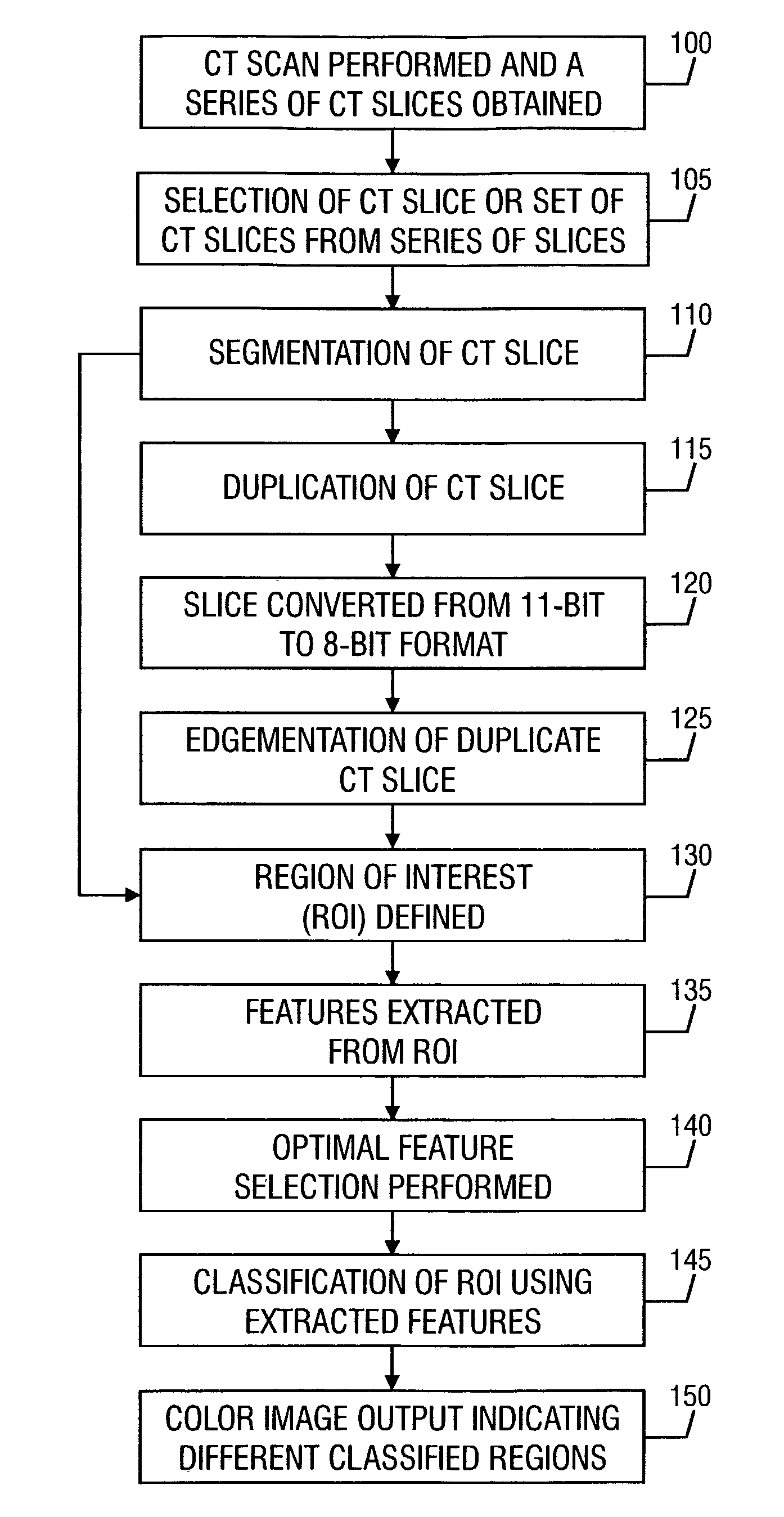
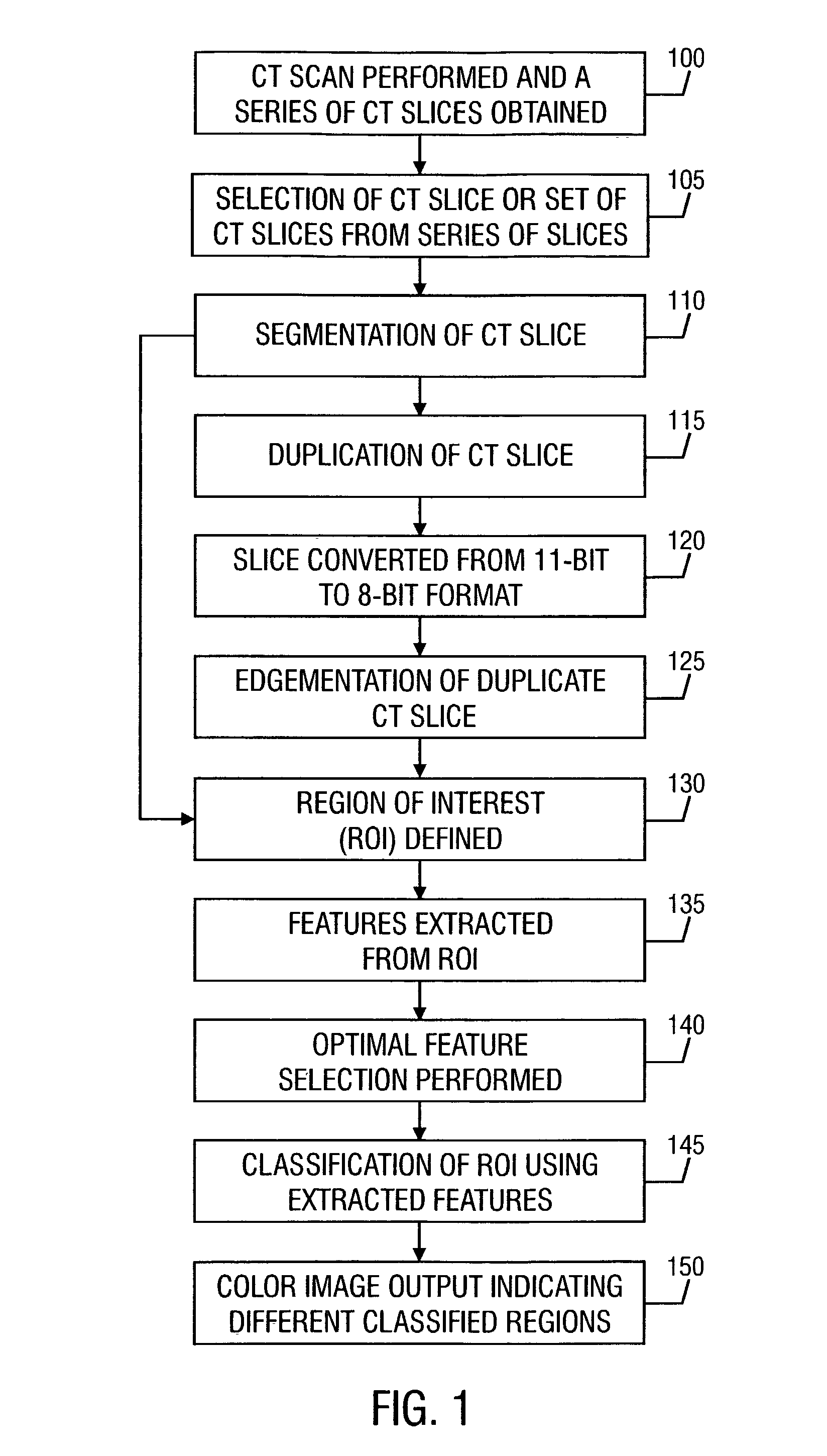
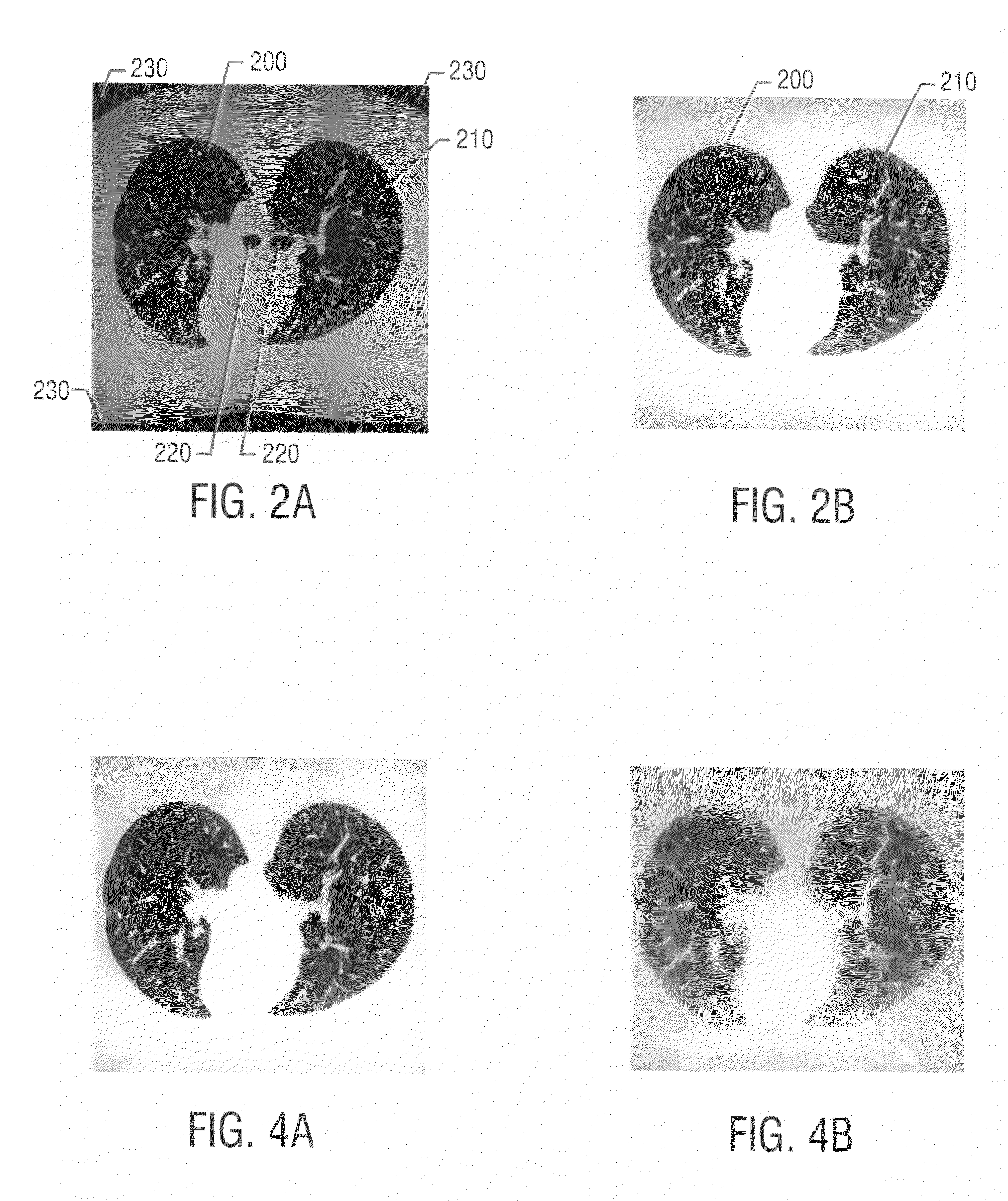
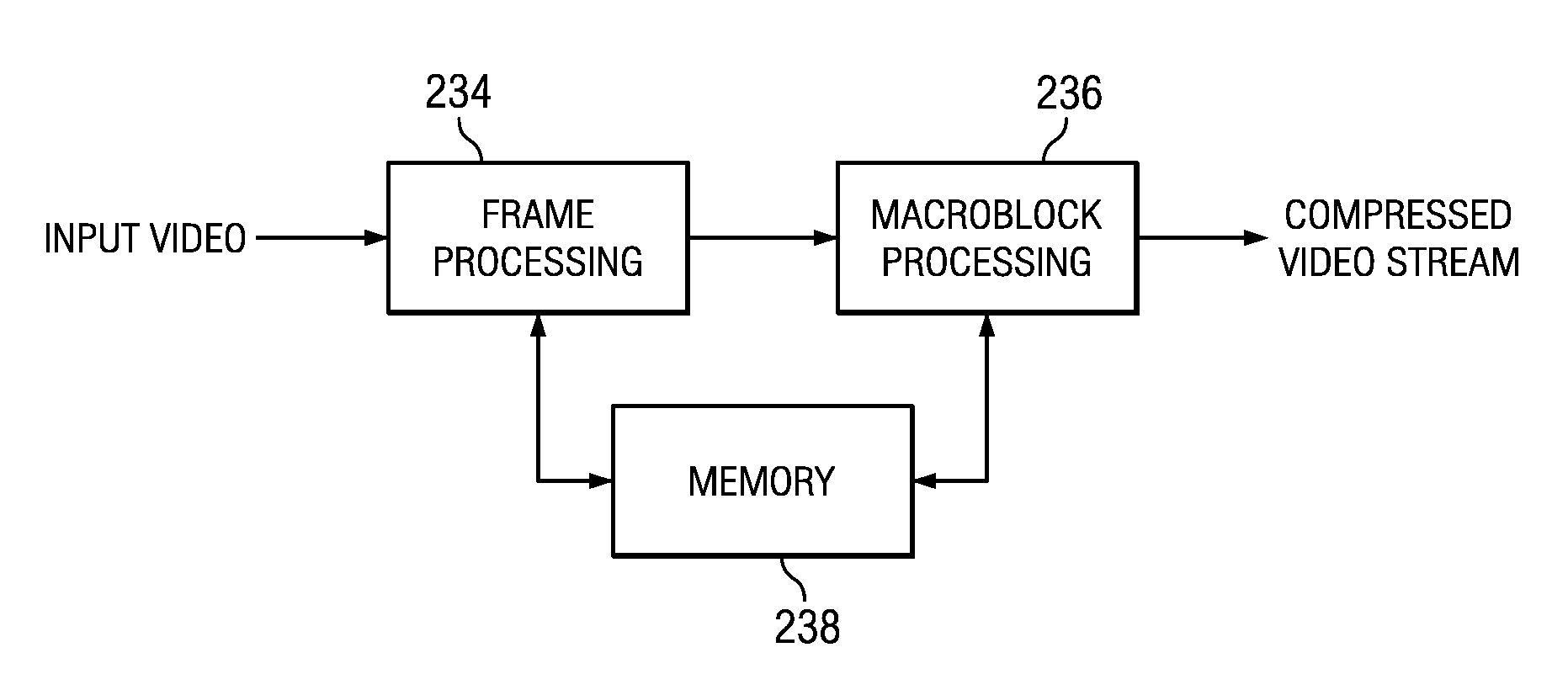
Patents
Literature
76 results about "Texture measure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
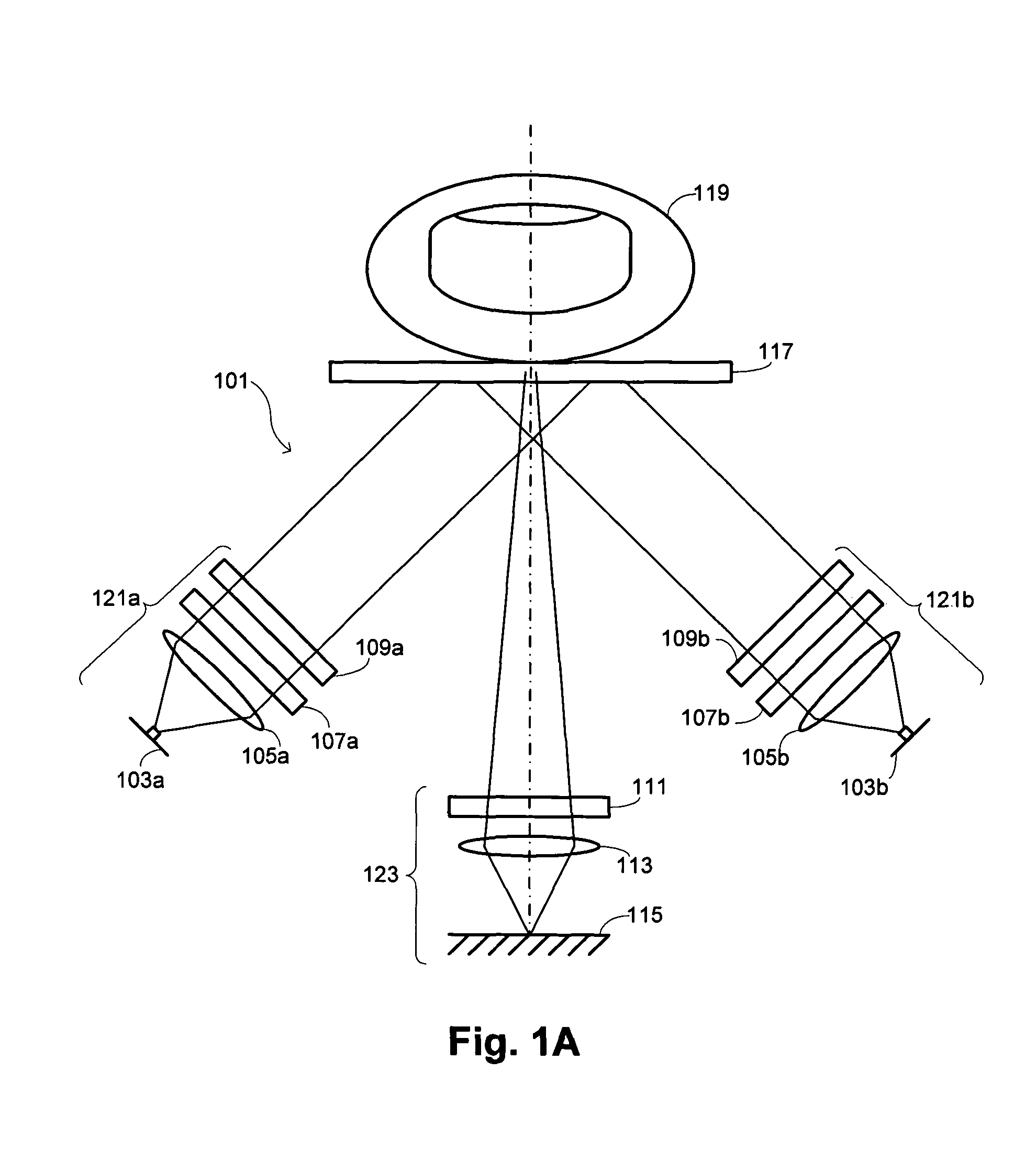
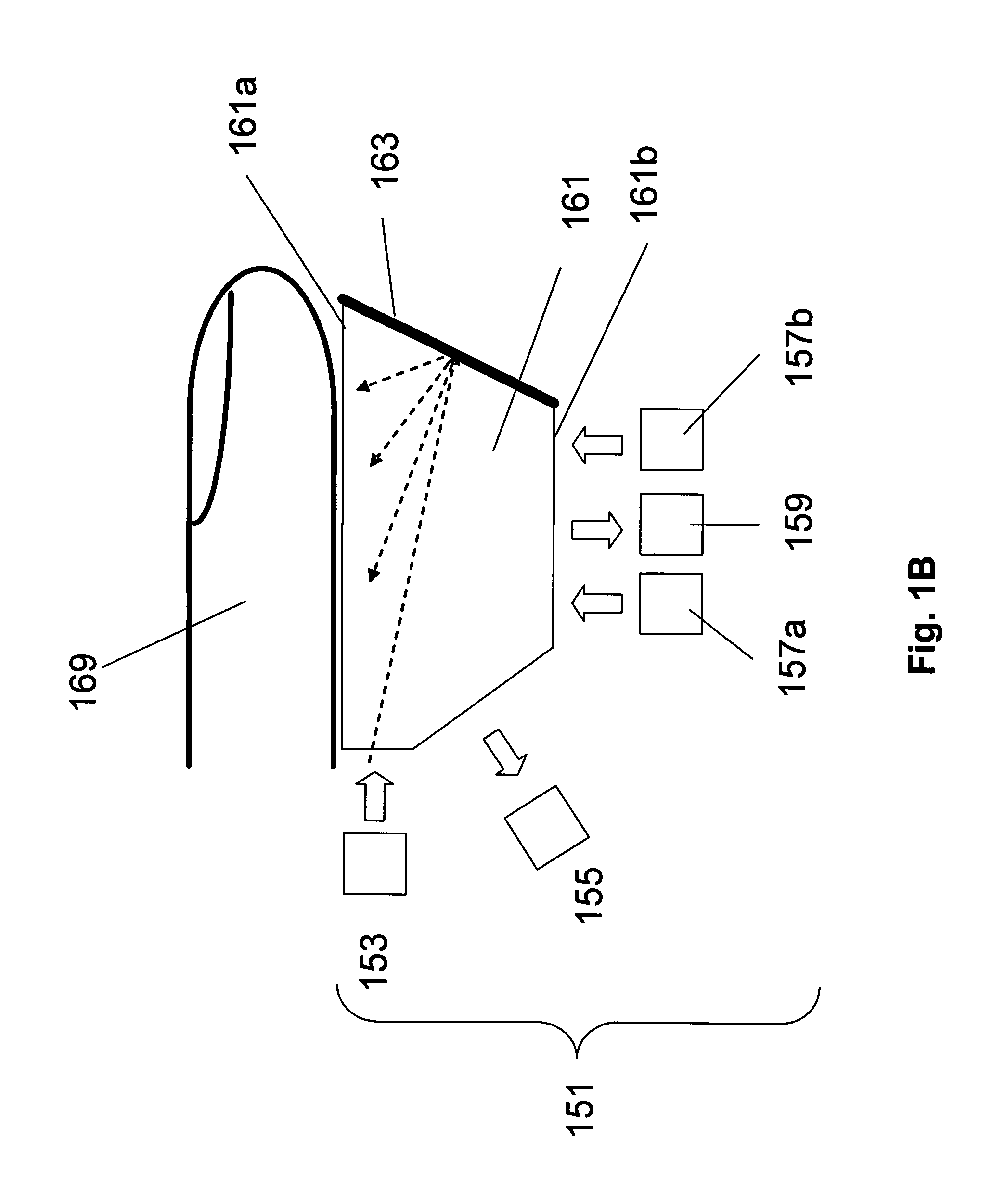
Comparative texture analysis of tissue for biometric spoof detection
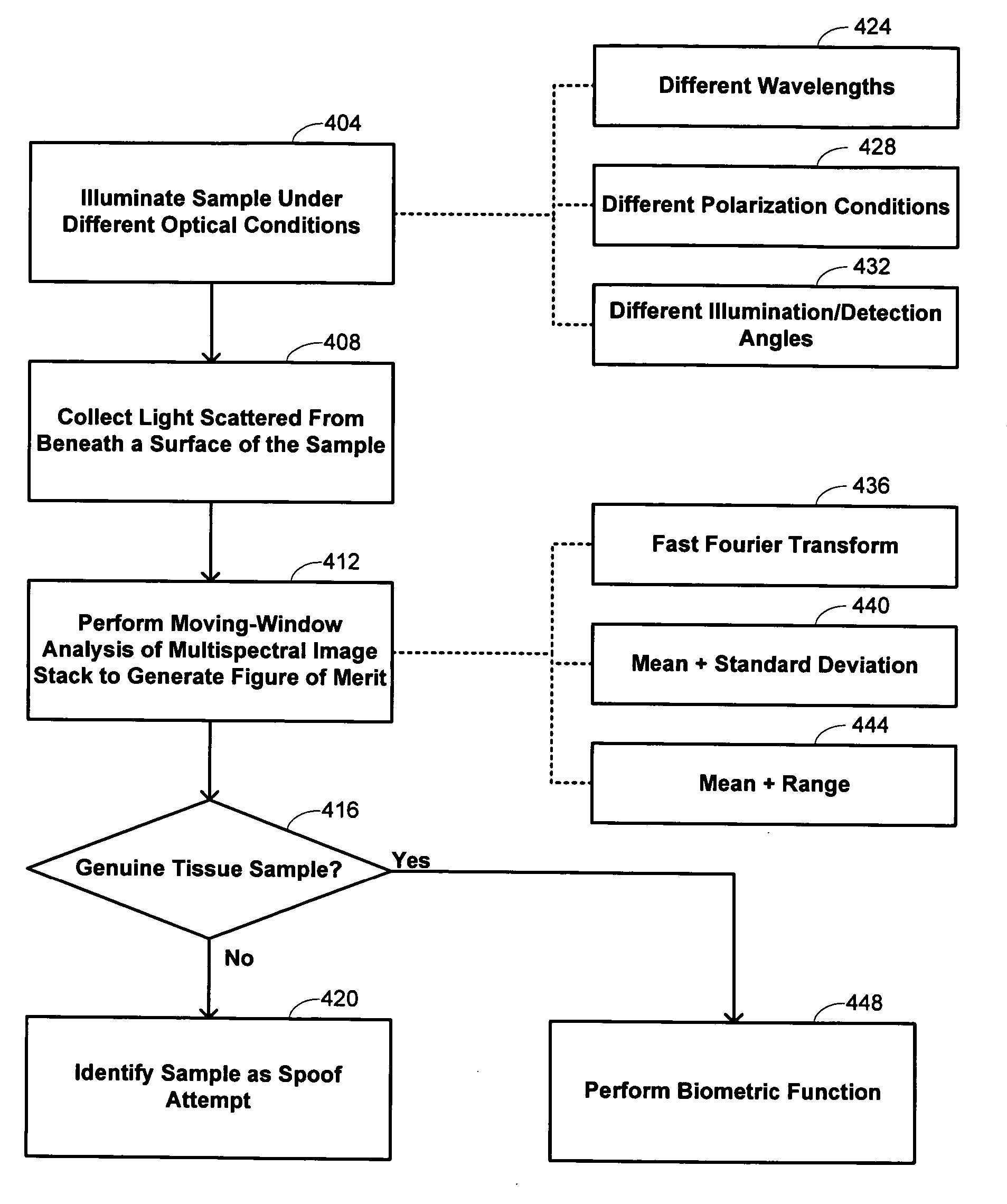
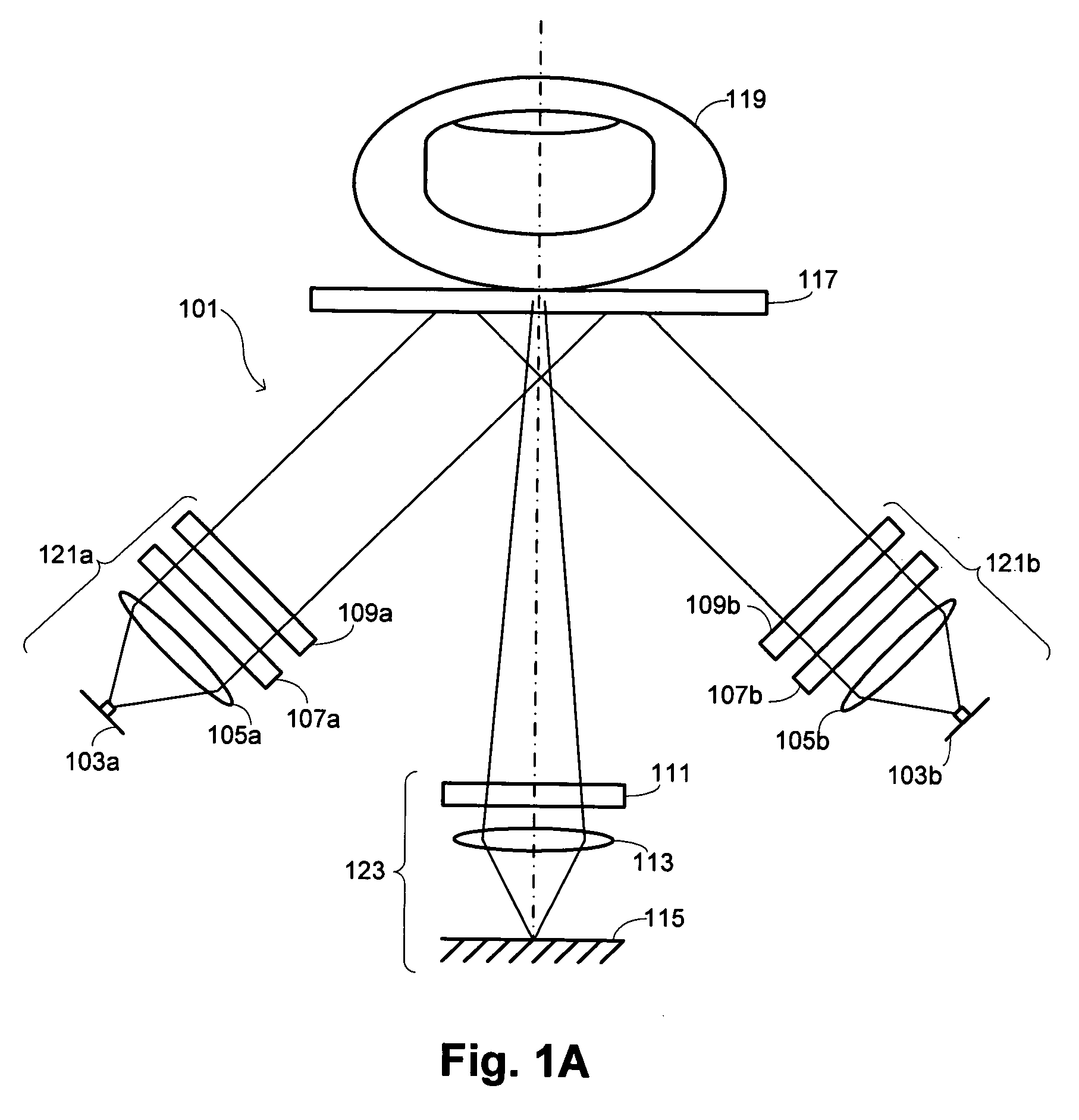
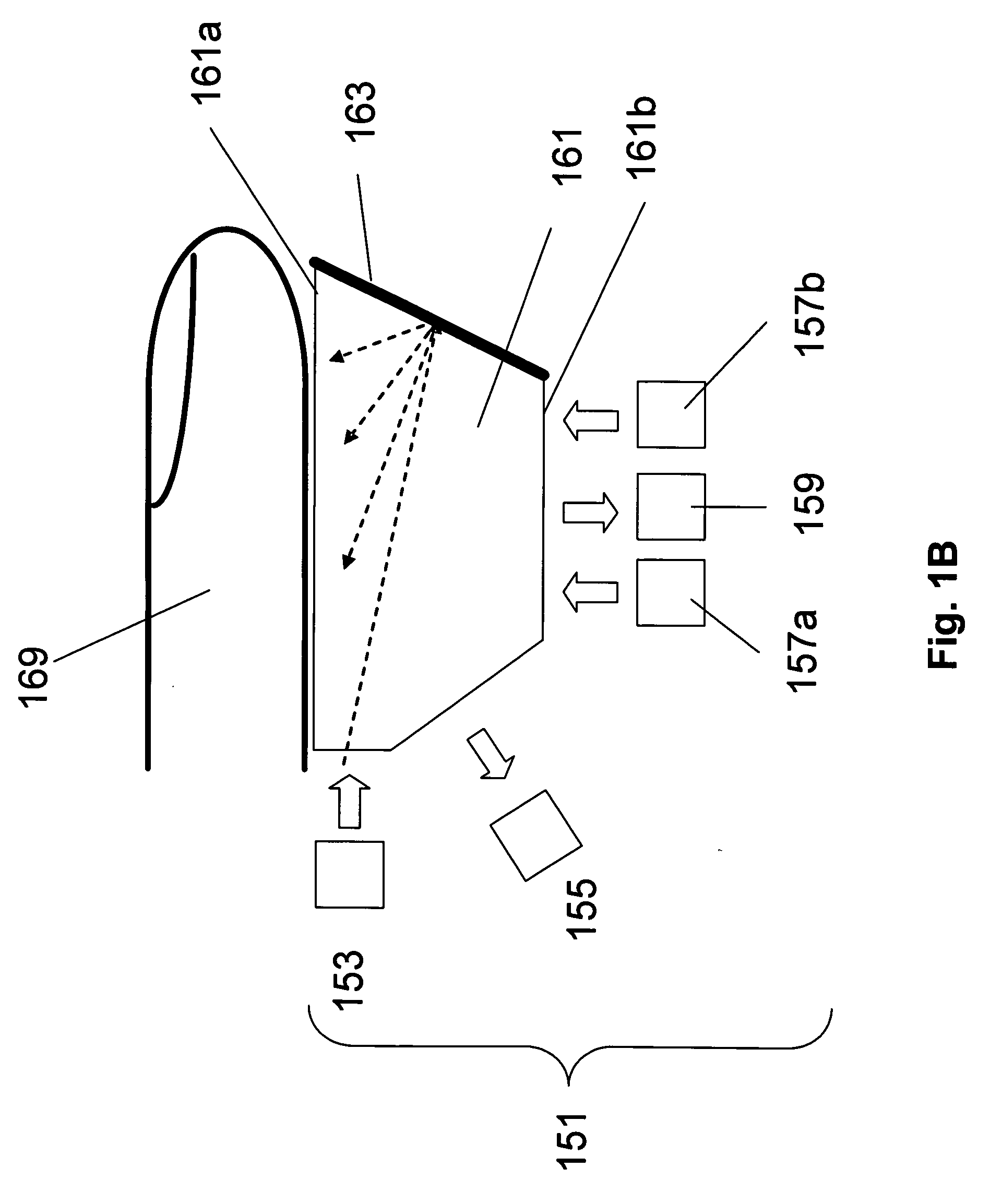
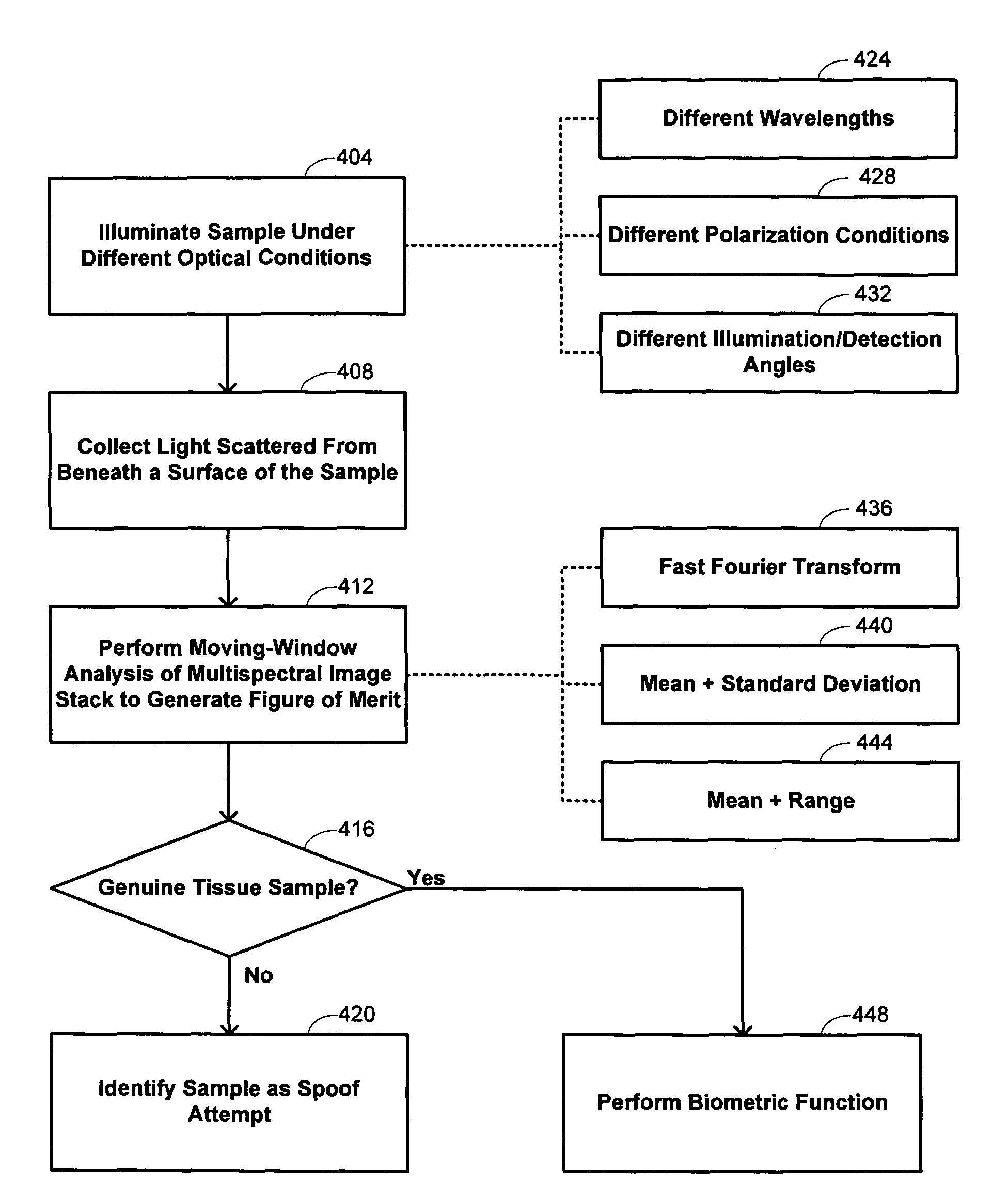
Methods are described of evaluating the genuineness of a sample presented for biometric evaluation. The sample is illuminated under distinct optical conditions. Light scattered from the sample is received. Multiple images are formed, each image being formed from the received light for one of the optical conditions. A set of texture measures is generated, each texture measure being generated from one of the images. It is determined whether the generated texture measures is consistent with the sample being authentic unconcealed biological tissue.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
Comparative texture analysis of tissue for biometric spoof detection
Methods are described of evaluating the genuineness of a sample presented for biometric evaluation. The sample is illuminated under distinct optical conditions. Light scattered from the sample is received. Multiple images are formed, each image being formed from the received light for one of the optical conditions. A set of texture measures is generated, each texture measure being generated from one of the images. It is determined whether the generated texture measures is consistent with the sample being authentic unconcealed biological tissue.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
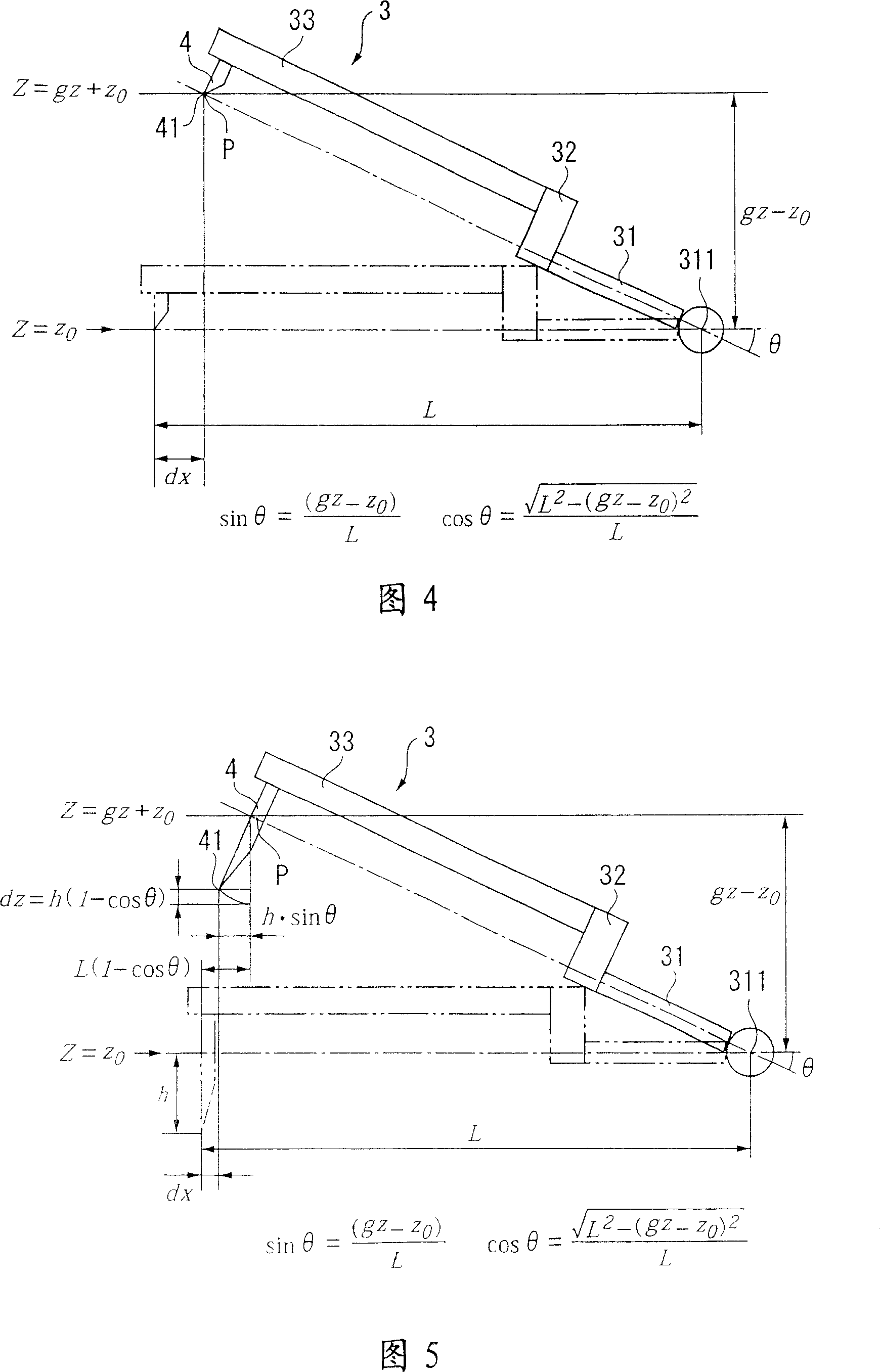
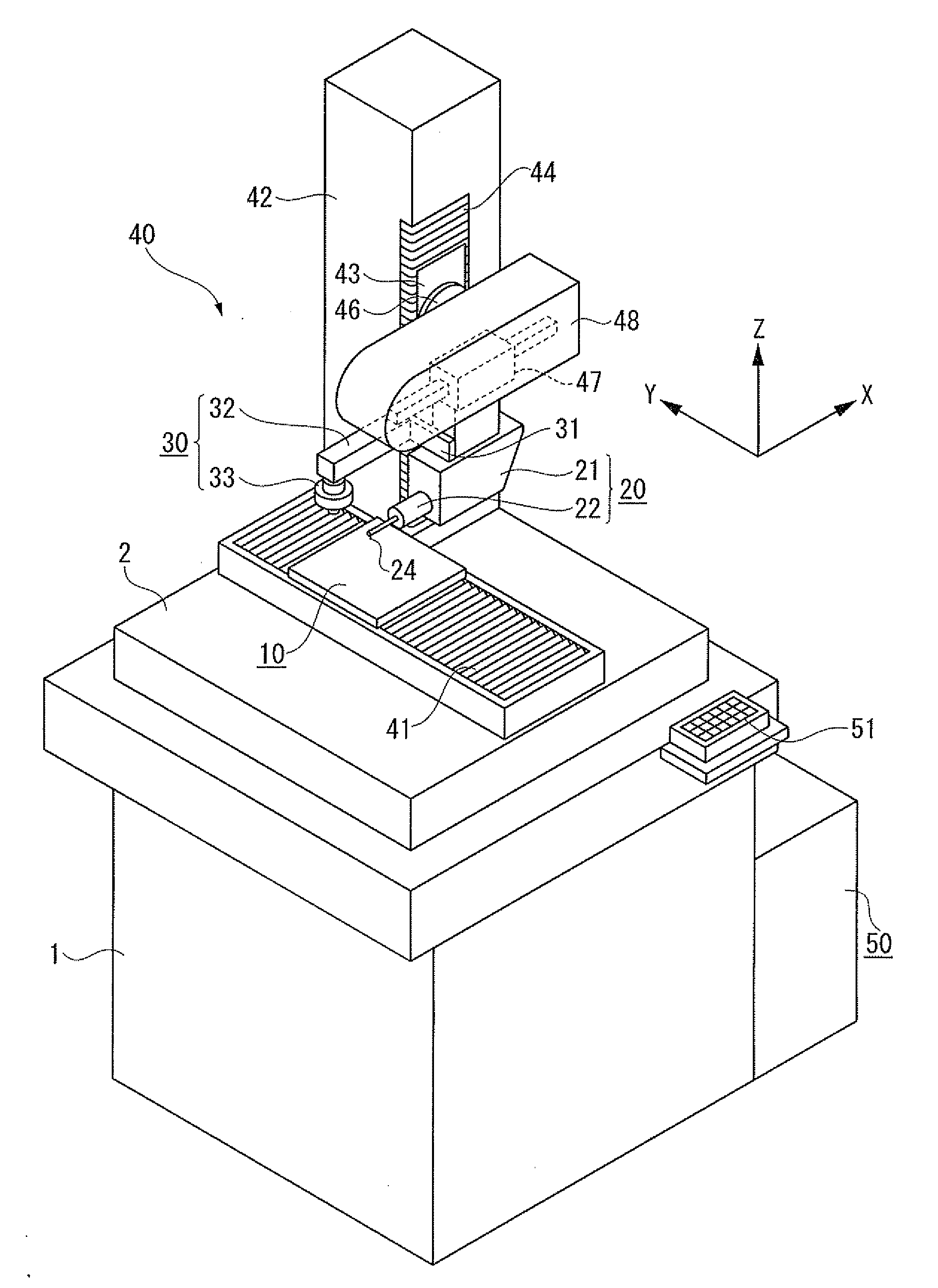
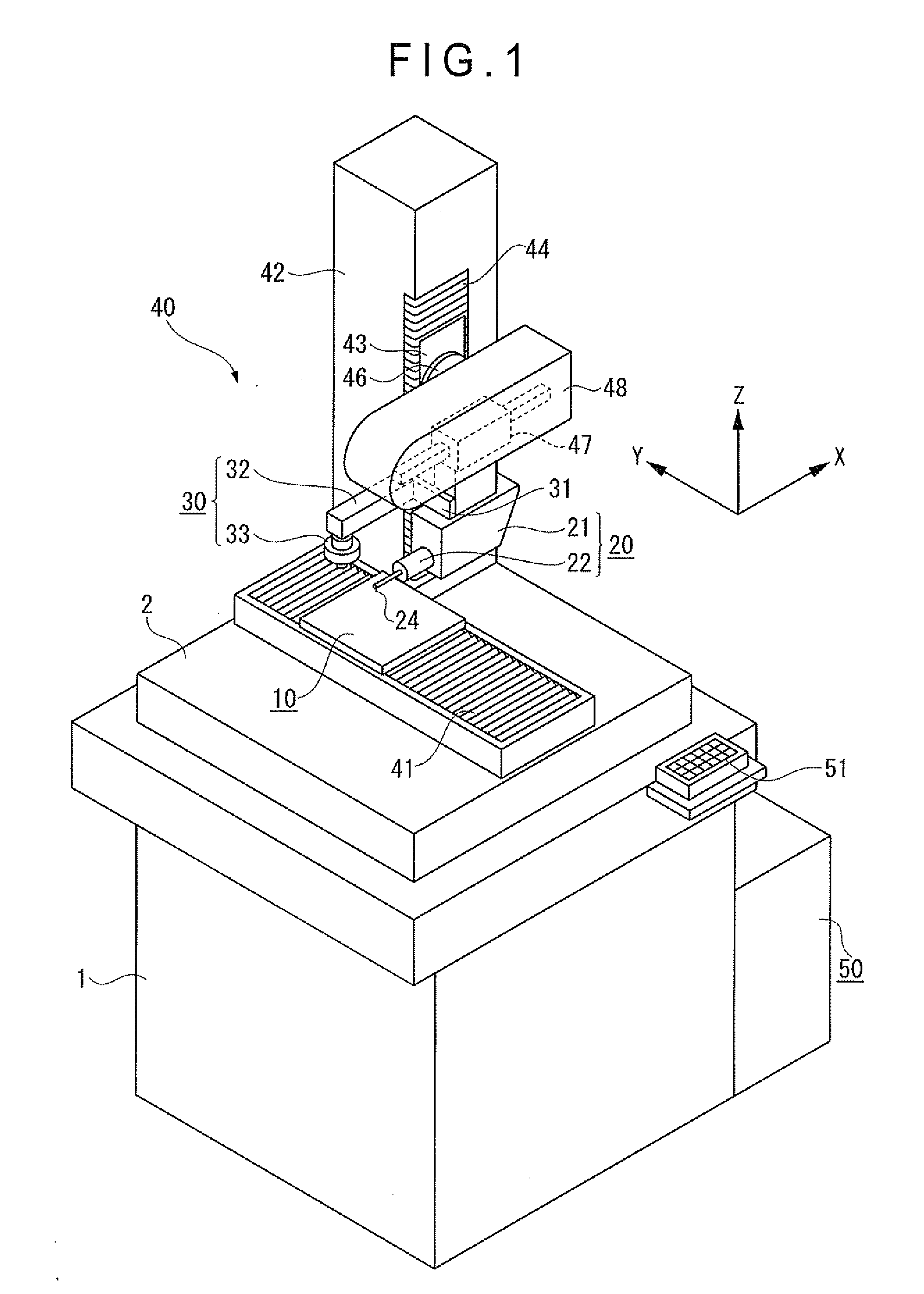
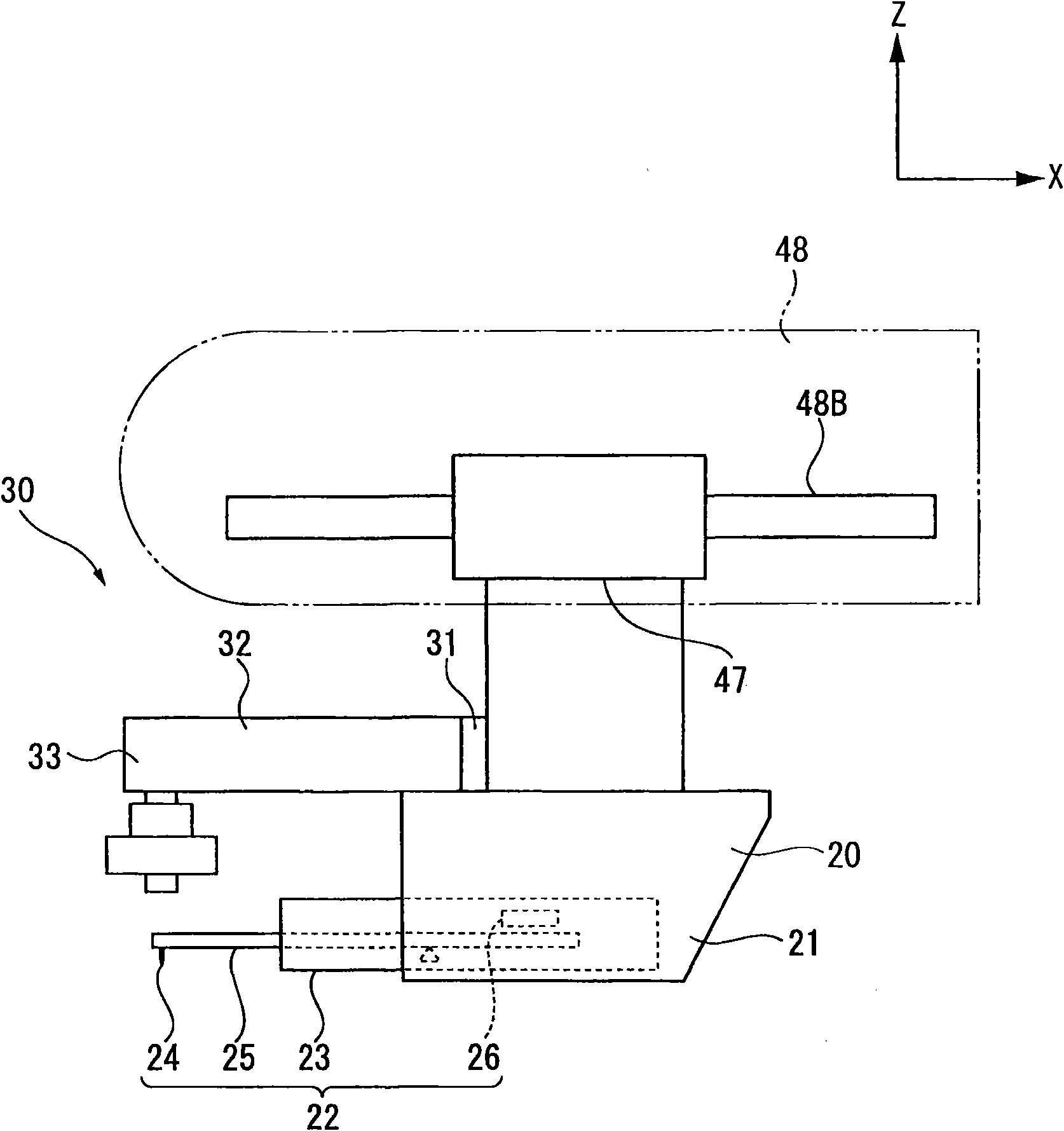
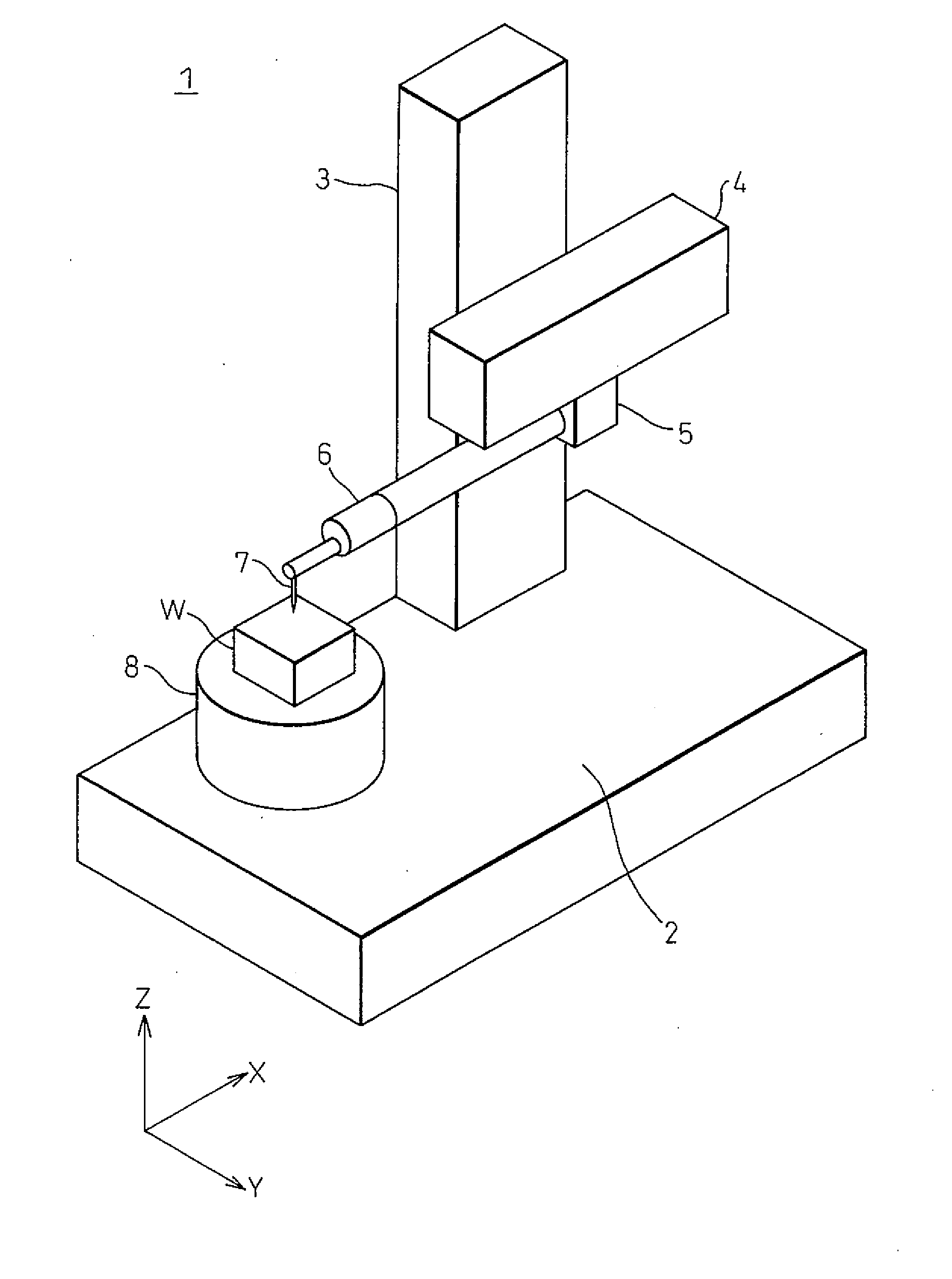
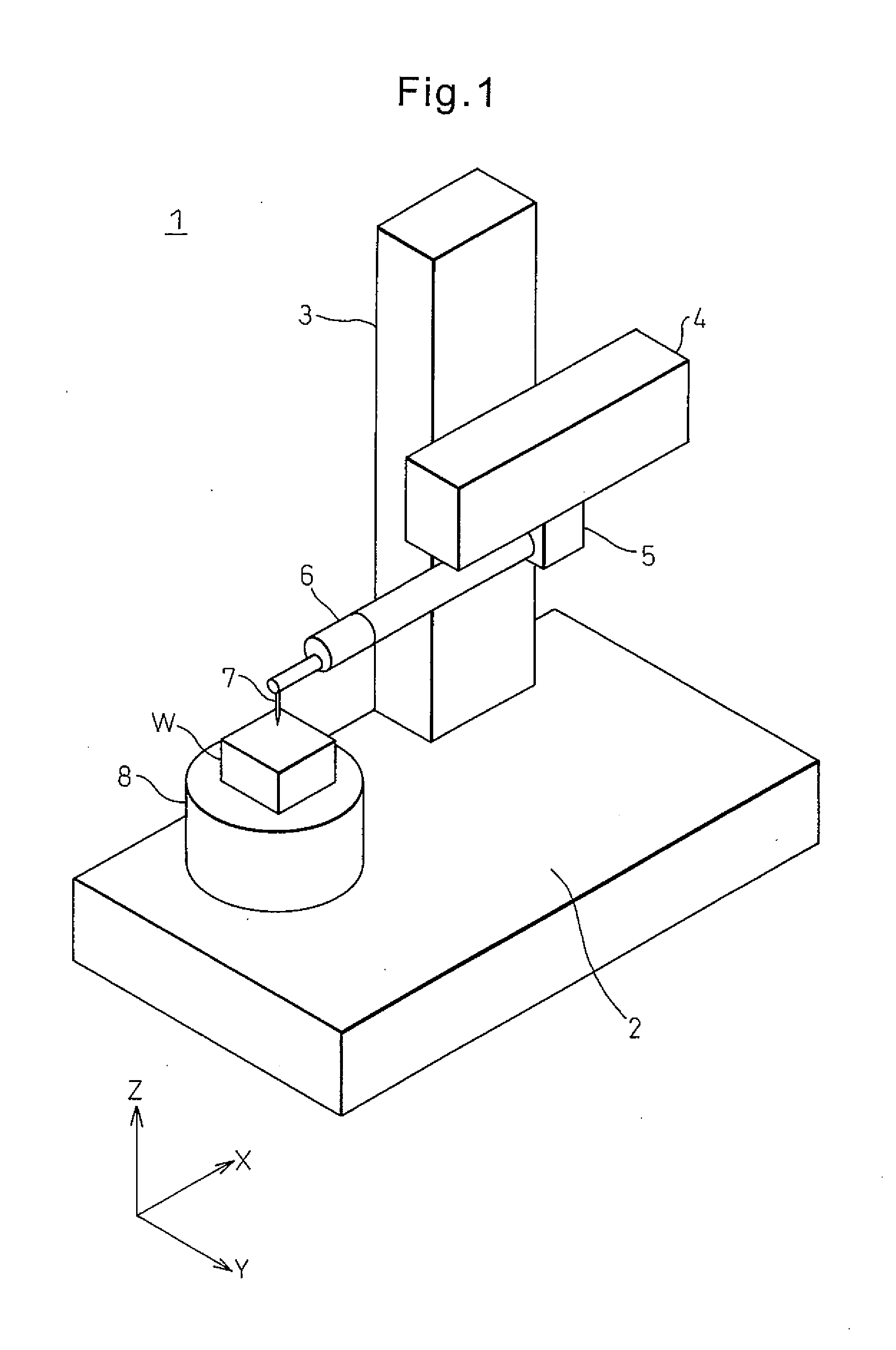
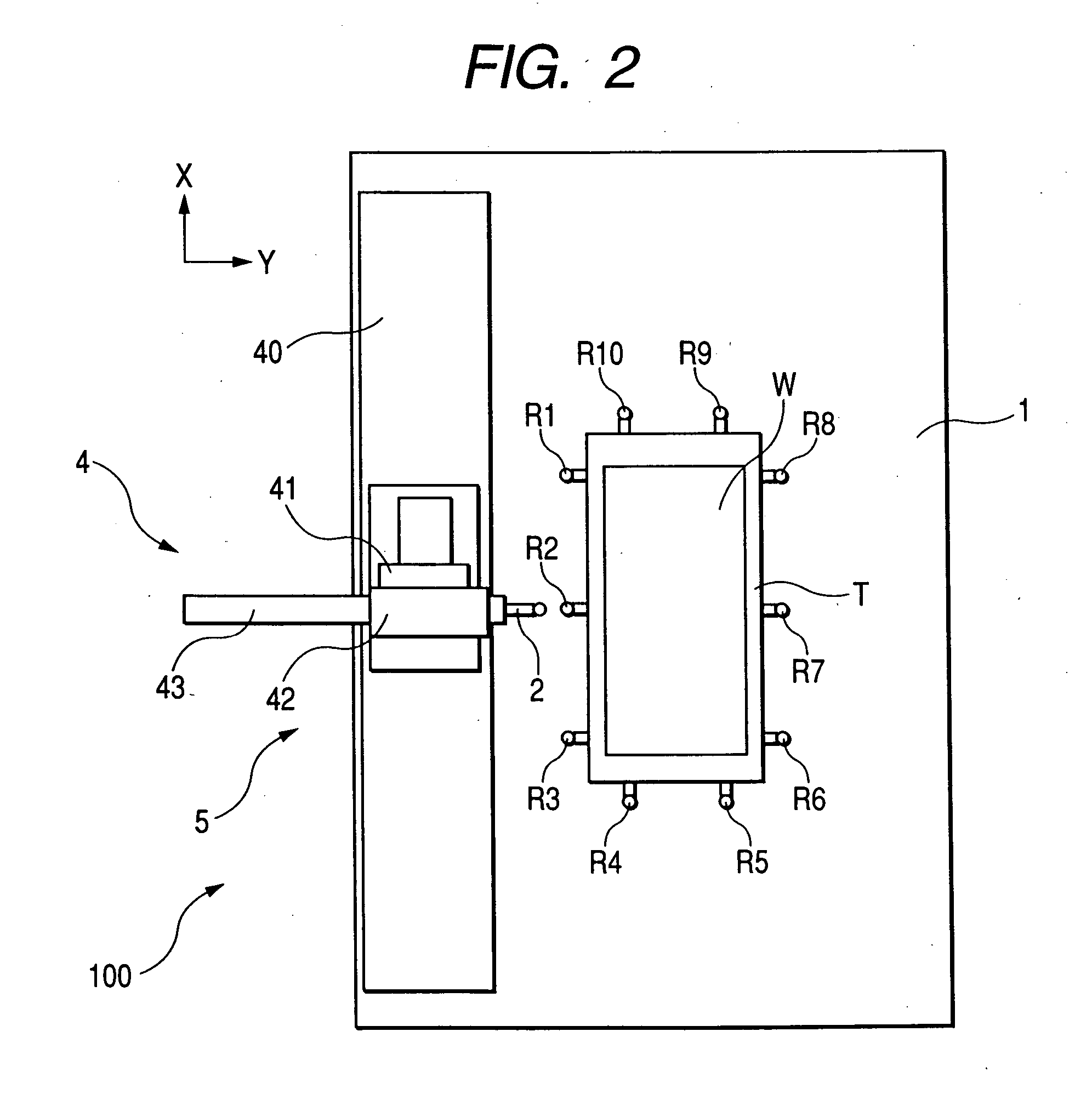
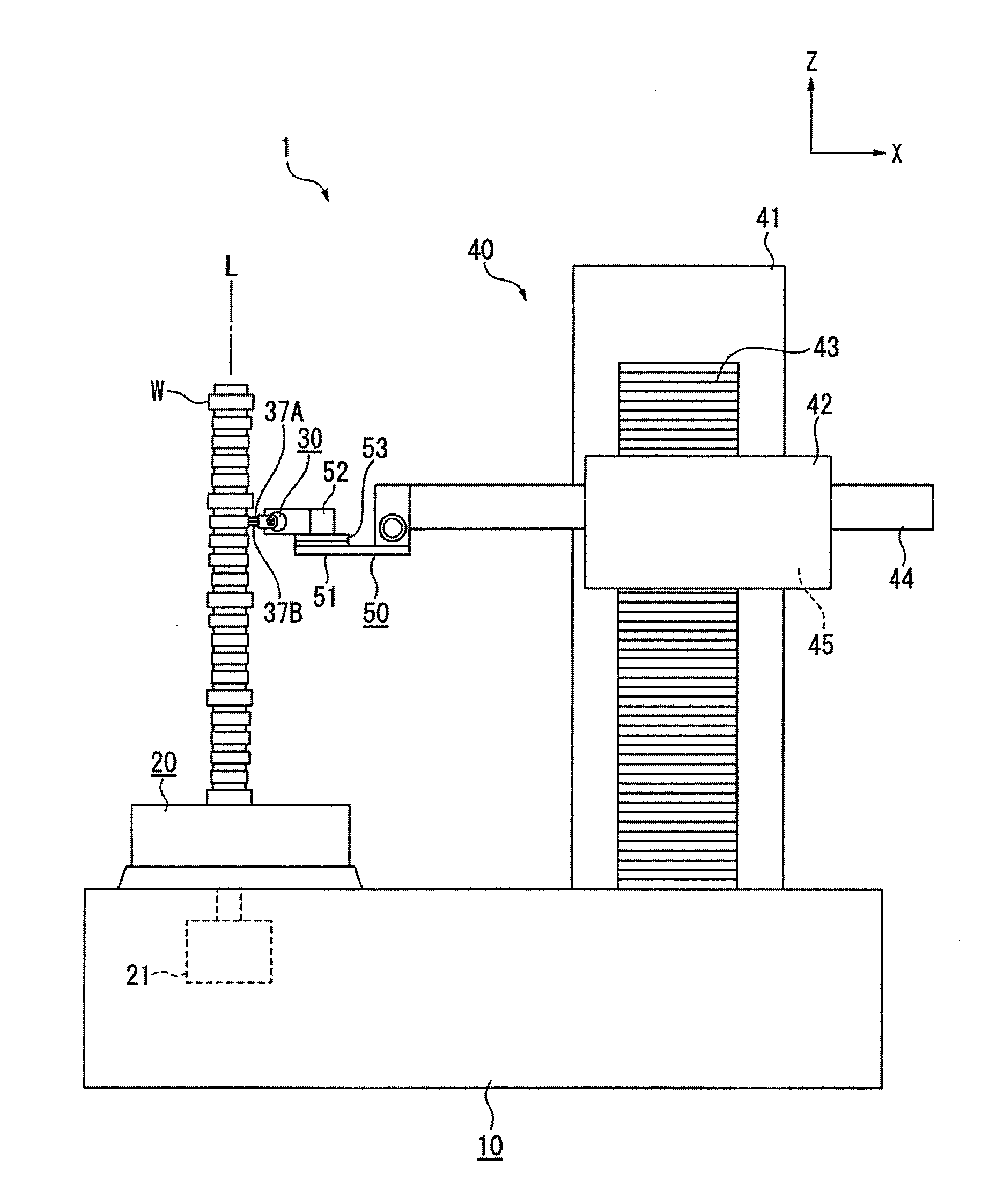
Width-measuring method and surface texture measuring instrument
ActiveUS20050132591A1Easy to measureSimple and accurate measurementMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsMechanical diameter measurementsMeasuring instrumentSurface roughness
A surface texture measuring instrument has a rotary table on which a workpiece is rotatably mounted, a Z-axis slider capable of moving in a Z-axis direction parallel to a rotation axis of the rotary table, an X-axis slider that is held by the Z-axis slider and is advanceable and retractable in an X-axis direction orthogonal to the rotation axis, a first arm that is held by the X-axis slider and is rotatable around a center line parallel to the X-axis, a second arm that is held by the first arm and is advanceable and retractable in a direction orthogonal to the X-axis, and a detector held by the second arm to measure a surface texture of the workpiece.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
