Patents
Literature
33 results about "Androgen independent prostate cancer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The oncoprotein BCL-2 is associated with the development of androgen-independent prostate cancer, due to its high levels of expression in androgen-independent tumours in advanced stages of the pathology. The upregulation of BCL-2 after androgen ablation in prostate carcinoma cell lines and in a castrated-male rat model further established a ...
Method of treating androgen independent prostate cancer
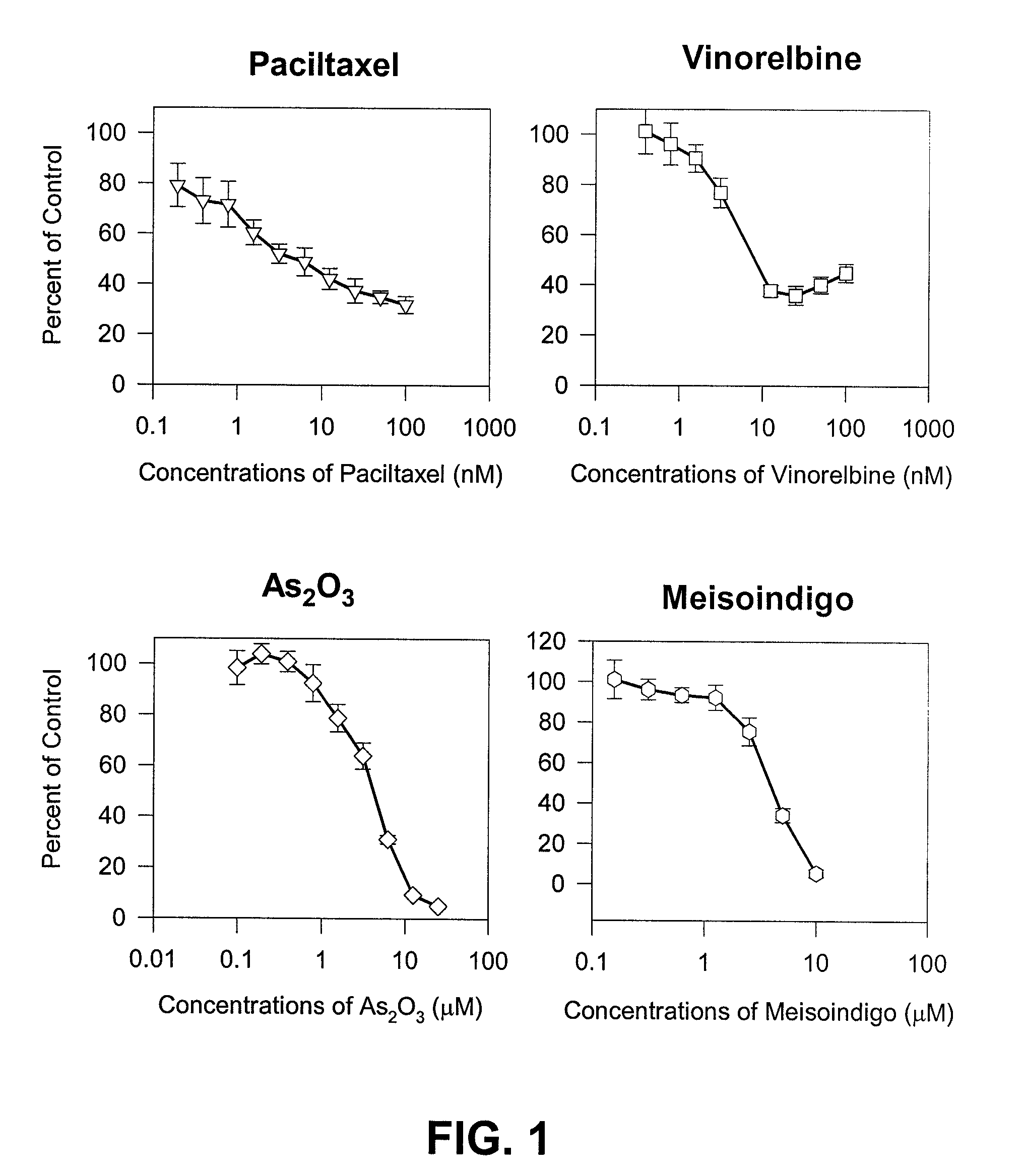
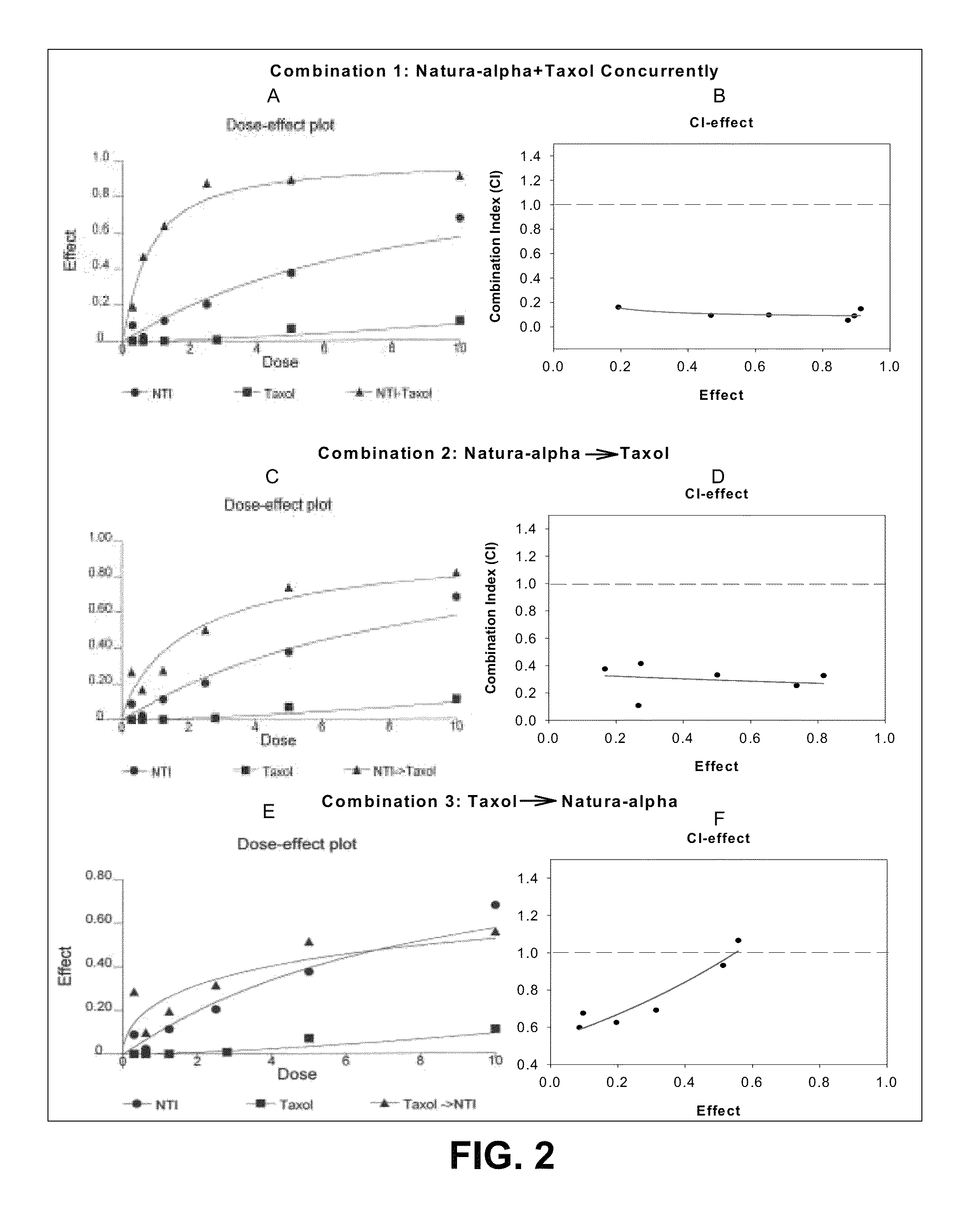
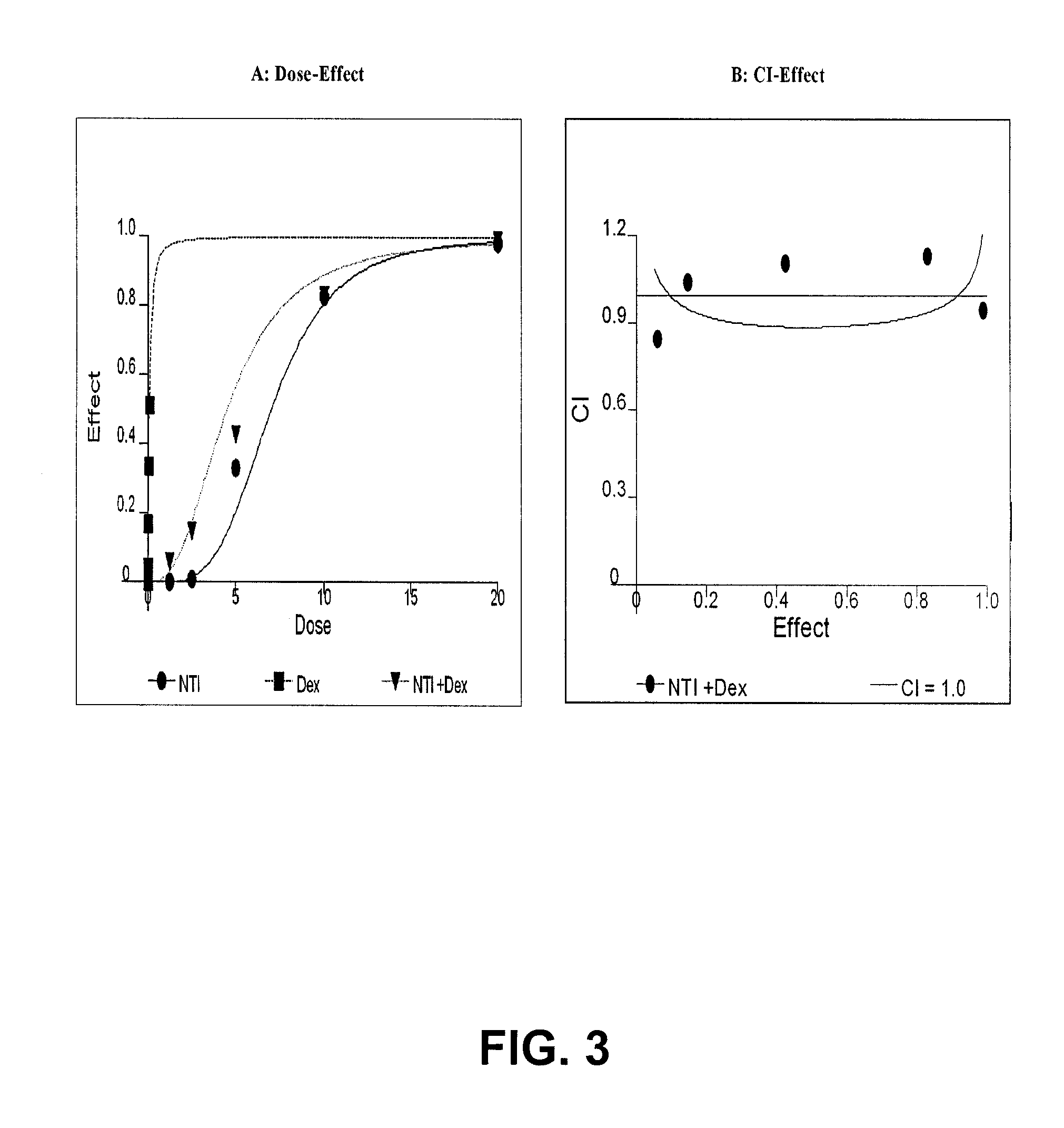
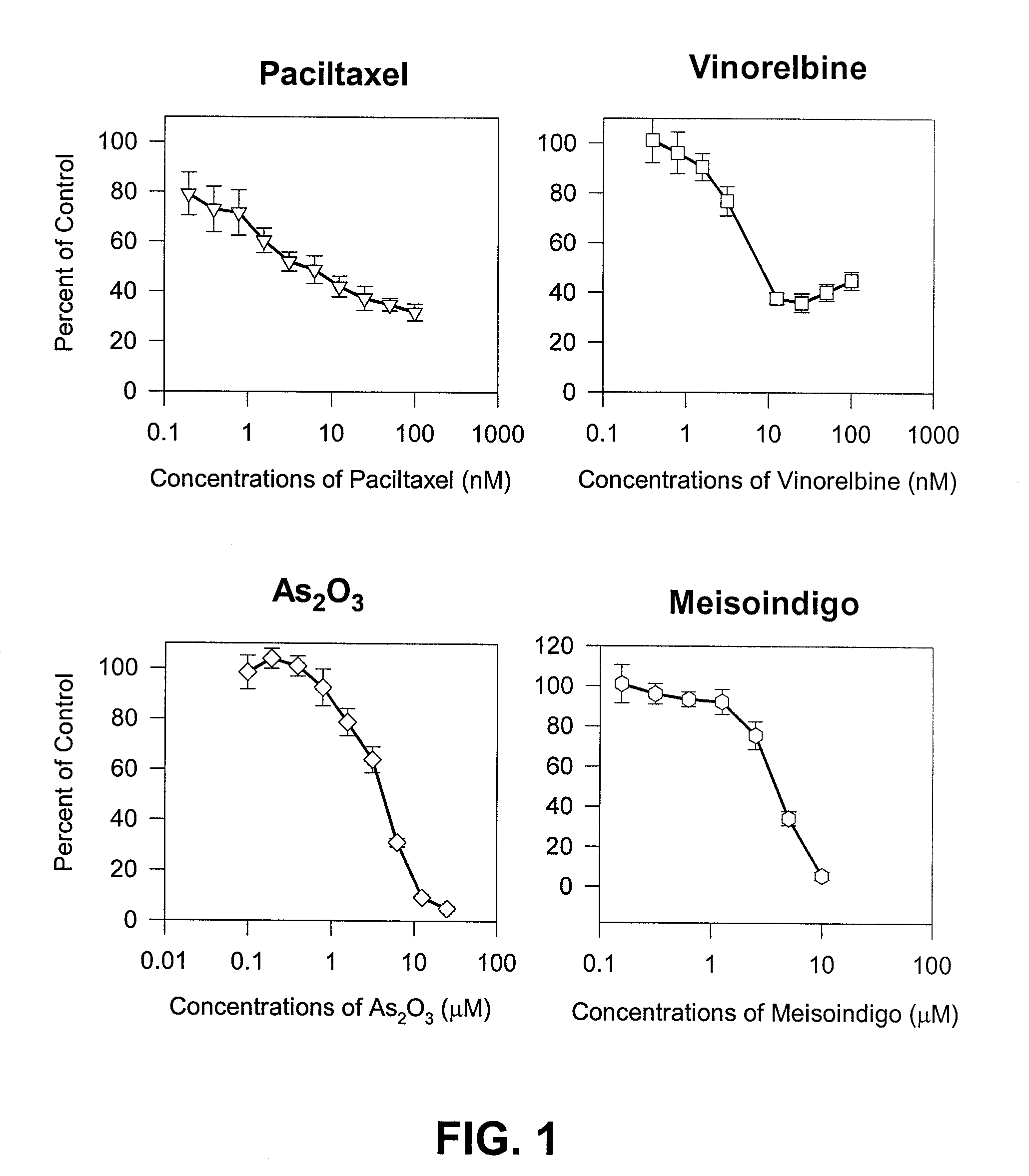
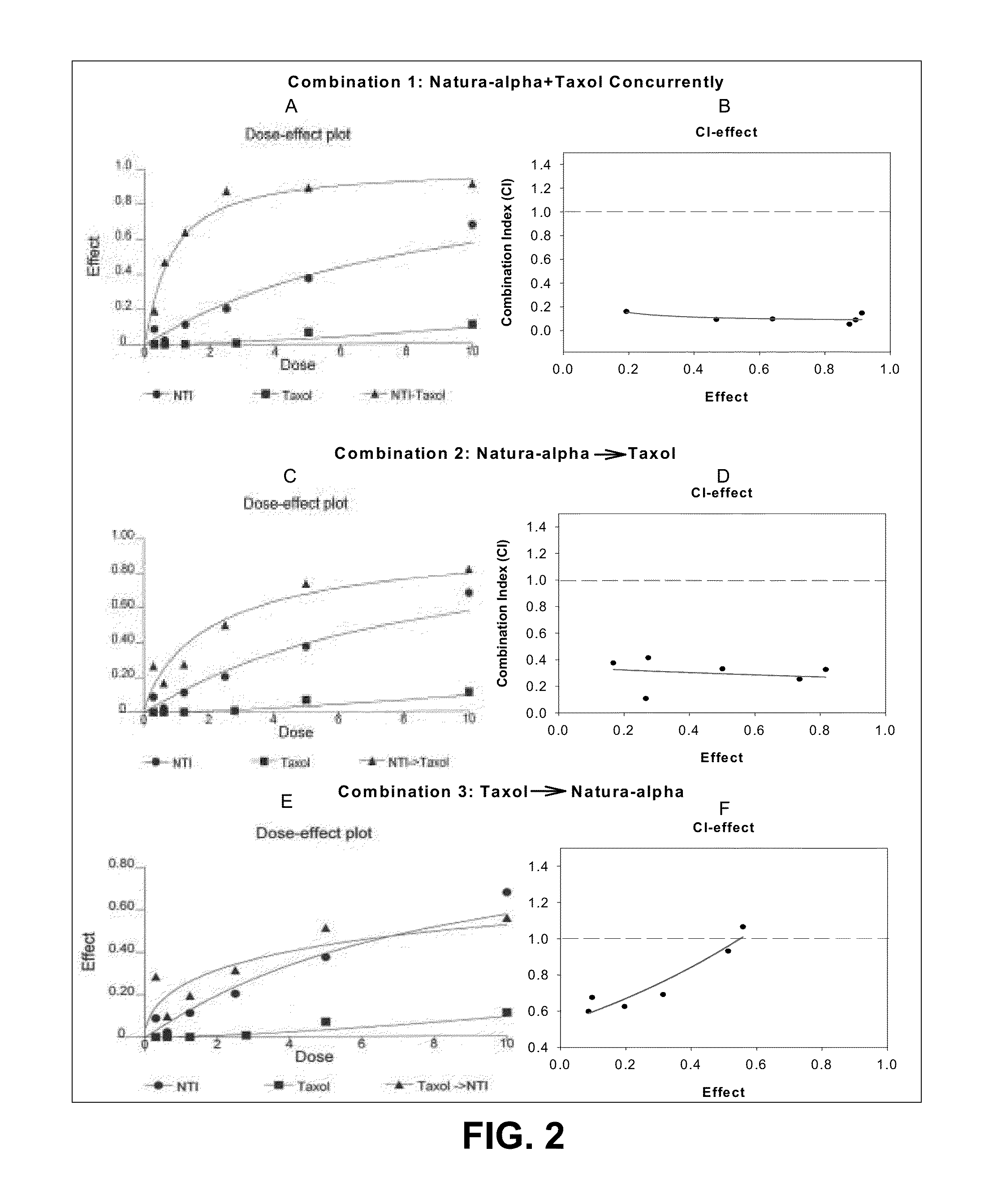
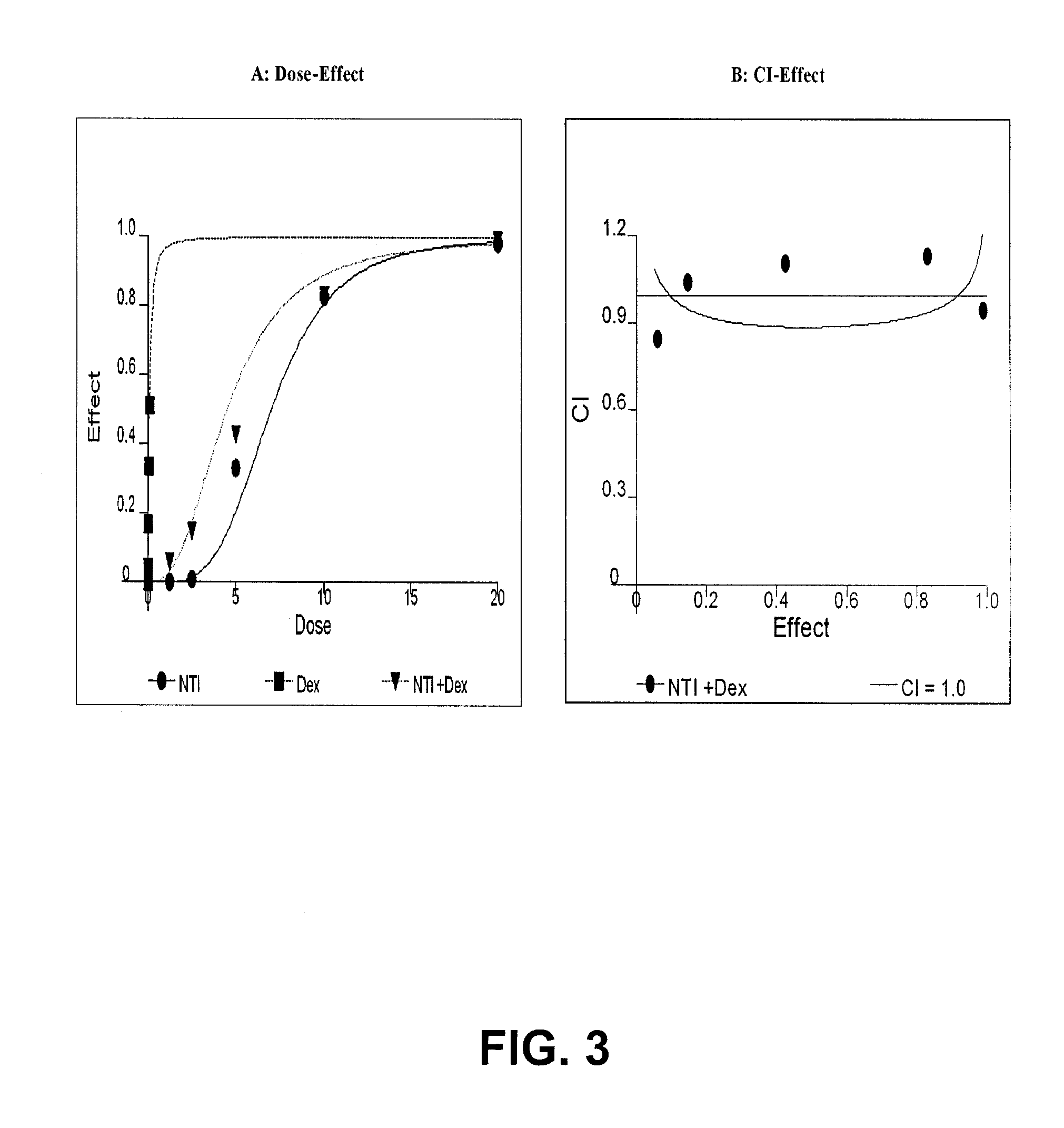
The present invention is directed to a method treating prostate cancer. The method comprises administering to a patient in need thereof at least one compound selected from N-methyl-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone; N-1-(β-D-O-triacetyl-xylopranosyl)-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone; and N-1-(β-D-O-triacetyl-xylopranosyl)-N′-methyl-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone. Preferably the compound is in an amount sufficient to inhibit growth, invasion, and / or metastasis of prostate cancer cells.
