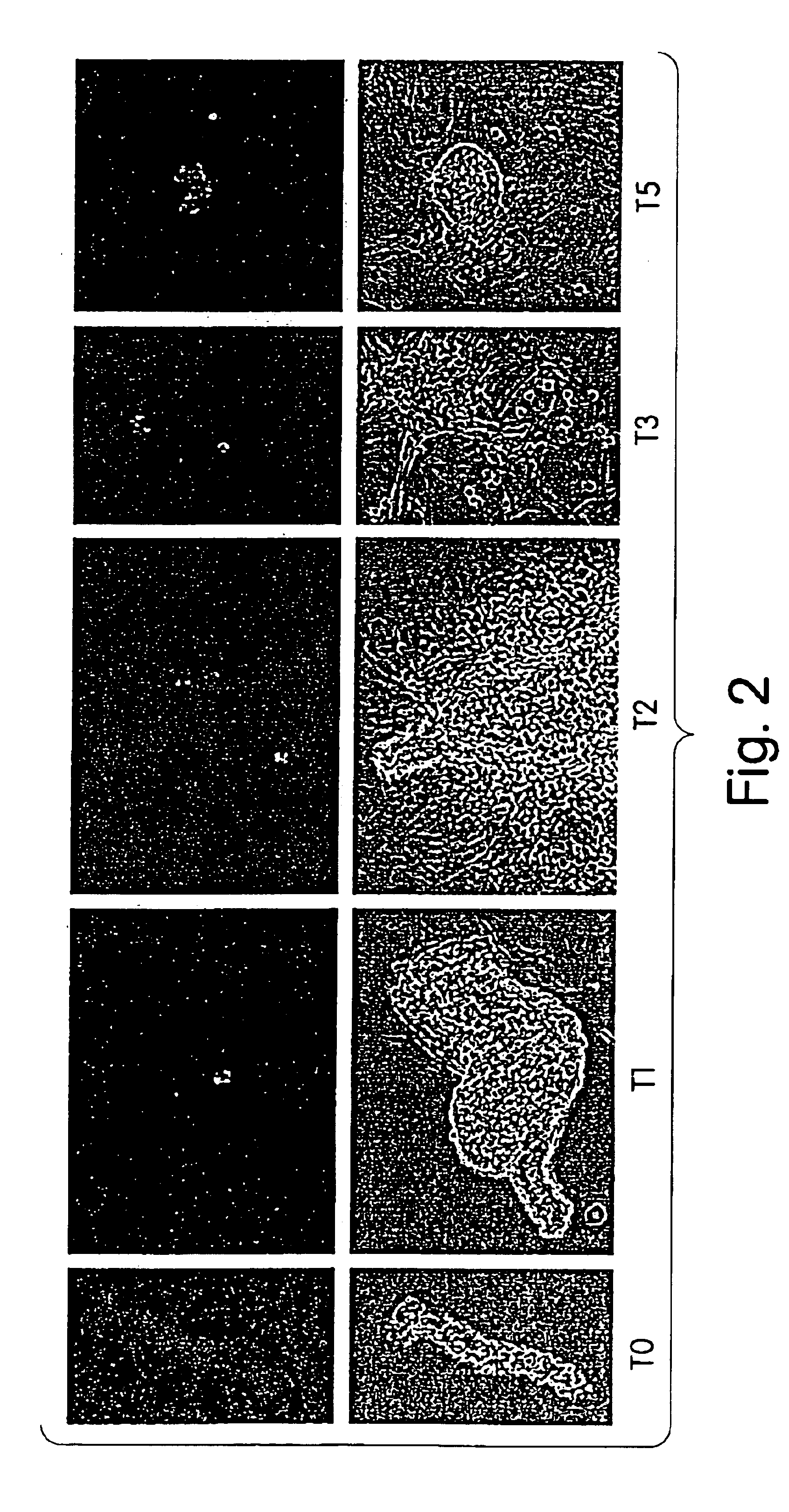
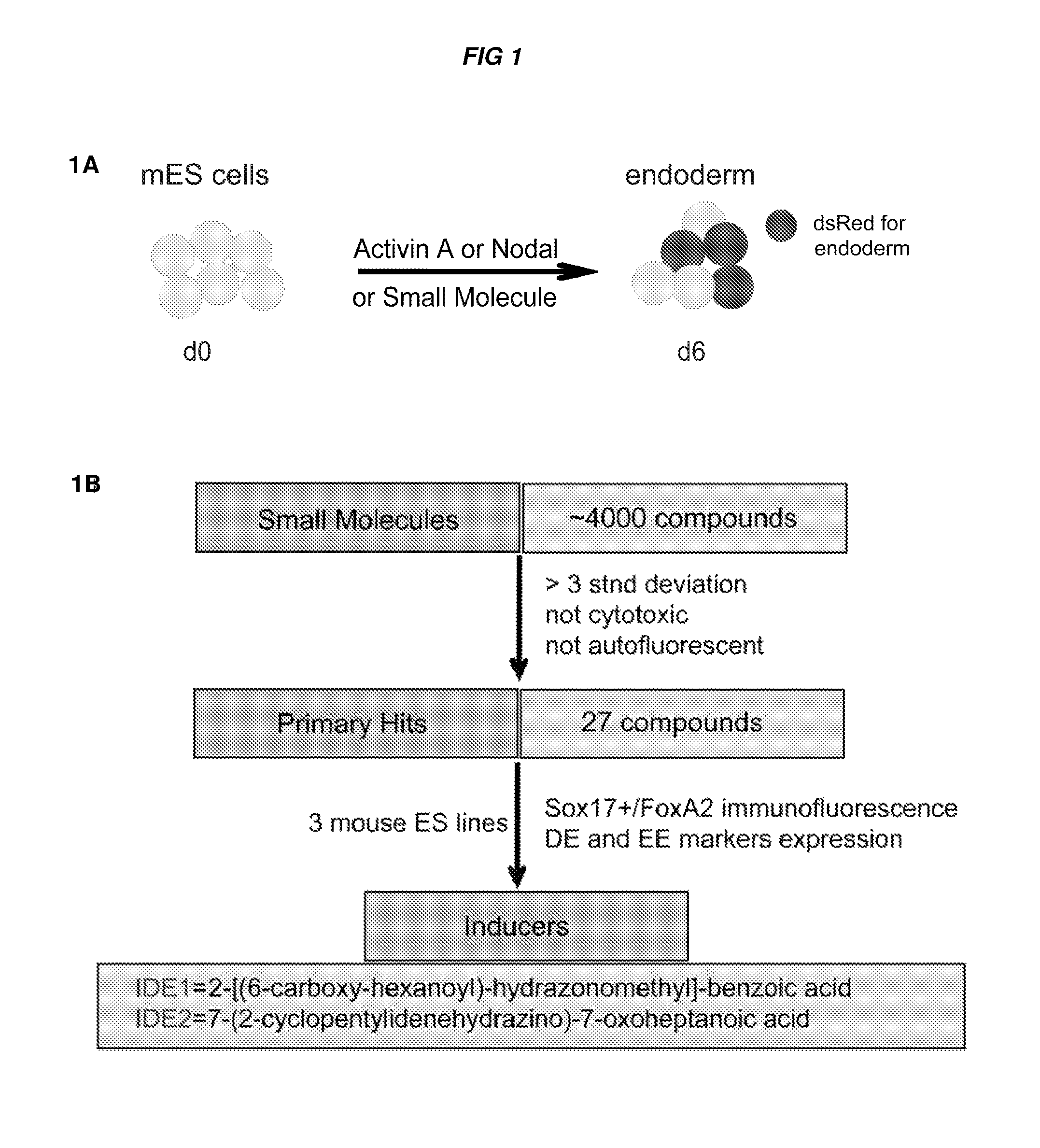
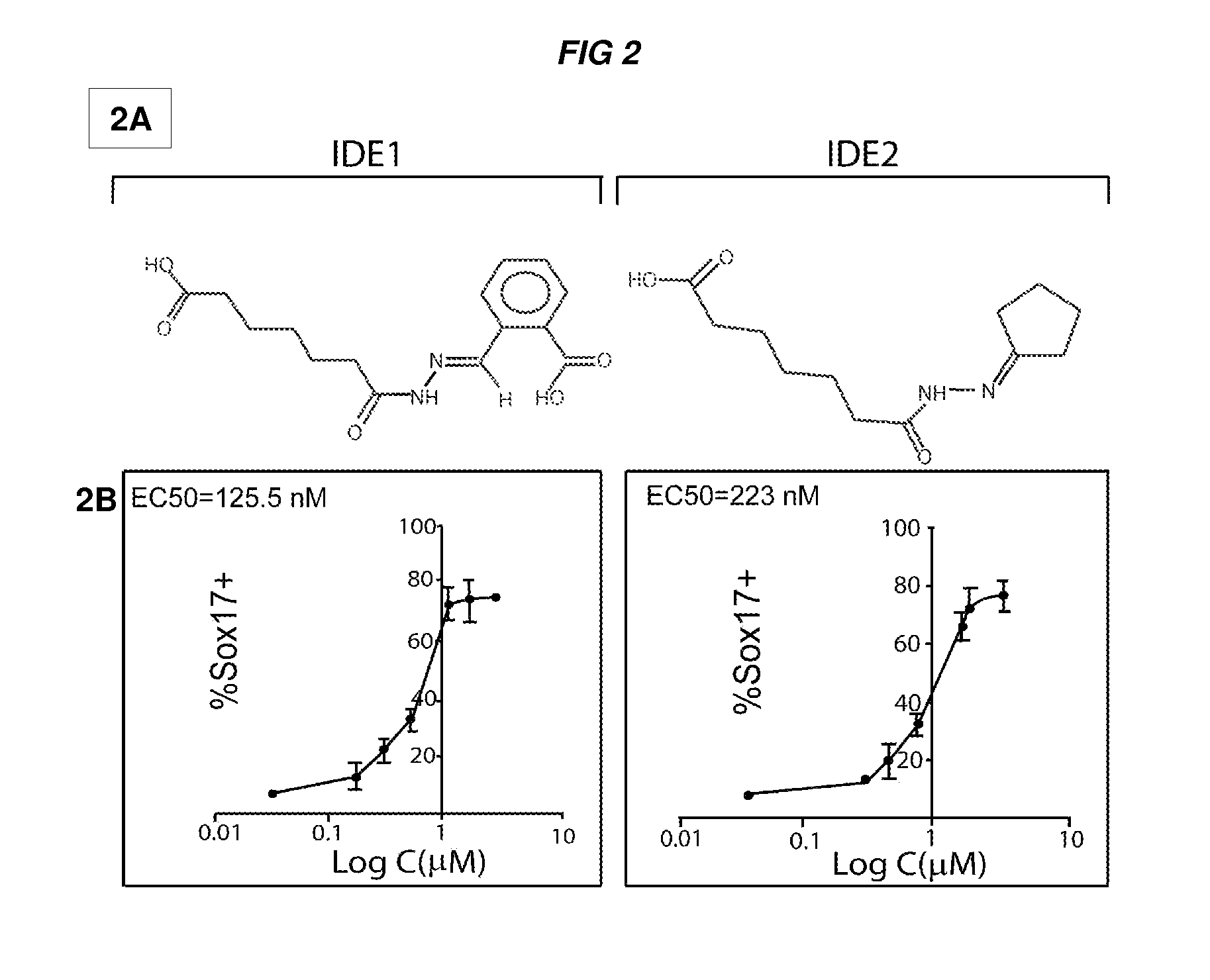
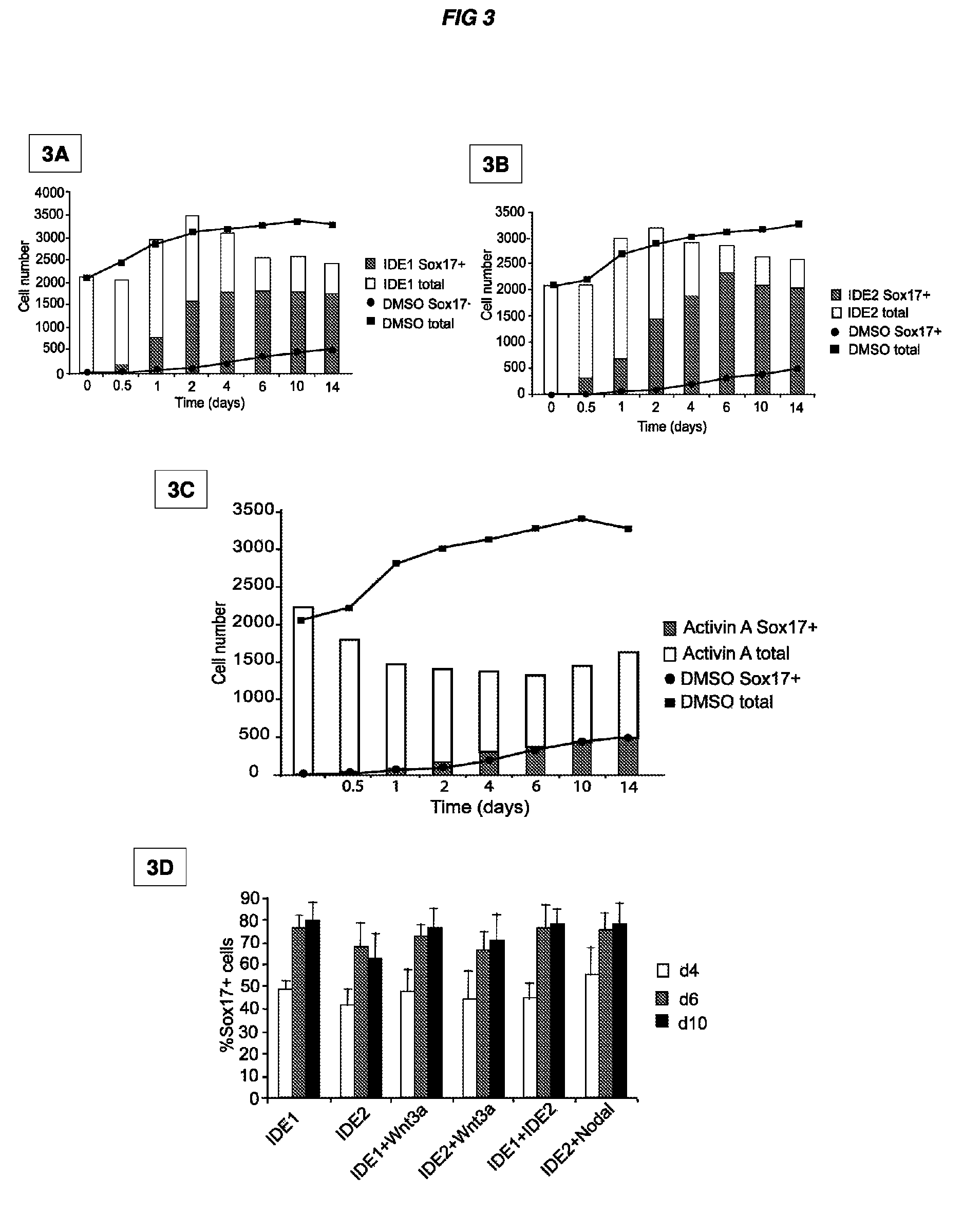
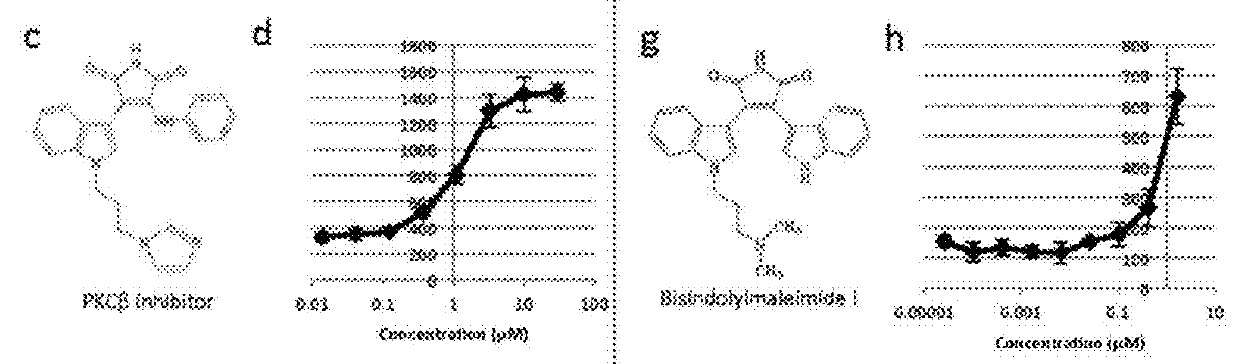
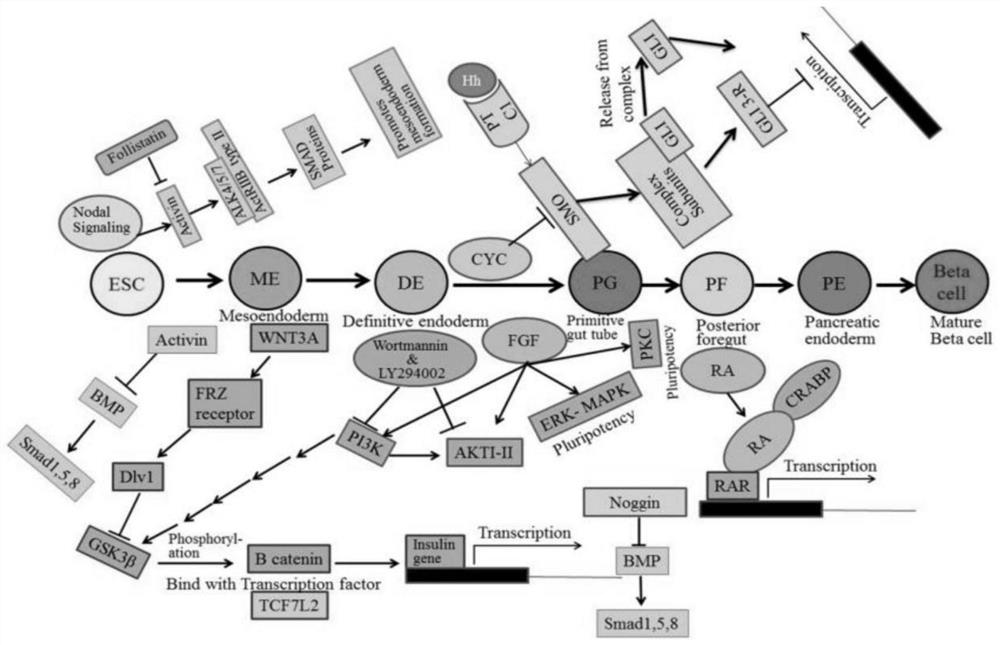
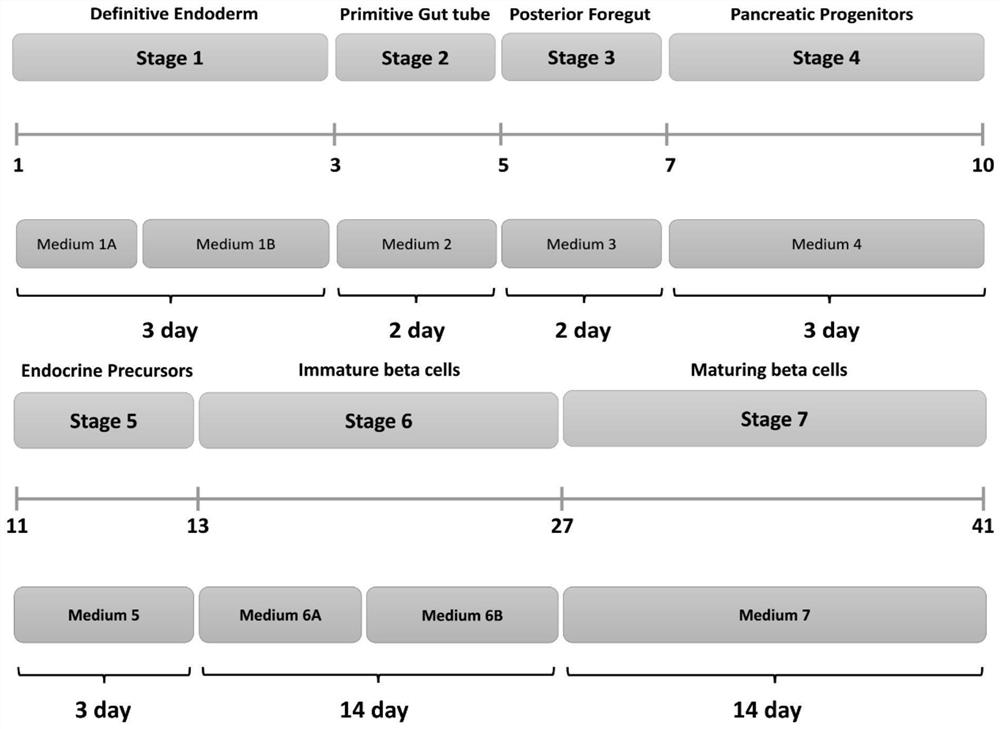
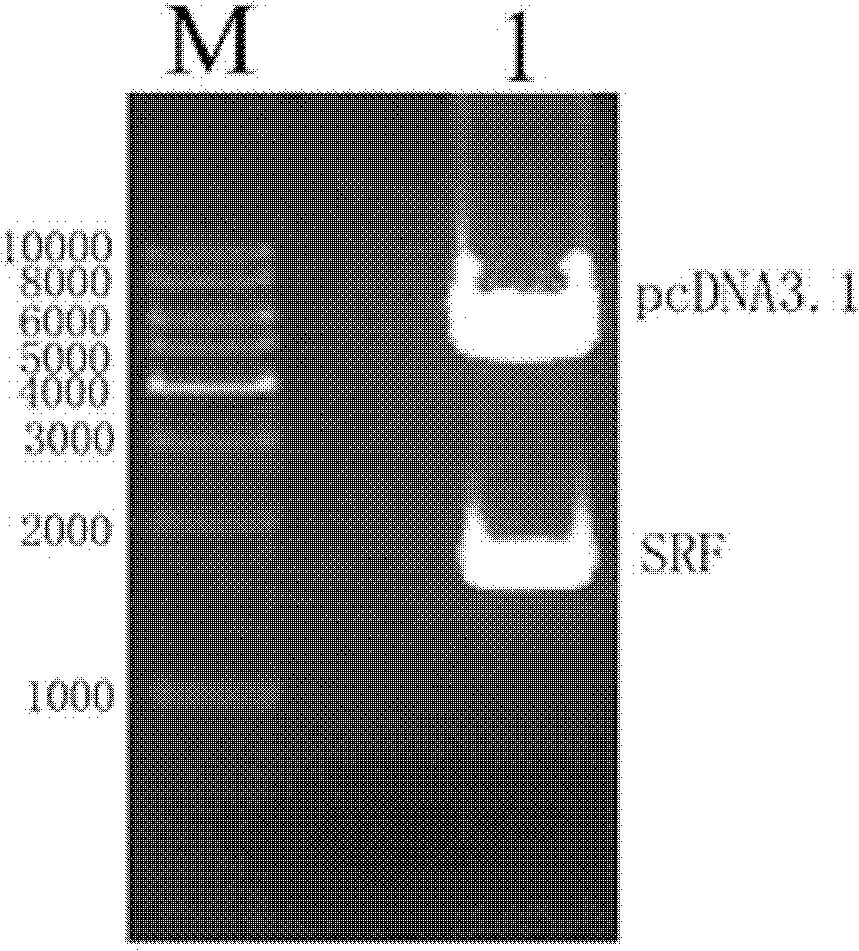Patents
Literature
58 results about "Pancreatic progenitor cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pancreatic progenitor cells are multipotent stem cells originating from the developing fore-gut endoderm which have the ability to differentiate into the lineage specific progenitors responsible for the developing pancreas.
