Patents
Literature
41 results about "Hiv gp120" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
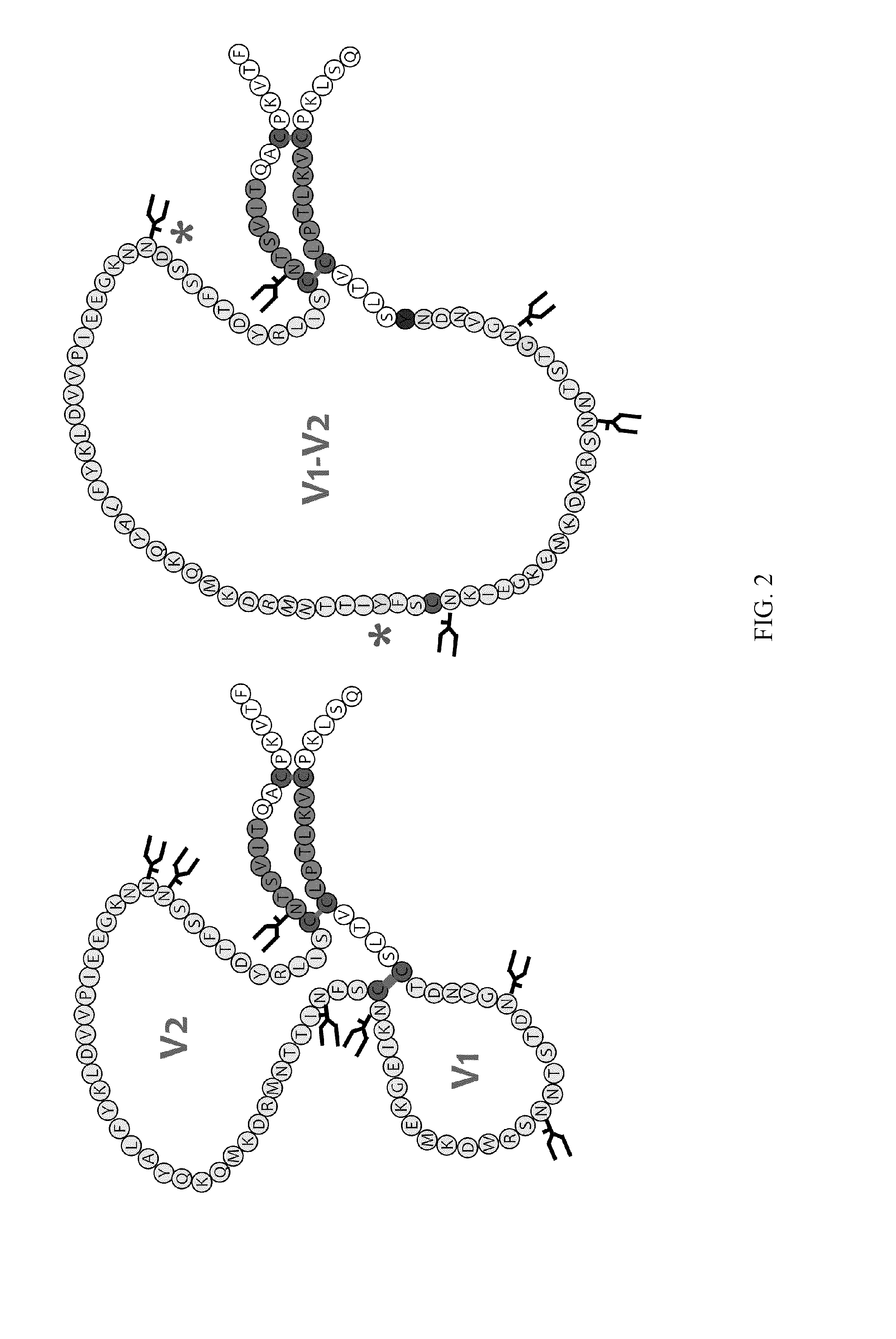
Gp120 is the name of the glycoprotein which forms the spikes sticking out of a HIV virus particle.
HIV envelope polypeptides
InactiveUS6042836ANo accumulationReduce capacitySugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsGeographic regionsHiv envelope
Owner:GENENTECH INC
HIV envelope polypeptides
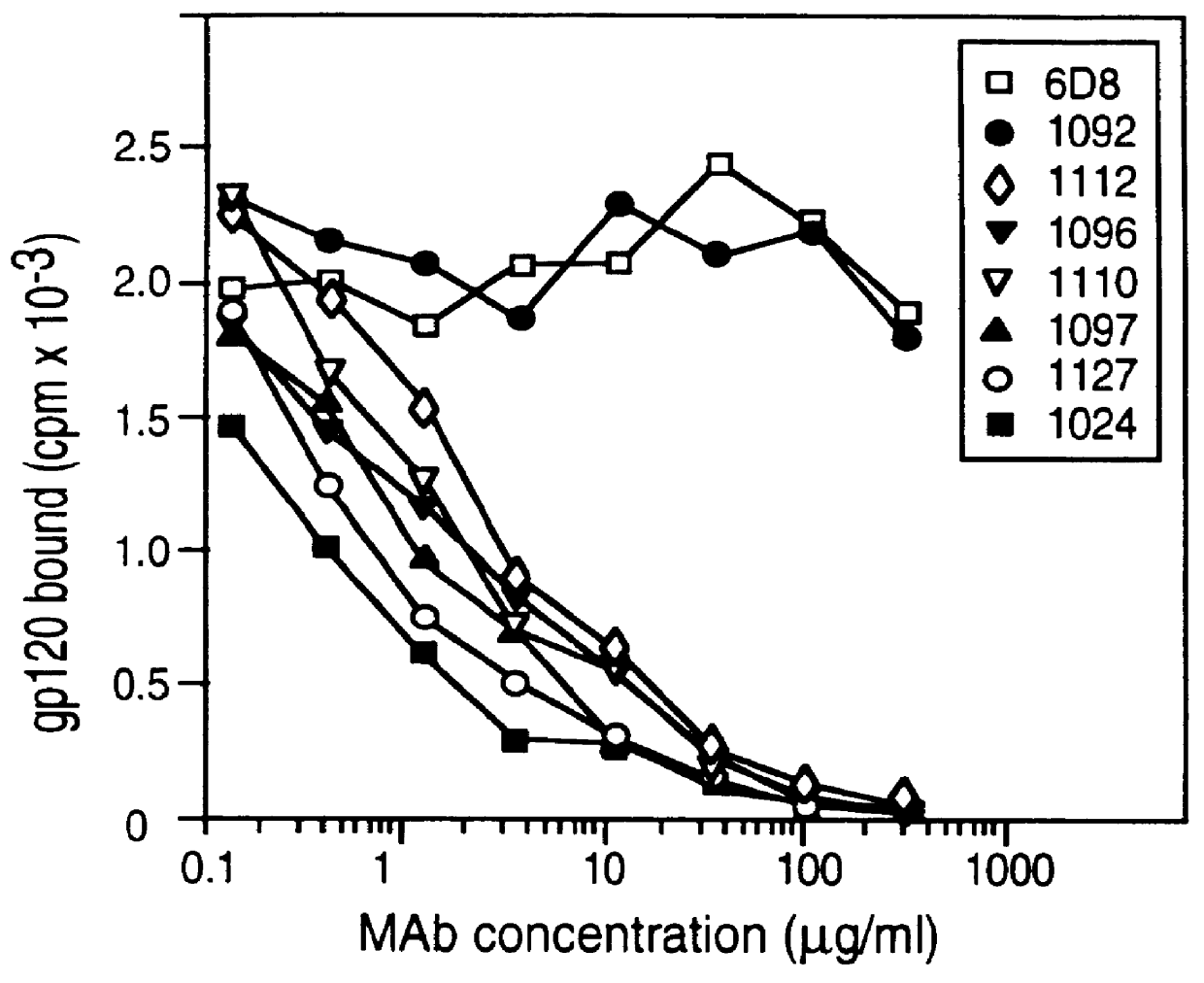
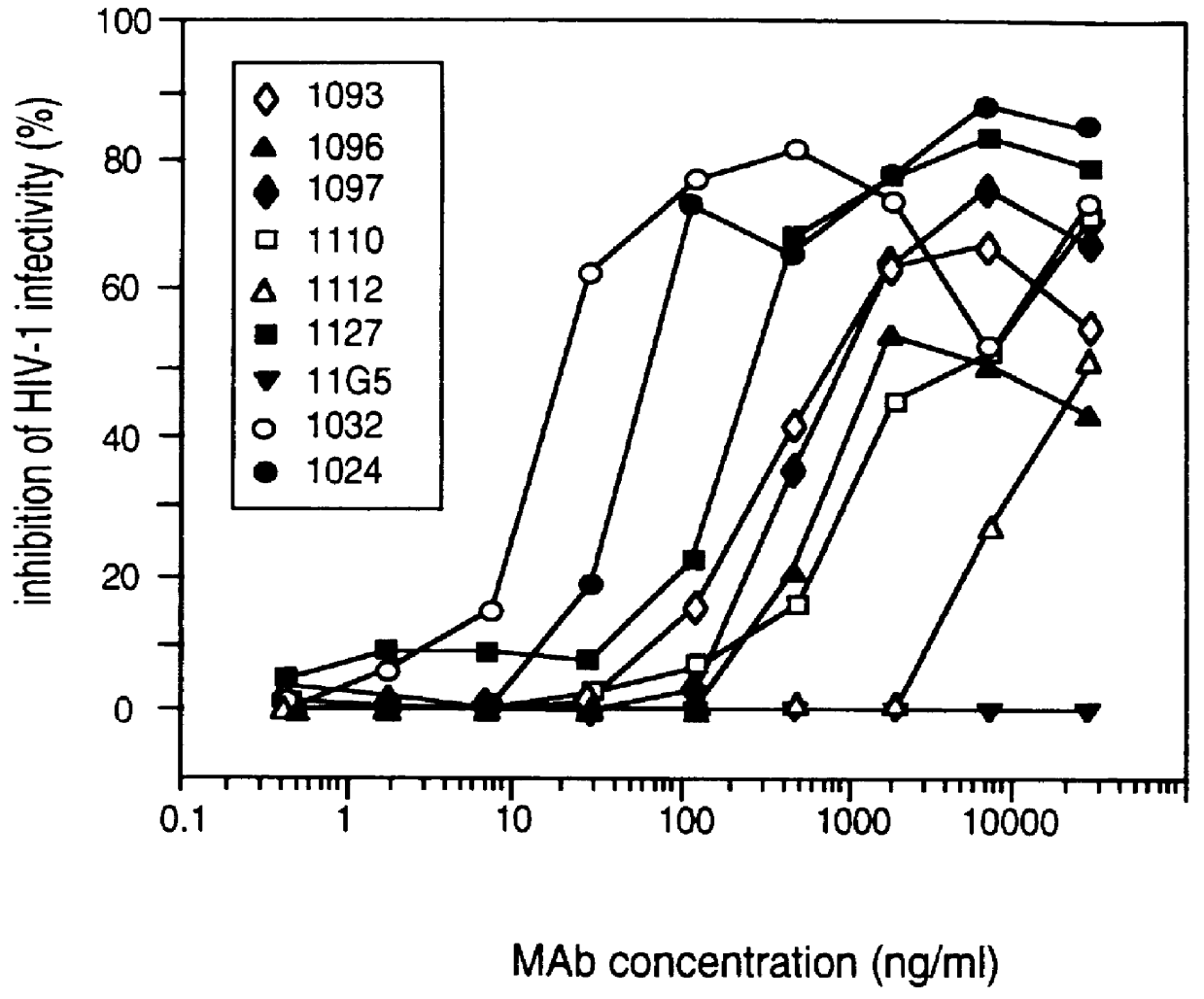
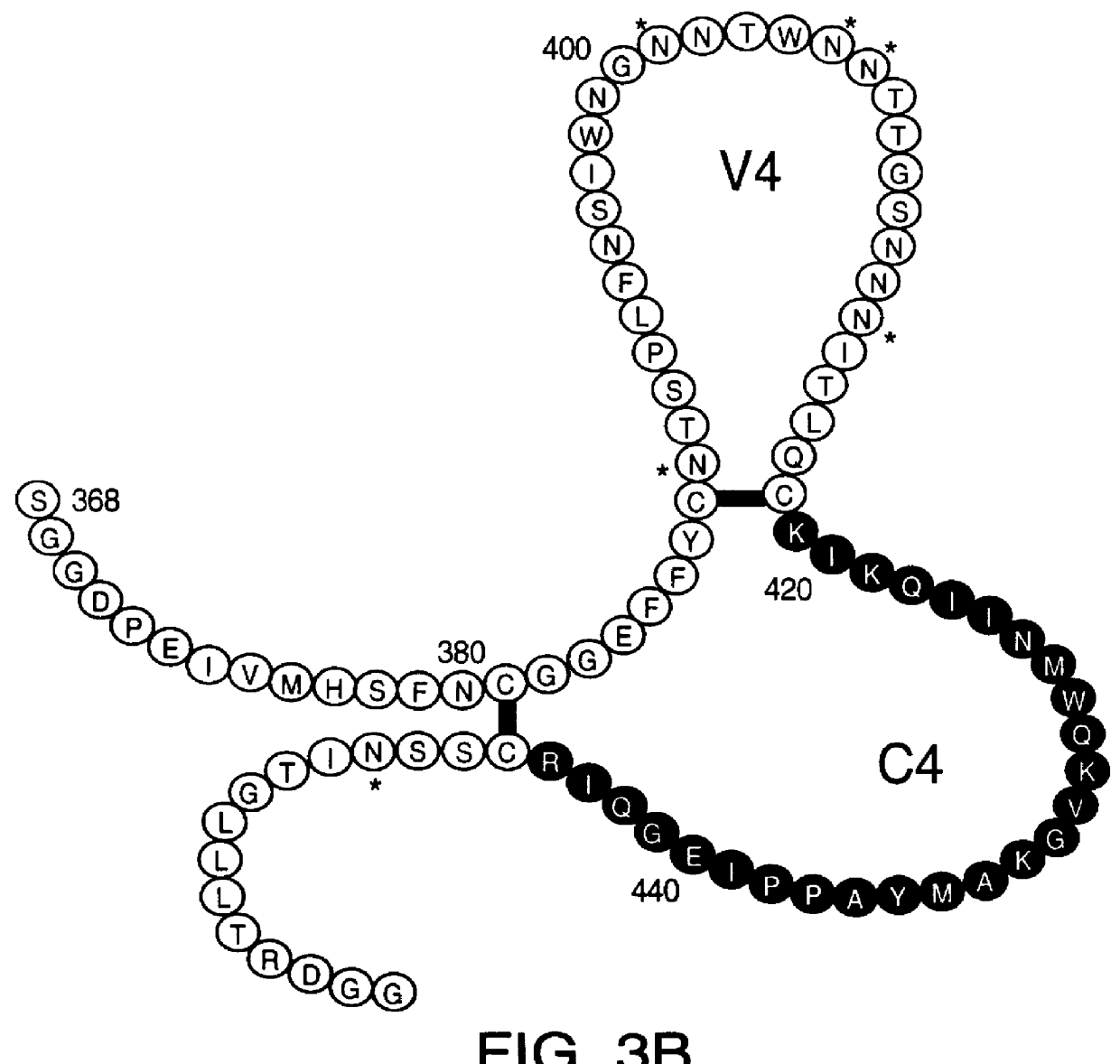
A method for the rational design and preparation of vaccines based on HIV envelope polypeptides is described. In one embodiment, the method for making an HIV gp120 subunit vaccine for a geographic region comprises determining neutralizing epitopes in the V2 and / or C4 domains of gp120 of HIV isolates from the geographic region and selecting an HIV strain having gp120 a neutralizing epitope in the V2 or C4-domain which is common among isolates in the geographic region. In a preferred embodiment of the method, neutralizing epitopes for the V2, V3, and C4 domains of gp120 are determined. At least two HIV isolates having different neutralizing epitopes in the V2, V3, or C4 domain are selected and used to make the vaccine. The invention also provides a multivalent HIV gp120 subunit vaccine. A DNA sequence encoding gp120 from preferred vaccine strains of HIV, GNE8 and GNE16, expression constructs comprising the GNE8-gp120 and GNE16-gp120 encoding DNA under the transcriptional and translational control of a heterologous promoter, and isolated GNE8-gp120 and GNE16-gp120 are also described.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
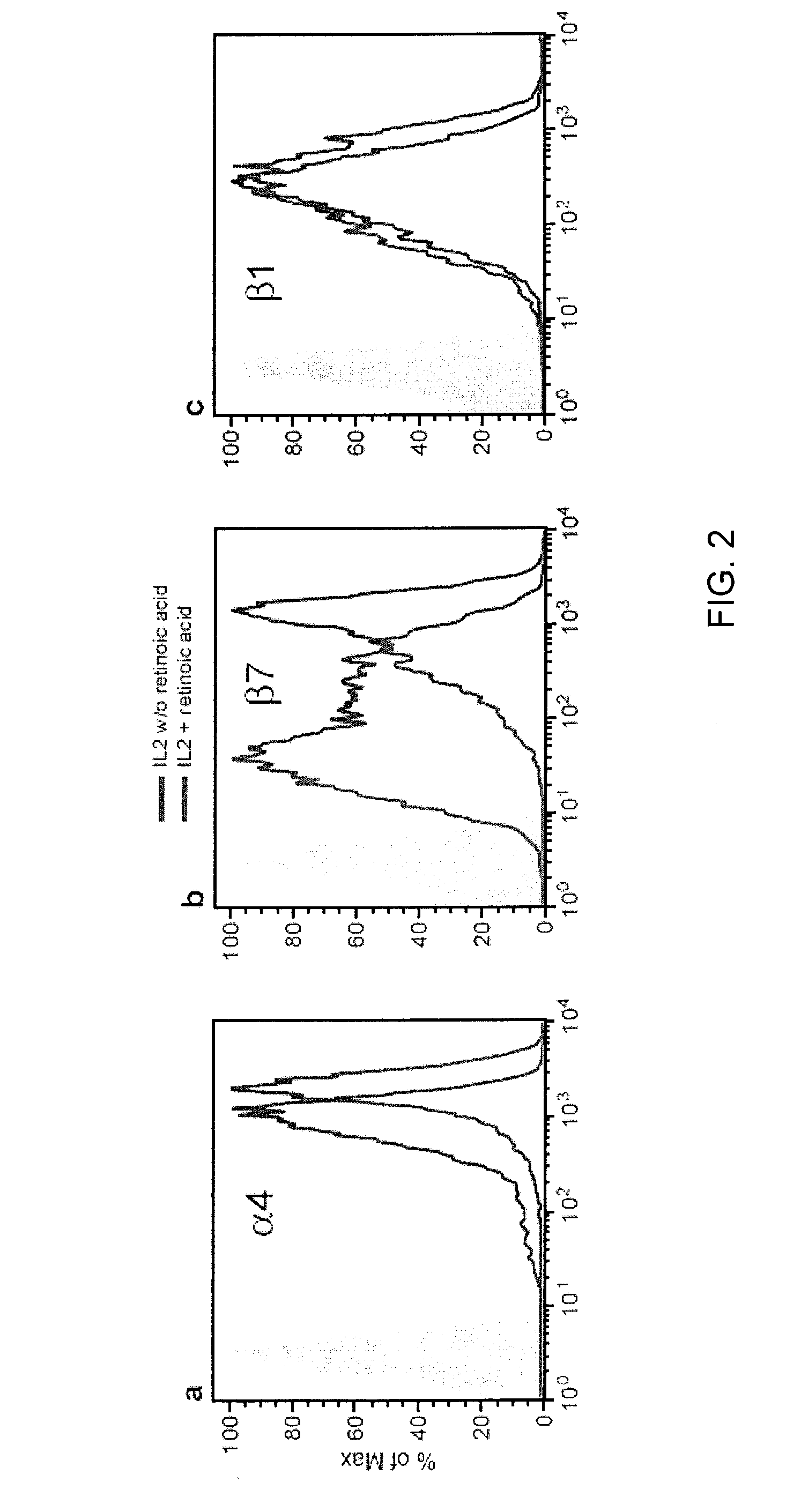
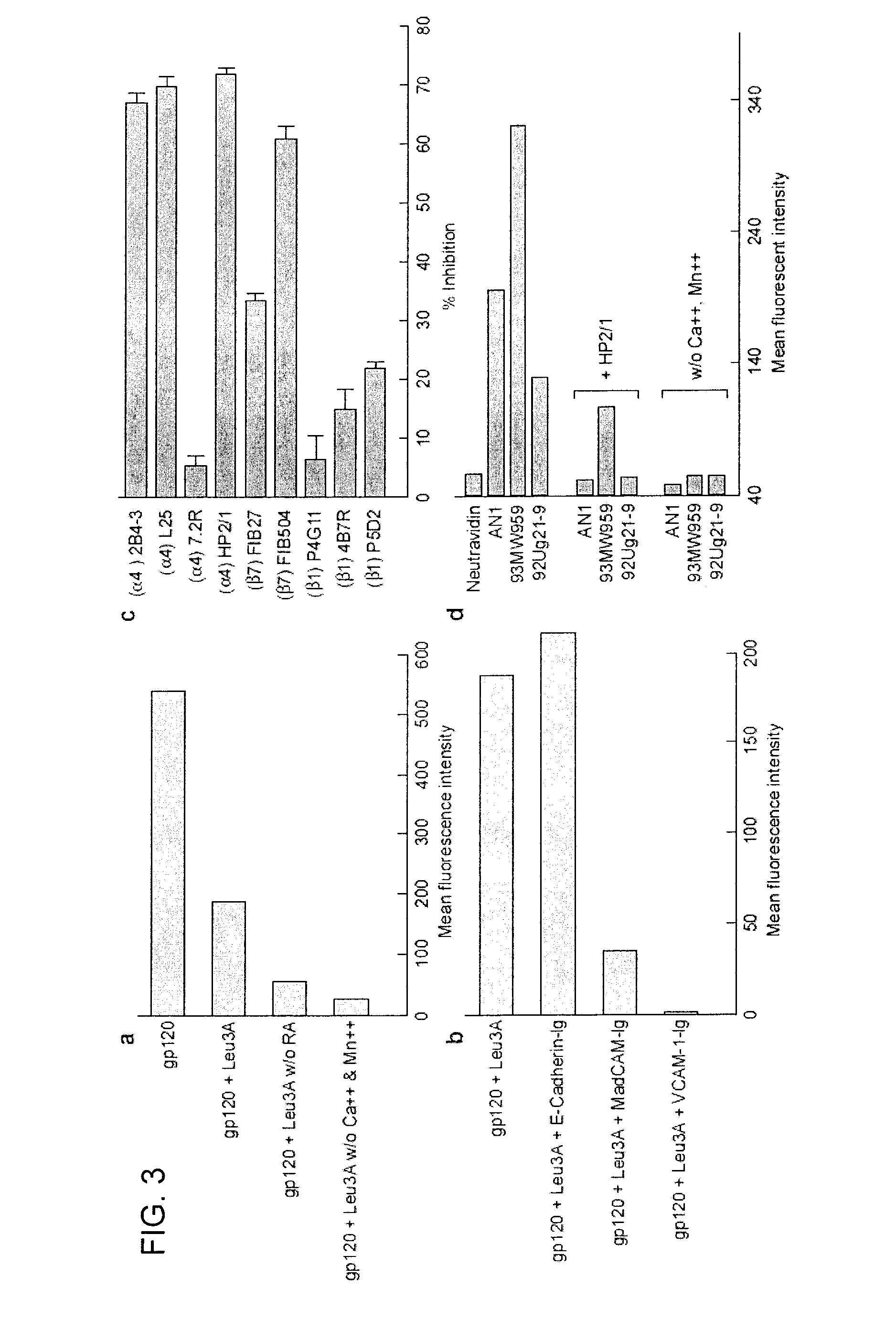
Use of antagonists of the interaction between HIV gp120 and a4b7 integrin
ActiveUS20110086024A1Infection efficiency can be decreasedLow efficiencyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMonoclonal antibodyΒ7 integrin
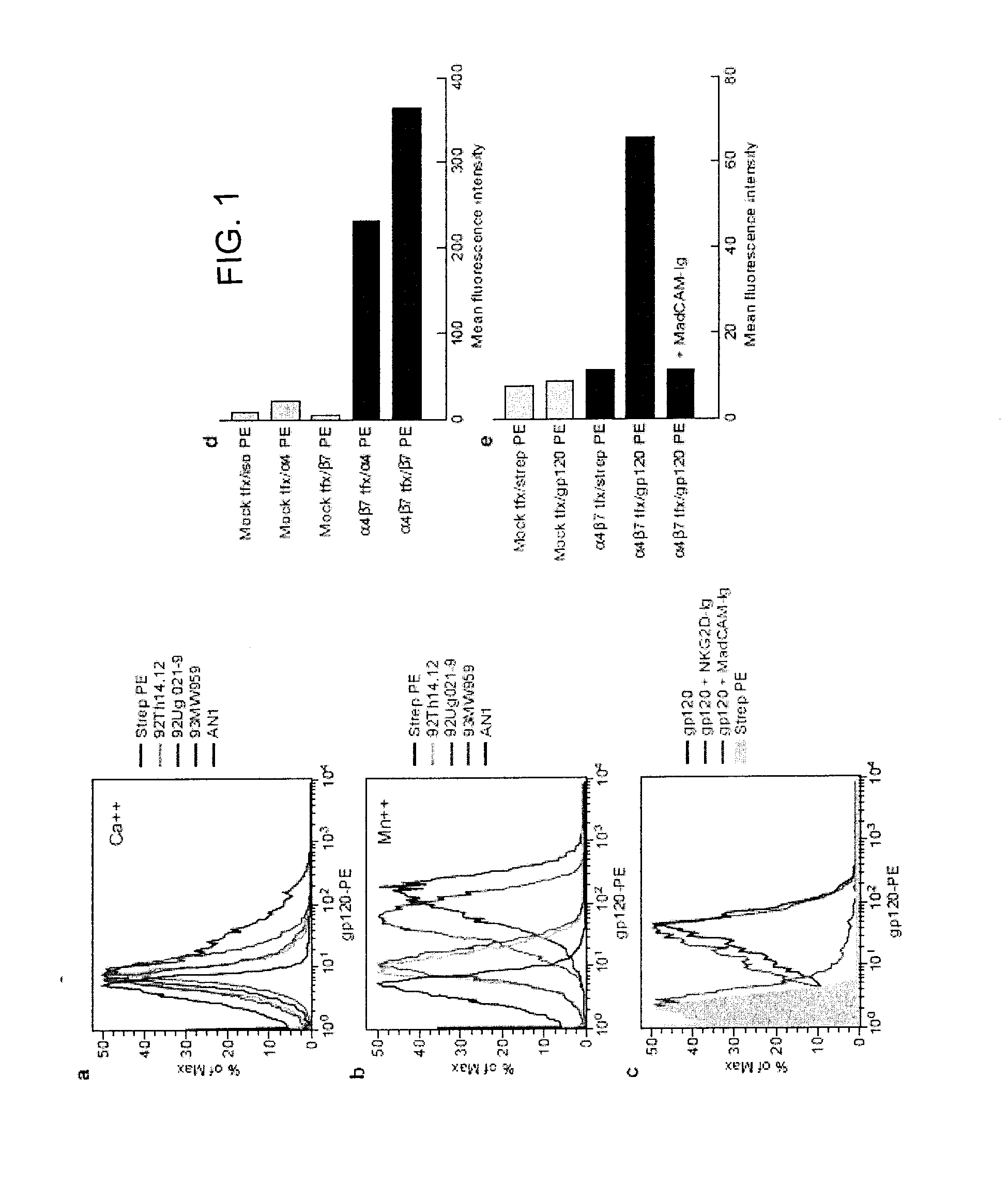