Owner:NATROGEN THERAPEUTICS INT
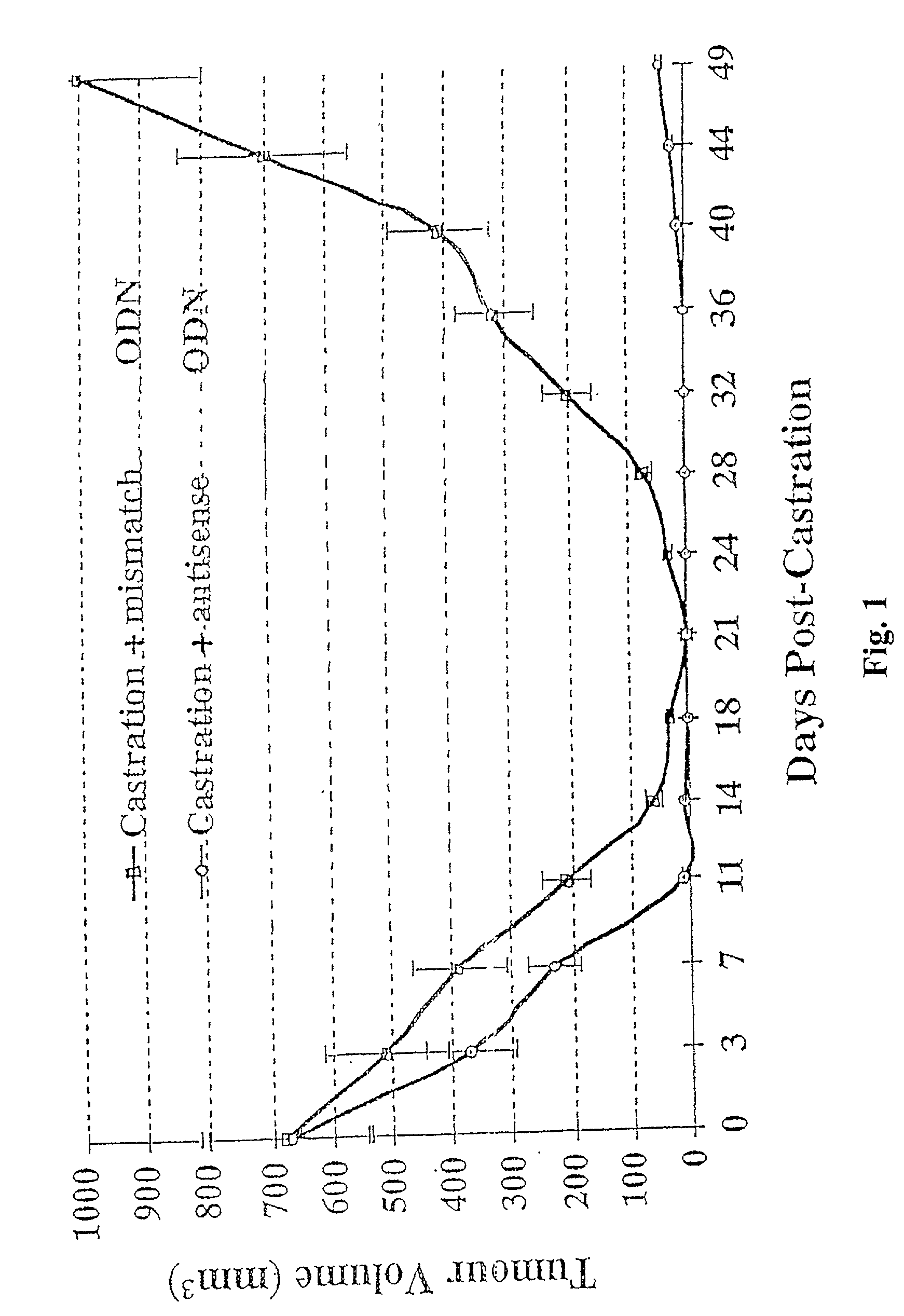
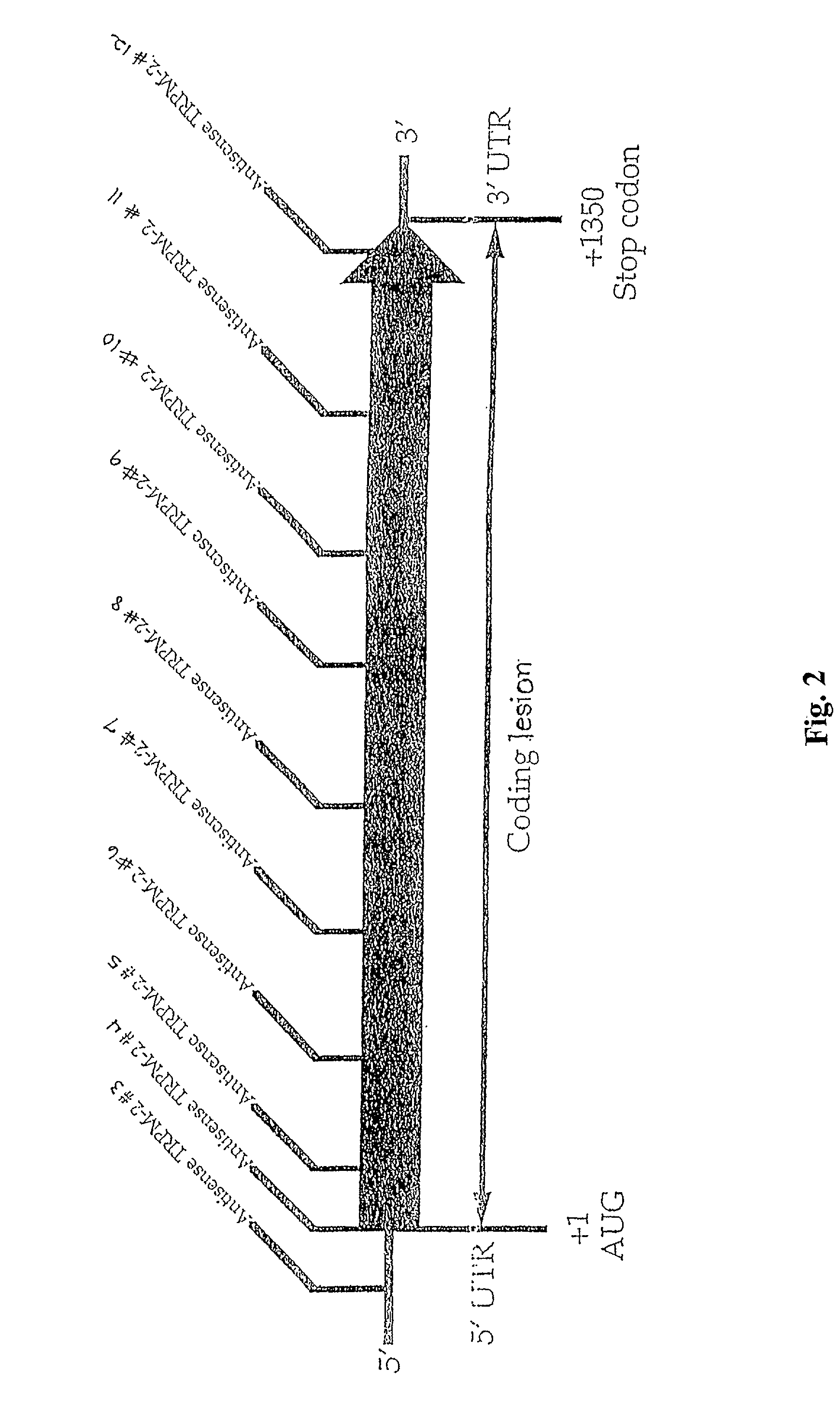
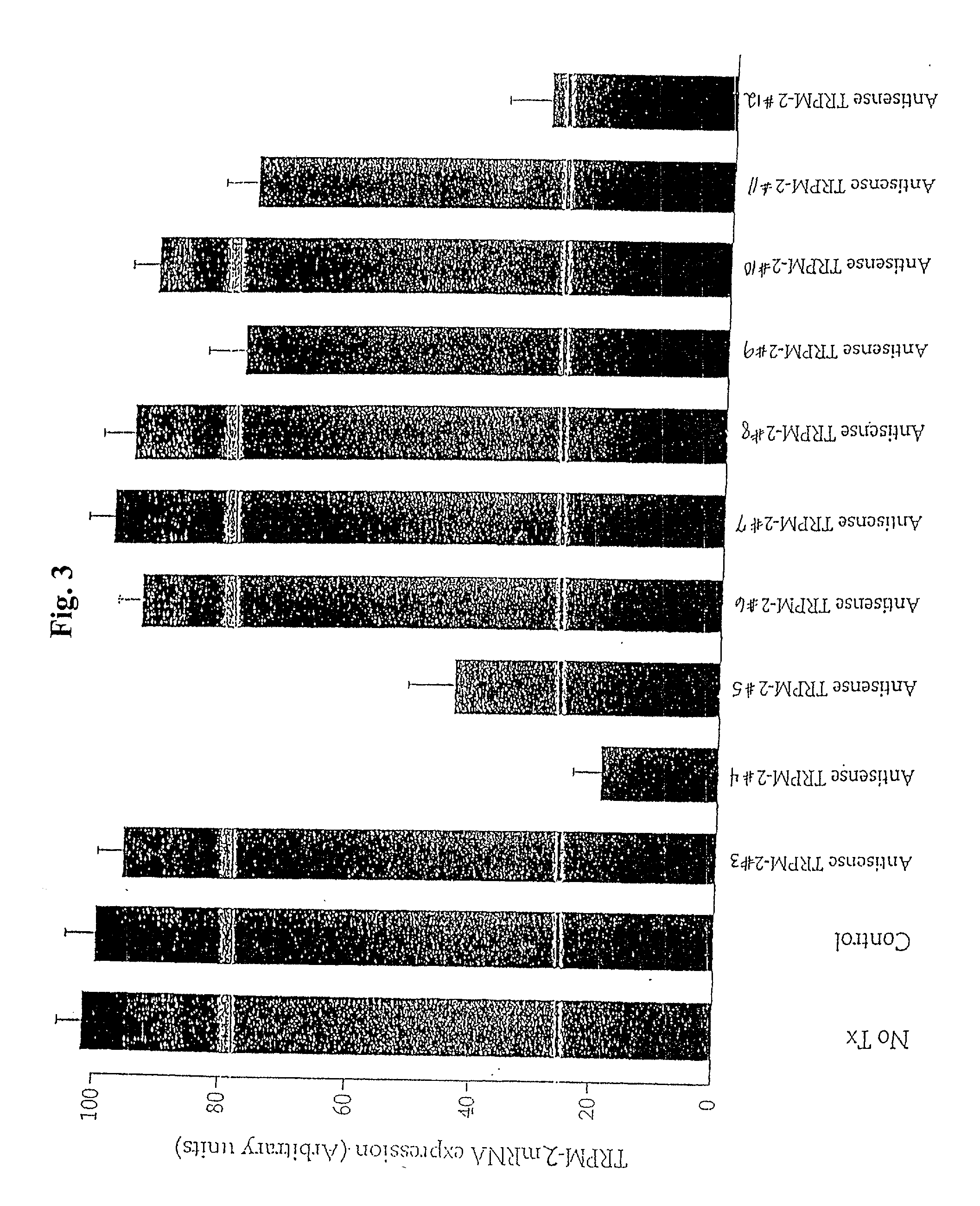
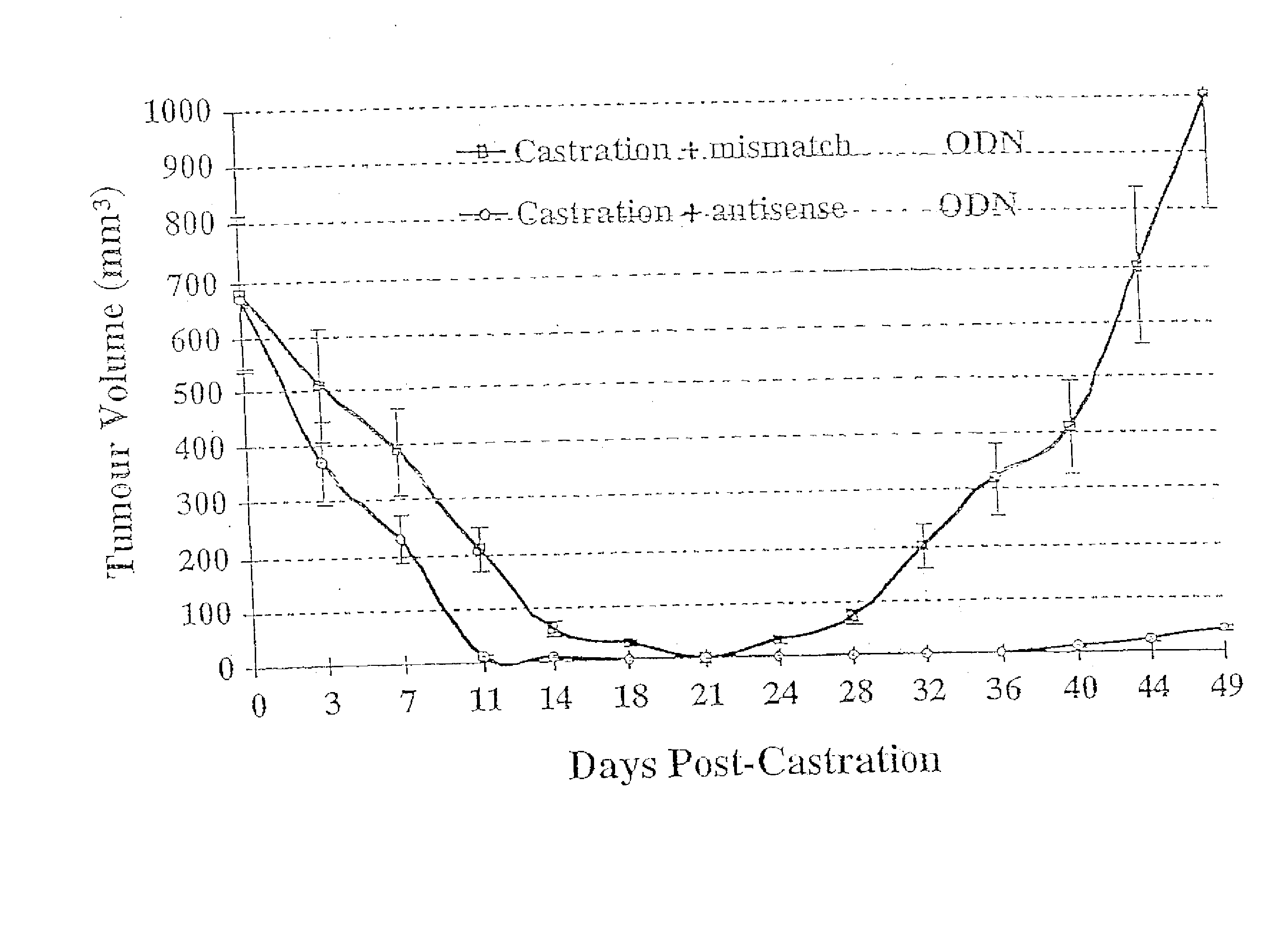
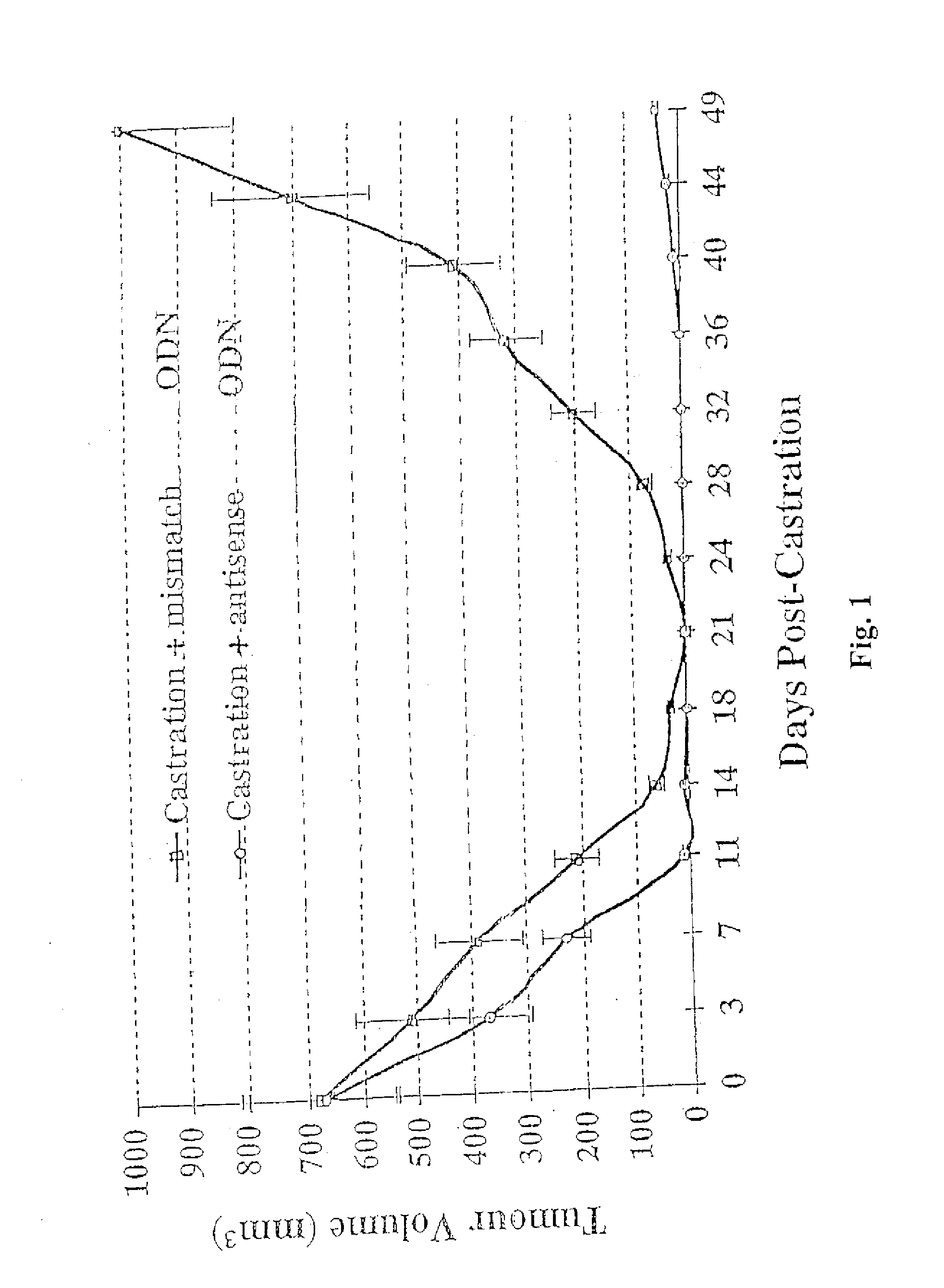
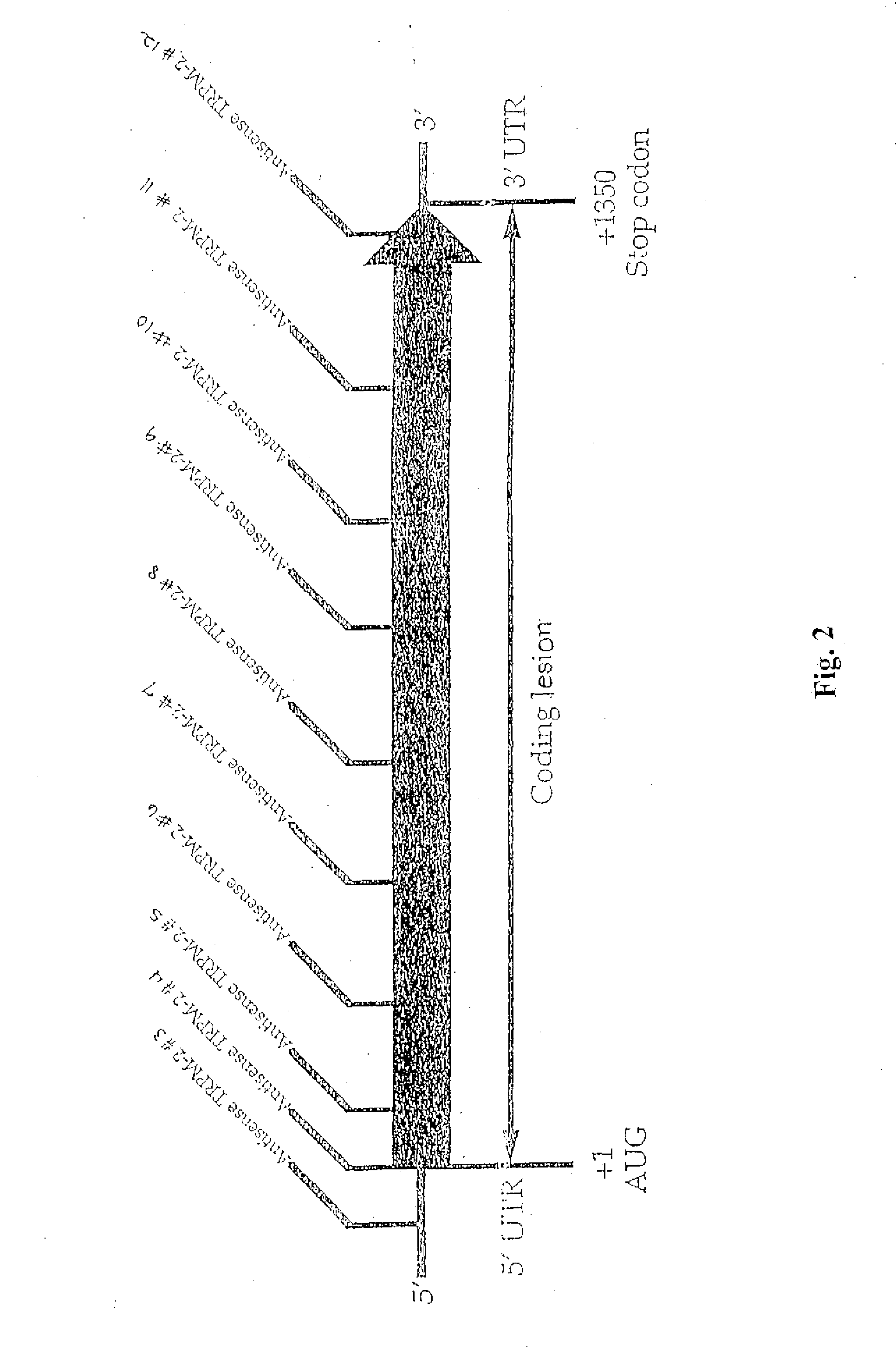
TRPM-2 antisense therapy
InactiveUS20020128220A1Increased chemosensitivityInhibit expressionApolipeptidesSugar derivativesDiseaseCancer type
It has now been determined that antisense therapy which reduces the expression of TRPM-2 provides therapeutic benefits in the treatment of cancer. In particular, such antisense therapy can be applied in treatment of prostate cancer and renal cell cancer. Addition of antisense TRPM-2 ODN to prostatic tumor cells in vivo is effective for delaying the onset of androgen independence. Thus, prostate cancer can be treated in an individual suffering from prostate cancer by initiating androgen-withdrawal to induce apoptotic cell death of prostatic tumor cells in the individual, and administering to the individual a composition effective to inhibit expression of TRPM-2 by the tumor cells, thereby delaying the progression of prostatic tumor cells to an androgen-independent state in an individual Combined use of antisense TRPM-2 and taxanes synergistically enhances cytotoxic chemosensitivity of androgen-independent prostate cancer. In addition, it has also been found that antisense TRPM-2 has beneficial effect for other cancer types. Specifically, antisense TRPM-2 ODN enhances chemosensitivity in human Renal cell cancer, a normally chemoresistant disease with no active chemotherapeutic agent having an objective response rate higher than 10%. Radiation sensitivity is also enhanced when cells expressing TRPM-2 are treated with antisense TRPM-2 ODN. Thus, the antisense TRPM-2 ODNs can be used to enhance hormone sensitivity, chemosensitivity and radiation sensitivity of a variety of cancer types in which expression of TRPM-2 has been observed.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
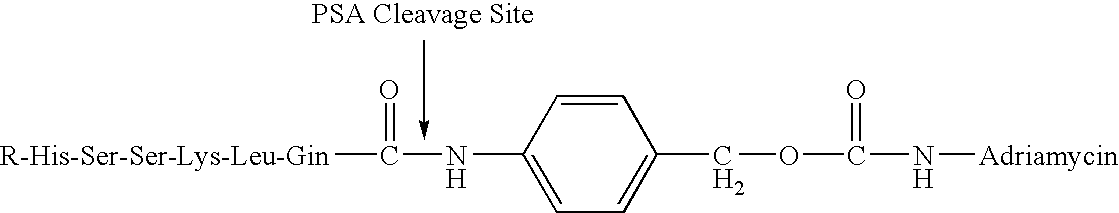
Drug complex for treatment of metastatic prostate cancer
InactiveUS20050233948A1Improve efficacyLow toxicityTripeptide ingredientsSaccharide peptide ingredientsProstate cancer cellAntigen
A drug complex for delivery of a drug or other agent to a target cell, comprising a targeting carrier molecule which is selectively distributed to a specific cell type or tissue containing the specific cell type; a linker which is acted upon by a molecule which is present at an effective concentration in the environs of the specific cell type; and a drug or an agent to be delivered to the specific cell type. In particular, a drug complex for delivering a cytotoxic drug to prostate cancer cells, comprising a targeting carrier molecule which is selectively delivered to prostate tissue, bone or both; a peptide which is a substrate for prostate specific antigen; and a cytotoxic drug which is toxic to androgen independent prostate cancer cells.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +2
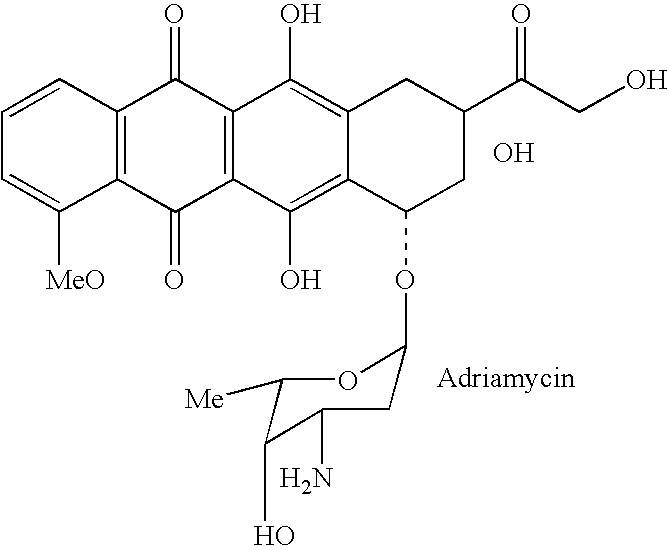
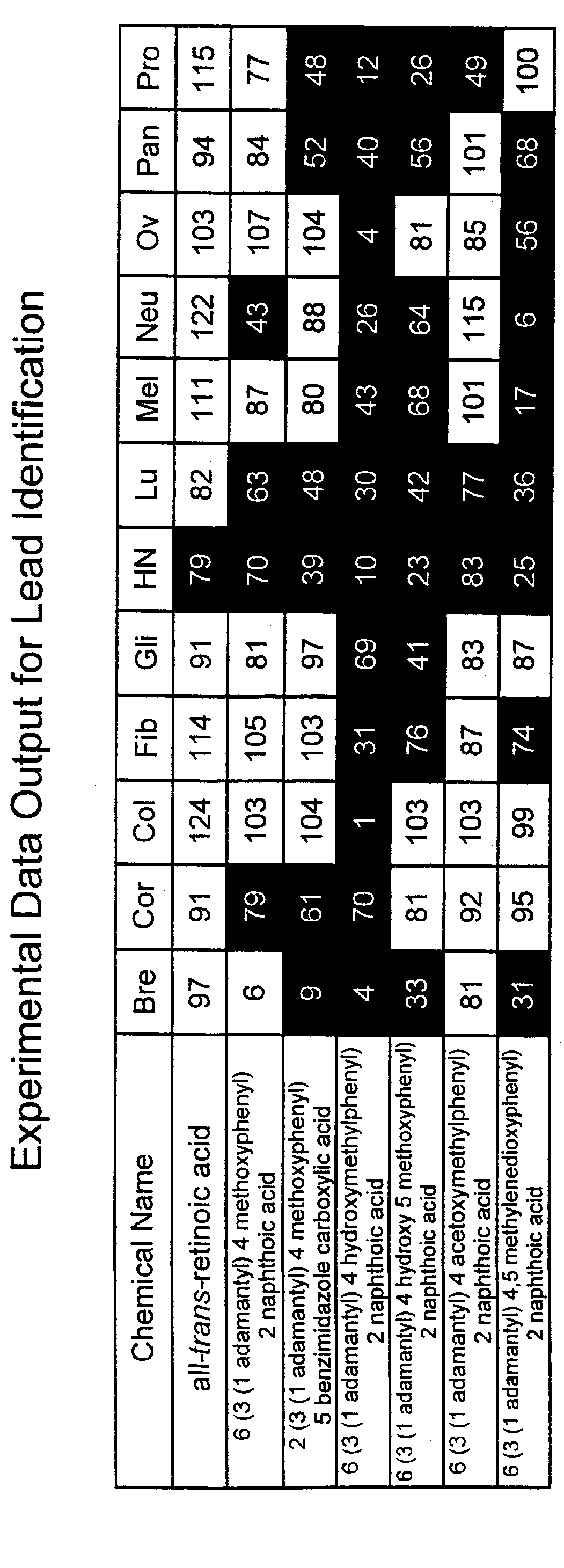
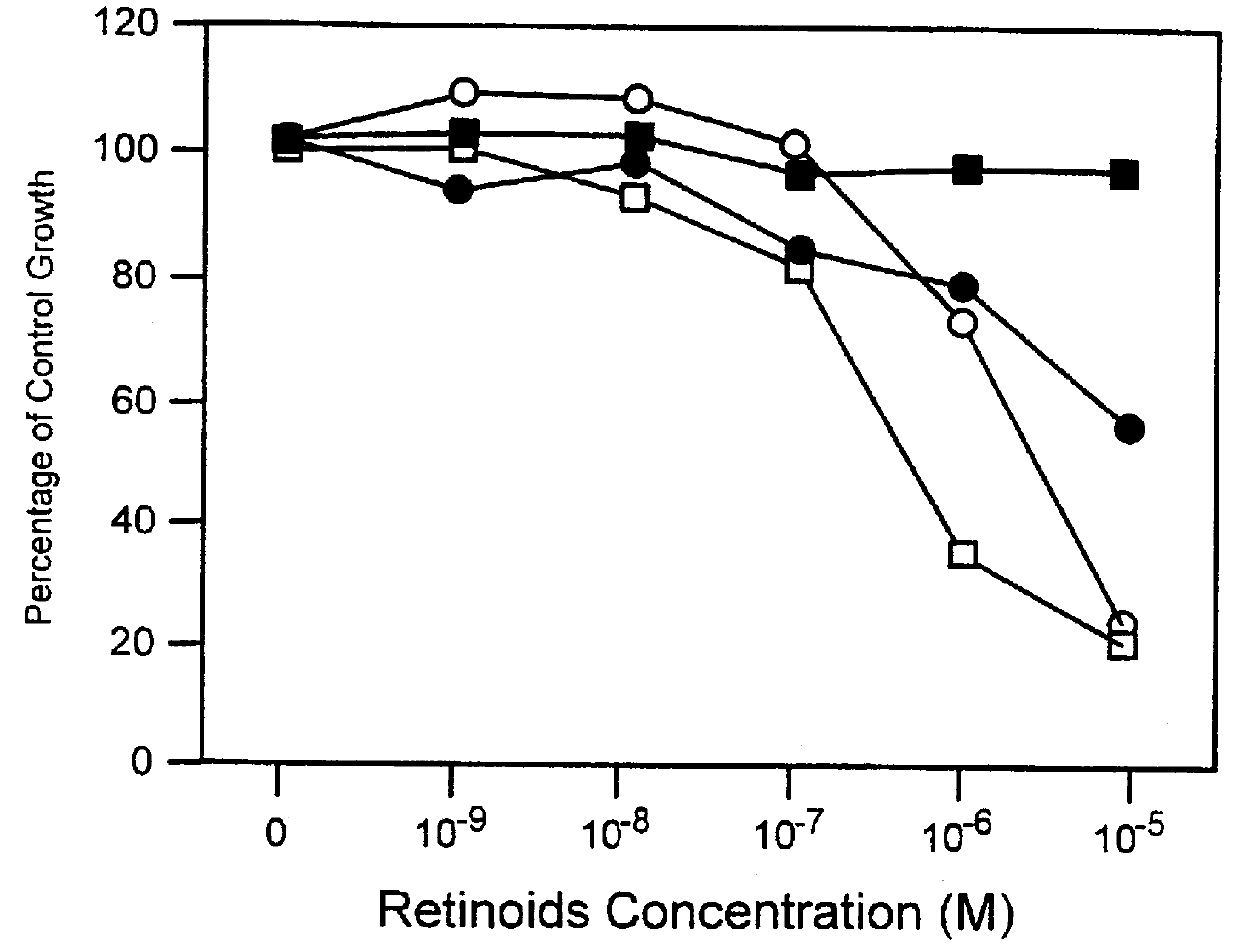
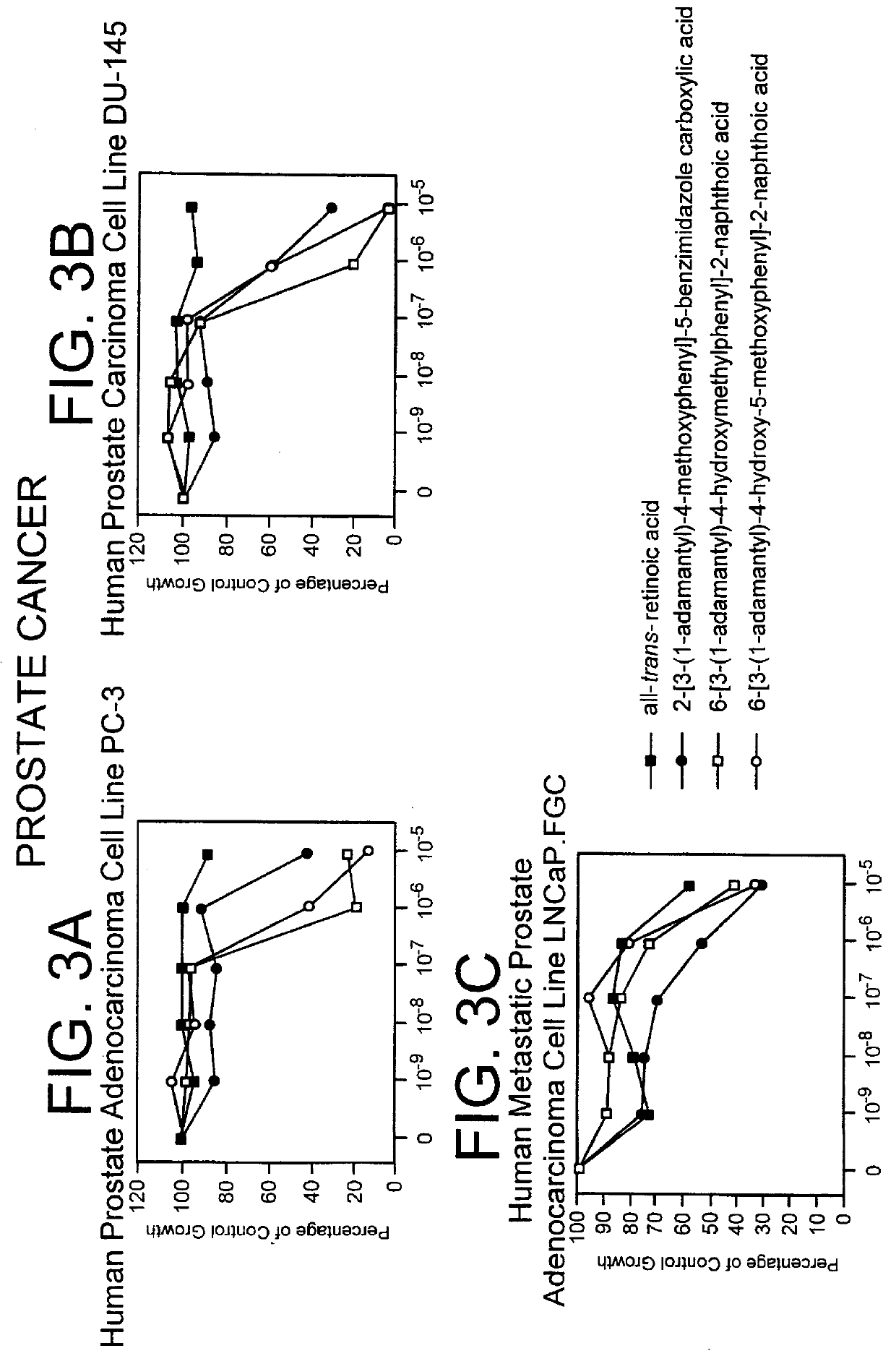
Apoptosis inducing adamantyl derivatives and their usage as anti-cancer agents
InactiveUS6127415APreventing and controlling photoinducedPreventing and controlling and chronologic agingBiocideCosmetic preparationsDiseaseAnticarcinogen
PCT No. PCT / US97 / 11564 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 14, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 14, 1999 PCT Filed Jul. 8, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 01132 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 15, 1998The present invention relates to specific adamantyl or adamantyl group derivative containing retinoid compounds induce apoptosis of cancer cells. These adamantyl retinoid derivatives are useful for the treatment of many cancers and solid tumors, especially androgen-independent prostate cancer, skin cancer, pancreatic carcinomas, colon cancer, melanoma, ovarian cancer, liver cancer, small cell lung carcinoma, non-small cell lung carcinoma, cervical carcinoma, brain cancer, bladder cancer, breast cancer, neuroblastoma / glioblastoma, and leukemia. Also, the invention relates to novel adamantyl or adamantyl group derivative compounds which are useful as active agents for the treatment or prevention of keratinization disorders and other dermatological conditions, and other diseases.