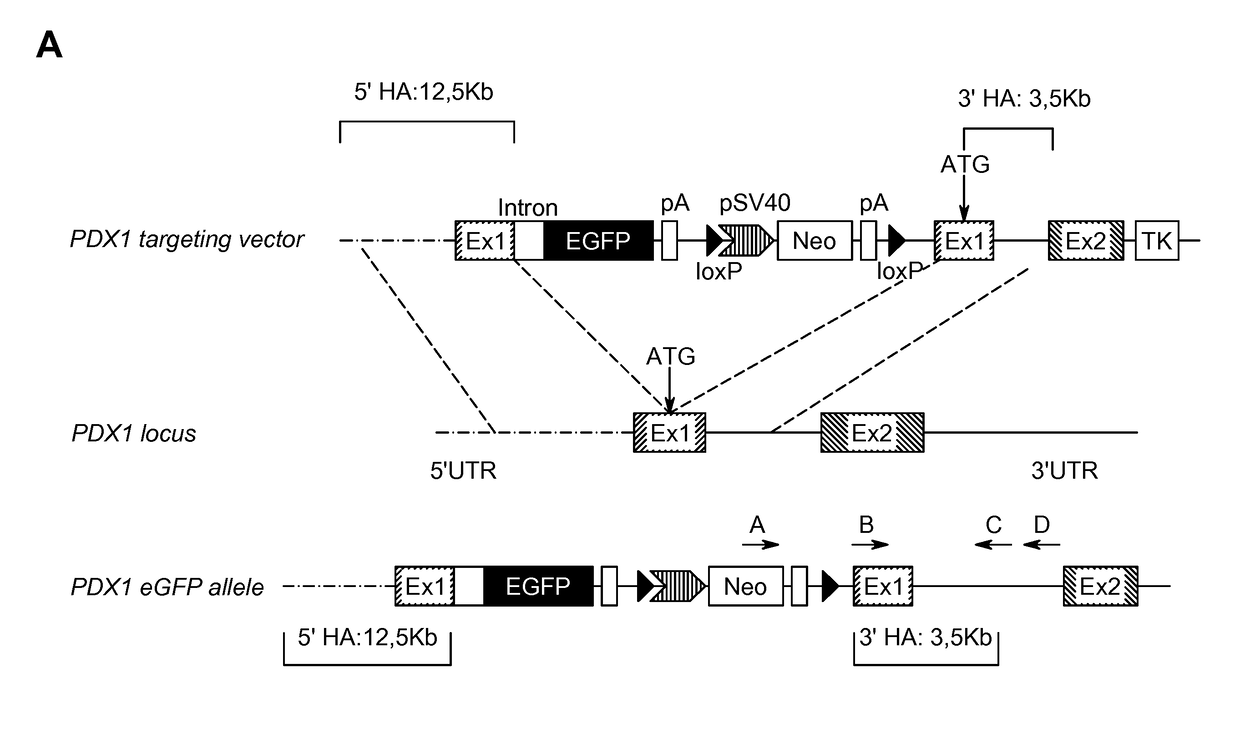
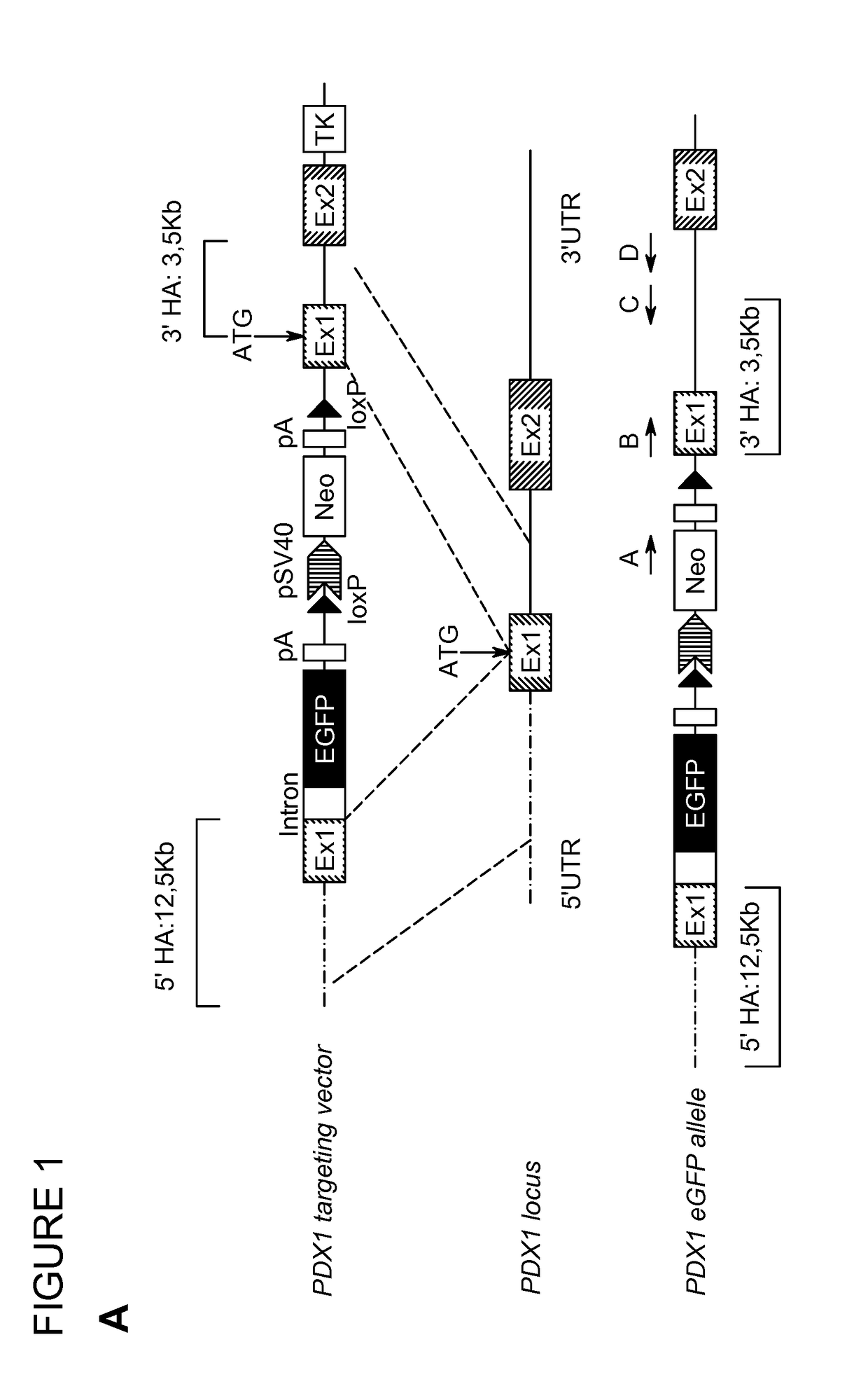
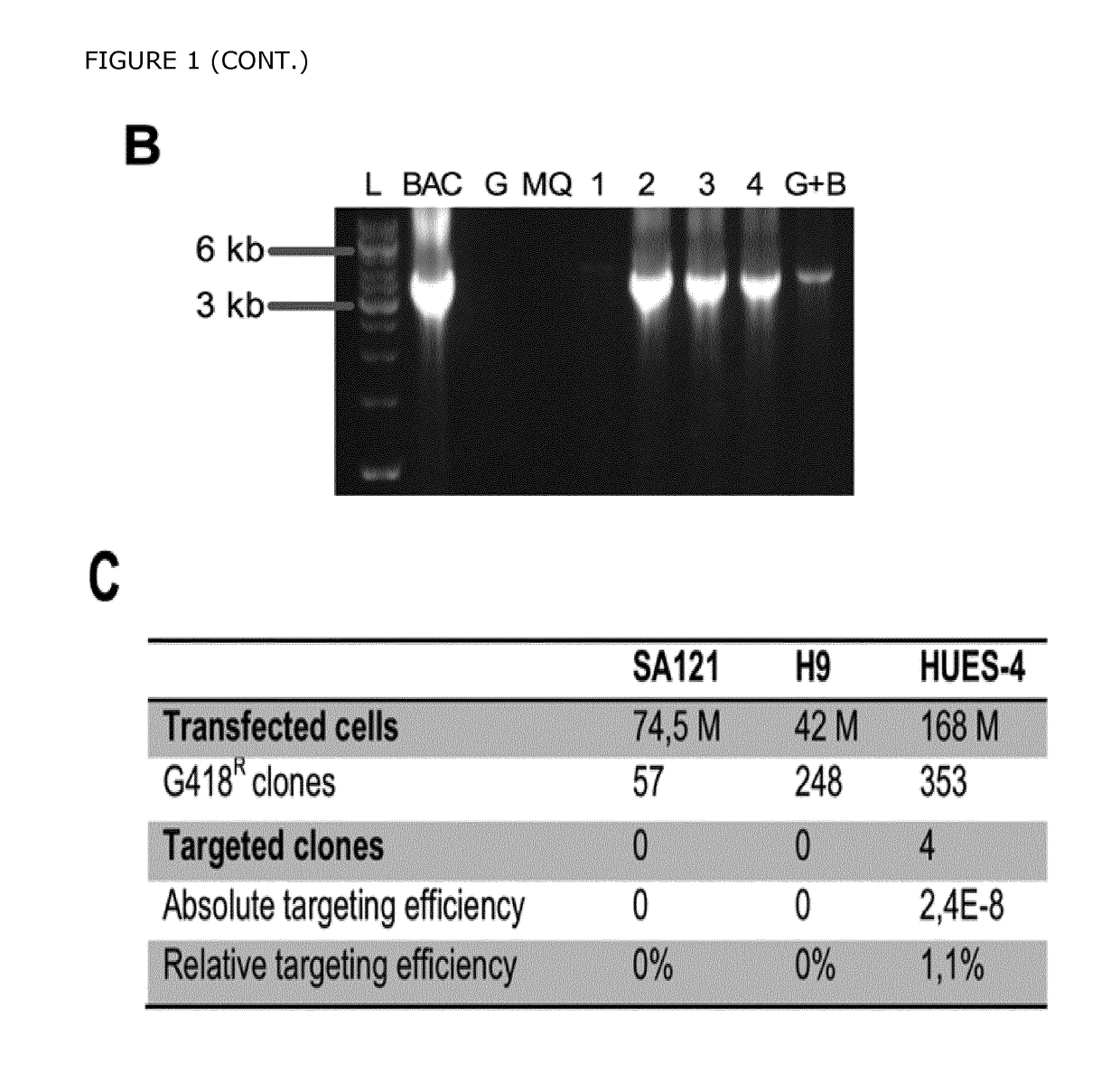
Methods and devices for differentiating pluripotent stem cells into cells of the pancreatic lineage
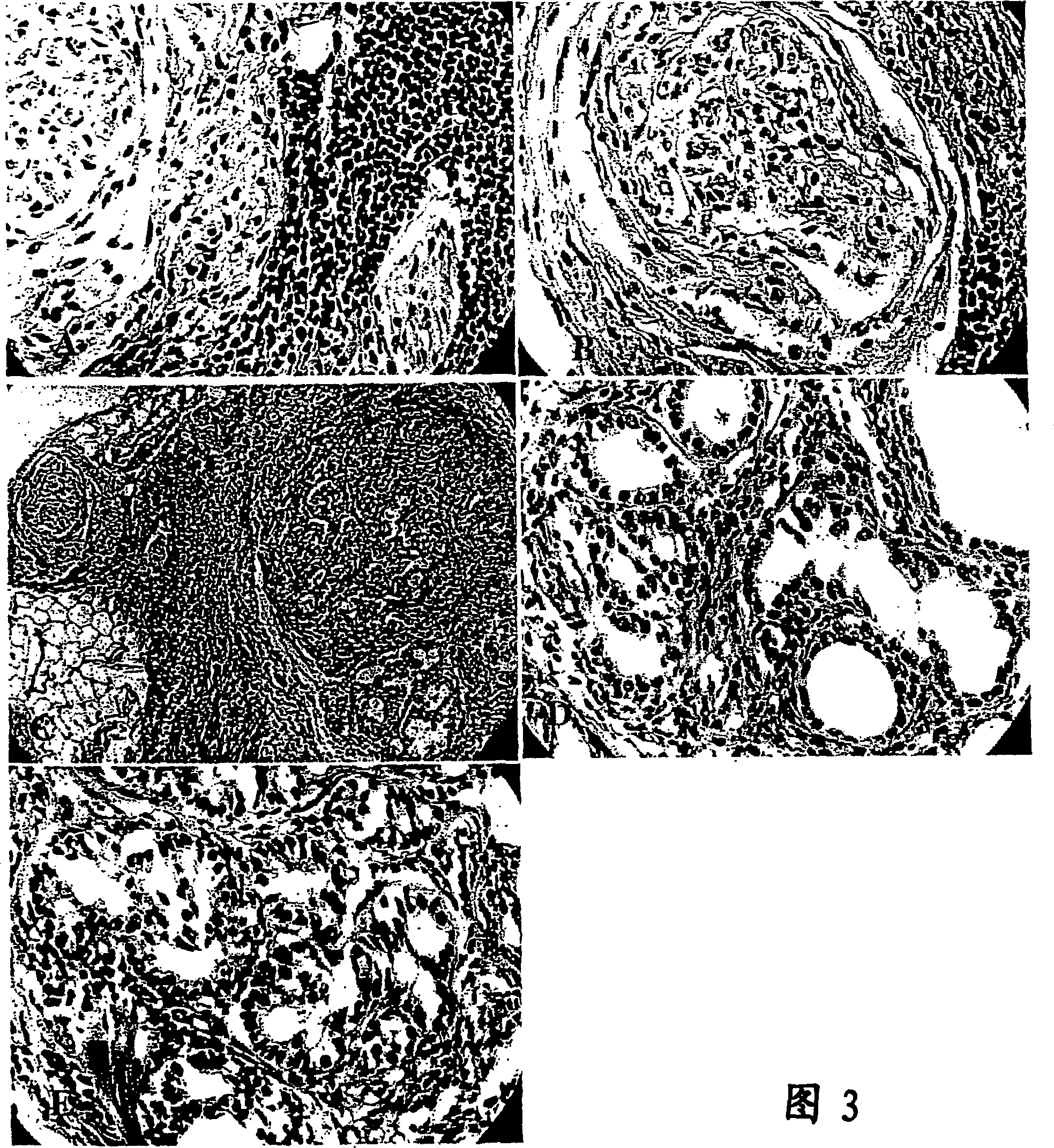
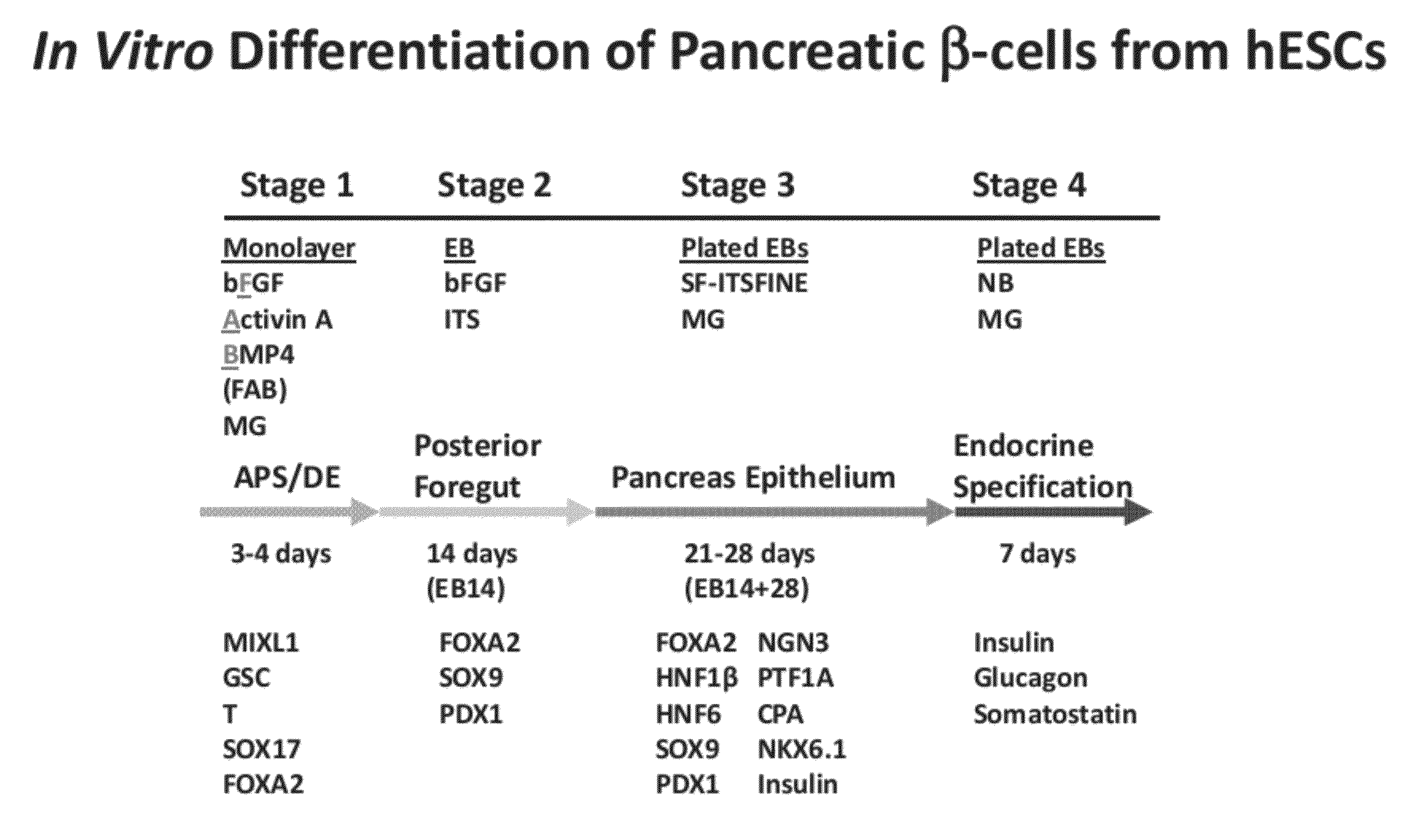
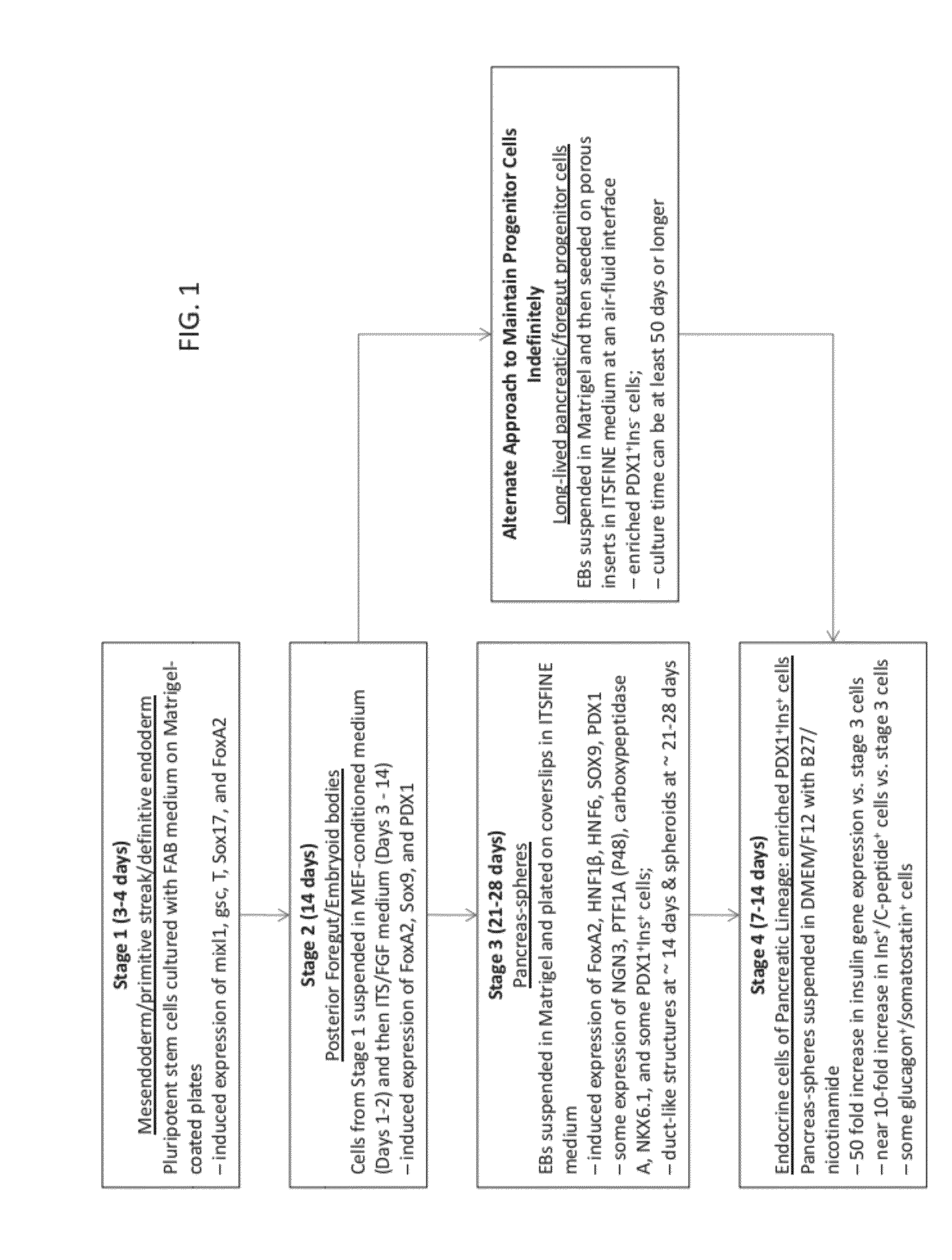
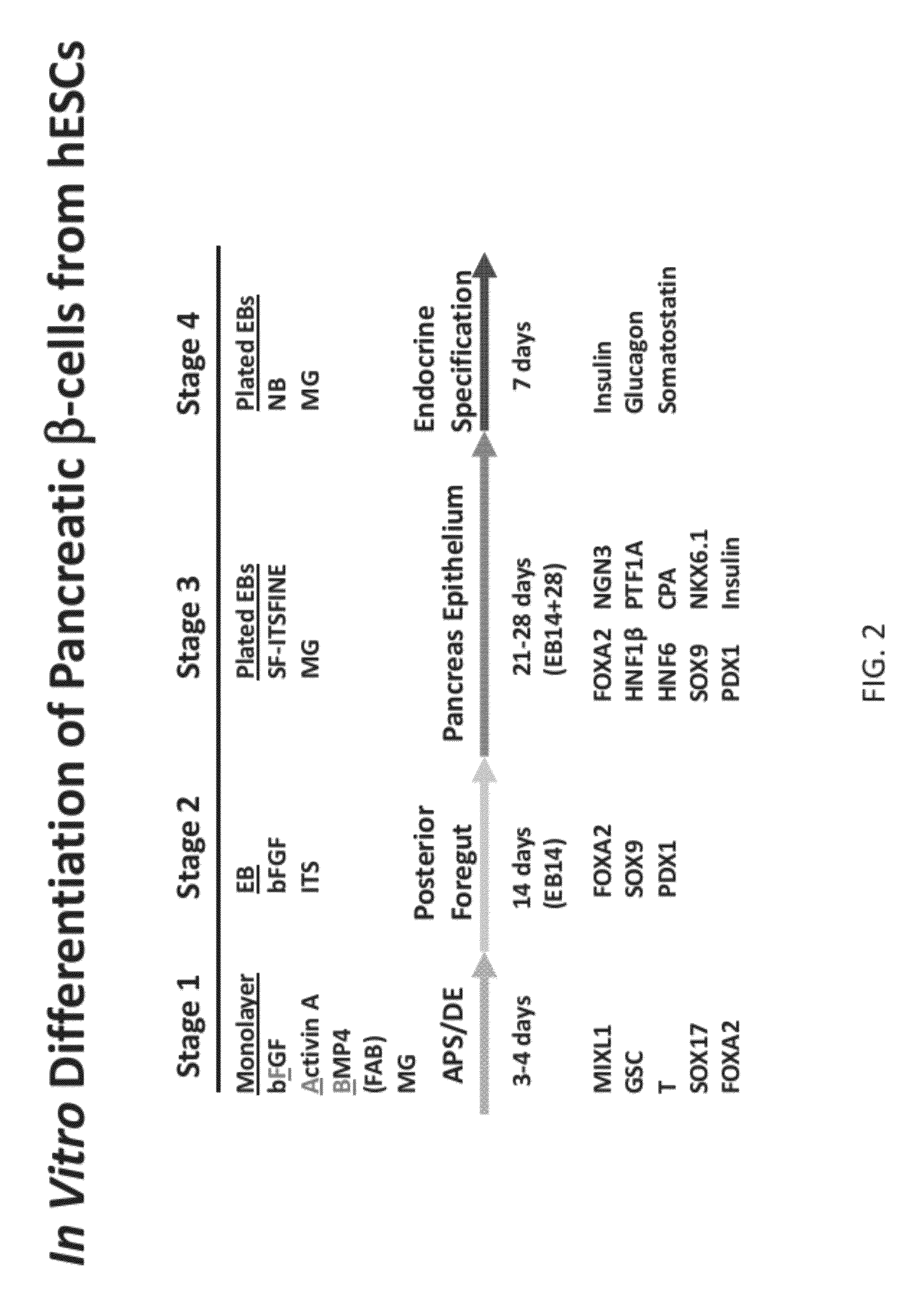
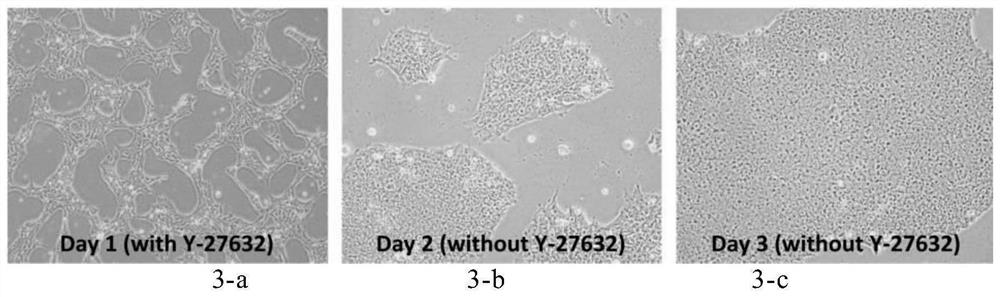
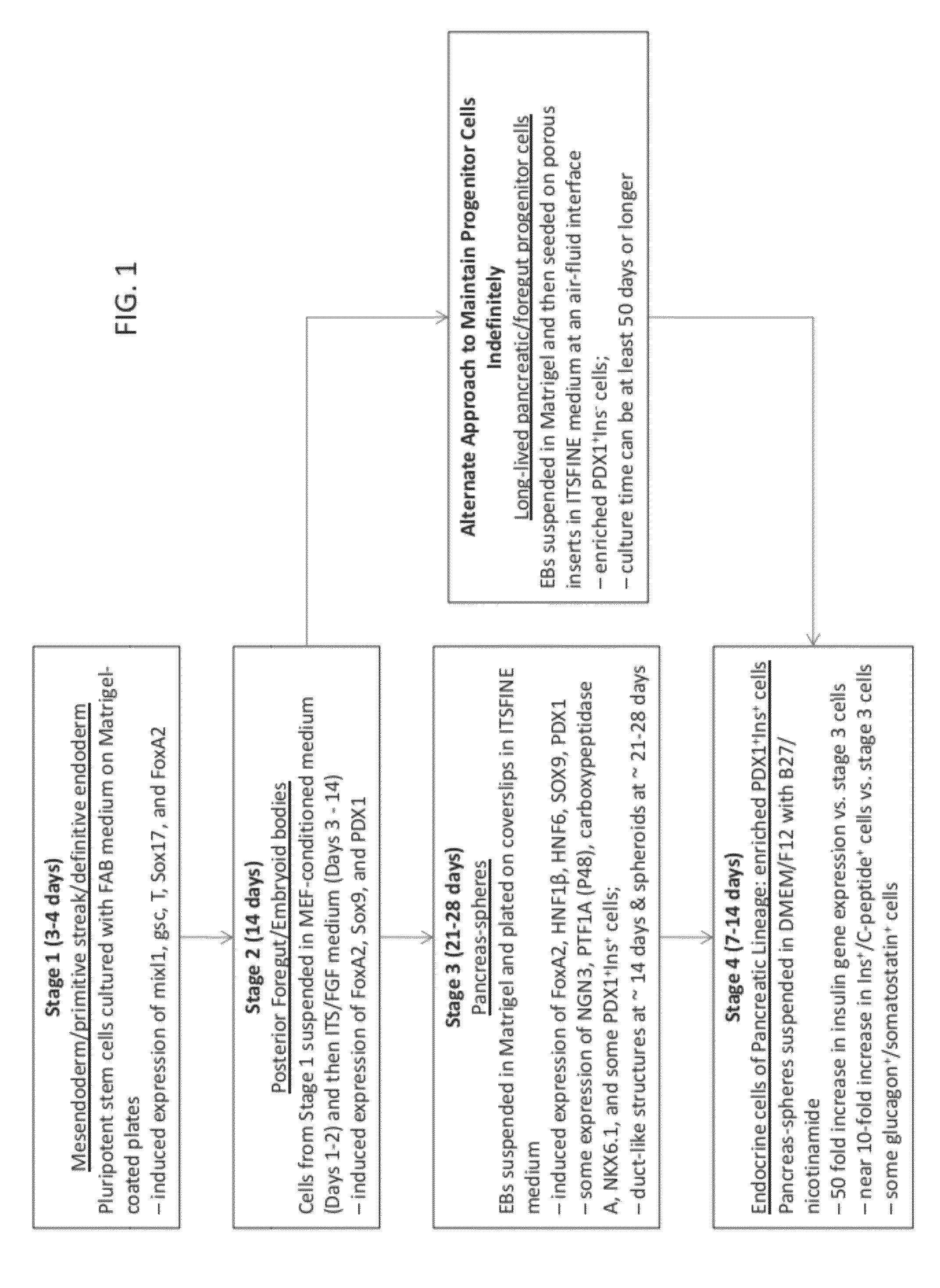
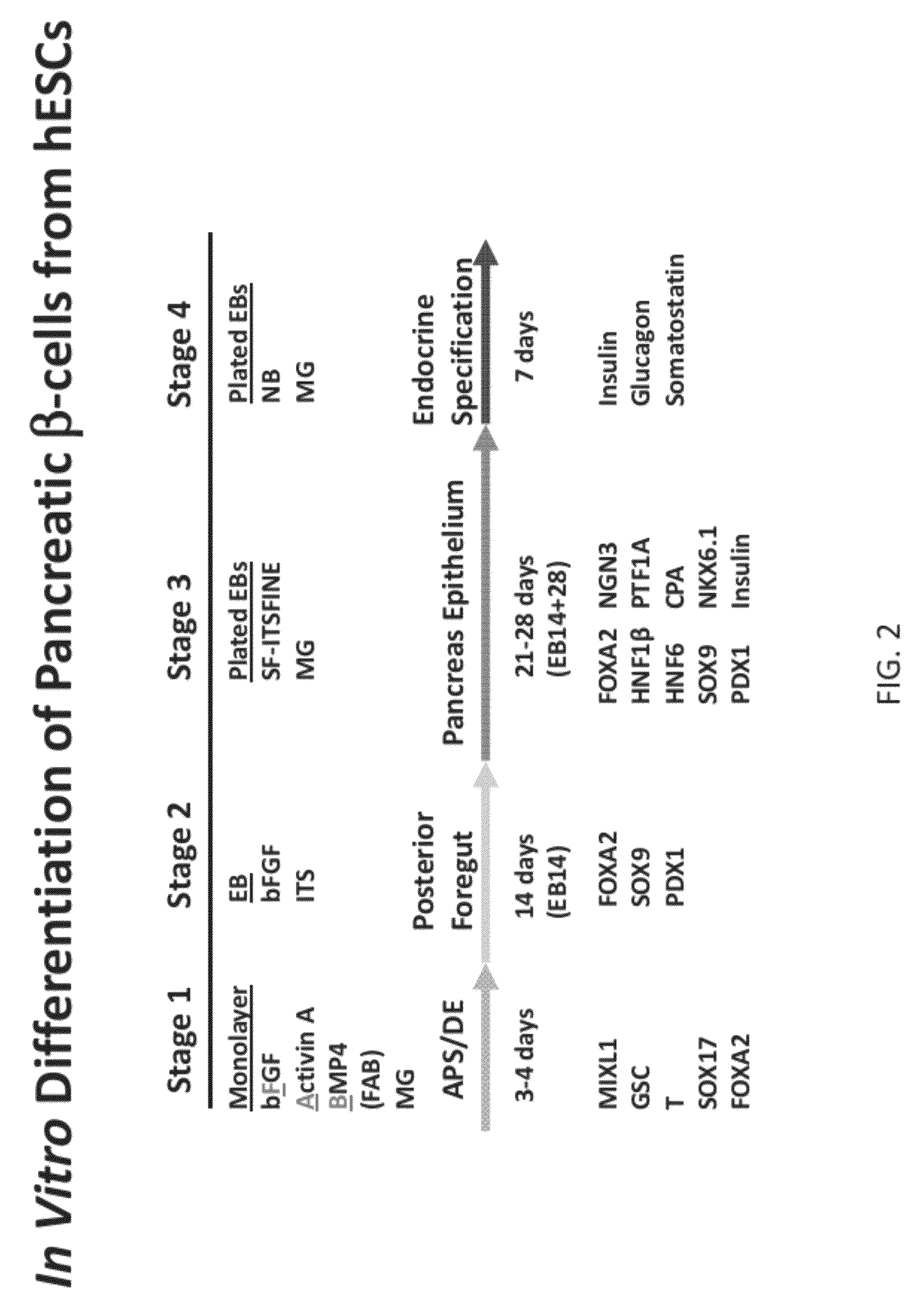
Methods and devices for culturing human pluripotent stem cells to produce cells of the pancreatic lineage are disclosed. The methods include steps of culturing the stem cells under conditions that induce the expression of mesendoderm / primitive streak and definitive endoderm markers in a chemically defined medium including an effective amount of i) fibroblast growth factor, ii) Activin A, and iii) bone morphogenetic protein. The methods further include the steps of culturing cells under conditions favoring the formation of at least one of intact embryoid bodies and pancreatic progenitor PDX1+ Ins− cells.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
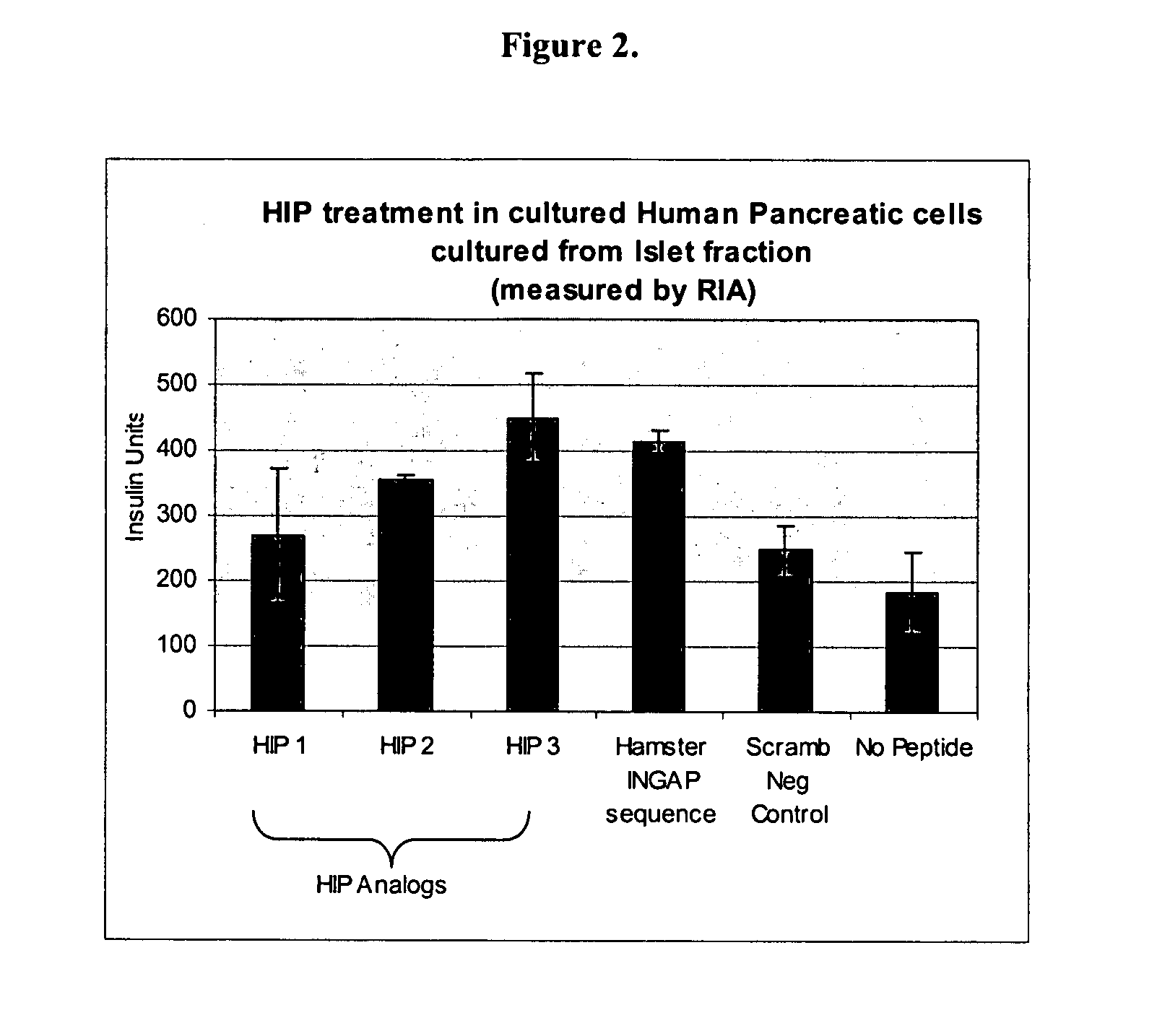
Peptides, derivatives and analogs thereof, and methods of using same
InactiveUS7393919B2Reduce needStimulating GLP-1 receptorsOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderHuman Proislet PeptideProgenitor
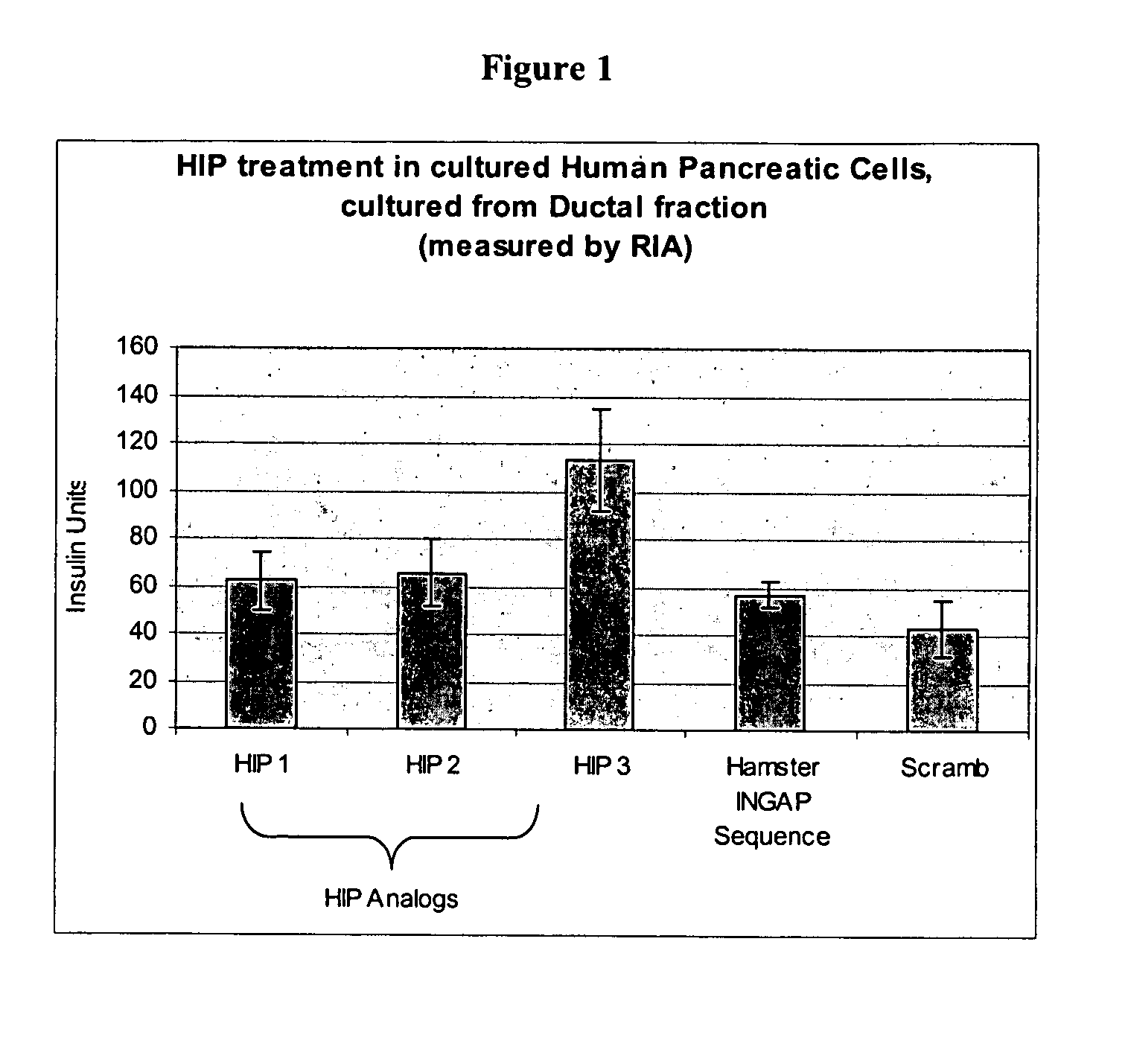
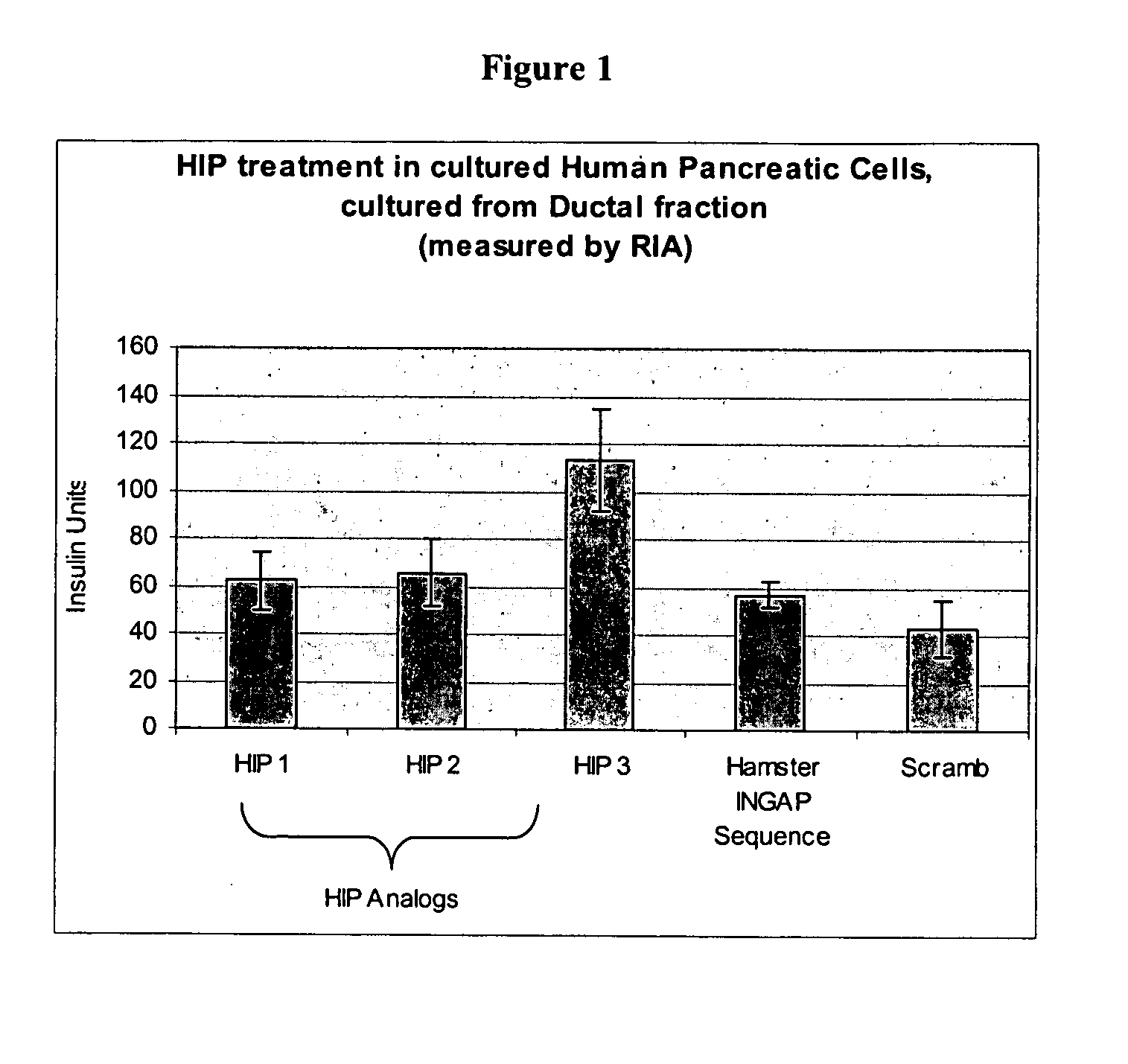
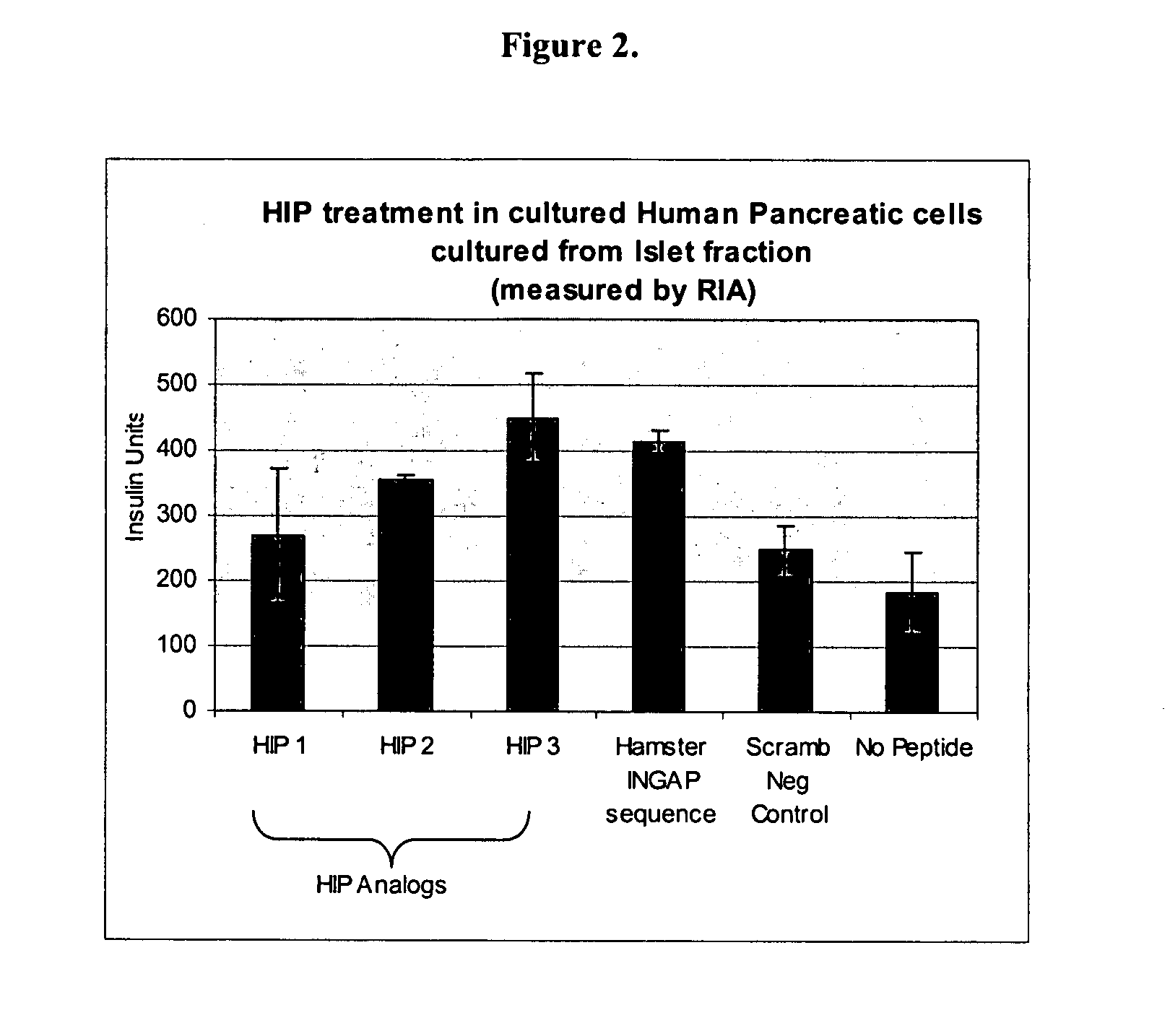
