Patents
Literature
49 results about "Implant size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
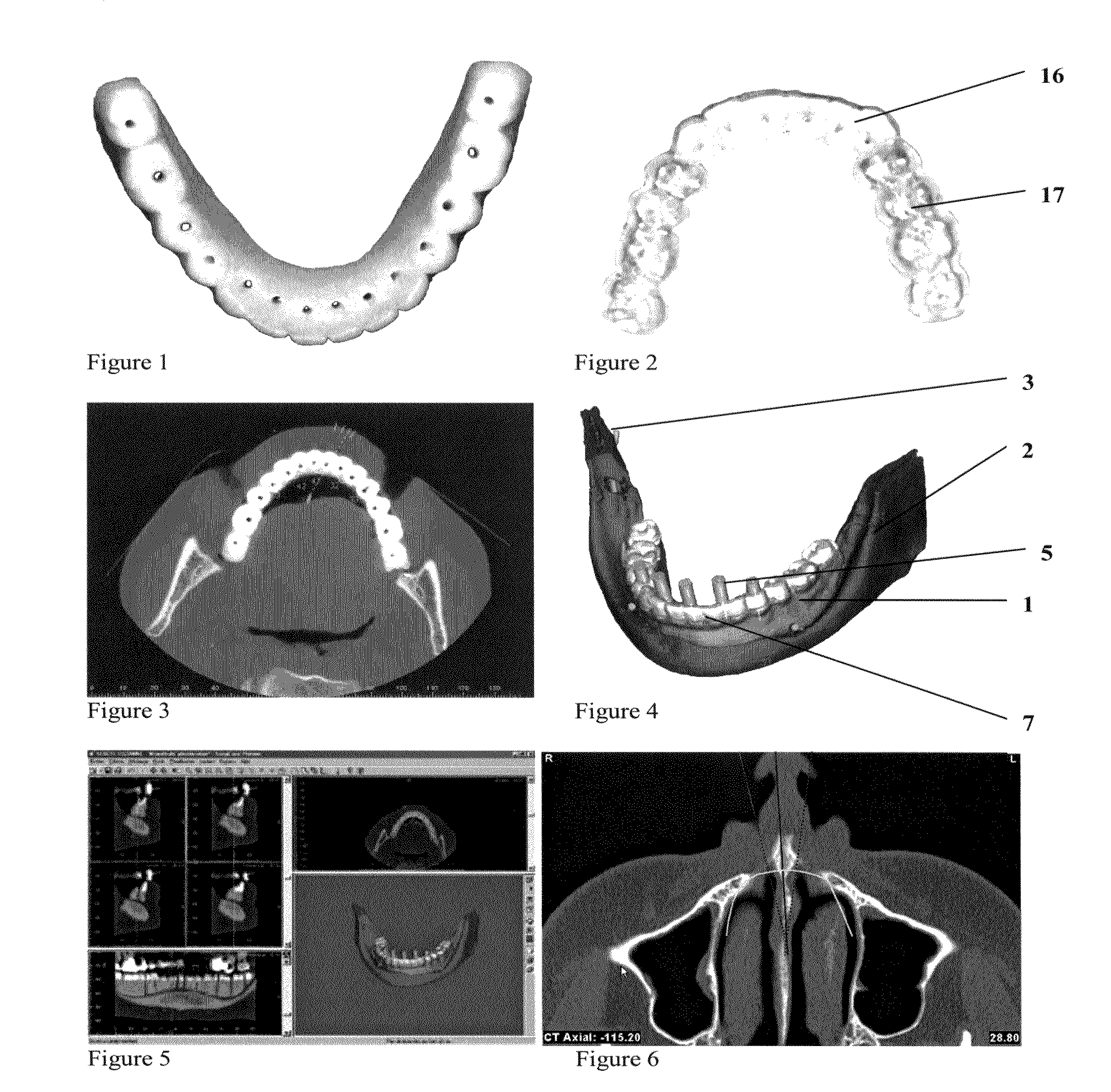
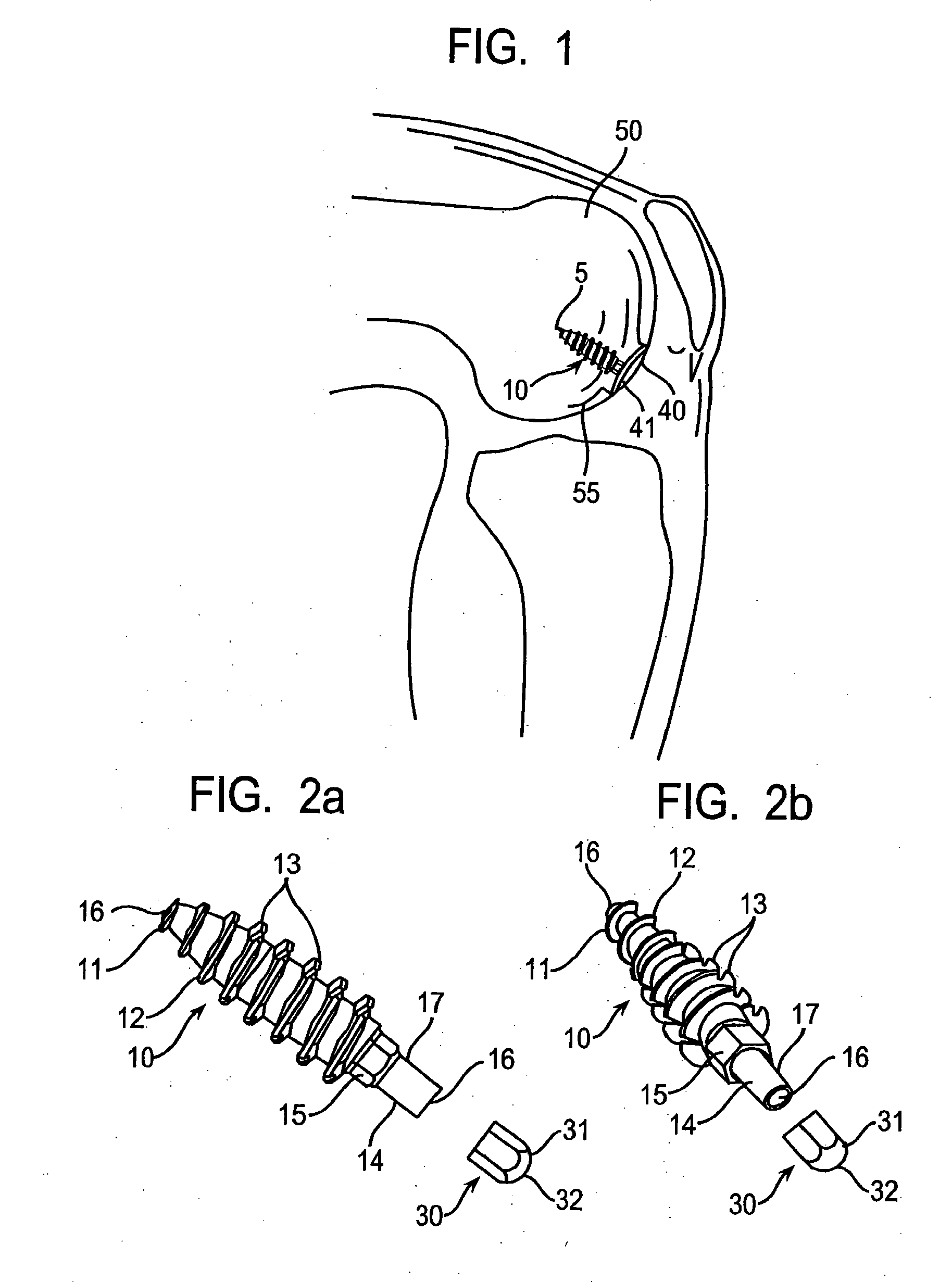
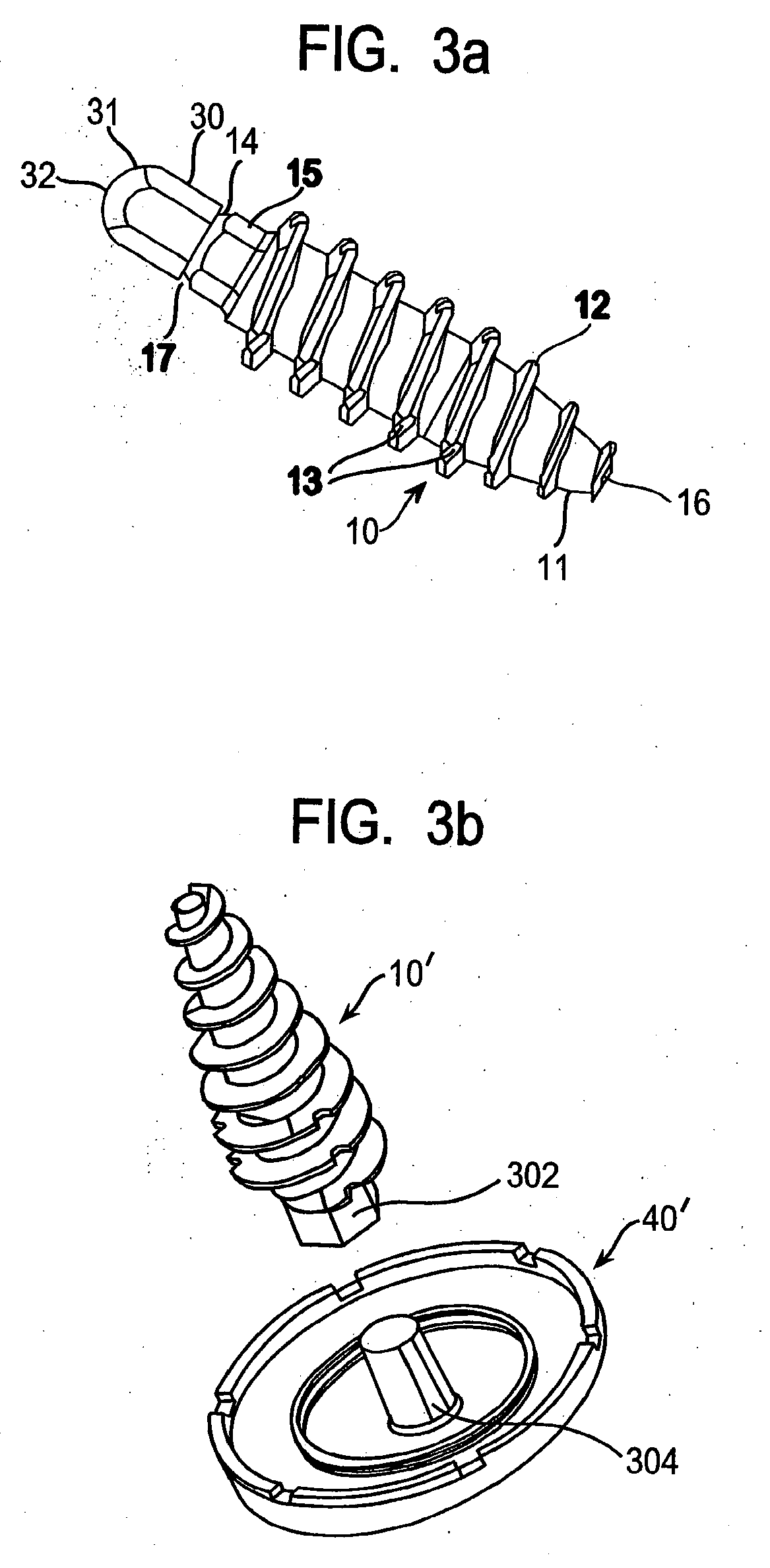
Method of and system for planning a surgery
ActiveUS20090043556A1Analogue computers for chemical processesDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgery procedureBiomedical engineering
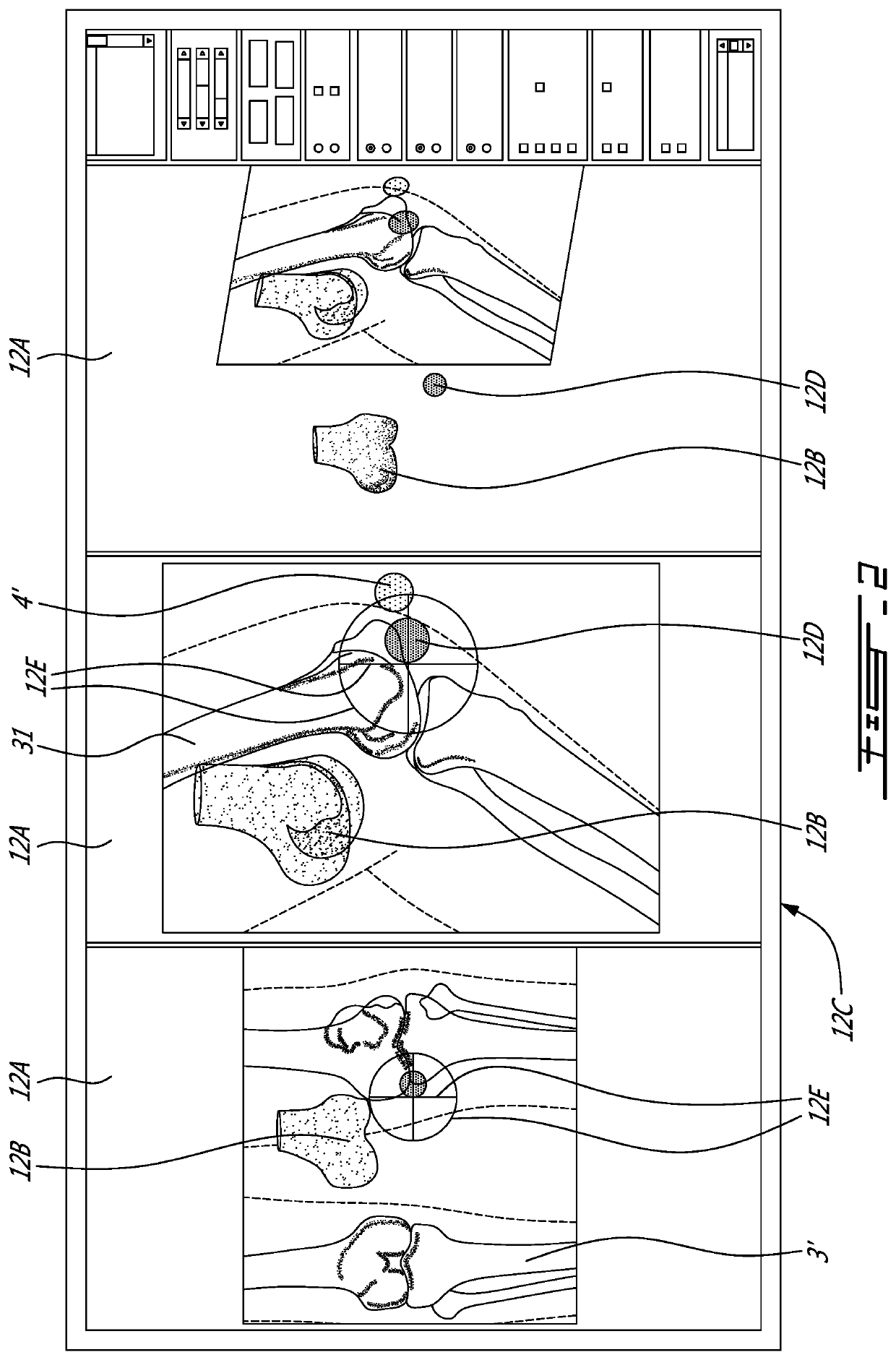
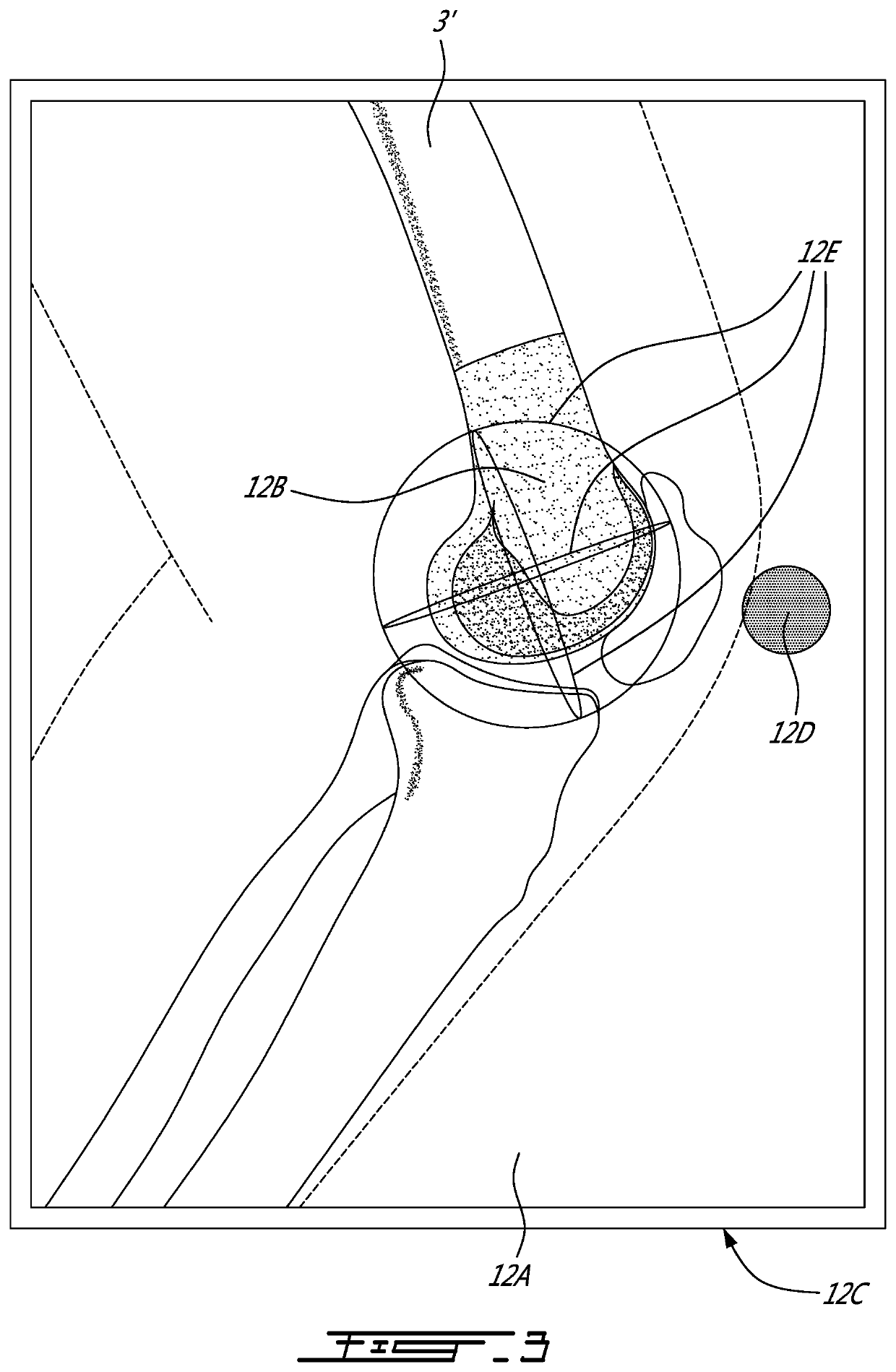
A system for virtually planning a size and position of a prosthetic implant for a bone on a patient includes a database containing pre-defined form factor information for a plurality of different implants and a circuit for obtaining surface shape information of the bone. The system further includes a circuit for defining baseline location parameters for an implant location in relation to a virtual representation of the bone based on the surface shape information and a circuit for assessing a fit calculation of each implant in relation to the virtual representation of the bone based on the form factor in formation and a plurality of fit factors at each of a plurality of incremental positions in relation to the bone. Still further, the system includes a circuit for selecting a best fit implant size and position from all of the fit calculations.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
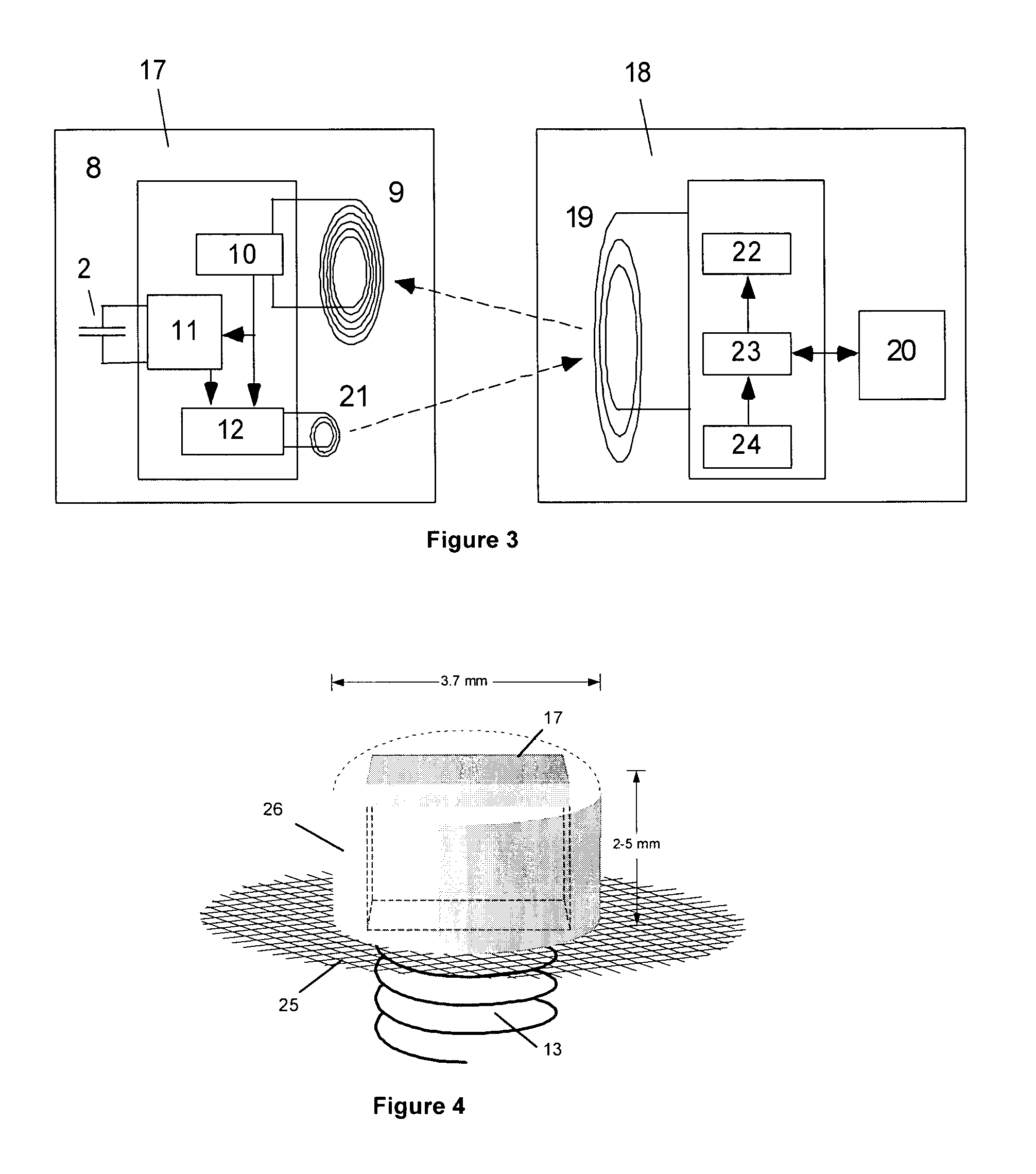
Wireless device and system for monitoring physiologic parameters
ActiveUS20090182206A1Minimal invasionSmall sizeElectrotherapyCatheterMonitor blood pressureSignal conditioning
A system for monitoring blood pressure and other physiologic parameters is provided. The system is designed such that it can be delivered to the patient with ease and minimal invasion. The system contains at least one self contained implantable sensing device consisting of a sensor, an electrical circuit for signal conditioning and magnetic telemetry, a biocompatible outer surface and seal, an anchoring method, and an external readout device. The implant is small in size so that it may be delivered to the desired location and implanted using a catheter, although direct surgical implantation is also possible. The circuit, sensor, and antenna for telemetry are packaged together and sealed hermetically to the biologic environment. The larger readout unit remains outside the body but proximal to the implant for minimizing communication distance.
Owner:UIM PRESSURE IMPLANT INC
System and method for joint resurface repair
InactiveUS7510558B2Enhance load bearing and load transfer propertyImprove the immunitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisArticular surfacesArticular surface
