Patents
Literature
30 results about "Paced Ventricular Rhythm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
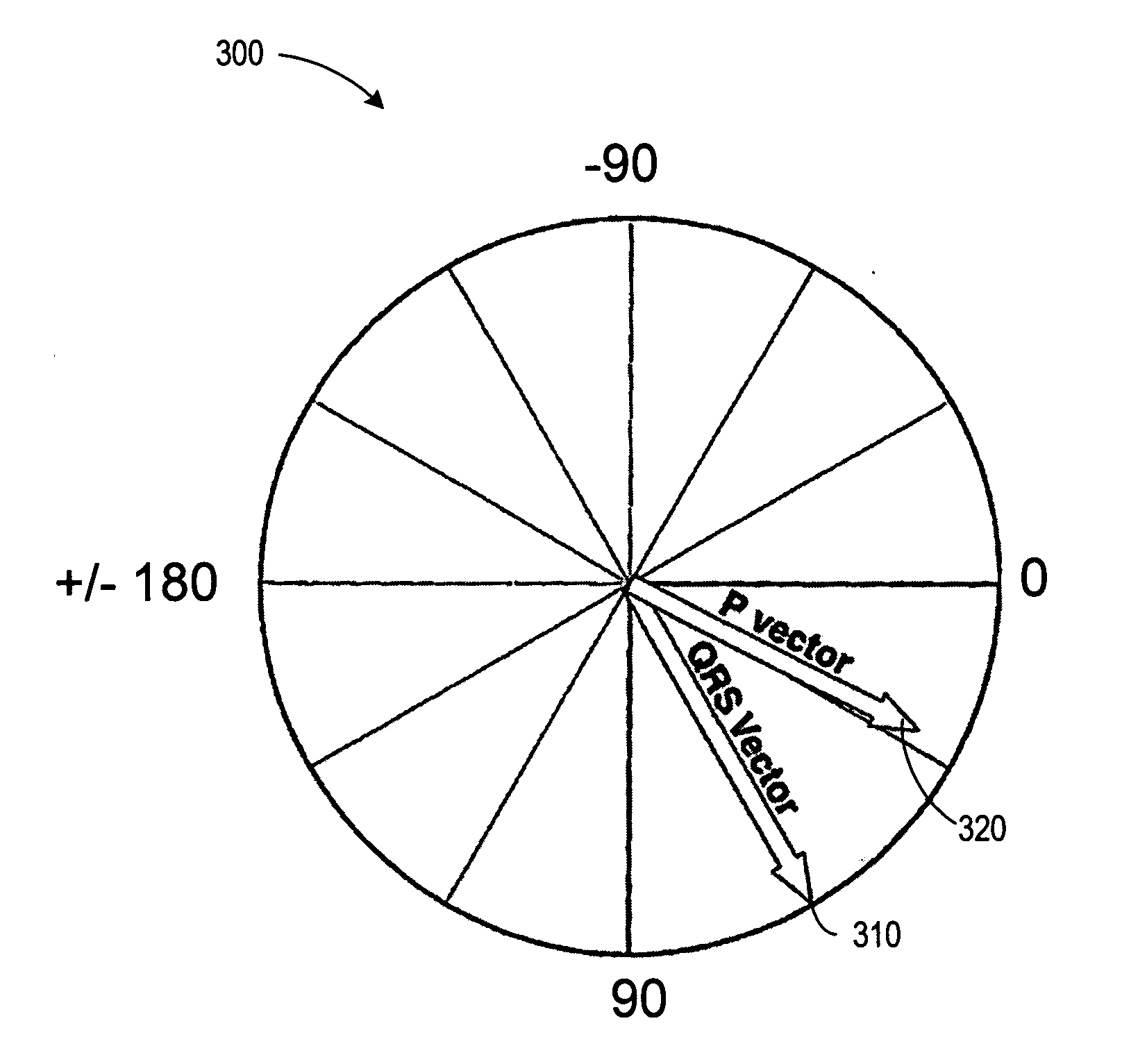
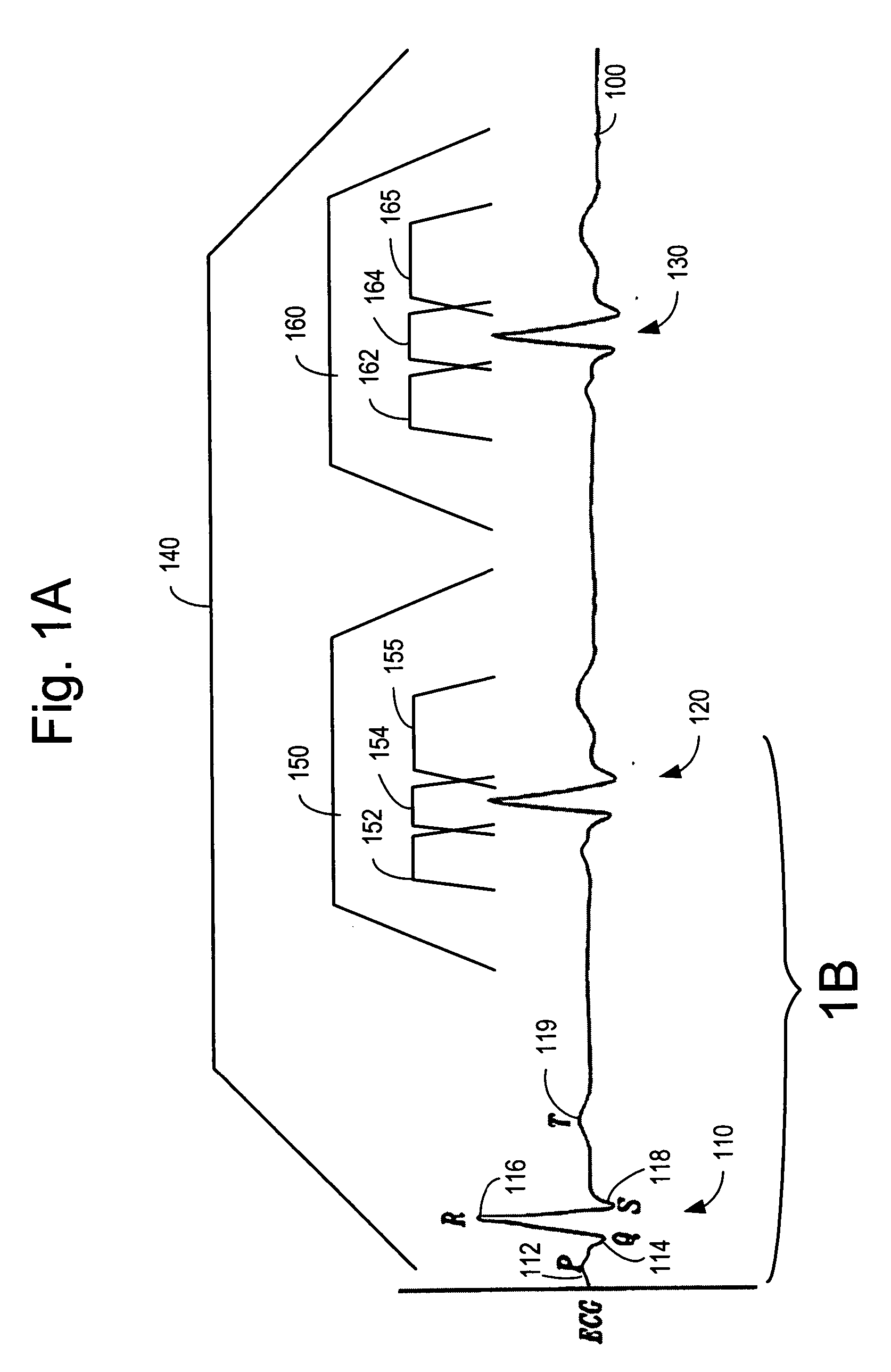
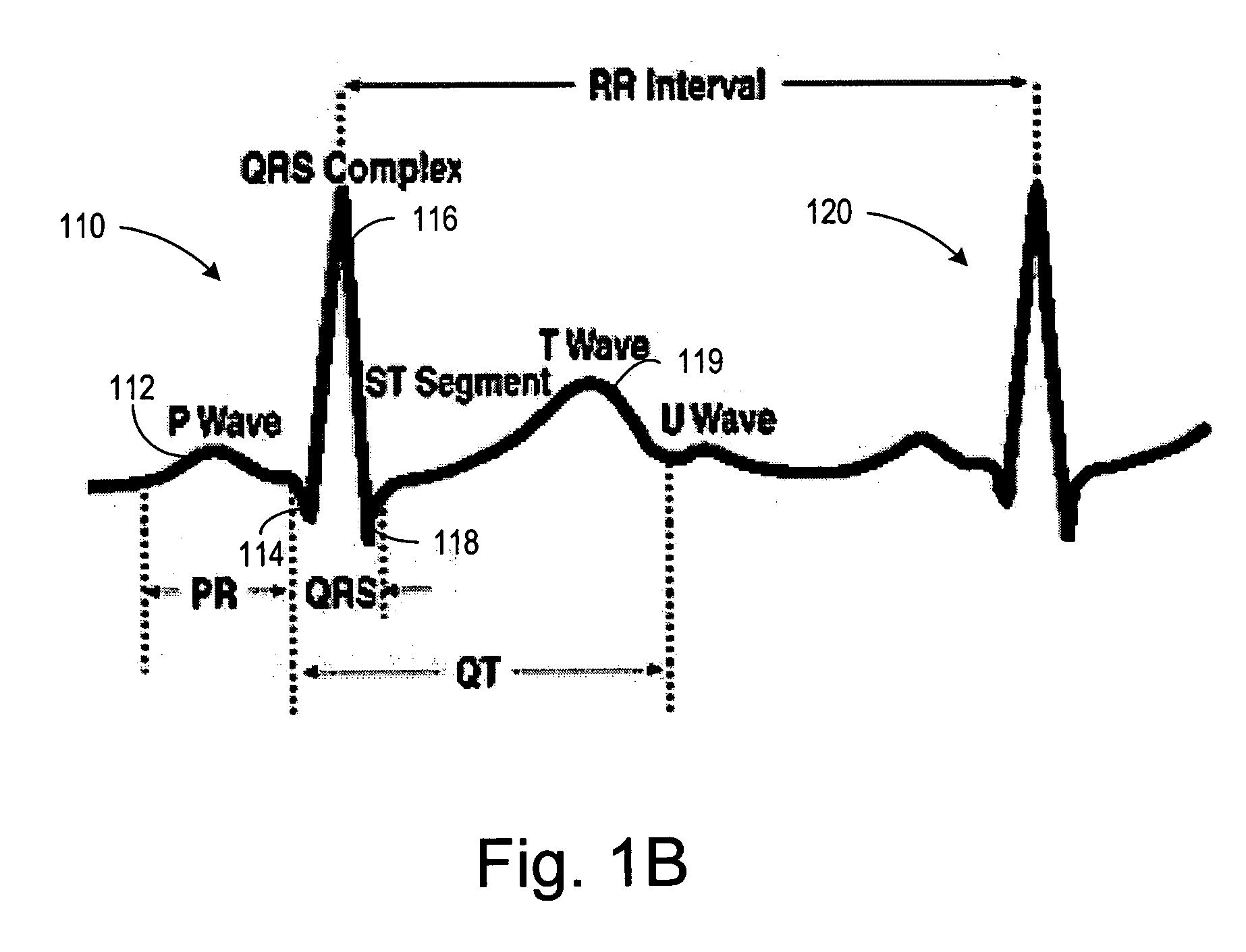
An electrocardiographic finding in which the ventricular rhythm is controlled by an electrical impulse from an artificial cardiac pacemaker. (CDISC)
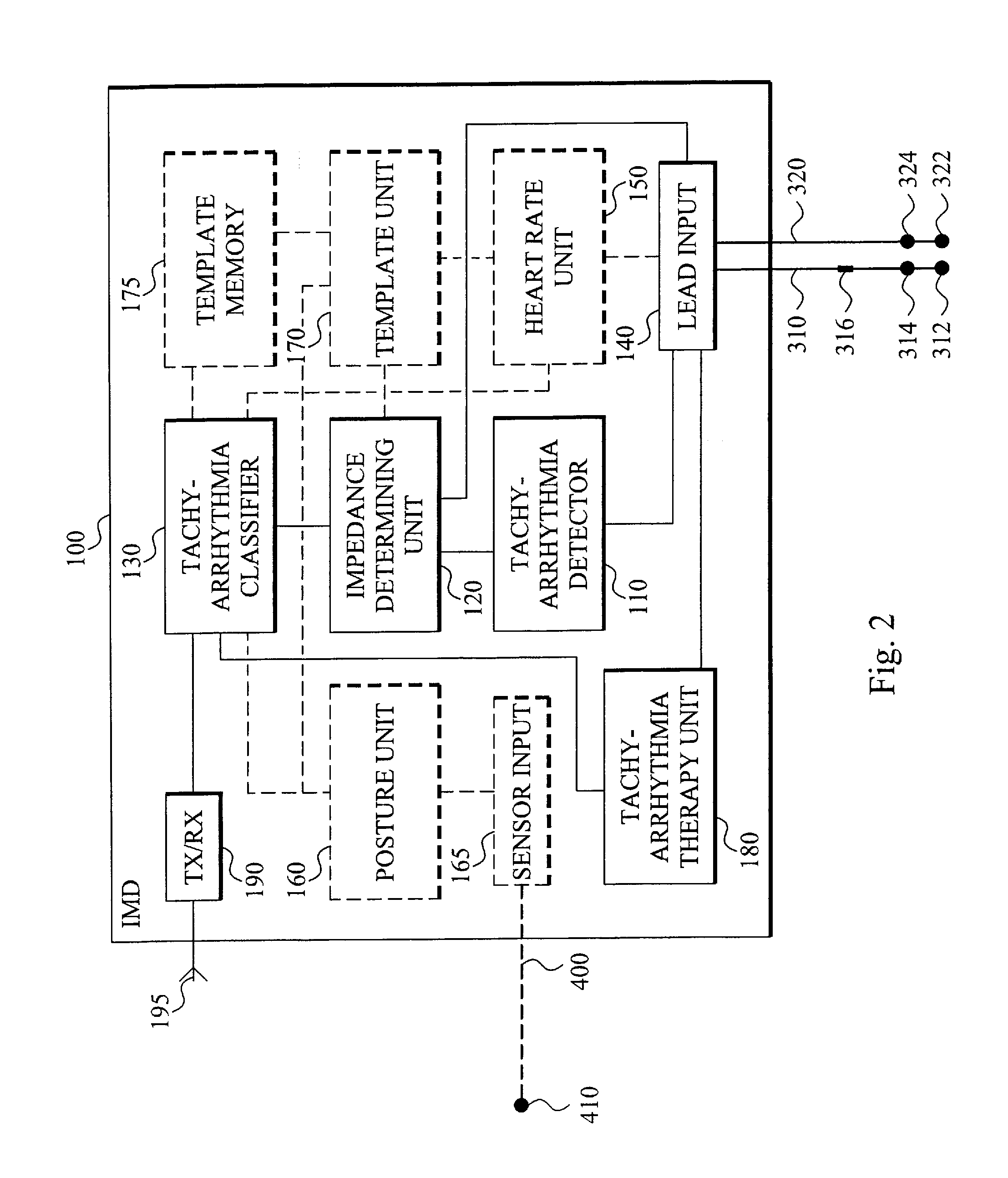
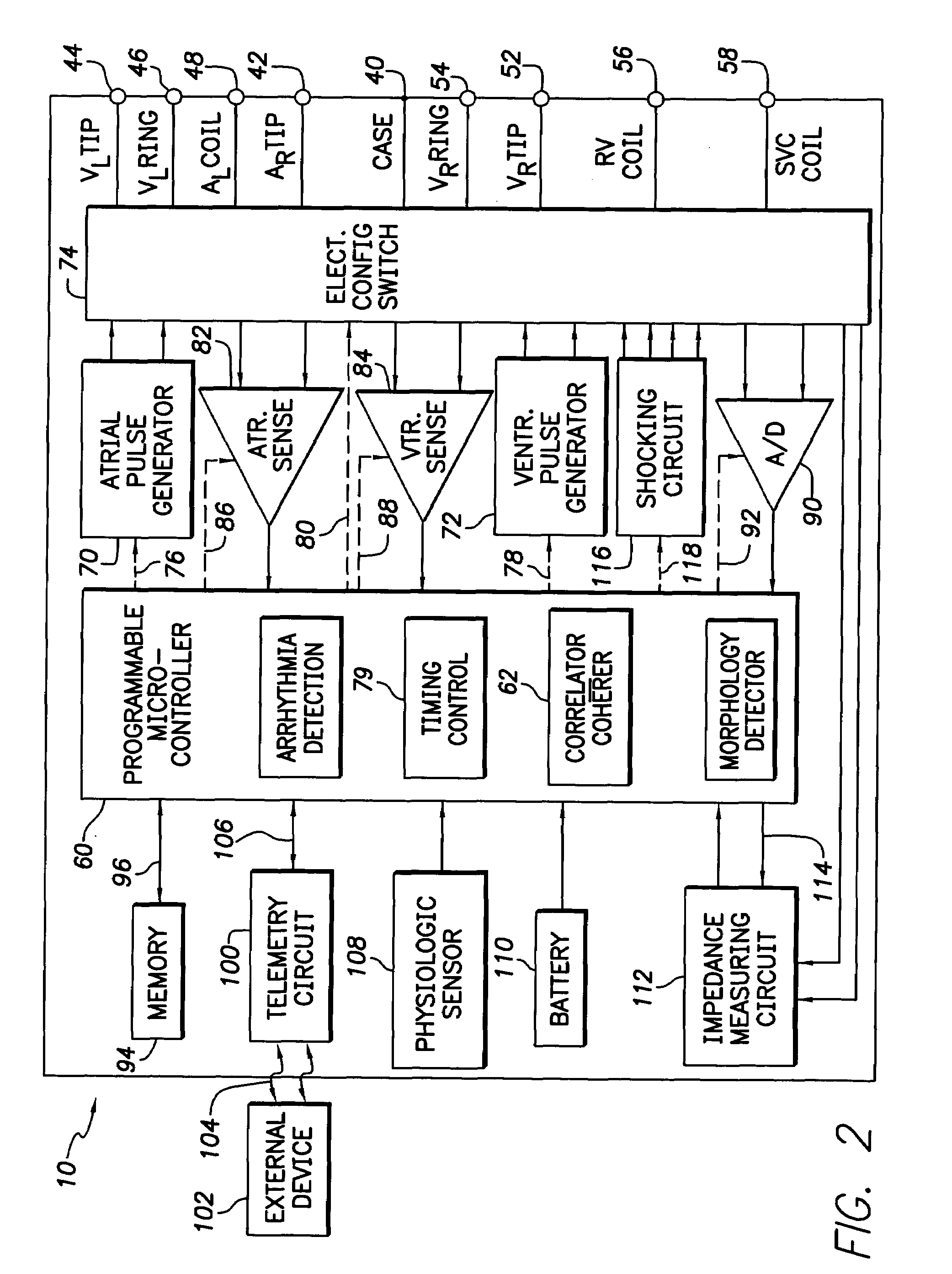
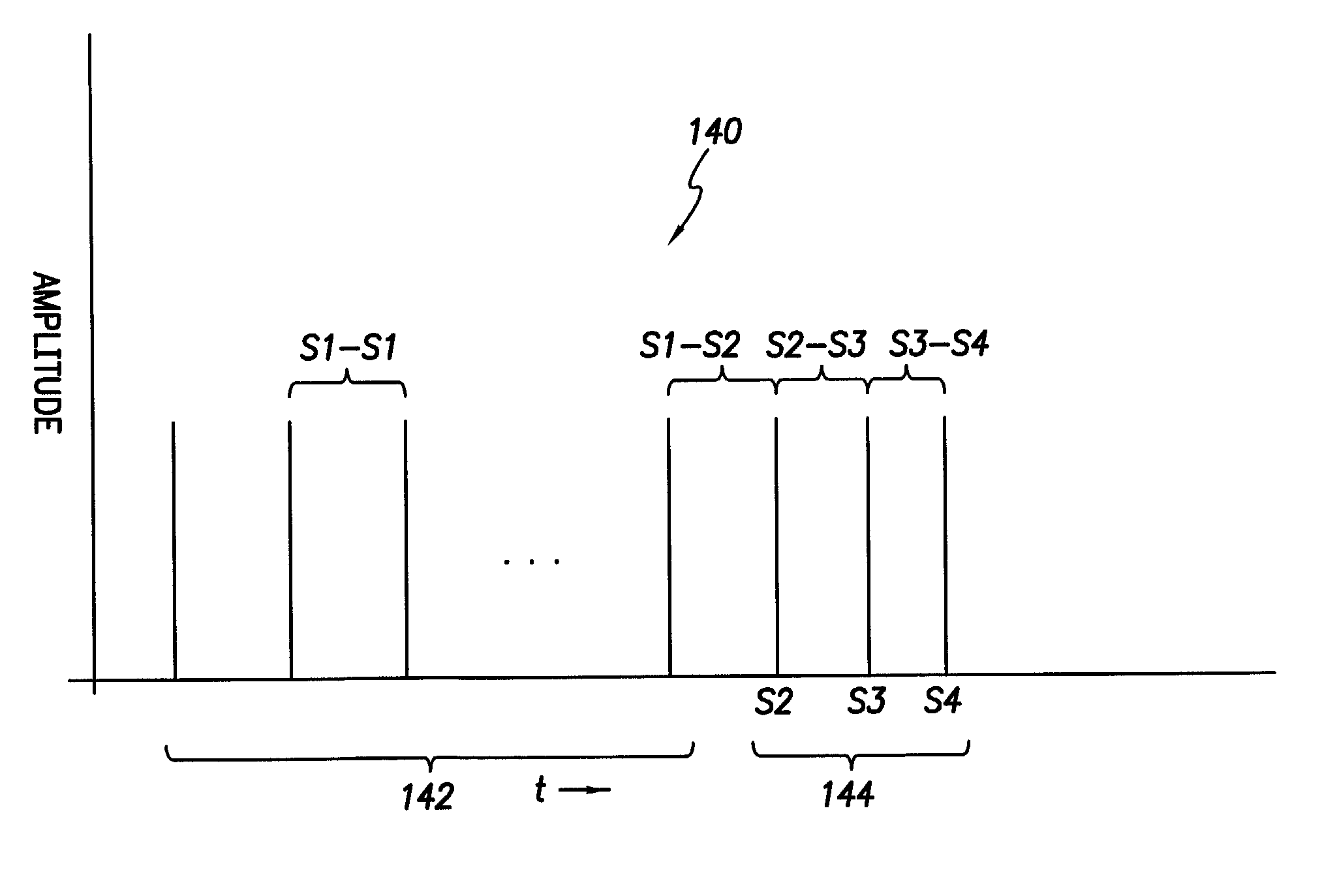
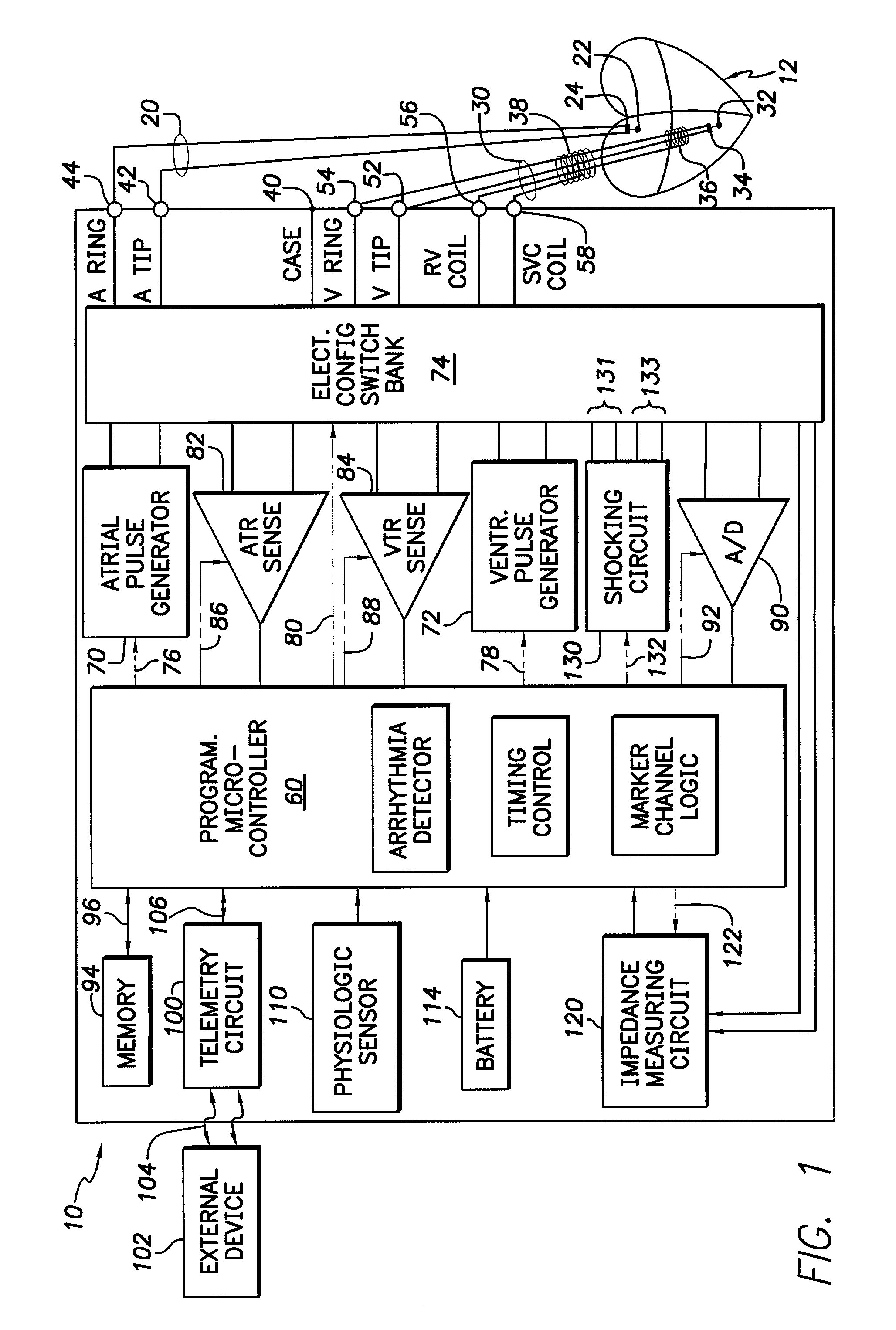
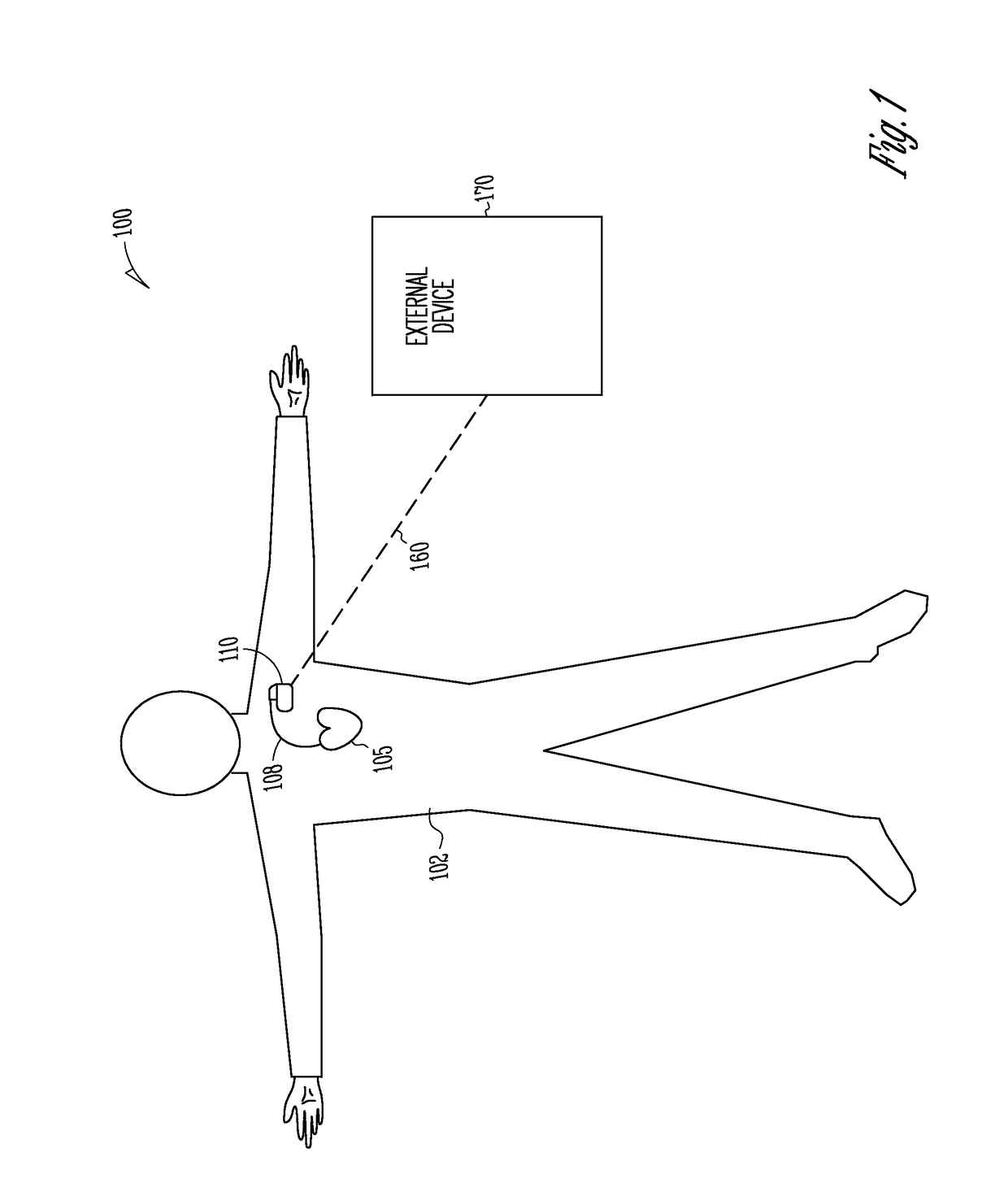
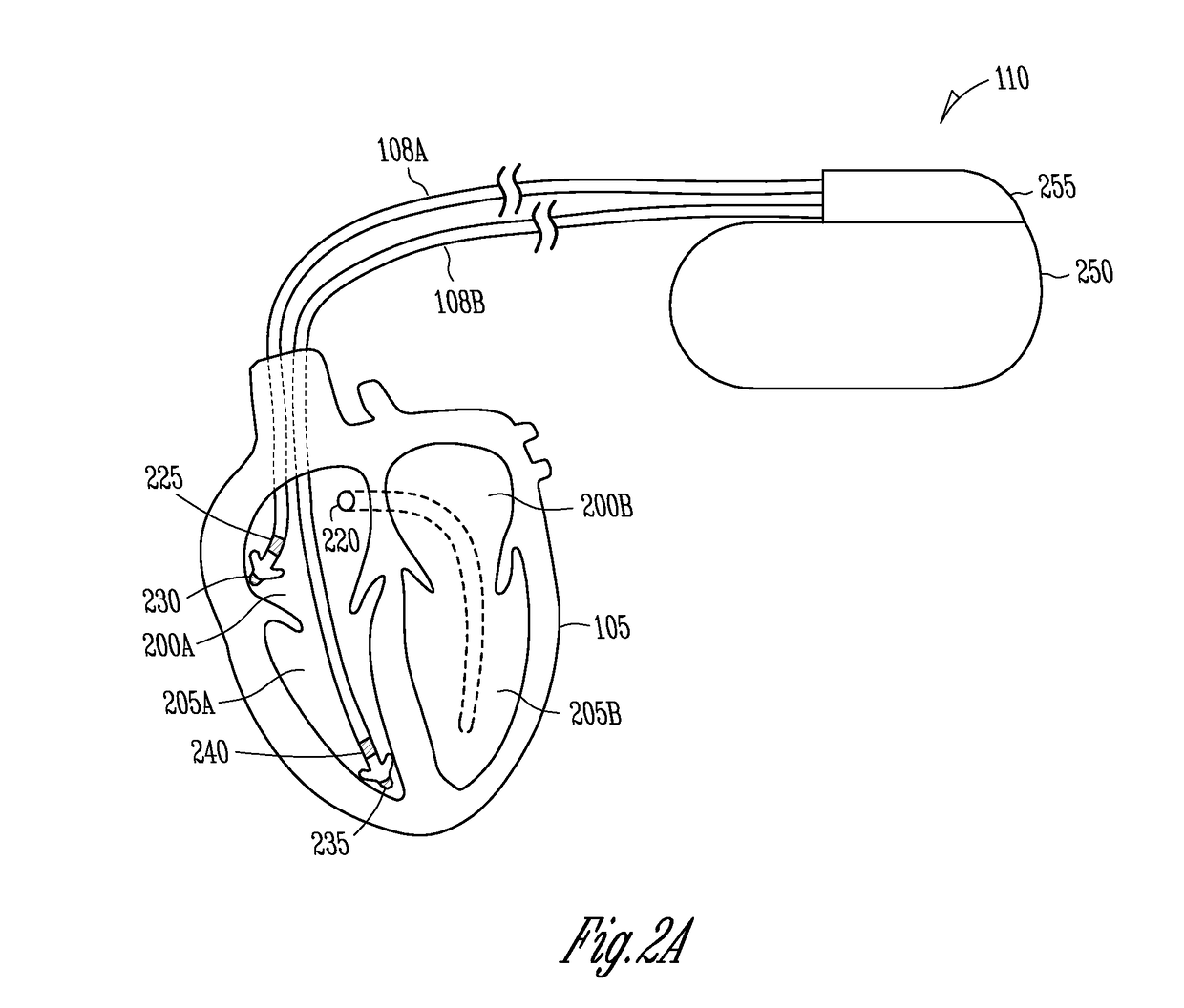
Arrhythmia discrimination using electrocardiograms sensed from multiple implanted electrodes
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems provide for monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation and pacing therapies, or a combination of these capabilities, including cardiac systems incorporating or cooperating with neuro-stimulating devices, drug pumps, or other therapies. Embodiments of the present invention relate generally to implantable medical devices employing automated cardiac activation sequence monitoring and / or tracking for arrhythmia discrimination. Embodiments of the invention are directed to devices and methods involving sensing a plurality of composite cardiac signals using a plurality of implantable electrodes. A source separation is performed using the sensed plurality of composite cardiac signals and the separation produces one or more cardiac signal vectors associated with one or more cardiac activation sequences that is indicative of ischemia. A change of the one or more cardiac signal vectors is detected using the one or more cardiac signal vectors. Cardiac arrhythmias are discriminated using the one or more cardiac signal vectors.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method for surgically implanting an electrode device
InactiveUS20080161894A1Reduce riskFew potential side effectSpinal electrodesSurgeryCarotid sinusRight ventricles
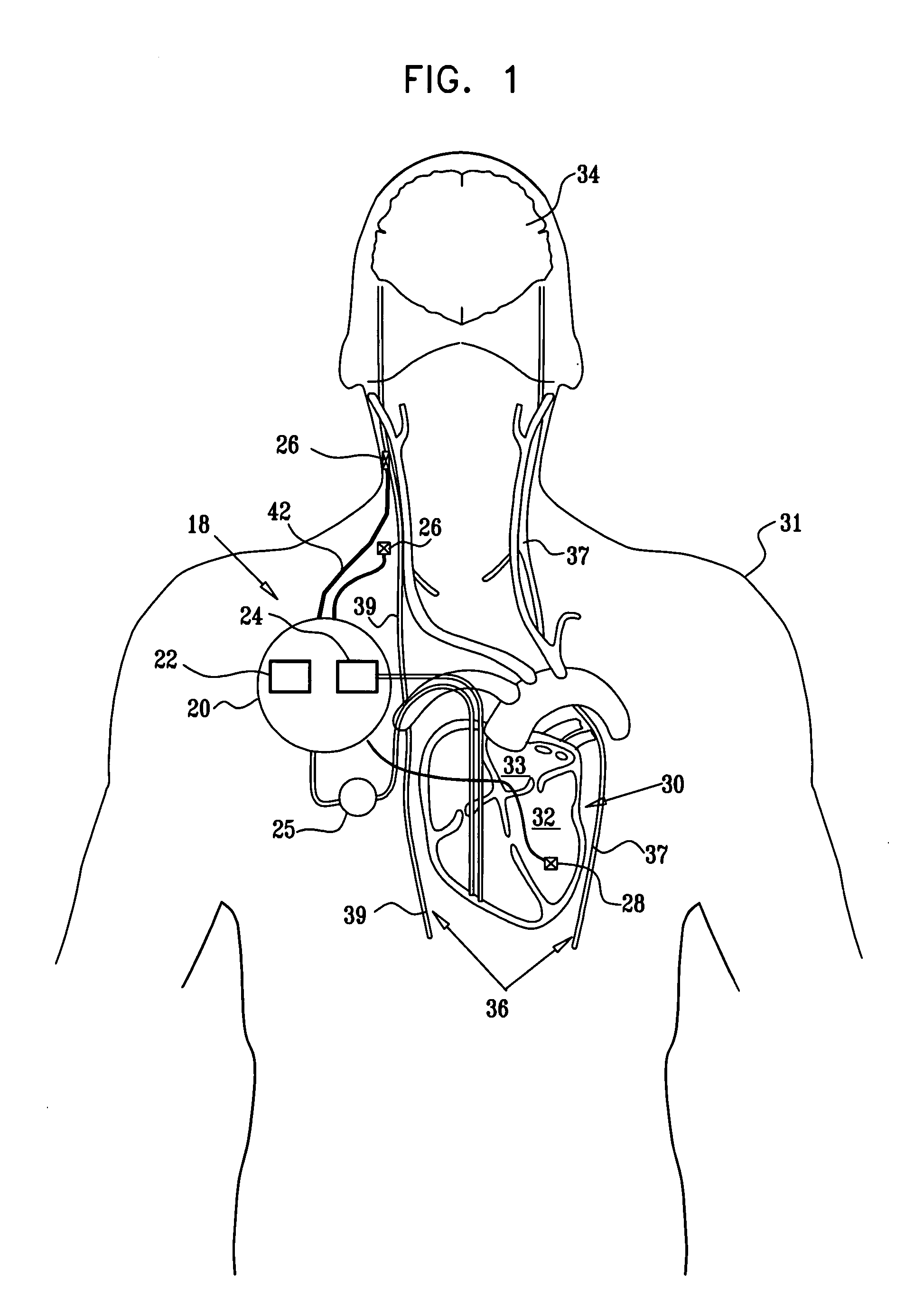
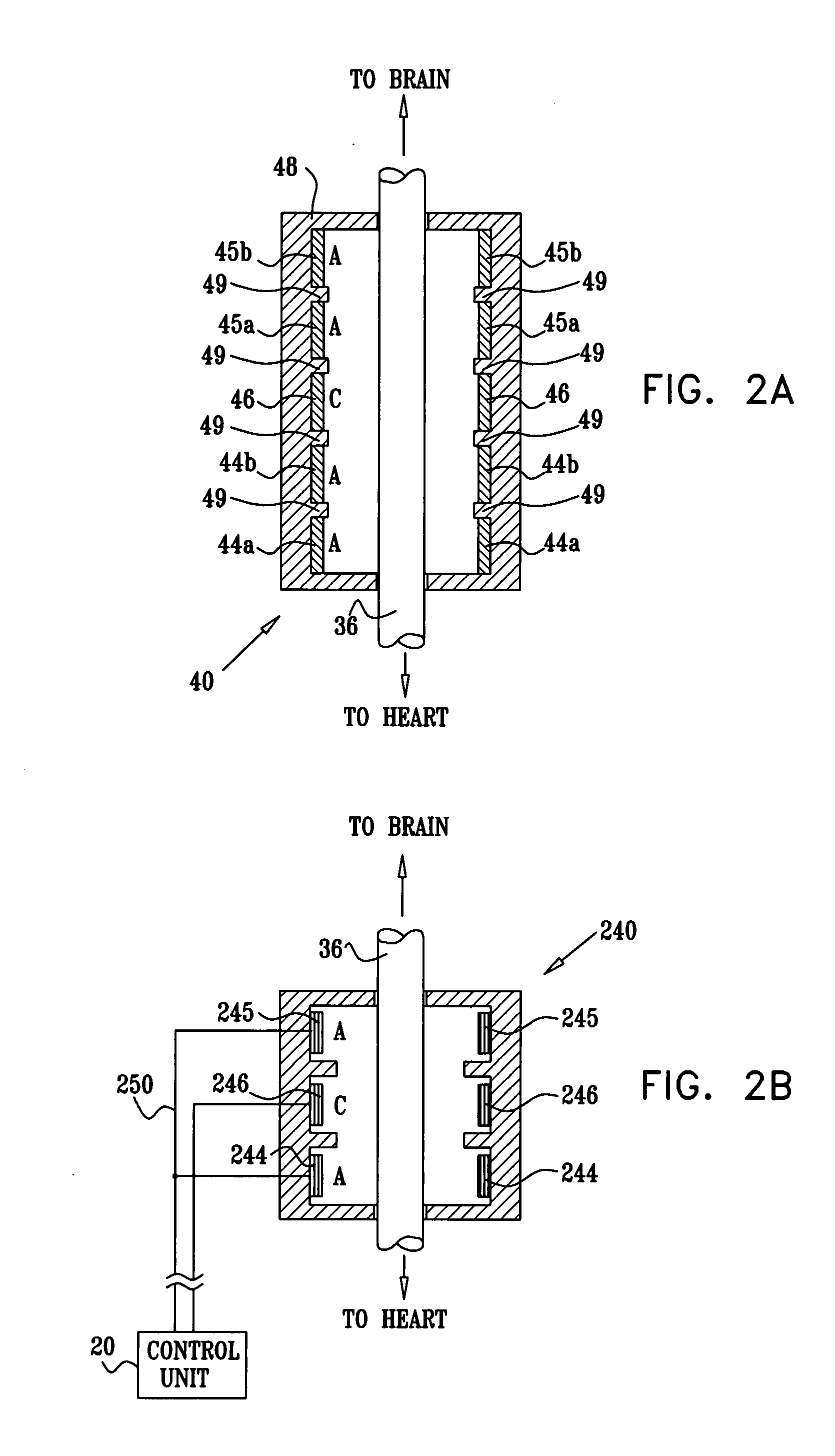
Apparatus is provided including an implantable sensor, adapted to sense an electrical parameter of a heart of a subject, and a first control unit, adapted to apply pulses to the heart responsively to the sensed parameter, the pulses selected from the list consisting of: pacing pulses and anti-arrhythmic energy. The apparatus further includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, and a jugular vein of the subject; and a second control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the site a current that increases parasympathetic tone of the subject and affects a heart rate of the subject. The first and second control units are not under common control. At least one of the control units is adapted to coordinate an aspect of its operation with an aspect of operation of the other control unit. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for defining the effect of atrial arrhythmias on cardiac performance and directing therapy using a plurality of intrinsically and extrinsically derived signals
ActiveUS7963925B1Ensure complianceLess timelyElectrotherapyOrgan movement/changes detectionDigital signal processingPatient demographics
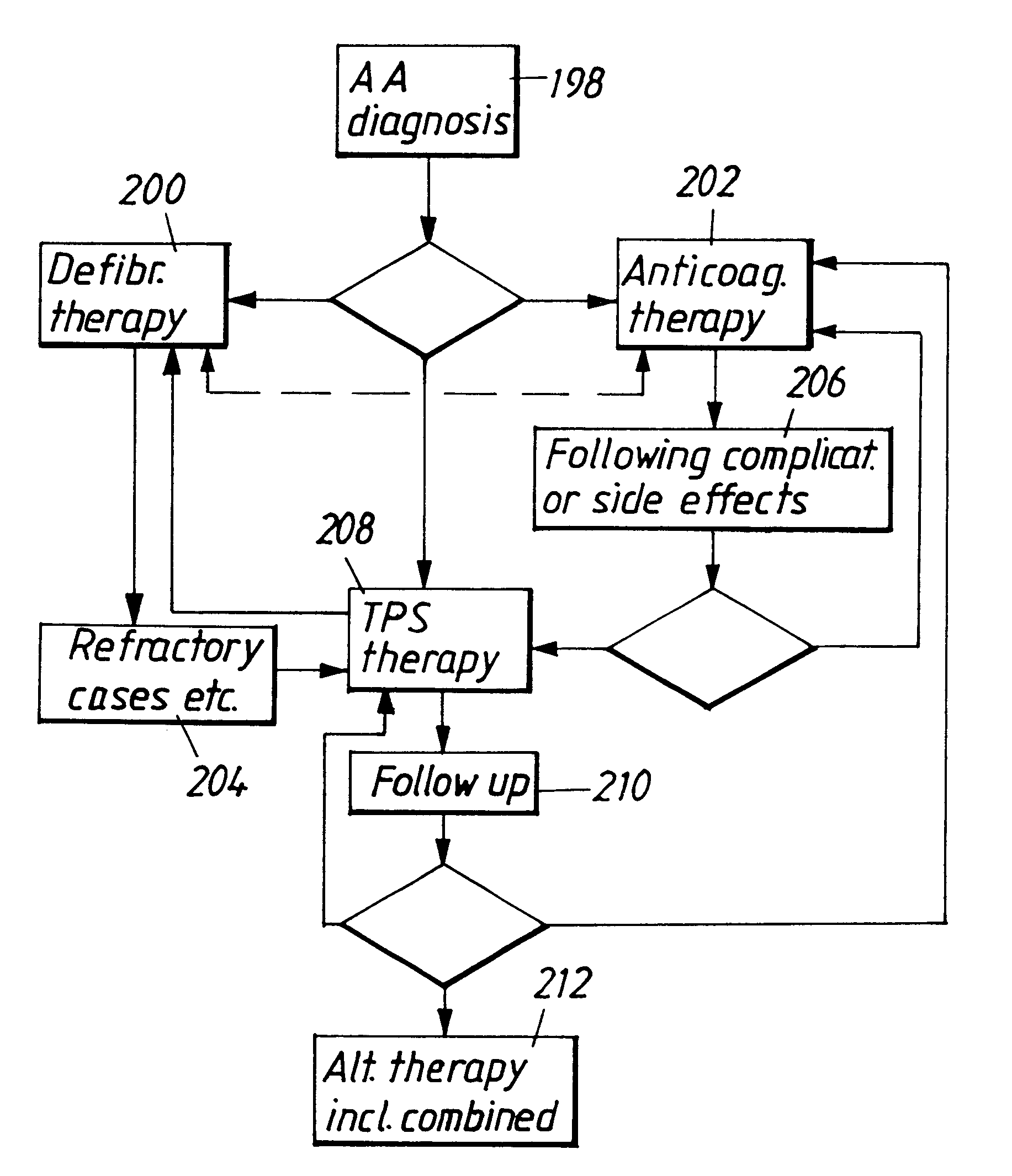
This invention describes methods and algorithms for processing a plurality of relevant signals / data intrinsic to a patient and / or derived from external diagnostic equipment for management of atrial arrhythmias. The intrinsic signals are acquired from intracardiac leads / sensors and analogous extrinsic data obtained from imaging equipment and patient demographics. These data are input into software algorithms that use digital signal processing to output informational data of clinical and technical relevance after comparisons are made to patients with access to this technology whose outcome under varying treatments is known. These combined data are used to define prognosis, make treatment suggestions, direct programming of cardiac devices and digitally convert intrinsically and extrinsically derived indices into a common metric. In a preferred embodiment, the intrinsically and extrinsically acquired data is utilized in the design of catheters and software algorithms for performing intracardiac procedures such as ablation of atrial arrhythmias.
