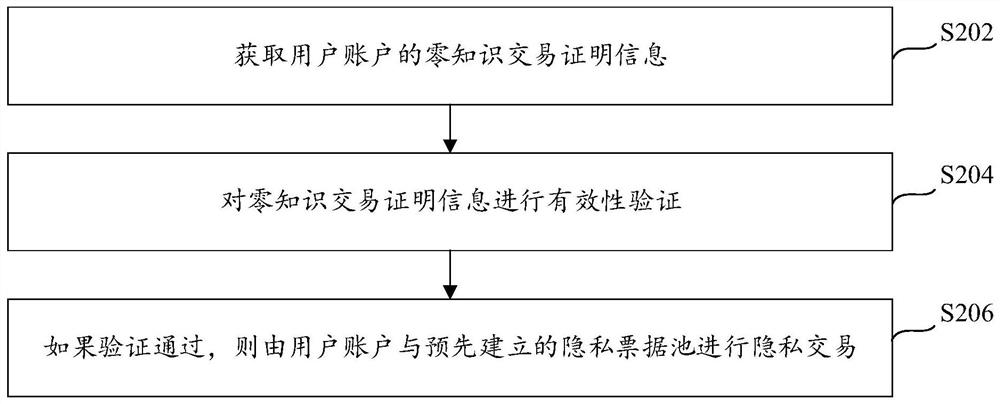
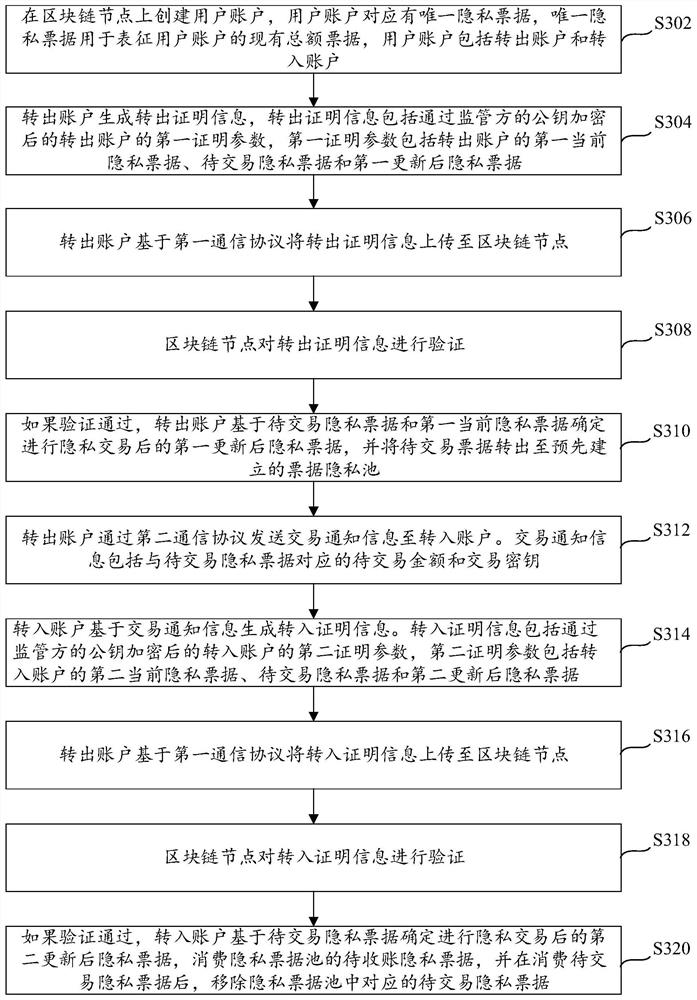
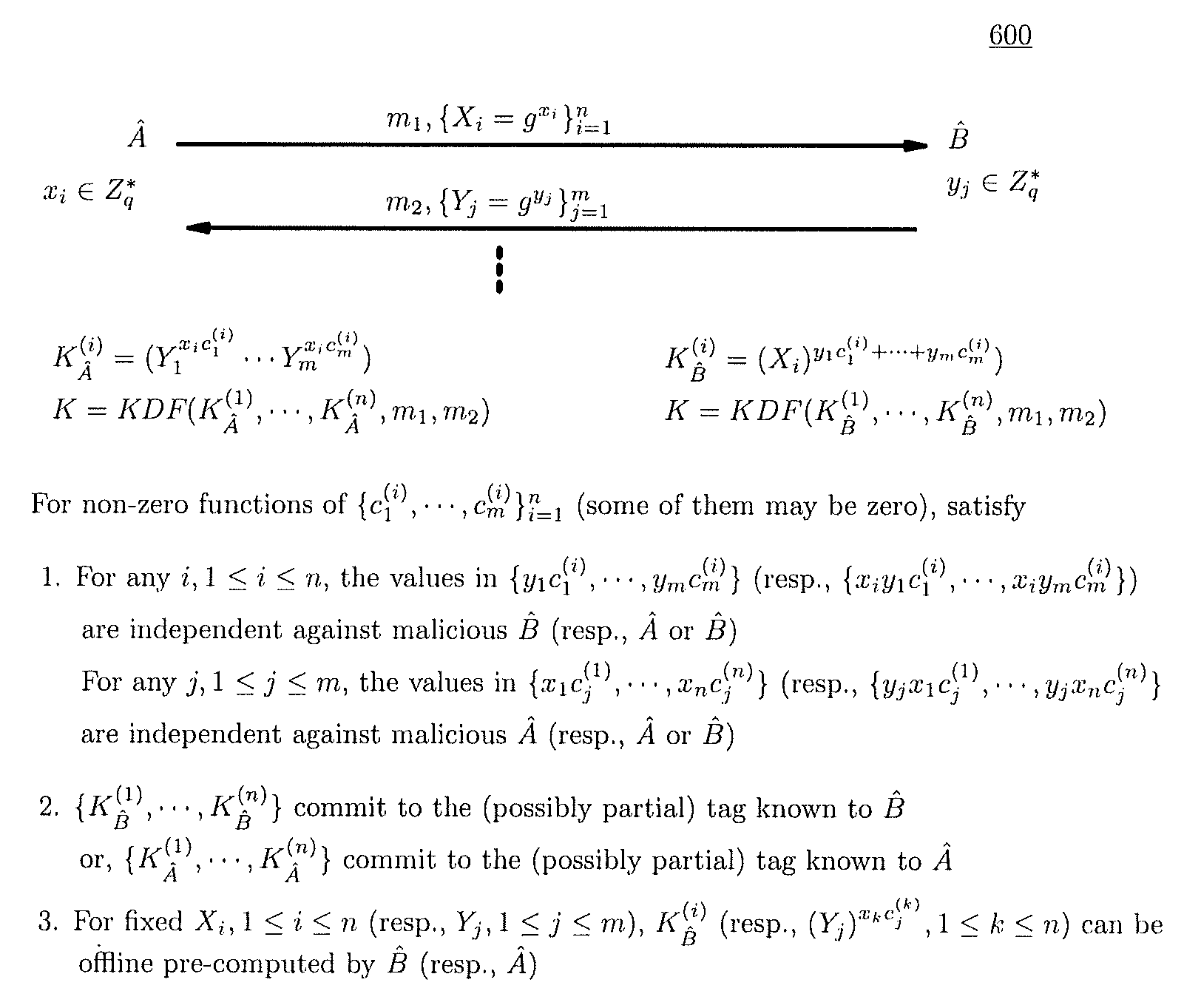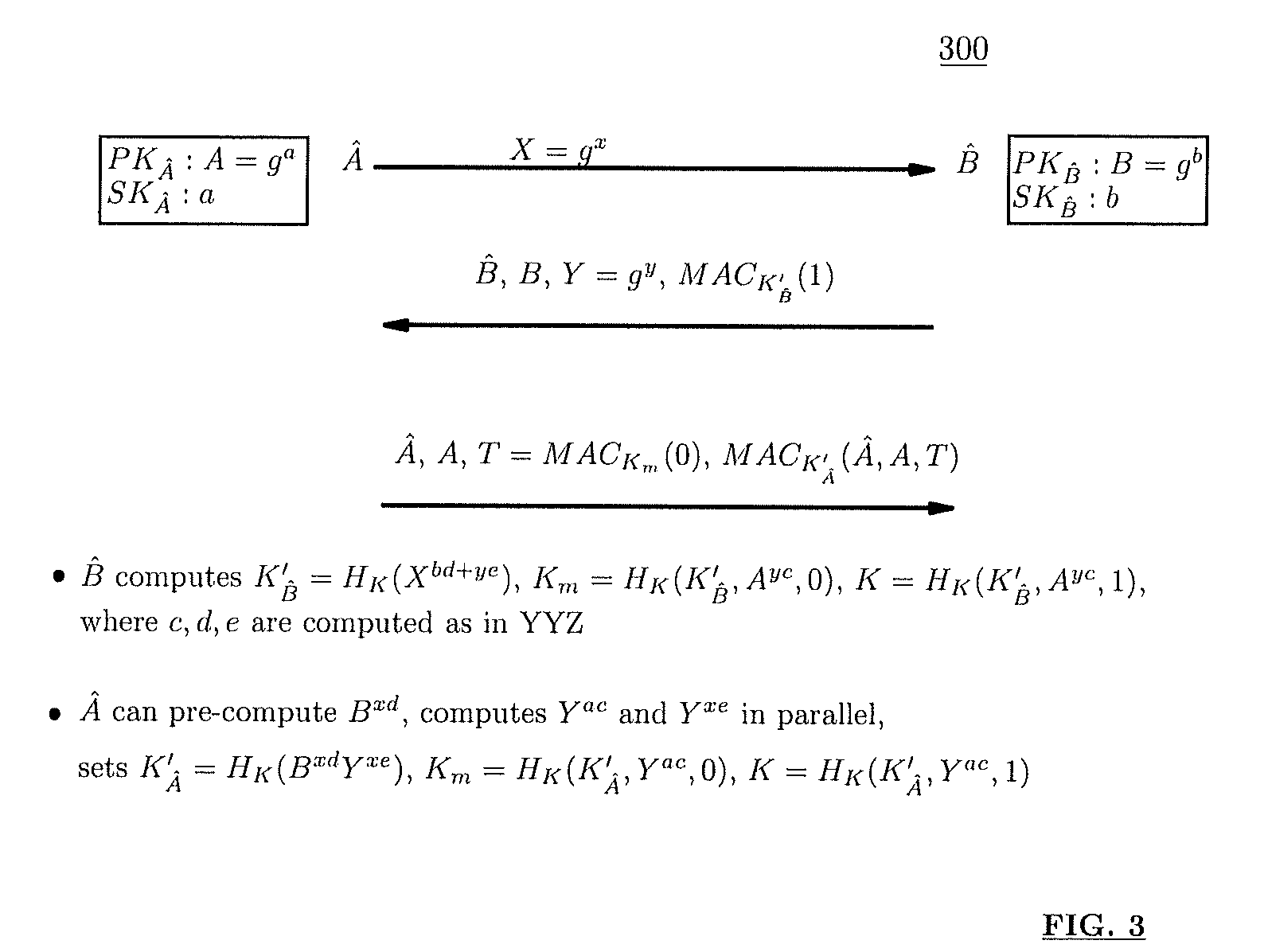Patents
Literature
113 results about "Proof of knowledge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cryptography, a proof of knowledge is an interactive proof in which the prover succeeds in 'convincing' a verifier that the prover knows something. What it means for a machine to 'know something' is defined in terms of computation. A machine 'knows something', if this something can be computed, given the machine as an input. As the program of the prover does not necessarily spit out the knowledge itself (as is the case for zero-knowledge proofs) a machine with a different program, called the knowledge extractor is introduced to capture this idea.
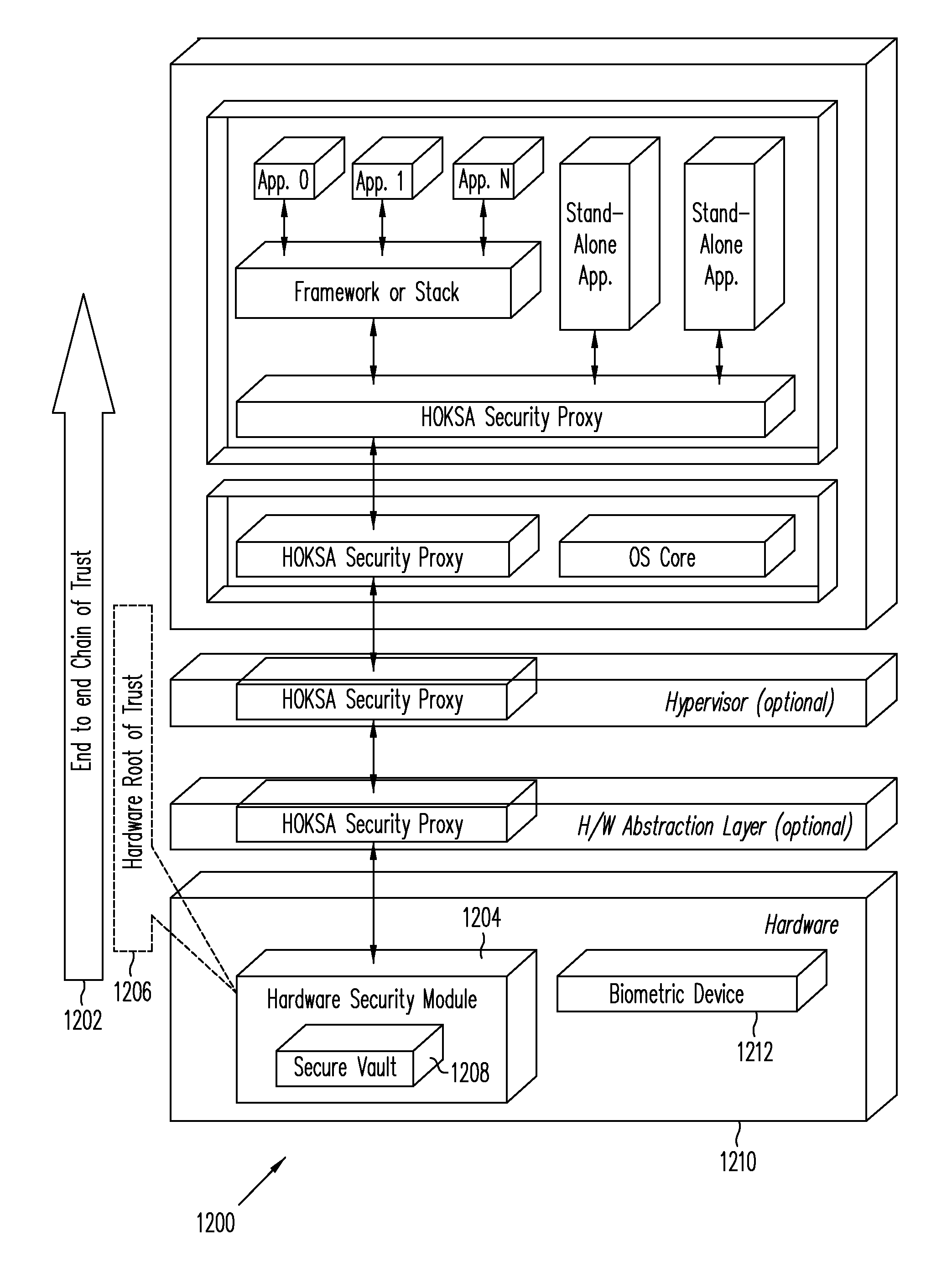
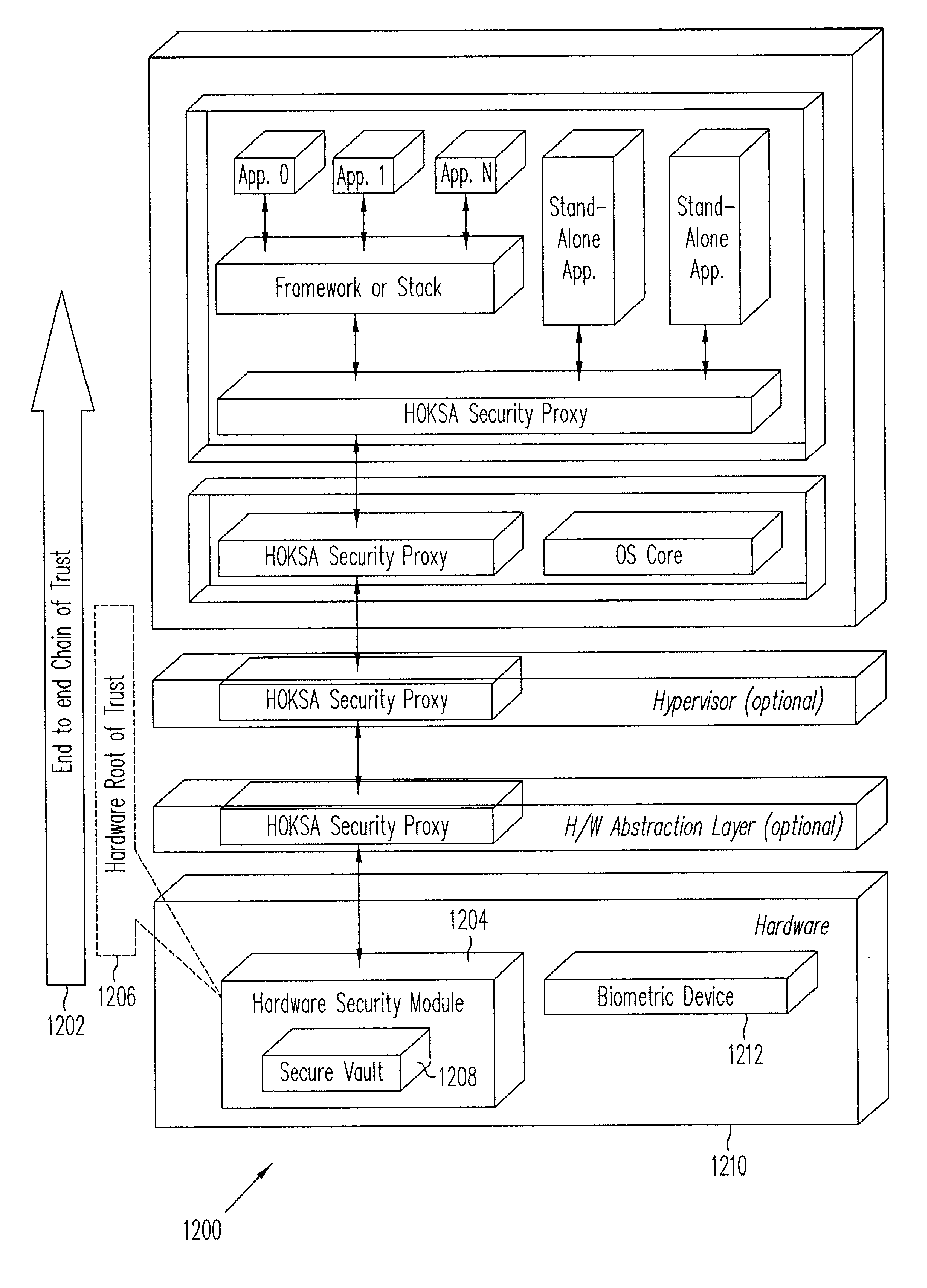
Hardware-Based Zero-Knowledge Strong Authentication (H0KSA)
InactiveUS20100306531A1Reduce riskUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationHardware security moduleChain of trust
Systems and methods are provided for a device to engage in a zero-knowledge proof with an entity requiring authentication either of secret material or of the device itself. The device may provide protection of the secret material or its private key for device authentication using a hardware security module (HSM) of the device, which may include, for example, a read-only memory (ROM) accessible or programmable only by the device manufacturer. In the case of authenticating the device itself a zero-knowledge proof of knowledge may be used. The zero-knowledge proof or zero-knowledge proof of knowledge may be conducted via a communication channel on which an end-to-end (e.g., the device at one end and entity requiring authentication at the other end) unbroken chain of trust is established, unbroken chain of trust referring to a communication channel for which endpoints of each link in the communication channel mutually authenticate each other prior to conducting the zero-knowledge proof of knowledge and for which each link of the communication channel is protected by at least one of hardware protection and encryption.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
Method and structure for self-sealed joint proof-of-knowledge and diffie-hellman key-exchange protocols
InactiveUS20100205443A1Robust resistance against malicious disclosureImproving security and privacy and efficiencyUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeCryptographic protocol
A method (and structure) for a party (the prover) to prove its knowledge, jointly and non-malleably, of multiple secret (fixed and / or ephemeral) Diffie-Hellman exponents (DH-exponents), corresponding to its public (fixed and / or ephemeral) DH-components and with respect to the public (fixed and / or ephemeral) challenging DH-components from another party (the verifier). The joint proof-of-knowledge (JPOK) consists of secrets made by multiplying multiple DH-secrets, which can be generated and verified by each party by its own secret DH-exponents and the public DH-components of both parties. To ensure the non-malleability of the JPOK, the method invented herein makes all these multiplied DH-secrets to be independent, and makes the session-tag committed to the multiplied DH-secrets. To preserve players' privacy and / or to improve protocol efficiency, the invented method makes the DH-secrets to be multiplied to further satisfy at least one of the following (besides above independence and commitments properties): (1) Deniability: all the DH-secrets to be multiplied can be computed out merely from the ephemeral secret DH-exponents and the public DH-components of both parties; (2) Pre-computability: a DH-secret involving a fixed DH-component of a party can be offline pre-computed by its peer; (3) Post-ID computability: a DH-secret involving an ephemeral DH-component of a party can be computed by its peer without knowing that party's identity and / or fixed DH-components. The secrets made by multiplying multiple DH-secrets can then be used to derive session-keys and to generate and verify authenticators between the parties. The invented method can also be used in parallel or subsequently by the parties, possibly with reserved player roles in different runs of the method, for mutual identifications, key confirmations, and for achieving more advanced cryptographic protocols in various settings.
