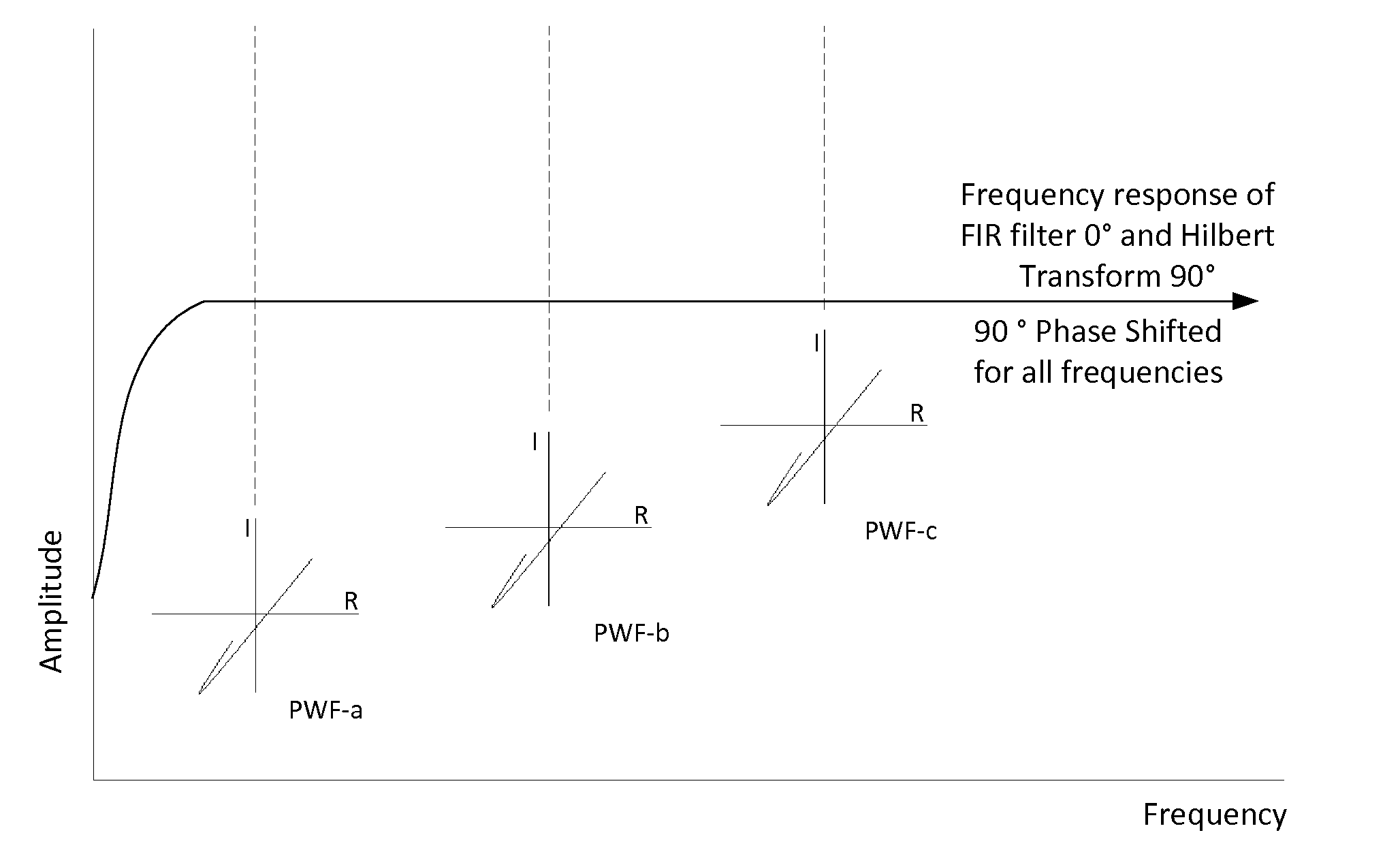Patents
Literature
47 results about "Impedance plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
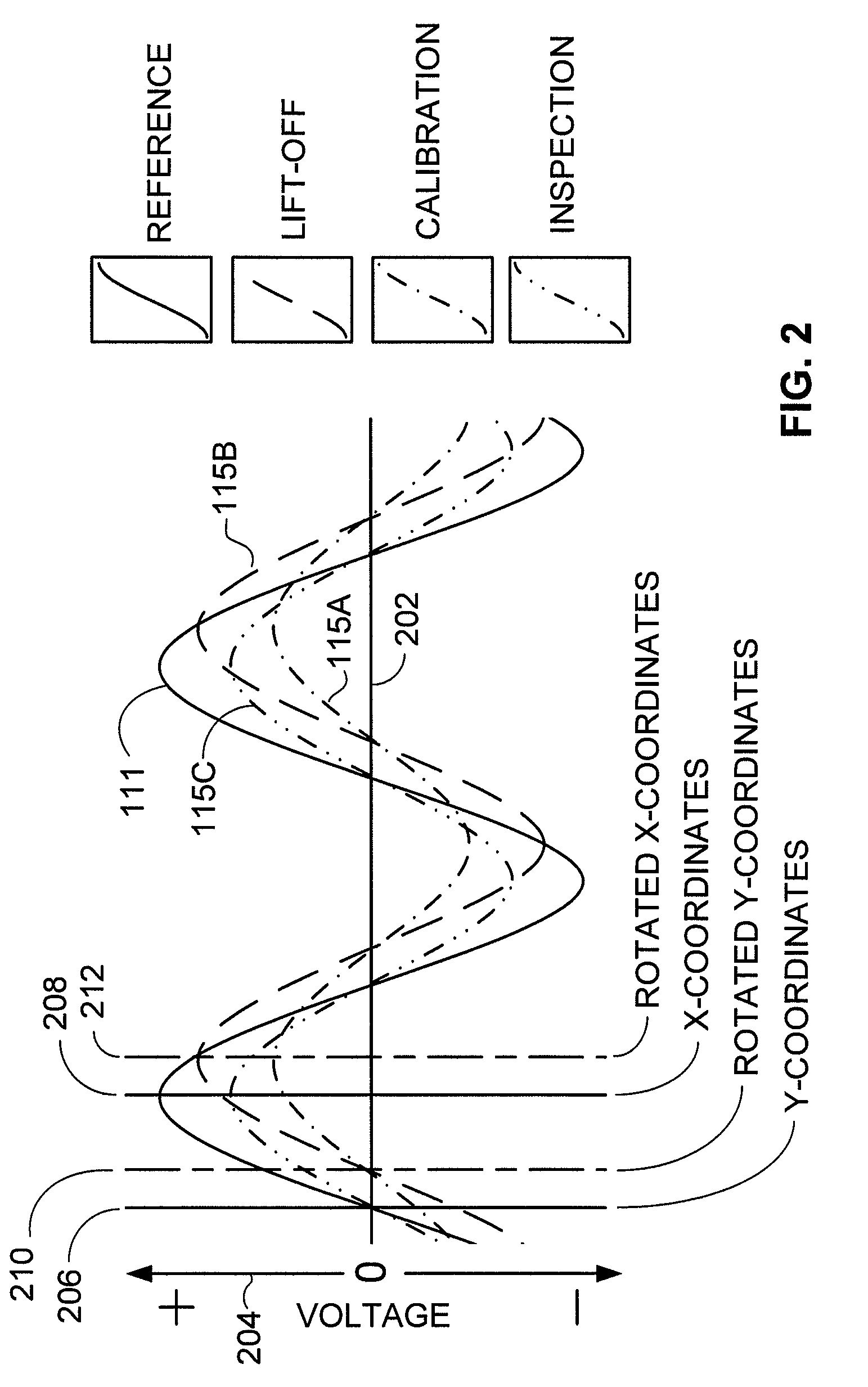
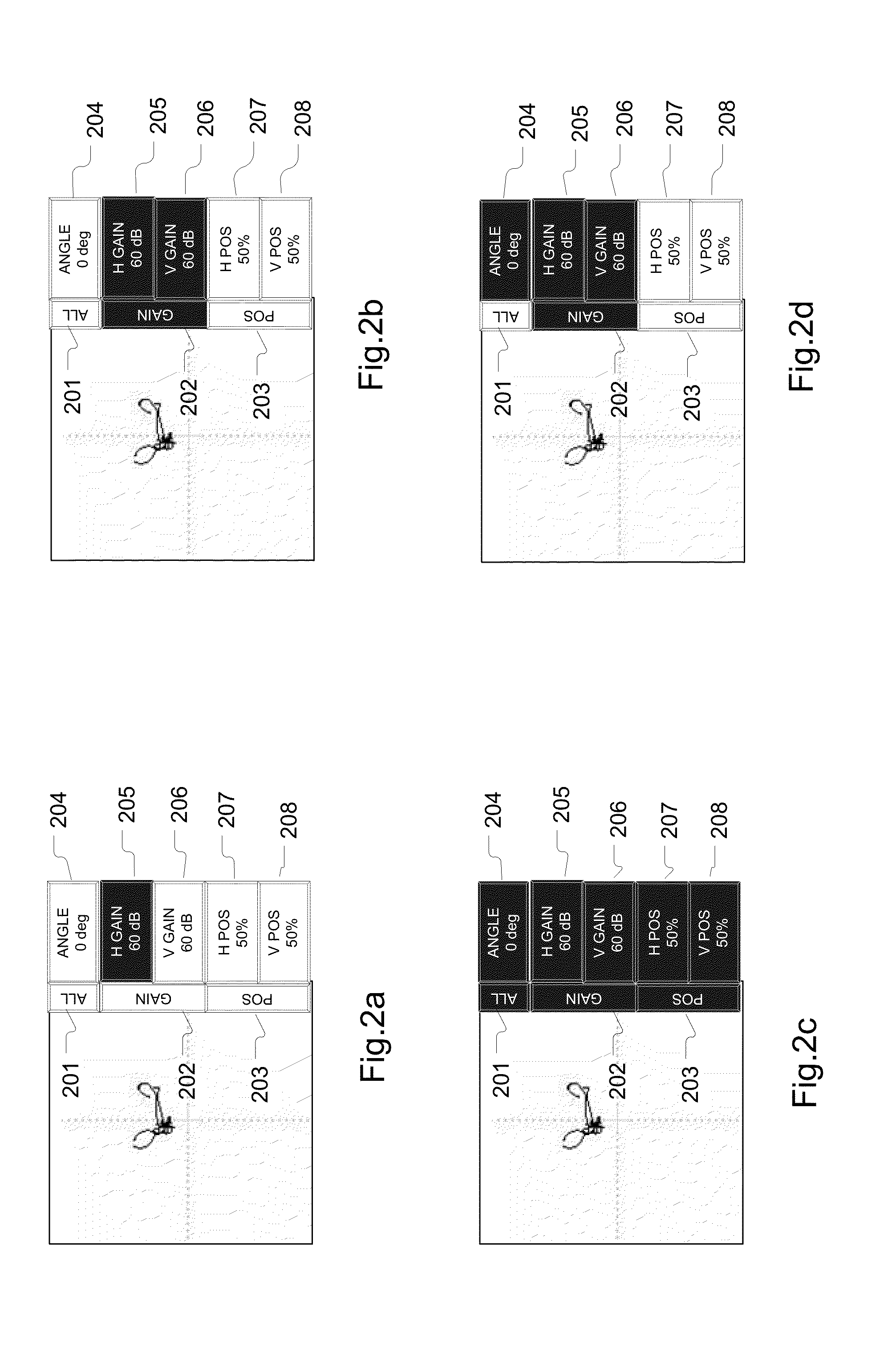
Display - Complex Impedance Plane (eddy scope) Electrical Impedance (Z), is the total opposition that a circuit presents to an alternating current. Impedance, measured in ohms, may include resistance (R), inductive reactance (X L), and capacitive reactance (X C).
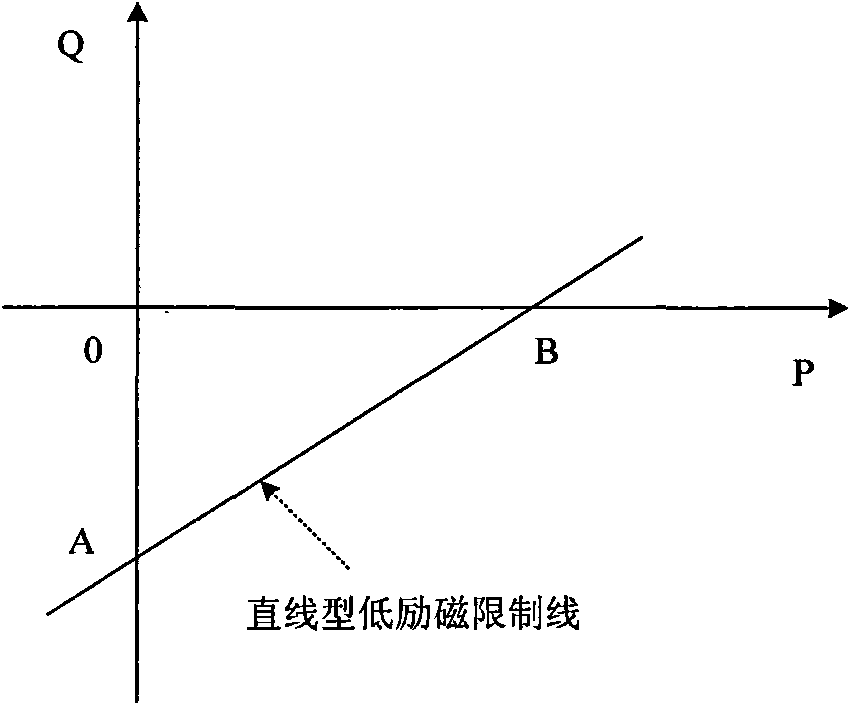
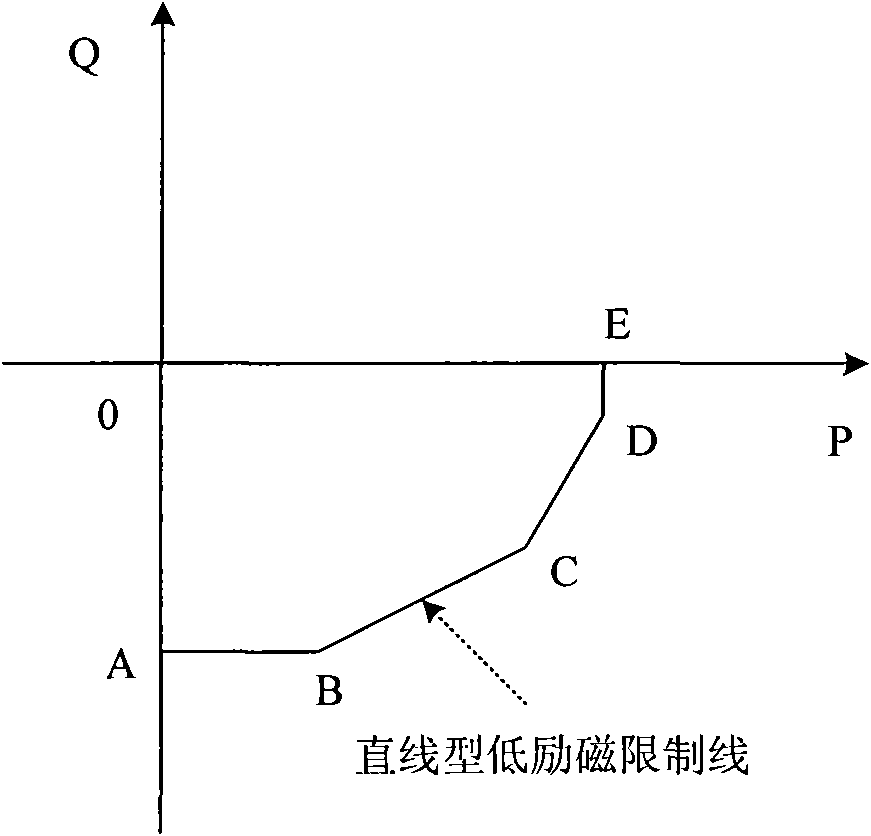
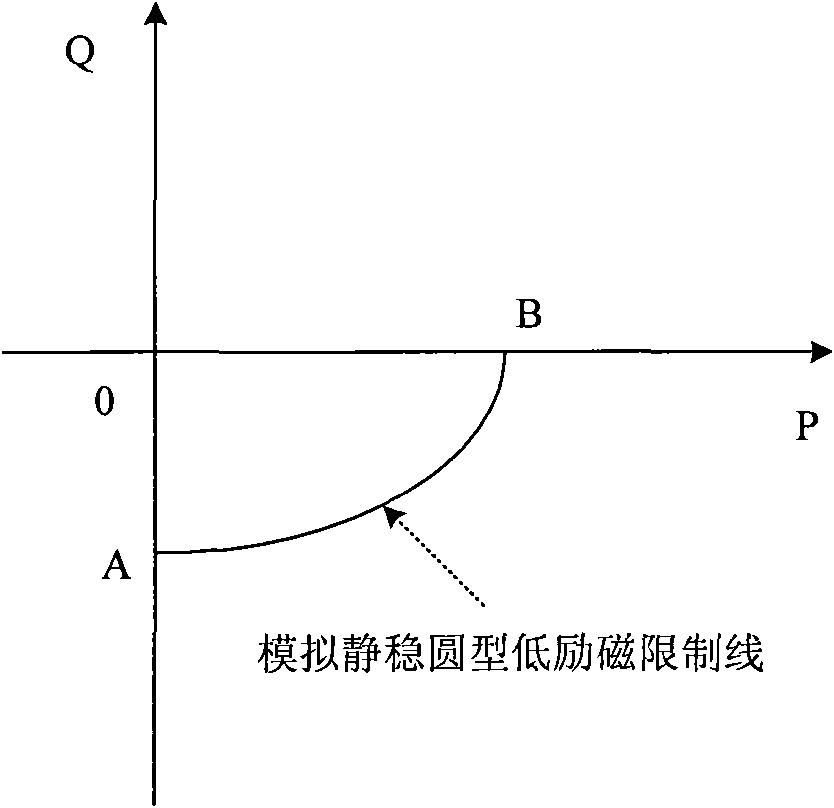
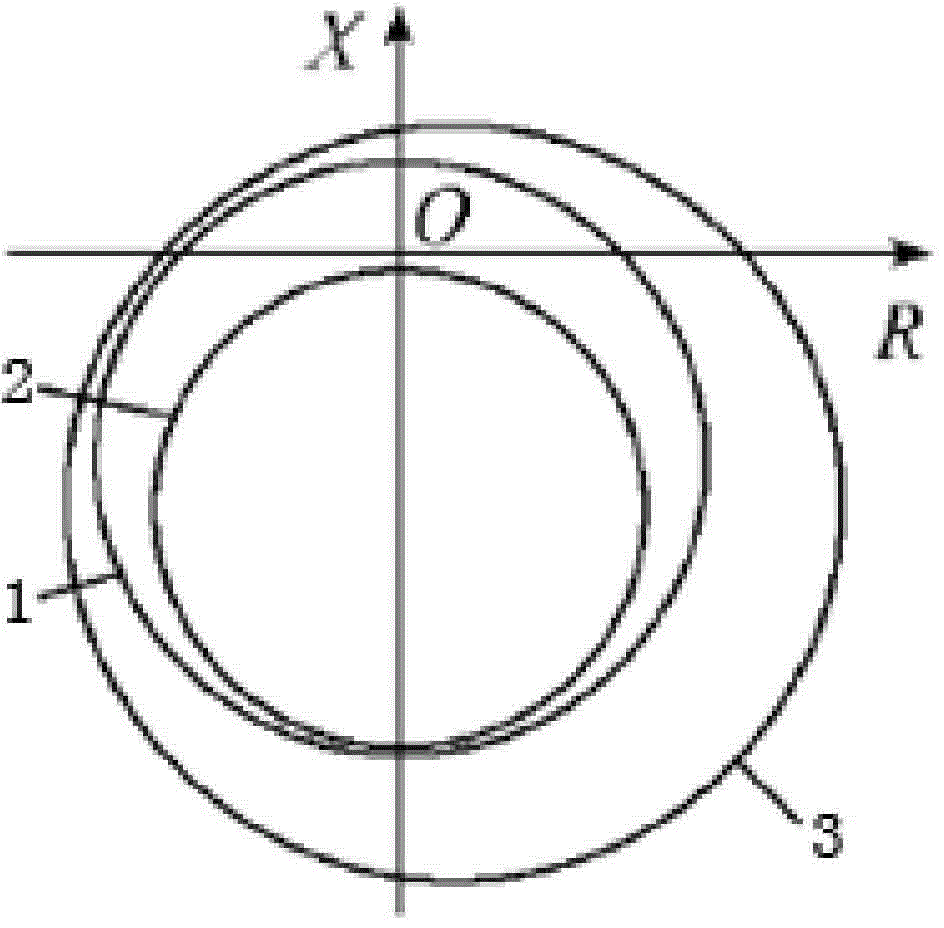
Method of limiting low excitation
ActiveCN101588153AFor a seamless fitPrevent accidental tripGenerator control by field variationTerminal voltageExcitation current
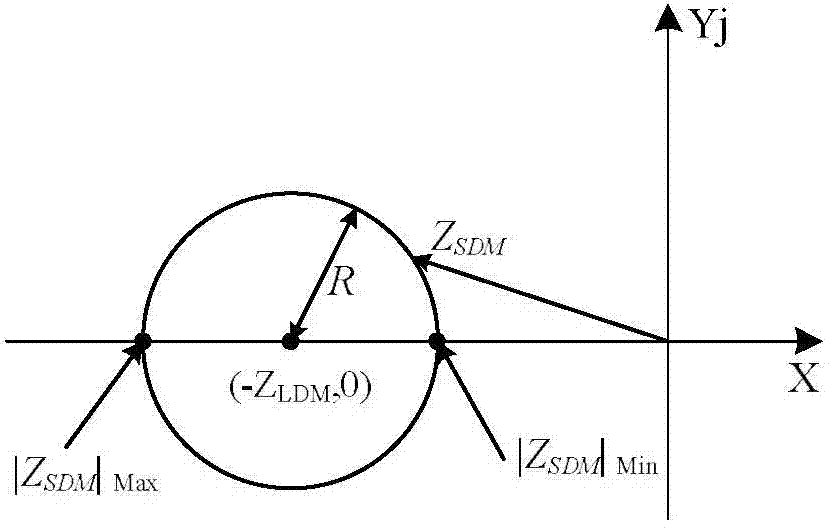
Method of limiting low excitation, calculating measured impedance of generator terminal by detecting generator terminal voltage and terminal current, when the measured impedance entering low excitation limited impedance circle, the low excitation limits prolong action of 40-60 ms on amplifying excitation current to maintain generator in stable operation situation, the low excitation limited impedance impedance circle covers static stable loss of excitation protection impedance circle to implement seamless connection with generator loss of excitation protection impedance criterion, and prevent the generator in low excitation operation, the low excitation is limited lagging behind the loss of excitation protection action, thereby generator error jump is caused. The invention is used in generator excitation regulation, comparing with former low extitation limiting method, the invention is more visualized, the loss of excitation protection and low excitation are all R-X impedance plane coordinate description and easy to cooperate with each other.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER +2
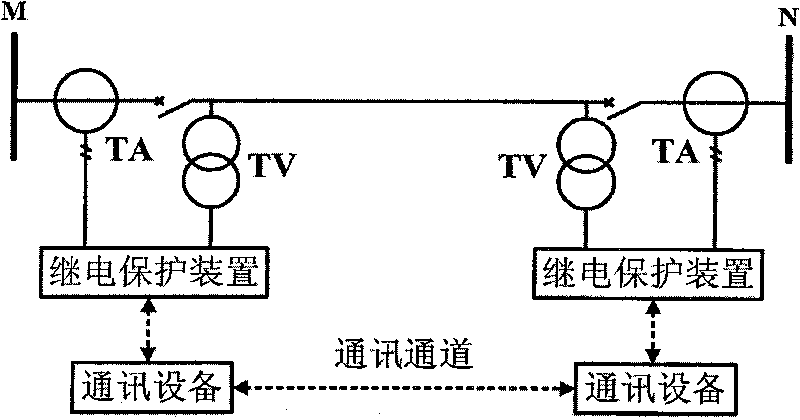
Method for pilot protection of circuit based on current capacity and voltage capacity at two ends
InactiveCN101741070AImprove reliabilityHigh sensitivityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
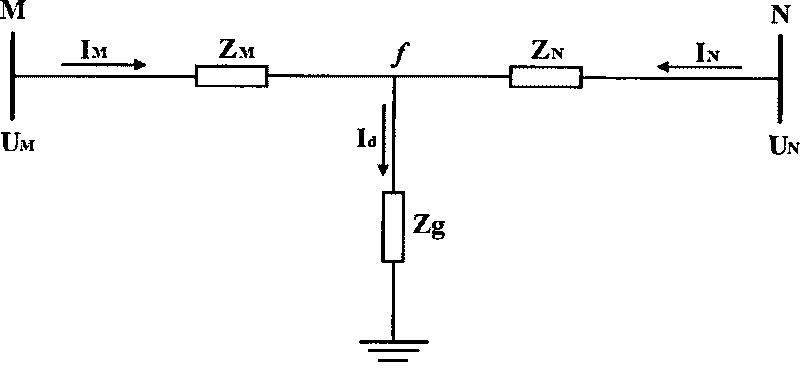
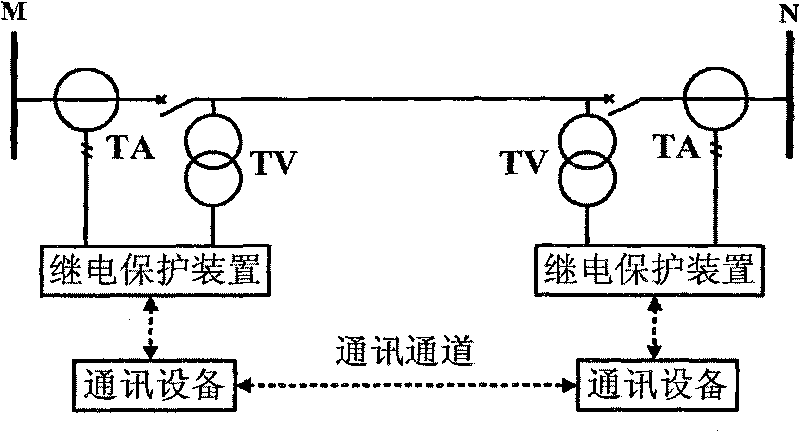
The invention relates to a method for pilot protection of a circuit based on the current capacity and the voltage capacity at two ends, which comprises the following steps that: 1) two ends of the circuit are provided with same relay protection devices, and each relay protection device measures the current capacity and the voltage capacity of the end and acquires the current capacity and the voltage capacity of the opposite end through a communication channel; 2) each relay protection device performs calculation according to the current capacities and the voltage capacities of the two ends at the same time, the branch impedance of each phase and / or the inter-phase branch impedance are calculated for an alternating current circuit, and the branch resistance is calculated for a direct current circuit; and 3) for the alternating current circuit, a +R axis region is set on an impedance plane as an action region, and the branch impedance falls into the region and is judged as an internal circuit fault, and for the direct current circuit, a fixed resistance value can be set, the branch impedance is smaller than the fixed resistance value and is judged as the internal circuit fault.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Composite steel pipe defect detecting device and composite steel pipe defect detecting method