Owner:STUART SCHECTER LLC
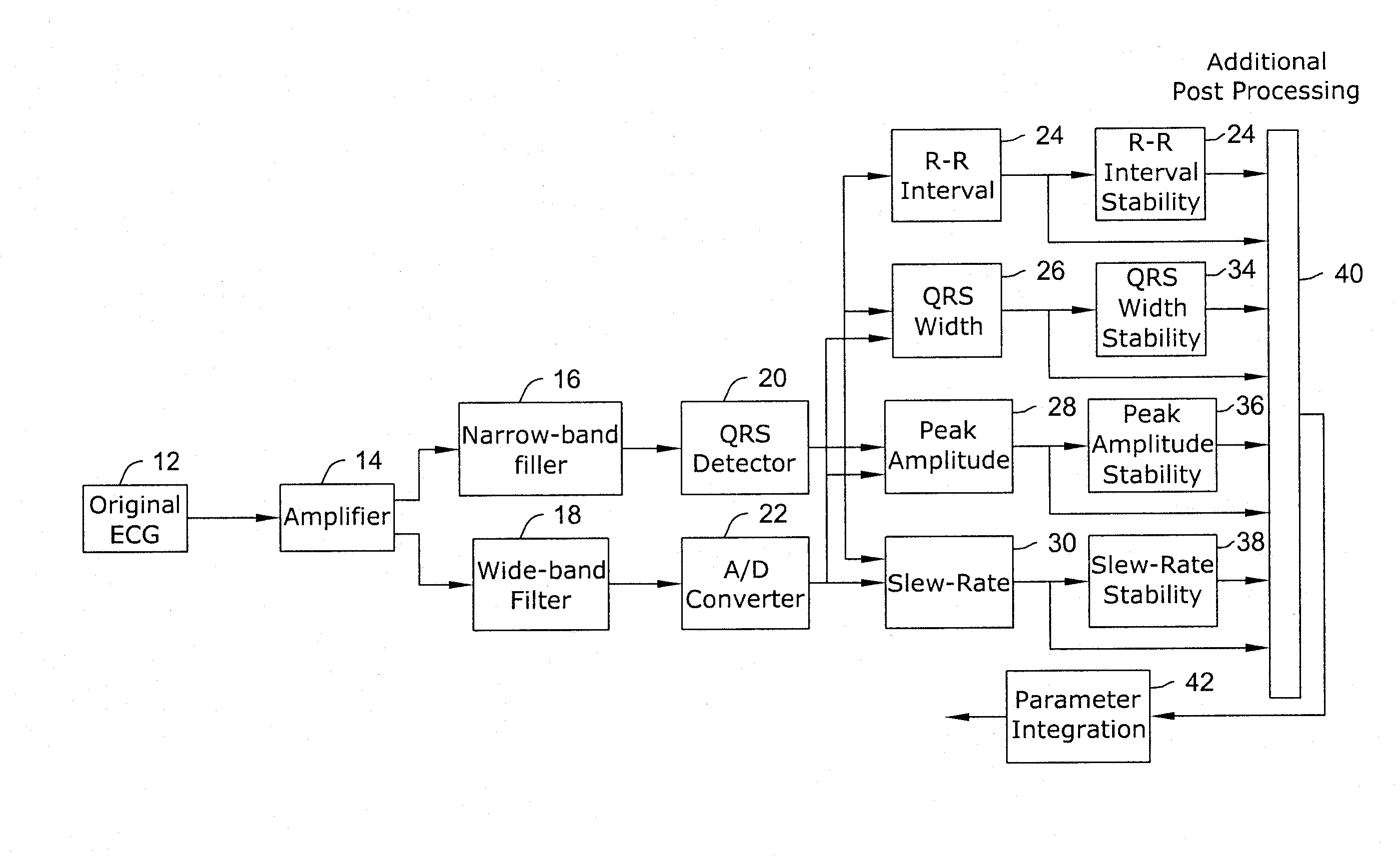
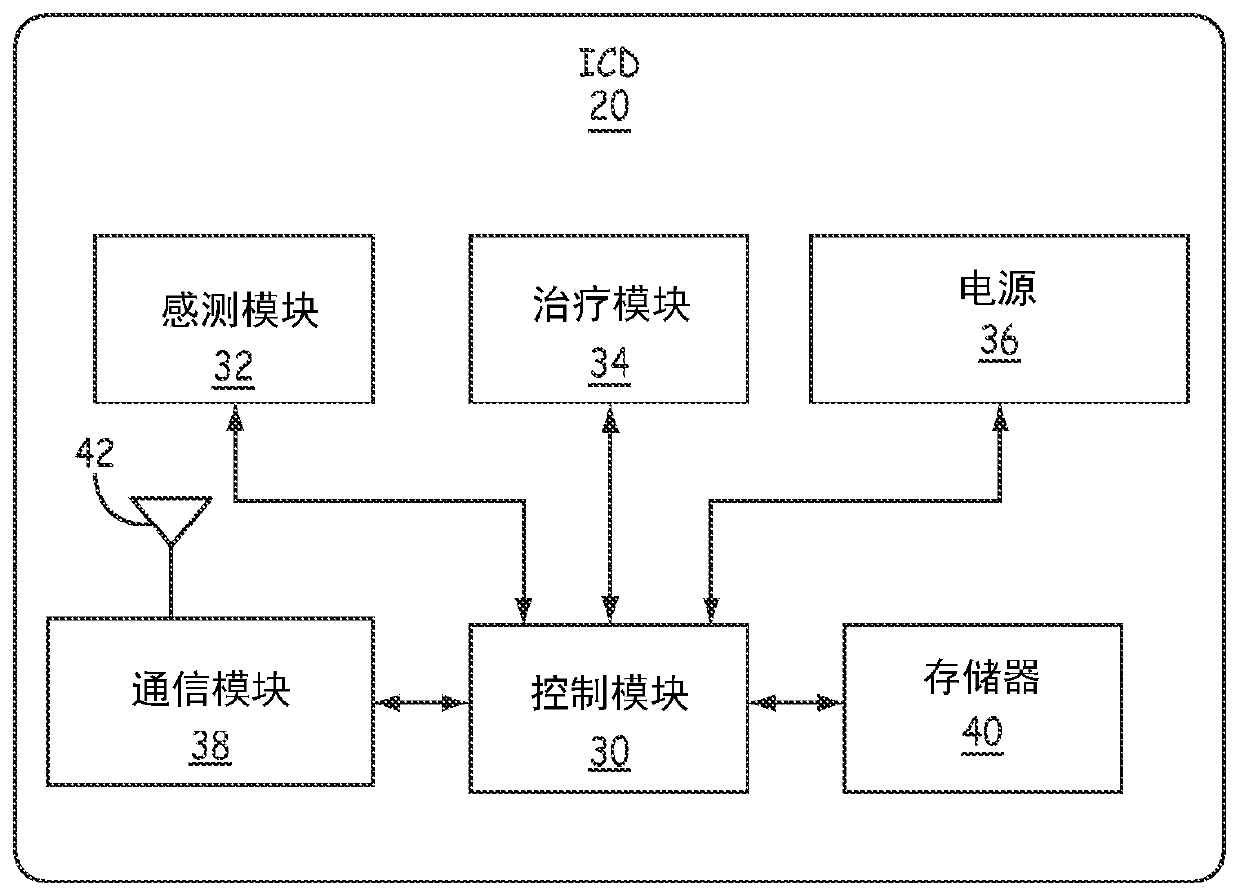
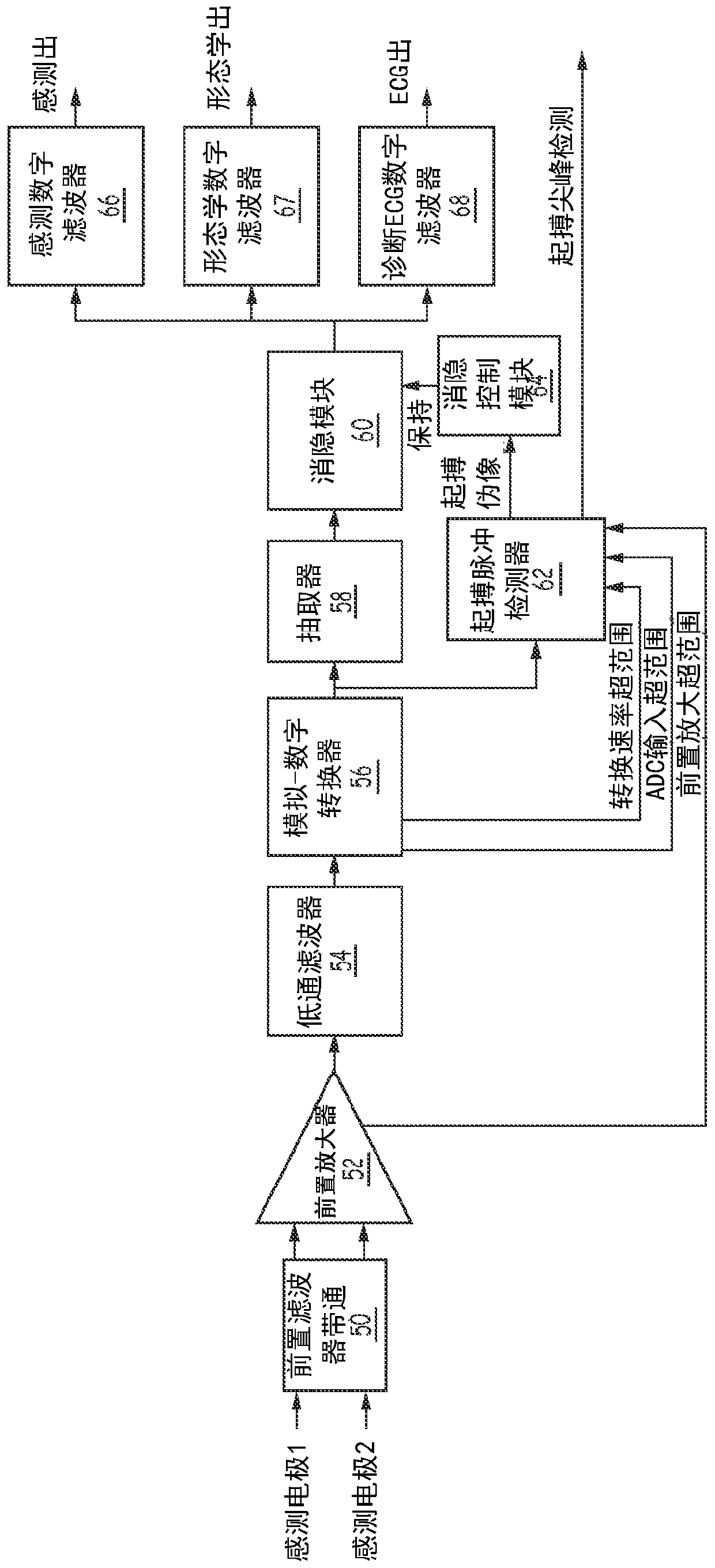
Apparatus and method of arrhythmia detection in a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter/defibrillator
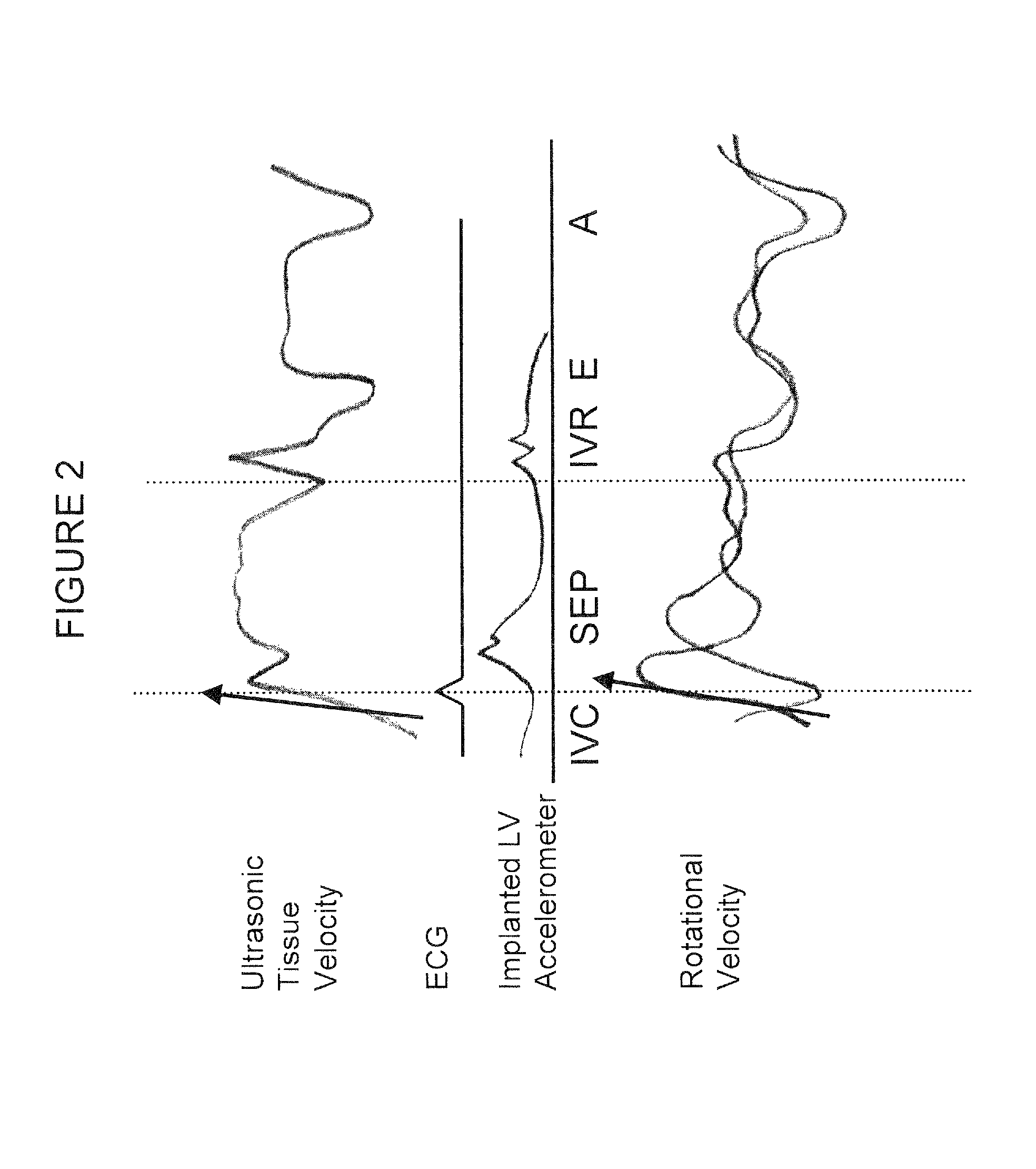
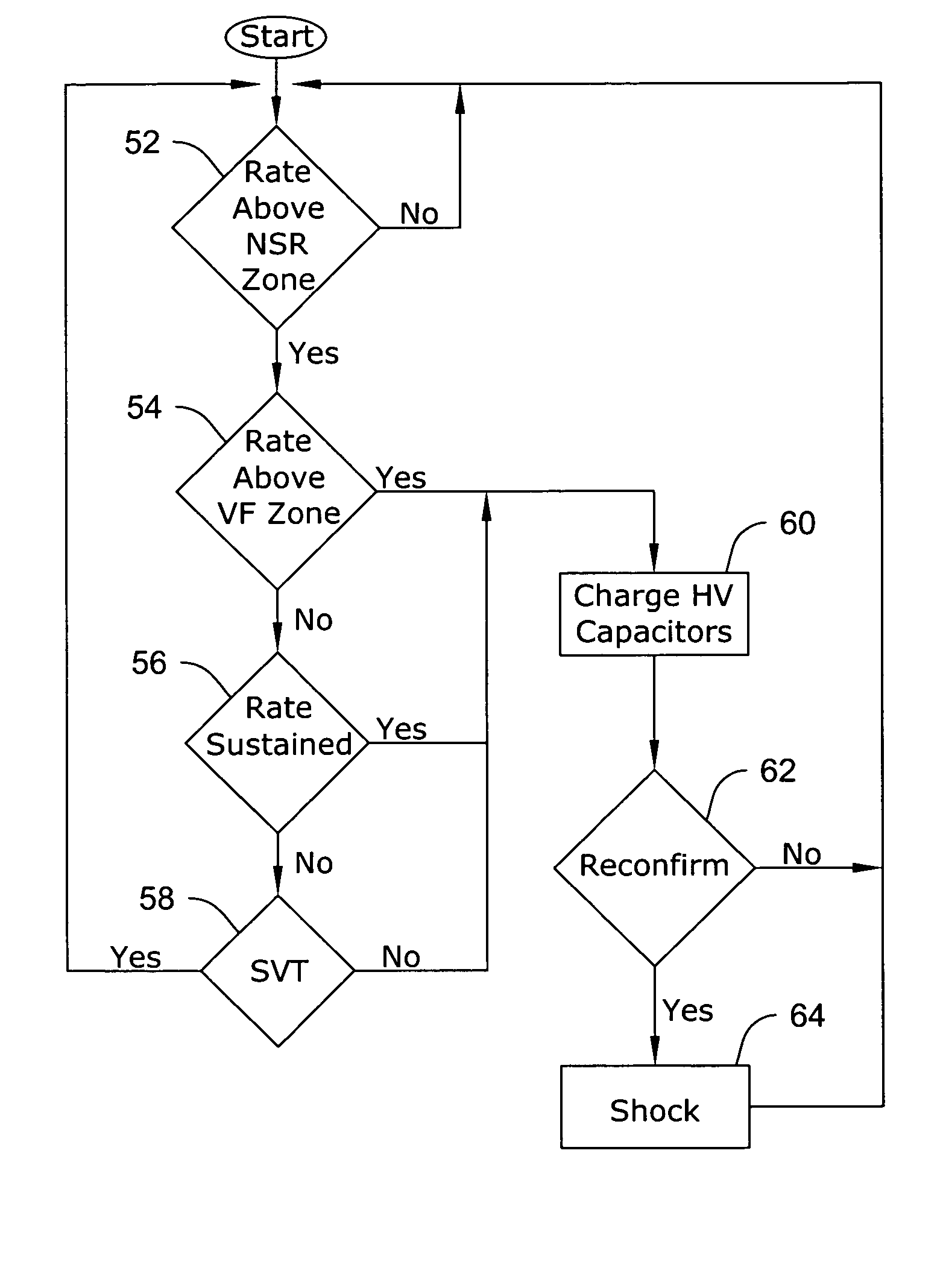
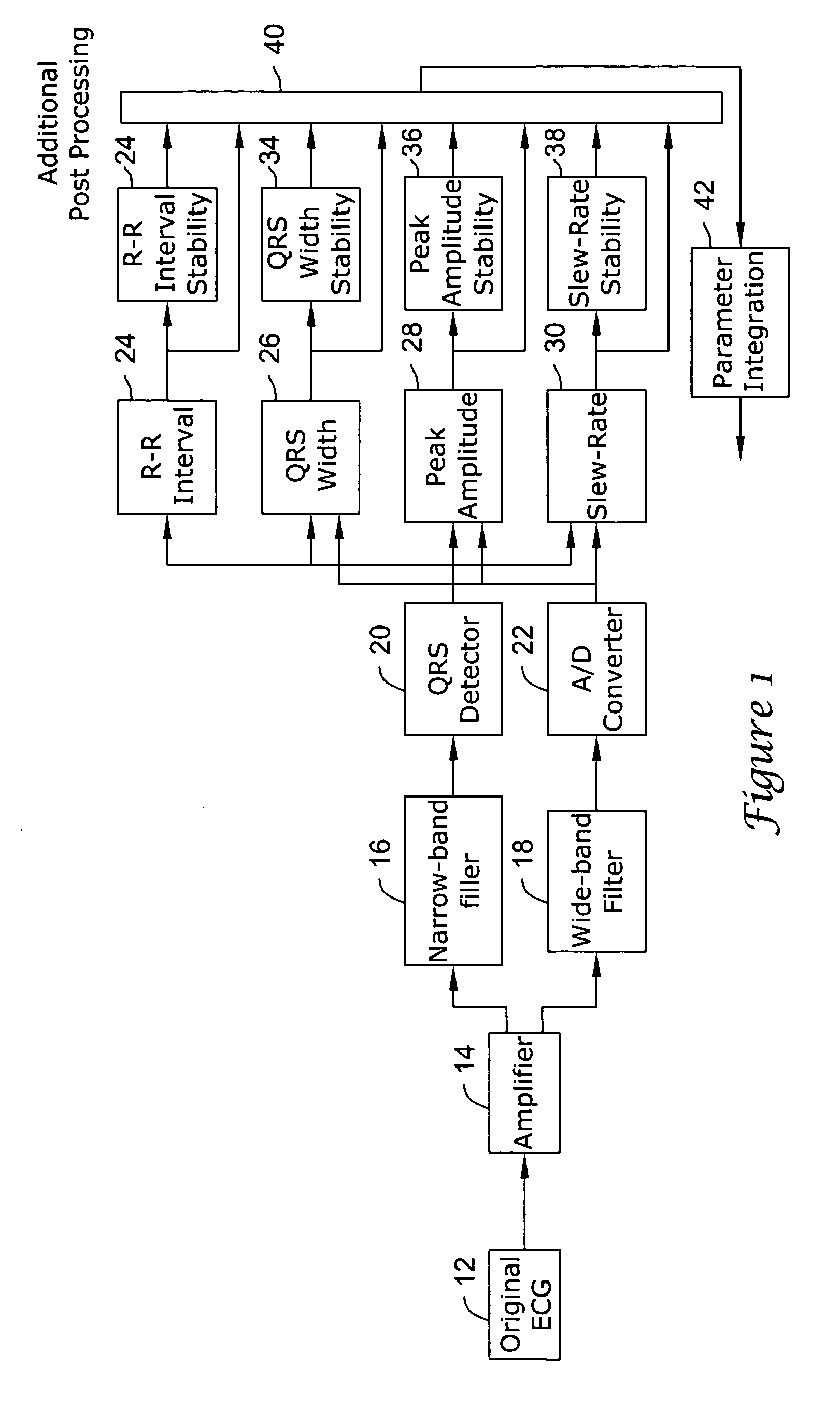
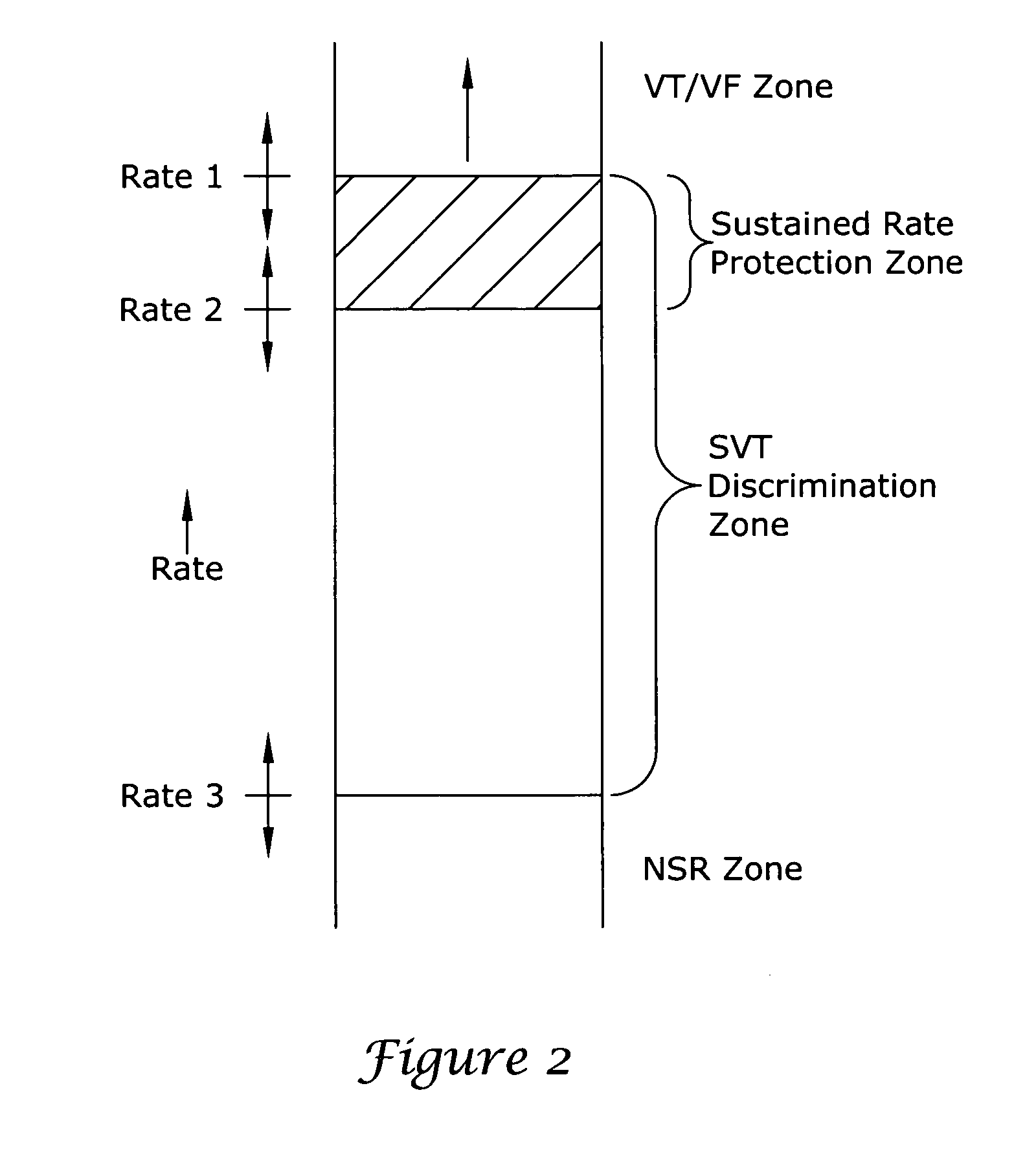
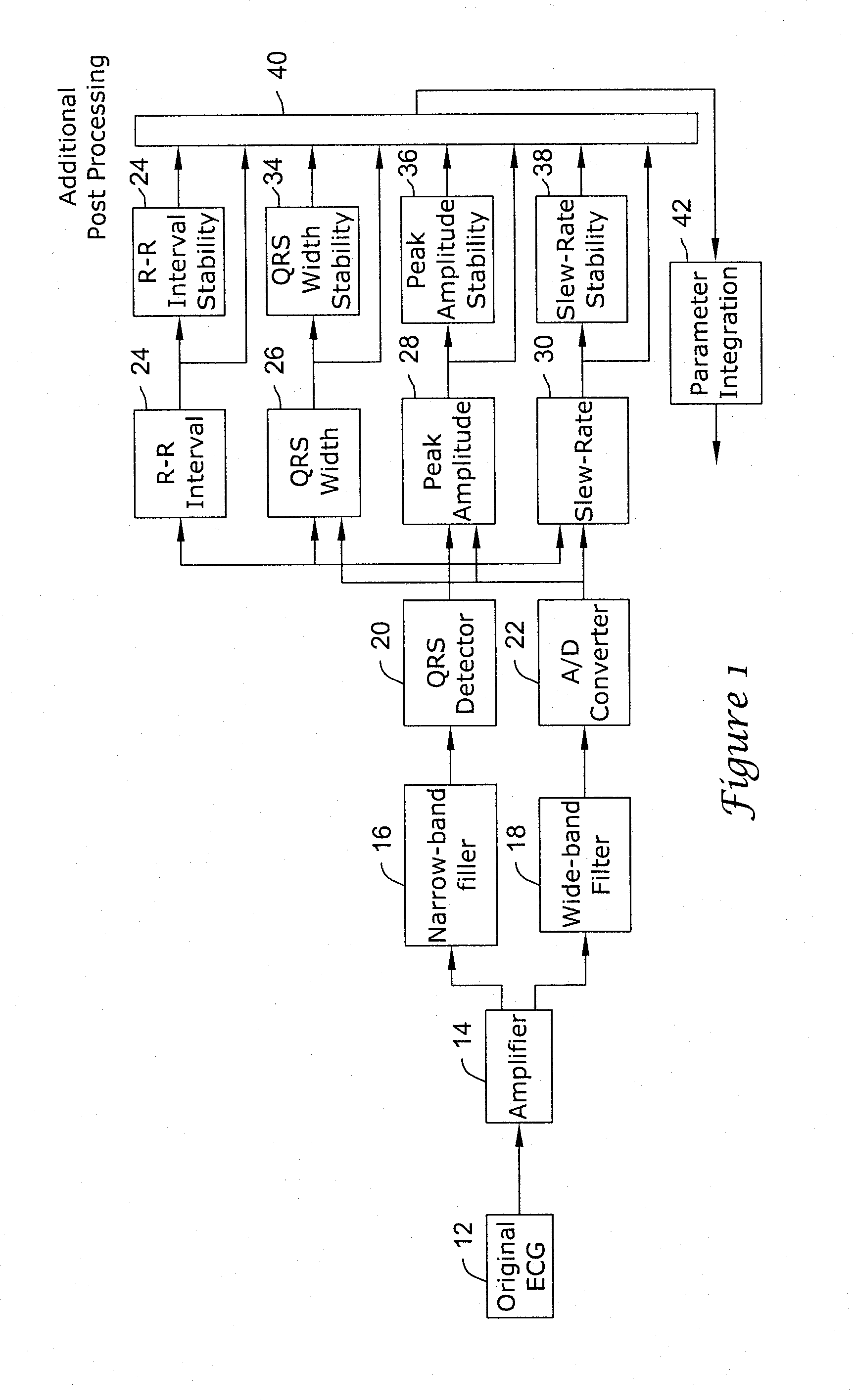
In a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter / defibrillator, cardiac arrhythmias are detected to determine necessary therapeutic action. Cardiac signal information is sensed from far field electrodes implanted in a patient. The sensed cardiac signal information is then amplified and filtered. Parameters such as rate, QRS pulse width, cardiac QRS slew rate, amplitude and stability measures of these parameters from the filtered cardiac signal information are measured, processed and integrated to determine if the cardioverter / defibrillator needs to initiate therapeutic action.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
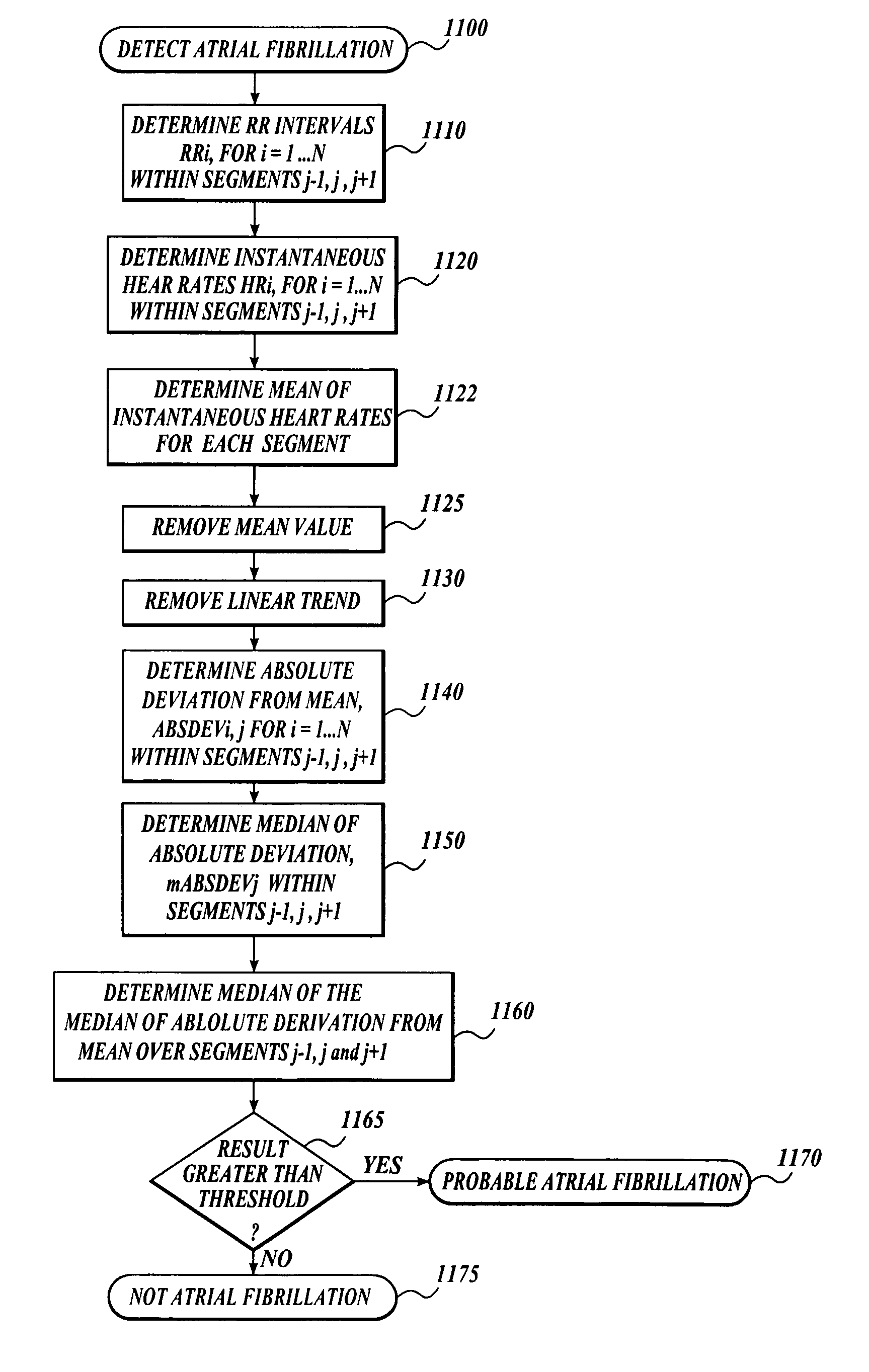
Long-term monitoring for discrimination of different heart rhythms
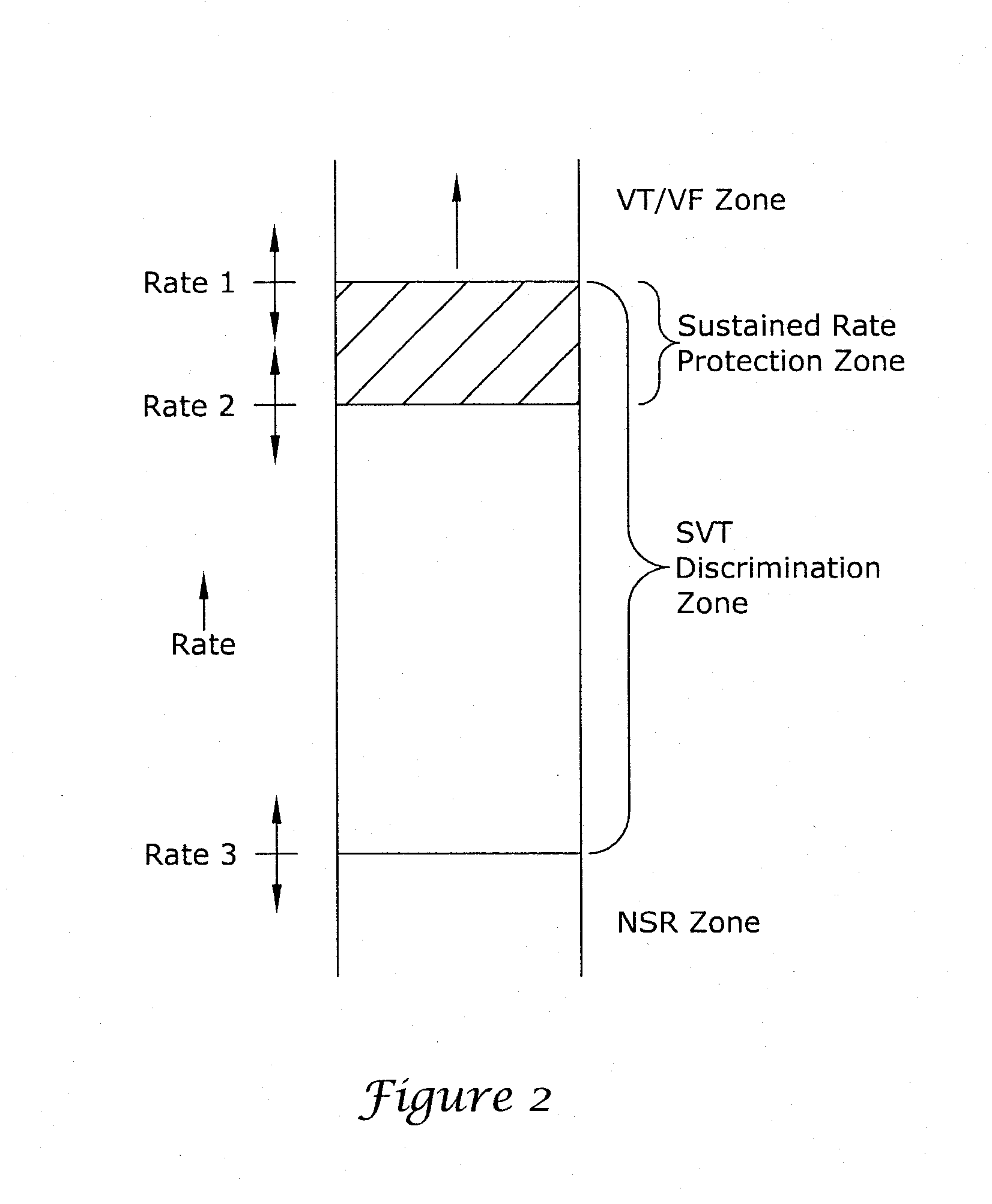
A method and a system for detection of an arrhythmia and discrimination between different types of arrhythmia to determine whether to administer an electric shock to the heart, the method comprising monitoring the electrical activity of a beating heart, selecting a number of heart beat intervals that will comprise an analysis segment; determining an instantaneous heart rate for each of the heart beat intervals with the segment; calculating the mean instantaneous heart rate for the segment; determining the variability of the instantaneous heart rates compared to a mean; using a linear combination of the mean and the non-linear value for comparison with a predetermined threshold to discriminate the type of arrhythmia to automatically decide if intervention is indicated.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Apparatus and Method of Arrhythmia Detection in a Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter/Defibrillator
In a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter / defibrillator, cardiac arrhythmias are detected to determine necessary therapeutic action. Cardiac signal information is sensed from far field electrodes implanted in a patient. The sensed cardiac signal information is then amplified and filtered. Parameters such as rate, QRS pulse width, cardiac QRS slew rate, amplitude and stability measures of these parameters from the filtered cardiac signal information are measured, processed and integrated to determine if the cardioverter / defibrillator needs to initiate therapeutic action.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
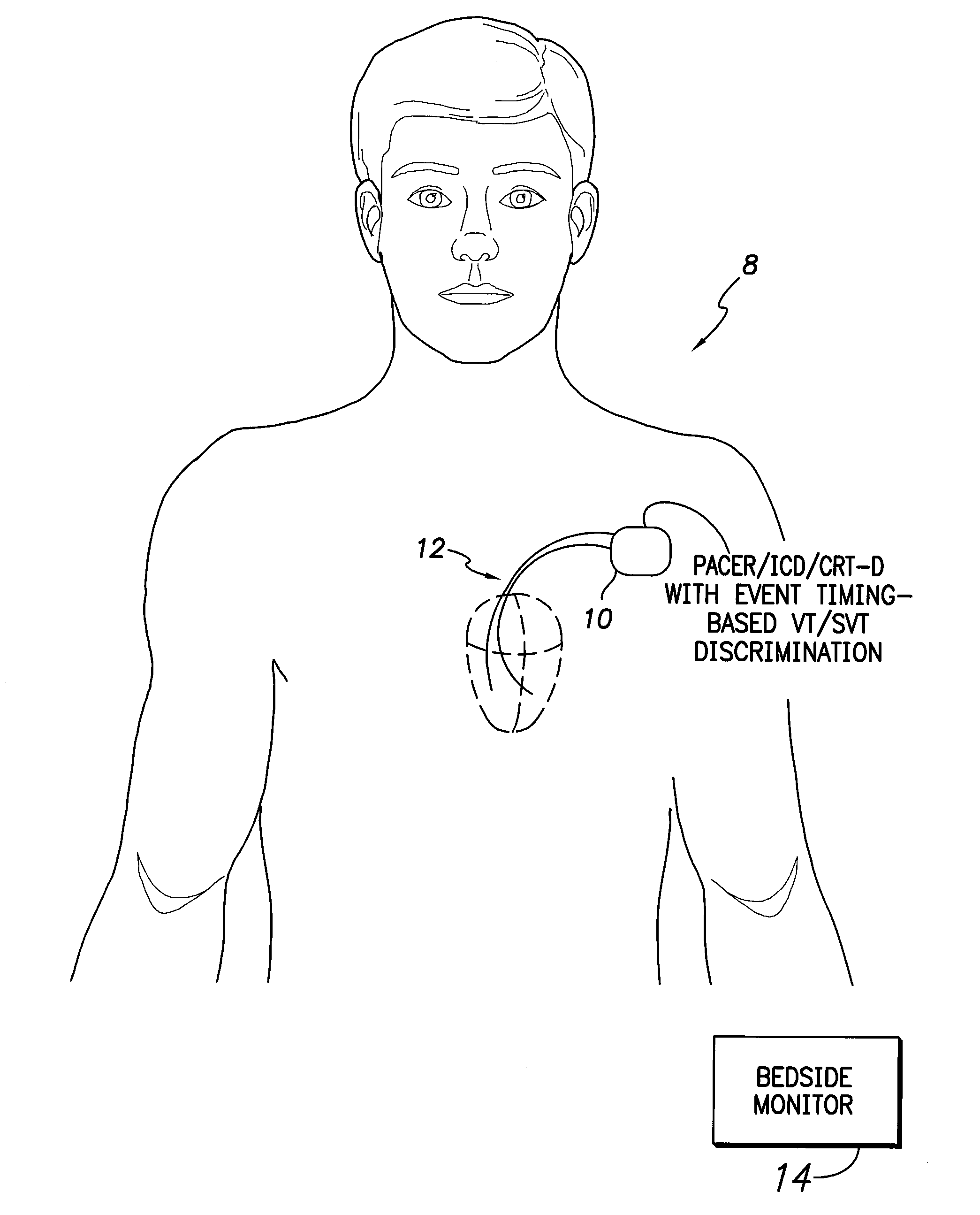
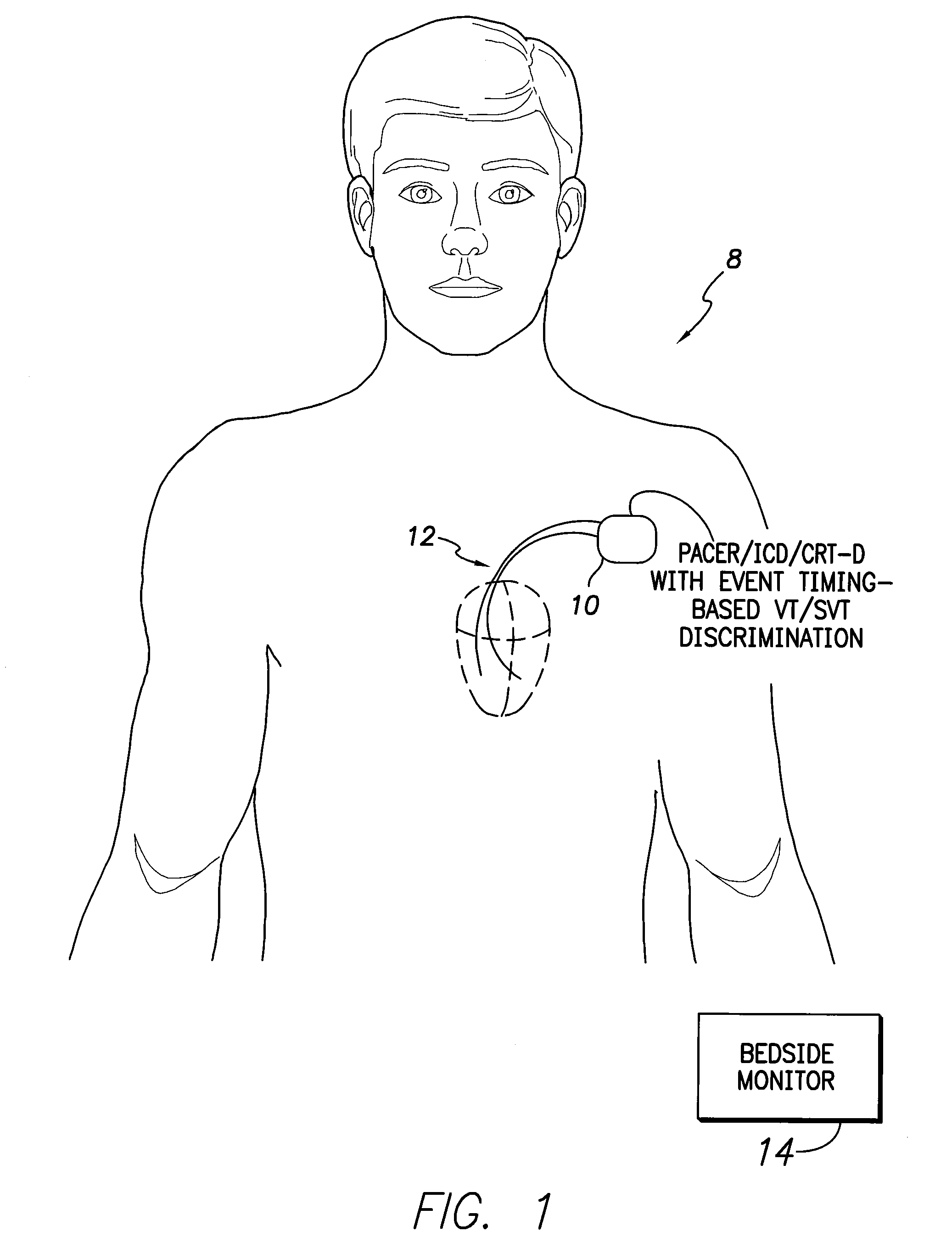
IMPLANTABLE MEDICAL DEVICE AND A METHOD COMPRISING MEANS FOR DETECTING AND CLASSIFYING VENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTMIAS (As Amended)
ActiveUS20100179411A1Reliable discriminationElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisVentricular volumeVentricular Tachyarrhythmias
In a method and implantable medical device for ventricular tachyarrhythmia detection and classification, upon detection of a ventricular tachyarrhythmia based on an electrocardiogram signal, cardiogenic impedance data representative of ventricular volume dynamics are collected and used for classifying the detected tachyarrhythmia as stable or unstable. In the latter case but typically not in the former case, defibrillation shocks or other forms of therapy are applied to combat the unstable ventricular tachyarrhythmia.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Systems and methods for leadless pacing and shock therapy