Owner:GALDERMA RES & DEV SNC
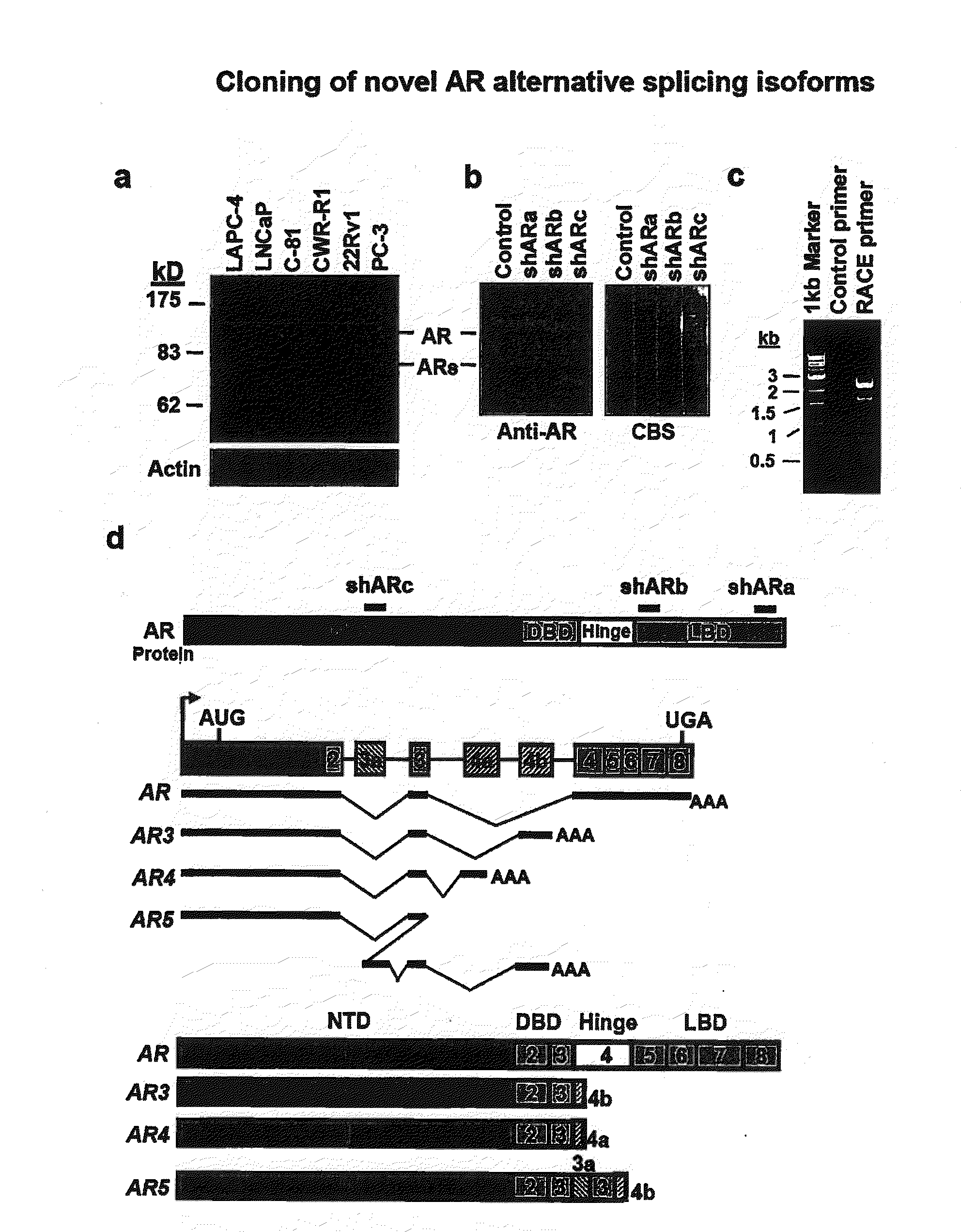
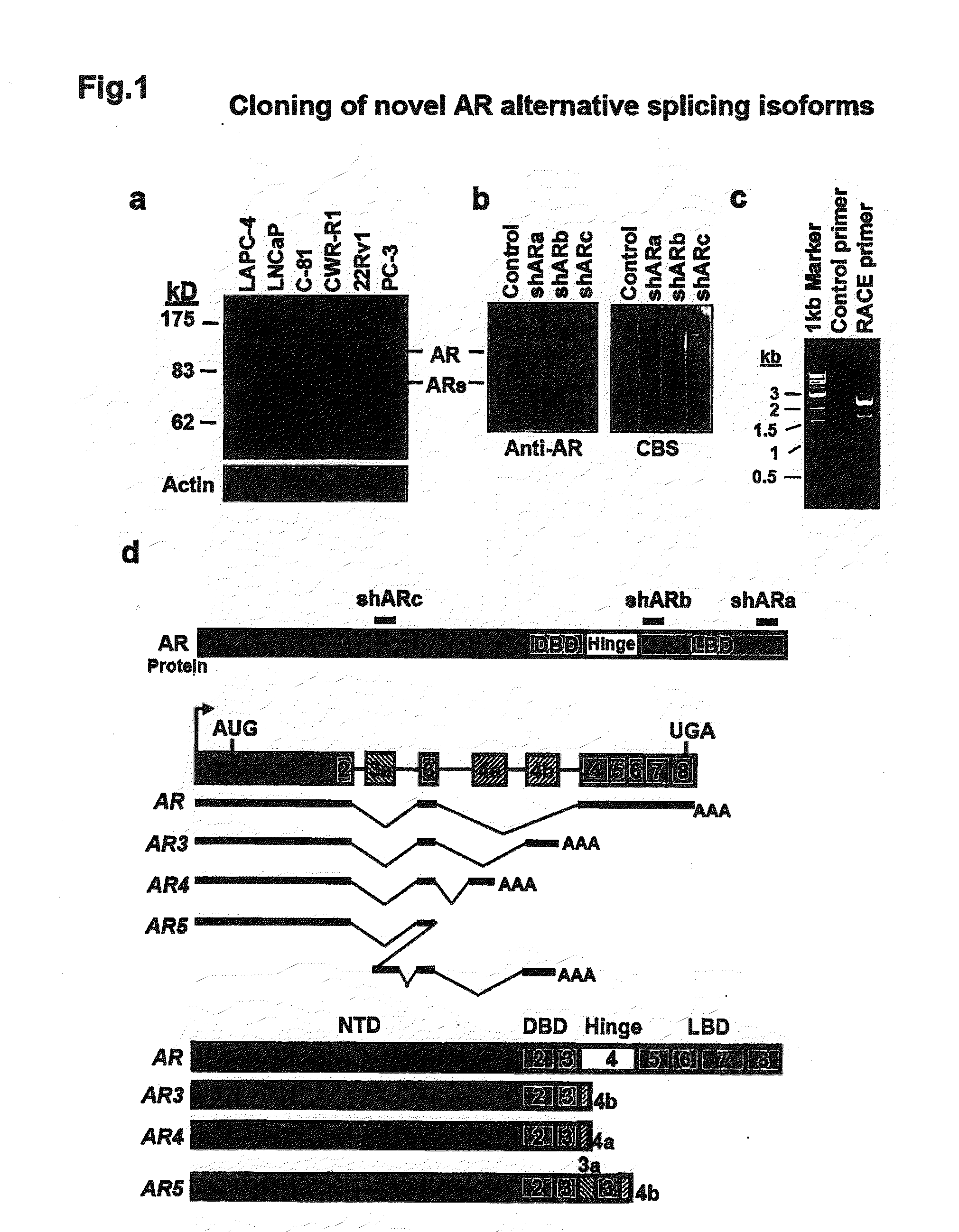
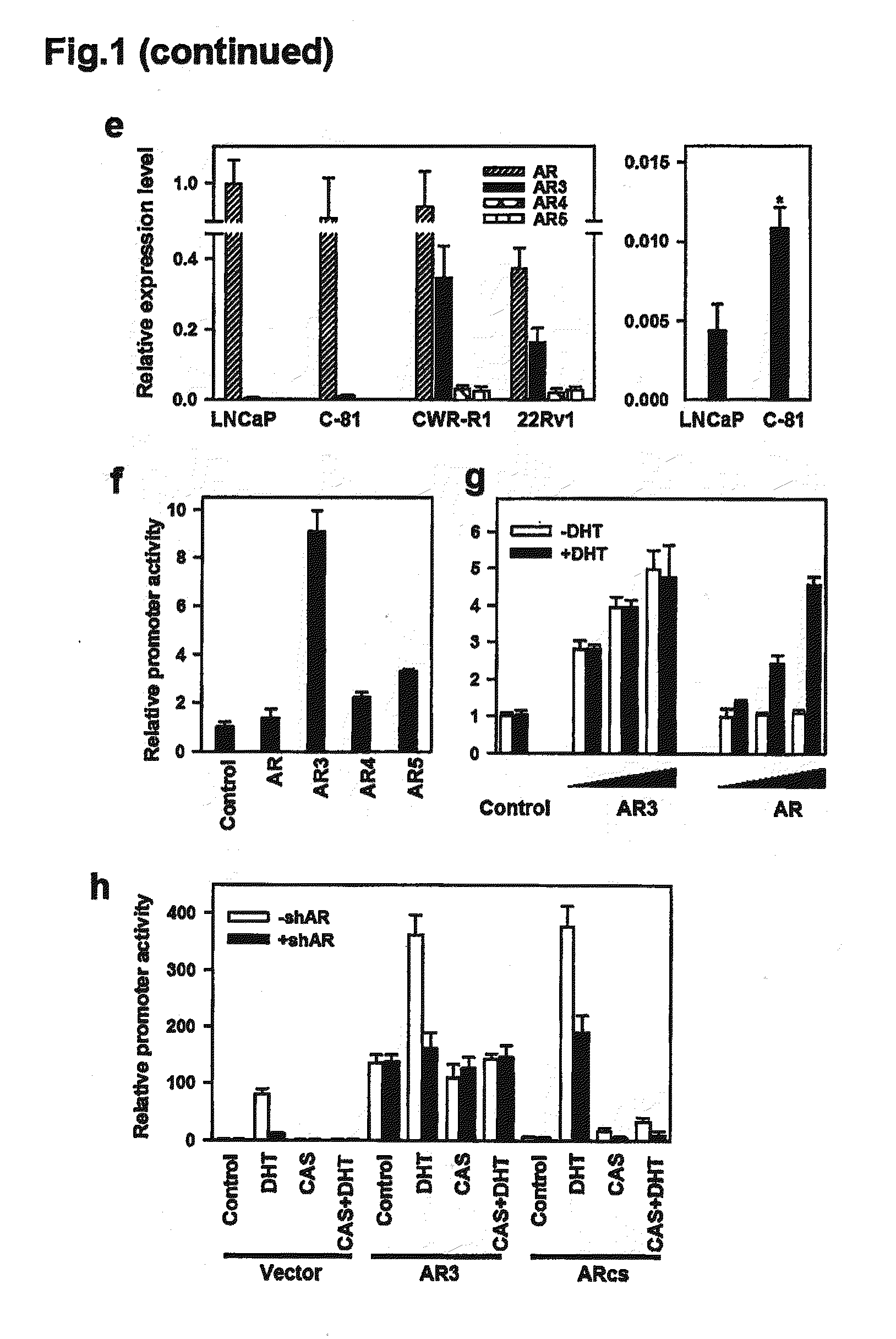
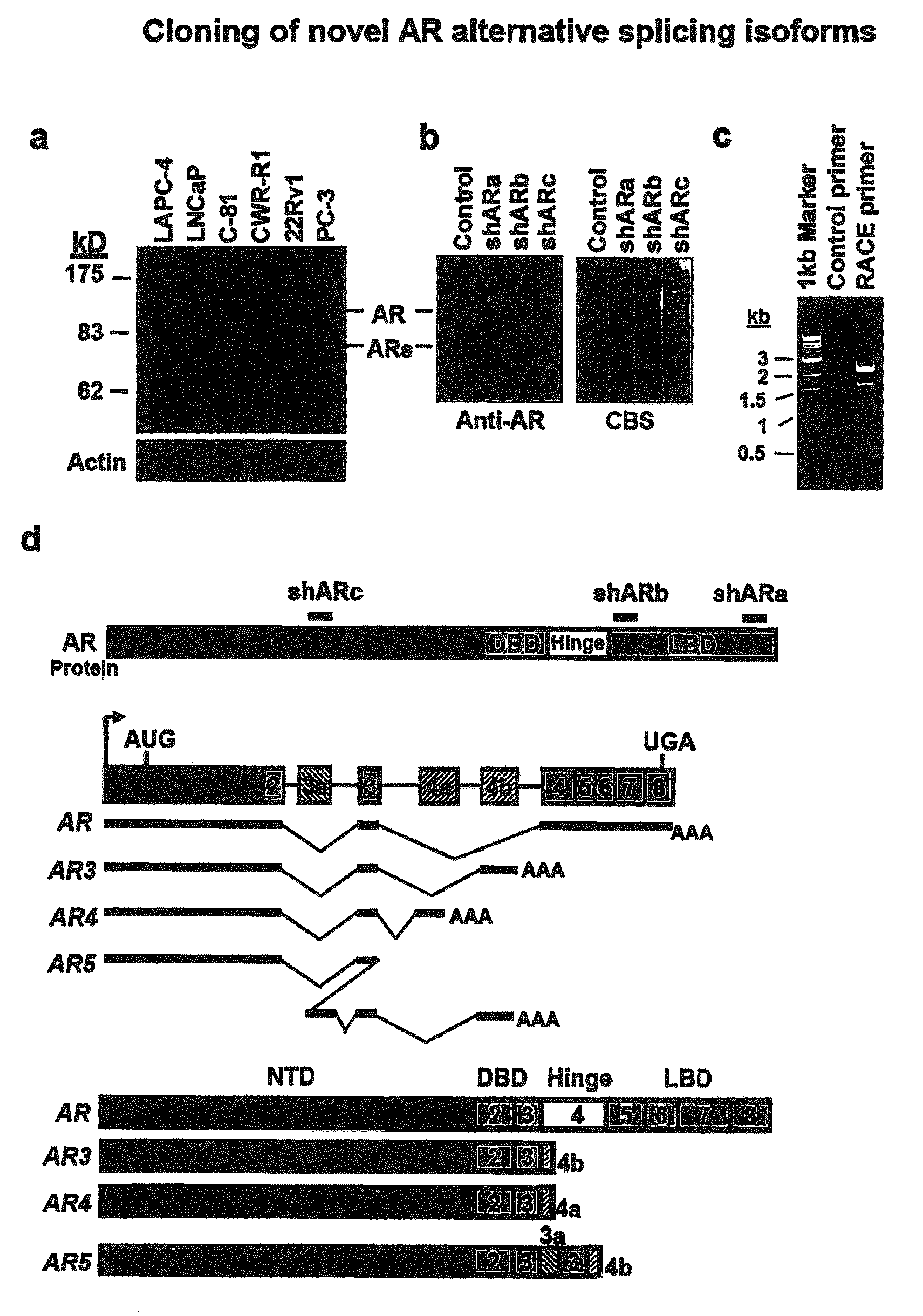
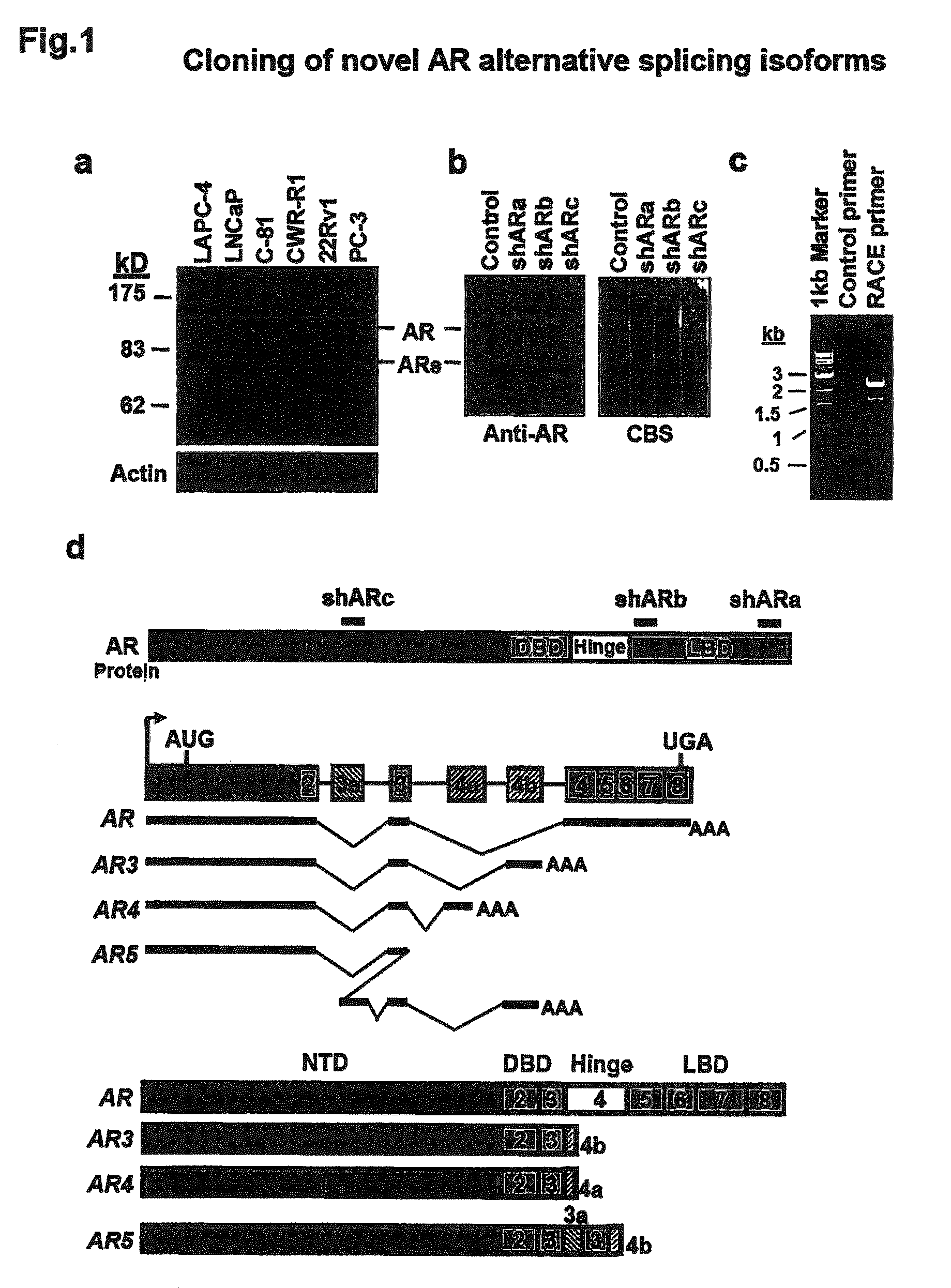
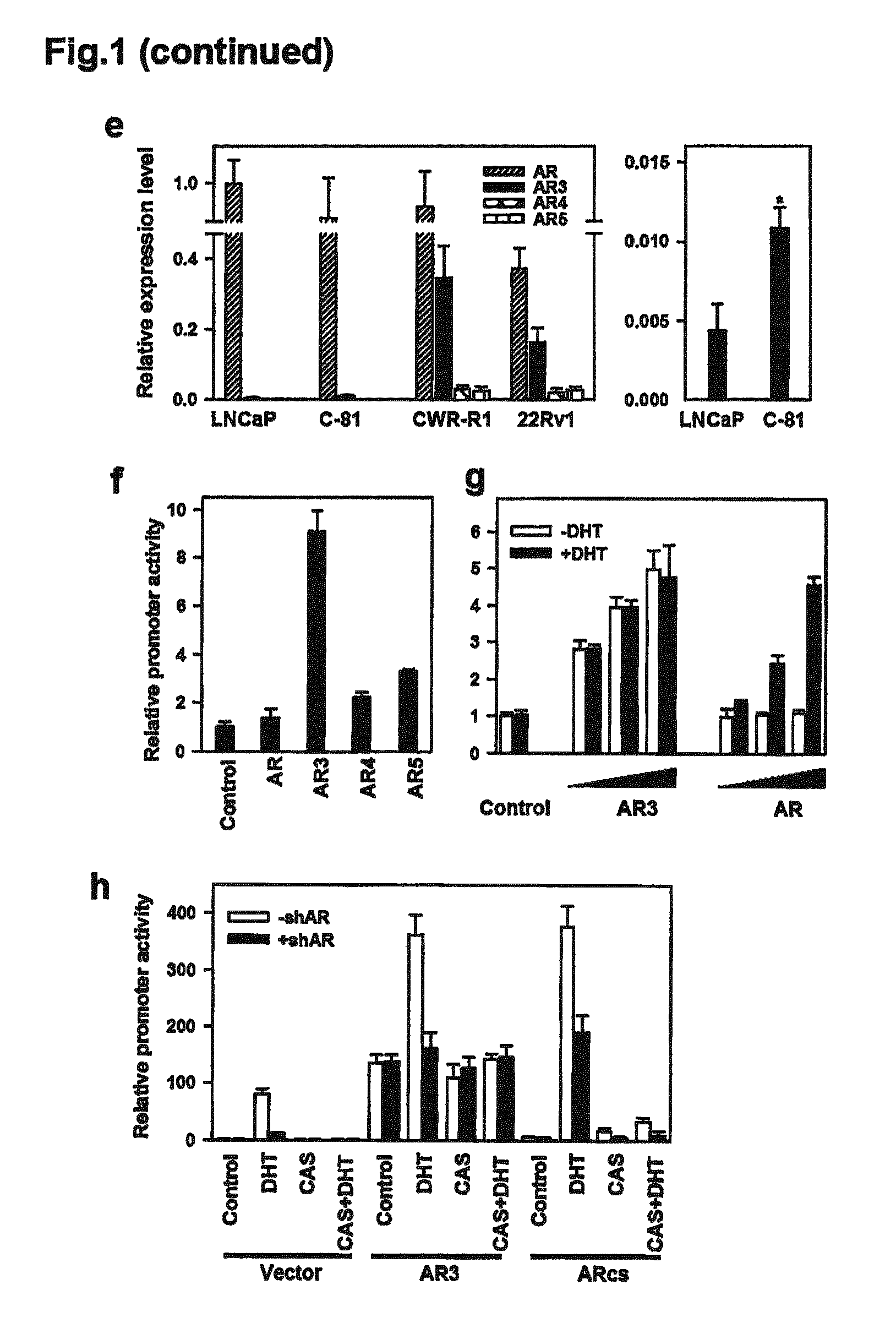
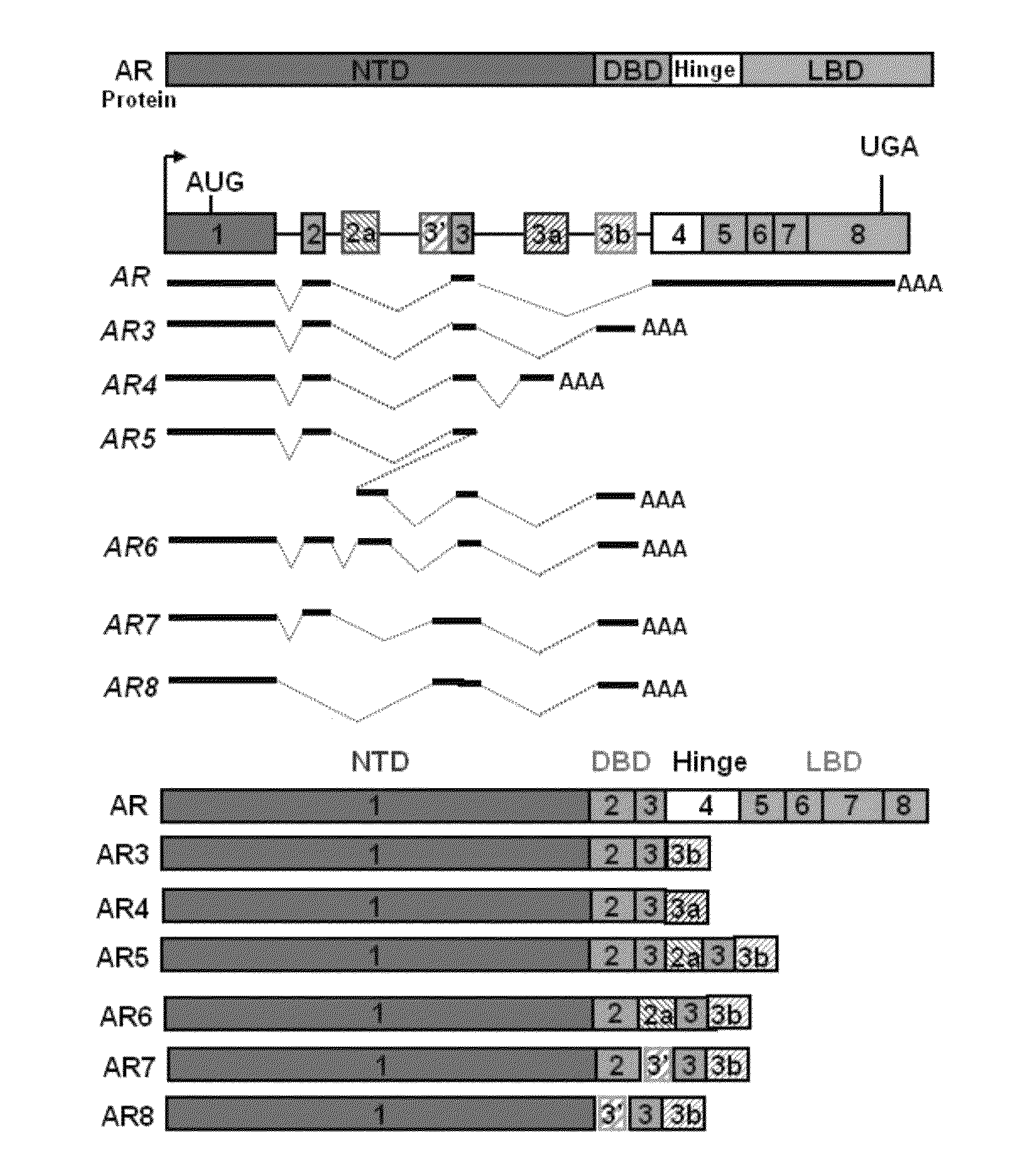
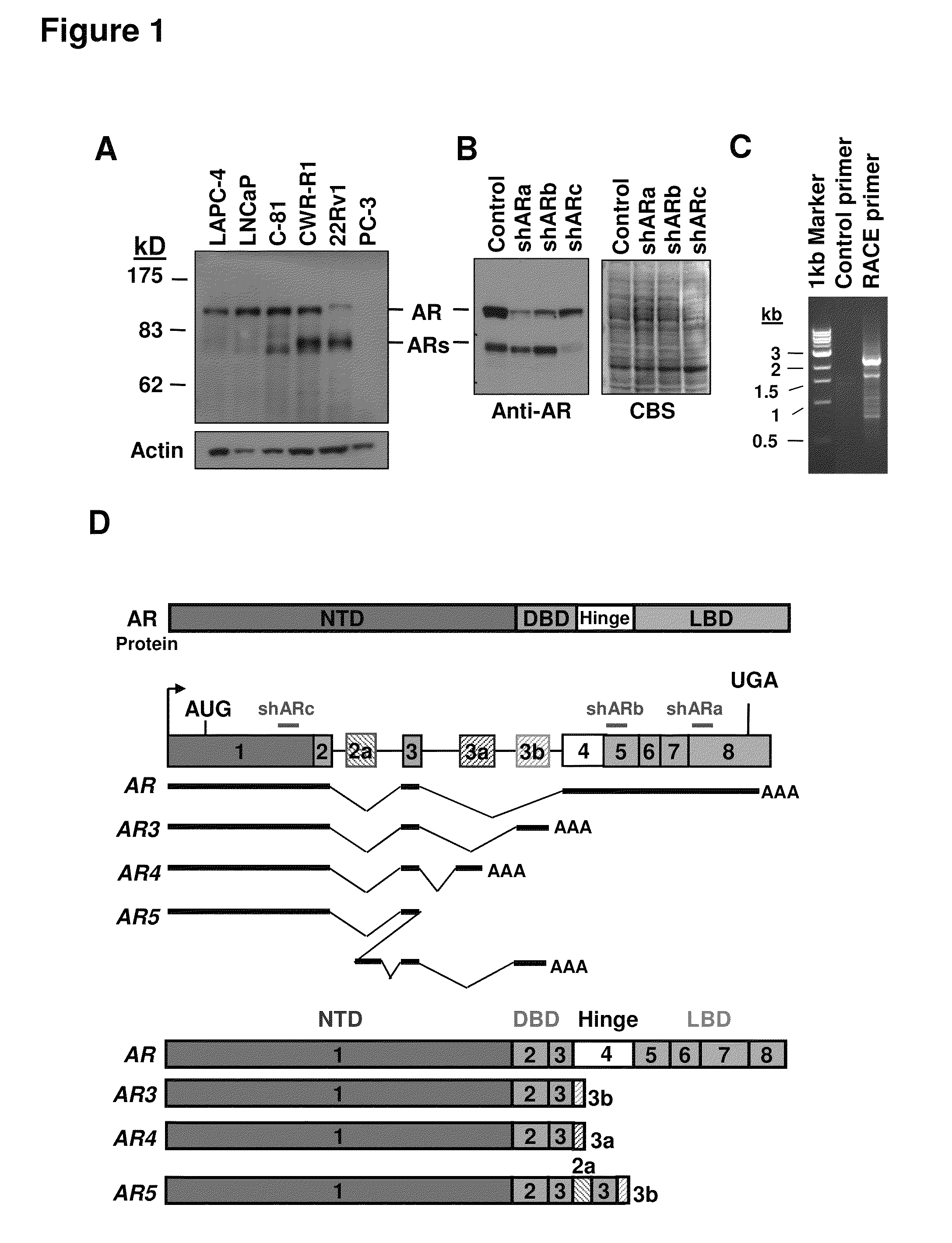
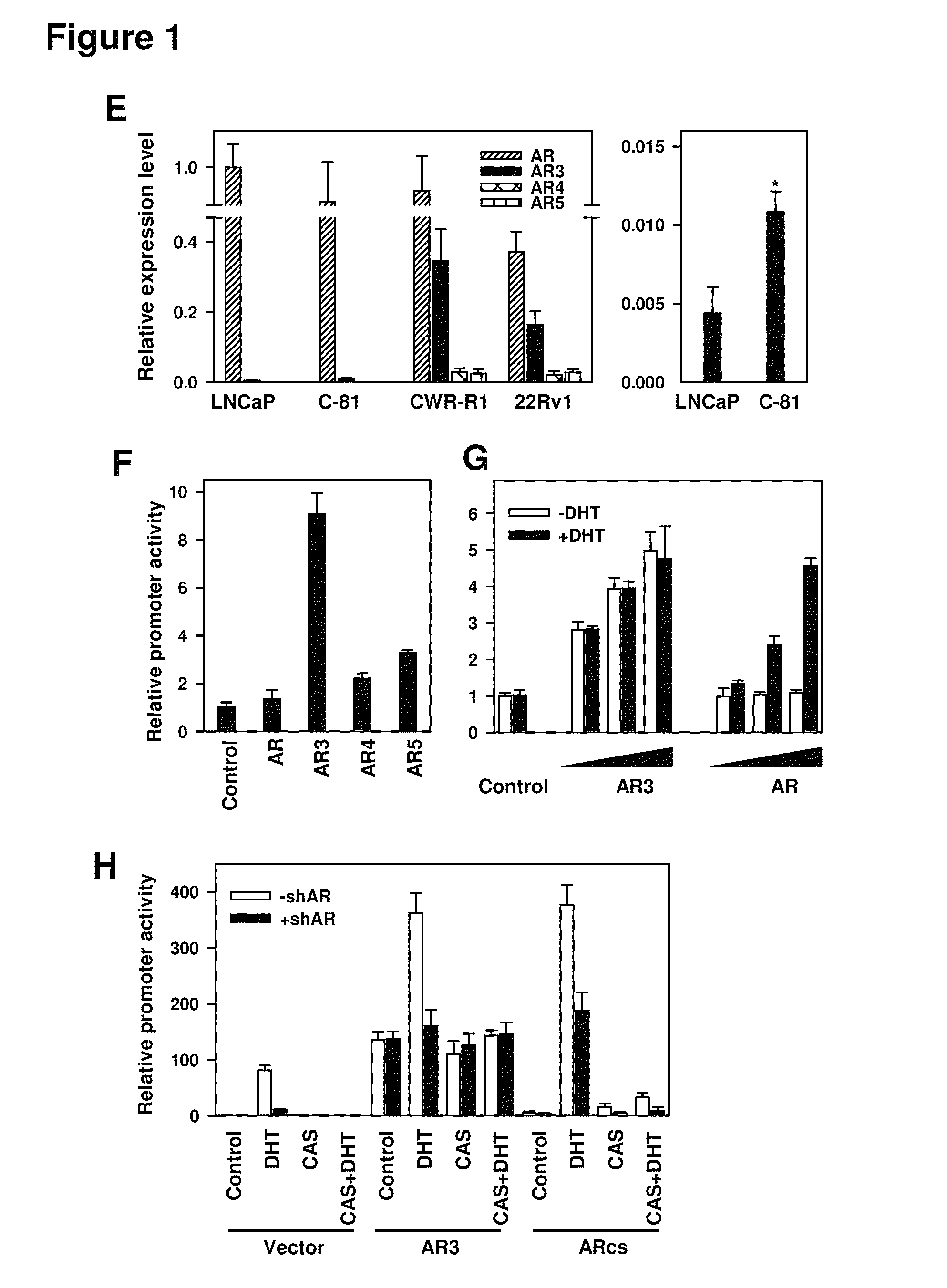
Novel human androgen receptor alternative splice variants as biomarkers and therapeutic targets
The present invention relates to novel androgen receptor splice variants (AR3, AR4, AR4b, AR5 and AR8) and variants and fragments thereof which have a role in the progression of androgen independent prostate cancer. The invention further relates to compositions and methods which can be used to identify and treat prostate cancer based on these novel androgen receptor splice variants, as well as methods for screening agents which modulate the activity and / or expression of the androgen receptor splice variants. Vectors, host cells and recombinant methods for producing the same and transgenic animals are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Human androgen receptor alternative splice variants as biomarkers and therapeutic targets
ActiveUS8133724B2Increase or decrease stabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAndrogen Receptor GeneAndrogen independent prostate cancer
The present invention relates to novel androgen receptor splice variants (AR3, AR4, AR4b, AR5 and AR8) and variants and fragments thereof which have a role in the progression of androgen independent prostate cancer. The invention further relates to compositions and methods which can be used to identify and treat prostate cancer based on these novel androgen receptor splice variants, as well as methods for screening agents which modulate the activity and / or expression of the androgen receptor splice variants. Vectors, host cells and recombinant methods for producing the same and transgenic animals are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
HRPCa9 and HRPCa10 nucleic acids and polypeptides
InactiveUS6872811B1Prevent and ameliorate symptomTumor rejection antigen precursorsBacteriaHybridization probeAndrogen independent prostate cancer
The invention concerns cDNA molecules encoding HRPCa 9 and HRPCa 10 both of which are constitutively expressed in the androgen-independent cell line, LN3 LNAcP and induced by testosterone in the androgen-dependent cell line, LNAcP.The invention provides isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding a polypeptide of the invention or biologically active portion thereof. The present invention also provides nucleic acid molecules which are suitable as primers or hybridization probes for the detection of nucleic acids encoding a polypeptide of the invention. The invention also provides screening assays which can be used to identify compounds useful for the treatment of prostate cancer (e.g., androgen-independent prostate cancer).
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
Human androgen receptor alternative splice variants
ActiveUS8841422B2Increase or decrease stabilityBacteriaReceptors for hormonesAndrogenAndrogen independent prostate cancer
The present invention relates to novel androgen receptor splice variants (AR3, AR4, AR4b, AR5 and AR8) and variants and fragments thereof which have a role in the progression of androgen independent prostate cancer. The invention further relates to compositions and methods which can be used to identify and treat prostate cancer based on these novel androgen receptor splice variants, as well as methods for screening agents which modulate the activity and / or expression of the androgen receptor splice variants. Vectors, host cells and recombinant methods for producing the same and transgenic animals are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Prophylactic / therapeutic agent for cancer
InactiveUS20110312898A1Organic active ingredientsTumor rejection antigen precursorsAndrogen independent prostate cancerOncology
A prophylactic / therapeutic agent for androgen-independent cancer is provided. A prophylactic / therapeutic agent for androgen-independent cancer includes a metastin derivative, and is particularly useful as a prophylactic / therapeutic agent for androgen-independent cancer, in particular, androgen-independent prostate cancer.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
TRPM-2 Antisense Therapy
InactiveUS20080064651A1Reduce expressionIncreased chemosensitivityApolipeptidesSugar derivativesDiseaseCancer type
