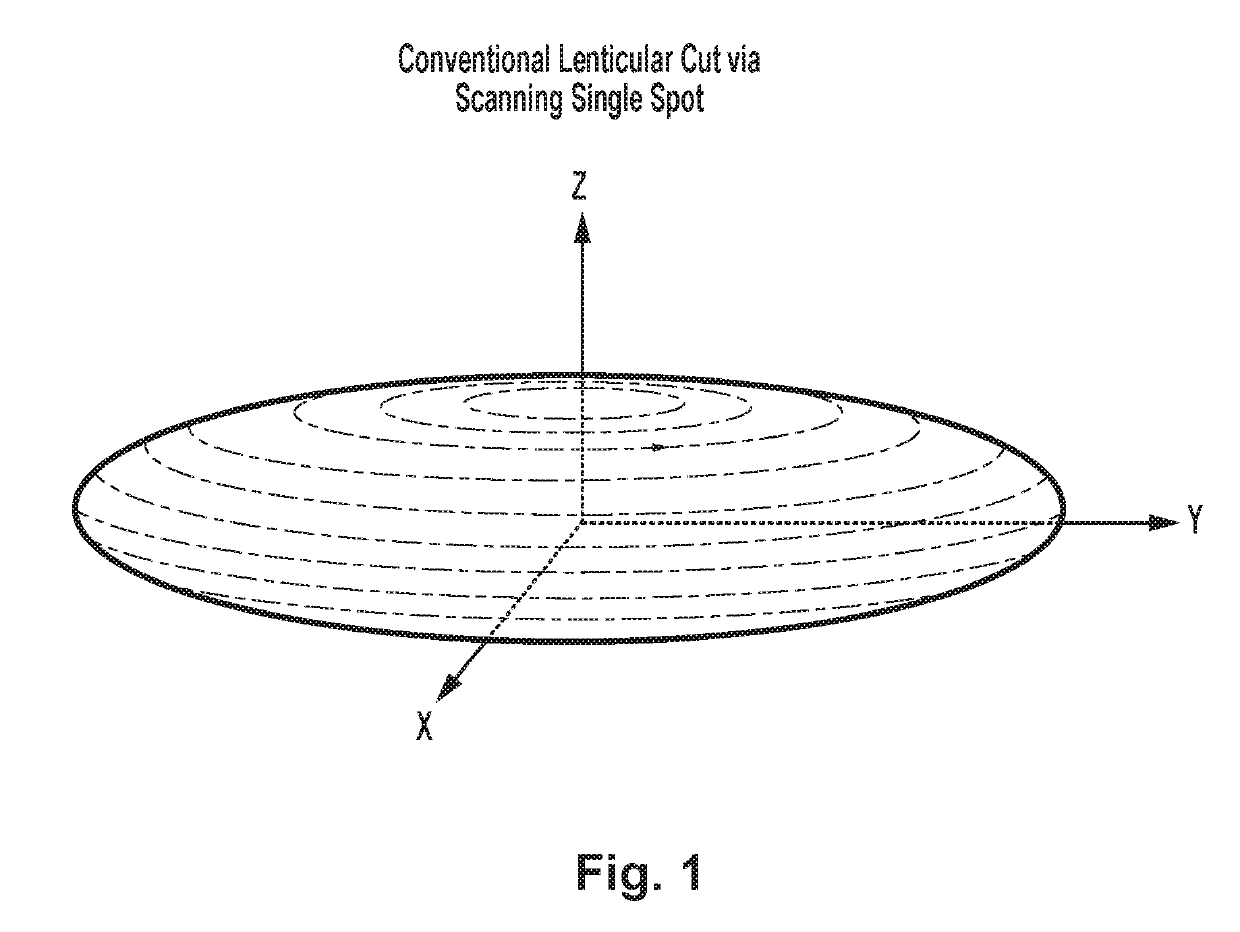
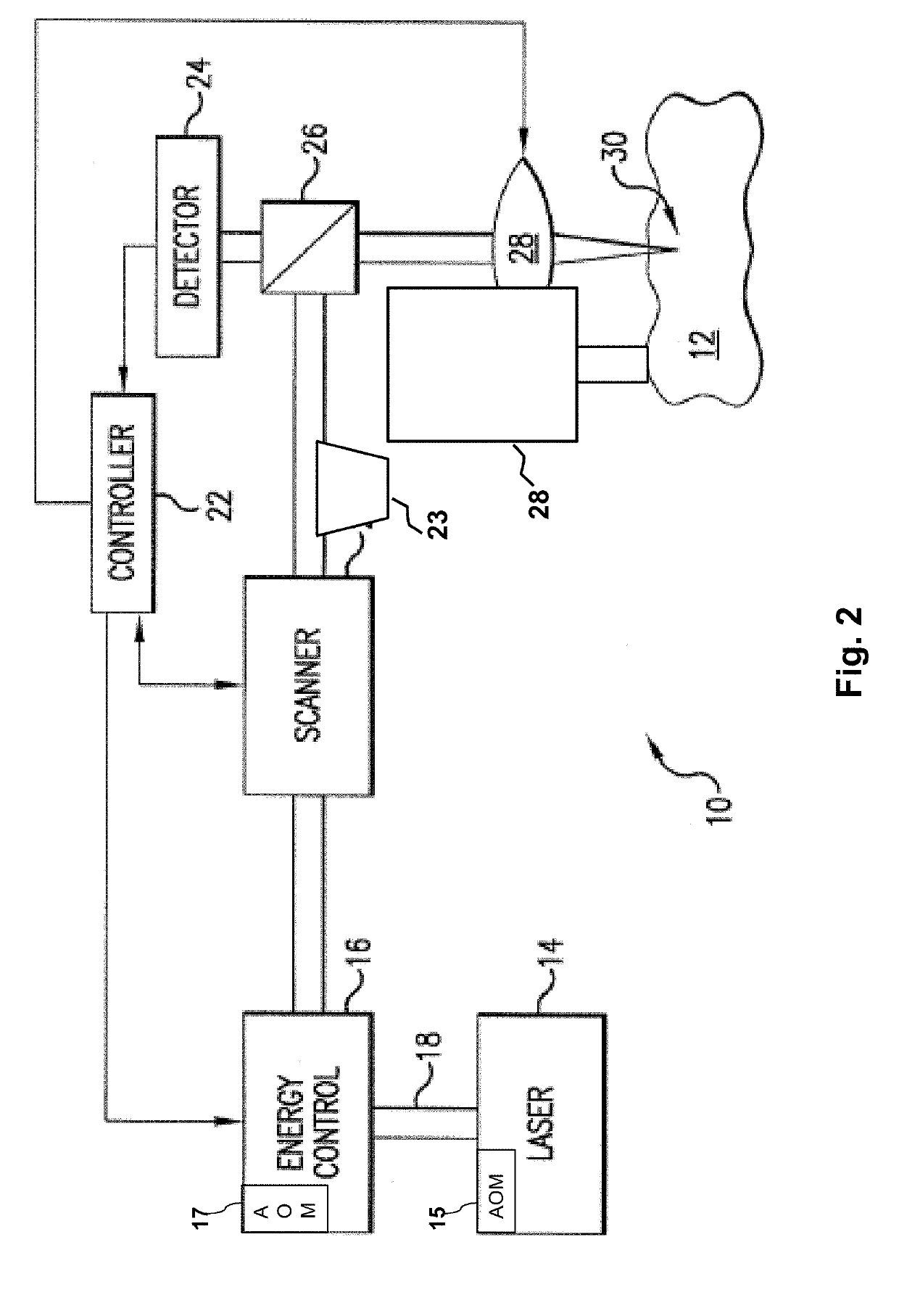
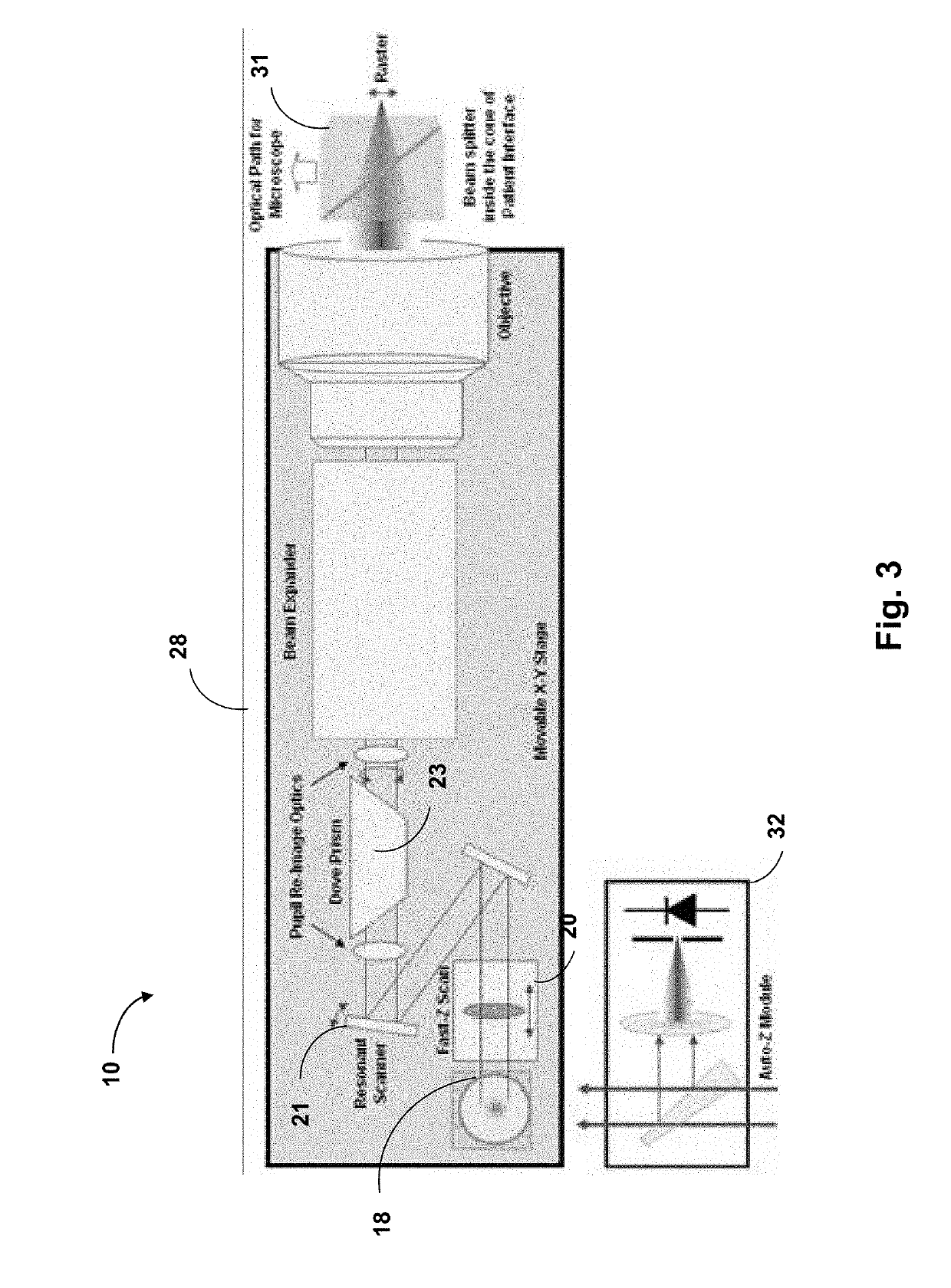
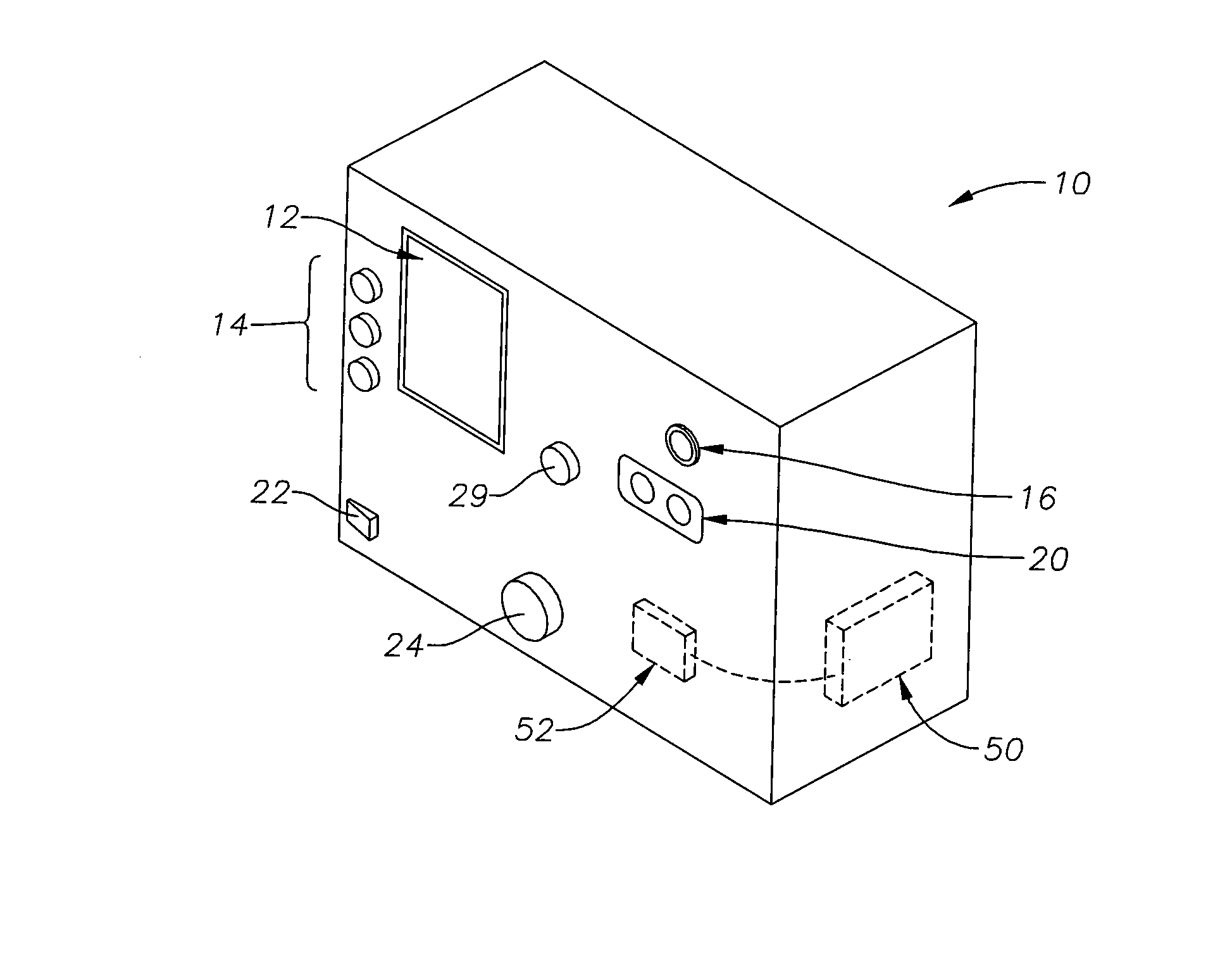
Patents
Literature
56 results about "Eye surgery laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
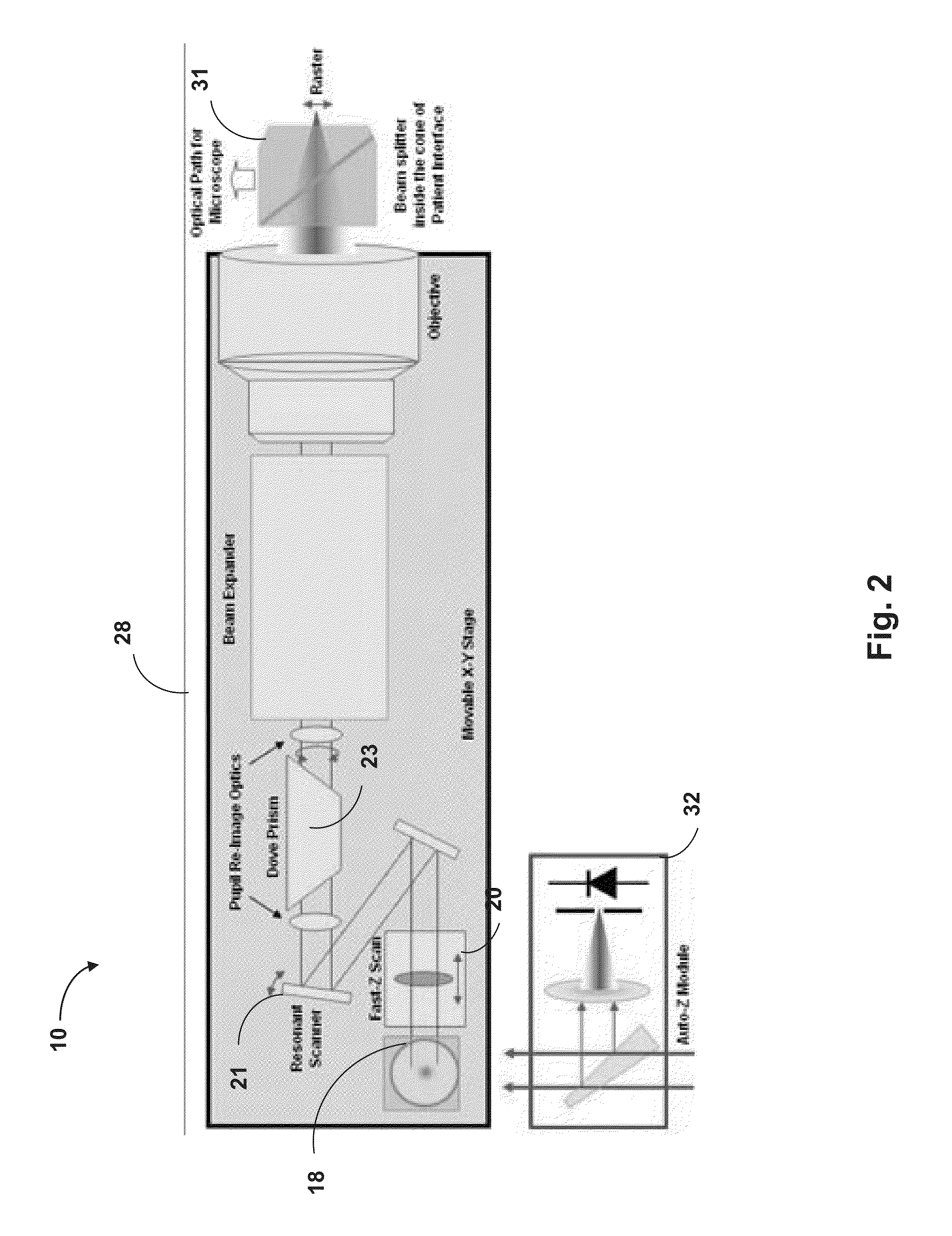
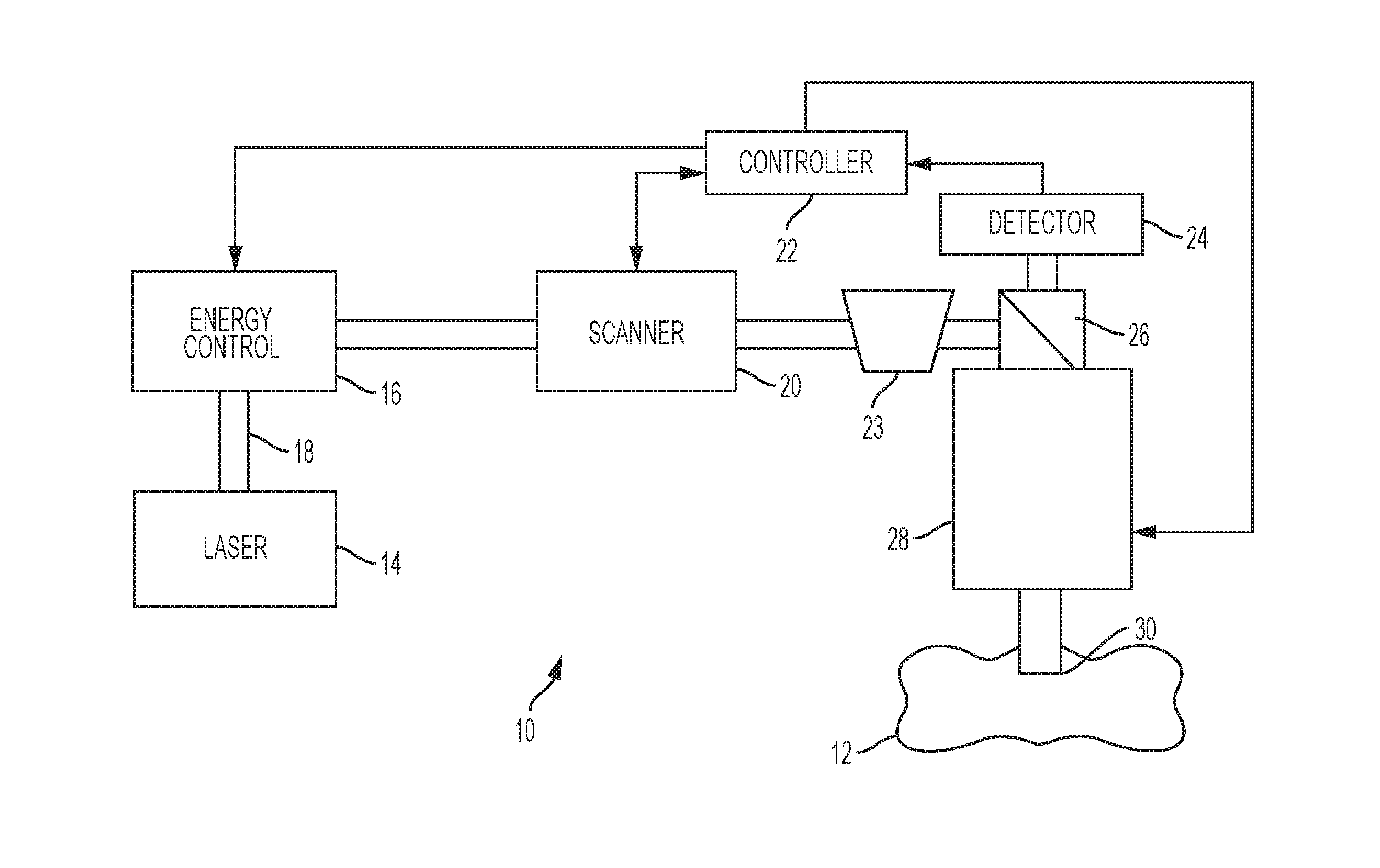
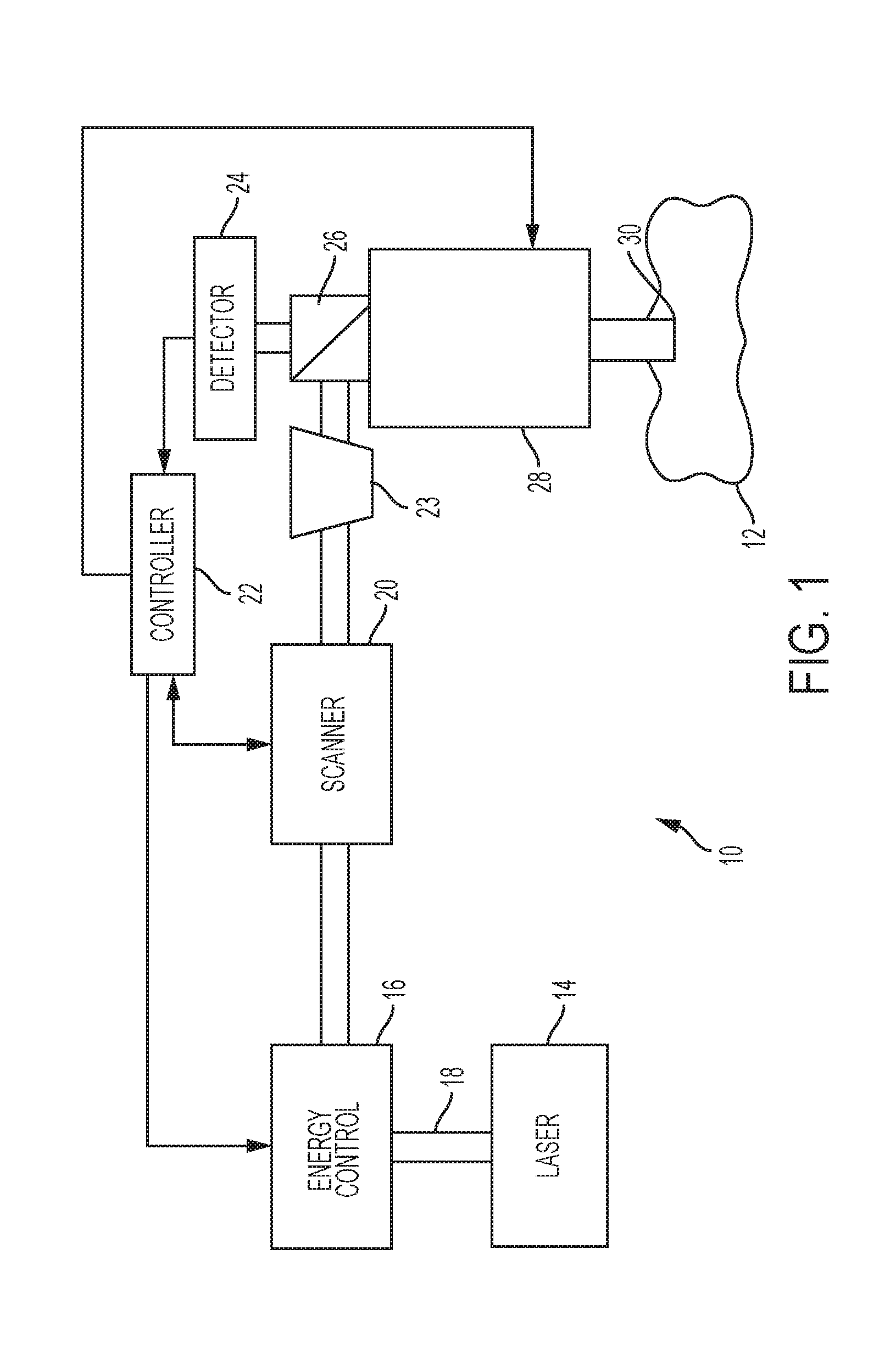
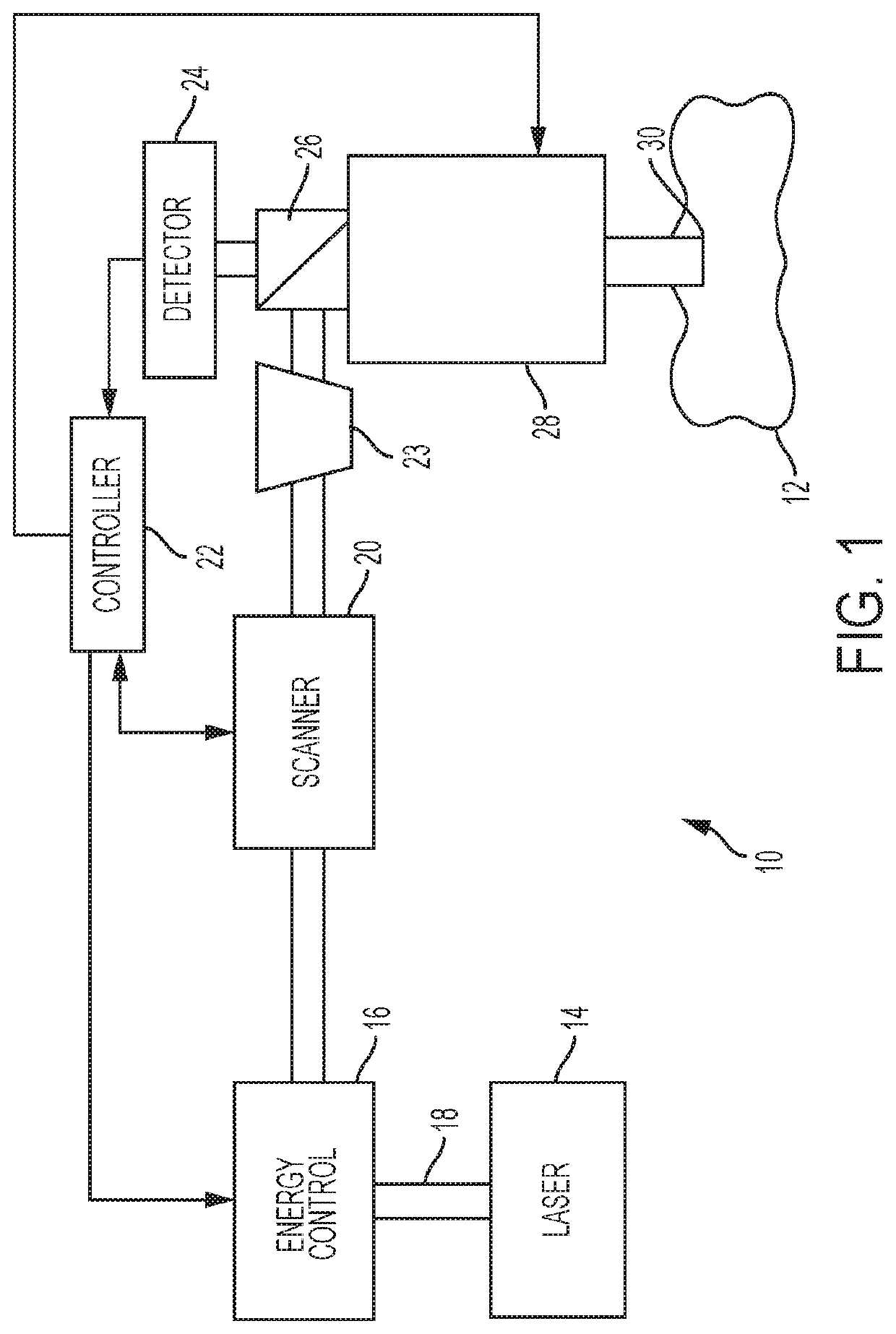
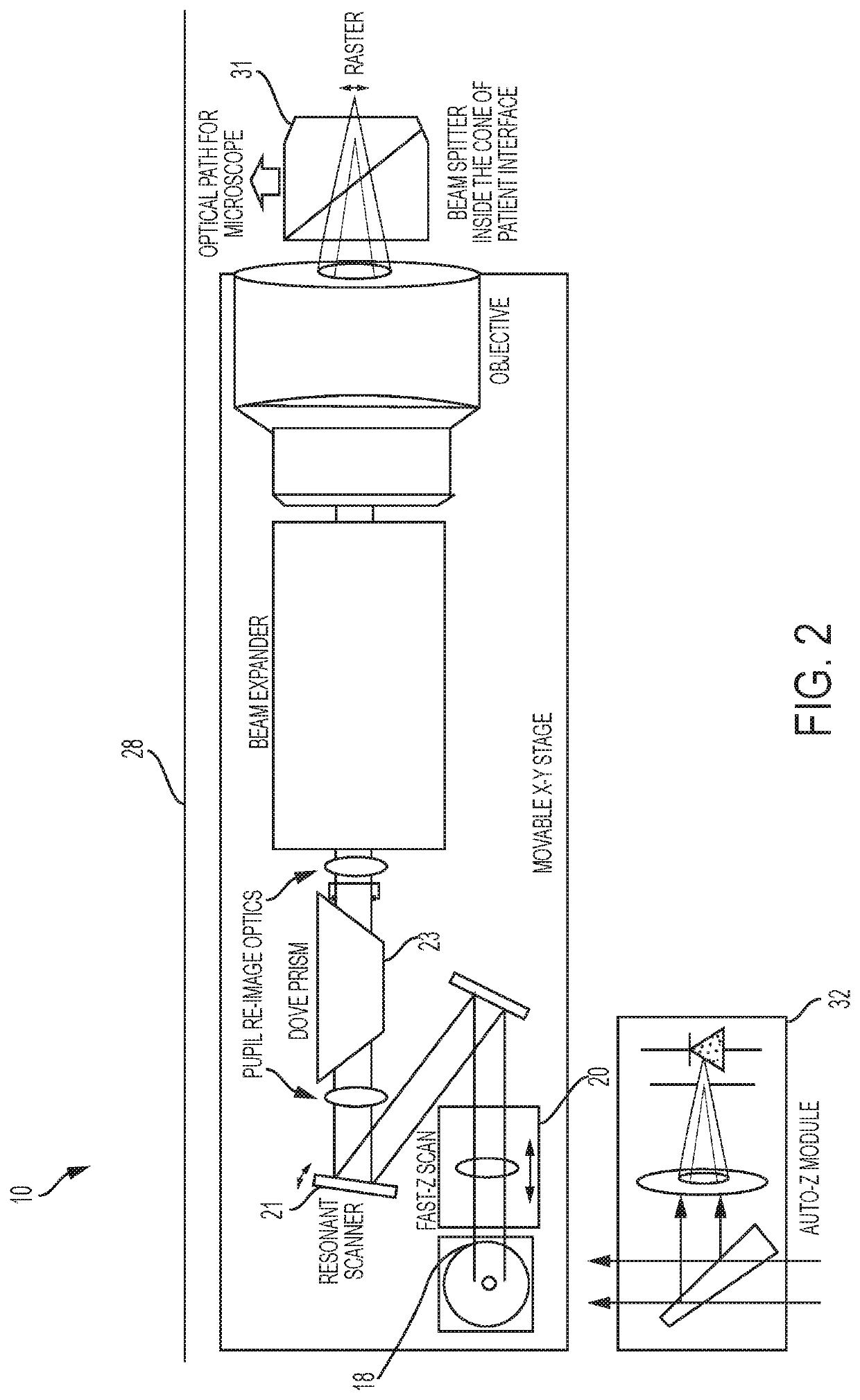
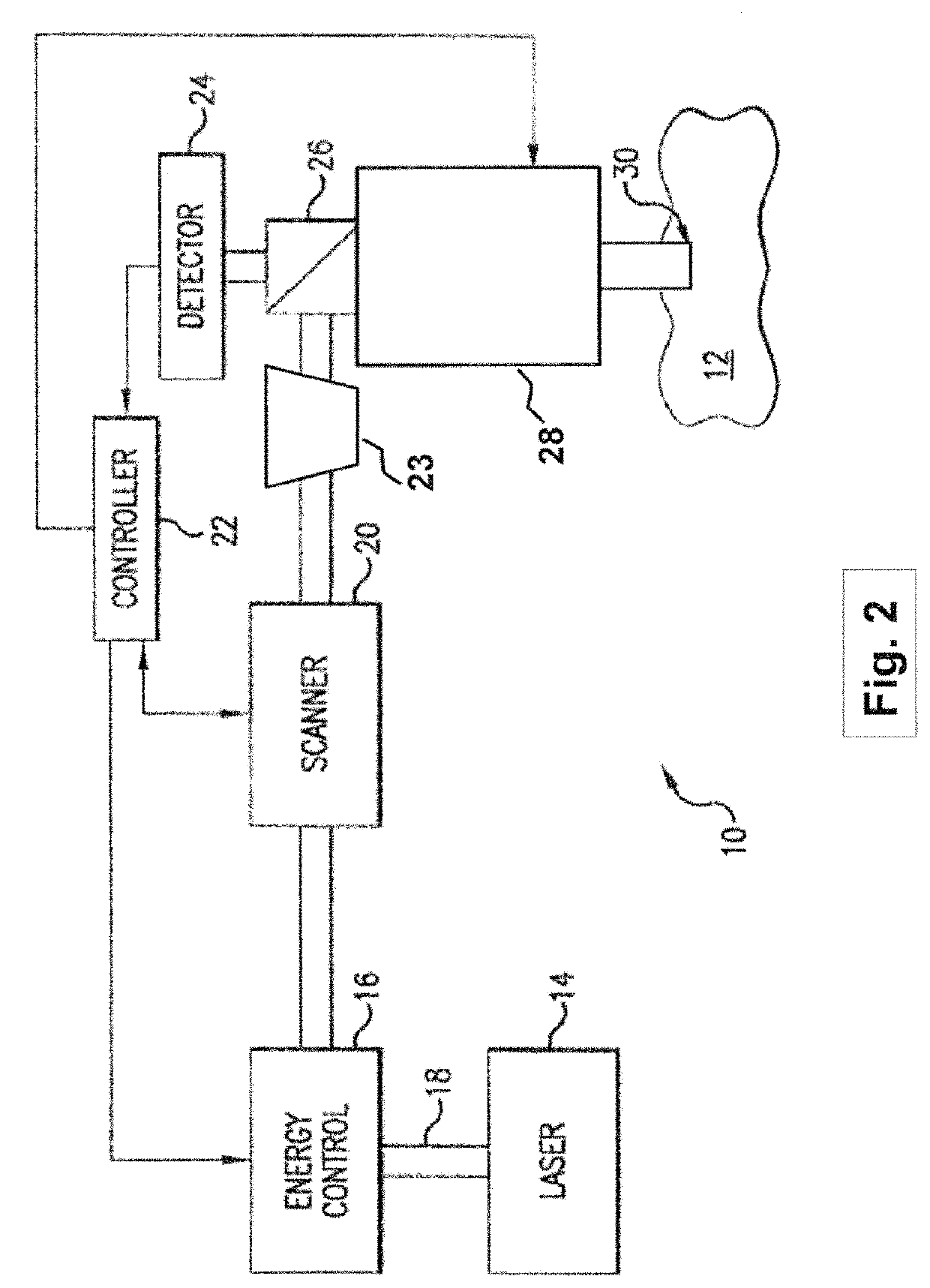
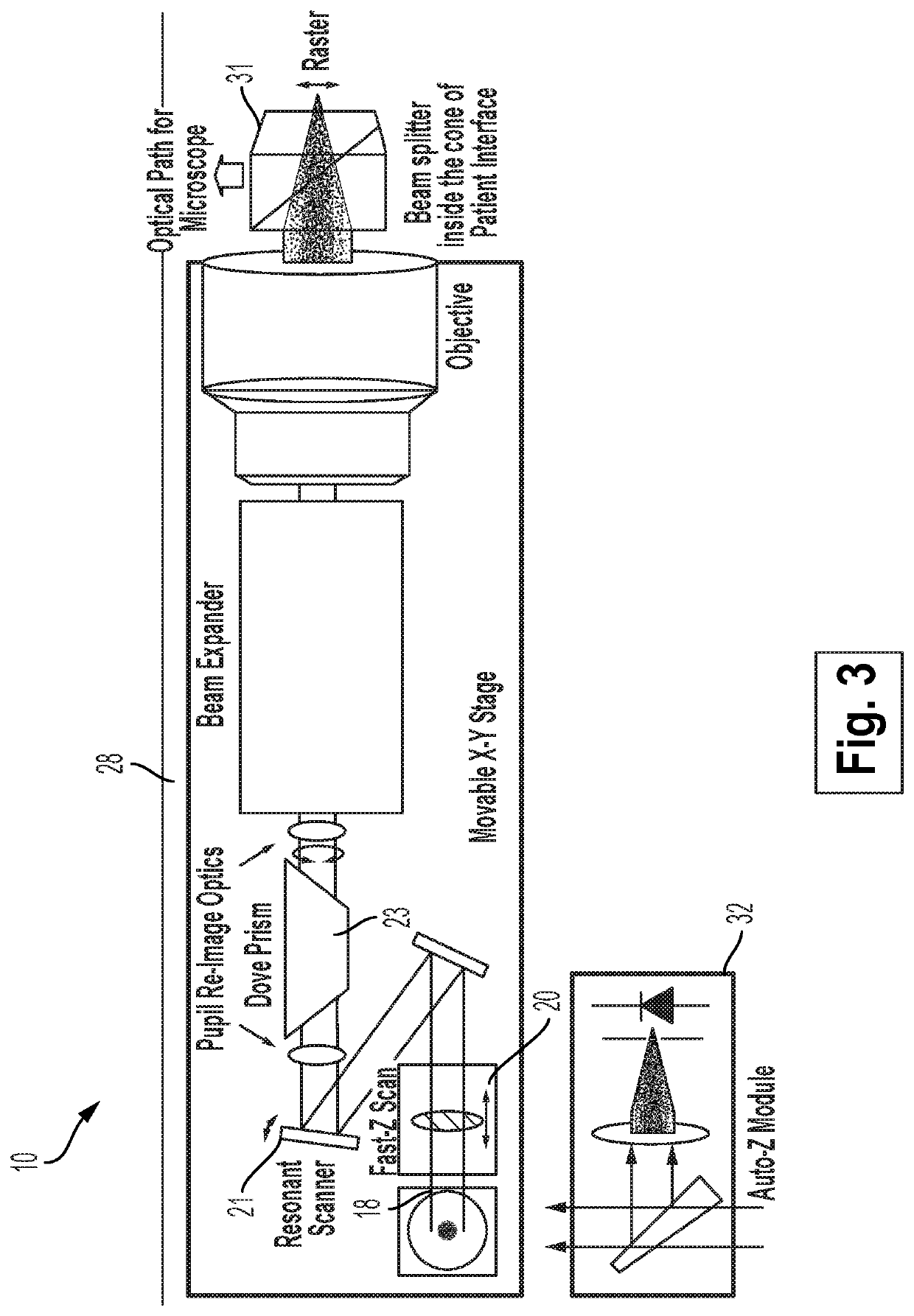
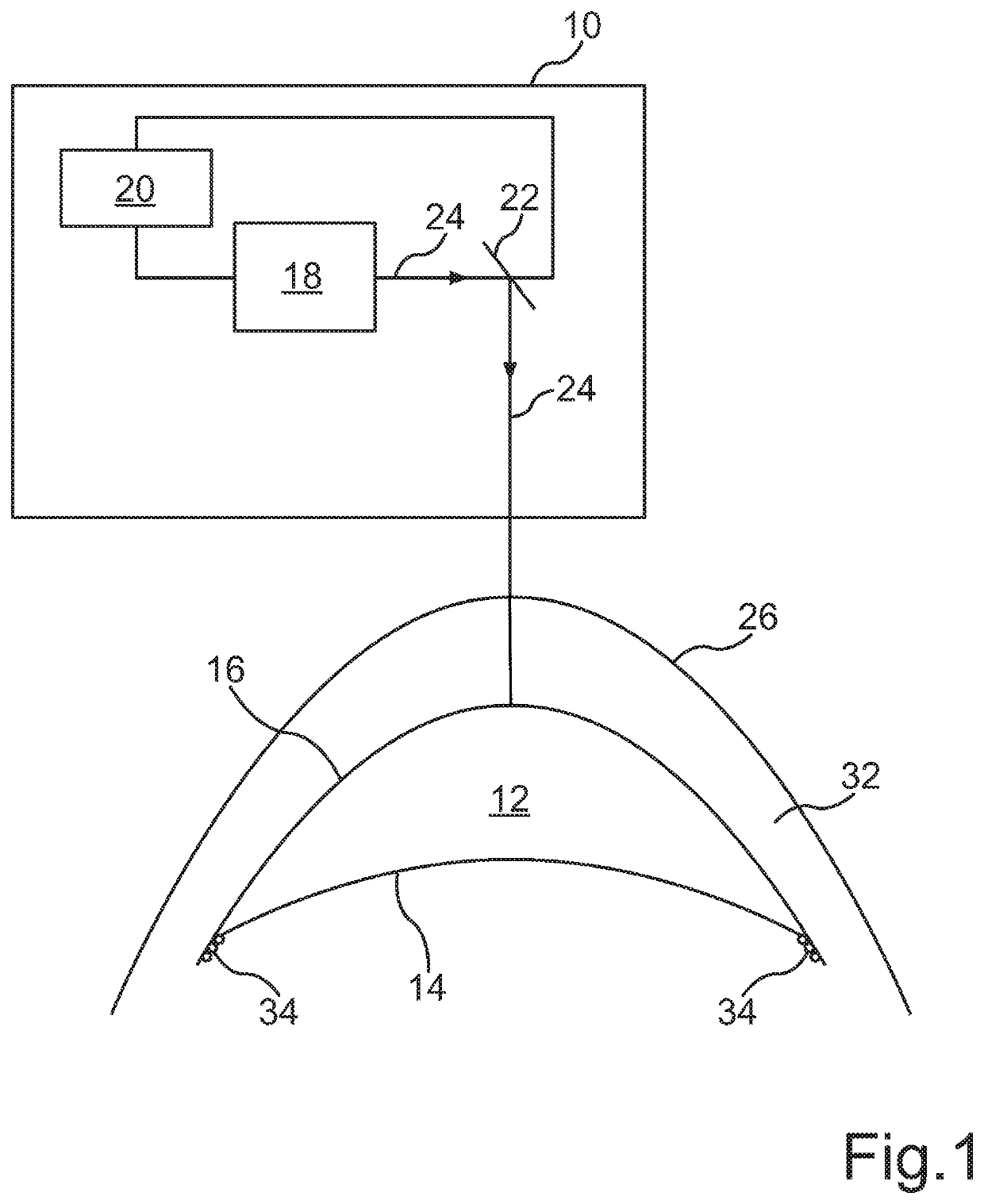
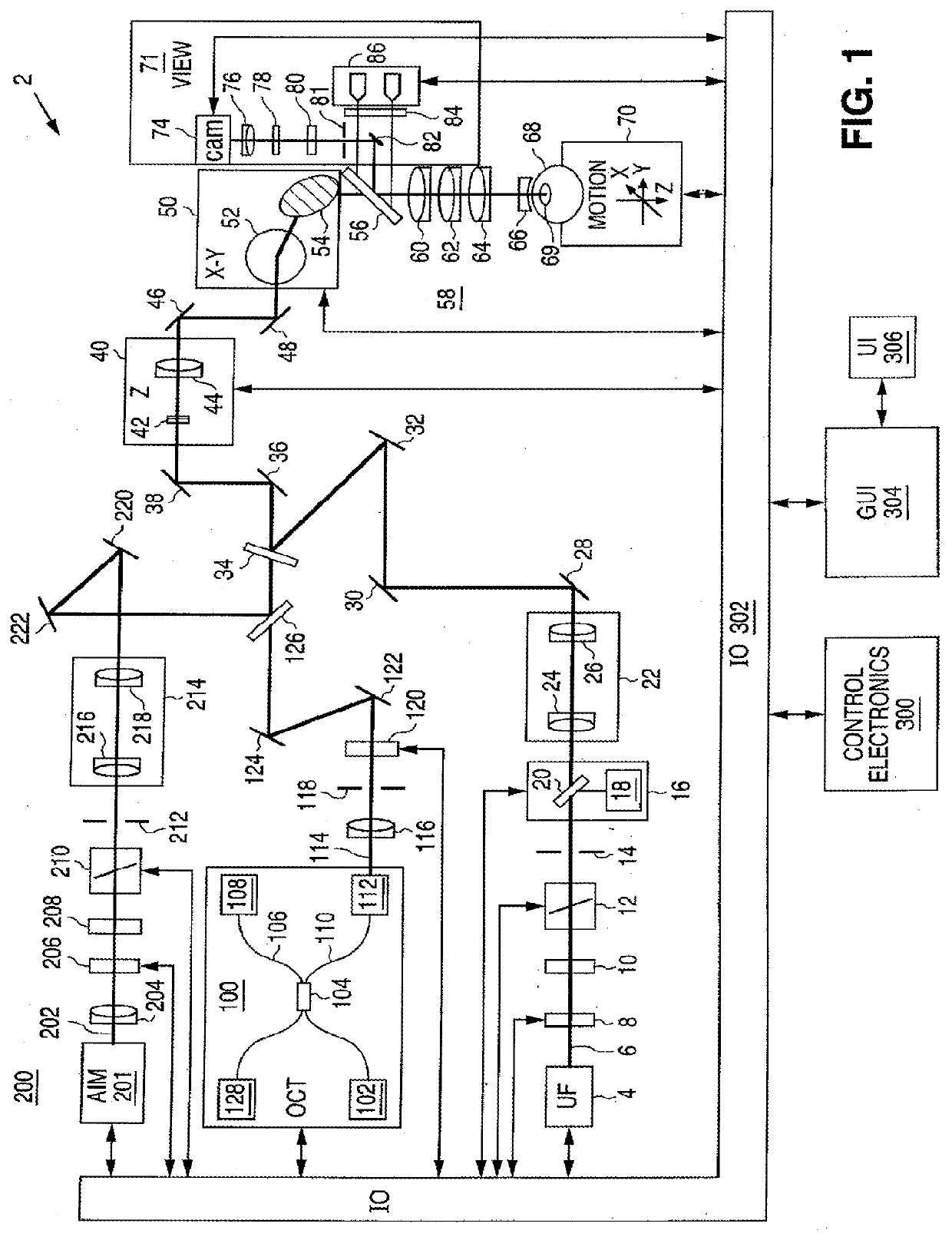
Optical System for Ophthalmic Surgical Laser
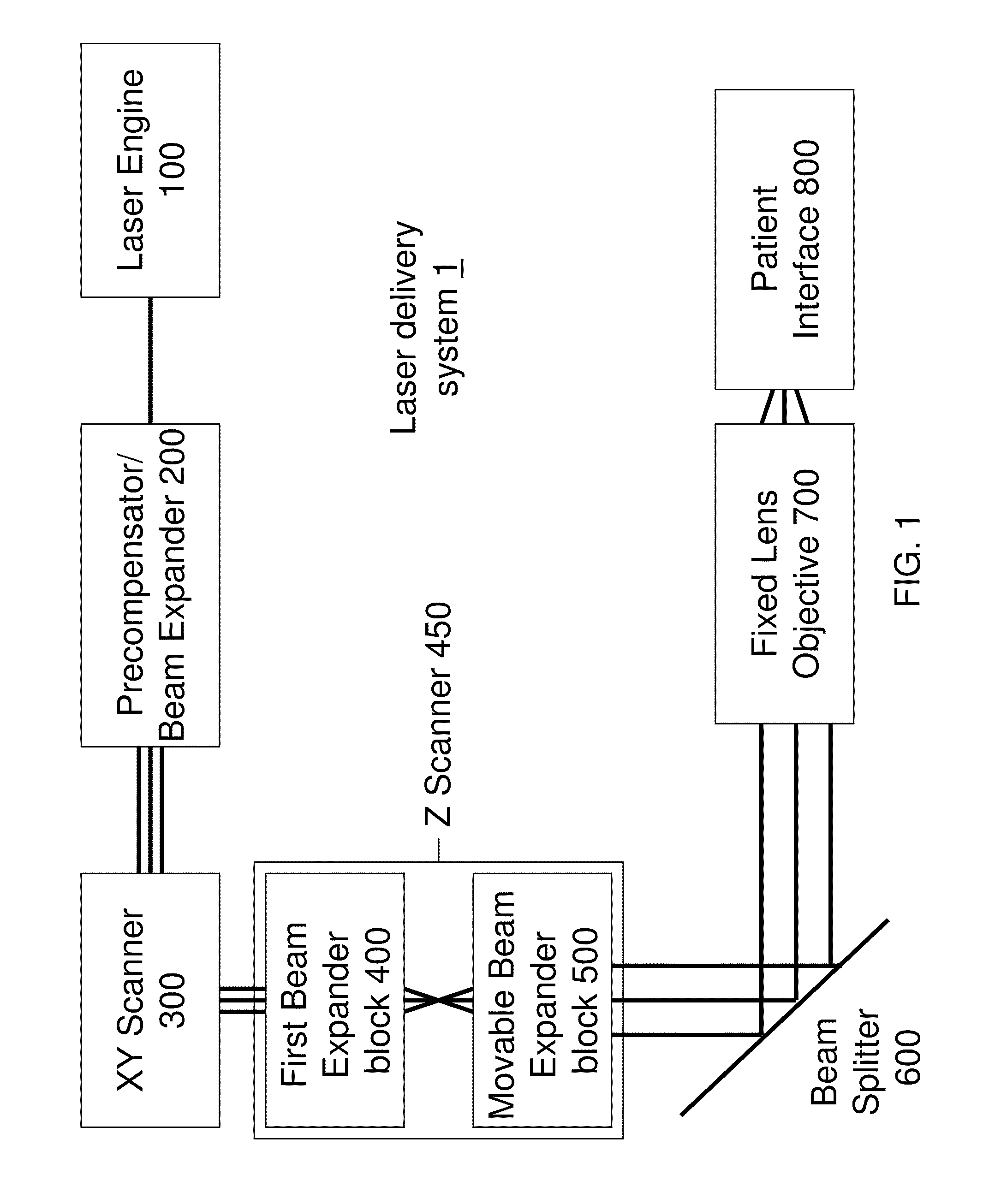
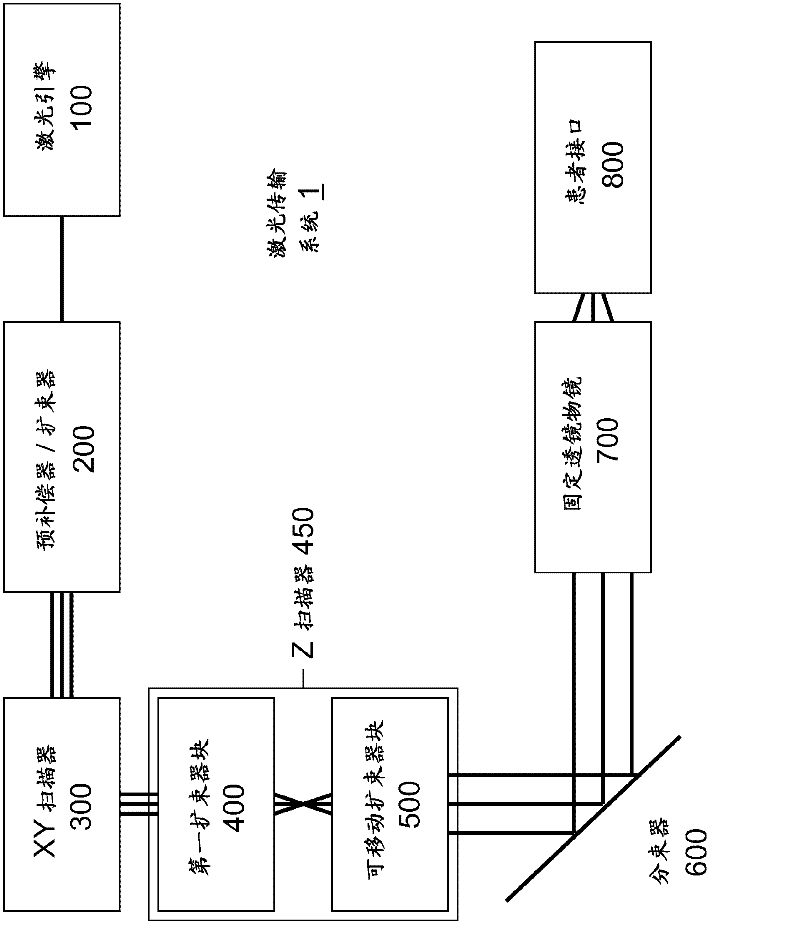
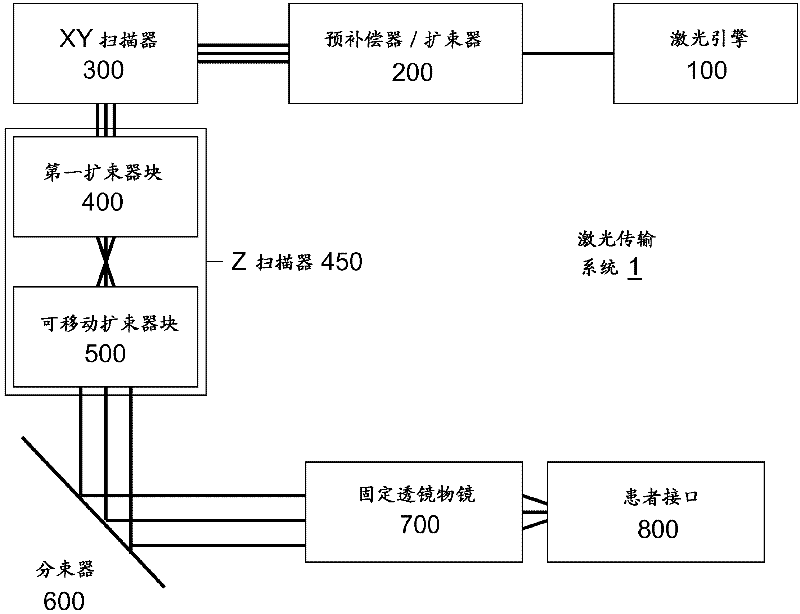
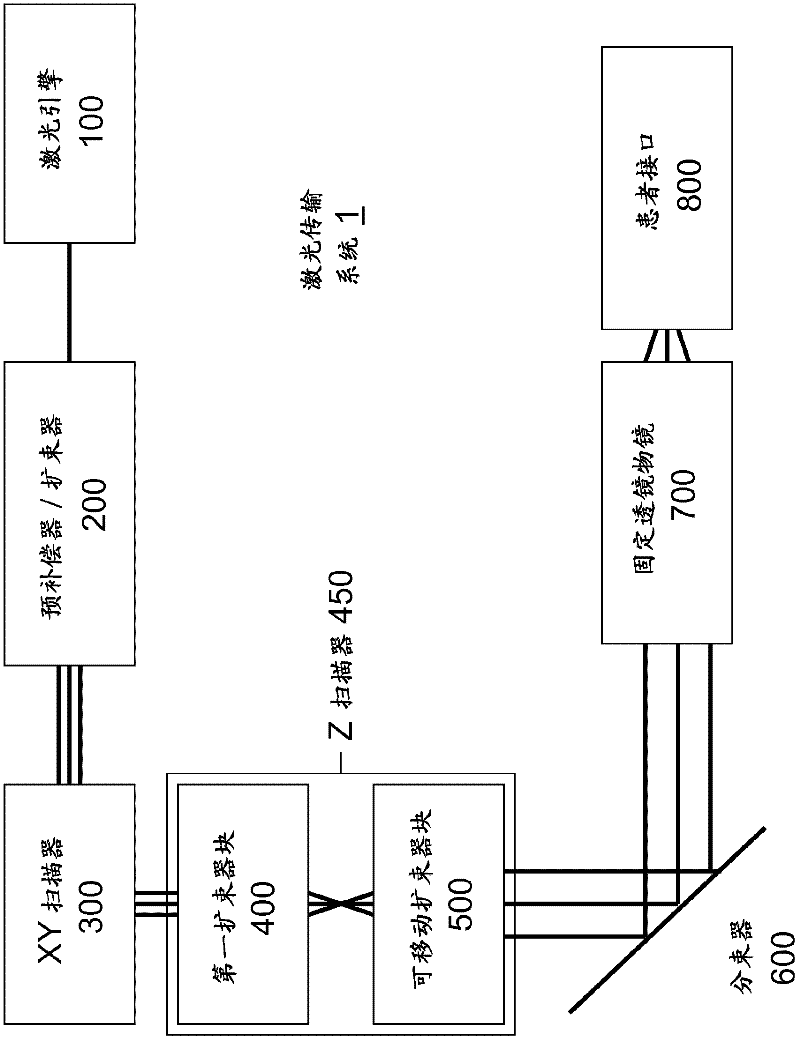
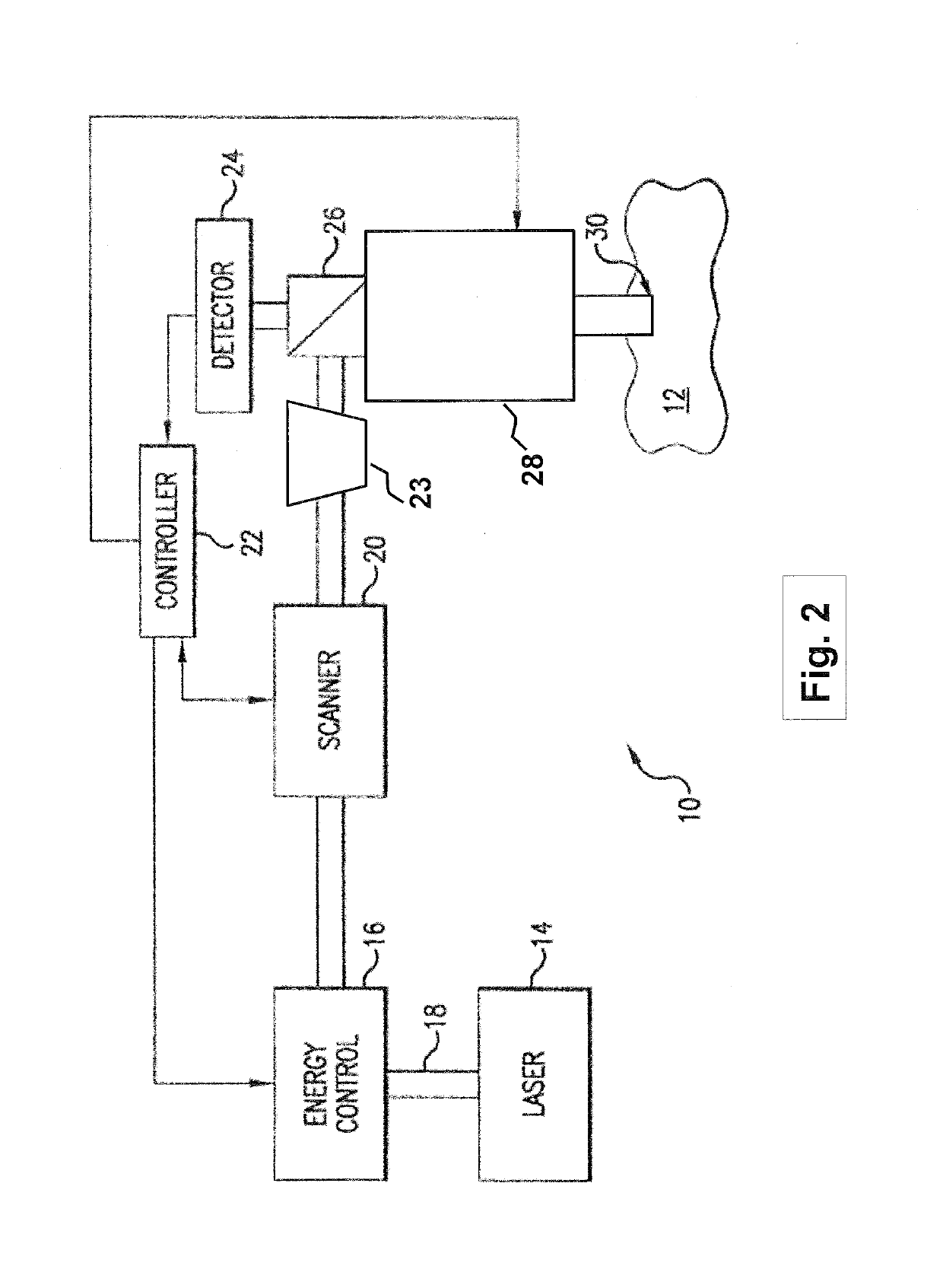
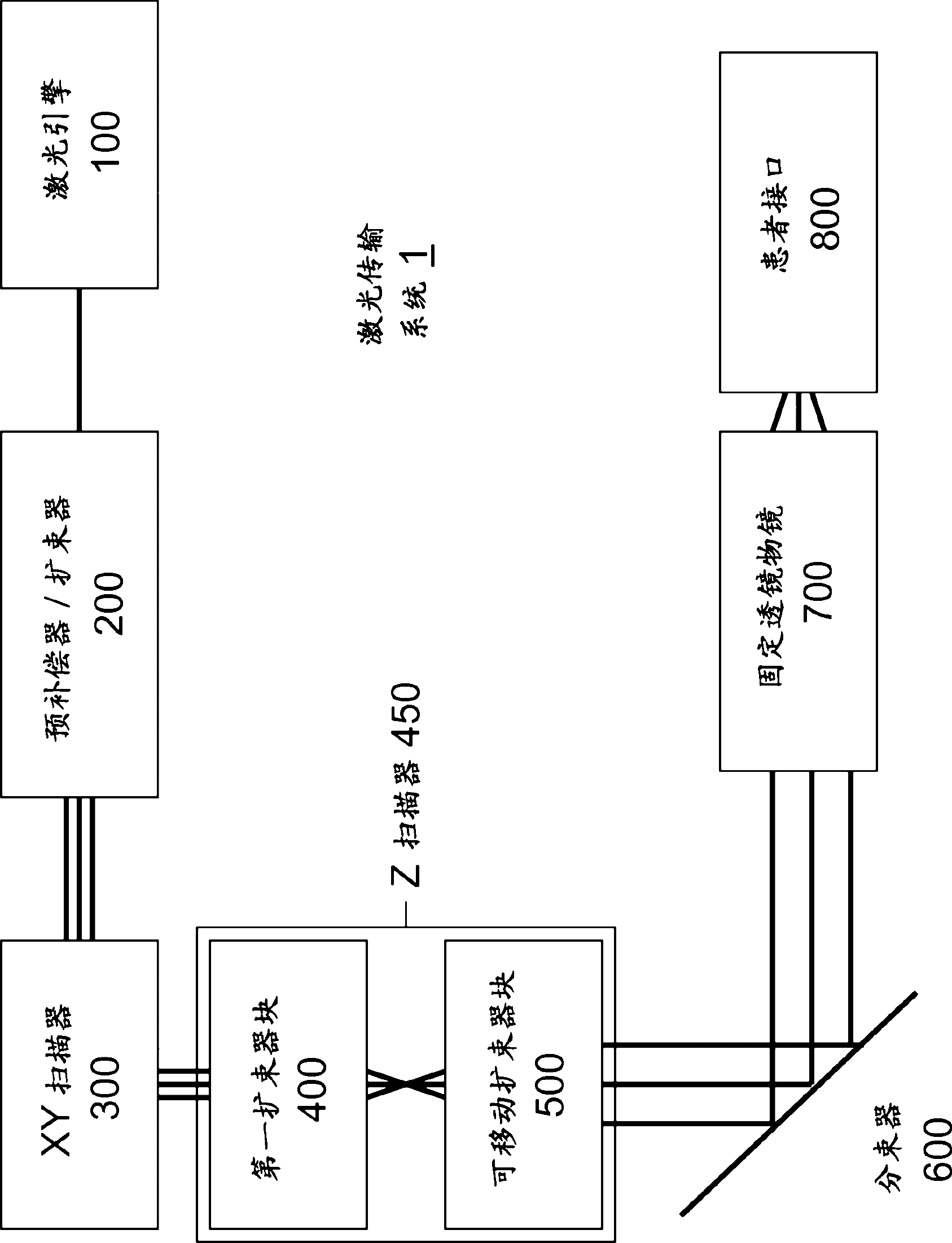
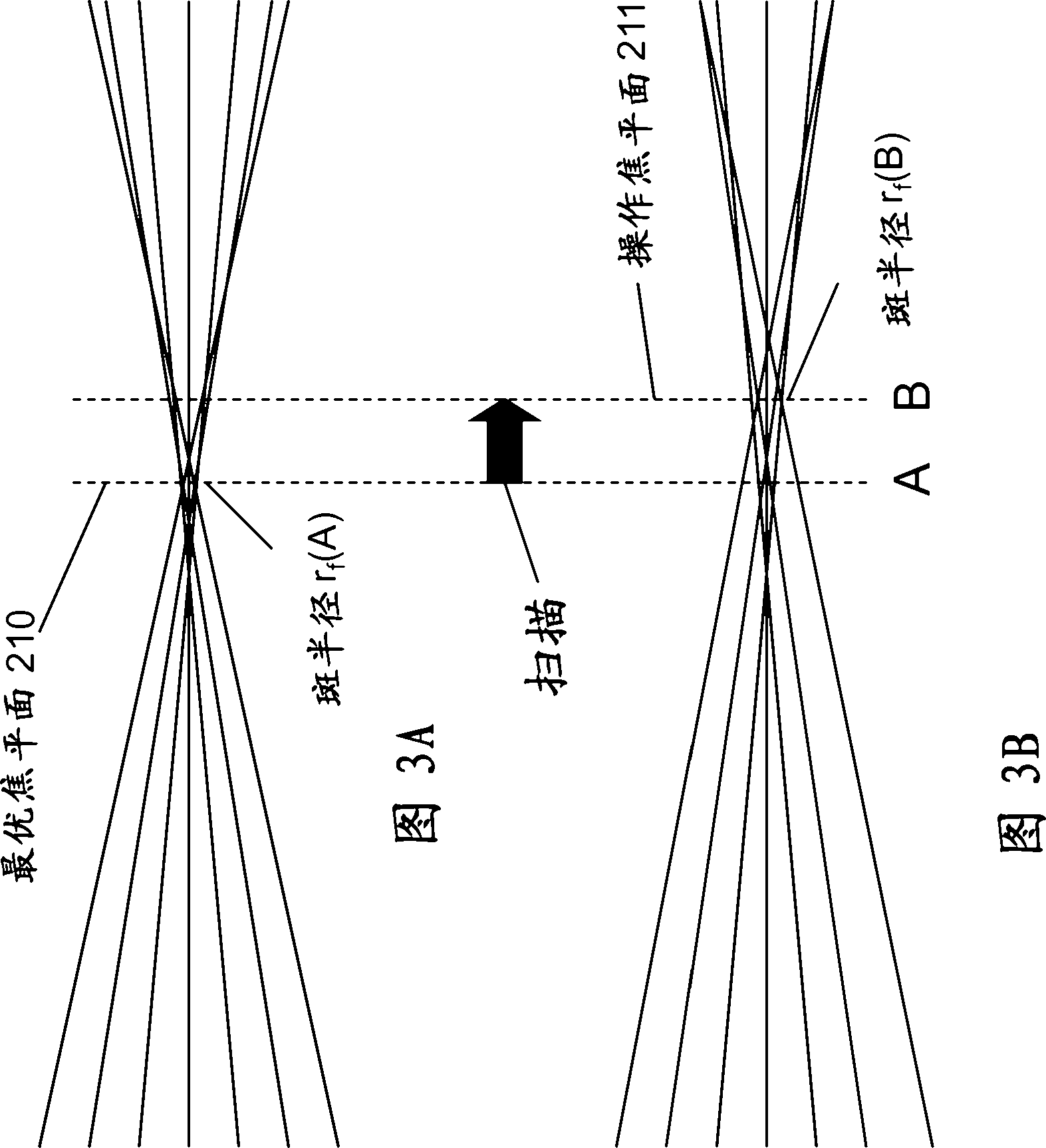
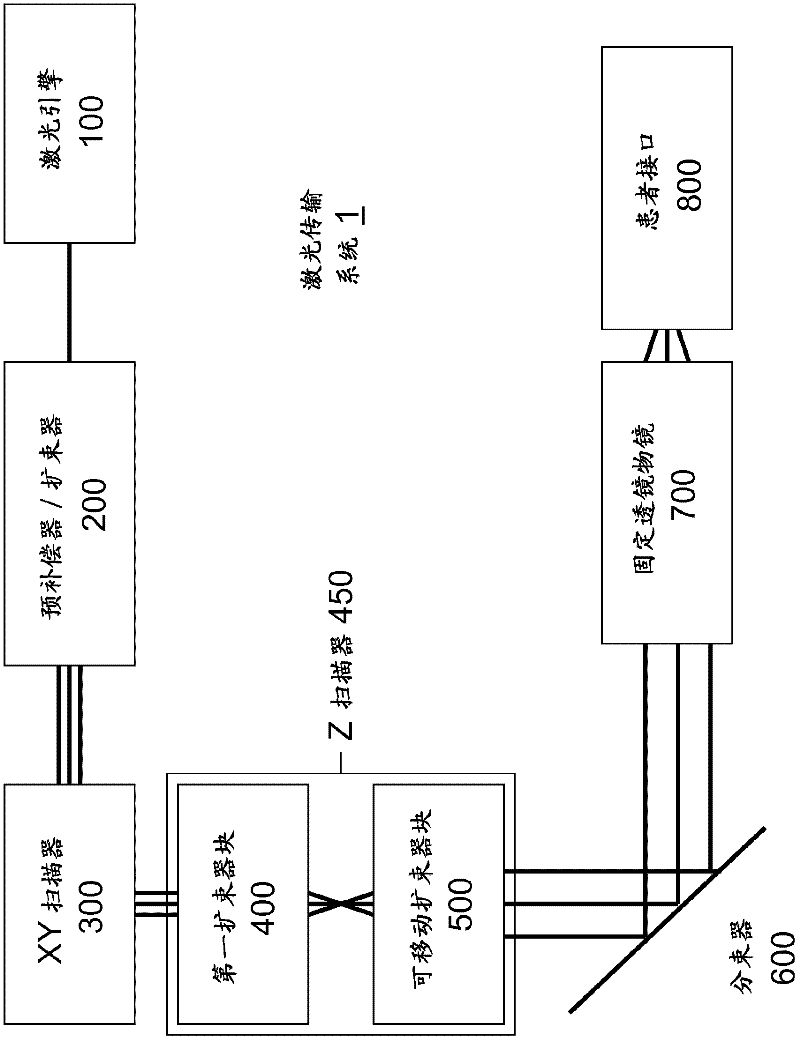
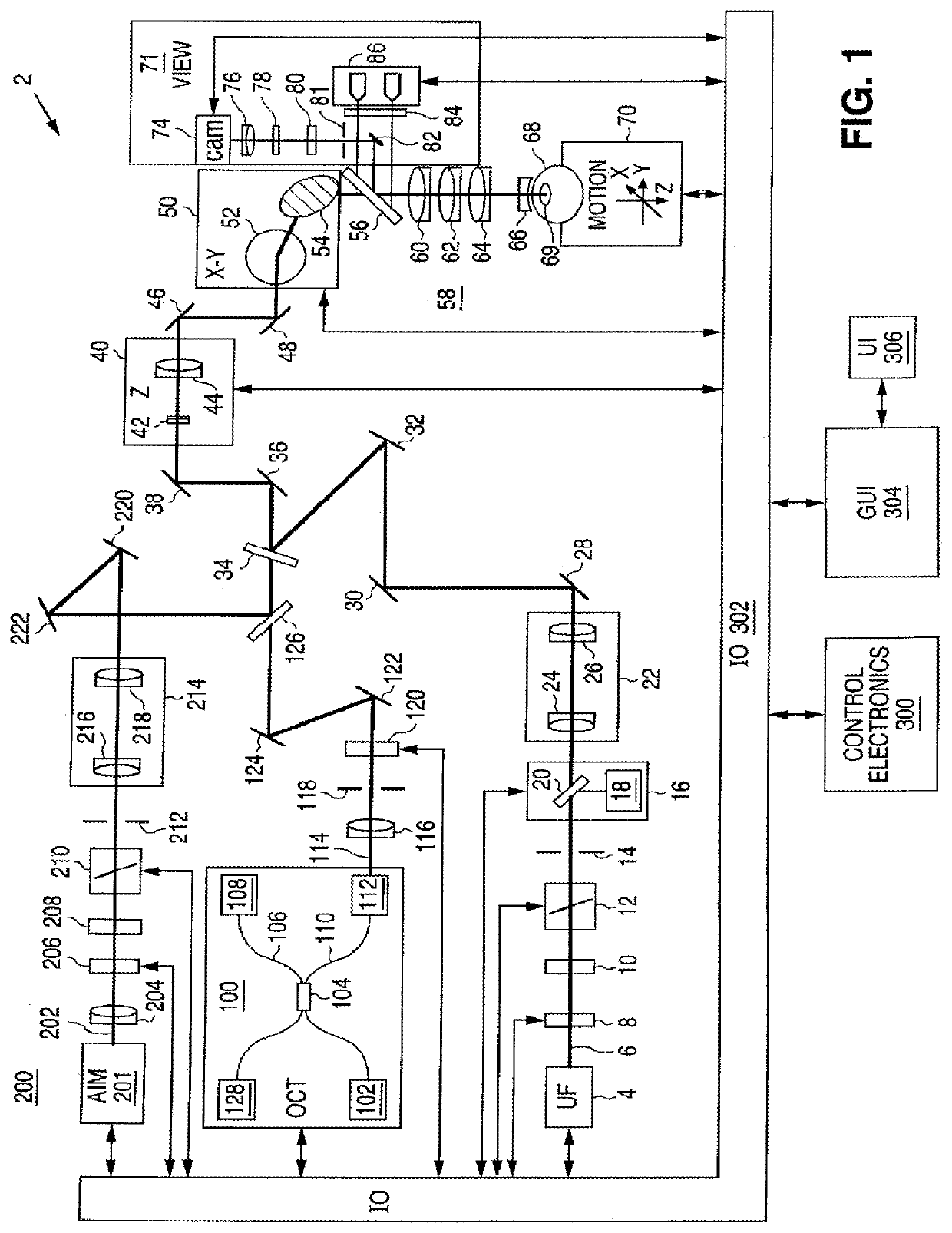
A laser delivery system for ophthalmic surgery includes a laser engine, configured to generate a laser beam, an optical block, to receive the laser beam generated by the laser engine and to precompensate an aberration of the laser beam, and an XY scanner, to receive, directly or indirectly, the precompensated laser beam outputted by the optical block and to scan the laser beam in a direction essentially transverse to an optical axis of the laser delivery system.
