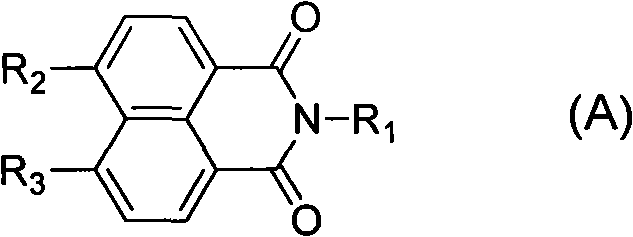
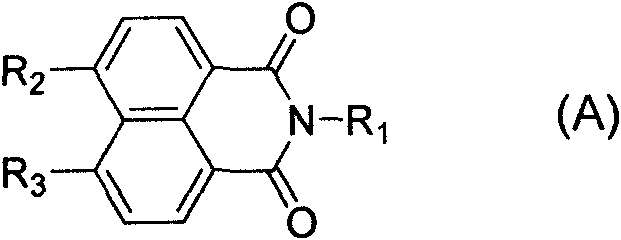
Patents
Literature
288 results about "Acinic cell carcinoma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
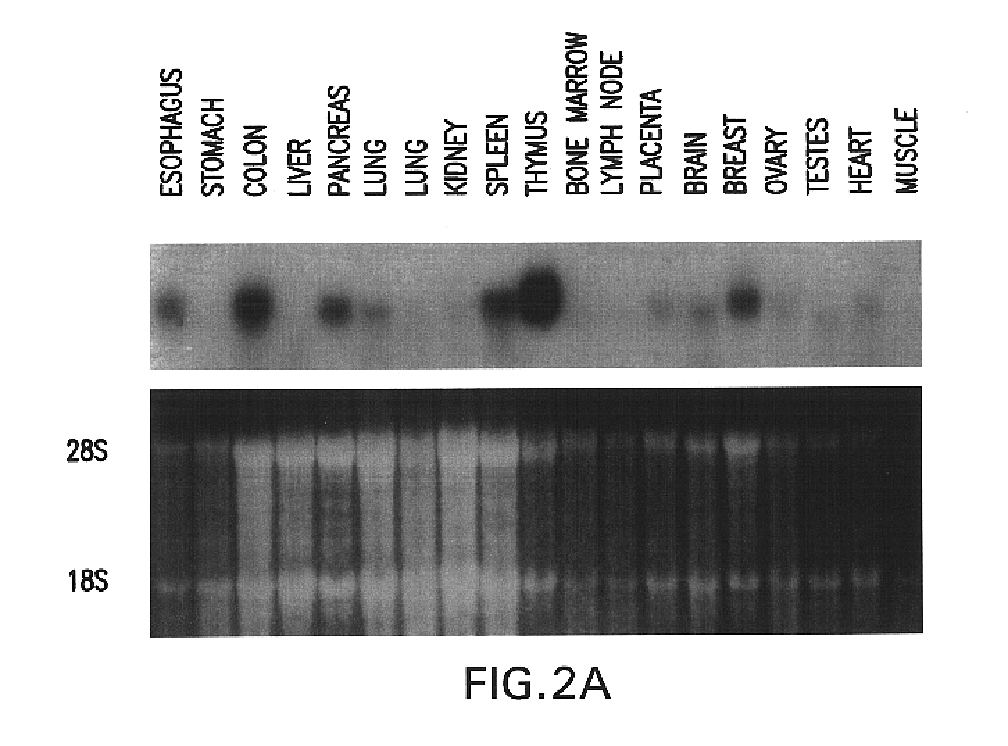
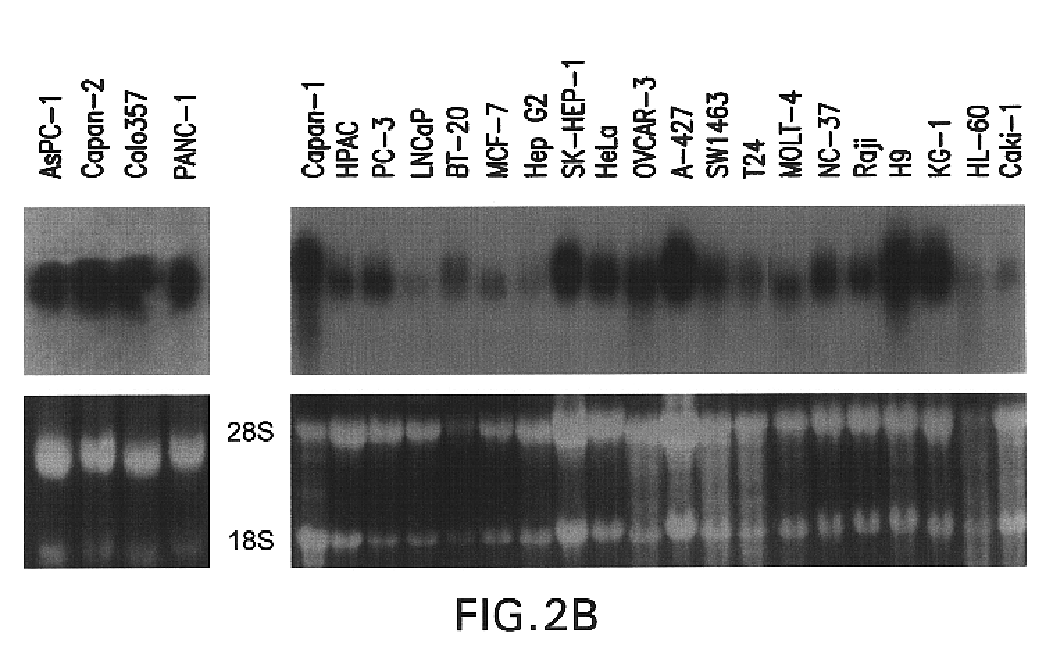
Acinic cell carcinoma is a malignant tumor representing 2% of all salivary tumors. 90% of the time found in the parotid gland, 10% intraorally on buccal mucosa or palate. The disease presents as a slow growing mass, associated with pain or tenderness in 50% of the cases. Often appears pseudoencapsulated.
Method of treating androgen independent prostate cancer
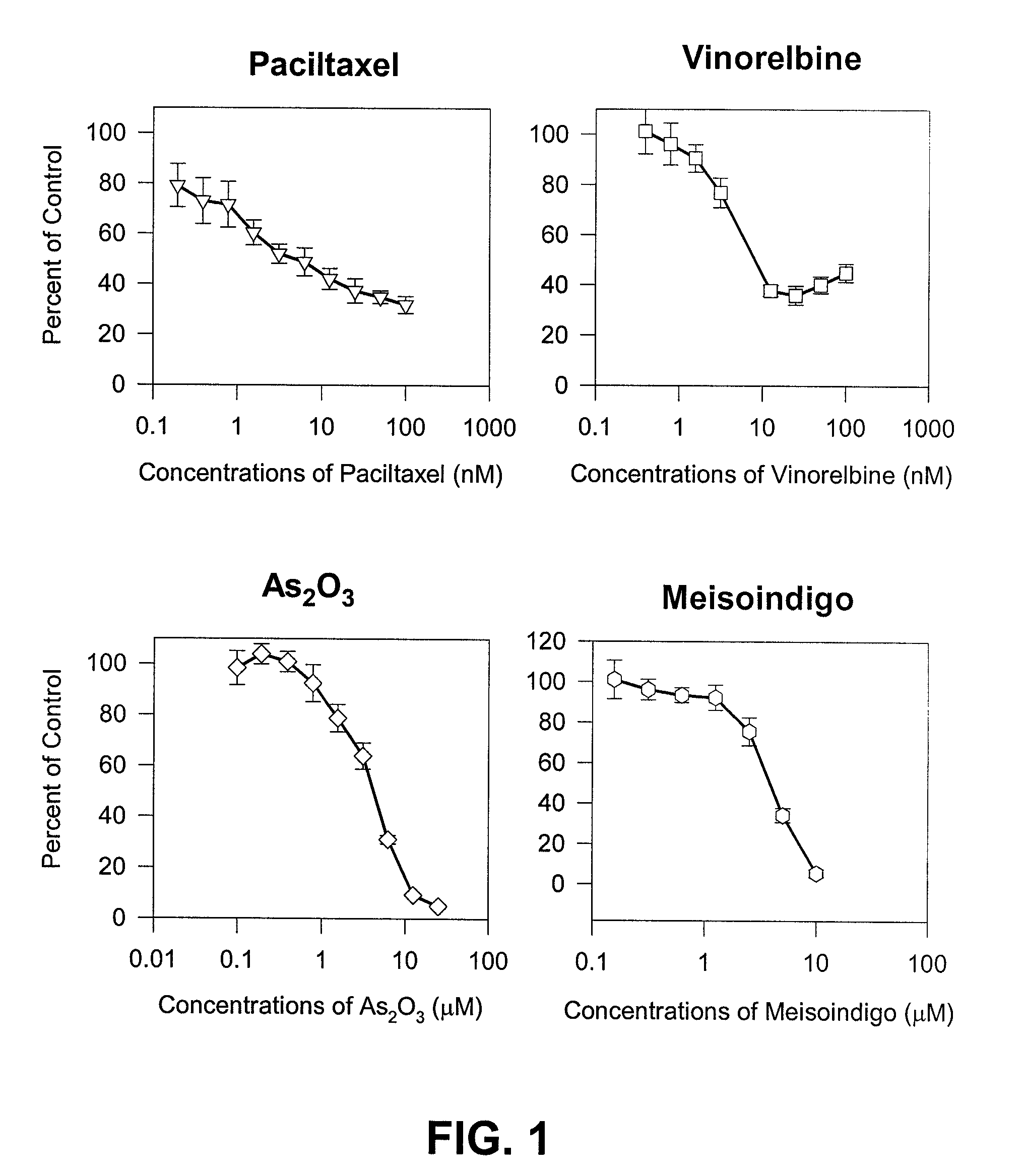
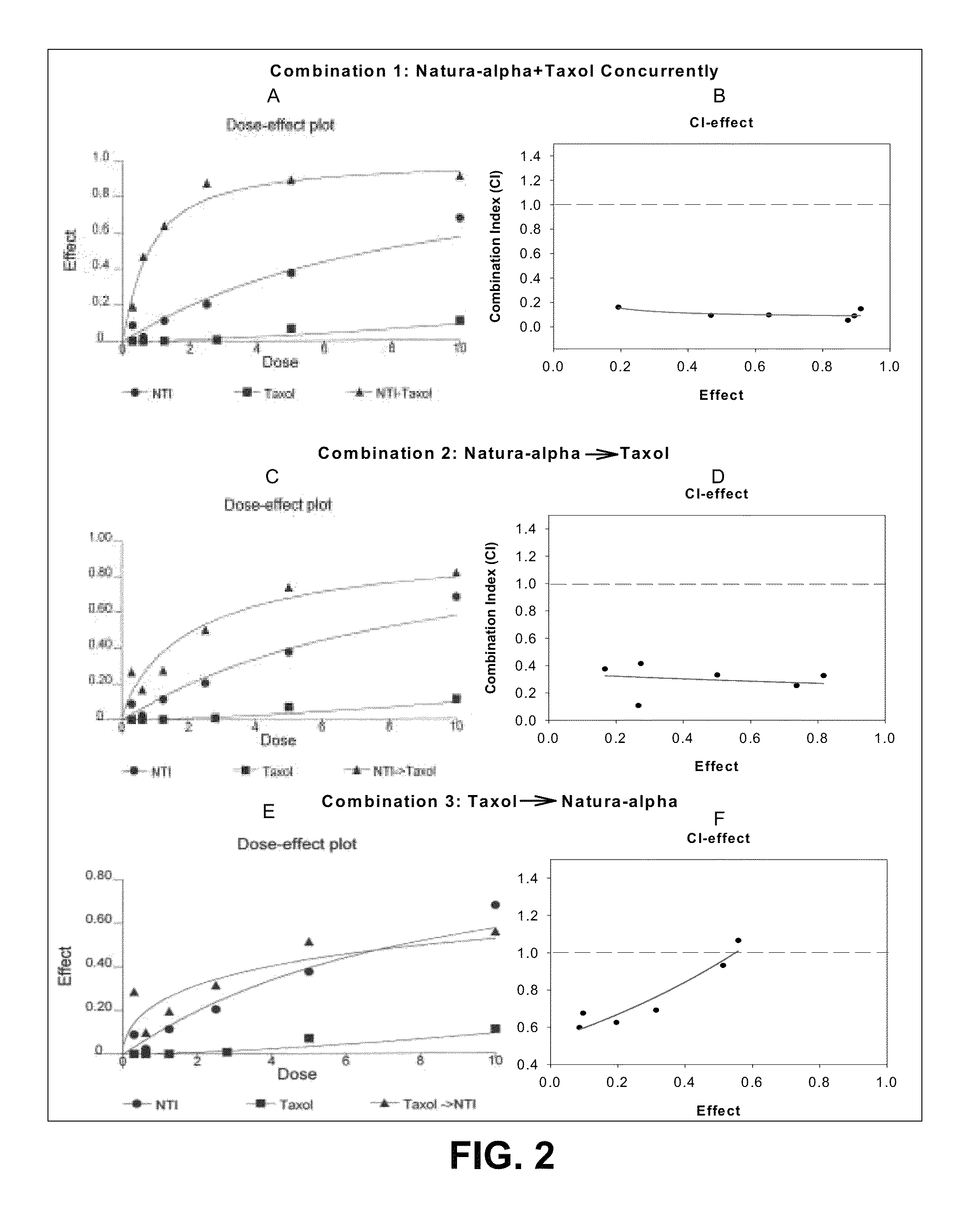
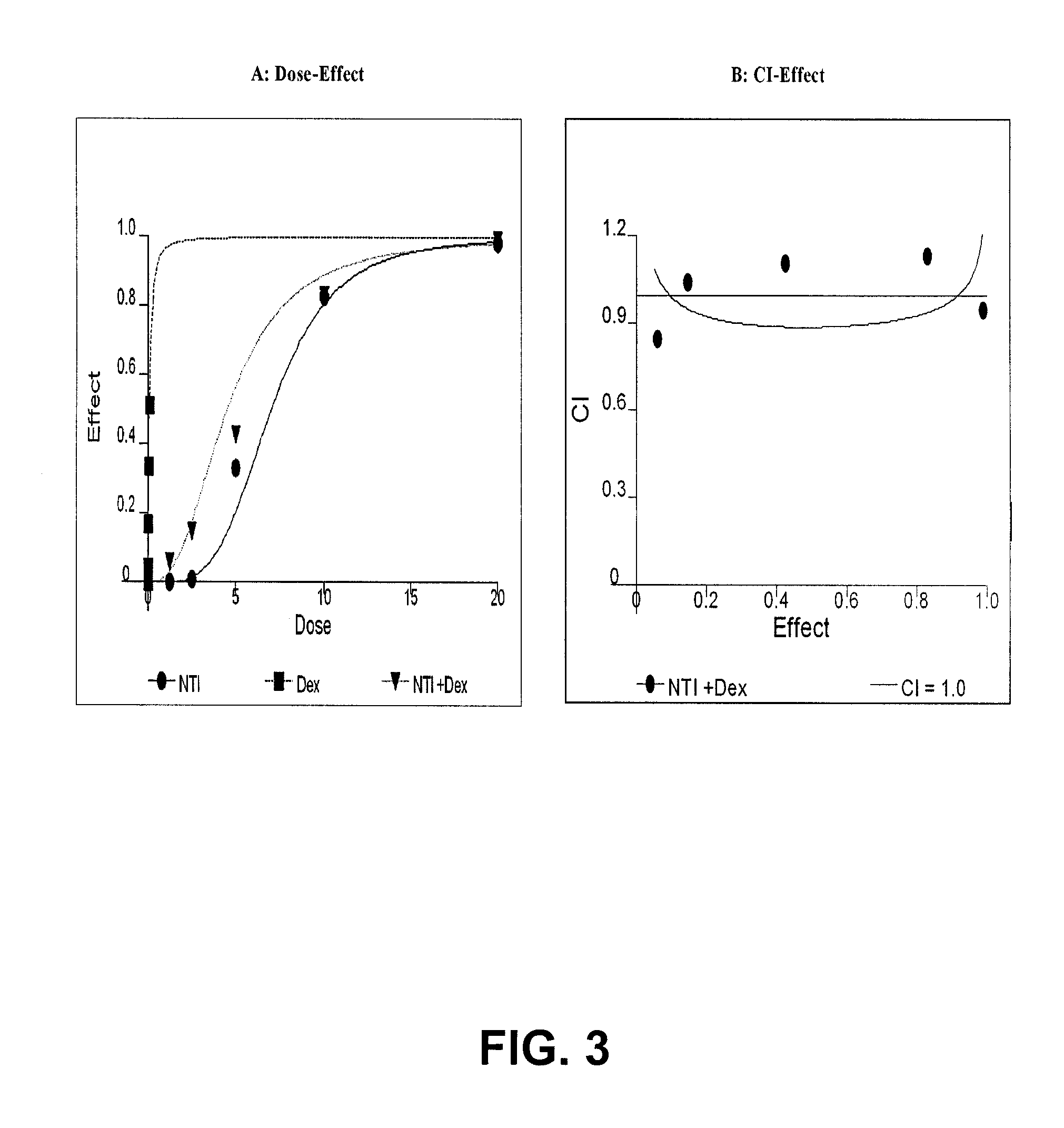
The present invention is directed to a method treating prostate cancer. The method comprises administering to a patient in need thereof at least one compound selected from N-methyl-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone; N-1-(β-D-O-triacetyl-xylopranosyl)-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone; and N-1-(β-D-O-triacetyl-xylopranosyl)-N′-methyl-Δ3,3′-dihydroindole-2,2′ diketone. Preferably the compound is in an amount sufficient to inhibit growth, invasion, and / or metastasis of prostate cancer cells.