Human proIslet Peptides (HIP) and HIP analogs and derivatives thereof, derived from or homologous in sequence to the human REG3A protein, chromosome 2p12, are able to induce islet neogenesis from endogenous pancreatic progenitor cells. Human proIslet Peptides are used either alone or in combination with other pharmaceuticals in the treatment of type 1 and type 2 diabetes and other pathologies related to aberrant glucose, carbohydrate, and / or lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, overweight, obesity, polycystic ovarian syndrome, eating disorders and the metabolic syndrome.
Owner:CUREDM GRP HLDG
Method and apparatus for cell culture using a two liquid phase bioreactor
InactiveUS20050176140A1Maximize growthMaximize proliferationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell phenotypeEmbryo
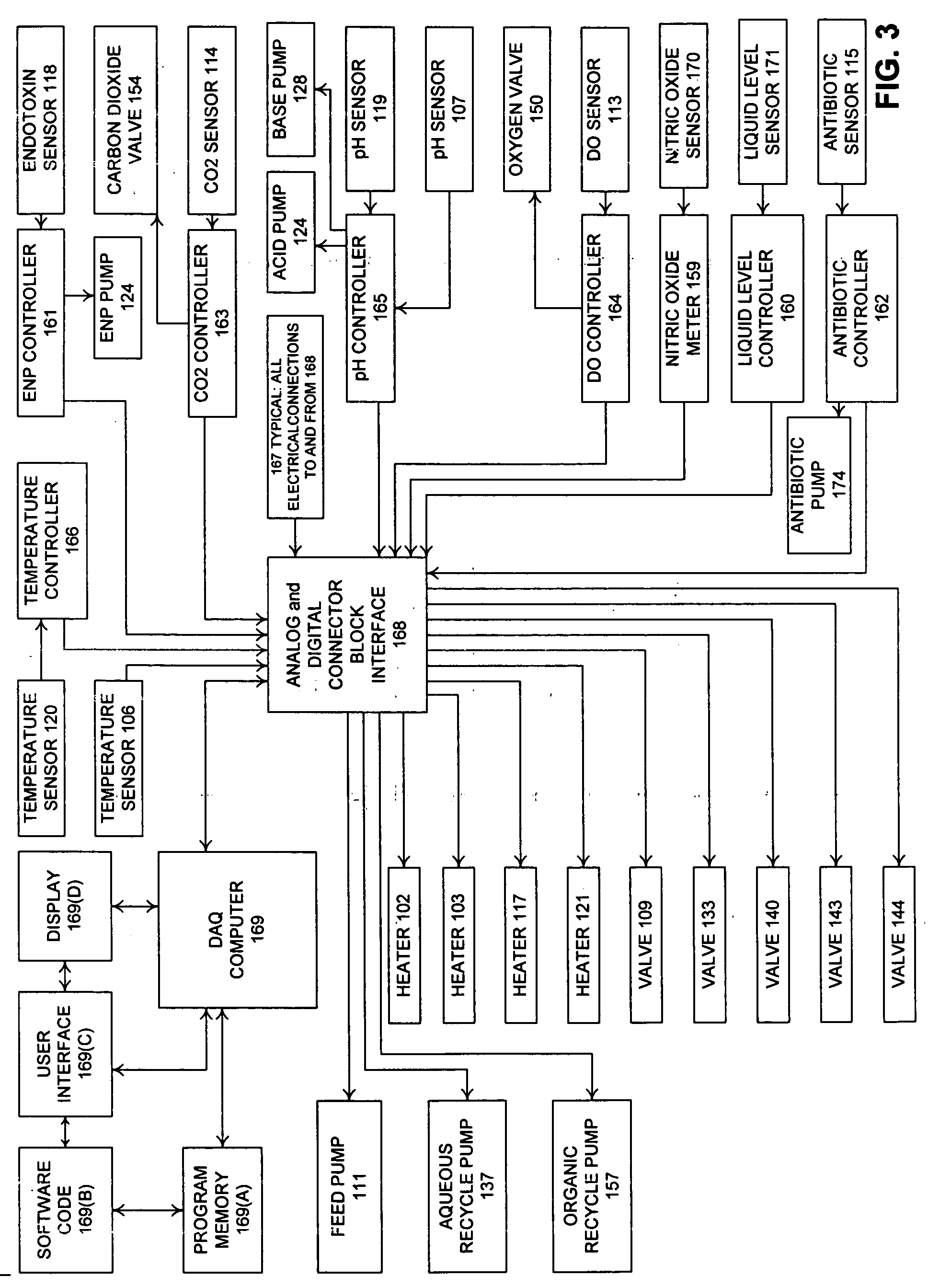
Advanced Bioreactor Cell Culture Technology presents a method of cell culturing and bioprocessing incorporating molecular biology techniques, advanced process control methodology, and a process control interface applied to a two liquid phase cell culture bioreactors to proliferate, grow, and expand non-differentiated precursor cells, embryonic stem (ES) cells, endocrine progenitor cells, pancreatic progenitor cells, pancreatic stem cells, pancreatic duct epithelial cells, nestin-positive islet-derived progenitor cells (NIPs), or pluripotent non-embryonic stem (PNES) cells in the bioreactor, and influence, stimulate, and induce the non-differentiated precursors and progenitors into fully differentiated beta cell phenotypes; including microprocessor control of cell culture process variables and data acquisition during bioprocessing. The invention may be applied to precursors and progenitor cells either transgenic or non-transgenic derived from animals and mammals.
Owner:BENEDICT DANIEL J +1
Peptides, derivatives and analogs thereof, and methods of using same