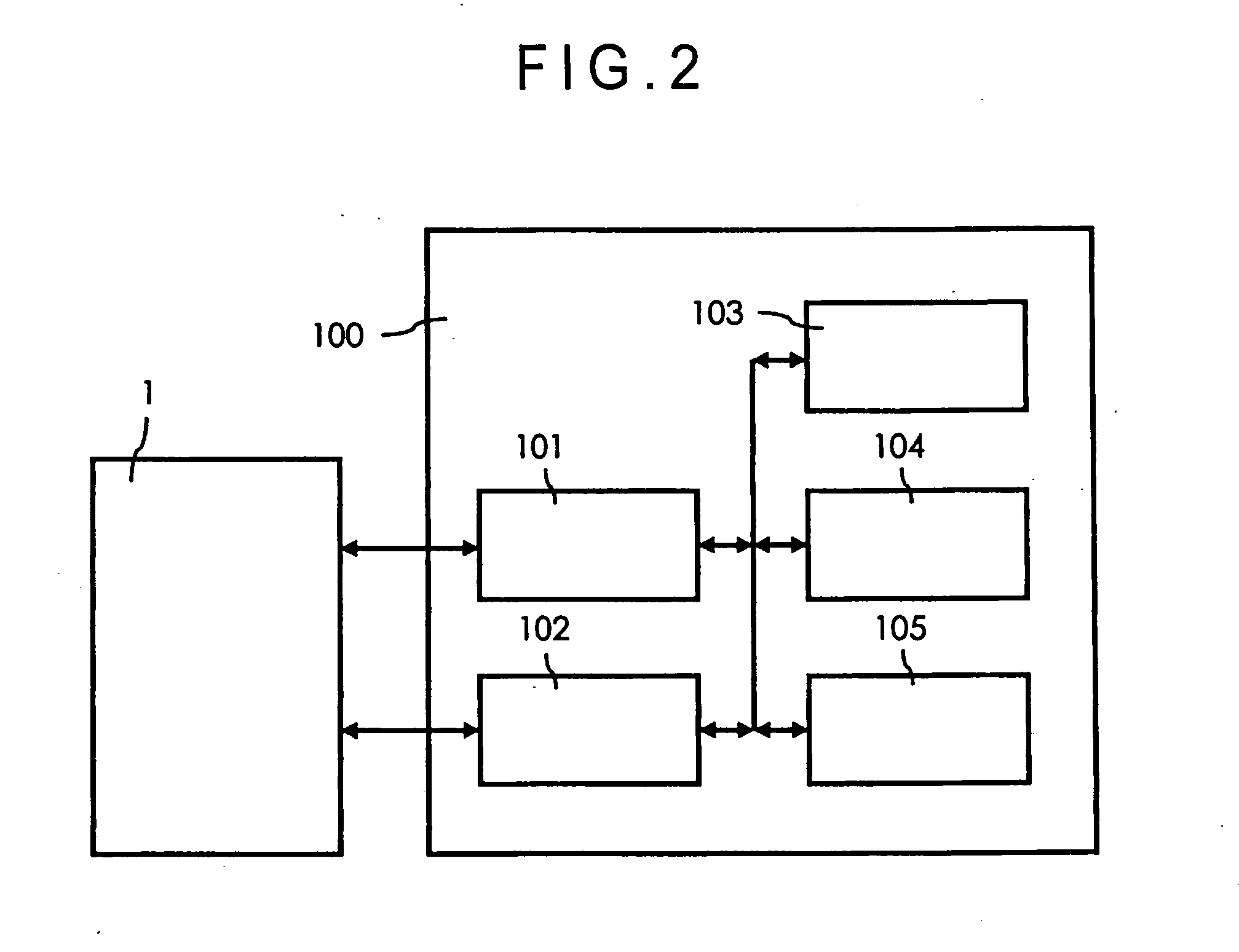
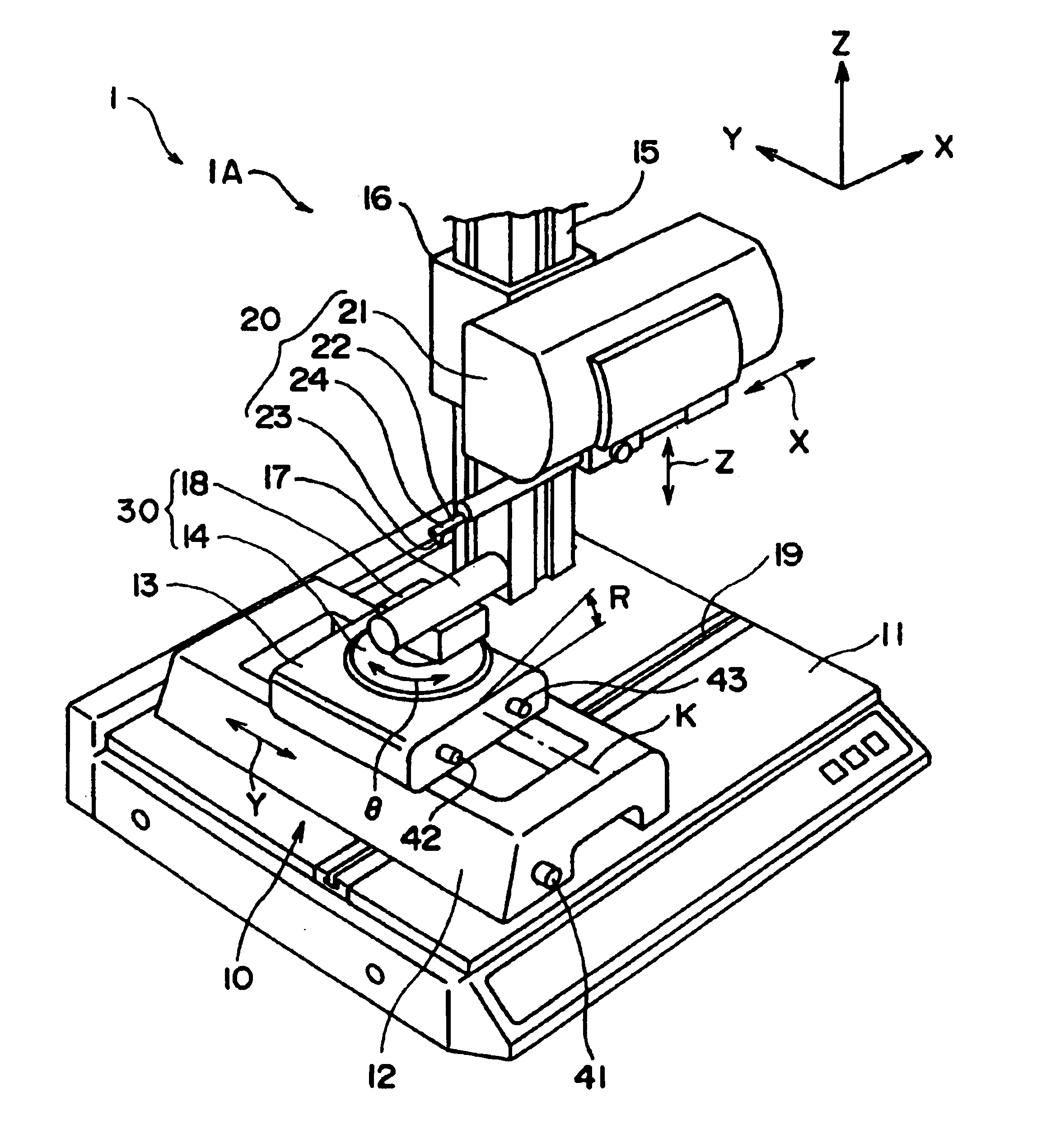
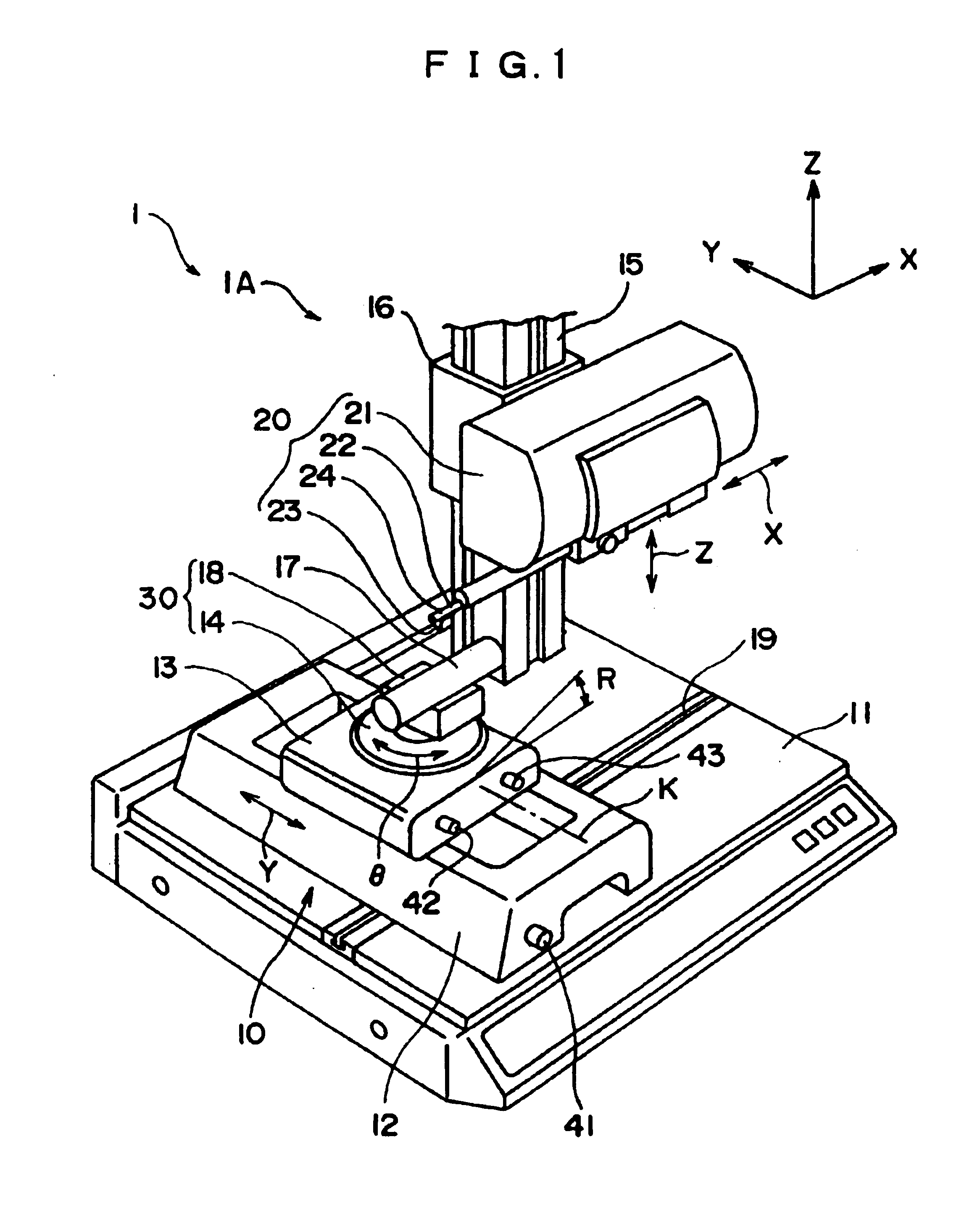
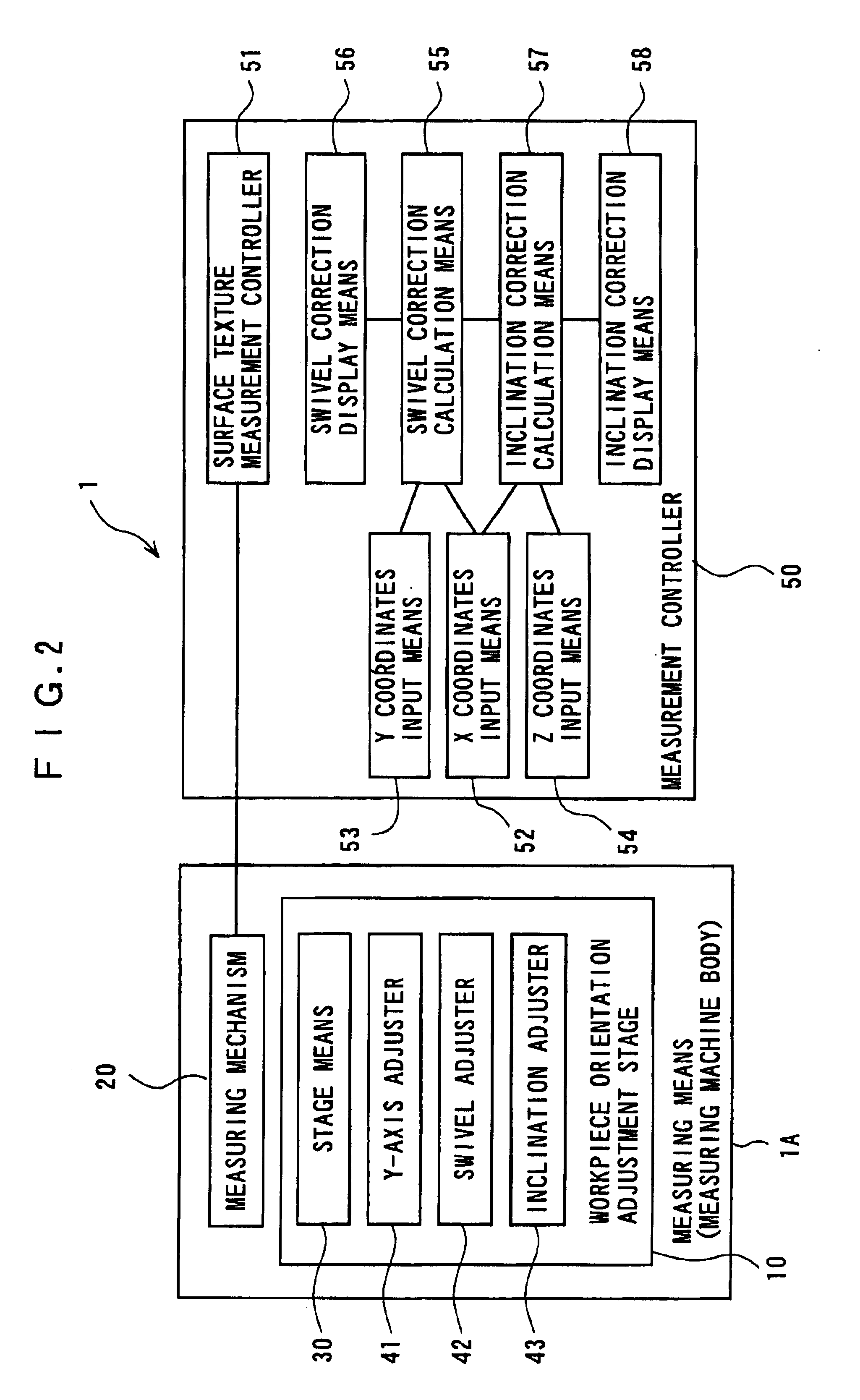
Surface texture measuring machine, leveling device for surface texture measuring machine and orientation-adjusting method of workpiece of surface texture measuring machine
InactiveUS6745616B1Scan accuratelyEasy to adjustMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsMeasurement/indication equipmentsOperabilityEngineering
In advance to measuring texture of the workpiece by a surface texture measuring machine (1), a workpiece orientation adjustment stage (10) is manually moved by the surface texture measuring machine (1) in accordance with calculated orientation correction amount of the workpiece, thus adjusting orientation of the workpiece. Since it is only necessary for an operator to operate respective adjustment means until reaching a displayed correction amount, operation thereof can be facilitated and orientation thereof can be highly accurately adjusted without impairing operability.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Methods and apparatuses for analyzing images
A method for automated analysis of textural differences present on an image volume. The image volume includes a plurality of volume elements, and each volume element has a gray level. The method includes defining a volume of interest (VOI); performing texture measures within the VOI; and classifying the VOI as belonging to a tissue pathology class based upon the texture measures. Computer readable media encoded with computer readable instructions for carrying out these functions. An apparatus that includes an image input adapted to receive a diagnostic medical image. The image includes a plurality of pixels, and each pixel has a particular gray level. The apparatus also includes a display for displaying a graphical user interface and the received image; and a processor adapted to perform texture measures on one or more groups of pixels within the image and classify each group of pixels to a tissue pathology class based upon the textures measures. The processor is further adapted to (1) associate a color to each group of pixels indicative of the group's tissue pathology class, (2) cause the display to display one or more of the colors on the image at the location of the associated group or groups of pixels, (3) permit a user to manually associate a tissue pathology class to a group of pixels, and (4) cause the display to display the manually-associated tissue pathology class.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Method and System for Low Complexity Adaptive Quantization
InactiveUS20110268180A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoFactor base
