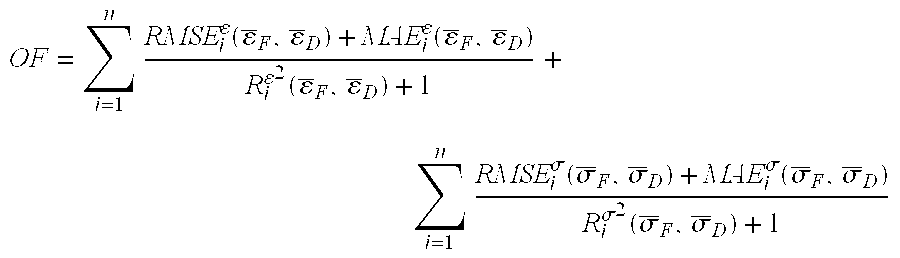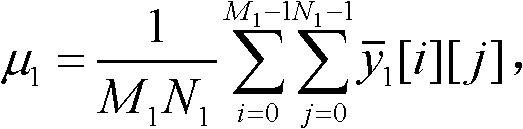Patents
Literature
30 results about "Spatial variance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
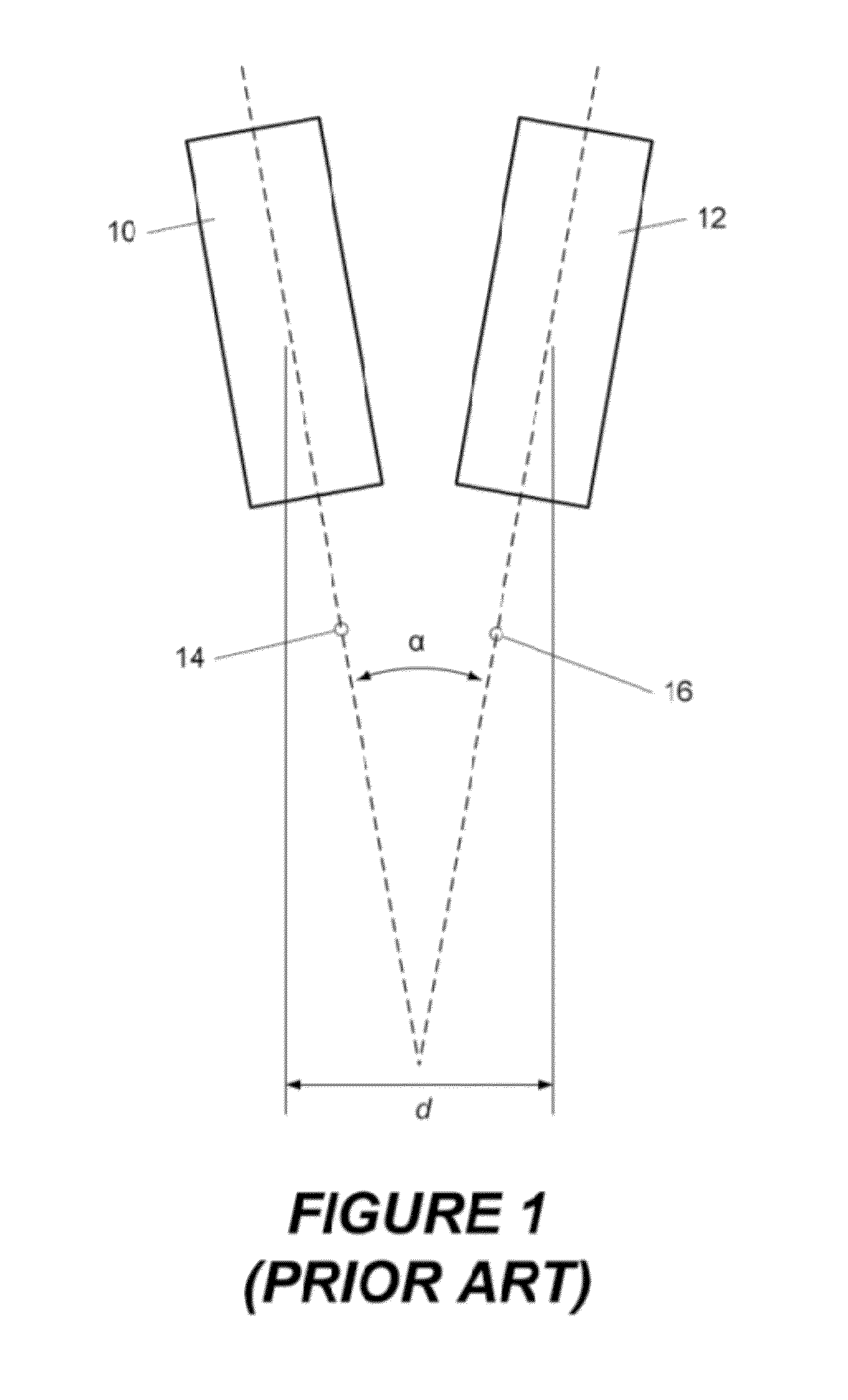
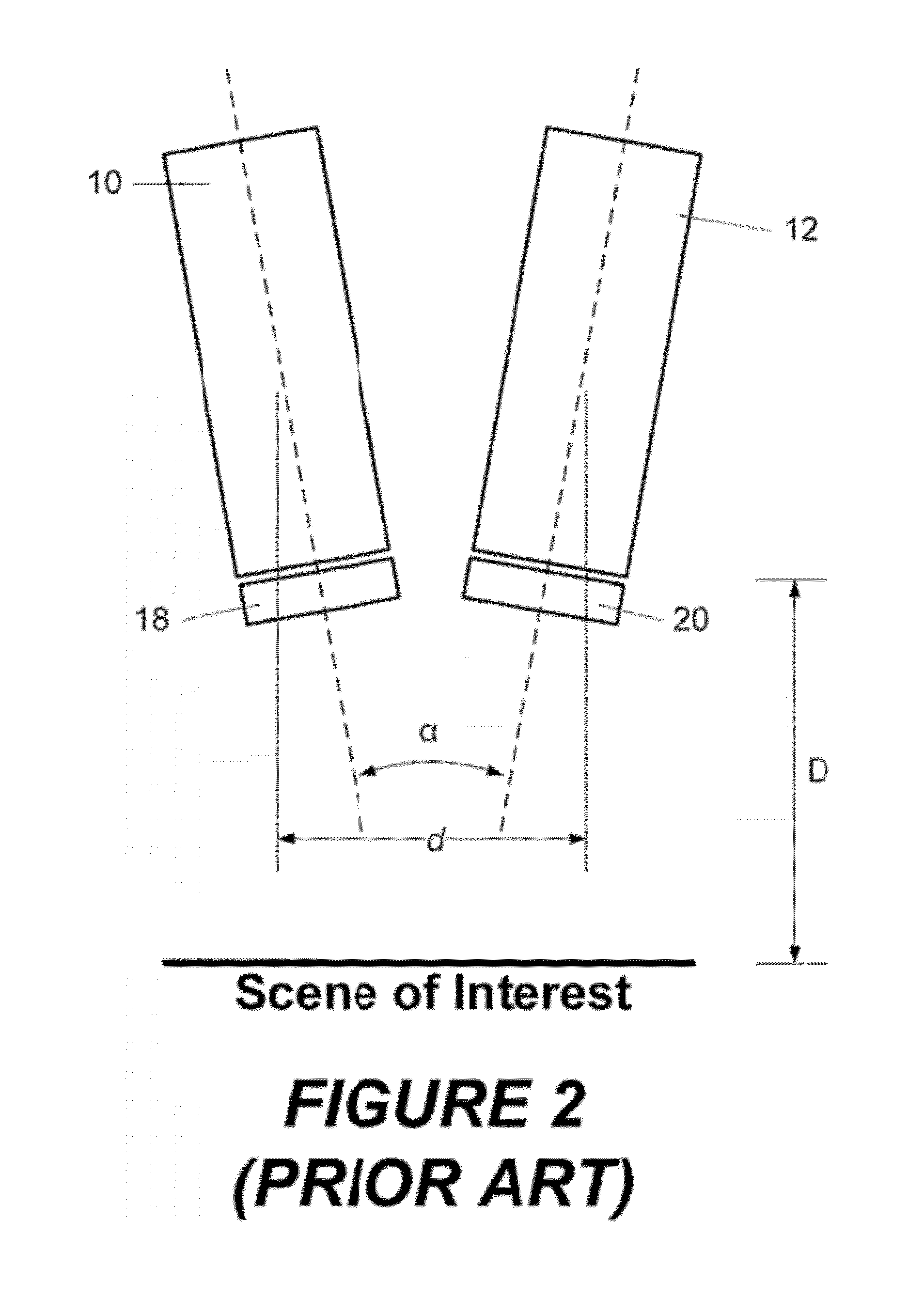
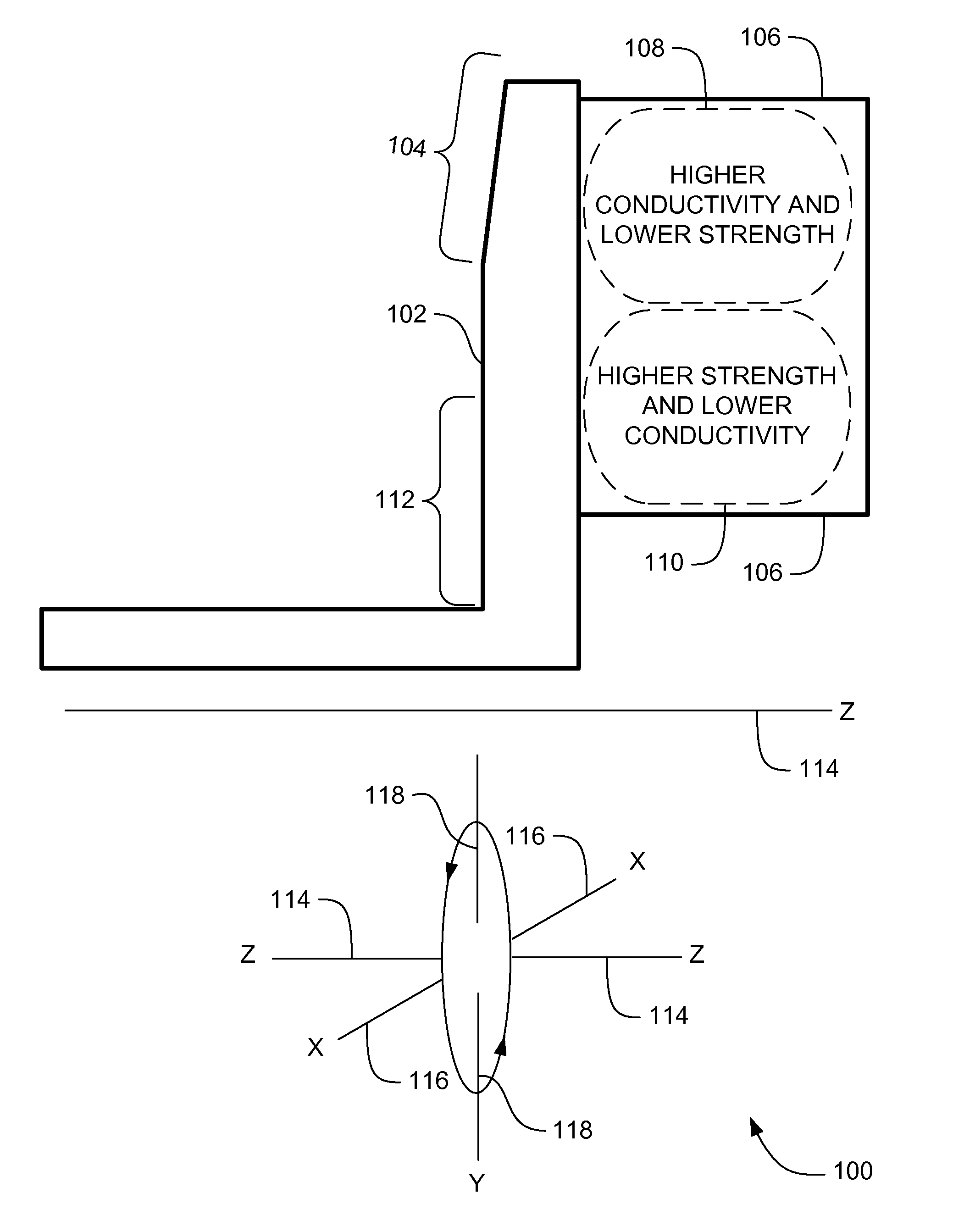
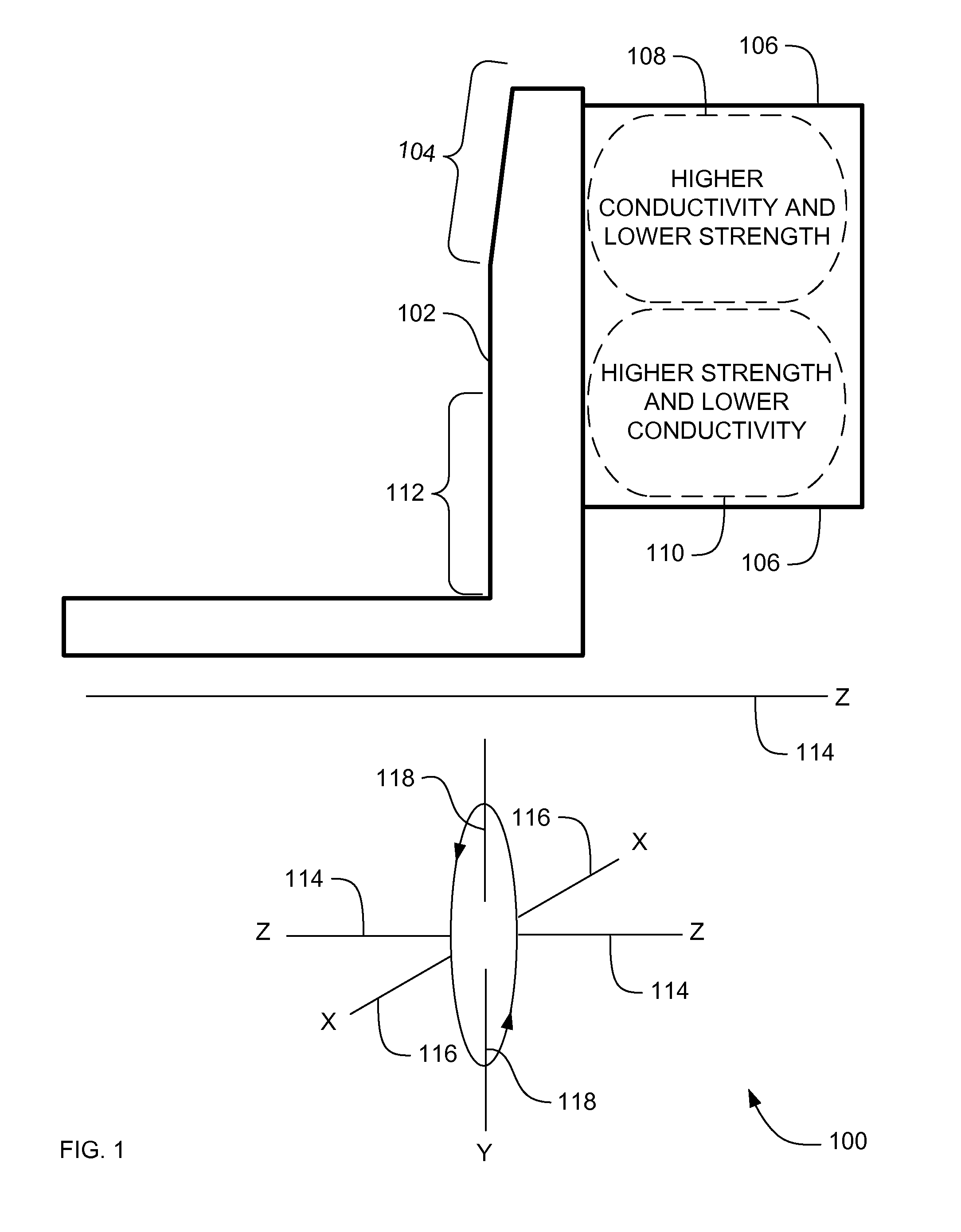
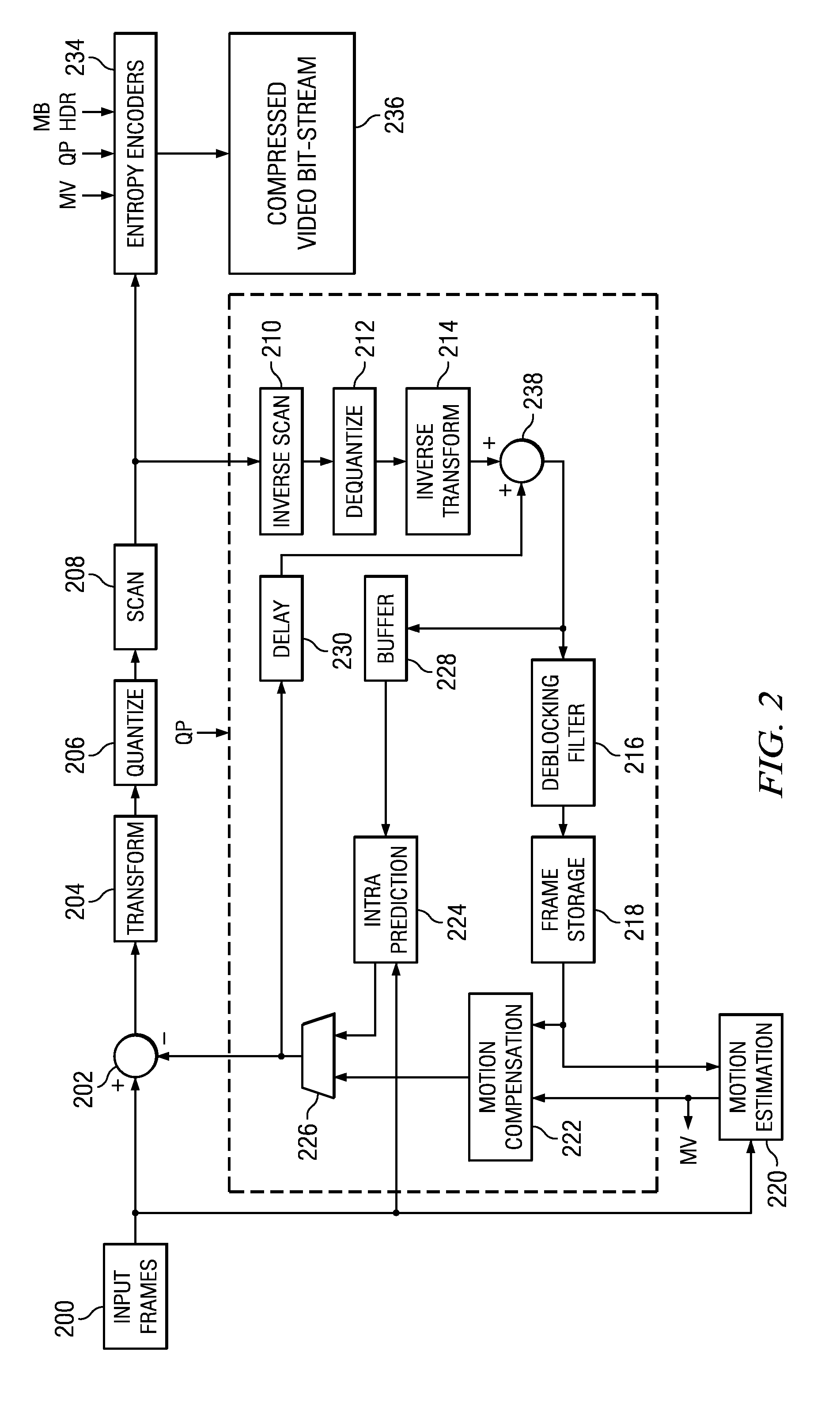
Systems, methods and apparatus of a composite X-Ray target
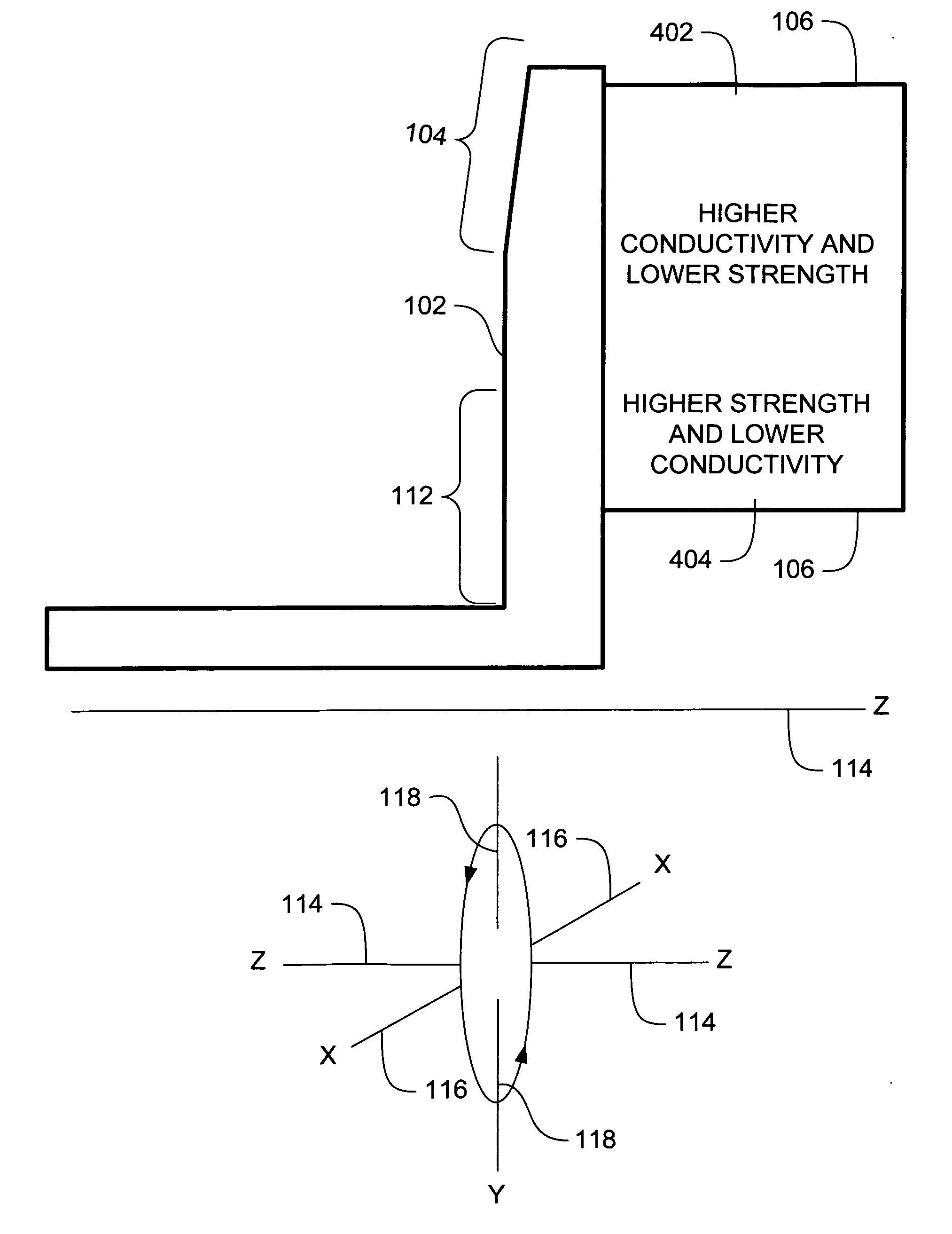
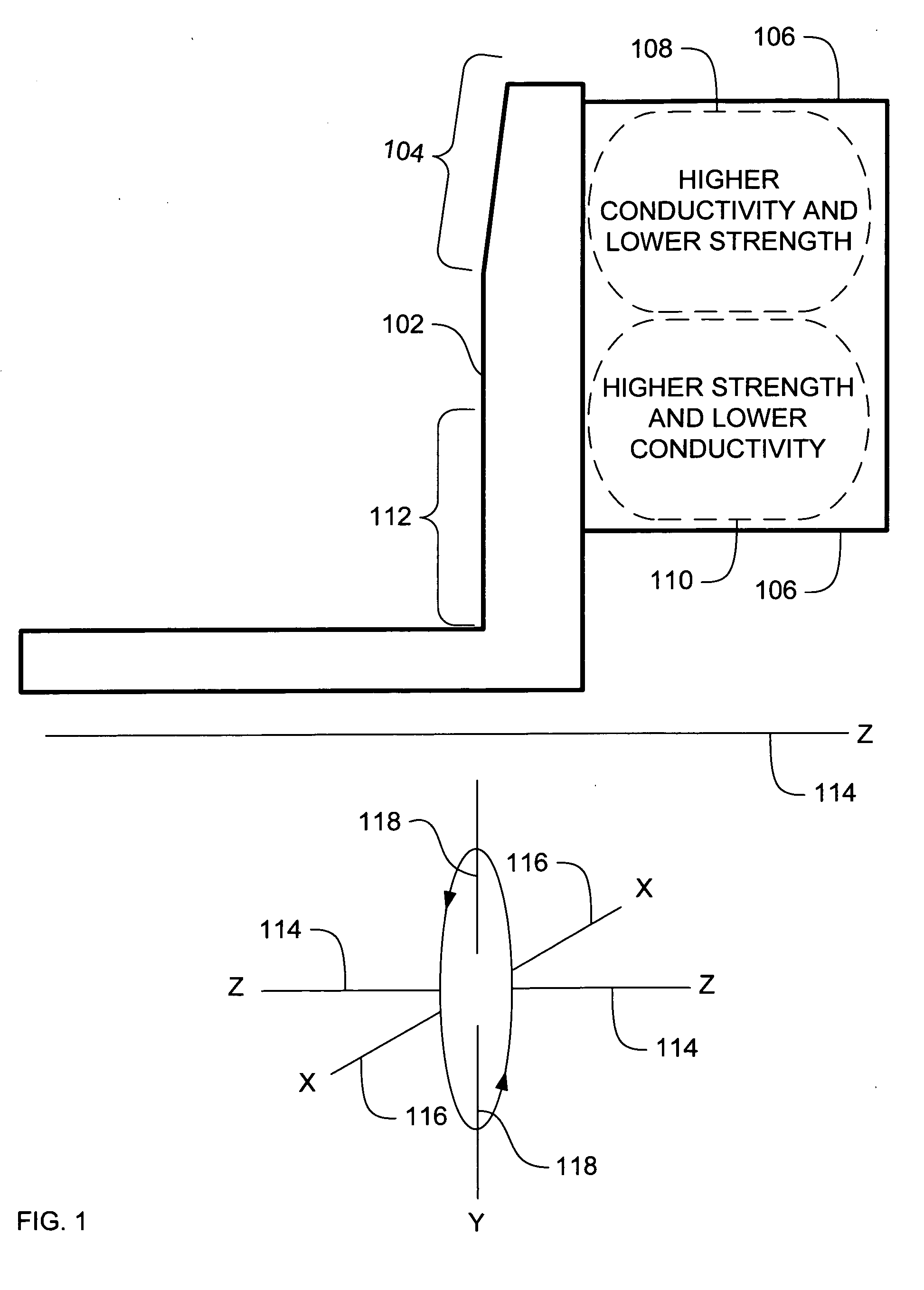
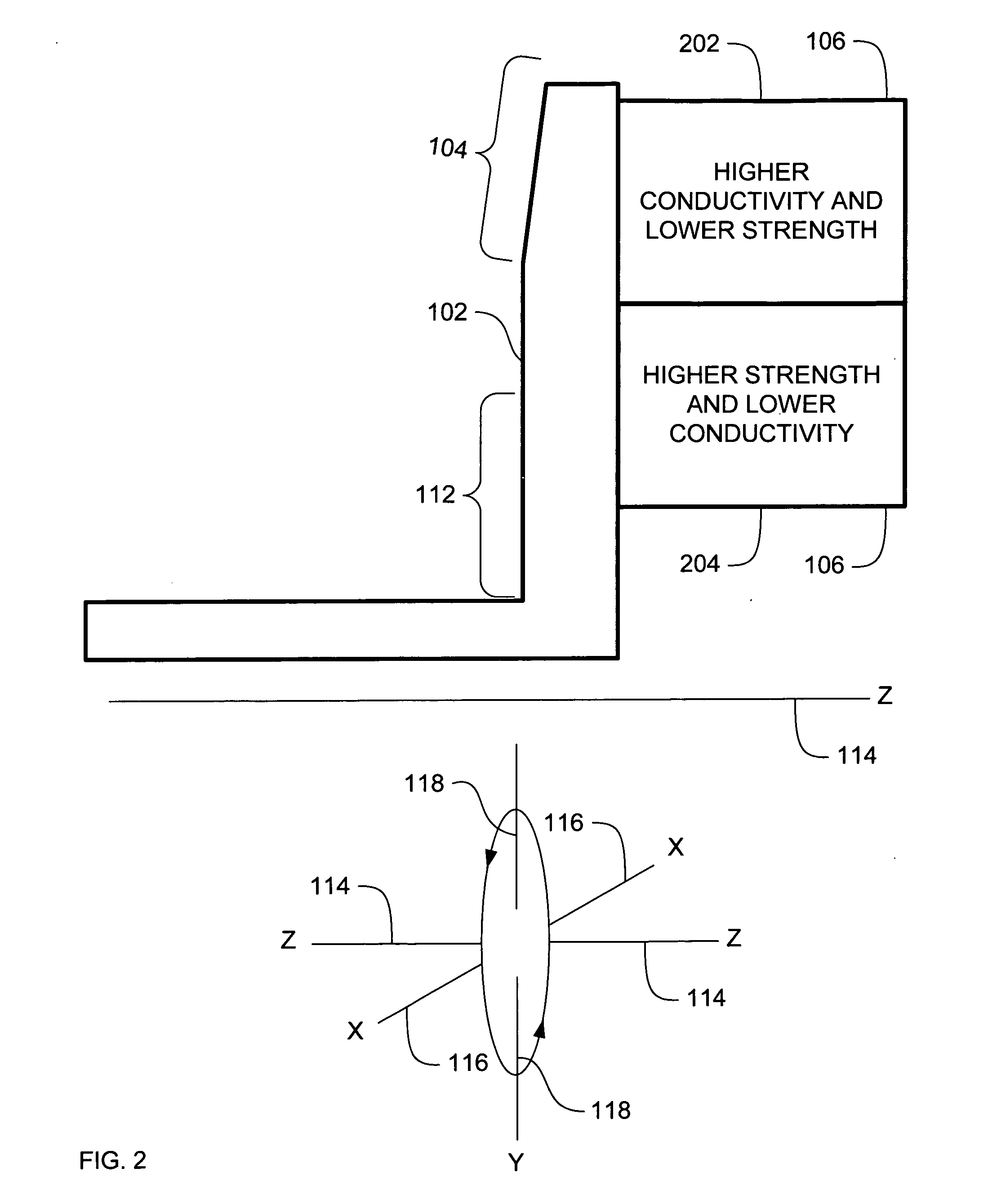
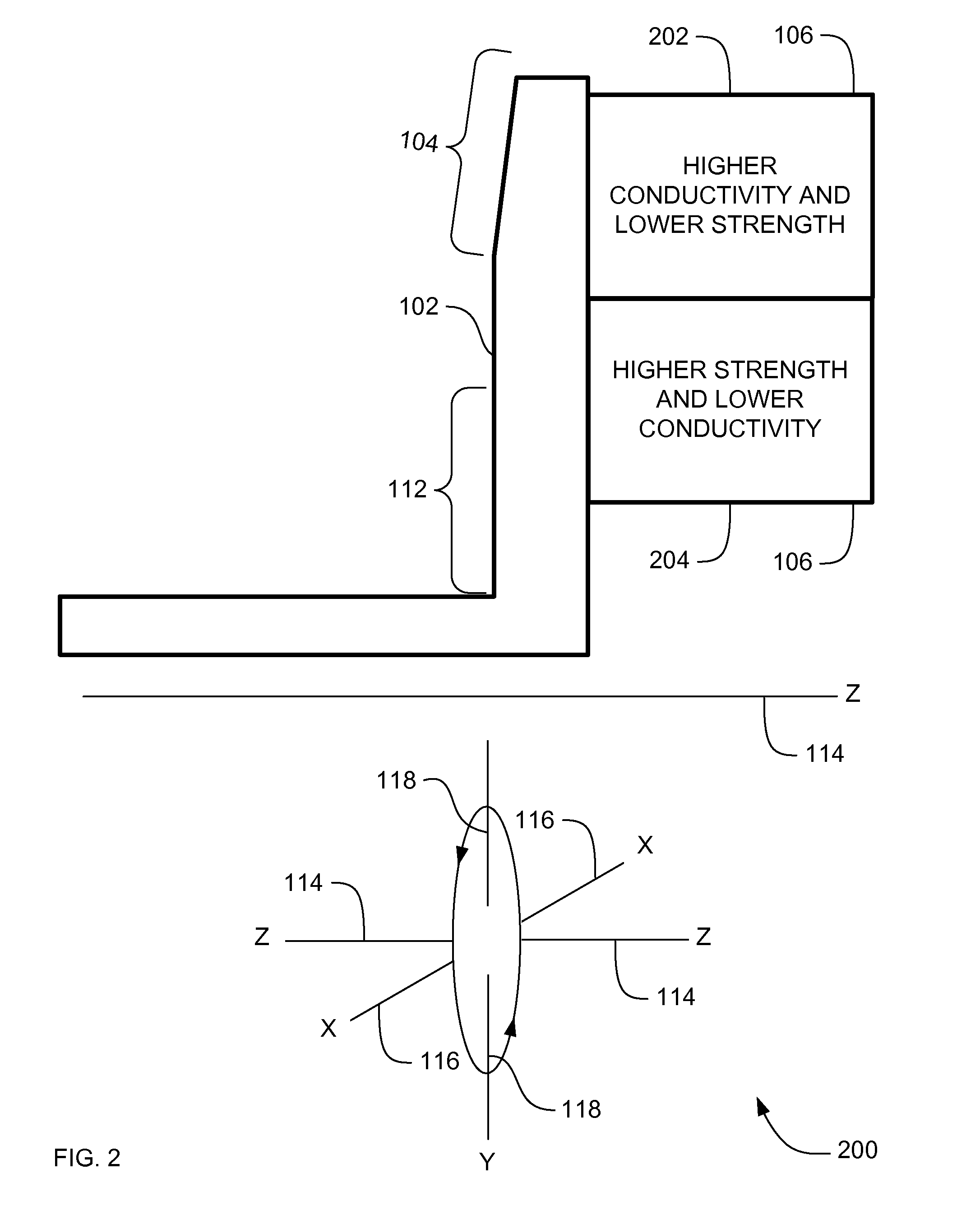
ActiveUS20070071174A1High mechanical strengthLow thermal conductivityX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesX-raySystems approaches
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which in some embodiments an X-Ray energy target includes composite material that varies spatially in thermal properties, and in some embodiments, the composite material varies spatially in strength properties. In some embodiments, the spatial variance is a continuum and in other embodiments, the spatial variance is a plurality of distinct portions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Motionless adaptive stereoscopic scene capture with tuneable liquid crystal lenses and stereoscopic auto-focusing methods
