Patents
Literature
356results about "Document inserters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
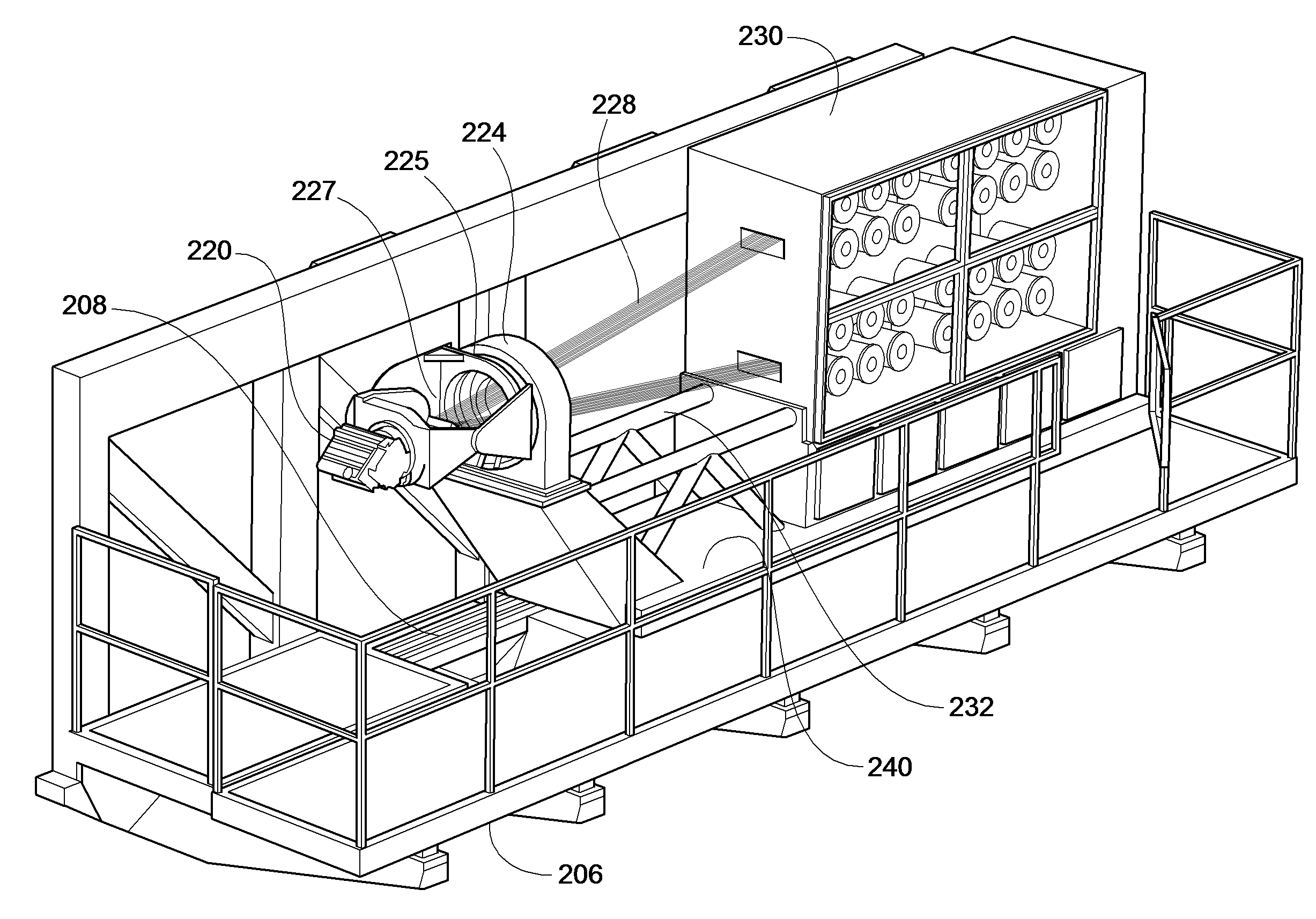
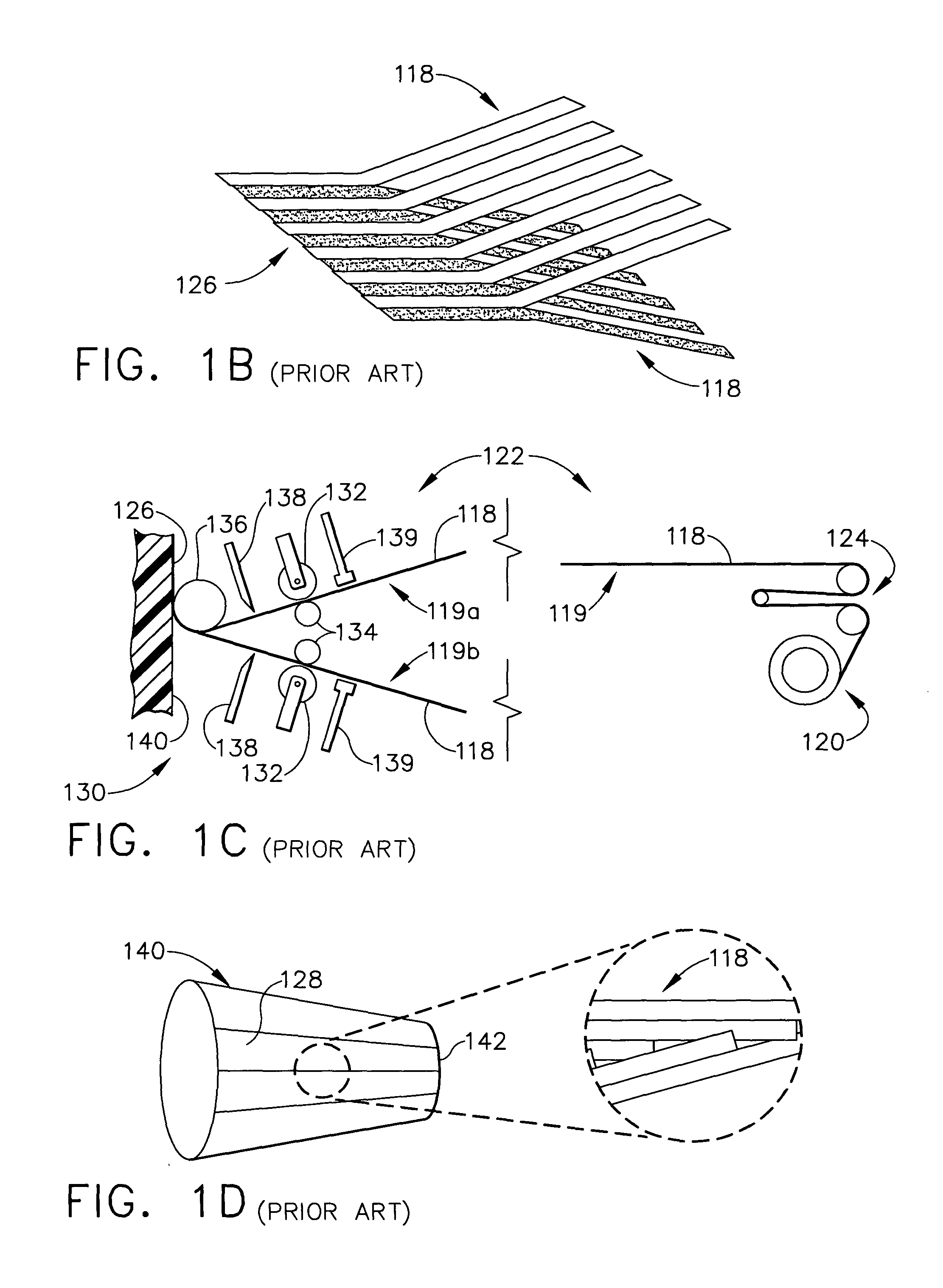
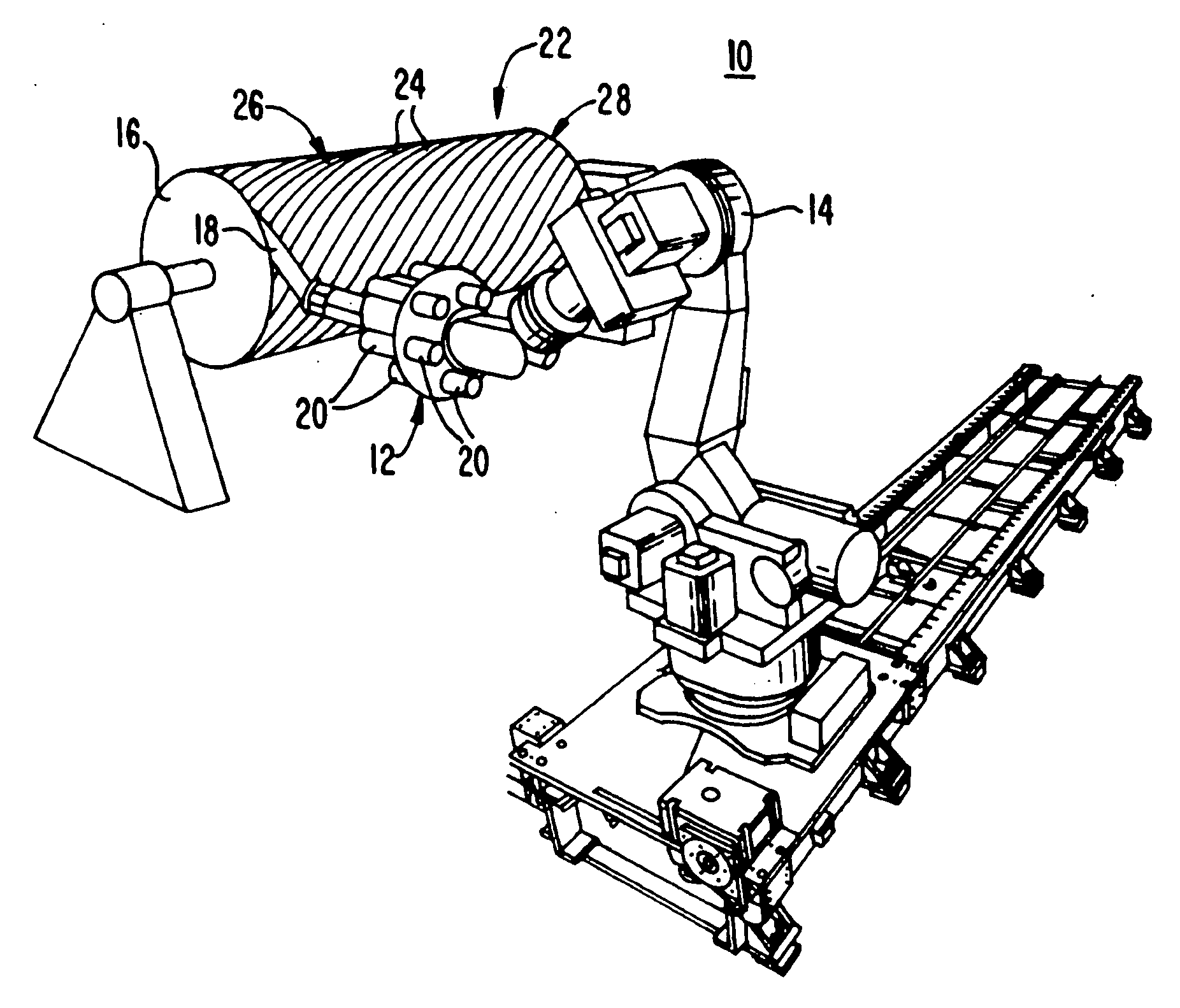
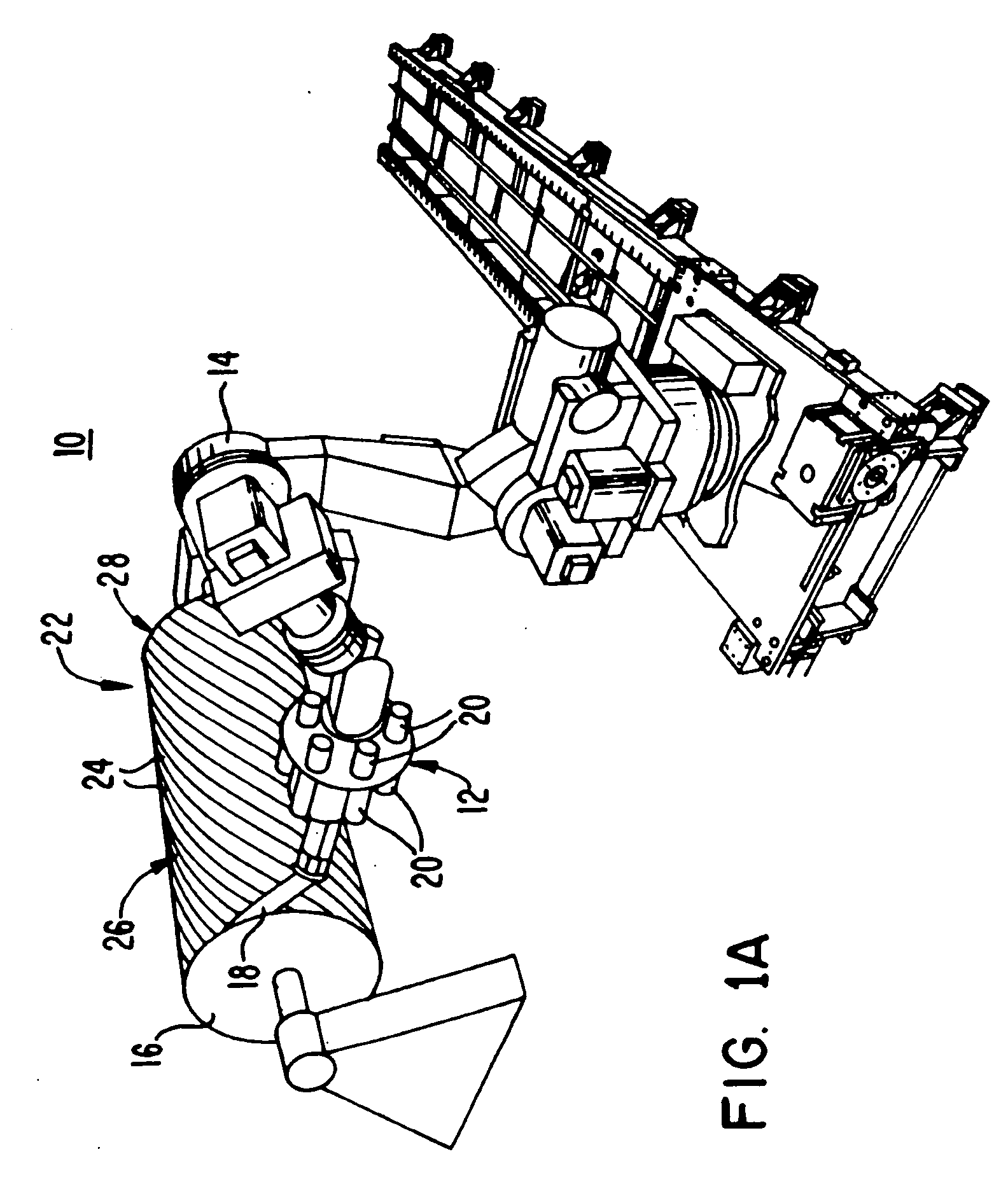
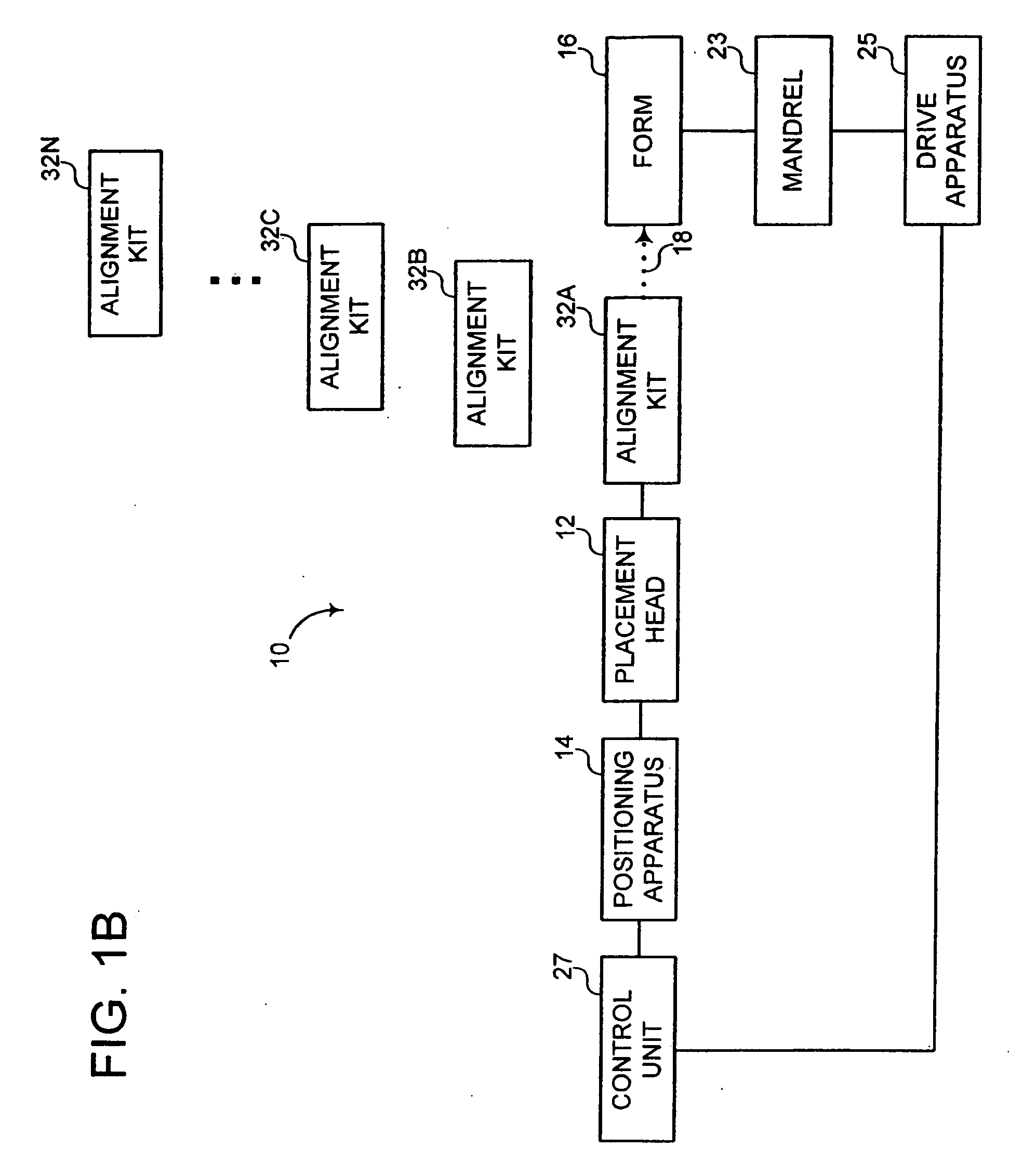
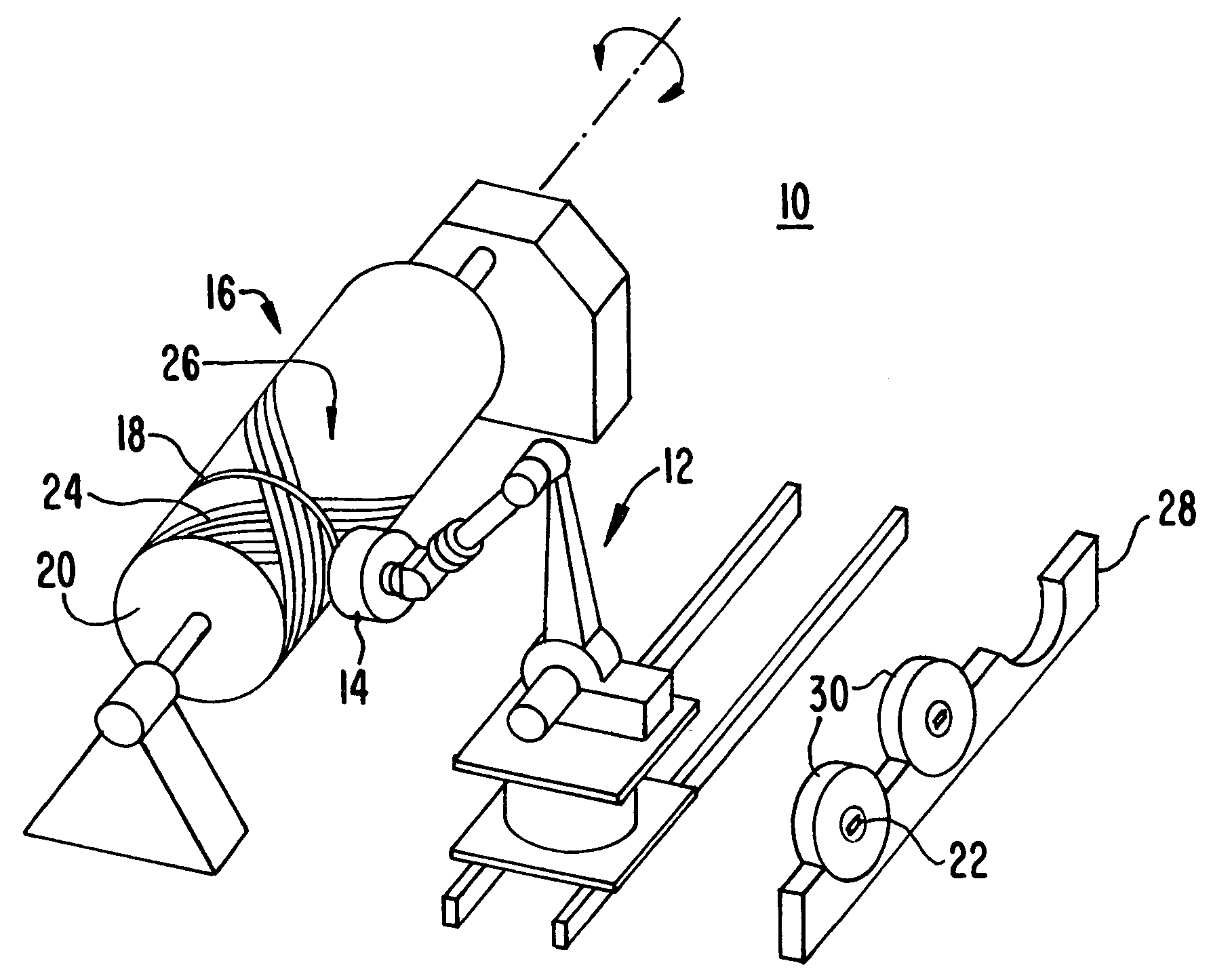
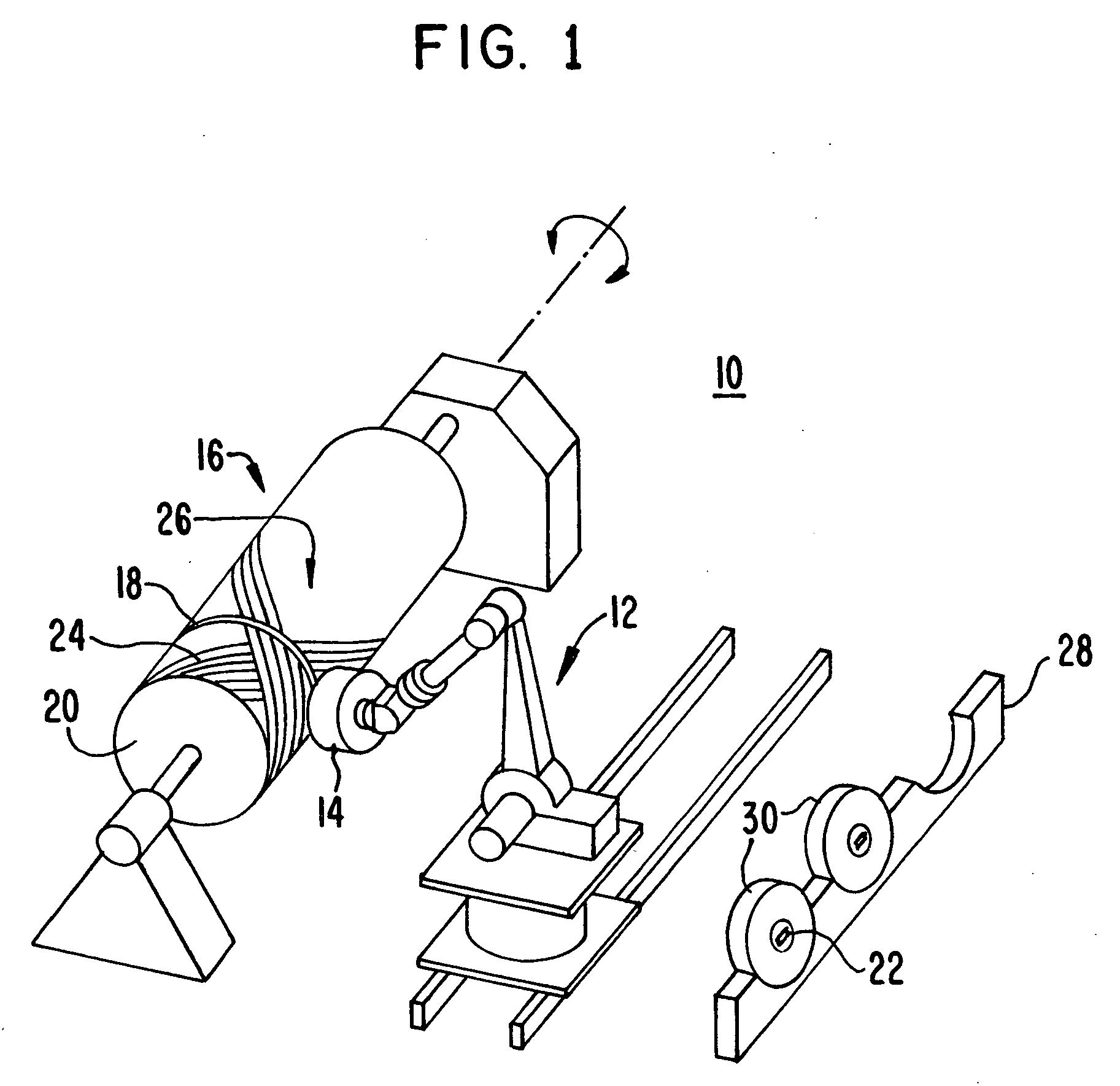
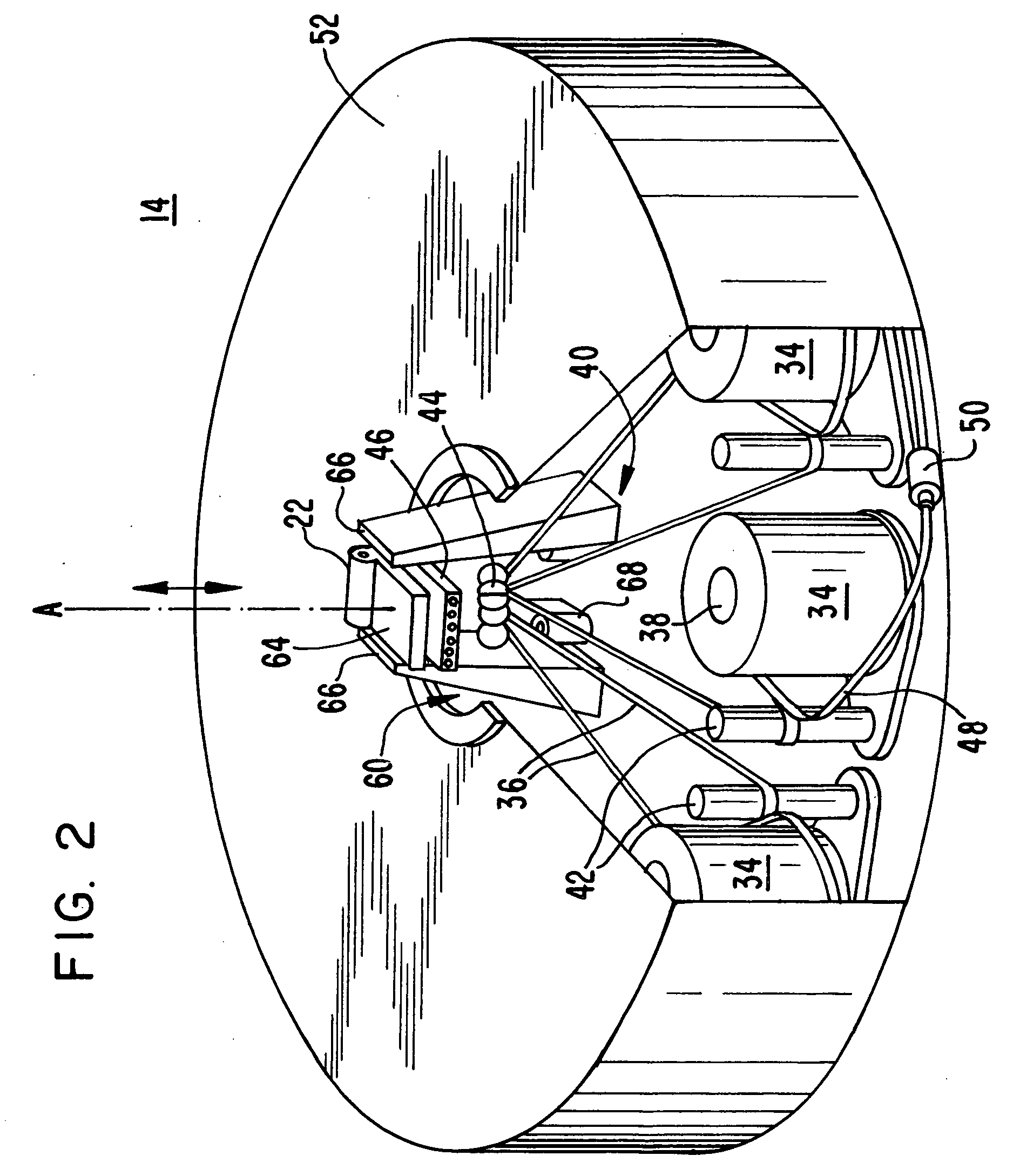
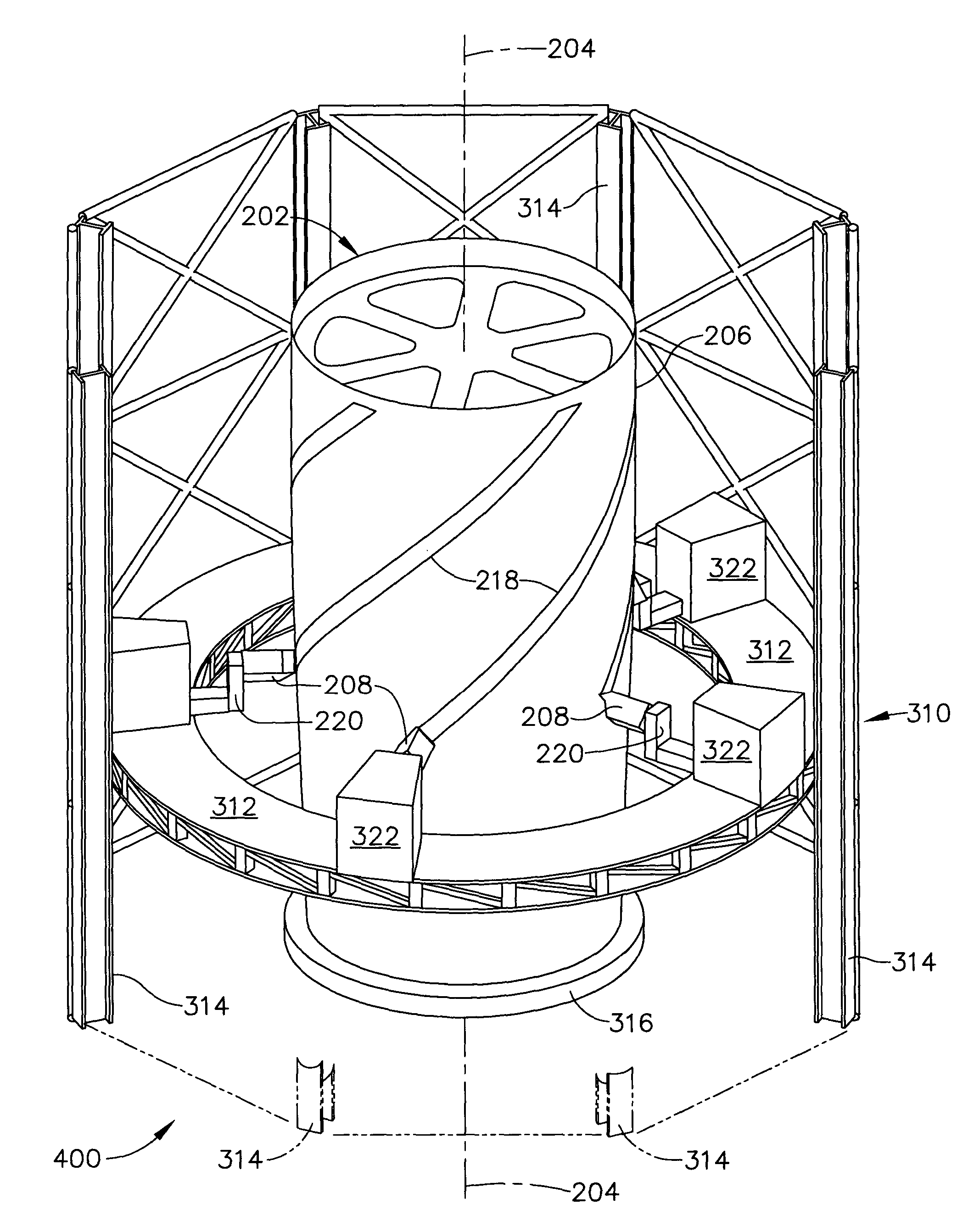
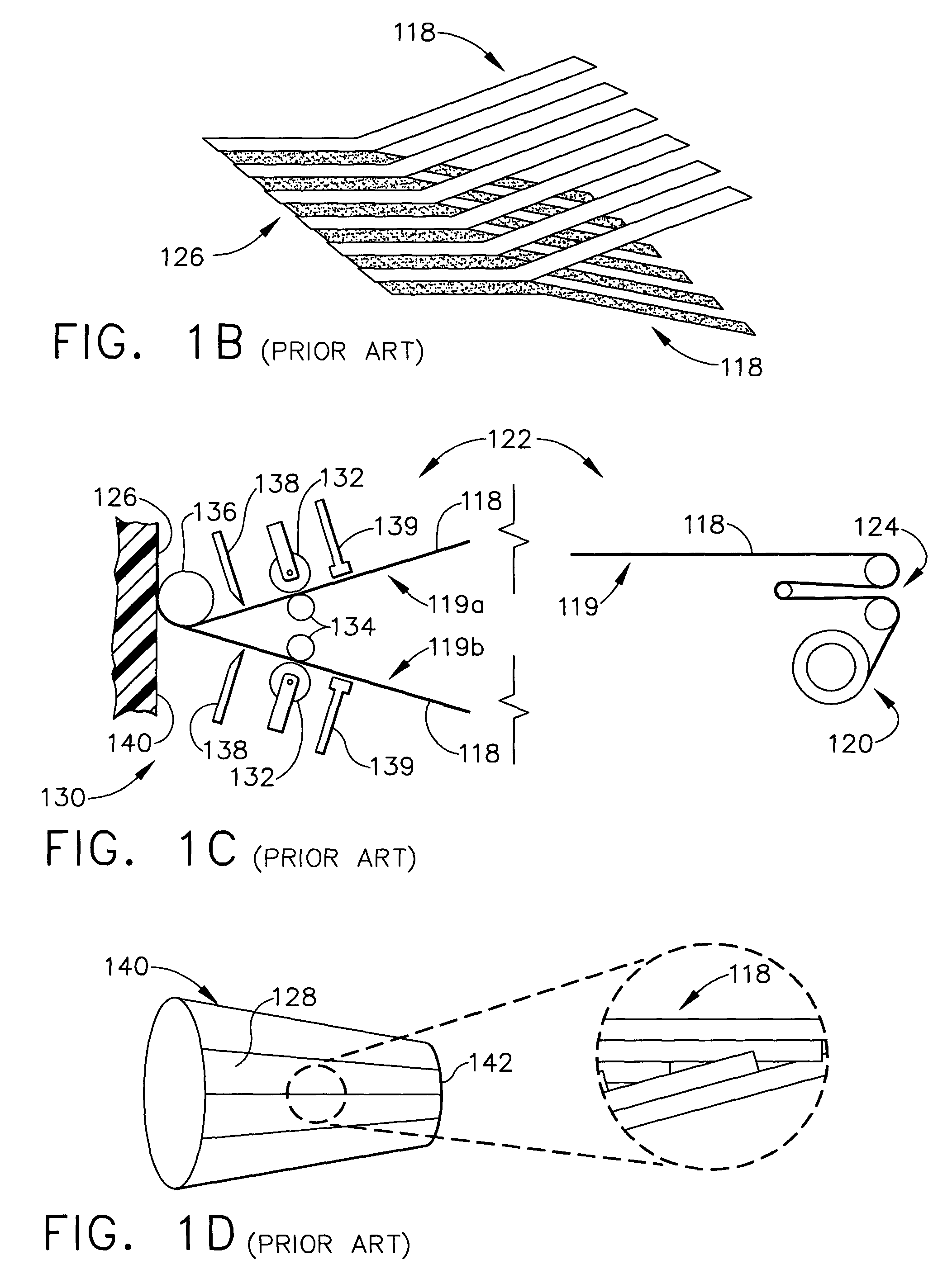
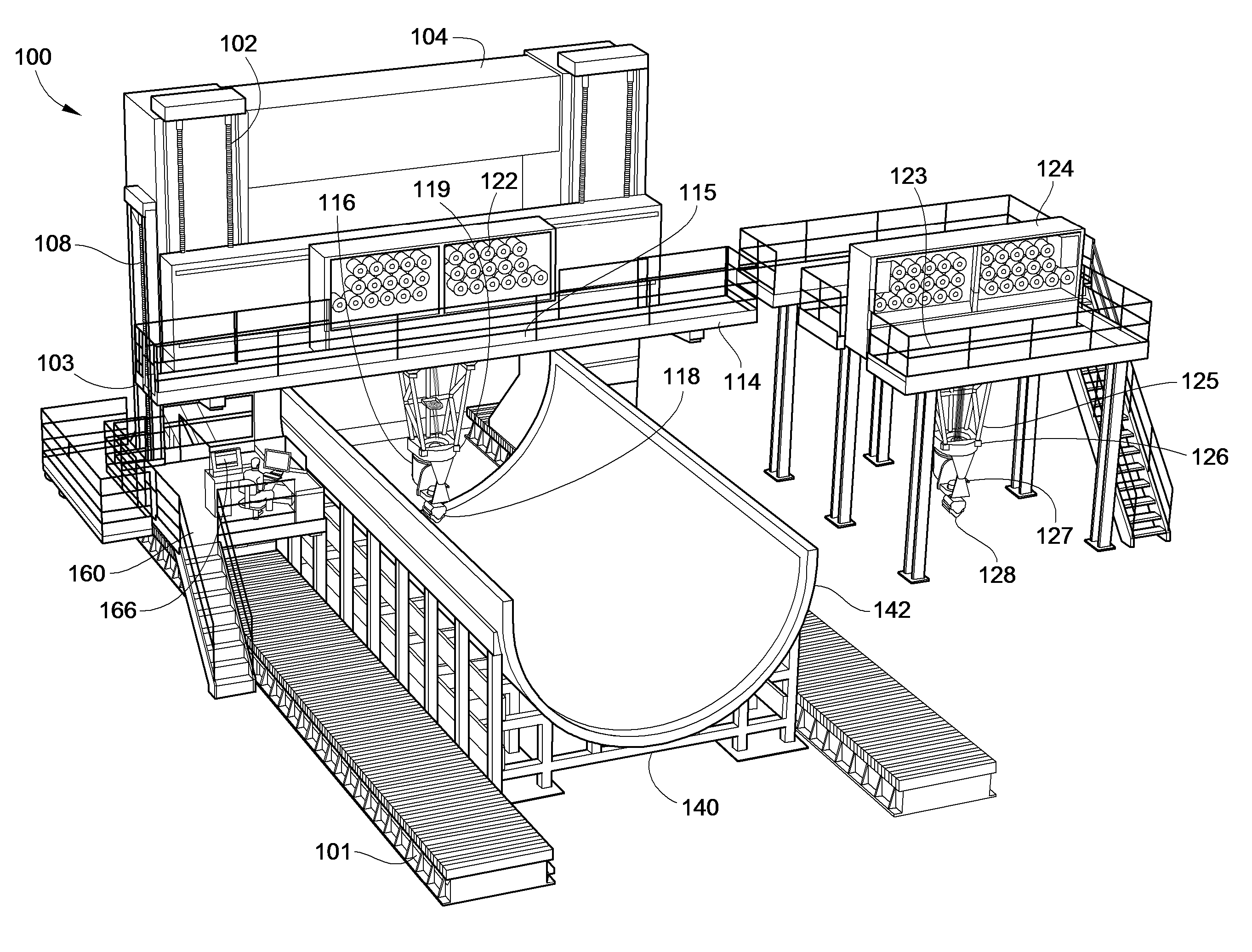
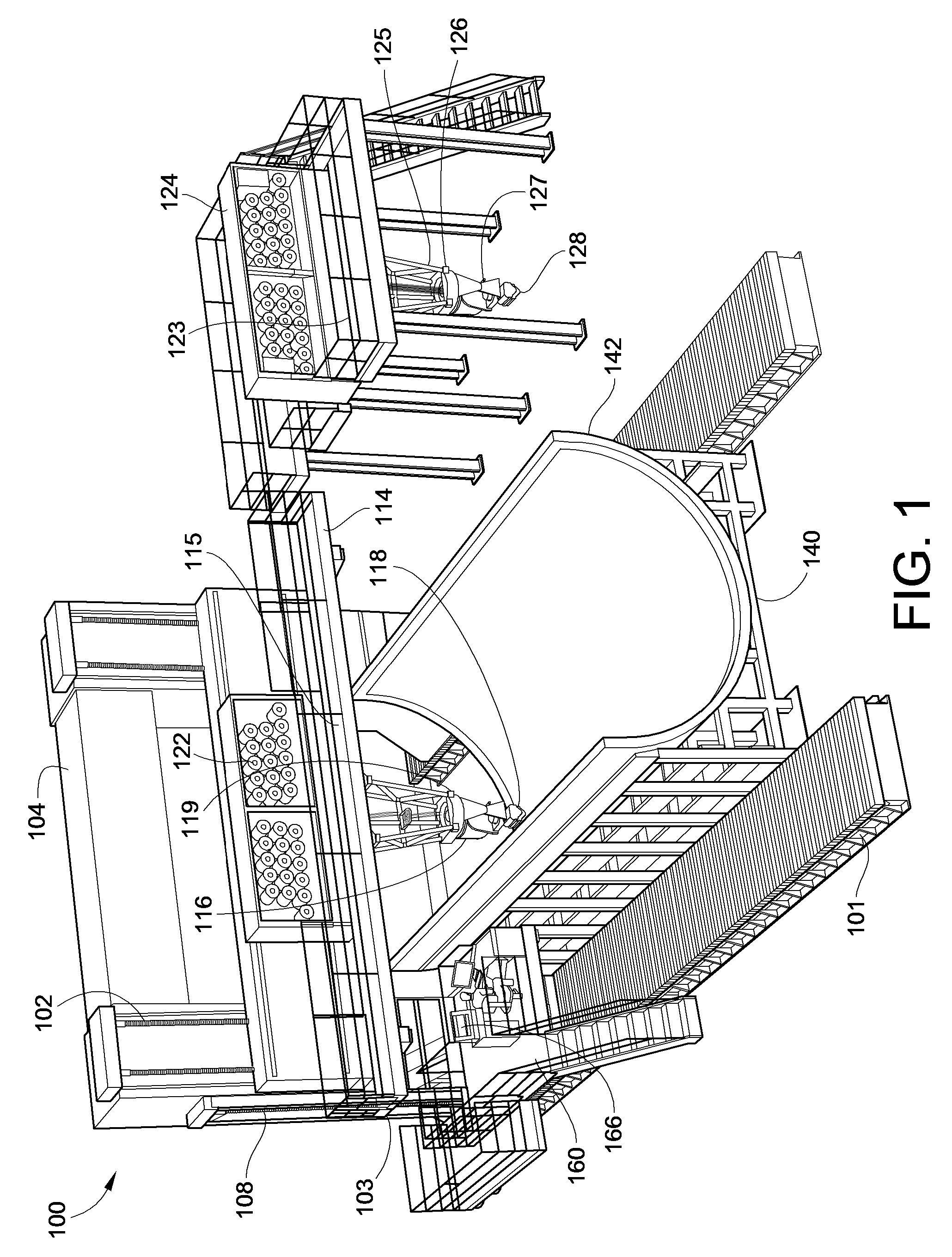
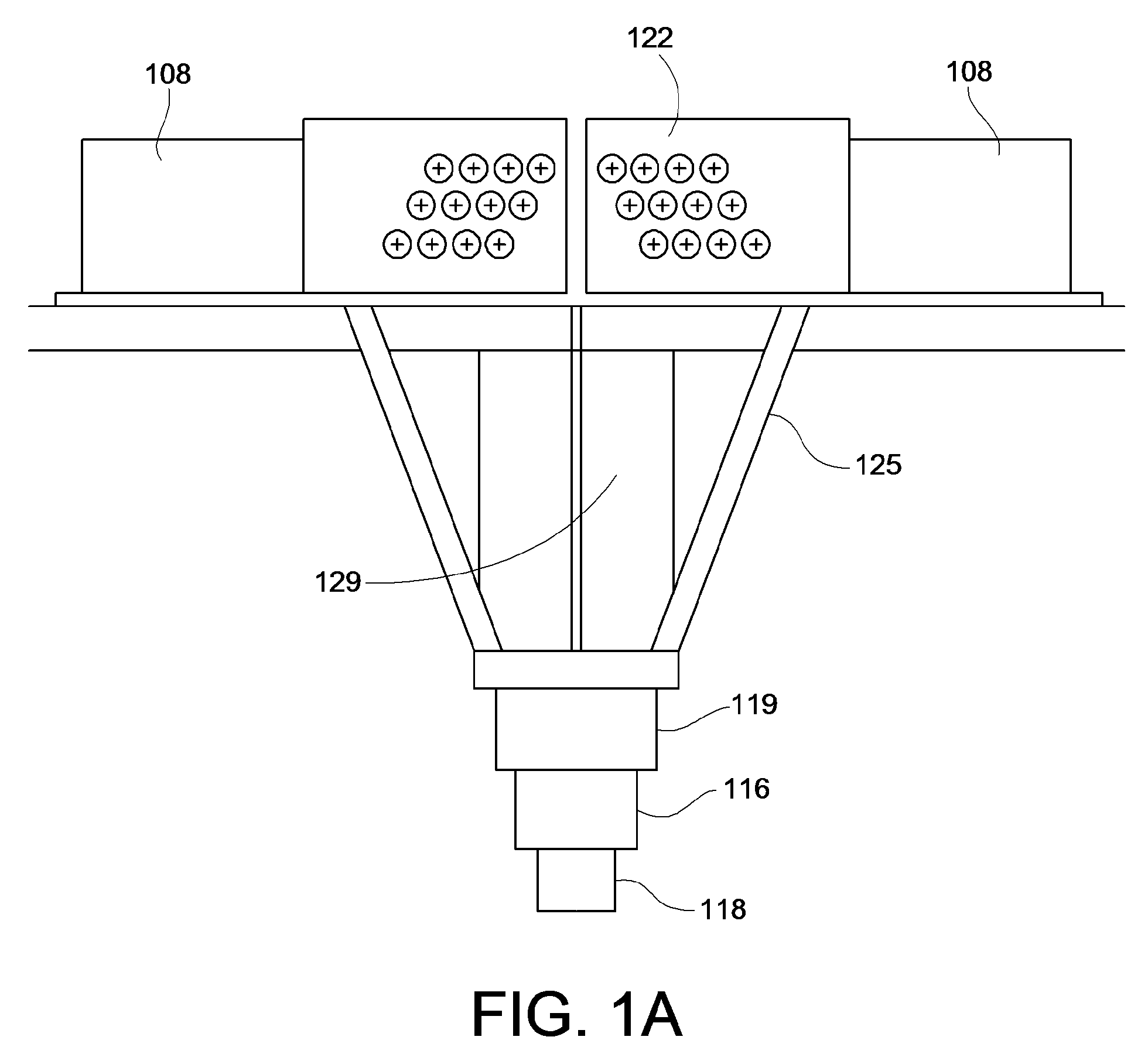
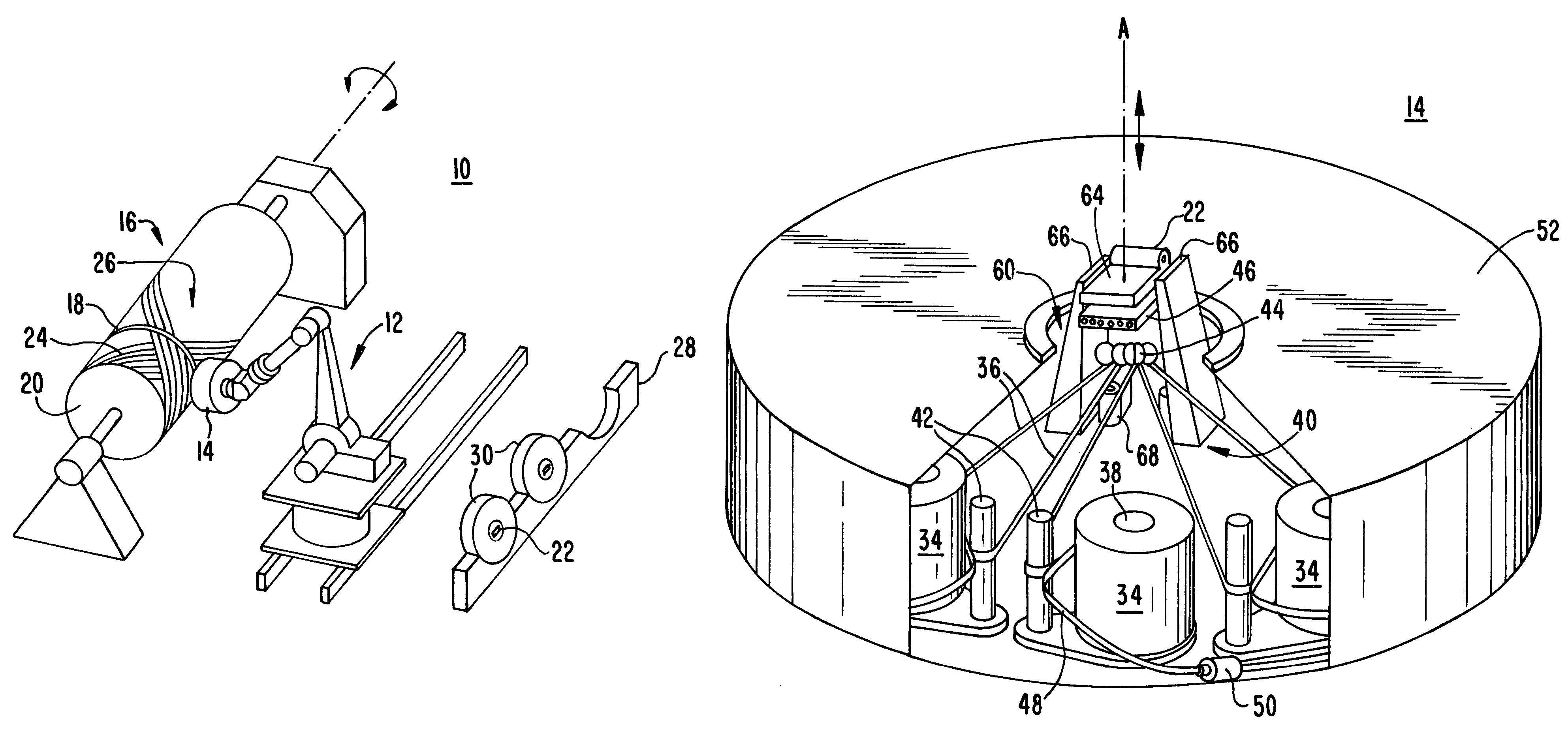
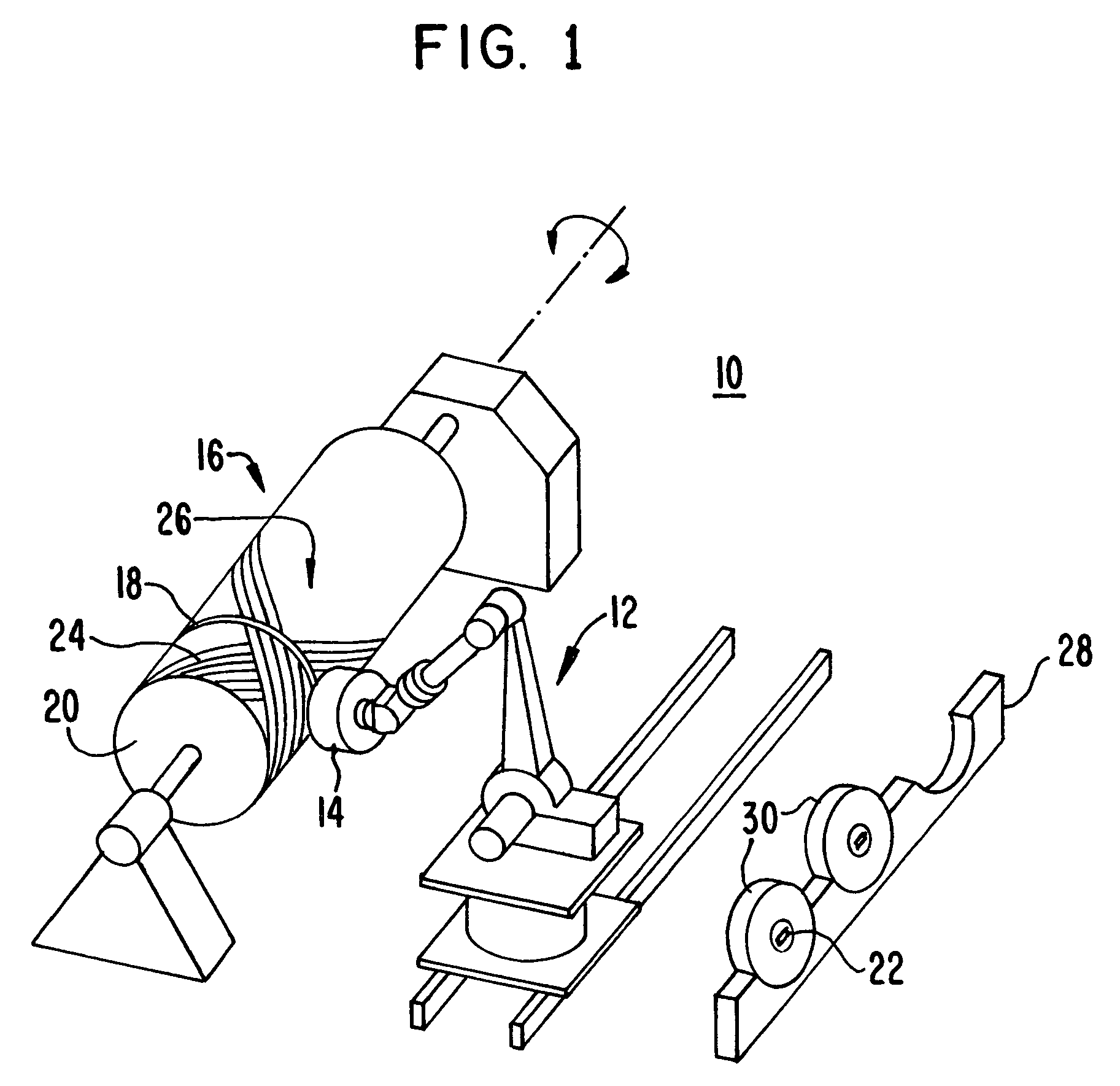
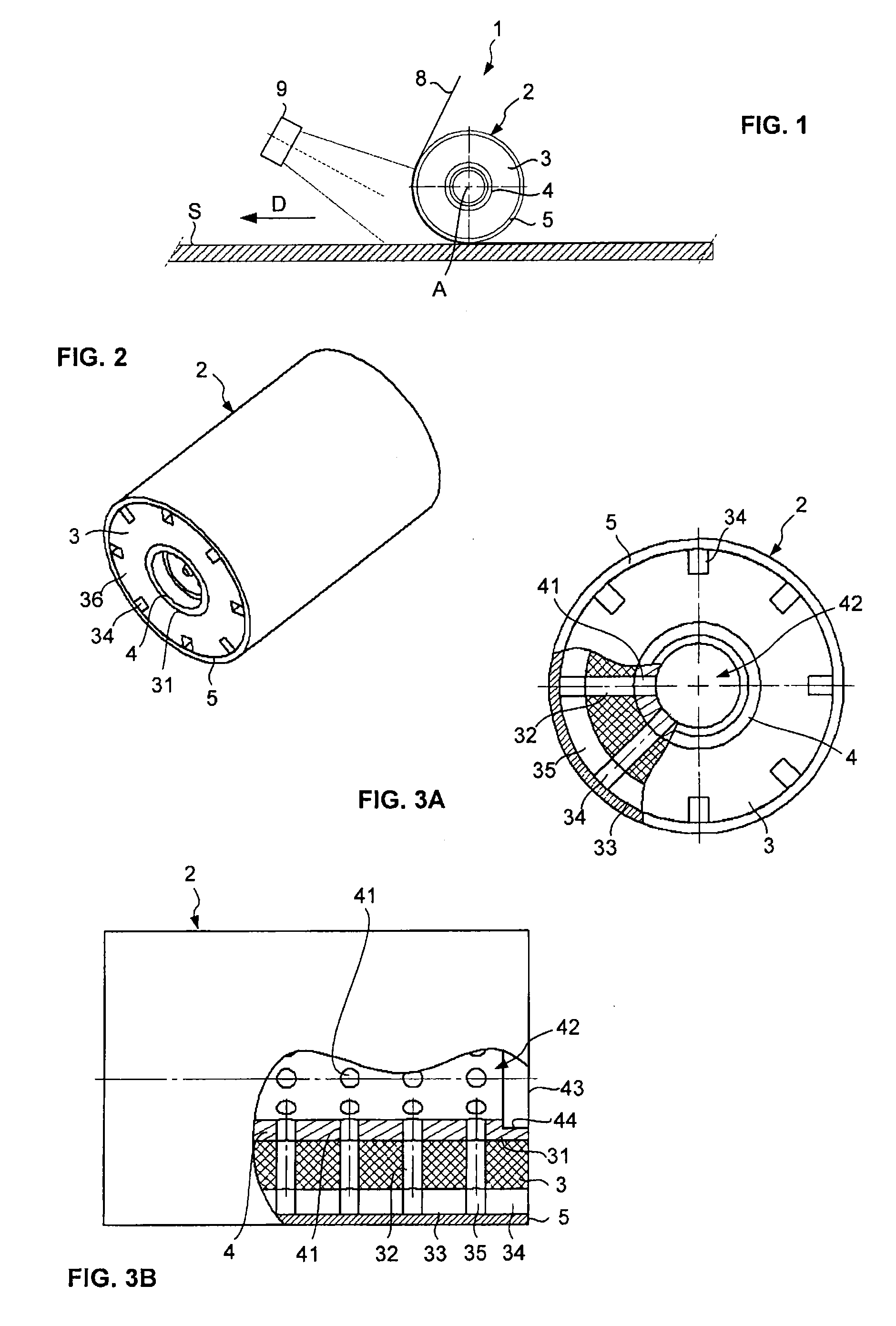
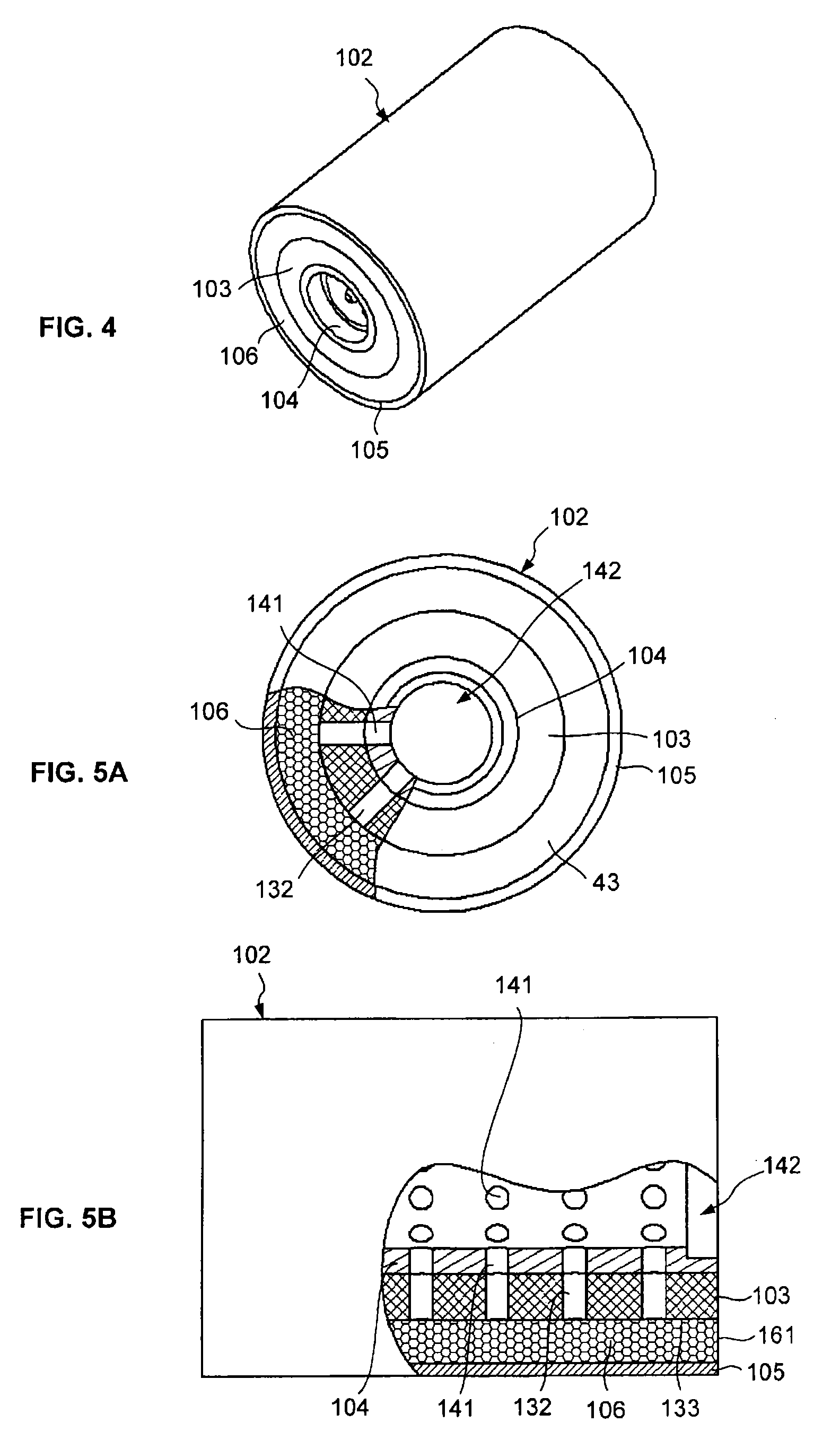
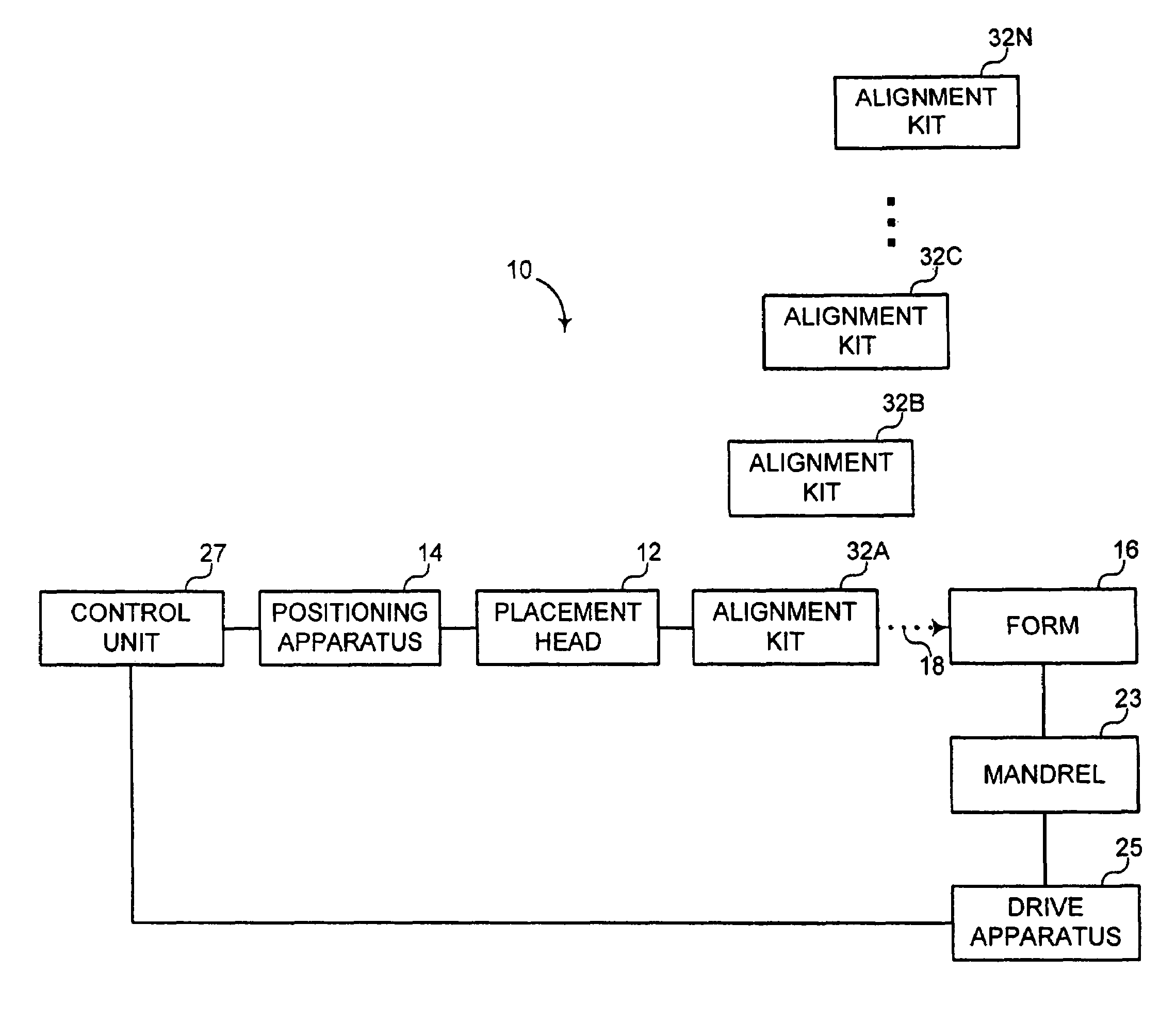
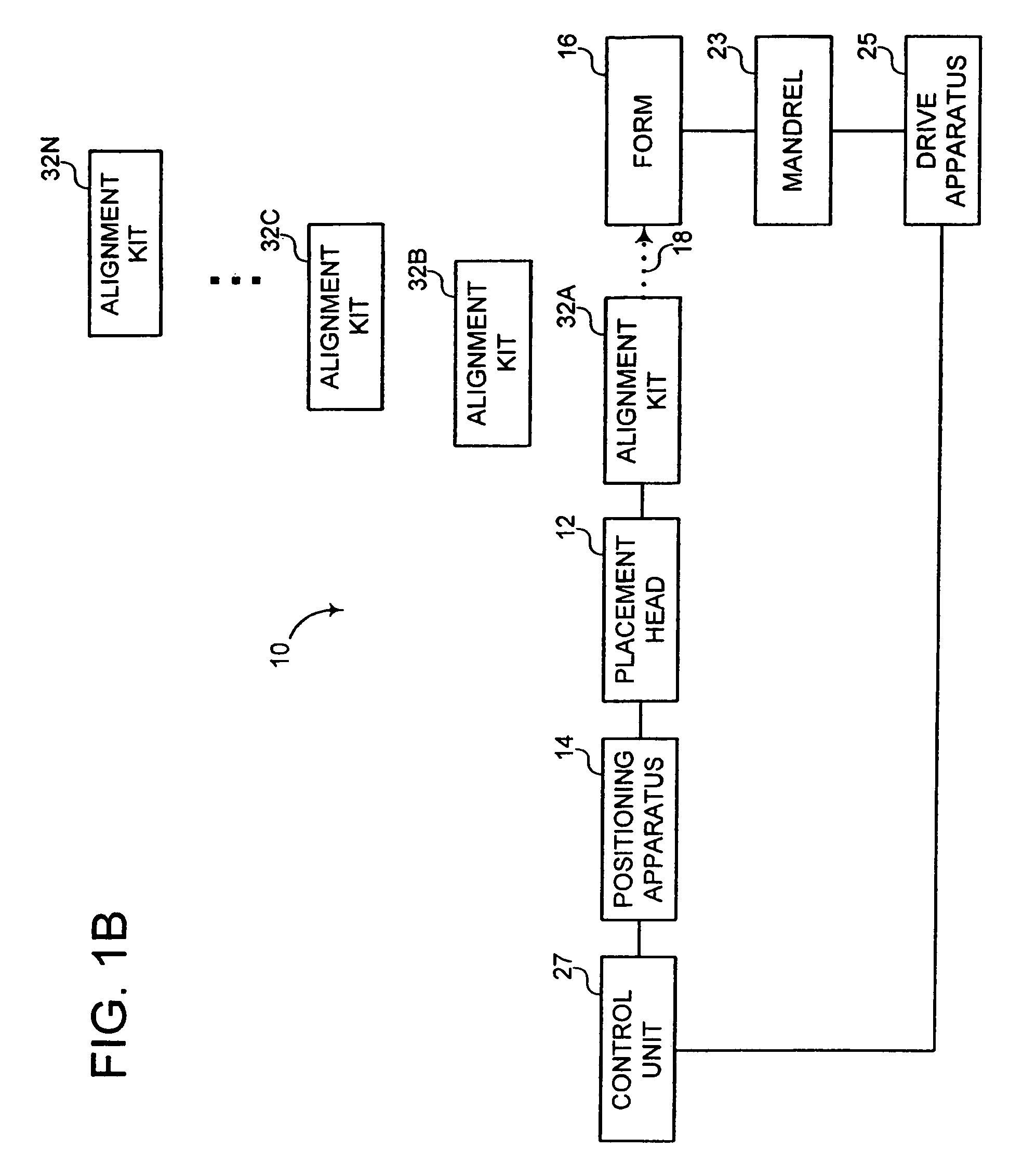
Fiber Placement Machine Platform System Having Interchangeable Head and Creel Assemblies
Owner:INGERSOLL MACHINE TOOLS
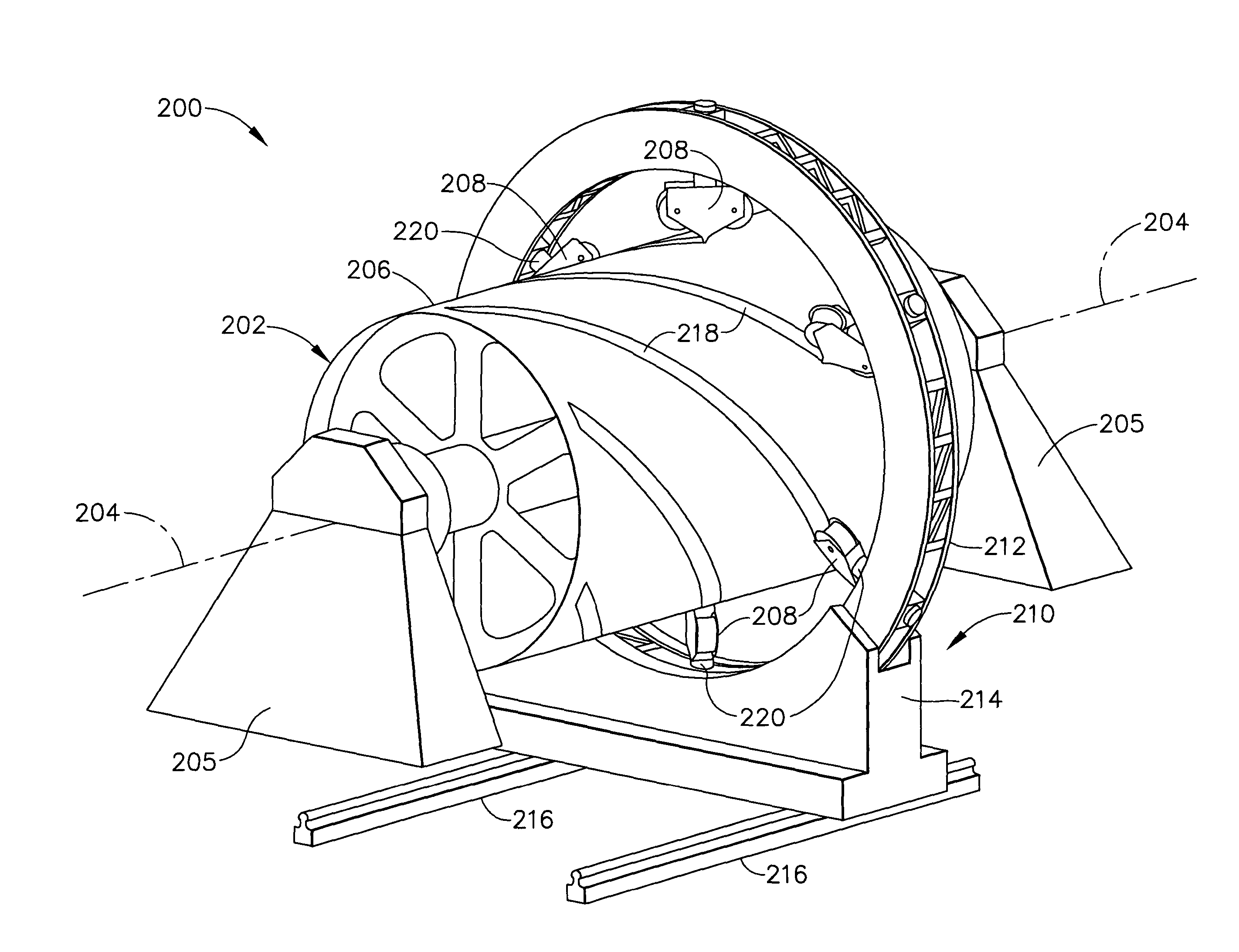
Multiple head automated composite laminating machine for the fabrication of large barrel section components
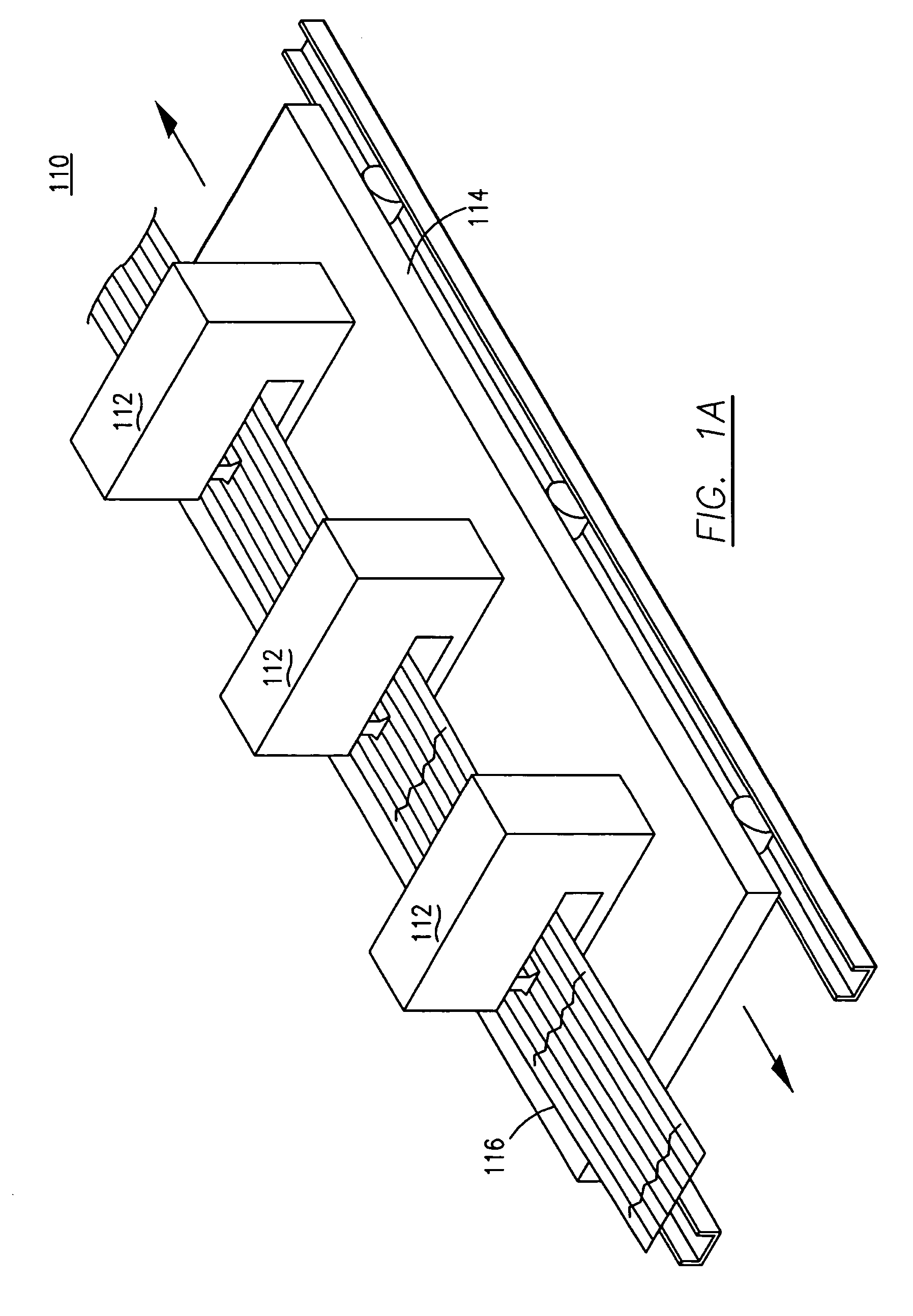
An aircraft part manufacturing device for automated composite lamination on a mandrel surface of a tool having a rotational axis includes a mechanical supporting structure that supports multiple material delivery heads. The tool is moveable and rotatable relative to the mechanical supporting structure. The mechanical supporting structure provides for axial translation of the material delivery heads relative to the mandrel surface while the mandrel surface is rotated for laying down courses of composite material over the entire mandrel surface of the tool. The position and movement