A generic bone implant, or set of standardized implants, is created based on using a guide device to develop an axis normal to an articular surface of bone and collecting only one or two data points. A generic cutting tool is used to cut the bone to a point where a generic implant can be used. Several improved tools relating to the procedure for using such an implant, as well as methods for using implants consistent with the invention are further described, including: single-axis and biaxial drill guide tools and methods, generic single-axis implant methods and devices, generic biaxial implant methods and devices, tools and methods for holding or delivering an implant, removal or revision tools and methods, digital measuring systems and methods, and set of measuring gauges for determining the appropriate implant dimensions.
Owner:ARTHROSURFACE
Implant for replacing a vertebra
InactiveUS6908485B2Quick installationFine adjustment of its lengthInternal osteosythesisBone implantBiomedical engineeringVertebra
The invention concerns an implant for replacing a vertebra at least partially, consisting of two parts adapted to be mutually connecting while enabling the adjustment of the implant total dimension, each part having an invariable dimension homologous with the implant dimensions. The parts form a screw-nut connection with each other.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
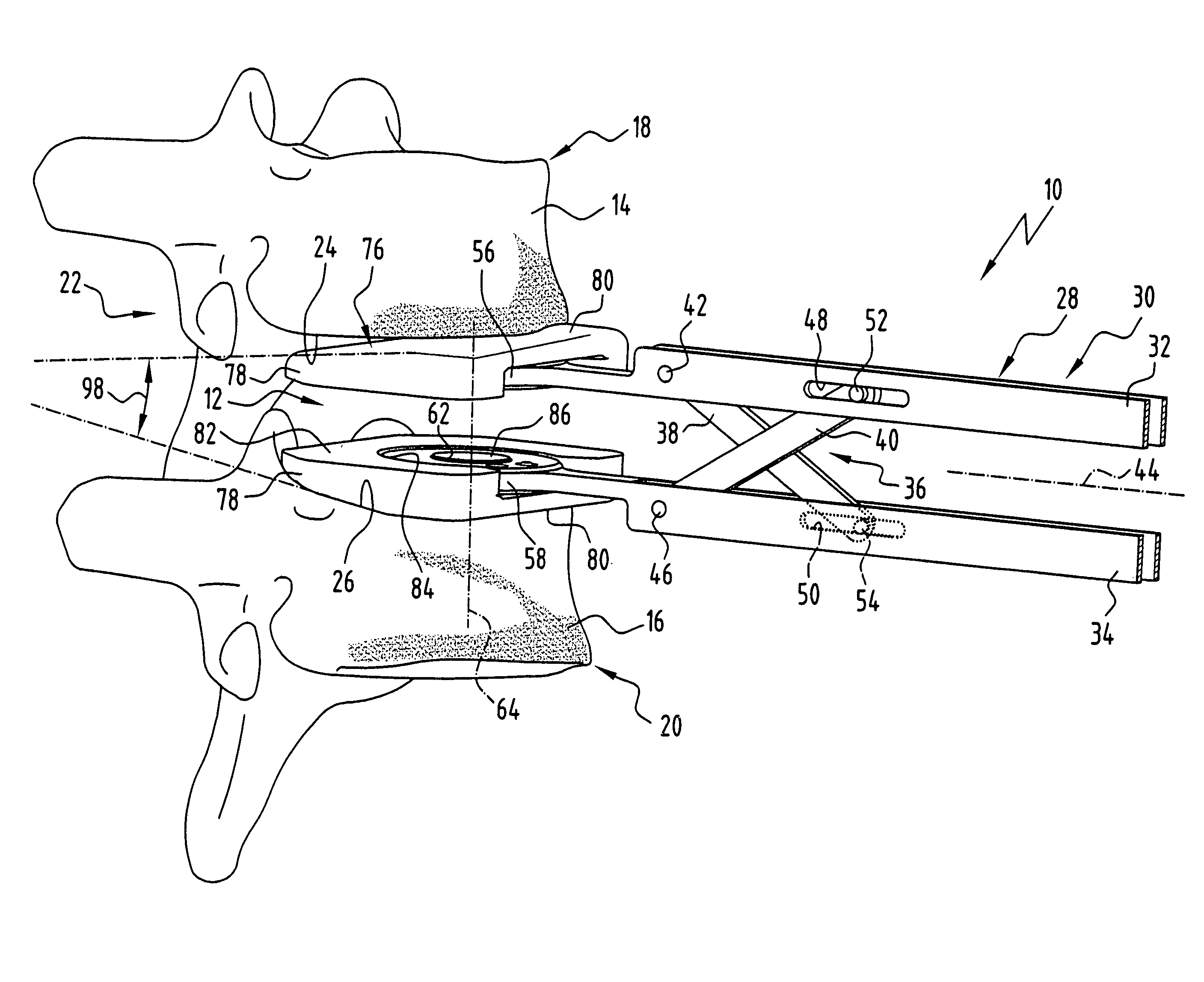
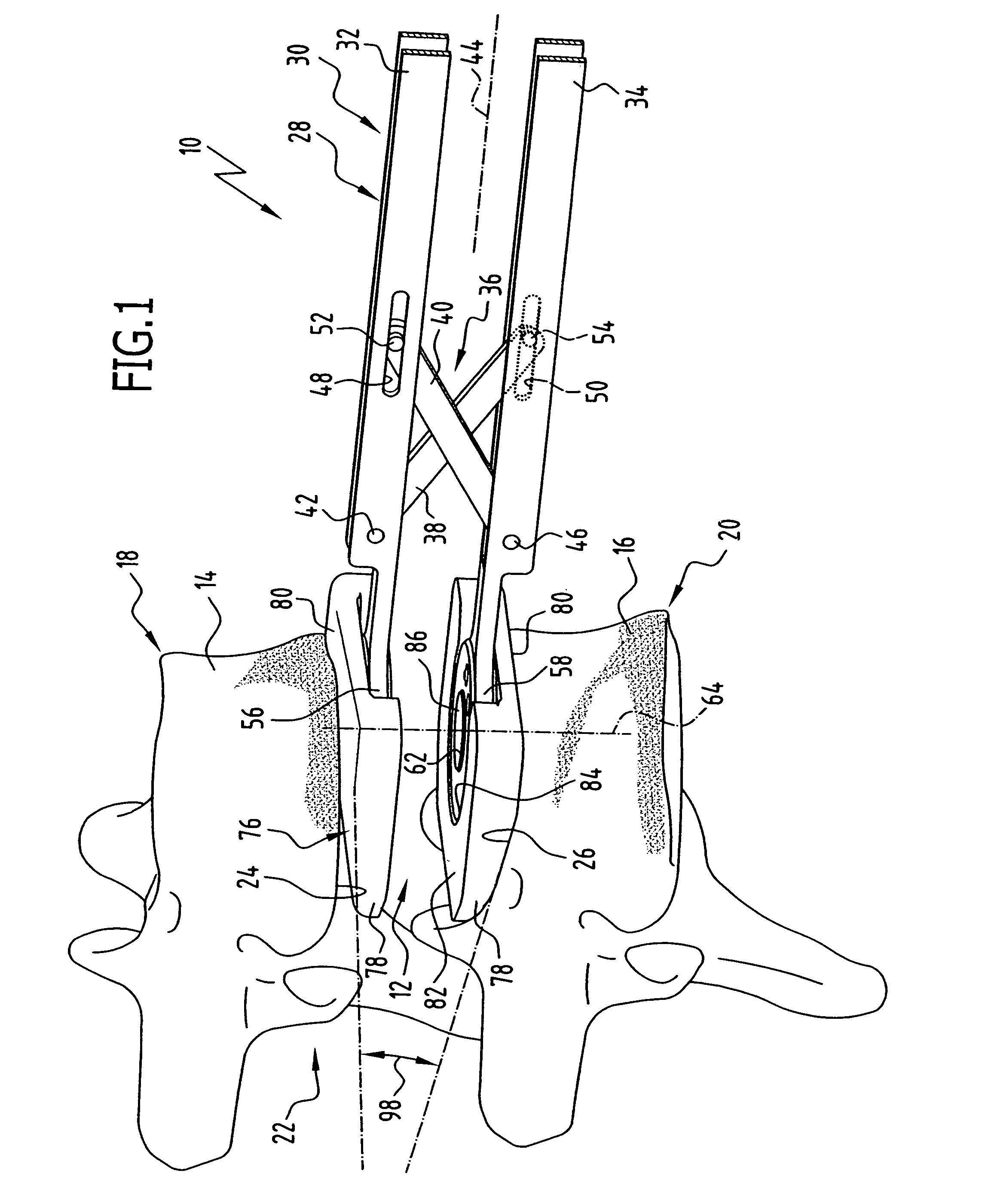
Spinal stabilization device and methods
Devices and methods for immobilizing adjacent vertebrae are disclosed including the utilization of one or more implants inserted between adjacent vertebrae and having protrusions thereon for substantially fixedly securing with the vertebrae. In one form, an implant may be inserted in a first orientation and then rotated to a second orientation having a larger profile. A second implant may also be inserted in the same vertebral space in the same manner. A trial spacer may be used to determine the proper implant size. In another form, an implant may be inserted already in the fusion orientation. The implants and trial spacer, as well as a spreader and / or a scraper for preparing the intervertebral space, may be inserted in the vertebral space with the same insertion tool. The inserter tool may include a threaded member for attachment with the implants or other devices.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
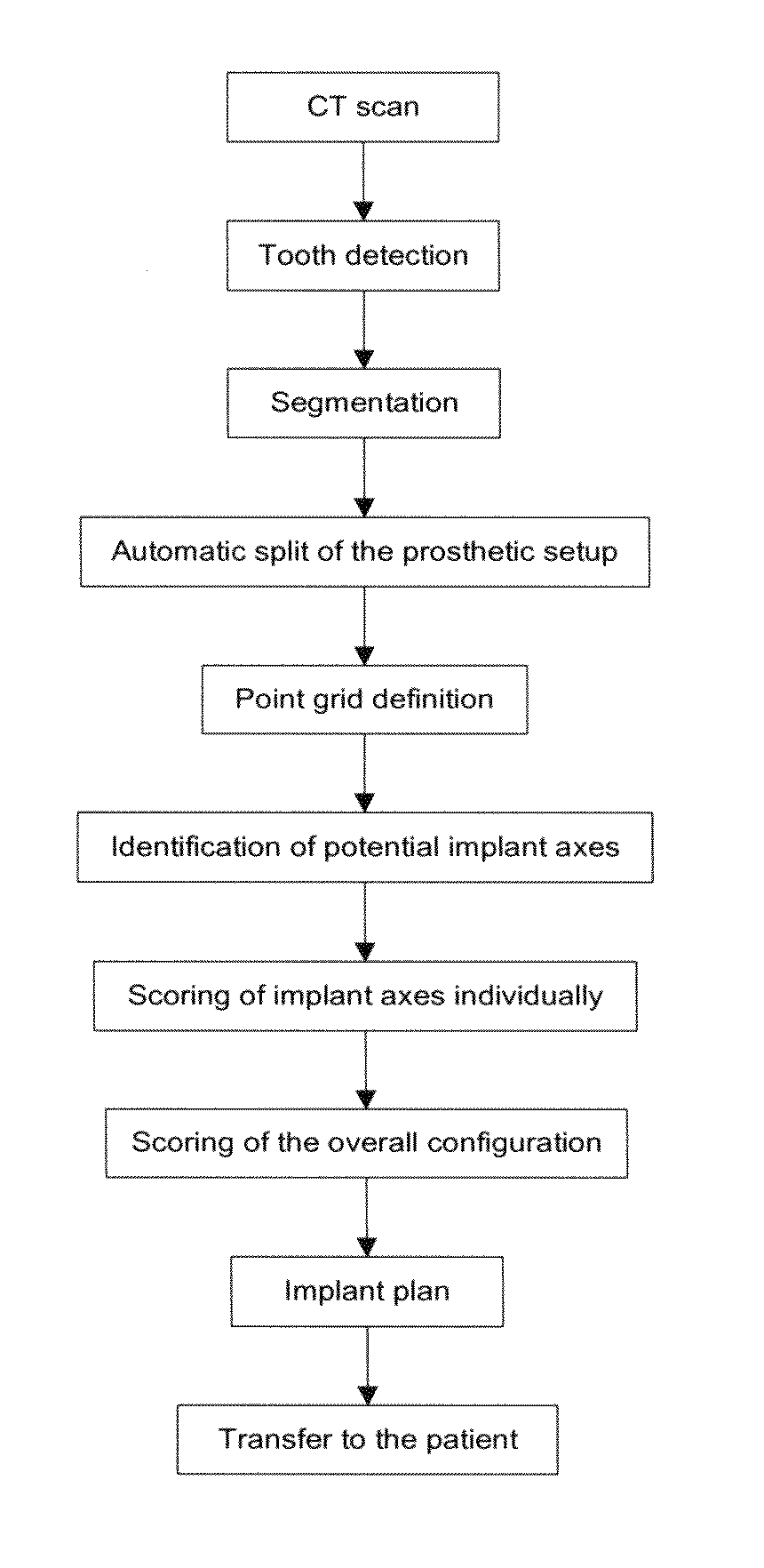
Method for (semi-) automatic dental implant planning
ActiveUS20090162813A1Simple methodOvercome disadvantagesDental implantsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDental implantOrthodontics
A method and system for (semi-) automatic dental implant planning (A) is described including (a) means for creating 3D models of a tooth setup (b) and / or means for creating 3D models of parts of the jaw, (c) means for detecting zones in the jaw where implants can (or optionally cannot be placed), (d) means for detecting restorative elements in the tooth setup, (e) means for determining candidate implant dimensions, positions, orientations and configurations, (f) means for obtaining implant plans, (g) means for comparing implant plans to each other or to given criteria, (h) means for selecting or improving an implant plan.