A method of encoding a block of pixels in a digital video sequence that includes computing an average texture measure for a plurality of blocks of pixels encoded prior to the block of pixels, computing a texture measure for the block of pixels, computing a block quantization step size for the block of pixels as the product of a quantization step size selected for a sequence of blocks of pixels comprising the block of pixels and a multiplication factor selected from a set of multiplication factors based on a ratio of the texture measure and the average texture measure, and quantizing the block of pixels using the block quantization step size.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Surface texture measuring instrument and calibration method thereof
InactiveCN100371672CReduce riskCalibration precisionProgramme controlPhotometry using reference valueMeasuring instrumentComputer science
In a calibration method for a surface texture measuring instrument which measures the surface of a workpiece and includes an arm that is supported to be swingable around a base point thereof and is provided with a contact point at an end for scanning the workpiece surface, the calibration method includes a measurement step for measuring a calibration gauge the cross section of which contains a part of a substantially perfect circle, an assignment step for assigning the detection results from the measurement step in an evaluation formula based on the equation of a circle in which the center coordinates of the calibration gauge are (xc, zc) and the radius is 'r', and a calibration step for calibrating each parameter based on the results obtained in the assignment step.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
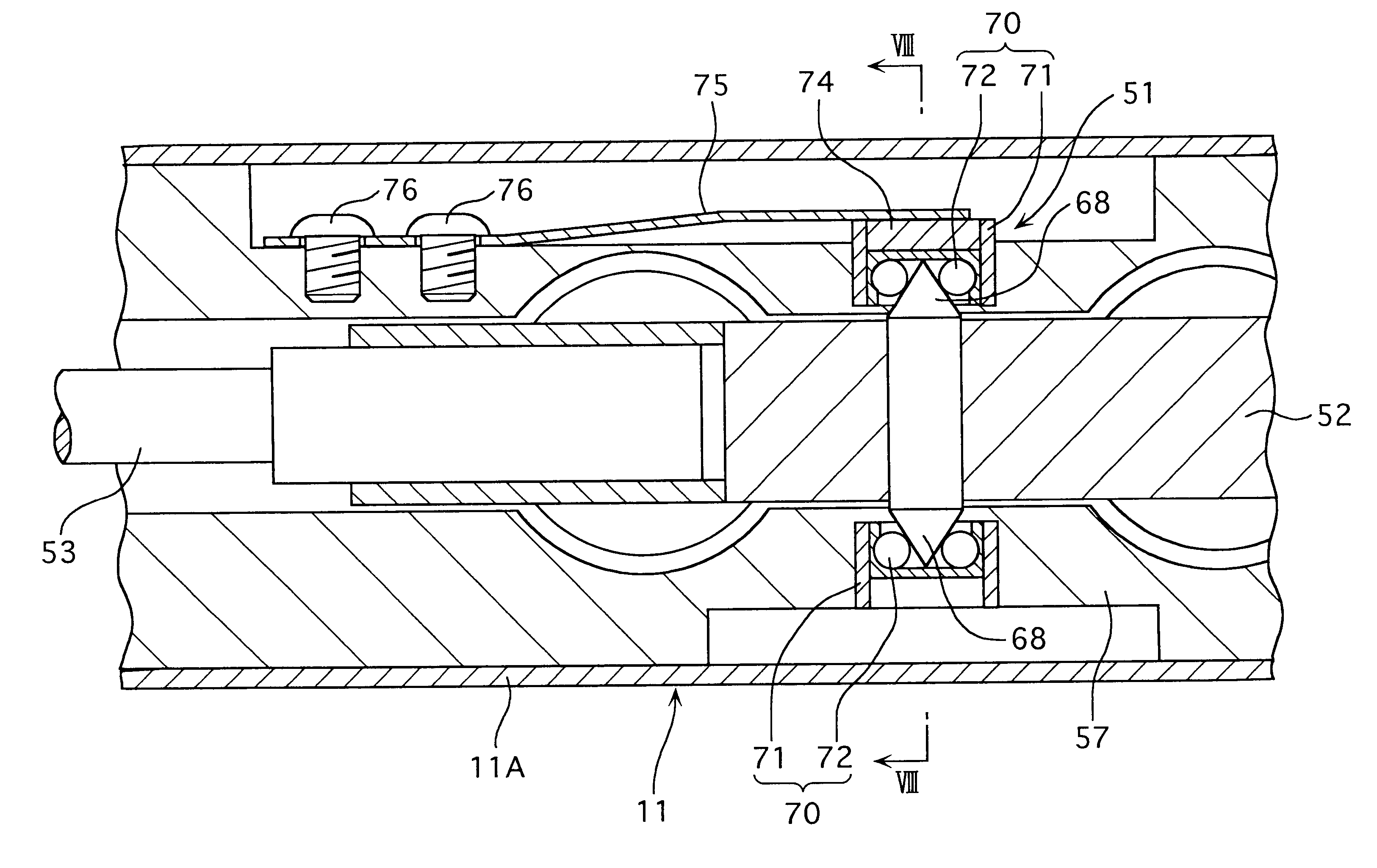
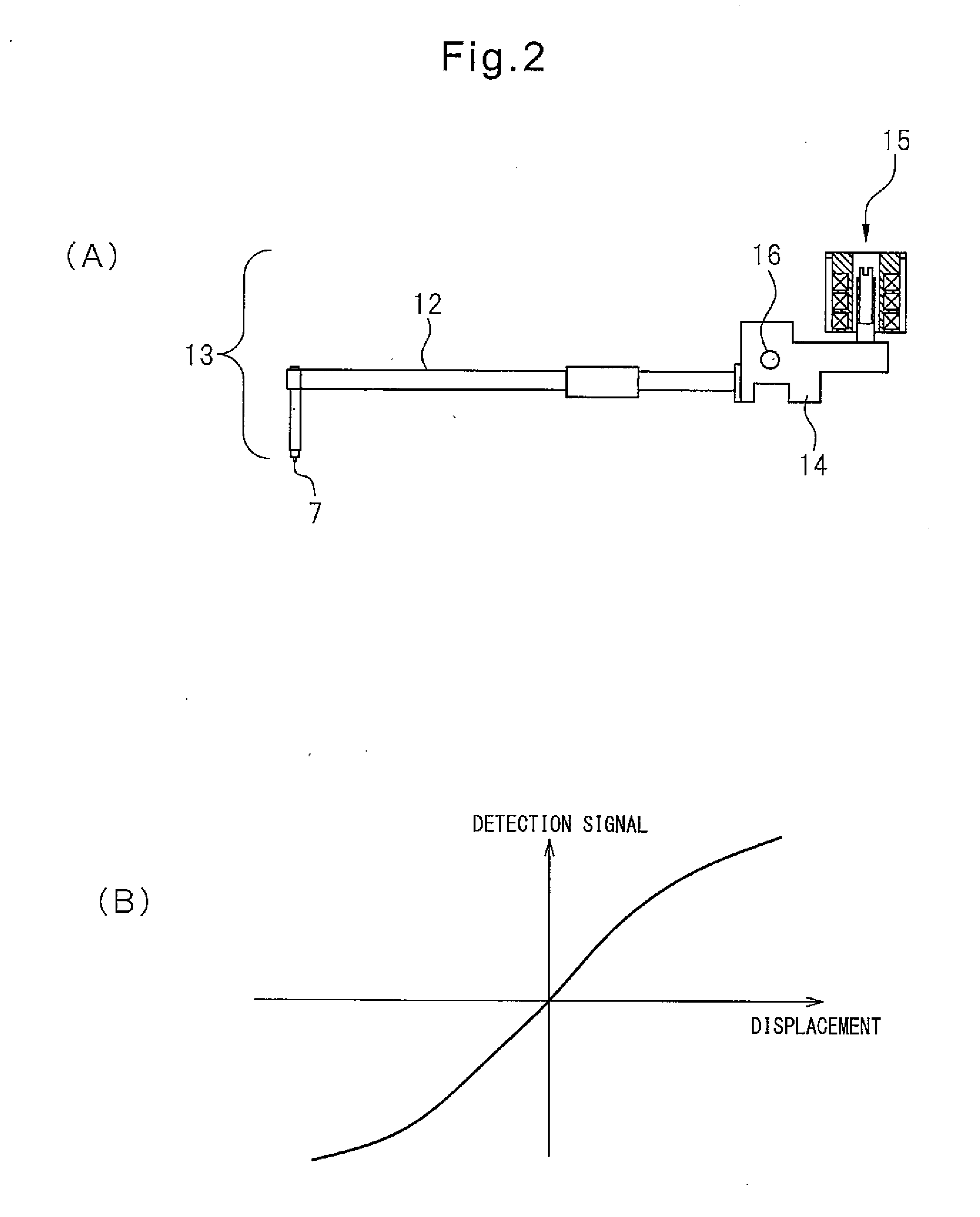
Detector for surface texture measuring instrument
InactiveUS6487897B1Rotary torque can be decreasedMinimize hysteresisFeeler-pin gaugesMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsBall bearingMeasuring instrument
An arm member (52) detachably provided with a stylus arm (53) is rotatably held by a casing (11), where pivots (68) respectively project from both sides of a rotation center of the arm member (52), a first ball bearing (70) engaging with one of the pivots (68) is fixed to the casing (11) and a second ball bearing (70) engaging with the other one of the pivots (68) is fixed to the second ball bearing (70). A leaf-spring (75) has one end fixed to the casing (11) and the other end fixed to the second ball bearing (70). Since the second ball bearing (70) does not shift relative to the leaf-spring (75), measuring pressure remains stable.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
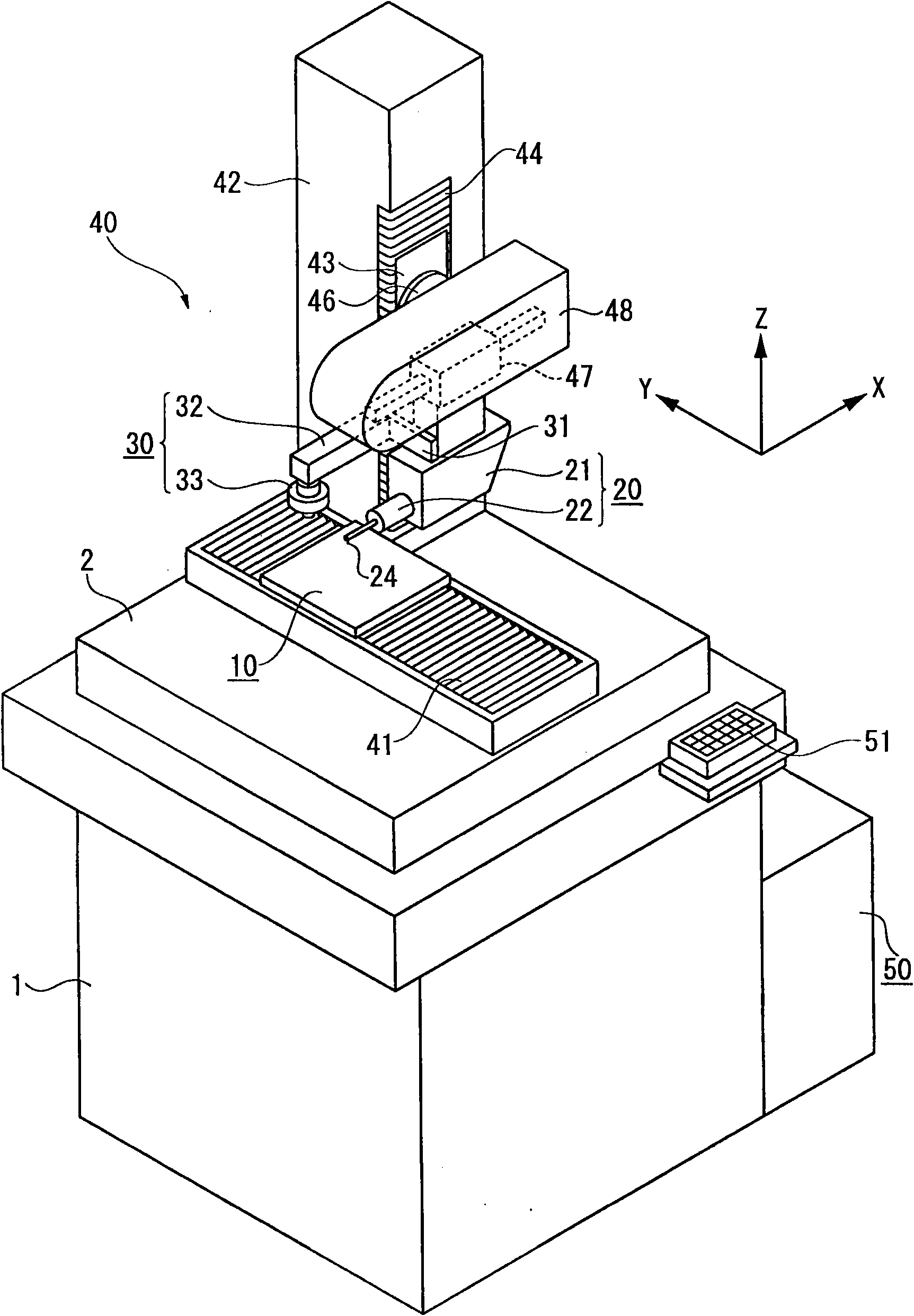
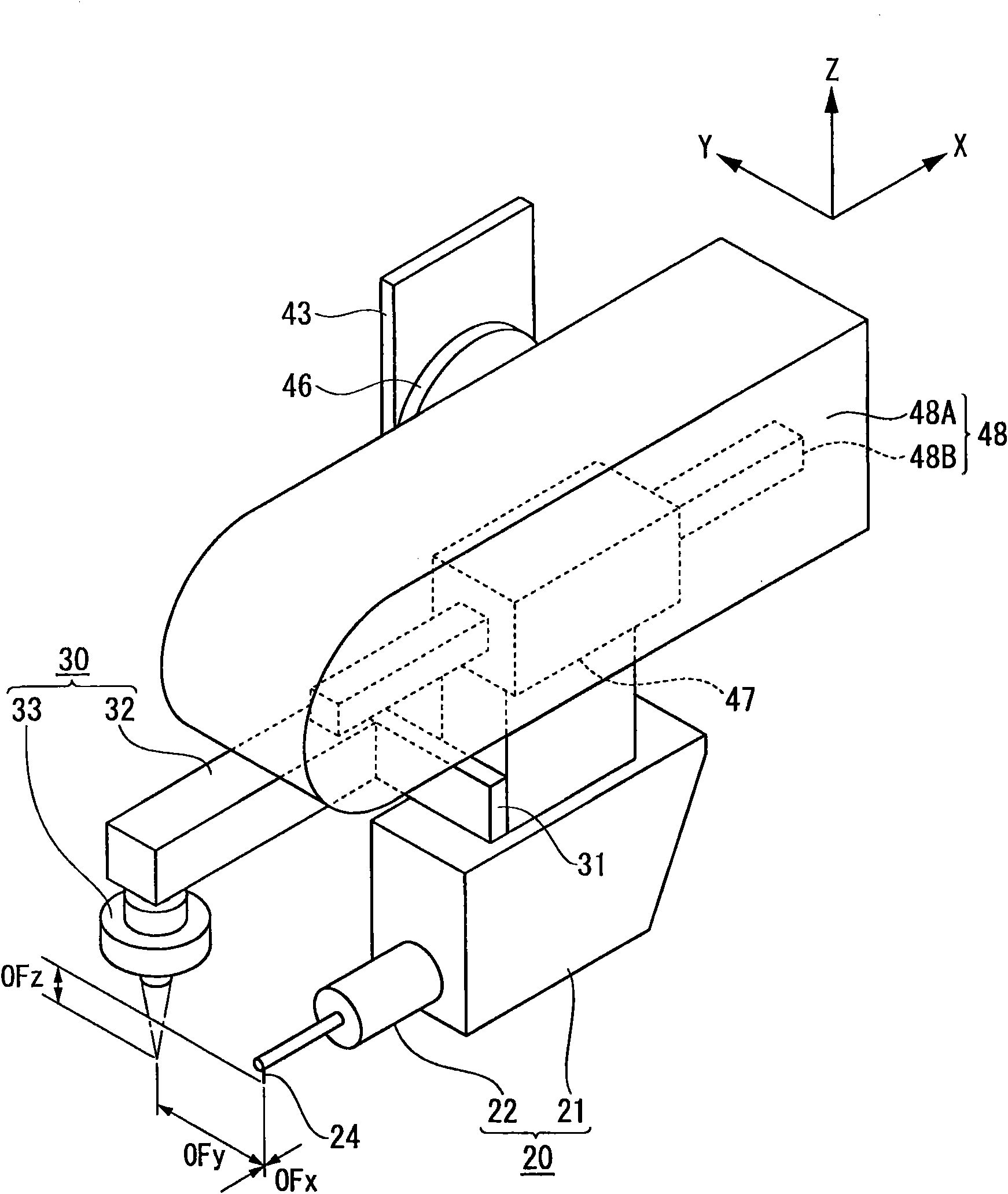
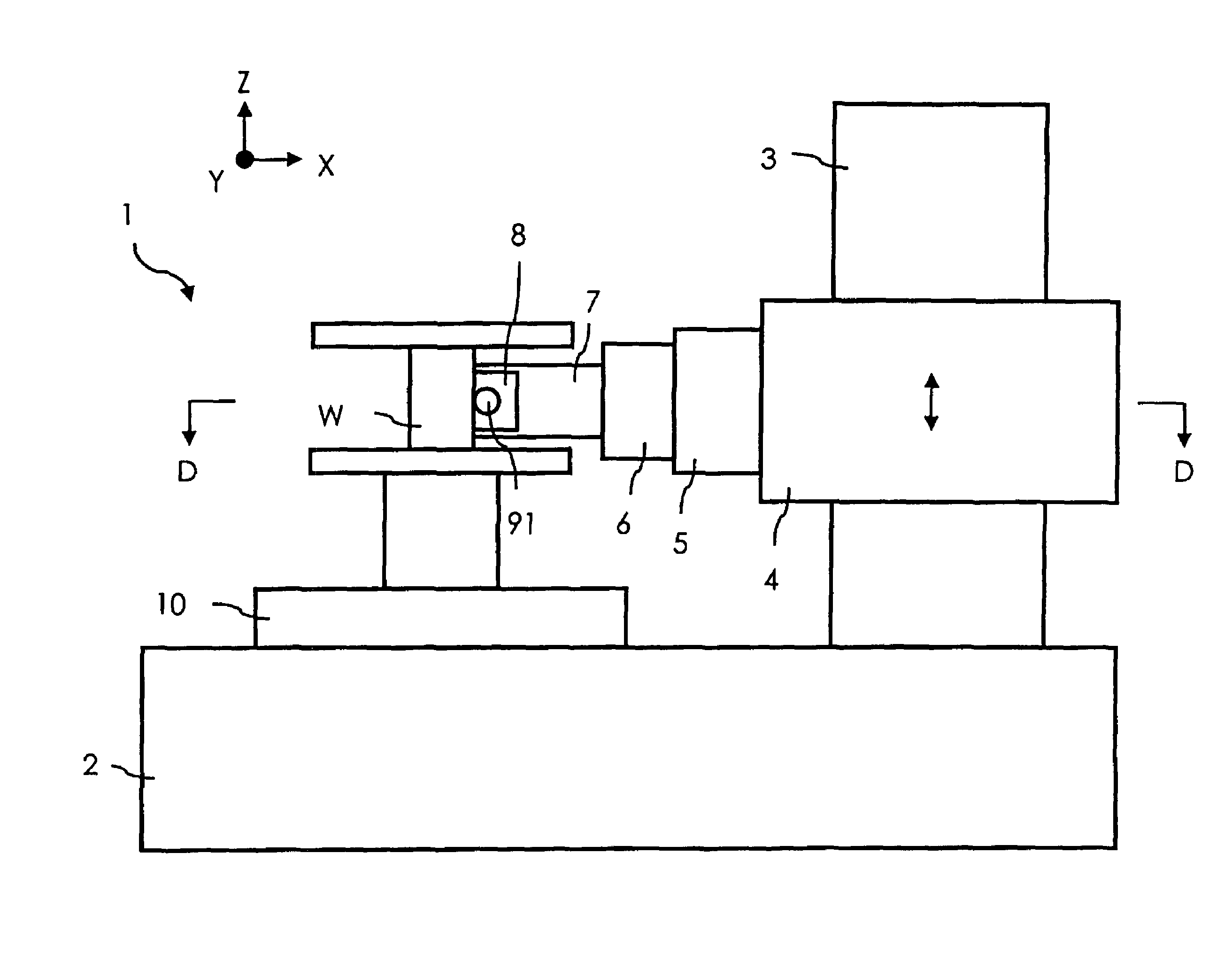
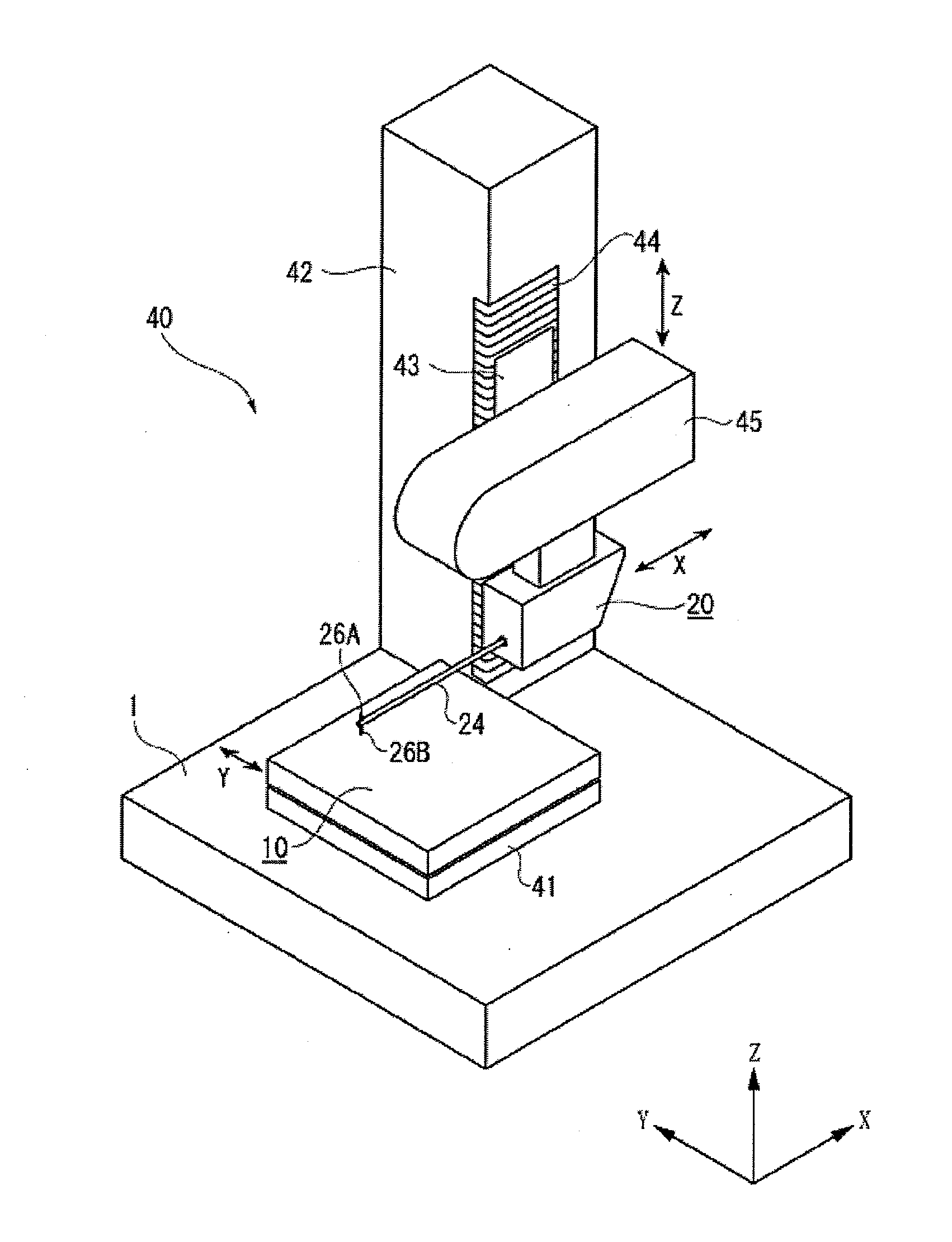
Surface texture measuring machine and a surface texture measuring method
ActiveUS20110083497A1Avoid interferenceReduce the burden onUsing optical meansMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsContact typeComputer vision