of each of the plurality of material delivery heads is individually adjustable. Arm mechanisms provide motion of each material delivery head in a direction normal to the mandrel surface; rotation about an axis normal to the mandrel surface; circumferential position adjustment in a hoop direction relative to the mandrel surface; and axial position adjustment relative to the other material delivery heads.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Tow width adaptable placement head device and method
InactiveUS20070029030A1Lamination ancillary operationsControlling laminationEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Modular head lamination device and method
A composite item is fabricated with a device. The device includes and end effector and a positioning device. The end effector places a tow. The end effector includes a spindle, compaction device, and a path. The spindle detachably secures a spool of tow and the path is disposed from the spool to the compaction device. The positioning device positions the end effector. The end effector is detachably secured to the positioning device.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
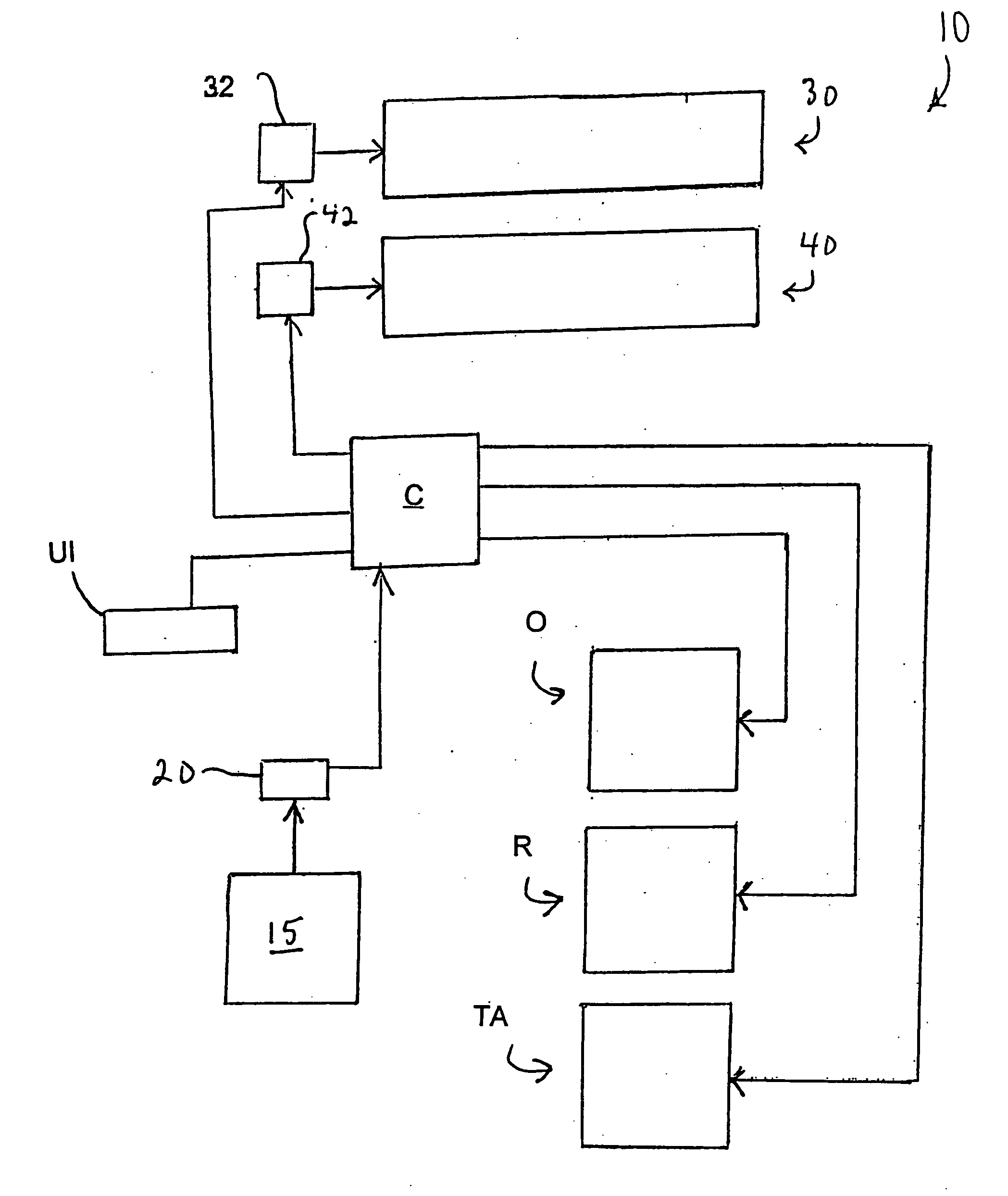
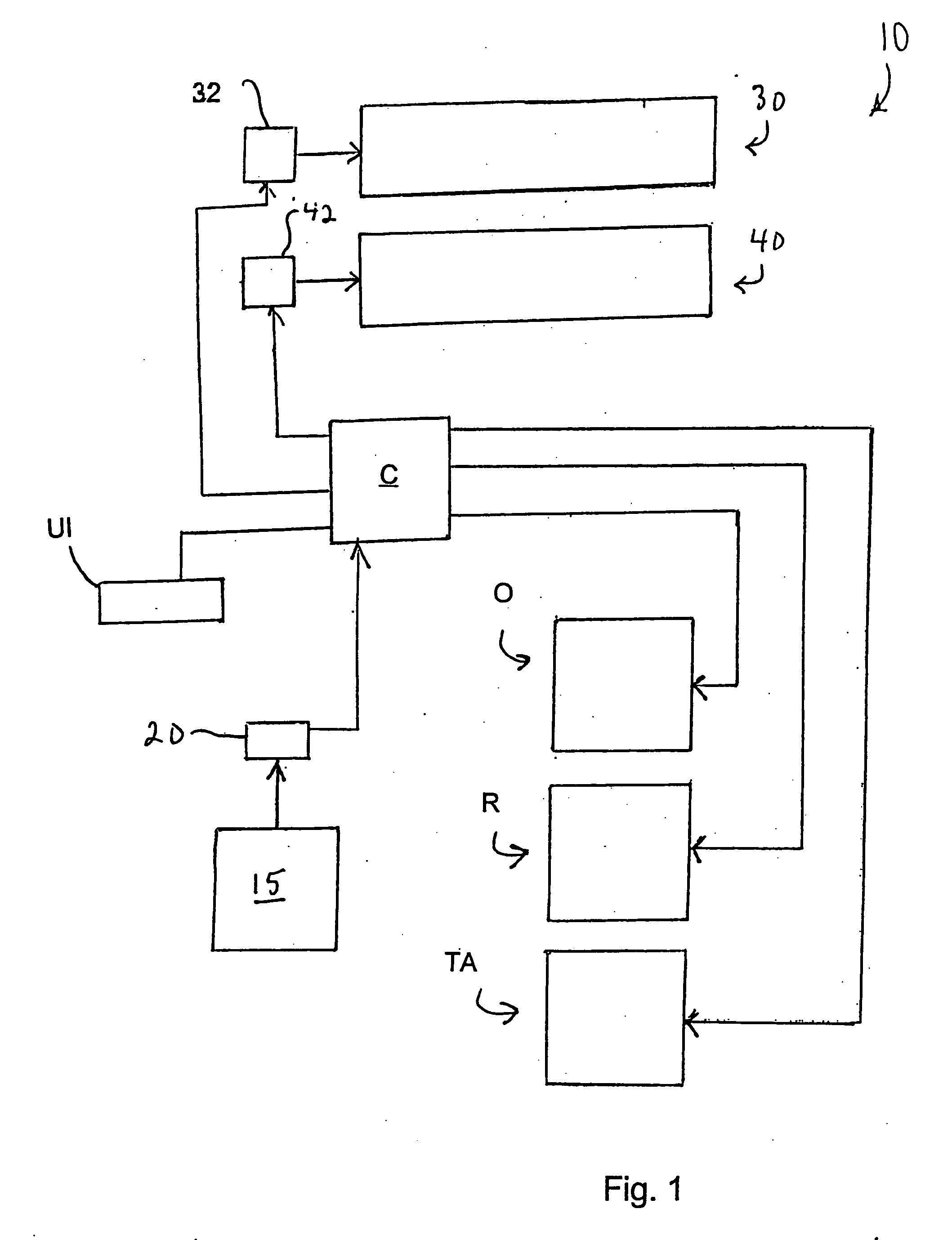
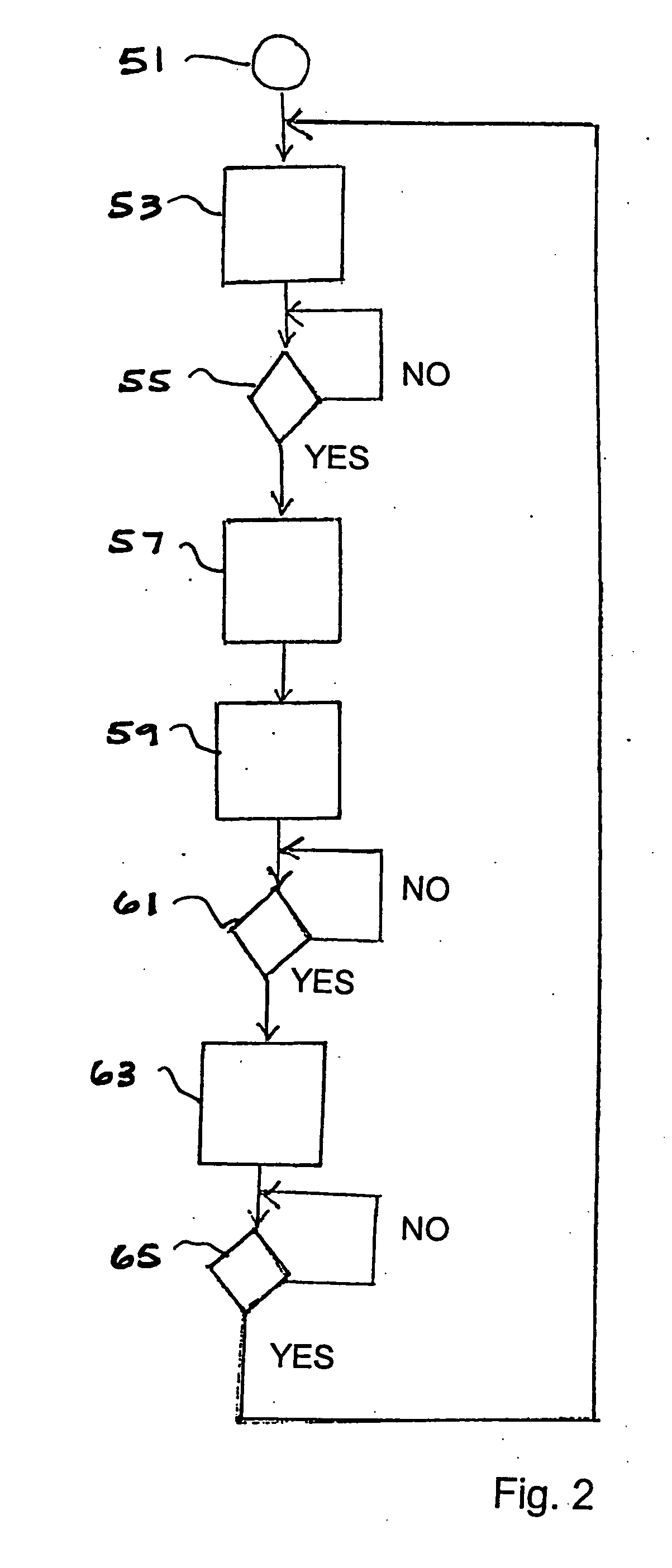
Inserting apparatus and method with controlled, master cycle speed-dependent actuator operations
InactiveUS20050246139A1Constant time lagEffective maintenanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsMotor driveMotion controller