Methods are provided for the treatment of a HIV infection. The methods can include administering to a subject with an HIV infection a therapeutically effective amount of an agent that interferes with the interaction of gp120 and α4 integrin, such as a α4β1 or α4β7 integrin antagonist, thereby treating the HIV infection. In several examples, the α4 integrin antagonist is a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to a α4, β1 or β7 integrin subunit or a cyclic hexapeptide with the amino acid sequence of CWLDVC. Methods are also provided to reduce HIV replication or infection. The methods include contacting a cell with an effective amount of an agent that interferes with the interaction of gp120 and α4 integrin, such as a α4β1 or α4β7 integrin antagonist. Moreover, methods are provided for determining if an agent is useful to treat HIV.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
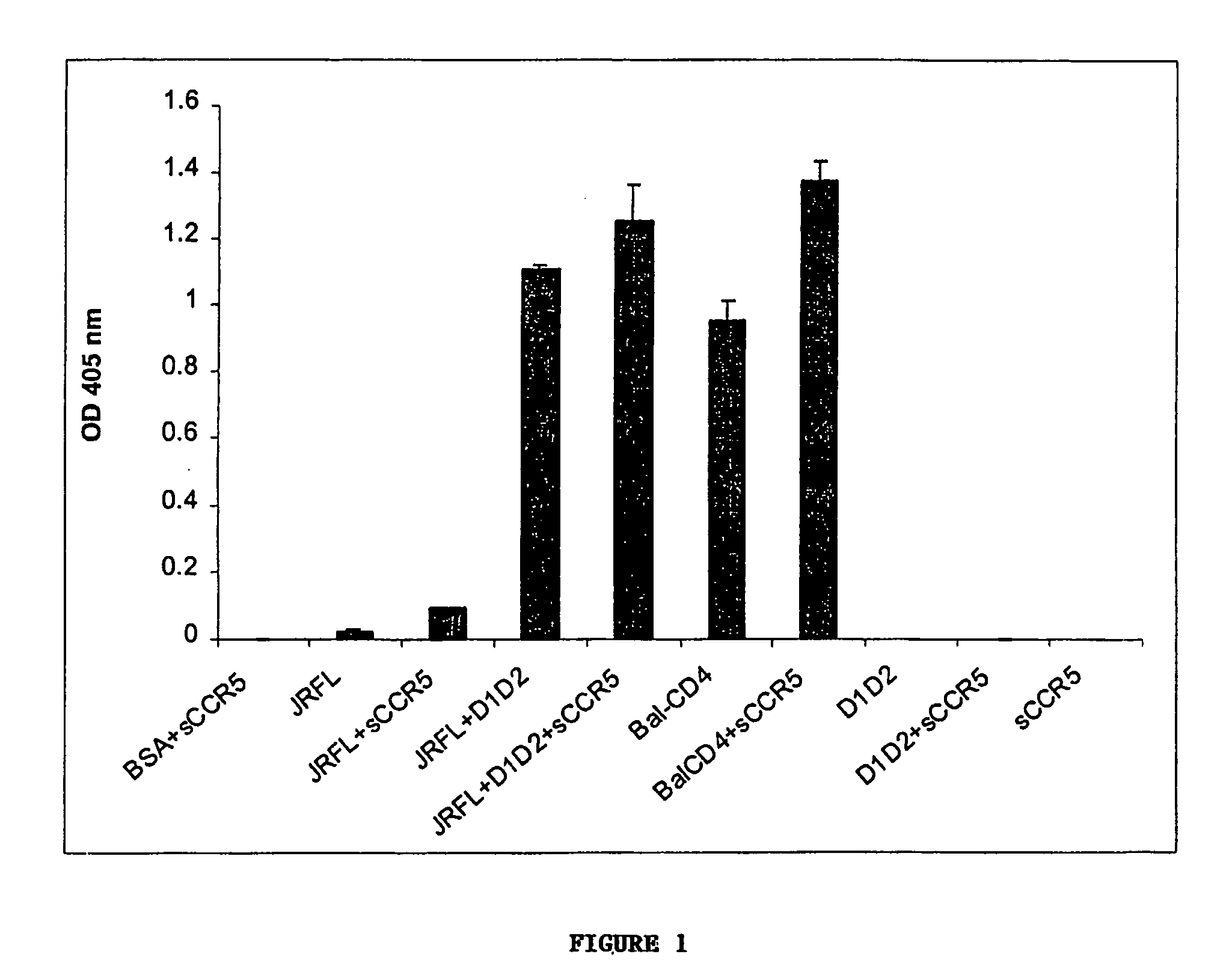
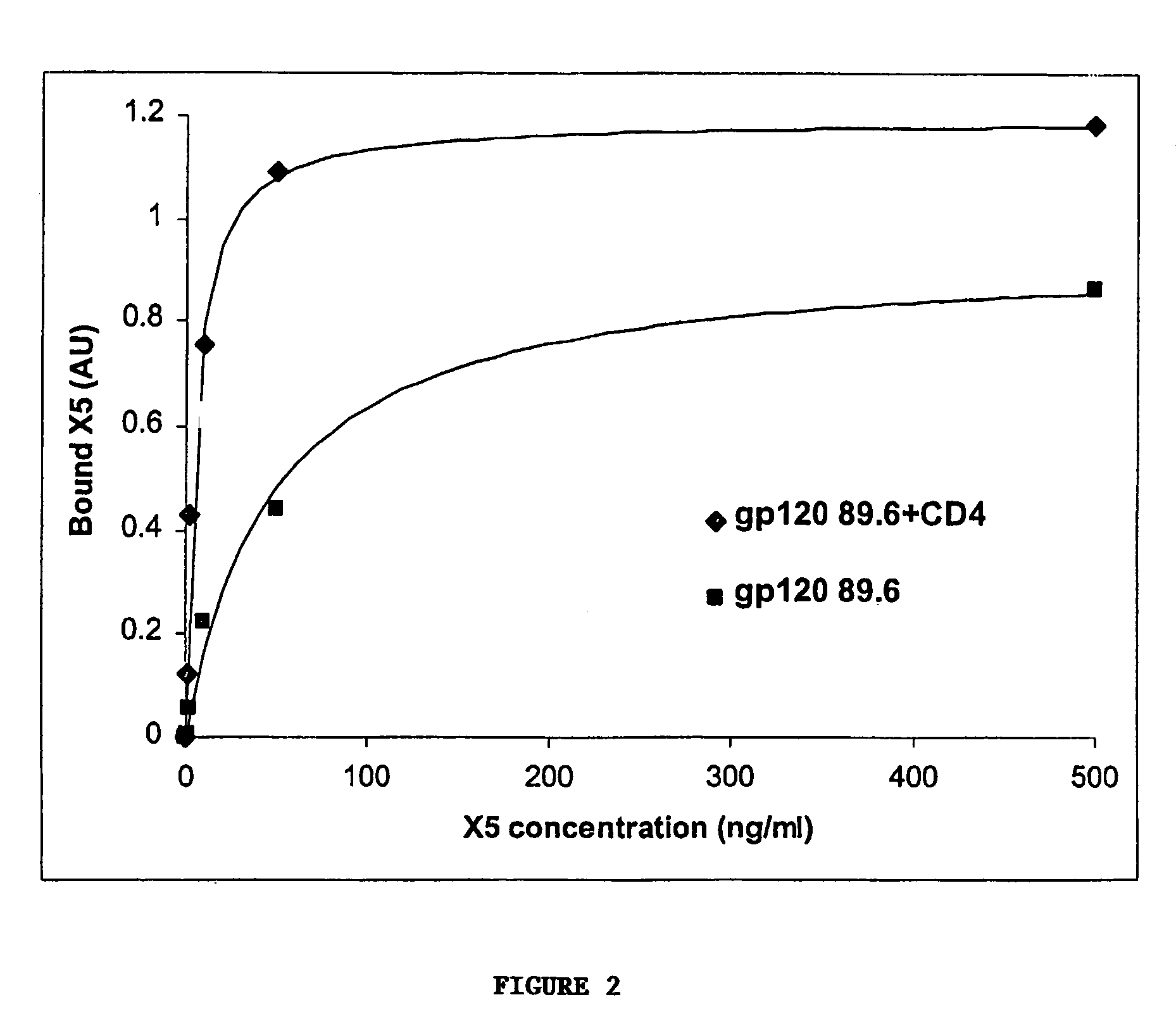
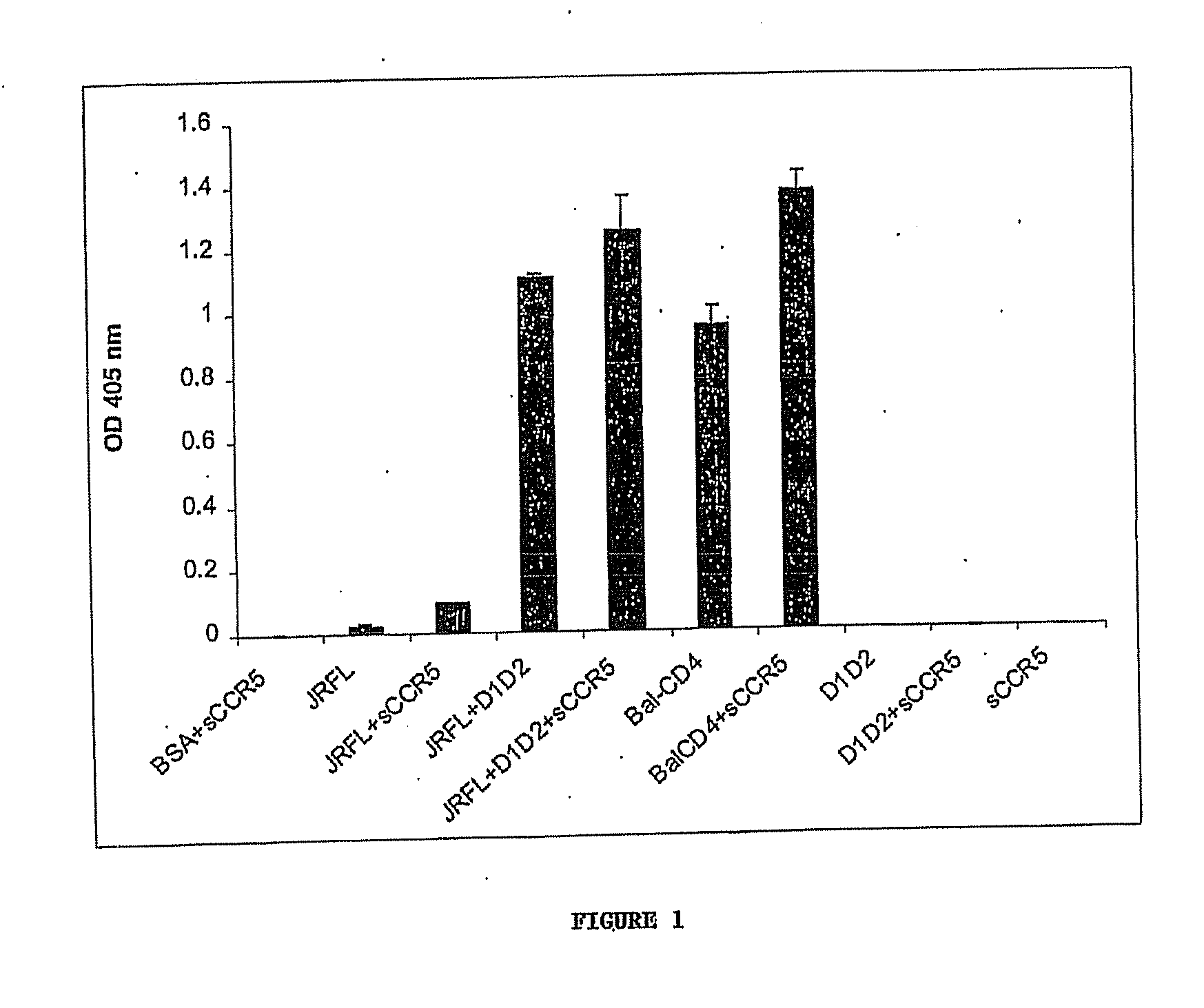
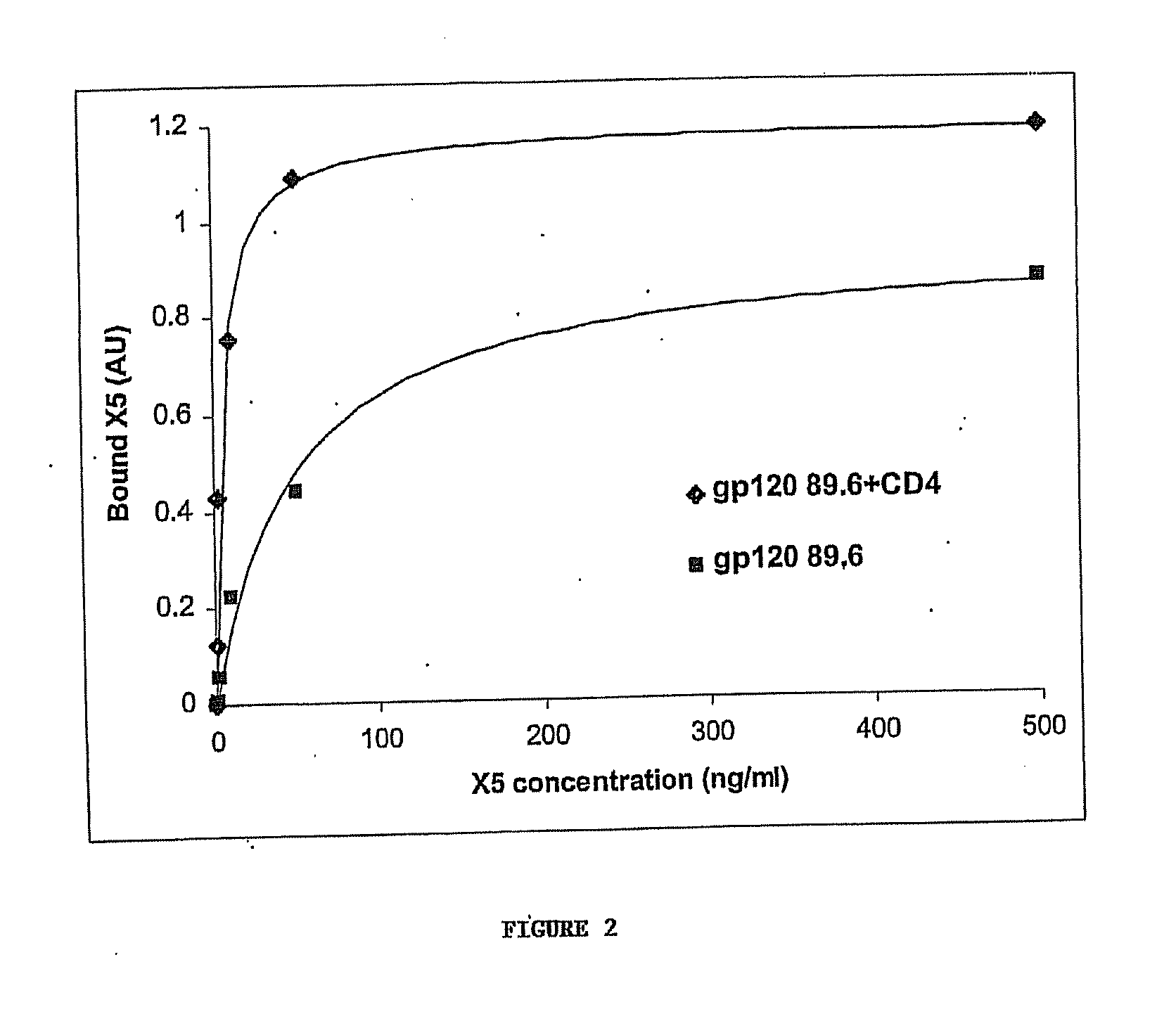
Broadly cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus selected by Env-CD4-co-receptor complexes
InactiveUS7223844B2Increase exposurePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody fragmentsMammal
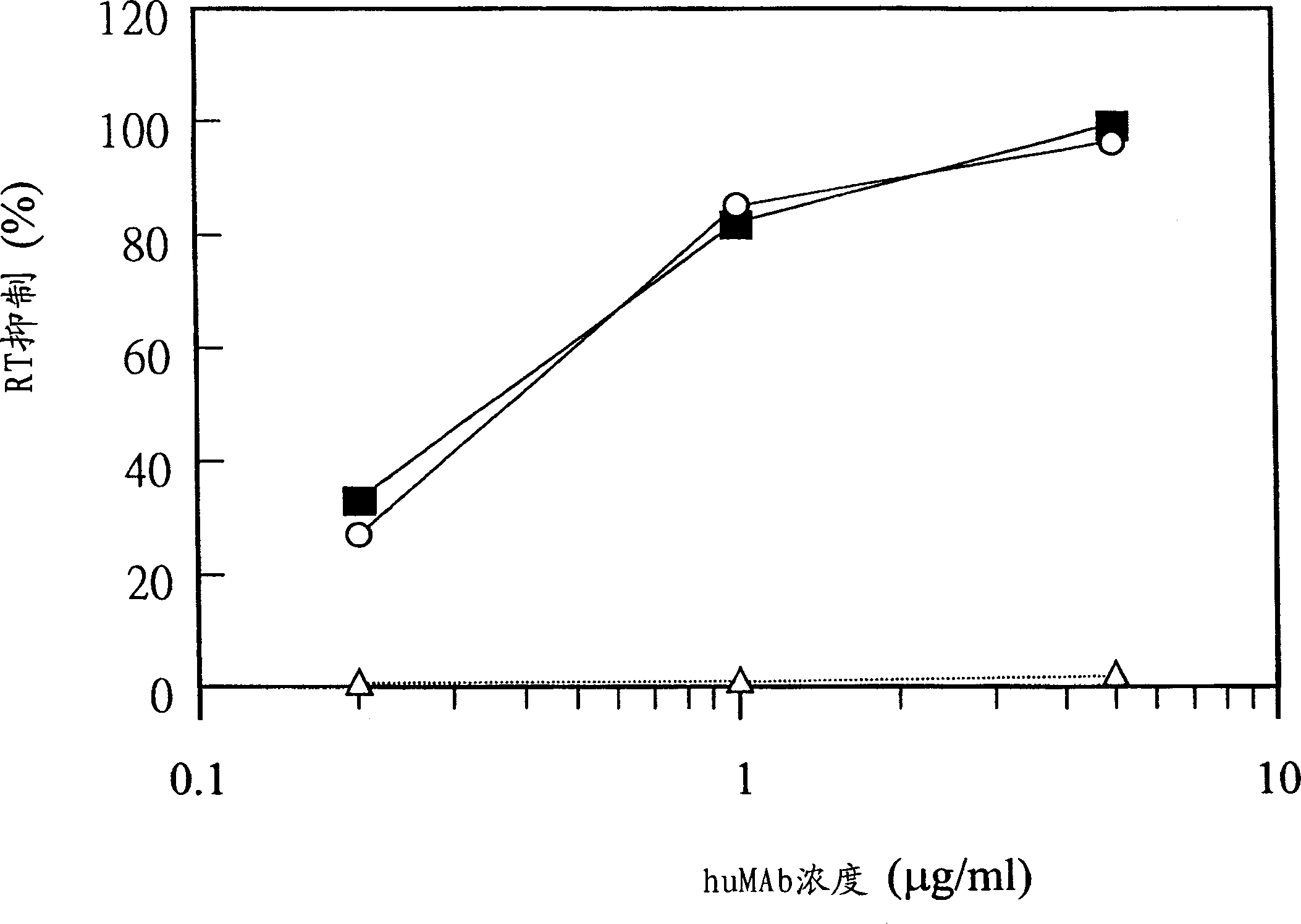
The present invention features antibodies and antibody fragments that specifically bind a CD4-inducible HIV gp120 epitope that is enhanced by binding a co-receptor for HIV, such as CCR5 or CXCR4, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies or antibody fragments. The invention also features nucleic acids encoding the antibodies or antibody fragments, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the nucleic acids encoding the antibodies or antibody fragments, vectors comprising the nucleic acids, and cells comprising the vectors. The invention further features methods of identifying antibodies or antibody fragments with broadly neutralizing activity against HIV. The invention also features methods of inhibiting HIV entry into cells and methods of inhibiting replication of HIV in mammals, using the antibodies and nucleic acids of the invention.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
Modified and fusion enhanced erythrocytes, cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110091973A1Short half-lifeGenetically modified cellsBlood/immune system cellsADAMTS ProteinsChemokine receptor CCR5