Owner:ALCON LENSX
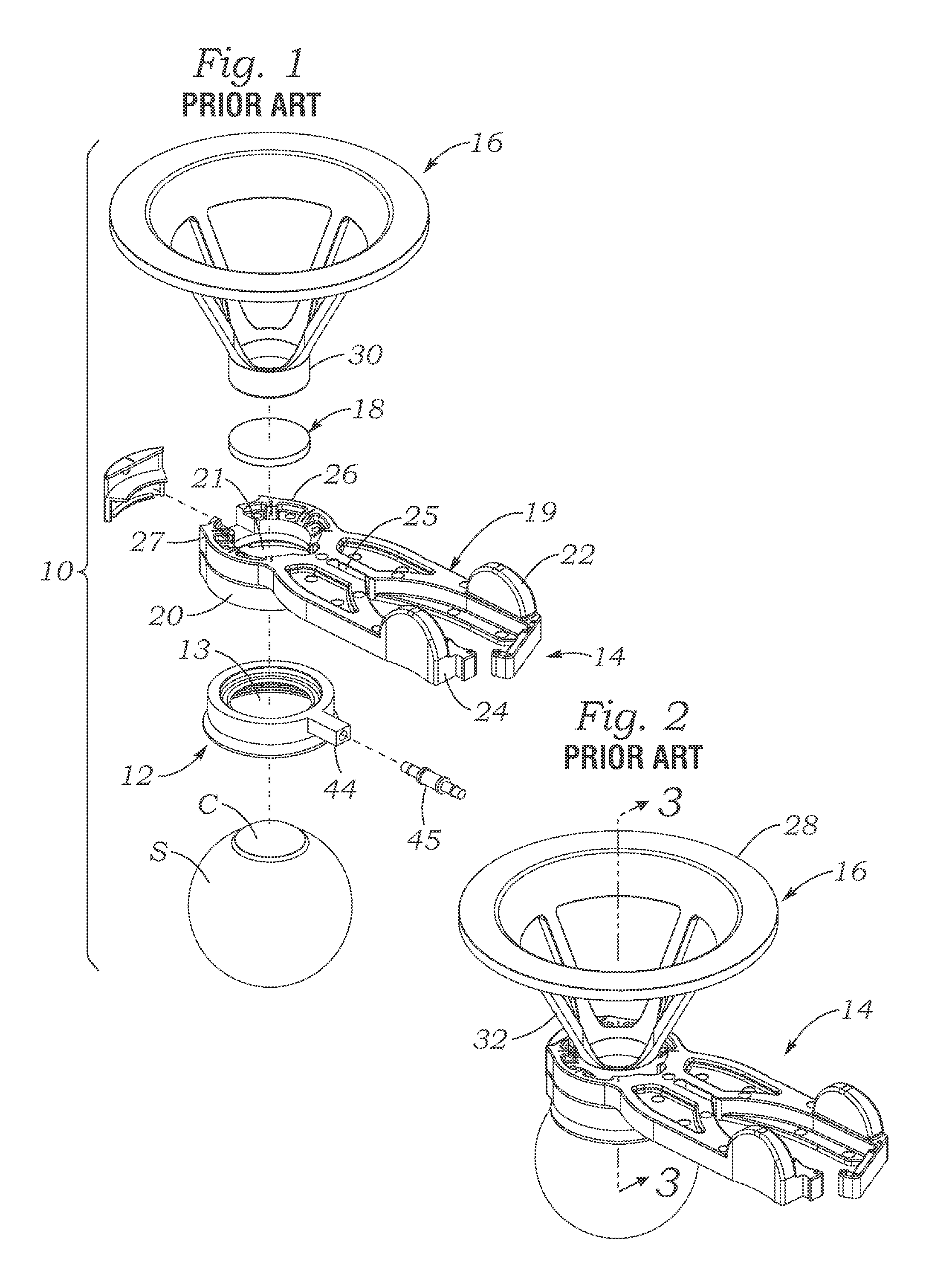
Hybrid ophthalmic interface apparatus
ActiveUS20140276673A1Sufficient flexibilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive index matchingDelivery system
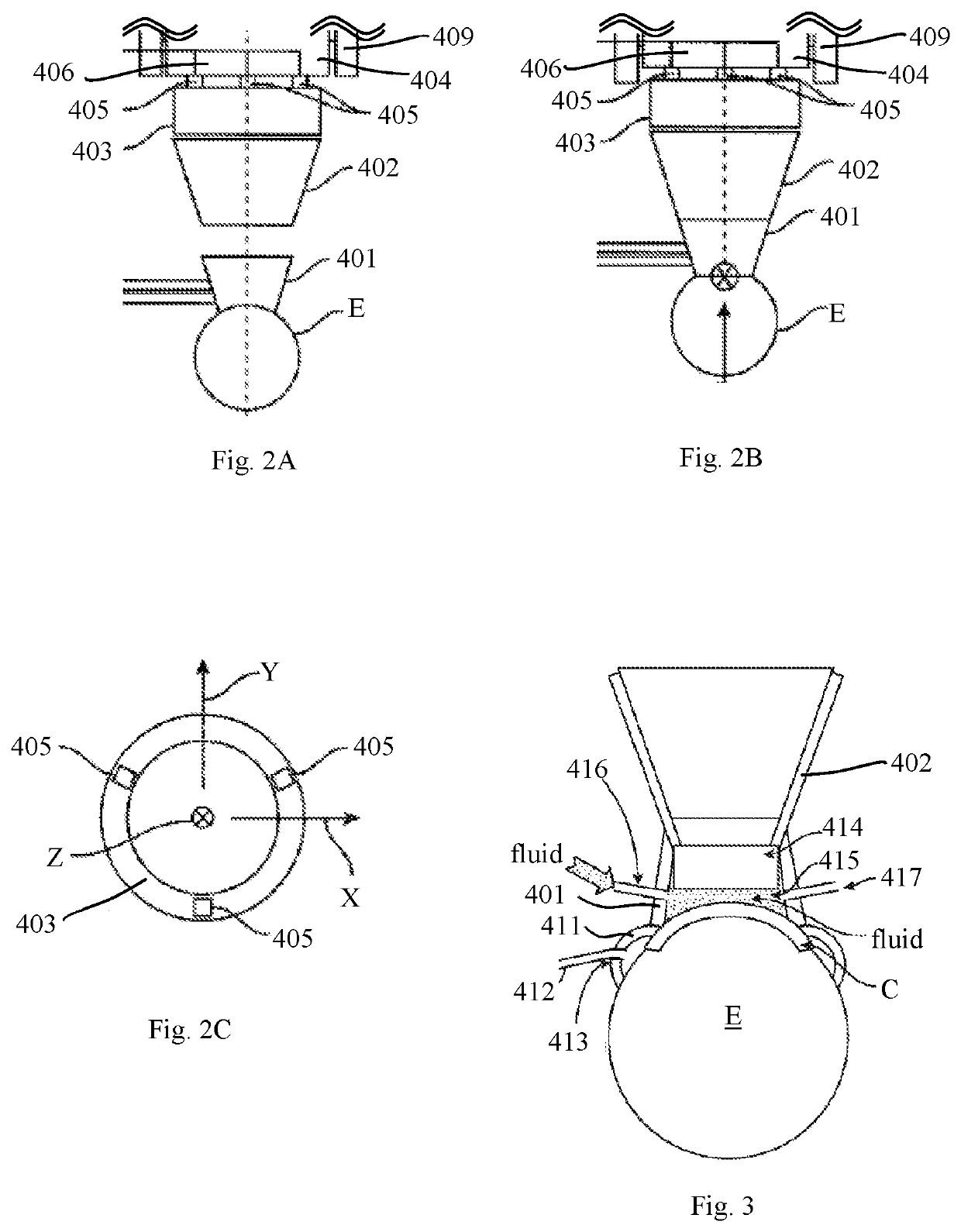
Apparatus and methods are provided for interfacing an ophthalmic surgical laser with an eye using a patient interface (PI). The PI may include a closed, fluid-filled bladder having fiducials that contacts and deforms to the eye. Or, the PI may have an applanation lens with an outer ring portion and an inner concave portion for receiving the apex of the cornea. Another PI features a suction ring with a flexible skirt for contacting the sclera that is non-circular and / or non-planar. A system for injecting an index matching fluid into the area above the eye may also be incorporated. An integrated system includes a co-molded lens cone and attachment ring, with a lens window at the bottom of the lens cone which provides a sealed volume for vacuum-attaching a laser delivery system above the lens cone.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
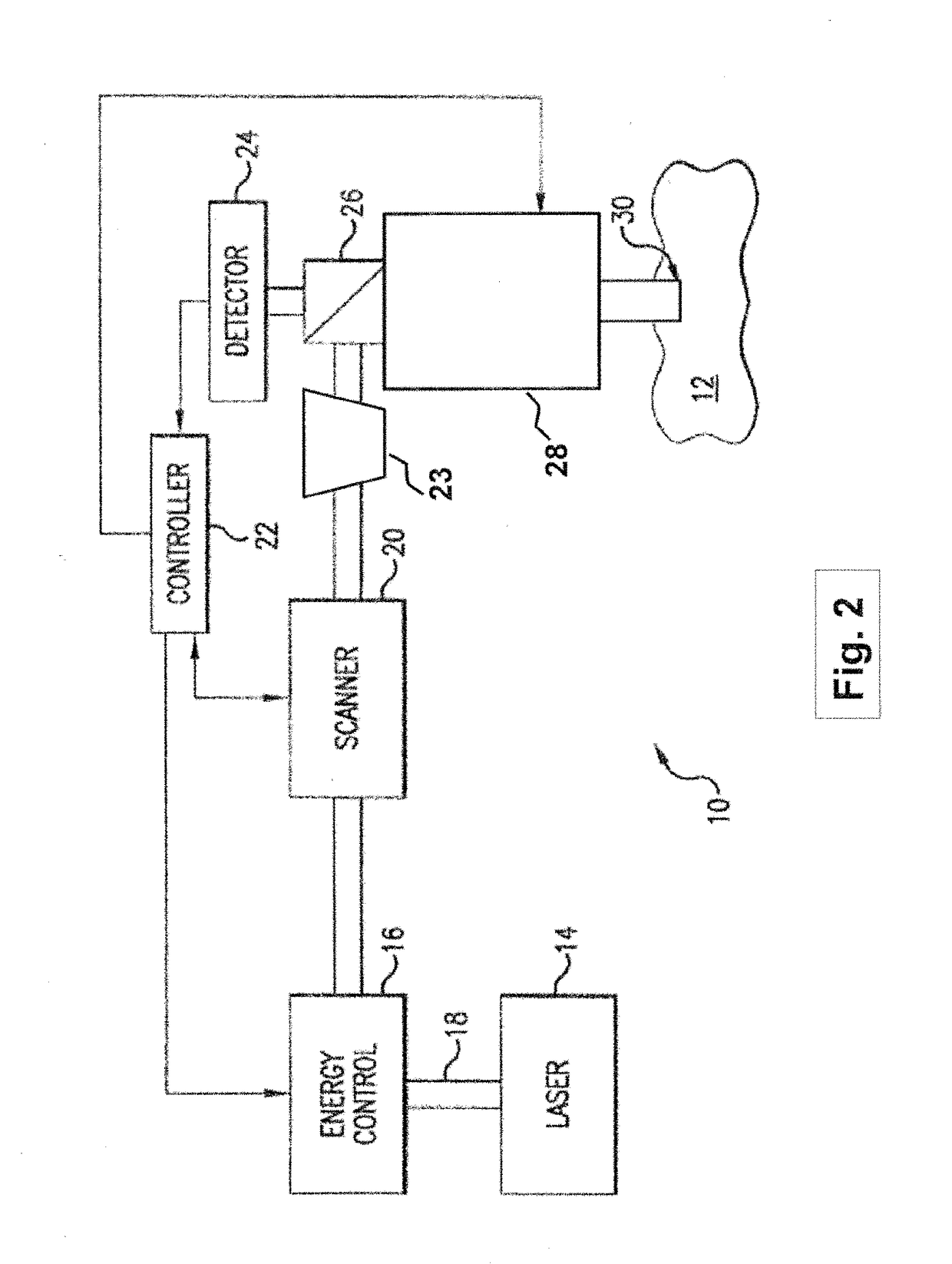
