Patents
Literature
36 results about "Consistency rules" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
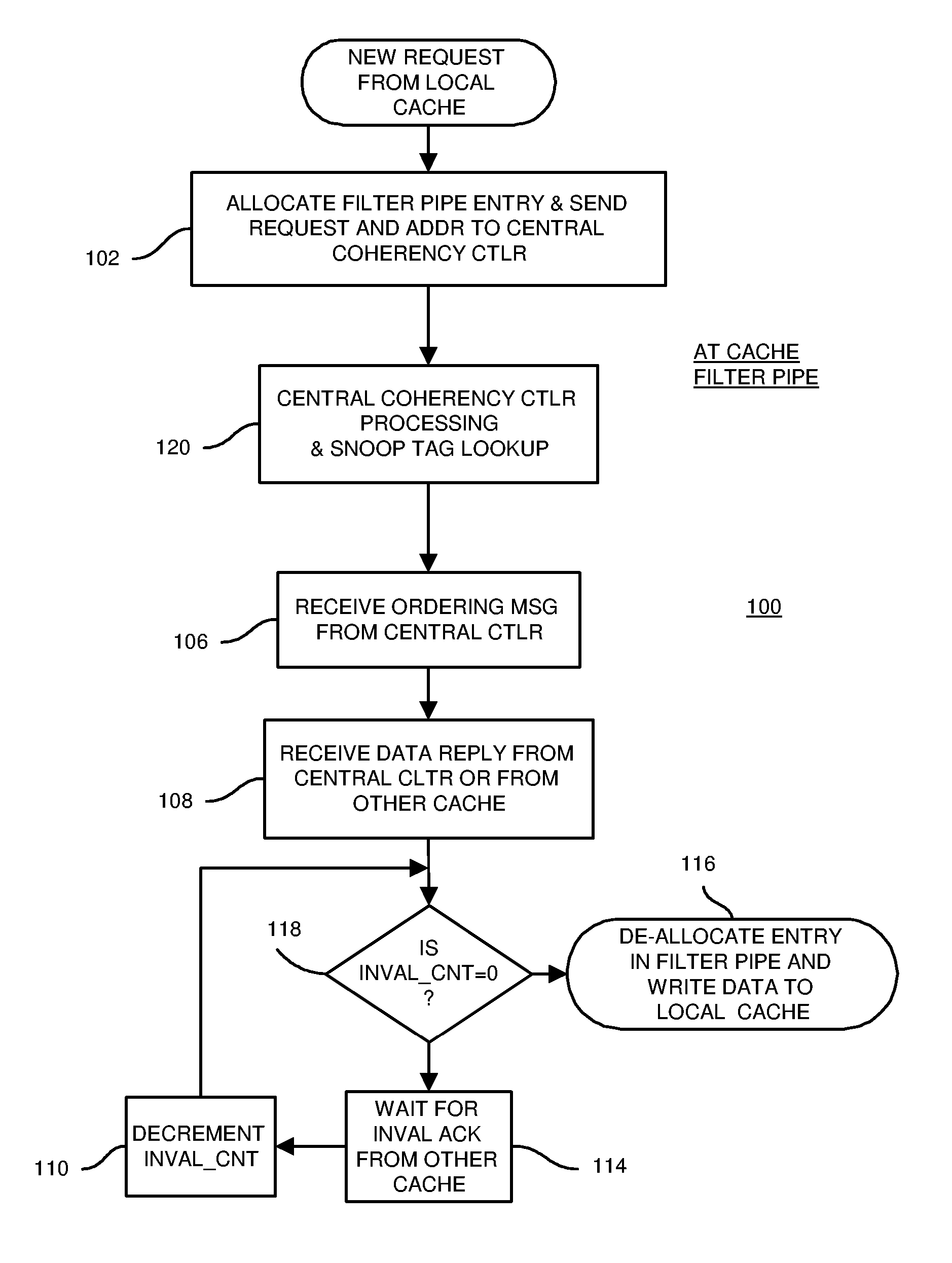
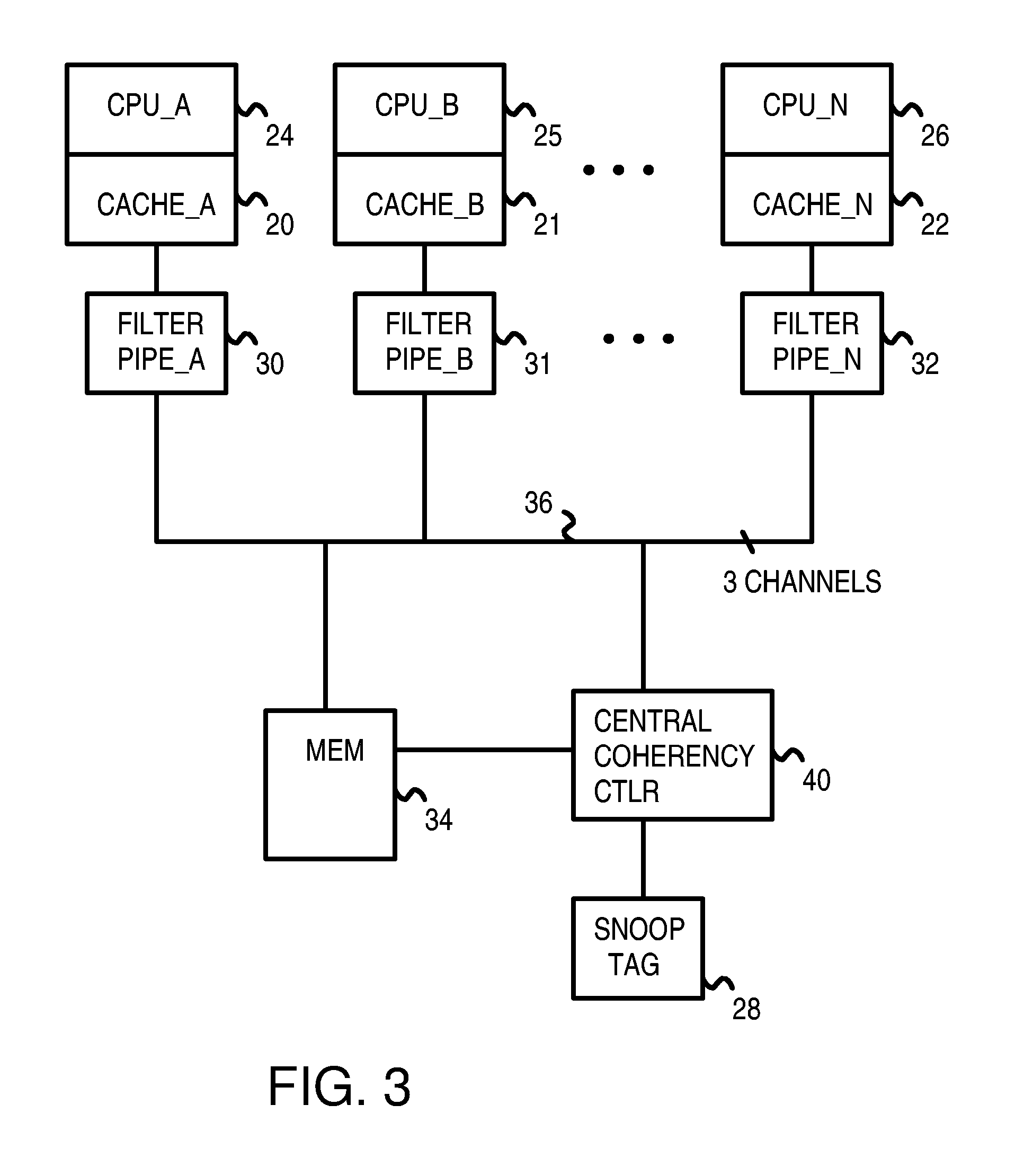
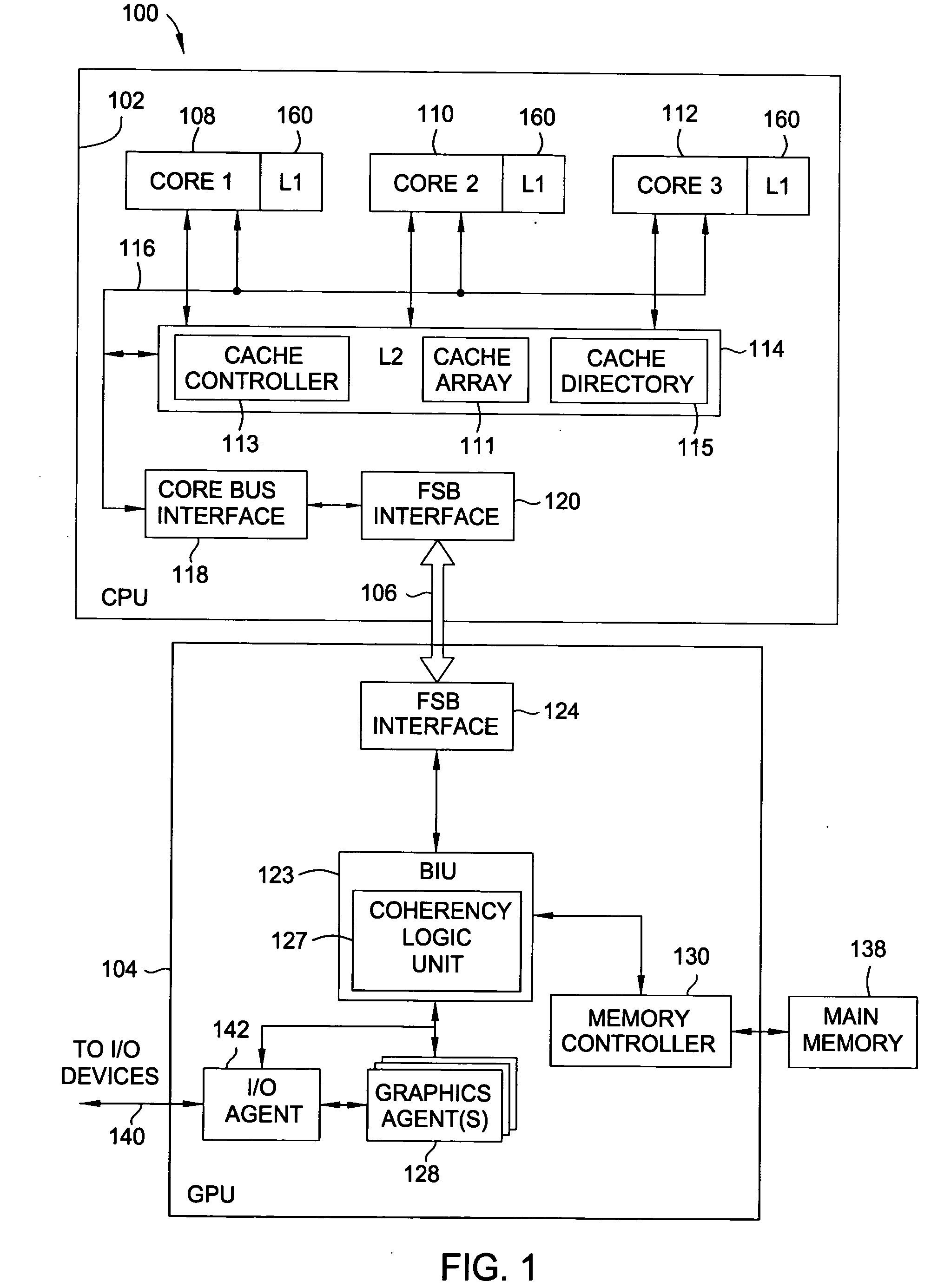
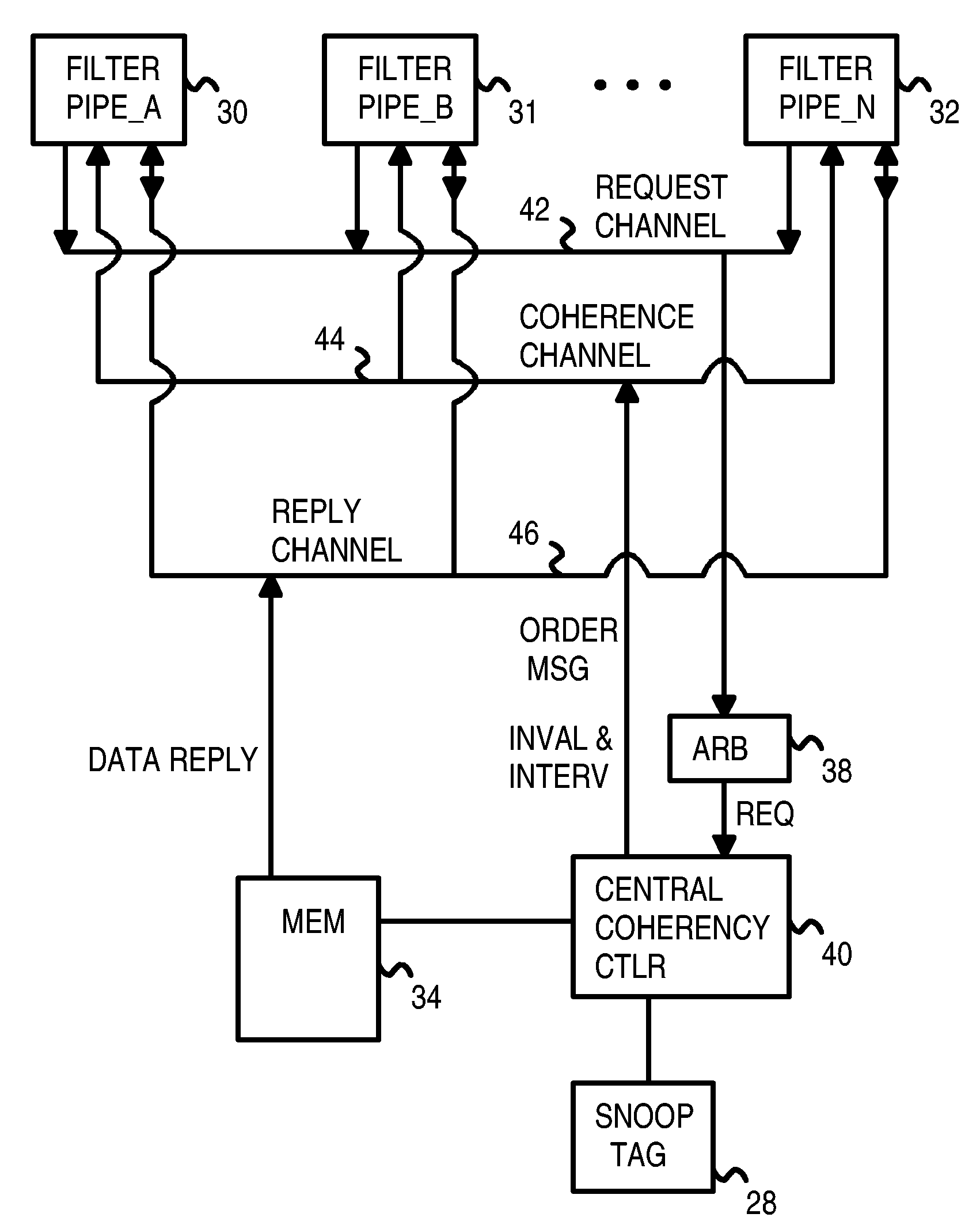
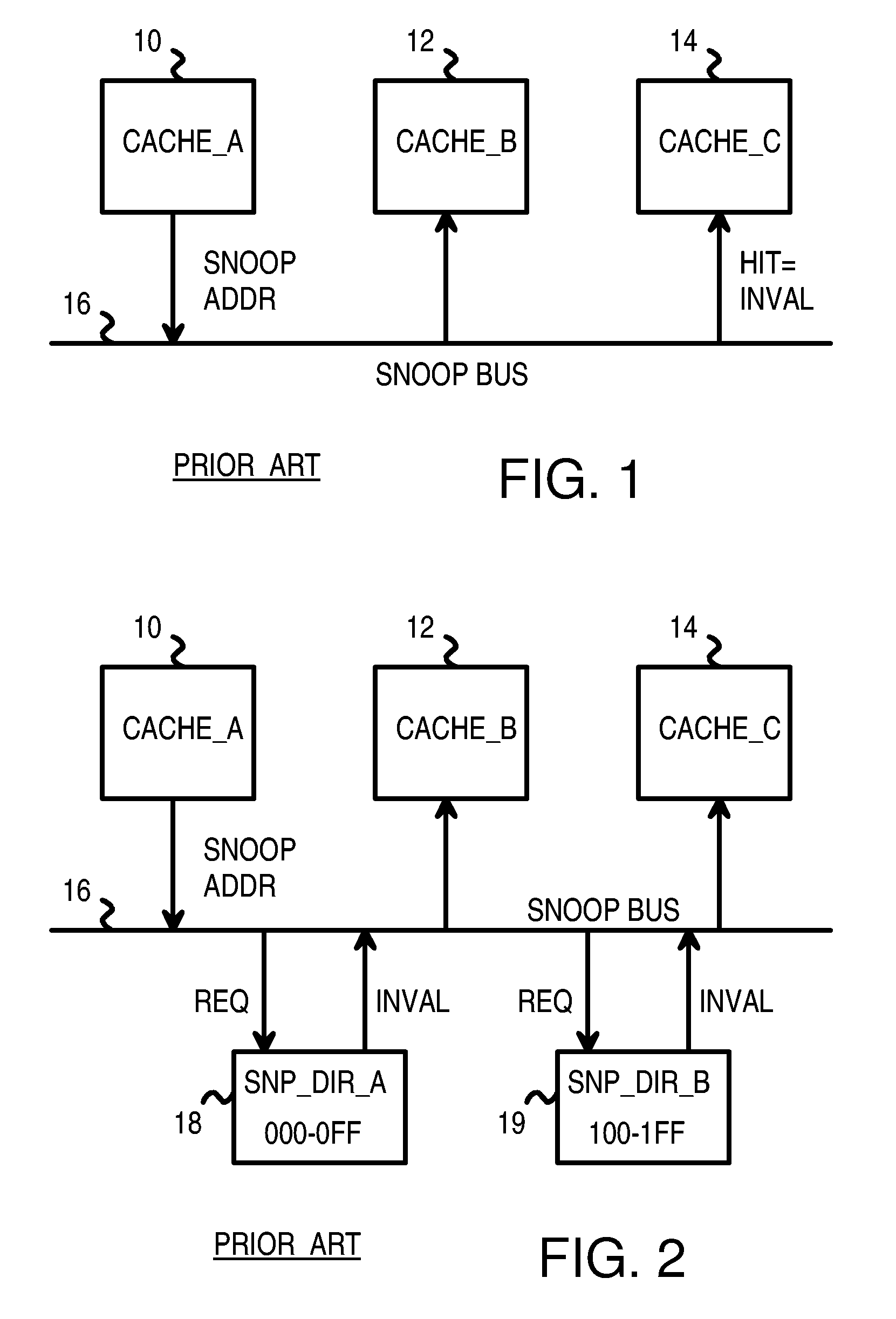
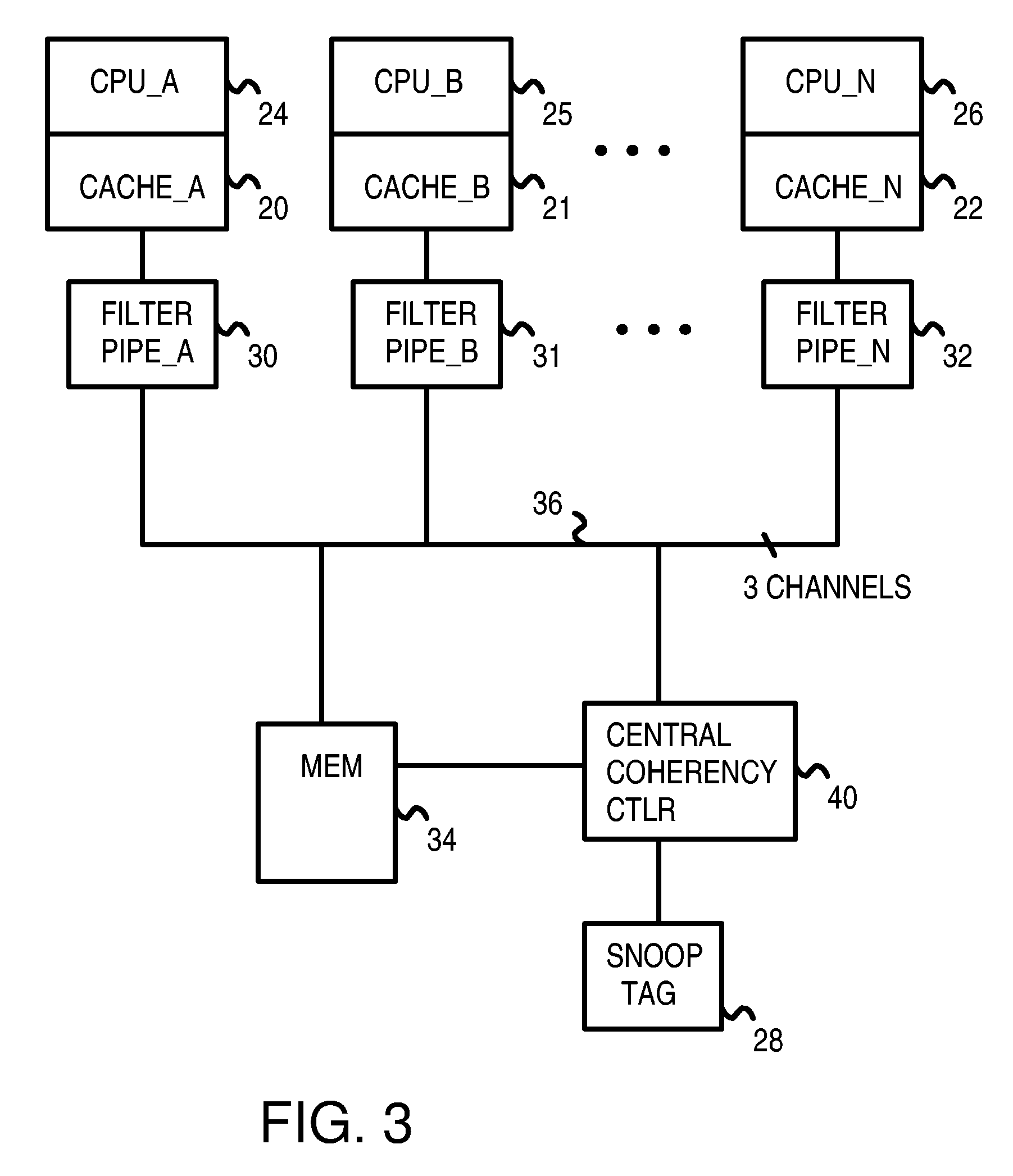
Distributed Cache Coherence at Scalable Requestor Filter Pipes that Accumulate Invalidation Acknowledgements from other Requestor Filter Pipes Using Ordering Messages from Central Snoop Tag
A multi-processor, multi-cache system has filter pipes that store entries for request messages sent to a central coherency controller. The central coherency controller orders requests from filter pipes using coherency rules but does not track completion of invalidations. The central coherency controller reads snoop tags to identify sharing caches having a copy of a requested cache line. The central coherency controller sends an ordering message to the requesting filter pipe. The ordering message has an invalidate count indicating the number of sharing caches. Each sharing cache receives an invalidation message from the central coherency controller, invalidates its copy of the cache line, and sends an invalidation acknowledgement message to the requesting filter pipe. The requesting filter pipe decrements the invalidate count until all sharing caches have acknowledged invalidation. All ordering, data, and invalidation acknowledgement messages must be received by the requesting filter pipe before loading the data into its cache.