Modified fusion enhanced erythrocytes (or other cell types and synthetic cells) including human viral receptor proteins, human viral coreceptor proteins and viral derived proteins capable of mediating entry of respective viruses into the modified erythrocytes, cells or pseudo-cells and the method of using the fusion enhanced modified erythrocytes, cells or pseudo-cells for the treatment or prevention of viral infections. The fusion enhanced modified erythrocytes comprises CD4 and at least one HIV coreceptor, such as CXCR4 or CCR5 and as well, at least one of cholesterol rafts, fusin, actin, a viral derived protein such as fusion peptide derived from HIV GP120 or HIV GP41 or a shorter protein derived from a long viral protein, such as a portion of HIV derived GP120, or HIV GP41 such as the 23 N-terminal peptide of the HIV-1 gp 41 protein (AVGIGALFLGFLGAAGSTMGARS) called FP23 (Fusion Peptide). These viral-fusion enhanced cells may also be electrostatic charge enhanced through further additions named in this invention. The modified erythrocytes, when administered to an HIV patient, bind to the plasma virus and induce the injection of the HIV ribonucleoprotein complex into the cells. The entrapped viral content is sequestered within said cell for at least the period of time that the cell maintains its outer membrane integrity. The virus is thereafter either degraded or deactivated within the erythrocytes, cells or pseudo-cells, or destroyed by erythrophagocytosis.
Owner:GLASER LARRY F
Therapeutic peptides and vaccines
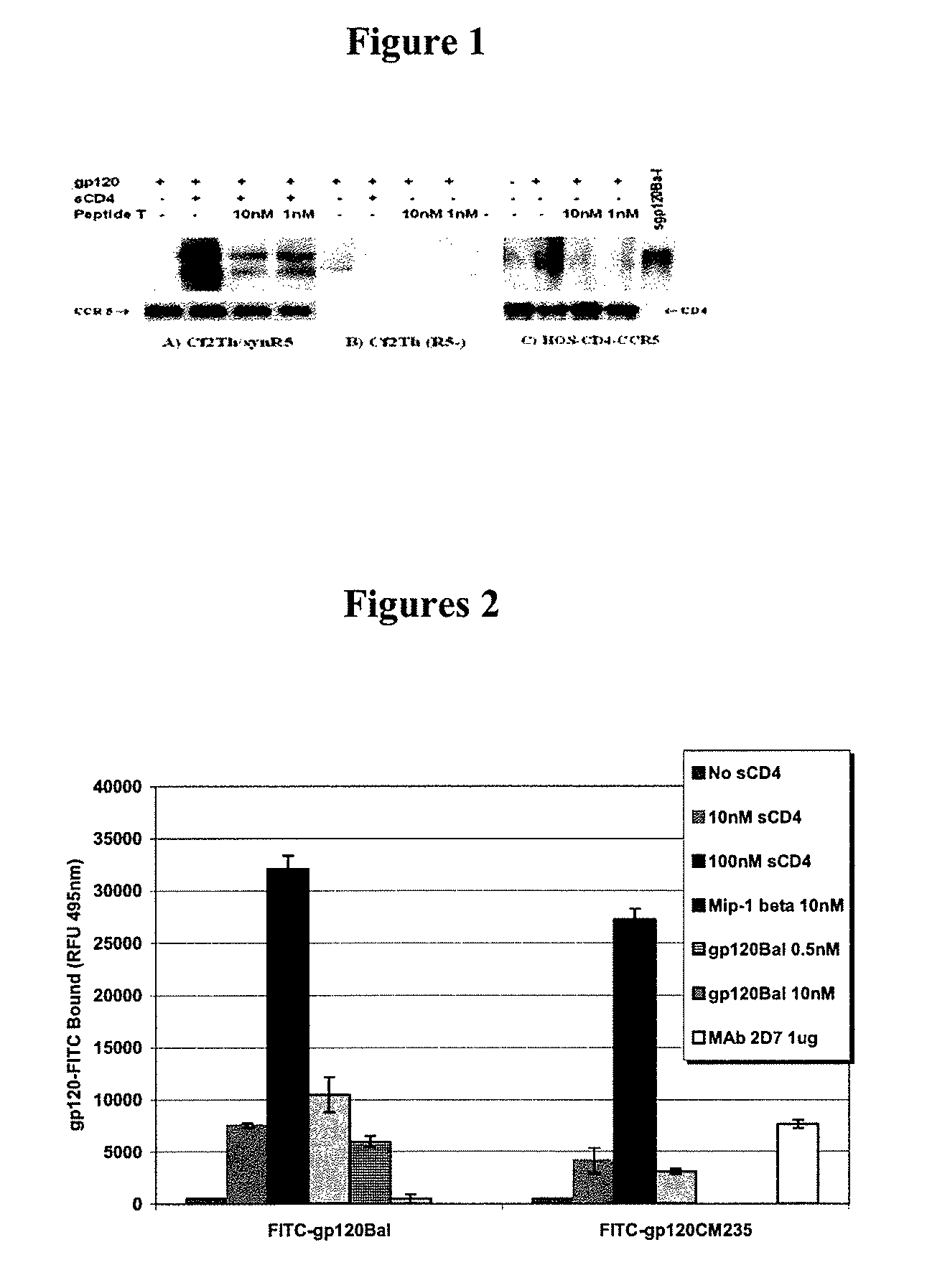
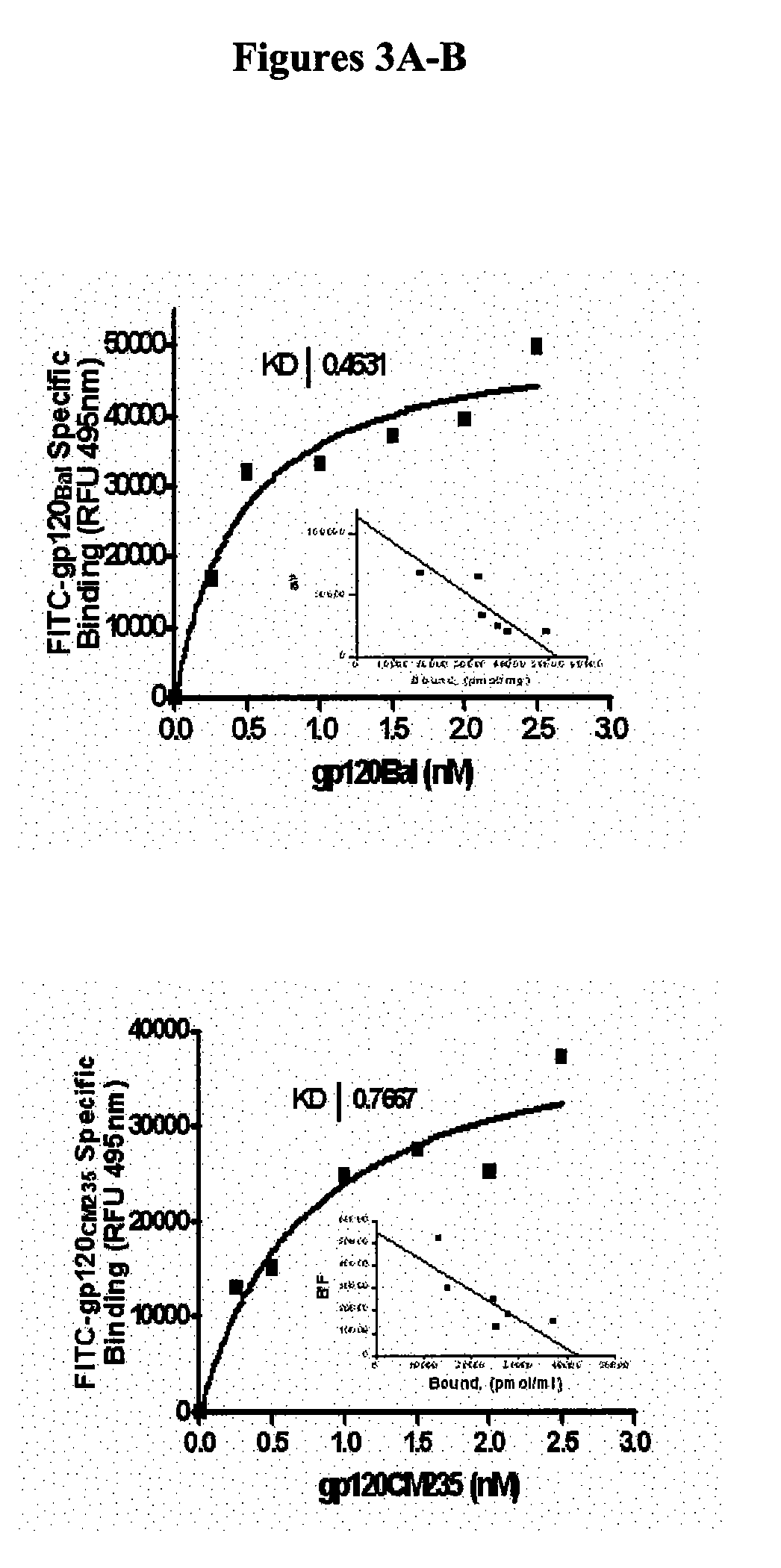
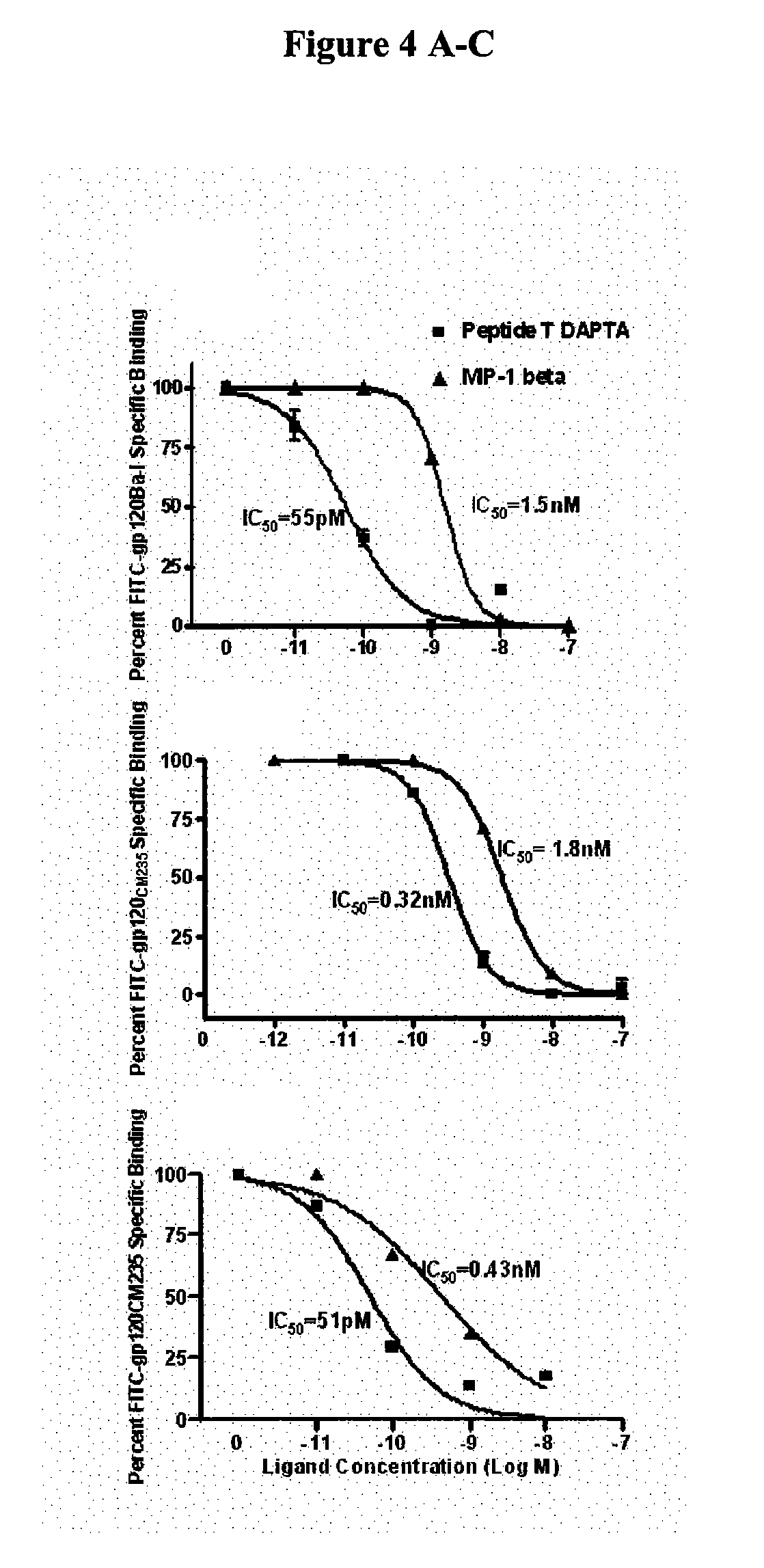
Compositions are disclosed that induce broadly HIV therapeutic and vaccine inducing antibodies against diverse HIV clades and relate to the ability to identify HIV gp120-derived short peptide sequence immunogens and various therapeutic compositions made from the identified peptides which compose CCR5 binding sites. Also disclosed are methods of selecting peptide sequences that are likely candidates for drugs which will offer effective treatment in such areas as Alzheimer's disease, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis and other diseases associated with the human inflammatory cascade as well as related retroviruses such as HTLV-1, the cause of tropical spastic paraparesis.