Owner:ANDREW C YAO
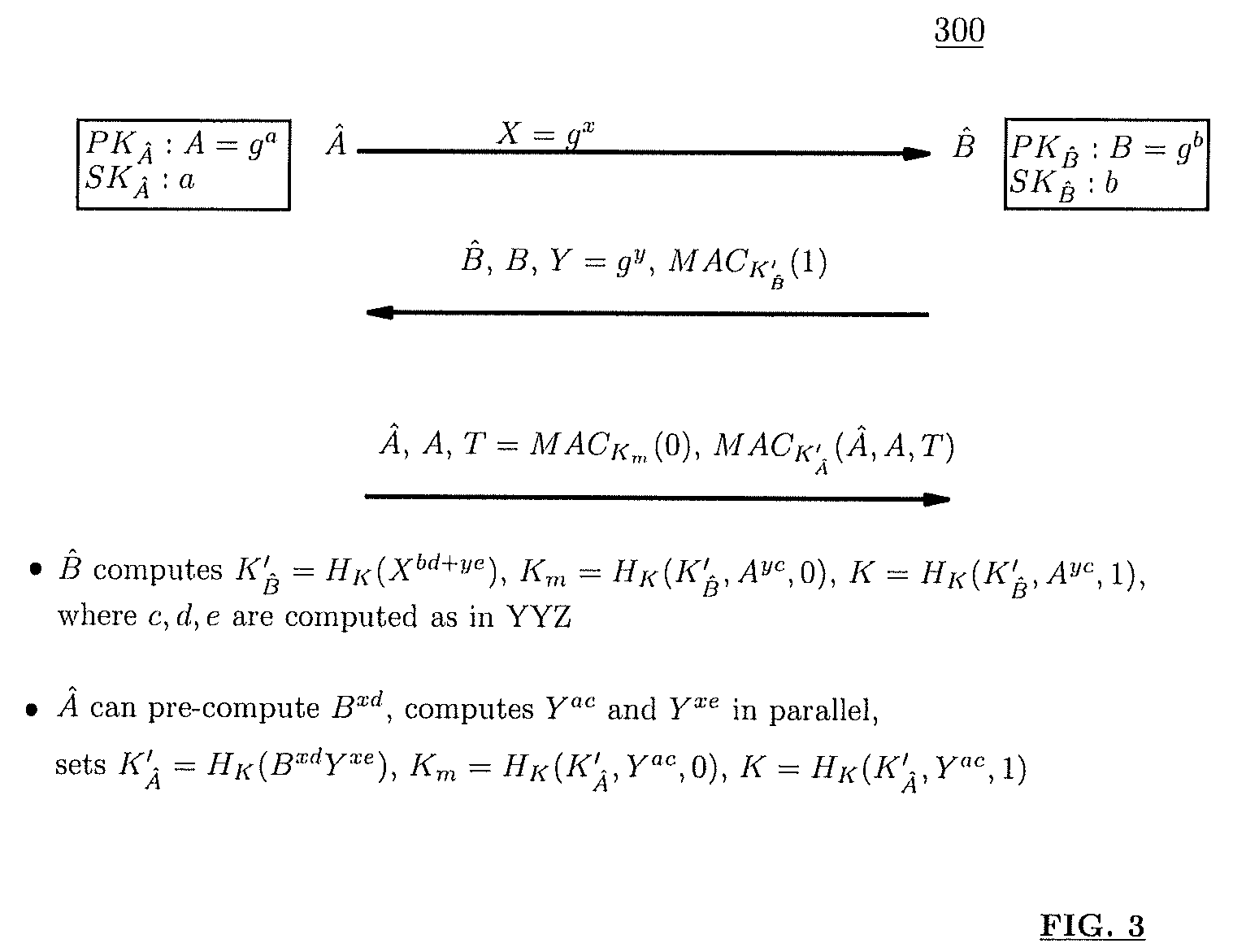
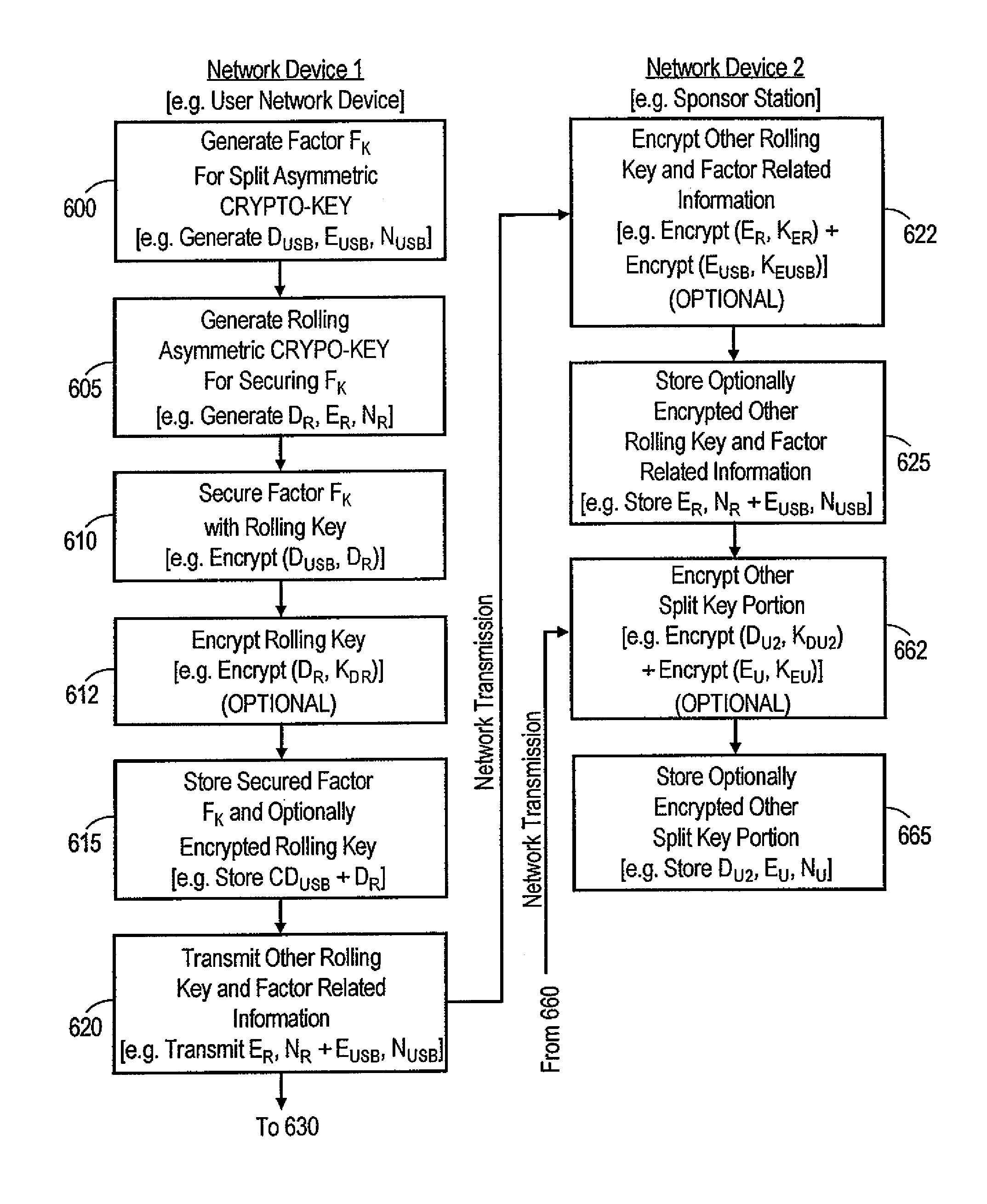
Asymmetric crypto-graphy with rolling key security
ActiveUS20070067618A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsGraphicsInformation processor
A system for securing information, includes a processor and storage device. The storage device stores information encrypted with one of a first private rolling key and a first public rolling key of an a first asymmetric rolling crypto-key, along with the one first rolling key. The processor has the logic to direct transmission, via a network, of proof of knowledge of the stored one first rolling key to authenticate a user, and of a request for the other of the first private rolling key and the first public rolling key. The processor receives the other first rolling key via the network, responsive to the directed transmission. The processor then decrypts the stored encrypted information with the received other first rolling key, and generates a second asymmetric rolling crypto-key having a second private rolling key and a second public rolling key. The processor encrypts the information with one of the second private rolling key and the second public rolling key. The processor also directs transmission of the other of the second private rolling key and the second public rolling key via the network. The storage device stores the information encrypted with the one second rolling key and the one second rolling key itself.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Method for Authenticating a Client Device to a Server Using a Secret Element
ActiveUS20160105414A1Controlling the riskUser identity/authority verificationCommunication with homomorphic encryptionClient-sideAuthentication
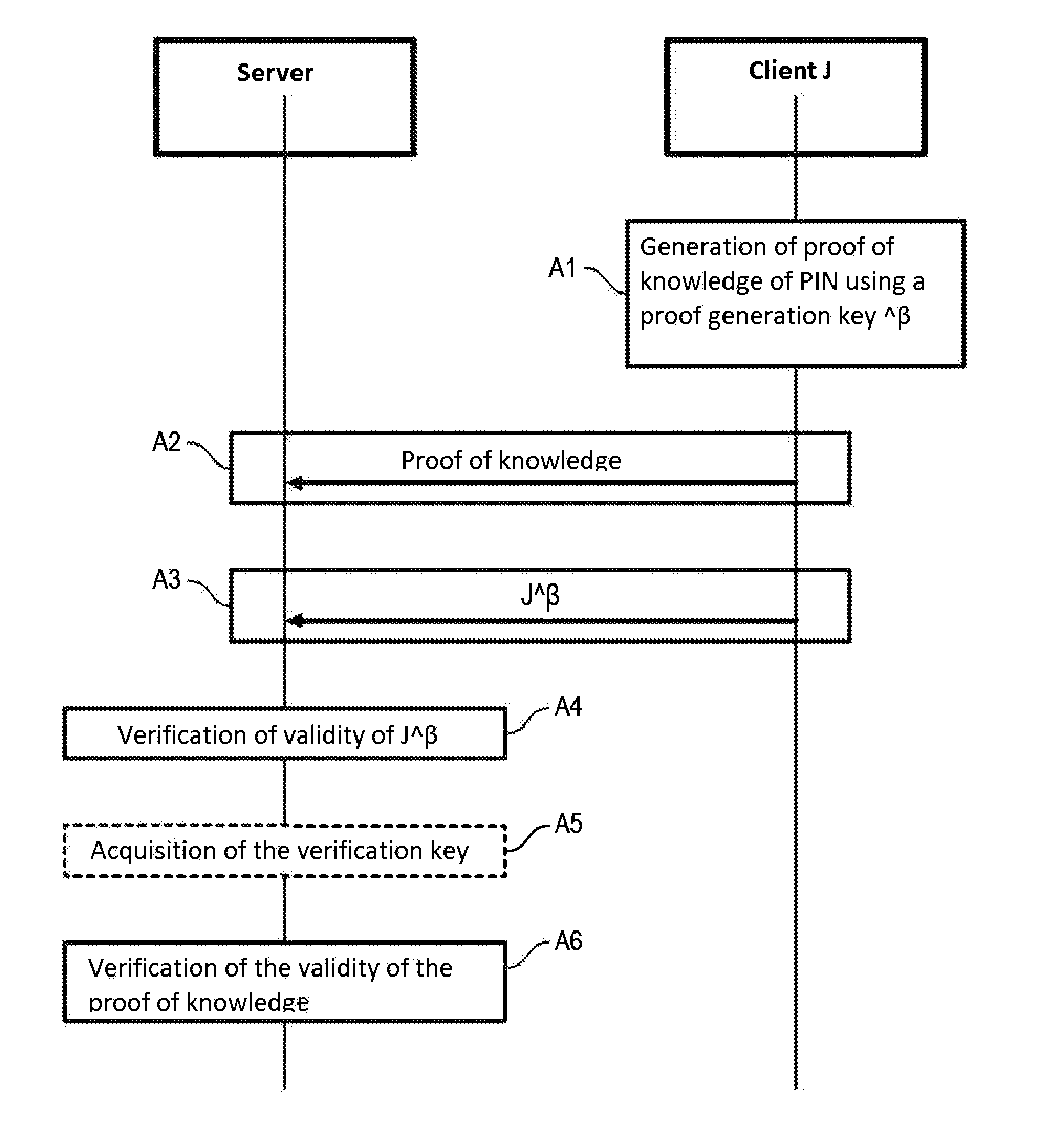
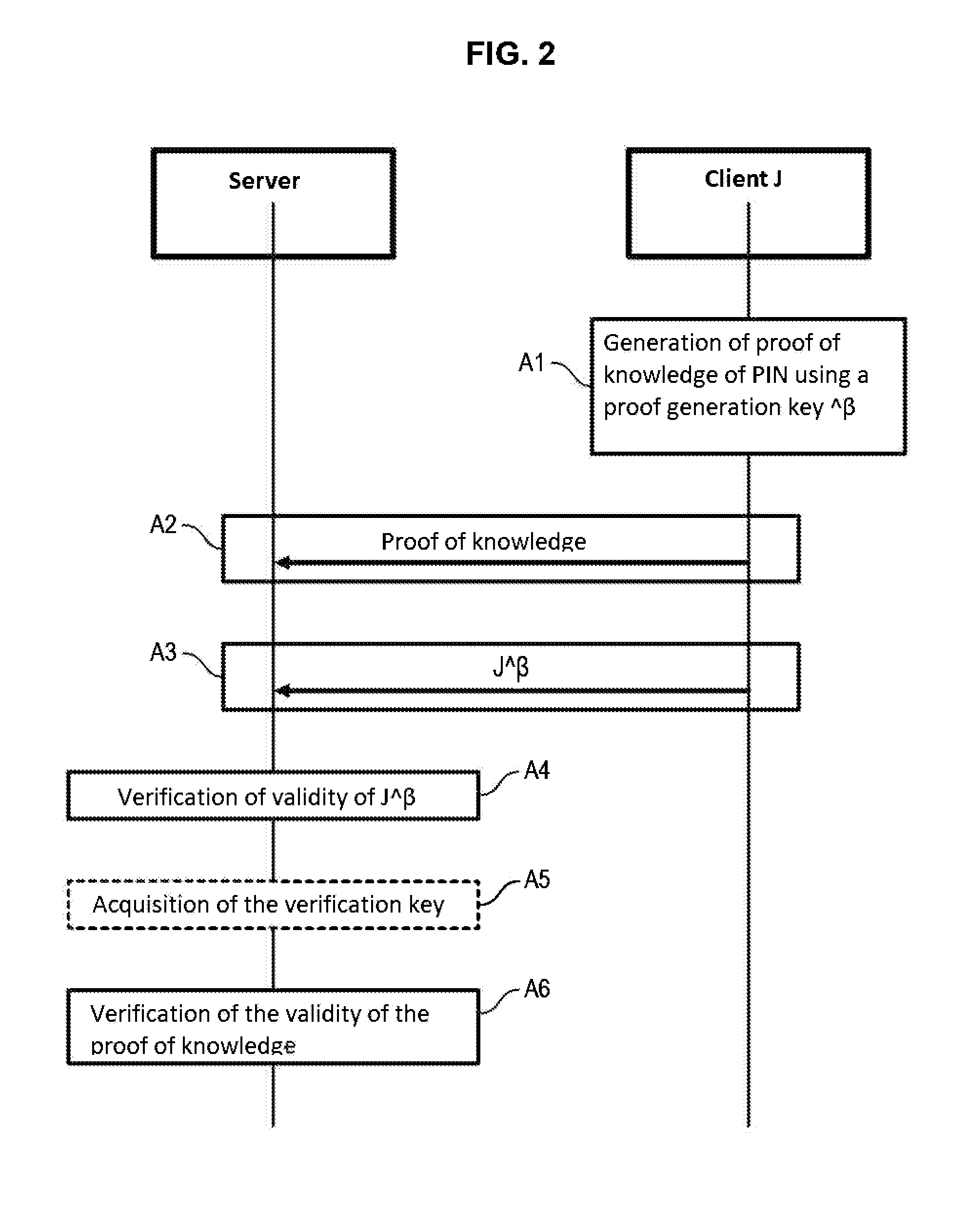
The invention relates to an authentication method for authenticating a client device having an authentication token generated by means of a pseudo-homomorphic function and based on a secret element (PIN) known only by the client device, to a server, comprising:the generation (A1), by the client device, of proof of knowledge of the secret element based on a proof generation key masked with a first mask data item, said masked proof generation key being dependent on said secret element,the transmission to the server by the client device, of said generated proof of knowledge of the secret element (A2) and of the authentication token (J) masked using the mask data item (A3),the verification of the validity of the masked authentication token (A4) and of the validity of the proof of knowledge by the server (A6) by a zero-knowledge proof, proving the knowledge of said secret element by the client device without revealing it.