In an inserting apparatus and method such as the continuous motion type, a motion controller electrically communicates with an encoder, a first motor driving an insert conveyor assembly, a second motor driving an envelope conveyor assembly, and an actuator operatively interfaced with a peripheral device. The motion controller controls insert conveyor assembly speed, envelope conveyor assembly speed, and the rotational position at which the actuator should be activated, based on the encoder signal. Once during every master cycle, the motion controller calculates the actuator activation position, and causes the first actuator to be activated at the calculated first actuator activation position.
Owner:BELL & HOWELL CO
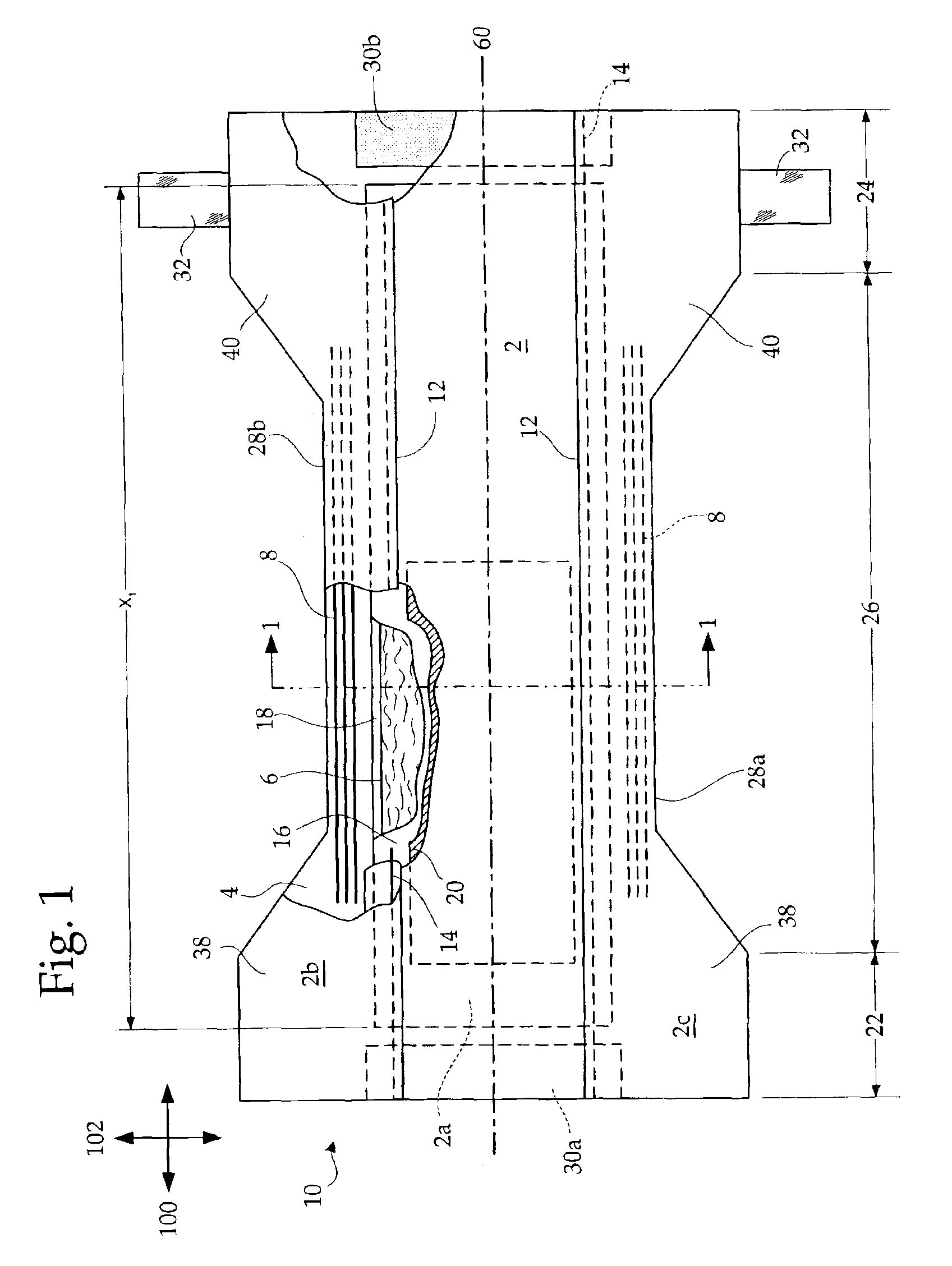
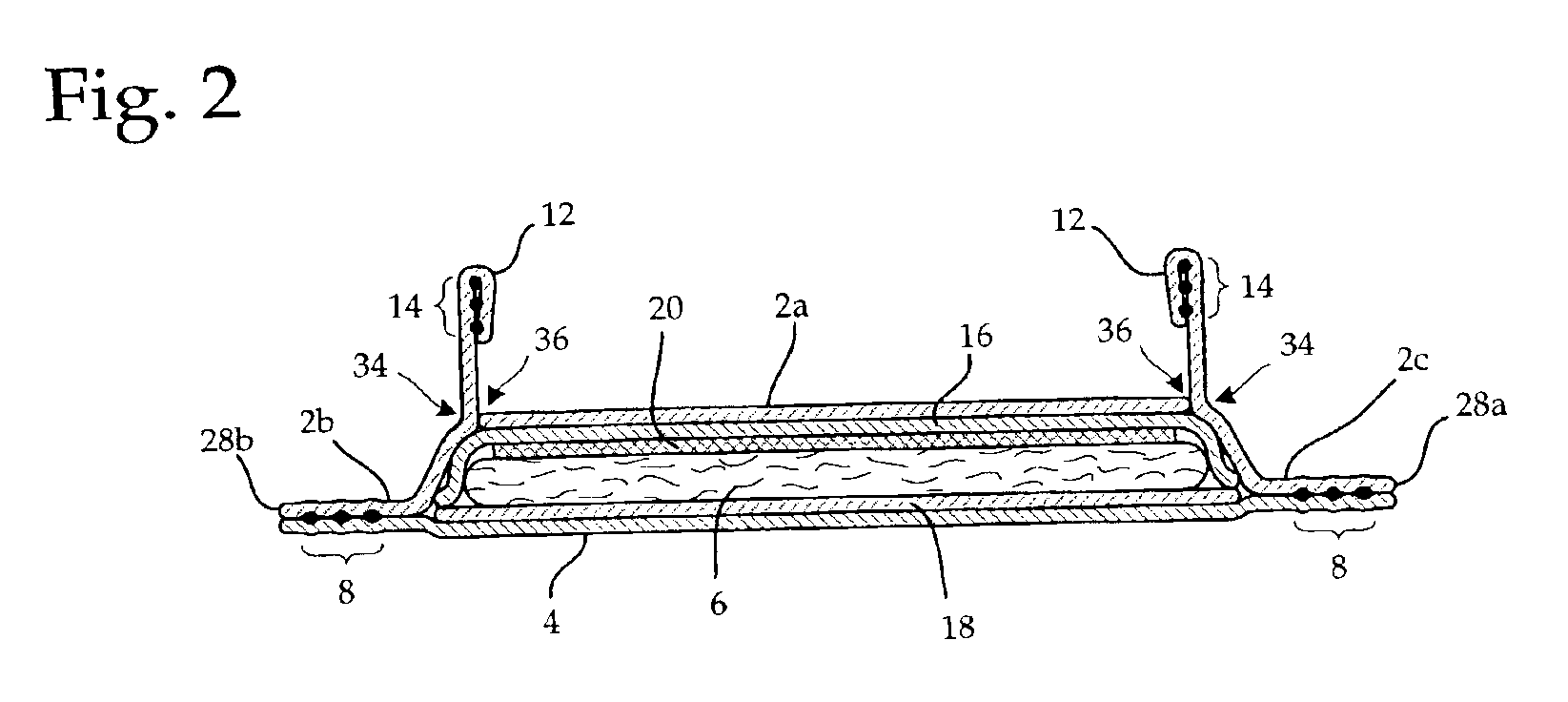
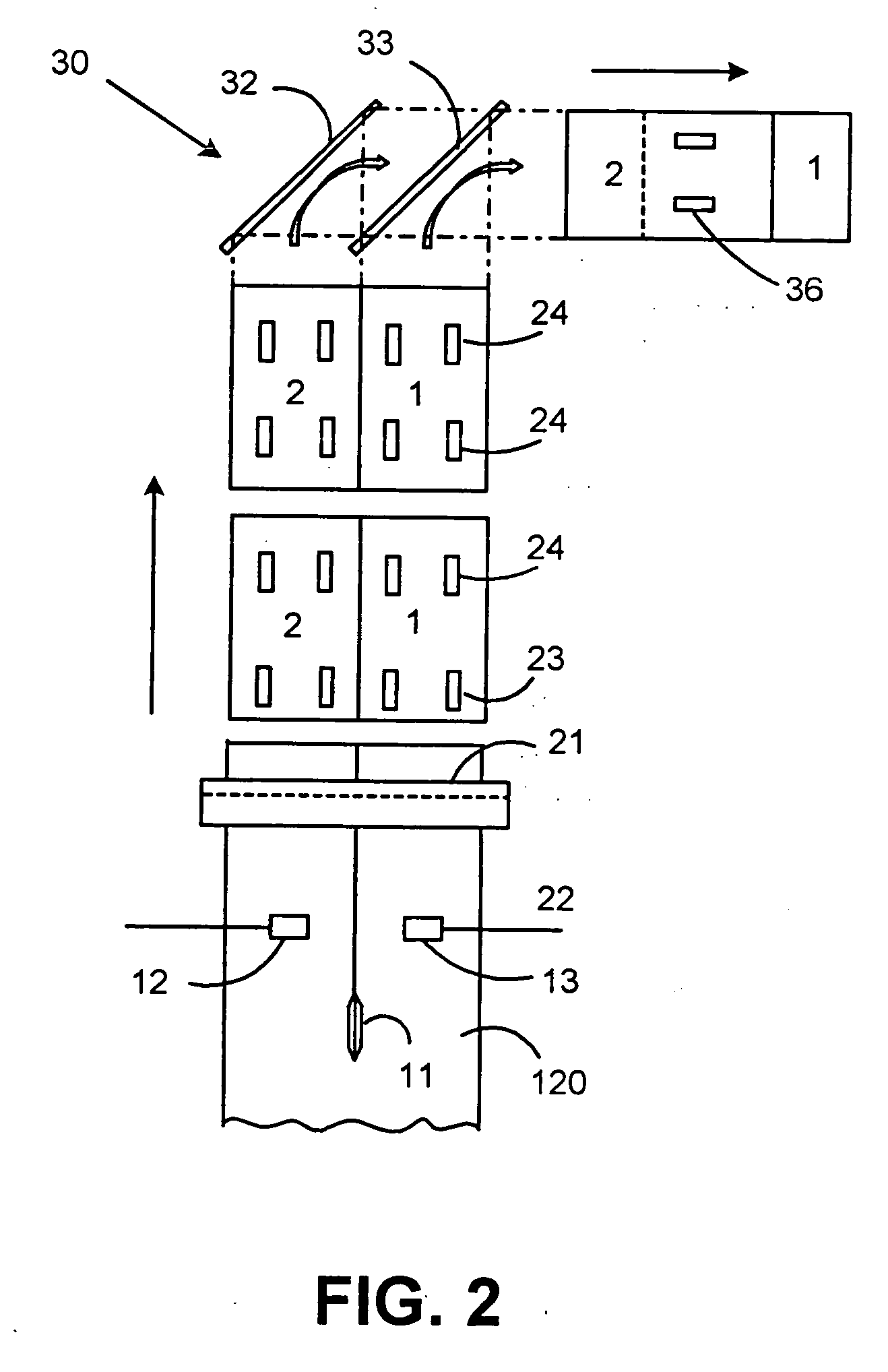
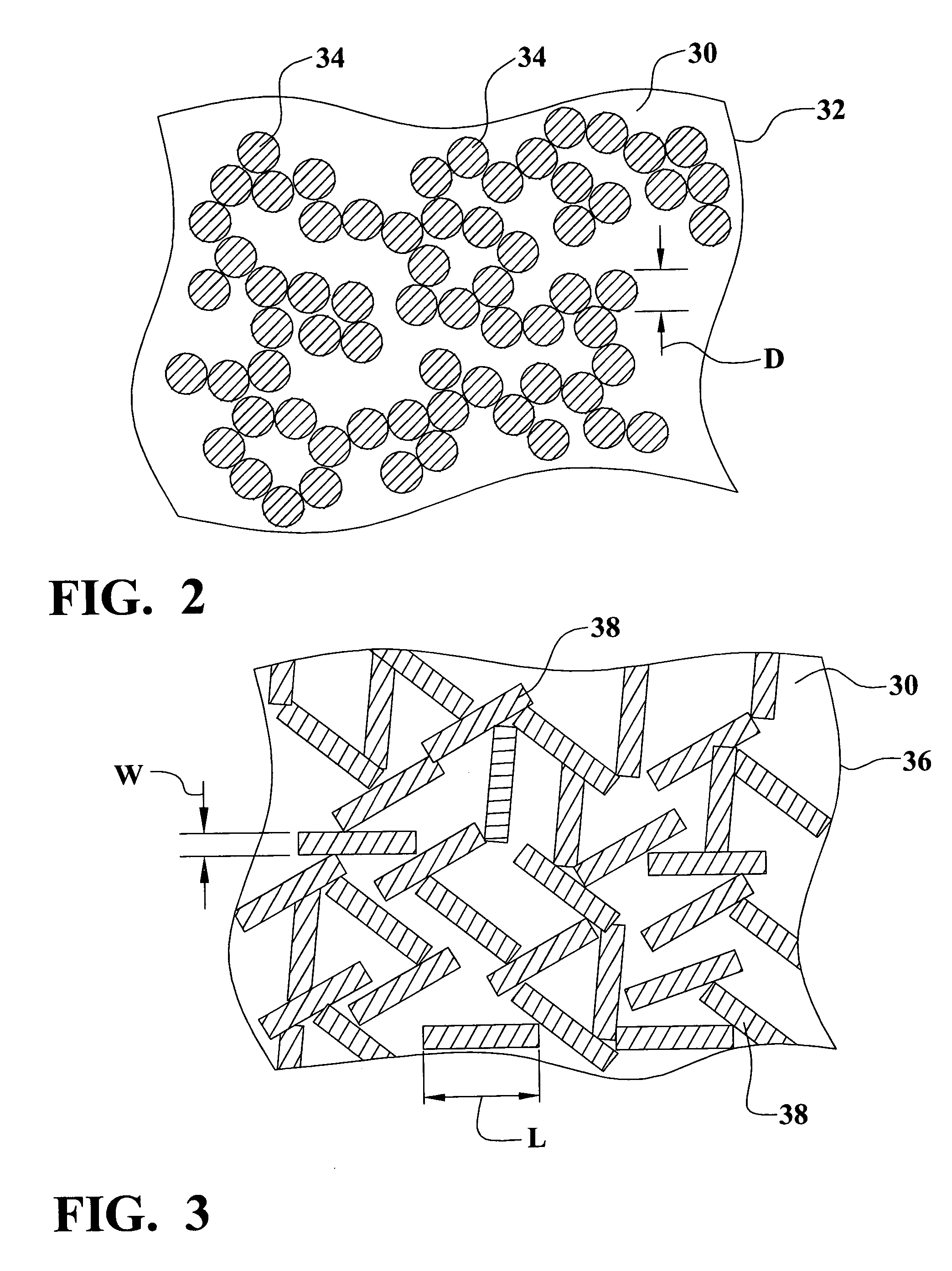
Method and apparatus for forming tow-based absorbent structures with a single casing sheet
InactiveUS6923926B2Easy to operateIncrease line speedMechanical working/deformationDough shapingParticulatesEngineering
An apparatus and method for forming tow-based absorbent structures having a single casing sheet are disclosed. The apparatus has a tow supply mechanism for providing tow material, a particulate matter supply mechanism for providing particulate matter, and a casing sheet supply mechanism for providing casing sheet material. The apparatus also has a vacuum draw roll having a foraminous center surface that has a width defined by a first edge and a second edge and is rotatable about a first axis. The vacuum draw roll is positioned to receive the tow material, the particulate matter and the casing sheet material to form a open core composite supply. The apparatus also has one or more angled surfaces positioned to create one or more obtuse angles in the open core composite supply, and one or more folders to further fold the one or more obtuse angles in the open core composite supply to form a folded core composite supply.