Owner:PEPTIDE ACCOUNT LLC
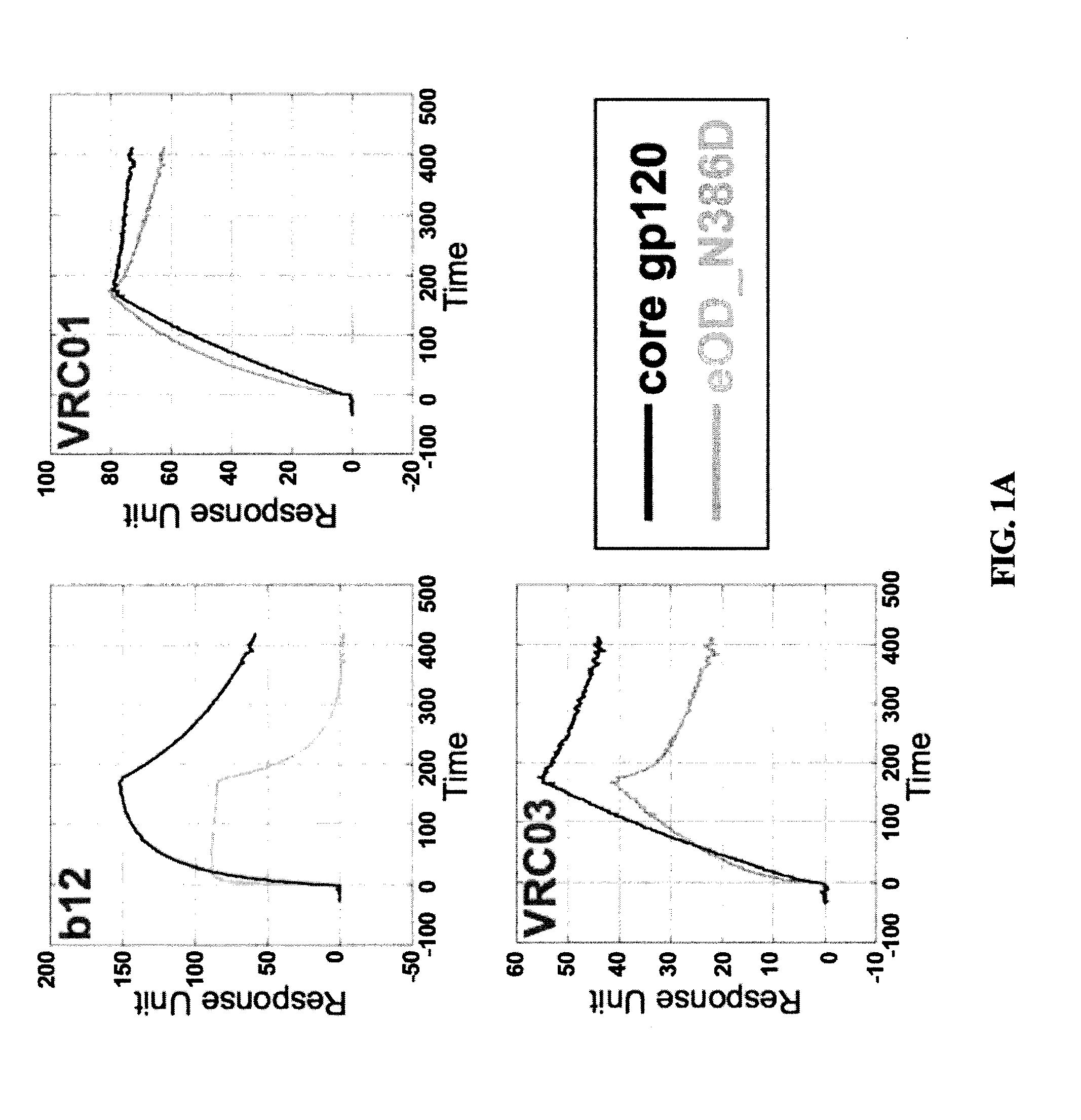
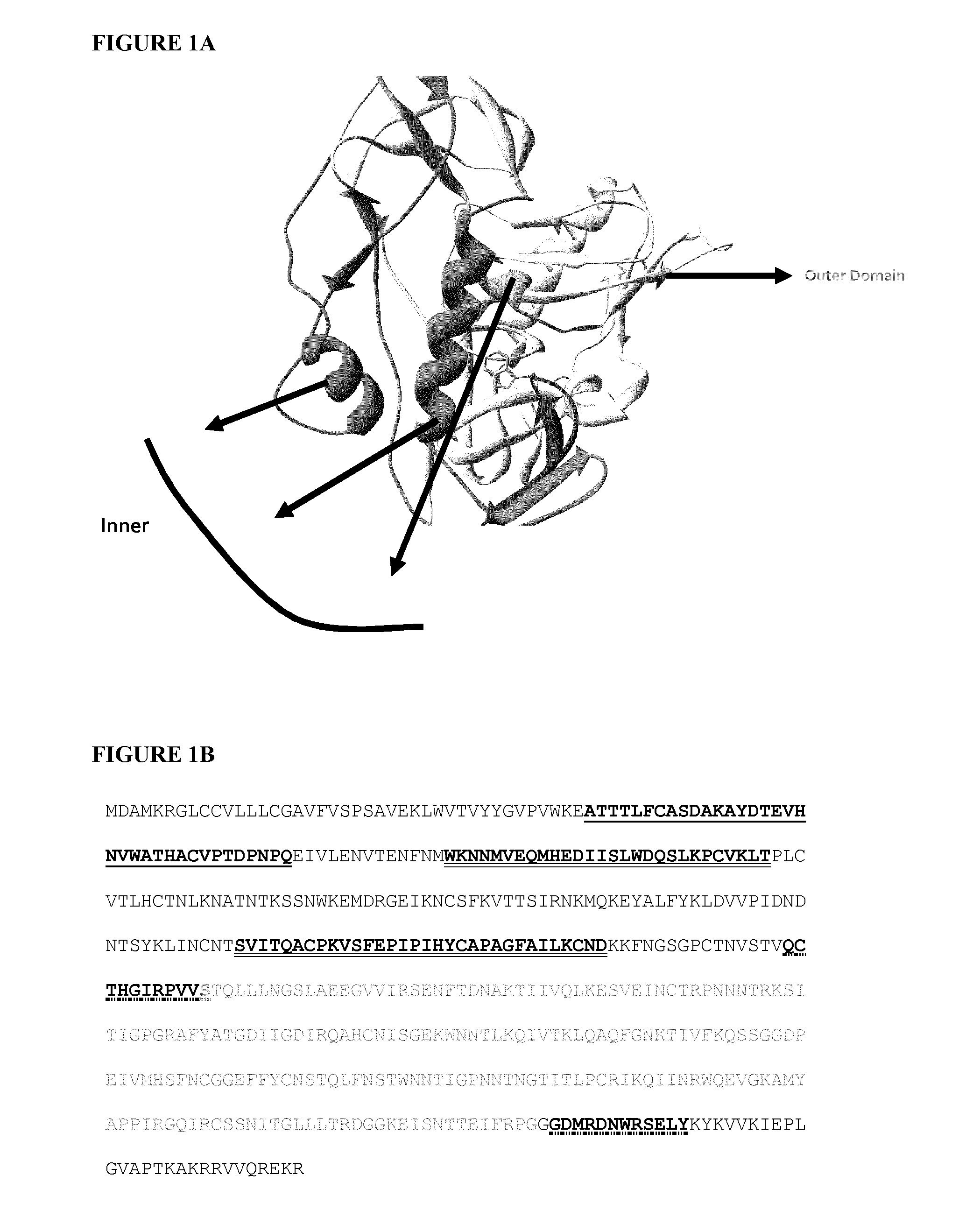
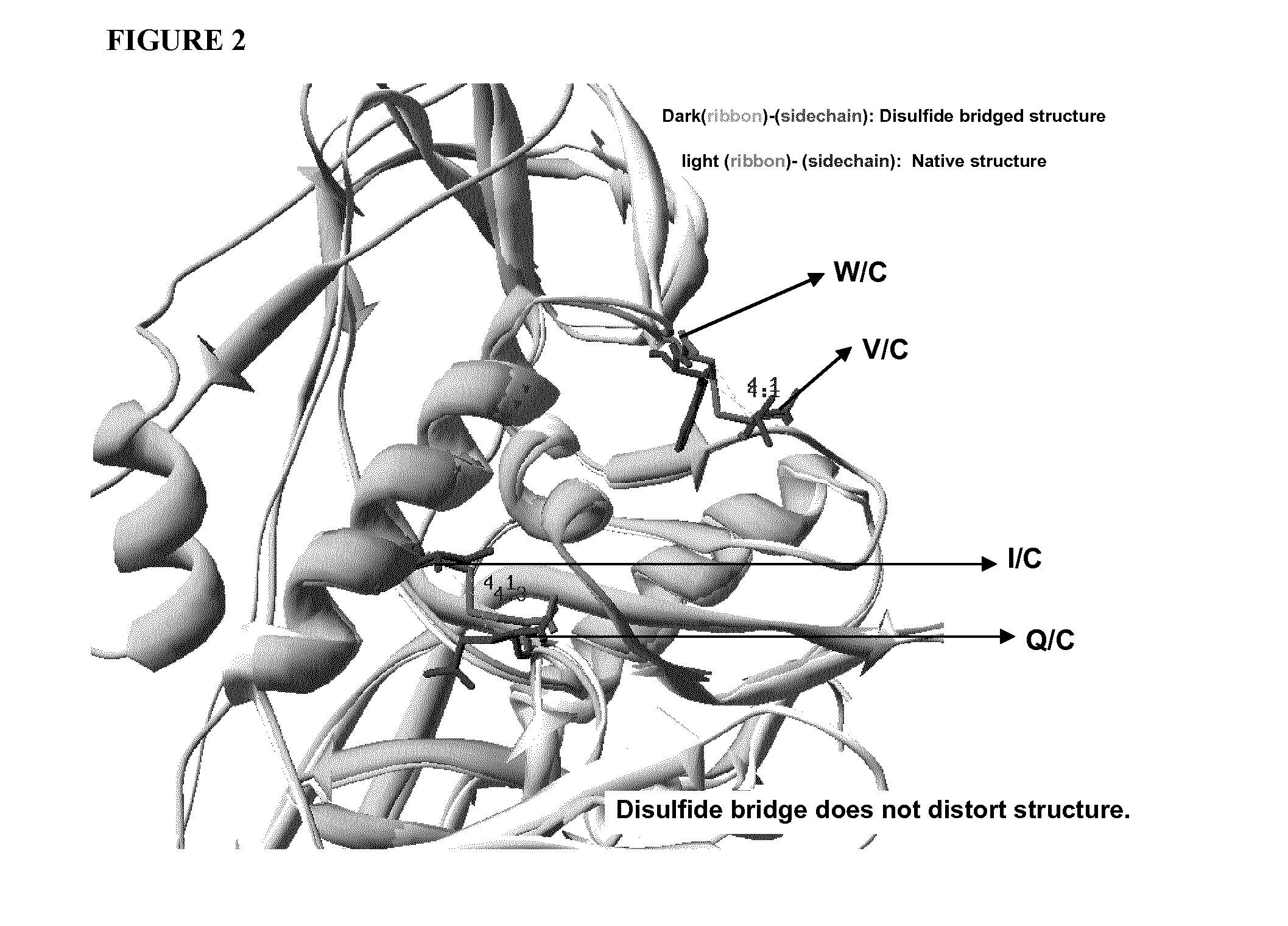
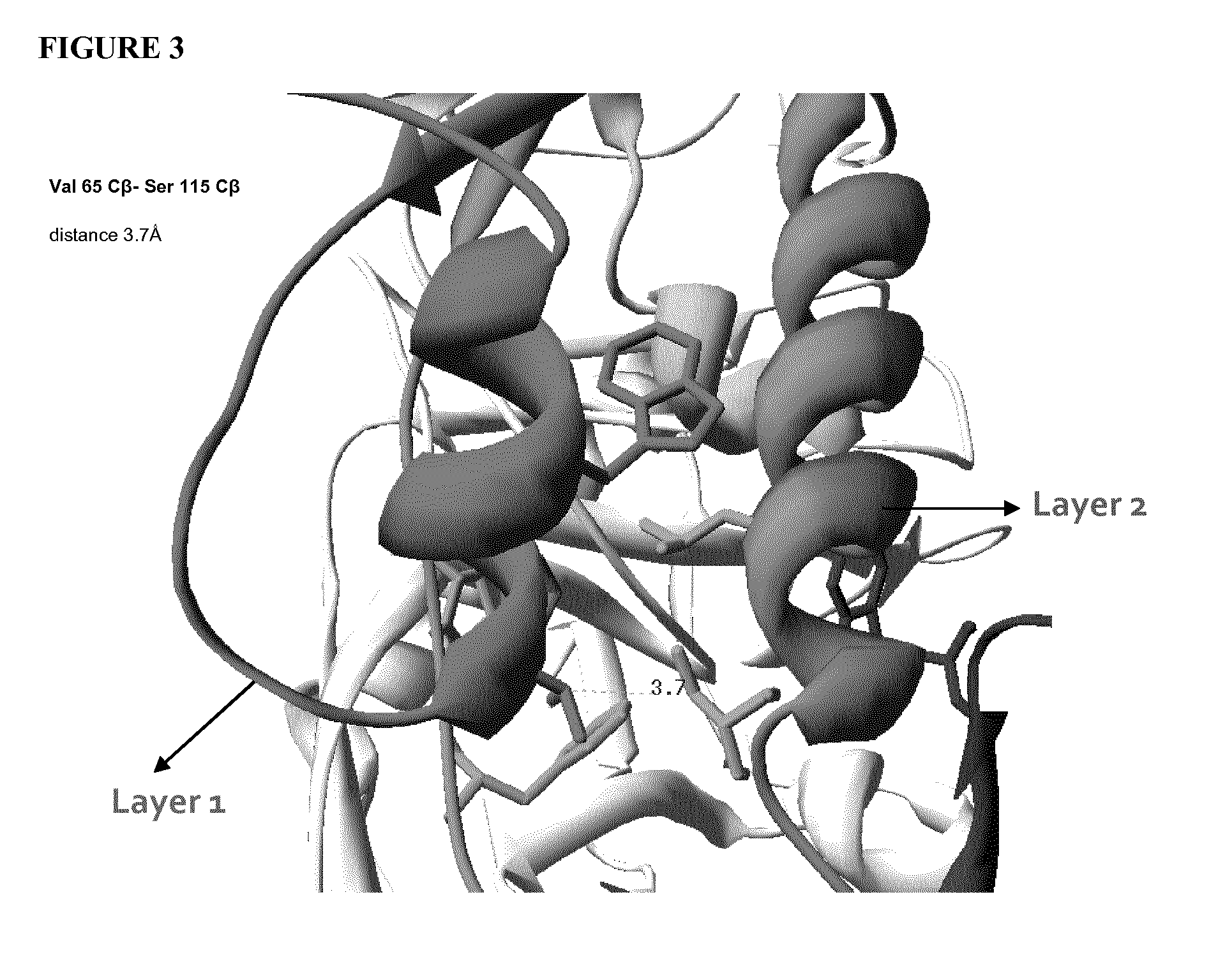
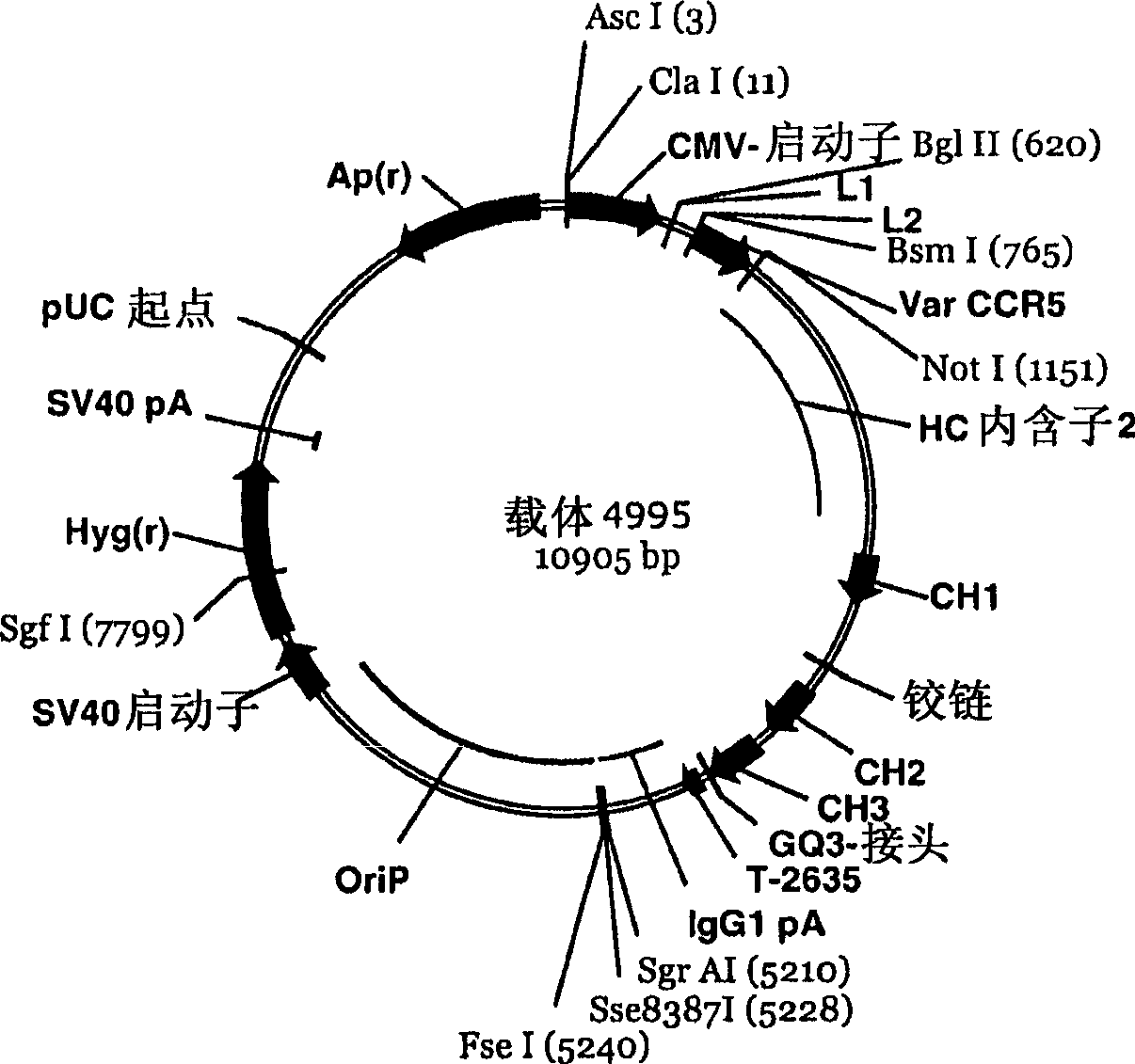
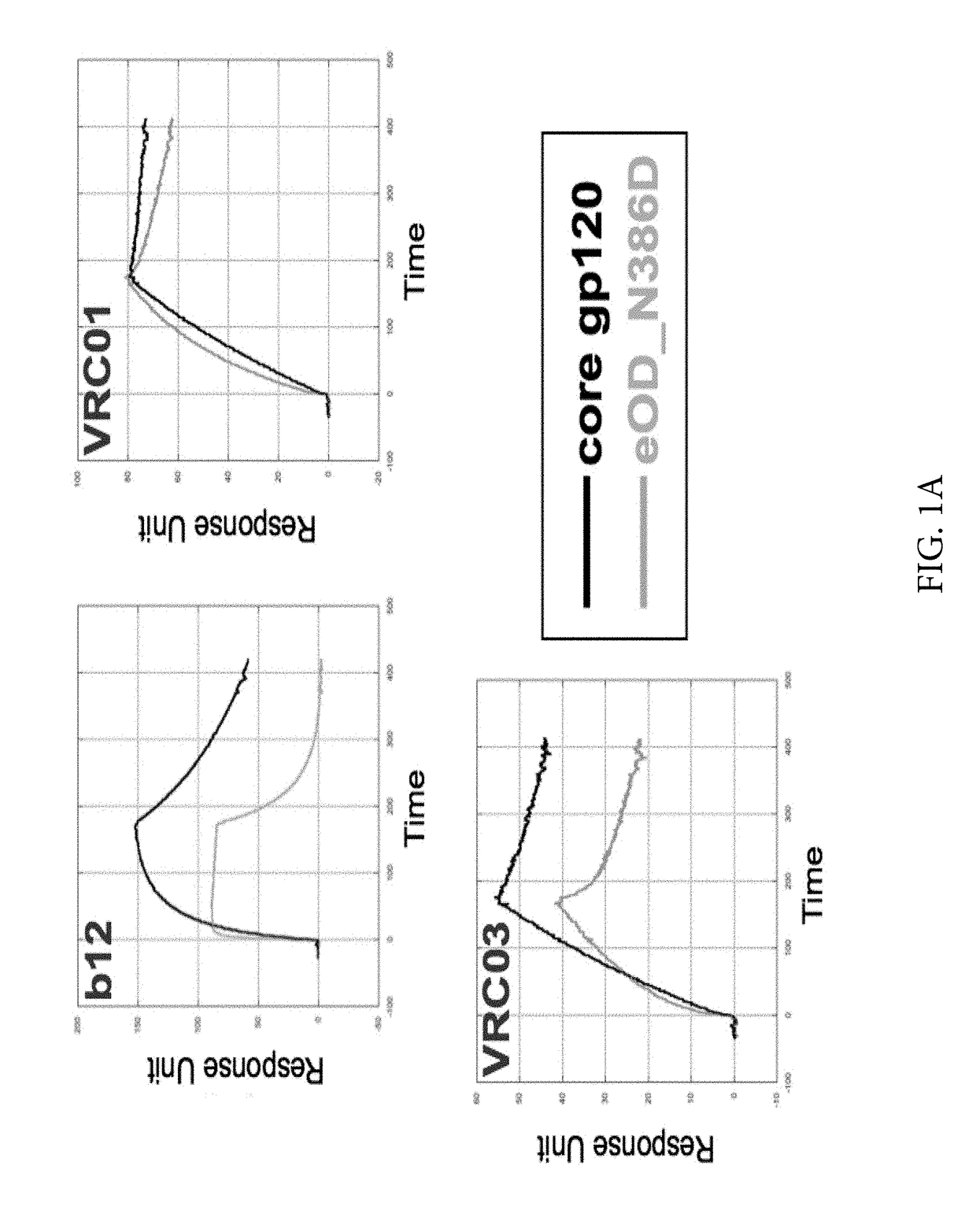
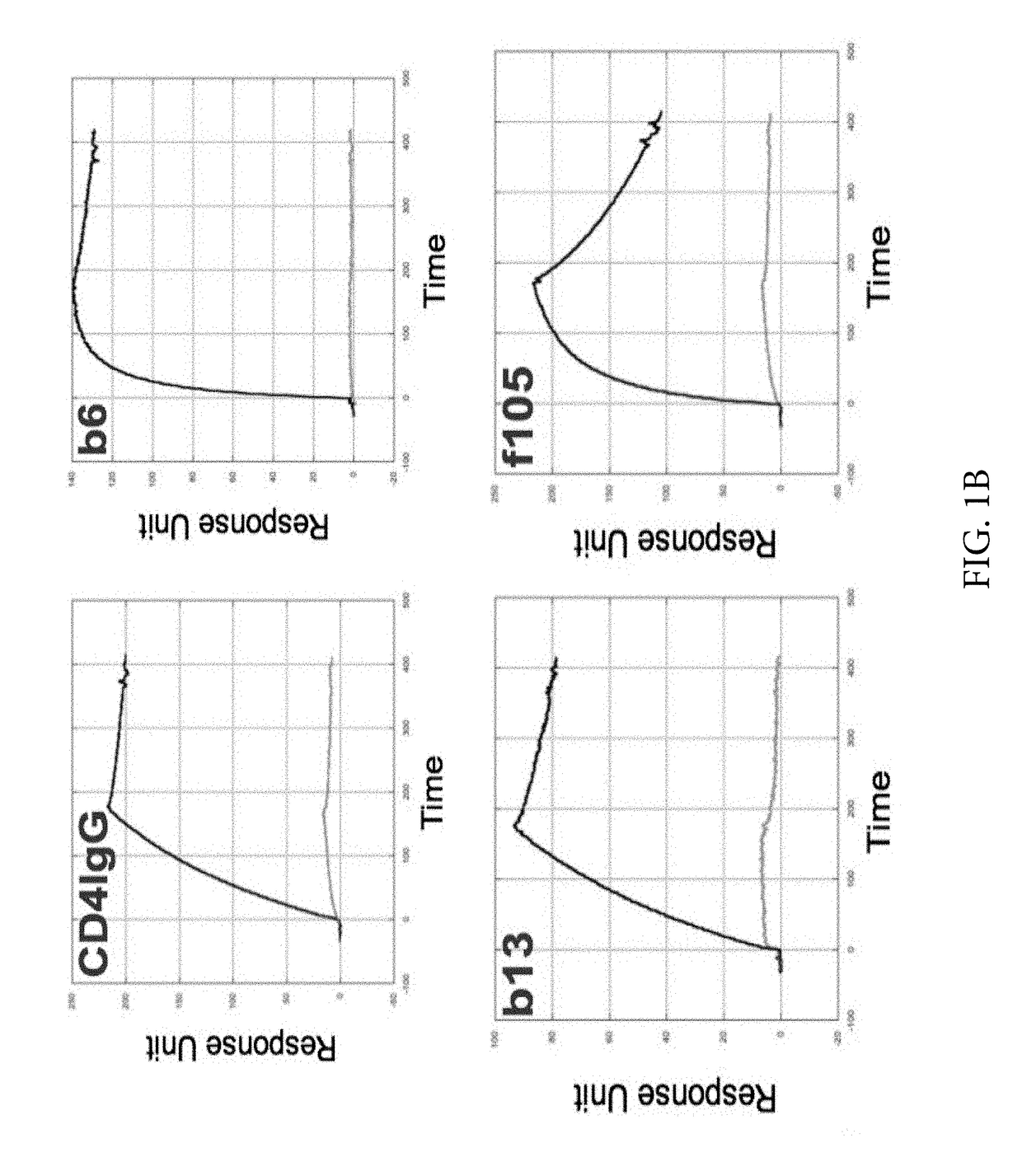
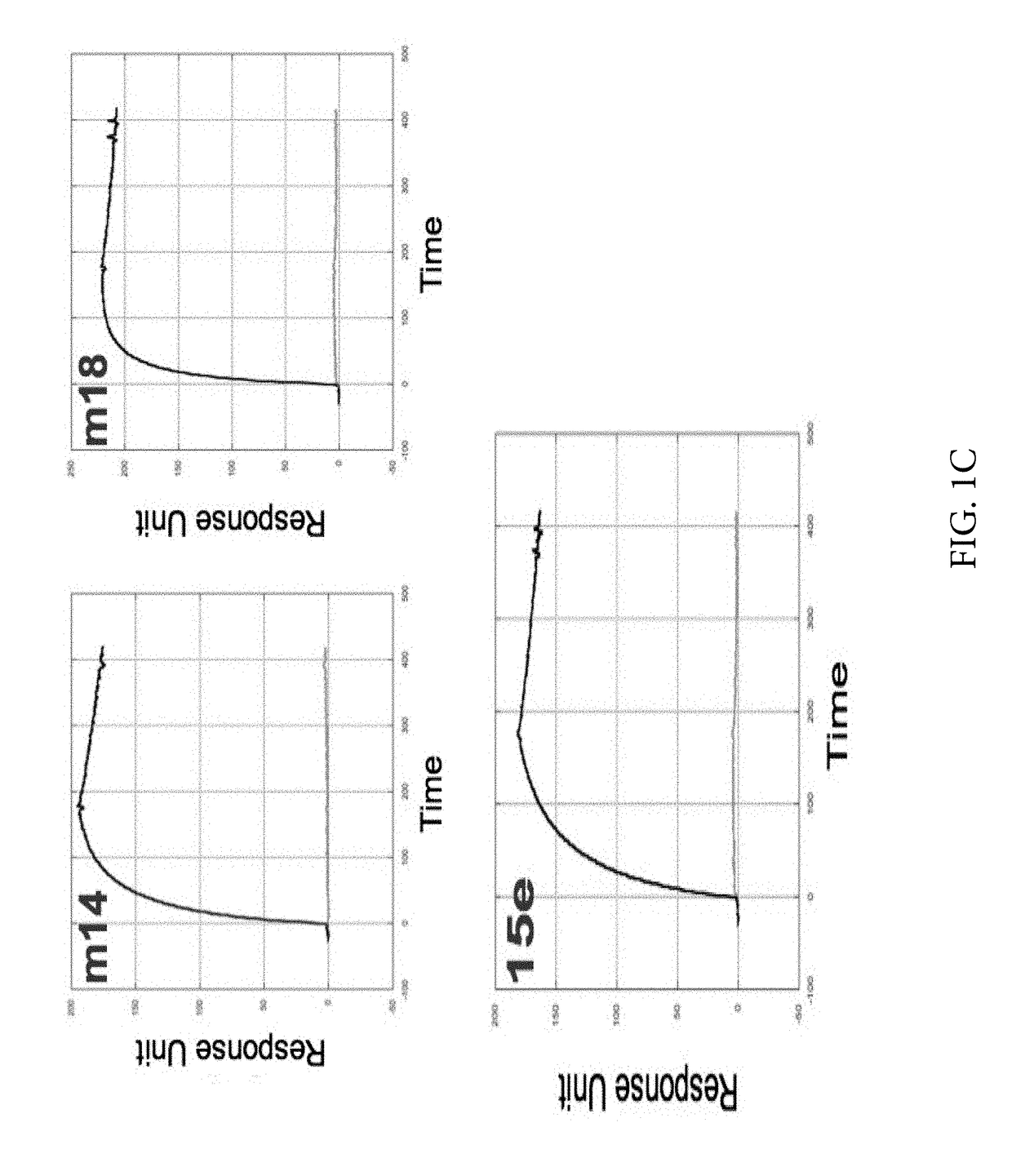
Engineered outer domain (EOD) of HIV gp120 and mutants thereof
InactiveUS20140322269A1Improve germline VRC0 bindingImprove bindingSugar derivativesVirus peptidesEpitopeBinding site
The invention relates to an engineered outer domain (eOD) of HIV gp120 and mutants thereof and methods of making and using the same. The mutant eODs may be advantageous for the elicitation of CD4-binding site (CD4bs)-directed broadly-neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) and / or improve binding to mature VRC01 and / or improve binding to germline VRC01 and the germlines of other VH1-2 derived broadly-neutralizing antibodies. The mutant eODs may also include glycan-masking mutations on eOD. The present invention also includes fusions of eOD to various protein multimers to enhance immunogenicity as well as the design of cocktails of different eODs that represent the full diversity of HIV sequences within the VRC01 epitope and surroundings.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +2
Preparation of full-length human antibody
InactiveCN1626669AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansImmunoglobulins against virusesAntigenHuman lymphocyte
The present invention provides a method for producing a fully humanized antibody that recognizes a predetermined antigen and does not rely on a human donor who has been exposed to the antigen. To achieve this, lymphocytes from natural human donors are immunized in vitro with an antigen of interest, and antibody-producing cells directed against said antigen are then identified. Because lymphocytes immunize in vitro rather than in vivo, it is possible to modulate the antigen or antigen fragment recognized by the antibody. A preferred antigen is an HIV gp120 peptide, especially the co-receptor binding region of gp120.
