Patents
Literature
102 results about "Limb amputation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
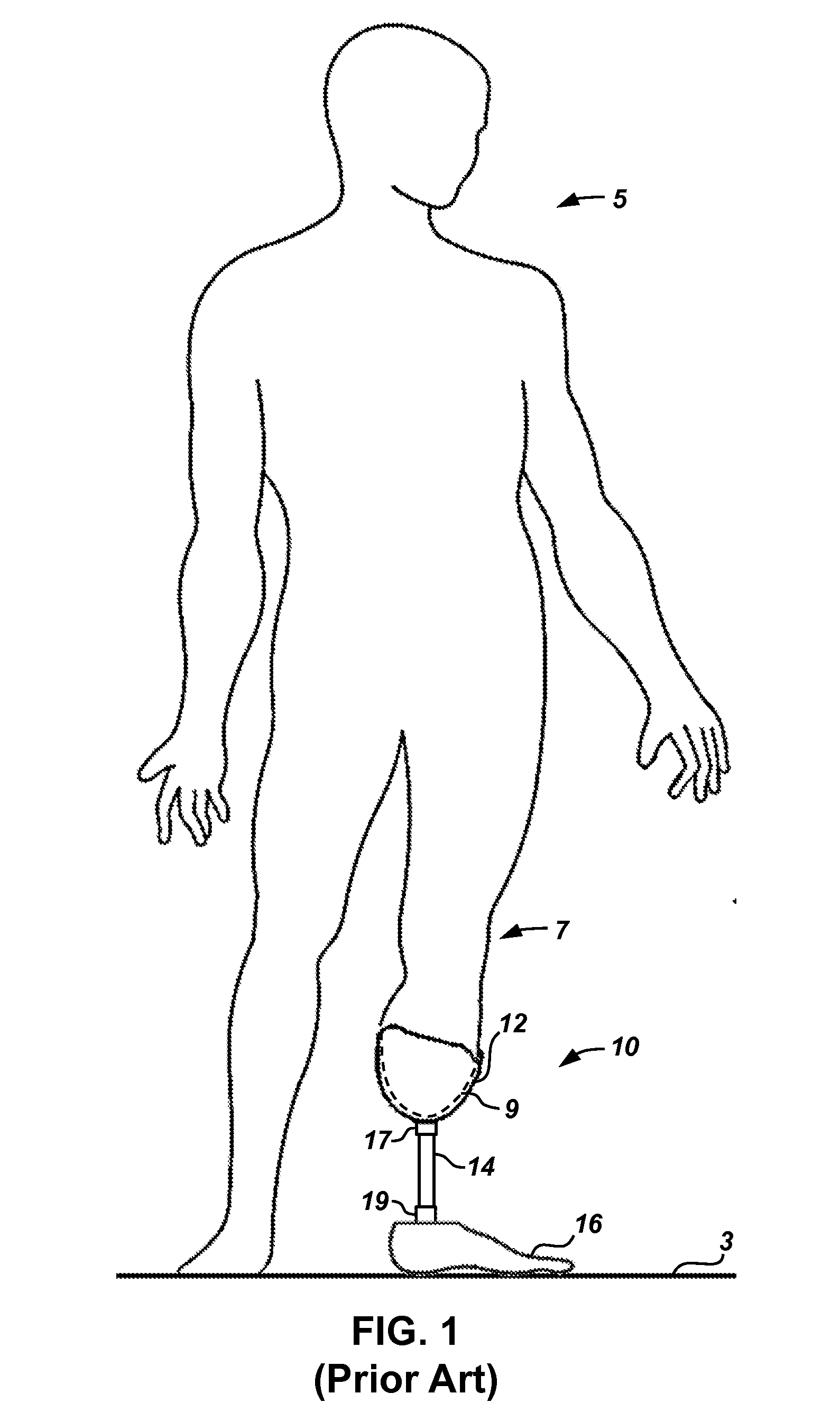
Lower limb, or leg, amputations can be divided into two broad categories - minor amputations and major amputations, Minor amputations generally refers to the amputation of digits. Major amputations are commonly referred to as below-knee amputation, above-knee amputation and so forth.
System, garment and method
ActiveUS20110015498A1Level of customizationSame compressionPerson identificationSensorsButtocksExternal pressure
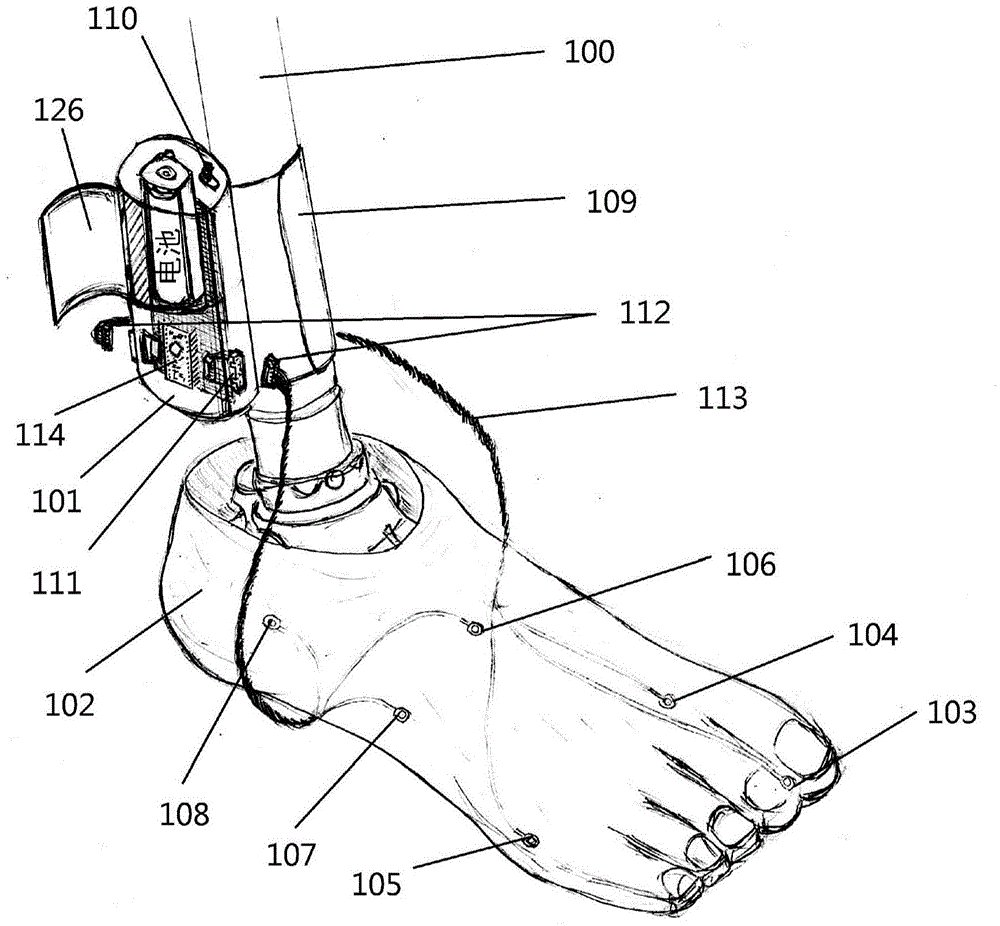
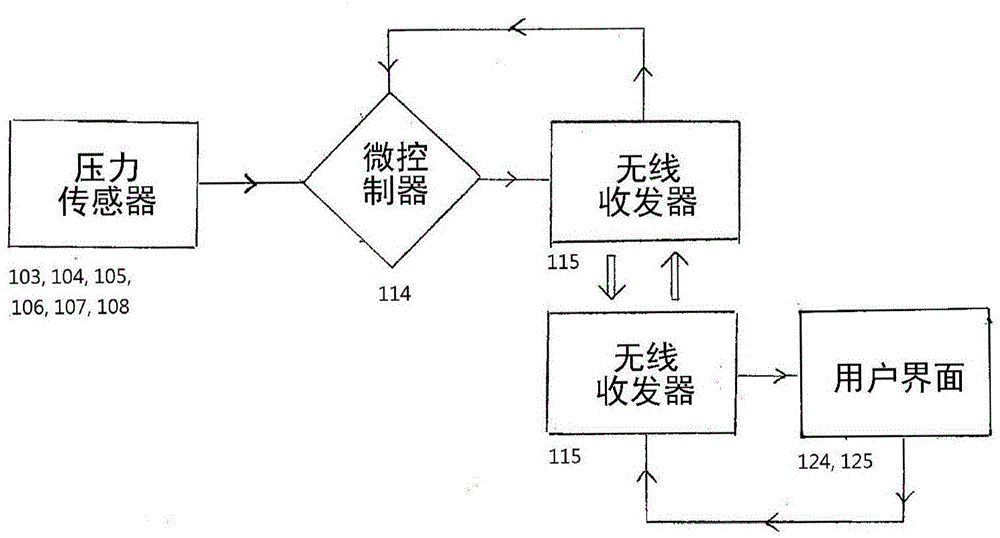
The present invention relates to a system and garment that incorporates sensors that can be used for measuring or monitoring pressure or forces in feet, the stumps of limbs of an amputee that are fitted with prosthetic devices, or any other parts of the body that are subject to forces such as the buttock while seated or when external pressure inducing devices are employed, such as for example, pressure bandages. The invention also relates to a method to monitor or diagnose any foot or limb related activity for recreational, sporting, military or medical reasons and is particularly aimed at the treatment of neuropathic or other degenerating conditions.
Owner:SENSORIA
Equilibrium-point prosthetic and orthotic ankle-foot systems, devices, and methods of use
ActiveUS20100185301A1Reduce and prevent likelihoodWeaken energyArtificial legsDiseasePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The present invention relates to a system for use in rehabilitation and / or physical therapy for the treatment of injury or disease. The system can enable an amputee to proceed over any surface without overbalancing. In particular the system is self-adapting to adjust the torque moment depending upon the motion, the extent of inclination, and the surface topography.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