A surface texture measuring machine includes: a stage, a contact-type detector having a stylus, an image probe, a relative movement mechanism and a controller. The controller includes: a center position calculating unit that, when the image probe enters position data of at least three points on a circular contour of a circular concave portion or a circular convex portion of an object, approximates the entered position data to a circle to obtain a center position of the circle; and a stylus setting unit that, after calculating the center position, operates the relative movement mechanism to position the stylus of the contact-type detector at the center position.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Surface texture measuring instrument
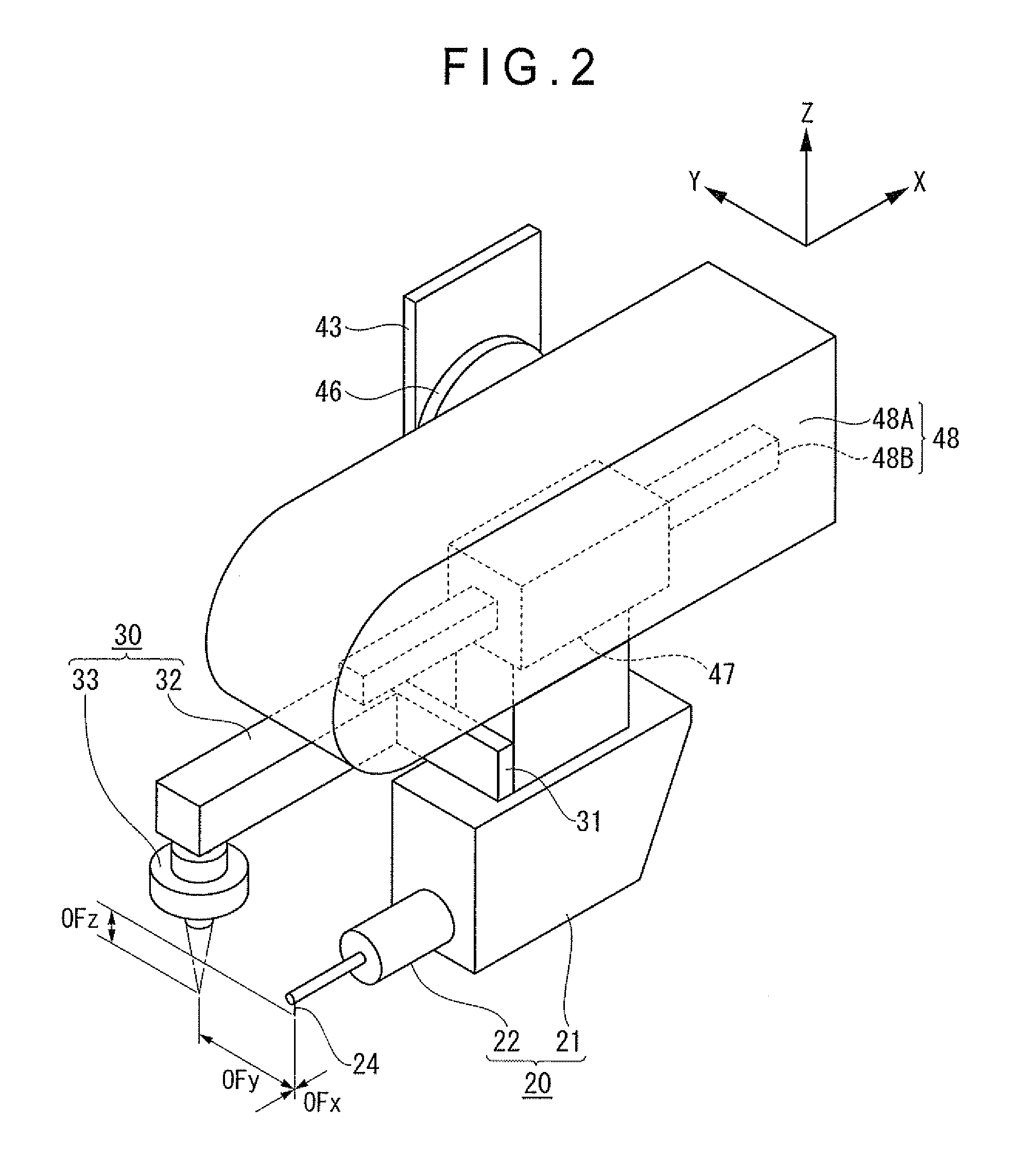
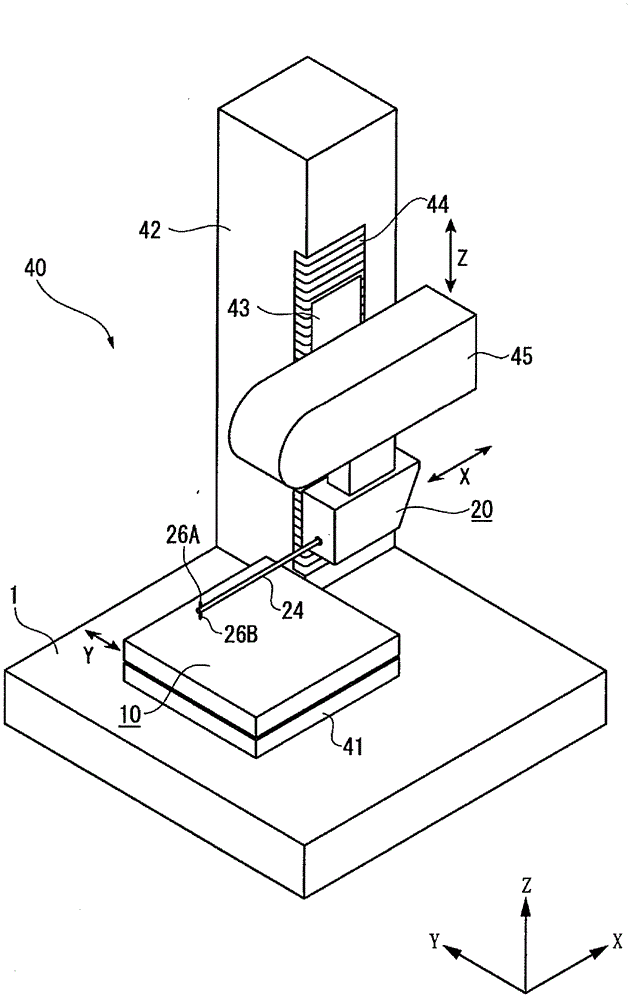
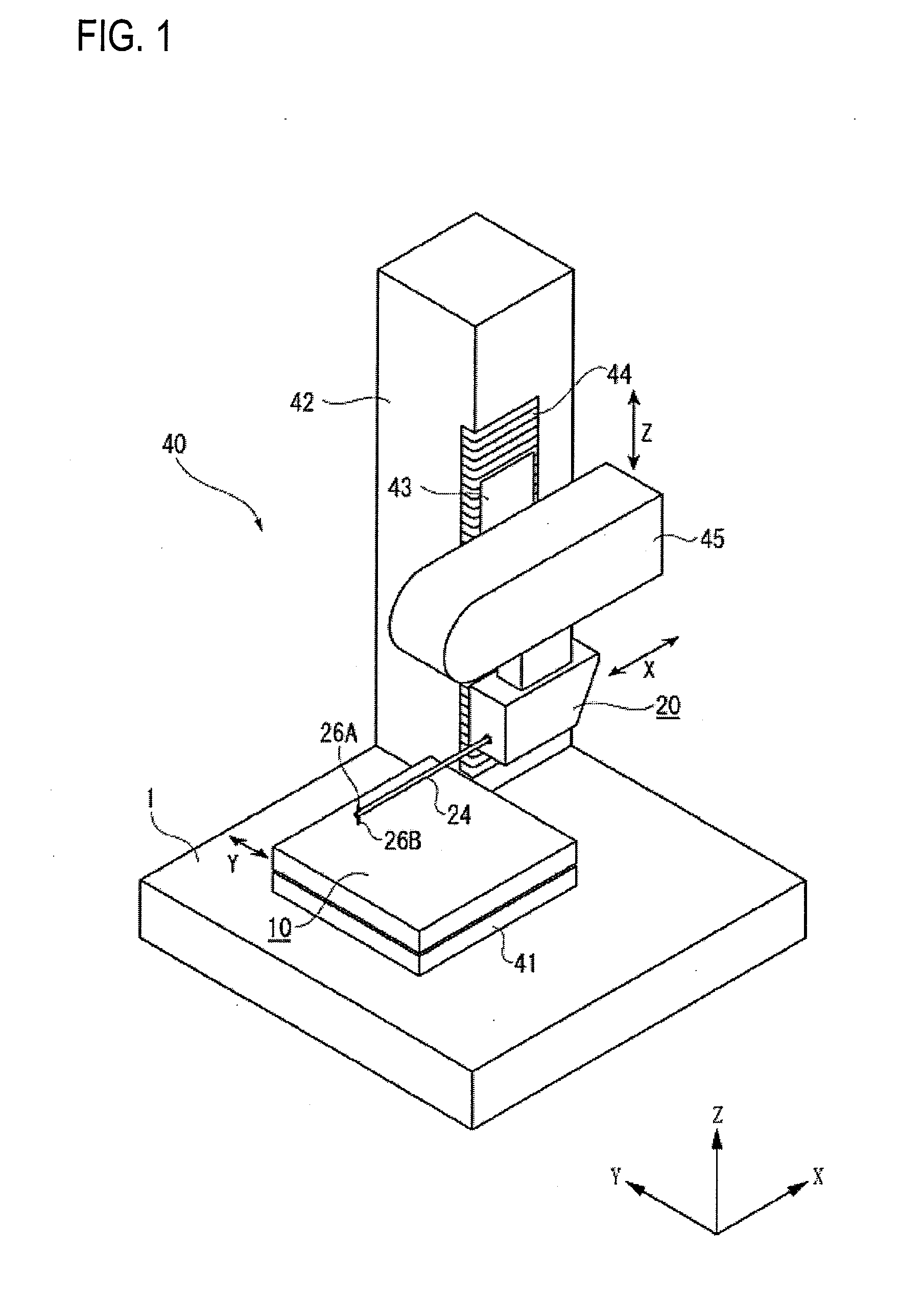
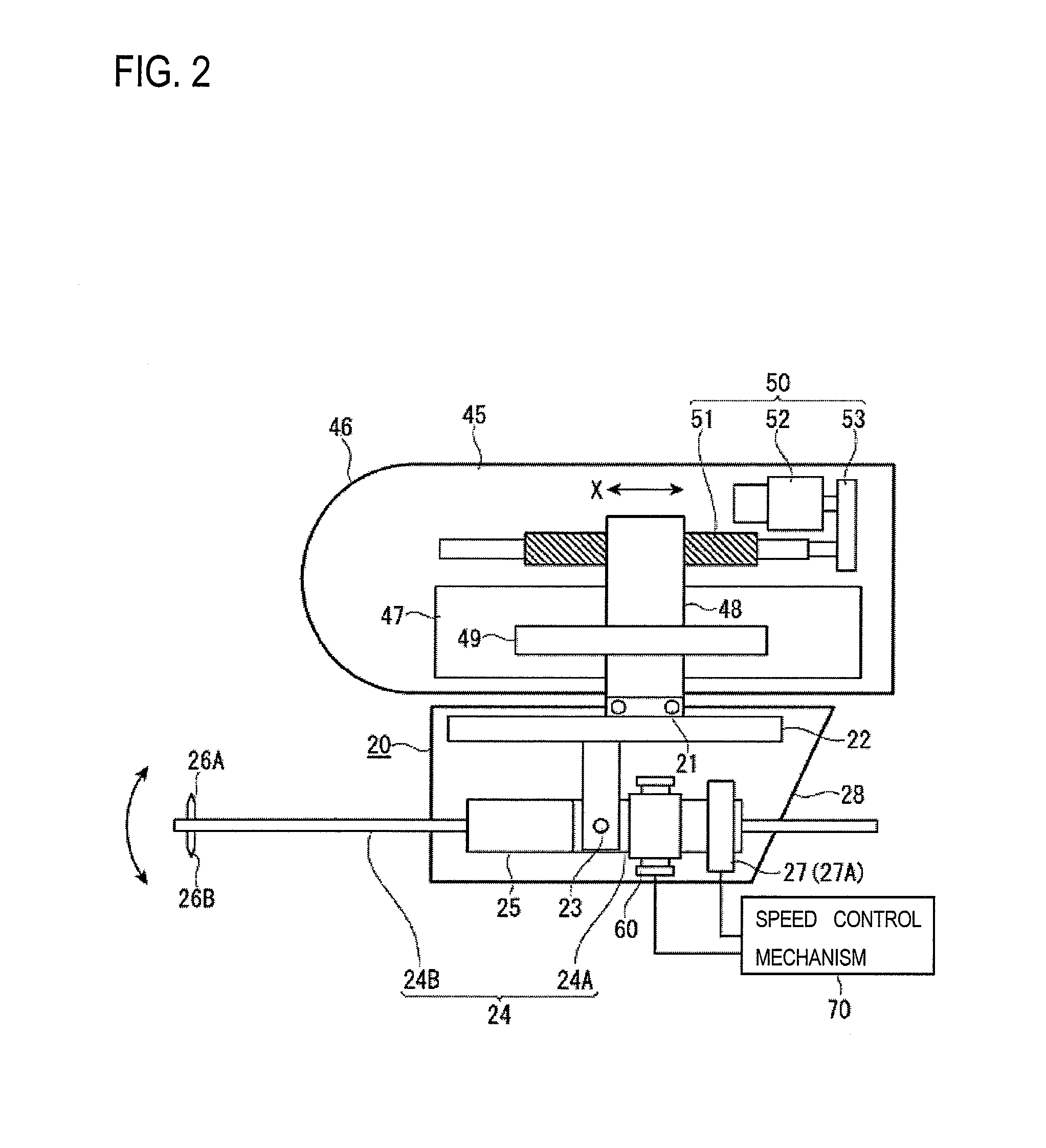
ActiveCN102749058AAvoid damageShock suppressionError compensation/eliminationMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsMeasuring instrumentEngineering
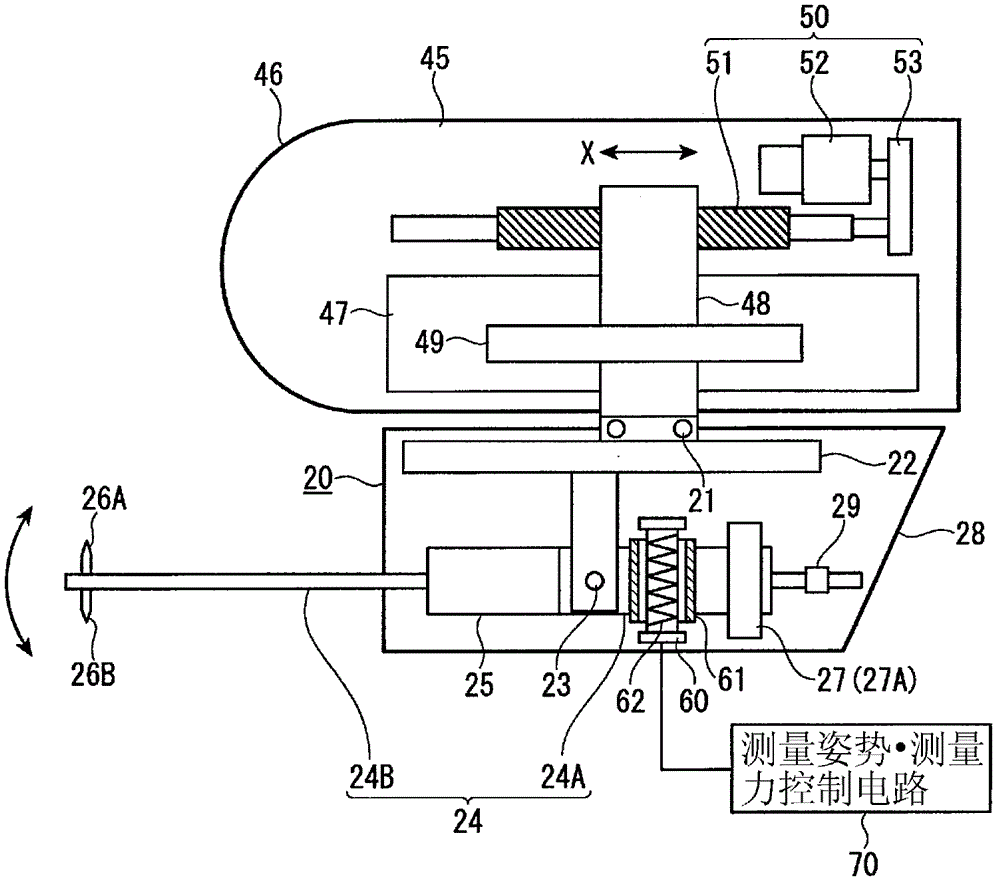
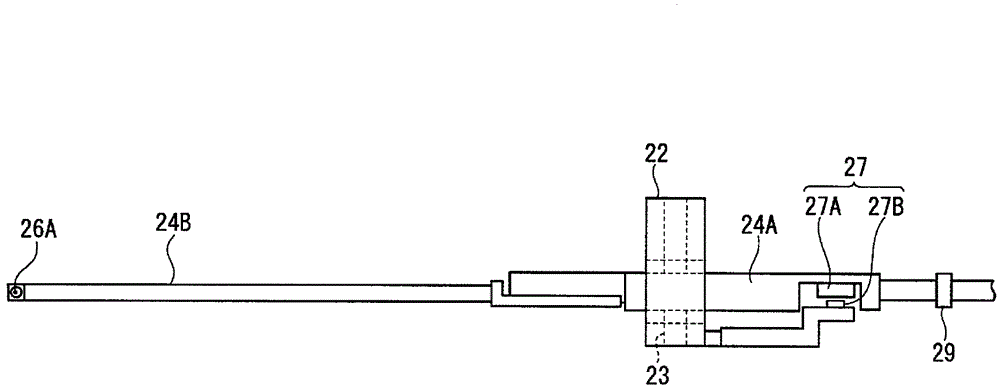
The invention provides a surface texture measuring instrument. In the surface texture measuring instrument, a measurement arm (24) includes: a first measurement arm (24A) that is supported by a bracket (22) around a support shaft (23) movably in a circular movement in a casing (28); and a second measurement arm (24B) having styluses (26A, 26B) that are attachably and detachably provided to an end of the first measurement arm (24A) via an attachment-detachment mechanism (25), the attachment-detachment mechanism (25) being arranged in the casing. A displacement detector (27) includes: a scale (27A) provided to the measurement arm; and a detection head provided to the bracket (22) to face the scale. A detecting surface of the scale is on an axis of the measurement arm and on a plane of the circular movement of the measurement arm.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Surface texture measuring machine and a surface texture measuring method
ActiveCN102042813AReduce the burden onAvoid interferenceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsContact typeComputer vision
A surface texture measuring machine includes: a stage, a contact-type detector (20) having a stylus, an image probe (30), a relative movement mechanism (40) and a controller (50). The controller (50) includes: a center position calculating unit that, when the image probe enters position data of at least three points on a circular contour of a circular concave portion or a circular convex portion of an object, approximates the entered position data to a circle to obtain a center position of the circle; and a stylus setting unit that, after calculating the center position, operates the relative movement mechanism to position the stylus of the contact-type detector at the center position.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Width-measuring method and surface texture measuring instrument
