Patents
Literature
43 results about "K space sampling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
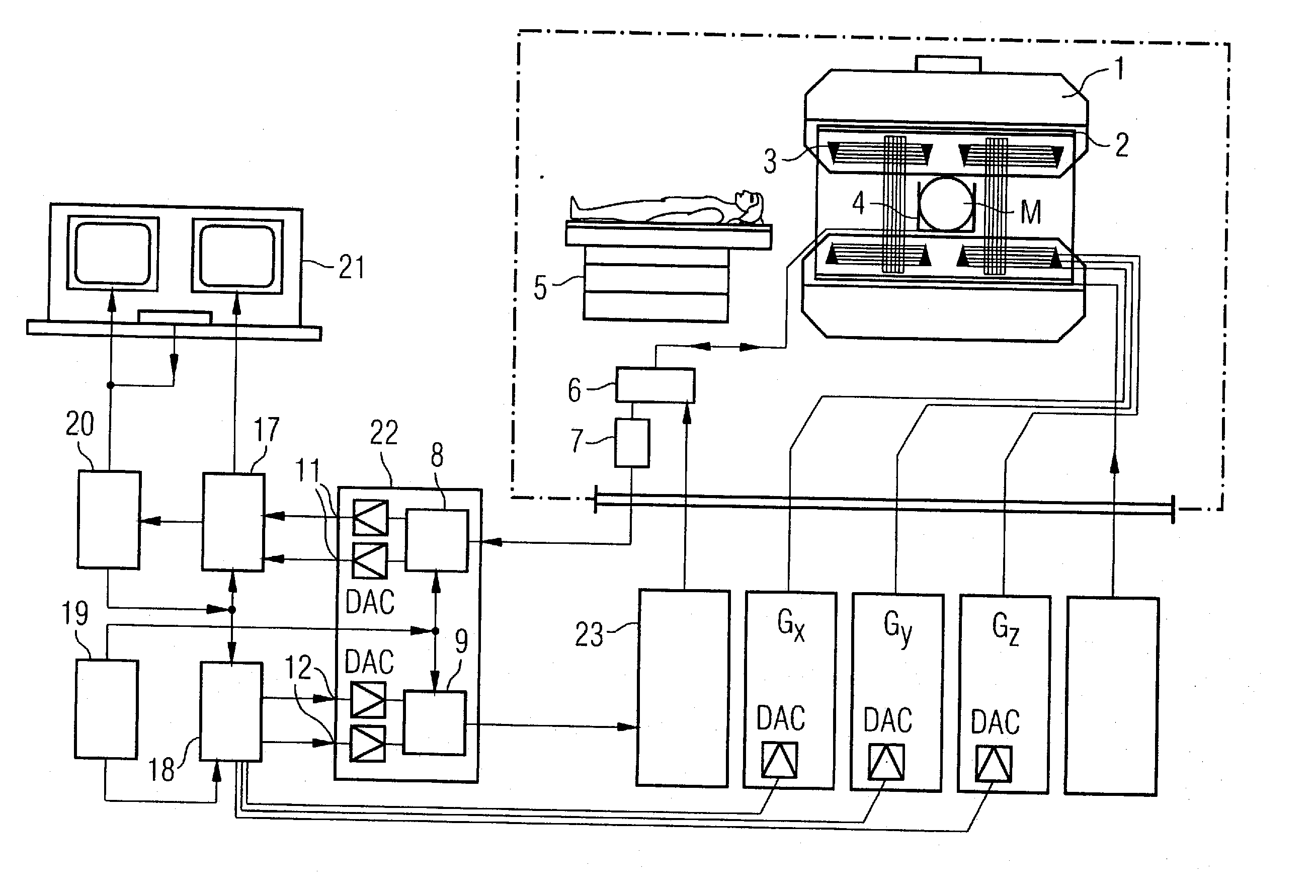
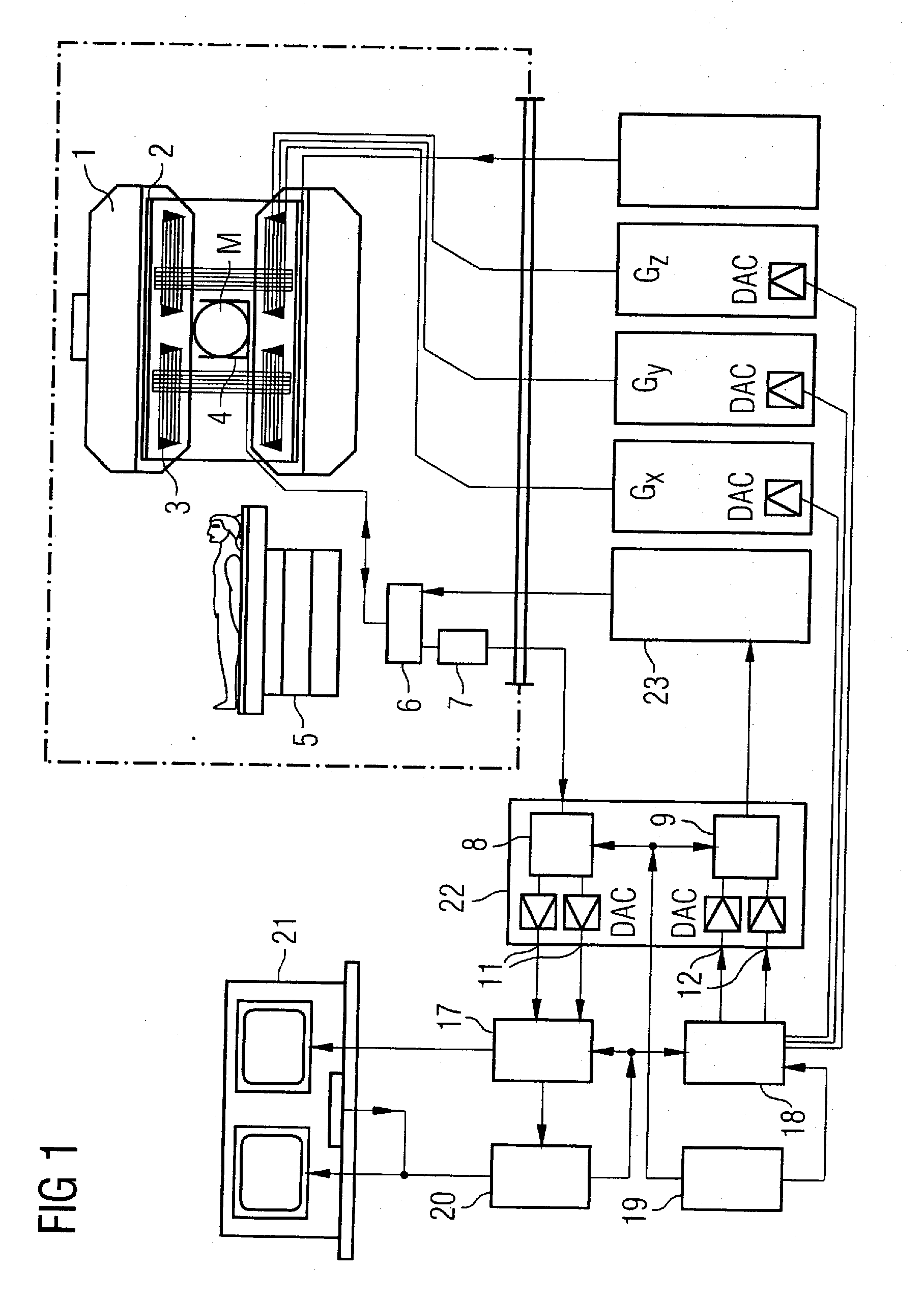
Magnetic resonance imaging with improved imaging contrast
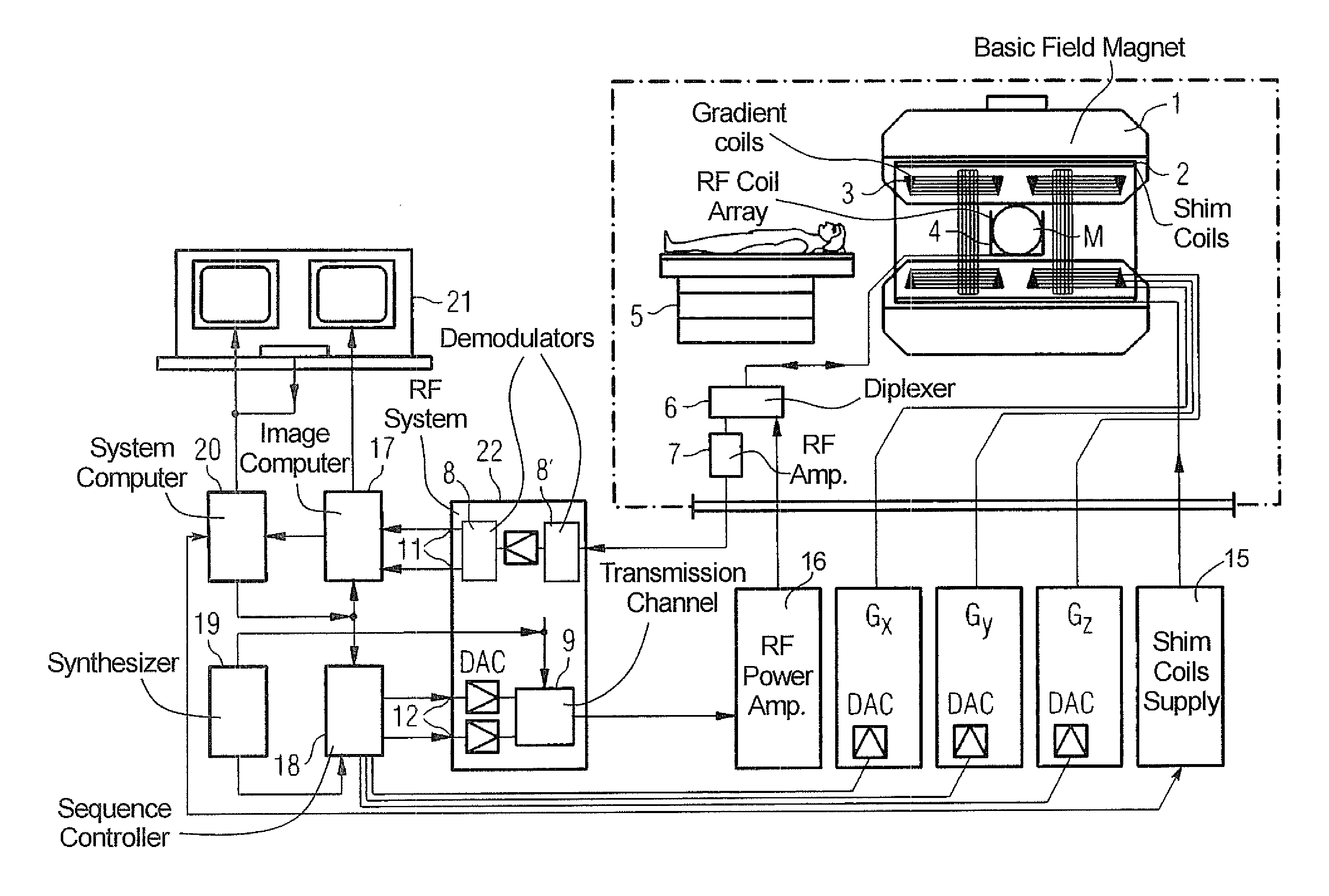
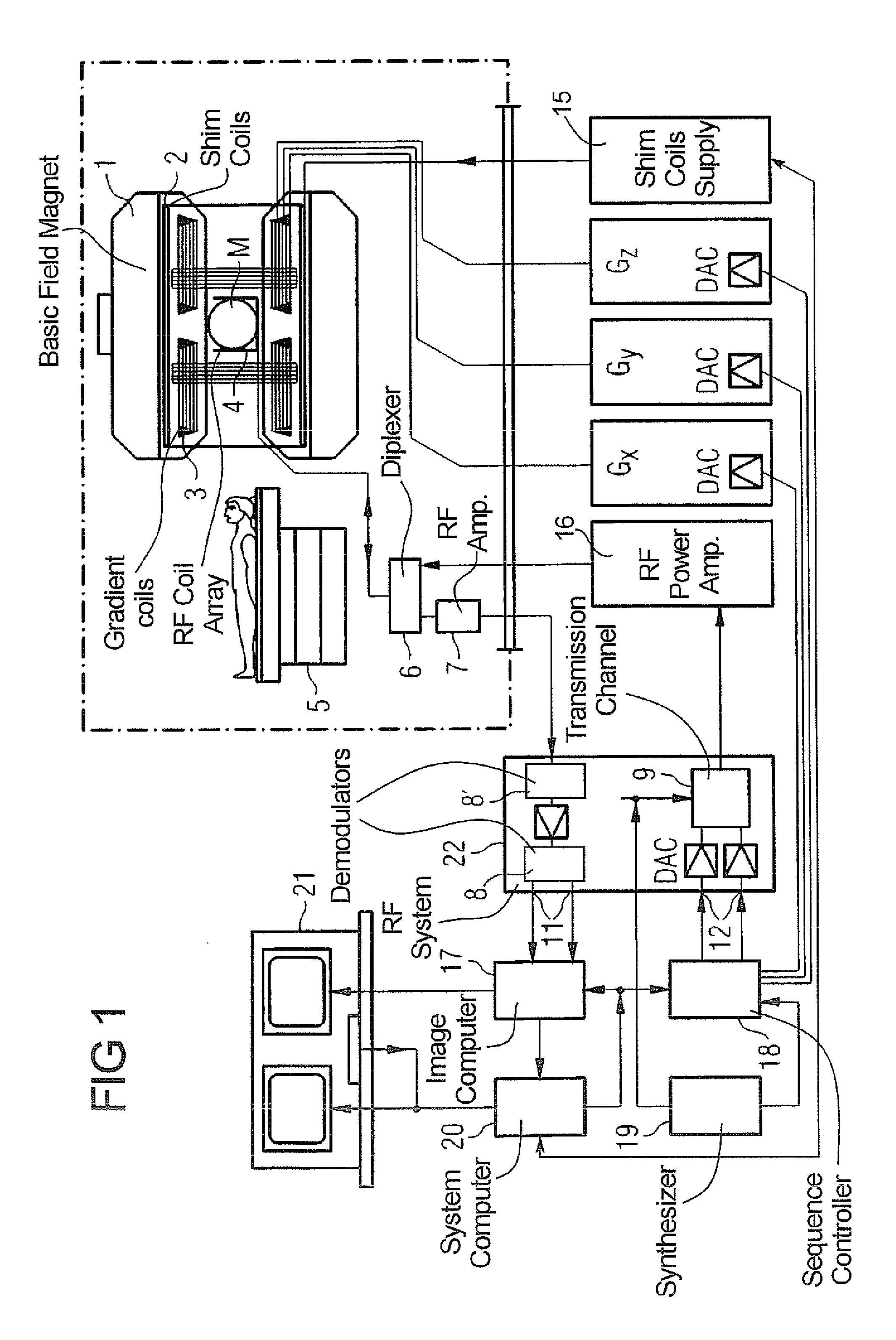
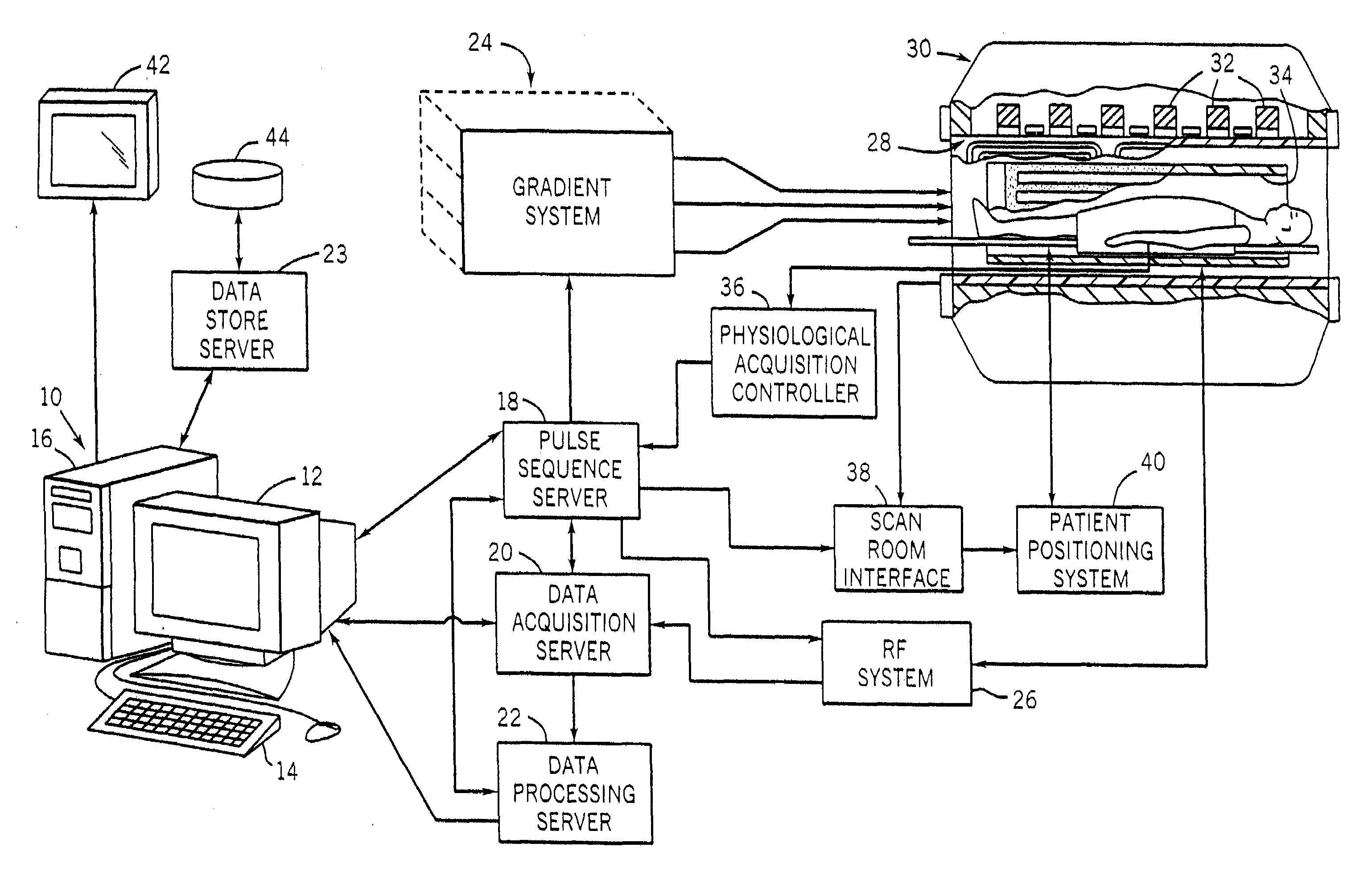
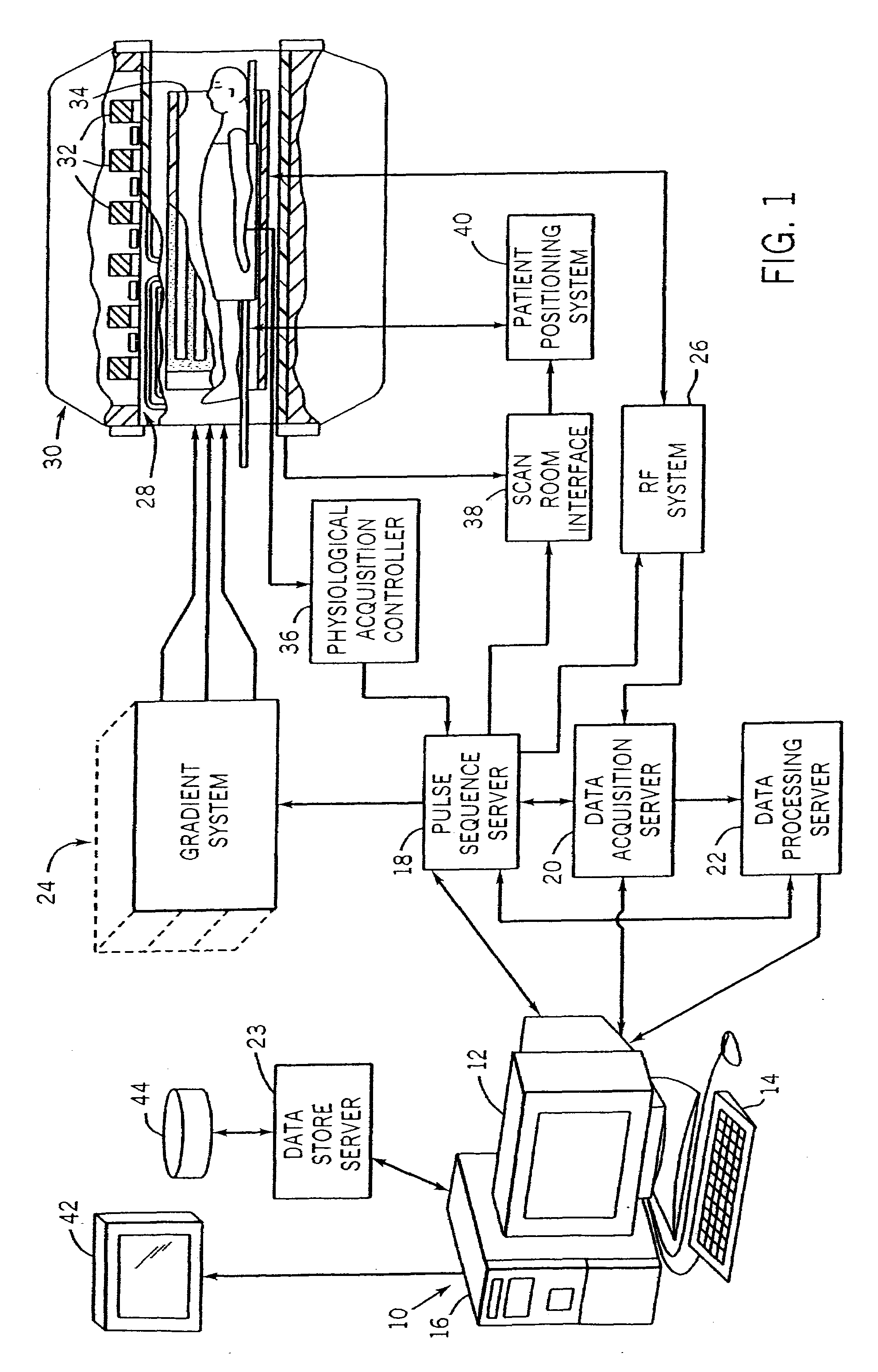
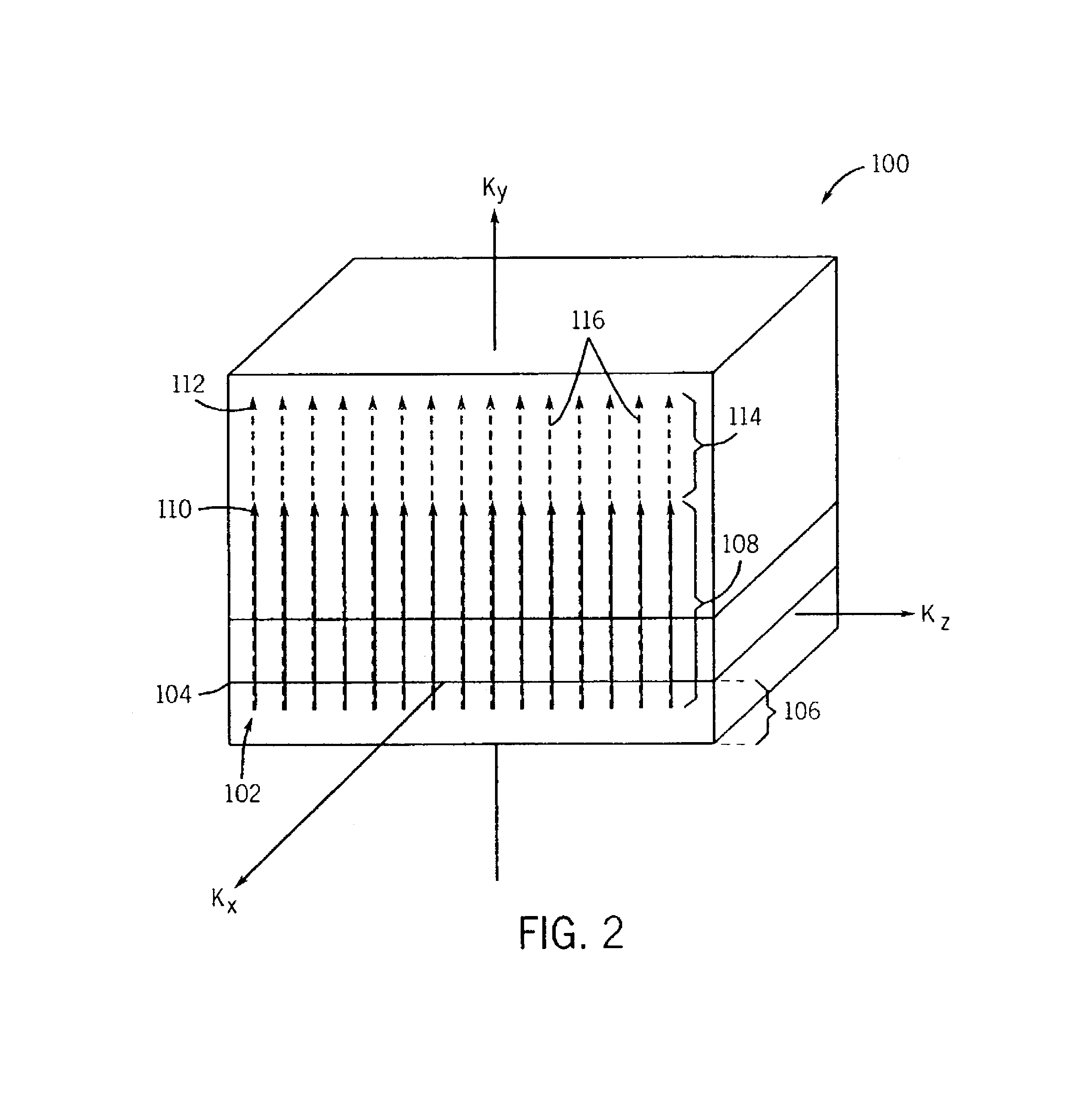
InactiveUS20120013336A1Minimize timeMinimal echo timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientObject based
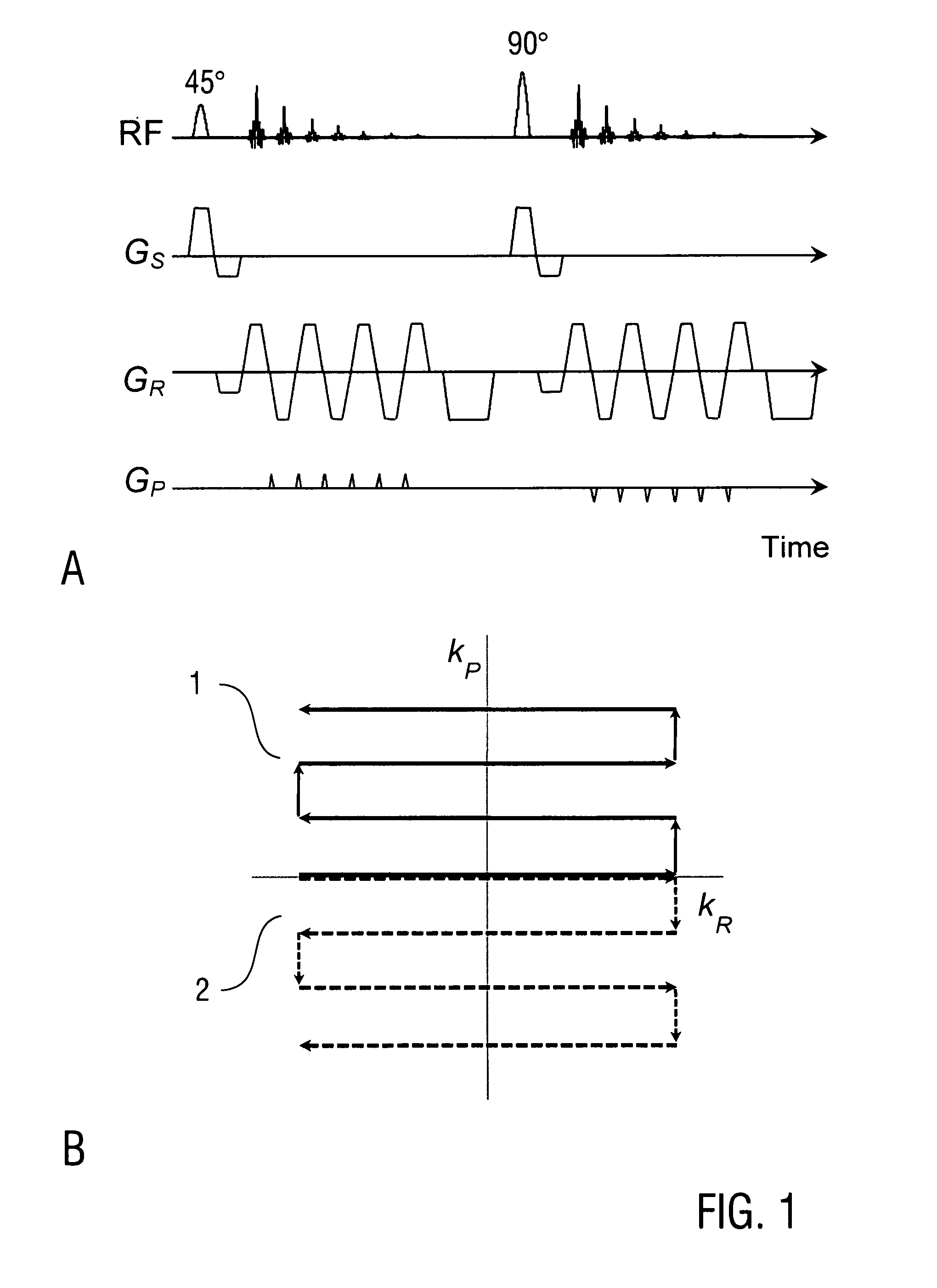
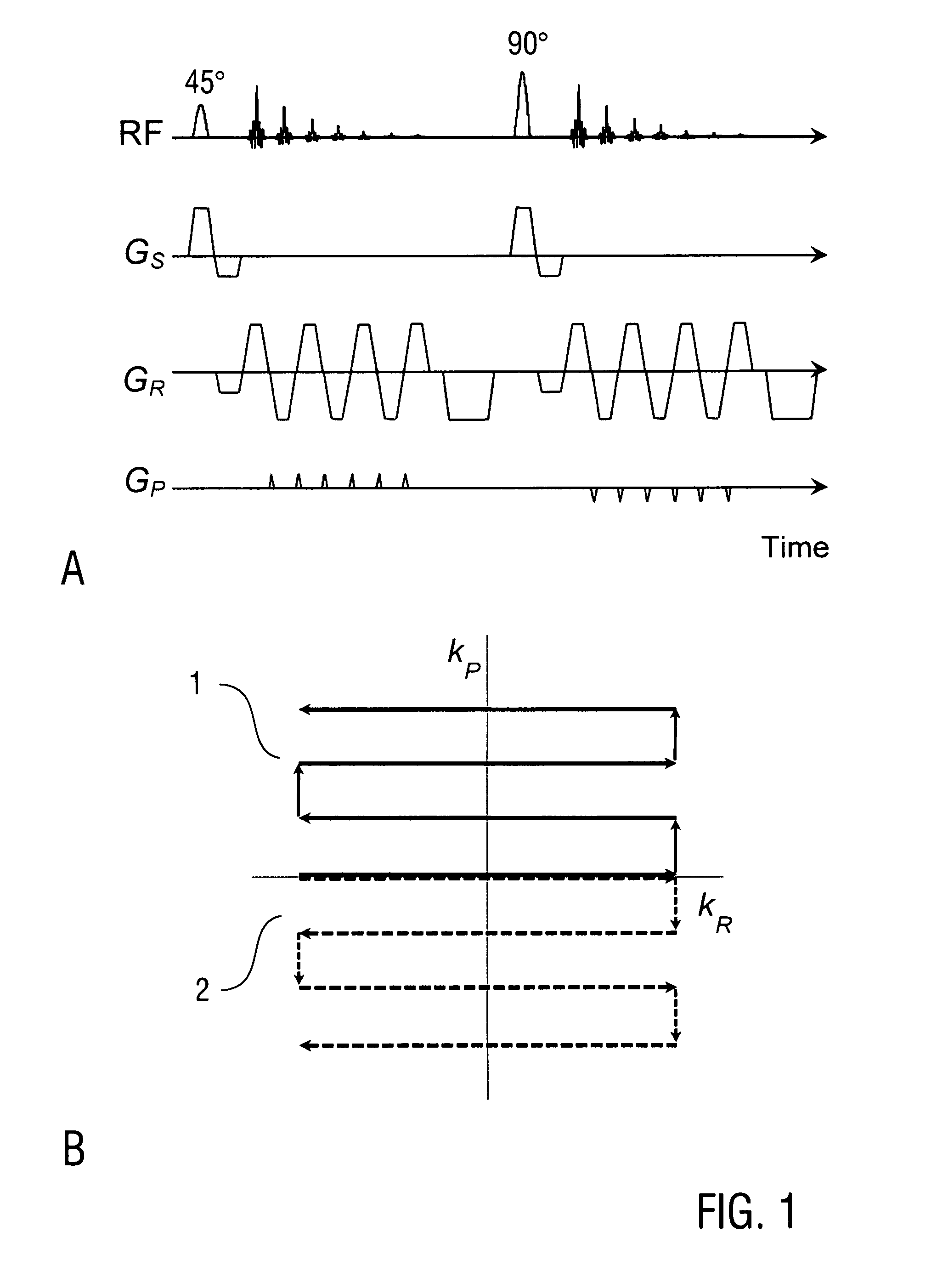
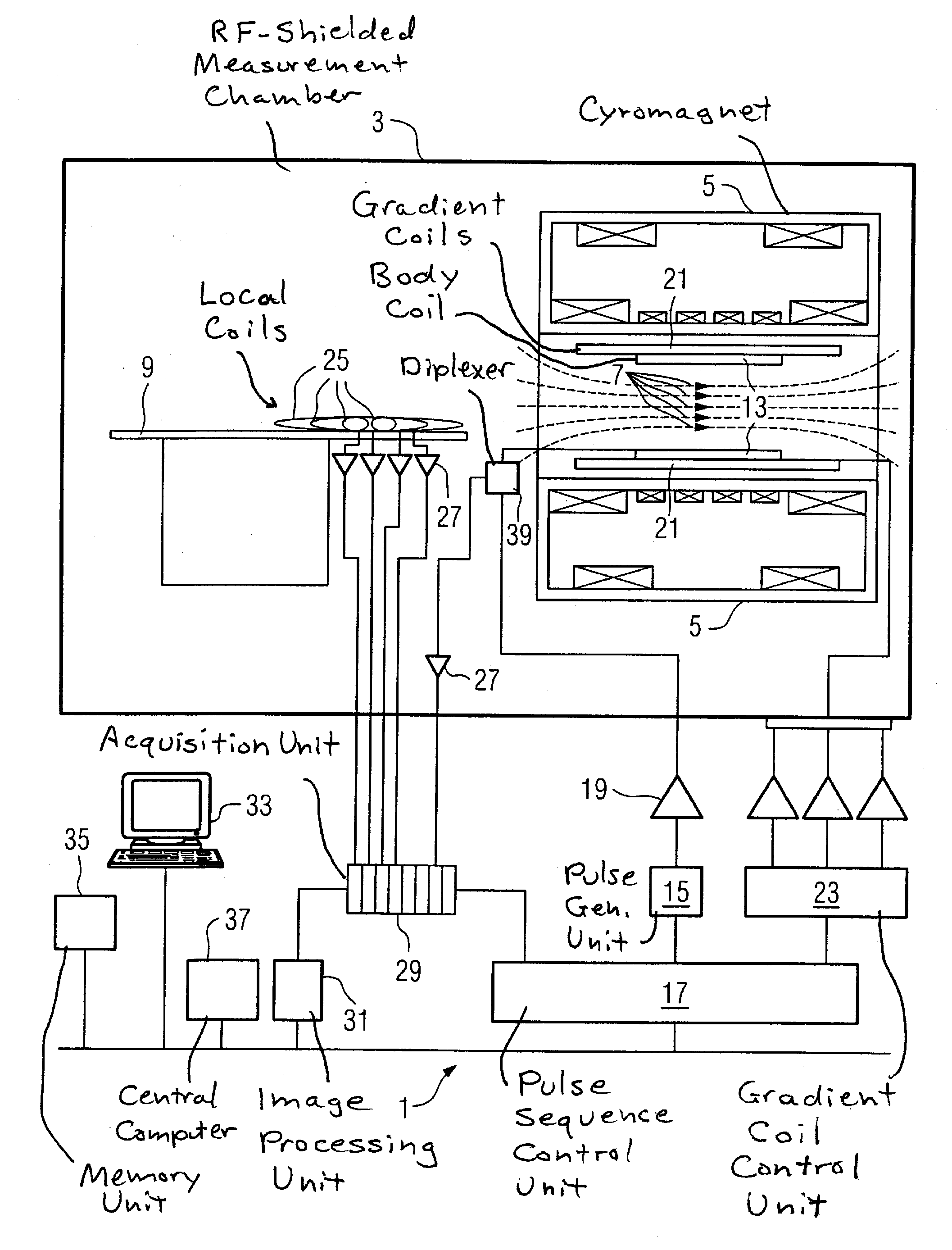
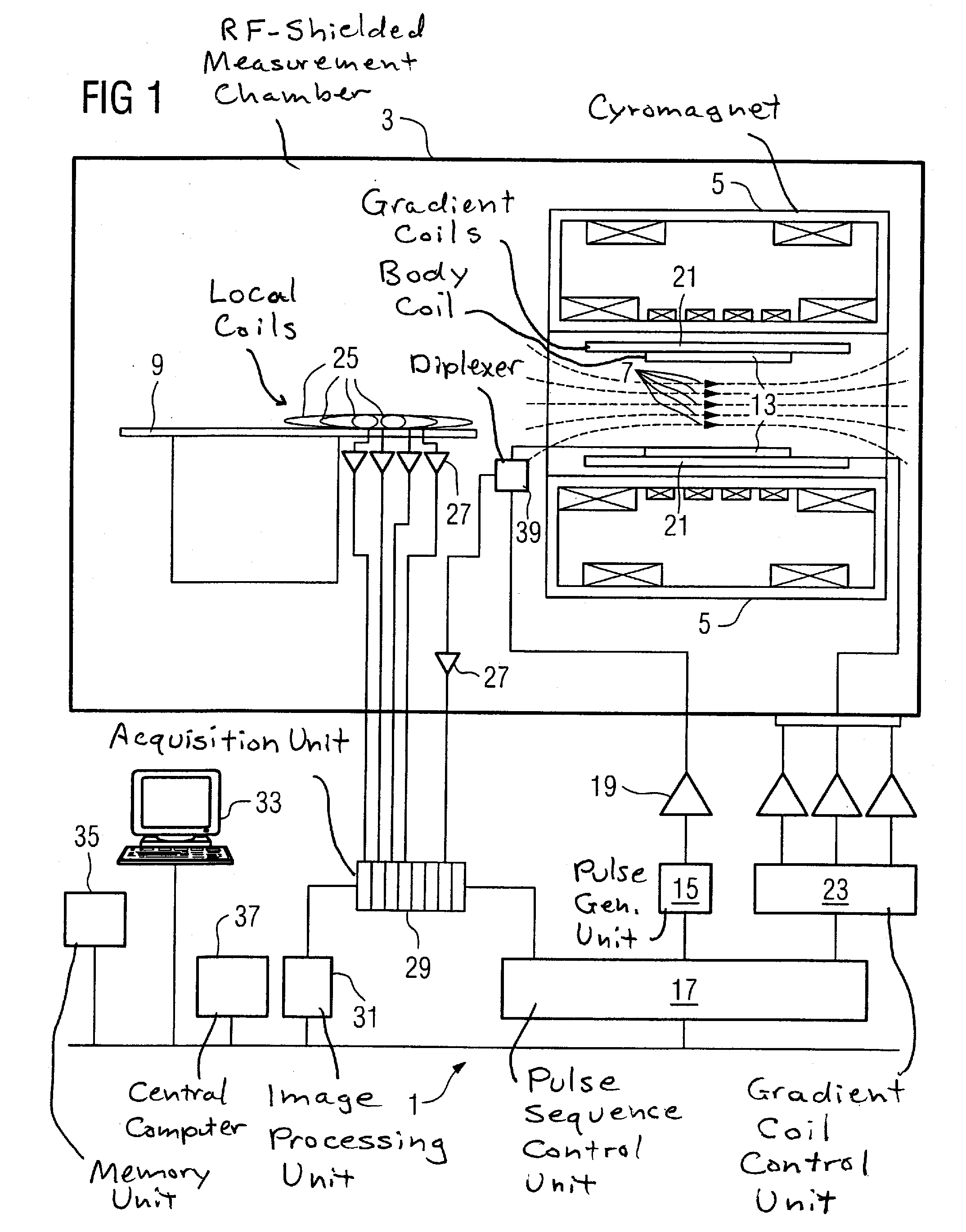
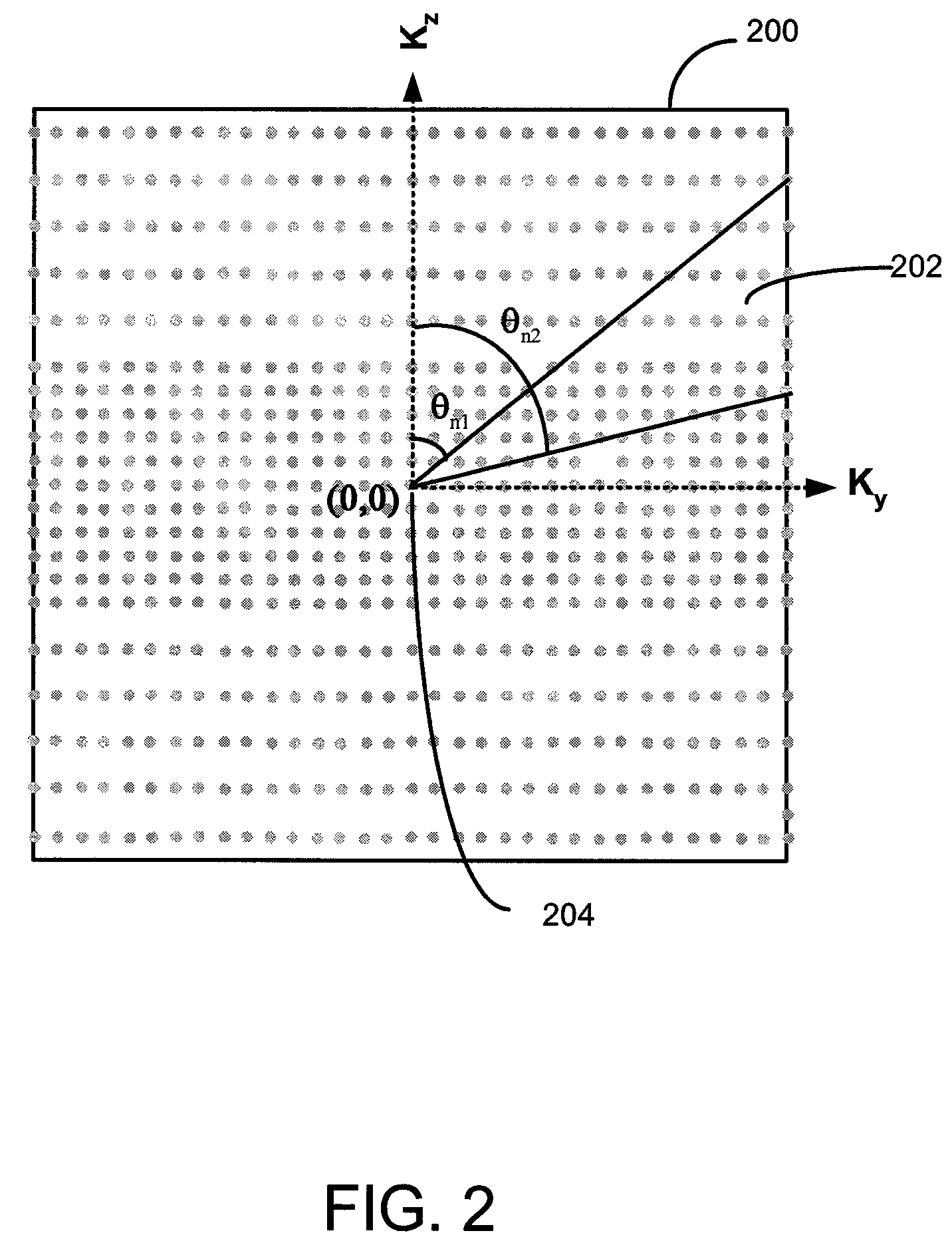
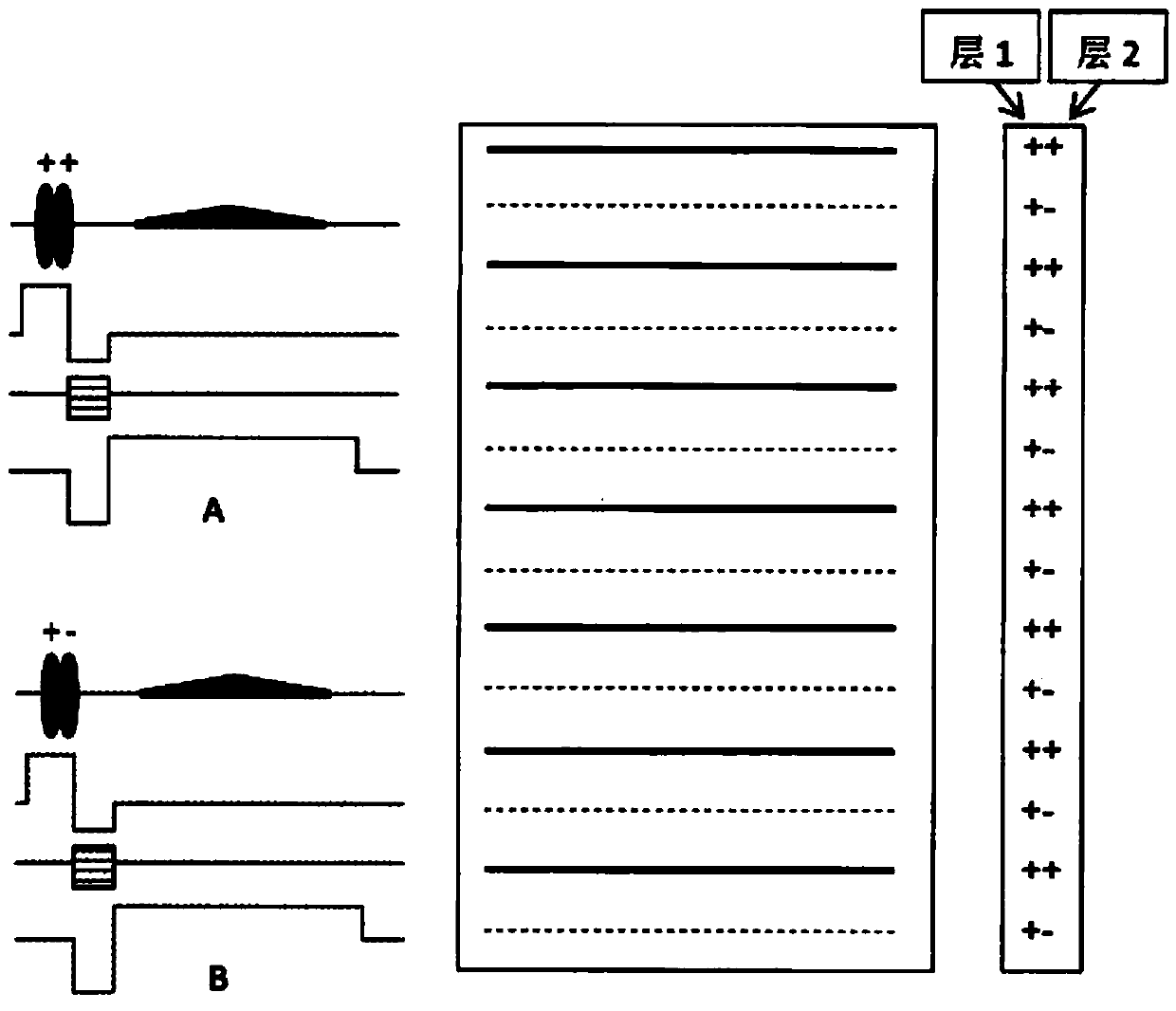
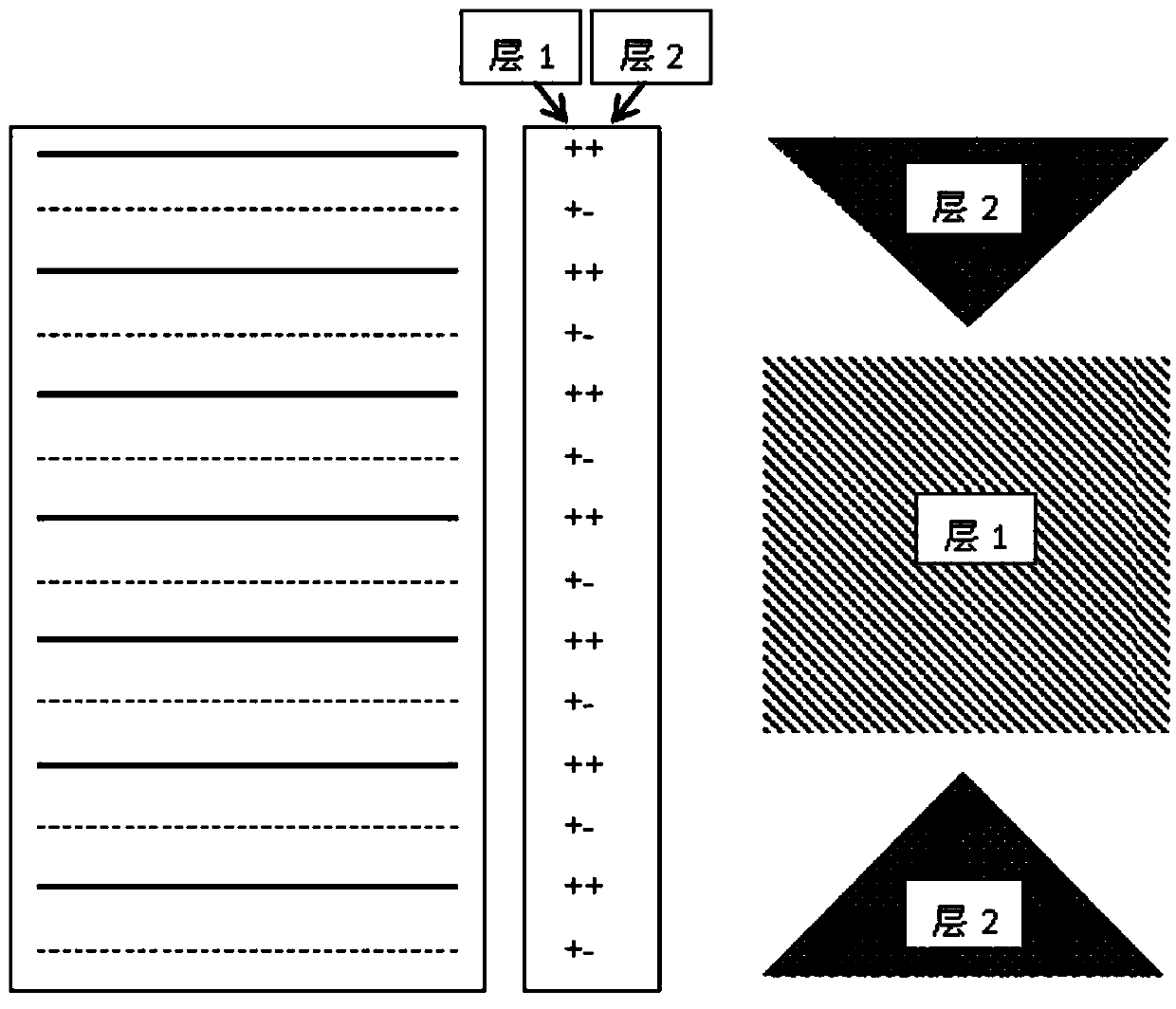
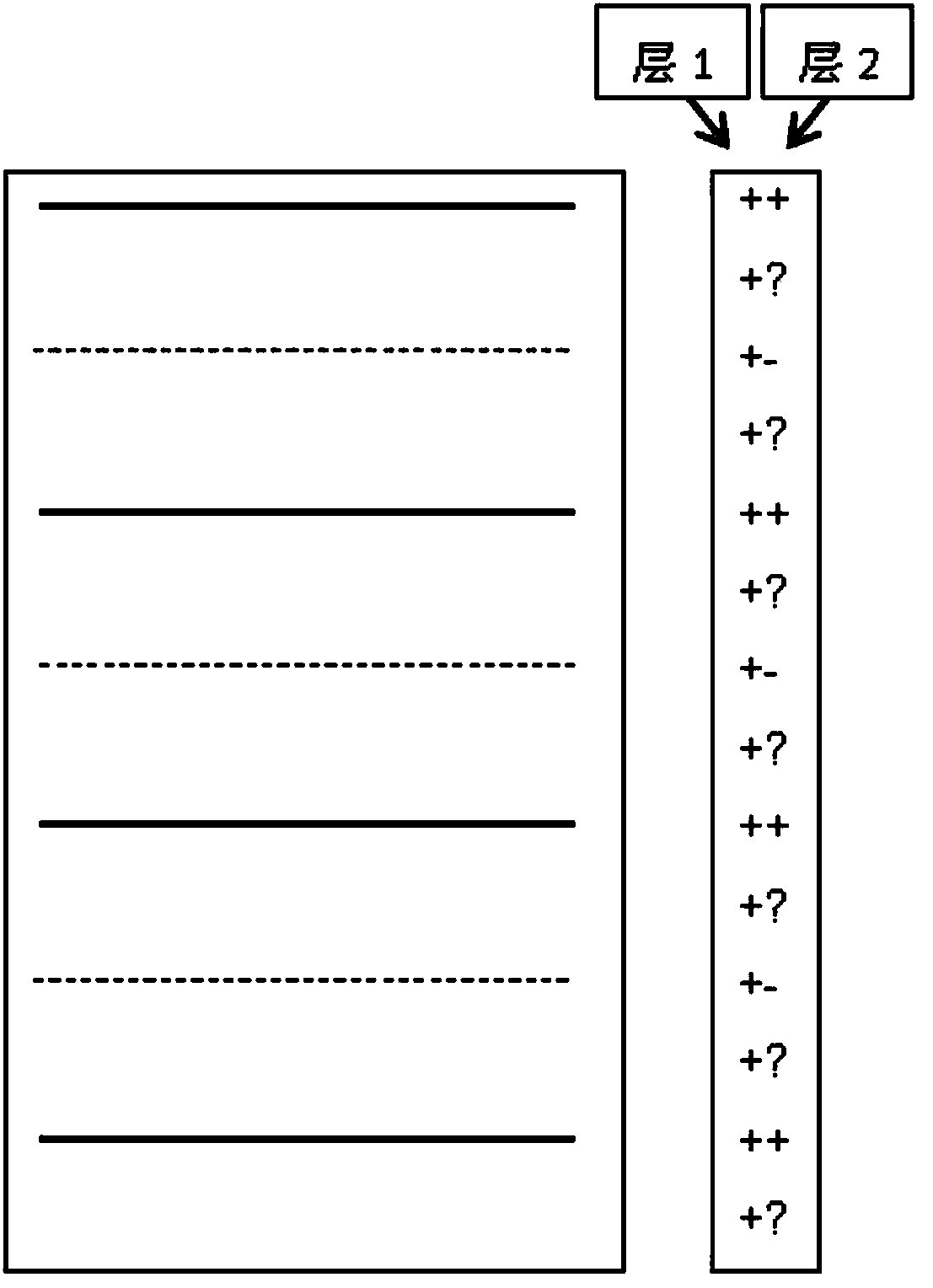
A method of magnetic resonance imaging of an object comprises the steps of arranging the object in a stationary magnetic field, subjecting the object to an excitation and encoding sequence of magnetic field gradients resulting in k-space sampling in two segments along the phase encoding direction, wherein the encoding sequence of the magnetic field gradients is selected such that the two segments in k-space are sampled along trajectories beginning with a central k-space line through the k-space center and continuing to opposite k-space borders of the two segments, collecting magnetic resonance signals created in the object, and reconstructing an image of the object based on the magnetic resonance signals, wherein one central k-space line is sampled in both of the two k-space segments, and intersegment phase and / or intensity deviations are corrected in both k-space segments using the magnetic resonance signals collected along the central k-space line. Furthermore, an imaging device for magnetic resonance imaging of an object is described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