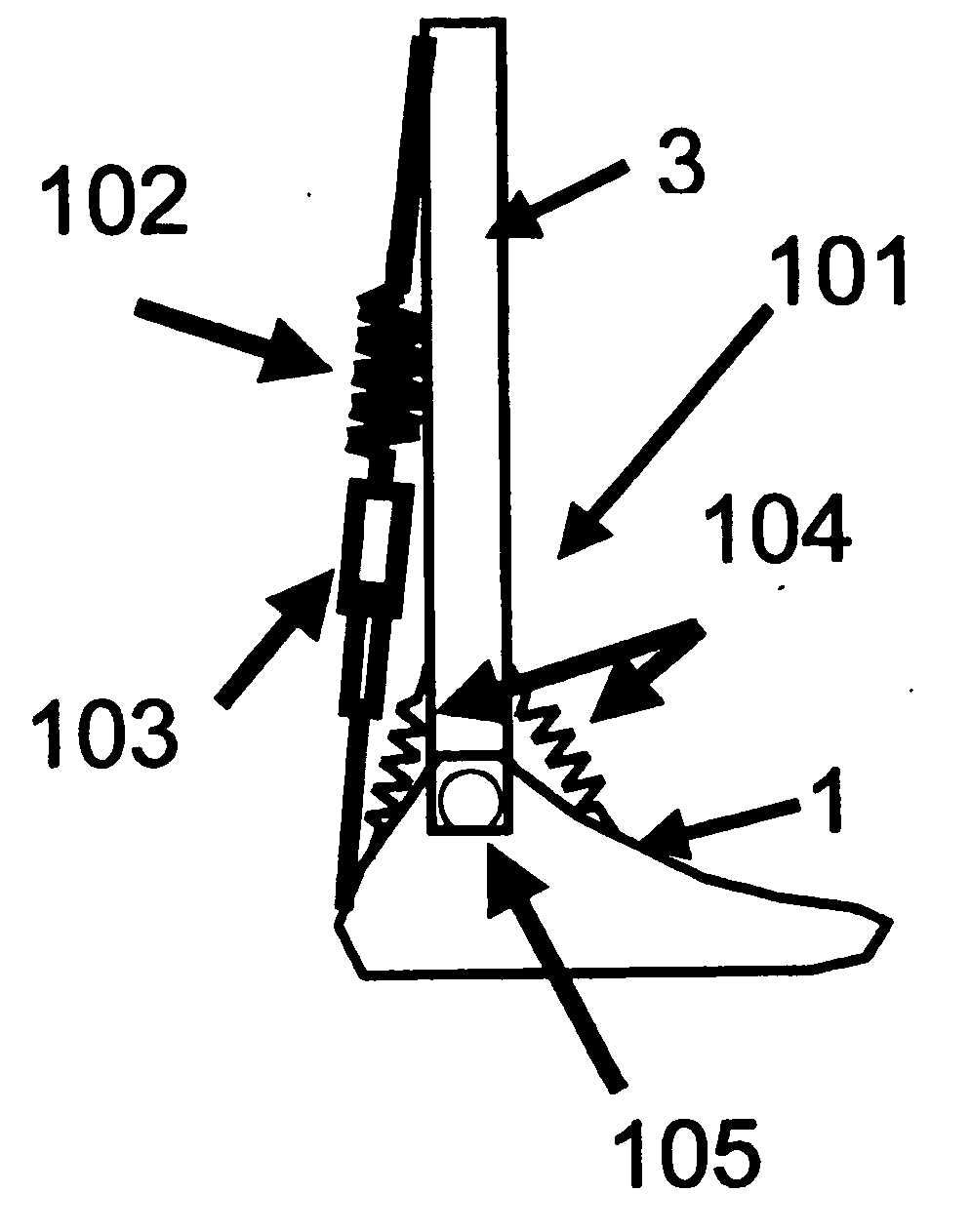
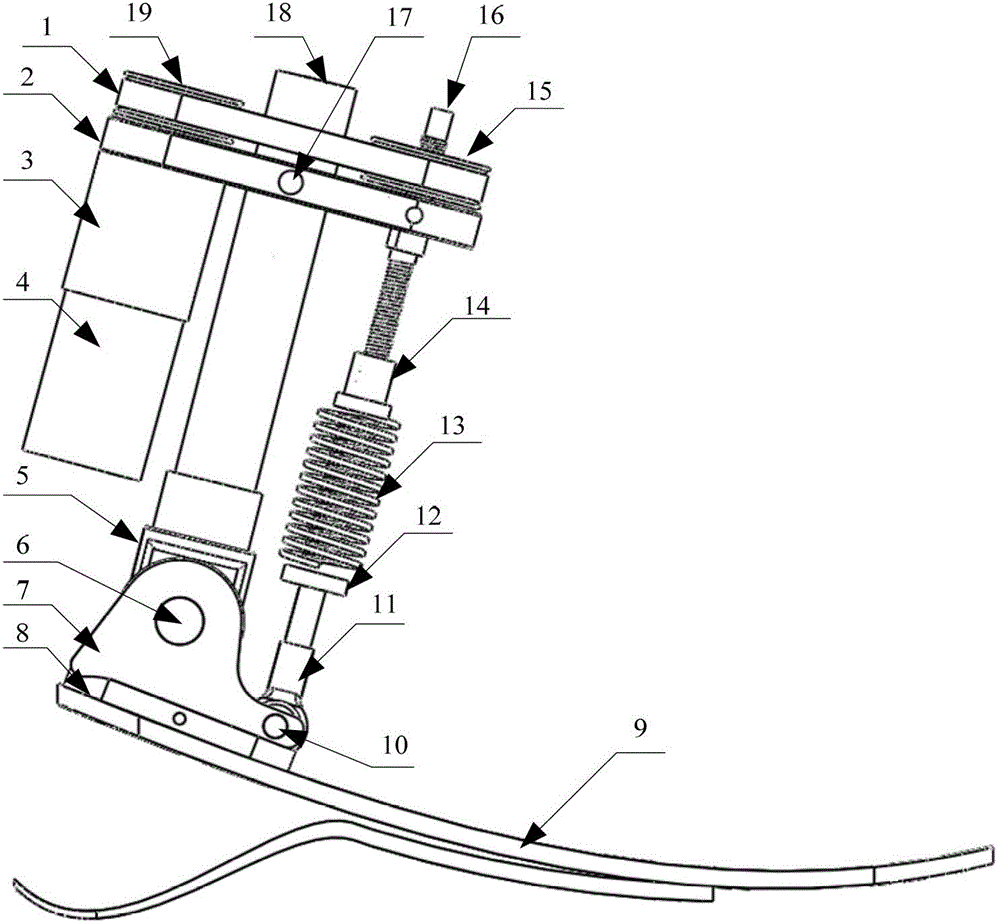
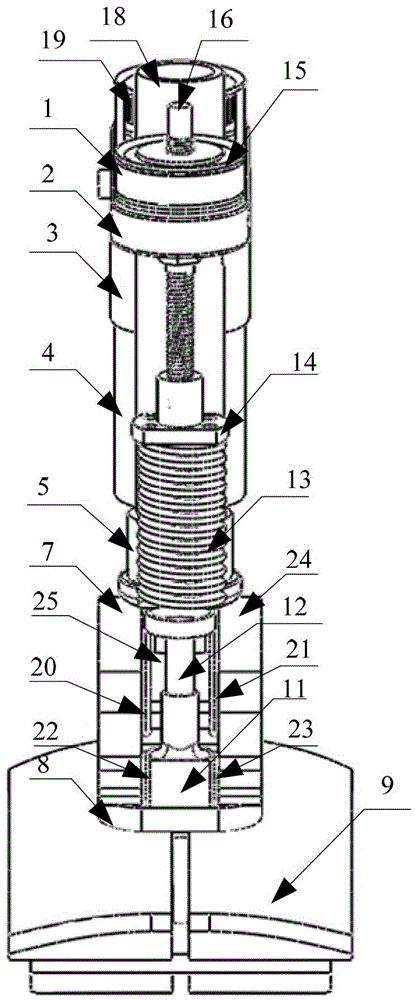
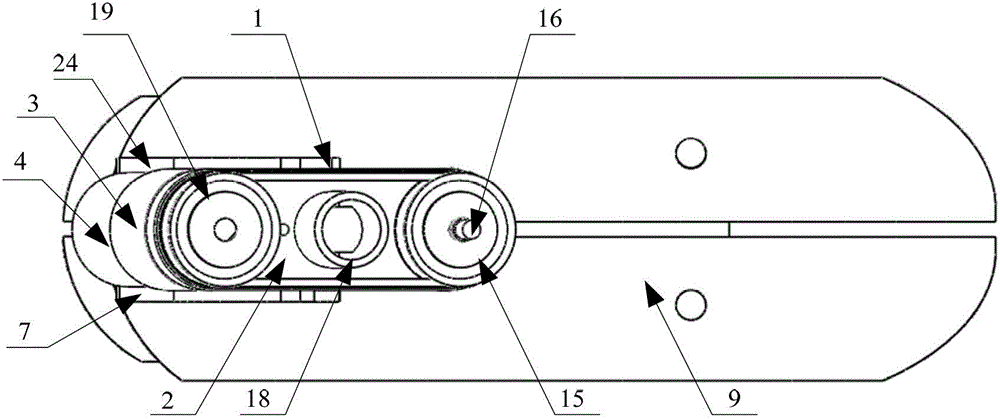
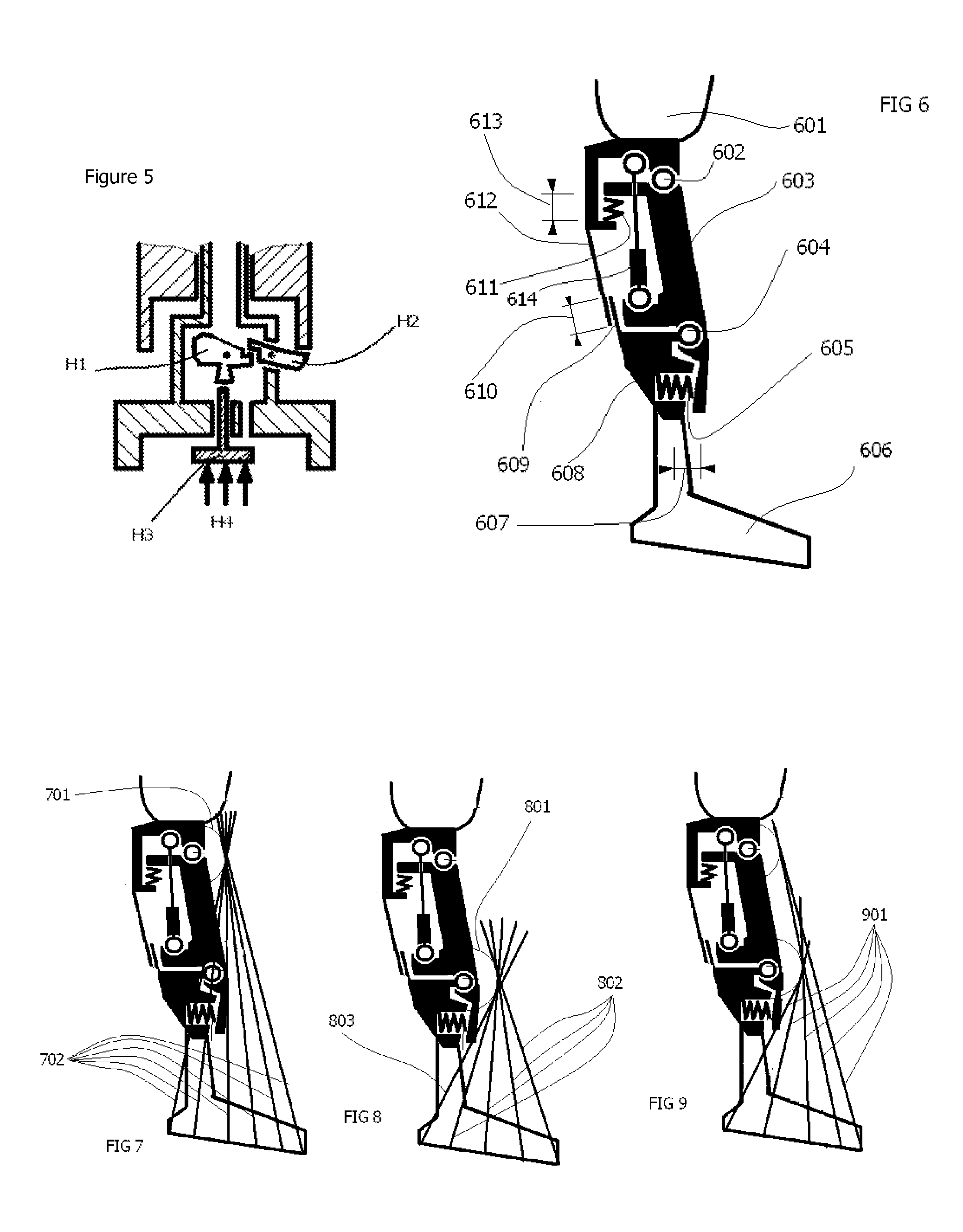
Automatic prosthesis for above-knee amputees
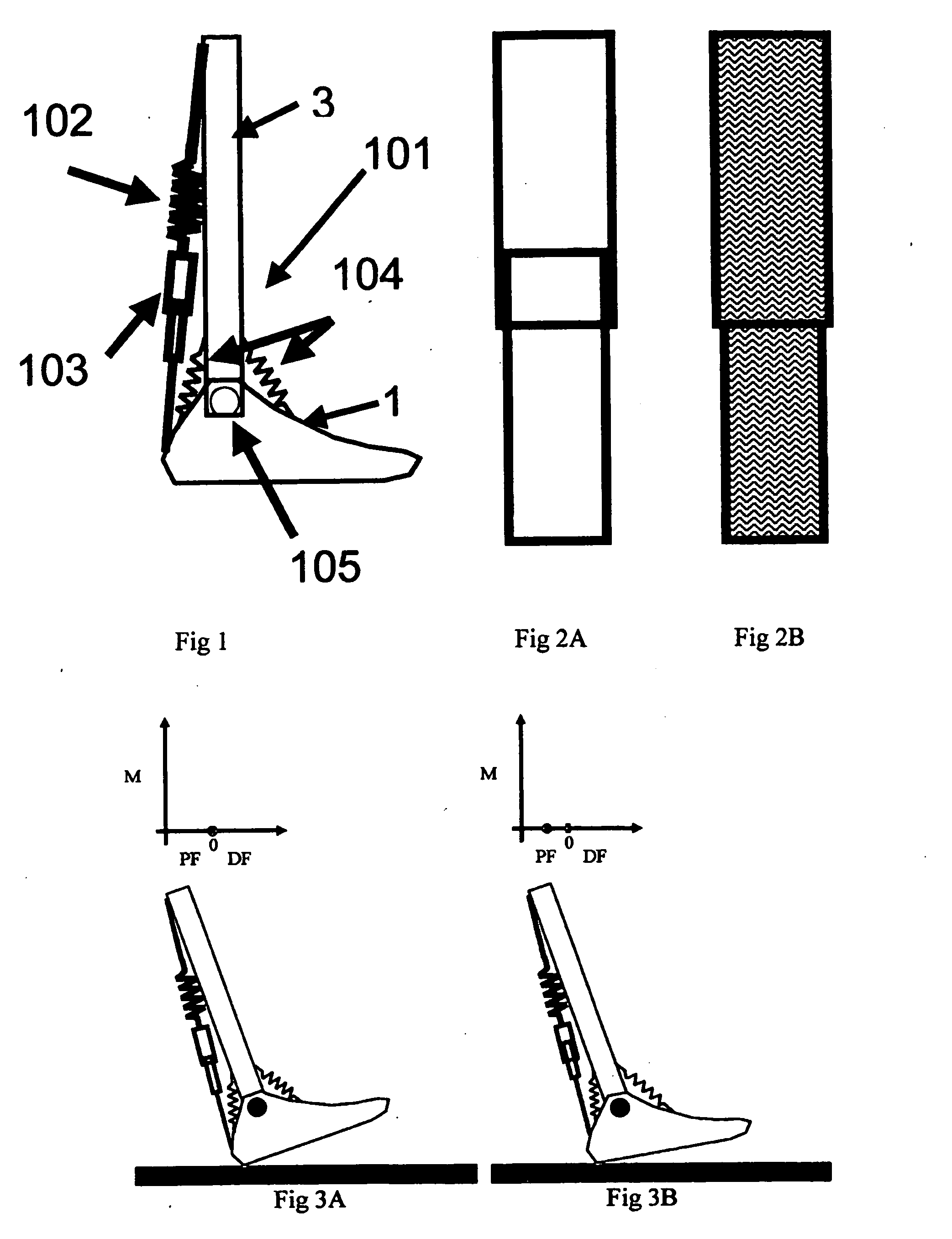
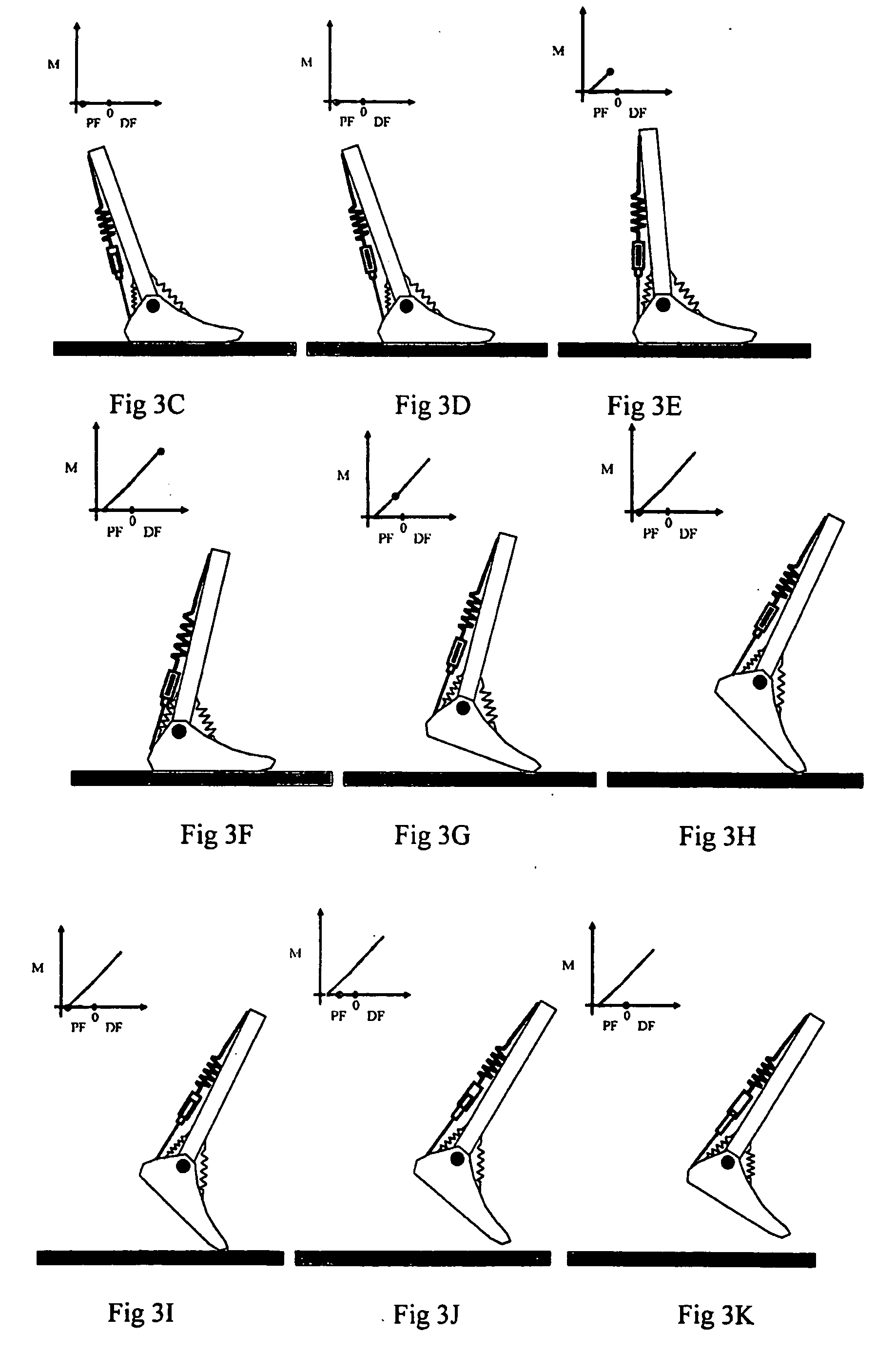
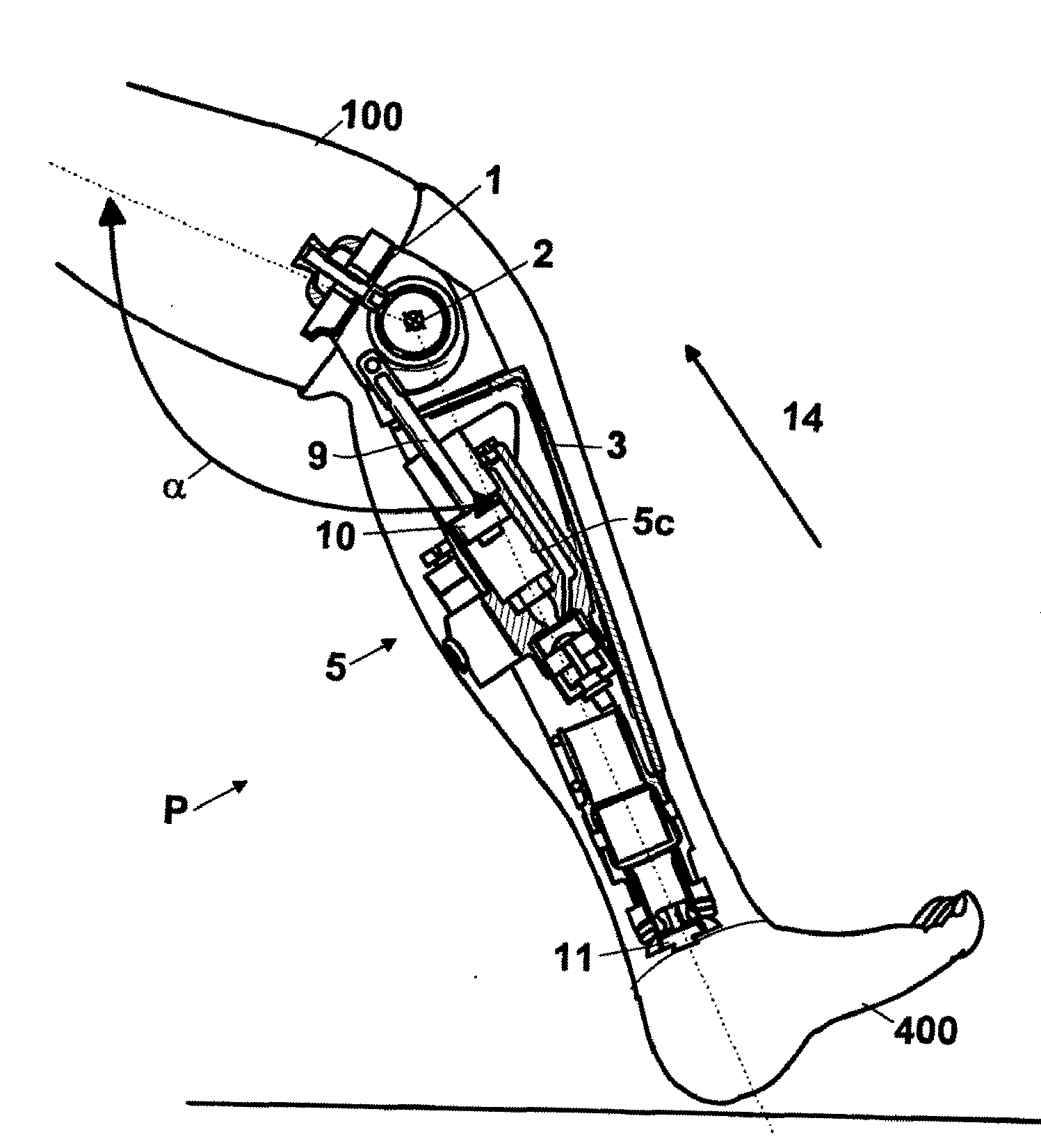
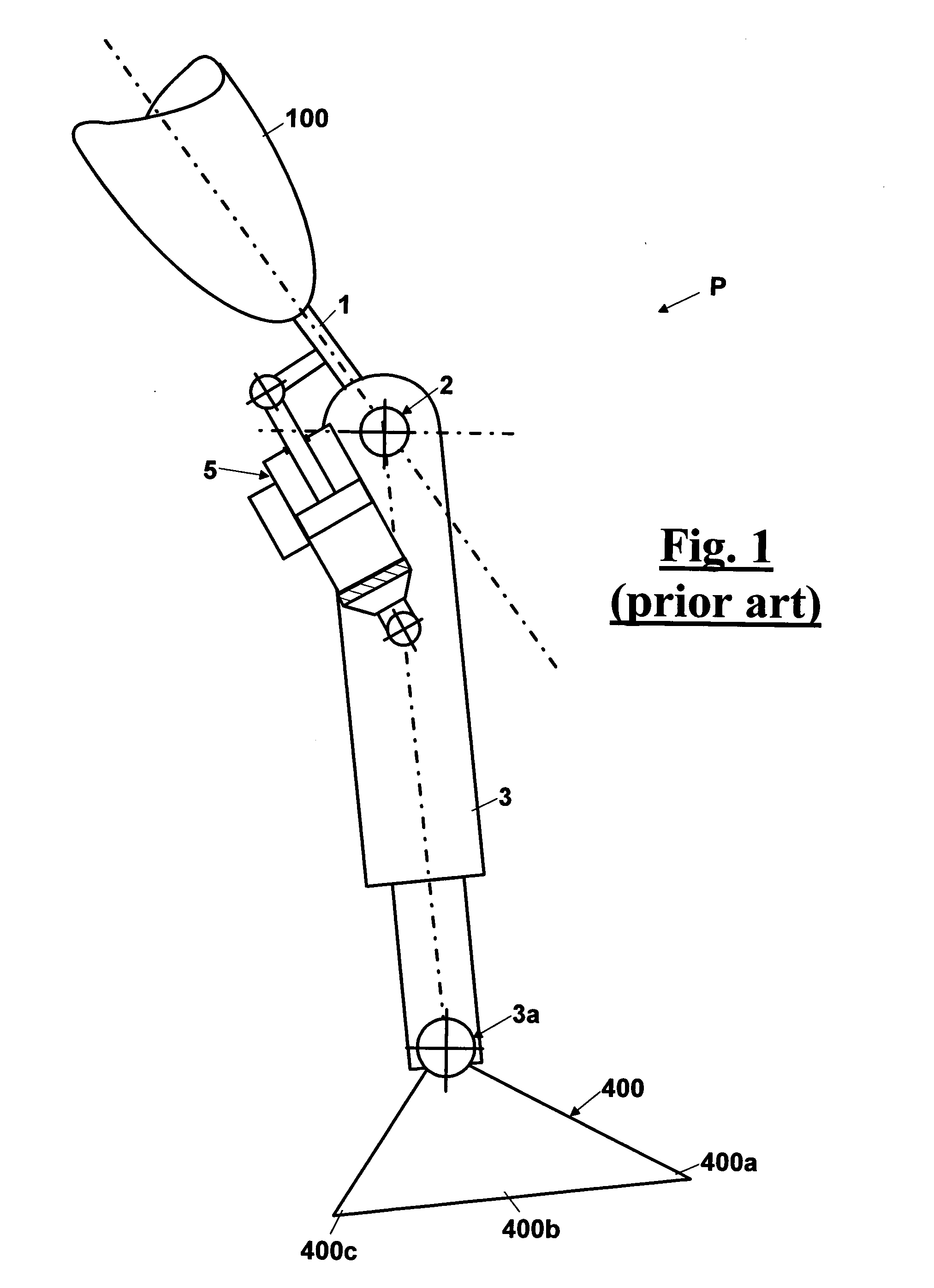
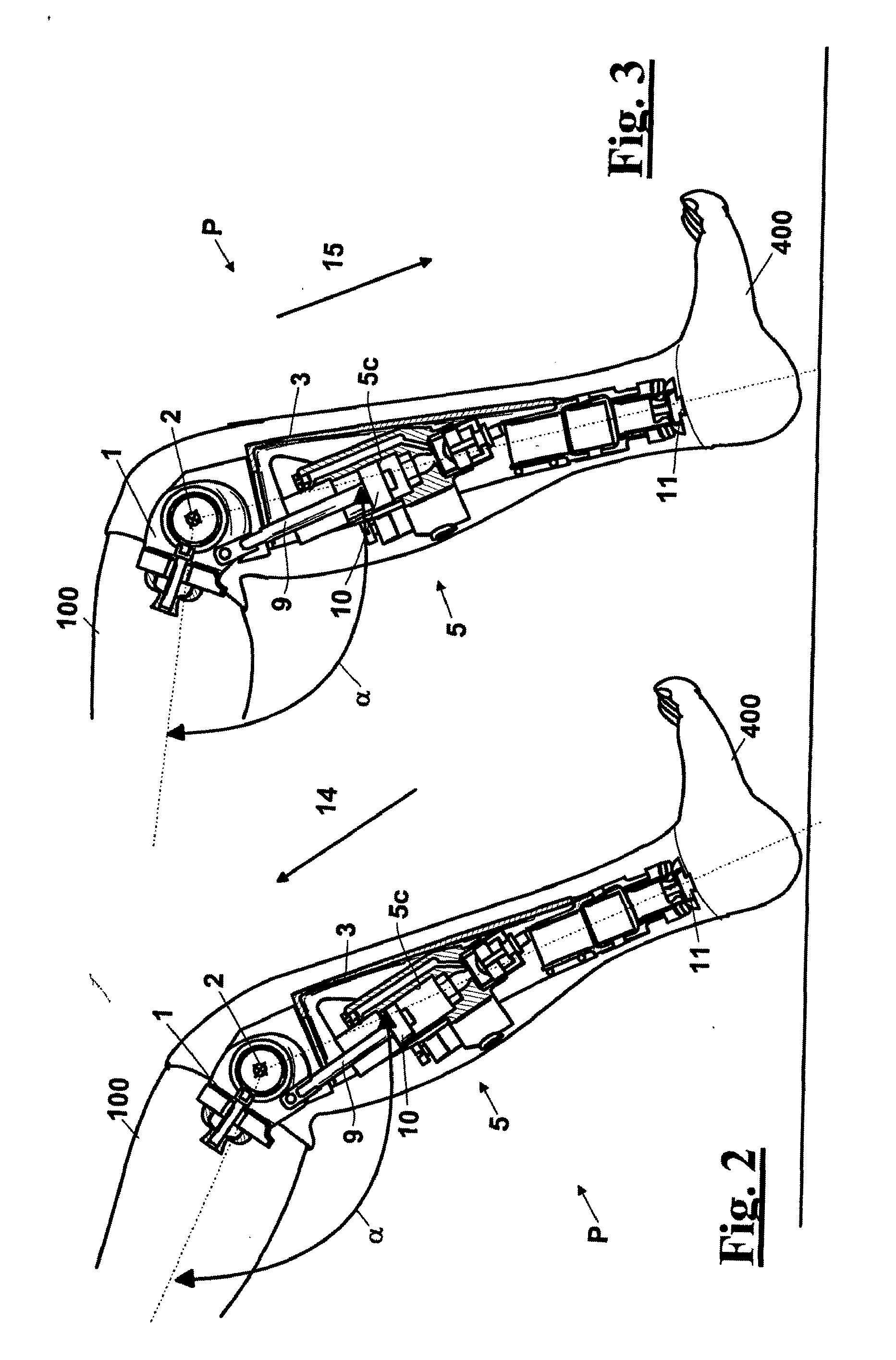
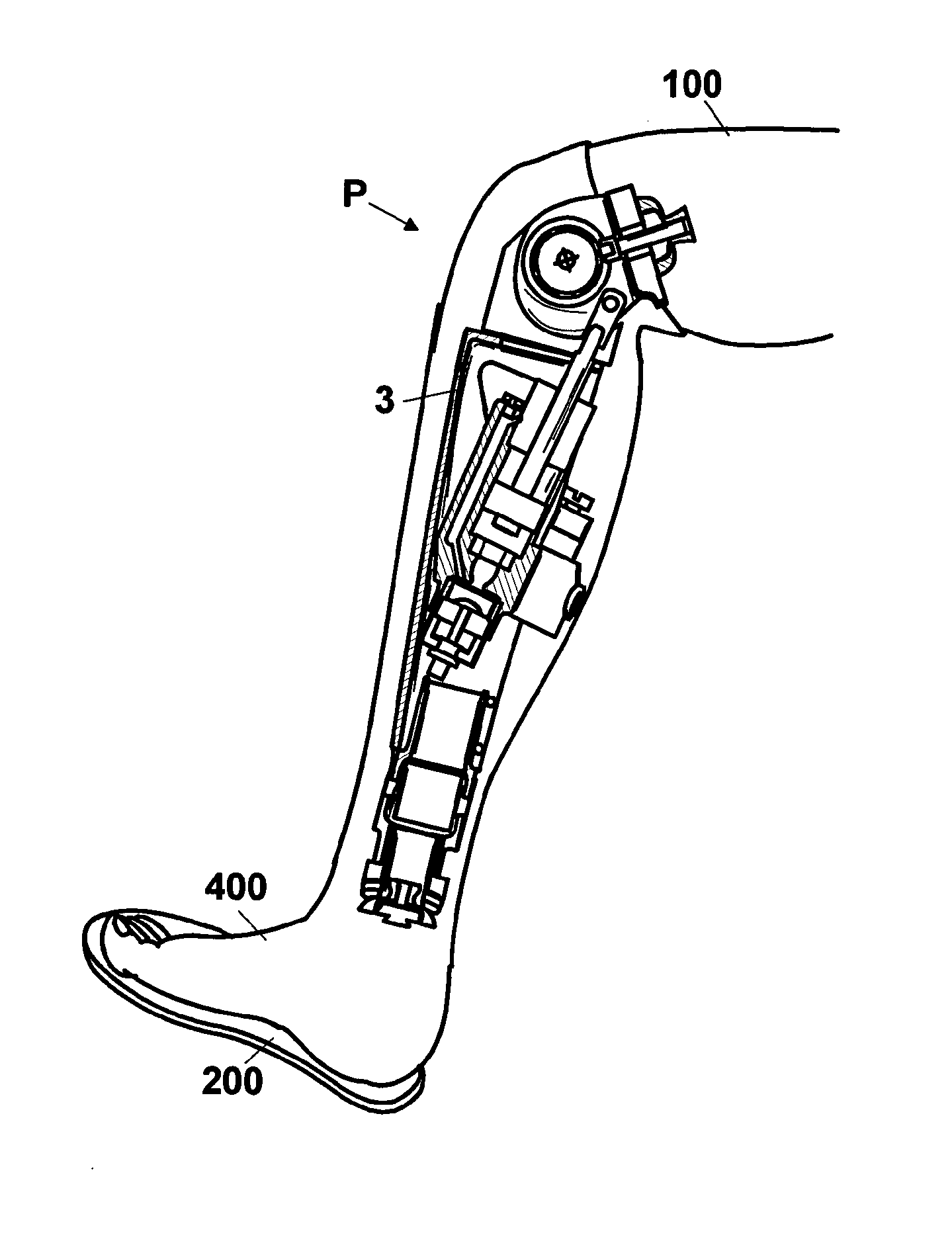
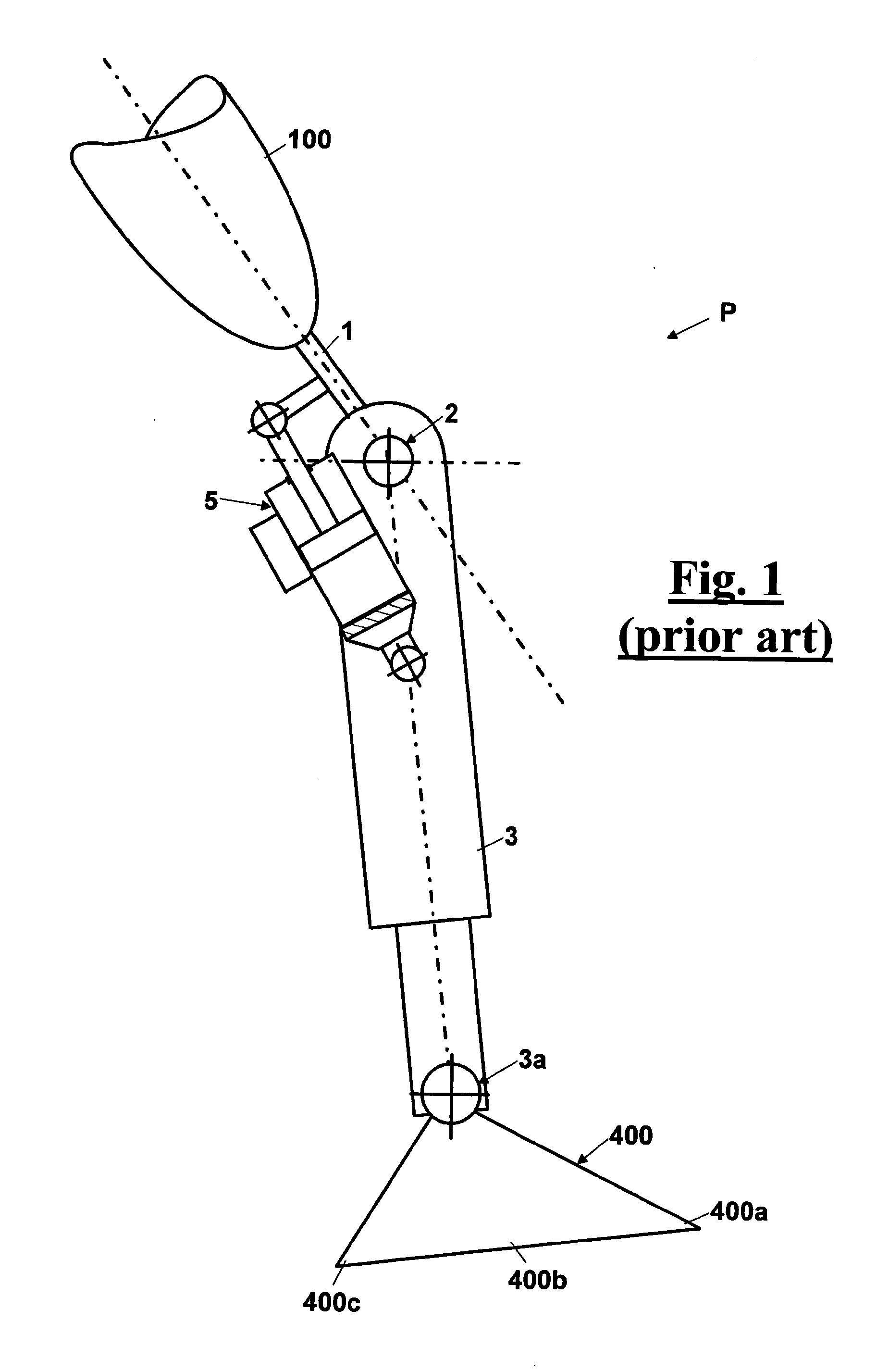
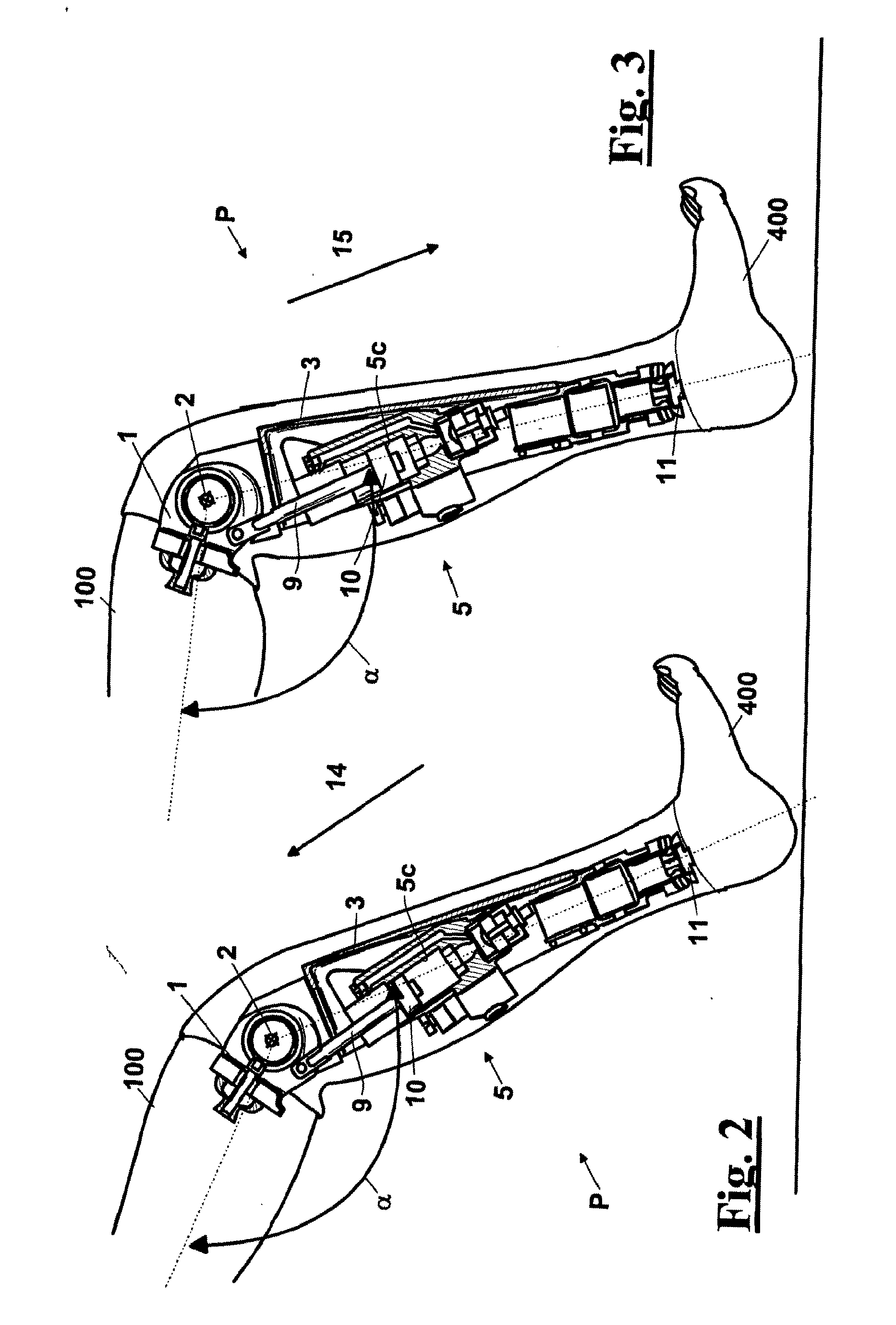
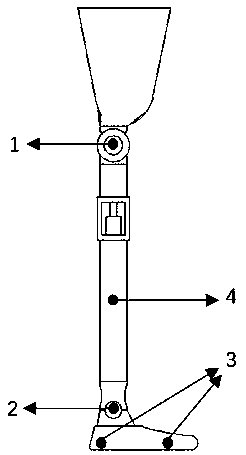
A above knee prosthesis (P) applied to femoral connection (100) of an amputee that comprises a upper hinge (1) connected to femoral connection of the patient, an articulation axis (2) with the function of reproducing the knee movements, a tibia-calf muscle unit (3) pivotally connected to the femoral•segment and a damper (5) that reproduces some functions of the calf muscle and ensures to the prosthesis to brake and to allow the sequential swing and stance phases typical of the gait. The damper comprises a cylinder (5c) wherein a piston (10) and a stem (9) act connected to each other and adapted to carry out a damping reaction of said damper responsive to the forces loaded on the prosthesis. In particular, a force transducer is provided in the damper arranged, in particular, in the stem with a microprocessor that receives a force signal from the transducer and operates means for adjusting the reaction of the damper responsive to the detected force signal.