InactiveUS20070087971A1Promoting beta cell regenerationIncrease satietyOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderHuman Proislet PeptideProgenitor
Human proIslet Peptides (HIP) and HIP analogs and derivatives thereof, derived from or homologous in sequence to the human REG3A protein, chromosome 2p12, are able to induce islet neogenesis from endogenous pancreatic progenitor cells. Human proIslet Peptides are used either alone or in combination with other pharmaceuticals in the treatment of type 1 and type 2 diabetes and other pathologies related to aberrant glucose, carbohydrate, and / or lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, overweight, obesity, polycystic ovarian syndrome, eating disorders and the metabolic syndrome.
Owner:CUREDM GRP HLDG
Methods for reprogramming cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20140038291A1Eliminate the problemGenetically modified cellsPancreatic cellsProgenitorReprogramming
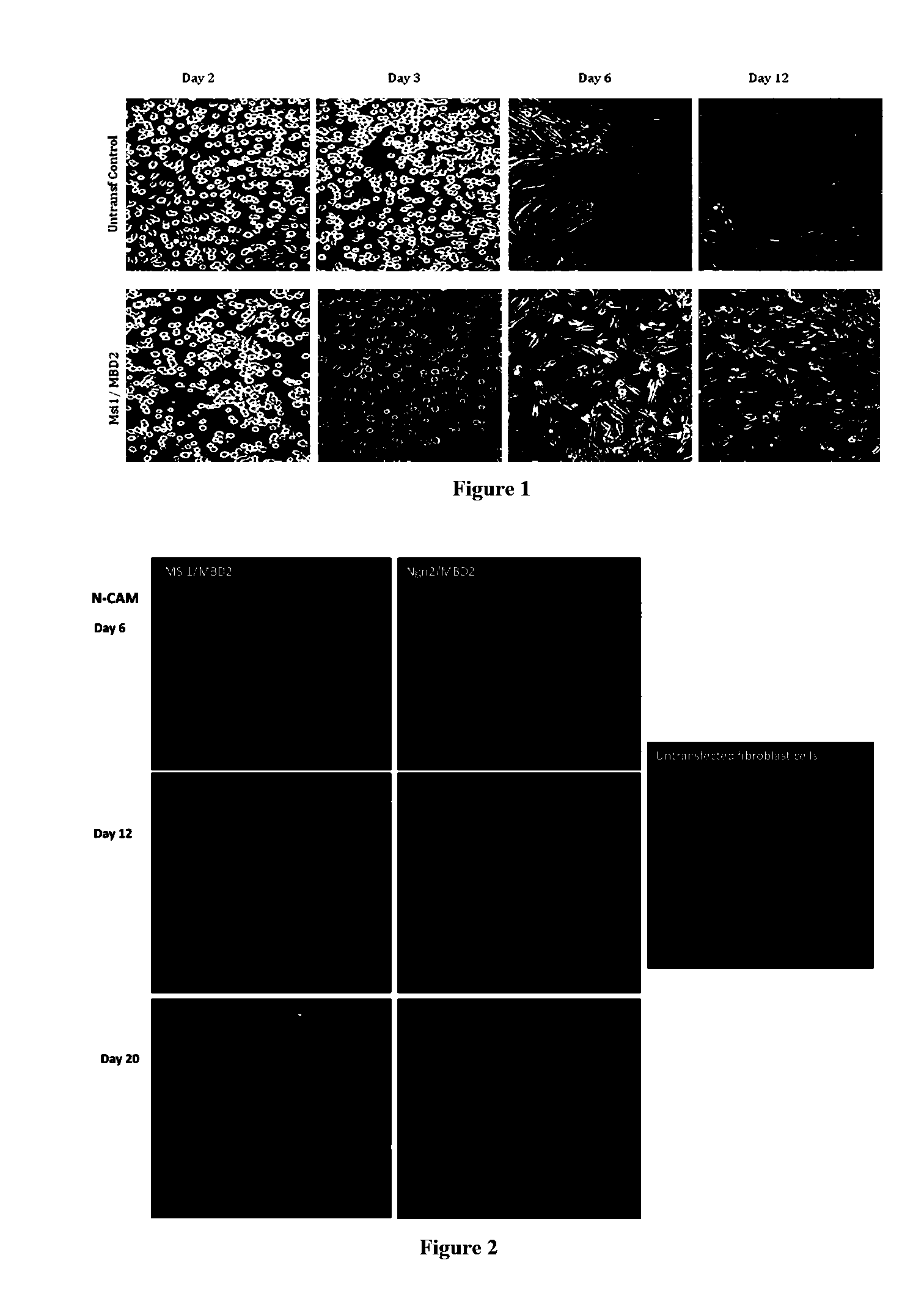
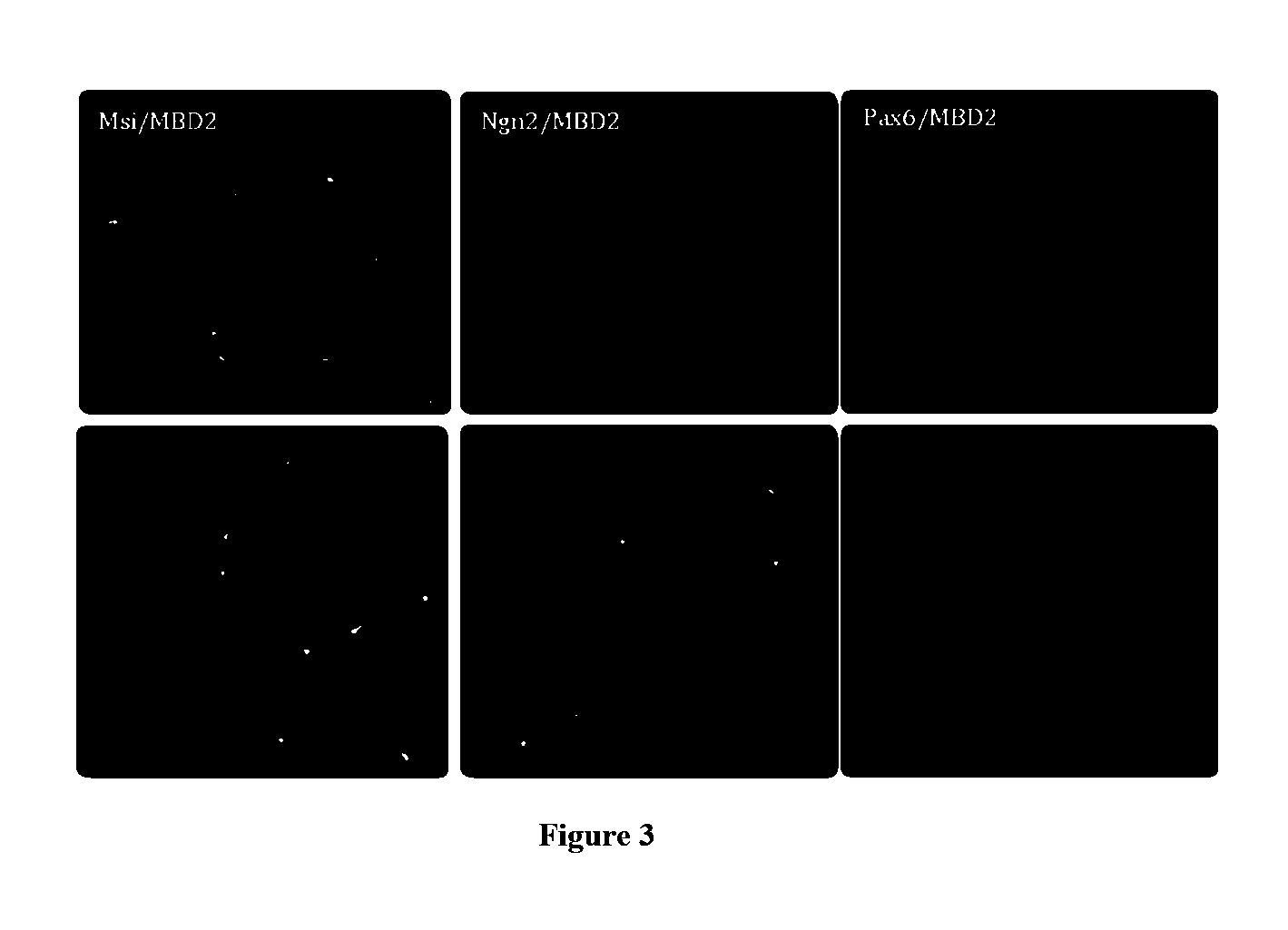
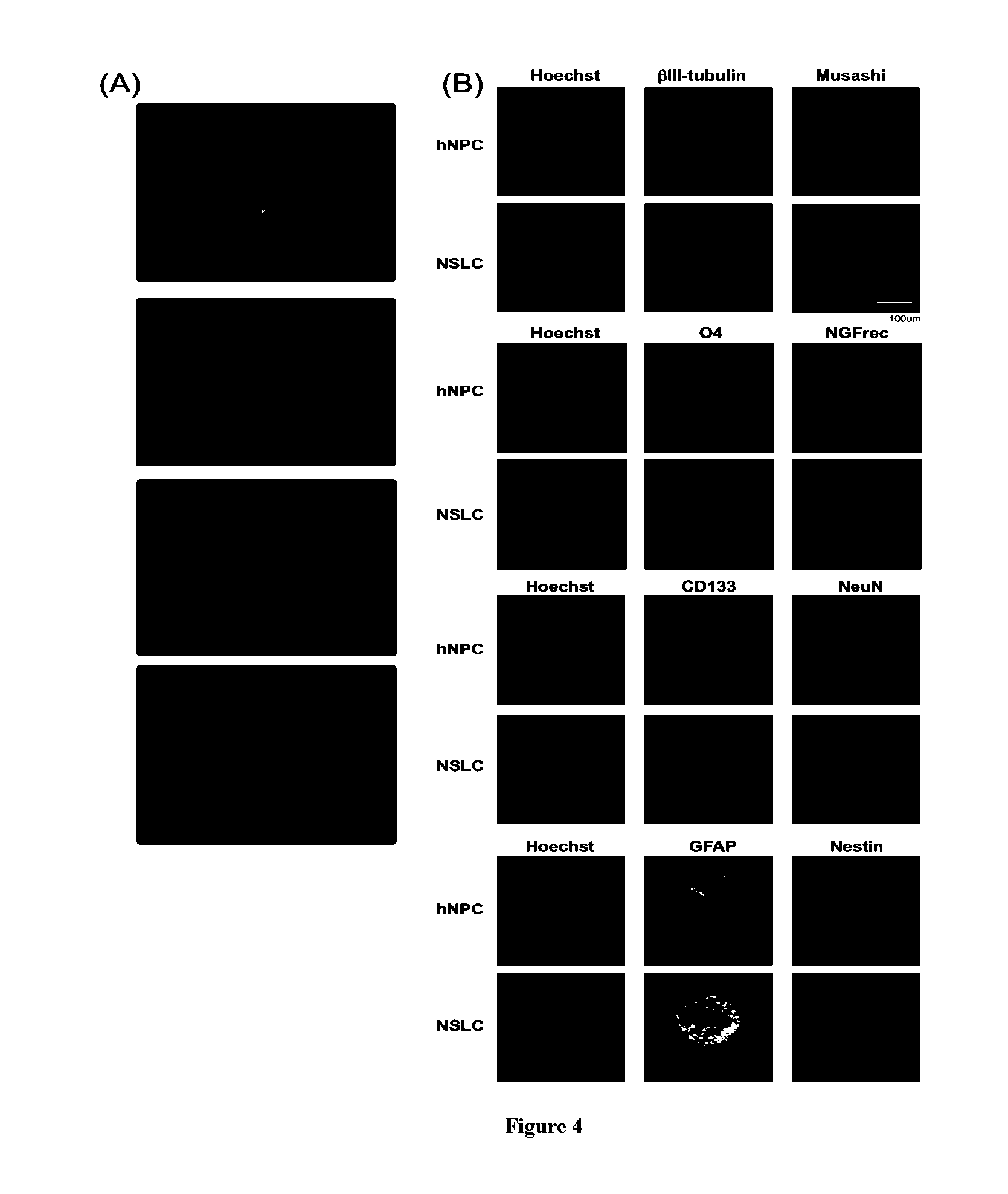
Described herein are reprogrammed cells, and methods for cell dedifferentiation, transformation and eukaryotic cell reprogramming. Also descried are cells, cell lines, and tissues that can be transplanted in a patient after steps of in vitro dedifferentiation and in vitro reprogramming. In particular embodiments the cells are Stem-Like Cells (SLCs), including Neural Stem-Like Cells (NSLCs), Cardiac Stem-Like Cells (CSLC), Hematopoietic Stem-Like Cells (HSLC), Pancreatic Progenitor-Like Cells, and Mesendoderm-like Cells. Also described are methods for generating these cells from human somatic cells and other types of cells. Also provided are compositions and methods of using of the cells so generated in human therapy and in other areas.
