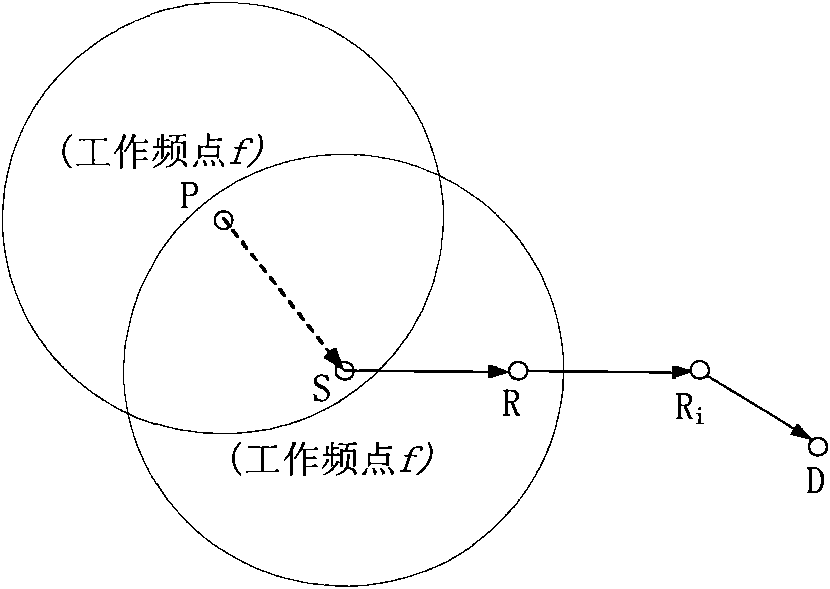
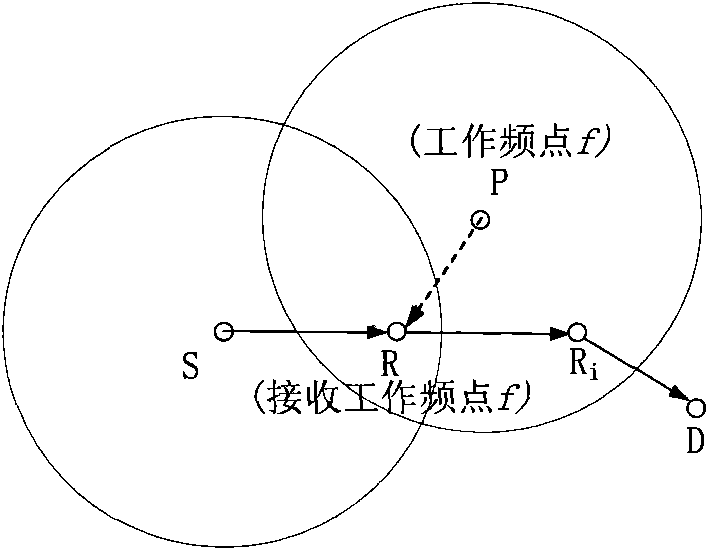
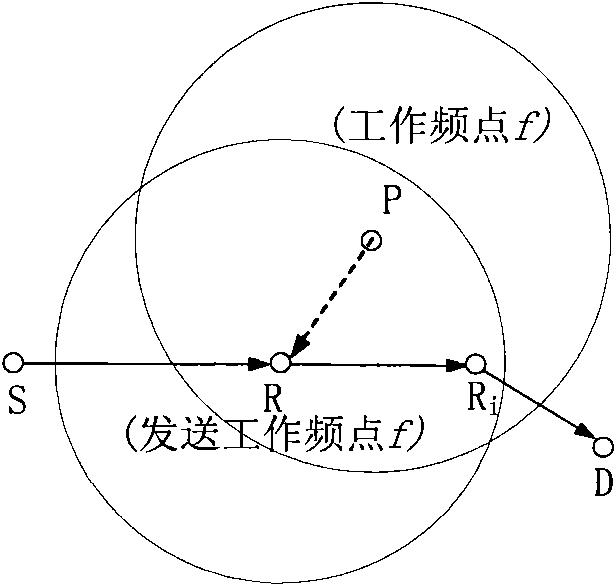
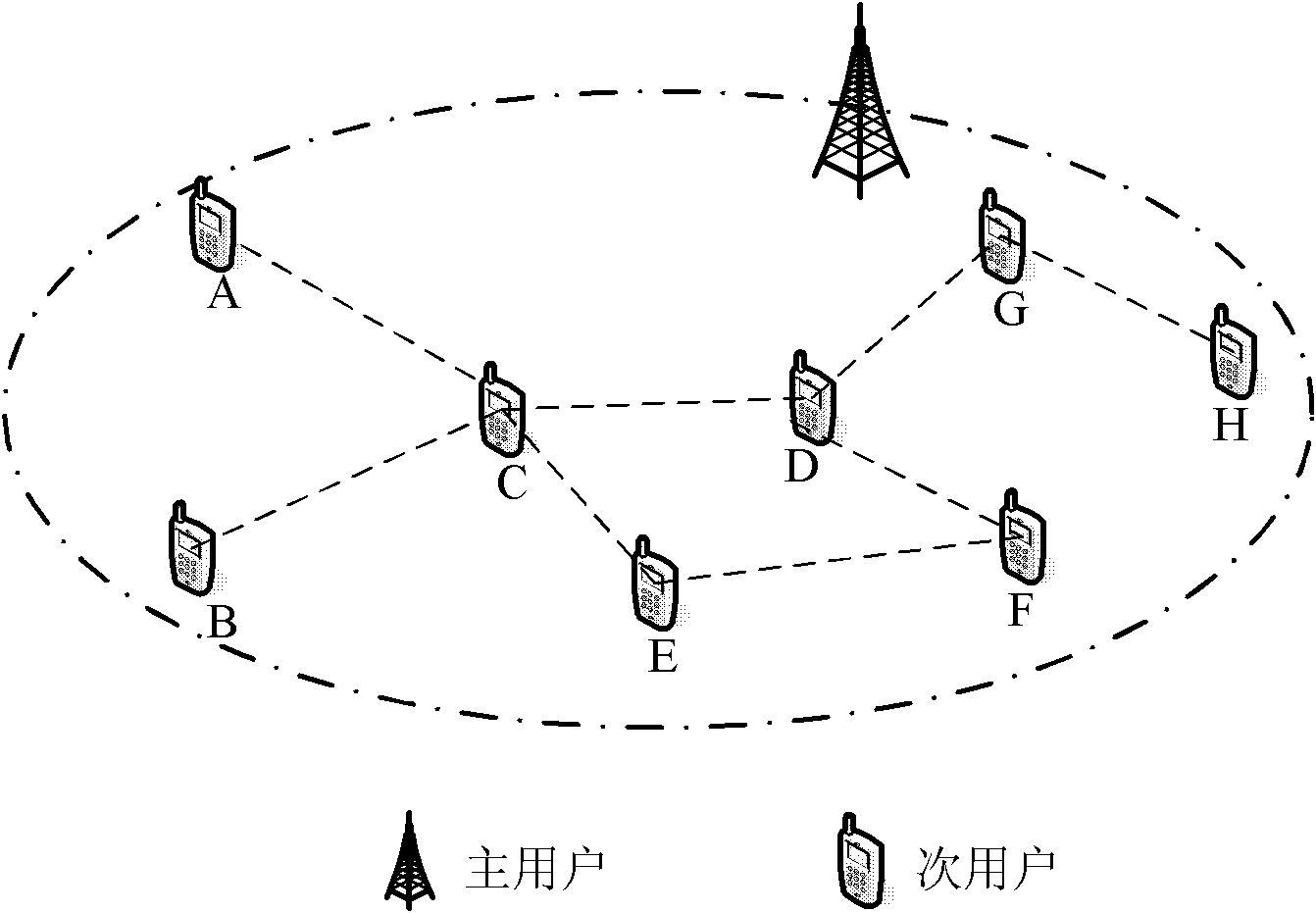
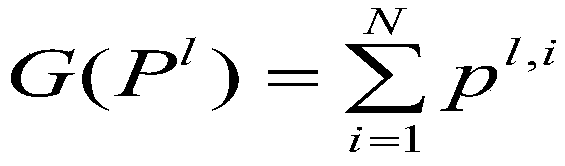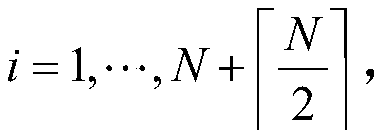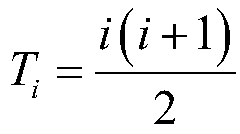Patents
Literature
36 results about "Socially distributed cognition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Distributed cognition is an approach to cognitive science research that deploys models of the extended mind (see, for example, the paper The Extended Mind) by taking as the fundamental unit of analysis "a collection of individuals and artifacts and their relations to each other in a particular work practice". "DCog" is a specific approach to distributed cognition (distinct from other meanings) which takes a computational perspective towards goal-based activity systems. DCog frameworks were originally developed in the mid-1980s by Edwin Hutchins, who continues to be the leading pioneer and whose research is based at the University of California at San Diego.
Distributed cognitive technology for intelligent emotional robot
InactiveCN101604204AInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman behaviorLanguage understanding
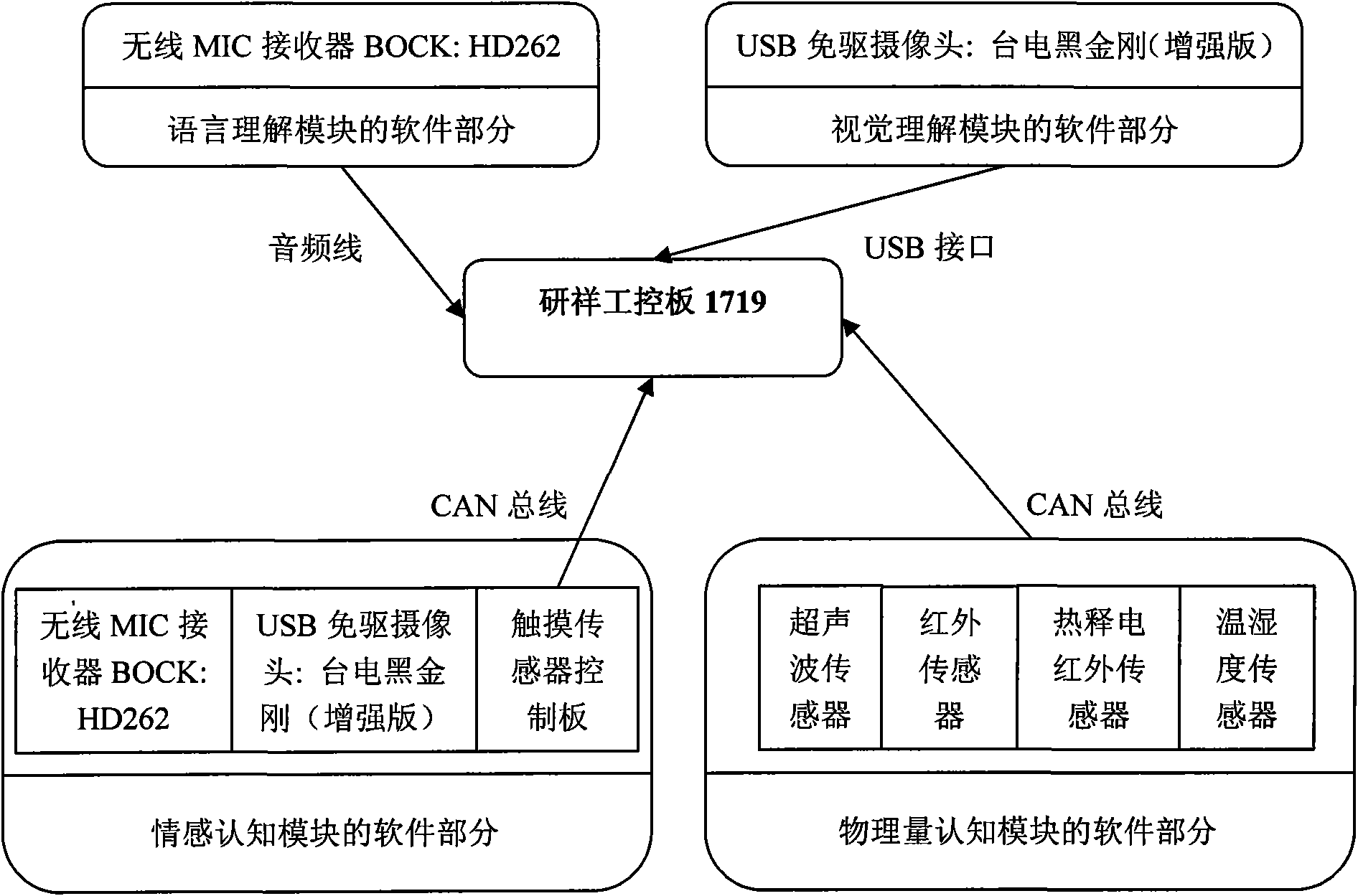
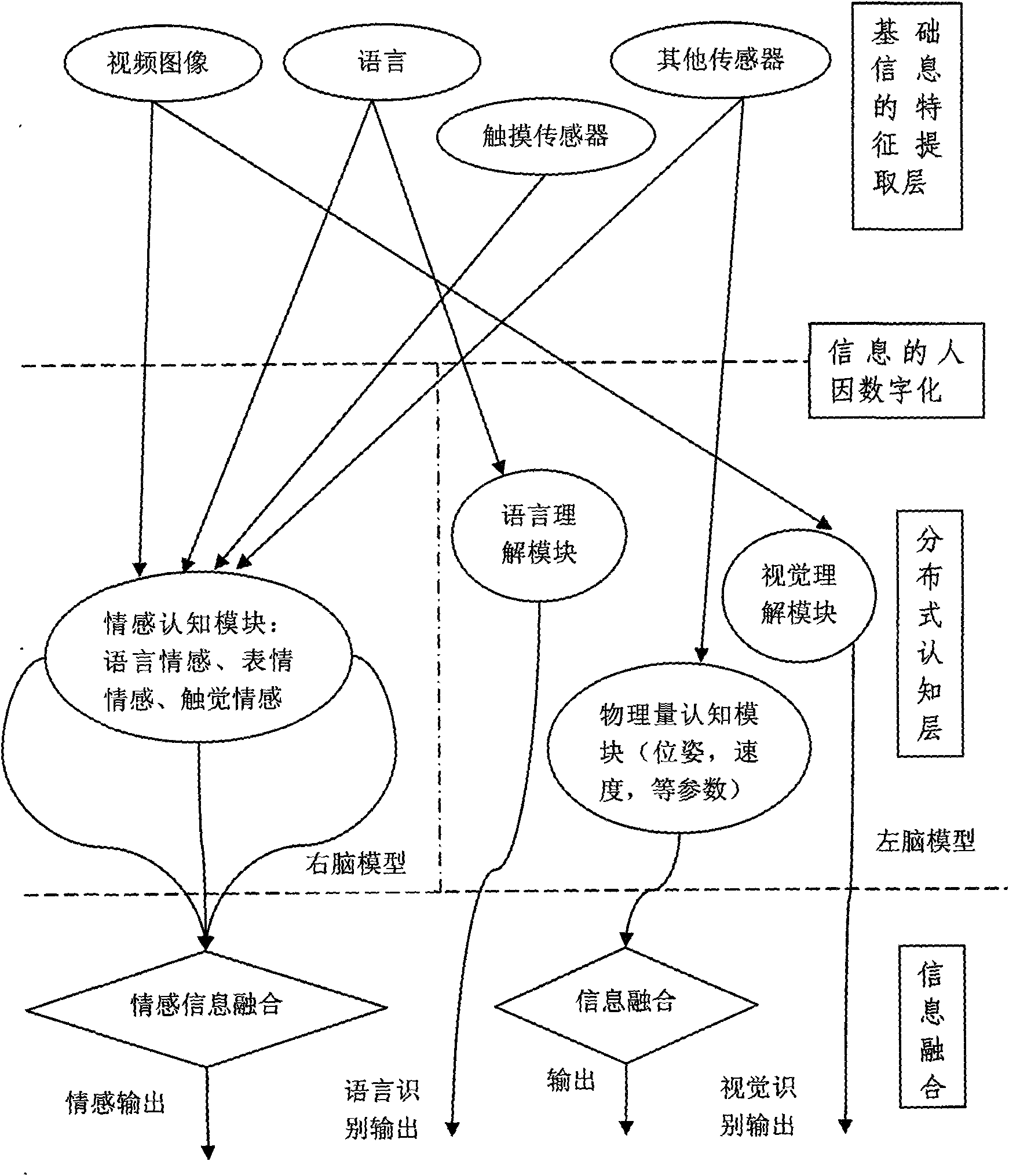
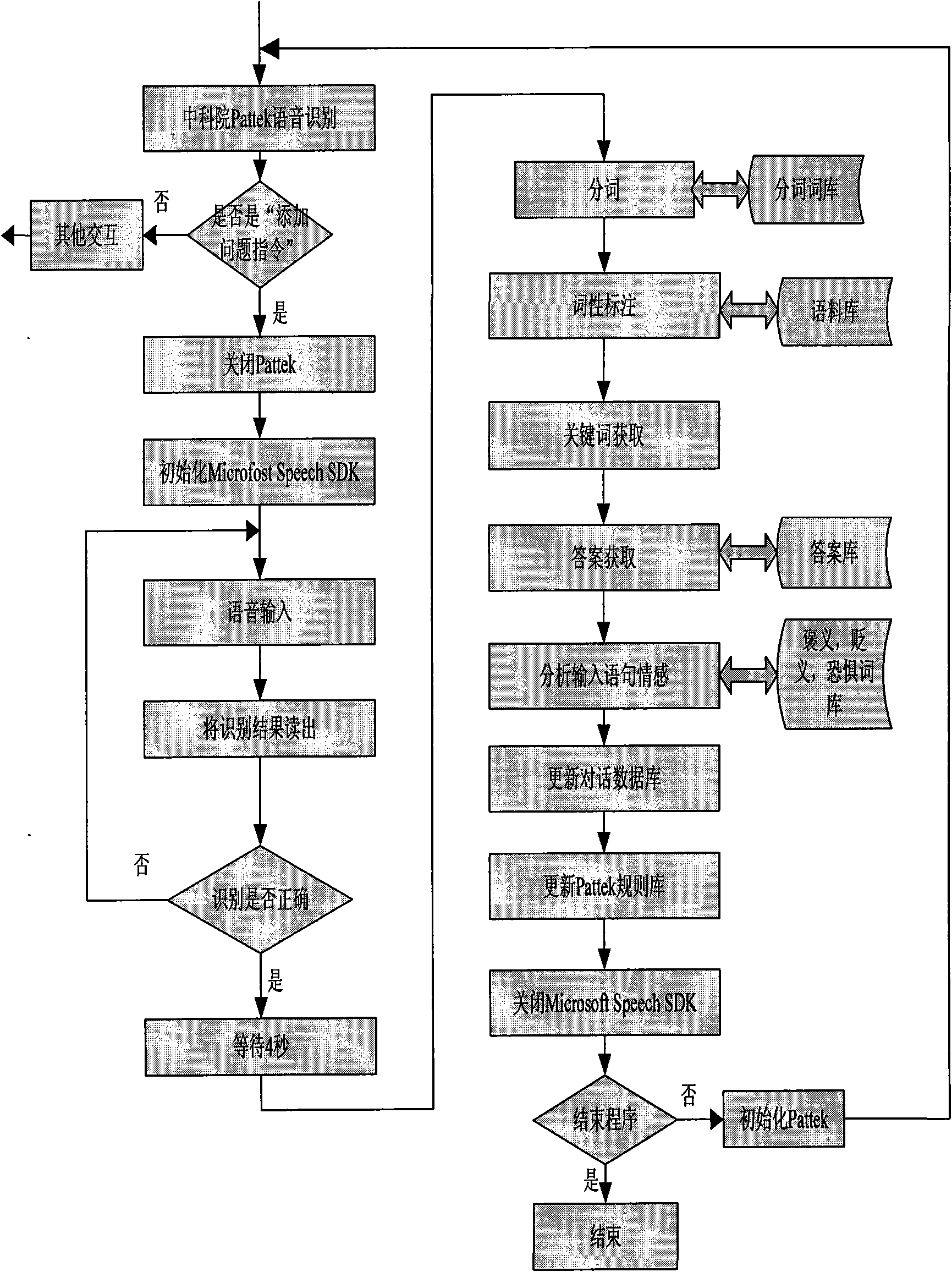
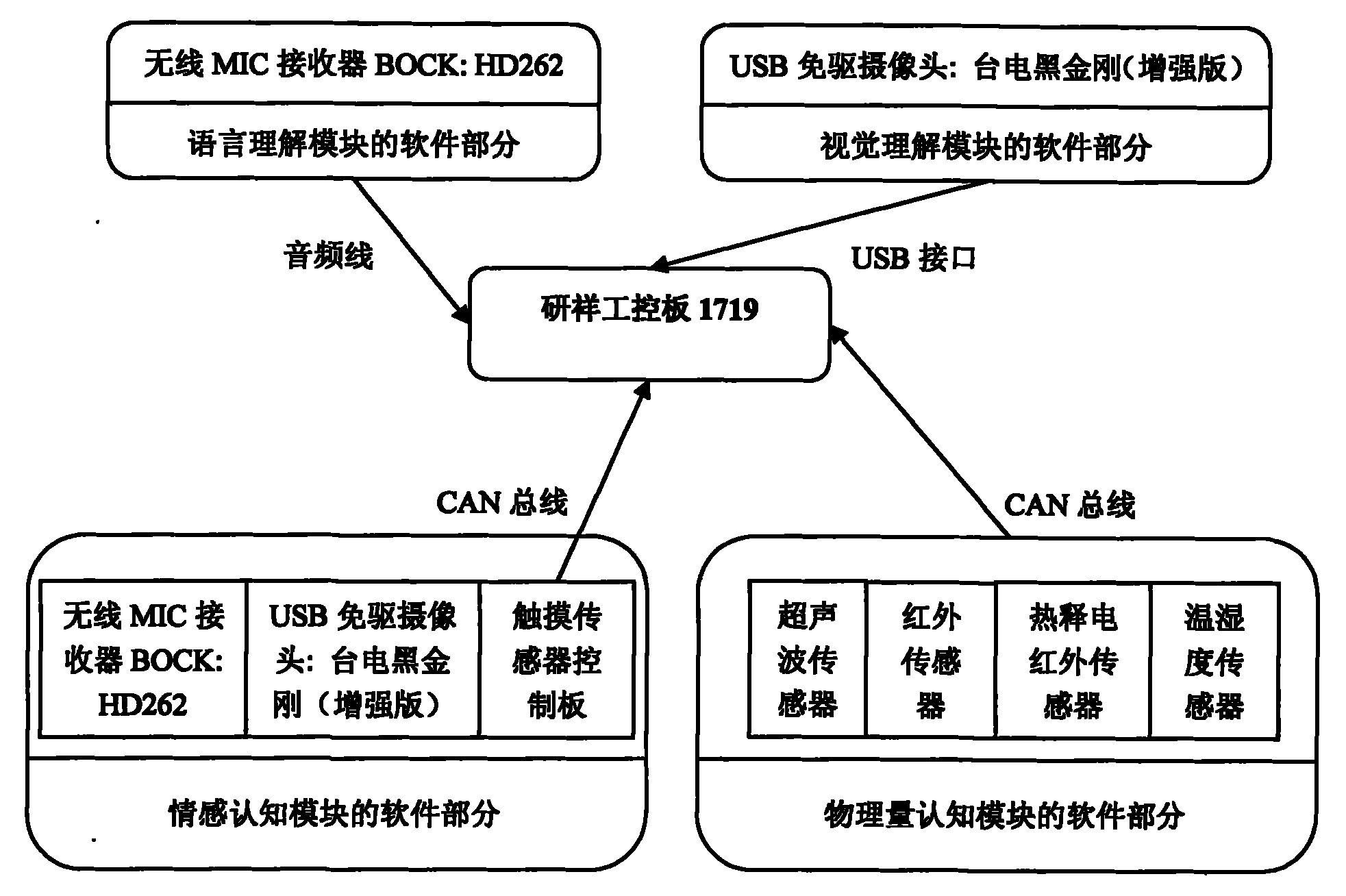
The invention provides distributed cognitive technology for an intelligent emotional robot, which can be applied in the field of multi-channel human-computer interaction in service robots, household robots, and the like. In a human-computer interaction process, the multi-channel cognition for the environment and people is distributed so that the interaction is more harmonious and natural. The distributed cognitive technology comprises four parts, namely 1) a language comprehension module which endows a robot with an ability of understanding human language after the steps of word division, word gender labeling, key word acquisition, and the like; 2) a vision comprehension module which comprises related vision functions such as face detection, feature extraction, feature identification, human behavior comprehension, and the like; 3) an emotion cognition module which extracts related information in language, expression and touch, analyzes user emotion contained in the information, synthesizes a comparatively accurate emotion state, and makes the intelligent emotional robot cognize the current emotion of a user; and 4) a physical quantity cognition module which makes the robot understand the environment and self state as the basis of self adjustment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
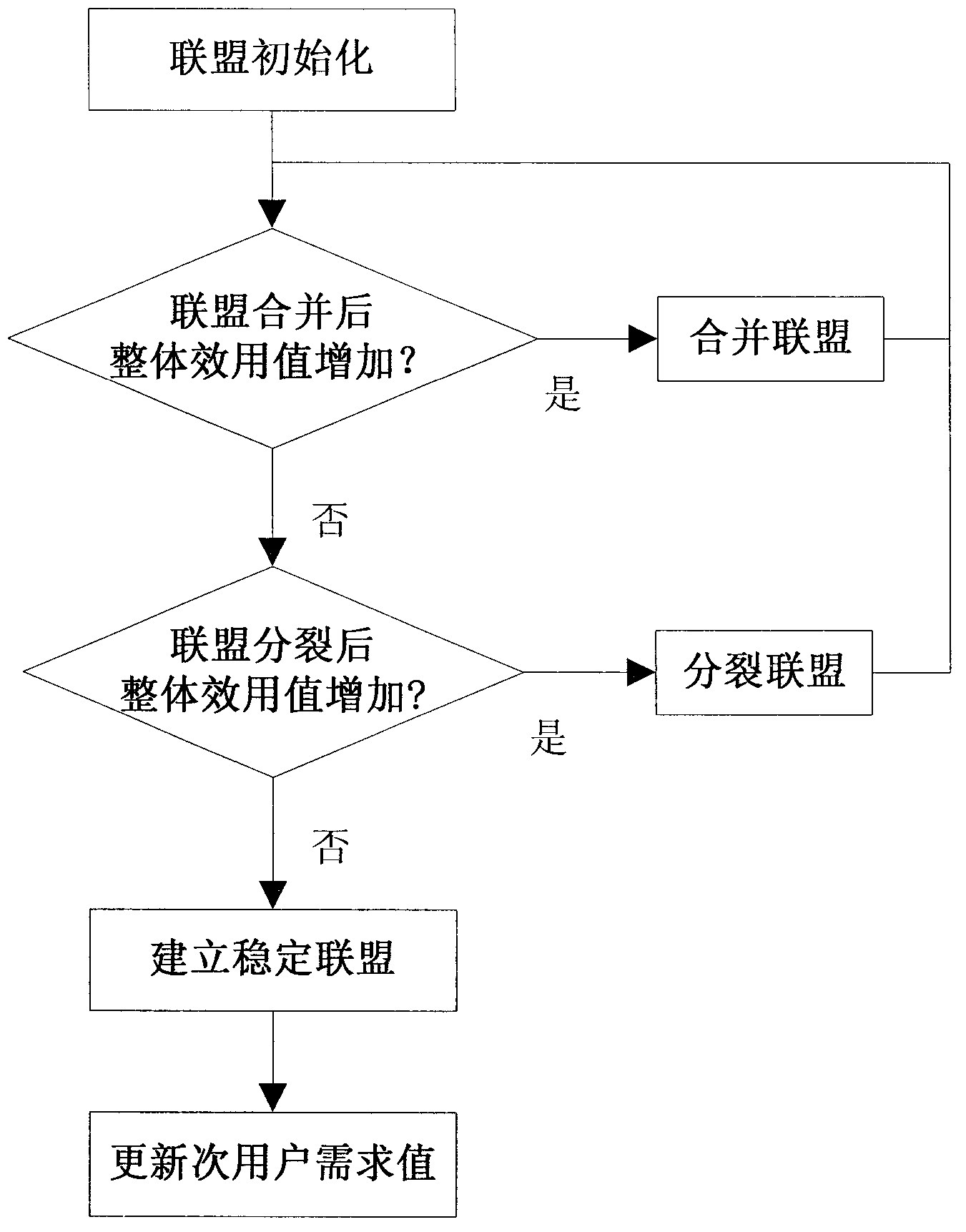
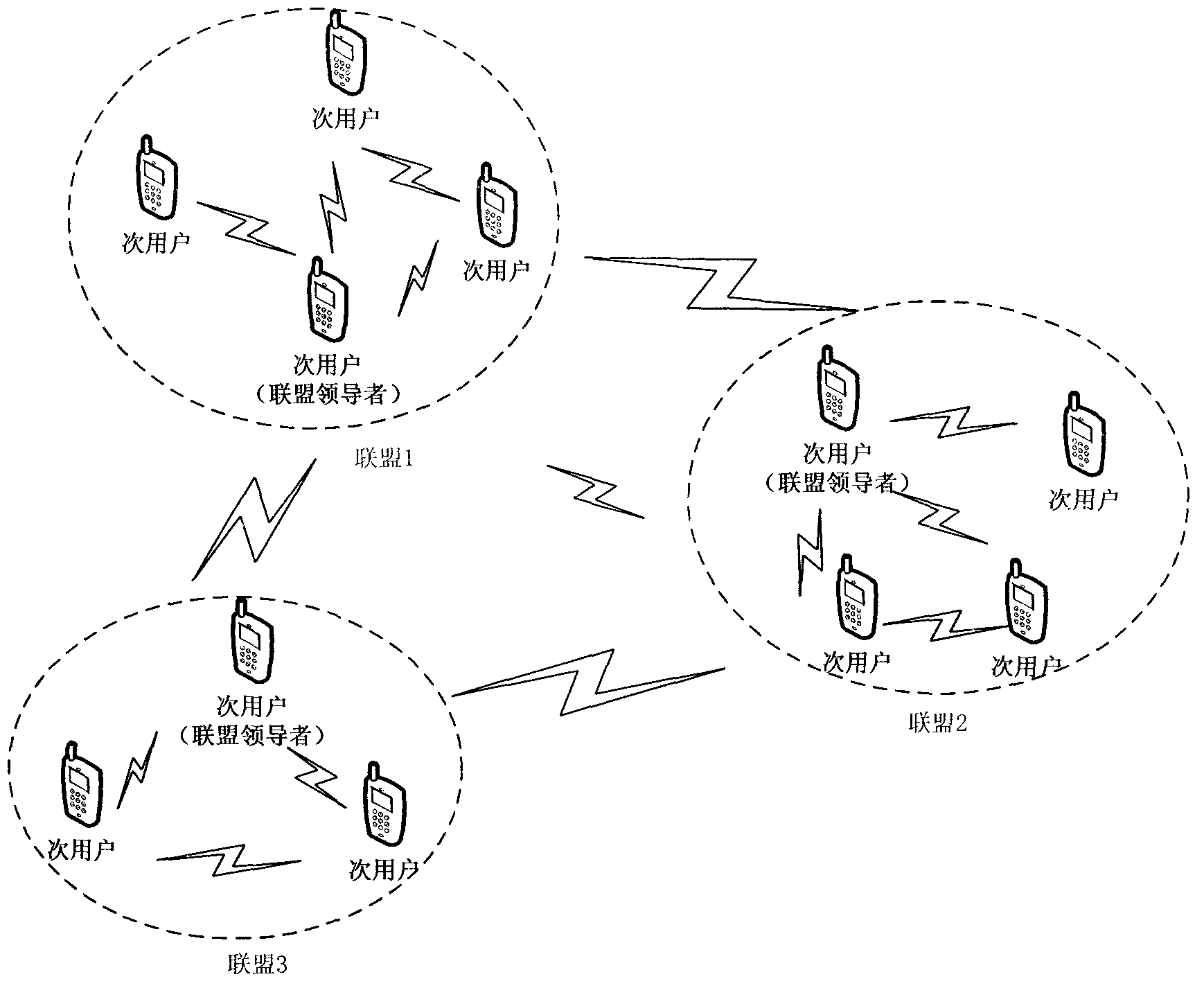
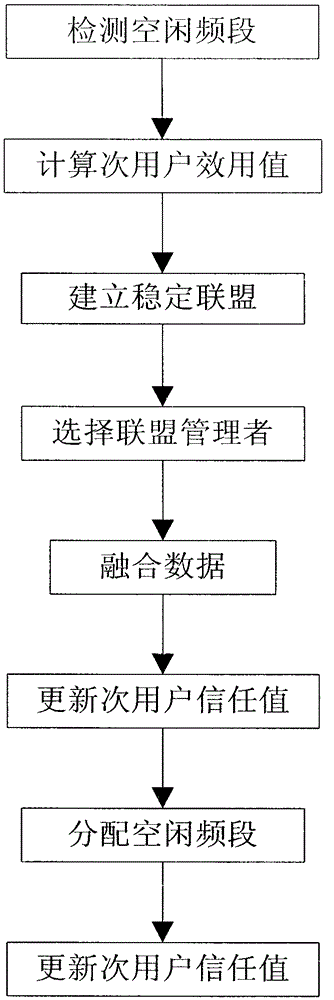
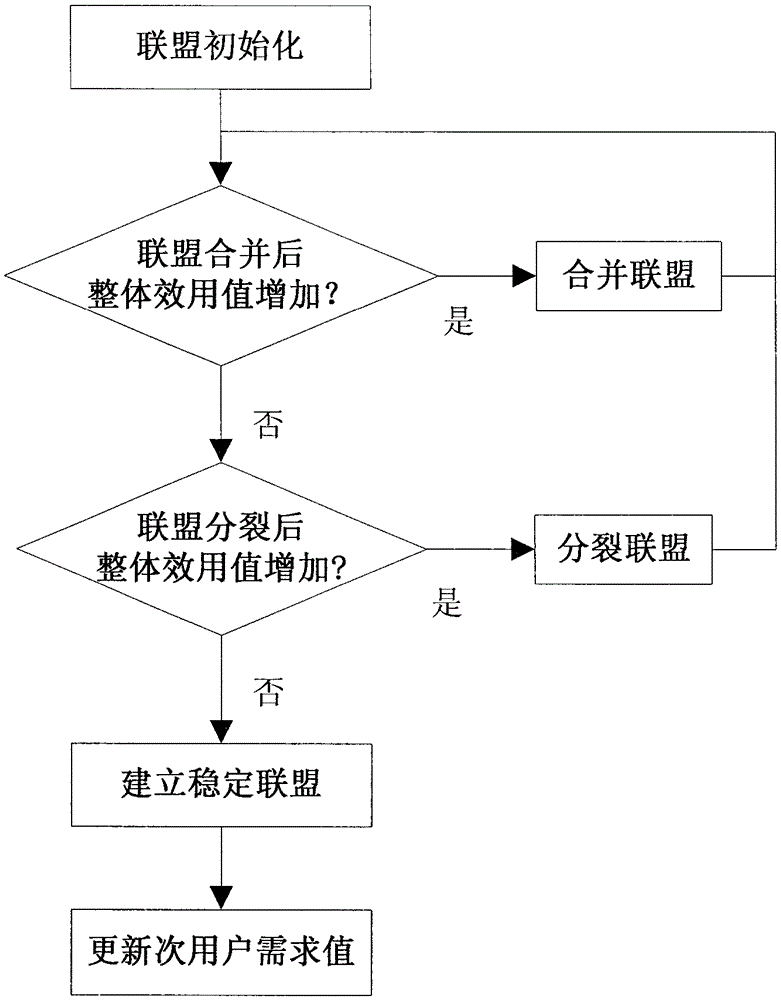
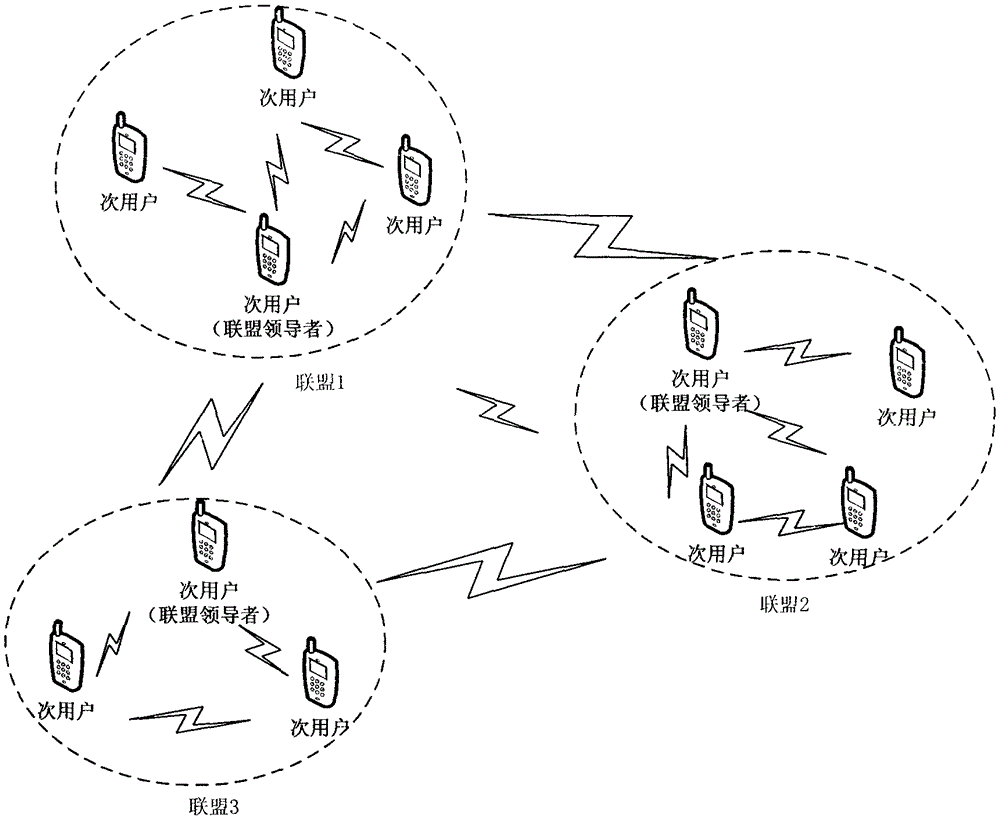
Distributed cognition wireless network spectrum allocation method based on coalition games
ActiveCN103260166AEnsure fairnessImprove satisfactionNetwork planningQuality of serviceFrequency spectrum
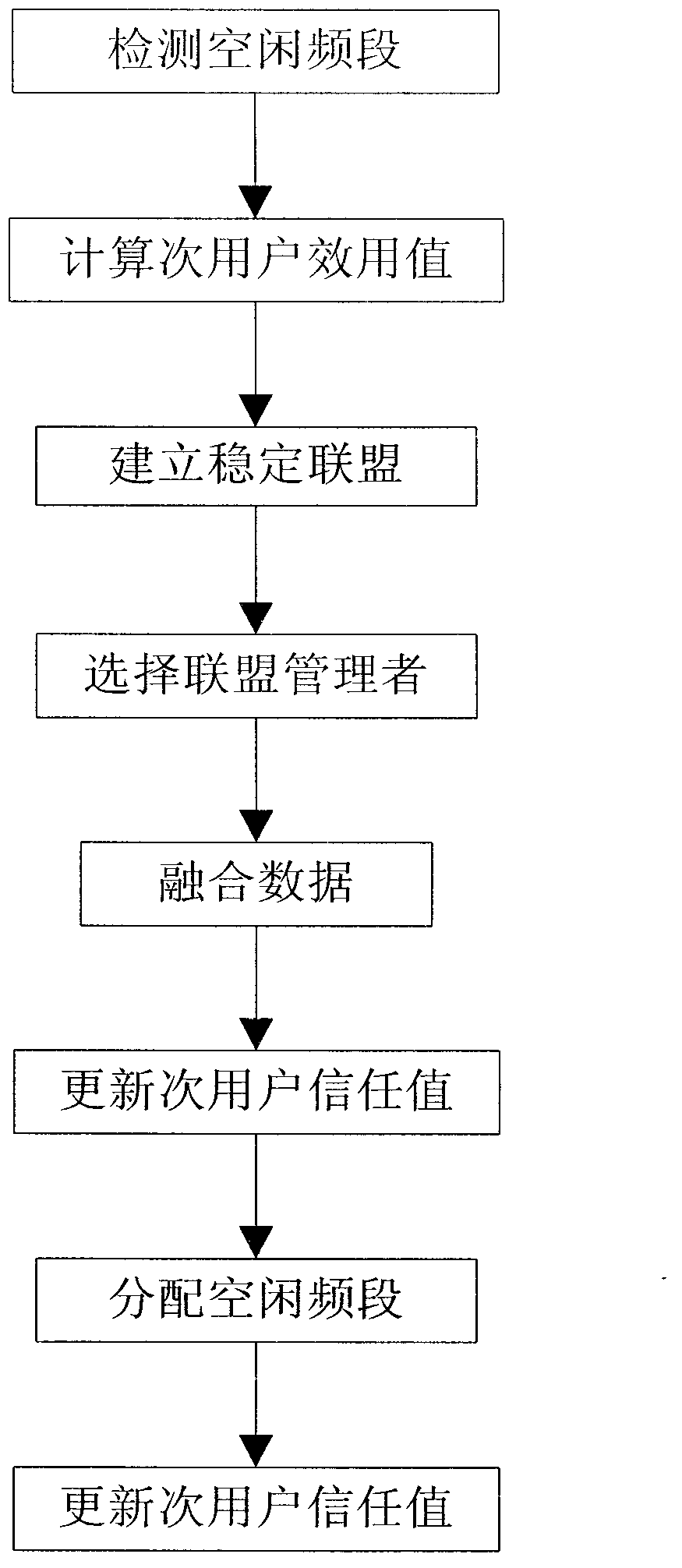
The invention discloses a distributed cognition wireless network spectrum allocation method based on coalition games. The problem that in the prior art, a cognition wireless network cannot fully use a totalization and whole and partial concept to allocate free frequency ranges is mainly solved. The method comprise the steps of detecting free frequency ranges, computing secondary user utility values, establishing stable coalition, selecting a coalition manager, merging data, refreshing secondary user trust values, allocating the free frequency ranges and refreshing the secondary user trust values. The method is fully combined with the advantages of the cognition wireless network, the trust values, participation values and requirement values are used to represent the utility values of a secondary user comprehensively, the secondary user satisfaction degree of the free frequency ranges and network service quality are improved, the secondary user is divided into the coalition to allocate spectrum resources, using ratio of the free frequency ranges and fairness of spectrum allocating are improved, and by refreshing the secondary user trust values, negative influence on a network from a vicious secondary user is lowered.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
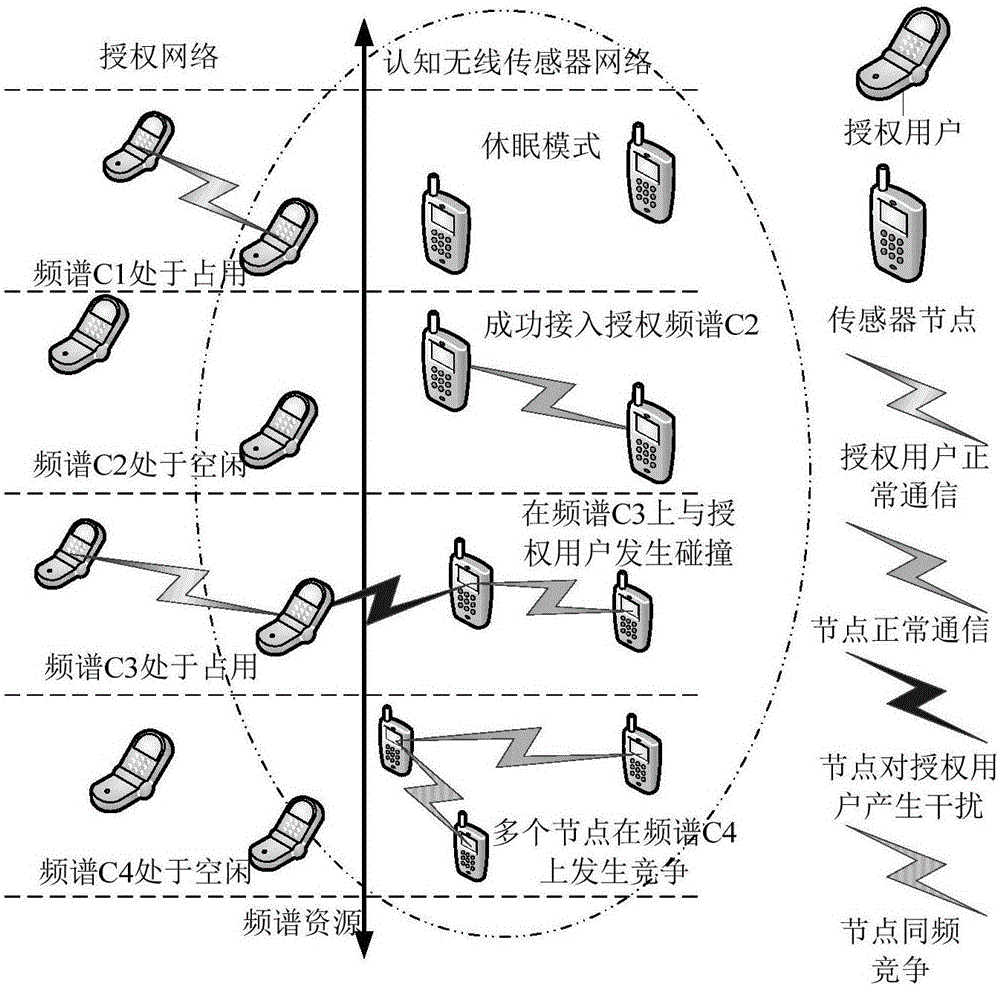
Method for spectrum allocation in distributed cognition wireless sensor network on basis of Q study
InactiveCN106358203AImprove efficiencyFast convergenceSpectral gaps assessmentNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumComputation complexity
