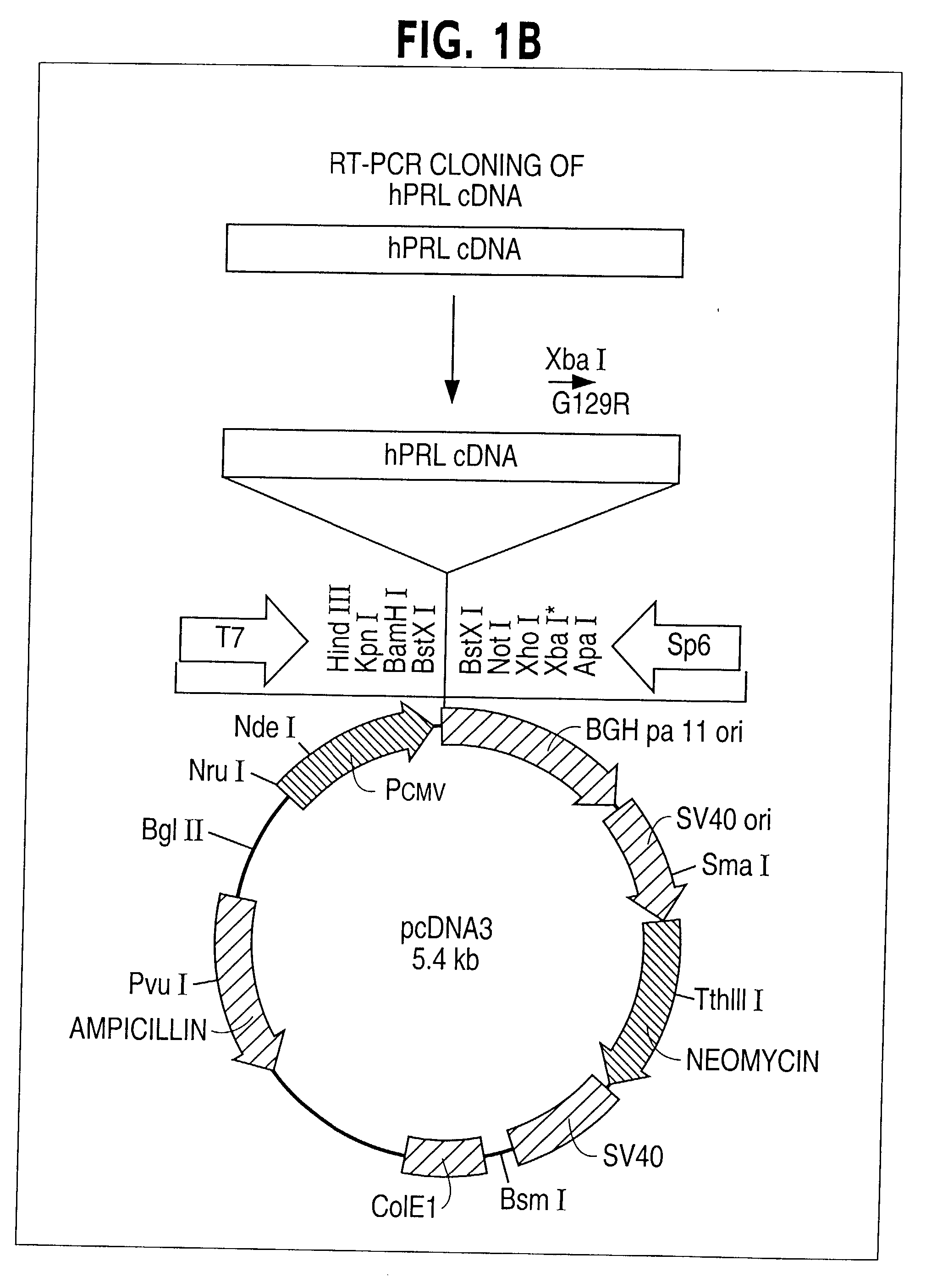
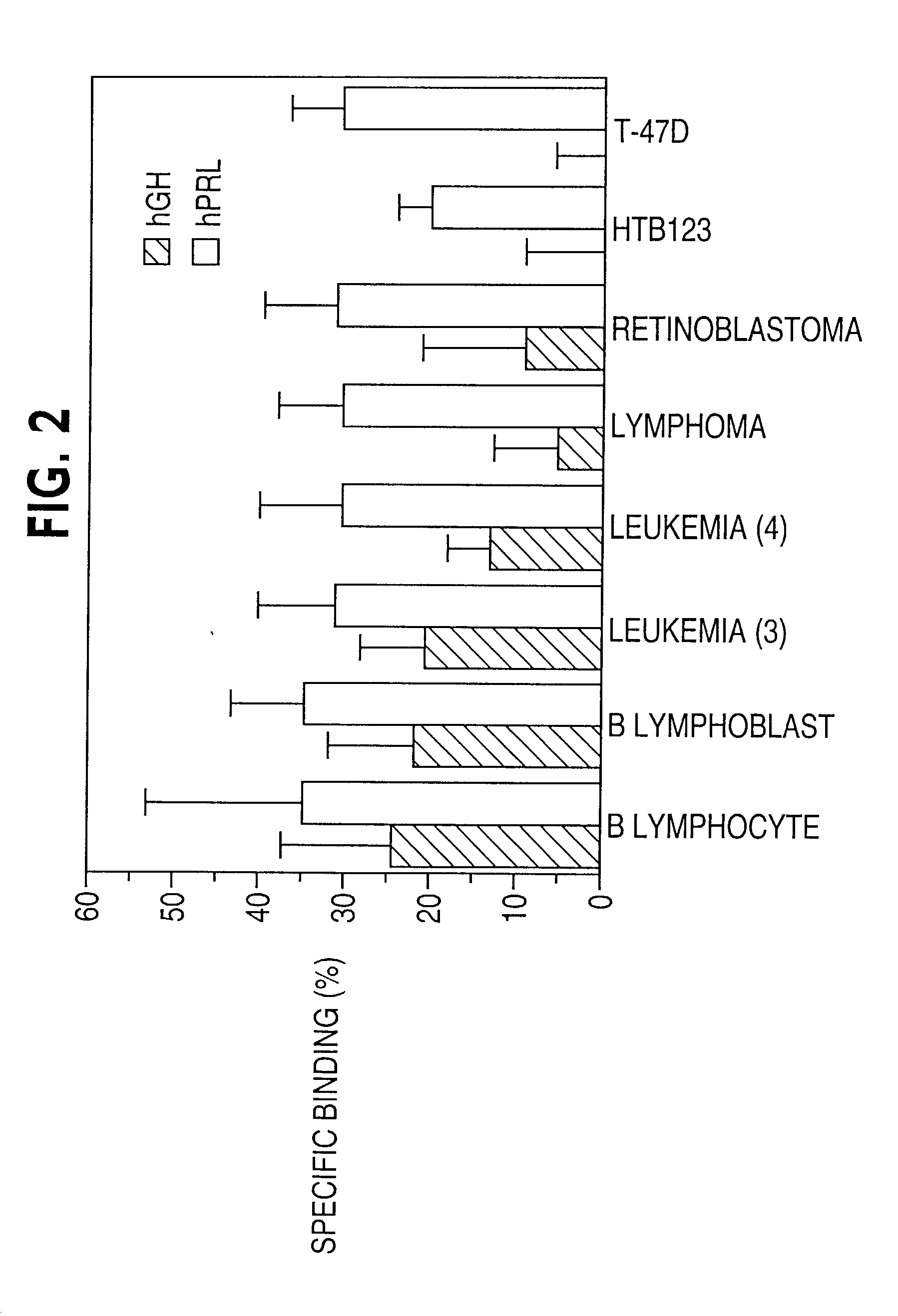
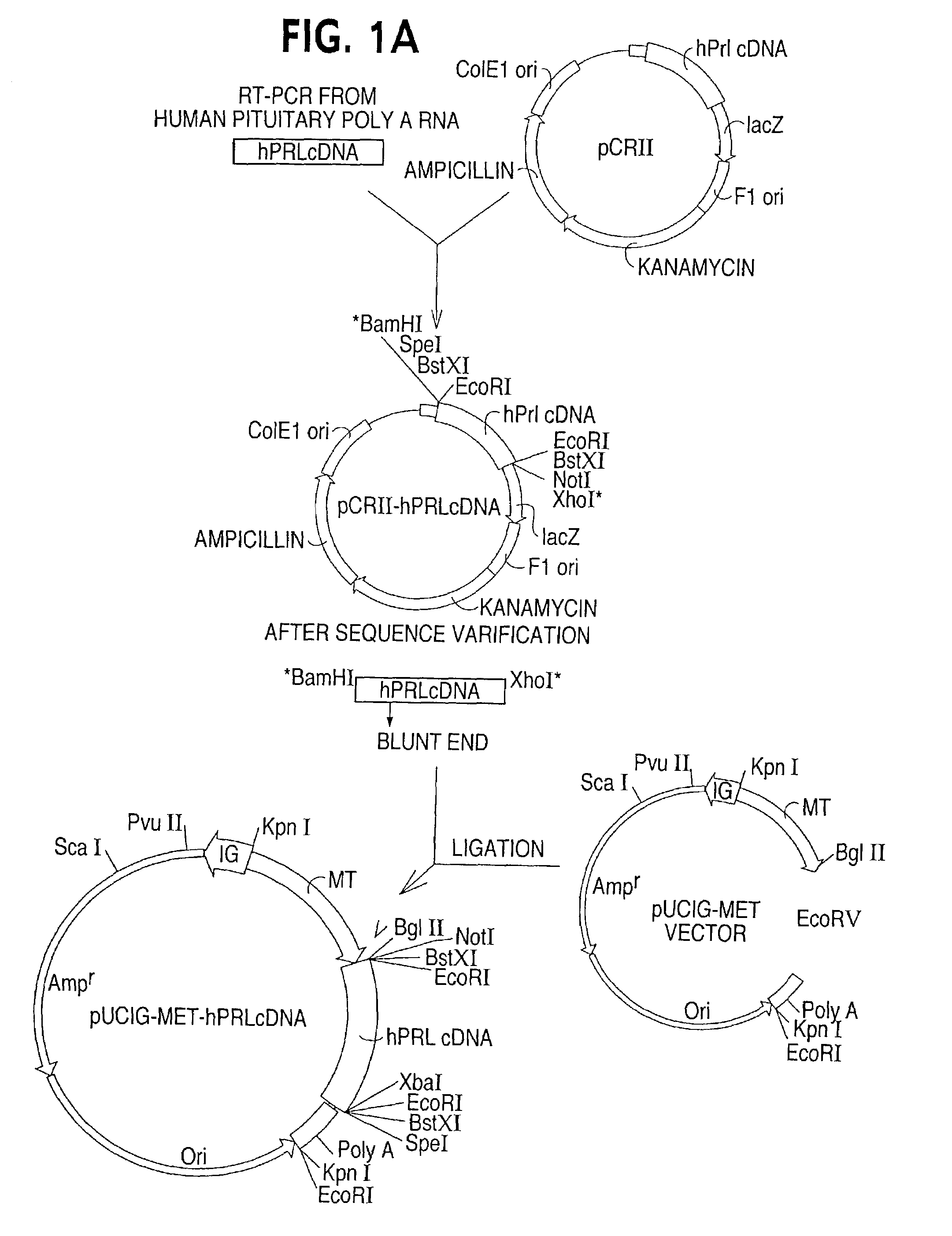
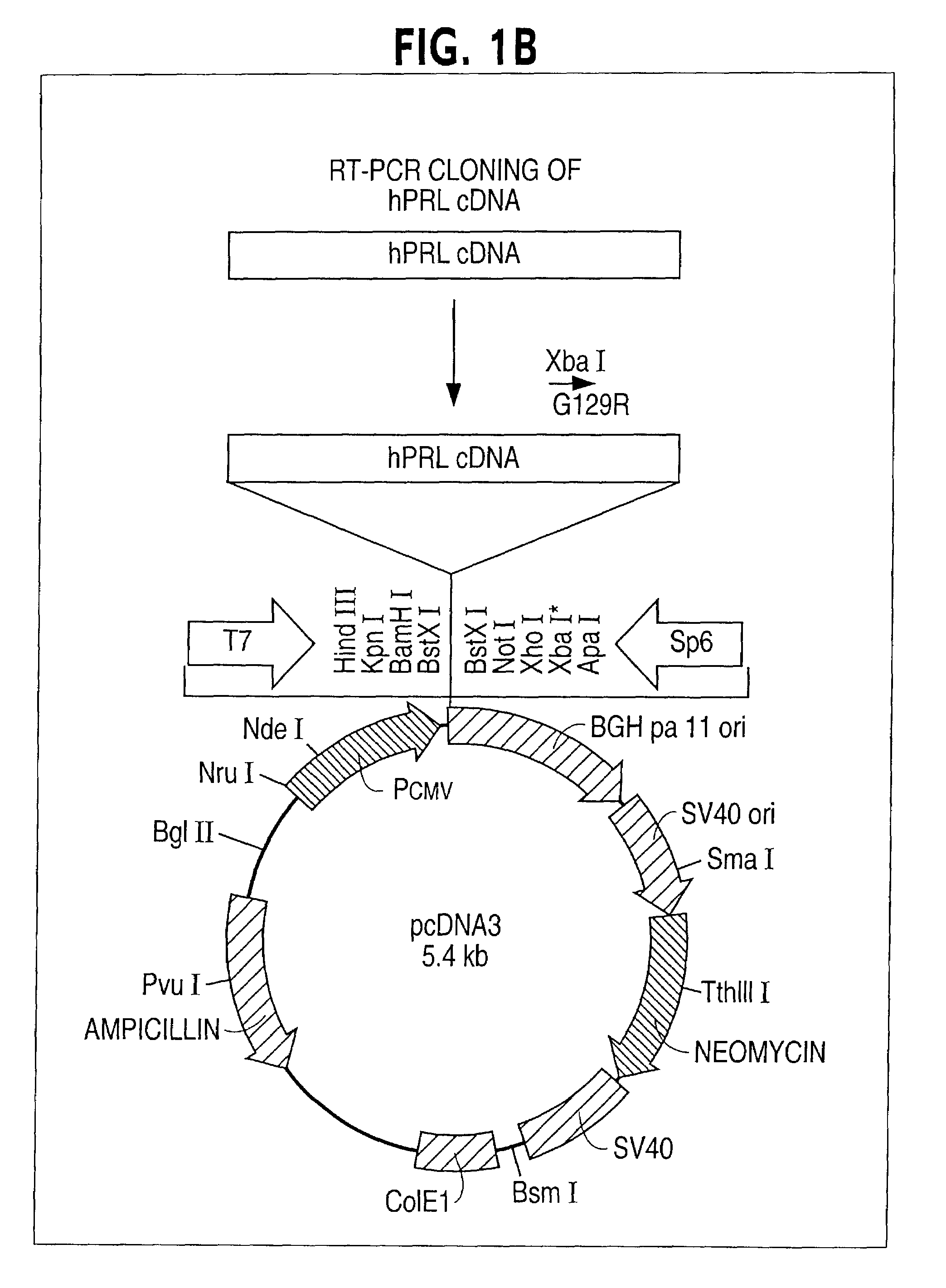
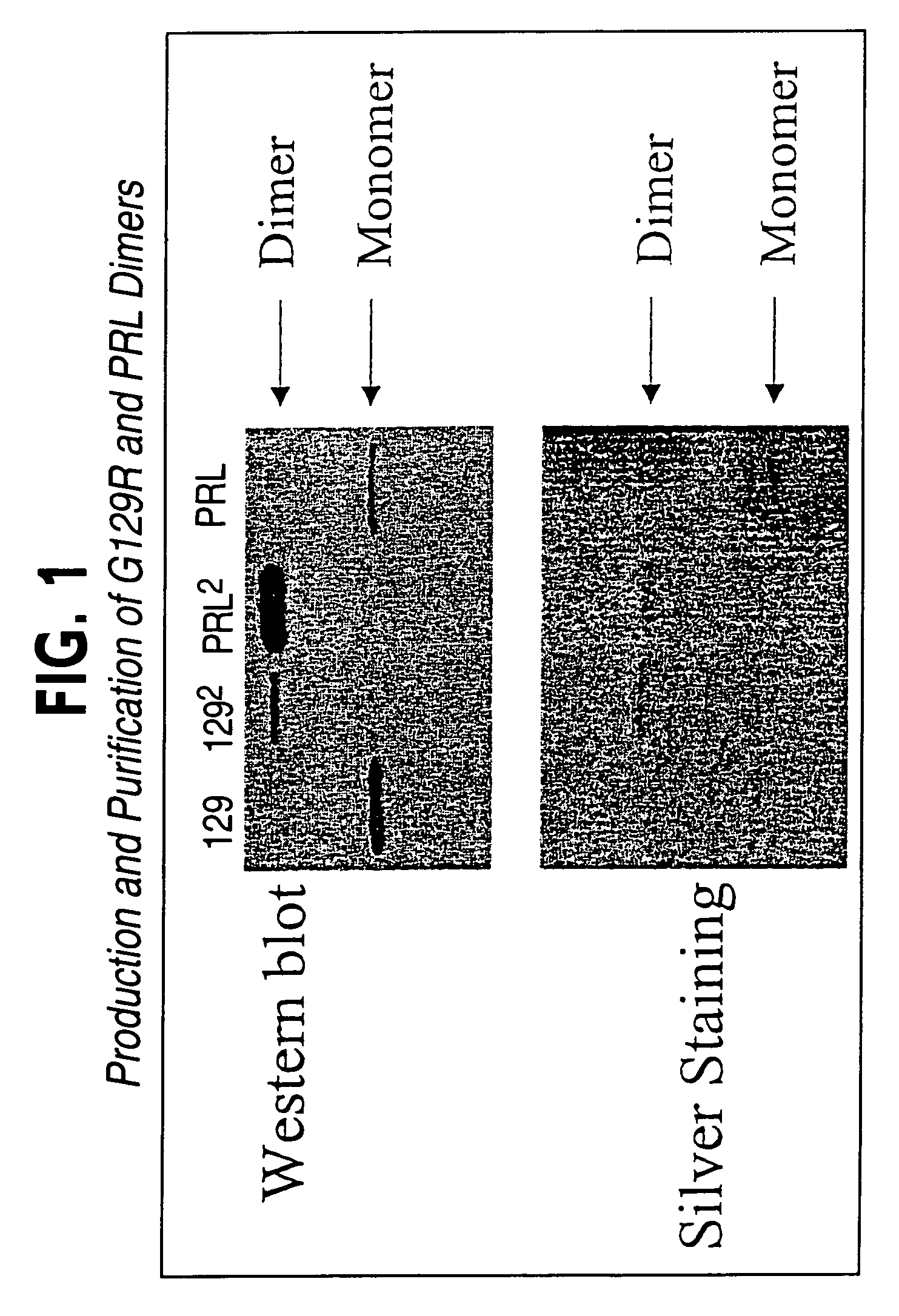
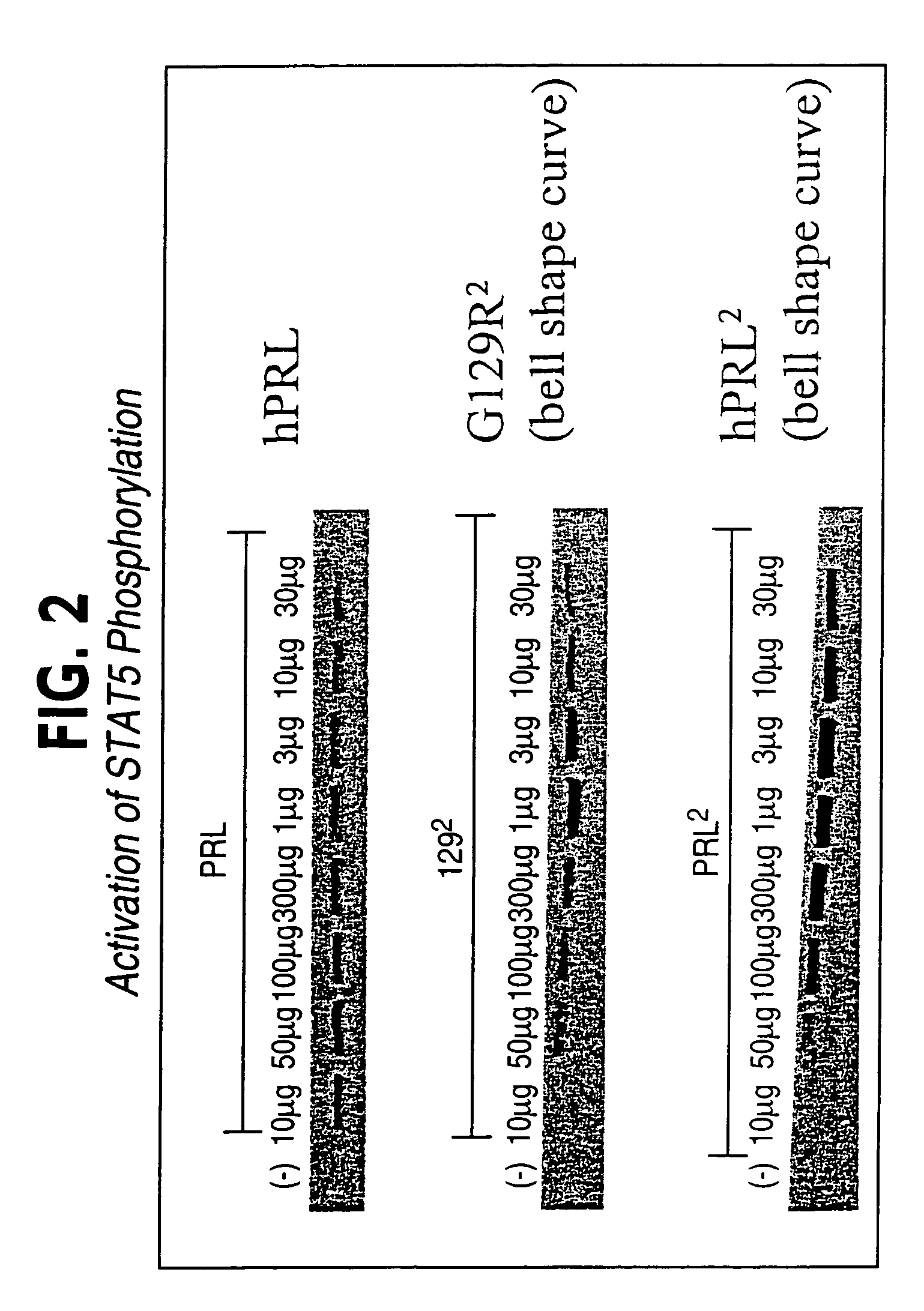
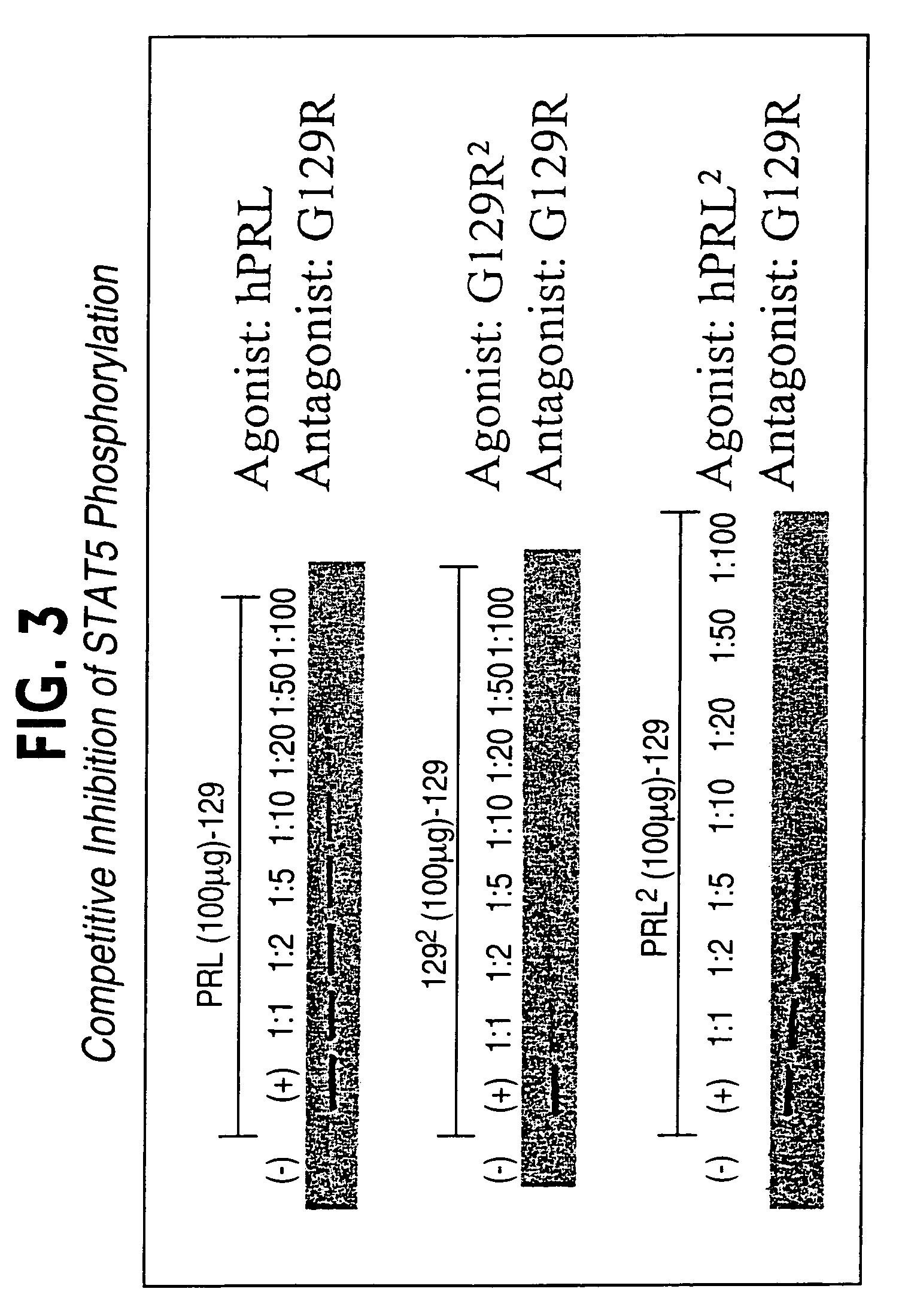
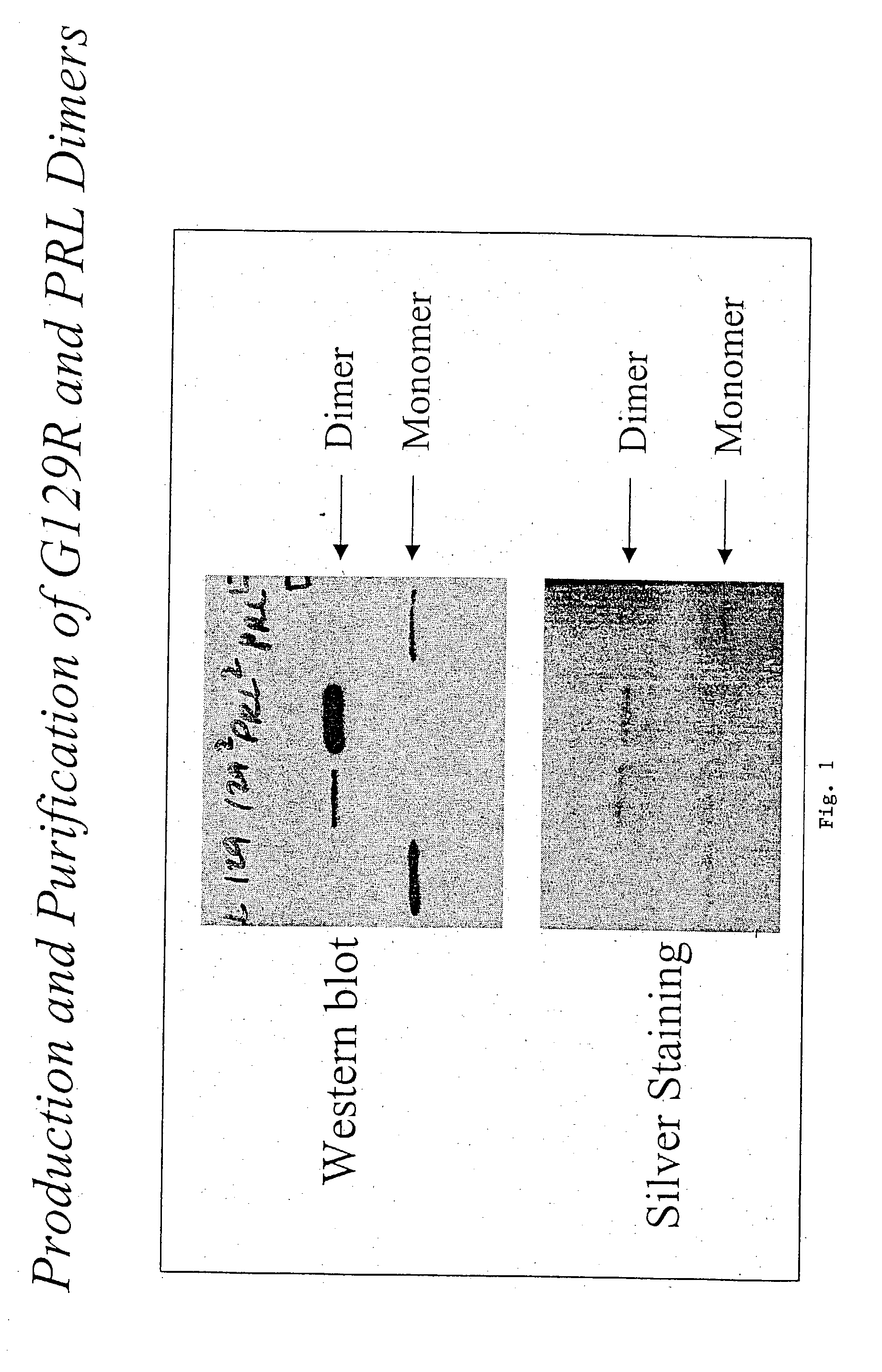
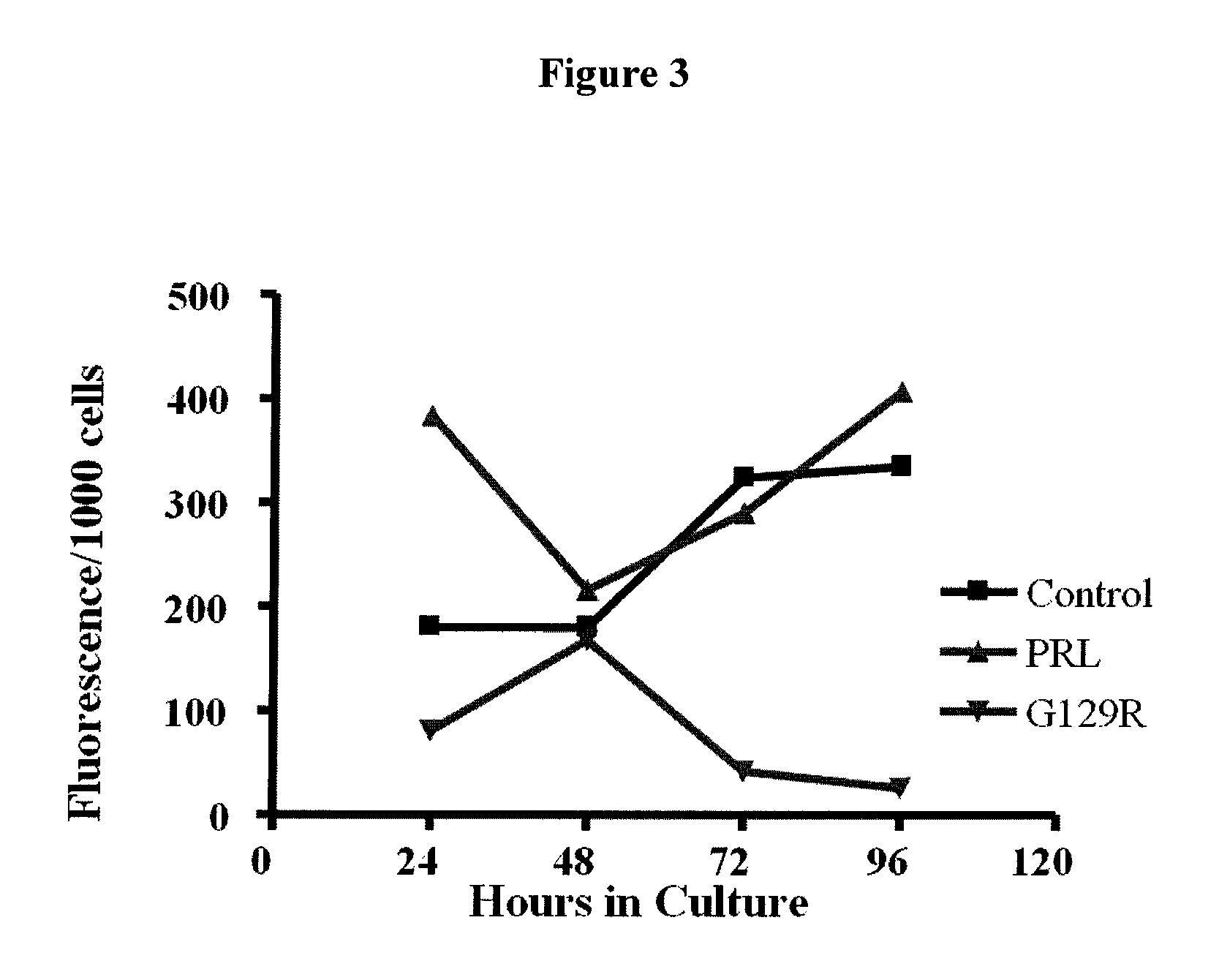