ActiveCN105102060ATransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart defibrillatorsCardioversionsElectrical stimulations
Techniques and systems for monitoring cardiac arrhythmias and delivering electrical stimulation therapy using a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator (SICD) and a leadless pacing device (LPD) are described. For example, the SICD may detect a tachyarrhythmia within a first electrical signal from a heart and determine, based on the tachyarrhythmia, to deliver anti-tachyarrhythmia shock therapy to the patient to treat the detected arrhythmia. The LPD may receive communication from the SICD requesting the LPD deliver anti-tachycardia pacing to the heart and determine, based on a second electrical signal from the heart sensed by the LPD, whether to deliver anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) to the heart. In this manner, the SICD and LPD may communicate to coordinate ATP and / or cardioversion / defibrillation therapy. In another example, the LPD may be configured to deliver post-shock pacing after detecting delivery of anti-tachyarrhythmia shock therapy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
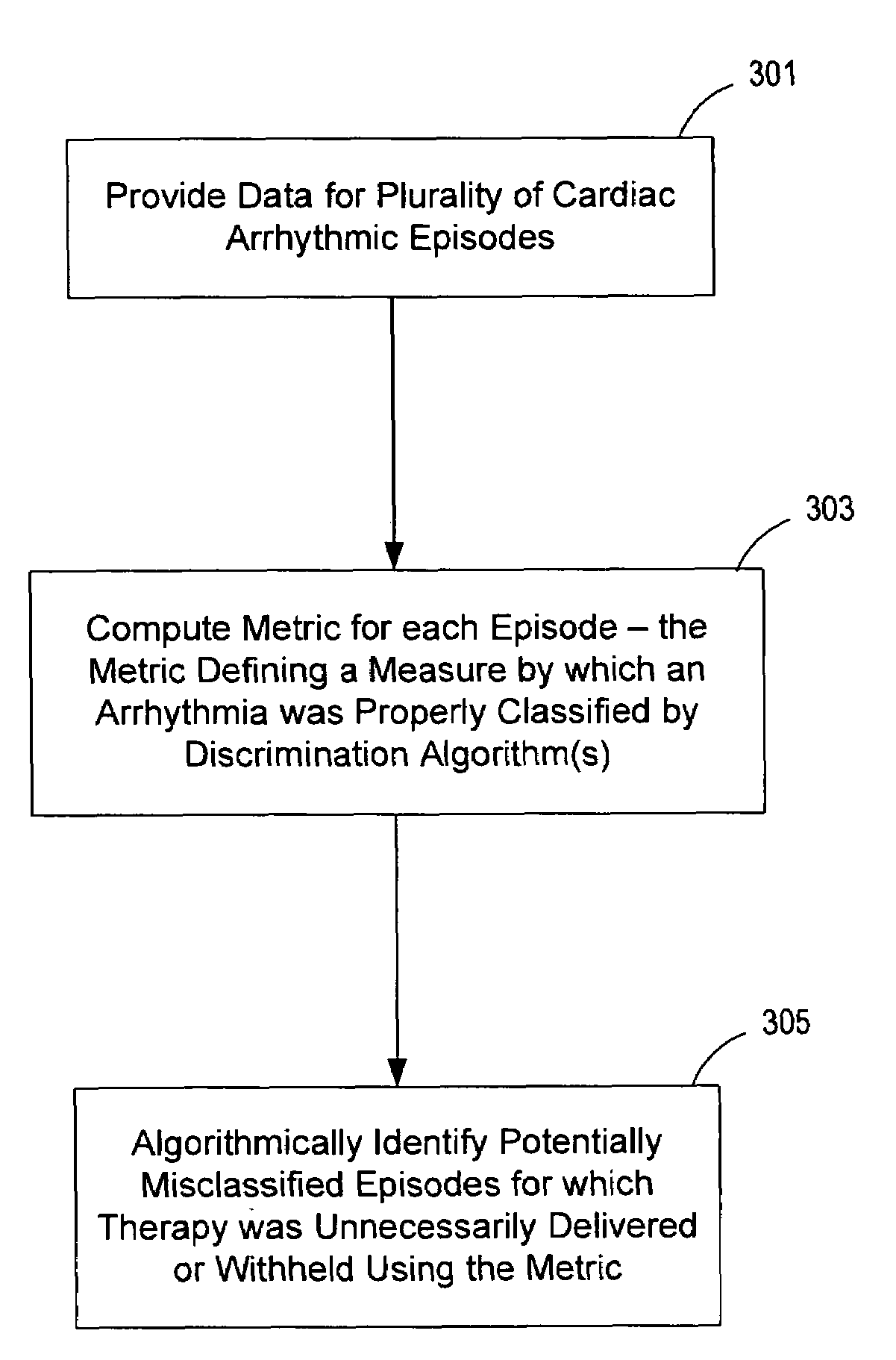
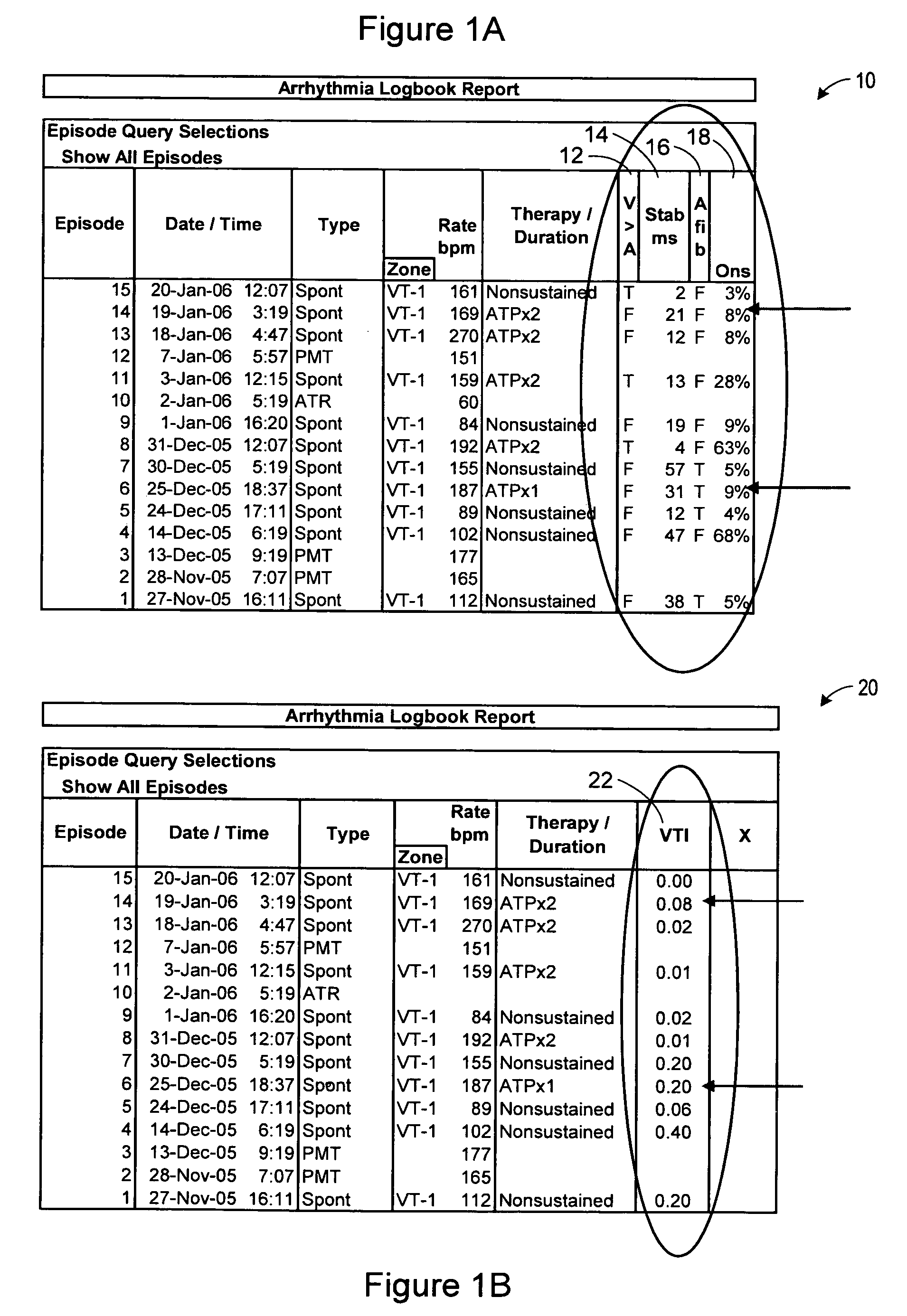
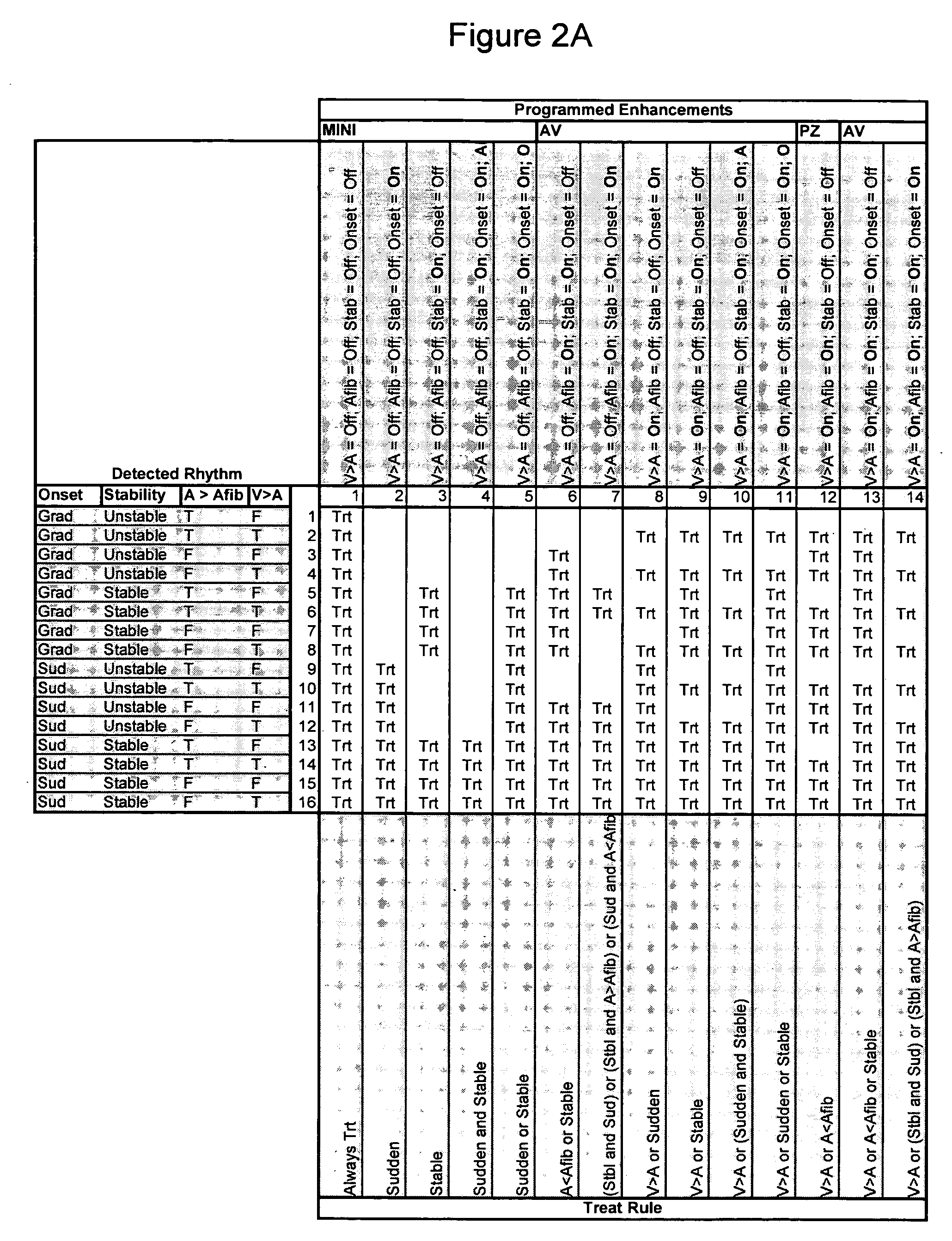
Method and apparatus for identifying potentially misclassified arrhythmic episodes
An implantable cardiac device is configured to classify cardiac arrhythmias using a plurality of arrhythmia discrimination algorithms. Data is provided that is associated with a plurality of cardiac arrhythmic episodes for which a cardiac electrical therapy was delivered or withheld by the implantable medical device based on the plurality of arrhythmia discrimination algorithms. A metric for each of the arrhythmic episodes is computed. The metric defines a measure by which the implantable cardiac device properly classified the arrhythmia. Potentially misclassified arrhythmic episodes of the plurality of cardiac arrhythmic episodes for which cardiac electrical therapy was inappropriately delivered or withheld are algorithmically identified using the metric.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
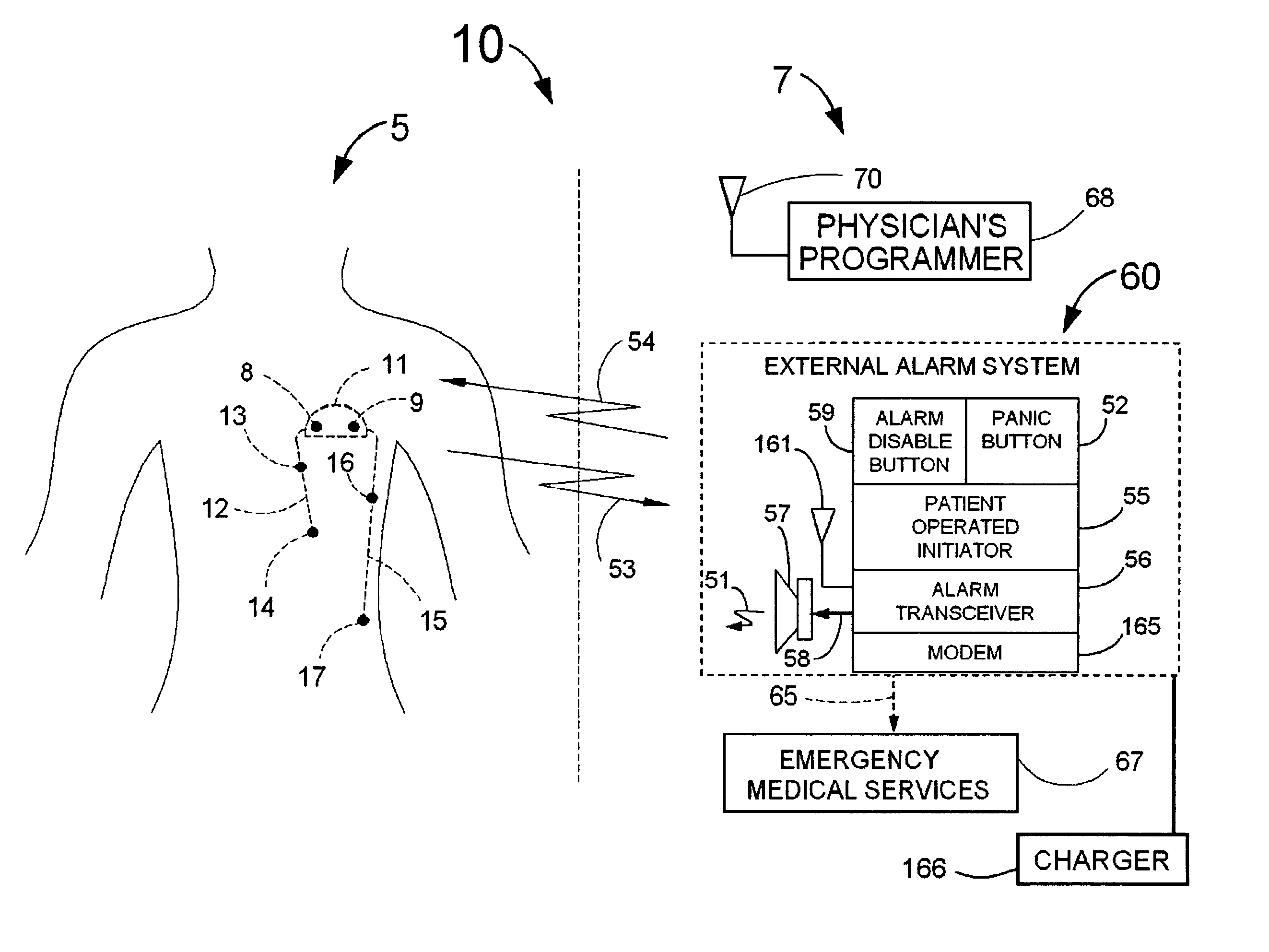
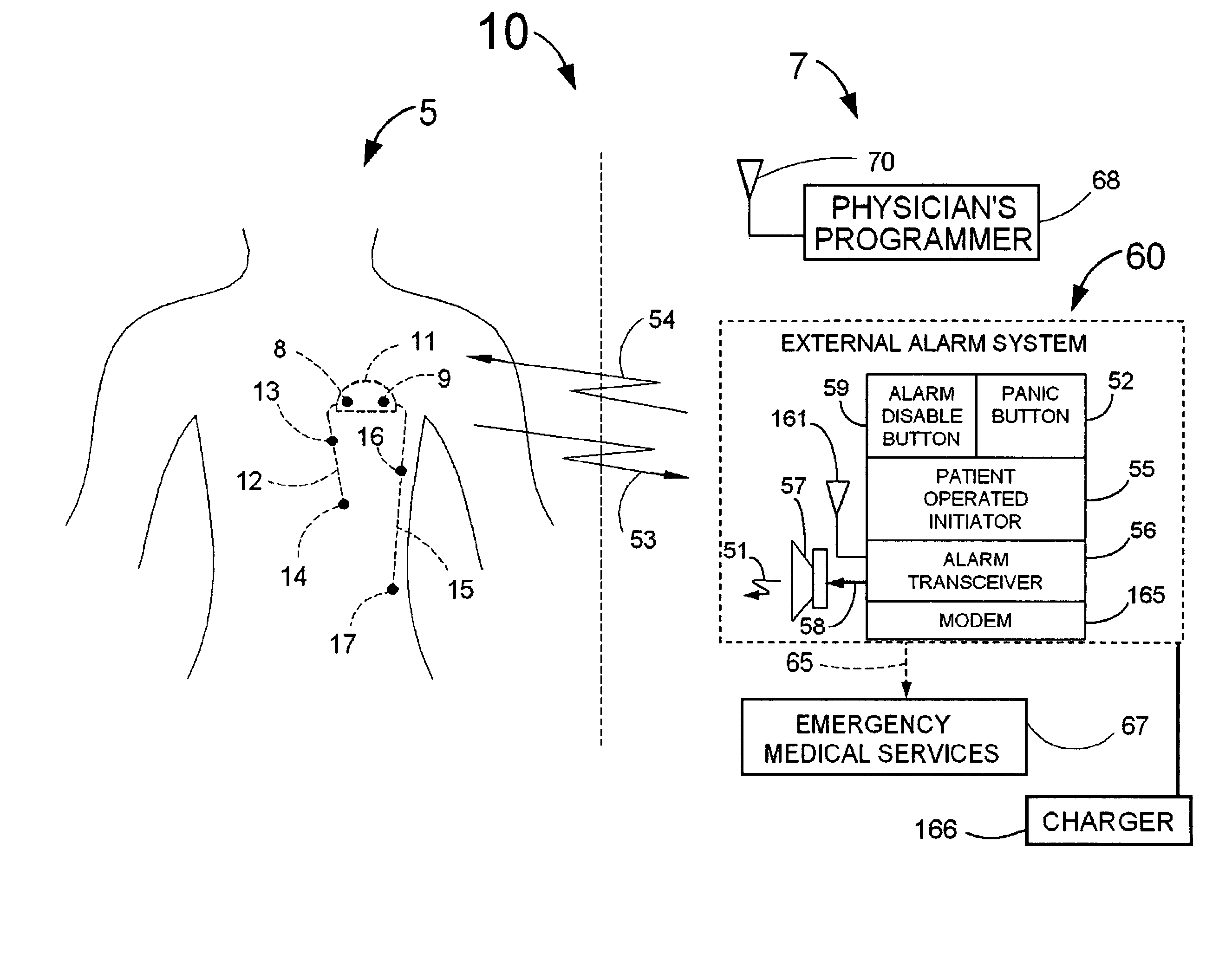
System for the detection of cardiac events
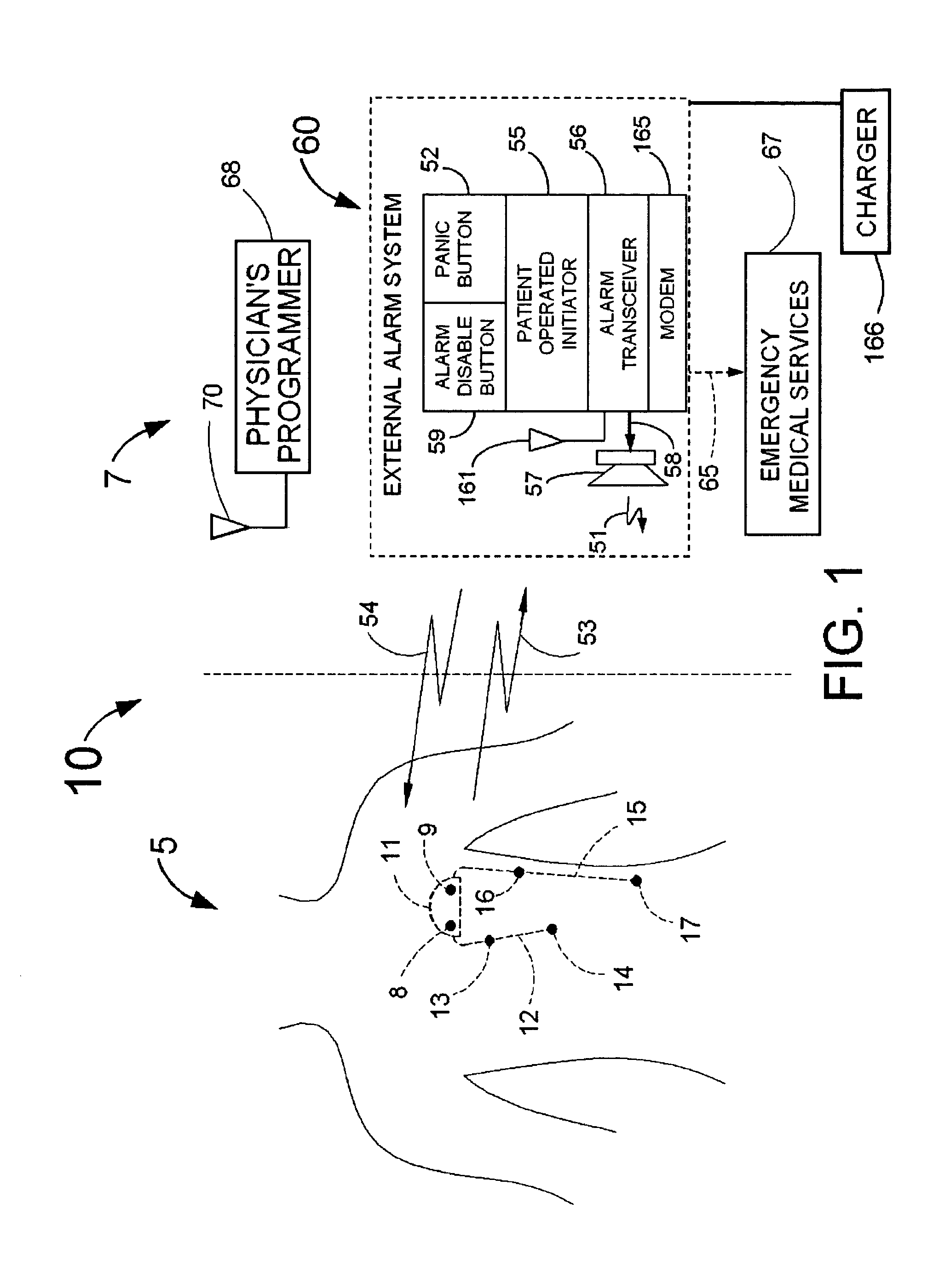
InactiveUS20080058660A1Improve abilitiesLow costElectrocardiographyCatheterIncreased heart rateCardiac pacemaker electrode
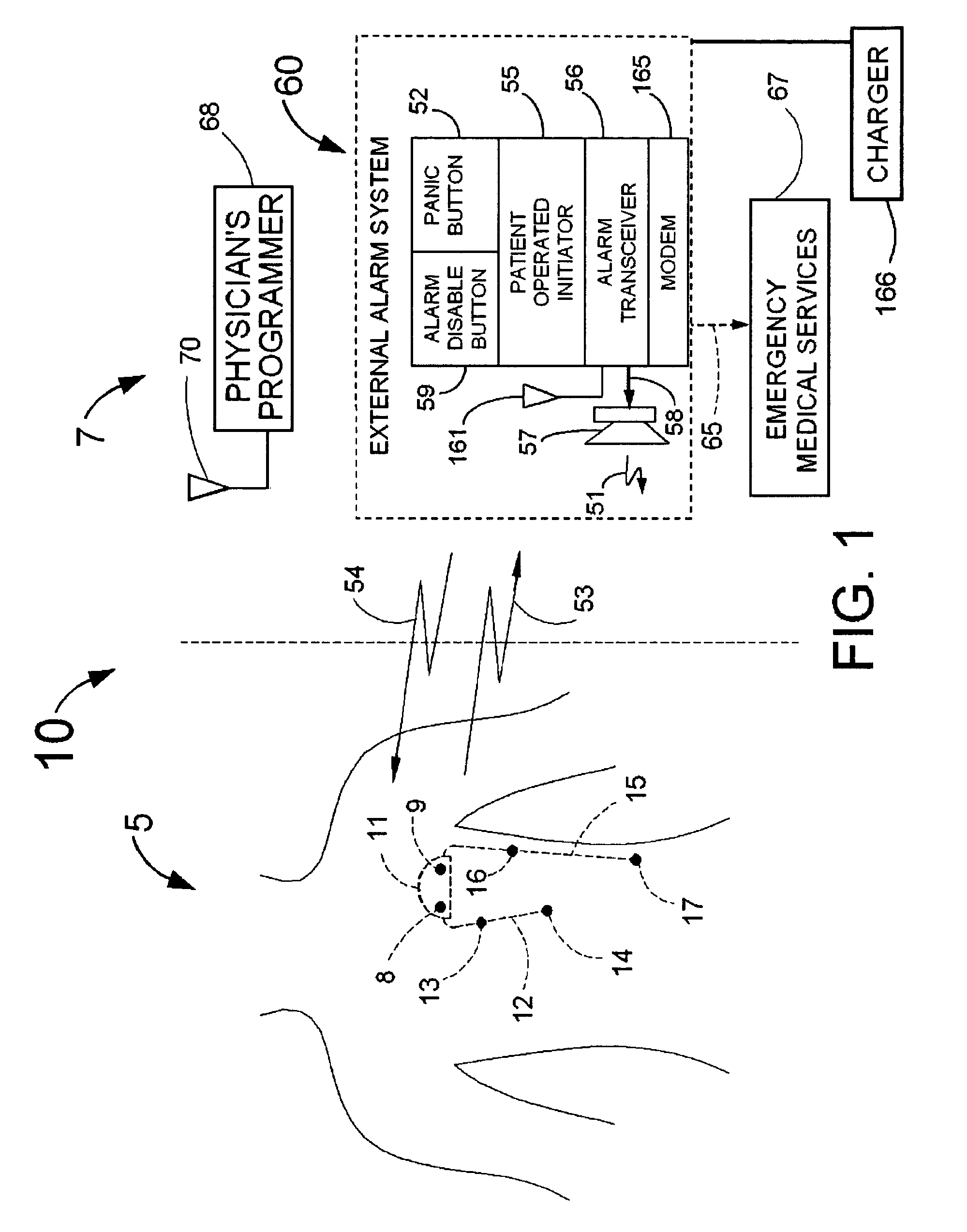
Disclosed is a system for the detection of cardiac events (a guardian system) that includes an implanted device called a cardiosaver, a physician's programmer and an external alarm system. The system is designed to provide early detection of cardiac events such as acute myocardial infarction or exercise induced myocardial ischemia caused by an increased heart rate or exertion. The system can also alert the patient with a less urgent alarm if a heart arrhythmia is detected. Using one or more detection algorithms, the cardiosaver can detect a change in the patient's electrogram that is indicative of a cardiac event within five minutes after it occurs and then automatically warn the patient that the event is occurring. To provide this warning, the guardian system includes an internal alarm sub-system (internal alarm means) within the cardiosaver and / or an external alarm system (external alarm means). If the guardian system is put into a pacemaker, the algorithm can utilize a different analysis of the electrogram depending on whether or not the pacemaker is actually pacing the heart.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Implantable cardiac stimulation device including a system for and method of automatically inducing a tachyarrhythmia
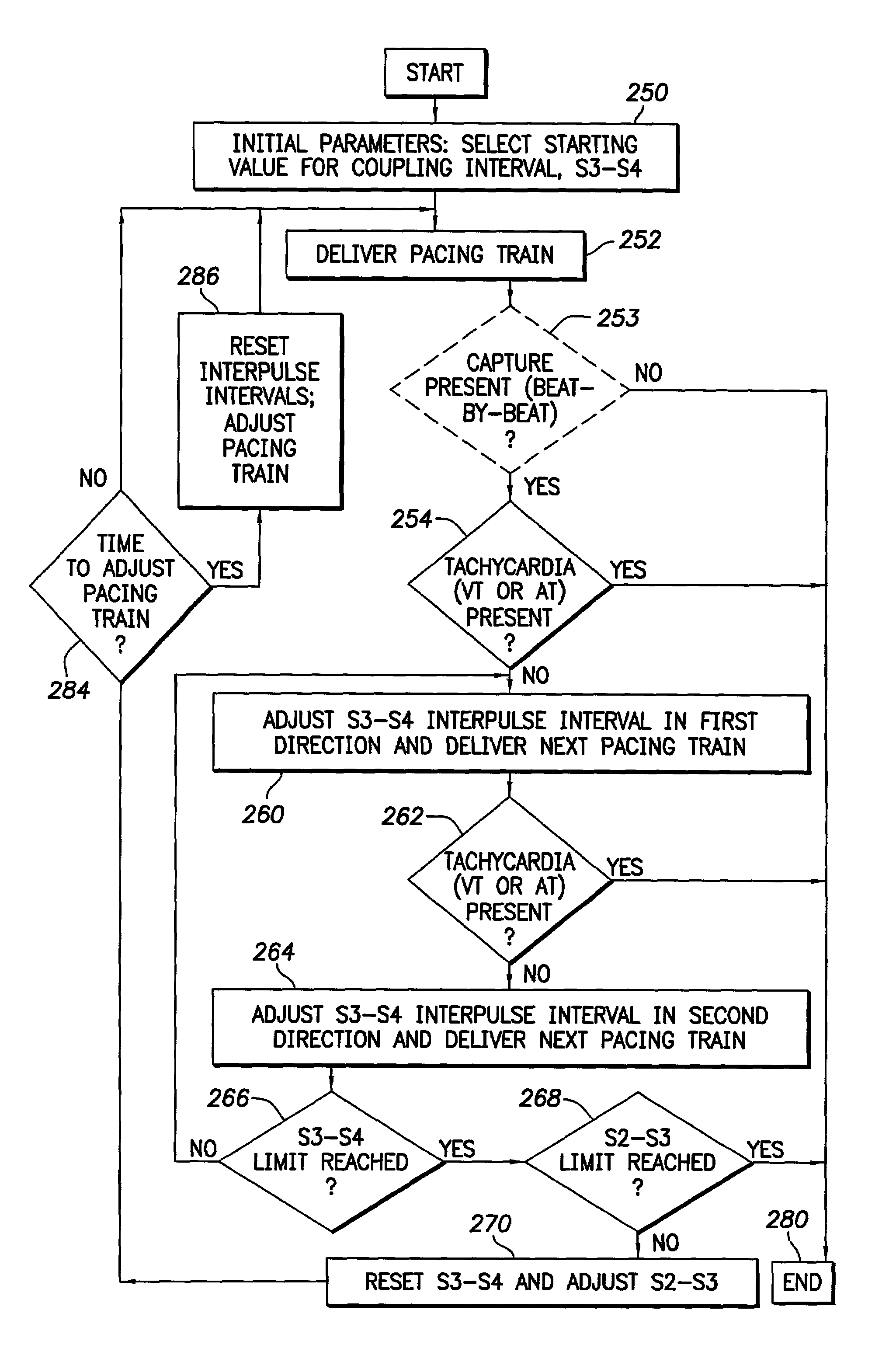