Owner:OFFICINE ORTOPEDICHE RIZZOLI SRL
System incorporating an insole pressure sensor and personal annunciator for use in gait assistive therapy
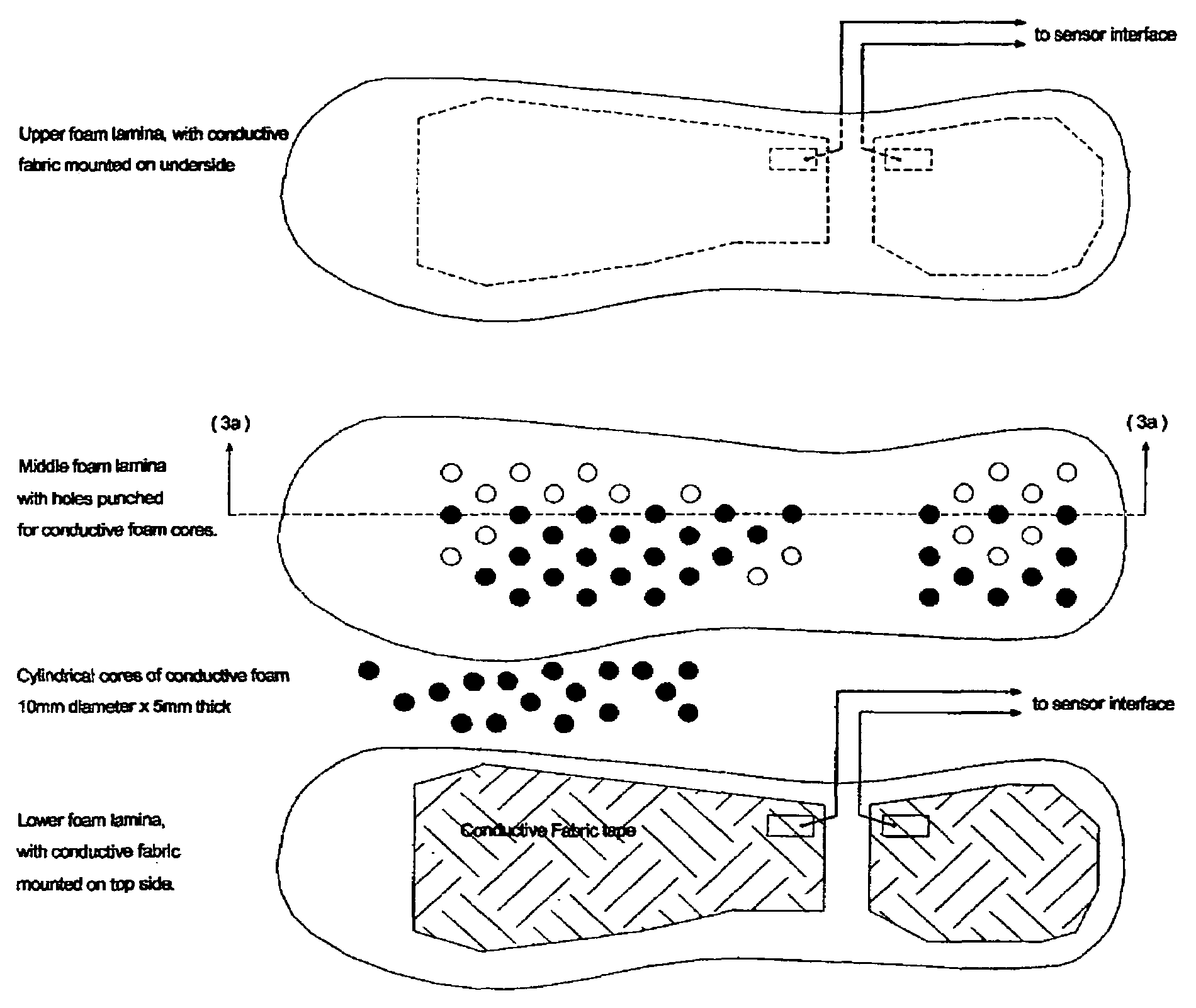
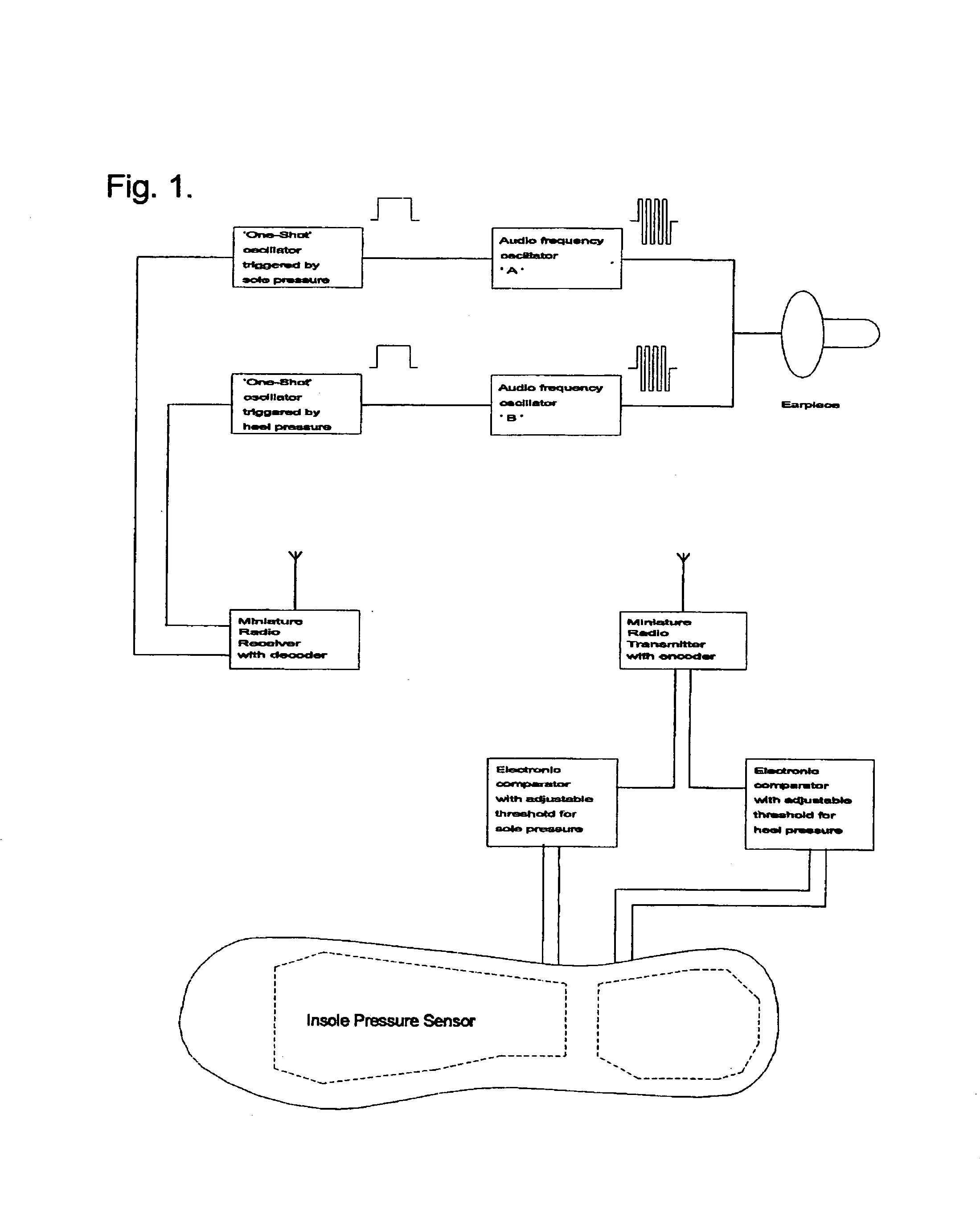
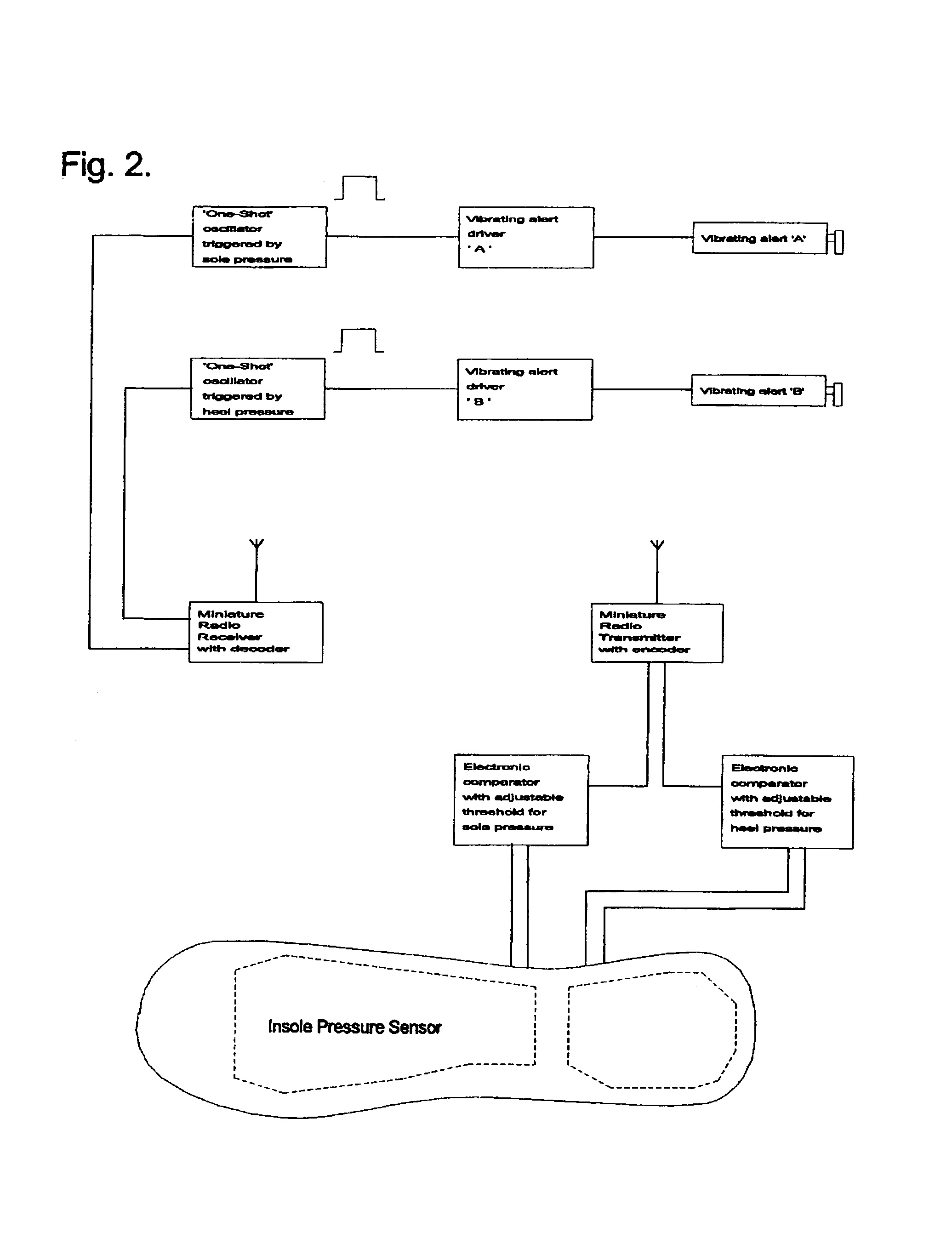
A gait assistive system designed to assist with the therapeutic treatment of subjects who have difficulty in walking, specifically those with a lack of sensation due to nerve damage or amputation, who are unable to tell when the foot makes contact with the floor. The system includes a removable insole placed inside the shoe which proportionally senses touchdown of the limb. The sensed touchdown is communicated to a transmitter and subsequently to a remotely positioned receiver to provide a desired bio-feedback of the sensed touchdown. The system can also include a second remotely located receiver that can be used to facilitate set up and / or adjustments of the system.
Owner:HASELHURST RICHARD S +1
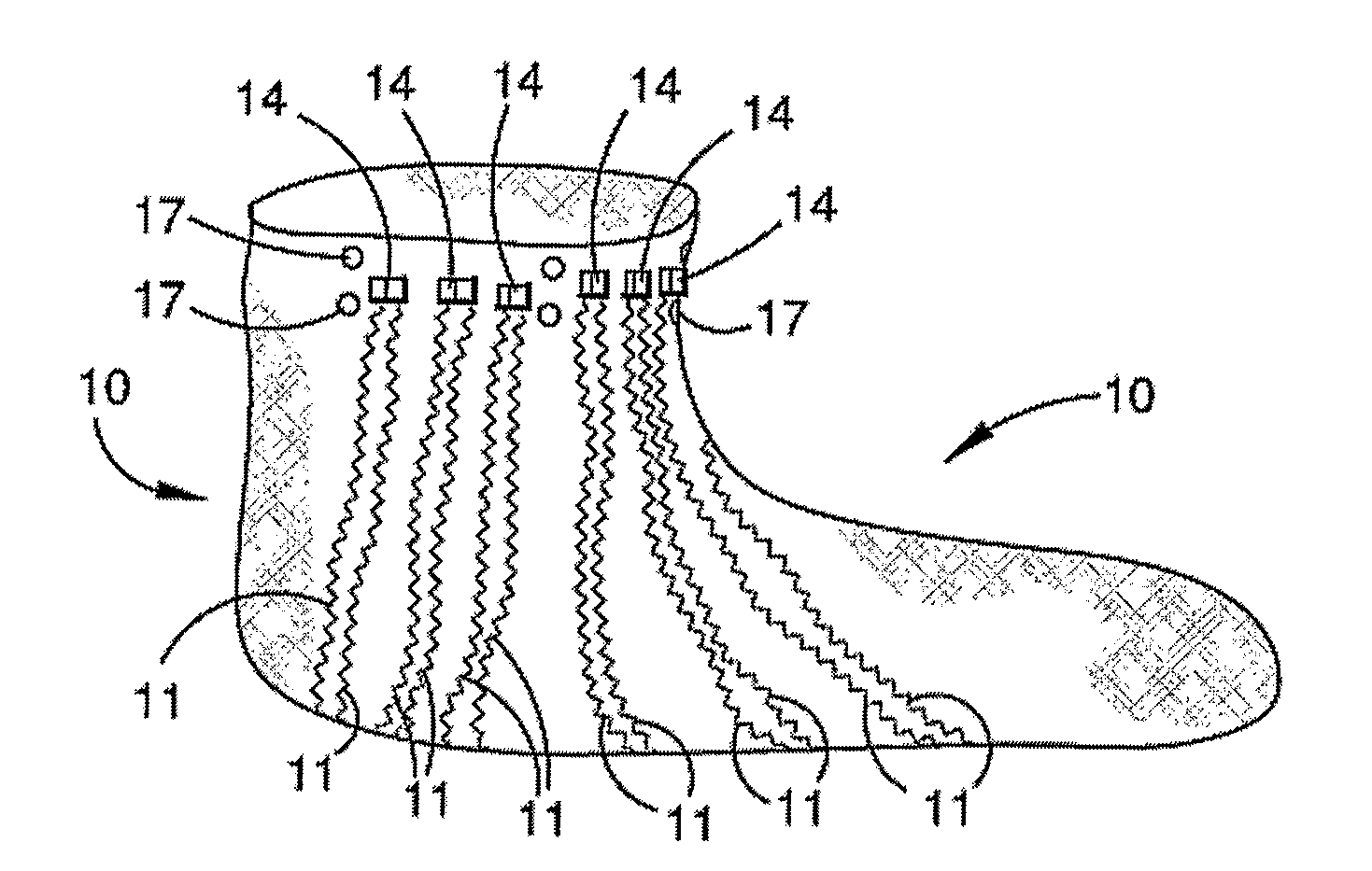
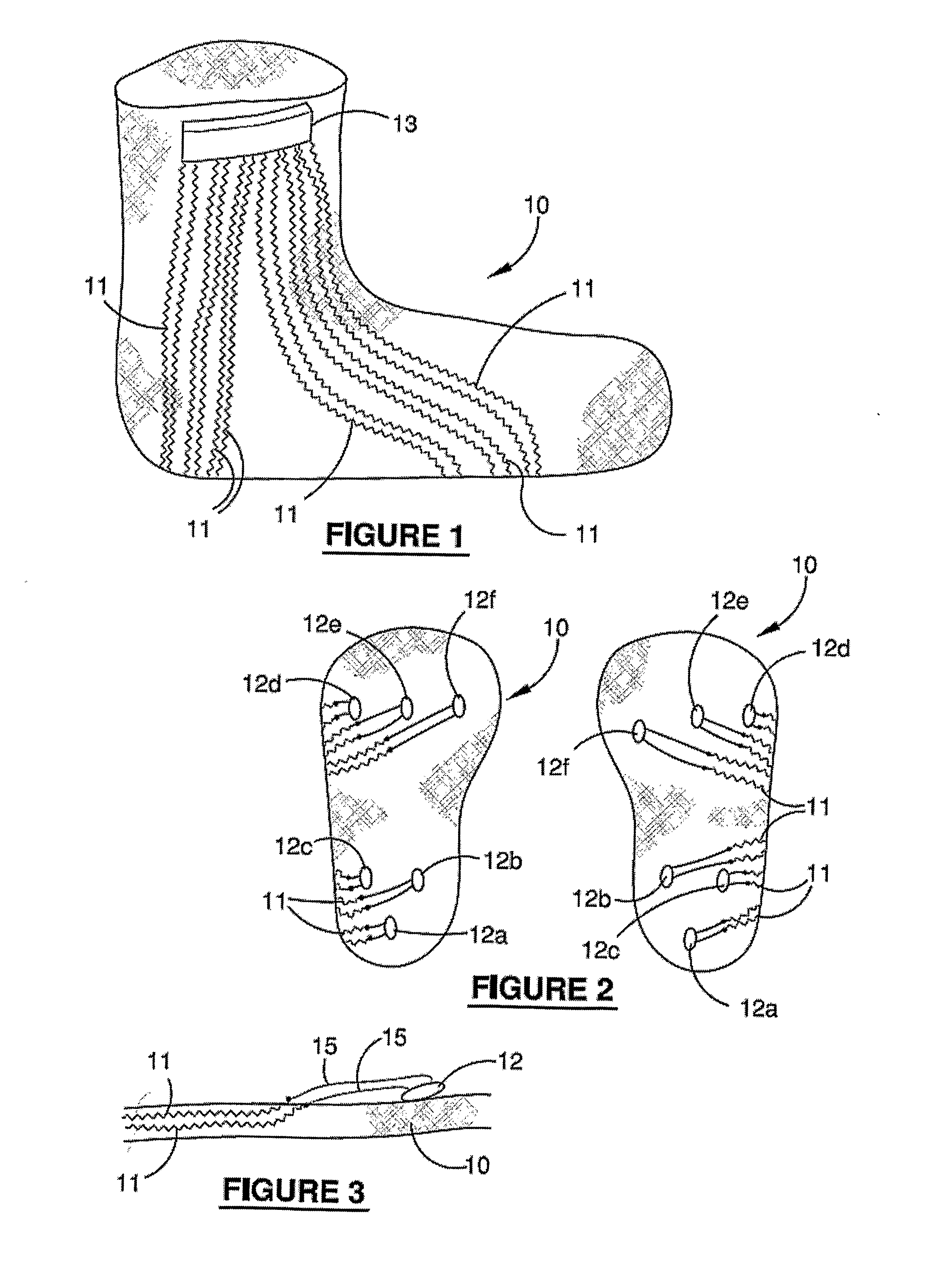
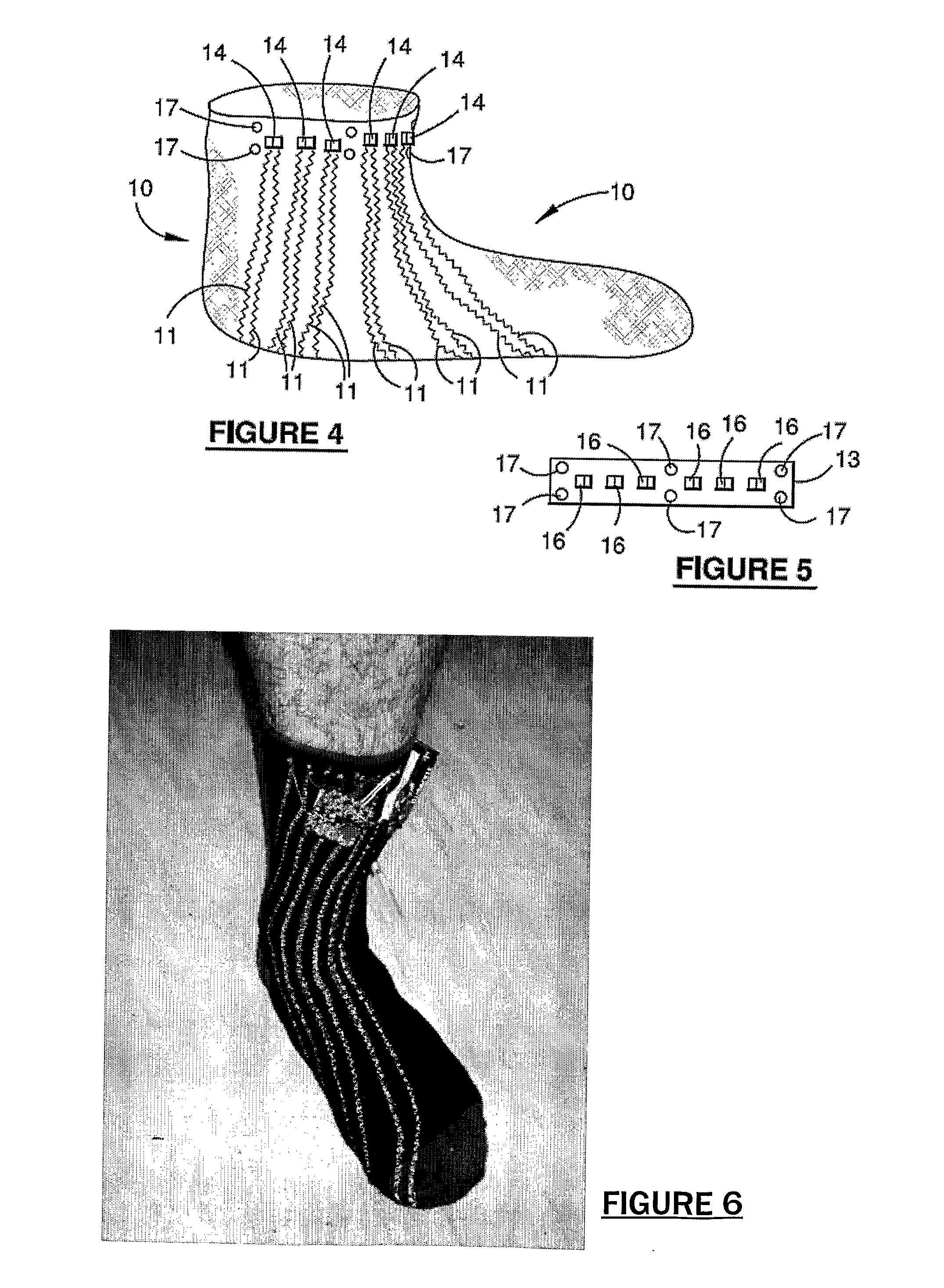
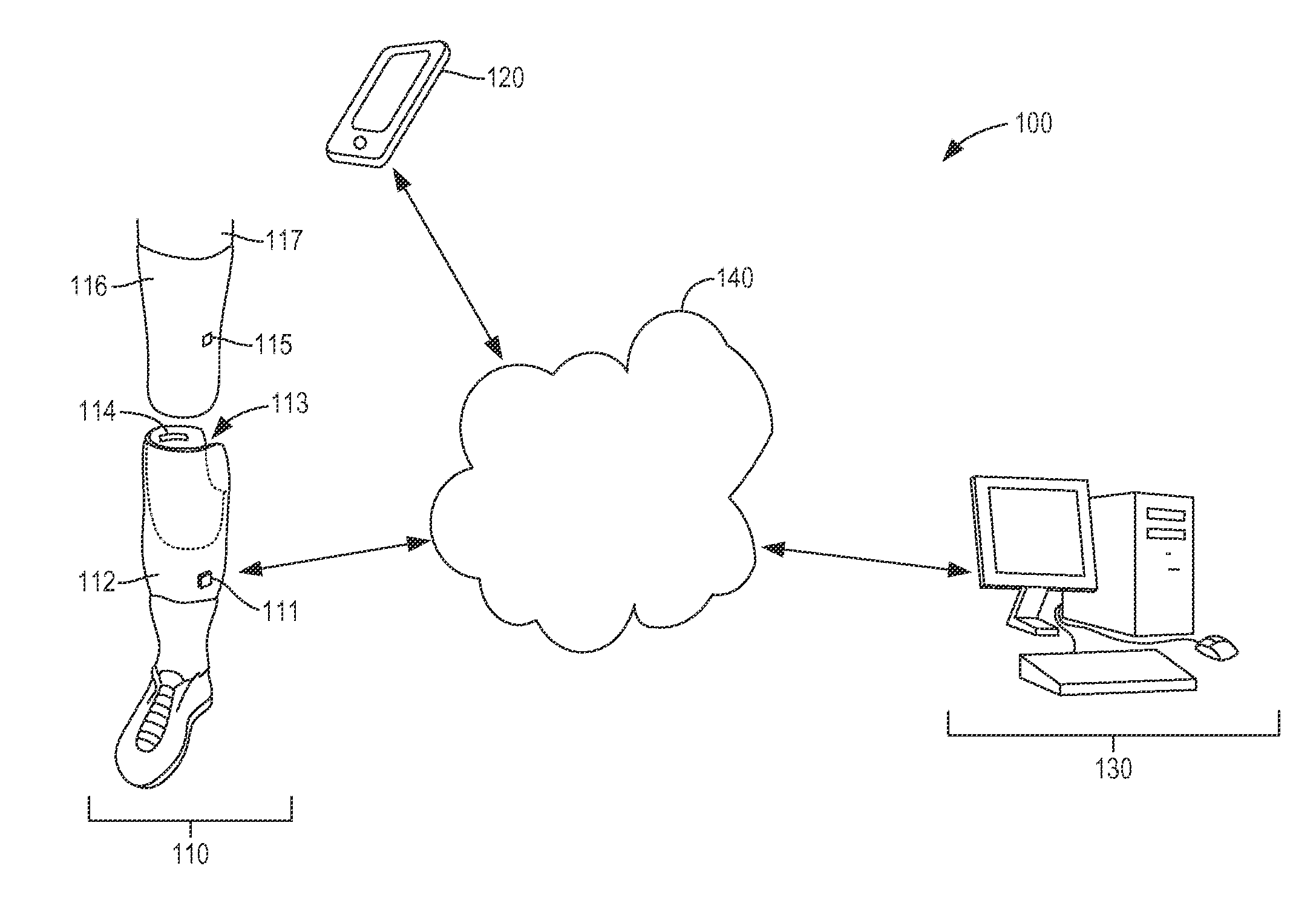
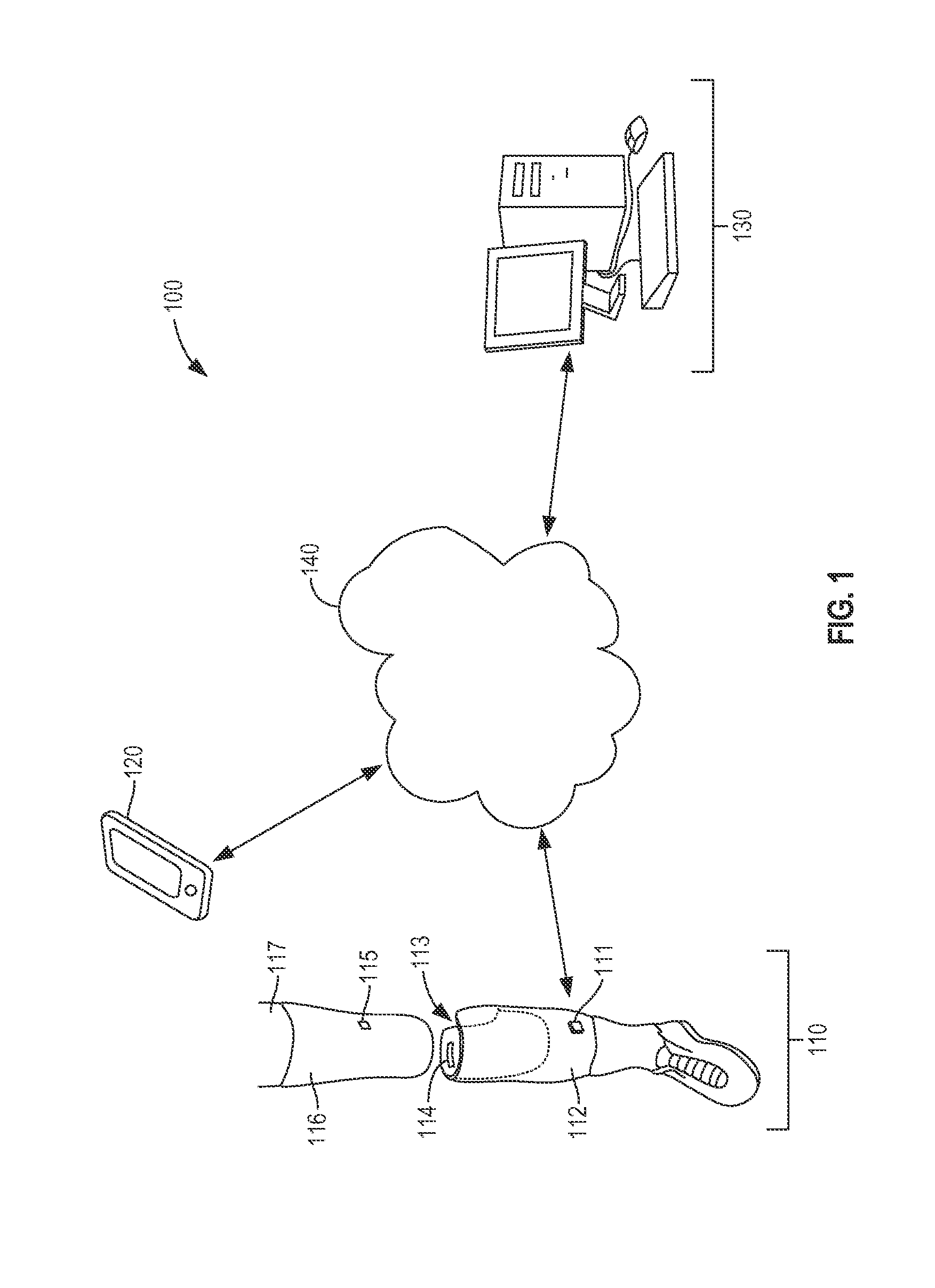
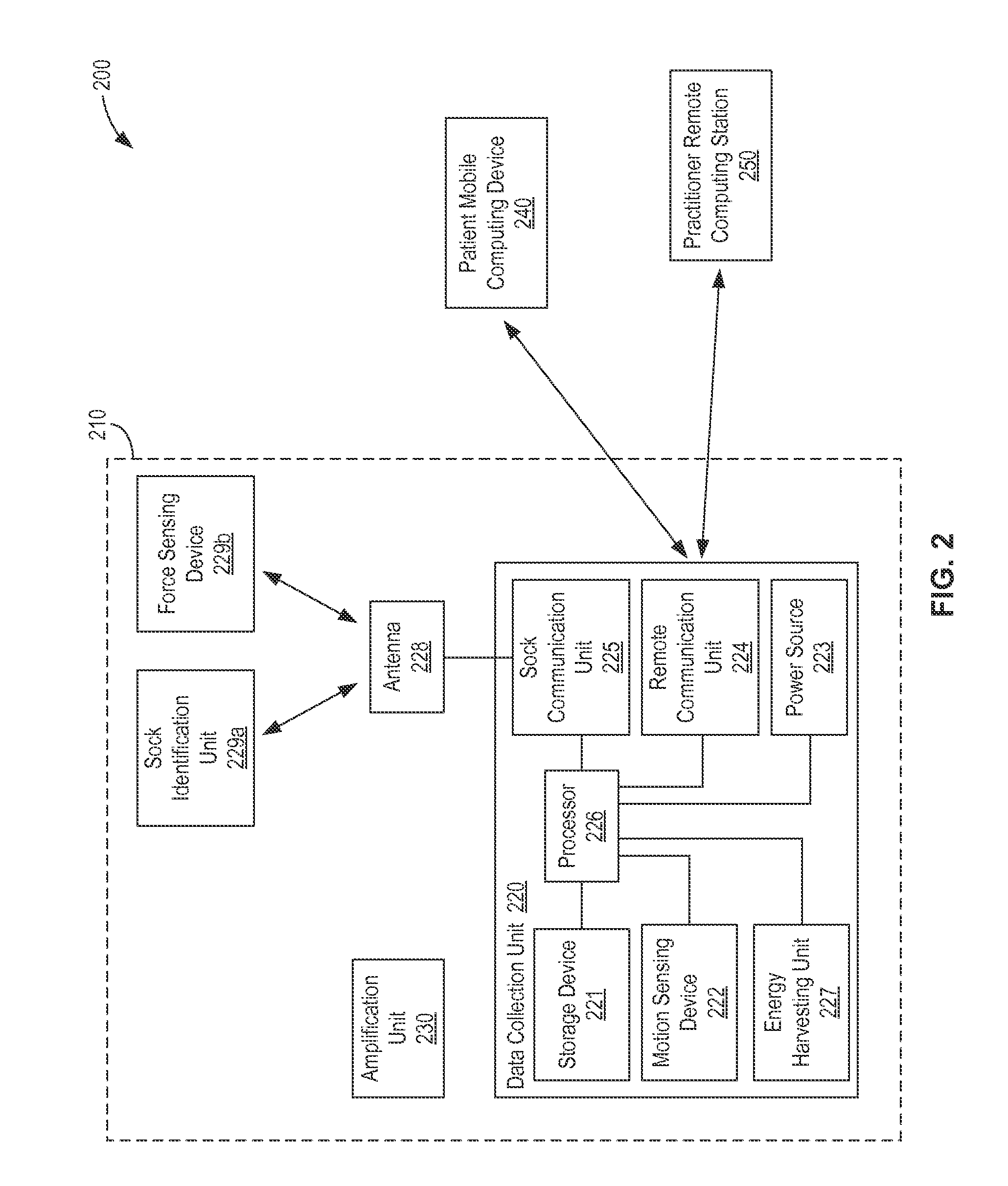
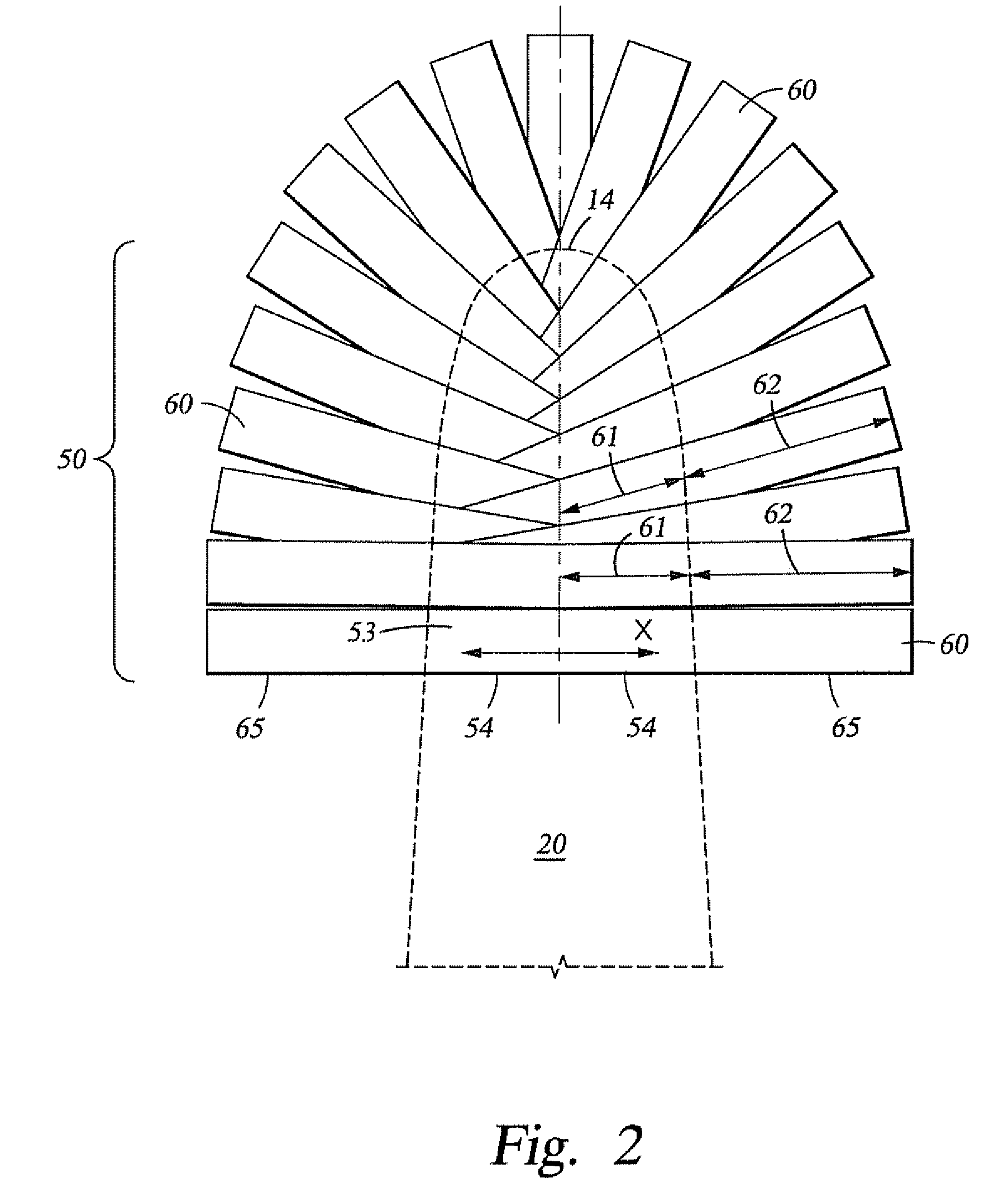
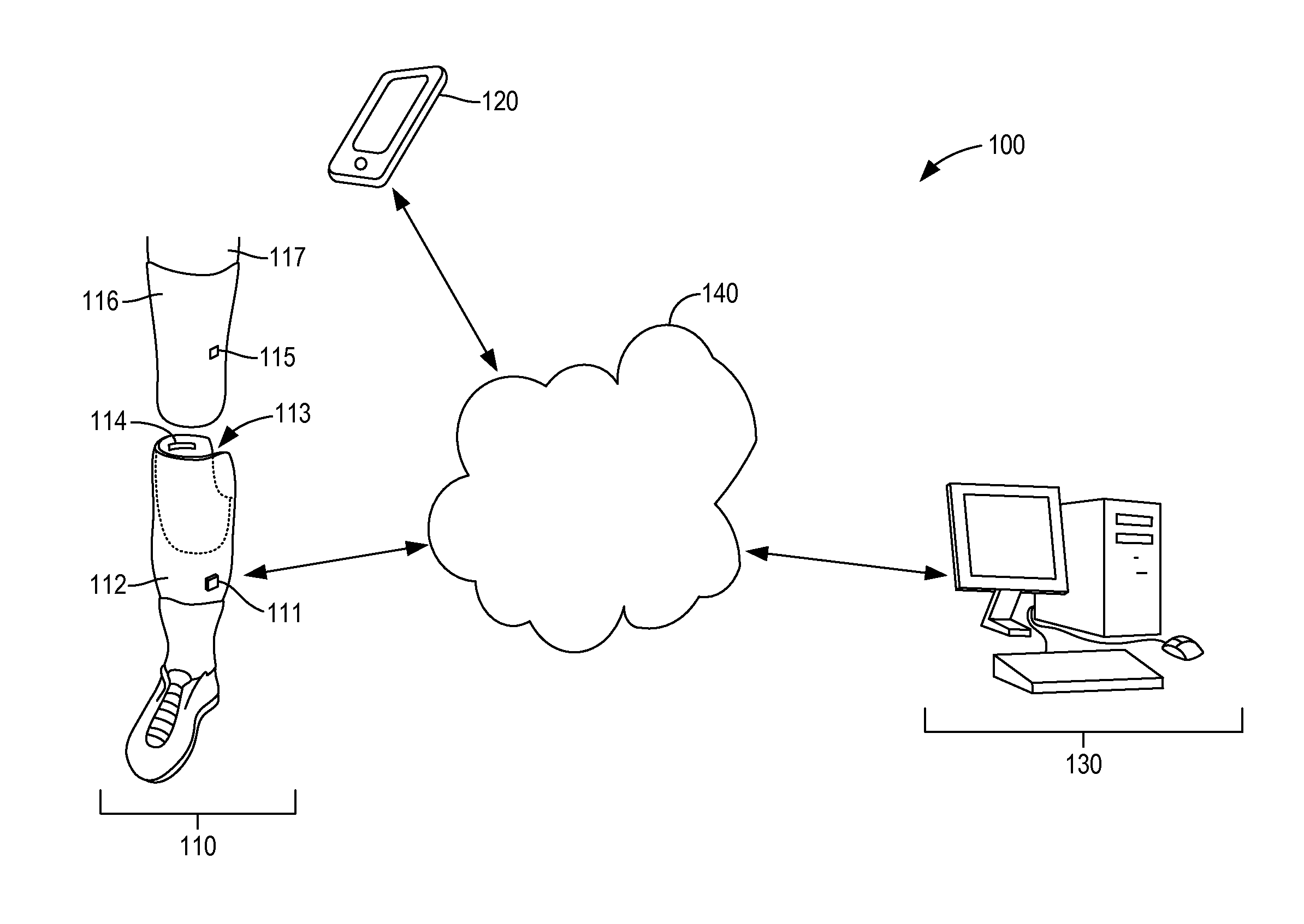
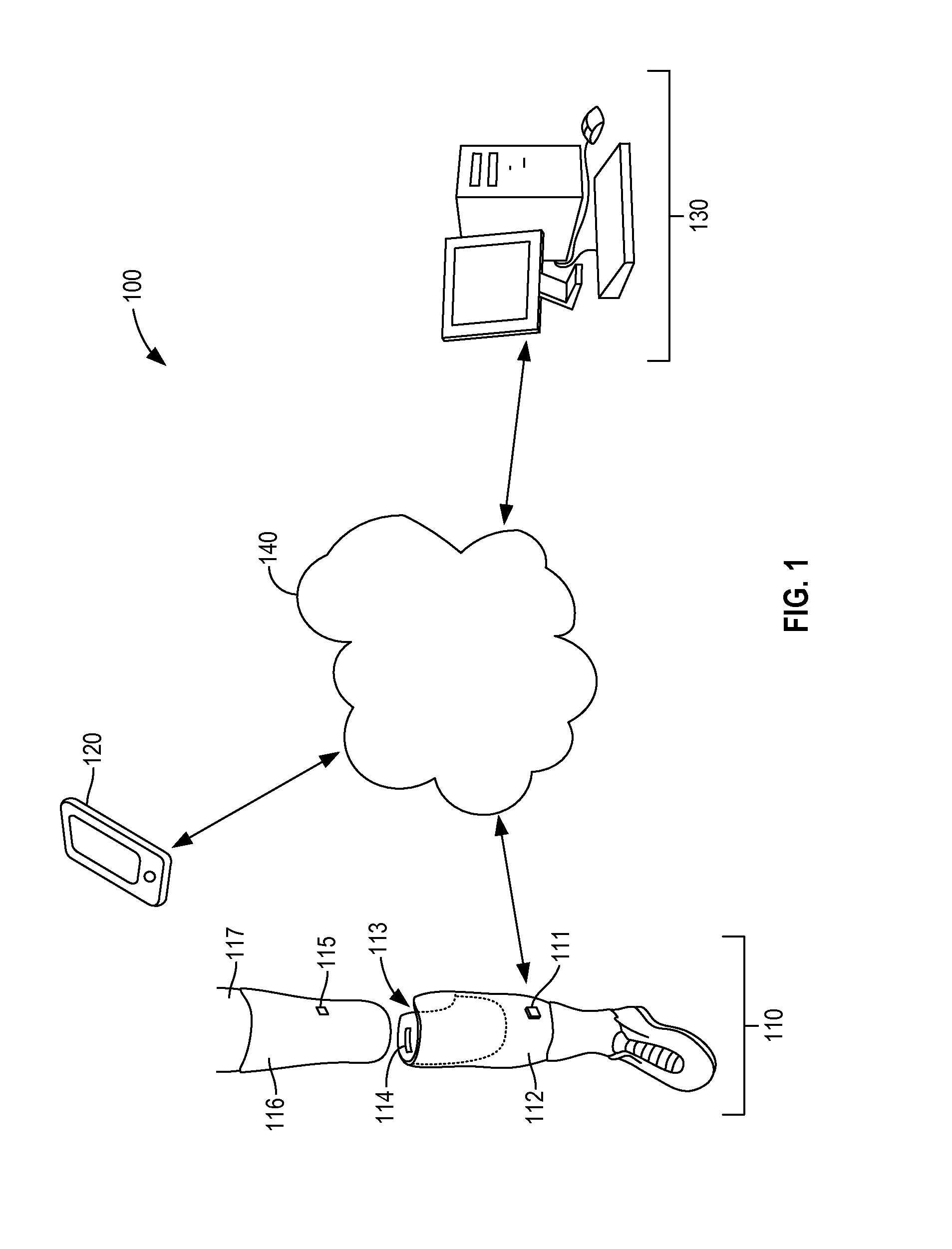
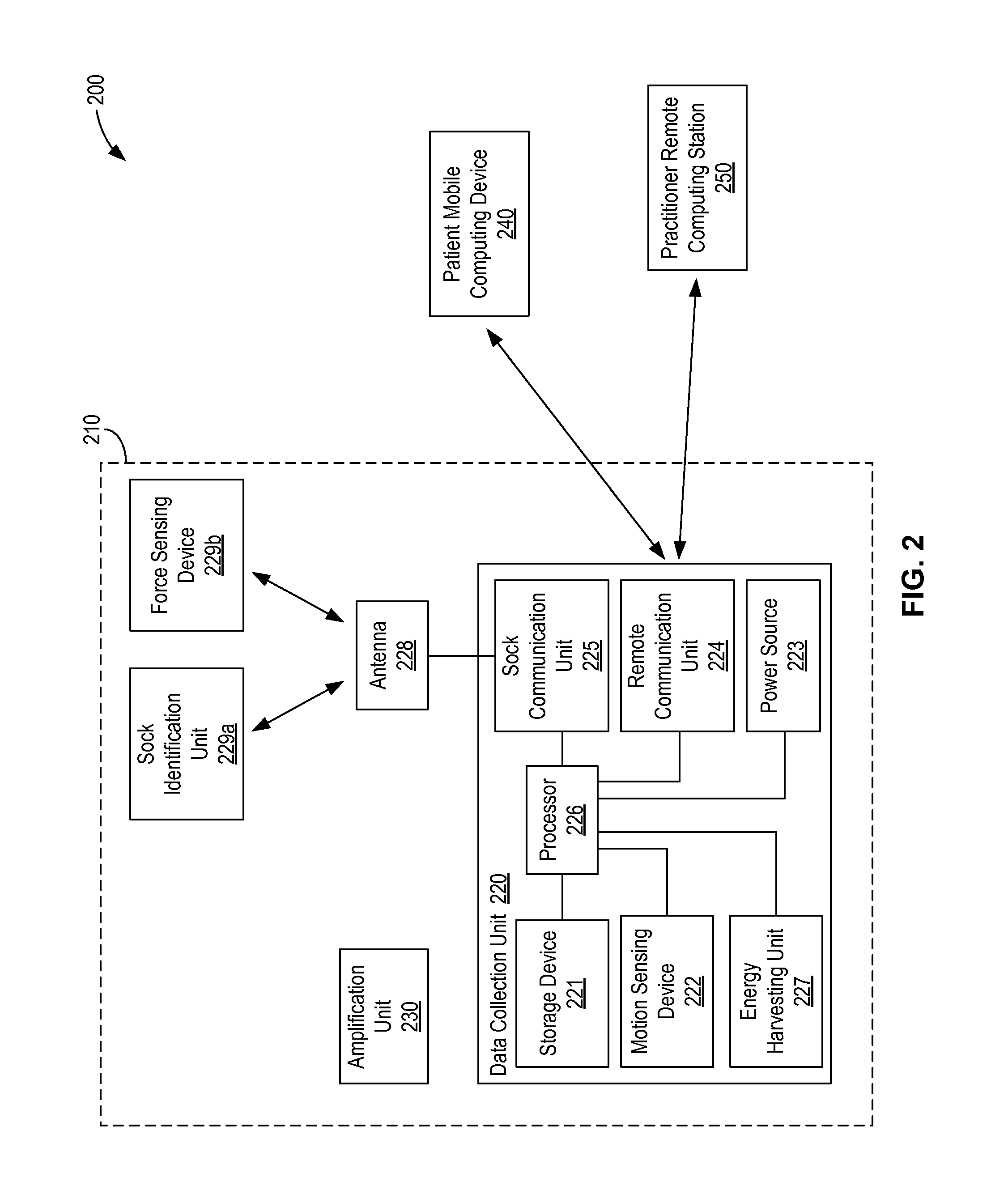
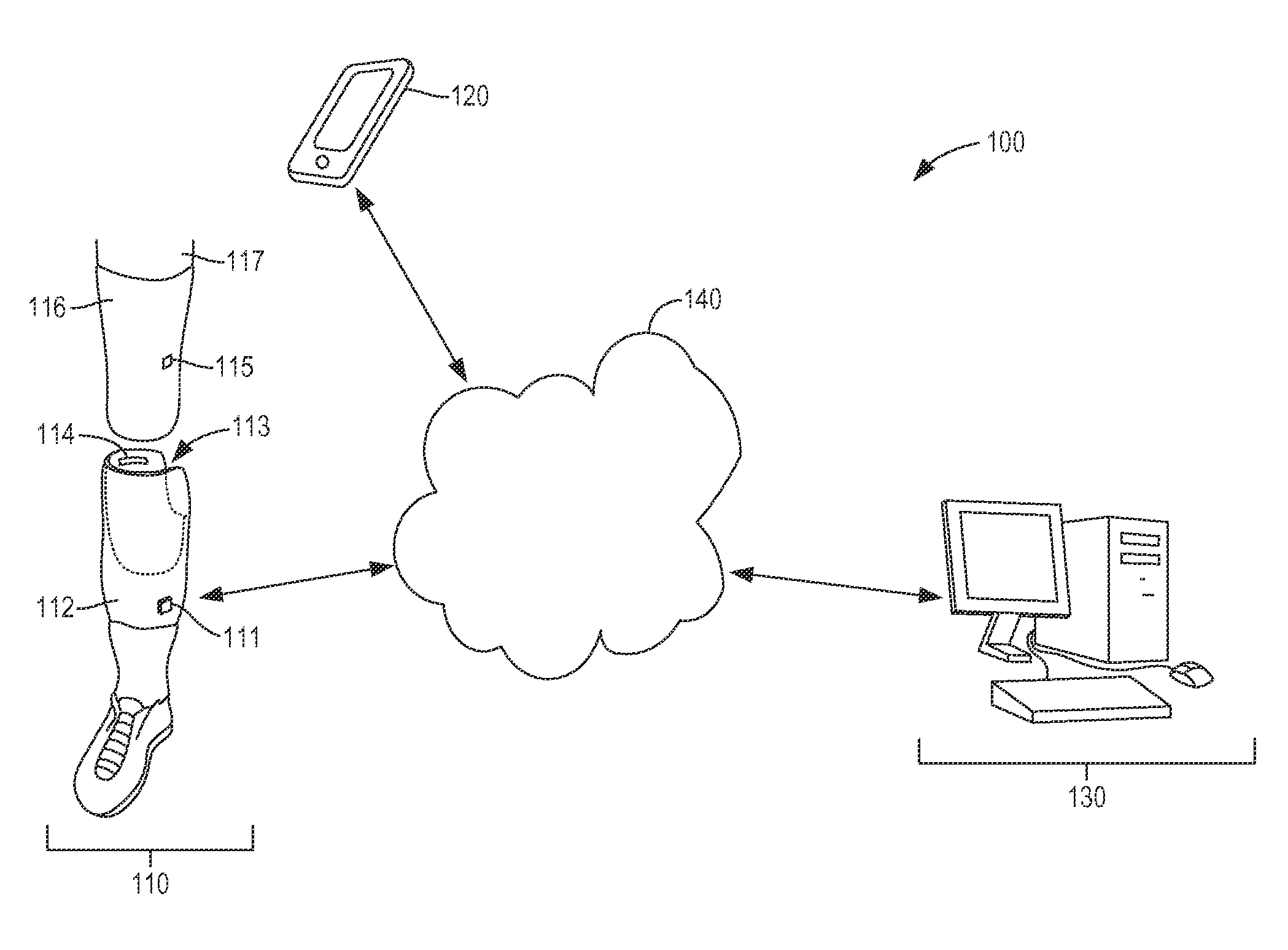
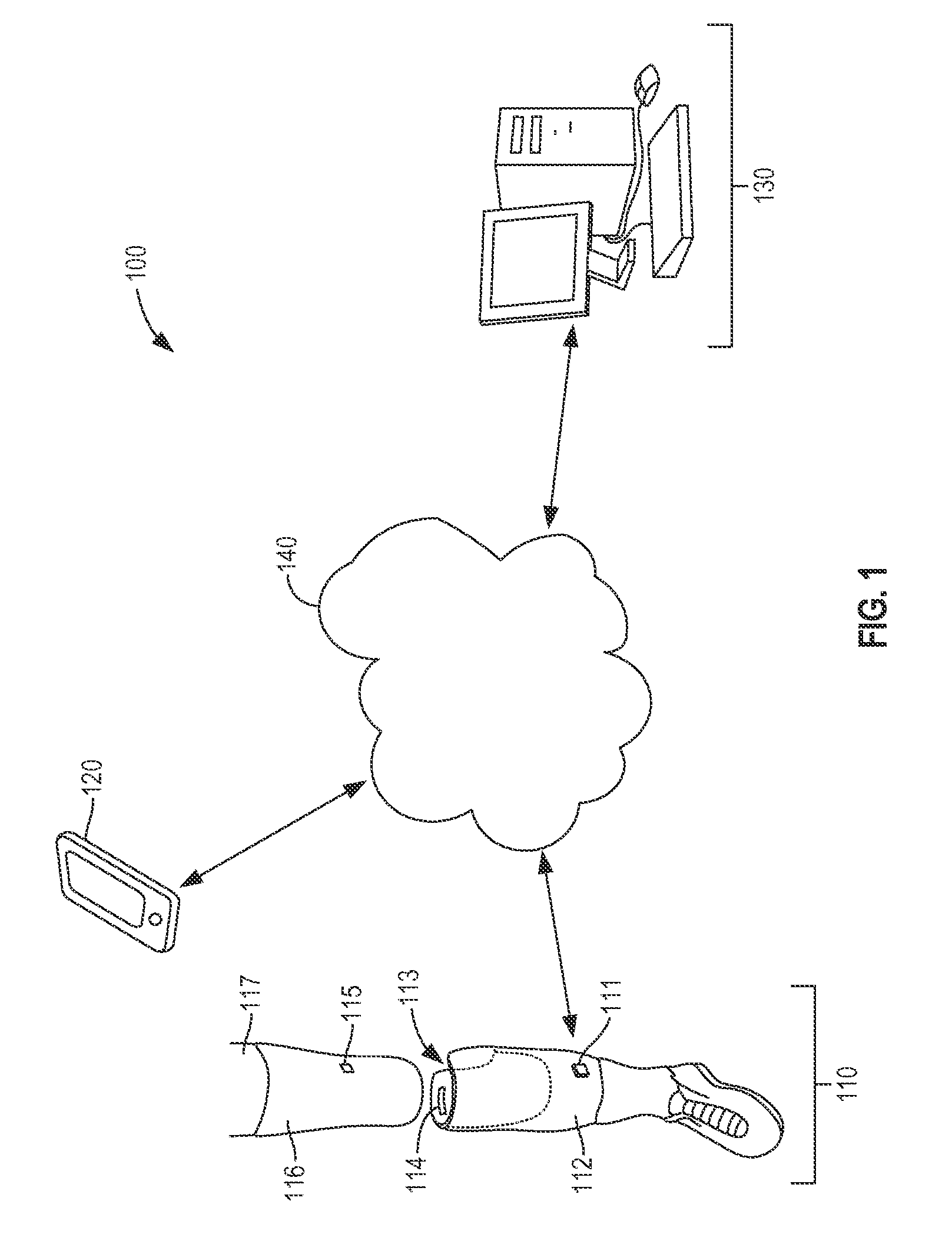
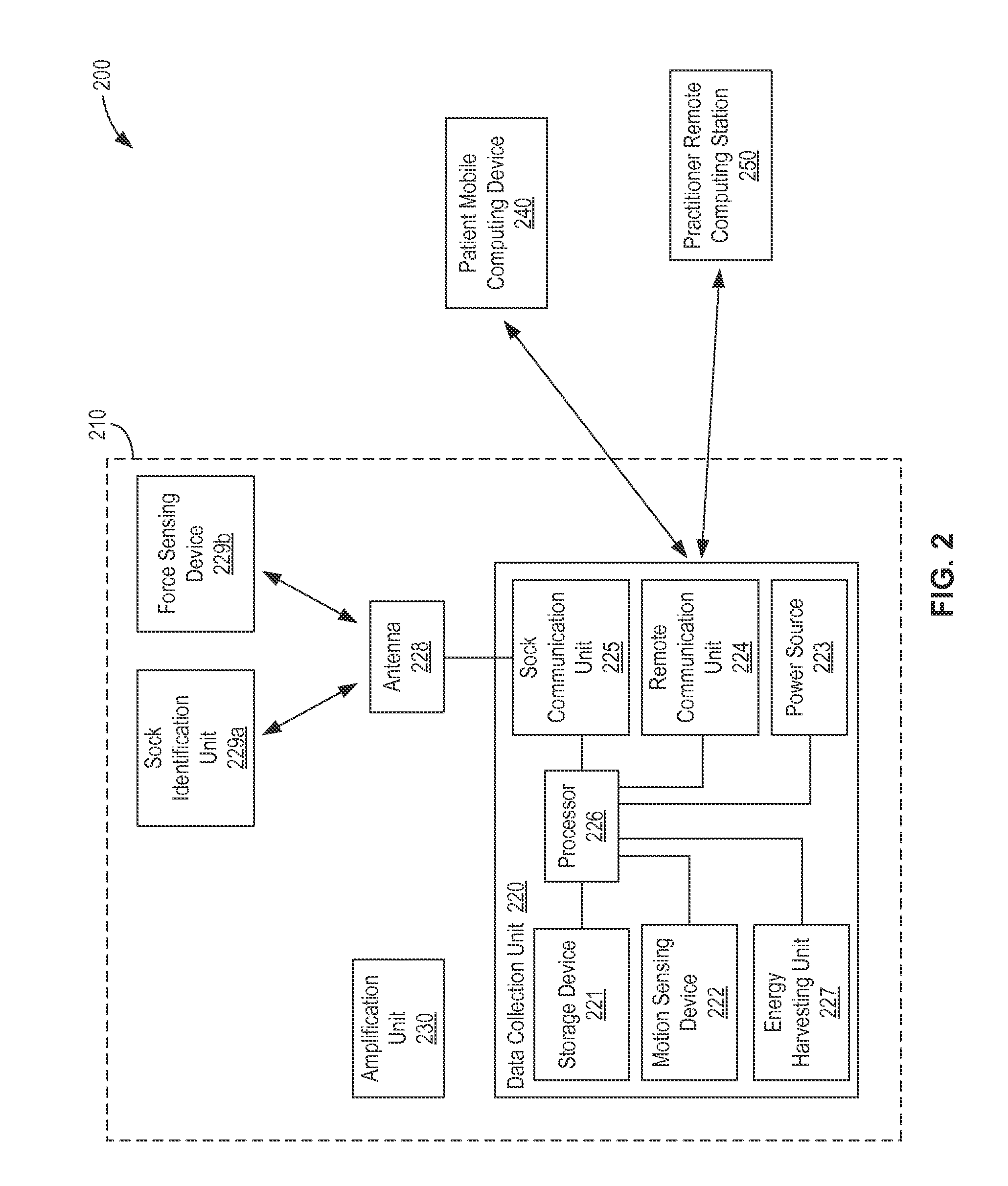
Limb volume accommodation in people with limb amputation
InactiveUS20120226197A1Improve patient outcomesImprove developmentPerson identificationTelemedicineMonitoring systemLimb amputation