Owner:CCL HLDG
Broadly cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus selected by env-cd4-co-receptor complexes
InactiveUS20070212349A1Animal cellsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody fragmentsNeutralizing antibody
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
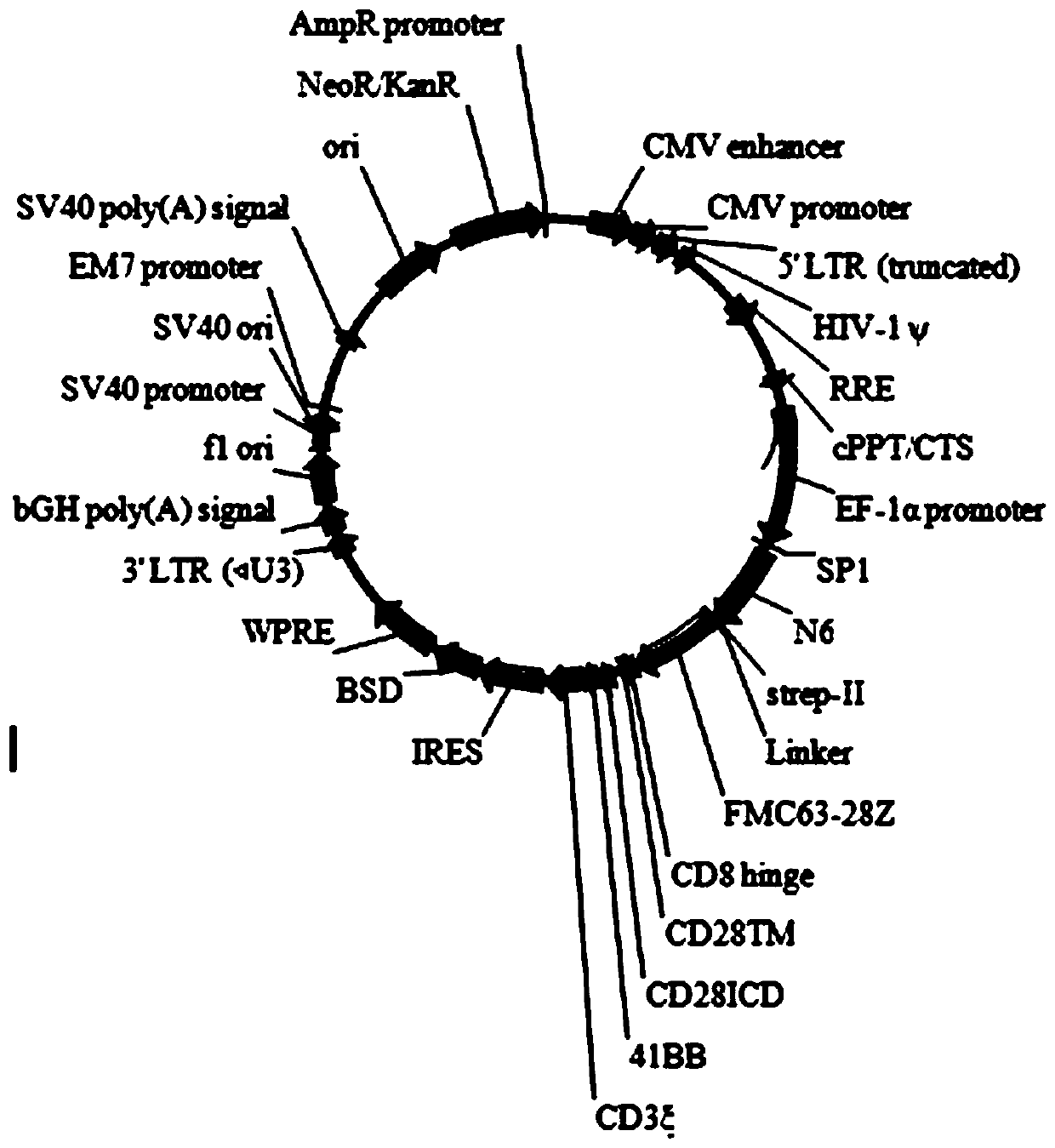
Bispecific chimeric antigen receptor for treating hematologic tumor complicated with HIV infection, gene thereof, and construction method and application of gene
ActiveCN111196858AAchieve the effect of treating two diseases at the same timeEasy to removeVirusesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSingle-Chain AntibodiesAntiendomysial antibodies
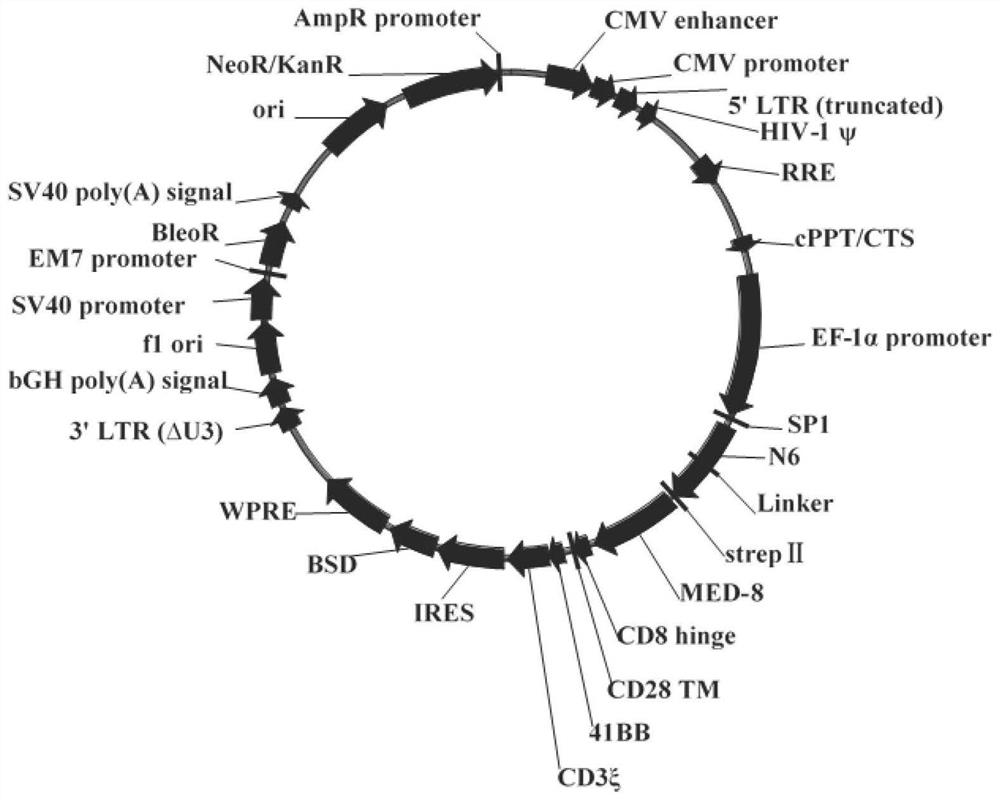
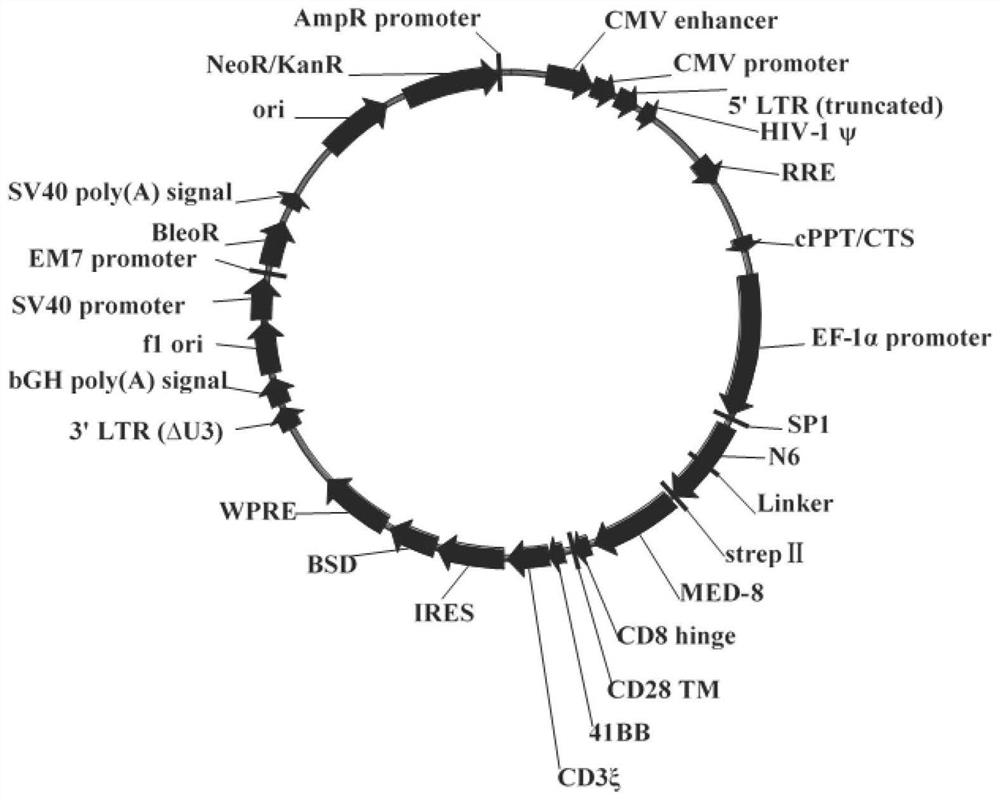
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of a recombinant gene of a bispecific chimeric antigen receptor for treating HIV infection complicated with blood tumor. The chimeric antigen receptor is formed by sequentially connecting a signal peptide, an HIV gp120 antigen specific single-chain antibody and an anti-CD19 single-chain antibody and then sequentially connecting witha CD28 transmembrane region, a CD28 intracellular structural domain (ICD), a 4-1BB costimulatory structural domain and a CD3zeta intracellular signal transduction structural domain in series, or the chimeric antigen receptor comprises: first CAR composed of the signal peptide, the chimeric antigen receptor, the HIV gp120 antigen specific single-chain antibody, the CD28 transmembrane region, the CD28-ICD, the anti-CD19 single-chain antibody, the CD8 transmembrane region, the CD28-ICD, the 4-1BB costimulatory structural domain and the CD3zeta intracellular signal transduction domain; and secondCAR composed of and the signal peptide, the anti-CD19 single-chain antibody, the CD8 transmembrane region in parallel, connecting the CD28-ICD, the 4-1BB costimulatory structural domain and the CD3zeta intracellular signal transduction domain, wherein the first CAR and the second CAR are sequentially connected in parallel.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Stabilized gp120
InactiveUS20150183835A1Reduced stabilityReduce interactionSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesEpitopeBinding site
The present invention provides an isolated polypeptide comprising an HIV gp120 polypeptide or soluble gp140 polypeptide stabilized in a conformation which exposes both CD4-bound and CD4-binding site epitopes. The invention also provides immunogenic compositions and methods of treating and preventing infection with HIV.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
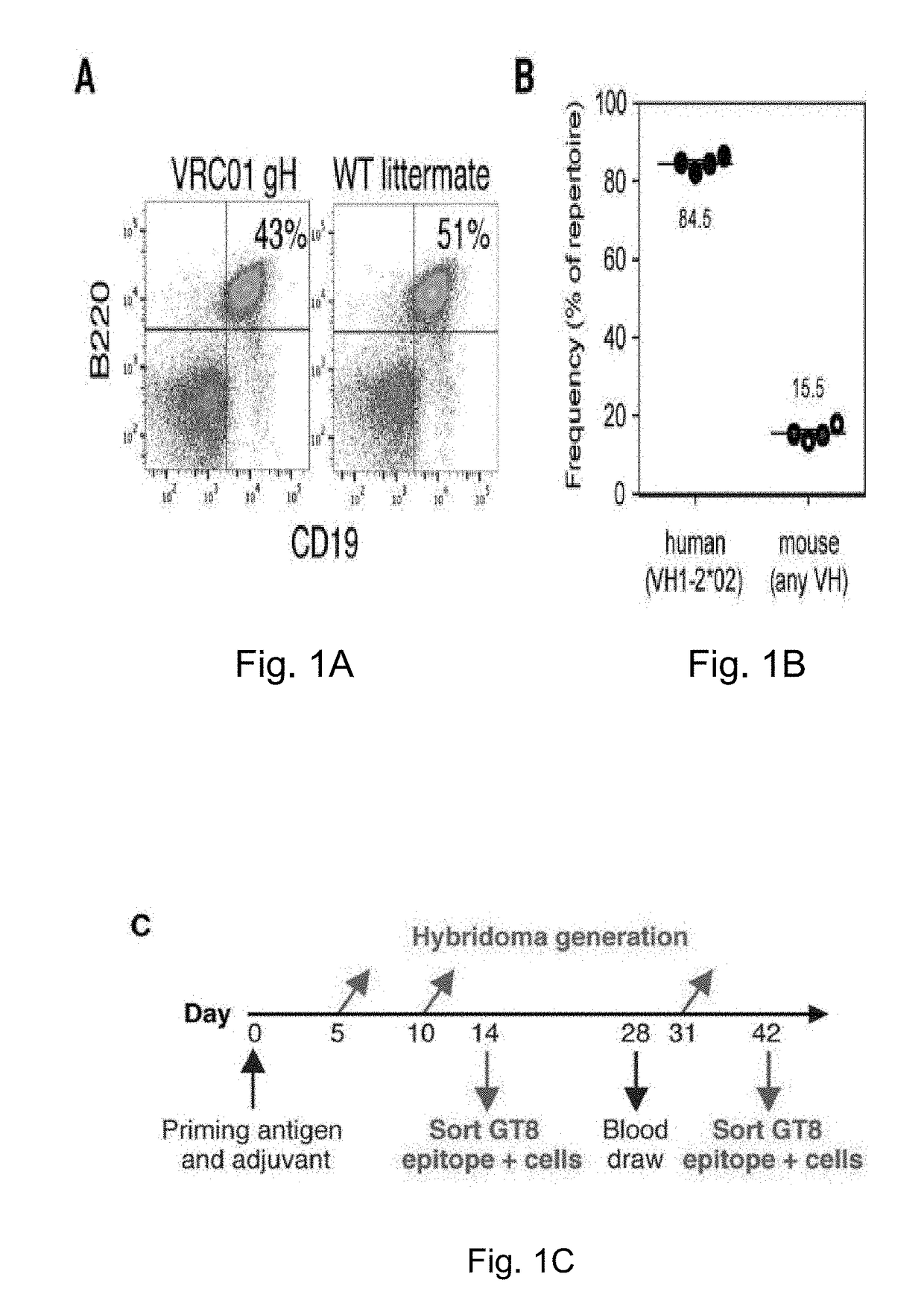
Engineered outer domain (EOD) of HIV gp120, mutants and use thereof
ActiveUS20180194809A1Elicit immune responseCompounds screening/testingViral antigen ingredientsHeavy chainMutant
The present invention relates to engineered outer domain (eOD) immunogens of HIV gp120 and mutants thereof and methods of making and using the same. The present invention also includes fusions of eOD to various protein multimers to enhance immunogenicity. The mutant eODs bind to neutralizing antibody precursors. The mutant eODs can activate germline precursors on the pathway to eliciting a broadly neutralizing antibody (bnAb) response. The invention also relates to immunized knock-in mice expressing germline-reverted heavy chains. Induced antibodies showed characteristics of bnAbs and mutations that favored binding to near-native HIV-1 gp120 constructs. In contrast, native-like immunogens failed to activate precursors. The invention also relates to rational epitope design that can prime rare B cell precursors for affinity maturation to desired targets.
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE +1
Therapeutic Peptides and Vaccines
Compositions are disclosed that induce broadly HIV theraputic and vaccine inducing antibodies against diverse HIV clades and relate to the ability to identify HIV gp120-derived short peptide sequence immunogens and various therapeutic compositions made from the identified peptides which compose CCR5 binding sites. Also disclosed are methods of selecting peptide sequences that are likely candidates for drugs which will offer effective treatment in such areas as Alzheimer's disease, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis and other diseases associated with the human inflammatory cascade as well as related retroviruses such as HTLV-1, the cause of tropical spastic paraparesis.
Owner:PEPTIDE ACCOUNT LLC
Anti-idiotype monoclonal antibodies as mimotopes of the HIV gp120 antigen
Novel anti-idiotype monoclonal antibodies are described which are capable of specifically reacting with the idiotype of human anti-gp120 antibodies, of inhibiting the binding between the gp120 antigen and human anti-gp120 antibodies, and of evoking a neutralising anti-gp120 immune response in an animal host to which they are administered. The anti-idiotype antibodies of the invention can be identified based on the amino acid sequences of the variable portions of their light and heavy chains. In addition, a method for obtaining a panel of anti-idiotype monoclonal antibodies, expression vectors and transformed host cells usable in a recombinant DNA procedure in order to generate the aforesaid anti-idiotype monoclonal antibodies, as well as the therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic use of such antibodies are disclosed.
Owner:POMONA RICERCA
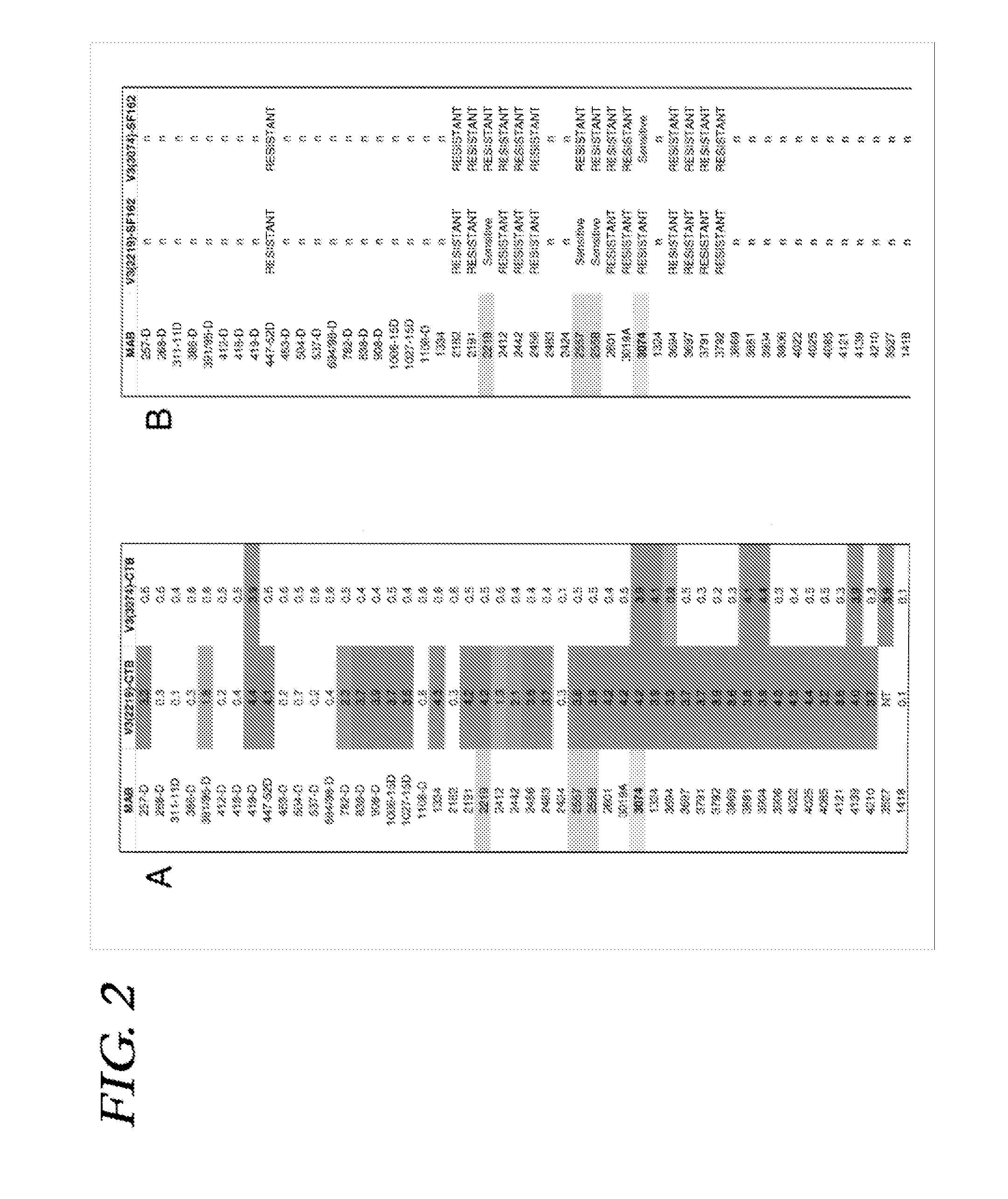
Immunogenic polypeptides comprising a modified loop peptide presenting the HIV-1 GP120 3074 mAb epitope and scaffold proteins containing said peptide
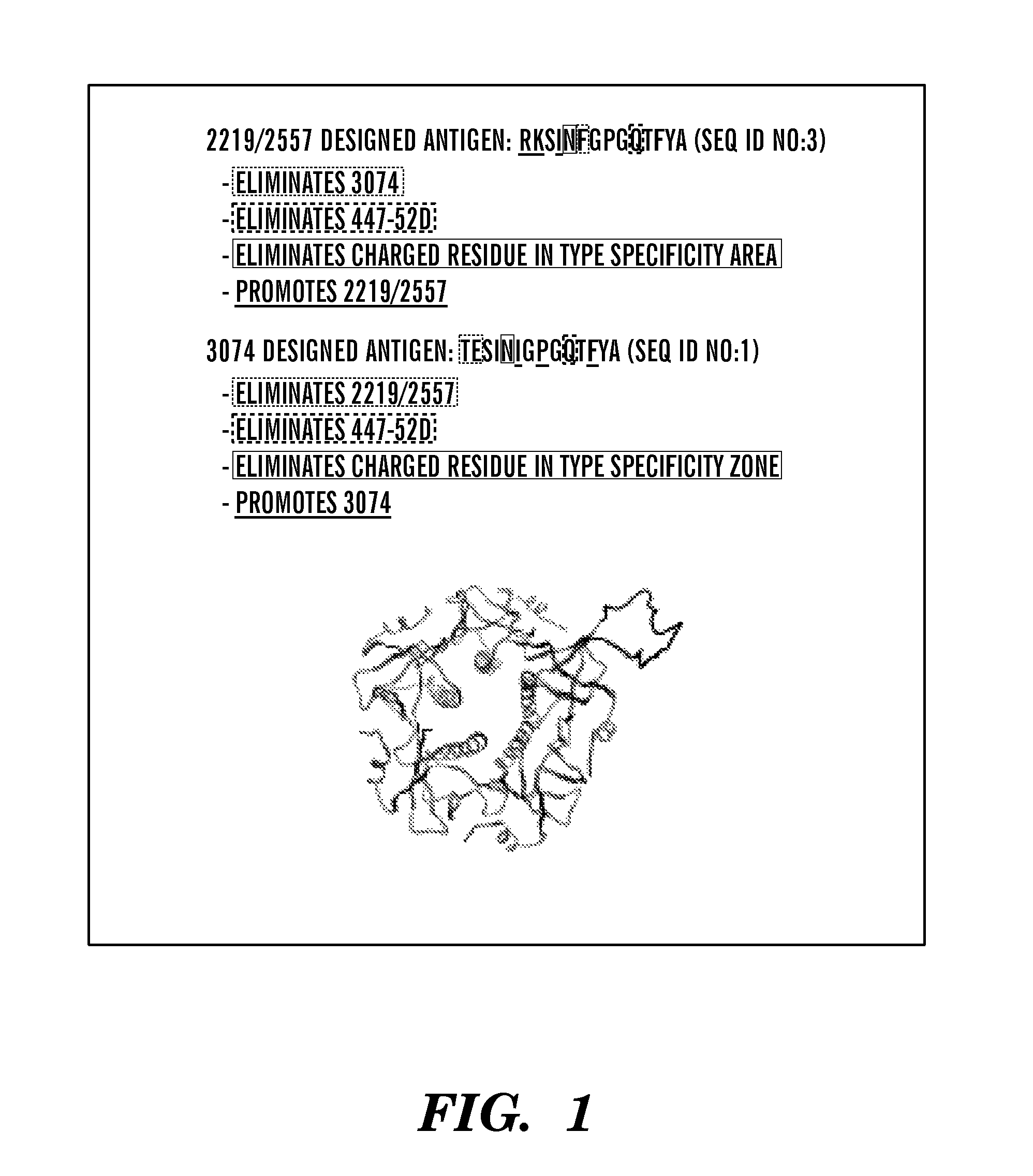
The present invention is directed to a recombinant immunogenic polypeptide. The polypeptide includes a loop peptide inserted into an immunogenic scaffold protein. The loop polypeptide has an amino acid sequence which presents the 3074 mAb- or the 2219 / 2557 mAb-targeted epitope of the HIV gp120 protein and not other known epitopes of the HIV gp120 protein. When used as an immunogen, the polypeptide induces an antibody response which neutralizes heterologous HIV-1 viruses in a pattern similar to that observed for the 3074 mAb- or the 2219 / 2557 mAb-targeted epitope, respectively. Pharmaceutical compositions containing the immunogenic polypeptide as well as methods of making and using it are also disclosed.