Owner:PARAGON TRADE BRANDS
Composite structural element fabricating device and method
ActiveUS20070029038A1Easy to produceAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentWelding/cutting auxillary devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
To fabricate a composite item, a device places a composite ply on a curved form at about 0° relative to a longitudinal axis of the form. The form includes a web surface and a cap surface. The device includes a web compaction roller and a set of guides. The web compaction roller compacts a composite material upon the web surface and generate a web ply. The set of guide rollers urges against the cap surface. The compaction roller is directed along the form by the guide rollers.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
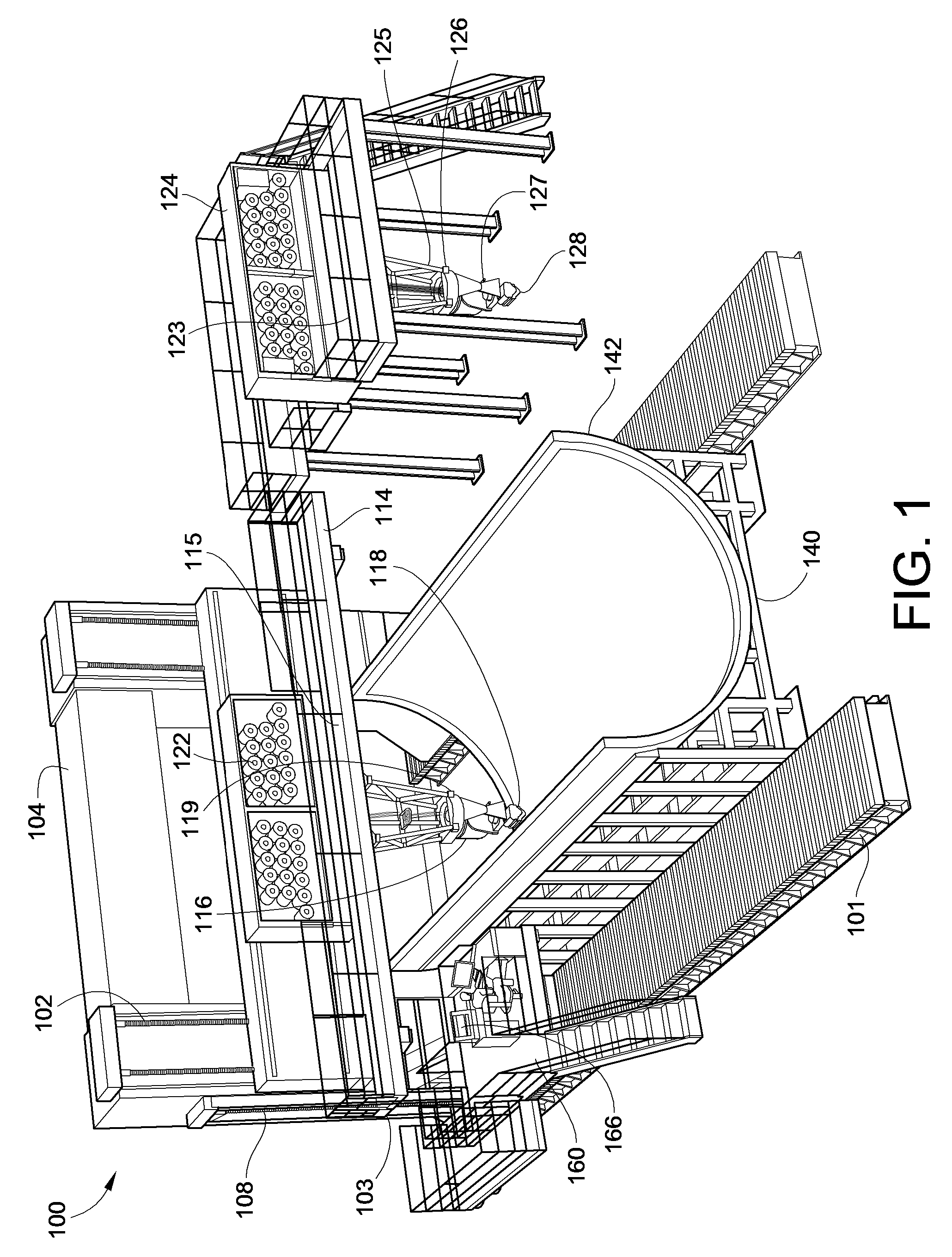
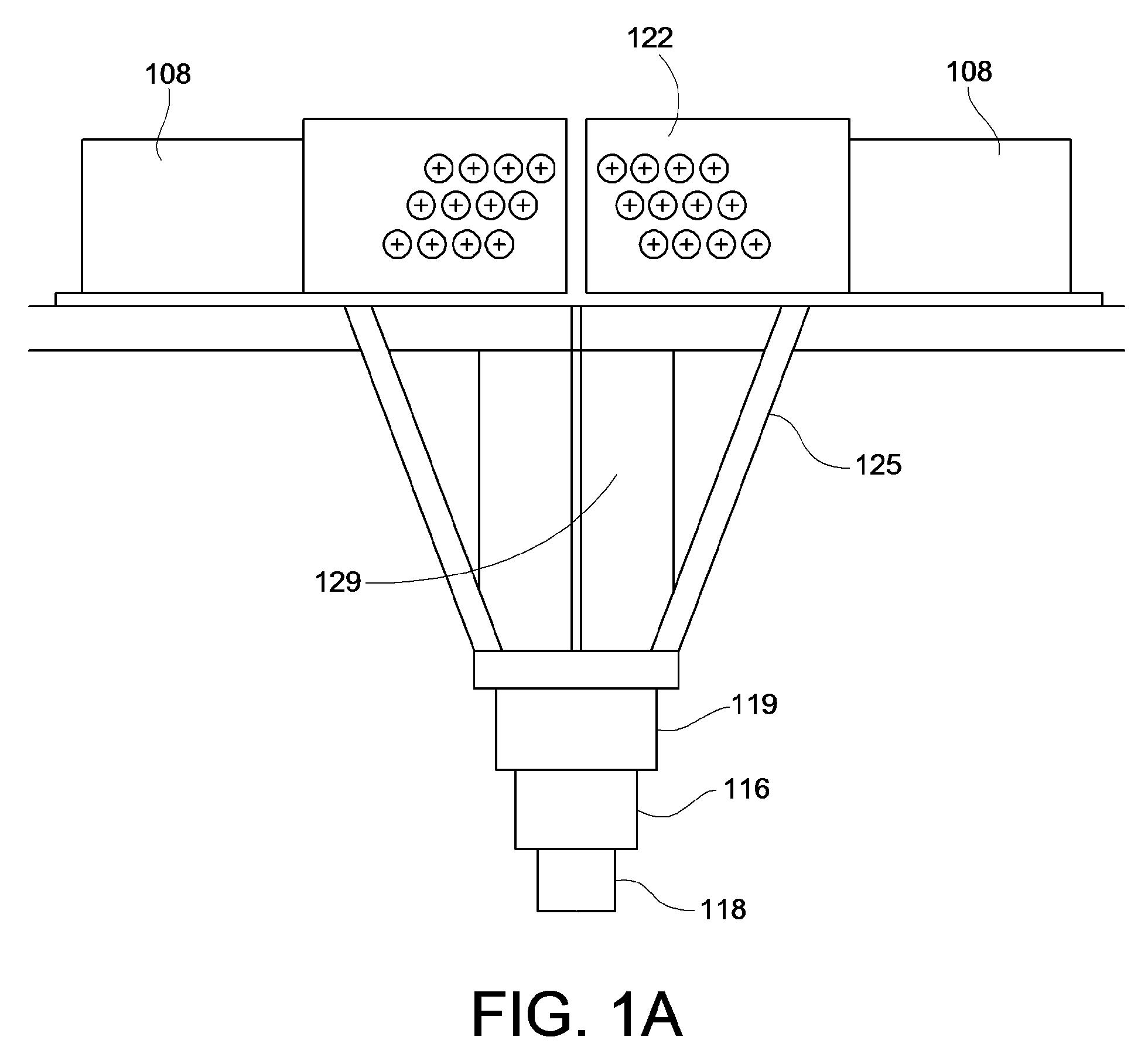
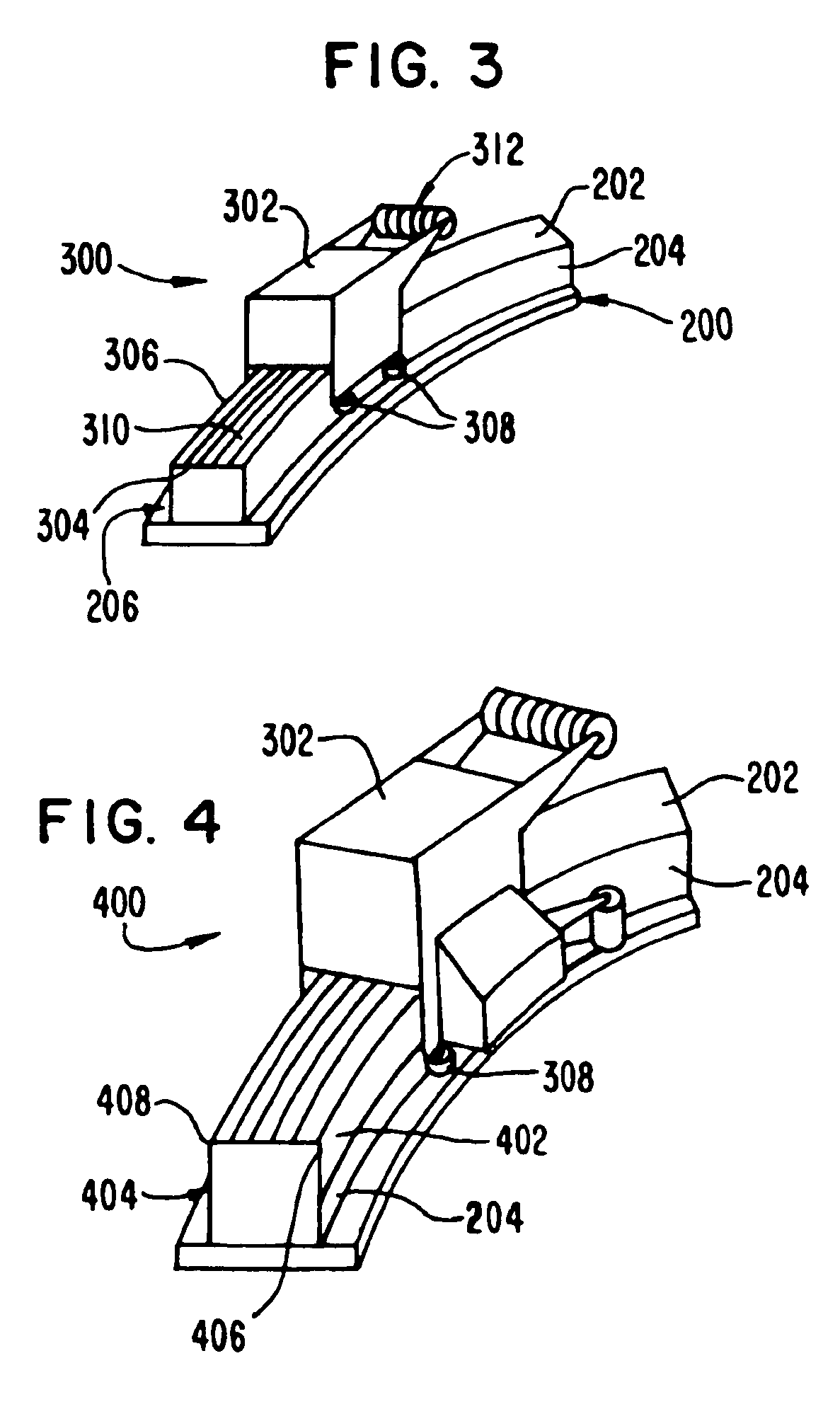
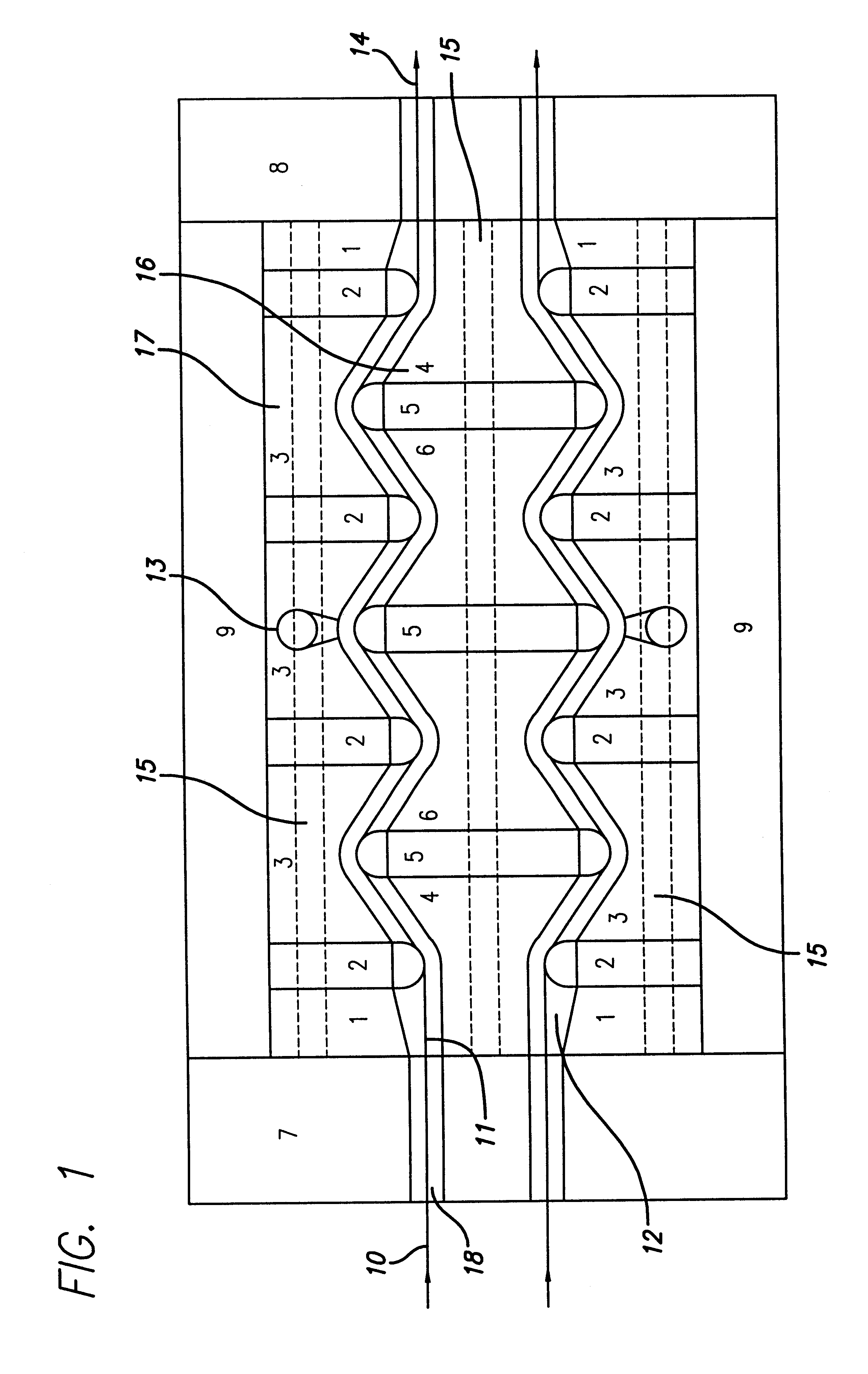
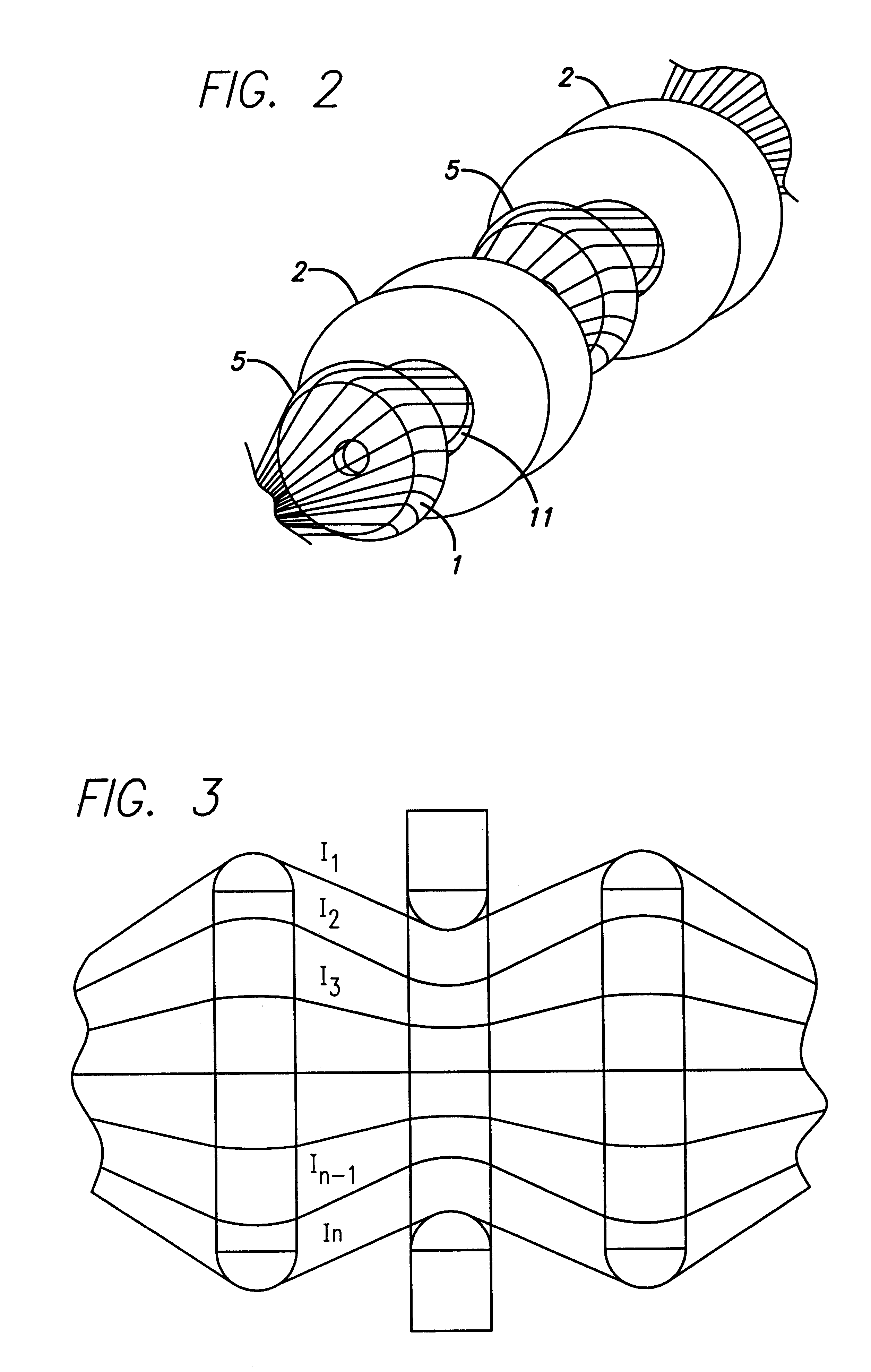
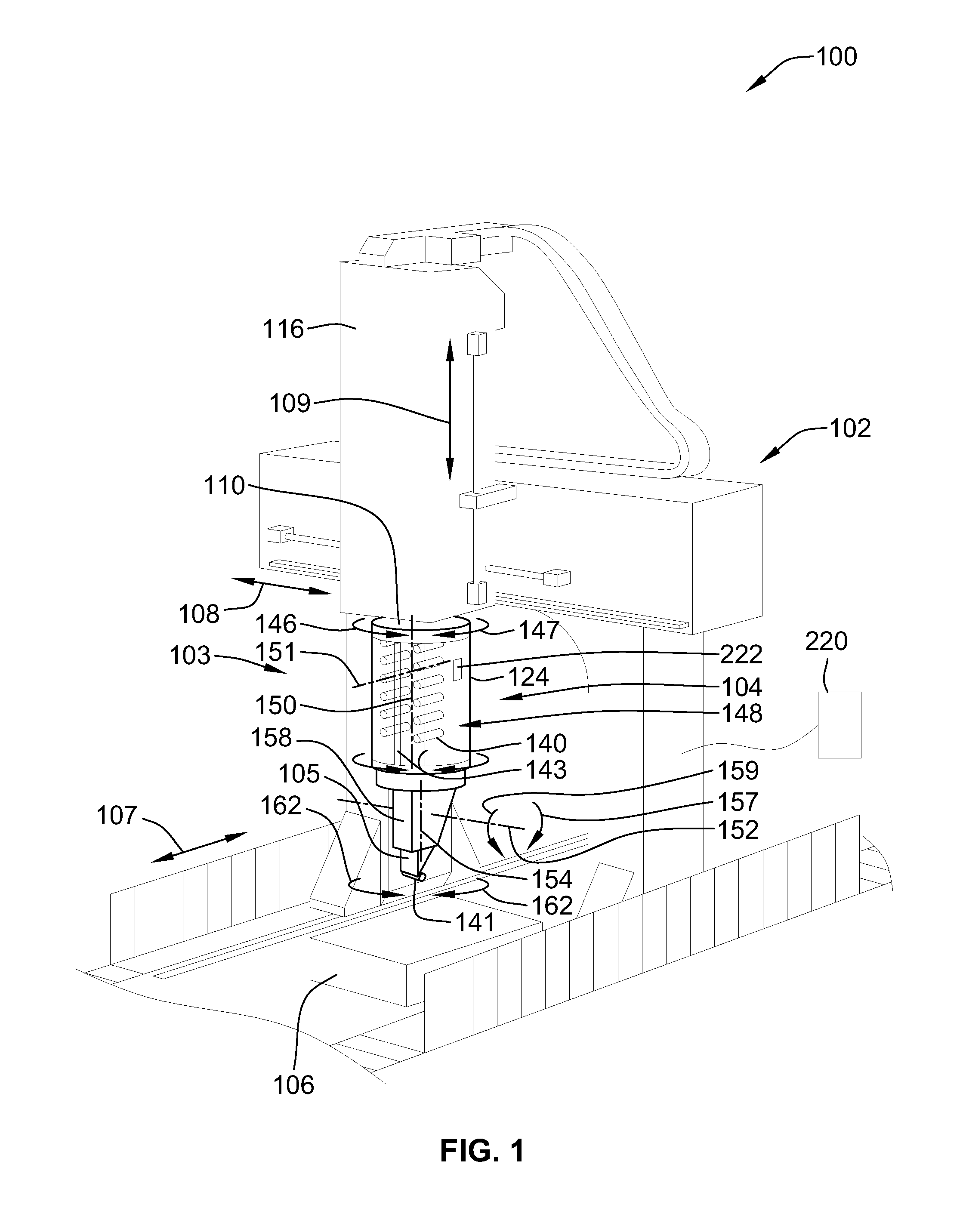
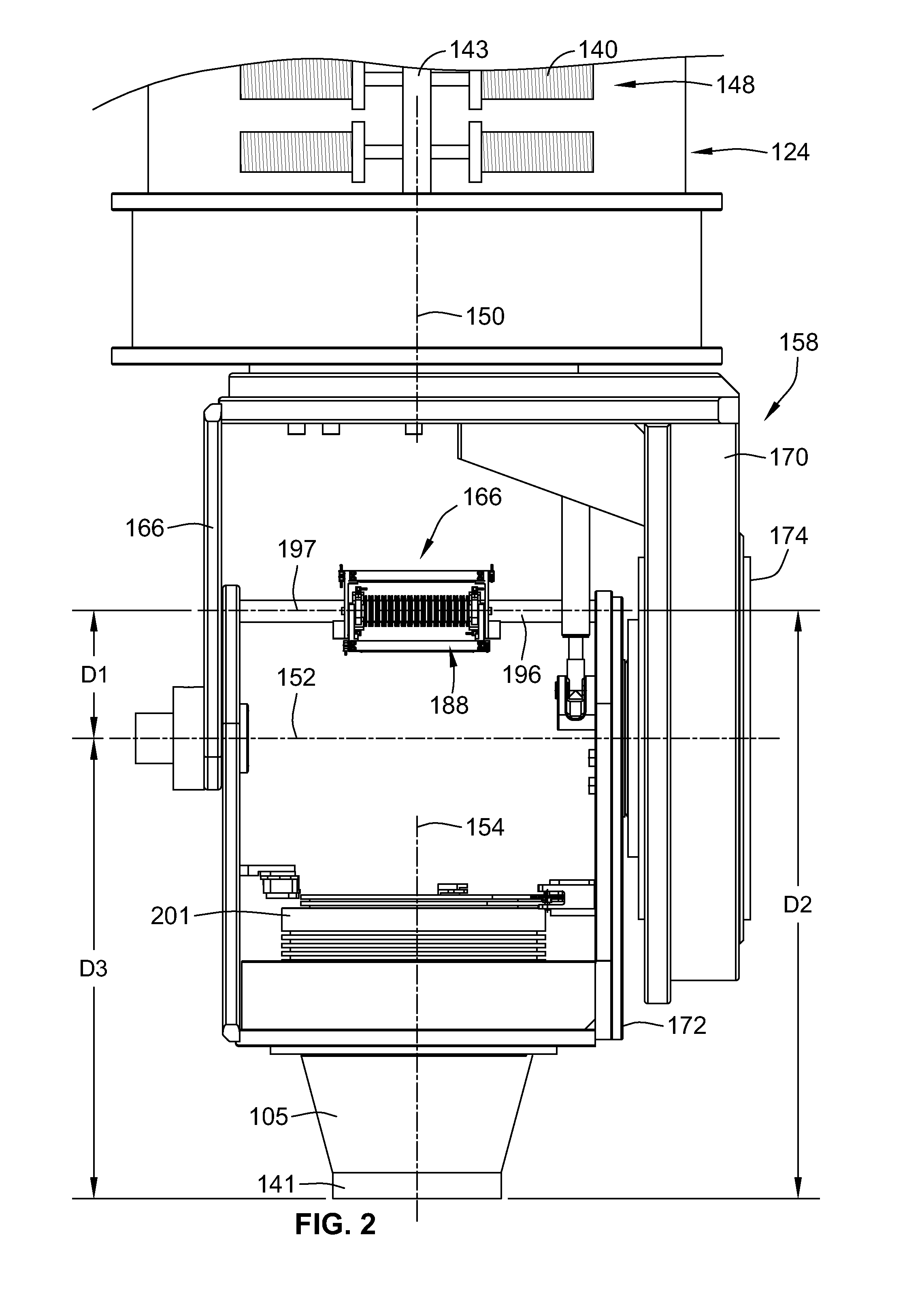
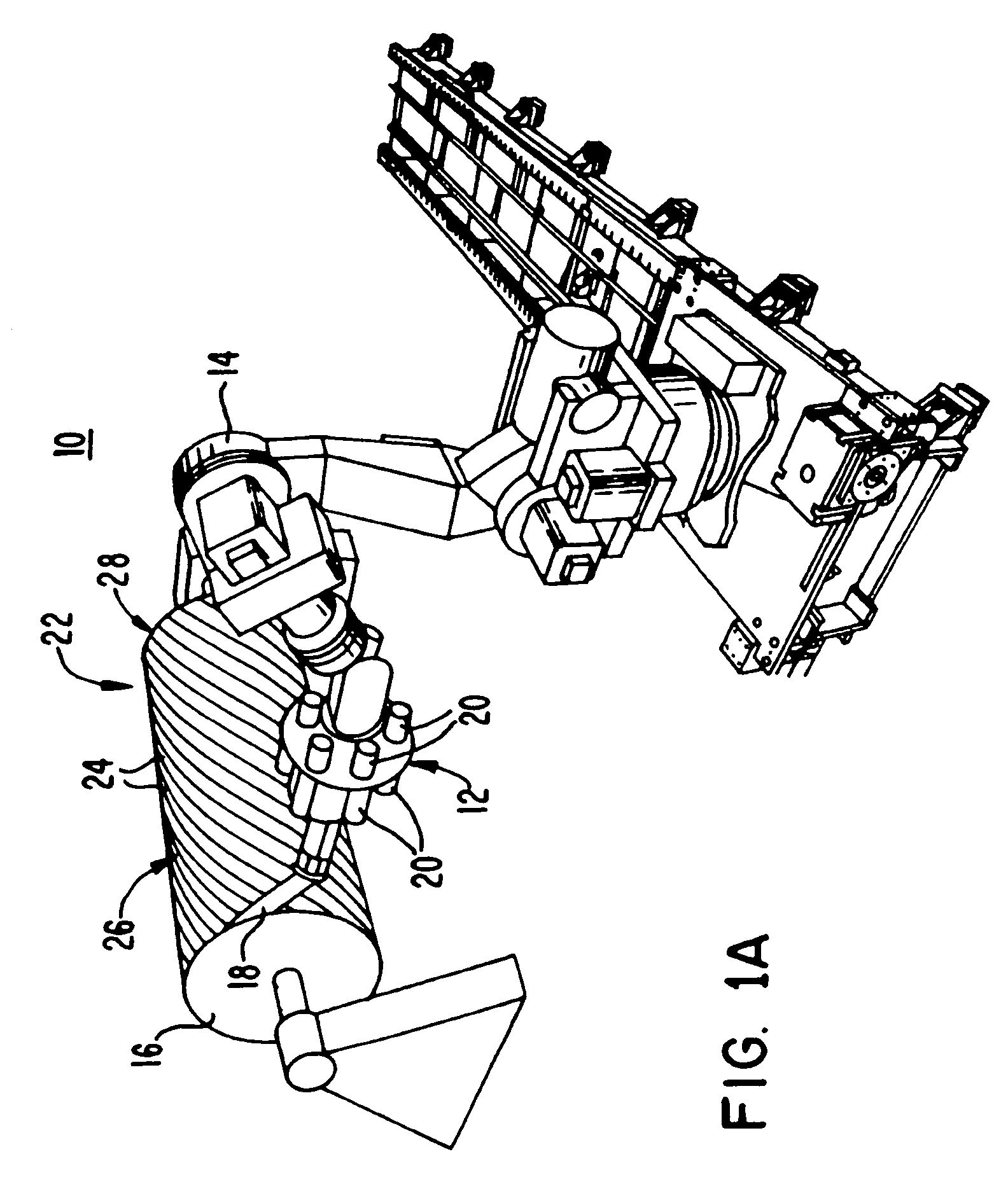
Fiber delivery apparatus and system having a creel and fiber placement head sans fiber redirect
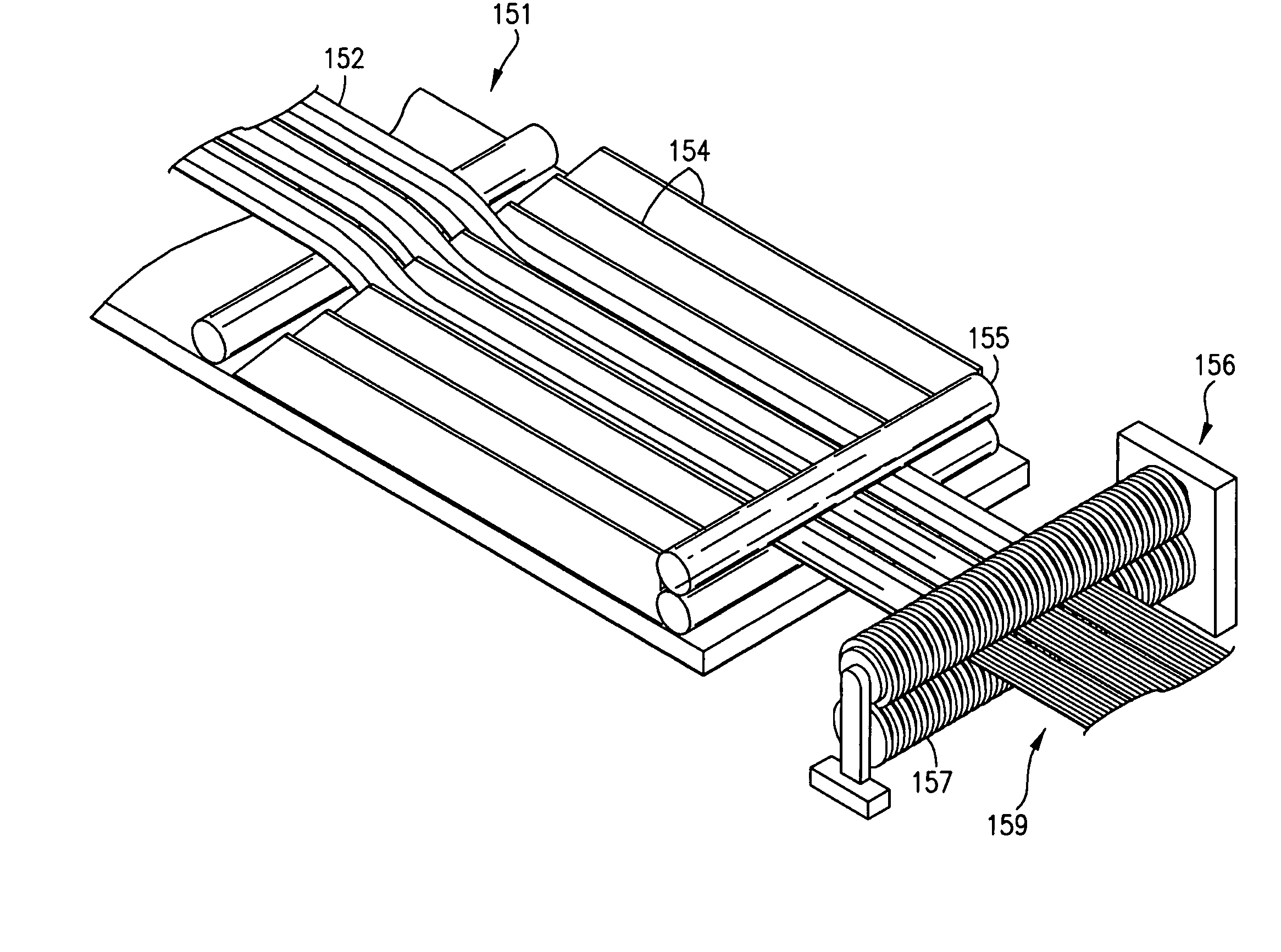
A fiber delivery apparatus having a creel assembly and a fiber placement head is provided. A plurality of fiber spools are stored in the creel assembly. The tow paths from the spools to the fiber placement head are substantially fixed such that movements orienting the fiber placement head relative to a tool are simultaneously applied to the fiber spools as well. As such, the length and orientation of the tow paths between the spools and the fiber placement head are constant.