Owner:NATROGEN THERAPEUTICS INT
Prostate specific antigen oligo-epitope peptide
The invention is a prostate specific antigen oligo-epitope peptide which comprises more than one PSA epitope peptide, which conforms to one or more human HLA class I motifs. The prostate specific antigen oligo-epitope peptide in combination with various HLA-class I molecules or interactions with various T-cell receptors elicits PSA specific cellular immune responses. The prostate specific antigen oligo-epitope peptide is useful as an immunogen in the prevention or treatment of prostatic cancer, in the inhibition of prostatic cancer cells and in the establishment and characterization of PSA-specific cytotoxic T-cell lines.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES DEPT OF THE GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC
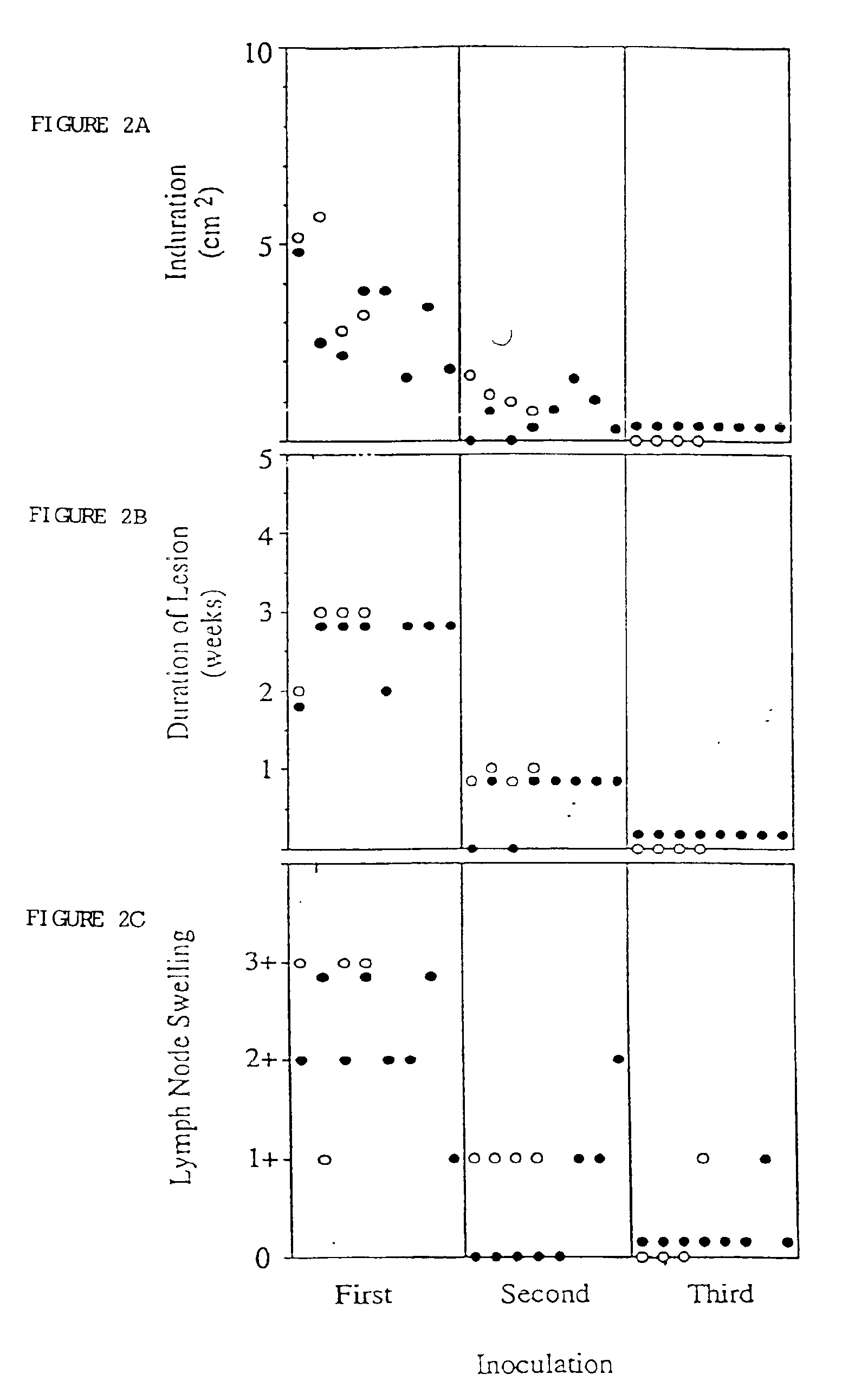
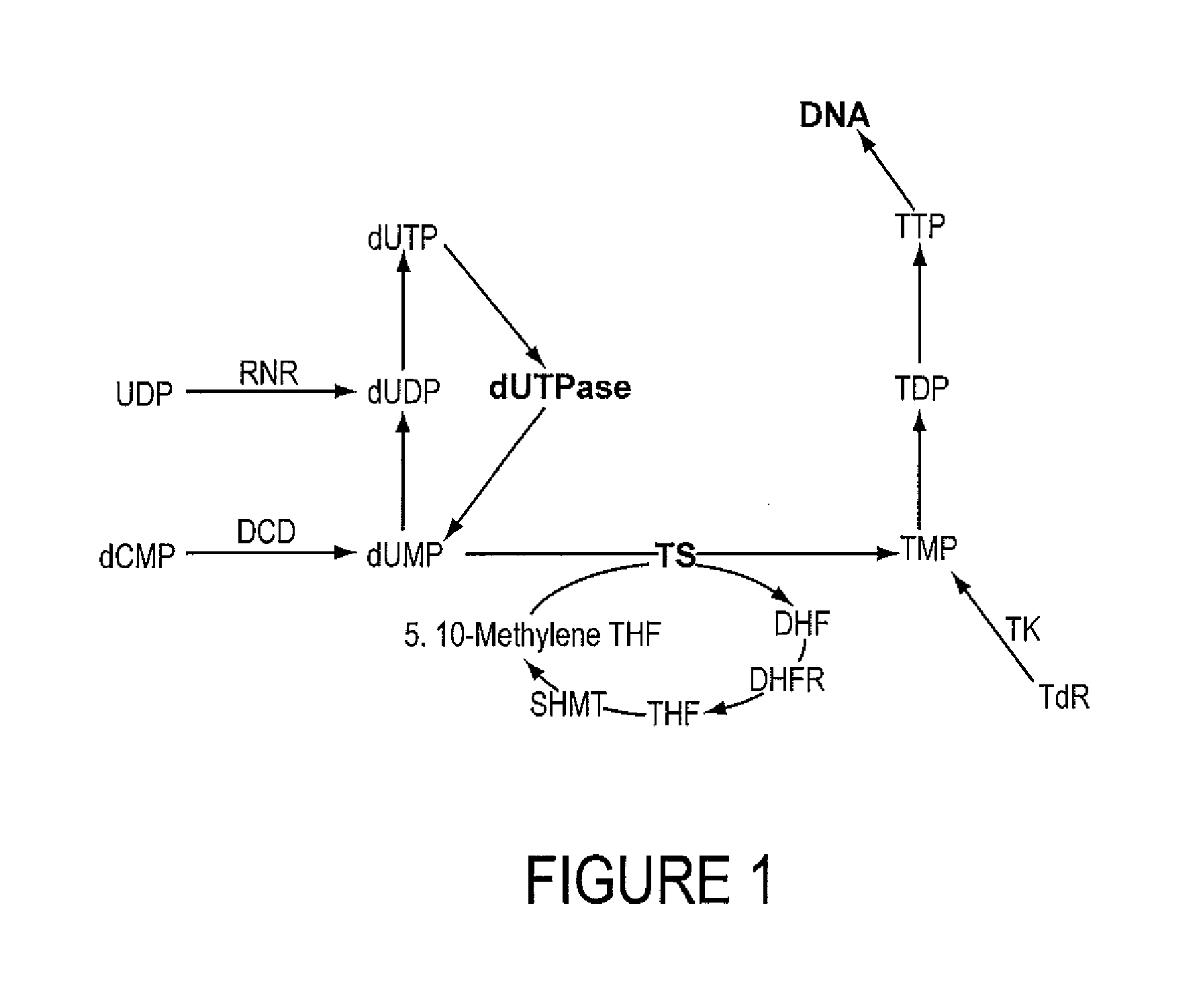
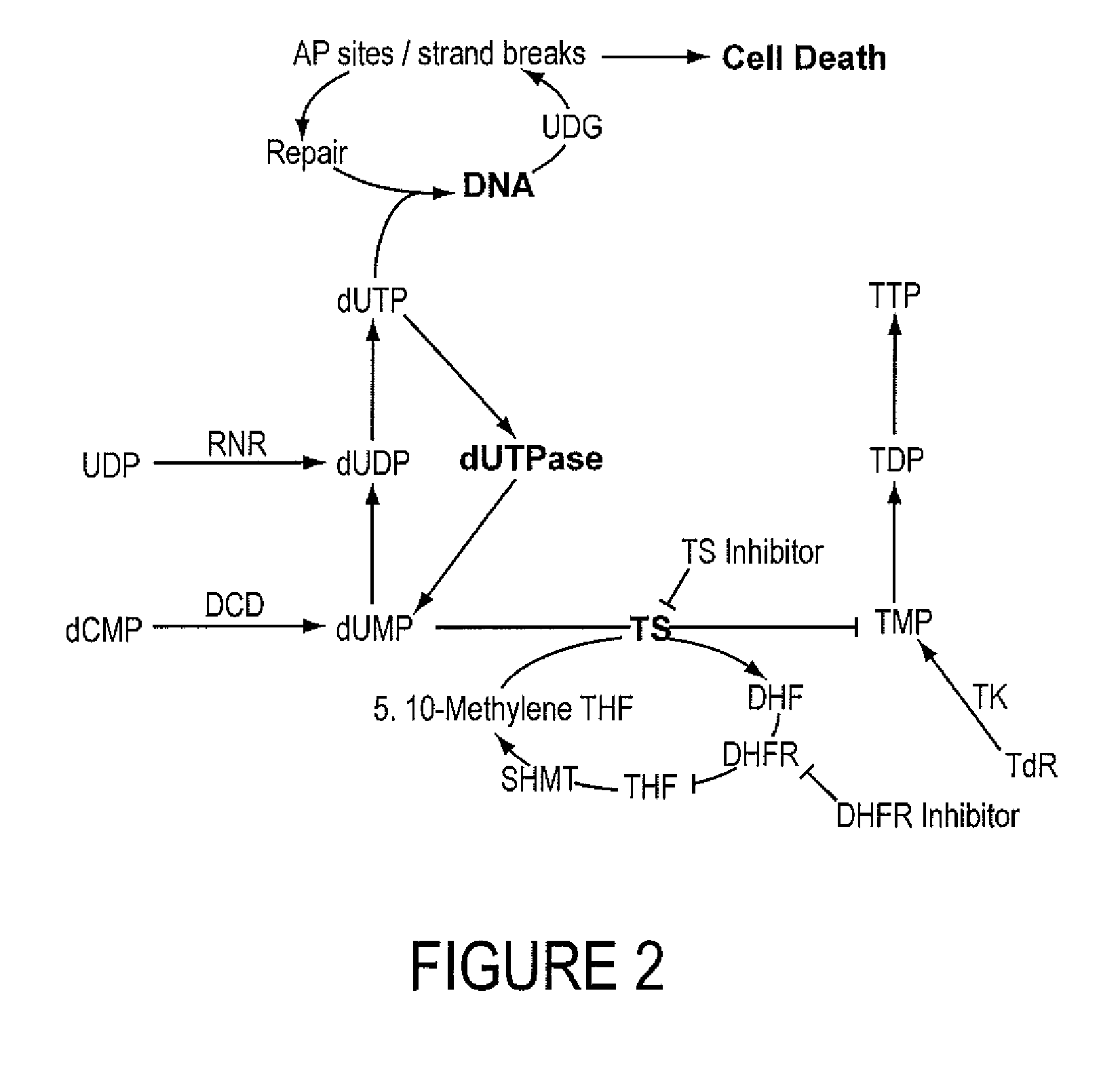
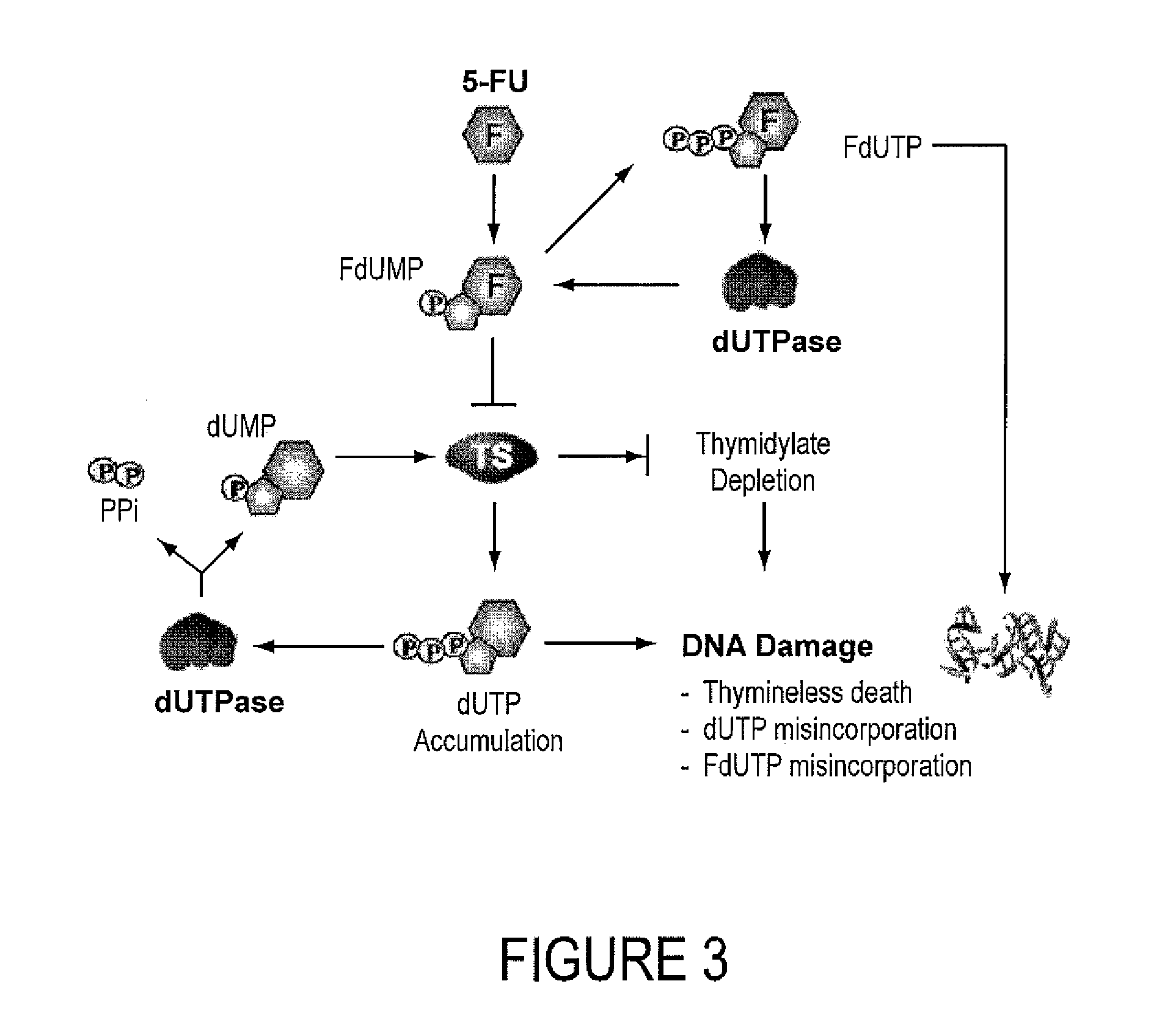
INHIBITORS OF dUTPase
InactiveUS20110212467A1Improve the immunitySuppresses dUTP poolOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryClinical efficacyUracil
Evidence demonstrating that elevated expression of dUTPase protects breast cancer cells from the expansion of the intracellular uracil pool, translating to reduced growth inhibition following treatment with 5-FU is provided. The implementation of in silica drug development techniques to identify and develop small molecule inhibitors of dUTPase are reported. As 5-FU and the oral 5-FU pro-drug capecitabine remain central agents in the treatment of a variety of malignancies, the clinical utility of a small molecule inhibitor to dUTPase represents a viable strategy to improve the clinical efficacy of these mainstay chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Novel pathways in the etiology of cancer
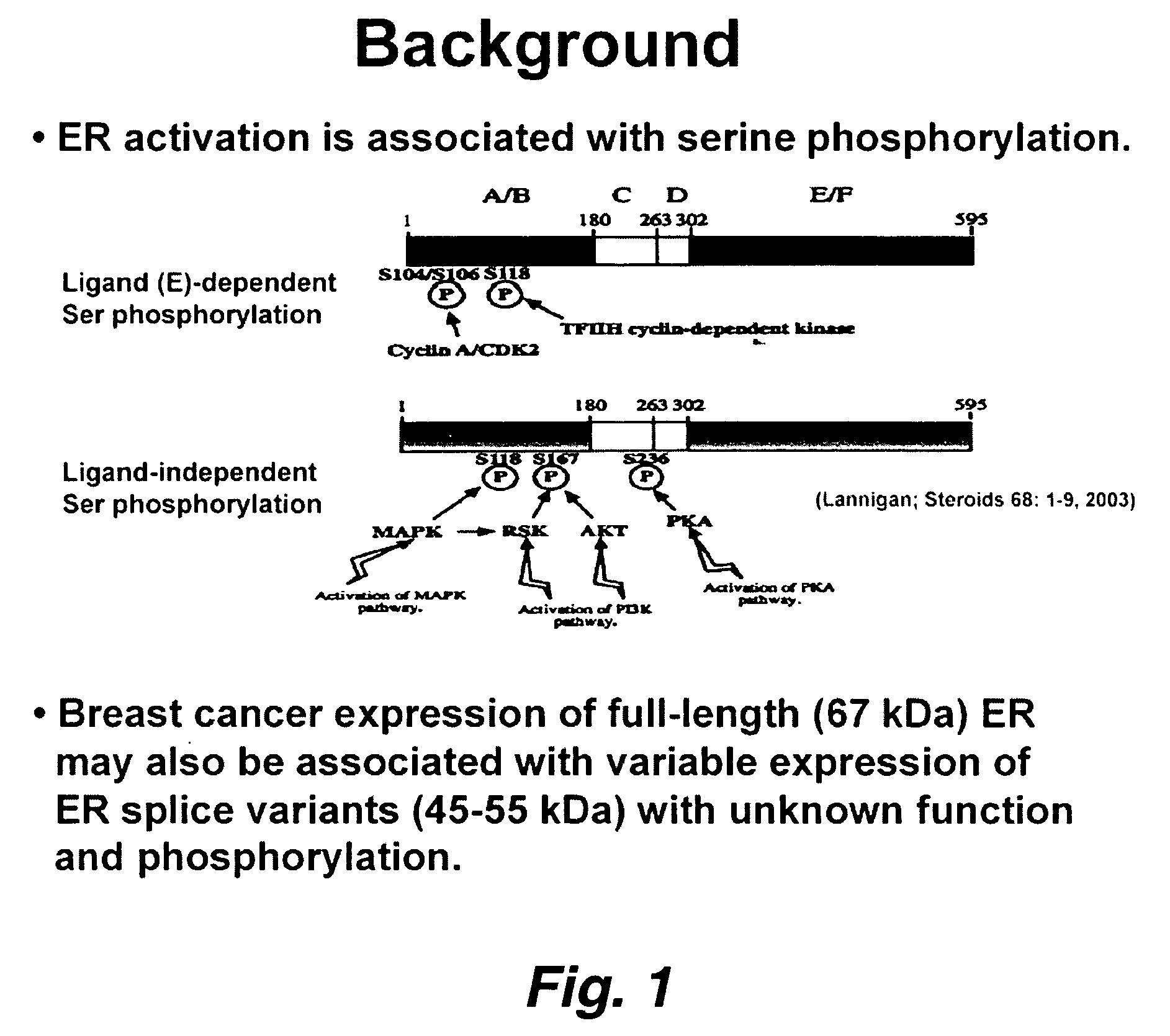
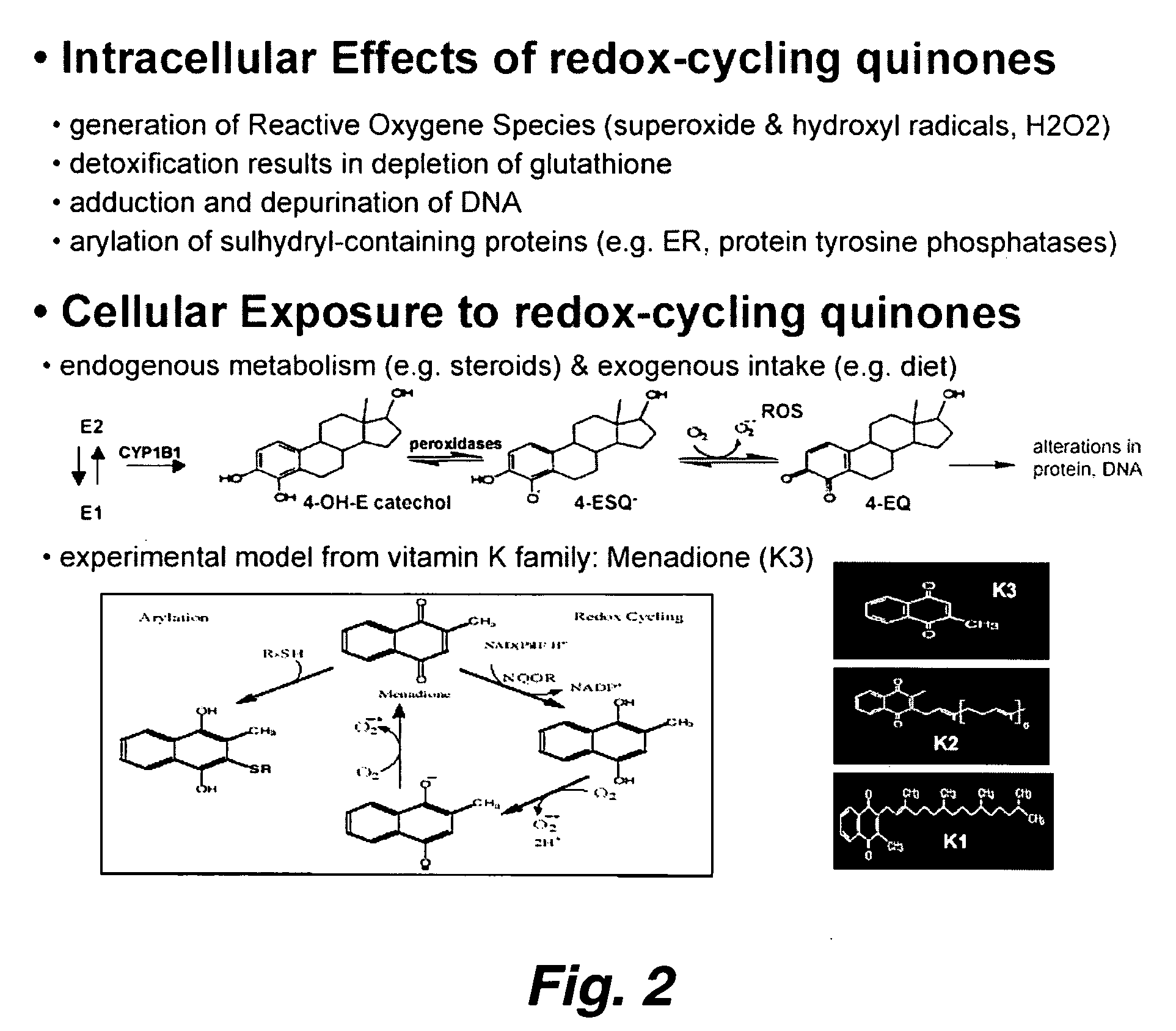
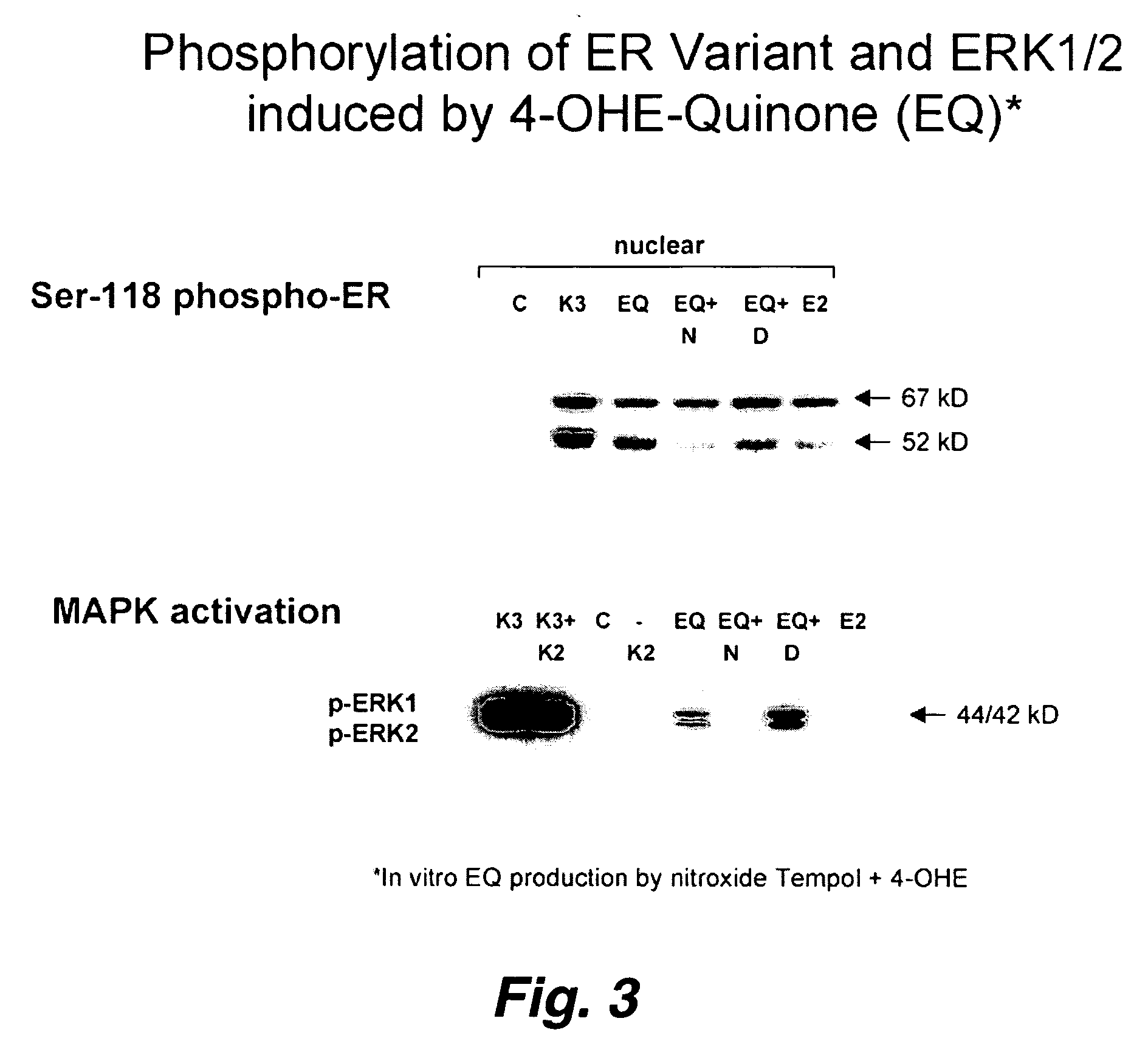
This invention pertains to the identification of two novel epithelial signaling pathways in ER-positive breast cancer s and the discovery that the cellular biology and (likely also the clinical outcome) of ER-positive breast cancer cells is unexpectedly altered when these signaling pathways are activated. The first pathway pertains to the discovery that NF-κB activation and / or DNA binding is implicated in the etiology of ER-positive breast (and other) cancers. The second pathway involves ligand-independent quinine-mediated ER activation by posphorylation (e.g. on SER-118 and SER-167 residues of ER) and nuclear translocation of full-length (67 kDA) ER as well as the phorphorylating activation of a truncated and nuclear-localized ER variant (˜52 kDa).
Owner:THE BUCK INST FOR RES ON AGING
Methods to inhibit growth of prostate cancer cells
InactiveUS7361338B2Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPassive ImmunizationsProstate cancer cell
A novel gene (designated 101P3A11 or PHOR-1) and its encoded protein, and variants thereof, are described wherein 101P3A11 exhibits tissue specific expression in normal adult tissue, and is aberrantly expressed in the cancers listed in Table I. Consequently, 101P3A11 provides a diagnostic, prognostic, prophylactic and / or therapeutic target for cancer. The 101P3A11 gene or fragment thereof, or its encoded protein, or variants thereof, or a fragment thereof, can be used to elicit a humoral or cellular immune response; antibodies or T cells reactive with 101P3A11 can be used in active or passive immunization.