Owner:MOLSOFT +2
Methods and compositions for inhibiting hiv-coreceptor interactions
InactiveUS20060116325A1Elicit immune responseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseImmunodeficiency virus
Novel methods and compositions are provided for inhibiting interactions between human immunodeficiency viruses (HIVs) and viral coreceptors, including CXCR4 and / or CCR5 coreceptors. The anti-coreceptor binding agent includes a novel peptide portion of the gp120 envelope protein of HIV-1, as well as peptide analogs and mimetics of this peptide, that specifically binds to, or modulates activity of, the coreceptors(s). The anti-coreceptor binding agent is useful as a prophylactic or therapeutic treatment to prevent or inhibit HIV binding to a susceptible cell and thereby reduces infection and / or moderates or treats related diseases. In alternative embodiments, the peptides, analogs and mimetics are effective to inhibit direct co-receptor binding by HIV virus, coreceptor binding by HIV gp120 proteins or peptides, HIV fusion with target host cells, HIV virion entry into host cells, HIV replication, and HIV transmission between cells and hosts. In more detailed embodiments, the anti-coreceptor binding agents of the invention are multi-tropic by exhibiting activity against HIV interactions with multiple, CXCR4 and CCR5, coreceptors.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
A conjugate of an antibody against CCR5 and an antifusogenic peptide
InactiveCN101500615AVirus peptidesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeavy chainHIV receptor
The current invention is related to a conjugate comprising one or more antifusogenic peptides and an antibody against an HIV gp120 binding cell surface receptor, characterized in that one to eight antifusogenic peptides are each conjugated to one terminus of the heavy and / or light chains of said antibody against an HIV gp120 binding cell surface receptor and to the pharmaceutical use of said conjugate.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Engineered outer domain (eOD) of HIV gp120 and mutants thereof
ActiveUS10221217B2Improve bindingImproving immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsEpitopeBinding site
The invention relates to an engineered outer domain (eOD) of HIV gp120 and mutants thereof and methods of making and using the same. The mutant eODs may be advantageous for the elicitation of CD4-binding site (CD4bs)-directed broadly-neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) and / or improve binding to mature VRC01 and / or improve binding to germline VRC01 and the germlines of other VH1-2 derived broadly-neutralizing antibodies. The mutant eODs may also include glycan-masking mutations on eOD. The present invention also includes fusions of eOD to various protein multimers to enhance immunogenicity as well as the design of cocktails of different eODs that represent the full diversity of HIV sequences within the VRC01 epitope and surroundings.
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE +2
Antibodies that target HIV gp120 and methods of use
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Recombinant fusion protein comprising HIV gp120 linked to an enhancing CD4 binding site mAb
Fusion proteins comprising a portion of the HIV-1 Env protein (gp120 and gp140) and single-chain fragment V regions (ScFv) of an enhancing antibody that exhibits binding specificity for HIV-1 Env protein are disclosed that may serve in immunogenic formulations for vaccination against HIV-1 infection, as well as methods of generating an immune response using the fusion proteins.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Multi-specific antibody targeting HIV gp120 protein and human CD3 molecule and application thereof
ActiveCN114316062AEasy to eliminateReduce loadHybrid immunoglobulinsAntiviralsSingle-Chain AntibodiesClinical efficacy
The invention discloses a multispecific antibody targeting HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) gp120 protein and human CD3 molecules and application of the multispecific antibody. The multi-specific antibody comprises an antibody specifically bound with gp120 and a single-chain antibody specifically bound with CD3 at the 471st-710th sites of which the amino acid sequence is sequence 1, and the antibody specifically bound with gp120 comprises a heavy chain variable region at the 1st-136th sites of which the amino acid sequence is sequence 1 and a light chain variable region at the 1st-125th sites of which the amino acid sequence is sequence 3, and the single-chain antibody is fused with the C terminal of the heavy chain of the antibody which is specifically combined with the gp120. The multispecific antibody targets different epitopes of gp120, the neutralizing effect of HIV viruses can be remarkably improved, the probability of generation of virus escape mutation is reduced, meanwhile, the viruses are better killed by targeting CD3 molecules, and the clinical curative effect of antibody treatment is improved.
Owner:珠海臻谱基因科技有限公司
Rapid selection method for HIV gp-120 variants
InactiveUS20140037667A1Increase affinity of antibodyQuick selectionVirusesBacteriaNeutralizing antibodyVirus
The invention relates to a method for rapid immunogen selection (RIS) based on the binding a library of recombinant viruses containing randomized HIV gp120 variants of a surface polypeptide displayed to said neutralizing antibodies. The invention relates as well to the use of the HIV gp120 immunogens isolated according to the RIS method of the invention in medicine for the treatment of diseases caused by a virus and in diagnosis for the identification of neutralizing antibodies in a patient.
Owner:LAB DEL DR ESTEVE SA +1
Anti-idiotype monoclonal antibodies mimicking the HIV gp120 CD4-binding (CD4bs)
Novel anti-idiotype monoclonal antibodies are described which are capable of specifically reacting with the idiotype of human anti-gp120 antibodies, of inhibiting the binding between the gp120 antigen and human anti-gp120 antibodies, and of evoking a neutralising anti-gp120 immune response in an animal host to which they are administered. The anti-idiotype antibodies of the invention can be identified based on the amino acid sequences of the variable portions of their light and heavy chains. In addition, a method for obtaining a panel of anti-idiotype monoclonal antibodies, expression vectors and transformed host cells usable in a recombinant DNA procedure in order to generate the aforesaid anti-idiotype monoclonal antibodies, as well as the therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic use of such antibodies are disclosed.
Owner:POMONA RICERCA
Bispecific chimeric antigen receptor targeting HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus-1) envelope protein as well as preparation method and application of bispecific chimeric antigen receptor
ActiveCN114163534AImprove broad spectrumImprove featuresAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiviralsAntigen receptorsBiology
The invention provides a bispecific chimeric antigen receptor targeting an HIV-1 virus envelope protein. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises (1) a recognition unit targeting an HIV-1 gp120 protein co-receptor binding site; (2) a recognition unit targeting other binding sites of HIV-1 gp120 (including but not limited to a CD4 binding site, a V1V2 glycan region, a V3 glycan region, a gp120-gp41 interface or a proximal membrane end external region on gp41); (3) a hinge and transmembrane region; and (4) an intracellular signal transduction domain; optionally, the chimeric antigen receptor further comprises (5) one or more co-stimulatory signal domains; preferably, according to the series connection sequence of the chimeric antigen receptor extracellular recognition domain, the far membrane end is a recognition unit of a targeted HIV-1 gp120 protein co-receptor binding site, and the near membrane end is a recognition unit of targeted HIV gp120 other binding sites. The invention provides a brand-new construction method of the HIV-1 virus envelope protein bispecific chimeric antigen receptor, immune cells modified by the HIV-1 virus envelope protein bispecific chimeric antigen receptor have stronger activating and killing capabilities, HIV-1 infected cells can be specifically recognized and killed, and the HIV-1 virus envelope protein bispecific chimeric antigen receptor has a good application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
A bispecific chimeric antigen receptor, gene, construction method and application for treating HIV infection
ActiveCN111704675BChange the way of industrializationGood clinical promotion valueAntiviralsMammal material medical ingredientsAntigenSingle-Chain Antibodies
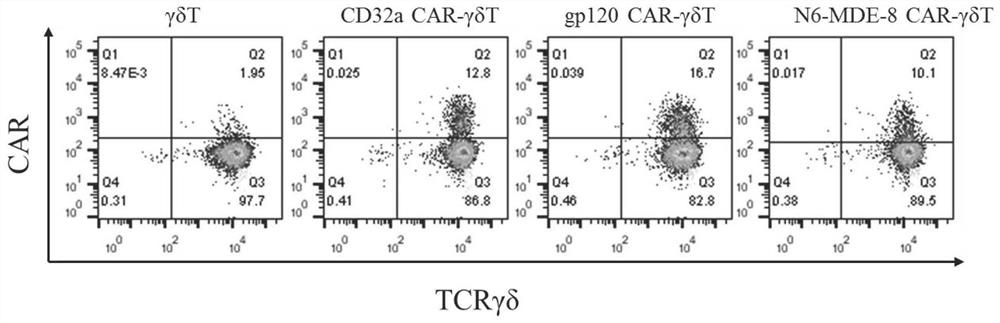
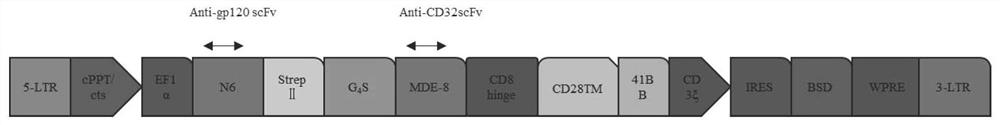
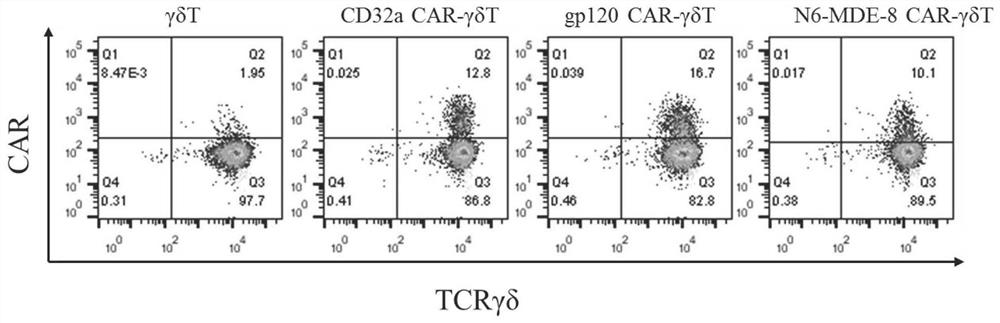
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a bispecific chimeric antigen receptor recombinant gene for treating HIV infection. The bispecific chimeric antigen receptor includes anti-CD32a single-chain antibody and anti-HIV gp120 single-chain antibody The coding nucleotide sequence of the anti-CD32a single-chain antibody and the coding nucleotide sequence of the anti-HIV gp120 single-chain antibody are connected in series in the bispecific chimeric antigen receptor coding gene. The bispecific chimeric antigen of the present invention targets the fusion protein gp120, a marker for HIV replication and proliferation, and the membrane protein CD32a, a marker for latency, to design dual-target CAR-T cells, which can completely eliminate HIV-infected target cells, It has great clinical promotion value.
Owner:WUHAN BIO RAID BIOTECH CO LTD
Bispecific chimeric antigen receptor for treating human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, gene, construction method and application of bispecific chimeric antigen receptor
ActiveCN111704675AChange the way of industrializationGood clinical promotion valueMammal material medical ingredientsAntiviralsAntigenSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention discloses a construction method for a recombination gene of a bispecific chimeric antigen receptor for treating a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and application thereof. The bispecific chimeric antigen receptor comprises an anti-CD32a single-chain antibody and an anti-HIV gp120 single-chain antibody; and a coding nucleotide sequence of the anti-CD32a single-chain antibody and a coding nucleotide sequence of the anti-HIV gp120 single-chain antibody are connected in series in a coding gene of the bispecific chimeric antigen receptor. According to the bispecific chimeric antigen receptor of the invention, by taking a marker fusion protein gp120 of HIV replication and proliferation and a marker envelop protein CD32a of the latent period as target points, a dual-target point CAR-T cell is designed, and thus, HIV infected target cells can be thoroughly eliminated; and the bispecific chimeric antigen receptor has great clinical promotion value.