A motionless adaptive focus stereoscopic scene capture apparatus employing tuneable liquid crystal lenses is provided. The apparatus includes at least two image sensors preferably fabricated as a monolithic stereo image capture component and at least two corresponding tuneable liquid crystal lenses preferably fabricated as a monolithic focus adjustment component. Using a variable focus tuneable liquid crystal lens at each aperture stop provides constant magnification focus control. Controlled spatial variance of a spatially variant electric field applied to the liquid crystal of each tuneable liquid crystal lens provides optical axis shift enabling registration between stereo images. A controller implements coupled auto-focusing methods employing multiple focus scores derived from at least two camera image sensors and providing multiple tuneable liquid crystal lens drive signals for synchronous focus acquisition of a three dimensional scene. Wafer manufacture provides a compact stereoscopic image capture apparatus for endoscopic surgery, optical inspection and entertainment applications.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
Systems, methods and apparatus of a composite X-Ray target
ActiveUS7382864B2High mechanical strengthLow thermal conductivityX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesX-raySystems approaches
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which in some embodiments an X-Ray energy target includes composite material that varies spatially in thermal properties, and in some embodiments, the composite material varies spatially in strength properties. In some embodiments, the spatial variance is a continuum and in other embodiments, the spatial variance is a plurality of distinct portions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
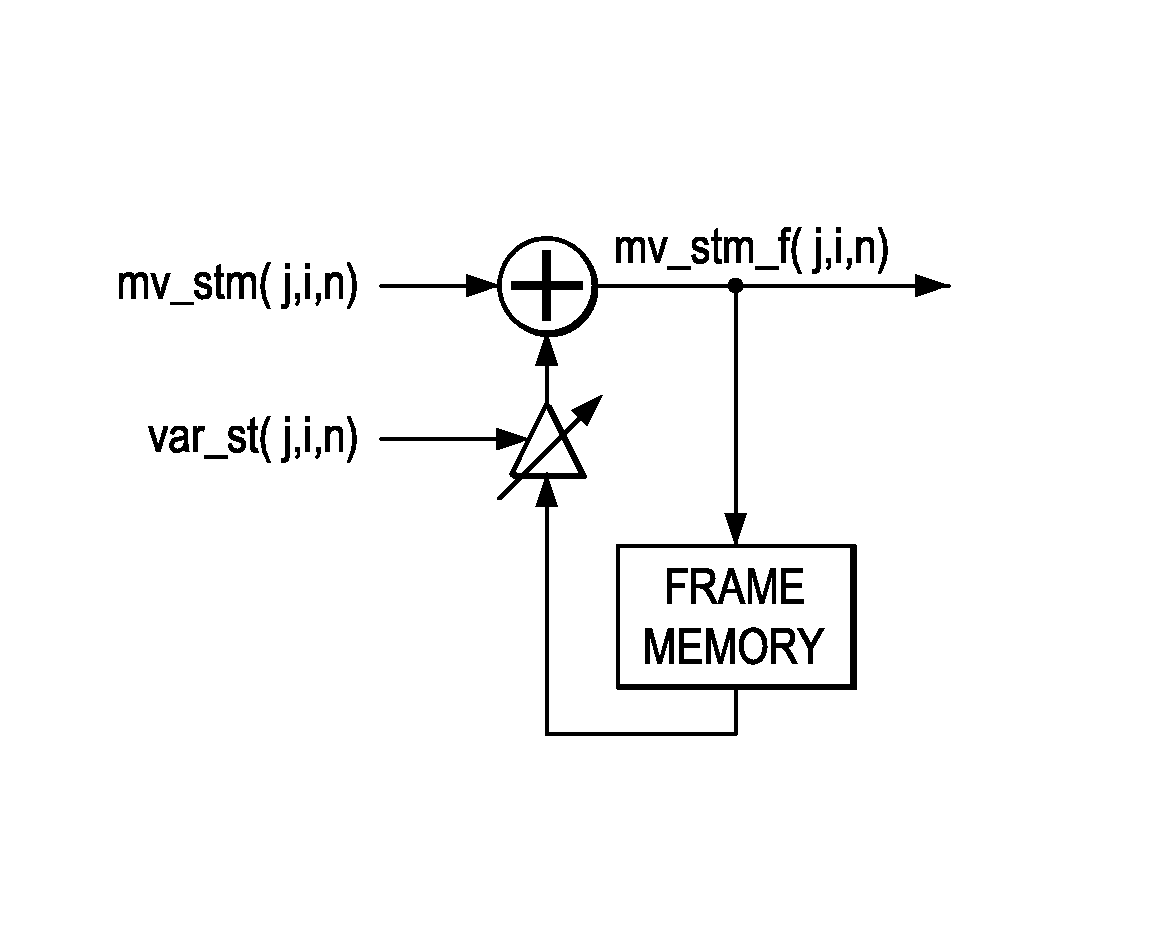
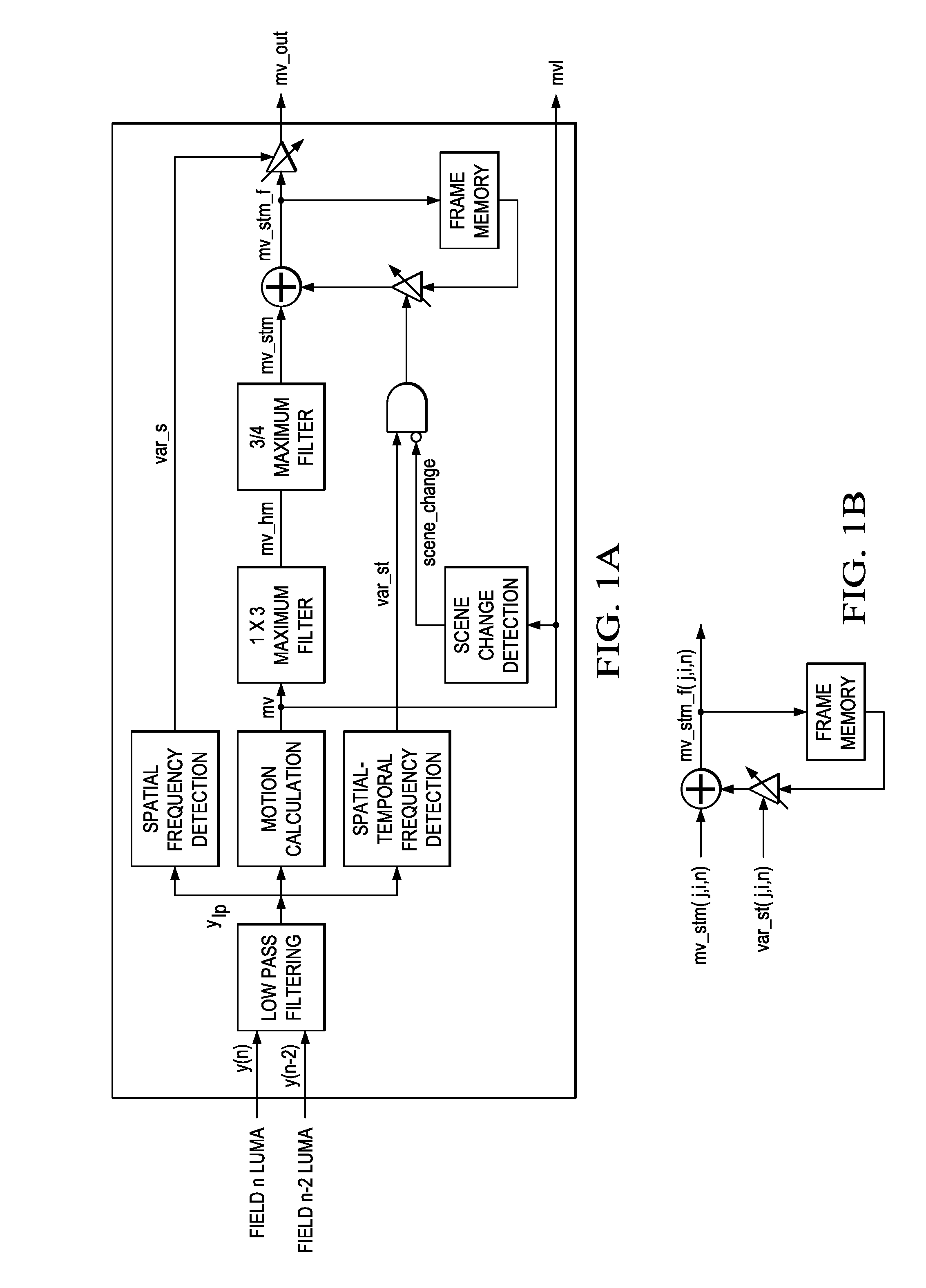
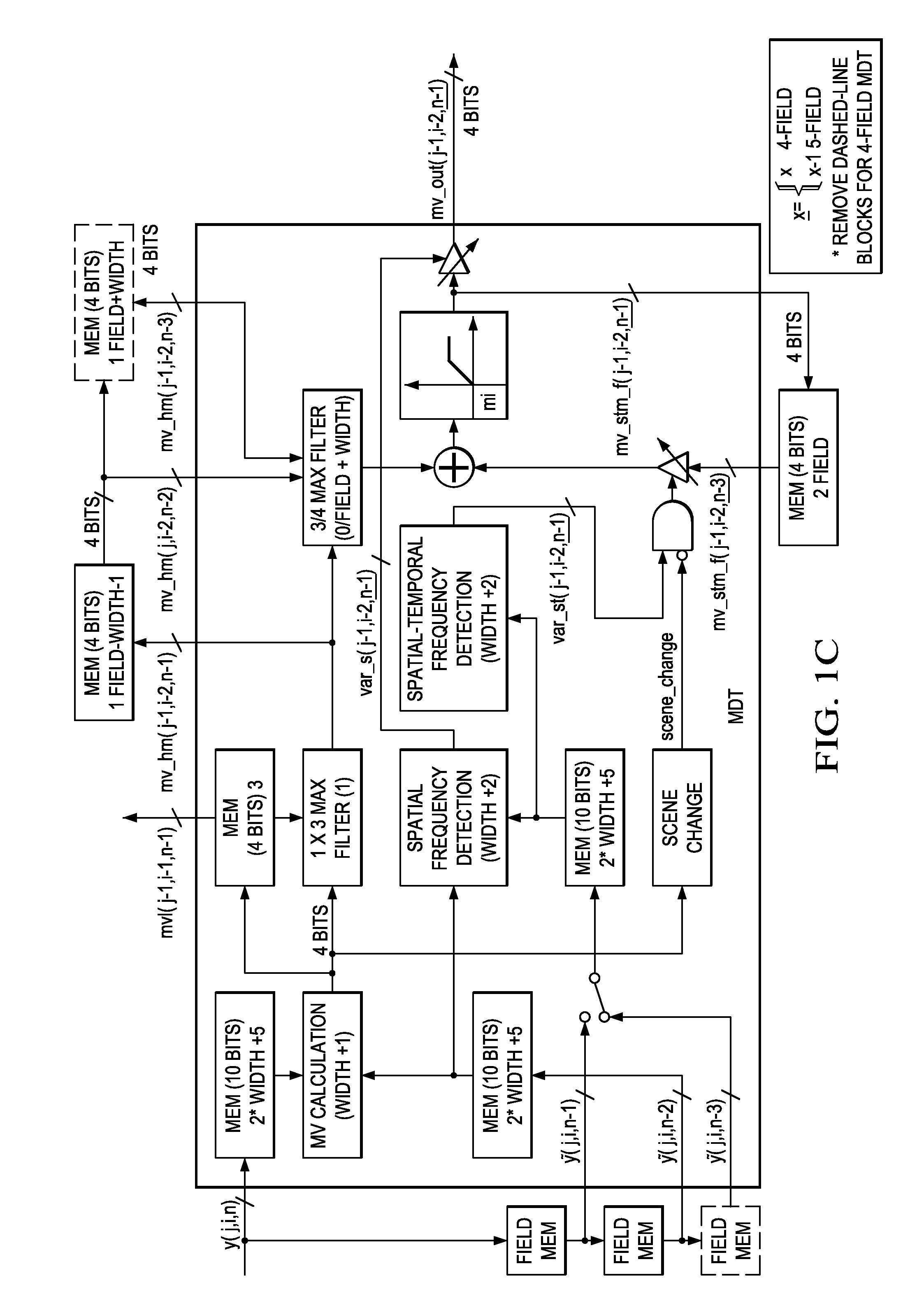
Motion detection for interlaced video
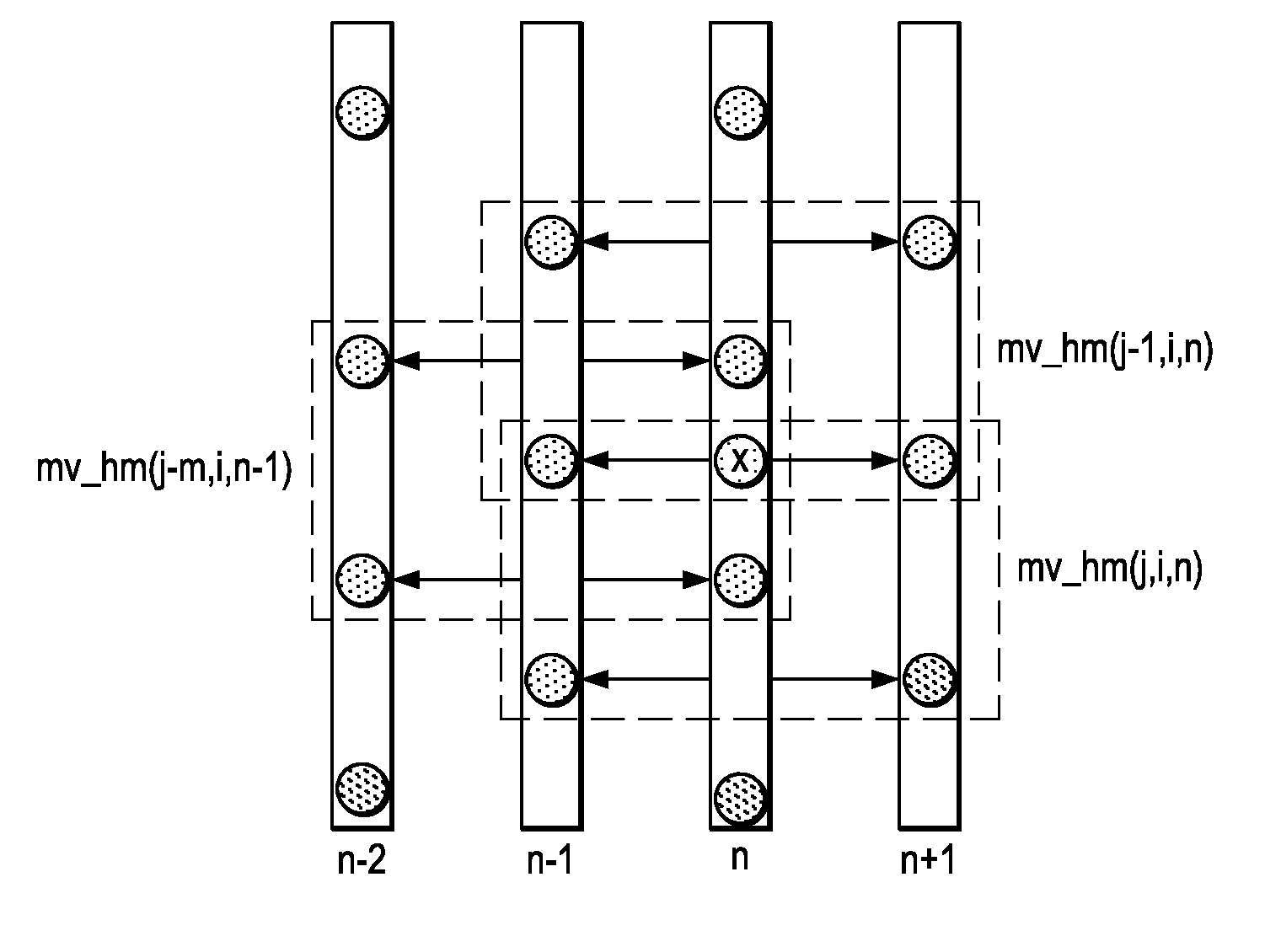
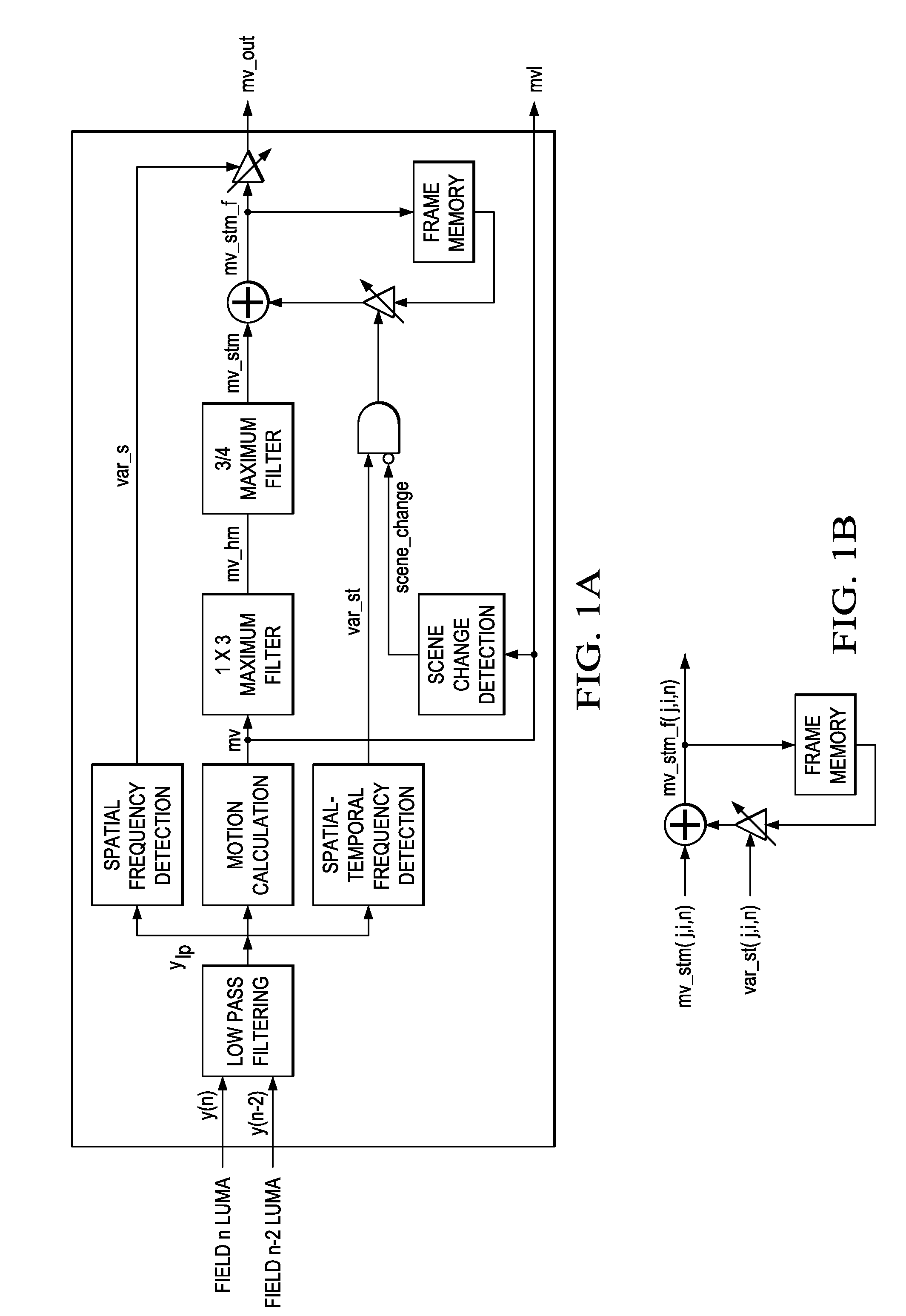
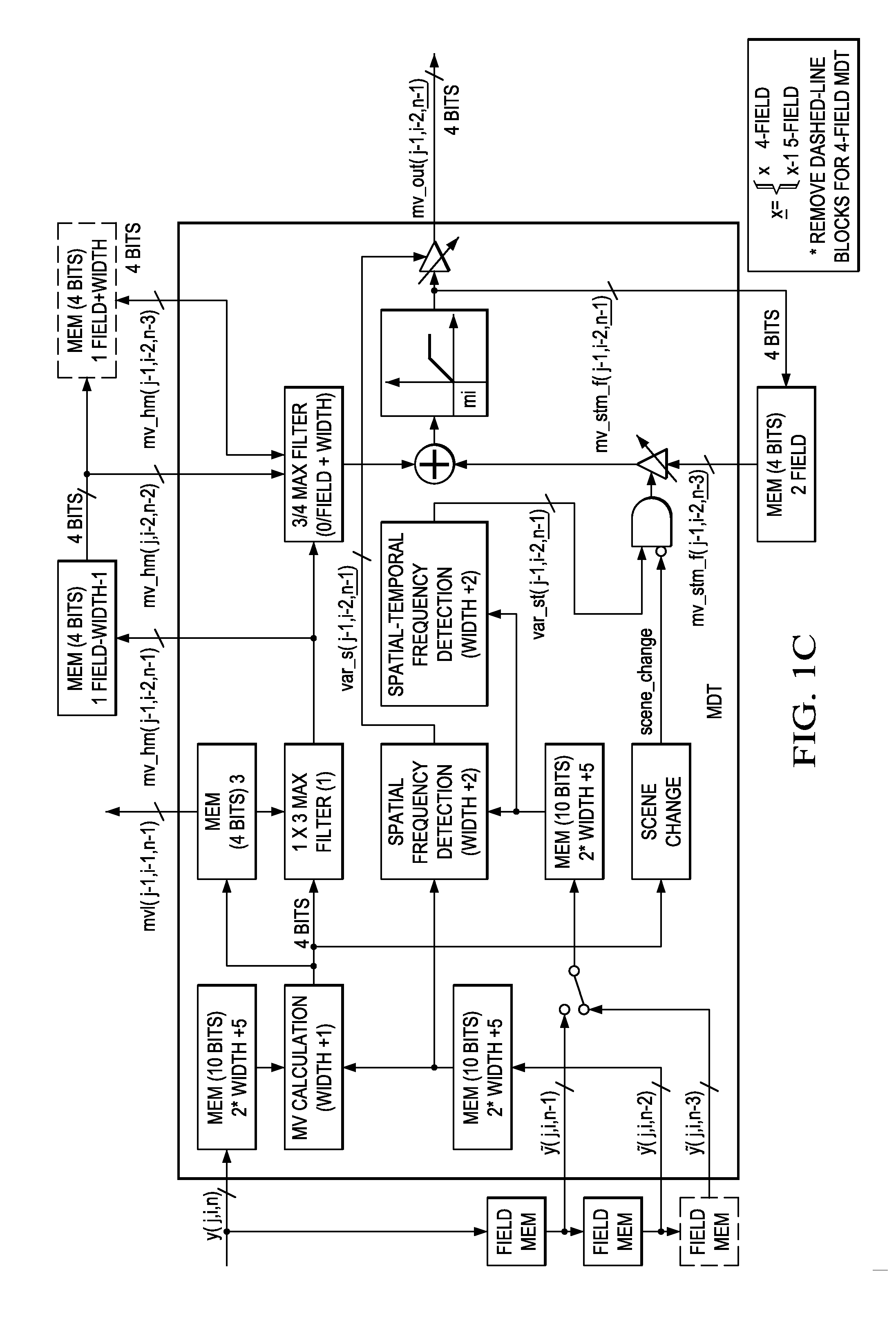
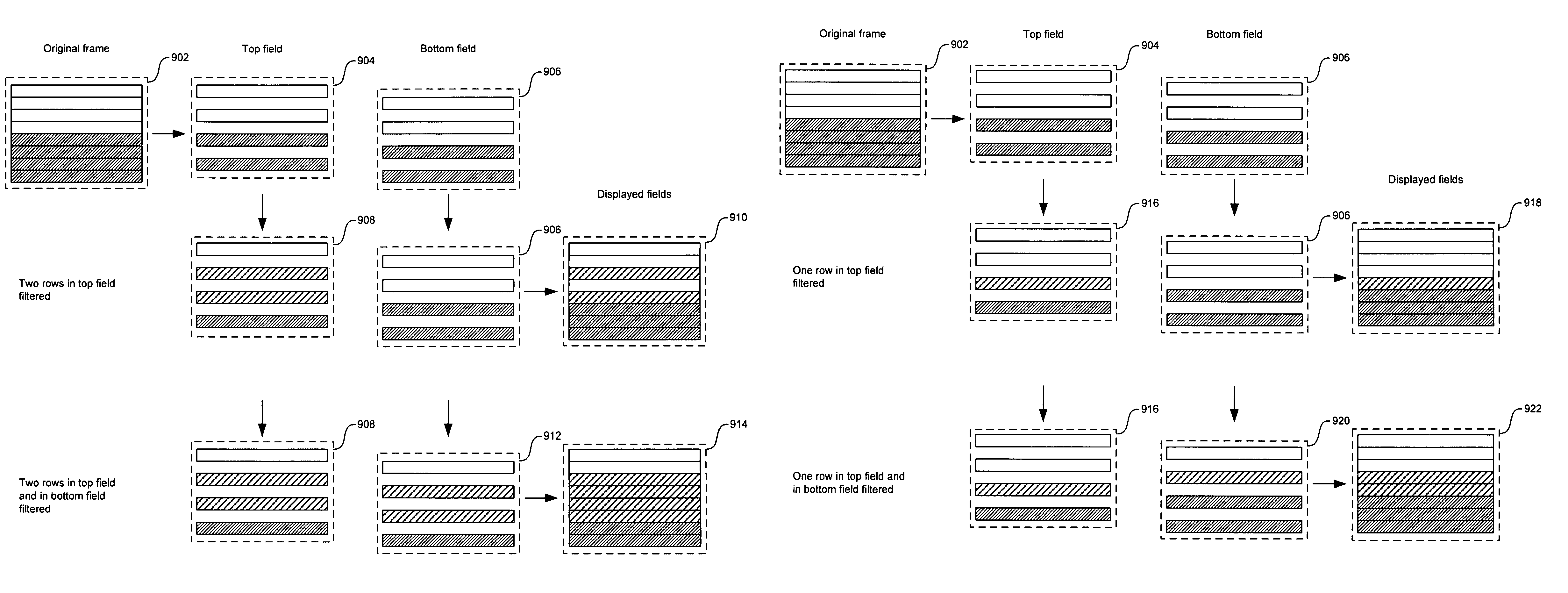