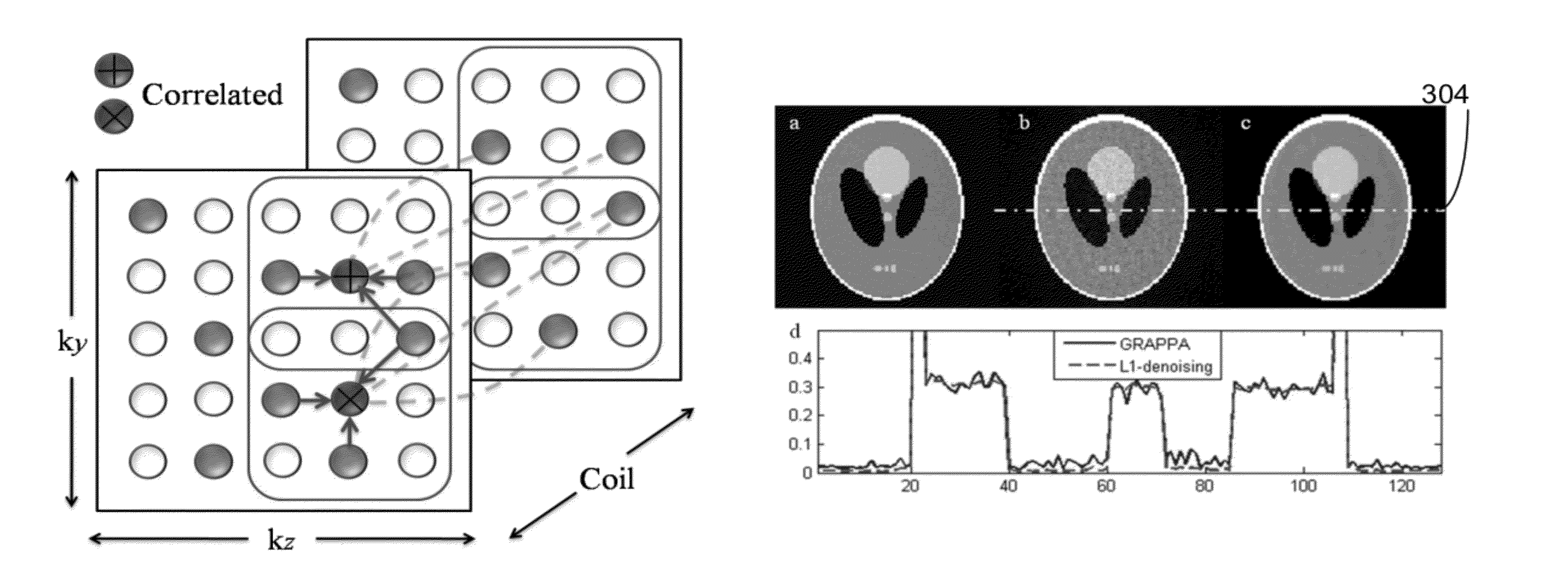
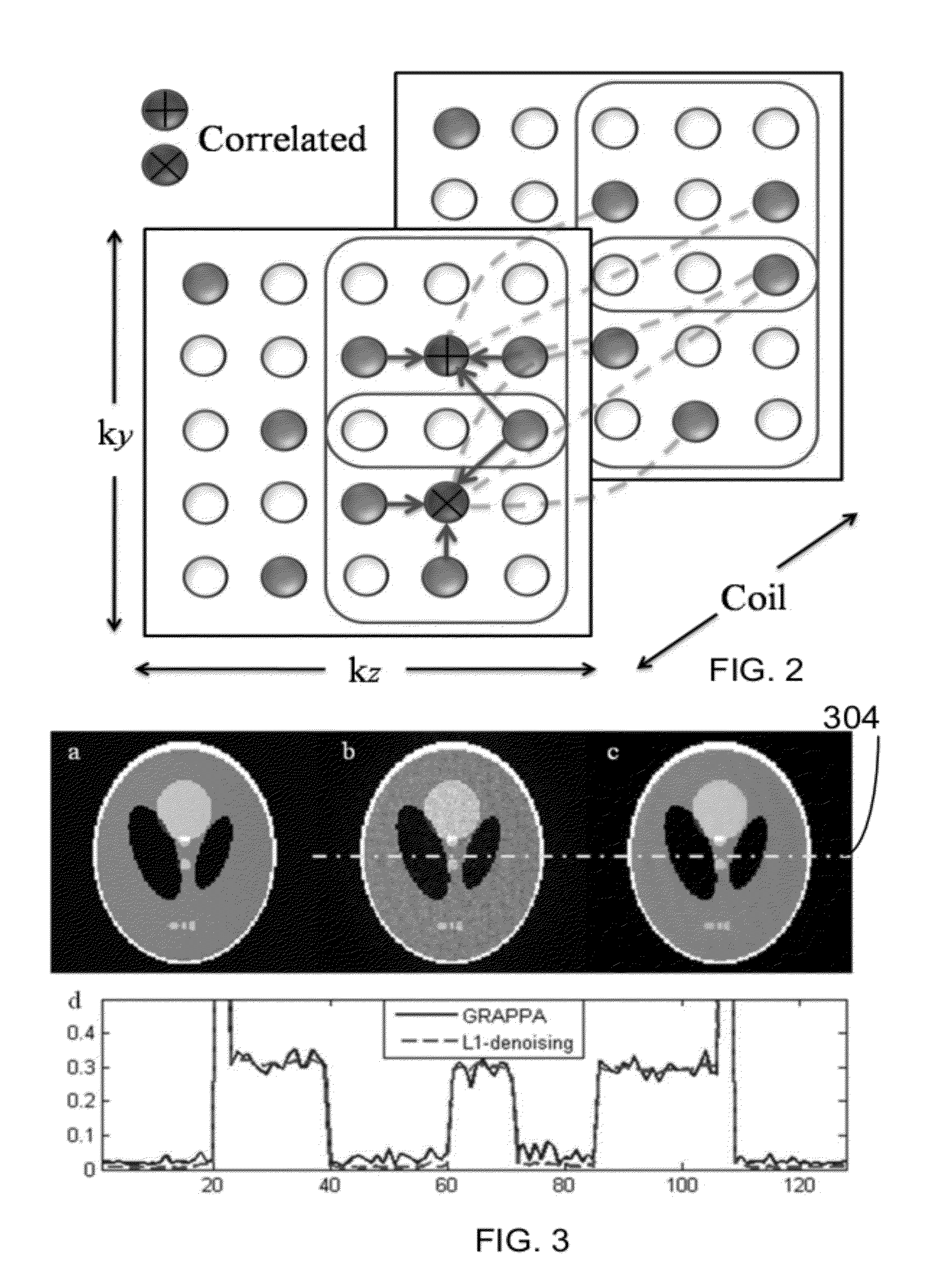
Autocalibrating parallel imaging reconstruction method from arbitrary k-space sampling with reduced noise
ActiveUS20120092009A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionParallel imagingReconstruction method
A computer implemented method for magnetic resonance imaging is provided. A 3D Fourier Transform acquisition is performed with two phase encode directions, wherein phase code locations are chosen so that a total number of phase encodes is less than a Nyquist rate, and closest distances between phase encode locations takes on a multiplicity of values. Readout signals are received through a multi-channel array of a plurality of receivers. An autocalibrating parallel imaging interpolation is performed and a noise correlation is generated. The noise correlation is used to weight a data consistency term of a compressed sensing iterative reconstruction. An image is created from the autocalibration parallel imaging using the weighted data consistency term. The image is displayed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
MR image reconstruction method and MR apparatus using propeller imaging
ActiveUS20060264735A1Simple (andReconstructed imageMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setResonance
In a magnetic resonance (MR) image reconstruction method and MR apparatus, for raw MR data are acquired with the propeller technique, and k-space sampling ensues in sub-data sets. The sample points of each sub-data set correspond to grid points of a Cartesian initial grid and the Cartesian initial grid of the sub-data sets can be brought into congruence by rotation: A Cartesian final grid is selected, and a calculation-based transfer of the data points of each sub-data set ensues to a respective new grid that exhibits the orientation of the respective sub-data set and the grid constants of the final grid, if the grid constants of the output grid