Owner:AZUL SYSTEMS
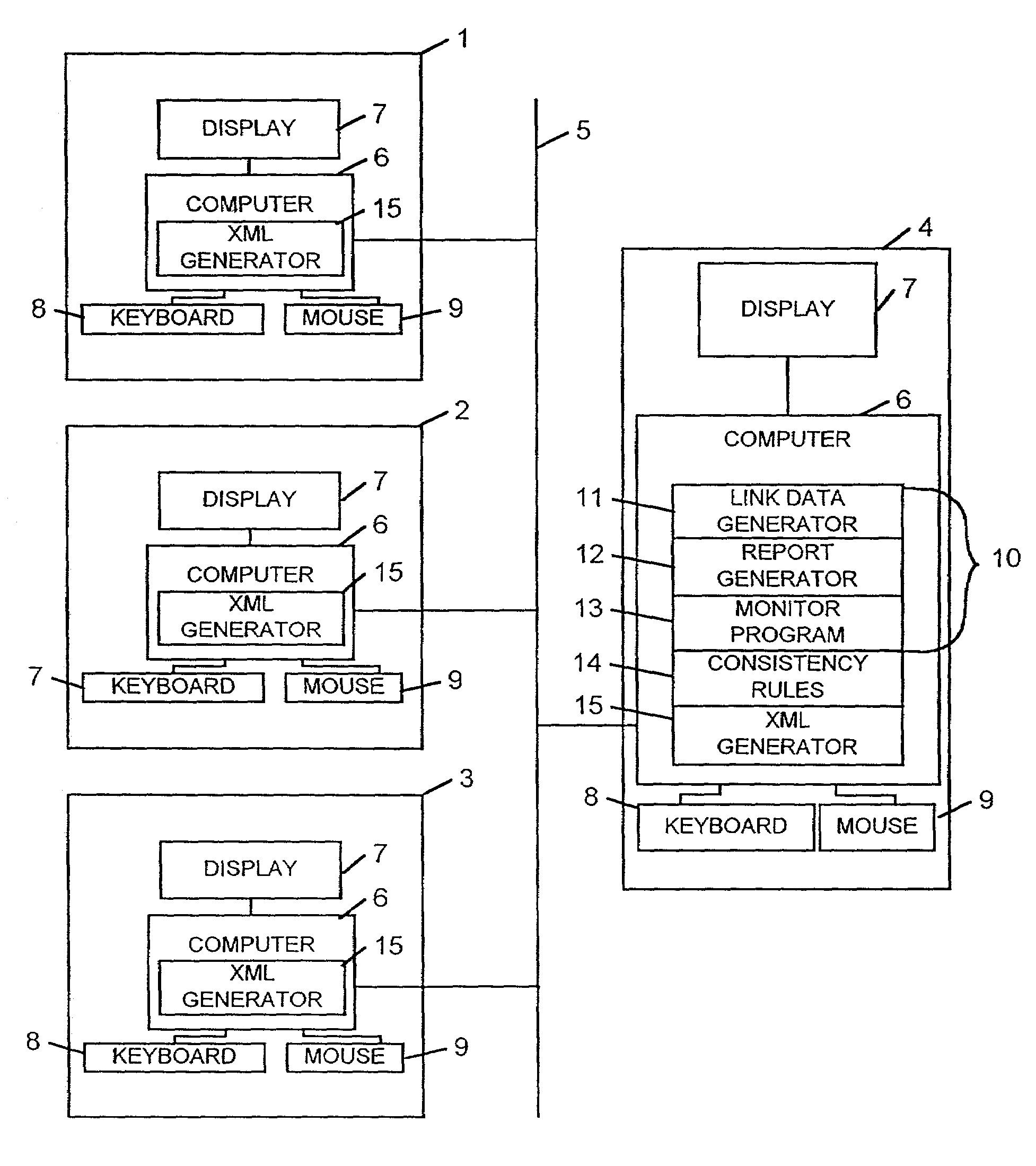
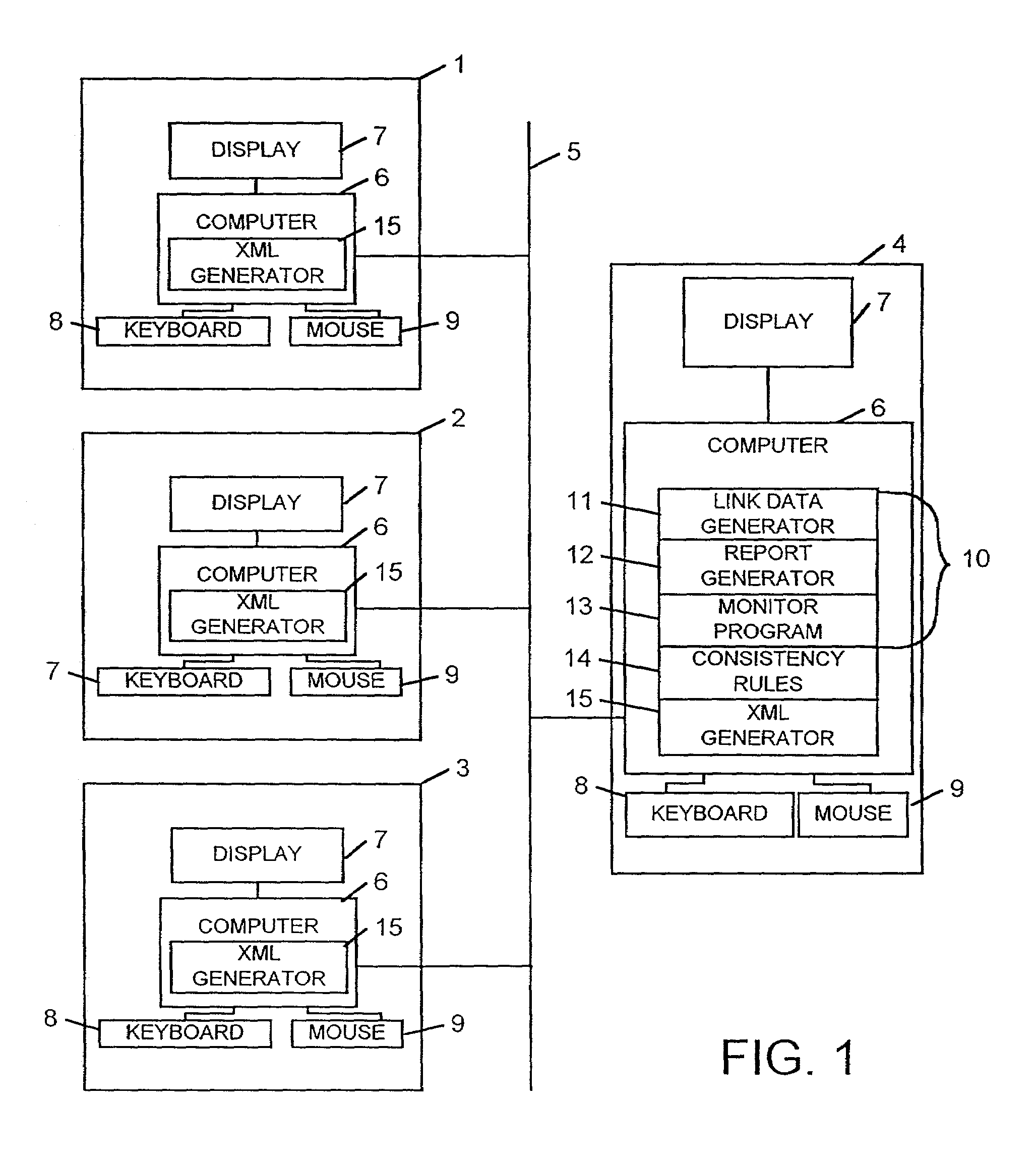
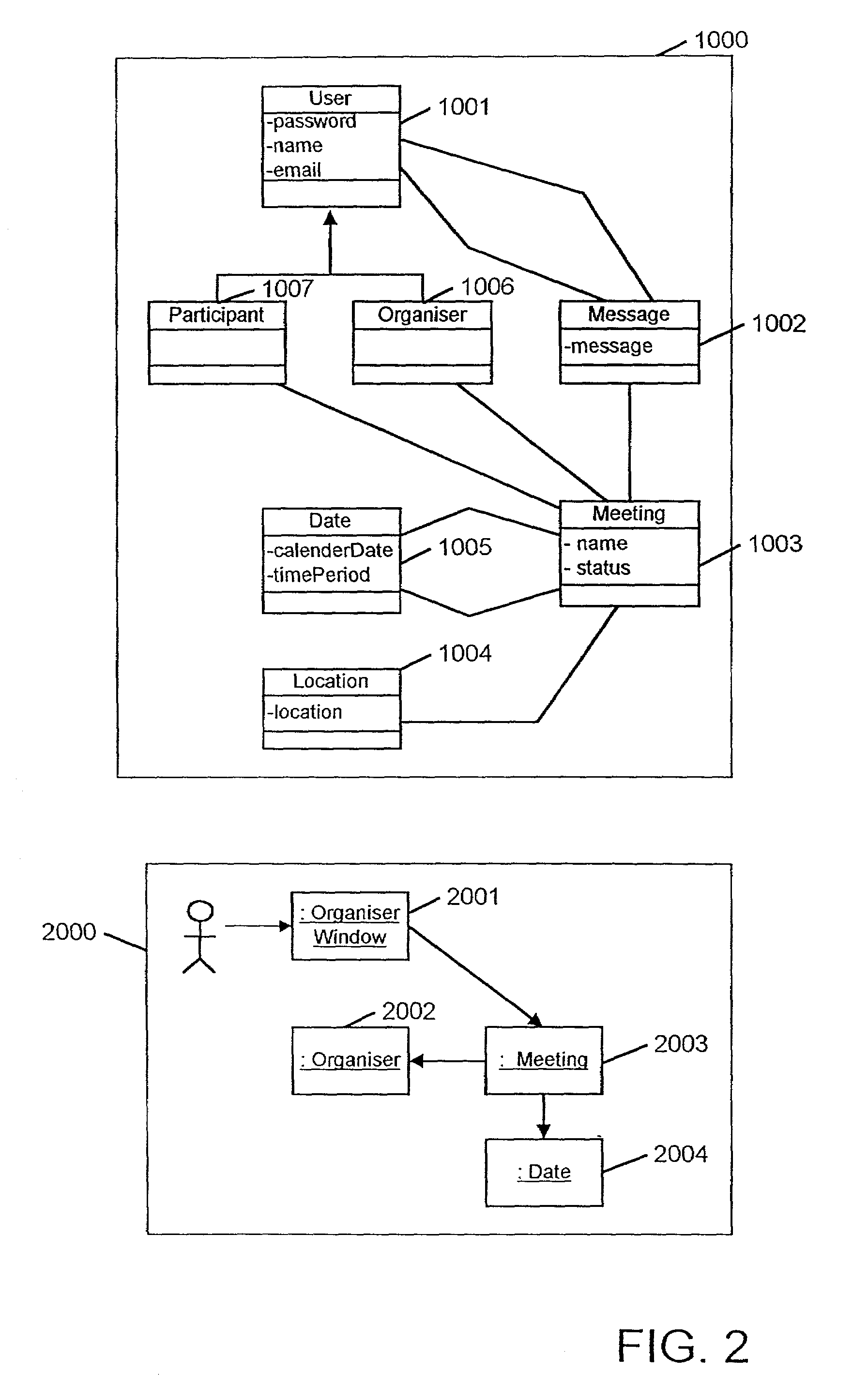
Method and apparatus for monitoring and maintaining the consistency of distributed documents
InactiveUS7143103B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalApplication softwareDatabase
A computer network comprising a plurality of terminals (1–4) connected via a communications network 5 is provided. In each of the terminals (1–4) application software (15) for generating XML source documents is provided. XML source documents created using the application software (15) are then sent to one of the terminals (4) having stored therein a consistency checker (10). The consistency checker (10) processes the source document together with a set of consistency rules (14) to generate an output presentation identifying data within the source documents which does or does not fulfil the requirements of consistency relationships defined by the consistency rules (14).
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON
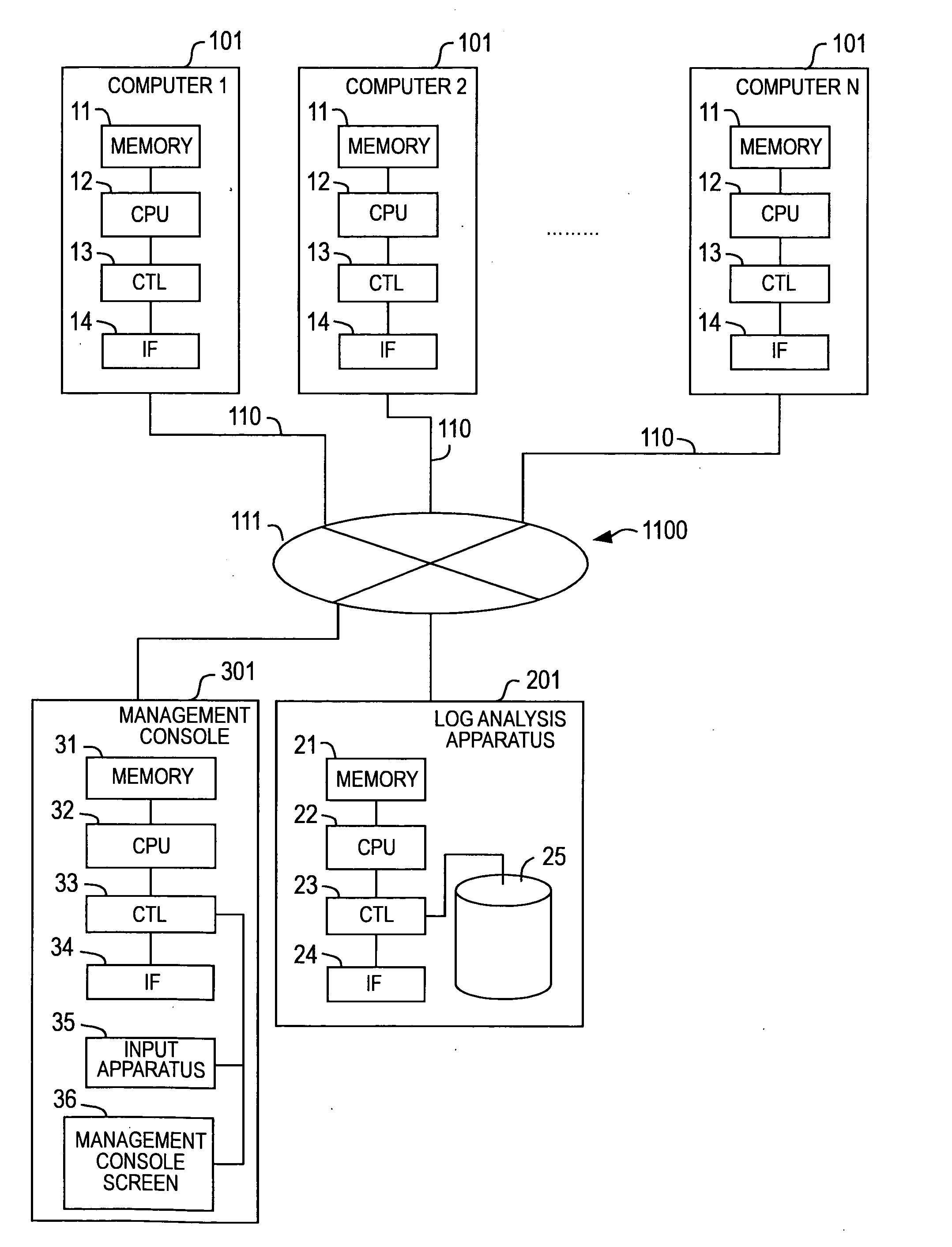
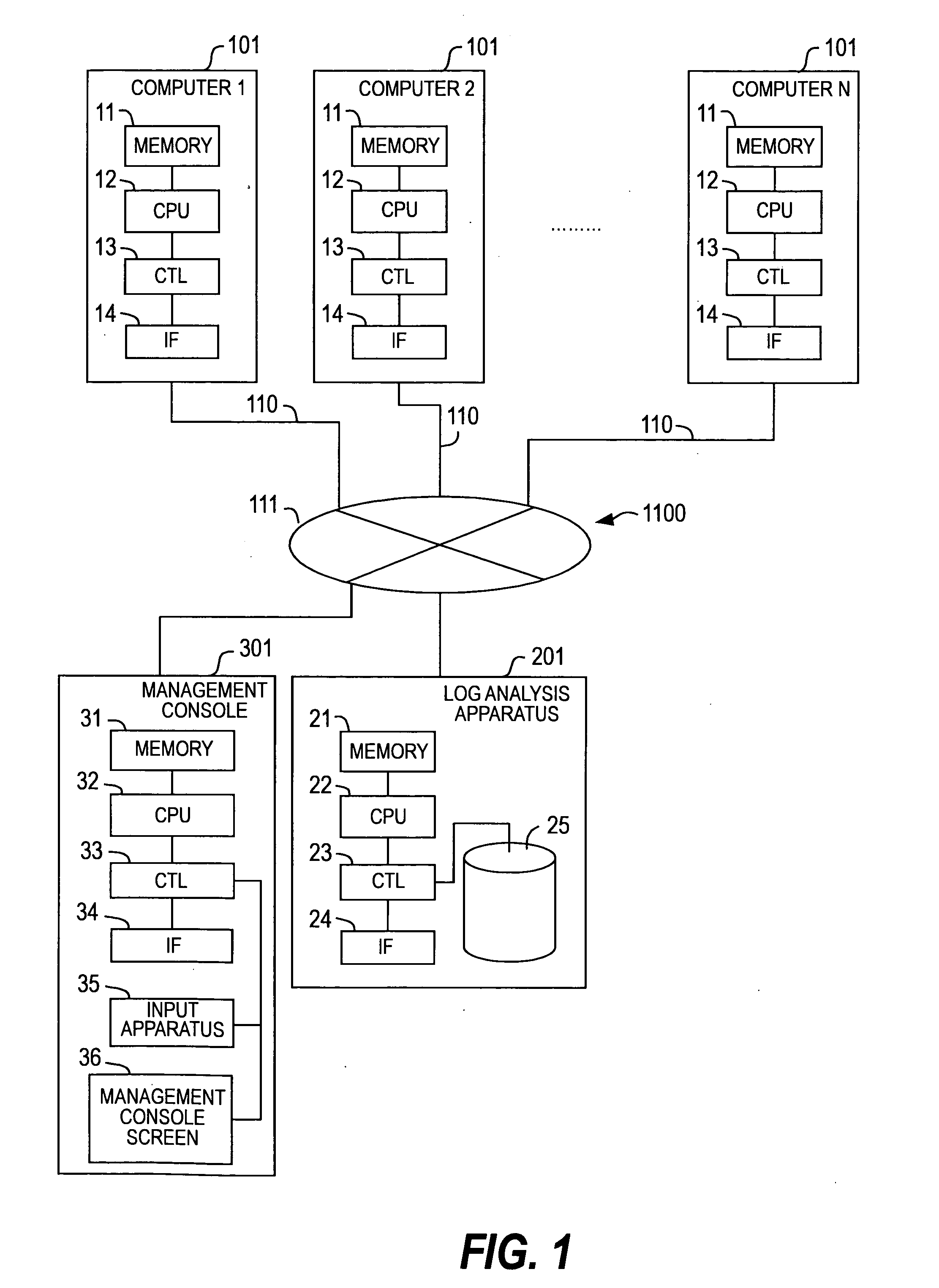
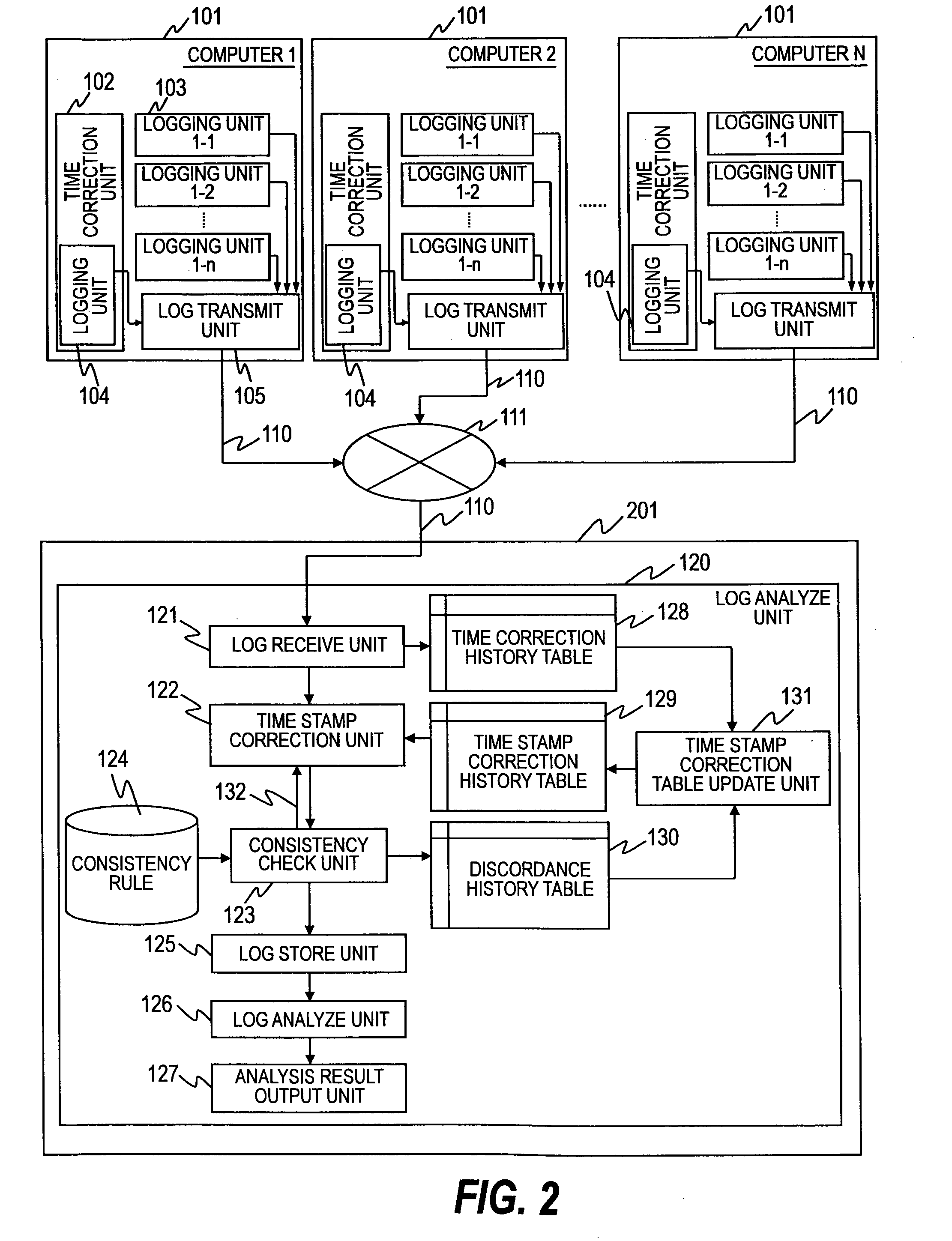
Method for analyzing data and data analysis apparatus
InactiveUS20080263105A1Avoid discontinuitiesAccurate understandingDigital data processing detailsTransmissionAnalysis dataData profiling
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for converting flat video to tridimensional video based on bidirectional tracing and characteristic points correction
InactiveCN101287142AGuaranteed conversion effectHigh degree of automationImage analysisSteroscopic systemsStereoscopic videoKey frame
The invention relates to a method for converting a plane video to a stereoscopic video, based on bidirectional tracking and characteristic dot correction, which pertains to the multimedia technical filed of computers. The method comprises the steps as follows: a whole plane video sequence is divided into subsequences which have relevant contents; a frame is appointed as a key frame; foreground object segmentation is carried out to the key frame, and corresponding depth maps and profile feature points are extracted; bidirectional tracking is carried out to obtain the profile feature points of a non-key frame; the profile feature points that do not meet the motion consistency rules is eliminated; the position of each profile feature point in the collection of the profile feature points of the non-key frame is adjusted to be on the profile of a corresponding foreground object so as to obtain the collection of the profile feature points corresponding to each non-key frame of the video subsequences and recover the foreground object profile of the non-key frame, thus the depth map sequence of an original plane video sequence is obtained; finally, a stereoscopic video sequence corresponding to the original plane video sequence is obtained. Based on the key frame, the method obtains the high-precision depth map of the video sequence, thus well realizing the conversion from the plane video to the stereoscopic video.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Distributed cache coherence at scalable requestor filter pipes that accumulate invalidation acknowledgements from other requestor filter pipes using ordering messages from central snoop tag
A multi-processor, multi-cache system has filter pipes that store entries for request messages sent to a central coherency controller. The central coherency controller orders requests from filter pipes using coherency rules but does not track completion of invalidations. The central coherency controller reads snoop tags to identify sharing caches having a copy of a requested cache line. The central coherency controller sends an ordering message to the requesting filter pipe. The ordering message has an invalidate count indicating the number of sharing caches. Each sharing cache receives an invalidation message from the central coherency controller, invalidates its copy of the cache line, and sends an invalidation acknowledgement message to the requesting filter pipe. The requesting filter pipe decrements the invalidate count until all sharing caches have acknowledged invalidation. All ordering, data, and invalidation acknowledgement messages must be received by the requesting filter pipe before loading the data into its cache.