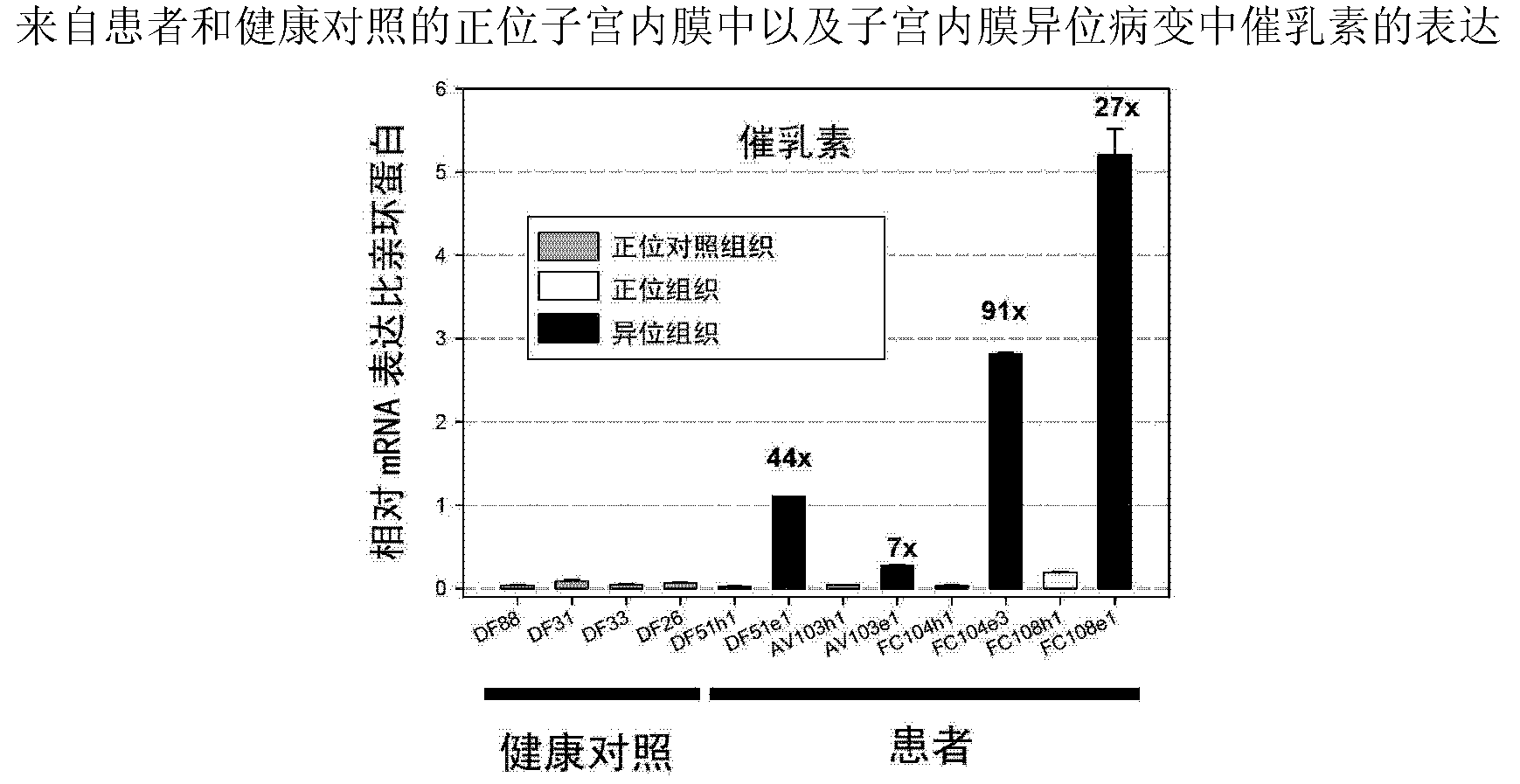
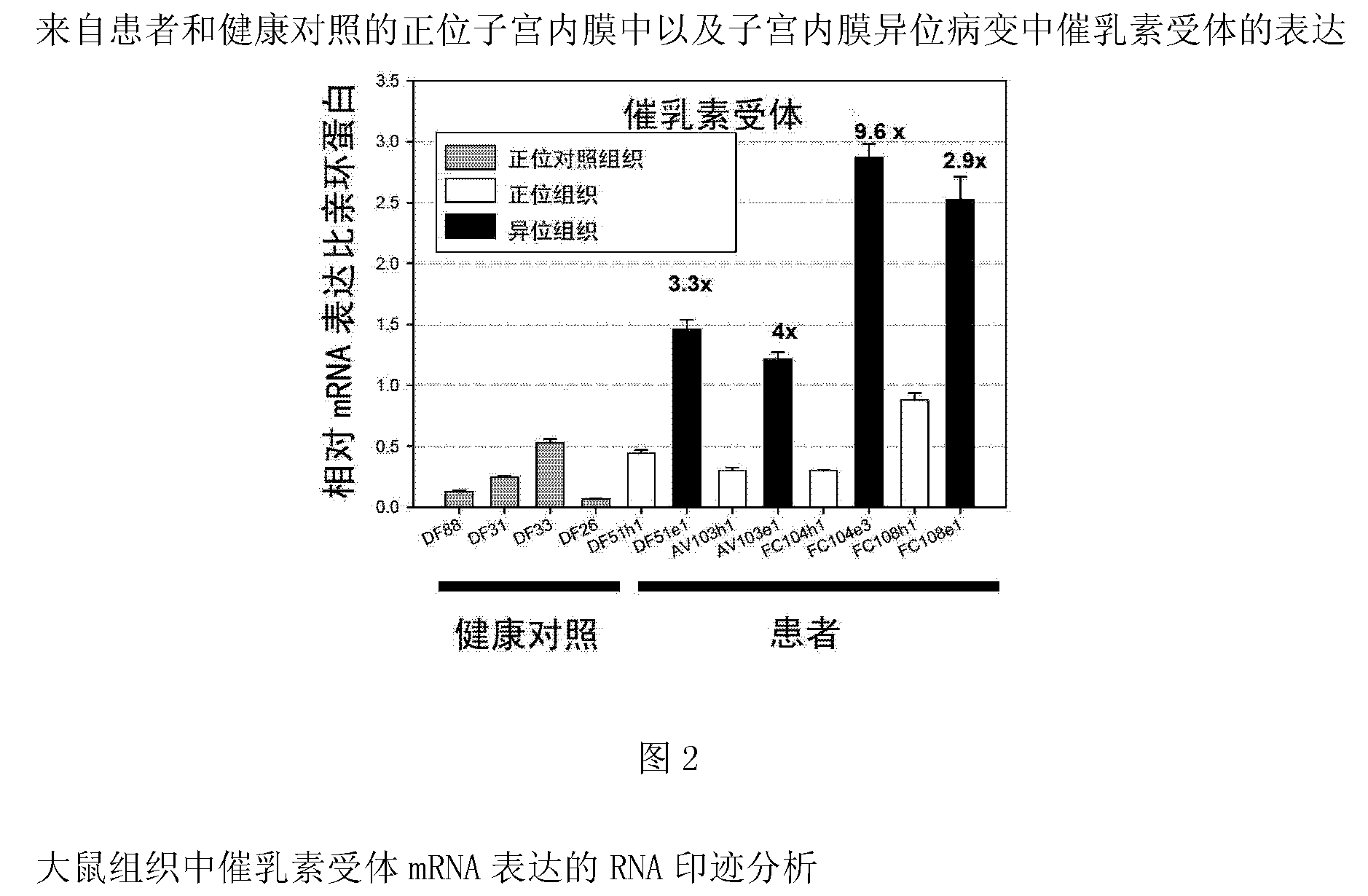
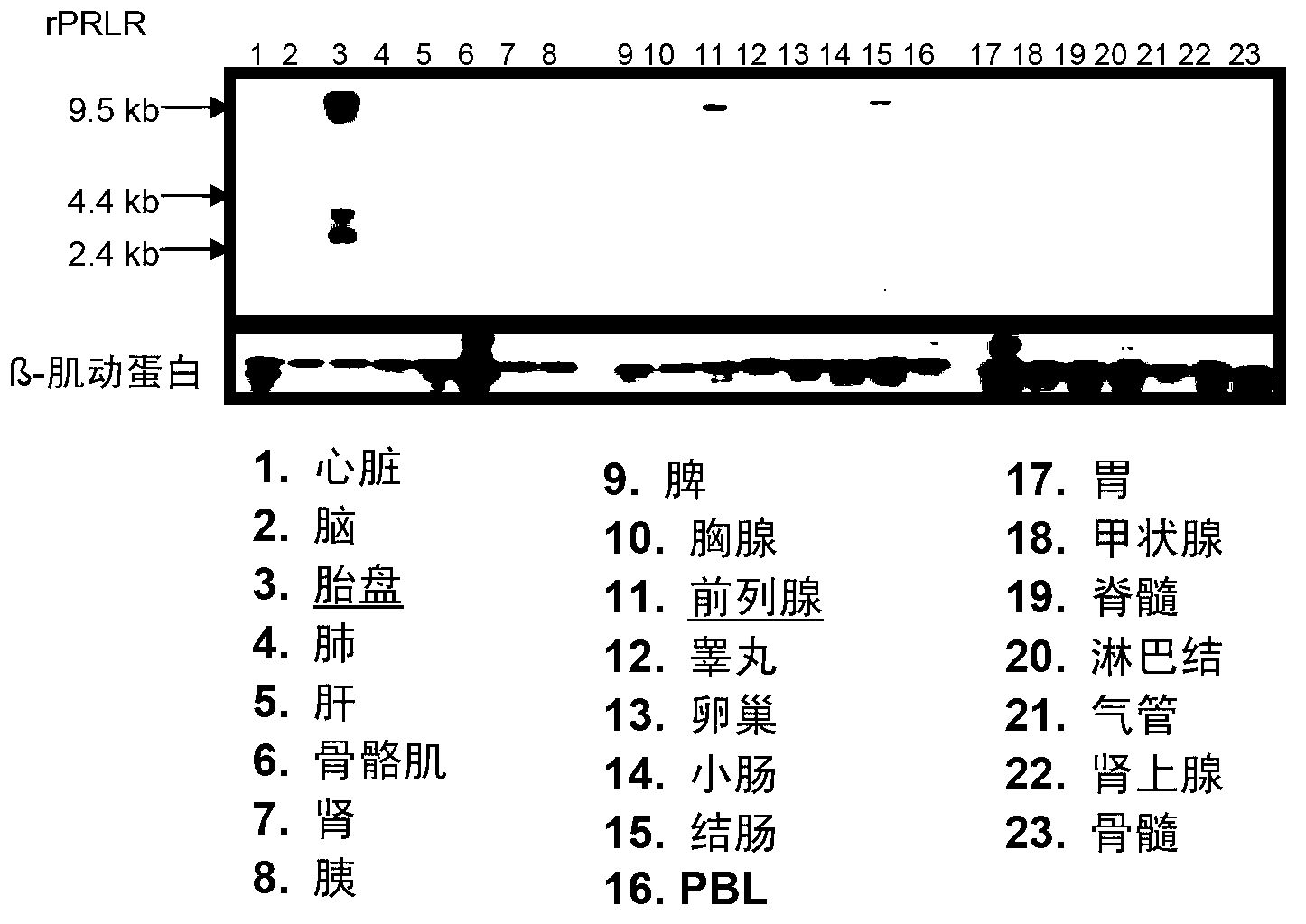
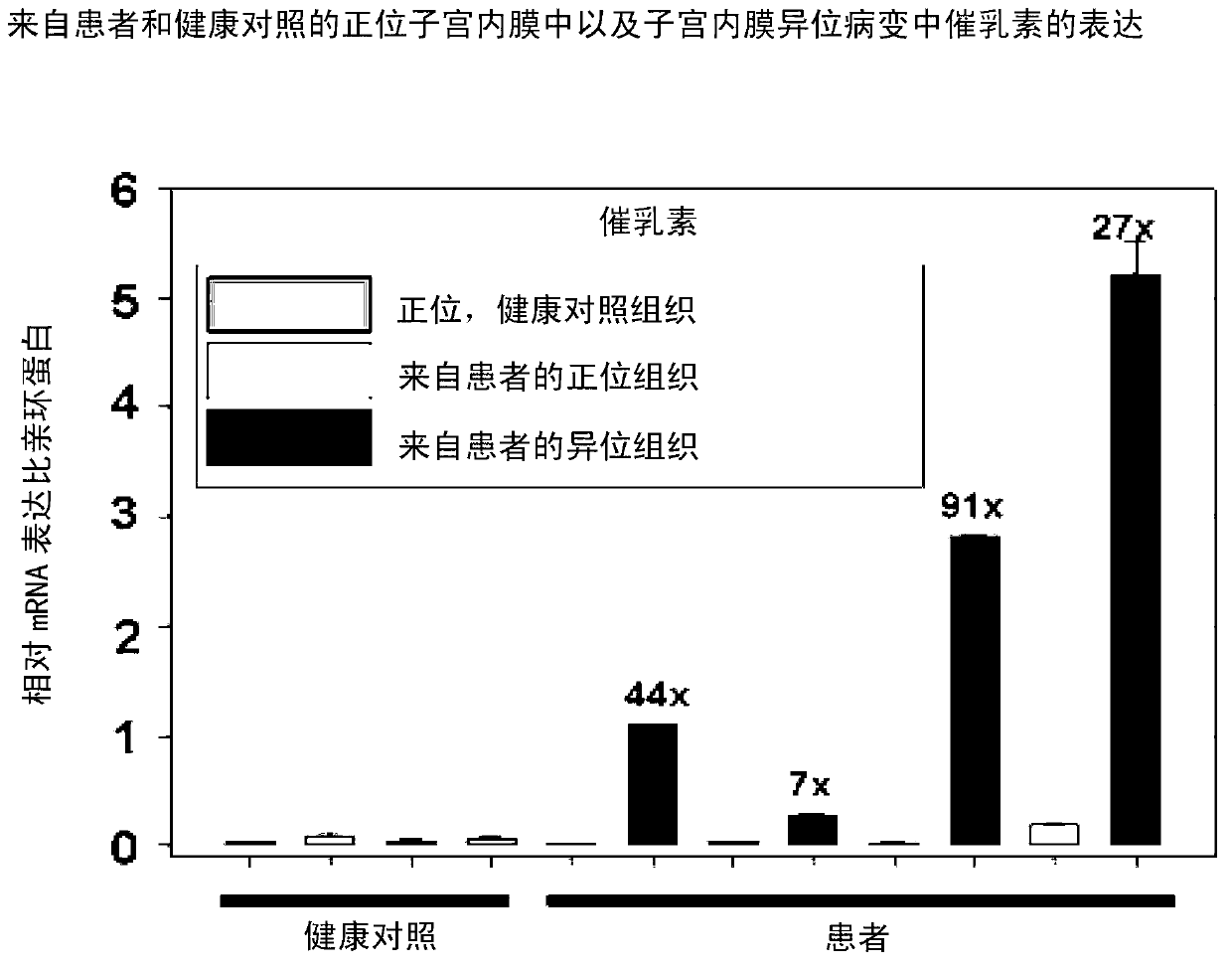
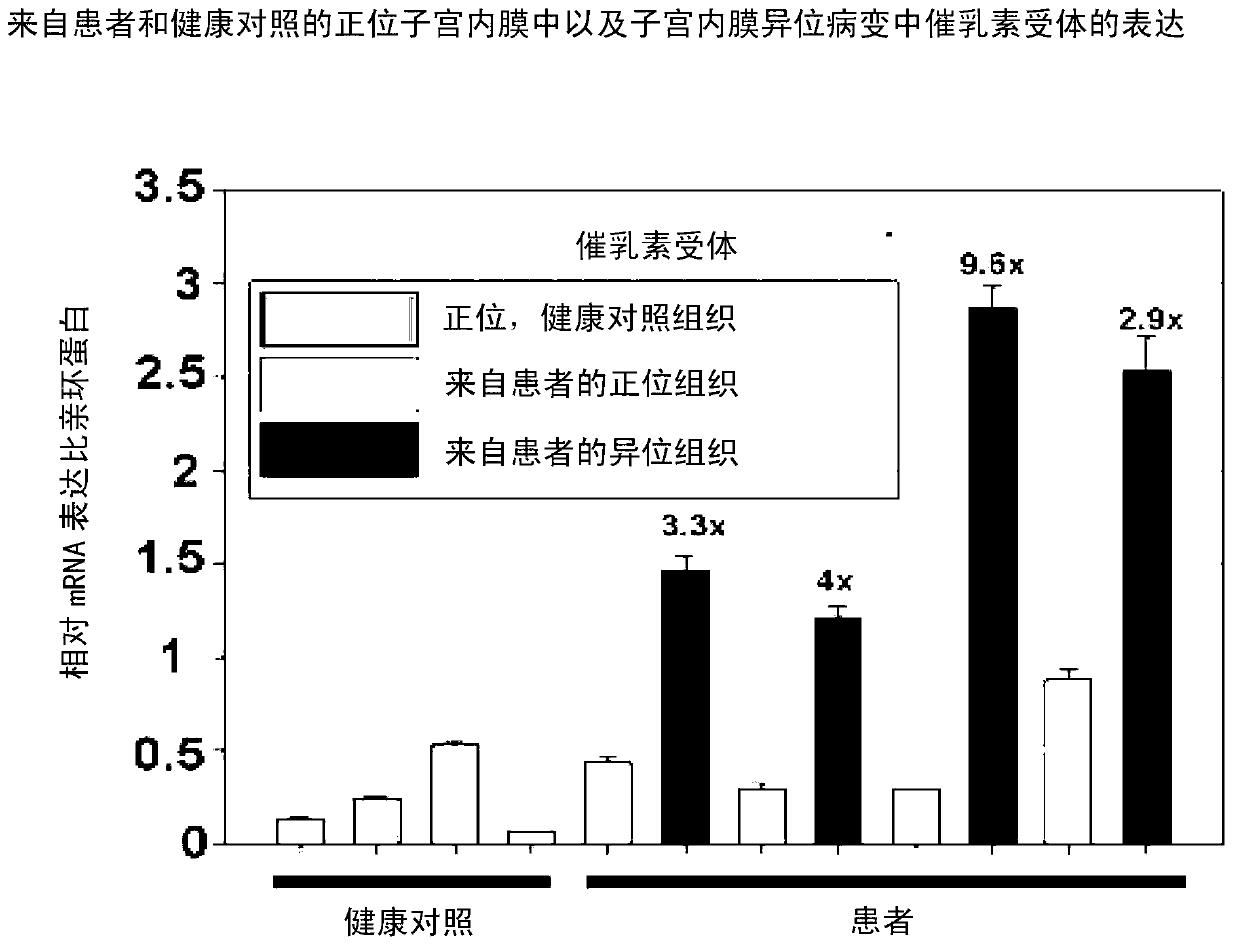
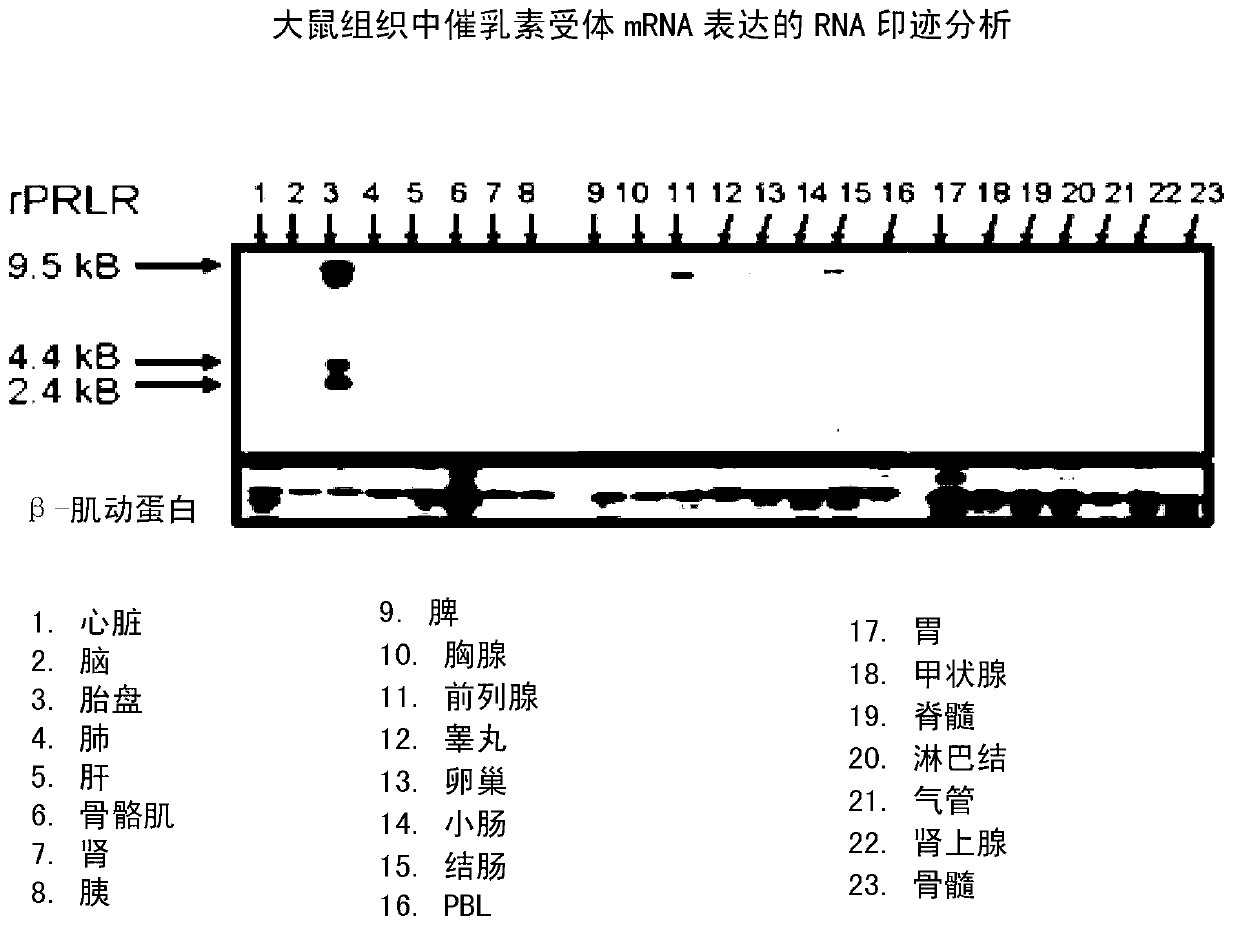
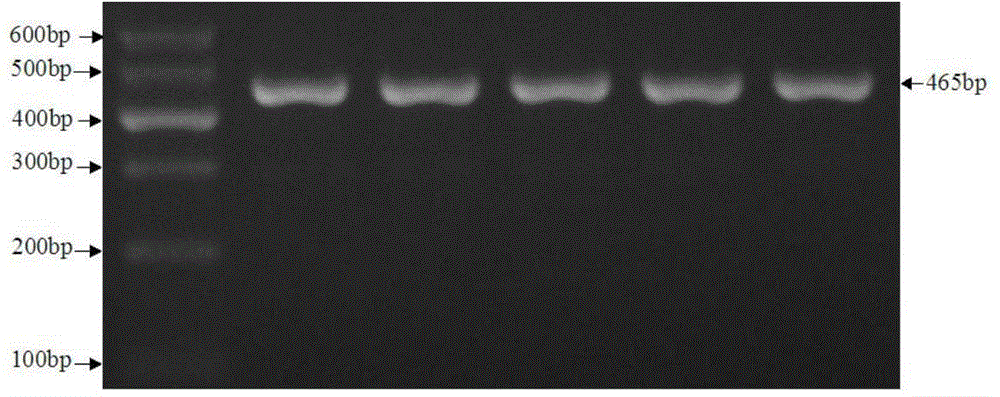
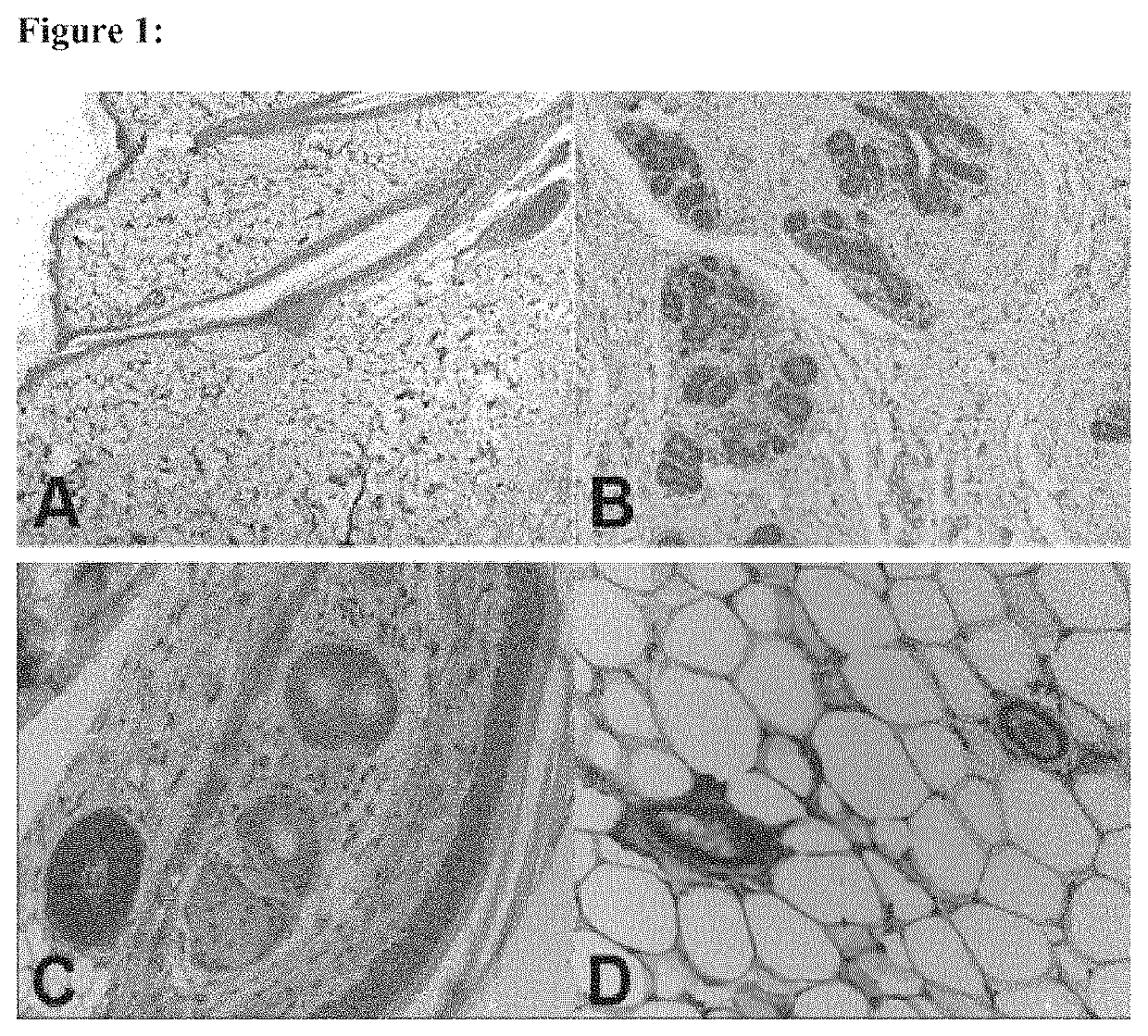
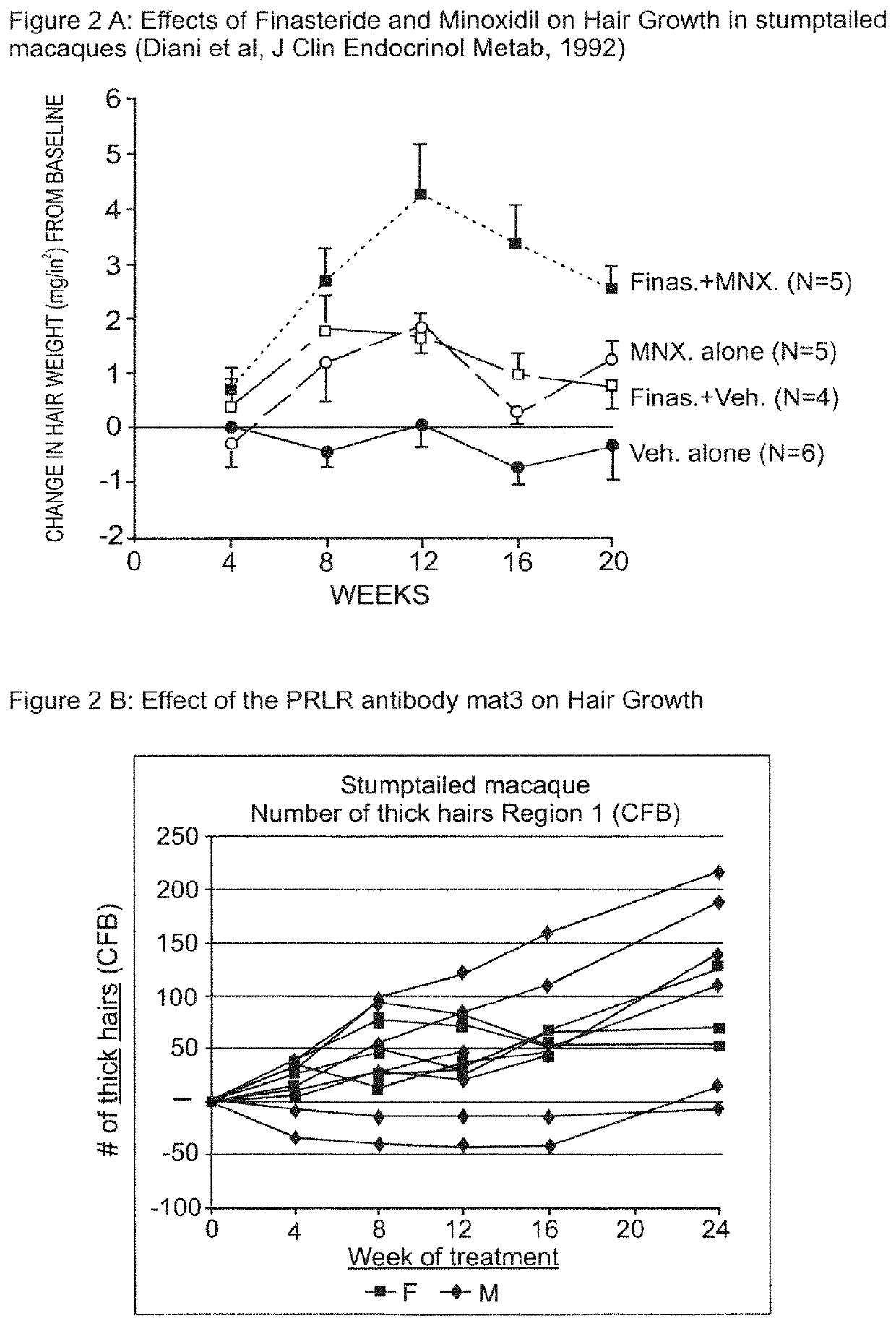
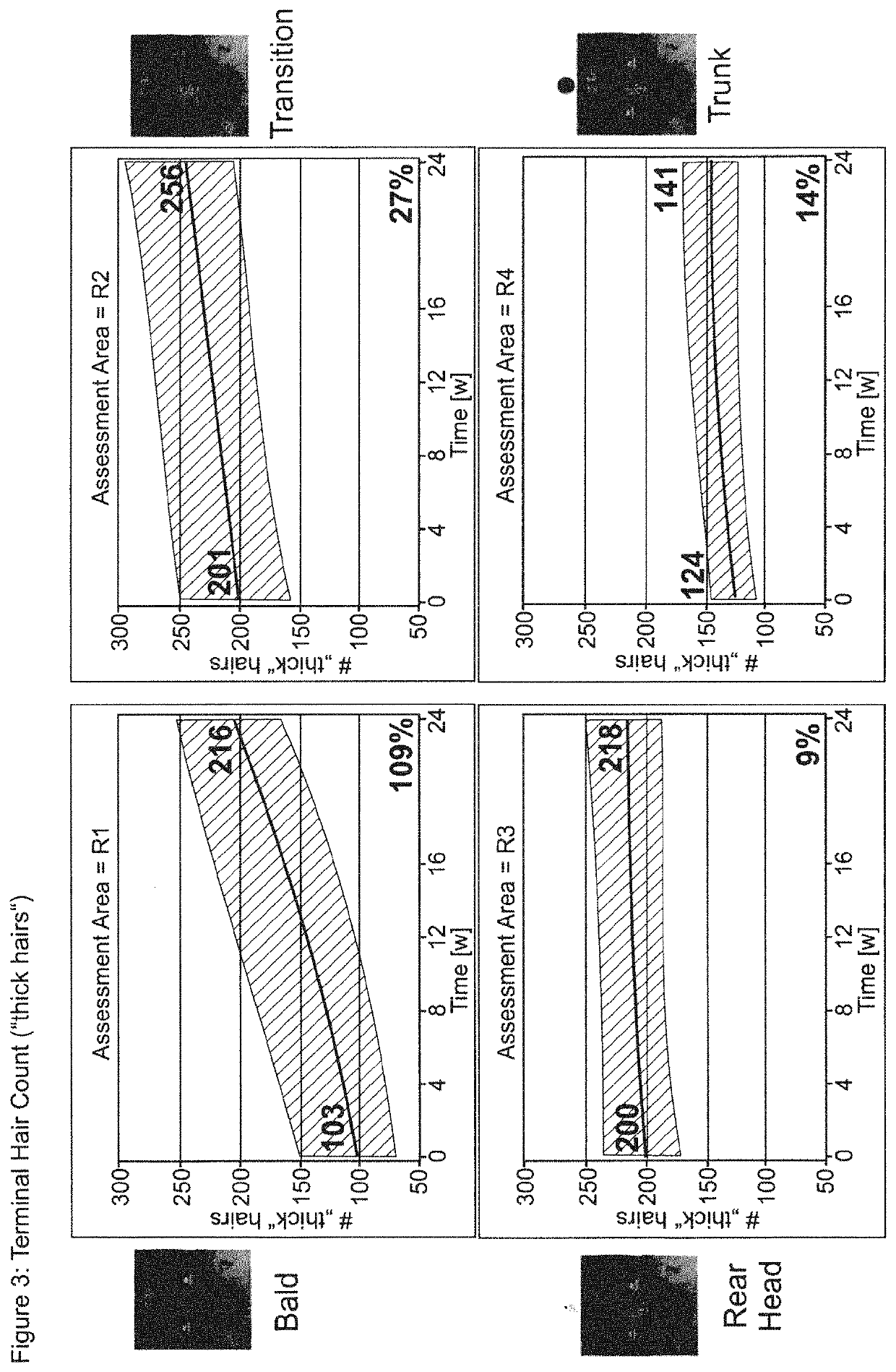