Owner:IDEMIA IDENTITY & SECURITY FRANCE
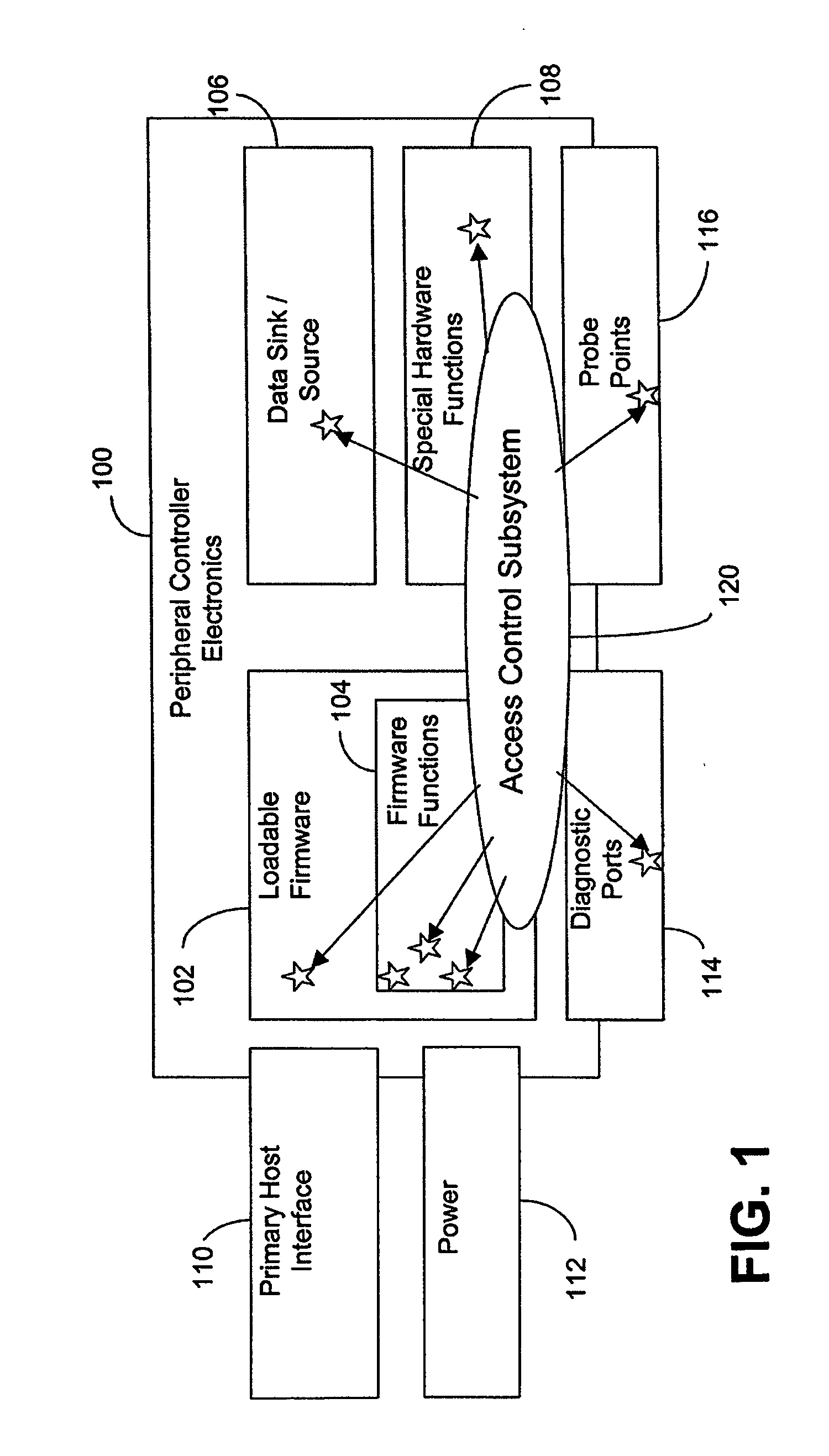
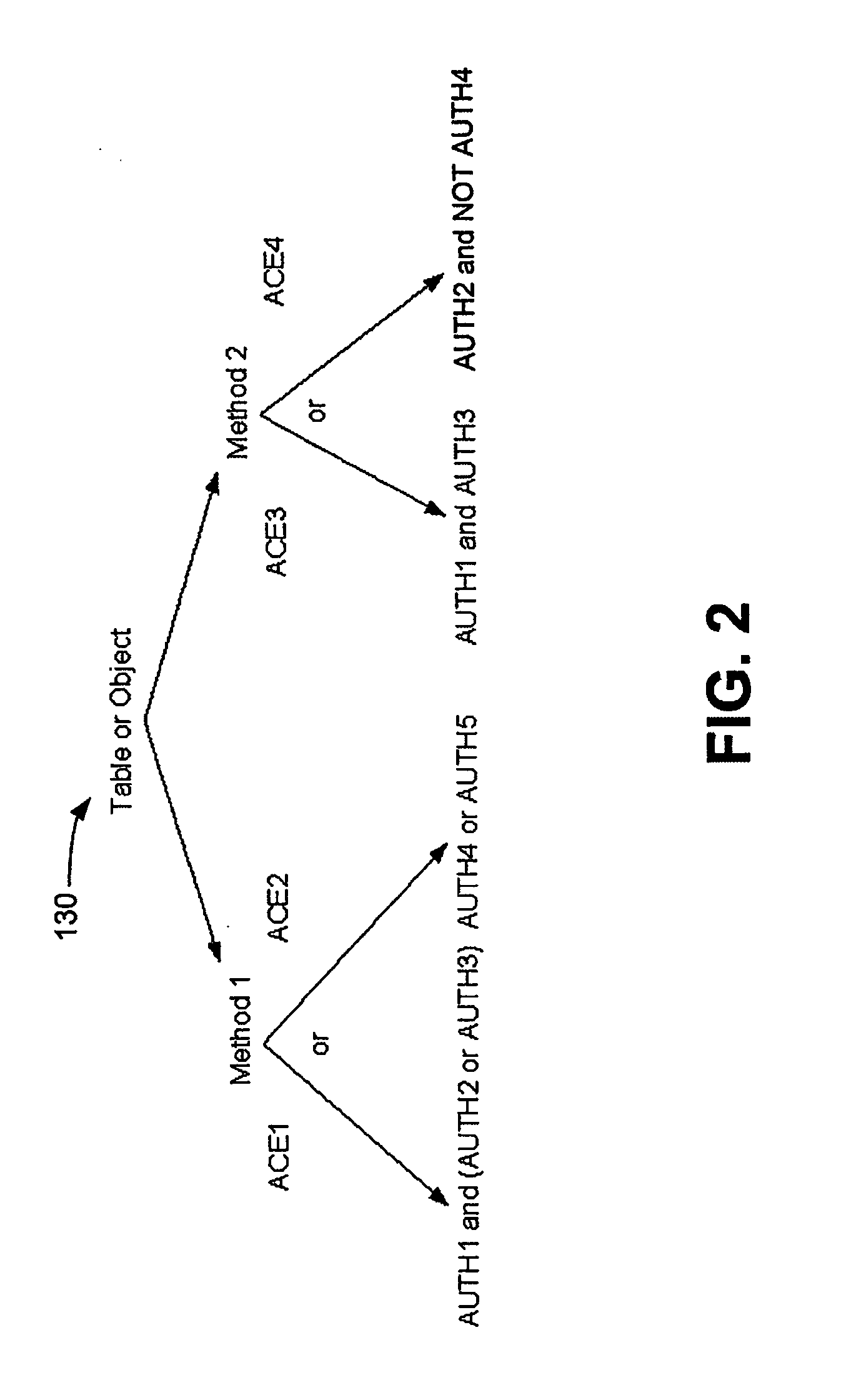
Versatile access control system
ActiveUS20070250915A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationControl systemVLAN access control list
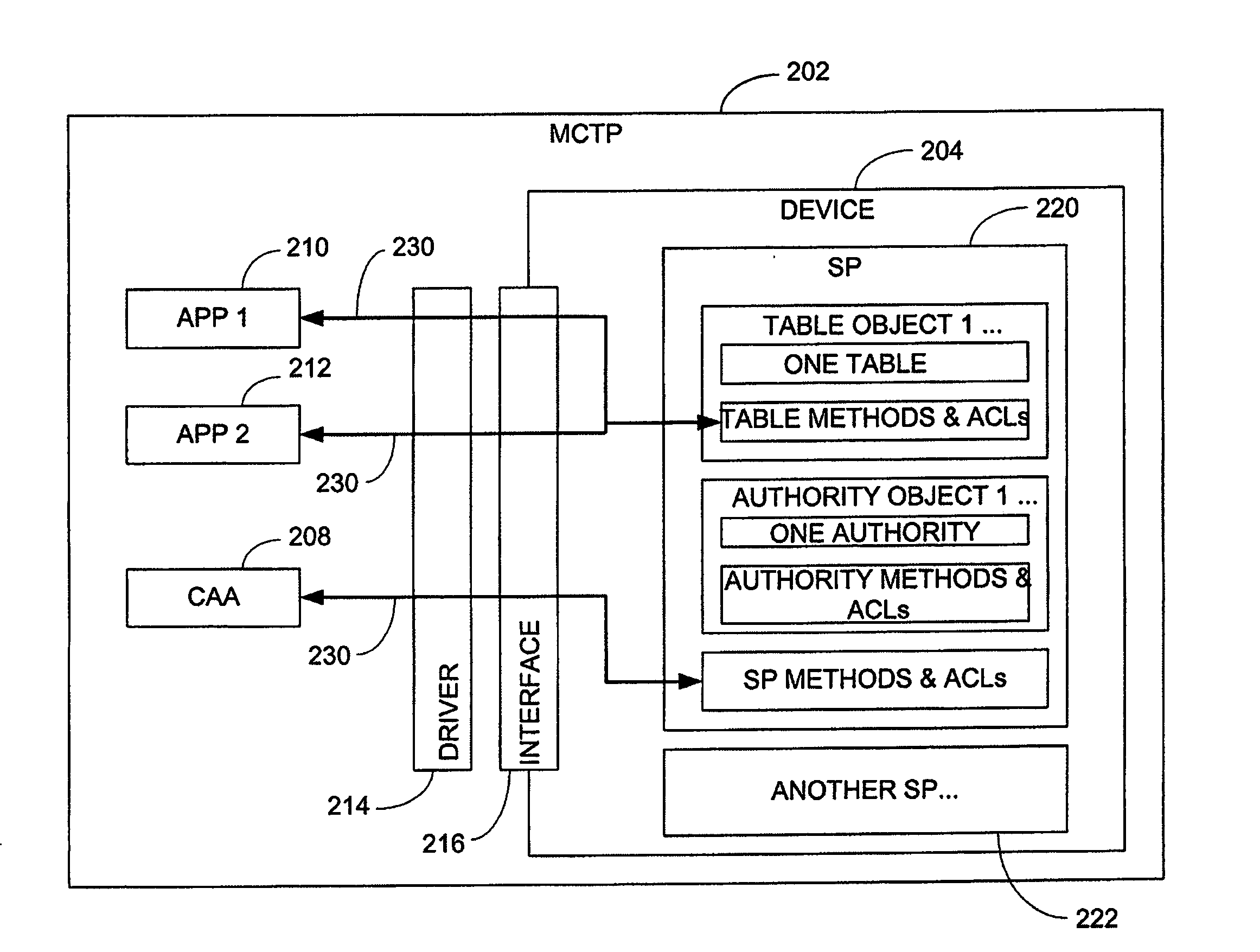
An access control system and method are provided, which include a plurality of authorities, a plurality of access control elements and an access control list. Each authority associates at least one of a plurality of proof of knowledge operations with at least one of a plurality of proof of knowledge credentials. Each access control element identifies a Boolean combination of at least one of the authorities. The access control list identifies one or more of the access control elements by which a method to be executed can be authenticated.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
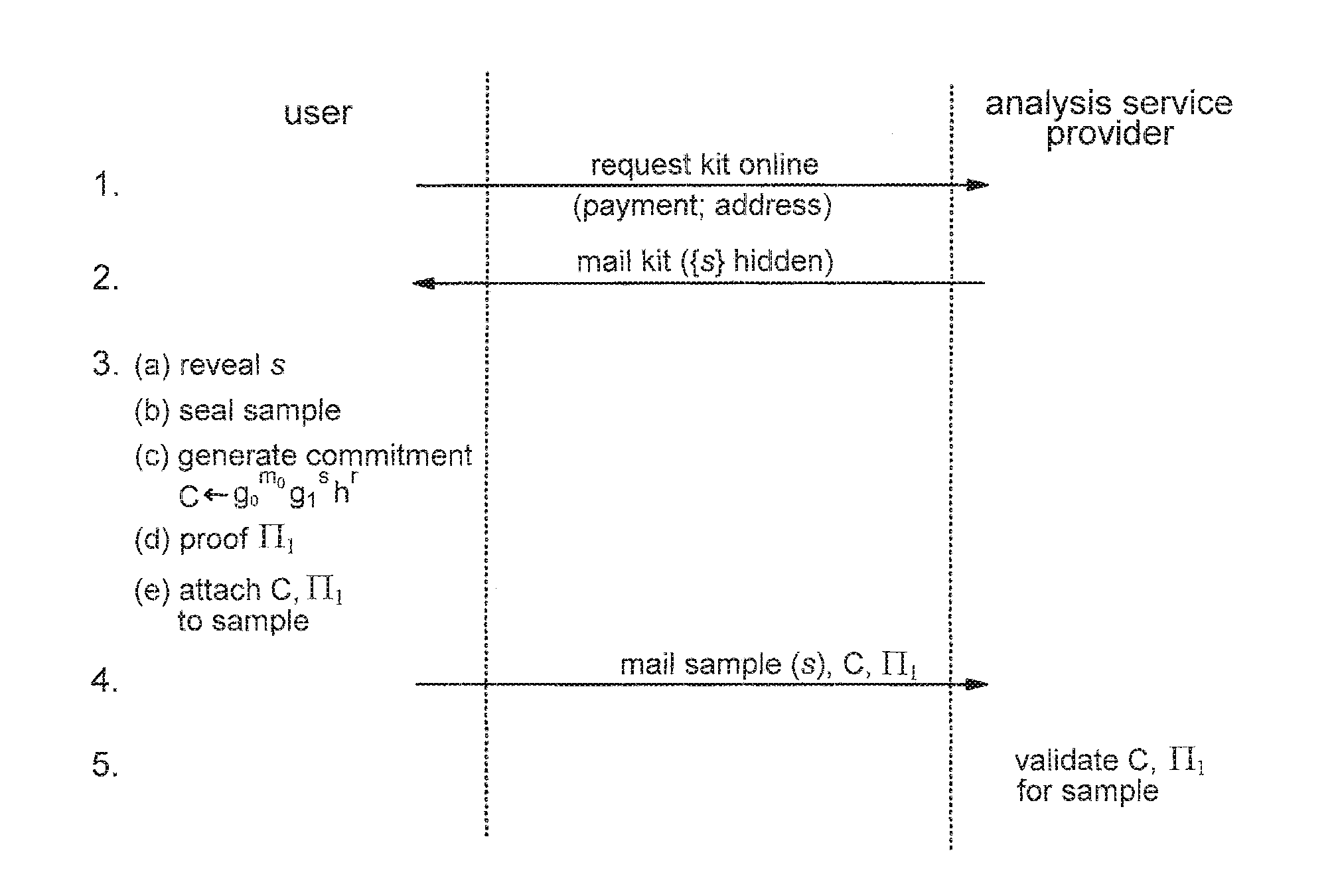
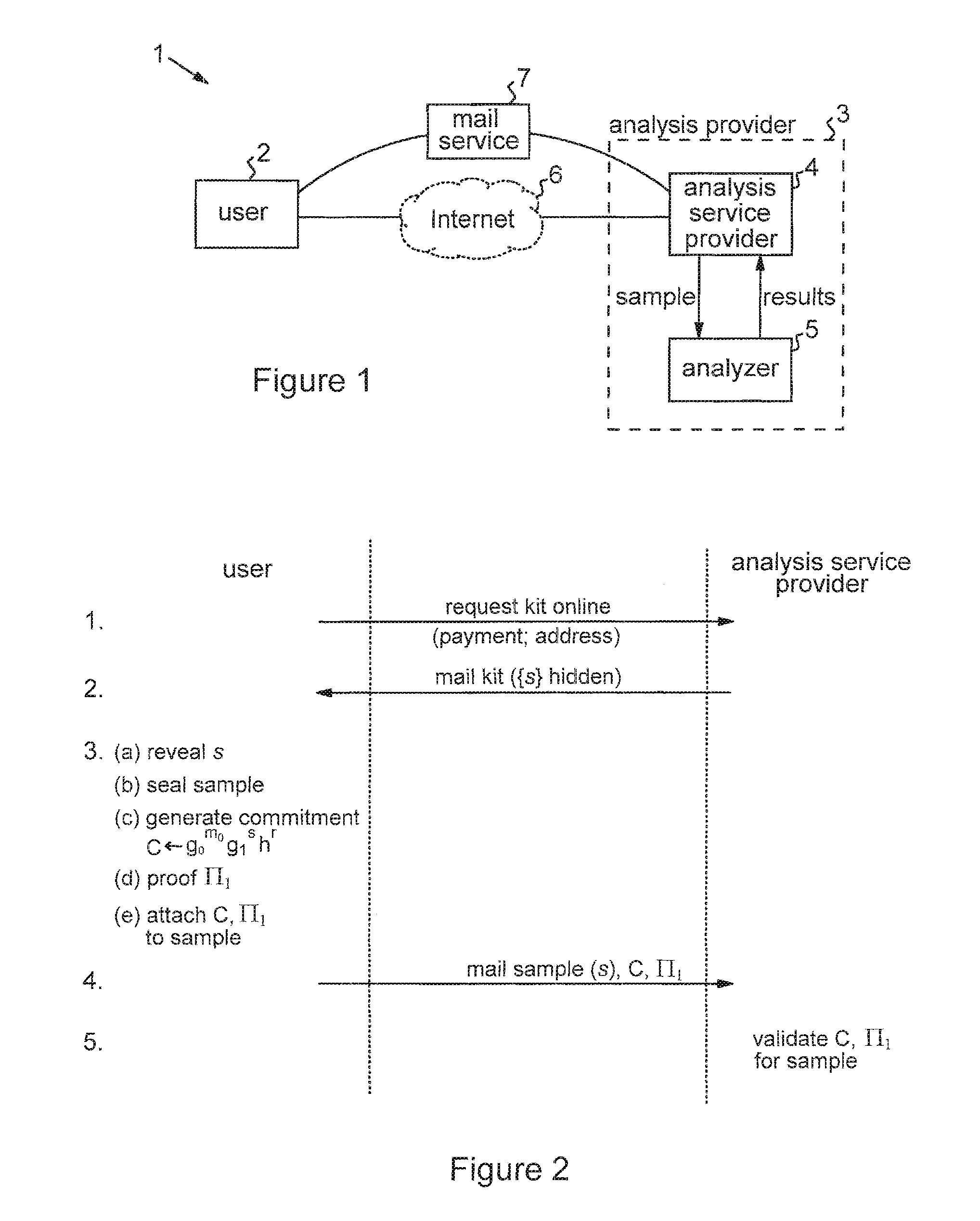
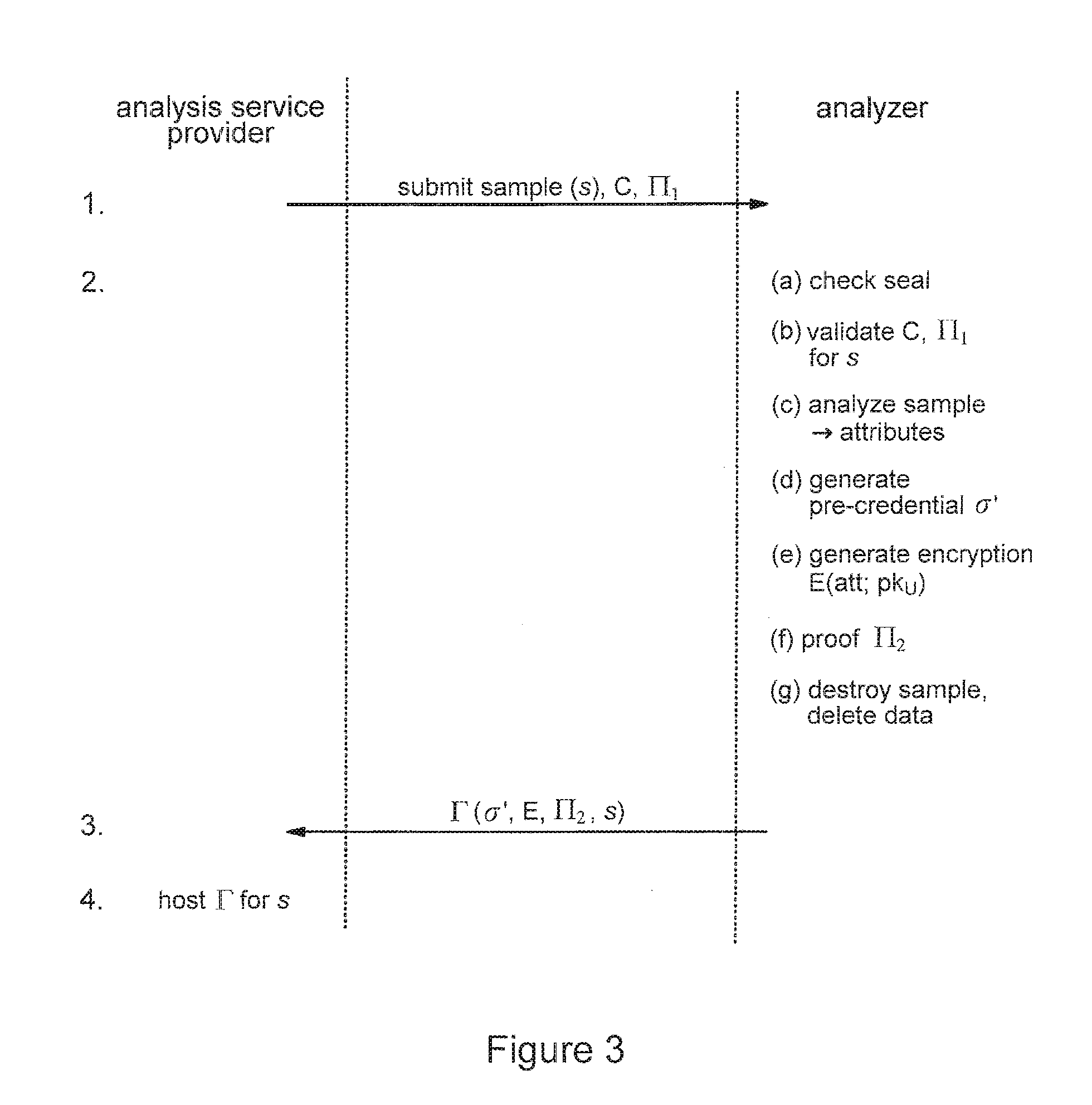
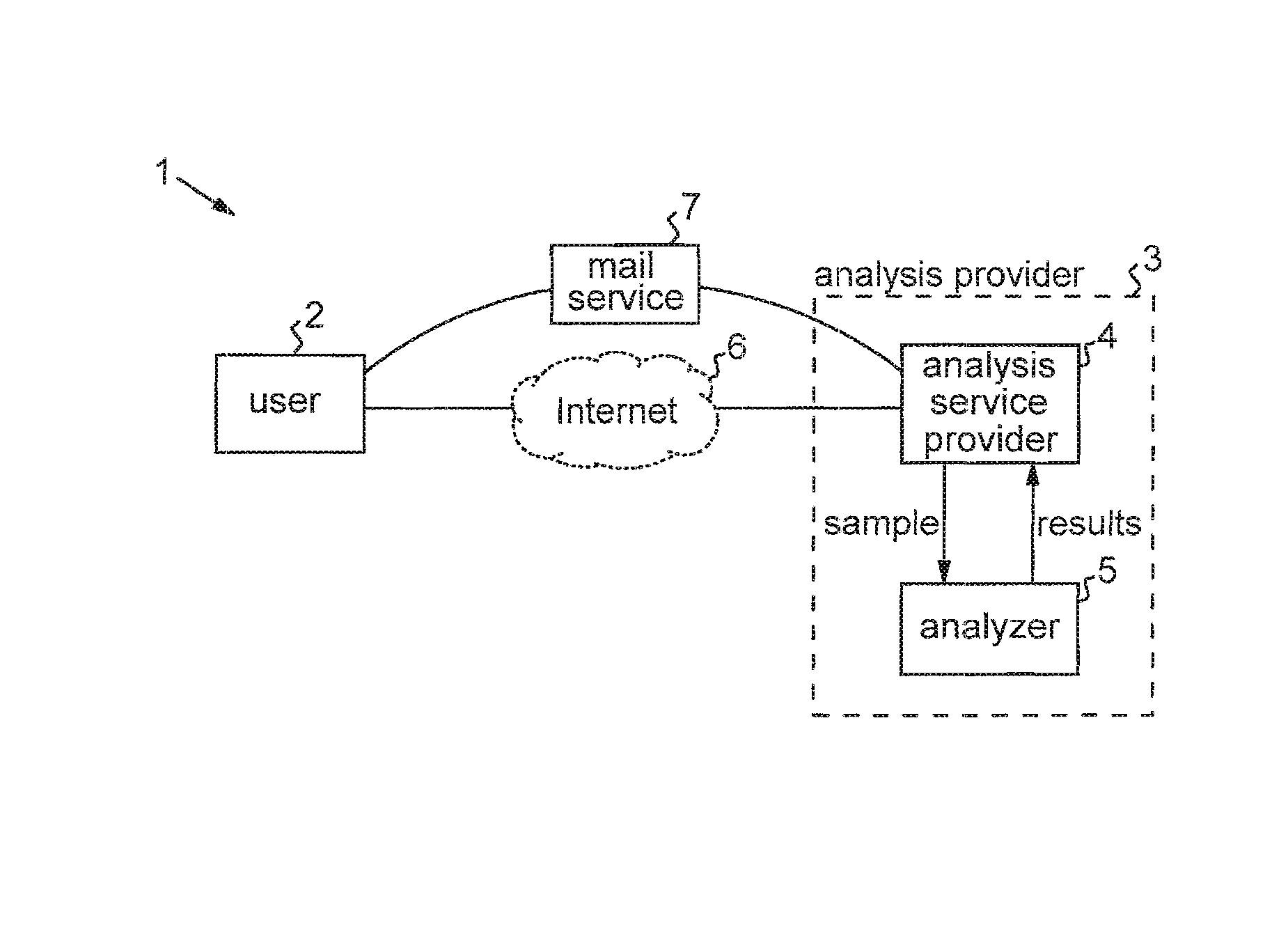
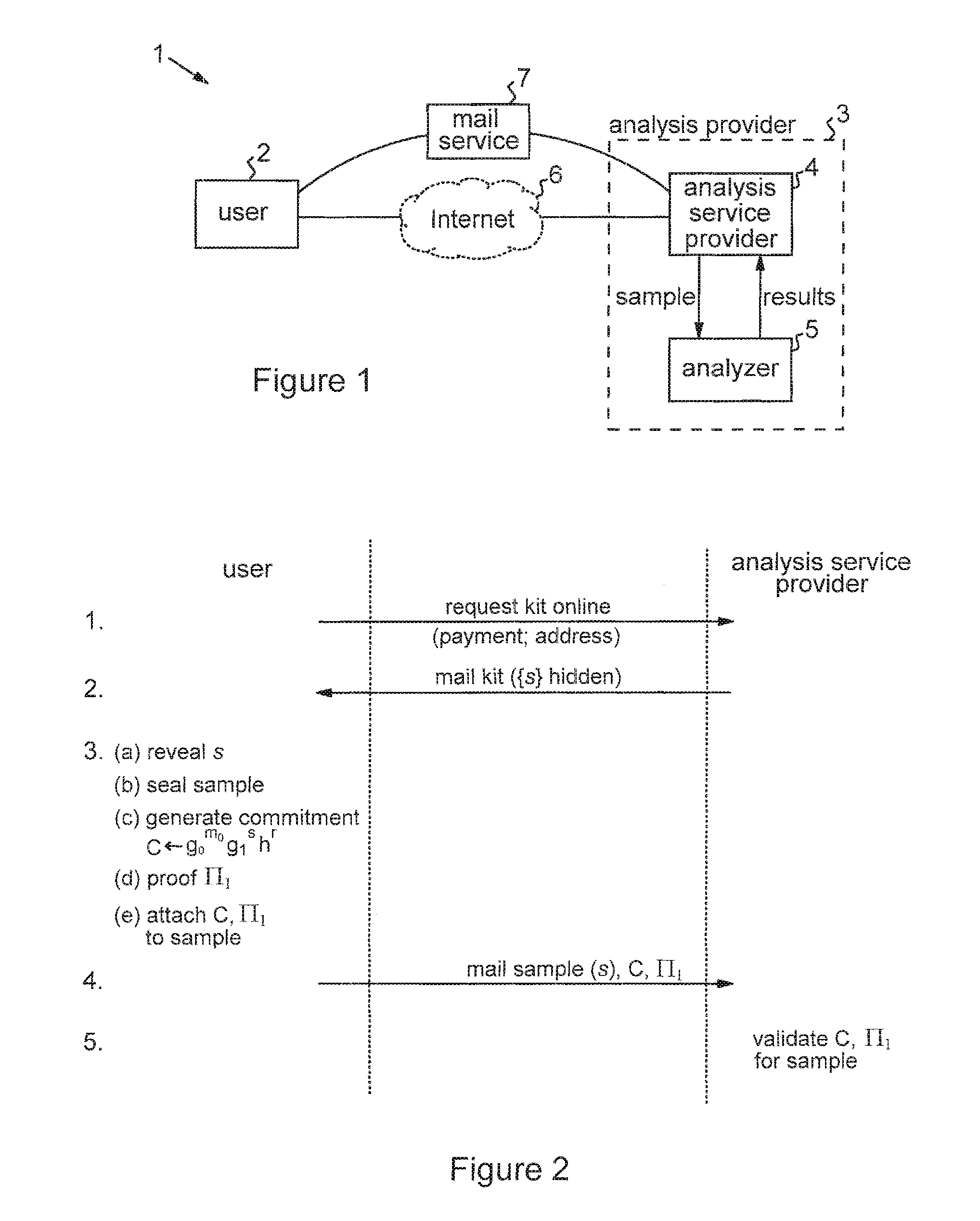
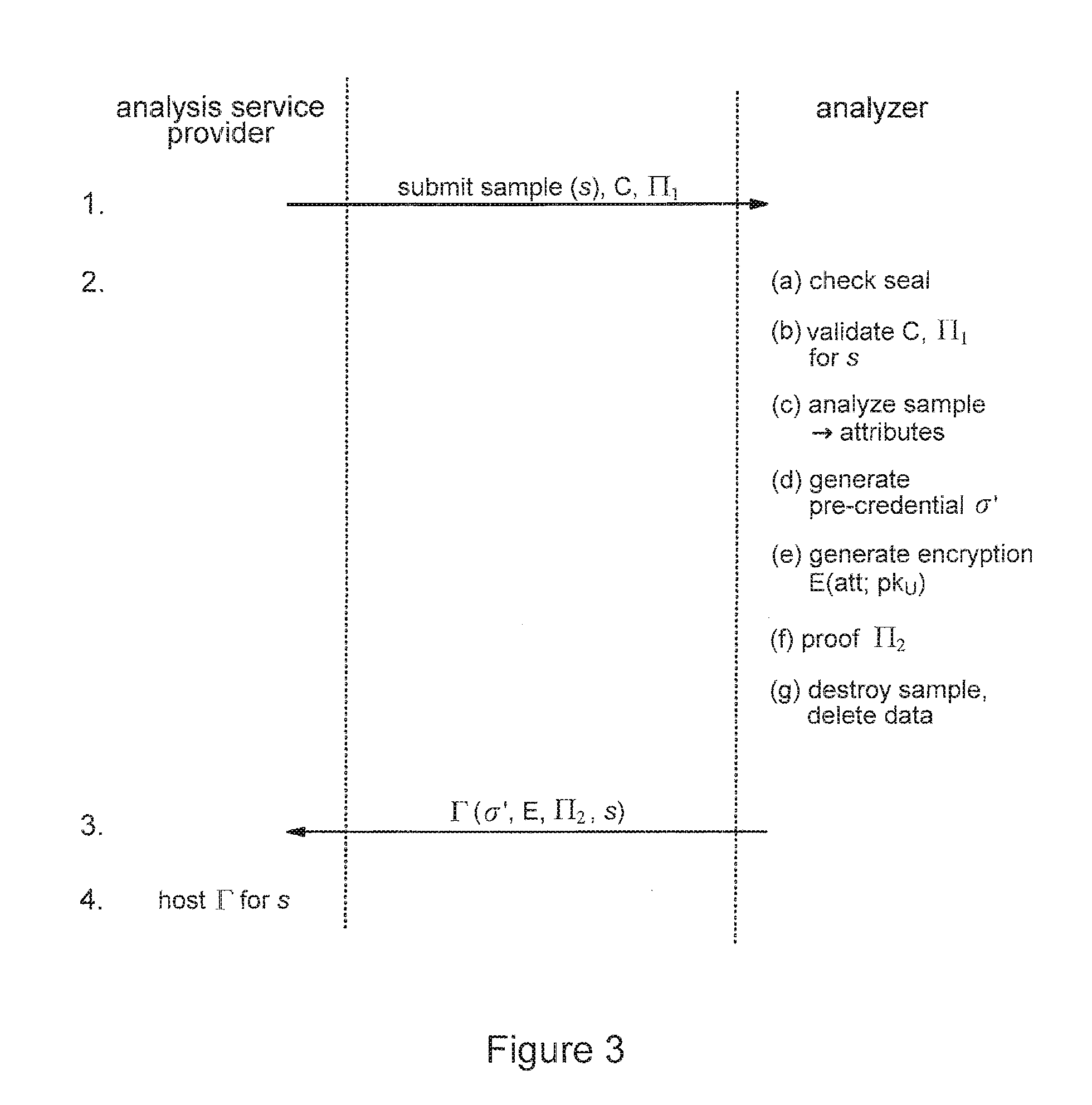
Privacy-sensitive sample analysis
InactiveUS20120005098A1Guaranteed usageIncrease constraintsDigital data authenticationAnonymous user systemsAnalysis sampleComputer science
Processes are described for provision of privacy-sensitive sample analysis results to a sample provider. The sample provider generates a cryptographic commitment encoding a secret value, r, and a sample identifier, s, associated with a sample container. The sample provider provides the commitment to an analysis provider in association with the sample container containing a sample for analysis. The analysis provider analyzes the sample to obtain a set of analysis results corresponding to the sample identifier, s, and generates a cryptographic pre-credential, σ′, corresponding to the sample identifier, s. The pre-credential, σ′, encodes the set of analysis results and the commitment. Completion of the pre-credential, σ′, requires knowledge of the secret value, r, in the commitment. In response to cryptographic proof of knowledge by the sample provider of at least the secret value, r, in the commitment encoded in the pre-credential, σ′, corresponding to the sample identifier, s, the analysis provider supplies the pre-credential, σ′, to the sample provider. The sample provider then completes the pre-credential, σ′ using the secret value, r, to obtain a cryptographic credential, σ, encoding the set of analysis results.