Owner:AGENSYS INC
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and treatment of cancer
The present invention relates to a novel gene, CaSm, that is highly expressed in cancer tissues and cell lines, especially pancreatic cancer. The full length cDNA of CaSm encodes a protein of 133 amino acids. CaSm contains the two Sm motifs found in the common snRNP proteins, with the greatest homology to the Sm G protein (60% similarity). The present invention further encompasses CaSm peptides, fusion proteins, host cell expression systems, antibodies to CaSm, antisense CaSM molecules, and compounds that modulate CaSm gene expression or CaSm activity. Antisense CaSm RNA is able to alter the transformed phenotype of pancreatic cancer cells by reducing their ability to form large colonies in soft agar when compared to untransfected cells. The present invention also encompasses methods for disease diagnosis, drug screening and the treatment of cancer.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
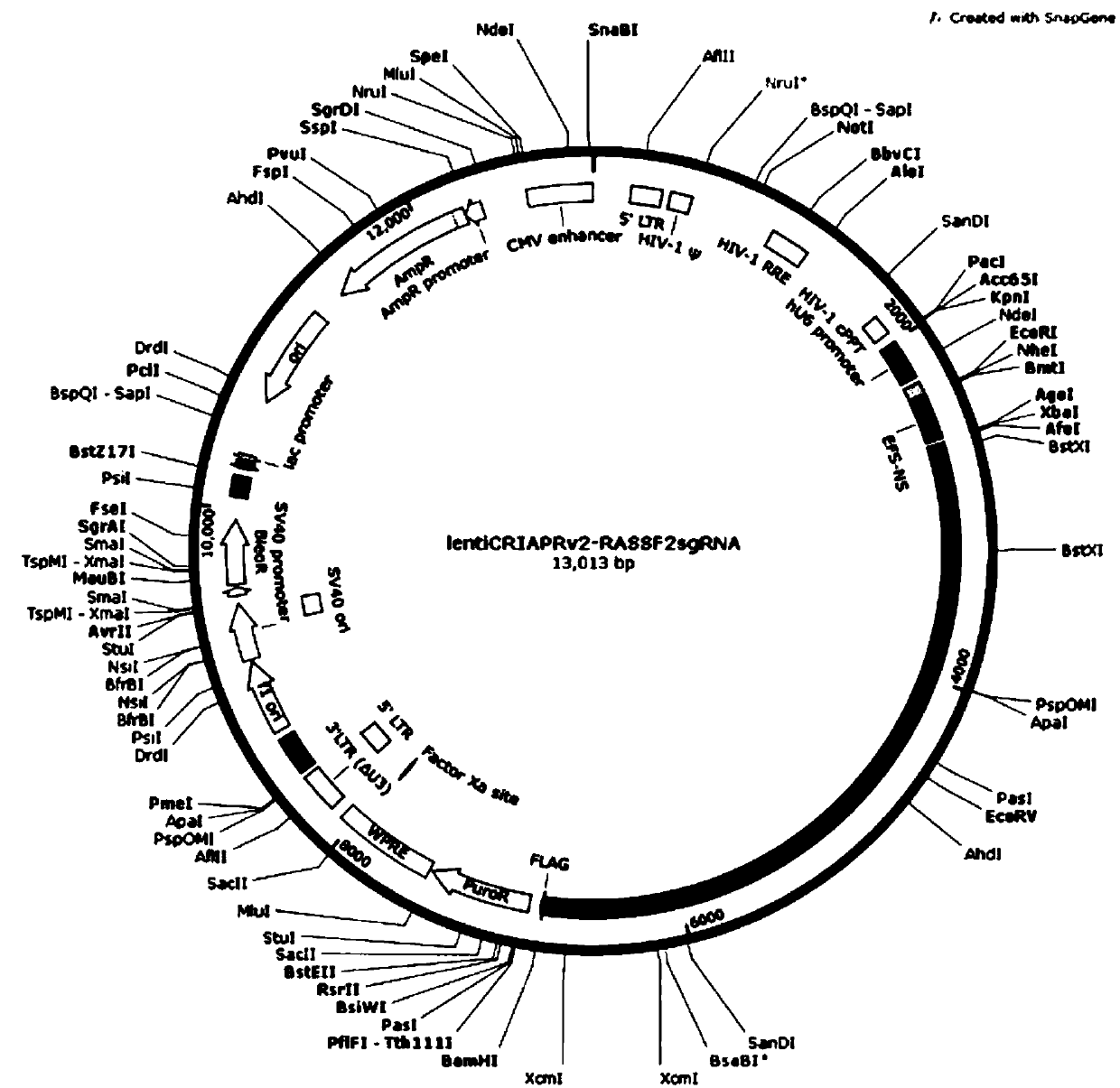
CRISPR-Cas9 targeting knockout of human breast cancer cell RASSF2 gene and specific sgRNA of RASSF2 gene
The invention discloses CRISPR-Cas9 targeting knockout of human breast cancer cell RASSF2 gene and specific sgRNA of RASSF2 gene. According to the method, the sgRNA of specific targeting RASSF2 gene is obtained, wherein the base sequence of the sgRNA is represented by SEQ ID NO.1; construction of the sgRNA of RASSF2 gene into a lentiviral vector system is carried out, wherein the lentiviral vectorsystem contains Cas9 protein; and at last, human breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 is infected with the CRISPR-Cas9 lentivirus containing the sgRNA so as to obtain a cell strain with obviously reduced RASSF2 protein expression level. The operation and the steps are simple; the sgRNA targeting performance is excellent; cutting efficiency on RASSF2 gene is high; the constructed CRISPR-Cas9 lentiviral vector system is high in knockout efficiency, and is capable of realizing specific knockout of RASSF2 gene to obtain human breast cancer cells without RASSF2 gene, so that powerful instrument is provided for study on the action mechanisms of RASSF2 in breast cancer celles.
Owner:OBIO TECH SHANGHAI CORP LTD
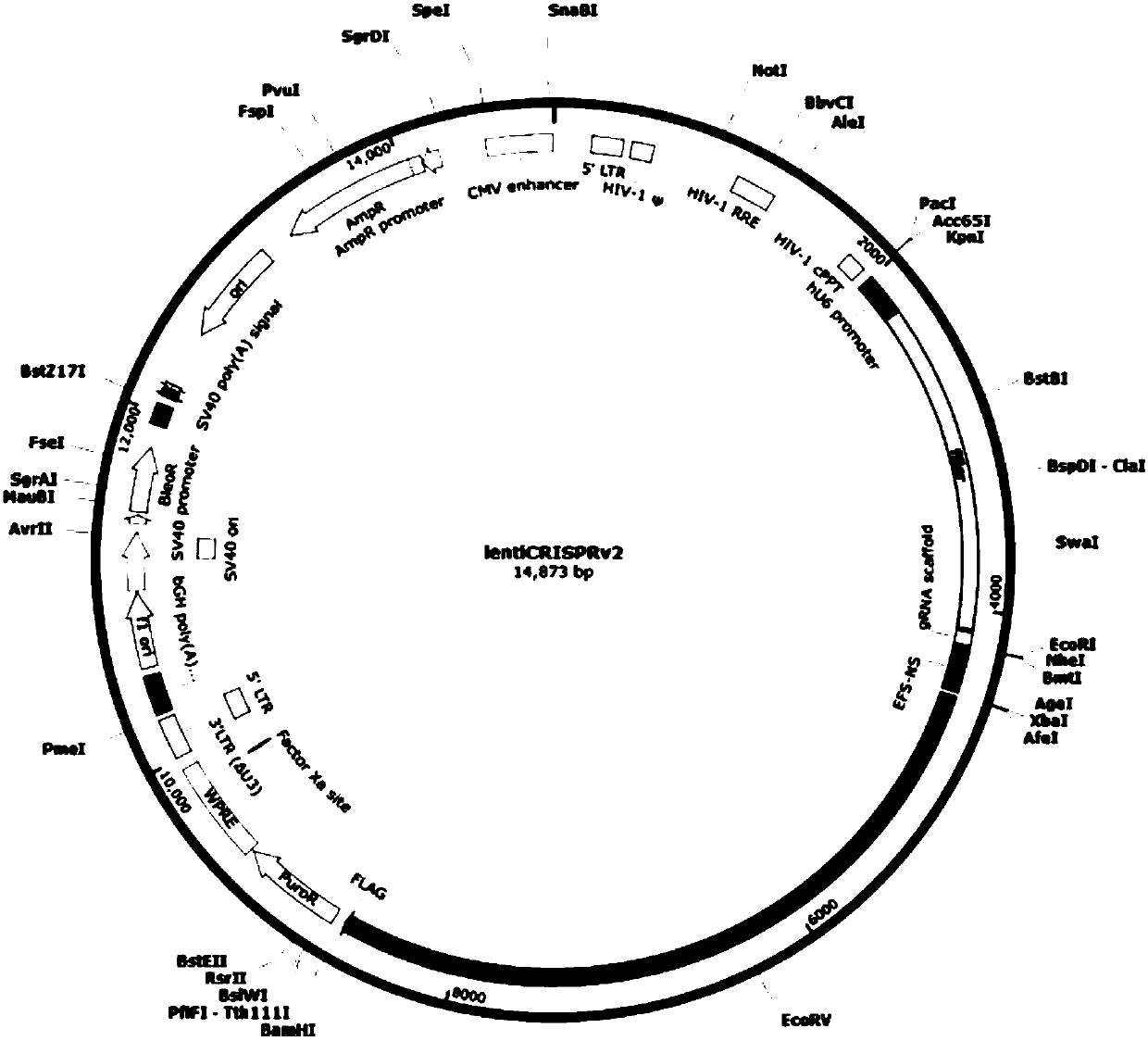
CRISPR-Cas9 targeted and knockout SLC30A1 gene and specific sgRNA of gene
The invention discloses a CRISPR-Cas9 targeted and knockout human breast cancer cell SLC30A1 gene and the specific sgRNA of the gene. Firstly, sgRNA for specific targeting of the SLC30A1 gene is obtained, and a base sequence of the sgRNA is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; secondly, the sgRNA of the SLC30A1 gene is constructed to a lentivirus vector system containing Cas9 proteins; finally, CRISPR / Cas9 lentivirus containing the sgRNA is infected with a human breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 to obtain a cell strain of which the SLC30A1 protein expression level is obviously reduced. The CRISPR-Cas9 targeted and knockout human breast cancer cell SLC30A1 gene and the specific sgRNA of the gene disclosed by the invention have the advantages of simple operation steps, good sgRNA targetability and high cuttingefficiency on the SLC30A1 gene; in addition, the constructed CRISPR / Cas9 lentivirus system has the advantage of high knockout efficiency and can specifically knock out the SLC30A1 gene so as to obtain the human breast cancer cell having the SLC30A1 gene knocked out; therefore, a powerful tool is provided for further researching an action mechanism of the SLC30A1 in breast cancer cells.
Owner:OBIO TECH SHANGHAI CORP LTD
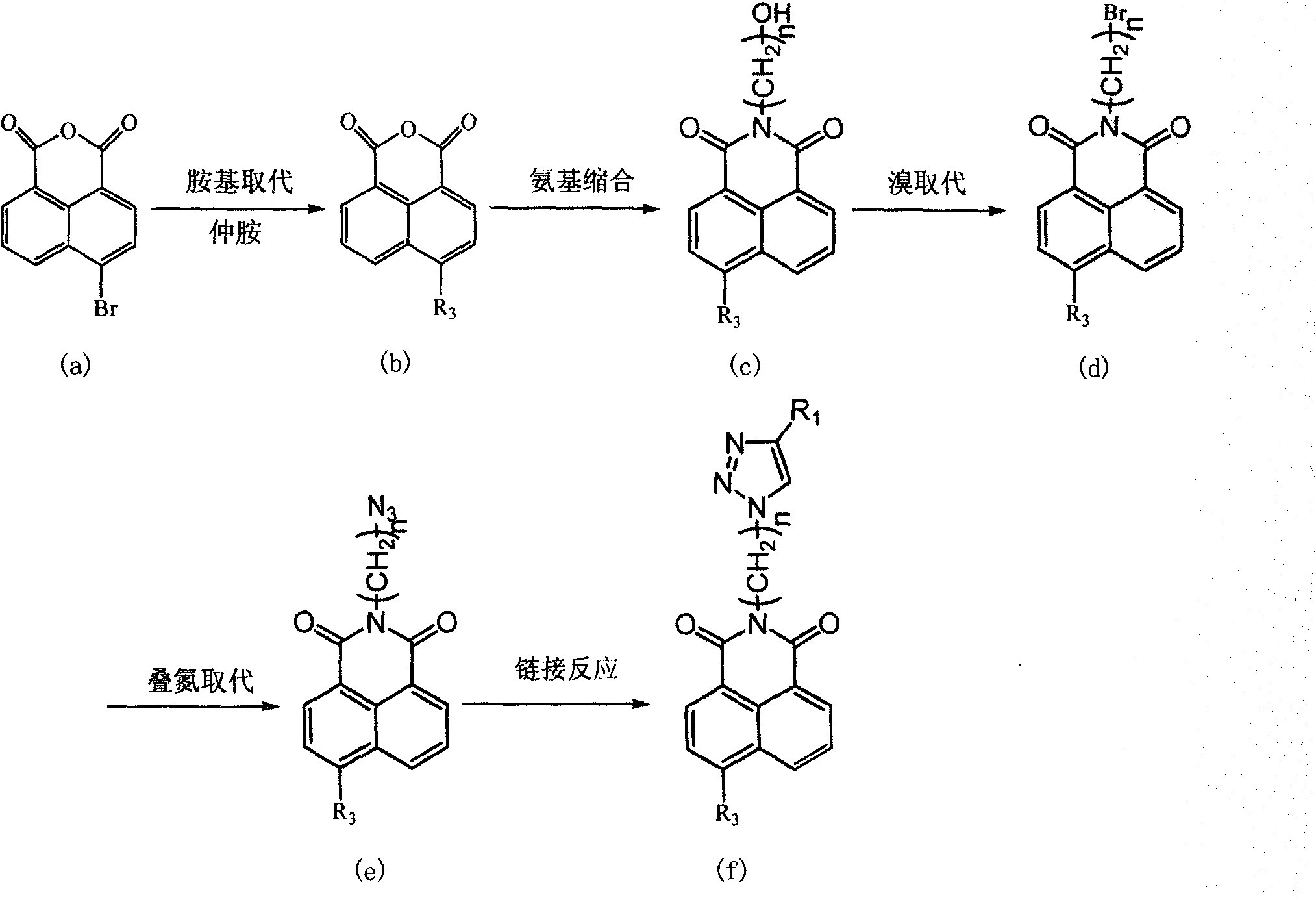
Anti-tumor compound containing triazole heterocyclic structure and application thereof
InactiveCN101628912AGood antitumor activityHigh inhibition rateOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAbnormal tissue growthSide chain
The invention discloses a class of anti-tumor compounds containing a triazole heterocyclic structure and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of medicinal chemistry. The compounds containing the triazole heterocyclic structure introduce quintuple 1,2,3-triazole ring in the form of side chains through the amino condensation, bromination, nitrine substitution, link reaction and other reactions on the basis of naphthalimide parent structure, select tetrazolium salt reduction to test 7721 hepatocellular in the experiment of inhibiting proliferation of tumor cells, and also select sulfonyl rhodamine B protein staining method to test MCF-7 breast cancer cells. The experiment results show that the anti-tumor compounds have wide anti-tumor activity and good inhibition effect on the normal growth of tumor cells derived from different tissues of liver cancer, breast cancer and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Genetic amplification of IQGAP1 in cancer
ActiveUS9157123B2Diminish invasivenessReduce spreadOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCell invasionFollicular thyroid cancer
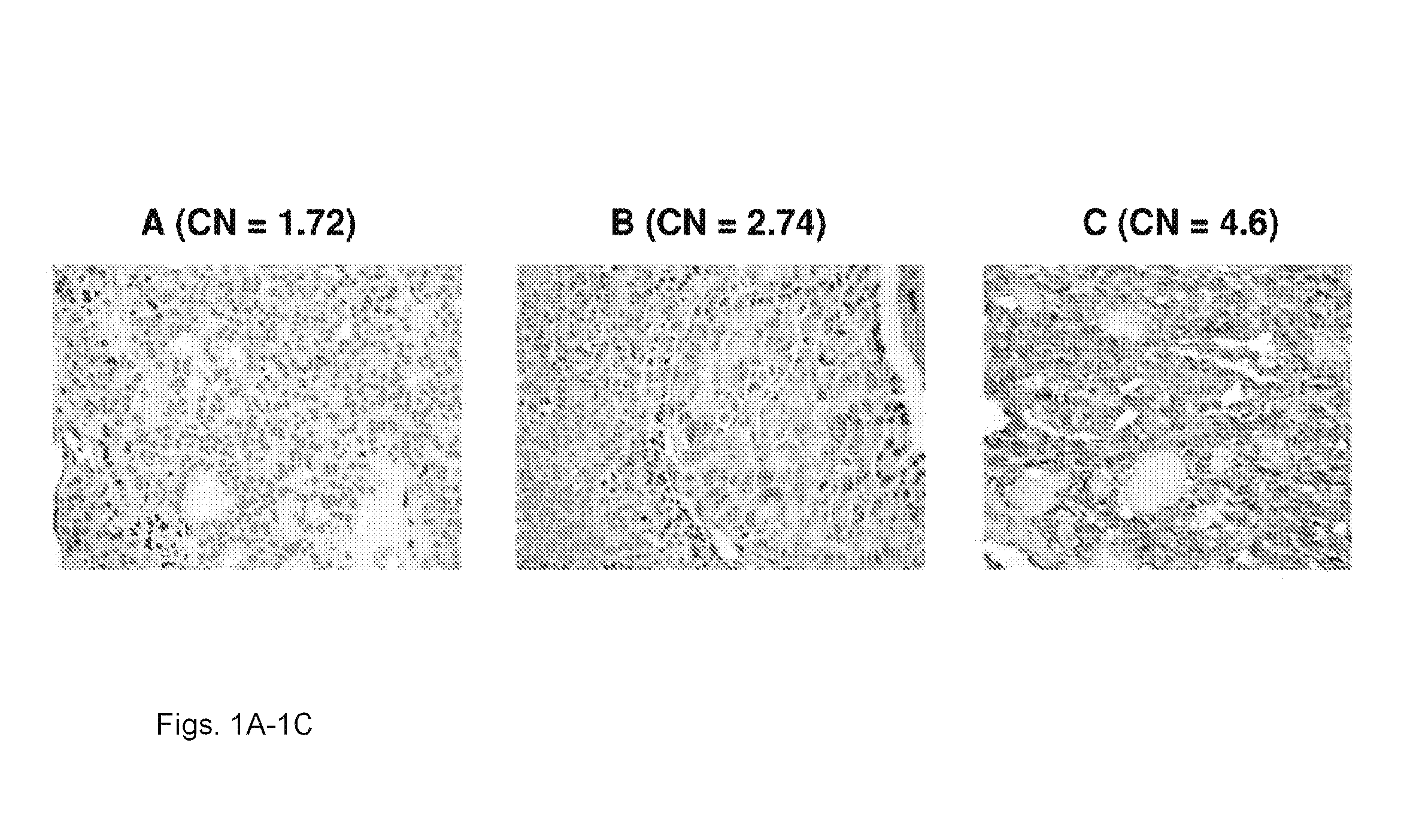
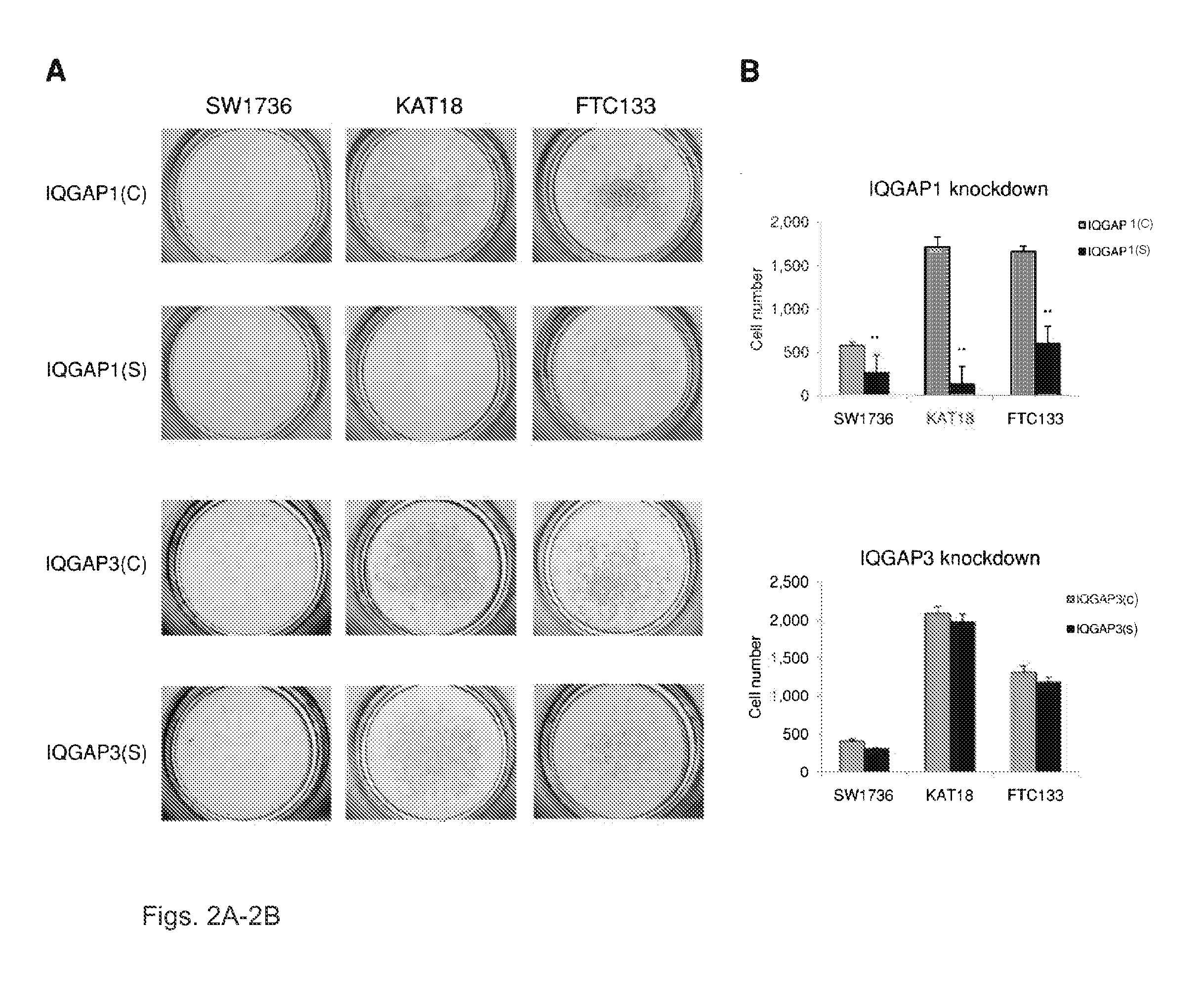