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Prolactin receptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
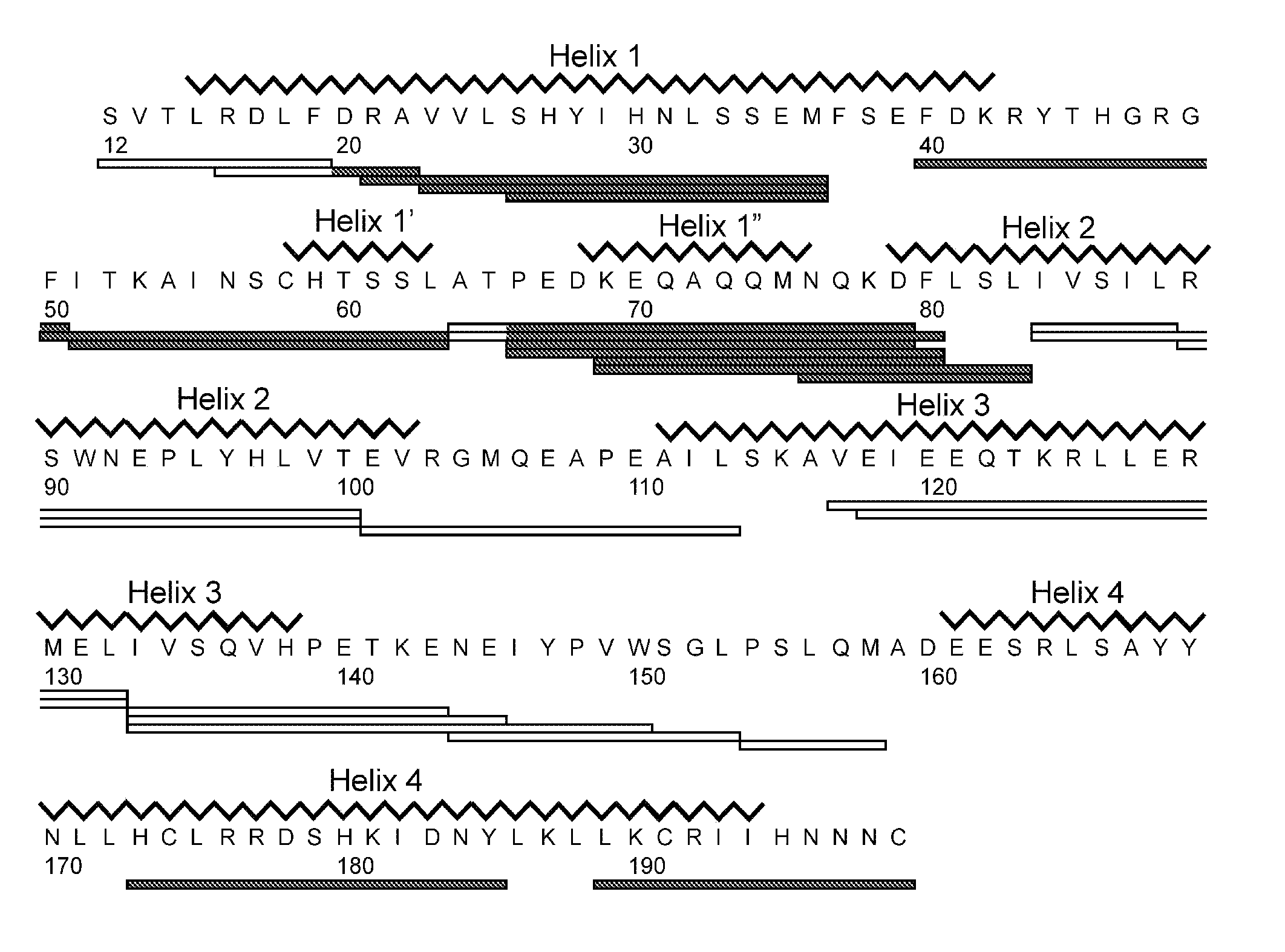
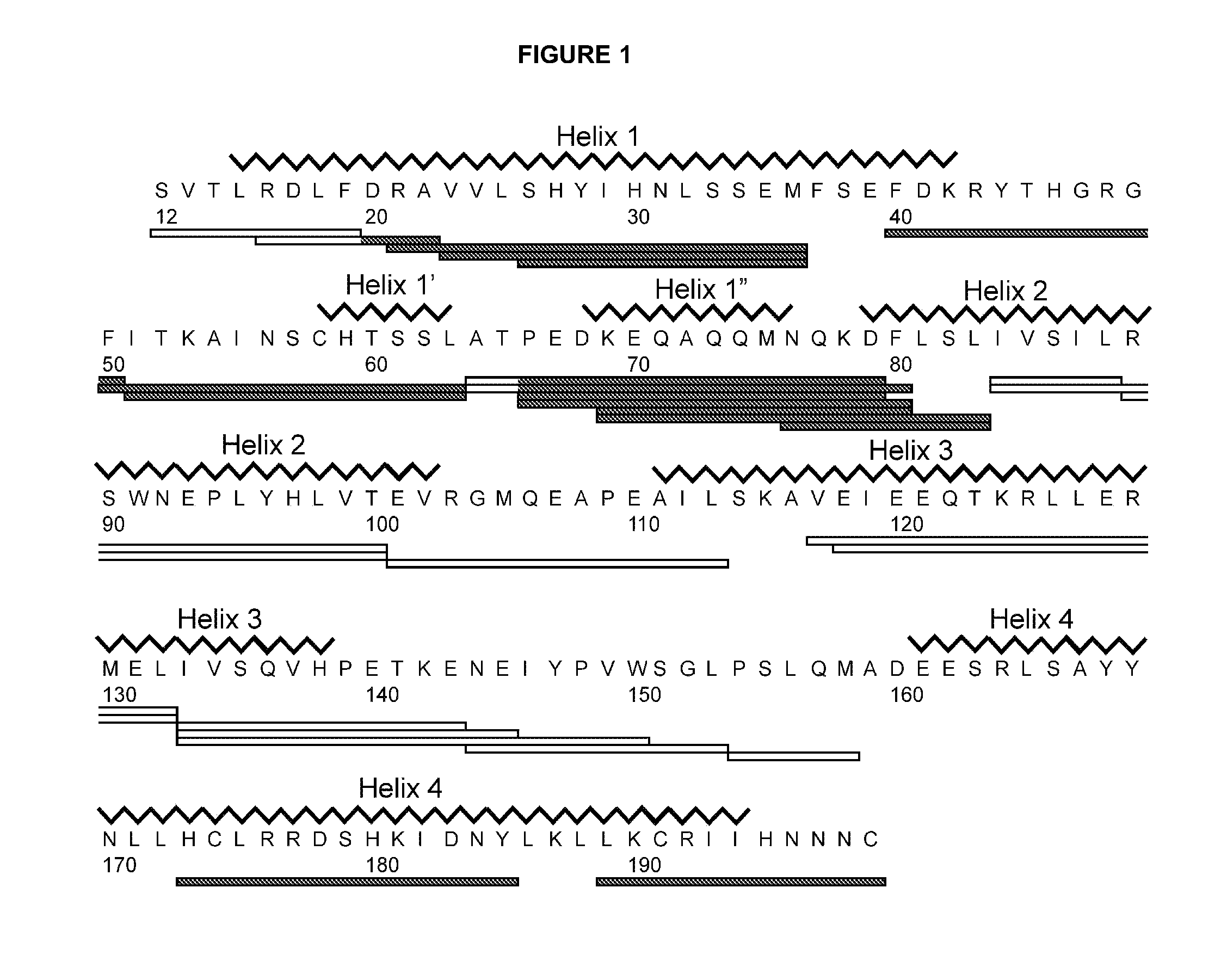
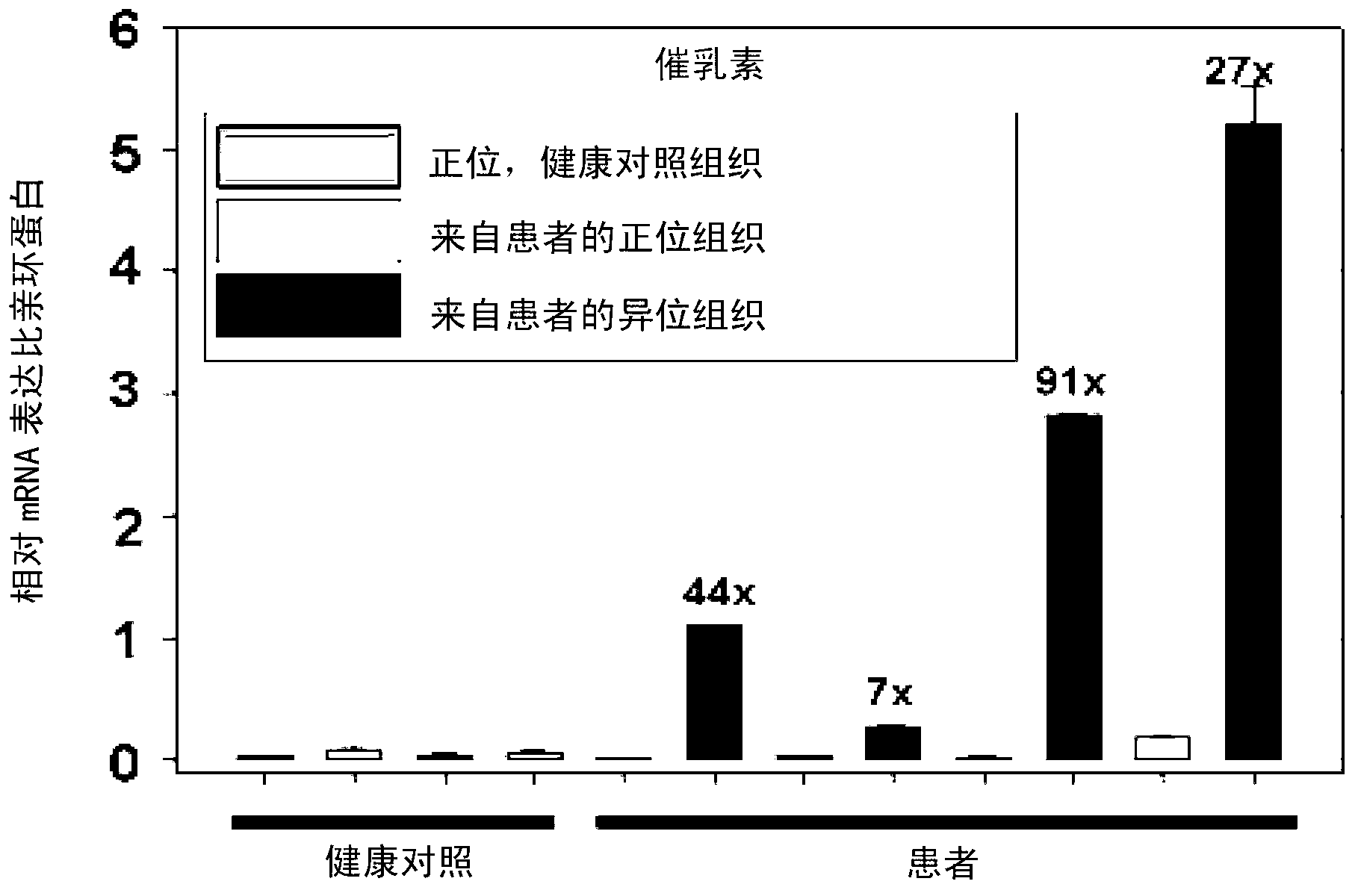
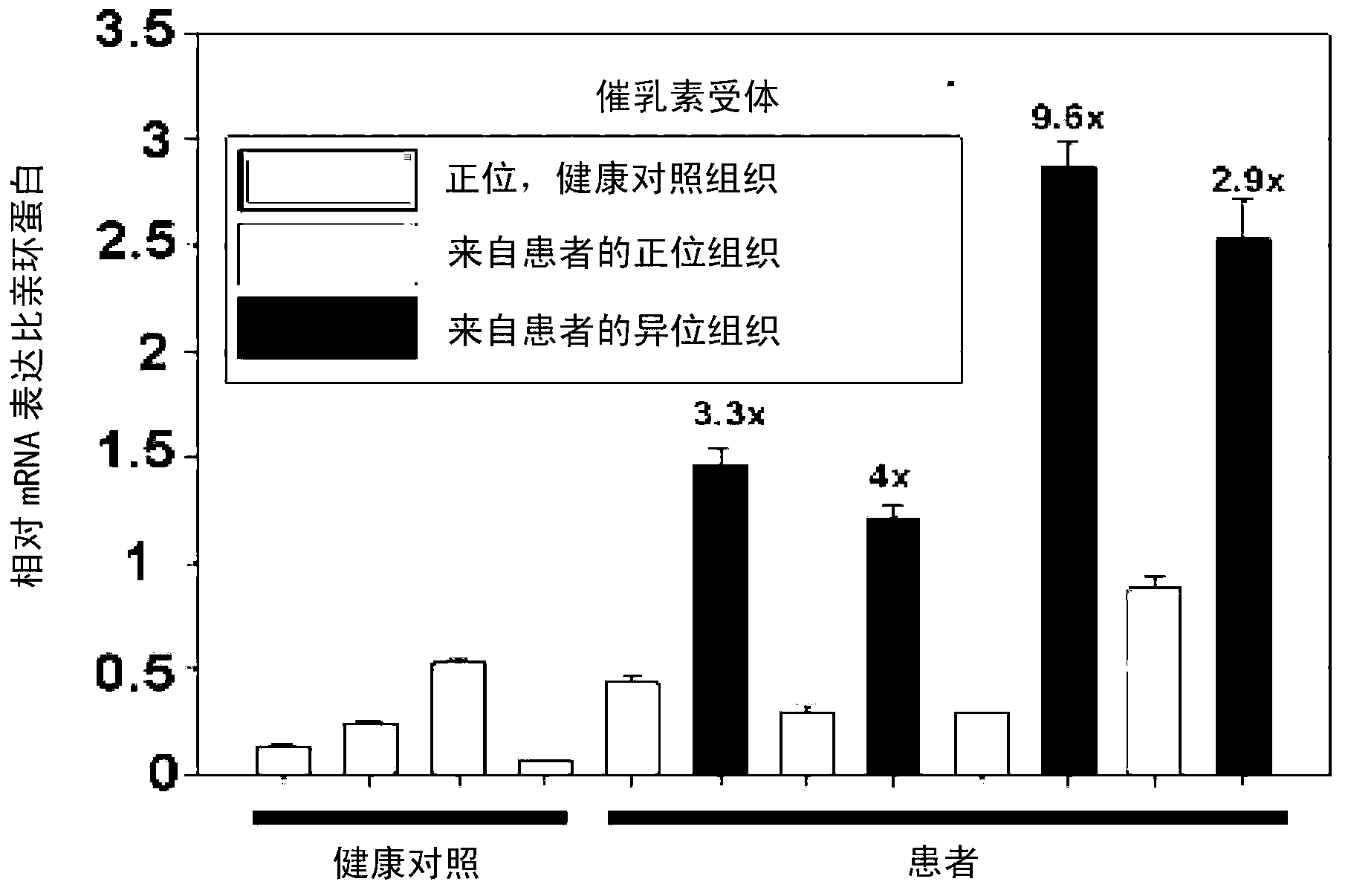
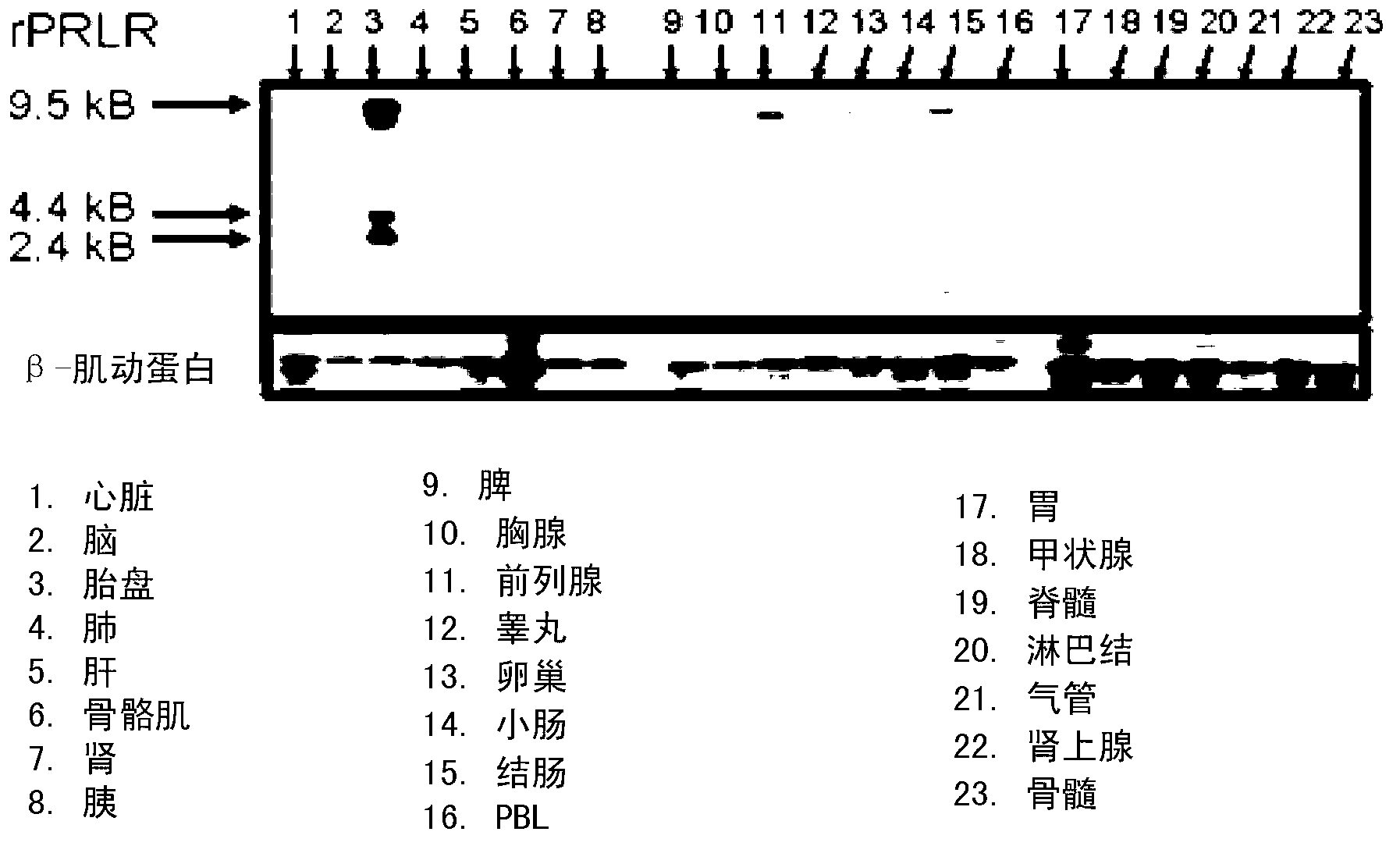
The prolactin receptor (PRLR) is a type I cytokine receptor encoded in humans by the PRLR gene on chromosome 5p13-14. The PRLR binds prolactin (PRL) as a transmembrane receptor. Thus the PRLR contains an extracellular region to bind PRL, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmatic region. The PRLR can also bind to and be activated by growth hormone (GH) and human placental lactogen (hPL), in addition to prolactin.