ActiveCN102680570AQuality assuranceAvoid interferenceMaterial magnetic variablesNon destructiveSignal on
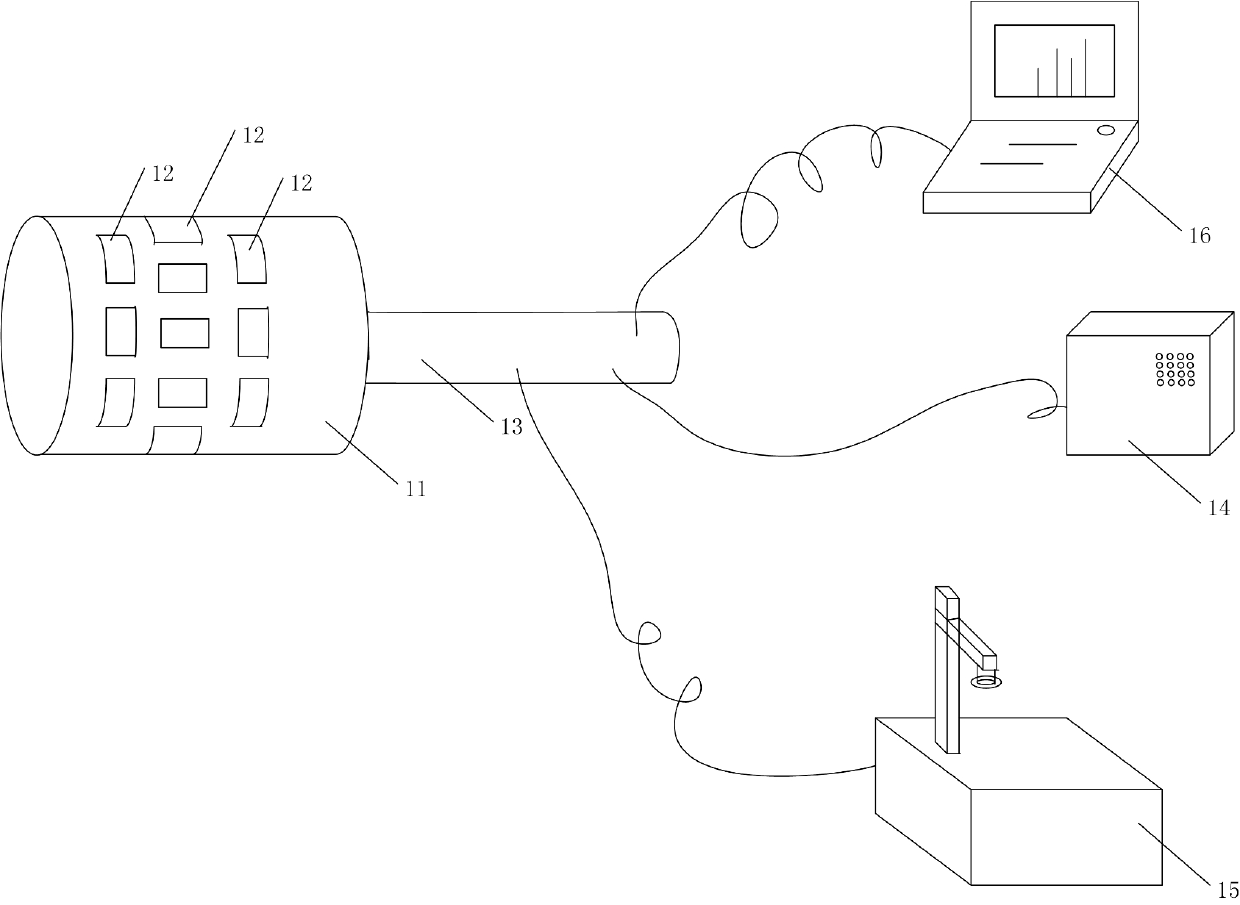
The invention provides a composite steel pipe defect detecting device and a composite steel pipe defect detecting method, and belongs to the technical field of non-destructive detection. The device comprises an eddy current probe, eddy current detection coils wrapped on the outer surface of the eddy current probe and a driving device connected with the eddy current probe. The method comprises the following steps of: (a) inserting the cylindrical eddy current probe into the inner wall of a composite steel pipe to be detected; (b) detecting the composite steel pipe to be detected by the eddy current detection coils wrapped on the outer surface of the eddy current probe to acquire eddy current signals, and executing a step (c) when the impedance amplitude of the detected eddy current signals on an impedance plane graph exceeds a set alarm amplitude range; executing a step (d) when the impedance amplitude of the detected eddy current signals on the impedance plane graph does not exceed the set alarm amplitude range; (c) recording the composite steel pipe to be detected as an unqualified composite steel pipe; and (d) recording the composite steel pipe to be detected with a qualified mark. By the device and the method, defects of the composite steel pipe to be detected are quickly detected with high sensitivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI HILONG ANTI CORROSION TECH ENG +1
Quick distinguishing method for zero-sequence directional elements of alternating-current and direct-current serial-parallel power grid
InactiveCN102508098AGuaranteed reliabilityImprove performanceElectrical testingAlternating currentImpedance plane
The invention relates to a quick distinguishing method for zero-sequence directional elements of an alternating-current and direct-current serial-parallel power grid. The quick distinguishing method includes computing sampling values of zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current according to sampling values of three-phase voltage and three-phase current at a protection mounting position; establishing a time-domain differential equation based on instantaneous sampling values of the zero-sequence voltage and the zero-sequence current; computing weights of zero-sequence resistance and zero-sequence inductance by the aid of the time-domain differential equation and a least square method; converting the weight of zero-sequence resistance and the zero-sequence inductance of a system to frequency domain, and computing power-frequency zero-sequence impedance; and judging whether forward or reverse grounding faults occur or not by means of judging whether an area of an impedance plane with the zero-sequence impedance is in a positive-direction action area or a negative-direction action area. The method is not affected by low-frequency weights, fractional harmonic waves or the fact that positive-sequence impedance is unequal to negative-sequence impedance after the alternating-current and direct-current serial-parallel power grid fails, reliability of computation results is guaranteed, action performances of the zero-sequence directional elements are far superior to those of various power-frequency directional elements based on full-period Fourier algorithm and semi-period Fourier algorithm, and the quick distinguishing method has an extremely important application value.