differ from those of the final grid. A calculation-based transfer of the data points of each sub-data set, or the data points of a respective new grid (if obtained) ensures to the final grid by the application of a rotation module followed by transformation of the acquired data into the image domain.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
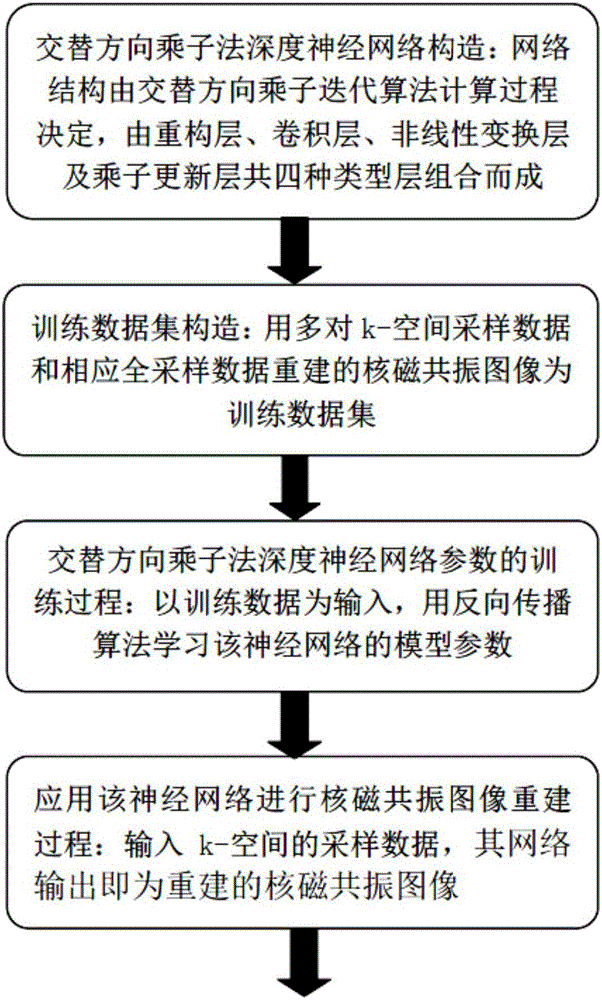
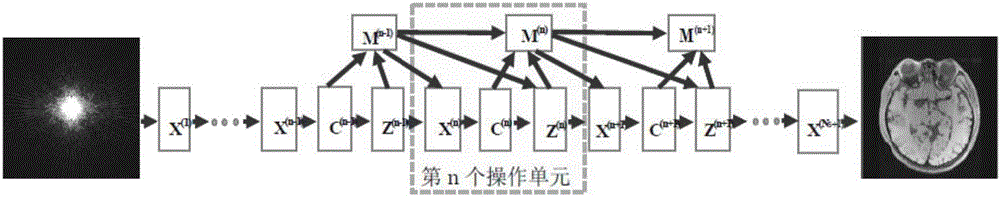
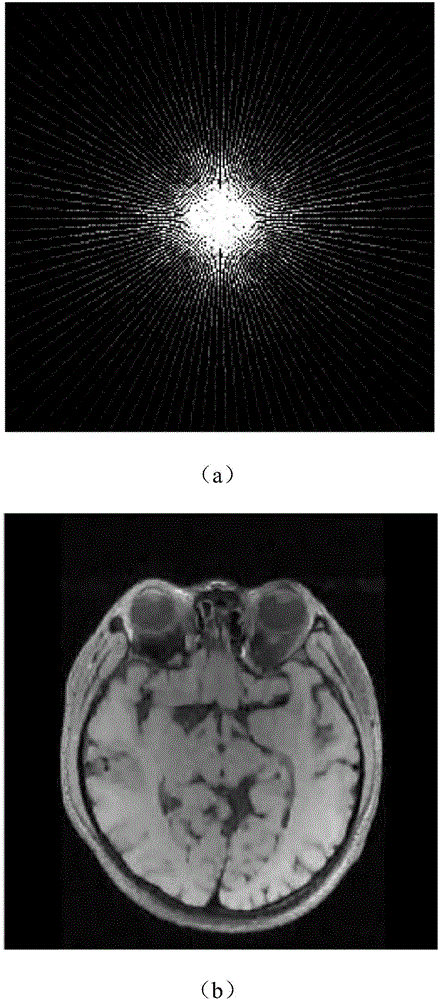
Compressed sensing nuclear magnetic resonance imaging method based on deep neural network
ActiveCN106373167AHigh precisionFast precisionReconstruction from projectionNeural learning methodsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceData set
The invention discloses a compressed sensing nuclear magnetic resonance imaging method based on a deep neural network. Through the method, a high-quality nuclear magnetic resonance image can be reconstructed with k-space low sampling data collected by a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging device. The method mainly comprises three steps: constructing an alternating direction multiplier deep neural network, training the parameters of the network, and applying the trained network to compressed sensing nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. A nuclear magnetic resonance image reconstructed with multiple pairs of sampling data at low sampling rate and corresponding full-sampling data is used as a training data set, and the model parameters of the alternating direction multiplier deep neural network are trained so that the output image of the deep neural network when sampling data at low sampling rate is used as input is as close as possible to an image reconstructed with full-sampling data. In application, k-space sampling data at given low sampling rate is input to a trained alternating direction multiplier deep neural network, and the output of the network is a reconstructed nuclear magnetic resonance image.