The invention discloses a method for spectrum allocation in a distributed cognitive wireless sensor network on the basis of Q study. The average throughput and the average energy efficiency ratio of the maximized distributed cognitive wireless sensor network are taken as objects, nodes in the cognitive wireless sensor network study from one another according to peripheral authorization frequency spectrum state change and allocation strategies of other nodes and finally adapt, the process is mapped into a distributed multi-agent Q study process, and the best spectrum allocation strategy is approximated by executing the best response Q study iterative algorithm in a timing sequence alternation mechanism. The method has the characteristics that the convergence speed is high, the calculation complexity is low, and the average throughput and the average energy efficiency ratio of the cognitive wireless sensor network are improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
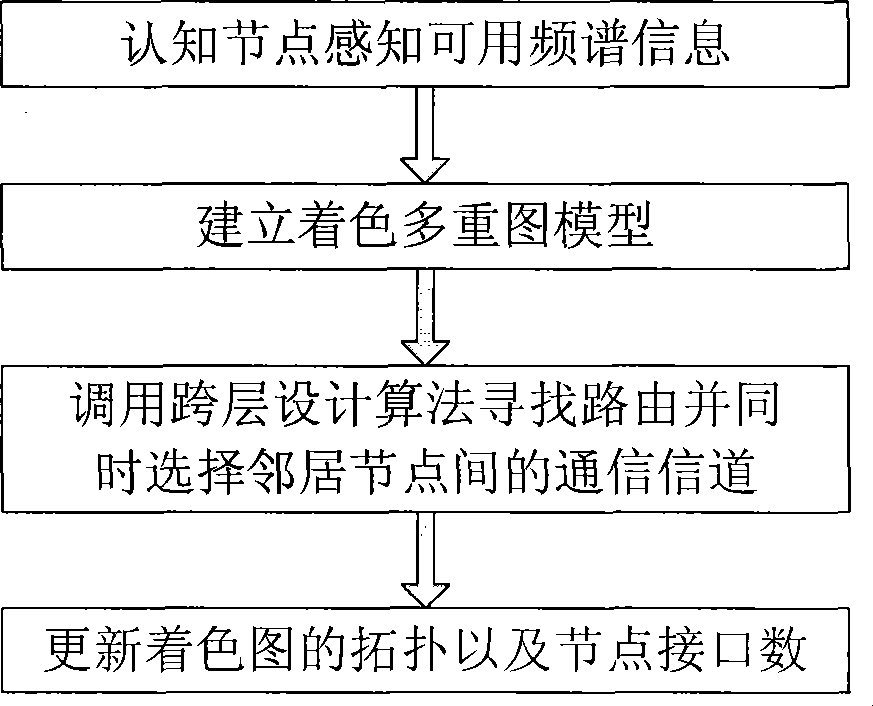
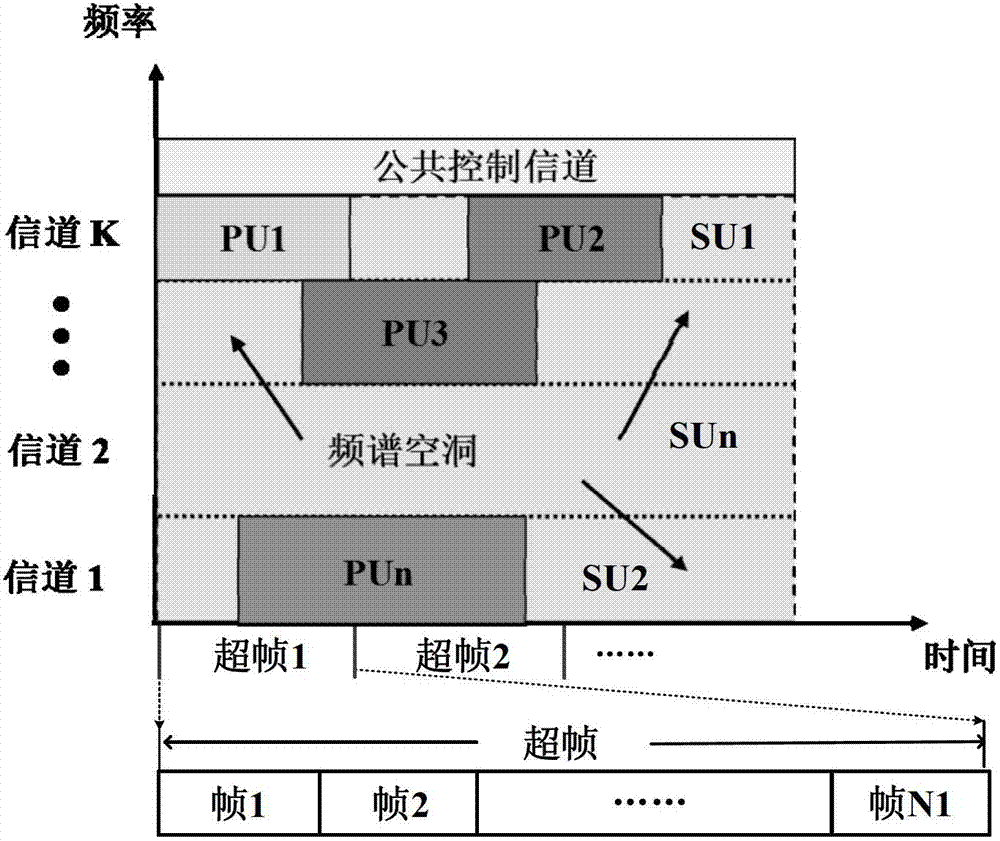
Routing method for distributed cognition radio network based on layer-striding design
InactiveCN101437273AOptimize adjacent hop interferenceMinimize routing hopsTransmission monitoringWireless communicationRadio networksFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a method for distributed type cognitive radio network routing based on cross-layer design, which belongs to the technical field of cognitive radio network. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a coloring multi-graph model according to useable frequency spectrum information acquired by node perception; transferring a cross-layer design routing algorithm to search the routing between a source node and a target node, and simultaneously selecting communication signal channels between adjacent nodes; and updating the topology of coloring multi-graph and interface number of the nodes. The routing method adopts the cross-layer design on the routing selection of a network layer and an MAC layer, and concretely optimizes routing hop number and adjacent hop interfere under the condition of lower time complexity. The method is applicable to radio network, next generation heterogeneous network and so on.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Frequency spectrum switching method in distributed cognitive radio network
InactiveCN101860937ASmooth switchingEnsure communication continuityWireless communicationFrequency spectrumSocially distributed cognition
The invention discloses a frequency spectrum switching method in a distributed cognitive radio network. Cognitive users establish and maintain the own preferred frequency point neighbor list and a route cache list. When the cognitive users as the source nodes detect the authorized users, the cognitive users performs the following steps of: updating the own preferred frequency point neighbor list; judging whether available frequency point exists between the cognitive users and the next hop neighbor node, if so, selecting a first new frequency point according to the available frequency point and transmitting data on the new frequency point, updating the available frequency point in the preferred frequency point neighbor list to available frequency point around the first new frequency point, and updating corresponding neighbor node; and otherwise, combining the route caching list for switching frequency spectrum. The invention takes route factor into consideration according to characteristics of the distributed network cognitive environment, provides the specific frequency spectrum switching flow and signaling design thereof and ensures completion of frequency spectrum switch, thereby ensuring the persistence of communication of the cognitive users.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
A Spectrum Sensing Method
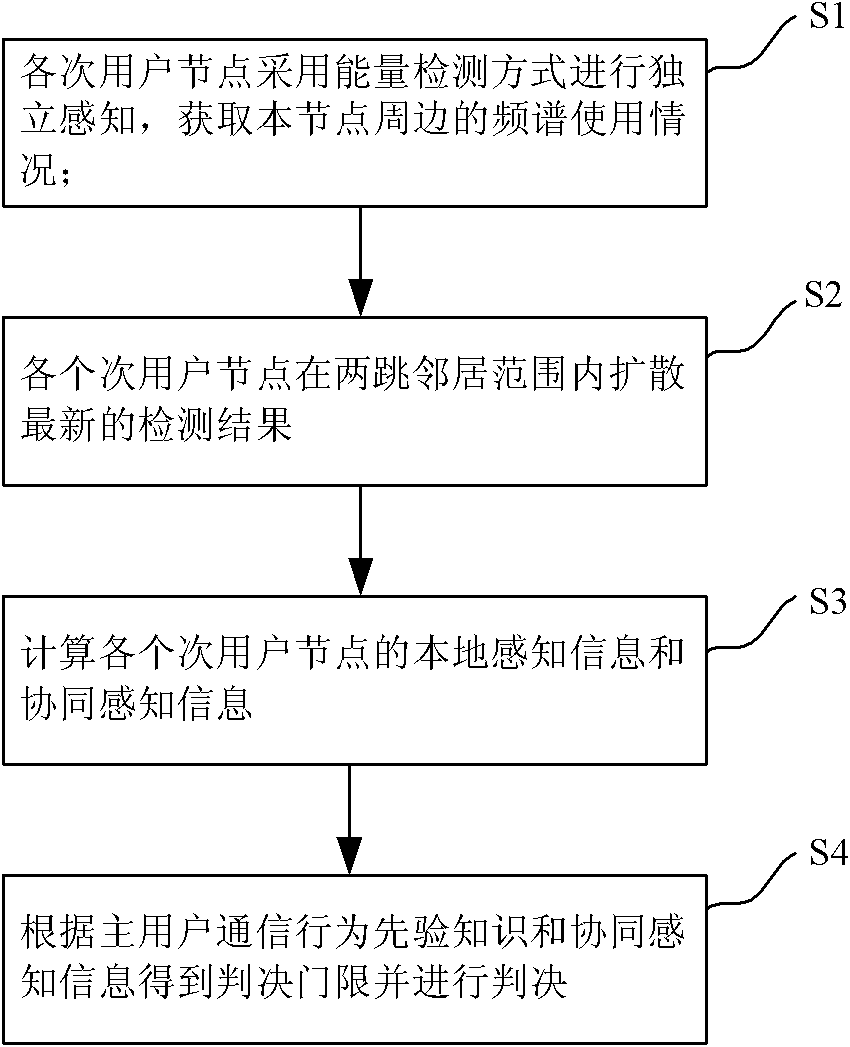
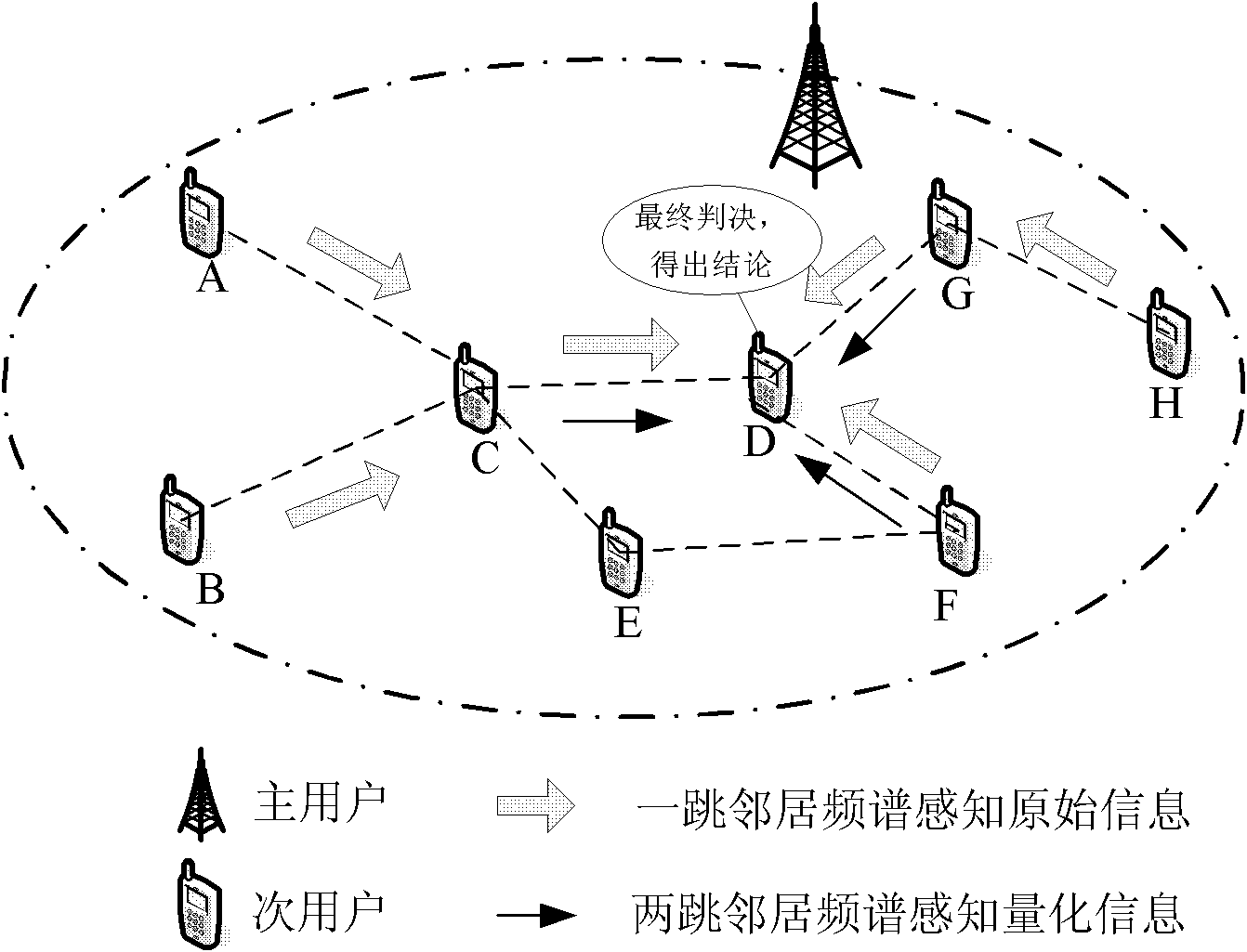
InactiveCN102291191AReduce the impactReduce complexityTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumSocially distributed cognition
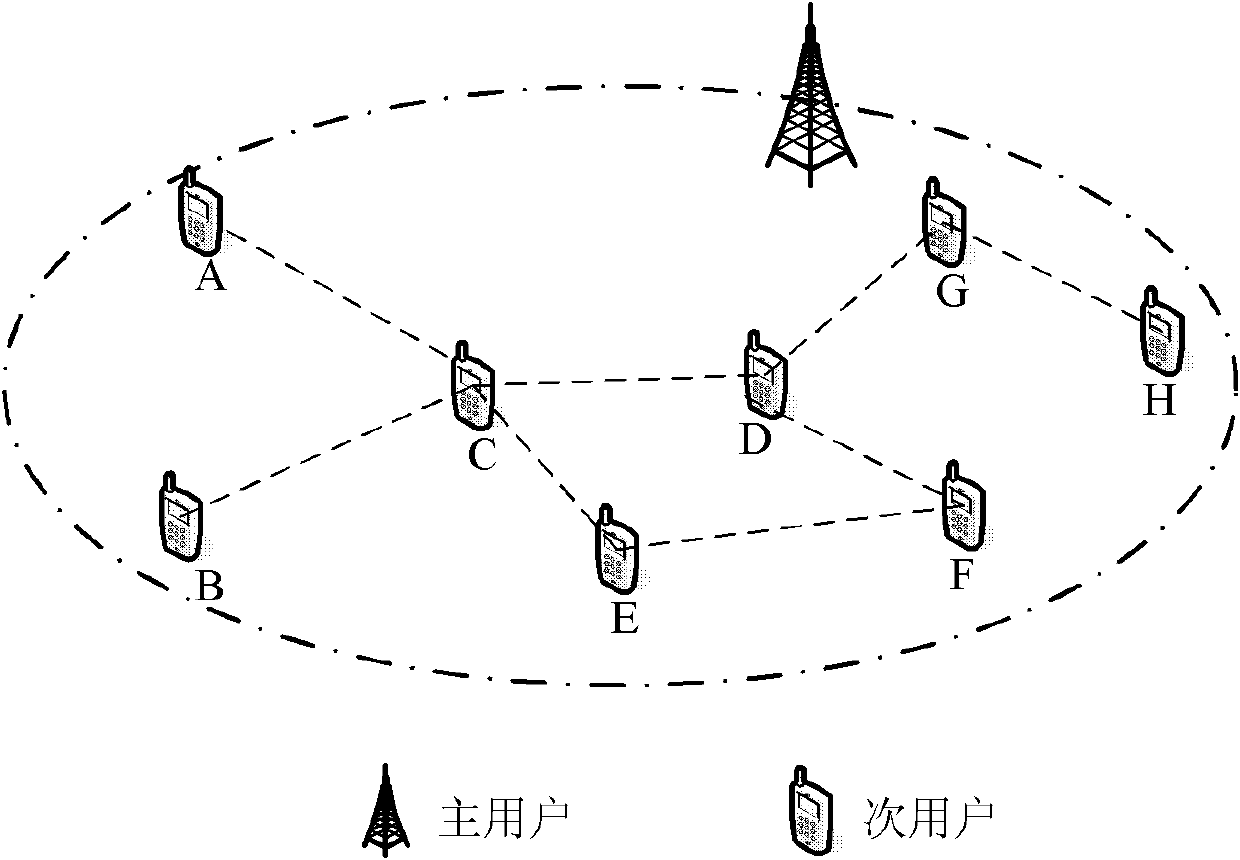
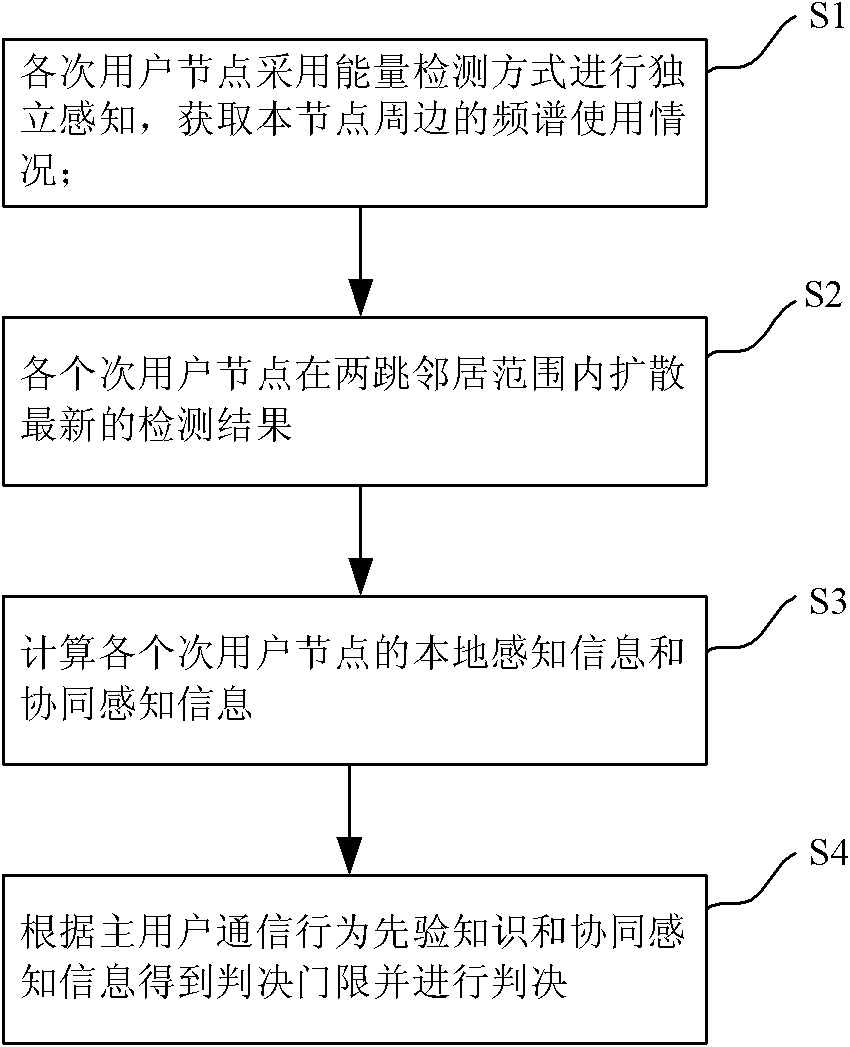
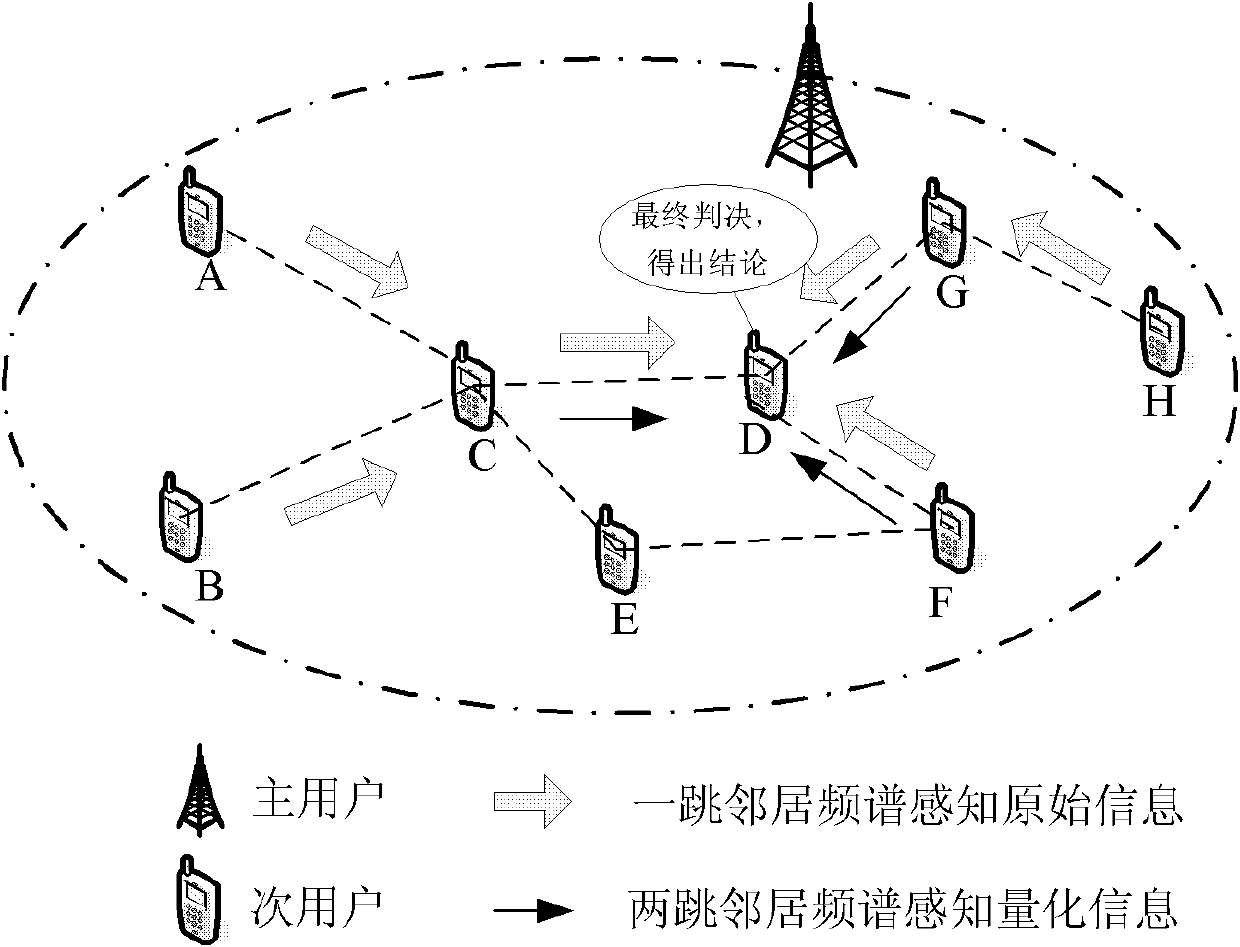