Owner:NOVAGENESIS FOUND
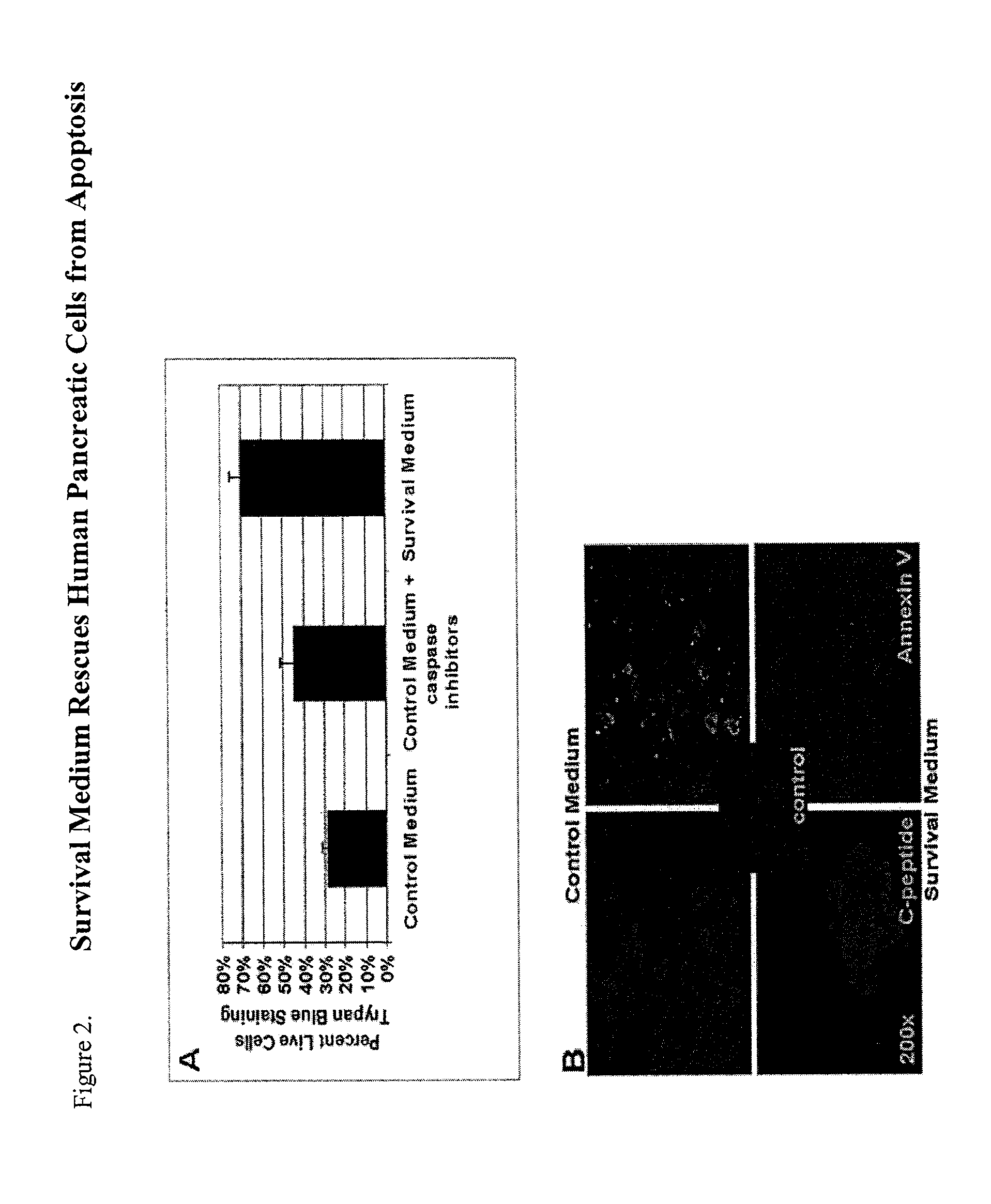
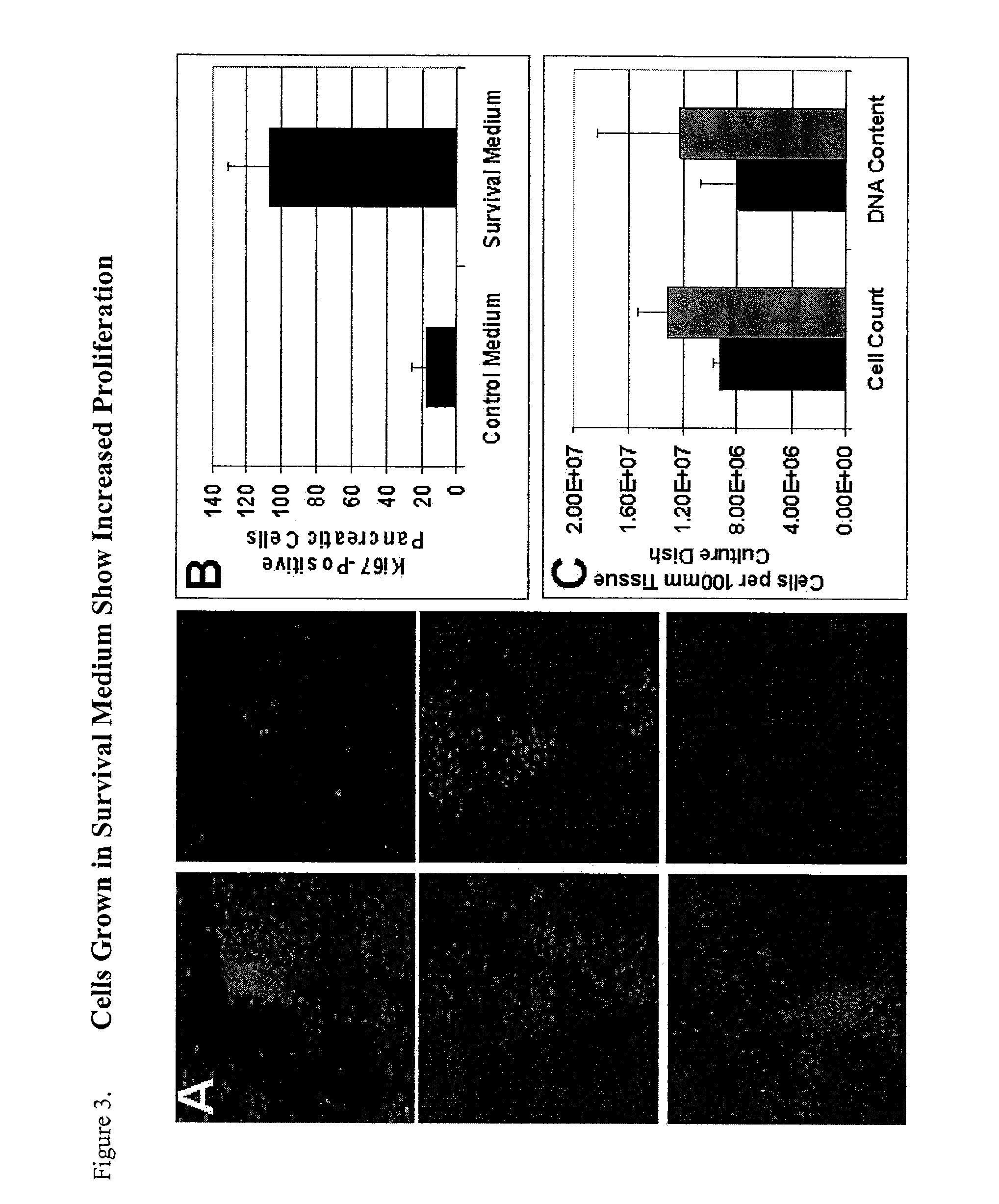
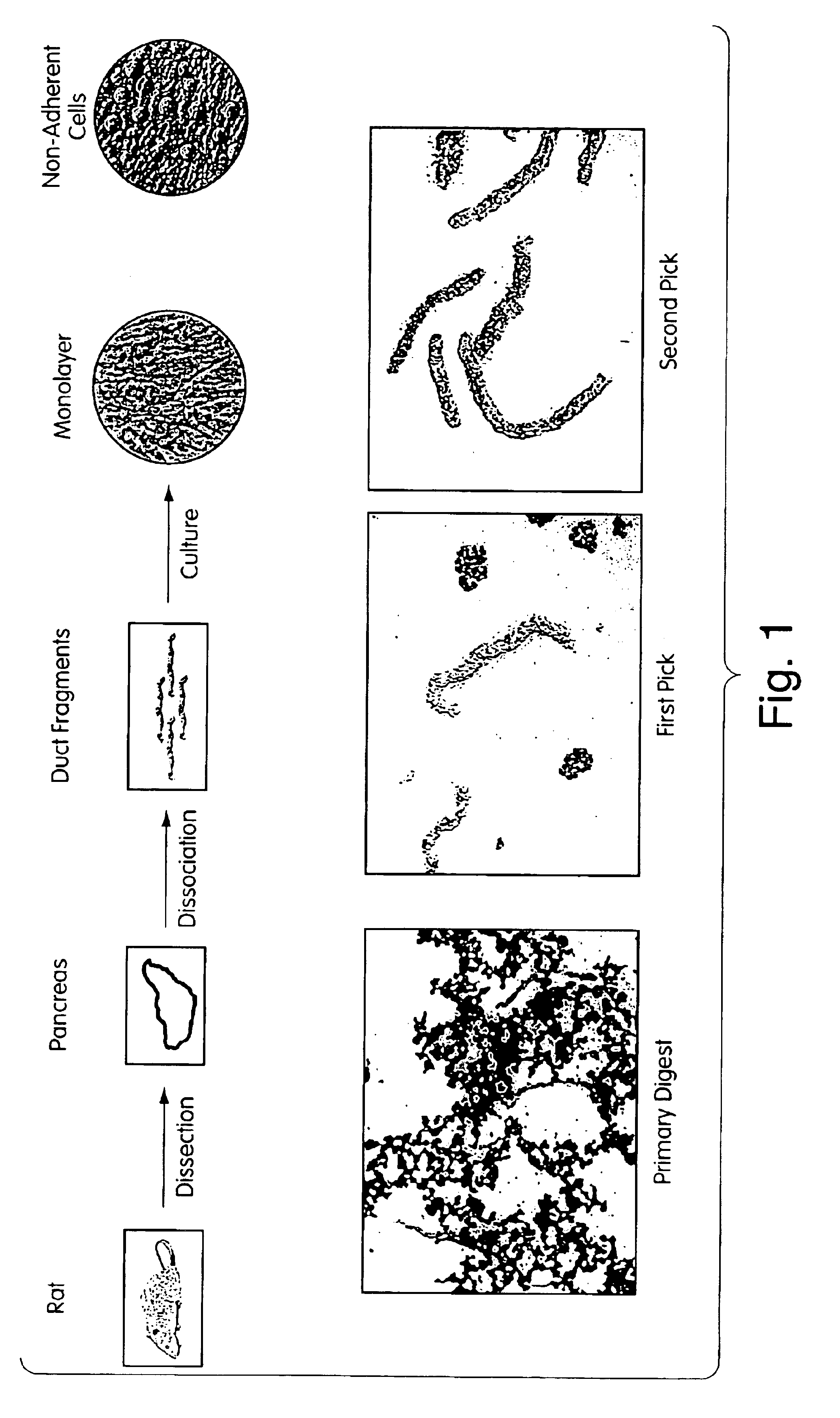
Method of improving cell proliferation of pancreatic progenitor cells in a pancreatic cell culture
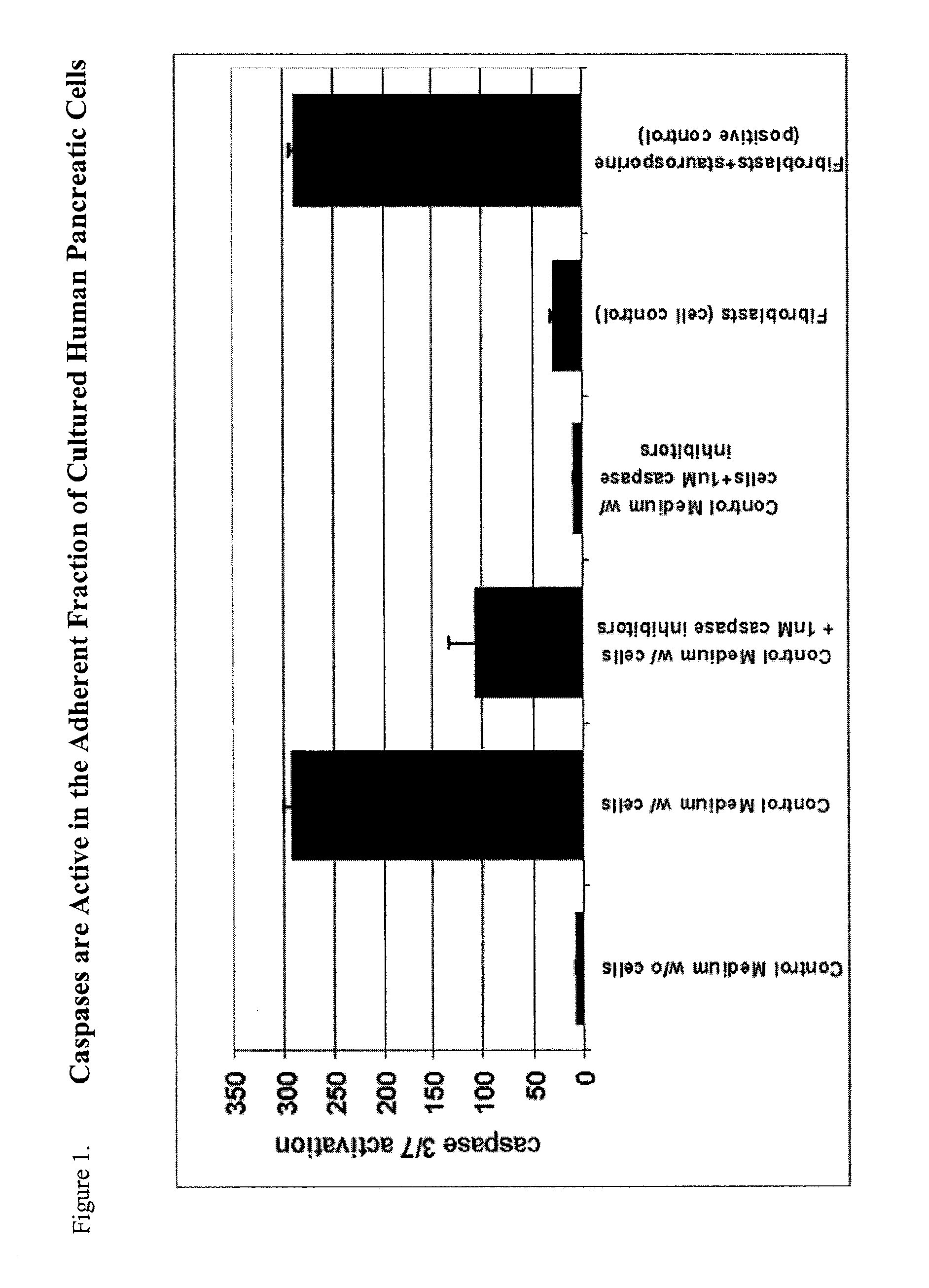
InactiveUS20100311166A1Increasing cell proliferationIncreased level of activationCell dissociation methodsMetabolism disorderProgenitorCaspase inhibitors
The invention relates to the discovery that the proliferation and survival of pancreatic progenitor cells can be enhanced by contacting the cells with, (1) a caspase inhibitor sufficient to reduce apoptosis in the pancreatic endocrine cells; and, (2) a growth factor in an amount sufficient to increase the level of activated Akt in the pancreatic endocrine cells.
Owner:RENEURON INC
Progenitor cells, methods and uses related thereto
The present invention relates to a substantially pure population of viable pancreatic progenitor cells, and methods for isolating such cells. The present invention further concerns certain therapeutic uses for such progenitor cells, and their progeny.
Owner:ES CELL INT
Compositions and methods for promoting the generation of definitive endoderm
ActiveUS8507274B2Efficiently and reproducibly differentiateImprove efficiencyUrea derivatives preparationMetabolism disorderGerm layerEpithelium
Certain embodiments disclosed herein are directed to a method of producing endoderm cells, such as definitive endoderm cells by exposing stem cells such as embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells to an effective amount of at least one compound described herein to differentiate the stem cells into the endoderm cells such as definitive endoderm cells. Differentated endoderm cells produced by the methods disclosed herein can be differentiated into pancreatic epithelium, and other endoderm derivatives such as thymus, liver, stomach, intestine and lung. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of producing pancreatic progenitor cells, such as Pdx1-positive pancreatic progenitor cells by exposing endoderm cells, such as definitive endoderm cells to an effective amount of at least one compound described herein to differentiate the definitive endoderm cells into Pdx1-positive pancreatic progenitor cells. Kits and compositions comprising Pdx1-positive pancreatic progenitor produced using the methods are also described.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Progenitor cells, methods and uses related thereto
The present invention relates to a substantially pure population of viable pancreatic progenitor cells, and methods for isolating such cells. The present invention further concerns certain therapeutic uses for such progenitor cells, and their progeny.