Owner:DENTSPLY IMPLANTS NV
Wireless device and system for monitoring physiologic parameters
ActiveUS7686762B1Delivered to the patient with ease and minimal invasionMinimal invasionElectrotherapyCatheterMonitor blood pressureSignal conditioning
A system for monitoring blood pressure and other physiologic parameters is provided. The system is designed such that it can be delivered to the patient with ease and minimal invasion. The system contains at least one self contained implantable sensing device consisting of a sensor, an electrical circuit for signal conditioning and magnetic telemetry, a biocompatible outer surface and seal, an anchoring method, and an external readout device. The implant is small in size so that it may be delivered to the desired location and implanted using a catheter, although direct surgical implantation is also possible. The circuit, sensor, and antenna for telemetry are packaged together and sealed hermetically to the biologic environment. The larger readout unit remains outside the body but proximal to the implant for minimizing communication distance.
Owner:UIM PRESSURE IMPLANT INC
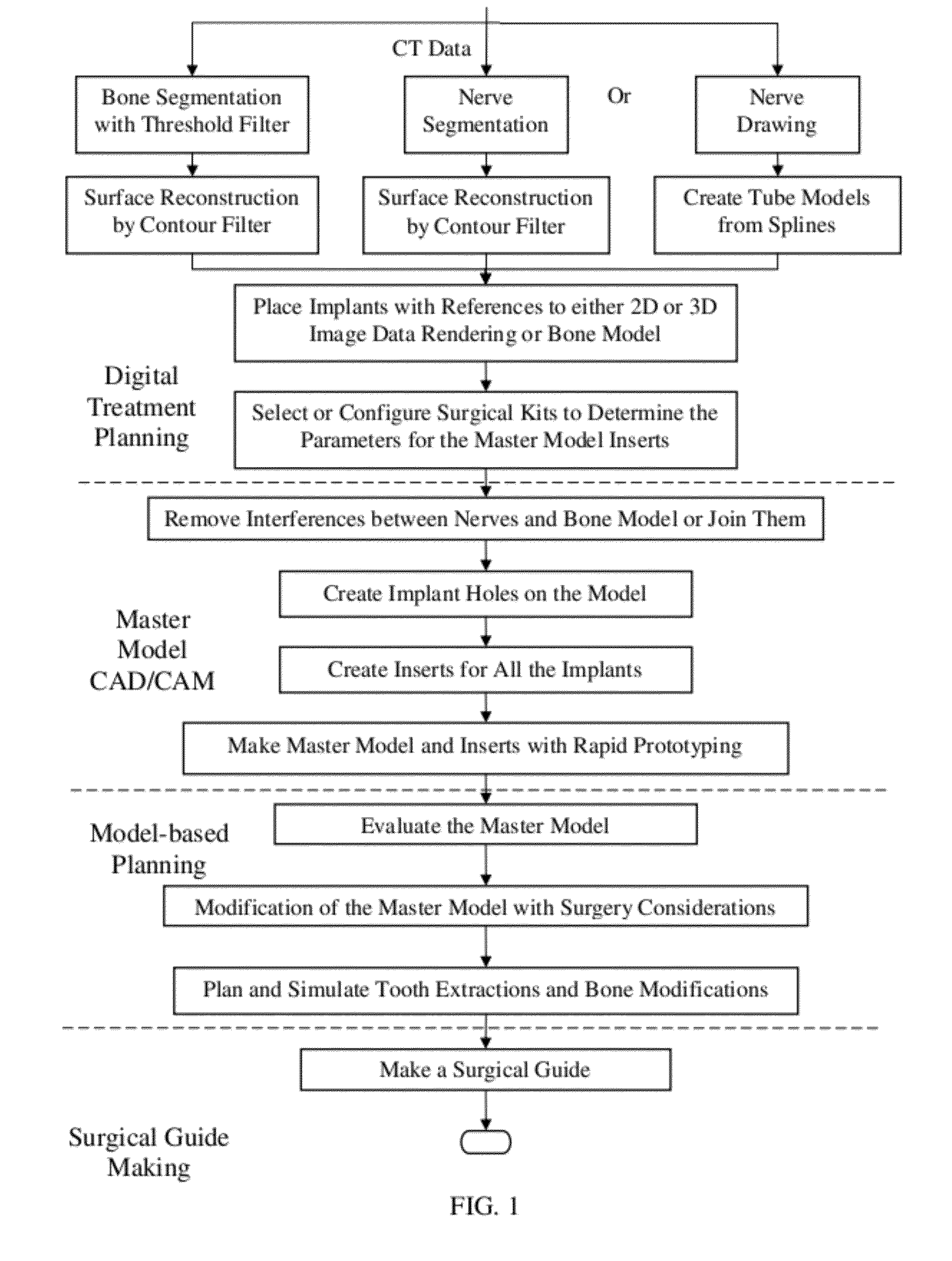
Hybrid method for dental implant treatment planning
InactiveUS20120046914A1Fast technologyDental implantsAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical operationAnatomical structures
A hybrid method for dental implant treatment planning and a corresponding approach to make a surgical guide. After digital treatment planning is performed with CT scan data, a master model is created, which embodies the patient anatomy and entire treatment plan. Jaw bone, tooth surfaces, soft tissues and nerves are all contained by the master model. The plan details including implant sizes and positions, surgical guide drill options, as well as the choice of a surgical kit, are all conveyed by the master model. Meanwhile, models of specially designed “implant inserts (or replicas)” are also generated, which have one end that fits into the implant holes on the master model and another end to make the surgical guide. The master model and inserts are manufactured with rapid prototyping technology. A surgical guide is later on made from them with conventional lab processes. A main characteristic of this approach is that the master model and the inserts are the physical embodiment of a virtual treatment plan. With them, the surgeons can continue the treatment planning for operations like tooth extractions and bone modifications before making the surgical guides. Therefore the treatment planning workflow is a combination of digital treatment planning and a physical model based planning, in other words, a hybrid approach. A differentiator in this invention is the generation of a closed solid model of the soft tissue, as part of the master model, from the scan data. This approach can be applied to create both bone-borne and tissue-borne surgical guides with low cost process, which is a big advantage over other approaches.
Owner:GAO FEI
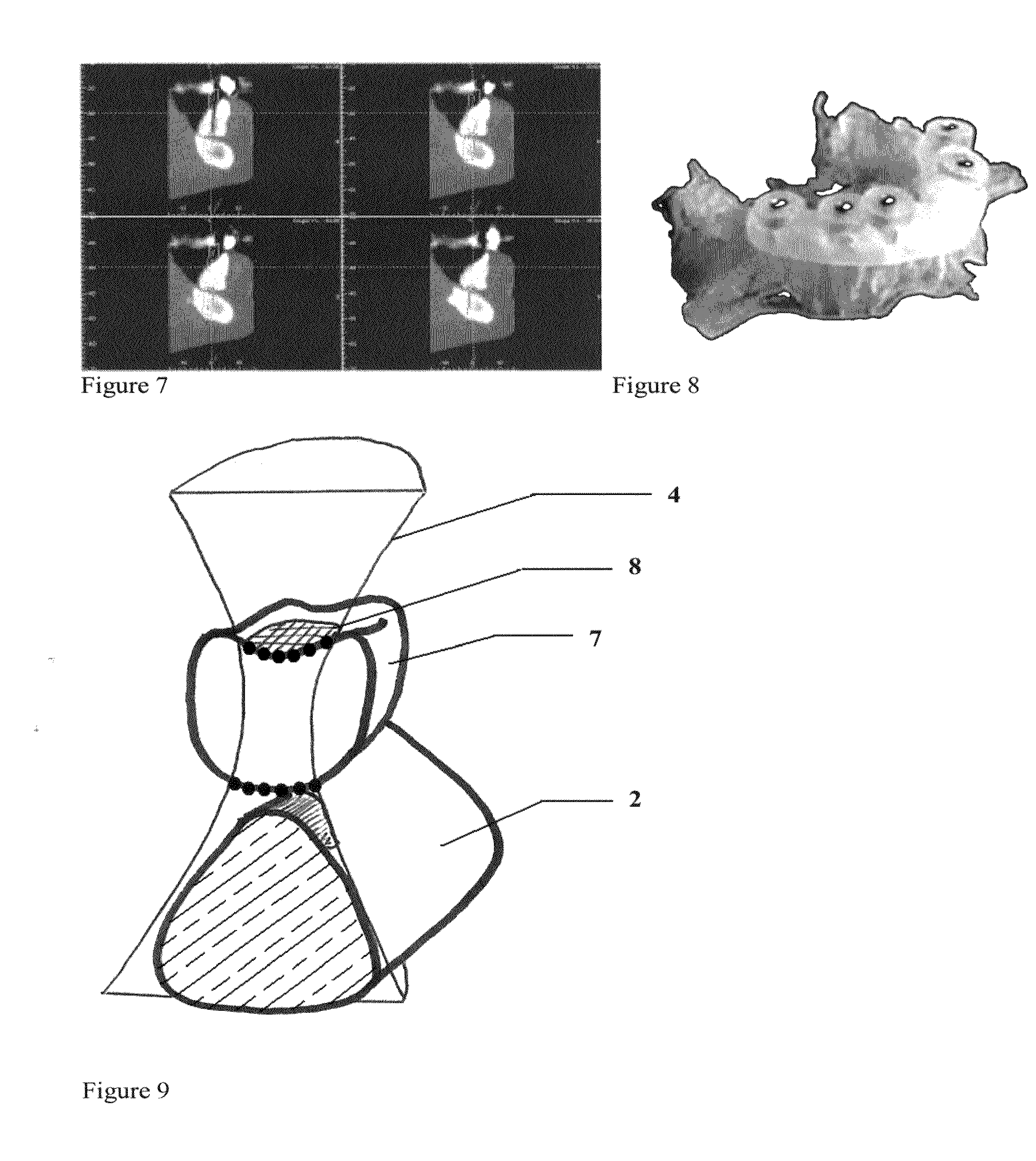
Selectively expanding spine cage, hydraulically controllable in three dimensions for vertebral body replacement
ActiveUS8480741B2Deterioration of over timeStrong implantInternal osteosythesisBone implantDistractionSpinal locomotion
A selectively expanding spine cage has a minimized diameter in its unexpanded state that is smaller than the diameter of the neuroforamen through which it passes in the distracted spine. The cage conformably engages between the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae to effectively distract the anterior disc space, stabilize the motion segments and eliminate pathologic spine motion. The cage enhances spinal arthrodesis by creating a rigid spine segment. Expanding selectively, the cage height increases and holds the vertebrae with fixation forces greater than adjacent bone and soft tissue failure forces in natural lordosis. Stability is thus achieved immediately, enabling patient function by eliminating painful motion. Greater distraction height is achieved without an increase in implant size through the use of interfitted stages.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Spinal stabilization device and methods
Devices and methods for immobilizing adjacent vertebrae are disclosed including the utilization of one or more implants inserted between adjacent vertebrae and having protrusions thereon for substantially fixedly securing with the vertebrae. In one form, an implant may be inserted in a first orientation and then rotated to a second orientation having a larger profile. A second implant may also be inserted in the same vertebral space in the same manner. A trial spacer may be used to determine the proper implant size. In another form, an implant may be inserted already in the fusion orientation. The implants and trial spacer, as well as a spreader and / or a scraper for preparing the intervertebral space, may be inserted in the vertebral space with the same insertion tool. The inserter tool may include a threaded member for attachment with the implants or other devices.