A system and method for use in an implantable cardiac stimulation device permits automatic induction of a tachyarrhythmia of a heart to permit the performance of an electrophysiological test of the heart. A pulse generator repeatedly delivers a group of first and second sets of pacing pulses to a chamber of the heart. The pacing pulses are separated in time by interpulse intervals to overdrive pace a chamber of the heart. A processor, coupled to the pulse generator, varies the second set of interpulse intervals according to a predetermined protocol after each group of pacing pulses is delivered to the chamber of the heart. The successive groups of pacing pulses are delivered to the heart until the tachyarrhythmia is induced.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
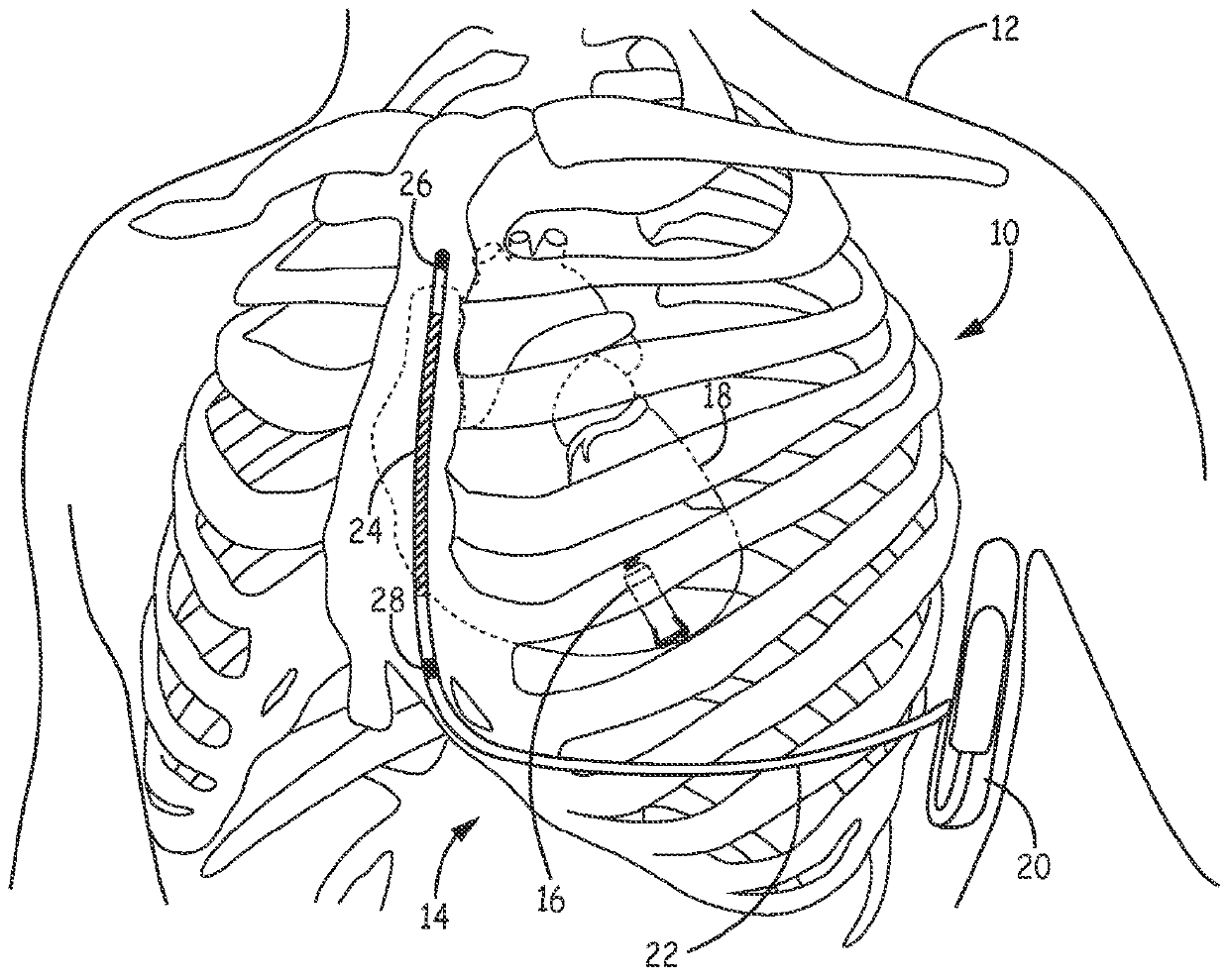
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) system including substernal lead
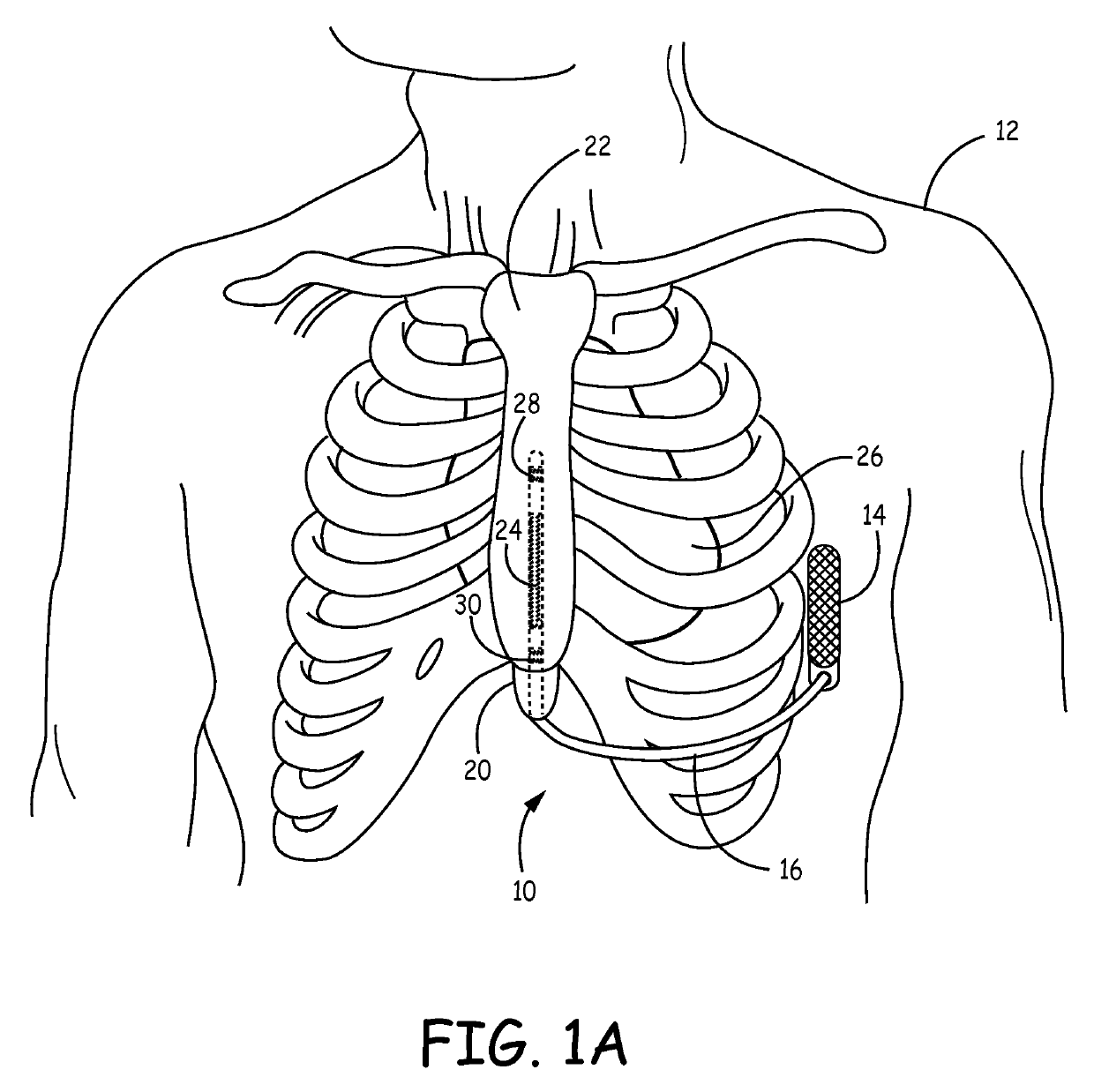
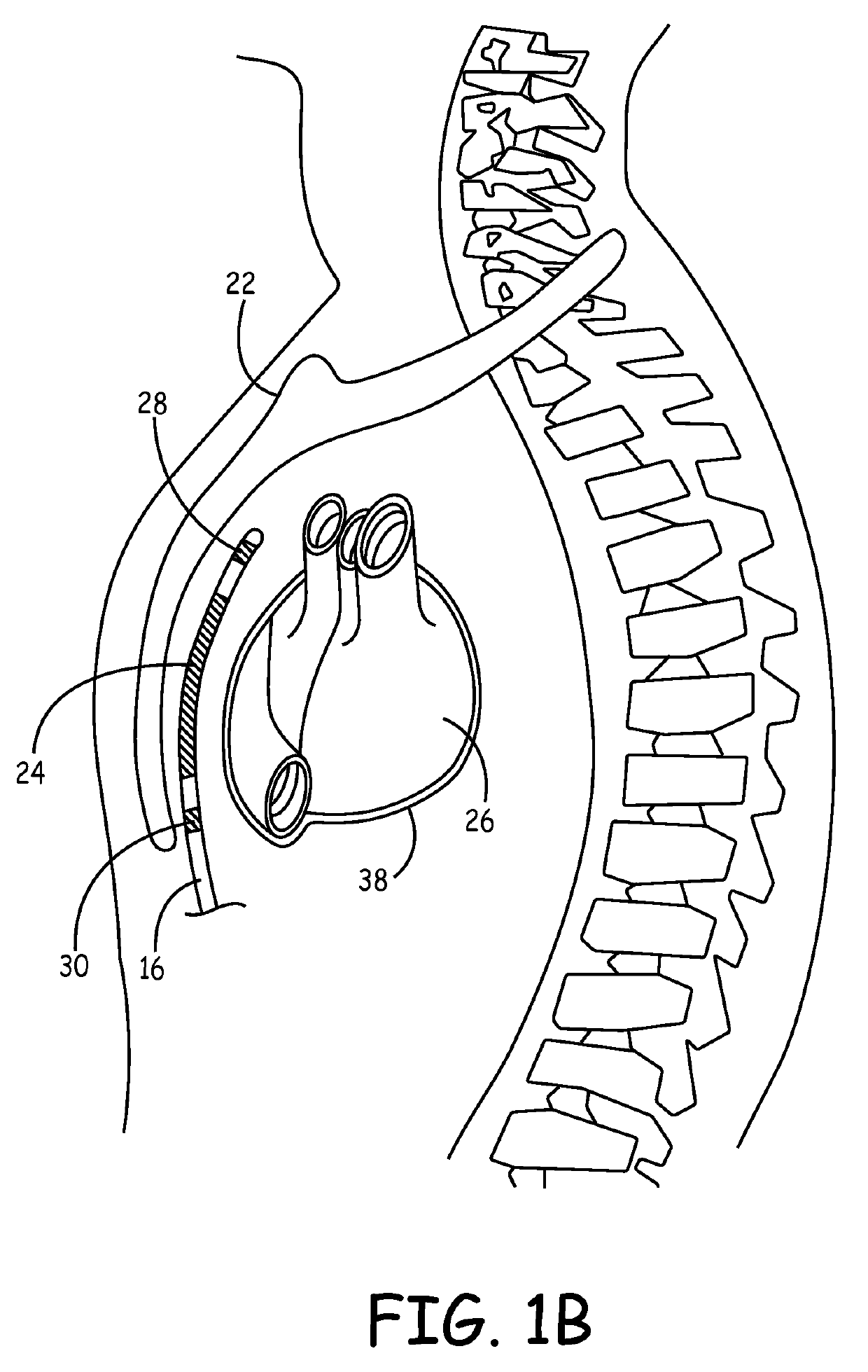
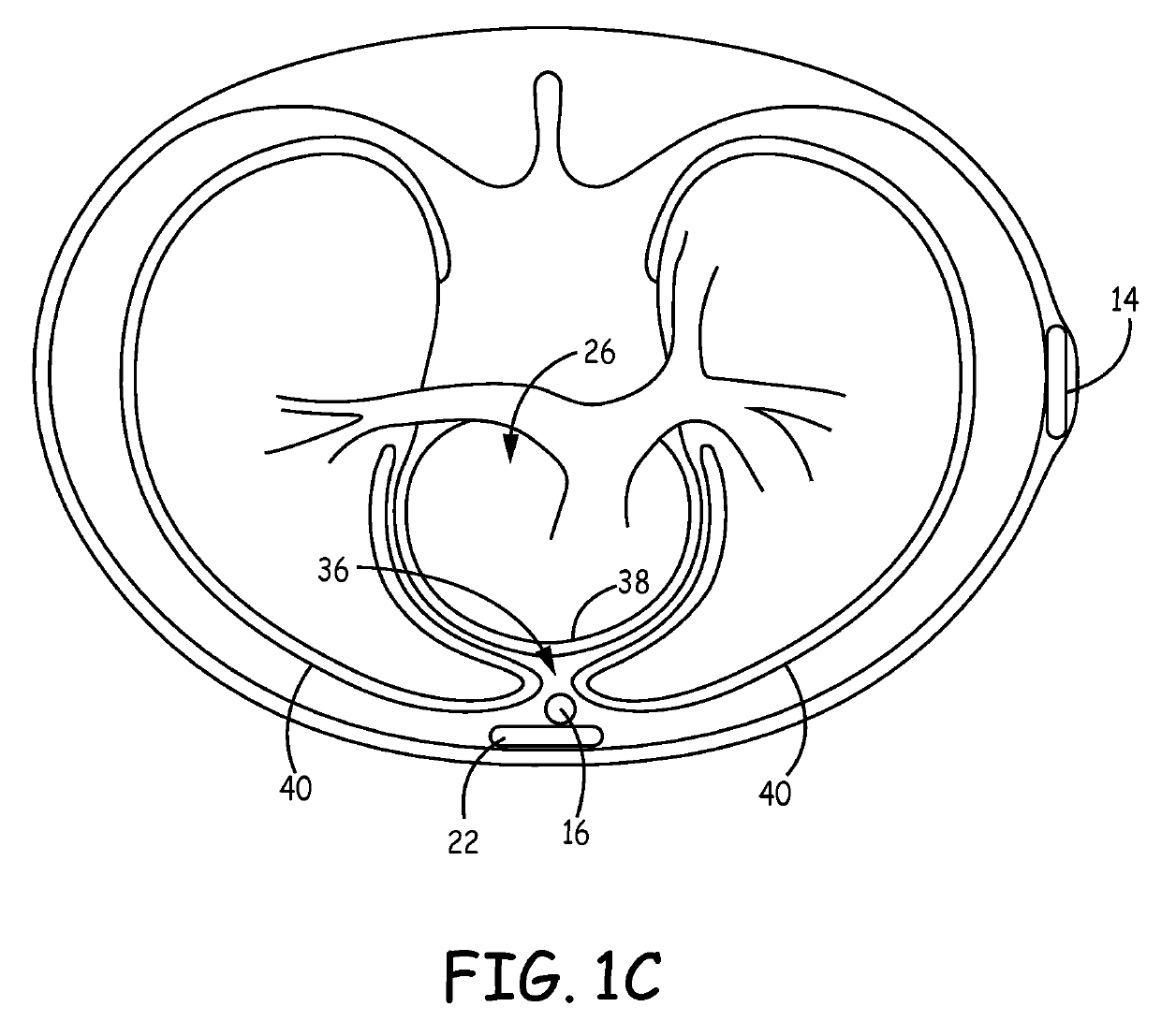
Substernal implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) systems and methods for providing substernal electrical stimulation therapy to treat malignant tachyarrhythmia, e.g., ventricular tachycardia (VT) and ventricular fibrillation (VF) are described. In one example, an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) system includes an ICD implanted in a patient and an implantable medical electrical lead. The lead includes an elongated lead body having a proximal end and a distal portion, a connector at the proximal end of the lead body configured to couple to the ICD, and one or more electrodes along the distal portion of the elongated lead body. The distal portion of the elongated lead body of the lead is implanted substantially within an anterior mediastinum of the patient and the ICD is configured to deliver electrical stimulation to a heart of the patient using the one or more electrodes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
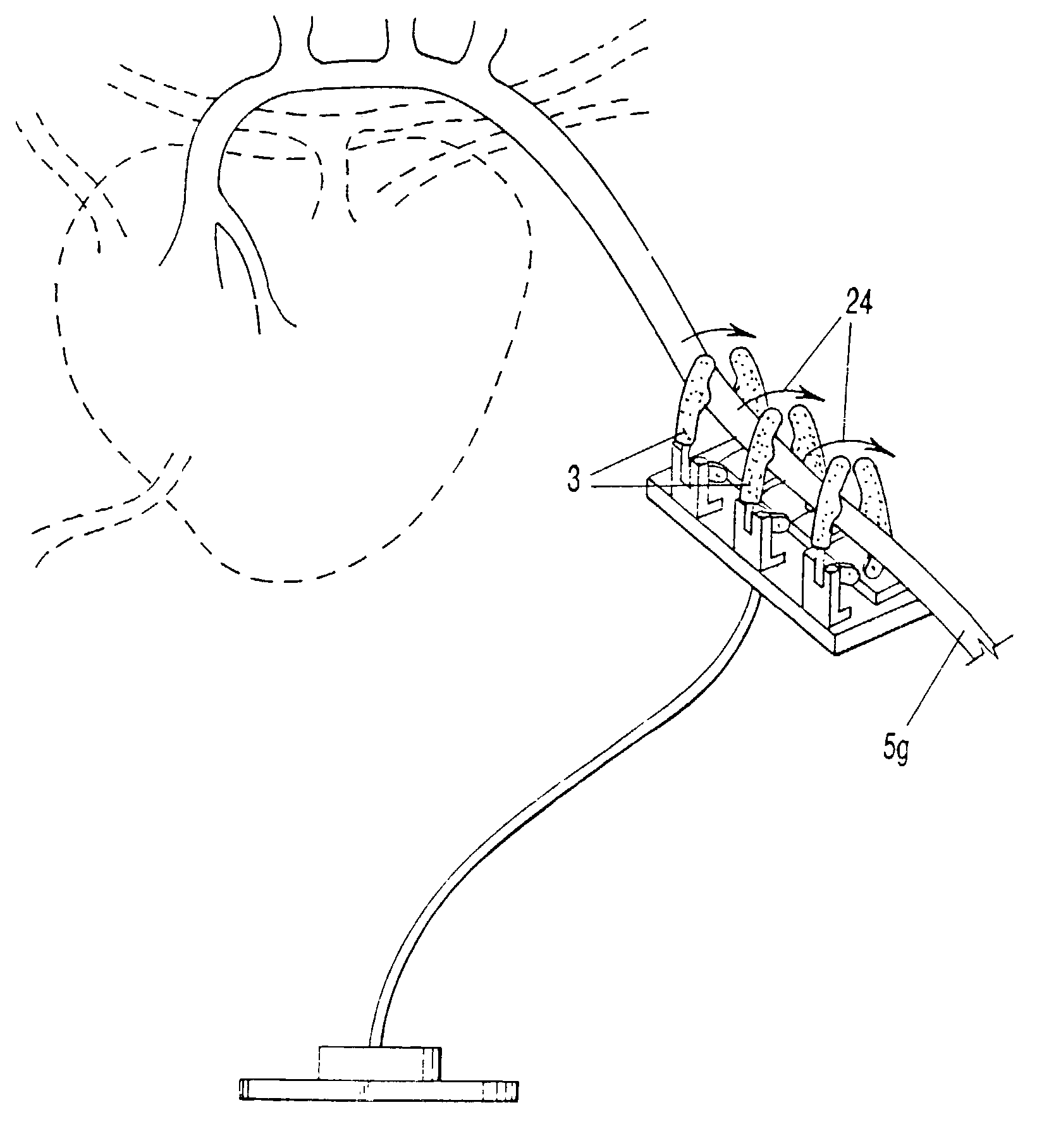
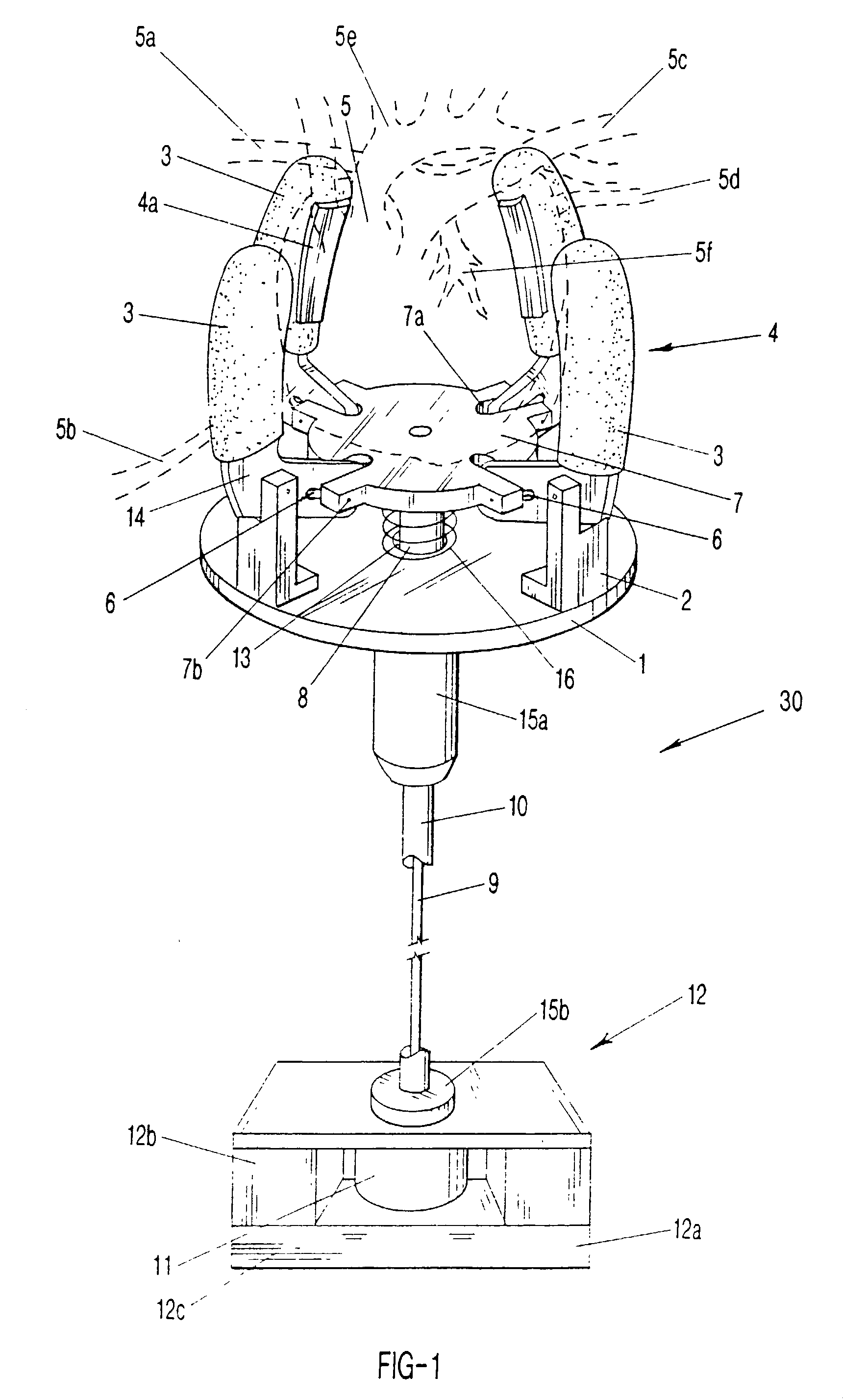
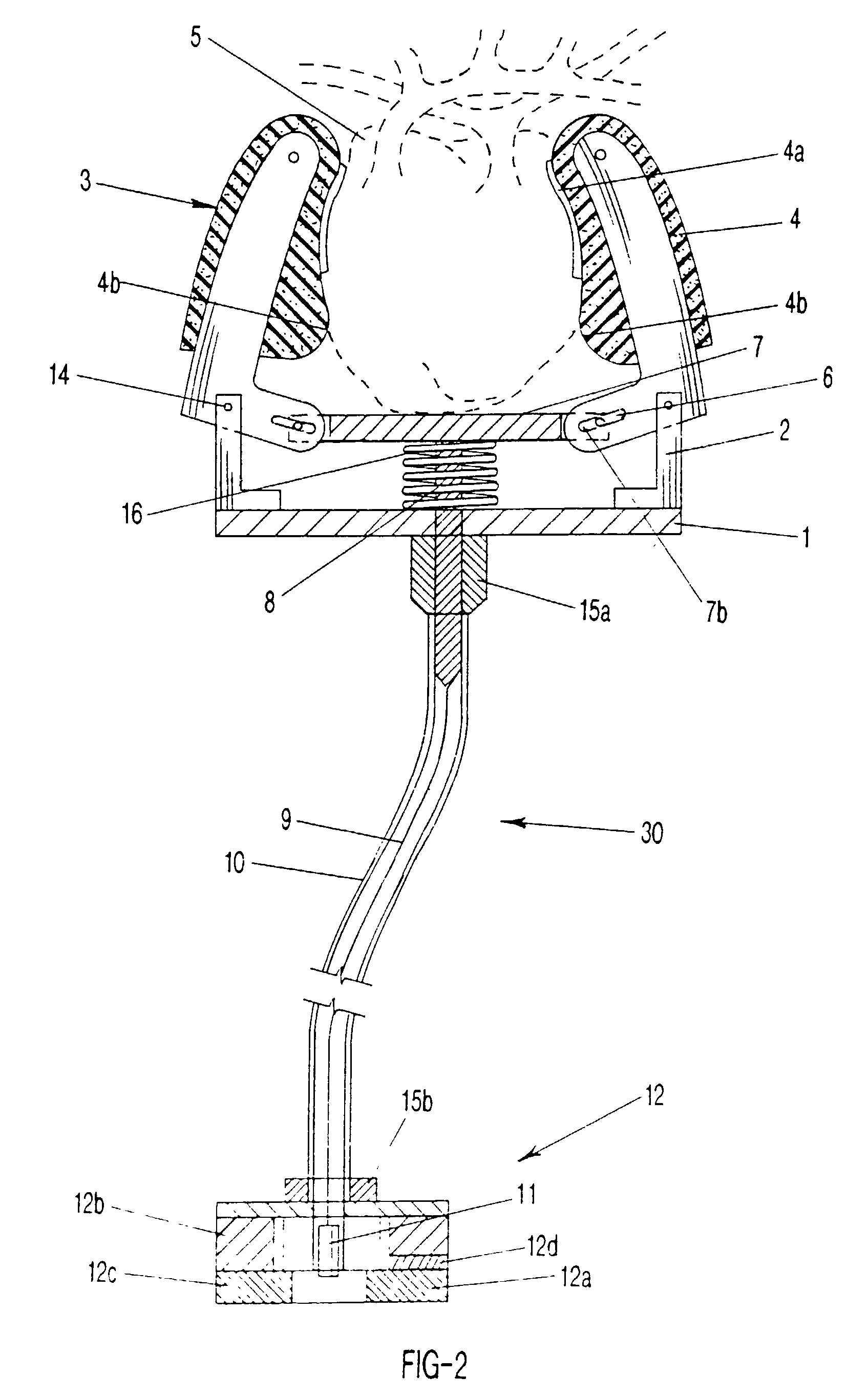
Electrically-controllable multi-fingered resilient heart compression devices
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
System for the detection of cardiac events
Disclosed is a system for the detection of cardiac events (a guardian system) that includes an implanted device called a cardiosaver, a physician's programmer and an external alarm system. The system is designed to provide early detection of cardiac events such as acute myocardial infarction or exercise induced myocardial ischemia caused by an increased heart rate or exertion. The system can also alert the patient with a less urgent alarm if a heart arrhythmia is detected. Using one or more detection algorithms, the cardiosaver can detect a change in the patient's electrogram that is indicative of a cardiac event within five minutes after it occurs and then automatically warn the patient that the event is occurring. To provide this warning, the guardian system includes an internal alarm sub-system (internal alarm means) within the cardiosaver and / or an external alarm system (external alarm means). If the guardian system is put into a pacemaker, the algorithm can utilize a different analysis of the electrogram depending on whether or not the pacemaker is actually pacing the heart.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
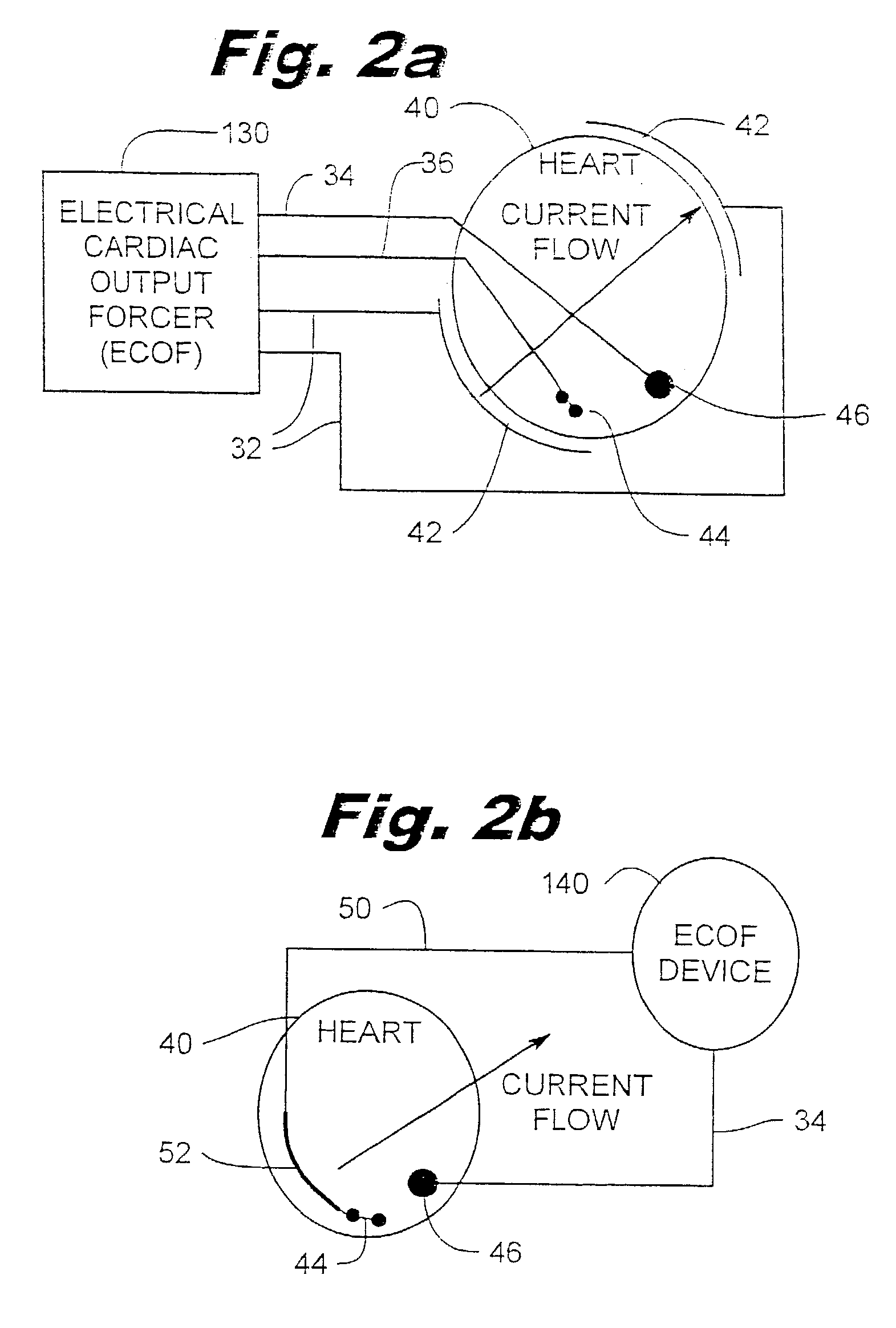
Method and apparatus for electrically forcing cardiac output in an arrhythmia patient
InactiveUS7706864B2Maintain consciousnessLife maintenanceHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeFibrillation
An electrical method and apparatus for stimulating cardiac cells causing contraction to force hemodynamic output during fibrillation, hemodynamically compromising tachycardia, or asystole. Forcing fields are applied to the heart to give cardiac output on an emergency basis until the arrhythmia ceases or other intervention takes place. The device is used as a stand alone external or internal device, or as a backup to an ICD, atrial defibrillator, or an anti-tachycardia pacemaker. The method and apparatus maintain some cardiac output and not necessarily defibrillation.
Owner:GALVANI
Method and apparatus for detecting atrial tachyarrhythmia using heart sounds