We examined IQGAP1 copy gain and its relationship with clinicopathologic outcomes of thyroid cancer and investigated its role in cell invasion and molecules involved in the process. We found IQGAP1 copy number (CN) gain ?3 in 1 of 30 (3%) of benign thyroid tumor, 24 of 74 (32%) follicular variant papillary thyroid cancer (FVPTC), 44 of 107 (41%) follicular thyroid cancer (FTC), 8 of 16 (50%) tall cell papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), and 27 of 41 (66%) anaplastic thyroid cancer, in increasing order of invasiveness of these tumors. A similar tumor distribution trend of CN ?4 was also seen. IQGAP1 copy gain was positively correlated with IQGAP1 protein expression. It was significantly associated with extrathyroidal and vascular invasion of FVPTC and FTC and, remarkably, a 50%-60% rate of multifocality and recurrence of BRAF mutation-positive PTC (P=0.01 and 0.02, respectively). The siRNA knock-down of IQGAP1 dramatically inhibited thyroid cancer cell invasion and colony formation. Co-immunoprecipitation assay showed direct interaction of IQGAP1 with E-cadherin, a known invasion-suppressing molecule, which was upregulated when IQGAP1 was knocked down. IQGAP1, through genetic copy gain, plays an important role in the invasiveness of thyroid cancer and represents a useful prognostic marker and therapeutic target for this and other cancers.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Products and preparation method of double chimeric antigen receptor gene modified T lymphocyte targeting breast cancer stem cells
InactiveCN105950561AMammal material medical ingredientsNGF-receptor/TNF-receptor superfamilySingle-Chain AntibodiesCytotoxicity
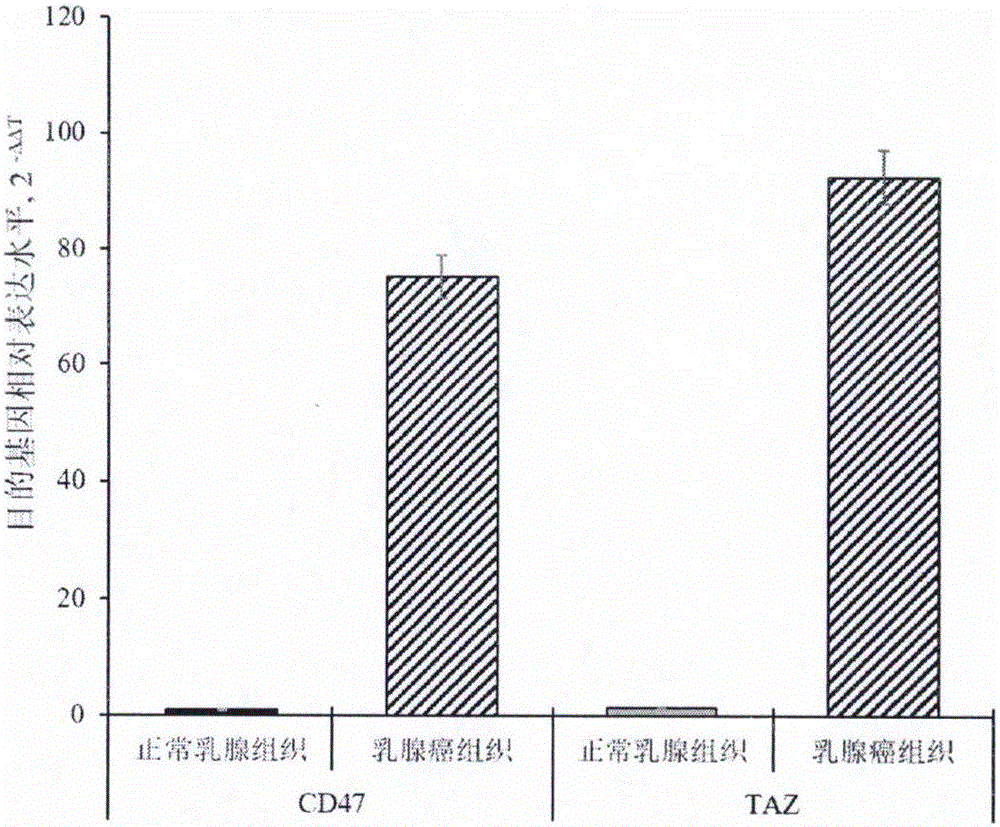
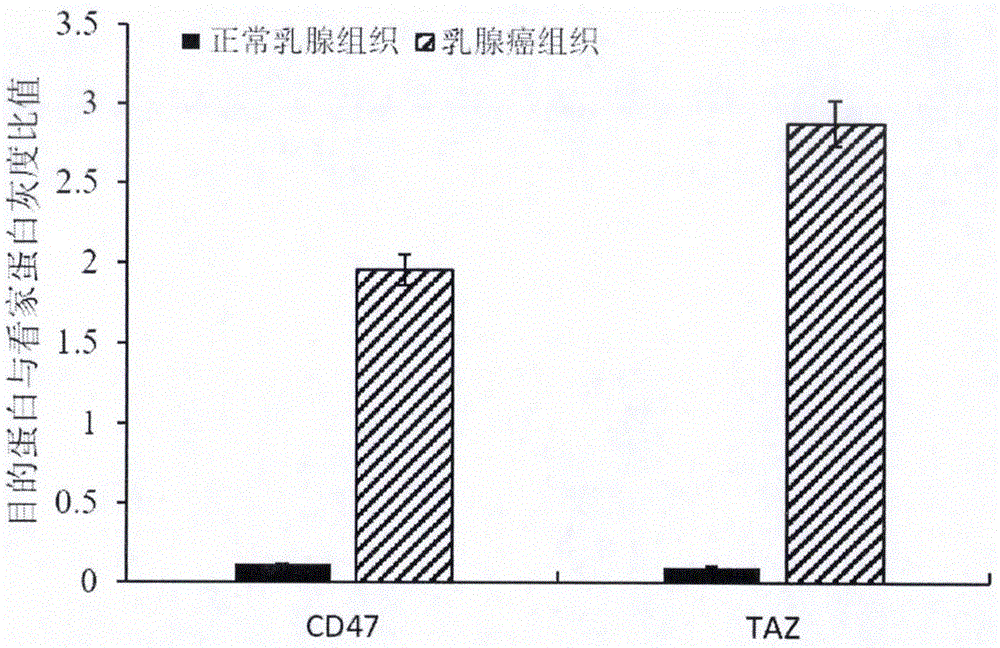
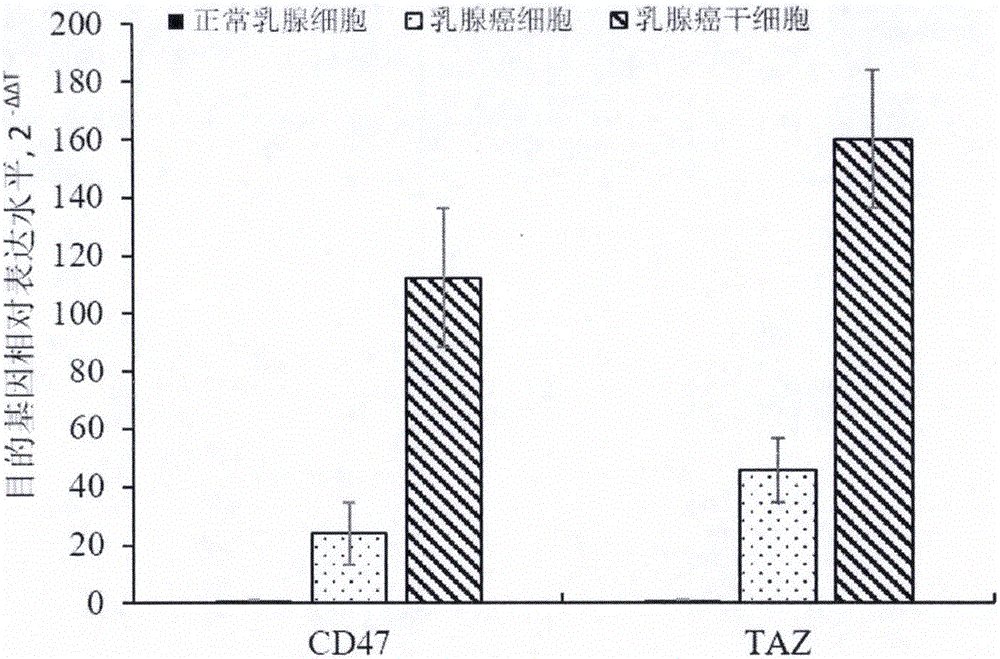
The invention provides a preparation method of a double chimeric antigen receptor gene modified T lymphocyte targeting breast cancer stem cells. The preparation method is characterized in that integrin-associated protein (CD47) and transcriptional coactivator (TAZ) are both highly expressed in breast cancer tissues, especially in the breast cancer stem cells; by established CD47 and TAZ over-expressed breast cancer cells, higher proliferation and metastasis capacity and cancer stem cell features are shown. Extracellular domain of the two breast cancer stem cell antigens CD47 and TAZ are targeted to generate monoclonal strains in specific binding under immunity action, and single-chain antibodies in specific binding with the CD47 and TAZ by genetic recombination are obtained to construct a human CD47 and TAZ containing double chimeric antigen receptor gene recombined to a virus vector to transfect human T lymphocyte. By high expression of the double chimeric antigen receptor gene in specific binding with human CD47 and TAZ expressing breast cancer stem cells, a first signal and a costimulatory signal can be activated to trigger anti-breast-cancer cytotoxicity, and high cytotoxicity in in-vivo and in-vitro anti-cancer experiments is achieved.
Owner:泰州市数康生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing docetaxel and sulforaphane loaded self-assembled nano-particle and application of nano-particle
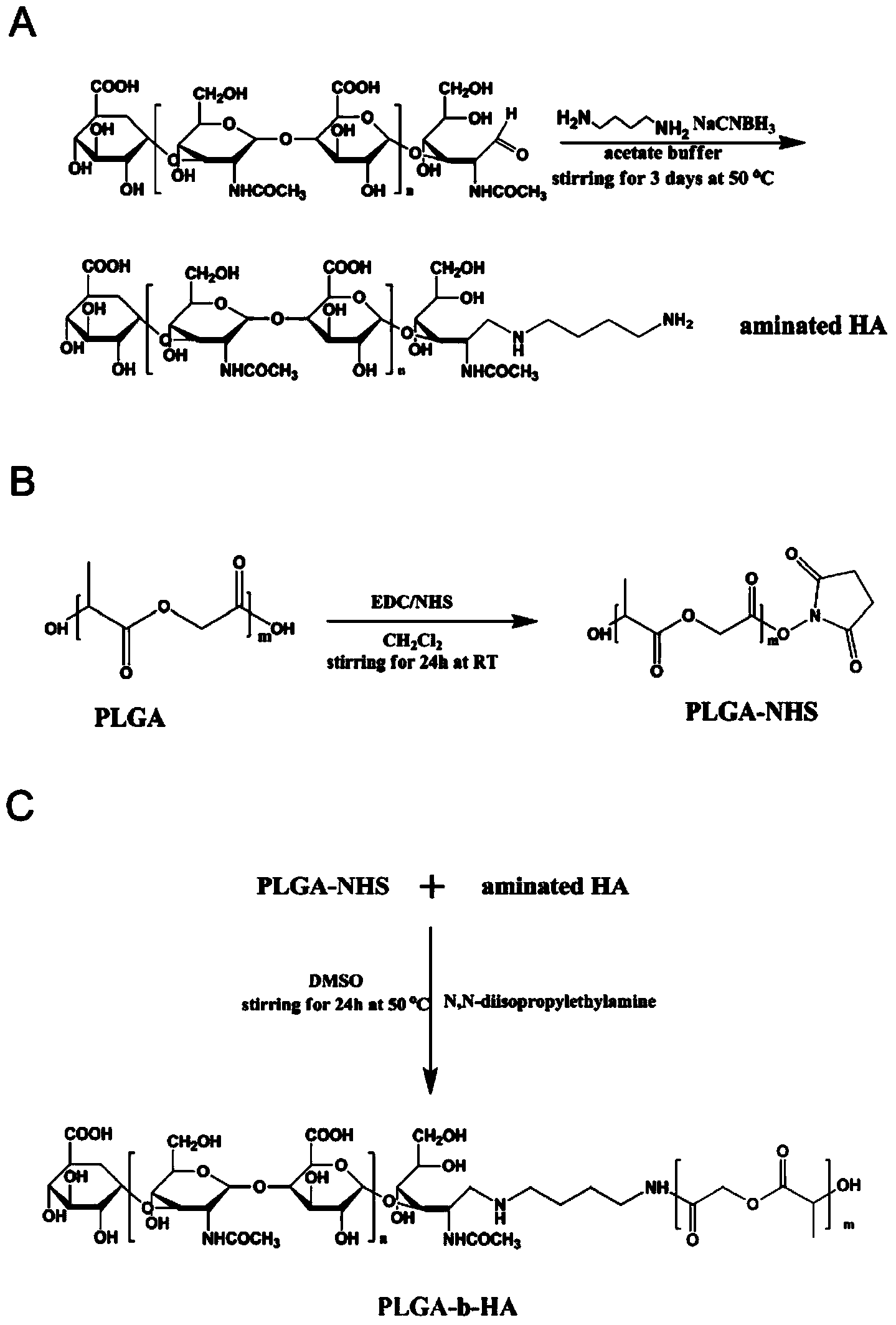
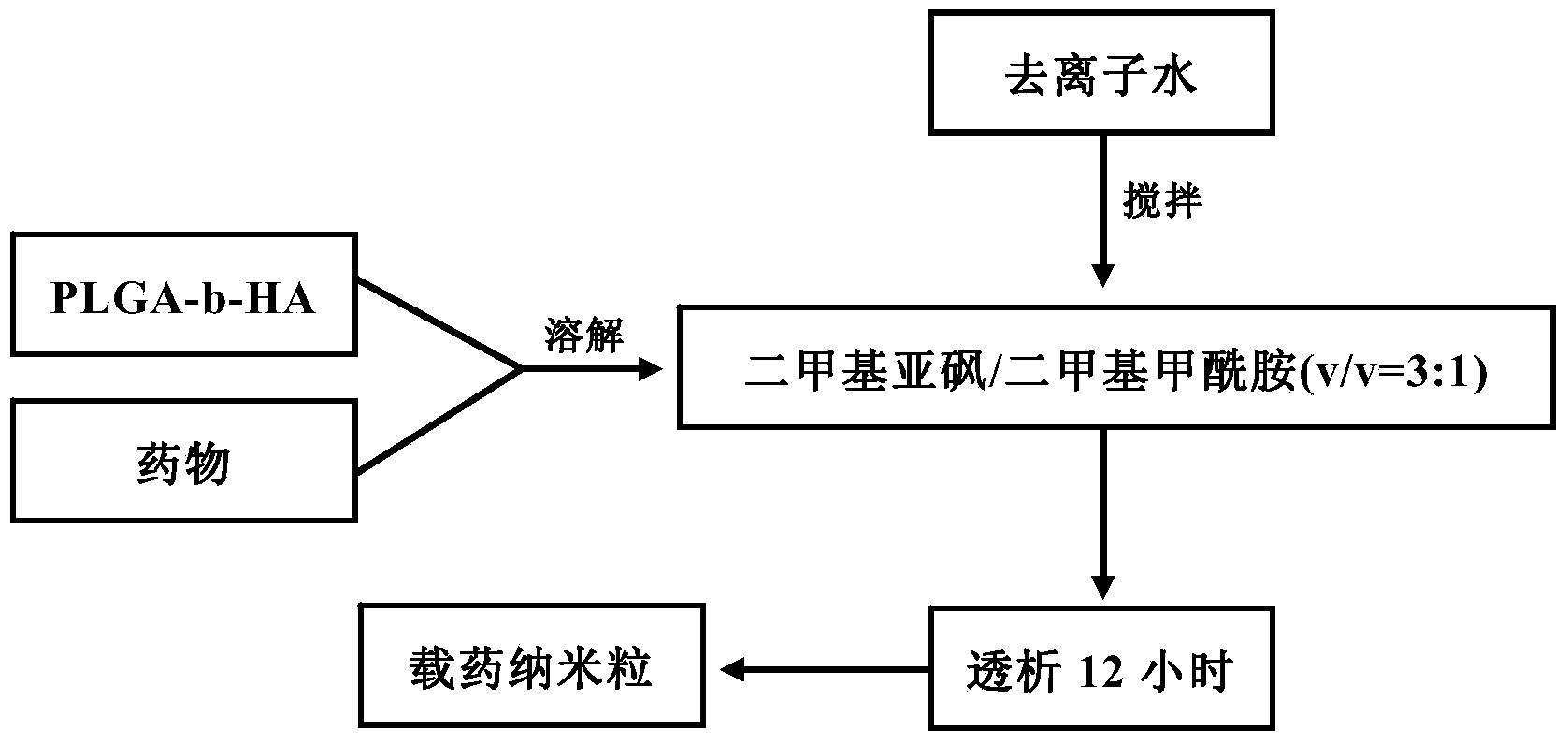
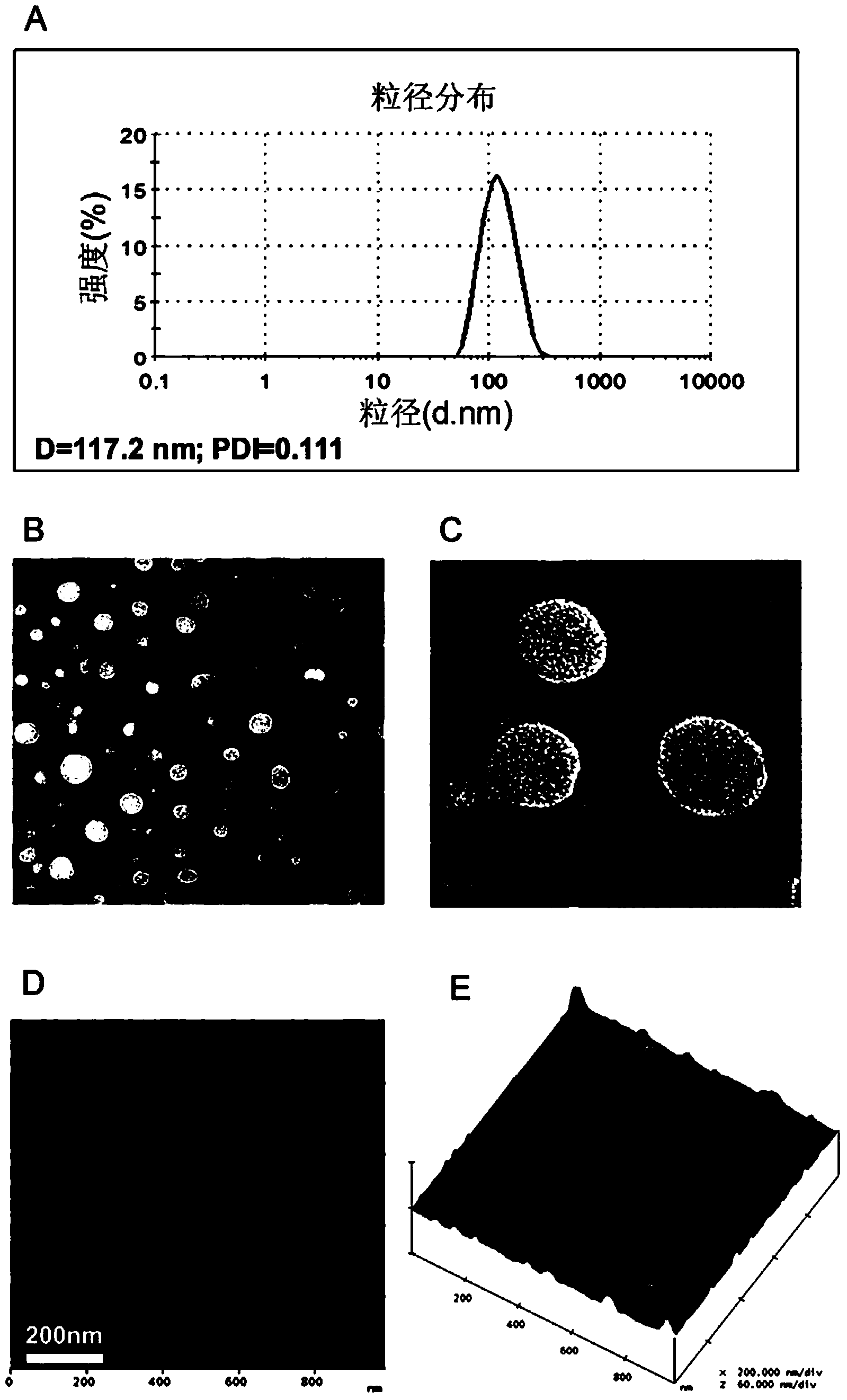
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, and provides a docetaxel and sulforaphane loaded hyaluronic acid modified poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) copolymer self-assembled nano-particle, a preparation method thereof and an application of the self-assembled nano-particle in preparing a medicine for treating breast cancer. The microscopic structure of the nano-particle comprises a hydrophobic PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)) core and a hydrophilic HA (hyaluronic acid) shell, wherein the PLGA core is used for wrapping a medicine DTX (docetaxel) or SFN (sulforaphane), and the hydrophilic shell HA can target a breast cancer stem cell highly expressing a CD44 receptor. In-vitro cytotoxicity tests indicate that the drug-loaded nano-particle can play a good role in resisting differentiation of mammary gland cells and breast cancer stem cells when compared with free medicines; in-vivo tumor inhibition experiments indicate that the drug-loaded medicine is more effective than free medicines and combined free medicines, and has a small systematic toxicity. The nano-particle can play a role in simultaneously performing target differentiating on mammary gland cells and breast cancer stem cells, and a new strategy is provided to treatment of breast cancer.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Antihuman ROR1 (receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor) monoclonal antibody and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104817642AIncrease productionProspects for industrial applicationMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionHeavy chain
The invention provides an antihuman ROR1 (receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor) monoclonal antibody and a preparation method and application thereof. The antibody is provided with a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region, each of the heavy chain variable region and the light chain variable region is provided with three CDRs (complementarity determining regions), the amino acid sequence of the CDR1 of the heavy chain variable region is SEQ ID NO:21 or NO:27, the amino acid sequence of the CDR2 is SEQ ID NO:22 or NO:28, and the amino acid sequence of the CDR3 is SEQ ID NO:23 or NO:29; the amino acid sequence of the CDR1 of the light chain variable region is SEQ ID NO:24 or NO:30, the amino acid sequence of the CDR2 is SEQ ID NO:25 or NO:31, and the amino acid sequence of the CDR3 is SEQ ID NO:26 or NO:32. The antibody is good in monomer stability and high in specificity, specific markers of the leukemia can be detected in advance by monitoring specific cells, ROR1 targets in breast cancer cells can be further combined, and silence experiment completion is facilitated.