Owner:XTANT MEDICAL HLDG INC
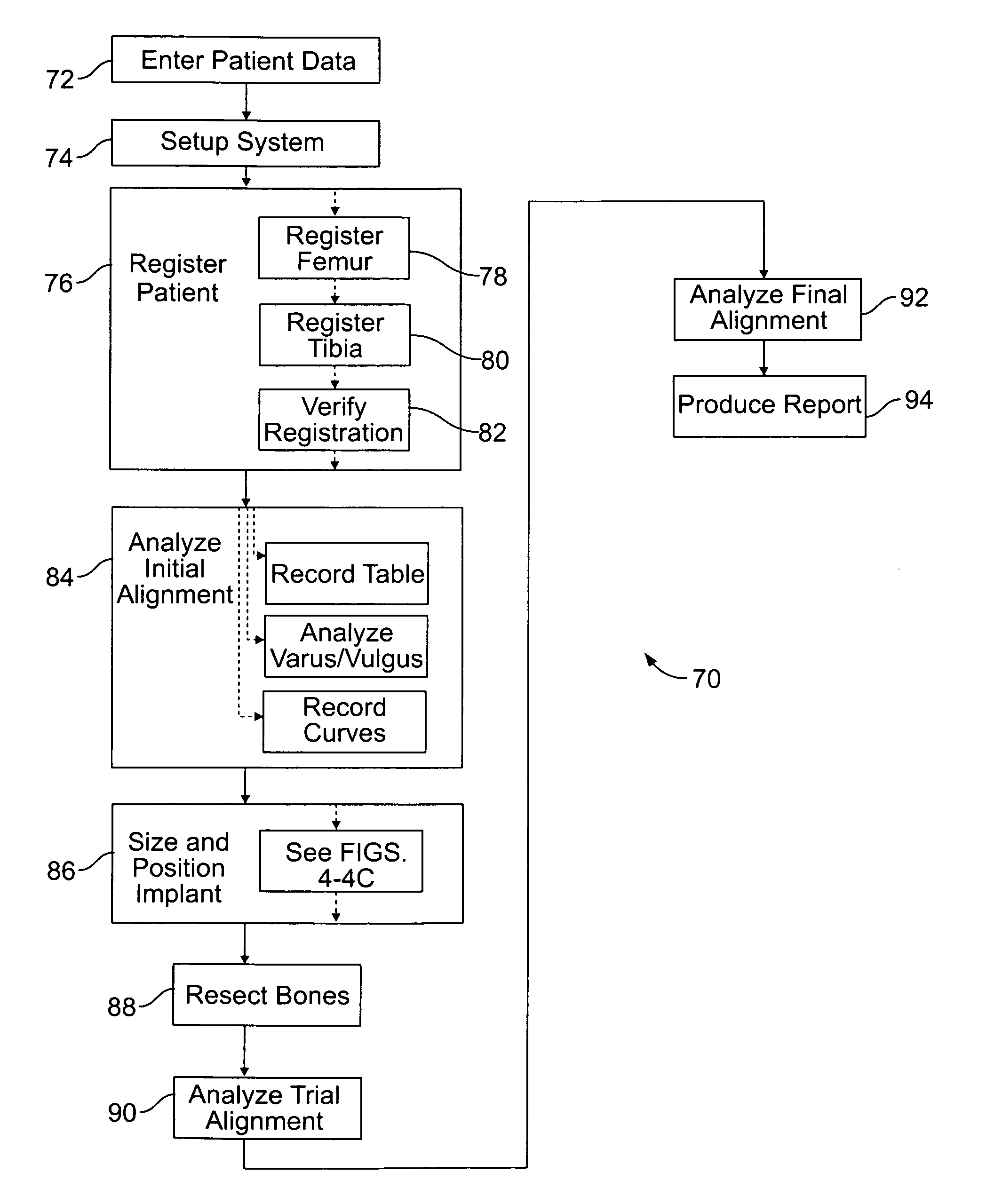
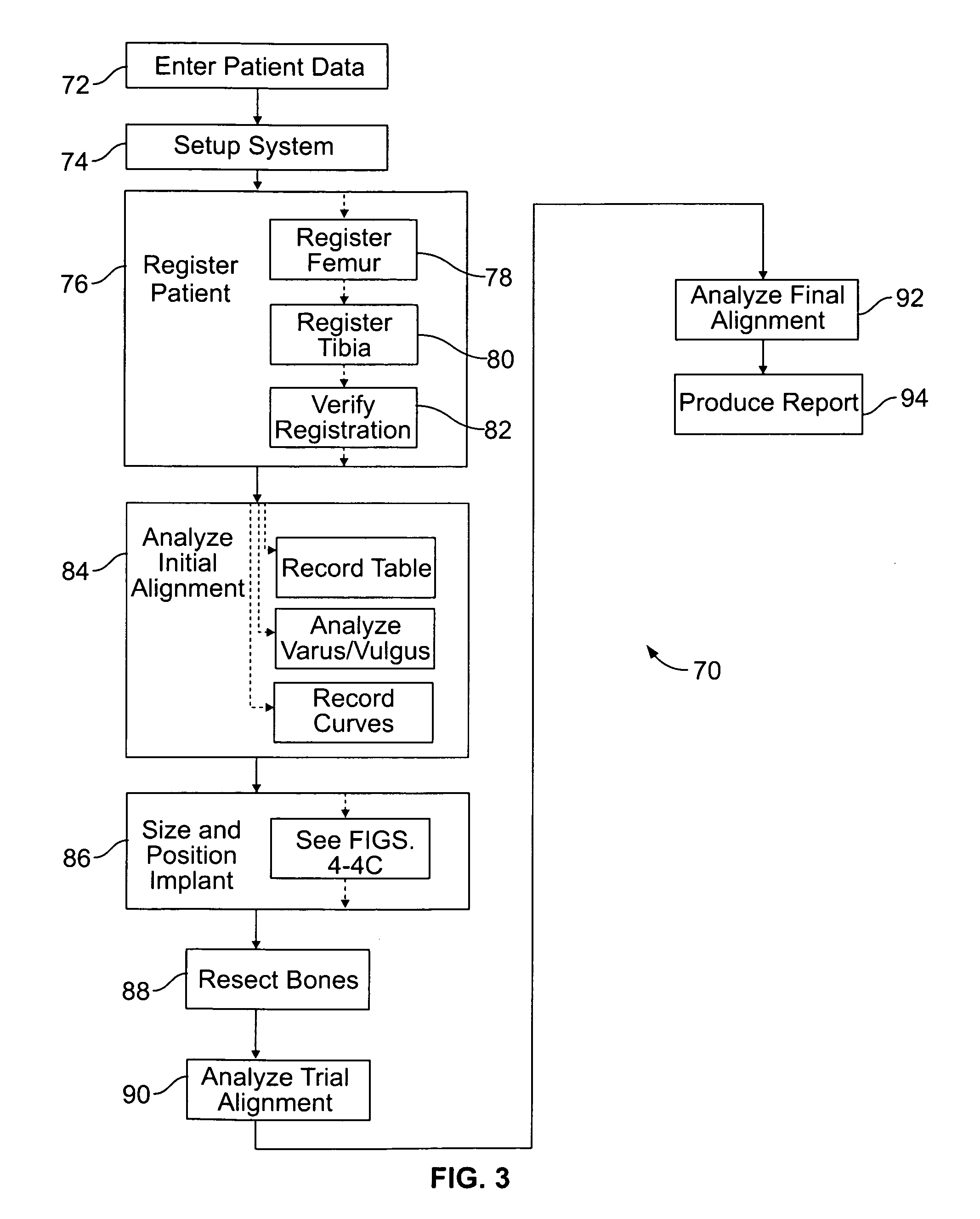
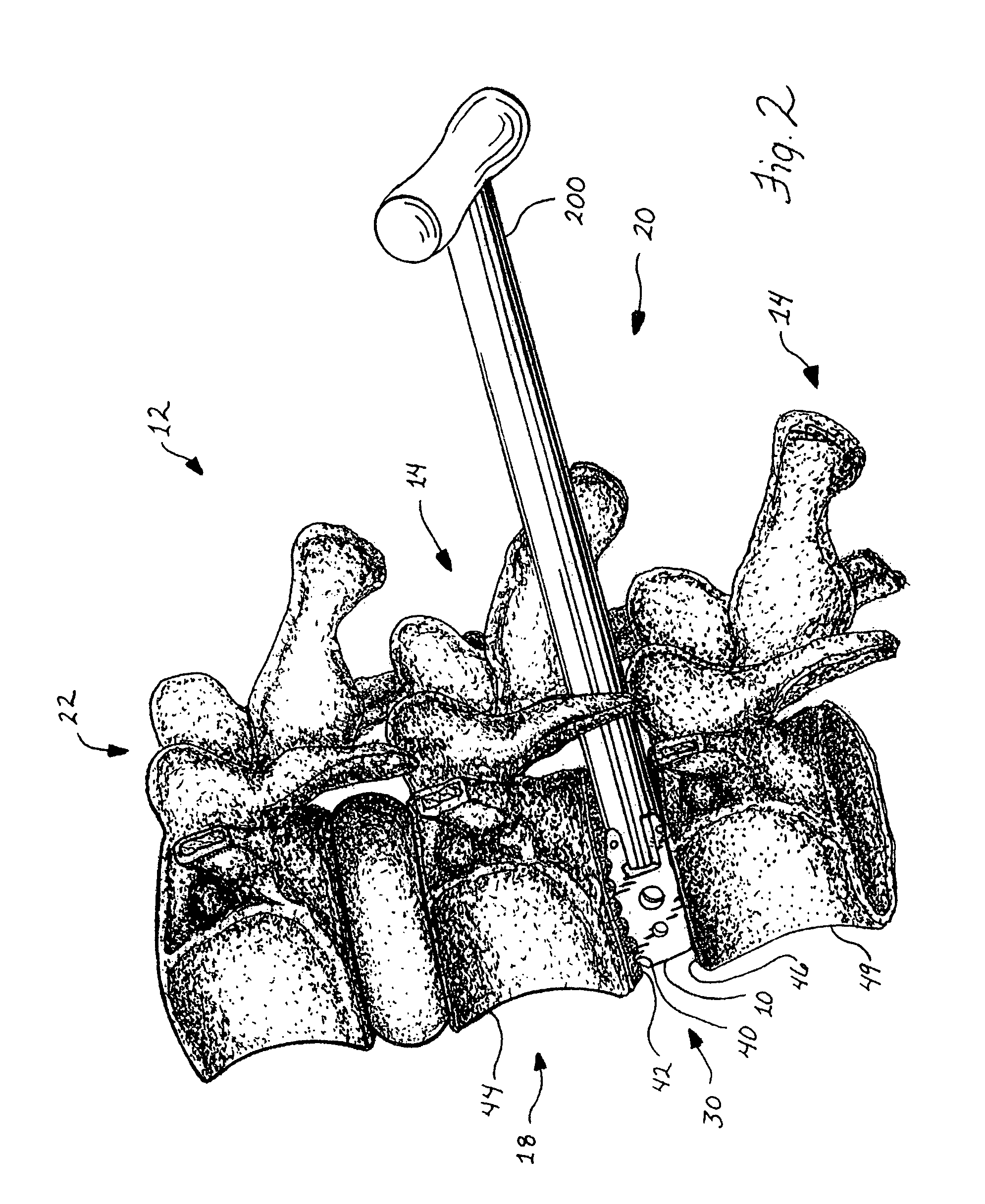
Method of and system for planning a surgery
ActiveUS8382765B2Medical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesMedicineSurgery procedure
A system for virtually planning a size and position of a prosthetic implant for a bone on a patient includes a database containing pre-defined form factor information for a plurality of different implants and a circuit for obtaining surface shape information of the bone. The system further includes a circuit for defining baseline location parameters for an implant location in relation to a virtual representation of the bone based on the surface shape information and a circuit for assessing a fit calculation of each implant in relation to the virtual representation of the bone based on the form factor in formation and a plurality of fit factors at each of a plurality of incremental positions in relation to the bone. Still further, the system includes a circuit for selecting a best fit implant size and position from all of the fit calculations.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Method for (semi-) automatic dental implant planning
ActiveUS8170327B2Simple methodOvercome disadvantagesDental implantsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDental implantOrthodontics
Owner:DENTSPLY IMPLANTS NV
Method of and System for Planning a Surgery
A system for virtually planning a size and position of a prosthetic implant for a bone on a patient includes a database containing pre-defined form factor information for a plurality of different implants and a circuit for obtaining surface shape information of the bone. The system further includes a circuit for defining baseline location parameters for an implant location in relation to a virtual representation of the bone based on the surface shape information and a circuit for assessing a fit calculation of each implant in relation to the virtual representation of the bone based on the form factor in formation and a plurality of fit factors at each of a plurality of incremental positions in relation to the bone. Still further, the system includes a circuit for selecting a best fit implant size and position from all of the fit calculations.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
In-vivo biodegradable medical implant
InactiveUS9119906B2The implementation process is simpleReduce internal stressSuture equipmentsBone implantMetallic materialsEngineering
In-vivo biodegradable medical implants, containing at least in part at least partially fine-grained metallic materials that are strong, tough, stiff and lightweight, are disclosed The in-vivo biodegradable implants are used in a number of stent applications, for fracture fixation, sutures and the like. The in-vivo biodegradable medical implants enable the reduction of implant size and weight and consequently result in reducing the release of implant degradation products into the body.
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
System and Method for Joint Resurface Repair
InactiveUS20090192516A1Enhance load bearing and load transfer propertyImprove the immunitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisArticular surfacesArticular surface
Owner:ARTHROSURFACE
Surgical instrument for determining the size of intervertebral implant
ActiveUS8585710B2Easy to adjustReduce in quantityMeasurement devicesPerson identificationArticular surfacesArticular surface
A surgical instrument is configured for determining the size and / or height of an intervertebral implant insertable into an intervertebral space between two adjacent vertebral bodies of two human or animal vertebrae. The implant includes a first abutment element for abutment against an articular surface of one of the two adjacent vertebral bodies and a second abutment element supported directly or indirectly on the first abutment element for abutment against an articular surface of the other of the two adjacent vertebral bodies. The instrument includes a holding part defining a longitudinal direction and at least one test implant, which includes a first and a second test-implant abutment element each having at least one abutment surface for abutment against one of the articular surfaces. A distal end of the holding part includes at least one abutment-element holding element for detachable connection to the at least one test implant 149.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Surgical implants, tools and methods for treating pelvic conditions
Described are pelvic implants (e.g., urinary incontinence sling, hammock, etc.) and method of implanting a pelvic implant that provide treatment for pelvic floor disorders such as incontinence, stress urinary incontinence, prolapse (e.g., cystocele, enterocele, rectocele, vault prolapse), fecal incontinence, and the like, wherein the implant and methods involve various features, such as the ability to adjust dimensions of an implant before, during, or after implantation.