The invention discloses a frequency spectrum sensing method. The frequency spectrum sensing method comprises the following steps of: independently sensing minor user nodes in an energy detecting mode, and acquiring the use conditions of frequency spectrums of the peripheries of the minor user nodes; acquiring a latest detection result by diffusing the minor user nodes within a two-hop neighbour range; computing the local sensing information and the synergetic sensing information of the minor user nodes; acquiring a judgment threshold according to master user communication behavior priori knowledges and the synergetic sensing information, and judging. According to the frequency spectrum sensing method disclosed by the invention, special appointed sink nodes or clustering computation is notneeded, the local sensing information diffusion of the minor user nodes is limited within the two-hop neighbour range, and the complexity and the synergetic spending of the synergetic detection of a distributed cognitive network are effectively reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and device for resisting spectrum sensing data falsification through distributed cognitive radio network
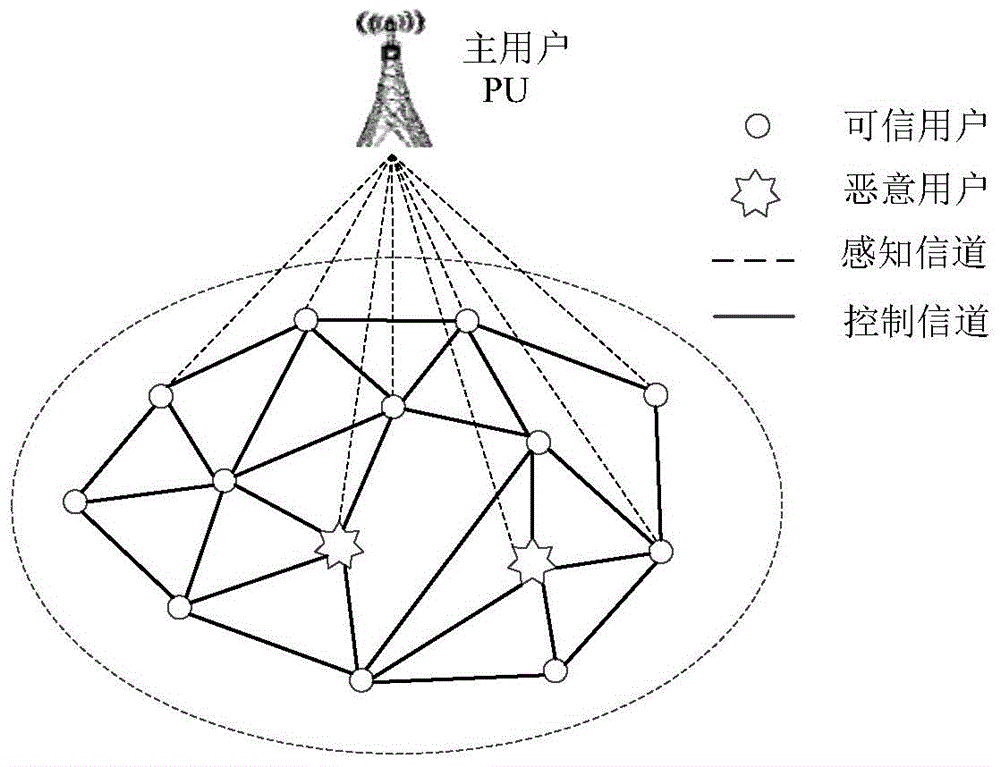
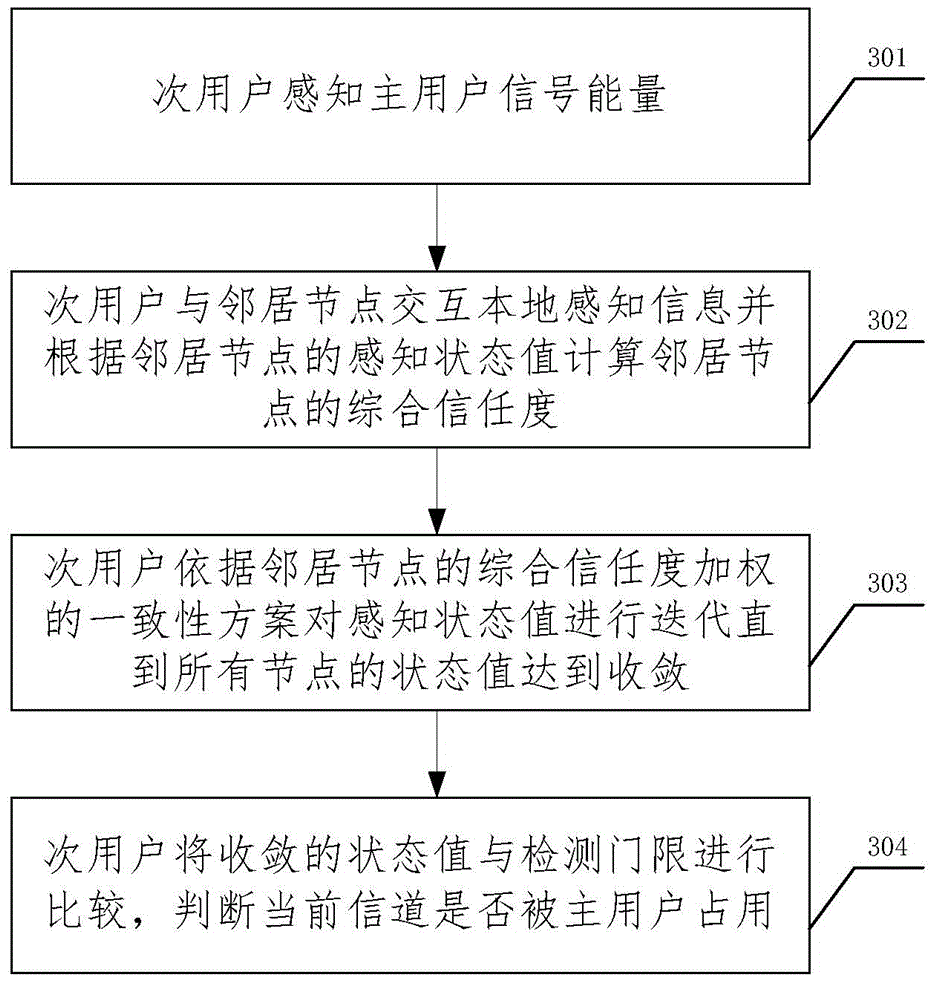
ActiveCN104618908AImprove securityDefense against SSDF attacksTransmissionSecurity arrangementSensing dataComputer network
The invention relates to the technical field of cognitive radio safety and discloses a method and a device for resisting spectrum sensing data falsification through a distributed cognitive radio network, wherein the method comprises the following steps: a secondary user perceives signal energy of a primary user; the secondary user interacts local perceptual information with a neighbor node and calculates comprehensive credibility of the neighbor node according to a cognitive state value of the neighbor node; the secondary user performs iteration on the cognitive state value according to a comprehensive credibility weighting consistence scheme of the neighbor node until state values of all nodes are converged; the secondary user compares the converged state value with a detection threshold and judges whether an existing channel is occupied or not by the primary user. The method can be used for resisting spectrum sensing data falsification launched by a malicious user, improving spectrum sensing safety in the cognitive network and resisting SSDFs of various forms very well on the condition of not having priority knowledge of number of intruders, a falsification strategy, and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Active spectrum sensing switching method
ActiveCN106507370AAvoid interferencePrediction is accurateModulated-carrier systemsData switching networksCognitive userIdle time
The invention relates to an active spectrum sensing switching method. The method mainly comprises the steps that a cognitive user senses and collects spectrum information of available channels; the cognitive user calculates to obtain next time slot idle probabilities of the channels, residual idle time correction factors of the channels and learning constants of cognitive user switching thresholds through long term observation; the cognitive user judges when to switch and which channel to switch; and the cognitive user carries out spectrum switching and recovers communication. According to the method, changes of the channels can be dynamically tracked and the spectrum can be switched rapidly; on-demand switching can be realized on the premise of not disturbing licensed users; the collision and switching times is effectively reduced; and the method can be applied to a spectrum switching process in a distributed cognitive radio network.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and system for probing distributed cognitive radio channel
InactiveCN101572897AReduce computational complexityImprove the ability to detect channels in real timeWireless communicationPropogation channels monitoringFusion centerFrequency spectrum
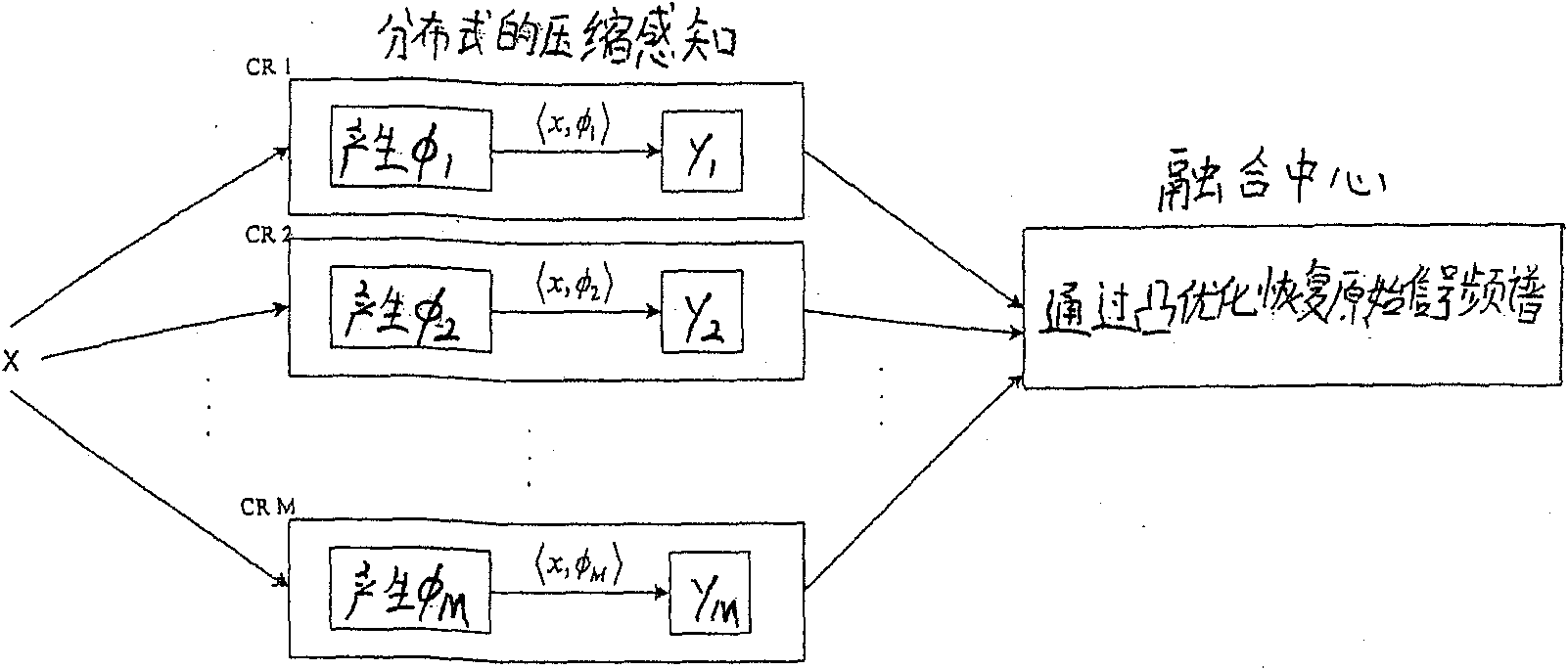
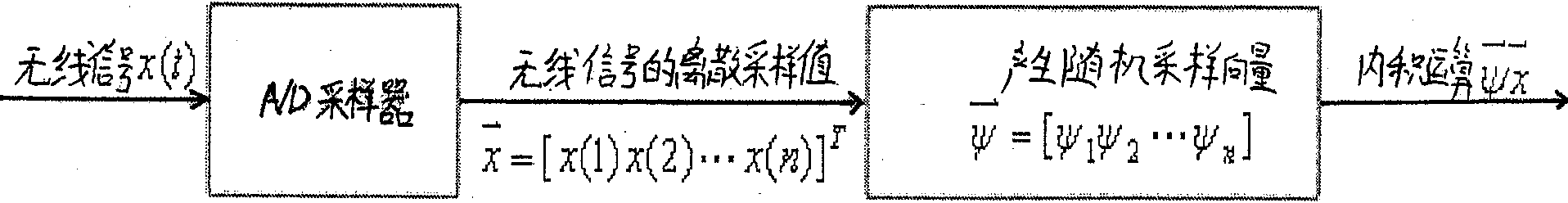
The invention provides a method and a system for probing a distributed cognitive radio channel. In a distributed cognitive network, random M users are selected, wherein M is less than N, and N is the length of discrete wireless signals; each user in the M users carries out inner product operation for respective wireless signals to acquire a compression sampling value respectively, and transmits the acquired compression sampling value to a fusion center; and the fusion center carries out frequency spectrum recovery for the wireless signals, and transmits back the frequency spectrum of the recovered wireless signals to each user terminal in the distributed cognitive network.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Multi-channel collaborative spectrum sensing method based on iterative filtering
InactiveCN103209037AImprove Spectrum Detection PerformanceEasy to detectTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumSocially distributed cognition
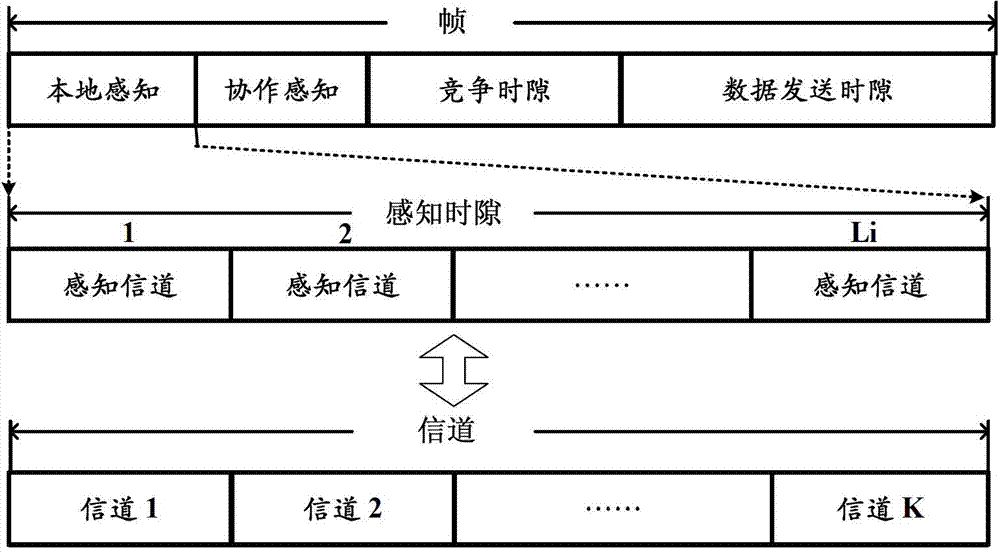