Owner:ACROBIOSYSTEMS INC
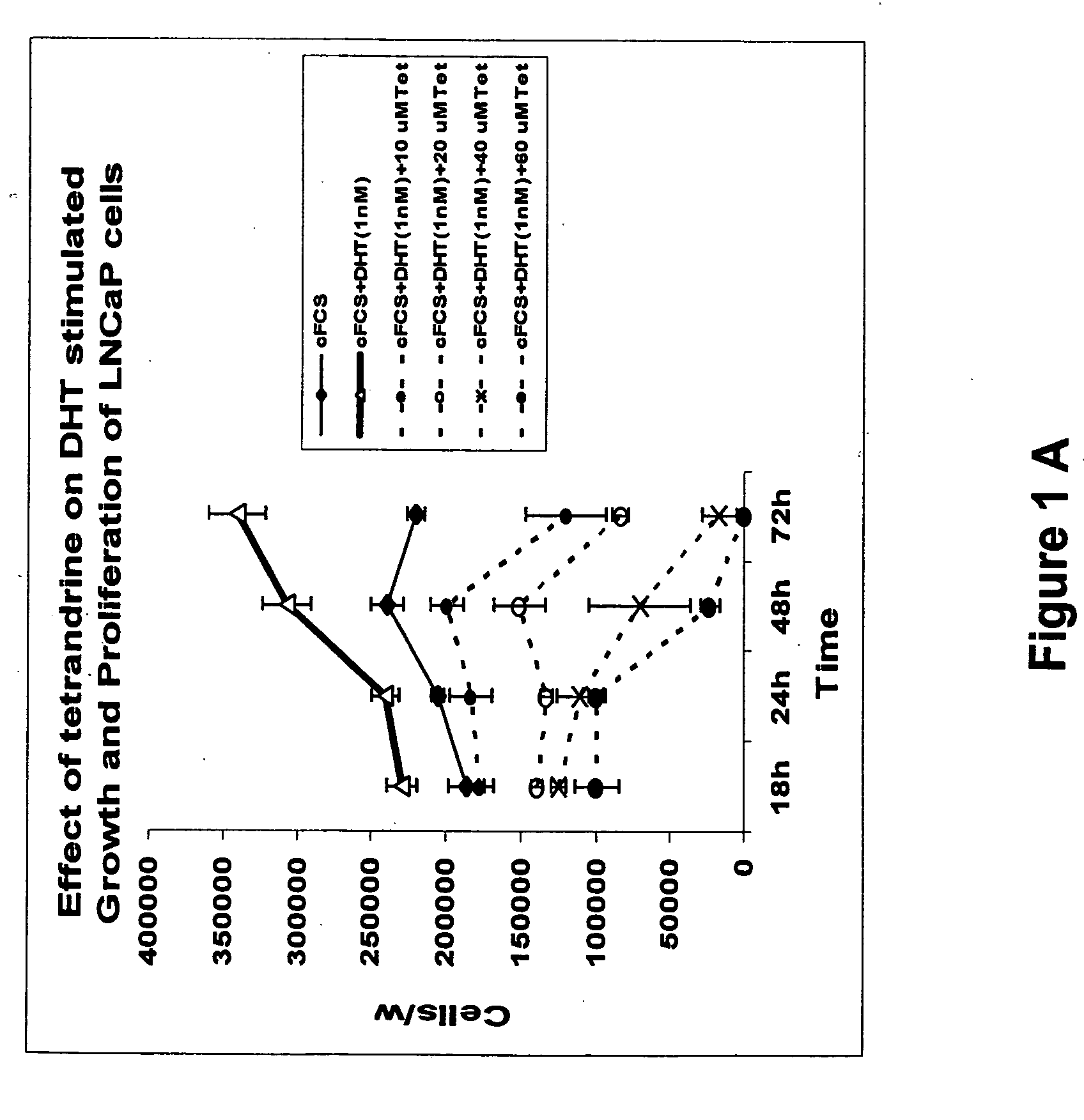
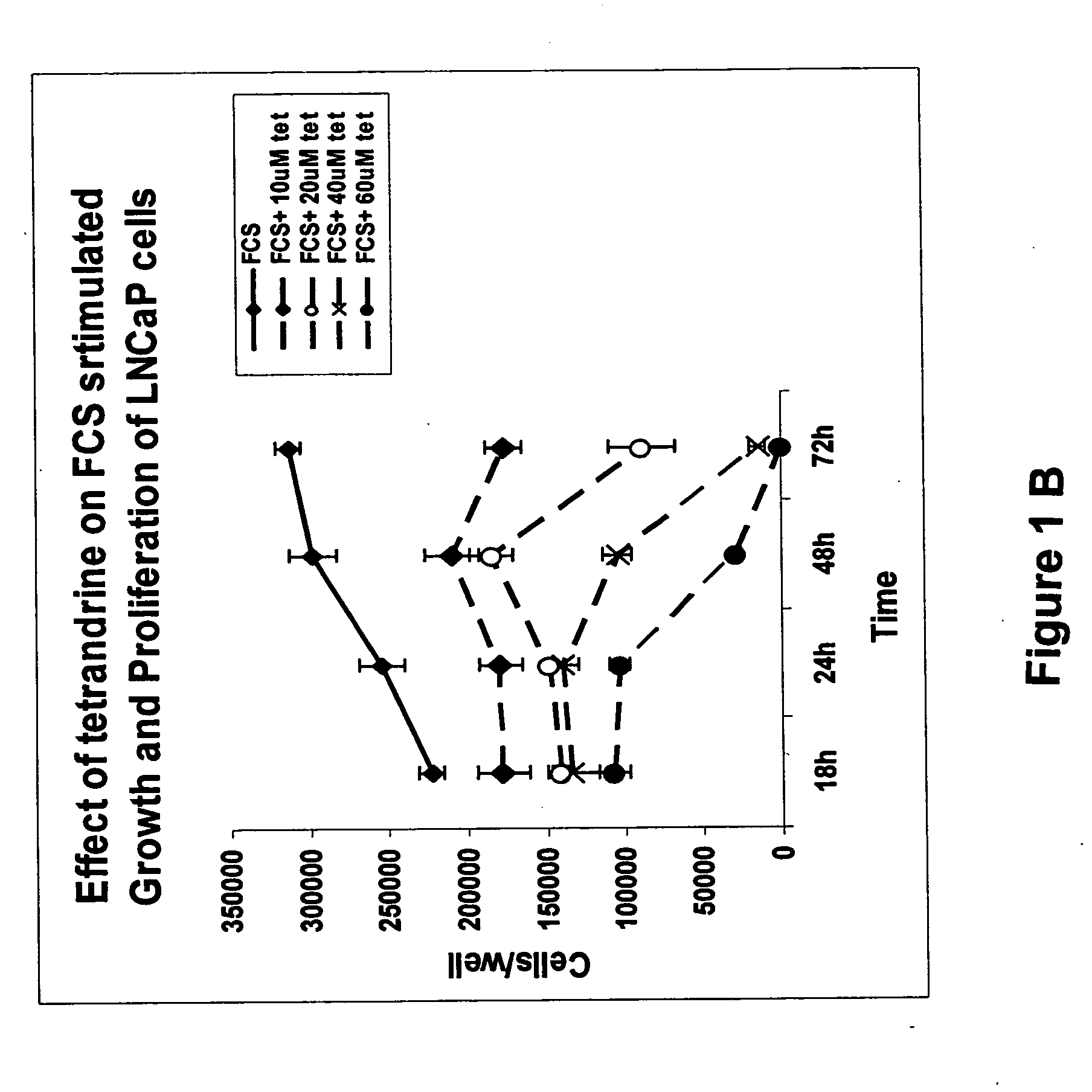
Treatment and prevention of prostate cancer
InactiveUS20050245559A1Treating and preventing prostate cancerBiocideAnimal repellantsProstate cancer cellIsoquinoline
The present invention provides novel methods of preventing and treating prostate cancer with tetrandrine, a bisphehol-isoquinoline alkaloid isolated from the Chinese herb Stephania tetrandra. The present invention also provides the use of tetrandrine for the manufacture of a pharmaceutical composition for treating prostate cancer. The tetrandrine can be used as any isomer of tetrandrine such as the (R,R), (S,S), (R,S), and (S,R) isomers and any combination of these isomers. The present invention also provides methods of inhibiting the growth of prostate cancer cells in vitro by contacting the cells with tetrandrine. The present invention also provides methods of inducing apoptosis in prostate cancer cells in vitro by contacting the cells with tetrandrine.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
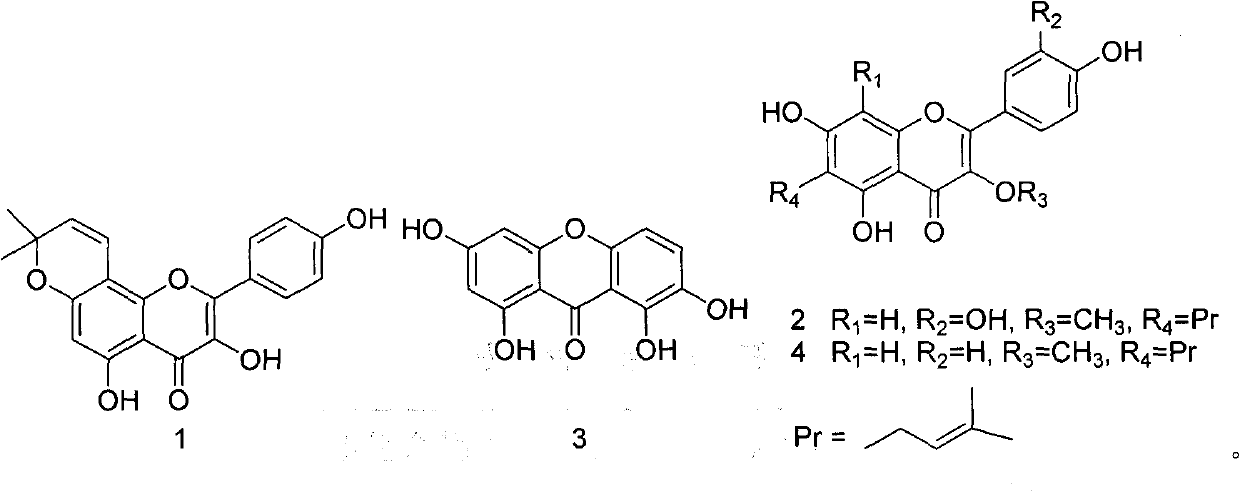
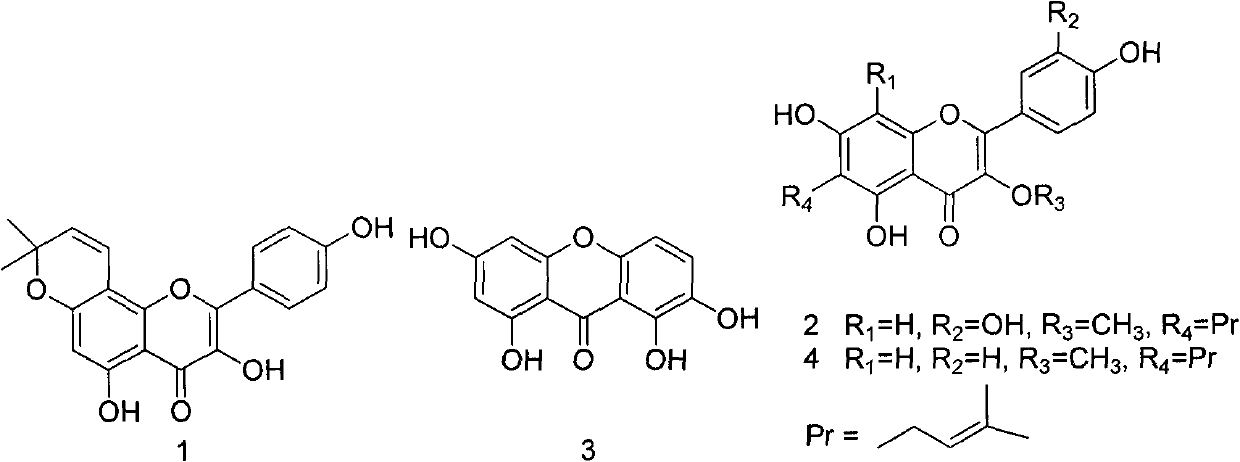
Application of flavonoids compounds to breast cancer resistance
ActiveCN102335165AInhibition of proliferative abilityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsStructural formulaHuman breast
The invention discloses application of four kinds of known flavonoids compounds to treatment of breast cancers. The four kinds of known flavonoids are known compoundes obtained by separating fruit of sinopodophyllum emodi and have structures shown as structural formulas 1-4 in the specification. Experiments on the effect of the kinds of compounds on inhibiting human breast cancer cells show that the series of compounds have a favorable effect on inhibiting the proliferation of the breast cancer cells.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
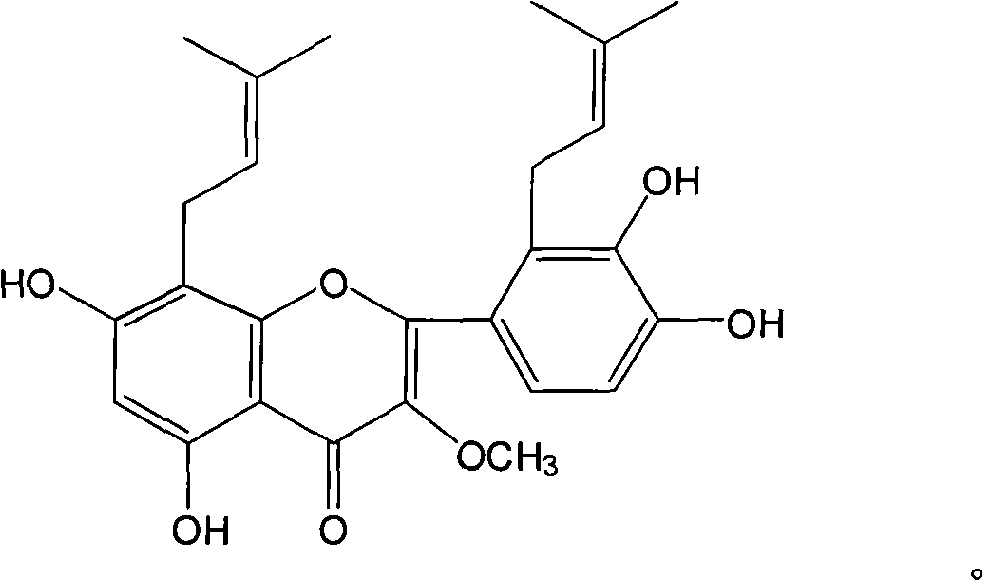
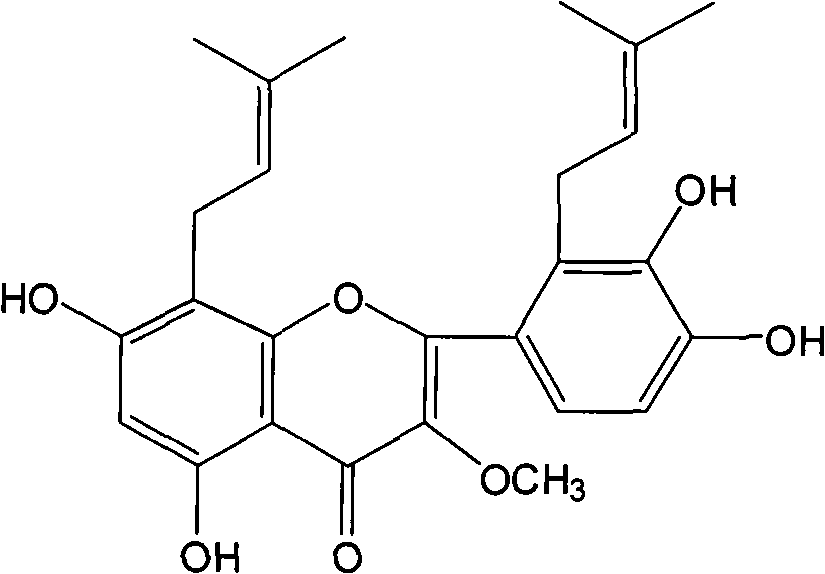
Isopentenyl flavone and application thereof
InactiveCN101648934AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryGynecologyAcinic cell carcinoma
The invention relates to an isopentenyl flavone and an application of the compound to the preparation of a medicament for treating breast cancer. The isopentenyl flavone is a new compound of 8,2'-diprenylquercetin3- methyl etherseparated from fructus podophylli. The experiment of the inhibited effect on human breast cancer cells shows that the isopentenyl flavone has good inhibited effect on the human breast cancer cells.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Inhibition of the Survival of Pancreatic Cancer by Cyclohexenone Compounds from Antrodia Camphorata
ActiveUS20110009494A1Enhance cancer therapeutic effectPromote growthBiocideOrganic chemistryPancreas tumorsCyclohexenone
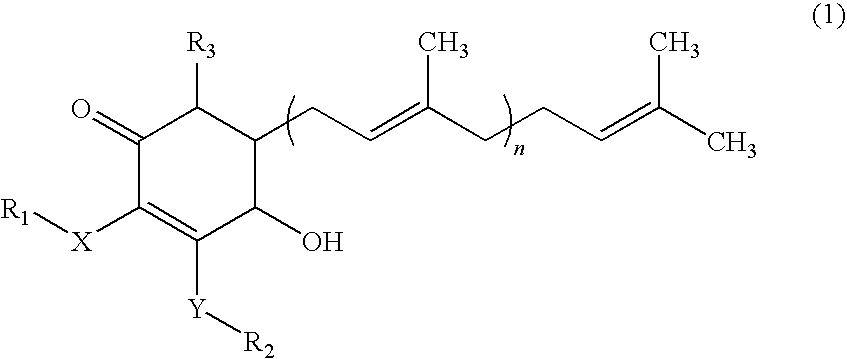
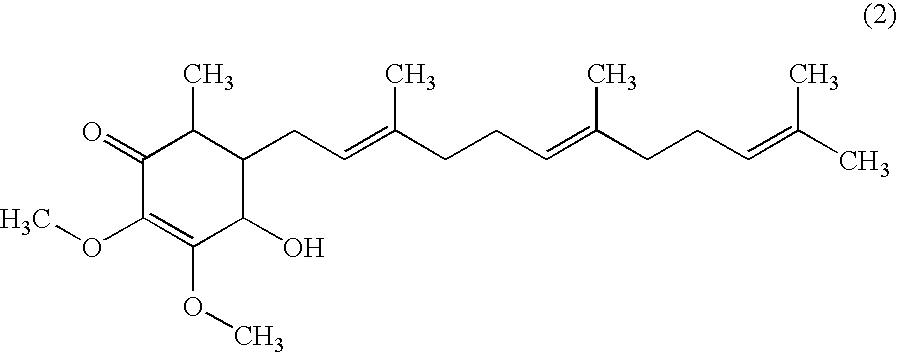
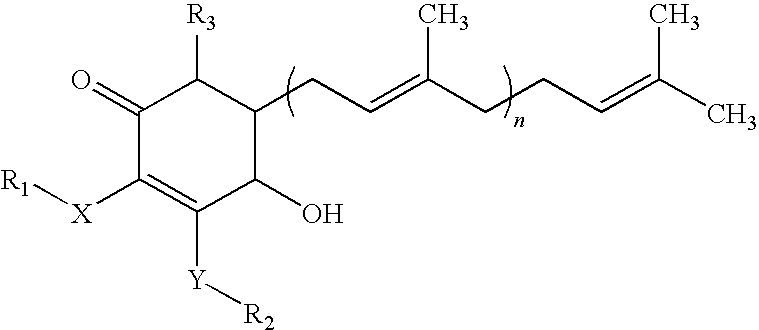
The present invention relates to a novel application of a compound. The compound 4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methyl-5-(3,7,11-trimethyl-dodeca-2,6,10-trienyl)-cyclohex-2-enone of the invention is isolated and purified from the extracts of Antrodia camphorata, which can be applied for inhibiting the survival of pancreatic cancer cells and be used as a pharmaceutical composition to inhibit the pancreatic tumor growth.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
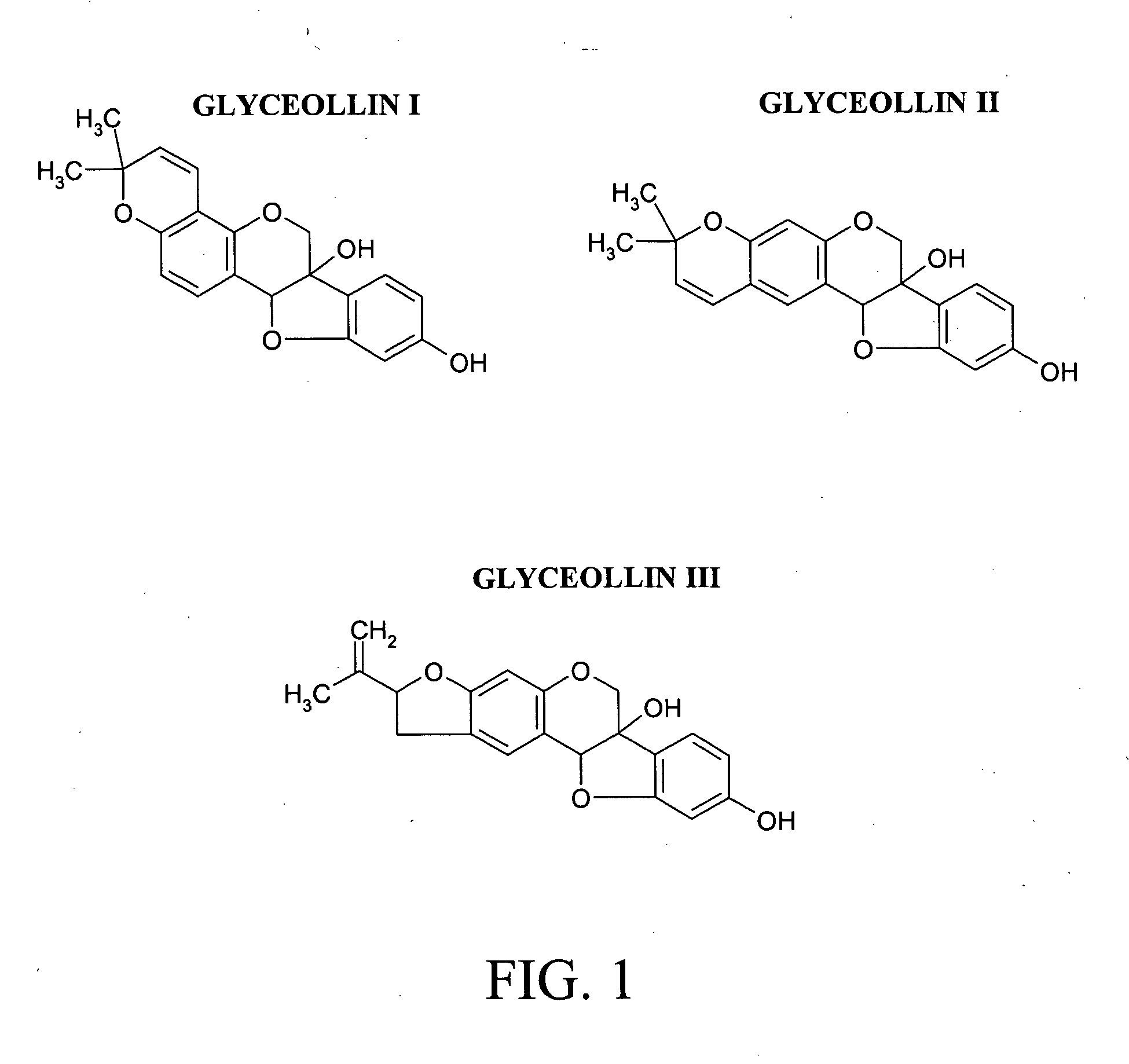
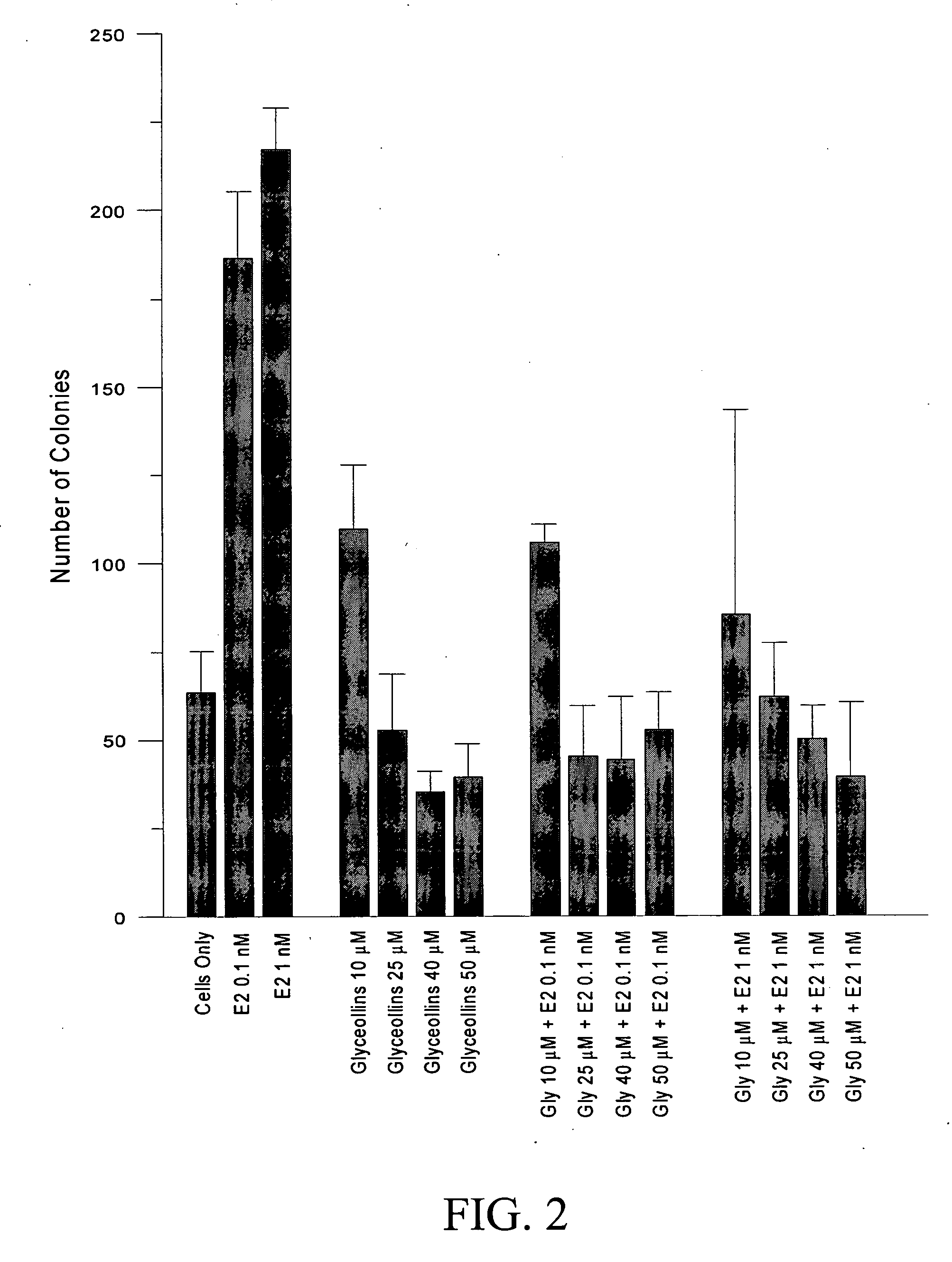
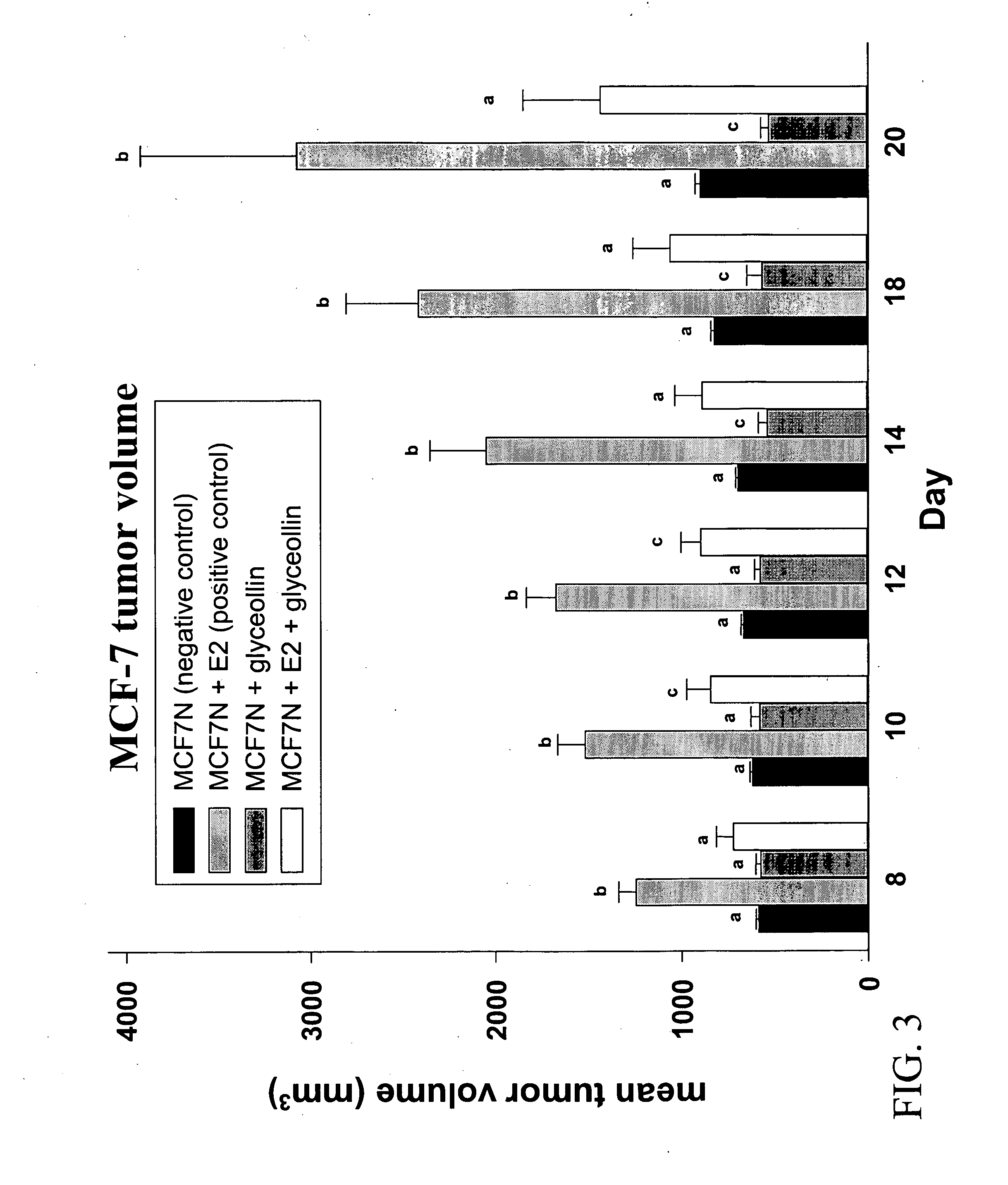
Antiestrogenic glyceollins suppress human breast and ovarian carcinoma proliferation and tumorigenesis
InactiveUS20060246162A1Preventing minimizing development growthOrganic active ingredientsBiocideStress inducedPhytochemical
The flavonoid family of phytochemicals, particularly those derived from soy, has received attention regarding their hormonal activity and their effects on human health and disease. The types and amounts of these compounds in soy and other plants are controlled by both constitutive expression and stress-induced biosynthesis. The health benefits of soy may therefore be dependent upon the amounts of the various hormonally active phytochemicals present. We have identified increased biosynthesis of the isoflavonoid phytoalexin compounds, Glyceollins I, II and III, in soy plants grown under stressed conditions (elicited soy), which exhibit marked anti-estrogenic effects on ER function. Here we demonstrate that specific glyceollins, isolated from elicited soy, displayed anti-estrogenic activity, suppressing basal and estrogen stimulated colony formation of ER-positive estrogen dependent breast cancer cells and inhibiting ER-dependent gene expression of progesterone receptor (PgR) and stromal derived factor-1 (SDF1 / CXCL12). Examining the effects of glyceollin on in vivo tumor formation / growth we demonstrate the ability of glyceollins to significantly suppress basal and estrogen-stimulated tumor growth of ER-positive MCF-7 breast and BG-1 ovarian carcinoma cells in ovariectomized female nude mice. We further demonstrate that the effects of glyceollins on suppression of tumor growth correlate with inhibition of estrogen stimulated PgR expression. In contrast to the uterotropic activity of tamoxifen the glyceollins displayed no uterine agonist activity. The Glyceollin (I-III) compounds may represent an important component of the health effects of soy as well as represent novel anti-estrogens useful in the prevention or treatment of breast and ovarian carcinoma.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