Motion detection in interlaced video fields, as useful in de-interlacing, includes spatial-temporal maximum filtering, temporal IIR filtering dependent upon spatial-temporal variance, and spatial variance dependent moving-still interpolation blending factor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
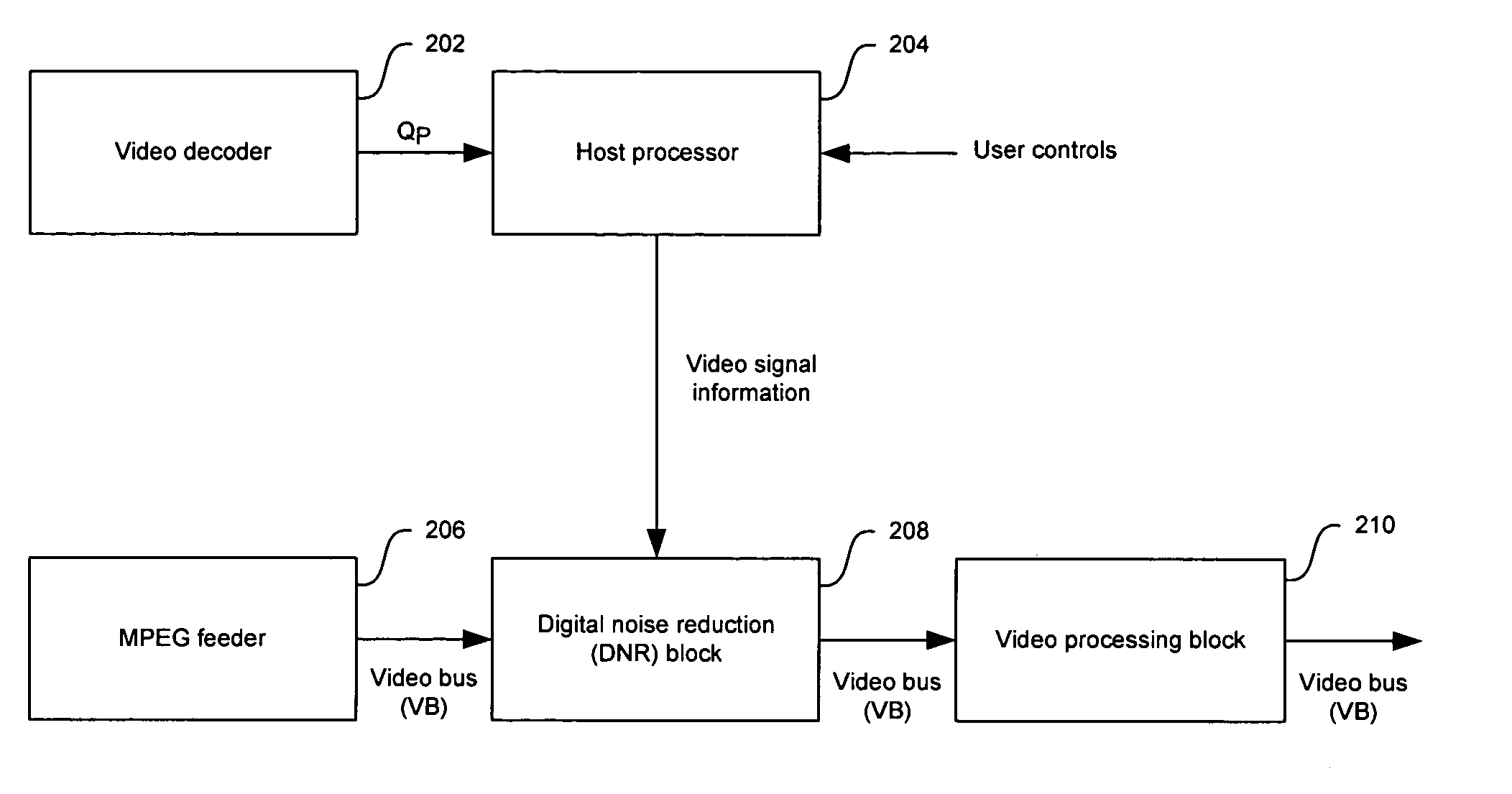
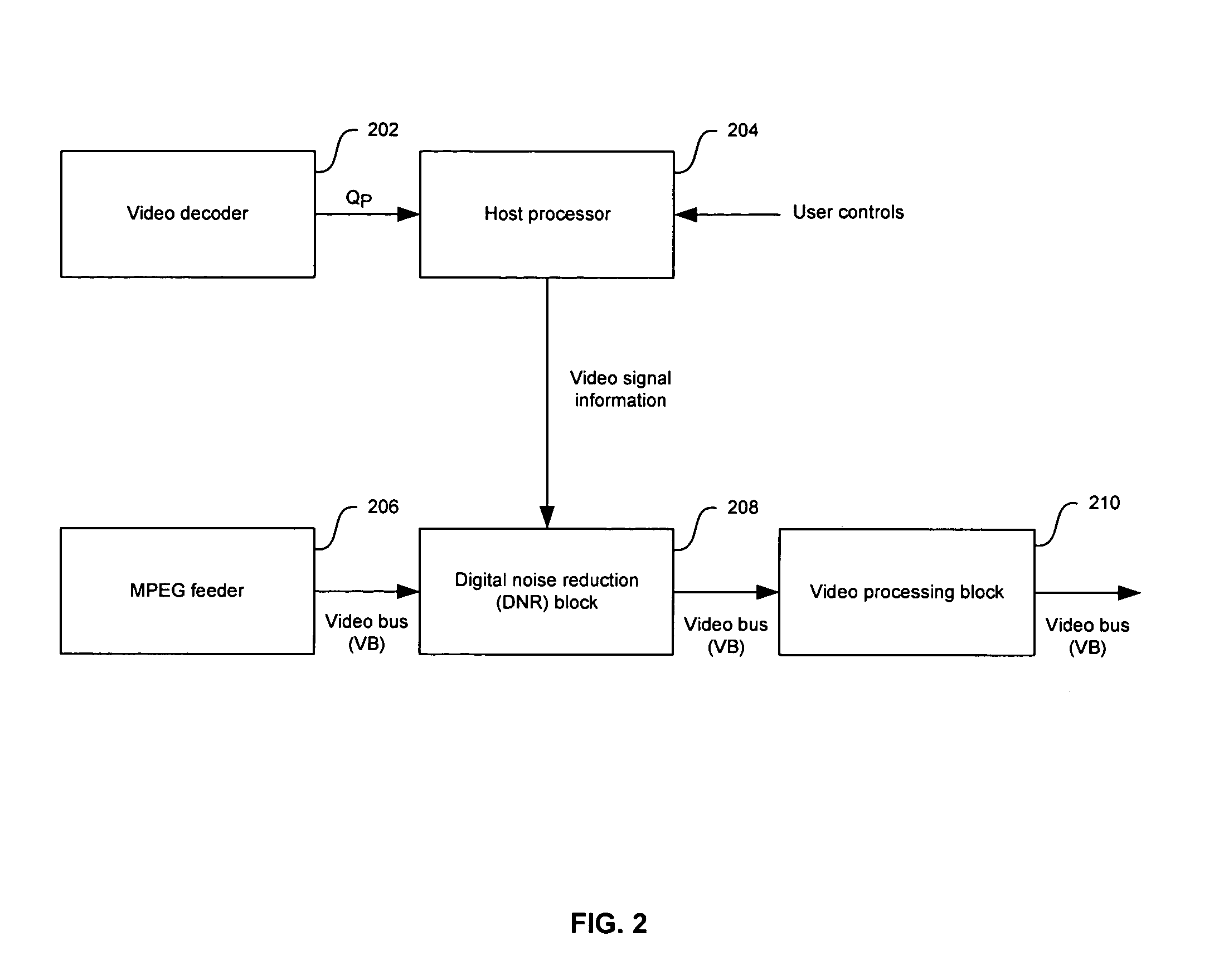
Method and system for block noise reduction
InactiveUS20060171467A1Block noise decreaseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionVertical edge
In a video system, a method and system for block noise reduction are provided. Edge parameters based on spatial variance may be determined to detect vertical edges that may result from block noise. These edge parameters may be determined serially. Once detected, pixels neighboring the vertical edges may be filtered and clamped to determine a vertical block noise reduction difference (BNR) parameter. Similarly, edge parameters based on spatial variance may be determined to detect horizontal edges that may result from block noise. These edge parameters may be determined serially. Once detected, pixels neighboring the horizontal edge may be filtered and clamped to determine a horizontal BNR difference parameter. The vertical and horizontal BNR difference parameters may be utilized to reduce block noise artifacts in the video image.