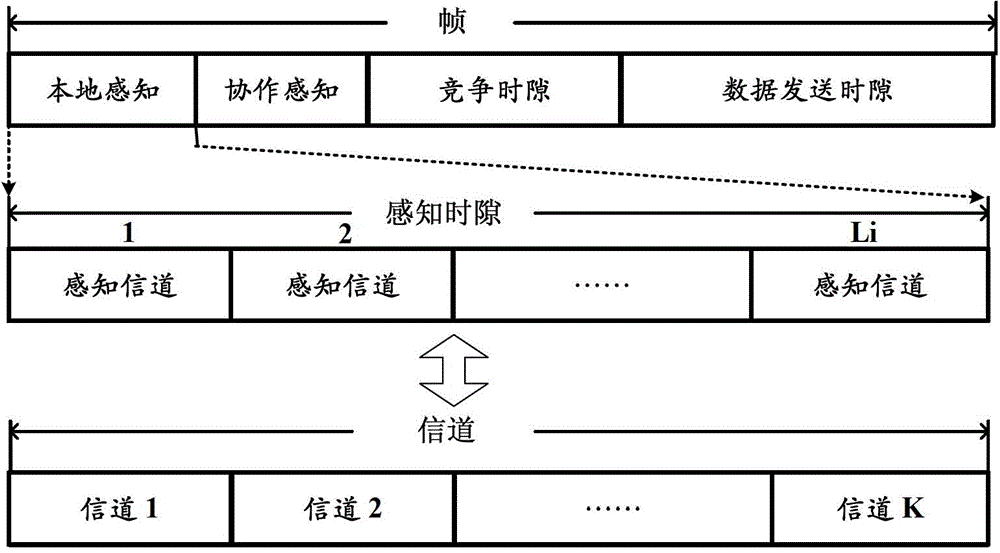
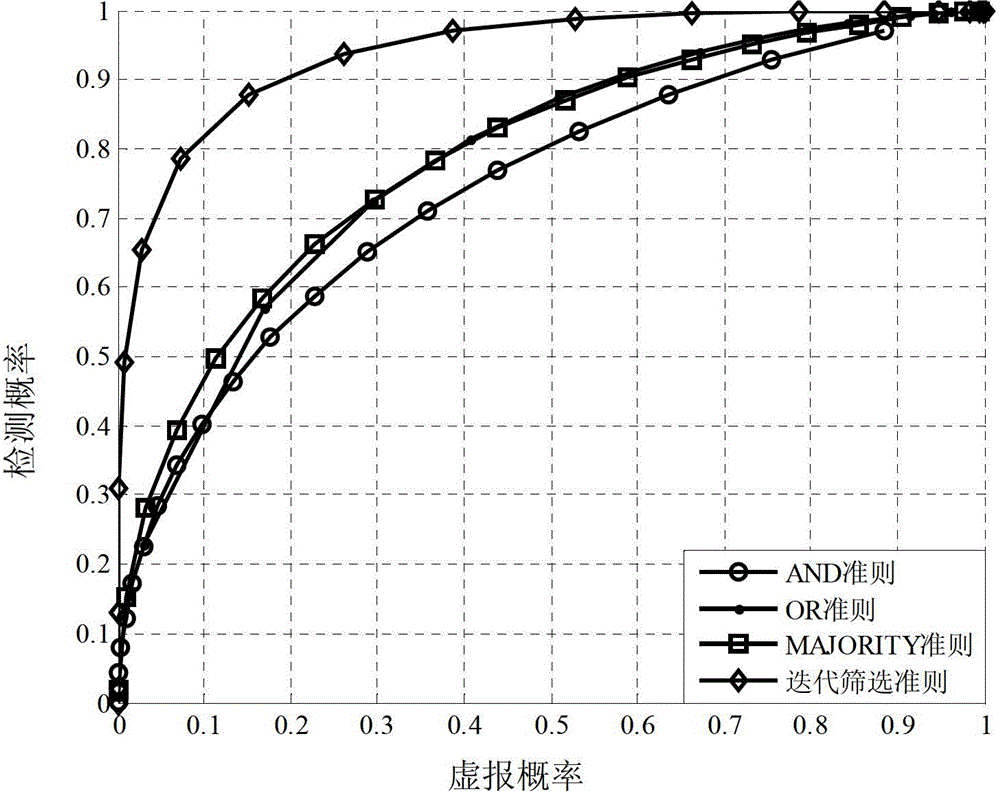
The invention discloses a multi-channel collaborative spectrum sensing method based on iterative filtering. The method includes: time is divided into time slices with fixed length through a reasonably designed frame structure. In each time slice, a secondary user with poor sensing performance is removed preferentially and does not participate in next round of cooperative spectrum sensing, and therefore the number of sensing users is reduced remarkably, and spectrum sensing performance is improved. Through design of the frame structure and a collaborative sensing scheme, the multi-channel collaborative spectrum sensing method based on the iterative filtering can solve problems of too much collaborative spectrum sensing users and malicious user interference existing in a distributed cognitive radio network. Theory analysis and simulation results show that: compared with an existing collaborative spectrum sensing method, the multi-channel collaborative spectrum sensing method based on the iterative filtering can effectively reduce the number of the secondary users participating in collaborative sensing in a loose condition, malicious interference users are removed, and simultaneously spectrum sensing performance of the cognitive radio network is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
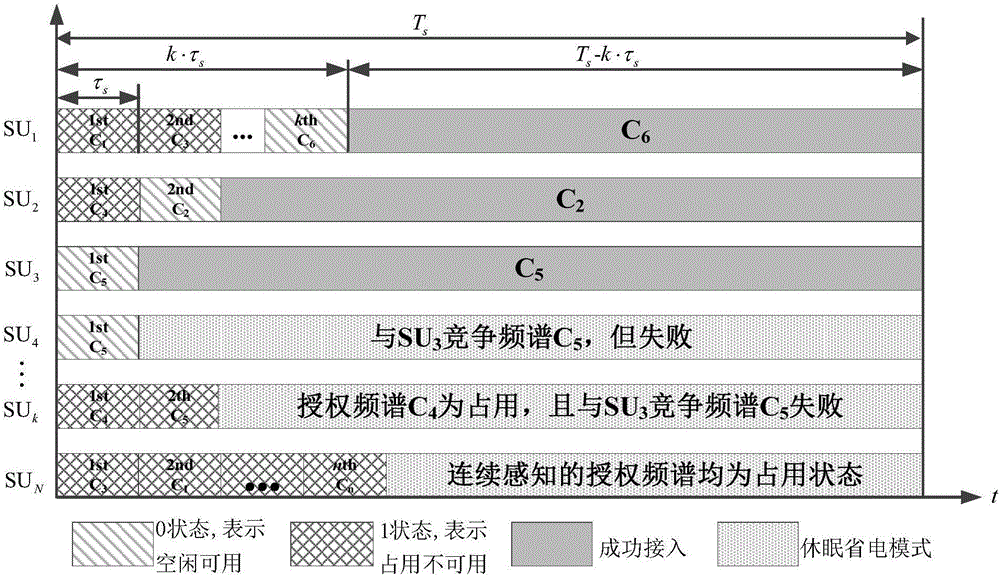
Spectrum access method for distributed cognitive radio system
InactiveCN102170706AGuaranteed stabilityGuarantee queue stabilityWireless communicationTelecommunicationsAccess method
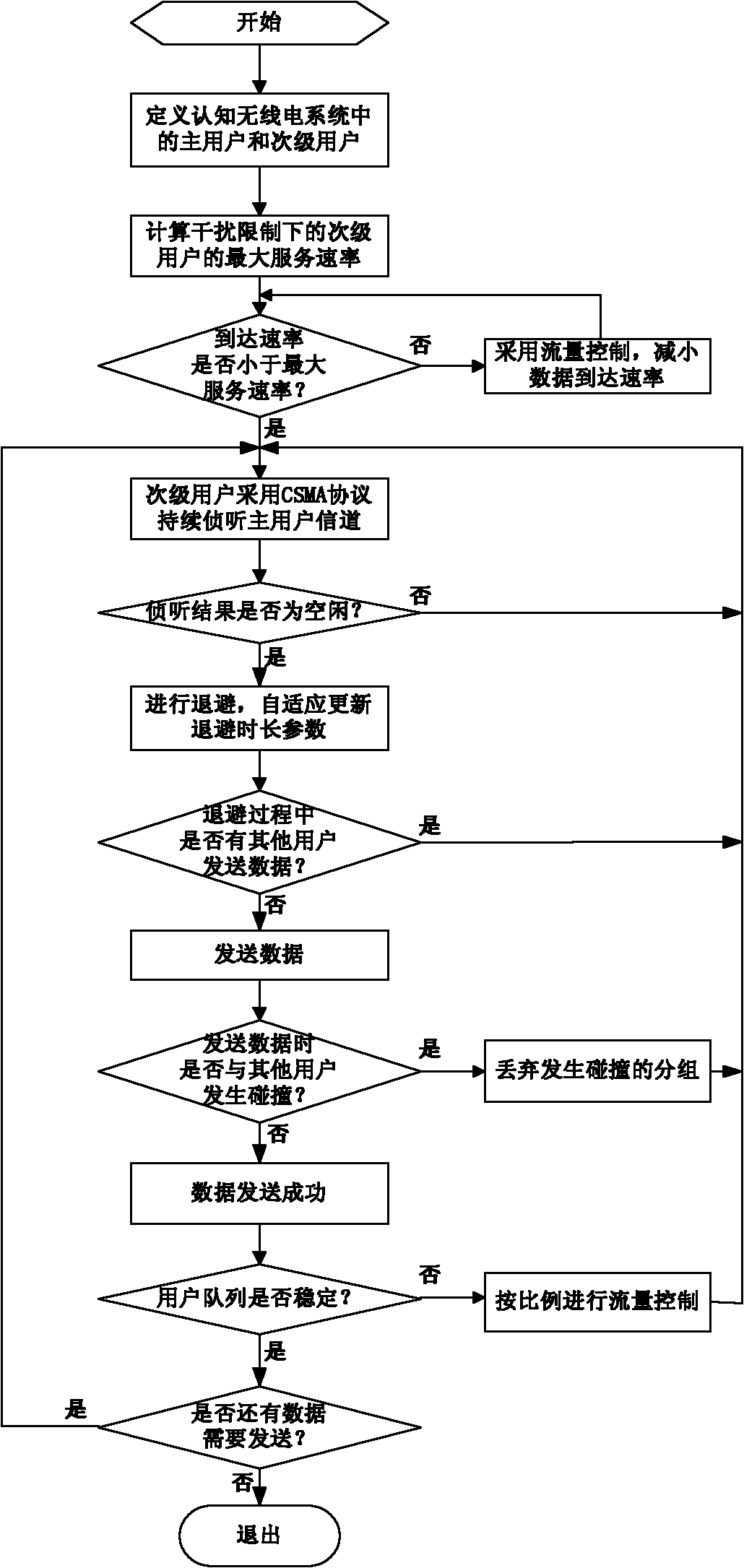
The invention discloses a spectrum access method for a distributed cognitive radio system, which mainly aims to solve the problem of low queue stability of secondary users in the conventional cognitive radio system. The method is implemented by the following steps of: 1) defining primary users and the secondary users in the cognitive radio system; 2) regulating the arrival rate of the secondary users to make the arrival rate of the secondary users lower than a maximum service rate under interference limitation; 3) continuously snooping channels of the primary users by adopting a carrier sensemultiple access (CSMA) protocol, and accessing the channels after snooping results indicate random withdrawal when idle by the secondary users; and 4) adaptively regulating withdrawal time length parameters by the secondary users to make the stable service rate close to the arrival rate to finally achieve queue stability. The method has the advantages that the queue stability of the secondary user is achieved and that primary and secondary user collision probability is lower than the interference limitation, and can be used for the cognitive radio system with strict requirements on queue delay in the field of wireless communication.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Routing and time slot distributing method on basis of main user protection in cognitive radio network
InactiveCN102724669AIncrease network capacityImprove throughputHigh level techniquesNetwork planningComputation complexitySocially distributed cognition
The invention discloses a routing and time slot distributing method on the basis of main user protection in a cognitive radio network for a distributive cognitive radio network. The method comprises the following steps of designing a reasonable chain measuring and routing information spreading mechanism to search a source-to-target node communication route for a secondary user in a network; and on the premise of not causing over interference to a main user, increasing flow of a throughput bottle-neck link in the route by using the time slot distributing method, so that the throughput of the secondary user in the network is improved. Through reasonable routing and time slot distribution, a primary user and the secondary user in the distributive cognitive radio network can use a frequency band authorized by the main user at the same time and over interference to the main user is not caused. Theoretical analysis and simulation result show that compared with the current routing algorithm, the method can reduce calculation complexity and efficiently increase the throughput of the secondary user simultaneously.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Security cooperative spectrum sensing method based on reputation mechanism and dynamic game