Owner:CURIS INC
Populations of pancreatic progenitor cells and methods of isolating and using same
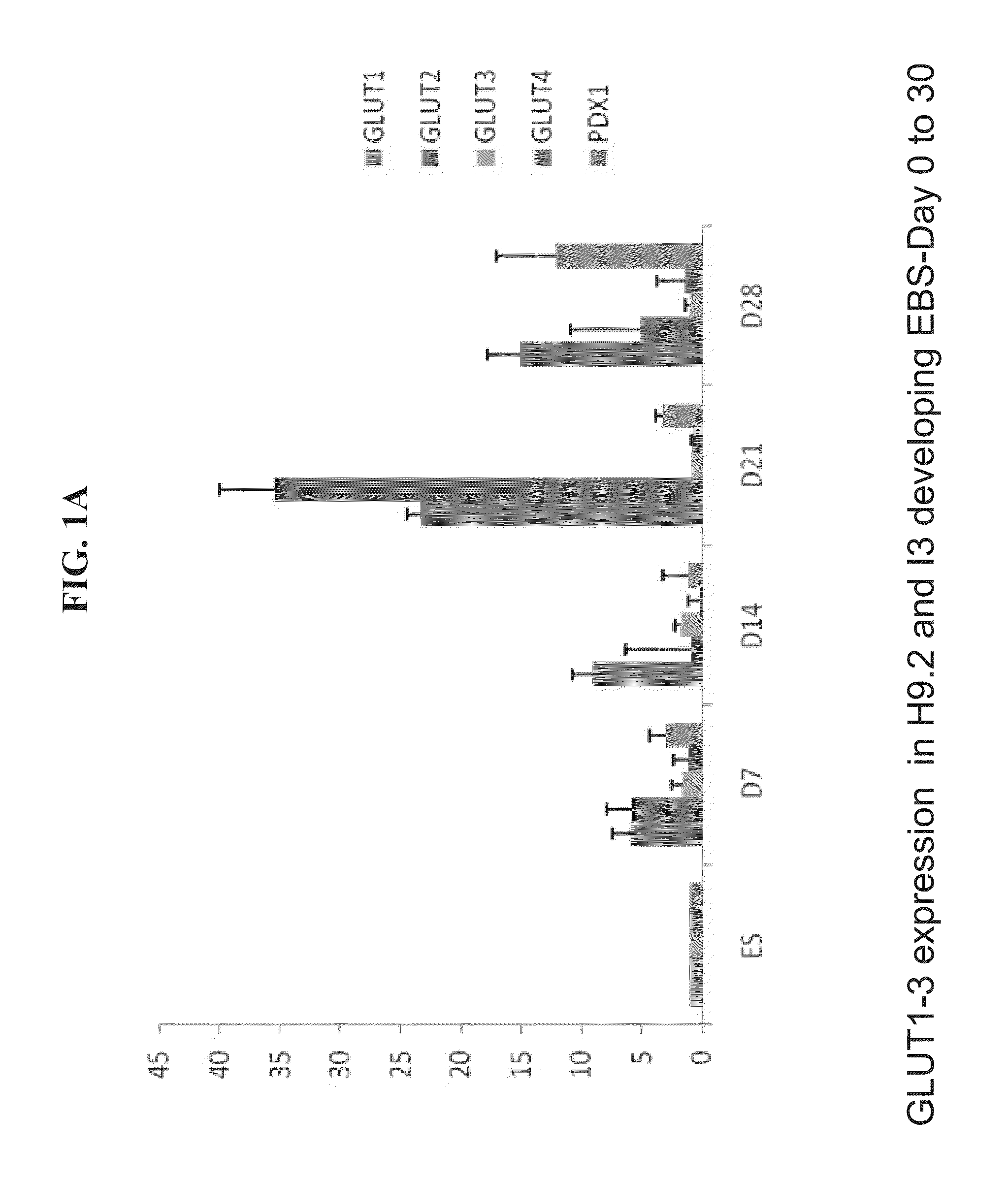
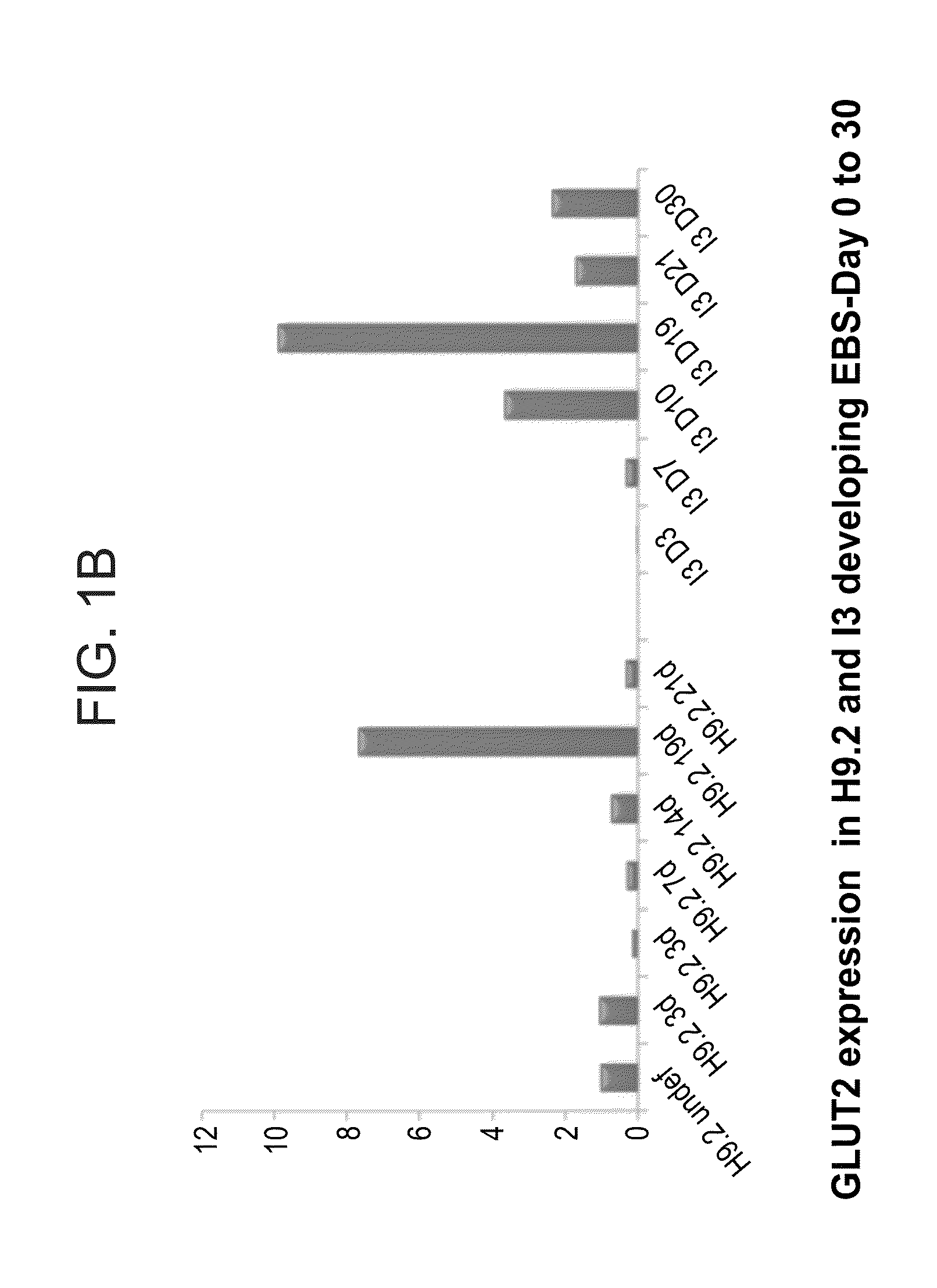
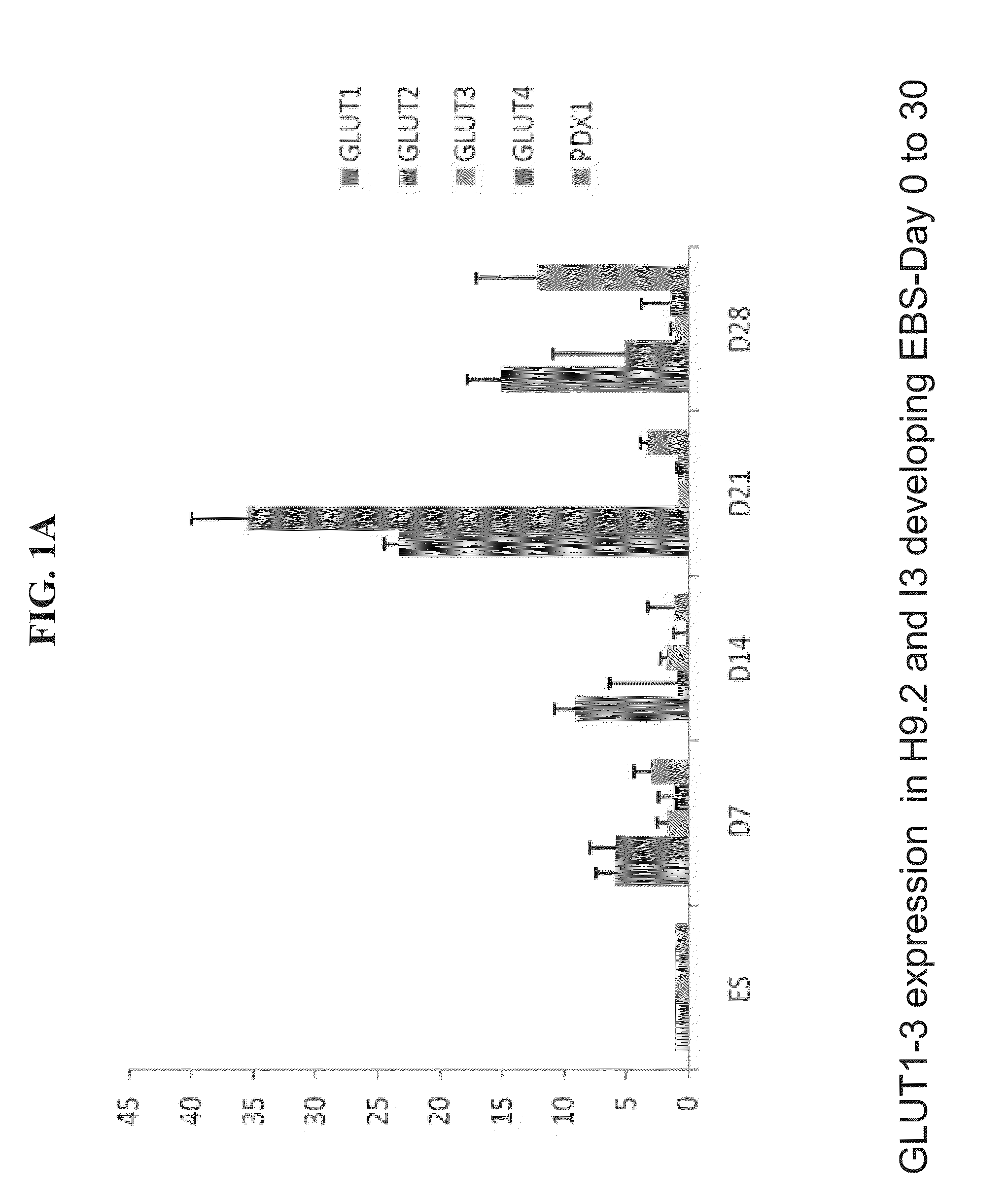
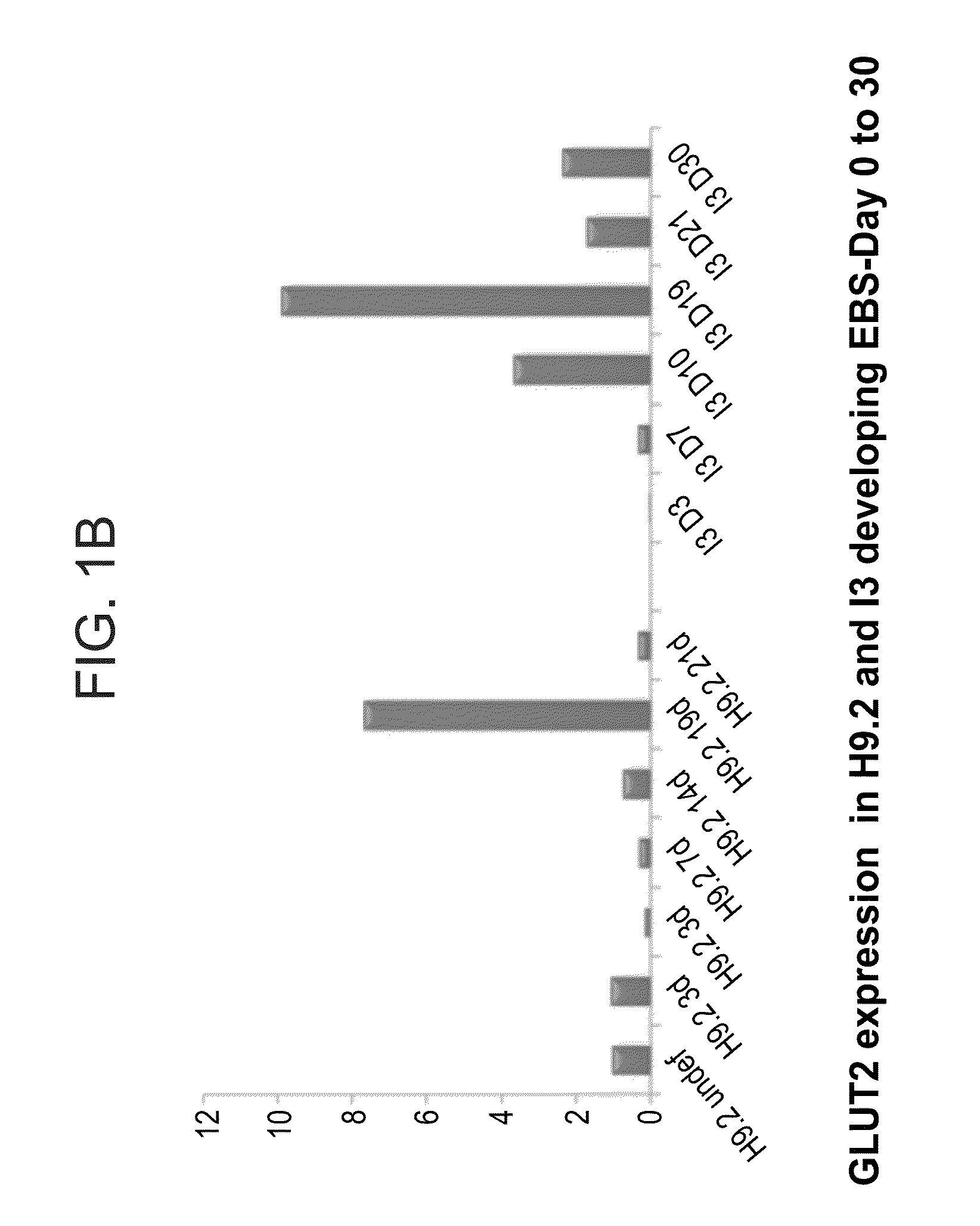
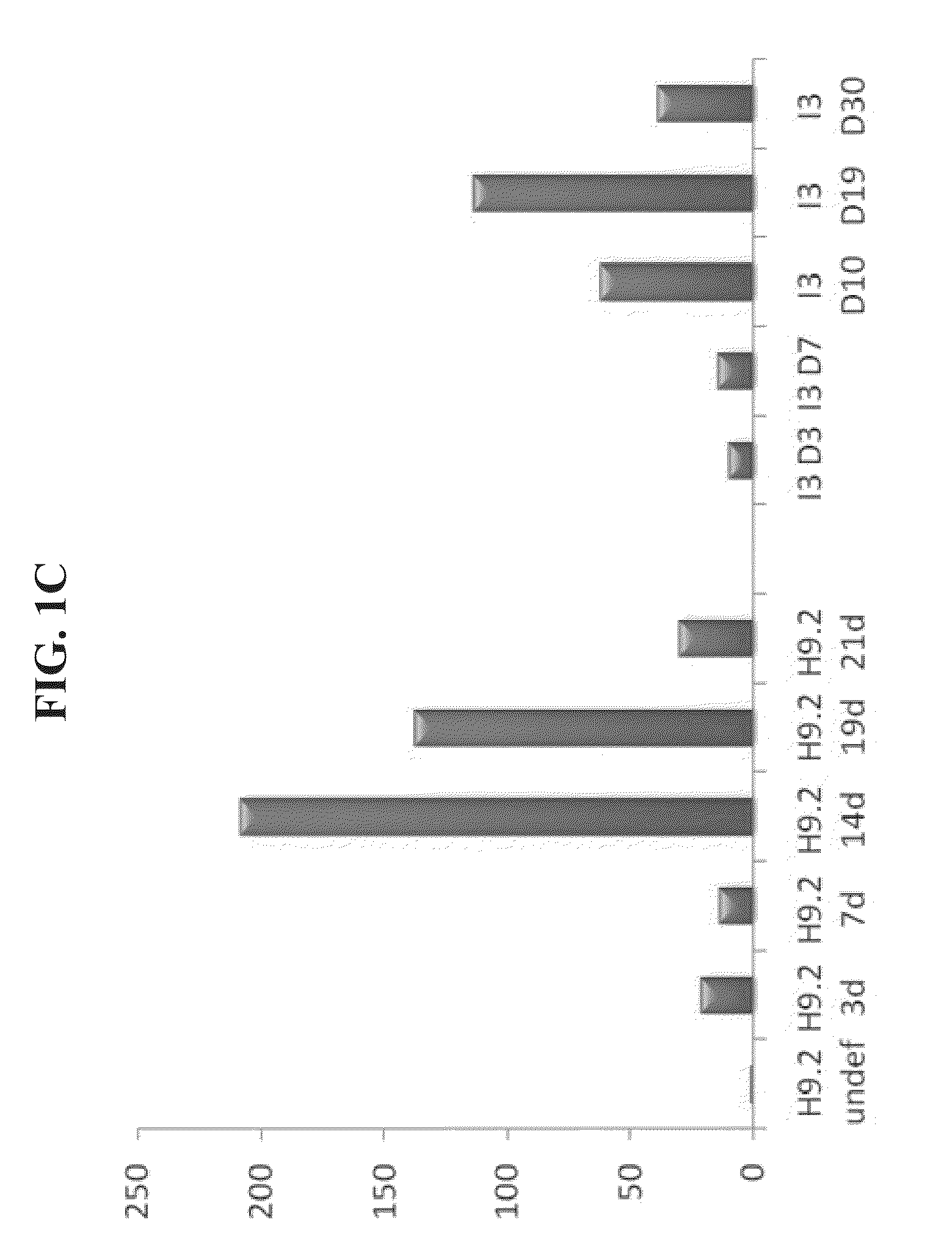
A method of generating pancreatic progenitor cells is disclosed. The method comprises:(a) differentiating stem cells under conditions such that at least a portion of the cells express glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) so as to generate GLUT2-expressing cells; and(b) enriching for the GLUT2-expressing cells so as to generate a population of GLUT2 enriched cells, wherein at least 80% of the population of GLUT2 enriched cells express GLUT2, thereby generating pancreatic progenitor cells.Isolated populations of cells generated according to the method, pharmaceutical compositions comprising same and uses thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Method for Proliferation of Pancreatic Progenitor Cells
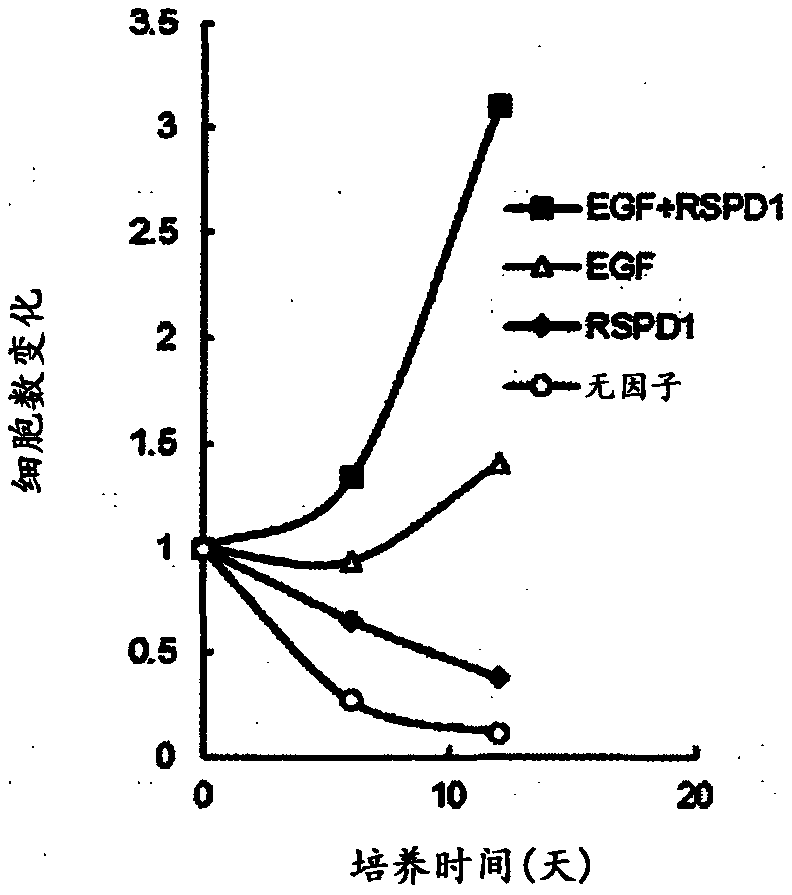
ActiveUS20170233700A1Improve efficiencyHigh purityPancreatic cellsArtificial cell constructsProgenitorEgf signaling
The present invention relates to a method for preparing highly pure pancreatic progenitor cells by using pluripotent stem cells such as ES cells or iPS cells as a source, inducing their differentiation into pancreatic progenitor cells, and culturing and proliferating the pancreatic progenitor cells. Specifically, the present invention relates to a method for proliferation of pancreatic progenitor cells, comprising the step of culturing the pancreatic progenitor cells in a medium containing (i) an EGF signal transduction activator and / or an FGF signal transduction activator and (ii) a ROCK inhibitor.
Owner:ORIZURU THERAPEUTICS INC
Compositions and methods for promoting the generation of definitive endoderm
ActiveUS20120088300A1Effectively lead to differentiationImprove efficiencyUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationGerm layerEpithelium
Certain embodiments disclosed herein are directed to a method of producing endoderm cells, such as definitive endoderm cells by exposing stem cells such as embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells to an effective amount of at least one compound described herein to differentiate the stem cells into the endoderm cells such as definitive endoderm cells. Differentated endoderm cells produced by the methods disclosed herein can be differentiated into pancreatic epithelium, and other endoderm derivatives such as thymus, liver, stomach, intestine and lung. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of producing pancreatic progenitor cells, such as Pdx1-positive pancreatic progenitor cells by exposing endoderm cells, such as definitive endoderm cells to an effective amount of at least one compound described herein to differentiate the definitive endoderm cells into Pdx1-positive pancreatic progenitor cells. Kits and compositions comprising Pdx1-positive pancreatic progenitor produced using the methods are also described.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Compositions and methods for promoting the generation of endocrine cells
ActiveUS20160032249A1Facilitate furtherMaximize chance of successOrganic active ingredientsPancreatic cellsProgenitorBiology
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for the generation of insulin positive β cells, for example by exposing Pdx+ pancreatic progenitor cells to one or more compounds, and compositions and kits comprising isolated populations of insulin positive cells.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Culture media and applications thereof, and differentiation methods of induced pluripotent stem cells into pancreatic islets
ActiveCN112251396AReduce immune riskImprove the level ofMetabolism disorderPancreatic cellsPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
The invention relates to the technical field of stem cells, and especially relates to culture media and applications thereof, and differentiation methods of induced pluripotent stem cells into pancreatic islets. In the provided differentiation methods, a differentiation process from iPS stem cells to pancreatic progenitor cells needs 14 days (2 weeks); and the process mainly includes following four steps:directional endoderm - archenteric canal -foregut / hindgut - pancreatic progenitor cells. The differentiation process from the pancreatic progenitor cells to functional islets needs about 31 days (1 month); and the process is mainly divided into following three steps: endocrine progenitor cells - early islets - islets in late functional maturity. Each of the above steps needs specific induction culture media; and the culture media can be formed by adding corresponding inducing factors into basic media, and the corresponding culture media need to be daily replaced for culture. Feeder layer cells are not needed during the whole induction of the method; and the adopted culture media have no animal-derived components, so that the risks of alloimmunization can be reduced.
Owner:ALLIFE MEDICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Methods and devices for differentiating pluripotent stem cells into cells of the pancreatic lineage
Methods and devices for culturing human pluripotent stem cells to produce cells of the pancreatic lineage are disclosed. The methods include steps of culturing the stem cells under conditions that induce the expression of mesendoderm / primitive streak and definitive endoderm markers in a chemically defined medium including an effective amount of i) fibroblast growth factor, ii) Activin A, and iii) bone morphogenetic protein. The methods further include the steps of culturing cells under conditions favoring the formation of at least one of intact embryoid bodies and pancreatic progenitor PDX1+Ins− cells.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Pancreatic stem cells
Pancreatic progenitor cells isolated from the pancreas of a mammal. The invention also includes pancreatic cells or neural cells differentiated from the pancreatic progenitor cells.