Owner:AMS RES CORP
Measuring system and method for oral implant repair space analysis
ActiveCN107647929AJudgment operation spaceSimple bite distance checkDental implantsImpression capsMissing toothMissed tooth
The invention discloses a measuring system for oral implant repair space analysis. The system comprises a first measuring unit for measuring degree of opening and a plurality of missing teeth gaps, asecond measuring unit for measuring a single missing tooth gap and bite distance, and a third measuring unit for measuring depth of gingiva. The first measuring unit, the second measuring unit and thethird measuring unit all comprise connecting rods and measuring heads arranged at upper ends of the connecting rods. The measuring units of the measuring system have simple structures, are easy to use, have accurate measured data, can accurately and rapidly measure specific spatial characteristics of a to-be-repaired position, and provides basis for design of key parameters of implant size, implant location or shape and structure of upper dummy and the like, and solves problems that current oral and model space analysis depends on clinical experience, is lack of accurate and efficient measurement methods.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
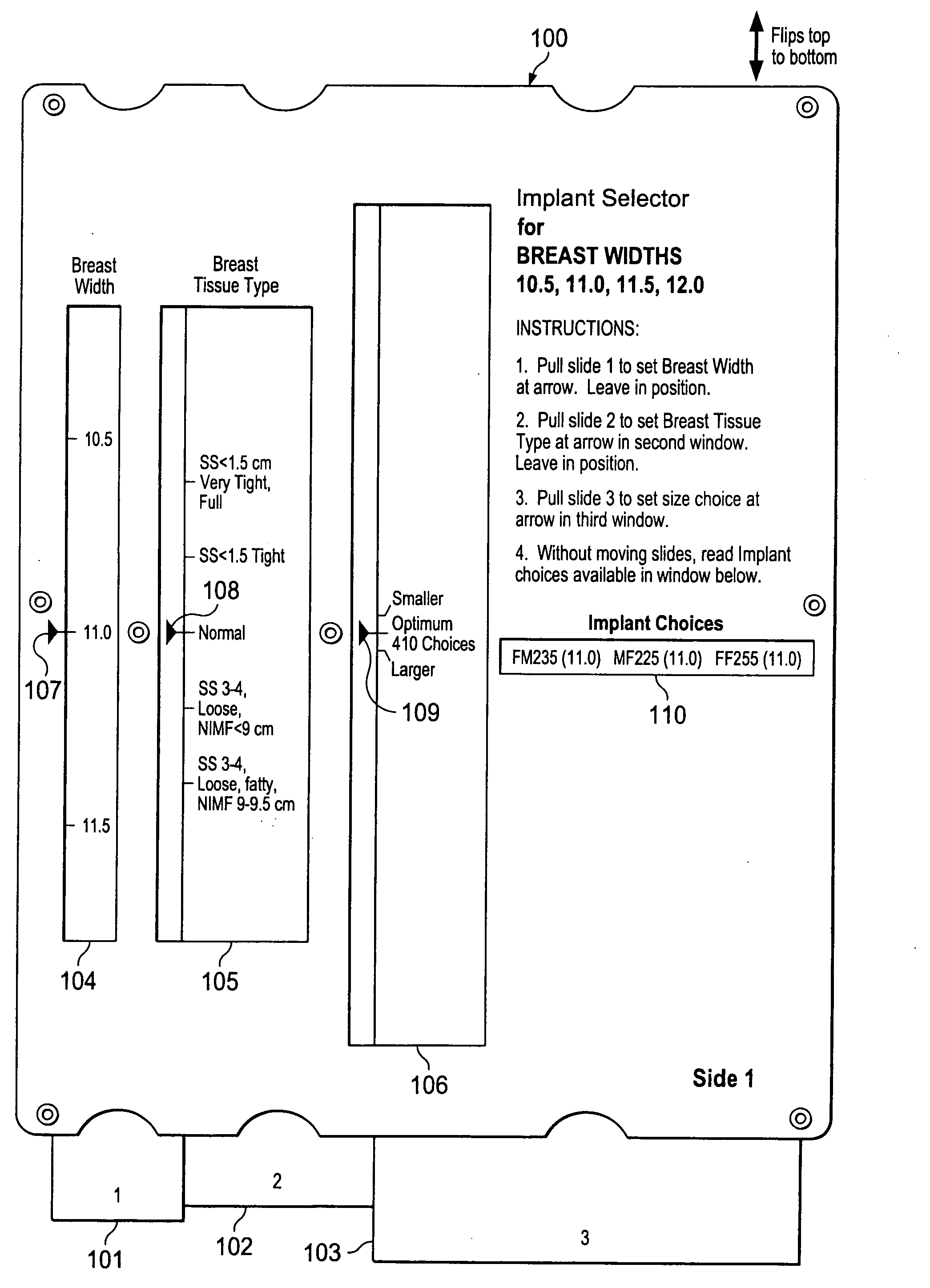
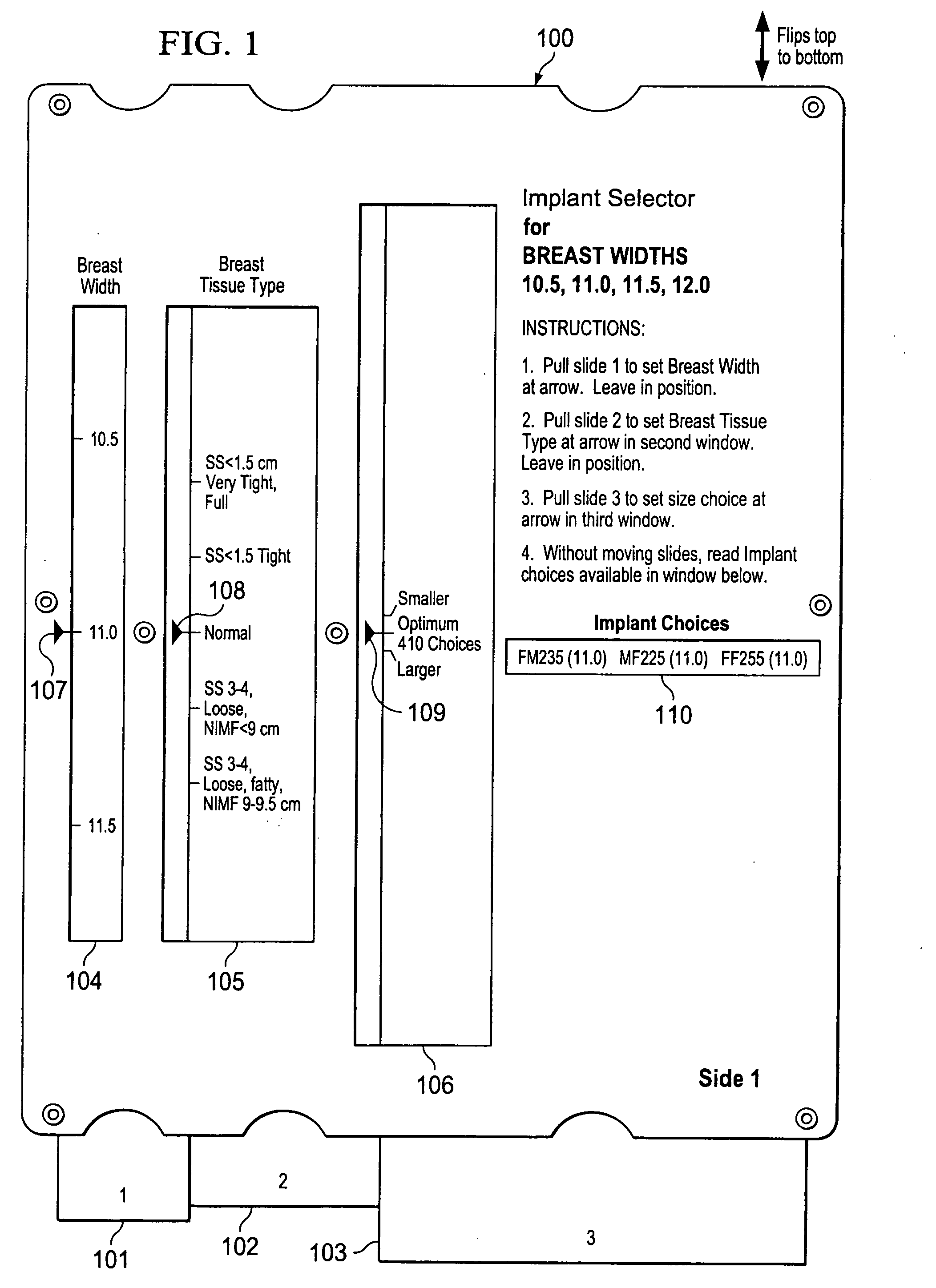
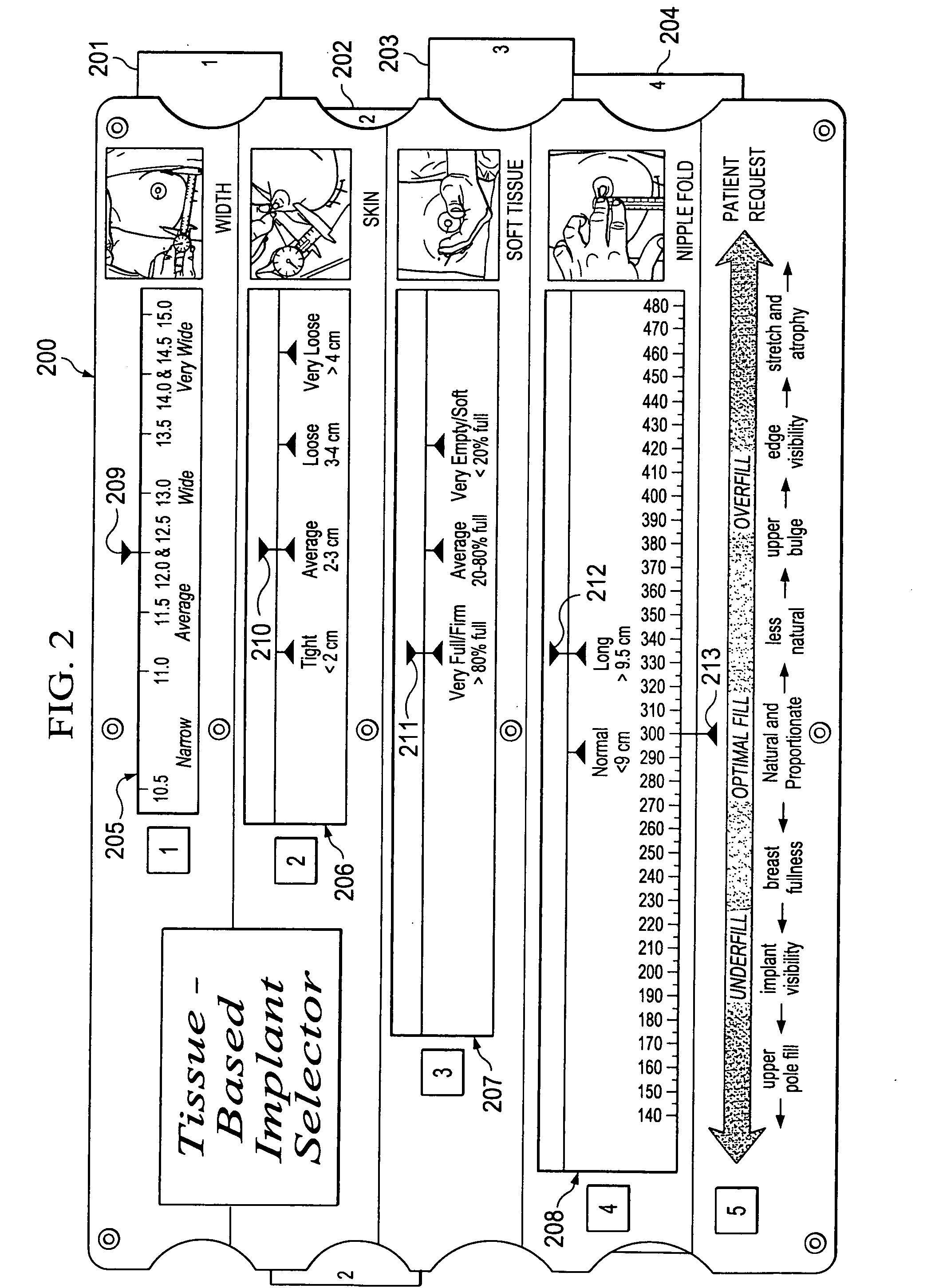
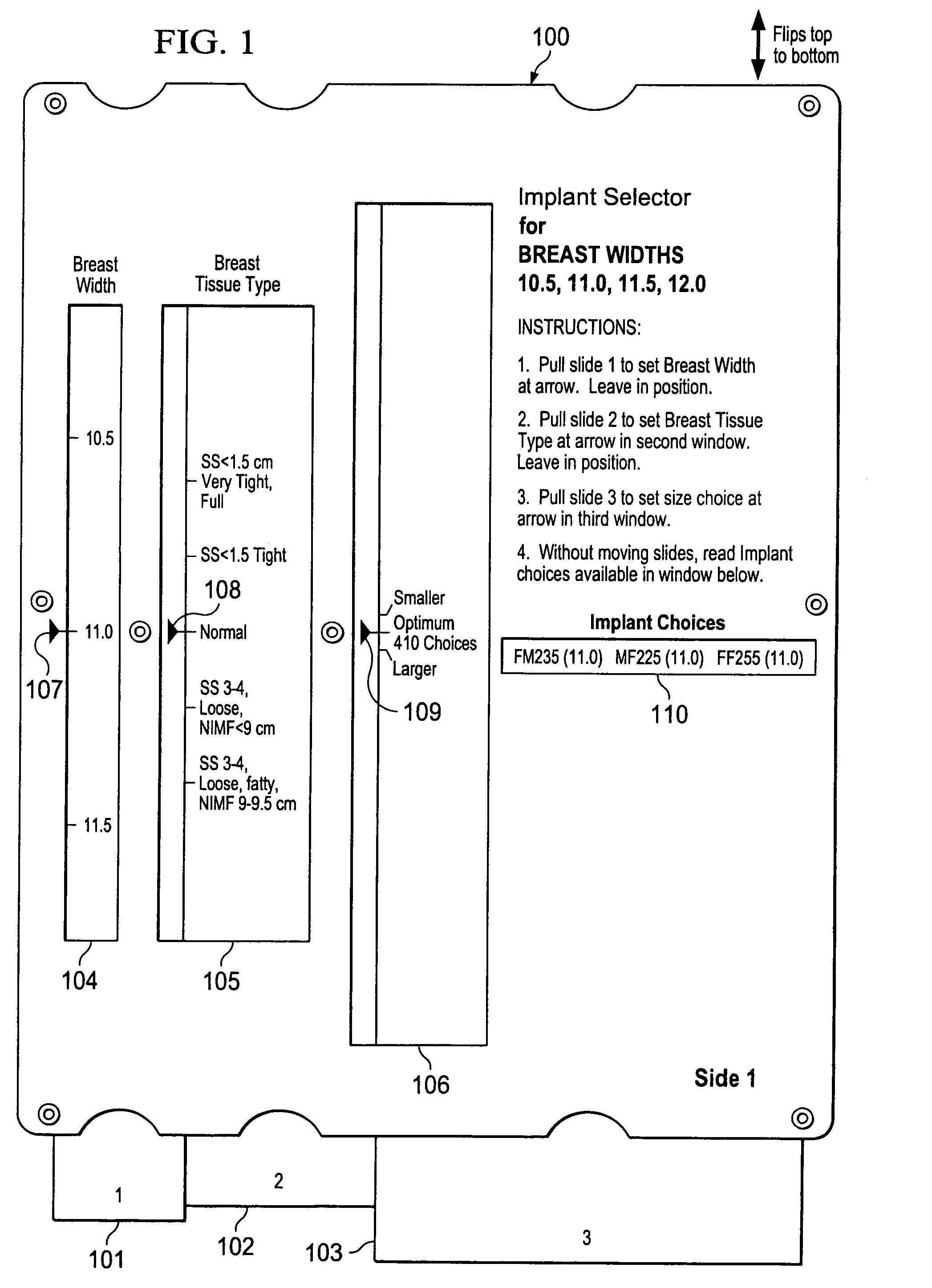
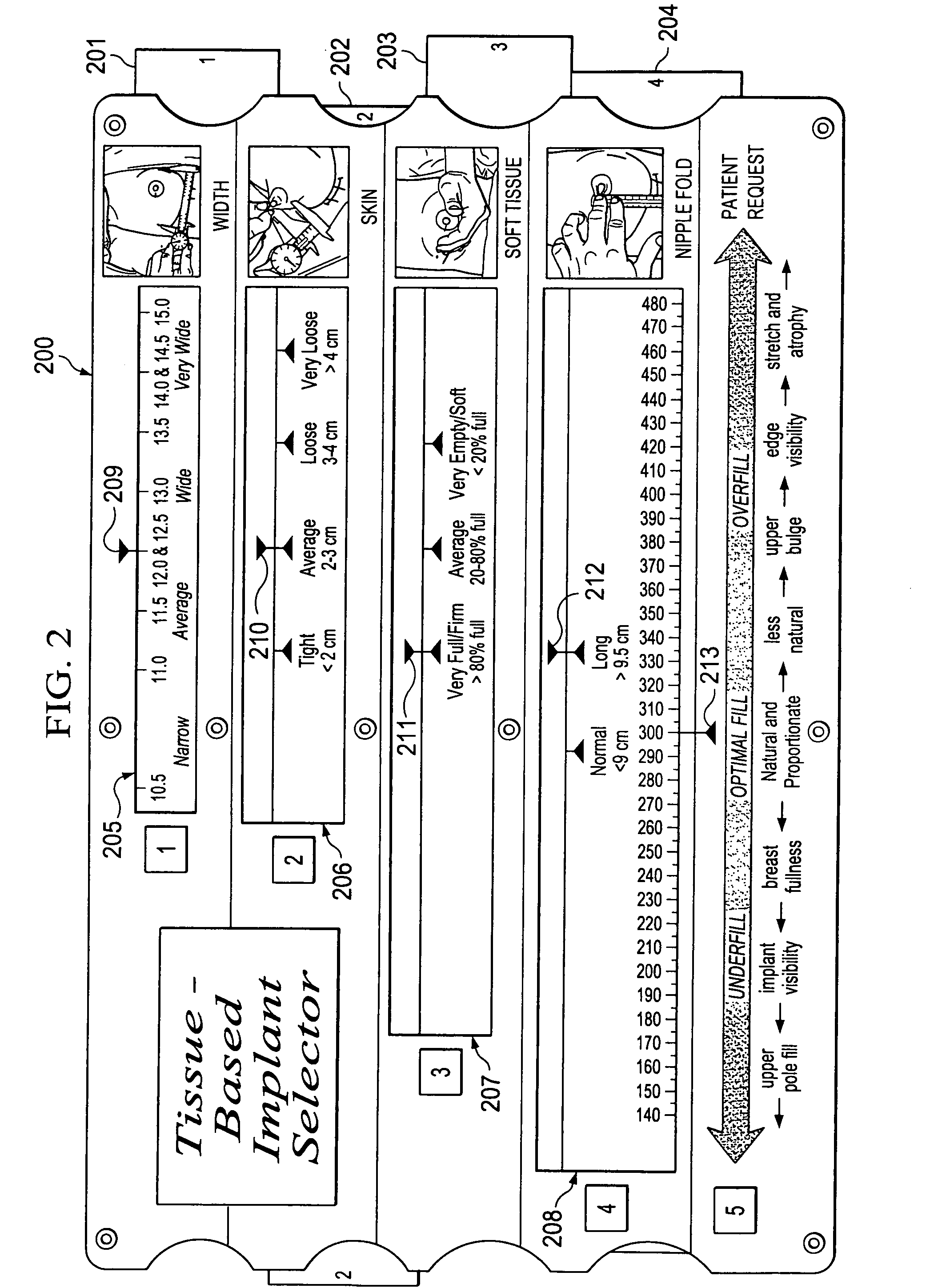
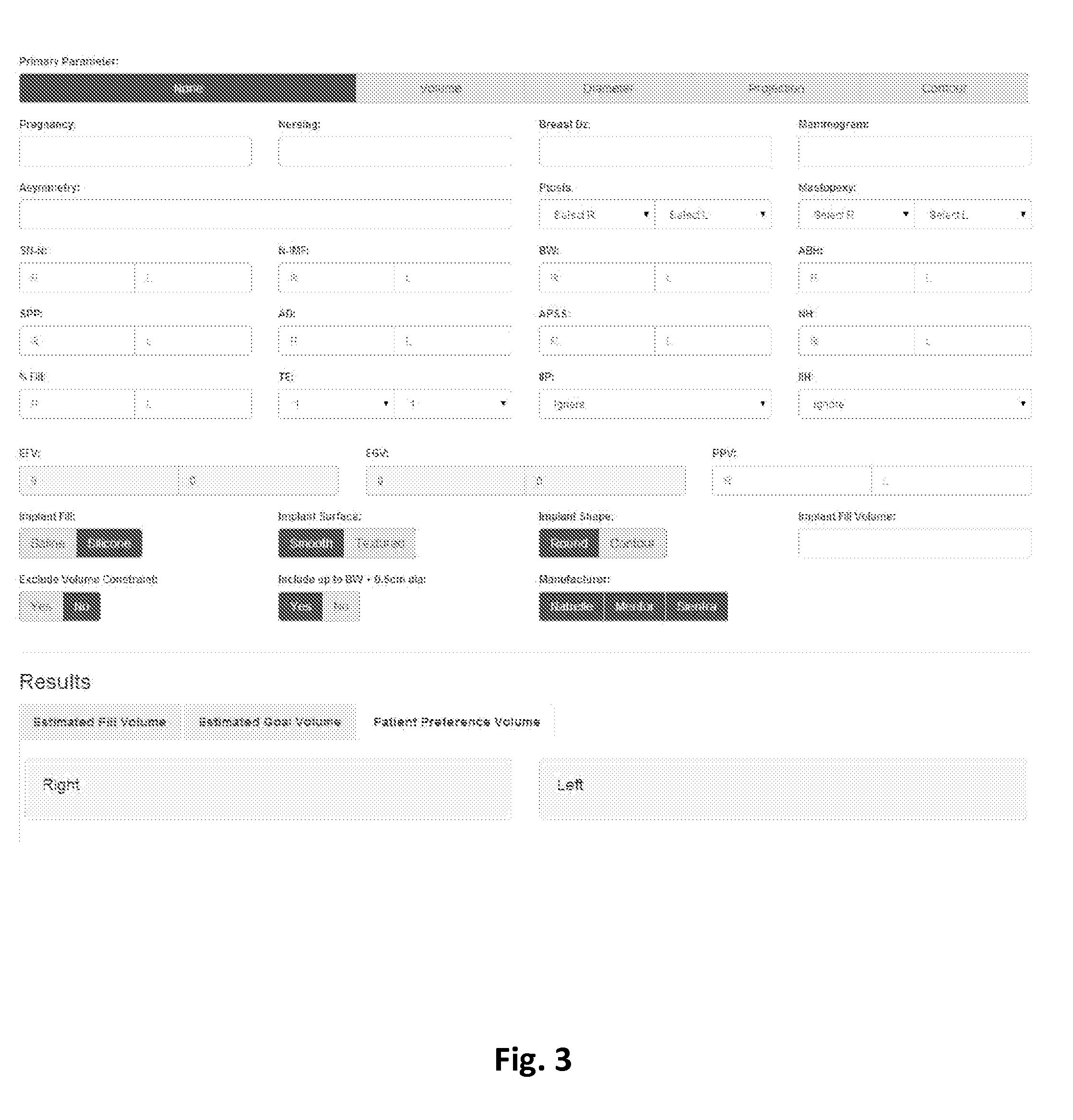
Breast implant selector systems
ActiveUS20090069891A1Easily and accurately selectEasy to useMedical simulationMammary implantsBreast implantBreast tissue
A breast implant selector system including a breast width selector for selecting breast width input information, a breast tissue type selector for selecting breast tissue type input information in response to breast width input information selected with the breast width selector, and an implant size selector for selecting implant size input information in response to the breast tissue type input information selected with the breast tissue type selector. A result indicator provides a result characterizing at least one suggested breast implant as a function of the input breast width, breast tissue type, and implant size input information.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
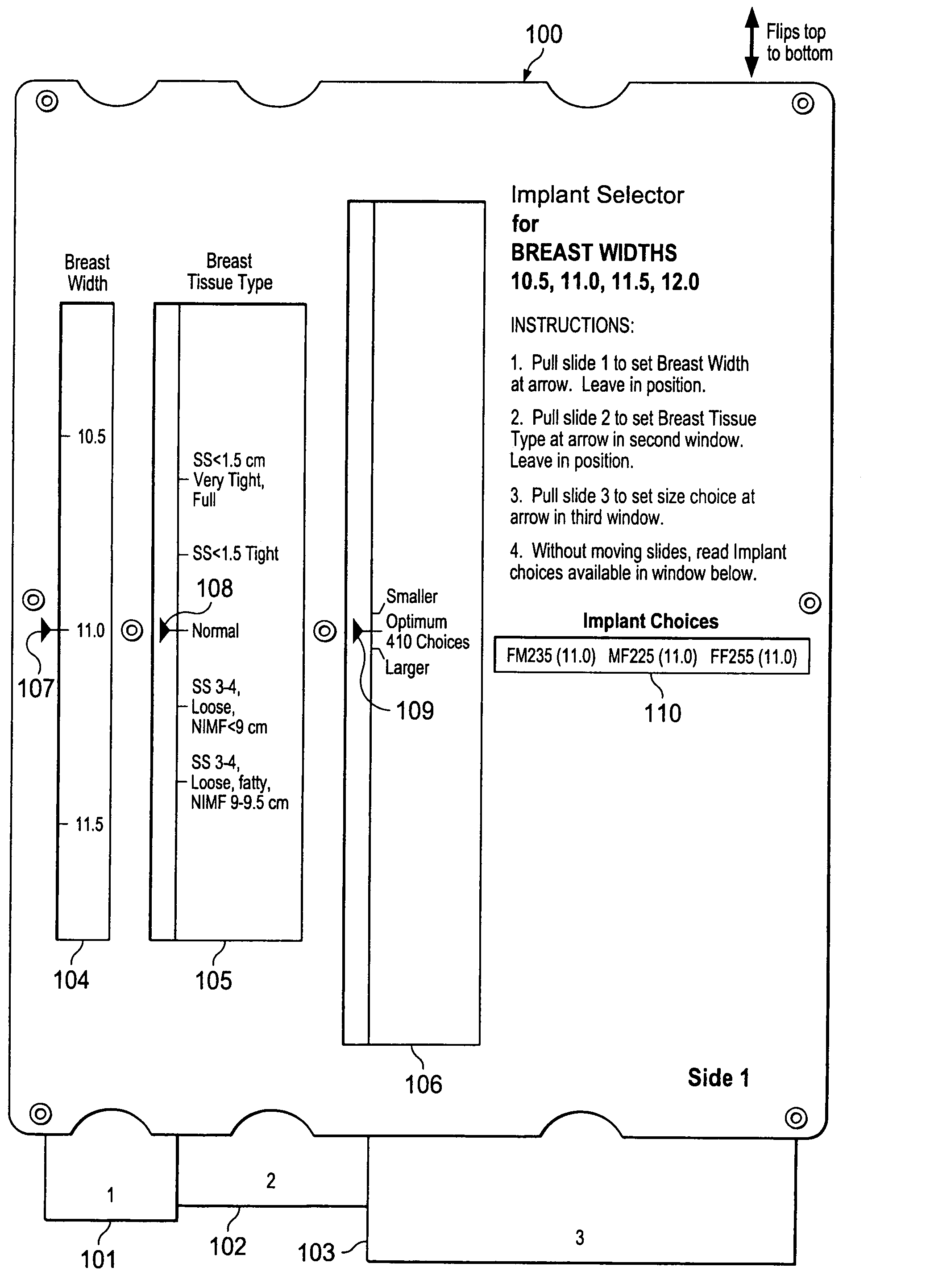
Breast implant selector systems
ActiveUS7685721B2Easily and accurately selectEasy to useMedical simulationMammary implantsBreast implantBreast tissue
A breast implant selector system including a breast width selector for selecting breast width input information, a breast tissue type selector for selecting breast tissue type input information in response to breast width input information selected with the breast width selector, and an implant size selector for selecting implant size input information in response to the breast tissue type input information selected with the breast tissue type selector. A result indicator provides a result characterizing at least one suggested breast implant as a function of the input breast width, breast tissue type, and implant size input information.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Optimizing patellar femoral mechanics through alternative depth referencing