It has now been determined that antisense therapy which reduces the expression of TRPM-2 provides therapeutic benefits in the treatment of cancer. In particular, such antisense therapy can be applied in treatment of prostate cancer and renal cell cancer. Addition of antisense TRPM-2 ODN to prostatic tumor cells in vivo is effective for delaying the onset of androgen independence. Thus, prostate cancer can be treated in an individual suffering from prostate cancer by initiating androgen-withdrawal to induce apoptotic cell death of prostatic tumor cells in the individual, and administering to the individual a composition effective to inhibit expression of TRPM-2 by the tumor cells, thereby delaying the progression of prostatic tumor cells to an androgen-independent state in an individual Combined use of antisense TRPM-2 and taxanes synergistically enhances cytotoxic chemosensitivity of androgen-independent prostate cancer. In addition, it has also been found that antisense TRPM-2 has beneficial effect for other cancer types. Specifically, antisense TRPM-2 ODN enhances chemosensitivity in human Renal cell cancer, a normally chemoresistant disease with no active chemotherapeutic agent having an objective response rate higher than 10%. Radiation sensitivity is also enhanced when cells expressing TRPM-2 are treated with antisense TRPM-2 ODN. Thus, the antisense TRPM-2 ODNs can be used to enhance hormone sensitivity, chemosensitivity and radiation sensitivity of a variety of cancer types in which expression of TRPM-2 has been observed.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
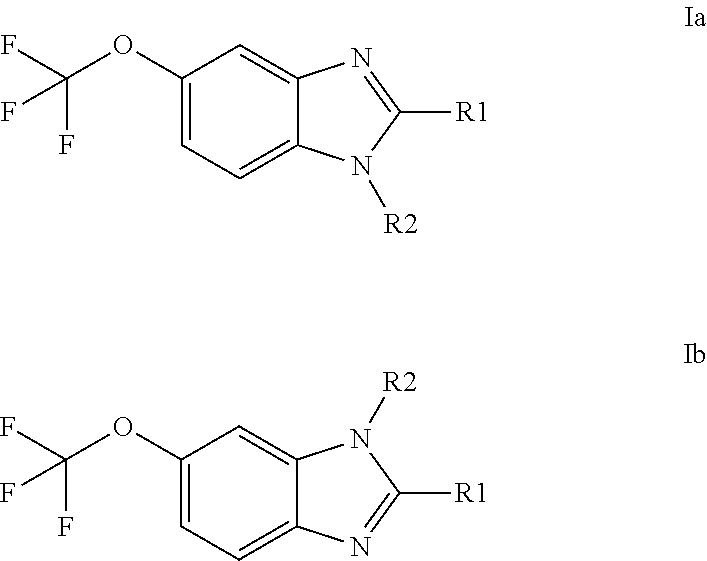
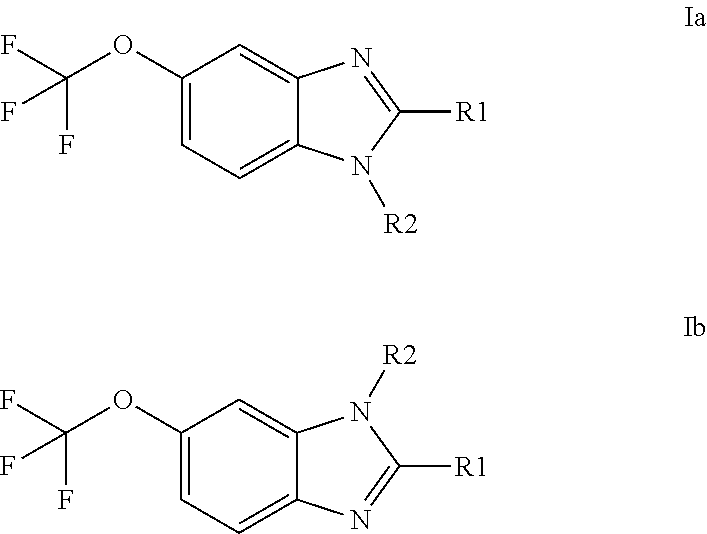
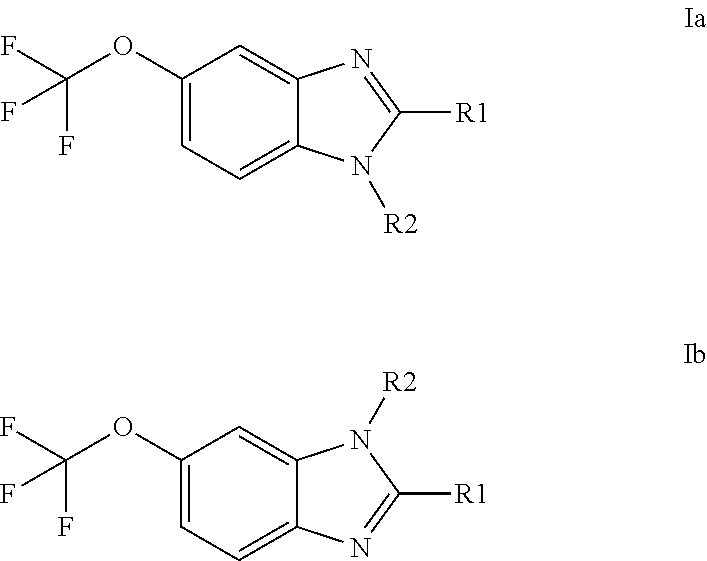
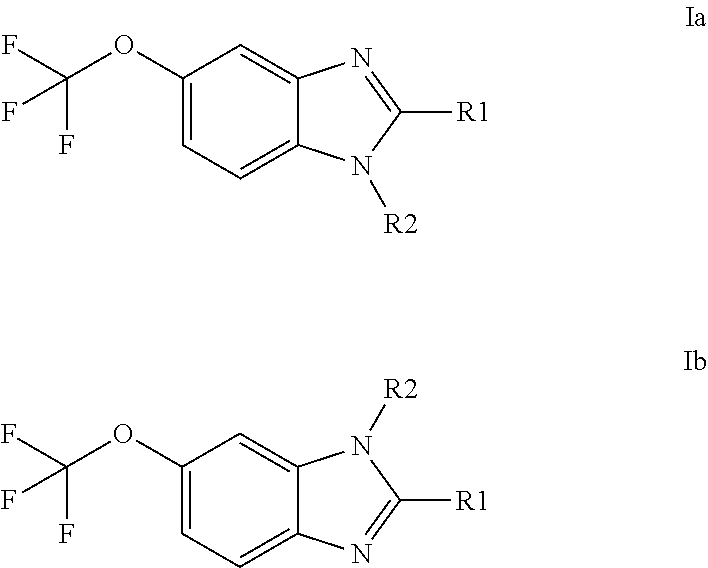
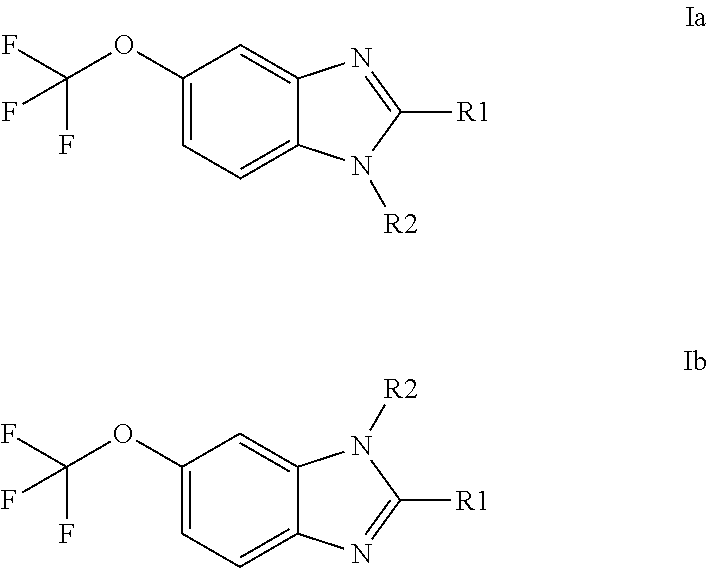
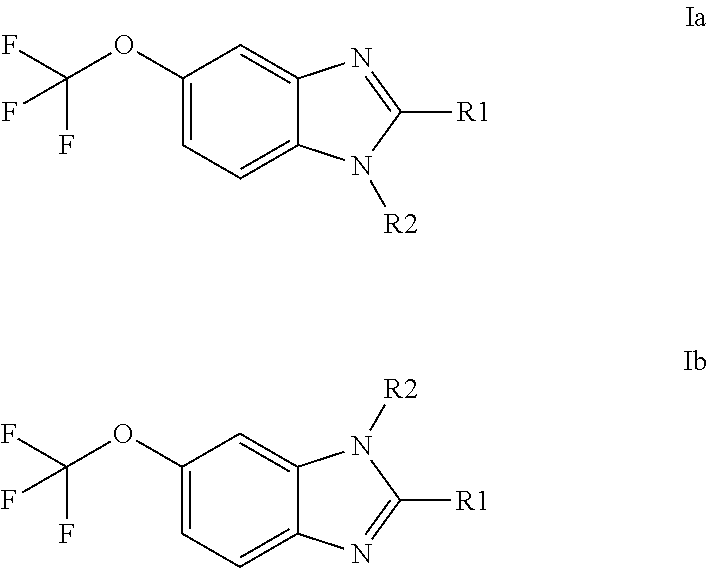
Anti-cancer agents based on 6-trifluoromethoxybenzimidazole derivatives and method of making
The present disclosure relates to novel compounds having the structural Formulas (1a,1b), stereoisomers, tautomers, racemics, prodrugs, metabolites thereof, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt and / or solvate thereof as chemotherapy agents for treating of cancer, particularly androgen-independent prostate cancer. The disclosure also relates to methods for preparing said compounds, and to pharmaceutical compositions comprising said compounds.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
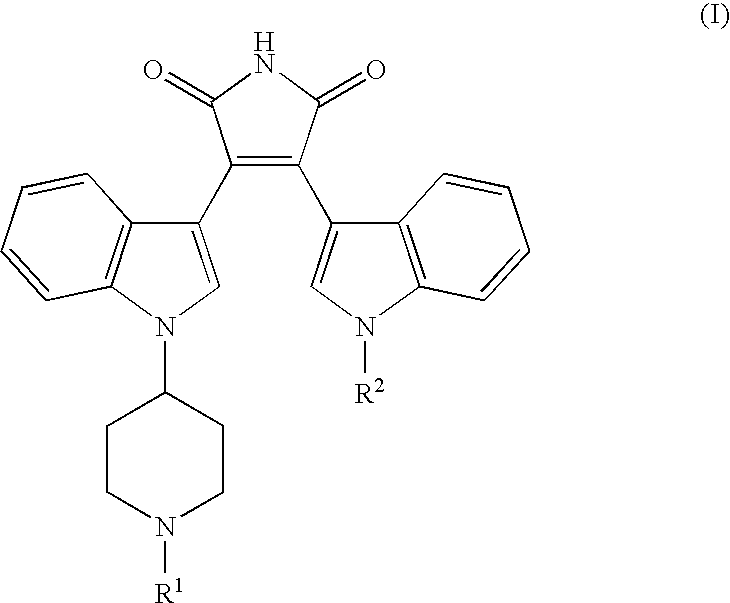
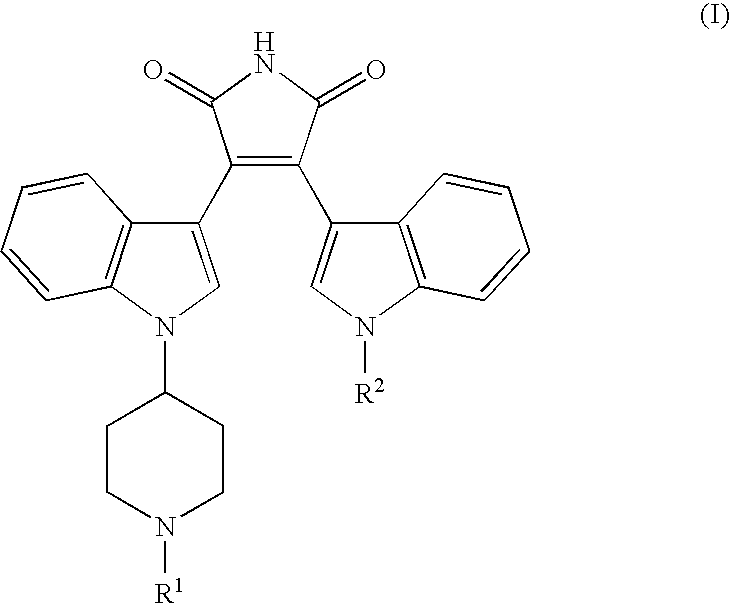
Bisindolyl maleimides useful for treating prostate cancer and akt-mediated diseases
The present invention provides a method of treating prostate cancer comprising administering to a patient in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the formula (I) wherein R1 and R2 are each independently hydrogen or C1-C4 alkyl; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. In a second embodiment, the invention provides a method of treating androgen-independent prostatic adenocarcinoma comprising administering to a patient in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. In a third embodiment, the invention provides a method of treating an AKT-mediated disease selected from the group consisting of glioblastoma, colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, and renal cell cancer, comprising administering to a patient in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Method of treating androgen independent prostate cancer
The present invention is directed to a method treating prostate cancer. The method comprises administering to a patient in need thereof at least one compound selected from N-methyl-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone; N-1-(β-D-O-triacetyl-xylopranosyl)-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone; and N-1-(β-D-O-triacetyl-xylopranosyl)-N′-methyl-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone. Preferably the compound is in an amount sufficient to inhibit growth, invasion, and / or metastasis of prostate cancer cells.
Owner:NATROGEN THERAPEUTICS INT
Murine Pten null prostate cancer model
InactiveUS20060064768A1Lower Level RequirementsHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorProstate cellsAndrogen independent prostate cancer
The invention provides a transgenic mouse and cell lines with a homozygous disruption of a chromosomal PTEN gene in prostate cells. The mouse progresses from hyperplasia to metastatic cancer and can be used to identify prostate cancer therapeutics and genes that are differentially regulated during androgen dependent and androgen independent prostate cancer progression.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of treating androgen independent prostate cancer
The present invention is directed to a method treating prostate cancer. The method comprises administering to a patient in need thereof at least one compound selected from N-methyl-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone; N-1-(β-D-O-triacetyl-xylopranosyl)-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone; and N-1-(β-D-O-triacetyl-xylopranosyl)-N′-methyl-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone. Preferably the compound is in an amount sufficient to inhibit growth, invasion, and / or metastasis of prostate cancer cells.