Owner:广州本影医疗科技有限公司
Magnetic resonance imaging with improved imaging contrast
InactiveUS8664954B2Minimize timeMinimal echo timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientObject based
A method of magnetic resonance imaging of an object comprises the steps of arranging the object in a stationary magnetic field, subjecting the object to an excitation and encoding sequence of magnetic field gradients resulting in k-space sampling in two segments along the phase encoding direction, wherein the encoding sequence of the magnetic field gradients is selected such that the two segments in k-space are sampled along trajectories beginning with a central k-space line through the k-space center and continuing to opposite k-space borders of the two segments, collecting magnetic resonance signals created in the object, and reconstructing an image of the object based on the magnetic resonance signals, wherein one central k-space line is sampled in both of the two k-space segments, and intersegment phase and / or intensity deviations are corrected in both k-space segments using the magnetic resonance signals collected along the central k-space line. Furthermore, an imaging device for magnetic resonance imaging of an object is described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
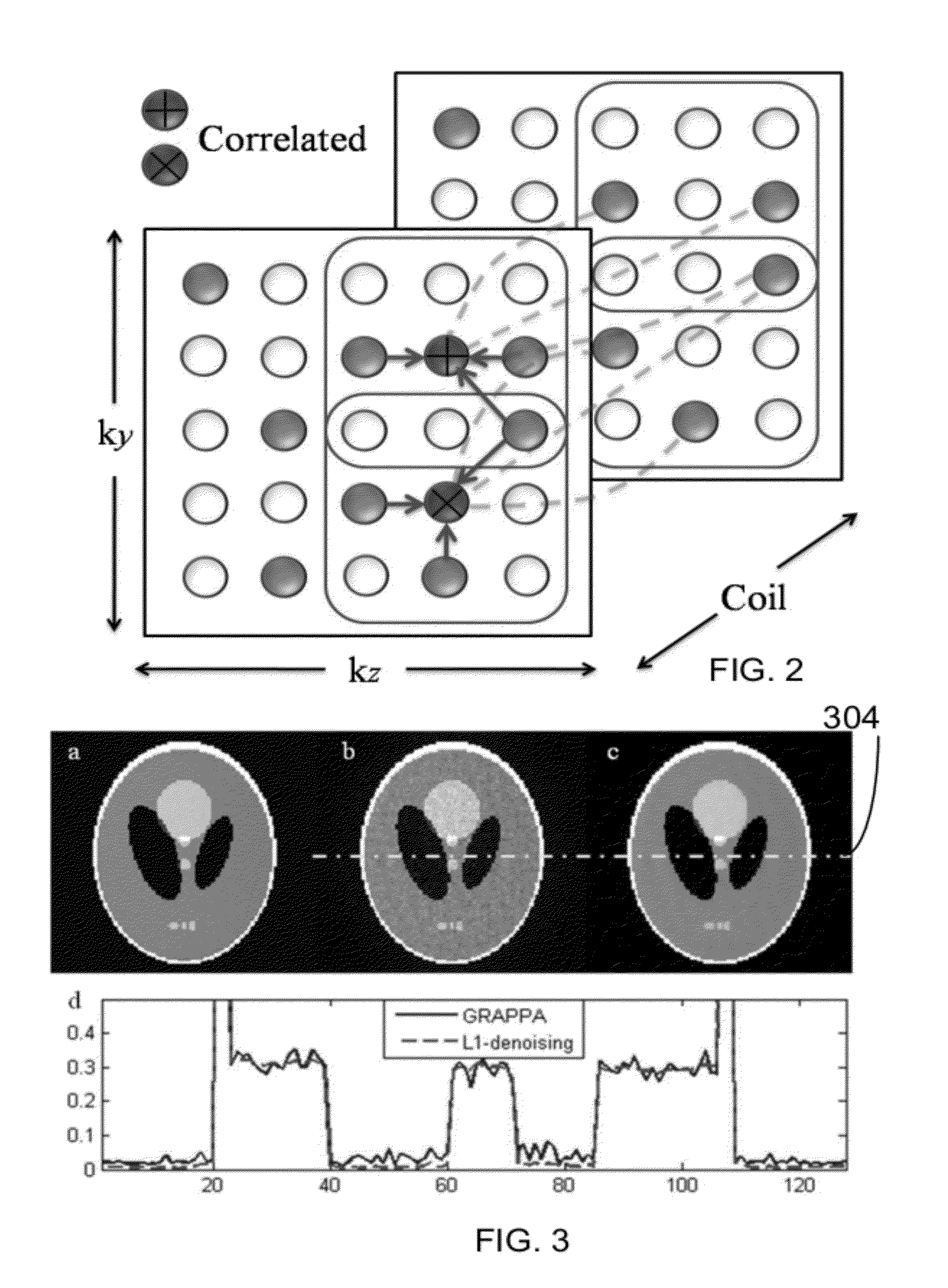
Multi-coil magnetic resonance data acquisition and image reconstruction method and apparatus using blade-like k-space sampling
ActiveUS20080129289A1Avoid disadvantagesImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceReconstruction method
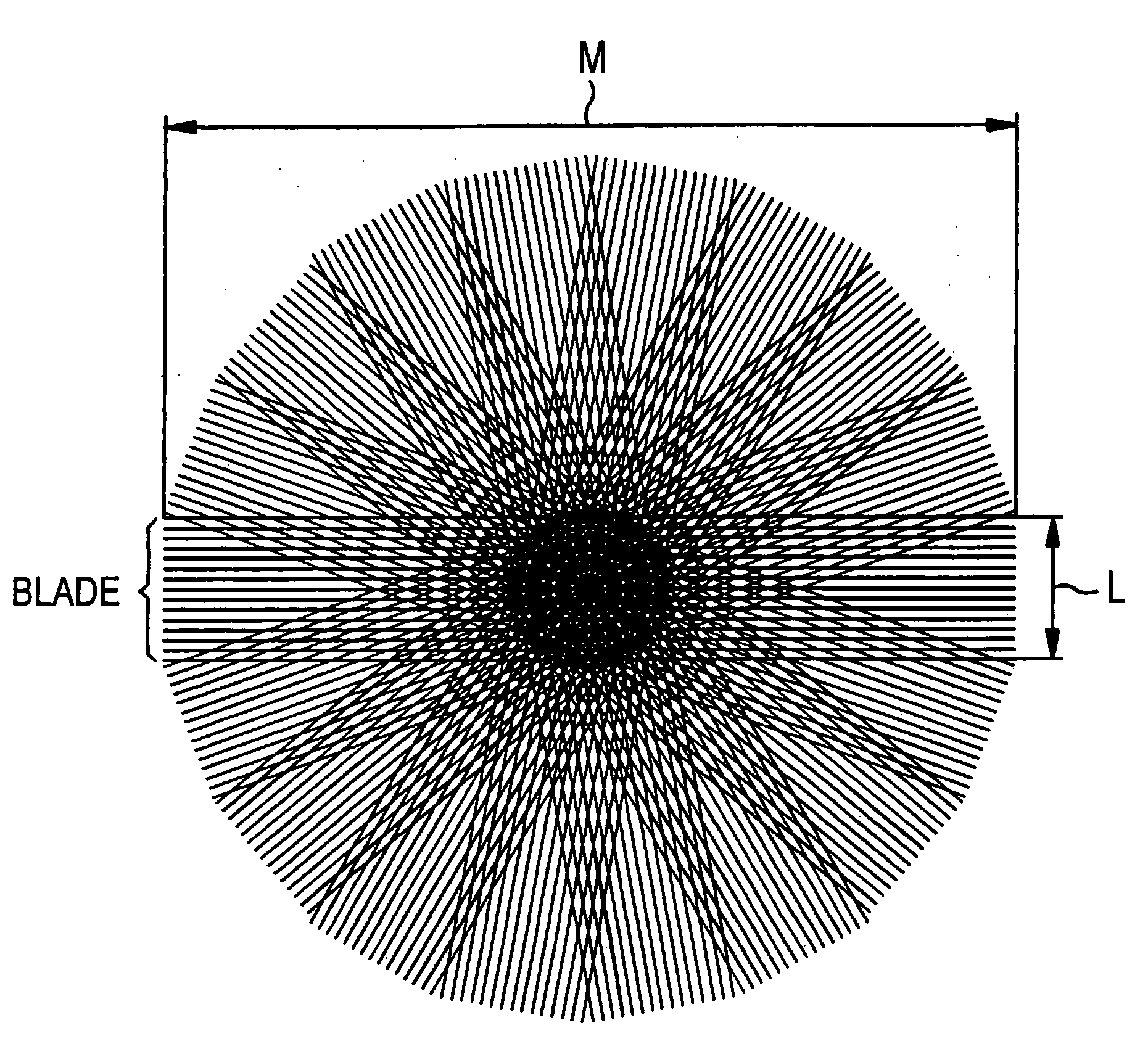
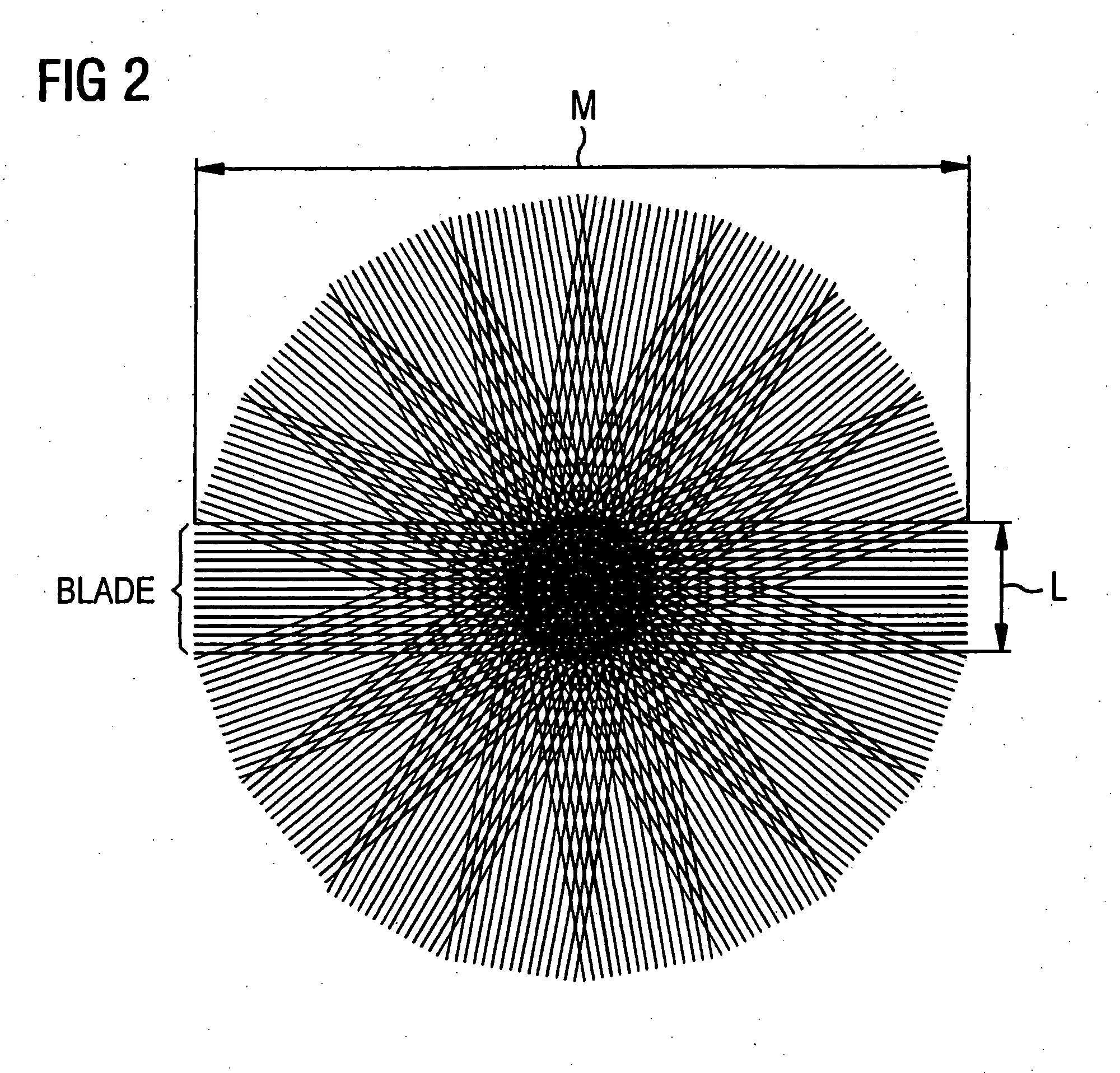
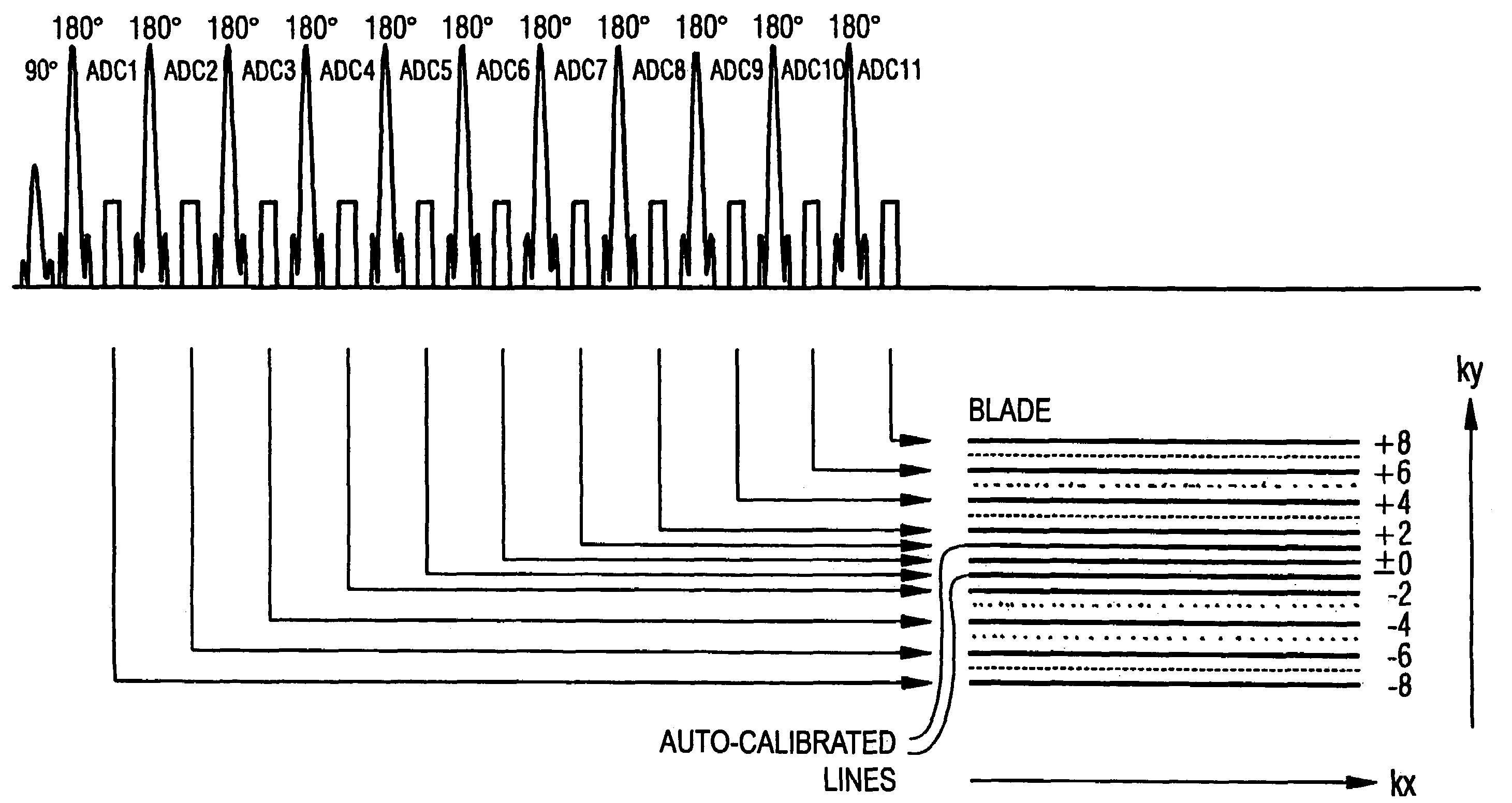
In a data acquisition and reconstruction method for magnetic resonance (MR) tomography, and a corresponding MR tomography apparatus, a blade-like sampling of k-space according to the PROPELLER method using a number of reception coils ensures with partial under-sampling of at least one blade of k-space such that the under-sampling ensues by regular omission of k-space lines in both boundary regions (with regard to the phase-encoding direction ky) of a blade such that only data in each A-th line of said boundary regions are acquired; with no k-space lines being omitted in the central region (with regard to the ky-direction) and thus at least one coil calibration line is obtained, selection of a suitable PPA method for completion of the blades and determination of the necessary coil calibration data necessary for the PPA reconstruction of a partial under-sampled blade from the central completely sampled region of said blade. PPA reconstruction via application of the selected PPA method selected in order to interpolate the non-measured or, respectively, omitted k-space lines of each blade, and execution of the PROPELLER reconstruction after the PPA reconstruction.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus for generating a measurement sequence executable by apparatus hardware
InactiveUS20080024129A1Optimal hardware utilizationImprove overall utilizationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceControl signalResonance
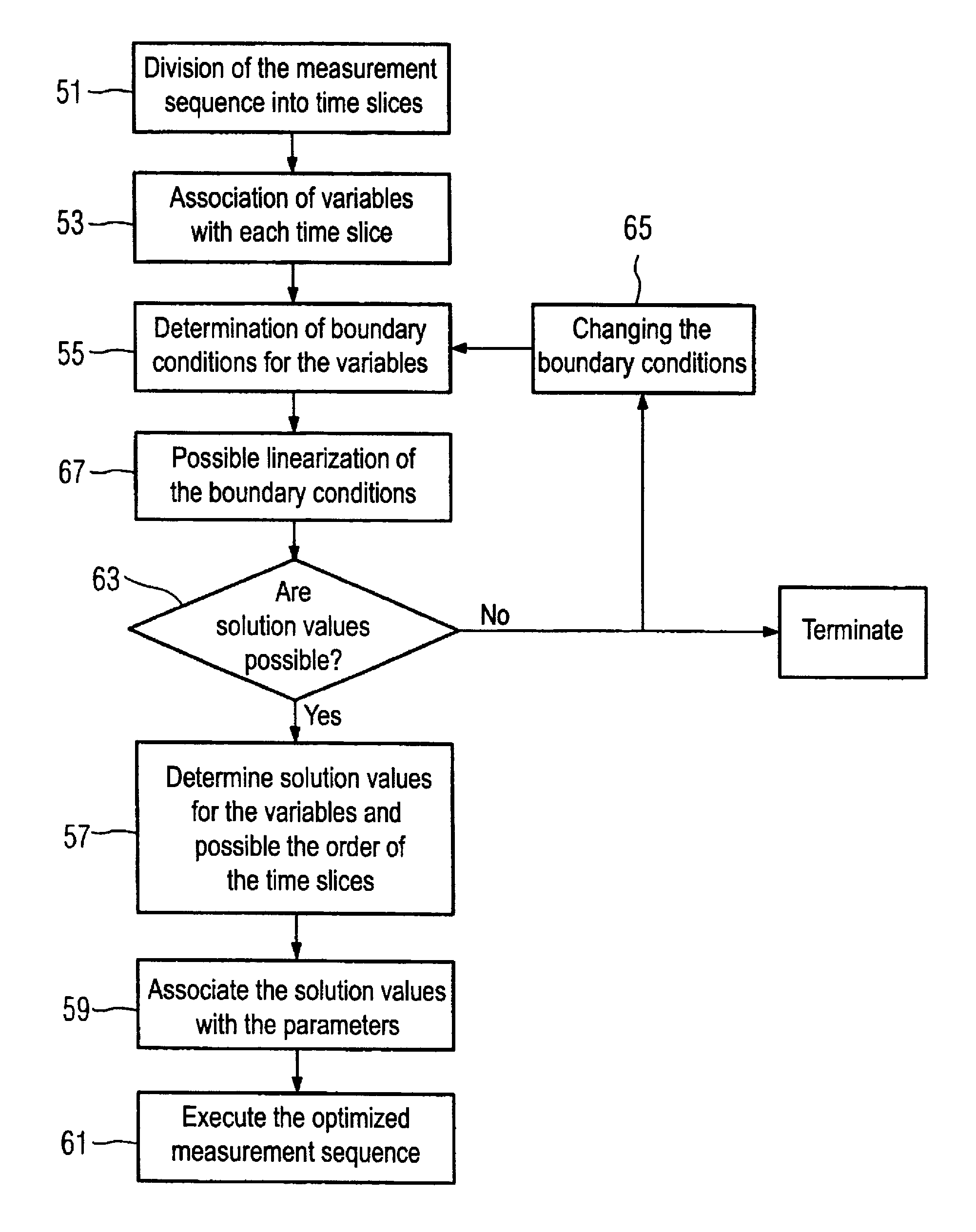
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus for generation of a measurement sequence that can be executed with the hardware of the magnetic resonance apparatus, a measurement sequence is generated as a series of time slices of different time slice types, with the control signals for the magnetic resonance apparatus during each time slice being determined using parameters describing these time slices. After division of the measurement sequence into a number of time slices dependent on the sequence type and on a k-space sampling type, descriptive variables are associated with the time slices. Value ranges of the variables are limited and / or the variables are set in relation to one another using boundary conditions. A determination ensues of solution values of the variables with which a predetermined target parameter of the measurement sequence is optimized. A measurement sequence executable on the hardware is attained by association of the solution values with the corresponding parameters of the time slices.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Multi-coil magnetic resonance data acquisition and image reconstruction method and apparatus using blade-like k-space sampling
ActiveUS7482806B2Avoid disadvantagesImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonancePropeller
In a data acquisition and reconstruction method for magnetic resonance (MR) tomography, and a corresponding MR tomography apparatus, a blade-like sampling of k-space according to the PROPELLER method using a number of reception coils ensures with partial under-sampling of at least one blade of k-space such that the under-sampling ensues by regular omission of k-space lines in both boundary regions (with regard to the phase-encoding direction ky) of a blade such that only data in each A-th line of said boundary regions are acquired; with no k-space lines being omitted in the central region (with regard to the ky-direction) and thus at least one coil calibration line is obtained, selection of a suitable PPA method for completion of the blades and determination of the necessary coil calibration data necessary for the PPA reconstruction of a partial under-sampled blade from the central completely sampled region of said blade. PPA reconstruction via application of the selected PPA method selected in order to interpolate the non-measured or, respectively, omitted k-space lines of each blade, and execution of the PROPELLER reconstruction after the PPA reconstruction.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and device for eliminating motion artifact of K spacial sampled data in MRI system
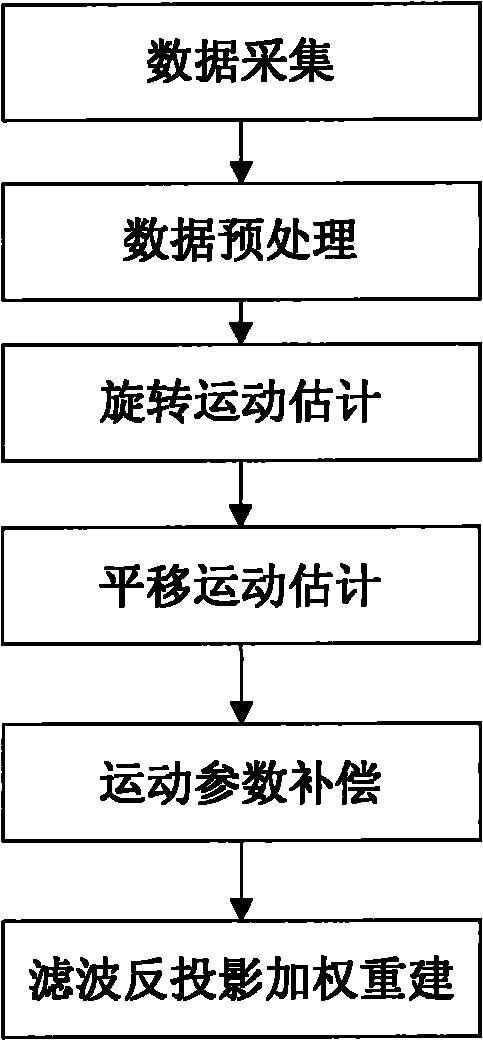
The invention relates to a method and a device for eliminating motion artifact of K spacial sampled data in a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system. The method comprises the following steps of: sampling data; preprocessing the data, namely ensuring the consistency of echo signal intensity, and moving the echo maximum to the center; estimating rotary motion, namely searching echo reference pairs between a rotary data tape and a basis data tape by utilizing frequency domain similarity, calculating relative angle offset among the reference pairs, establishing a rotary motion equation set, and introducing a constraint condition to solve rotary motion parameters; estimating translational motion, namely establishing a translational equation set to solve translational motion parameters according to a data consistency principle equivalent equation and the rotation angle obtained in the last step; compensating motion parameters, namely performing motion compensation on the motion parameters solved in the step 3 and the step 4; and performing filtered backprojection weighted reestablishment, namely adopting a filtered backprojection method for weighted reestablishment. The method or the device can effectively inhibit motion artifact.