Owner:XJ ELECTRIC +2
Multi-lateral current magnitude voltage magnitude based transformer relay protecting method
InactiveCN101764392AInternal fault differentiationImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectricityTransformer
The invention provides a multi-lateral current magnitude voltage magnitude based transformer relay protecting method, which has the advantages of convenience, reliability, sensitivity and the like. The method comprises the following steps that: 1) a relay protection device acquires sampling values of three-phase voltage and current on each side of the transformer, and calculates out the current magnitude and the voltage magnitude on each side of each phase of winding; 2) the relay protection device calculates the branch impedance of each phase of the winding according to the current magnitude and the voltage magnitude; and 3) a +R axis area is set on an impedance plane as an action area, and failure inside the transformer is determined when the branch impedance drops in the region more than the set time.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Simplified impedance plane bondtesting inspection
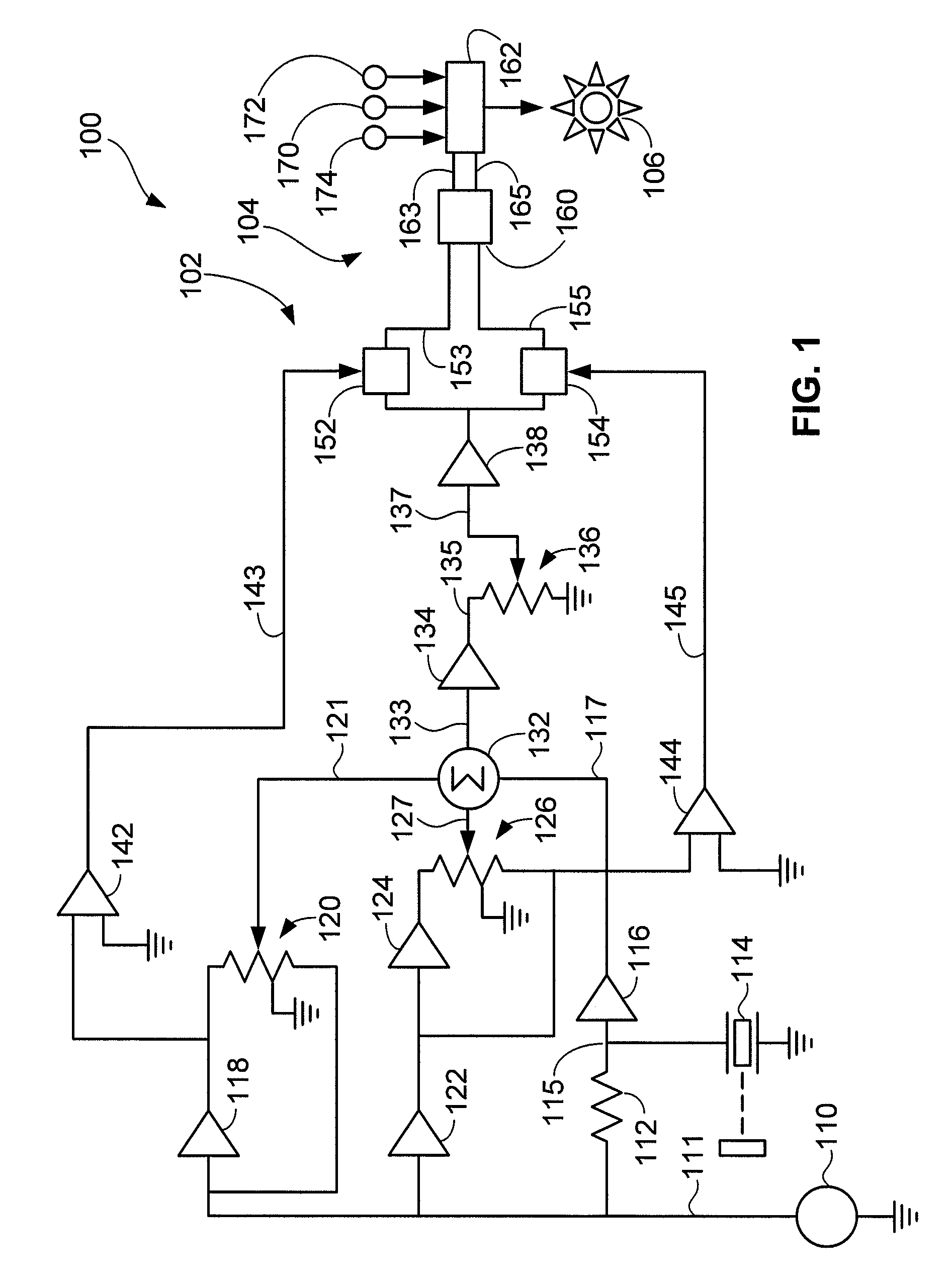
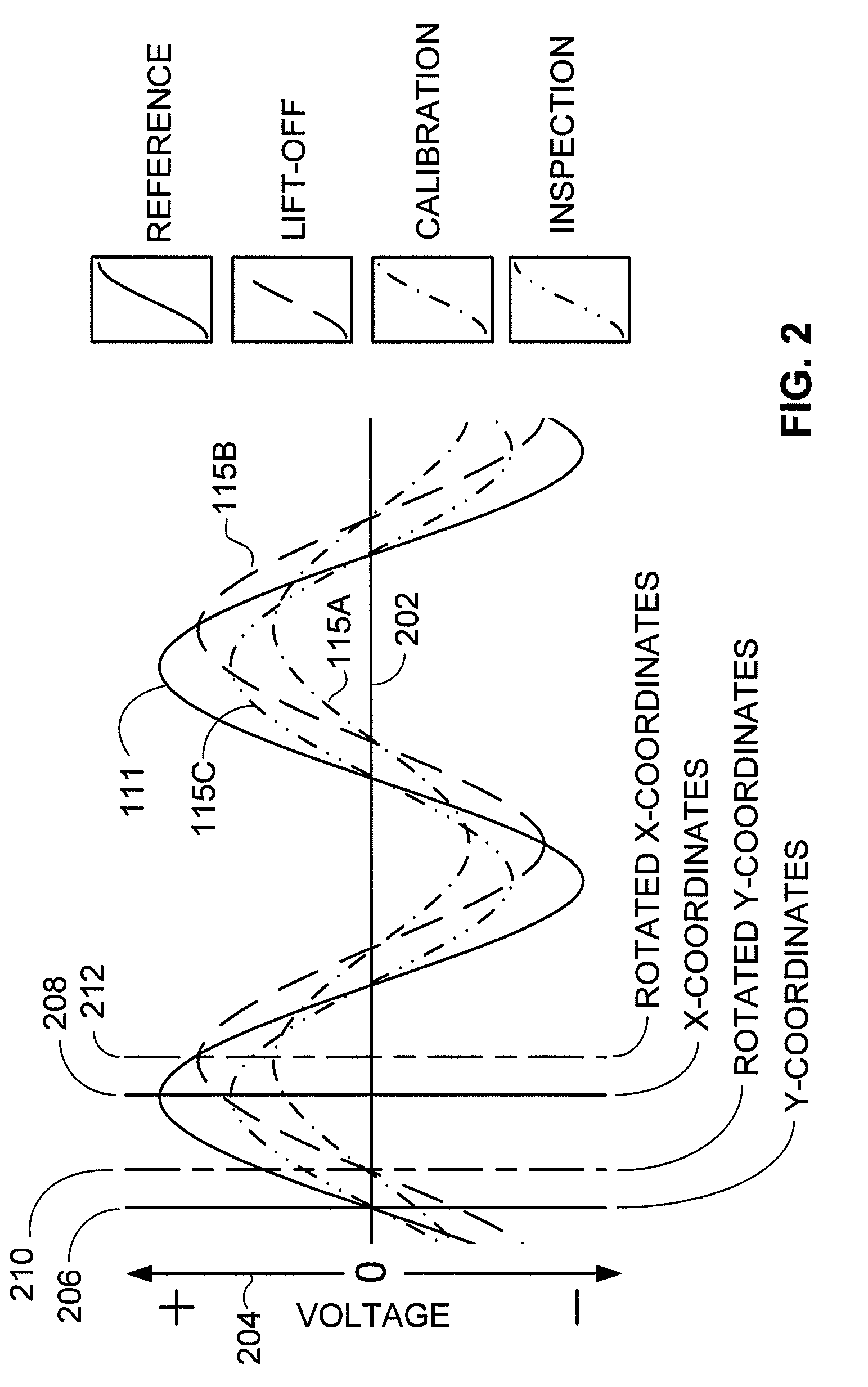
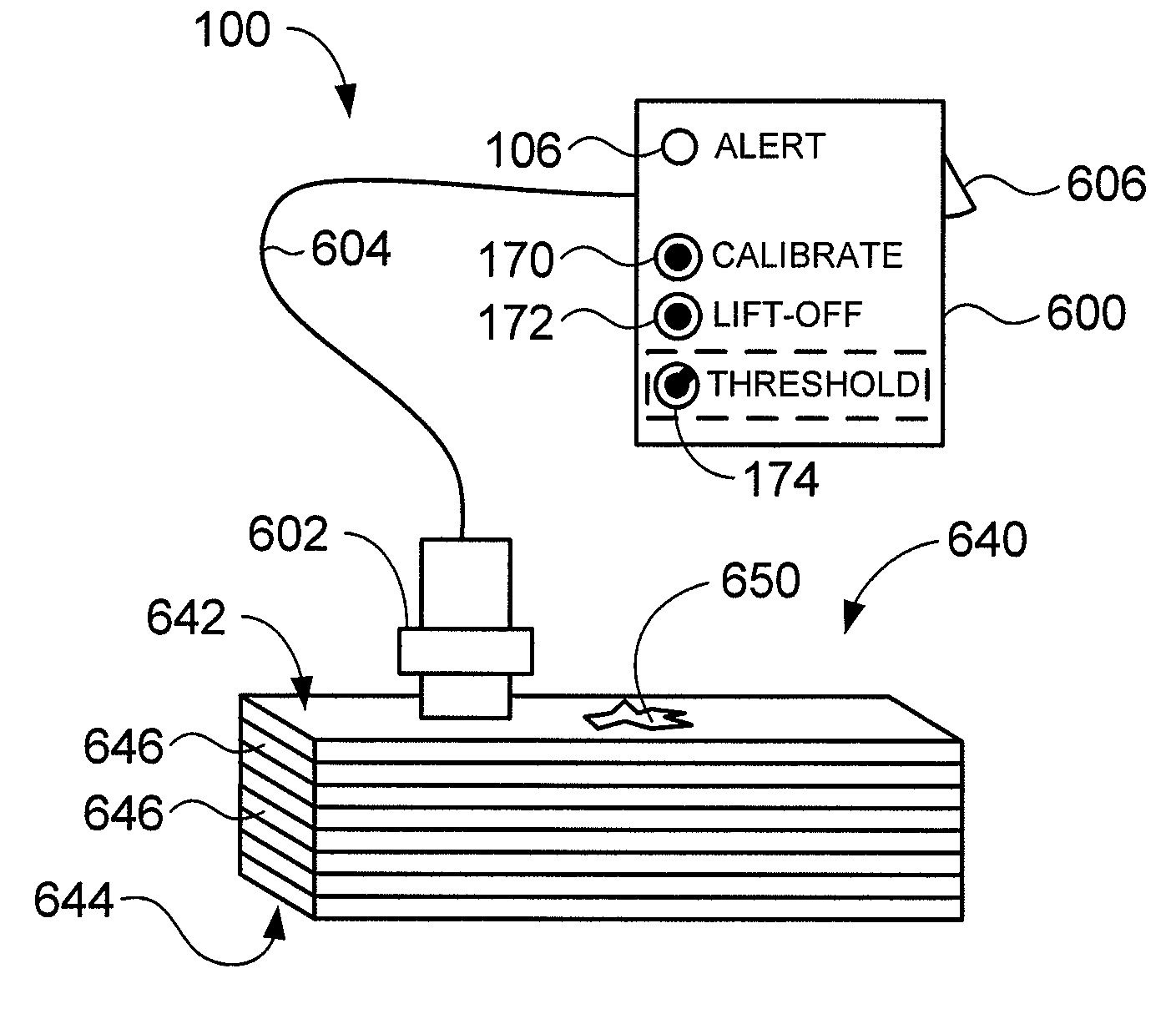
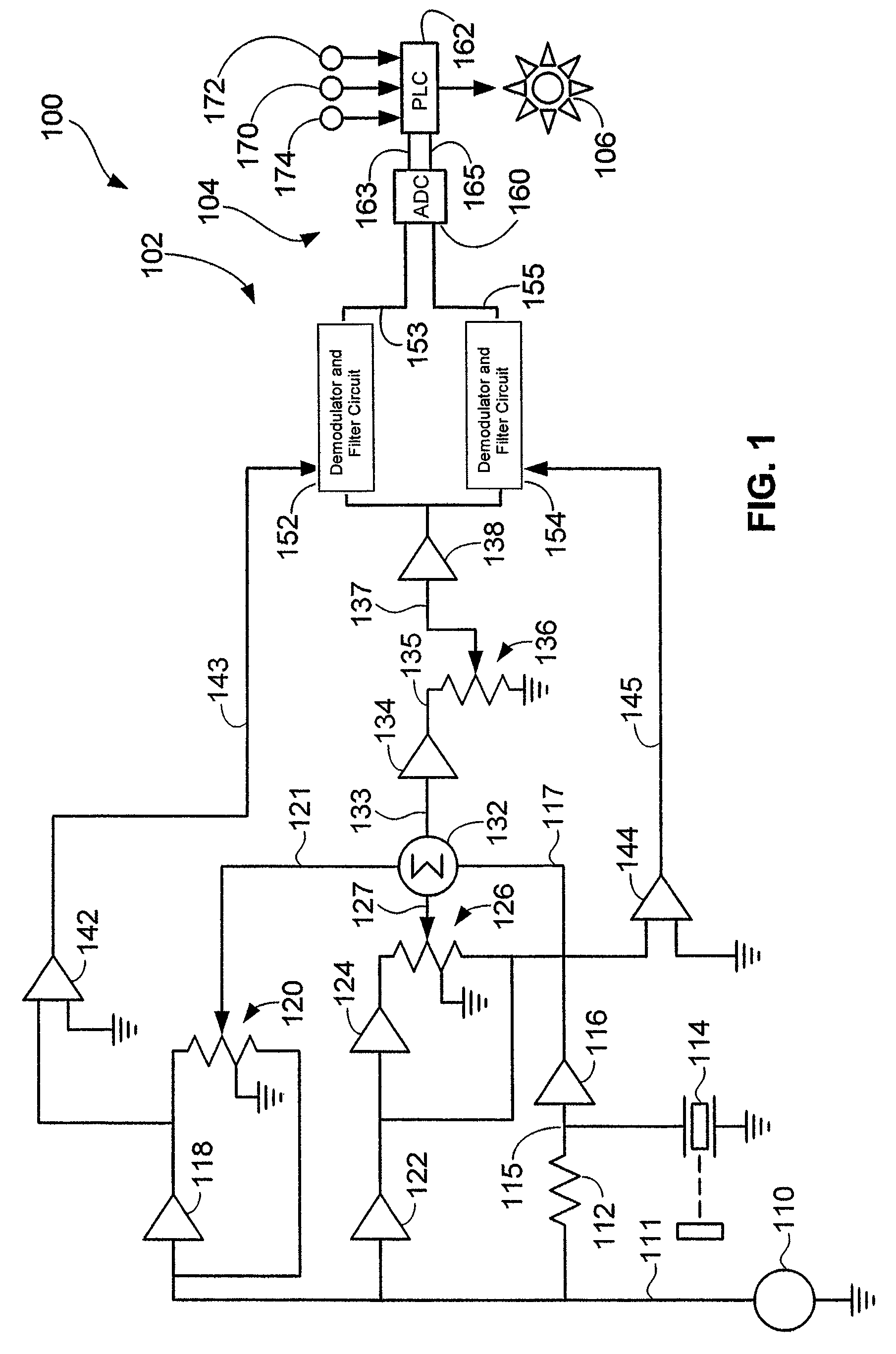
ActiveUS20080156096A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResonant frequencyUltrasonic sensorTransducer
An NDI system includes an ultrasonic transducer and an electronic device having an indicator, such as a light source. The electronic device energizes the transducer, receives sinusoidal signals from the transducer, determines impedance-plane coordinates corresponding to quadrature-phase separated components of the sinusoidal signals, and automatically activates the indicator if impedance-plane coordinates exceed a preset threshold. The system may be used in methods of inspecting layered structures such as composite aircraft components and repair patches applied to such structures.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Simplified impedance plane bondtesting inspection
ActiveUS7574915B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResonant frequencyUltrasonic sensorTransducer
An NDI system includes an ultrasonic transducer and an electronic device having an indicator, such as a light source. The electronic device energizes the transducer, receives sinusoidal signals from the transducer, determines impedance-plane coordinates corresponding to quadrature-phase separated components of the sinusoidal signals, and automatically activates the indicator if impedance-plane coordinates exceed a preset threshold. The system may be used in methods of inspecting layered structures such as composite aircraft components and repair patches applied to such structures.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
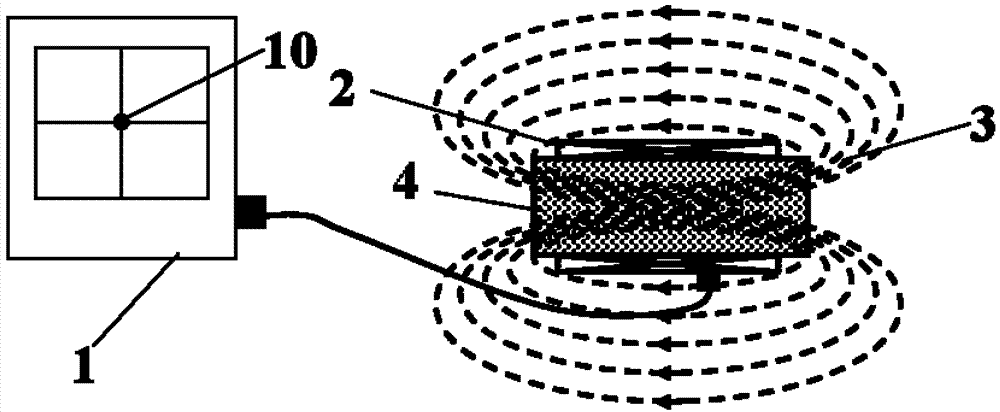
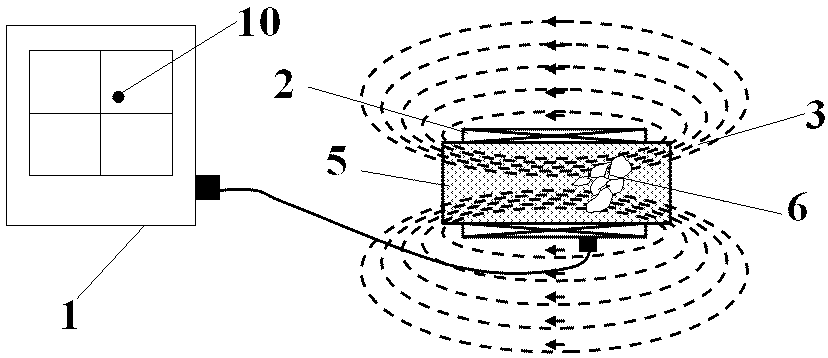
Device and method for non-contact magnetic induction impedance plane projection imaging
ActiveCN103006185ASimple structureEasy to implementSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateElectrical resistance and conductanceImpedance distribution