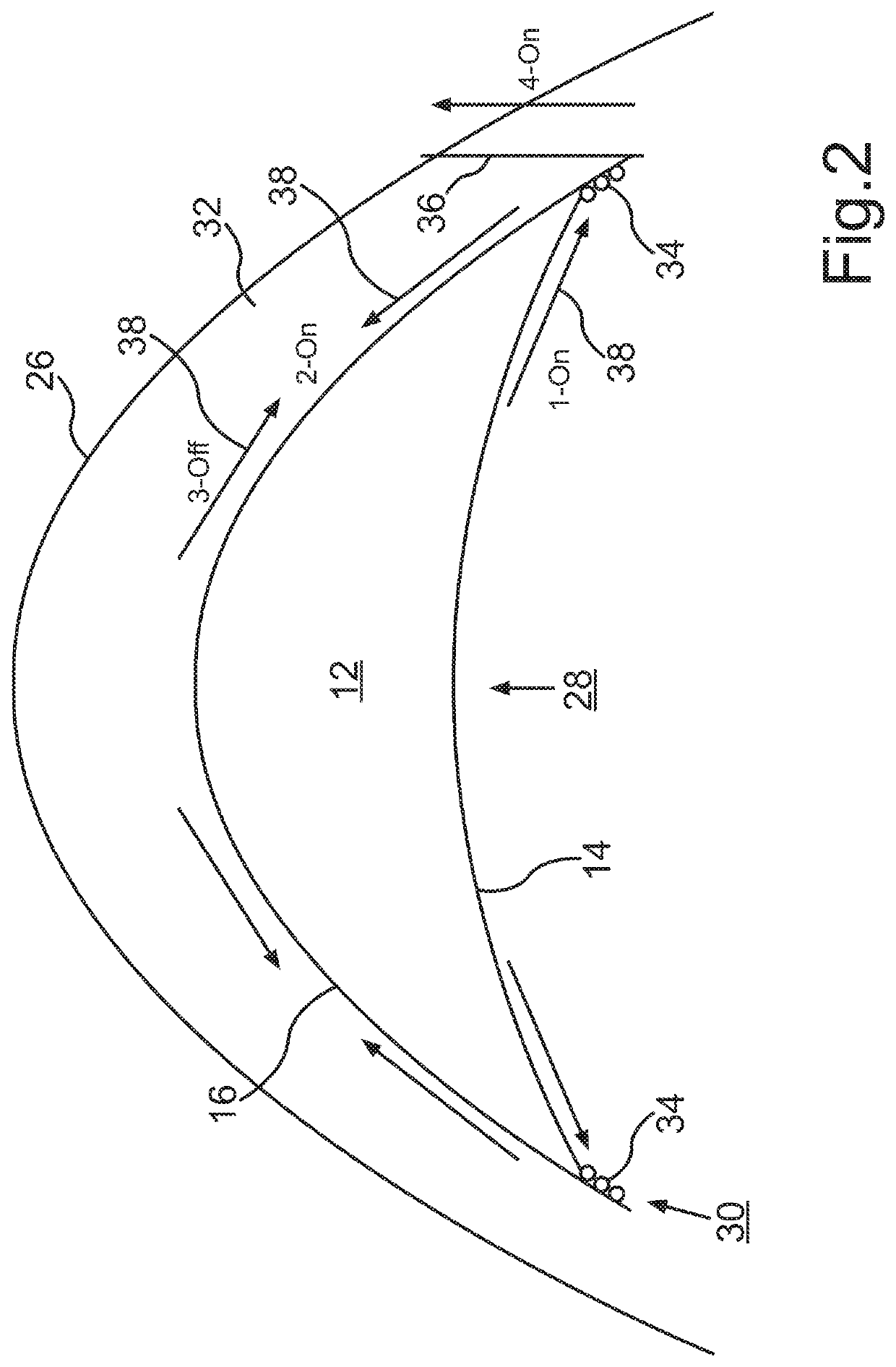
Systems and methods for synchronized three-dimensional laser incisions
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for creating synchronized three-dimensional laser incisions. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser delivery system for delivering a pulsed laser beam to a target in a subject's eye, an XY-scan device to deflect the pulsed laser beam, a Z-scan device to modify a depth of a focus of the pulsed laser beam, and a controller configured to synchronize an oscillation of the XY-scan device and an oscillation of the Z-device to form an angled three-dimensional laser tissue dissection.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Optical system with movable lens for ophthalmic surgical laser
An eye-surgical laser system includes a laser source, to generate a laser beam, an XY scanner, to scan a focal spot of a received laser beam in an XY direction essentially transverse to an optical axis of the laser system, and a lens group, disposed in the optical path between the laser source and the XY scanner, to receive the laser beam generated by the laser source, to precompensate an aberration of the laser beam, and to forward the precompensated laser beam to the XY scanner, the lens group having a movable lens, movable in a Z direction along an optical axis.