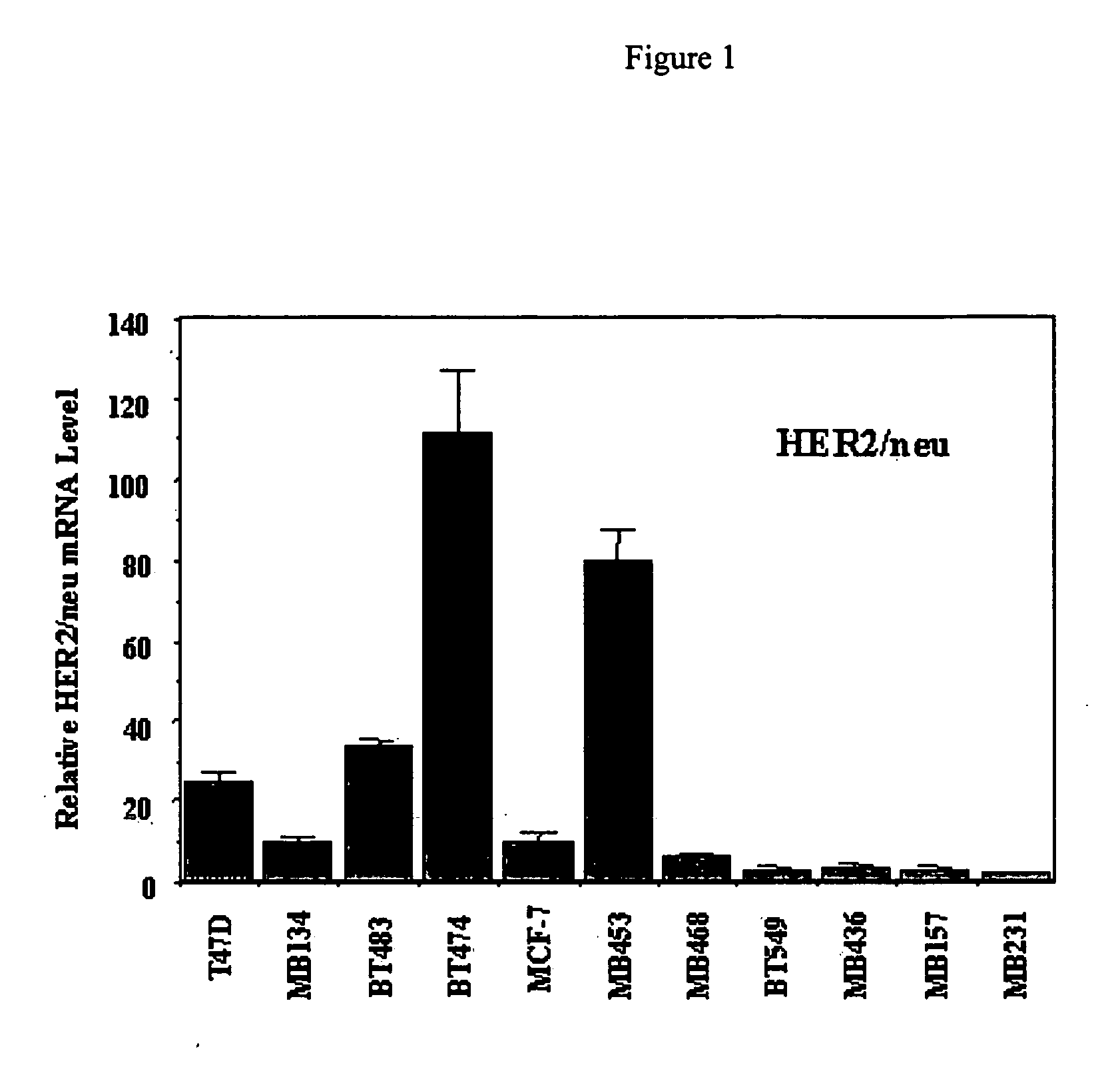
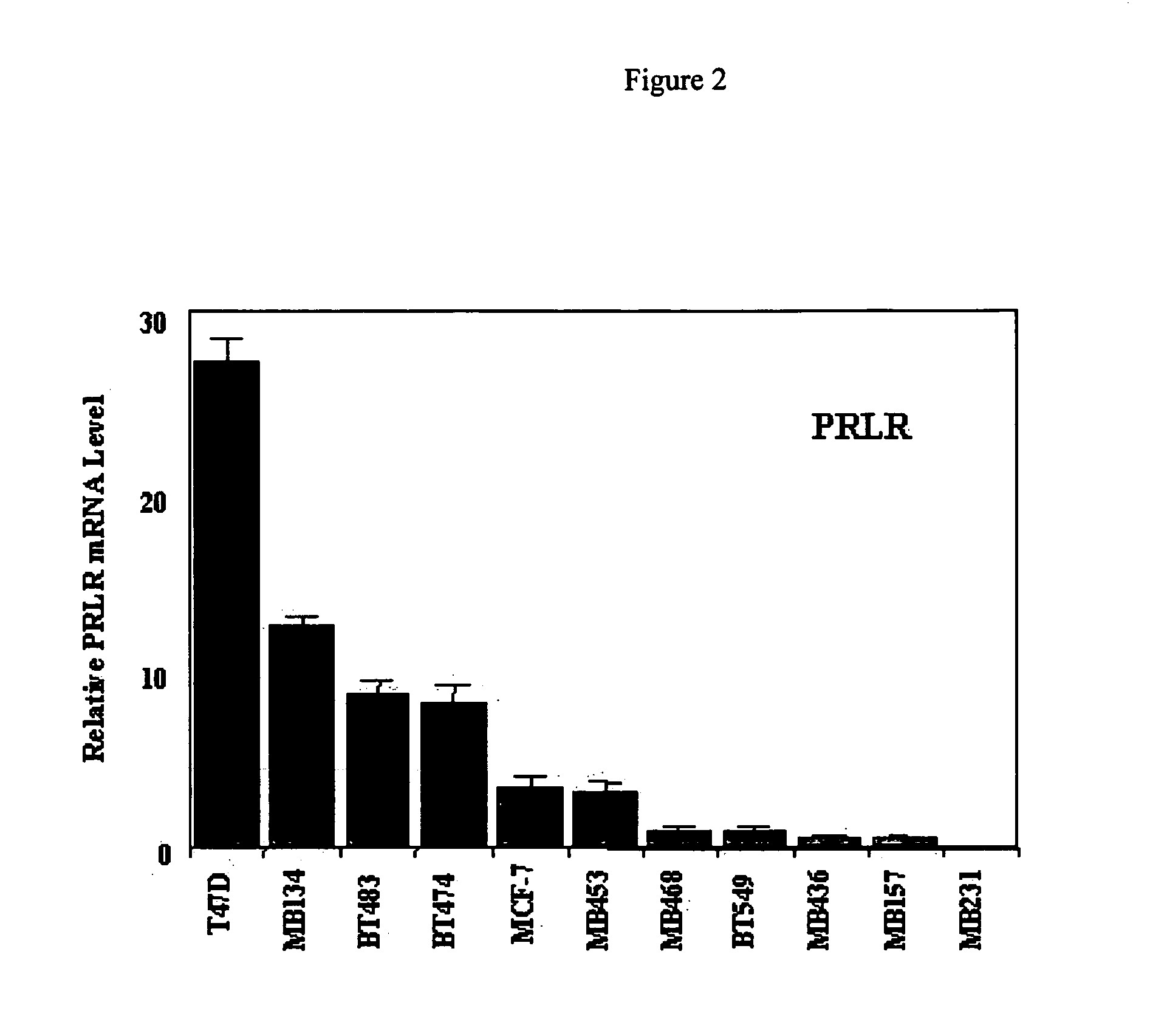
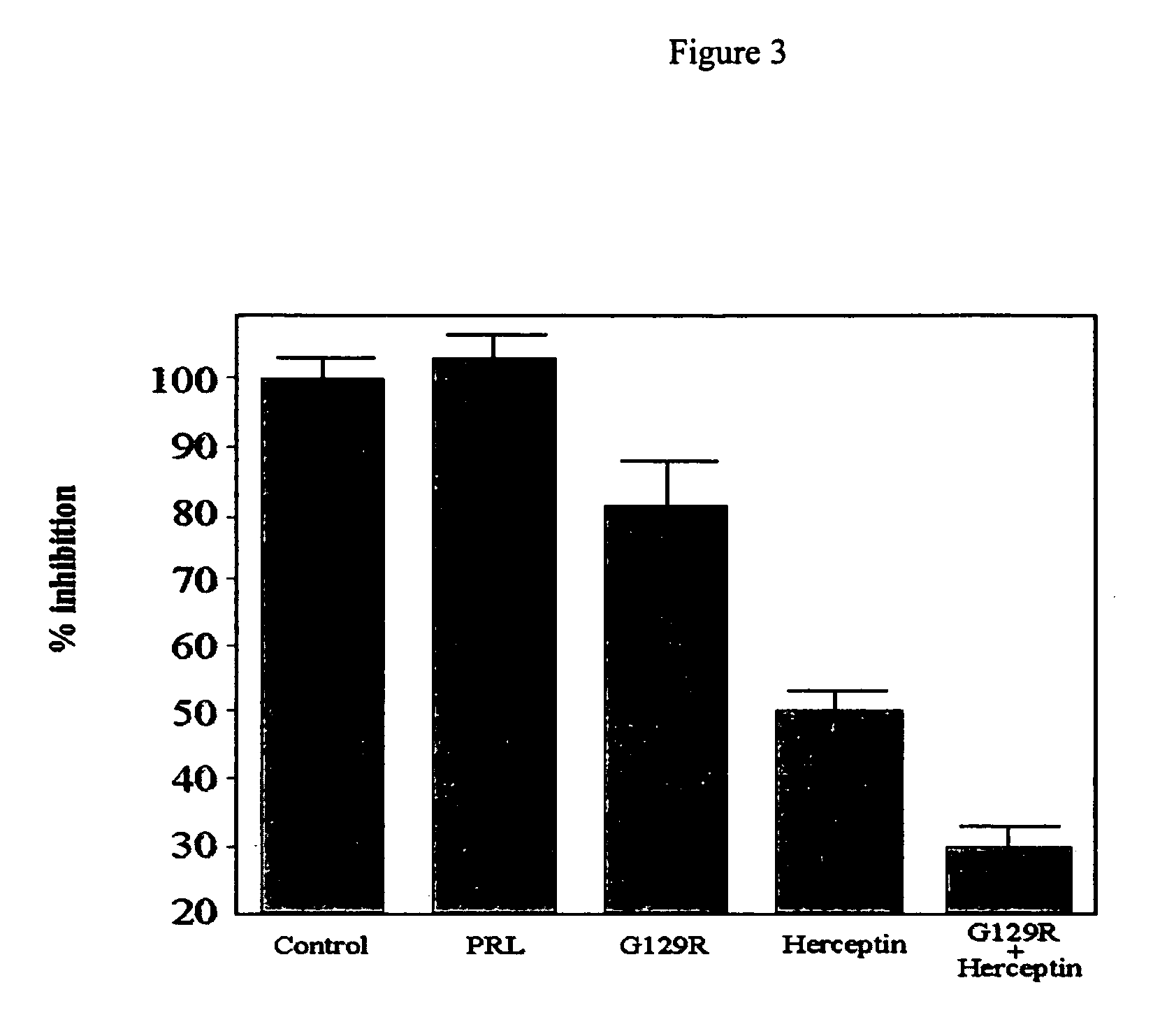
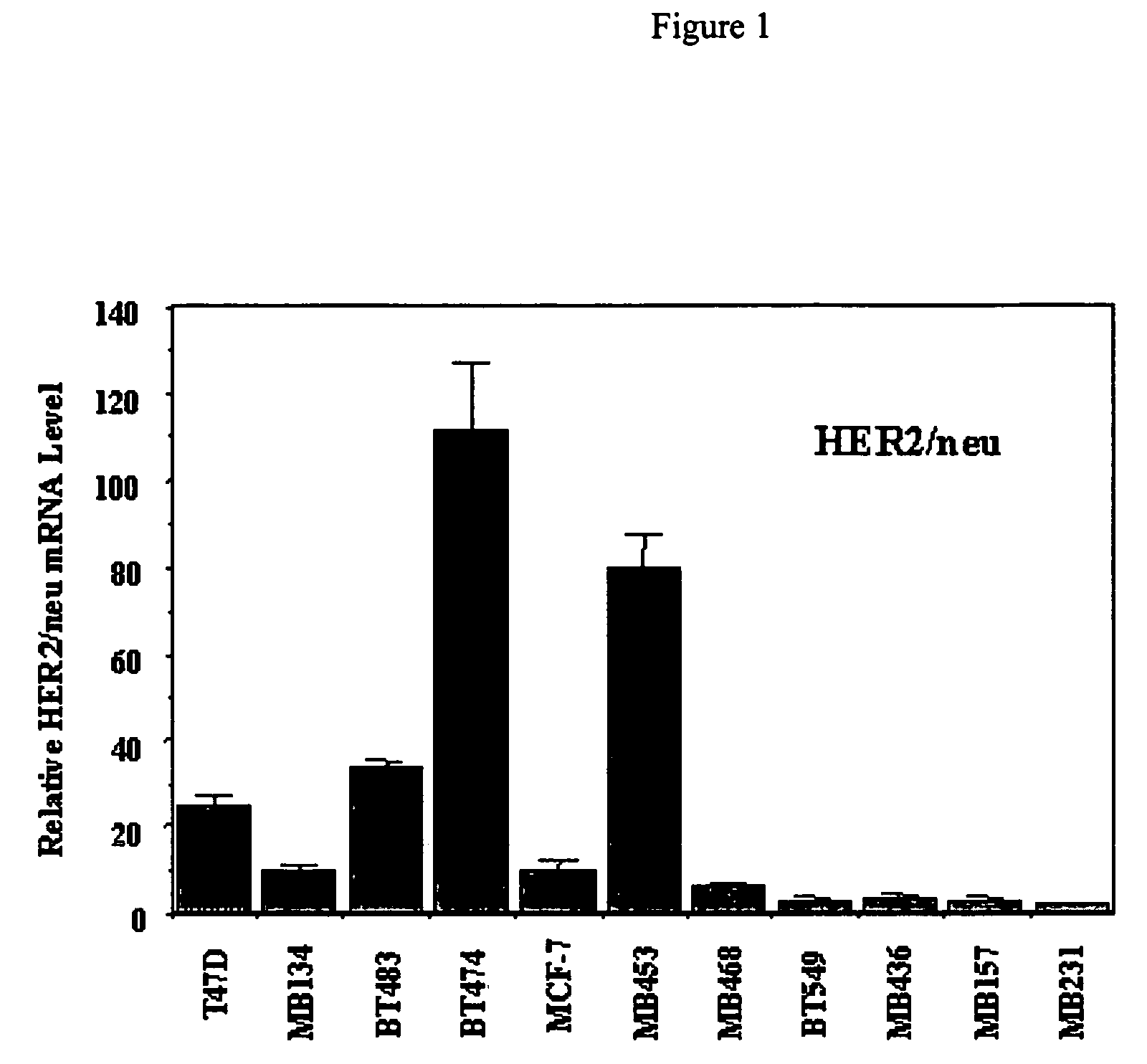
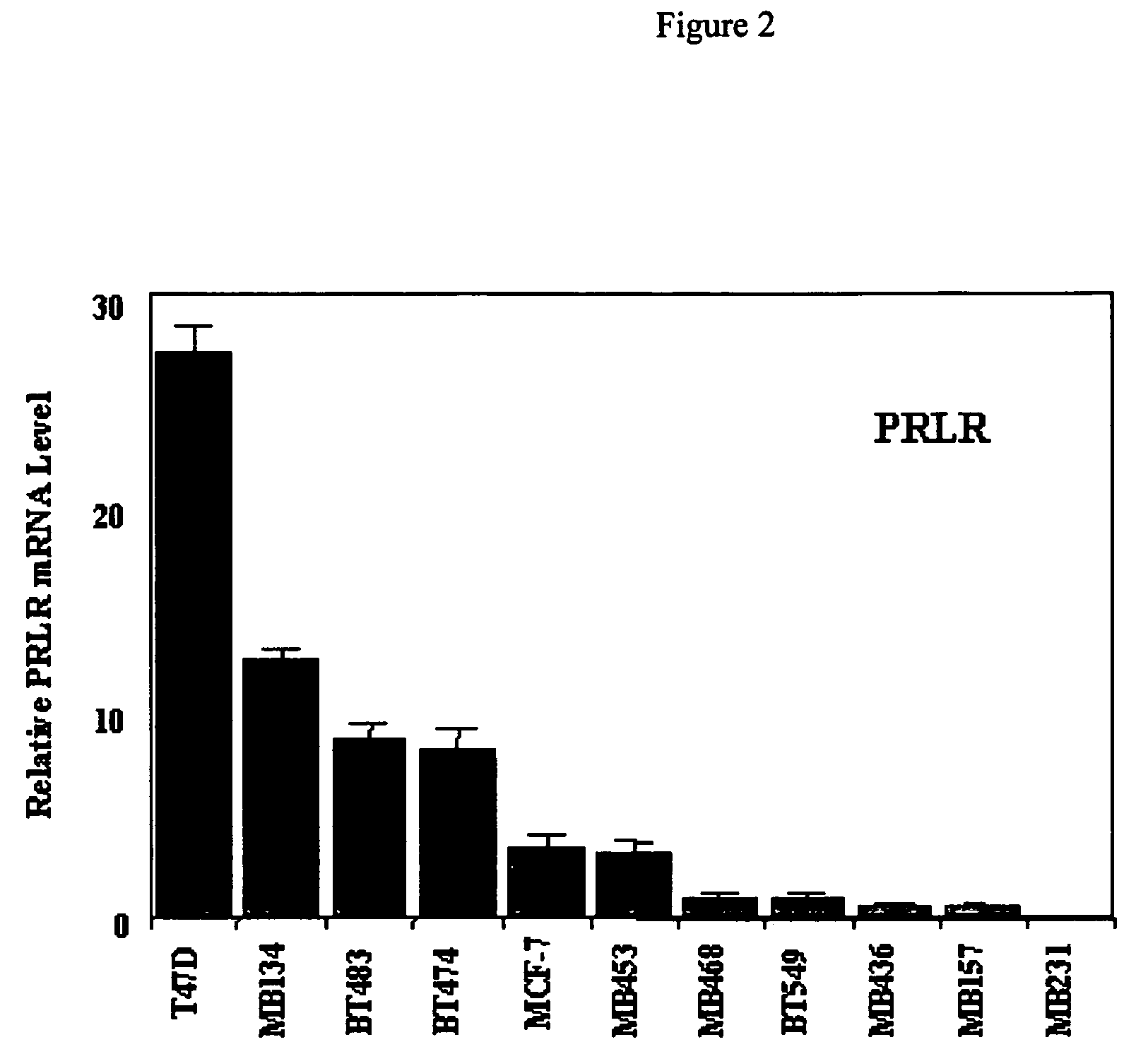
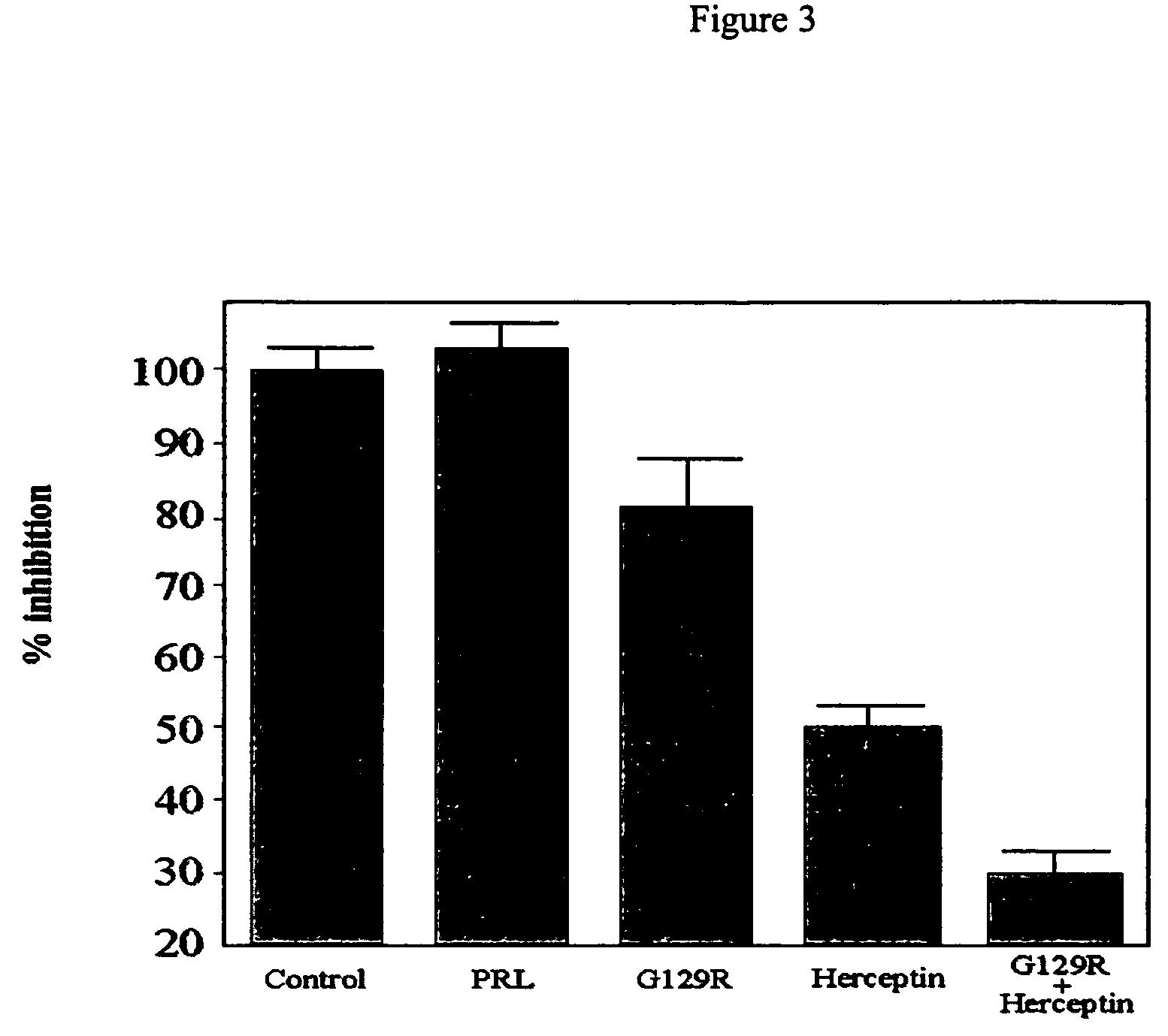
Use of prolactin receptor antagonists in combination with an agent that inactivates the HER2/neu signaling pathway
InactiveUS20050271626A1Slow tumor growthInhibit cell proliferationBiocideHormone peptidesProlactin receptorAntagonist
The present invention describes compositions and methods for inhibiting cell proliferation comprising a prolactin receptor antagonist and an agent that inactivates the HER2 / neu signaling pathway, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:ONCOLIX
Use of anti-prolactin agents to treat proliferative conditions
InactiveUS20030022833A1Induce inhibitionPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseHuman cancer
Owner:ONCOLIX
Use of anti-prolactin agents to treat proliferative conditions
InactiveUS7115556B2Reduced availabilityPrevent proliferationHormone peptidesOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseHuman cancer
Owner:ONCOLIX
Methods And Compositions For The Treatment Of Prolactin-Receptor Related Disorders
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the treatment, diagnosis, prevention, or amelioration of one or more symptoms of a prolactin receptor-related condition, including, for example, a cancer such as breast cancer or prostate cancer, by administering a growth hormone-based prolactin receptor antagonist and zinc, or administering a growth hormone-based prolactin receptor antagonist to a tissue with an effective local concentration of zinc. The invention further provides pharmaceutical compositions of growth hormone-based prolactin receptor antagonists and zinc useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:TERCICA
Multi-gene pyramiding breeding method for thoroughbred milk goats
InactiveCN102605064AAccurately estimate breeding valuesImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementExonProlactin receptor
The invention discloses a multi-gene pyramiding breeding method for thoroughbred milk goats. Genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a milk goat continuously giving birth to two or more lambs is used as a template, four pairs of primers respectively expand intron 2 and exon 10 of a prolactin receptor gene and an untranslation region (5'UTR) and exon 1 of luteotropin beta calcmeurin 5', the sizes of expanded products are judged by agarose gel electrophoresis, site mutation of the expanded products of the four pairs of primers are screened by DNA sequencing technology, then polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is used for performing genetic typing and gene frequency analysis for SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) of four sites of the prolactin receptor gene and the luteotropin beta calcmeurin, the relation of polymorphism of a multiple-birth milk goat individual (F1 generation) and the number of born lamps and the relation of different genetype combinations and the number of the born lamps are analyzed, parental generation (F0 generation) is reviewed, filial generation (F2 generation) is tracked, the relation of the genetype combination of an ewe individual and the number of the born lamps is detected, and contribution of different genetypes in terms of prolific trait formation is analyzed.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Use of Prolactin Receptor Antagonist and Chemotherapeutic Drug for Treating Ovarian Cancer
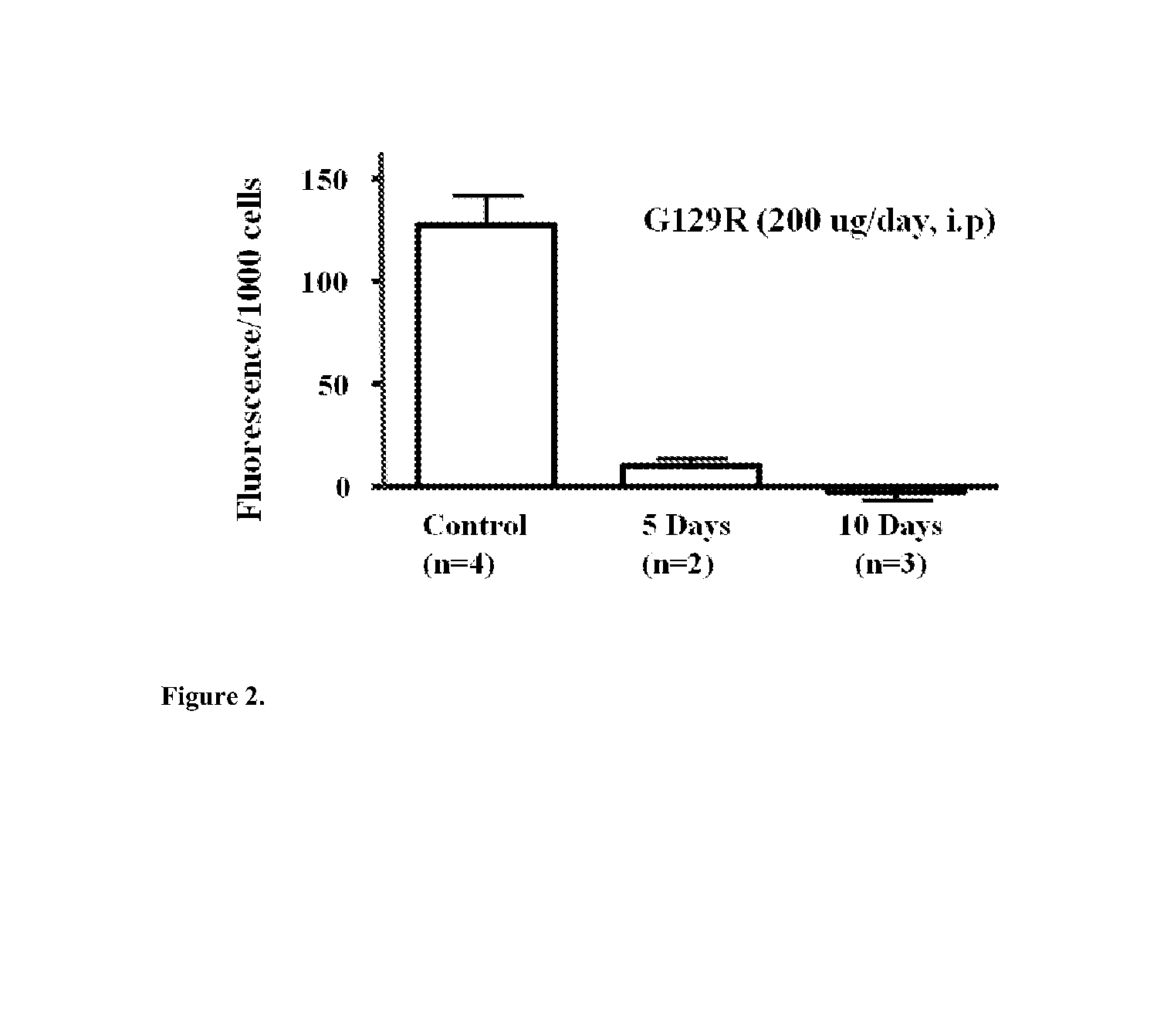
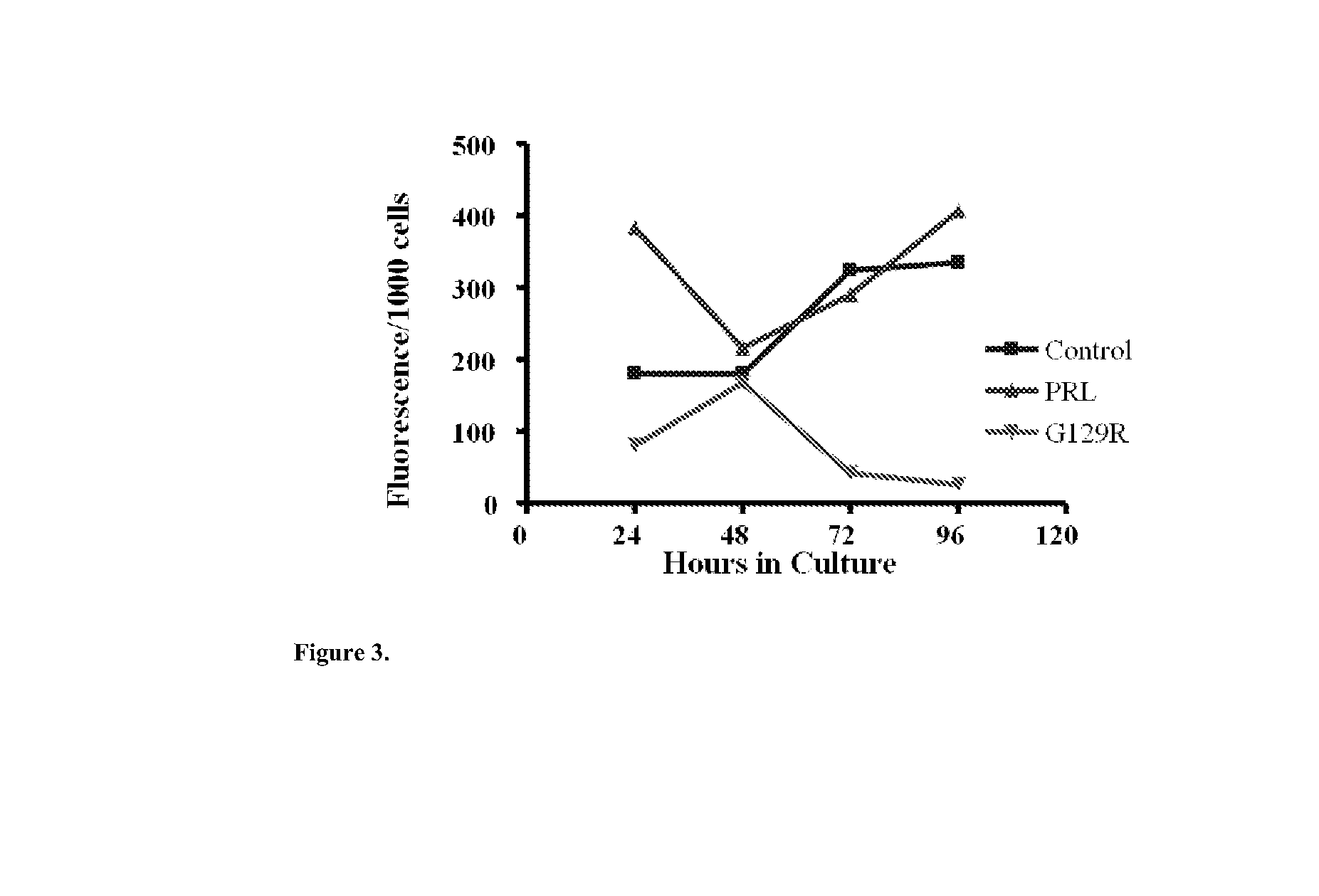
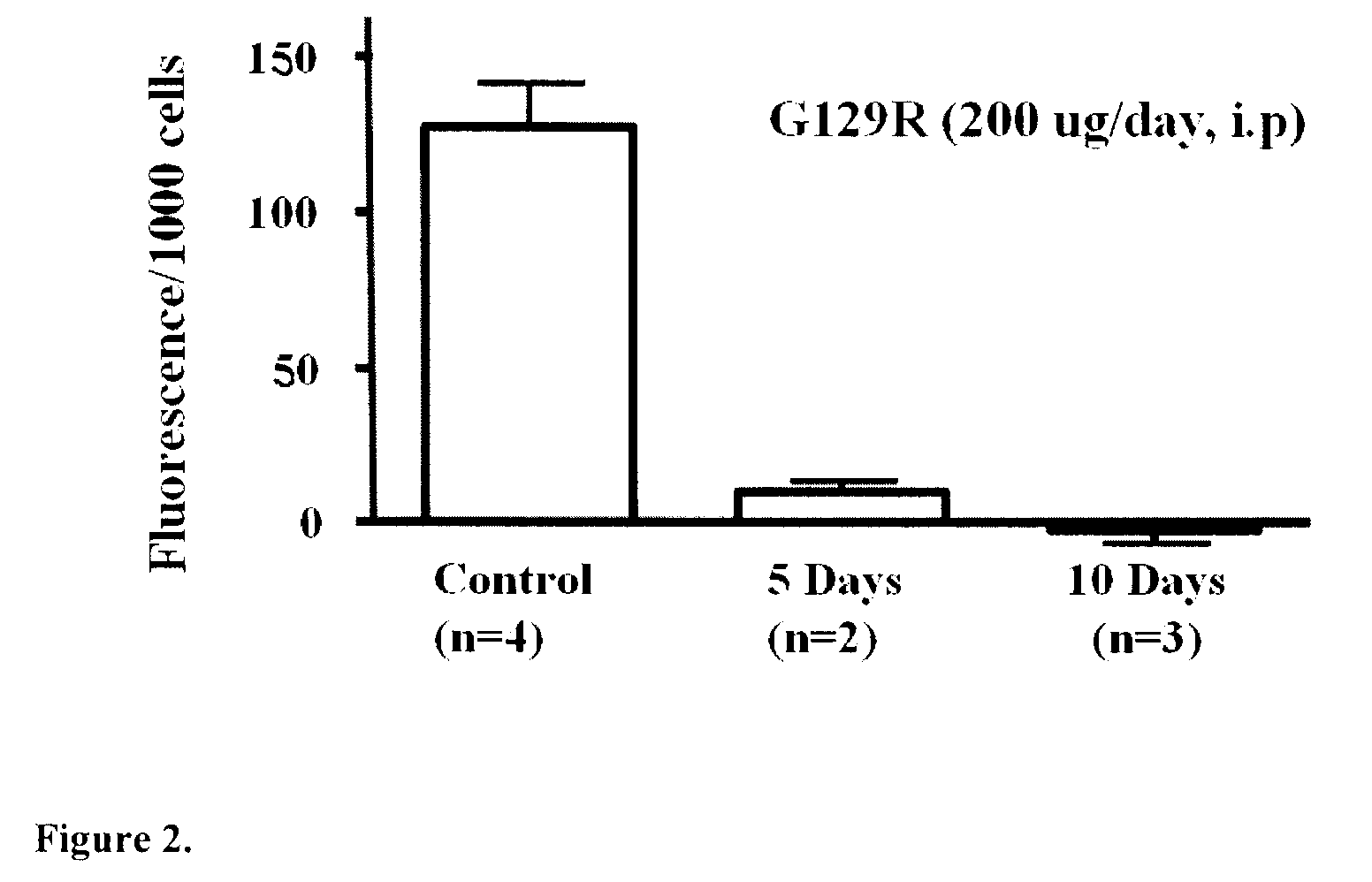
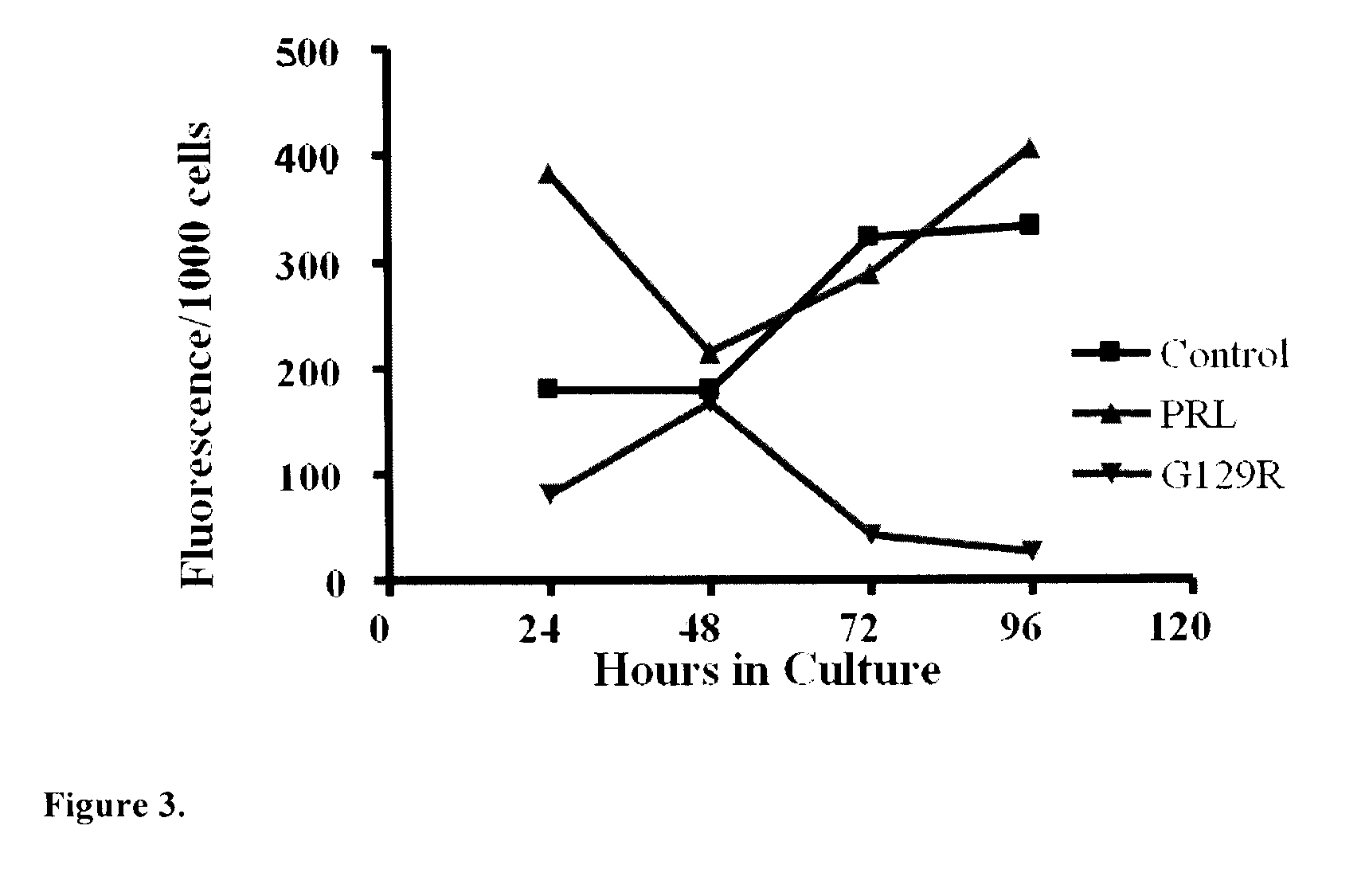
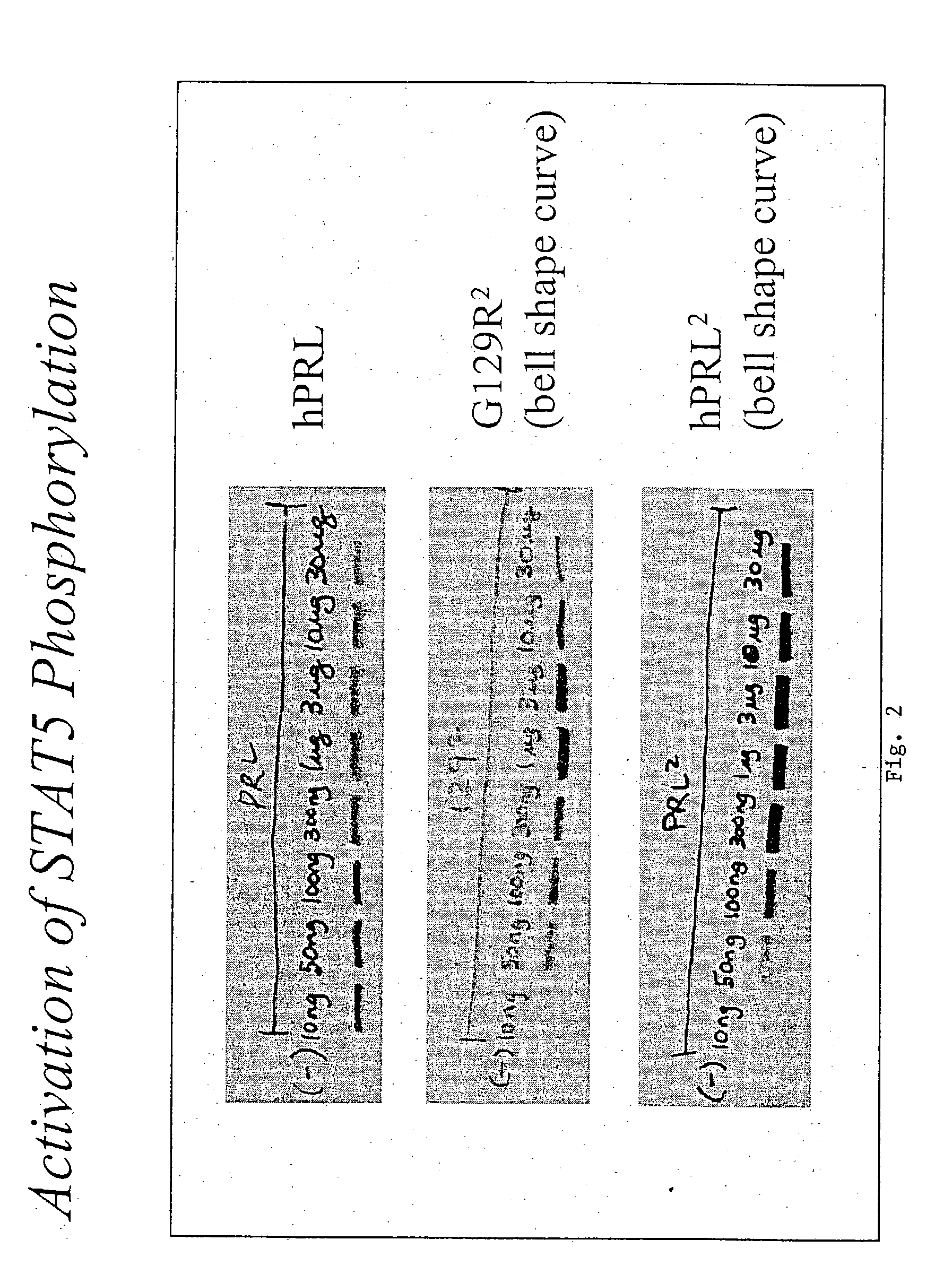
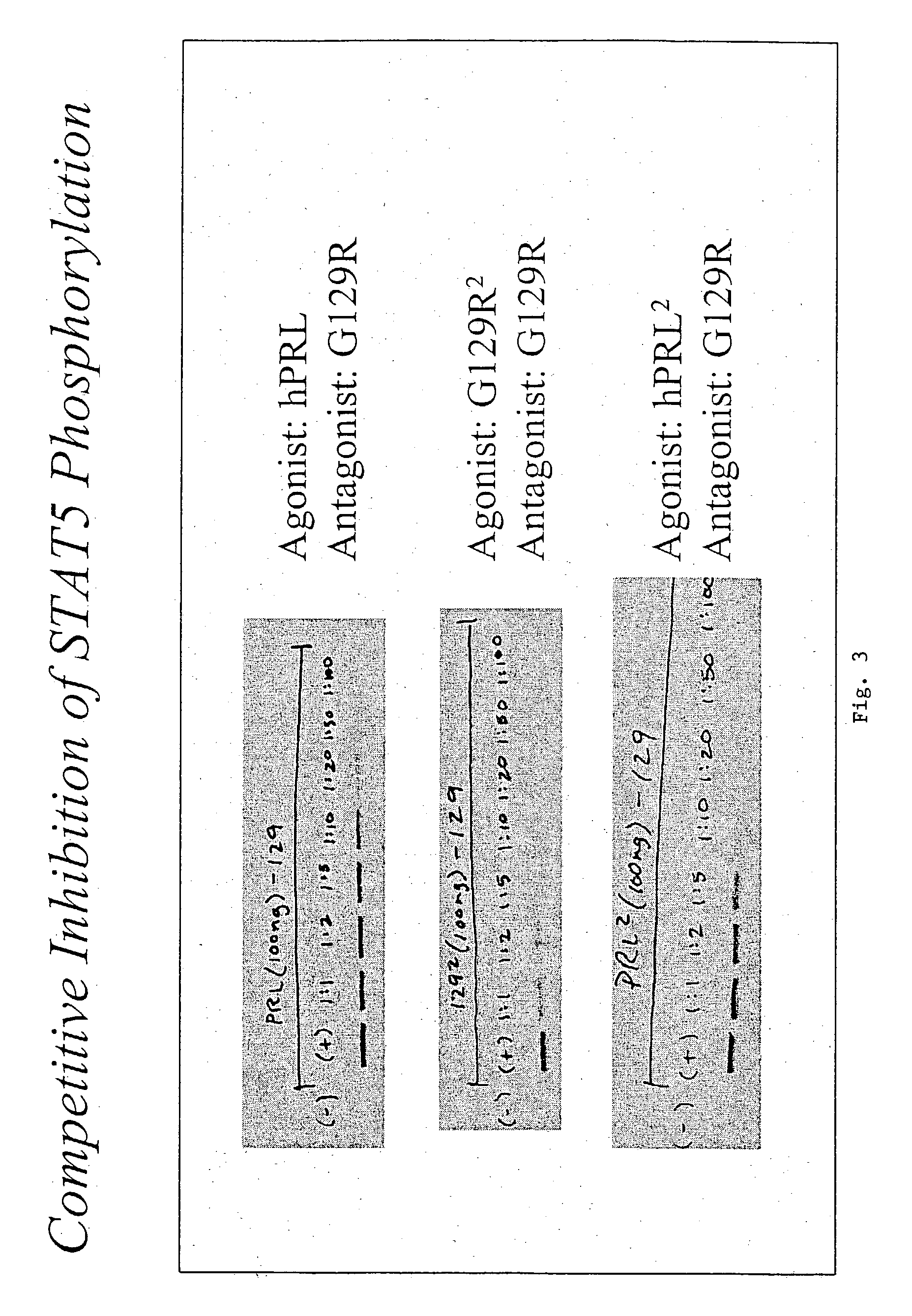
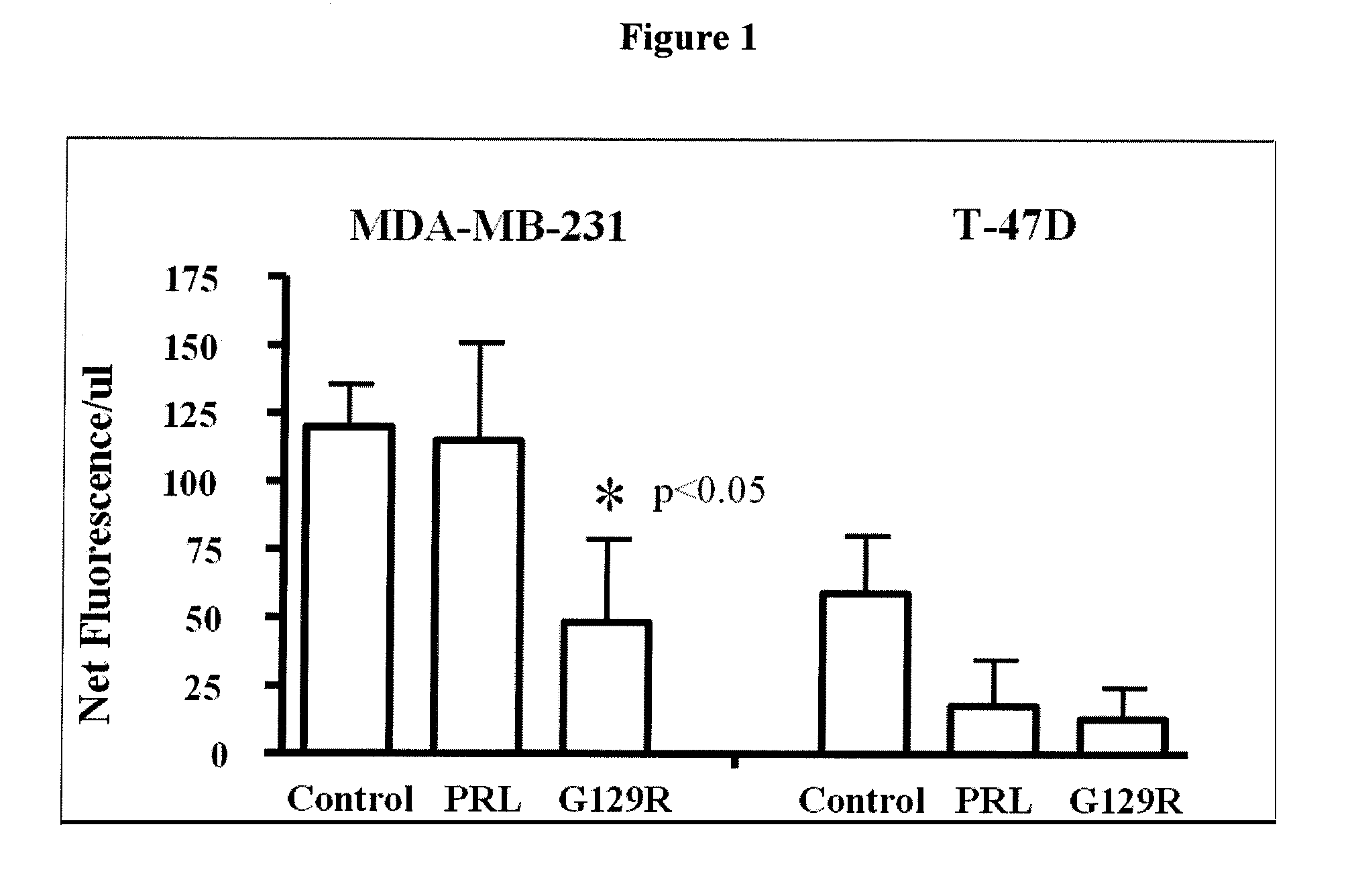
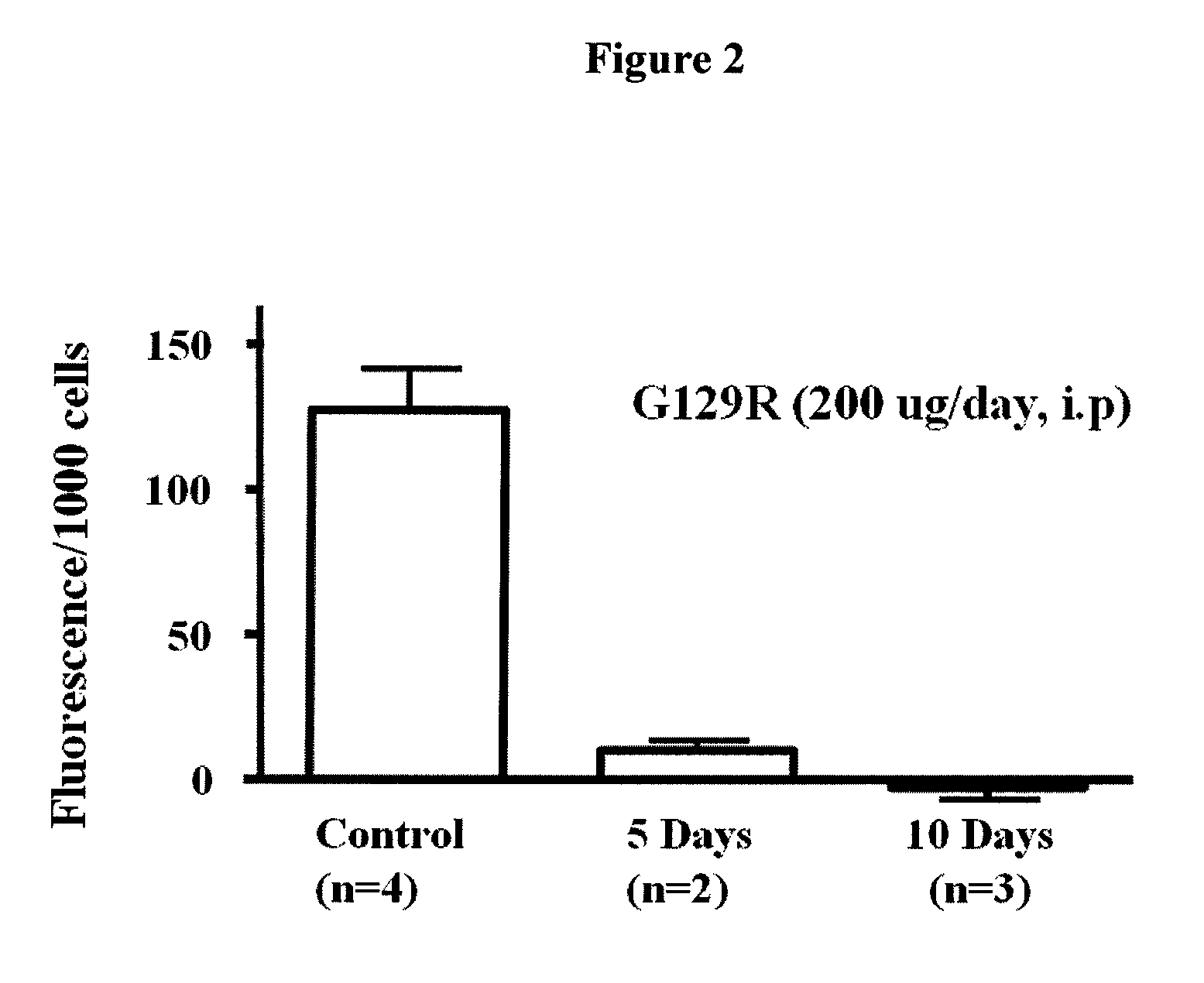
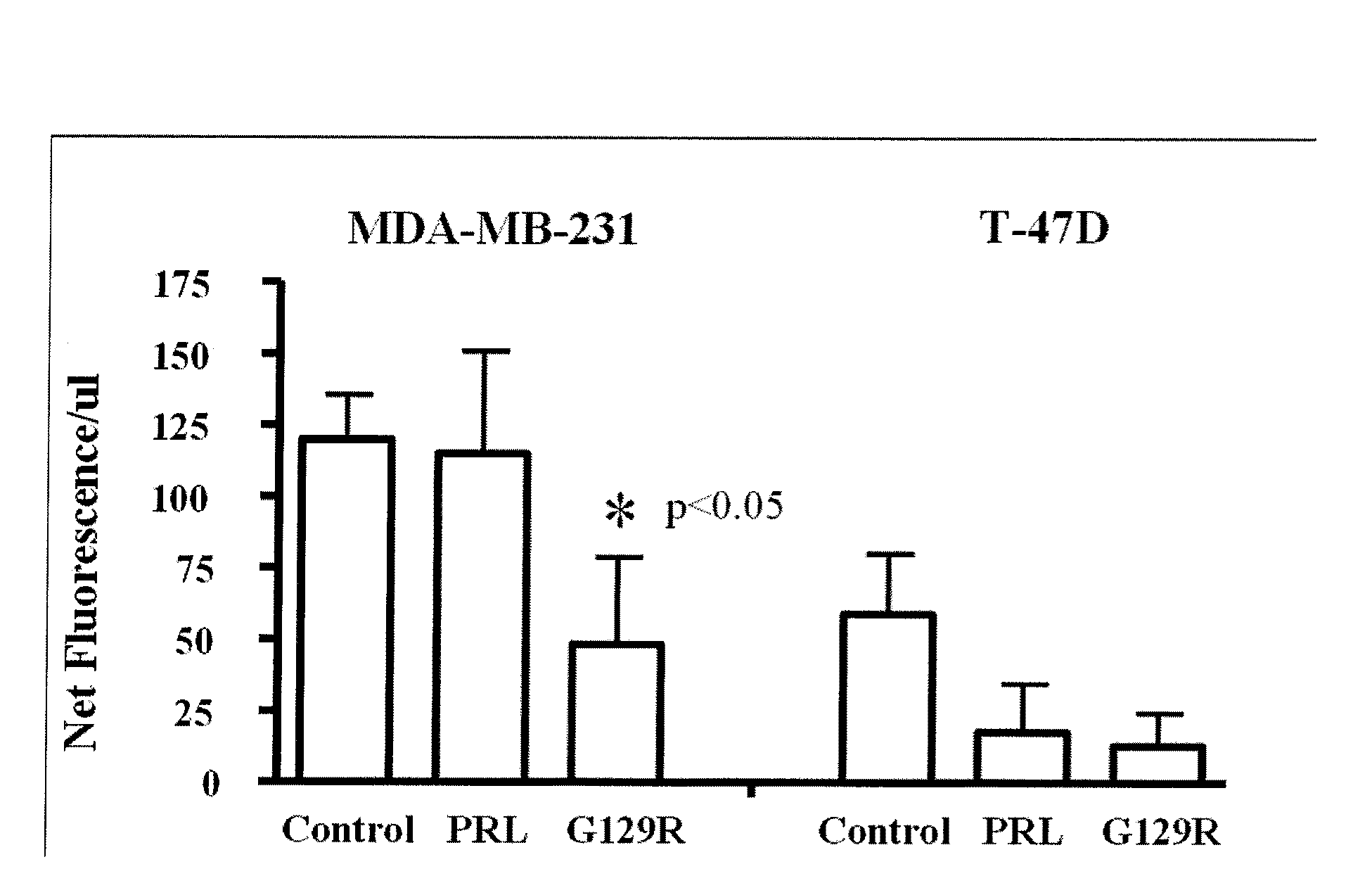
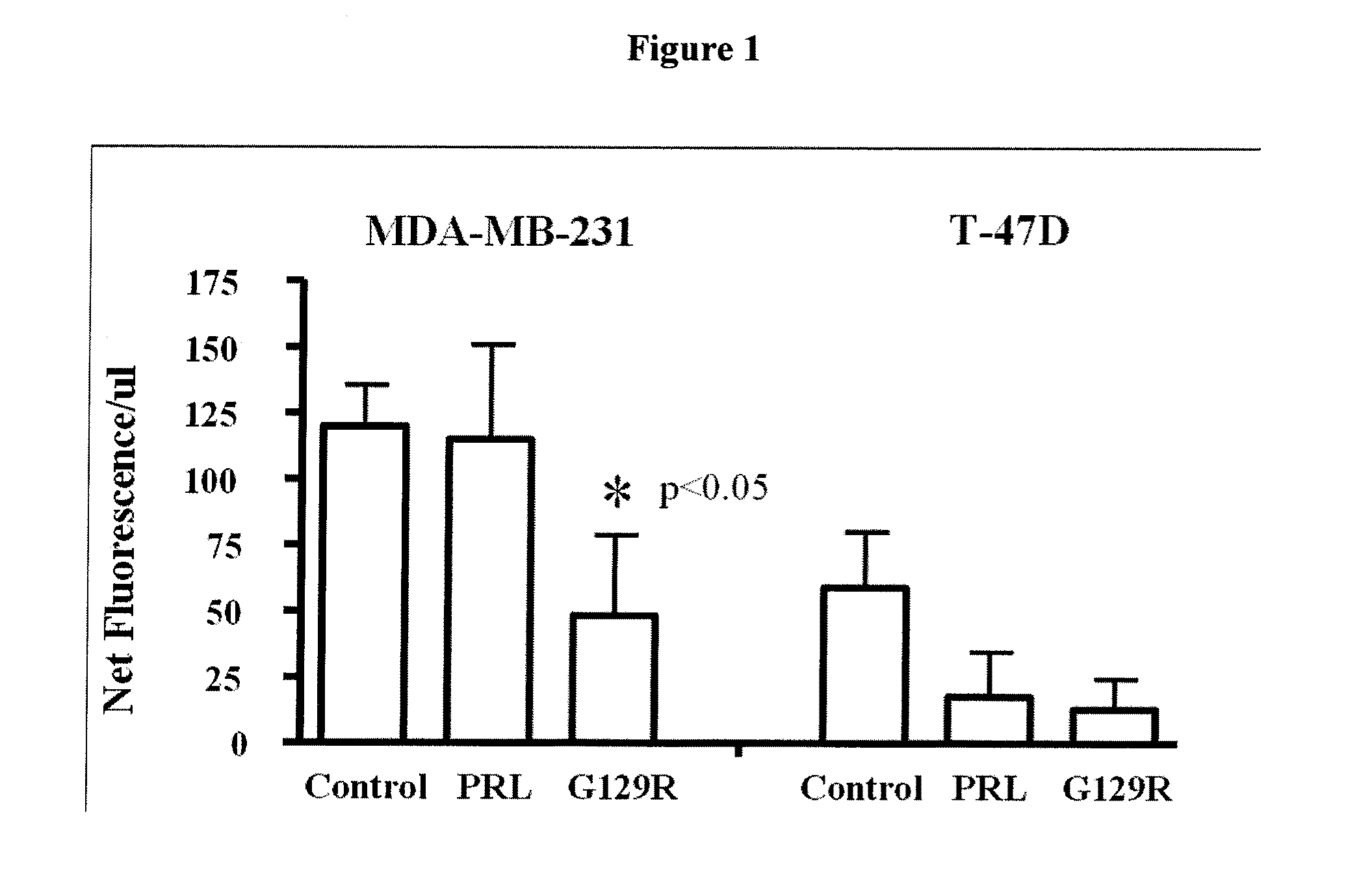
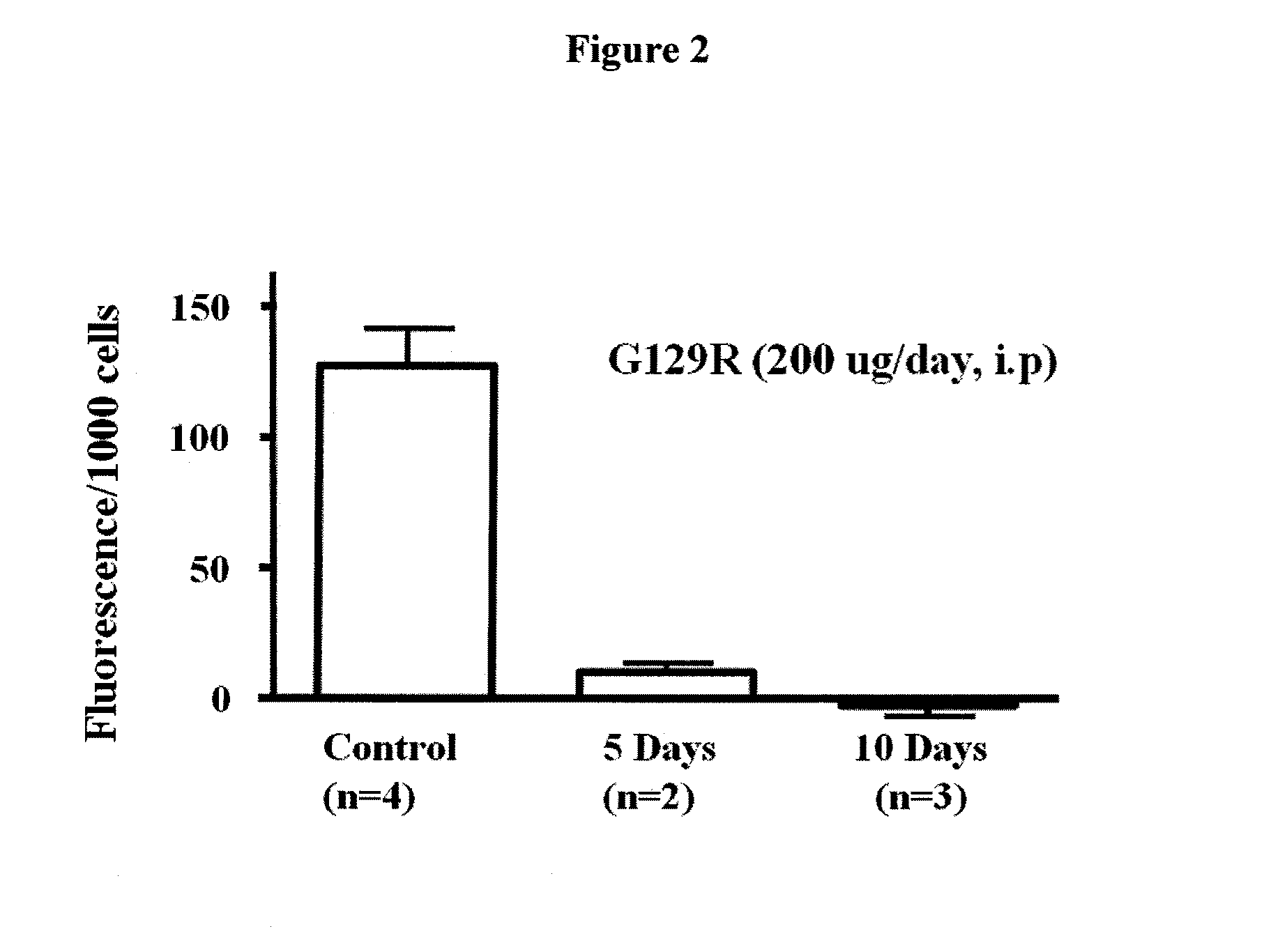
The present invention relates generally to the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment, and more particularly to compositions and methods that may be useful for eliminating cancer cells with stem-like characteristics. The disclosed compositions and methods may also be useful for managing breast cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer or endometrial (uterine) cancer with metastases; and visualizing the cancer cells in patient's body. The compositions of the instant invention include human prolactin receptor antagonist G129R.