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
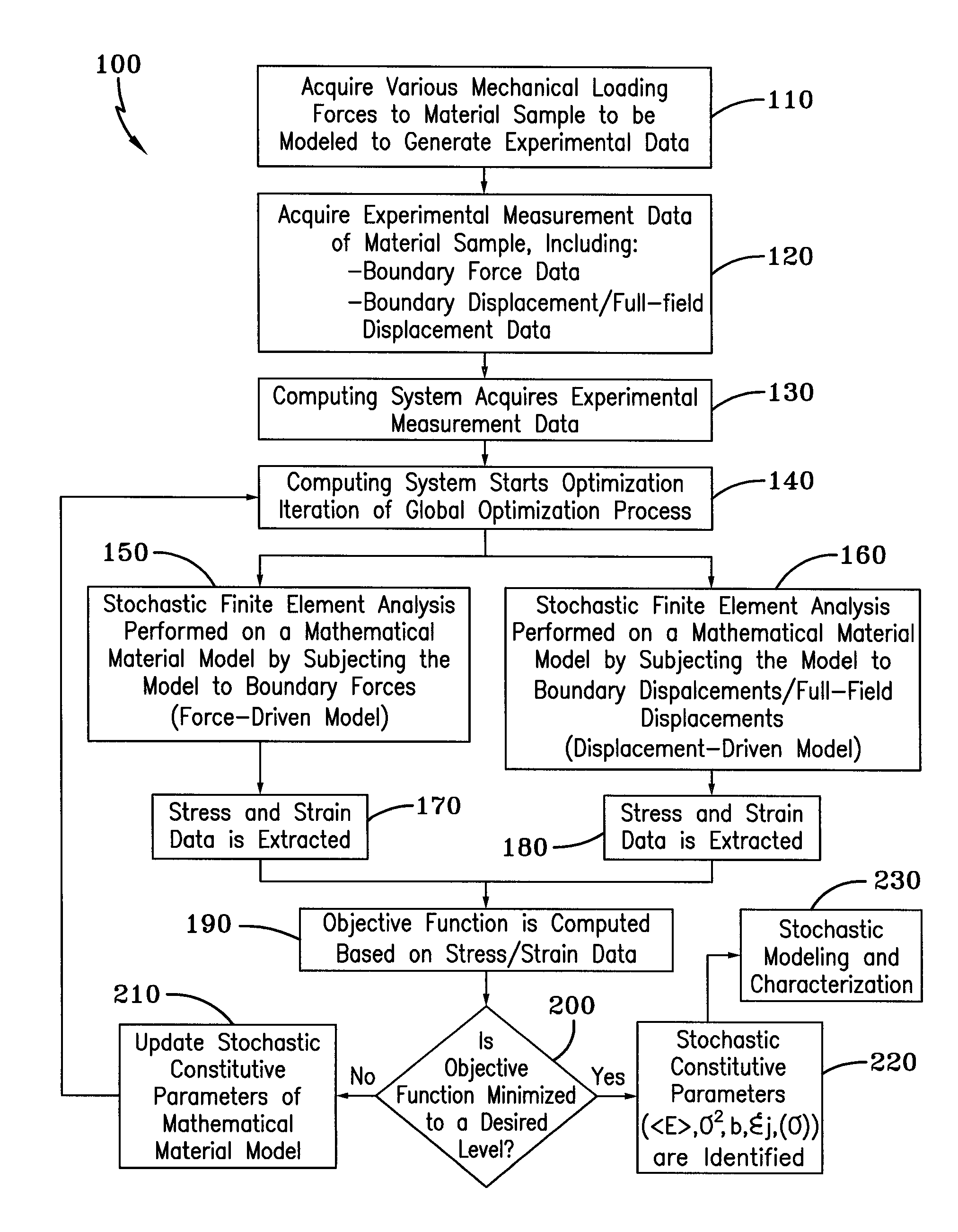
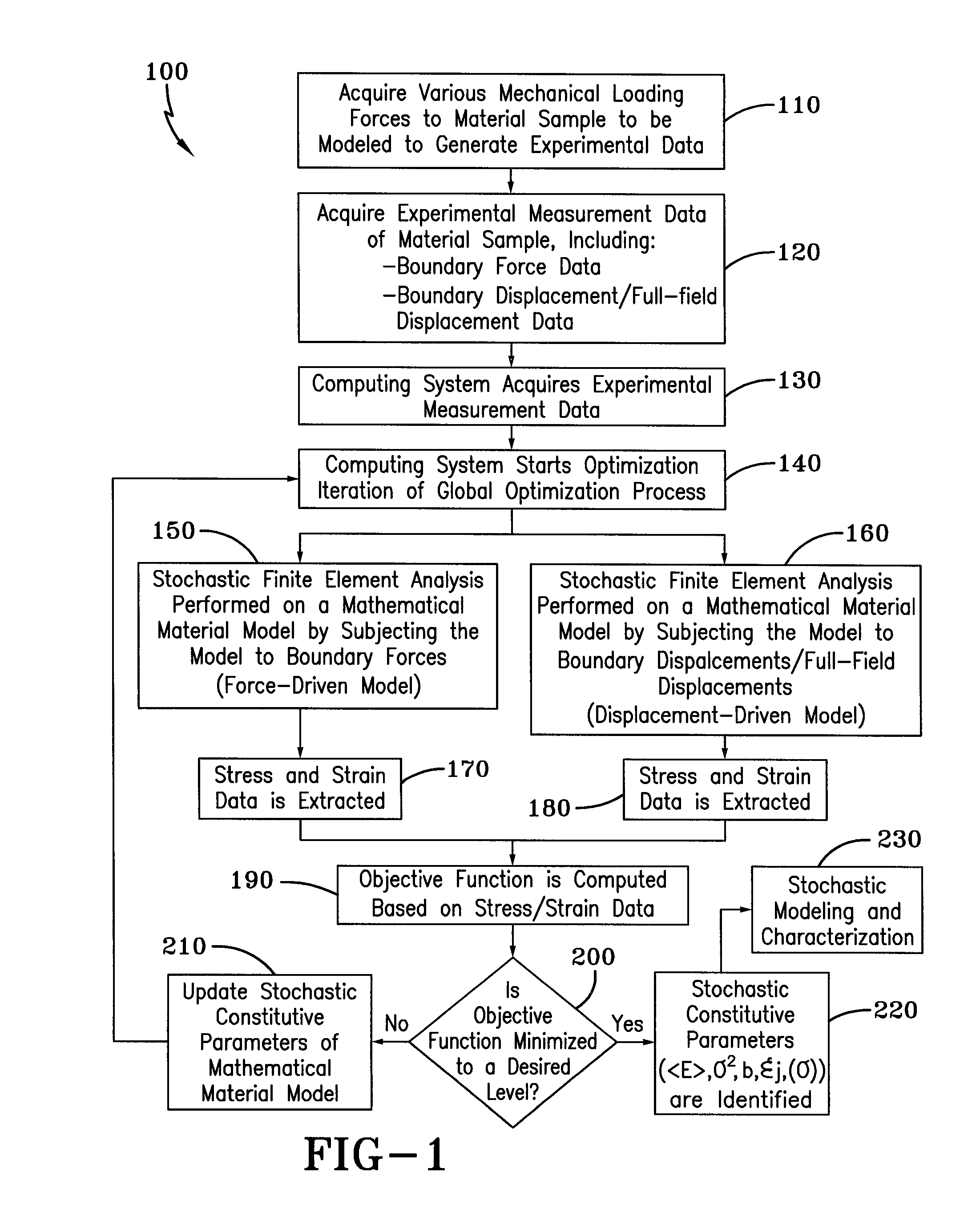
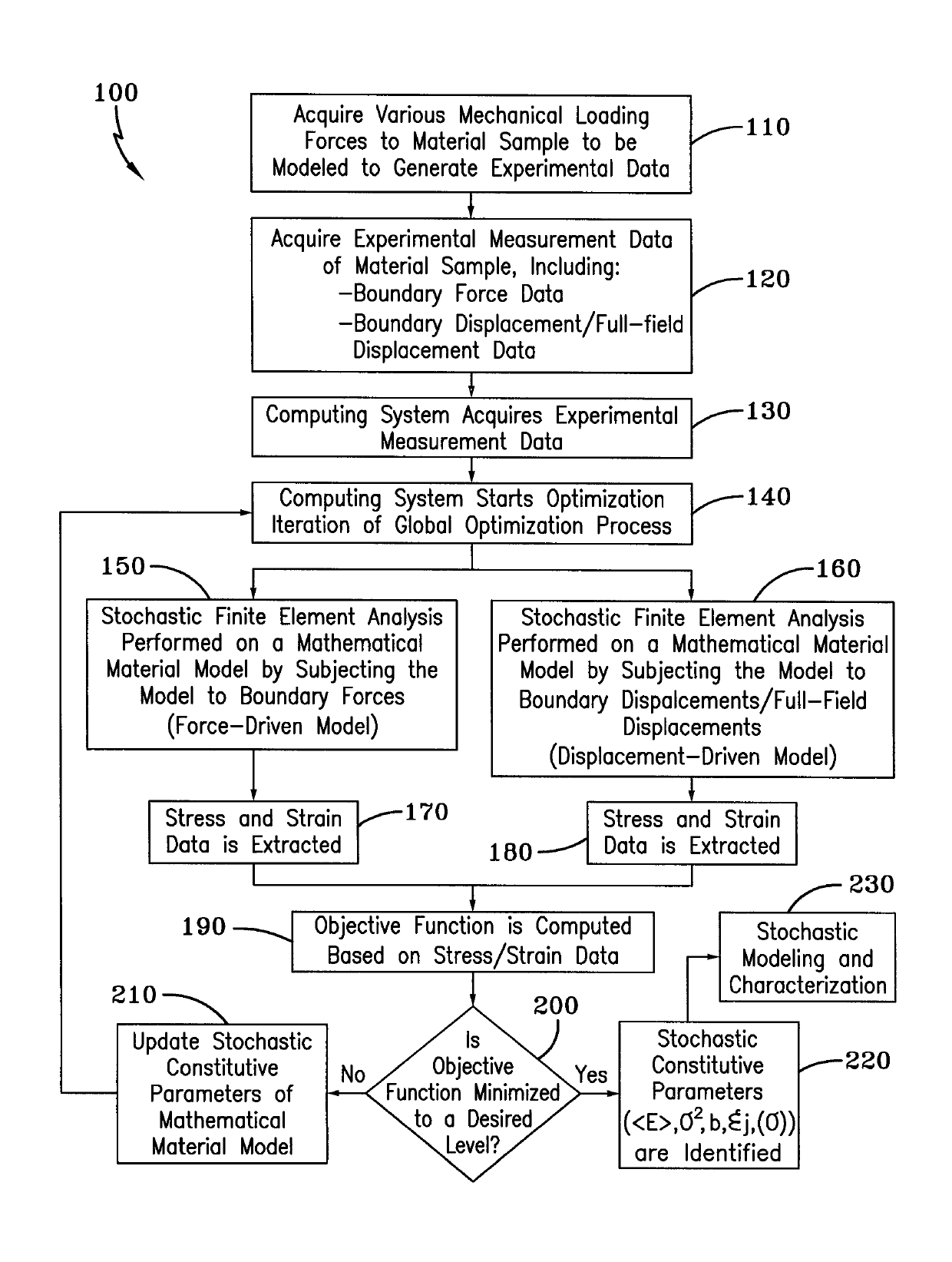
Method for Identifying Stochastic Information of Heterogeneous Materials
InactiveUS20150057988A1Minimize objective functionComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationRandom materialsElement analysis
A method for identifying stochastic information of a heterogeneous material utilizes physical loading measurements that are input into a global optimization process. The optimization process executes, in parallel, a force-driven non-linear finite element simulation and a displacement-driven finite element simulation of a constitutive model of the heterogeneous material. The constitutive models model the spatially varying random material properties (i.e. stochastic properties) using the Karhunen-Loeve expansion, thereby introducing the stochastic parameters, including spatial mean, spatial variance, and correlation length for example into the