In knee-replacement surgery, restoration is achieved with respect to the patellar femoral joint in the distal plane is, thereby optimizing patellar femoral mechanics. The depth of the trochlea is increased with increasing implant size. In the preferred embodiment, this is achieved by referencing the extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region, and resecting the distal femur in accordance with the extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region. As an alternative, the invention provides for distal femoral and proximal tibial components having bone-contacting and articulating surfaces which account for the measured extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region. A method of preparing a distal femur according to the invention includes the steps of installing a rod or stem within the intramedullary canal, and attaching a referencing fixture thereto. The extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region is measured using the referencing fixture, and the distal femur is resected in accordance with the extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region. The method typically further includes the step of placing a spacer between the referencing fixture and the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region. The preferred alternative embodiment of the invention involving the use of modified components proceeds similarly, except that after measuring the extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region using the referencing fixture, distal femoral and proximal tibial components are implanted having bone-contacting and articulating surfaces which take the measurement into account.
Owner:MASINI MICHAEL A
Artificial joint replacement assisting device, artificial joint replacement assisting method using same, and assisting system
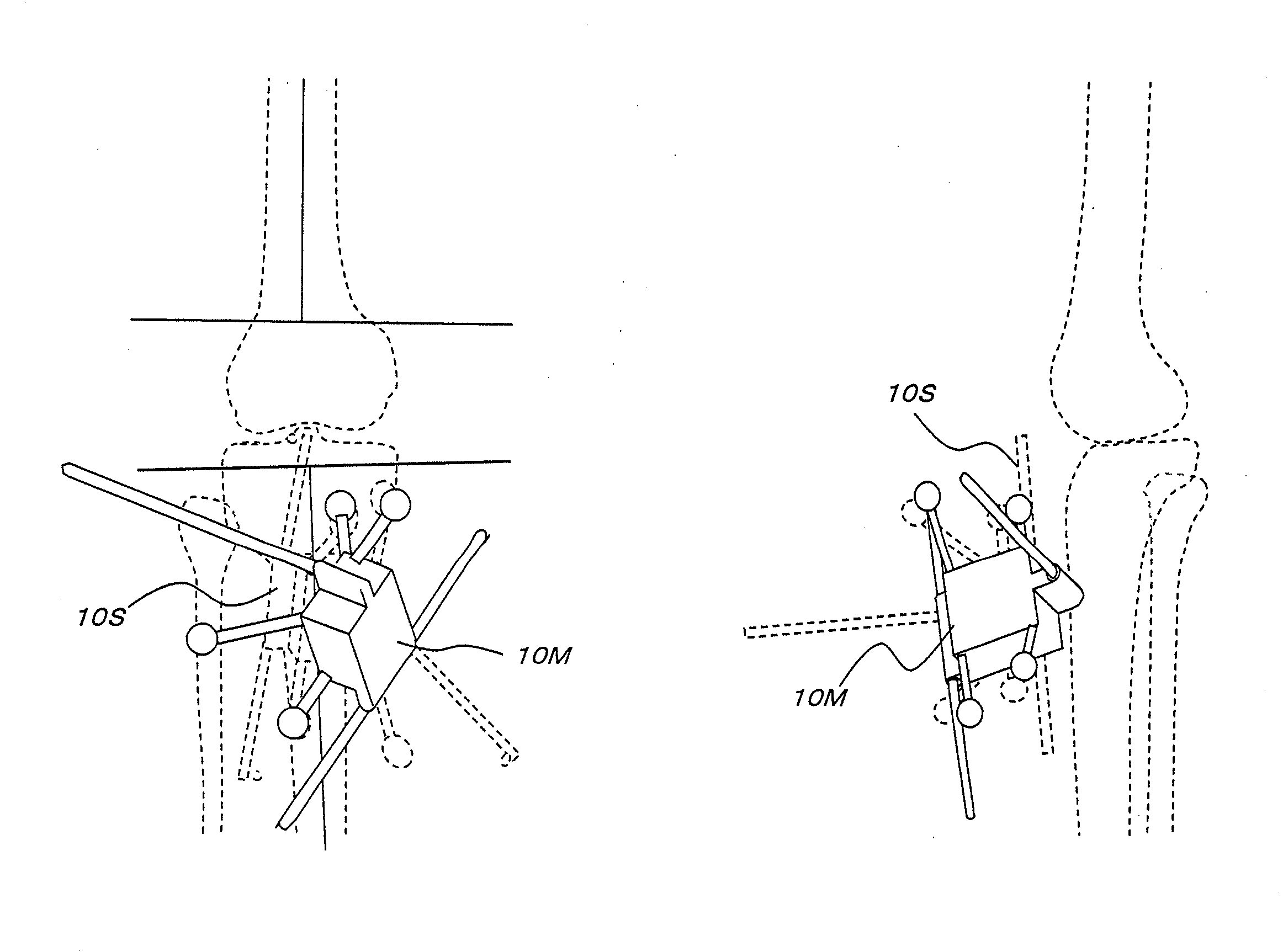
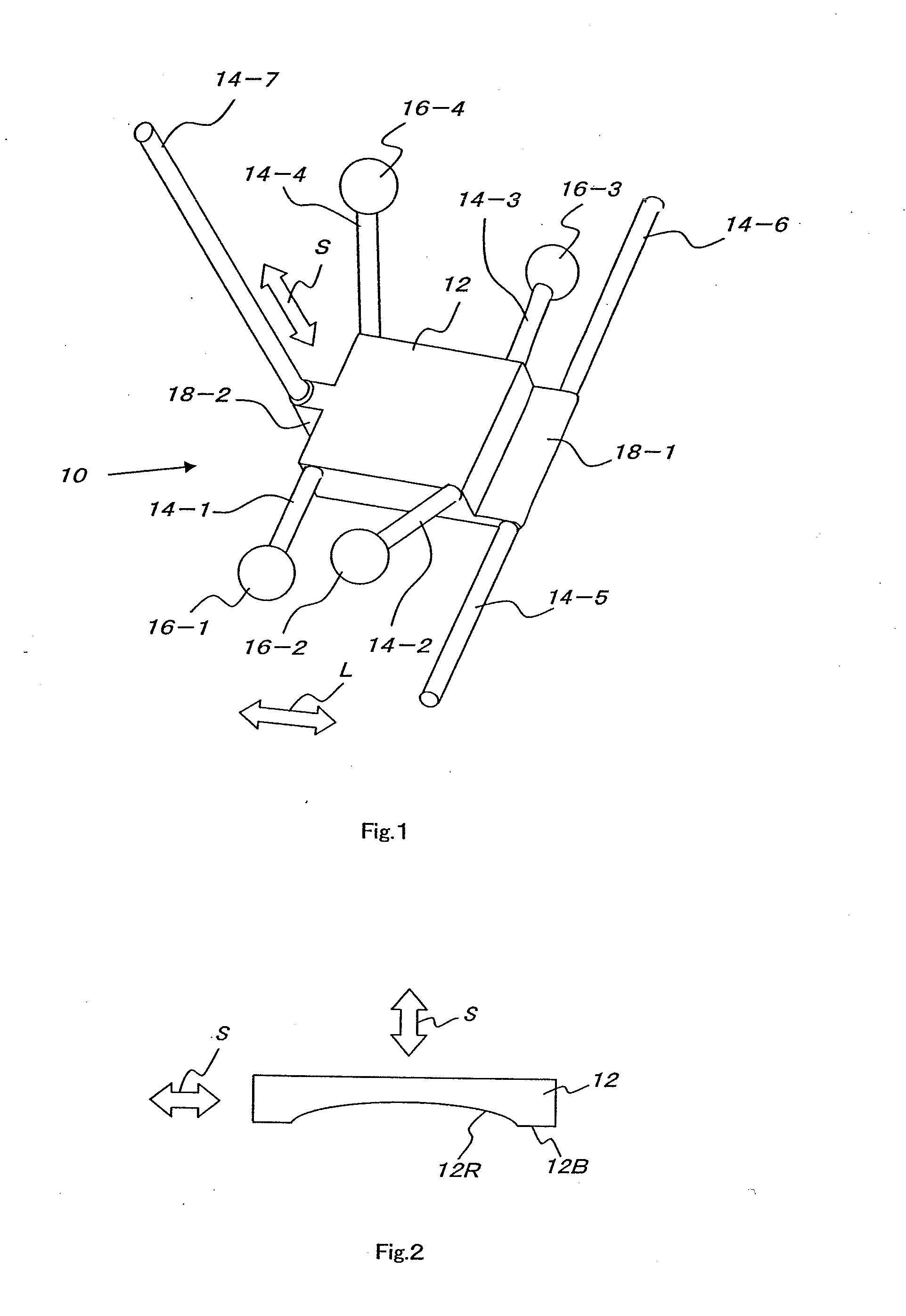
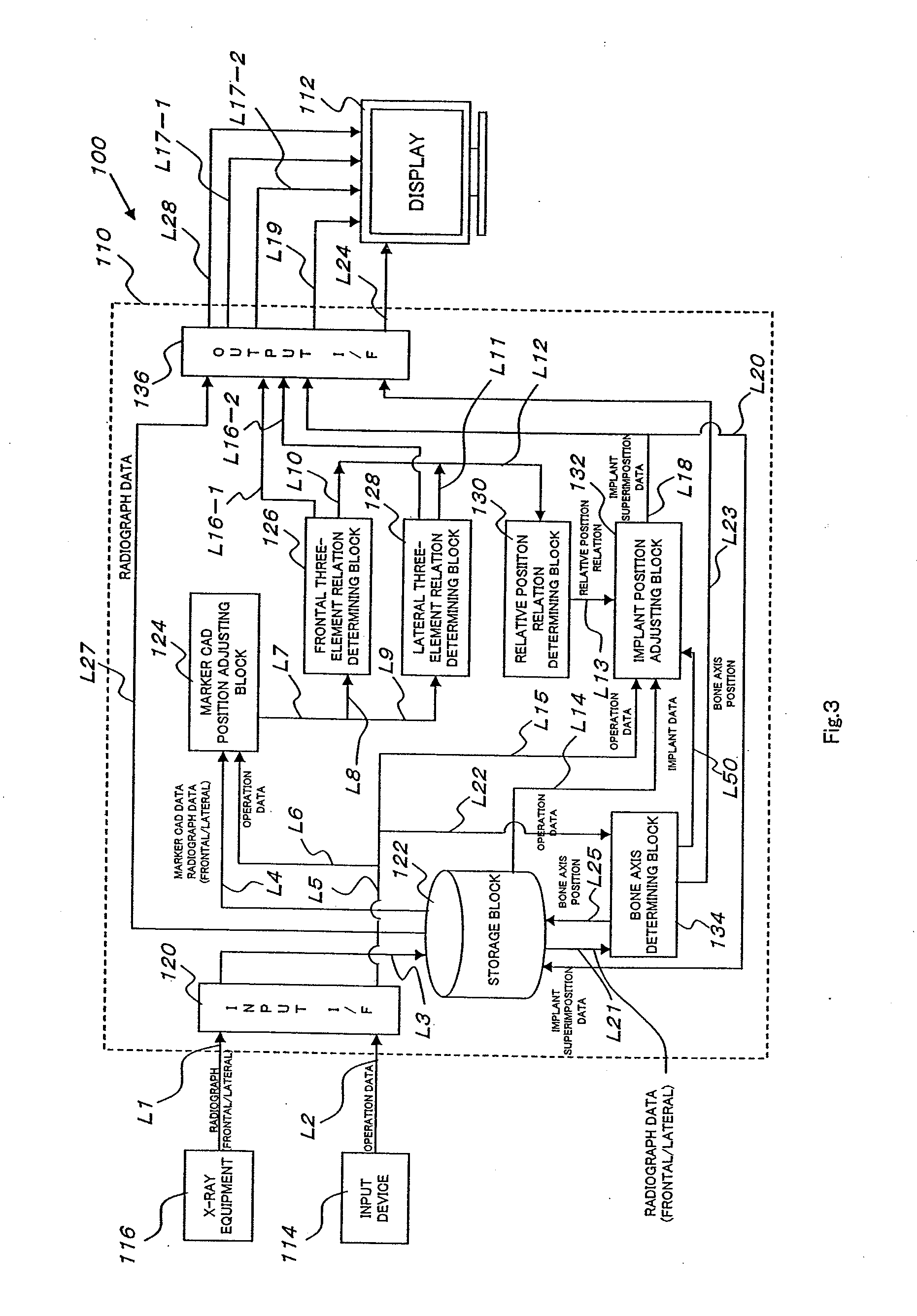
InactiveUS20100094308A1Accurately determineAdequate implant positionJoint implantsDiagnostic markersArtificial jointsX-ray
A technique of adequately determining the position of the bone resection plane of artificial joint replacement and the size of the implant. The three-dimensional relative position relation (the three-dimensional position relation between the relation among frontal three elements and the relation among lateral three elements) among the five elements, i.e., a frontal The source of X-ray (FS), the plane (PS) to which the frontal radiograph belongs, a lateral The source of X-ray (FL), the plane (PL) to which the lateral radiograph belongs, a lateral The source of X-ray (FL), the plane (PL) to which the lateral radiograph belongs, and three-dimensional CAD data is determined (S7), shade images (IU, IL) of three dimensional CAD data on the implant are superimposed in an adequate position shown in the radiograph, and the images are displayed on a display (112) (S9, S10).
Owner:TATSUMI ICHIRO +1
Dental implant system
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Device and method for determining proper screw or implant size during orthopedic surgery
