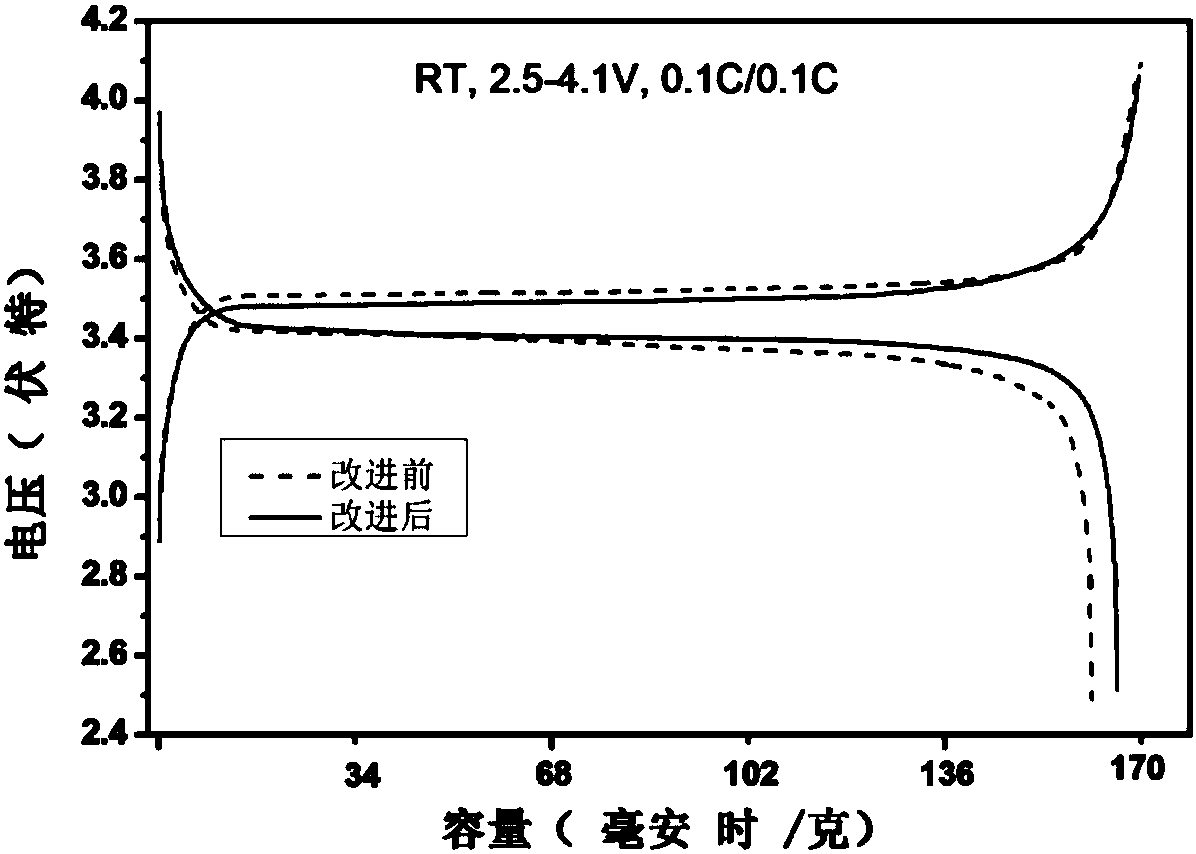
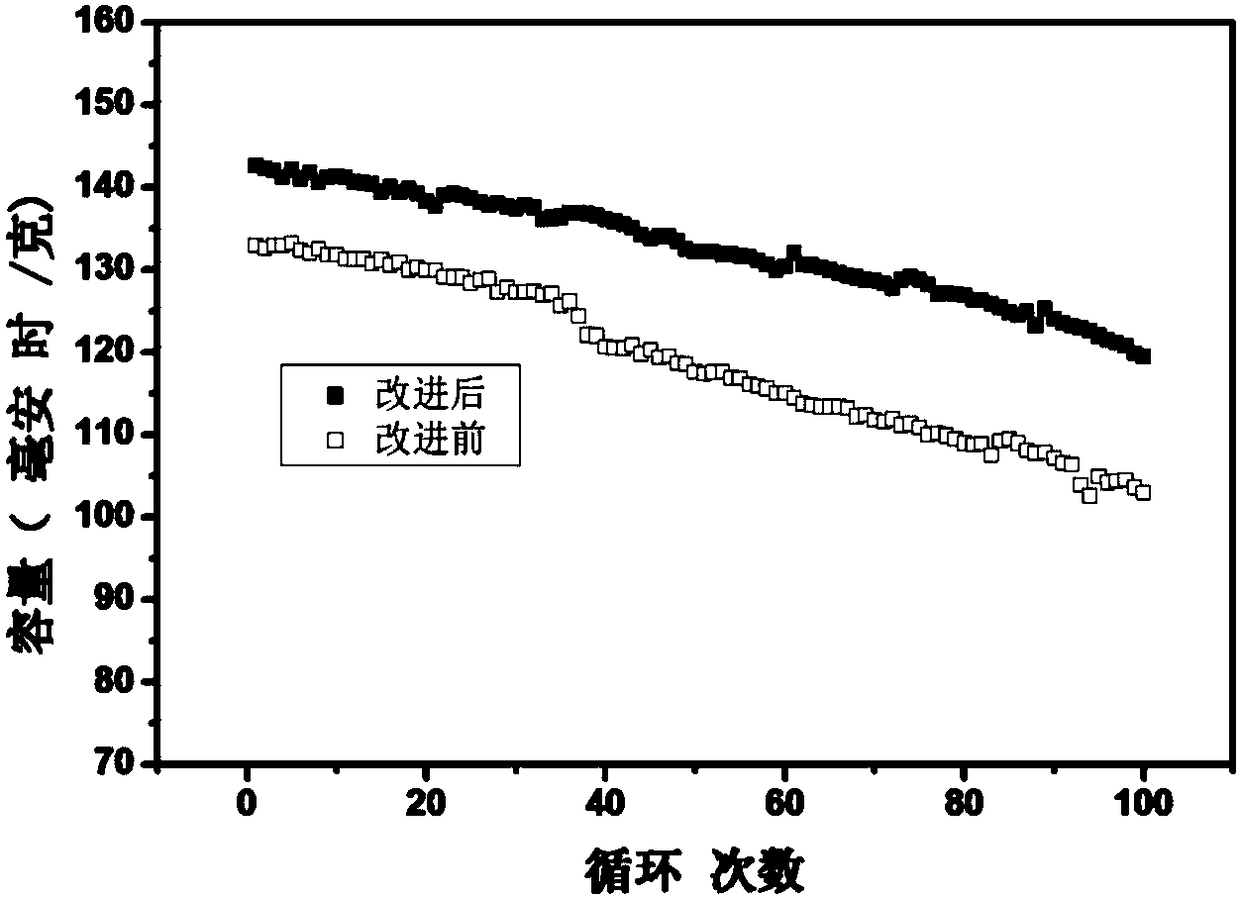
Preparation method of lithium ion battery electrode material
A lithium-ion battery and electrode material technology, applied in battery electrodes, non-aqueous electrolyte battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of electrode material structure deformation, low electronic conductivity, high energy consumption, etc., to achieve changing distribution, high electronic Effects of conductivity and high degree of graphitization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
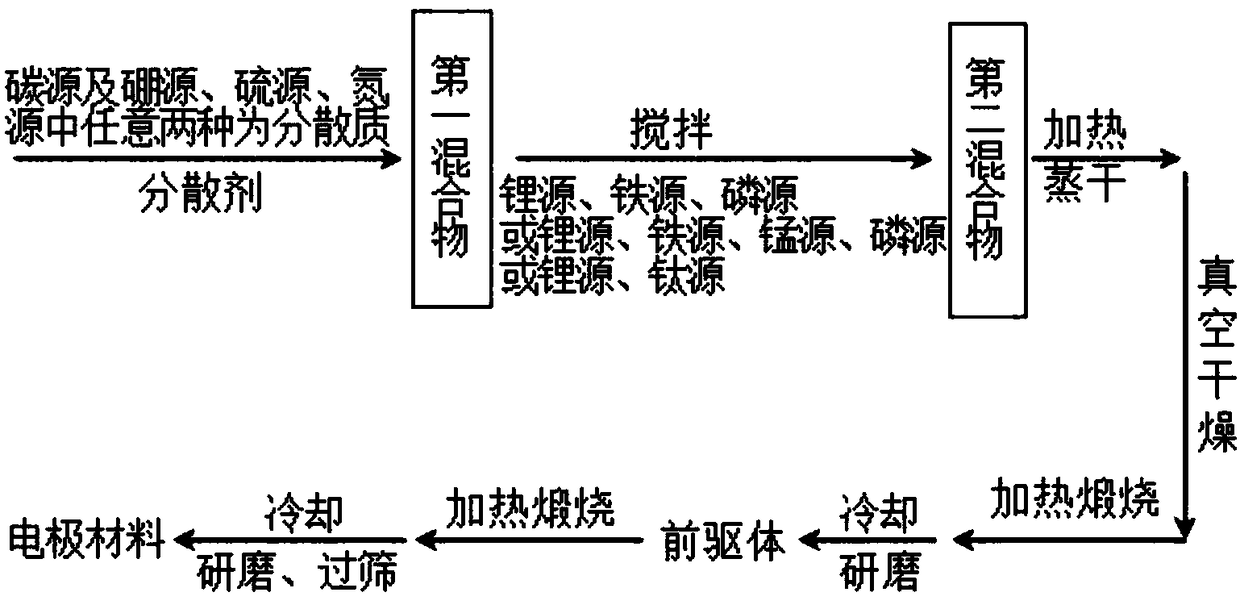
[0040] The present embodiment provides a kind of preparation method of lithium-ion battery electrode material, specifically as follows:
[0041] Add 3g of citric acid, tetraphenylboronic acid, and dibenzyl disulfide to 100g of V (去离子水) :V (乙醇) = 4:1 mixed dispersant, stirred evenly in the reactor to form the first mixture. Add 0.5 g of lithium carbonate, ferrous oxalate, and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate to the first mixture in sequence according to the molar ratio of Li:Fe:P of 1:1:1, and stir evenly to form the second mixture. The second mixture was heated at 80° C. and stirred at 300 rpm until the