ActiveUS7036238B2Scan accuratelyIncrease the areaMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsMechanical diameter measurementsRotary stageMeasuring instrument
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Surface texture measuring instrument
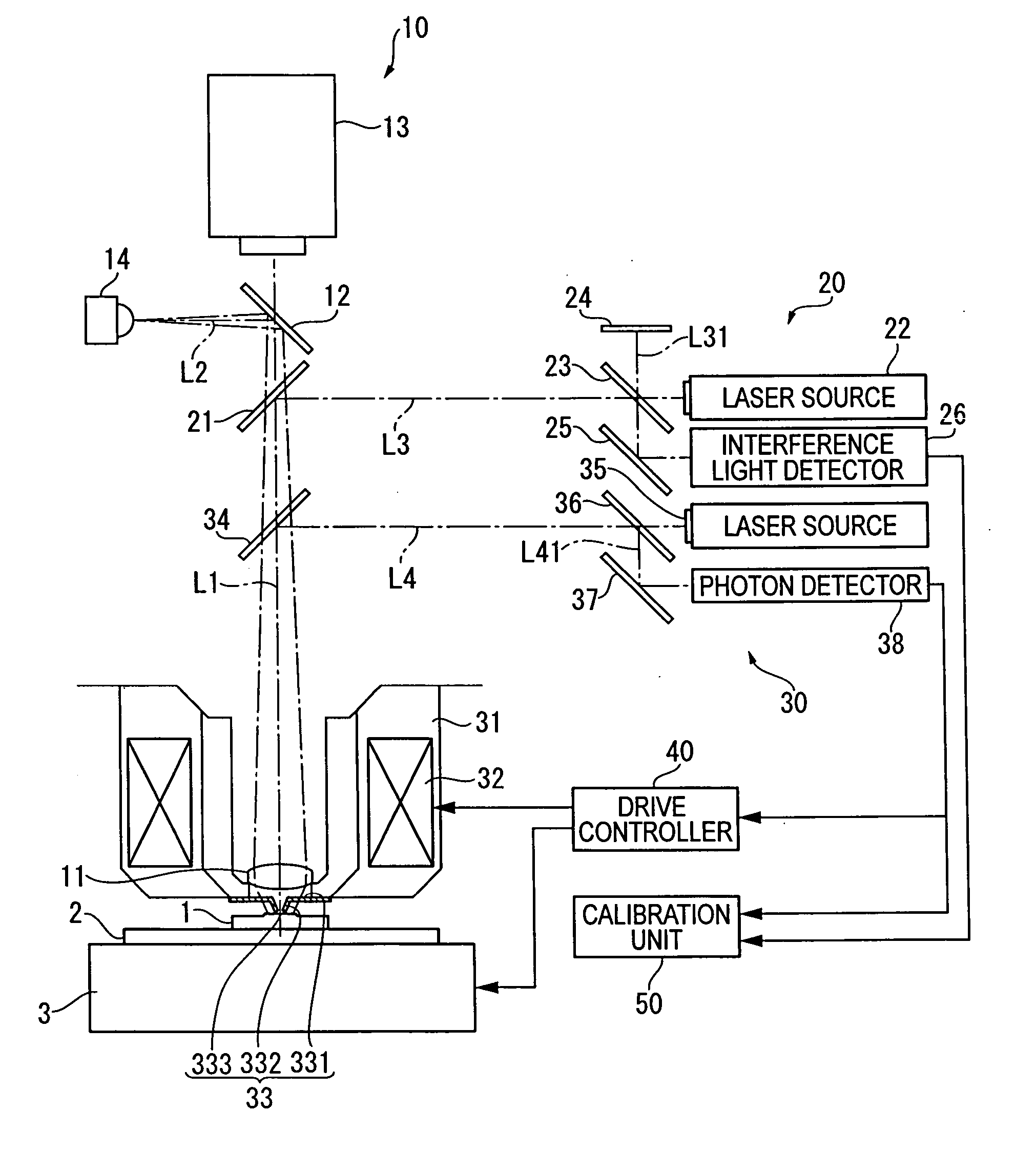
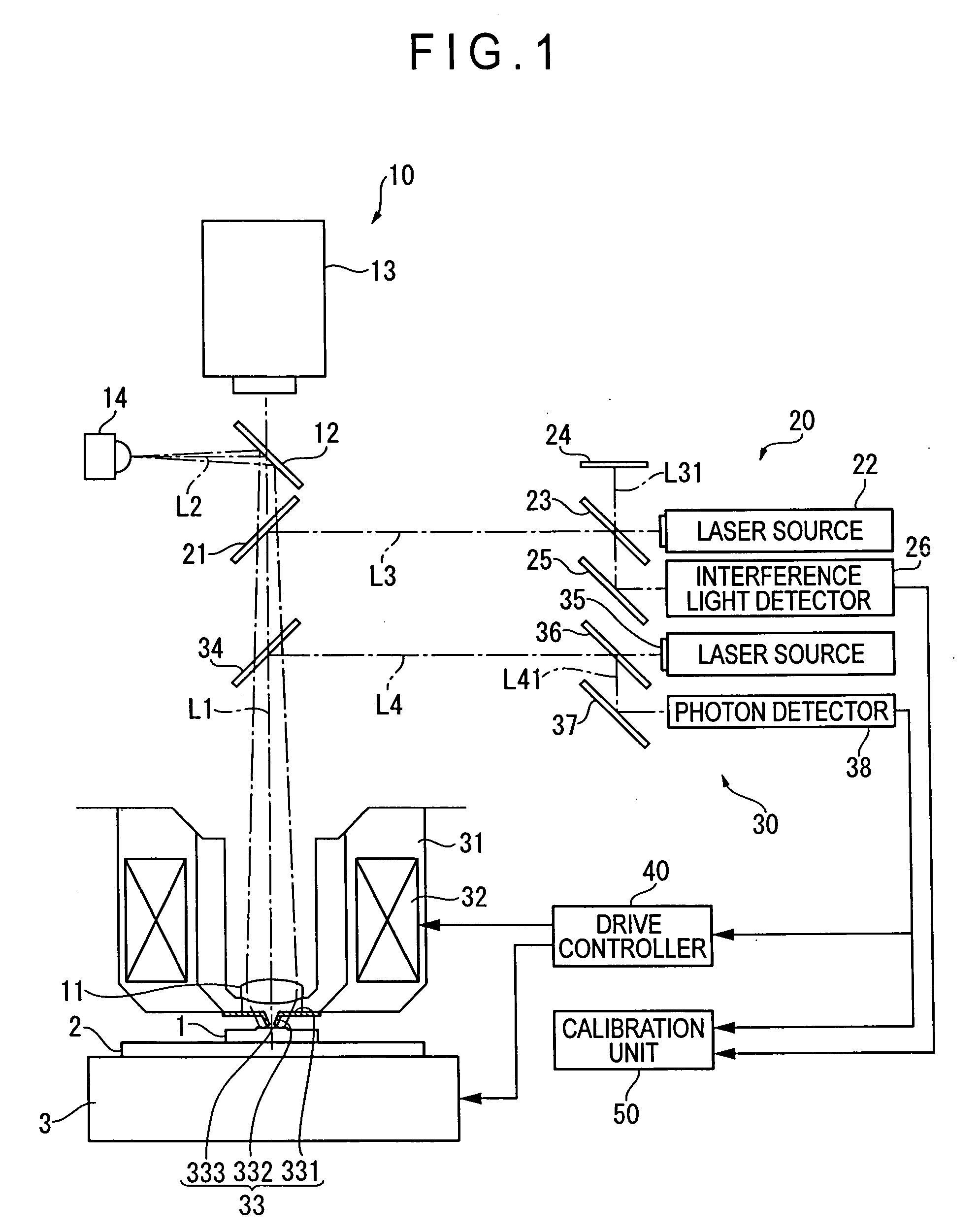
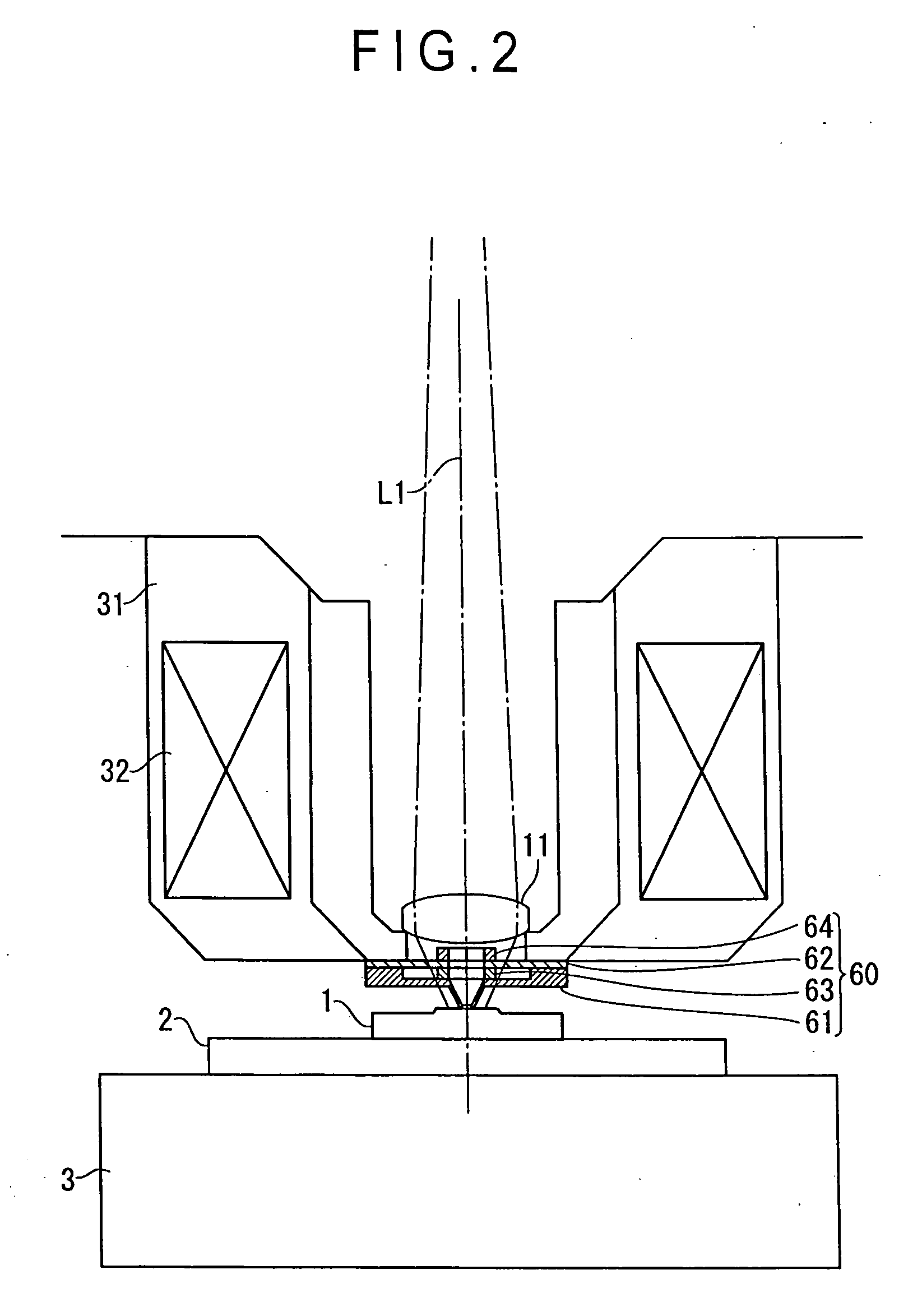
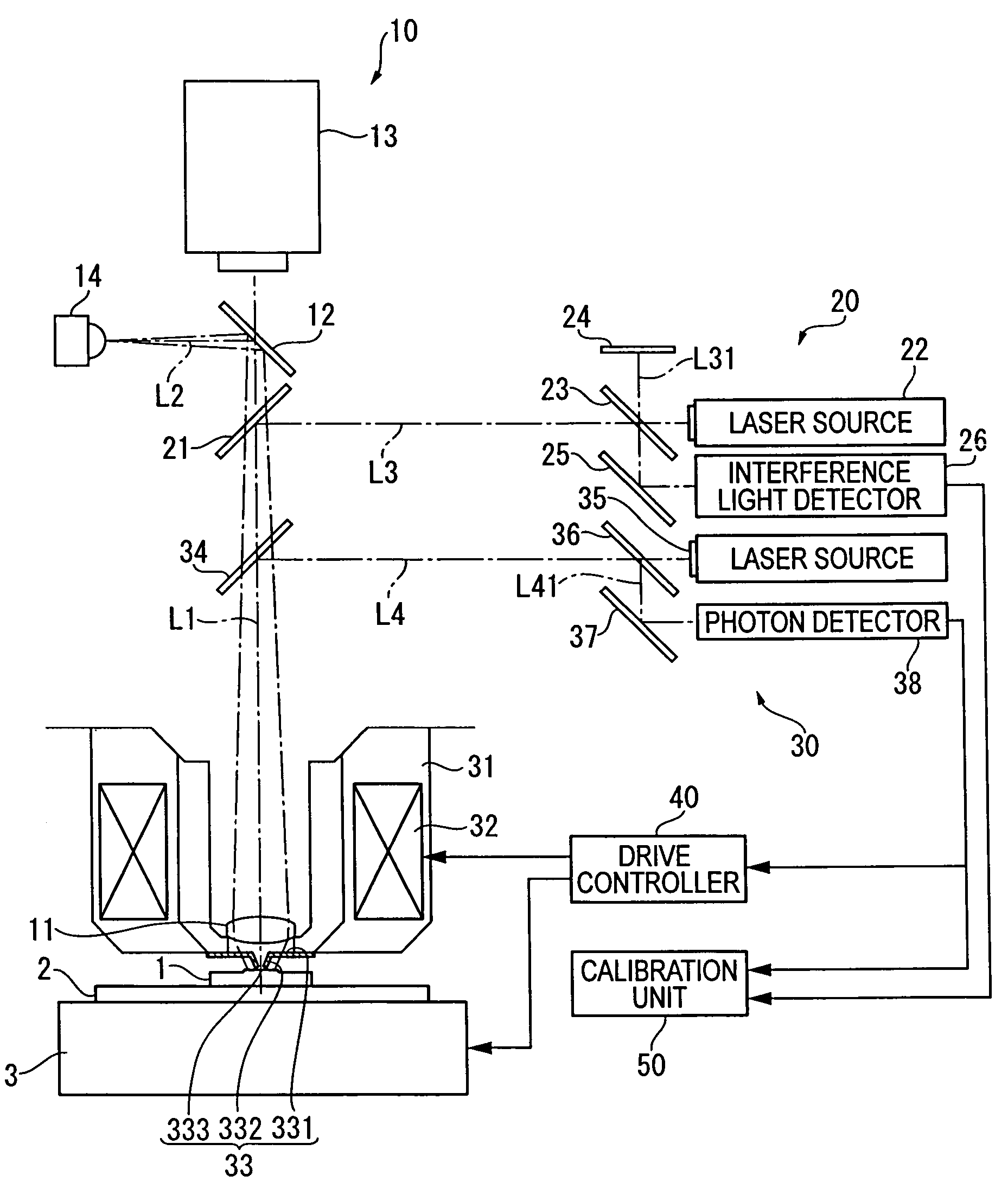
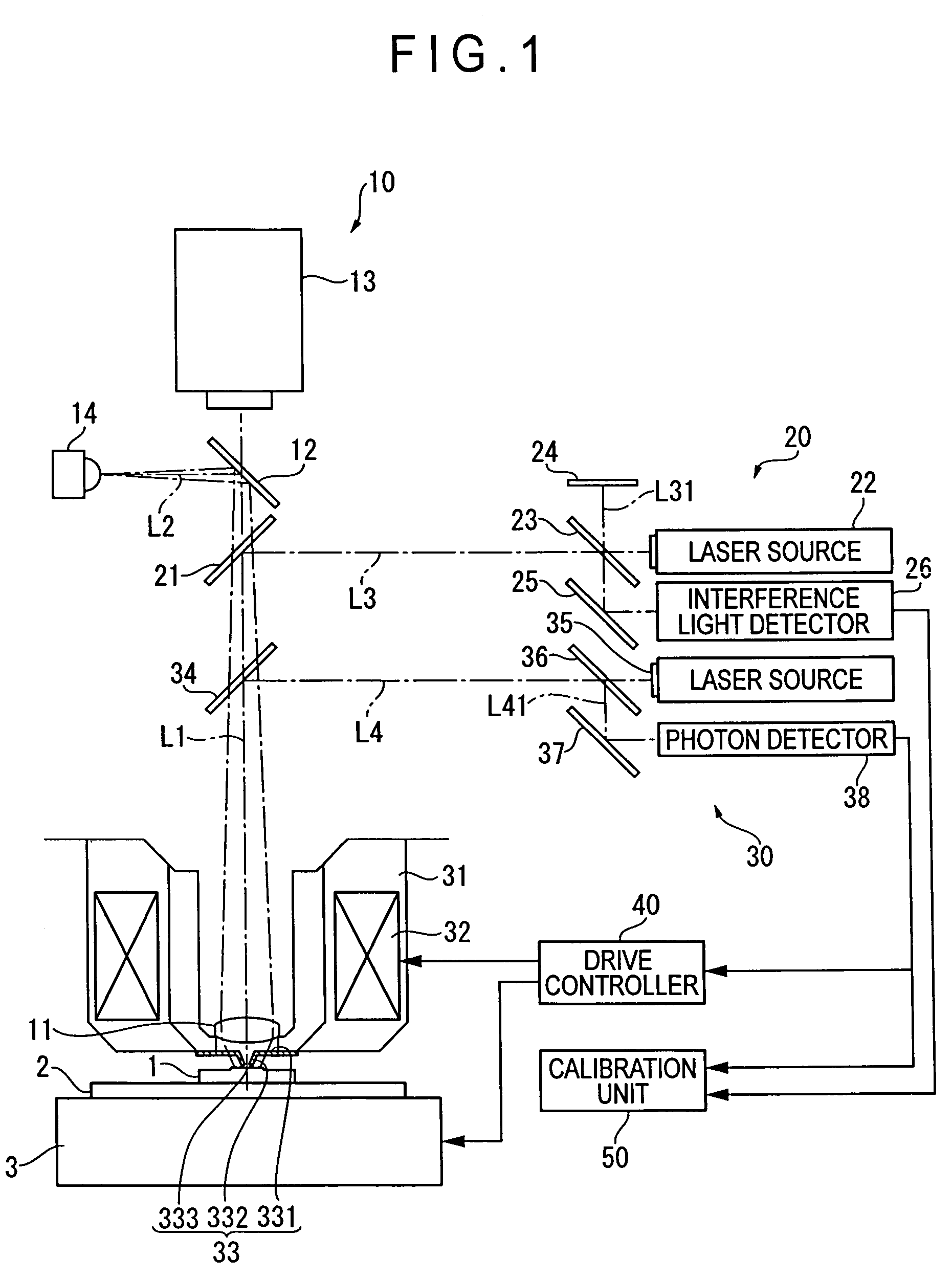
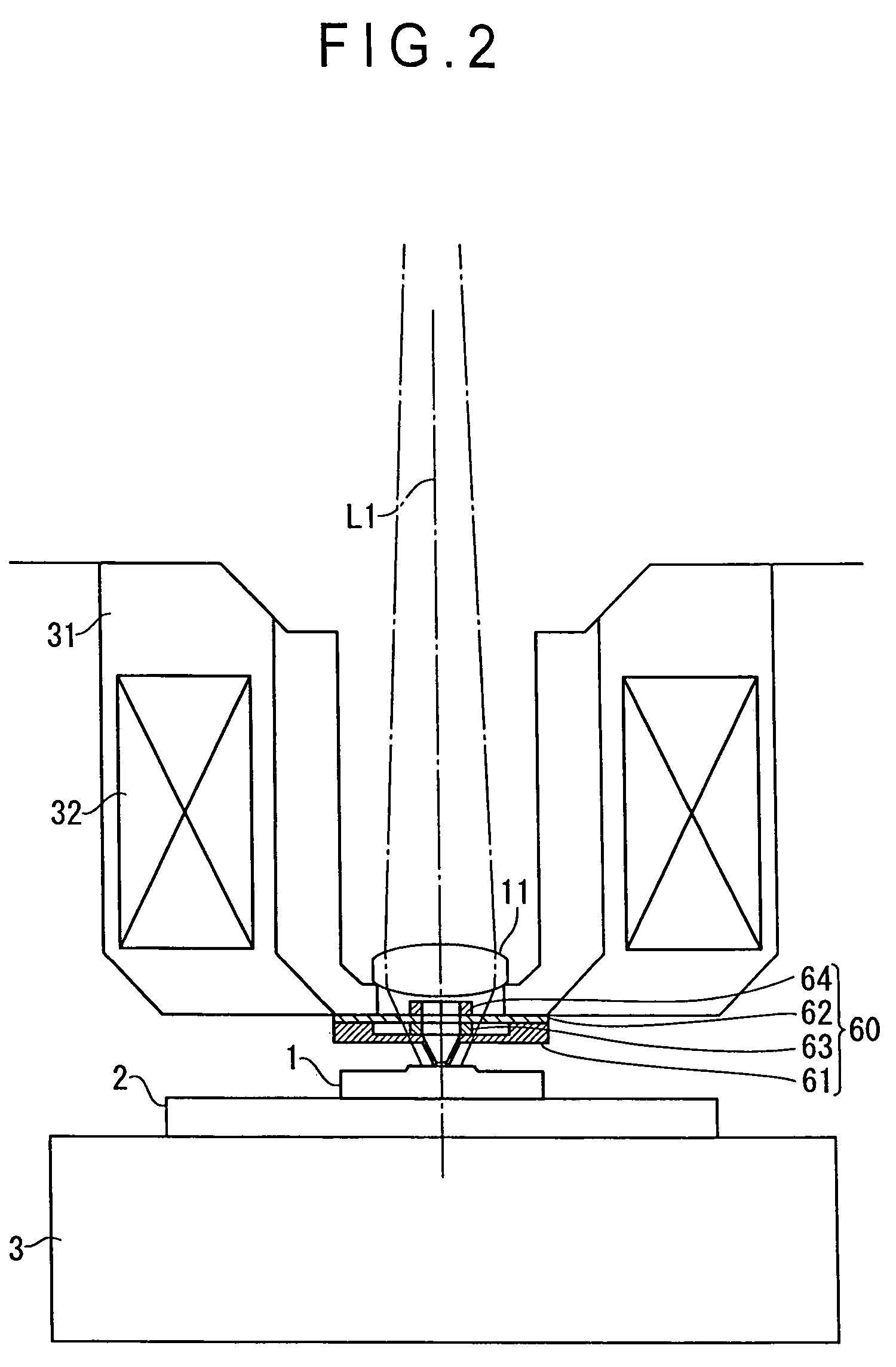
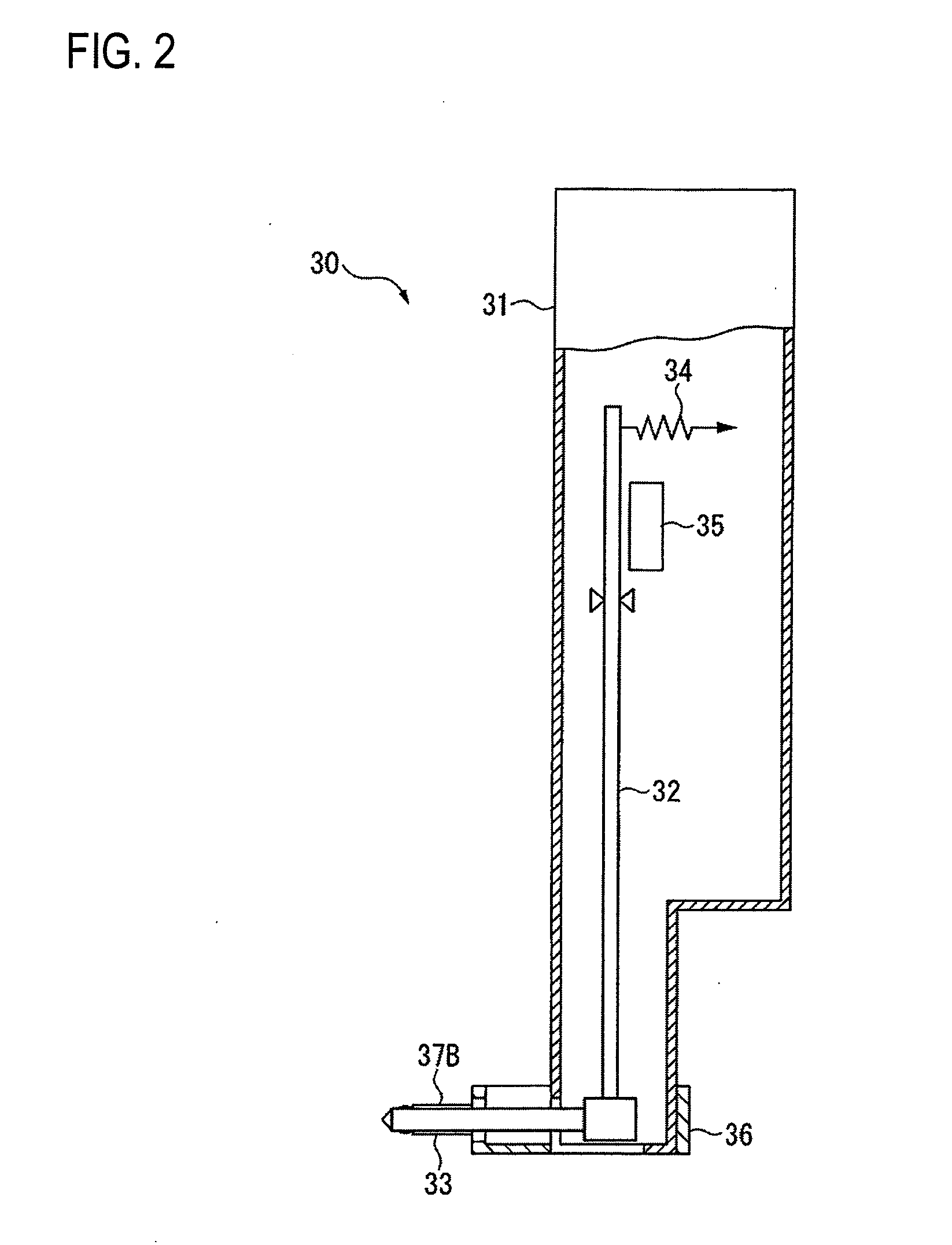
ActiveUS20060109480A1High precision calibrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMeasuring instrumentScattering effect
A surface texture measuring instrument provided with a near-field measuring unit (30) including a near-field probe (33) that forms a near-field light at a tip end thereof when a laser beam is irradiated, a laser source (35) that generates the laser beam to be irradiated on the near-field probe (33), a detection element (38) that detects scattering effect of the near-field light generated when the near-field probe (33) is moved close to a workpiece (1), and an actuator (32) that displaces the near-field probe (33) and the workpiece (1) in a direction moving close to / away from each other, includes: a laser length-measuring unit (20) that measures a relative distance between a reference position and the workpiece (1) in the vicinity of the tip end of the near-field probe (33) or a relative distance between the reference position and the near-field probe (33).
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
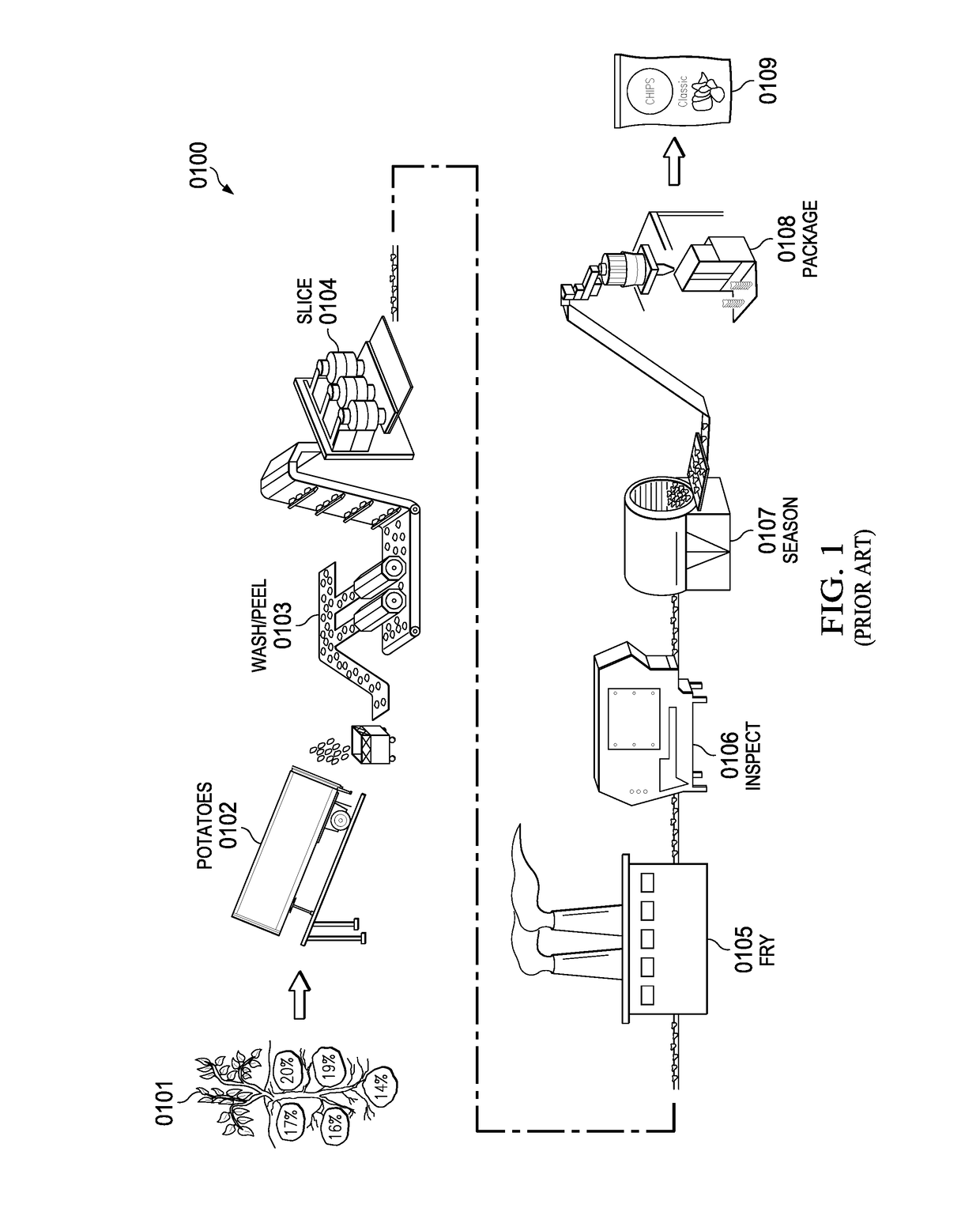
Feedback control of food texture system and method
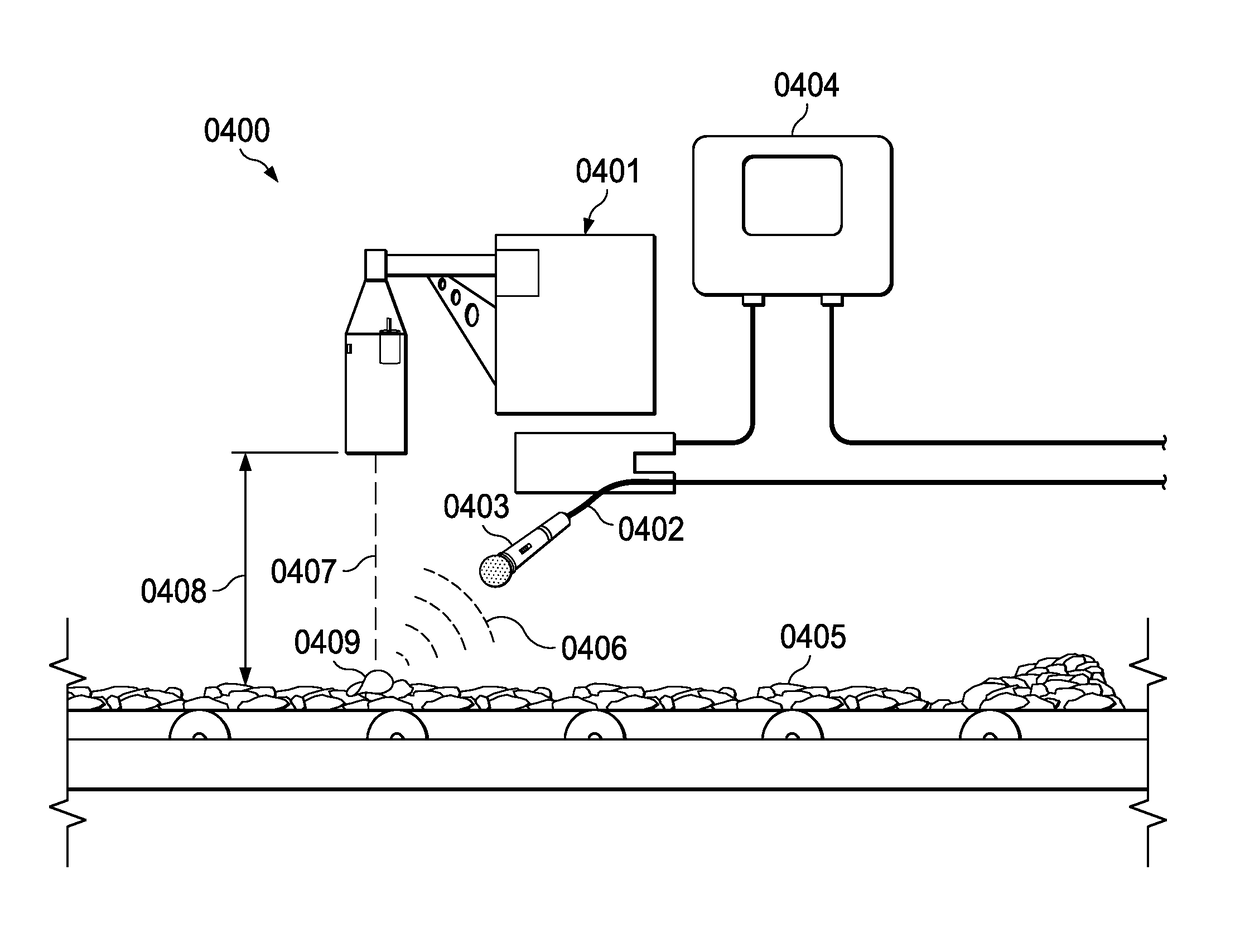
ActiveUS20170089869A1Testing starch susbtancesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesControl systemEngineering
A feedback and feedforward as well as a statistical predictive control system and method for continuously controlling texture of a food snack in a manufacturing process. The feedback system includes a quantitative texture measuring tool that is positioned downstream of a food processing unit. The texture measuring tool continuously measures a texture attribute of food snack from the food processing unit and feeds back texture attribute information to a controller that controls input parameters to food processing unit such that the texture attribute of a resultant food snack falls within an acceptable limit. The texture measuring tool comprises an excitation tool that strikes the food snack and produces an acoustic signal that is processed by a data processing unit. The data processing unit identifies relevant frequencies in the acoustic signal and quantitatively measures a texture attribute based on a correlated model that includes the relevant frequencies.