Owner:IBM CORP
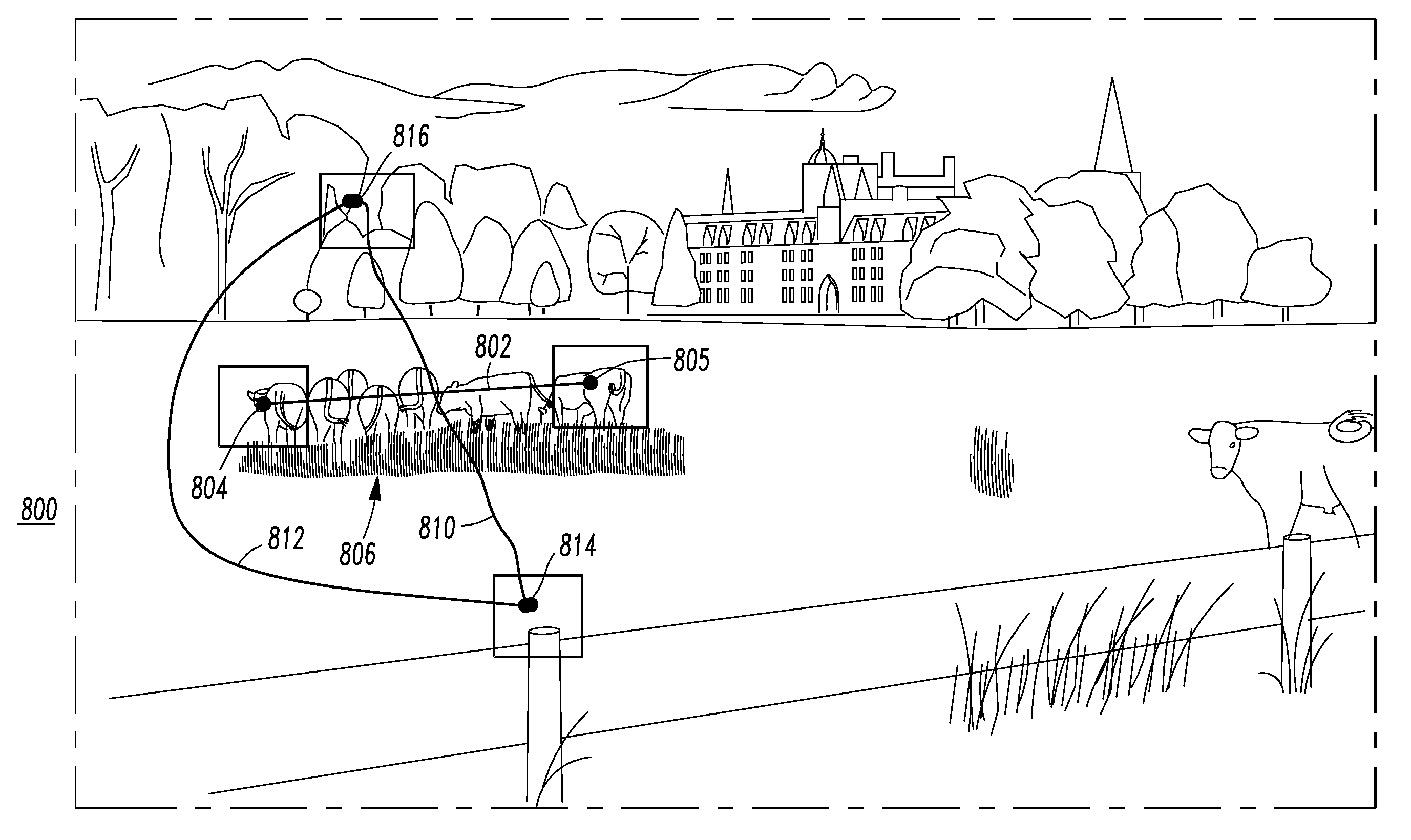
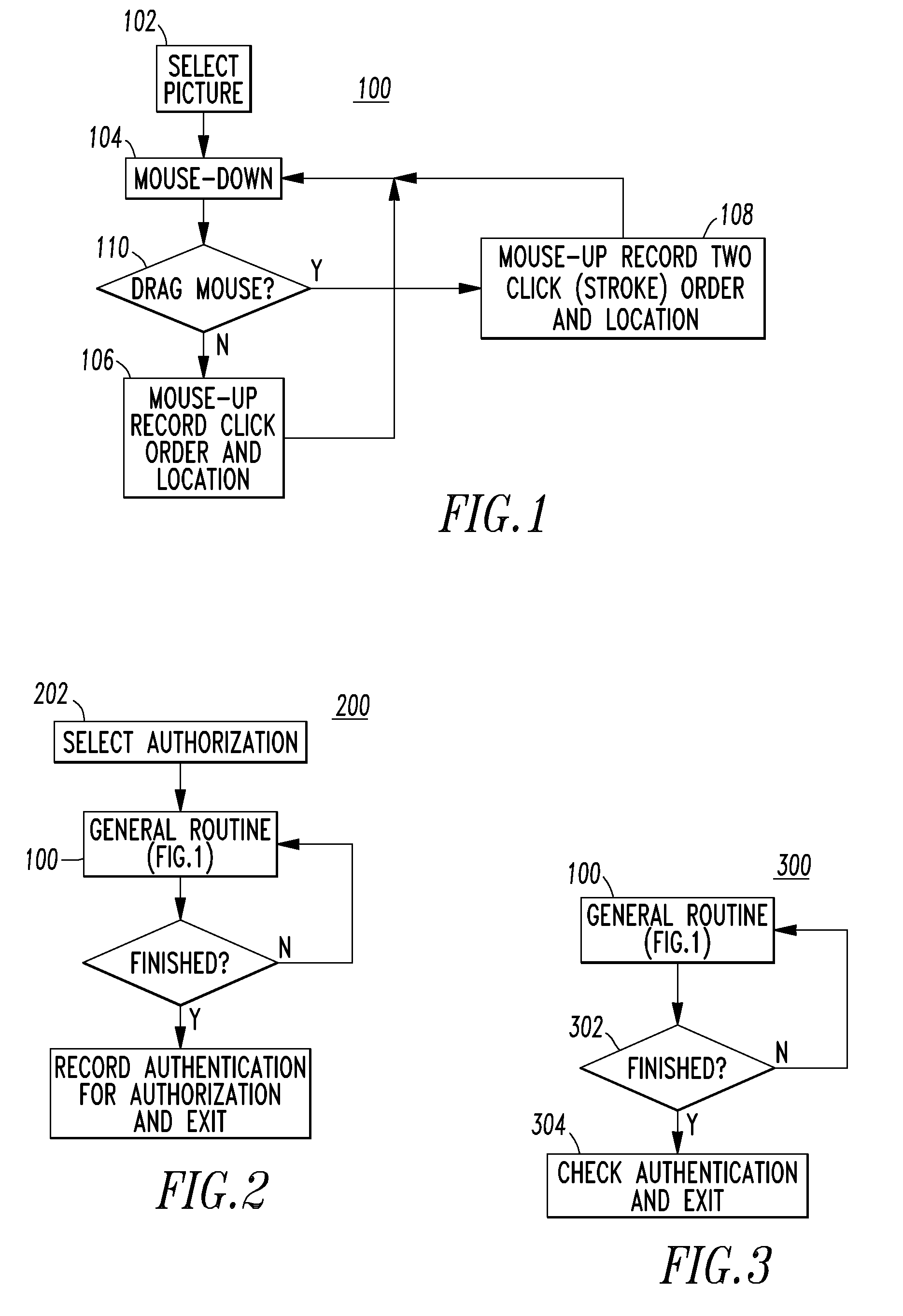
Method and system for processor or web logon
ActiveUS8813183B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareDisplay device
A system is for a proof of knowledge enrollment or authentication. The system includes a processor having an input, an output and a routine; and a display having an image from the output of the processor. The routine is structured to input from the input of the processor a plurality of different position selections and / or a plurality of different path selections on the image. The routine is further structured to authenticate the proof of knowledge as a function of the plurality of different position selections and / or the plurality of different path selections on the image.
Owner:ANTIQUE BOOKS
Privacy-sensitive sample analysis
InactiveUS8825555B2Guaranteed usageIncrease constraintsDigital data authenticationBiological testingAnalysis sampleComputer science
Processes are described for provision of privacy-sensitive sample analysis results to a sample provider. The sample provider generates a cryptographic commitment encoding a secret value, r, and a sample identifier, s, associated with a sample container. The sample provider provides the commitment to an analysis provider in association with the sample container containing a sample for analysis. The analysis provider analyzes the sample to obtain a set of analysis results corresponding to the sample identifier, s, and generates a cryptographic pre-credential, σ′, corresponding to the sample identifier, s. The pre-credential, σ′, encodes the set of analysis results and the commitment. Completion of the pre-credential, σ′, requires knowledge of the secret value, r, in the commitment. In response to cryptographic proof of knowledge by the sample provider of at least the secret value, r, in the commitment encoded in the pre-credential, σ′, corresponding to the sample identifier, s, the analysis provider supplies the pre-credential, σ′, to the sample provider. The sample provider then completes the pre-credential, σ′ using the secret value, r, to obtain a cryptographic credential, σ, encoding the set of analysis results.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
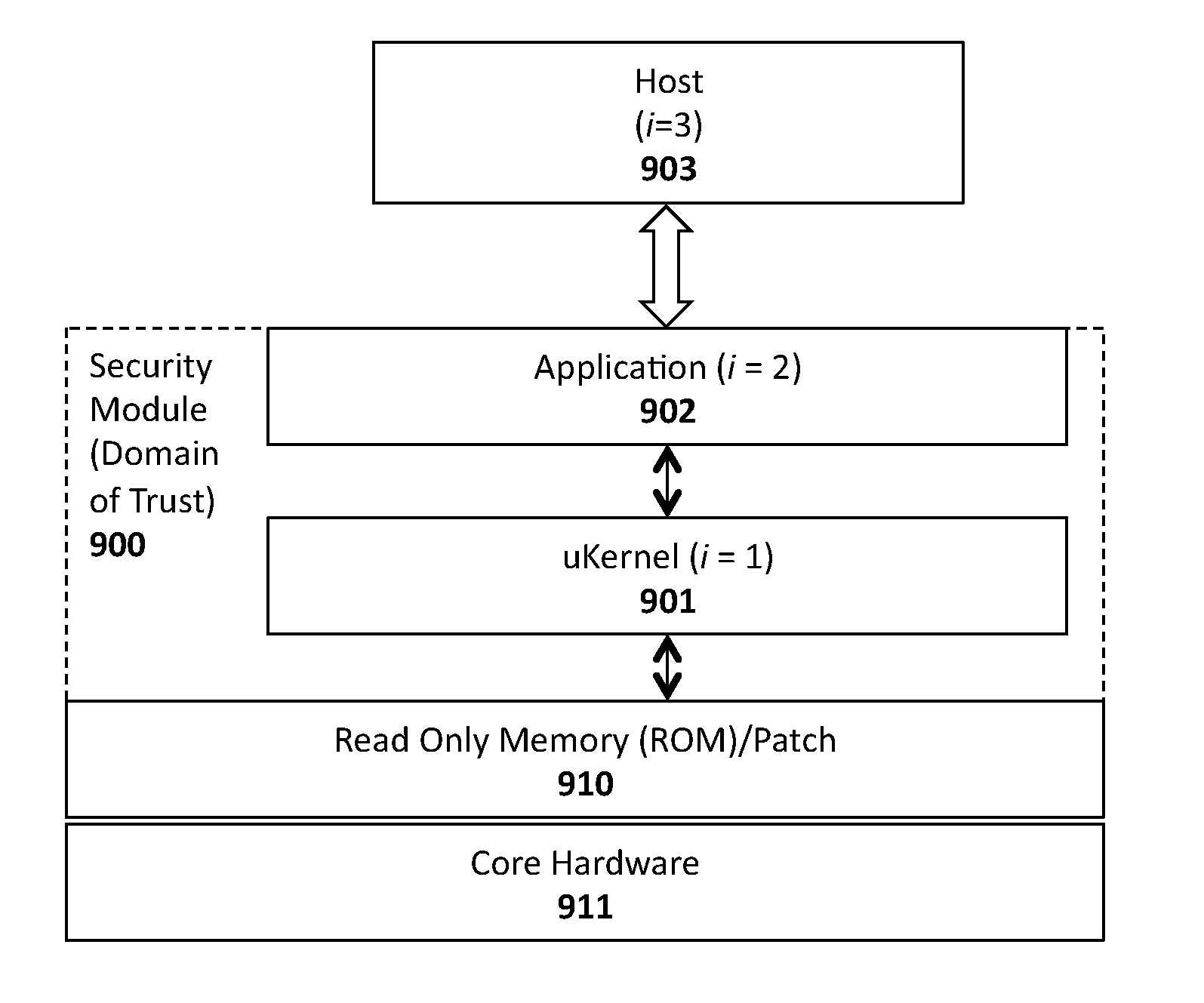
Apparatus and method for implementing zero-knowledge proof security techniques on a computing platform
InactiveUS20150095655A1Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionProcessing coreA domain
An apparatus and method for zero knowledge proof security techniques within a computing platform. One embodiment includes a security module executed on a processing core to establish a domain of trust among a plurality of layers by sending a challenge from a verification layer to a first prover layer, the challenge comprising an indication of at least one selected option; in response to receiving the challenge, generating first verification information at the first prover layer based on the secret and the indication of the selected option; sending the first verification information to at least a second prover layer, the second prover layer generating second verification information based on the first verification information and the indication of the selected option; and performing a verification operation at the verification layer using the second verification information based on the selected option.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and structure for self-sealed joint proof-of-knowledge and diffie-hellman key-exchange protocols
InactiveUS8464060B2Robust resistance against malicious disclosureImproving security and privacy and efficiencyUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeComputer science
A method (and structure) for a party (the prover) to prove its knowledge, jointly and non-malleably, of multiple secret (fixed and / or ephemeral) Diffie-Hellman exponents (DH-exponents), corresponding to its public (fixed and / or ephemeral) DH-components and with respect to the public (fixed and / or ephemeral) challenging DH-components from another party (the verifier). The joint proof-of-knowledge (JPOK) consists of secrets made by multiplying multiple DH-secrets, which can be generated and verified by each party by its own secret DH-exponents and the public DH-components of both parties. To ensure the non-malleability of the JPOK, the method makes all these multiplied DH-secrets to be independent, and makes the session-tag committed to the multiplied DH-secrets. In addition, the invented method makes the DH-secrets to be multiplied to further satisfy at least one of the following: (1) deniability; (2) pre-computability; and (3) post-ID computability.
Owner:ANDREW C YAO
Asymmetric crypto-graphy with rolling key security
ActiveUS8099607B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsGraphicsNon symmetric
A system for securing information, includes a processor and storage device. The storage device stores information encrypted with one of a first private rolling key and a first public rolling key of an a first asymmetric rolling crypto-key, along with the one first rolling key. The processor has the logic to direct transmission, via a network, of proof of knowledge of the stored one first rolling key to authenticate a user, and of a request for the other of the first private rolling key and the first public rolling key. The processor receives the other first rolling key via the network, responsive to the directed transmission. The processor then decrypts the stored encrypted information with the received other first rolling key, and generates a second asymmetric rolling crypto-key having a second private rolling key and a second public rolling key. The processor encrypts the information with one of the second private rolling key and the second public rolling key. The processor also directs transmission of the other of the second private rolling key and the second public rolling key via the network. The storage device stores the information encrypted with the one second rolling key and the one second rolling key itself.
Owner:VMWARE INC
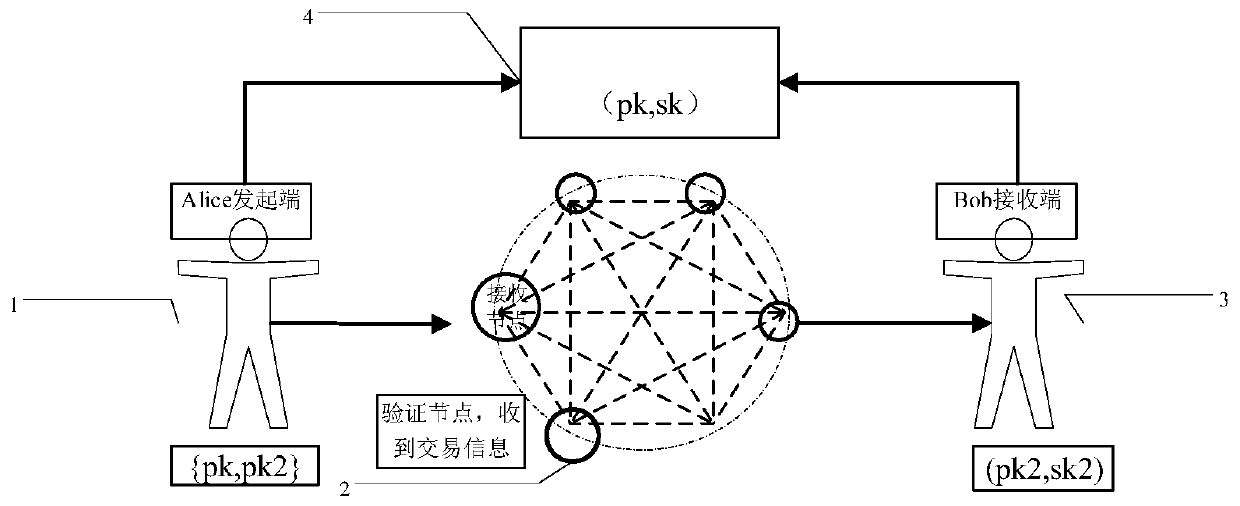
Identity management and authentication system and method based on block chain and zero knowledge proof
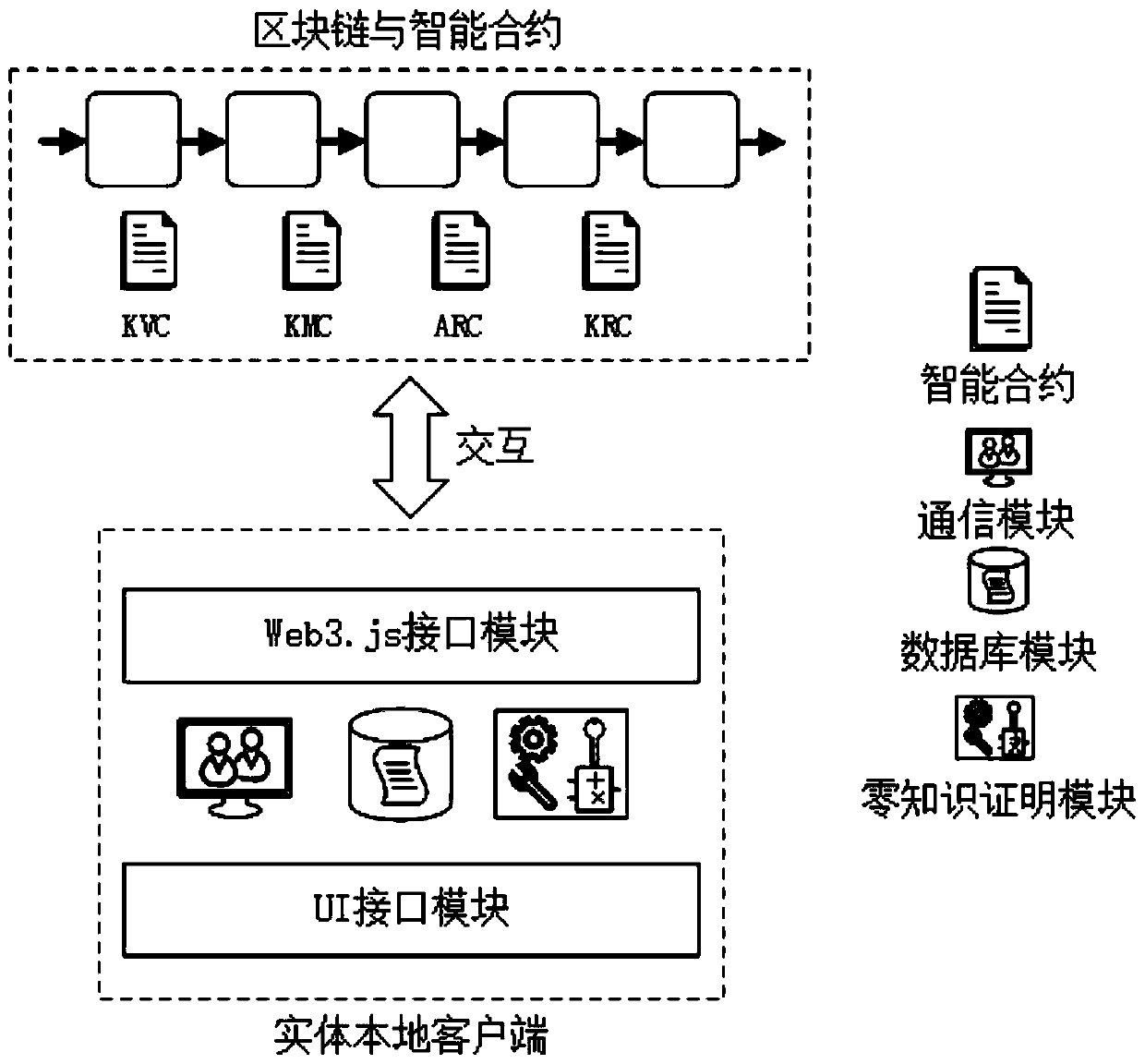
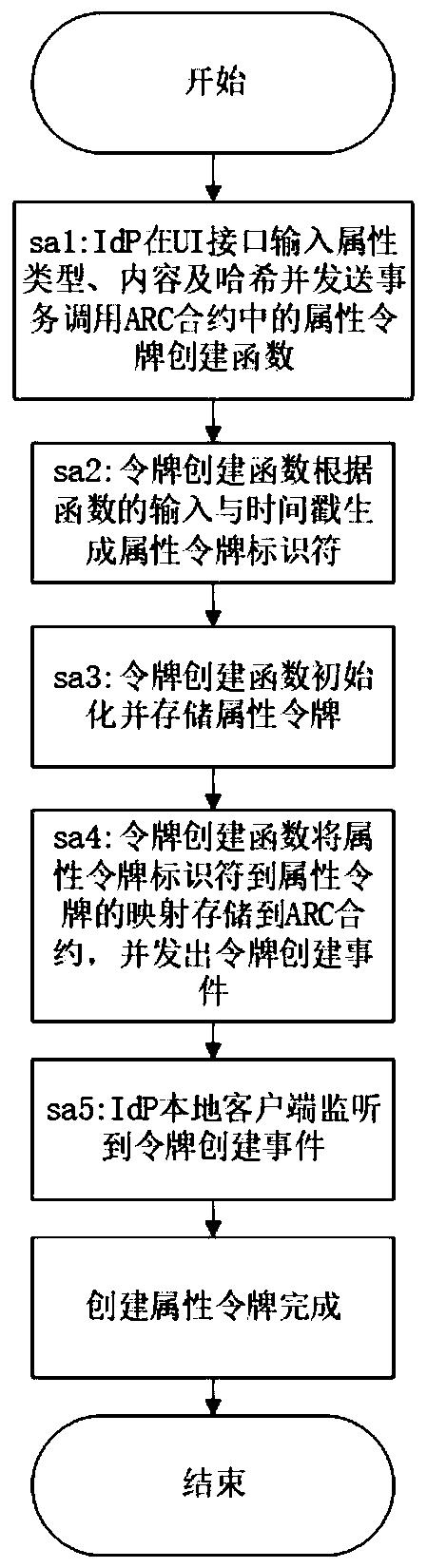
ActiveCN111447073AImplement anonymous authenticationSolve the problem that the mapping relationship is exposed to everyoneDatabase management systemsUser identity/authority verificationEngineeringSmart contract
The invention provides an identity management and authentication system and method based on a block chain and zero knowledge proof. The identity management and authentication system comprises an on-chain smart contract and an off-chain entity local client. The on-chain intelligent contract comprises the following contracts: an attribute warehouse contract, a knowledge management contract, a knowledge verification contract and a key warehouse contract. The off-chain entity local client comprises the following modules: a UI interface module, a web3.js interface module, a zero knowledge proof module, a communication module and a database module. The identity management and authentication method comprises the steps of attribute token creation, attribute hidden token creation, identity information authentication and attribute token logout. According to the invention, the ownership of the user to the attribute is not disclosed in the blockchain, the problem that the identity management system in the blockchain discloses the mapping relationship between the personal identifier and the personal identity information to the owner is solved, and the privacy of the user identity information isensured.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Set membership proofs in data processing systems
InactiveUS20090300347A1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracySecuring communicationData processing systemComputer security
A method and apparatus for proving and a method and apparatus for verifying that a secret value is a member of a predetermined set of values. The proving mechanism receives a set of signatures which has respective values in the predetermined set signed using a private key. The proving mechanism sends to the verifying mechanism a commitment on the secret value of the proving mechanism. The proving mechanism and verifying mechanism then communicate to implement a proof of knowledge protocol demonstrating knowledge by the proving mechanism of a signature on the secret value committed to in the commitment, thus proving that the secret value is a member of the predetermined set.