solution evaporated to dryness to form a solid. Then vacuum-dry at 80°C for 10h, then heat to 350°C for 4h under nitrogen atmosphere at a rate of 5°C per minute for calcination, then cool and grind. Then, it is heated to 800° C. for 15 hours at a heating rate of 5° C. per minute and calcined for 15 hours. The obtained solid product is ground and sieved to obtain a boron-sulfur ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The present embodiment provides a kind of preparation method of lithium-ion battery electrode material, specifically as follows:
[0050] 3g of sucrose, ethylphenylboronic acid, and thiophene were sequentially added into deionized water with a total mass of 30g according to the C:B:S molar ratio of 1:0.01:0.01, and stirred uniformly in the reactor to form the first mixture. Add 0.5 g of lithium nitrate, ferrous acetate, and ammonium phosphate to the first mixture in sequence according to the molar ratio of Li:Fe:P of 0.9:1:1, and stir to form a second mixture. The second mixture was heated at 70°C and stirred at 200 rpm until the solution evaporated to dryness to form a solid. Then vacuum-dried at 70°C for 8h, then heated to 250°C for 3h under an argon atmosphere at a rate of 1°C per minute and then calcined for 3h, cooled and ground. Then, it is heated to 700° C. for 8 hours at a heating rate of 1° C. per minute and calcined for 8 hours. The obtained solid product is ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The present embodiment provides a kind of preparation method of lithium-ion battery electrode material, specifically as follows:
[0053] Add 3 g of glucose, 4-aminophenylboronic acid, and sulfonated polystyrene into deionized water with a total mass of 150 g in sequence according to the C:B:S molar ratio of 1:0.1:0.1, and stir evenly in the reactor to form the first mixture . Add 0.5 g of lithium hydroxide, iron phosphate, and diammonium hydrogen phosphate to the first mixture in sequence according to the molar ratio of Li:Fe:P of 1.1:1:1, and stir evenly to form the second mixture. The second mixture was heated at 90°C and stirred at 400 rpm until the solution evaporated to dryness to form a solid. Then vacuum dry at 100°C for 12h, then heat to 450°C for 5h under nitrogen atmosphere at a rate of 20°C per minute for calcination, then cool and grind. Then, it is heated to 1000° C. for 30 hours at a heating rate of 20° C. per minute and calcined for 30 hours. The obtai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com