Azithromycin ophthalmic in-situ gel and preparation method thereof
A technology of azithromycin and in-situ gel, which is applied in the direction of medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, and pharmaceutical formulations. To achieve excellent bioadhesion, improve patient compliance, and improve bioavailability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
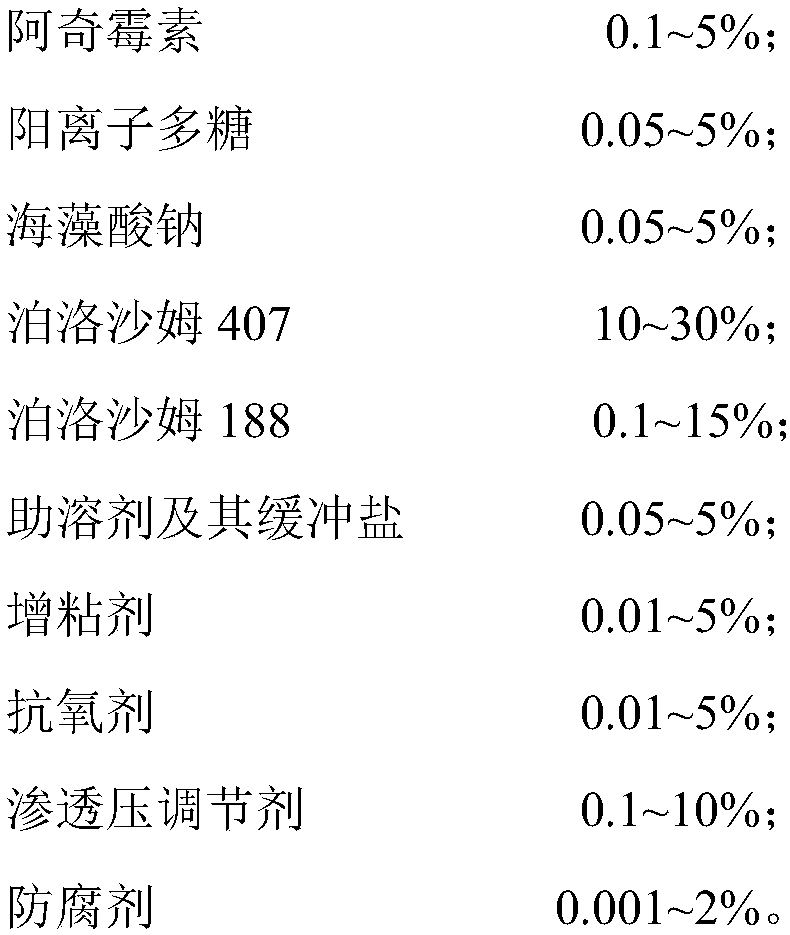
[0037] An azithromycin ophthalmic in situ gel, which comprises the following components by weight percentage of raw materials:
[0038]
[0039] Preparation:
[0040] 1) Dissolving citric acid and sodium citrate with water for injection, the amount of water for injection is 50% to 80% of the total water for injection, and then adding azithromycin, carboxylated chitosan, L-cysteine, Mannitol and benzalkonium chloride were continuously stirred and dissolved, then the prescribed amount of poloxamer 407 and poloxamer 188 were added, stirred evenly, and refrigerated at 4°C overnight to allow it to swell and dissolve slowly to obtain a clear, non-toxic Agglomerate, evenly dispersed solution, adjust the pH to 6.5 with sodium hydroxide pH regulator, filter and sterilize through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane to form solution I, and set aside;
[0041] 2) Weigh the prescribed amount of sodium alginate and hypromellose, slowly add to the heated water for injection, the amount of wat...
Embodiment 2
[0044] An azithromycin ophthalmic in situ gel, which comprises the following components by weight percentage of raw materials:
[0045]
[0046] Preparation:
[0047] 1) Dissolving citric acid and sodium citrate with water for injection, the amount of water for injection is 50% to 80% of the total water for injection, and then adding azithromycin, carboxylated chitosan, L-cysteine, Mannitol and benzalkonium chloride were continuously stirred and dissolved, then the prescribed amount of poloxamer 407 and poloxamer 188 were added, stirred evenly, and refrigerated at 4°C overnight to allow it to swell and dissolve slowly to obtain a clear, non-toxic Agglomerate, evenly dispersed solution, adjust the pH to 6.5 with sodium hydroxide pH regulator, filter and sterilize through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane to form solution I, and set aside;
[0048] 2) Weigh the prescribed amount of sodium alginate and hypromellose, slowly add to the heated water for injection, the amount of wat...
Embodiment 3
[0051] An azithromycin ophthalmic in situ gel, which comprises the following components by weight percentage of raw materials:
[0052]
[0053] Preparation:
[0054] 1) Dissolve citric acid and sodium citrate with water for injection, the amount of water for injection is 50-80% of the total amount of water for injection, and then add azithromycin, chitosan, L-cysteine, mannitol and Benzalkonium chloride, stir continuously to dissolve, then add the prescribed amount of poloxamer 407 and poloxamer 188, stir well, refrigerate overnight at 4°C, let it swell and dissolve slowly, and obtain a clear, lump-free solution 1. For the uniformly dispersed solution, adjust the pH to 6.5 with sodium hydroxide pH regulator, filter and sterilize through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane to form solution I, and set aside;
[0055] 2) Weigh the prescribed amount of sodium alginate and hypromellose, slowly add to the heated water for injection, the amount of water for injection is 20-50% of the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com