Owner:IBM CORP
Anonymous selectable credential system and method therefor
InactiveUS20080075281A1Computational cost for the user to prove any portion of his full set of rights is constantEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital data processing detailsUser PrivilegeComputer science
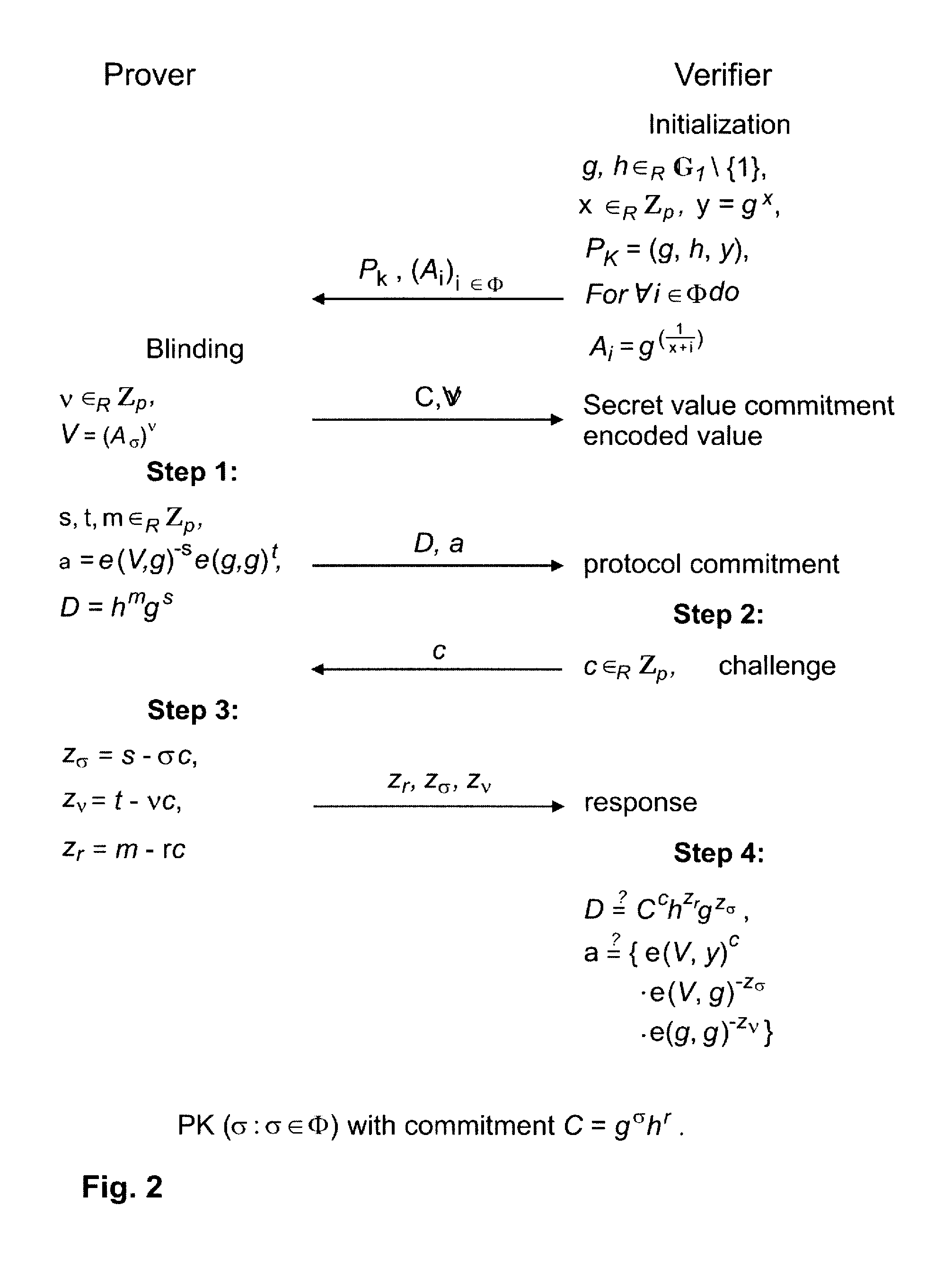
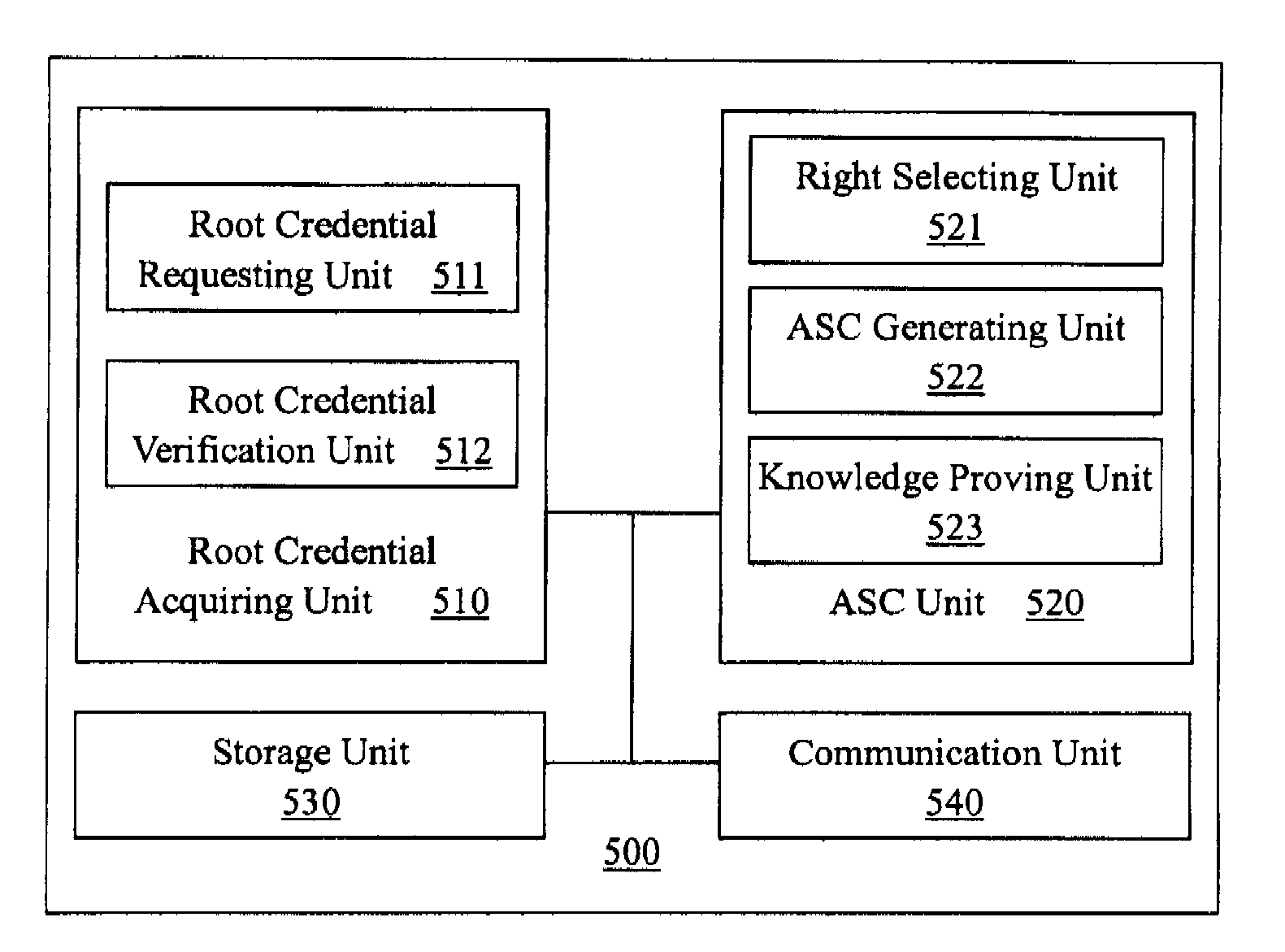
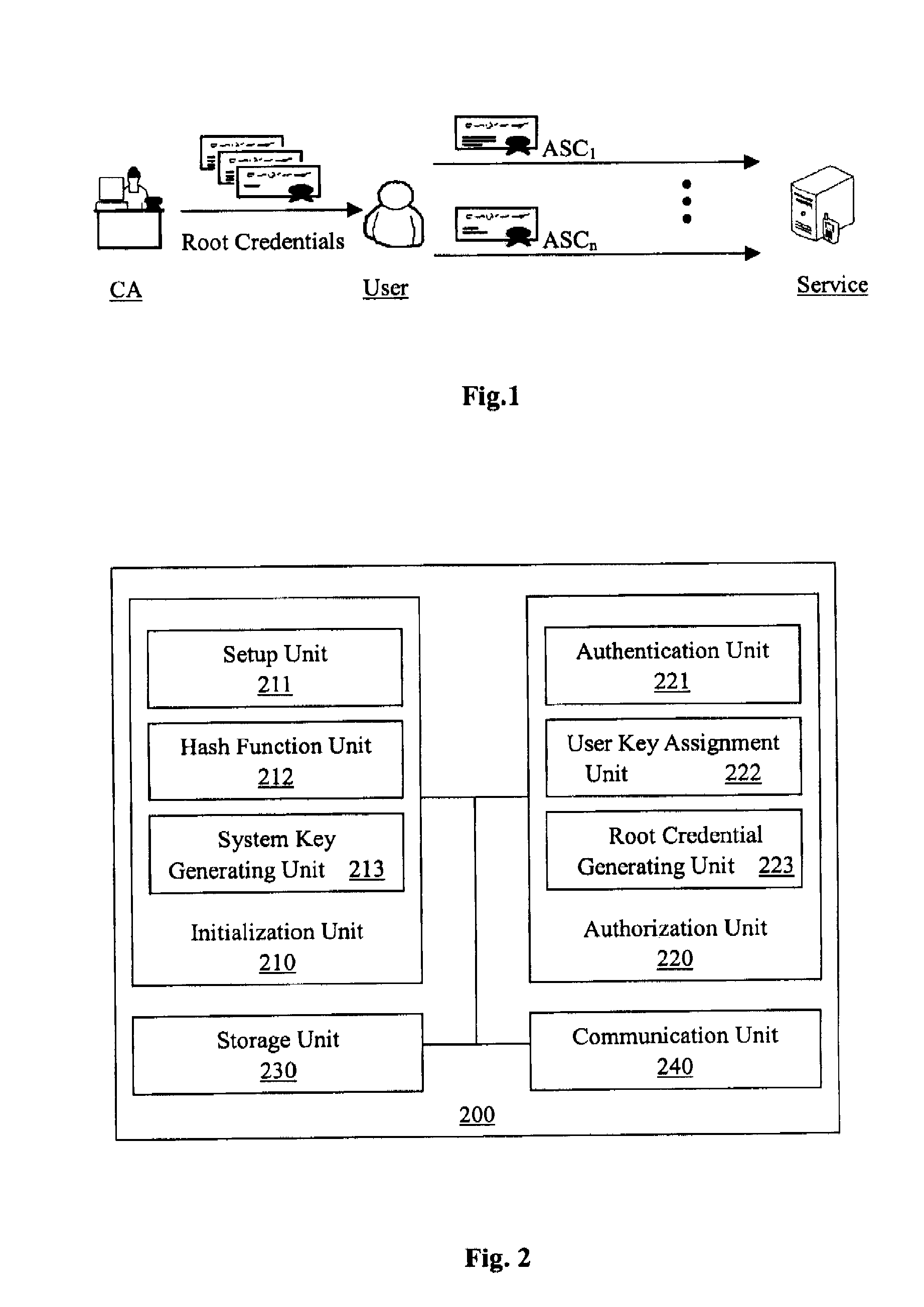
The present invention provides an anonymous selectable credential system and method therefor. In the system, a credential authority issues root credentials to a user for certain user rights. The user generates an anonymous selectable credential from the root credentials that correspond to a selected set of user rights, and presents the anonymous selectable credential to a service. Using the anonymous selectable credential, the user can prove to the service through a knowledge proof that the selected set of user rights was granted by the credential authority. Then the service may provide service to the user according to the verified user rights. By generating and presenting different anonymous selectable credentials, the user could remain anonymous no matter how many times he / she accessed one or more services. The user can selectively prove any portion of his / her full set of rights, and no matter how many rights is to be proved, the computational cost is basically the same as that for proving only one right.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
Zero-knowledge proof data interaction method, node and equipment
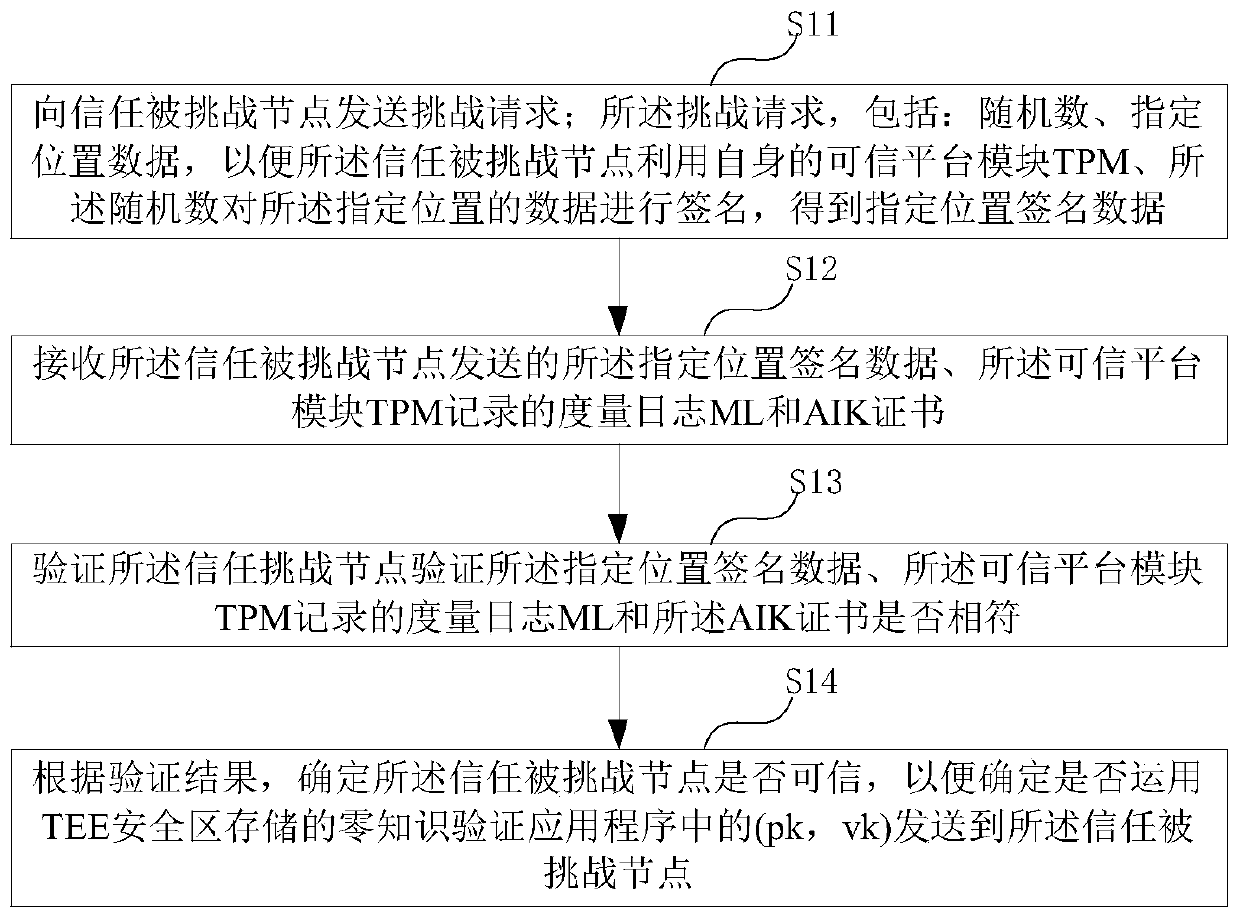
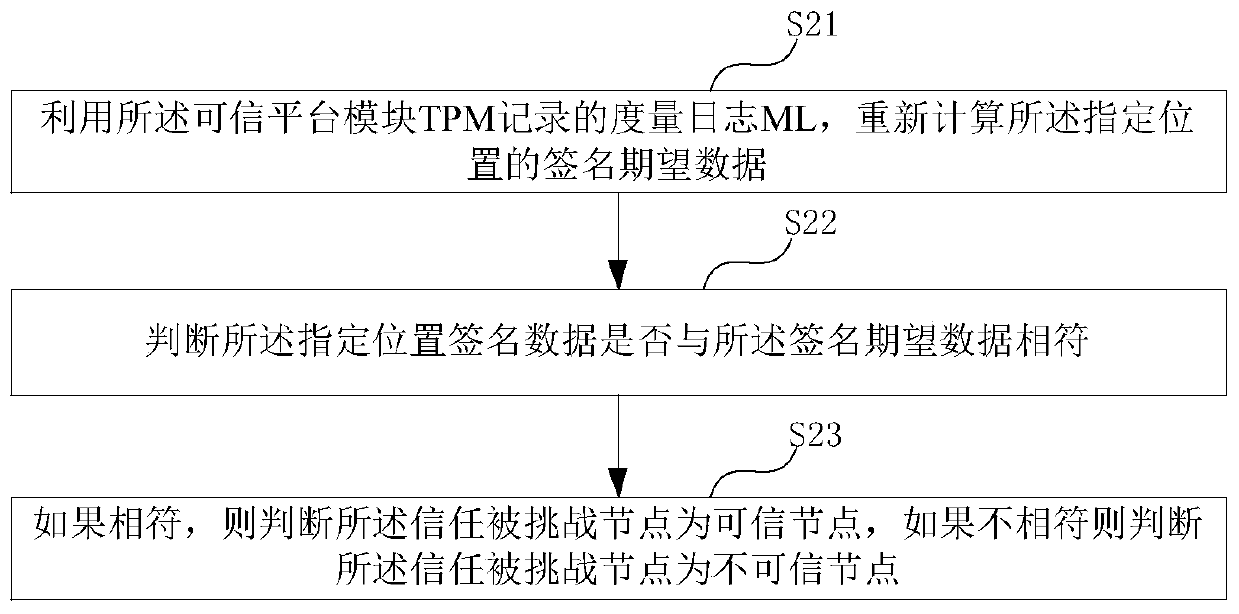
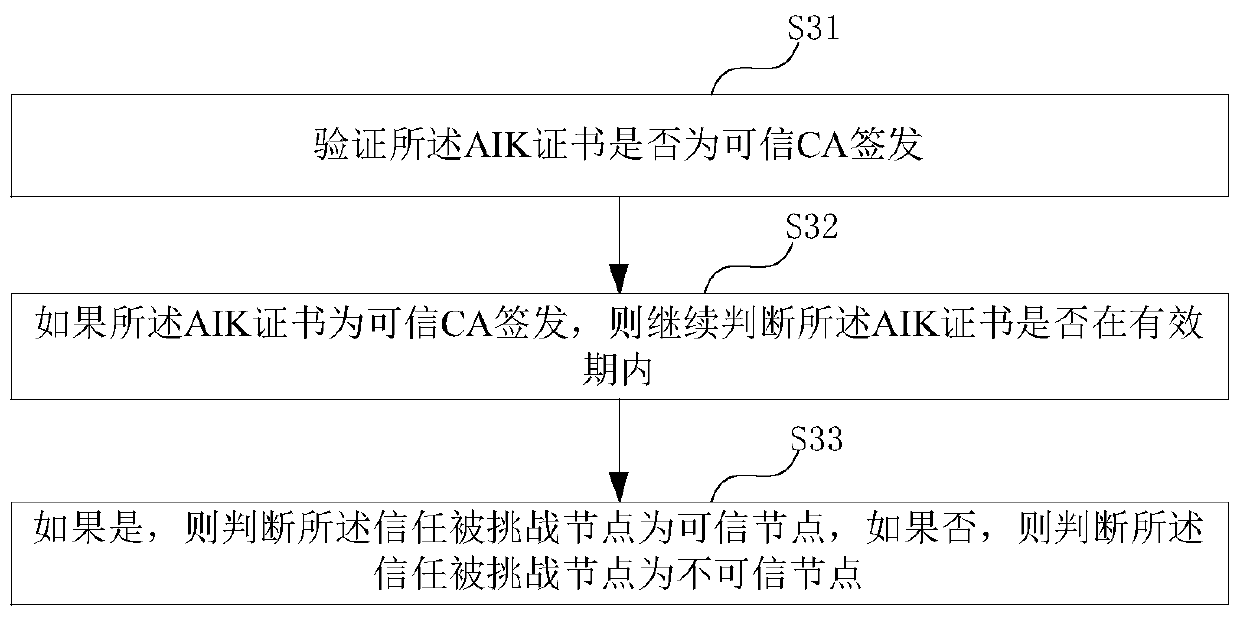
ActiveCN110768791AKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputer networkTrusted Platform Module
The embodiment of the invention provides a zero-knowledge proof data interaction method, which is used for a trust challenge node and comprises the following steps of sending a zero-knowledge challenge request to a trust challenged node, wherein the challenge request comprises a random number and specified position data, so that the trusted challenged node signs the data of the specified positionby using a trusted platform module (TPM) of the trusted challenged node and the random number to obtain specified position signature data; receiving the specified position signature data sent by the trusted challenged node, and a measurement log ML and an AIK certificate recorded by the trusted platform module TPM; verifying whether the trust challenge node verifies that the specified position signature data and the measurement log ML recorded by the trusted platform module TPM are consistent with the AIK certificate or not; and according to the verification result, determining whether the trusted challenged node is trusted or not, so as to determine whether to transmit the (pk, vk) in the zero-knowledge verification application stored in the TEE security area to the trusted challenged node or not.