Owner:SEABERG RAEWYN +2
In vitro pancreatic differentiation of pluripotent mammalian cells
This invention relates to the in vitro differentiation of pluripotent cells into pancreatic progenitors by i) culturing pluripotent cells in a definitive endoderm (DE) medium comprising a TGFp ligand, fibroblast growth factor ( FGF), bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), a PI3K inhibitor and optionally a GSK3 β inhibitor to produce a population of definitive endoderm cells, ii) culturing the definitive endoderm cells in a first pancreatic medium comprising an activin antagonist; FGF; retinoic acid; and a BMP inhibitor to produce a population of dorsal foregut cells; iii) culturing the dorsal foregut cells in a second pancreatic medium comprising FGF, retinoic acid, a BMP inhibitor, and a hedgehog signalling inhibitor, and; iv) culturing the endoderm cells in a third pancreatic medium comprising FGF. The progenitor cells thus produced may be further differentiated into pancreatic endocrine cells. These methods may be useful, for example, in producing pancreatic cells for therapy or disease modelling.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
Human pancreatic epithelial progenitor cells and methods of isolation and use thereof
The invention discloses a substantially pure population of human pancreatic progenitor cells and methods of isolating and culturing the pancreatic progenitor cells. By carefully manipulating the microenvironment of the pancreatic progenitor cells, multiple passages are attainable wherein the pancreatic progenitor cells do not senesce and furthermore, are capable of becoming functional exocrine or endocrine cells. In addition, several methods of use of human pancreatic progenitor cells are disclosed herein.
Owner:RAVEN BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
Method for inducing human mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into insulin-secreting cells in vitro
InactiveCN102618500AHigh transfection efficiencyImprove securityVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsProgenitorInsulin Secreting Cell
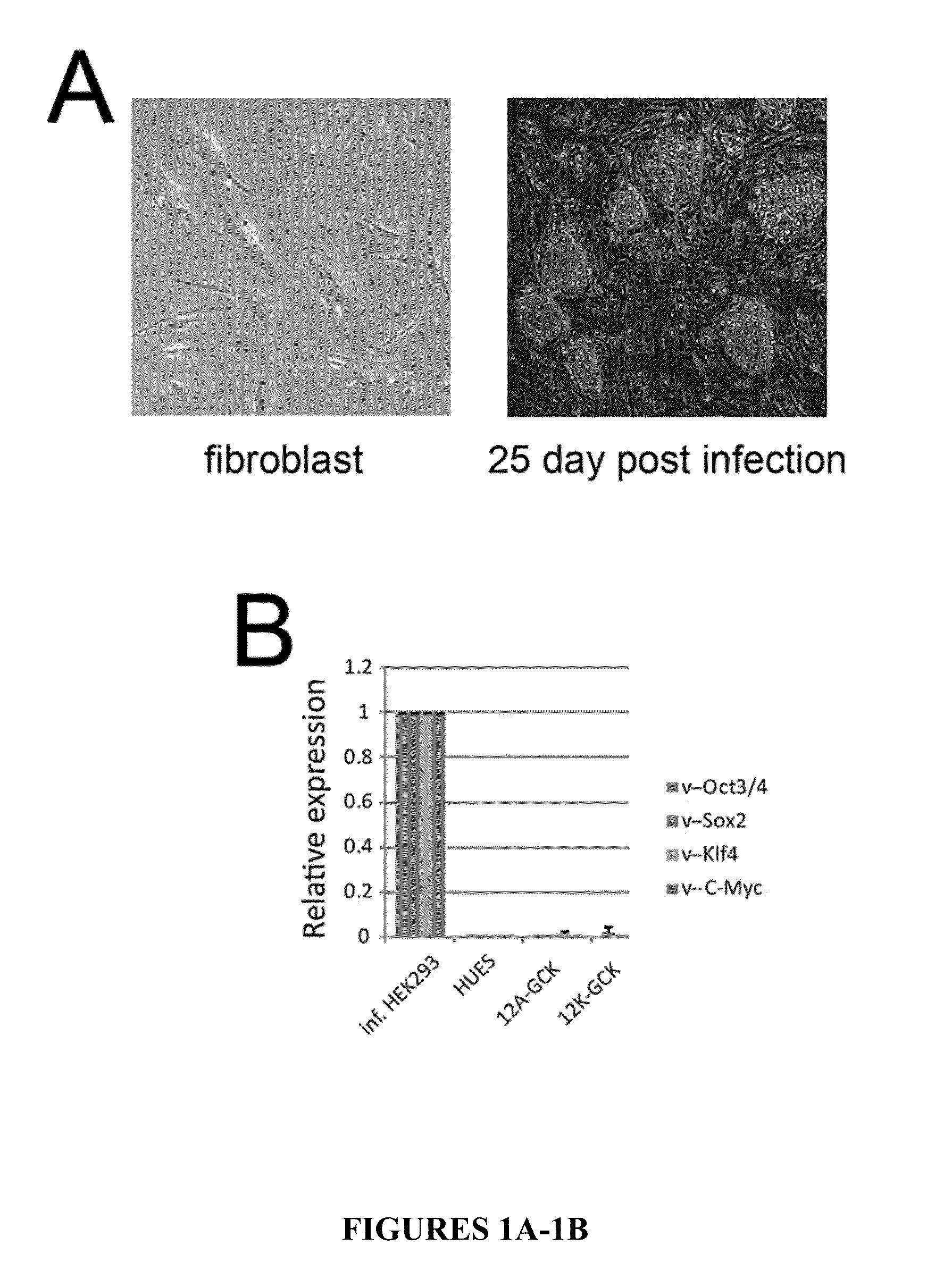
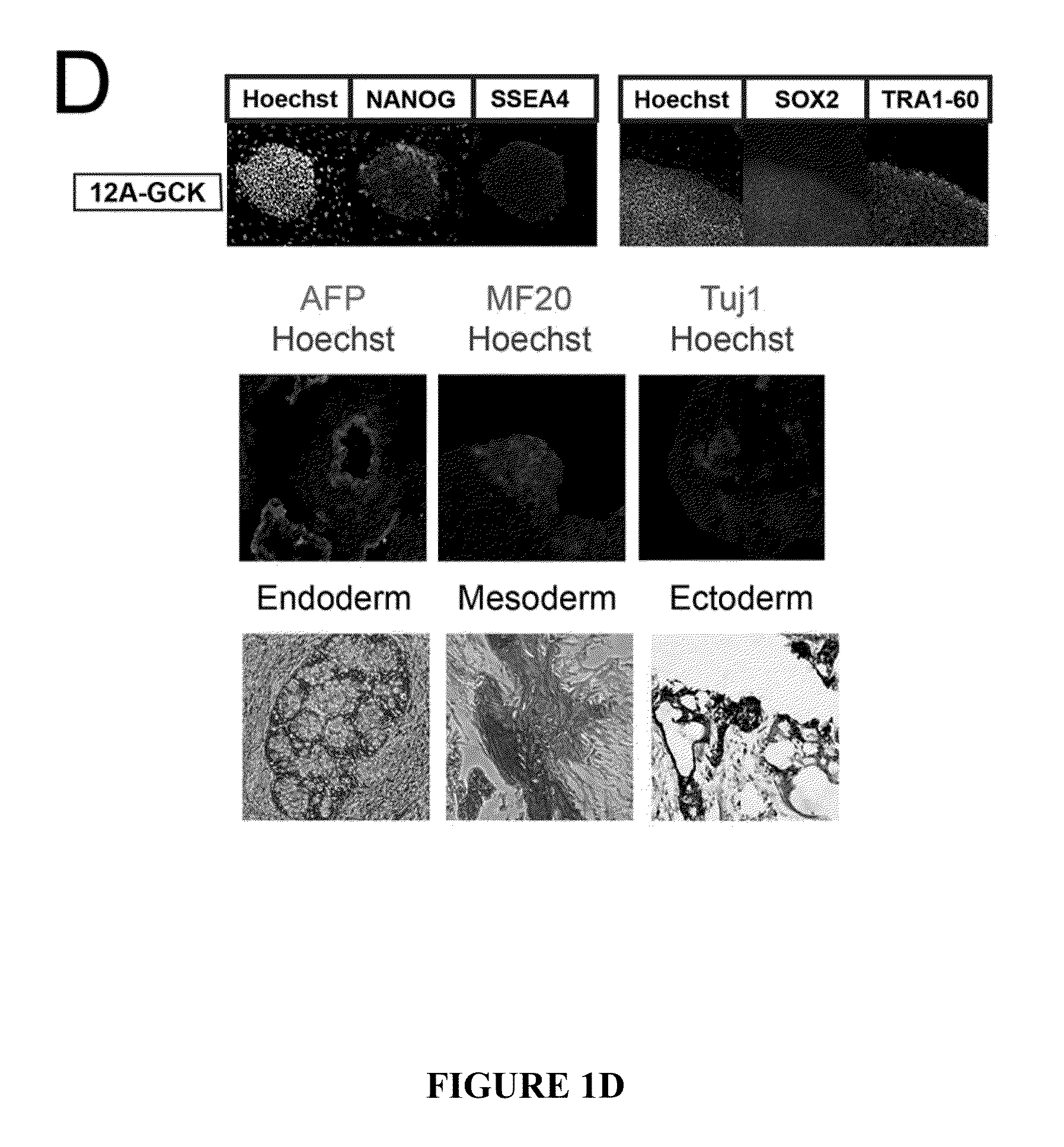
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine, in particular to a method for inducing human mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into insulin-secreting cells in vitro, which includes, according to the technical scheme, constructing recombinant eukaryotic expression plasmids of SRF (serum response factor) gene; preliminarily inducing human mesenchymal stem cells into nestin cells first; further inducing the nestin cells into pancreatic progenitor cells; transfecting an eukaryotic expression vector containing the SRF gene to the cells above; and finally inducing the cells into insulin-secreting cells, wherein the eukaryotic expression vector comprises pEGFP (plasmid enhanced green florescence protein), pcDNA or pCMV. By the method, new seed cell sources for cell therapy of diabetes mellitus are provided, new theoretical and experimental basis is provided for directed induction of mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into insulin-secreting cells and clinical application of the insulin-secreting cells, and new models for drug development and screening related to the insulin-secreting cells are provided.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for generating beta cells
The invention is directed to methods for generating pancreatic progenitor cells, insulin producing cells or endoderm cells using embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. The present invention also relates to an isolated population comprising pancreatic progenitor cells or a insulin-producing cells, compositions and their use in the treatment of diabetes
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Identification Of Novel Cell Surface Markers For Pancreatic Progenitor Cells And Definite Endodermal Cells
Methods of identifying, isolating and qualifying pancreatic progenitor cells and definite endodermal cells. An isolated population of pancreatic progenitor cells, including at least 75% of cells having a TROP-2+ and / or TROP-2+ / GPR50+ expression pattern and an isolated population of definite endodermal cells, including at least 50% of cells having a SOX17+ / SOX7+ / GSC+ / CER+ / FOXA2+ / CXCR4+ / NANOG expression pattern. Nucleic acid constructs including a reporter protein under the transcriptional regulation of SOX17 regulatory sequence or of PDX1 regulatory sequence, and cells comprising same, and methods and kits using same.
Owner:STEM CELL THERAPEUTICS
Pancreatic small cells and uses thereof
The present invention provides mammalian pancreatic progenitor cells (“small cells”) and methods for their isolation and propagation. The pancreatic small cells are derived from adult pancreatic tissue and are characterised by their small size. The small cells are quiescent or undergo a very slow cell cycle when maintained in cell culture. Small cells secrete synaptophysin and islet hormones and are predominantly found in small, growing islets as small clusters. The present invention further provides for the use of the pancreatic small cells in transplantation and the treatment of diabetes mellitus, and for the genetic engineering of the small cells in order to produce recombinant proteins in vivo.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Human pancreatic epithelial progenitor cells and methods of isolation and use thereof