Owner:ONCOLIX
Materials and Methods for Producing Animals With Short Hair
ActiveUS20160081313A1Improve productivityImprove embryo survivalAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAnimal scienceProviding material
The subject invention provides materials and methods for producing animals with short hair length. In a preferred embodiment, this is accomplished by altering in the animal the nucleotide sequence that encodes the prolactin receptor (PRLR) protein such that a truncated version of the protein is produced. Advantageously, and surprisingly, the truncated protein produced according to the subject invention retains lactogenic functionality, but causes the animal to have a short-hair coat.
Owner:ACCELIGEN INC
Breeding method of multi-gene pyramiding of fine breed milk goats
InactiveCN101845506AAccurately estimate breeding valuesImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeExon
The invention discloses a breeding method of multi-gene pyramiding of fine breed milk goats, which comprises the following steps: using genome DNA of milk goats continuously bearing two or more than two goats as a template; using four pairs of primers for respectively amplifying intrones 2 and exons 10 of prolactin receptor genes, and the 5' non-translational region (5' UTR) and exons 1 of luteotropin beta subunit genes; using agarose gel electrophoresis for carrying out size determination on each amplifying product; adopting the DNA sequencing technology for sieving and checking the site-directed mutation of the amplifying products of the four pairs of the primers; then, using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for carrying out gene typing and gene frequency analysis on the SNPs of the four sites of the prolactin receptor genes and the luteotropin beta subunit genes; analyzing the relationship between the goat bearing number and the polymorphism of the high-yield milk goat individuals (generation F1) and the relationship between different gene type combinations and the goat bearing number; tracing to the parent generation (generation F0); tracking filial generation (generation F2); detecting the relationship between the goat bearing number and the gene type combinations of the female goat individuals; and analyzing the contribution of different gene types in the prolific trait formation.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Neutralizing prolactin receptor antibodies and their therapeutic use
The present invention is directed to neutralizing prolactin receptor antibodies 002-H06 and antigen binding fragments, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in the treatment or prevention of benign disorders and indications mediated by the prolactin receptor such as endometriosis, adenomyosis, non-hormonal female contraception, benign breast disease and mastalgia, lactation inhibition, benign prostate hyperplasia, fibroids, hyper- and normoprolactinemic hair loss, and cotreatment in combined hormone therapy to inhibit mammary epithelial cell proliferation. The antibodies of the invention block prolactin receptor-mediated signaling.
Owner:BAYER IP GMBH
Compositions and methods for visualizing and eliminating cancer stem cells
The present invention relates generally to the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment, and more particularly to compositions and methods that may be useful for eliminating cancer cells with stem-like characteristics. The disclosed compositions and methods may also be useful for managing breast cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer or endometrial (uterine) cancer with metastases; and visualizing the cancer cells in patient's body. The compositions of the instant invention include human prolactin receptor antagonist G129R.
Owner:ONCOLIX
Receptor-mediated delivery: compositions and methods
InactiveUS20090317855A1Inhibit expressionImprove the level ofGenetic material ingredientsTissue cultureProstate cancer cellCancer cell