Owner:北京八分量信息科技有限公司
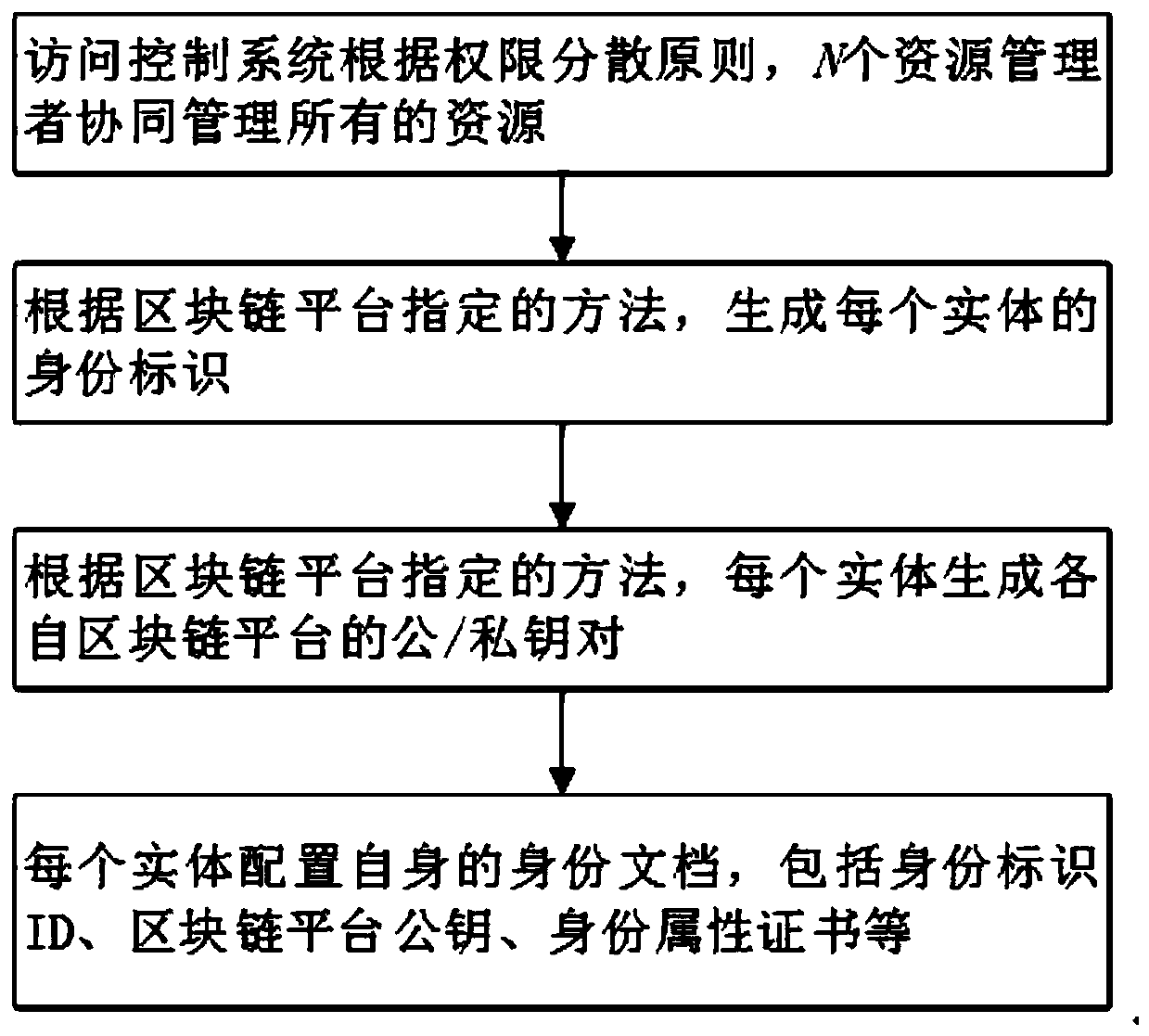
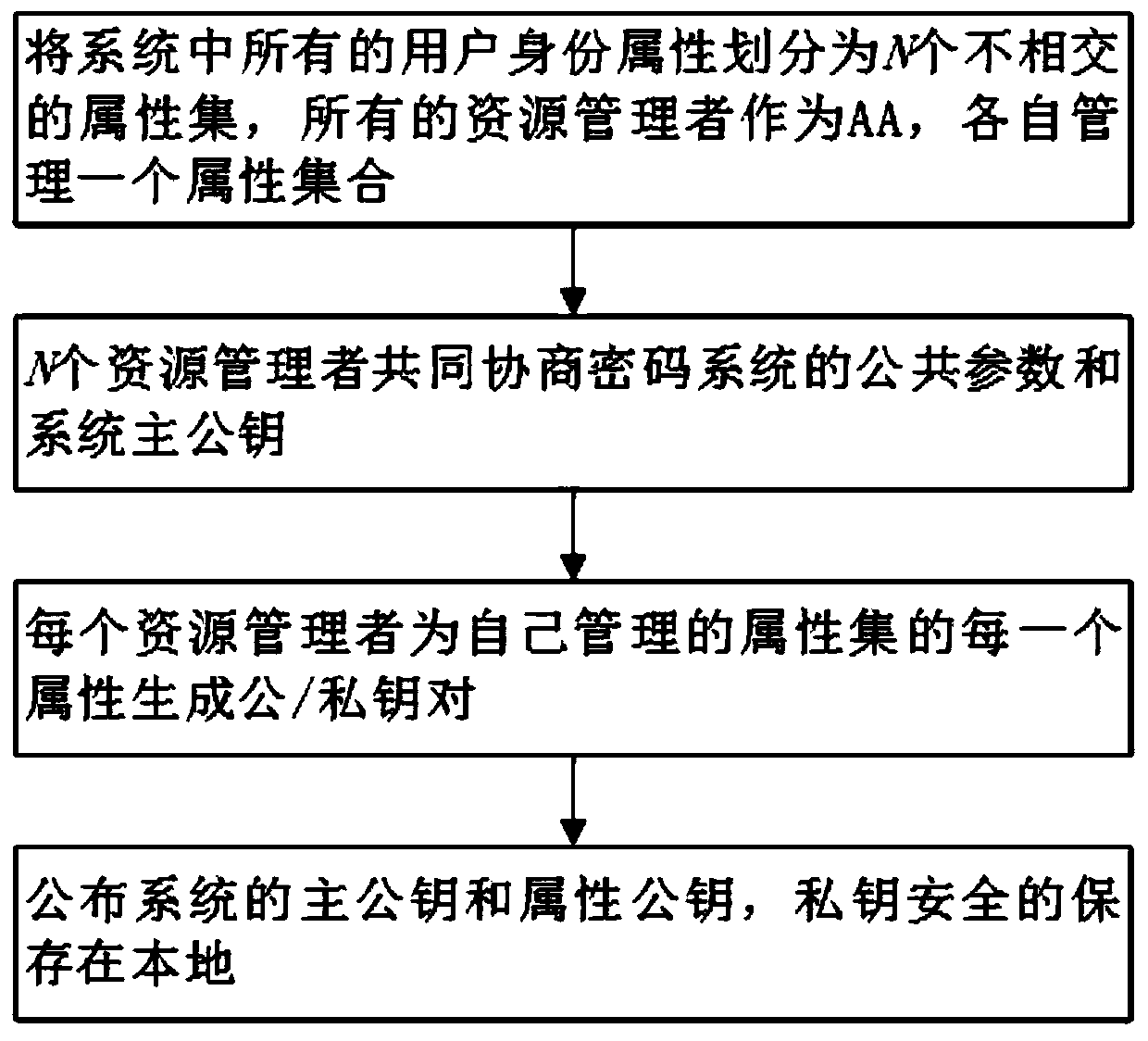
Collaborative fine-grained access control method based on block chain
ActiveCN111147460AImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesTrusted authorityRing signature
The invention discloses a collaborative fine-grained access control method based on a block chain. According to the invention, identities and attribute certificates of entities in a system are managedby utilizing a blockchain-based identity management technology, so the method does not depend on TP; each entity in the system can manage own identity and attribute certificate in a self-organizing manner; the overall safety of the system is improved; in addition, technologies such as zero knowledge proof and ring signature are utilized, so it is ensured that identity privacy of the user cannot be leaked in the transaction process; under the condition that a trusted center does not exist, the system master key is generated by negotiation of all resource managers in the system, an attribute cryptographic mechanism of a multi-attribute authoritative key strategy under the condition of not depending on credible authority is solved, cooperative key generation and resource access based on a block chain are realized, and the security of each entity in the system is greatly improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Hardware-based zero-knowledge strong authentication (h0KSA)
ActiveUS20150288521A1Reduce riskUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationHardware security moduleChain of trust
Owner:PAYPAL INC
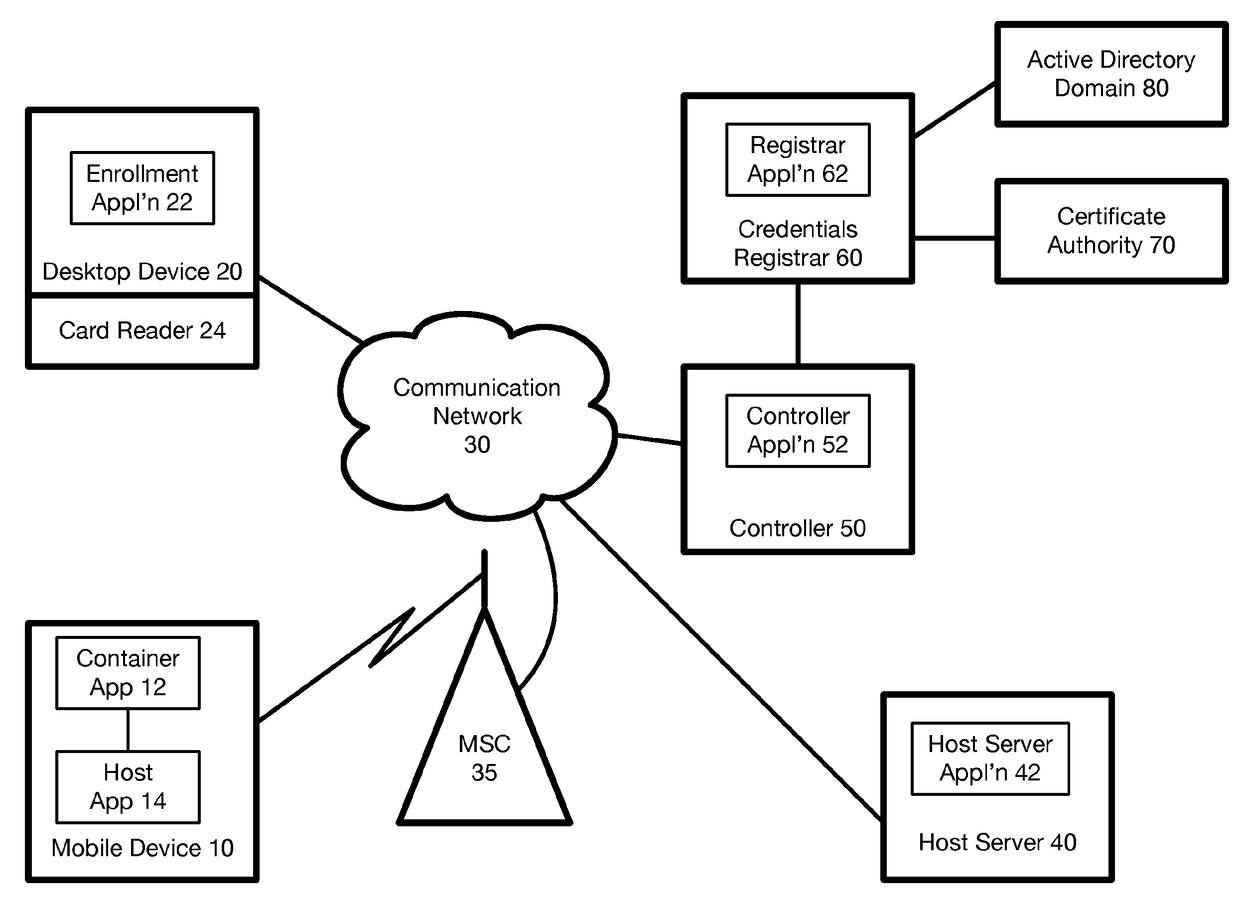
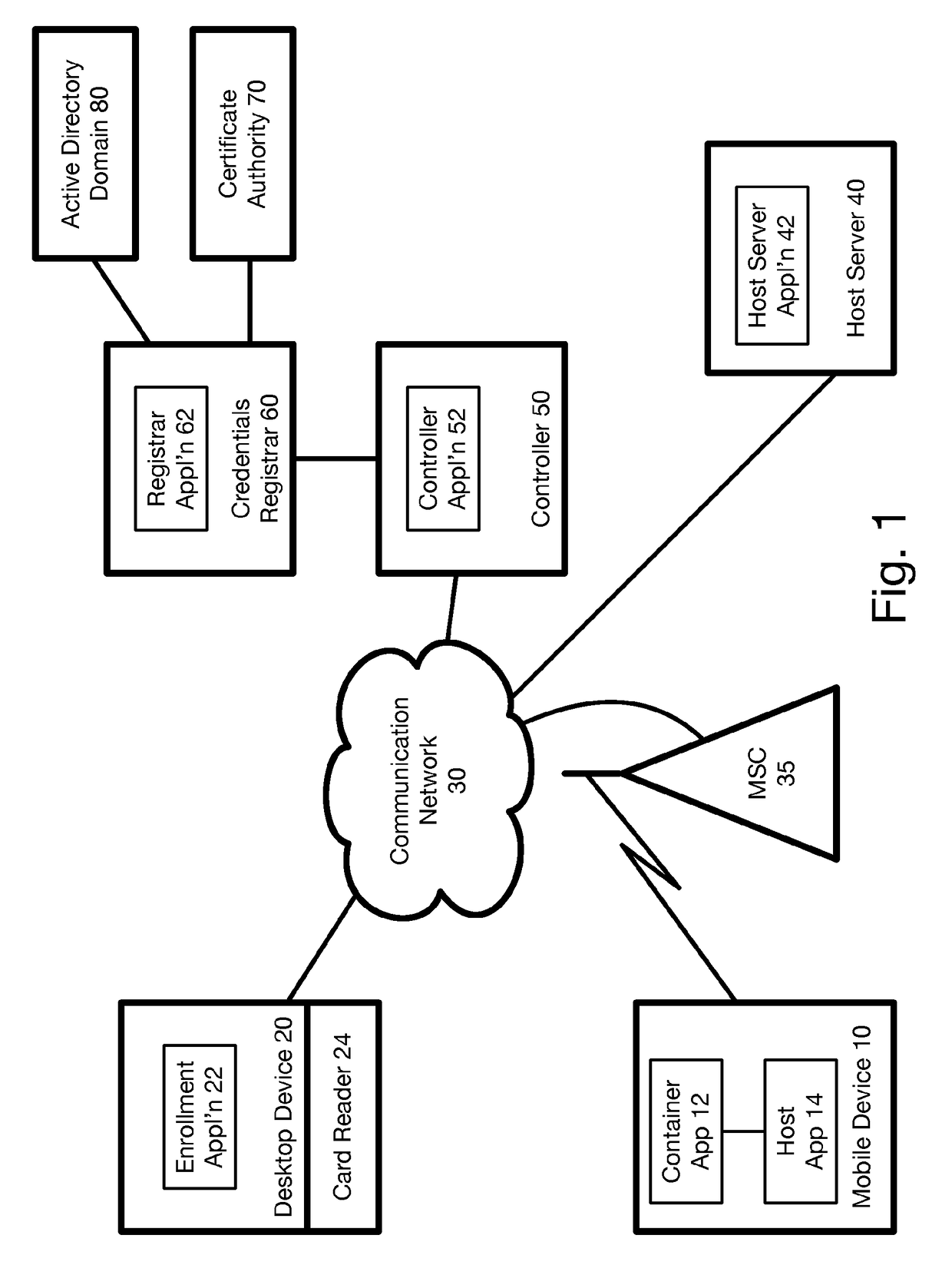
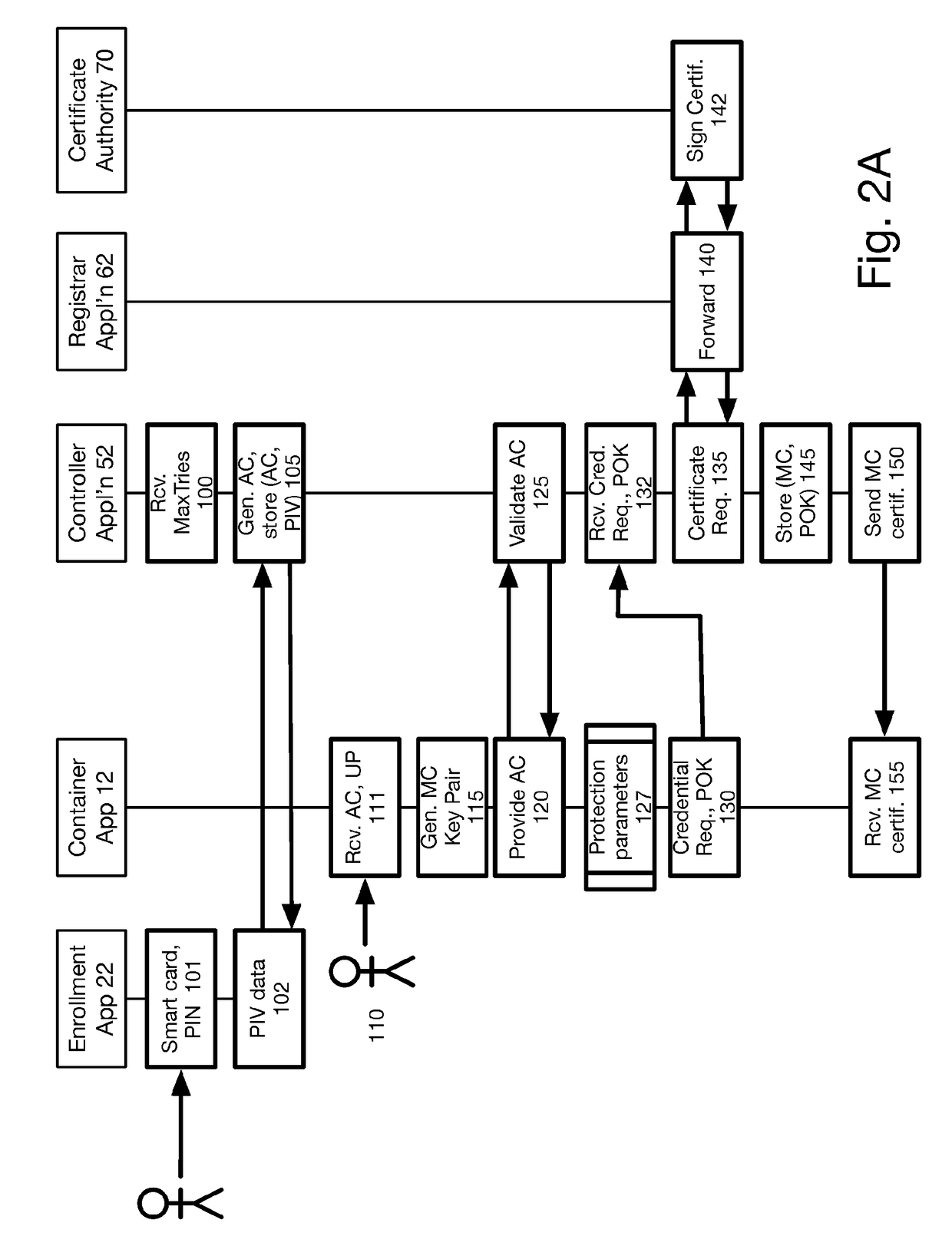
Method and system for issuing and using derived credentials
ActiveUS20180041494A1Improve access securityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital data authenticationPasswordSmart card
At a mobile device, a password is used to create a proof of knowledge (POK). The POK is stored in a controller accessible via a communication network. The POK ensures that the controller can detect an incorrect password from the mobile device, and that the mobile device cannot be subject to a brute force attack to determine the DC stored in the mobile device. After a predetermined number of unsuccessful attempts to enter the password, the controller blocks further attempts, thereby restoring protection against a brute force attack that was lost going from a standalone smart card to mobile-device-based derived credentials. A portion of Derived Credentials, needed to authenticate the user of a mobile device, is stored in the controller, further increasing the difficulty of unauthorized use.
Owner:ROUTE1
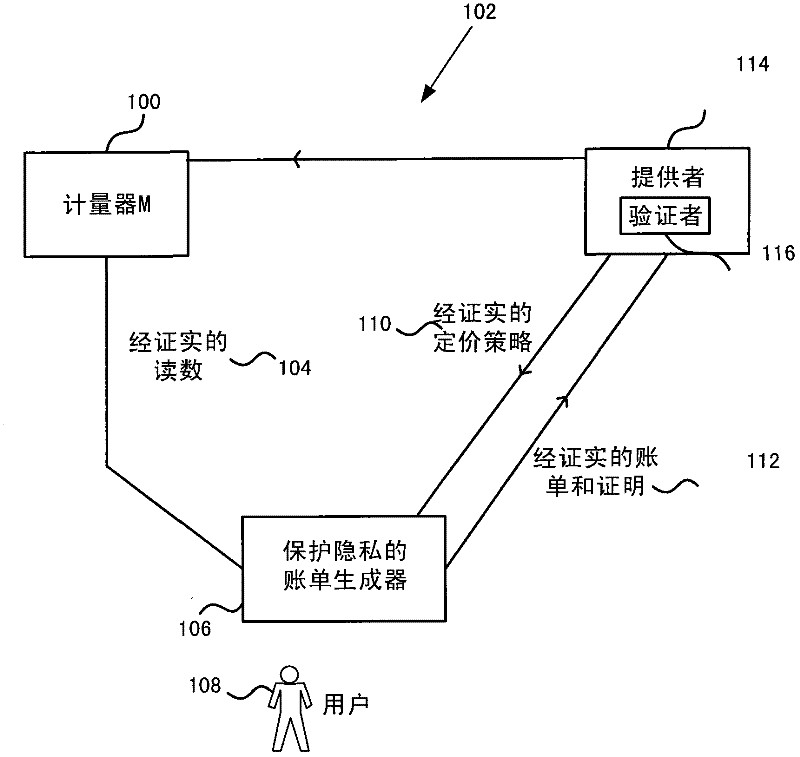
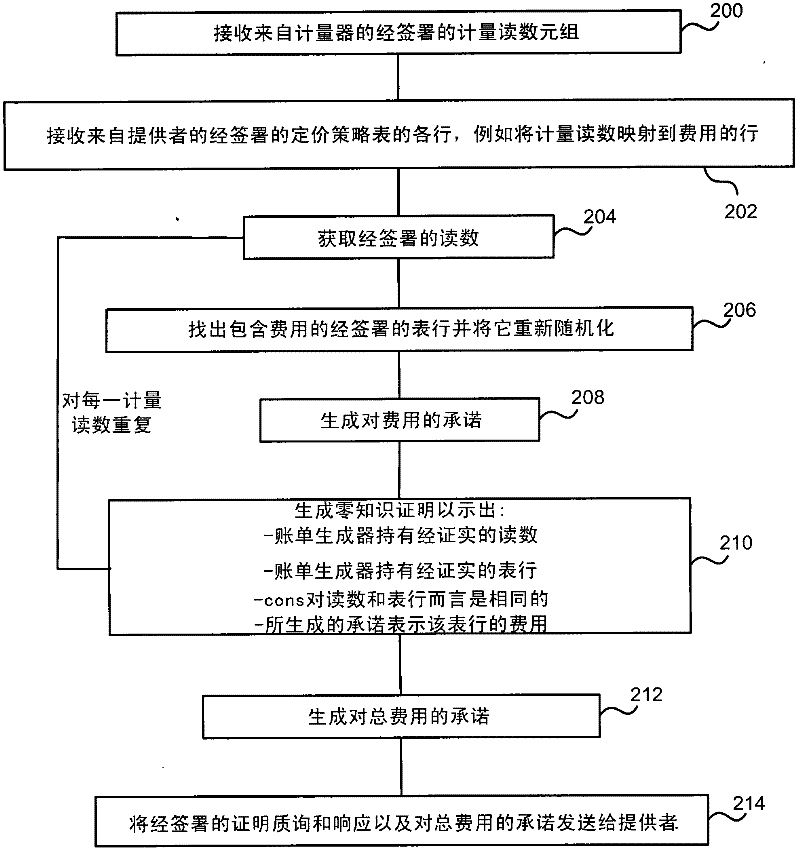
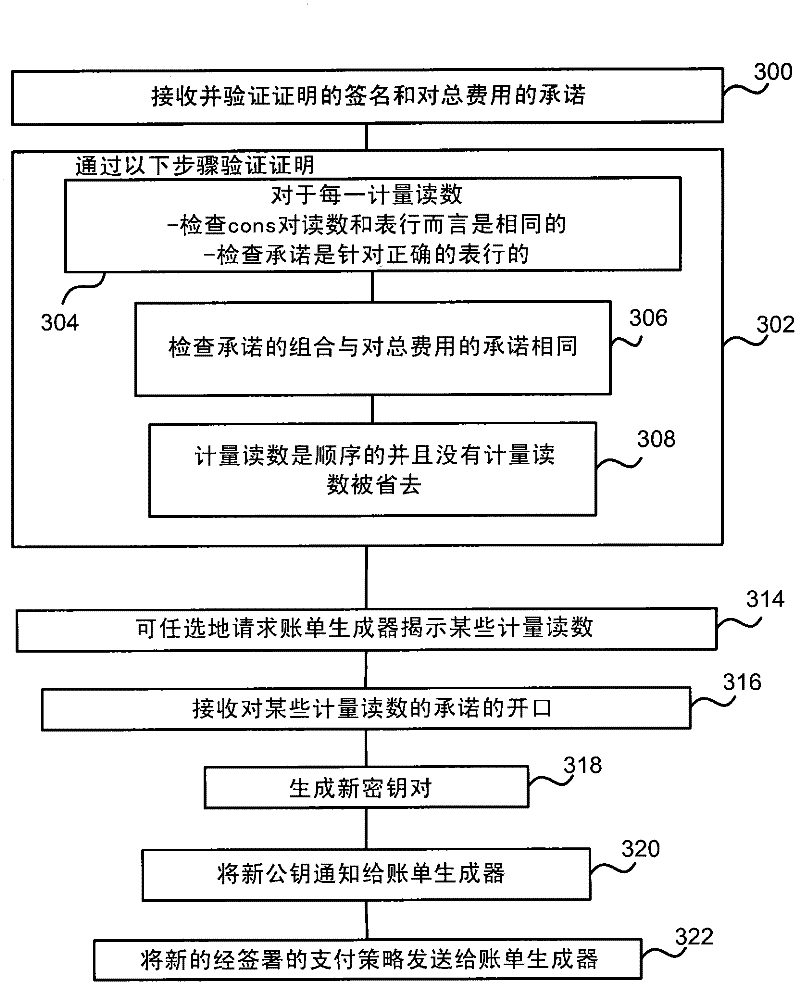
Privacy-preserving metering
InactiveCN102446329AUser identity/authority verificationPayment architectureElectricityTraffic congestion
The invention relates to privacy-preserving metering. Privacy protecting metering is described such as for electricity, gas or water metering, metering use of cloud computing resources, traffic congestion charging and other metering applications. In examples, fine grained user consumption data is kept private and not disclosed to a provider of a resource consumed by the user. In examples, a bill generator receives certified meter readings and a certified pricing policy and generates a bill which omits fine grained user consumption data. For example, the bill generator generates a zero knowledge proof that the bill is correct and sends that proof to a provider together with the bill. In examples a provider is able to check that the bill is correct using the zero knowledge proof without finding out the user's private consumption data. In an embodiment the pricing policy is stored as signed rows of a table to enable efficient generation of the zero knowledge proof.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Supervisable blockchain construction method based on group signature
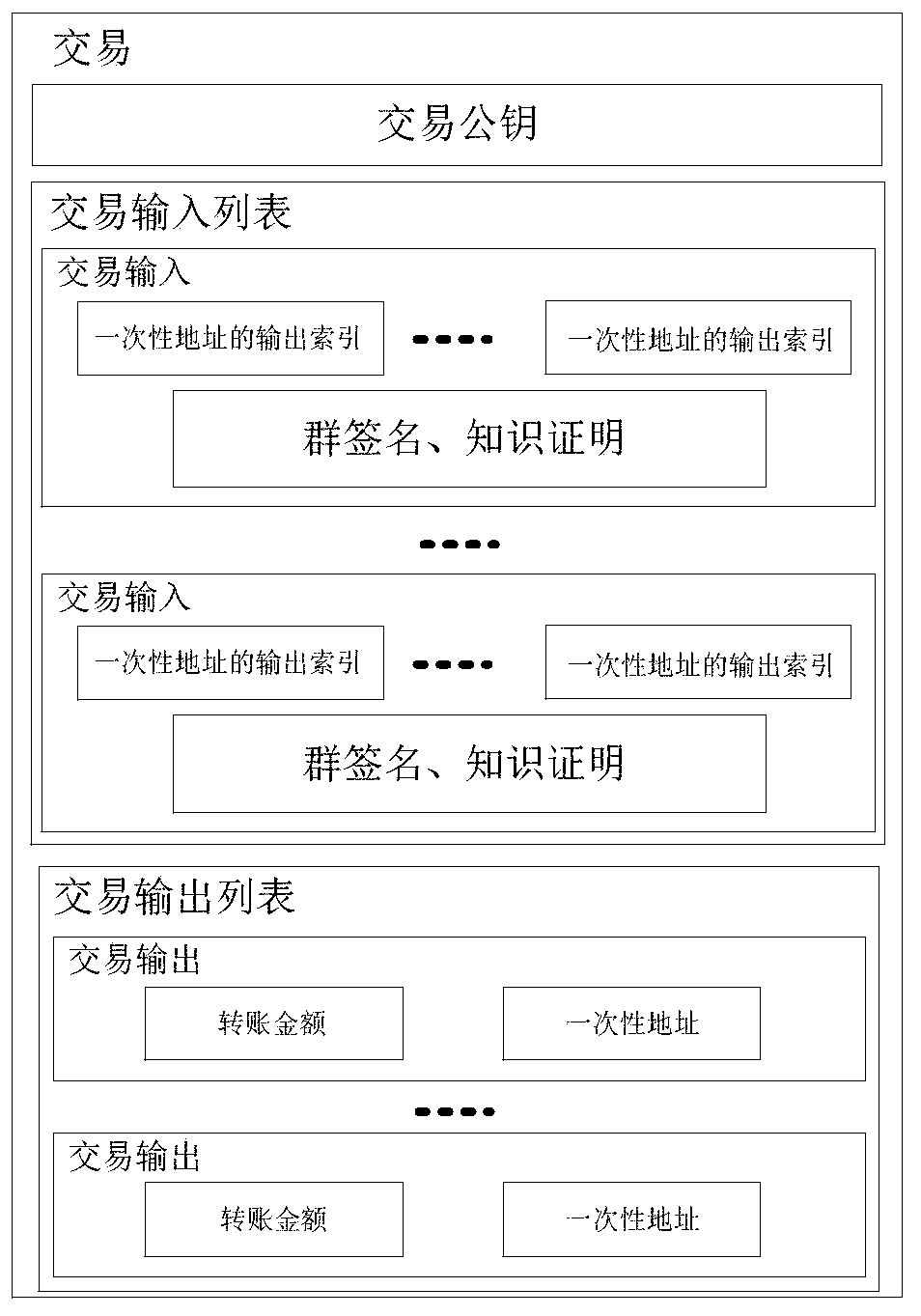
ActiveCN111010280AEnsure safetyPrevent double spendingKey distribution for secure communicationFinanceUser needsSoftware engineering
The invention provides a supervisable blockchain construction method based on group signature. A group administrator, a blockchain user and a blockchain verification node are included, wherein the blockchain user needs to register to the group administrator to obtain a user private key; a group signature is generated by using the user private key, and a knowledge proof is generated by using a local secret number; and the blockchain verification node verifies the group signature by using the group public key and verifies the knowledge proof in the transaction, thereby ensuring that the transactions of all blockchains are generated by registered users, preventing the users from being blurred, and enabling a group administrator to recover the identities of the users through the group privatekey and the group signature to realize supervision. According to the method, the traceability, the non-linkability and the supervisibility of user transaction can be realized at the same time, the supervisibility problem of the blockchain is solved, the method is directly applied to the blockchain adopting a UTXO mode, and the supervisibility is provided by performing adaptive transformation on the block chain.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Block chain-based data storage proving method and device, equipment and storage medium
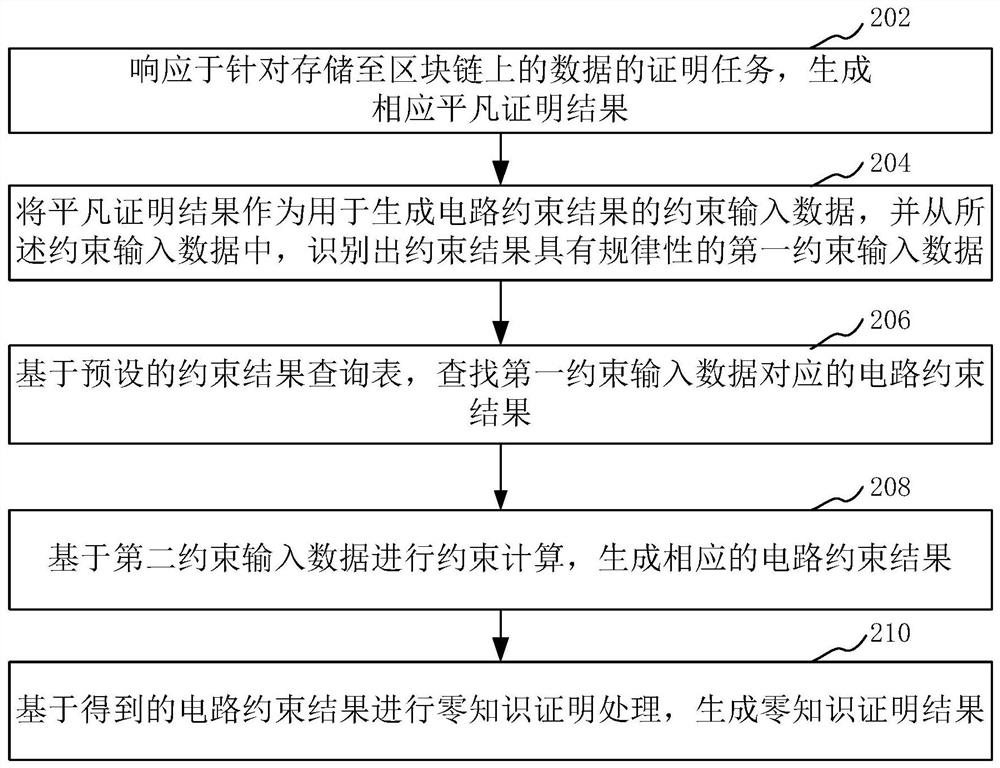
ActiveCN113177225AAvoid Complicated Constraint CalculationsSave resourcesRelational databasesDigital data protectionAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a block chain-based data storage proving method and device, equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of generating a corresponding trivial certification result in response to a certification task for data stored on a block chain; taking the trivial proof result as constraint input data used for generating a circuit constraint result, and identifying first constraint input data of which the constraint result has regularity from the constraint input data; based on a preset constraint result query table, searching a circuit constraint result corresponding to the first constraint input data; performing constraint calculation based on the second constraint input data to generate a corresponding circuit constraint result, wherein the second constraint input data is the constraint input data except the first constraint input data in the constraint input data; and performing zero-knowledge proof processing based on the obtained circuit constraint result to generate a zero-knowledge proof result. The scheme can save system resources and improve efficiency.