A cardiac rhythm management system senses a cardiac signal indicative of heartbeats and an acoustic signal indicative of heart sounds and detects atrial tachyarrhythmia based on the sensed cardiac and acoustic signals. In various embodiments, the system senses the cardiac and acoustic signals without using an atrial lead, thus allowing for, for example, monitoring atrial fibrillation burden in a heart failure patient who does not wear an implantable device with an atrial lead. In various embodiments, the system detects heartbeats and heart sounds, measures parameters associated with the detected heartbeats and heart sounds, and detects one or more specified types of atrial tachyarrhythmia using the measured parameters. In various embodiments, the measured parameters are selected from heart rate, heart sound amplitude, cycle length variability, and systolic and diastolic intervals.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Implantable cardiac stimulation device providing accelerated defibrillation delivery and method
An implantable cardiac stimulation device provides accelerated delivery of defibrillation therapy to a patient's heart. The device includes a sensing circuit that provides right and left heart cardiac activity signals and a detector that detects an accelerated arrhythmia of the patient's heart and establishes a plurality of accelerated cardiac rate zones including a fibrillation rate zone and at least one intermediate rate zone. A classifier responsive to the right and left heart cardiac activity signals classifies an accelerated arrhythmia as one of fibrillation and tachycardia responsive to the detector detecting an accelerated arrhythmia having a cardiac rate within the at least one intermediate rate zones. A therapy circuit applies defibrillation to the heart responsive to the classifier classifying an accelerated arrhythmia as fibrillation and anti-tachycardia pacing to the heart responsive to the classifier classifying an accelerated arrhythmia as tachycardia.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Implantable cardiac stimulation device including a system for and method of automatically inducing a tachyarrhythmia
A system and method for use in an implantable cardiac stimulation device permits automatic induction of a tachyarrhythmia of a heart to permit the performance of an electrophysiological test of the heart. A pulse generator repeatedly delivers a group of first and second sets of pacing pulses to a chamber of the heart. The pacing pulses are separated in time by interpulse intervals to overdrive pace a chamber of the heart. A processor, coupled to the pulse generator, varies the second set of interpulse intervals according to a predetermined protocol after each group of pacing pulses is delivered to the chamber of the heart. The successive groups of pacing pulses are delivered to the heart until the tachyarrhythmia is induced.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Heart stimulator for administering antithrombus therapy
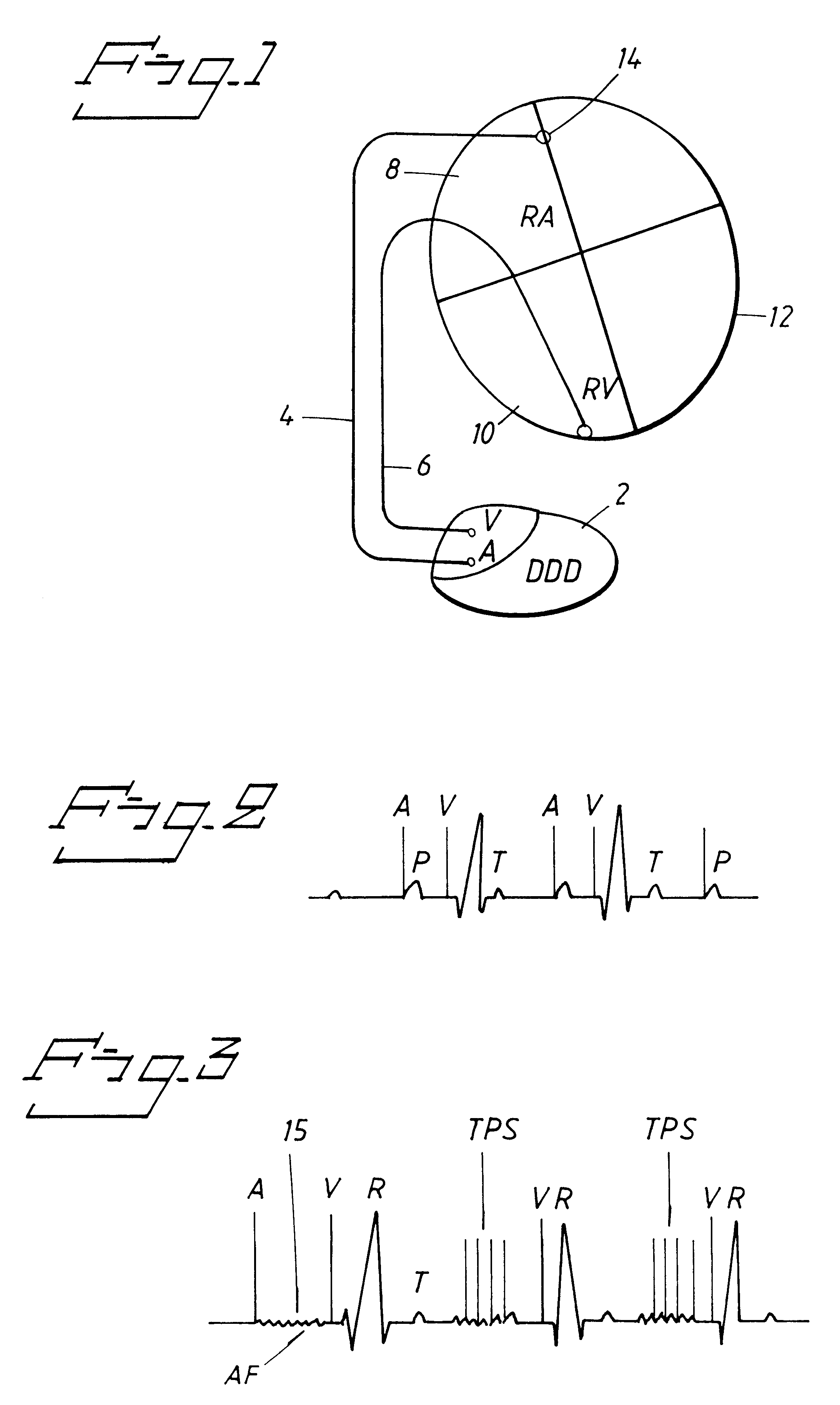
InactiveUS6731981B1Improve efficiencyInhibition formationHeart defibrillatorsParoxysmal AFHemodynamics
A heart stimulator has a stimulation energy delivering assembly, including at least one lead adapted for implantation in contact with cardiac tissue, and an atrial arrhythmia detector, and a control unit connected to the stimulation energy delivering assembly and to the detector. The control unit controls the stimulation energy delivering assembly to deliver at least one atrial arrhythmia abolishing therapy and, if continued atrial arrhythmia is detected, to deliver antithrombus stimulation energy pulses of lower energy than a defibrillation shock, but with different timing and with sufficient energy for producing atrial contraction for increasing hemodynamic blood transportation away from the atrium and for preventing thrombi formation in the atrium. For a patient suffering from a chronic or paroxysmal non-curable atrial arrhythmia, the control unit controls the stimulation energy delivering assembly to deliver the antithrombus energy without any preceding arrhythmia abolishing therapy.