Owner:NATROGEN THERAPEUTICS INT
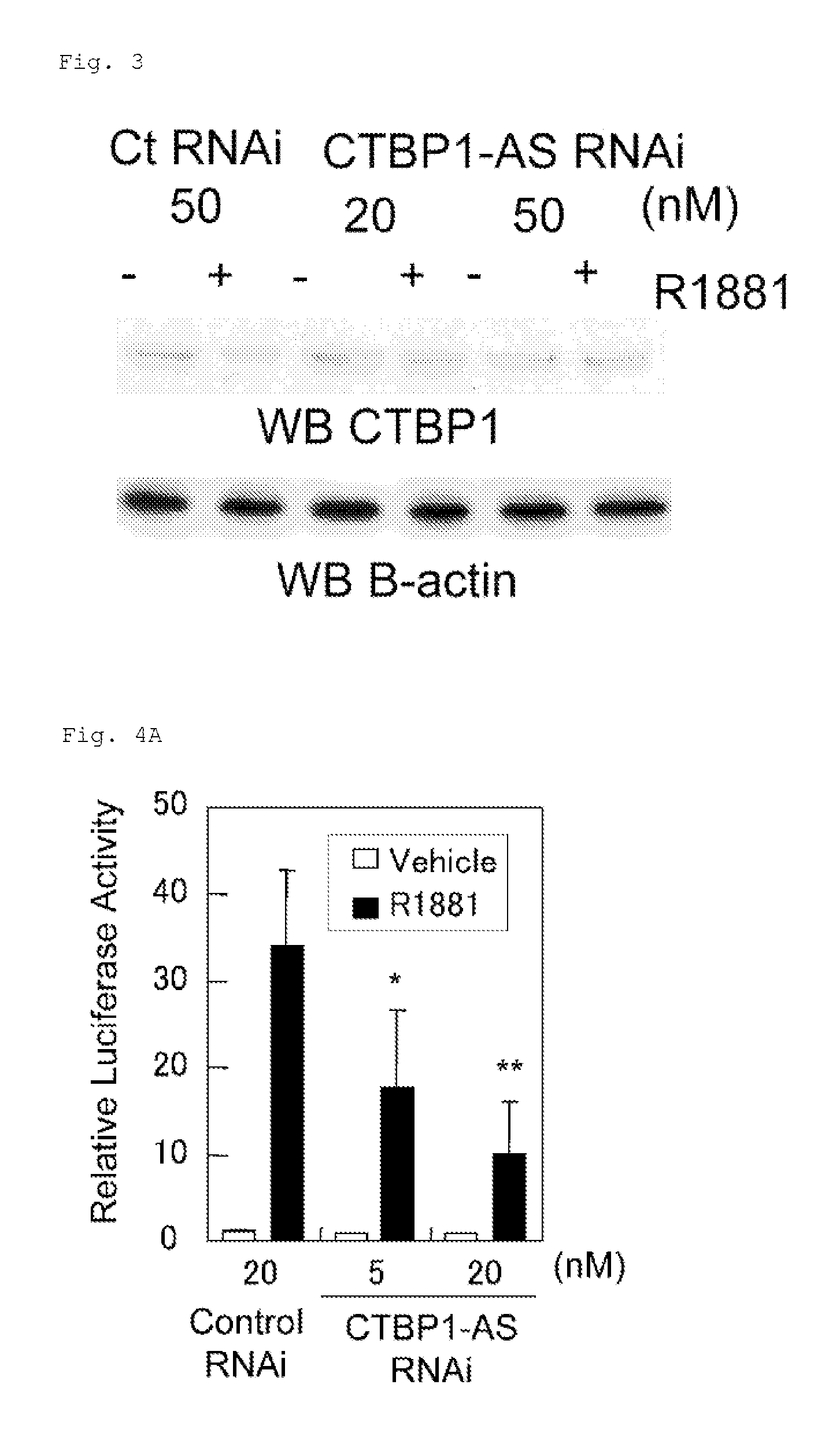
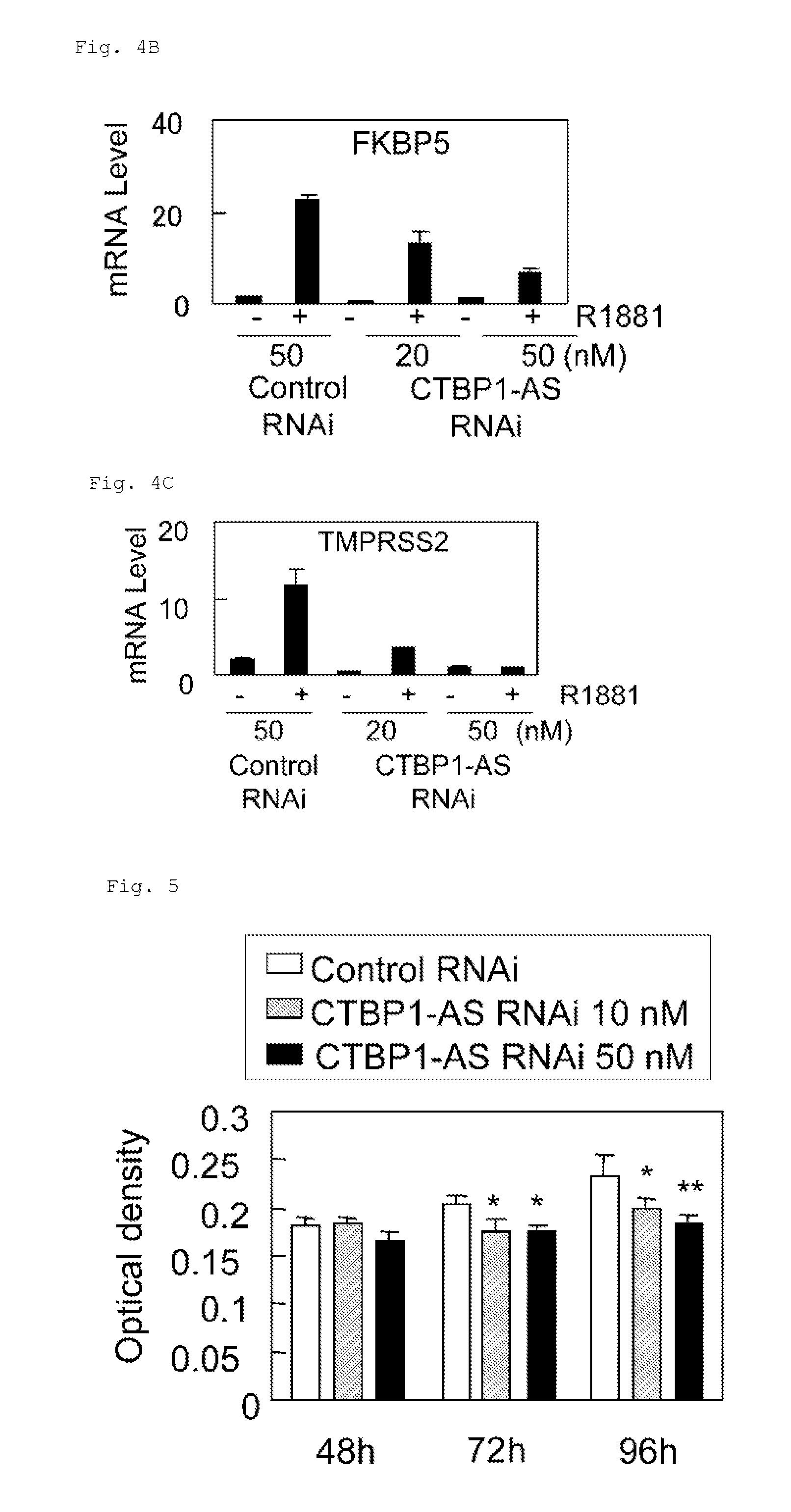
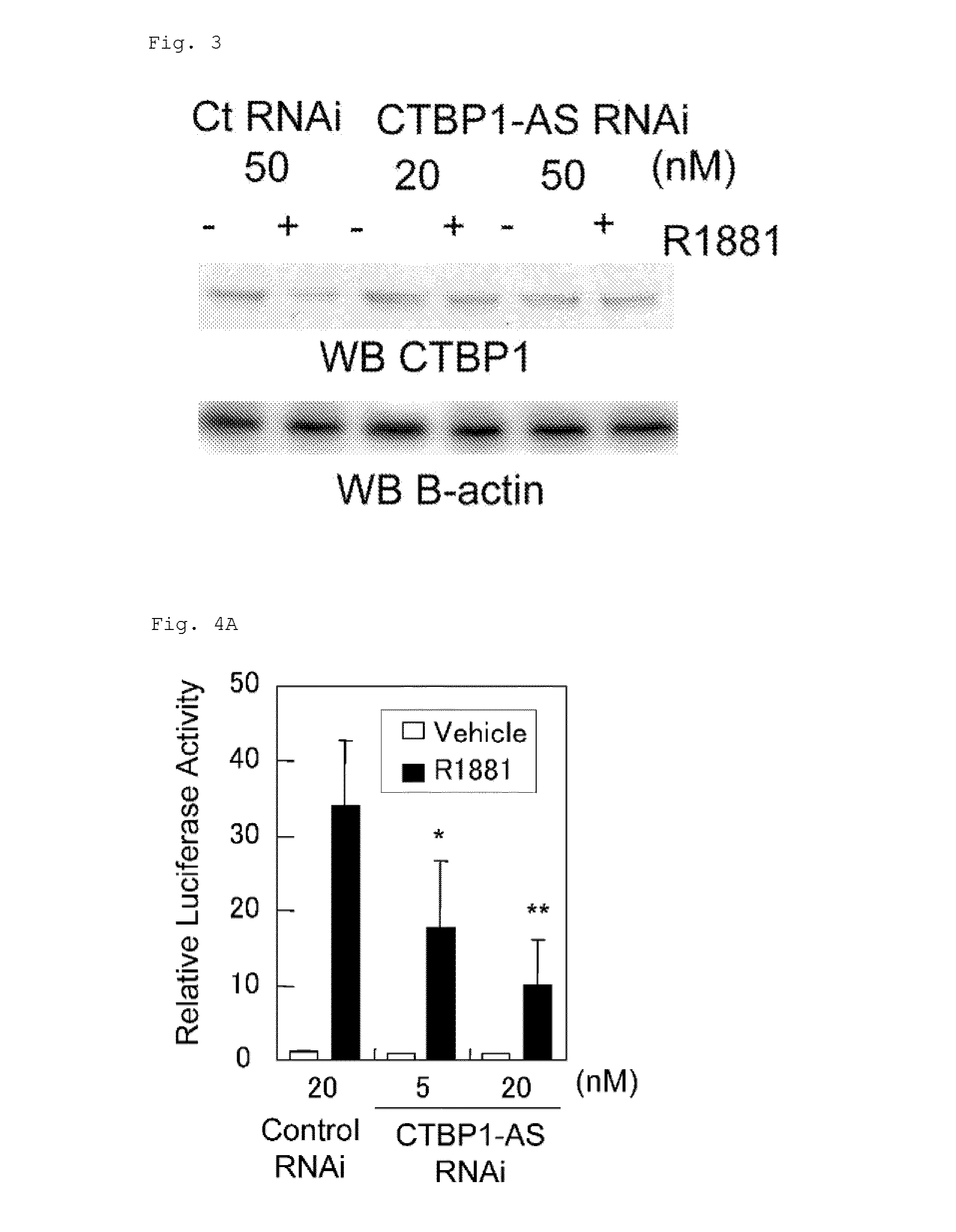
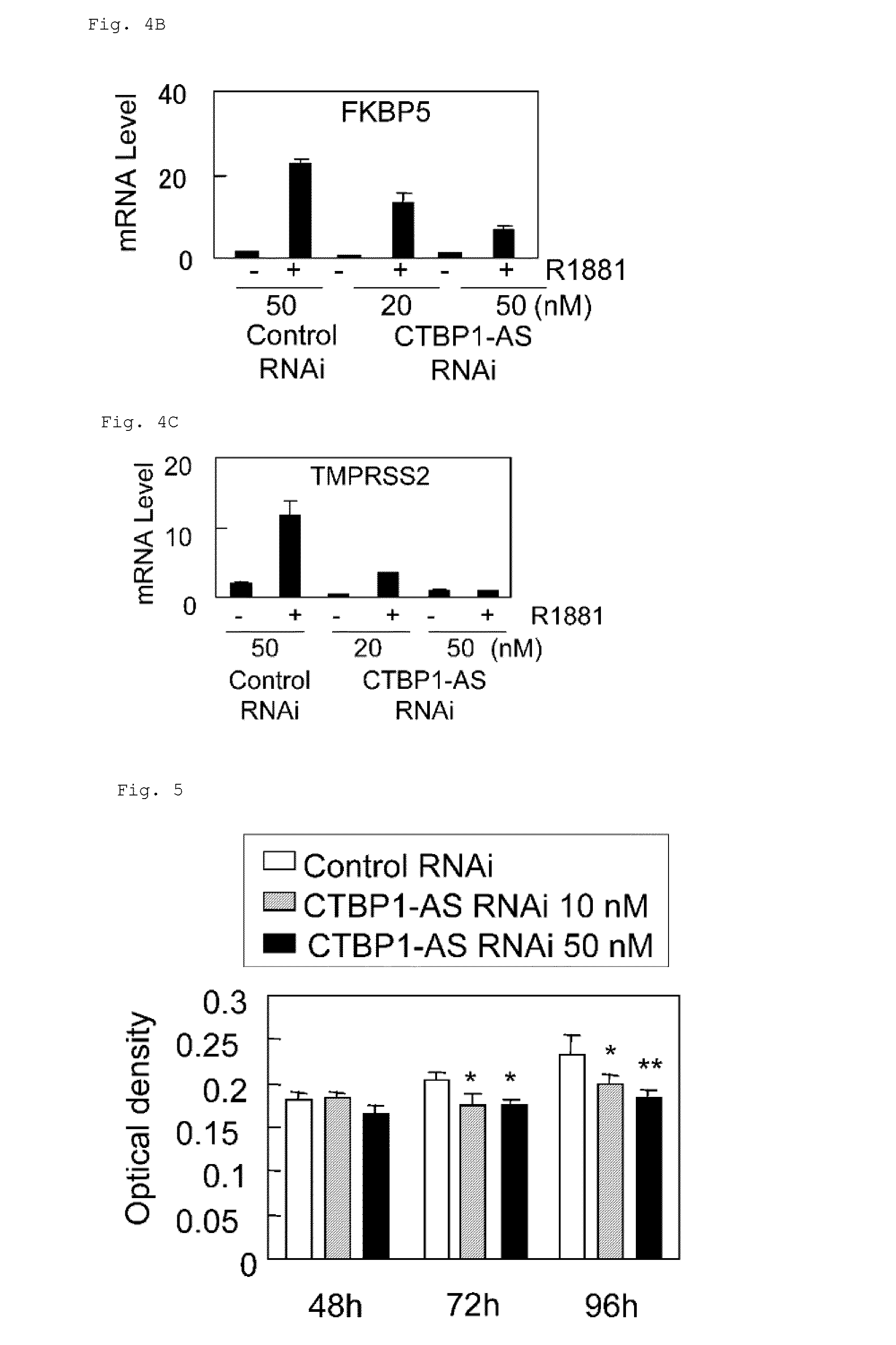
Cell growth inhibitor and screening method thereof
InactiveUS20130184327A1Growth inhibitionSuppresses transcriptional activity of signalOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesBinding siteScreening method
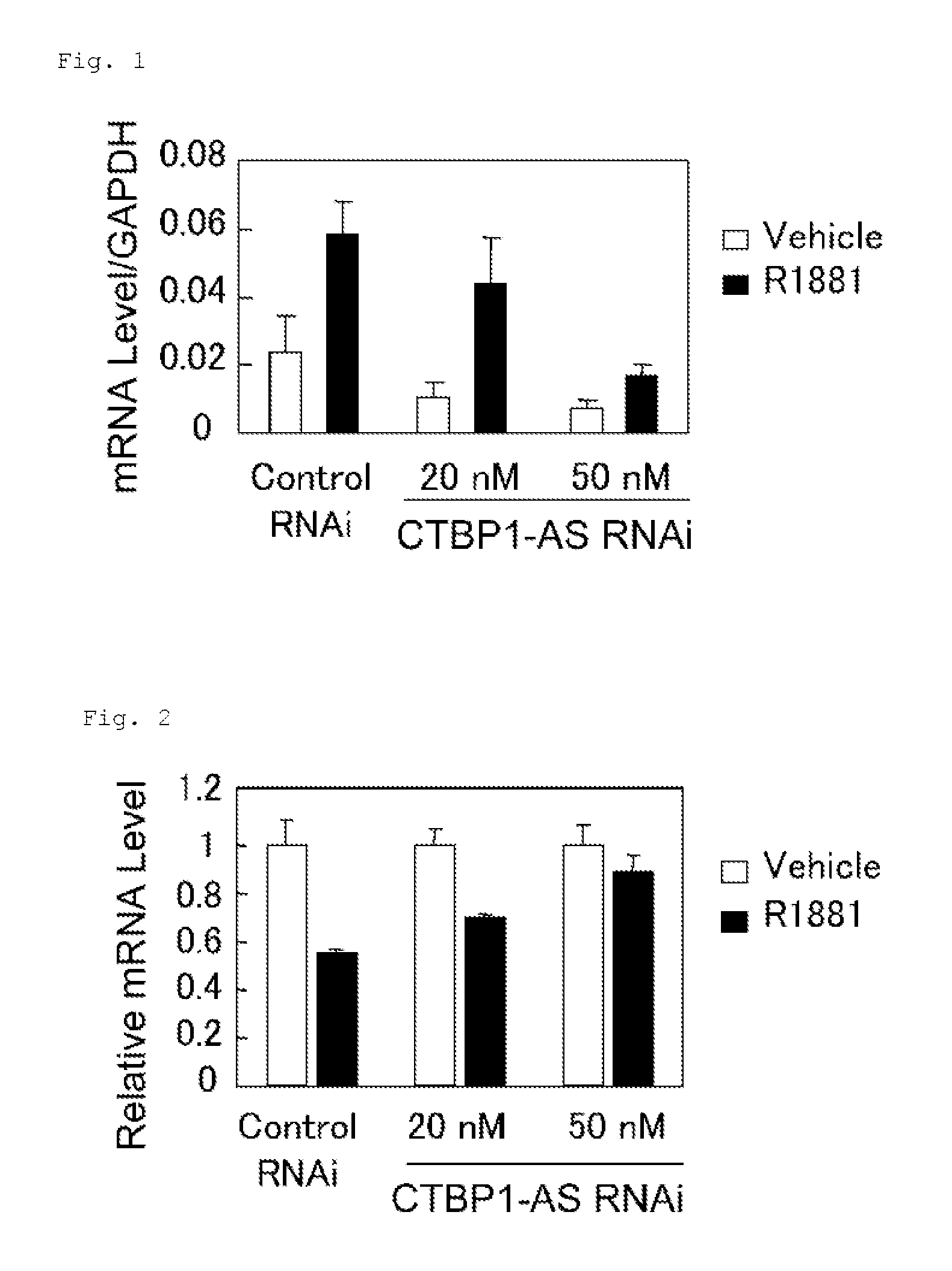
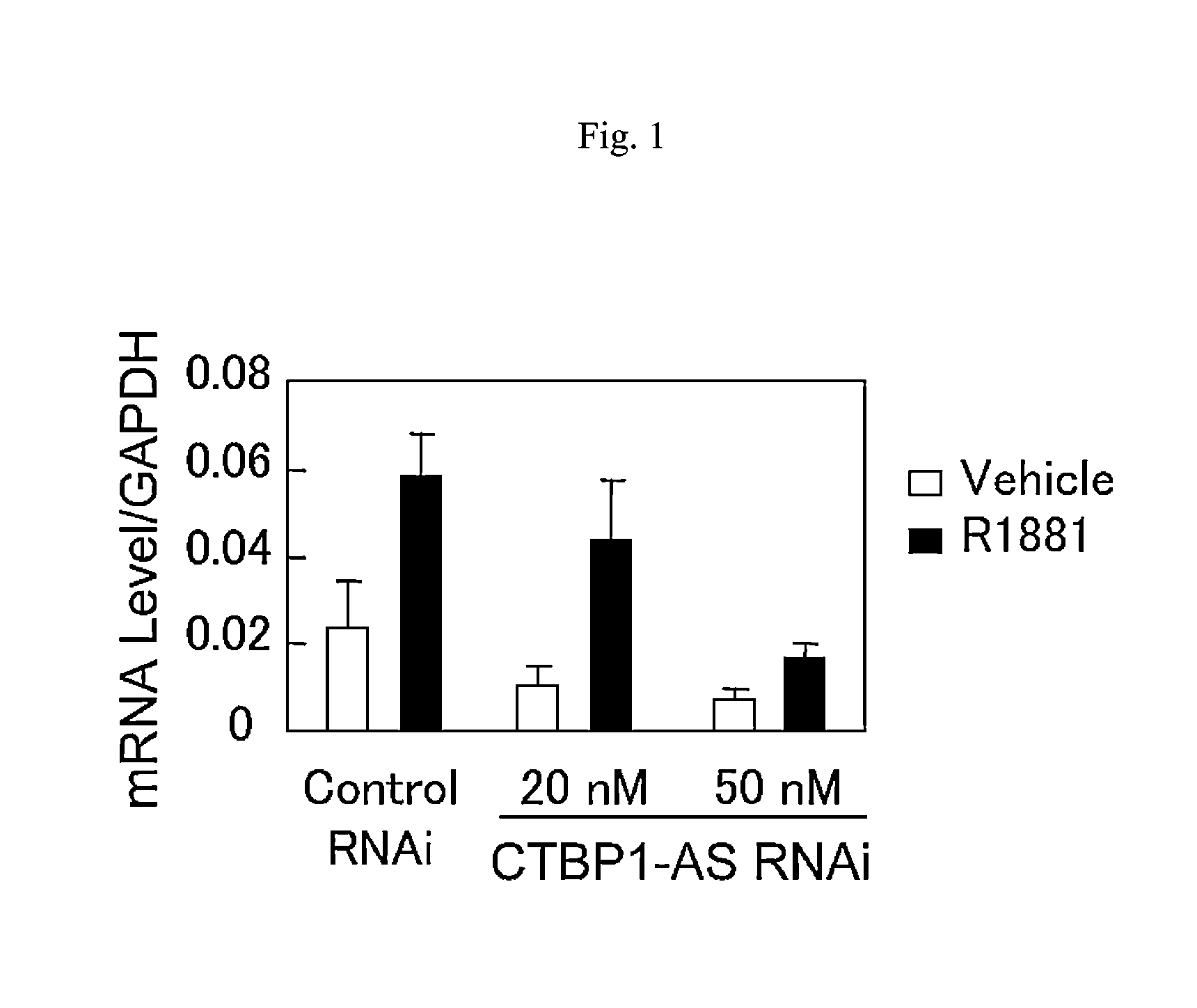
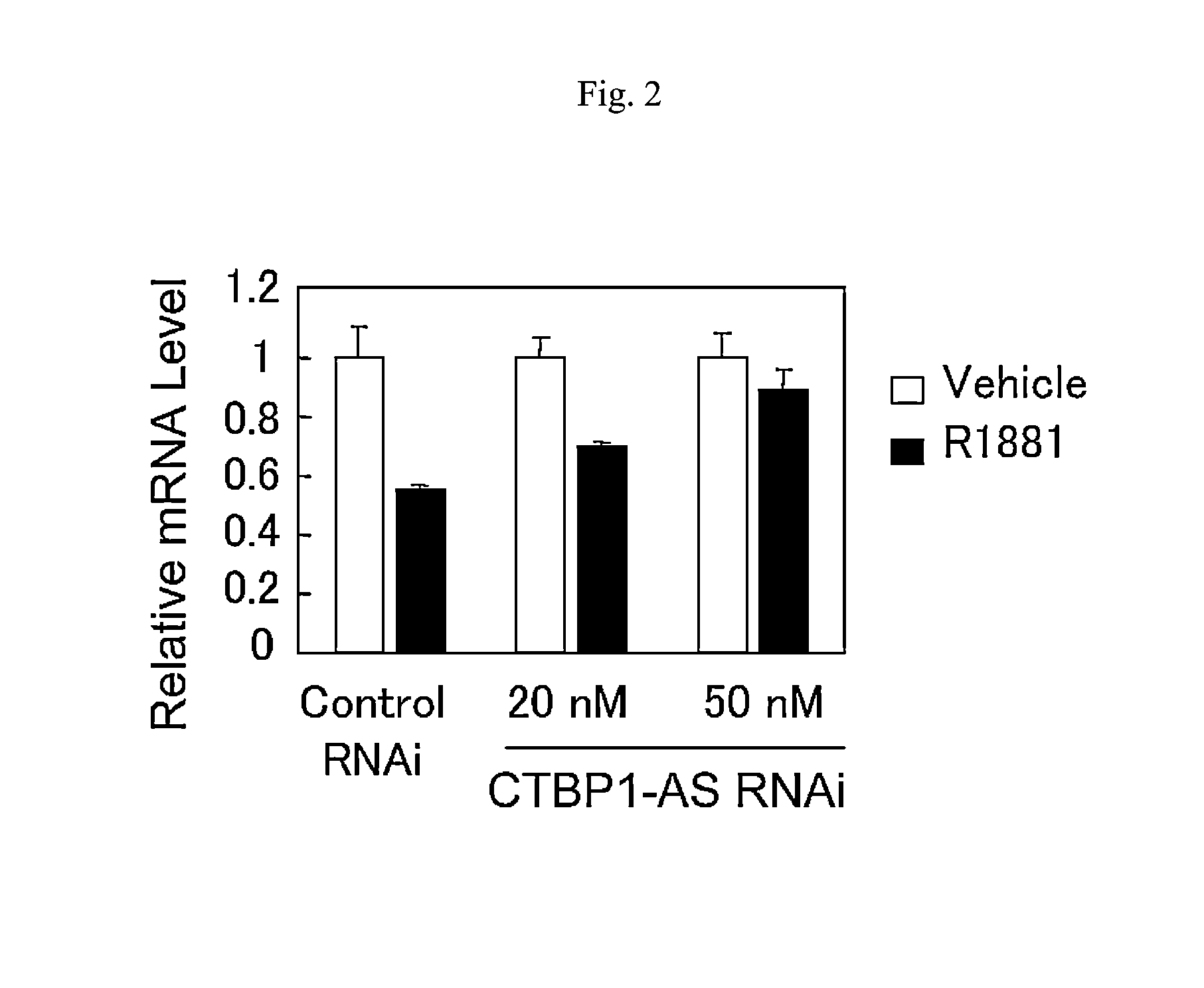
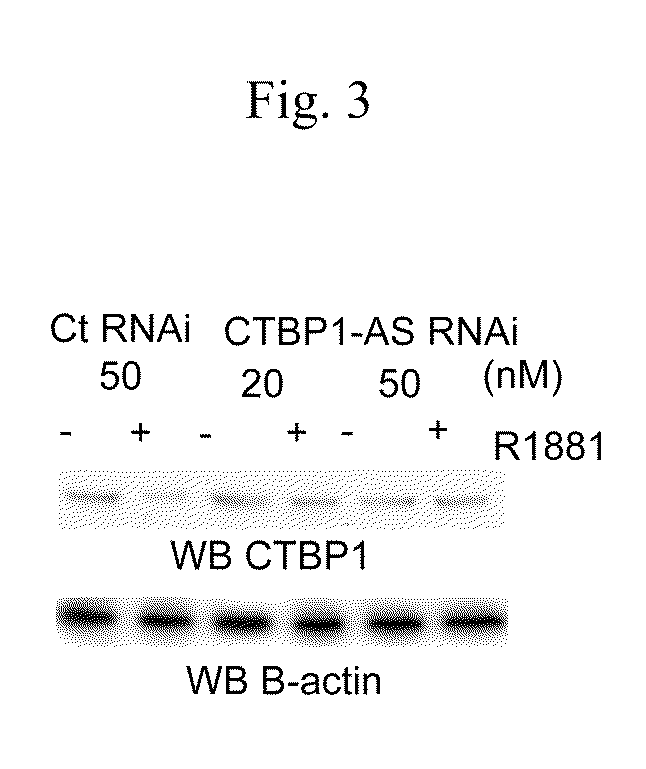
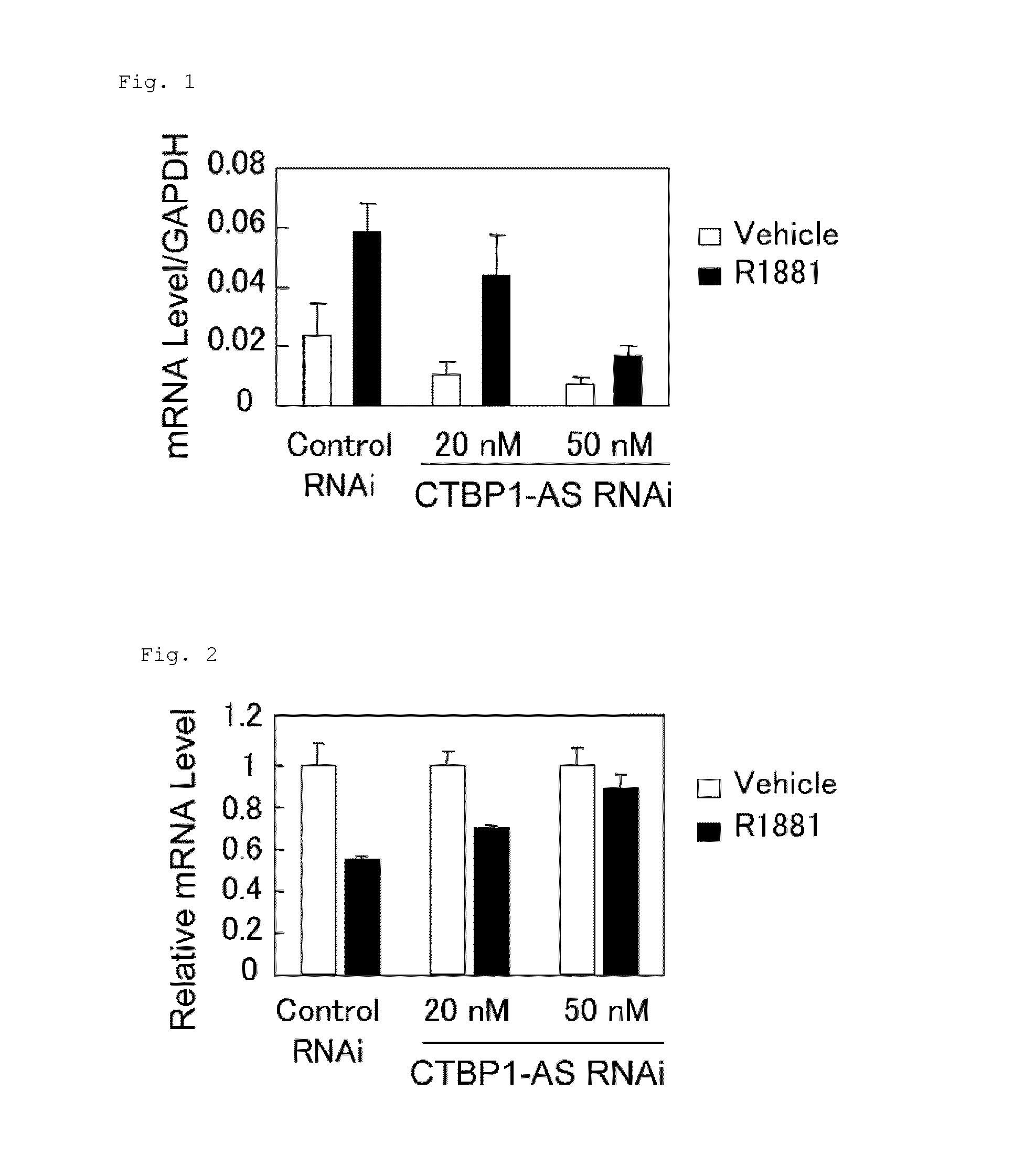
An object is to provide a cell growth inhibitor also effective for androgen-independent prostate cancer. The present invention provides a cell growth inhibitor having, as an active ingredient, an expression inhibitor or function inhibitor of an antisense RNA (CTBP1-AS) expressed in the vicinity of an androgen receptor (AR) binding site of a C-terminal binding protein (CTBP1) gene.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
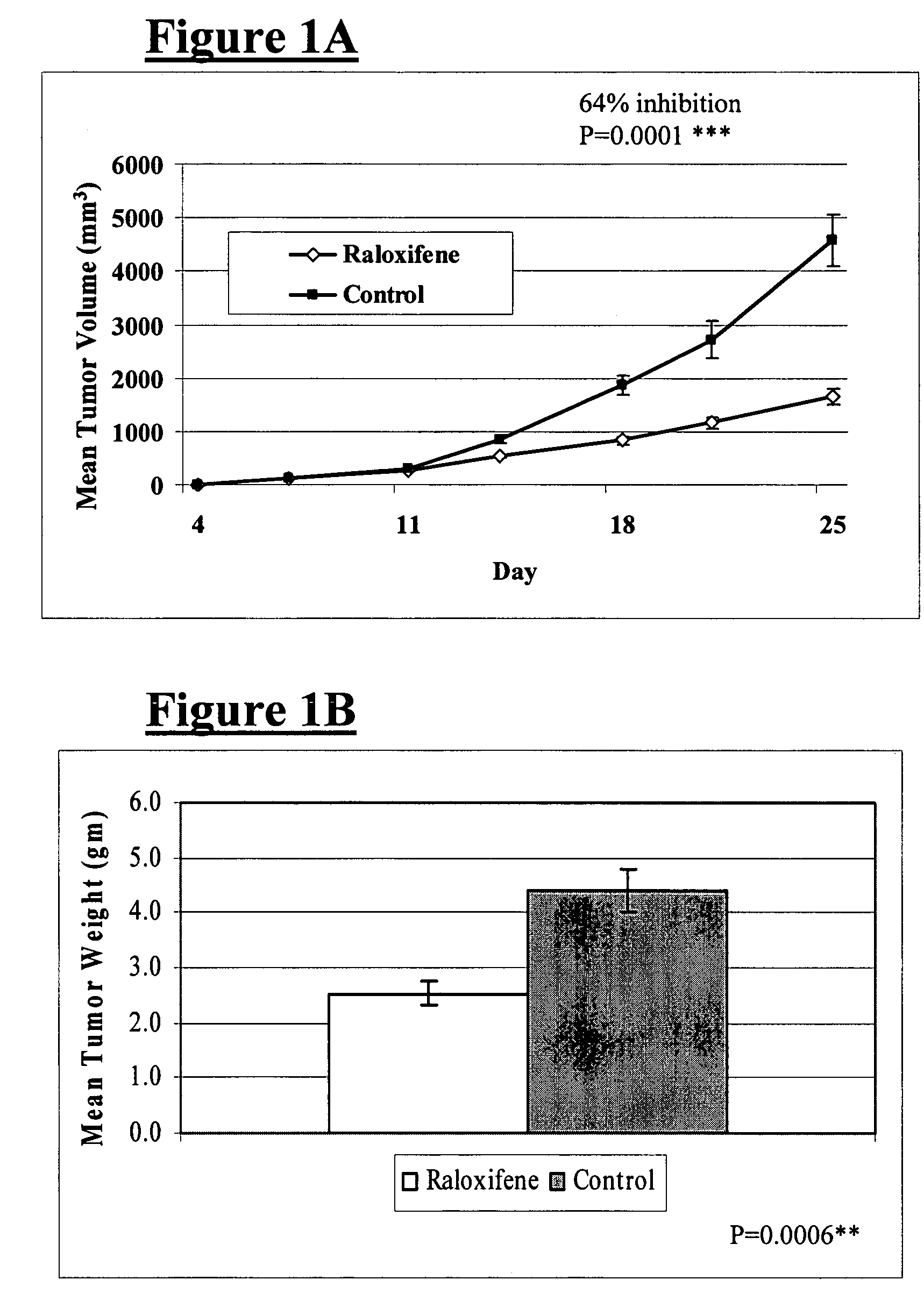
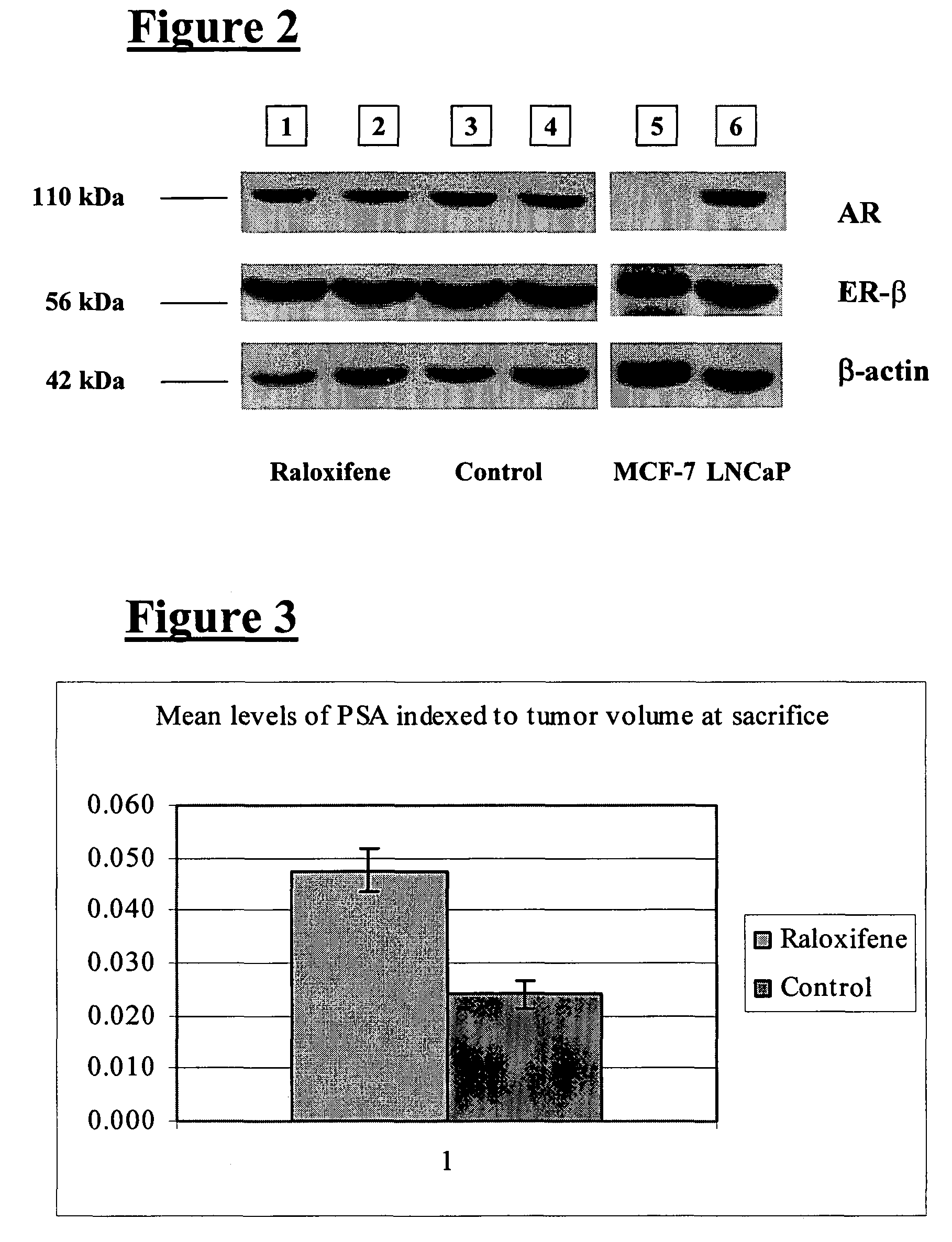
Use of benzothiopenes to treat and prevent prostate cancer
Disclosed herein is a method for treating and preventing prostate cancer, and particularly androgen-independent prostate cancer, the method including administering to a mammal a benzothiopene having the formulaor pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs thereof, wherein R and R1 are each independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, —COR2, —COR3, and R4; R2 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C14 alkyl, C1-C3 chloroalkyl, C1-C3 fluoroalkyl, C5-C7 cycloalkyl, C1-C4 alkoxy, and phenyl; R3 is phenyl with at least one substitution selected from the group consisting of C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 alkoxy, hydroxy, nitro, chloro, fluoro, trichloromethyl, and trifluoromethyl; R4 is selected from the group consisting of C1-C4 alkyl, C5-C7 cycloalkyl, and benzyl; and R5 is selected from the group consisting of oxygen and —C═O. The method may further include the administration of an estrogen lowering drug to enhance efficacy of the compound of the present invention.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
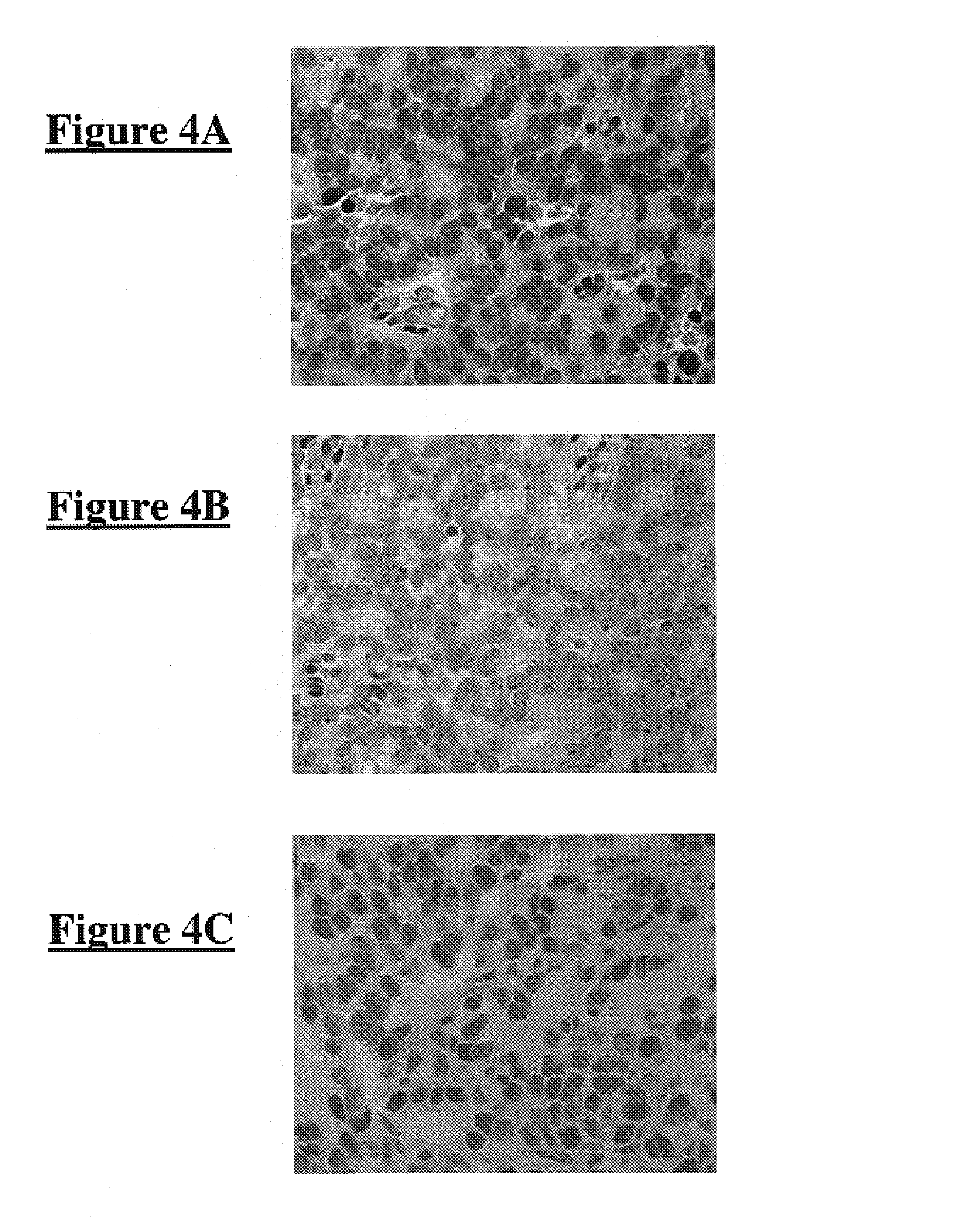
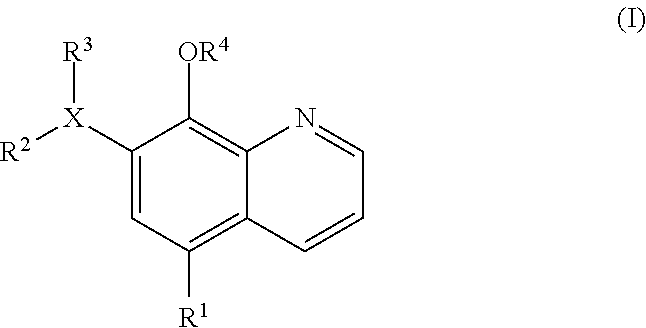
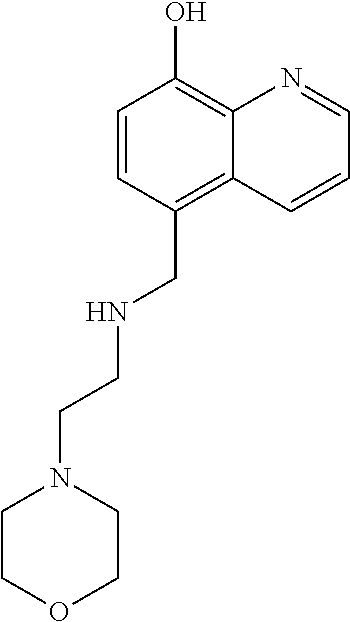
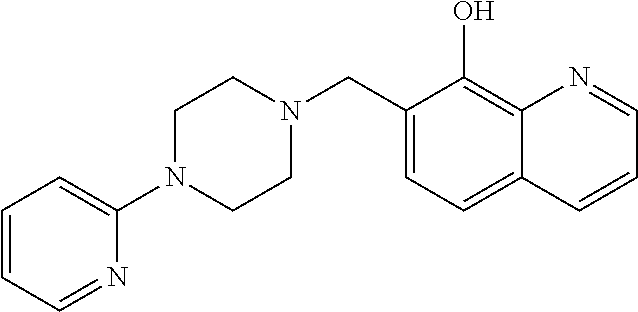
Inhibitors of JMJD2C as Anticancer Agents
The present disclosure provides compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and related methods for the treatment of cancer, e.g., castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Specifically, the present disclosure provides a series of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives which show cytotoxic effects on androgen-independent prostate cancer cells.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Cell growth inhibitor and screening method thereof