Owner:深圳市名竹科技有限公司
Blockchain node data safety interaction method and first interaction node
PendingCN111429138AProtect transaction privacyGuaranteed legalityDigital data protectionPayment protocolsCiphertextInternet privacy
According to the blockchain node data safety interaction method and the first interaction node provided by the invention, the transaction information is encrypted by using the homomorphic encryption technology, the blockchain account book only stores the ciphertext, and the transaction information is invisible to a non-transaction participant on the chain, so that the transaction privacy of the user is effectively protected; in the prior art, homomorphic encrypted transaction information cannot be verified whether to be legal or not, a zero knowledge proof technology is used for performing range proof on the transaction amount in an invisible state of the transaction amount, each node of the block chain network can participate in verification after receiving broadcast transaction, and theservice legality and public verifiability of the transaction are ensured.
Owner:INDUSTRIAL AND COMMERCIAL BANK OF CHINA
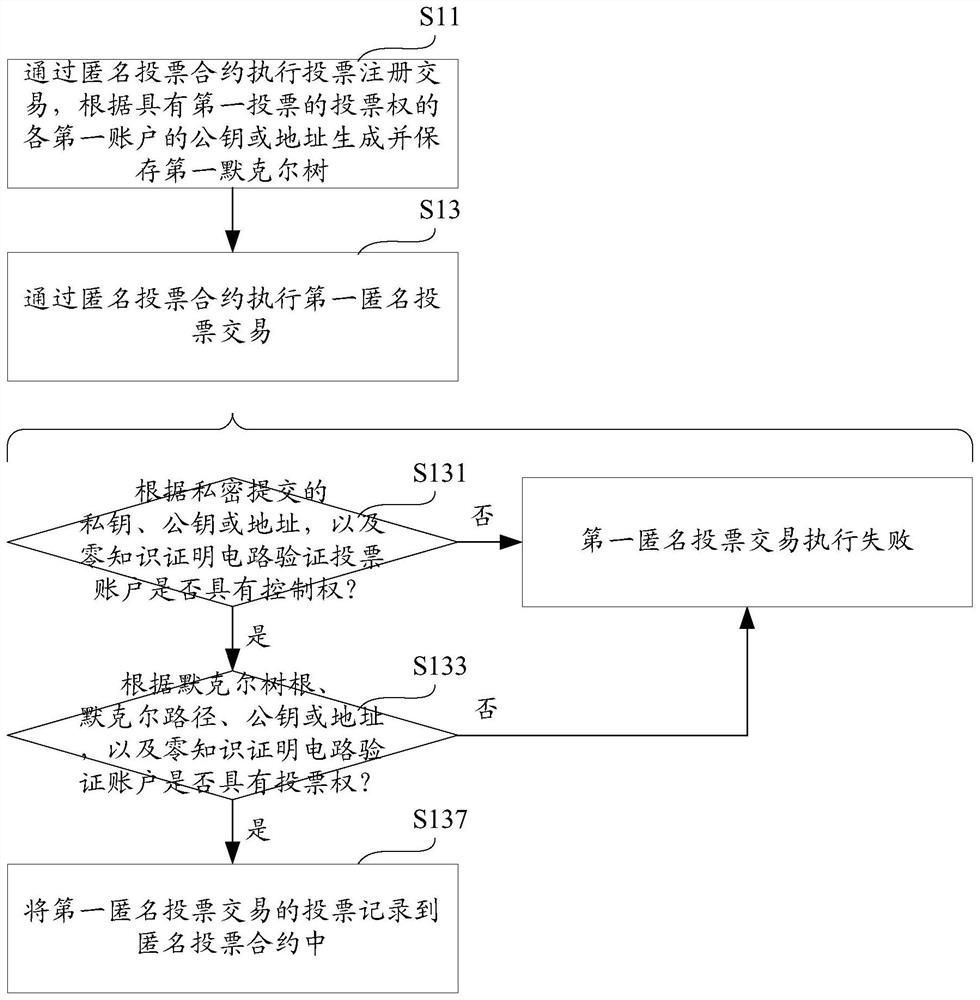
Blockchain anonymous voting method, computer equipment and storage medium
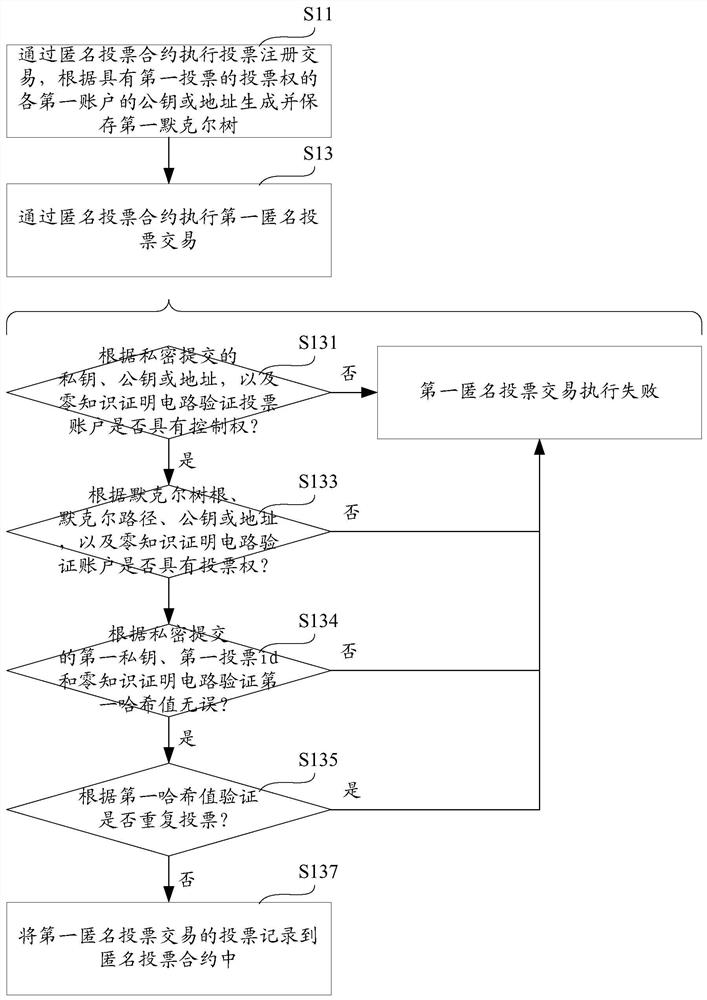
ActiveCN112968881ARealization of anonymous votingSolve the problem that different votes are difficult to distinguishUser identity/authority verificationCommunication with homomorphic encryptionPathPingEngineering
The invention provides a blockchain anonymous voting method, computer equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: executing a voting registration transaction, and generating and storing a first Merkel tree according to a first public key or a first address of each first account with the voting right of a first vote; executing the first anonymous voting transaction: according to a first private key submitted privately, a first public key submitted privately or a first address submitted privately, and a zero-knowledge proof circuit, verifying whether a second account of anonymous voting has the control right of the first address: if not, determining that the execution of the first anonymous voting transaction fails; according to a first Merkel tree root of public submission, a first Merkel path of private submission, a first public key or a first address of private submission, and a zero-knowledge proof circuit, verifying whether the second account has the voting right of the first voting: if not, determining that the execution of the first anonymous voting transaction fails; if yes, recording votes of the first anonymous voting transaction into the contract. According to the invention, anonymous voting on the blockchain is realized.
Owner:HANGZHOU FUZAMEI TECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for anonymous cryptocurrency transactions
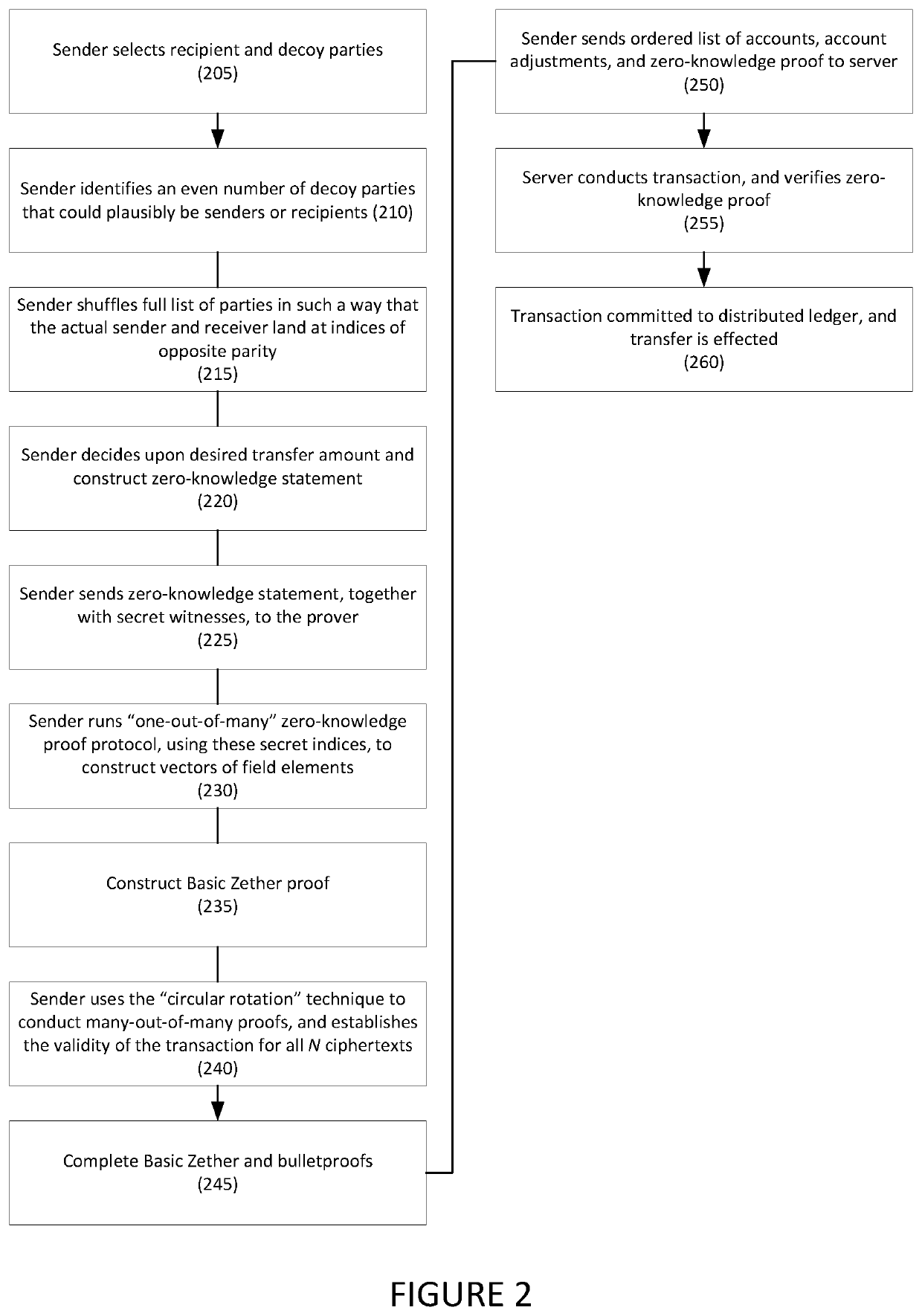
ActiveUS20200342452A1User identity/authority verificationAnonymous user systemsPaymentComputer network
Systems and methods for anonymous cryptocurrency transactions are disclosed. A method may include: receiving, from the electronic device associated with a sender of a cryptocurrency transaction, a zero-knowledge statement comprising a shuffled and anonymized list of participants comprising the sender, a receiver of the cryptocurrency transaction, and a plurality of decoy participants, a transfer amount, and a remaining balance, and a secret witness, wherein each participant is associated with an index; generating one-out-of-many proofs for the sender and the receiver based on their associated indices; generating a Basic Zether proof for the transfer amount and the remaining balance; conducting many-out-of-many proofs with parameters chosen for an anonymous payment setting; and constructing a zero-knowledge proof for the zero-knowledge statement. The sender sends an ordered list of the participants and the zero-knowledge proof to a verifier using the FiatShamir transform, and the verifier verifies the zero-knowledge proof.
Owner:CONSENSYS SOFTWARE INC
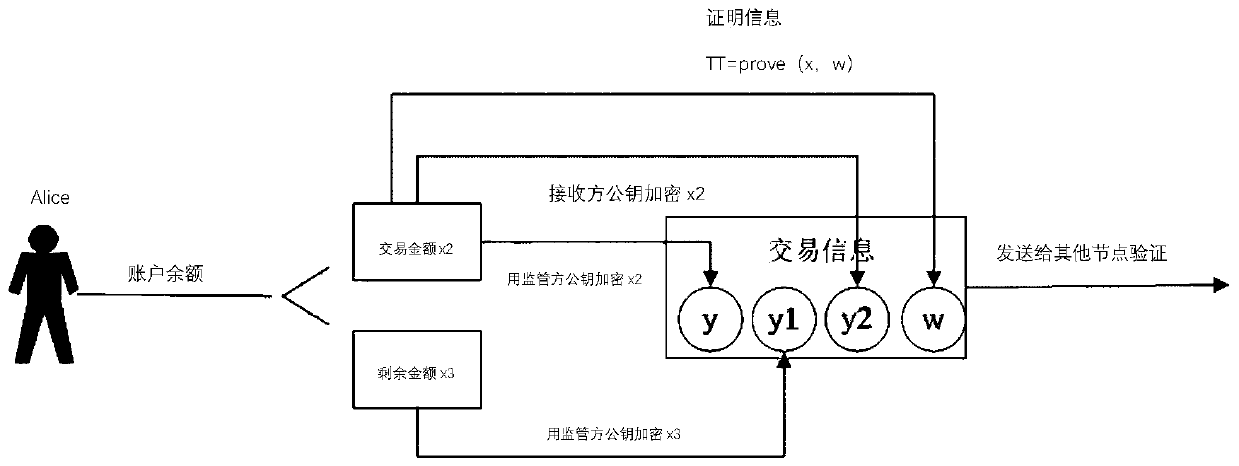
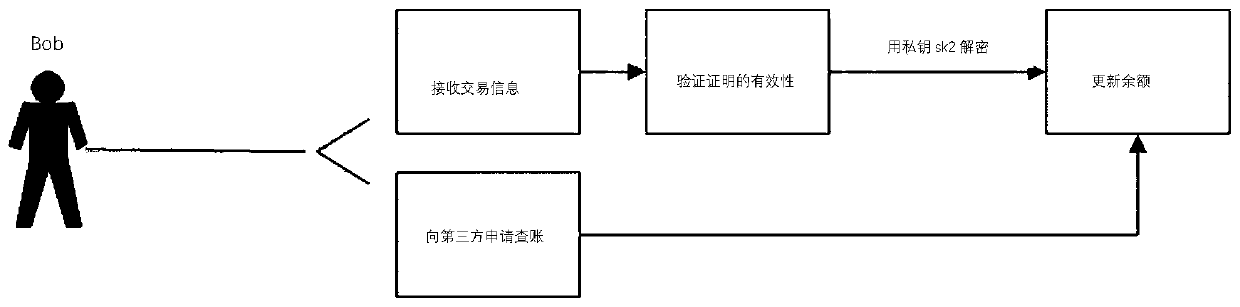
Privacy transaction method and device, zero knowledge proof system and privacy transaction architecture model
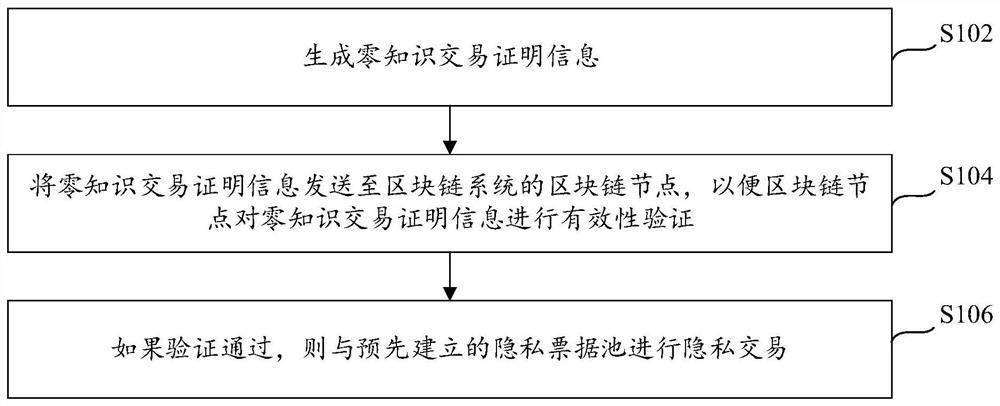
ActiveCN112288434ALow costReduce costs (such as time costsPayment protocolsInternet privacyEngineering
The invention provides a private transaction method and device, a zero-knowledge proof system and a private transaction architecture model, relates to the technical field of block chains, and is applied to a private transaction method of a client, and the method comprises the steps: generating zero-knowledge transaction proof information; wherein the zero-knowledge transaction certification information comprises certification parameters of a user account encrypted by a public key of a supervisor; wherein the certification parameters comprise a current private bill of the user account, a to-be-transacted private bill and an updated private bill; uploading the zero-knowledge transaction proof information to a blockchain node of a blockchain system, so that the blockchain node performs validity verification on the zero-knowledge transaction proof information; if the verification is passed, carrying out private transaction with a pre-established private bill pool; the private bill pool isused for storing private bills to be transacted. According to the invention, the bill management cost is reduced, higher safety guarantee can be provided during transaction, and the legality and compliance of the transaction are guaranteed.
Owner:NETEASE (HANGZHOU) NETWORK CO LTD
Power data uploading system and method based on zero-knowledge proof
PendingCN113660092ASolve storageSolve the problem of data credibilityUser identity/authority verificationOriginal dataSoftware engineering
The invention relates to a power data uploading system and method based on zero knowledge proof. The system comprises a plurality of power utilization unit modules, a plurality of block chain side chains and a block chain main chain; the plurality of power utilization unit modules are respectively connected with the block chain main chain through the corresponding block chain side chains; the power utilization unit module is used for collecting power utilization original data and uploading the original data and a signature to the block chain side chain, and the block chain side chain is used for processing the received original data to obtain statistics / description of the data, generating a zero-knowledge proof, and uploading the statistics / description and the zero-knowledge proof of the data to a block chain main chain; and the block chain main chain is used for receiving the statistics / description of the data and the zero-knowledge proof, verifying the correctness of the zero-knowledge proof through the smart contract, and archiving, recording and displaying the zero-knowledge proof if the verification is passed. According to the invention, the problem of expanding the block chain storage capability and the data credibility in the energy data uploading process can be solved.