ActiveCN104993890AAccelerate the speed of obtaining the reputation value of collaborative sub-usersHigh speedTransmission monitoringSensing dataFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a security cooperative spectrum sensing method based on a reputation mechanism and a dynamic game. The method combines the credibility transfer process of a secondary user. If the secondary user exceeds the one-hop communication range of a neighbor secondary user, then the neighbor secondary user broadcasts the reputation value previously established by the moving secondary user to a secondary user within the one-hop communication range, so that when the moving secondary user participates in cooperation, the speed of acquiring the reputation value by a cooperative spectrum sensing requester can be accelerated. Thereafter, a dynamic game method is run, and the secondary user is stimulated to participate in cooperation through the utility function of the cooperative spectrum sensing requester and the cooperative spectrum sensing secondary user, and the cooperative spectrum sensing security is improved in combination with the reputation value weight distribution. According to the security cooperative spectrum sensing method based on the reputation mechanism and the dynamic game provided by the invention, the convergence speed of the credibility evaluation of the moving secondary user in a distributed cognitive radio network can be improved, the cooperation fairness can be guaranteed and the collaborators are stimulated to participate in cooperation actively, the SSDF (Spectrum Sensing Data Falsification) attack can be effectively resisted and the spectrum sensing rate can be improved.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
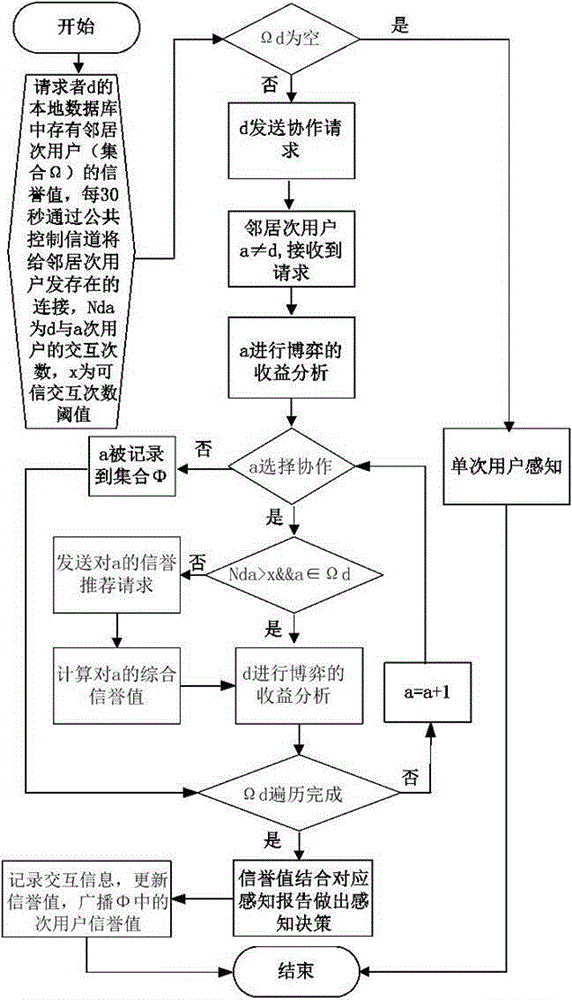
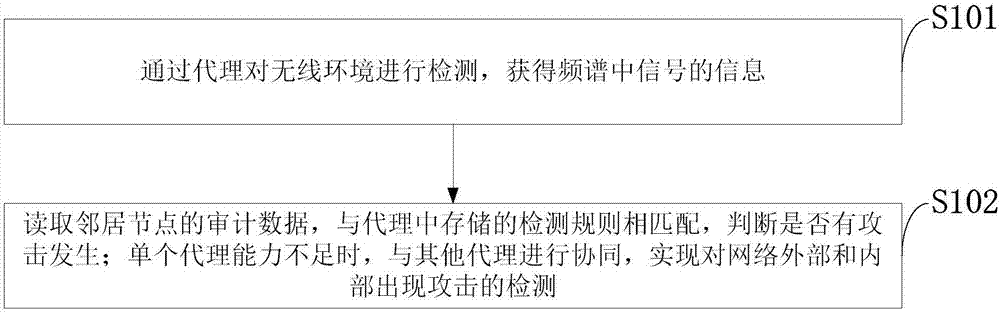
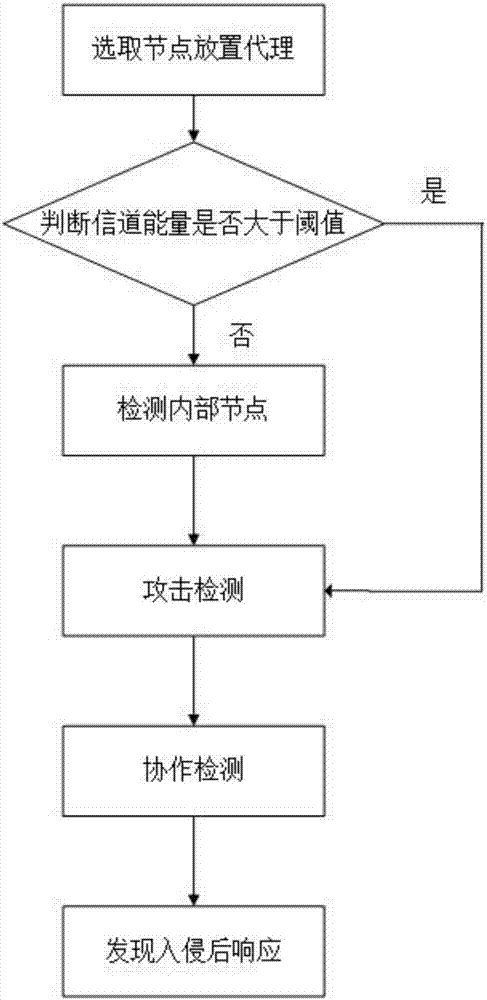
Agent-based intrusion detection method for cognitive wireless network
ActiveCN107426212ATransmissionSecurity arrangementSocially distributed cognitionAnt colony optimization algorithms
The invention belongs to the field of cognitive wireless network technology, and discloses an agent-based intrusion detection method for a cognitive wireless network. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a node placement agent; determining whether the channel energy is greater than a threshold; detecting an internal node; performing attack detection; performing cooperative detection; and giving a response after the intrusion is detected. According to the agent-based intrusion detection method disclosed by the invention, attacks in a distributed cognitive wireless network are detected by using an agent-based intrusion detection system, the shortcoming of only performing single attack detection in existing security schemes can be overcome, and the overall security and robustness of the cognitive wireless network can be realized; and during detection, the attacks that occur inside the network can be detected through the coordination of multiple agents by using an ant colony optimization algorithm, the shortcomings that the computing power of secondary users is weak and a single agent cannot detect all known attacks can be overcome, and the high efficiency of the detection can be guaranteed.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Channel initialization method for distributed cognitive radio network
InactiveCN102256265ASolve the problem of initial networking difficultiesOptimize the transmission pathNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork planningSocially distributed cognitionIdle channel
The invention belongs to wireless communication technical field, and discloses a channel initialization method for a distributed cognitive radio network. The method is characterized in that: through monitoring idle channels, N channel machines capture a Beacon message sent by a root node, and a whole monitoring process is divided into a crude capture phase and a fine capture phase, wherein a preset root node plays a dominant role in whole channel initialization, and other nodes connect with a network through capturing the Beacon message and according to a message in a notification; after connecting with the network, a common node sends an Info message to a superior node to report locally perceptive available channel information, step by step the information is gathered at the root node, thus the root node can calculate available idle channels in the whole network, and a problem of an initial networking difficulty caused by inconsistence of available channels of each node is effectively solved. According to a mechanism of periodically broadcasting Beacon messages, a network access problem of a delayed network node is effectively solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
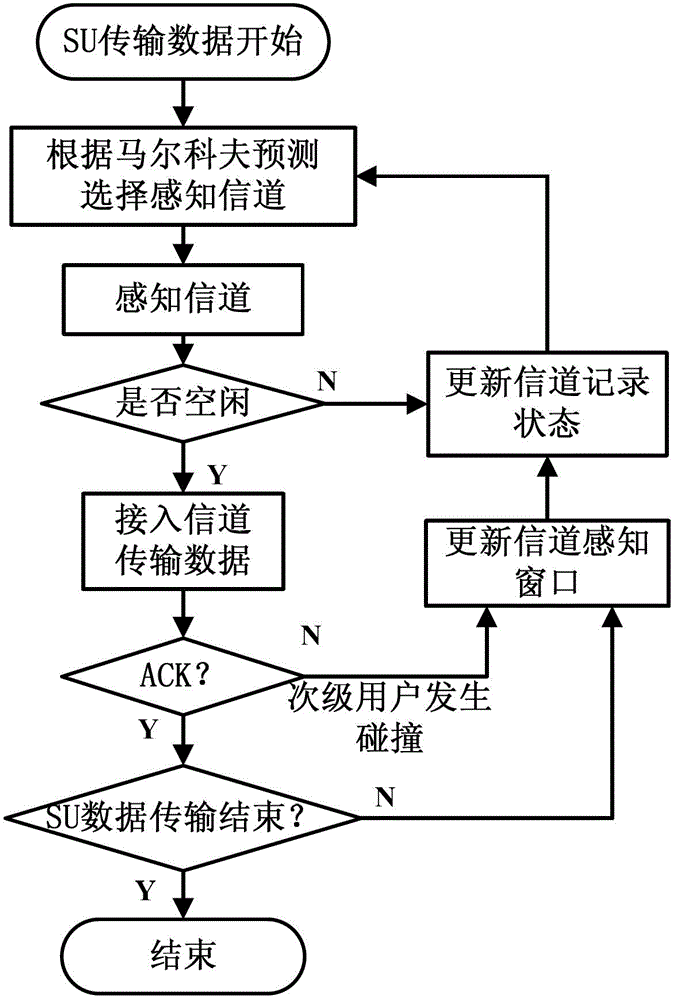
Multi-channel perceptual sequence optimizing method on basis of Markov prediction in distributive cognitive radio network