Owner:PACESETTER AB
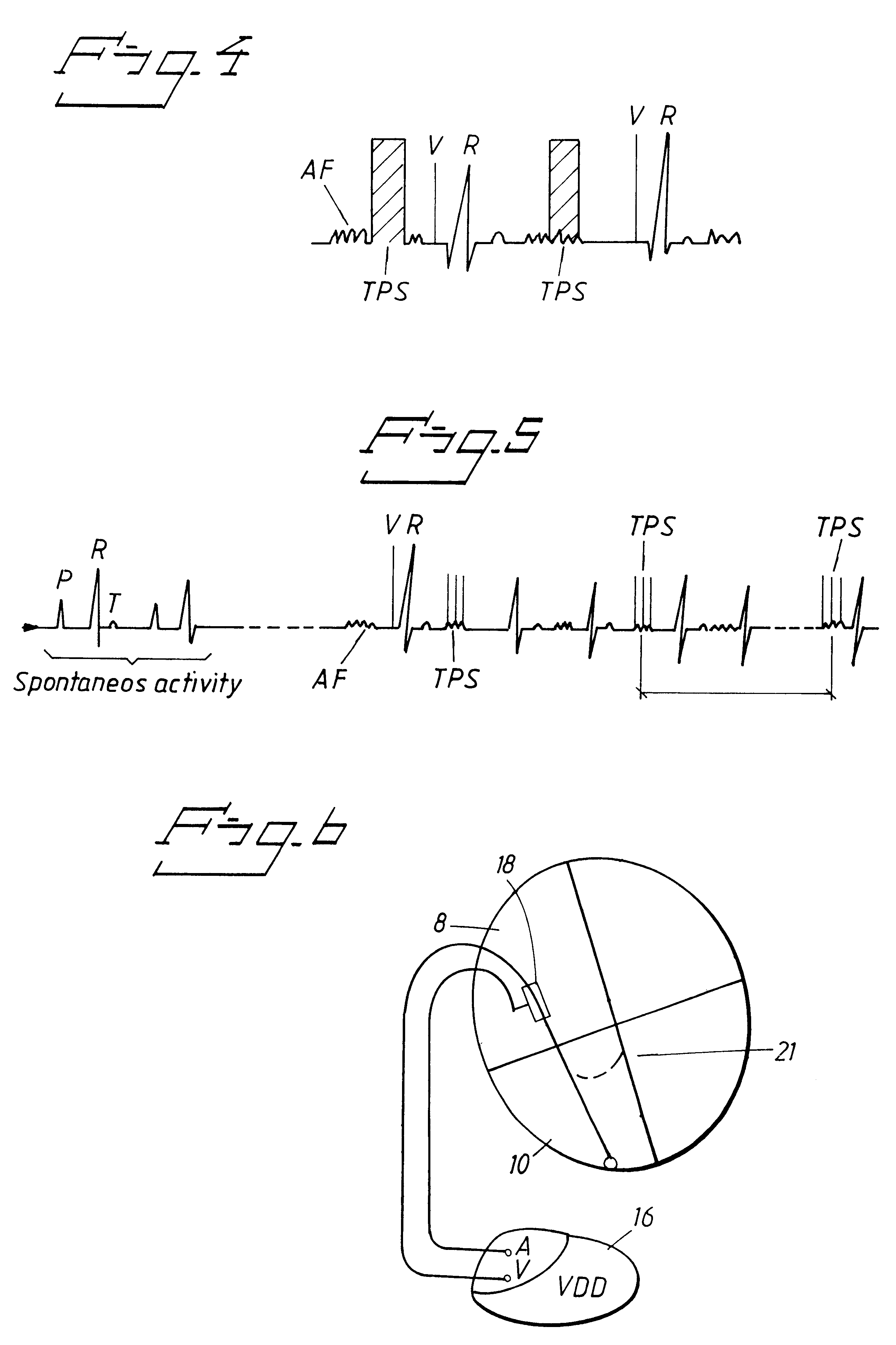
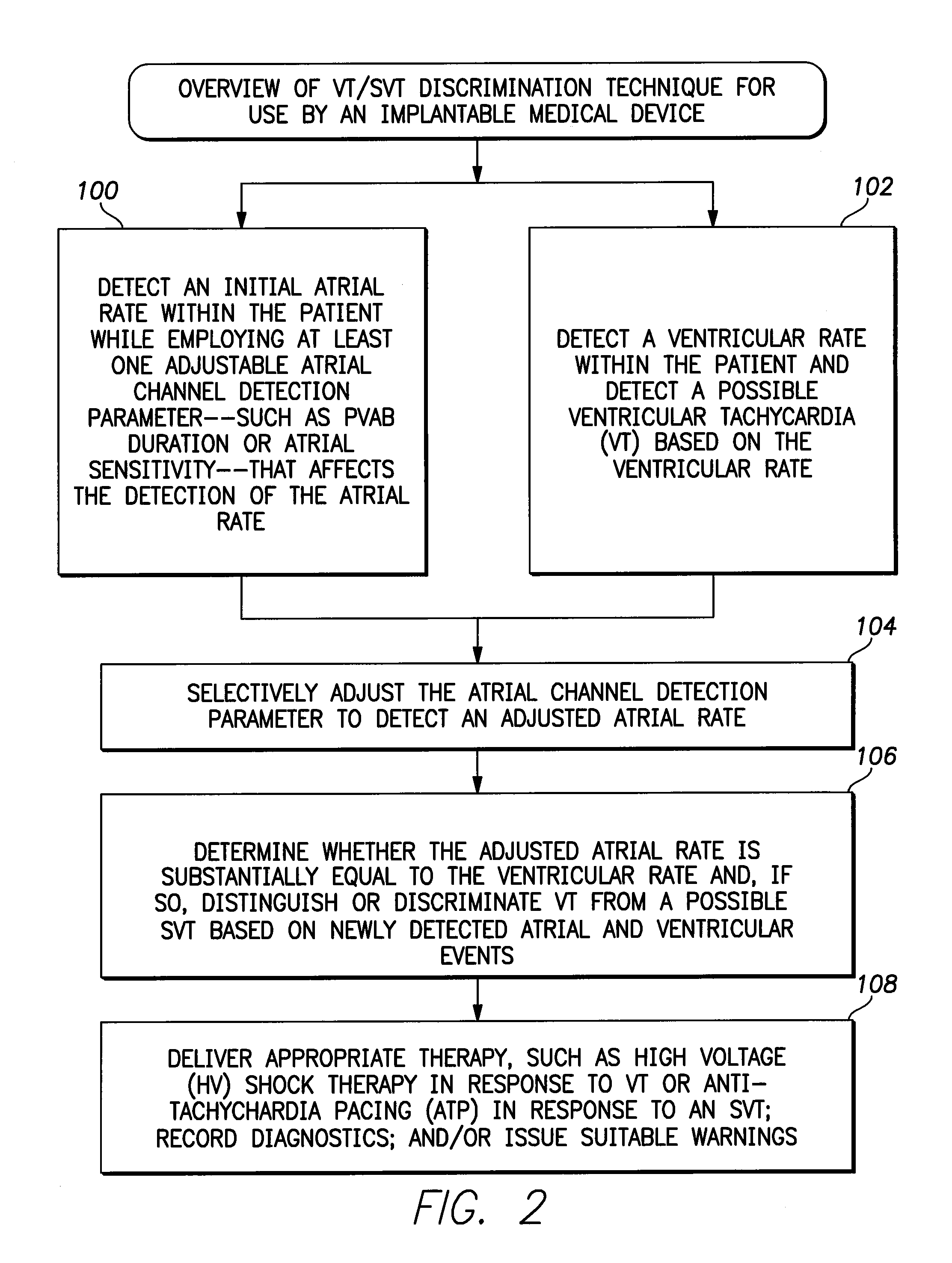
Systems and methods for use with an implantable medical device for discriminating vt and svt be selectively adjusting atrial channel sensing parameters
ActiveUS20110282405A1Increase chanceAssessment of atrioventricular (AV) association stabilityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular rateVentricular tachycardia
Techniques are described for discriminating ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) in circumstances when the ventricular rate exceeds the atrial rate (i.e. V>A). In one example, an initial atrial rate is detected while employing adjustable atrial channel detection parameters that can affect the detection of the true atrial rate—such as a post-ventricular atrial blanking (PVAB) interval or an atrial channel sensitivity level. If the ventricular rate exceeds a VT rate zone threshold with V>A, the device does not immediately deliver high voltage shock therapy as done in other devices. Rather, the device instead selectively adjusts the atrial channel detection parameter(s) to determine if the true atrial rate is equal to the ventricular rate. If so, then such is an indication that the arrhythmia might be SVT rather than VT and various discrimination procedures are employed to distinguish SVT from VT before therapy is delivered.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Systems and methods for use with an implantable medical device for discriminating VT and SVT based on ventricular depolarization event timing
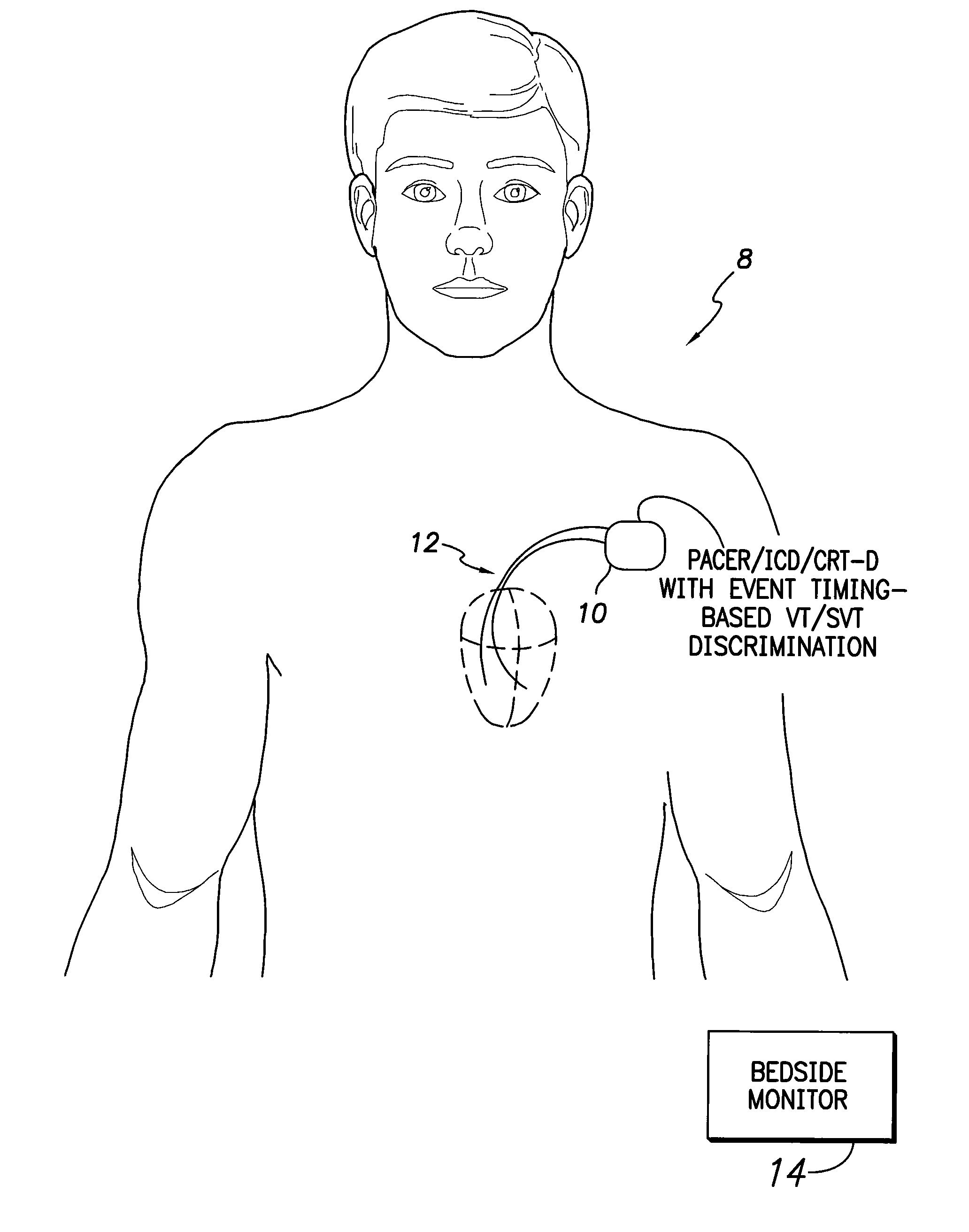
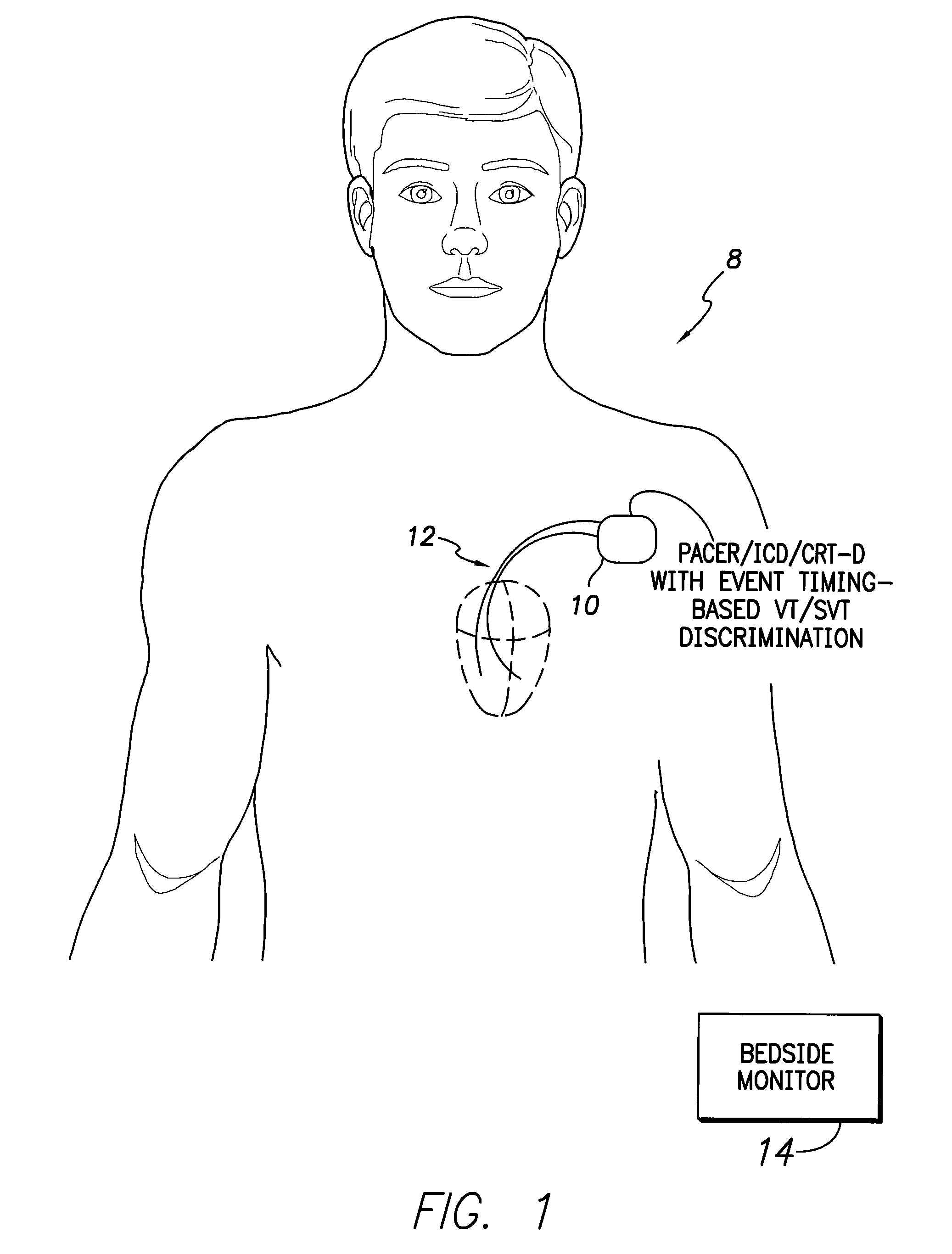
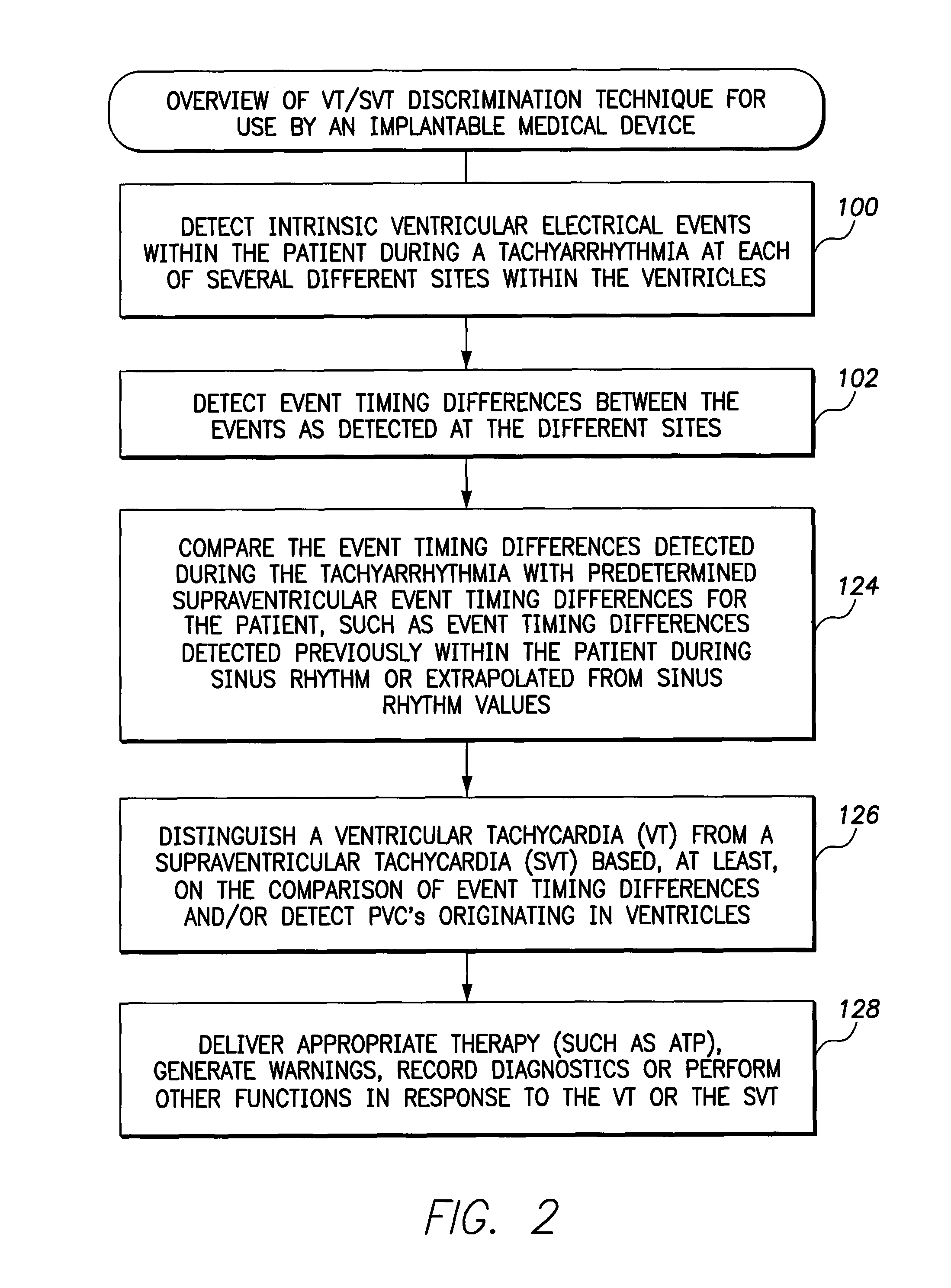
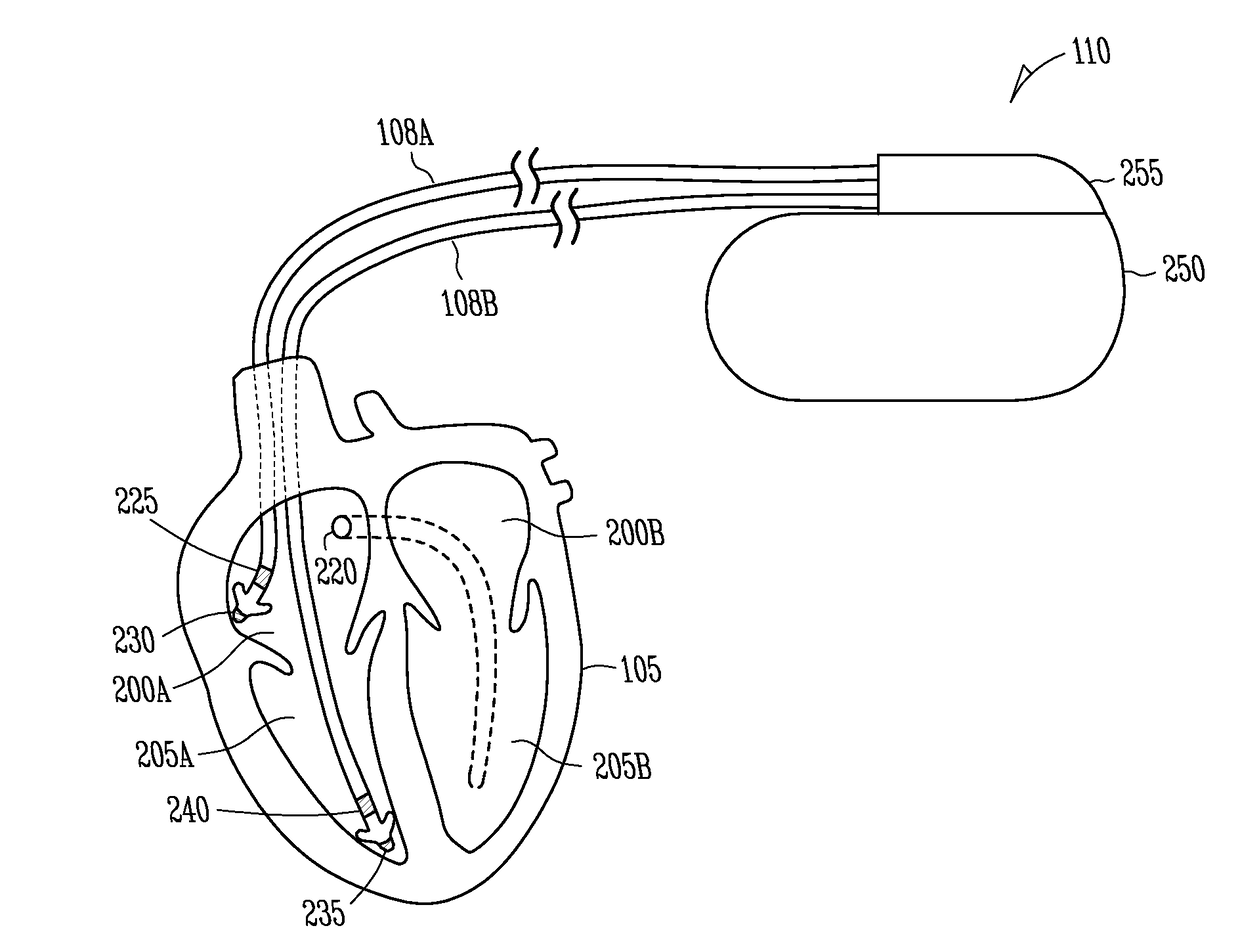
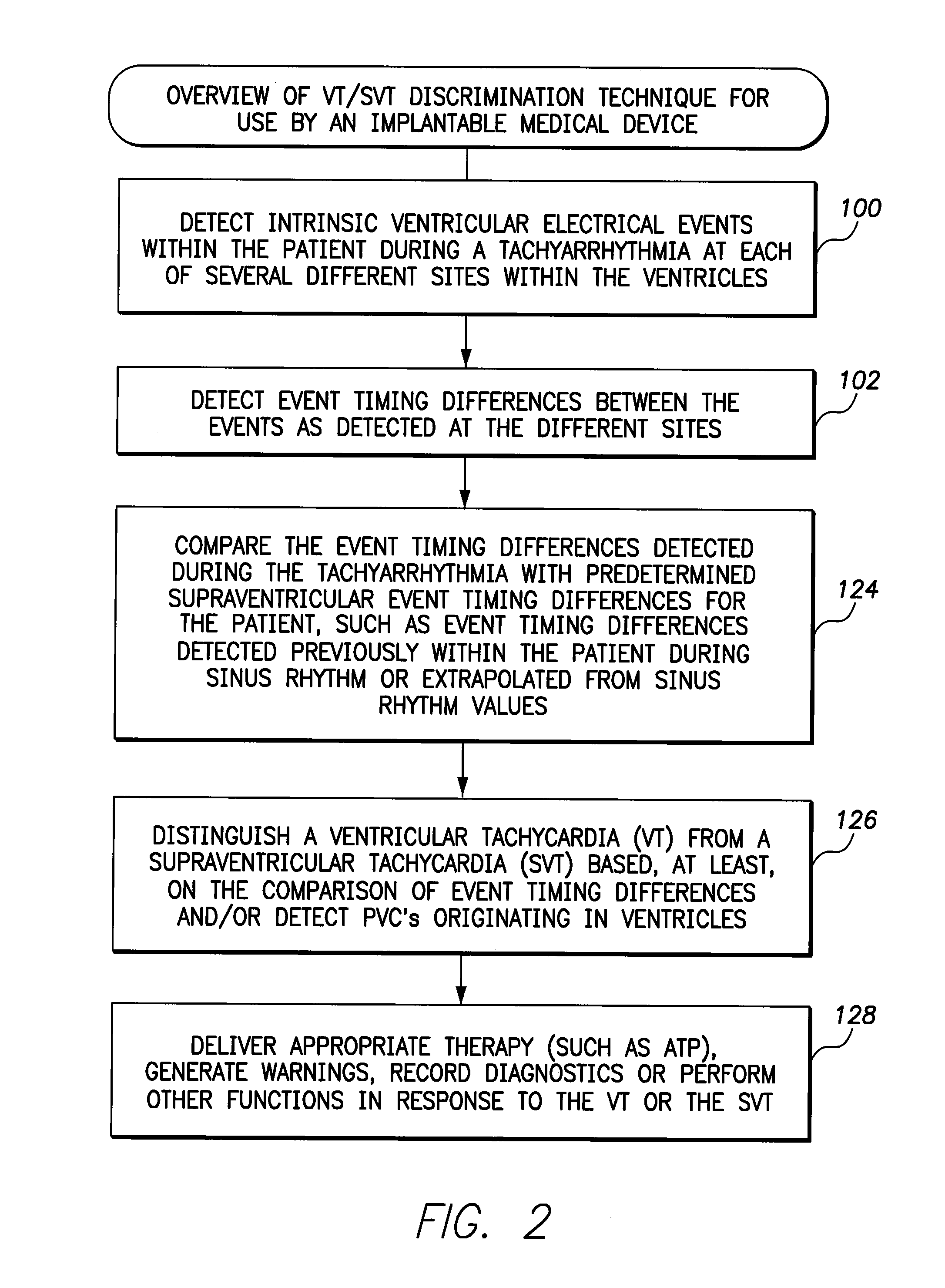
ActiveUS8165675B2Efficiently and reliably distinguishedElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMulti siteWaveform analysis
Techniques are described for discriminating ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) using an implantable medical device capable of multi-site ventricular sensing. In one example, ventricular depolarization events are detected within a patient by the implantable device during a tachyarrhythmia, at both a left ventricular sensing site and a right ventricular sensing site. Ventricular event timing differences are then ascertained. The device compares the ventricular event timing differences detected during the tachyarrhythmia with predetermined supraventricular event timing differences for the patient, such as event timing differences previously detected within the patient during sinus rhythm or extrapolated from sinus rhythm values. The device then distinguishes VT from SVT based on the comparison of the event timing differences detected during the tachyarrhythmia with the predetermined supraventricular event timing differences. Morphological waveform analysis can also be performed, when needed, to further distinguish VT from SVT.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
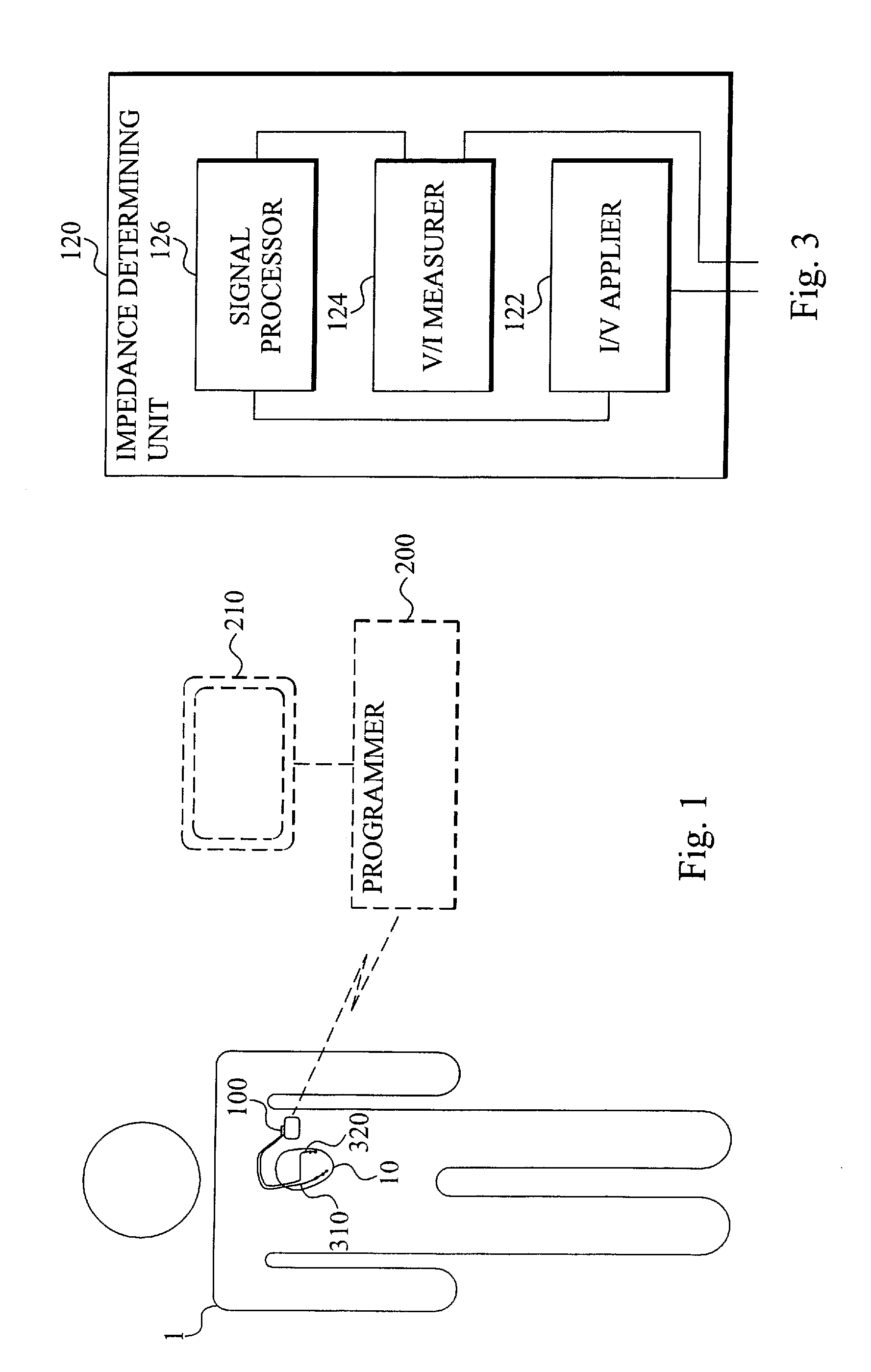
Intracardiac impedance and its applications
A system to measure intracardiac impedance includes implantable electrodes and a medical device. The electrodes sense electrical signals of a heart of a subject. The medical device includes a cardiac signal sensing circuit coupled to the implantable electrodes, an impedance measurement circuit coupled to the same or different implantable electrodes, and a controller circuit coupled to the cardiac signal sensing circuit and the impedance measurement circuit. The cardiac signal sensing circuit provides a sensed cardiac signal. The impedance measurement circuit senses intracardiac impedance between the electrodes to obtain an intracardiac impedance signal. The controller circuit determines cardiac cycles of the subject using the sensed cardiac signal, and detects tachyarrhythmia using cardiac-cycle to cardiac-cycle changes in a plurality of intracardiac impedance parameters obtained from the intracardiac impedance signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Systems and methods for use with an implantable medical device for discriminating vt and svt based on ventricular depolarization event timing