Compositions and methods for delivering an agent to a cell comprising a prolactin receptor are provided. Also provided is a method of inhibiting a breast, ovarian or prostate cancer cell, where the method includes a step of contacting the cell with a complex comprising a prolactin receptor ligand linked to at least one of an RNAi-inducing agent, a polynucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide, an miRNA, a cytotoxic moiety, a chemotherapeutic moiety, a radioactive moiety or a nanoparticle. Methods of detecting a cancer cell expressing a prolactin receptor are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Multimeric ligands with enhanced stability
InactiveUS7632809B2Increased serum half-lifeImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSomatotropic hormoneGrowth hormone
Owner:ONCOLIX
Multimeric ligands with enhanced stability
InactiveUS20040033948A1Reduced responseReducing cachexia and protein lossPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGrowth hormoneAgonist
The present invention provides compositions and methods for making multimeric proteins to increase stability over their monomer. For example, more stable growth hormone and prolactin receptor agonists are provided.
Owner:ONCOLIX
Compositions and methods for visualizing and eliminating cancer stem cells
InactiveUS8754035B2In-vivo radioactive preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellLymphatic Spread
The present invention relates generally to the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment, and more particularly to compositions and methods that may be useful for eliminating cancer cells with stem-like characteristics. The disclosed compositions and methods may also be useful for managing breast cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer or endometrial (uterine) cancer with metastases; and visualizing the cancer cells in patient's body. The compositions of the instant invention include human prolactin receptor antagonist G129R.
Owner:ONCOLIX
Neutralizing prolactin receptor antibodies and their therapeutic use
Owner:BAYER IP GMBH
Method for predicating milk yield of small tailed han sheep by virtue of BMPR (bone morphogenetic protein receptor )-1B or PRLR (prolactin receptor) gene SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) lotus
ActiveCN104087677AEnough intakeShorten the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementBone morphogenetic protein 6Molecular level
The invention relates to the raise livestock field, and discloses a method for predicating milk yield of small tailed han sheep by virtue of BMPR(bone morphogenetic protein receptor )-1B or PRLR (prolactin receptor) gene SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) lotus. The method comprises the following steps: extracting a small tailed han sheep genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid); amplifying a sequence of SNP lotus-containing BMPR-IB A746G or a sequence of SNP lotus-containing PRLR gene; judging an E2-C34T mutant gene type of the BMPR-IB A746G or PRLR gene. The method disclosed by the invention can be applied to carrying out feeding and management according to difference of milk secretion control gene types, and can be used for improving the milk secretion amount, guaranteeing that a lamb has enough milk intake, improving the survival rate and reducing the breeding economic loss. The method disclosed by the invention provides a molecular-level technical support for predicating and molecularly selecting the milk yield of small tailed han sheep; by applying the method disclosed by the invention, the survival rate and development rate of the lambs are greatly improved, so that better breeding economic benefits are produced, and therefore, the method has good application prospect.
Owner:新疆维吾尔自治区畜牧科学院中国-澳大利亚绵羊育种研究中心
Materials and methods for producing animals with short hair
ActiveUS10716298B2Improve productivityImprove survivalSugar derivativesReceptors for hormonesPhysiologyNucleotide sequencing
The subject invention provides materials and methods for producing animals with short hair length. In a preferred embodiment, this is accomplished by altering in the animal the nucleotide sequence that encodes the prolactin receptor (PRLR) protein such that a truncated version of the protein is produced. Advantageously, and surprisingly, the truncated protein produced according to the subject invention retains lactogenic functionality, but causes the animal to have a short-hair coat.