Owner:WUHAN BIO RAID BIOTECH CO LTD
Immunogenic polypeptides having an immunogenic scaffold protein and a loop peptide, presenting a 3074- or 2219/2557- monoclonal antibody-targeted epitope, which is present in the HIV gp120 protein
ActiveUS20130287804A1Bridging the gapPeptide/protein ingredientsVirus peptidesCyclic peptideHeterologous
Owner:MOLSOFT +2
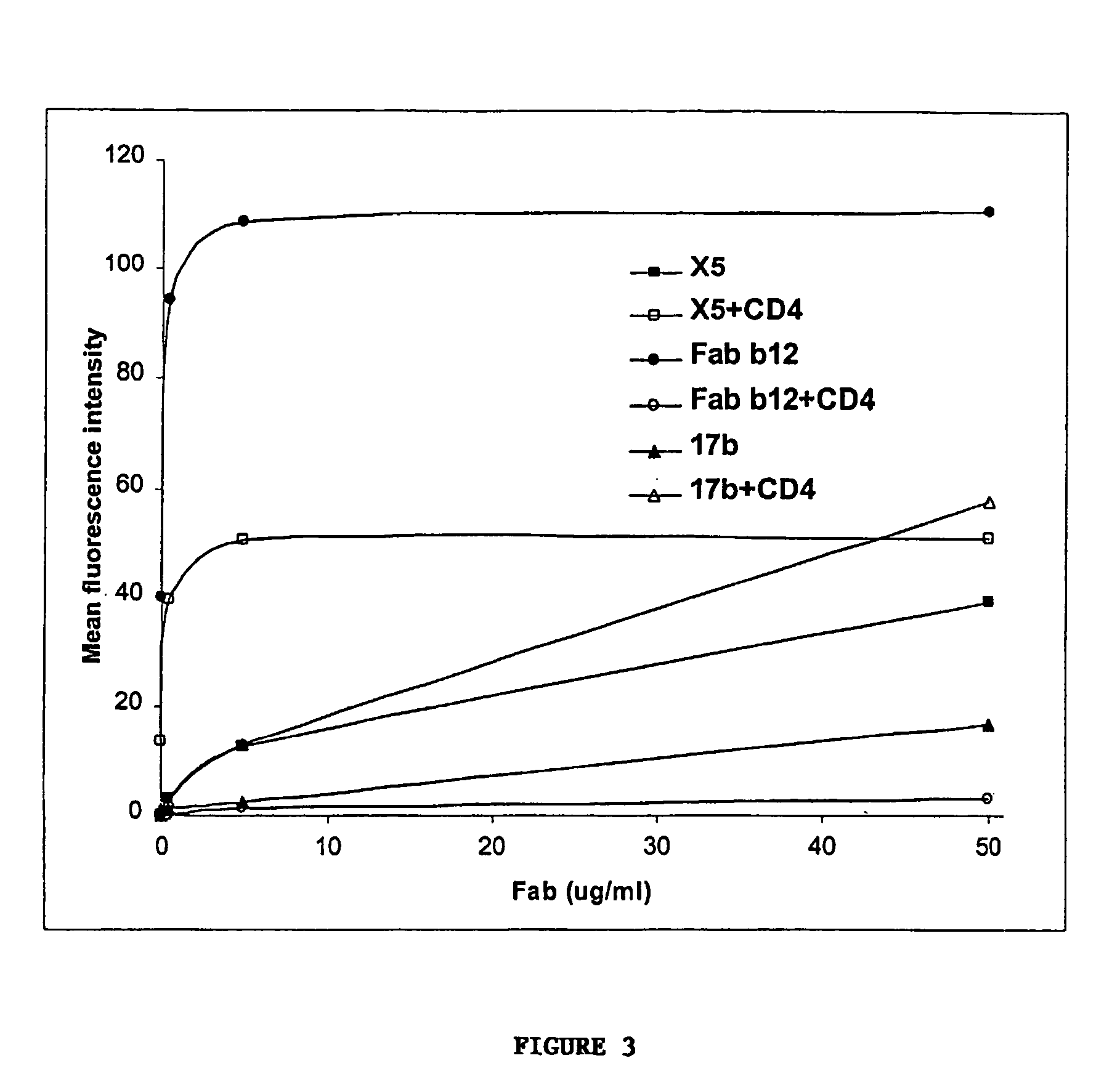
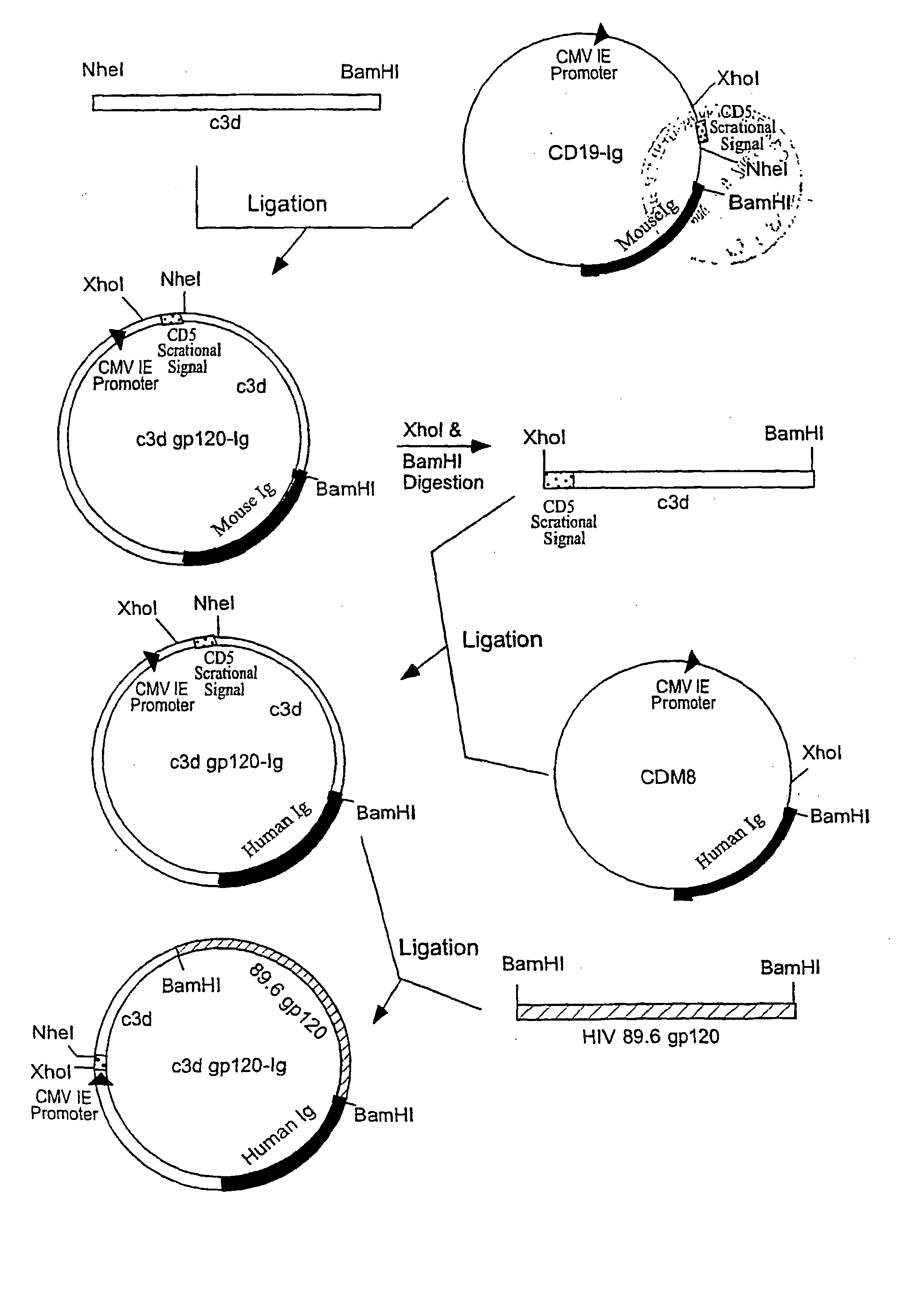
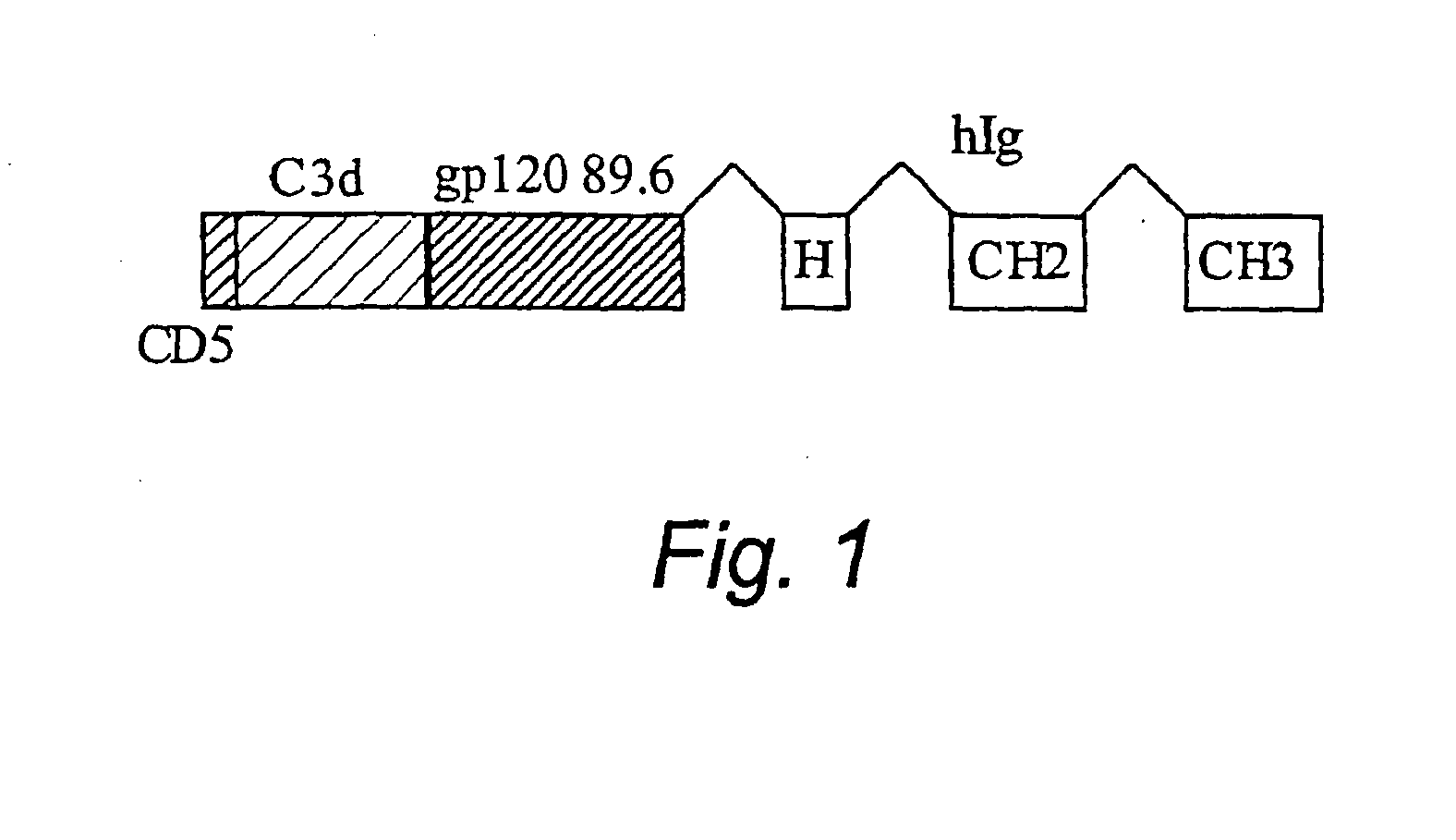
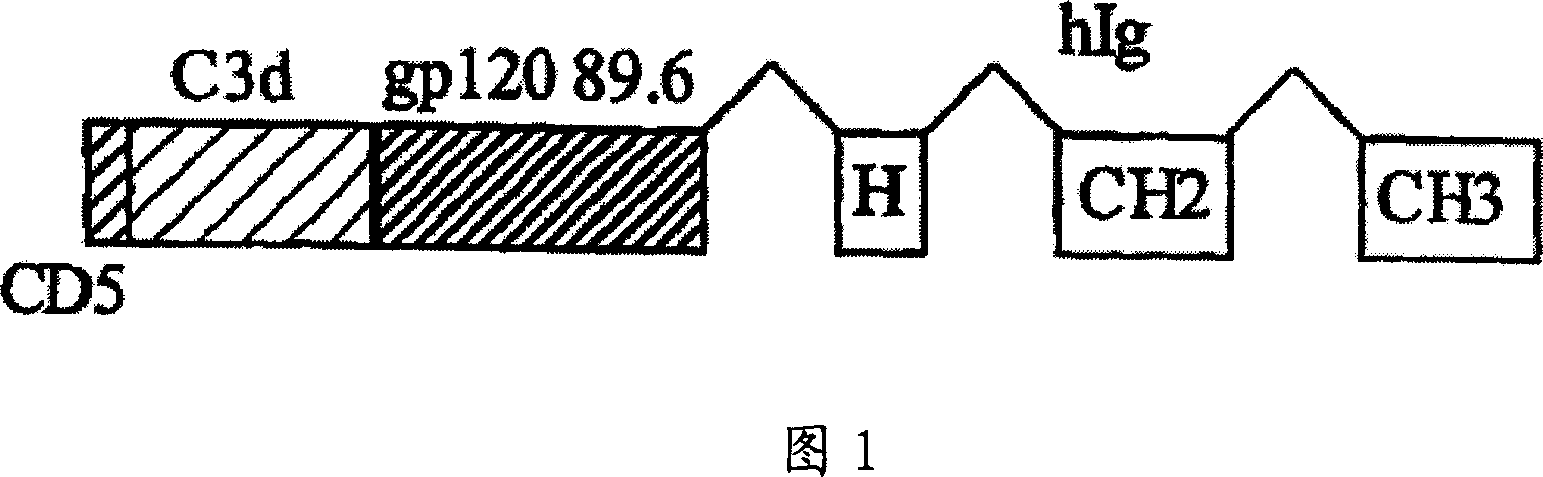
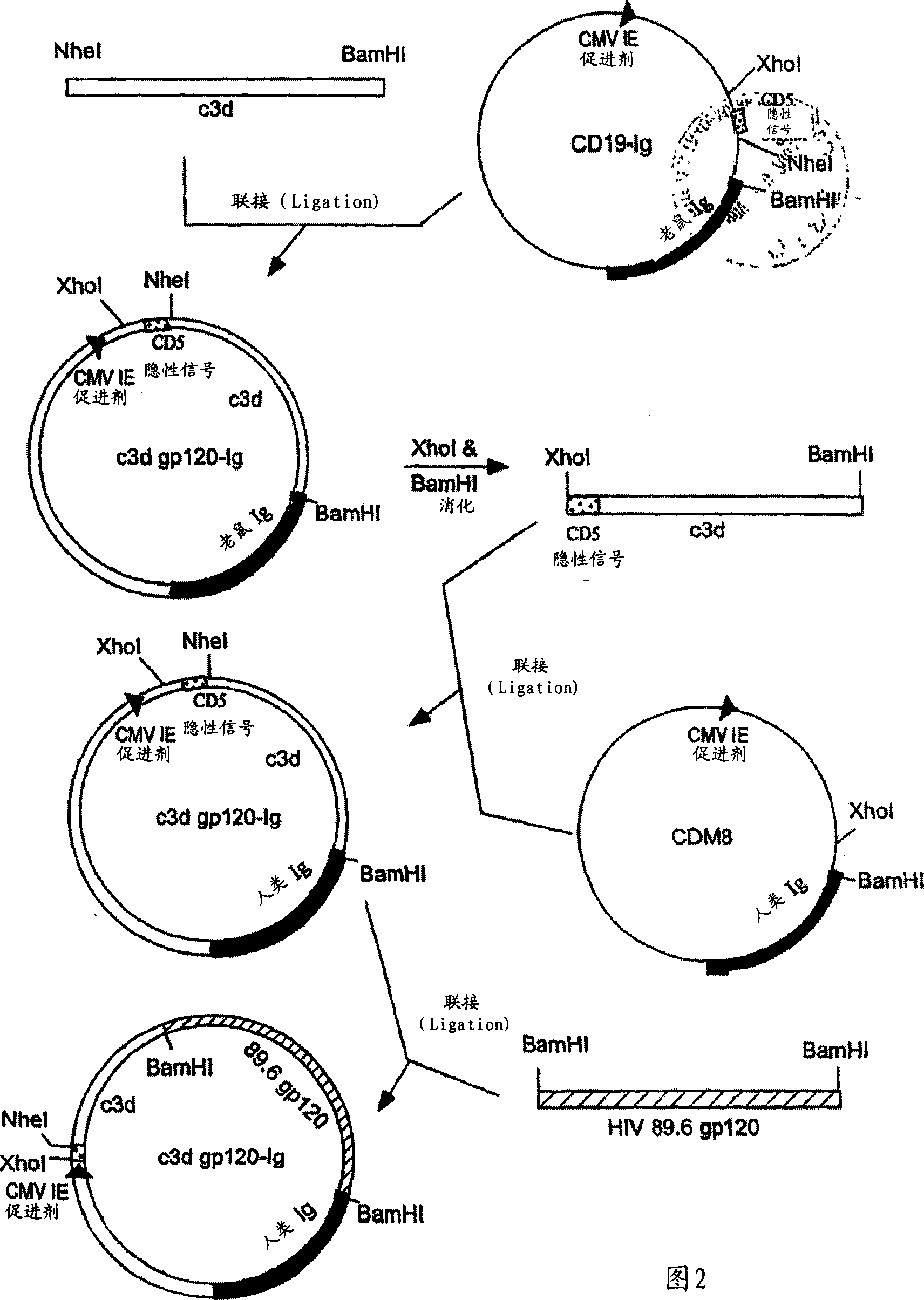
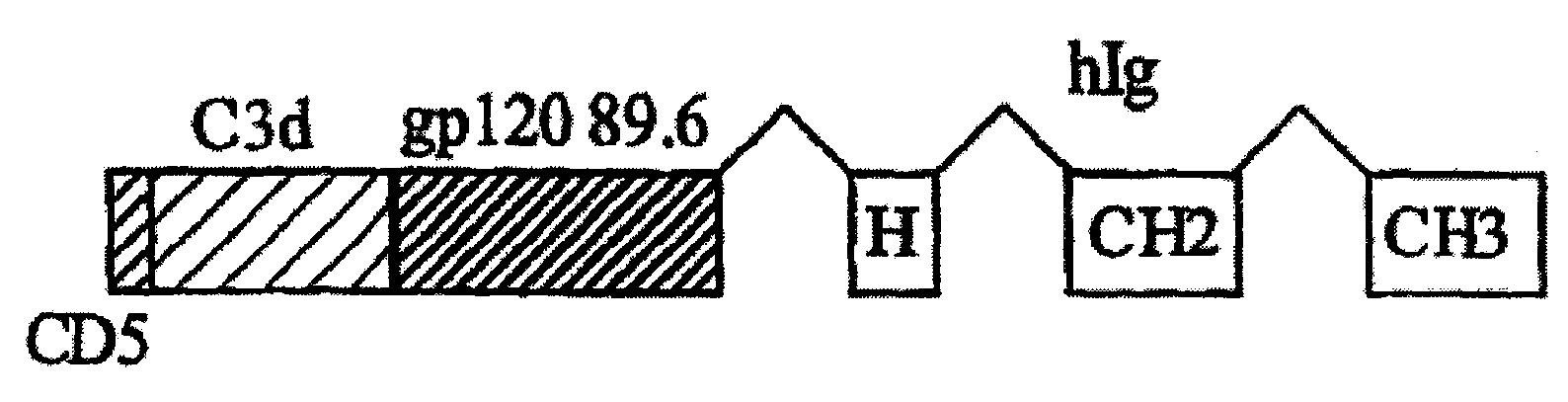
IgG Fc/HIV-gp120/C3d fusion protein
Owner:DUKE UNIV
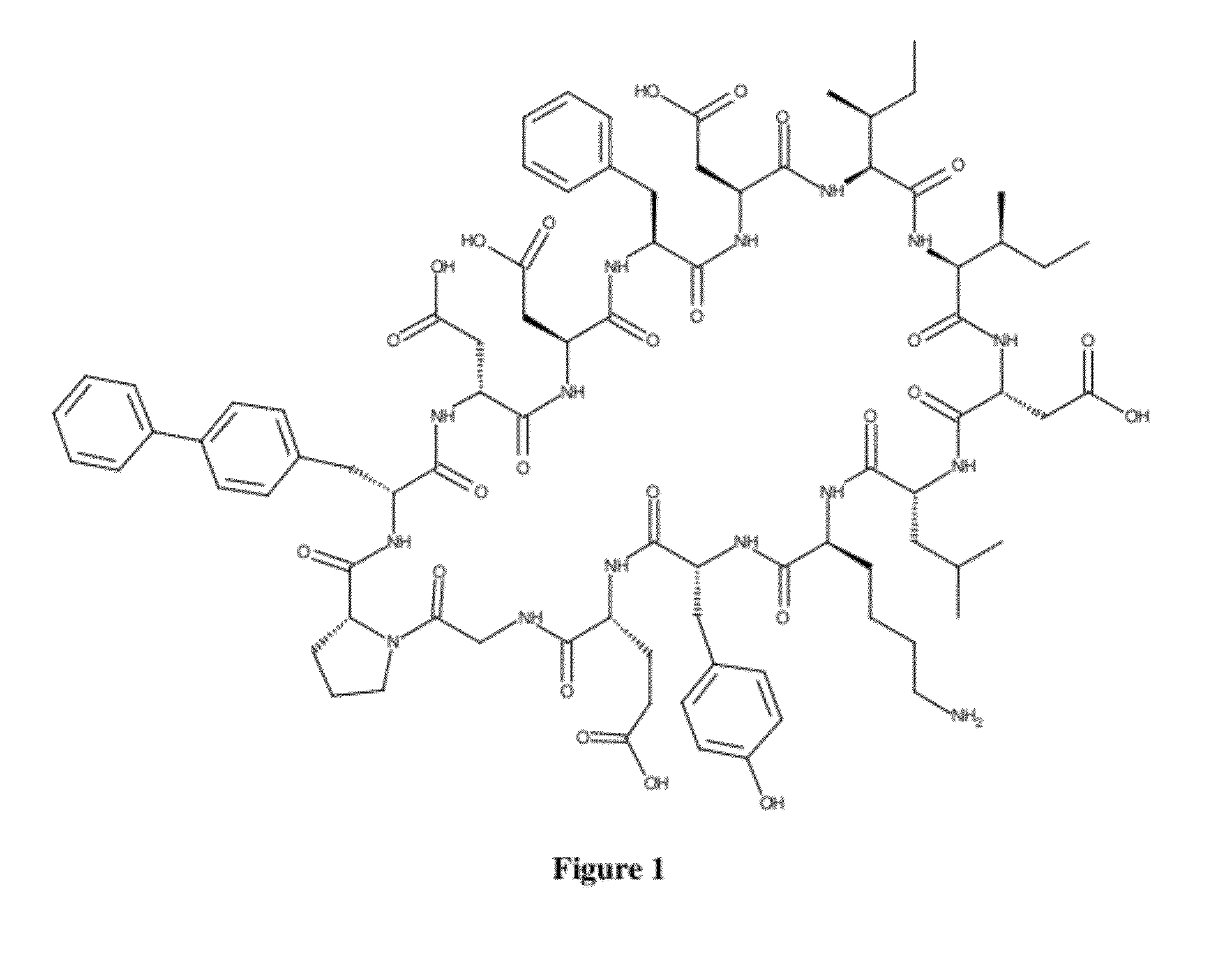
Designer Cyclic Peptides - HIV gp120 Antagonists and their Applications
InactiveUS20120270806A1Avoid enteringIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMicrobiological testing/measurementCyclic peptideStructure and function
The present invention is concerned with a novel composition of matter—a cyclic peptide derived from computer modeling studies that modulates the structure and function of the HIV main envelope protein gp120. The compound is capable of binding to the CD4-binding region of gp120 (this defines it as a CD4 mimic), and can be used for the purposes of: (1) controlling and preventing HIV infections, (2) detecting, isolating and purifying gp120. Contrary to examples of prior art that involved CD4 mimics being either small molecules or macromolecules, the present invention is concerned with the class of “large small molecules” that may offer a satisfactory balance between the activity and drug-like properties. Modified variants of the prototype compound that can be reasonably considered its derivatives are also claimed.
Owner:CZYRYCA PRZEMYSLAW
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com