The invention discloses a device and a method for non-contact magnetic induction impedance plane projection imaging. An alternating current magnetic field is generated in an excitation coil by introducing alternating sinusoidal current, a measured object with certain conductivity is arranged in the alternating current magnetic field, the inside of the measured object generates same-frequency alternating eddy current due to electromagnetic induction, measuring coils which are arranged into a plane in a matrix way are used for respectively detecting magnetic filed signals caused by the alternating current eddy current, according to the relationship of the measuring signals and the impedance distribution of the measured object, the impedance distribution condition of the part of the measured object corresponding to each measuring coil is respectively calculated, and all calculating results form an impedance plane projection image according to the positions of the measuring coils.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
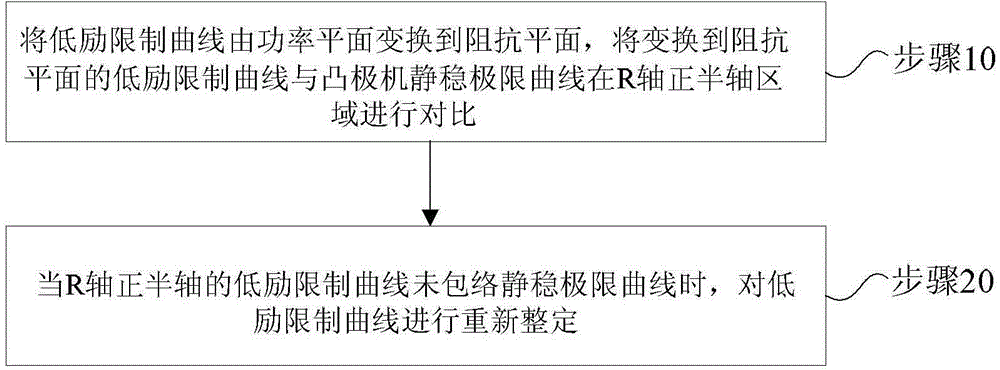
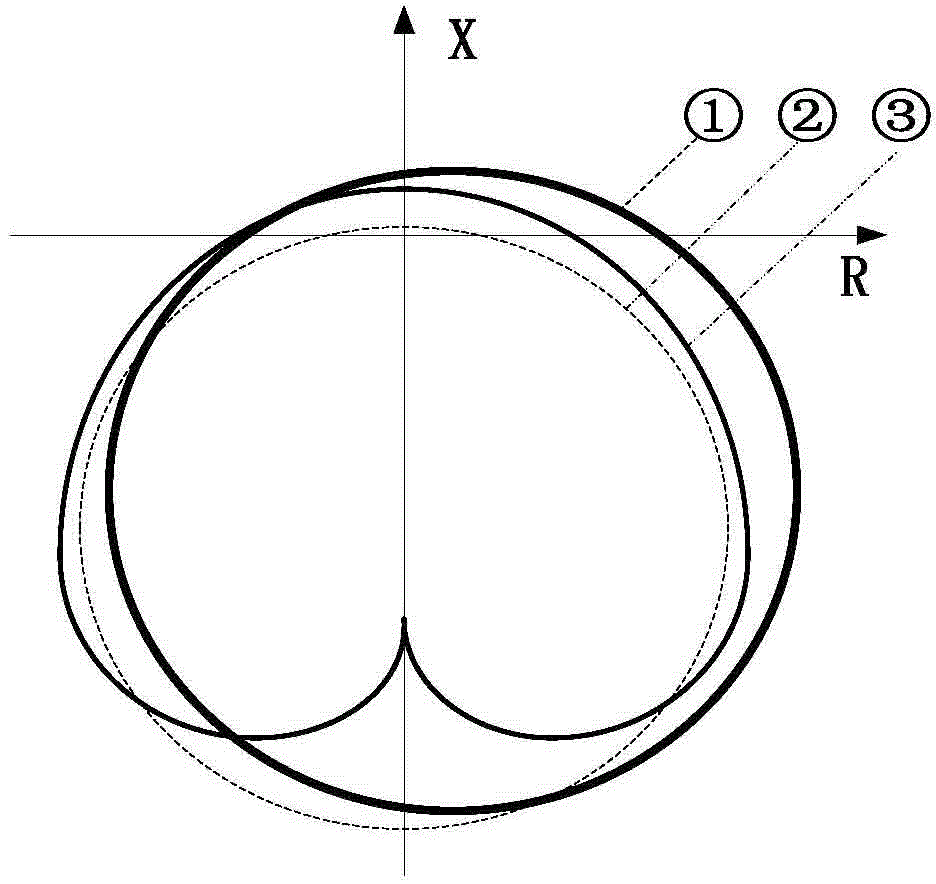
Method and device for matching and setting low-excitation limitation and field loss protection of salient-pole machine
ActiveCN104701816AEnsure reasonable cooperationGet the most out of your controlsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringVoltage stability
The invention provides a method and a device for matching and setting low-excitation limitation and field loss protection of a salient-pole machine, which are used for guaranteeing reasonable matching of the low-excitation limitation and field loss protection of the salient-pole machine. The method comprises the following steps: converting a low-excitation limitation curve to an impedance plane from a power plane, comparing the low-excitation limitation curve converted to the power plane with a static voltage stability limitation curve of the salient-pole machine in an R-axis positive semi-axis area; when the low-excitation limitation curve of the R-axis positive semi-axis area does not include the static voltage stability limitation, re-setting the low-excitation limitation curve. According to the technical scheme adopted by the invention, the reasonable matching between the low-excitation limitation and field loss protection of the salient-pole machine is guaranteed, technical basis is provided for power dispatching production management in a facilitated manner, the control and protection functions of the motor are brought into full play, the network source coordination level is improved, the safe and efficient operation of the energy resources are realized, and the power is guaranteed to safely and economically feed out.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRICAL POWER RES INST +4
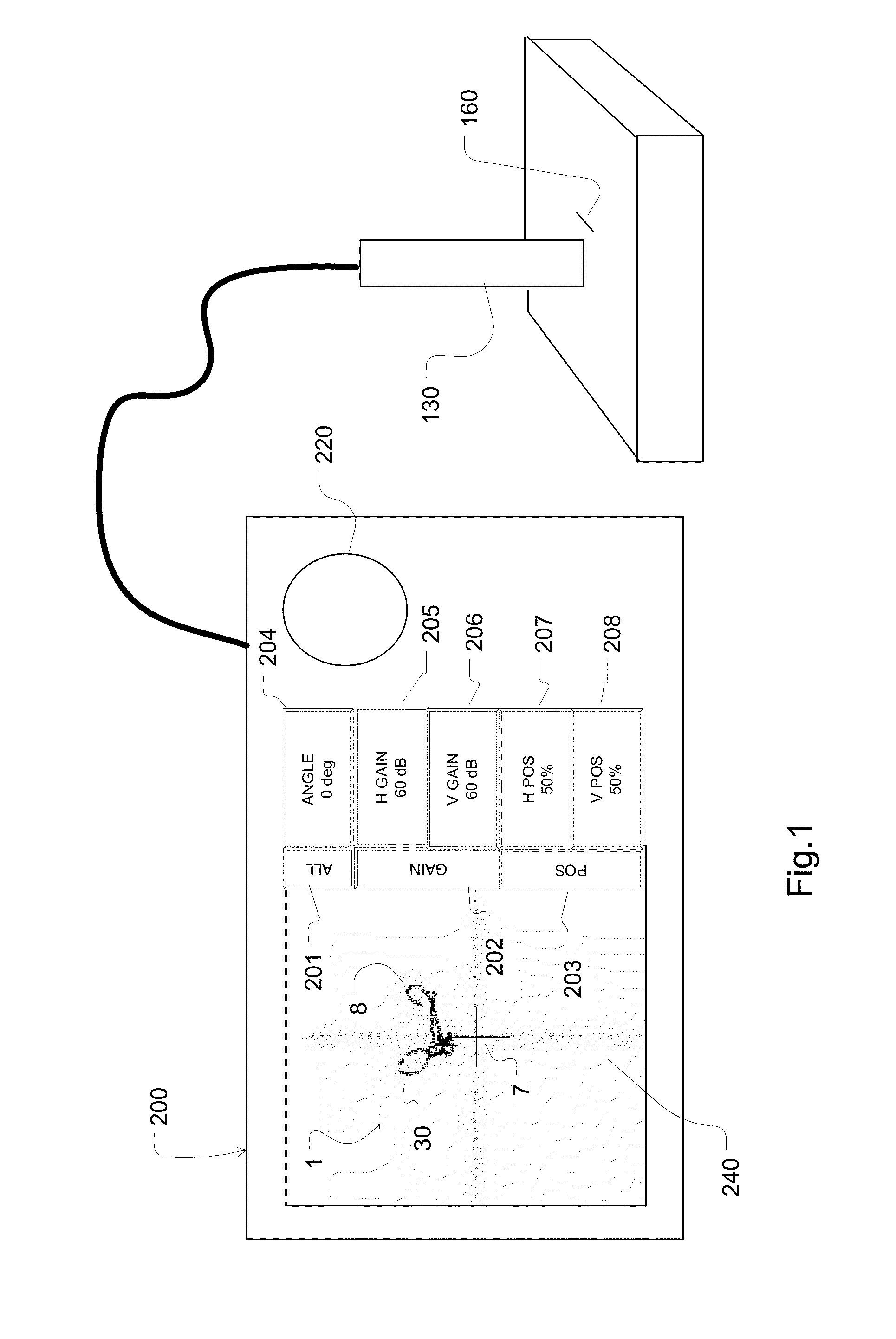
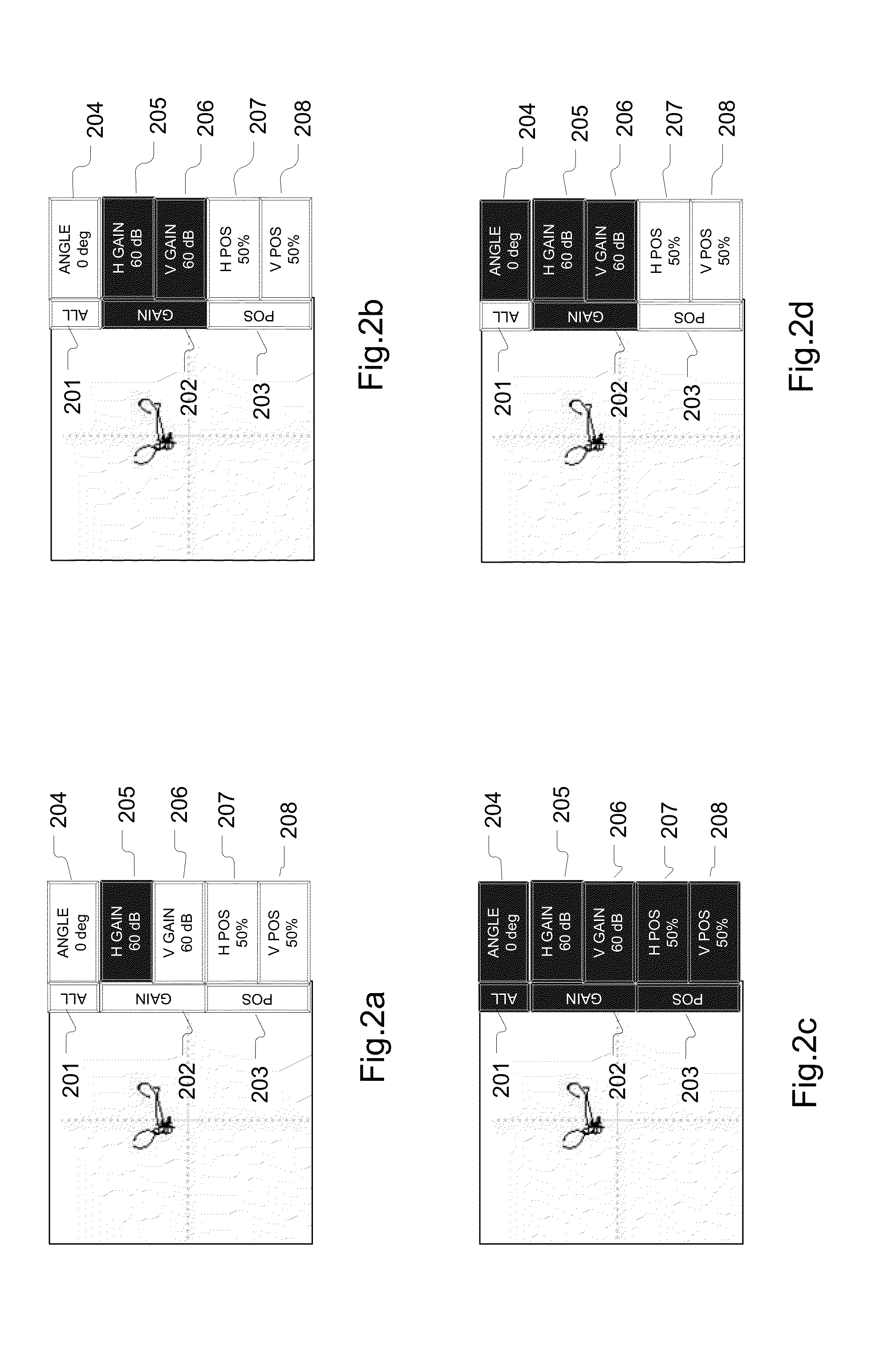
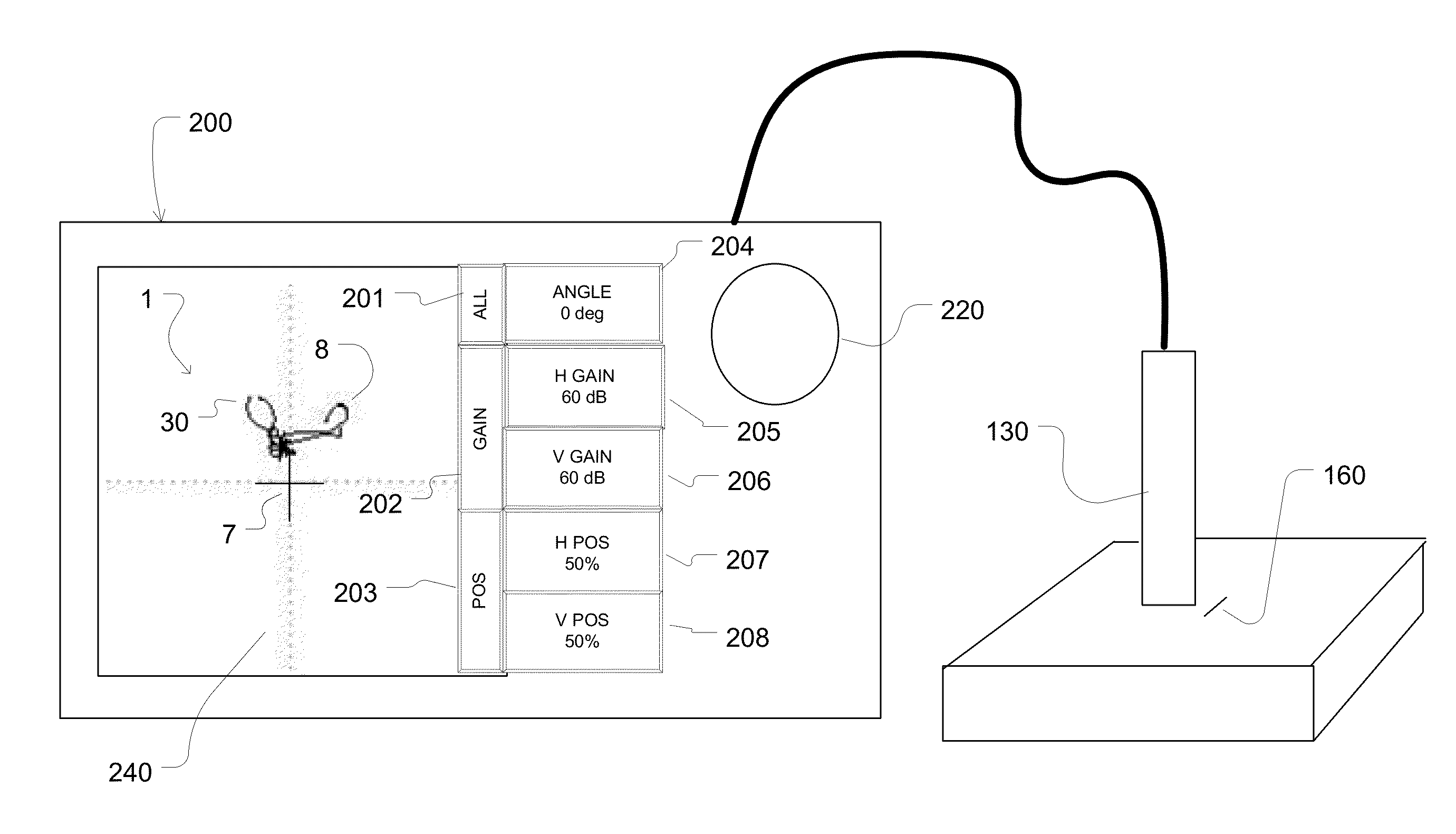
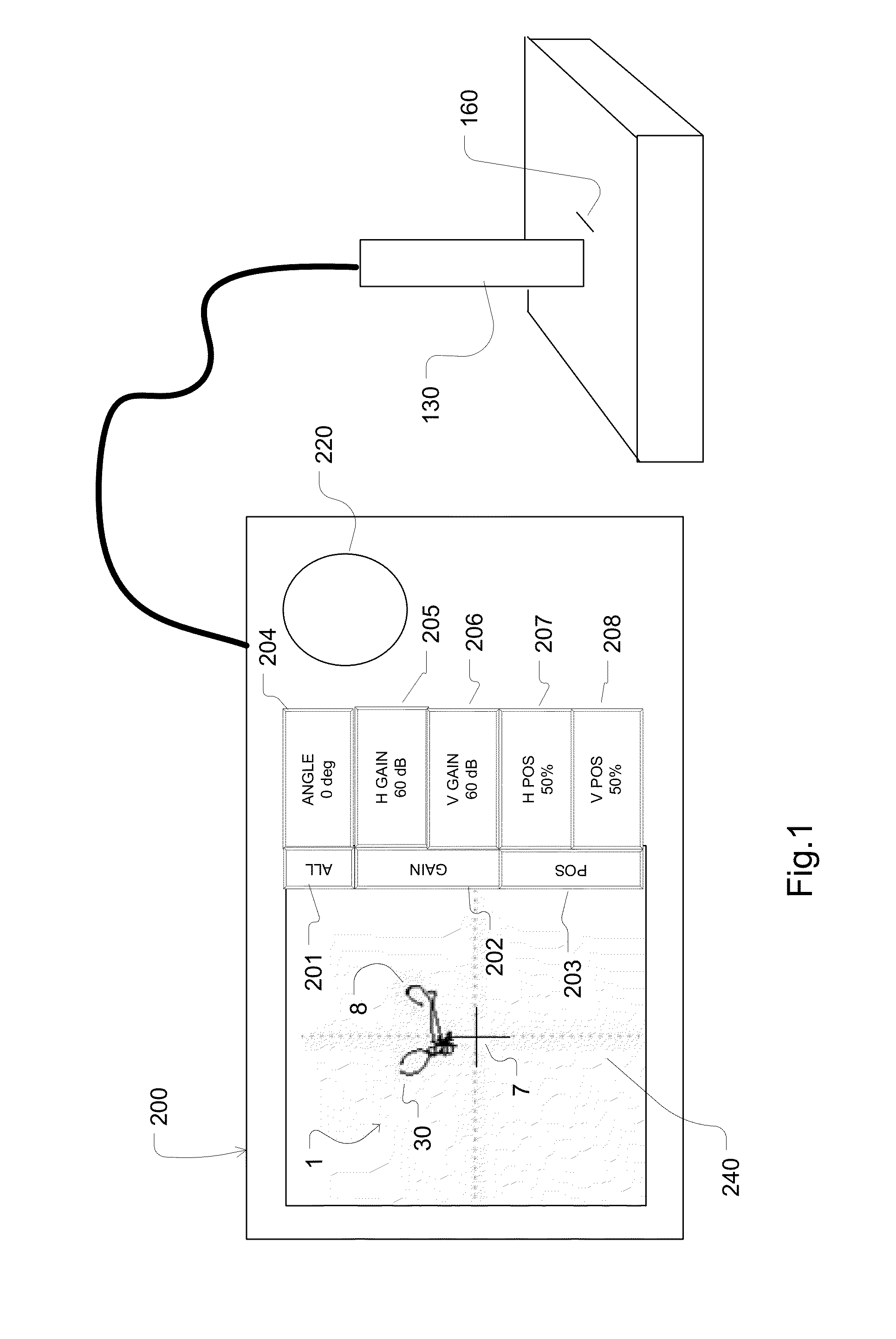
Method of manipulating impedance plane with a multi-point touch on touch screen
ActiveUS20140028608A1Simplified and intuitive operationImprove user experienceInput/output processes for data processingMaterial magnetic variablesNon destructiveTouchscreen
A touch screen is disclosed which responds to a user's touch for re-drawing, re-scaling, re-translating and re-positioning an impedance plane signal received from non-destructive testing equipment, such as an eddy current sensor. The impedance plane is manipulated by slidingne, two or more fingers simultaneously to an end position to effectuate a complete re-drawing operation of the image.