Owner:XINGAOYI MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
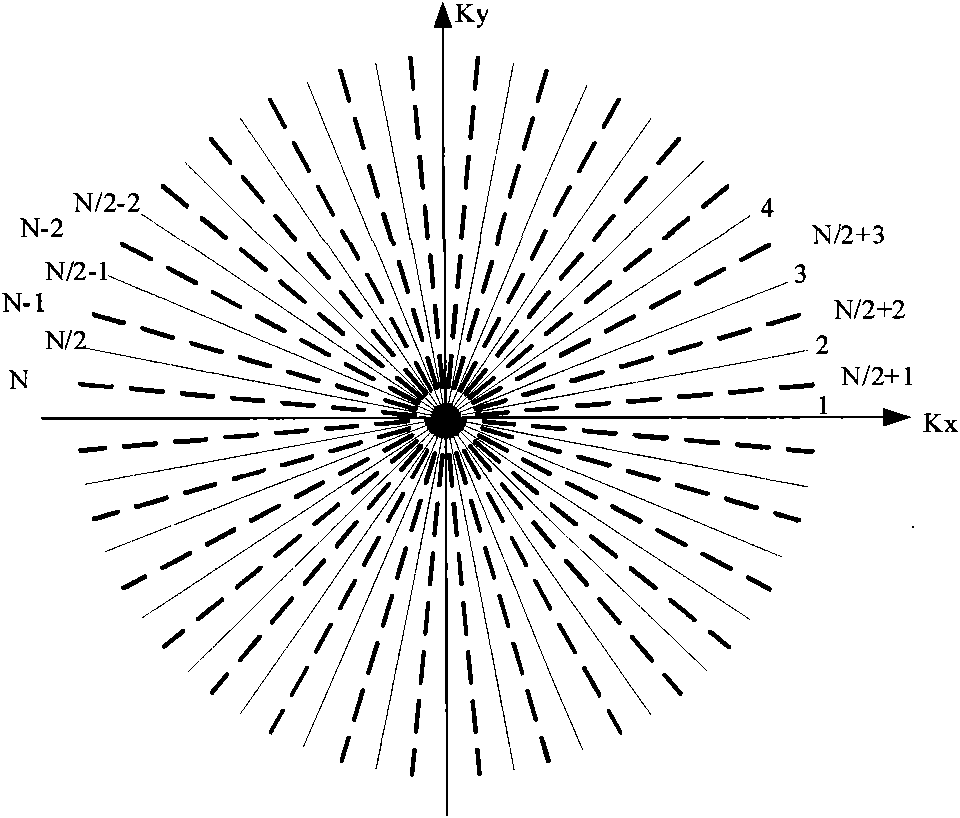
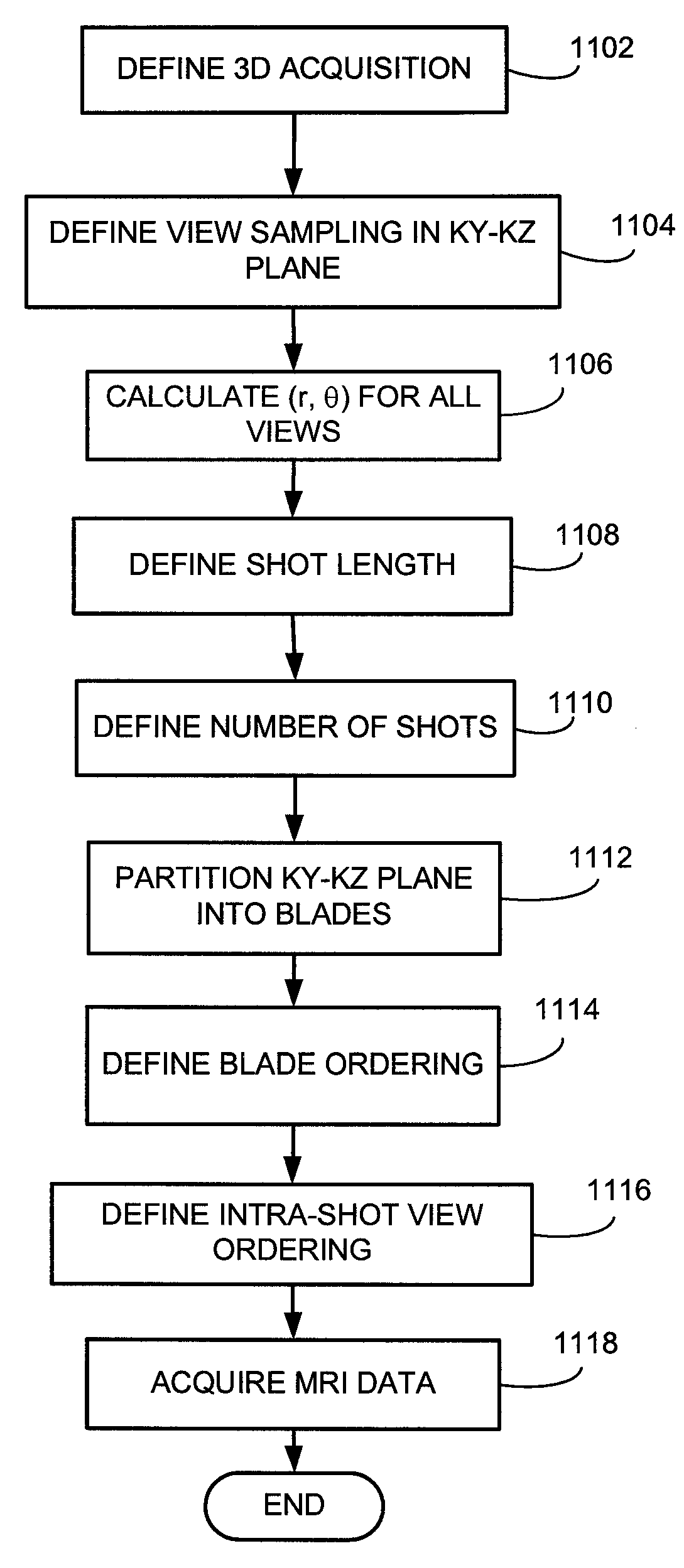
Method and apparatus for acquiring magnetic resonance imaging data
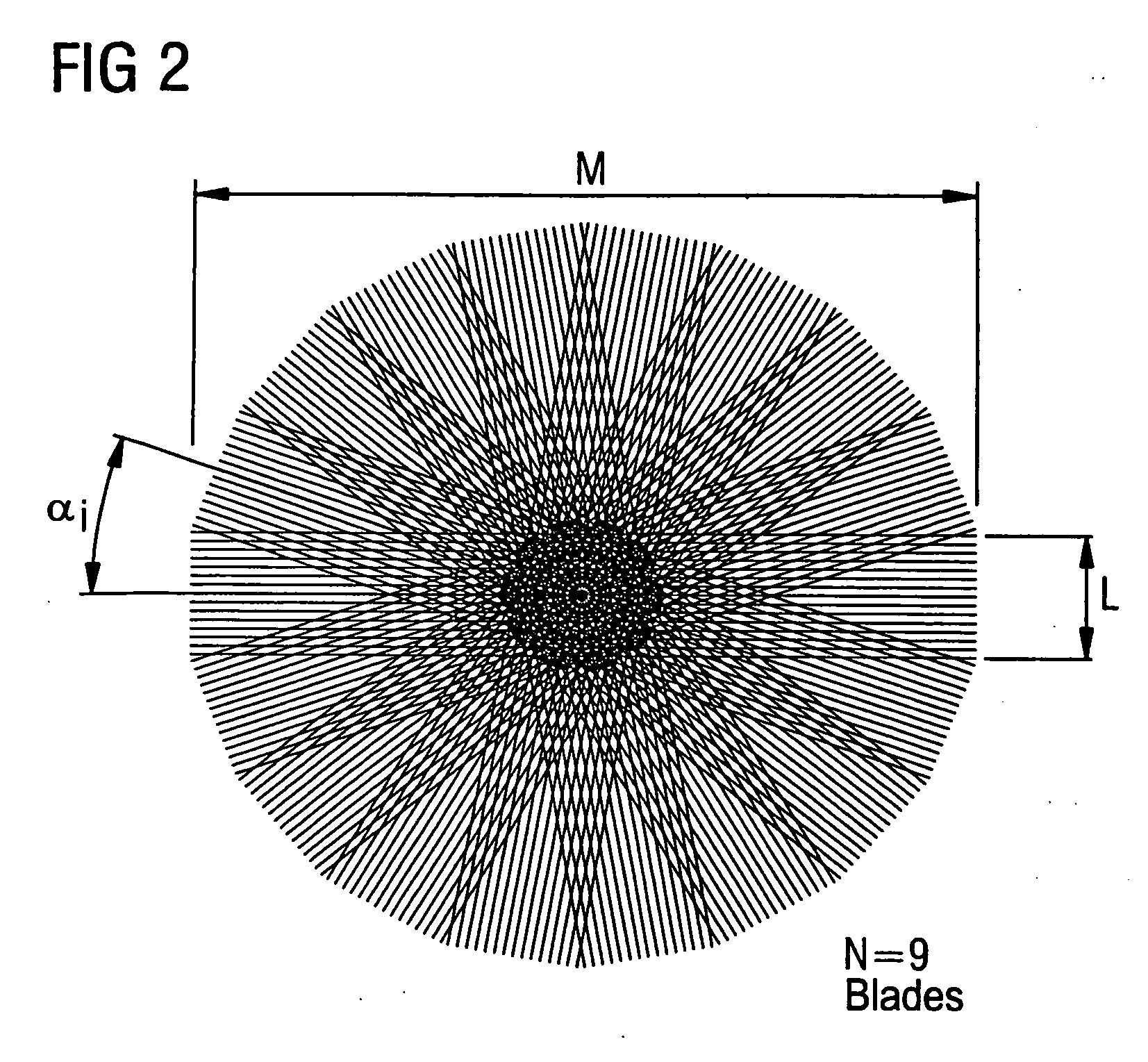
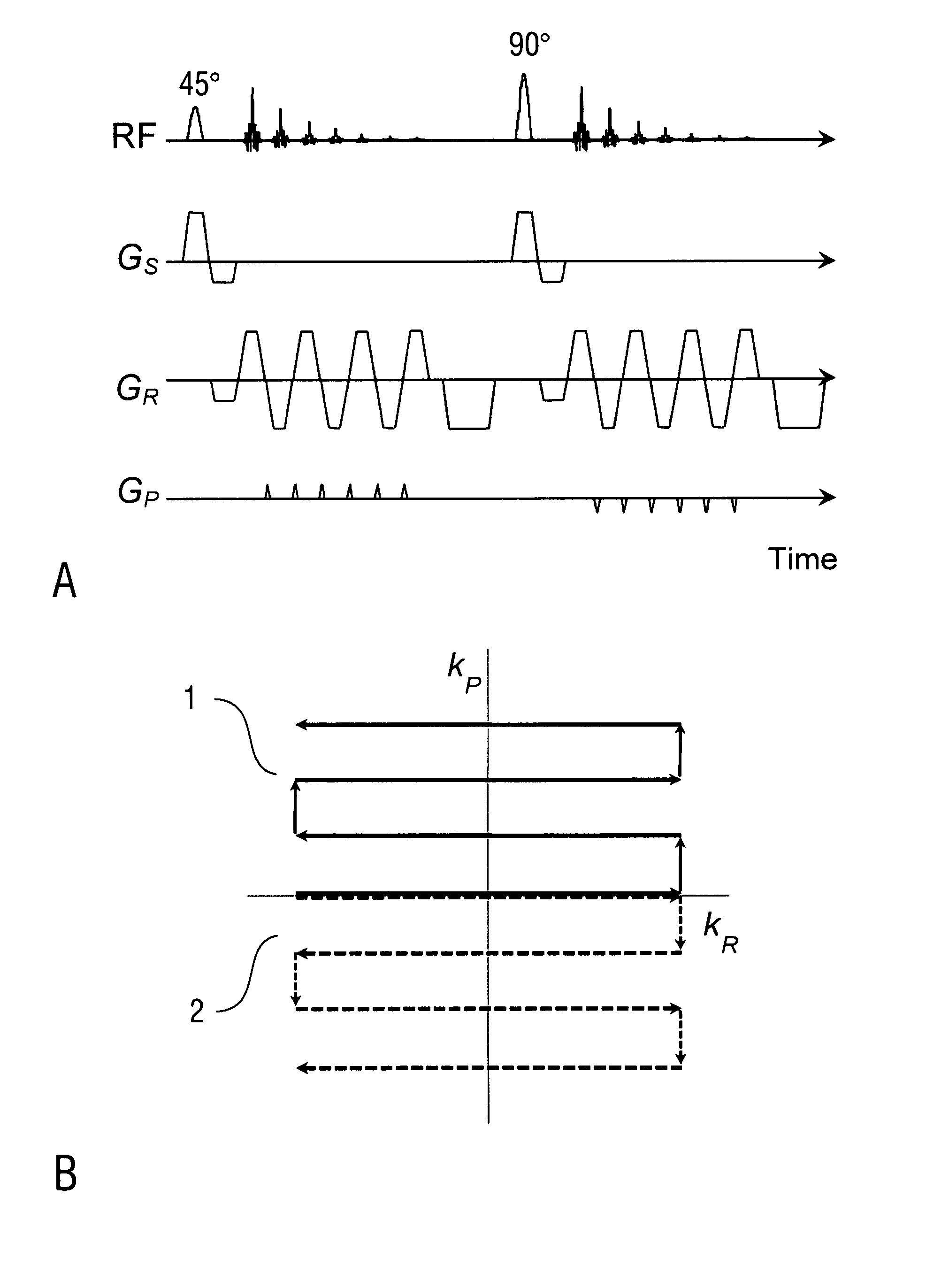
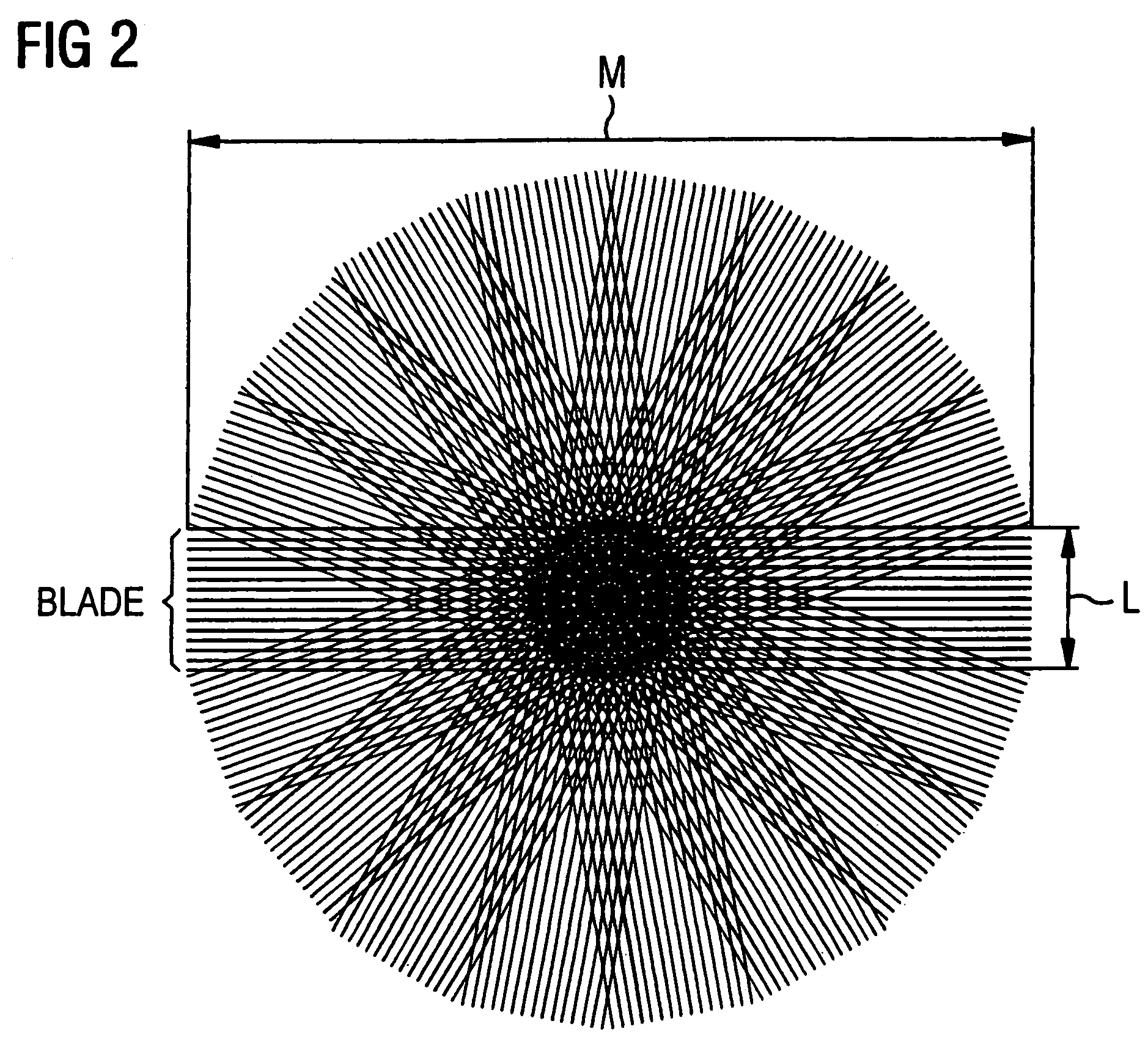
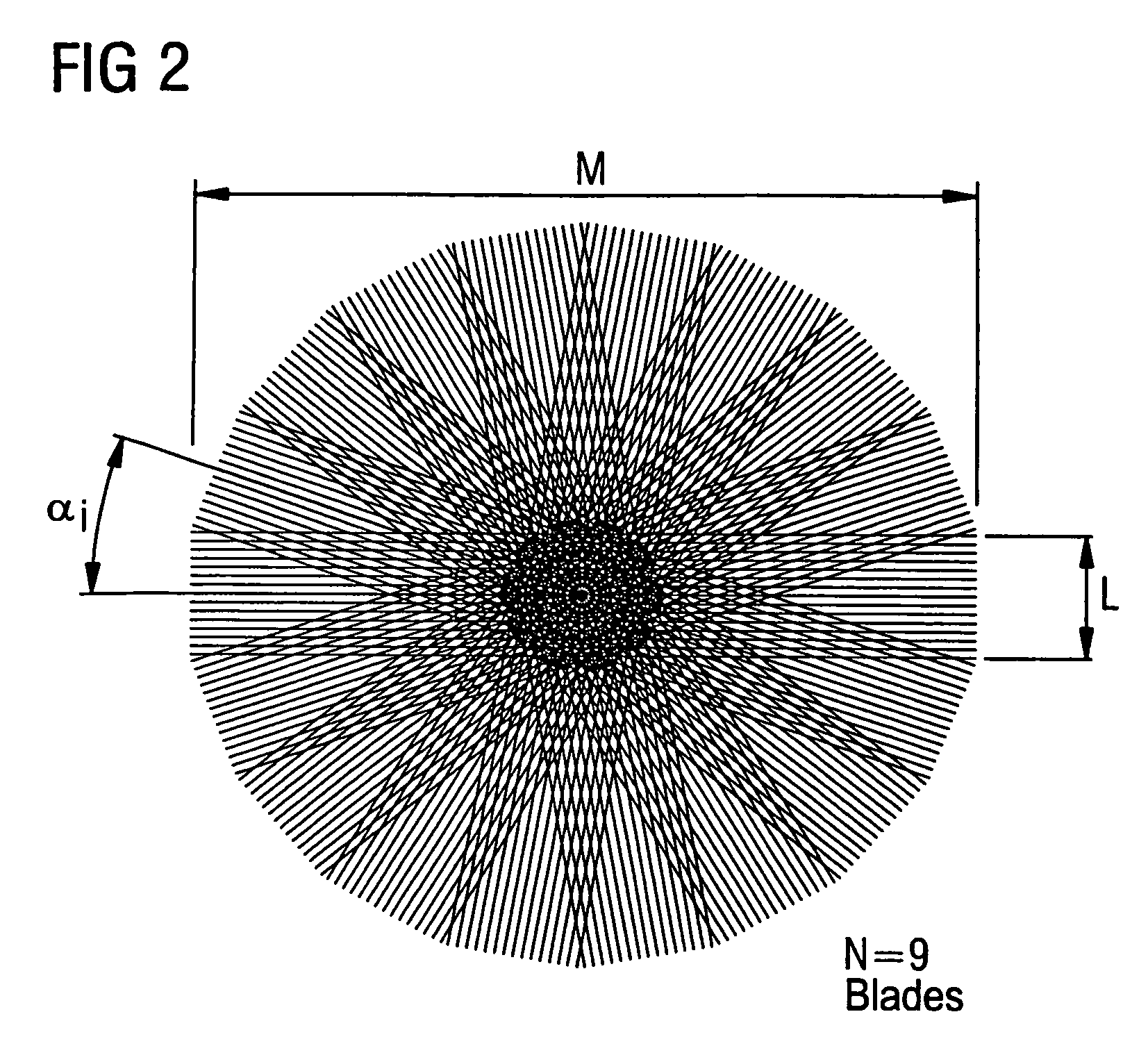
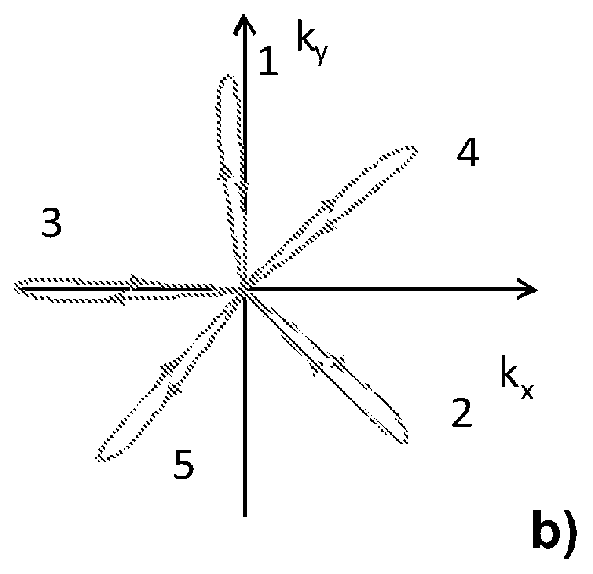
A multi-shot three-dimensional (3D) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data view-ordering strategy for uniform or variable density k-space sampling schemes is presented. The ky-kz plane is partitioned into multiple wedge-shaped “blades” (or radial fan beams). The angular size of individual blades may be adjusted according to the desired number of views for each blade. Each blade includes views near the origin that contain low-frequency information about the imaged object such that views having the most desirable characteristics may be used to fill the central portions of k-space.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic resonance frequency and phase position double-encoding sampling method and image reconstruction method
ActiveCN103389481AReduce data volumeReduced sampling timeMagnetic measurementsData acquisitionReconstruction method
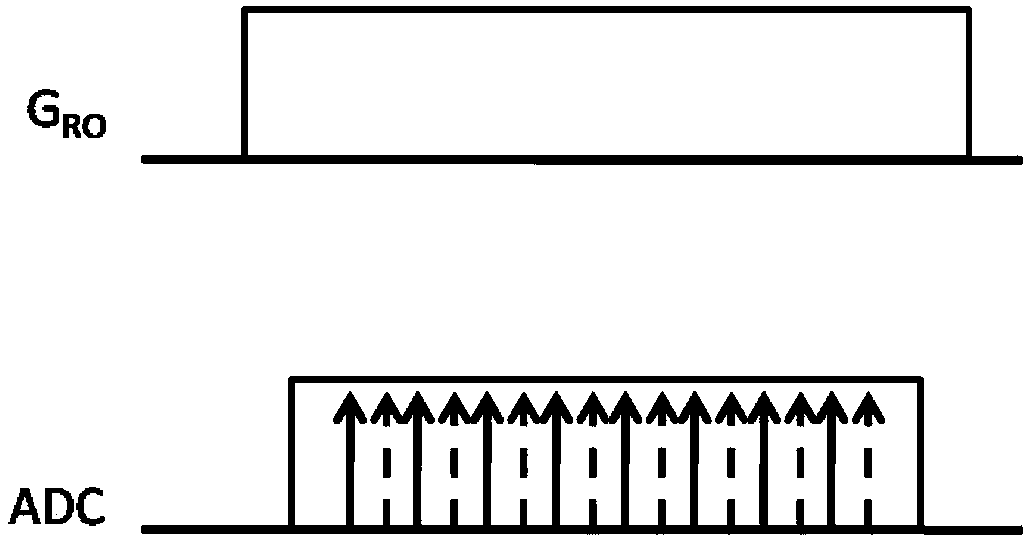
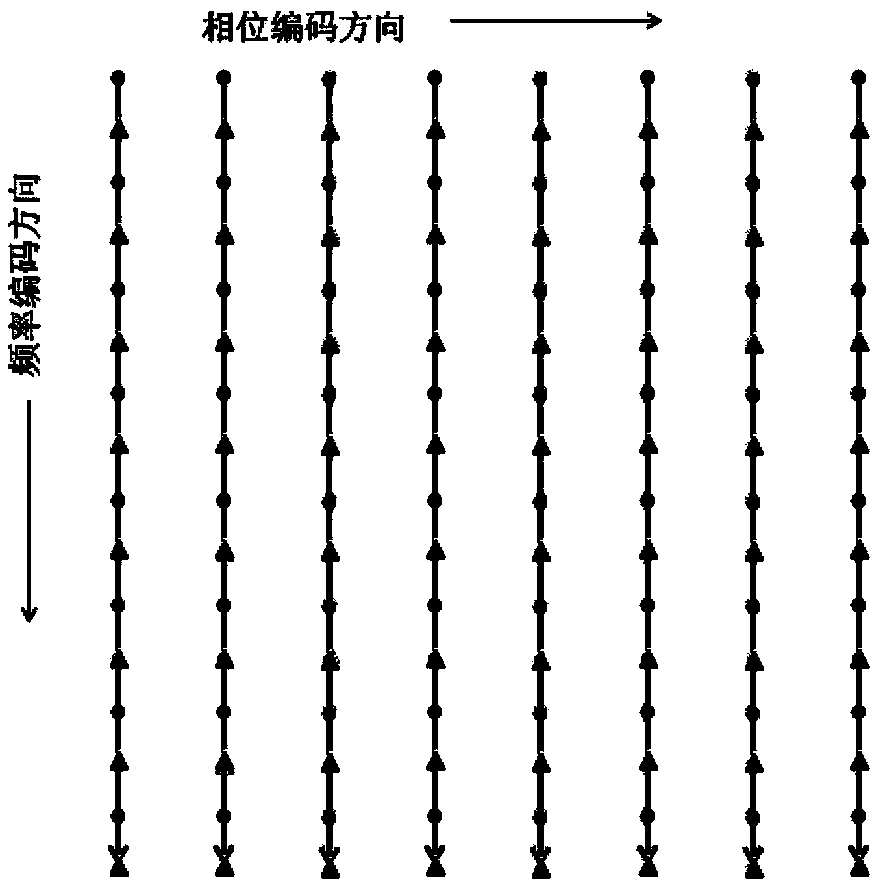
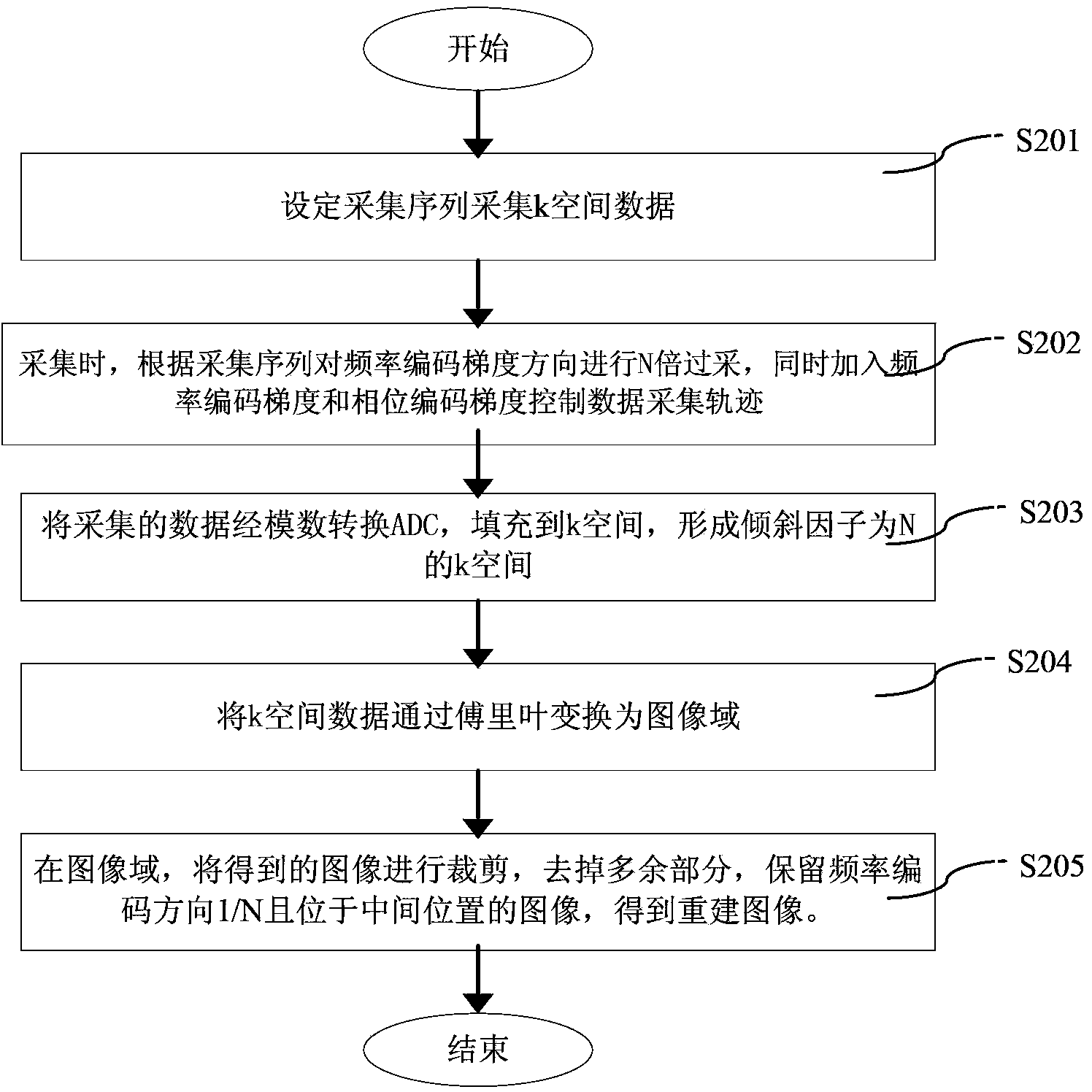
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance frequency and phase position double-encoding sampling method and an image reconstruction method. The sampling method comprises the following steps of (a) setting an acquisition sequence and acquiring k-space data; (b) performing N-time over-sampling to the frequency encoding gradient direction according to the acquisition sequence during acquisition and simultaneously adding frequency encoding gradient and phase position encoding gradient to control data acquisition tracks; (c) filling the data acquired in the step (b) into a k-space through an analog to digital converter (ADC) to form the k-space with an inclination factor N, wherein data points of the k-space are distributed along the frequency encoding gradient direction and the phase position encoding gradient direction in an inclined N*m rows*n columns mode, and (N-1) blank data points are filled between every two adjacent actually acquired data points in the frequency encoding direction and the phase position encoding direction, the N is an integer larger than 1, and the m and the n are positive integers. The magnetic resonance frequency and phase position double-encoding sampling method enables phase positions and frequency to be encoded simultaneously so as to control the k-space sampling tracks, enables acquisition times to be less than the acquisition s times of a traditional acquisition s mode, shortens the total acquisition time and enables reconstructed images not to have image artifacts basically.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
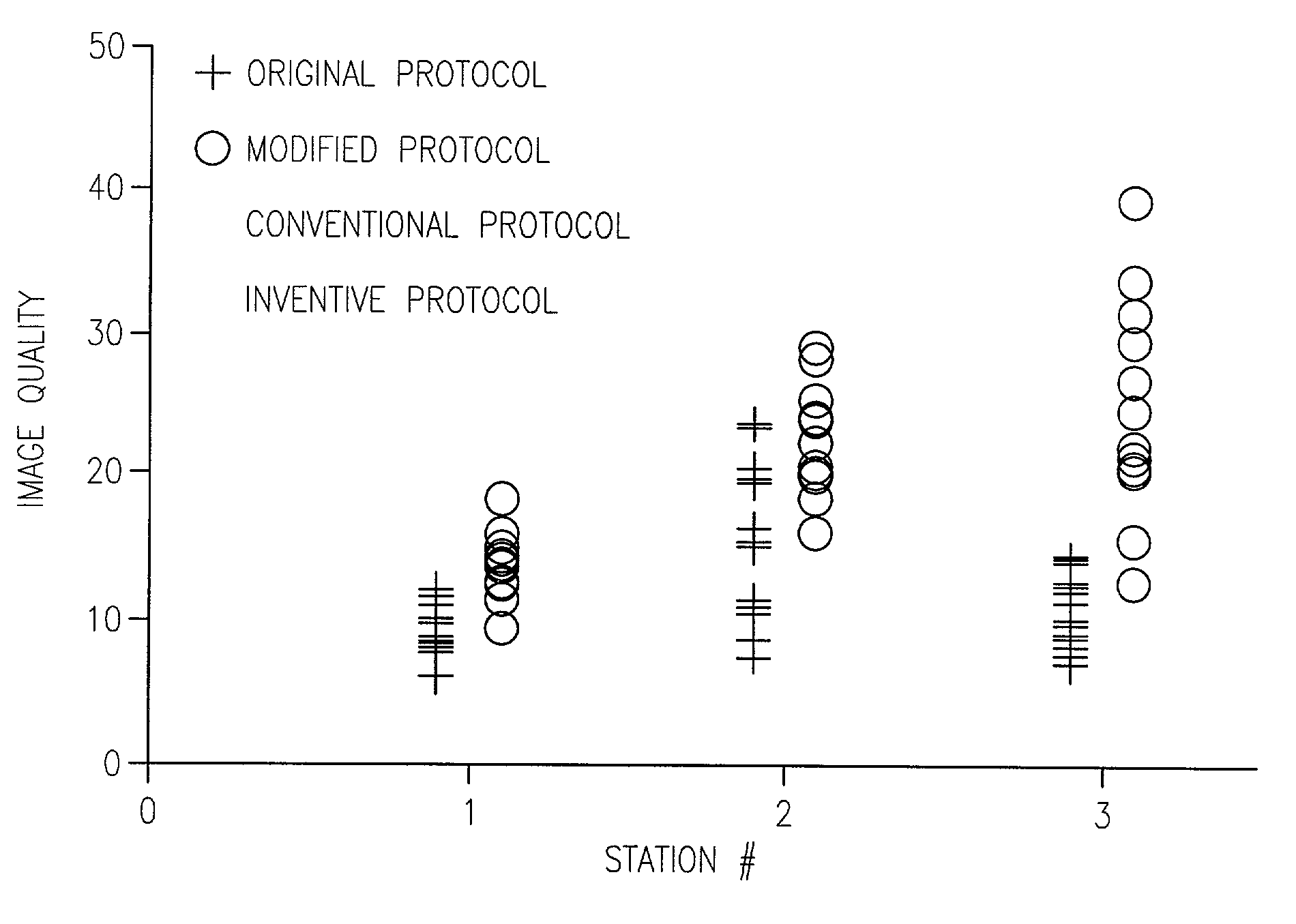
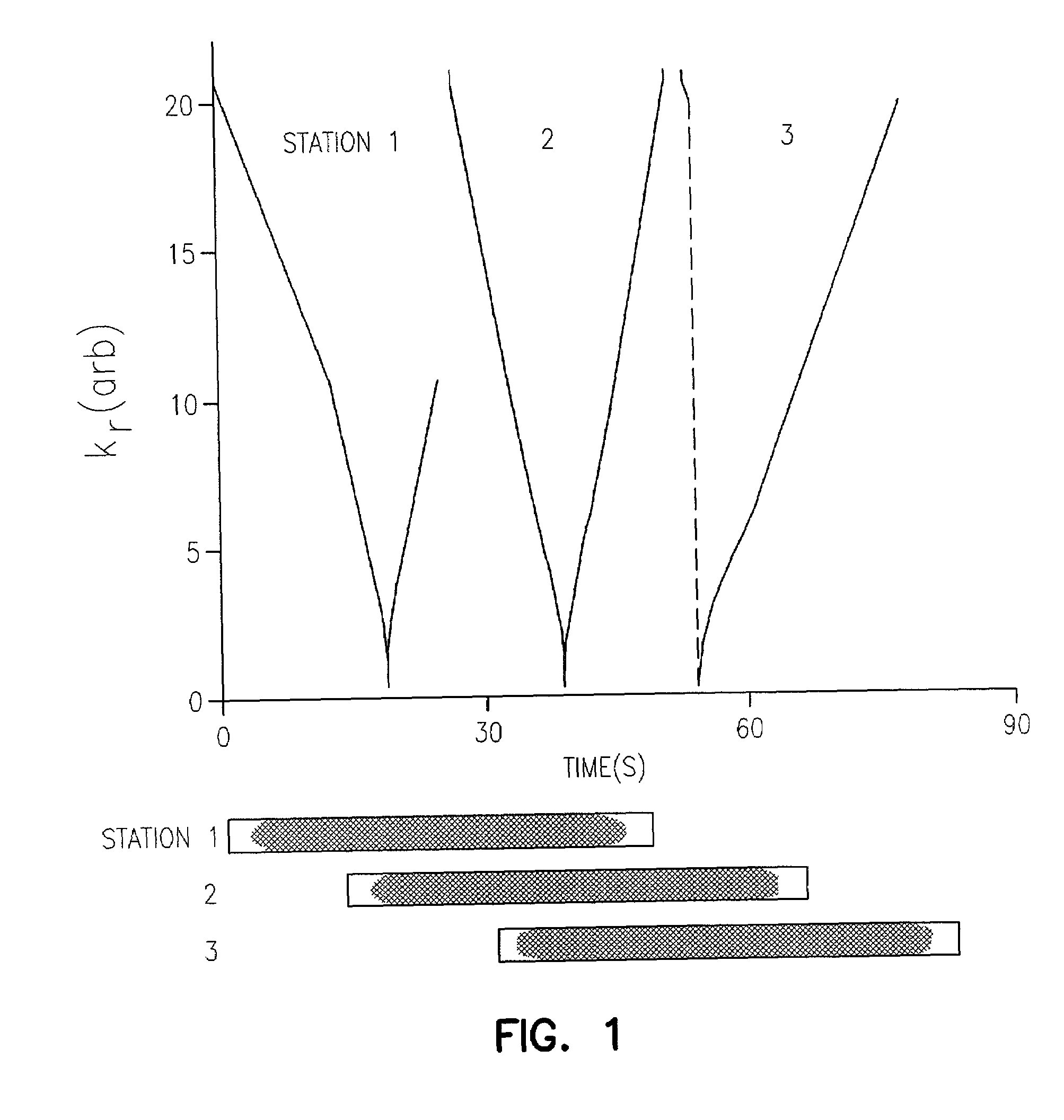
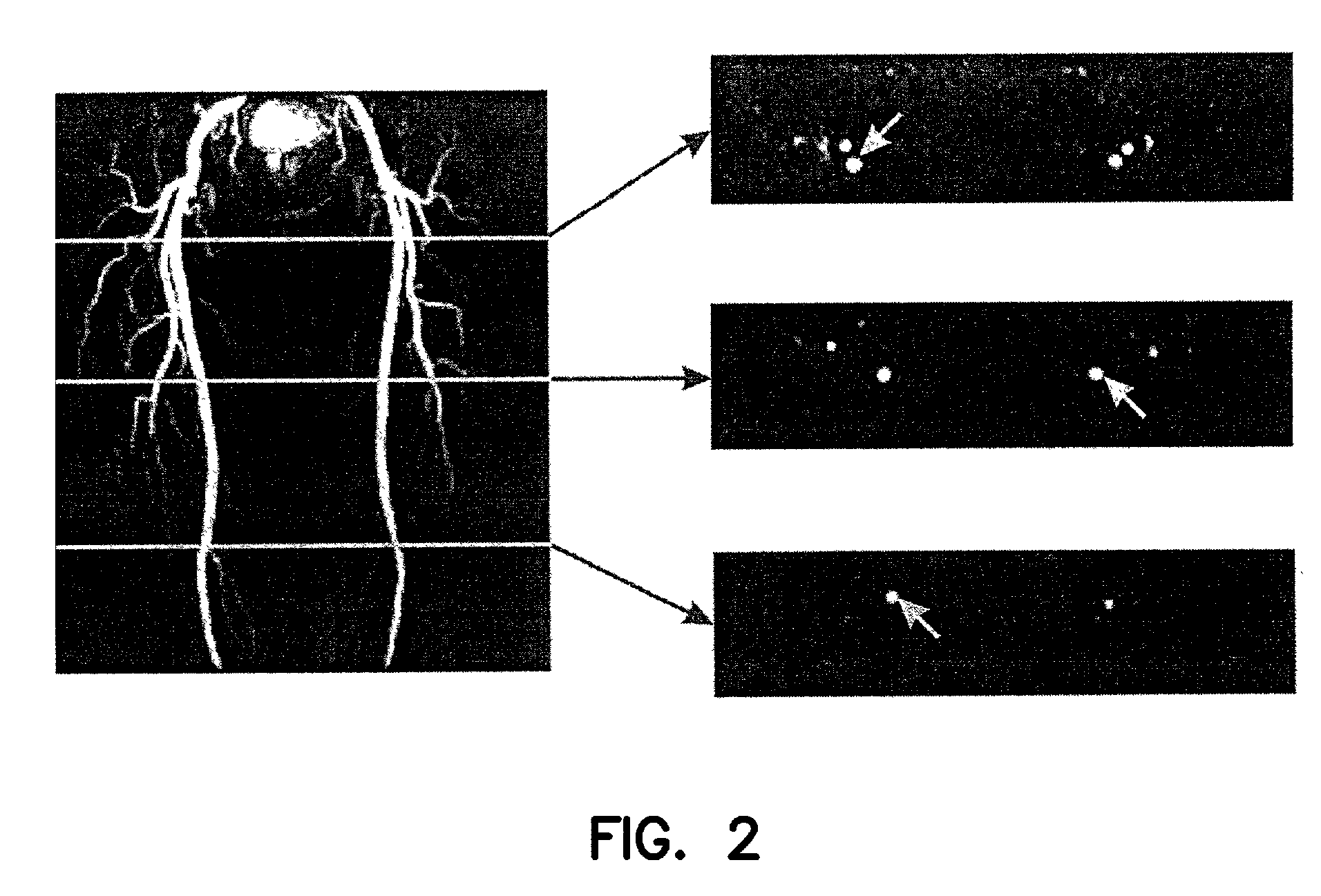
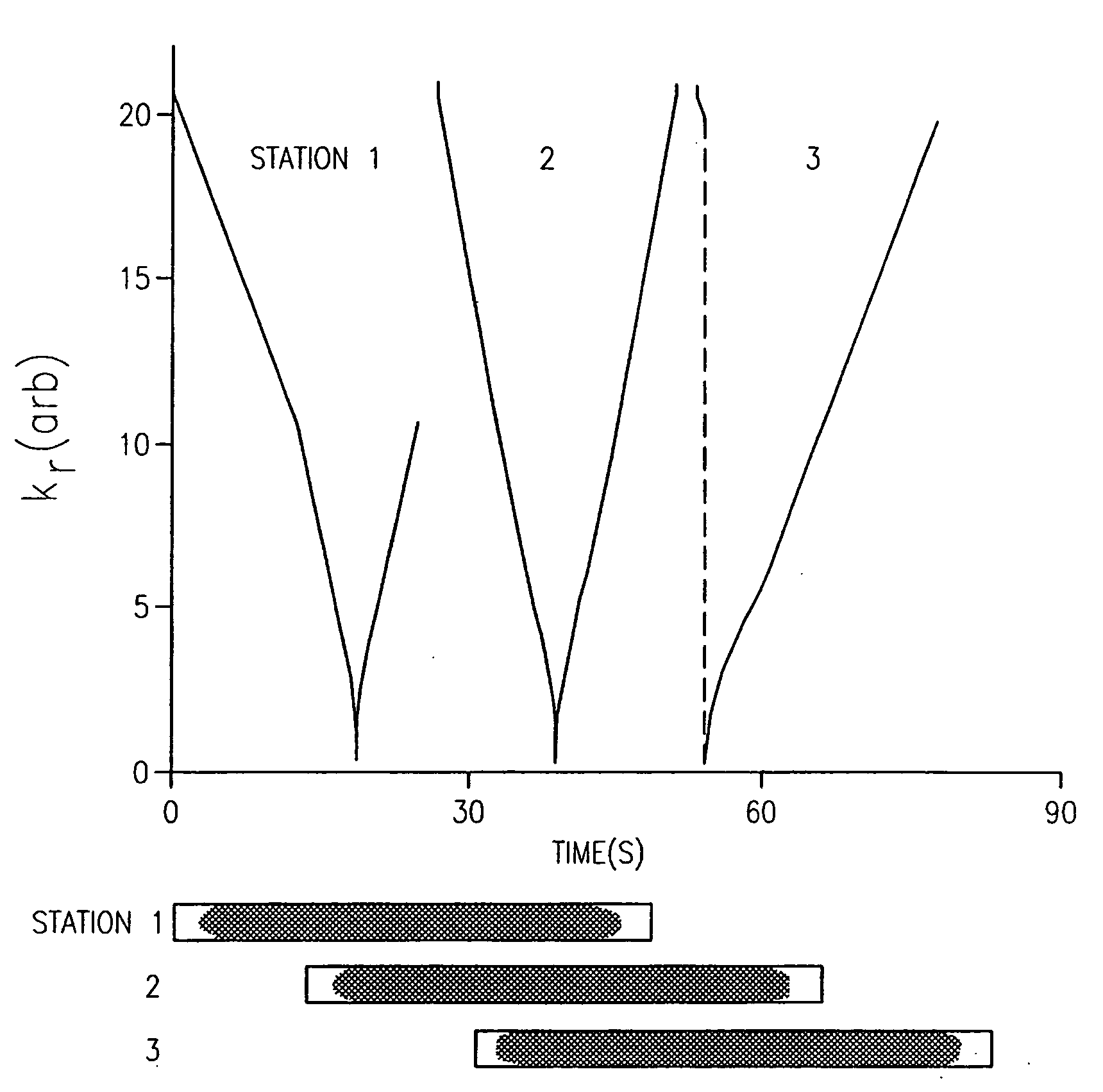
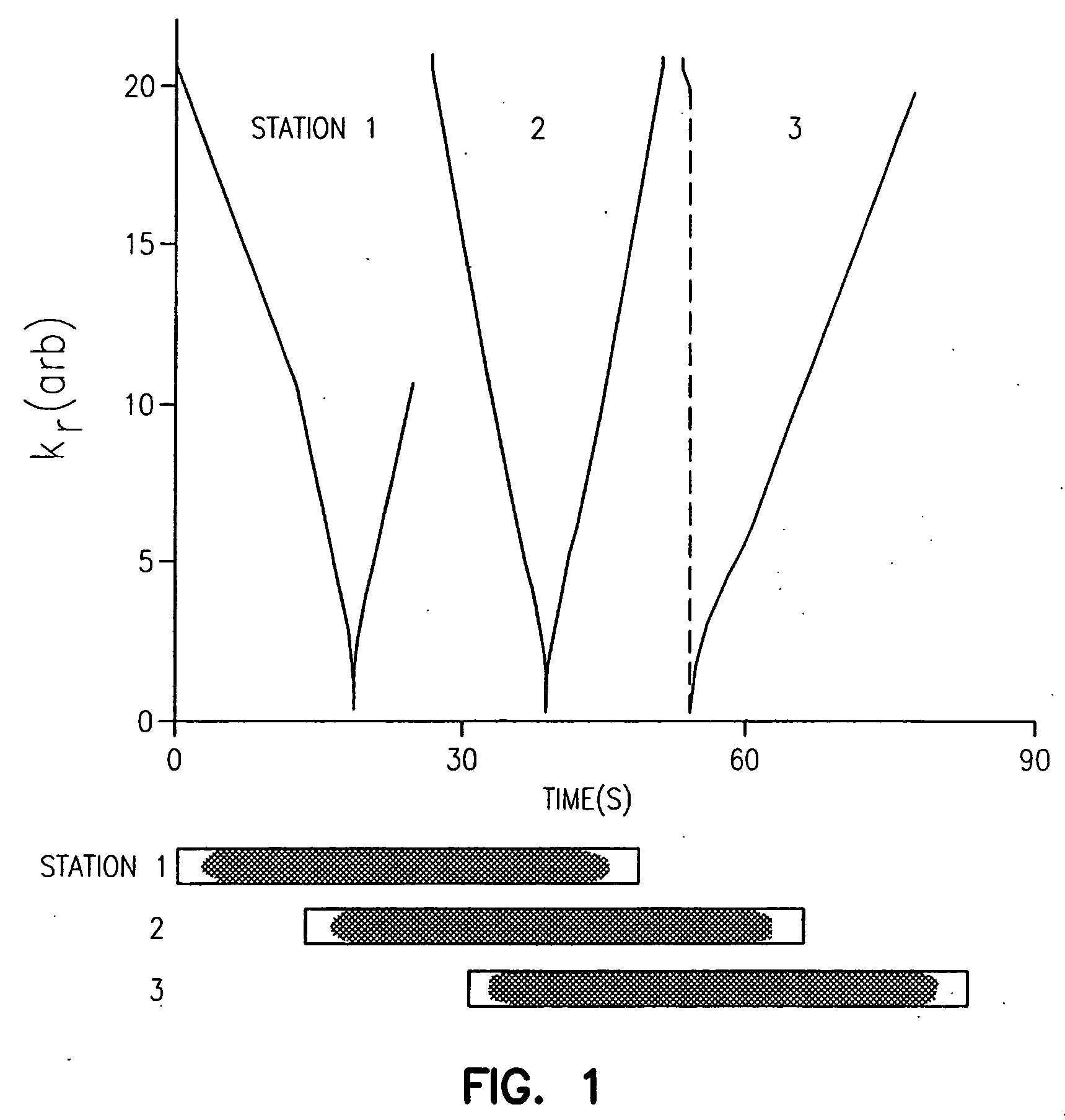
Method and apparatus for anatomically tailored k-space sampling and recessed elliptical view ordering for bolus-enhanced 3D MR angiography
InactiveUS7003343B2Increasing dose sharingMinimize timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityBlood vessel
Current bolus chase magnetic resonance angiography is limited by the imaging time for each station. Tailoring the density of k-space sampling along the anterior-posterior direction of the coronal station allows a substantial decrease in scan time that leads to greater contrast bolus sharing among stations and consequently a significant improvement in image quality. Fast arterial-venous transit in the carotid arteries requires accurate, reliable timing of the acquisition to the bolus transit to maximize arterial signal and minimize venous artifacts. The rising edge of the bolus is not utilized in conventional elliptical-centric view ordering because the critical k-space center must be acquired with full arterial enhancement. The invention provides a recessed elliptical-centric view ordering scheme is introduced in which the k-space center is acquired a few seconds following scan initiation. The recessed view ordering is shown to be more robust to timing errors in a patient studies.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and apparatus for anatomically tailored k-space sampling and recessed elliptical view ordering for bolus-enhanced 3D MR angiography