Owner:AZUL SYSTEMS
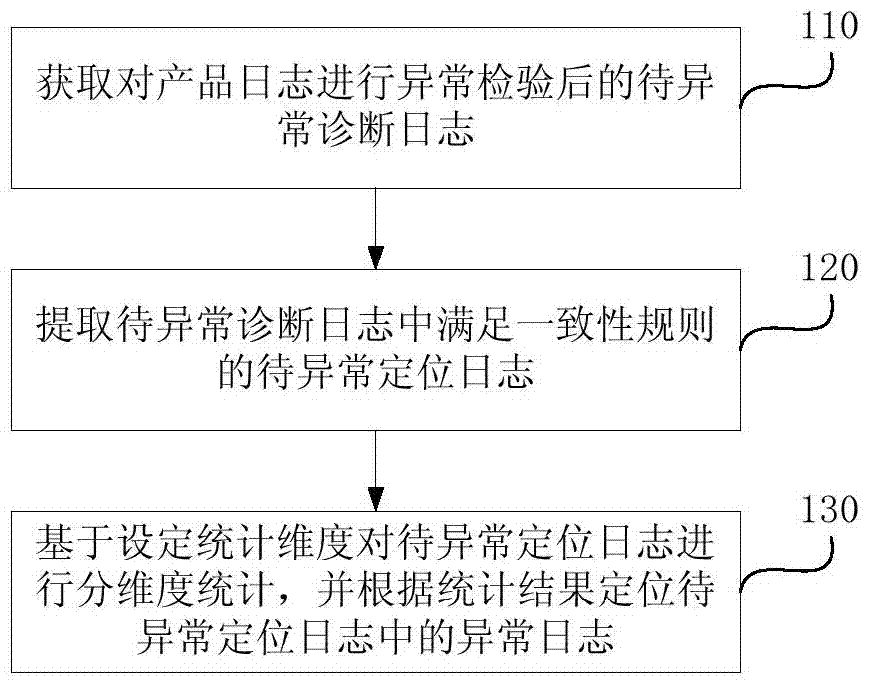
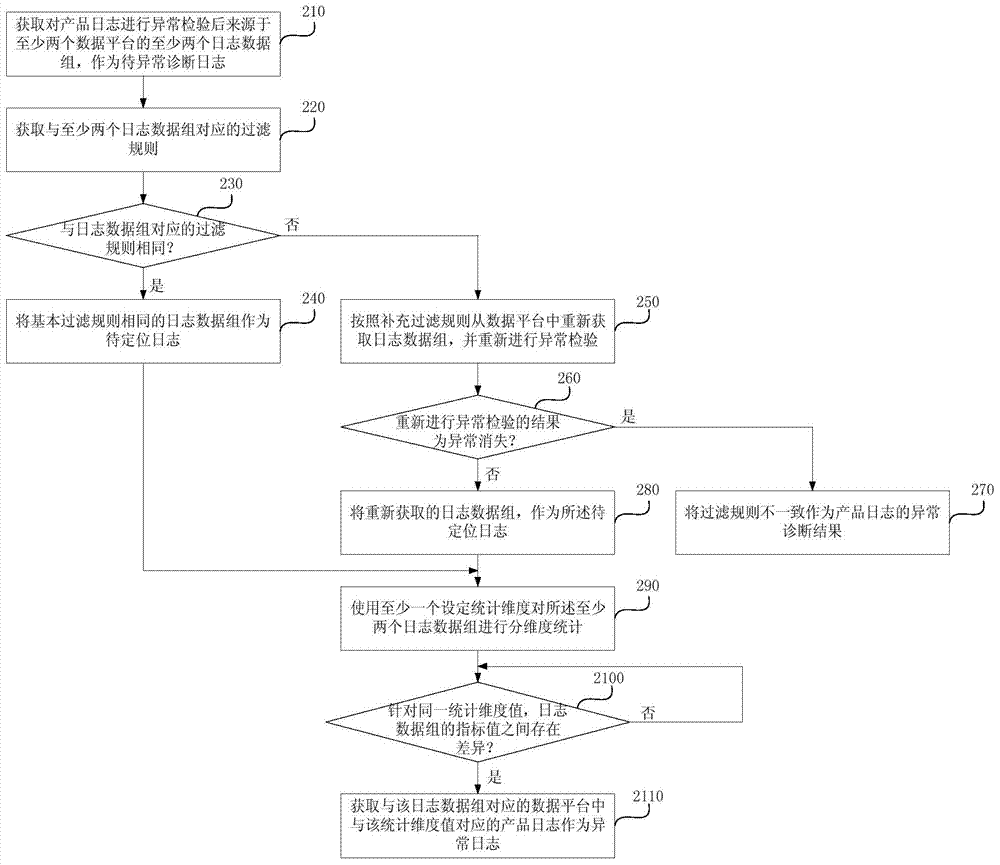
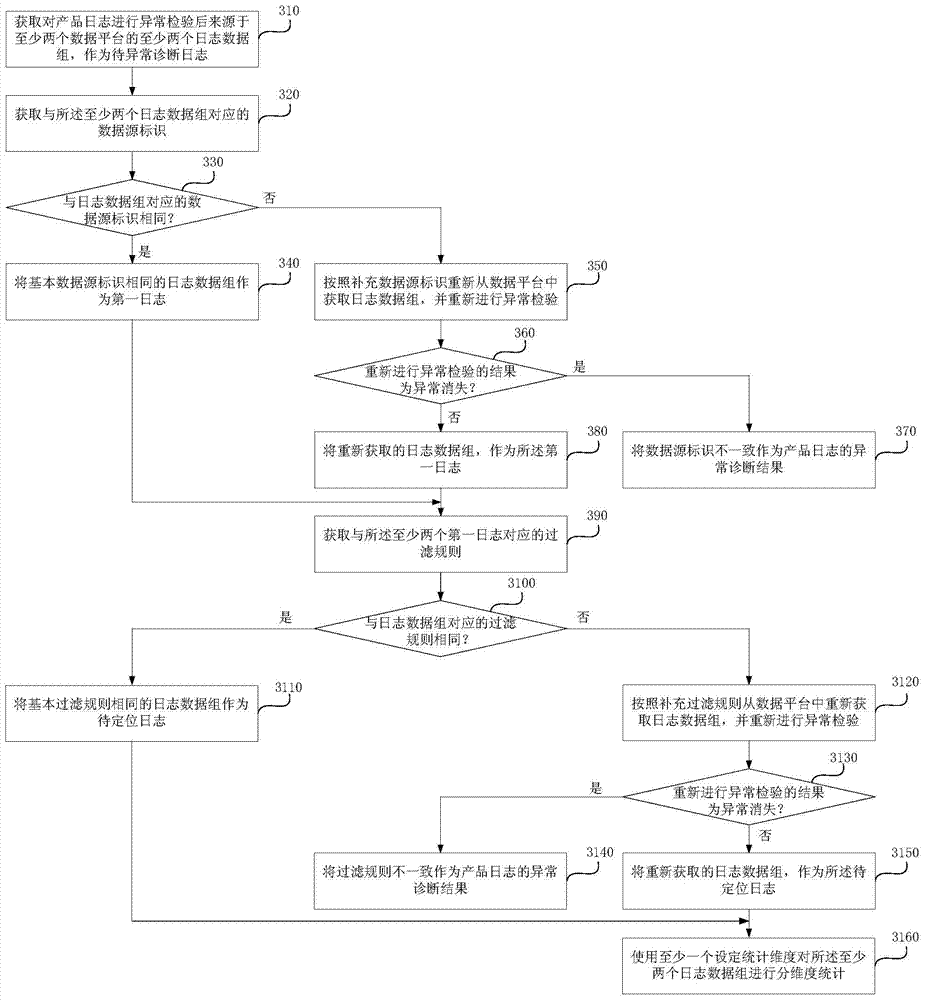
Abnormity diagnosis method and device of product logs
ActiveCN104268064AImprove work efficiencyReduce investmentHardware monitoringSpecial data processing applicationsDiagnosis methodsData mining
Owner:深圳太乐文化科技有限公司
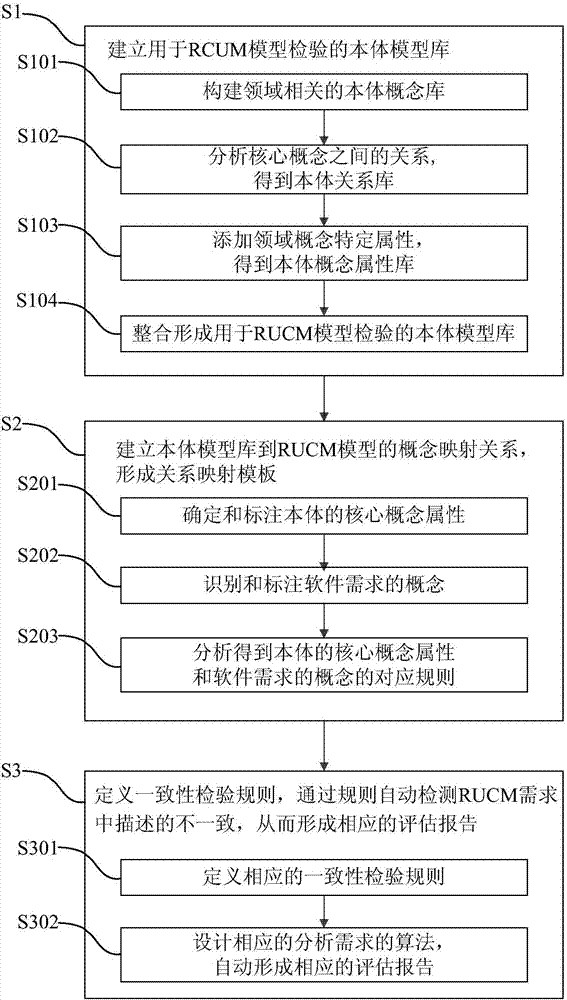
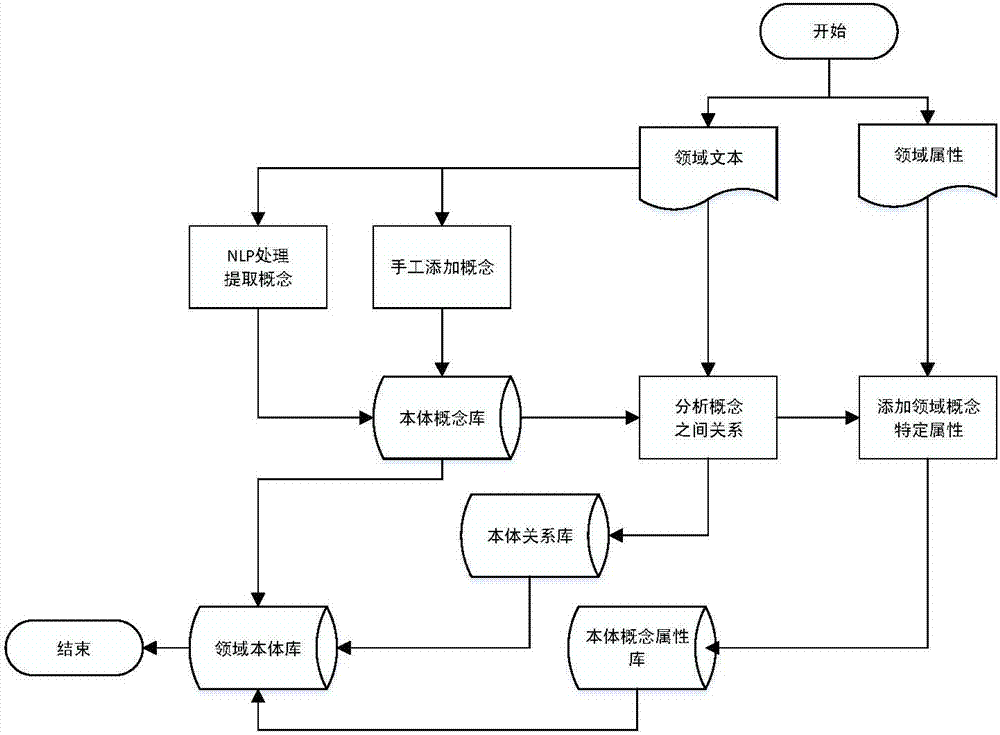
Consistency checking method for RUCM model based on body
The invention relates to a consistency checking method for an RUCM model based on a body. The method comprises the following steps: modeling domain knowledge to form a domain body model containing domain concepts, relations among the domain concepts and associated attributes of the domain concepts; with core concepts in a body library, establishing and analyzing mapping relations from related concepts in the body library to concepts of the RUCM model; and finally, checking a non-uniformity defect in the RUCM model according to the uniformity rule by definition. The RUCM model supporting checking of a body model is designed in an extended manner. An algorithmic tool for uniformity checking of the RUCM model is provided based on the body. The consistency checking method for an RUCM model based on the body has the following beneficial effects: non-uniformity is avoided when field knowledge is utilized for rapidly and efficient examination of demands; meanwhile, repeated labor is solved; and accuracy and integrality of demands are provided.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
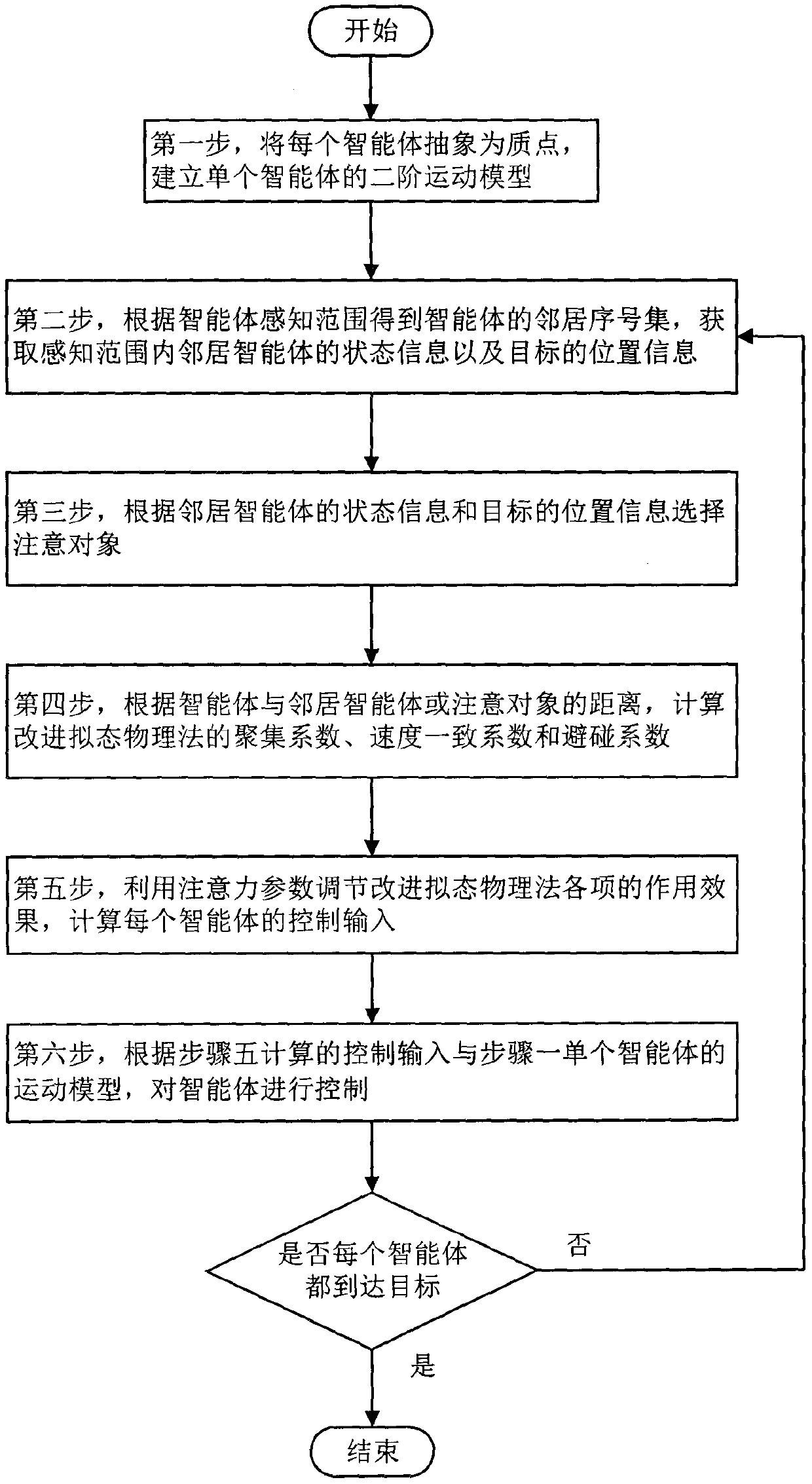
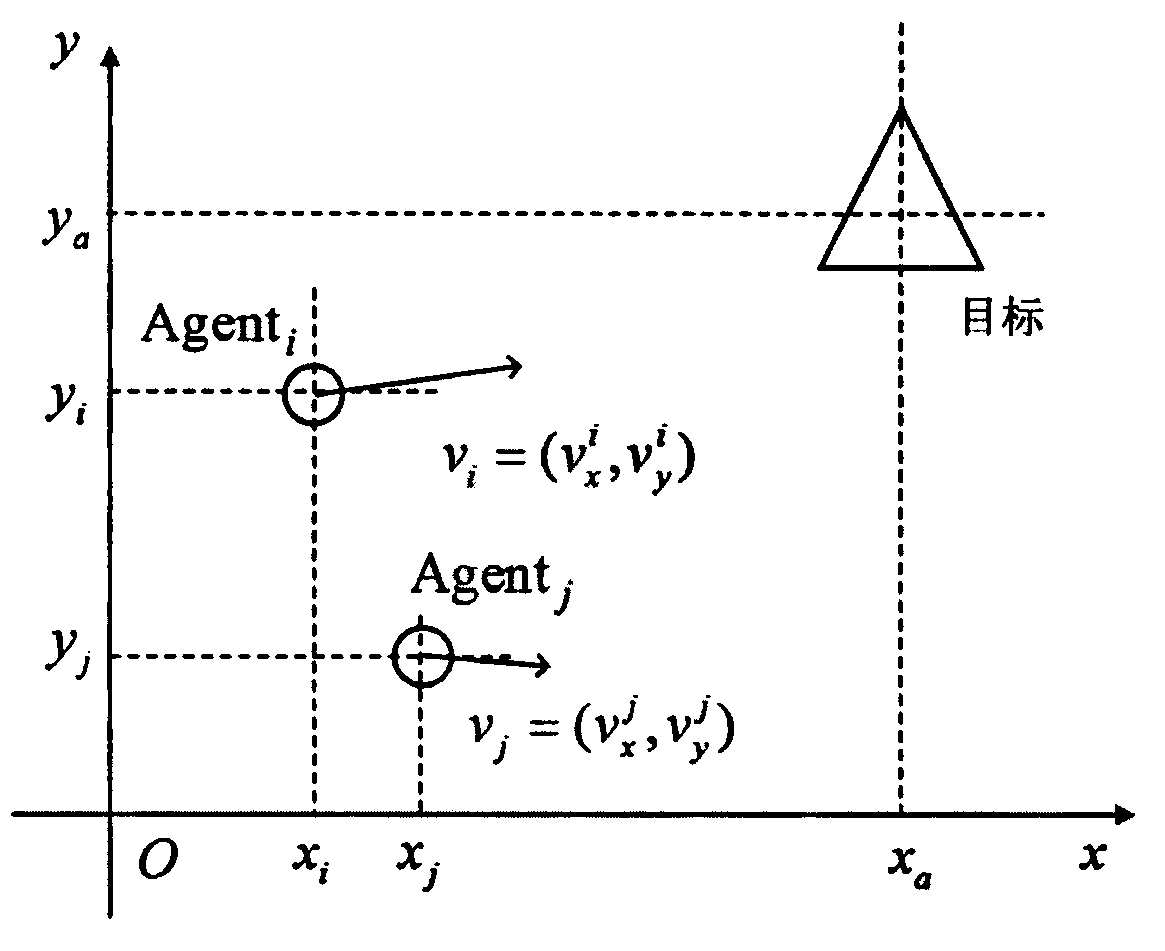
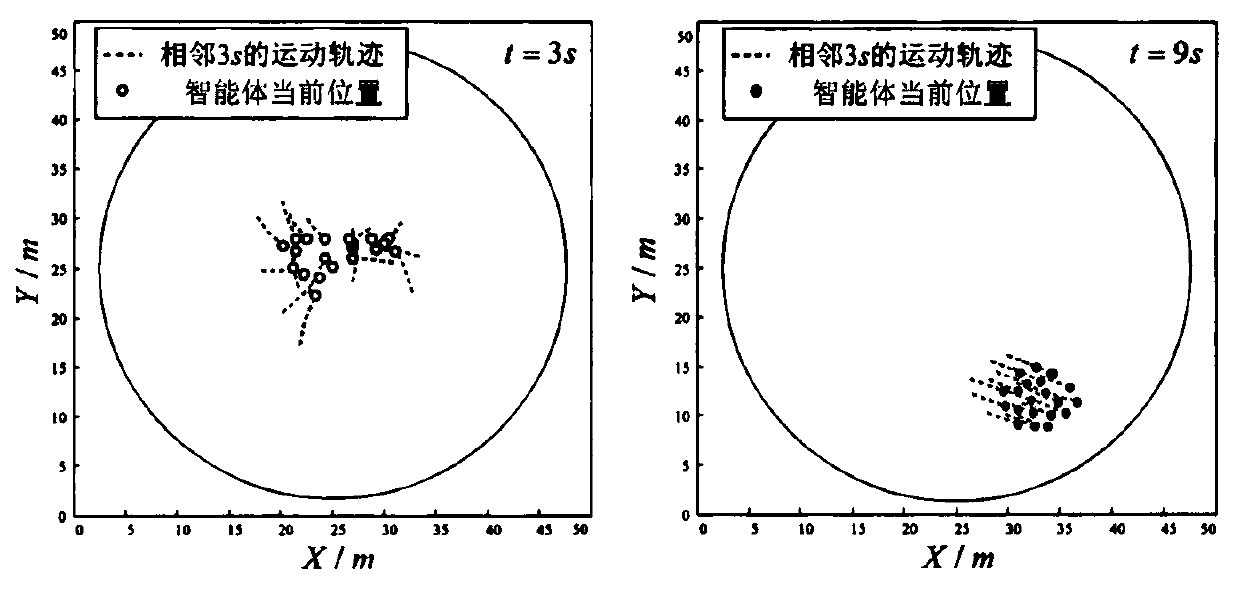
Multi-agent system motion control method based on improved physicomimetics
ActiveCN110275527AAchieving Gathering MovementSolve the boundary oscillation problemAutonomous decision making processPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimulationMulti-agent system
The invention discloses a multi-agent system motion control method based on improved physicomimetics, and relates to the field of multi-agent coordinated motion control. The method comprises the steps of: firstly establishing a motion model of a single agent, and describing the motion rules of the multiple agents by using a method of physicomimetic force; then, combineing the physicomimetics with classic cohesion, separation and speed consistency rules, and calculating a cohesion coefficient and a speed consistency coefficient by using the distance and the relative velocity speed; then, improving the effects of various items of the physicomimetics by attention parameter adjustment so that the agent selectively follow other agents or targets; finally, adjusting the