Application of phosphodiesterase4 inhibitor ZL-n-91 in preparing medicine for treating prostate cancer proliferation and transfer
ActiveCN107714686AStrong specificityLittle side effectsPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsProstate cancer cellCytology
The invention discloses application of a phosphodiesterase4 (PDE4) inhibitor ZL-n-91 in preparing medicine for treating prostate cancer proliferation and transfer. Animal experiments and cytology experiments of mice are utilized to show that the phosphodiesterase4 inhibitor ZL-n-91 disclosed by the invention can obviously inhibit prostate cancer cell proliferation and transfer, so that the phosphodiesterase4 inhibitor ZL-n-91 is indicated to hopefully become an important target of prostate cancer proliferation and transfer researches, a foundation is provided for preparing medicine for resisting prostate cancer proliferation and transfer, and the phosphodiesterase4 inhibitor ZL-n-91 has a good development and application prospect.
Owner:SHENZHEN HANHUI PHARM TECH CO LTD
Application of gene marker in diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer
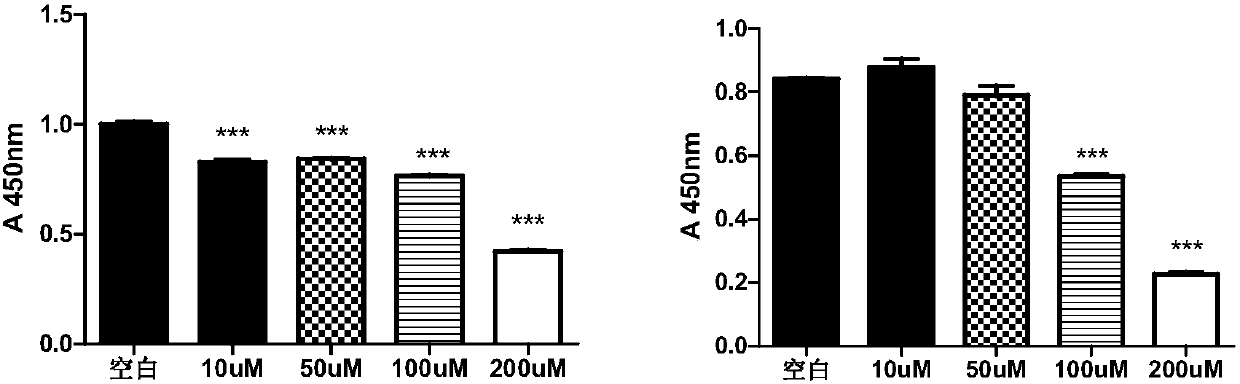
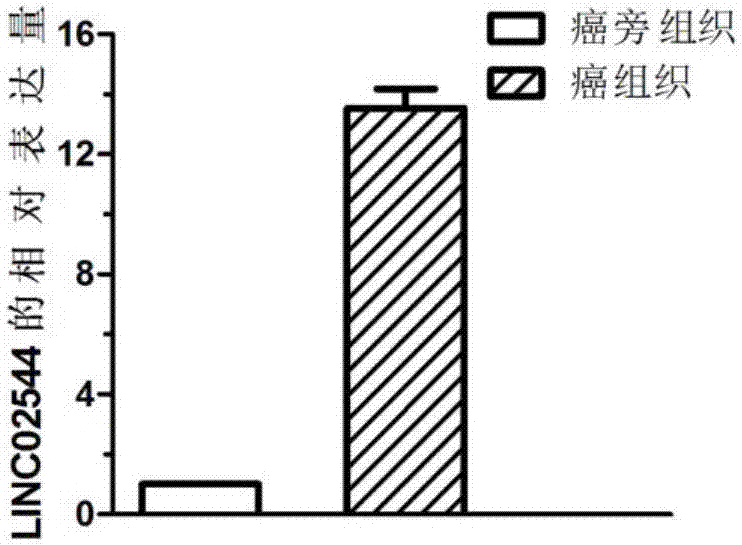
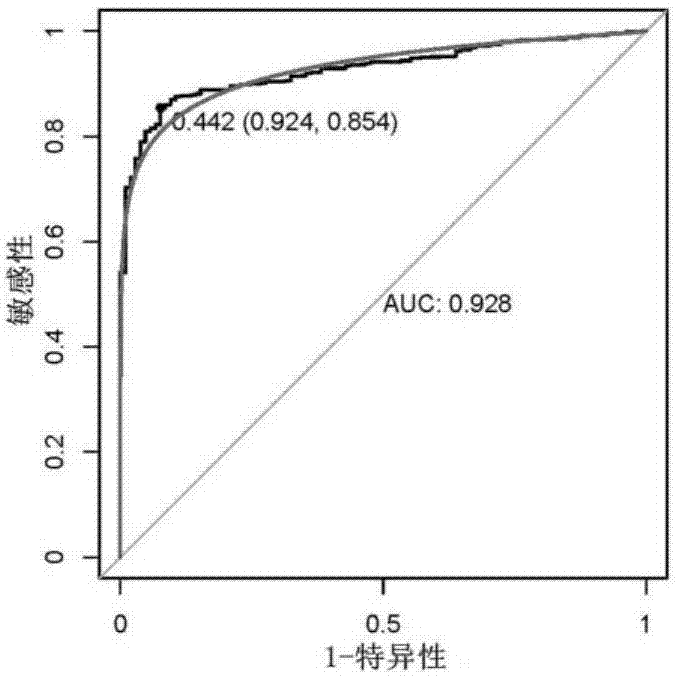
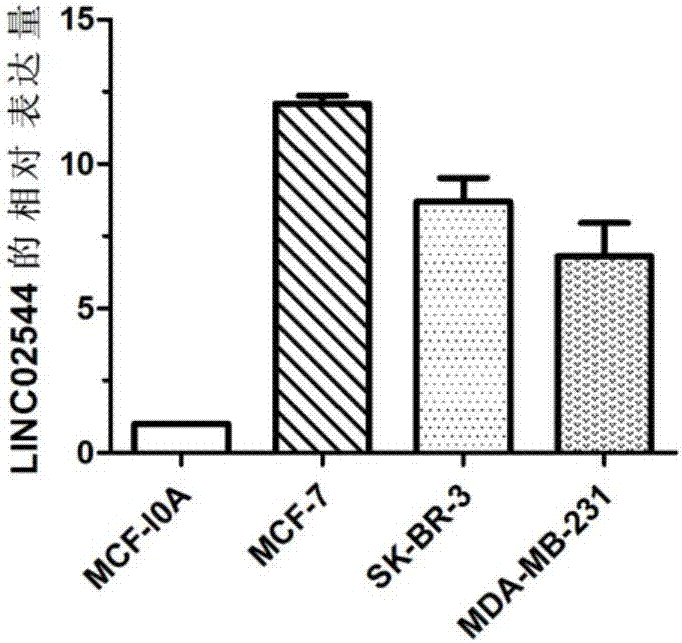
The invention discloses an application of a gene marker in diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. The gene is LINC02544, the invention firstly discovers that expression of LINC02544 in a breast cancer patient is obviously up-regulated, and verification is further carried out through QPCR, so that LINC02544 can be applied to diagnosis of the breast cancer as a biomarker. The invention also discloses that proliferation of breast cancer cells can be effectively inhibited and migration and attack rates of the breast cancer cells can be reduced by reducing expression of LINC02544, so that LINC02544 can be applied to treatment of the breast cancer and shift thereof as a drug target.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
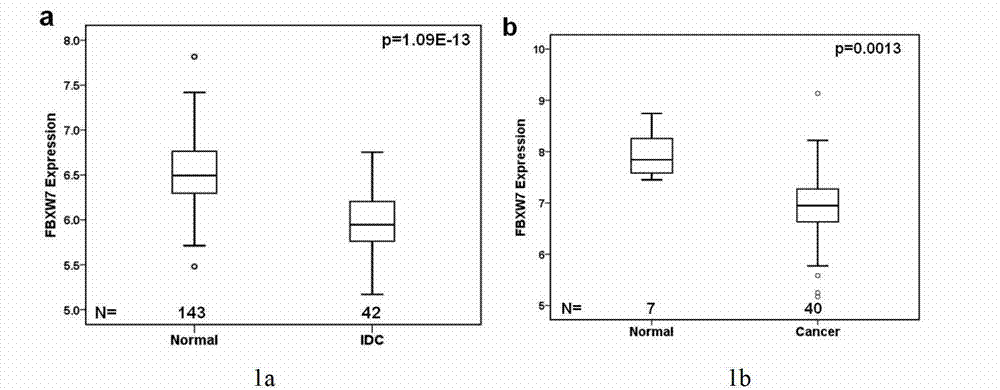
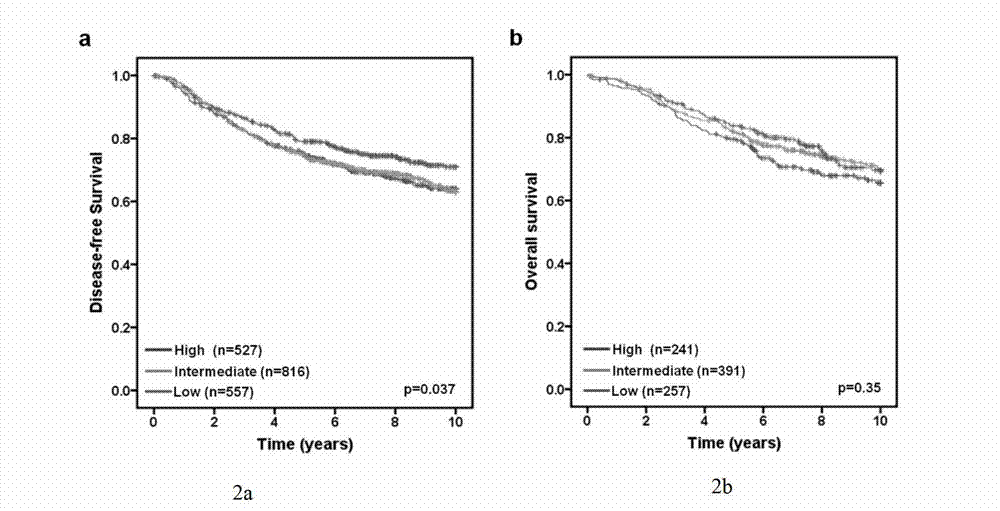
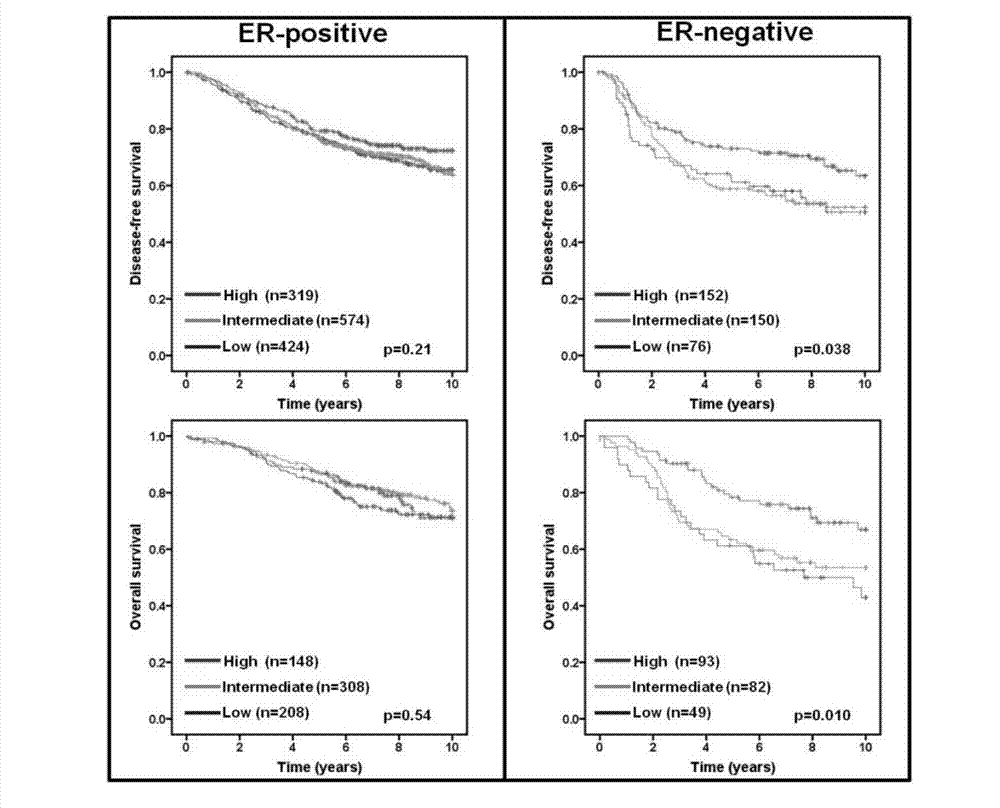
Application of cancer suppressor gene FBXW7 in preparation of drugs used for preventing or treating breast tumors, expression vector and diagnosis medicine
ActiveCN103191443ARealize detectionGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividualized treatmentPrognostic prediction
The invention discloses application of a cancer suppressor gene FBXW7 in preparation of drugs used for preventing or treating breast tumors, an expression vector and a diagnosis medicine, belonging to the field of medical biotechnology. Specifically, the invention provides application of the cancer suppressor gene FBXW7 in preparation of drugs used for preventing or treating breast tumors, the expression vector constructed from the gene FBXW7 and a vector pcDNA3.1 and a preparation method thereof, and the breast tumor diagnosis medicine at least including a pair of primers capable of specific amplification of the gene FBXW7 and composed of an upstream primer and a downstream primer. Expression of the cancer suppressor gene FBXW7 is closely related to breast cancer molecular subtyping; the cancer suppressor gene FBXW7 has specific low expression in a breast cancer with high grade malignancy and exerts an inhibitory effect on growth of breast cancer cells. Thus, screening of breast cancers with low expression of the gene has significant meaning to prognostic prediction of the breast cancers; and specific recovery of expression of the cancer suppressor gene in breast cancer cells provides a novel approach for targeted individualized treatment of the breast cancers.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Separation method of breast cancer stem cells
InactiveCN103243075AGuaranteed separation efficiencyGuaranteed purityTumor/cancer cellsCancer cellMagnetic bead
The invention provides a separation method of breast cancer stem cells and belongs to the field of cell separation. The separation method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a hydrothorax single-cell suspension; (2) carrying out immunomagnetic bead negative sorting, and separating and removing non-breast-cancer cells, so as to obtain breast cancer epithelial cell sap; and (3) carrying out enrichment and purification on the breast cancer epithelial cell sap obtained in the step (2) by utilizing a non-adhesive culture method, so as to obtain breast cancer stem cell spheroids. Compared with the prior art, the separation method has the beneficial effects that the surfaces of the cells obtained by utilizing the separation method are not interfered by antibodies and magnetic beads; the separation efficiency of the breast cancer cells and the purity of the breast cancer cells after the breast cancer stem cells are enriched can be guaranteed; and not only can a small quantity of breast cancer epithelial cells be effectively separated, but also the separation time is shortened, and the production cost is lowered, so that the separation method is safe and effective.
Owner:四川全组生命科技有限公司
Compositions and methods for targeted tumor therapy
The present invention relates to a method of treating a human patient having one or more tumor cells. In one embodiment, the method comprises the step of implanting at or around the site of one or more tumor cells in the patient a cell population comprising one or more prostate cancer cells characterized in that the one or more prostate cancer cells have the propensity of metastasizing to skeleton and soft tissues which represent one or more lethal phenotypes of human prostate cancer.