Owner:FRITO LAY NORTH AMERICA INC
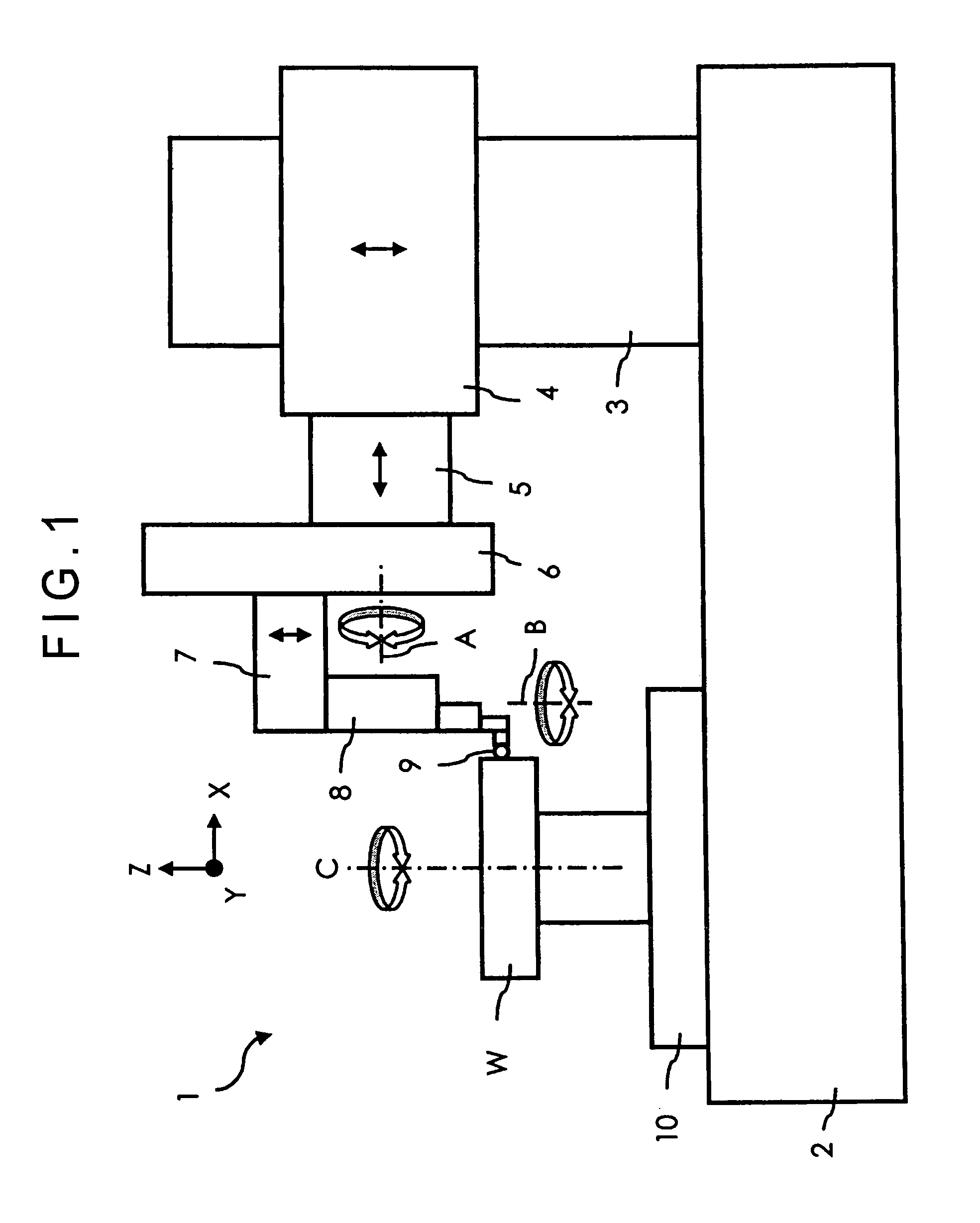
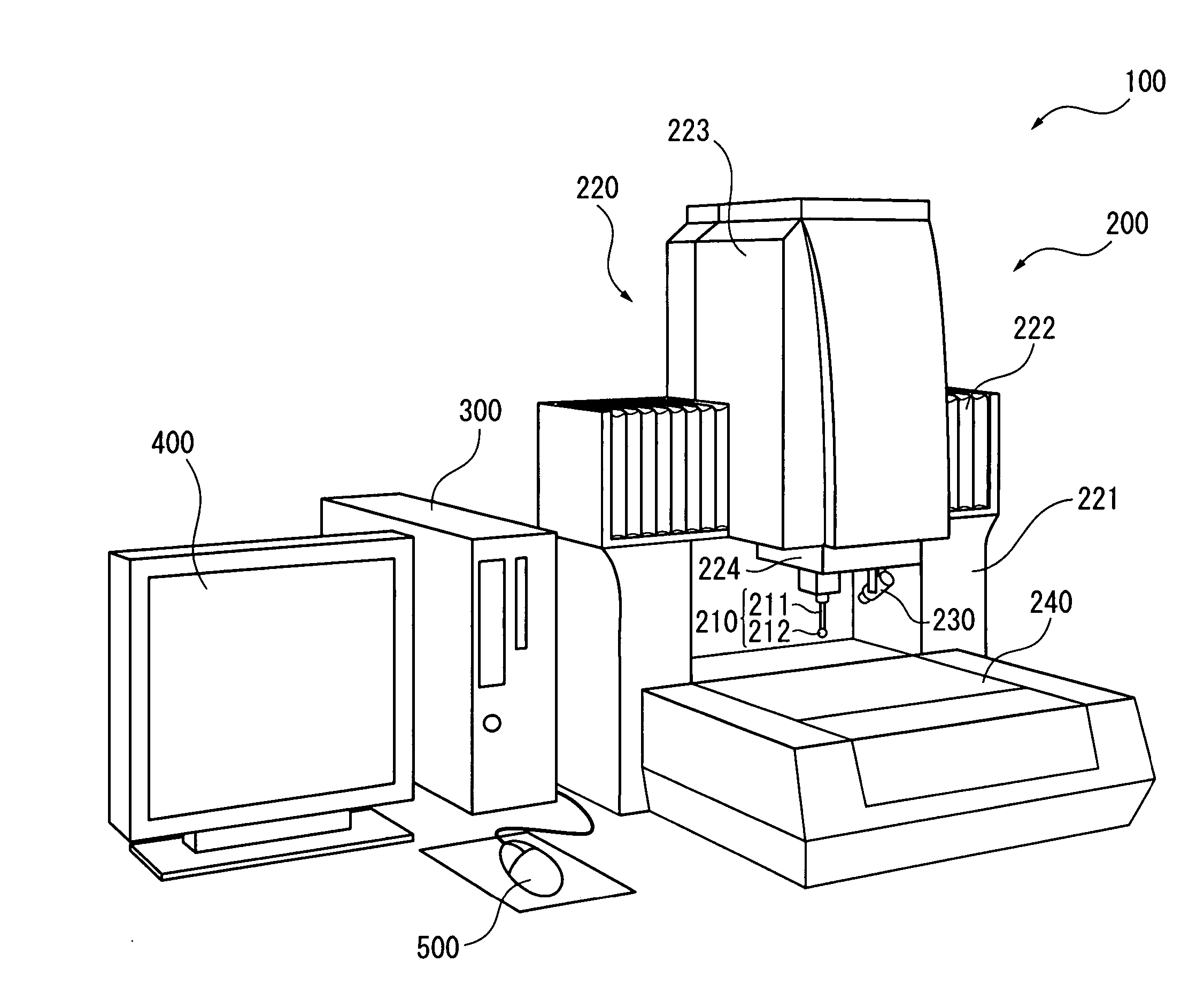
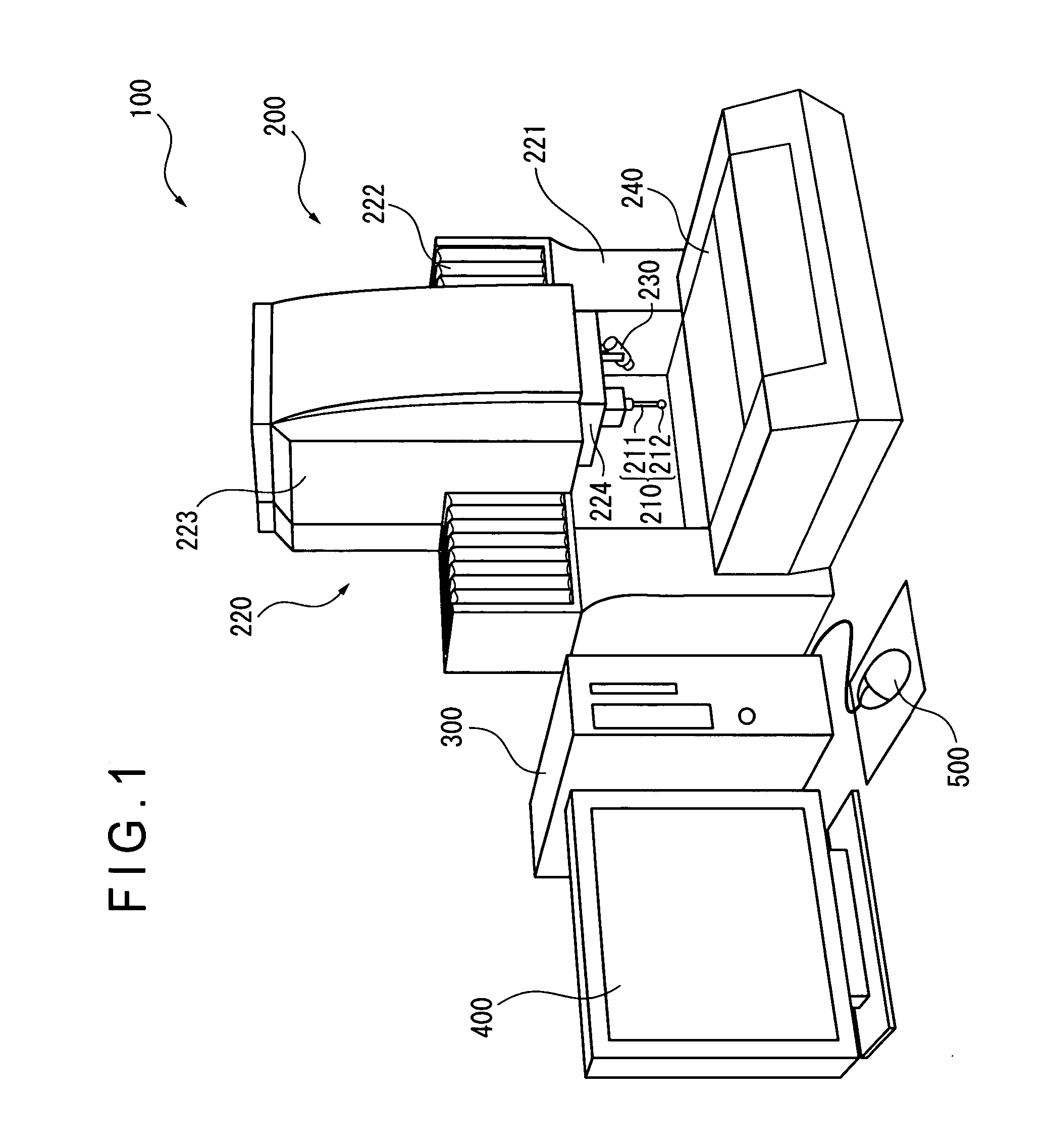
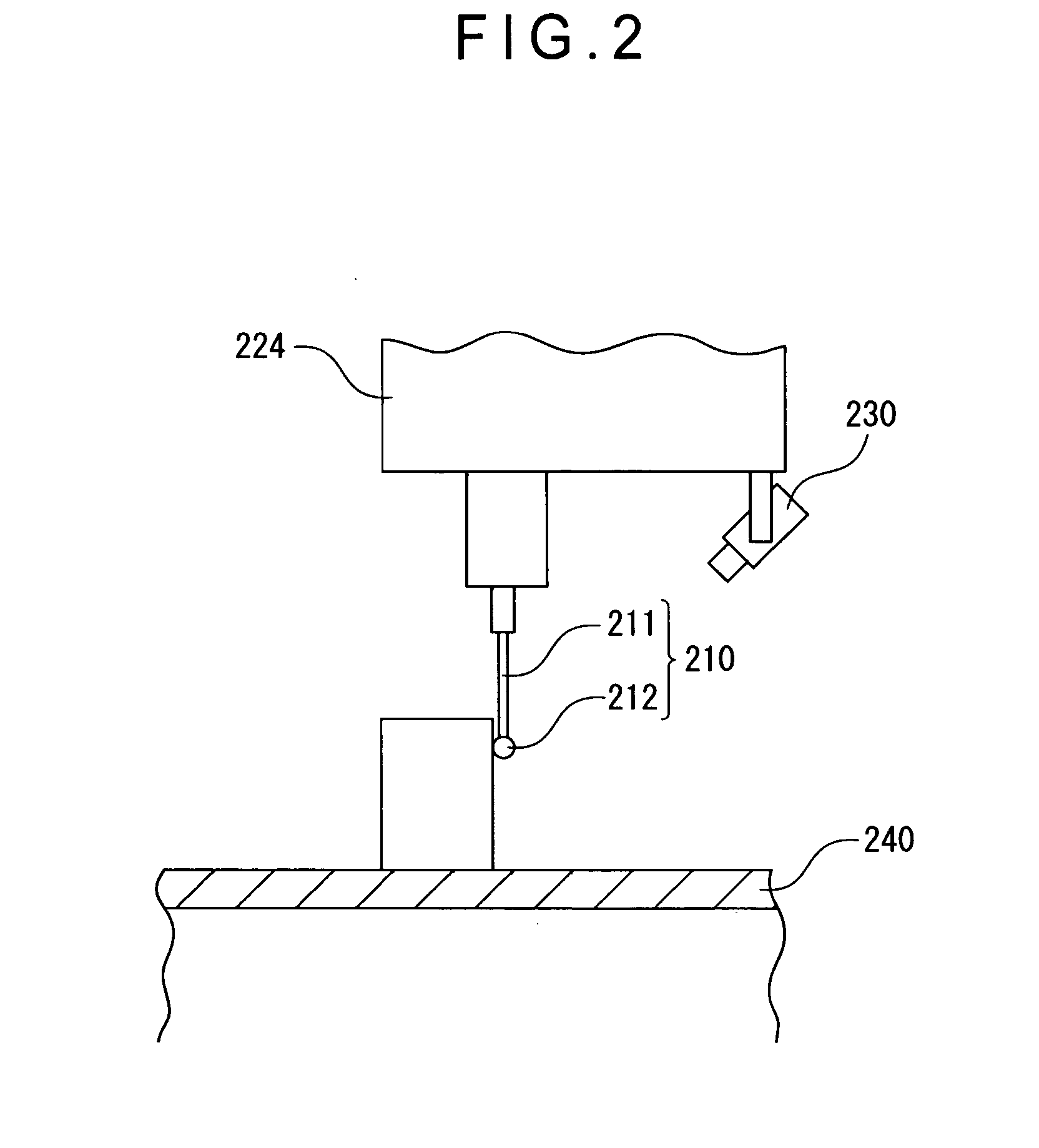
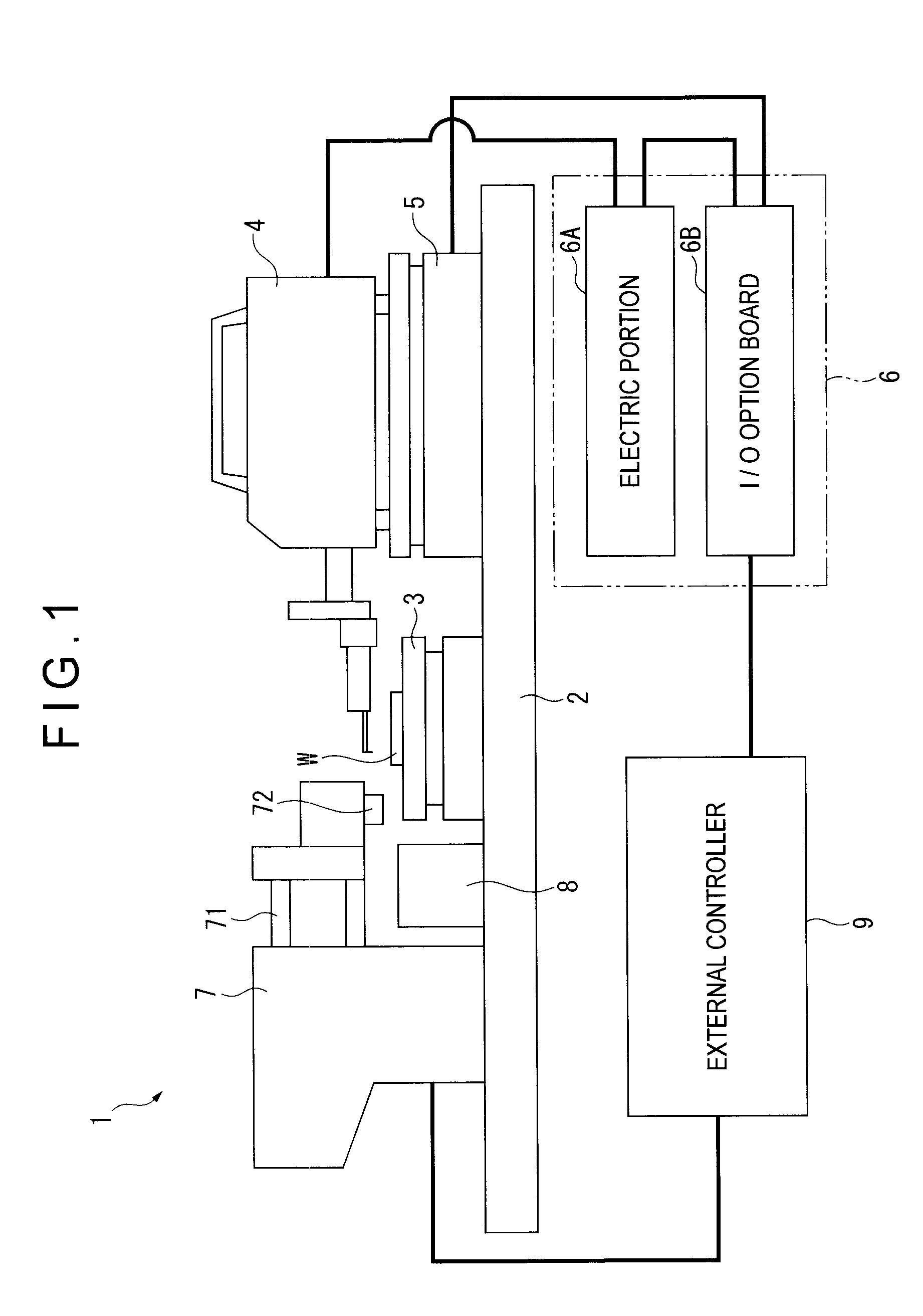
Probe observing device and surface texture measuring device
InactiveUS20070086620A1High measurement accuracyEasy to operateCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansImaging processingMeasurement device
Provided is a probe observing device, including: a camera (230) for taking an image of a probe (210 ); an image processing unit (330) for processing data on the image taken by the camera (230); a monitor (400) for displaying the image data processed by the image processing unit (330); and a mouse (500) for inputting an instruction for image processing through manual operation. The image processing unit (330) includes an image data processing unit (350) for processing the image data in accordance with the instruction inputted by the mouse. The camera (230) includes a low-magnification lens system, and is provided to be fixed in position with respect to the probe (210) such that the probe (210) enters the view field of the camera (230).
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Measurement texture geometric feature reconstruction method based on photometric stereo
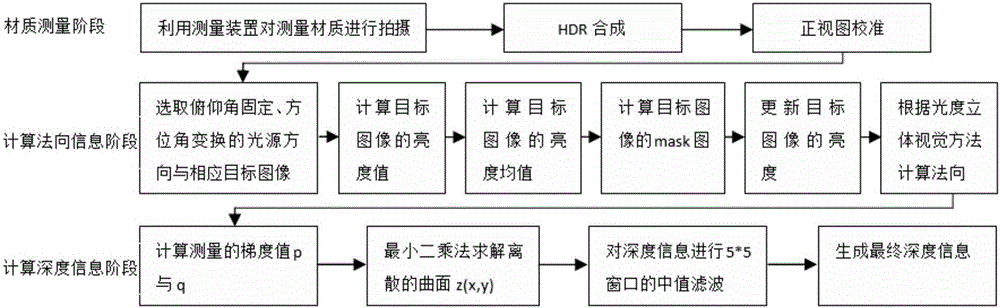
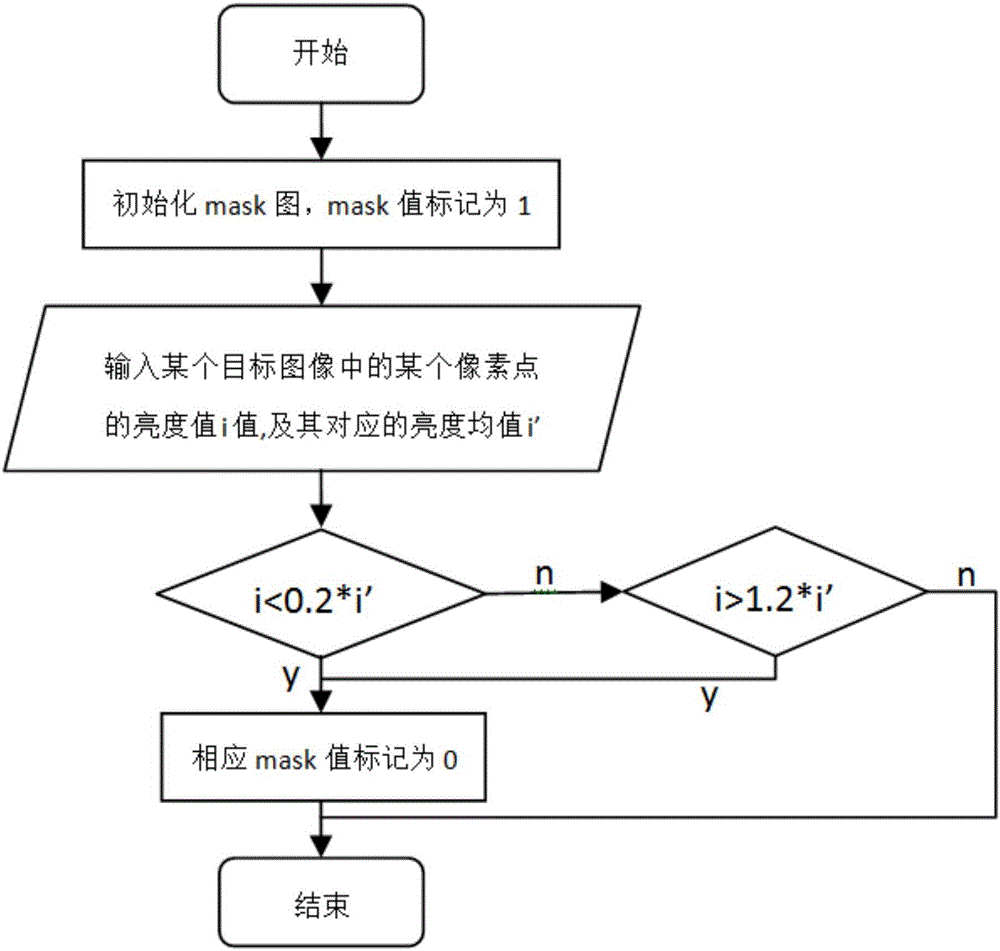
ActiveCN105787989AAccurate calculationImage rendering3D-image renderingReconstruction methodDiffuse reflection
The invention discloses a measurement texture geometric feature reconstruction method based on photometric stereo. The method is characterized in that utilizing a realistic texture measuring device in a camera light source array mode to collect BTF data under different angle light sources and viewing angles; with measurement texture multi-view angle information being combined, optimizing a photometric stereo method and reconstructing normal information of the measurement texture; and reconstructing depth information of the measurement texture through a least square method in a measurement gradient field according to the normal information. More accurate normal information can be calculated when the input image sequence is influenced by non-Lamertian diffuse reflection parts of highlight and shadow and the like in the stage of calculating shadow information of the surface of the texture, and in the stage of calculating the depth information, influence of noise of the measurement gradient field on the depth is reduced through filtering.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
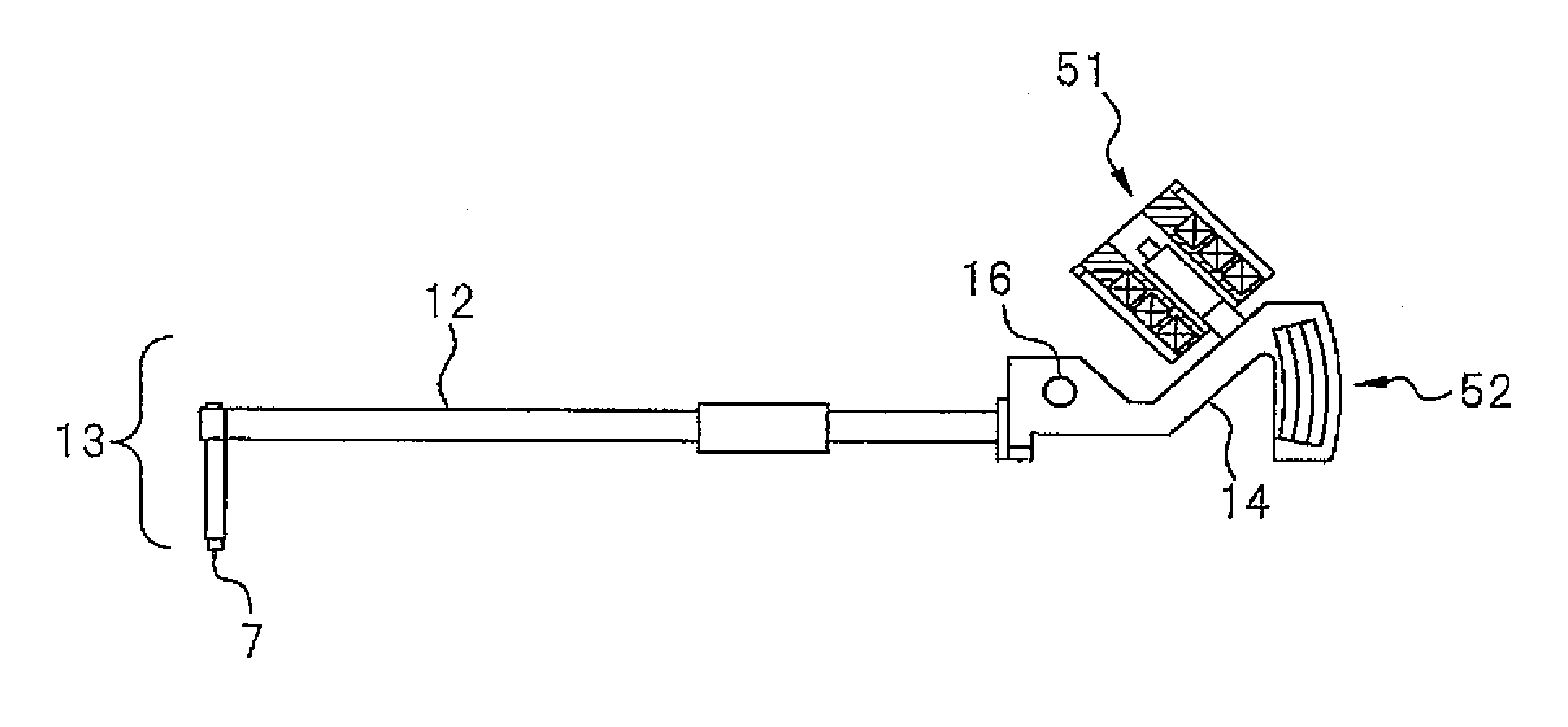
Contour and surface texture measuring instrument and contour and surface texture measuring method
ActiveUS20140331511A1High resolutionImprove linearityMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsMeasuring instrumentLinearity
A contour and surface texture measuring instrument for measuring a contour and surface texture of a surface of a work W, whose configuration is simple and which can be implemented at a low cost, and which generates a displacement signal having a high resolution and high linearity in a wide measurement range is disclosed, the contour and surface texture measuring instrument having a measurement part 13 having a probe 13 configured to come into contact with the surface of the work W and to change its position vertically, a feed mechanism 14 configured to relatively move the work with respect to the probe, an arm 12 having the measurement part at one end and configured to transfer a displacement of the probe and to rotate with a pivot 16 as a center, and a differential transformer-type detection mechanism 51 and a scale-type detection mechanism 52 attached to the arm or a position interlocked with the arm and configured to detect a displacement of the probe.
Owner:TOKYO SEIMITSU
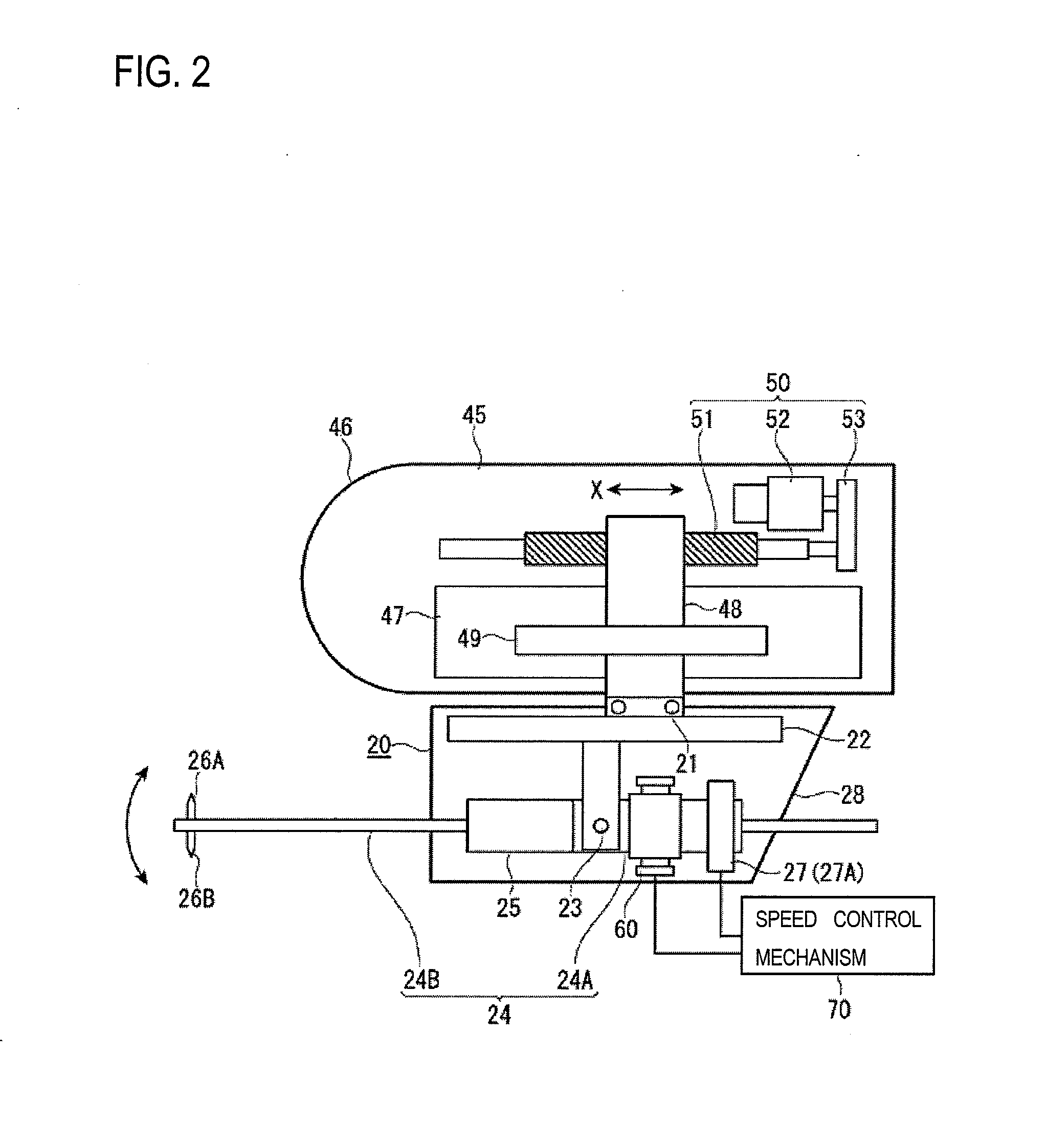
Surface texture measuring apparatus
ActiveUS20120227476A1Not easy to damageAvoid damageMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsRelative motionEngineering
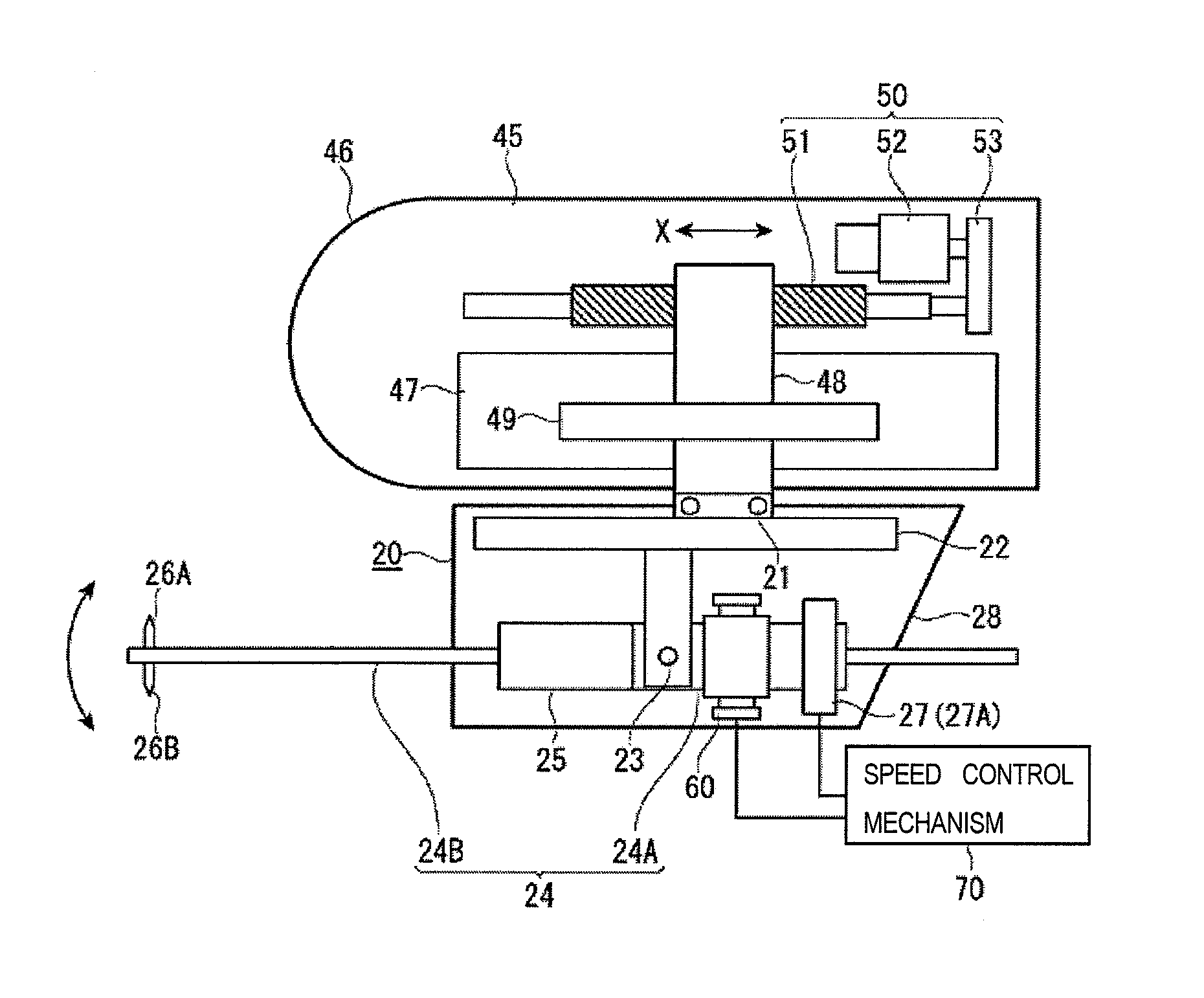
A surface texture measuring apparatus includes a stylus displacement detector having a measurement arm which is able to swing, a pair of styli provided at a tip of the measurement arm, and a detection unit configured to detect swing amounts of the measurement arm, a stage configured to mount the subject of measurement thereon, and a relative movement mechanism configured to cause a relative movement between the detector and the stage. The apparatus includes a posture switching mechanism configured to switch a posture of the measurement arm between a posture in which the measurement arm is urged in one swing direction and a posture in which the measurement arm is urged in the other swing direction, and a speed control mechanism configured to control a switching speed of posture switching of the measurement arm to a preset speed when the posture of the measurement arm is switched by the posture switching mechanism.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Surface texture measuring instrument and measuring method
ActiveUS20100018298A1Easy to operateCompact configurationPrecision positioning equipmentMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsMeasurement deviceMeasuring instrument
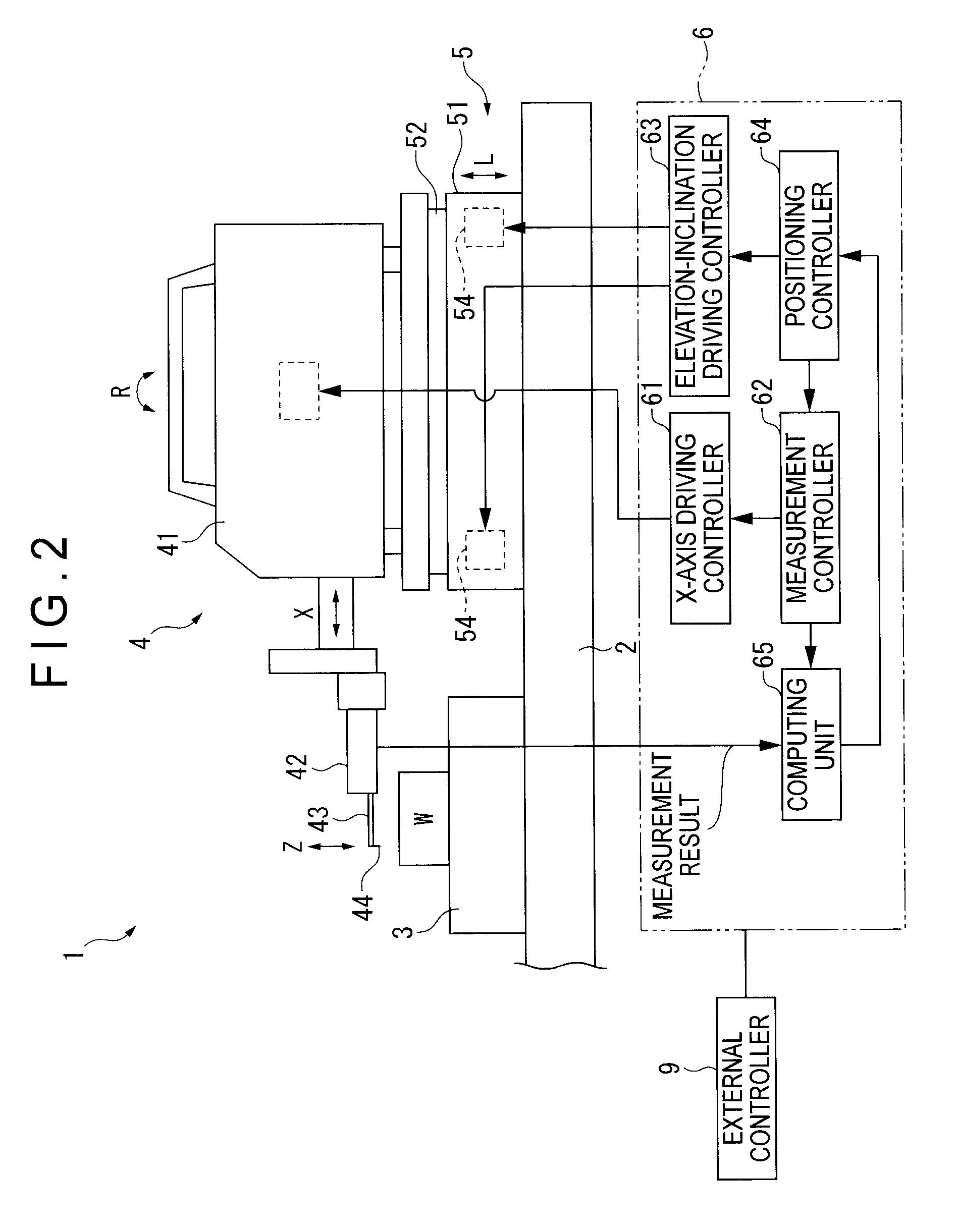
A surface texture measuring instrument includes: a measuring device that includes a detector for detecting surface texture of a workpiece and an X-axis movement mechanism for moving the detector in a measurement direction; an elevation inclination adjuster capable of adjusting an elevation position and an inclination angle of a table on which the measuring device is mounted; a stage on which the workpiece is mounted; and a controller that controls the measuring device and the elevation inclination adjuster. The controller includes: a measurement controller that controls the X-axis movement mechanism to conduct a preliminary measurement and main measurement of the workpiece; a computing unit that acquires a result of the preliminary measurement from the detector and obtains an inclination angle of the workpiece at which the workpiece is inclined to the measurement direction; and a positioning controller for adjusting the inclination angle of the table based on the obtained inclination angle.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Surface texture measuring instrument
ActiveUS7319528B2High precision calibrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMeasuring instrumentScattering effect
A surface texture measuring instrument provided with a near-field measuring unit (30) including a near-field probe (33) that forms a near-field light at a tip end thereof when a laser beam is irradiated, a laser source (35) that generates the laser beam to be irradiated on the near-field probe (33), a detection element (38) that detects scattering effect of the near-field light generated when the near-field probe (33) is moved close to a workpiece (1), and an actuator (32) that displaces the near-field probe (33) and the workpiece (1) in a direction moving close to / away from each other, includes: a laser length-measuring unit (20) that measures a relative distance between a reference position and the workpiece (1) in the vicinity of the tip end of the near-field probe (33) or a relative distance between the reference position and the near-field probe (33).