A prosthetic sock monitoring system is disclosed. The sock monitoring system includes a storage device and a data collection unit. The data collection unit is operable to receive data from at least one sensor coupled to a prosthetic sock that is wearable by a patient, and store the received data in the storage device. A prosthetic sock is also disclosed. The sock comprises material shaped to fit over at least a portion of the residual limb of the patient and a thickness adapted for inserting the residual limb into the socket of the prosthesis while the sock is fitted over the residual limb. The sock also comprises one or more of a sock identification unit and a force sensing device.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Active-passive type ankle joint prosthesis and movement mode thereof
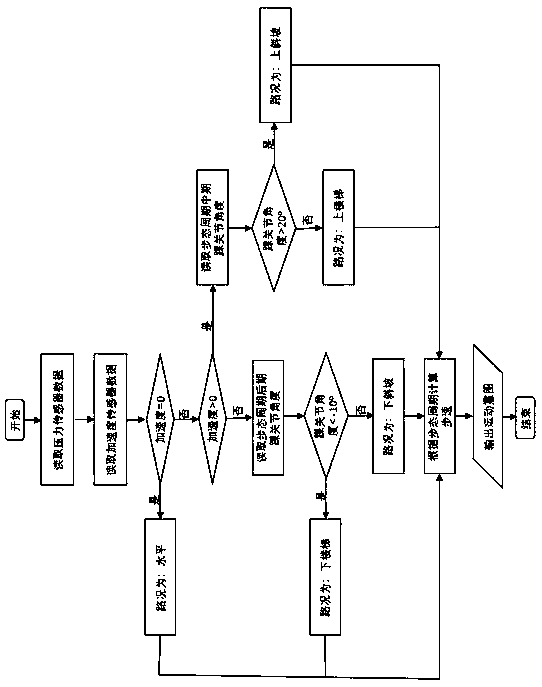
The invention discloses an active-passive type two-degrees-of freedom ankle joint prosthesis, comprising a carbon fiber energy storage sole, a motor, a speed reducer, a motor fixing supporting seat, a belt pulley transmission device, a carbon fiber pipe, a ball screw, an energy storage springs, joint bearings, energy storage rubber rings and joint supporting seats, wherein the carbon fiber energy storage sole is connected with the carbon fiber pipe through the joint supporting seats; the motor fixing supporting seat is connected with the carbon fiber pipe through an active pin; the motor is fixedly arranged on one end of the motor fixing supporting seat; the ball screw is fixedly arranged on the other end of the motor fixing supporting seat; two ends of the motor fixing supporting seat are connected by the belt pulley transmission device; the energy storage springs areis connected with a ball screw nut; and the energy storage rubber rings are connected with the joint bearings and the joint supporting seats through a shaft. The ankle joint prosthesis provided by the invention not only can completely provide required energy for human