models. Stress and strain values for both the force-driven and displacement driven finite element analyses are input into an objective function, whereupon the finite element simulations are updated after each iteration of the optimization process is performed until the objective function is minimized to a desired level. This results in the identification of optimized stochastic parameters associated with the heterogeneous material under investigation.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
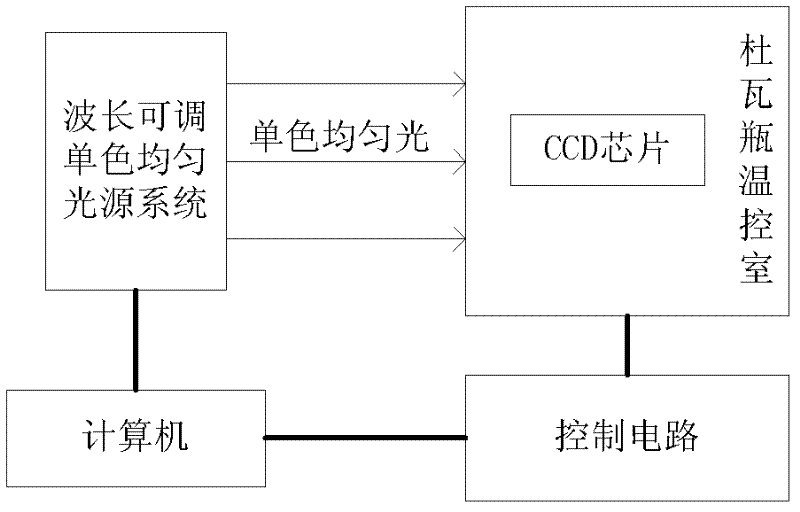
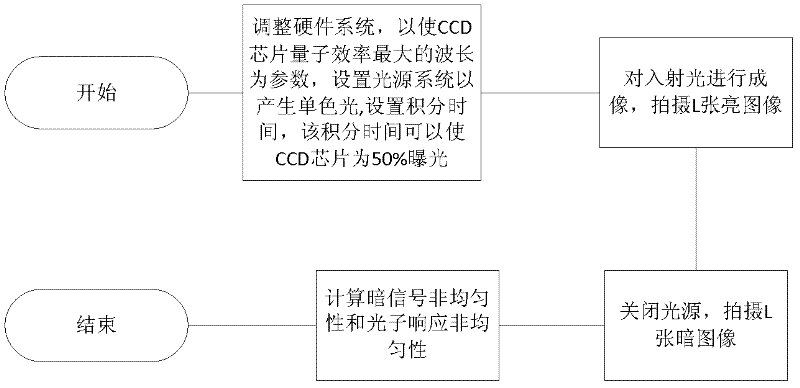
Method for measuring dark signal non-uniformity and photon response non-uniformity of photons of CCD (charge coupled device) chip
InactiveCN102508144ASpatial non-uniformity is accurateIncrease signal strengthTesting optical propertiesIndividual semiconductor device testingMeasurement precisionImage sequence
The invention discloses a method for measuring dark signal non-uniformity and photon response non-uniformity of a CCD (charge coupled device) chip, which mainly solves the problem of insufficient measurement precision of performance parameters of a CCD of the prior art. The method