motion of the agents through the improved physicomimetics so as to realize the cohesion motion, the speed consistency, and the group motion of the multi-agent system under a multi-objective environment. The method mainly solves the boundary oscillation of the classic multi-agent system motion control algorithm during the cohesion motion and the group motion problem of the multi-agent system in the multi-objective environment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
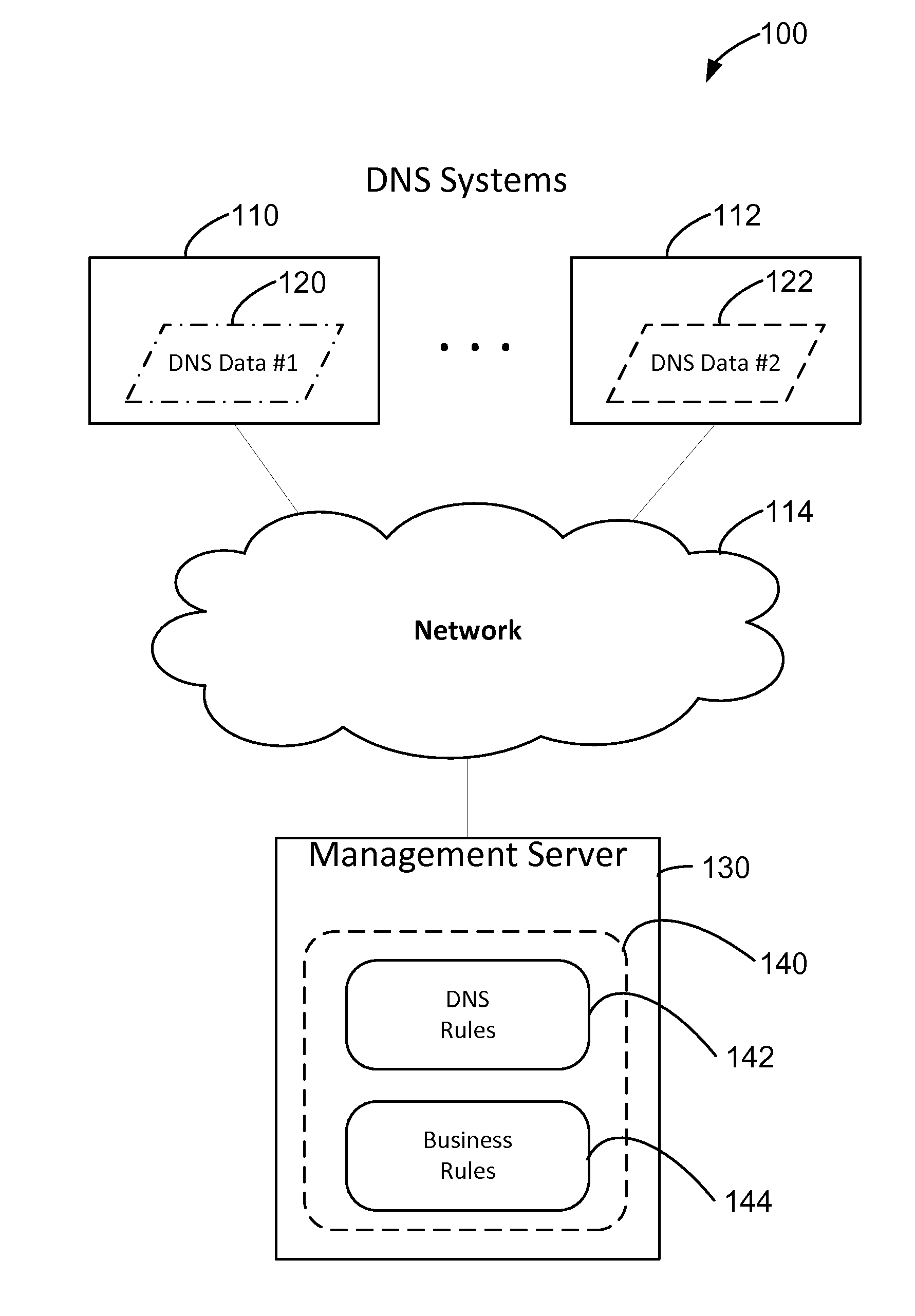
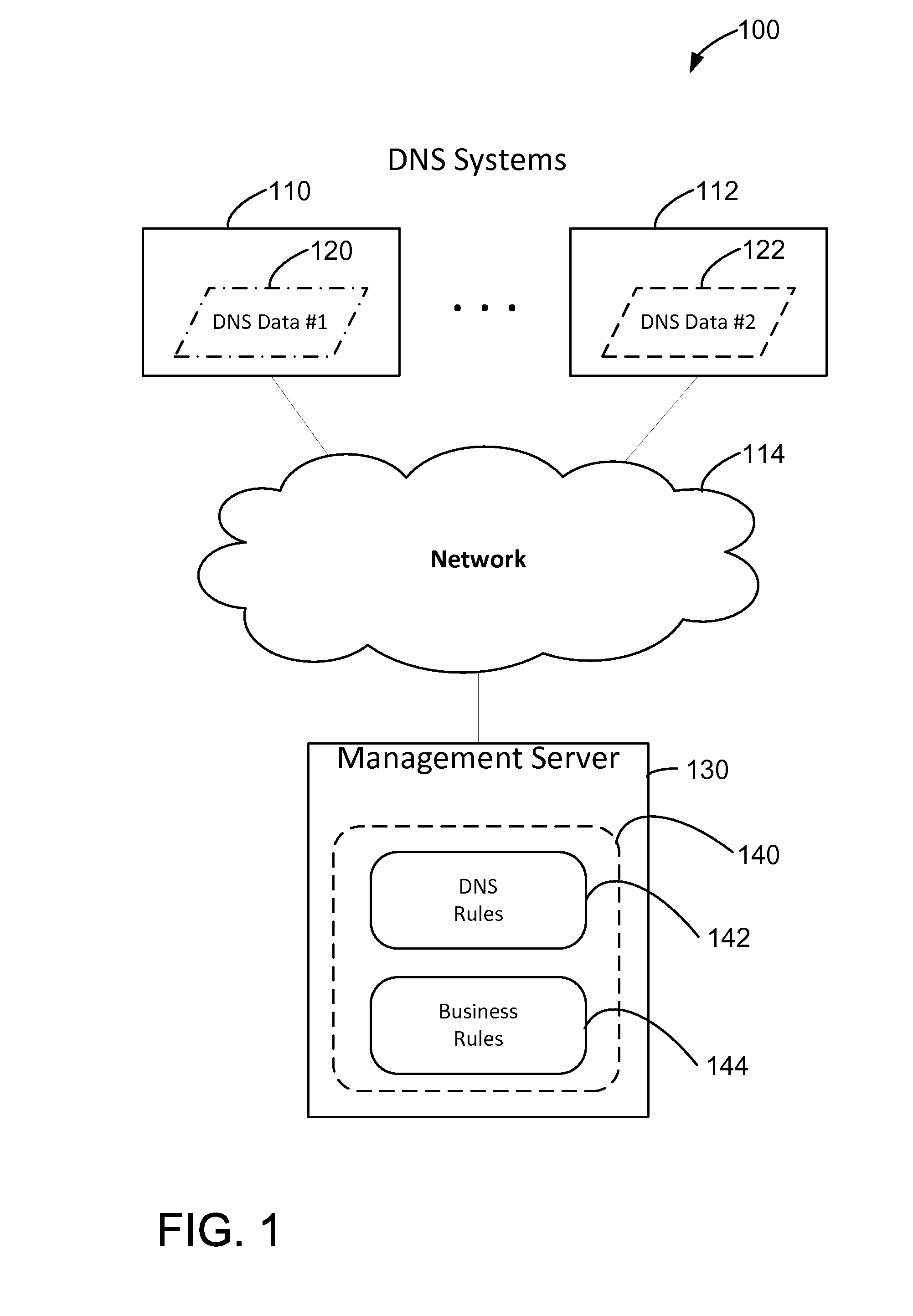
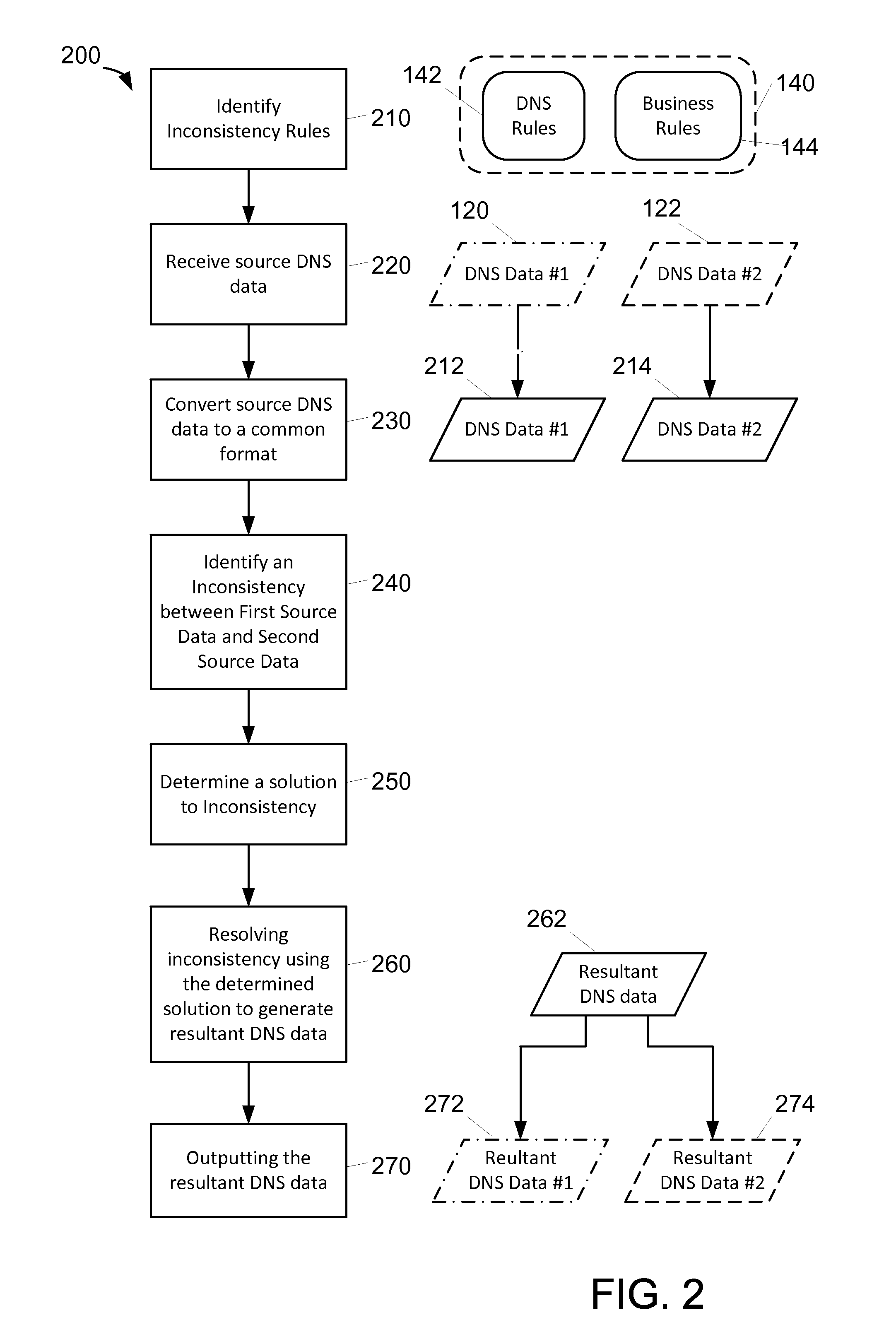
Systems and methods for resolving data inconsistencies between domain name systems
In one aspect, a computer-implemented method for managing Domain Name System (DNS) information is provided. The method uses a computing device having a processor and a memory. The method includes receiving, in the memory, source DNS data from a plurality of DNS systems including at least first source data from a first source system and second source data from a second source system. The method also includes identifying, by the processor, an inconsistency between the first source data and the second source data. The inconsistency includes an inconsistency type. The method further includes determining a solution to the inconsistency by applying one or more rules from a plurality of inconsistency rules based at least in part on the inconsistency type associated with the inconsistency. The method also includes resolving the inconsistency using the determined solution including generating resultant DNS data.
Owner:MASTERCARD INT INC
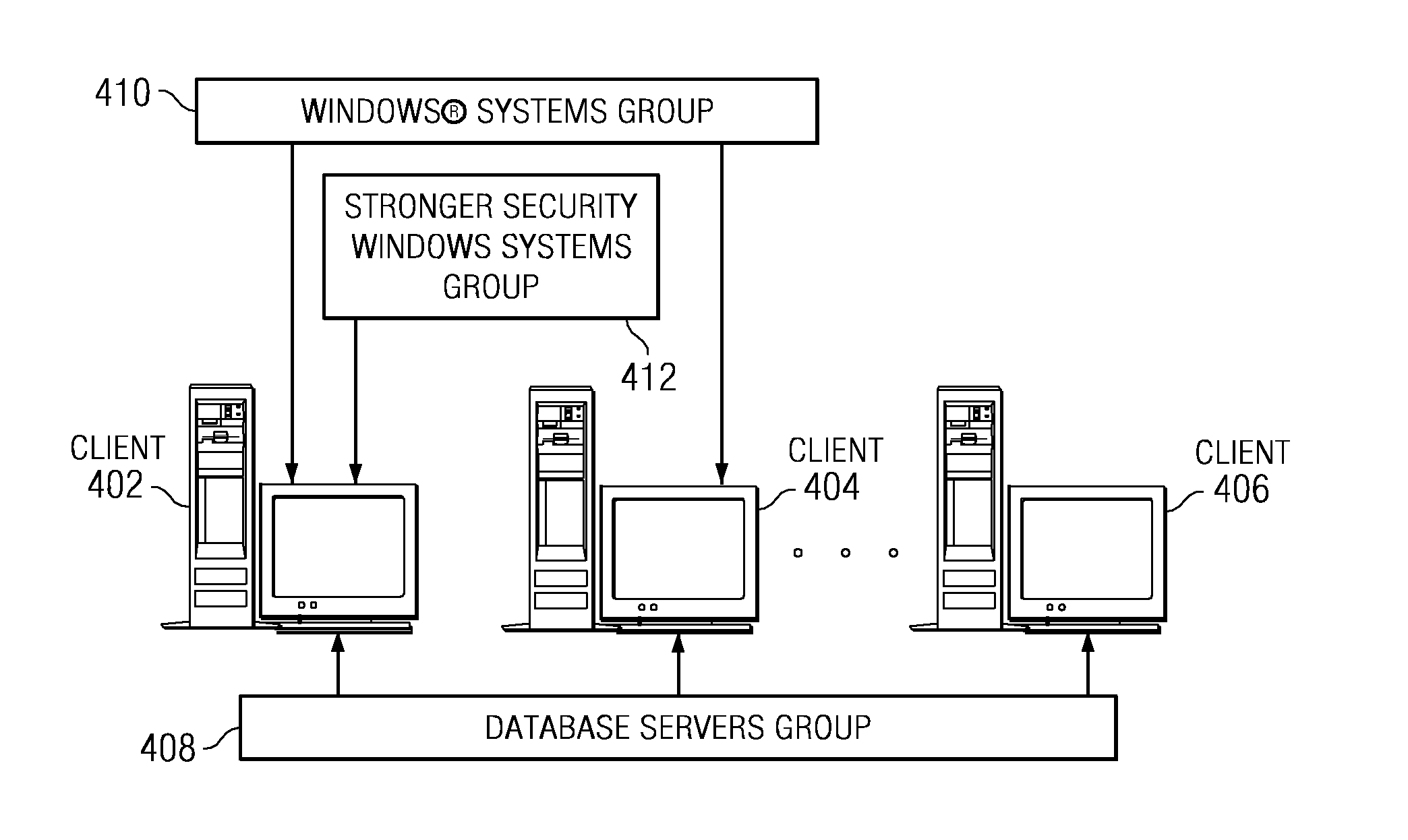
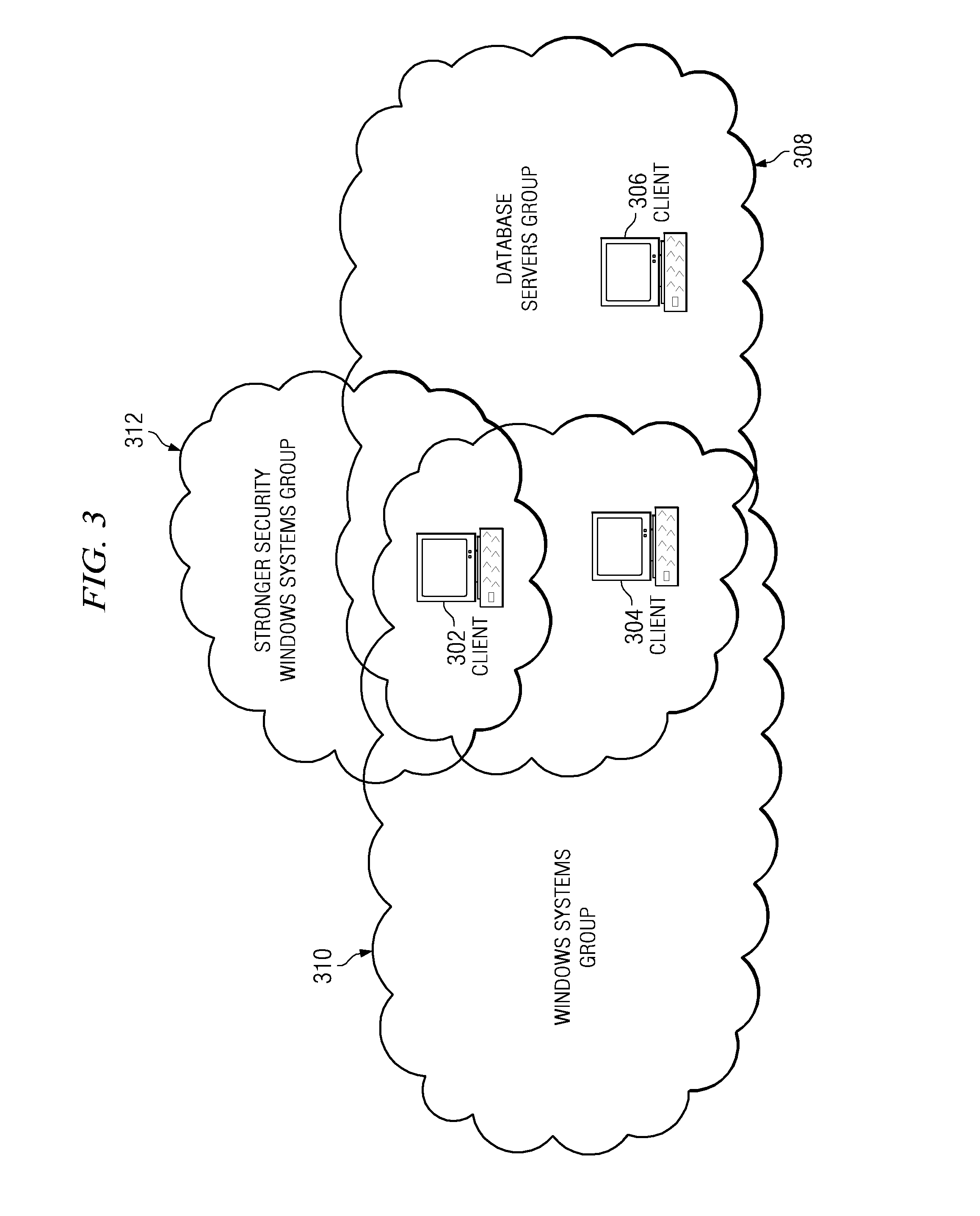
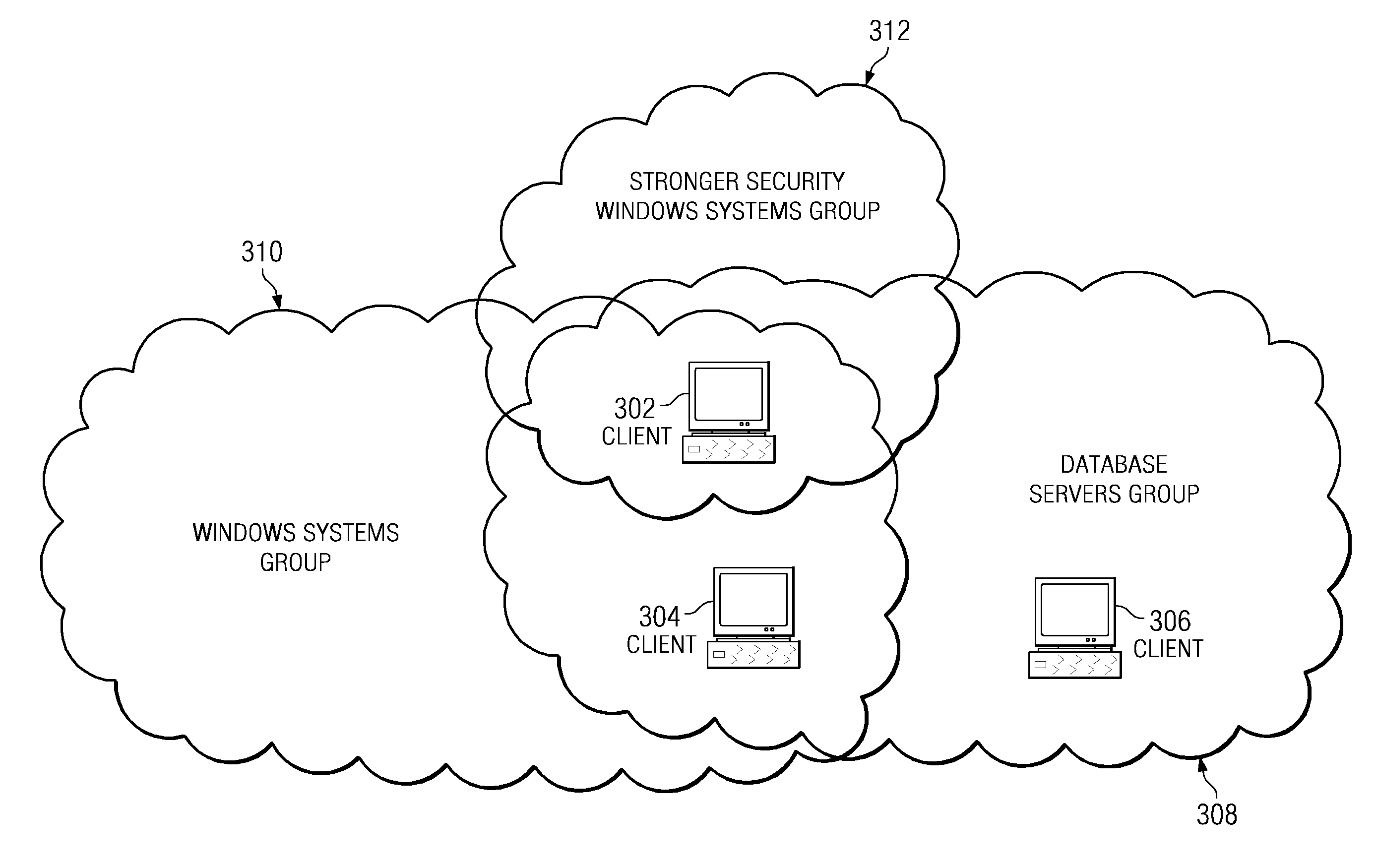
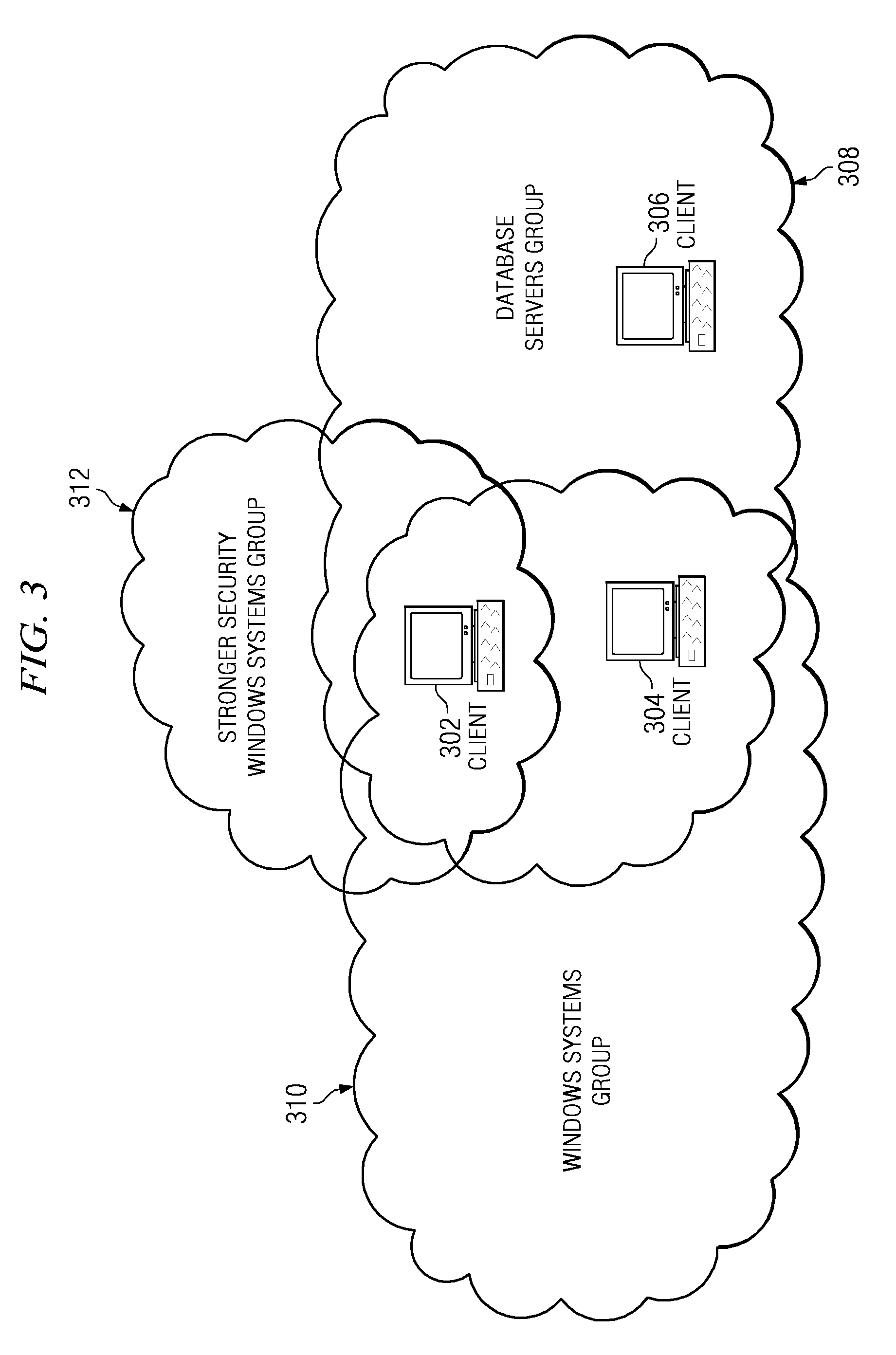
Applying compliance standards to a computer within a grouping hierarchy
InactiveUS20080120686A1Digital computer detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsData processing systemData mining
A computer implemented method, data processing system, and computer usable program code are provided for applying compliance standards to a set of computers. A set of computer groupings containing the set of computers is identified. Each computer in the set of computers is included in at least one computer group in the set of computer groupings. A set of compliance rules is identified for each of the set of computer groupings. Configuration information for the set of computers is acquired and the configuration information for each of the set of computers is compared to the set of compliance rules for each of the set of computer groupings to which each computer in the set of computers is included. Compliance results are generated for each computer in the set of computers.