gait, but also can adapt to various landforms; in addition, the ankle joint prosthesis can completely imitate movement angles of a human ankle joint on a sagittal plane or a coronal plane; and therefore, the normal walking requirement of an amputation patient can be satisfied better.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
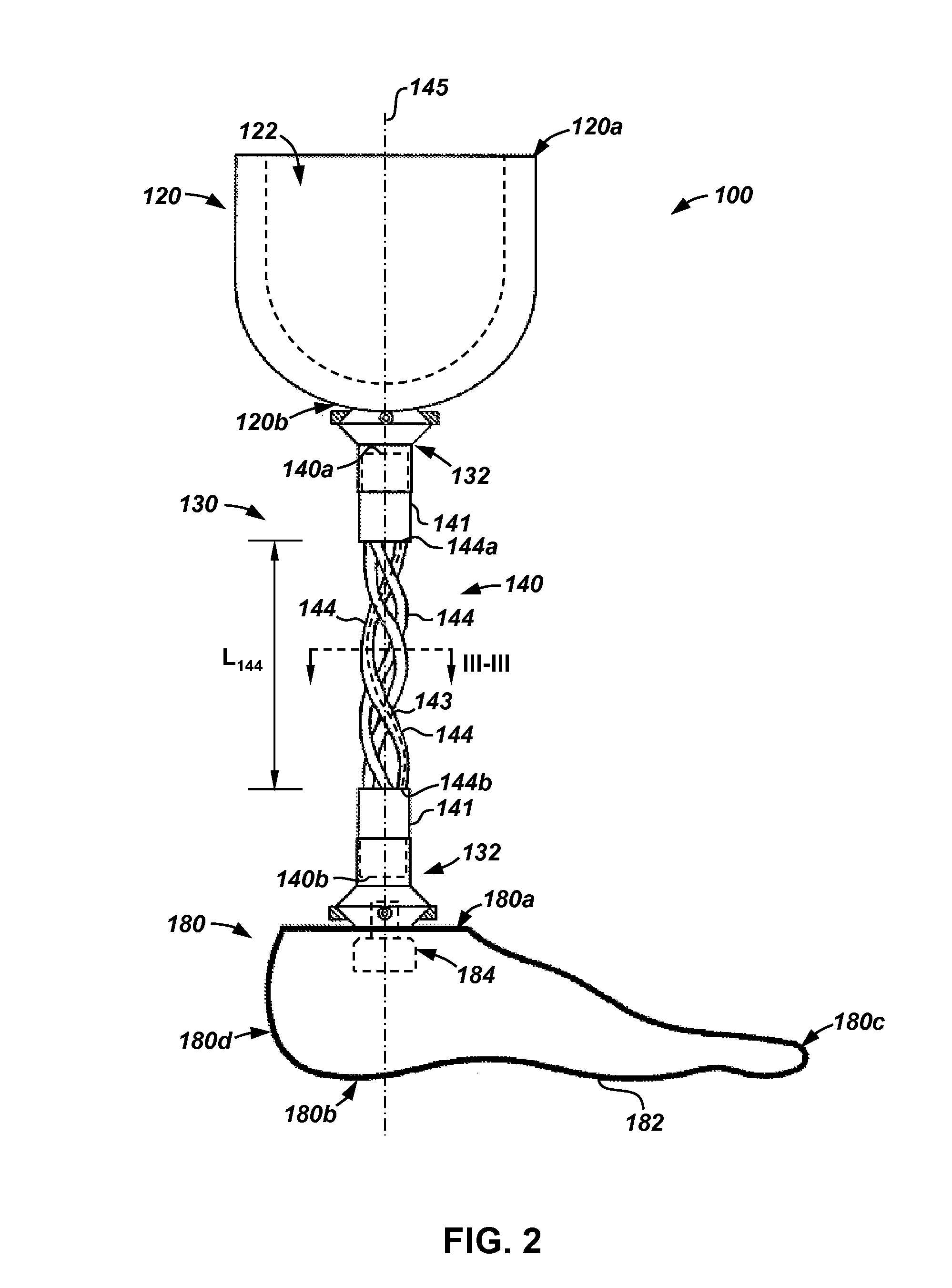
Lap Joint For Prosthetic Foot
Apparatus and methods for a prosthetic foot for attachment to a socket worn by an amputee. In an embodiment, the prosthetic foot comprises a body including a forefoot portion and a heel portion. In addition, the prosthetic foot comprises at least one attachment member extending from the body and conformable to the socket.
Owner:WILSON MICHAEL T
Limb Volume Accommodation in People With Limb Amputation
InactiveUS20140288669A1Easy to determineFunction increaseTelemedicineMedical equipmentMonitoring systemLimb amputation
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Enhanced crutch walker
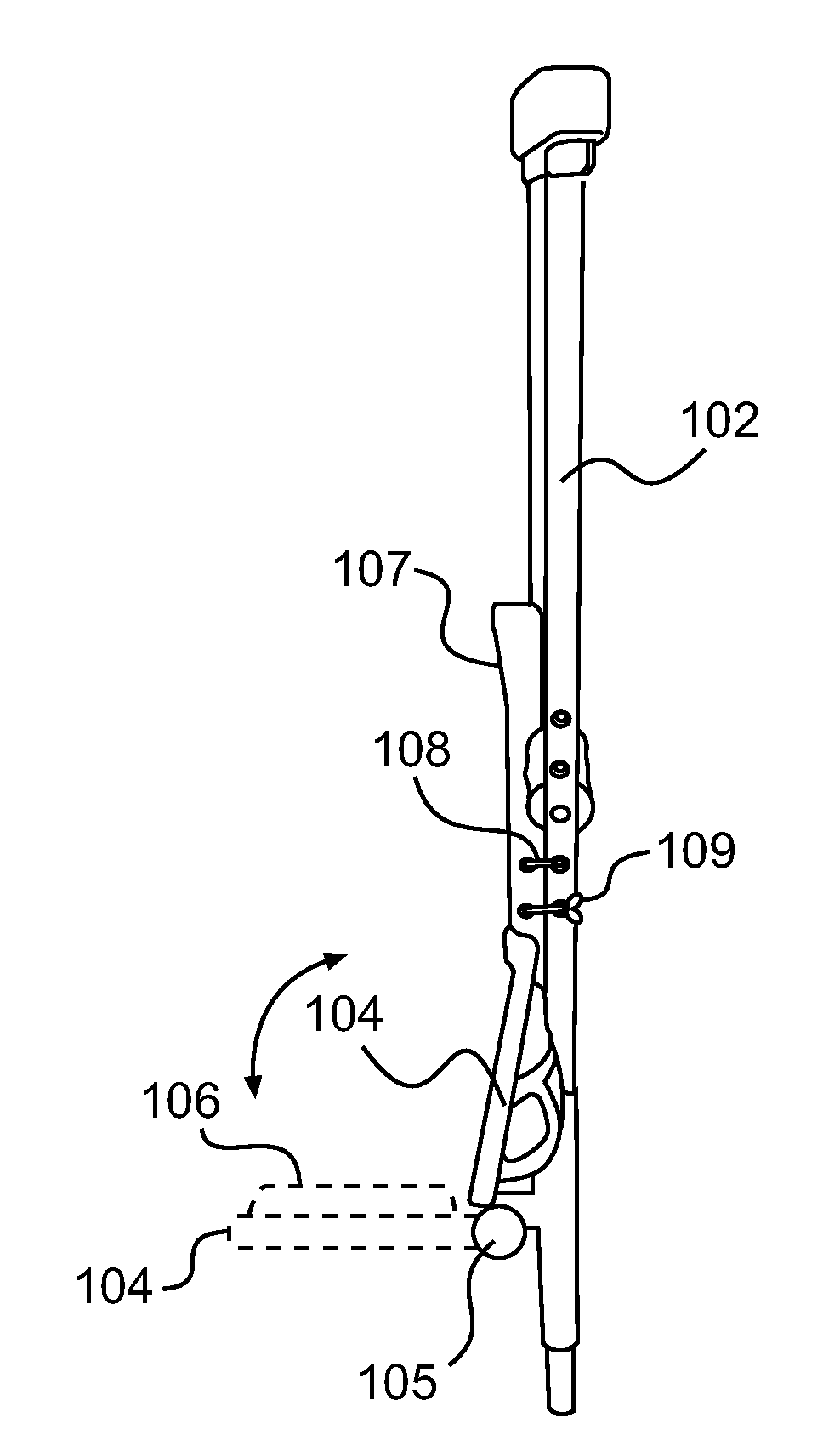
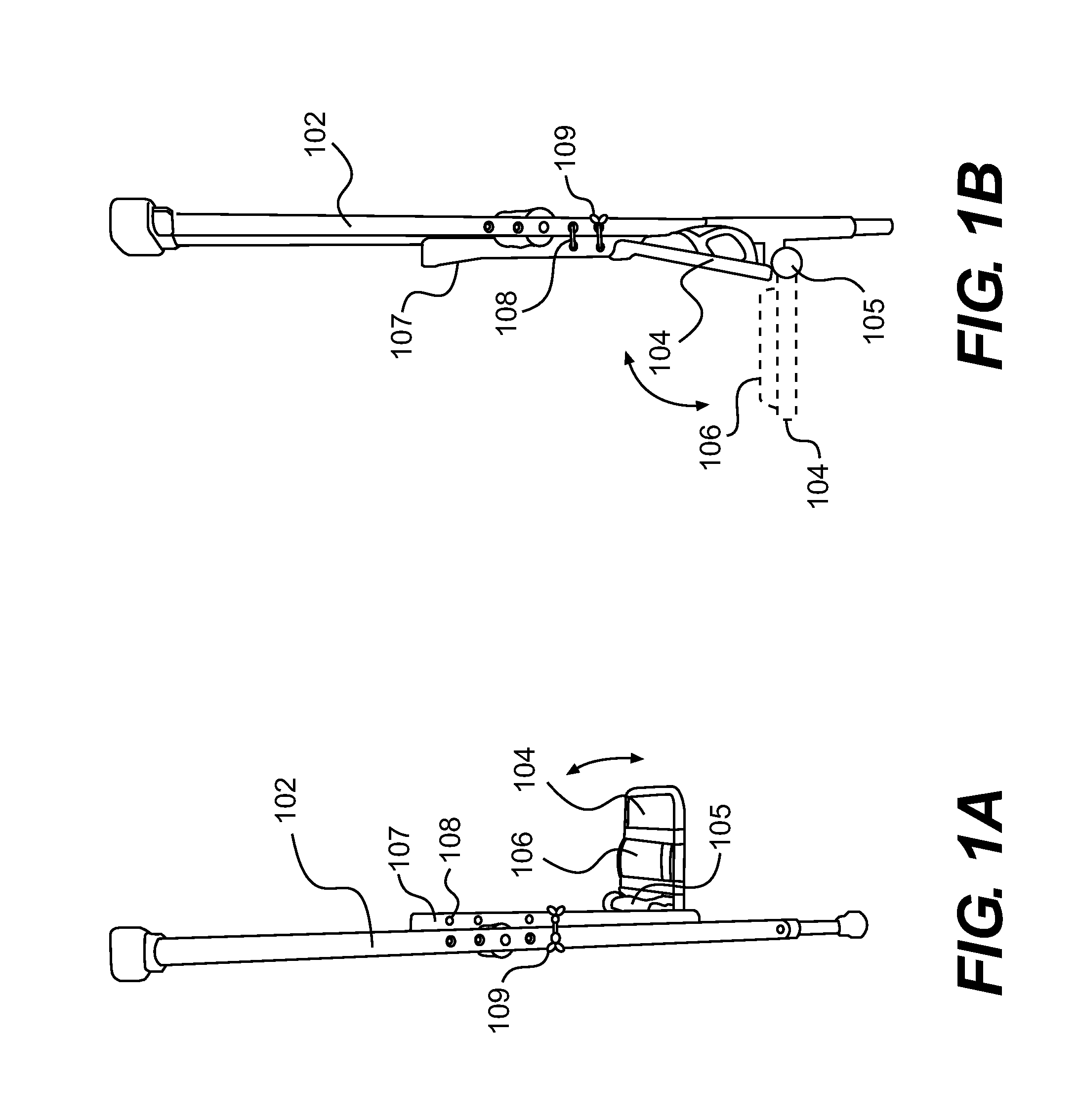
InactiveUS20100269872A1Relieve discomfortRelieve pressureWalking sticksCrutchesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationKnee support
A knee support attachable to a medical crutch for supporting an injured or amputated knee of a user of the medical crutch is provided. The knee support is held in a first extended position when in use and a second folded position when not in use. The knee support includes a base plate affixed to the medical crutch for supporting a knee placed thereon, and a soft padding covering the base plate for providing a cushioned support to the knee placed thereon. The knee support provides hands-free feature for the user. The position of the base plate is adjustable along the holes or the length of the medical crutch.