Owner:INGERSOLL MACHINE TOOLS
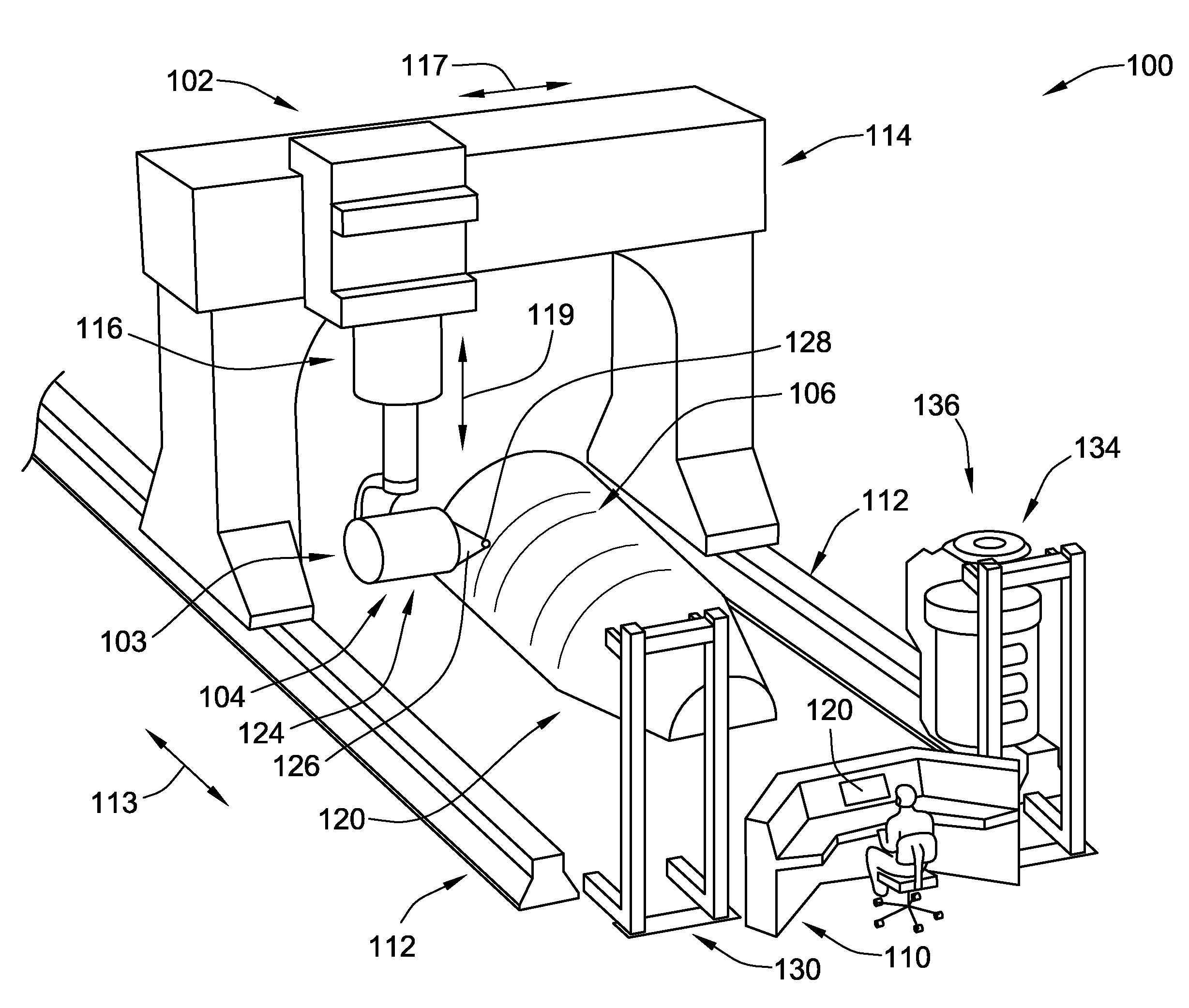
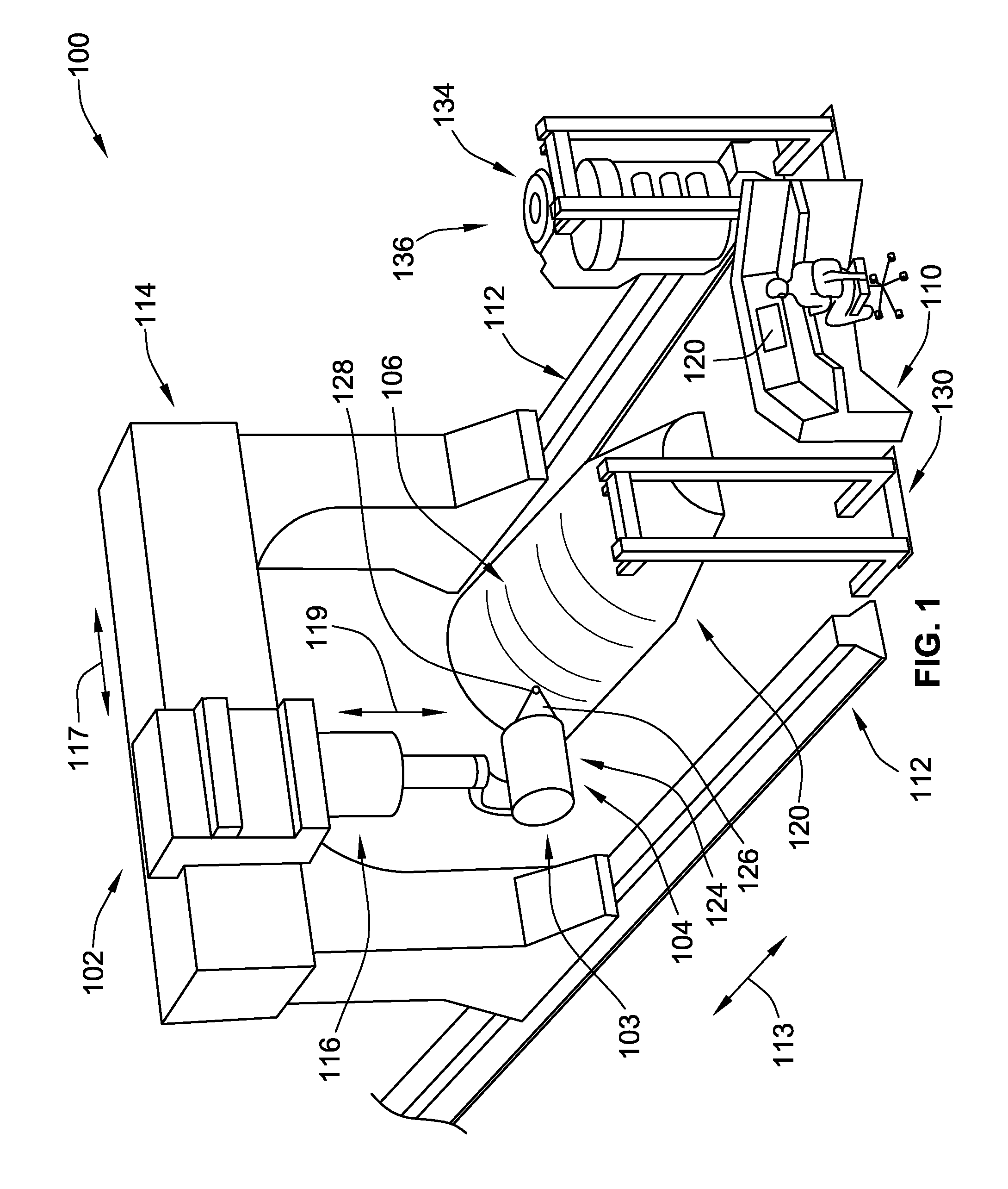
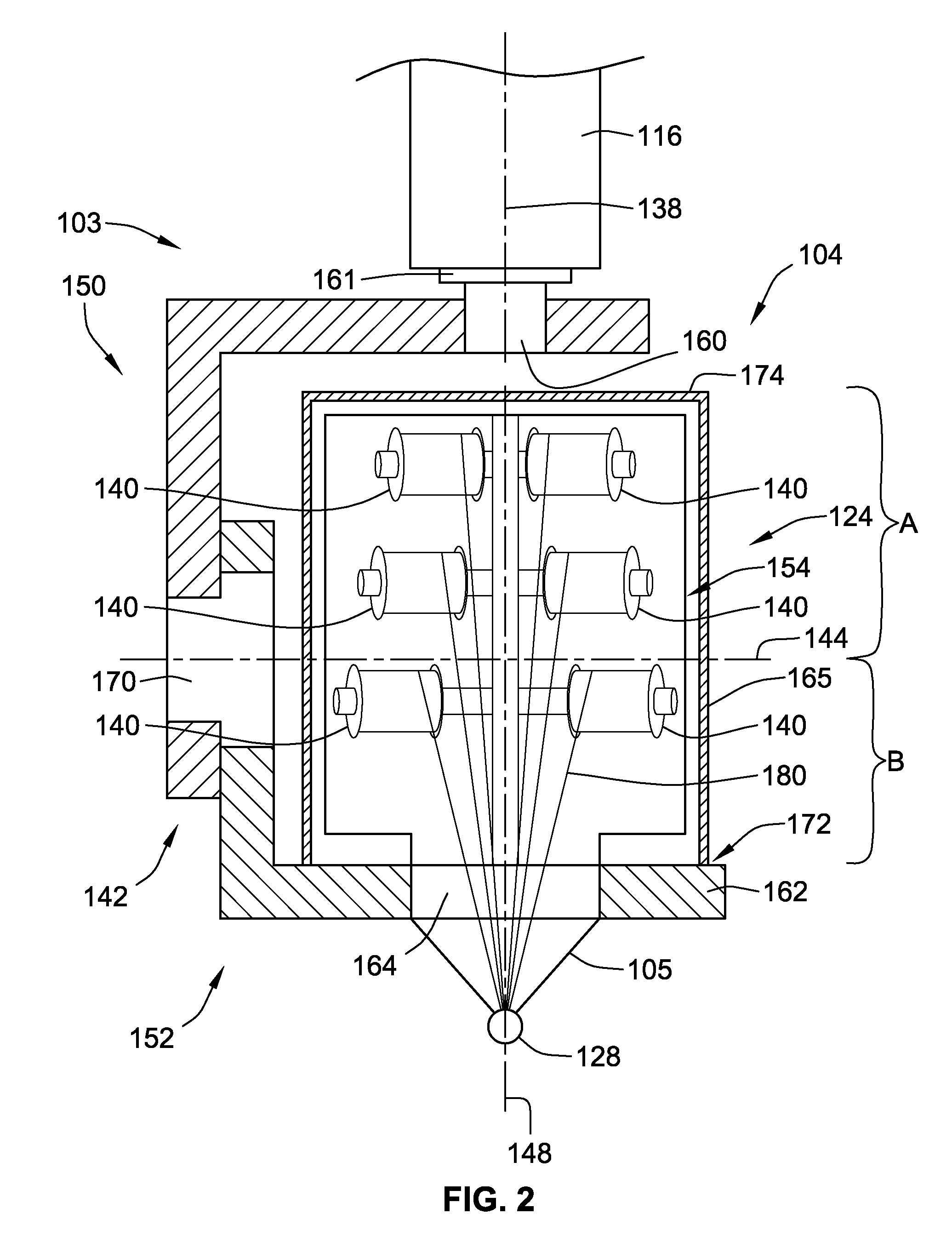
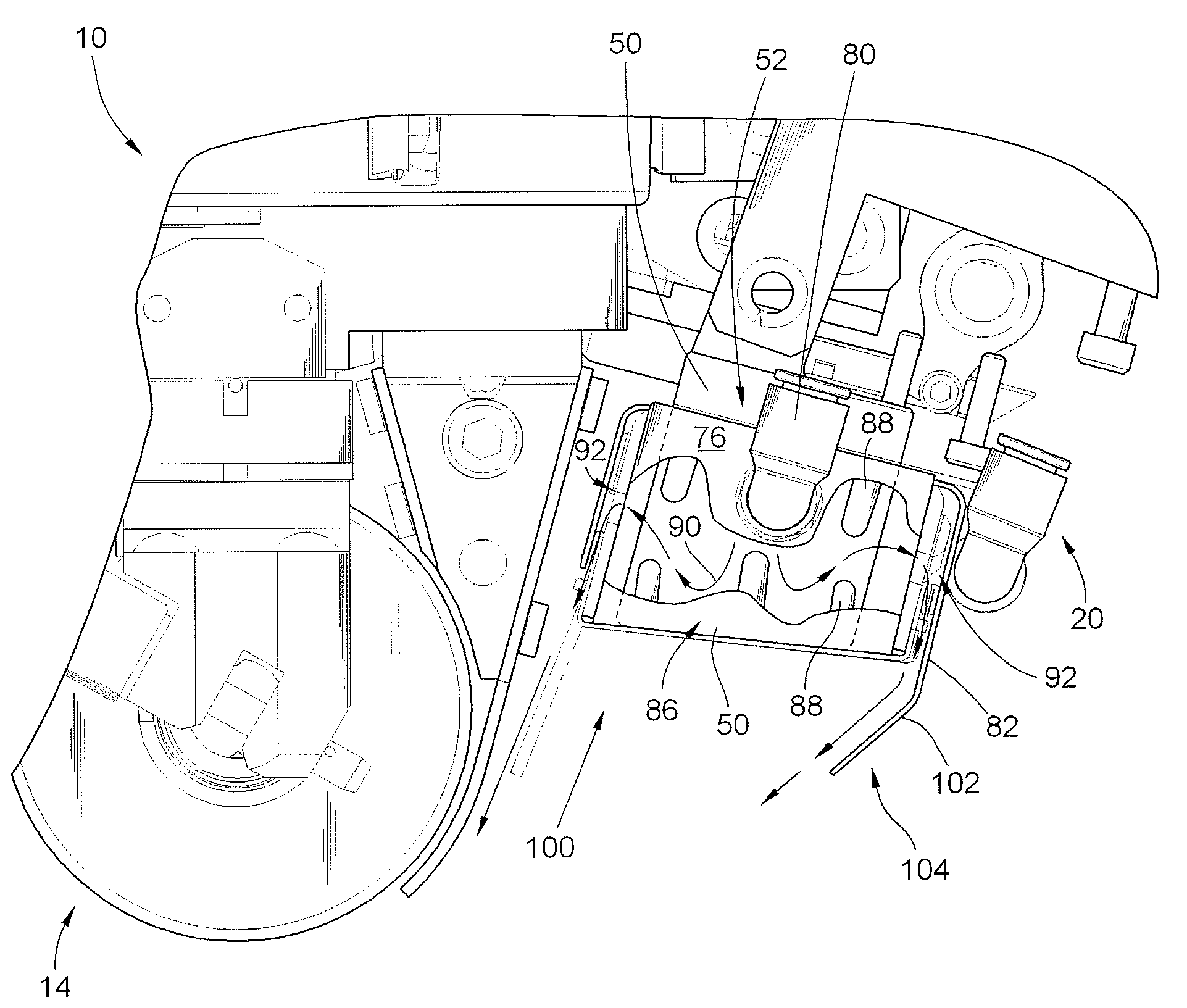
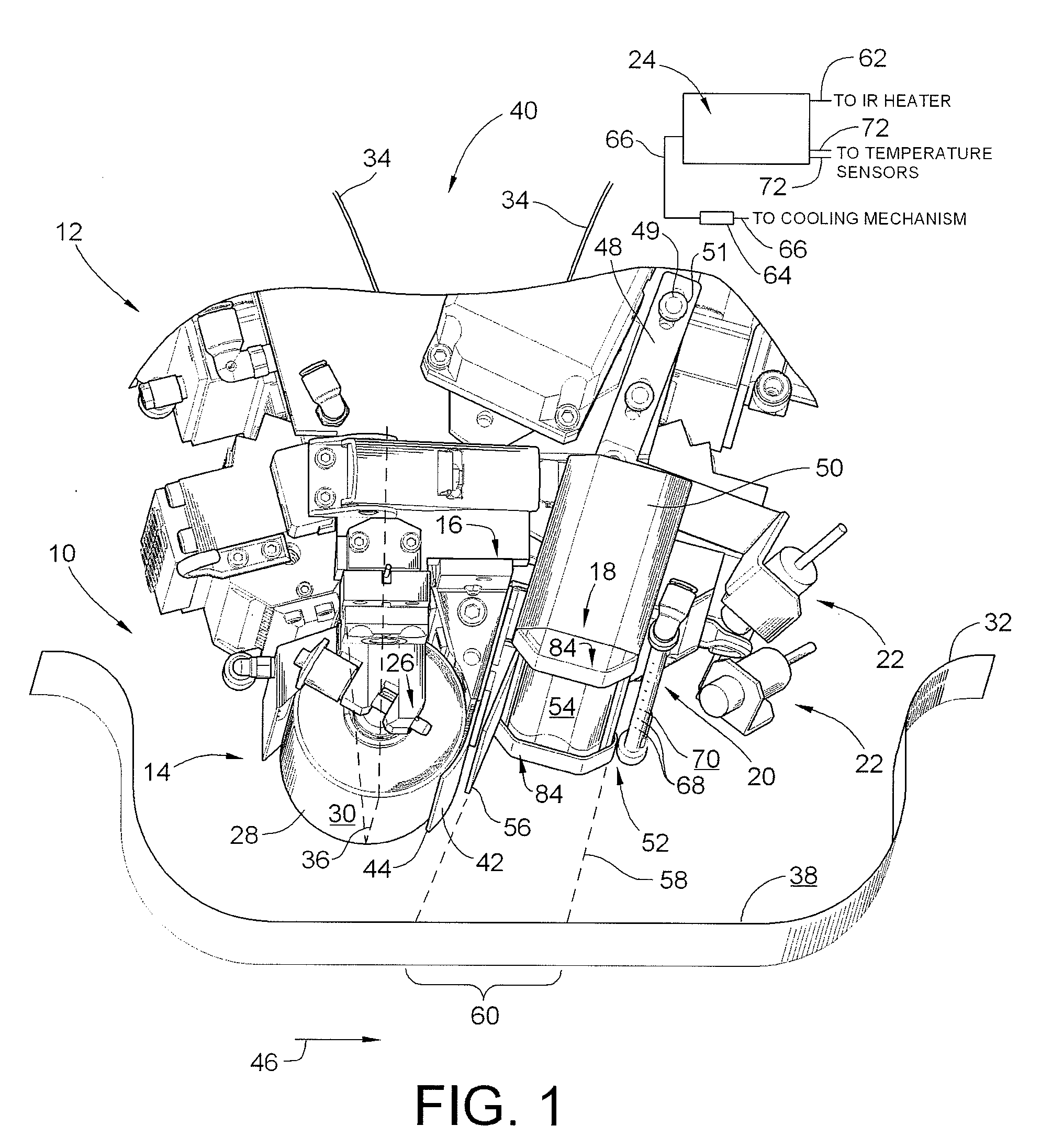
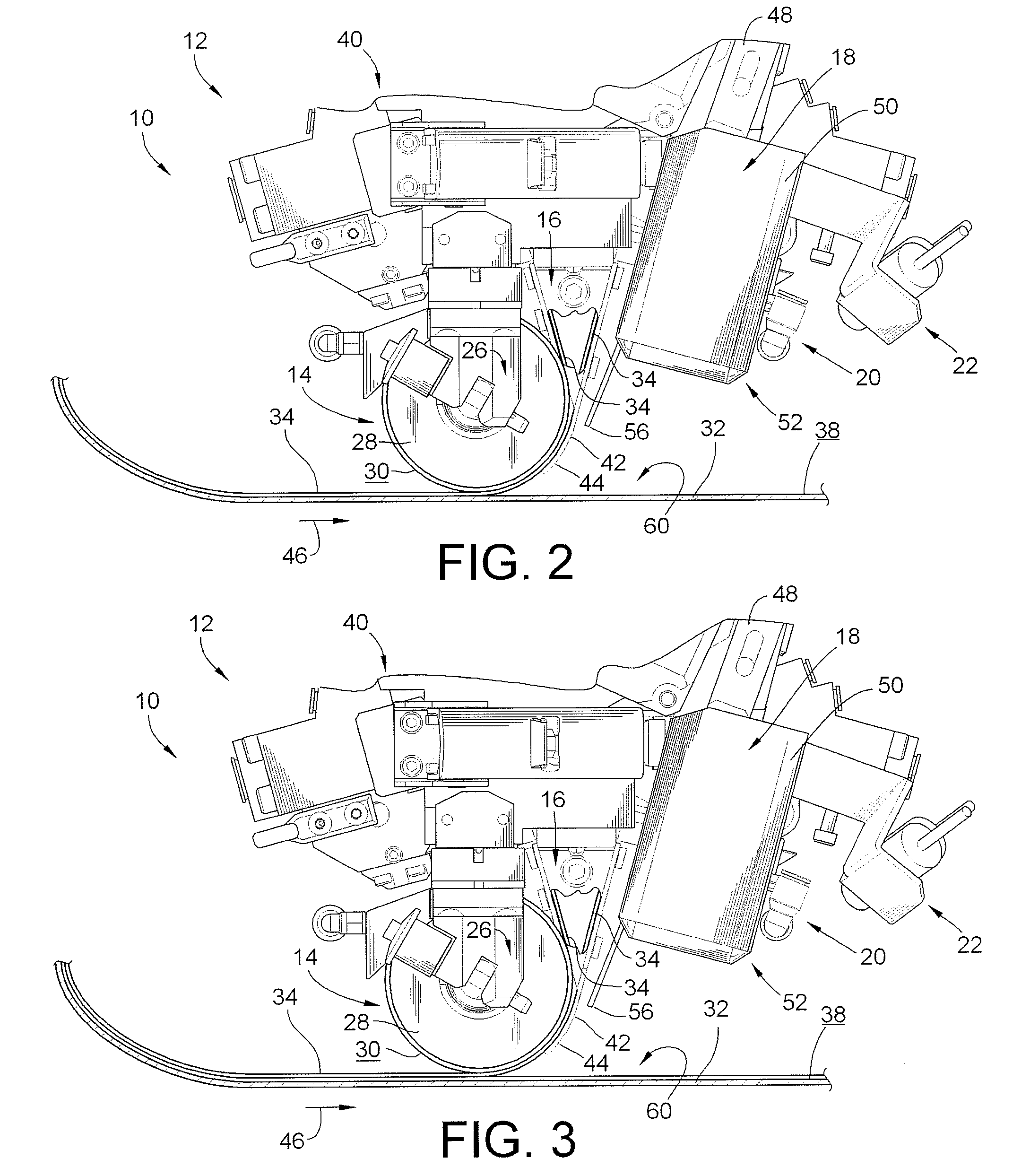
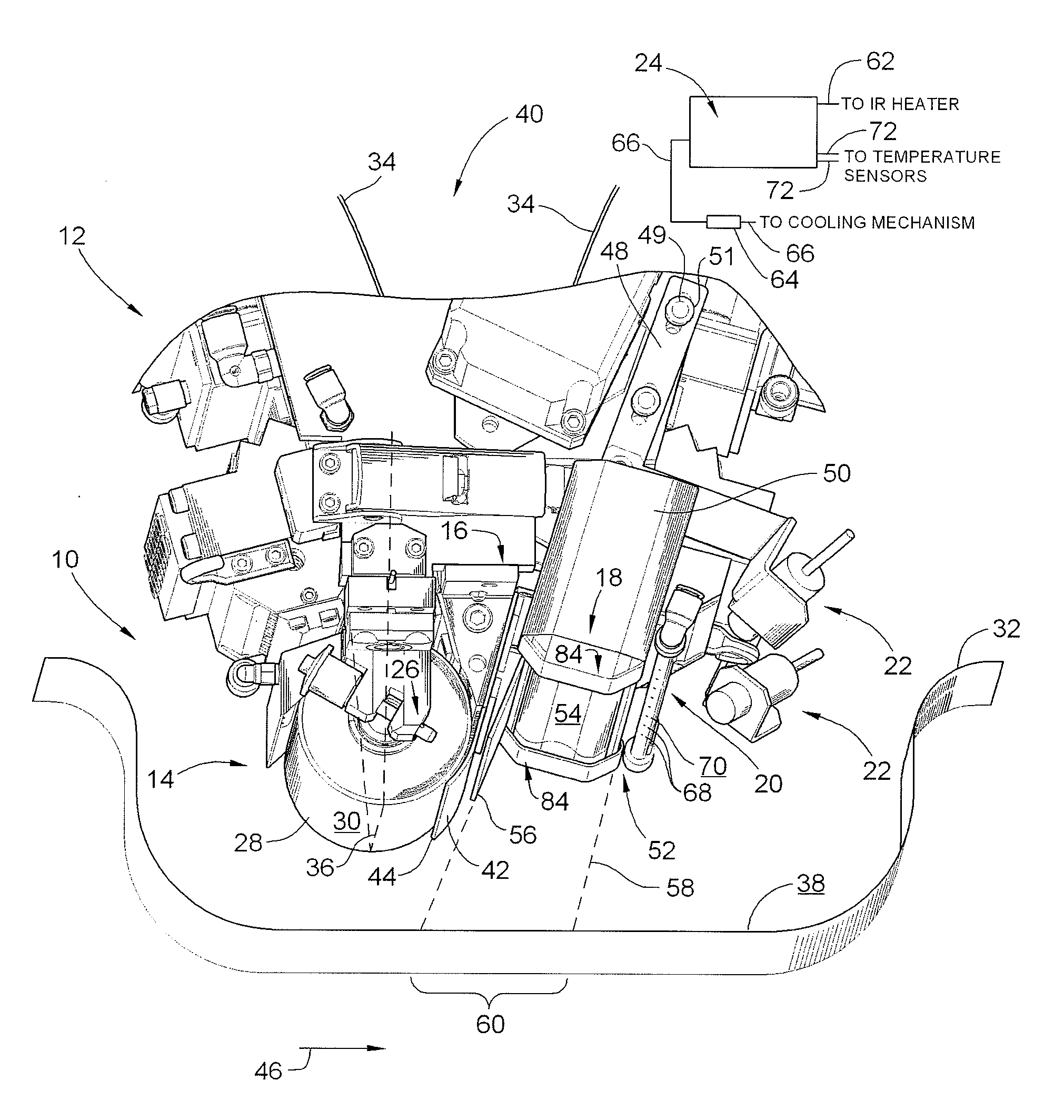
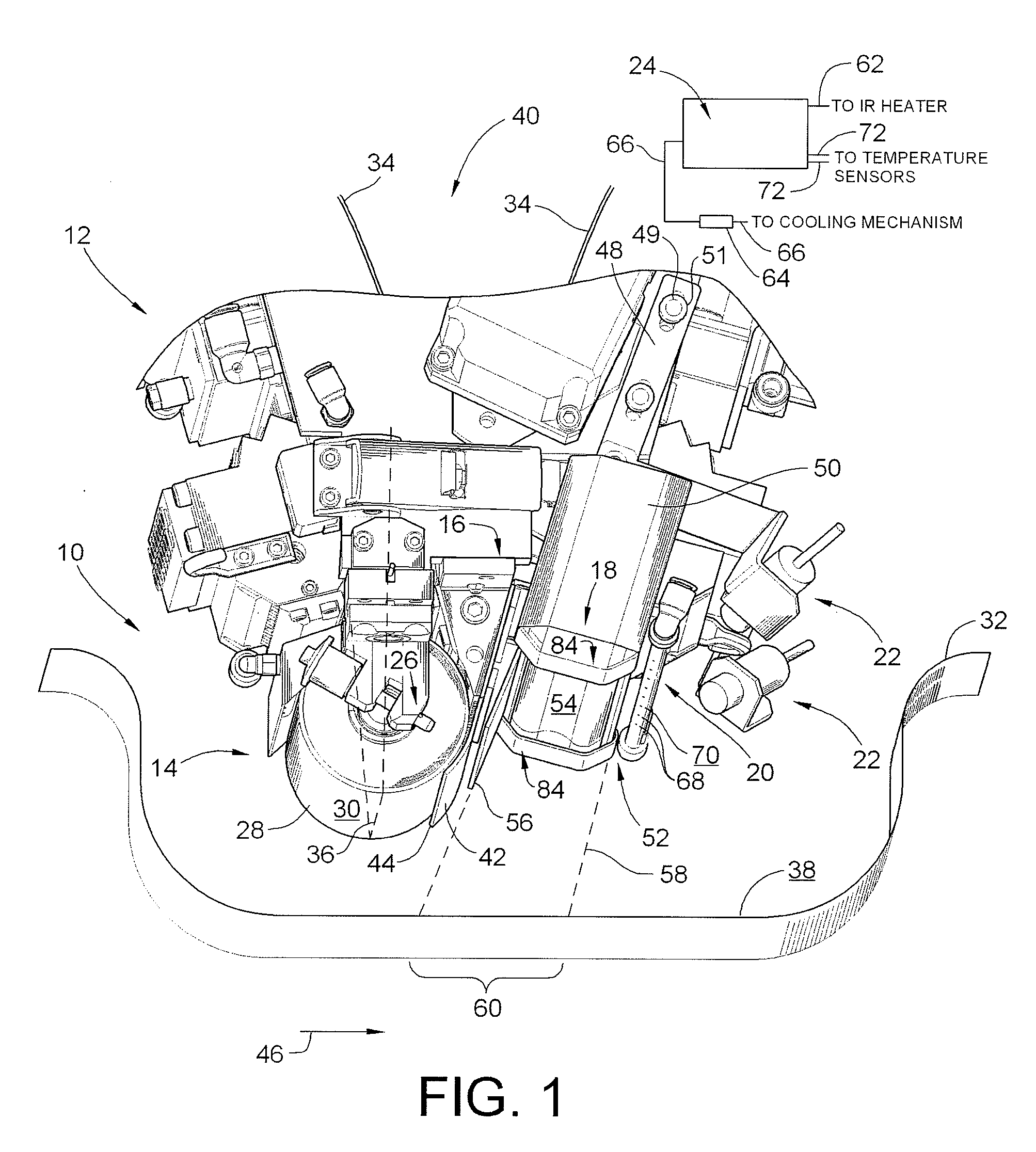
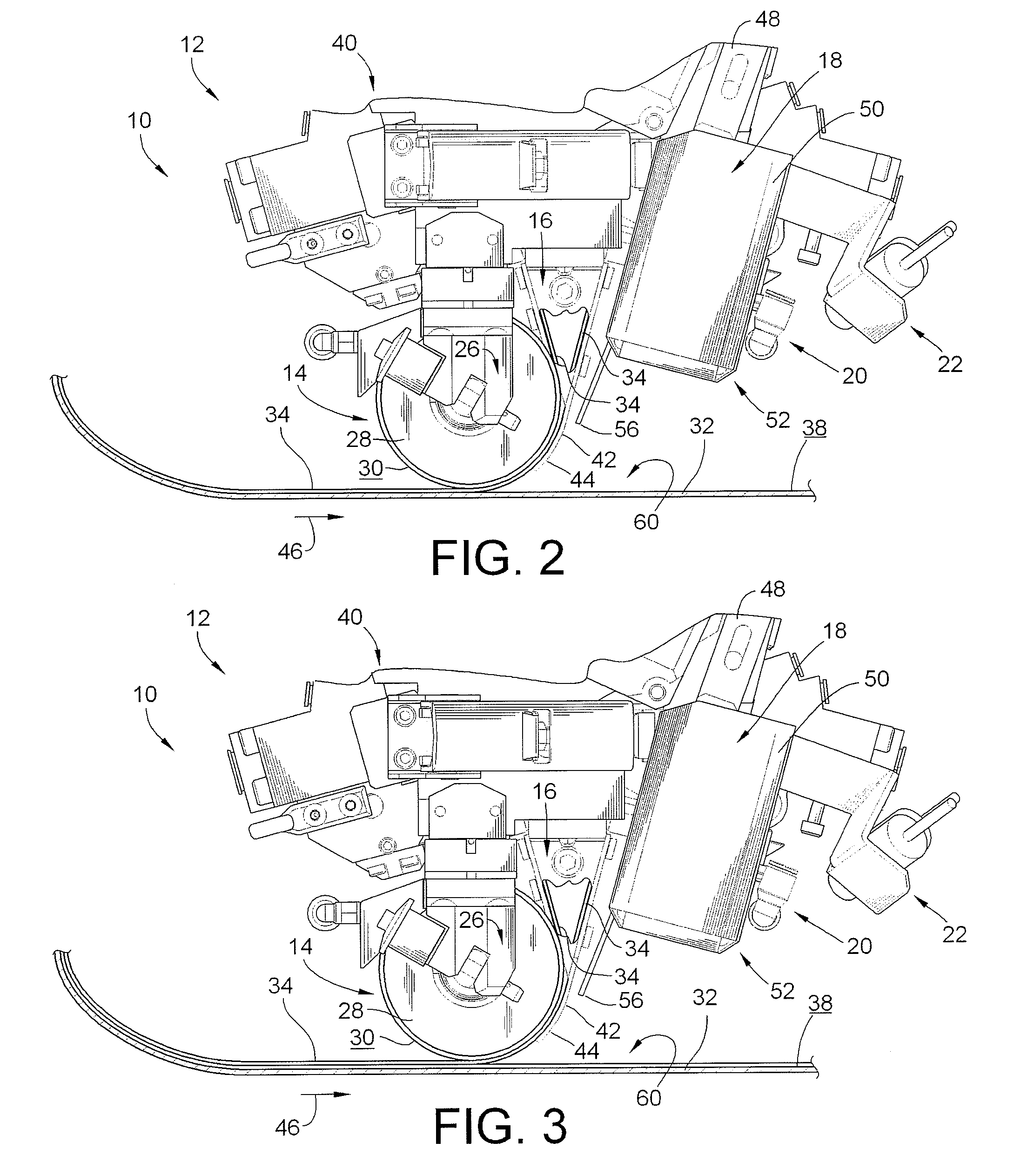
System and method for heating carbon fiber using infrared radiation in a fiber placement machine
ActiveUS7731816B2Heating fastInexpensive and quick to reactLamination ancillary operationsLaminationFiberCarbon fibers
An apparatus comprising a fiber placement head assembly and an infrared heating assembly is provided. The fiber placement head assembly includes a compaction roller assembly and a feeder assembly. An infrared heating assembly, a cooling mechanism, temperature sensors, and a controller are operably coupled to the fiber placement head assembly. The infrared heating assembly includes an infrared heater that generates a heating profile. The heating profile defines a heating zone on either a tool or previously laid tows. If the burn point of either the tool or previously laid tows within the heating zone is approached, the controller, which receives temperature readings from the temperature sensors, simultaneously disables the infrared heater and activates the cooling mechanism. As such, the tool and the previously laid tows are protected from being ruined due to an over temperature condition.
Owner:INGERSOLL MACHINE TOOLS
Process for manufacturing resin-coated fibers composite and an application thereof
InactiveUS6270851B1Prevent fracture of the fiber filamentsMaximize molten resin penetrating timeLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsEngineeringFibrous composites
An apparatus for producing a resin coated fiber composite of a rod shape, tubular-shape or plate shape comprises a plurality of first members having an annular shape with a semi-circular ring shaped internal surface, second members having a disc shape with a semicircular ring shaped external surface, first connectors for assembling the first members, second connectors for assembling the second members, an outer die member semi-assembled with the first members and connectors, an inner die member semi-assembled with the second members and connectors, a heater, an inlet nozzle and an outlet nozzle, a zigzag shaped tunnel formed between the inner and outer die members for providing a narrow flow path of the fiber filaments, and resin inlet ports to fill the molten resin in the zigzag shaped tunnel and pressurize the flow path of the fiber filaments. A process for preparing a resin coated fiber composite of a rod-shape, tubular-shape or plate-shape comprises steps of spreading fiber filaments by passing the fiber filaments through a first member having a convex-concave portion to prevent fracture of the fiber filaments, and sequentially tensioning through a series of first and second members all along a narrow flow path to maximize molten resin penetrating surface area, impregnating pressurized molten resin into the fiber filaments continuously by passing the fiber filaments through a series of the first and second members all along the narrow flow path of a zigzag shaped tunnel to maximize molten resin penetrating time, and wherein pressurization of the molten resin maximizes penetration of molten resin into pores of the fiber filaments and minimizes possibility of resin degradation, stranding the resin-coated fiber filaments through a final set of the first members having the convex-concave portion for strengthening the fiber filaments, and integrating and pultruding the resin-coated fiber filaments continuously by passing the fiber filaments all along the narrow flow path of the zigzag shaped tunnel to form a desired diameter through the outlet nozzle.
Owner:SAMBARK LFT
Multiple head automated composite laminating machine for the fabrication of large barrel section components
An aircraft part manufacturing device for automated composite lamination on a mandrel surface of a tool having a rotational axis includes a mechanical supporting structure that supports multiple material delivery heads. The tool is moveable and rotatable relative to the mechanical supporting structure. The mechanical supporting structure provides for axial translation of the material delivery heads relative to the mandrel surface while the mandrel surface is rotated for laying down courses of composite material over the entire mandrel surface of the tool. The position and movement of each of the plurality of material delivery heads is individually adjustable. Arm mechanisms provide motion of each material delivery head in a direction normal to the mandrel surface; rotation about an axis normal to the mandrel surface; circumferential position adjustment in a hoop direction relative to the mandrel surface; and axial position adjustment relative to the other material delivery heads.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
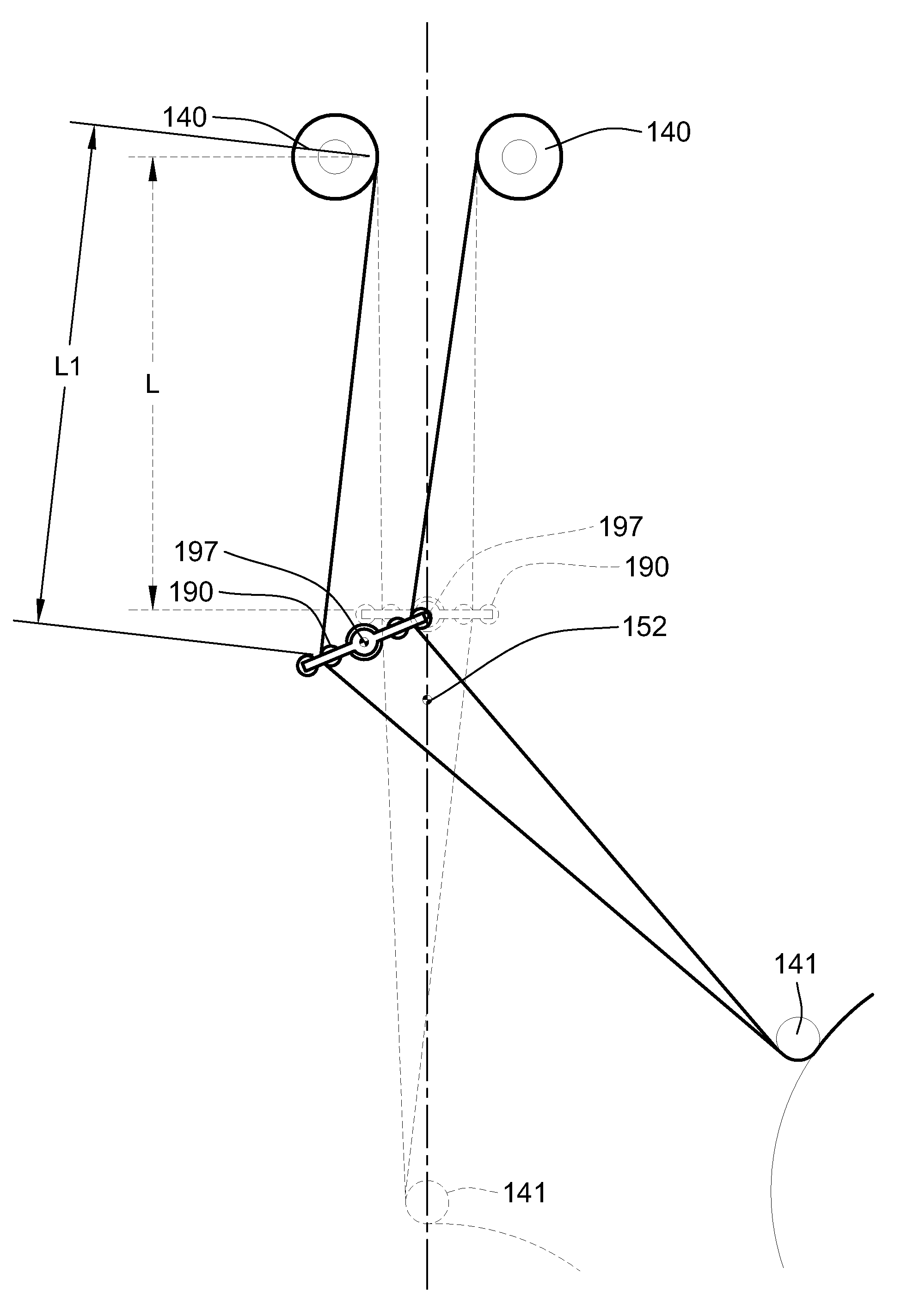
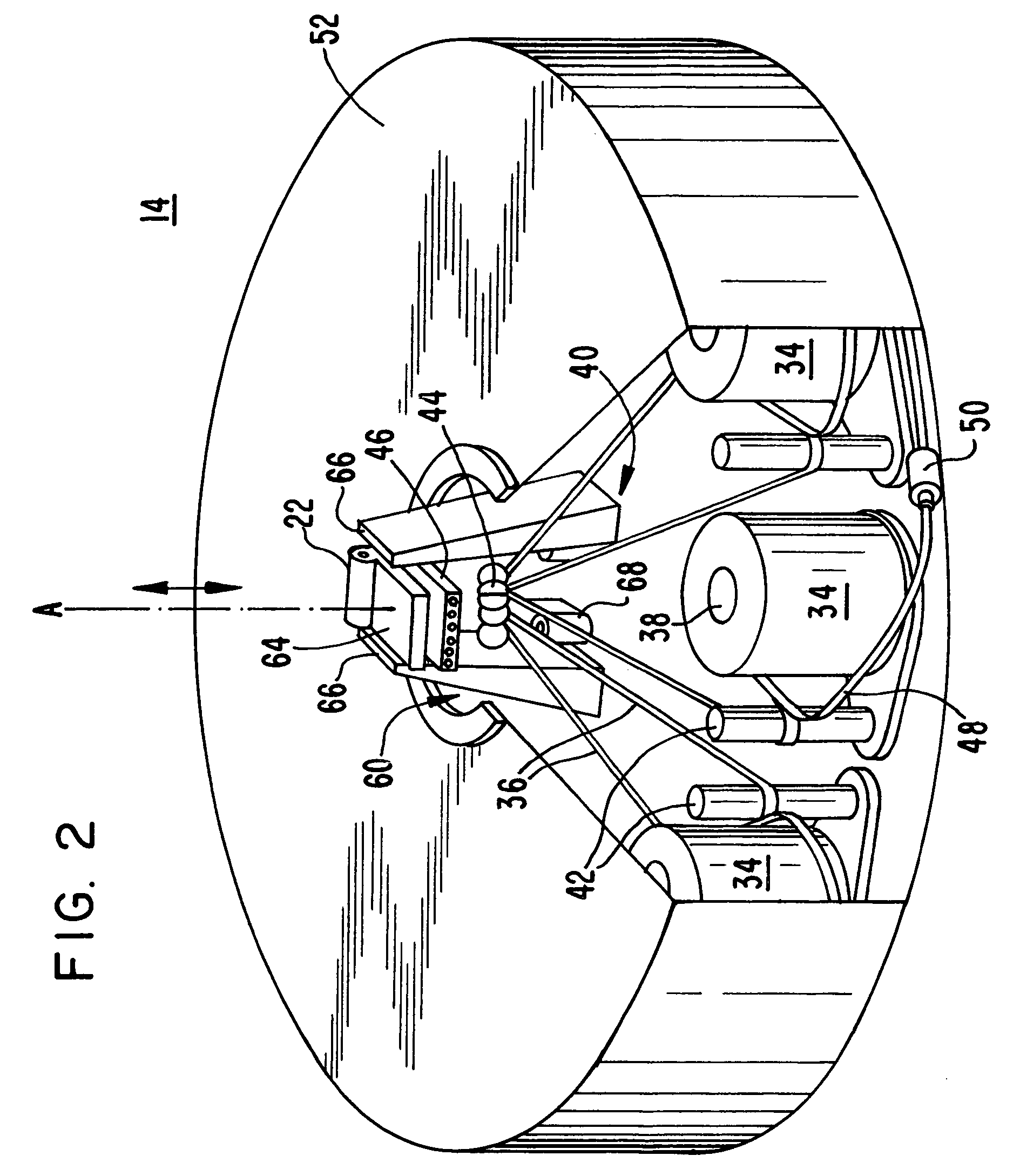
Fiber placement machine platform system having interchangeable head and creel assemblies
Owner:INGERSOLL MACHINE TOOLS
Fiber delivery apparatus and system having a creel and fiber placement head with polar axis of rotation
ActiveUS8534338B2Improve protectionReduce any negative affects on fiber towsEngine sealsLamination ancillary operationsFiberDegrees of freedom
A fiber placement system including positioner and a fiber delivery apparatus having a creel assembly and a fiber placement head is provided. The positioner moves the entire fiber delivery apparatus including the creel assembly and the fiber placement head via at least three linear degrees of freedom. The fiber delivery apparatus includes an articulating wrist for moving the fiber placement head relative to the creel assembly. The fiber placement apparatus is substantially free of linear degrees of freedom within the fiber tow paths between the spools and the fiber placement head. One or more rotational degrees of freedom may be provided along the tow path. In one embodiment, the interface between the fiber delivery apparatus and the positioner is laterally offset such that a portion of the creel axially overlaps with vertical ram of the positioner.