ActiveUS20190000405A1Accurate and Precise MeasurementsPromote recoverySurgical needlesForeign body detectionMedicineFluorescence
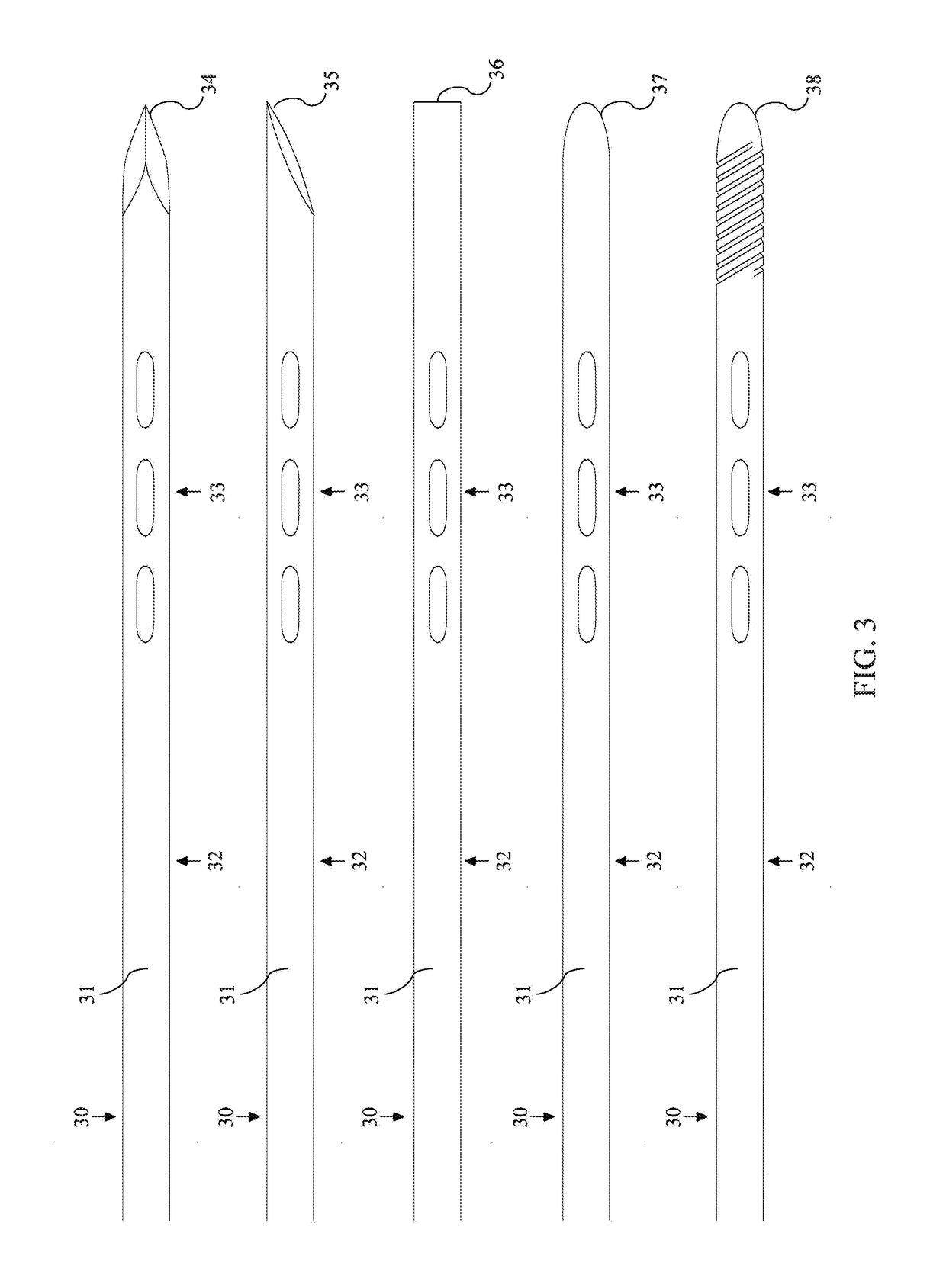
The devices and methods described herein refer to a guidewire, sometimes referred to as a K-wire, for use during varying orthopedic surgeries. The guidewire allows for the measurement of objects and distances inside the patient's body when used in tandem with x-ray or fluoroscopy imaging. Also, the devices and methods described herein act as a guide to accurately insert an instrument or implant, in the correct orientation, to the surgical site. The guidewire comprises a measurement segment that comprises one or more markers placed at known distances from the distal end of the guidewire. The markers, when used in tandem with fluoroscopy and / or x-ray imaging, provide users with a reference for measuring objects and distances inside the body. The markers can have many possible designs or configurations such as, but not limited to, visualization windows, grooves, notches, and / or material inserts.
Owner:SURGENTEC LLC
Systems and methods for sizing, inserting and securing an implant intervertebral space
InactiveCN101534752APrevent reversalPrevent retractionSpinal implantsIntervertebral spaceSpinal implant
A prosthetic spinal implant having a deployable securing mechanism that is deployable into a portion of the vertebral space for affixing the implant between the vertebrae, the securing mechanism having tactile feedback means comprising a surface for transmitting tactile feedback during deployment of the securing mechanism. A spinal implant having deployable securing means that interface with the implant to prevent the deployable securing means from retracting after deployment. An implant that utilizes its resilient properties to provide the user with tactile feedback with which the user may ascertain the position of the securing mechanism. A system and tools for sizing and implanting implants with the aforementioned characteristics.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Knee replacement surgical cut planes estimation for restoring pre-arthritic alignment
ActiveUS11439467B1Improve stabilityMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesComputer-aided planning/modellingCoronary arteriesPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A computer-aided pre-operative planning tool with interactive surgeon interface for total knee replacement implements a method that allows implant size selection, implant positioning, and surgical cut planes estimation (with construction of corresponding surgical jig), based upon a series of coronal, axial and sagittal image slices of a patient's leg. Limb alignment and corresponding surgical cut planes are defined based upon joint anatomical-matching analysis to minimize joint wear and restore a pre-arthritic alignment (rather than an always fully neutral alignment). Using the interface, a surgeon has the option to adjust the varus / valgus alignment within recommended bounds between the pre-arthritic and fully neutral alignments. Implant size may be selected based on a best fit to the patient's leg obtained from analysis of the images.