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
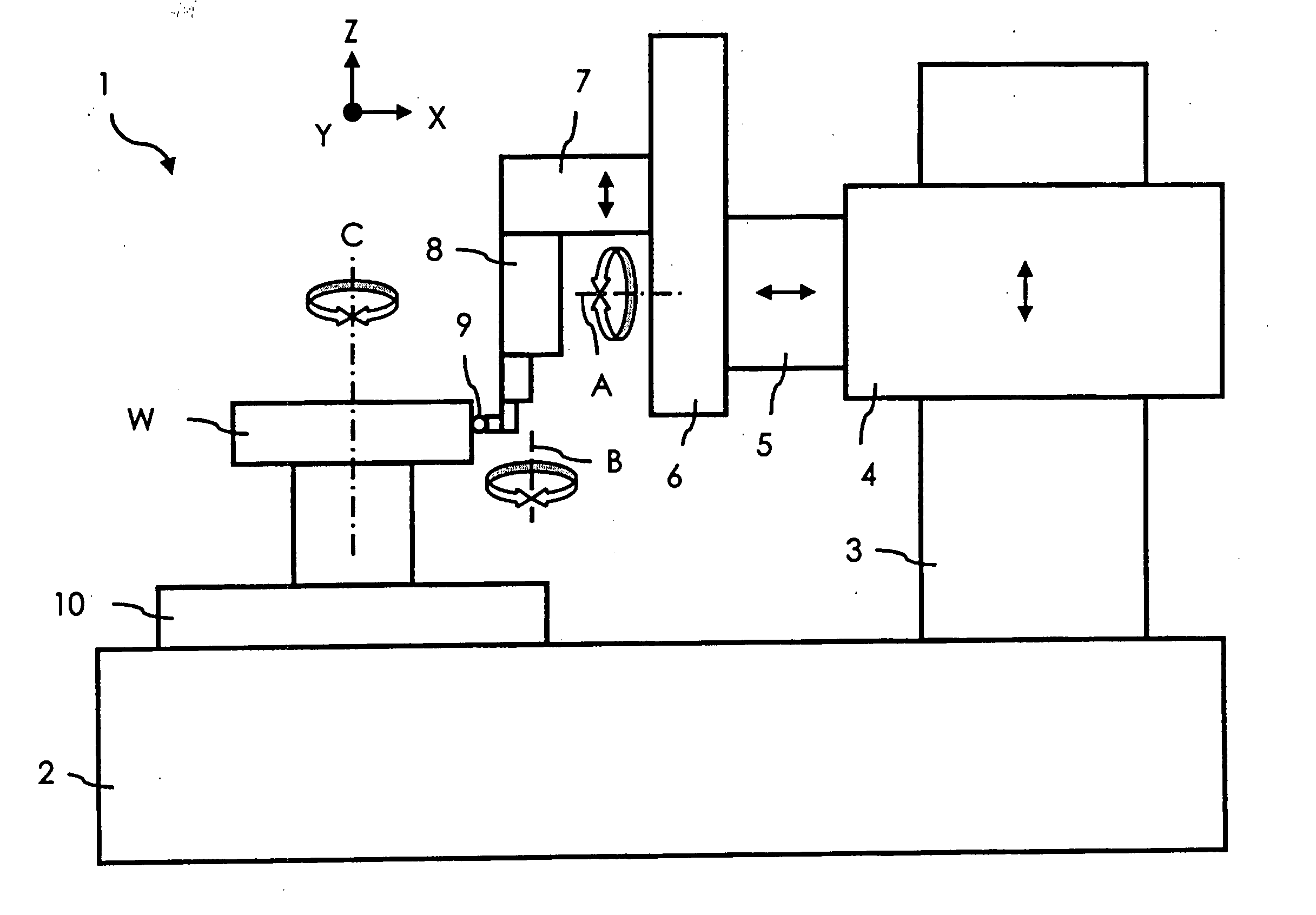
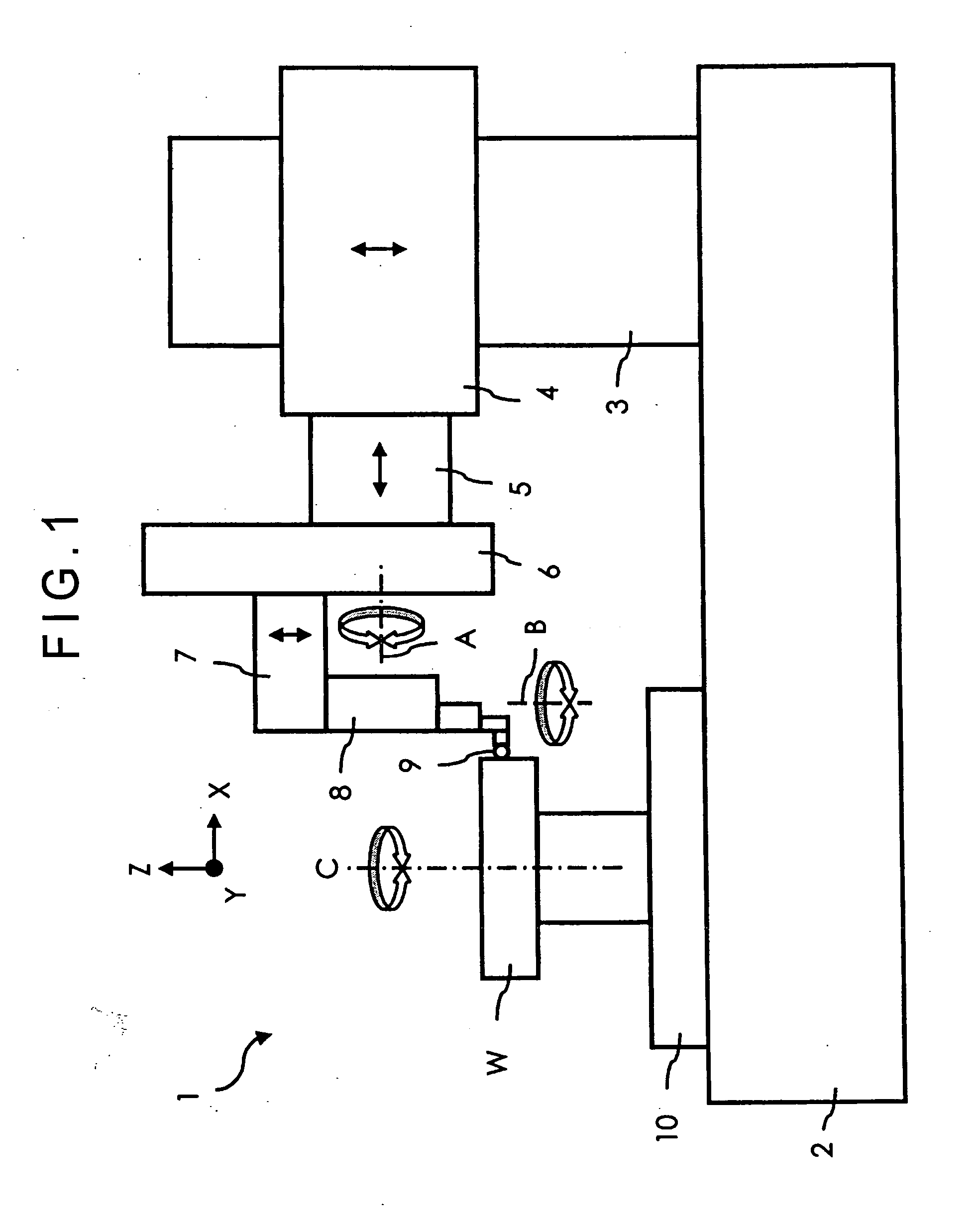
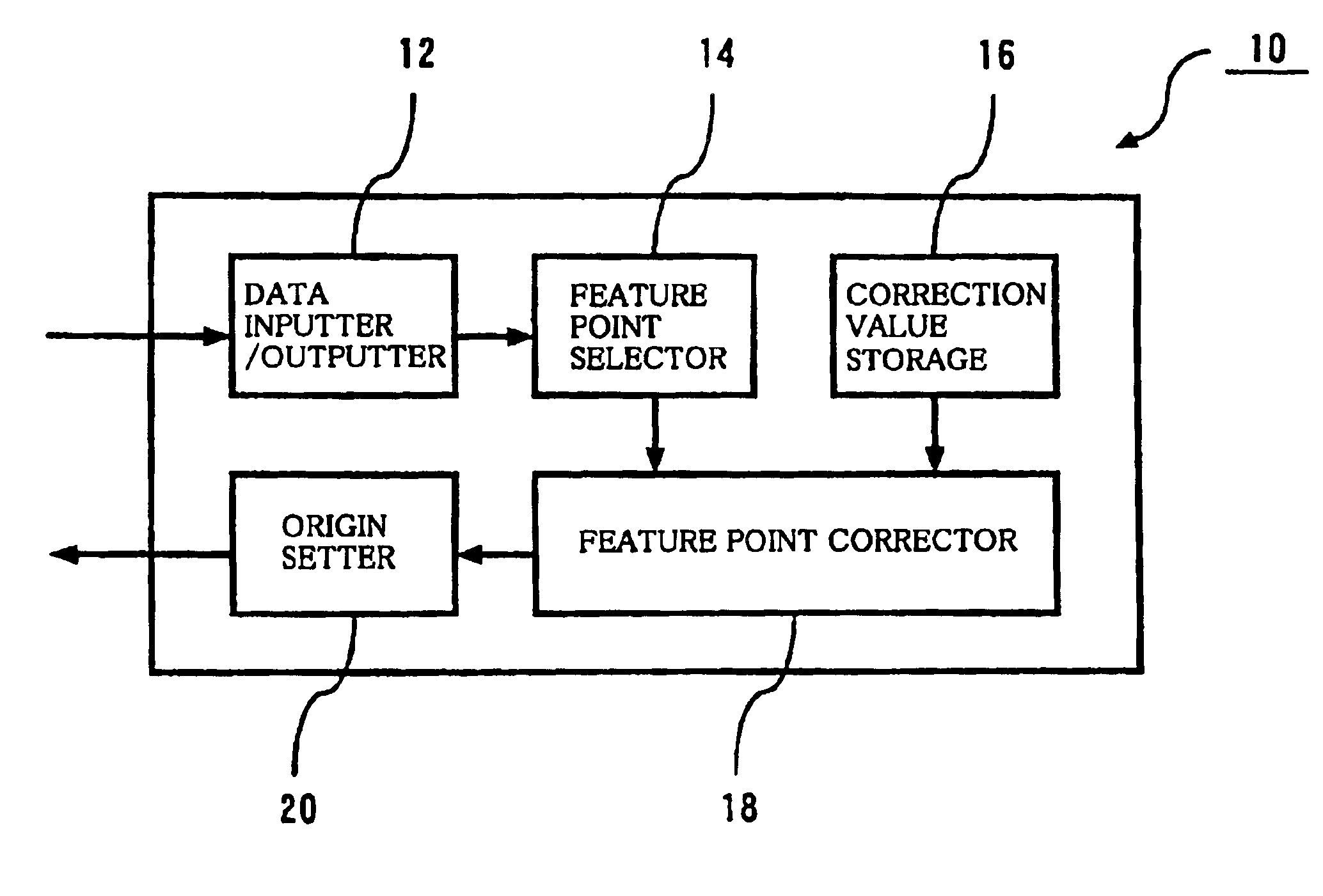
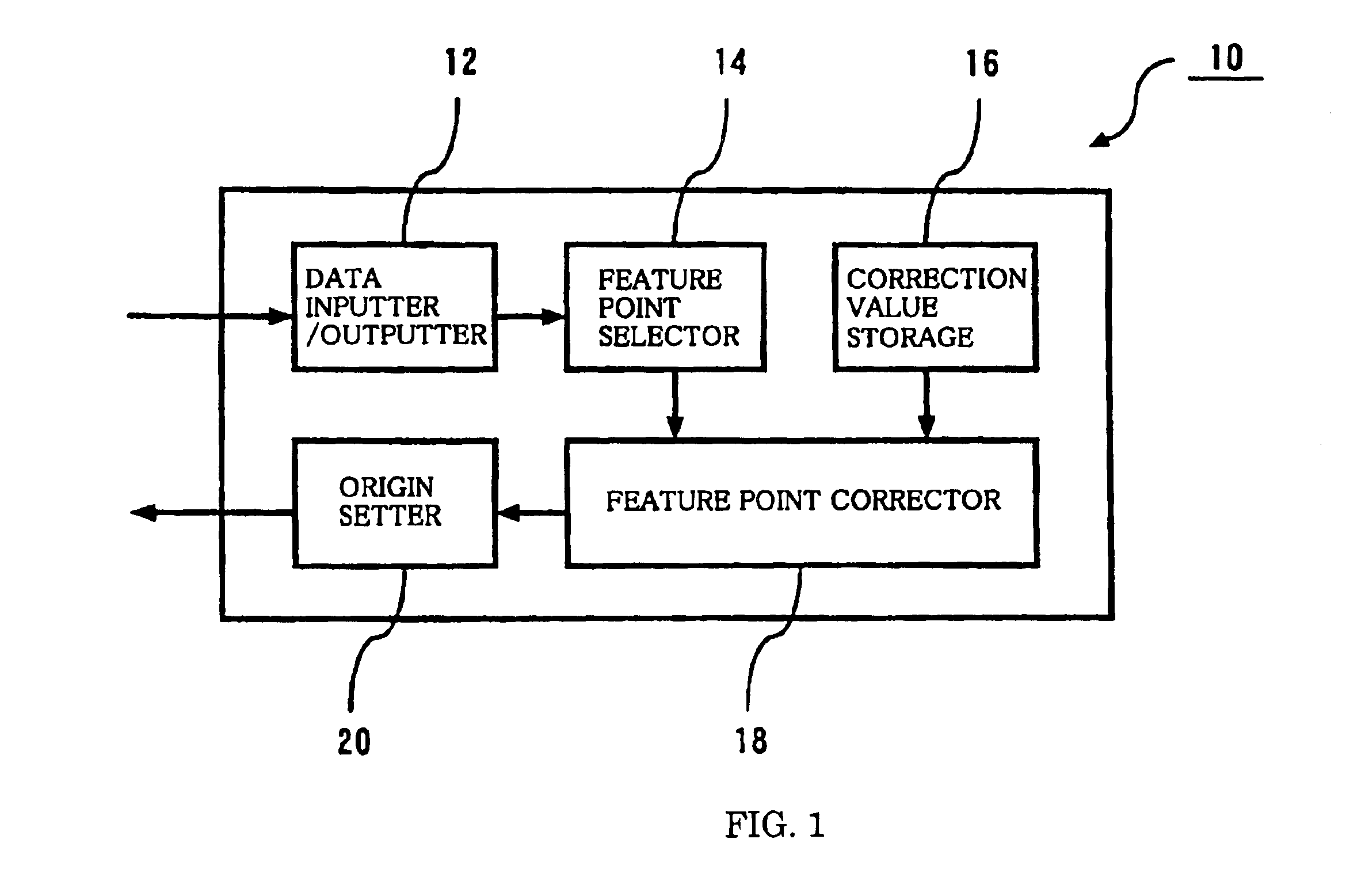
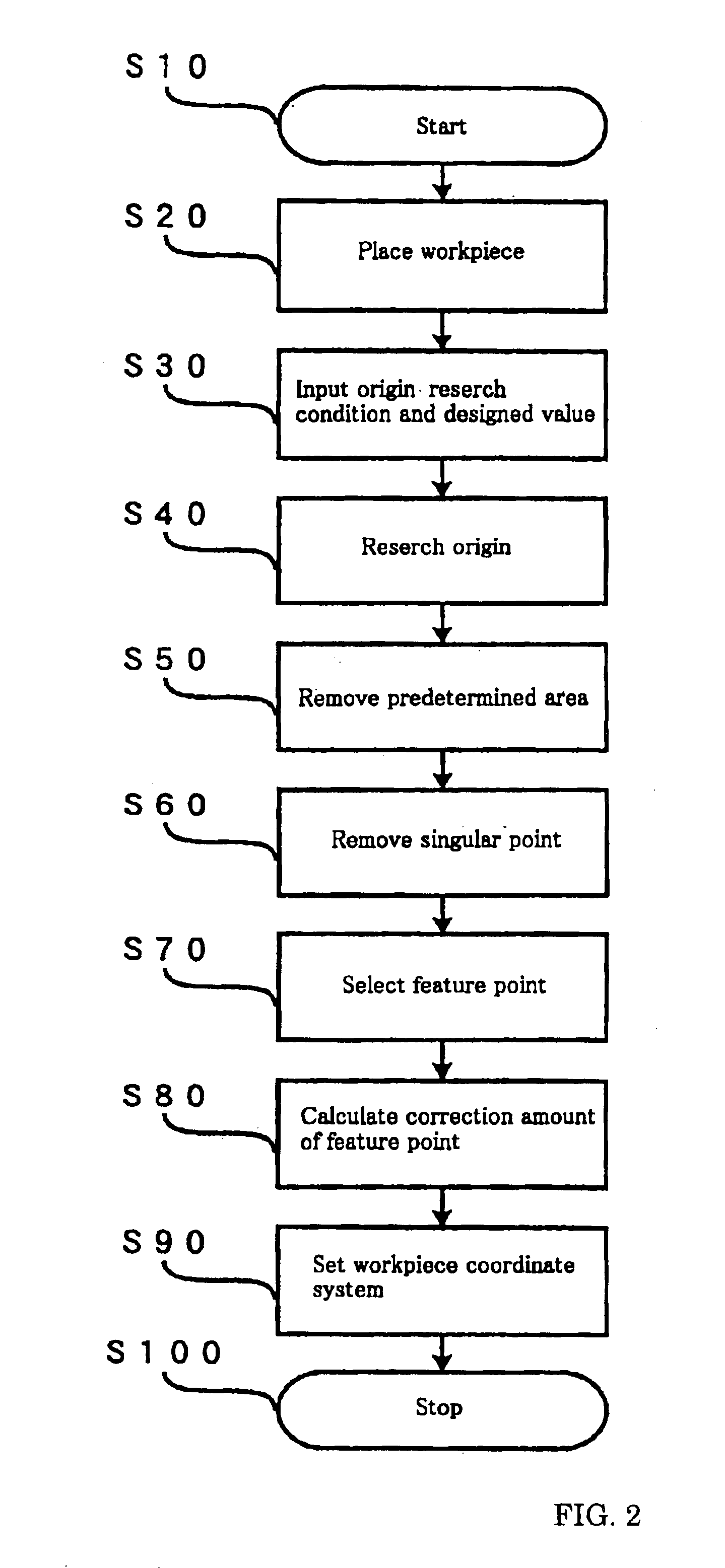
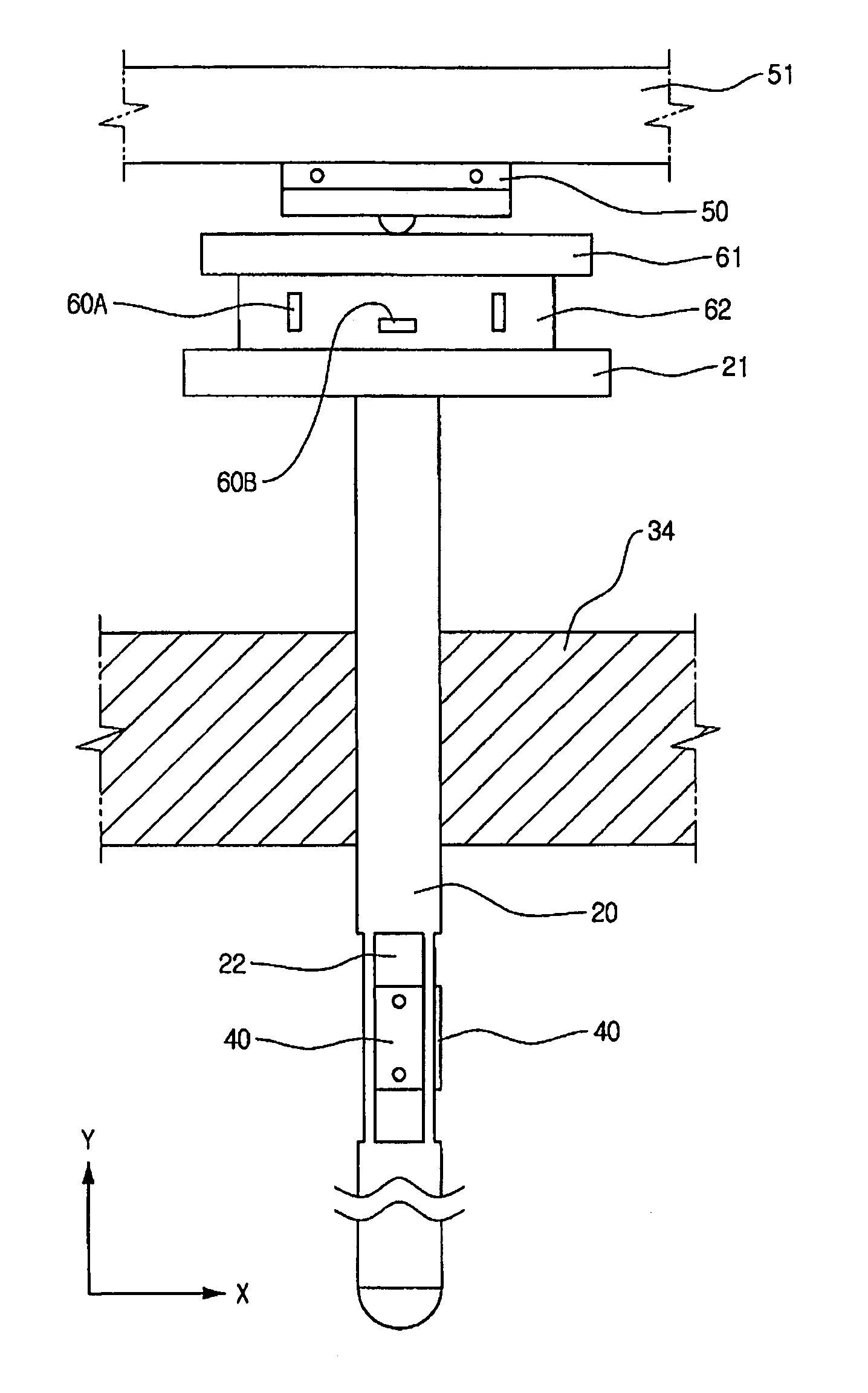
Workpiece coordinate system origin setting method, workpiece coordinate system origin setting program and workpiece coordinate system origin setting device of a surface property measuring machine
ActiveUS6895359B2Accurately and easily originDrawing from basic elementsFeeler-pin gaugesAcquired characteristicAlgorithm
The object of the invention is to provide a method, a program and a device that can set accurately and easily the origin of the coordinate system of a workpiece based on the result obtained by a surface texture measuring machine scanning over a feature area on the surface of the workpiece. The device comprises a data inputter for inputting data obtained by scanning a feature area including at least a feature point area and a non-feature point area of the surface of a workpiece, a feature point selector for extracting the feature points of the data by statistically processing the data inputted into the data inputter and an origin setter for setting the origin of a workpiece coordinate system relative to an origin setting target point of the workpiece based on the coordinate values of the feature point obtained by the feature point selector.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
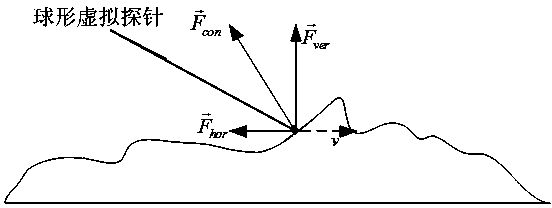
Texture force measuring method in force tactile representation
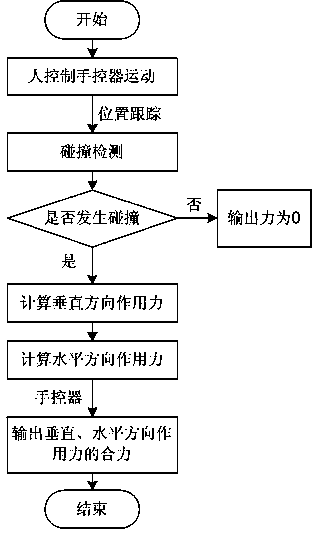
ActiveCN103439030AEmbodies stiffness propertiesImprove realismForce measurementTouch PerceptionEngineering
The invention discloses a texture force measuring method in force tactile representation. The texture force is decomposed to an acting force in the vertical direction and an acting force in the horizontal direction by considering surface factors of an objective texture and movement speed and active press force in the exploring process with human hands. The acting force in the vertical direction is divided into an objective factor acting force and a subjective factor acting force, wherein the objective factor acting force is determined by height of a microcosmic contour on the surface of the texture measured and surface stiffness characteristic. In consideration of change of normal acceleration in the contact process reflecting changes of speed and pressure of human hands in the moving process, the subjective factor acting force is the function of the normal acceleration, and the normal acceleration in simulation is a linear interpolation function of the measured acceleration under different pressures and at different speeds. The acting force in the horizontal direction can be frictional resistance when a probe streaks the surface of the texture and is determined by the pressure in the vertical direction and the dynamic friction coefficient of the texture material.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Mount table, surface texture measuring machine and surface texture measuring method
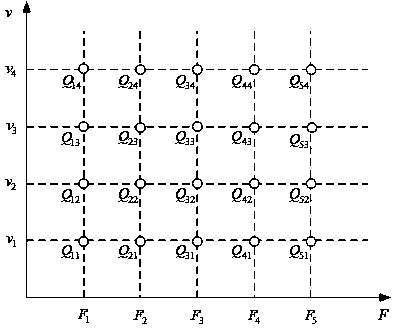
ActiveUS20050223579A1Accurate connectionAccurately synthesizedMechanical measuring arrangementsEngineeringTexture measure
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Contour and surface texture measuring instrument and contour and surface texture measuring method
ActiveUS9074865B2High resolutionImprove linearityMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsMeasuring instrumentLinearity
Owner:TOKYO SEIMITSU
Surface texture measuring instrument
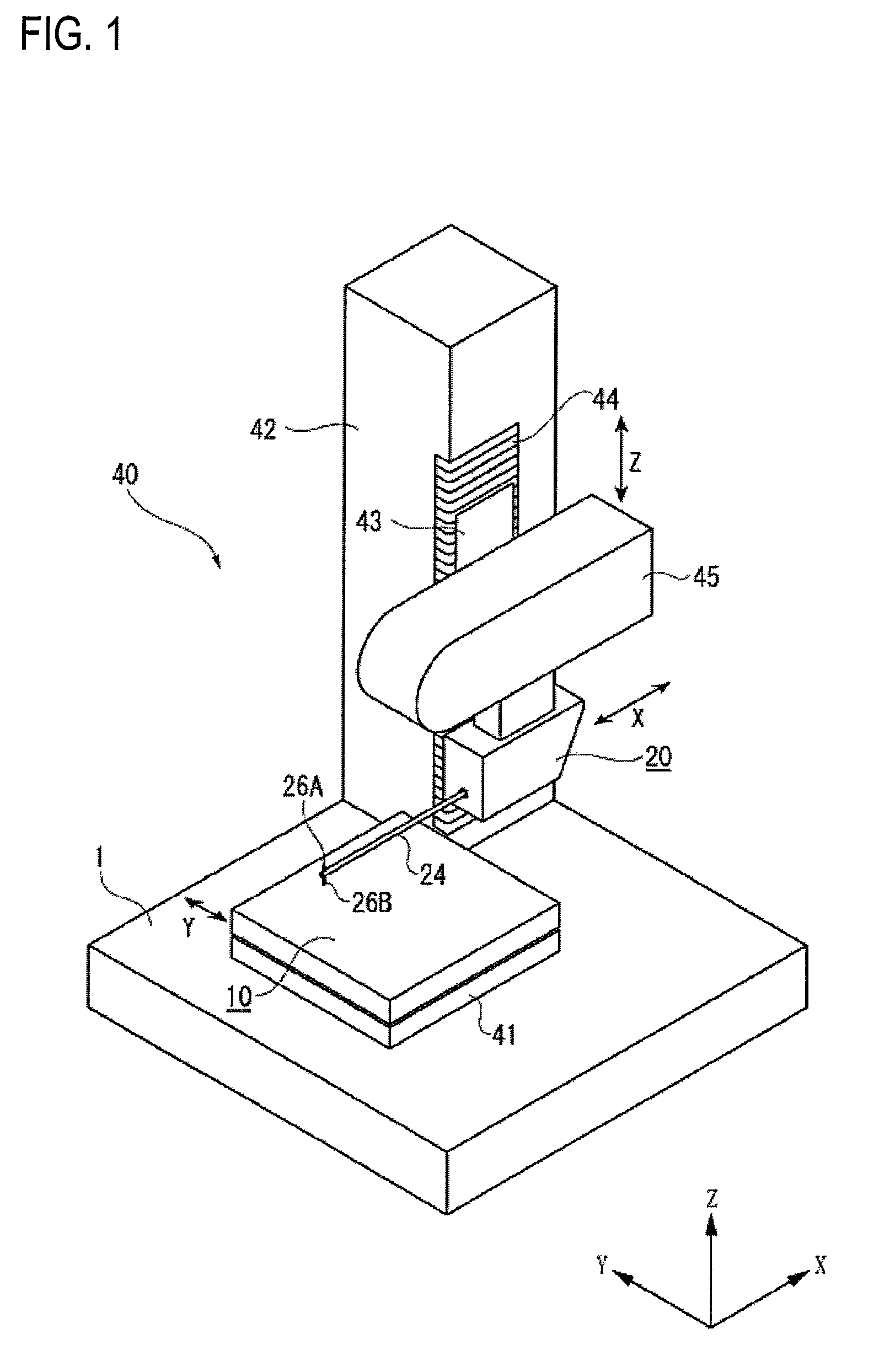
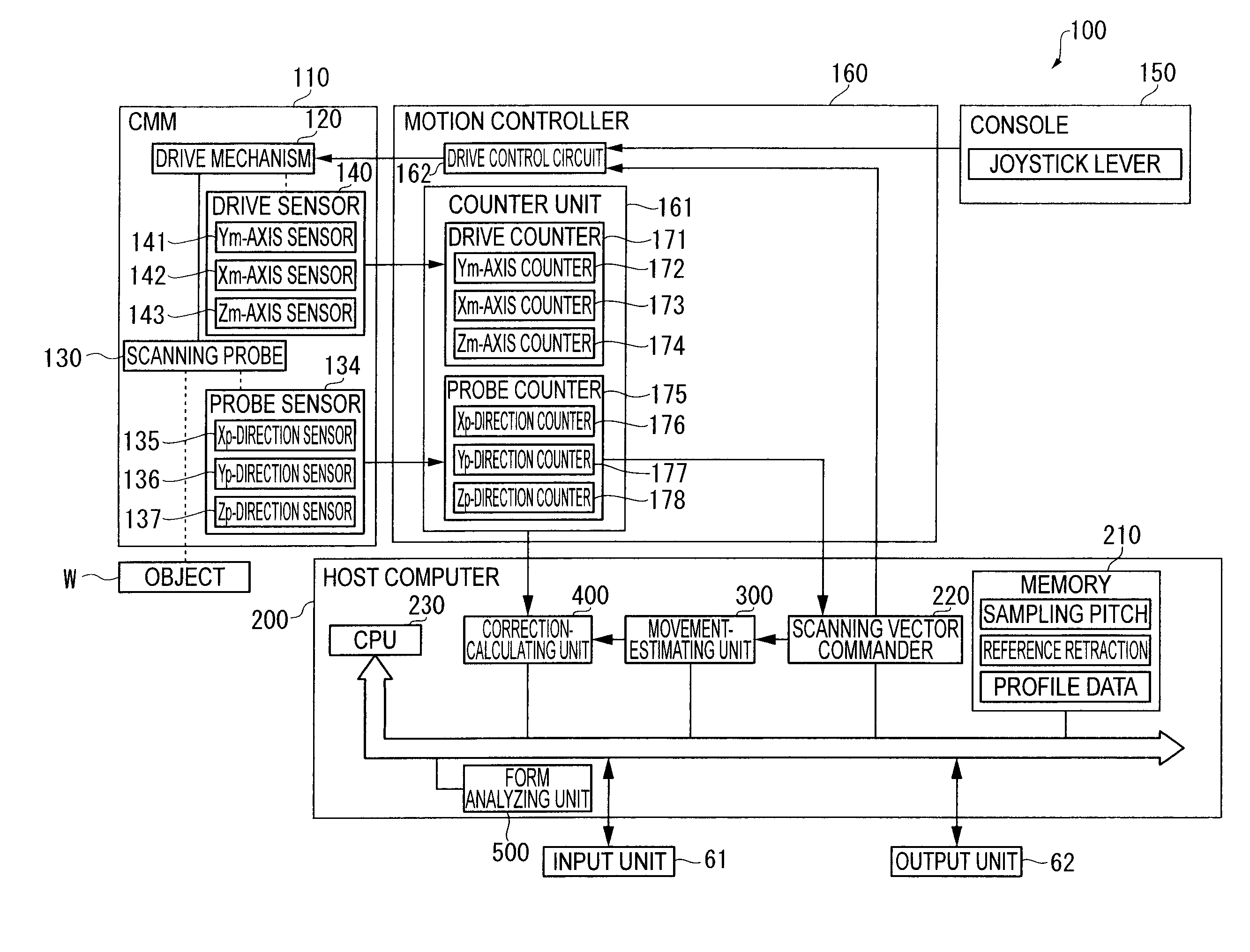
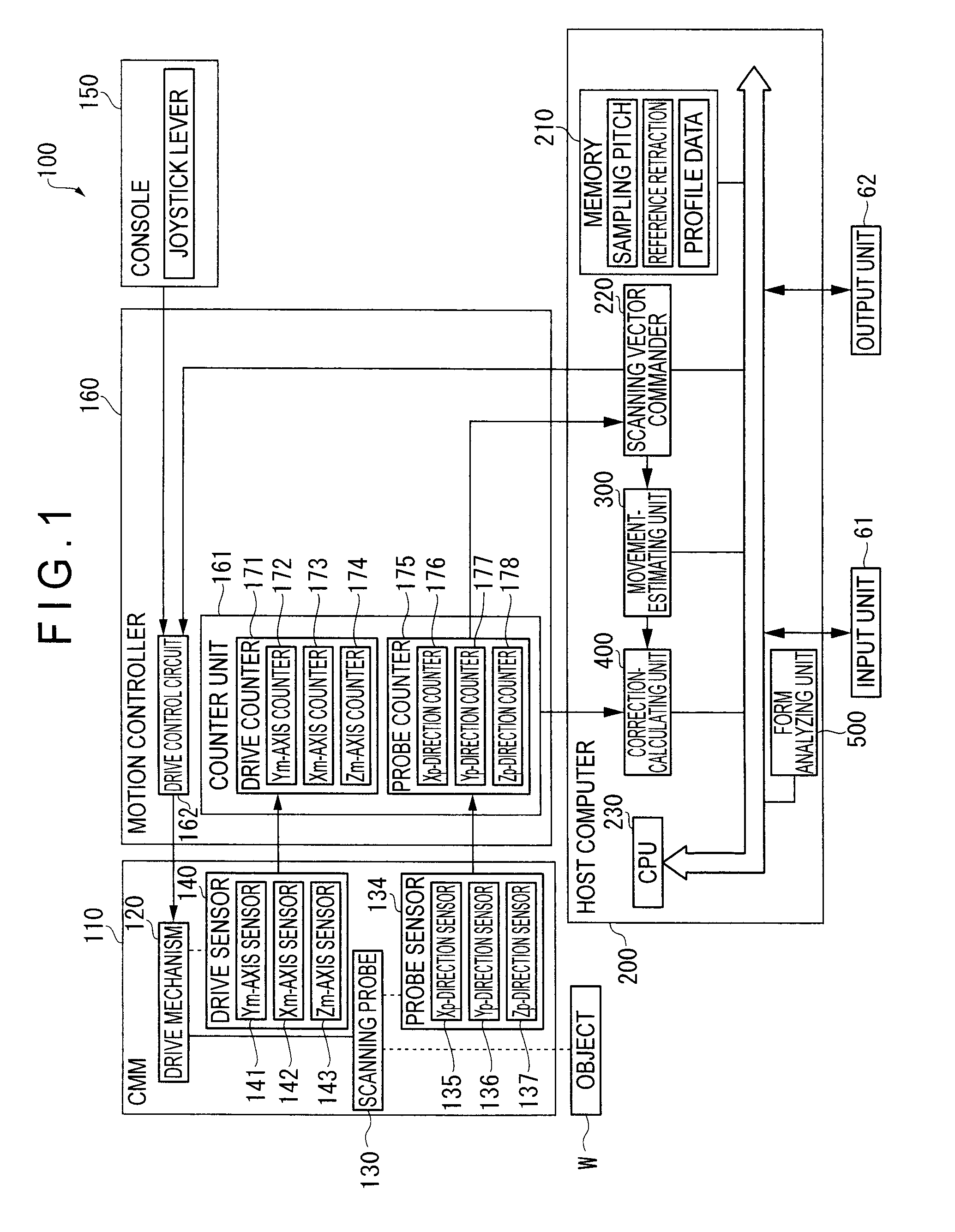
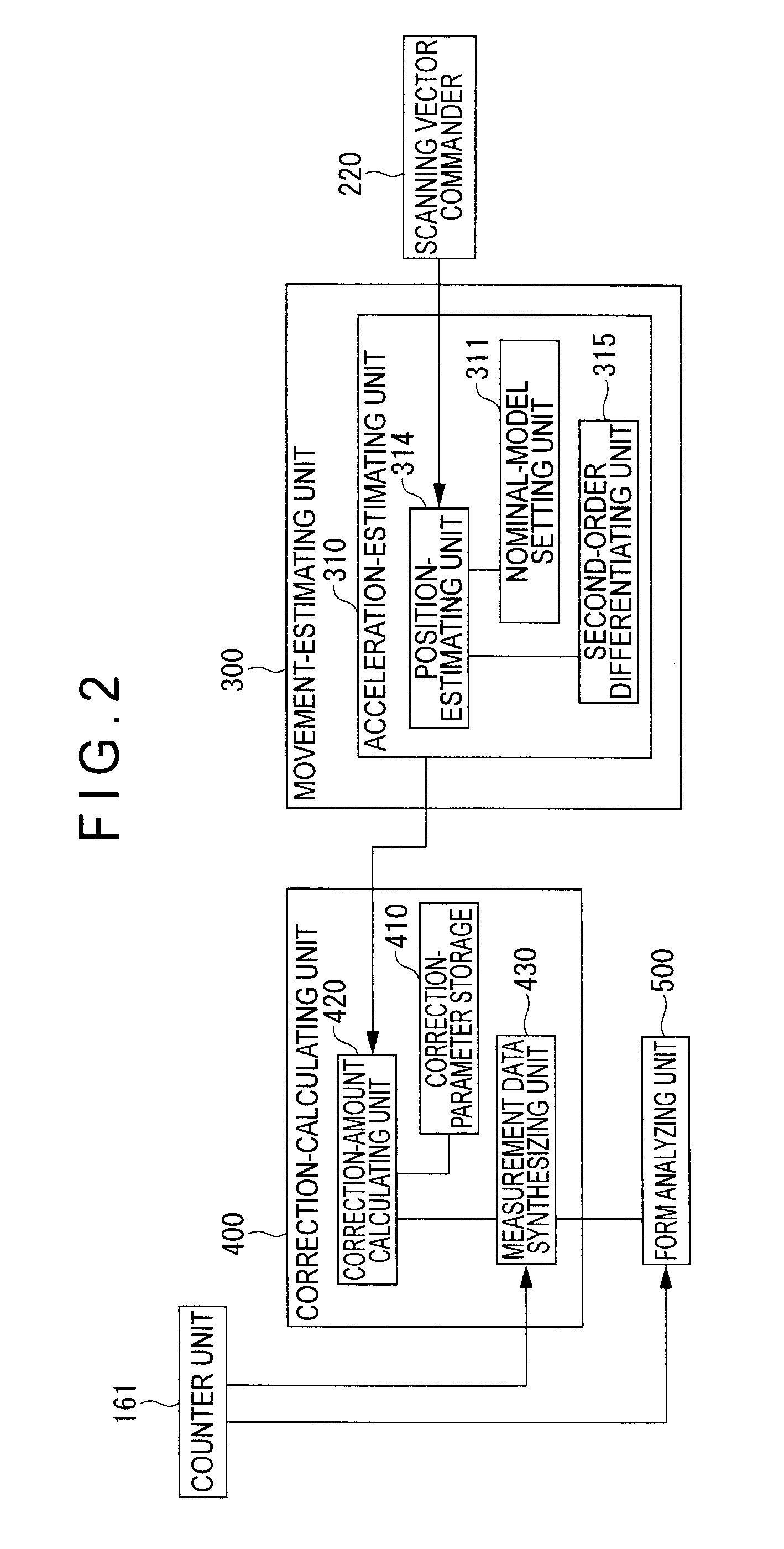
ActiveUS20090037128A1Erroneous outputAccurate calculationDigital data processing detailsTemperatue controlObservational errorMeasuring instrument
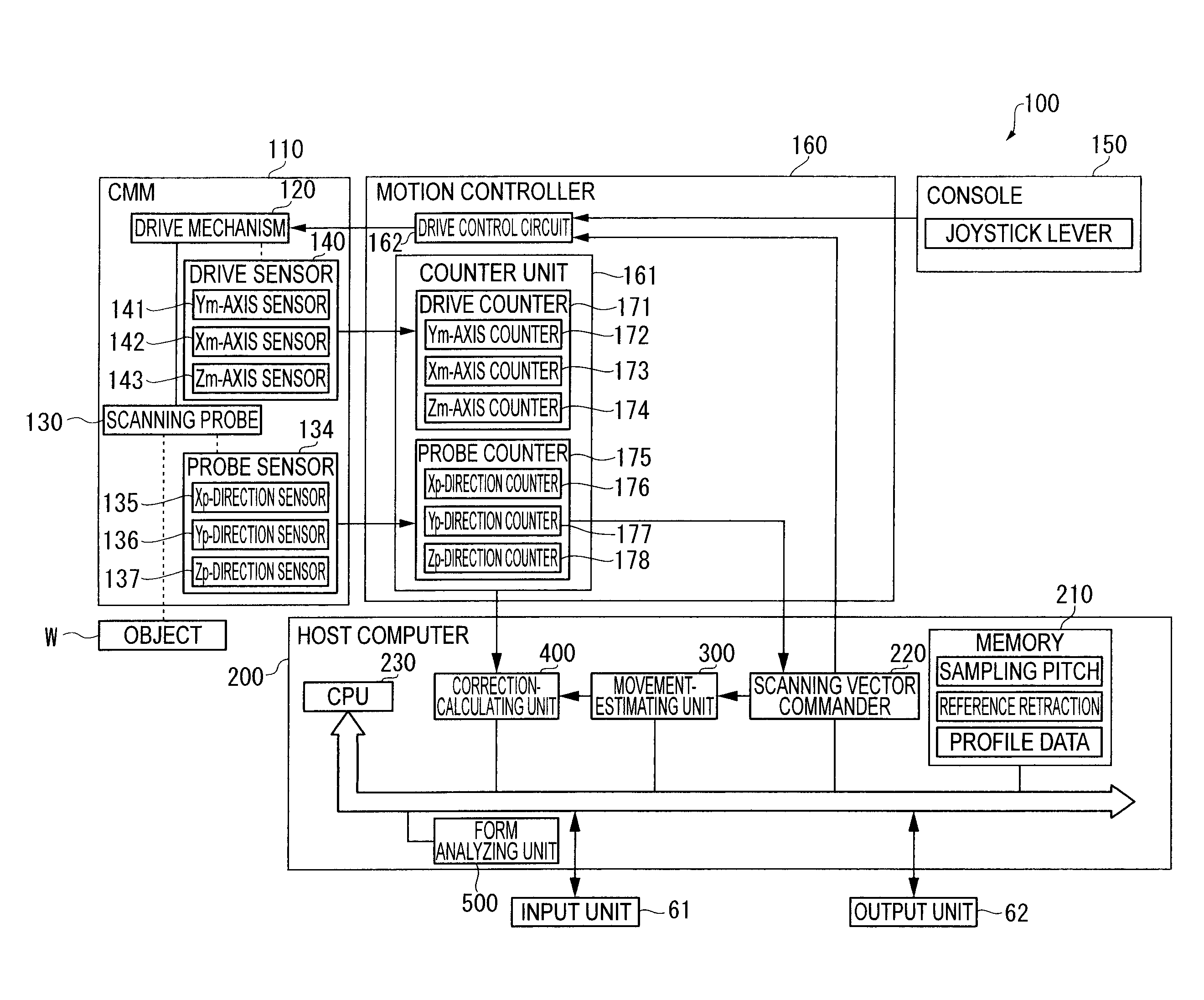
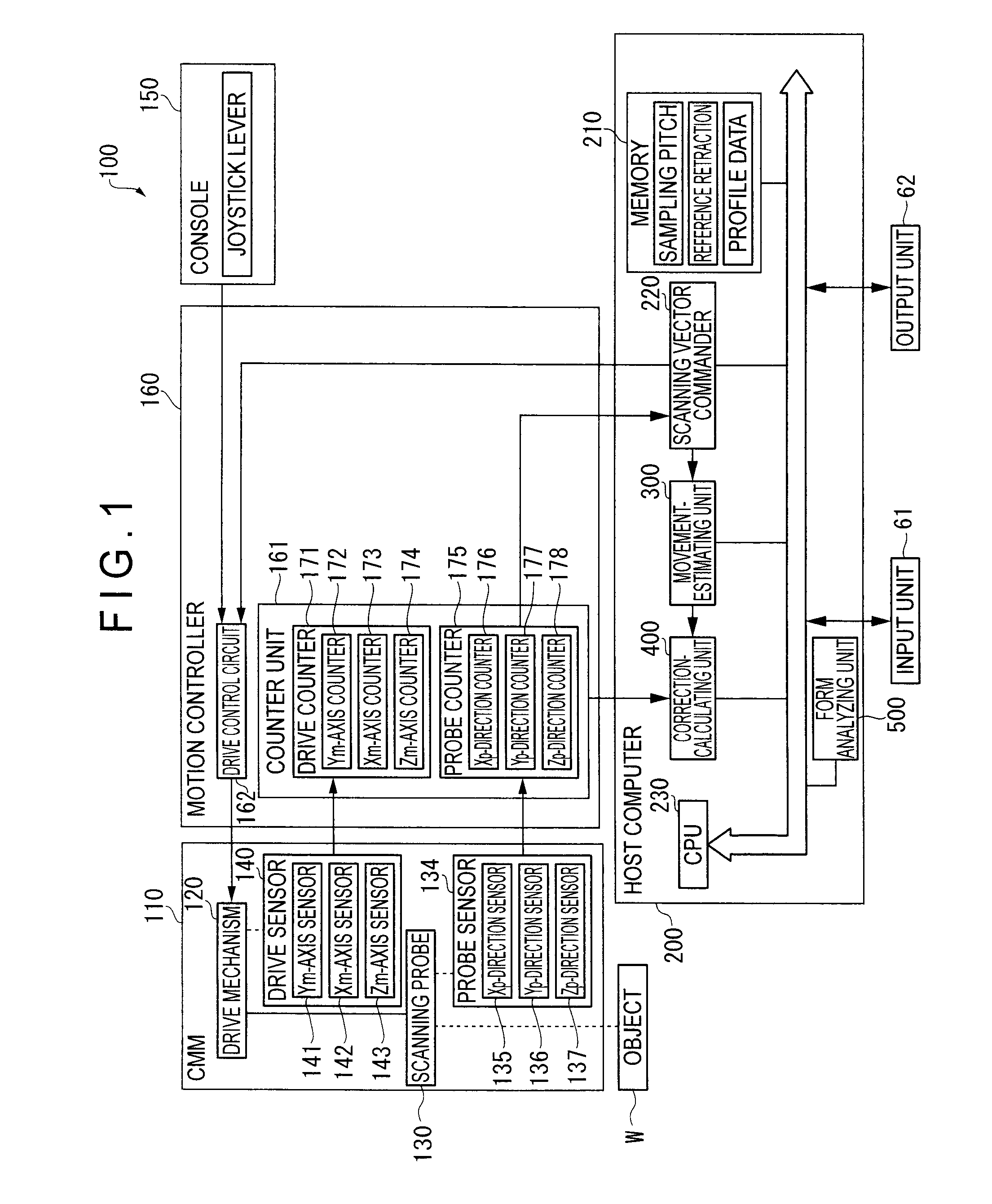
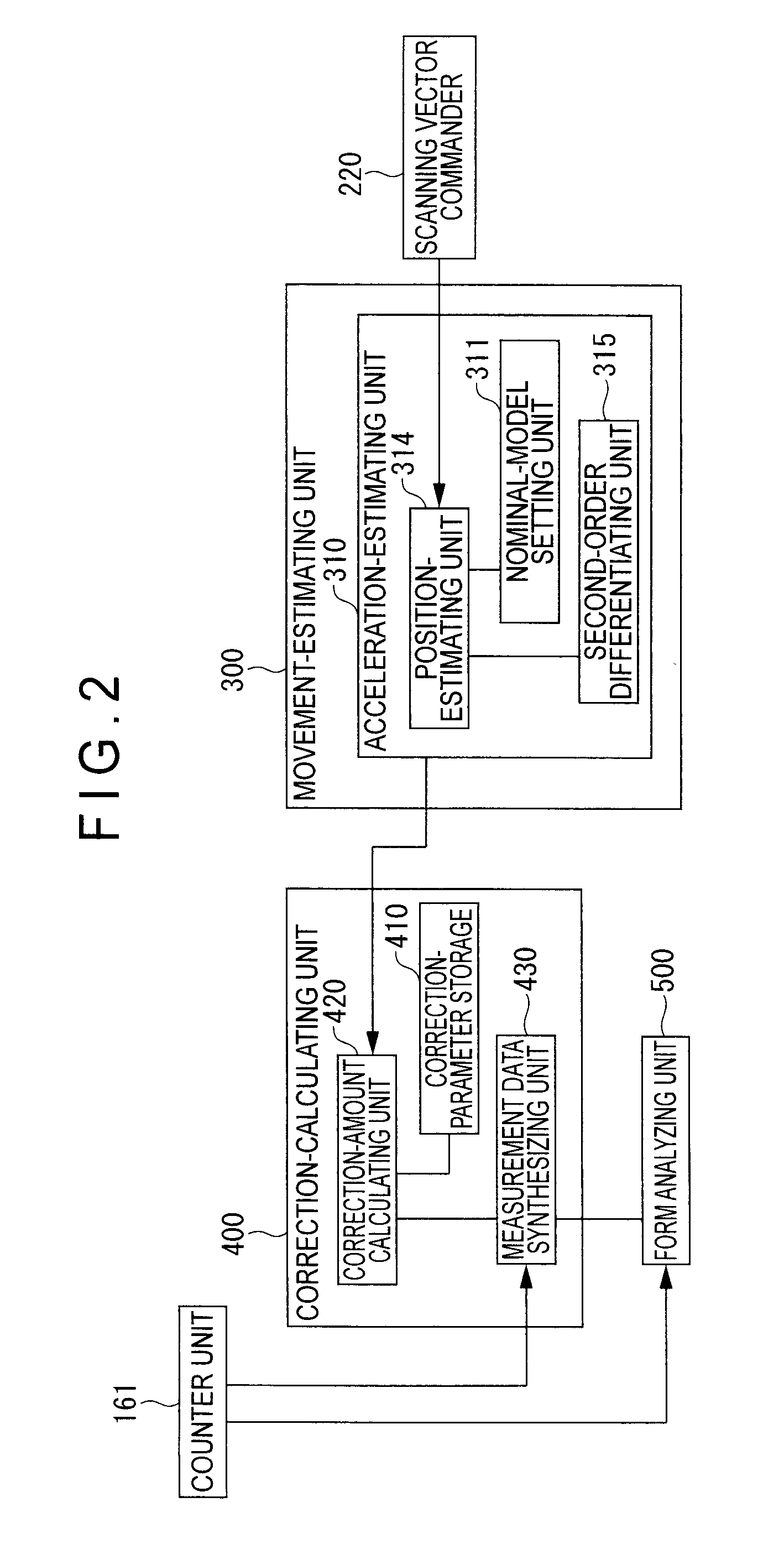
A surface texture measuring instrument includes: a movement-estimating unit for estimating a movement condition of a drive mechanism based on a scanning vector command issued by a scanning vector commander to calculate an estimated operation state quantity; and a correction-calculating unit for correcting a detection value of a drive sensor in accordance with the estimated operation state quantity calculated by the movement-estimating unit. The movement-estimating unit includes: a nominal-model setting unit in which a nominal model representing signal transfer function of the scanning vector command from the issuance of the scanning vector command to a reflection on a movement position of the scanning probe is stored. The correction-calculating unit includes a correction-amount calculating unit that calculates a correction amount for correcting a measurement error generated on account of deformation during the drive of the drive mechanism based on the estimated operation state quantity; and a measurement data synthesizing unit that synthesizes the detection value of the drive sensor and a detection sensor and the correction amount calculated by the correction-amount calculating unit to acquire a measurement data.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
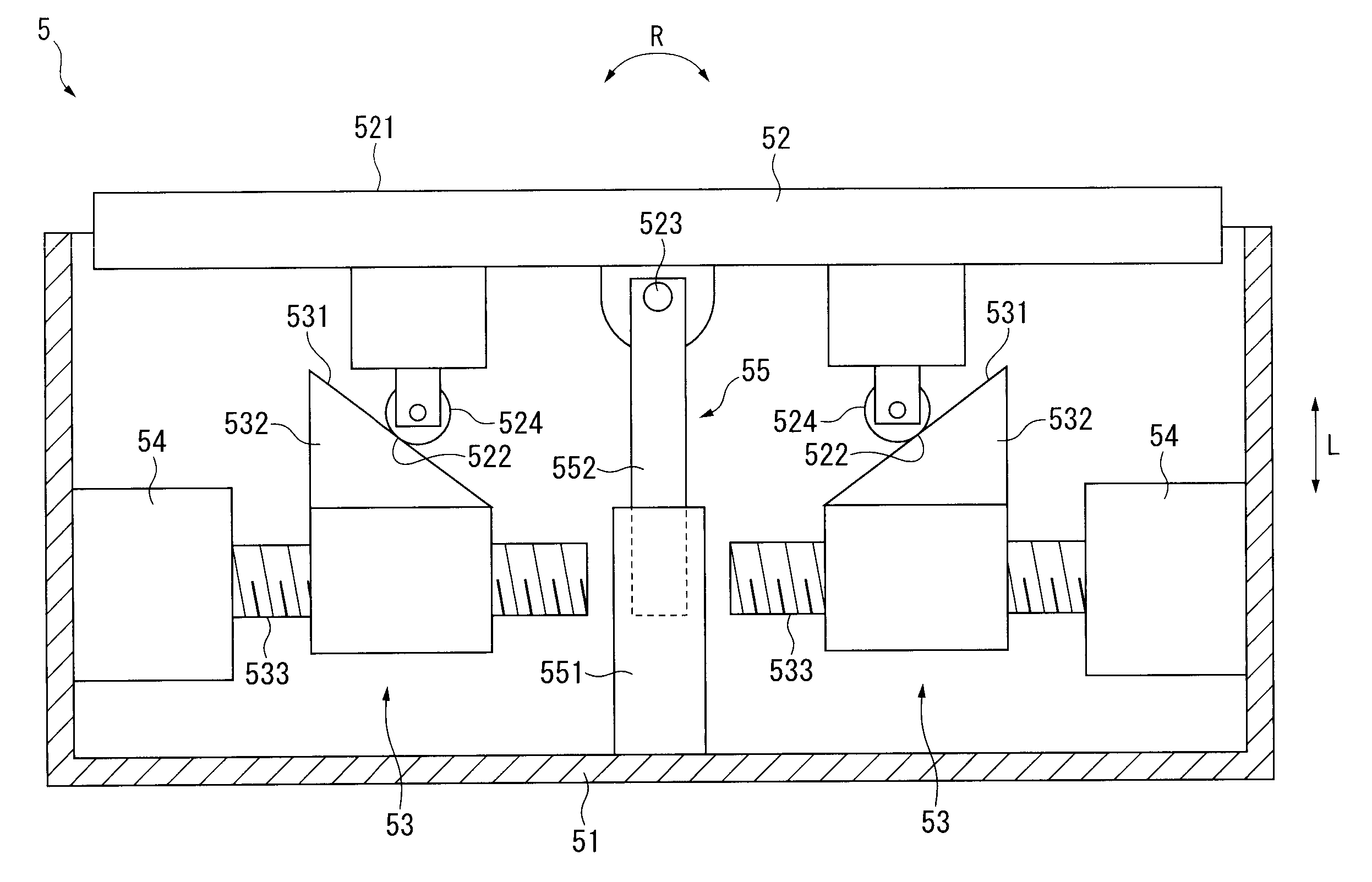