Owner:ALCON LENSX
Optical system for ophthalmic surgical laser
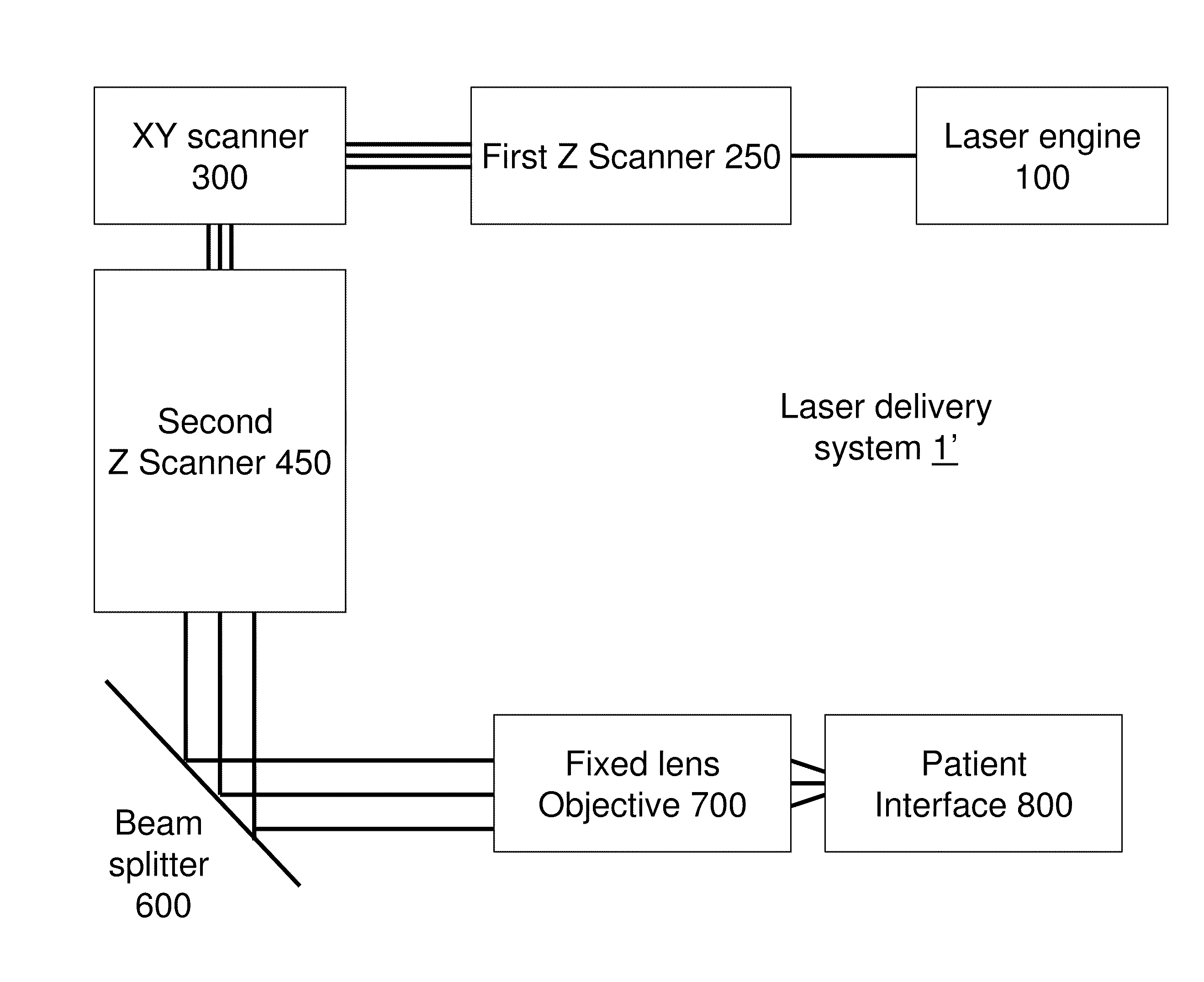
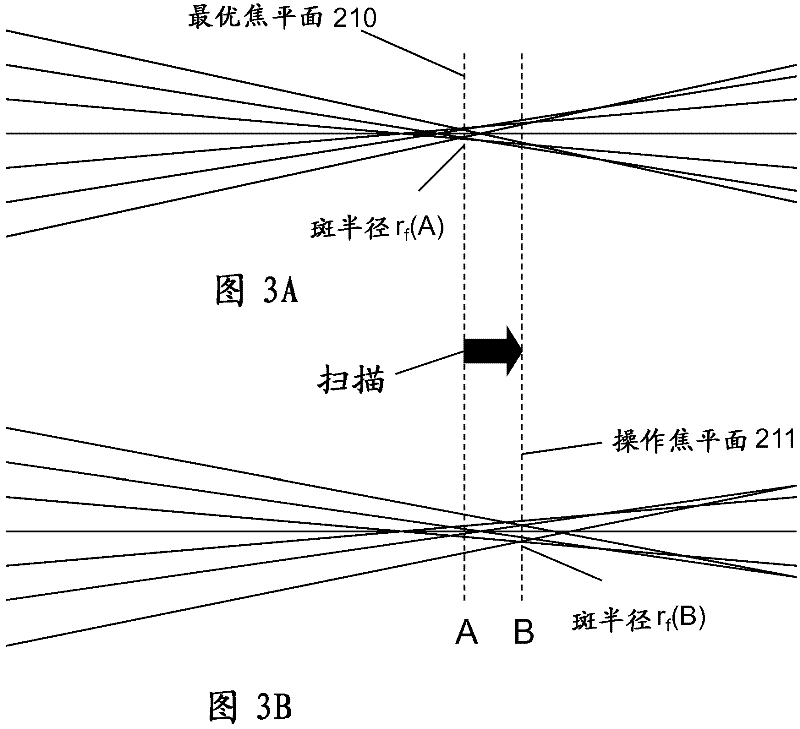
A laser system for ophthalmic surgery includes a laser source to produce a surgical pulsed laser beam, an XY scanner to scan the surgical pulsed laser beam in XY transverse directions, a Z scanner, to scan the XY scanned laser beam along a Z axis, an objective, to focus the XYZ scanned beam into a focal spot in a target region, and a computational controller, to use a computational process to control at least one of the Z scanner and the XY scanner, to control an optical distortion of the focused scanned beam.
Owner:ALCON INC
Optical system for ophthalmic surgical laser
A laser system for ophthalmic surgery includes a laser source, to generate a pulsed laser beam, an XY scanner, to receive the pulsed laser beam, and to output an XY-scanning beam, scanned in two directions transverse to a Z axis, a Z scanner, to receive the XY-scanning beam, and to output an XYZ-scanning beam, scanned in addition along the Z axis, the Z scanner including a first lens group to output a beam having an intermediate focal plane, and a movable lens group to receive the beam through the intermediate focal plane and to collimate the beam in a variable manner, and an objective to receive the collimated beam from the Z scanner and to focus the beam into a focal spot in a target region.
Owner:ALCON INC
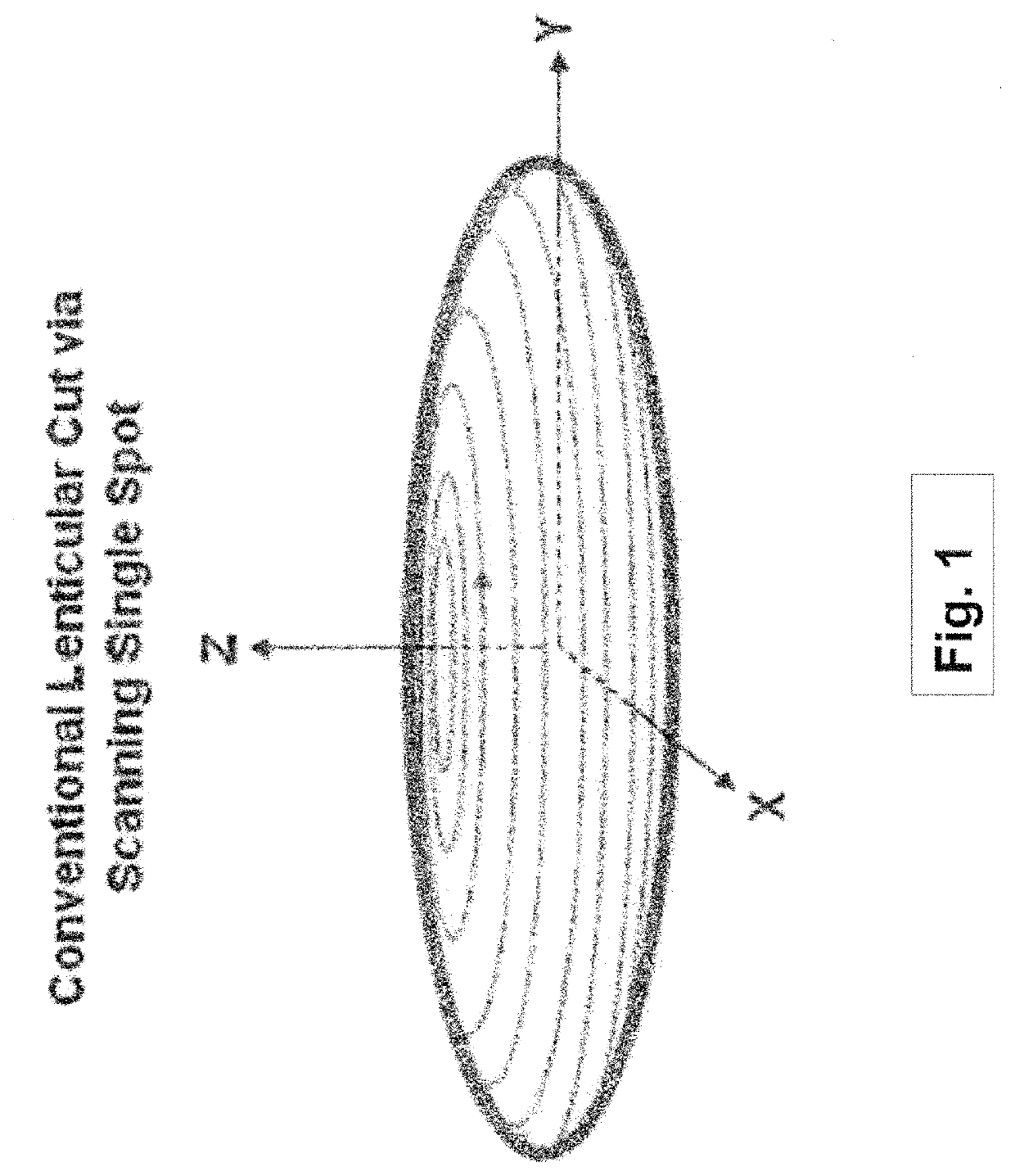
Systems and methods for lenticular laser incision
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Systems and methods for lenticular laser incision
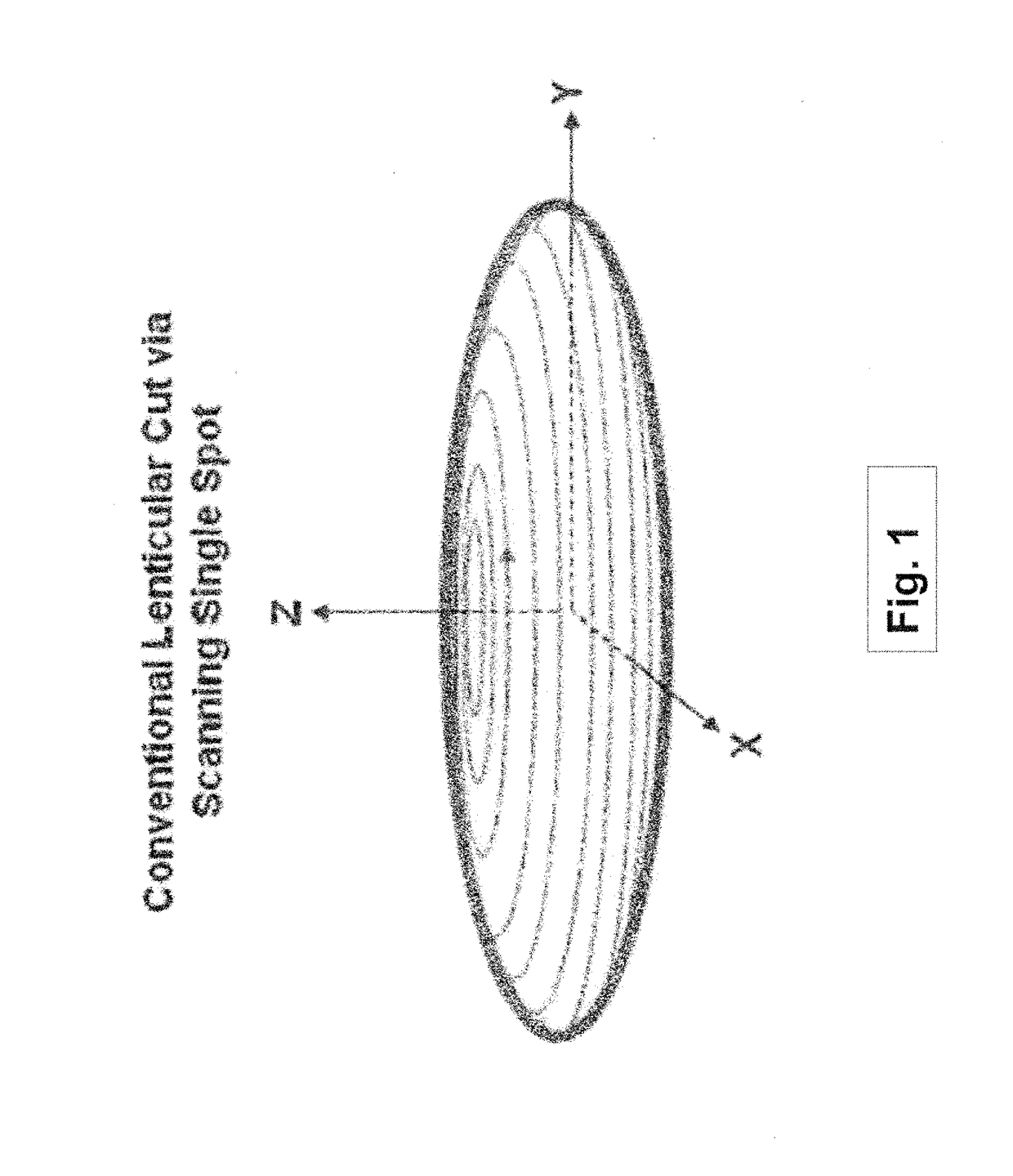
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for lenticular laser incision. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser delivery system for delivering a pulsed laser beam to a target in a subject's eye, an XY-scan device to deflect the pulsed laser beam, a Z-scan device to modify a depth of a focus of the pulsed laser beam, and a controller configured to form a top lenticular incision and a bottom lenticular incision of a lens in the subject's eye, where each of the top and bottom lenticular incision includes a center spherical portion and an edge transition portion that is not located on the same spherical surface as the spherical portion but has a steeper shape.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Systems and methods for femtosecond laser photorefractive keratectomy
ActiveUS20160250074A1Correct distortionConvenient treatmentLaser surgeryFemto second laserLaser procedure
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for photorefractive keratectomy. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser source generating a pulsed laser beam and a laser delivery system delivering the pulsed laser beam to a cornea of an eye. A patient interface couples to and constrains the eye relative to the laser delivery system. A controller controls the laser delivery system to perform an anterior surface volume dissection on the cornea.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
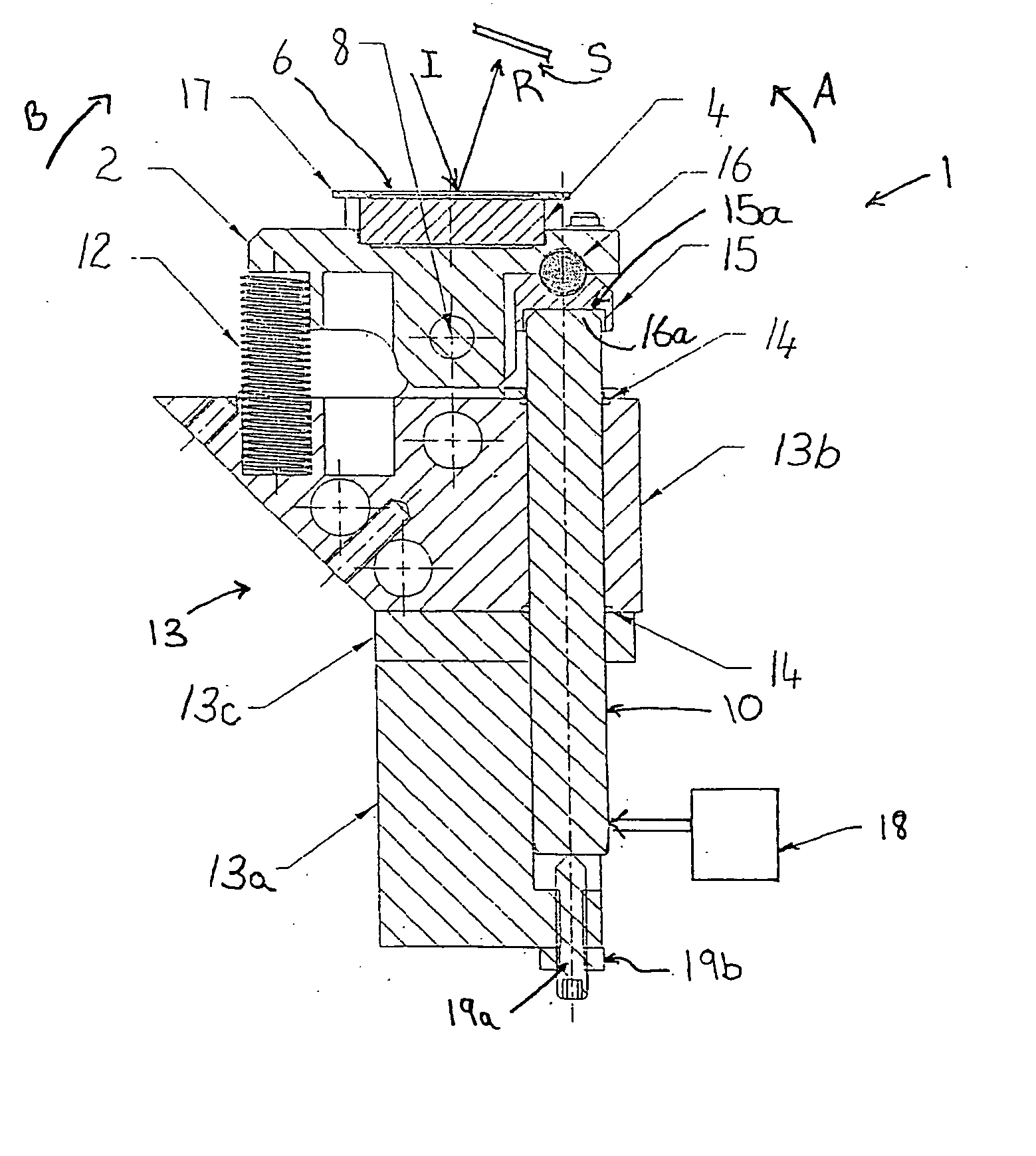
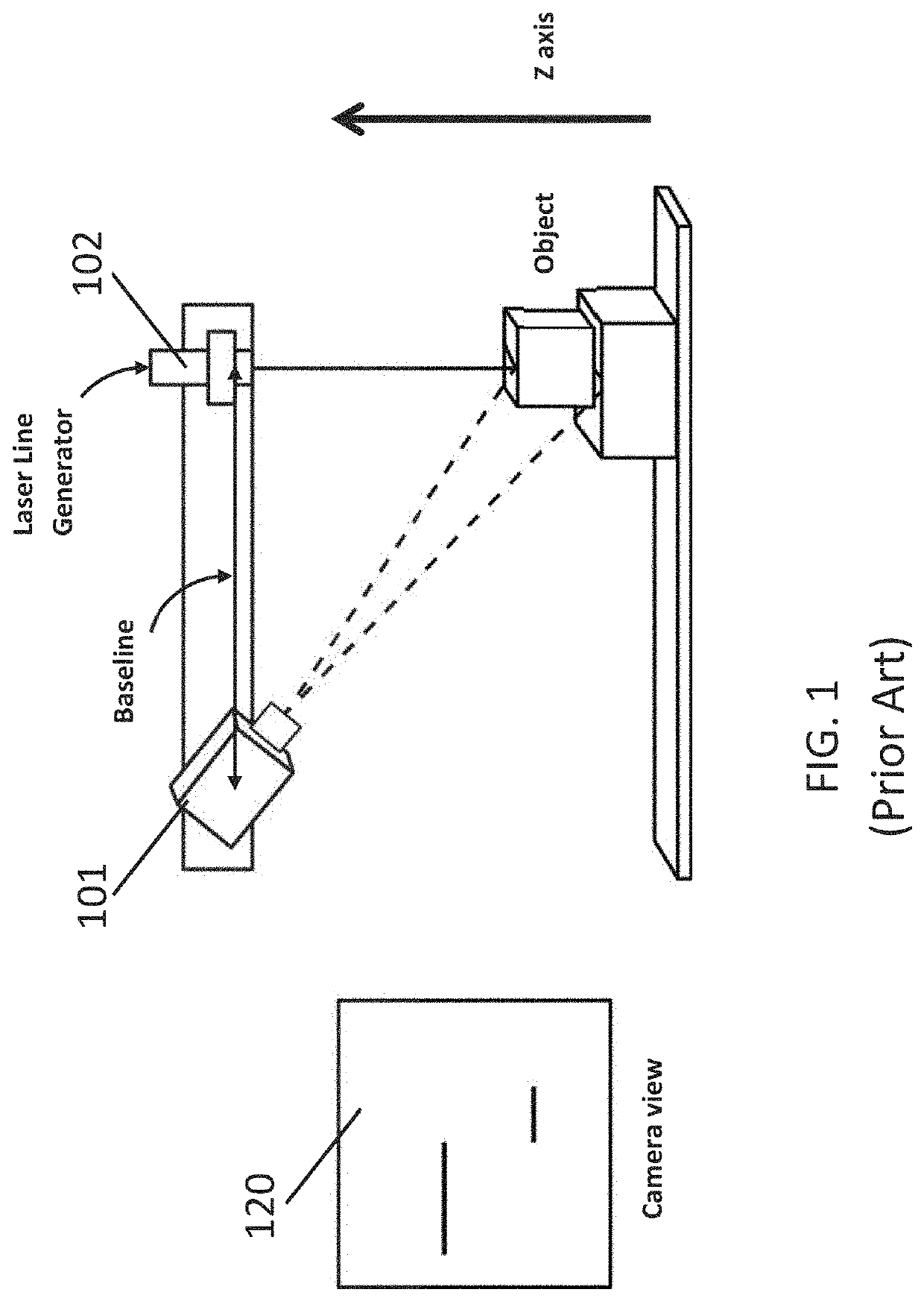
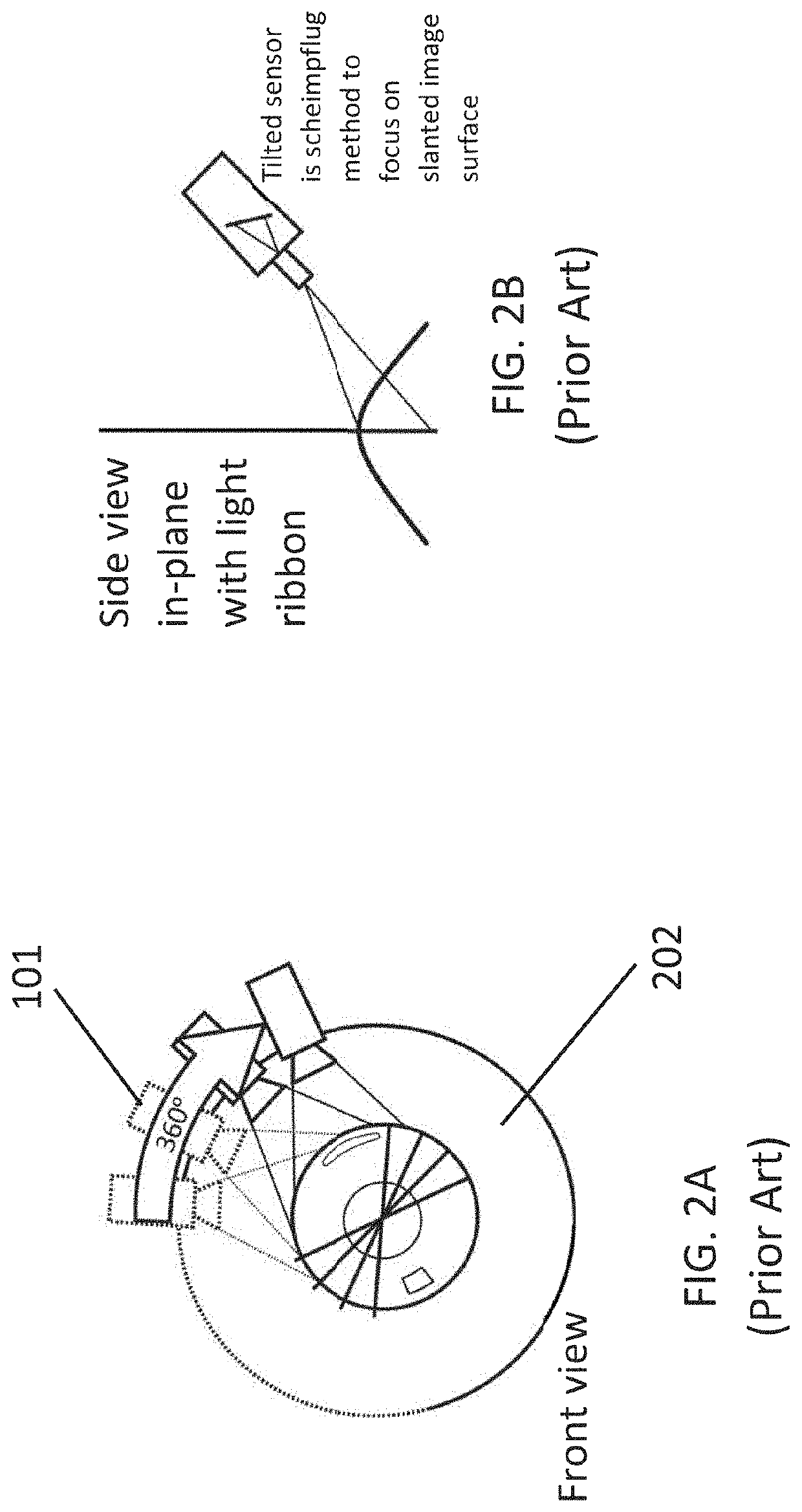
Scanning device and method of scanning an optical beam over a surface
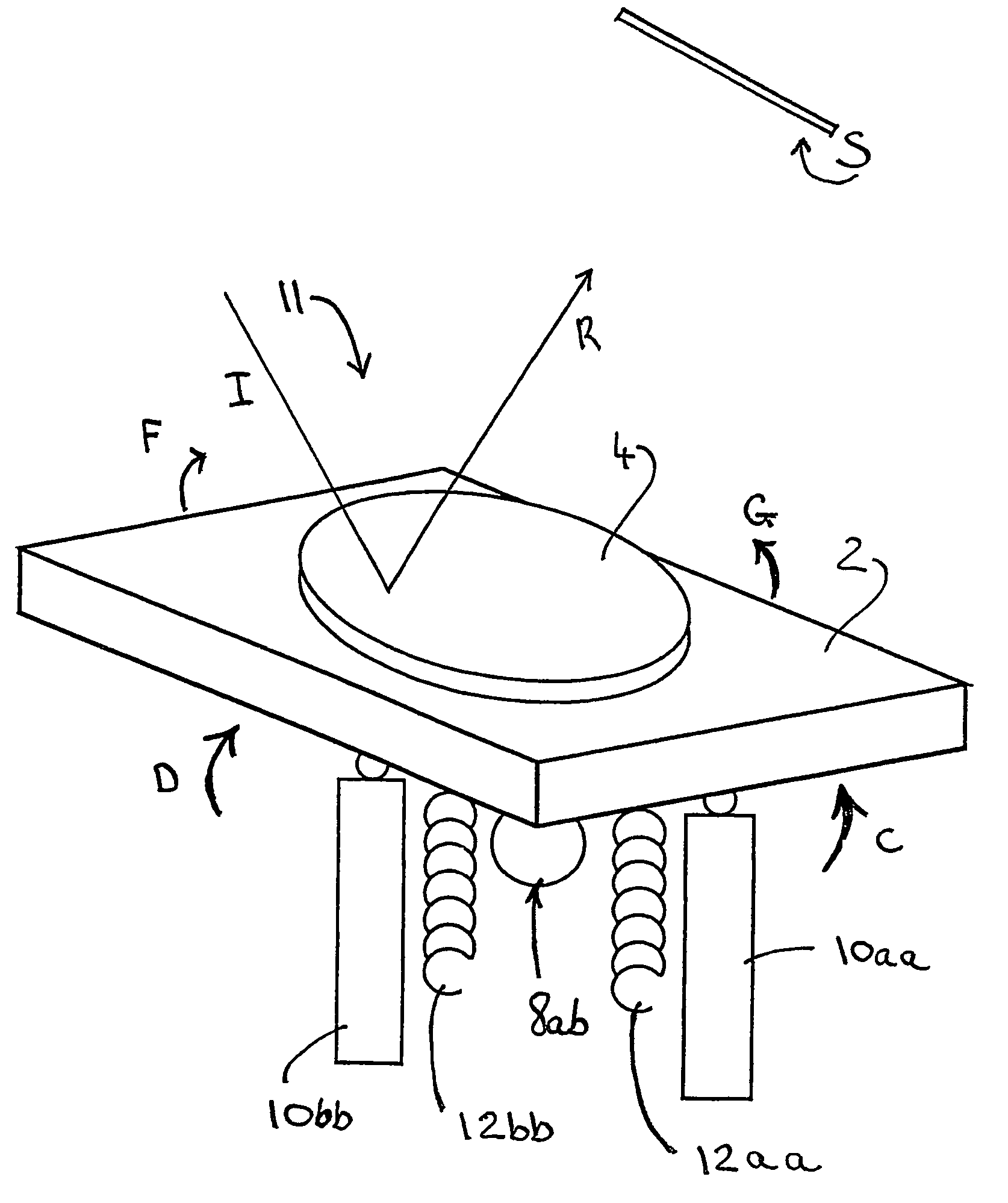
An optical scanning device (1) to scan an optical beam over a surface (S). The optical scanning device (1) uses a piezoelectric actuator (10) acting on a platform (2) that carries a mirror (4) to pivot the platform (2) about a pivot (8). Voltage is applied to the piezoelectric actuator (10) to pivot the platform (2) about the pivot (8). Changes in the applied voltage result in the angle at which the beam is reflected by the mirror (4) being altered. In this way, the reflected beam (R) can be scanned to different locations on the surface (S). Providing two such optical scanning devices (1a, 1b) or using two piezoelectric actuators (10aa, 10bb) acting on a single platform (2) enables two dimensional scanning of the surface (S) by the optical scanning device / s (1,1a, 1b). The optical scanning device (1) of the present invention may be used in refractive eye surgery laser apparatus.