InactiveCN102724680AImprove throughputReduce the number of perceptionsEnergy efficient ICTHigh level techniquesSocially distributed cognitionData transmission
The invention discloses a multi-channel perceptual sequence optimizing method on the basis of Markov prediction in a distributive cognitive radio network. The method comprises the following steps of: under the limitation condition that a cognitive network has a plurality of opportunistic access authorization channels and a primary user can only sense and access to one channel, estimating the available probability of each channel on the basis of the Markov prediction, optionally selecting the channel with relatively high available probability to sense, and according to a sensing result, determining whether to access to the channel to transmit data or not; and under the condition that a plurality of primary users access to the cognitive network simultaneously, providing a frequency domain sensing window adjusting strategy, so that the collision probability among the primary users is reduced. By the method, the primary users can quickly sense the available channels to transmit data, the sensing times of the primary users are reduced, the sensing efficiency of the primary users and the throughput of the cognitive network are improved, and energy is saved for the primary users. A simulation result shows that when the statistical information of the authorization channels is different, compared with the strategy of randomly selecting the sensing channel, the method can obviously improve the sensing efficiency of the primary users and the throughput of the cognitive network.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Multi-channel collaborative spectrum sensing method based on iterative filtering
InactiveCN103209037BImprove Spectrum Detection PerformanceEasy to detectTransmission monitoringSocially distributed cognitionComputer science
The invention discloses a multi-channel collaborative spectrum sensing method based on iterative filtering. The method includes: time is divided into time slices with fixed length through a reasonably designed frame structure. In each time slice, a secondary user with poor sensing performance is removed preferentially and does not participate in next round of cooperative spectrum sensing, and therefore the number of sensing users is reduced remarkably, and spectrum sensing performance is improved. Through design of the frame structure and a collaborative sensing scheme, the multi-channel collaborative spectrum sensing method based on the iterative filtering can solve problems of too much collaborative spectrum sensing users and malicious user interference existing in a distributed cognitive radio network. Theory analysis and simulation results show that: compared with an existing collaborative spectrum sensing method, the multi-channel collaborative spectrum sensing method based on the iterative filtering can effectively reduce the number of the secondary users participating in collaborative sensing in a loose condition, malicious interference users are removed, and simultaneously spectrum sensing performance of the cognitive radio network is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
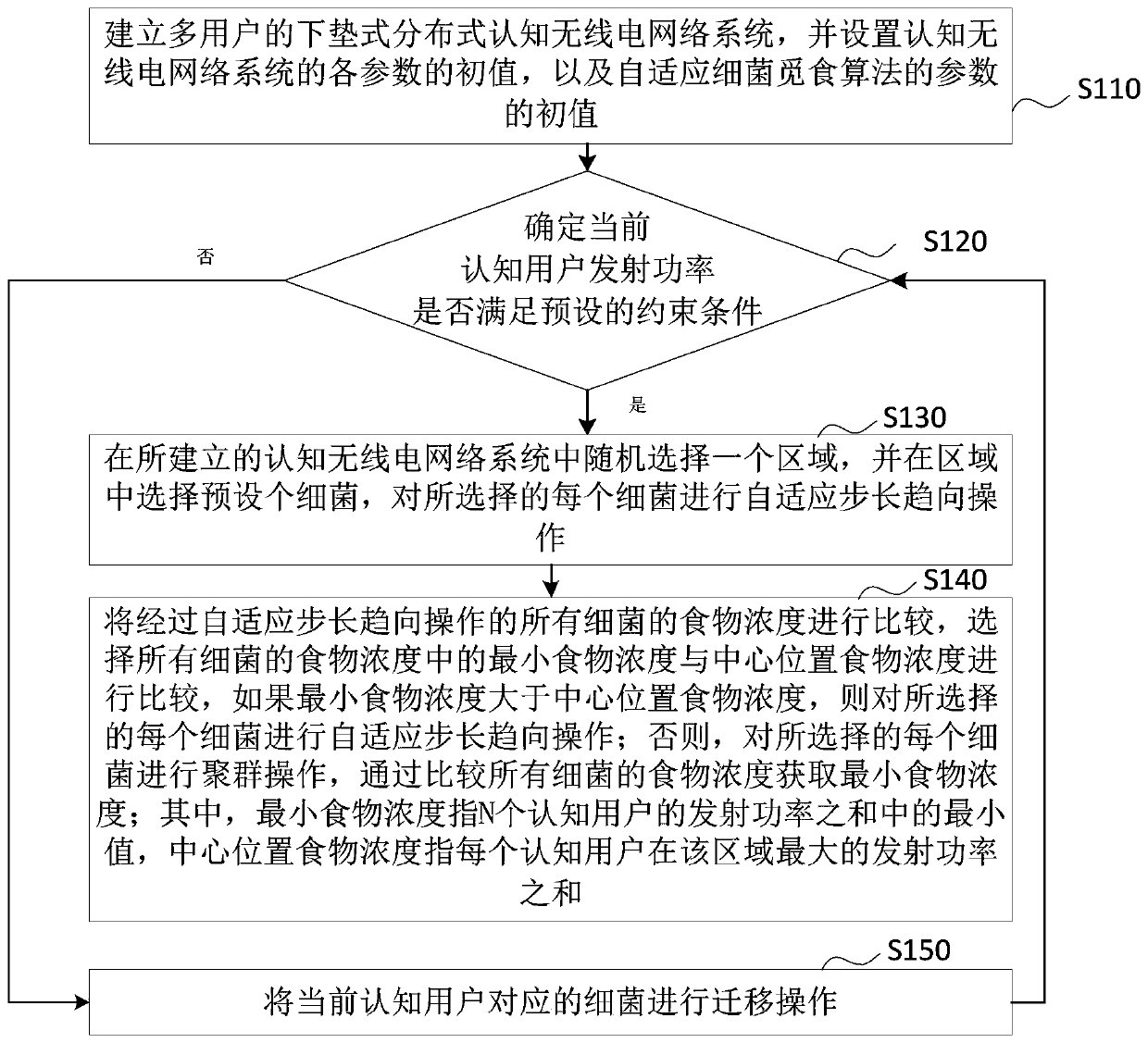
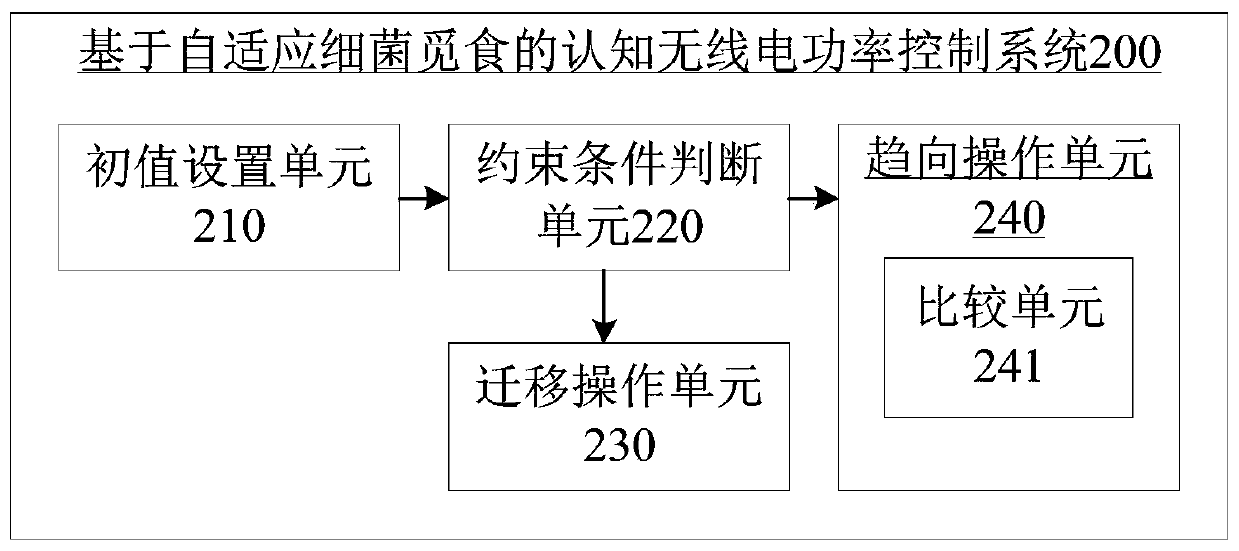
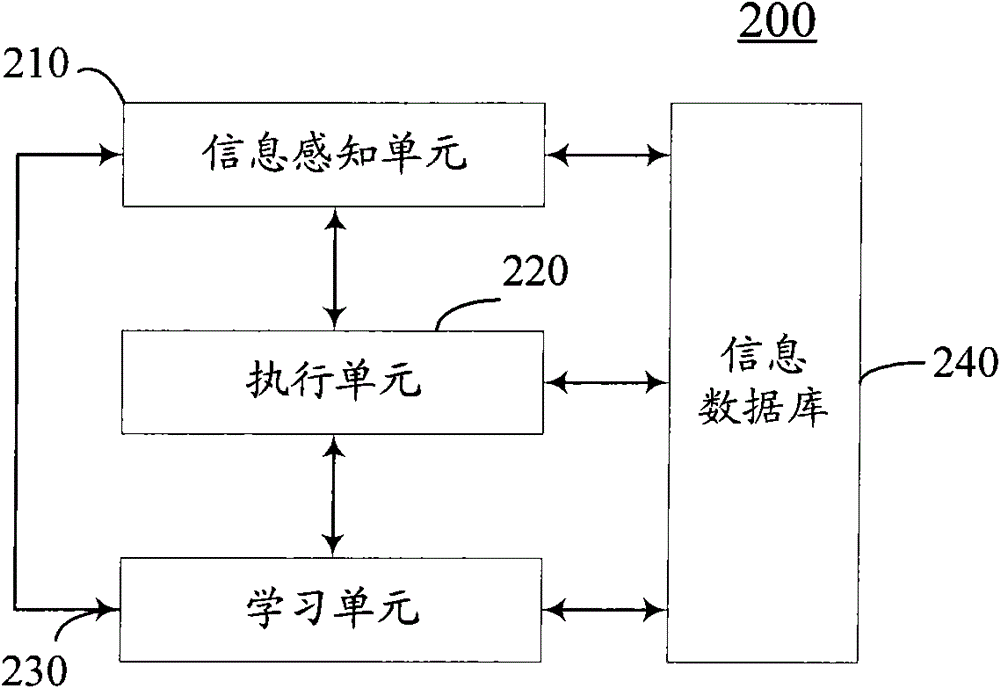
Cognitive radio power control method and system based on adaptive bacterial foraging
ActiveCN106954255ACognitive Spectrum UtilizationGuaranteed communication qualityPower managementCognitive userFrequency spectrum
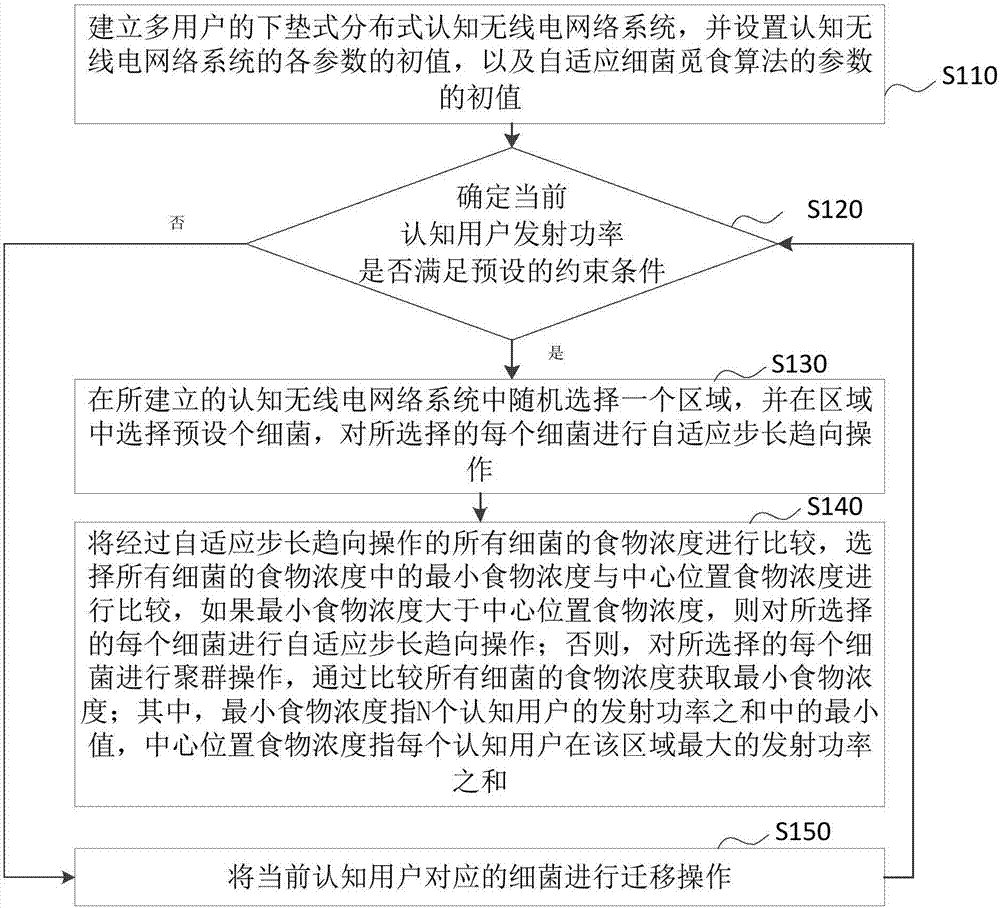
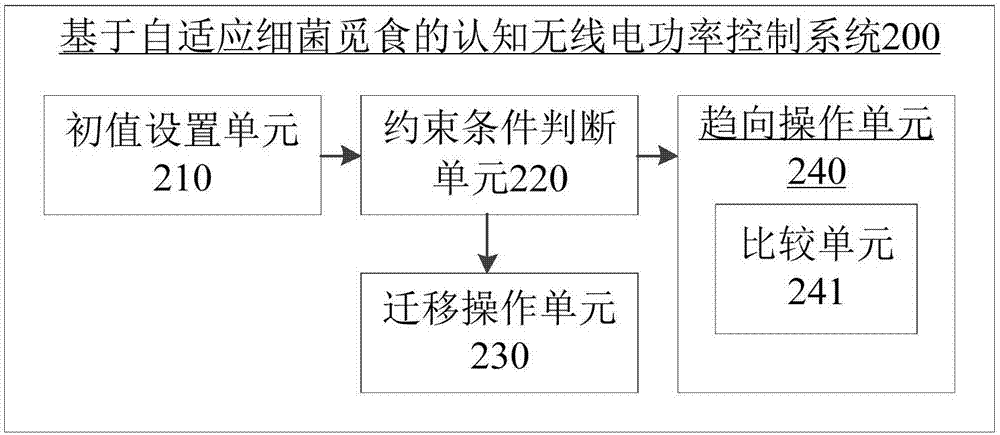
The invention provides a cognitive radio power control method and system based on adaptive bacterial foraging. The method includes the steps of establishing a multiuser underlying distributed cognitive radio network system, and setting initial values of parameters of the cognitive radio network system and initial values of parameters of an adaptive bacterial foraging algorithm; and then determining whether the transmitting power of current cognitive users meets preset constraints, and controlling the power of the cognitive users using the adaptive bacterial foraging algorithm to obtain the minimum value of the sum of the transmitting power of the cognitive users. According to the invention, the communication quality of the authorized users can be guaranteed, an adverse effect of the transmitting power of the cognitive users on a cognitive device is avoided, the cognitive users are allowed to have less energy consumption, the run time of the network is extended, and a better cognitive network spectrum utilization rate is thus gained.