Owner:THARP EDWARD
Lower-limb prosthesis alignment and gait analysis auxiliary system adopting foot pressure sensing technology
The invention provides an auxiliary system which is capable of assisting a limb prosthesis orthopedic doctor to assemble lower-limb prosthesis and helping an amputee to improve gait on the basis of a foot pressure signal of the amputee. The auxiliary system comprises a main circuit box, a sole pressure sensor assembly and an interface program, and the interface program is applied to a user interface. According to the auxiliary system, the main circuit box and the sole pressure sensor assembly are used together and are transmitted to the user interface in a wireless mode. The auxiliary system mainly operates on the basis of the principles of computing and displaying standing and swinging times of the amputee during walking as well as a reference pressure center path during walking and standing, and comparing with corresponding standard data, so as to suggest the orthopedic doctor in the adjustment of the lower-limb prosthesis alignment and the gait of the amputee. The auxiliary system disclosed by the invention is helpful for the limb prosthesis orthopedic doctor in the adjustment of the lower-limb prosthesis alignment, the assessment of the gait of the amputee after alignment and in the gait training of the amputee.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
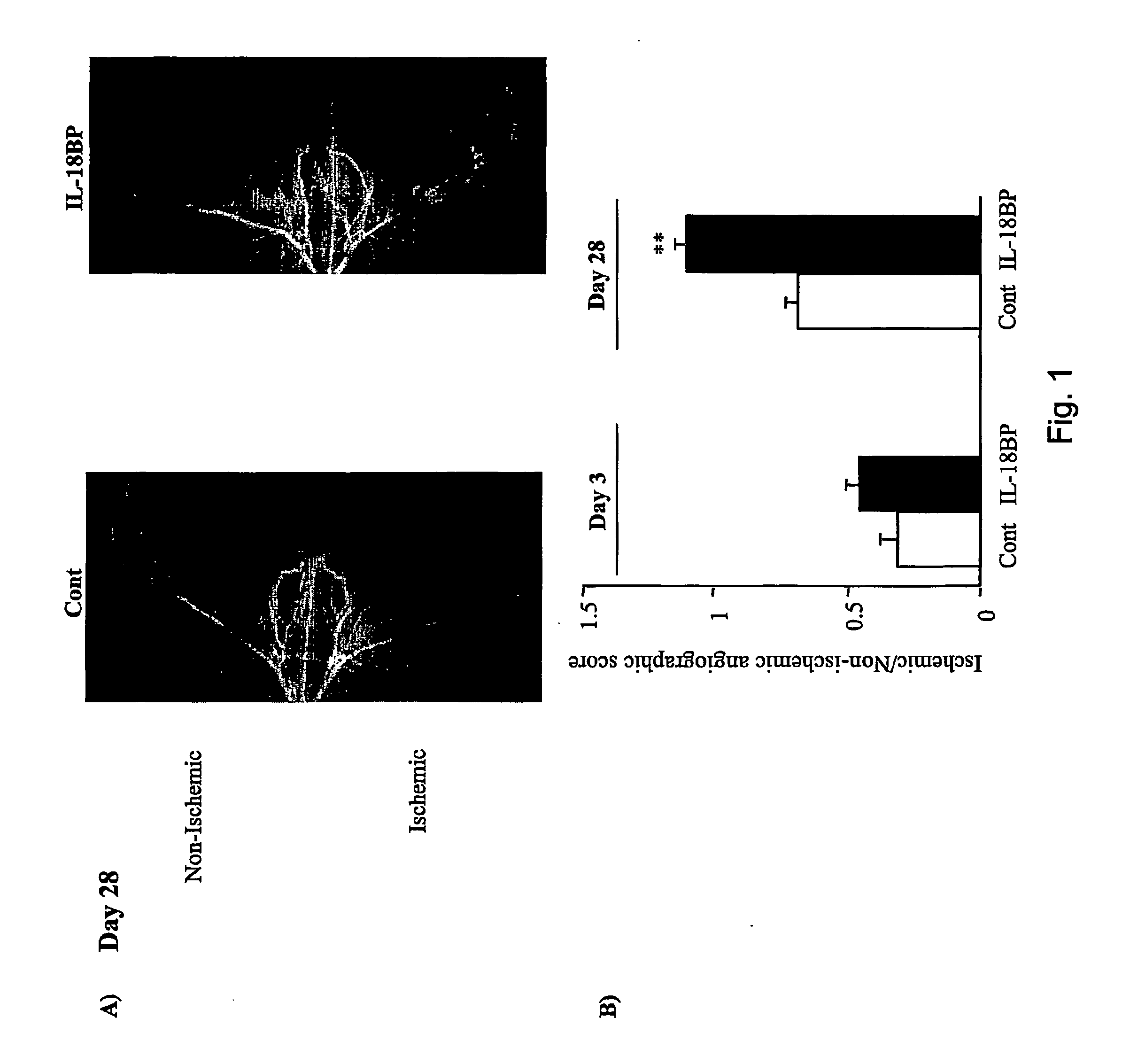
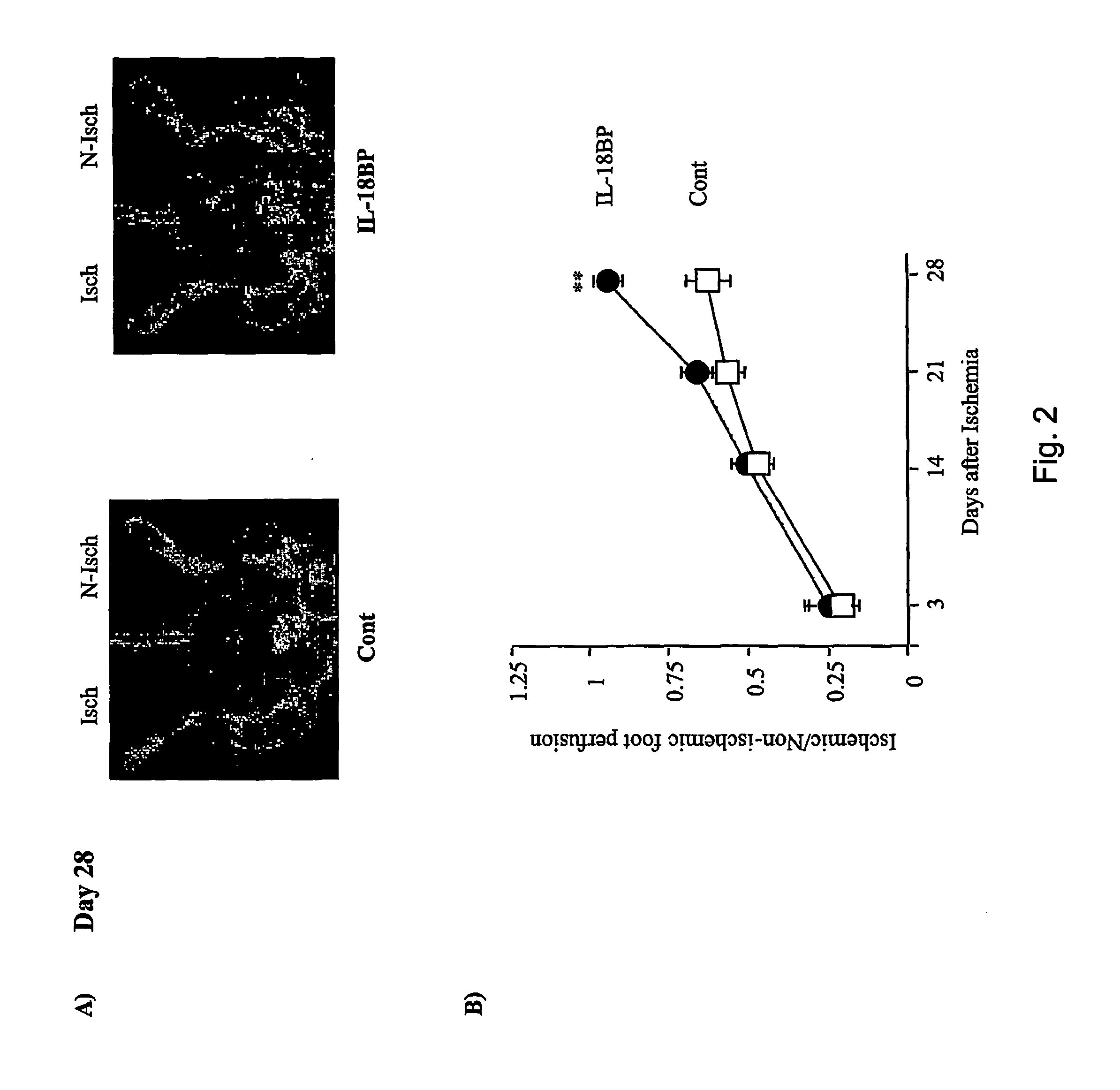
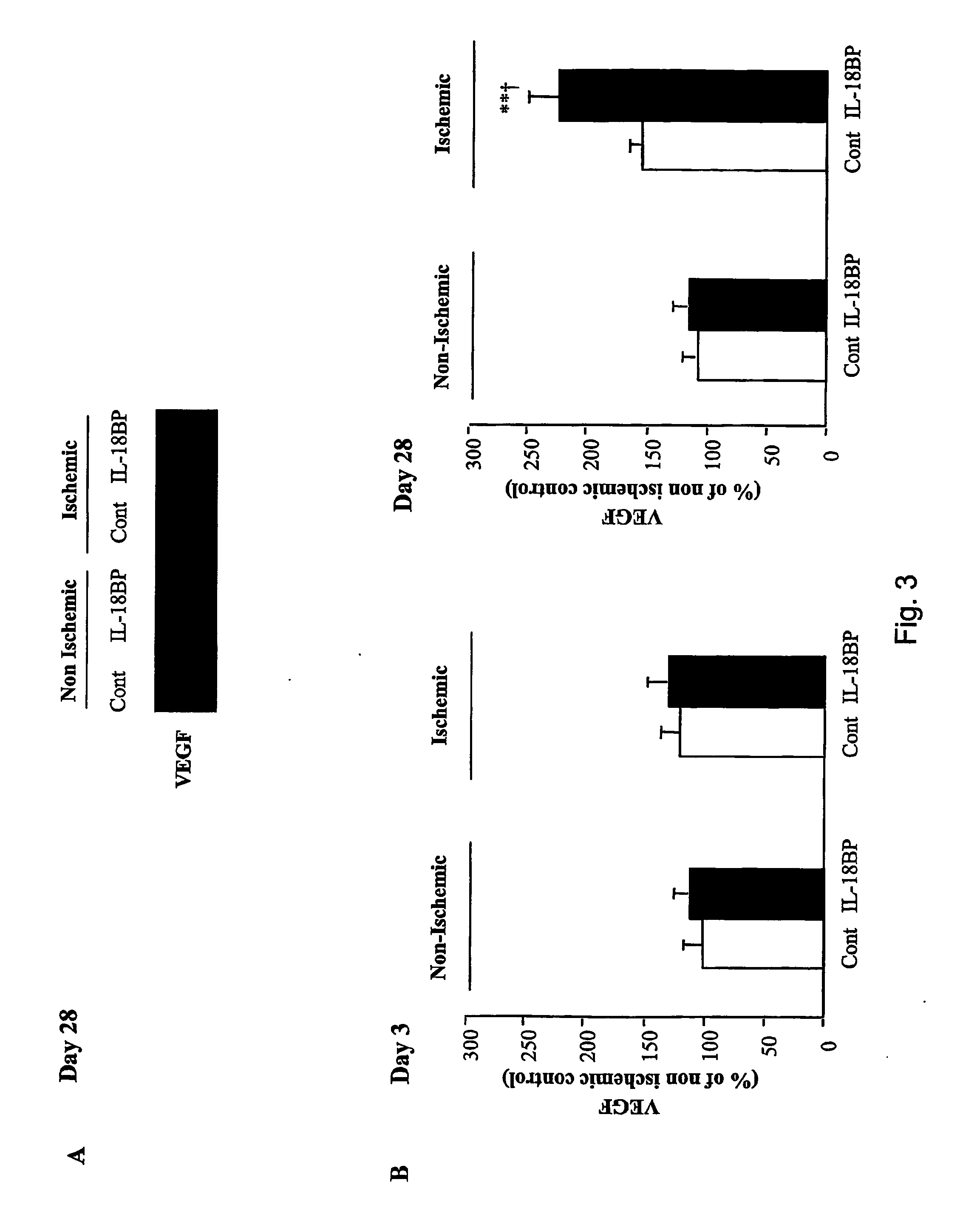
Use of il-18 inhibitors for treatment and/or prevention of peripheral vascular diseases
ActiveUS20060233799A1Increased endogenous productionEffective inhibiting amountPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsVascular diseaseLimb amputation
The invention relates to the use of an inhibitor of IL-18 in the preparation of a medicament for treatment and / or prevention of peripheral vascular diseases. The invention further relates to the use of an IL-18 inhibitor for prevention of limb amputation.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA +1
Prosthesis having movement lock
The present invention relates to artificial limbs generally and joints for same. The present invention provides hydraulic functional units whereby enabling movement of artificial joints to closely correspond with natural human movement. In the provision of realistic joints, as used in prosthetic limbs, an important aspect in achieving realistic movement is providing a different operating characteristic to the joint when under load. One important characteristic of an artificial leg for achieving a natural-looking walking gait corresponding with those of a stabilized knee, i.e. a knee resisting flexion when under load, is when it bears at least some of the weight of the amputee. Properties of resilient mechanical members are utilized to enable a hydro-mechanical system to be controlled so that it releases a low joint resistance mode relative to a default high resistance mode. The invention also permits alternative embodiments such as electronic, electro fluidic or electromechanical means.
Owner:BOENDER JENNIFER
Limb volume accommodation in people with limb amputation
InactiveUS8784340B2Easy to determineFunction increasePerson identificationTelemedicineMonitoring systemLimb amputation
A prosthetic sock monitoring system is disclosed. The sock monitoring system includes a storage device and a data collection unit. The data collection unit is operable to receive data from at least one sensor coupled to a prosthetic sock that is wearable by a patient, and store the received data in the storage device. A prosthetic sock is also disclosed. The sock comprises material shaped to fit over at least a portion of the residual limb of the patient and a thickness adapted for inserting the residual limb into the socket of the prosthesis while the sock is fitted over the residual limb. The sock also comprises one or more of a sock identification unit and a force sensing device.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
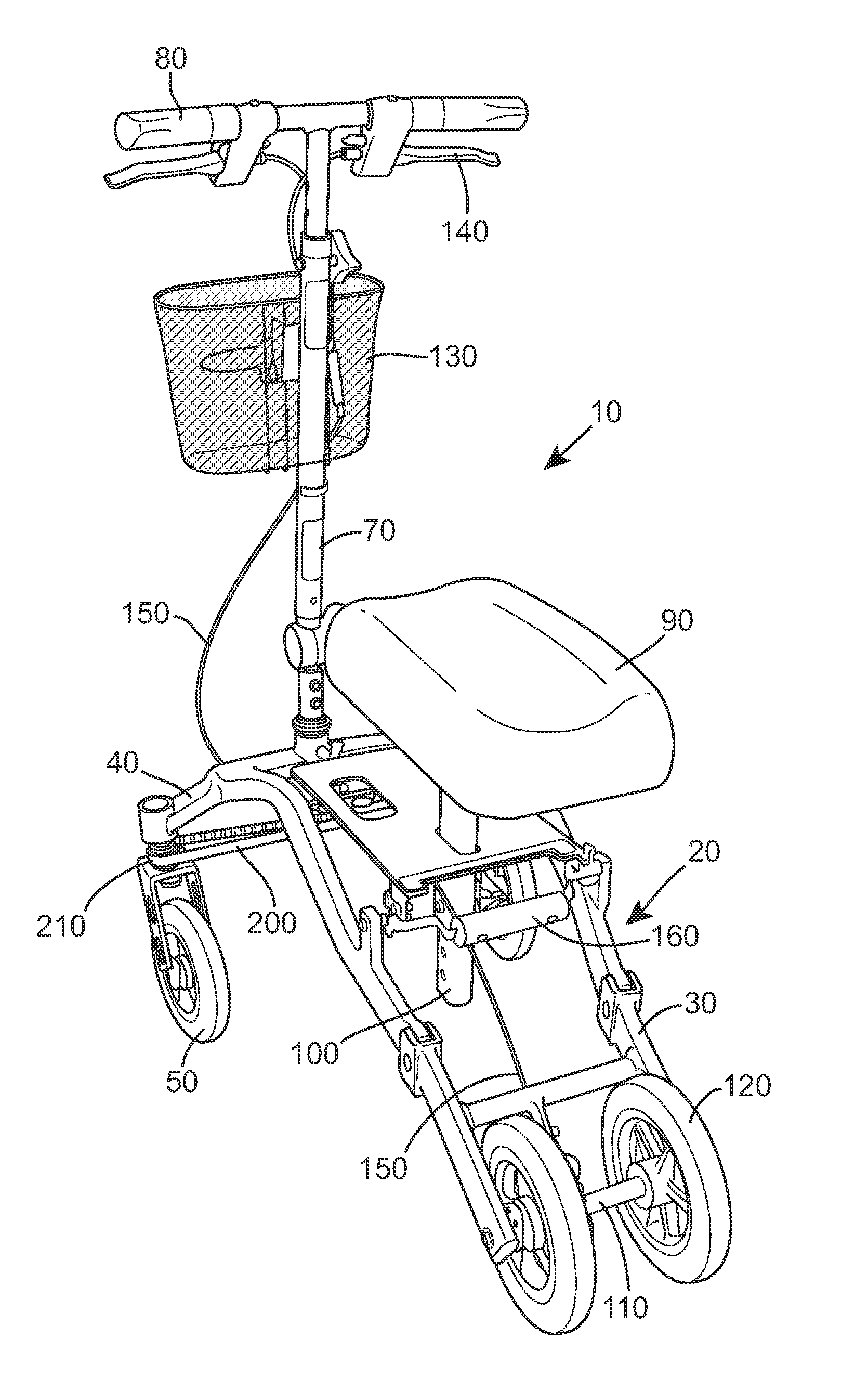
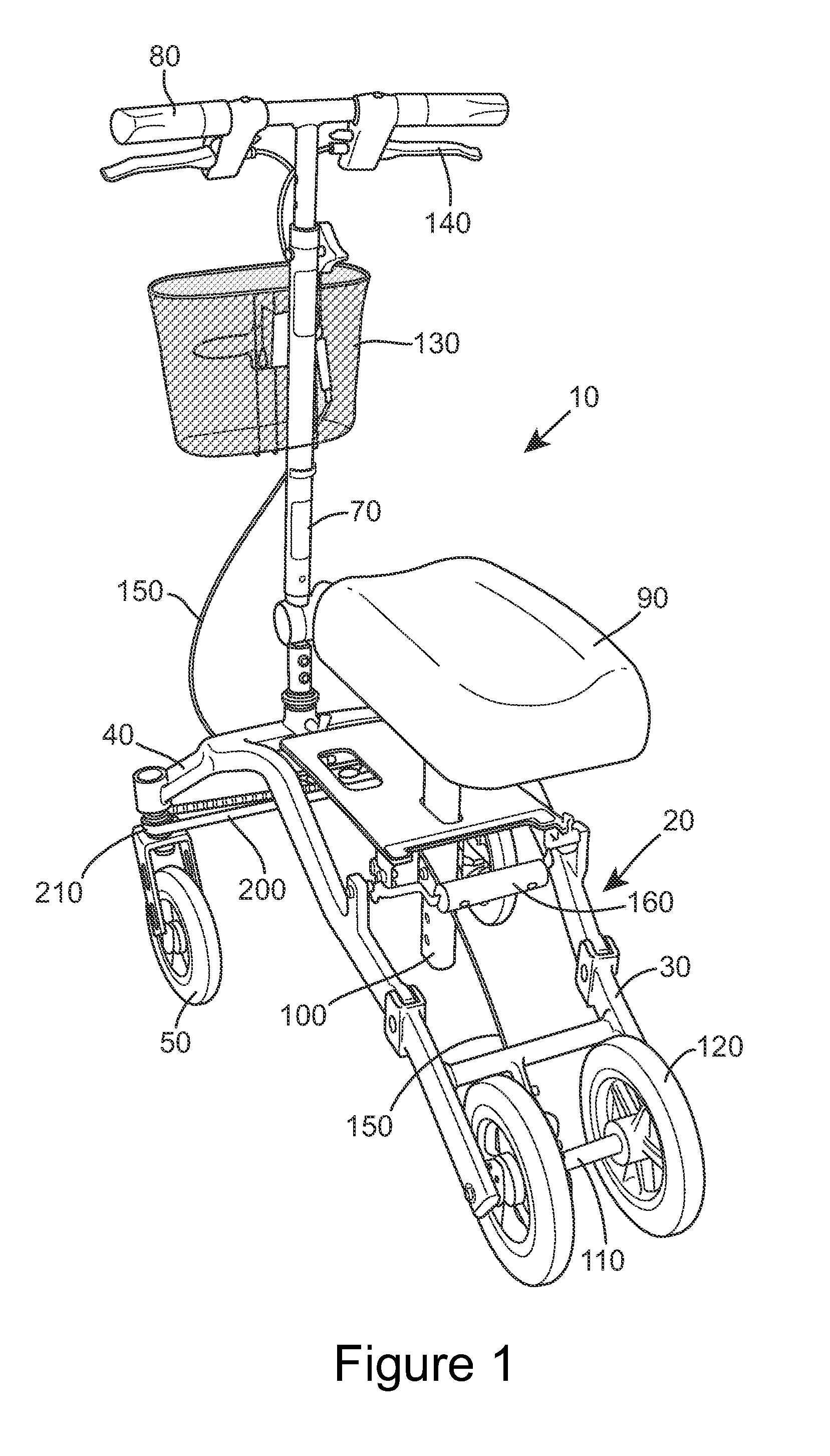
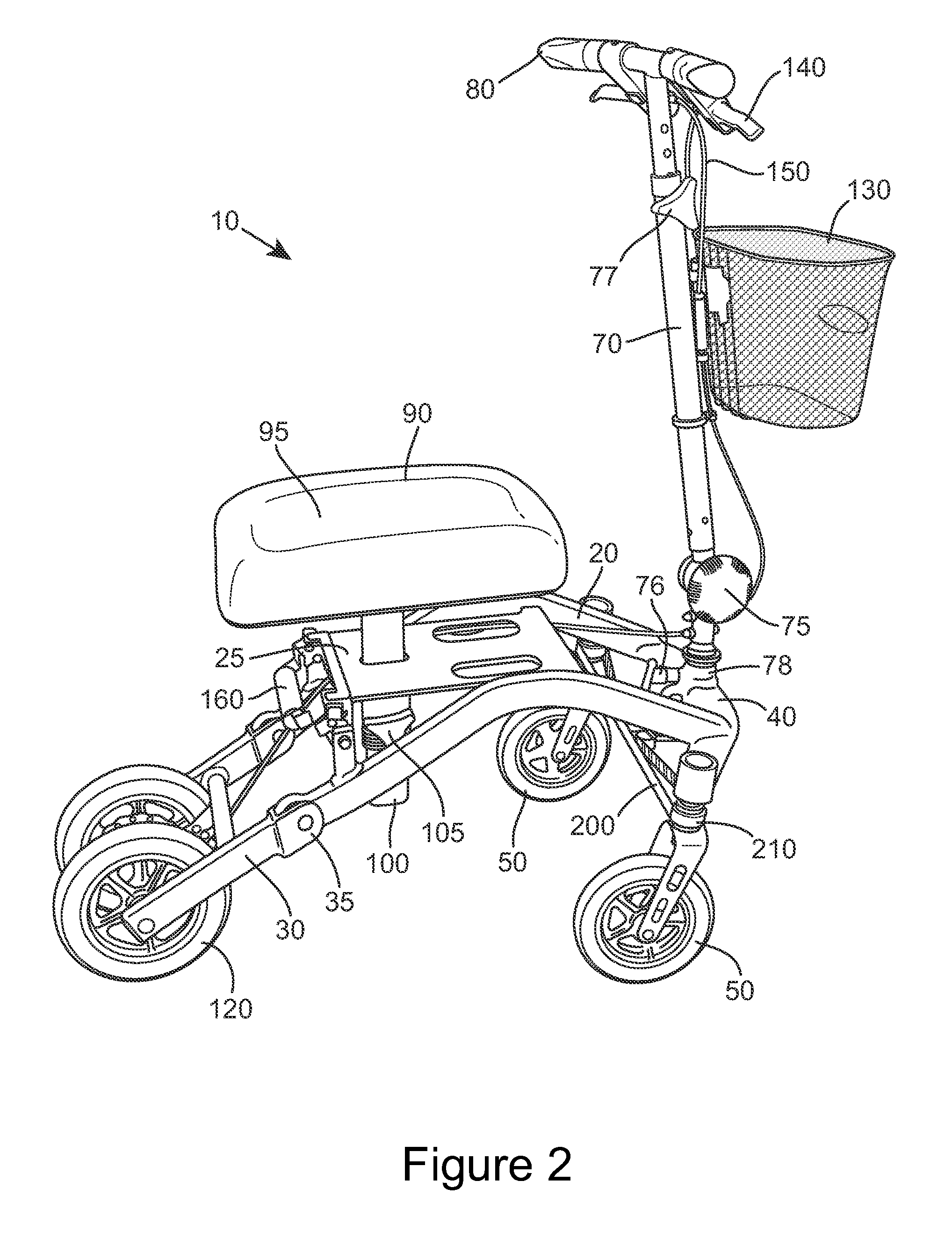
Knee-walker
ActiveUS20140097592A1No loss of stabilityMore finely controlledFoot-driven leversWheel based transmissionSteering columnEngineering
Knee-walkers allow amputees and individuals with injuries to maintain independent movement. Their stability and steering is very important. The invention comprises a knee-walker (10) comprising a frame (20), at least two ground-engaging wheels (50) at the front, a seat (90), a steering column (70), and a steering belt (200) linking the steering column to the two front wheels, the two front wheels being steered by rotation of the steering column and consequent rotation of the belt.
Owner:SMITH PAUL
Prosthesis having movement lock
The present invention relates to artificial limbs generally and joints for same. The present invention provides hydraulic functional units whereby enabling movement of artificial joints to closely correspond with natural human movement. In the provision of realistic joints, as used in prosthetic limbs, an important aspect in achieving realistic movement is providing a different operating characteristic to the joint when under load. One important characteristic of an artificial leg for achieving a natural-looking walking gait corresponding with those of a stabilised knee, i.e. a knee resisting flexion when under load, is when it bears at least some of the weight of the amputee. Properties of resilient mechanical members are utilized to enable a hydro-mechanical system to be controlled so that it releases a low joint resistance mode relative to a default high resistance mode. The invention also permits alternative embodiments such as electronic, electro fluidic or electromechanical means.
Owner:BOENDER JENNIFER
Knee joint prosthesis testing system and testing method
The invention belongs to the technical field of prosthetic testing devices, and particularly relates to a knee joint prosthesis testing system and a testing method. The testing system comprises a hipjoint drive system, a bionic thigh, a frame, a horizontal movement module and a ground reaction force module. According to the prosthesis testing platform, movement of the stump of an amputee can be simulated in a gait cycle by an automatic control system, ground reaction force is provided for the tested prosthesis, and an accurate testing environment is provided for the intelligent knee joint assembled at a joint by matching a movement curve of real human lower limbs. Compared with the previous prosthesis testing equipment, the test platform can actively provide the ground reaction force forthe prosthesis, and input of the ground reaction force in the prosthesis testing process is more accurate; and prosthesis testing in the circumstances of horizontal walking at different speeds, goingup and down the slope, going up and down stairs and the like can be achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Diagnostic System and Method for Amputation Risk Factor Identification and Amputation Prevention
A computer implemented diagnostic amputation prevention system and method for evaluating risk factors and generating risk assessments and recommendations for diabetic patients at risk for amputation is provided. The system includes a diagnostic computer having a neurological / vascular module configured to electronically query and receive information related to pedal pulses, monofilament testing device results, or combinations thereof. A skeletal module electronically queries and receives Osseous Deformity information, and a database stores and aggregates the received information. A results module identifies risk factors using the aggregated information and generates diagnostics and recommendations based on factors including the amount, type, and particular combination of identified risk factors. The diagnostics and recommendations include identification of amputation risk assessment categories, explanation of risk categories, identified risk factors, recommendations for treatment, and combinations thereof.