Owner:CLVR
Optical system for ophthalmic surgical laser
An ophthalmic laser system includes a laser source, to generate a pulsed laser beam, an XY scanner, to receive the pulsed laser beam, and to output an XY-scanning beam, scanned in two directions essentially transverse to an optical axis, and a multi-functional Z scanner, to receive the XY-scanning beam, to output an XYZ-scanning beam, having a numerical aperture NA and a focal spot in a target region, and to modify the numerical aperture NA essentially independently from scanning a Z focal depth of the focal spot along the optical axis.
Owner:ALCON INC
Hybrid ophthalmic interface apparatus
Apparatus and methods are provided for interfacing an ophthalmic surgical laser with an eye using a patient interface (PI). The PI may include a closed, fluid-filled bladder having fiducials that contacts and deforms to the eye. Or, the PI may have an applanation lens with an outer ring portion and an inner concave portion for receiving the apex of the cornea. Another PI features a suction ring with a flexible skirt for contacting the sclera that is non-circular and / or non-planar. A system for injecting an index matching fluid into the area above the eye may also be incorporated. An integrated system includes a co-molded lens cone and attachment ring, with a lens window at the bottom of the lens cone which provides a sealed volume for vacuum-attaching a laser delivery system above the lens cone.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Systems and methods for high speed modulation of a resonant scanner in ophthalmic laser applications
An ophthalmic surgical laser system includes: a laser that produces a pulsed laser beam having a pulse energy and pulse repetition rate; a high frequency fast scanner; an XY-scan device; a Z-scan device; and a controller. The controller controls the high frequency scanner to produce a scan line having a scan width; controls the XY-scan device and the Z-scan device to carry out of first sweep of the scan line in a first sweep direction and to carry out a second sweep of the scan line in a second sweep direction that is not parallel to the first sweep direction thereby defining an overlap region. At least one of the pulse energy, repetition rate, XY-scan speed, and the scan width is varied so as to accelerate the cutting speed and reduce the exposure of ophthalmic tissue in the overlap region to multiple exposures of laser pulses configured to modify ophthalmic tissue.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
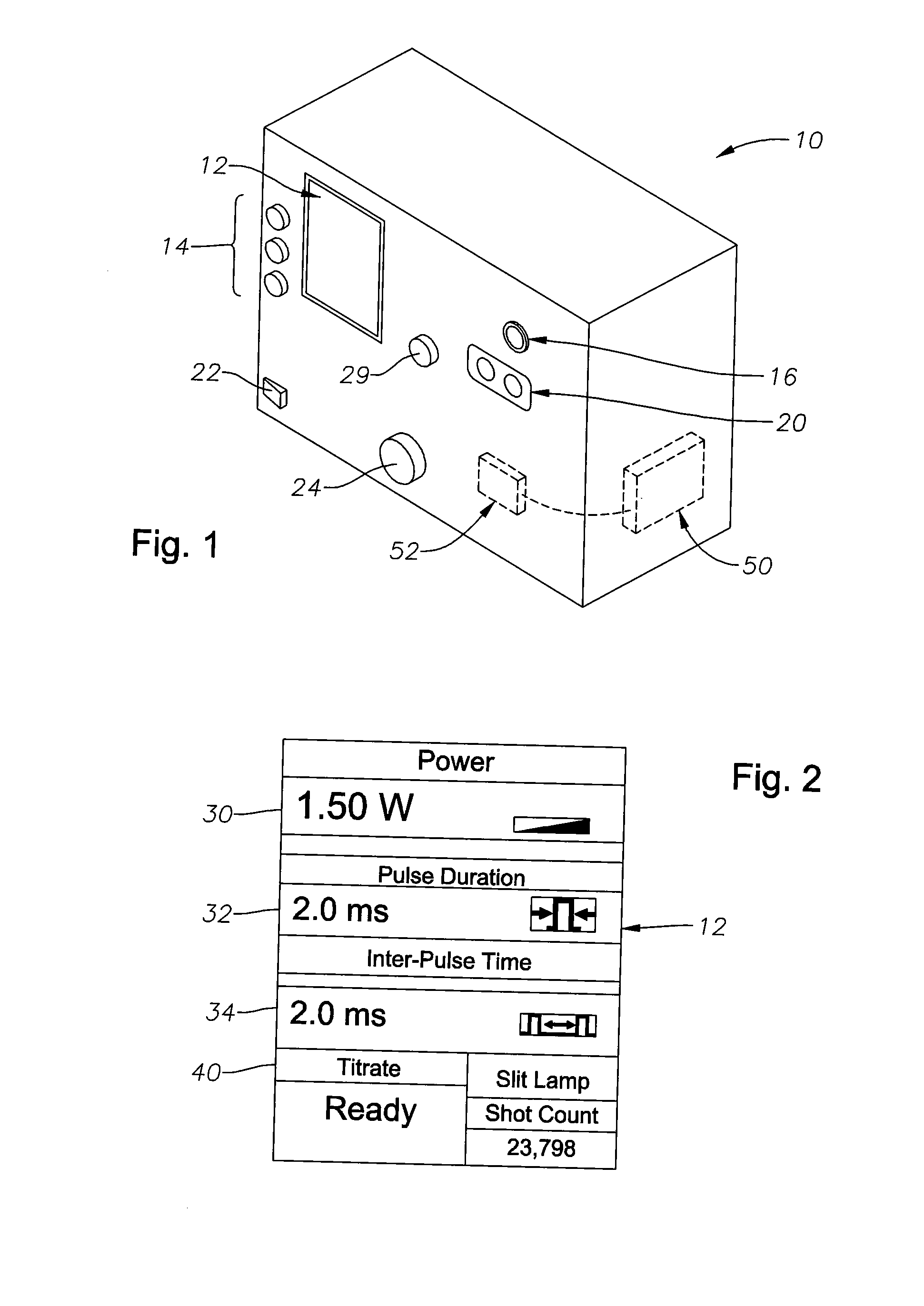
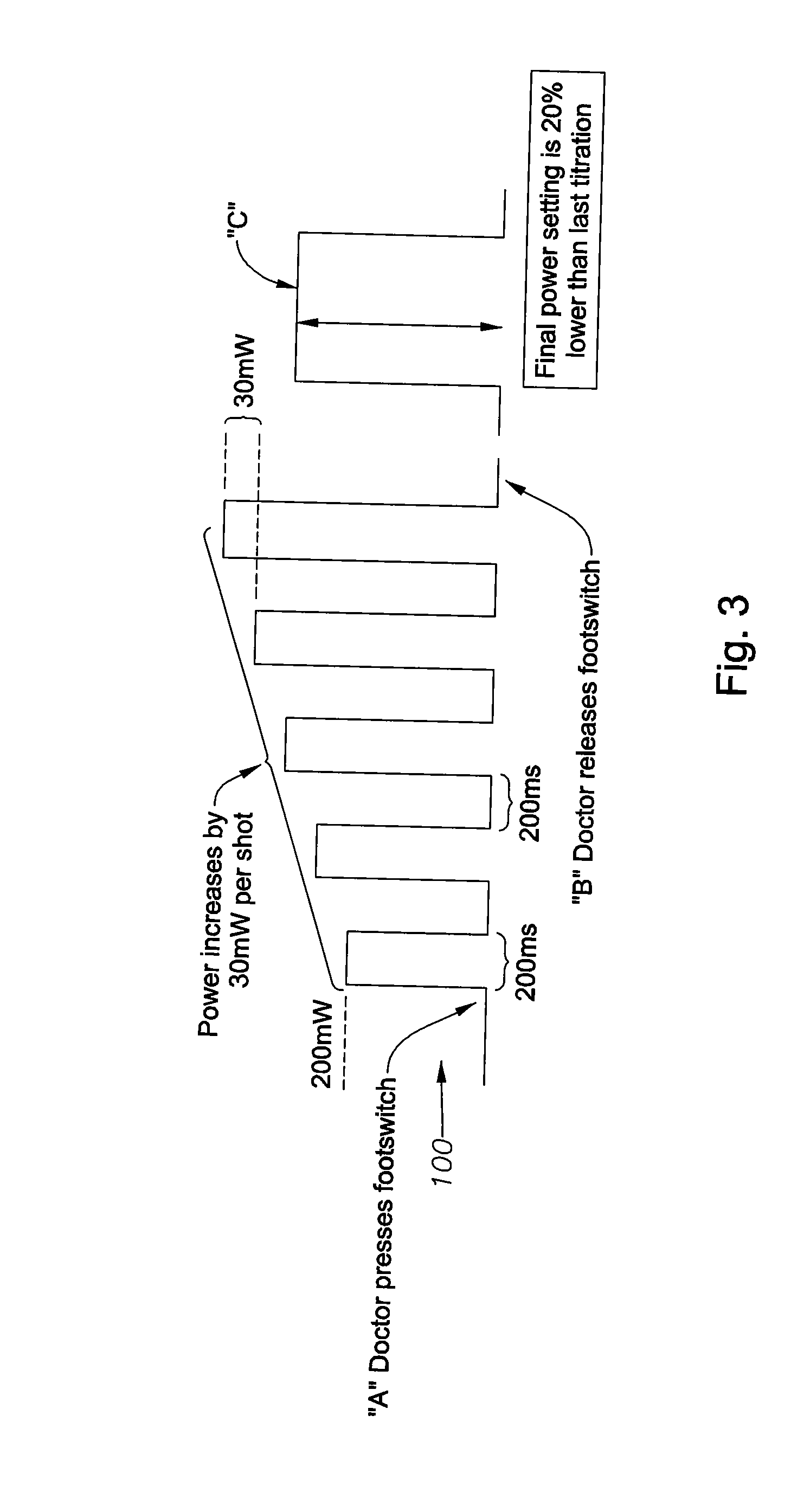
Apparatus and method for auto-titrating a laser
ActiveUS20080004609A1Transition quickly and efficientlySpeed up the flowLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsUser inputReady to use
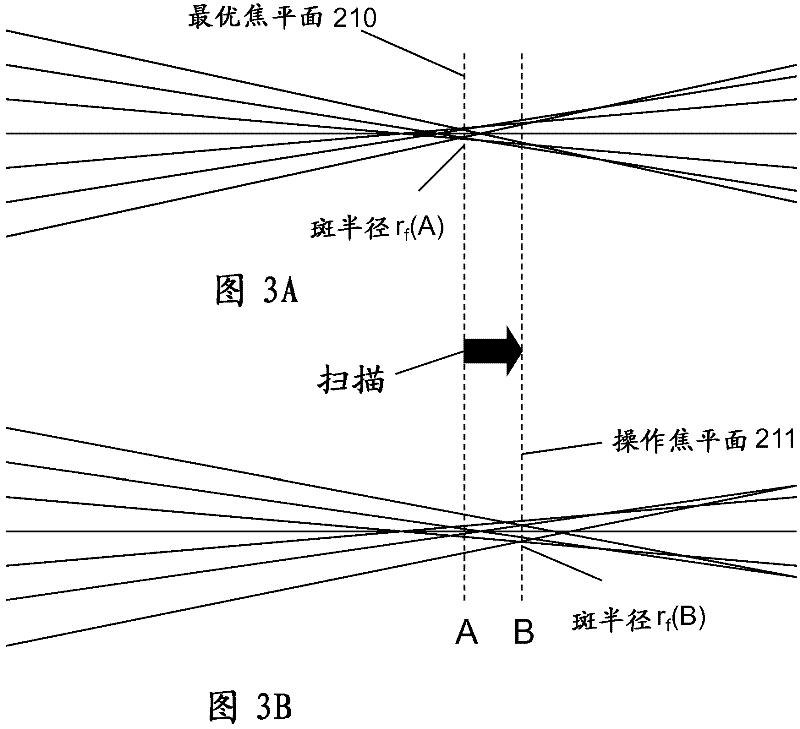
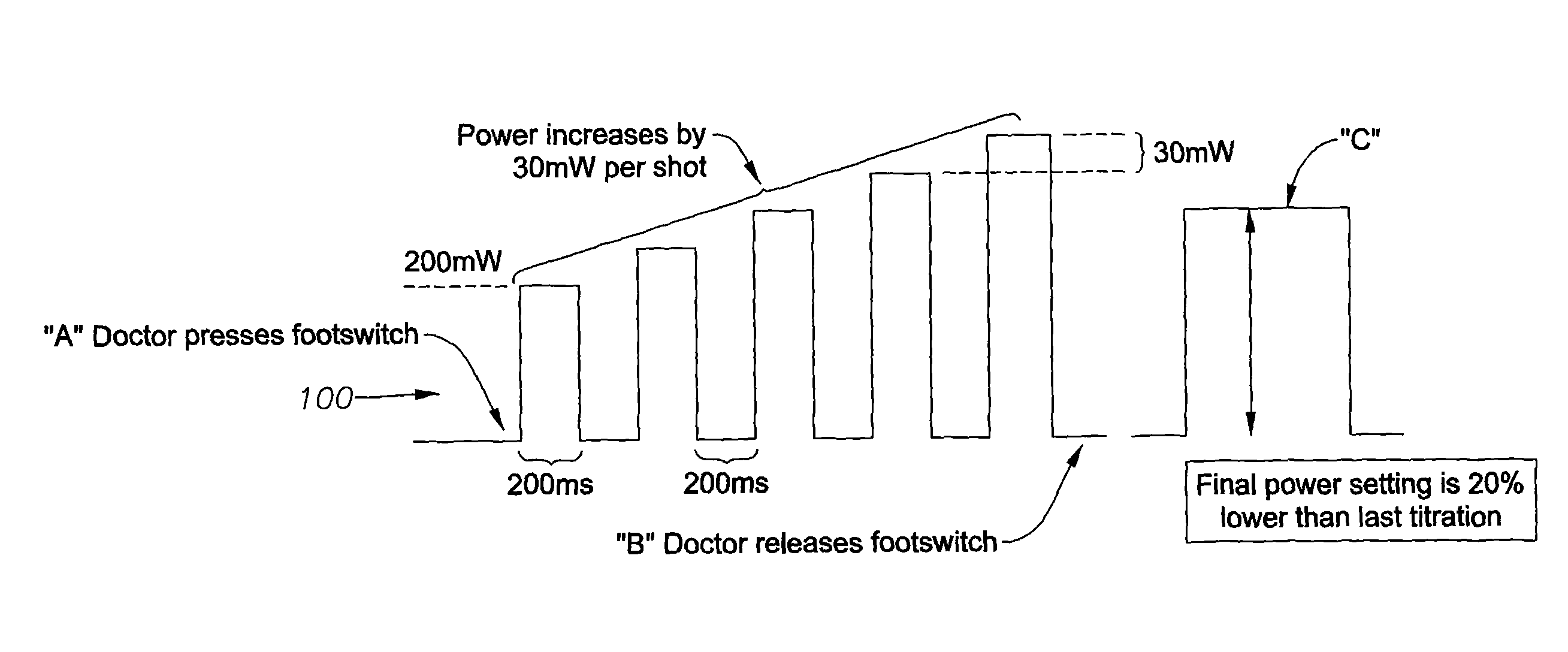
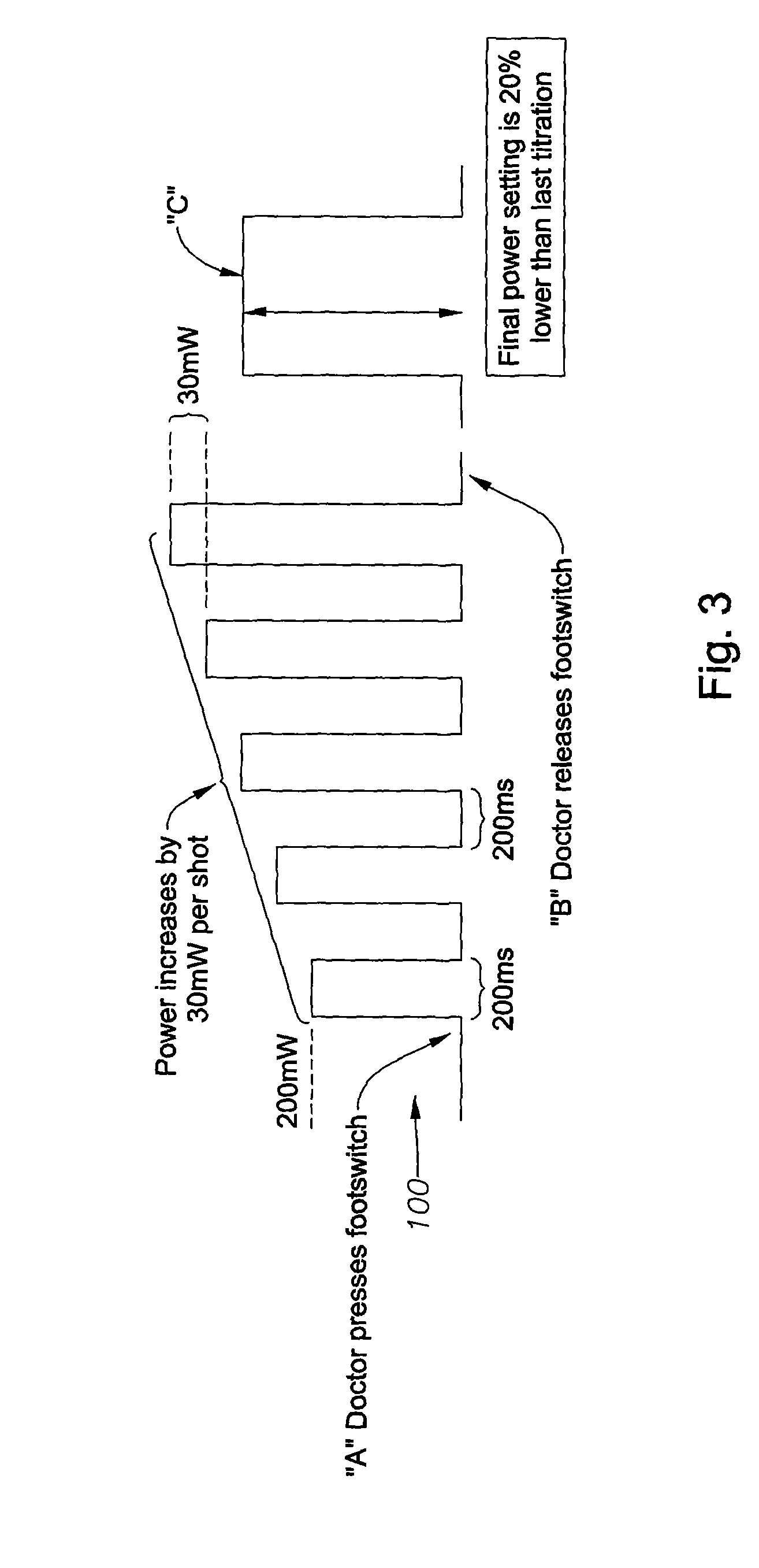
An apparatus and method for auto-titrating a surgical laser are disclosed. One embodiment of the method comprises: providing an algorithm, wherein the algorithm is operable to configure the laser based on one or more user inputs; providing a first user input operable to cause the algorithm to execute and fire the laser in a defined pattern; providing a second user input, in response to an observed condition, operable to cause the laser to stop firing and to cause the algorithm to determine one or more laser parameter values and configure the laser based on the one or more laser parameter values, wherein a final laser power value when the laser stops firing is an input to the algorithm and wherein the algorithm determines the one or more laser parameters based on the final laser power value. The method can further comprise placing the laser in a “ready” (surgical) mode, either automatically by the auto-titration algorithm or via another user input. Once in a ready mode, a user, such as a surgeon, can perform a surgical procedure with the automatically configured laser. The user inputs can be provided by activating a control switch, such as the footswitch typically used by ophthalmic surgeons to control the operation of an ophthalmic surgical laser.