The invention discloses a substantially pure population of human pancreatic progenitor cells and methods of isolating and culturing the pancreatic progenitor cells. By carefully manipulating the microenvironment of the pancreatic progenitor cells, multiple passages are attainable wherein the pancreatic progenitor cells do not senesce and furthermore, are capable of becoming functional exocrine or endocrine cells. In addition, several methods of use of human pancreatic progenitor cells are disclosed herein.
Owner:RAVEN BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC +1
Purification method for pancreatic precursor cells derived from pluripotent stem cells and amplification method therefor
InactiveCN109415689AImprove qualityReduce batch-to-batch variationPancreatic cellsDead animal preservationInduced pluripotent stem cellPurification methods
Disclosed are: a culture method for pancreatic precursor cells derived from pluripotent stem cells, said culture method comprising step (A) for three-dimensionally culturing pancreatic precursor cellsderived from pluripotent stem cells in a medium that contains a factor belonging to the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family and / or a factor belonging to the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, and (2) a Wnt agonist; a production method for islet cells from pancreatic precursor cells derived from pluripotent stem cells, said production method comprising step (E) for inducing the differentiation of the pancreatic precursor cells cultured by the aforesaid method into islet cells; and a cryopreservation method for pancreatic precursor cells derived from pluripotent stem cells, said cryopreservation method comprising step (F) for freezing the pancreatic precursor cells cultured by the aforesaid method.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Populations of pancreatic progenitor cells and methods of isolating and using same
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Methods for pancreatic tissue regeneration
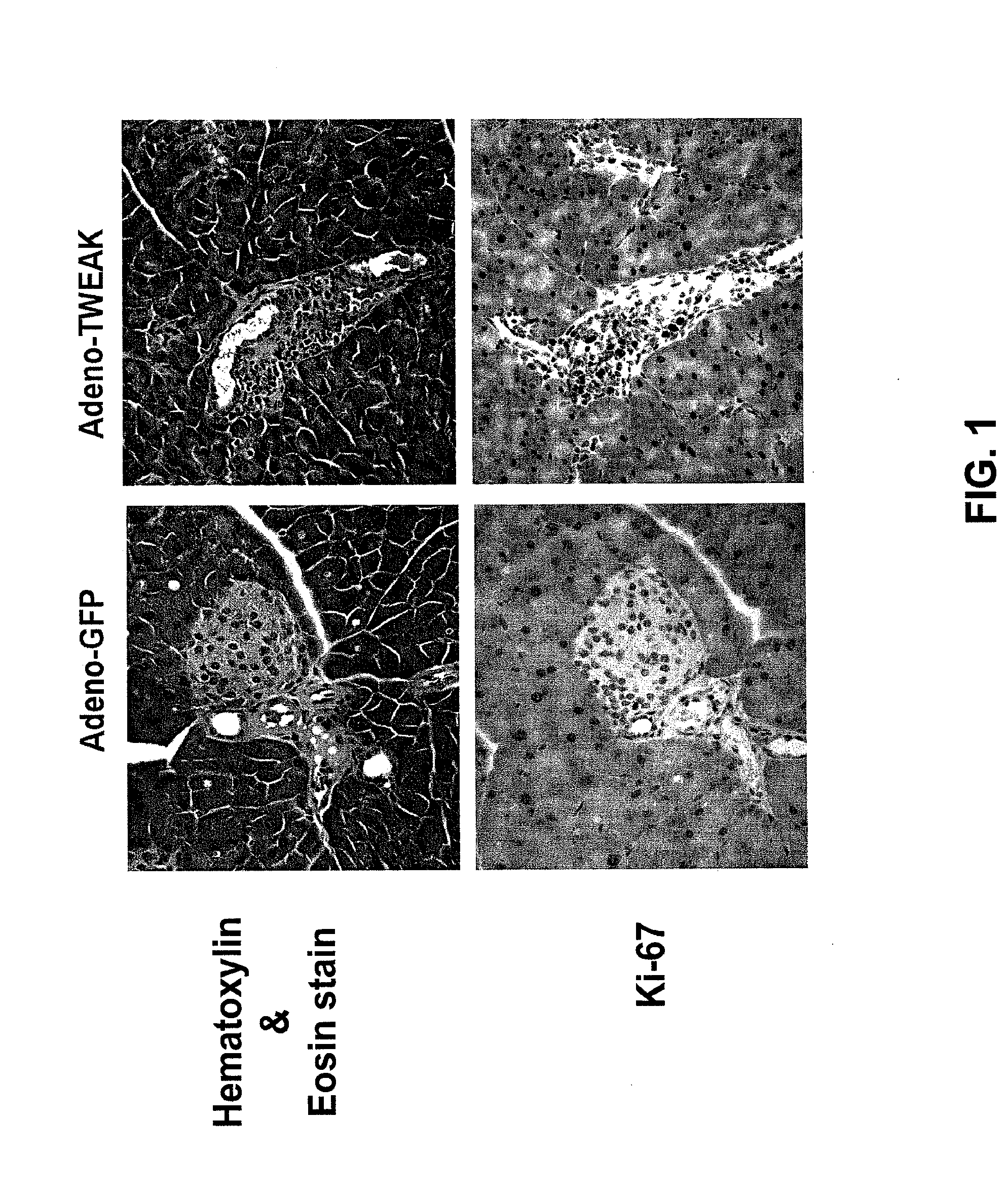
Disclosed are methods of expanding populations of pancreatic cells or inducing the generation of pancreatic progenitor cells in a subject or in culture using a therapeutically effective amount of a TWEAK receptor agonist. These methods may be used to treat diseases or conditions where enhancement of pancreatic progenitor cells for cell replacement therapy is desirable, including, e.g., diabetes and conditions that result in loss of all or part of the pancreas.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Method for generating pancreatic hormone-producing cells
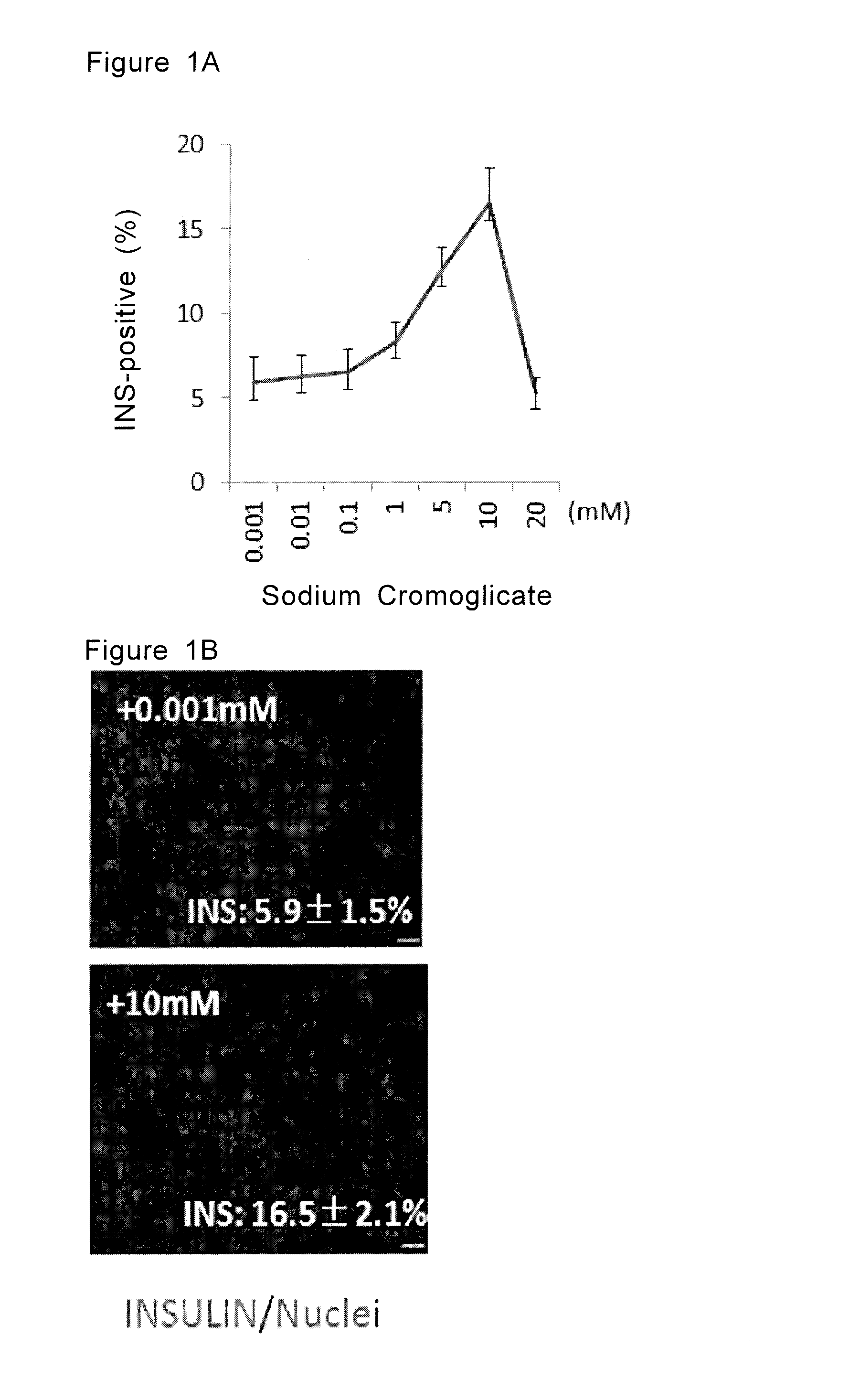
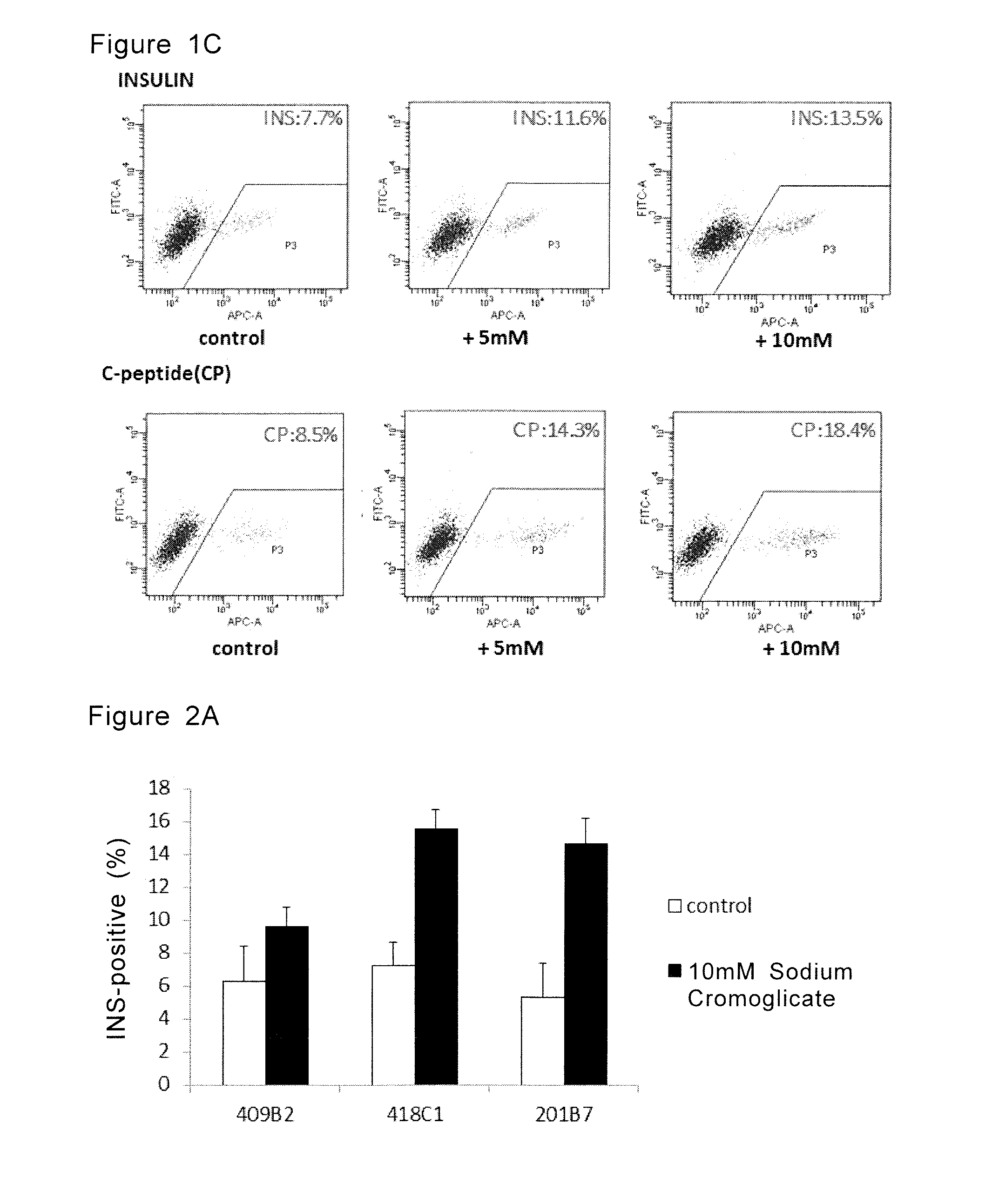
ActiveUS20160289642A1Generate efficientlyUseful in treatmentPancreatic cellsCulture processMedicinePancreatic hormone
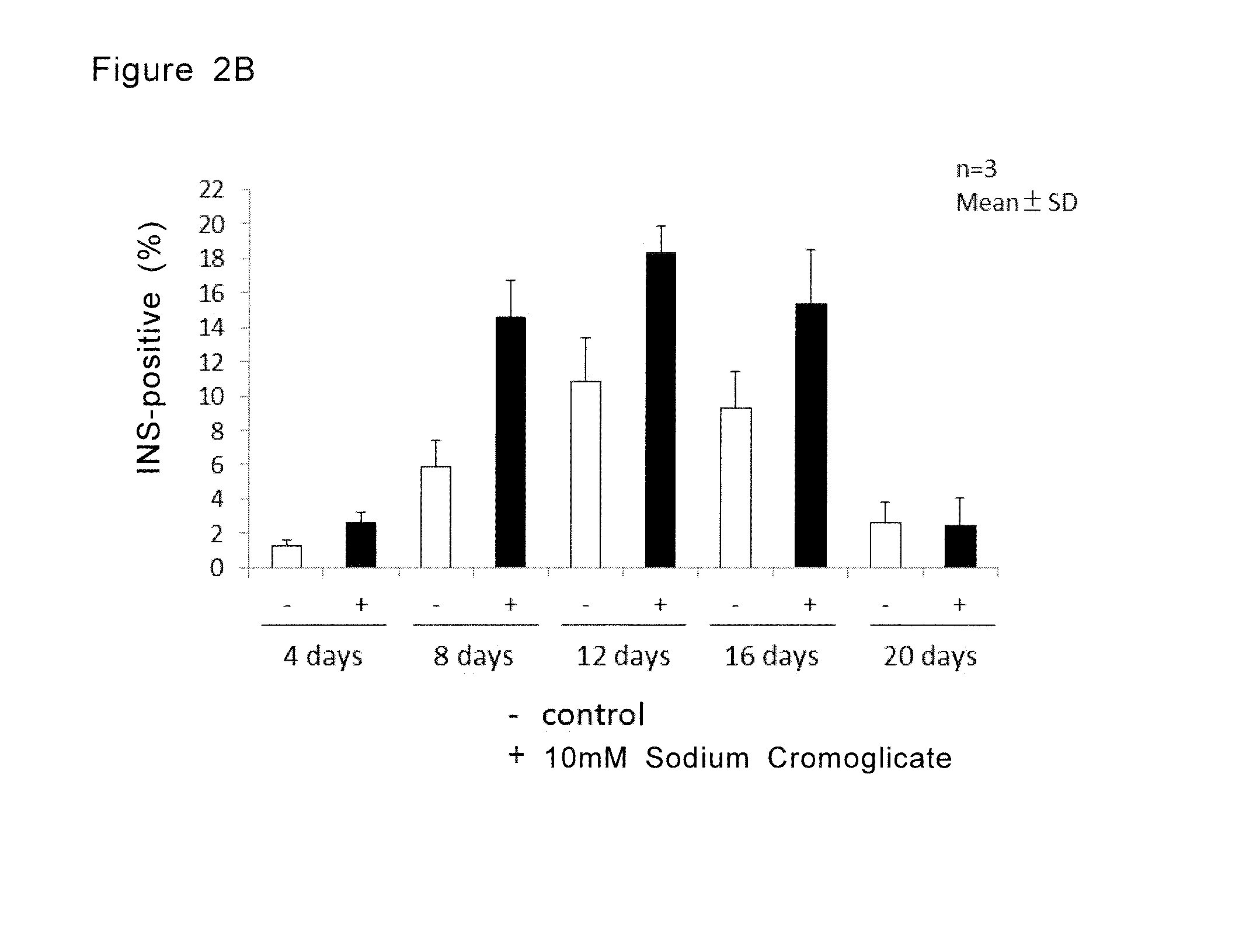
Provided is a method for inducing pancreatic hormone-producing cells from pancreatic progenitor cells efficiently. The method comprises a step of culturing the cells in a culture medium comprising sodium cromoglicate.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
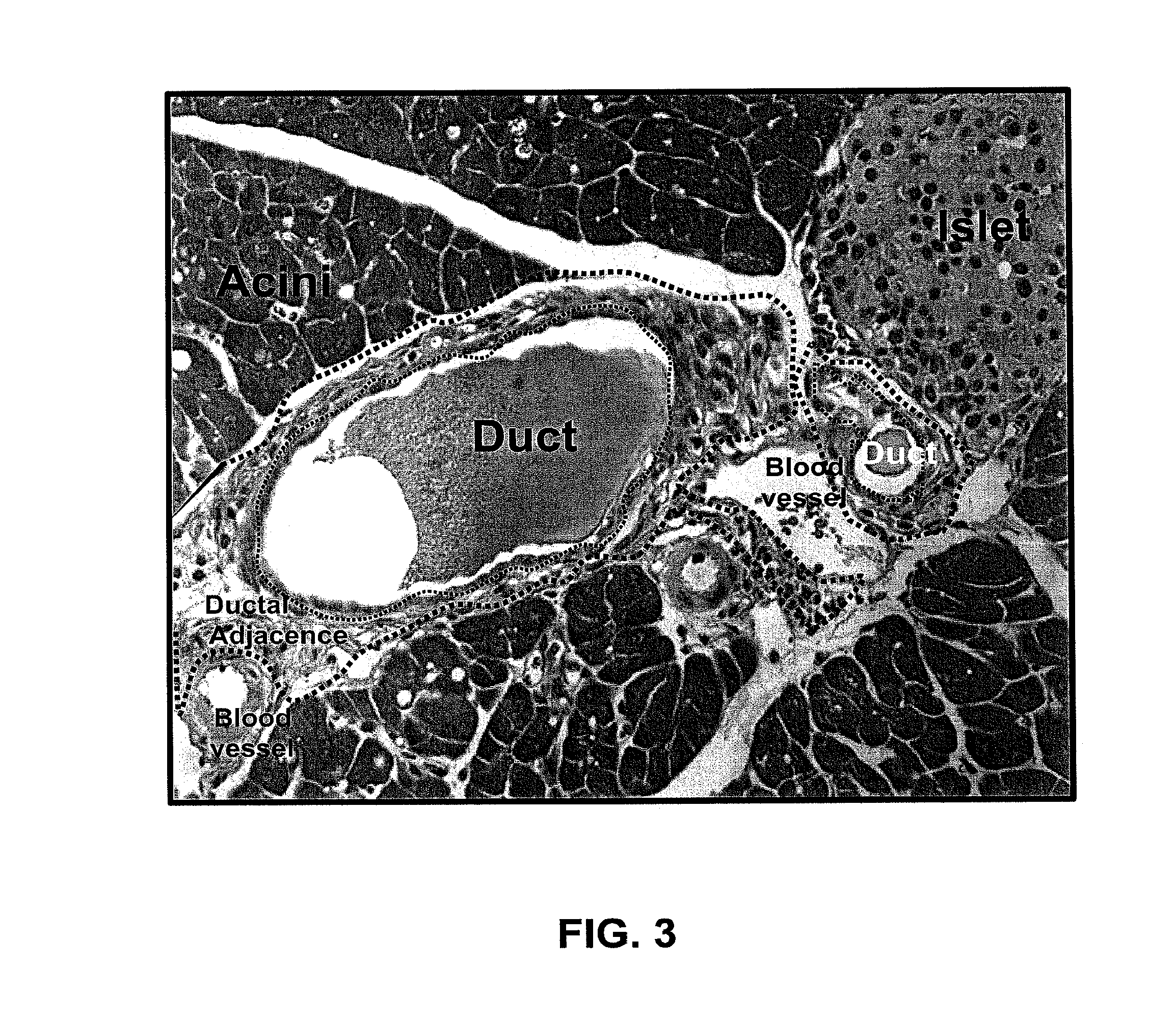
Isolation of bona fide pancreatic progenitor cells
The present invention relates to a method for isolating bona fide pancreatic progenitor cells and to cell populations enriched for bona fide pancreatic progenitor cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN
Pancreatic progenitor 1 gene and its uses
Methods for isolating pancreatic progenitor 1 genes are provided. The pancreatic progenitor 1 nucleic acid compositions find use in identifying homologous or related proteins and the DNA sequences encoding such proteins; in producing compositions that modulate the expression or function of the protein; and in studying associated physiological pathways. In addition, modulation of the gene activity in vivo is used for prophylactic and therapeutic purposes, such as identification of cell type based on expression, and the like.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Selection of pancreatic progenitors
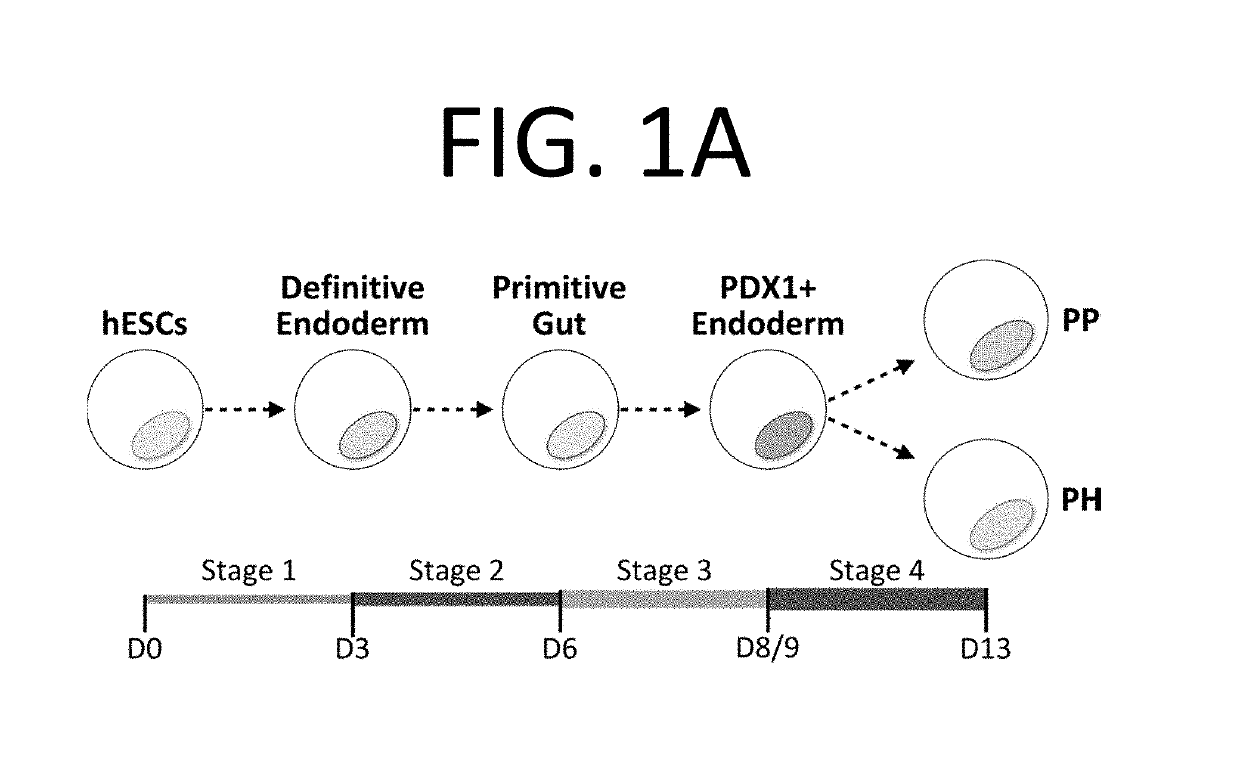
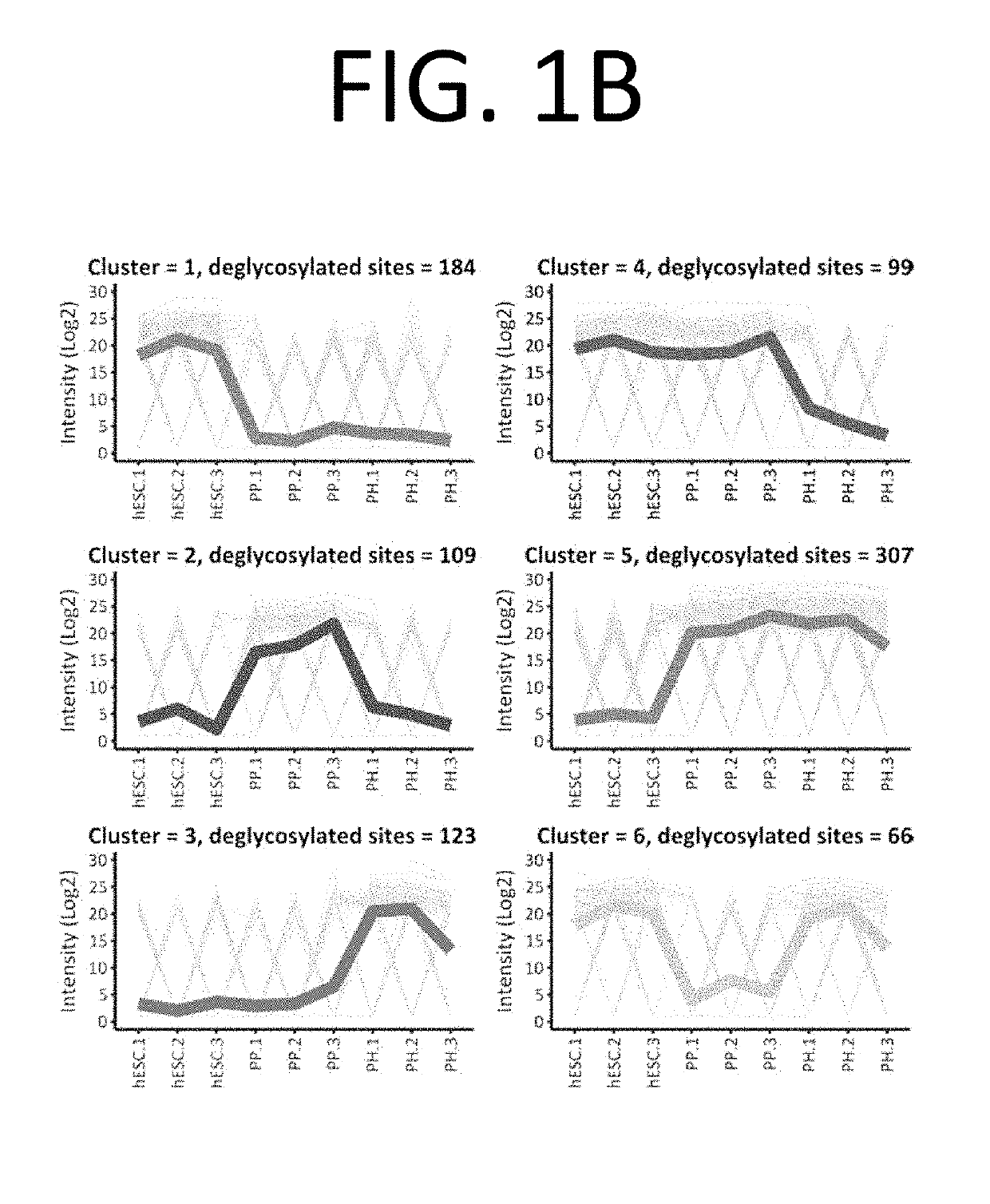
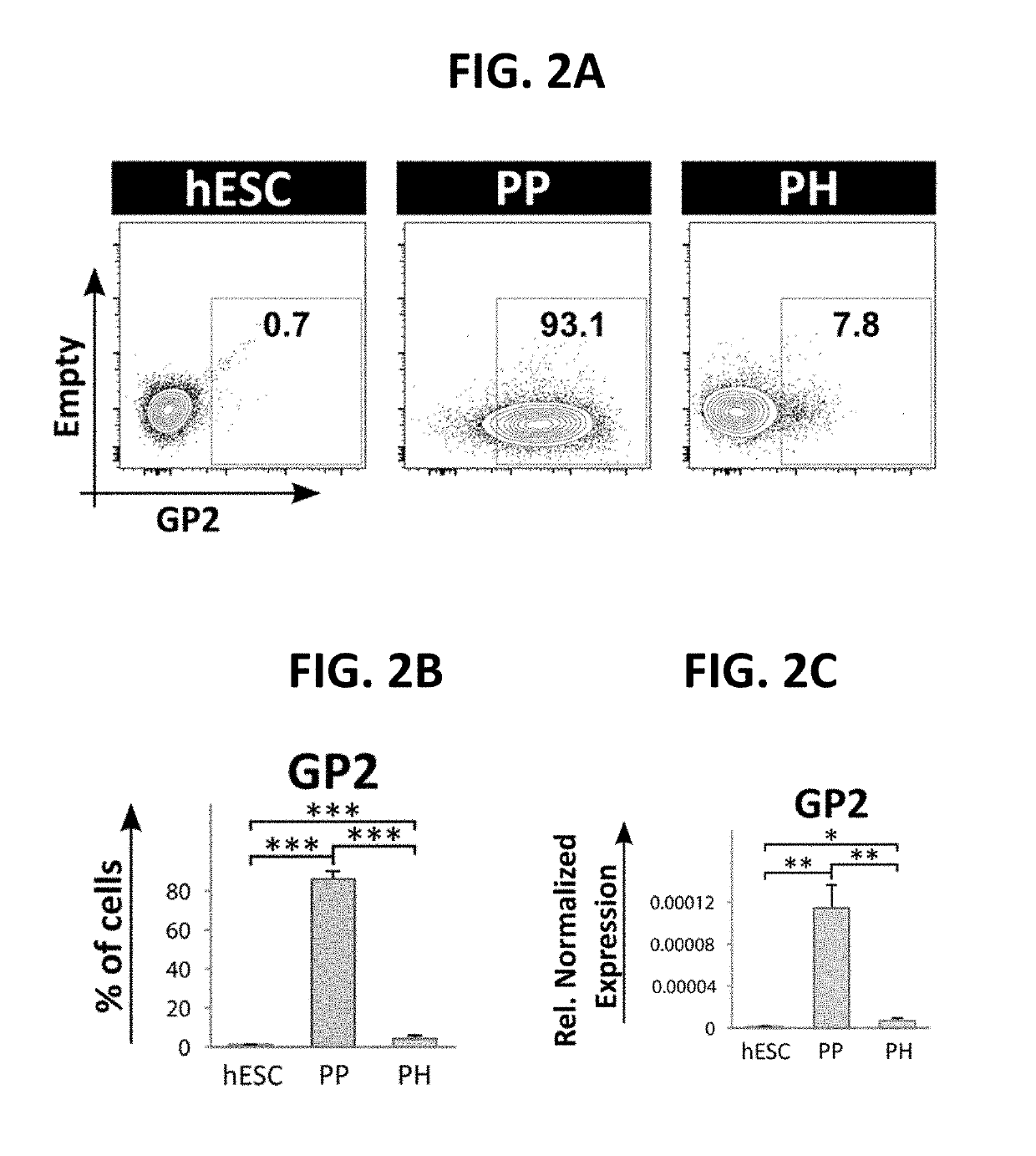
There is described herein a method for enriching / purifying a population of cells for pancreatic progenitor cells, the method comprising: a) providing the population cells, the population comprising pancreatic progenitor cells; and b) performing at least one of steps (i)-(v): (i) selecting for cells from the population that express at least one protein listed in cluster 2; (ii) selecting for cells from the population that express at least one protein listed in cluster 5; (iii) deselecting for cells from the population that express at least one protein listed in cluster 1; (iv) deselecting for cells from the population that express at least one protein listed in cluster 3; and (v) deselecting for cells from the population that express at least one protein listed in cluster 6.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com