Owner:CHUNG LELAND F +1
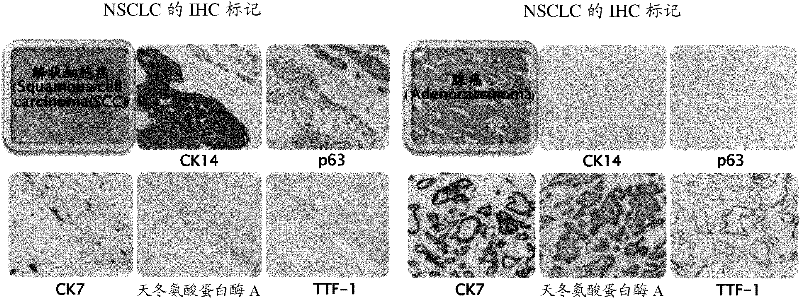
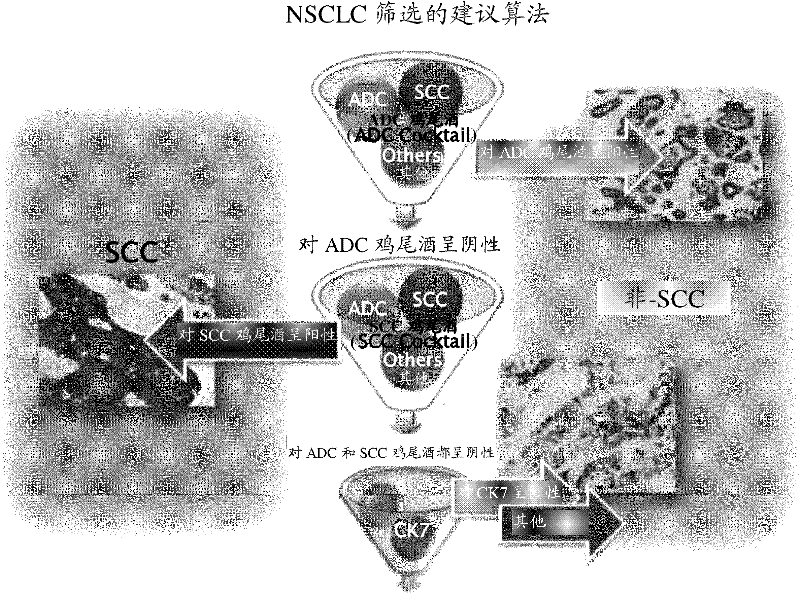
Cocktail antibody for determining histological type of carcinoma, determination kit and determination method
InactiveCN102405238AHigh precisionImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingAdenocarcinomaSquamous Carcinomas
Disclosed are a cocktail antibody, which is useful in determining the histological type of carcinoma, and a determination method using the same. Also disclosed is a determination kit. A cocktail antibody to be used for determining the histological type of lung carcinoma, characterized by comprising a combination of ADC cocktail antibody, which undergoes antigen-antibody reactions with Napsin-A localizing in the cytoplasm of adenocarcinoma and TTF-1 localizing in the cell nucleus thereof, with SCC cocktail antibody, which undergoes antigen-antibody reactions with CK14 localizing in the cytoplasm of squamous cell carcinoma and p63 localizing in the cell nucleus thereof.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOYAMA
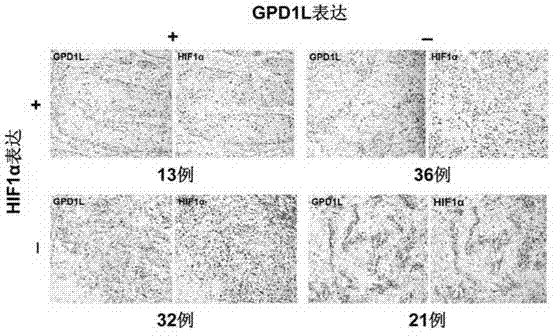
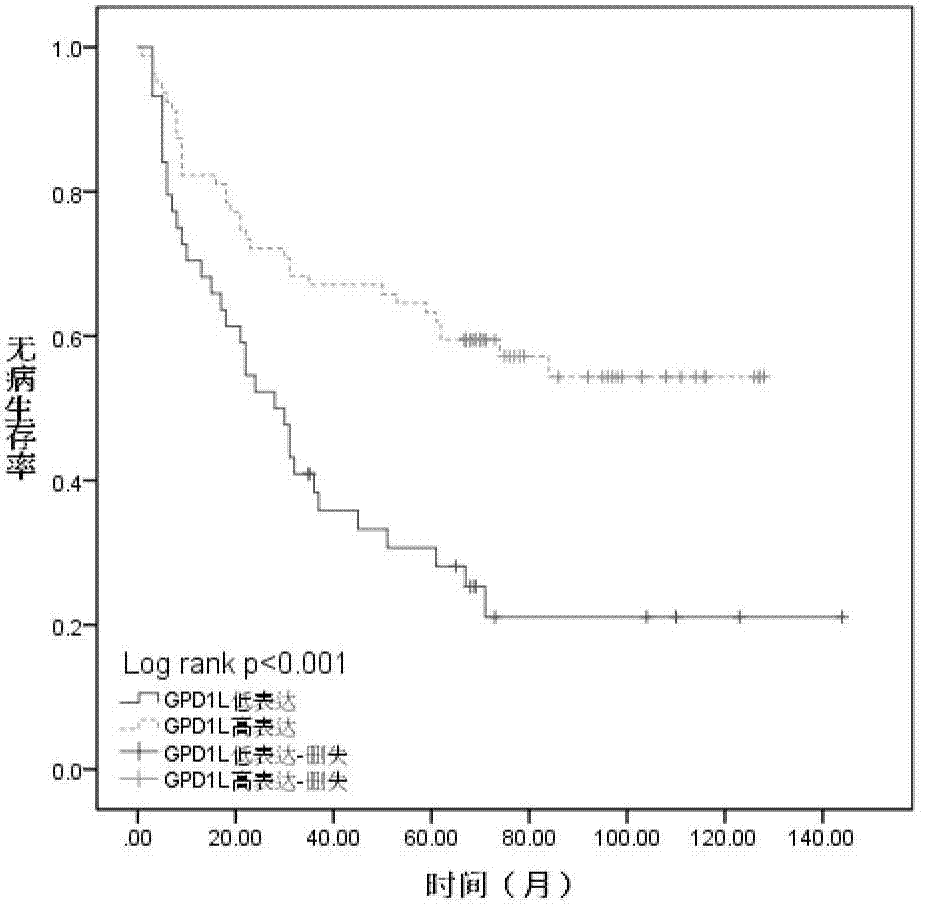
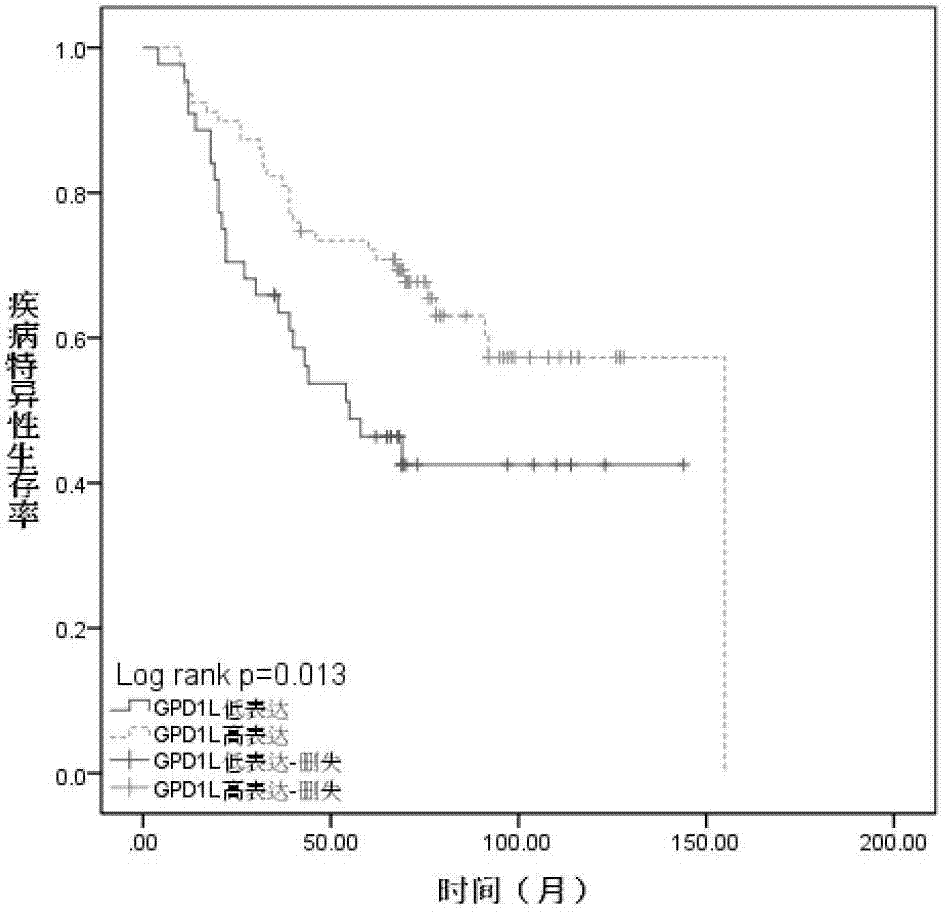
Biological marker of oral cavity oropharynx squamous-cell carcinoma and application of biological marker
ActiveCN104267191AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresDisease diagnosisBiological testingLymphatic SpreadSmall-cell carcinoma
The invention provides a biological marker of oral cavity oropharynx squamous-cell carcinoma and application of the biological marker. The biological marker is GPD1L and / or HIF1 alpha, and especially a combination of the GPD1L and the alpha. According to the invention, by detecting expression levels of the GPD1L and / or the HIF1 alpha, oral cavity oropharynx squamous-cell carcinoma auxiliary diagnosis, oral cavity oropharynx squamous-cell carcinoma patient prognosis, and / or prognosis cervical lymph node metastasis prediction can be performed.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SCHOOL OF STOMATOLOGY
Application of ingenane diterpene compound in preparation of antitumor drug
ActiveCN104622865AHigh activityGood choiceCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationChemical recyclingSide effectMedicine
The invention discloses an application of an ingenane diterpene compound in preparation of antitumor drug. The ingenane diterpene compound is one or more of the ingenane diterpene compound shown in a formula (1). The ingenane diterpene compound can obviously inhibit the propagation activity of breast cancer cells, compared with a traditional tumor therapeutic method, tumor inhibitory effect is good, toxic and side effects are little, targeting property is strong, the ingenane diterpene compound has no damage to normal cells, security can be guaranteed at maximum degree, the ingenane diterpene compound provides a latent novel medicine development purpose for treating breast cancer, and can be a further research as an anti-breast cancer candidate medicine.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of biomarker as target to diagnosis and treatment of lung adenocarcinoma
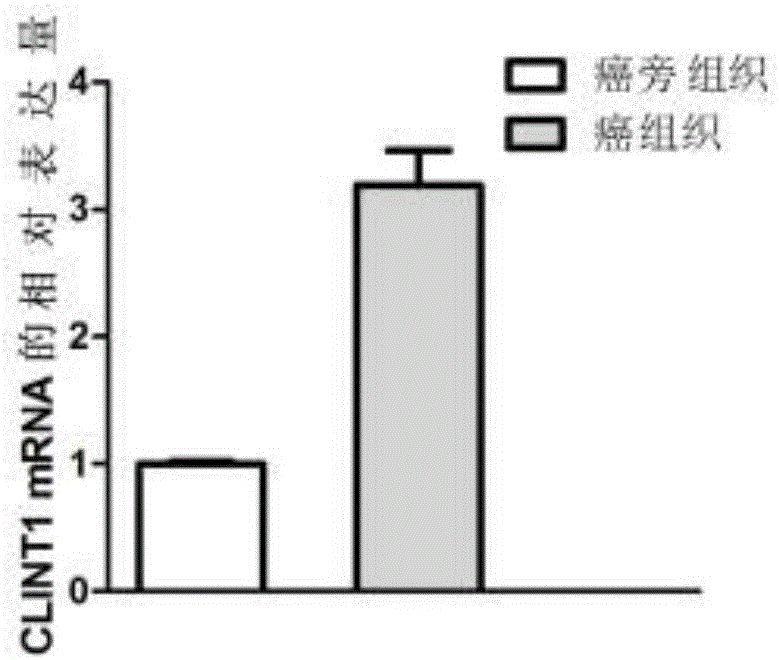
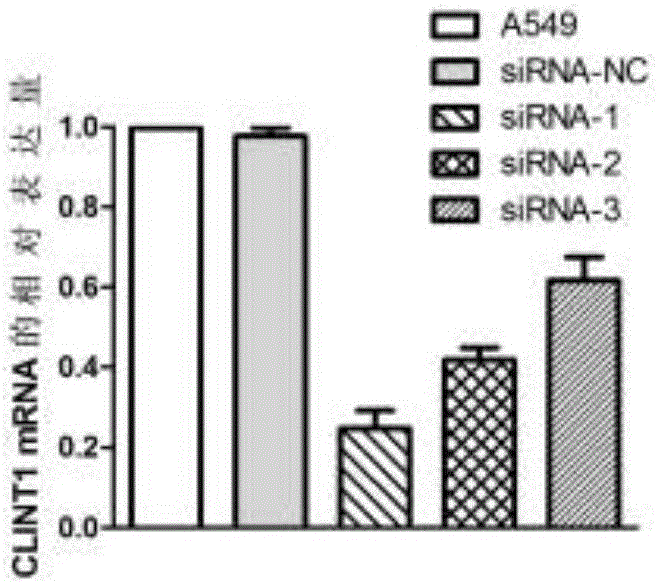
ActiveCN106729756AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAdenocarcinoma lung cancerDrug target
The invention discloses application of a biomarker as a target to the diagnosis and the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma. Particularly, the biomarker is CLINT1. The worldwide incidence rate of the lung adenocarcinoma continuously increases; an effective biomarker is needed to diagnose and / or treat the lung adenocarcinoma. The application is proven through an experiment; the expression, in a patient suffered from the lung adenocarcinoma, of the CLINT1 is up-regulated; the multiplication and the invasion of a lung adenocarcinoma cell can be inhibited by decreasing the expression of a CLINT1 gene. Prompted, the CLINT1 disclosed by the invention can be used as a marker for the early diagnosis of the lung adenocarcinoma; meanwhile, the gene can be also used as a potential drug target spot for treating the lung adenocarcinoma; the foundation is provided for the accurate medical treatment of the lung adenocarcinoma.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
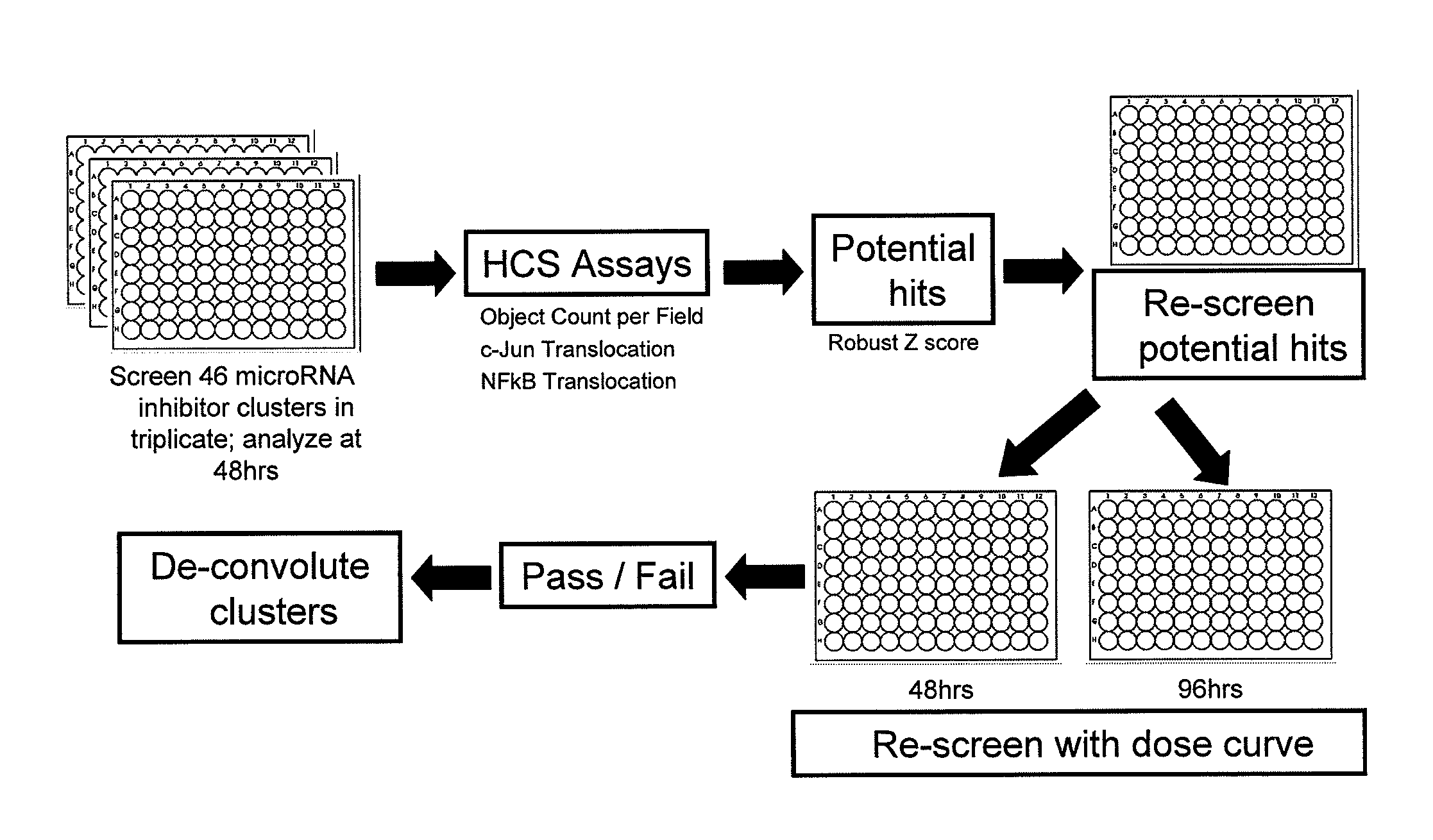
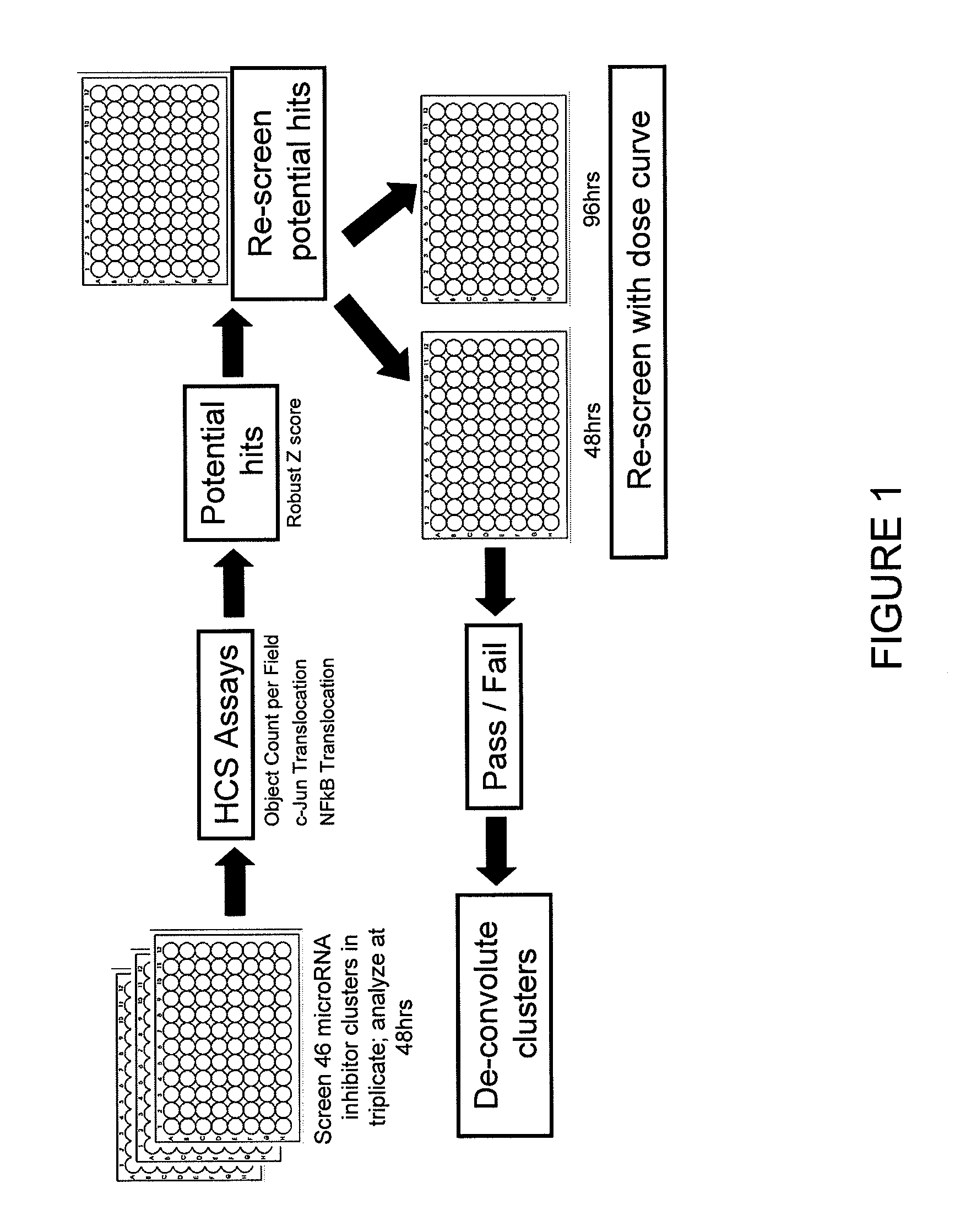
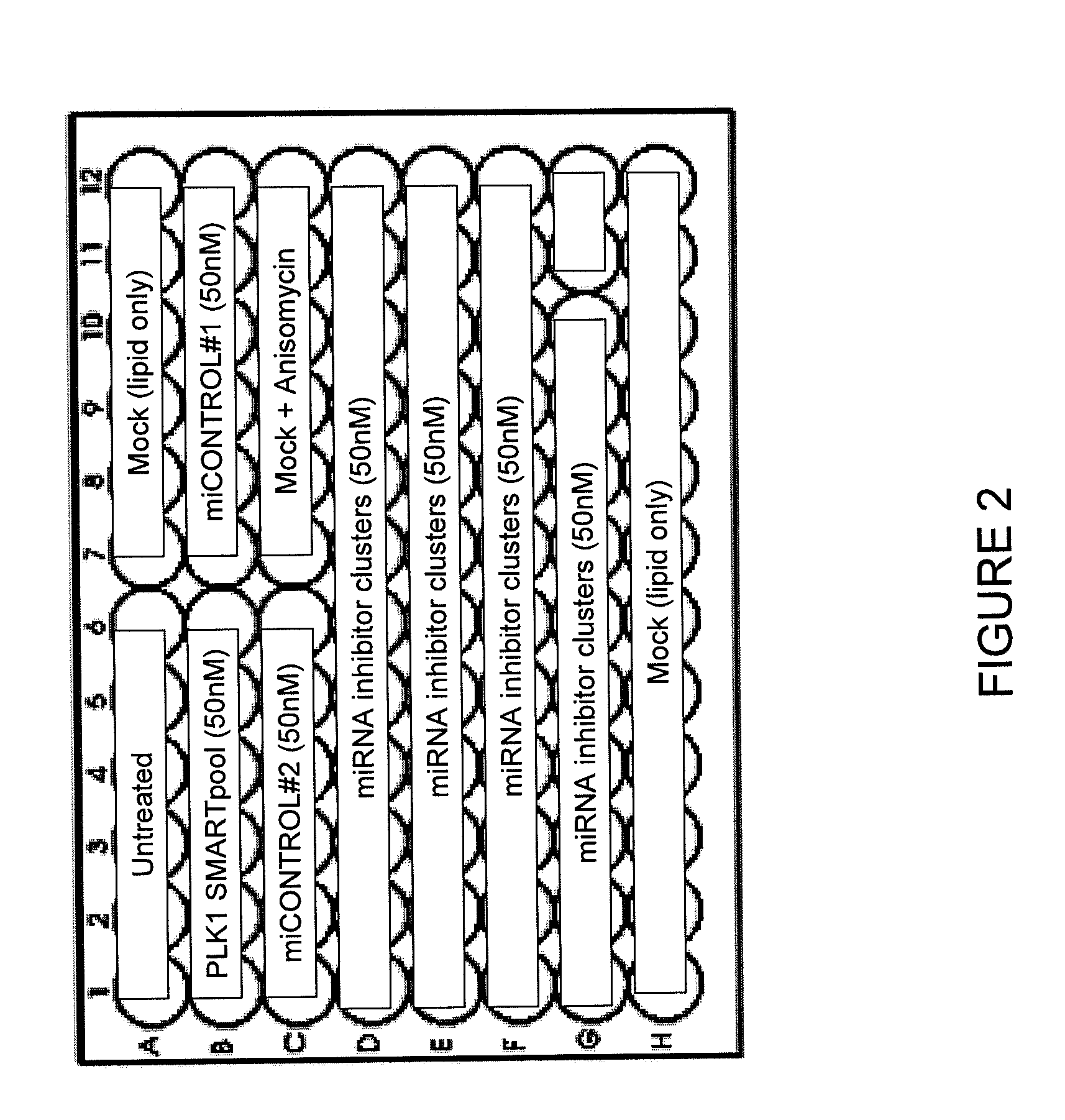
Screening of micro-rna cluster inhibitor pools
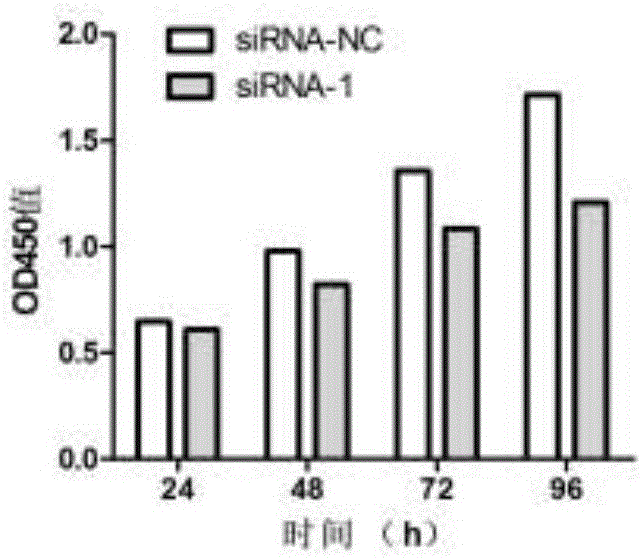
InactiveUS20100273856A1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementNuclear translocationAcinic cell carcinoma
The disclosure provides methods for inhibiting the activity of a miRNA cluster in a cell, and also for screening a cell for a phenotype(s) of interest resulting from inhibition of a miRNA cluster. The methods use a cluster pool which comprises at least one miRNA inhibitor specific for each miRNA in the miRNA cluster. MiRNA inhibitors are described that induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells and hence are useful in the treatment of breast cancer. The disclosure also provides pharmaceutical compositions which are useful for the treatment of breast cancer; methods for inducing the nuclear translocation of NF-κB in a breast cancer cell; methods for inducing the nuclear translocation of c-Jun in a breast cancer cell; method for inhibiting the nuclear translocation of NF-κB in a breast cancer cell; and methods for providing prognostic medical information relating to breast cancer progression.