Owner:ALCON INC
Systems and methods for femtosecond laser photorefractive keratectomy
ActiveUS10716705B2Convenient treatmentCorrect distortionLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFemto second laserLaser procedure
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for photorefractive keratectomy. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser source generating a pulsed laser beam and a laser delivery system delivering the pulsed laser beam to a cornea of an eye. A patient interface couples to and constrains the eye relative to the laser delivery system. A controller controls the laser delivery system to perform an anterior surface volume dissection on the cornea.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
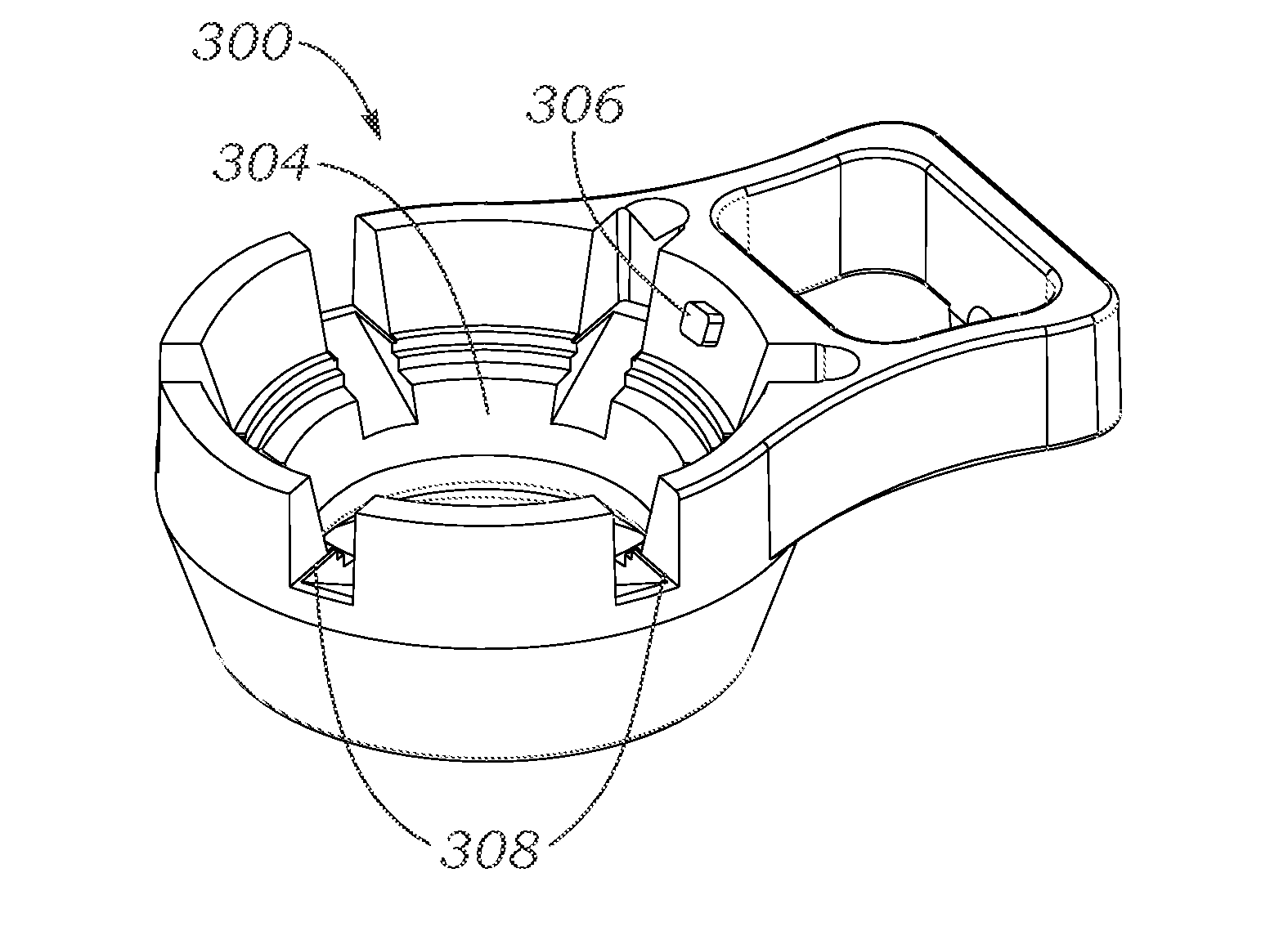
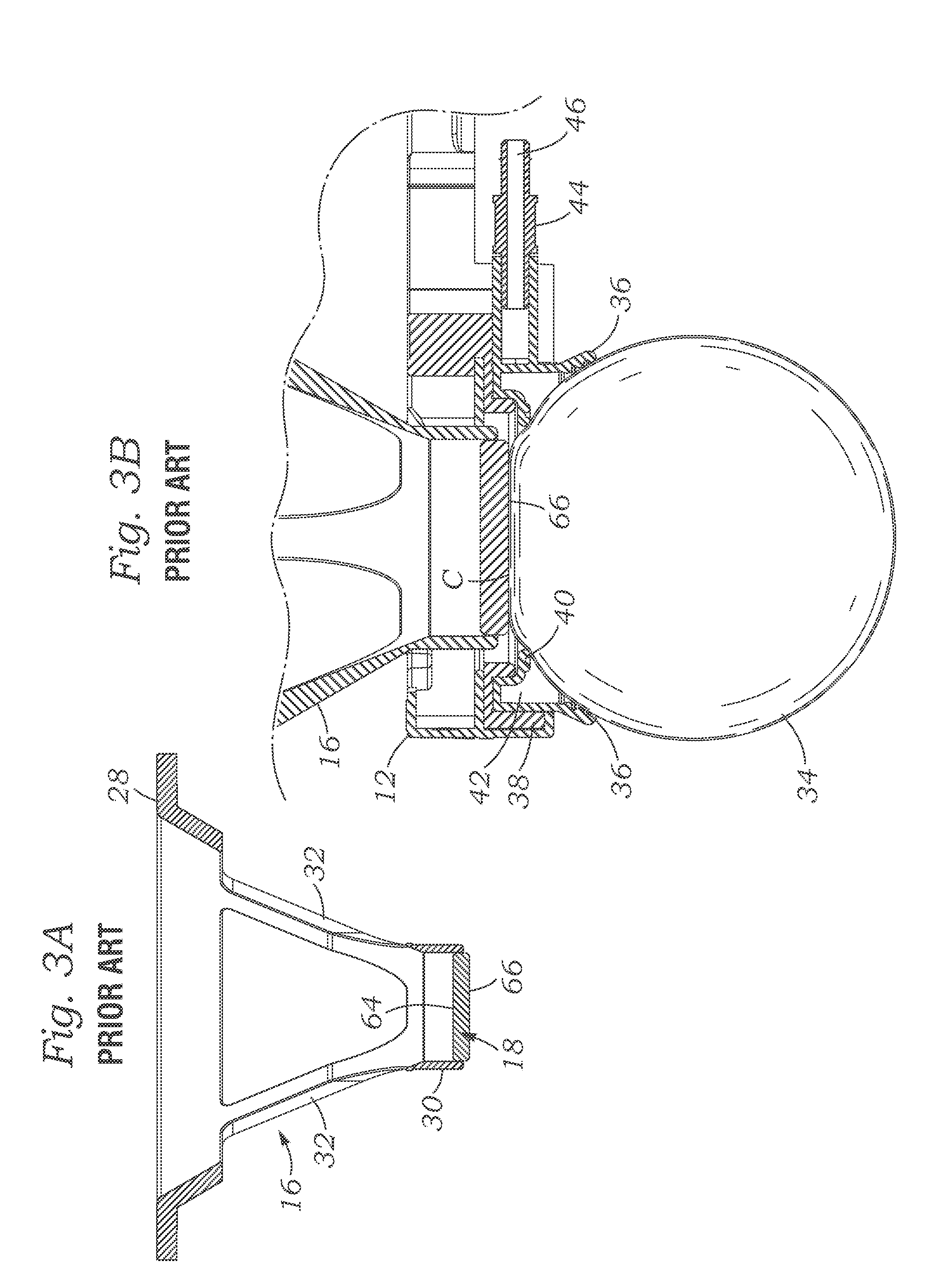
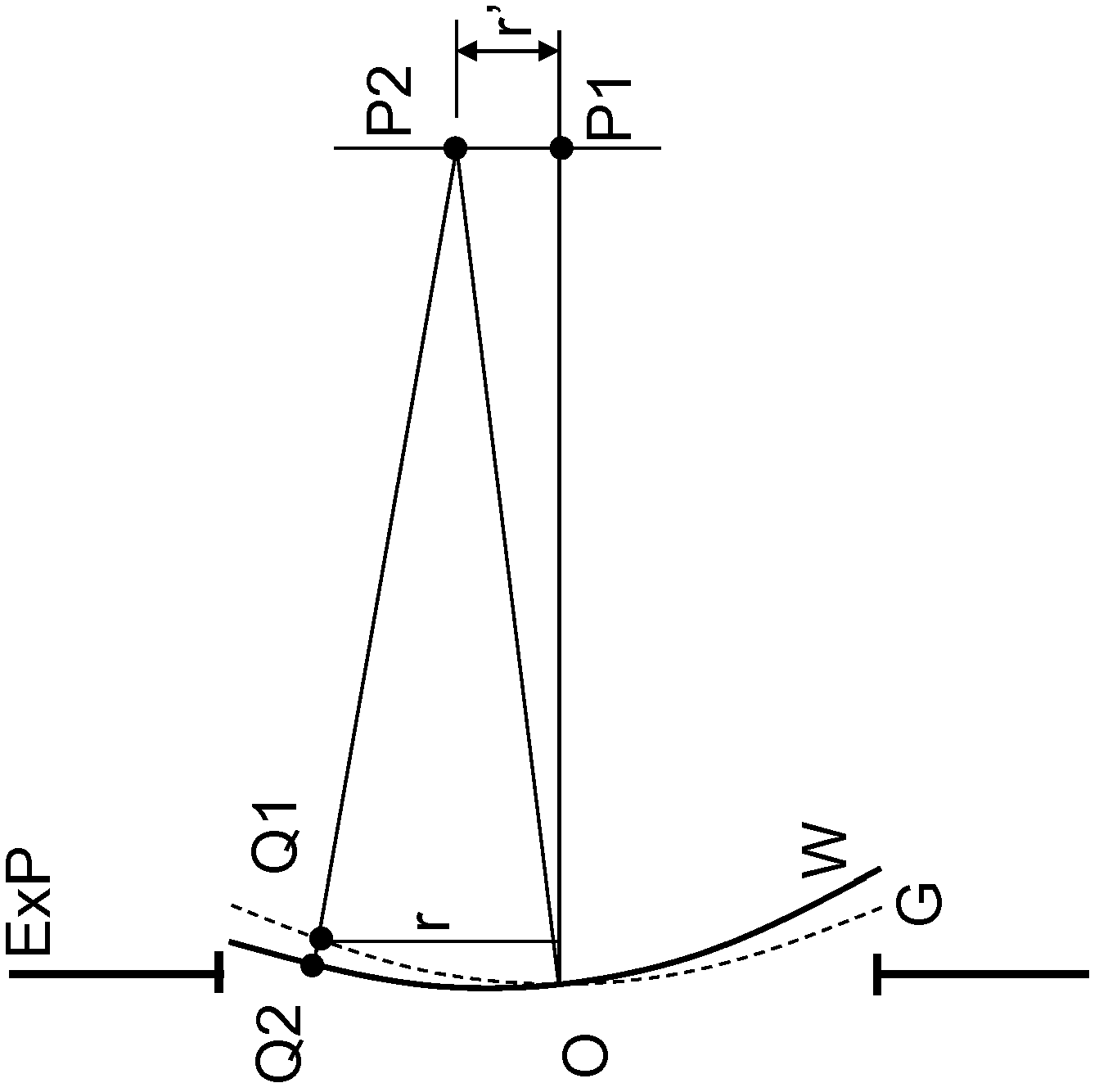
Patient interface with variable applanation
A variable-applanation patient interface can include a lens support system, attachable to a distal end of an ophthalmic surgical laser system; a contact lens, supported by the lens support system and configured to make contact with an eye-surface; and an adjustable coupler, coupled to at least one of the lens support system and the contact lens, and configured to be coupled to a non-central region of the eye-surface, to accommodate the contact lens to contact a central region of the eye-surface with a central applanation, to enable a change between the central applanation and an extended applanation, and to accommodate the contact lens to contact an extended region of the eye-surface larger than the central region with the extended applanation.
Owner:ALCON INC +1
Femtosecond laser system and methods for photorefractive keratectomy
ActiveUS20190125584A1Minimize disruptionLess discomfortLaser surgeryFemto second laserLaser procedure
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for lenticular laser incision. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser delivery system for delivering a pulsed laser beam to a target in a subject's eye, an XY-scan device to deflect the pulsed laser beam, a Z-scan device to modify a depth of a focus of the pulsed laser beam, and a controller configured to form a top lenticular incision and a bottom lenticular incision of a lens in the subject's eye, or just a bottom lenticular incision.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Optical system for ophthalmic surgical laser
A laser system for ophthalmic surgery includes a laser engine to generate a pulsed laser beam, and an XY scanner, to receive the generated pulsed laser beam, and to output a scanning laser beam, the XY scanner including an X scanner, including two X scanning mirrors, and a Y scanner, including two Y scanning mirrors. The XY scanner can modify essentially independently an angle the outputted scanning laser beam makes with an optical axis, and a position at which the outputted scanning laser beam intersects a subsequent reference plane perpendicular to the optical axis.
Owner:ALCON INC
Apparatus and method for auto-titrating a laser
ActiveUS8308716B2Transition quickly and efficientlySpeed up the flowLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsUser inputControl switch