includes steps of selecting the wavelength eta corresponding to the maximum quantum efficiency of the CCD chip, setting a wavelength-adjustable monochromatic uniform light source, and generating monochromatic light with the wavelength eta; then selecting integration time required to realize 50% exposure of the CCD chip, and adopting the integration time as a parameter to control the CCD chip to shoot two groups of image sequences and upload the two groups of image sequences to a computer; and computing parameters of the dark signal non-uniformity DSNU and the photon response non-uniformity PRNU of the CCD chip by means of computing a total average gray value and a spatial variance according to the two groups of images. The method has the advantages of high measurement precision and fine stability, and can be used for assessing performances of CCD chips.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
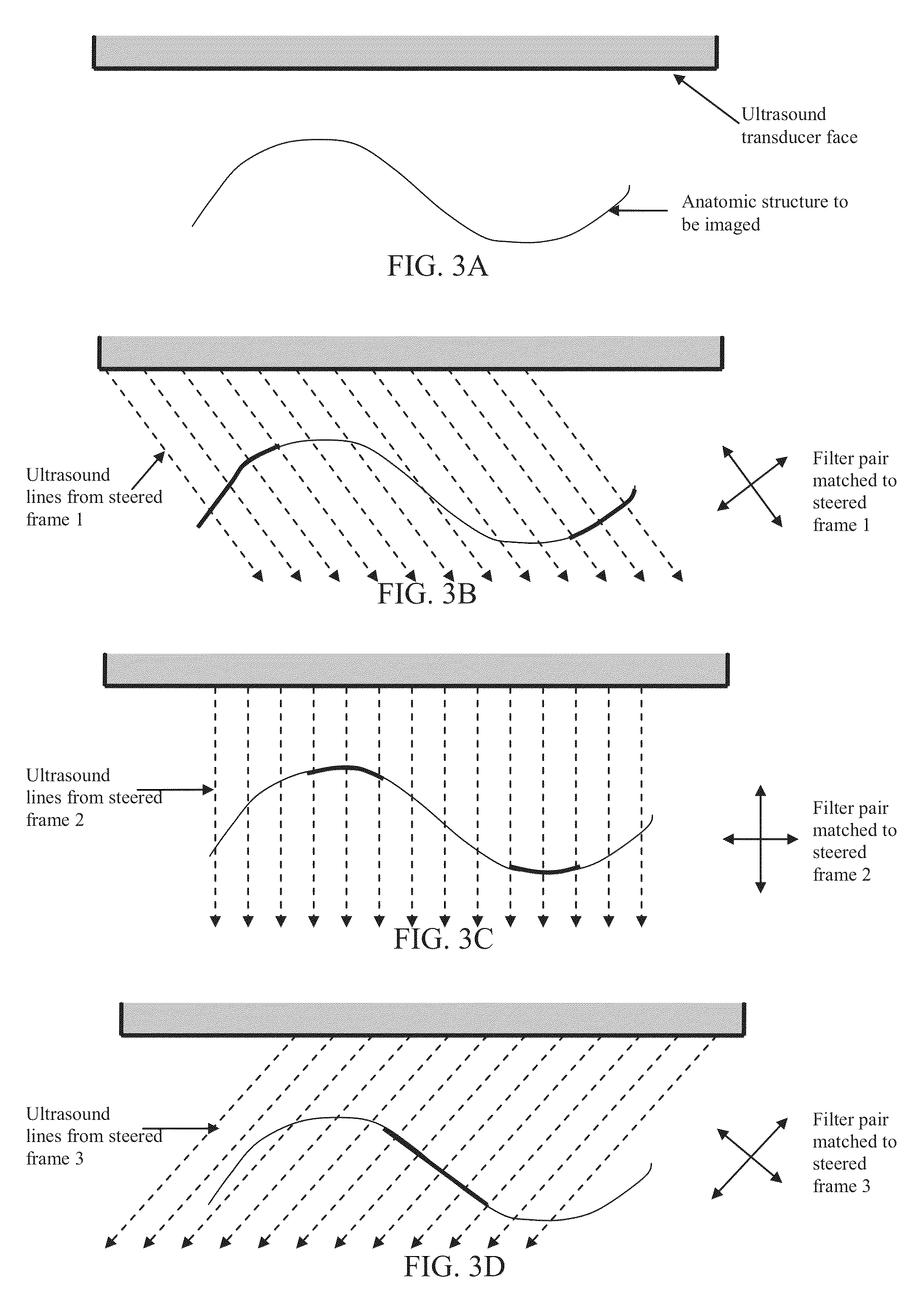
Component Frame Enhancement for Spatial Compounding in Ultrasound Imaging
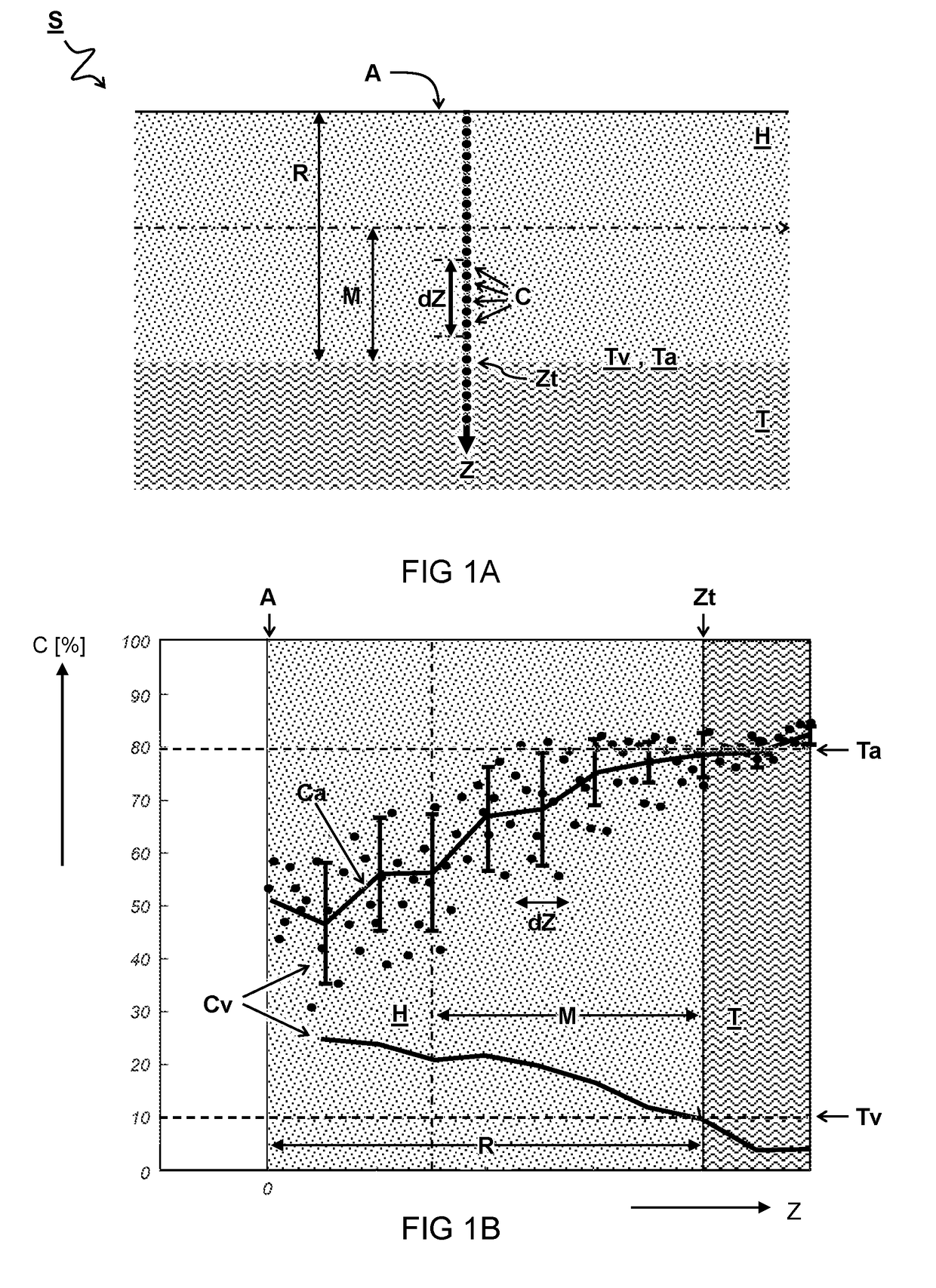
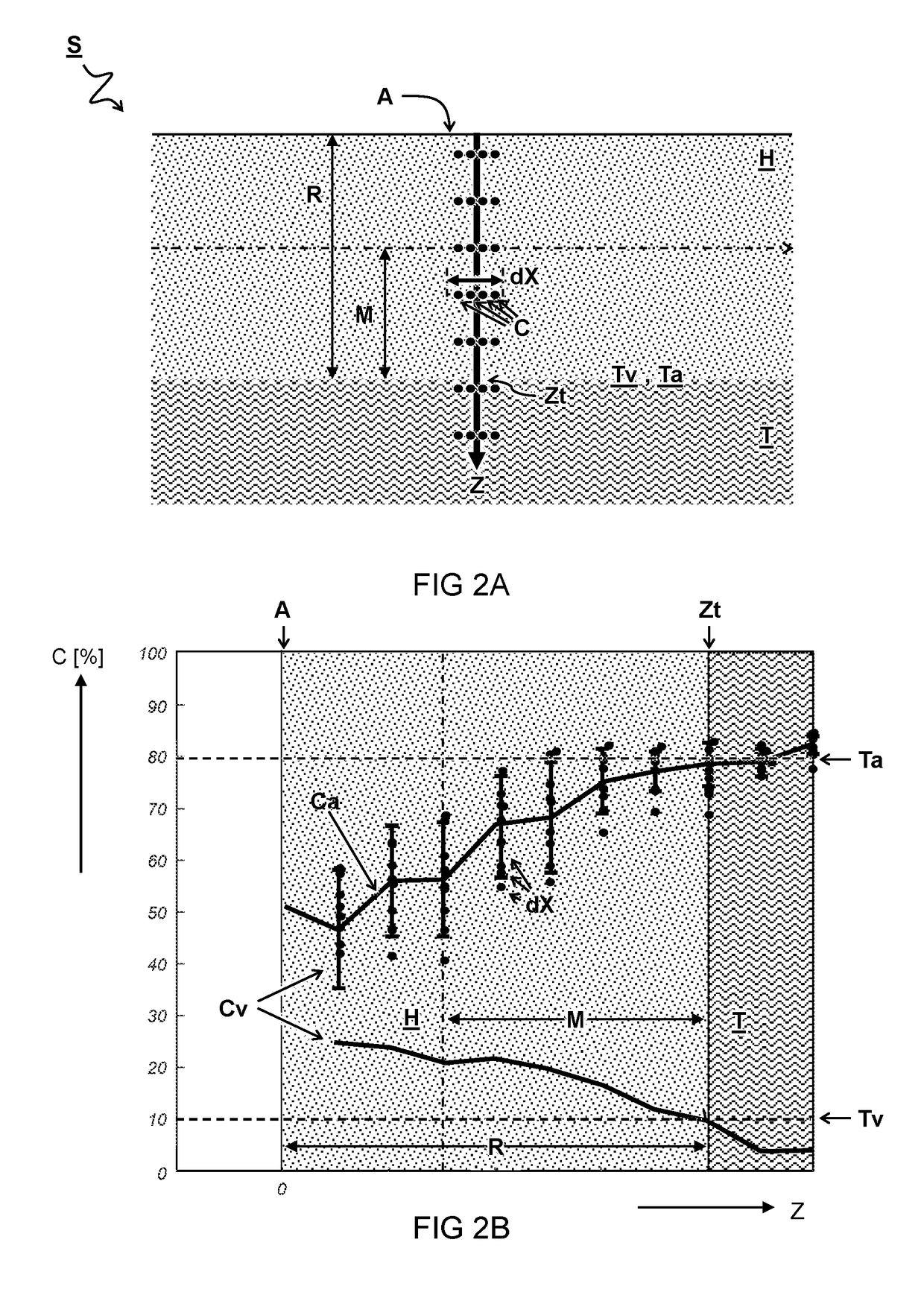
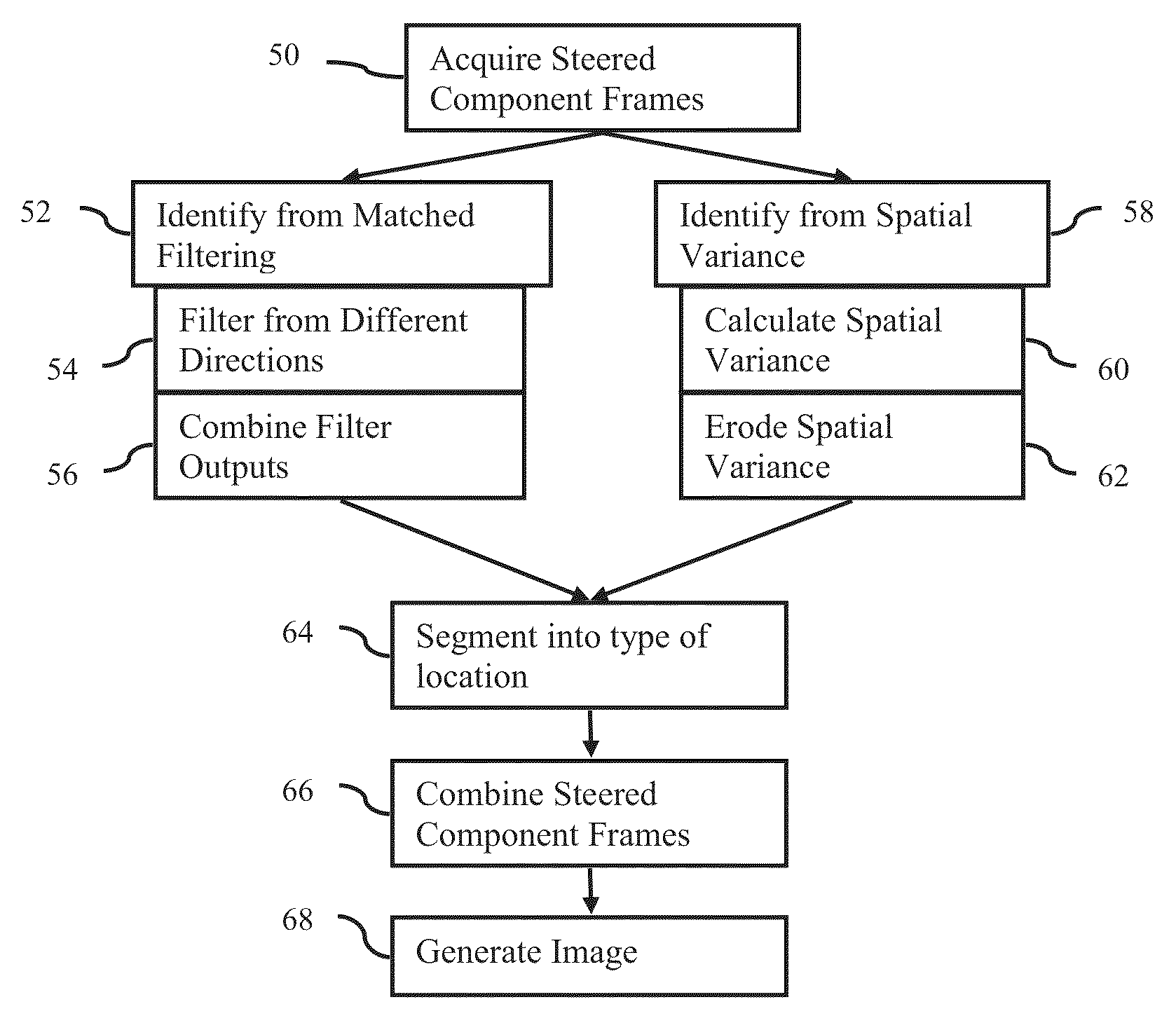
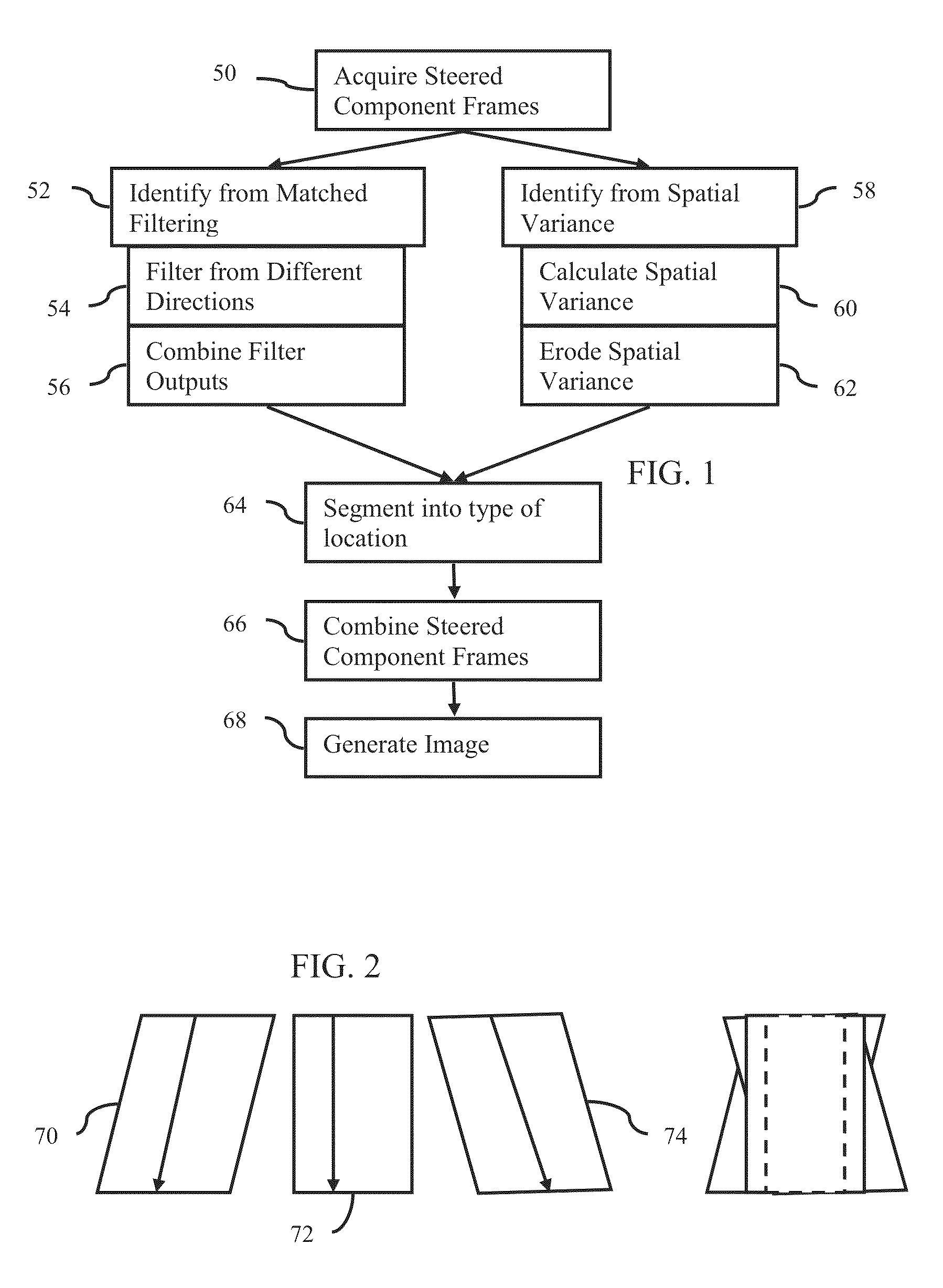