Owner:INGERSOLL MACHINE TOOLS
Composite structural element fabricating device and method
To fabricate a composite item, a device places a composite ply on a curved form at about 0° relative to a longitudinal axis of the form. The form includes a web surface and a cap surface. The device includes a web compaction roller and a set of guides. The web compaction roller compacts a composite material upon the web surface and generate a web ply. The set of guide rollers urges against the cap surface. The compaction roller is directed along the form by the guide rollers.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
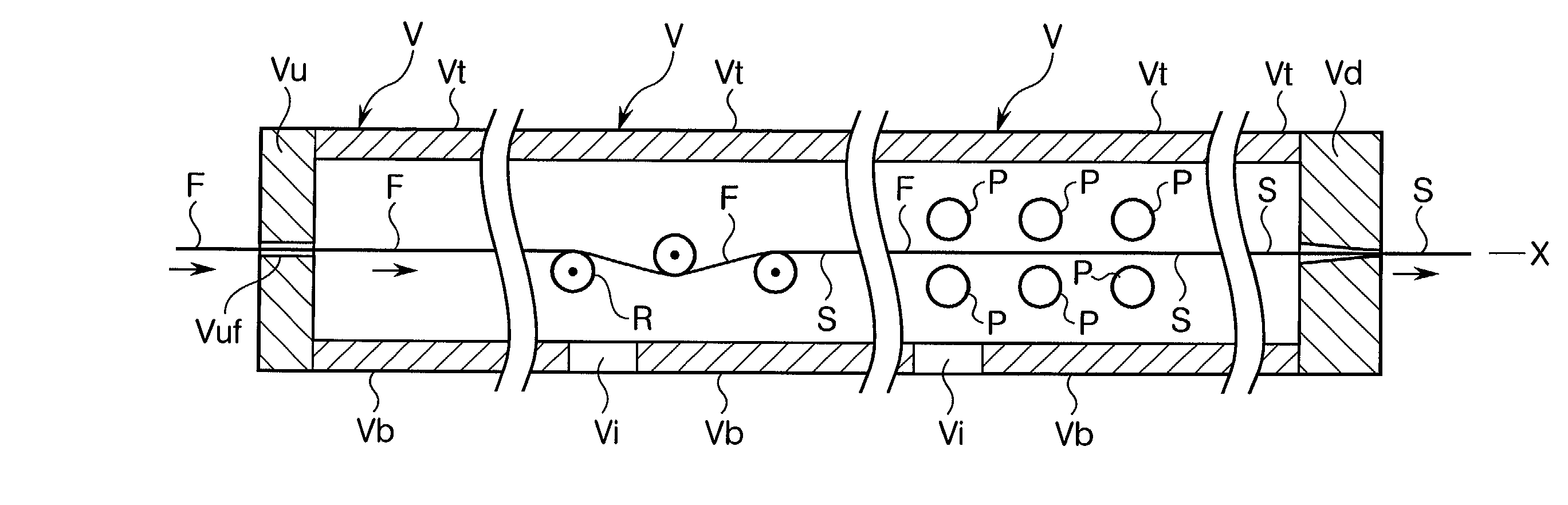
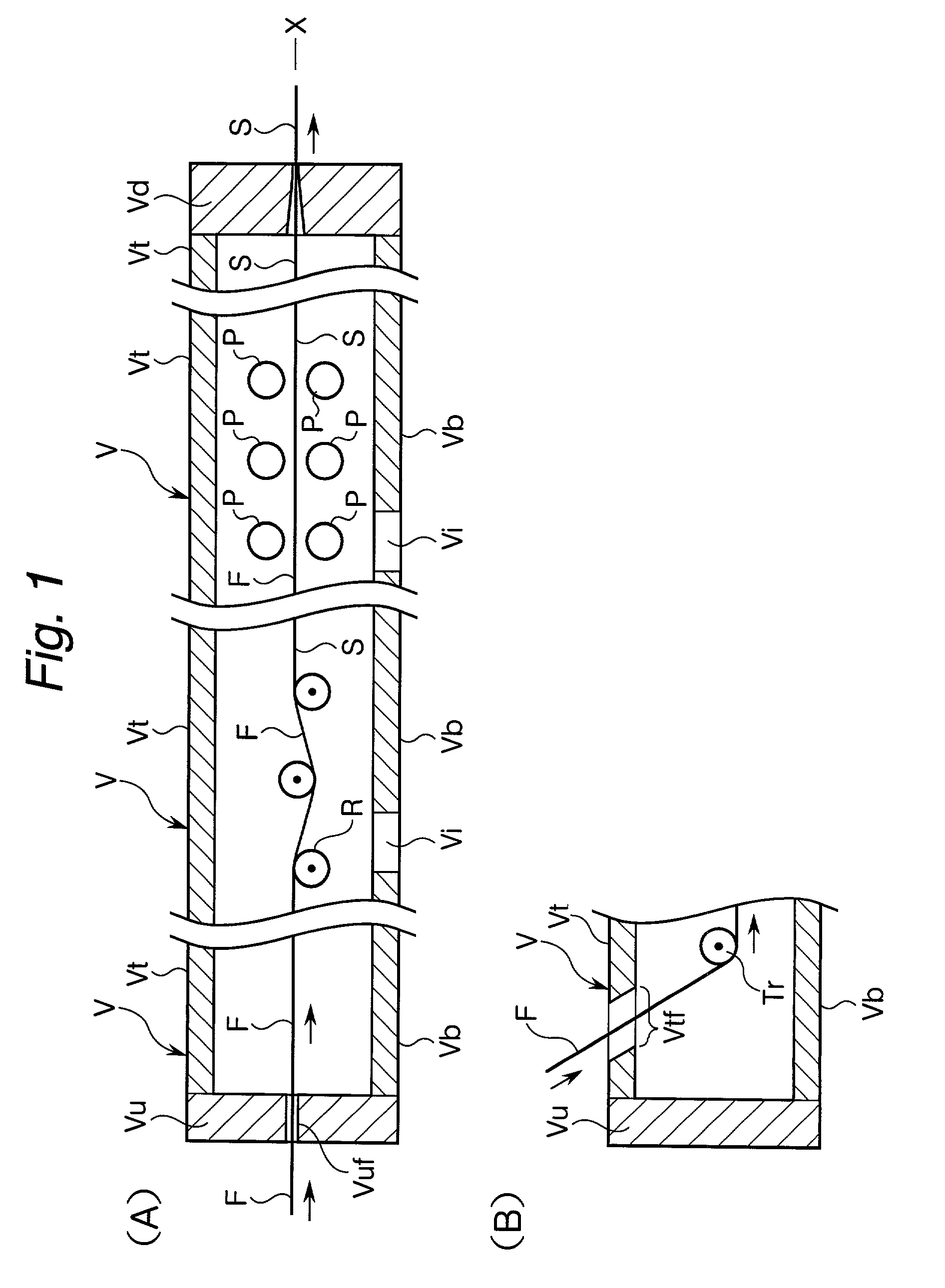
Apparatus and method for manufacture and use of composite fiber components
ActiveUS20050037195A1Add featureEnhance another featureLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsPre stressPre stressing
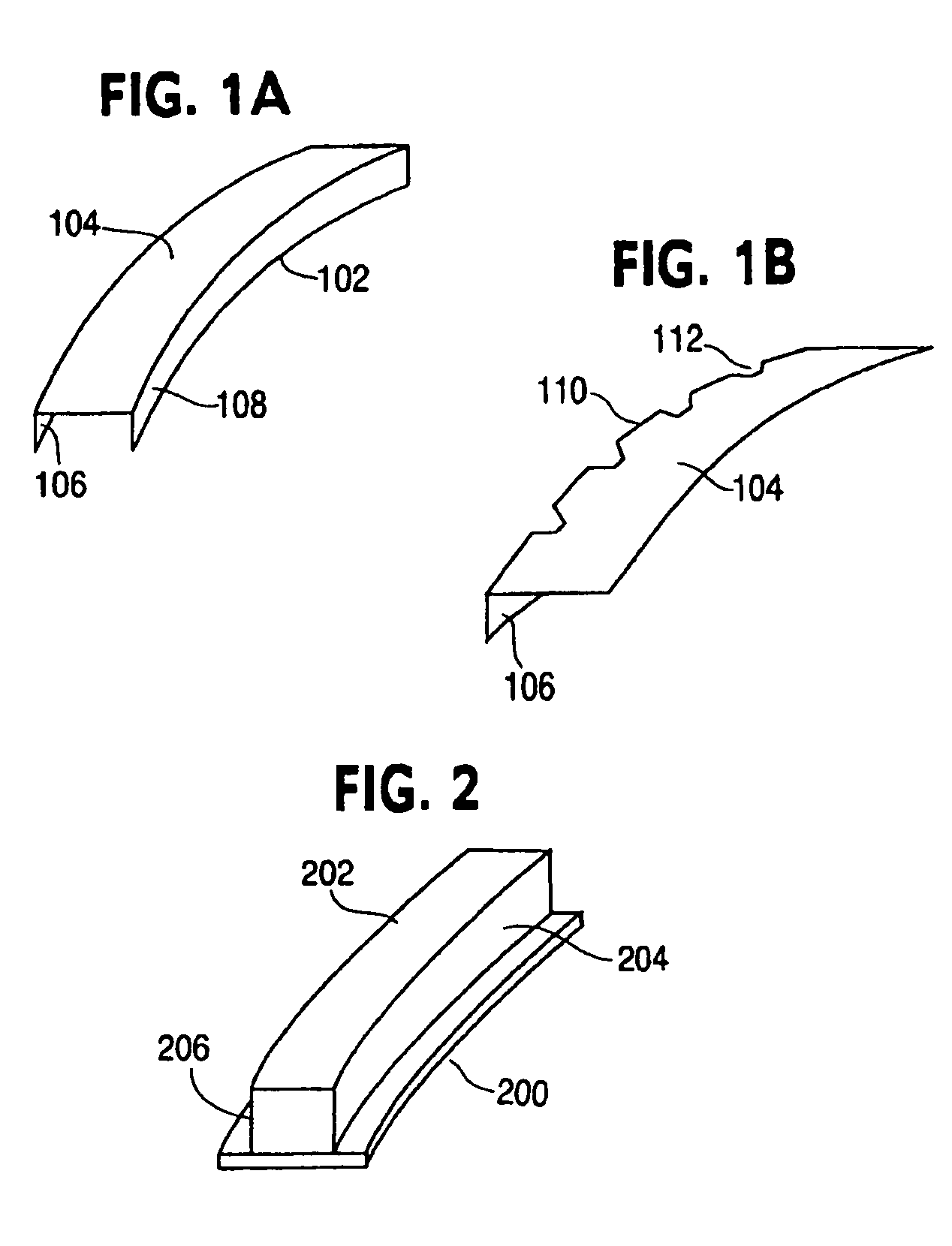
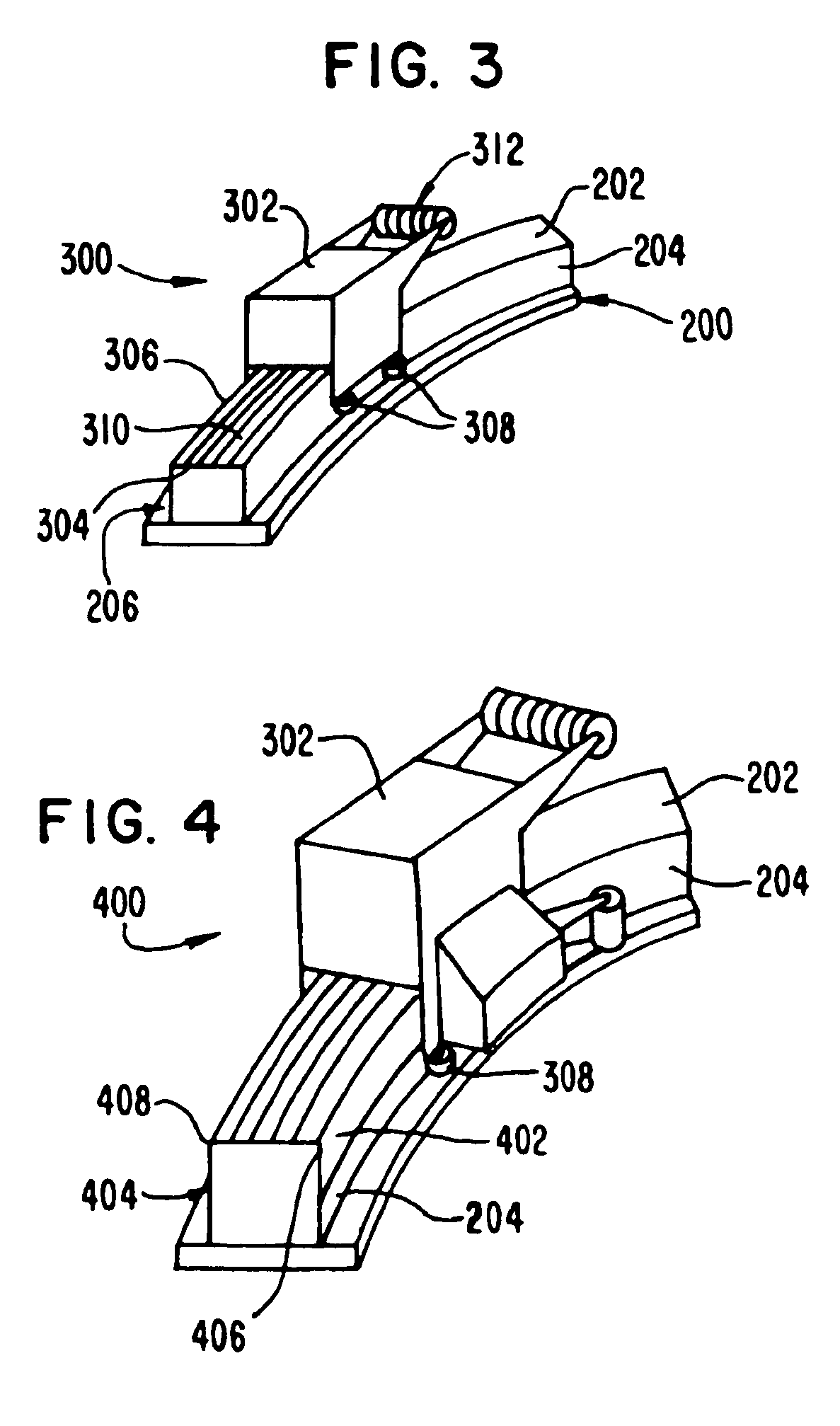
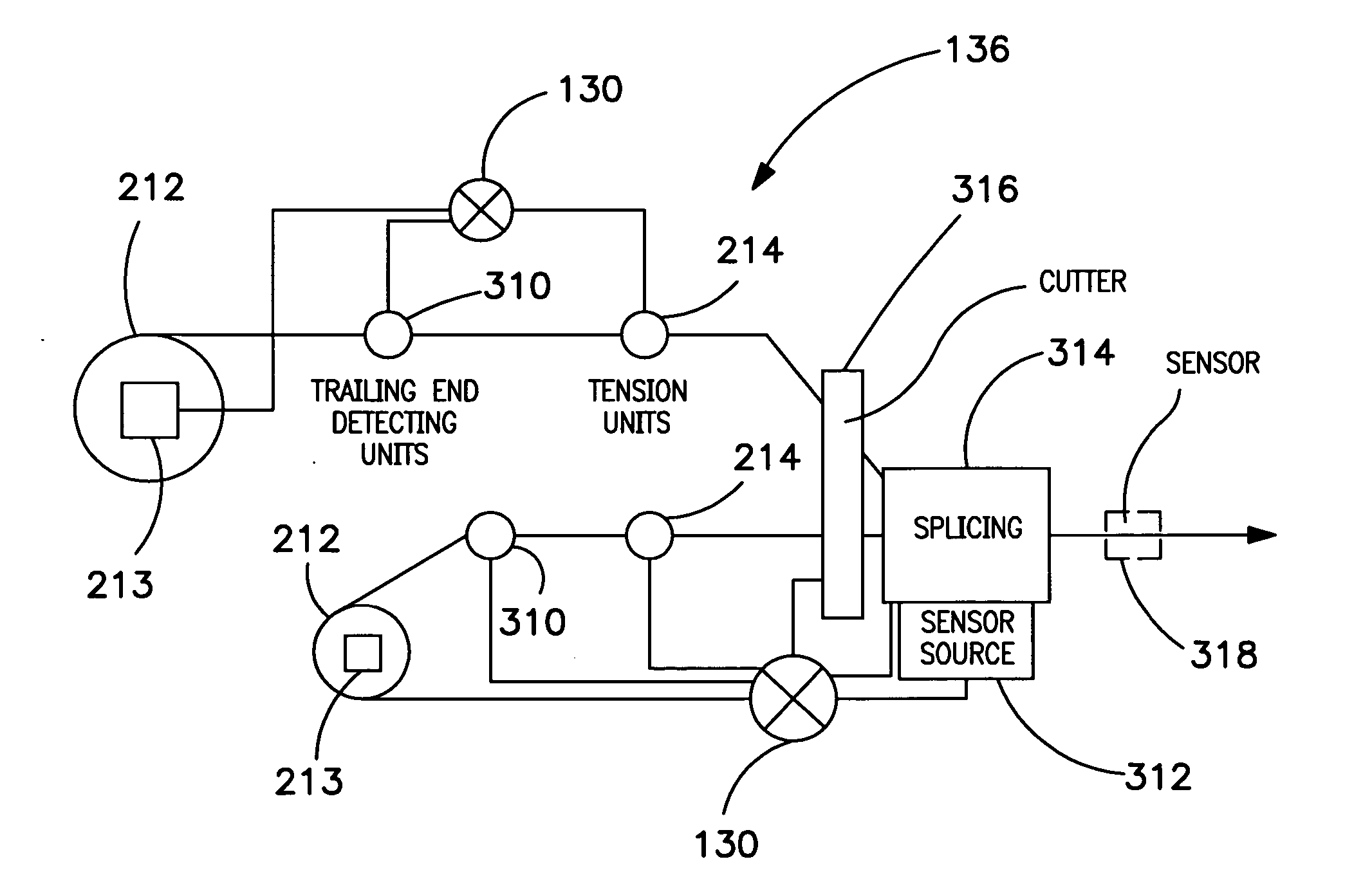
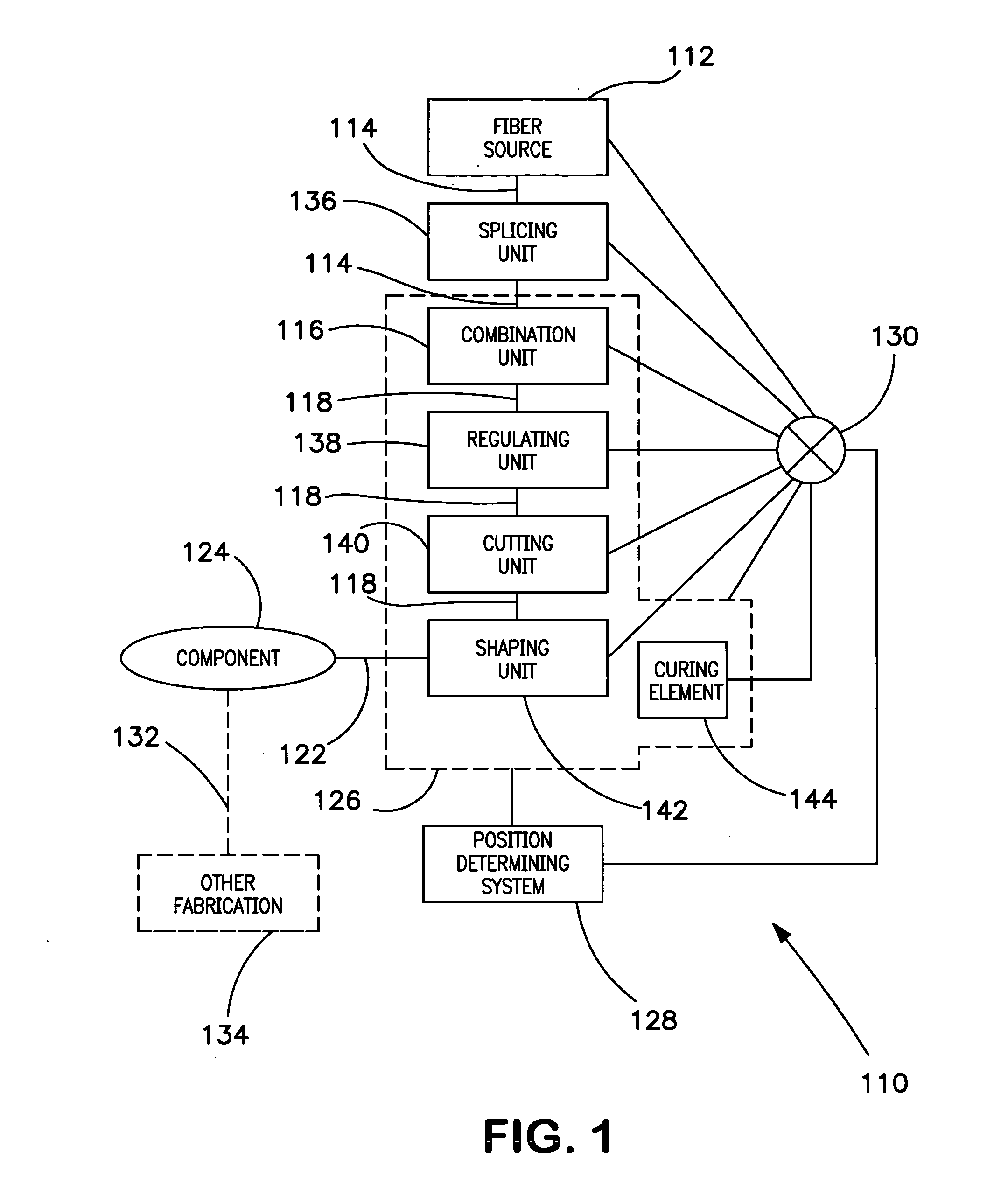
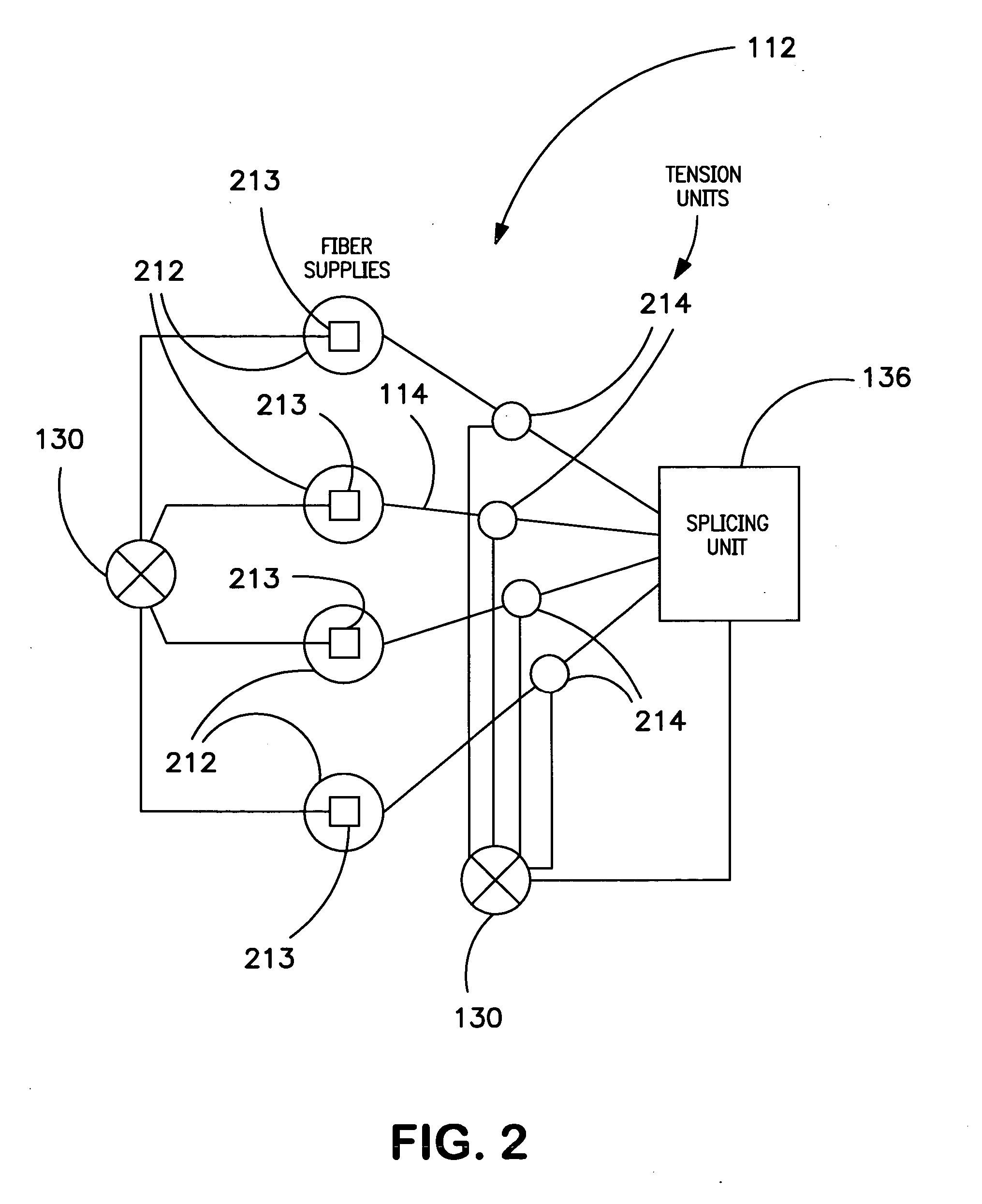
A fiber lay-up apparatus and method includes one or more fiber sources from at least one fiber supply wherein a fiber may be fed under tension to provide a pre-stress to the fiber. The fiber lay-up apparatus may include a resin impregnator for impregnating a fiber with a resin. The fiber may be impregnated under pressure to reduce friction, to provide a motive force to move the fiber through the impregnator, or to enhance control over impregnation. The fiber may be shaped by a fiber shaping unit including one or more active or passive shaping members that provide enhanced control over the shape and placement of the fiber as the fiber leaves the fiber lay-up apparatus. A cutting element for cutting a fiber as it is being layed-up may be positioned proximal to the one or more shaping members, and may enable the fiber lay-up apparatus to end the lay-up of one fiber (or set of fibers) and begin the lay-up of a new fiber (or set of fibers) without delay. A UV or other curing element may be provided downstream from the cutting element. A splicing unit may be employed to detect when a fiber supply is exhausted, and may splice a trailing end of an exhausted fiber supply to a leading end of a new fiber supply to provide a continuous (or substantially continuous) fiber feed. The splicing unit may also splice at least one sensor into a fiber being fed from the at least one fiber supply to provide information about the fiber either before, during, or after the fiber is layed-up.
Owner:LIGNUM VITAE
Reinforced composites and system and method for making same
InactiveUS20050048273A1Easy to smoothFacilitates rapidTailstocks/centresConfectioneryMechanical engineeringPressure sensitive
A detailed embodiment of the invention described herein includes a method and apparatus for pultrusion of a plastic member having a non-wood (e.g., bamboo) reinforced core. The apparatus includes an input and series of die assemblies for taking bamboo tape and embedding it in an appropriately shaped composite member. The die assembly may include a finger die, an encapsulation die, a forming die, and a chilling die. A pultrusion unit maintains production at an efficient and desired rate by use of pressure sensitive clamps to pull the product forward through the prior die units. A colorizer unit and embossing unit allow particular appearances to be produced in the end product. Alternative embodiments are also shown including the processing of bamboo into tape and ribbon forms usable by a pultrusion machine.