An apparatus and method for auto-titrating a surgical laser are disclosed. One embodiment of the method comprises: providing an algorithm, wherein the algorithm is operable to configure the laser based on one or more user inputs; providing a first user input operable to cause the algorithm to execute and fire the laser in a defined pattern; providing a second user input, in response to an observed condition, operable to cause the laser to stop firing and to cause the algorithm to determine one or more laser parameter values and configure the laser based on the one or more laser parameter values, wherein a final laser power value when the laser stops firing is an input to the algorithm and wherein the algorithm determines the one or more laser parameters based on the final laser power value. The method can further comprise placing the laser in a “ready” (surgical) mode, either automatically by the auto-titration algorithm or via another user input. Once in a ready mode, a user, such as a surgeon, can perform a surgical procedure with the automatically configured laser. The user inputs can be provided by activating a control switch, such as the footswitch typically used by ophthalmic surgeons to control the operation of an ophthalmic surgical laser.
Owner:ALCON INC
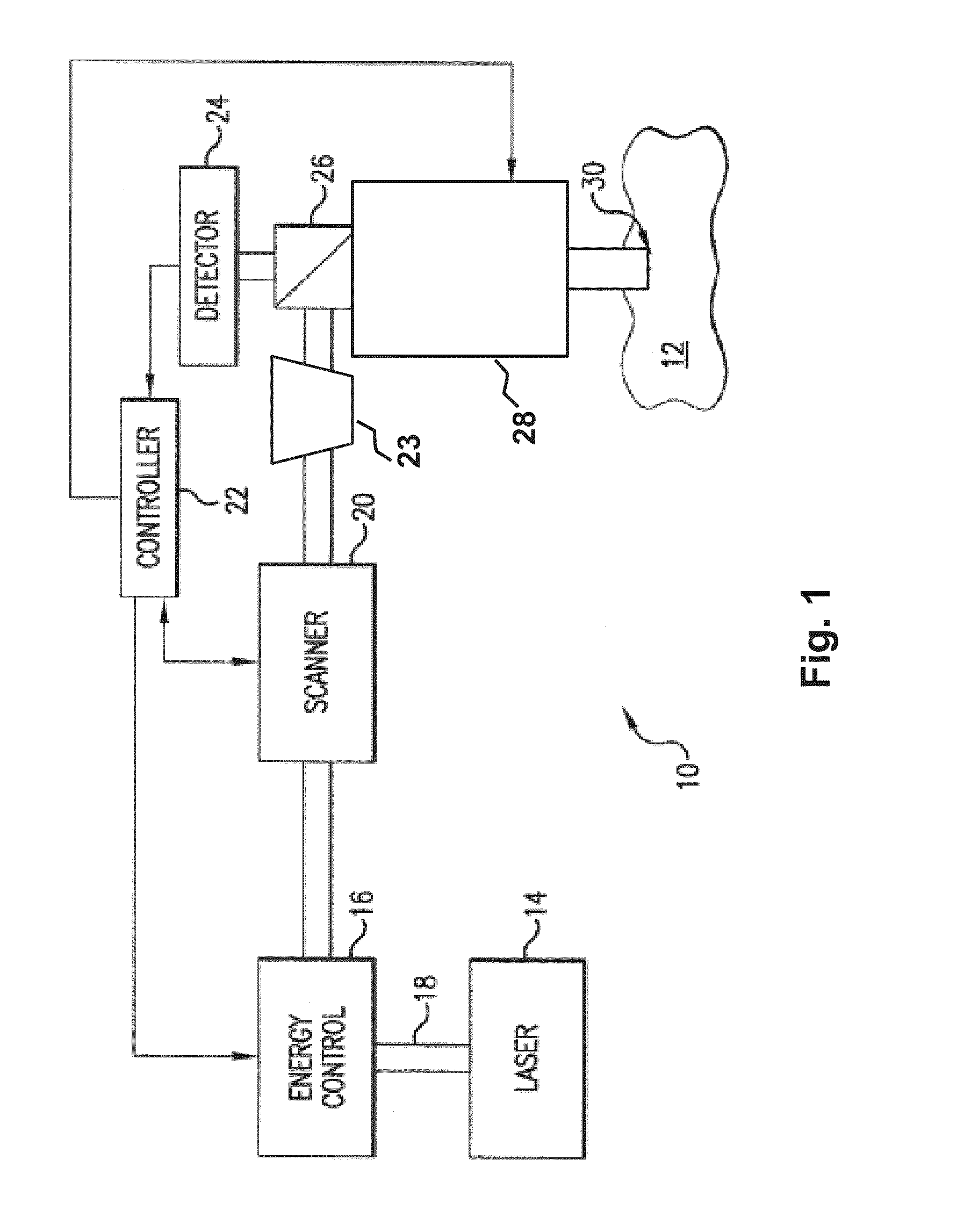
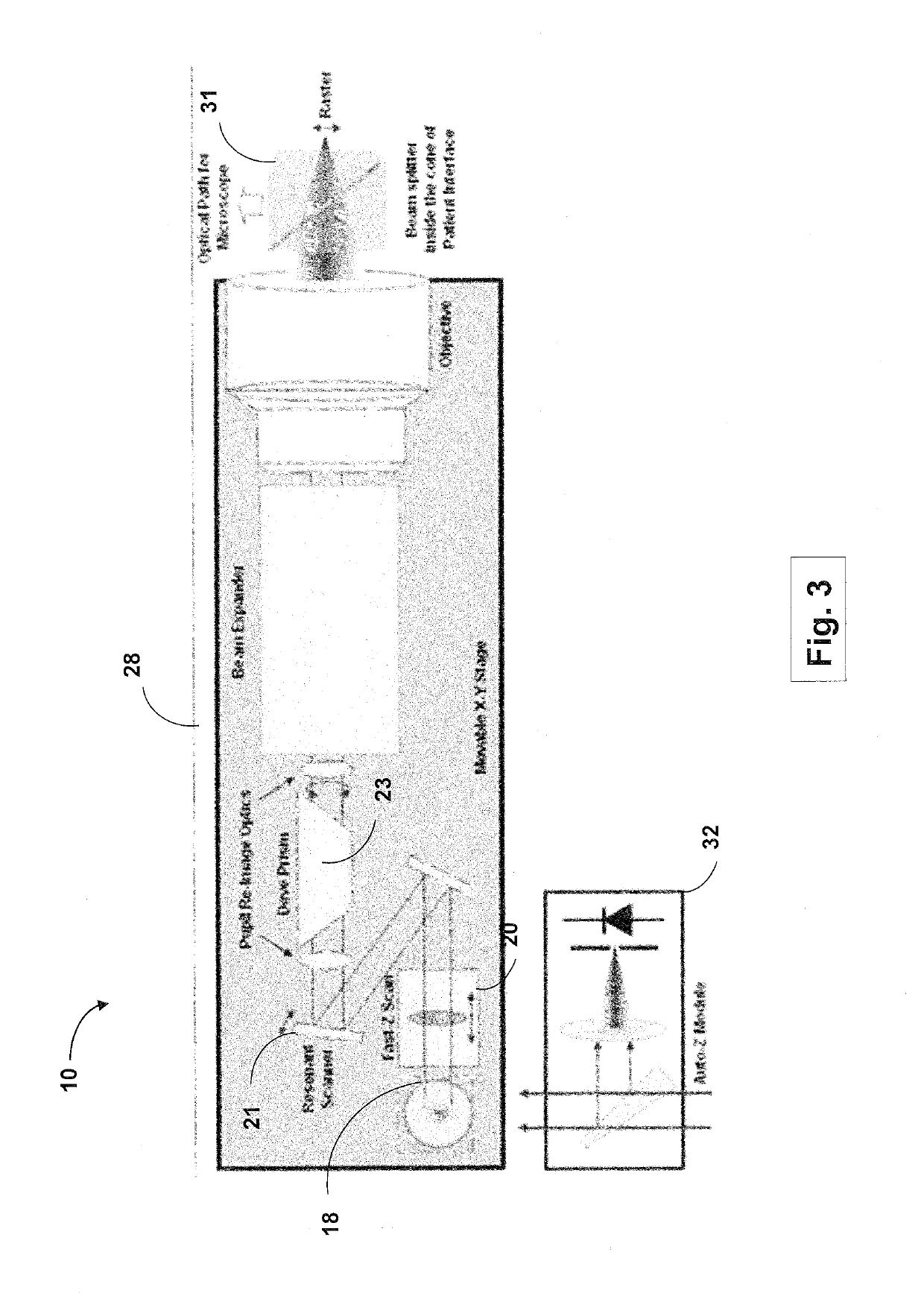
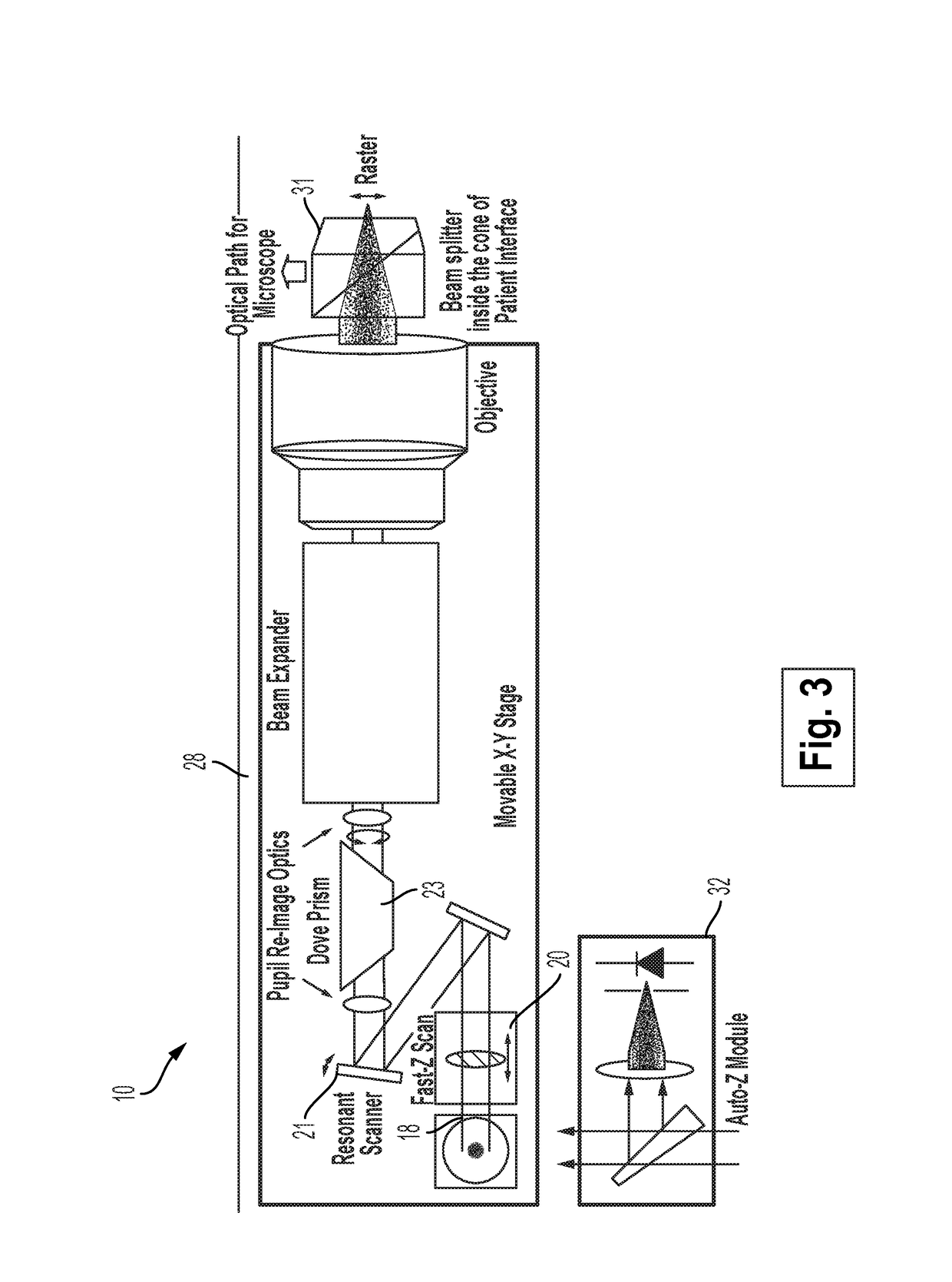
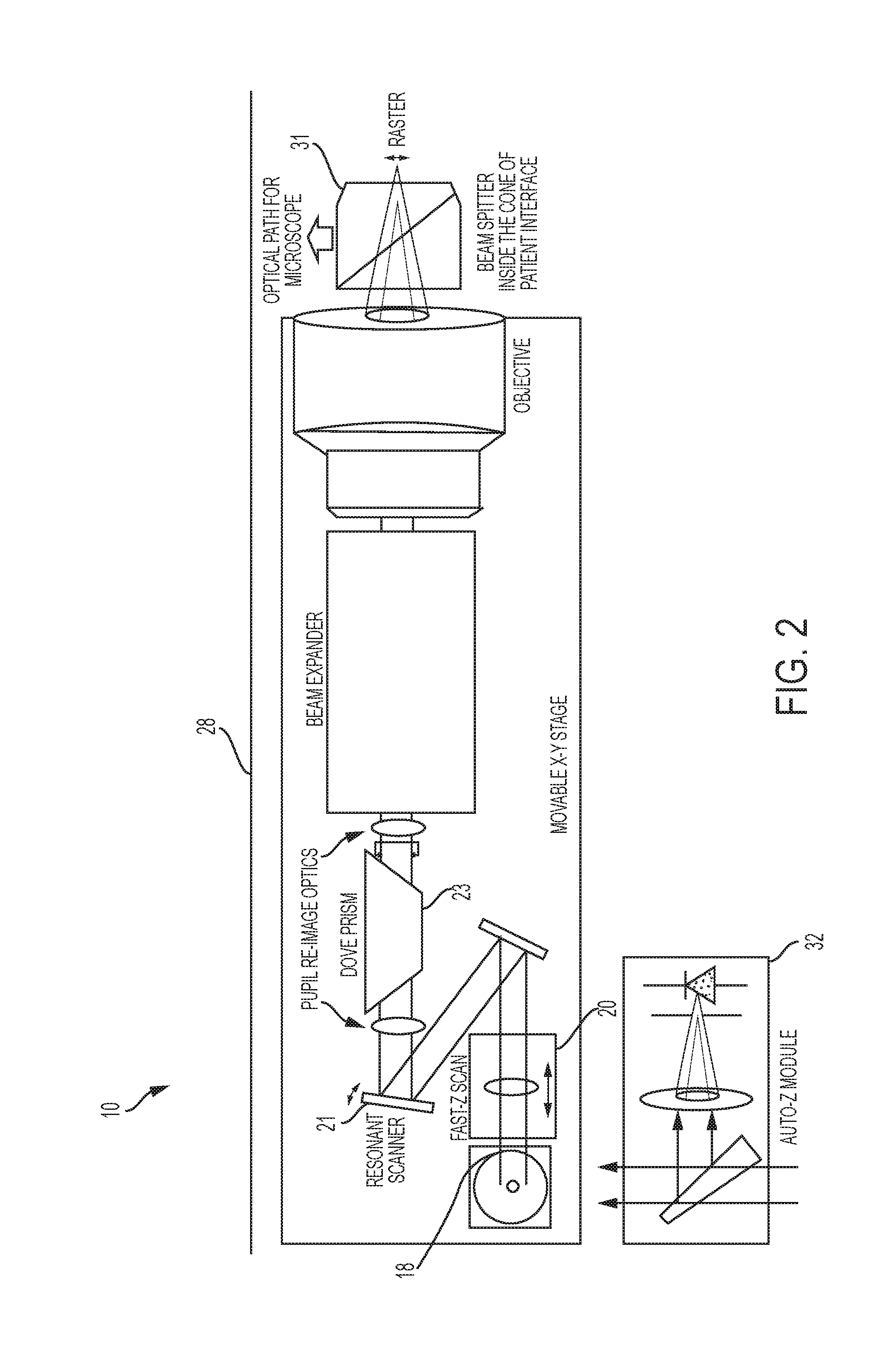
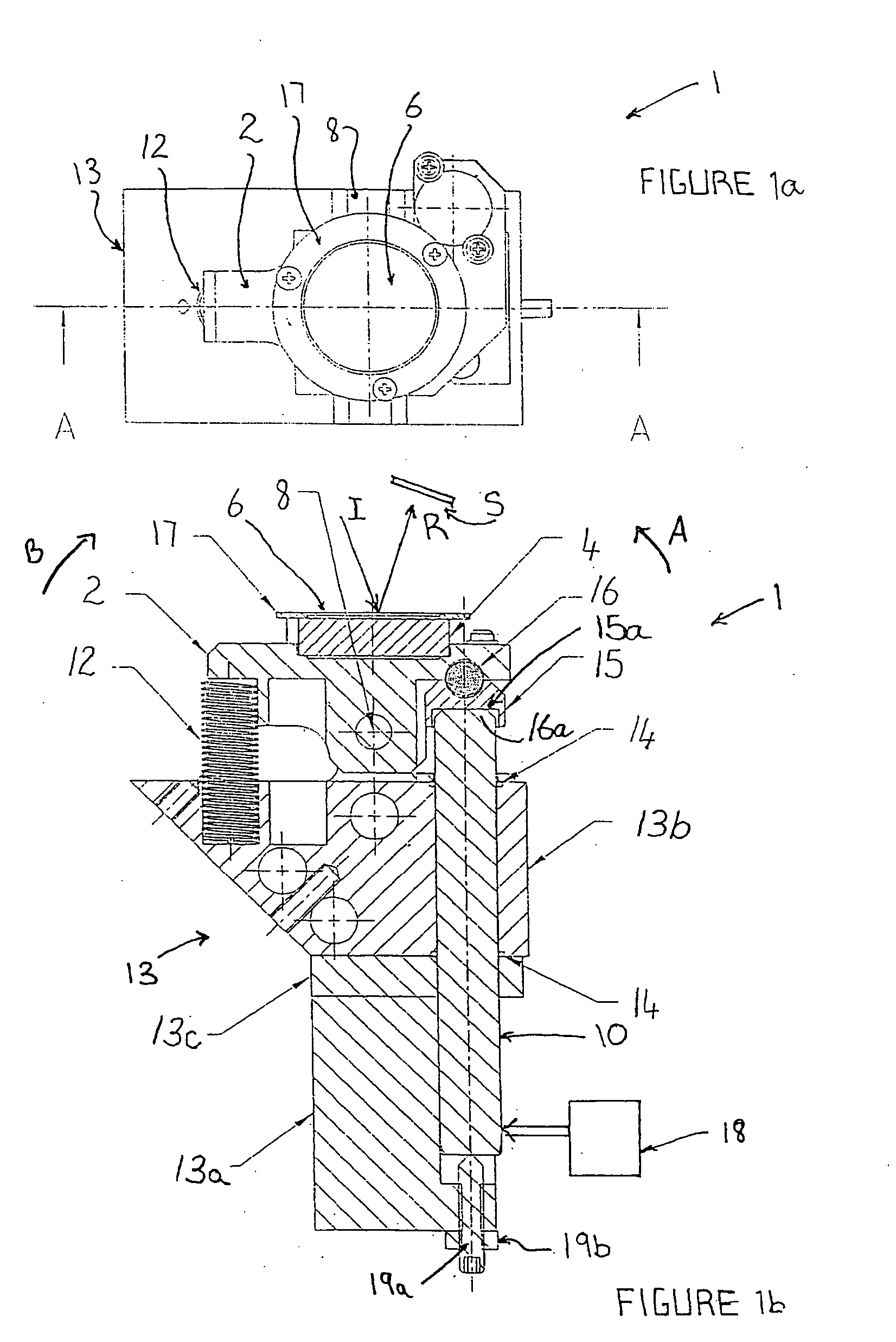
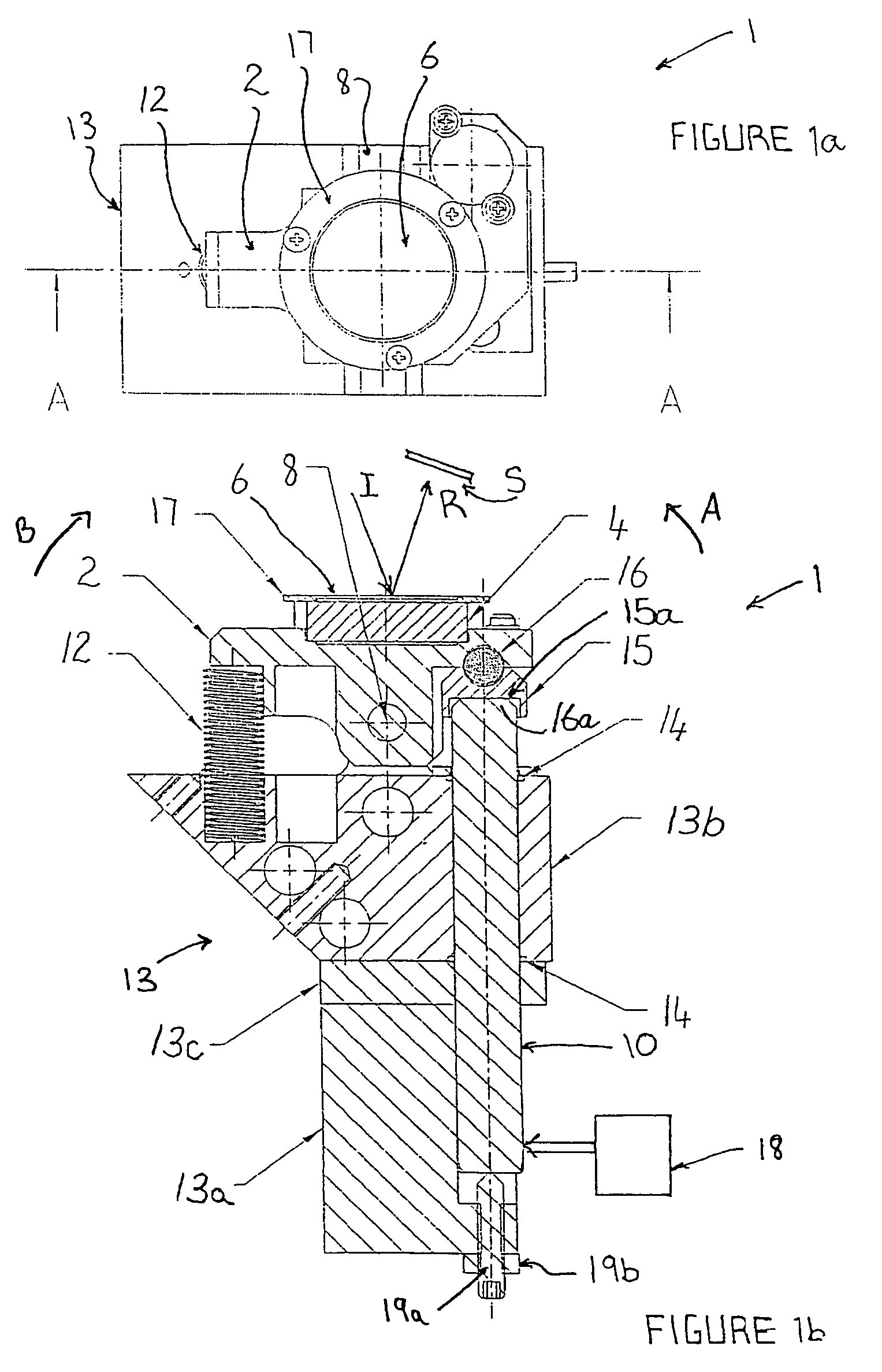
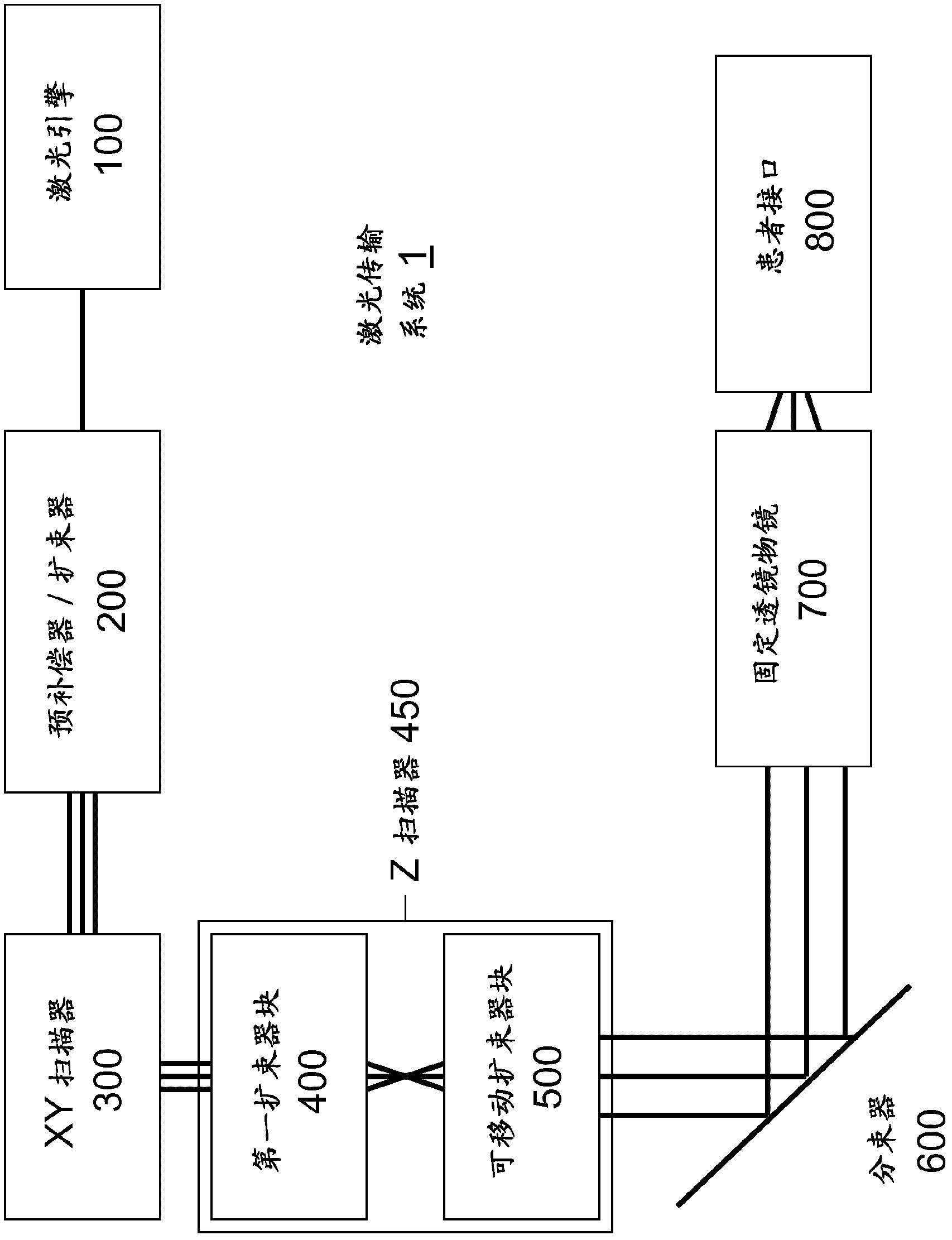
Ophthalmic surgery laser system and method for utilizing same for ophthalmic surgery
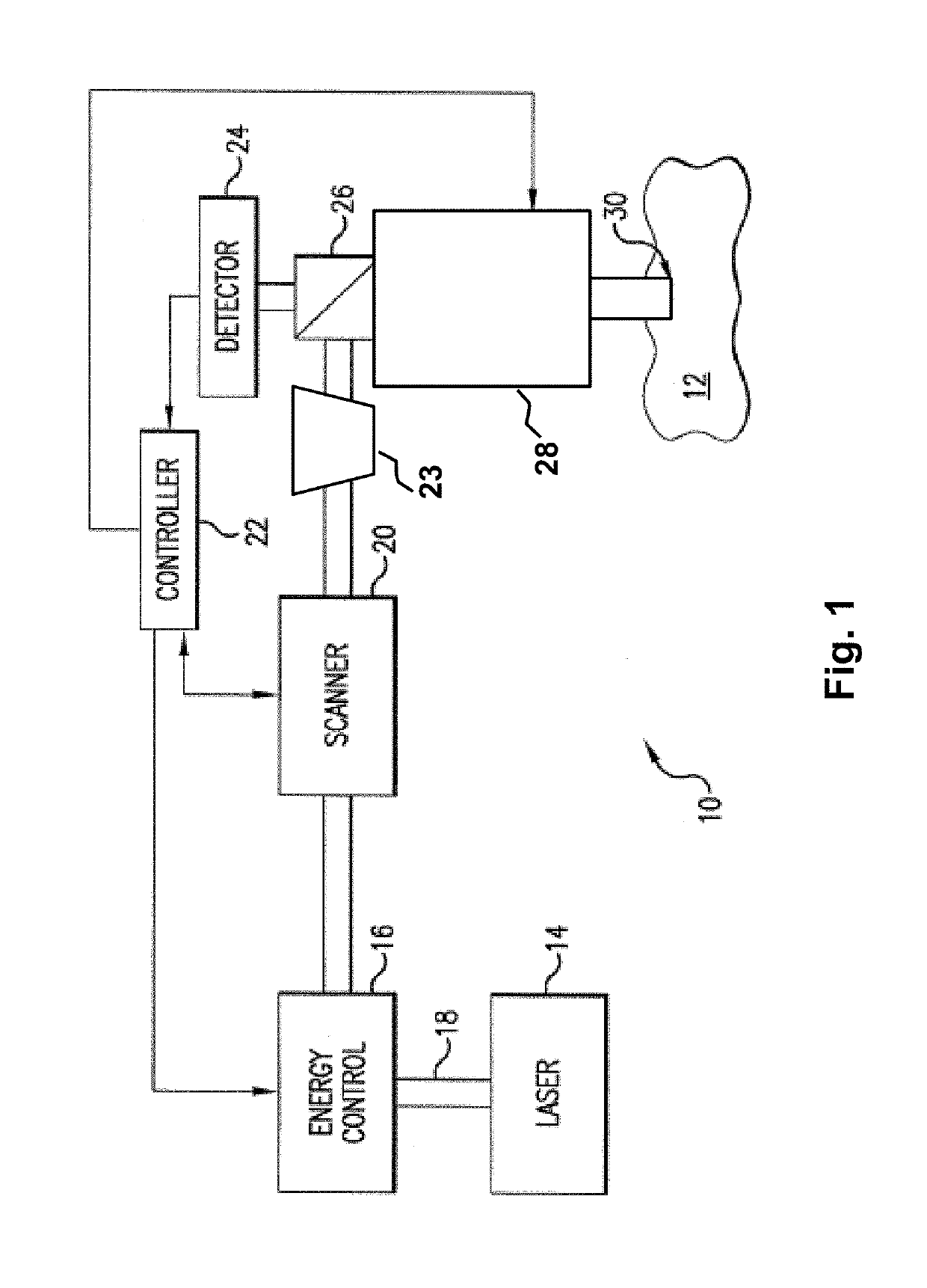
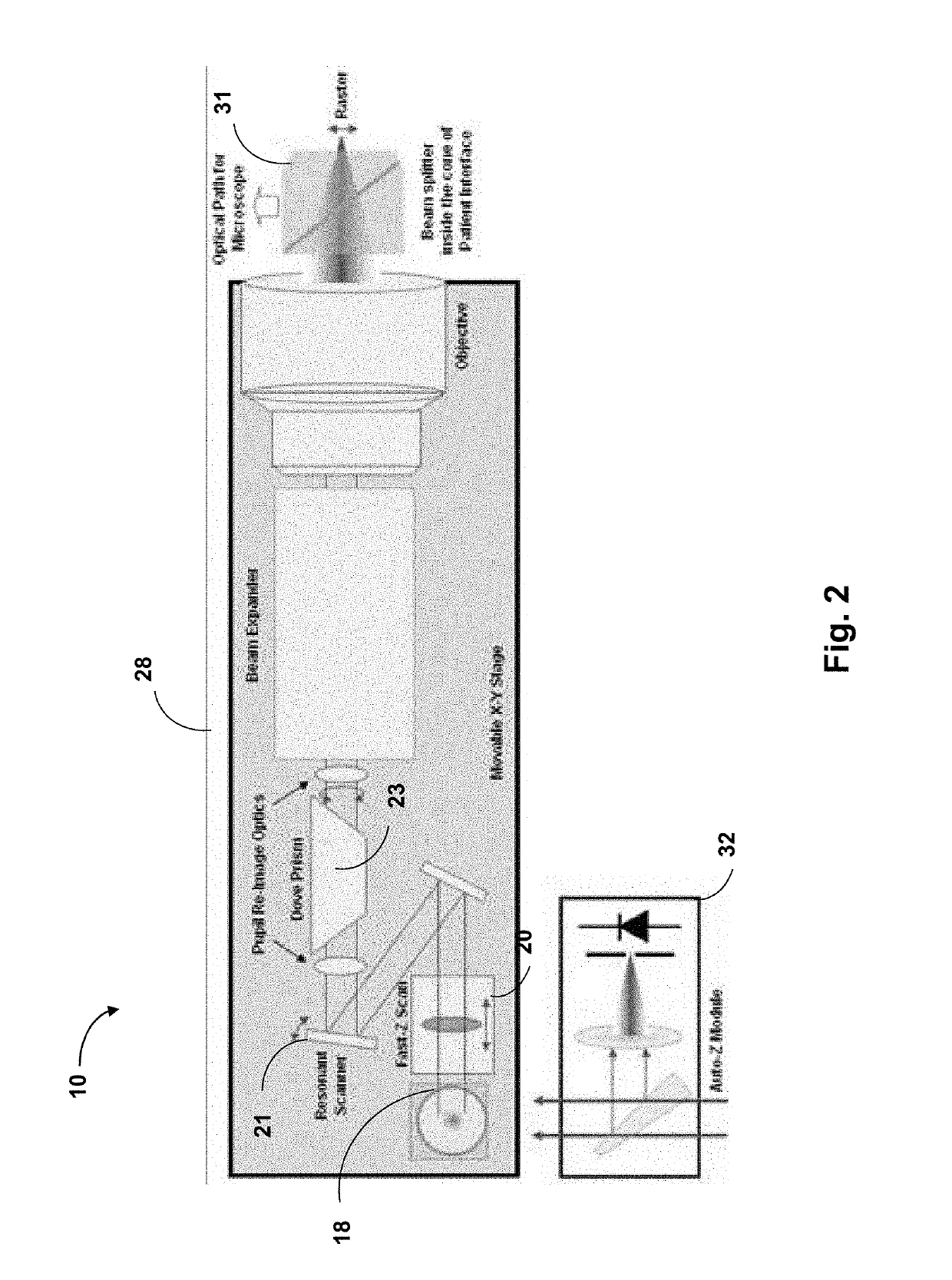
An ophthalmic surgery laser system and method of laser delivery for an ophthalmic surgery laser system are disclosed herein. Embodiments of the system and method are directed to an ophthalmic surgery laser system including a laser engine, a laser guide, and a laser shaper. Embodiments of the system and method are directed to a laser delivery system for an ophthalmic surgery laser system. Embodiments of the system and method are directed to an ophthalmic surgery laser system including additional functionality such as laser scanning confocal microscopy, 3D laser scanning, and laser beam diagnostics. Embodiments further include the use of a lower power illumination source.
Owner:DRAKE PRECISION OPTICS INC
Systems and methods for lenticular laser incision
Embodiments of this invention generally relate to ophthalmic laser procedures and, more particularly, to systems and methods for lenticular laser incision. In an embodiment, an ophthalmic surgical laser system comprises a laser delivery system for delivering a pulsed laser beam to a target in a subject's eye, an XY-scan device to deflect the pulsed laser beam, a Z-scan device to modify a depth of a focus of the pulsed laser beam, and a controller configured to form a top lenticular incision and a bottom lenticular incision of a lens in the subject's eye, where each of the top and bottom lenticular incision includes a center spherical portion and an edge transition portion that is not located on the same spherical surface as the spherical portion but has a steeper shape.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Optical system for ophthalmic surgical laser
A laser system for ophthalmic surgery includes a laser source to produce a pulsed laser beam, an XY scanner to scan the pulsed laser beam in XY directions transverse to a Z axis, a Z scanner, to scan the XY scanned laser beam along the Z axis, and an objective, to focus the XYZ scanned laser beam into a target region.