Owner:LINKEDIN
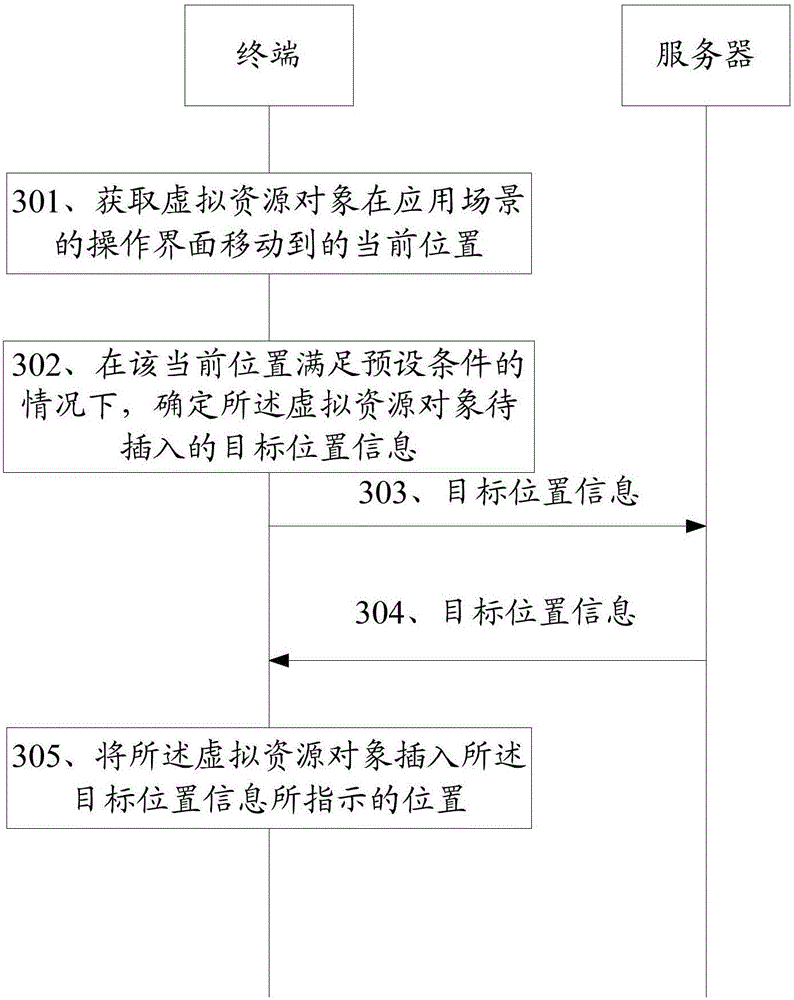
Insertion method of virtual resource object in application, and terminals
InactiveCN106598433AAccurate insertionImprove experienceVideo gamesInput/output processes for data processingComputer terminalConsistency rules
Embodiments of the present invention disclose an insertion method of a virtual resource object in an application, and terminals. Through adoption of the method and terminals, a user can insert the virtual resource object accurately and conveniently, so that the user experience is improved. The method comprises the steps that the terminal acquires a current position of the virtual resource object in an operation interface of an application scenario; if the current position meets a preset condition, the terminal determines information of a target position in which the virtual resource object is to be inserted; the terminal sends the information of the target position to a server; the terminal receives the information of the target position sent by the server, wherein the information of the target position is sent after the server determines that the information of the target position passes verification of a consistency rule; and the terminal inserts the virtual resource object in a position indicated by the target position.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
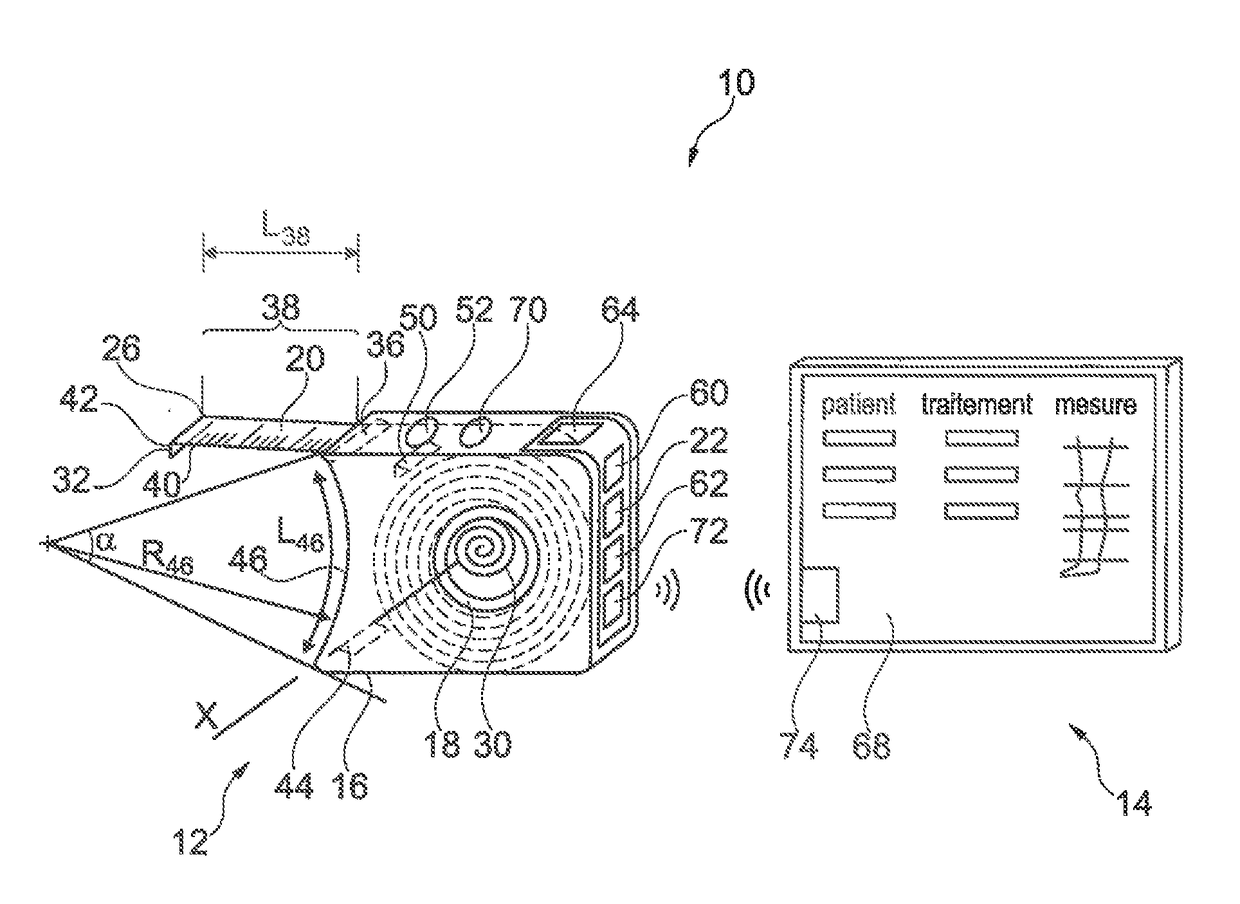
Device for taking a measurement
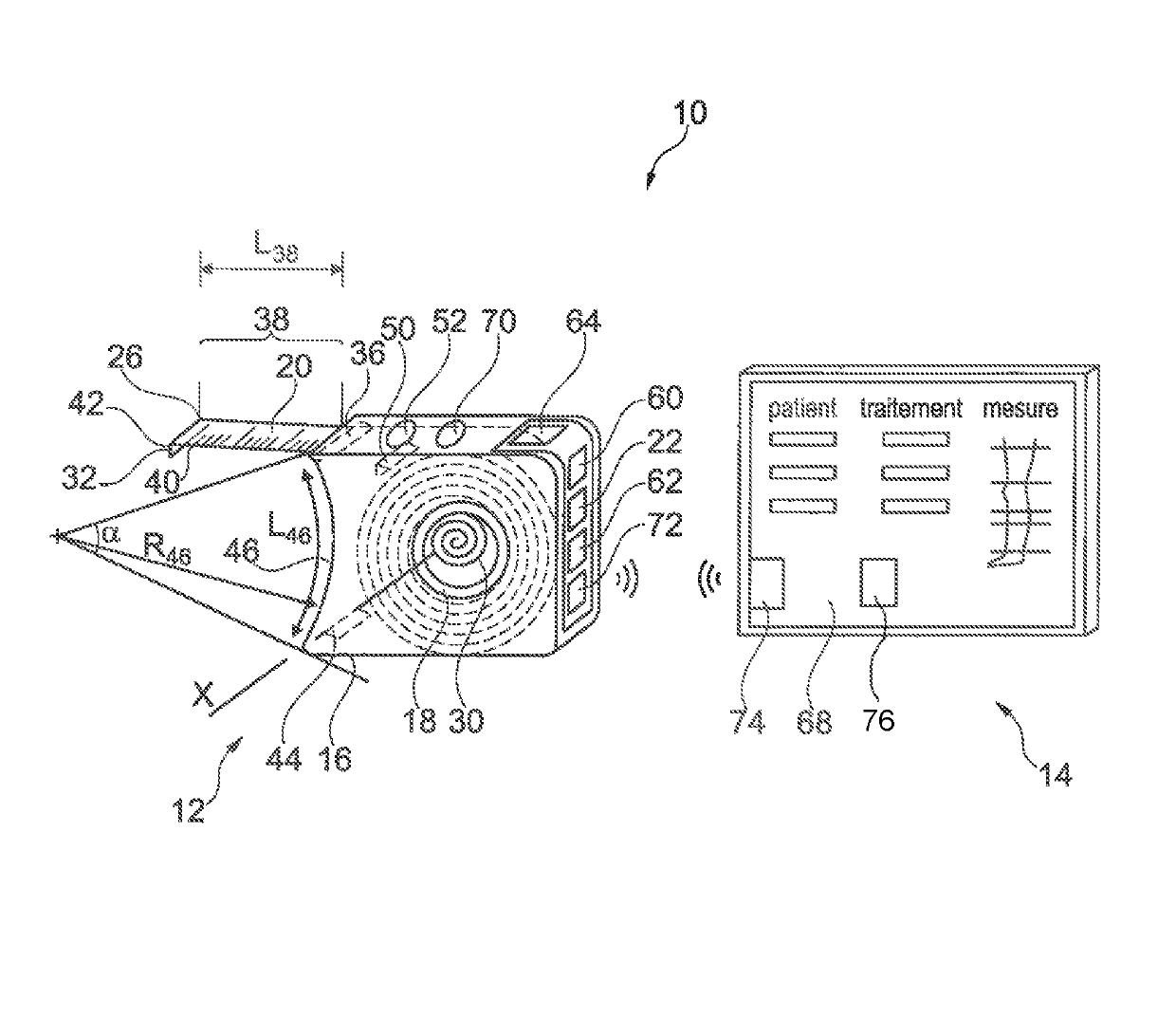
ActiveUS20170360331A1SensorsConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyComputer moduleConsistency control
A device for taking a measurement of a dimension of a part of the body of a patient, includes: an electronic tape measure having a portable housing, a winder accommodated in the housing, a tape which is partially wound on the winder and of which a portion, called the “unwound portion”, extends outside the housing, and a measuring module for a measurement, relative to the unwound portion; a consistency control module for checking the consistency of the measurement by at least one consistency rule and at least one context datum; and an alert module for delivering an alert if an inconsistency is detected by the consistency control module.