Owner:ACCELIGEN INC
Method for diagnosis and treatment of prolactin associated disorders
InactiveUS20150133383A1Reduce cell proliferationReduce spreadHormone peptidesCompound screeningDiseaseSOCS2
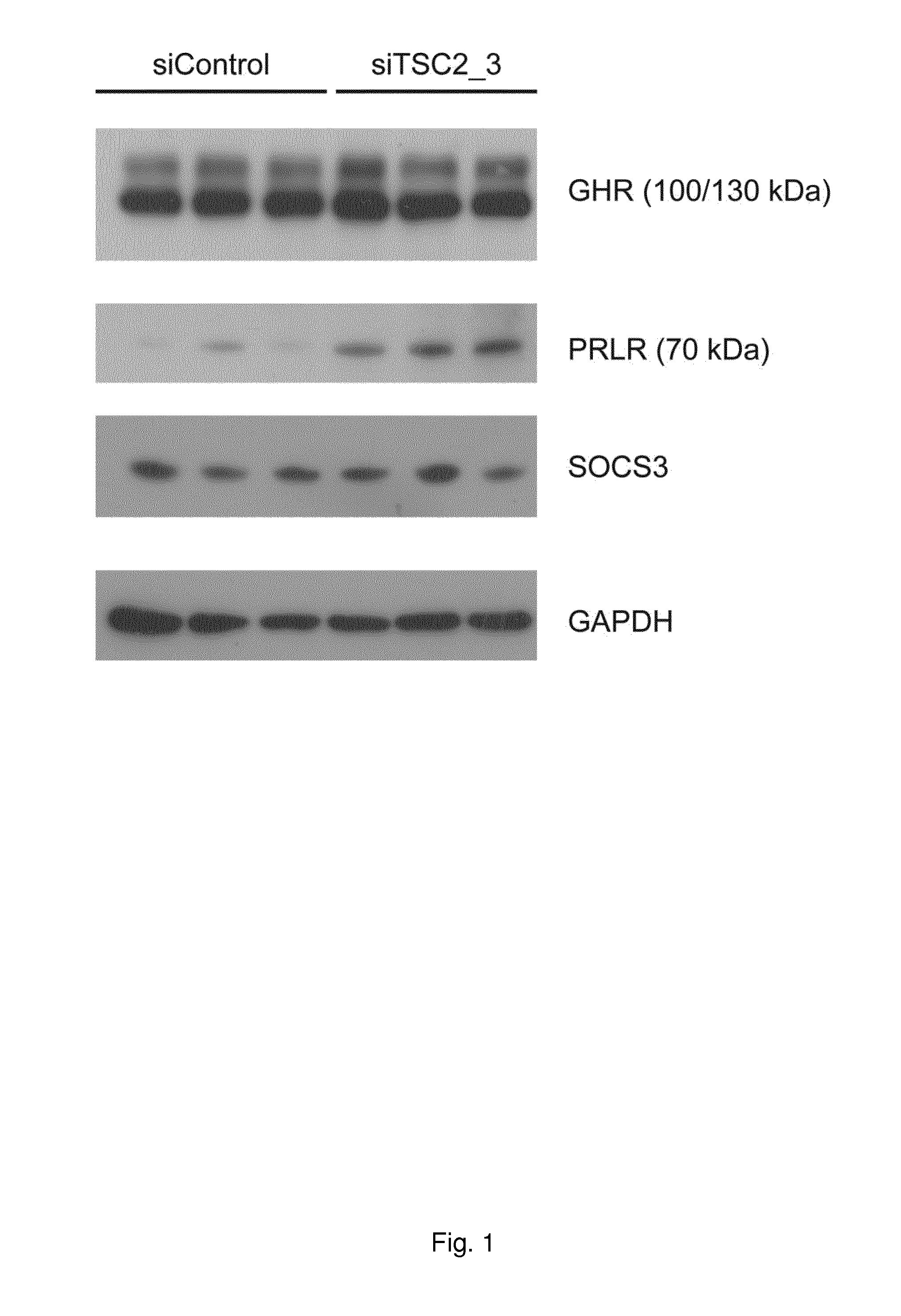
The present invention concerns methods and tools for determining a specific treatment of a prolactin associated disorder. The treatment is selected based on the expression pattern of growth hormonereceptor (GHR), prolactin receptor (PrlR) and the suppressors SOCS2 and TCS2.
Owner:PROREC BIO
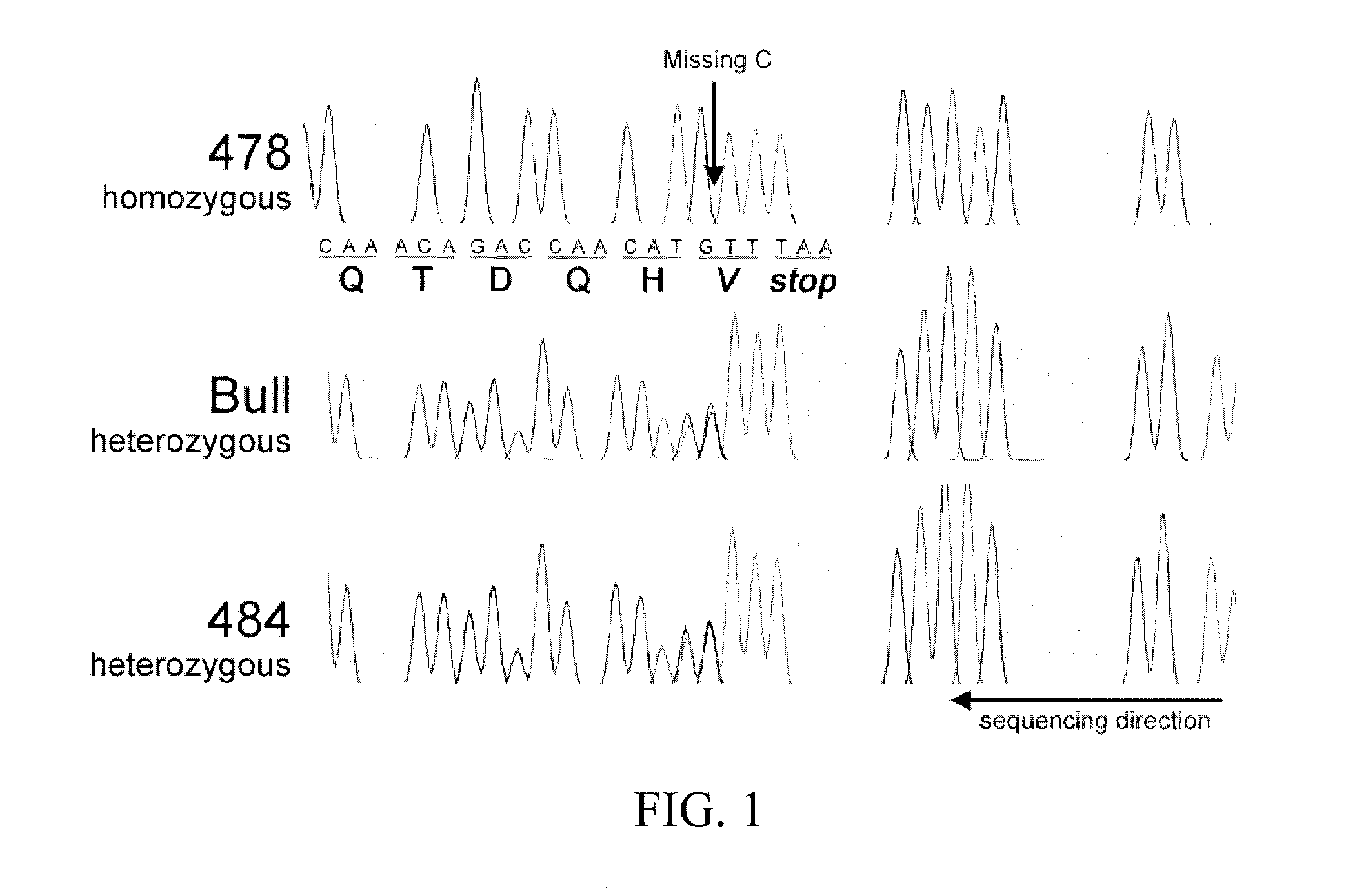
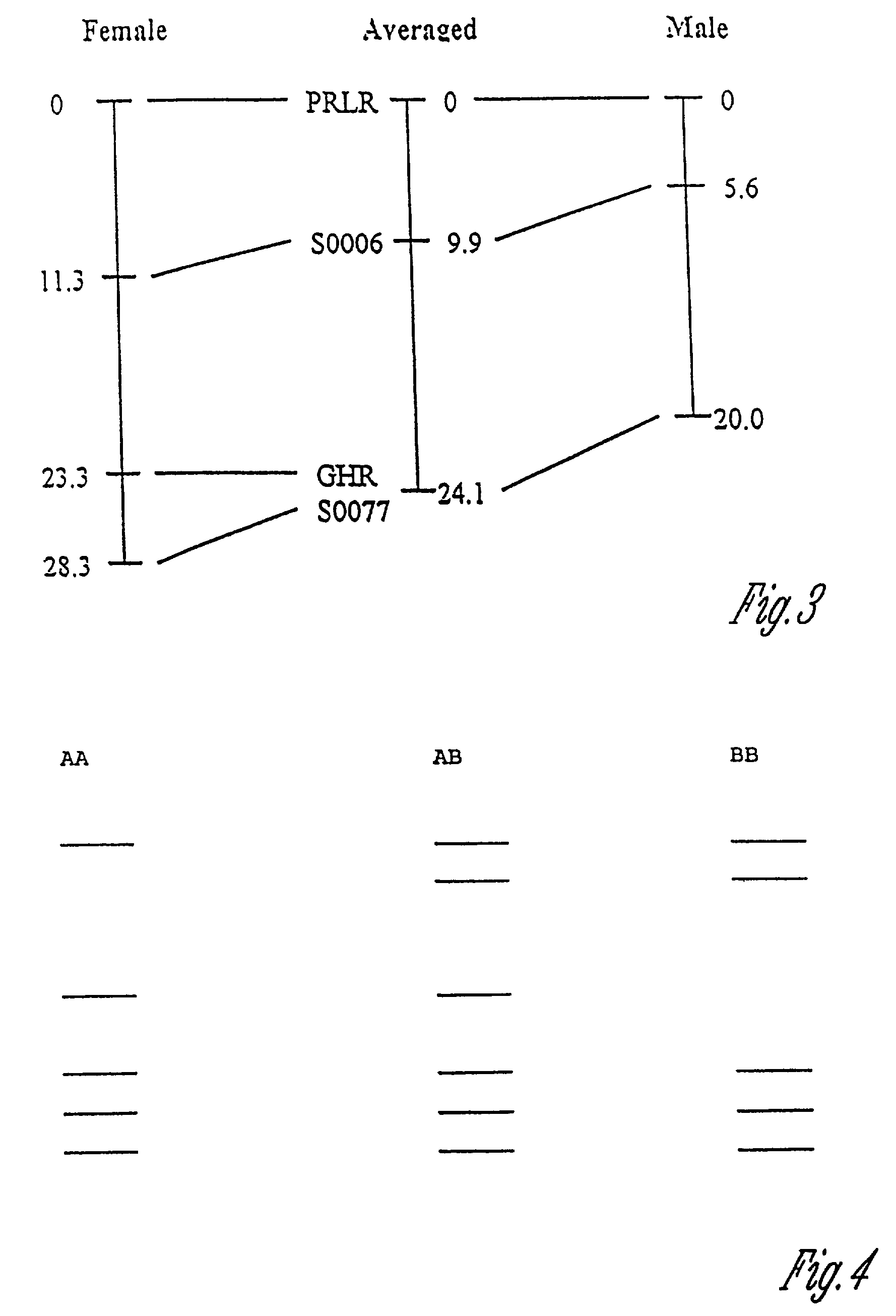
Prolactin receptor gene as a genetic marker for increased litter size in animals
InactiveUS7081335B2Immunoglobulin superfamilyMicrobiological testing/measurementLitterProlactin receptor
Disclosed herein are genetic markers for animal litter size, methods for identifying such markers, and methods of screening animals to determine those more likely to produce larger litters and preferably selecting those animals for future breeding purposes. The markers are based upon the presence or absence of certain polymorphisms in the prolactin receptor gene.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
Compositions and methods for visualizing and eliminating cancer stem cells
InactiveUS20100215577A1Peptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisLymphatic SpreadCancer cell
The present invention relates generally to the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment, and more particularly to compositions and methods that may be useful for eliminating cancer cells with stem-like characteristics. The disclosed compositions and methods may also be useful for managing breast cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer or endometrial (uterine) cancer with metastases; and visualizing the cancer cells in patient's body. The compositions of the instant invention include human prolactin receptor antagonist G129R.
Owner:ONCOLIX
Neutralizing prolactin receptor antibodies and their therapeutic use
The present invention is directed to the neutralizing prolactin receptor antibody 006- H07, and antigen binding fragments, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in the treatment or prevention of benign disorders and indications mediated by the prolactin receptor such as endometriosis, adenomyosis, non-hormonal female contraception, benign breast disease and mastalgia, lactation inhibition, benign prostate hyperplasia, fibroids, hyper- and normoprolactinemic hair loss, and cotreatment in combined hormone therapy to inhibit mammary epithelial cell proliferation. The antibodies of the invention block prolactin receptor-mediated signaling.
Owner:BAYER IP GMBH
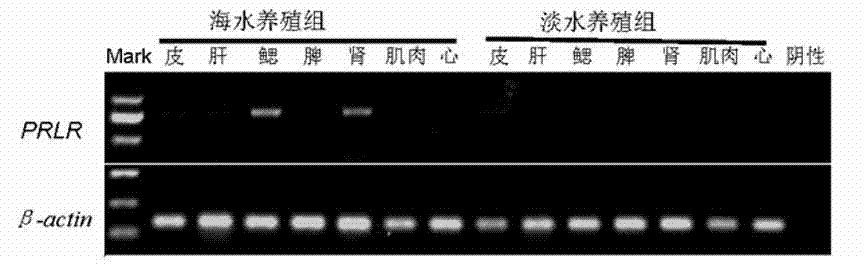
Method for judging lateolabrax japonicus aquatic water
InactiveCN103667518AEfficient identificationSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFresh water organismTotal rna
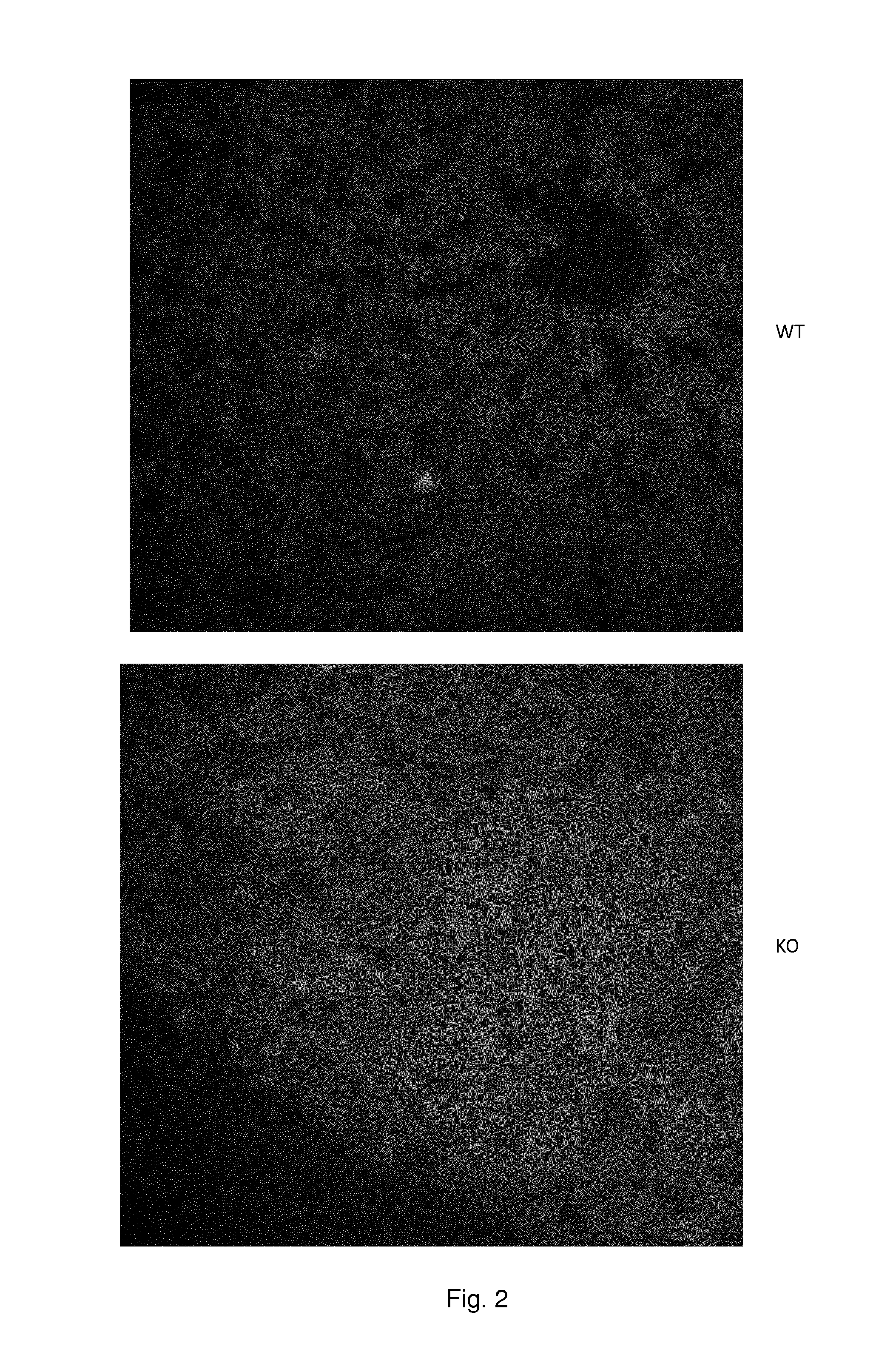
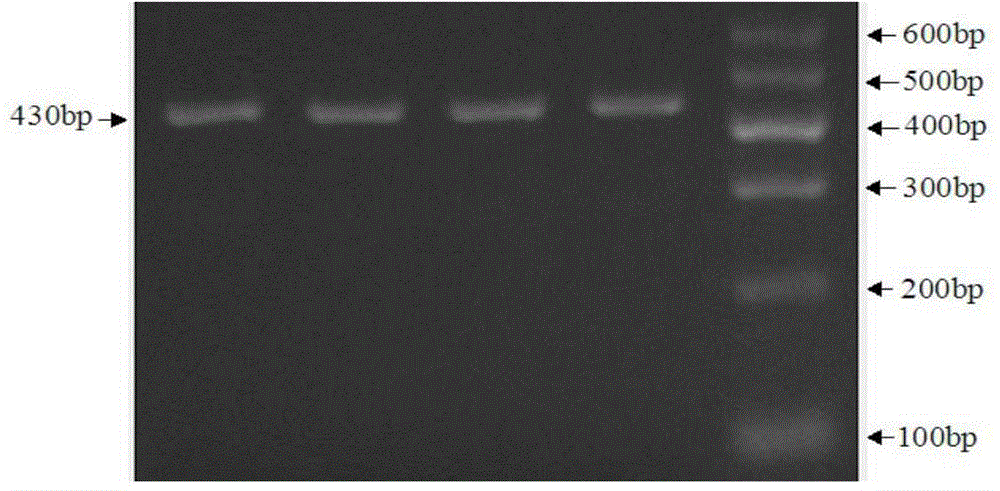
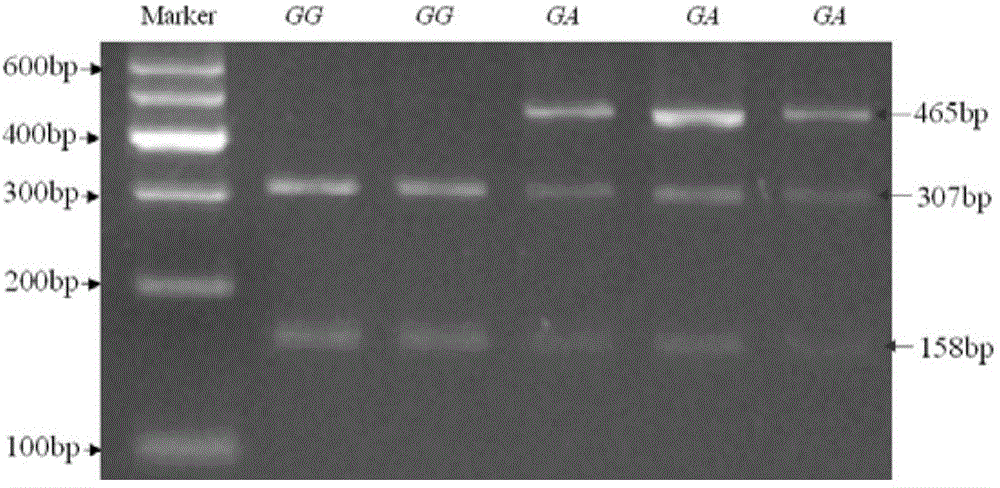
The invention discloses a method for judging lateolabrax japonicus aquatic water. The method specifically comprises the following steps: extracting total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) from lateolabrax japonicus tissues to be judged, and synthesizing a first cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) chain; amplifying a prolactin receptor via a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); observing whether a prolactin receptor expression strap exists on the gel electrophoresis picture of a PCR amplification product or not in order to judge whether lateolabrax japonicus under detection is cultured in fresh water or sea water. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and accurate, and can be applied to supervision in the field of aquatic products.
Owner:苏州市阳澄湖国家现代农业示范区发展有限公司
Prolactin receptor gene as a genetic marker for increased litter size in animals
InactiveUS20060099639A1Small sizeImmunoglobulin superfamilySugar derivativesLitterProlactin receptor
Disclosed herein are genetic markers for animal litter size, methods for identifying such markers, and methods of screening animals to determine those more likely to produce larger litters and preferably selecting those animals for future breeding purposes. The markers are based upon the presence or absence of certain polymorphisms in the prolactin receptor gene.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Human prolactin receptor antibody and application thereof
InactiveCN102250244AIncrease capacityIncrease diversityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsHeavy chainBiological Immunotherapy
The invention discloses a human prolactin receptor antibody, which comprises a heavy chain Fd fragment variable region and a light chain variable region, wherein the amino acid sequence of the heavy chain Fd fragment variable region is shown as SEQ ID No.2, and the amino acid sequence of the light chain variable region is shown as SEQ ID No.4. The invention also discloses a gene for encoding the antibody and application of the antibody in preparation of medicines for treating human breast cancer. A human prolactin receptor hPRLR antibody with high specificity and high affinity is obtained and has potential application prospect in biological immunotherapy of breast cancer.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Receptor-mediated delivery: compositions and methods
InactiveUS9127293B2Genetic material ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesProstate cancer cellCancer cell
Compositions and methods for delivering an agent to a cell comprising a prolactin receptor are provided. Also provided is a method of inhibiting a breast, ovarian or prostate cancer cell, where the method includes a step of contacting the cell with a complex comprising a prolactin receptor ligand linked to at least one of an RNAi-inducing agent, a polynucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide, an miRNA, a cytotoxic moiety, a chemotherapeutic moiety, a radioactive moiety or a nanoparticle. Methods of detecting a cancer cell expressing a prolactin receptor are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Neutralizing prolactin receptor antibodies and their therapeutic use
The present invention is directed to pharmaceutical compositions containing one or more neutralizing prolactin receptor antibodies and antigen binding fragments, and their use in the treatment or prevention of benign disorders and indications mediated by the prolactin receptor such as endometriosis, adenomyosis, non-hormonal female contraception, benign breast disease and mastalgia, lactation inhibition, benign prostate hyperplasia, fibroids, hyper- and normoprolactinemic hair loss, and cotreatment in combined hormone therapy to inhibit mammary epithelial cell proliferation. The composition of the invention blocks prolactin receptor-mediated signaling.
Owner:BAYER IP GMBH
A method for breeding milk-producing traits of dairy goats using double-gene polymerization effect
InactiveCN103468819BAccurately estimate breeding valuesImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryGene typeGenotype
The invention discloses a method for selecting milk production characters to breed a milk goat by utilizing the double gene polymerization effect. Milk goat genome DNA serves as a template, two pairs of primers are used for amplifying the exon 9 of a gene of a PRLR and the intron 1 of a gene of an ELF5 respectively, agarose gel electrophoresis with the concentration of 1.5% is used for judging the sizes of the amplified products, the locus mutations of the amplified products of the two pairs of primers are screened based on the DNA sequencing technique, then, the agarose gel electrophoresis with the concentration of 3.5% is used for carrying out genetic typing and gene frequency analyzing on SNPs of the two locuses of the gene of the PRLR and the gene of the ELF5, the relation between different gene type combinations and the milk production characters is analyzed, and the optimal gene combination is screened out.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Use of prolactin receptor antagonists in combination with an agent that inactivates the HER2/neu signaling pathway
InactiveUS8754031B2Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsVasopressin AntagonistsNK1 receptor antagonist
The present invention describes compositions and methods for inhibiting cell proliferation comprising a prolactin receptor antagonist and an agent that inactivates the HER2 / neu signaling pathway, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:ONCOLIX
Prolactin receptor antibody for male and female pattern hair loss
InactiveUS20210128728A1High systemic prolactinCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsFemale pattern alopeciaObstetrics
Owner:BAYER PHARMA AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com