InactiveUS20050203377A1Increasing dose sharingMinimize timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityImage quality
Current bolus chase magnetic resonance angiography is limited by the imaging time for each station. Tailoring the density of k-space sampling along the anterior-posterior direction of the coronal station allows a substantial decrease in scan time that leads to greater contrast bolus sharing among stations and consequently a significant improvement in image quality. Fast arterial-venous transit in the carotid arteries requires accurate, reliable timing of the acquisition to the bolus transit to maximize arterial signal and minimize venous artifacts. The rising edge of the bolus is not utilized in conventional elliptical-centric view ordering because the critical k-space center must be acquired with full arterial enhancement. The invention provides a recessed elliptical-centric view ordering scheme is introduced in which the k-space center is acquired a few seconds following scan initiation. The recessed view ordering is shown to be more robust to timing errors in a patient studies.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus for generating a measurement sequence executable by apparatus hardware
InactiveUS7443166B2Improve utilizationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsBiological testingControl signalResonance
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus for generation of a measurement sequence that can be executed with the hardware of the magnetic resonance apparatus, a measurement sequence is generated as a series of time slices of different time slice types, with the control signals for the magnetic resonance apparatus during each time slice being determined using parameters describing these time slices. After division of the measurement sequence into a number of time slices dependent on the sequence type and on a k-space sampling type, descriptive variables are associated with the time slices. Value ranges of the variables are limited and / or the variables are set in relation to one another using boundary conditions. A determination ensues of solution values of the variables with which a predetermined target parameter of the measurement sequence is optimized. A measurement sequence executable on the hardware is attained by association of the solution values with the corresponding parameters of the time slices.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method of reducing imaging time in propeller-MRI by under-sampling and iterative image reconstruction
InactiveUS20090129648A1Reduce in quantityEnhance the imageMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityAcquisition time
A method for reducing PROPELLER MRI data acquisition times, by combining k-space under-sampling and iterative reconstruction using NUFFT, while maintaining similar image quality as in PROPELLER MRI with sufficient k-space sampling. Iterative image reconstruction using NUFFT minimizes image artifacts produced with conventional PROPELLER image reconstruction in under-sampled acquisitions. The data acquisition and image reconstruction parameters are selected in order to achieve image quality similar to that of sufficiently-sampled PROPELLER acquisitions for significantly shorter imaging time. An advantage of using under-sampled PROPELLER imaging is a reduction in acquisition time by as much as 50% without introducing significant artifacts, and while maintaining other benefits of PROPELLER imaging.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
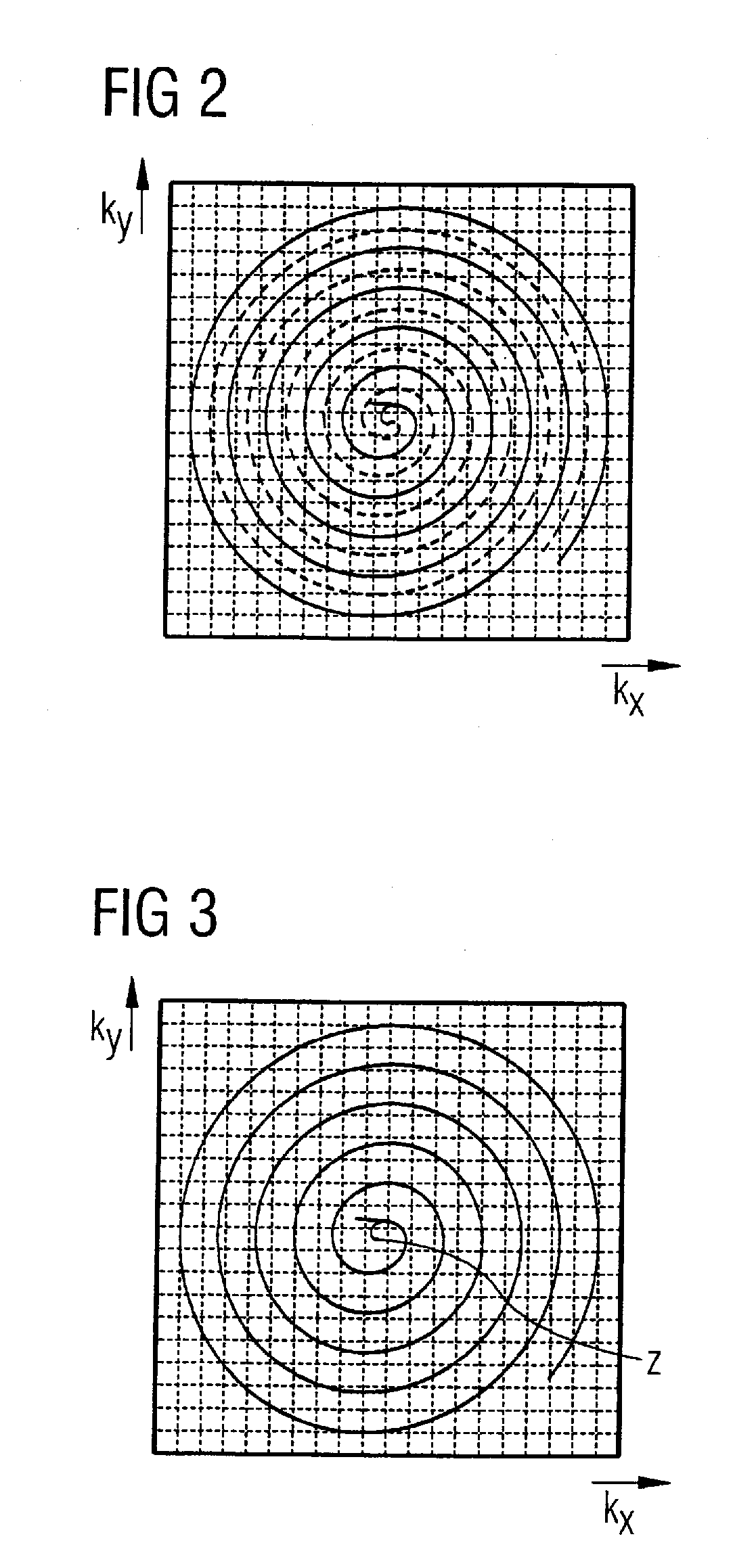
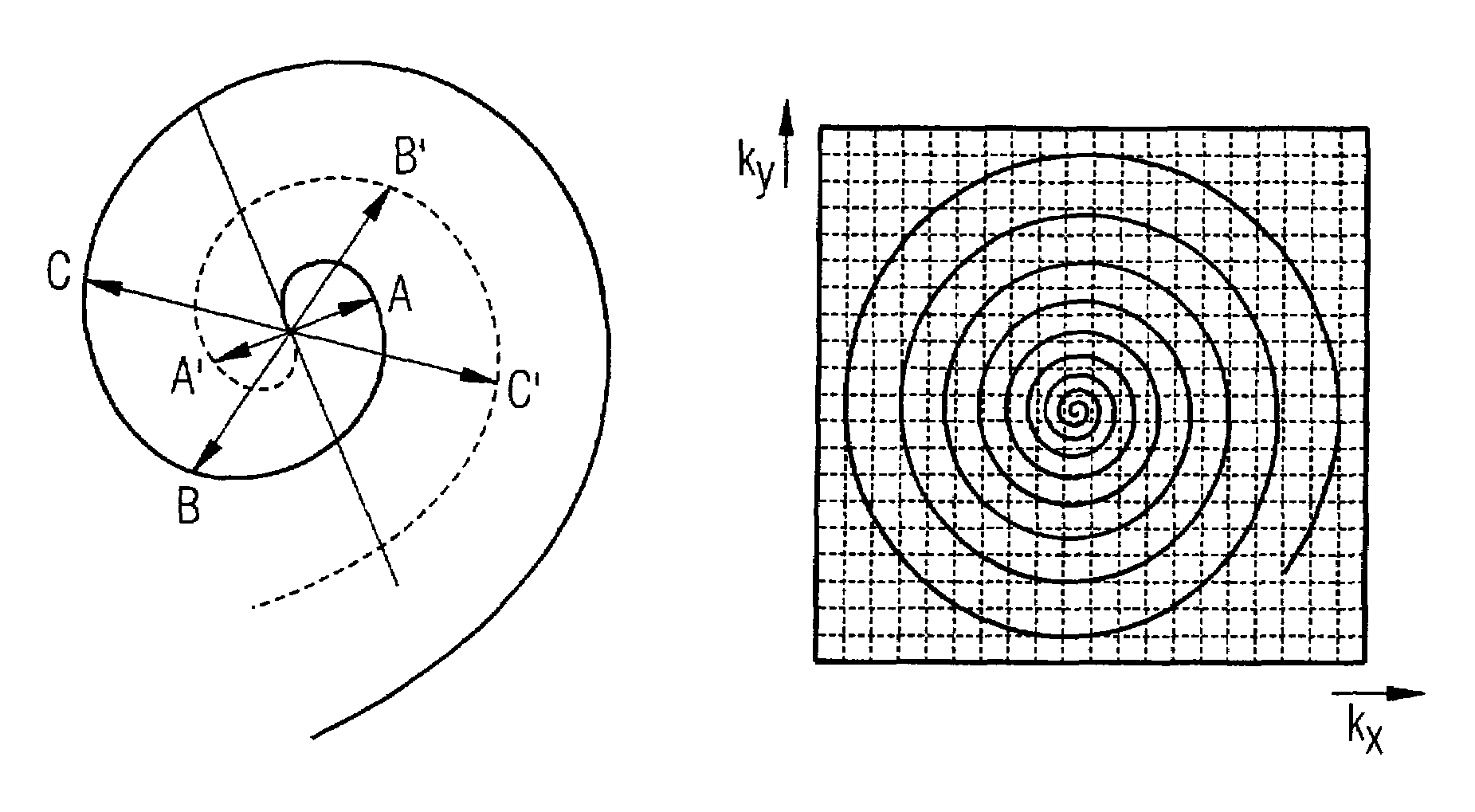
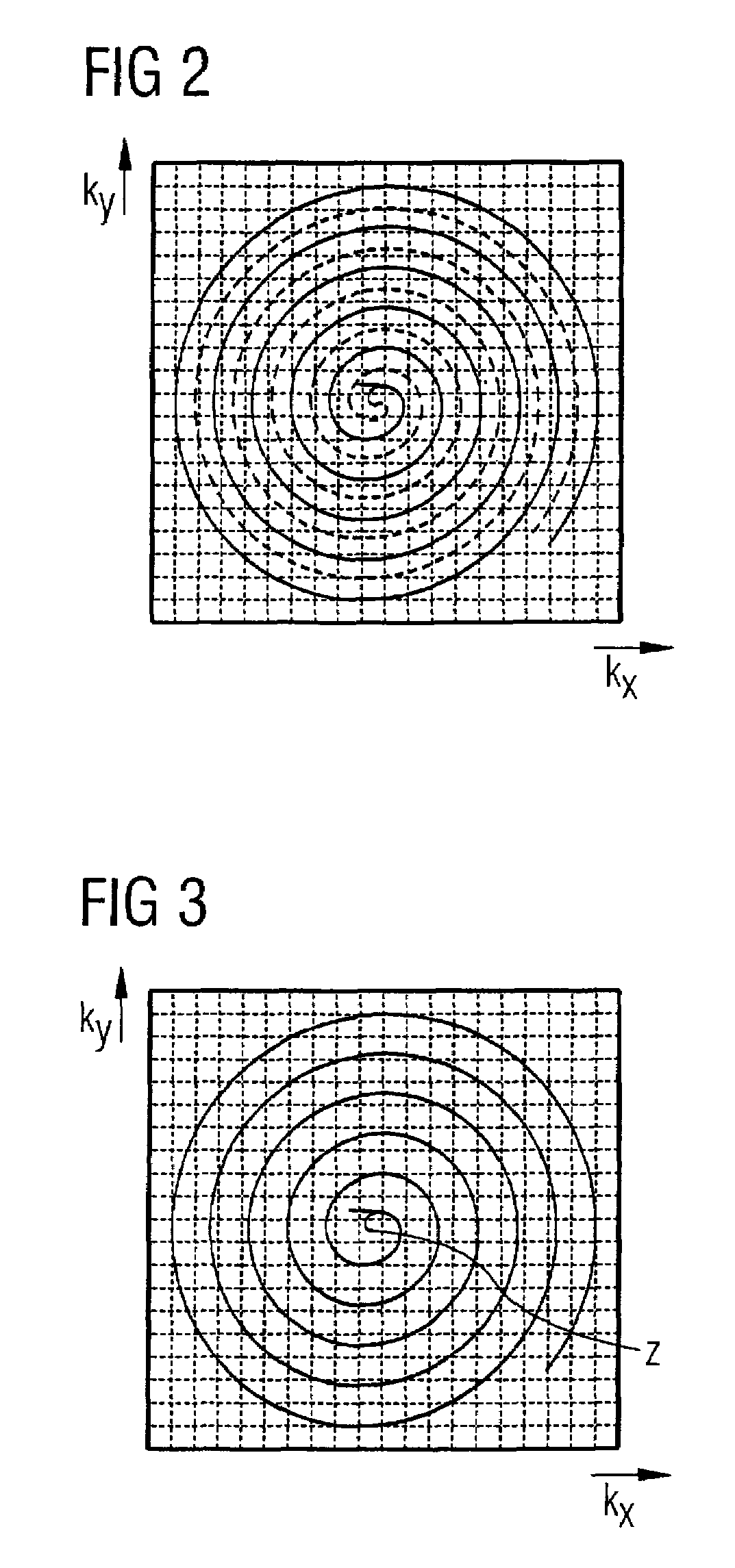
Method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging in magnetic resonance tomography
InactiveUS20080021303A1Shorten readout durationShorten the durationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringComplete dataResonance