Owner:HINKES MARK
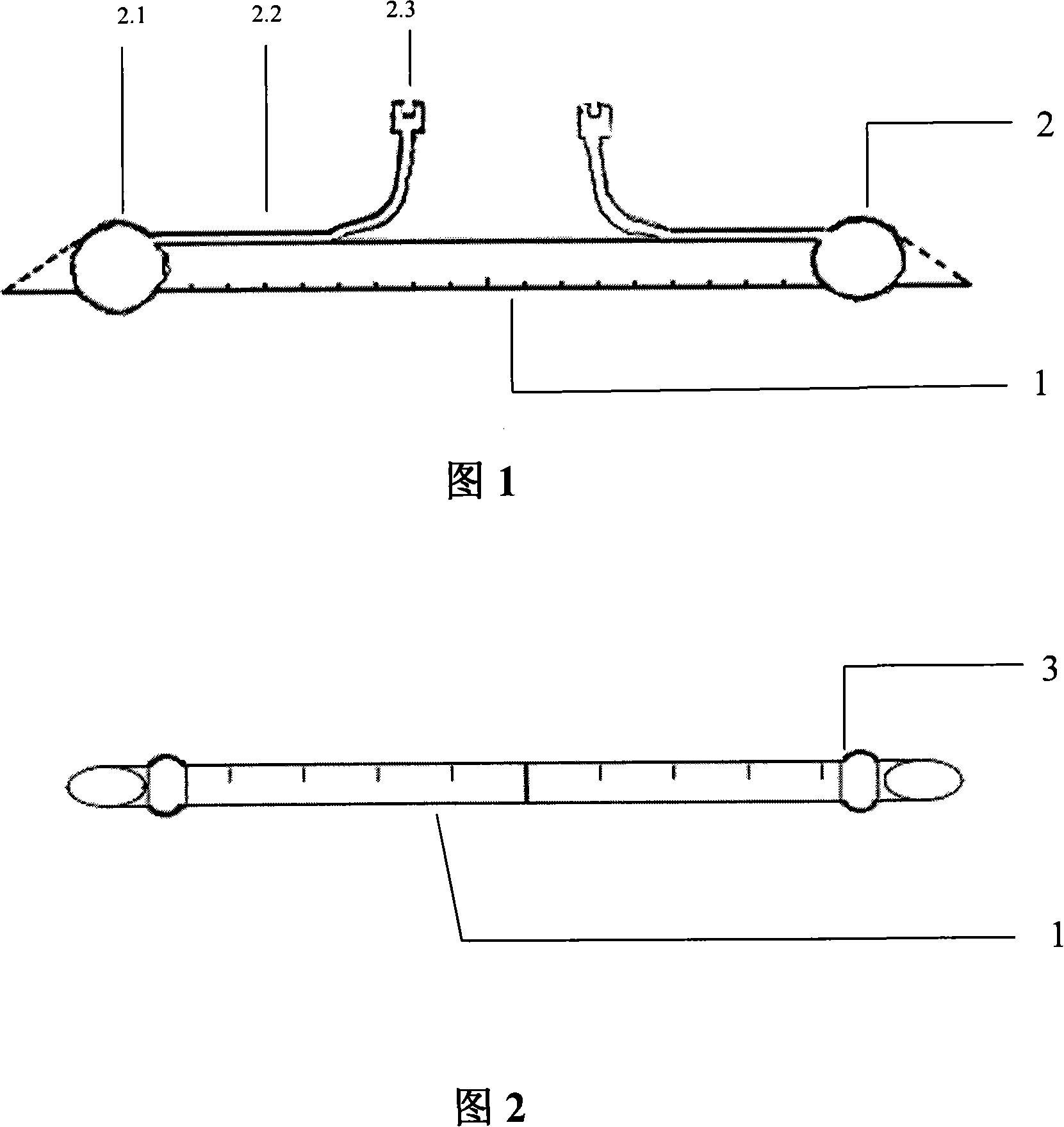
Arteria blood turning tube with fixing structure
The invention relates to the technical field of medical devices, which is an arteri-blood flow diverting pipe with fixed structure and for first aid of limb blood vessel wounds. The invention consists of a blood flow diverting pipe (1) and a fixed structure; pipe tops on both ends of the blood flow diverting pipe are inclined; a color strip with calibration can be arranged longitudinally on the pipe wall of the blood flow diverting pipe (1). A self-sticking blood stopper film can be coated on the pipe wall of the middle section of the blood flow diverting pipe; the fixed structure consists of two saccules (2) or two fixed rings (3); each saccule (2) consists of a saccule body (2.1), a saccule pipe (2.2) and an air supply valve (2.3); the two saccules bodies are respectively wrapped on the pipes on both ends of the blood flow diverting pipe; the fixed rings (3) are pipe wall circular heaves on both ends of the blood flow diverting pipe. The invention has the advantages of simple structure and convenience in use, plays the role of quickly stopping the blood from flowing out so as to ensure blood supply to the limbs through building temporary channels on the blood vessel breakage ends, reduces the risk of limb amputation, and meets the time requirements of diversion or sending for treatment afterwards.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Bionic passive flexible low-energy-consumption ankle and foot prosthesis based on rigid-flexible coupling
ActiveCN111150528AImprove experienceLow costArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
The invention aims to provide a bionic passive flexible low-energy-consumption ankle and foot prosthesis based on rigid-flexible coupling. The bionic passive flexible low-energy-consumption ankle andfoot prosthesis based on the rigid-flexible coupling comprises a shank part, and a foot part; the shank part comprises an upper shell, an upper shell connecting plate piece, an auxiliary metatarsal dorsiflexion limit assembly, a middle shell, a passive support and upper-middle shell connecting piece, a lower shell, an introversion and extroversion limit assembly, and a passive support and middle-lower shell connecting piece; the upper shell, the upper shell connecting plate piece, the auxiliary metatarsal dorsiflexion limit assembly, the middle shell and the lower shell are all made of hard materials; and the passive support and upper-middle shell connecting piece and the passive support and middle-lower shell connecting piece are both made of soft materials. The bionic passive flexible low-energy-consumption ankle and foot prosthesis based on the rigid-flexible coupling has the characteristics of being high in flexibility, self-stabilized, self-balanced, impact-resistant and the like;and thus, the bionic passive flexible low-energy-consumption ankle and foot prosthesis based on the rigid-flexible coupling is capable of perfecting natural-gait walking of an amputee, and improvingself-walking energy efficiency of the amputee.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Composite pylon for a prosthetic device
Owner:WILSON MICHAEL THOMAS
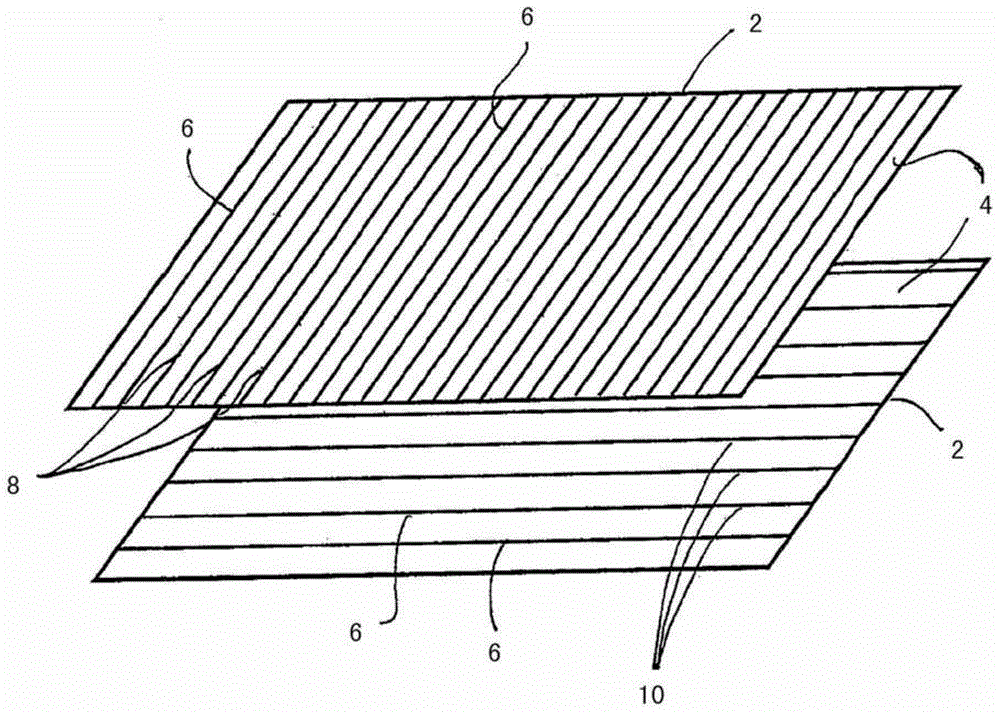
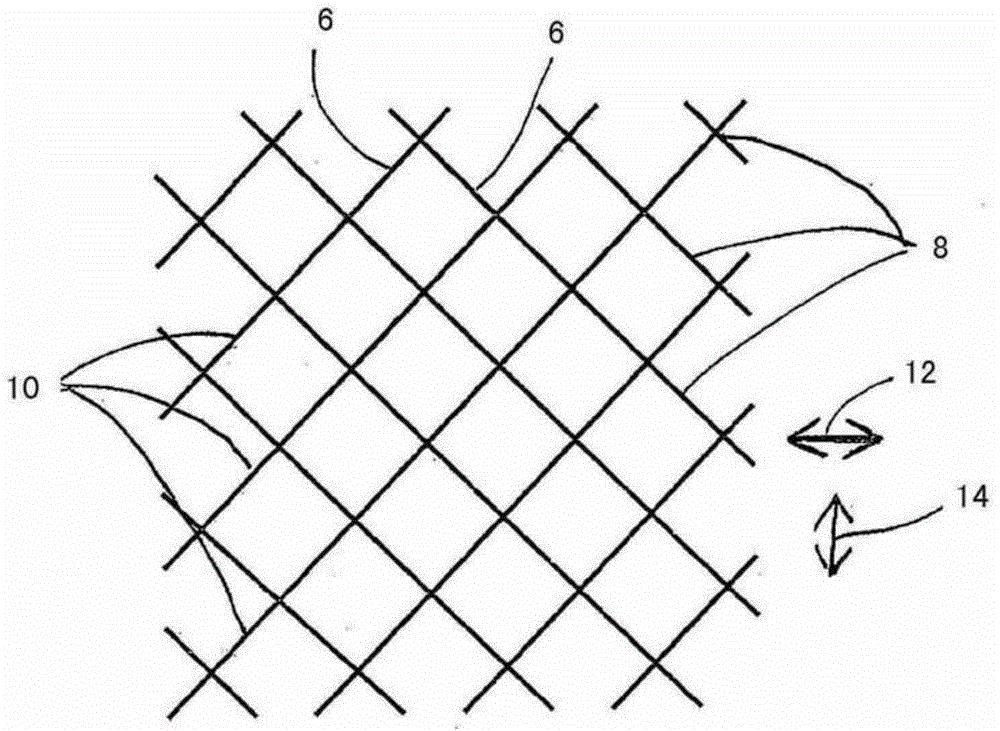
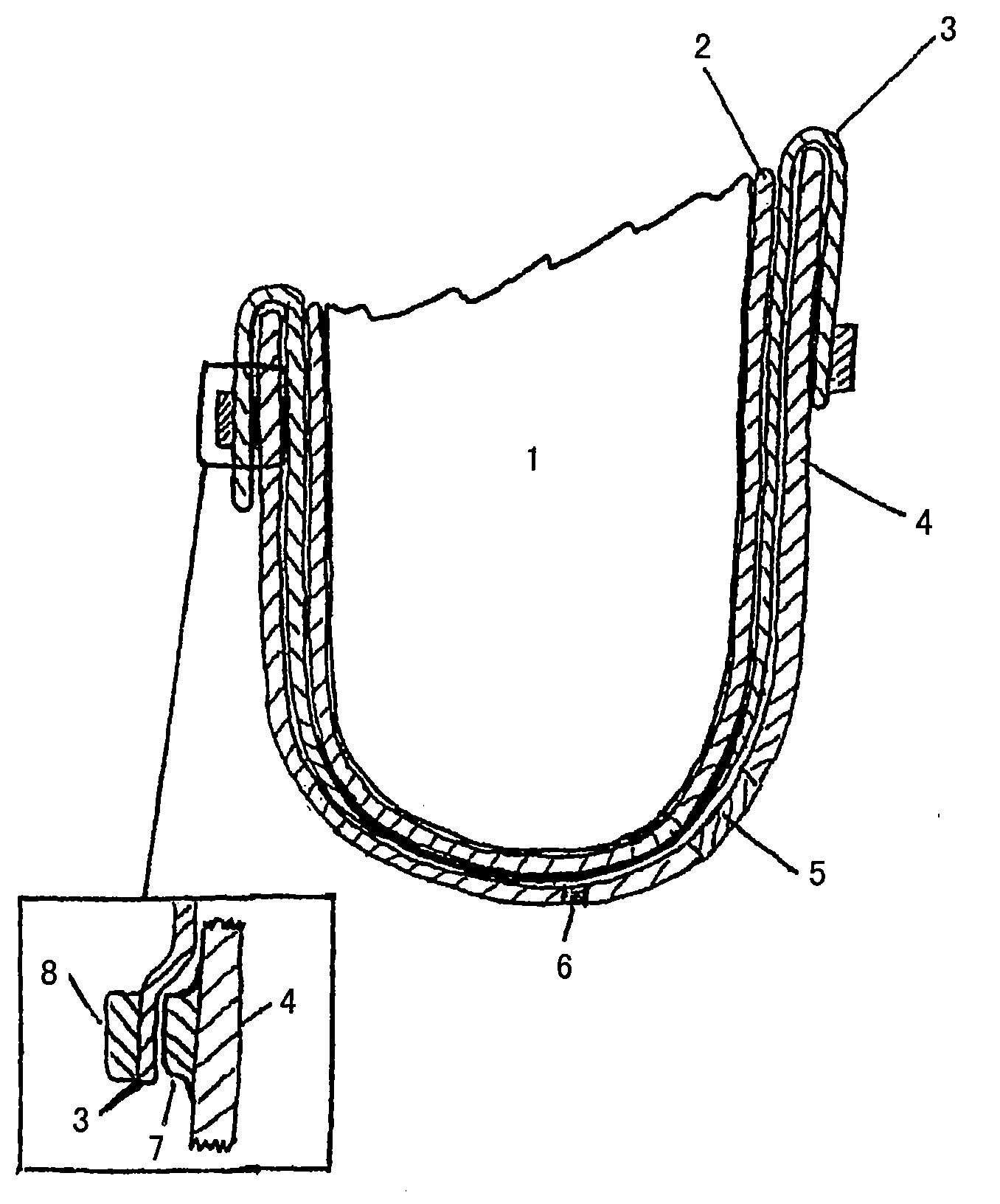
Liner for a prosthesis, and prosthesis
ActiveCN104684510ASimplify and reduce production methodsReduce manufacturing costProsthesisFiberProsthesis
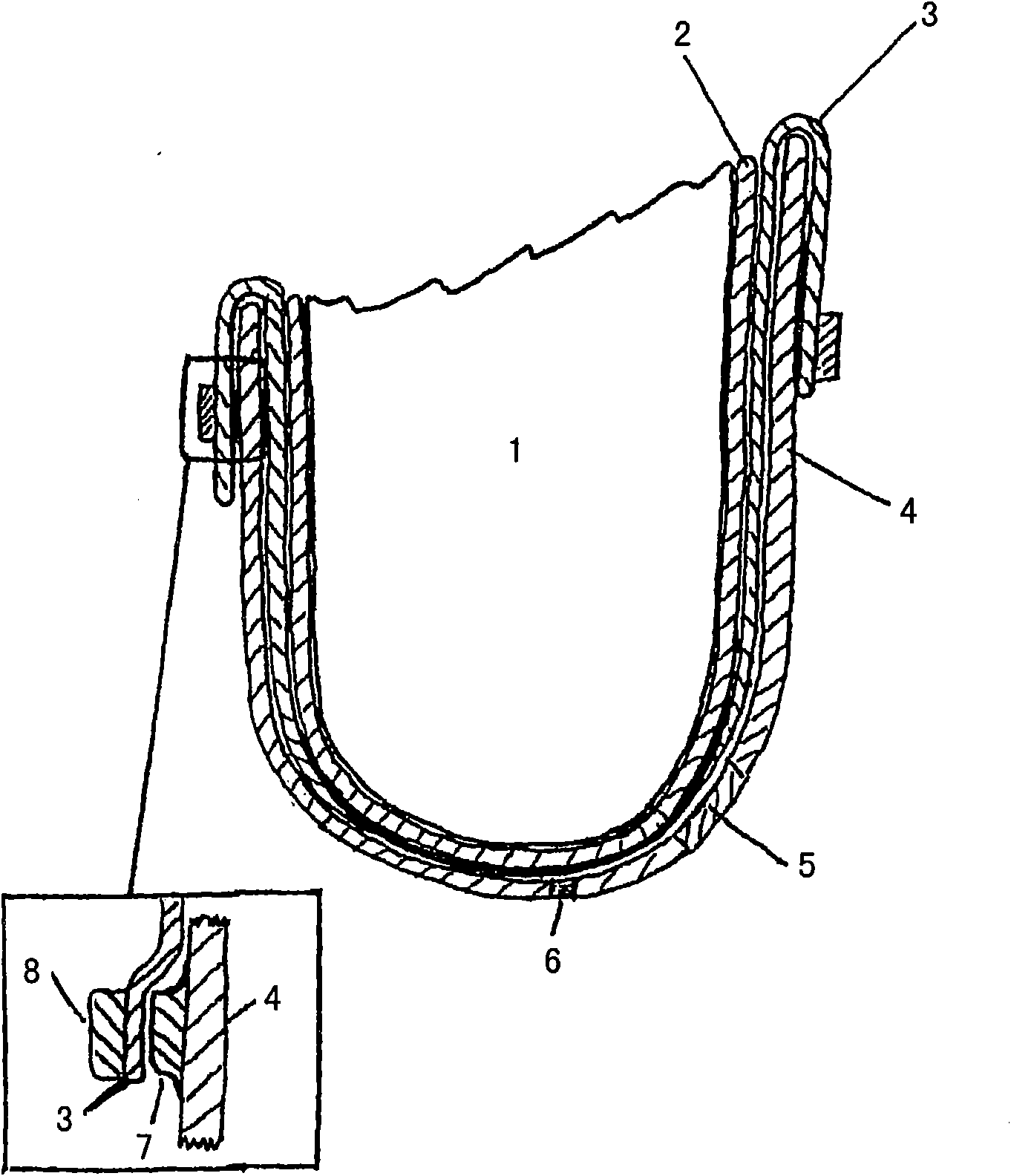
The invention relates to a liner (16) for a prosthesis, which liner (16) has a proximal opening, for receiving an amputation stump, and a distal end lying opposite the proximal opening, and it is produced from a liner material (4), wherein a longitudinal direction of the liner (16) extends from the proximal opening to the distal end, and a circumferential direction runs perpendicular to the longitudinal direction, wherein the liner (16) has a plurality of fibres (6), which are made from an inelastic material and are arranged in such a way that a lengthening of the liner (16) in the longitudinal direction results in a shortening of the liner (16) in the circumferential direction, and vice versa, wherein the liner (16) has non-slip means (26) which, when the liner (16) is fitted in place, prevent the liner (16) from slipping on the amputation stump.
Owner:OTTO BOCK HEALTHCARE IP GMBH & CO KG
Automatic prosthesis for above-knee amputees
A above knee prosthesis (P) applied to femoral connection (100) of an amputee that comprises a upper hinge (1) connected to femoral connection (100) of the patient, an articulation axis (2) with the function of reproducing the knee movements, a tibia-calf muscle unit (3) pivotally connected to the femoral segment (1) and a damper (5) that reproduces some functions of the calf muscle and ensures to the prosthesis (P) to brake and to allow the sequential swing and stance phases typical of the gait. The damper (5) comprises a cylinder (5c) wherein a piston (10) and a stem (9) act connected to each other and adapted to carry out a damping reaction of said damper responsive to the forces loaded on the prosthesis. In particular, a force transducer is provided in the damper (5) arranged, in particular, in the stem (9) with a microprocessor that receives a force signal from the transducer and operates means for adjusting the reaction of the damper responsive to the detected force signal. Exemplary embodiments are equipped with means for adjusting the gait parameters during a gait cycle, means for exploiting the energy dissipated by the prosthesis, means to assist the charge and the change of batteries, means to know the direction and / or the intensity of resultant forces transmitted through the prosthesis.
Owner:OFFICINE ORTOPEDICHE RIZZOLI SRL
Artificial limb movement intention identification method and device based on source-end fusion
PendingCN110742712AOvercoming complexityOvercoming Computational ComplexityMeasurement devicesProsthesisFoot ankle jointSimulation
The present invention discloses an artificial limb movement intention identification method and device based on source-end fusion. A processor collects ground bearing reaction force distribution condition through a pressure sensor arranged on soles of artificial limbs, judges gait cycles and calculates walking speed; road conditions of walking on a flat ground, going upstairs, going up a slope, going downstairs and going down a slope are distinguished through data acquired by an acceleration sensor arranged at artificial limb knee joint positions; going upstairs, going up a slope, going downstairs and going down a slope are distinguished by combining an angle sensor data of artificial foot ankle joint positions, and finally a processor judges movement intention of amputees according to walking speed and road conditions. According to the walking speed and road conditions, the processor controls artificial limbs to change actions according to the walking speed and road conditions, helpsthe artificial limbs to accurately make corresponding action, enables the amputees not need to exert force to change the actions of the artificial limbs, saves more labor of the amputees during use processes of the artificial limbs, and also enables the gait cycles to be more natural.
Owner:浙江臻行科技有限公司
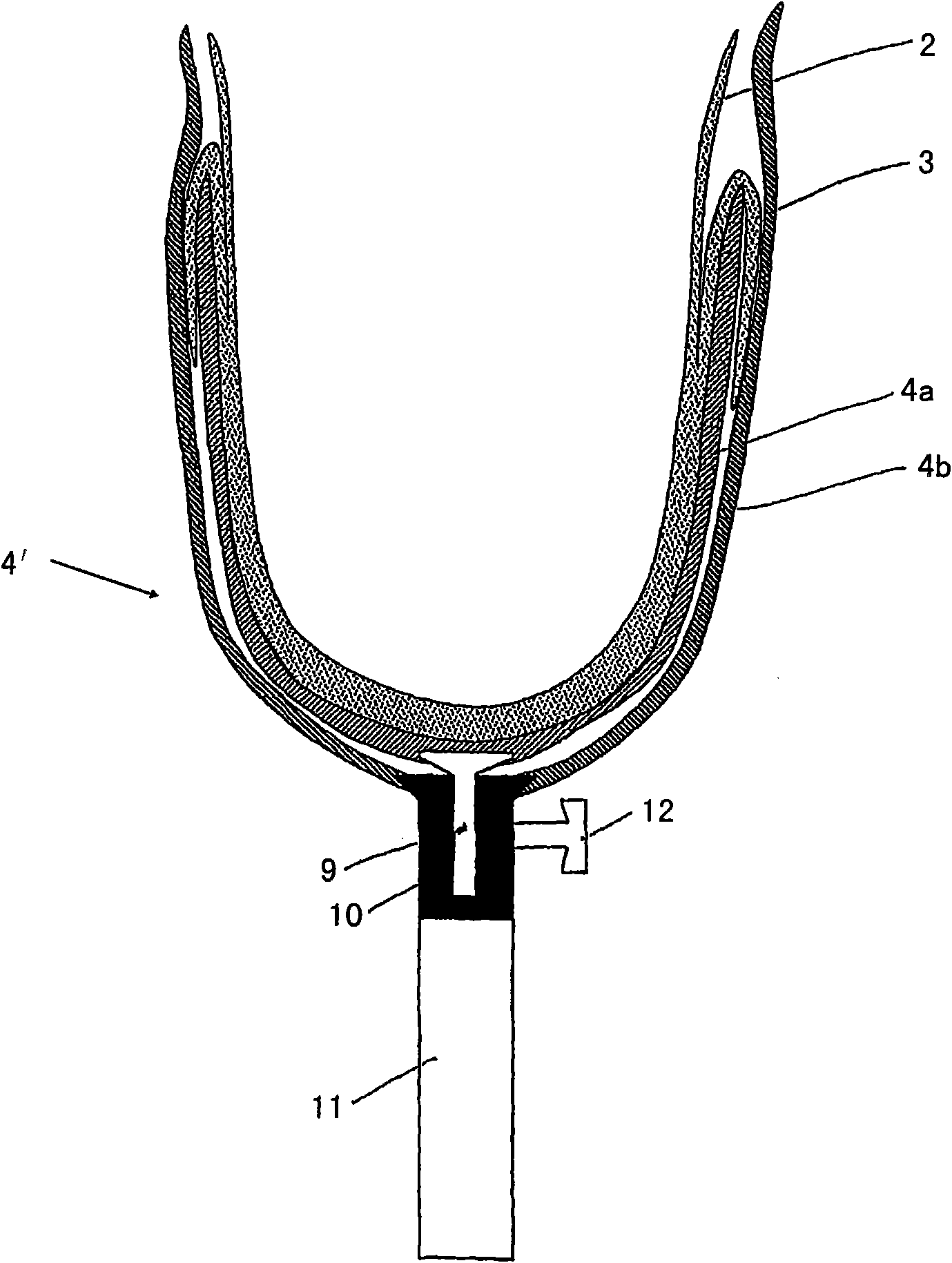
Liner for vacuum sockets, and use of the liner
A liner for vacuum sockets for receiving amputation stumps and for use in prosthetic sockets, wherein the liner has a double wall made up of an inner liner (2) and of an outer liner (3), permits improved sealing by a vacuum between liner and prosthetic socket (4) by virtue of the fact that the inner liner (2) and the outer liner (3) are fixedly connected to each other in the middle third and / or distal third and that the outer liner (3) is designed to provide a seal with the prosthetic socket (4).
Owner:OTTO BOCK HEALTHCARE IP GMBH & CO KG
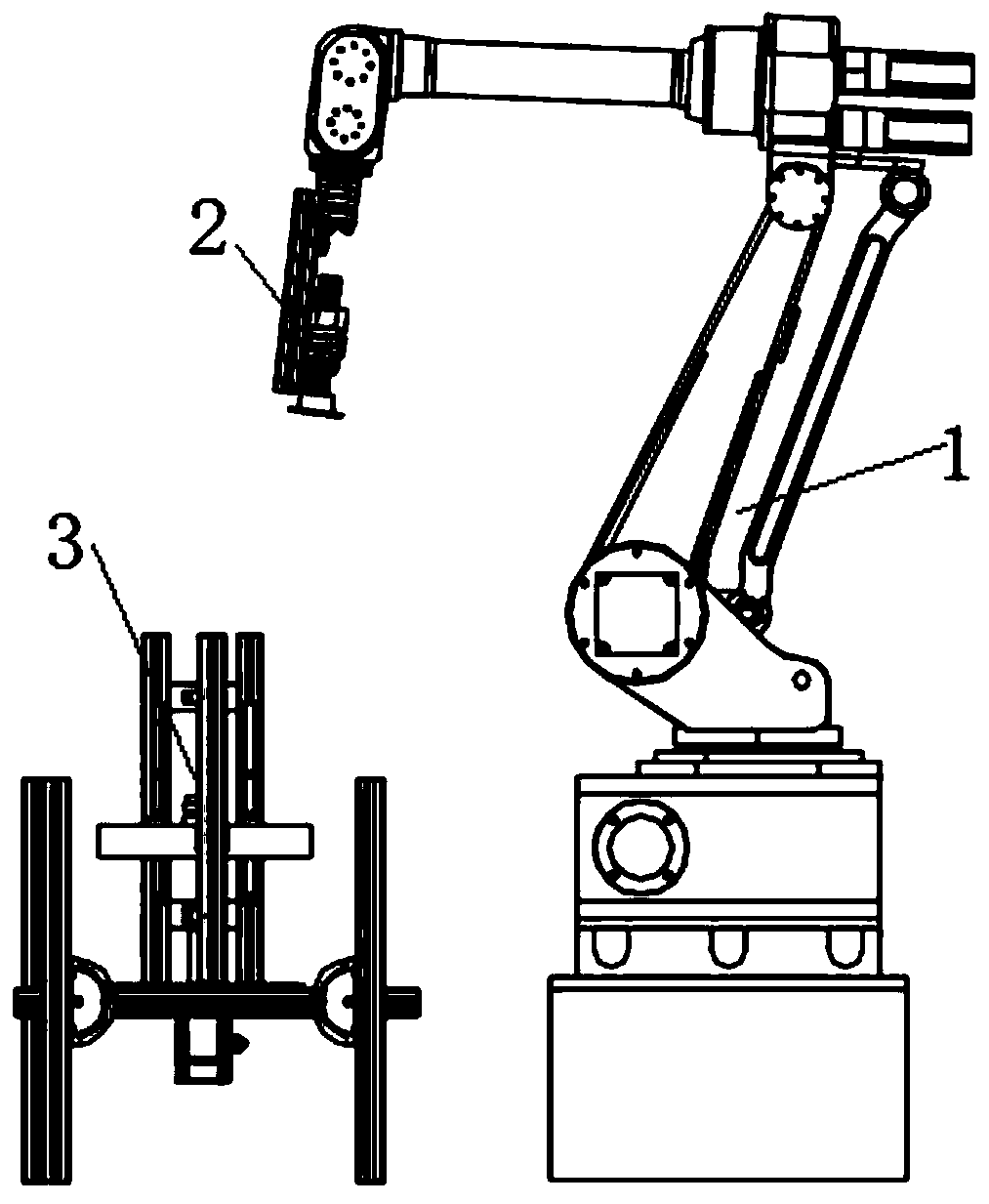
Industrial robot based knee-joint prosthesis testing device and testing methods
ActiveCN111588522ASimple structure to useFlexible and convenient controlArtificial legsKnee JointEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of prosthesis testing, and specifically relates to an industrial robot based knee-joint prosthesis testing device and testing methods. The device includesan industrial robot, a Bionic thigh and a ground reaction force module. The device can realize the prosthesis testing under environments of horizontally walking at different speeds, going up and downslopes and going up and down stairs by simulating the movement of the residual limbs of patients with knee amputation within a gait cycle; the device can adjust the ground reaction force on the foot of prosthesis, so that the inputting of the ground reaction force during prosthesis testing can be more accurate, and accurate testing environments can be provided for the intelligent keen joints assembled on an interface; and as the industrial robot is used, a testing system can be more convenient and flexible in using and simpler in structure.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Modular prosthetic arm system
Modular arm prosthesis, for amputations higher than the level of the forearm. With the feature of being modular, which gives us an advantage that reduces the repair time by replacing the module quickly. The Socket-stump module which can be adjusted to several stumps thanks to its pneumatic system for grip, decreases the level of customization of each prosthesis thus reducing the manufacturing time and cost of production of each prosthesis, as well as its easy control by means of myoelectric sensors.