InactiveUS8853182B2Growth inhibitionInhibition of transcriptional activityOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAndrogenScreening method
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
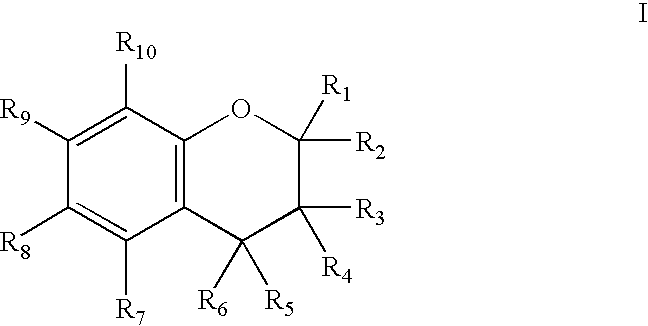
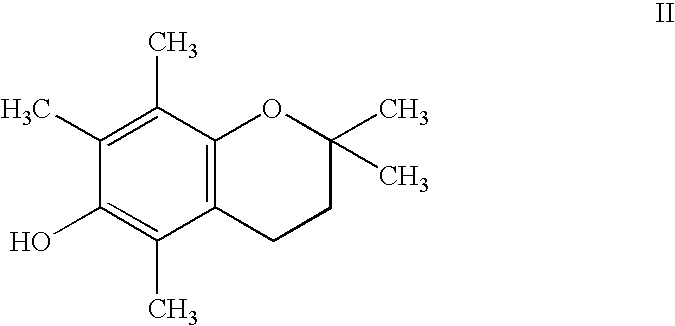
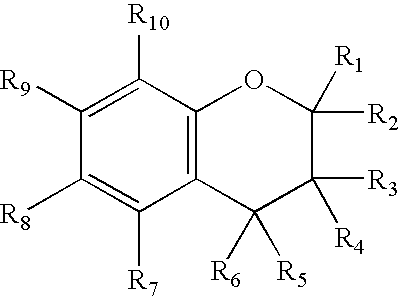
Chroman-Derived Compounds For The Treatment Of Cancer
The present invention provides methods for inhibiting the growth of androgen-independent prostate cancer tumor cells in a human comprising administering to the human. The invention further provides pharmaceutical and nutraceutical compositions containing chroman-derived compounds useful in the alleviation of cancer.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
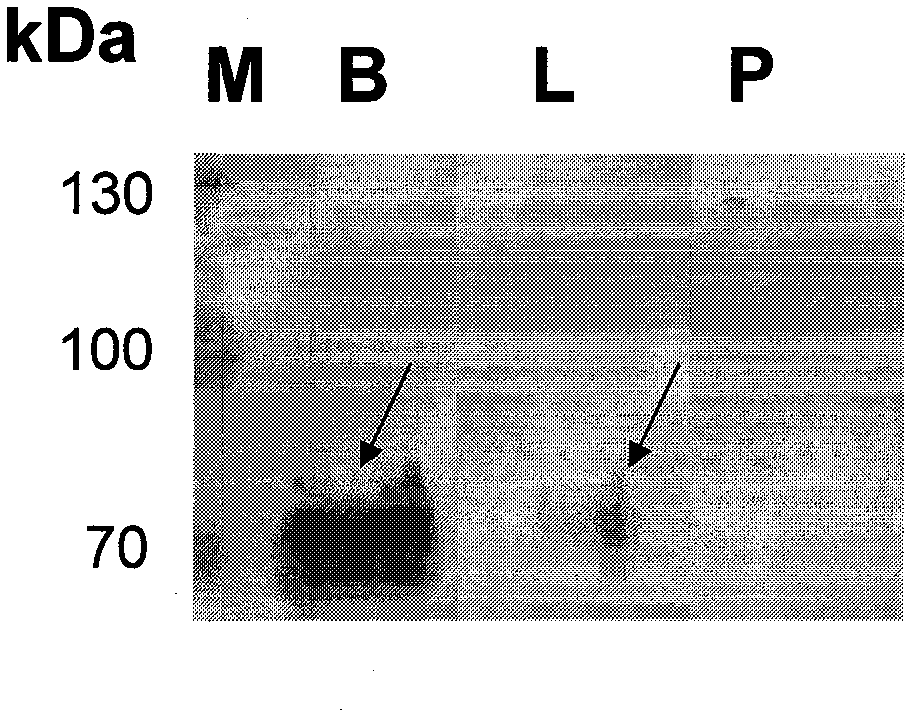
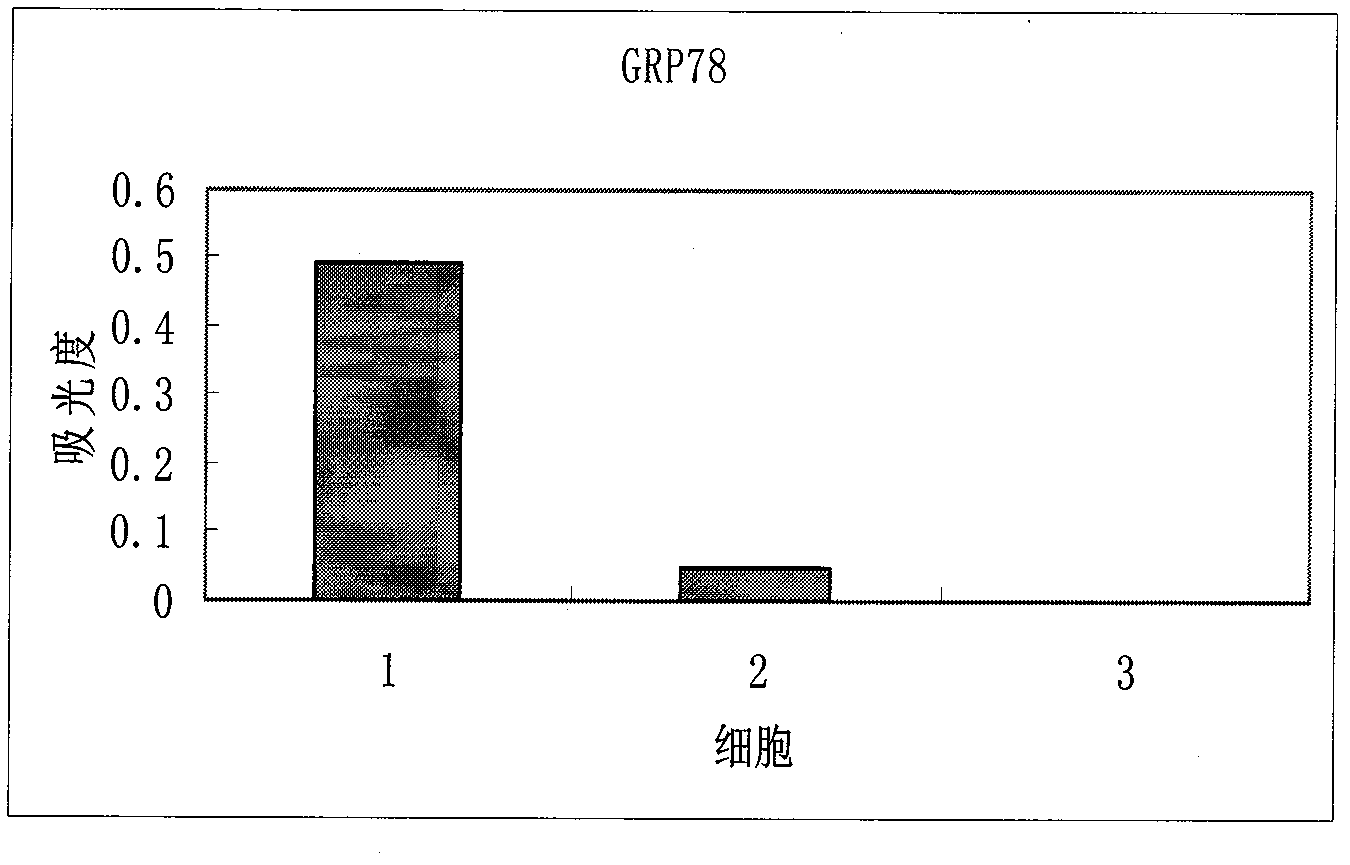
ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) kit for detecting prostate cancer
The compositions of three kinds of cell proteins of a benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH-1) cell, an androgen dependence prostate cancer cell LNCaP and an androgen non-dependence prostate cancer cell PC-3 are compared by adopting a dimensional electrophoresis method. Through mass spectrum analysis and database retrieval, two difference proteins of GRP78 and Annexin A2 are determined. Through Western Blotting detection on the expression of the two difference proteins in the three kinds of cells, the GRP78 and the Annexin A2 are finally determined to be used as sign proteins for detecting the prostate cancer. The invention also discloses a preparation and a use methods of the ELISA kit for detecting the prostate cancer.
Owner:NAT RES INST FOR FAMILY PLANNING
Method for the treatment of prostate cancer
A method for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer comprises administering to a patient suffering from advanced prostate cancer an androgen suppressing amount of a luteinizing hormone releasing hormone agonist analog and an amount of calcitriol sufficient to enhance the effectiveness of the luteinizing hormone releasing hormone agonist analog against the cancer relative to treatment with the luteinizing hormone releasing hormone agonist analog alone. Preferably the calcitriol is in the form of a stabilized, injectable solution of calcitriol in isotonic saline containing about 1 to about 30 milligrams per milliliter of calcitriol and a sufficient quantity of nonionic surfactant to solubilize the calcitriol therein. Preferably the a luteinizing hormone releasing hormone agonist analog is a nonapeptide or decapeptide agonist, such as leuprolide, goserelin or salts thereof. The method of the present invention affords a surprisingly improved efficacy for treatment of advanced prostate cancer such as androgen-independent prostate cancer (AIPC) or hormone refractory prostate cancer (HRPC) in comparison to treatment with a luteinizing hormone releasing hormone agonist analog alone.