Owner:DHARMACON INC
Application of formononetin in preparing medicine for treating breast cancer
InactiveCN103393638APrevent proliferationAntiproliferative activityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellNormal cell
The invention discloses a novel use of formononetin in pharmacy, and in particular discloses an application of formononetin in preparing a medicine for treating breast cancer. The applicants discover that formononetin can remarkably inhibit cell proliferation of breast cancer for the first time and discover through experiments that formononetin retards cell cycle by way of inactivating IGF1 / IGF1R-PI3K / AKT, so that formononetin generates good activity of inhibiting cell proliferation of breast cancer, and can be used as a cell cycle retardant to replace tamoxifen to inhibit cell proliferation of breast cancer so as to prevent and treat breast cancer. In addition, the applicants in experiments further discover that formononetin can be used as the cycle retardant for cancer cells and has specific targeting to normal cells as an agonist, so that formononetin has very high development value and real application value.
Owner:GUILIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Mitochondrial delivery of 3-bromopyruvate
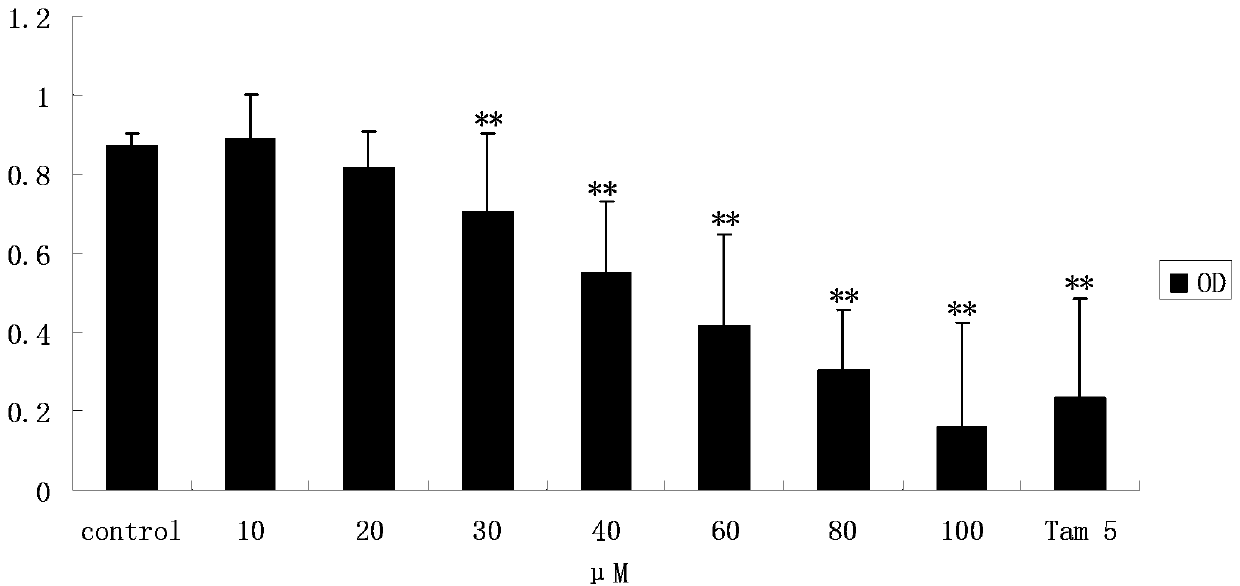
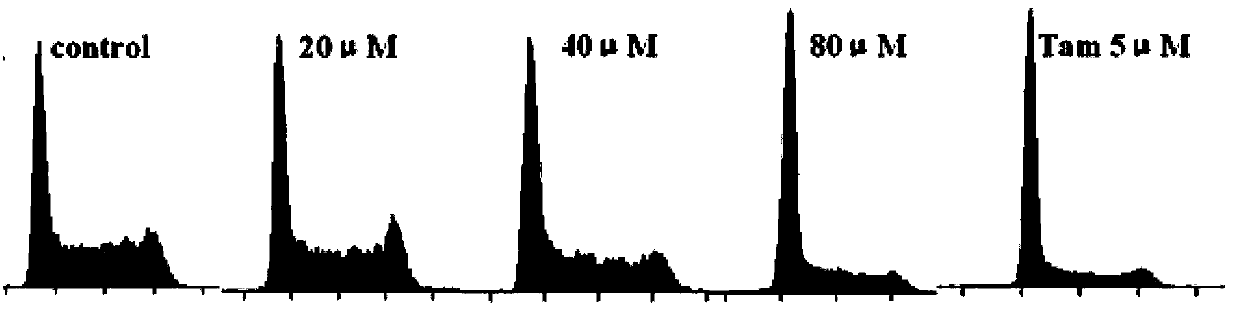
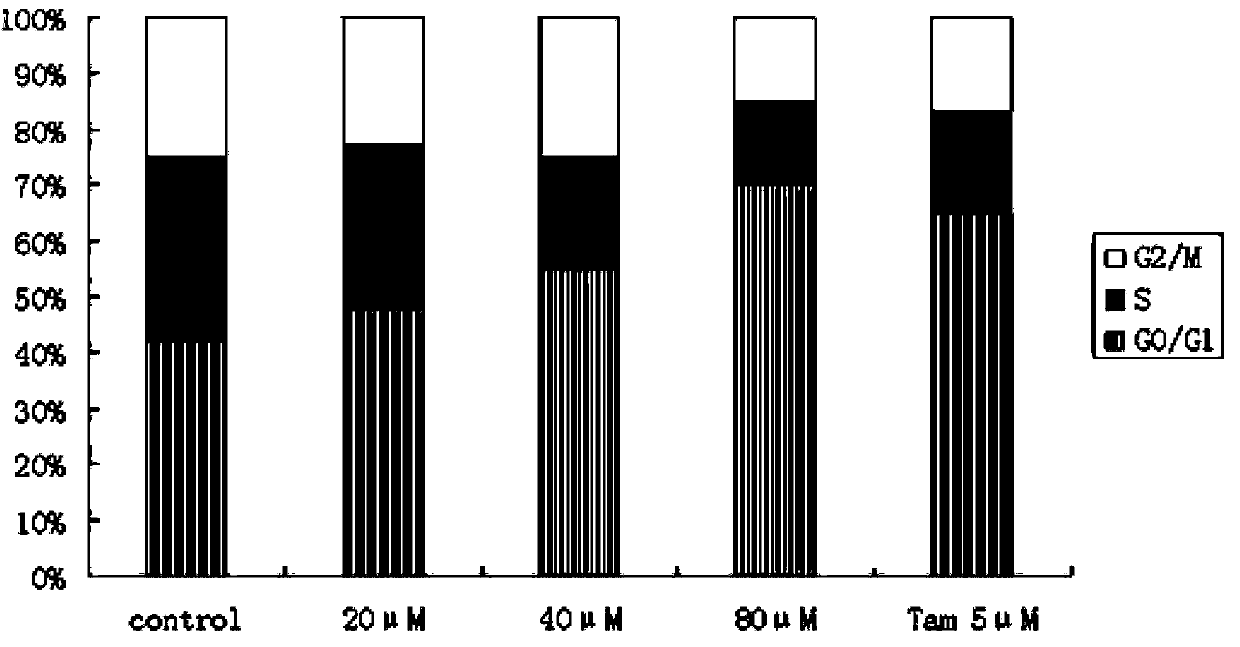
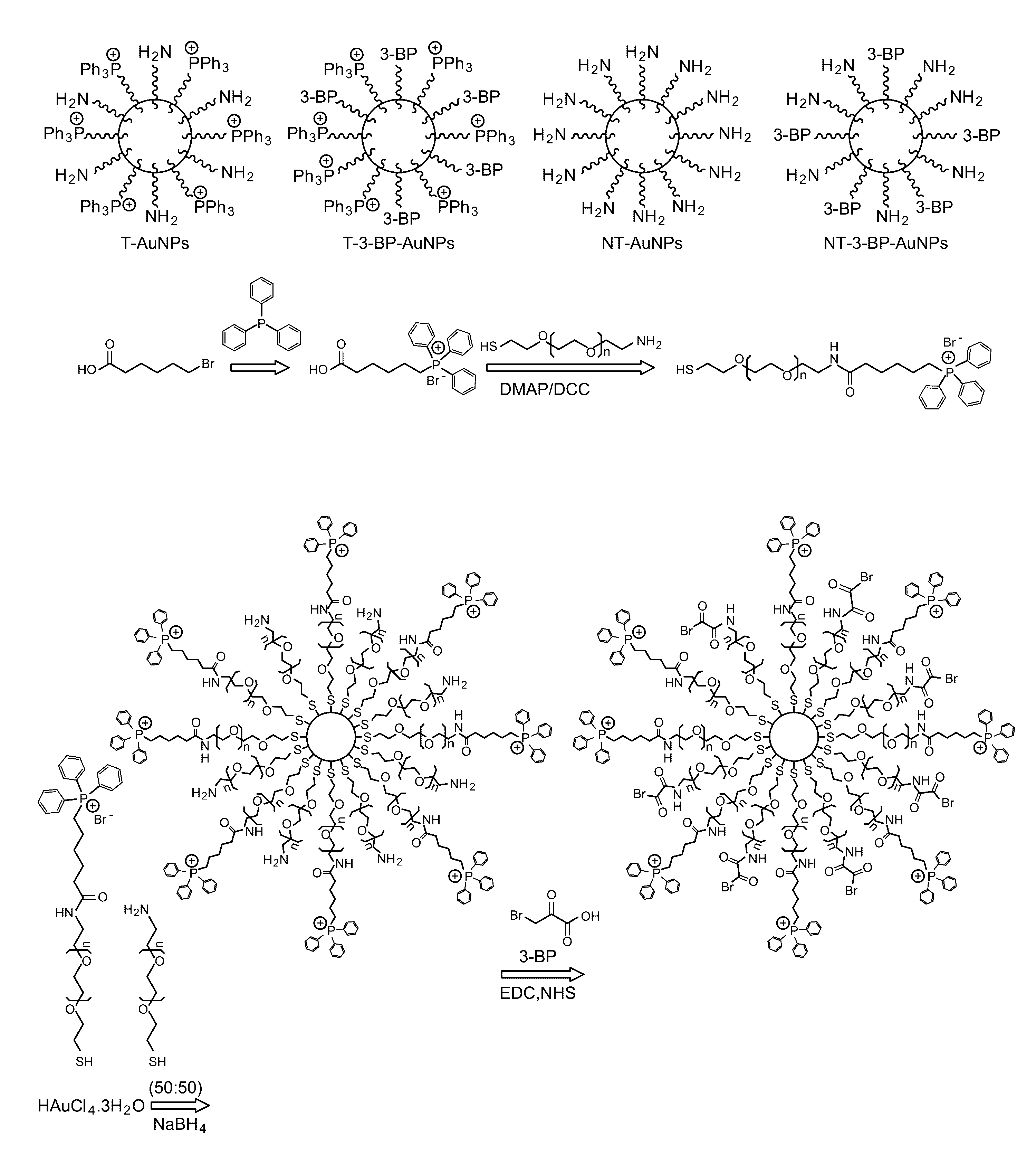
ActiveUS20170014361A1Good curative effectLow toxicityPowder deliveryDrug photocleavageProstate cancer cellCancer cell
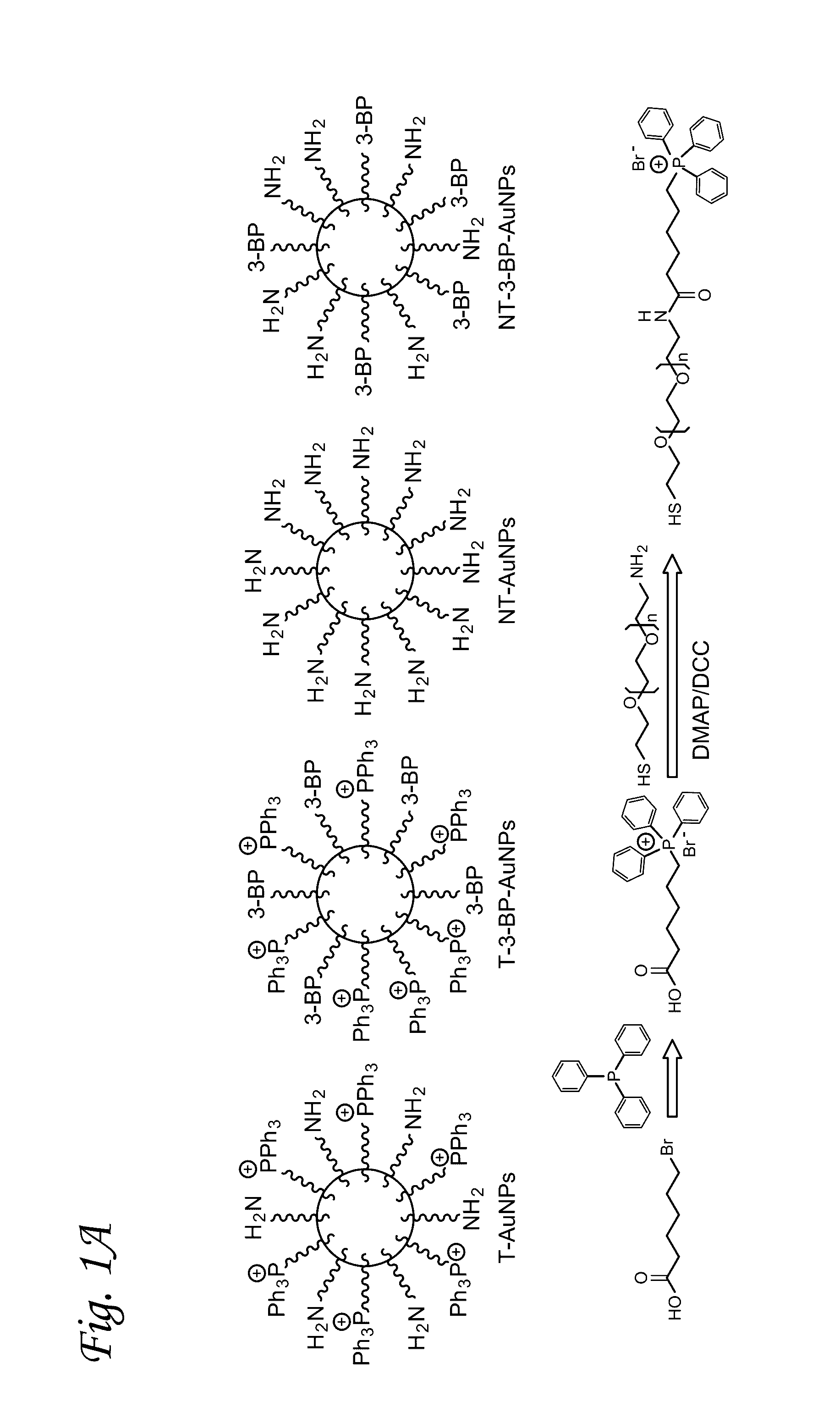
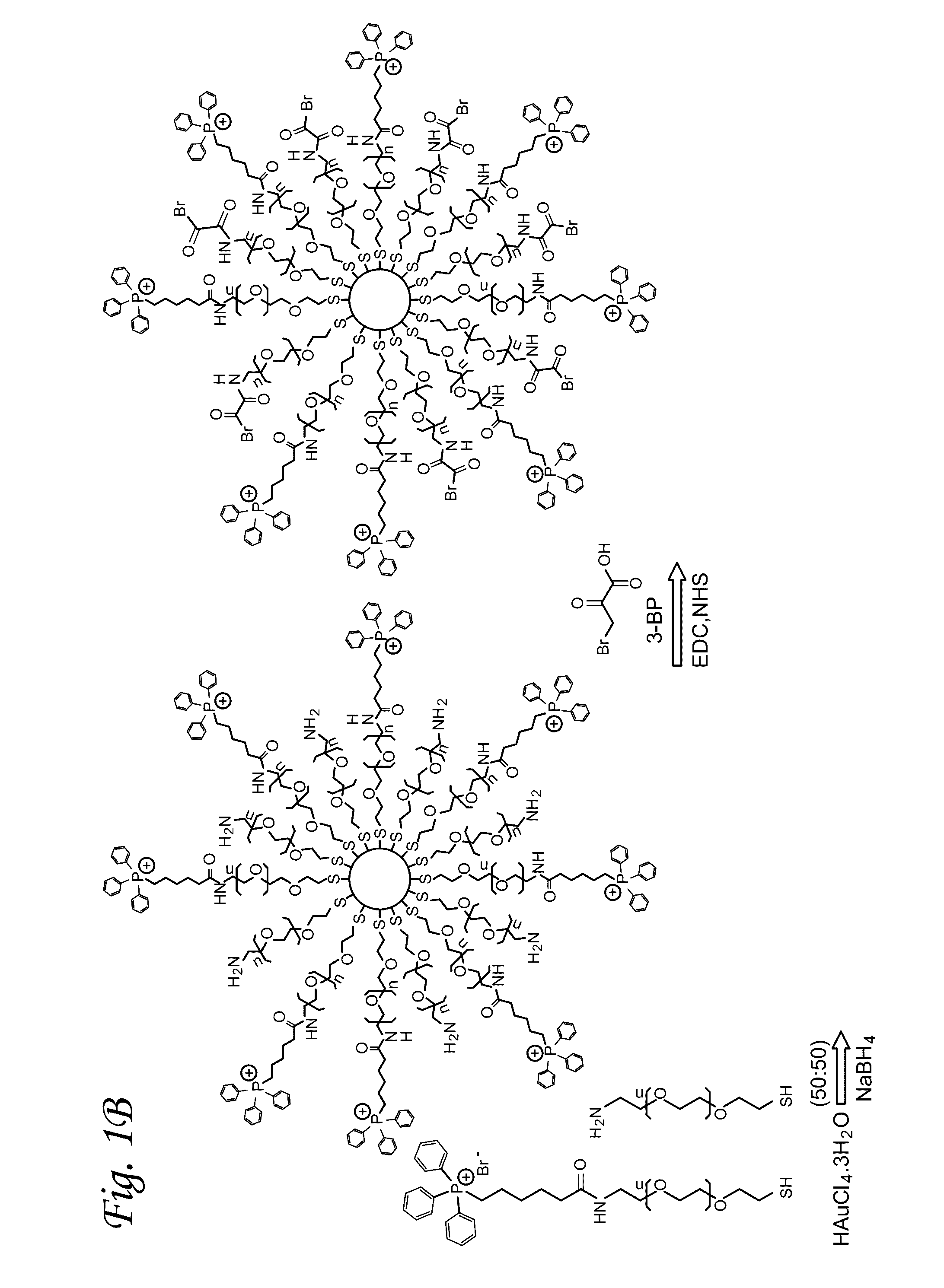
A mitochondria targeted gold nanoparticle (T-3-BP-AuNP) decorated with 3-bromopyruvate (3-BP) and delocalized lipophilic triphenylphosphonium (TPP) cations to target the mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm) was developed for delivery of 3-BP to cancer cell mitochondria by taking advantage of higher Δψm in cancer cell compared to normal cells. This construct showed remarkable anticancer activity in prostate cancer cells compared to non-targeted construct NT-3-BP-AuNP and free 3-BP. Anticancer activity of T-3-BP-AuNP was further enhanced upon laser irradiation by exciting the surface plasmon resonance band of AuNP and thereby utilizing a combination of 3-BP chemotherapeutic and AuNP photothermal effects. T-3-BP-AuNPs showed markedly enhanced ability to alter cancer cell metabolism by inhibiting glycolysis and demolishing mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in prostate cancer cells. Our findings demonstrated that mitochondria targeted and concerted chemo-photothermal treatment of glycolytic cancer cells with a single NP may have promise as a new anticancer therapy.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com