Owner:CORLYTE PRODS
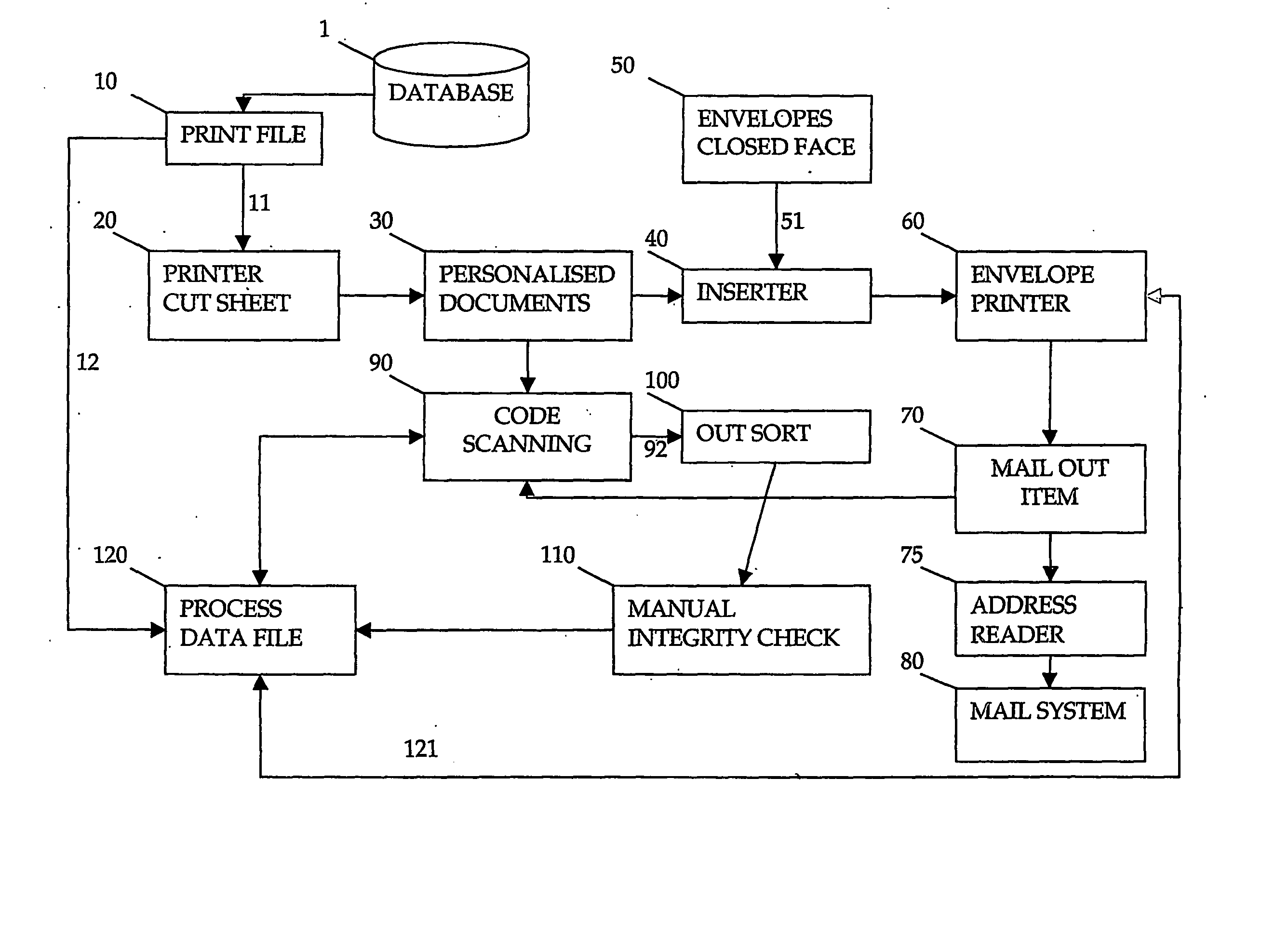
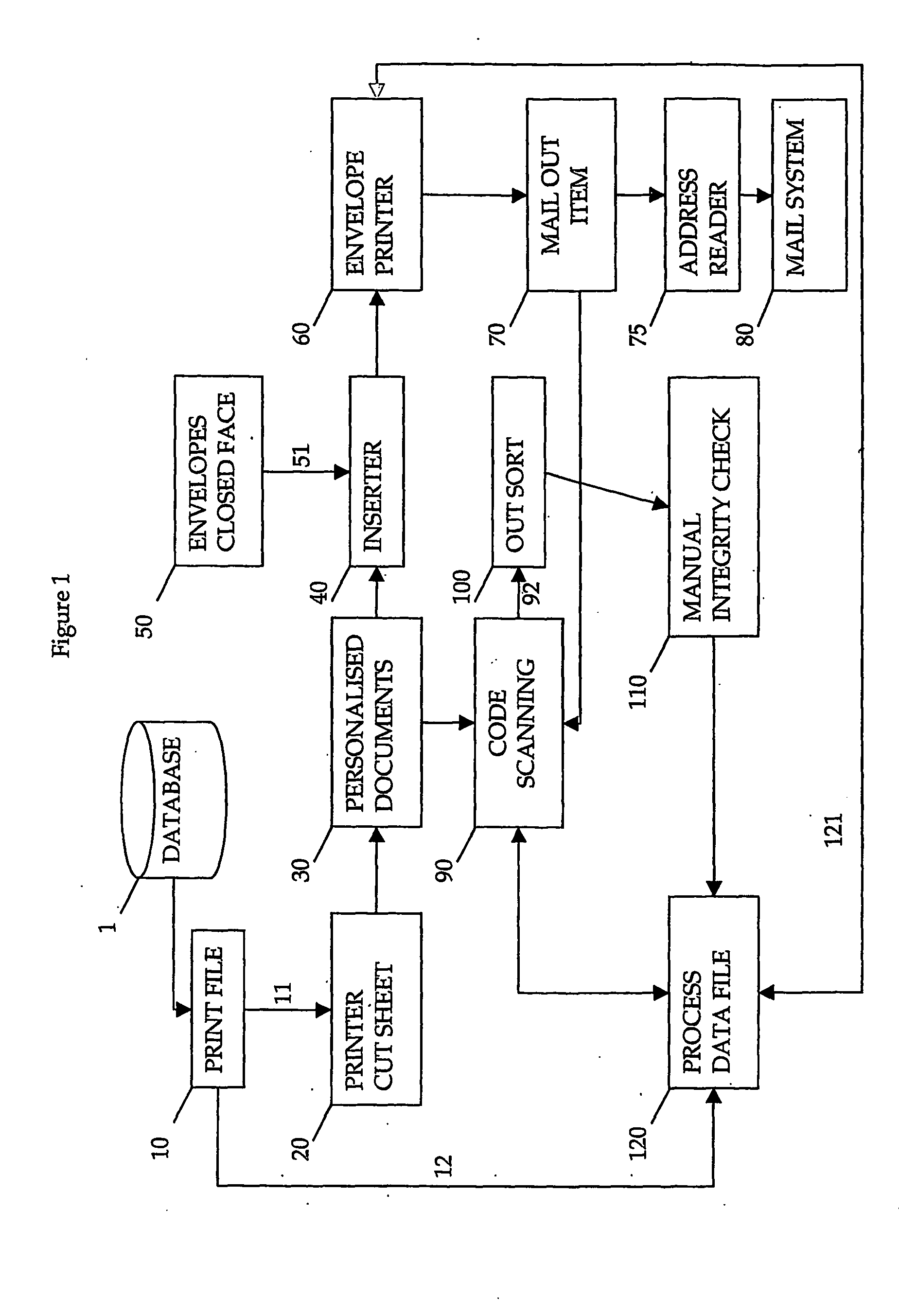
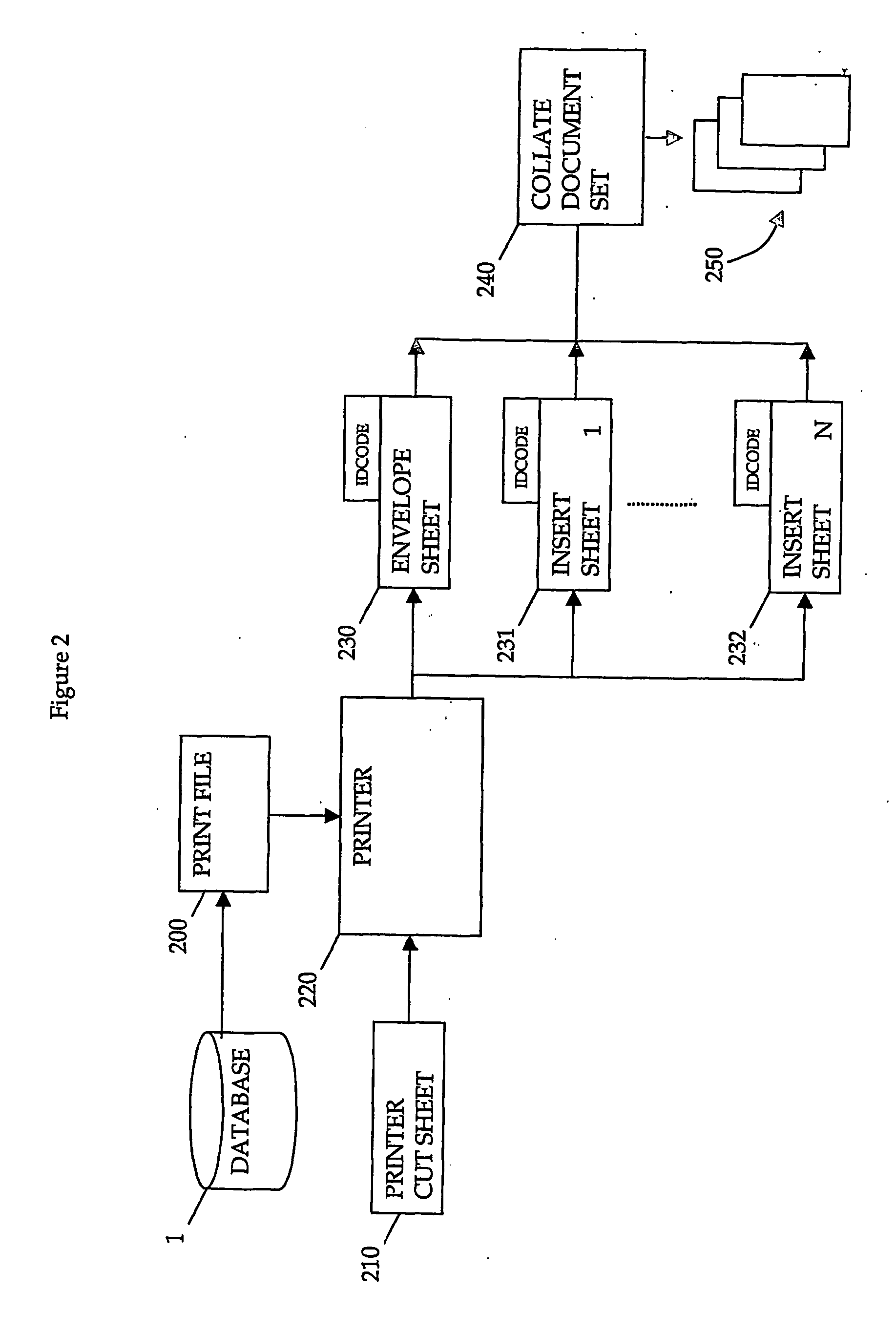
Method and apparatus for forming a document set
InactiveUS20060284360A1Reduce complexityReduces varietyOther printing matterBag making operationsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ENVELOPMENTS
Modular head lamination device and method
A composite item is fabricated with a device. The device includes and end effector and a positioning device. The end effector places a tow. The end effector includes a spindle, compaction device, and a path. The spindle detachably secures a spool of tow and the path is disposed from the spool to the compaction device. The positioning device positions the end effector. The end effector is detachably secured to the positioning device.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
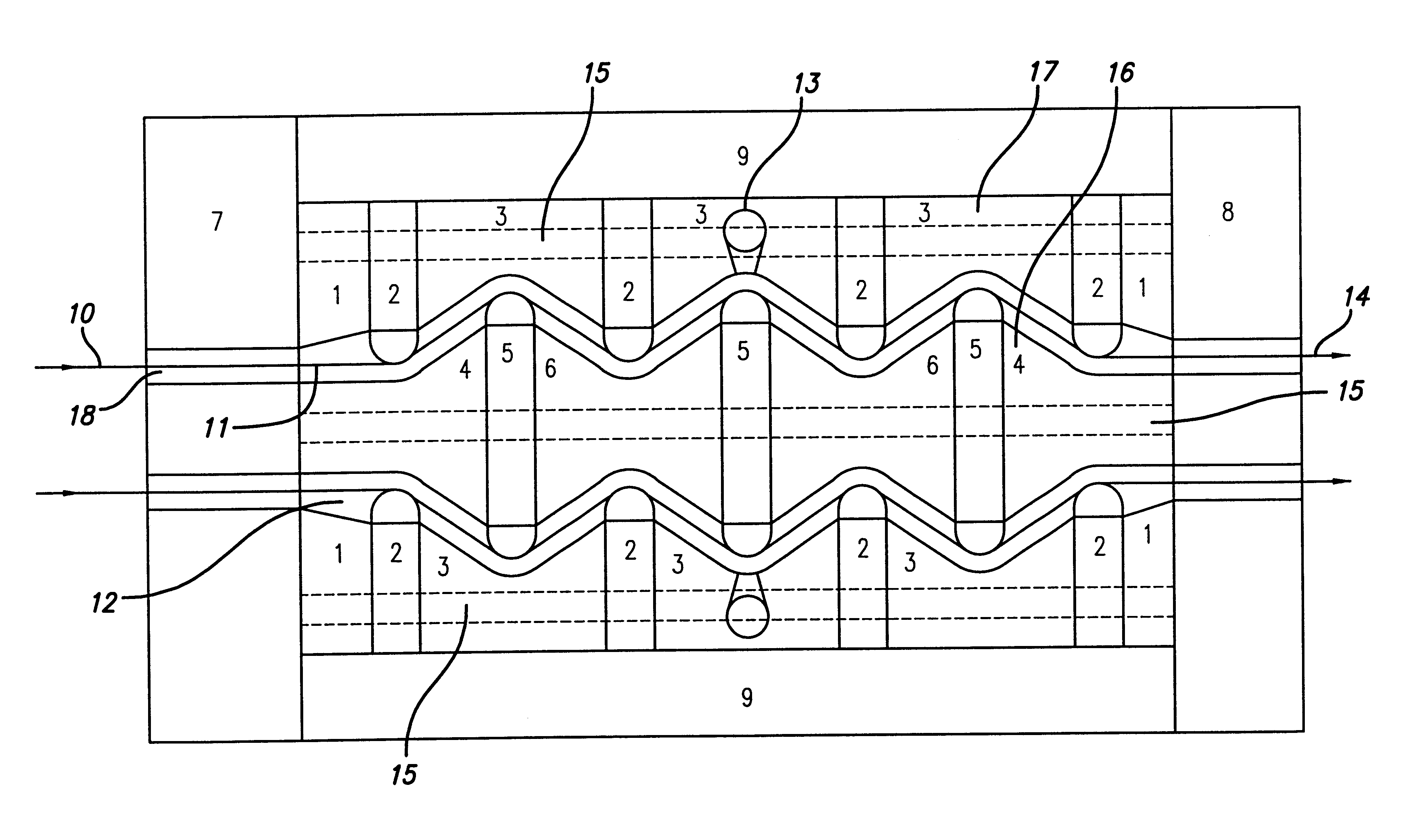
Device for producing thermoplastic resin continuous length sections reinforced with long fibers
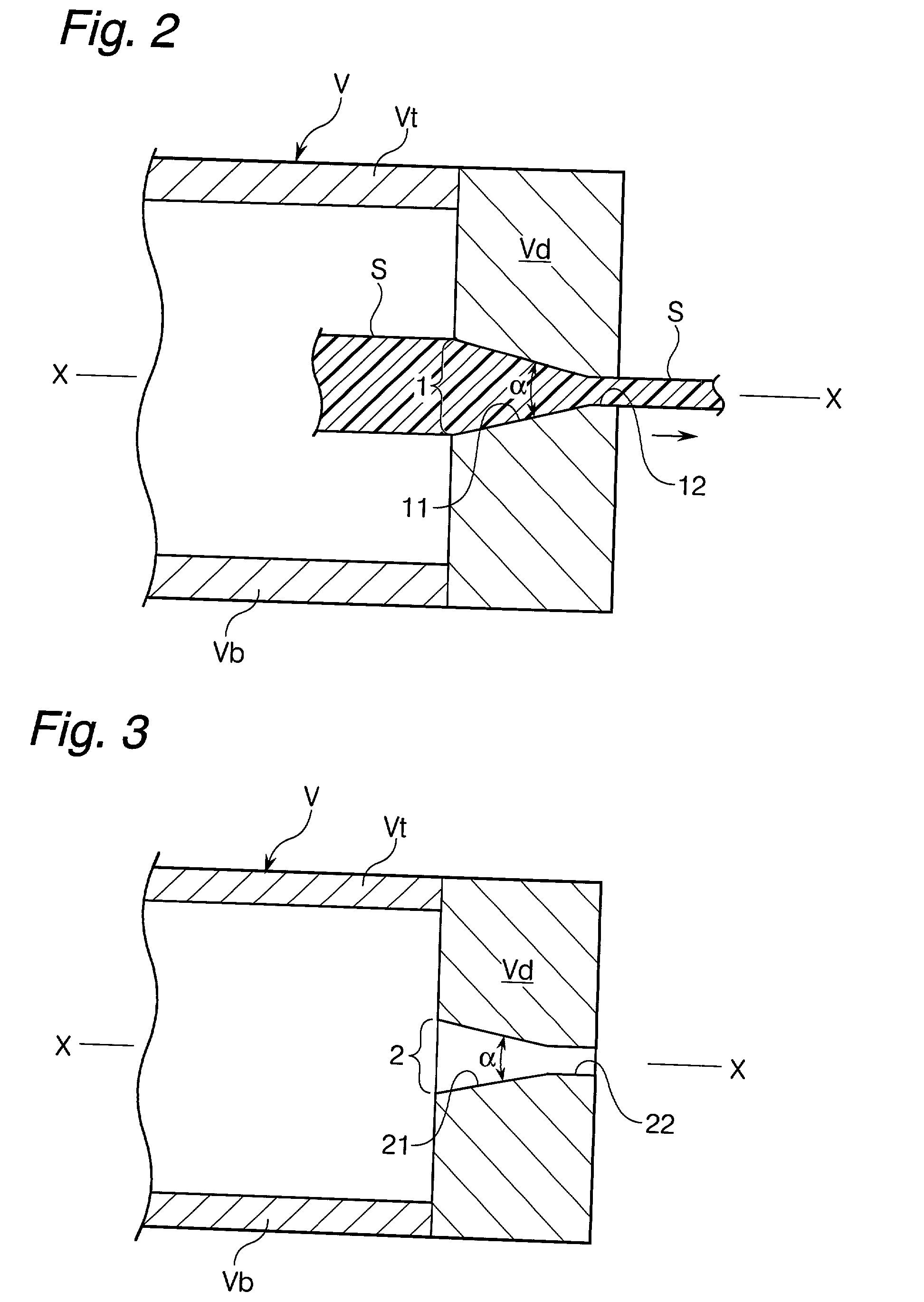
In a pultrusion device for producing continuous length sections prepared from thermoplastic resins reinforced with long fibers, the vertical angle (.alpha.) of an upstream conical surface of a conical portion, which constitutes a shaping nozzle perforated through the downstream end wall of the device ranges from 15 to 35 degrees and the shaping nozzle has a land portion having a length of 1 to 5 mm in the downstream area subsequent to the upstream conical surface. According to this pultrusion device for producing continuous length sections prepared from thermoplastic resins reinforced with long fibers, the long fibers never undergo any breakage nor fluffing during the opening treatment and this accordingly leads to the substantial reduction of pill-formation. As a result, the opening-impregnation device of the present invention provided at least with the downstream end wall carrying the shaping nozzle (including the land portion) can stably and continuously be operated over a long period of time, without any trouble such as those encountered in the conventional devices.
Owner:JNC CORP
Desk pad organizer system
A desk organizer tray, comprising a tray portion, an extension portion extending from the tray portion, and an attachment element applied to the extension portion. The tray portion contains a receptacle for holding desktop items. The tray portion is constructed of a plurality of superimposed board members, each of which contains a hole pattern. The hole patterns of the board members are in registration with one another to form the receptacle. The extension portion includes a board member that extends from the tray portion. The board members of the tray portion are mounted on the board member of the extension portion. The attachment element is applied to the board member of the extension portion. The attachment element serves to attach a desk pad to the extension portion, adjacent to the tray portion.
Owner:MEADWESTVACO CORP
System and Method for Heating Carbon Fiber Using Infrared Radiation in a Fiber Placement Machine
ActiveUS20070187021A1Heating fastInexpensive and quick to reactMechanical working/deformationLamination ancillary operationsFiberCarbon fibers
An apparatus comprising a fiber placement head assembly and an infrared heating assembly is provided. The fiber placement head assembly includes a compaction roller assembly and a feeder assembly. An infrared heating assembly, a cooling mechanism, temperature sensors, and a controller are operably coupled to the fiber placement head assembly. The infrared heating assembly includes an infrared heater that generates a heating profile. The heating profile defines a heating zone on either a tool or previously laid tows. If the burn point of either the tool or previously laid tows within the heating zone is approached, the controller, which receives temperature readings from the temperature sensors, simultaneously disables the infrared heater and activates the cooling mechanism. As such, the tool and the previously laid tows are protected from being ruined due to an over temperature condition.
Owner:INGERSOLL MACHINE TOOLS
Fiber application machine comprising a flexible compacting roller with a thermal regulation system
A fiber application machine for the production of parts made of composite materials comprising a compacting roller for applying on an application surface a band formed of at least a resin pre-impregnated flat fiber, and a heating system able to emit a heat radiation towards the band. The compacting roller comprises a rigid central tube provided with radial holes, and a cylinder made of an elastically deformable, flexible material, assembled on the central tube, and having a fluid communication assembly that brings the radial holes into fluid communication with the external surface of the cylinder. The machine includes a thermal regulation system that injects a thermal regulation fluid in the central tube internal passage.
Owner:CORIOLIS GRP
Motion control system and method for a high speed inserter input
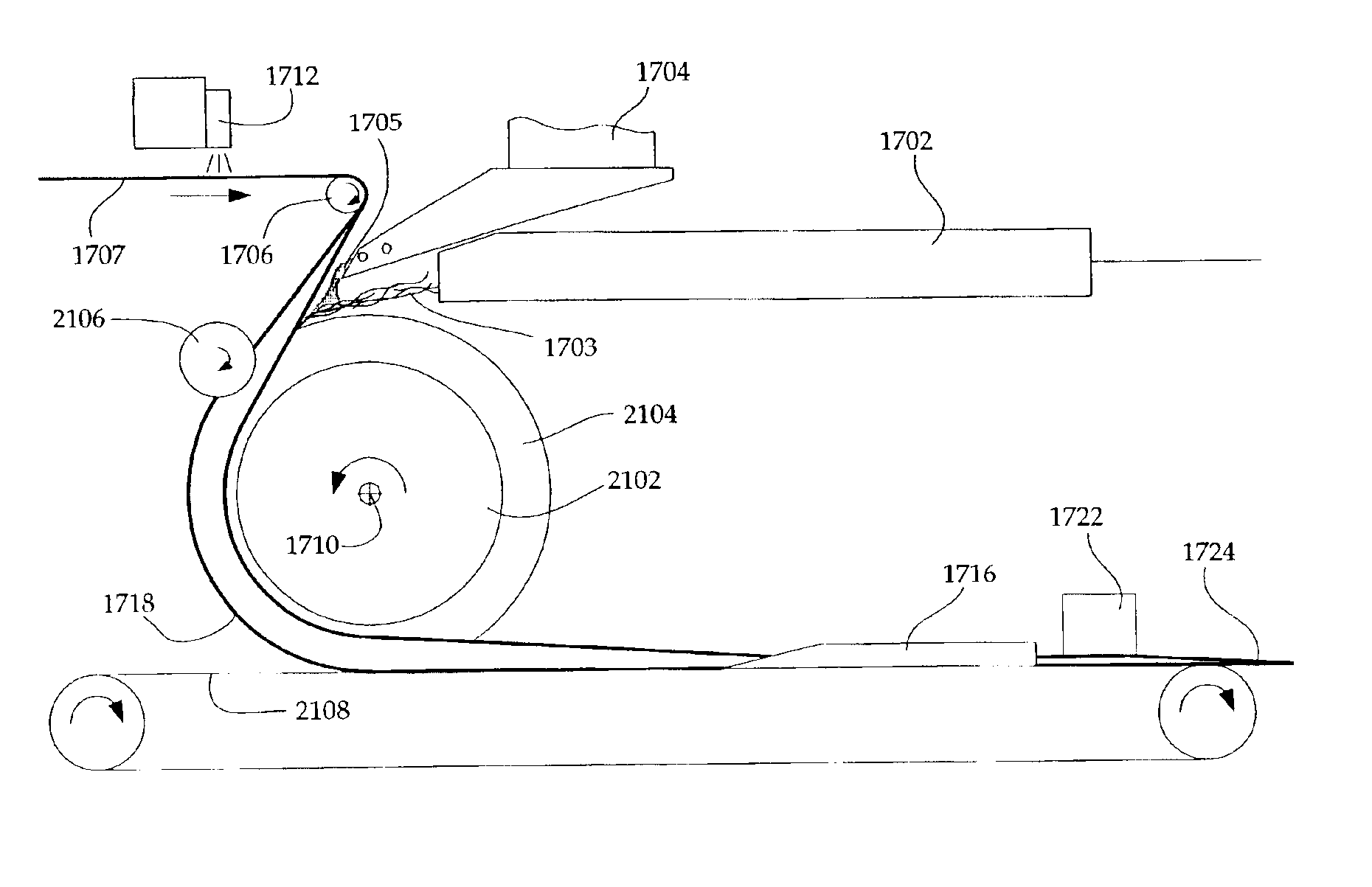
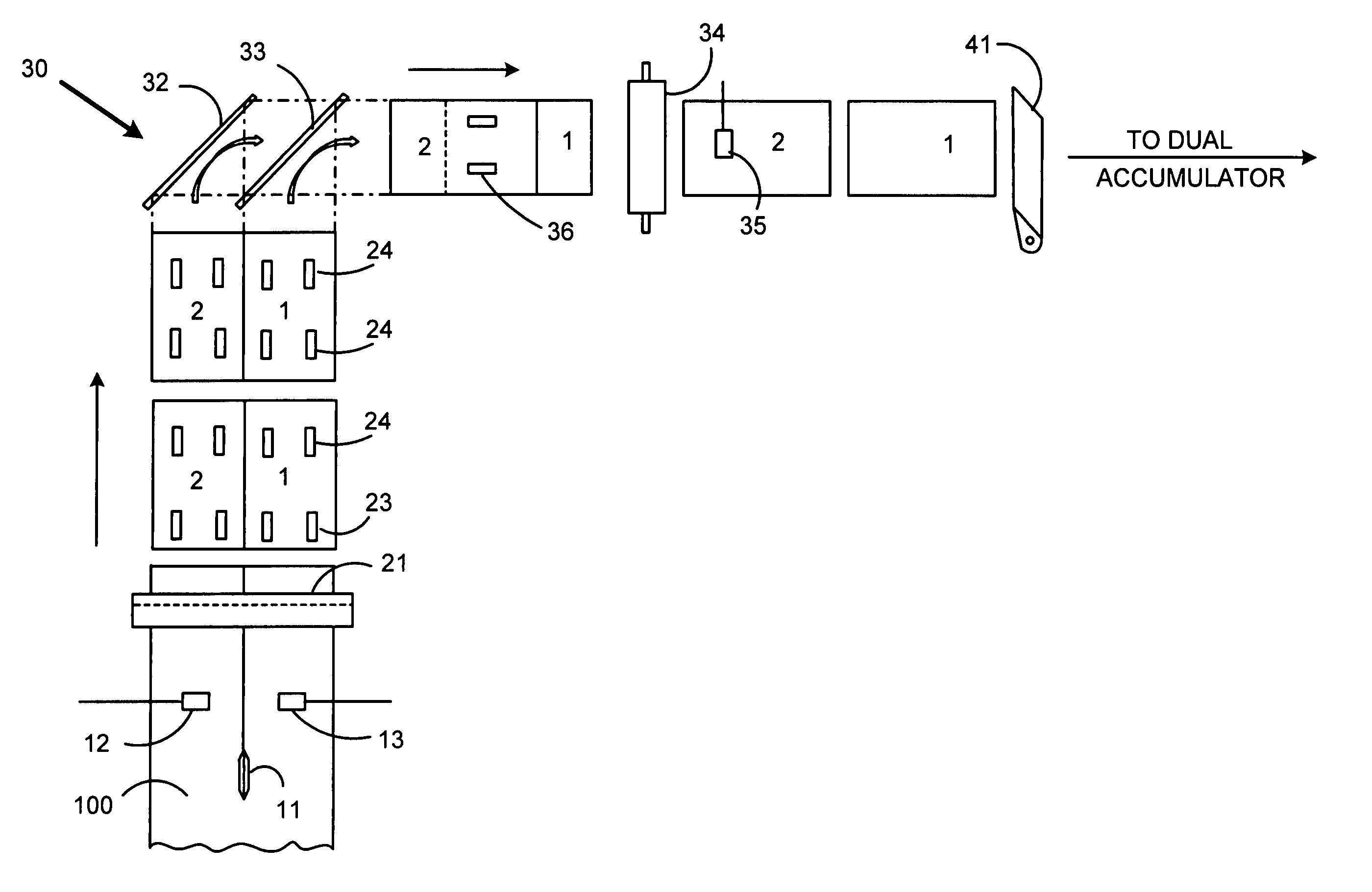
InactiveUS20060156876A1Faster and accurate and reliable high speed cuttingImprove throughputFunction indicatorsPile receiversControl systemPaper document
A high speed input system for an inserter machine. The system controlling a guillotine cutter, a cutter transport, and an upstream web handler transport to increase throughput for mail production. The controller is programmed to control the high speed input module in accordance with a repeating cycle. The cycle time is determined as an amount of time between a first web feed request and an earliest possible time that a subsequent second web feed request can be acted upon. A cutter transport motion control profile initiates feeding of a document length of web after receiving the first feed request. The cutter motion control profile causes the cutter blade to begin descending when the cutter transport has moved the web a trigger distance, calculated such that the cutter blade will first make contact with the web immediately when the web has been halted by the cutter transport motion profile. A web handler transport profile moves the web the document length at velocities and accelerations less than the velocities and accelerations of the cutter transport. At the end of the cycle, the web handler transport causes the web to be transported at a nominal velocity selected to maintain an appropriate amount of the web loop in the web handler. Within the web handler a control loop expands and contracts as the downstream cutter transport stops and starts as the cutter blade cuts the web in each cycle.