Owner:LAB INNOTHERA SAS
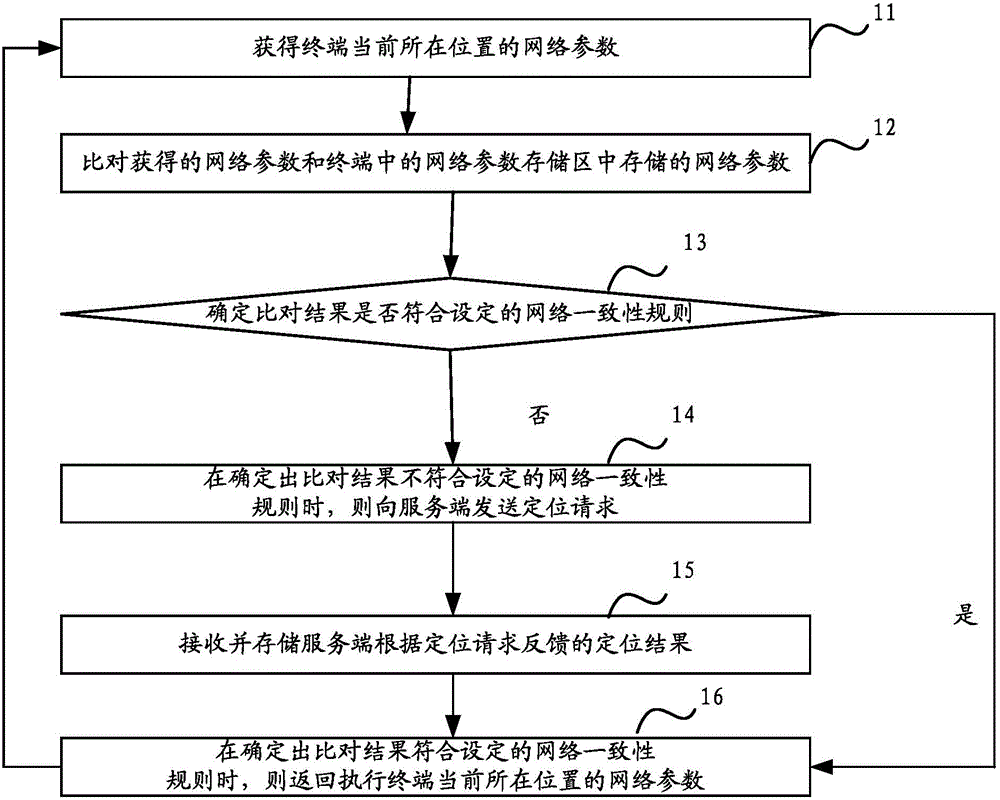
Positioning monitoring method and device
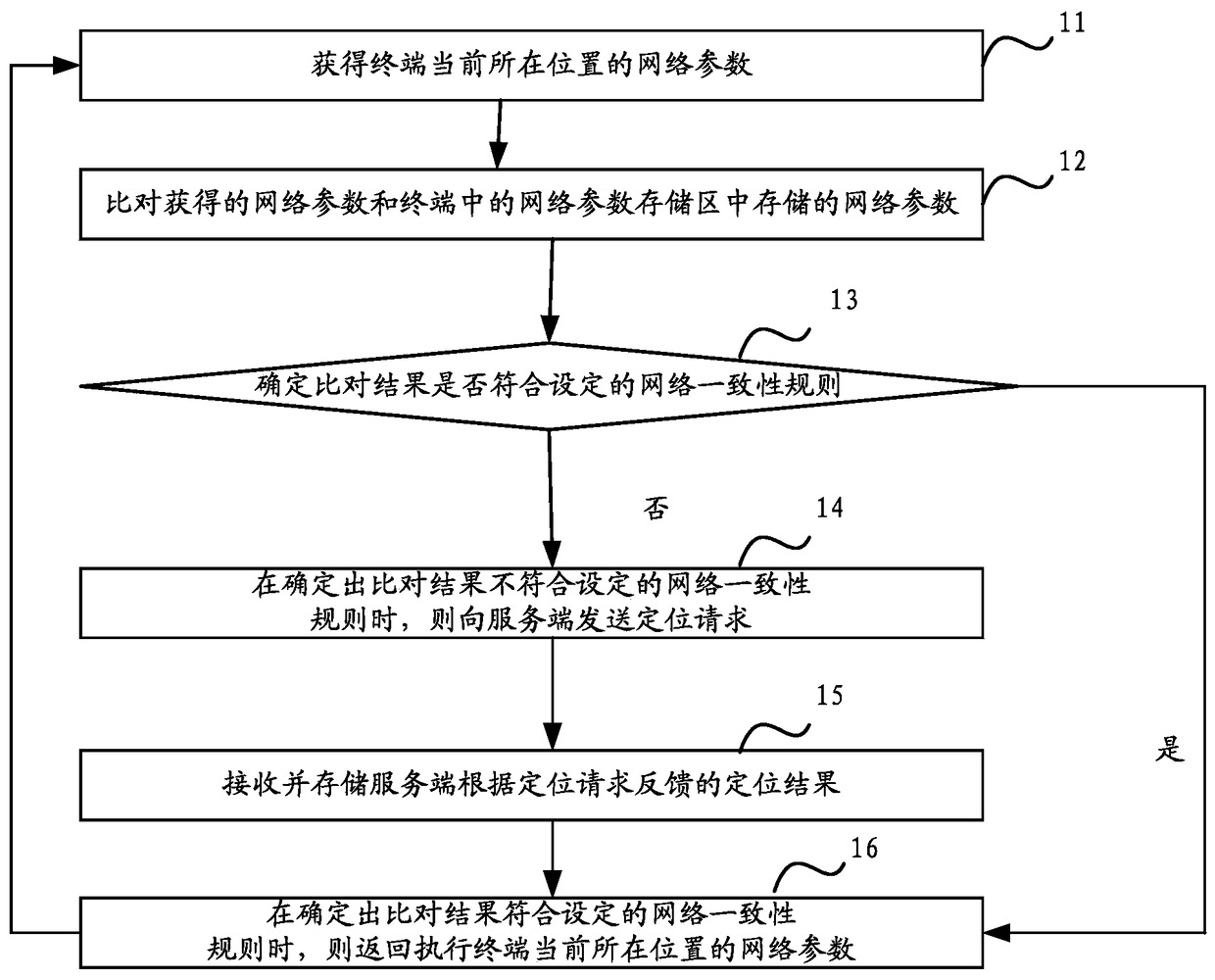
ActiveCN104703214AGuaranteed real-timeGuaranteed validityWireless communicationConsistency rulesServer-side
The invention discloses a positioning monitoring method and device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the network parameter of the current position of a terminal; comparing the acquired network parameter with a network parameter stored in a network parameter storage region in the terminal; when a comparison result is determined to be inconsistent with a set network parameter consistency rule, sending a positioning request to a server side, wherein the network parameter consistency rule indicates whether or not the difference value of the network parameter varying due to position variation of the terminal is within a set range; and receiving and storing a positioning result fed back by the server side according to the positioning request. The type of the sent positioning request and the content of the request can be determined according to a current network state, so that the positioning monitoring efficiency is increased.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Method for analyzing data and data analysis apparatus
InactiveUS7809681B2Eliminate time lagAvoid discontinuitiesDigital data processing detailsTransmissionAnalysis dataData profiling
Owner:HITACHI LTD
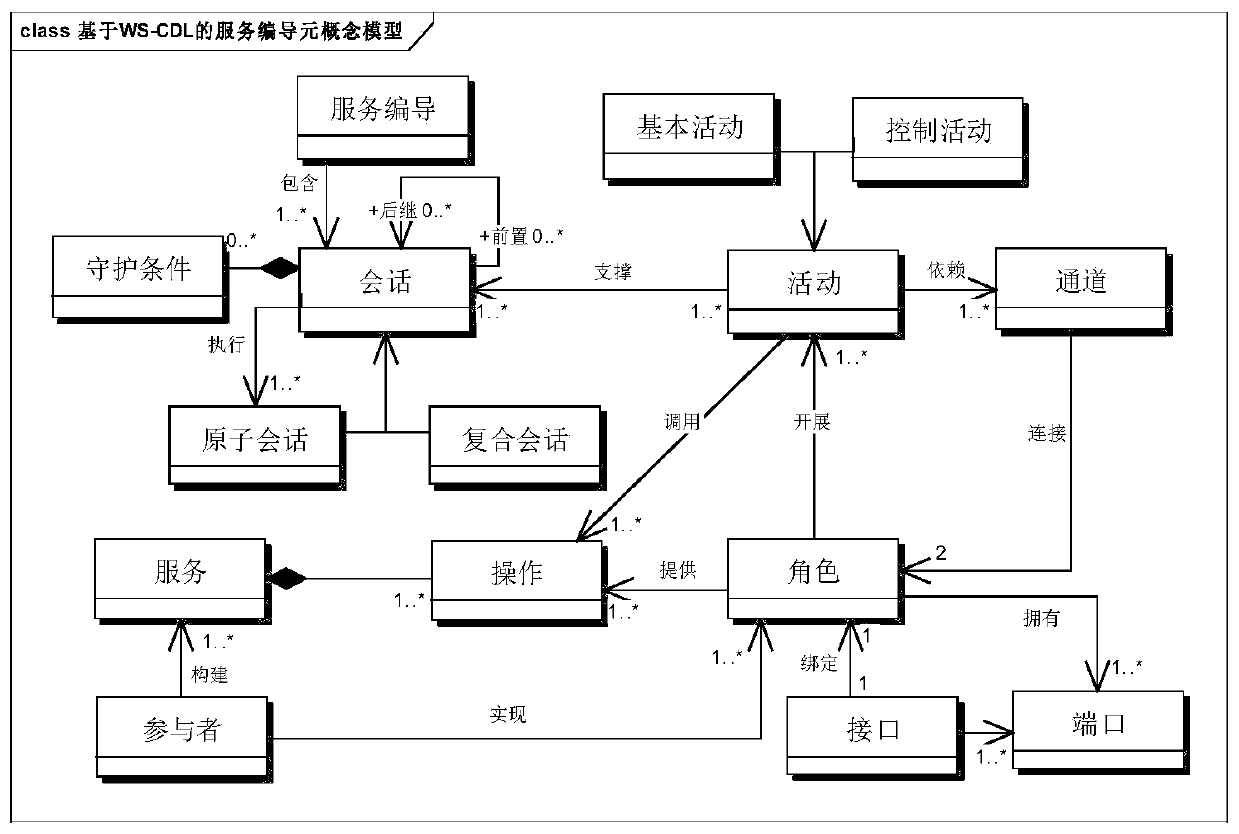
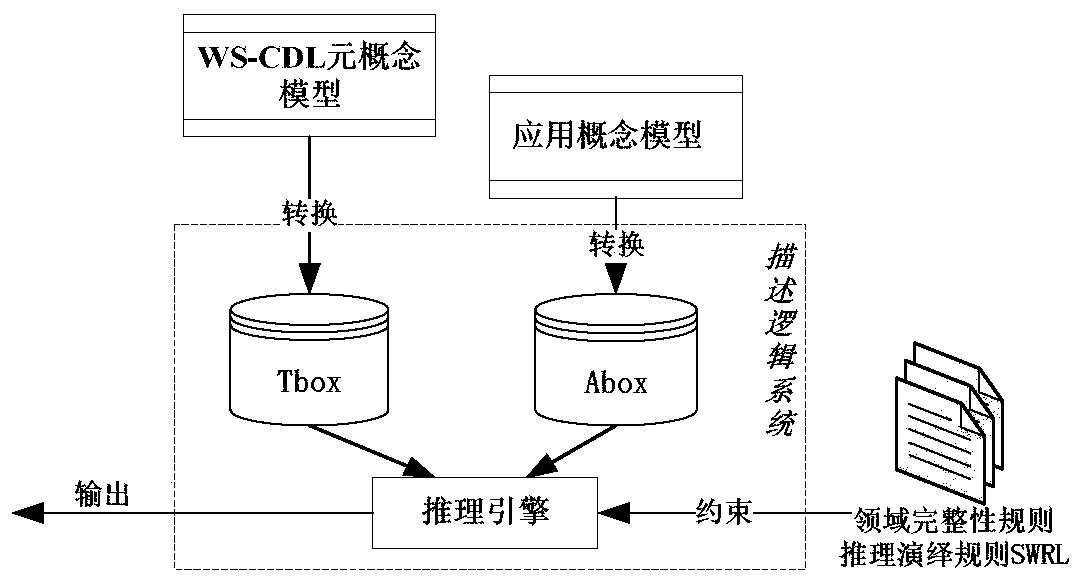
A service compilation model formalized verification method based on description logic
InactiveCN109784491AWith multiplexingCapable of describingOffice automationInference methodsSystem verificationValidation methods
The invention discloses a service compilation model formalized verification method based on description logic. The method comprises the steps of defining a WS- CDL based service compilation element concept models and domain rules, wherein the service compilation element concept models comprise service compilation elements and element relation sets, and the domain rules comprise consistency rules,integrity rules and deductive reasoning rules; Establishing an application concept model by combining the service compilation element concept model according to the service cooperation requirements ofthe users; According to the verification method based on the SHOIND, a service compilation element concept model, an application concept model and a field rule are converted, and data consistency andintegrity verification and rule-based reasoning verification are achieved. The method has the description capability, the automation degree and the verification efficiency of a traditional system verification method, does not have the problem of state explosion, and also has obvious advantages in the aspects of reasoning decidability, knowledge reuse and the like.
Owner:ARMY ENG UNIV OF PLA +1
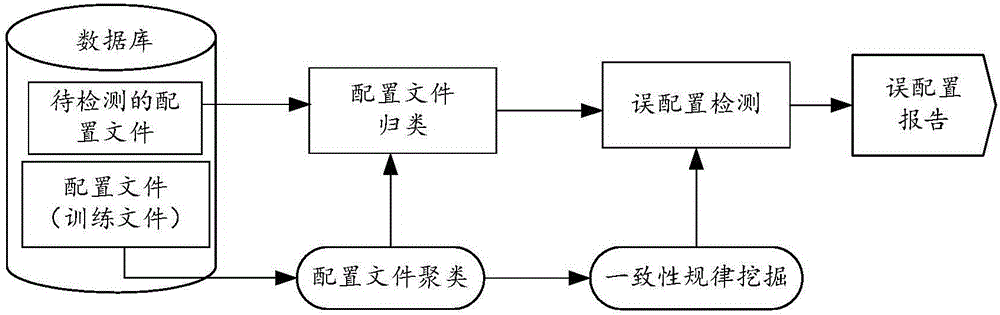
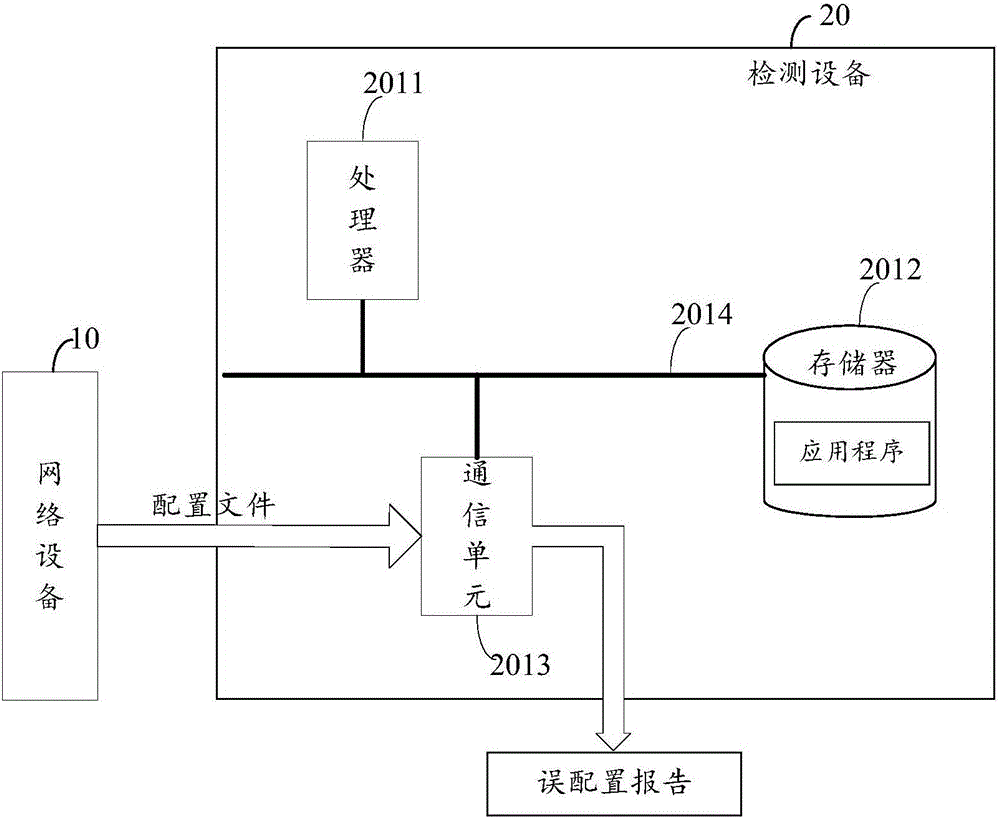
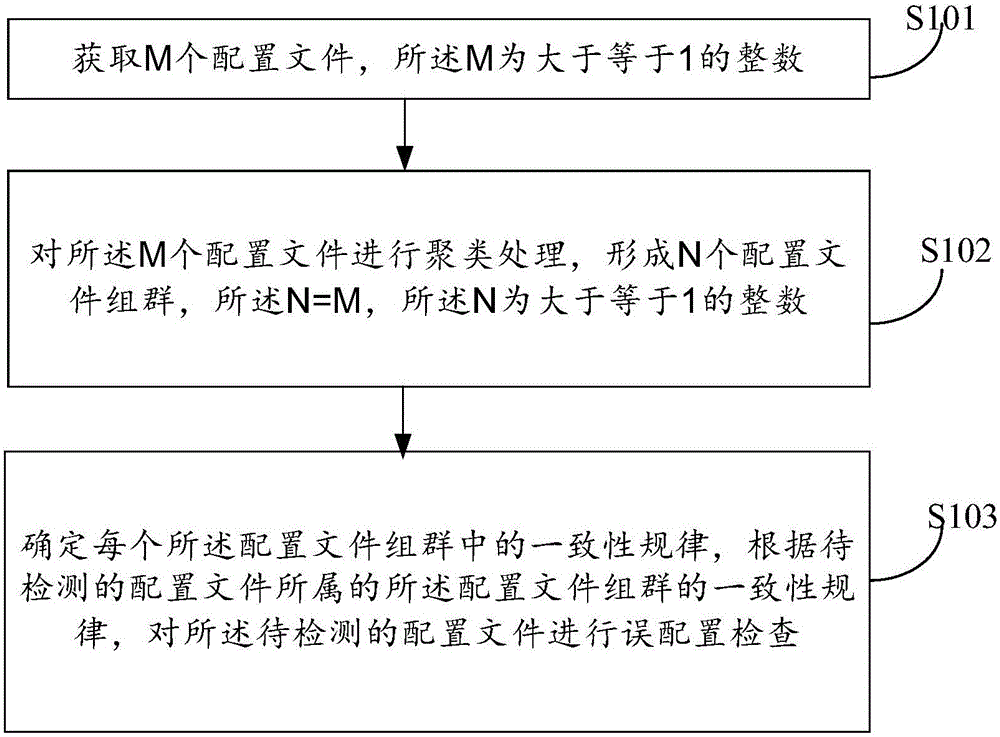
Mis-configuration detection method of network element equipment and detection device
ActiveCN105847065AImprove solution efficiencyImplement automatic detectionData switching networksNetwork managementData mining
The invention, which relates to the data mining and network management field, discloses a mis-configuration detection method of network element equipment and a detection device. Therefore, problems of low mis-configuration detection efficiency and flexibility due to investment of lots of manpower and time during the existing mis-configuration detection process can be solved. The method comprises: M configuration files are obtained; clustering processing is carried out on the M configuration files to form N configuration file groups; each configuration file group is processed and a consistency rule of each configuration file group is determined; and according to the consistency rule of the configuration file group which a to-be-detected configuration file belongs to, mis-configuration checking is carried out on the to-be-detected configuration file.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
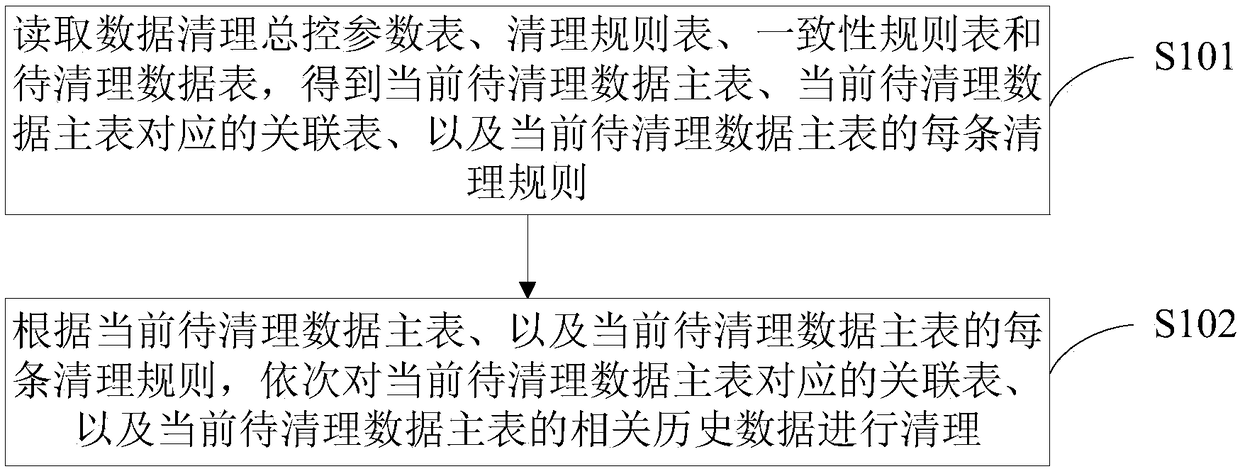
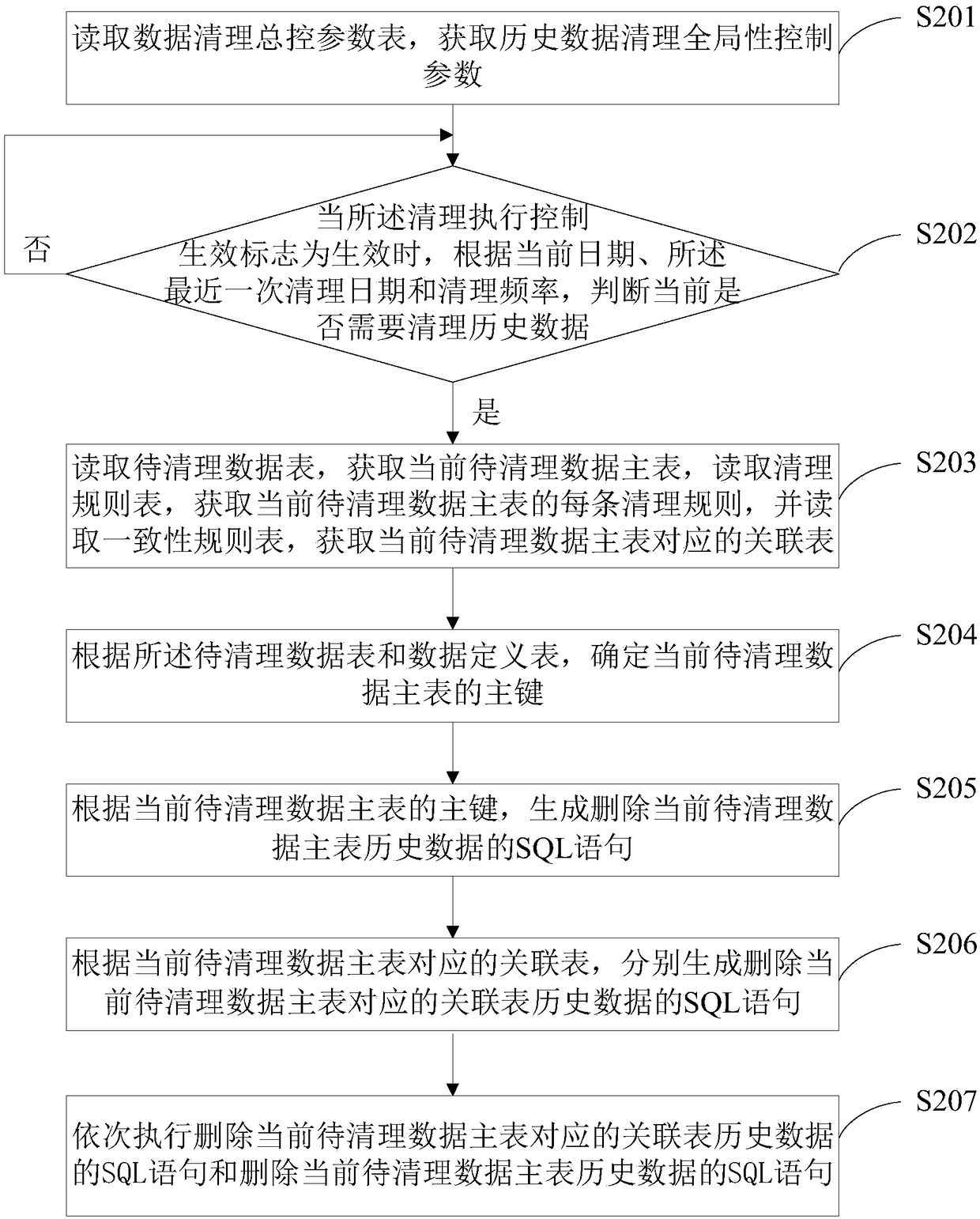
Automatic cleaning method and device for historical data
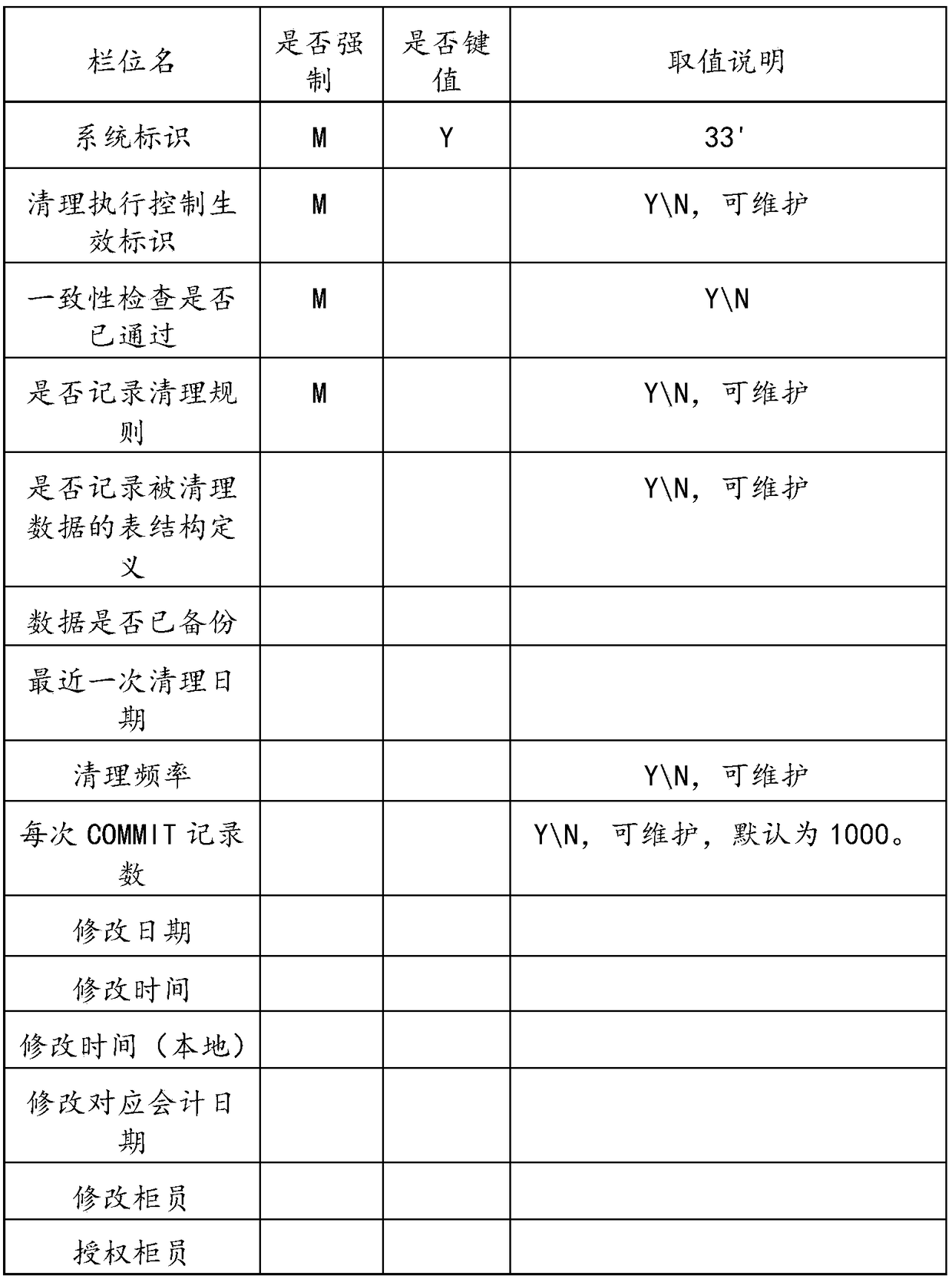
ActiveCN108319694AEnsure consistencySpecial data processing applicationsConsistency rulesControl parameters
The invention discloses an automatic cleaning method and device for historical data. The method comprises the steps that a data cleaning general control parameter list, a cleaning rule list, a consistency rule list and a to-be-cleaned data list are read to obtain a current to-be-cleaned data main list, an association list corresponding to the current to-be-cleaned data main list and each cleaningrule of the current to-be-cleaned data main list; according to the current to-be-cleaned data main list and each cleaning rule of the current to-be-cleaned data main list, relevant historical dada ofthe current to-be-cleaned data main list and association list corresponding to the current to-be-cleaned data main list is cleaned. According to a configurable cleaning rule, historical data is automatically cleaned, and the data consistency among the data lists is ensued during the cleaning of the historical data.