Owner:PROYECTOS OFTALMOLOGICOS S A DE CV
Lap joint for prosthetic foot
Apparatus and methods for a prosthetic foot for attachment to a socket worn by an amputee. In an embodiment, the prosthetic foot comprises a body including a forefoot portion and a heel portion. In addition, the prosthetic foot comprises at least one attachment member extending from the body and conformable to the socket.
Owner:WILSON MICHAEL T
Amputation dressings
InactiveUS20130267882A1Avoid infectionPromote wound healingFinger bandagesFeet bandagesWound dressingLimb amputation
The invention relates to devices, systems and methods for caring for amputations (e.g., limb amputations, digit amputations). Specifically, the invention relates to devices and systems (e.g., dressing systems) for secure placement of wound dressing material (e.g., dressing material, bandage material) on the body of a subject.
Owner:VOLKER MONICA ANN
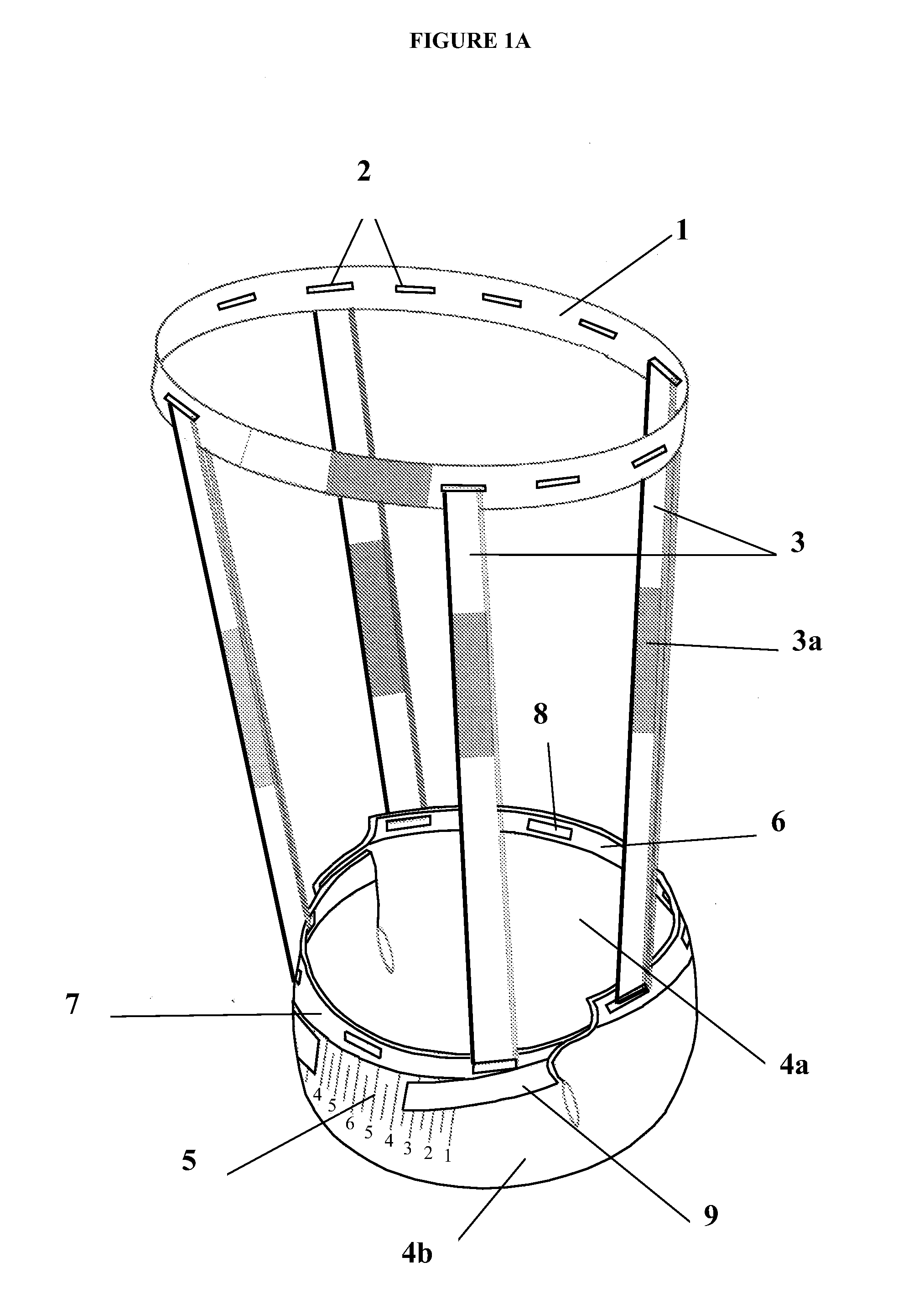
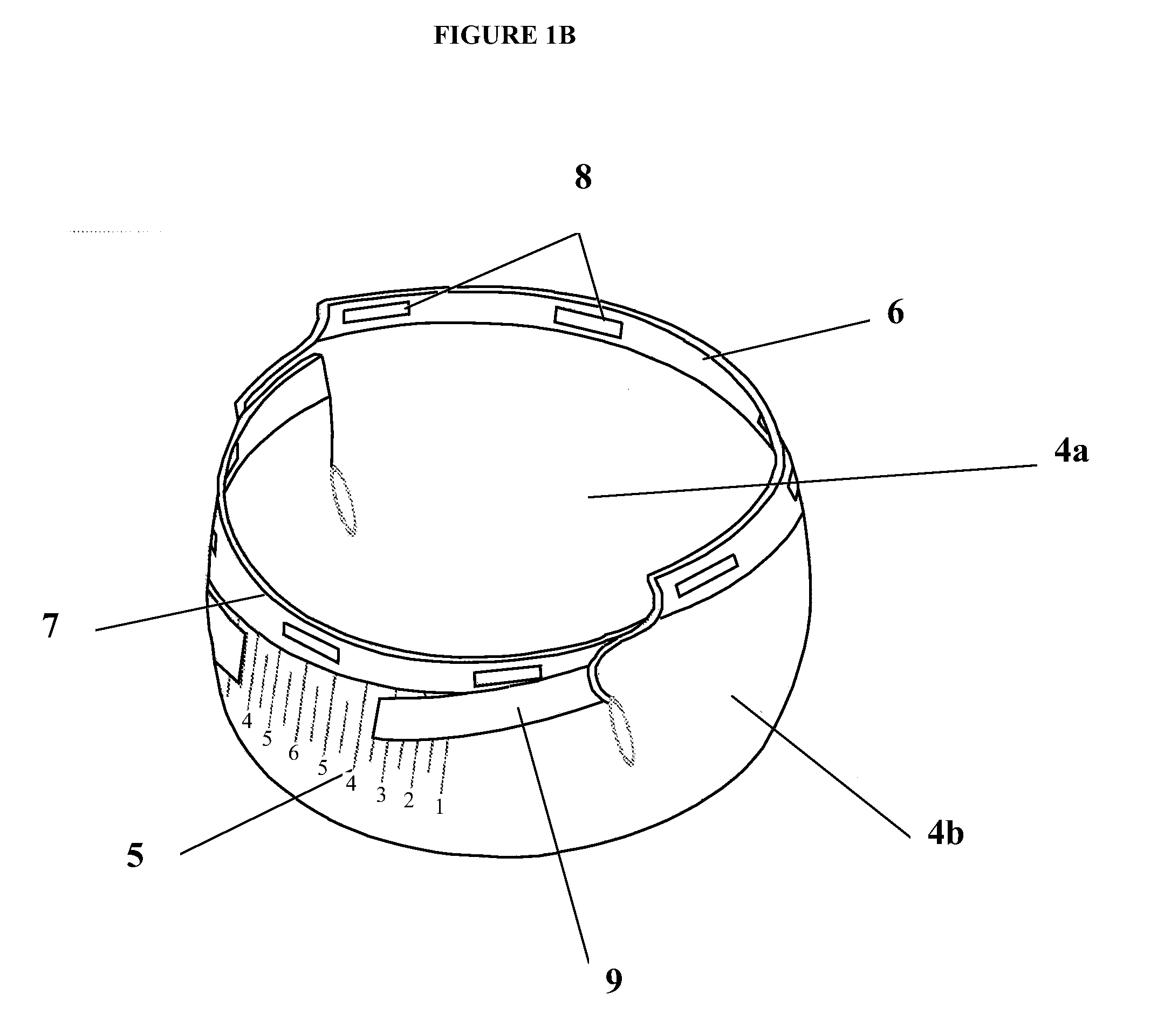
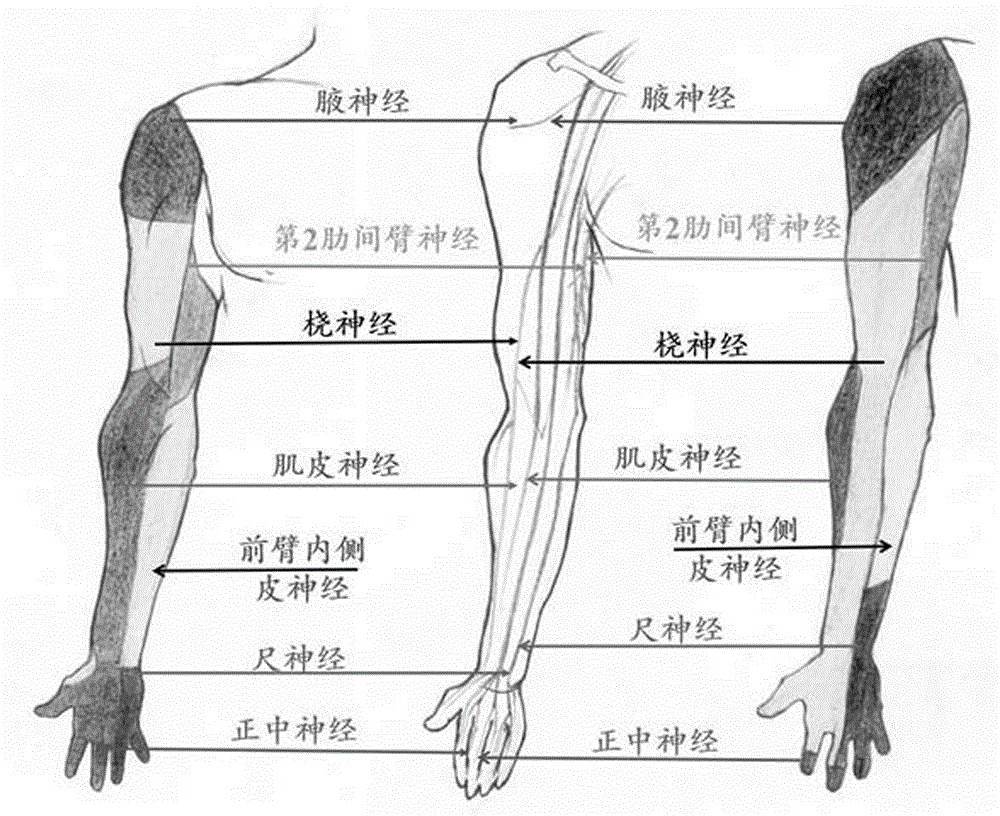
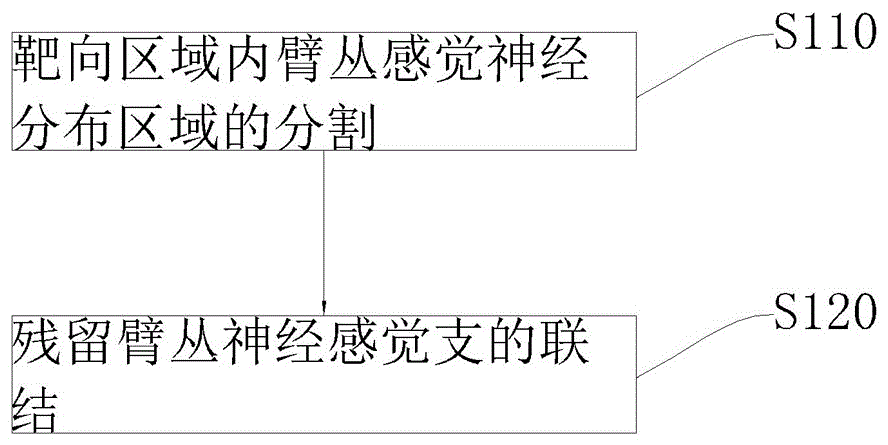
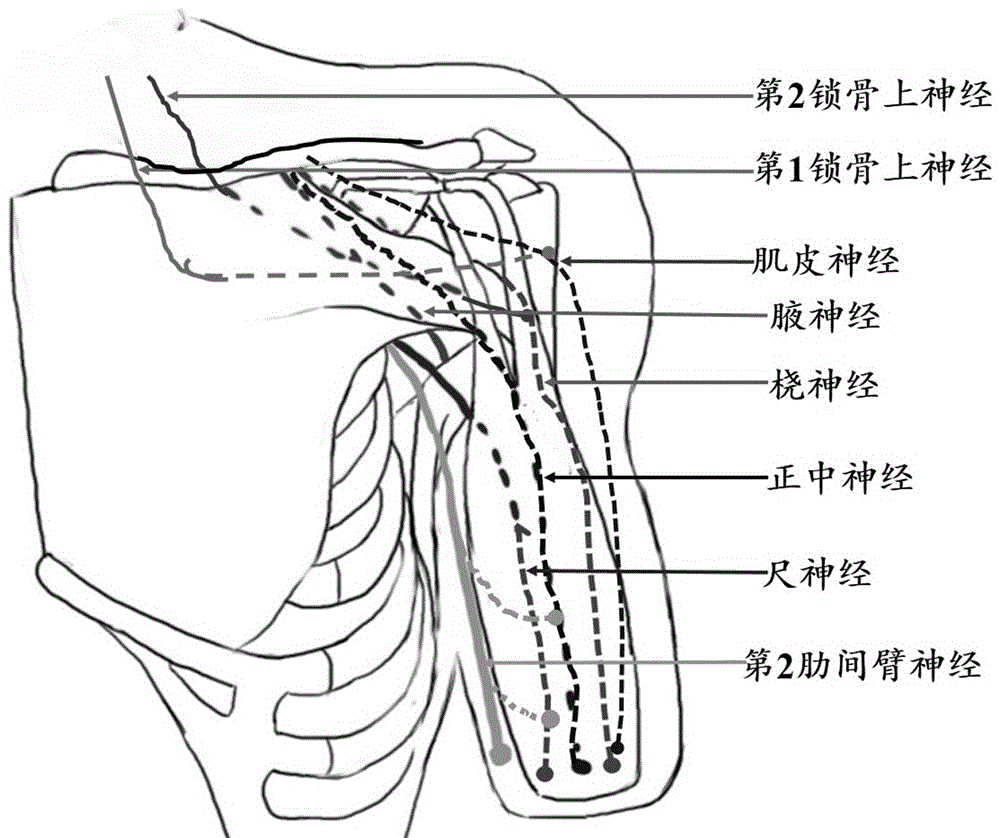
Method for reconstructing sensory nerve functions of amputation upper limbs and method for sensory nerve and artificial limb interfaces
InactiveCN105769396AFeeling resolvedThe technical method is simpleProsthesisSomesthetic areaPlexus brachialis
The invention discloses a method for reconstructing sensory nerve functions of amputation upper limbs and a method for reconstructing sensory nerve and artificial limb interfaces.The method for reconstructing the sensory nerve functions of the amputation upper limbs includes steps of separating sensory branches of various nerve bundles of remaining brachial plexus nerves of amputation patients and connecting the nerve sensory branches with sensory nerves in target sensory regions; adding different sensory sensors into nerve artificial limbs, timely transmitting external stimulation in contact with the artificial limbs to the target sensory regions of the limbs of the amputees by the aid of a stimulation input process and further transmitting the external stimulation in contact with the artificial limbs to sensory center regions of the brains of the amputees by the aid of the reconstructed target sensory regions of the limbs.The methods have the advantages that the brachial plexus nerves remained after the upper limbs of the amputation patients are amputated are connected into the selected target sensory regions, sensory innervation regions of the limbs can be reconstructed in the target sensory regions by the brachial plexus nerves, the limb sensory functions lost due to amputation can be reconstructed, and accordingly interfaces functions of remaining limb sensory and multifunctional nerve artificial limb sensory can be implemented.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
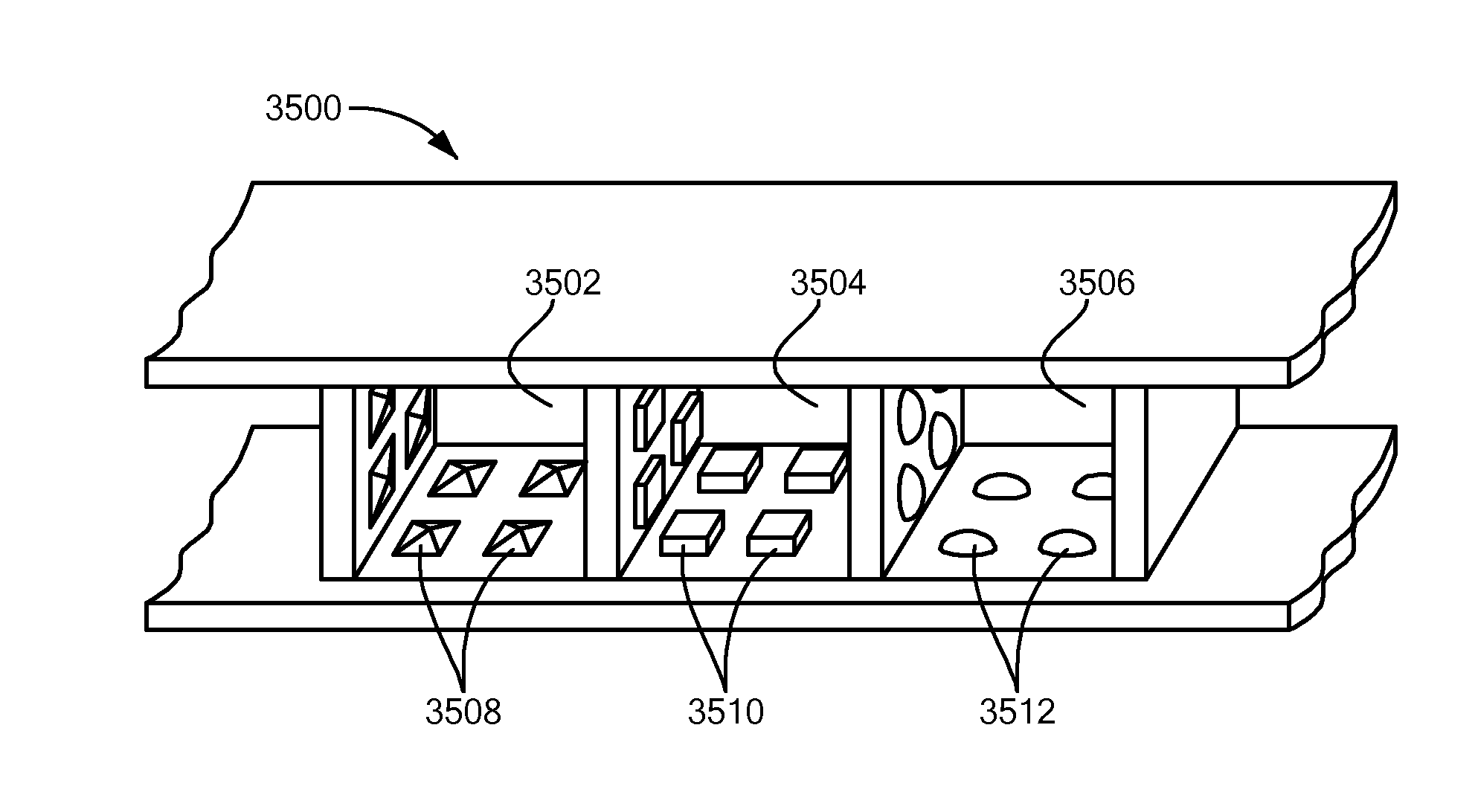
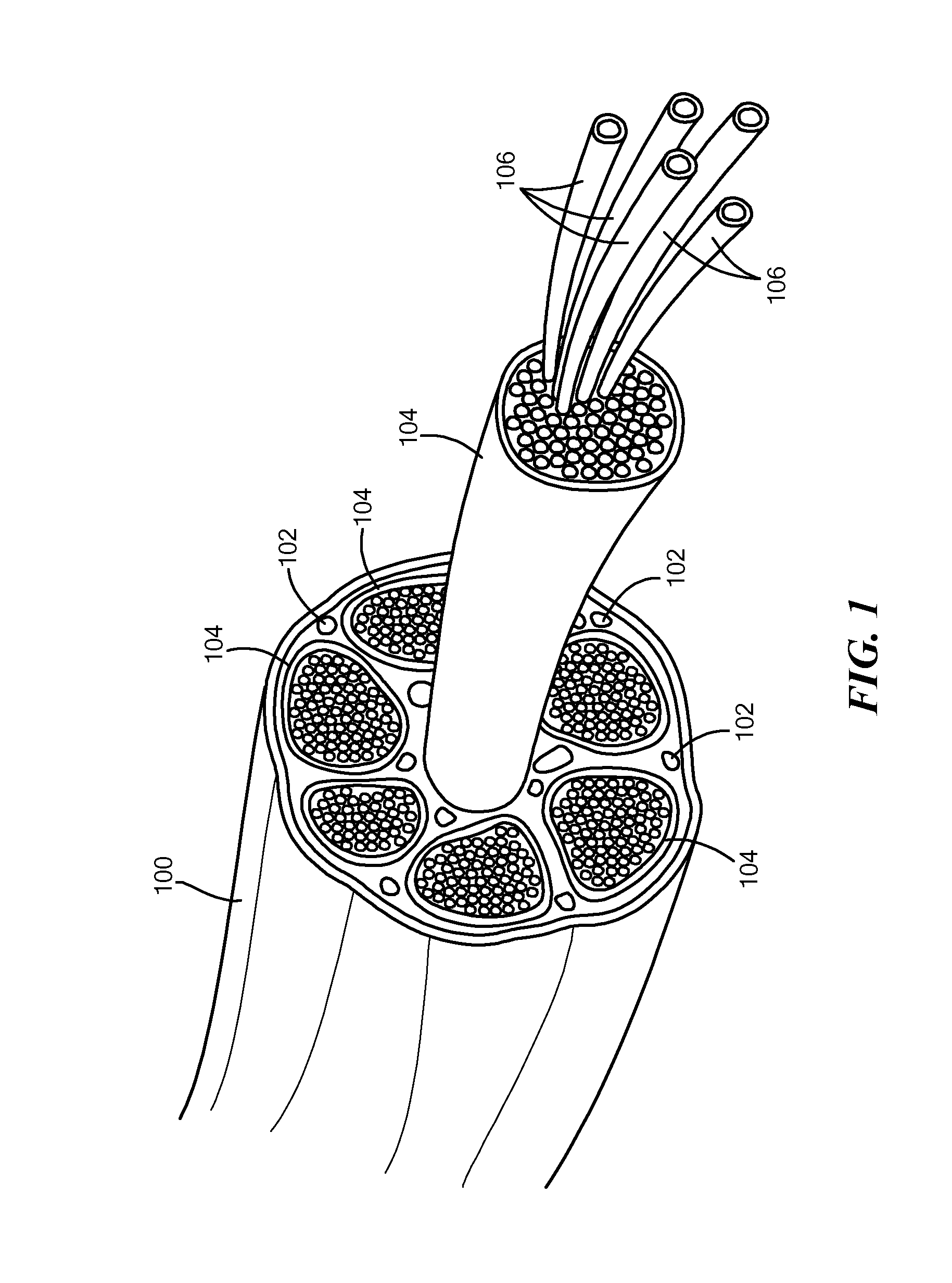
Multi-Layered Micro-Channel Electrode Array with Regenerative Selectivity
ActiveUS20150217109A1Enhanced differentiated geometric guidanceStrong specificitySpinal electrodesElectromyographyChannel geometryEfferent
A scaffold defines a plurality of channels, into which axons of a severed nerve may regenerate, such as after limb amputation. Each channel includes a corresponding electrode. Regenerating axons may make electrical contact with the electrodes. Each channel is at least partially filled with a growth factor selected to selectively stimulate axon regeneration. Adjacent channels may include different growth factors, so as to attract different types of axons, for example efferent axons and afferent axons, to each of the adjacent channels. The growth factors may be distributed in the channels so as to present a gradient across a geometry of each channel. This gradient provides enhanced differentiated geometric guidance to the axons, thereby yielding better specificity, in terms of which axons regenerate into which channels. Topography, such as geometric patterns in walls, ceilings and floors of the channels, may also be used to selectively encourage axon regeneration into the channels.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com