Owner:GENIX THERAPEUTICS
Prophylactic/therapeutic agent for cancer
InactiveCN102333520AOrganic active ingredientsTumor rejection antigen precursorsOncologyAndrogen independent prostate cancer
A prophylactic / therapeutic agent for androgen-independent cancer is provided. A prophylactic / therapeutic agent for androgen-independent cancer includes a metastin derivative, and is particularly useful as a prophylactic / therapeutic agent for androgen-independent cancer, in particular, androgen-independent prostate cancer.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Method of Inhibiting Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation
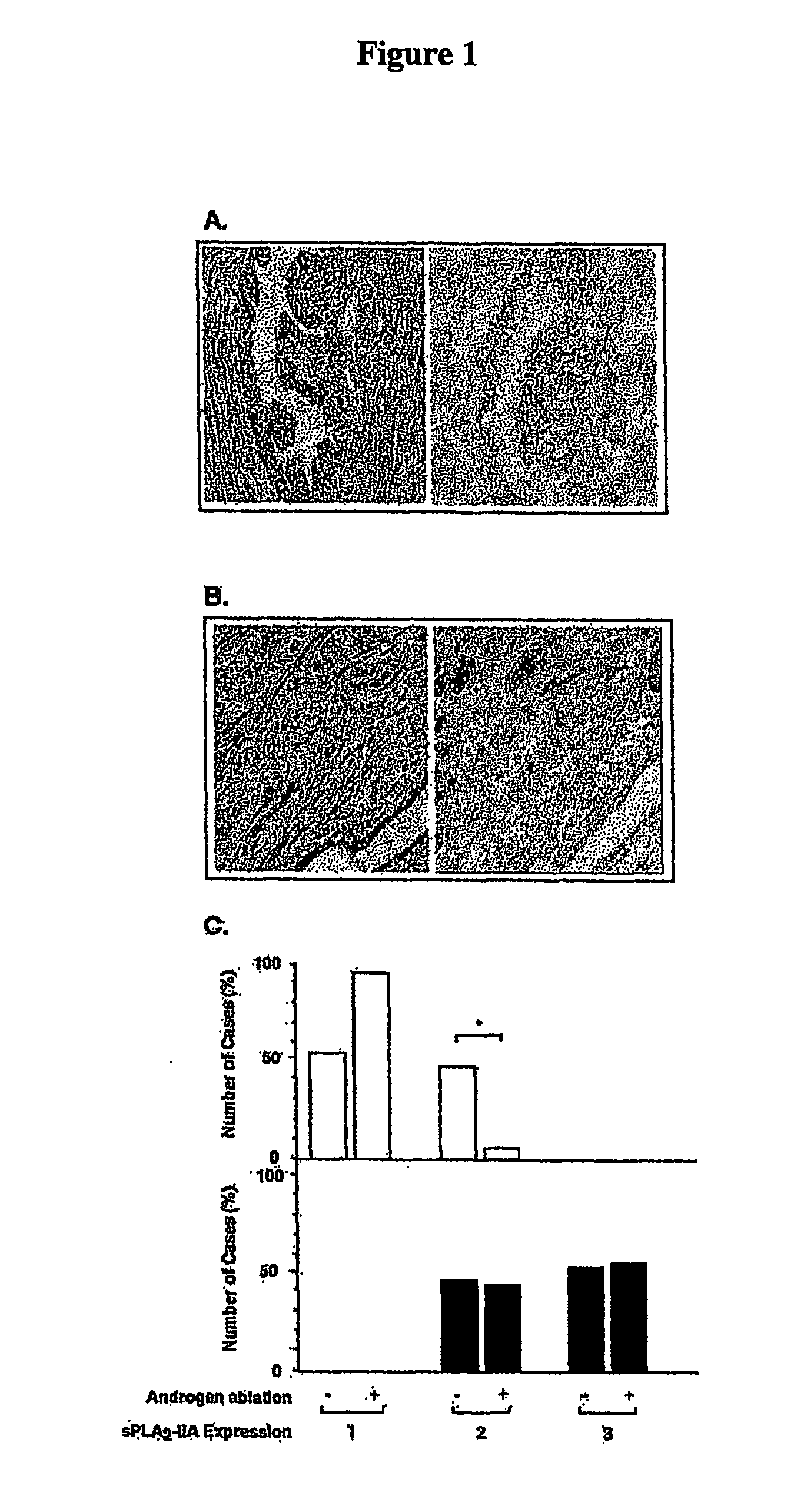
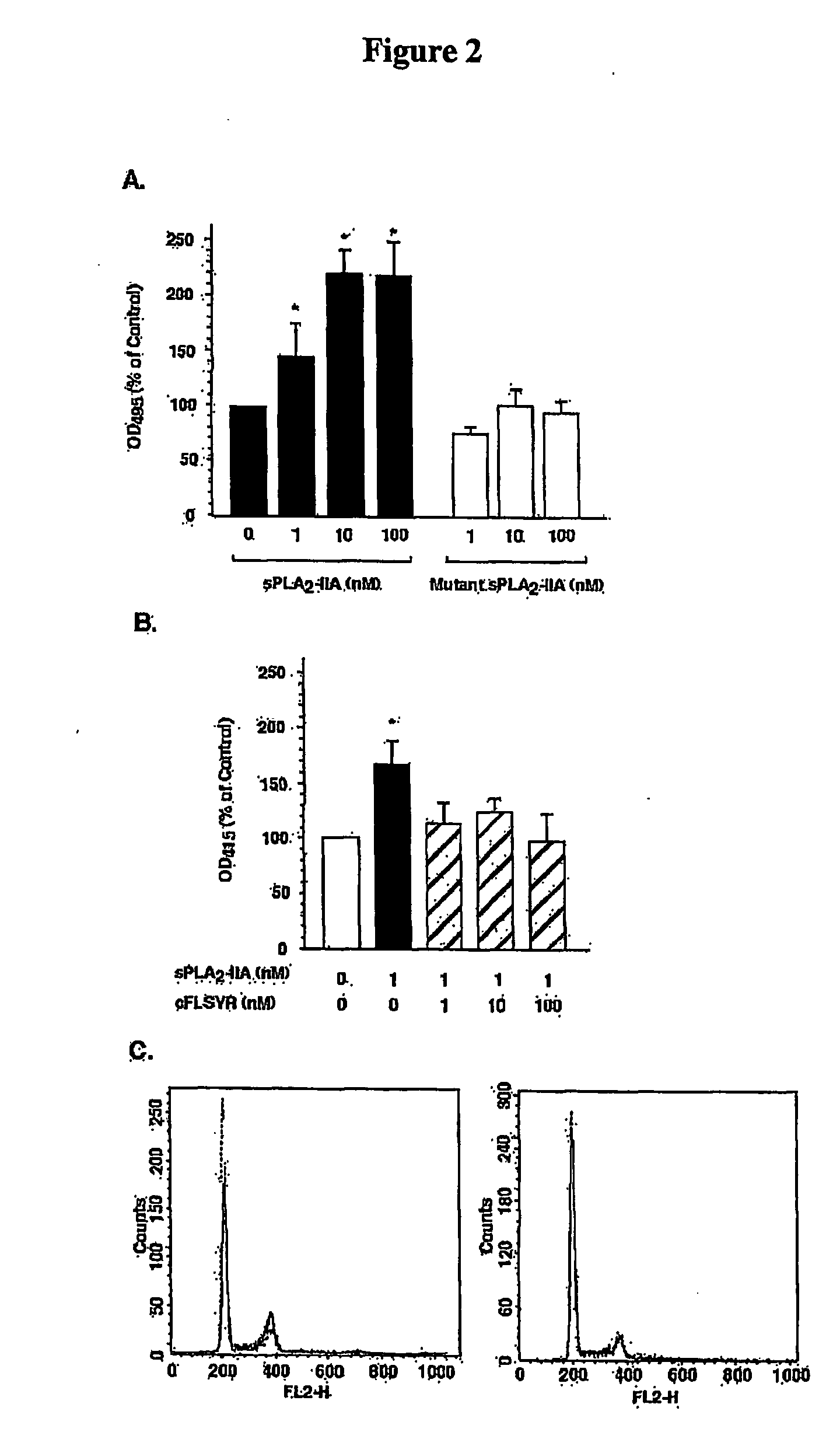
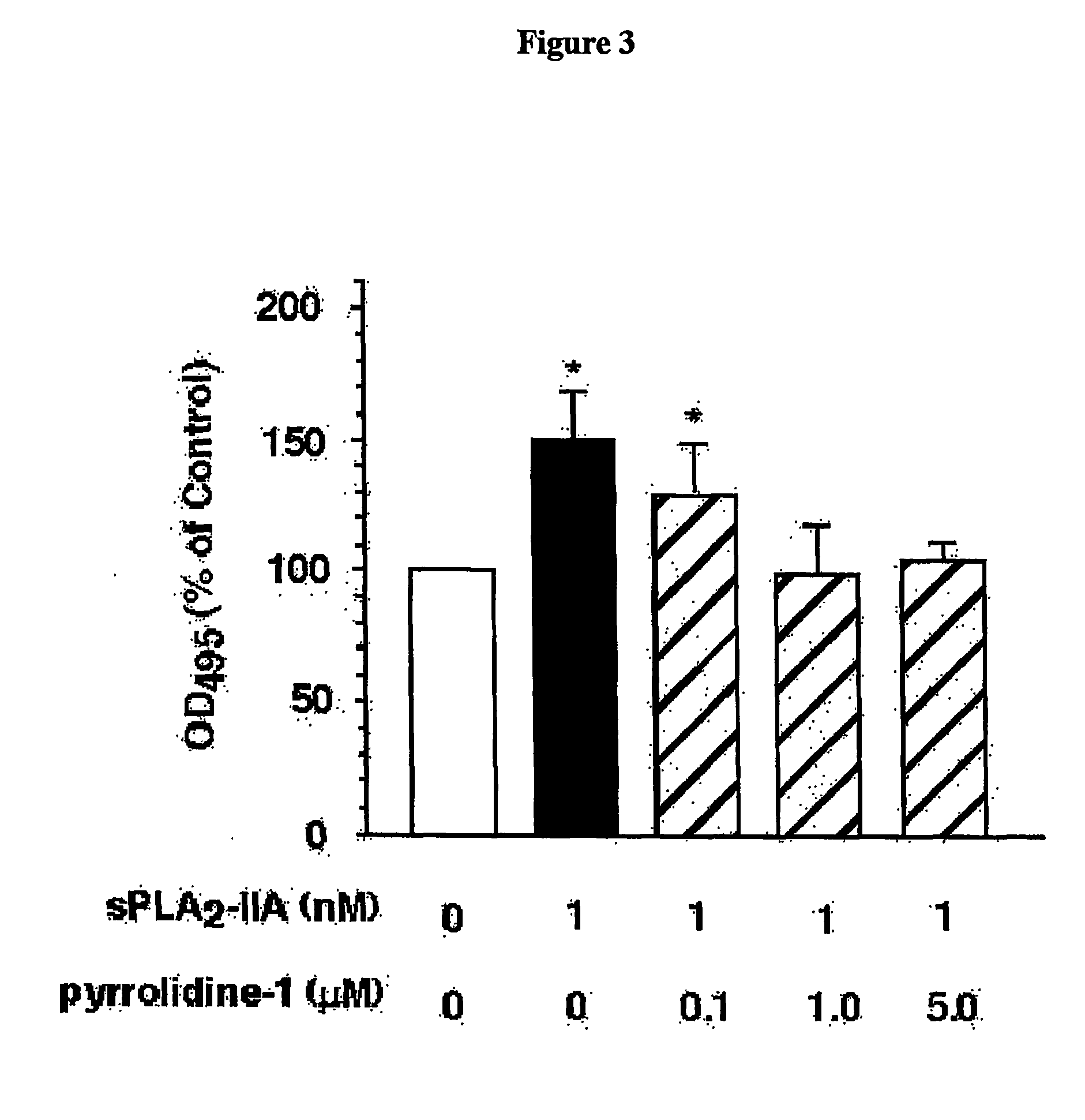
The present invention relates to a method of inhibiting or reducing the proliferation of prostate cancer cells, such as androgen independent prostate cancer (AIPC) cells, the method comprising administering to the cells a PLA2 inhibitor. In one embodiment the PLA2 inhibitor is a conformationally constrained molecule derived from a peptide consisting essentially of amino acid residues 70-74 of a human sPLA2-IIA protein, or the equivalent residues in other sPLA2 proteins.
Owner:SCOTT KIERAN FRANCIS
Cell growth inhibitor and screening method thereof
InactiveUS8796240B2Growth inhibitionInhibit expressionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsBinding siteScreening method
An object is to provide a cell growth inhibitor also effective for androgen-independent prostate cancer. The present invention provides a cell growth inhibitor having, as an active ingredient, an expression inhibitor or function inhibitor of an antisense RNA (CTBP1-AS) expressed in the vicinity of an androgen receptor (AR) binding site of a C-terminal binding protein (CTBP1) gene.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
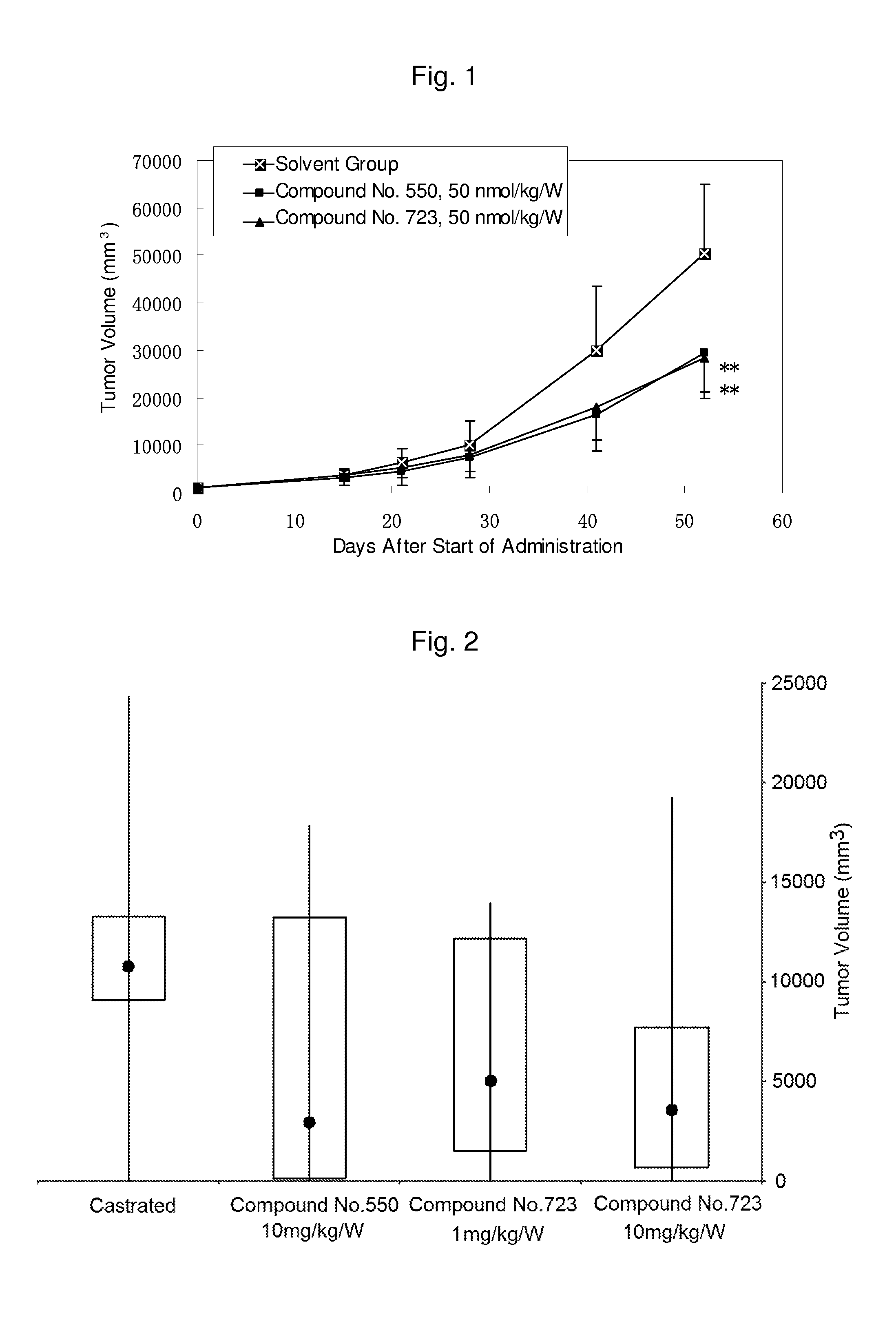
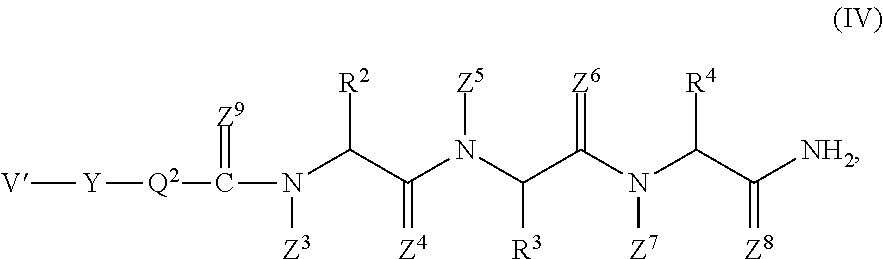
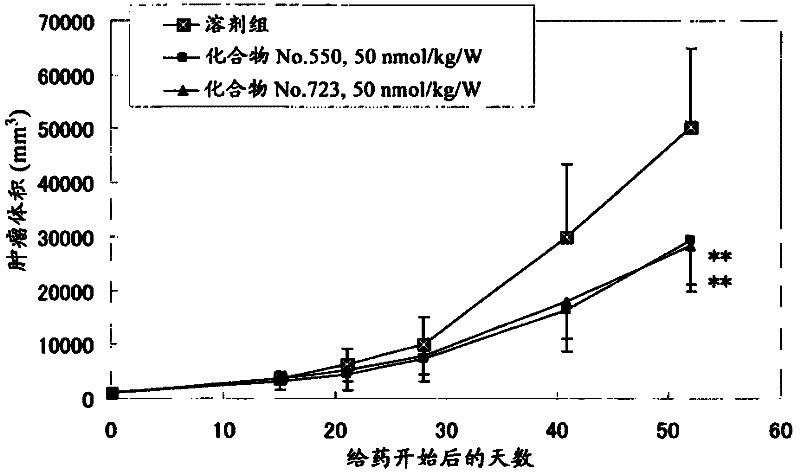
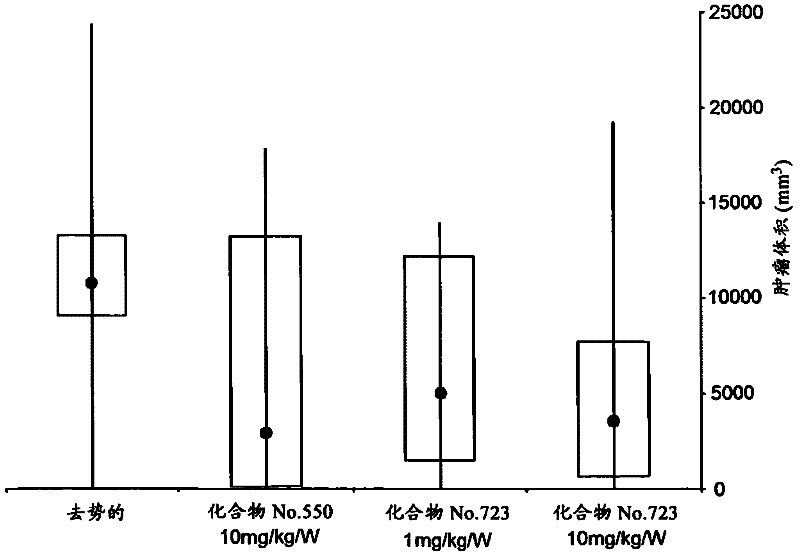
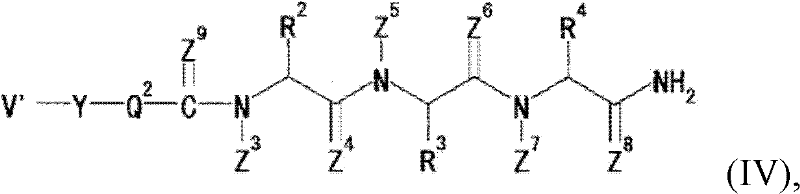
Pyrrolo [1,2-c] imidazole derivatives for use in the prophylaxis or treatment of cancer which is refractory to known cancer therapies
InactiveUS20140256693A1Impede acquisitionPrevent recurrenceOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAndrogenMedicine
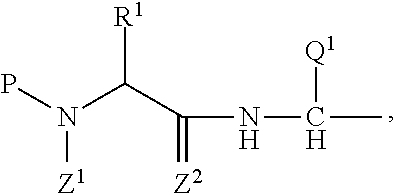
The present invention mainly aims to provide a drug for the prophylaxis or treatment of androgen-independent prostate cancer, which is highly useful as a pharmaceutical agent. The present invention provides a drug for the prophylaxis or treatment of androgen-independent prostate cancer, containing a steroid C17,20 lyase inhibitor, particularly, a compound represented by the formula (I):wherein n is an integer of 1 to 3, and Ar is an aromatic ring optionally having substituent(s), or a salt thereof or a prodrug thereof.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
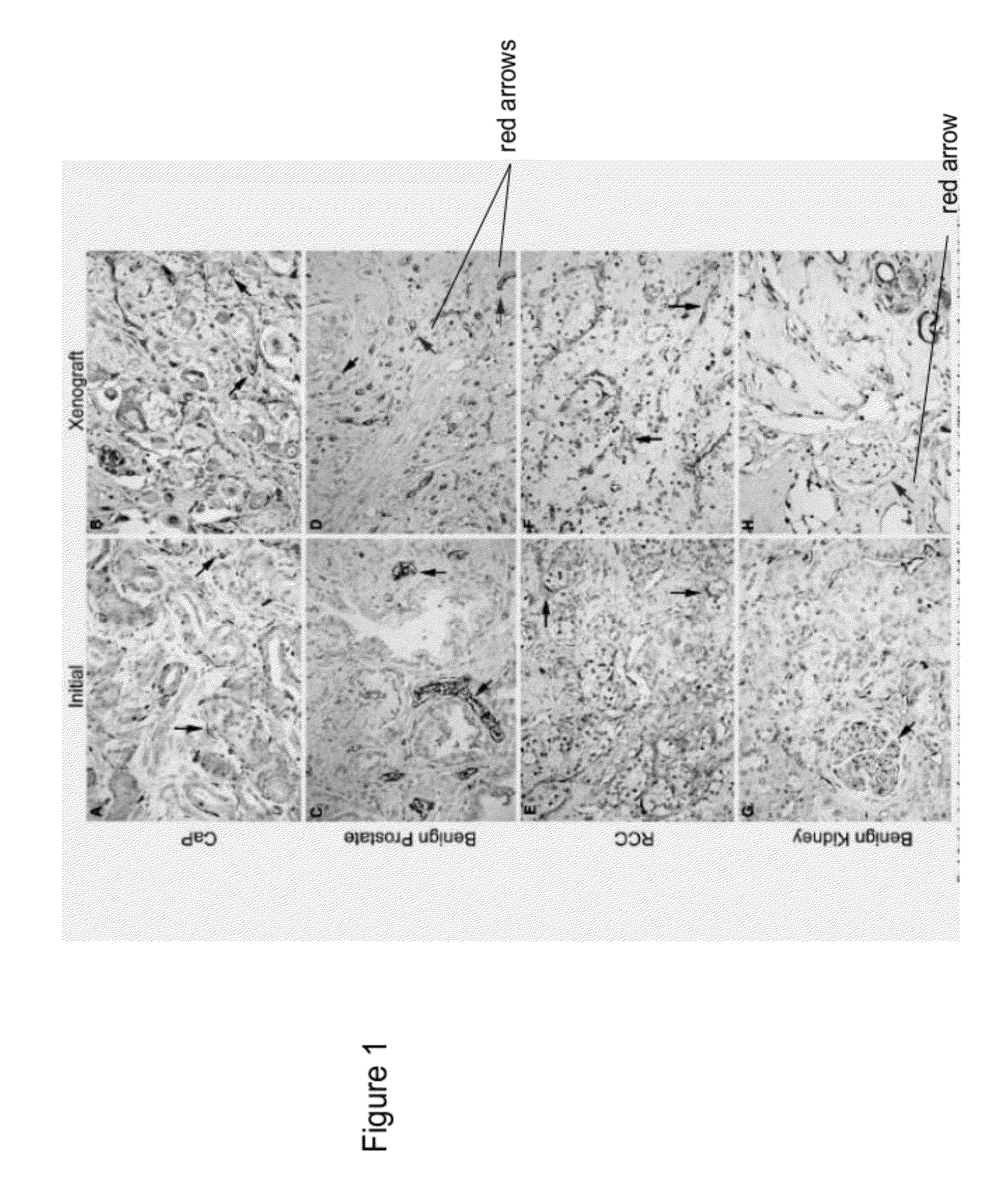
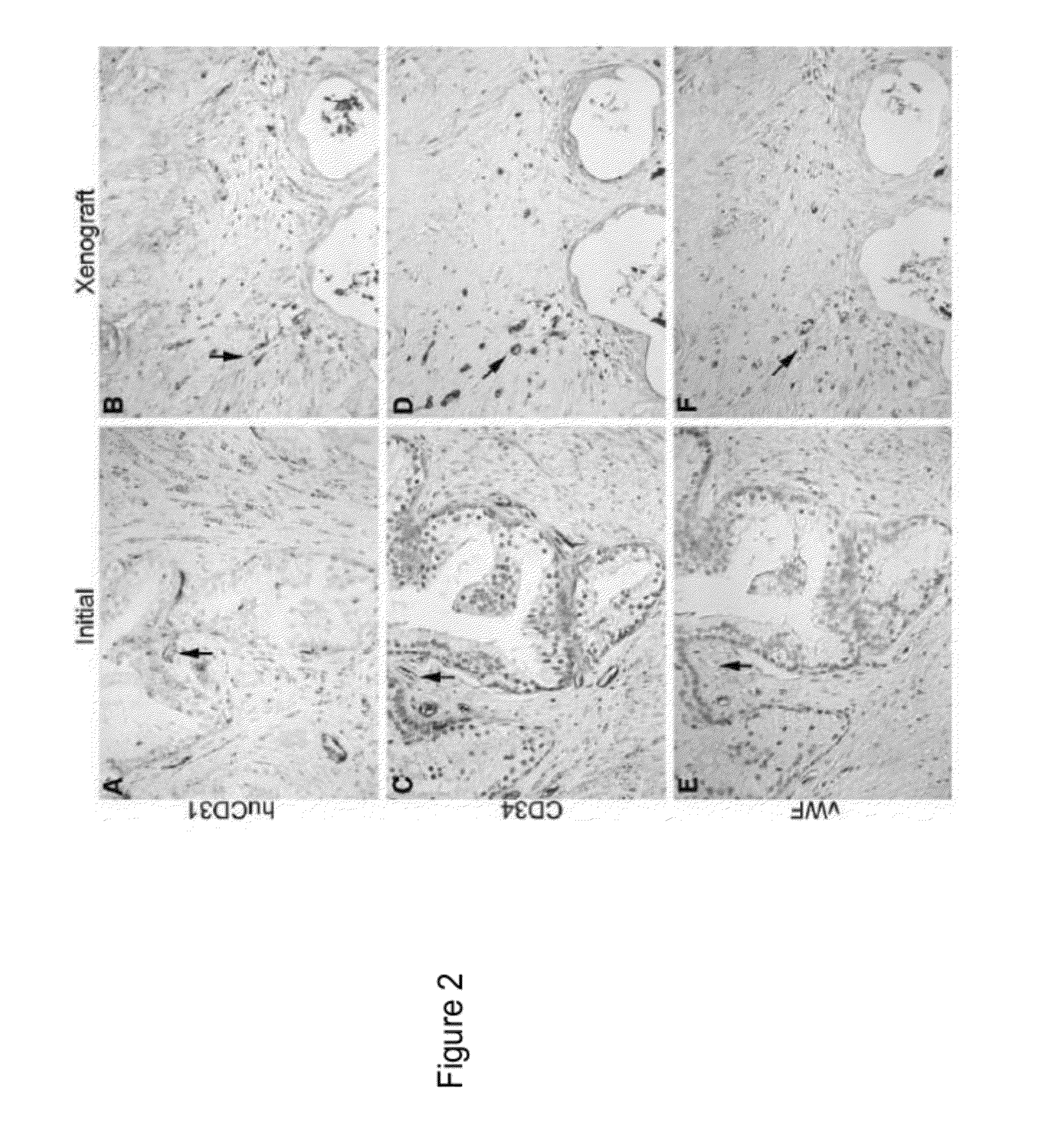
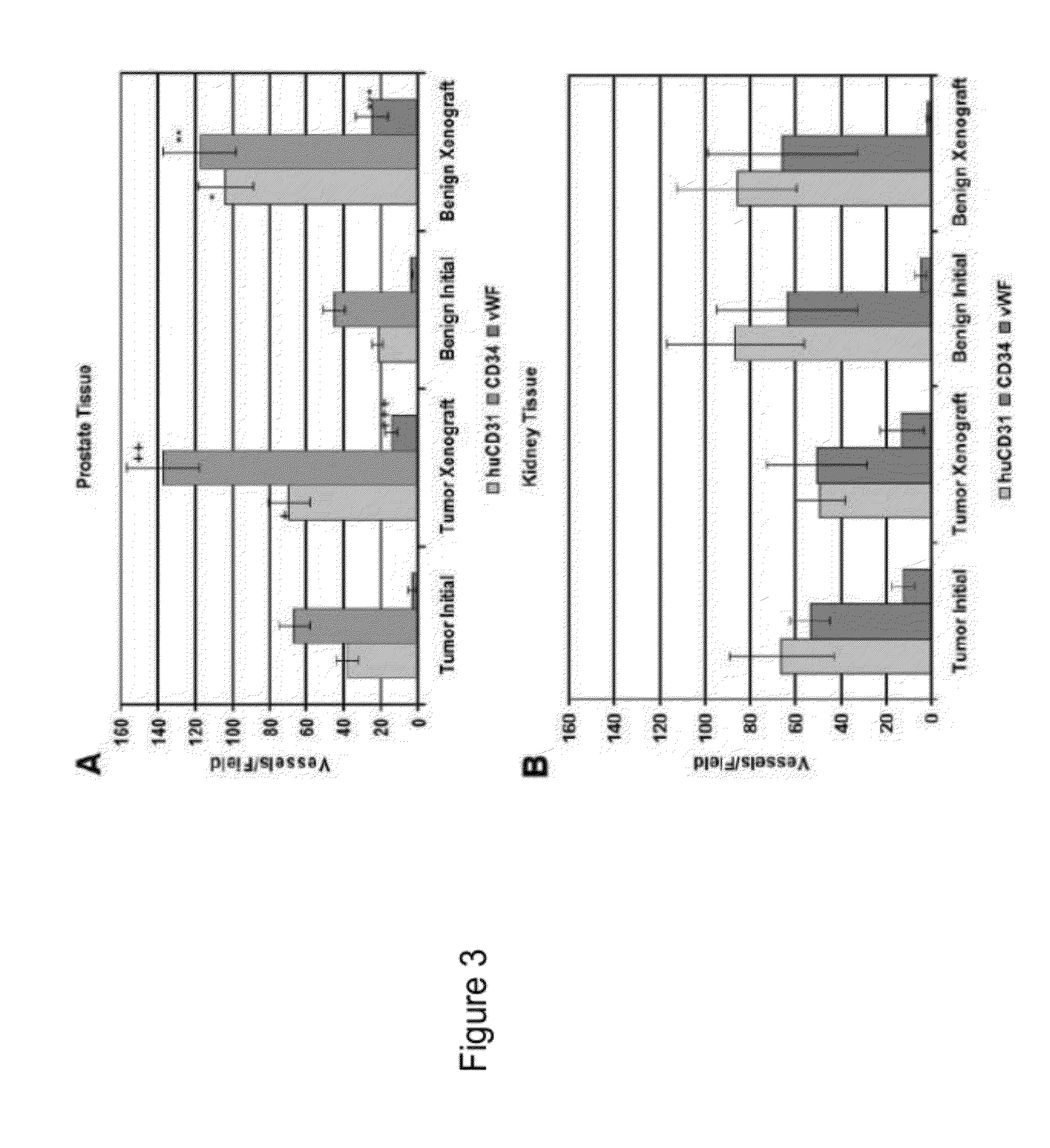
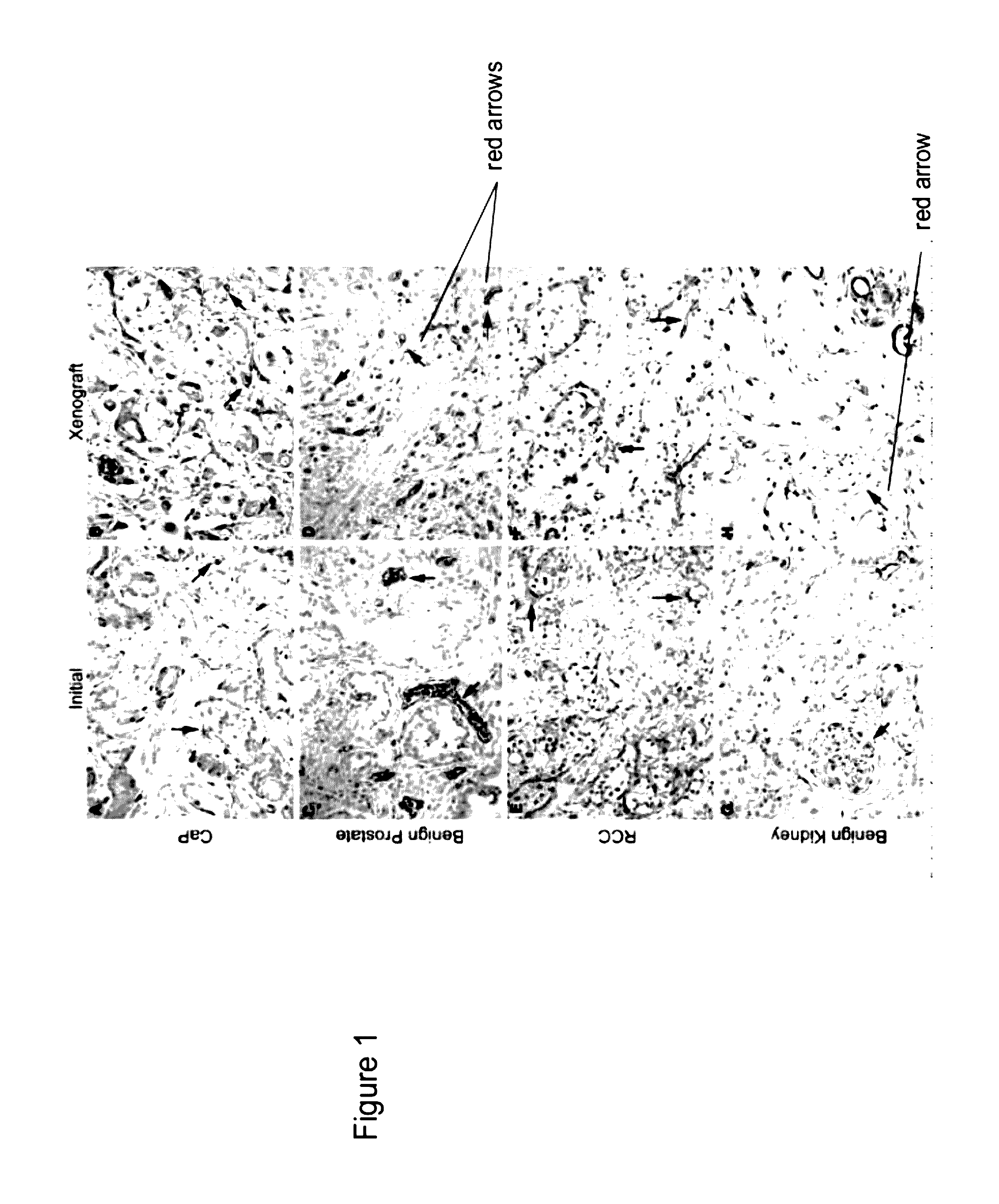
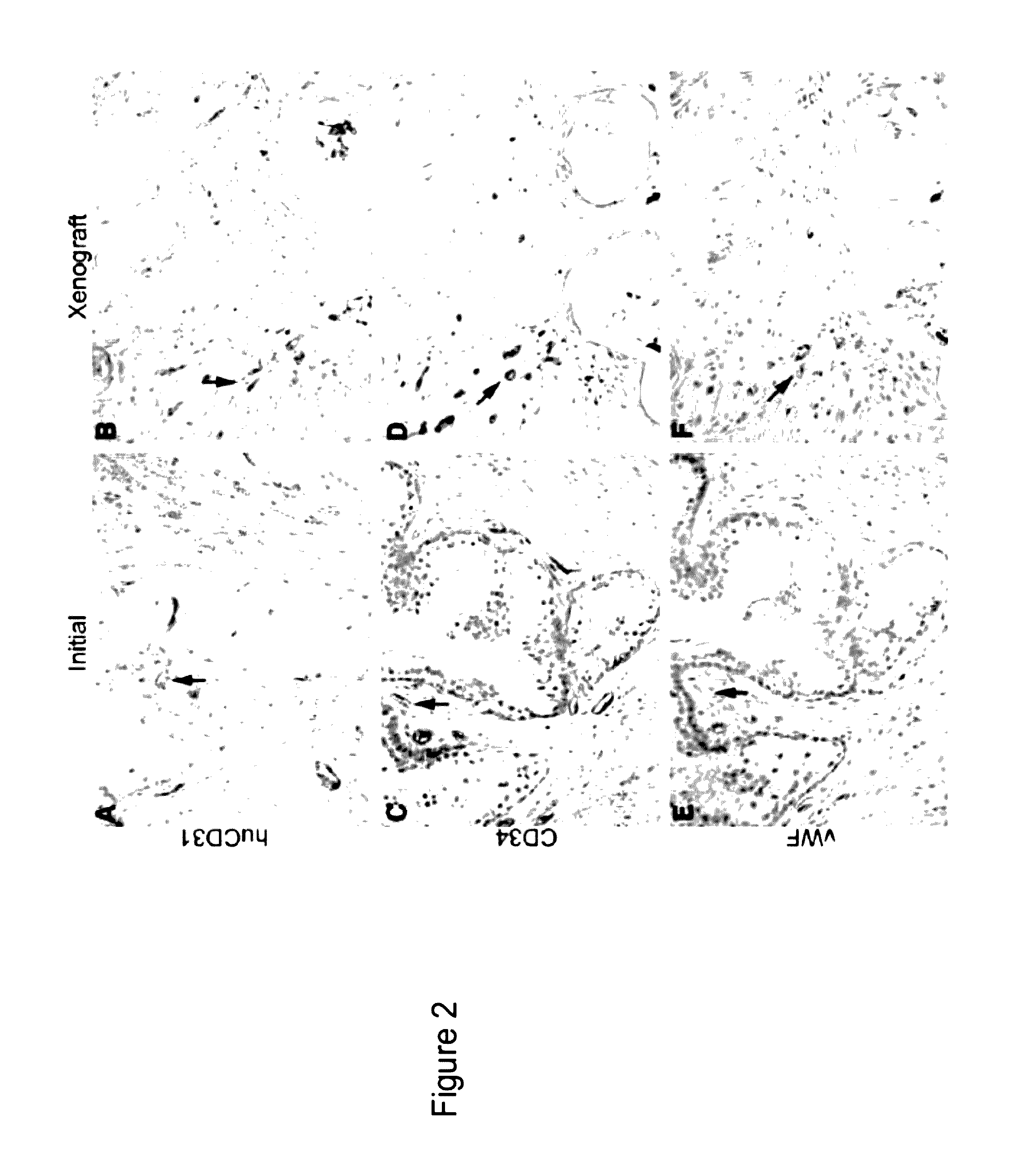
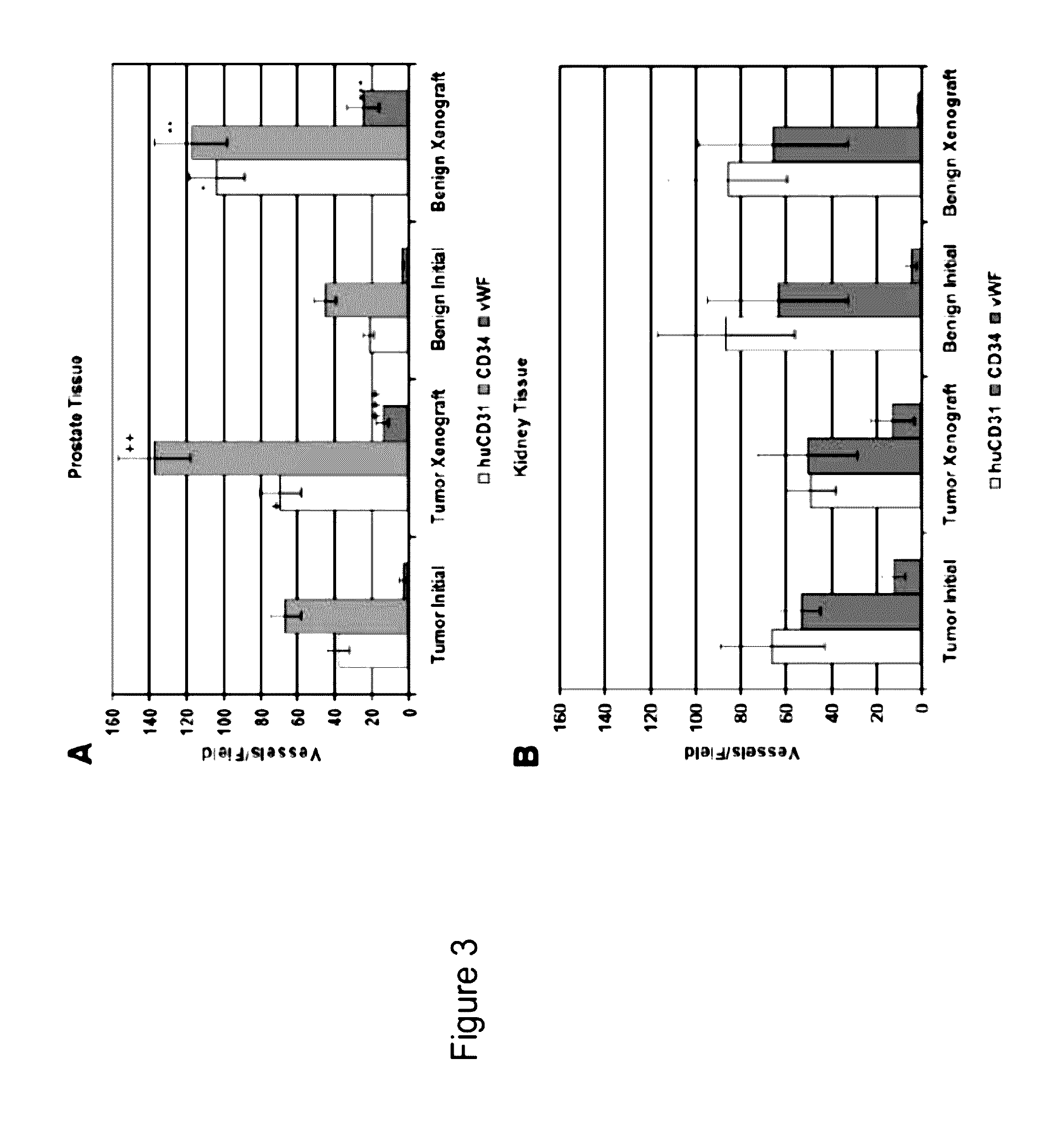
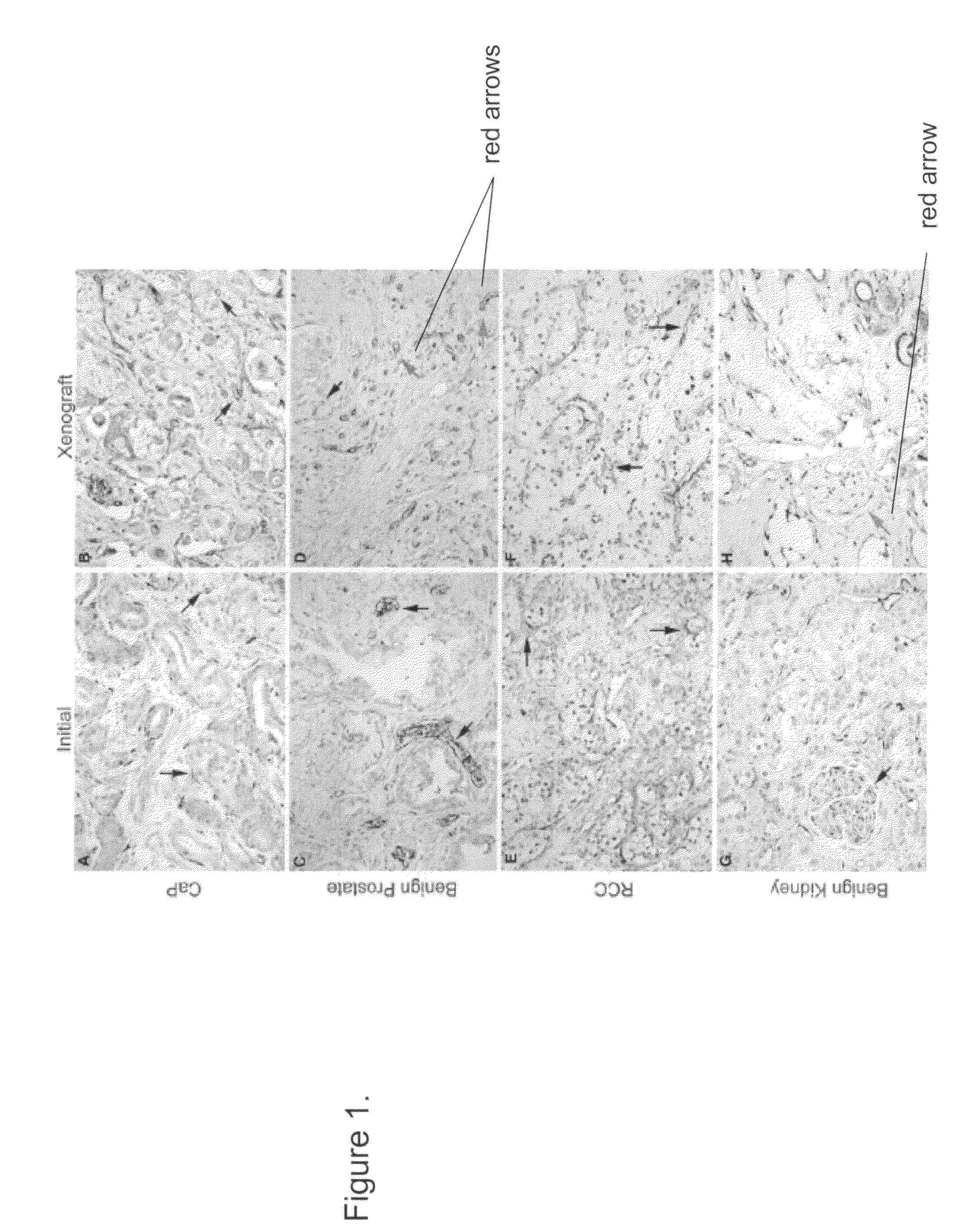
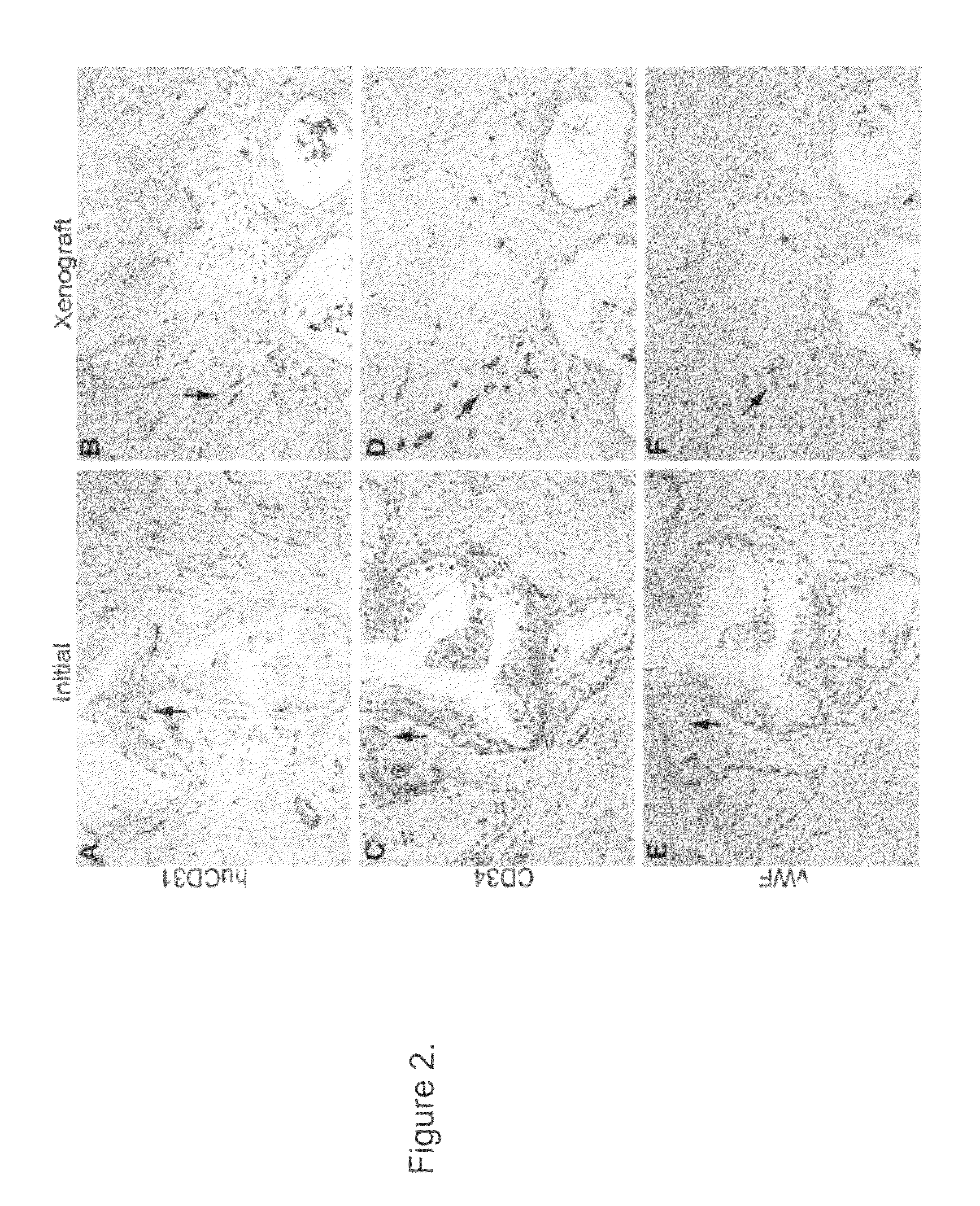
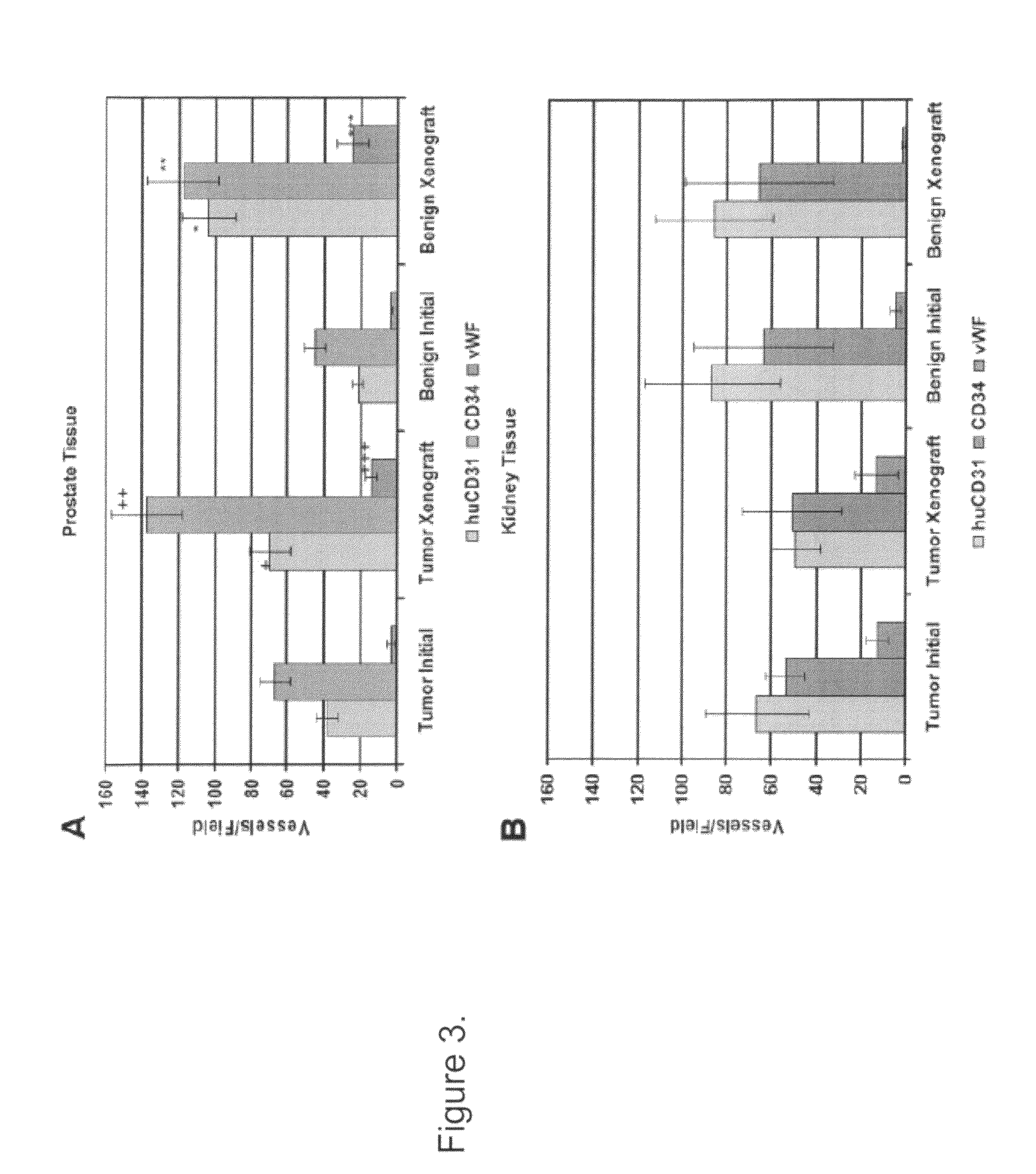
Methods For Evaluating and Implementing Prostate Disease Treatments
Provided is a method for evaluating test agents as candidates for treating prostatic diseases, including benign prostatic hyperplasia and androgen dependent and androgen independent prostate cancer. The method comprises providing a mouse comprising a human prostate primary xenograft, where the xenograft contains blood vessels that include human endothelial cells, initiating androgen deprivation in the mouse, administering to the mouse a test agent within a period of 1-7 days after initiating the androgen deprivation, and determining a reduction in human epithelial cells in the xenografts and / or a reduction in number of the endothelial cells or blood vessels in the xenograft. Also provided is a method for treating an individual for human prostate cancer or benign prostatic hyperplasia. The method comprises initiating androgen deprivation in the individual and administering to the individual an agent capable of inducing apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells within a period of 1-7 days of initiating androgen deprivation.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Methods for evaluating and implementing prostate disease treatments