Owner:OLYMPUS NDT
Method and device for generator out-of-step protection
InactiveCN104242245ALow costImprove compatibilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric machine testingEngineeringDynamo
The invention provides a method and a device for generator out-of-step protection. The method comprises the steps of A, obtaining the total impedance of a generator to an infinite bus, B, determining the isostatic boundary circle of the impedance plane of the infinite bus according to the total impedance, C, converting the isostatic boundary circle into a isostatic boundary circle on the impedance plane of a generator terminal, D, measuring the impedance of the generator terminal, when the impedance of the generator terminal goes in from the right side of the isostatic boundary circle and out from the left side of the isostatic boundary circle in predetermined time, confirming out-of-step acceleration of the generator and performing out-of-step acceleration protection, and when the impedance of the generator terminal goes in from the left side of the isostatic boundary circle and out from the right side of the isostatic boundary circle in the predetermined time, confirming out-of-step deceleration of the generator and performing out-of-step deceleration protection. According to the method and the device for generator out-of-step protection, the out-of-step faults can be detected in the first period of oscillation and the power swing is excellent.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Quick distinguishing method for zero-sequence directional elements of alternating-current and direct-current serial-parallel power grid
InactiveCN102508098BGuaranteed reliabilityImprove performanceElectrical testingAlternating currentImpedance plane
Owner:XJ ELECTRIC +2
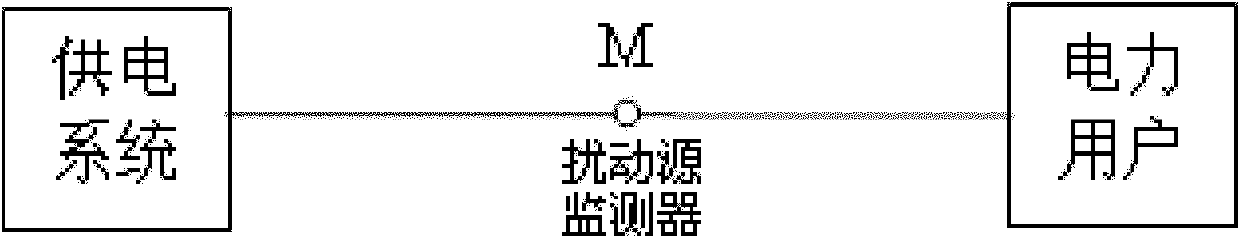
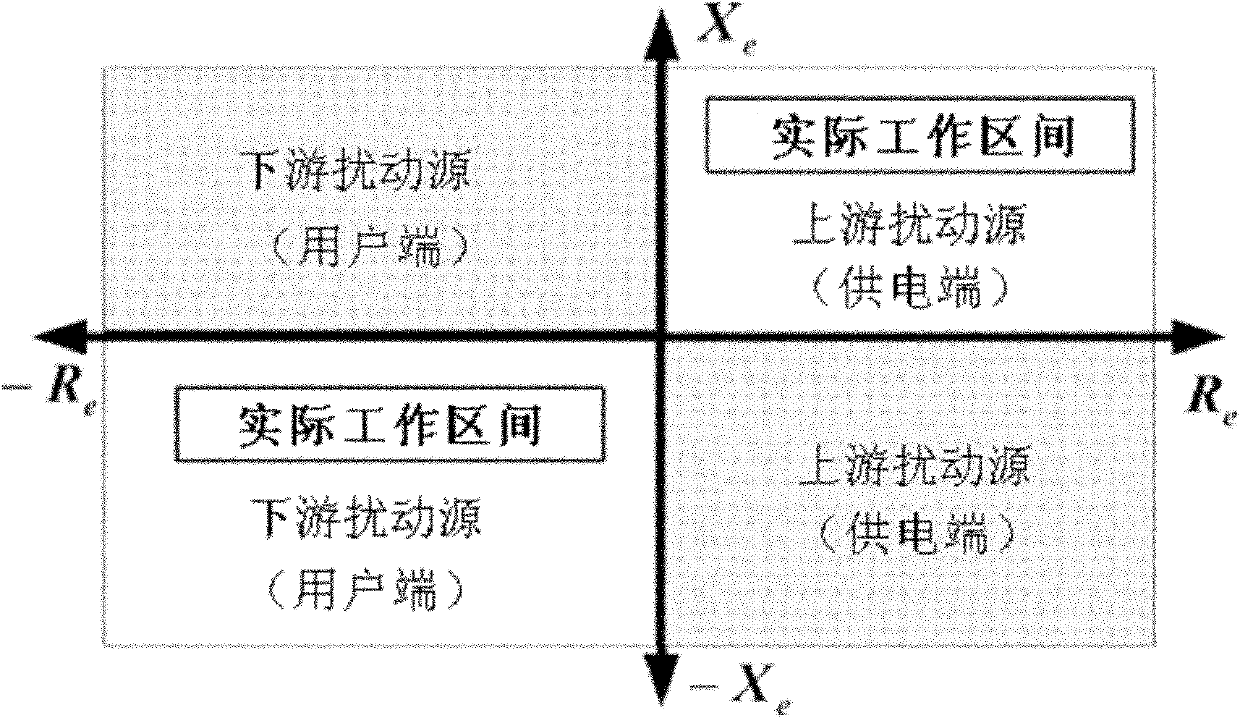
Method for positioning disturbance source of power system based on high-order harmonic equivalent impedance property
InactiveCN102044876AAccurately determine the locationHarmonic reduction arrangementAc network to reduce harmonics/ripplesDemarcation pointHarmonic
The invention relates to a method for positioning a disturbance source of a power system based on high-order harmonic equivalent impedance property. A monitor of the disturbance source is arranged at a demarcation point of a power supply system and a user side, and the monitor of the disturbance source can catch voltage and current waveform containing disturbance at an M point so as to judge the disturbance is from upper stream or lower stream, wherein the power supply system side is arranged at the upper stream, and the user side is arranged at the lower stream; once the occurrence of one disturbance is measured at the detection point, the equivalent impedance Ze is calculated, wherein (Vpre, Ipre) and (Vduring, Iduring) are five-order harmonic negative-sequence voltage and current measured at the measuring point M before and during the occurrence of the disturbance; if the Ze falls in a first quadrant of an impedance plane diagram, the disturbance source is determined to be positioned on the power supply system side; and if the Ze falls in a third quadrant of the impedance plane diagram, the disturbance source is determined to be positioned on the user side.
Owner:DONGYING POWER SUPPLY COMPANY STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER
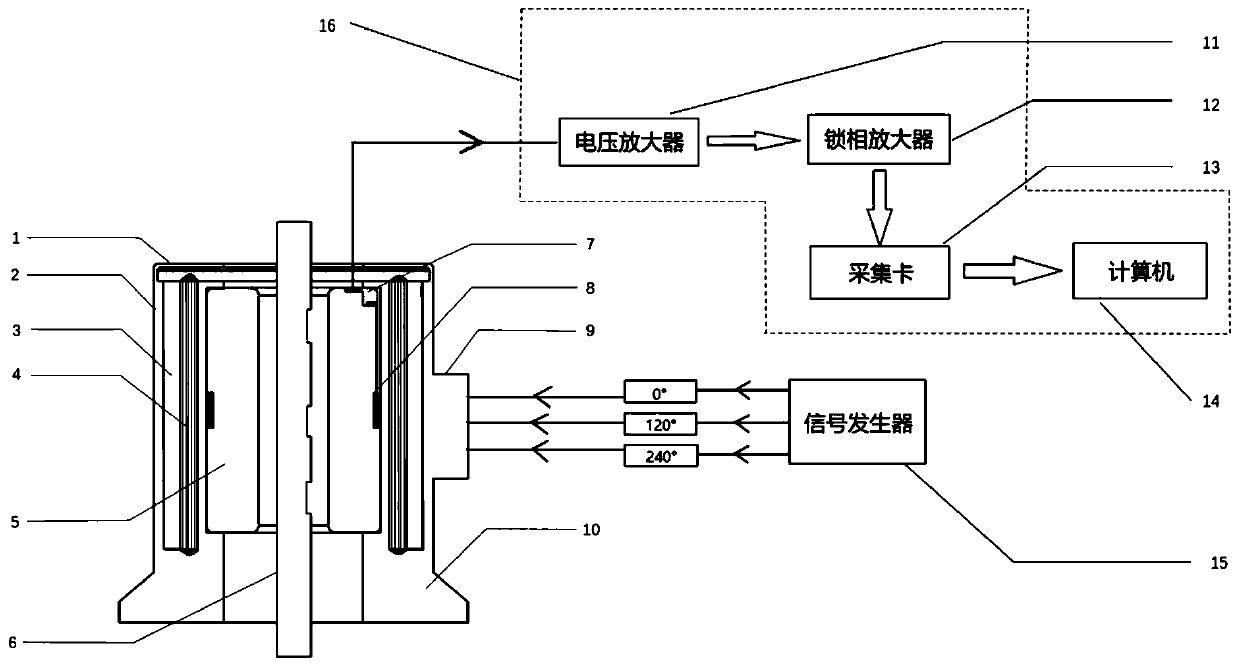
External penetrating rotating magnetic field detecting method for sucker rods
PendingCN111287733AUniform quadrupole rotating magnetic fieldContinuous scanConstructionsEngineeringSucker rod
The invention discloses an external penetrating rotating magnetic field detecting method for sucker rods. The detecting method comprises the following steps: a uniform rotating magnetic field generated by an excitation coil induces an annular eddy on the surface of a sample, and the annular eddy can be disturbed by defects at any angle on the sample; a detection coil picks up all axial disturbancesignals caused by the defects; voltage signals generated by the detection coil are amplified by a voltage amplifier and are received by a lock-in amplifier for processing, and real and imaginary voltage signals of defect signals are output; the signals are collected by a computer, and a variation curve is displayed on a front panel in real time by a LabVIEW program; and an impedance plan is drawnin MATLAB based on the real and imaginary data, and specific circumferential positions of the defects are judged according to image angles. The generated rotating magnetic field is more uniform and sensitive to the defects in all directions, so that all the axial disturbance signals generated by the defects can be picked up without being affected by lifting, and the method is suitable for the sucker rods with different outer diameters, and precise positions of the defects can be determined by a subsequent data processing method.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Co-chord multi-arc phase comparison loss of synchronism protection method