Surface texture measuring apparatus
ActiveUS8915124B2Not easy to damageAvoid damageMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsMeasurement/indication equipmentsEngineeringTexture measure
A surface texture measuring apparatus includes a stylus displacement detector having a measurement arm which is able to swing, a pair of styli provided at a tip of the measurement arm, and a detection unit configured to detect swing amounts of the measurement arm, a stage configured to mount the subject of measurement thereon, and a relative movement mechanism configured to cause a relative movement between the detector and the stage. The apparatus includes a posture switching mechanism configured to switch a posture of the measurement arm between a posture in which the measurement arm is urged in one swing direction and a posture in which the measurement arm is urged in the other swing direction, and a speed control mechanism configured to control a switching speed of posture switching of the measurement arm to a preset speed when the posture of the measurement arm is switched by the posture switching mechanism.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Surface texture measuring instrument
ActiveUS7715999B2Accurate calculationTemperatue controlDigital data processing detailsObservational errorMeasuring instrument
A surface texture measuring instrument includes: a movement-estimating unit for estimating a movement condition of a drive mechanism based on a scanning vector command issued by a scanning vector commander to calculate an estimated operation state quantity; and a correction-calculating unit for correcting a detection value of a drive sensor in accordance with the estimated operation state quantity calculated by the movement-estimating unit. The movement-estimating unit includes: a nominal-model setting unit in which a nominal model representing signal transfer function of the scanning vector command from the issuance of the scanning vector command to a reflection on a movement position of the scanning probe is stored. The correction-calculating unit includes a correction-amount calculating unit that calculates a correction amount for correcting a measurement error generated on account of deformation during the drive of the drive mechanism based on the estimated operation state quantity; and a measurement data synthesizing unit that synthesizes the detection value of the drive sensor and a detection sensor and the correction amount calculated by the correction-amount calculating unit to acquire a measurement data.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Surface texture measuring instrument
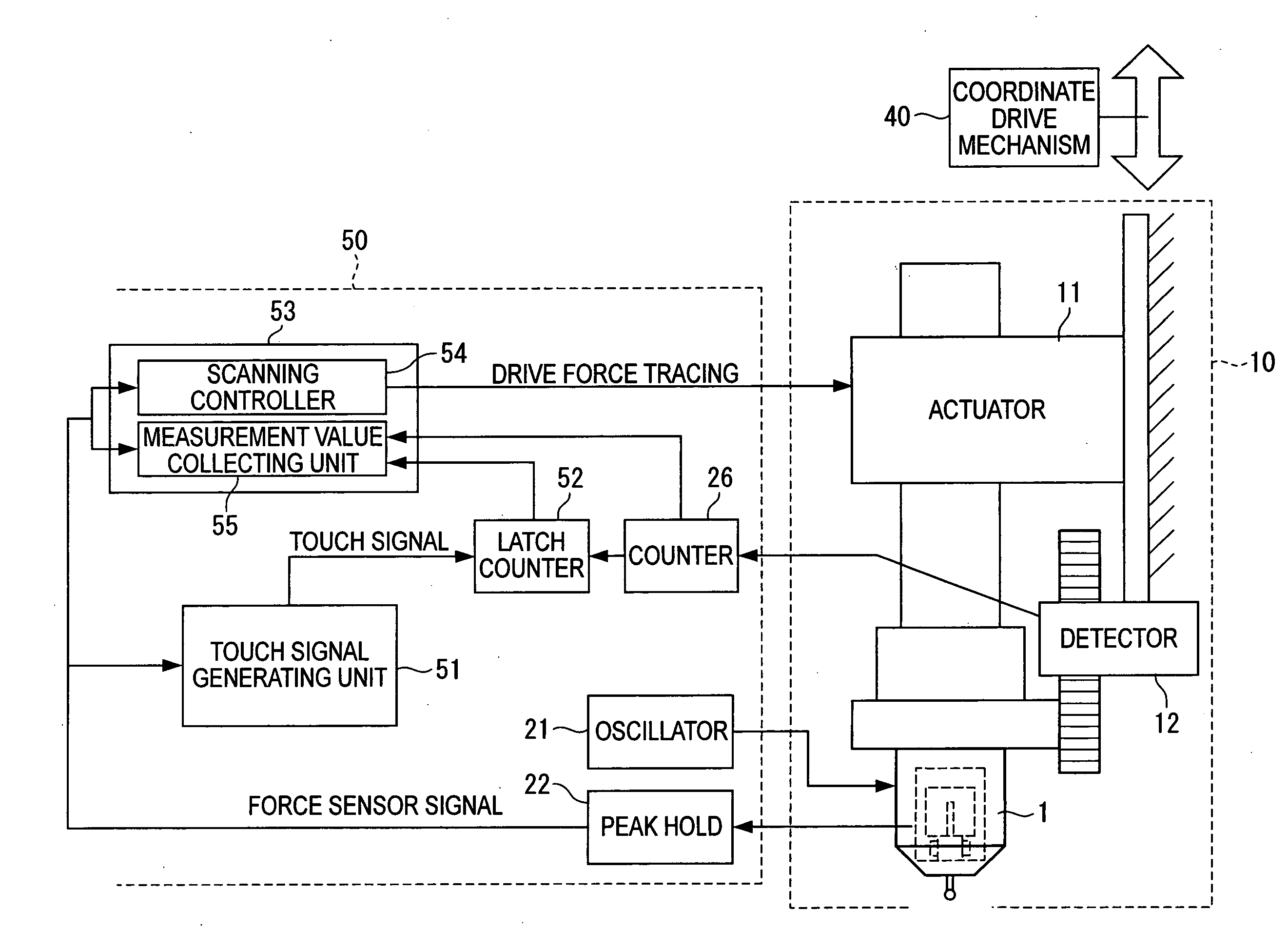
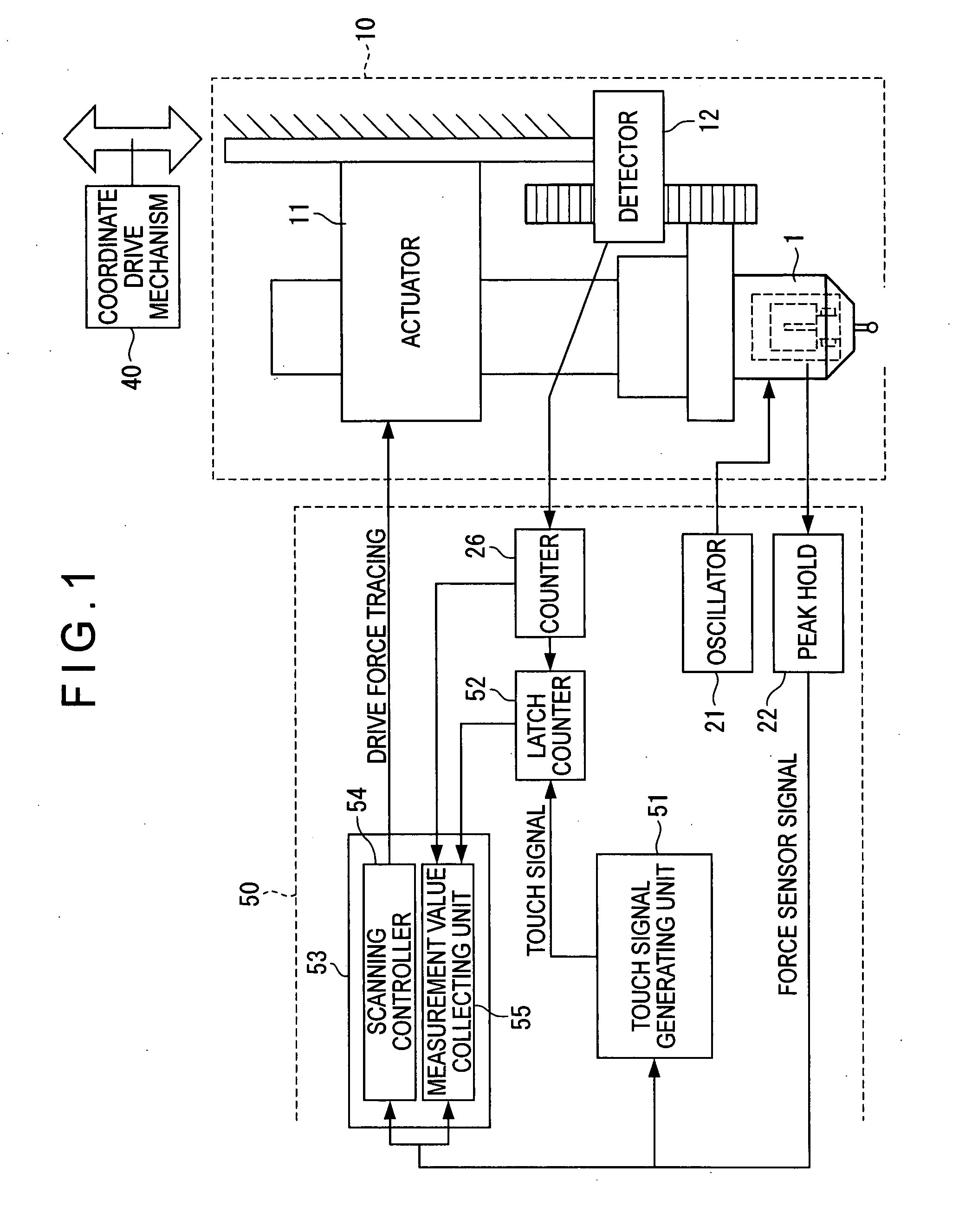
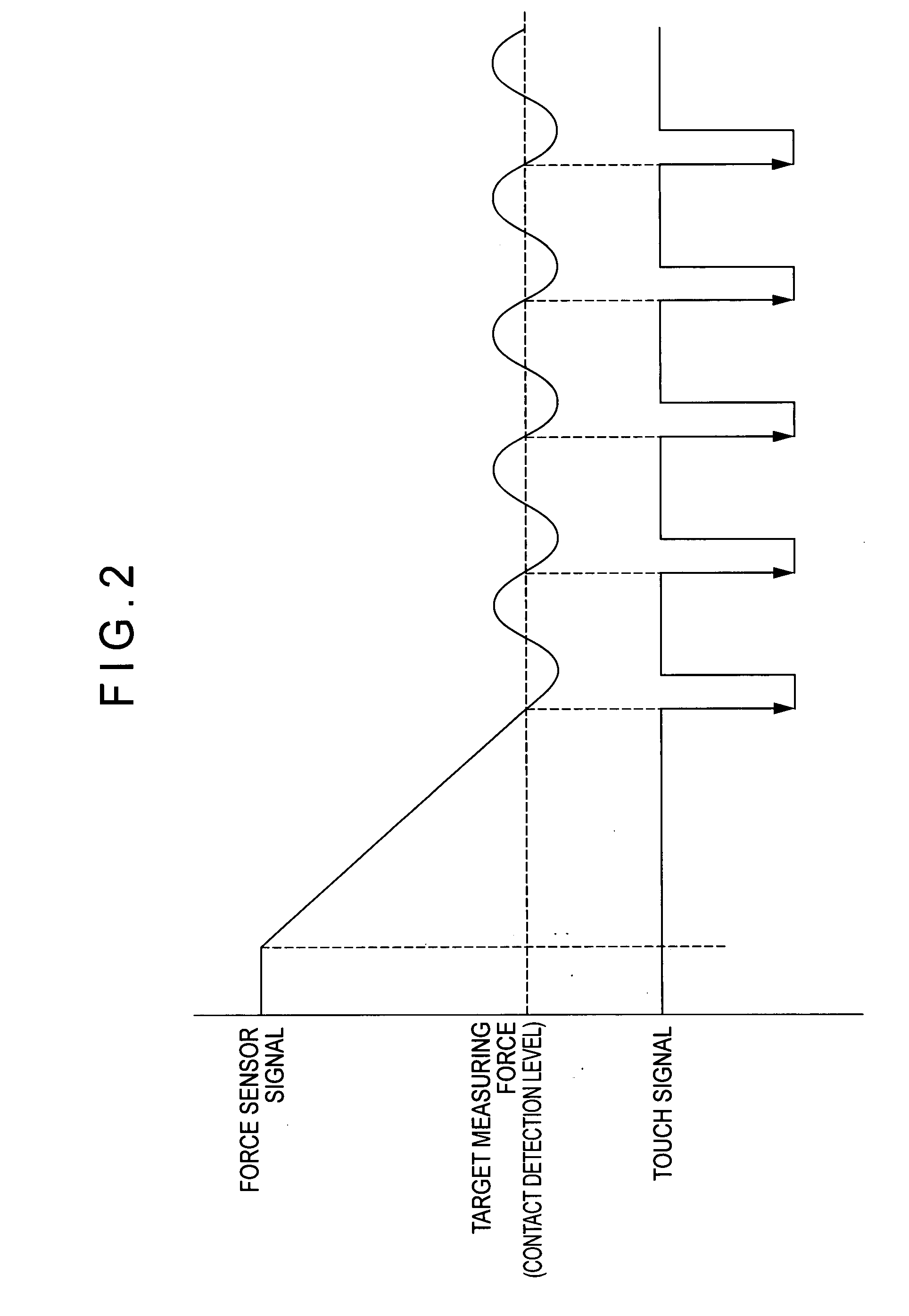
ActiveUS20070295100A1Small levelAccurate detectionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesElectric/magnetic contours/curvatures measurementsMeasuring instrumentClassical mechanics
A surface texture measuring instrument includes a force sensor (1), an actuator (11) and a detector (12). The surface texture measuring instrument further includes: a scanning controller (54) that collects a detection signal from the force sensor (1) and drives the actuator such that the detecting signal coincides with a target measurement value; a touch signal generator (51) that generates a touch signal when the detection signal from the force sensor (1) coincides with the target measurement value; and a measurement value collecting unit (55) that collects a measurement value from a counter (26) at a predetermined time interval in a state where a fluctuation range of the detection signal from the force sensor (1) is within a preset range when a scanning controller is in operation, the latch counter (52) collecting a measurement value from a latch counter (52) each time the touch signal is generated in a state where the detection signal from the force sensor (1) oscillates and an amplitude exceeds the preset range.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Surface texture measuring device
ActiveUS20110138895A1Efficient measurementBlocking may occurMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsElectric signalTexture measure
A surface texture measuring device includes a rotation driving device configured to rotate a measured substance, a roughness detector including a stylus provided displaceably at a tip of a detector main body and at least one skid provided at the tip of the detector main body and in the proximity of the stylus and outputting displacement of the stylus based on the skid as an electric signal, and a detector driving device configured to drive a detector holder. The detector holder includes a guide member driven by the detector driving device, a slide member configured to hold the roughness detector and provided slidably in a displacement direction of the stylus to the guide member, and an urging member configured to urge the slide member so that the skid always comes in contact with the measurement face of the measured substance.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Texture measuring apparatus and method
ActiveUS7997126B2Expressing texture of an objectAccurate expressionElectric/magnetic roughness/irregularity measurementsMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsMeasurement deviceTexture measure
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com