Owner:BANK OF CHINA
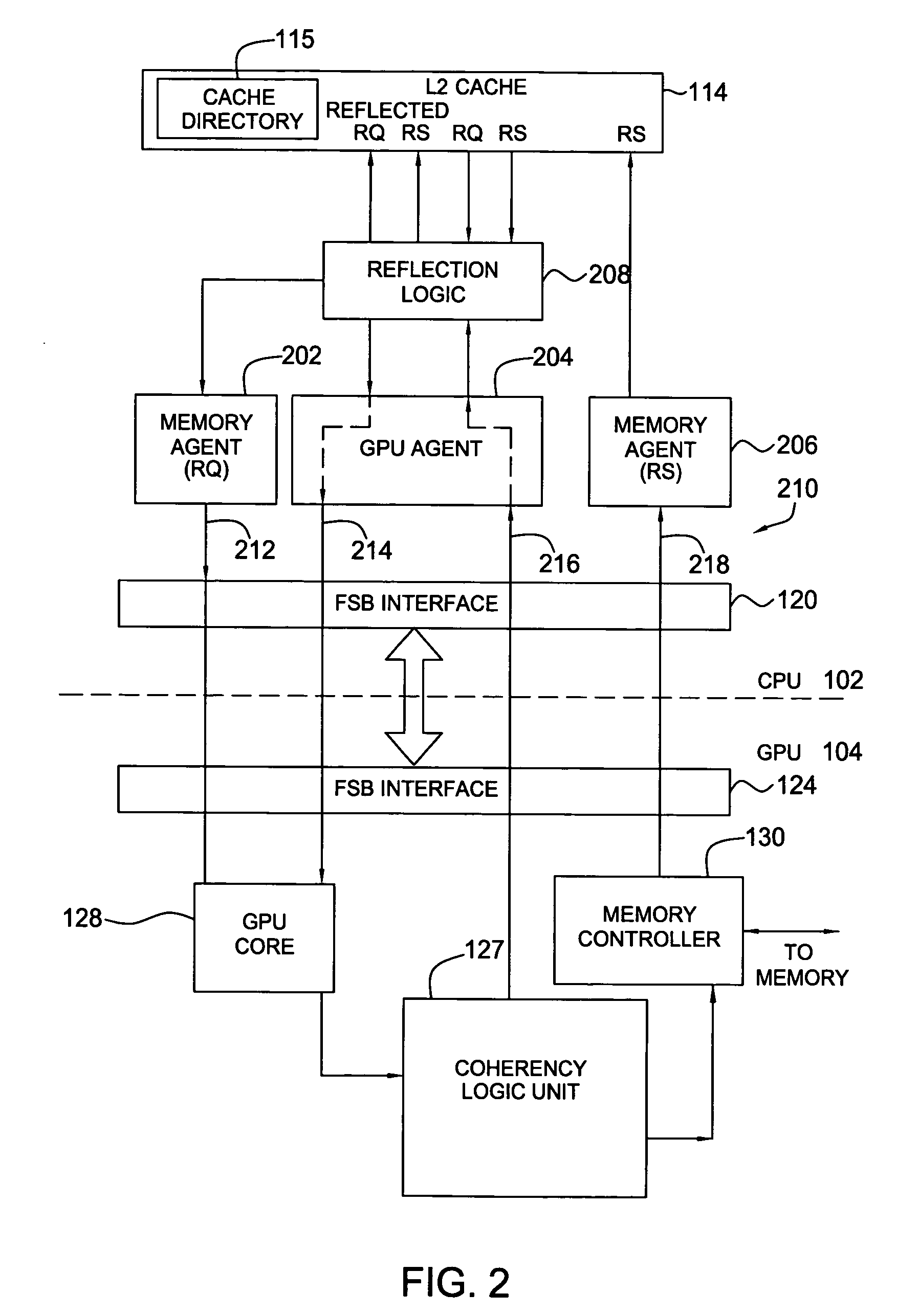
Technique to share information among different cache coherency domains
ActiveUS20120200585A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationImage memory managementGraphicsProcessing core
A technique to enable information sharing among agents within different cache coherency domains. In one embodiment, a graphics device may use one or more caches used by one or more processing cores to store or read information, which may be accessed by one or more processing cores in a manner that does not affect programming and coherency rules pertaining to the graphics device.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
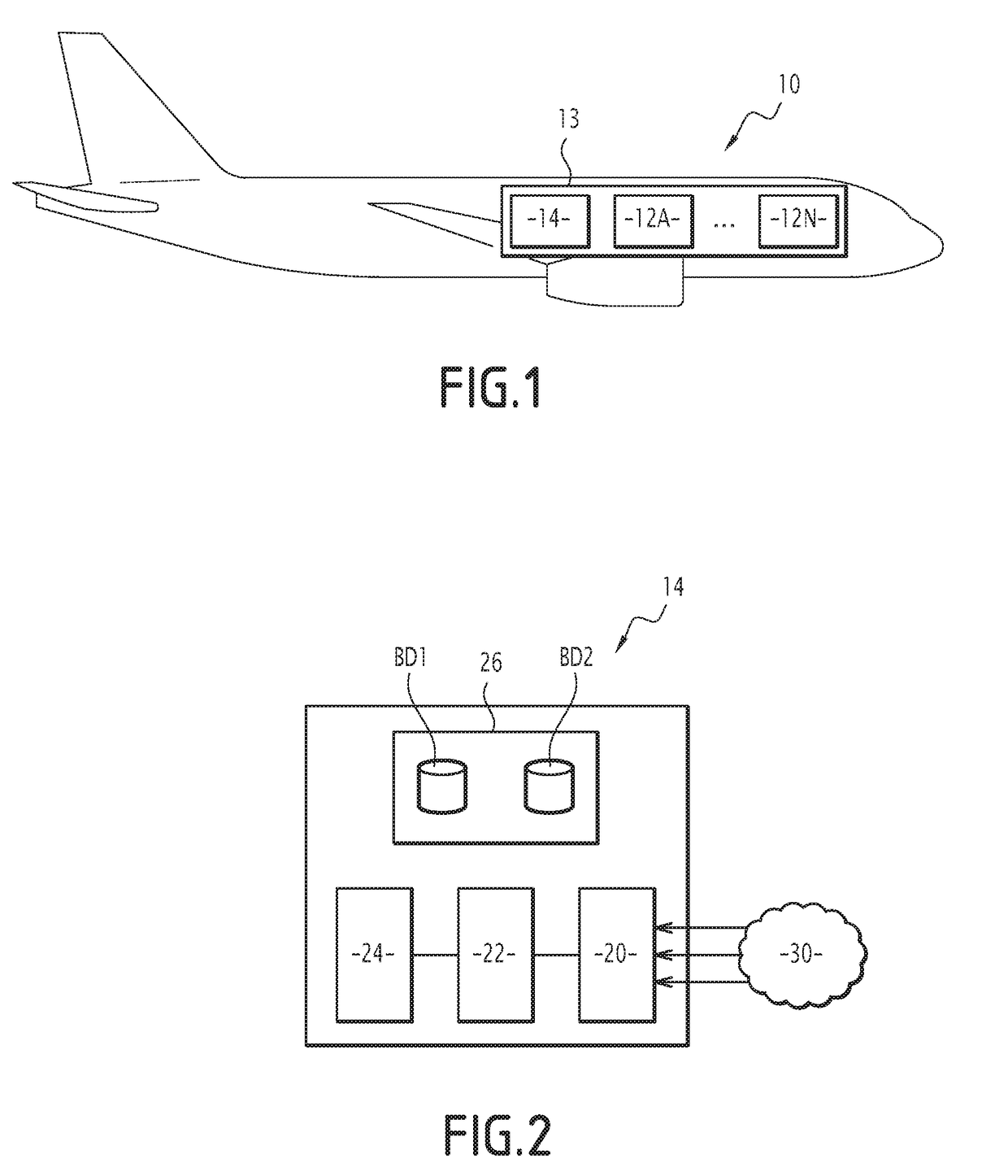
Method for testing the integrity of the avionics of an aircraft, associated device and computer program product
ActiveUS20190073841A1Optimization mechanismRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesElectric testing/monitoringAviationComputer science
A testing method including defining a plurality of test periods, and for each current test period collecting flight data from at least two separate avionics systems operating independently, analyzing consistency between the data collected during the previous test period, and / or between the data and flight data collected during an earlier test period, while verifying a plurality of predetermined consistency rules, and when at least one of these rules is not verified, generating an alert relative to a loss of integrity of the avionics.
Owner:THALES SA
An automatic calibration algorithm for multi-group multi-line laser radar
ActiveCN106872963BDisambiguating QuestionsCoordinate Transformation AccurateWave based measurement systemsData synchronizationRadar systems
The invention discloses an automatic calibration algorithm for a multi-group multi-line laser radar. The automatic calibration algorithm is implemented as follows: S1, a coordinate transformation relation initial value Tguess of a laser radar A and a laser B is estimated; S2, local sub map M construction is carried out on point cloud data collected by the laser radar A; S3, on the basis of hypotheses of data synchronization and track synchronization, the point data P<n>B are transformed to positions at the local sub map M at a time n by T<n>A and the Tguess and a near point at the local sub map M is found out by using a nearest neighbor point cloud searching algorithm; S4, on the basis of an environment consistency constraint, a multi-group calibration relation T<n>cali; between the laser radar A and the laser radar B is calculated; and S5, an abnormal sample point in a multi-group calibration matrix is eliminated by using a random sampling consistency rule and then averaging is carried out to obtain Tcali. According to the automatic calibration algorithm, a coordinate relationship between radars can be calibrated automatically only according to synchronization radar of the laser radar sensor, so that the operation becomes efficient and convenient; and the automatic calibration algorithm can be applied to calibration of a multi-radar system.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
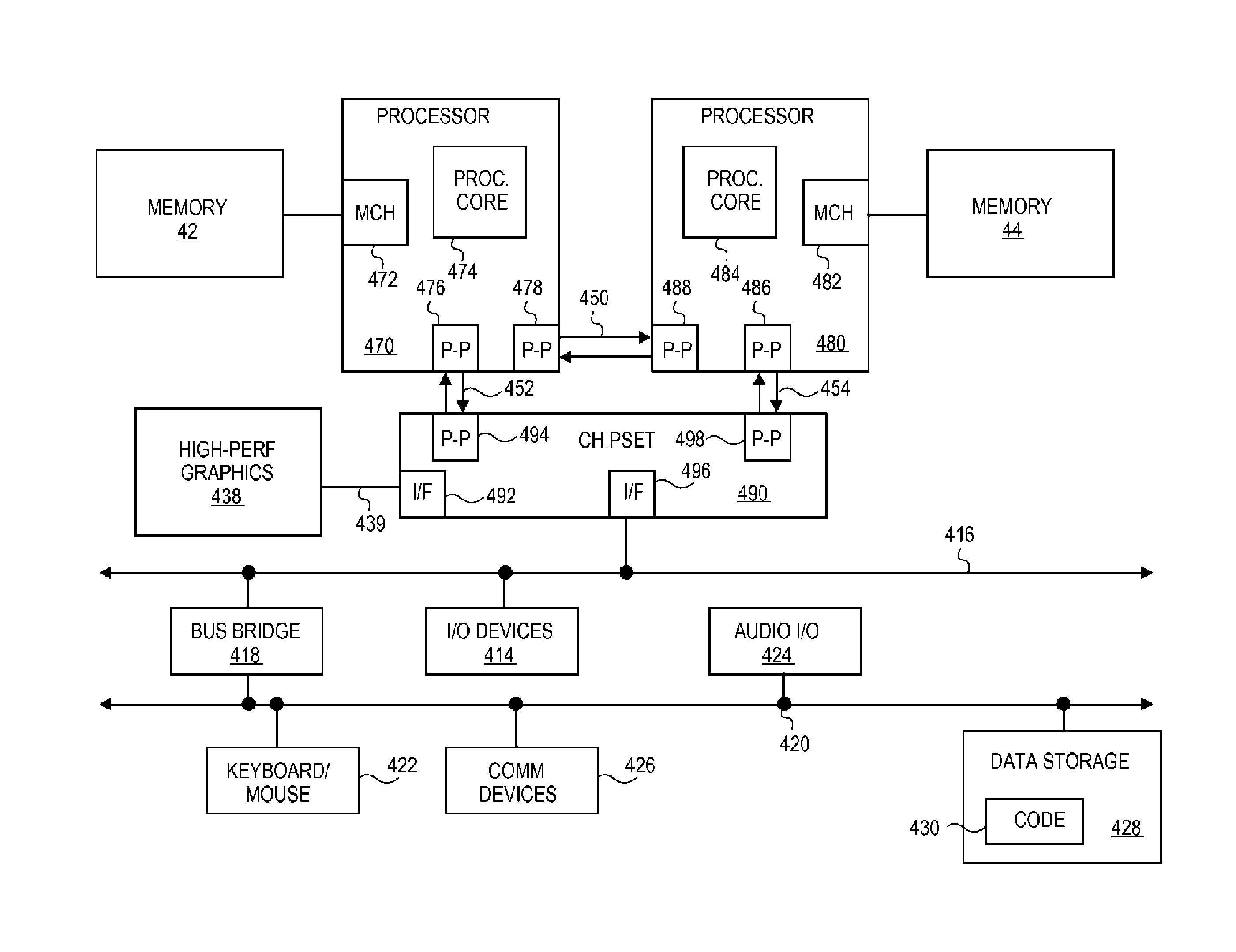
Low latency coherency protocol for a multi-chip multiprocessor system
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
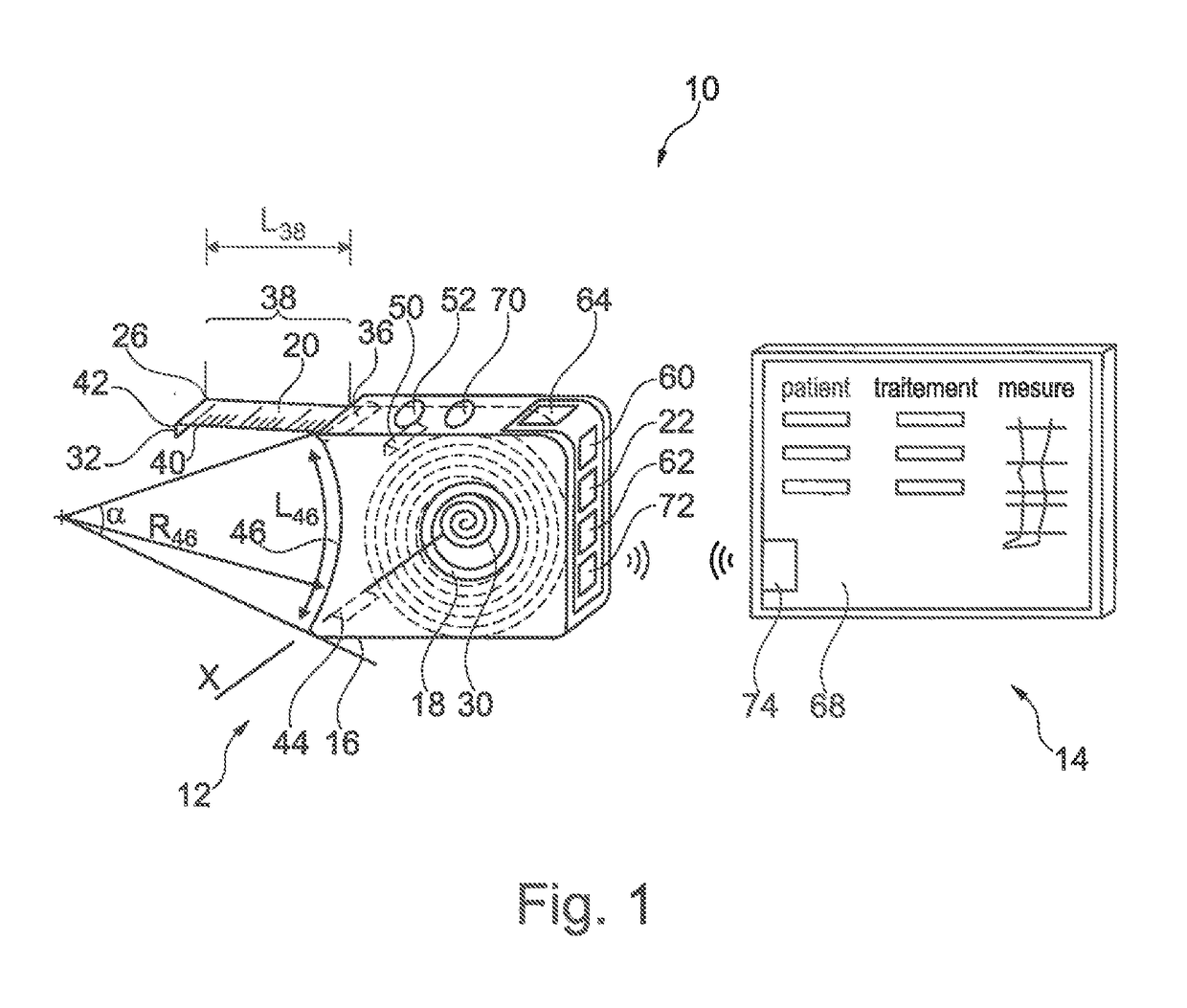
Device for taking a measurement
ActiveUS10349867B2SensorsConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyComputer moduleConsistency control
A device for taking a measurement of a dimension of a part of the body of a patient, includes: an electronic tape measure having a portable housing, a winder accommodated in the housing, a tape which is partially wound on the winder and of which a portion, called the “unwound portion”, extends outside the housing, and a measuring module for a measurement, relative to the unwound portion; a consistency control module for checking the consistency of the measurement by at least one consistency rule and at least one context datum; and an alert module for delivering an alert if an inconsistency is detected by the consistency control module.