In a method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging in magnetic resonance tomography using spiral-shaped k-space sampling, the underlying k-matrix is under-sampled such that an additional spiral is obtained by point mirroring of the measured values at the center of the k-matrix. This additional spiral forms a complete data set of the k-matrix together with the first spiral for imaging the output information.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Modeling and validation methods for compressed sensing and MRI
PendingCN107615089AImprove signal encodingImprove decoding performanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceValidation methods
A computer implemented method is provided that judiciously applies or manages randomness, incoherence, nonlinearity and structures involved in signal encoding or decoding. The method in a magnetic resonance imaging example comprises acquiring data samples in accordance with a k-space sampling pattern, identifying a signal structure in an assembly of the acquired data samples, and finding a resultconsistent with both the acquired data samples and the identified signal structure.
Owner:朱宇东
MR image reconstruction method and MR apparatus using propeller imaging
ActiveUS7840049B2Simple (andReconstructed imageMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setResonance
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method of autocalibrating parallel imaging interpolation from arbitrary K-space sampling with noise correlations weighted to reduce noise of reconstructed images
ActiveUS8638096B2Character and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase correlationPhase Code
A computer implemented method for magnetic resonance imaging is provided. A 3D Fourier Transform acquisition is performed with two phase encode directions, wherein phase code locations are chosen so that a total number of phase encodes is less than a Nyquist rate, and closest distances between phase encode locations takes on a multiplicity of values. Readout signals are received through a multi-channel array of a plurality of receivers. An autocalibrating parallel imaging interpolation is performed and a noise correlation is generated. The noise correlation is used to weight a data consistency term of a compressed sensing iterative reconstruction. An image is created from the autocalibration parallel imaging using the weighted data consistency term. The image is displayed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
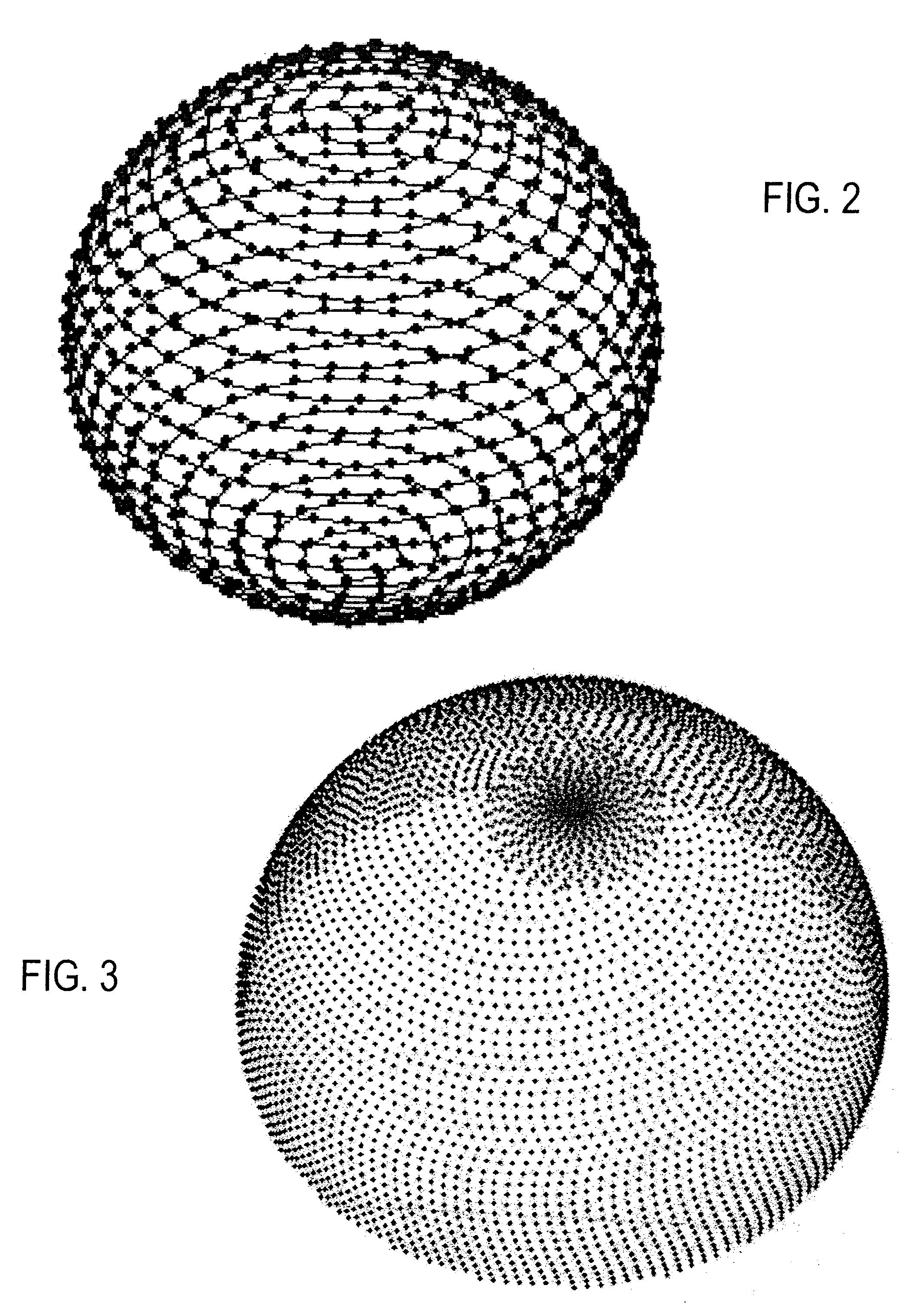
Accelerated Shells Trajectory MRI Acquisition
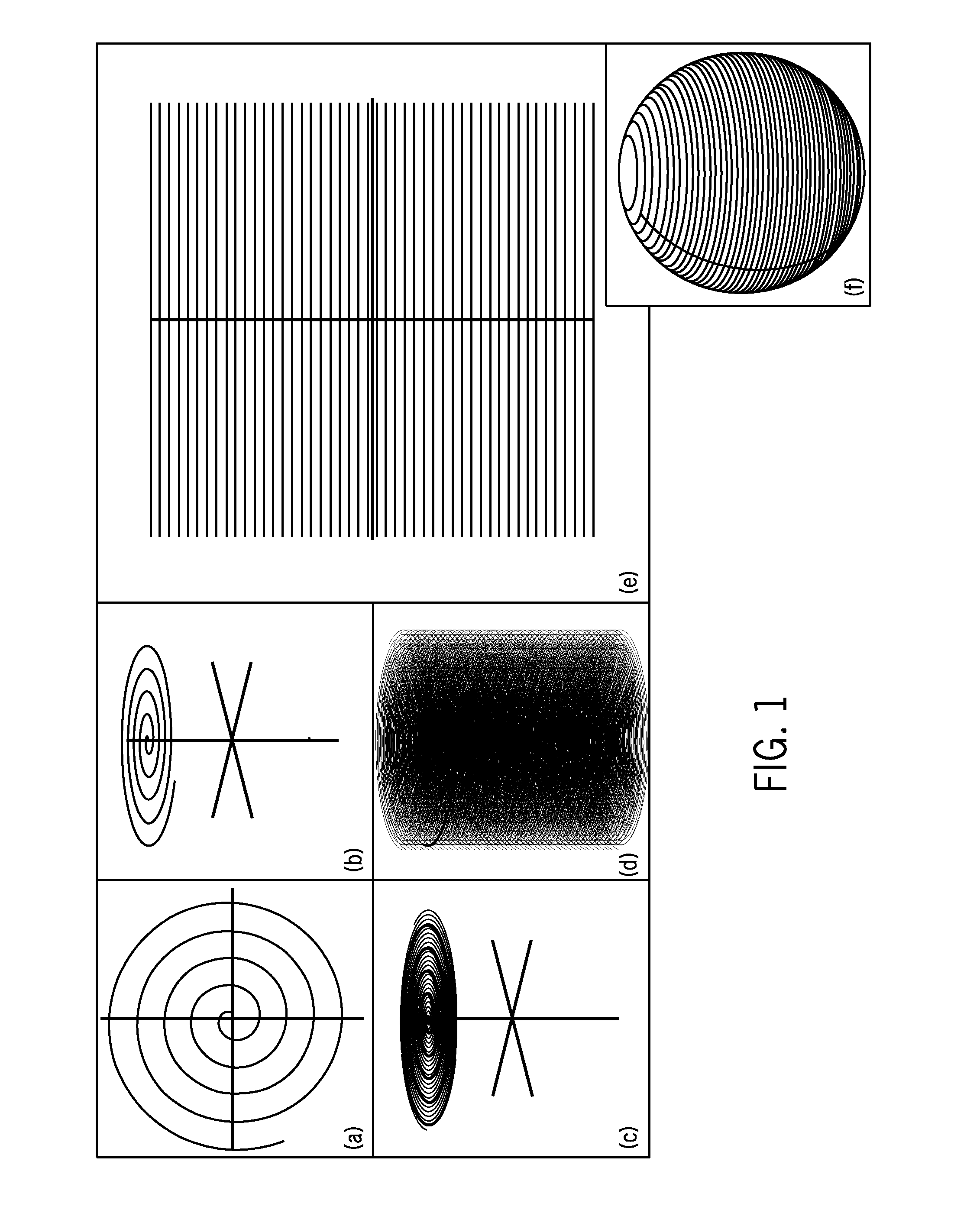
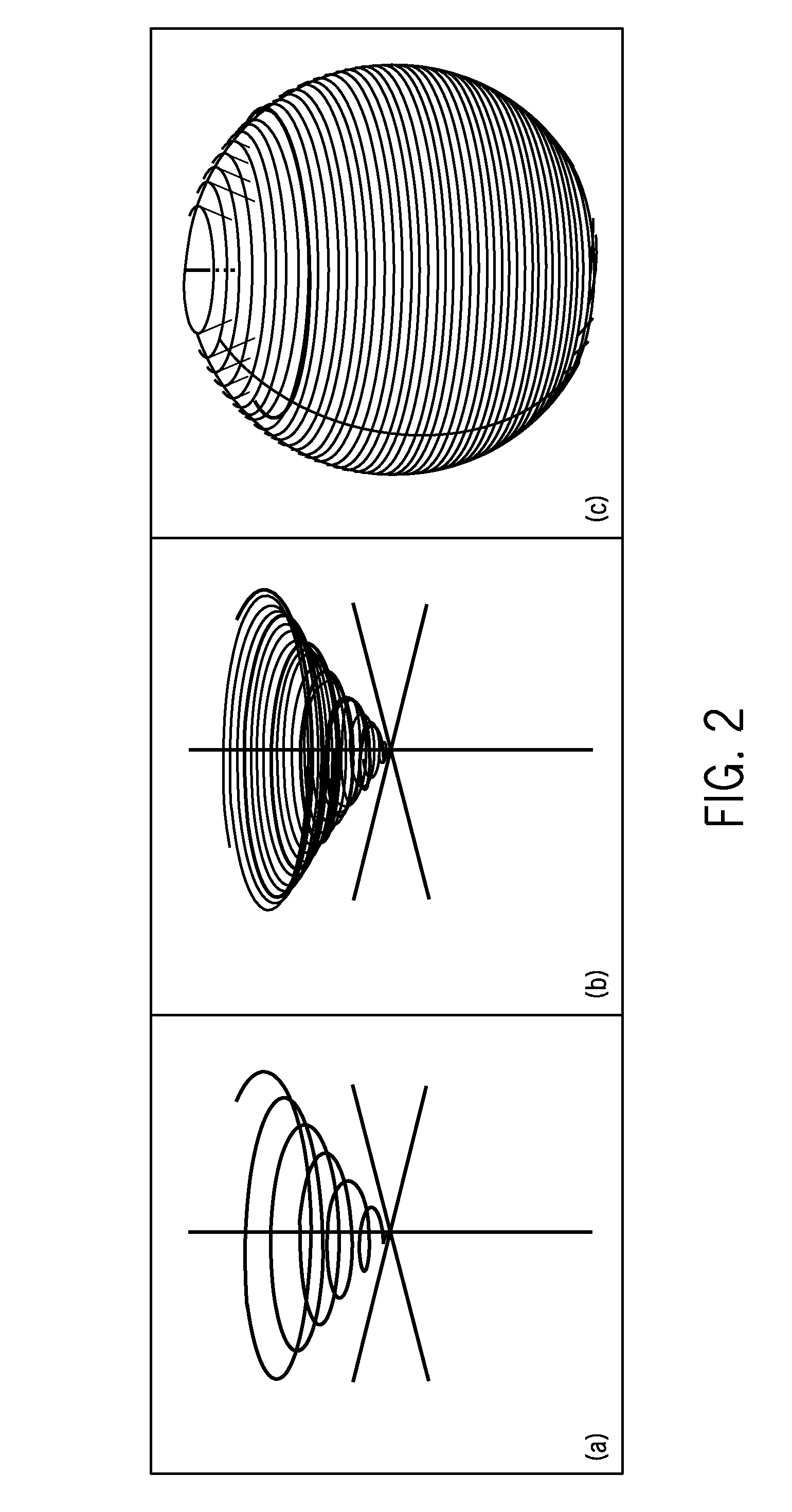
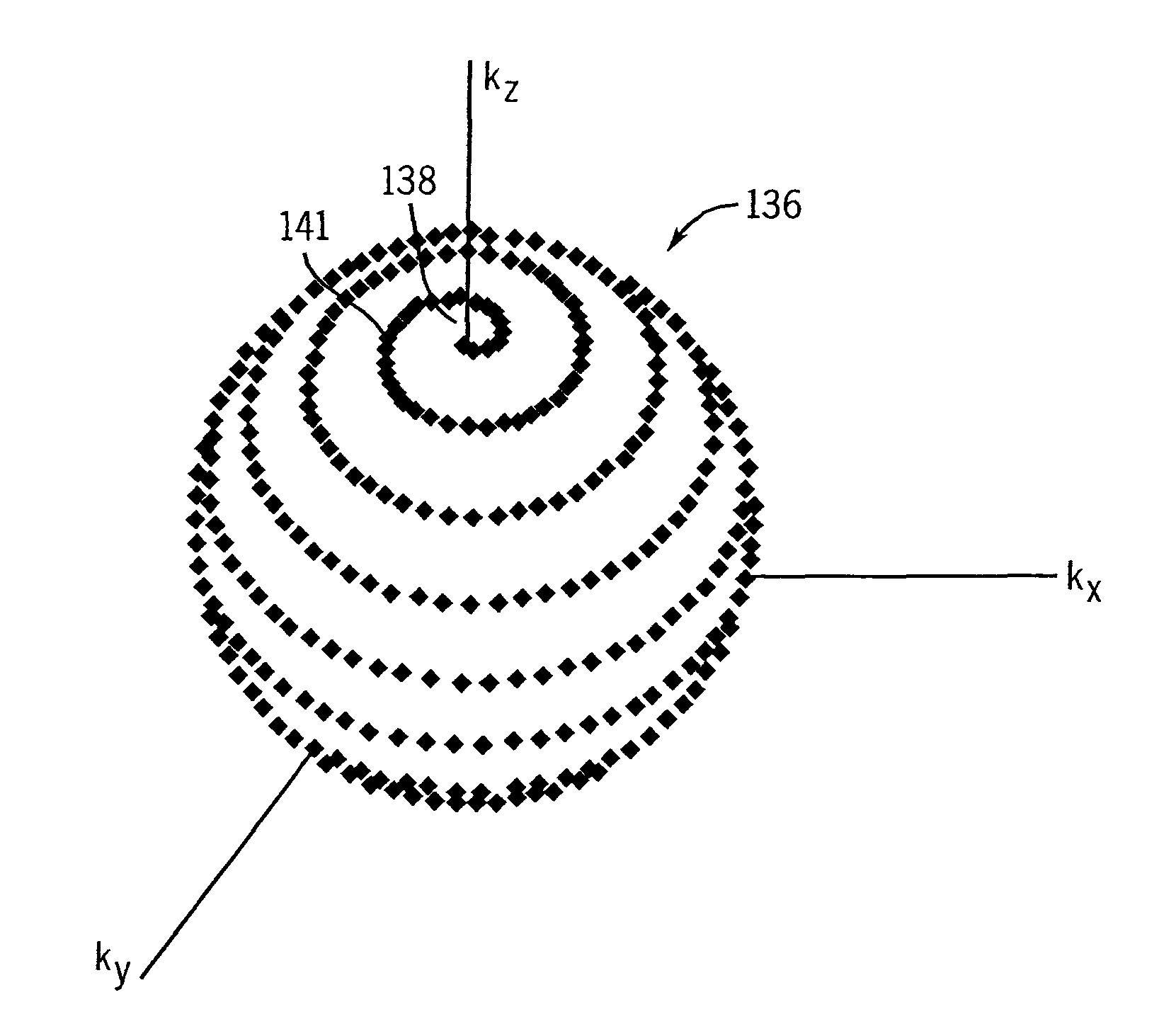
ActiveUS20080045828A1Shorter TR and signal readout durationReduce contributionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFat suppressionPulse sequence
An MRI k-space data set is acquired using a series of shell k-space sampling trajectories of different radii. Off-resonance effects are reduced and fat-suppression can be improved by using a shorter TR for pulse sequences that sample at smaller radii. At larger radii sampling is repeated with the central axis of the shell sampling trajectory tilted such that the polar regions of shells acquired at the same radii are sampled by the other shell.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
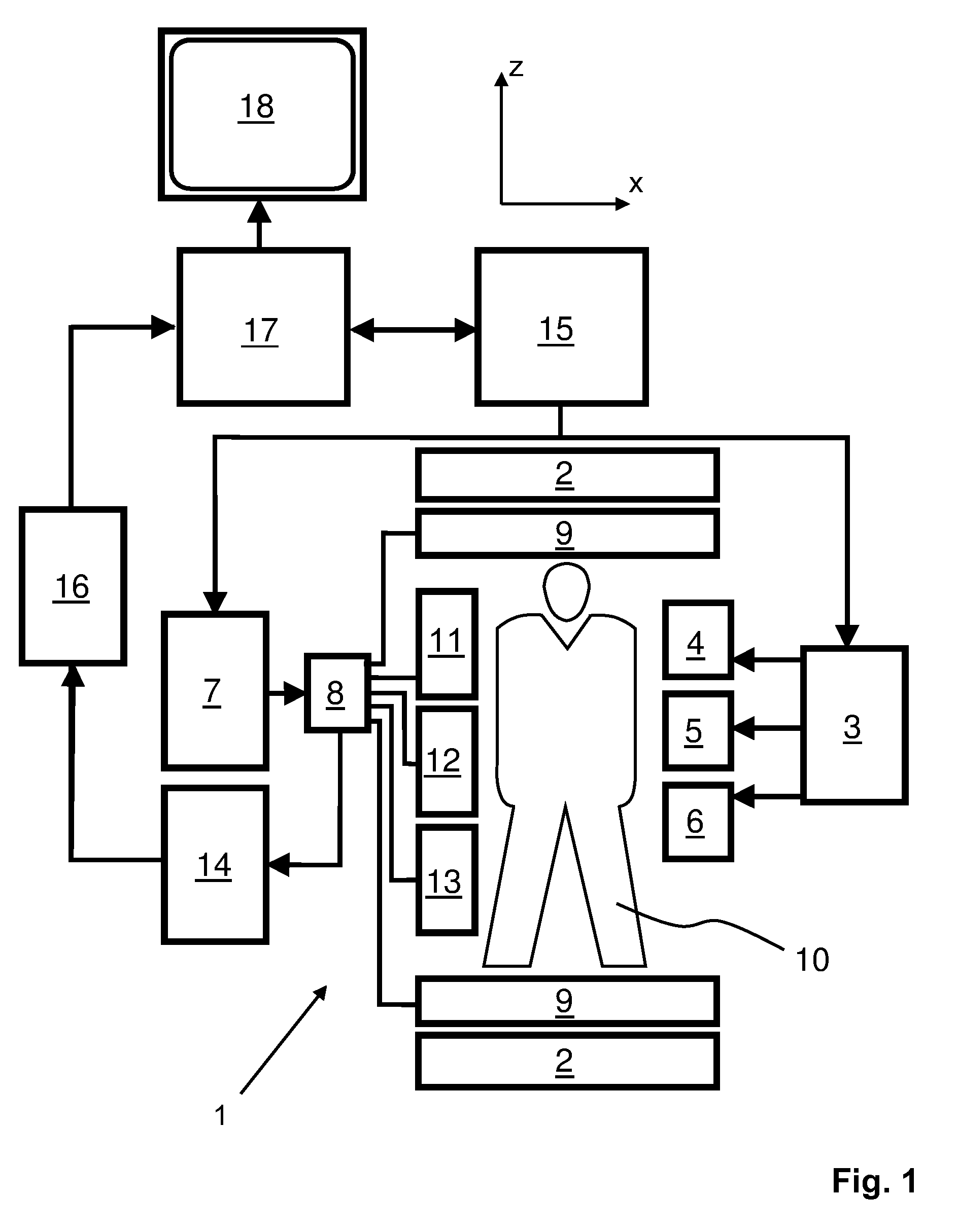
Mr image reconstruction using compressed sensing
ActiveUS20160291106A1Short scan timeNoise level causedMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsComputer scienceCompressed sensing
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of an object (10) placed in an examination volume of a MR device (1). The method comprises the steps of: subjecting the object (10) to an imaging sequence for acquiring MR signal data, wherein the MR signal data are acquired as a function of k-space position and time by using an irregular k-space sampling pattern with sub-sampling of k-space; reconstructing MR image data from the MR signal data, which MR image data comprise spatial dimensions and a frequency dimension, sparsity of the MR image data in a transform domain being exploited for suppressing sub-sampling artefacts in the MR image data. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) and to a computer program.