Owner:ALCON LENSX
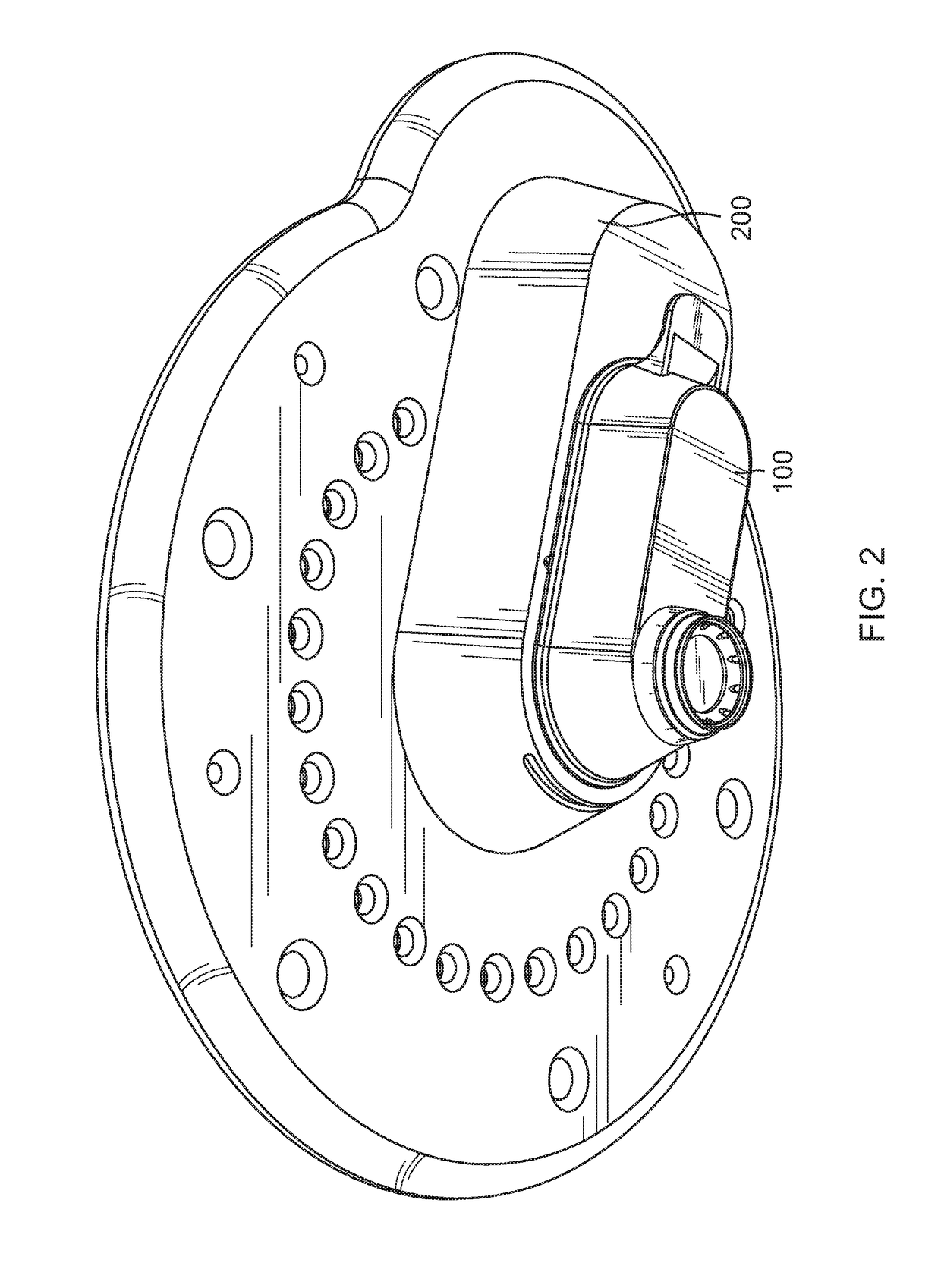
Patient interface device for ophthalmic surgical laser system
ActiveUS10966864B2Easy constructionEasy to useLaser surgeryProsthesisOphthalmology departmentReoperative surgery
Apparatus and method for interfacing an ophthalmic surgical laser system with a patient's eye using a single-piece patient interface (PI). The PI includes a hollow shell, with an applanation lens and a flexible skirt at its lower end. Through channels are formed around the applanation lens to connect the spaces above and below the lens. When the PI is coupled to the laser system and the eye, the upper rim of the shell forms a seal with the laser system and the flexible skirt forms a seal with the eye. A vacuum is applied to the interior of the shell via a vacuum port on the laser system, and the vacuum is communicated to the space enclosed by the applanation lens, the skirt and the eye through the channels around the lens. A magnetic mechanism is also provided to hold the PI shell to the laser system.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Method for controlling an eye surgical laser and treatment device
ActiveUS20200297537A1Treatment duration is reducedLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsErbium lasersPulse sequence
Owner:SCHWIND EYE TECH SOLUTIONS GMBH
Patient interface device for ophthalmic surgical laser system
Apparatus and method for interfacing an ophthalmic surgical laser system with a patient's eye using a single-piece patient interface (PI). The PI includes a hollow shell, with an applanation lens and a flexible skirt at its lower end. Through channels are formed around the applanation lens to connect the spaces above and below the lens. When the PI is coupled to the laser system and the eye, the upper rim of the shell forms a seal with the laser system and the flexible skirt forms a seal with the eye. A vacuum is applied to the interior of the shell via a vacuum port on the laser system, and the vacuum is communicated to the space enclosed by the applanation lens, the skirt and the eye through the channels around the lens. A magnetic mechanism is also provided to hold the PI shell to the laser system.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
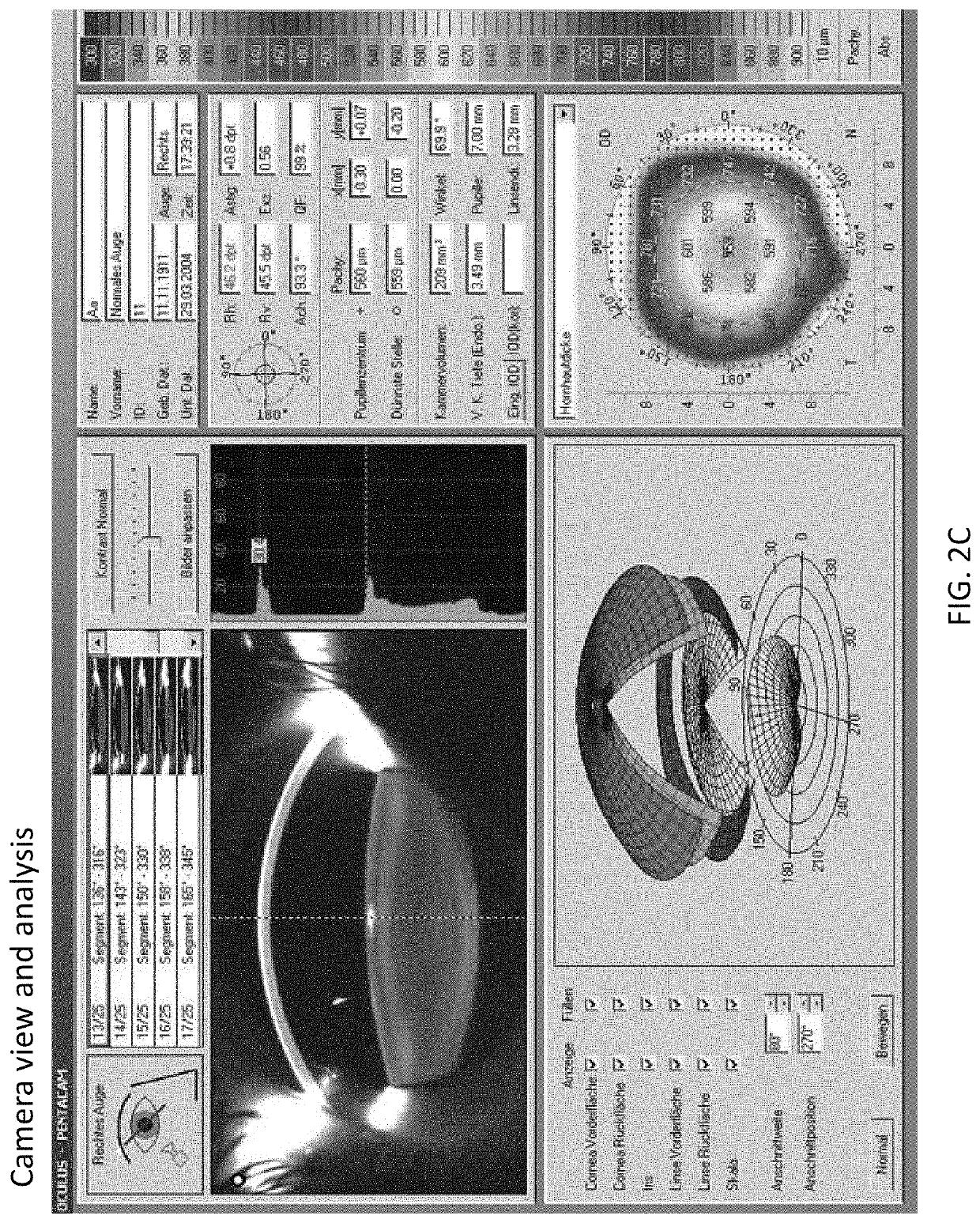
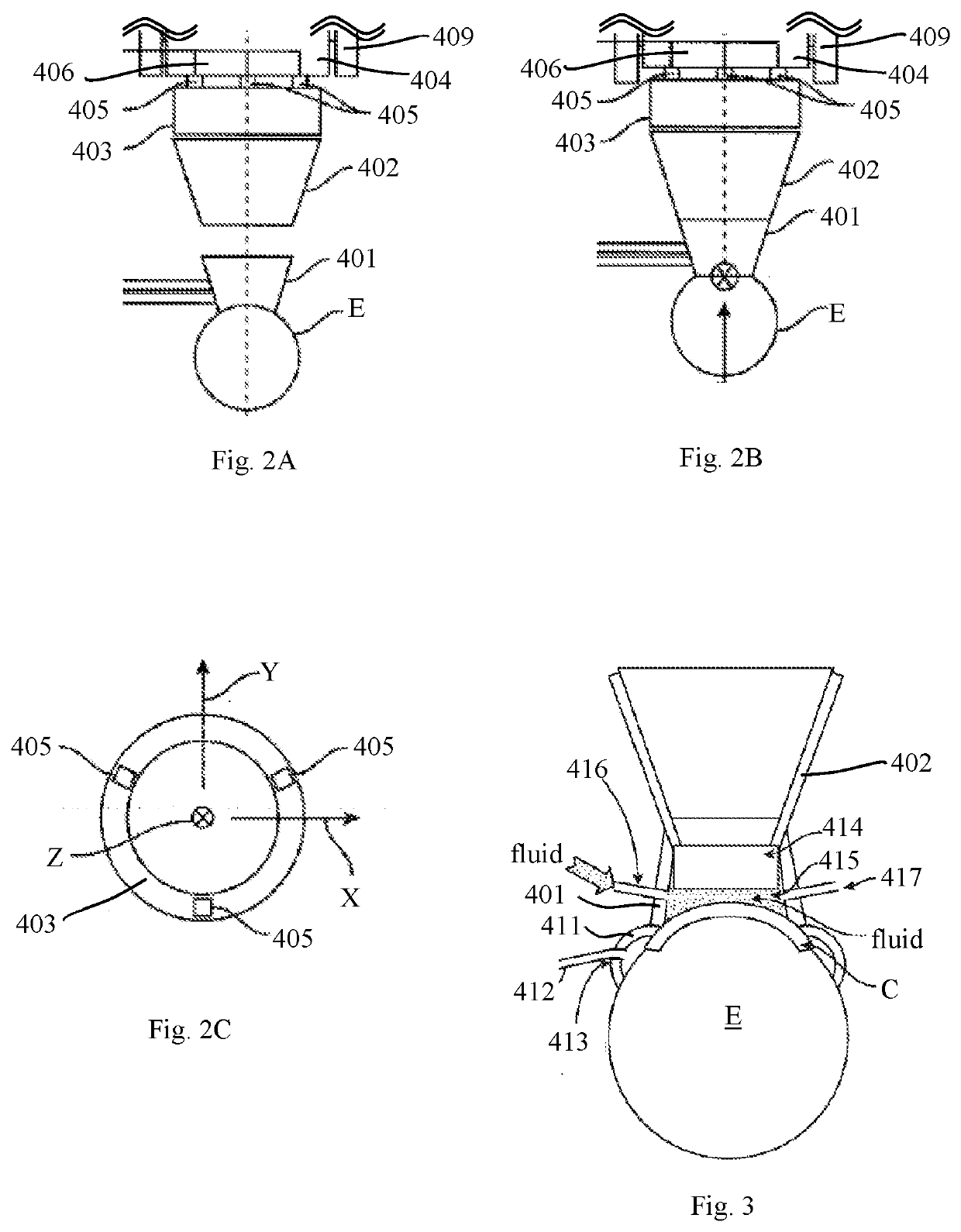
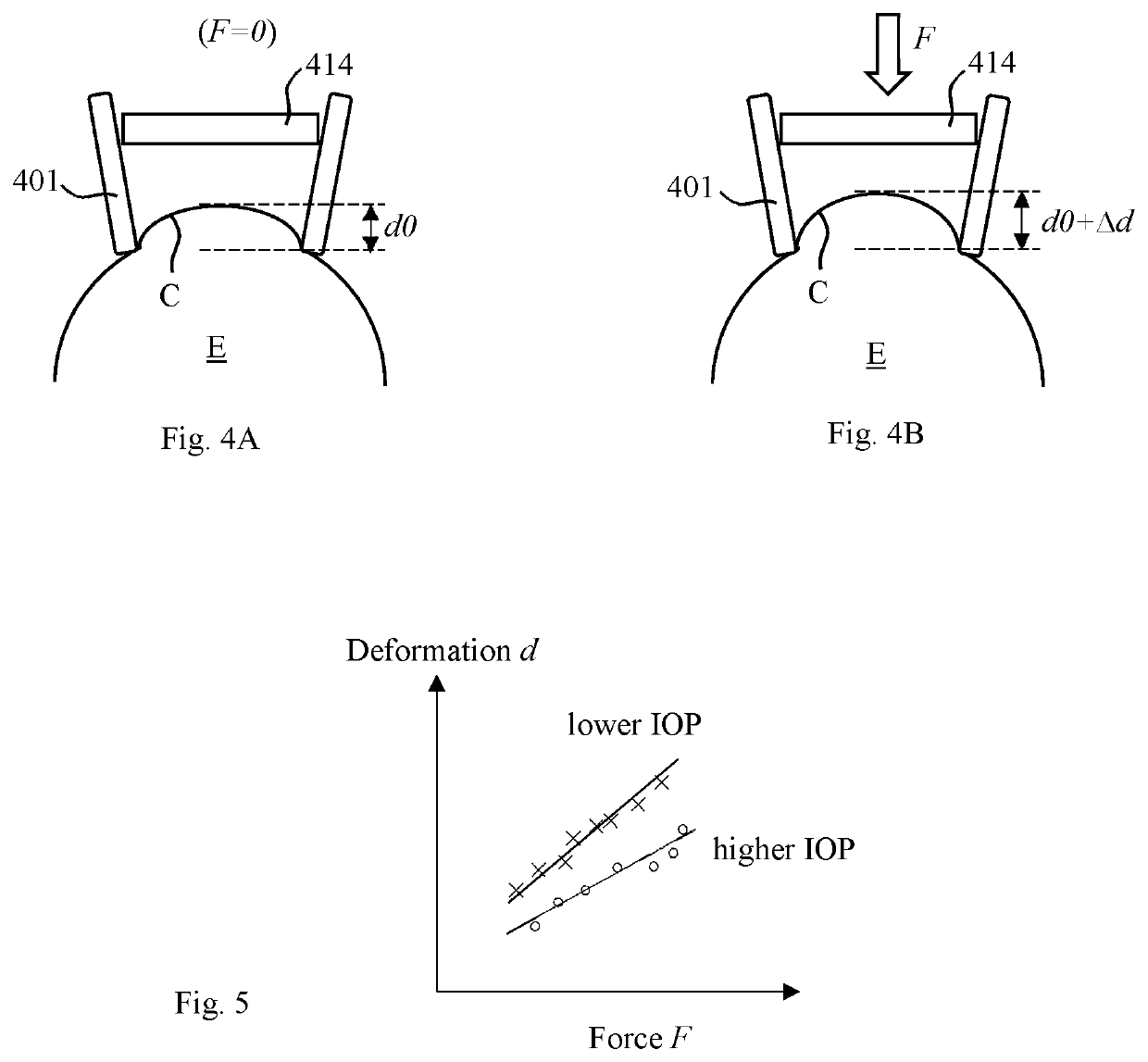
Intraocular pressure measurement for an eye docked to a laser system
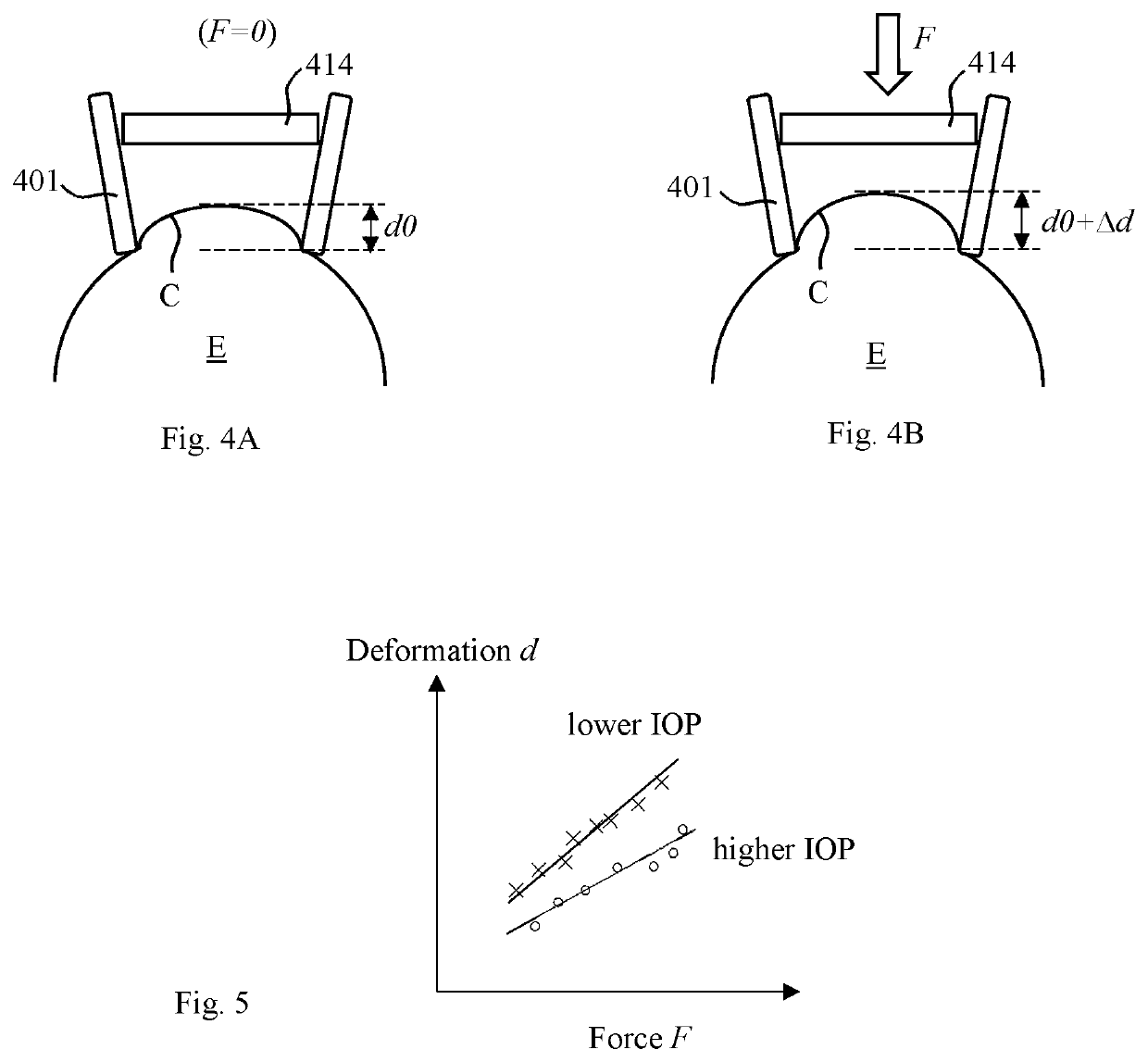
A method for measuring the intraocular pressure (IOP) of an eye docked to an ophthalmic surgical laser system via a patient interface assembly. While the eye is docked to the laser system, and as the vertical force exerted on the eye by the patient interface fluctuates as the patient breaths and moves, the amount of corneal deformation is continuously measured by an optical coherence tomography device of the laser system and the force exerted on the eye is continuously measured by force sensors integrated in the patient interface assembly. Based on the real-time force signal and real-time corneal deformation signal, a controller calculates a linear relationship between force and corneal deformation, and determines the IOP of the docked eye by comparing a slope of the linear relationship against a pre-established slope vs. IOP calibration curve. The IOP of the docked eye can be used when setting laser treatment parameters.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Intraocular pressure measurement for an eye docked to a laser system
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Passivation method of excimer laser gas configuration device
ActiveCN102517540BStable output energyAnti-corrosionSolid state diffusion coatingOptoelectronicsProduct gas
The invention relates to a passivation method of an excimer laser gas configuration device. The method is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out passivation preprocessing: cleaning the excimer laser gas configuration device to remove impurities therein, and blowing the excimer laser gas configuration device by N2; 2, carrying out passivation processing: inletting a mixed gas of F2 and He to the excimer laser gas configuration device, maintaining a constant temperature and a constant pressure for a period of time, and blowing the excimer laser gas configuration device by N2; and 3, inletting N2 to the excimer laser gas configuration device, and sealing to complete the passivation of the excimer laser gas configuration device. The He gas with small molecular weight and strong diffusion capability is used to substitute N2 used in the prior art, and passivation temperature conditions are changed, so an oxidation film which is stable and compact is tough and firm because of the increased penetration degree, thereby the further corrosion of a metal matrix can be effectively controlled. A configured excimer laser which has the advantages of stable output energy and uniform energy distribution can completely satisfy requirements of laser treatment for ophthalmic operations and costs low.
Owner:GUANGDONG SOUTHCHINA SPECIAL GAS INST
Patient interface device for ophthalmic surgical laser system
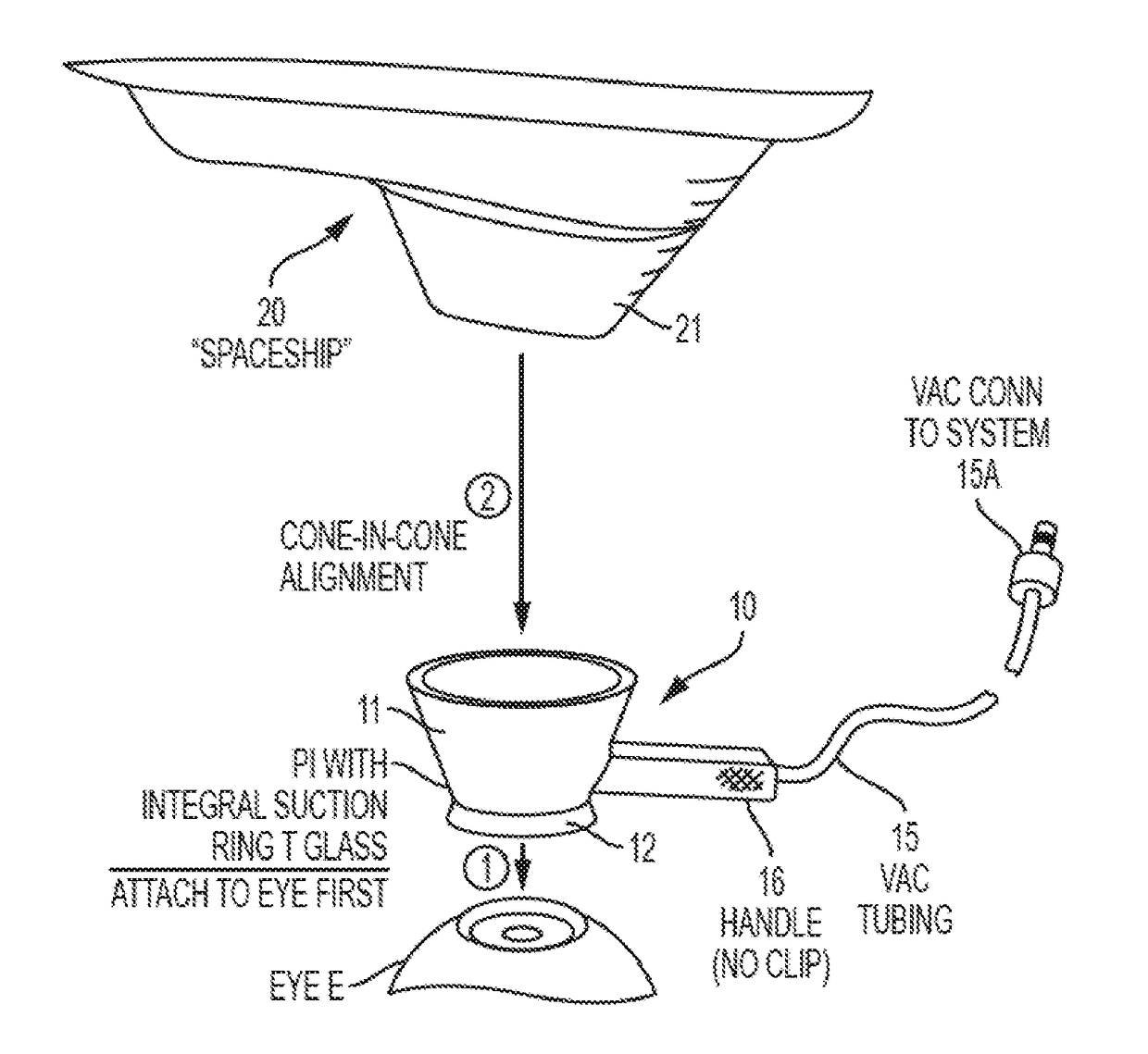
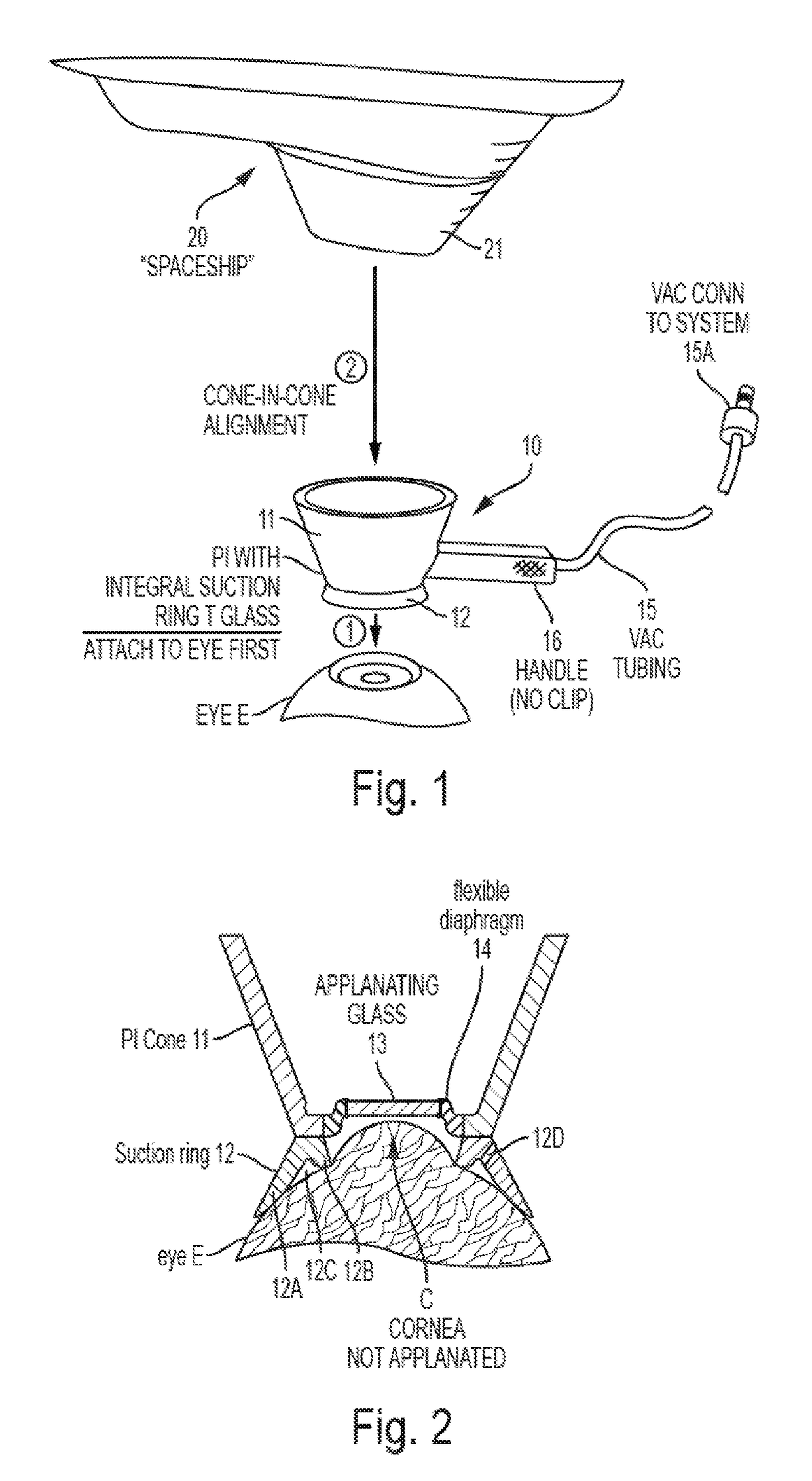
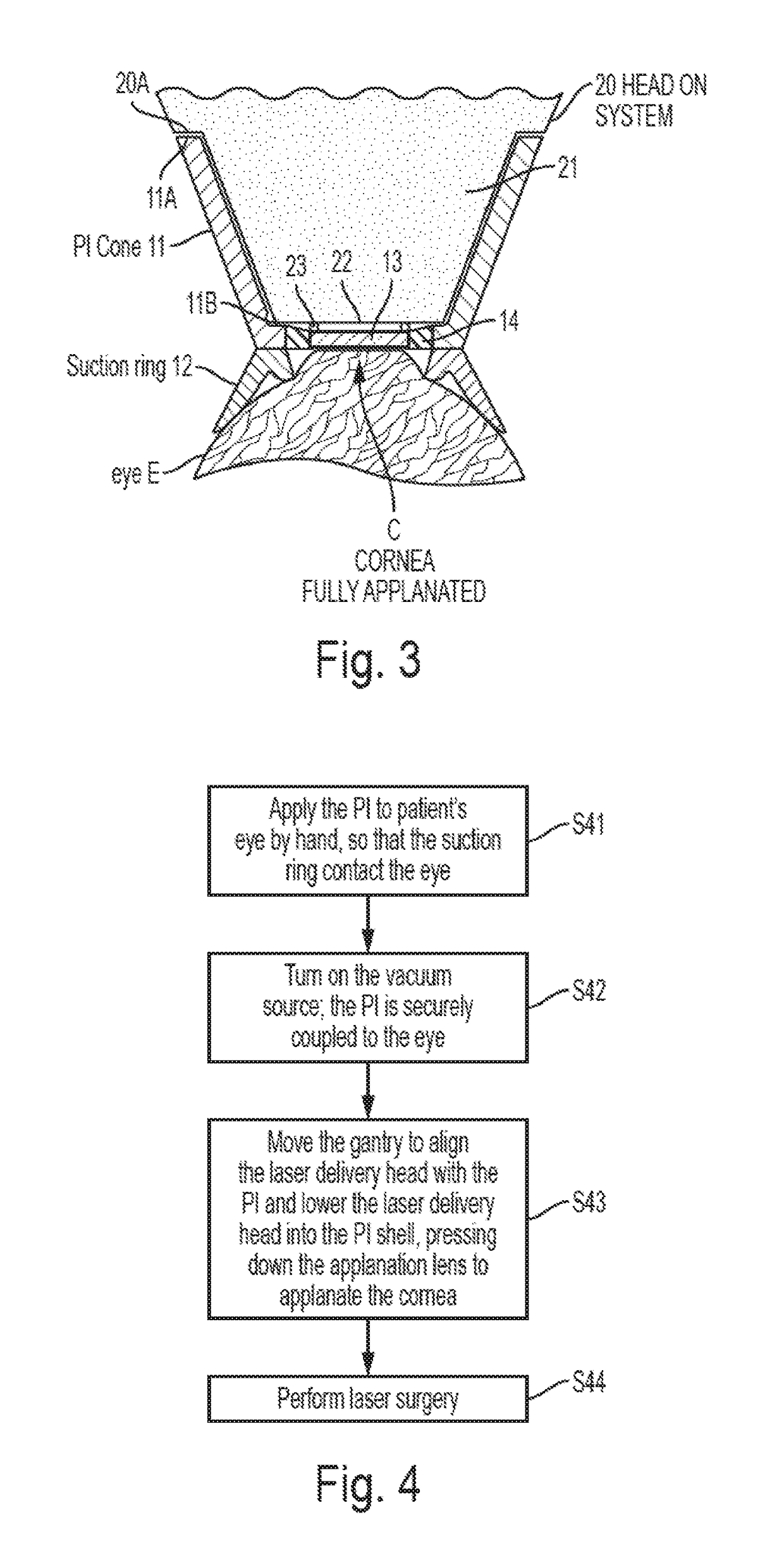
A single-piece patient interface device (PI) for coupling an patient's eye to an ophthalmic surgical laser system, which includes a rigid shell, a flexible suction ring joined to a lower edge of the shell, an applanation lens, and a flexible annular diaphragm which joins the applanation lens to the shell near the lower edge of the shell. The flexible diaphragm allows the applanation lens to move relative to the shell, including to shift in longitudinal and lateral directions of the shell and to tilt. In operation, the surgeon first secures the PI to the patient's eye by hand, and then couples the laser system to the PI by lowering the laser delivery head into the PI shell. During the lowering process, the laser delivery head presses the applanation lens down relative to the PI to applanate the cornea of the eye.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com