Owner:LAB INNOTHERA SA
Applying compliance standards to a computer within a grouping hierarchy
InactiveUS7870594B2Digital computer detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsData processing systemStructure of Management Information
Owner:LINKEDIN
User interface conformance
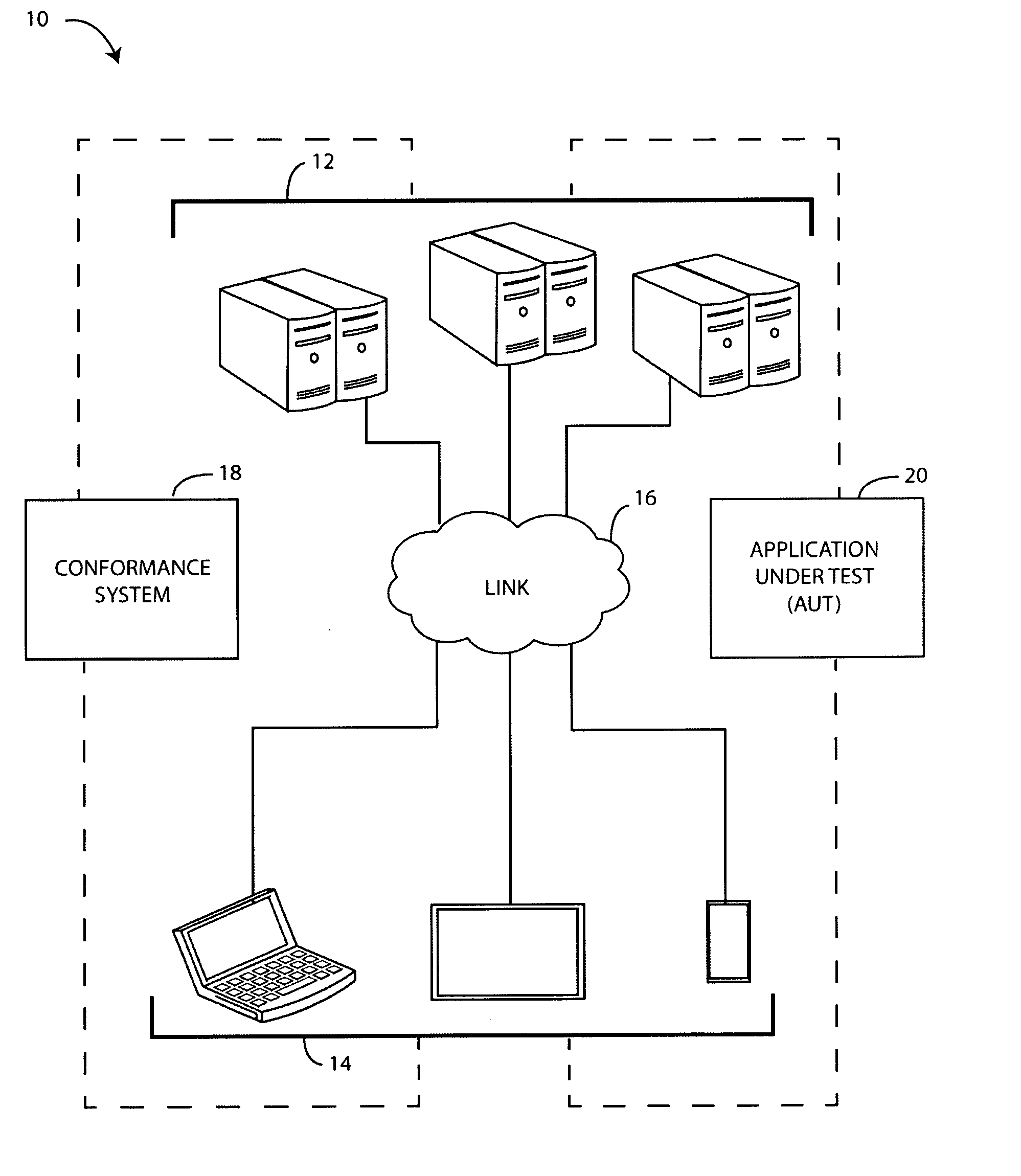
InactiveUS20160132427A1Software testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsApplication softwareData treatment
Verifying user interface conformance can include deriving a conformance rule set based on desired user interface characteristics identified through an examination of mockup data for the user interface. That mockup data includes a visual representation of the desired characteristics. Conformance data can then be generated based on differences between the desired characteristics and actual characteristics. Those differences are identified by processing the conformance rule set against screen capture data of the user interface as produced by an application under test. The screen capture data includes a visual representation of the actual characteristics of the user interface.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Technique to share information among different cache coherency domains
ActiveUS20130117509A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGraphicsInformation sharing
A technique to enable information sharing among agents within different cache coherency domains. In one embodiment, a graphics device may use one or more caches used by one or more processing cores to store or read information, which may be accessed by one or more processing cores in a manner that does not affect programming and coherency rules pertaining to the graphics device.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
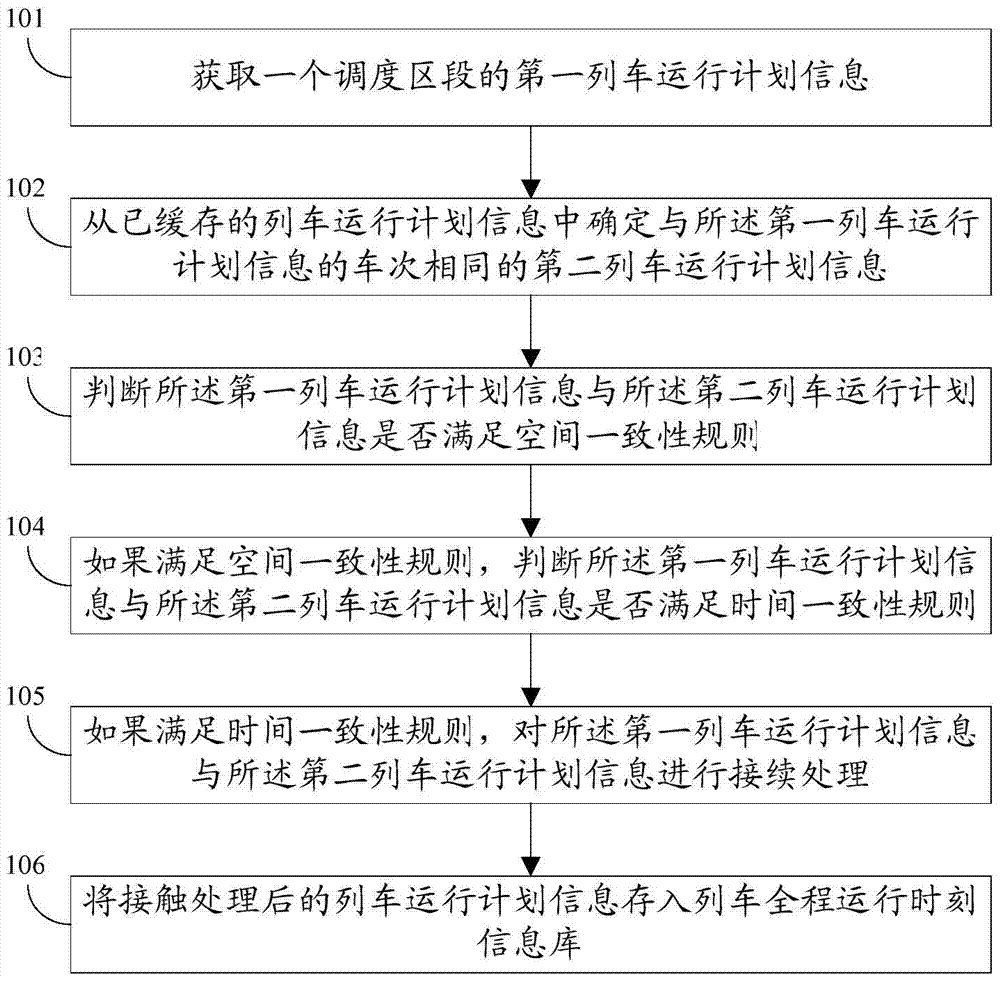
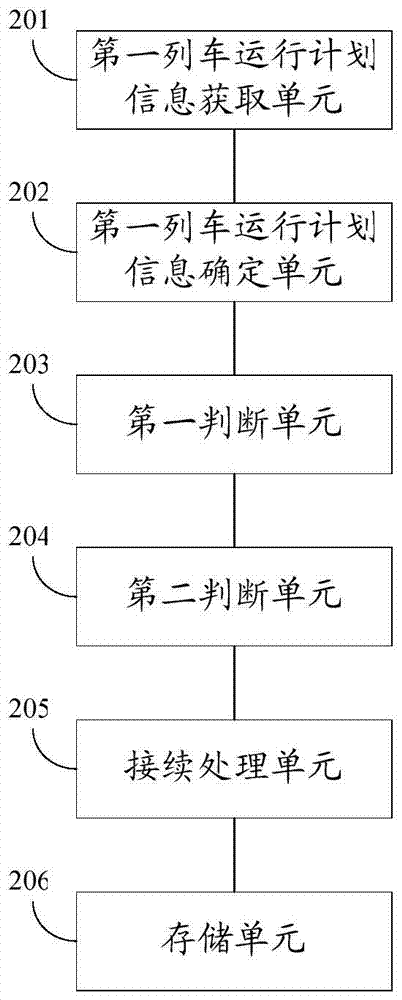
A method and system for generating time information of a train's entire running time
The invention discloses a method and a system for generating time information for the whole train running. The method includes: obtaining the first train operation plan information of a dispatching section; determining the second train operation plan information that is the same as the train number of the first train operation plan information from the cached train operation plan information; judging the Whether the first train operation plan information and the second train operation plan information satisfy the spatial consistency rule and the time consistency rule at the same time; The plan information is processed continuously; the train operation plan information after the contact processing is stored in the train full-time operation time information database. By adopting the method or system of the present invention, it is possible to integrate and generate the whole train running time information according to the train running plan information of each dispatching section.
Owner:CRSC RESEARCH & DESIGN INSTITUTE GROUP CO LTD +1
Automated compliance management
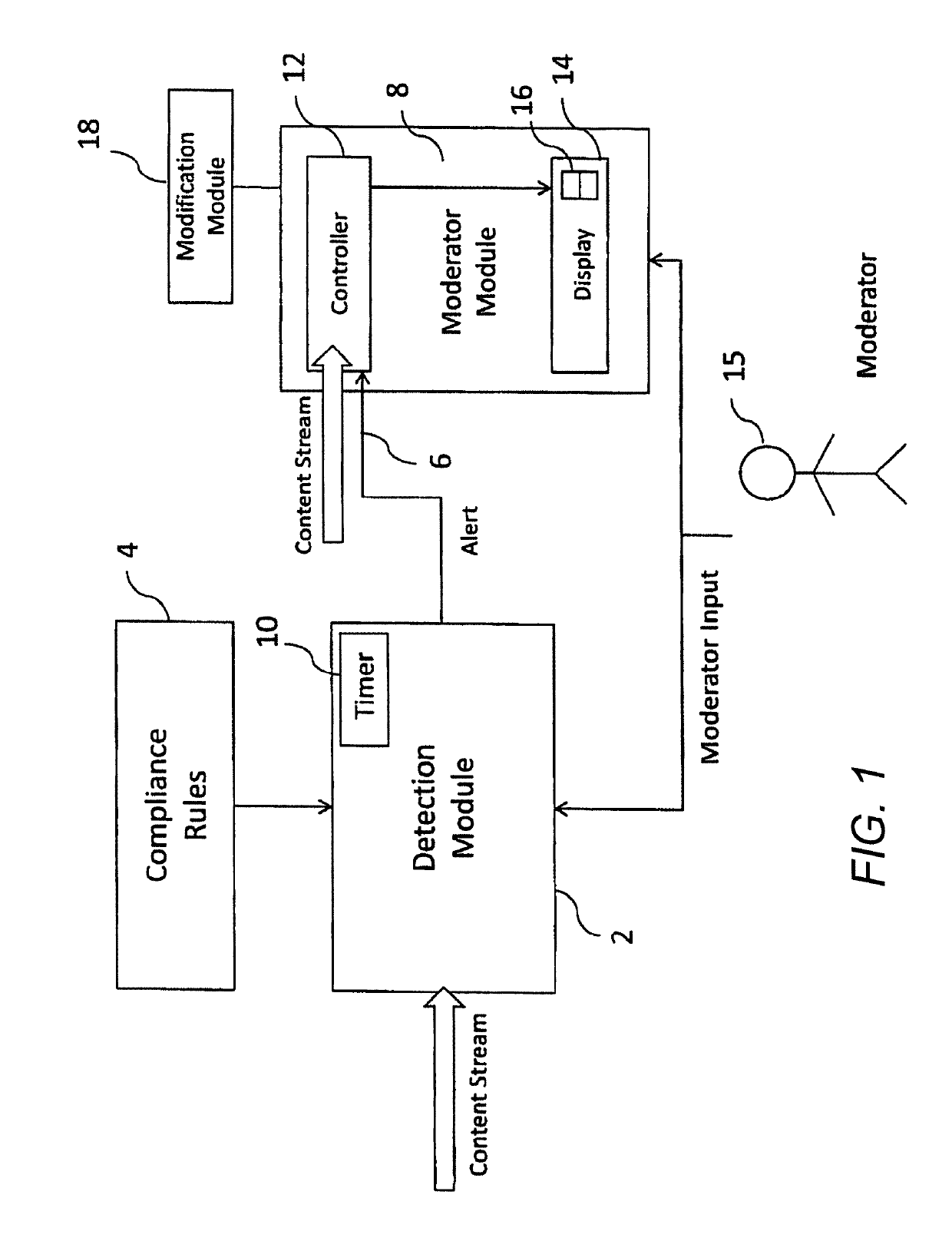
ActiveUS10298999B2Reduce in quantityEfficient processingBroadcast components for monitoring/identification/recognitionSelective content distributionDigital contentComputerized system
There is disclosed a computer system for analysing content, comprising: a detection module connected to receive at least one piece of digital content, the detection module being operable to access a set of compliance rules and compare the received at least one piece of digital content with the set of compliance rules, the detection module further being configured to generate an alert if the result of the analysis indicates a breach of at least one of the rules; a moderator module connected to receive the alert, the moderator module configured to enable output to a moderator based only on the piece of digital content which caused the alert to be generated, whereby the moderator can assess a modification to be made to the piece of content which caused the alert to be generated.
Owner:PRJ HLDG CO LLC
A positioning monitoring method and device
ActiveCN104703214BGuaranteed real-timeGuaranteed validityWireless communicationConsistency rulesServer-side
The invention discloses a positioning monitoring method and device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the network parameter of the current position of a terminal; comparing the acquired network parameter with a network parameter stored in a network parameter storage region in the terminal; when a comparison result is determined to be inconsistent with a set network parameter consistency rule, sending a positioning request to a server side, wherein the network parameter consistency rule indicates whether or not the difference value of the network parameter varying due to position variation of the terminal is within a set range; and receiving and storing a positioning result fed back by the server side according to the positioning request. The type of the sent positioning request and the content of the request can be determined according to a current network state, so that the positioning monitoring efficiency is increased.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Method and apparatus for reliable mashup
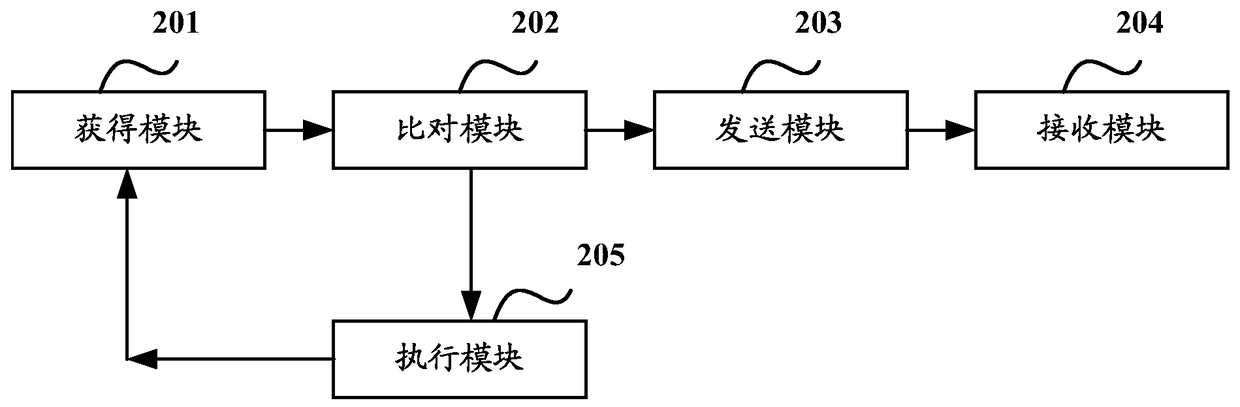
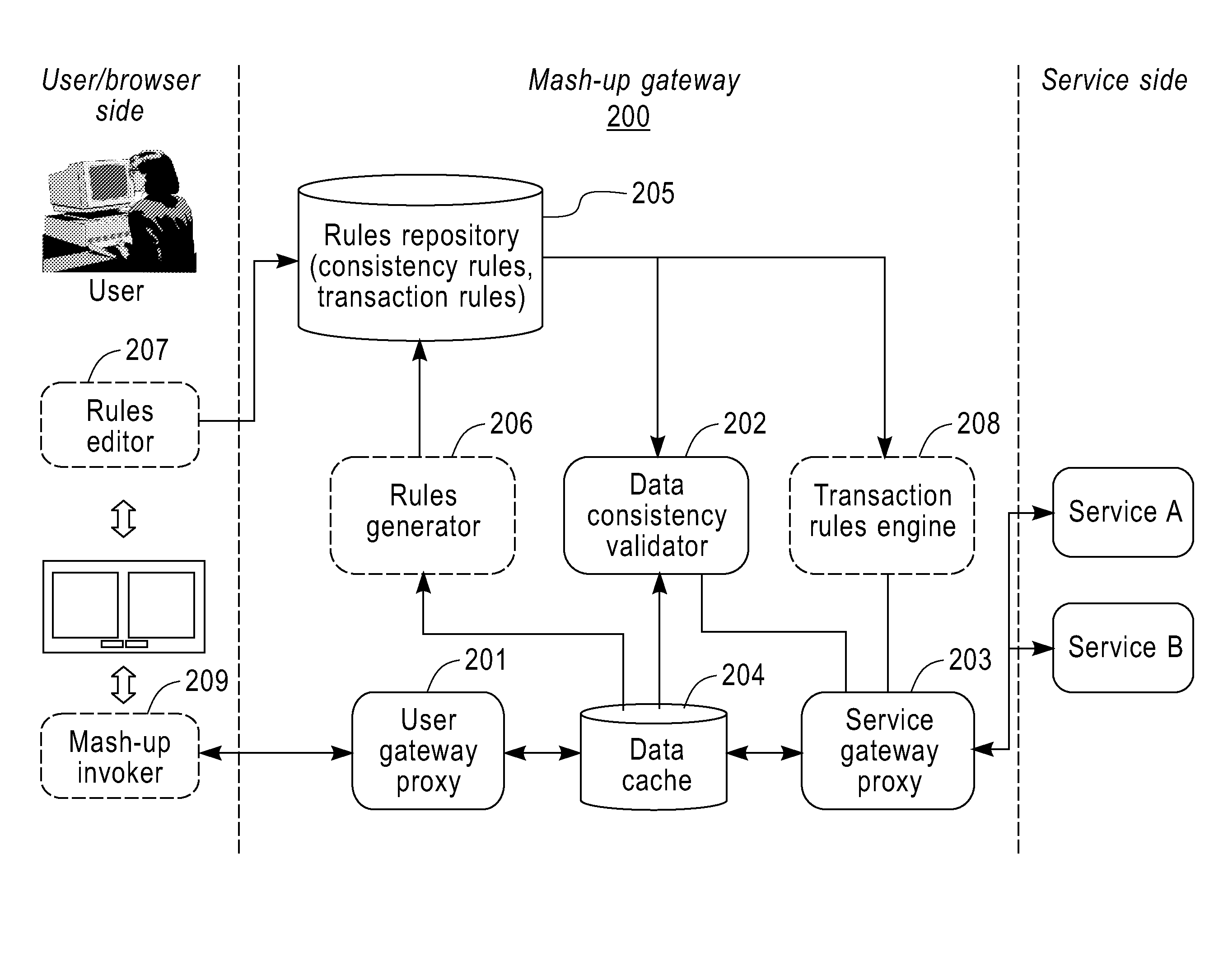
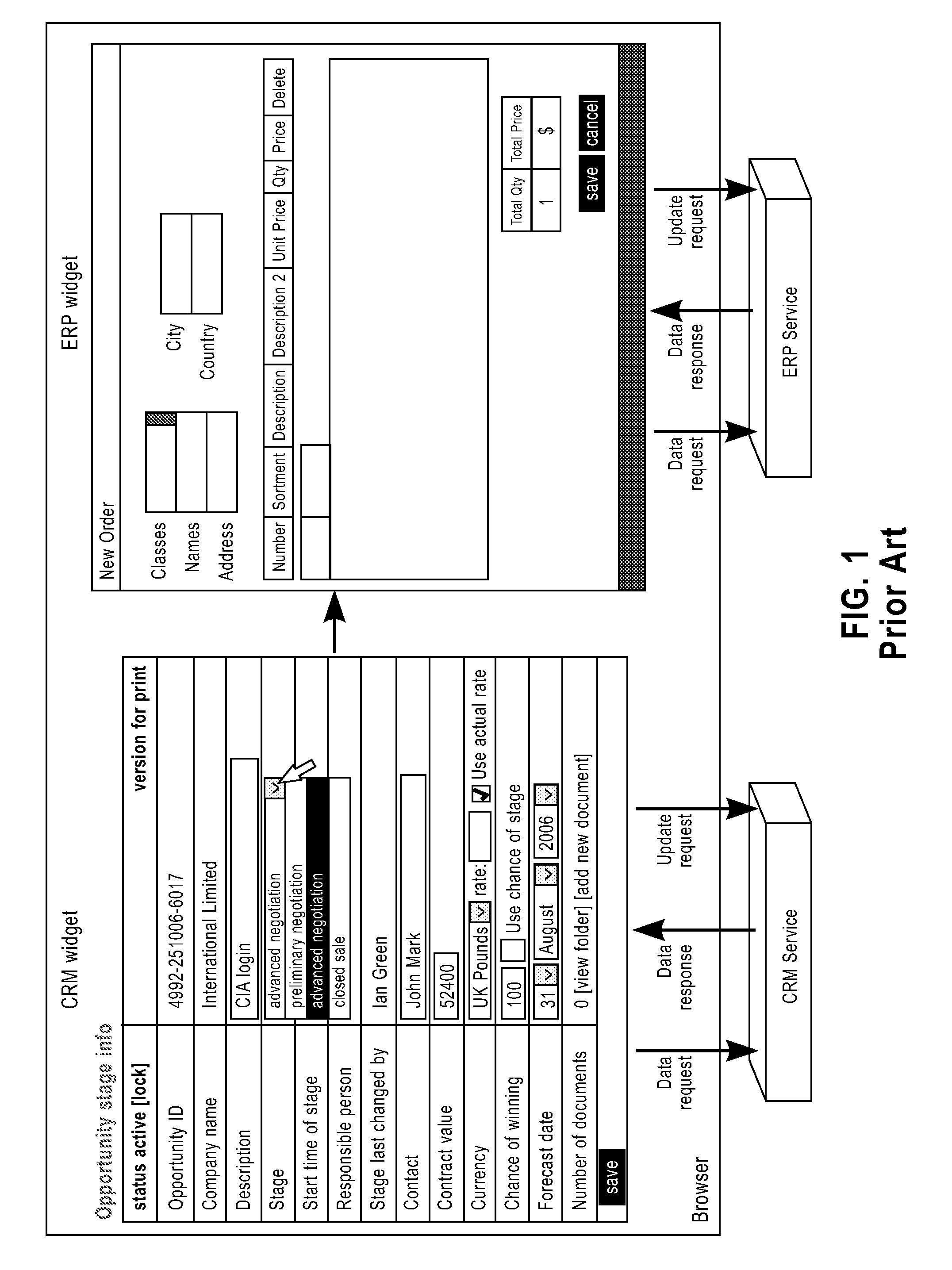
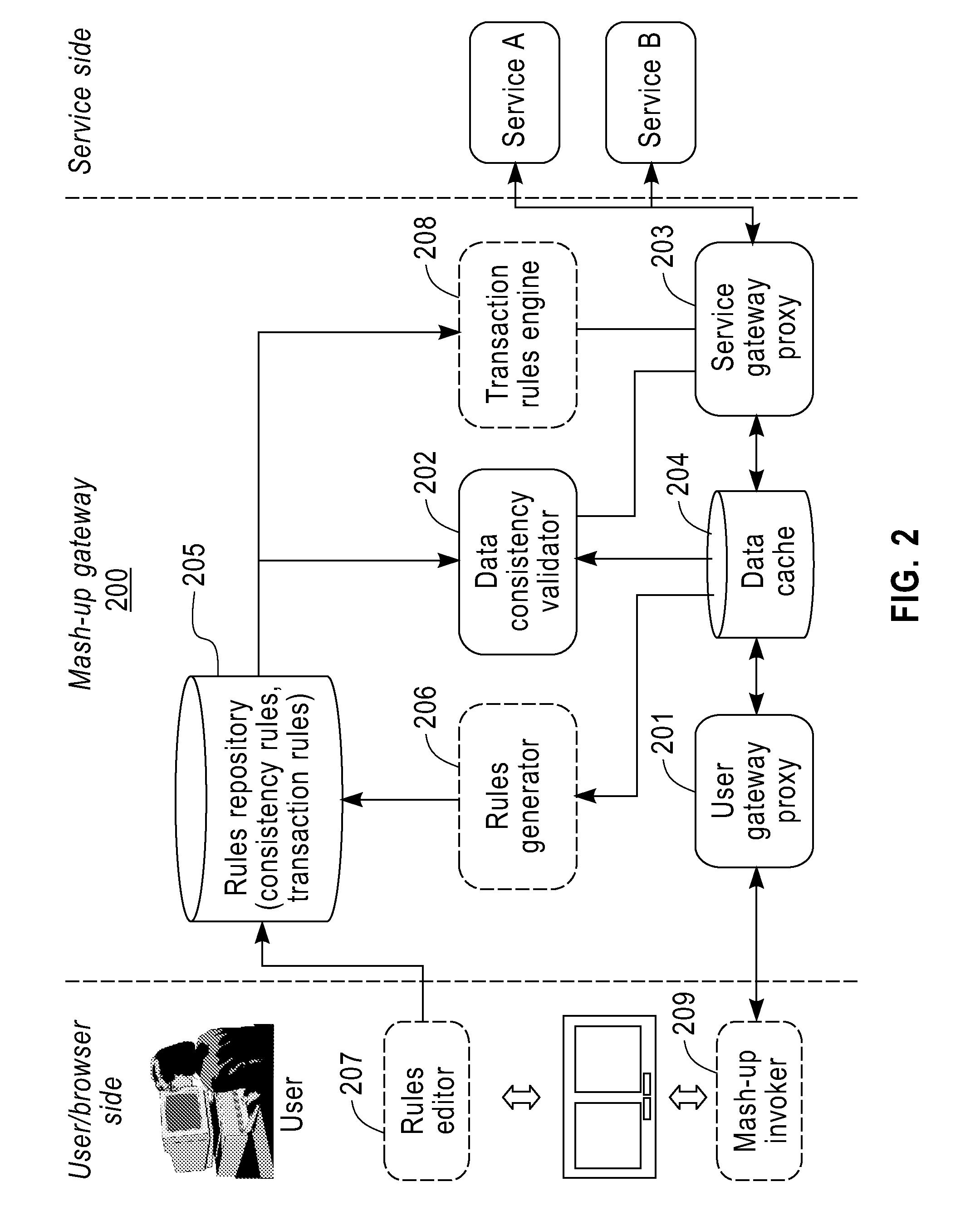
InactiveUS8316079B2Keep a lightweight and agile development experienceMultiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationClient-sideDatabase
A method and apparatus for reliable mashup. The method includes the steps of: intercepting a data update request submitted by a client browser to one or more of a plurality of services for providing mashup page data; performing consistency validation on the data update request using consistency rules; and, in response to a successful validation, forwarding the data update request to the one or more of the plurality of services.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com