Owner:KONINKLILJKE PHILIPS NV
MR image reconstruction using compressed sensing
ActiveUS9964615B2Short scan timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsCompressed sensingComputer science
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of an object (10) placed in an examination volume of a MR device (1). The method comprises the steps of: subjecting the object (10) to an imaging sequence for acquiring MR signal data, wherein the MR signal data are acquired as a function of k-space position and time by using an irregular k-space sampling pattern with sub-sampling of k-space; reconstructing MR image data from the MR signal data, which MR image data comprise spatial dimensions and a frequency dimension, sparsity of the MR image data in a transform domain being exploited for suppressing sub-sampling artefacts in the MR image data. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) and to a computer program.
Owner:KONINKLILJKE PHILIPS NV
Method for homogenizing resolution in magnet resonance tomography measurements using non-linear encoding fields
ActiveUS20110241678A1High densityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionImage resolutionTomography
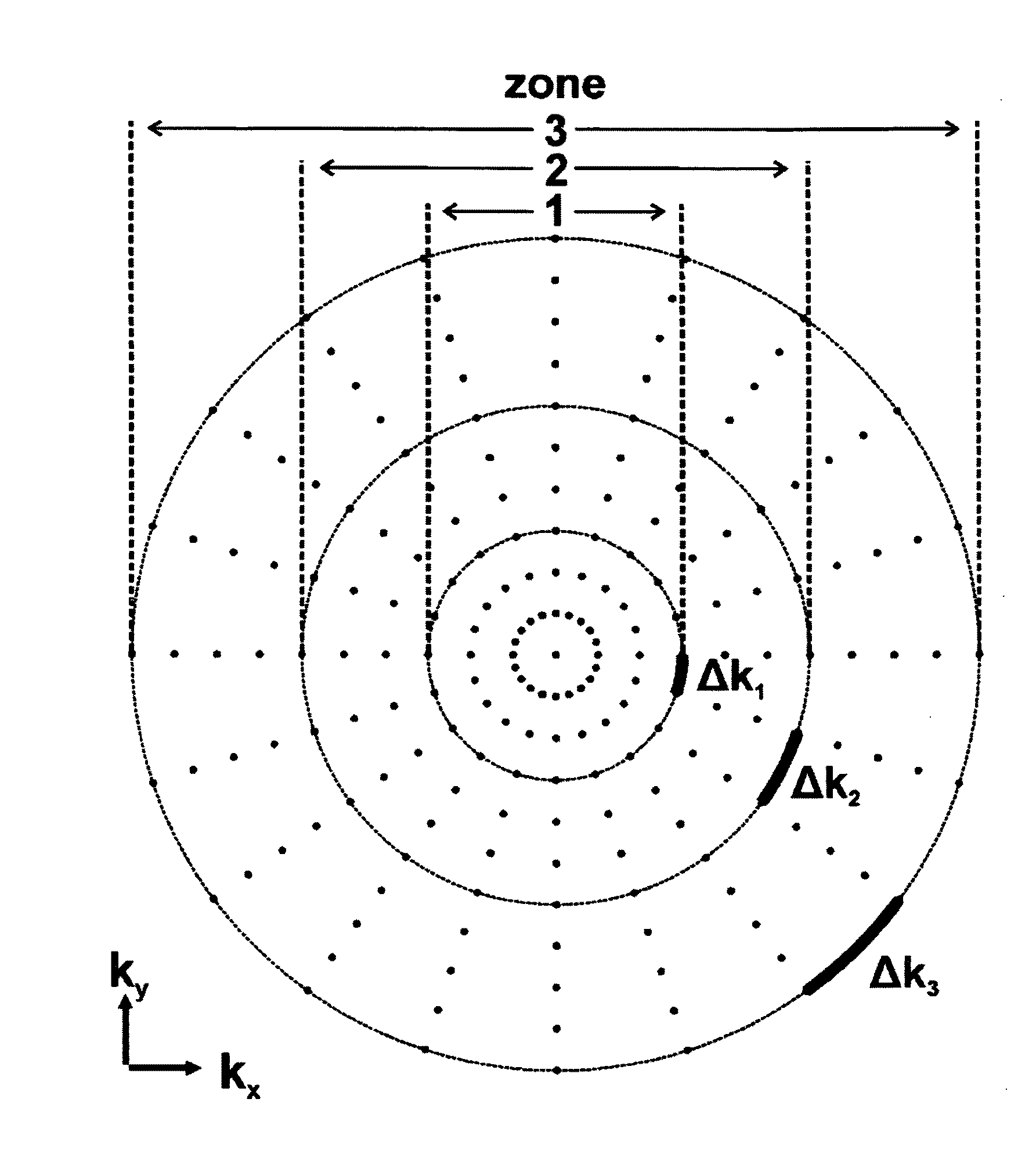
A method for magnetic resonance (=MR) imaging, wherein non-linear gradient fields are applied for the purpose of spatial encoding to acquire images of an object to be imaged and wherein the magnet resonance signal radiated from the object to be imaged is sampled on grids in time, to thereby obtain sampling points, is characterized in that the object to be imaged is mapped completely in regions of stronger gradient fields by increasing the density of the sampling points in the center of k-space, and additional sampling points are specifically acquired in the outer regions of k-space according to a k-space sampling pattern depending on the desired distribution of the resolution in the measurement, wherein the MR measurement is calculated with the additional sampling points. An MR imaging method is thereby provided by means of which homogenized resolution is achieved in the MR measurements using non-linear gradient fields for spatial encoding.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
Magnetic resonance image acquiring and reconstructing method and apparatus
ActiveCN104181481AFast imagingMake up for the problem of lower signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Resonance
The invention provides a magnetic resonance image acquiring and reconstructing method. In two-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging, K space is acquired and reconstructed by parallel acquisition using an n-slice acceleration method and a GRAPPA method, wherein the n is more than or equal to 2. By changing a K space undersampling and reconstructing method, a multi-slice stimulation acquiring method and a conventional GRAPPA technique can be combined and used simultaneously. Thus, a problem of damage, to the continuity of the phase modulation circulation of the K space, caused by the multi-slice stimulation acquiring method in conventional K space sampling is solved. Therefore, imaging speed is further increased and interlayer separation compensates a problem of decrease in a signal-to-noise ratio caused by parallel acceleration processing. Further, the invention provides a magnetic resonance image acquiring and reconstructing apparatus.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
System and Method for Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Three-Dimensional, Distributed, Non-Cartesian Sampling Trajectories
ActiveUS20150051479A1Simplify requirementsChoose simpleDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsComputer scienceK space sampling
A system and method for sampling k-space is provided that substantially simplifies the demands placed on the clinician to select and balance the tradeoffs of a particular selected sampling methodology. In particular, the present invention provides particularly advantageous sampling methodologies that simplify the selection of a particular k-space sampling methodology and, furthermore, the tradeoffs within a particular sampling methodology.
Owner:DIGNITY HEALTH
Magnetic resonance dynamic imaging sampling method and image reconstruction methods
InactiveCN107993271AFlexible sampling methodDownsamplingImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMultiple frameResonance
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance dynamic imaging sampling method which includes the steps of acquiring multi-frame images and allocating k-space sampling point positions of different frameimages to form a position complementary or approximately complementary relationship, wherein after being combined, the sampling point positions of different frame images form a complete sampling or approximately complete sampling k-space, which is called a combined k-space. A variety of magnetic resonance reconstruction methods can be used to reconstruct images, such as a compressive sensing method, a method based on prior images or reference images, and a parallel reconstruction method (GRAPPA, SENSE, and variants thereof). The invention also discloses two methods for performing image reconstruction on the sampling method. Compared with a traditional under-sampling method, the technology can further reduce the sampling rate, reduce the number of samples, further reduce the scanning time,and improve the quality of reconstruction results.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
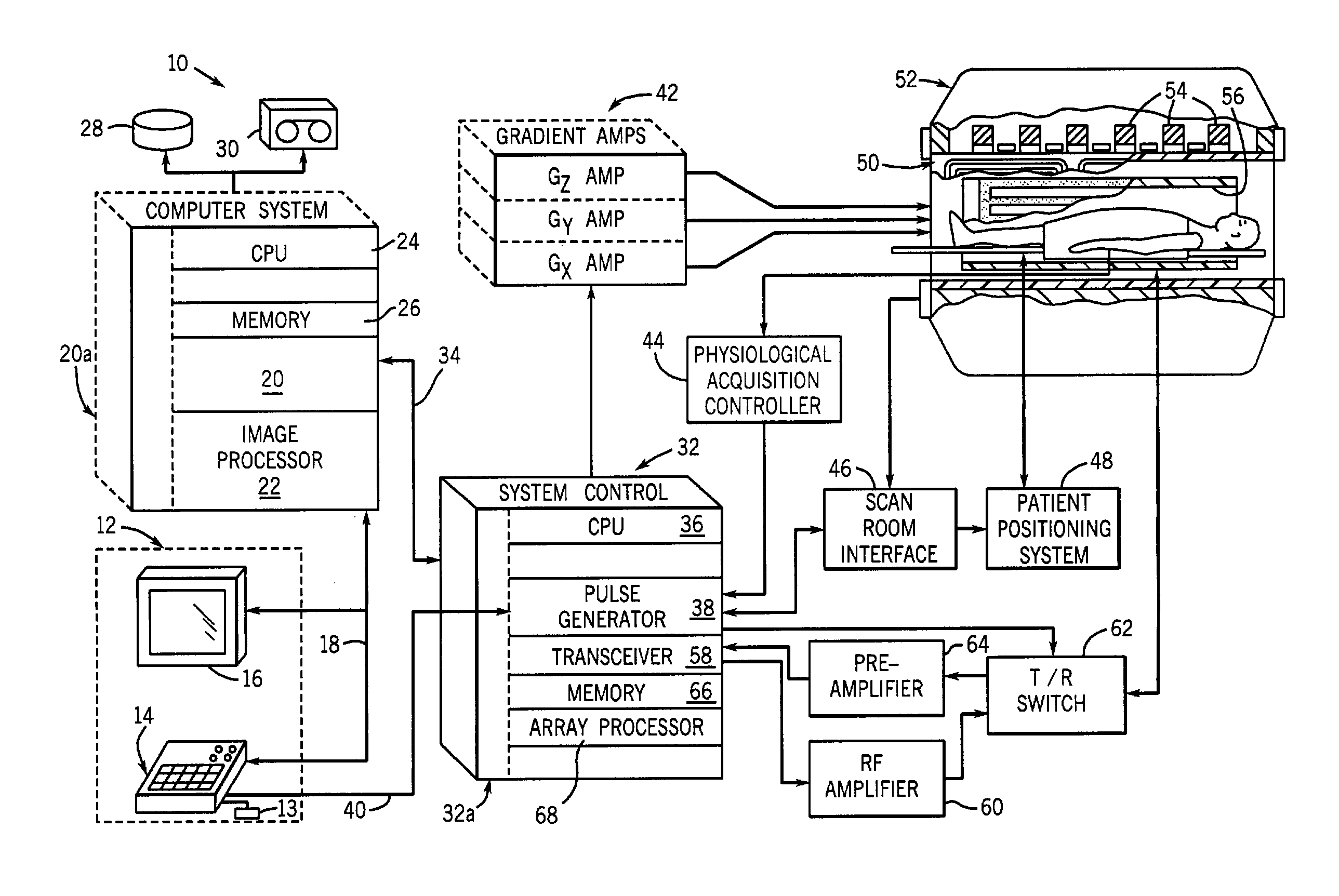
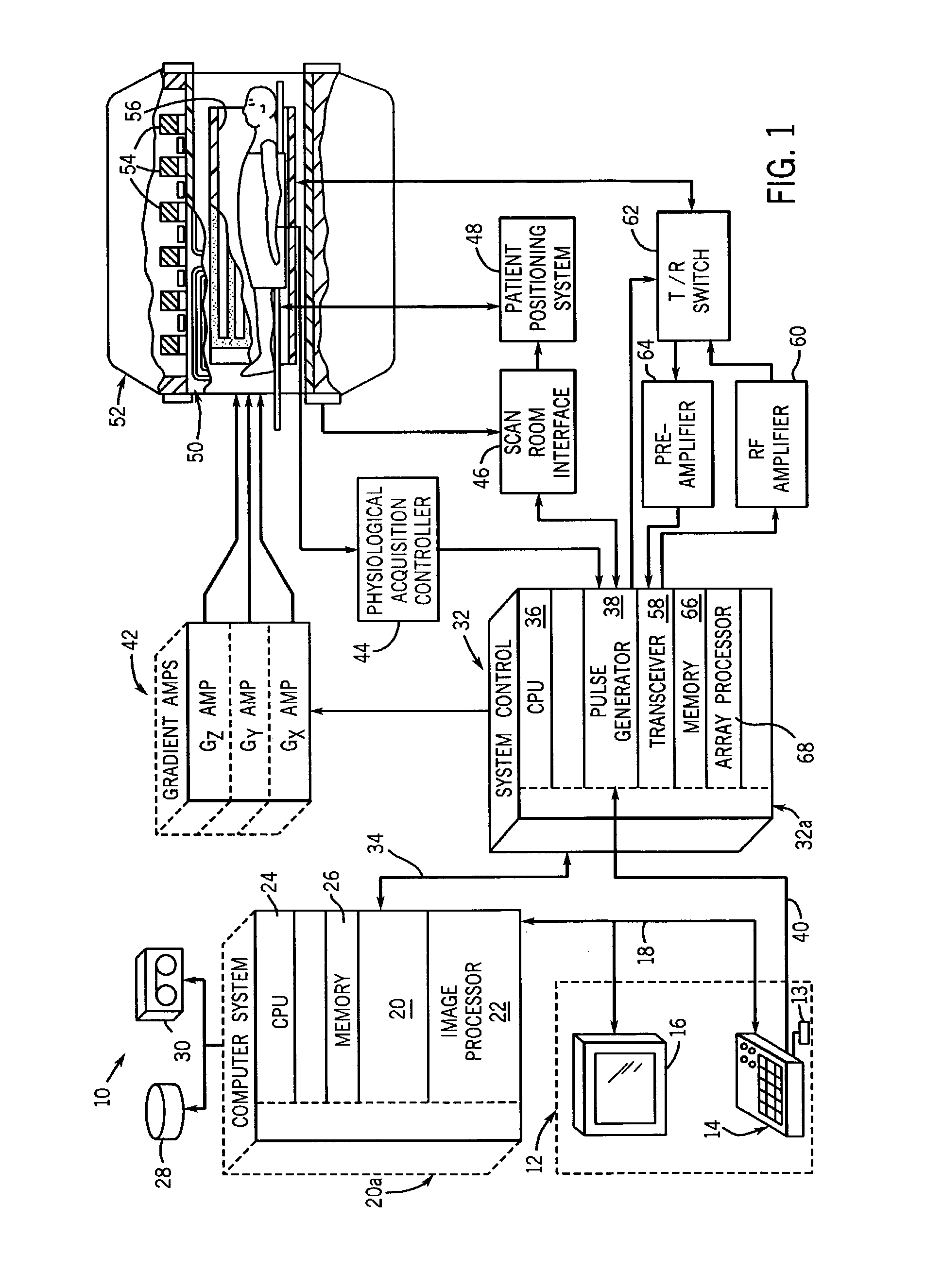
Method and apparatus for breath-held MR data acquisition using interleaved acquisition
ActiveUS7797031B1Minimal temporal and spatial discrepancies or inaccuraciesImage producedDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVentricular volumeCardiac cycle
A method and apparatus are presented for quickly acquiring MR cardiac images in a time equivalent to a single breath-hold. MR data acquisition is segmented across multiple cardiac cycles. MR data acquisition is interleaved from each phase of a first cardiac cycle with MR data from each phase of a subsequent cardiac cycle. Preferably, low spatial frequency data are interleaved between multiple cardiac cycles, and the subsequent cardiac cycle acquisition includes sequential acquisition of high spatial frequency data at the tail end of the acquisition window. An MR image can then be reconstructed with data acquired from each of the acquisitions that reduce ghosting and artifacts. MR images are reconstructed using this interleaved variable temporal k-space sampling technique to produce volume images of the heart within a single breath-hold. Images can be acquired throughout the cardiac cycle to measure ventricular volumes and ejection fractions. Single phase volume acquisitions can also be performed to assess myocardial infarction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging in magnetic resonance tomography
InactiveUS7719270B2Shorten the durationImage can be preventedMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringComplete dataData set
In a method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging in magnetic resonance tomography using spiral-shaped k-space sampling, the underlying k-matrix is under-sampled such that an additional spiral is obtained by point mirroring of the measured values at the center of the k-matrix. This additional spiral forms a complete data set of the k-matrix together with the first spiral for imaging the output information.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for accelerating magnetic resonance imaging using varying k-space sampling density and phase-constrained reconstruction
A method is presented for accelerating magnetic resonance imaging. In 3D MRI, the k-space in the phase encoding plane is divided into two symmetric parts and three asymmetric parts. Different sampling densities are applied in different parts. Images are reconstructed by iteratively minimizing a cost function when random sampling is applied in each part. A phase constraint term is added into the cost function to improve the quality of the reconstruction by exploiting the conjugate symmetry of k-space.
Owner:ALBERT LUDWIGS UNIV FREIBURG
Accelerated shells trajectory MRI acquisition
ActiveUS8095202B2Shorter TR and signal readout durationReduce contributionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFat suppressionPulse sequence
An MRI k-space data set is acquired using a series of shell k-space sampling trajectories of different radii. Off-resonance effects are reduced and fat-suppression can be improved by using a shorter TR for pulse sequences that sample at smaller radii. At larger radii sampling is repeated with the central axis of the shell sampling trajectory tilted such that the polar regions of shells acquired at the same radii are sampled by the other shell.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com