ActiveUS20110106194A1Efficiently and reliably distinguishedElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsMulti siteWaveform analysis
Techniques are described for discriminating ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) using an implantable medical device capable of multi-site ventricular sensing. In one example, ventricular depolarization events are detected within a patient by the implantable device during a tachyarrhythmia, at both a left ventricular sensing site and a right ventricular sensing site. Ventricular event timing differences are then ascertained. The device compares the ventricular event timing differences detected during the tachyarrhythmia with predetermined supraventricular event timing differences for the patient, such as event timing differences previously detected within the patient during sinus rhythm or extrapolated from sinus rhythm values. The device then distinguishes VT from SVT based on the comparison of the event timing differences detected during the tachyarrhythmia with the predetermined supraventricular event timing differences. Morphological waveform analysis can also be performed, when needed, to further distinguish VT from SVT.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Implantable neurostimulator-implemented method for managing tachyarrhythmia through vagus nerve stimulation
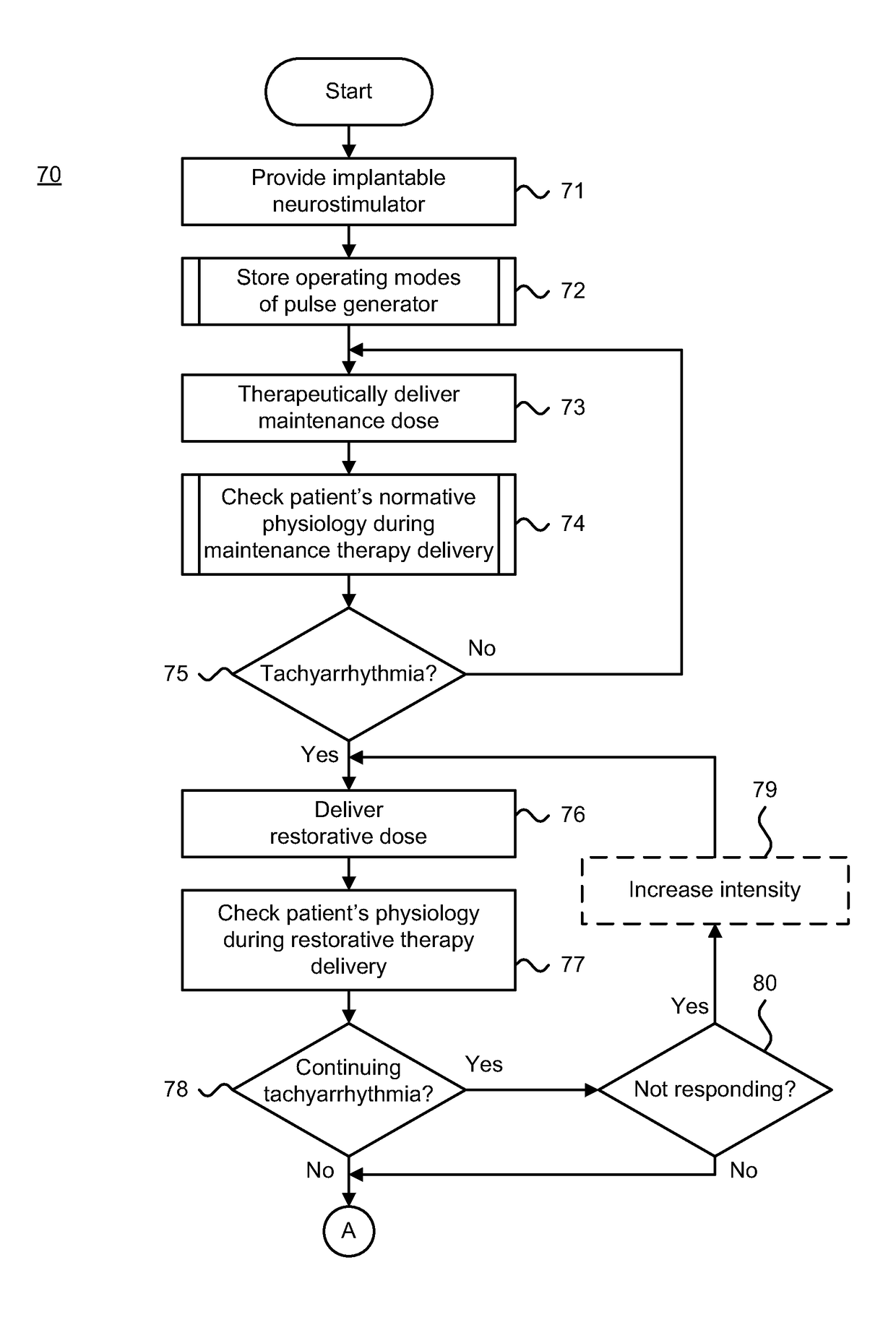
An implantable neurostimulator-implemented method for managing tachyarrhythmias through vagus nerve stimulation is provided. An implantable neurostimulator, including a pulse generator, is configured to deliver electrical therapeutic stimulation in a manner that results in creation and propagation (in both afferent and efferent directions) of action potentials within neuronal fibers of a patient's cervical vagus nerve. Operating modes of the pulse generator are stored. A maintenance dose of the electrical therapeutic stimulation is delivered to the vagus nerve via the pulse generator to restore cardiac autonomic balance through continuously-cycling, intermittent and periodic electrical pulses. A restorative dose of the electrical therapeutic stimulation is delivered to prevent initiation of or disrupt tachyarrhythmia through periodic electrical pulses delivered at higher intensity than the maintenance dose. The patient's normative physiology is monitored via a physiological sensor, and upon sensing a condition indicative of tachyarrhythmia, is switched to delivering the restorative dose to the vagus nerve.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Intracardiac impedance and its applications
A system to measure intracardiac impedance includes implantable electrodes and a medical device. The electrodes sense electrical signals of a heart of a subject. The medical device includes a cardiac signal sensing circuit coupled to the implantable electrodes, an impedance measurement circuit coupled to the same or different implantable electrodes, and a controller circuit coupled to the cardiac signal sensing circuit and the impedance measurement circuit. The cardiac signal sensing circuit provides a sensed cardiac signal. The impedance measurement circuit senses intracardiac impedance between the electrodes to obtain an intracardiac impedance signal. The controller circuit determines cardiac cycles of the subject using the sensed cardiac signal, and detects tachyarrhythmia using cardiac-cycle to cardiac-cycle changes in a plurality of intracardiac impedance parameters obtained from the intracardiac impedance signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Intracardiac impedance and its applications
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
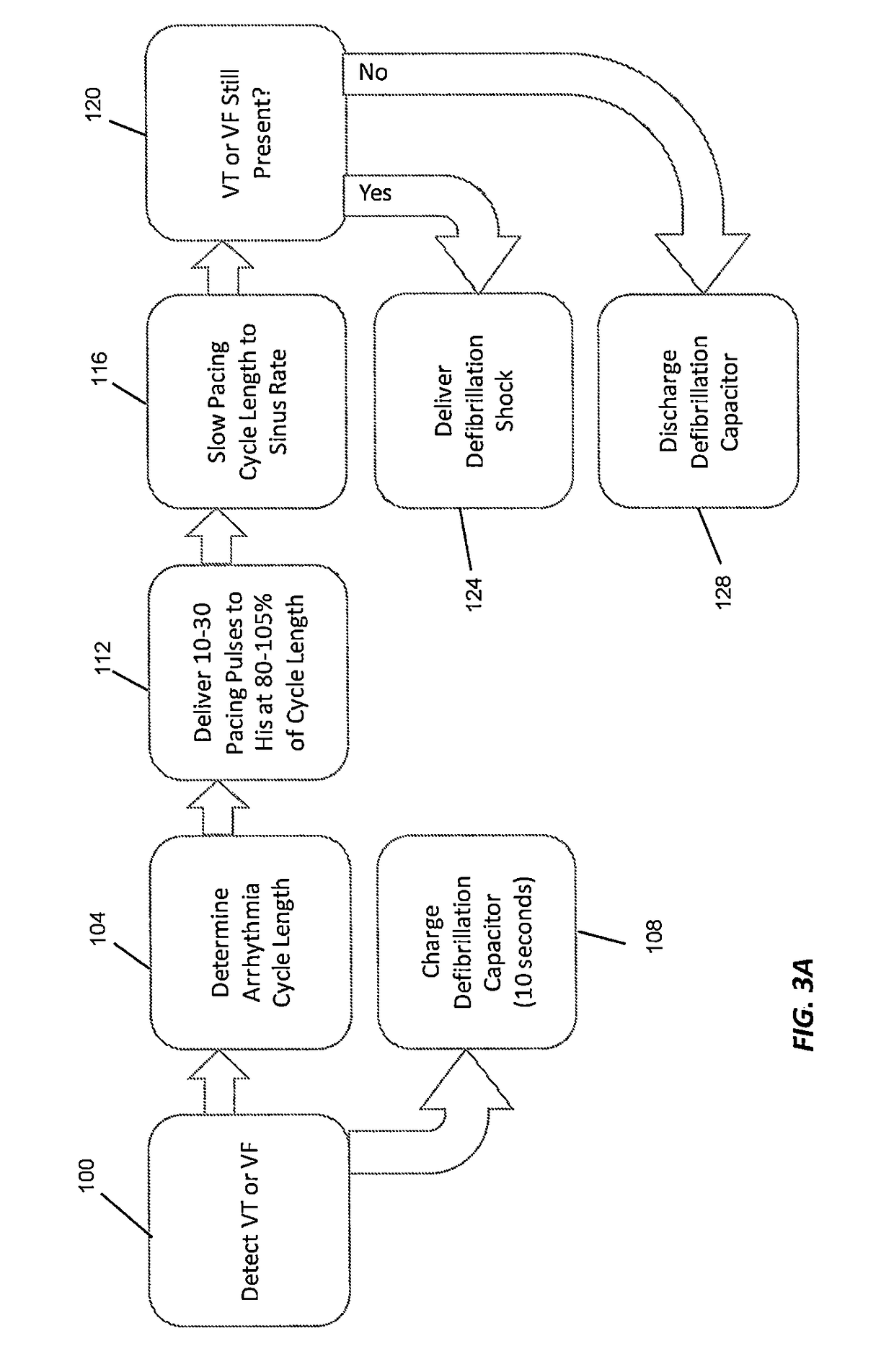
Implantable cardiac devices and methods for delivering low energy, pain-free defibrillation signals for ventricular arrhythmias