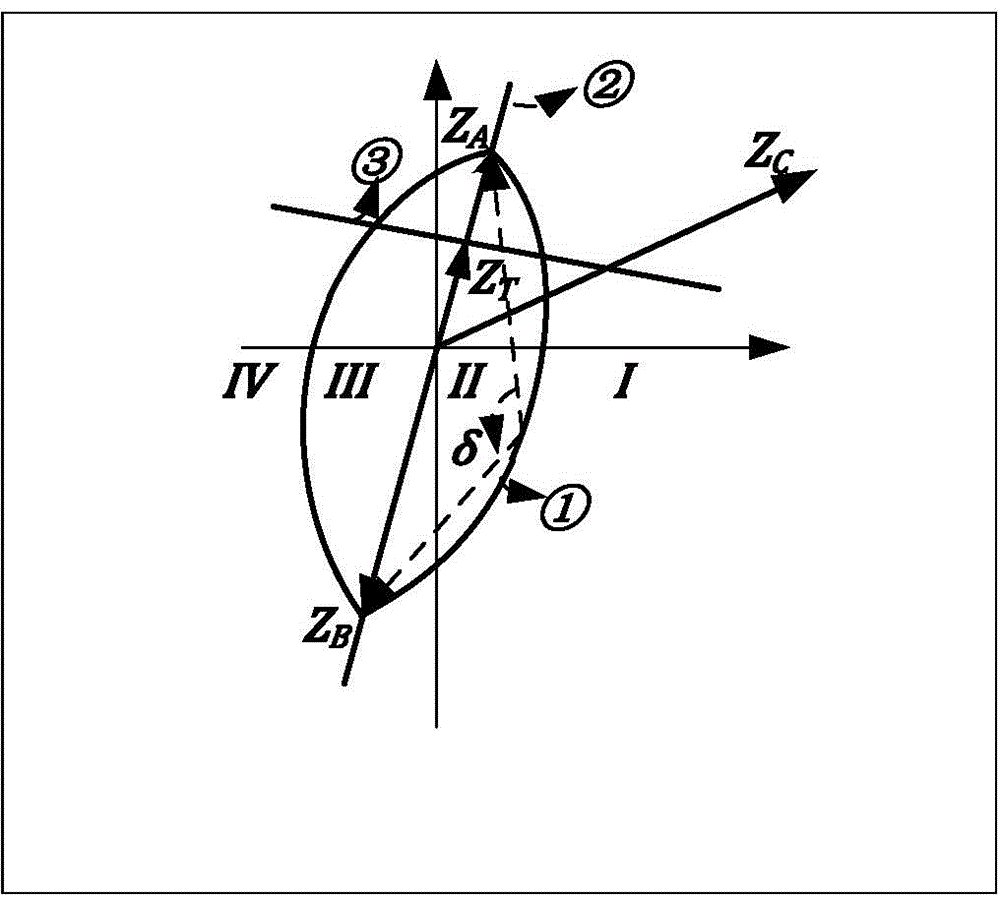
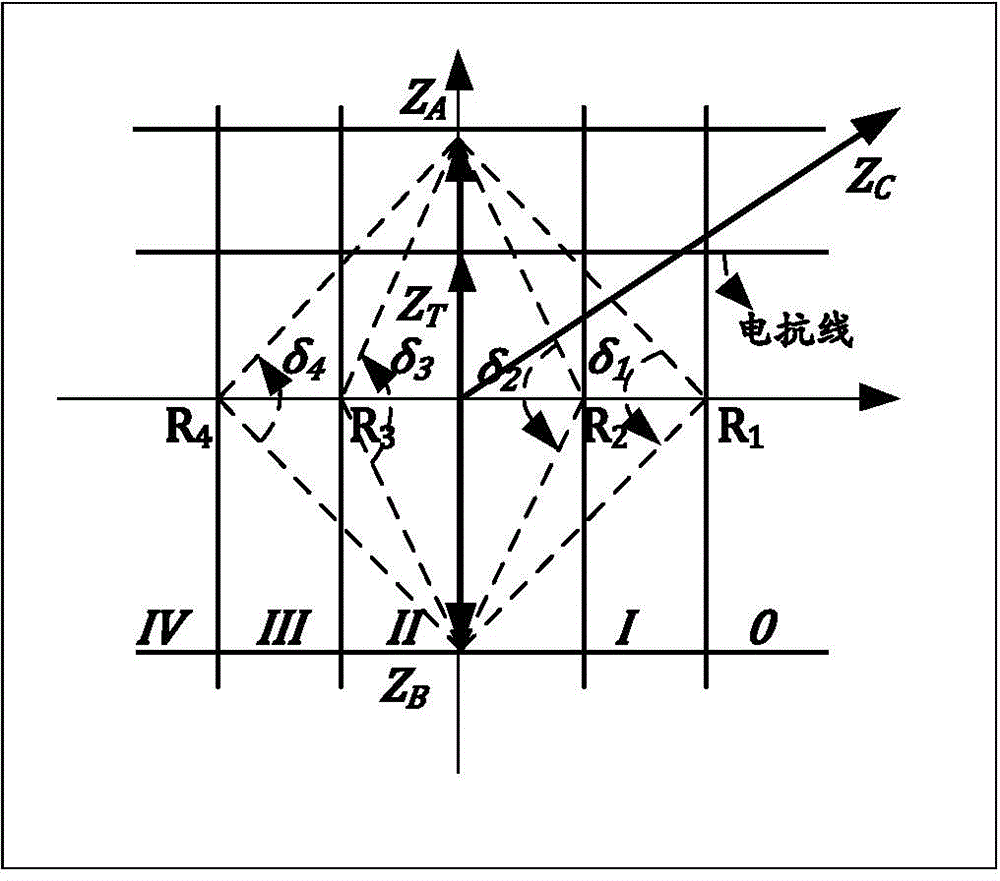
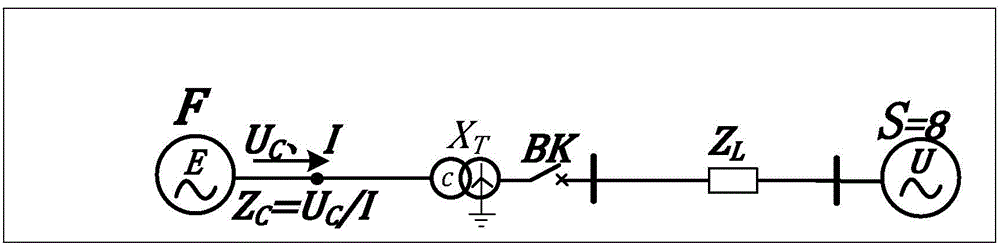
ActiveCN104410046ASimplify computational problemsSimple calculationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsComputation processEngineering
The invention relates to a co-chord multi-arc phase comparison loss of synchronism protection method. According to the method, an impedance plane is divided into five areas according to change of power angle Delta: 00-Delta 1, Delta 1-Delta 2, Delta 2-Delta 3, Delta 3-Delta 4, and Delta 4-3600, arc boundaries and reactance line boundaries of the five areas are divided, the area, in which measured impedance value ZC corresponding to current power angle Delta is, is detected according to the arc boundaries, historical logic of the ZC passing through the areas and dwell time thereof in the areas are judged, and whether a unit is in a step out state is confirmed; and the judgment result is generator step out or motor step out, pole slipping is recorded for once, and protection actuating signal is sent out through setting number of times of pole slipping. The Delta 1 and Delta 2 boundaries of the arc are corresponding to static stability boundary Delta J and moving stability boundary Delta M of the power angle of the unit, thereby being used as a boundary for unit step out logical judgment, being capable of preprocessing or warning early before step out, and simplifying loss of synchronization protection criteria; only sin Delta X value and cos Delta X value are needed, two multiplication computation are added in run, and then logic judgment is realized. The setting calculation process is simplified, and protection operation efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANJING GUODIAN NANZI WEIMEIDE AUTOMATION CO LTD
Circuit and method of providing a stable display for eddy current instruments
ActiveUS20160146759A1Reasonable variation rangeConstant signal sizeMaterial magnetic variablesFinite impulse responseSignal on
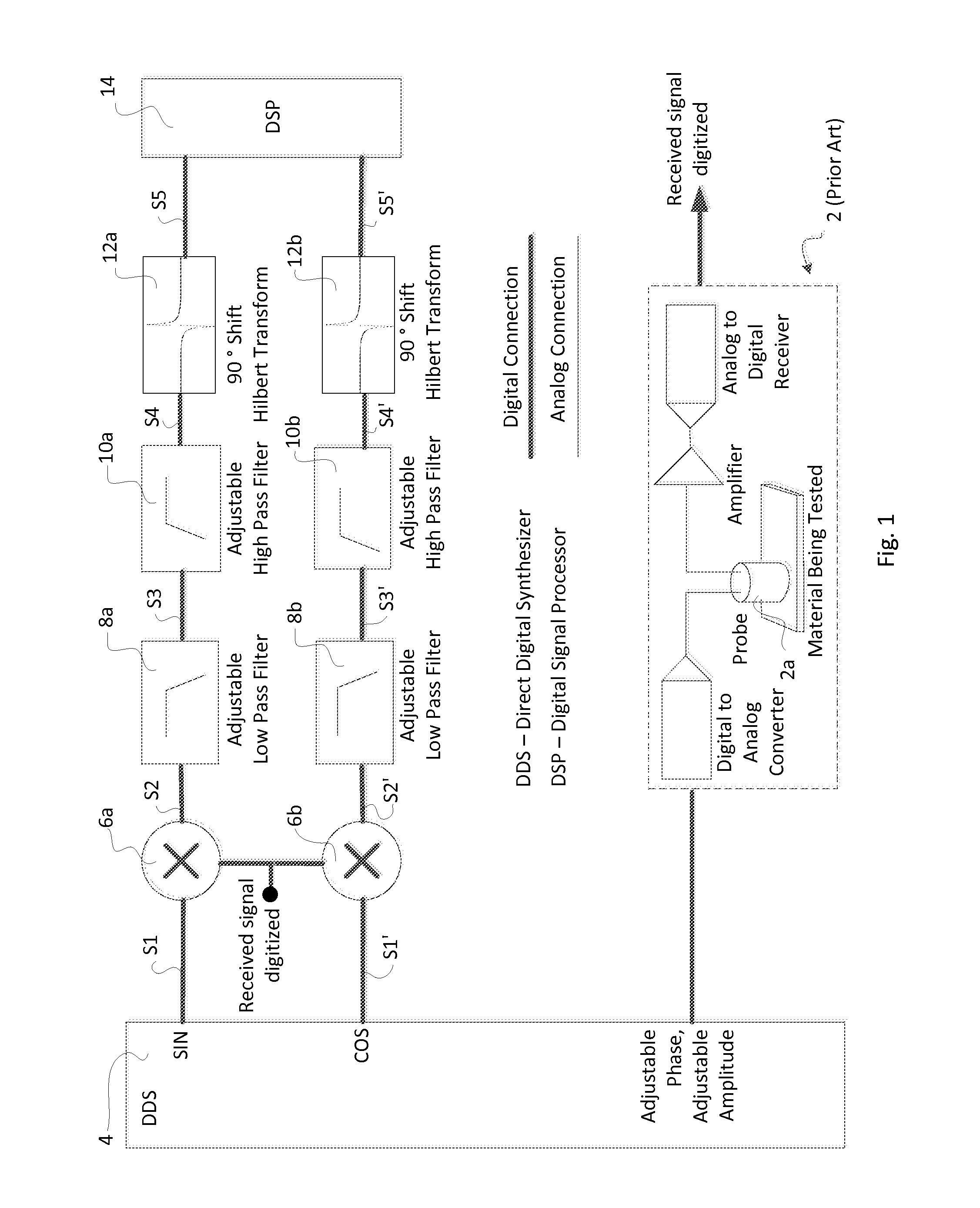
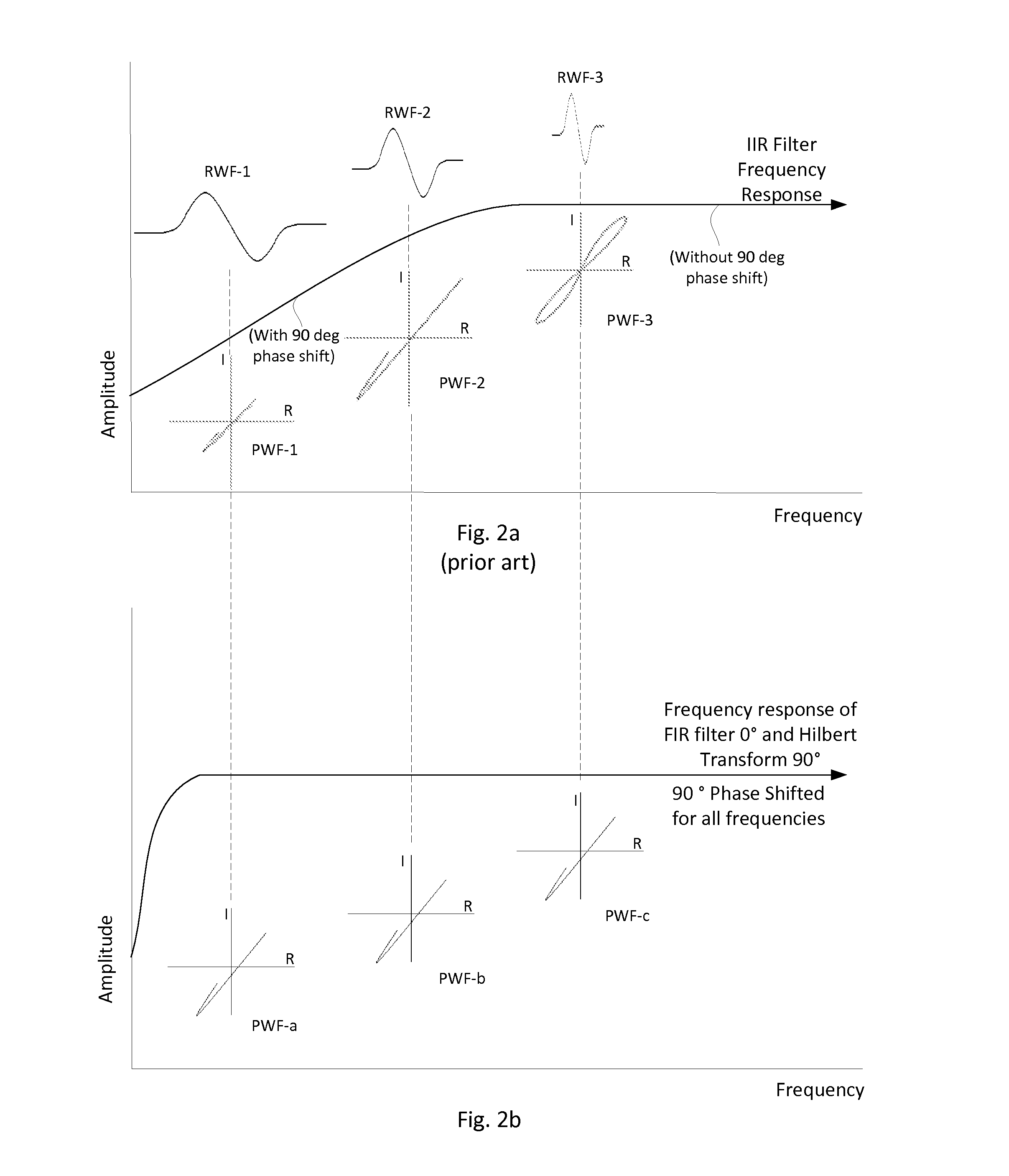
A rotary bolt hole eddy current inspection scanner using a differential eddy current probe, the circuitry of the scanner is embodied with a filtering circuit with three filters: FIR (Finite Impulse Response), a low pass filter, and a phase control filter (by means of a Hilbert transform). The result from a scan of a bolt hole is an output signal on an impedance plane exhibiting a “backwards 6” shape of stable size when the scanner changes its rotating rate significantly.
Owner:OLYMPUS AMERICA
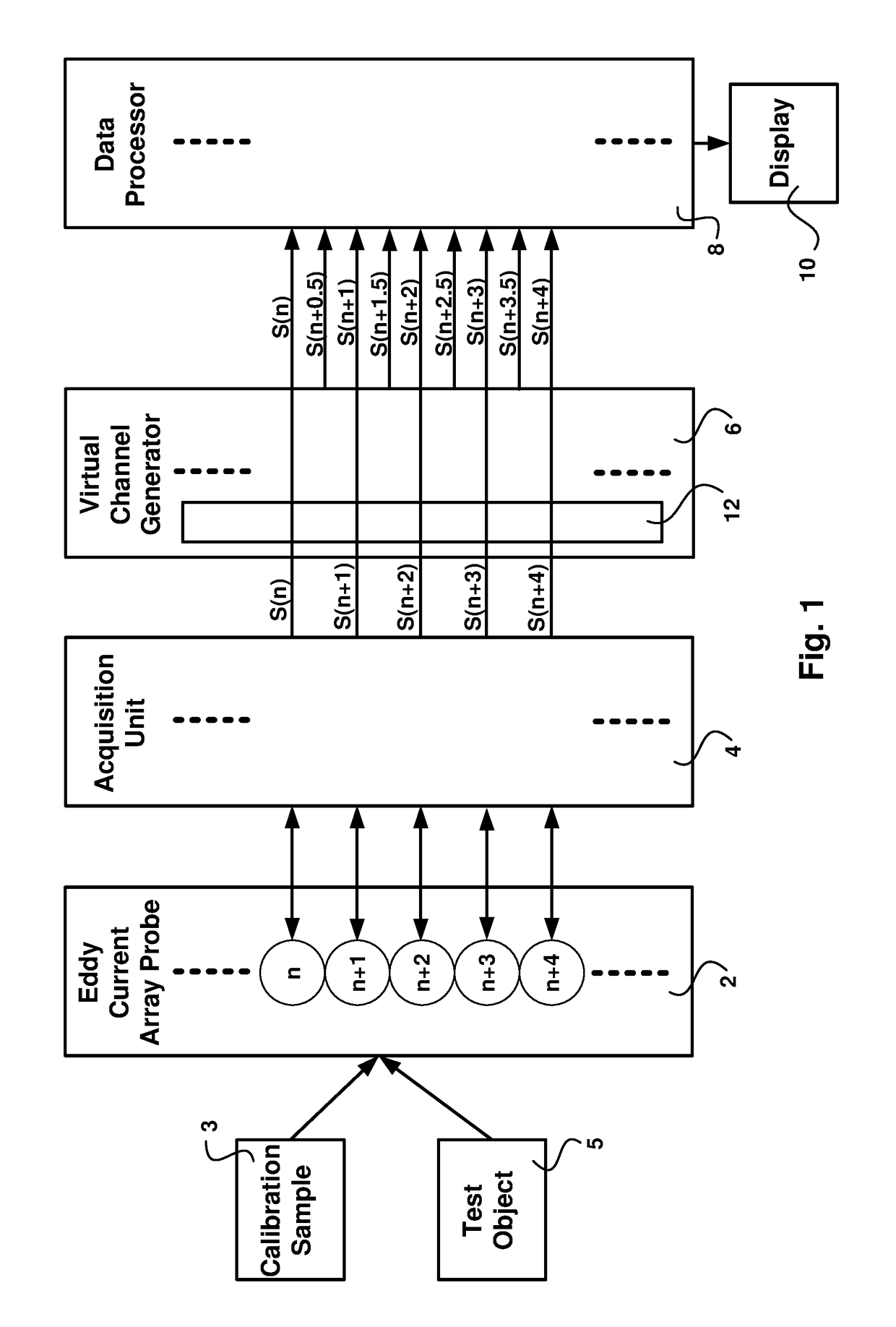
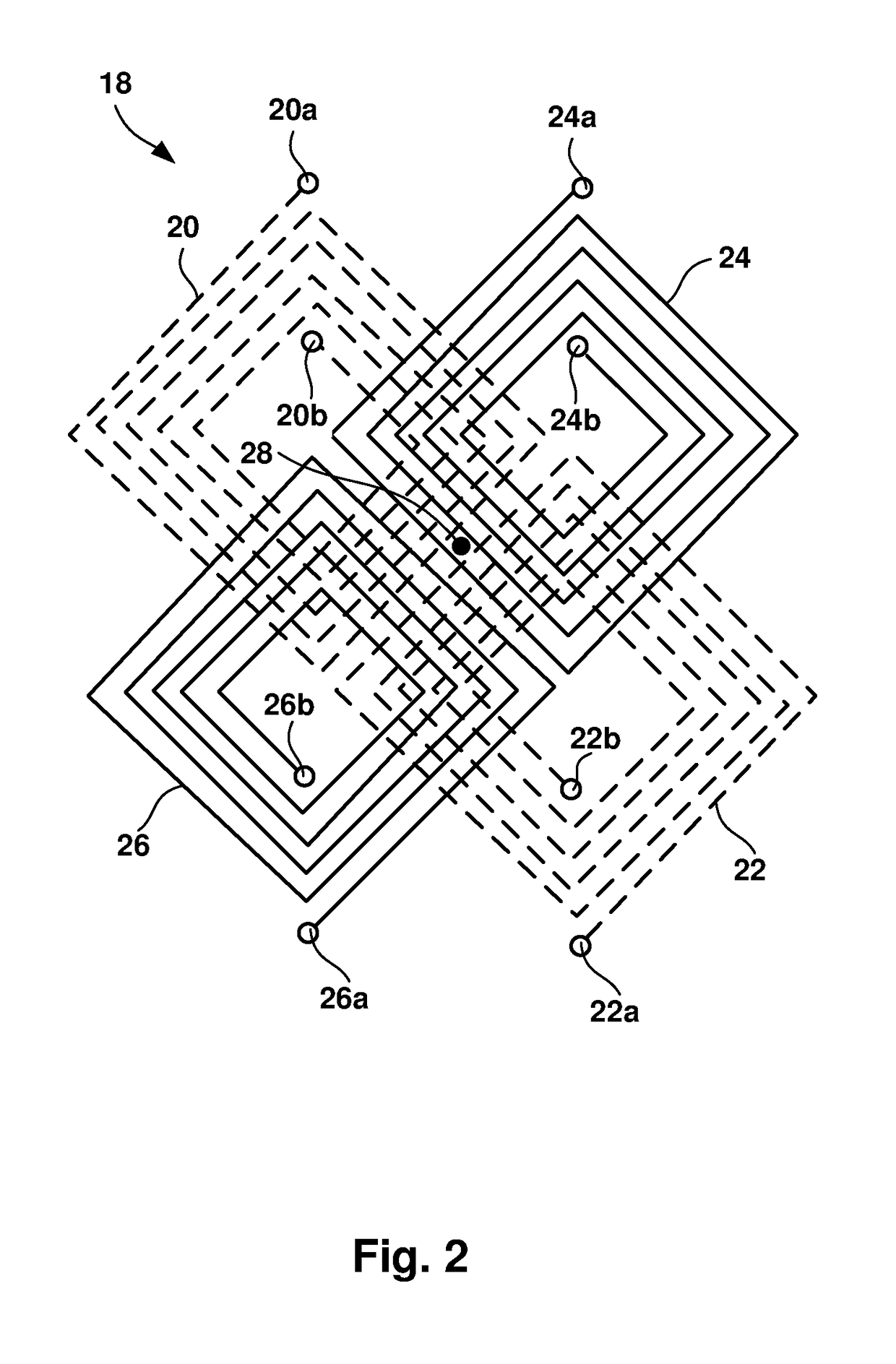
Virtual channels for eddy current array probes
ActiveUS20180217099A1Improved probe sensitivityImproved defect imagingMaterial magnetic variablesLong axisComputer science
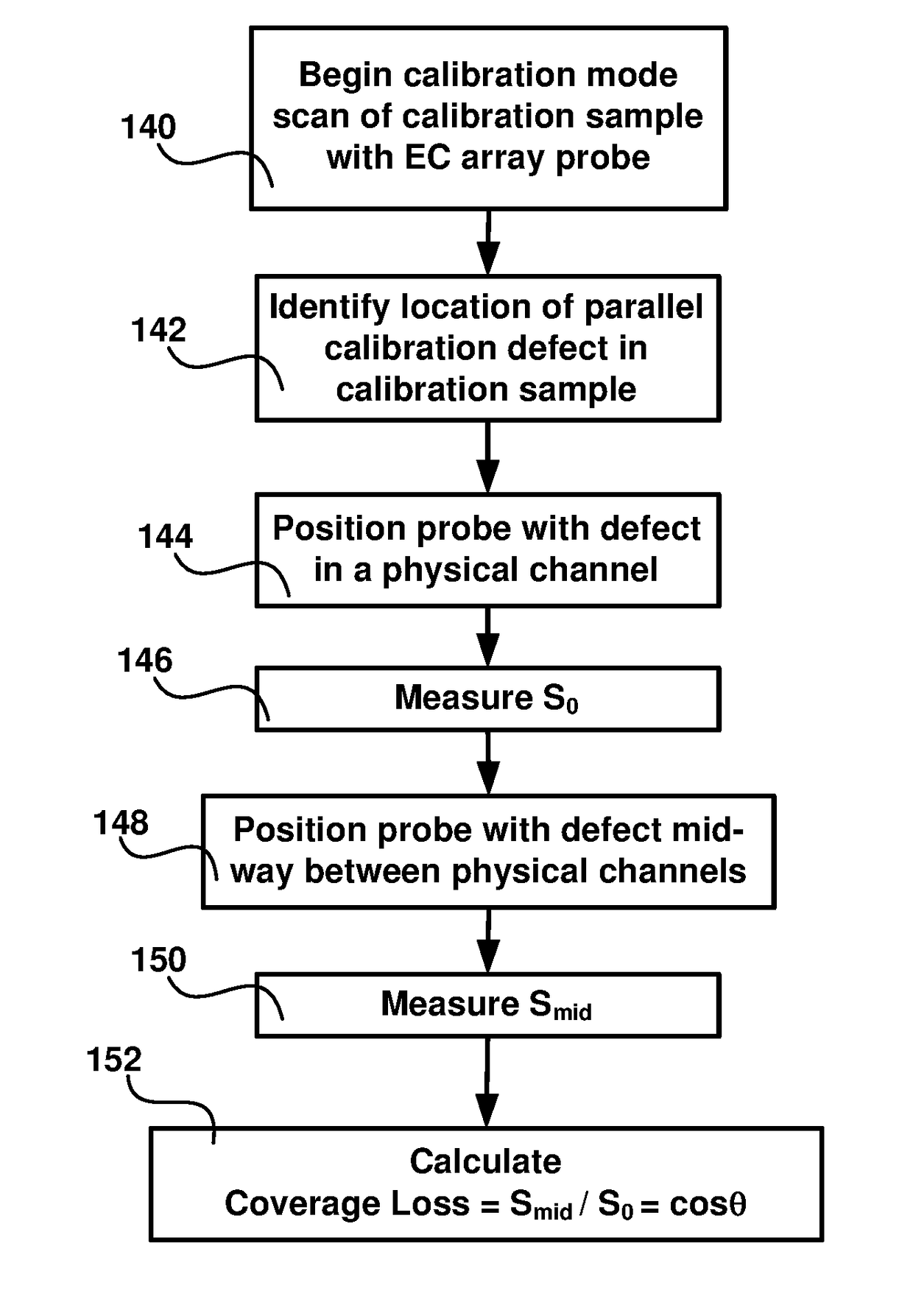
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for generating virtual inspection channels mid-way between the physical inspection channels of an eddy current array probe, thereby reducing the coverage loss and improving defect sizing and imaging. The method is based upon a calibration to determine the mid-channel coverage loss for parallel defects having their long axis parallel to the scanning direction. Based on the coverage loss measurement, a vector analysis system is constructed enabling generation of virtual channel signals which are available for processing in the same way as physical channels, with impedance plane representation including real and / or imaginary signal components. The system differentiates between parallel and perpendicular defects and employs different algorithms to generate virtual channel signals for parallel and perpendicular defect orientations.