Provided is a method for evaluating test agents as candidates for treating prostatic diseases, including benign prostatic hyperplasia and androgen dependent and androgen independent prostate cancer. The method comprises providing a mouse comprising a human prostate primary xenograft, where the xenograft contains blood vessels that include human endothelial cells, initiating androgen deprivation in the mouse, administering to the mouse a test agent within a period of 1-7 days after initiating the androgen deprivation, and determining a reduction in human epithelial cells in the xenografts and / or a reduction in number of the endothelial cells or blood vessels in the xenograft. Also provided is a method for treating an individual for human prostate cancer or benign prostatic hyperplasia. The method comprises initiating androgen deprivation in the individual and administering to the individual an agent capable of inducing apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells within a period of 1-7 days of initiating androgen deprivation.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Methods for evaluating and implementing prostate disease treatments
Provide is a method for evaluating test agents as candidates for treating prostatic diseases, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and androgen dependent and androgen independent prostate cancer. The method comprises providing a mouse comprising a human prostate primary xenograft, where the xenograft contains blood vessels that include human endothelial cells, initiating androgen deprivation in the mouse, administering to the mouse a test agent within a period of 1-7 days after initiating the androgen deprivation, and determining a reduction in human epithelial cells in the xenografts and / or a reduction in number of the endothelial cells or blood vessels in the xenograft. Also provided is a method for treating an individual for human prostate cancer or benign prostatic hyperplasia. The method comprises initiating androgen deprivation in the individual and administering to the individual an agent capable of inducing apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells within a period of 1-7 days of initiating androgen deprivation.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Anti-cancer agents based on 6-trifluoromethoxybenzimidazole derivatives and method of making
The present disclosure relates to novel compounds having the structural Formulas (1a,1b), stereoisomers, tautomers, racemics, prodrugs, metabolites thereof, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt and / or solvate thereof as chemotherapy agents for treating of cancer, particularly androgen-independent prostate cancer. The disclosure also relates to methods for preparing said compounds, and to pharmaceutical compositions comprising said compounds.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![Pyrrolo [1,2-c] imidazole derivatives for use in the prophylaxis or treatment of cancer which is refractory to known cancer therapies Pyrrolo [1,2-c] imidazole derivatives for use in the prophylaxis or treatment of cancer which is refractory to known cancer therapies](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/53d79340-0a28-438f-9eae-33af2d3710d3/US20140256693A1-20140911-D00001.png)
![Pyrrolo [1,2-c] imidazole derivatives for use in the prophylaxis or treatment of cancer which is refractory to known cancer therapies Pyrrolo [1,2-c] imidazole derivatives for use in the prophylaxis or treatment of cancer which is refractory to known cancer therapies](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/53d79340-0a28-438f-9eae-33af2d3710d3/US20140256693A1-20140911-D00002.png)
![Pyrrolo [1,2-c] imidazole derivatives for use in the prophylaxis or treatment of cancer which is refractory to known cancer therapies Pyrrolo [1,2-c] imidazole derivatives for use in the prophylaxis or treatment of cancer which is refractory to known cancer therapies](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/53d79340-0a28-438f-9eae-33af2d3710d3/US20140256693A1-20140911-C00001.png)