Owner:LENTO MEDICAL INC
Method and system for pre-operative implant sizing
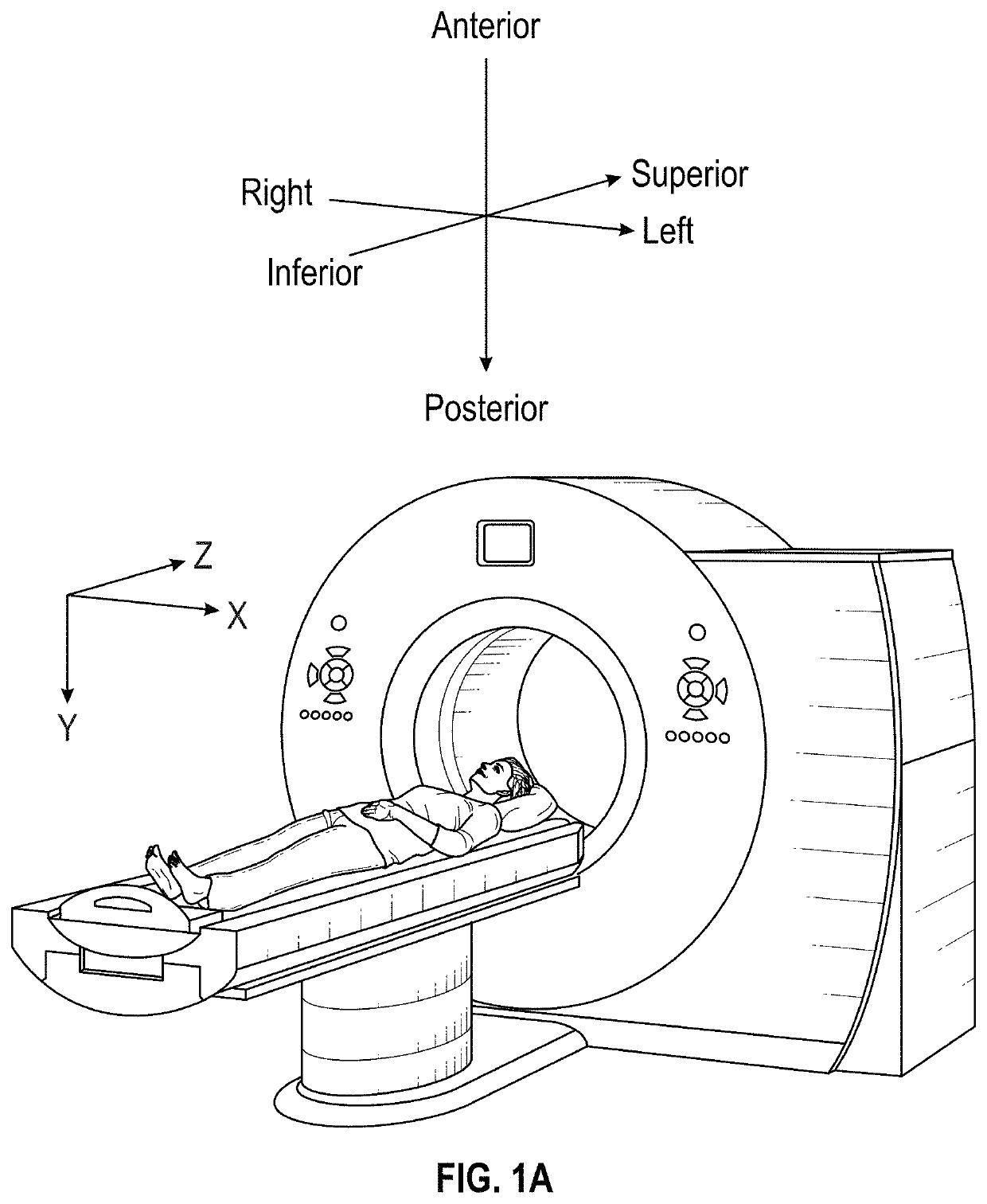
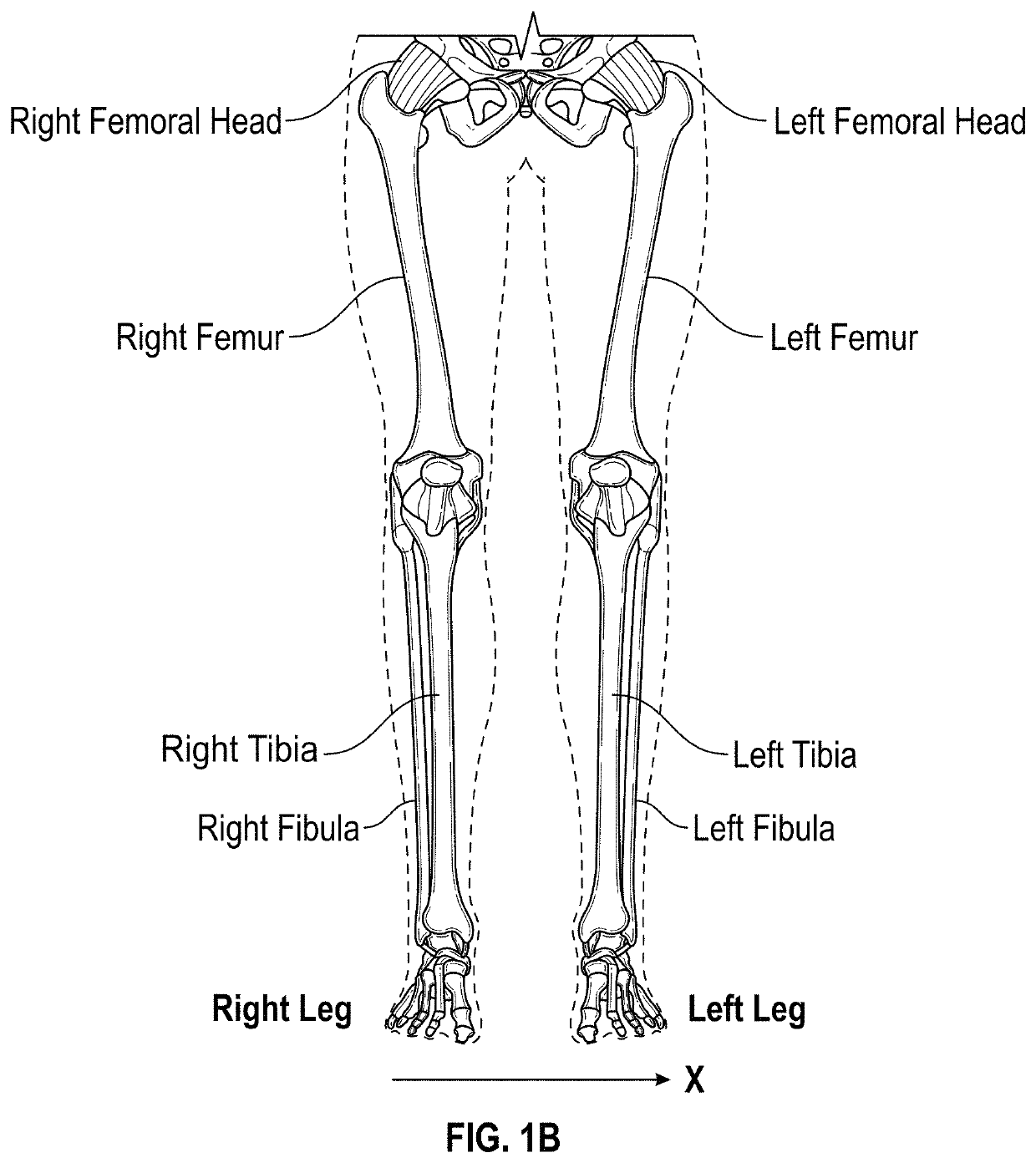
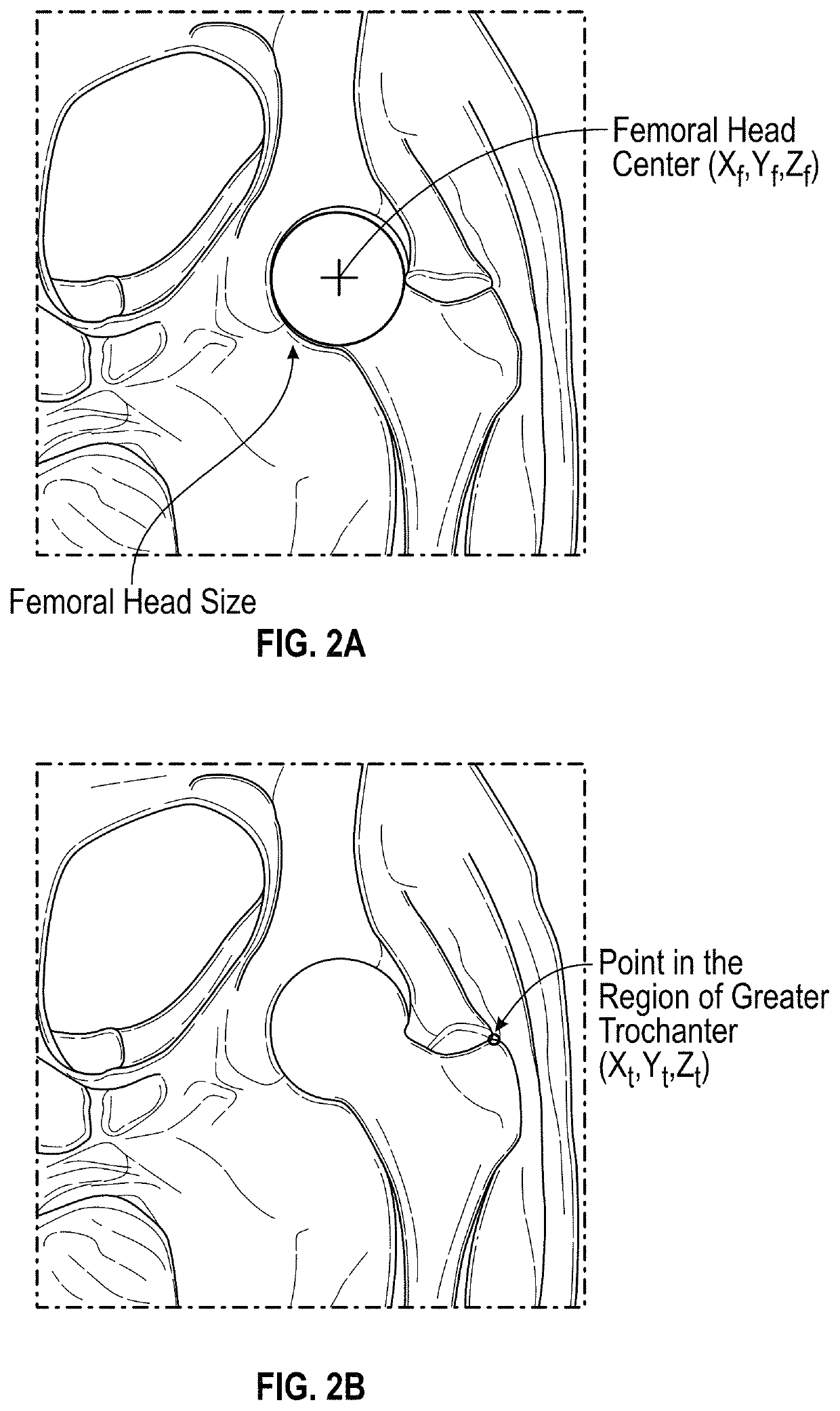
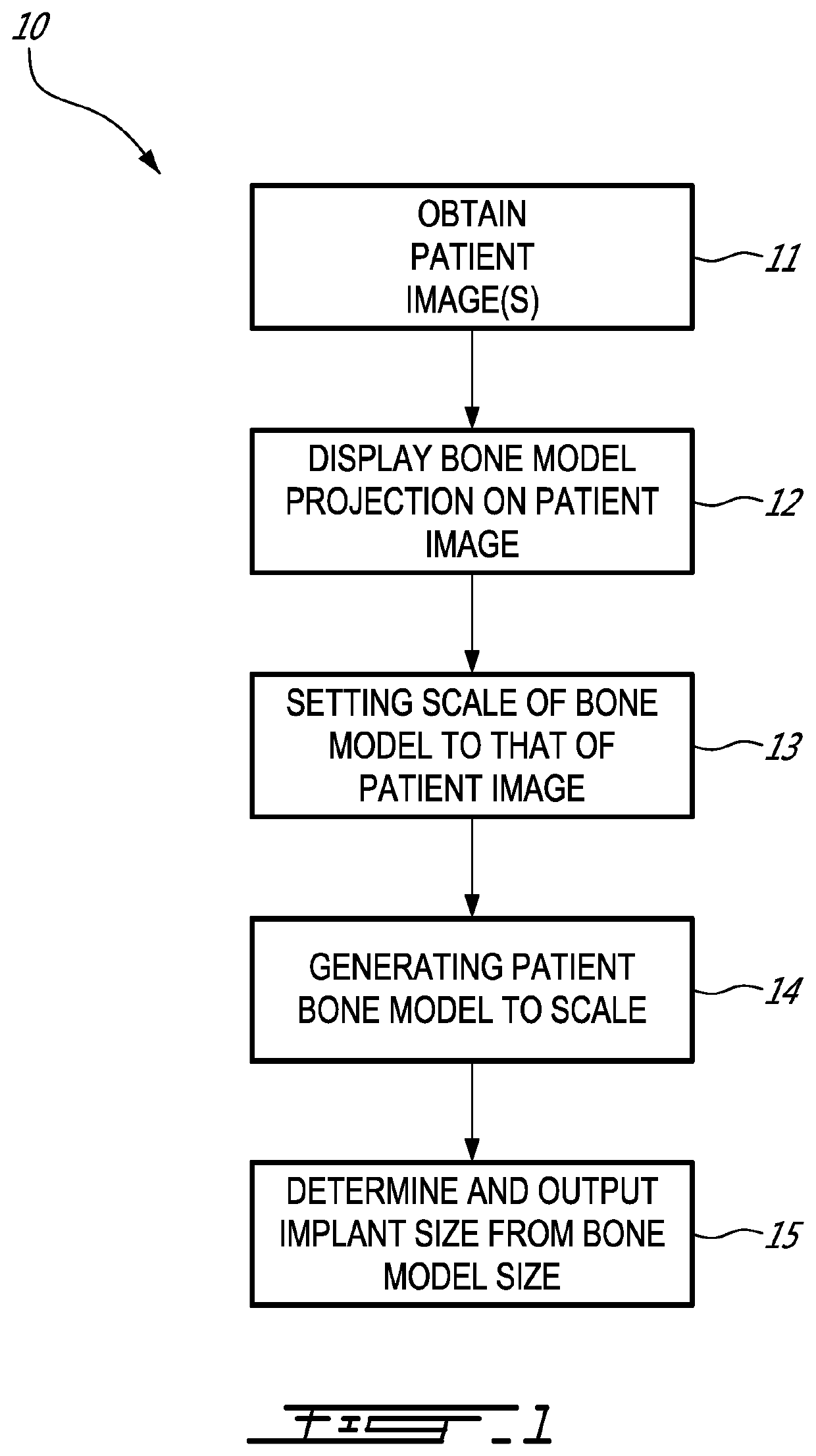
A system for sizing an implant for a patient pre-operatively comprises a processor unit. A non-transitory computer-readable memory may be communicatively coupled to the processing unit and comprising computer-readable program instructions executable by the processing unit for obtaining at least one radiographic patient image of at least one patient bone with a scale marker relative to the bone, the scale marker having a known geometry, setting a scale of the at least one radiographic patient image using the known geometry of the scale marker, generating a three-dimensional bone model representative of the at least one patient bone using the at least one radiographic patient image and the scale, identifying an implant size and / or an implant model using implant models and dimensions of the three-dimensional bone model based on said scale, and outputting the implant size and / or the implant model for the patient.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
Systems and methods for determining suitability of a mechanical implant for a medical procedure
InactiveCN106021876ADiagnosticsComputer-aided planning/modellingBiomedical engineeringMedical procedure
Owner:SANDANCE TECH
Cutting machine for resizing raw implants during surgery
ActiveUS10603175B2Improve accuracyIncrease speedAdditive manufacturing apparatusDiagnosticsPoint cloudReoperative surgery
Provided is a method for forming an implant with an autonomous manufacturing device. The method includes accessing a first computer-readable reconstruction of a being's anatomy; accessing a second computer-readable reconstruction of an implant; accessing a third computer-readable reconstruction comprising the first computer-readable reconstruction superimposed with the second computer readable reconstruction; generating at least one computer-readable trace from a point cloud; and forming an implant with an autonomous manufacturing device, wherein the autonomous manufacturing device forms the implant into a shape defined by at least one dimension of the computer-readable trace.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods and devices for breast implant surgery and selection
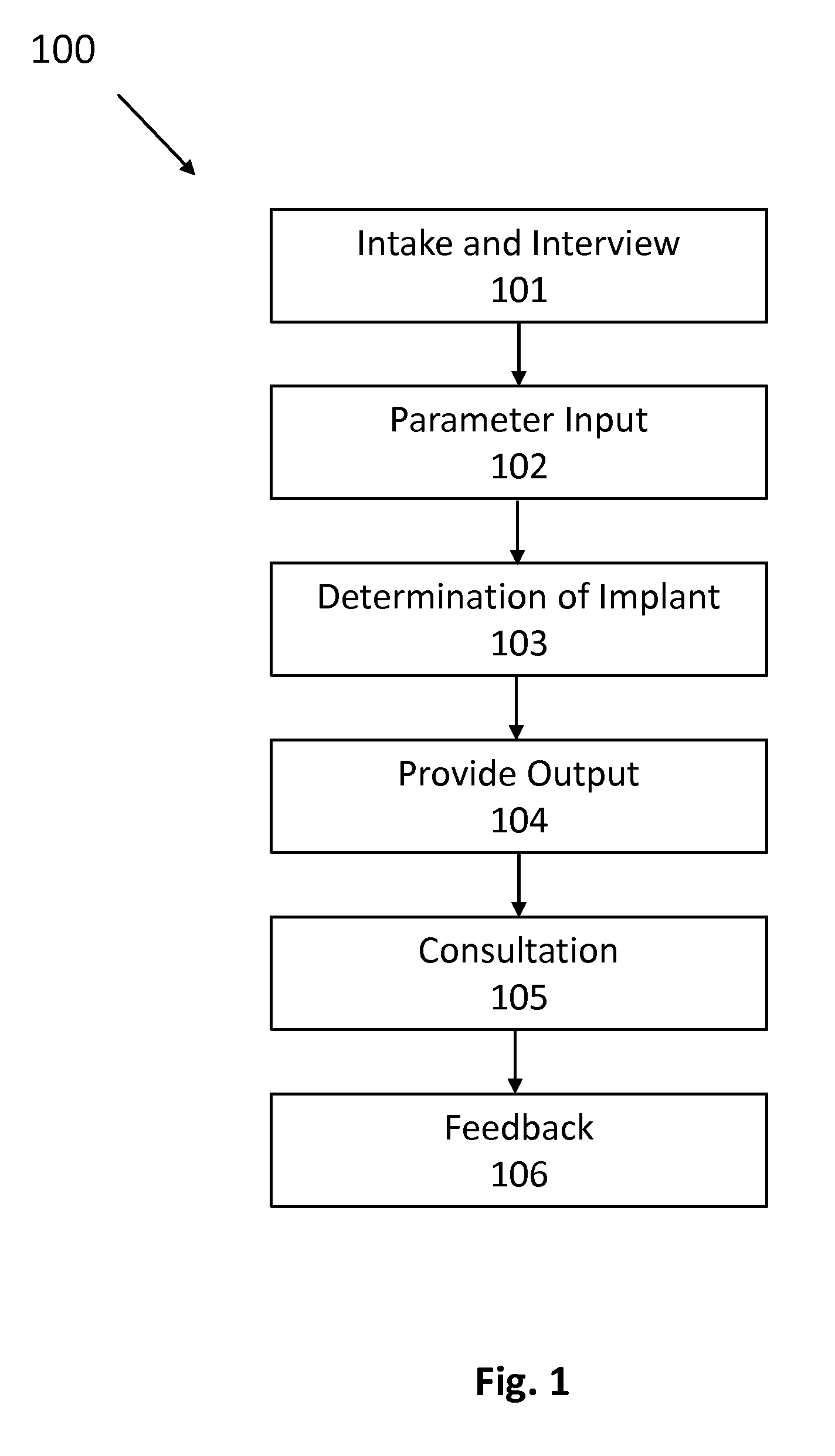
InactiveUS20150367581A1Minimal thicknessMore flexibleProgramme controlMammary implantsBreast implantSize determination
The present disclosure provides several processes, algorithms, and devices for breast implant surgery. An algorithm of the present disclosure can receive input from a user, surgeon, patient, and determine an appropriate or desired implant size or shape. The algorithm can prompt the user for adjustment and / or prioritization of certain parameters, and adjust the implant determination accordingly. Two-dimensional (2D) sizers of the present disclosure can be used during implant surgery to assist in determining an appropriate amount of pocket dissection. The 2D sizers can be inserted into a partially dissected cavity to determine whether the cavity is the correct size, and the doctor can then perform more dissection if needed. The processes and devices of the present disclosure can also be used with other imaging devices and a printer to provide implants on site.
Owner:TANTILLO MICHAEL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com