Owner:JILIN INST OF CHEM TECH
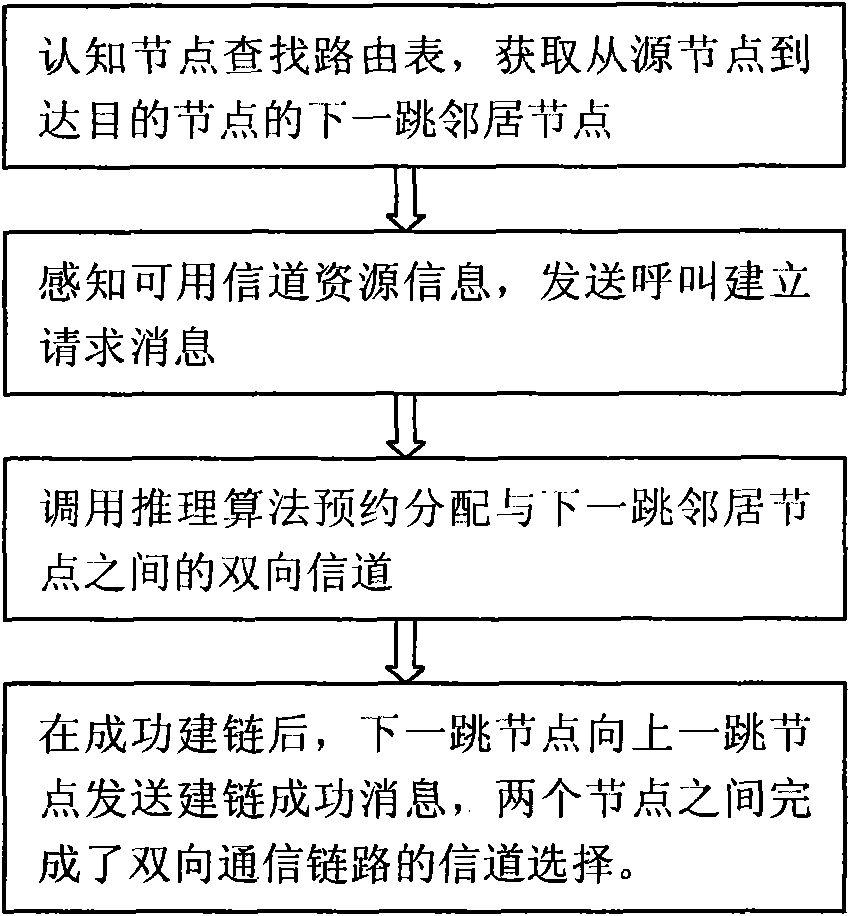
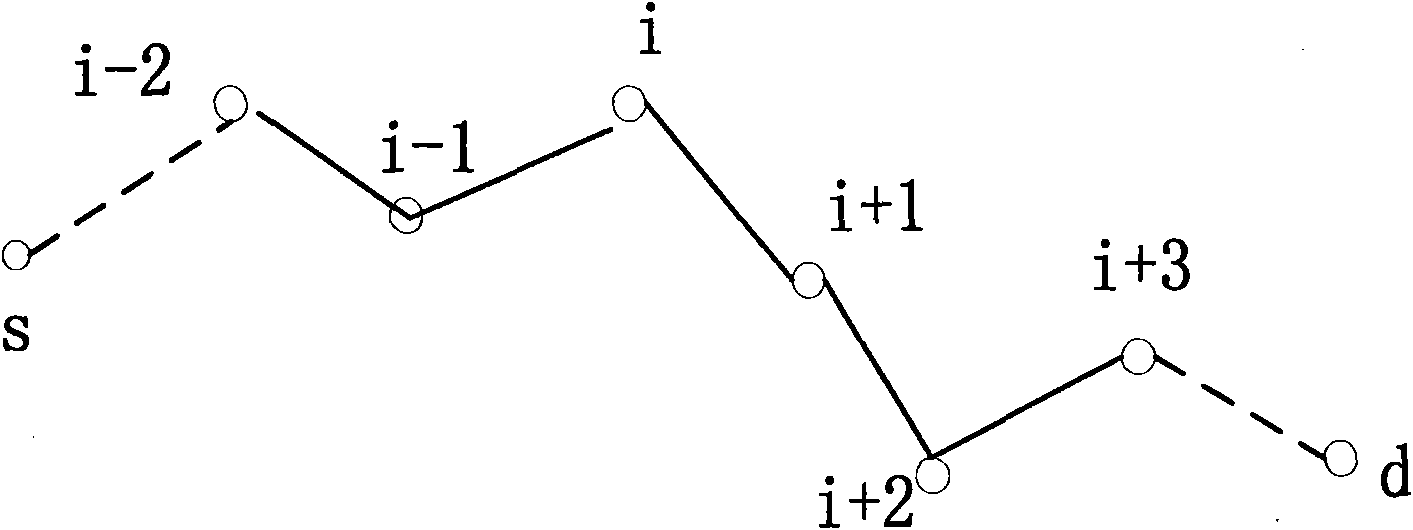
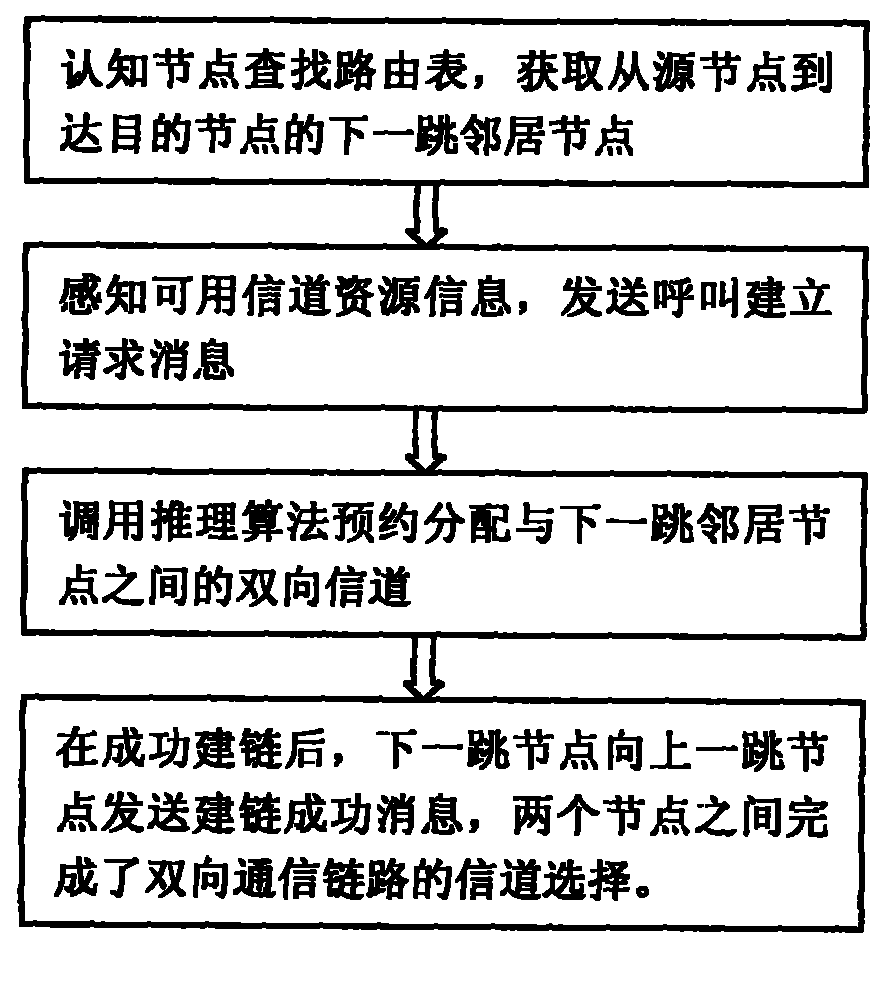
Distributed cognitive radio network two-way channel reservation link constructing method
InactiveCN101873598AIncrease profitConnection managementNetwork planningQuality of serviceFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a distributed cognitive radio network two-way channel reservation link constructing method which belongs to the technical field of cognitive radio networks, and mainly comprises the following steps: a node uses the perceptive capability of a radio terminal to spectrum holes, adopts the idea that a predecessor link reserves a public channel for a subsequent link as possible, reserves and distributes the channel resources of each link in a router from a source node to a target node hop by hop through a conflict prevention channel selection method, and establishes a two-way business transmission path from the source node to the target node. The method realizes channel pre-reservation and distribution in router selection, reduces collision and conflict, realizes the high-efficiency reuse of network resources, provides service quality ensuring capability for two-way multi-hop business transmission under the distributed environment, is applicable to cognitive radio networks, distributed multi-hop networks, wireless local are networks, next generation of heterogeneous networks and other application occasions.
Owner:CHONGQING TELECOMMUNICATION INSTITUTE
Distributed cognitive technology for intelligent emotional robot
InactiveCN101604204BInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionHuman behavior
The invention provides distributed cognitive technology for an intelligent emotional robot, which can be applied in the field of multi-channel human-computer interaction in service robots, household robots, and the like. In a human-computer interaction process, the multi-channel cognition for the environment and people is distributed so that the interaction is more harmonious and natural. The distributed cognitive technology comprises four parts, namely 1) a language comprehension module which endows a robot with an ability of understanding human language after the steps of word division, word gender labeling, key word acquisition, and the like; 2) a vision comprehension module which comprises related vision functions such as face detection, feature extraction, feature identification, human behavior comprehension, and the like; 3) an emotion cognition module which extracts related information in language, expression and touch, analyzes user emotion contained in the information, synthesizes a comparatively accurate emotion state, and makes the intelligent emotional robot cognize the current emotion of a user; and 4) a physical quantity cognition module which makes the robot understand the environment and self state as the basis of self adjustment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
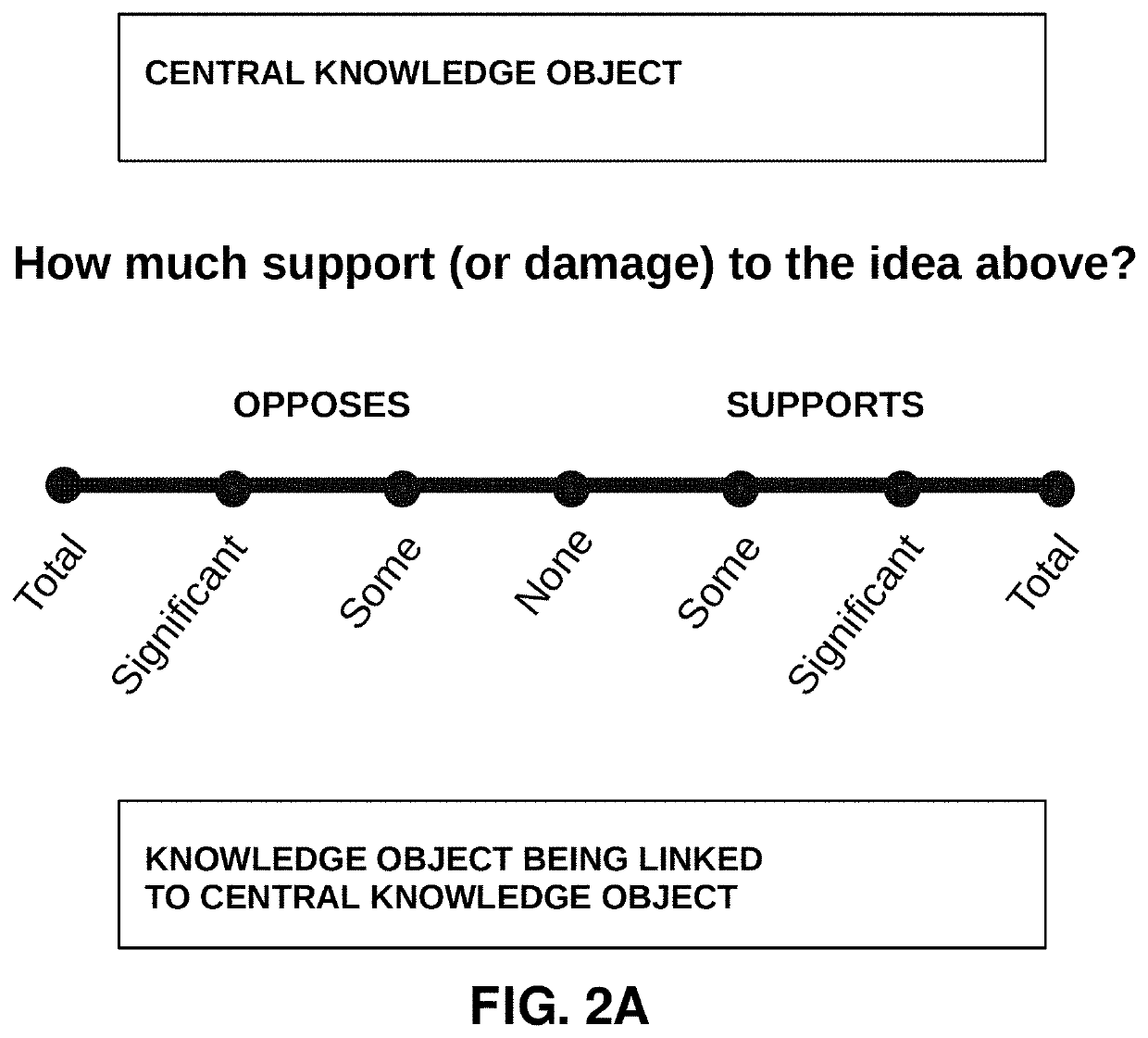
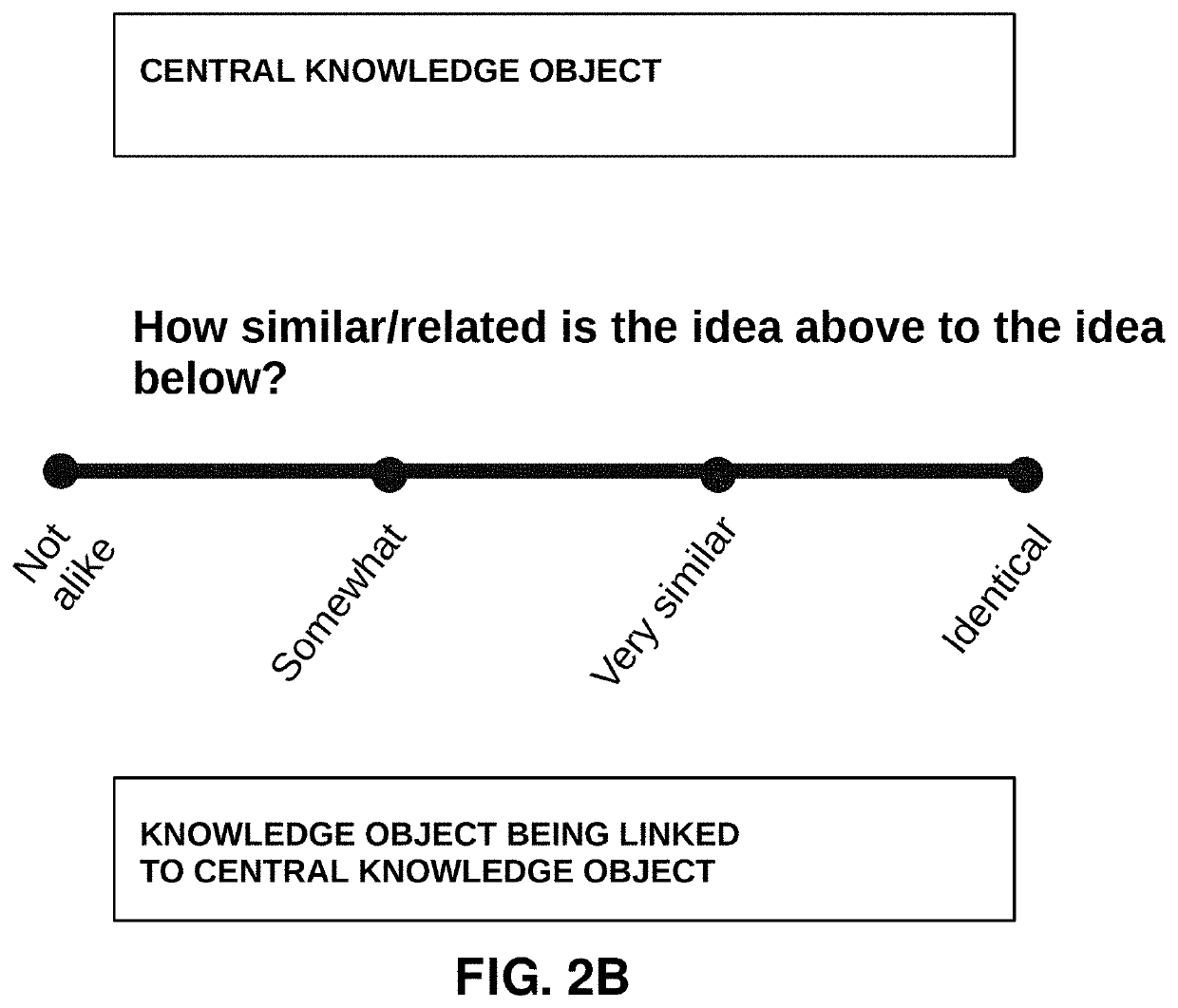
Computer-aided methods and systems for distributed cognition of digital content comprised of knowledge objects
PendingUS20210342408A1Reduced stateEnhance positive stateData processing applicationsWebsite content managementDigital contentSocially distributed cognition
Methods and systems for distributed cognition of digital content include receiving submissions from community members regarding a knowledge object. Each community member has a reputation value and each submission includes an evaluation value representing an evaluation of the knowledge object by the community member. A consensus evaluation is determined based on a calculated combination of the evaluation values in the submissions received and the reputation values of the respective community members who submitted the submissions. While submissions are being received, the consensus evaluation of the knowledge object is iteratively updated based on submissions received, being a calculated combination of the evaluation values in the submissions received and the reputation values of the respective community members who submitted the submissions. Additionally, the reputation value for each community member who submitted the submissions is iteratively updated based on a determined contribution of the respective community member's submission to the updated consensus evaluation.