Owner:OLYMPUS AMERICA +1
Method of manipulating impedance plane with a multi-point touch on touch screen
ActiveUS8698778B2Input/output processes for data processingMaterial magnetic variablesNon destructiveTouchscreen
A touch screen is disclosed which responds to a user's touch for re-drawing, re-scaling, re-translating and re-positioning an impedance plane signal received from non-destructive testing equipment, such as an eddy current sensor. The impedance plane is manipulated by slidingne, two or more fingers simultaneously to an end position to effectuate a complete re-drawing operation of the image.
Owner:OLYMPUS NDT
Method for detecting discontinuity of nonmetallic material by utilizing eddy current impedance plane detector
ActiveCN103940902AEasy to automate detectionRealize automated detectionMaterial magnetic variablesMetallic materialsComputational physics
The invention discloses a method for detecting discontinuity of a nonmetallic material by utilizing an eddy current impedance plane detector. The method is characterized in that by utilizing the characteristics that magnetic induction intensity and distribution of a magnetic field are changed caused by medium change in the magnetic field based on an electromagnetic field principle, and the discontinuity of the nonmetallic material is detected by utilizing the eddy current impedance plane detector. The current nondestructive testing theoretical limit is broken through, an electromagnetic eddy current detection method is applied to discontinuity detection of the nonmetallic material, the detection efficiency is improved, and automatic detection of the discontinuity of the nonmetallic material is easily realized.
Owner:EDDYSUN (XIAMEN) ELECTRONICS CO LTD
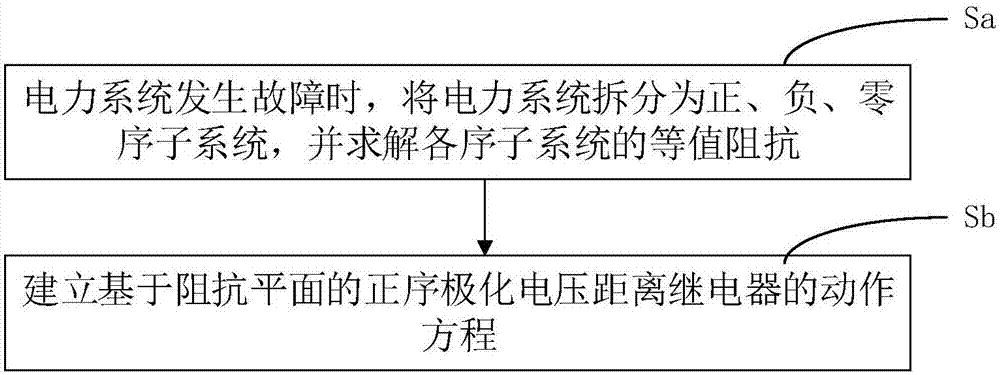
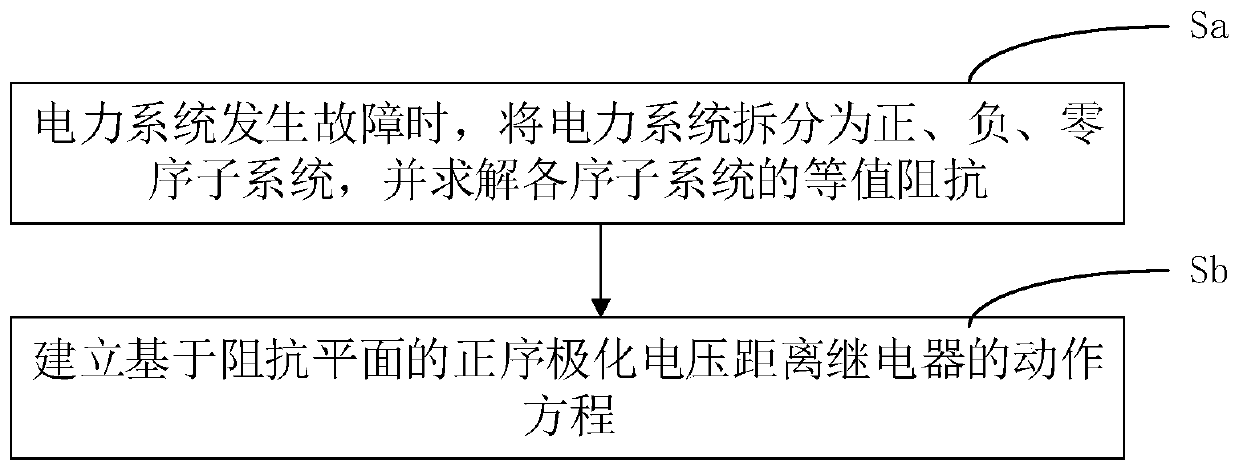
Positive sequence polarization voltage relay control analyzing method and system based on impedance plane
ActiveCN107968387AReflect a change in the mode of operationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationElectric power systemEngineering
The invention relates to an analysis method for analyzing the action behavior of a positive sequence polarization voltage distance relay based on an impedance plane. The analysis method comprises thestep that the action behavior of the positive sequence polarization voltage distance relay is analyzed through the constructed impedance plane. The step further comprises the steps that Sa when a power system fails, the power system is divided into positive, negative and zero sequence subsystems, and the equivalent impedance of each sequential subsystem is solved; and Sb, an action equation of thepositive sequence polarization voltage distance relay based on the impedance plane is established. The analysis method of the relay uses current and voltage data to calculate the positive, negative and zero sequence impedances of the system in real time, so that the behavior of distance protection can be analyzed point by point; the calculated zero, positive and negative sequence impedances of the system are accurate; and the change of one operating mode of the power system can be reflected in real time.
Owner:南京合智电力科技有限公司 +1
Design method for improving limiting sensibility of eddy current detection by using resonant frequency change
ActiveCN103760234AIncrease limit sensitivityIncreased Eddy Current Detection Limit SensitivityMaterial magnetic variablesFirst generationInstrument design
The invention discloses a design method for improving the limiting sensibility of eddy current detection by using a resonant frequency change. A quartz crystal oscillator in an eddy current detection instrument is replaced with a frequency generated by a resonance circuit; an eddy current detection coil is used as an inductor part of the resonance circuit; the eddy current detection instrument designed through the method can obtain a resonant eddy current detection impedance signal chart comprising amplitude, phase and frequency information; the eddy current detection instrument has the work characteristics of a first generation of resonant eddy current instruments, meanwhile, has the advantages of a second generation of impedance plane analysis eddy current instruments; the limiting sensibility of the eddy current detection is further improved through the combination of the two mechanisms.
Owner:EDDYSUN (XIAMEN) ELECTRONICS CO LTD
L-shaped impedance matching network design method
InactiveCN106650087ADesign quick successEasy to operateCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsCapacitanceImpedance matching
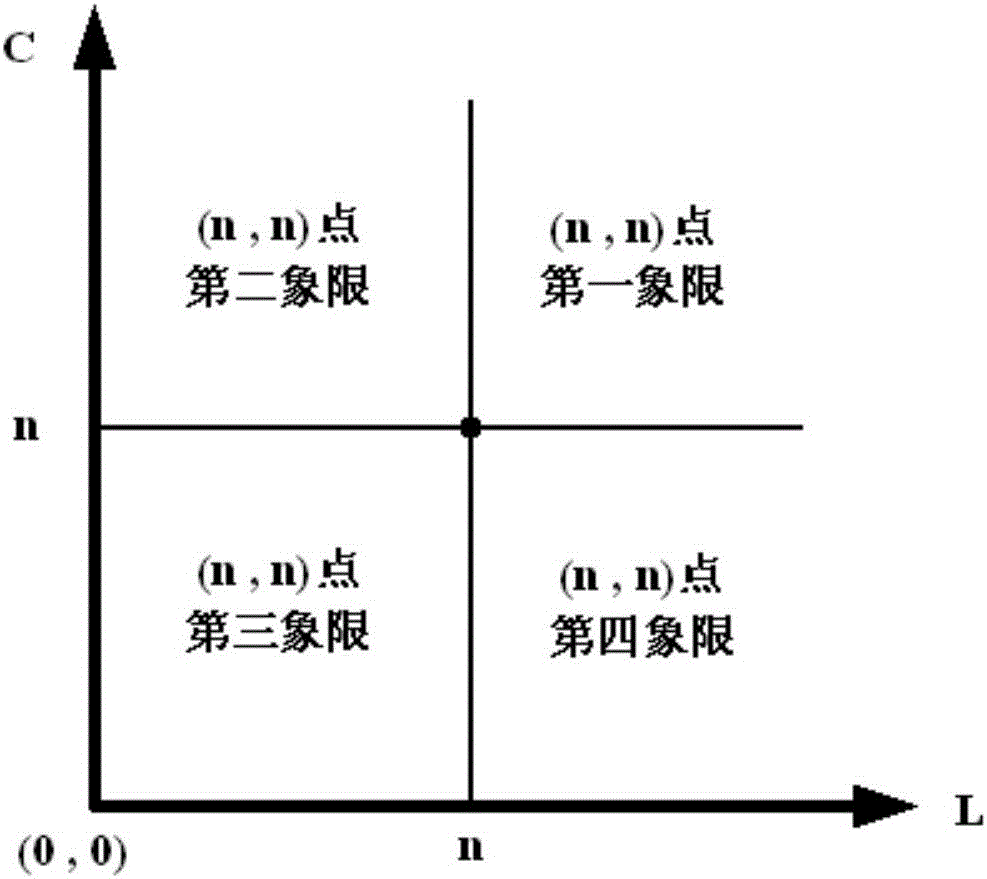
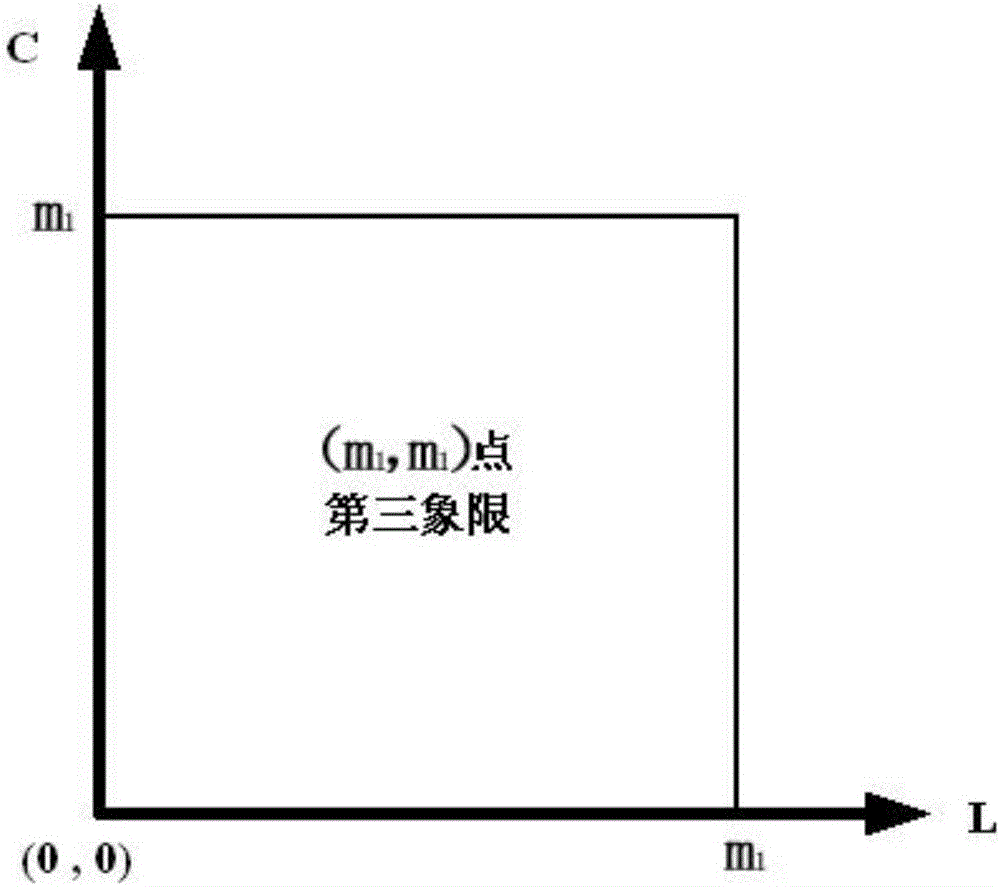
The invention discloses an L-shaped impedance matching network design method, comprising the steps of establishing a two-dimensional impedance plane and selecting a starting point in the two-dimensional impedance plane; designing an L-shaped impedance matching network according to the starting point, and measuring a characteristic impedance value Z (n, n), then judging whether the starting point is the matching point, and if so, designing the L-shaped impedance matching network according to the matching point; otherwise, continuing to implement; increasing capacitance and inductance values corresponding to the starting point, and measuring a corresponding characteristic impedance value Z (m, m); continuing to implement when Z (m, m) is closer to the center of the graph than Z (n, n), otherwise re-selecting; increasing the corresponding capacitance and inductance values, and judging that the matching point is located in the third quadrant of the impedance plane at the previous point of the point when the distance between Z (m, m) and the center of the original image of the Smith is larger than the starting distance; and reducing the range of the matching point to obtain a final matching region, and designing the L-shaped impedance matching network.