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
Tow width adaptable placement head device and method
InactiveUS7681615B2Lamination ancillary operationsControlling laminationEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Fiber application machine comprising a flexible compacting roller with a thermal regulation system
A fiber application machine for the production of parts made of composite materials comprising a compacting roller for applying on an application surface a band formed of at least a resin pre-impregnated flat fiber, and a heating system able to emit a heat radiation towards the band. The compacting roller comprises a rigid central tube provided with radial holes, and a cylinder made of an elastically deformable, flexible material, assembled on the central tube, and having a fluid communication assembly that brings the radial holes into fluid communication with the external surface of the cylinder. The machine includes a thermal regulation system that injects a thermal regulation fluid in the central tube internal passage.
Owner:CORIOLIS GRP
Method and apparatus for continuous molding of fiber reinforced plastic member with curvature
ActiveUS20060083806A1Avoid loadHigh strengthLabelling non-rigid containersConfectioneryShell moldingEngineering
In a continuous molding apparatus equipped with a long core 10 having a curvature disposed on a plane, a release film supplied from a lower release film feeder 20 is sent onto the core 10, and prepreg sheets supplied from a prepreg sheet feeder 30 are laminated thereon and preformed. A release film supplied from a release film feeder 40 is disposed on top of the laminated body, before the body is sent into a hot press 50. A puller 60 moves the laminated body without loading tension thereto. The laminated body enters a postcure device 70 in which thermosetting of the material is completed.
Owner:JAMCO
Low cost electronic toys and toy components manufactured from conductive loaded resin-based materials
InactiveUS20060003667A1Characteristic can be alteredDollsSelf-moving toy figuresElectrical conductorMetal fibers
Toys and toy components are formed of a conductive loaded resin-based material. The conductive loaded resin-based material comprises micron conductive powder(s), conductive fiber(s), or a combination of conductive powder and conductive fibers in a base resin host. The percentage by weight of the conductive powder(s), conductive fiber(s), or a combination thereof is between about 20% and 50% of the weight of the conductive loaded resin-based material. The micron conductive powders are metals or conductive non-metals or metal plated non-metals. The micron conductive fibers may be metal fiber or metal plated fiber. Further, the metal plated fiber may be formed by plating metal onto a metal fiber or by plating metal onto a non-metal fiber. Any platable fiber may be used as the core for a non-metal fiber. Superconductor metals may also be used as micron conductive fibers and / or as metal plating onto fibers in the present invention.
Owner:INTEGRAL TECHNOLOGY INC
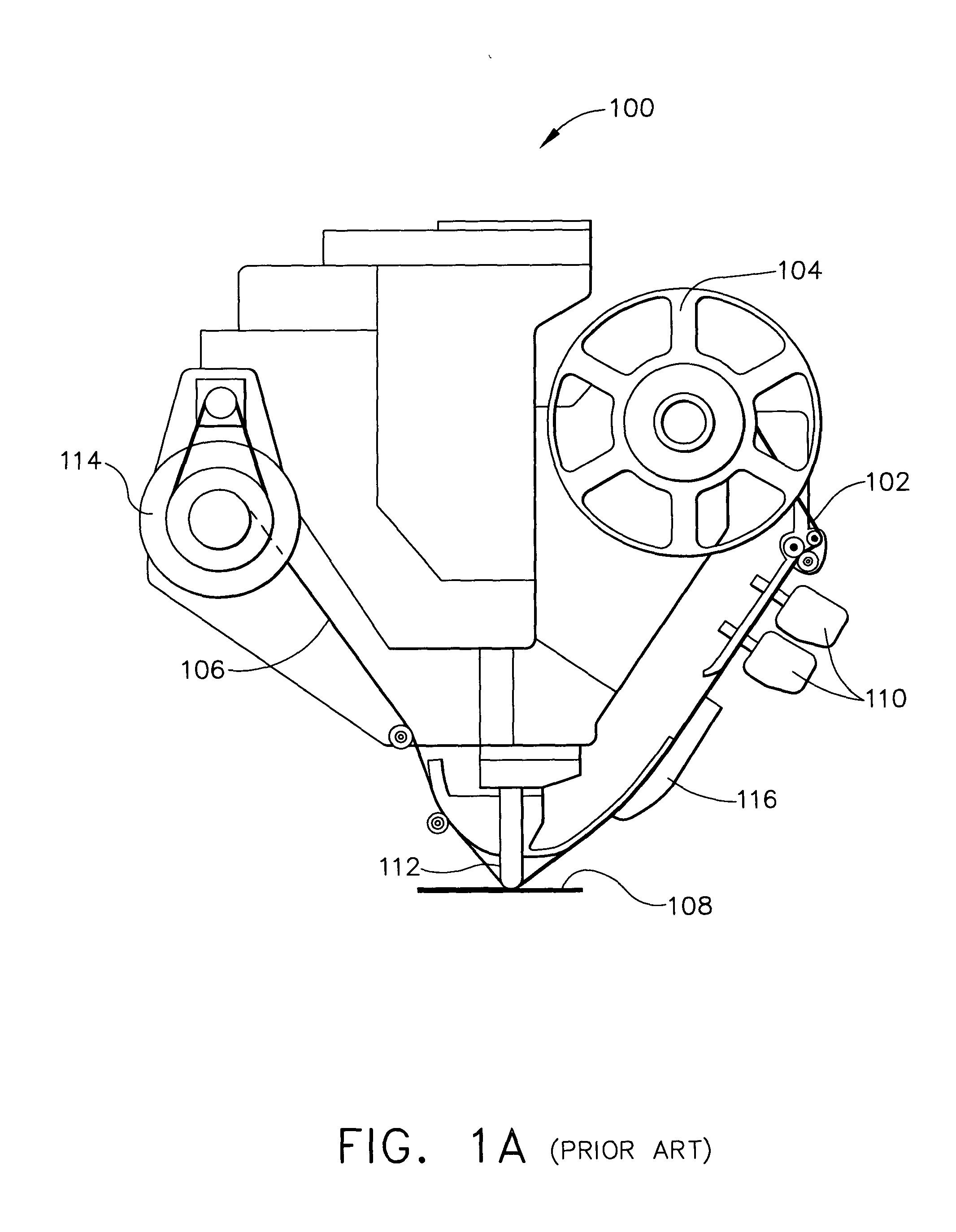
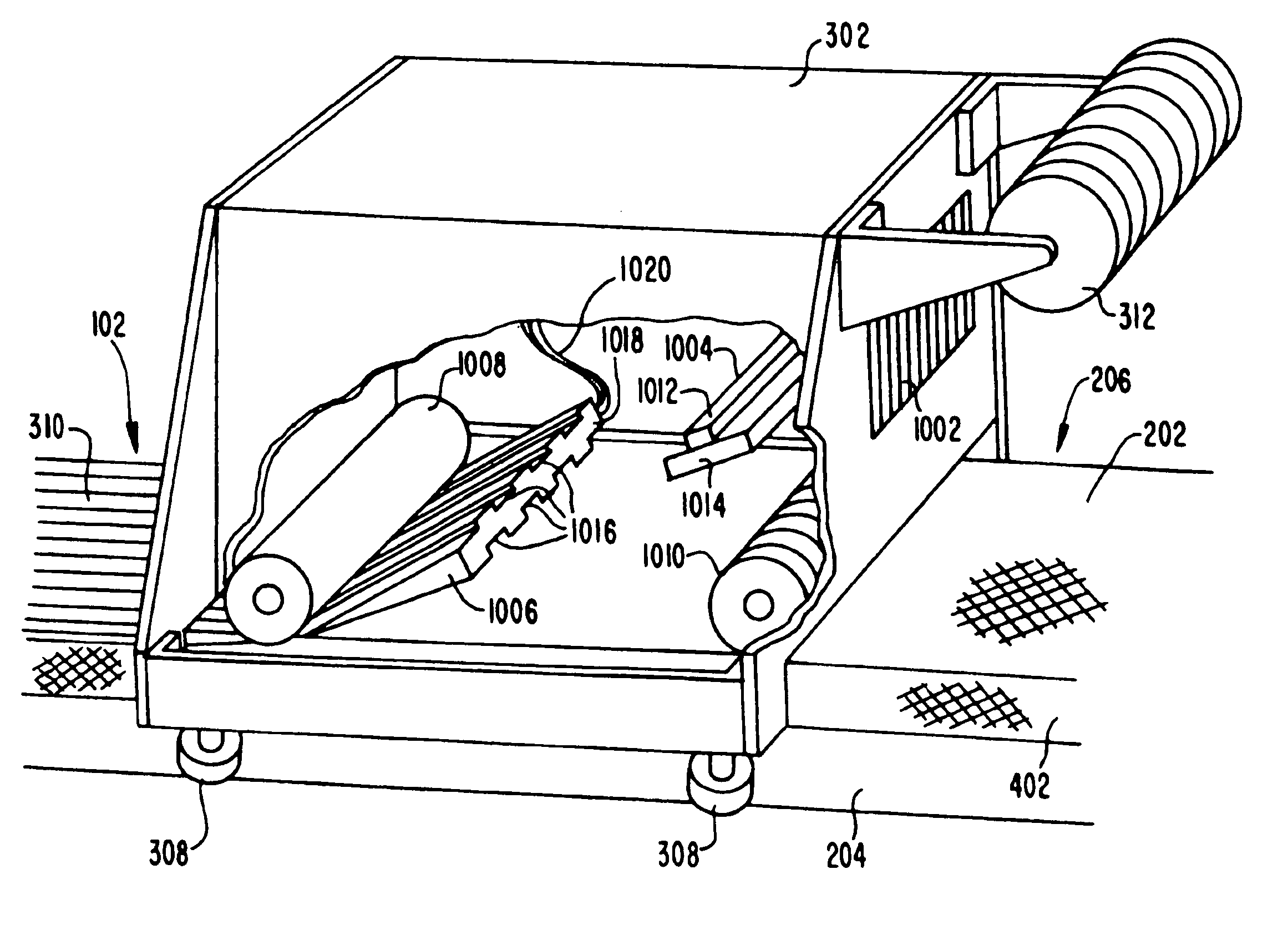
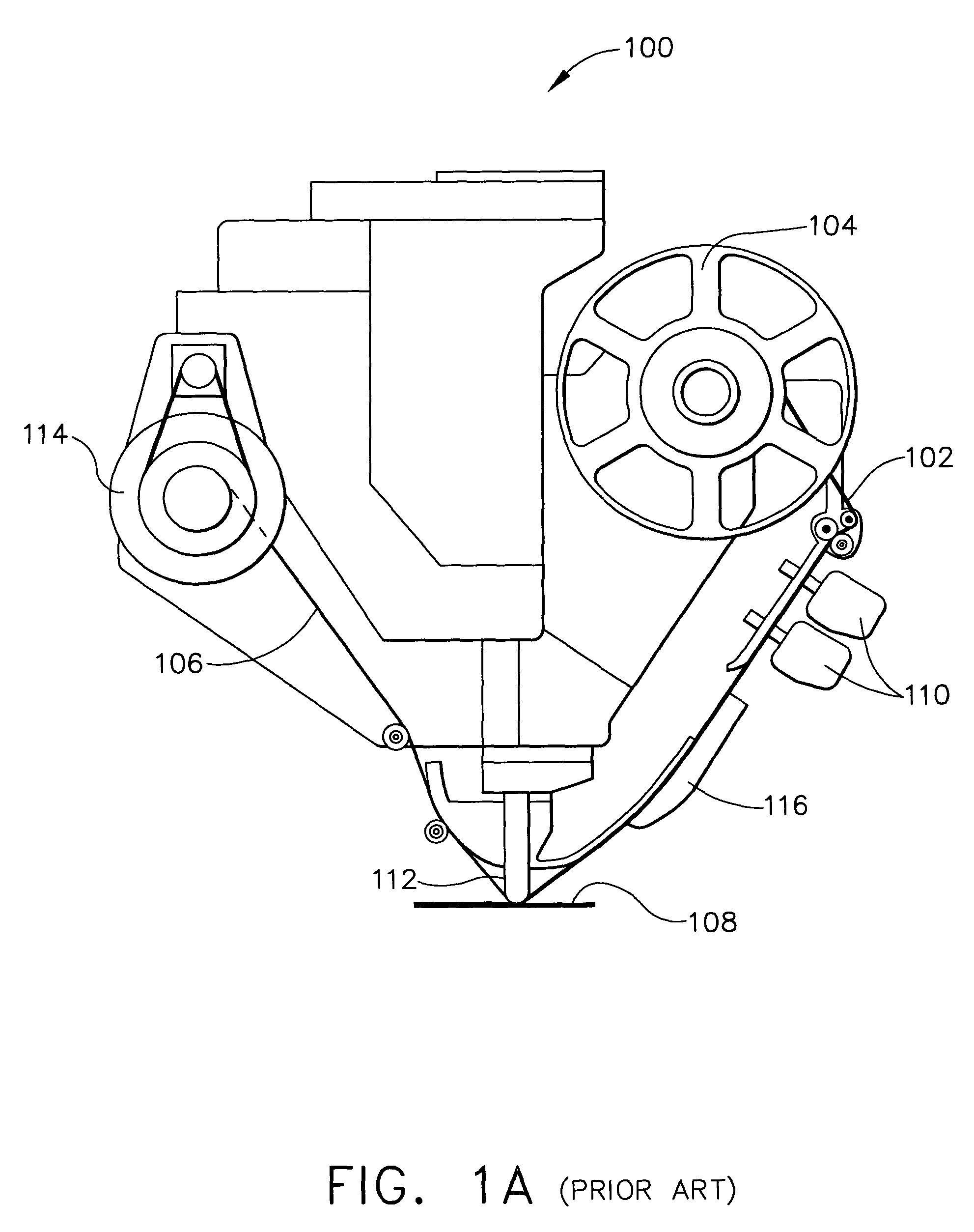
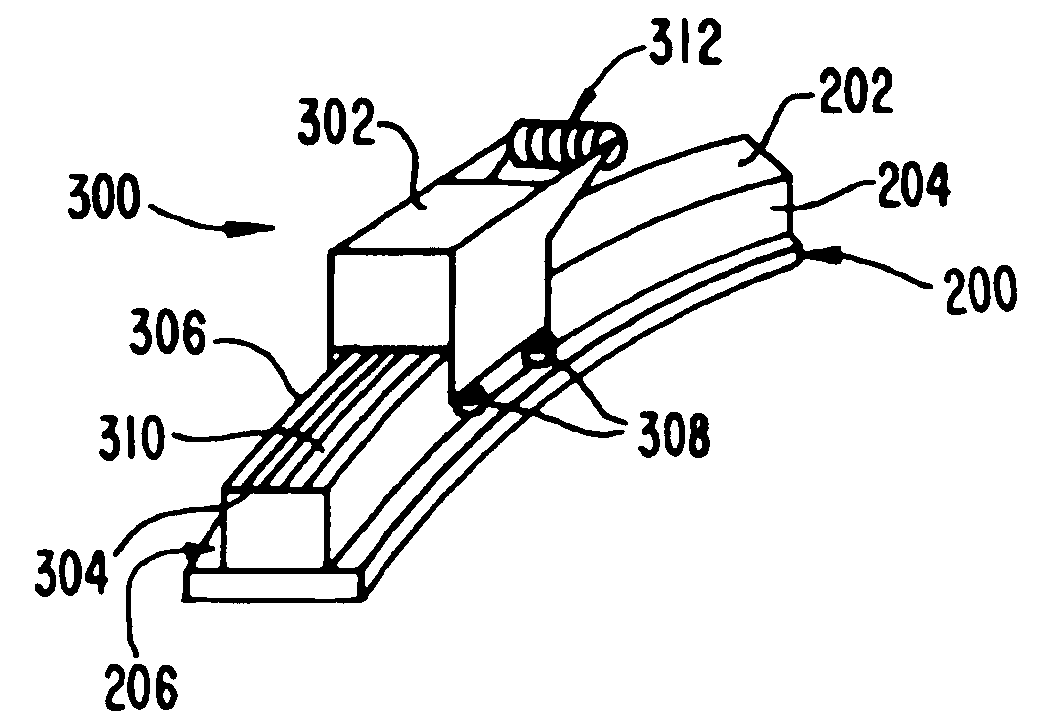
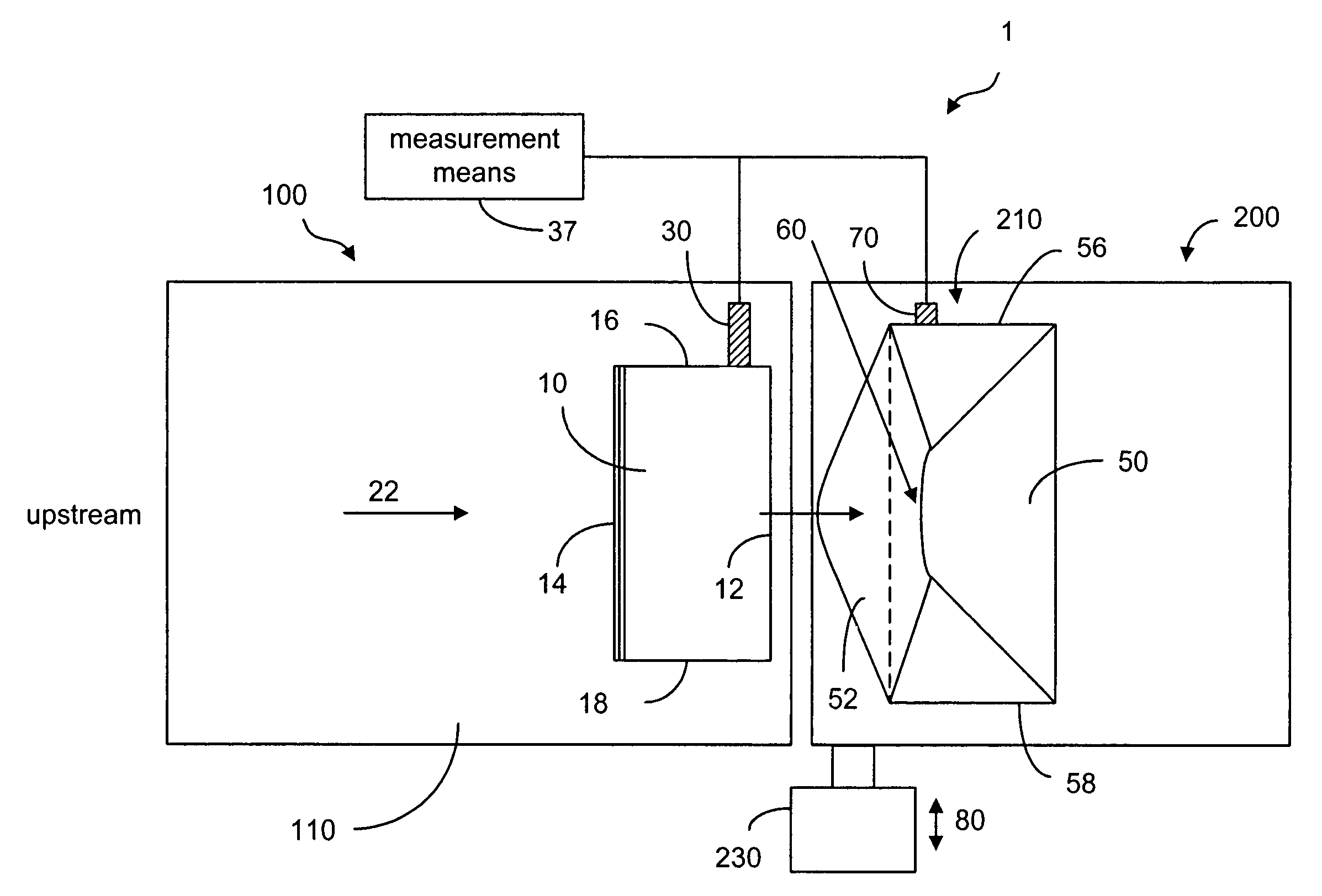
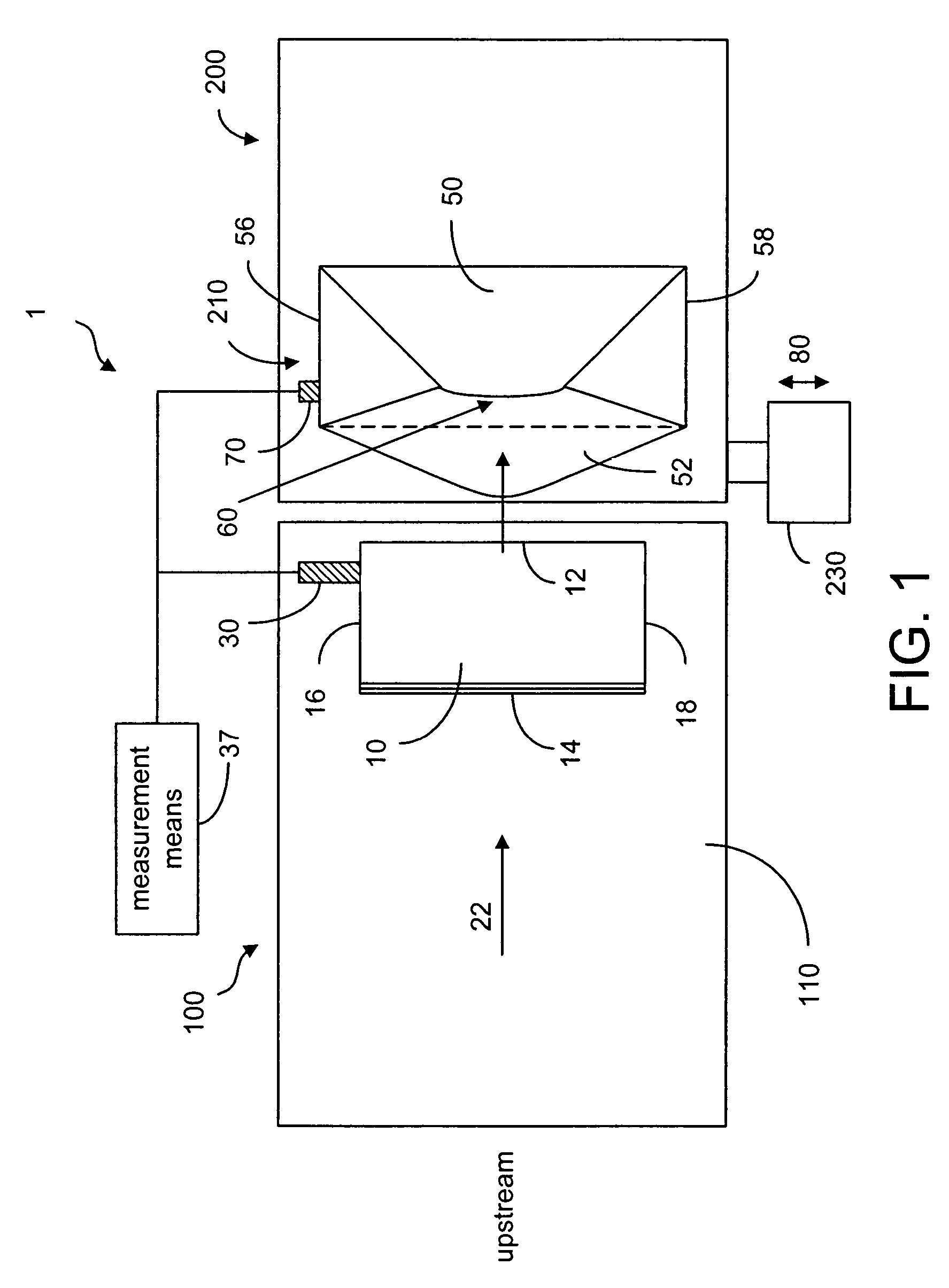
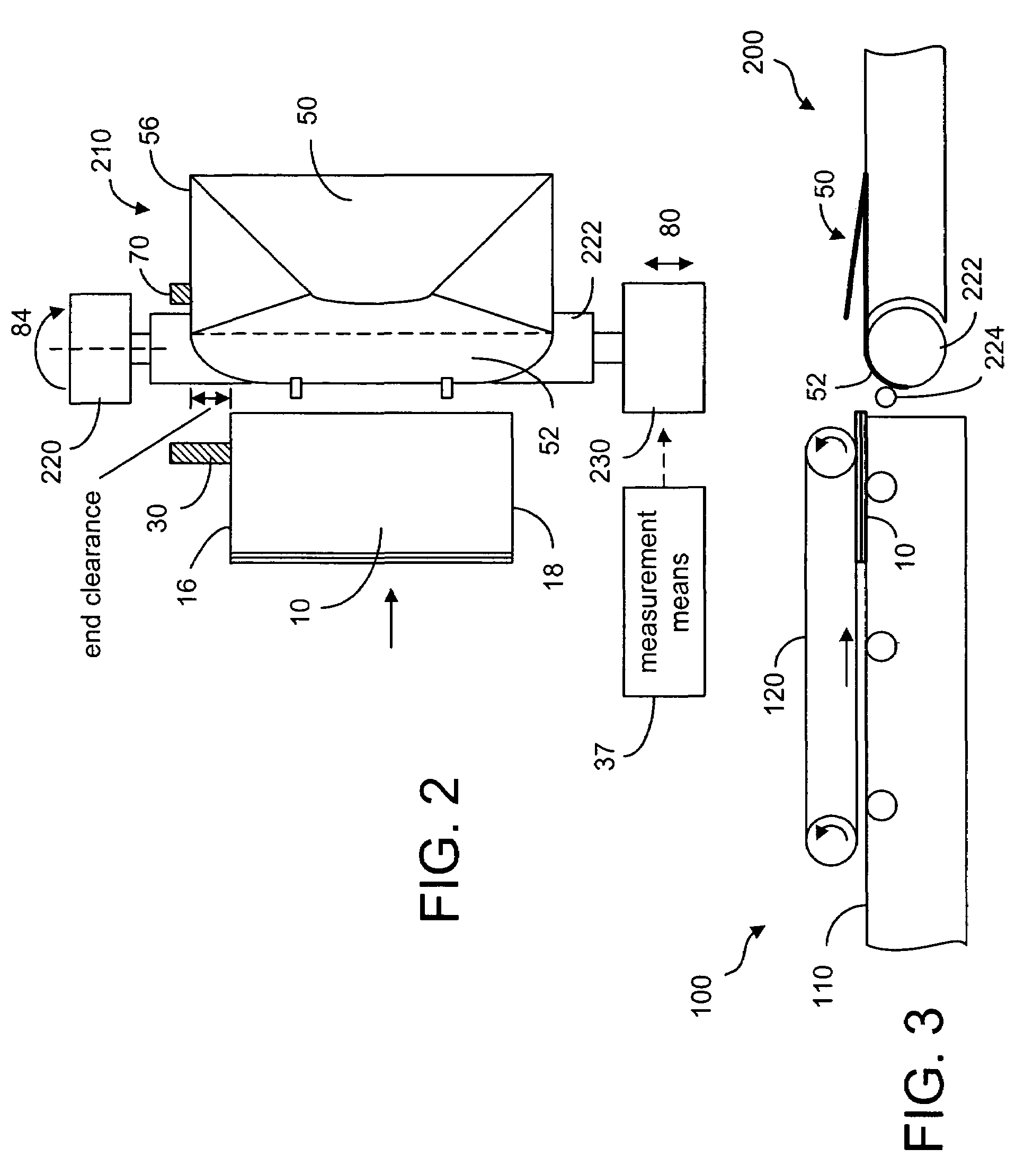
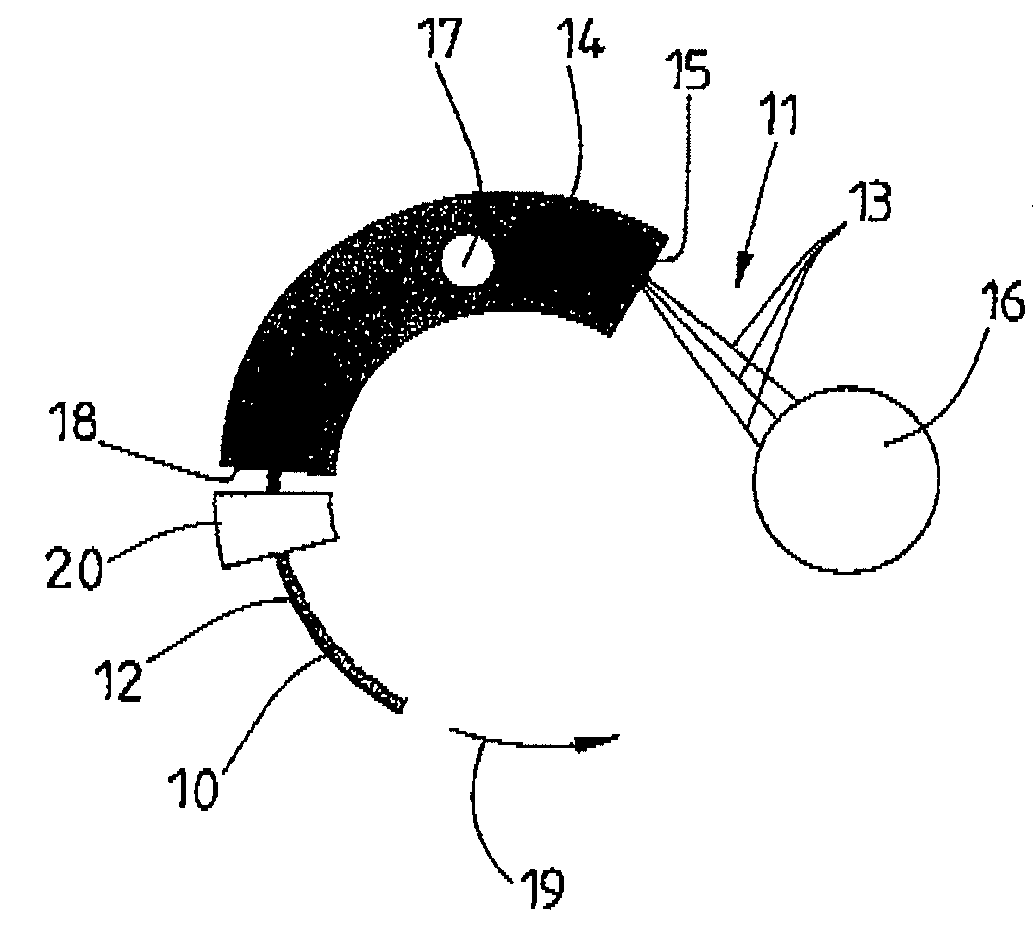
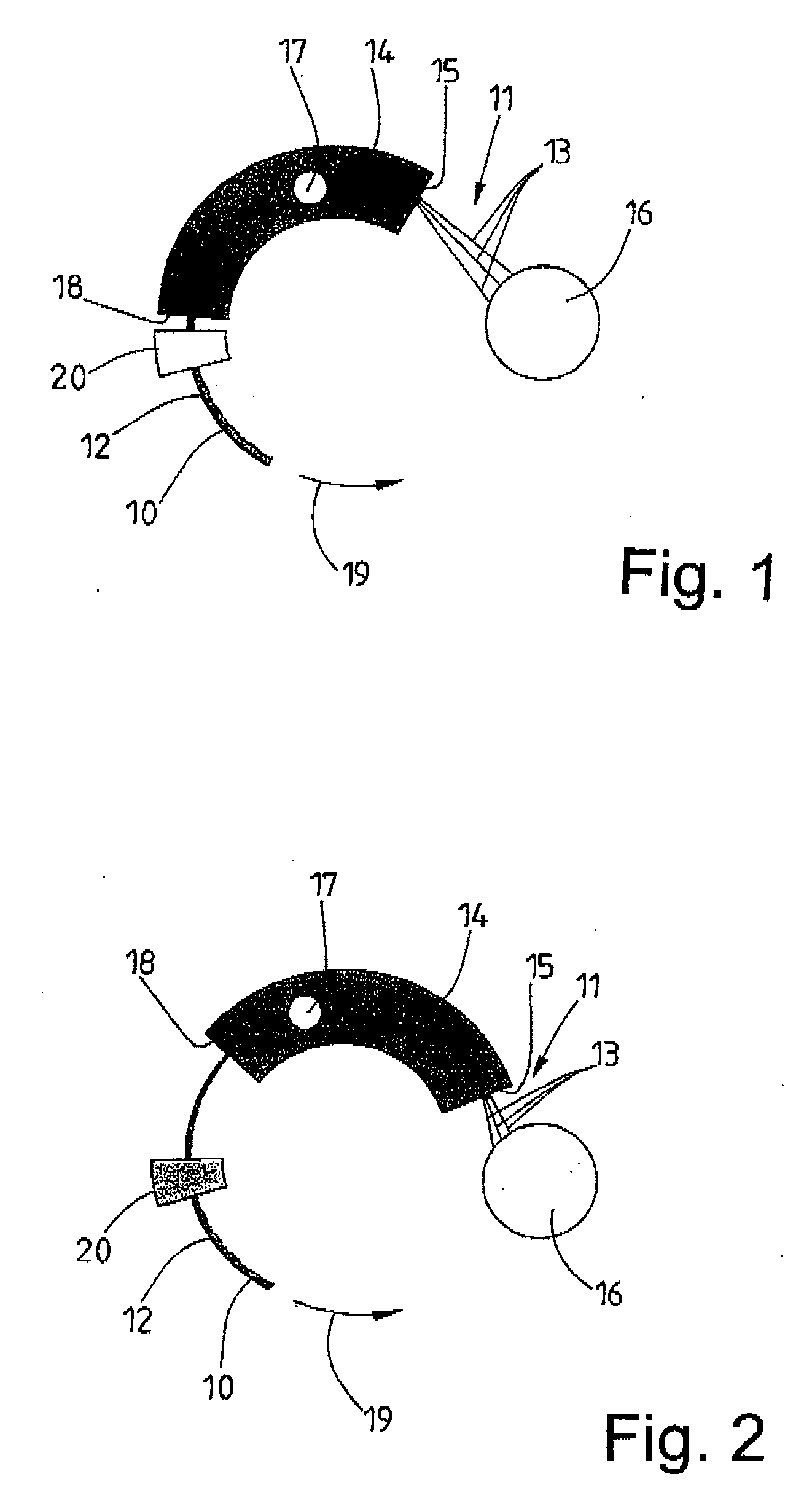
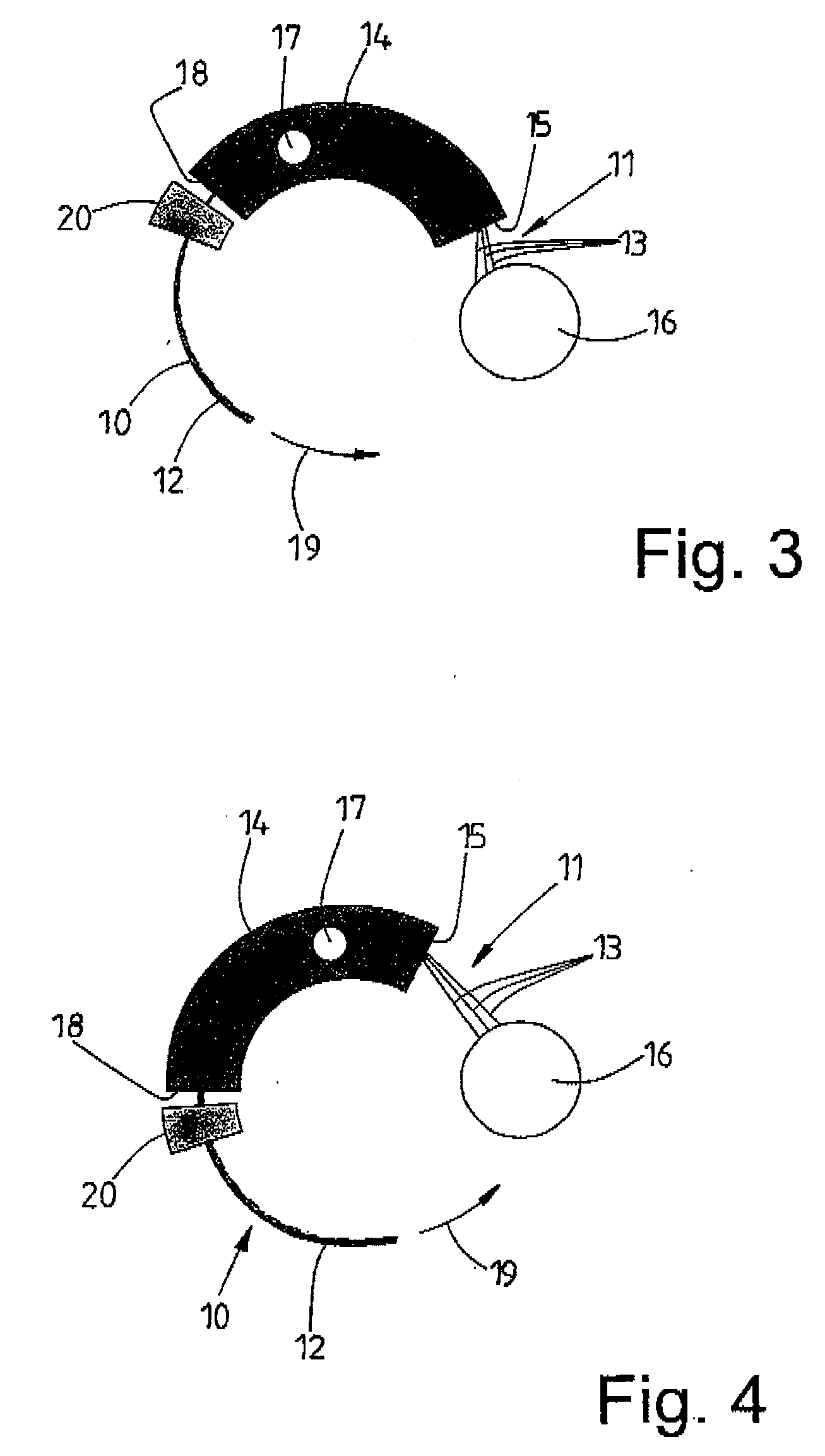
Method and device for aligning a receiving envelope in a mail inserter
In a mail inserter having an envelope movement mechanism to move an envelope into an insertion station and a feeder to move a pack of insert material into an insertion position so that the insert material can be inserted into the envelope, a linear array of optical sensing elements is used to determine the position of one edge of the insert material and another linear array of optical sensing elements is used to determine the position of one edge of the receiving envelope in order to make sure that there is sufficient end clearance between the insert material and the receiving envelope. A stepper motor is used to adjust the envelope position, if the end clearance is outside a predetermined range.
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
Method and device for the production of a plastic profile
In the production of elongate plastic profiles (10), which usually takes place by the pultrusion process, the cured plastic profile (10) emerging from a die (14) is pulled through the stationary die (14) by a take-off device. This process only makes it possible to produce straight plastic profiles (10). The invention envisages producing curved plastic profiles (10) by using a die (14) corresponding to the curvature of the plastic profile (10). For moving the cured part of the plastic profile (10) out of the die (14), it is provided that the die (14) is moved back step by step in relation to the stationary plastic profile (10) counter to the direction of production (19). In order that the plastic profile (10) remains stationary in relation to the die (14) as this takes place, it is securely held outside the die (14) by a holding means (20) during the moving back of the die (14).
Owner:3B LUX SARL
System and method for providing sheets to an inserter system using a rotary cutter
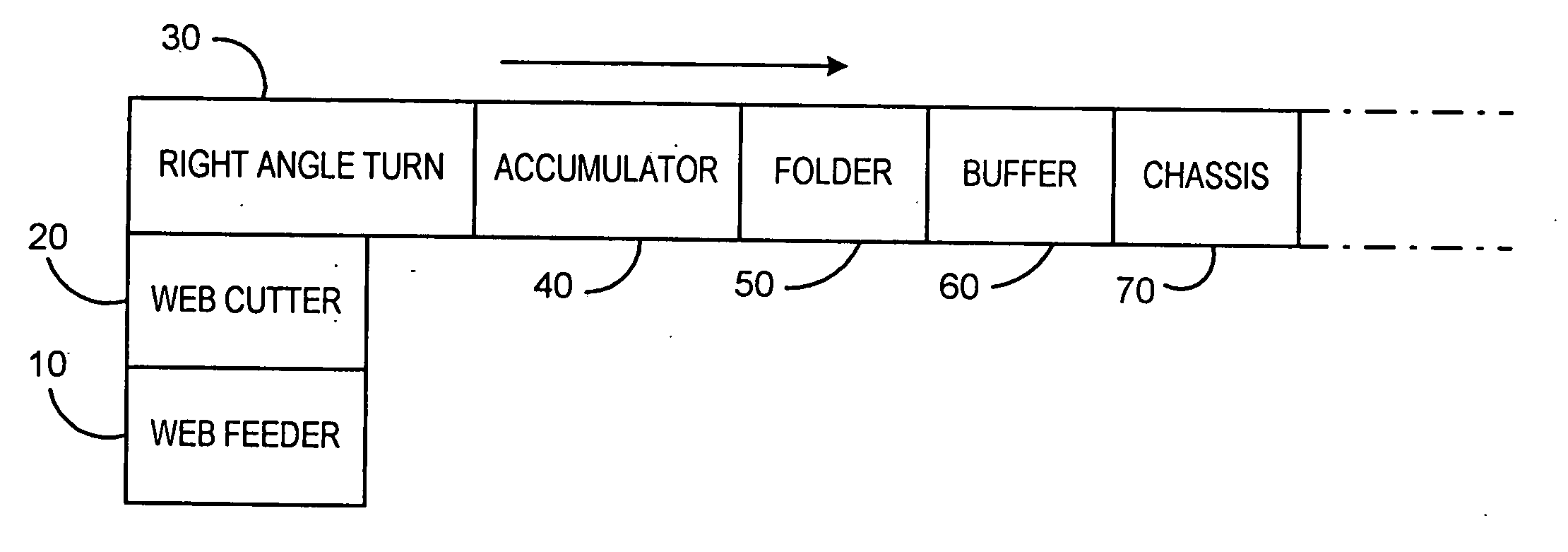
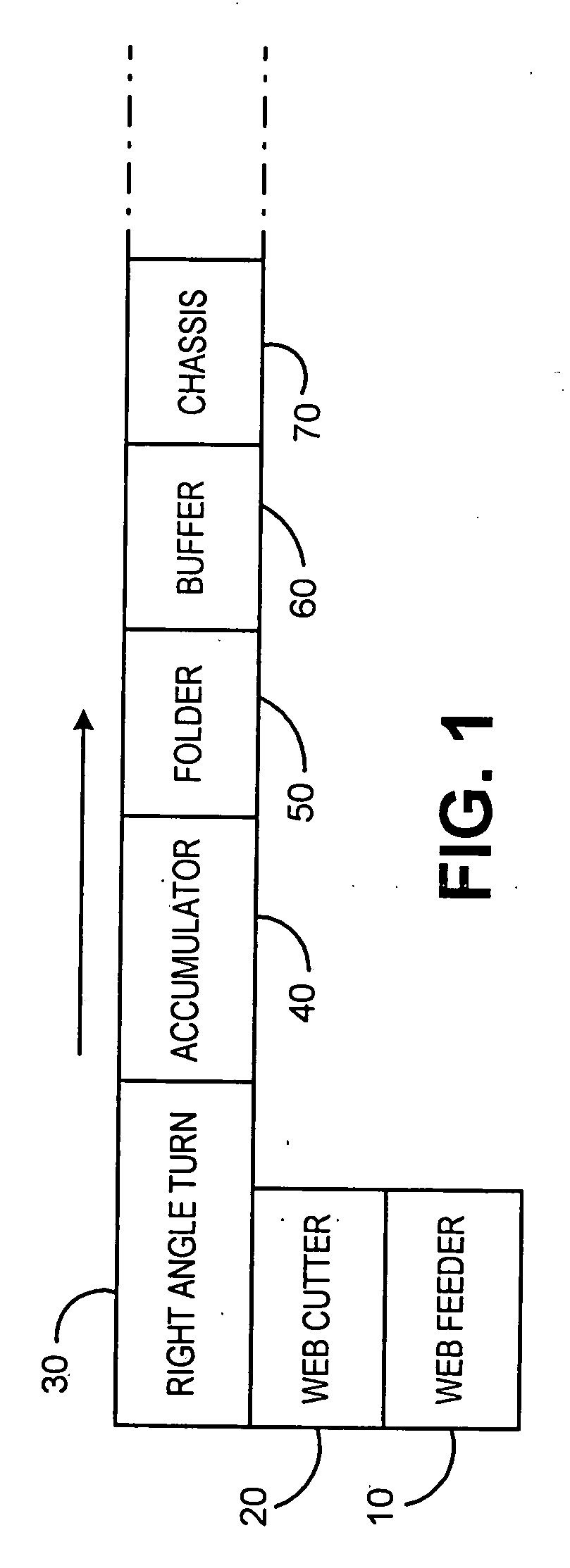
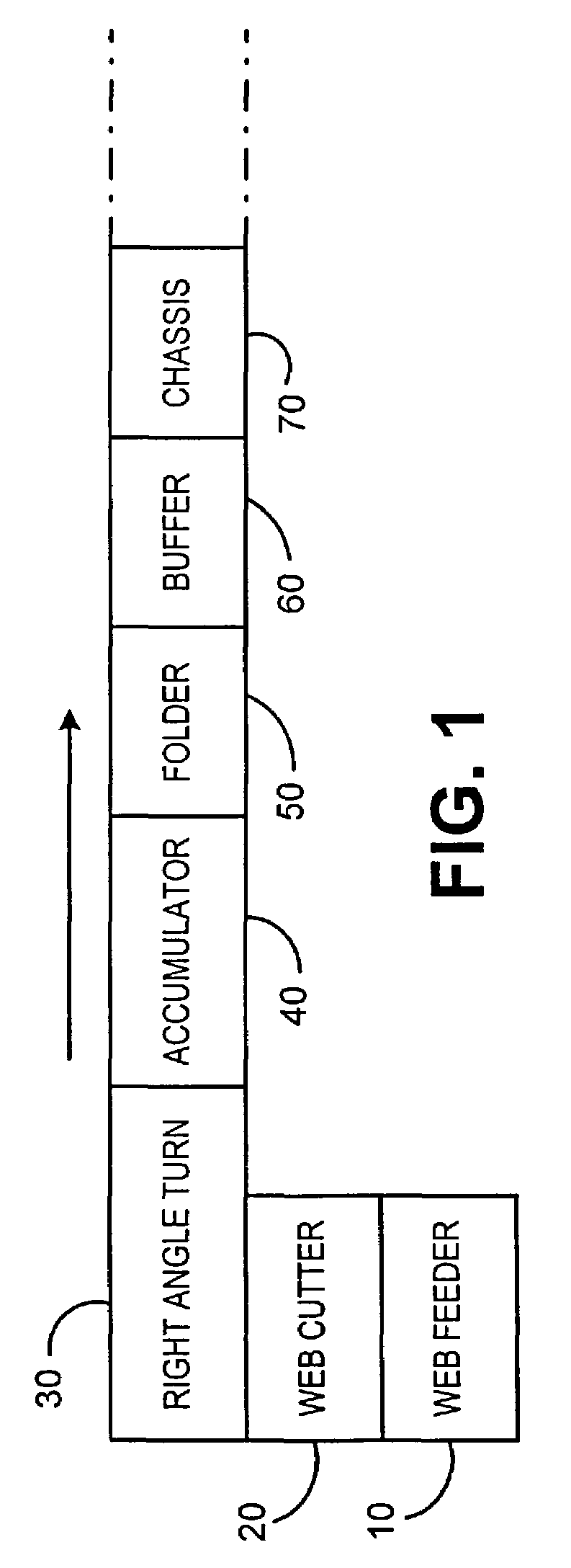
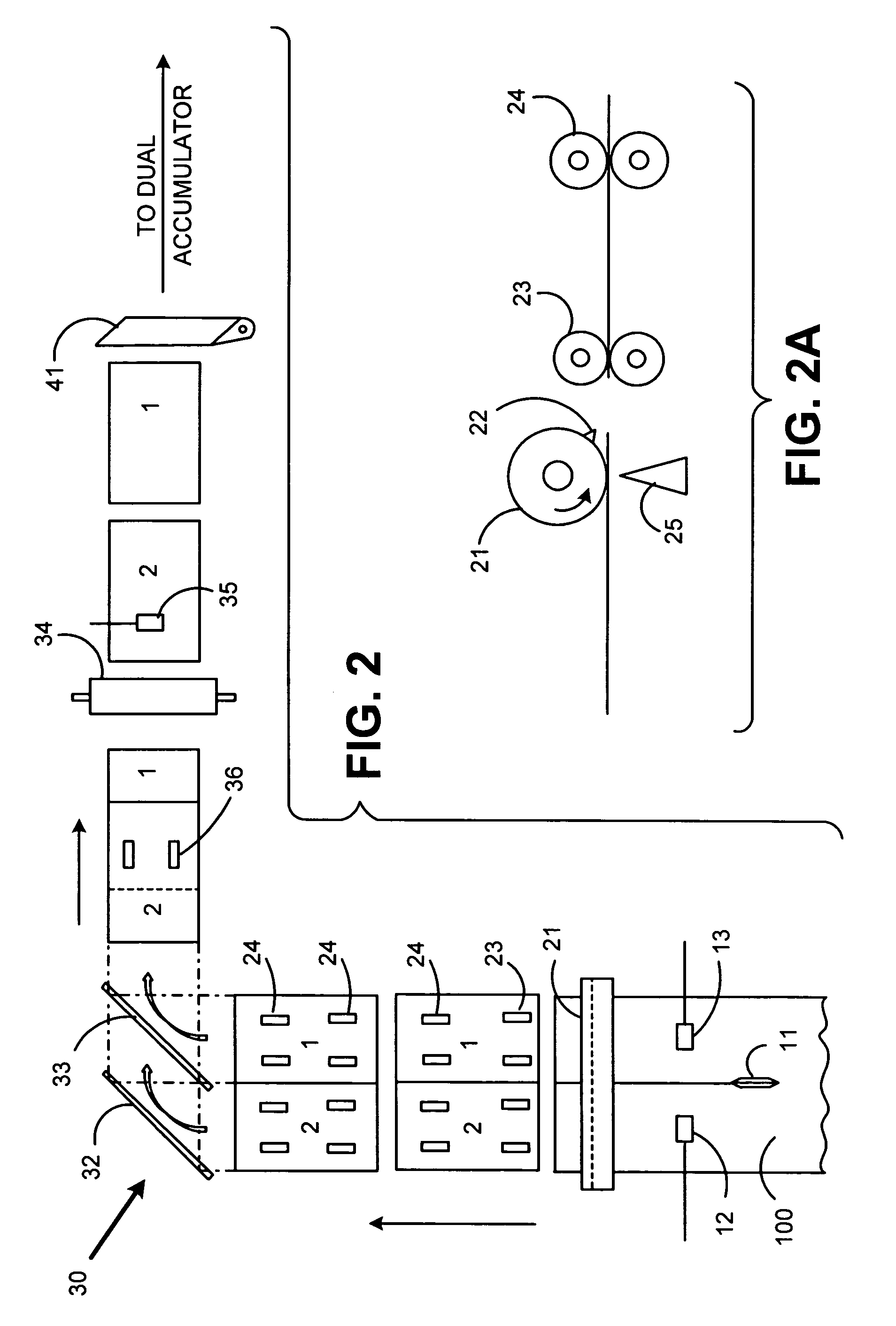
InactiveUS7021184B2Without significant lengthening of a buffer moduleSmall footprintSortingMetal working apparatusEngineeringPaper sheet
An inserter input system including a web feeder providing a web of printed material to be split by a web slitting knife along the web's direction of travel. The split web is then cut transverse to the direction of travel by a rotary cutter operating at a first velocity, resulting in side-by-side individual sheets. Downstream of the rotary cutter, a right angle turn mechanism receives each of the side-by-side sheets and reorients them by ninety degrees. Further the right angle turn reorients the sheets into a serial shingled arrangement. A high speed separation nip pulls individual shingled sheets out from the shingled arrangement. The speed of the separation nip is such that a predetermined gap between the previously shingled sheets is formed. In a further preferred embodiment of the present invention, the speed of the rotary cutter and right angle turn mechanism are controlled to adjust a quantity of sheets that would be generated from displacement traveled due to inertia during a deceleration of the system to a stop.
Owner:DMT SOLUTIONS GLOBAL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com