Owner:BIG IDEA LAB INC
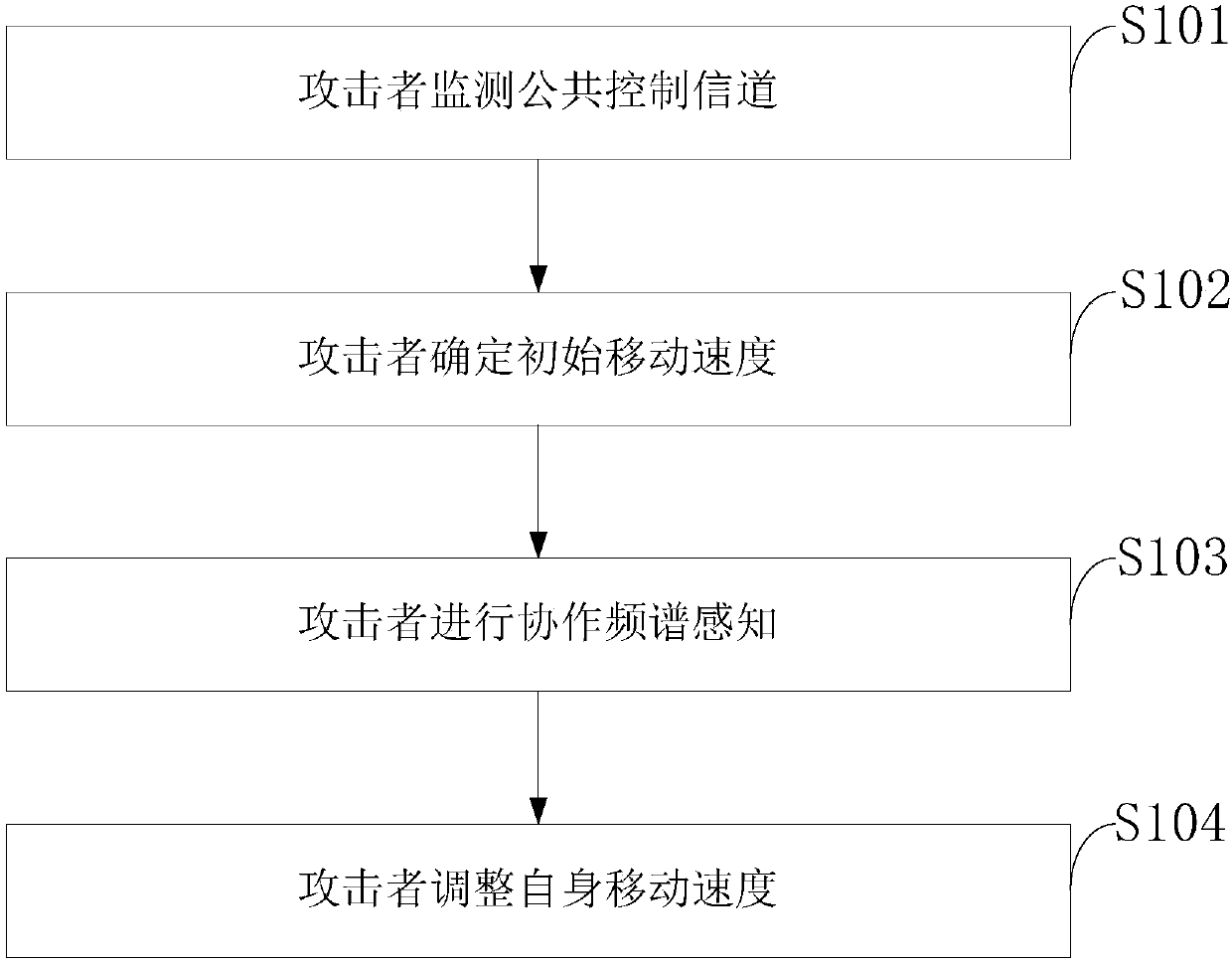
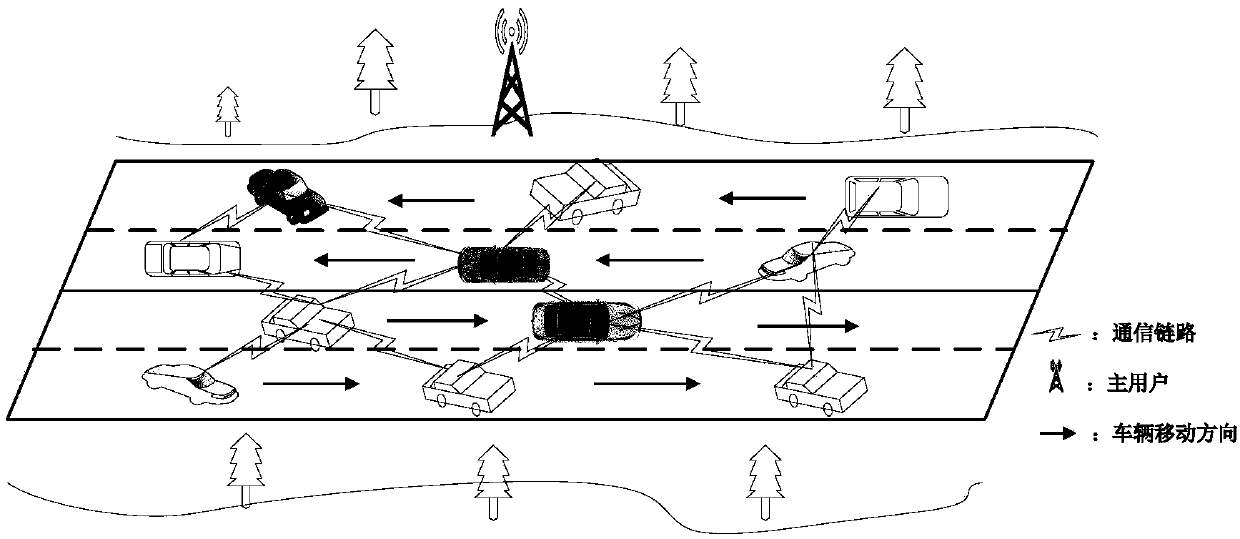
Spectrum sensing data tampering attack method, and distributed cognitive vehicle-mounted network
InactiveCN108156593AGuaranteed accuracyGuarantee authenticityParticular environment based servicesIn-vehicle communicationSensing dataFrequency spectrum
The invention belongs to the technical field of vehicle-mounted communication, and discloses a spectrum sensing data tampering attack method, and a distributed cognitive vehicle-mounted network. The method comprises the following steps: an attacker monitors a common control channel, the attacker determines an initial moving speed, the attacker performs cooperative spectrum perception, and the attacker adjusts an own movement speed. According to the spectrum sensing data tampering attack method, according to the distribution condition of neighbor nodes of the attacker, the change rates of the neighbor nodes of the attacker and the current movement speed of the attacker, the movement speed of the attacker is dynamically adjusted to realize the quick change of the neighbor nodes, when the attacker detection difficulty is increased, the proliferation of erroneous sensing data across the entire network is accelerated, so that the spectrum sensing data are tampered more effectively, and theattack is more flexible.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
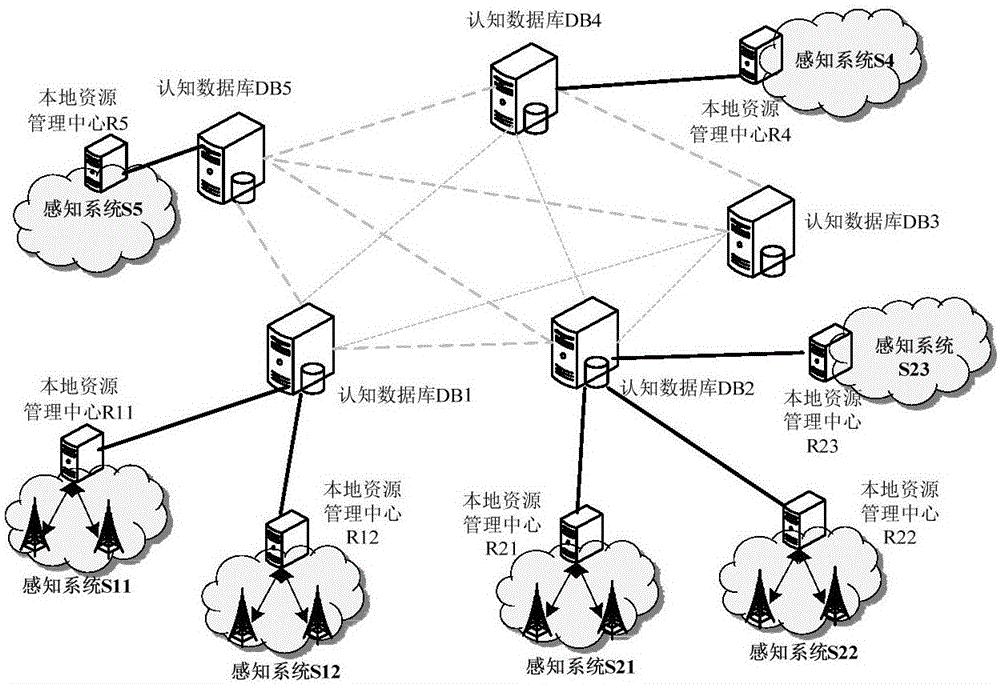
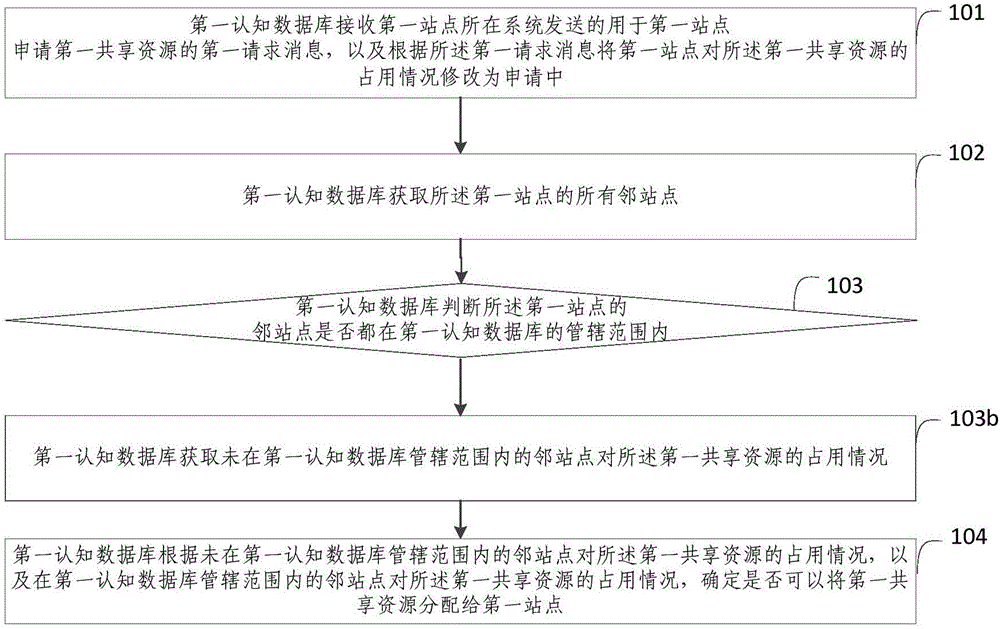
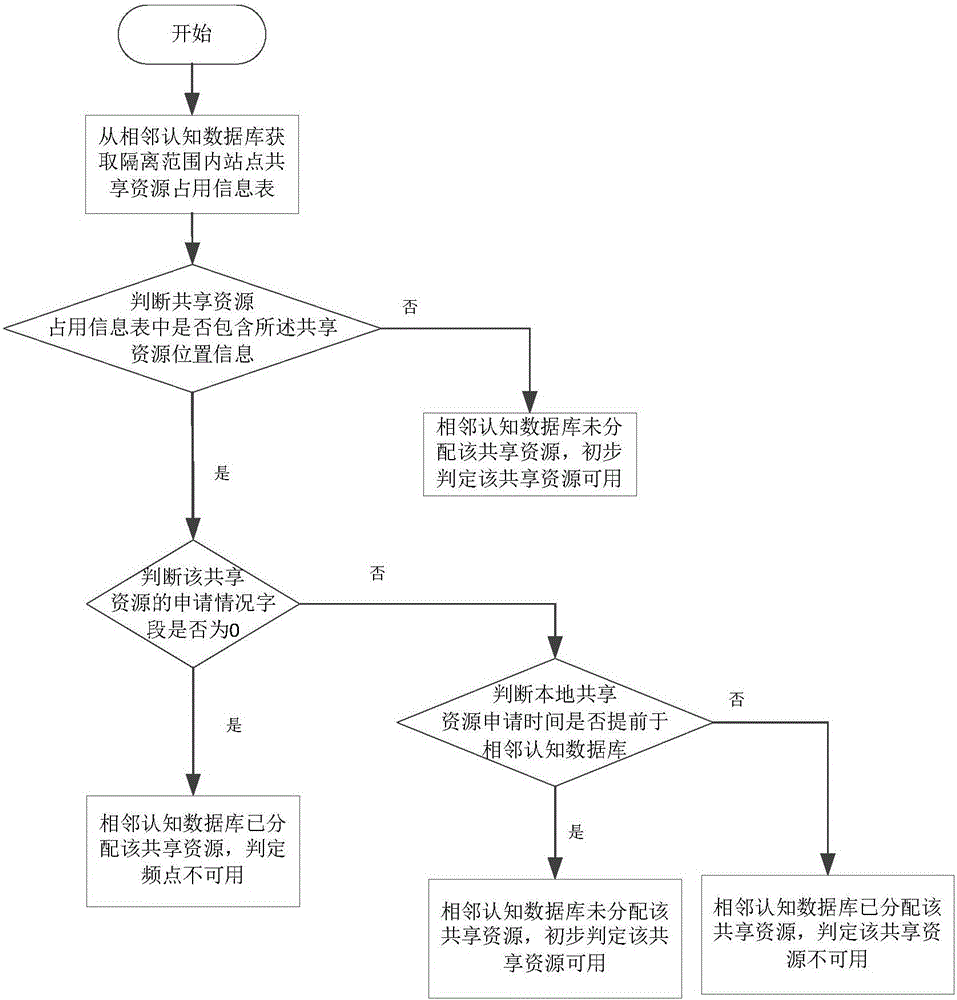
Conflict avoiding method based on distributed cognitive database, and cognitive database
InactiveCN106412923AGet timely application statusObtain frequency occupancy status in timeNetwork planningSocially distributed cognitionShared resource
The invention provides a conflict avoiding method based on a distributed cognitive database, and the cognitive database. The method includes: a first cognitive database receives a first request message sent by a system in which a first site is located, and modifying the occupation condition of a first shared resource as the pending state by the first site according to the first request message, wherein the first request message is used for applying the first shared resource by the first site; the first cognitive database obtains all adjacent sites of the first site; whether the adjacent sites are in a jurisdiction range of the first cognitive database is determined, and if not, the occupation condition of the first shared resource by the adjacent sites which are not in the jurisdiction range of the first cognitive database is obtained; and whether the first shared resource is distributed to the first site is determined according to the occupation condition of the first shared resource by the adjacent sites which are not in the jurisdiction range of the first cognitive database and the occupation condition of the first shared resource by the adjacent sites which are in the jurisdiction range of the first cognitive database. According to the method, the same shared resource can be prevented from being simultaneously allocated to the adjacent sites.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH
Spectrum allocation method based on alliance game in distributed cognitive wireless network
ActiveCN103260166BImprove service qualityOvercome the requirement of only considering the number of frequency bands for secondary usersNetwork planningQuality of serviceFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a distributed cognition wireless network spectrum allocation method based on coalition games. The problem that in the prior art, a cognition wireless network cannot fully use a totalization and whole and partial concept to allocate free frequency ranges is mainly solved. The method comprise the steps of detecting free frequency ranges, computing secondary user utility values, establishing stable coalition, selecting a coalition manager, merging data, refreshing secondary user trust values, allocating the free frequency ranges and refreshing the secondary user trust values. The method is fully combined with the advantages of the cognition wireless network, the trust values, participation values and requirement values are used to represent the utility values of a secondary user comprehensively, the secondary user satisfaction degree of the free frequency ranges and network service quality are improved, the secondary user is divided into the coalition to allocate spectrum resources, using ratio of the free frequency ranges and fairness of spectrum allocating are improved, and by refreshing the secondary user trust values, negative influence on a network from a vicious secondary user is lowered.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
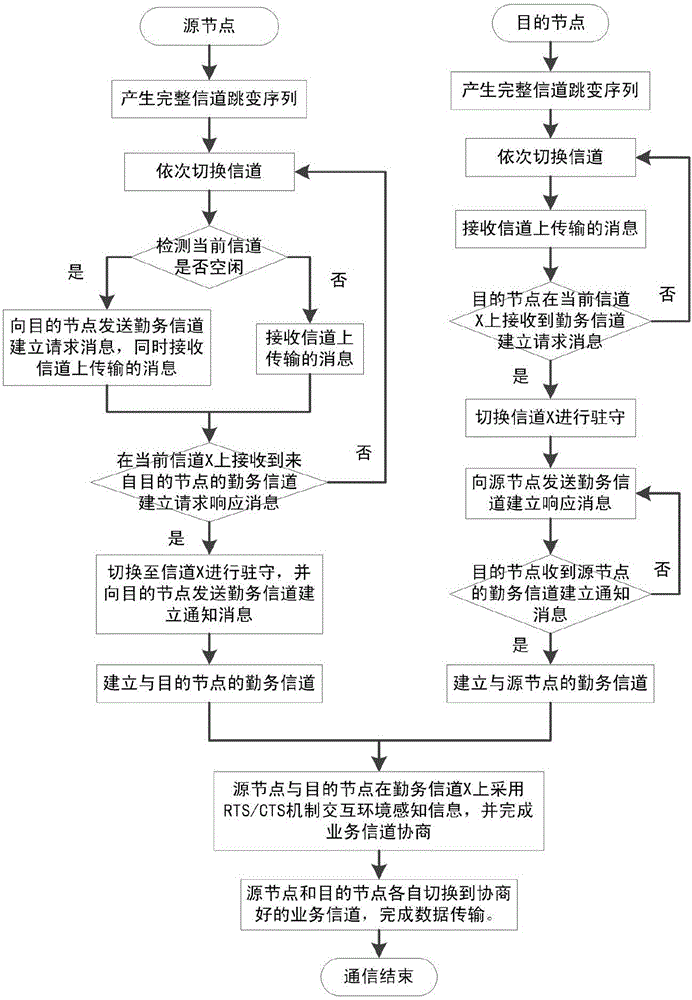
Service channel establishing method suitable for time asynchronous cognitive node
ActiveCN106535358ARealize intersectionEffective support for negotiationConnection managementTransceiverSocially distributed cognition
The invention provides a service channel establishing method suitable for a time asynchronous cognitive node, meanly used for solving the problem that the cognitive node establishes service channels in a plurality of shared control channels in a distributed wireless network. According to the invention, a hop sequence of cognitive node channels is established by means of the sub sequence combination mode based on hop channels and fixed channels, and an information channel intersection time slot format of repeating transceiver in multi time slot is designed. The invention is suitable in time asynchronous distributed cognitive radio network environment, and by means of the service channel establishing method suitable for a time asynchronous cognitive node provided by the invention, the channel intersection and information interaction for a plurality of cognitive nodes with symmetric identities in a plurality of shared control channels can be achieved, the service channels can be established, and the realization of the environment perception information interaction of cognitive nodes and the negotiation of business channels can be supported.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Cognitive radio power control method and system based on adaptive bacterial foraging
ActiveCN106954255BCognitive Spectrum UtilizationGuaranteed communication qualityPower managementCognitive userAnimal Foraging
The invention provides a cognitive radio power control method and system based on adaptive bacterial foraging. The method includes the steps of establishing a multiuser underlying distributed cognitive radio network system, and setting initial values of parameters of the cognitive radio network system and initial values of parameters of an adaptive bacterial foraging algorithm; and then determining whether the transmitting power of current cognitive users meets preset constraints, and controlling the power of the cognitive users using the adaptive bacterial foraging algorithm to obtain the minimum value of the sum of the transmitting power of the cognitive users. According to the invention, the communication quality of the authorized users can be guaranteed, an adverse effect of the transmitting power of the cognitive users on a cognitive device is avoided, the cognitive users are allowed to have less energy consumption, the run time of the network is extended, and a better cognitive network spectrum utilization rate is thus gained.
Owner:JILIN INST OF CHEM TECH
Cognitive network architecture and self-configuring method thereof
The invention discloses a centralized cognitive network system with cognitive capabilities and a distributed cognitive network system with cognitive capabilities. The centralized cognitive network system comprises at least one iNode for sensing network information of jurisdiction area thereof; a Root-iNote for receiving the network information and respectively establishing a configuration access plan for each iNode according to the network information; a CN (communicating net)- OAM (operation administration and maintenance) subsystem for obtaining the configuration access plan from the Root-iNote and respectively building communication link with related iNode based on the configuration access plan, wherein the communication link based on the iNode downloads related configuration parameters from the CN-OAM subsystem so as to perform self-configuration by use of the configuring parameters.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Frequency spectrum sensing method
InactiveCN102291191BReduce complexityReduce distractionsTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumSocially distributed cognition
The invention discloses a frequency spectrum sensing method. The frequency spectrum sensing method comprises the following steps of: independently sensing minor user nodes in an energy detecting mode, and acquiring the use conditions of frequency spectrums of the peripheries of the minor user nodes; acquiring a latest detection result by diffusing the minor user nodes within a two-hop neighbour range; computing the local sensing information and the synergetic sensing information of the minor user nodes; acquiring a judgment threshold according to master user communication behavior priori knowledges and the synergetic sensing information, and judging. According to the frequency spectrum sensing method disclosed by the invention, special appointed sink nodes or clustering computation is notneeded, the local sensing information diffusion of the minor user nodes is limited within the two-hop neighbour range, and the complexity and the synergetic spending of the synergetic detection of a distributed cognitive network are effectively reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A Secure Collaborative Spectrum Sensing Method Based on Reputation Mechanism and Dynamic Game
ActiveCN104993890BAccelerate the speed of obtaining the reputation value of collaborative sub-usersHigh speedTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumSocially distributed cognition
The present invention relates to a secure collaborative spectrum sensing method based on reputation mechanism and dynamic game. The method combines the reputation transfer process of secondary users. If a secondary user exceeds the one-hop communication range of a neighboring secondary user, the neighboring secondary user will move. The reputation value previously established by the secondary user is broadcast to the secondary users within its one-hop communication range, which speeds up the speed at which the reputation value is obtained by the cooperative spectrum sensing requester when the mobile secondary user participates in cooperation. Then run the dynamic game method, through the utility function of the cooperative spectrum sensing requester and the cooperative spectrum sensing secondary user, so as to encourage the secondary users to participate in the cooperation, and combine the reputation value weight distribution to improve the security of the collaborative spectrum sensing. The invention improves the convergence speed of mobile secondary user reputation evaluation in the distributed cognitive wireless network, ensures the fairness of cooperation and encourages collaborators to actively participate in cooperation, can effectively resist SSDF attacks, and simultaneously improves the frequency spectrum detection rate.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
A Service Channel Establishment Method Applicable to Time Asynchronous Cognitive Nodes
ActiveCN106535358BRealize intersectionEffective support for negotiationConnection managementTransmission path multiple useTransceiverSocially distributed cognition
The invention provides a service channel establishing method suitable for a time asynchronous cognitive node, meanly used for solving the problem that the cognitive node establishes service channels in a plurality of shared control channels in a distributed wireless network. According to the invention, a hop sequence of cognitive node channels is established by means of the sub sequence combination mode based on hop channels and fixed channels, and an information channel intersection time slot format of repeating transceiver in multi time slot is designed. The invention is suitable in time asynchronous distributed cognitive radio network environment, and by means of the service channel establishing method suitable for a time asynchronous cognitive node provided by the invention, the channel intersection and information interaction for a plurality of cognitive nodes with symmetric identities in a plurality of shared control channels can be achieved, the service channels can be established, and the realization of the environment perception information interaction of cognitive nodes and the negotiation of business channels can be supported.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com