Owner:XIAN HUAXUN MICROELECTRONICS
Method for estimating differential mode interference noise impedance of equipment
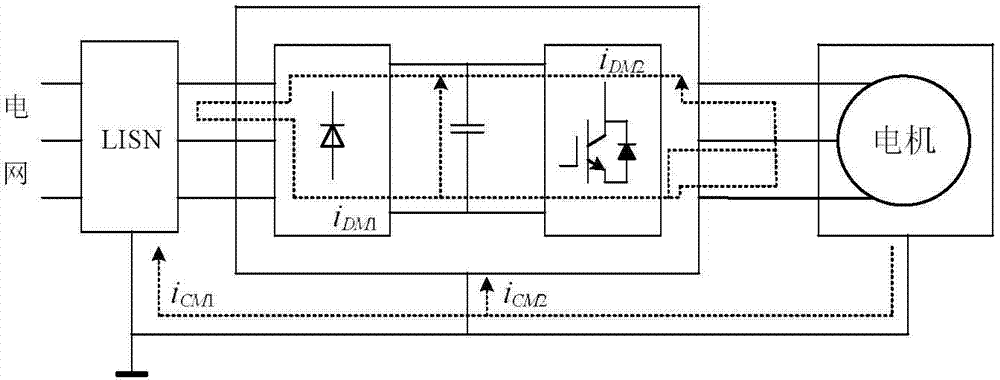
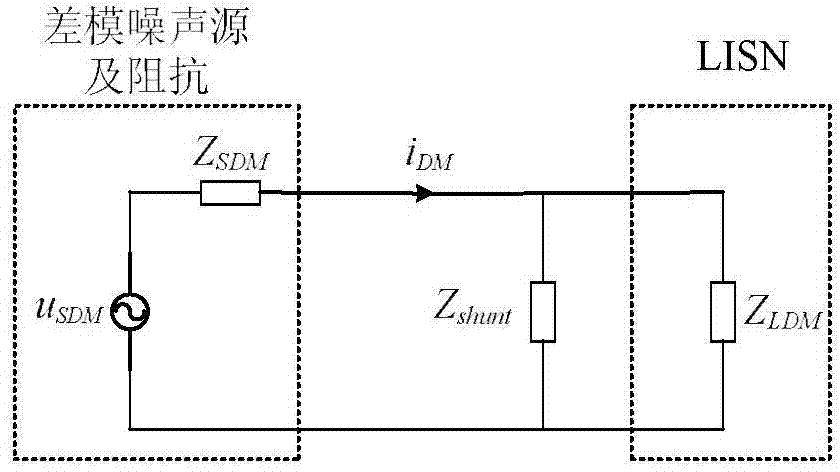
InactiveCN104849560AAddressing the Impact of Design IssuesNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceEstimation methodsElectromagnetic interference
The invention discloses a method for measuring and estimating differential mode interference noise impedance through insertion loss. According to the method, a known impedance amplitude element is inserted into a circuit to measure voltage before and after the element is inserted so as to obtain the insertion loss value of the element. A noise source impedance amplitude range is obtained by drawing an impedance plane graph. According to the method, the operation is simple and easy, the experimental condition is simple, and the result precision is relatively high. The impedance value estimated by the estimation method is compared with a measured value of a laboratory, and the compared result indicates that the estimation range precision is high. Moreover, the estimation method also can be suitable for a system with unknown impedance, the impedance value estimated by the method is beneficial to later-stage filter parameter design, and the results also can provide effective data for an electromagnetic interference protective problem.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting magnetization direction of non-magnetized anisotropic magnetic steel
ActiveCN104020425ARealize continuous automatic detectionRealize full inspectionMagnetic property measurementsElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetic anisotropy
The invention discloses a method for detecting magnetization direction of non-magnetized anisotropic magnetic steel. According to the method, non-magnetized anisotropic magnetic steel which has correct magnetization direction and has the same specification with magnetic steel to be detected is used as first standard magnetic steel and non-magnetized anisotropic magnetic steel which has incorrect magnetization direction and has the same specification with the magnetic steel to be detected is used as second standard magnetic steel; reactance and resistance are respectively detected by the adoption of an eddy current inspection instrument; resistance of the magnetic steel is taken as a horizontal coordinate and reactance of the magnetic steel is taken as a vertical coordinate to make an impedance plane diagram of the magnetic steel; an oval area is delimited in the impedance plane diagram to be used as a magnetization direction qualified area according to a position marked as the first standard magnetic steel and a position marked as the second standard magnetic steel in the impedance plane diagram; and detection of magnetization direction of the magnetic steel is converted to detection of position of the magnetic steel in the impedance plane diagram. The method provided by the invention has advantages as follows: continuous automatic detection of the magnetic steel in a non-magnetic environment is realized; detection efficiency is high; costs are low; full inspection of mass production can be realized; and detectivity of the detection is high.
Owner:NINGBO YUNSHENG +4
A Design Method for Improving the Sensitivity of Eddy Current Detection Limit by Resonant Frequency Variation
ActiveCN103760234BIncrease limit sensitivityIncreased Eddy Current Detection Limit SensitivityMaterial magnetic variablesResonanceInductor
The invention discloses a design method for improving the limit sensitivity of eddy current detection by changing the resonance frequency. The frequency generated by the resonance circuit is used to replace the quartz crystal oscillator in the eddy current detection instrument. The eddy current detection coil is used as the inductance part of the resonance circuit. Through this method design The eddy current detection instrument can obtain the impedance signal diagram of the resonant eddy current detection including amplitude, phase and frequency information. In addition to the working characteristics of the first generation resonant eddy current instrument, it also has the advantages of the second generation impedance plane analysis eddy current instrument. The superposition of mechanisms further improves the limit sensitivity of eddy current detection.
Owner:EDDYSUN (XIAMEN) ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-lateral current magnitude voltage magnitude based transformer relay protecting method
InactiveCN101764392BInternal fault differentiationImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectricityTransformer
The invention provides a multi-lateral current magnitude voltage magnitude based transformer relay protecting method, which has the advantages of convenience, reliability, sensitivity and the like. The method comprises the following steps that: 1) a relay protection device acquires sampling values of three-phase voltage and current on each side of the transformer, and calculates out the current magnitude and the voltage magnitude on each side of each phase of winding; 2) the relay protection device calculates the branch impedance of each phase of the winding according to the current magnitudeand the voltage magnitude; and 3) a +R axis area is set on an impedance plane as an action area, and failure inside the transformer is determined when the branch impedance drops in the region more than the set time.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
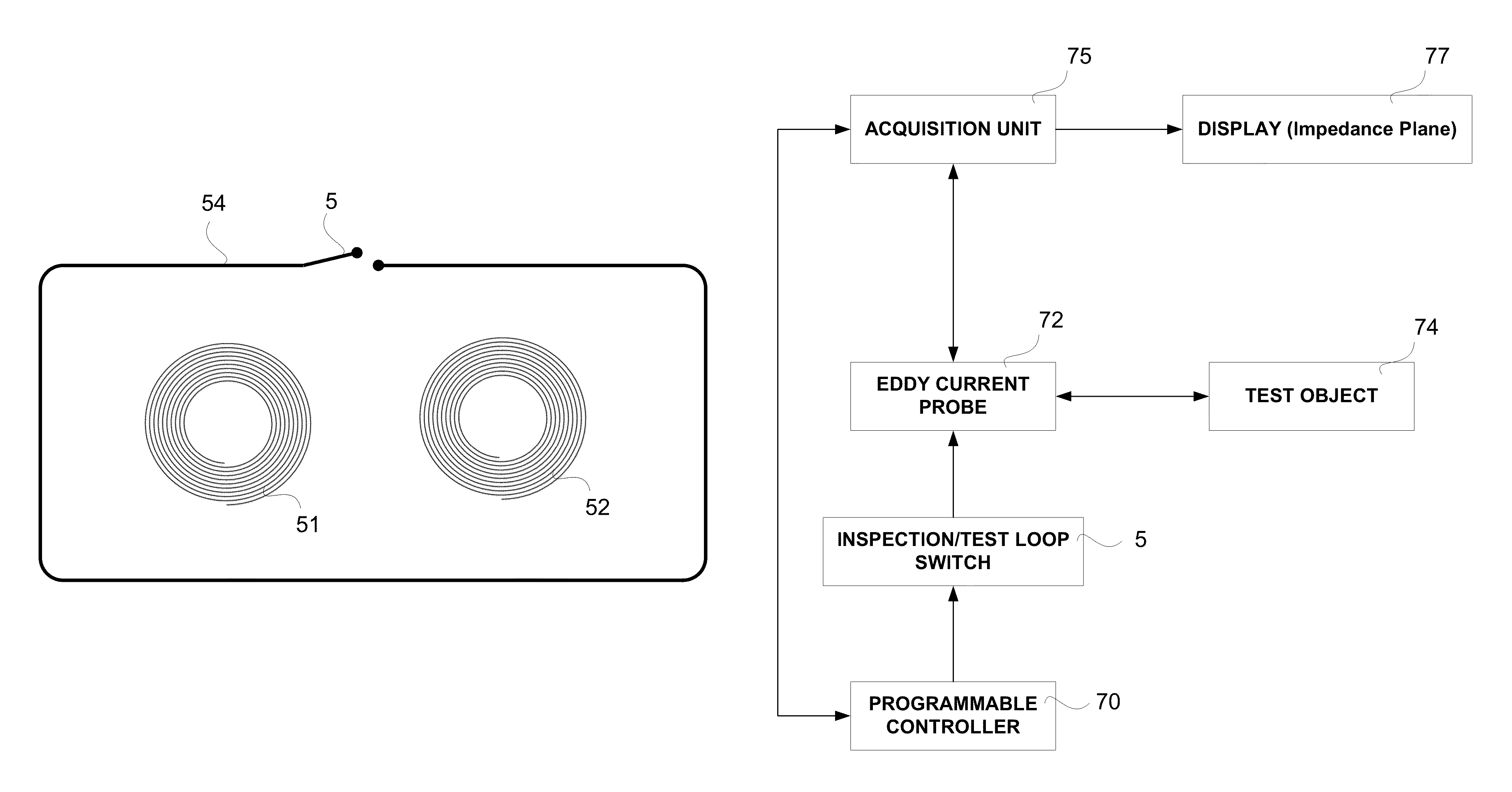
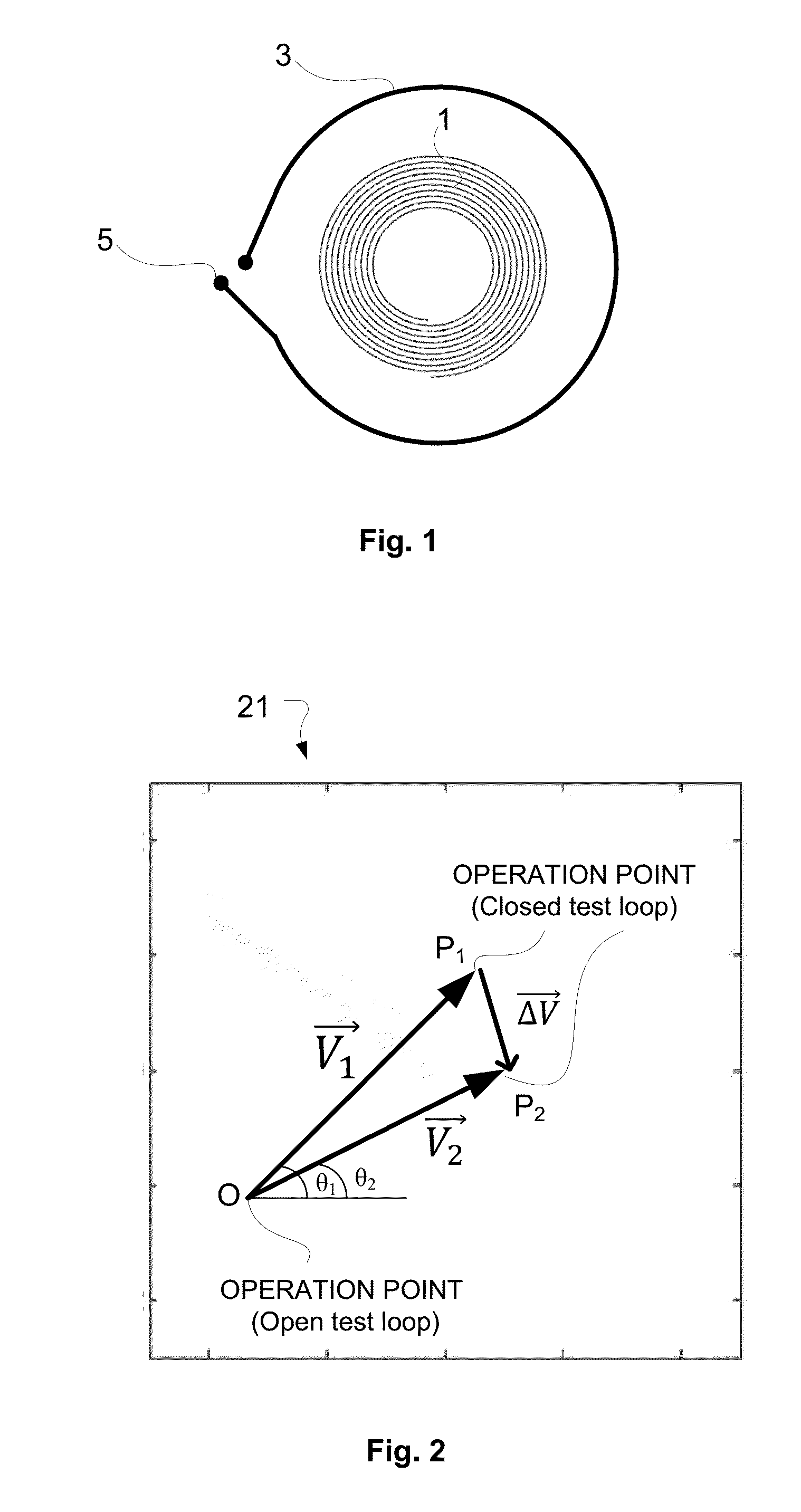
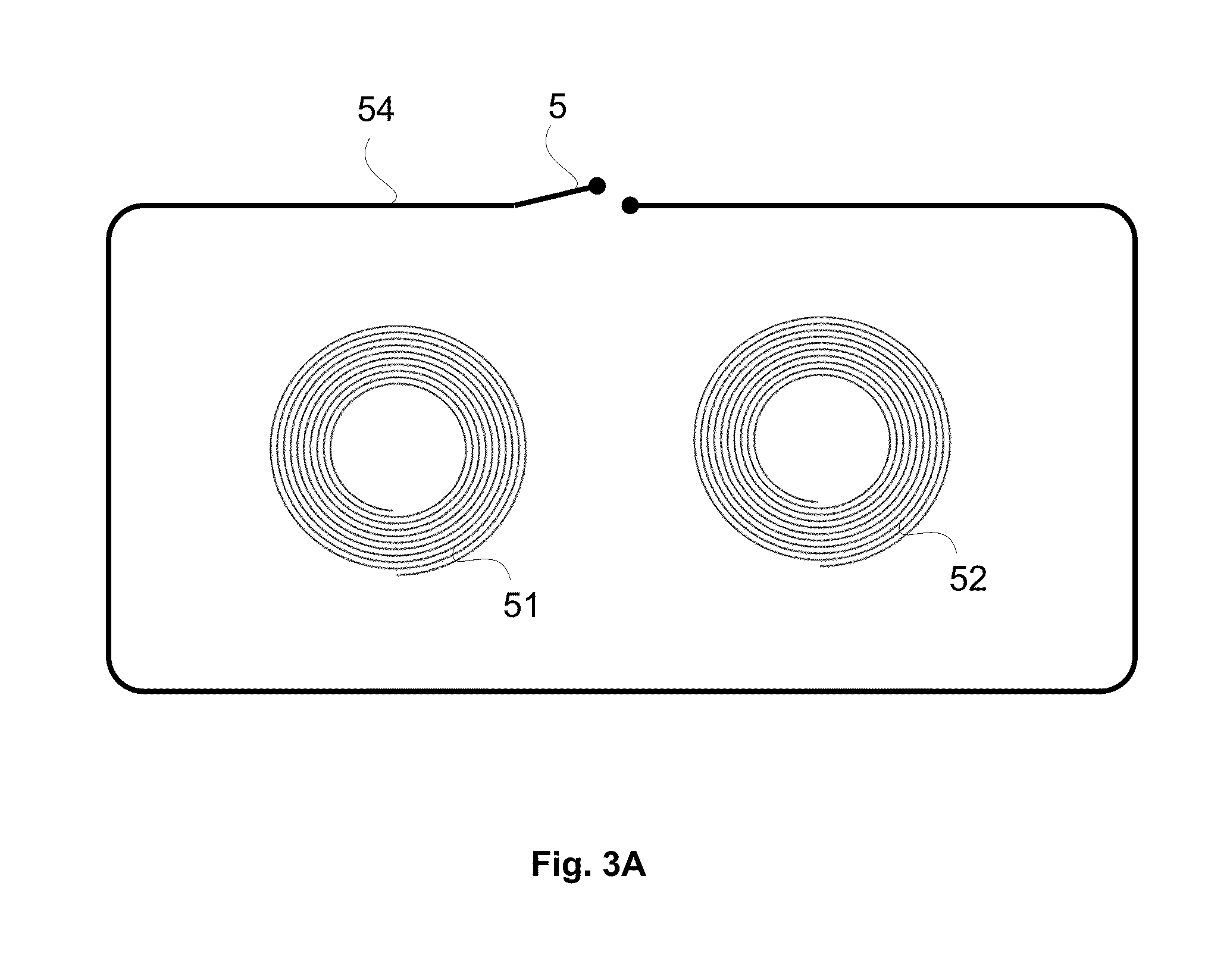
Method for monitoring the integrity of an eddy current inspection channel
ActiveUS9316618B2Magnetic property measurementsMaterial magnetic variablesDisplay deviceVisual perception
An eddy current object testing system includes an EC probe and an acquisition channel which is configured to receive an EC signal from the EC probe and to generate a visual output, namely an impedance plane representation, of the output. A display is coupled to the acquisition channel to display the visual output. The at least one probe is provided with a test loop substantially surrounding it and has a series switch which can be selectively closed or opened to thereby cause the image plane to assume a state that is indicative of a fault, if any, in the EC probe.
Owner:OLYMPUS NDT
Device and method for non-contact magnetic induction impedance plane projection imaging
ActiveCN103006185BSimple structureEasy to implementSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateElectrical resistance and conductanceImpedance distribution
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Relay Control Method Based on Impedance Plane Analysis of Positive Sequence Polarization Voltage
ActiveCN107968387BReflect a change in the mode of operationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationElectric power systemEngineering
The invention relates to an analysis method for analyzing the action behavior of a positive sequence polarization voltage distance relay based on an impedance plane. The analysis method comprises thestep that the action behavior of the positive sequence polarization voltage distance relay is analyzed through the constructed impedance plane. The step further comprises the steps that Sa when a power system fails, the power system is divided into positive, negative and zero sequence subsystems, and the equivalent impedance of each sequential subsystem is solved; and Sb, an action equation of thepositive sequence polarization voltage distance relay based on the impedance plane is established. The analysis method of the relay uses current and voltage data to calculate the positive, negative and zero sequence impedances of the system in real time, so that the behavior of distance protection can be analyzed point by point; the calculated zero, positive and negative sequence impedances of the system are accurate; and the change of one operating mode of the power system can be reflected in real time.
Owner:南京合智电力科技有限公司 +1
Generator out-of-step protection method and device
InactiveCN104242245BLow costImprove compatibilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric machine testingEngineeringDynamo
The invention provides a method and a device for generator out-of-step protection. The method comprises the steps of A, obtaining the total impedance of a generator to an infinite bus, B, determining the isostatic boundary circle of the impedance plane of the infinite bus according to the total impedance, C, converting the isostatic boundary circle into a isostatic boundary circle on the impedance plane of a generator terminal, D, measuring the impedance of the generator terminal, when the impedance of the generator terminal goes in from the right side of the isostatic boundary circle and out from the left side of the isostatic boundary circle in predetermined time, confirming out-of-step acceleration of the generator and performing out-of-step acceleration protection, and when the impedance of the generator terminal goes in from the left side of the isostatic boundary circle and out from the right side of the isostatic boundary circle in the predetermined time, confirming out-of-step deceleration of the generator and performing out-of-step deceleration protection. According to the method and the device for generator out-of-step protection, the out-of-step faults can be detected in the first period of oscillation and the power swing is excellent.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com