Owner:STATE GRID TIANJIN ELECTRIC POWER +1
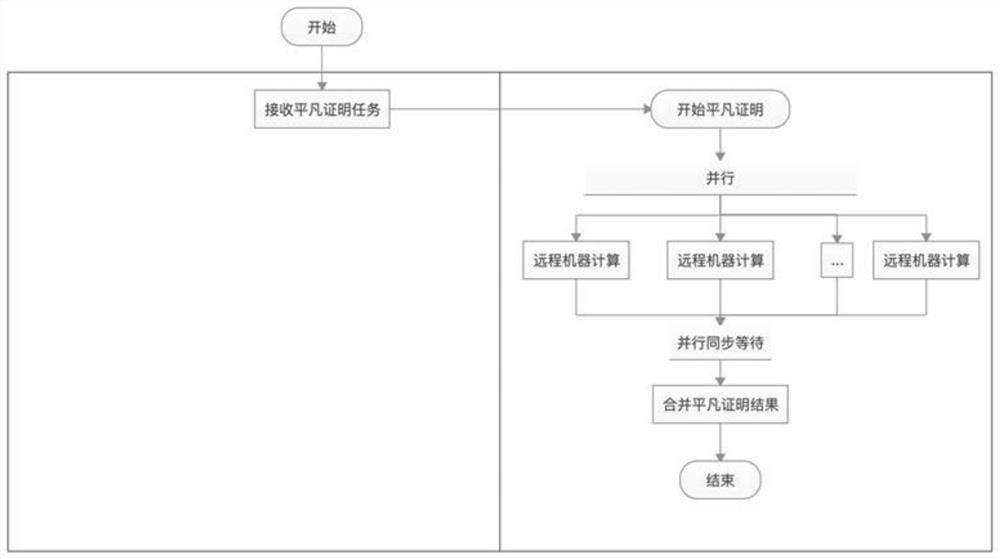
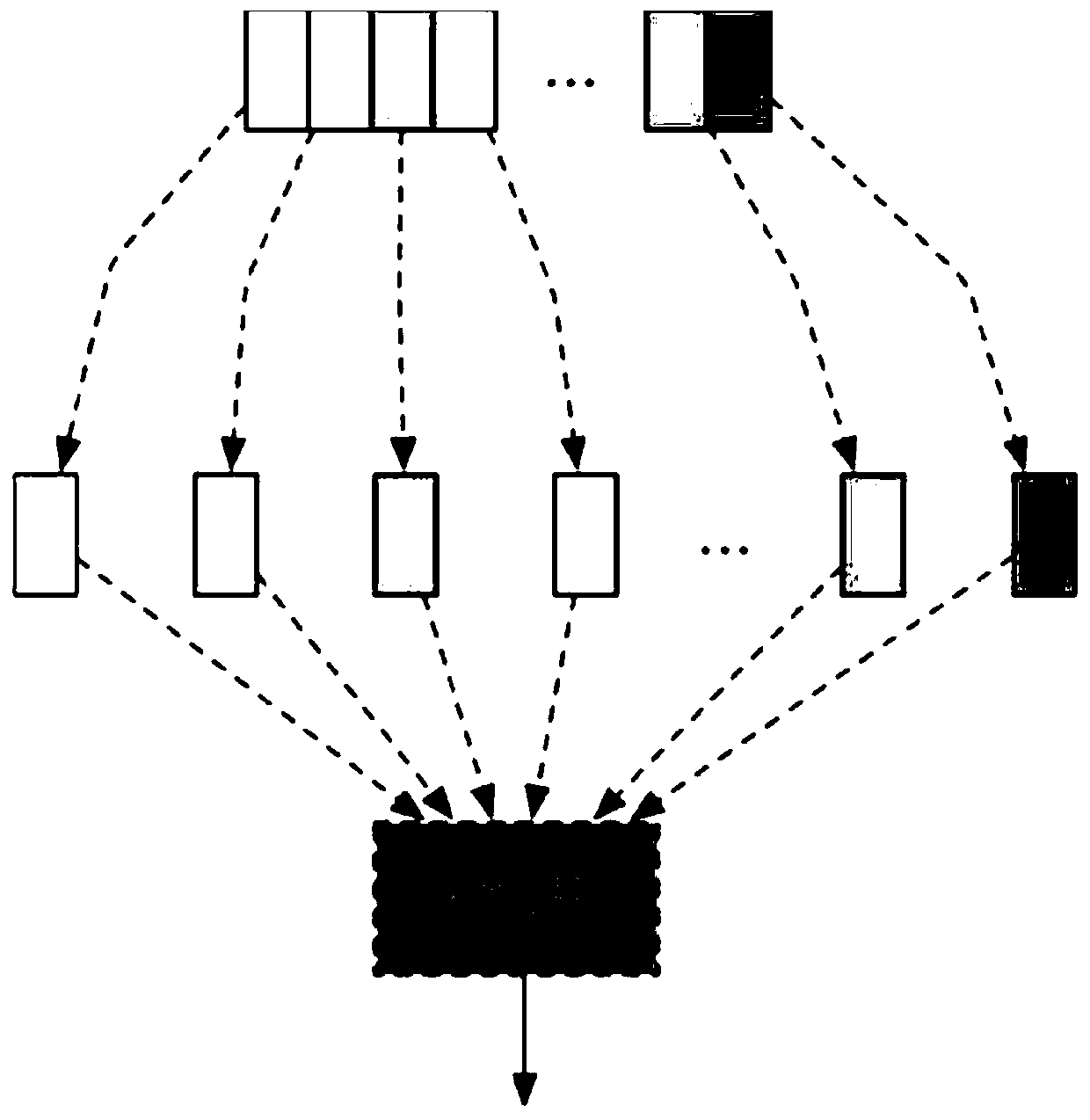
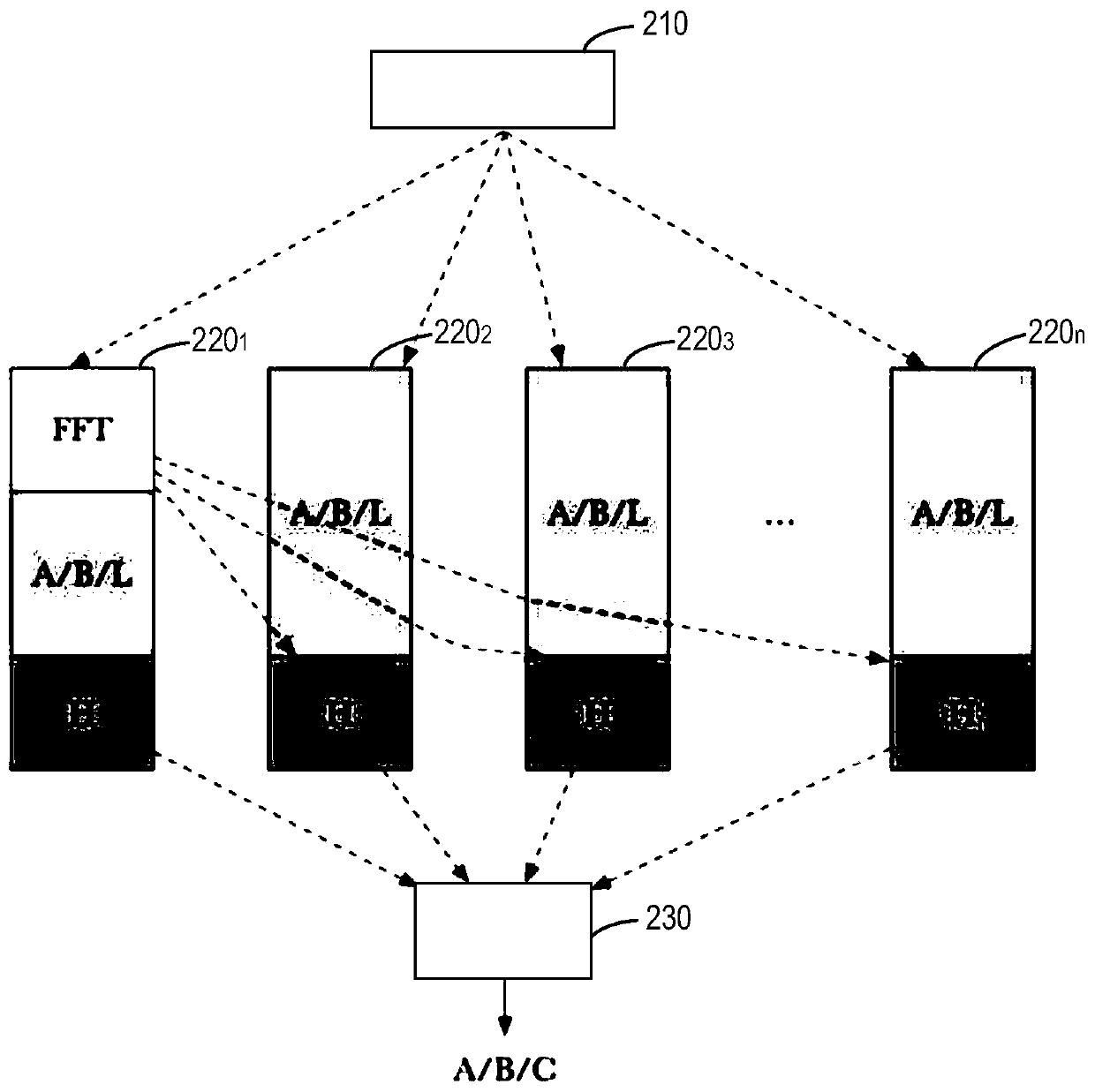
Method and device for obtaining zero knowledge proof based on distributed processing, medium and system
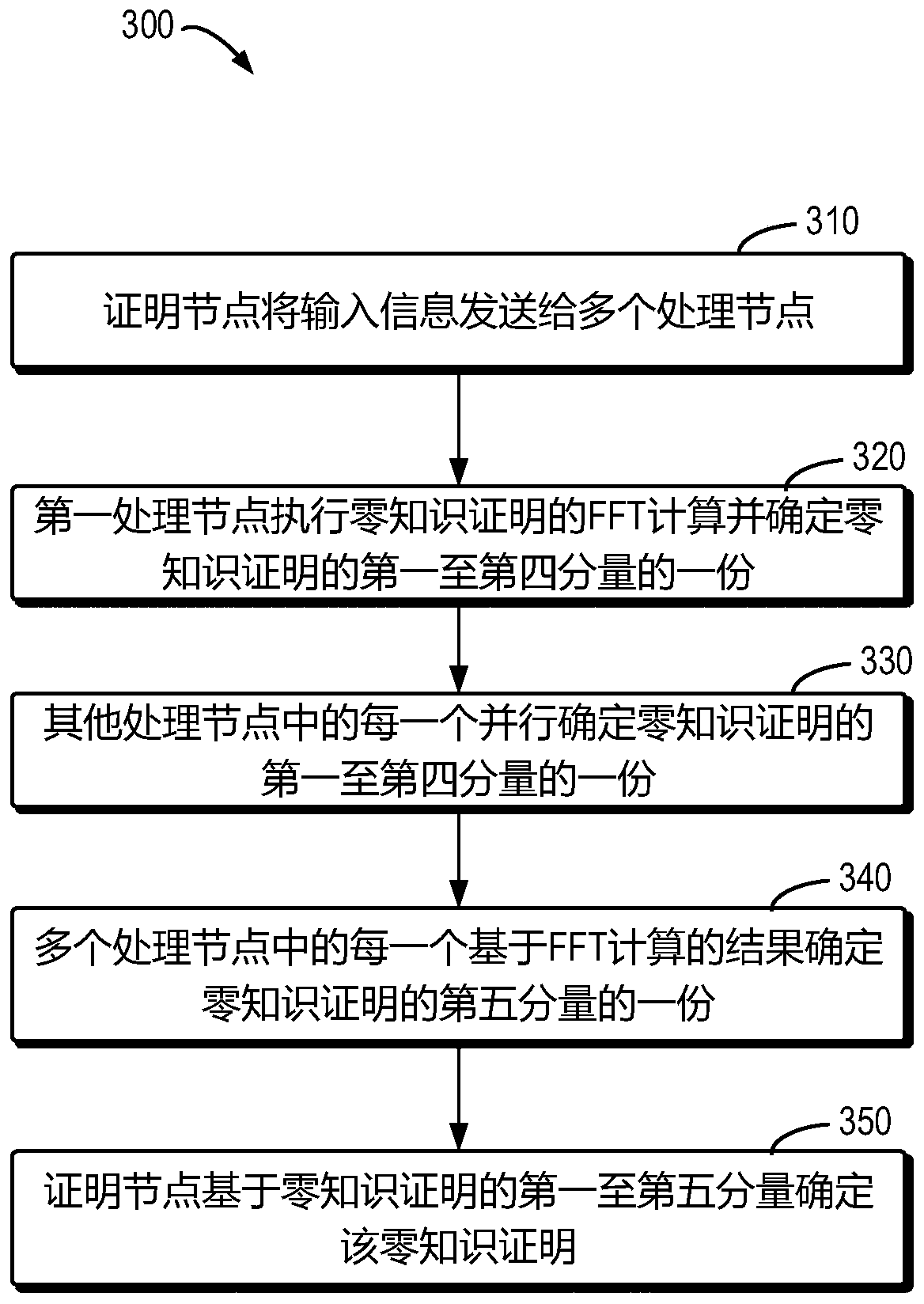
The invention provides a method and device for obtaining a zero knowledge proof based on distributed processing, a computer readable storage medium and a system for storing data in a blockchain. The method comprises the following steps: a proof node sends input information to a plurality of processing nodes; the first processing node performs FFT calculation of zero knowledge proof based on the input information, and determines one of the first to fourth components of the zero knowledge proof; other processing nodes except the first node in the plurality of processing nodes determine one of the first to fourth components of the zero knowledge proof in parallel; each of the plurality of processing nodes determines one part of a fifth component of the zero knowledge proof based on a result of the FFT calculation; and the proof node determines the first to fifth components based on the respective parts of the first to fifth components of the zero knowledge proof of the plurality of processing nodes, thereby obtaining the zero knowledge proof.
Owner:上海致居信息科技有限公司
Zero-knowledge proof method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN113569294AEnsure safetyBroad application spaceDigital data processing detailsDigital data protectionThird partyNon-interactive zero-knowledge proof
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Block chain zero-knowledge proving anonymous certificate verification method and system based on DID identity
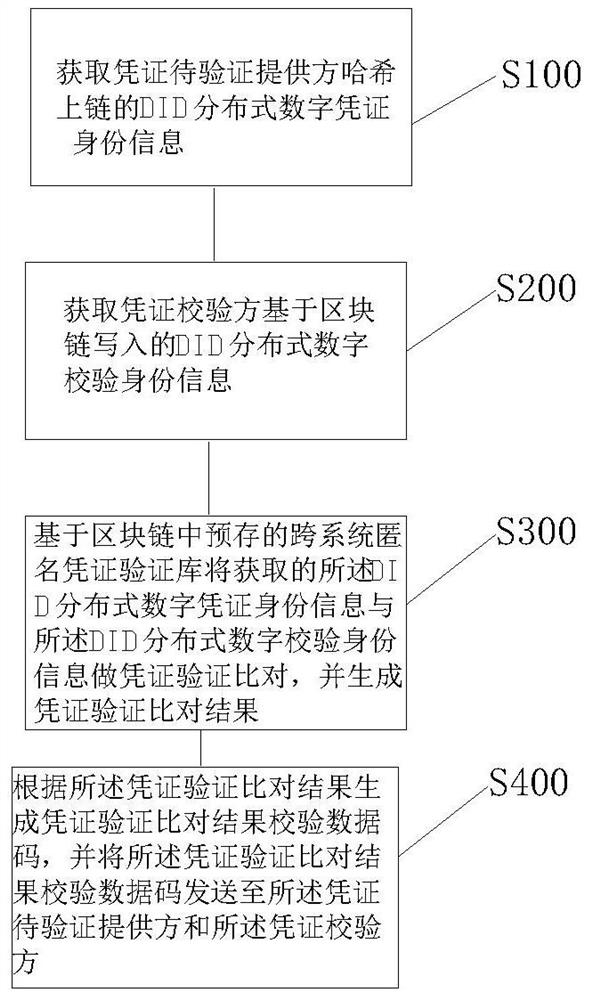
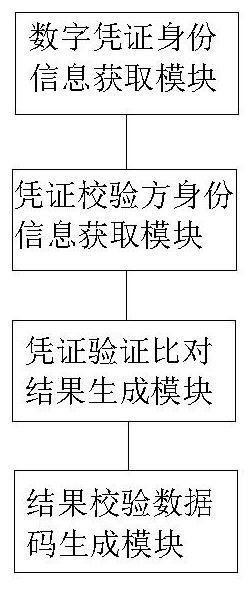
ActiveCN113037493ASolving Data Consistency IssuesRealize data sharingUser identity/authority verificationEnergy efficient computingComputer networkTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a DID identity-based block chain zero-knowledge proof anonymous certificate verification method and system. The method comprises the steps of obtaining DID distributed digital certificate identity information of a certificate to-be-verified provider in a Hash chain; obtaining DID distributed digital verification identity information written by a certificate verification party based on the block chain; then, on the basis of a cross-system anonymous certificate verification library pre-stored in a block chain, carrying out certificate verification comparison on the acquired DID distributed digital certificate identity information and the DID distributed digital verification identity information, and generating a certificate verification comparison result; finally, according to the voucher verification comparison result, generating a voucher verification comparison result verification data code, and sending the voucher verification comparison result verification data code to the voucher to-be-verified provider and the voucher verification party. According to the method, the problem of data consistency of a distributed system in the prior art is solved, the personal identification information is protected, and tampering is prevented.
Owner:上海泰砥科技有限公司
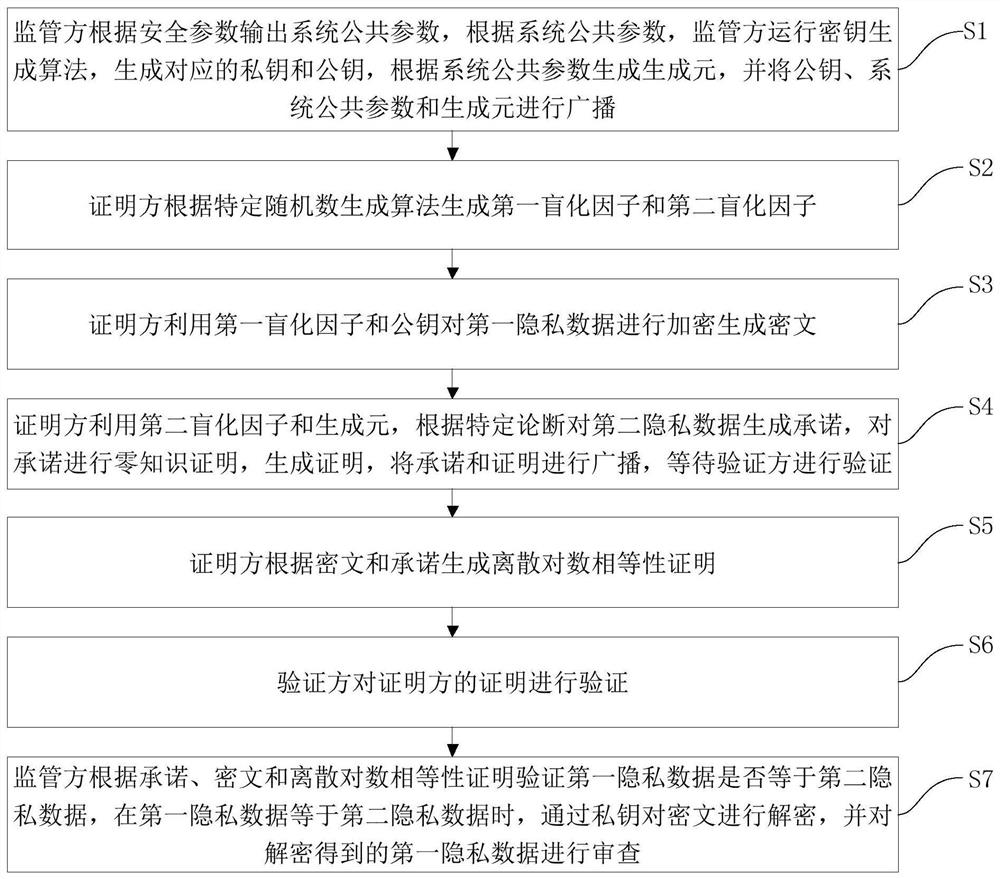
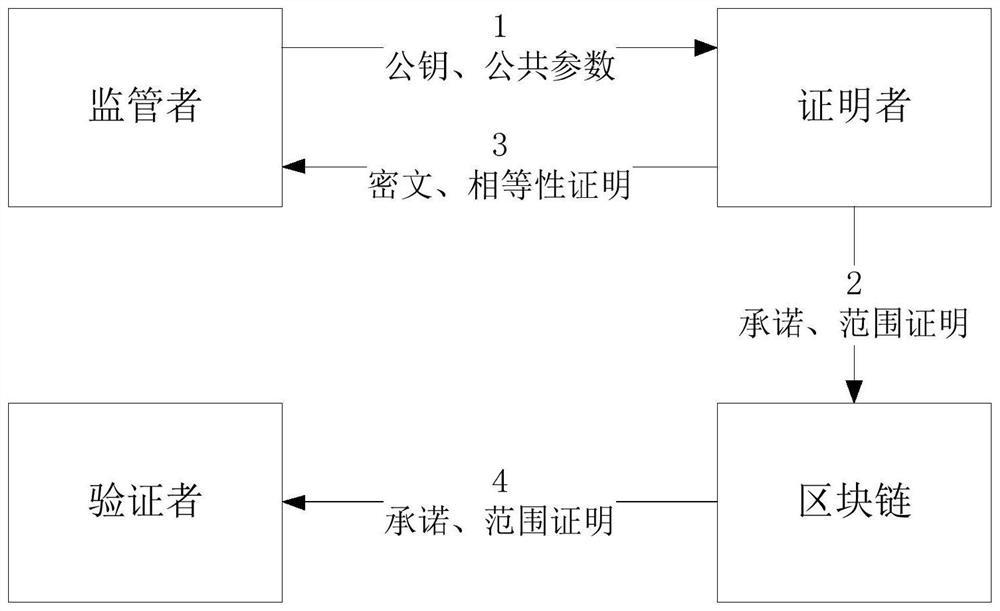
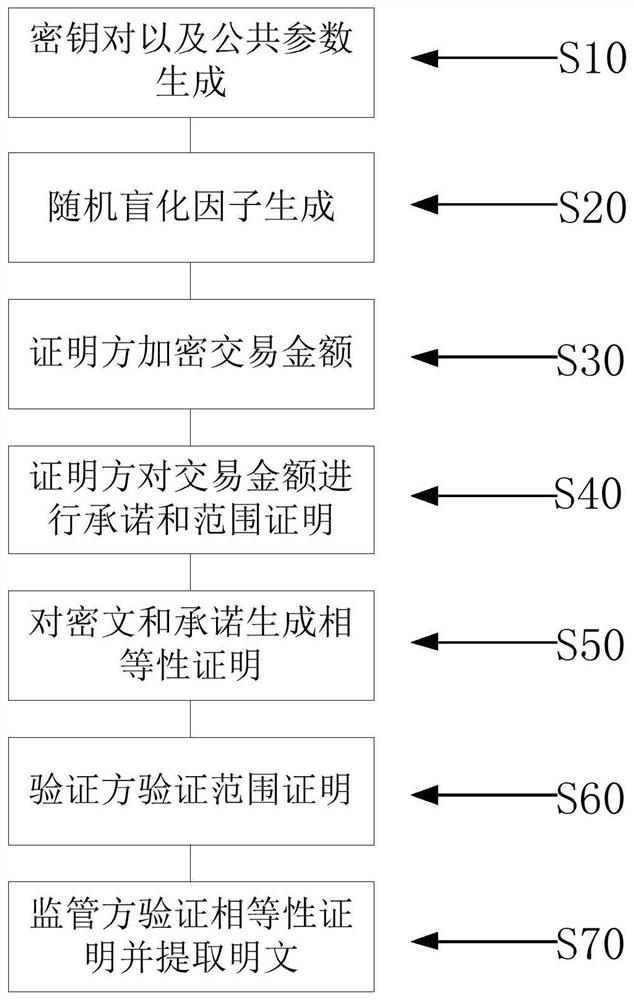
Supervisable zero-knowledge proof method and device based on discrete logarithm equality proof
The invention discloses a supervisable zero-knowledge proof method and device based on discrete logarithm equality proof, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a public parameter of a supervisable zero-knowledge proof system, a public key and a private key for data encryption and extraction, and a committed generator, and disclosing the public parameter, the public key and the generator; enabling the proving party to encrypt the private data; enabling the proving party to perform commitment and zero-knowledge proving on the private data; enabling the proving party to generate discrete logarithm equality proving for the ciphertext and the commitment; enabling the proving party to send the commitment and zero knowledge proof broadcast, the ciphertext and the equality proof to the supervising party; enabling the verification party to verify the zero-knowledge proof and verifies the validity of the data; enabling the supervisor to verify the discrete logarithm equality proof and judge whether the data encrypted by the proof party is uplink data or not; and enabling the supervisor to extract the data in the ciphertext according to the equality proof verification result and audits the data. According to the method, an efficient supervision scheme without interaction is constructed by adopting asymmetric encryption, and the supervision requirement of a supervisor is met in a scene of protecting data privacy by using zero knowledge proof.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com