ActiveUS20180318594A1Reduce inductionProne to arrhythmogenesisHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsSignal generatorCardiac device
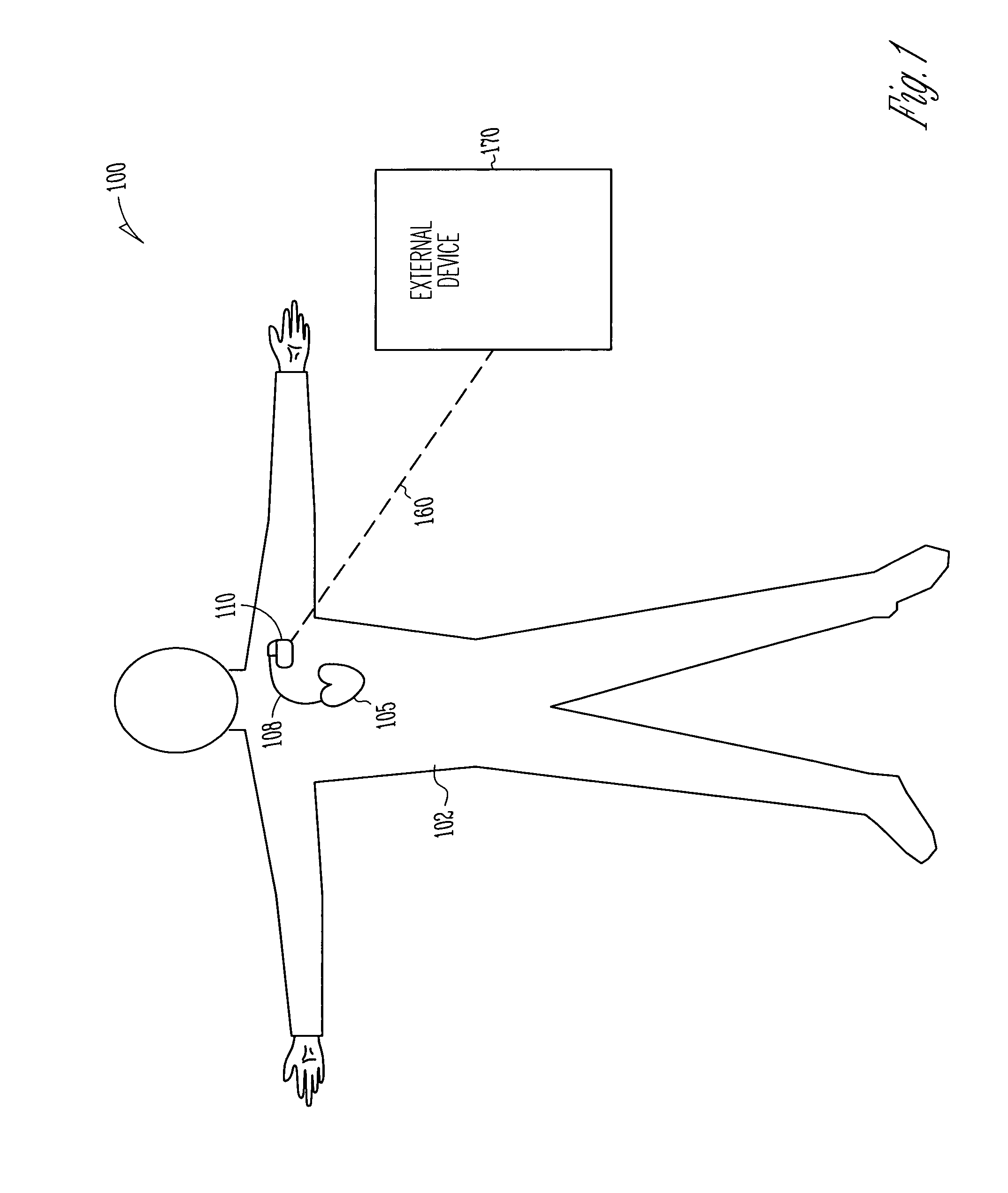
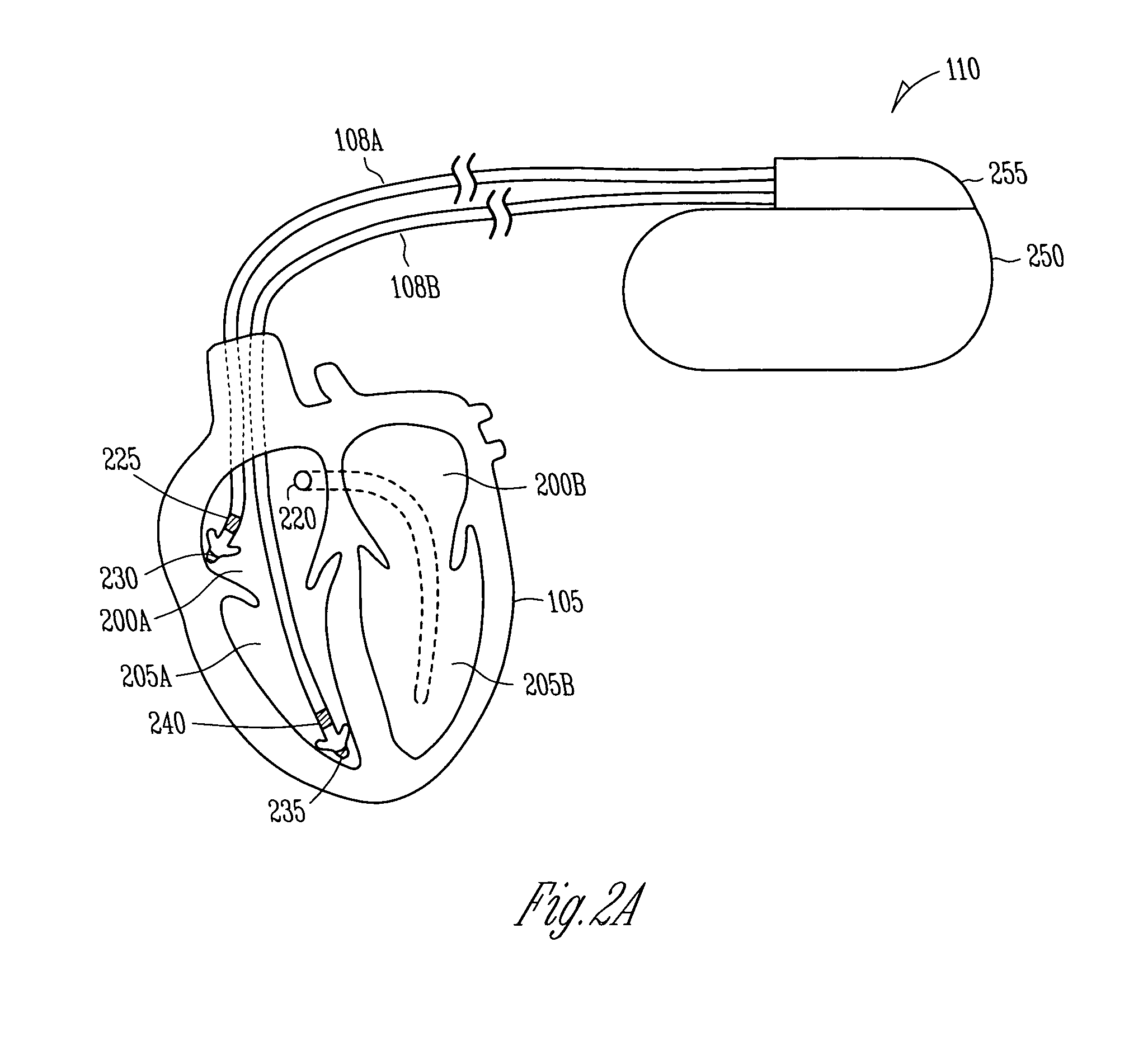
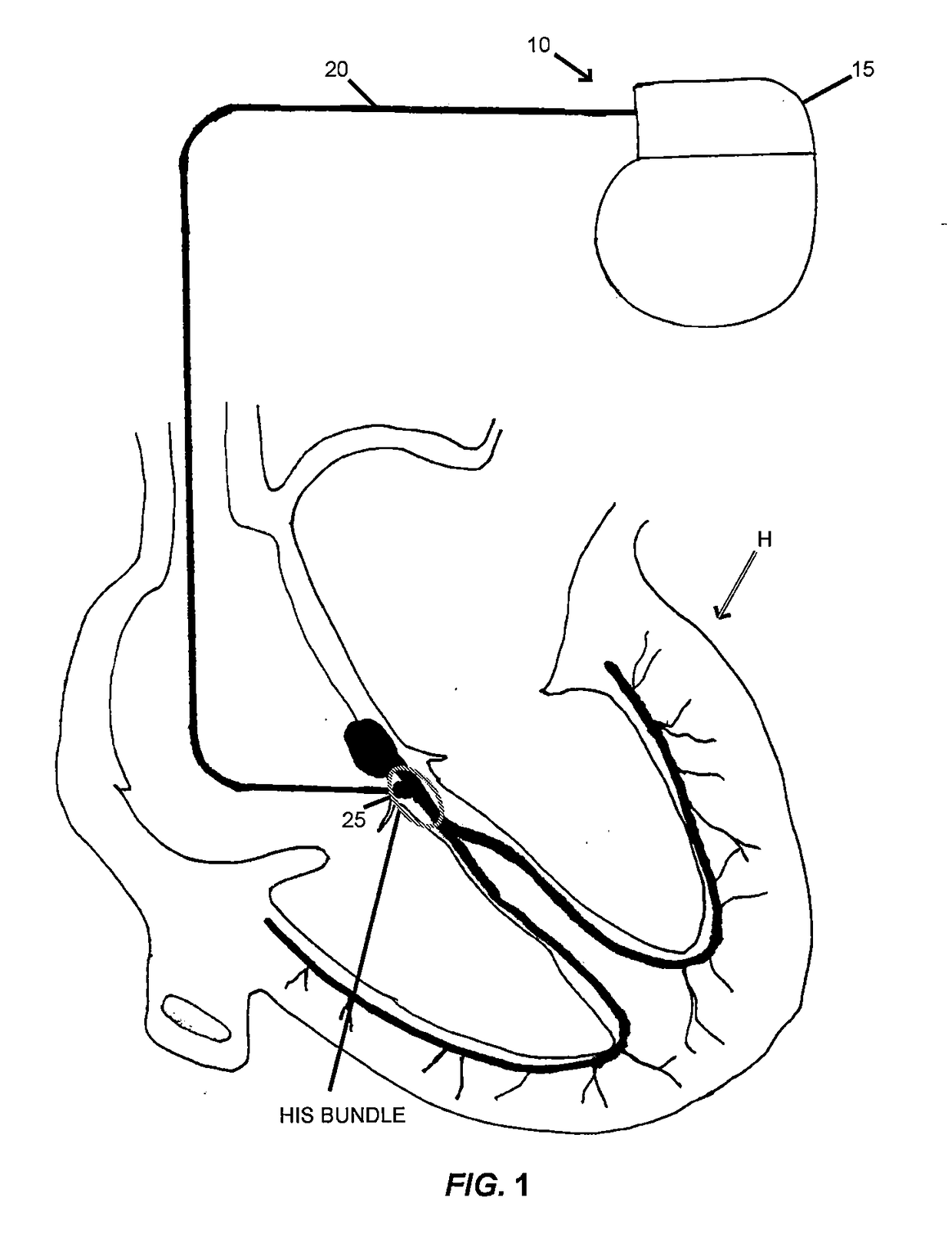
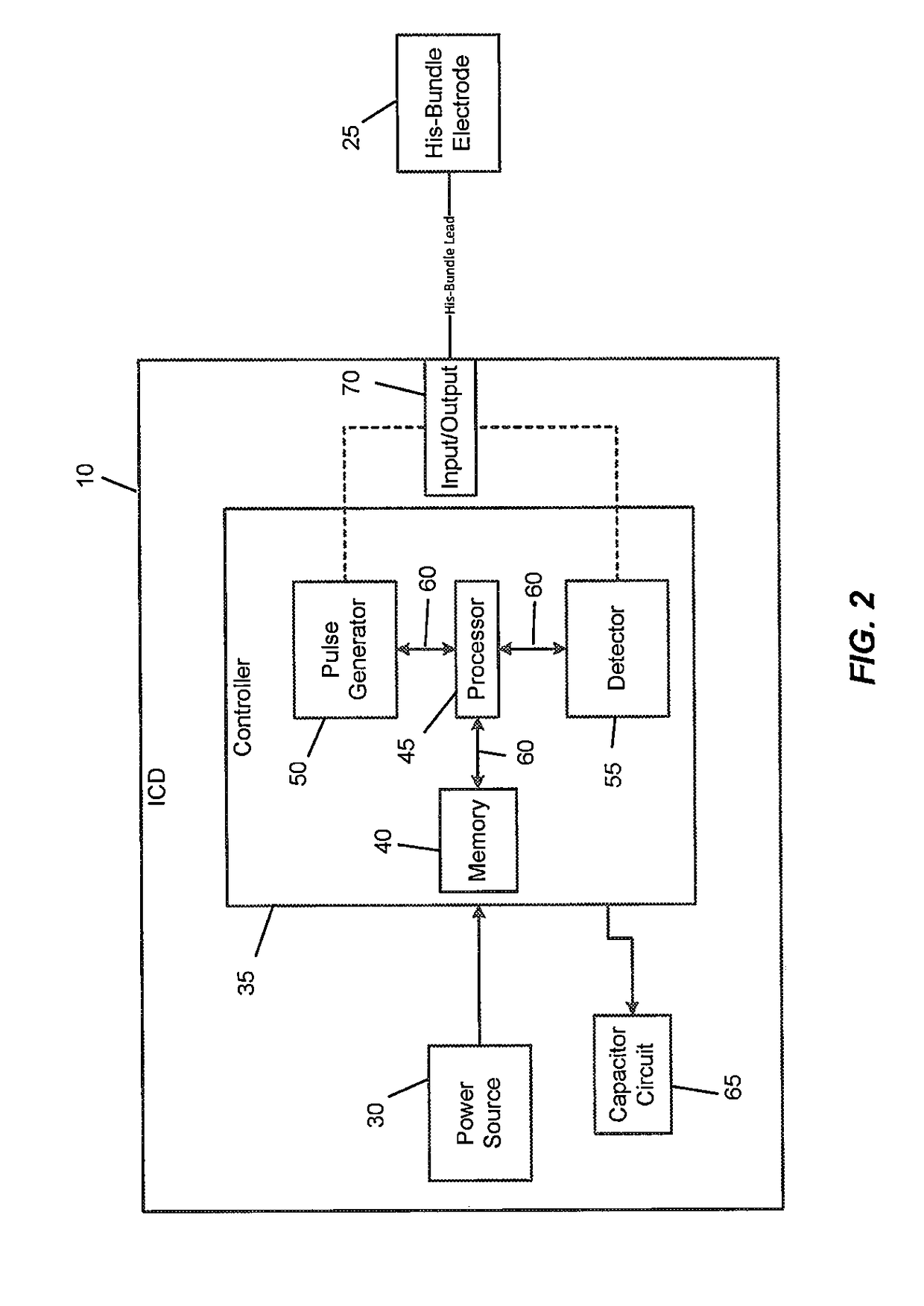
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) and methods of detection and treatment of dangerous and life-threatening heart rhythms by delivering real-time, customized low-energy pacing pulses to specific anatomy in the heart. The ICD includes a power source, a controller, powered by the power source, including an electronic processor, a memory, and a signal generator. The ICD also includes a lead coupled to the controller and an electrode that is in electrical communication with a His-bundle of a patient's heart. The ICD detects a ventricular arrhythmia of the patient's heart using the controller, and is configured to provide a pulsed defibrillation signal to the electrode to terminate the ventricular arrhythmia.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
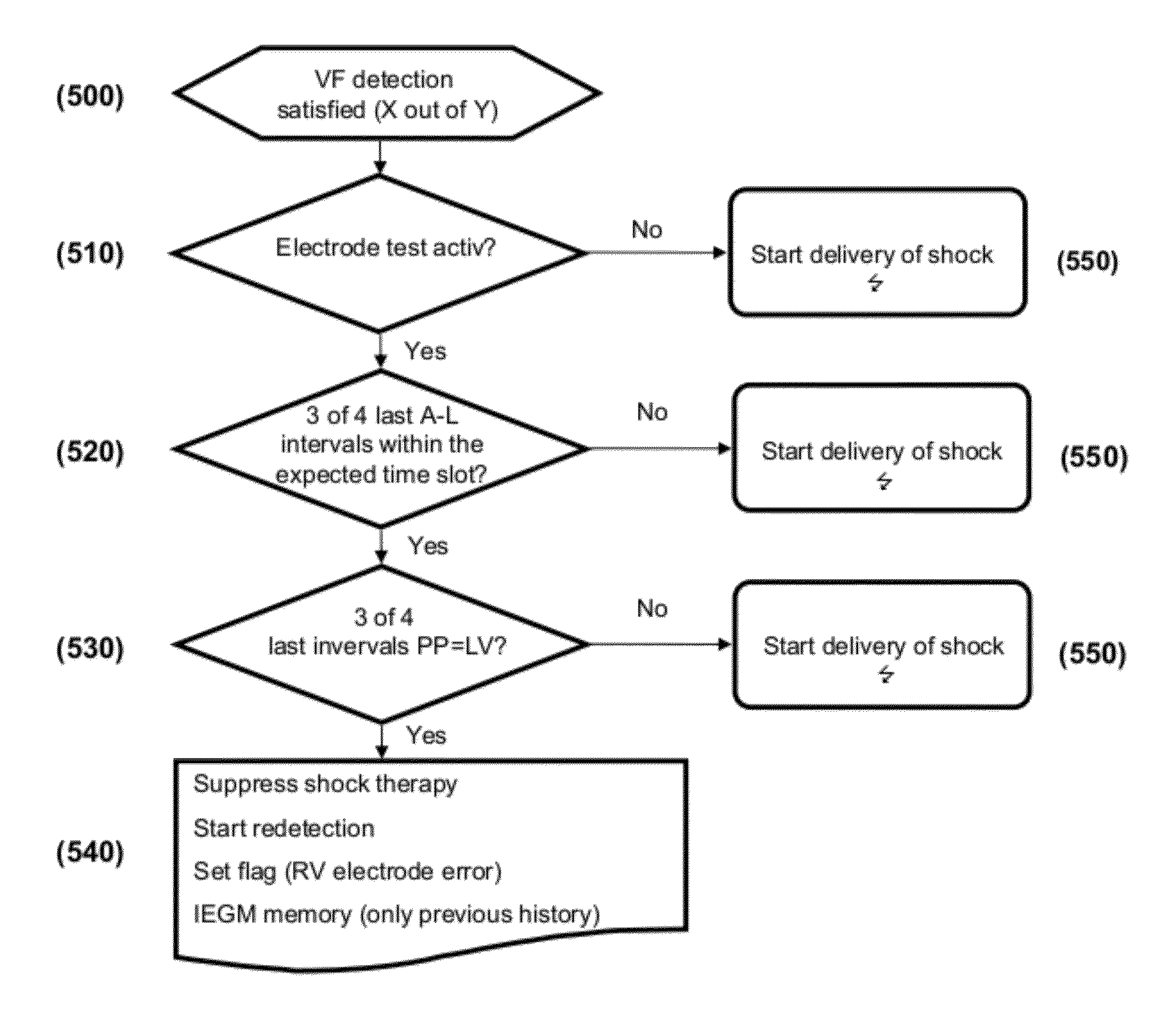
Cardiac stimulator for treatment of tachycardiac arrhythmias of the heart
ActiveUS8280507B2Avoid transmissionInternal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringRhythmCardiac Ventricle
An implantable antitachycardiac cardiac stimulator has at least one right-ventricular sensing unit, a defibrillation shock generator and a control unit, as well as an additional detection unit for detecting ventricular events which operates independently of the right-ventricular detection electrode, and an evaluation unit (e.g., as an additional component of the control unit) which suppresses the delivery of a defibrillation shock on reliable detection of the normal rhythm via the additional detection unit.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) tachyarrhythmia detection modification in response to detected pacing
ActiveCN106456014BHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringImplantable cardioverter-defibrillator
An implantable medical device includes a sensing module configured to obtain electrical signals from one or more electrodes, and a control module configured to process the electrical signals from the sensing module according to a tachyarrhythmia detection algorithm to monitor tachyarrhythmia. The control module detects initiation of a pacing string delivered by the second implantable medical device, determines a type of the detected pacing string, and modifies a tachyarrhythmia detection algorithm based on the detected type of pacing string.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
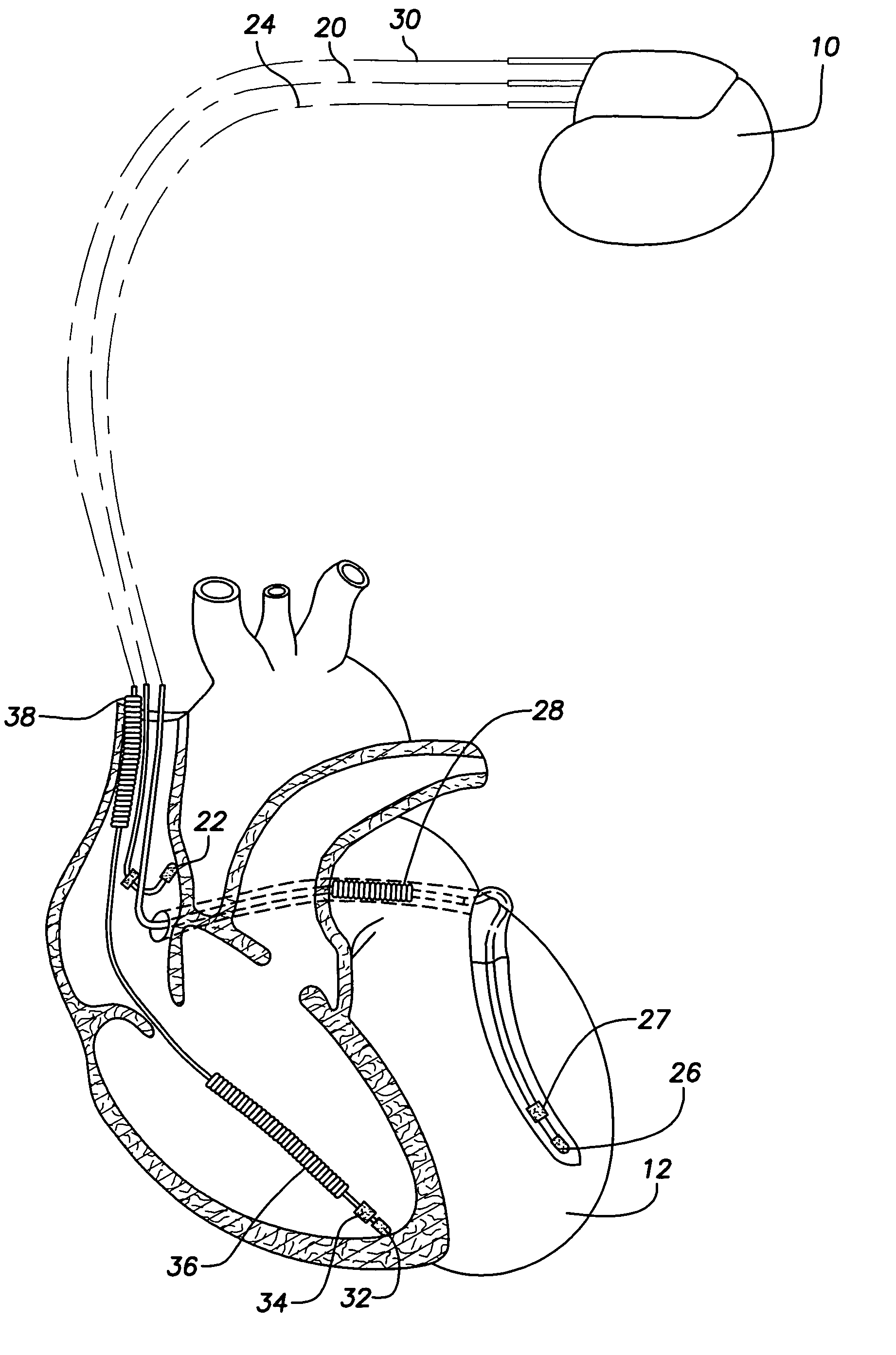
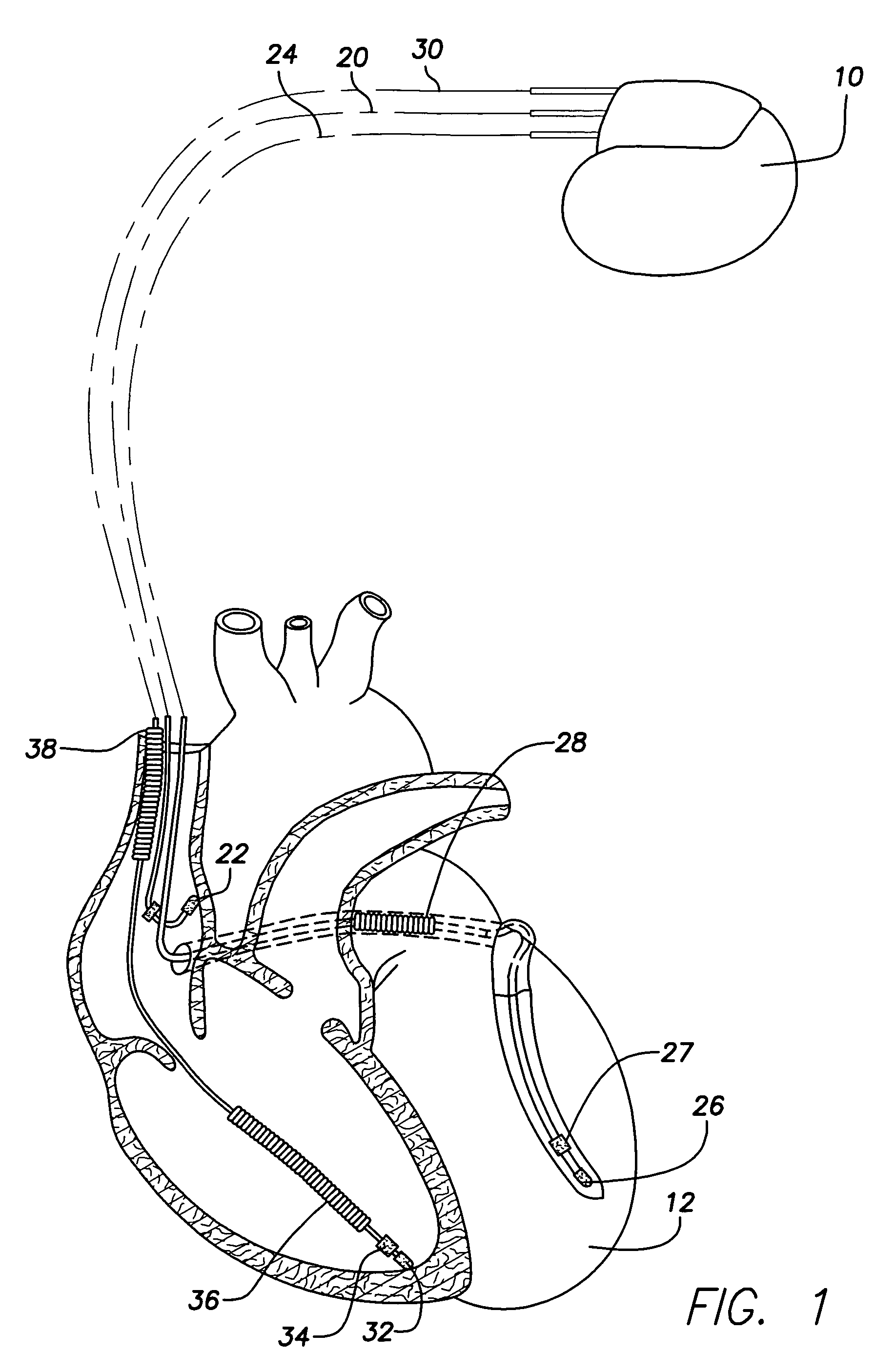
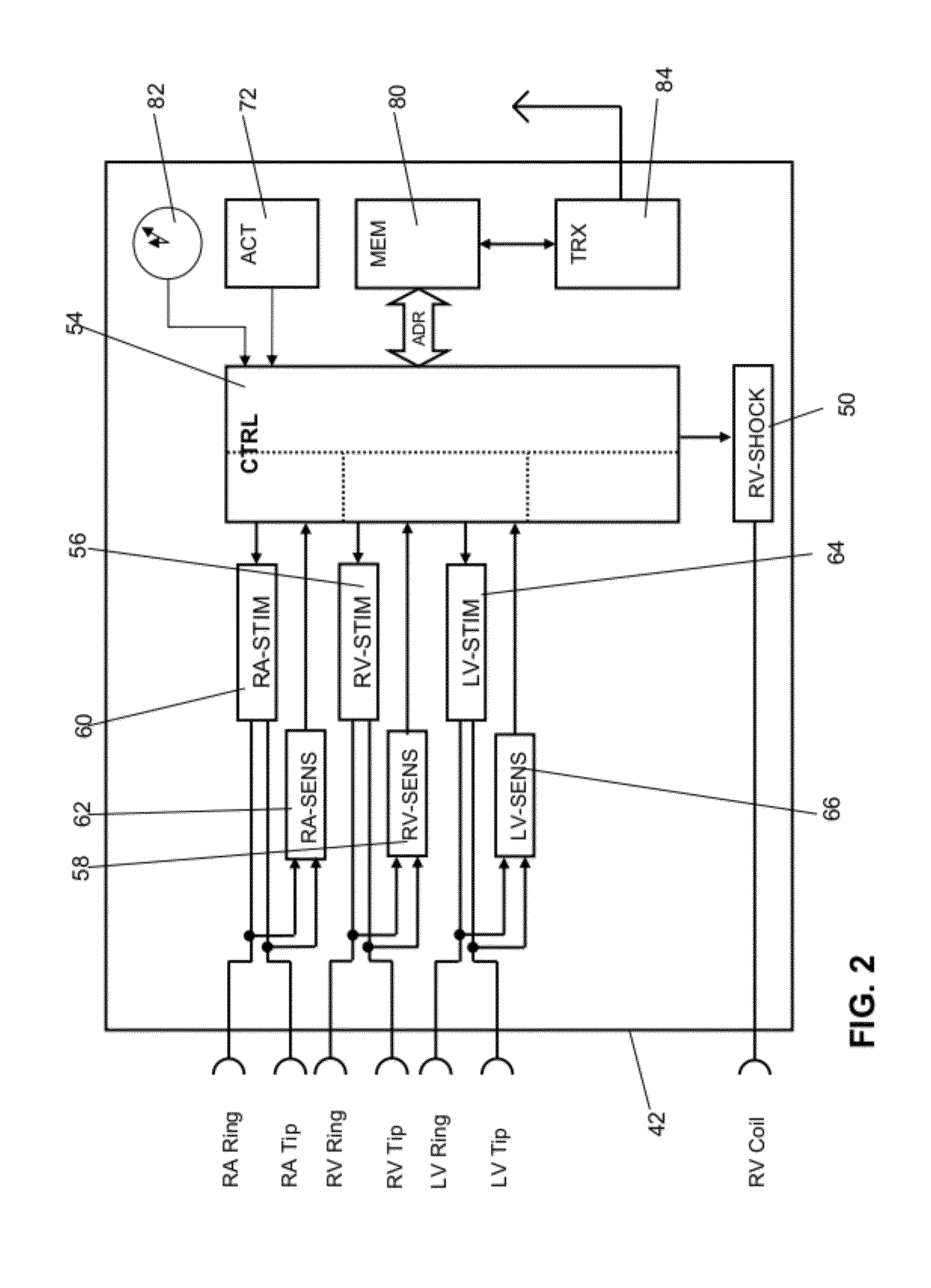
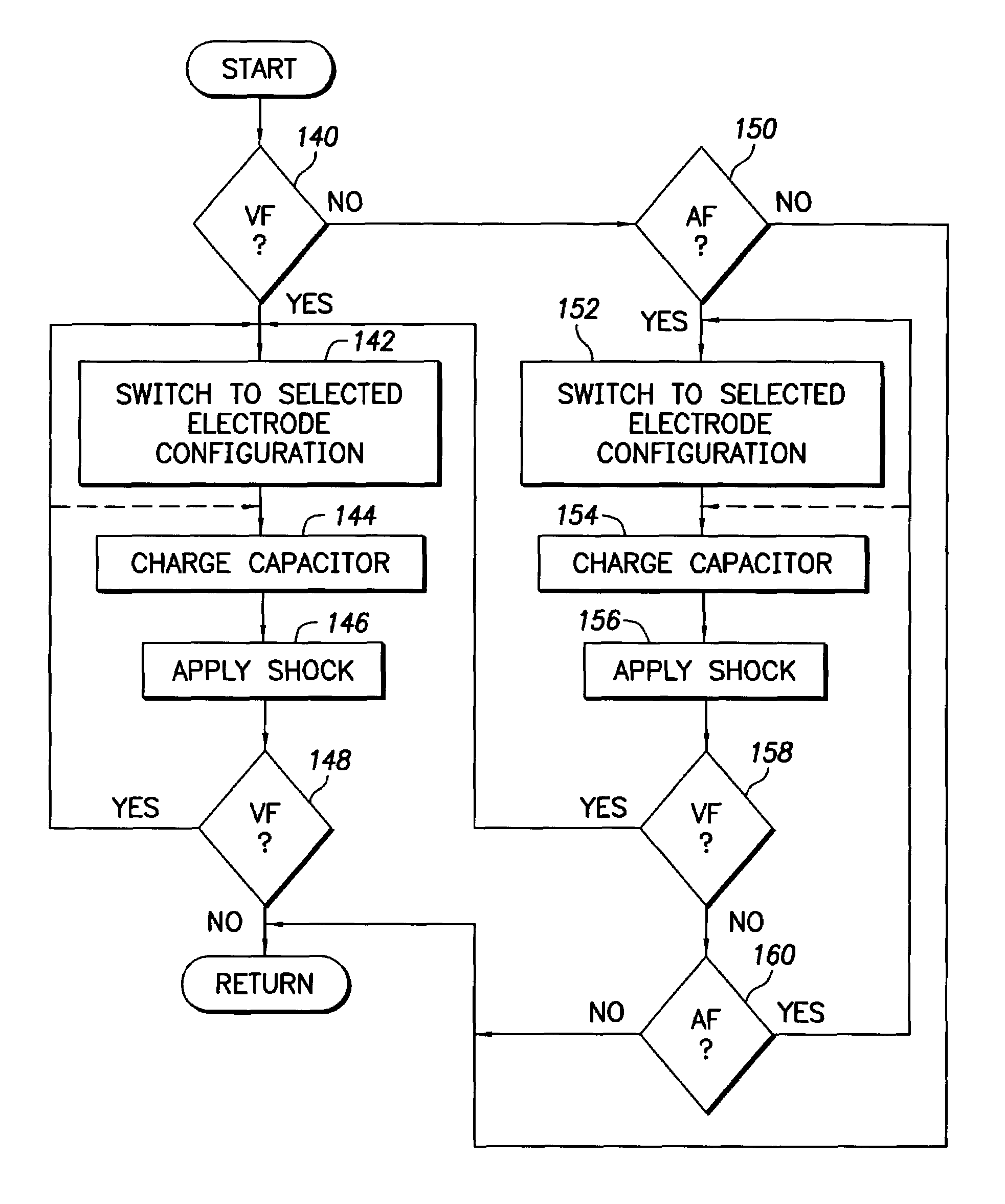
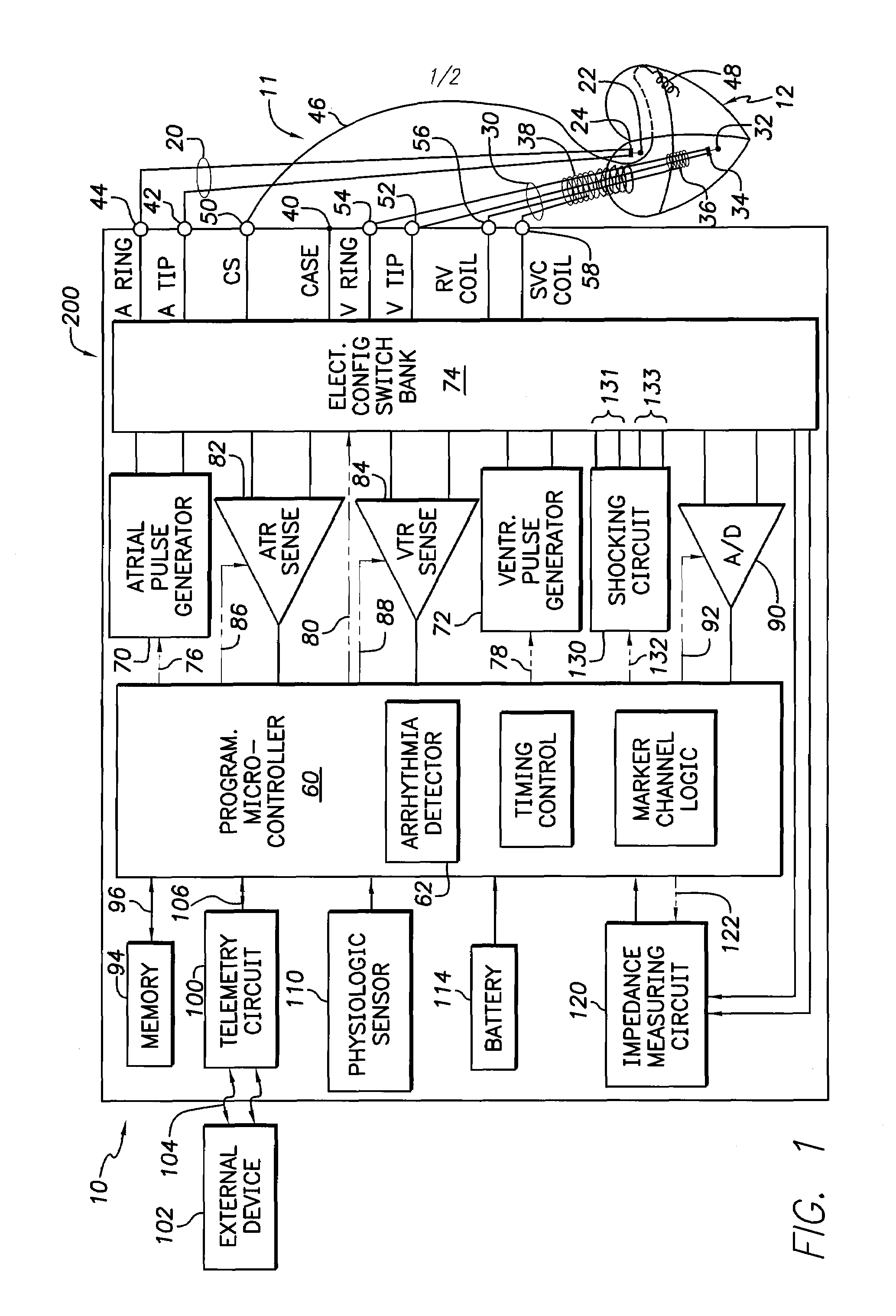
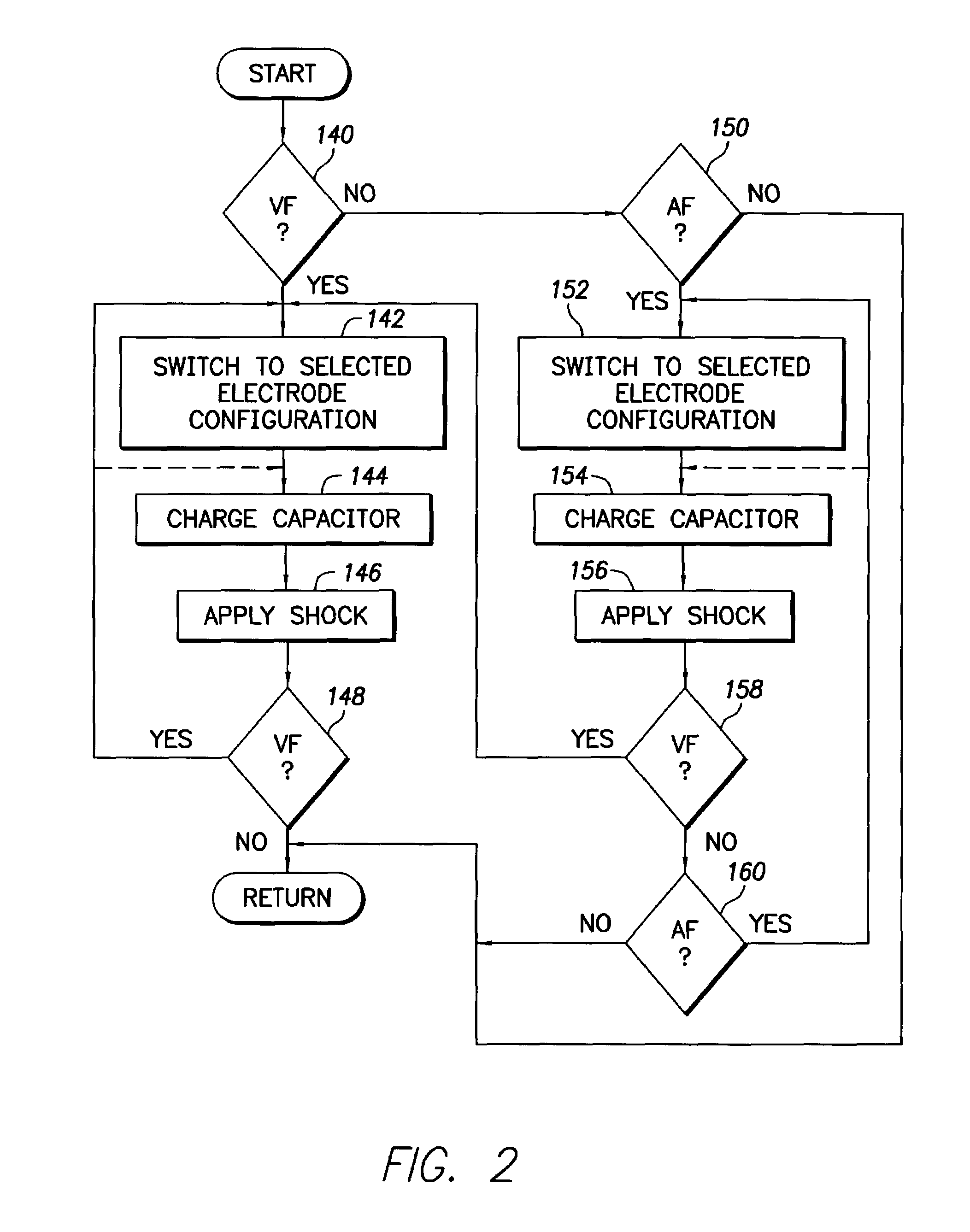
Dual-chamber implantable cardiac stimulation system and device with selectable arrhythmia termination electrode configurations and method
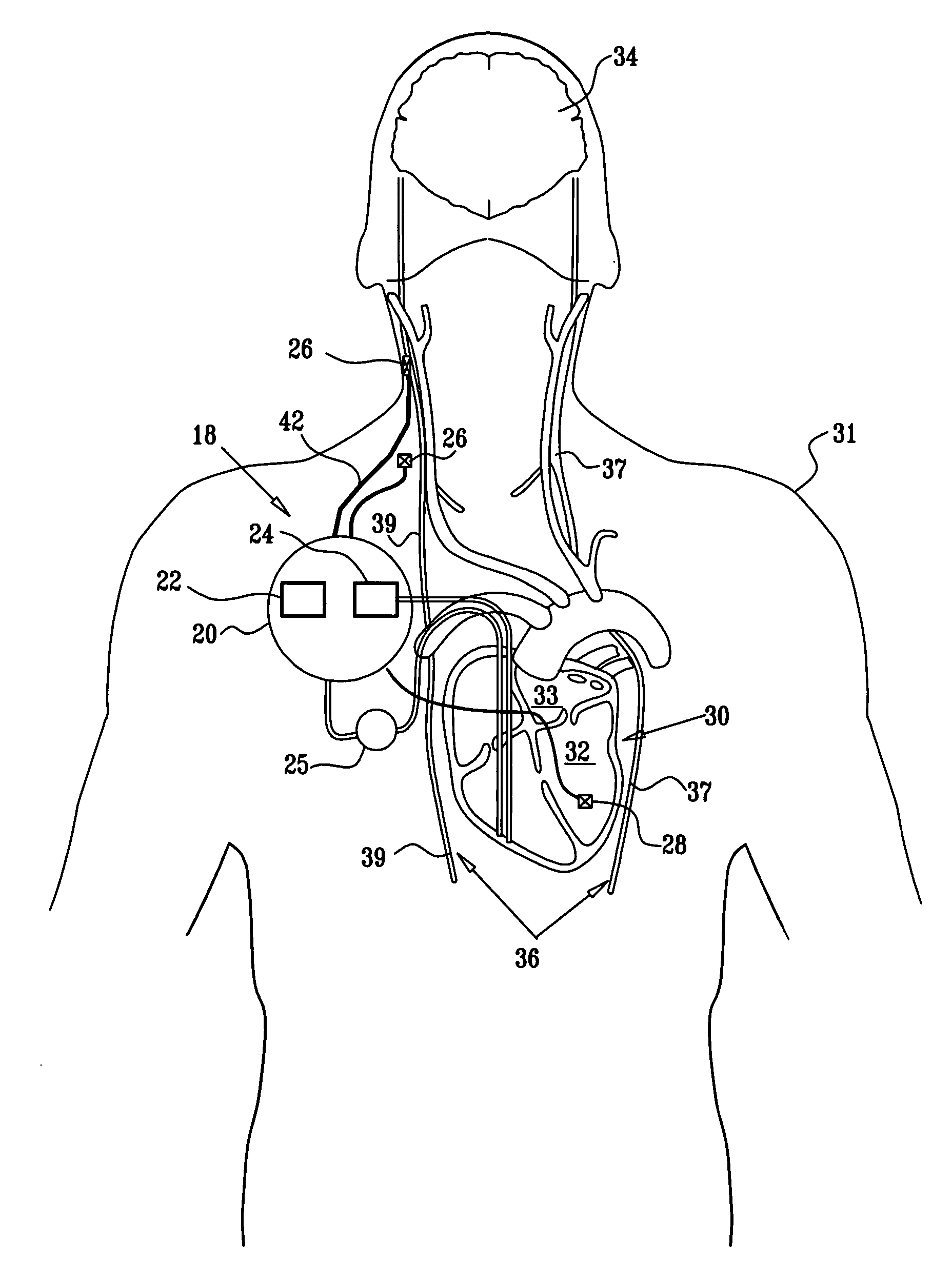
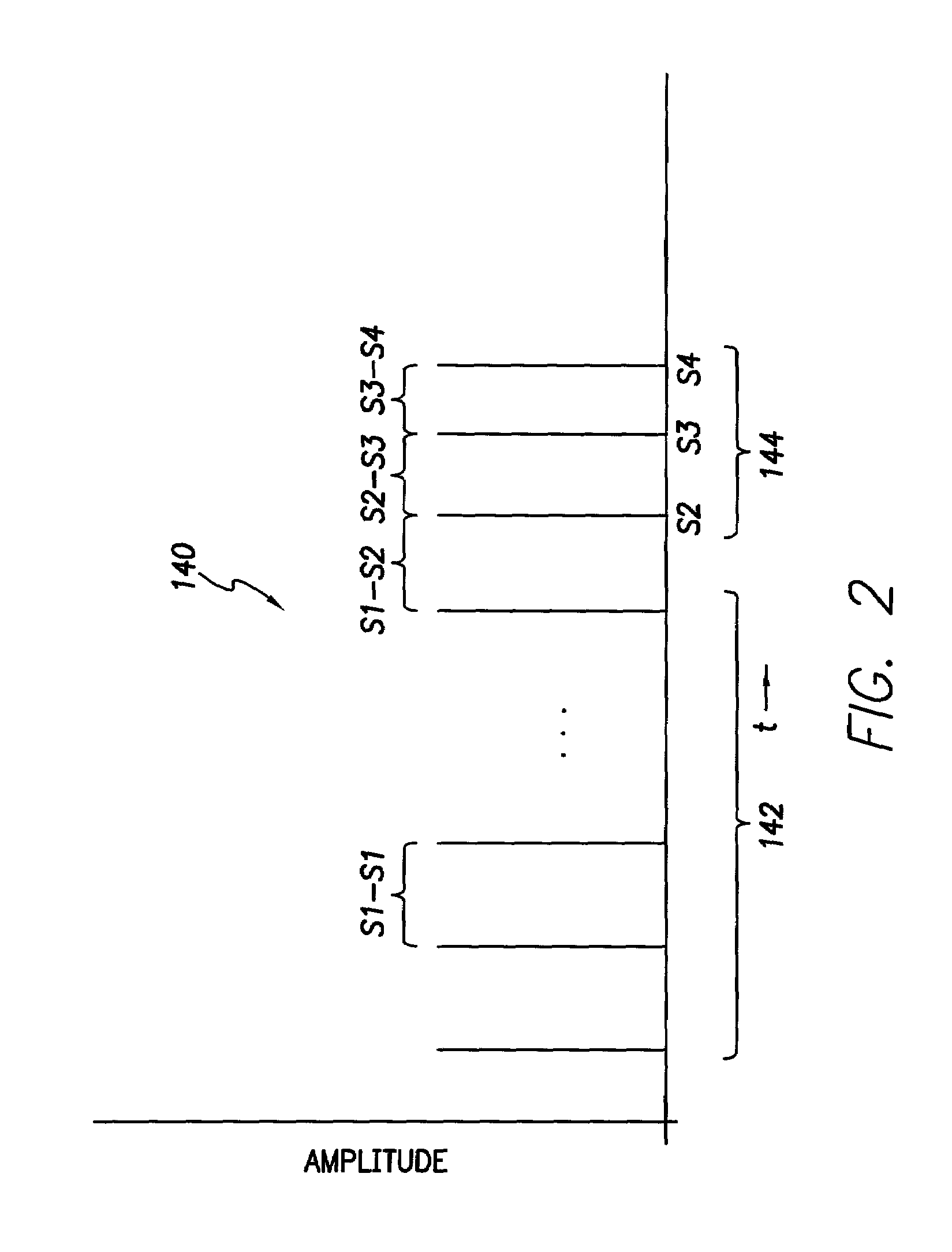
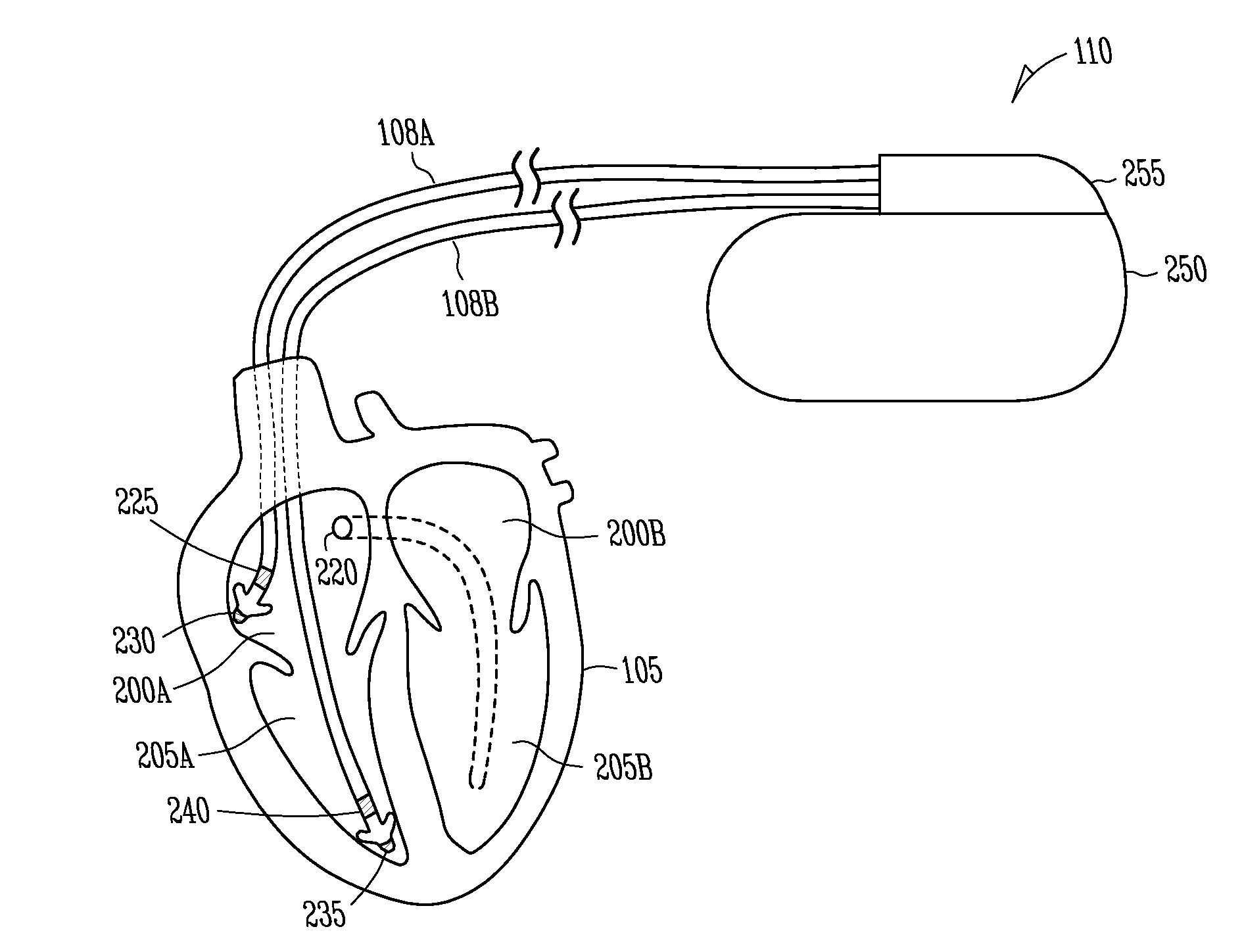
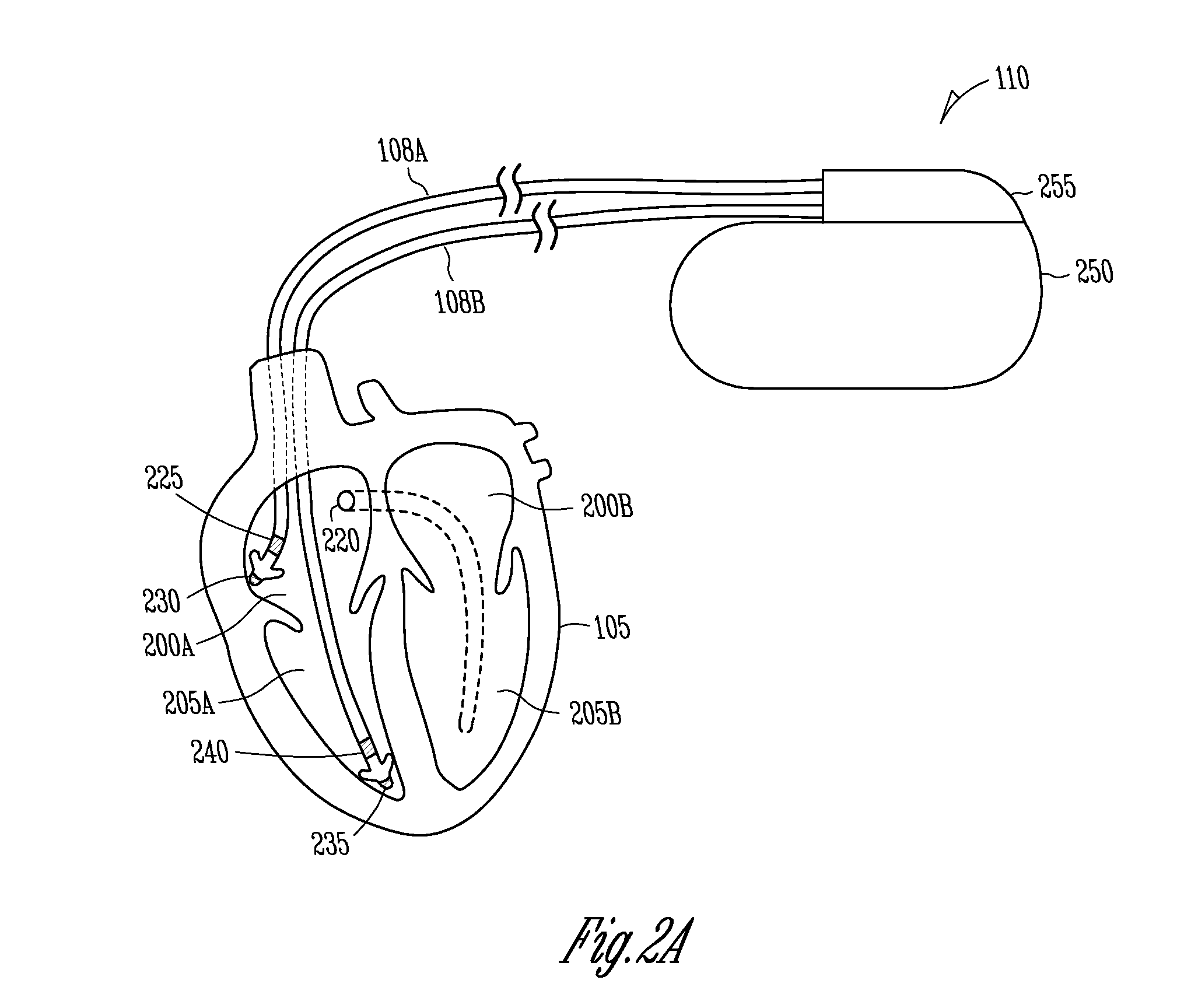
InactiveUS7212859B1Minimum of perceived discomfortMaintain validityHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac stimulationPaced Ventricular Rhythm
An implantable cardiac stimulation system delivers arrhythmia termination pulses to the ventricles and the atria of a heart. The system includes an implantable cardiac stimulation device, including a conductive enclosure, ventricular arrhythmia termination pulse generator, and an atrial arrhythmia termination pulse generator. A first electrode configuration, including the conductive enclosure, is arranged to be coupled to the ventricular pulse generator to terminate ventricular arrhythmias and a second electrode configuration, electrically independent from the conductive enclosure and confined within the heart, is arranged to be coupled to the atrial pulse generator to terminate atrial arrhythmias.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com