ActiveUS20130294665A1Character and pattern recognitionAcoustic wave reradiationUltrasound imagingAnatomical structures
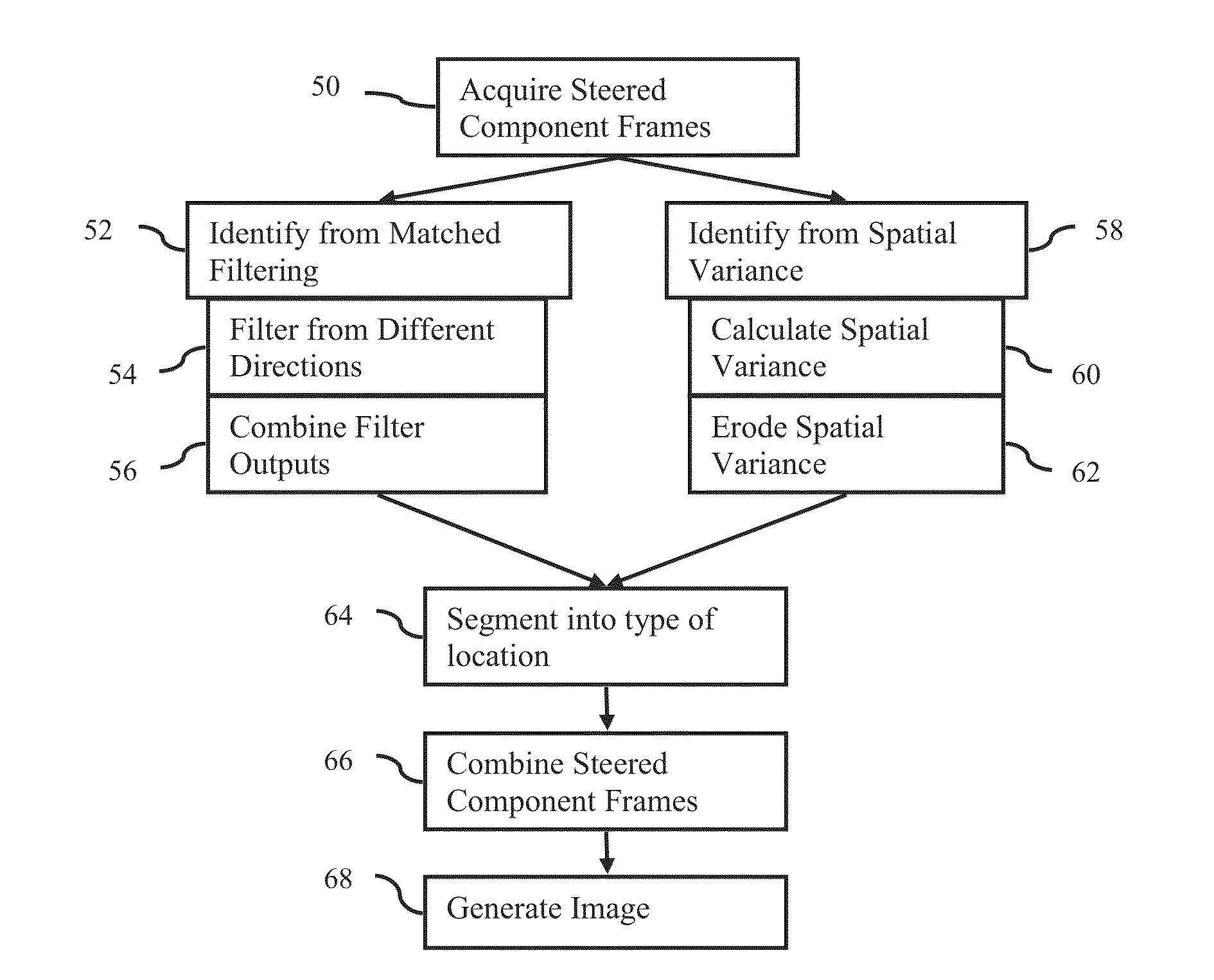
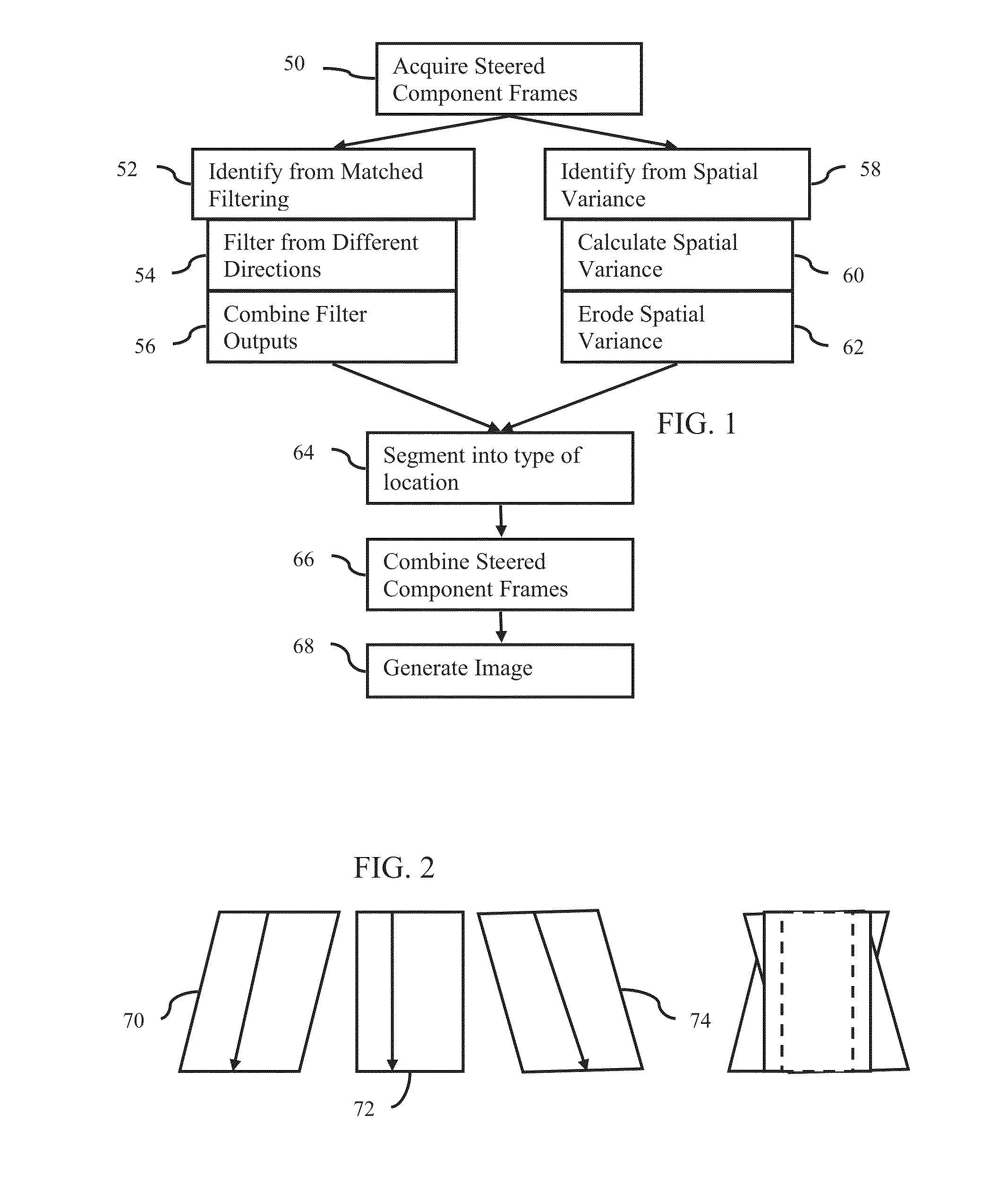
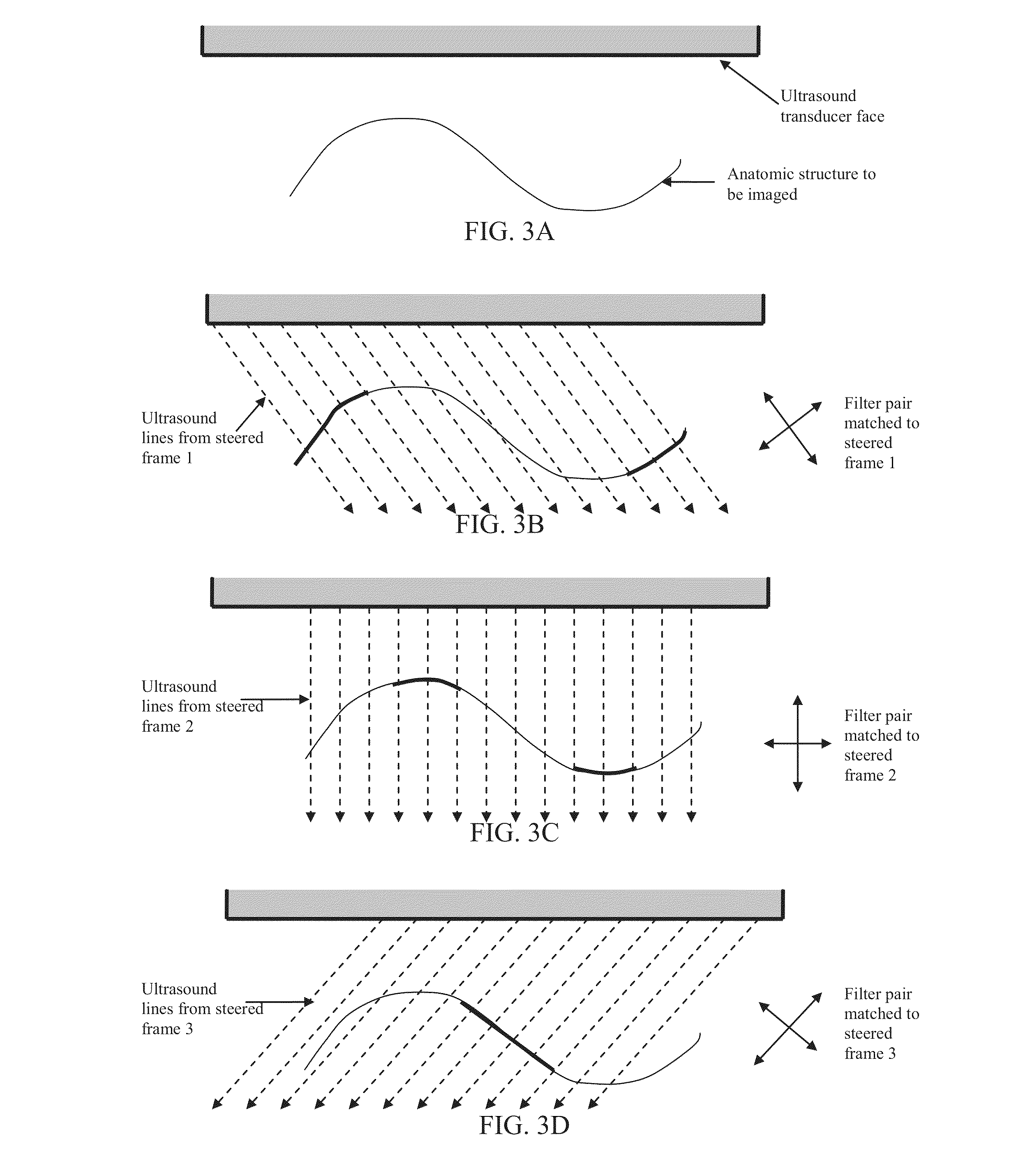
Steered spatial compounding is provided in ultrasound imaging. Component frames of data associated with different spatial response are processed to identify different sources of signals. Matched filtering and / or spatial variance with erosion distinguish between sources of signals, such as distinguishing between (1) anatomical structure and (2) soft tissue and / or noise. The locations in the patient are segmented by the source of signals and different compounding is applied for the different sources.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
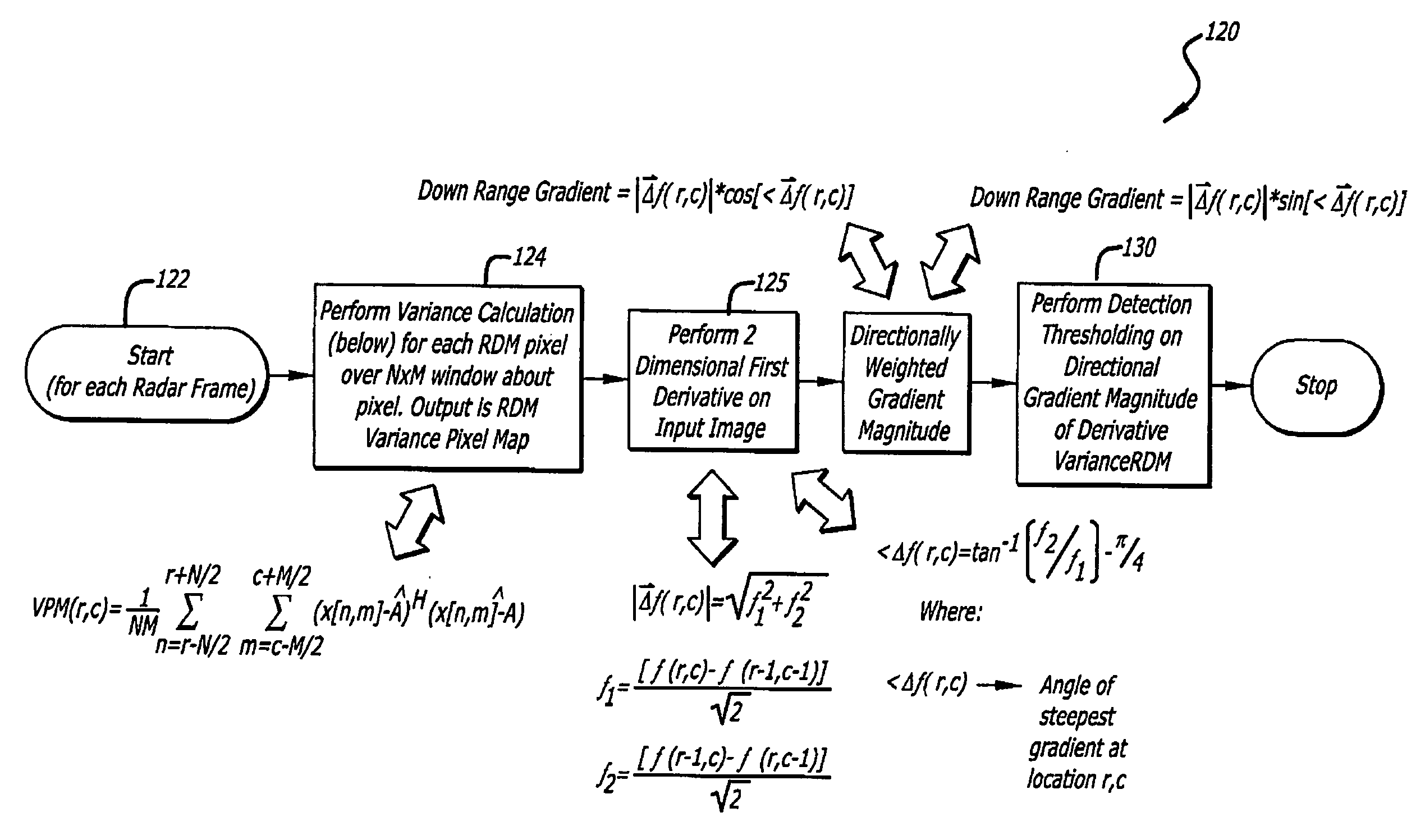
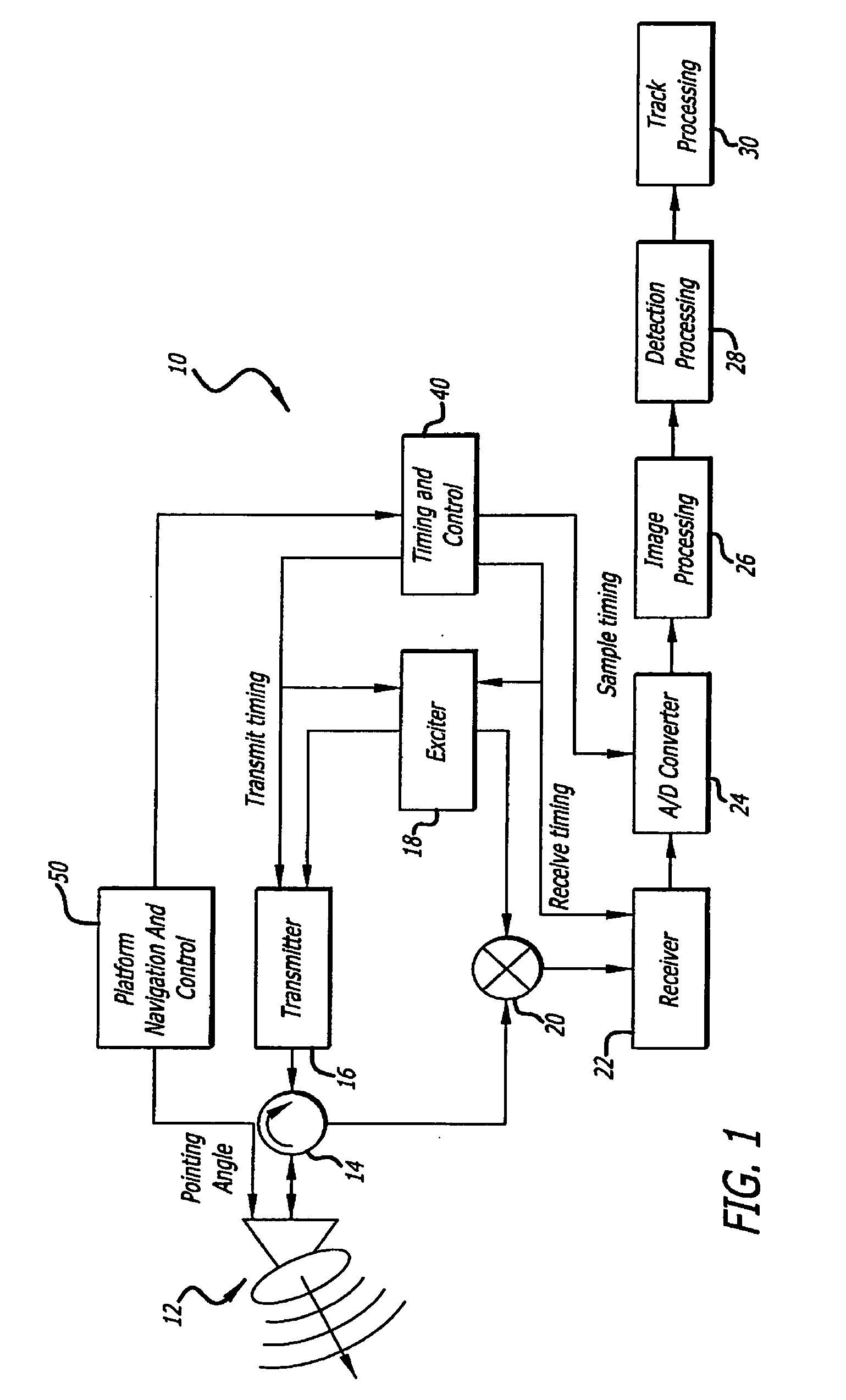
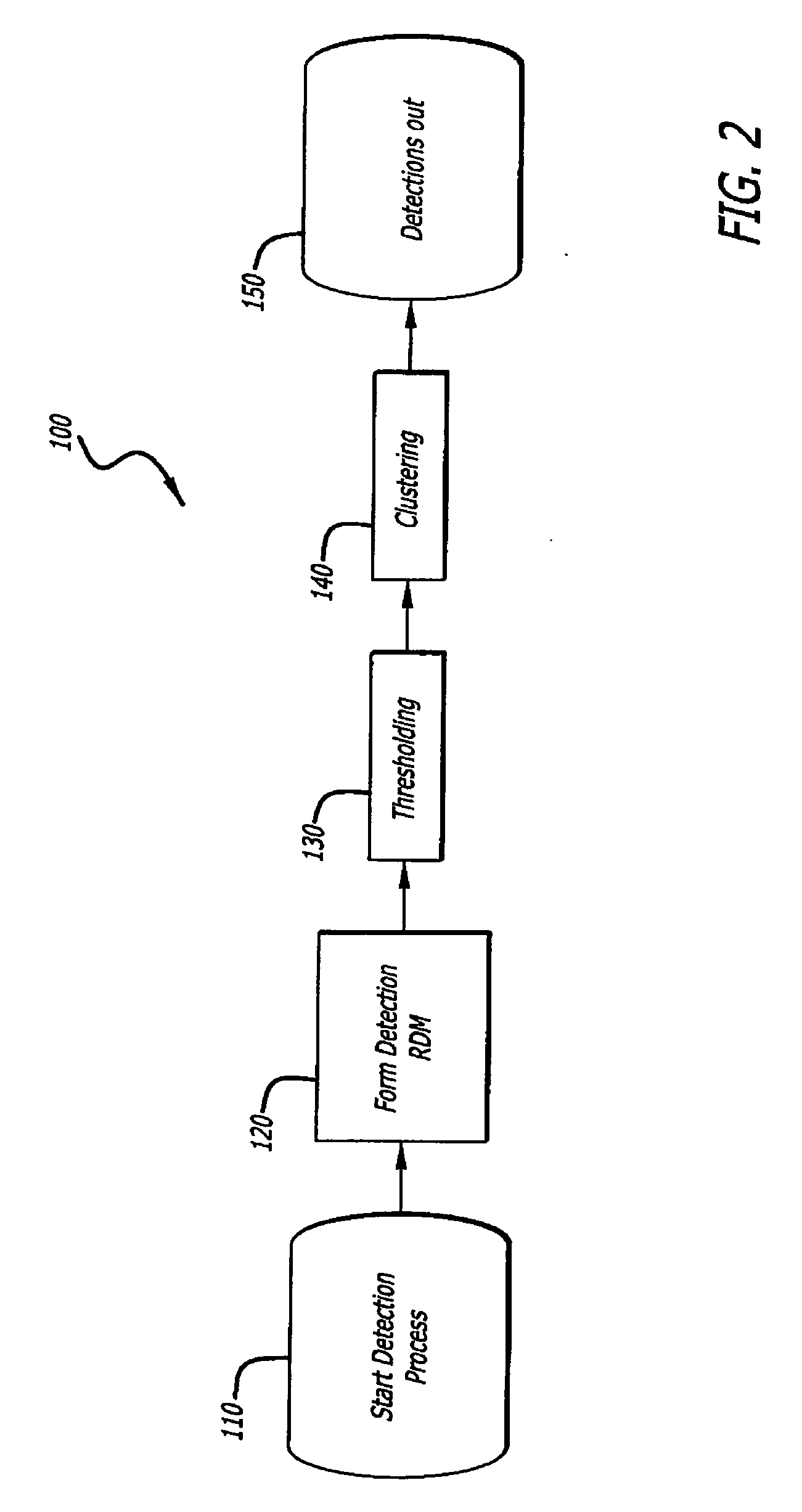
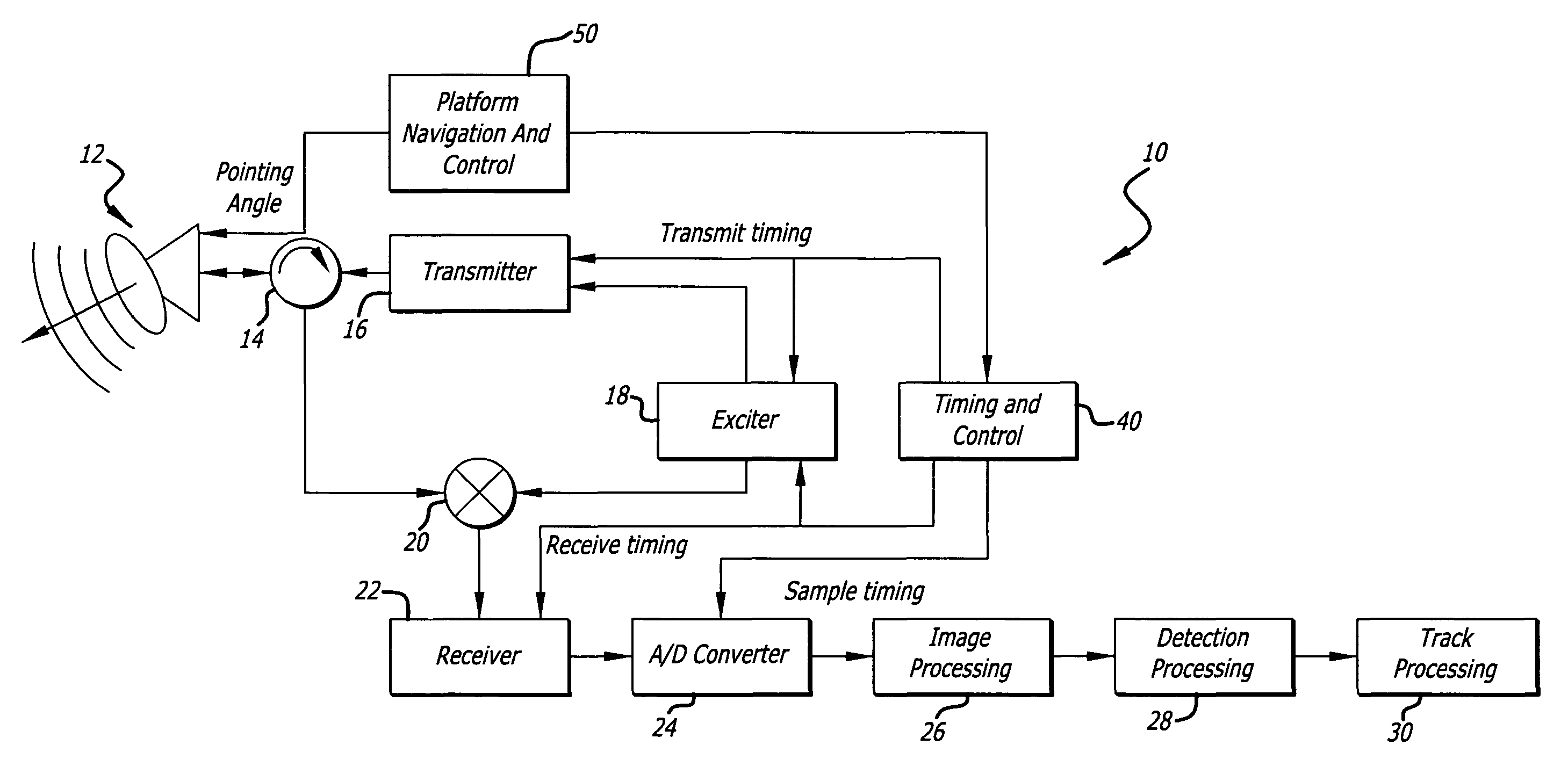
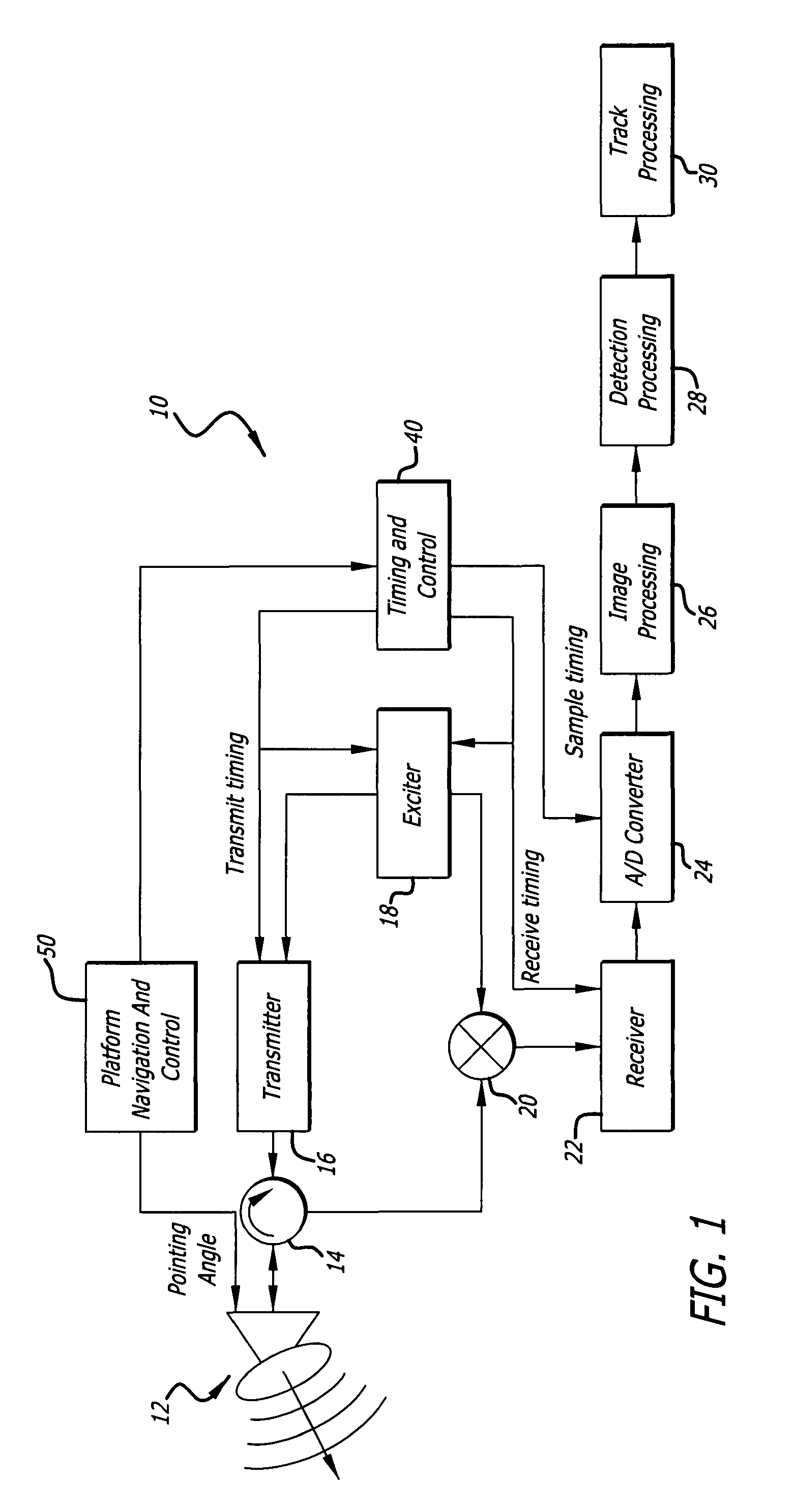
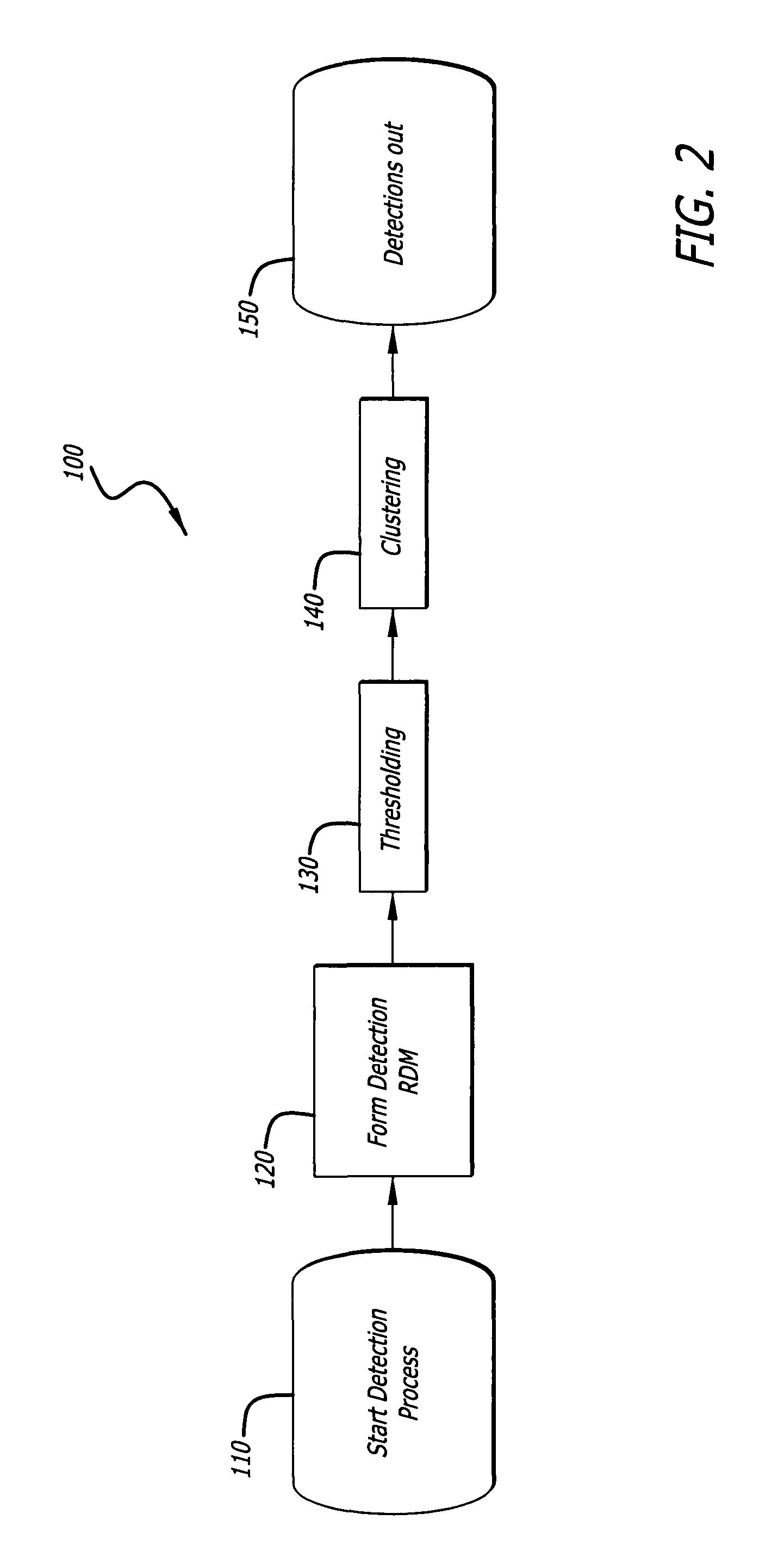
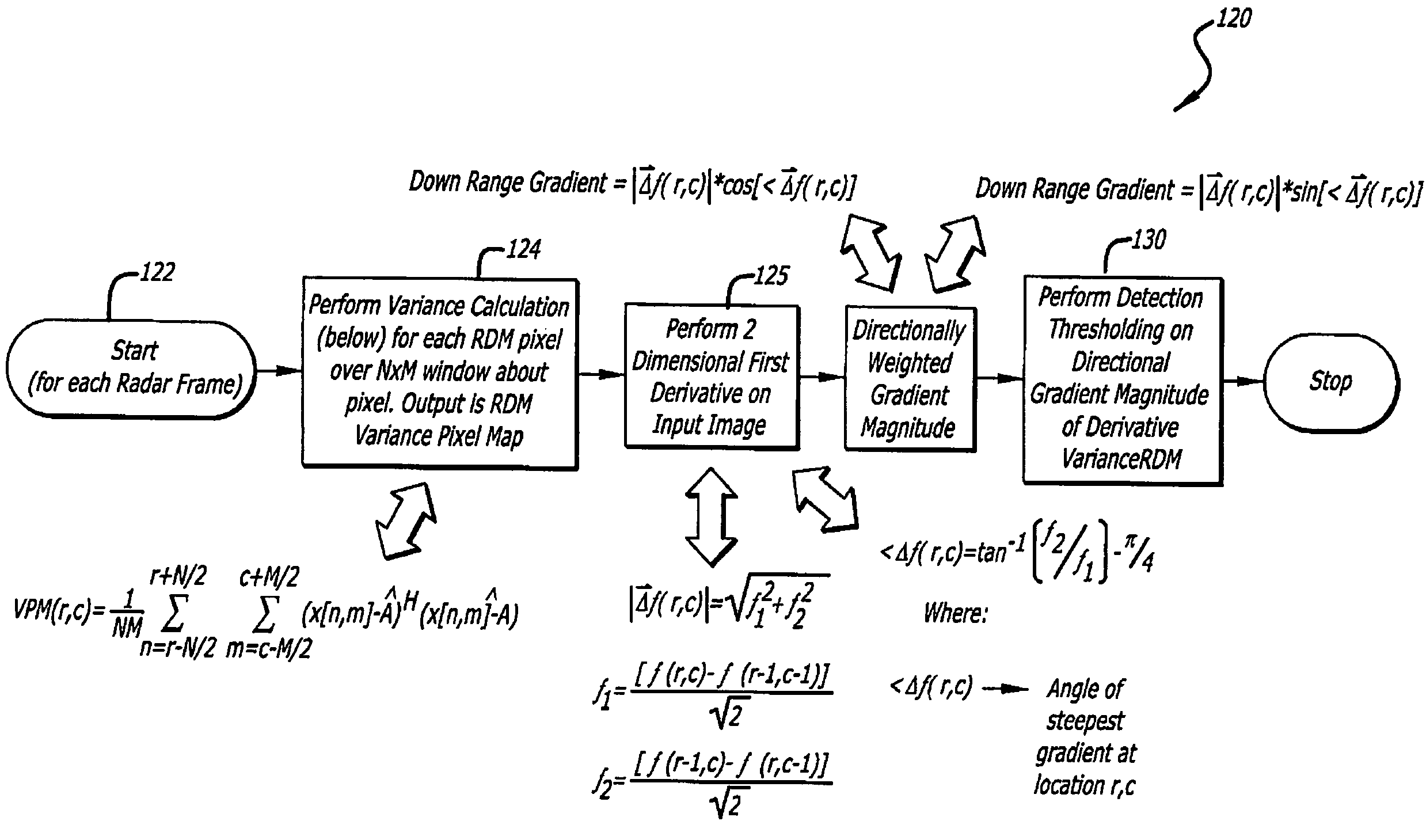
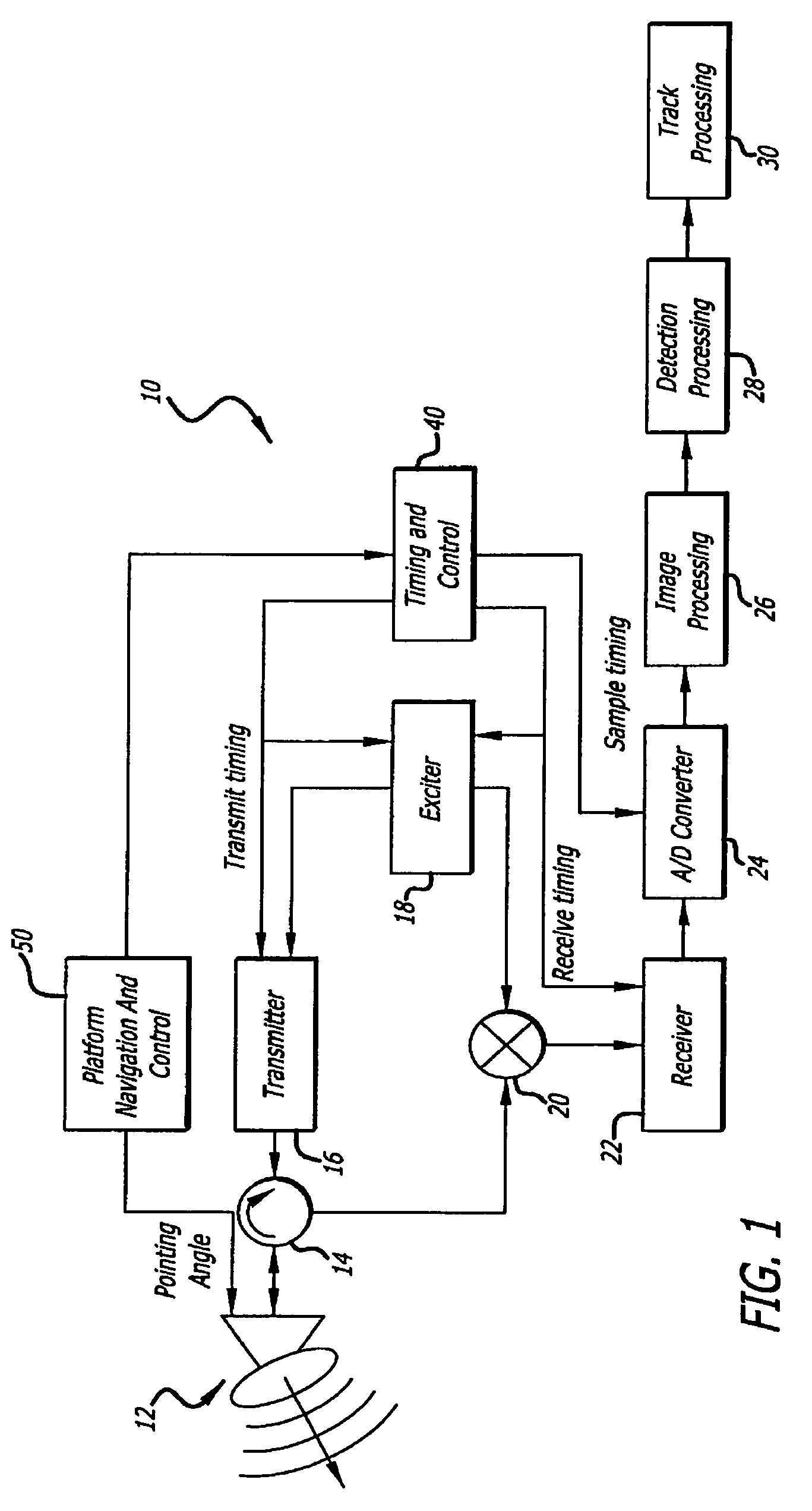
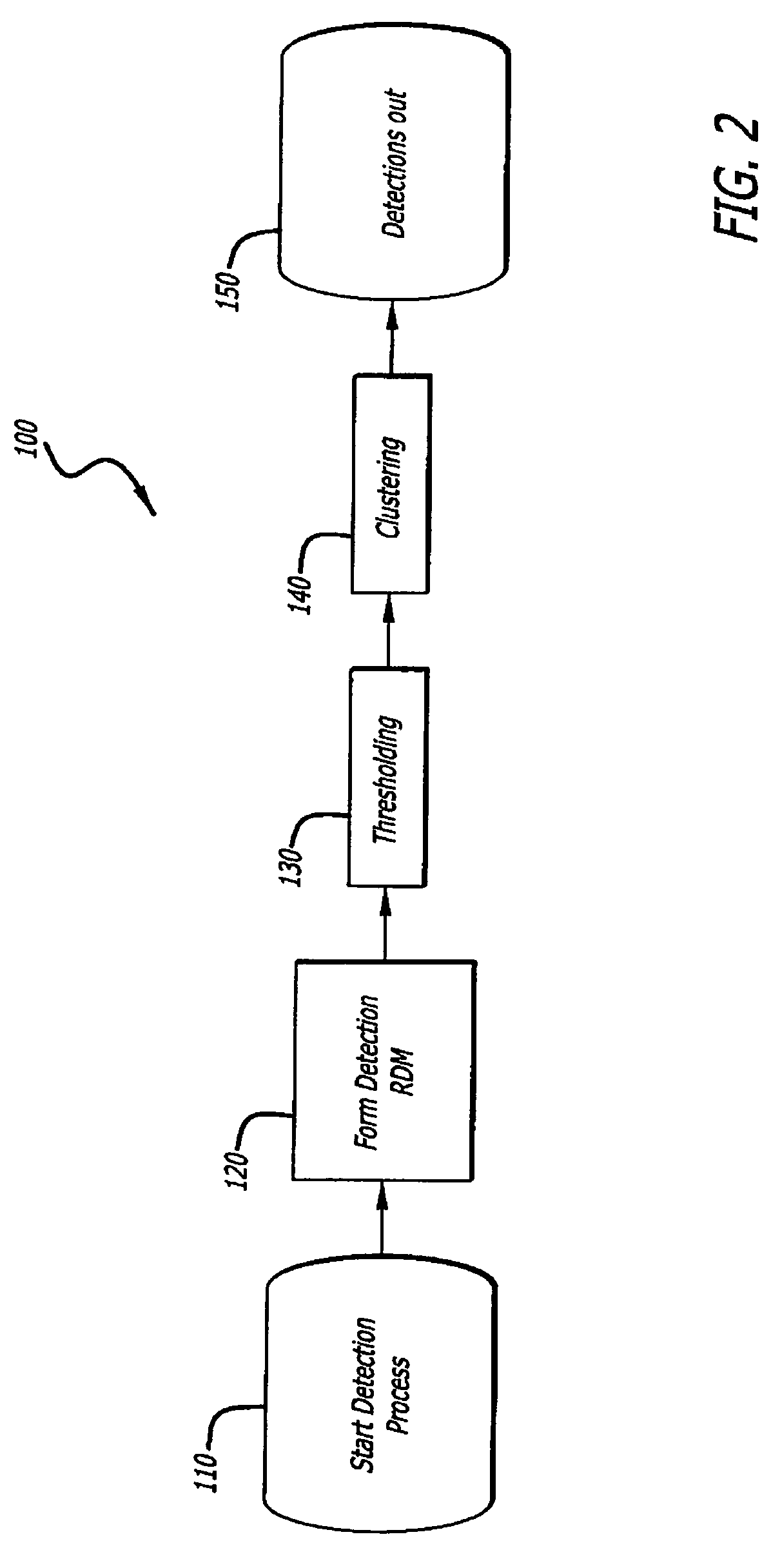
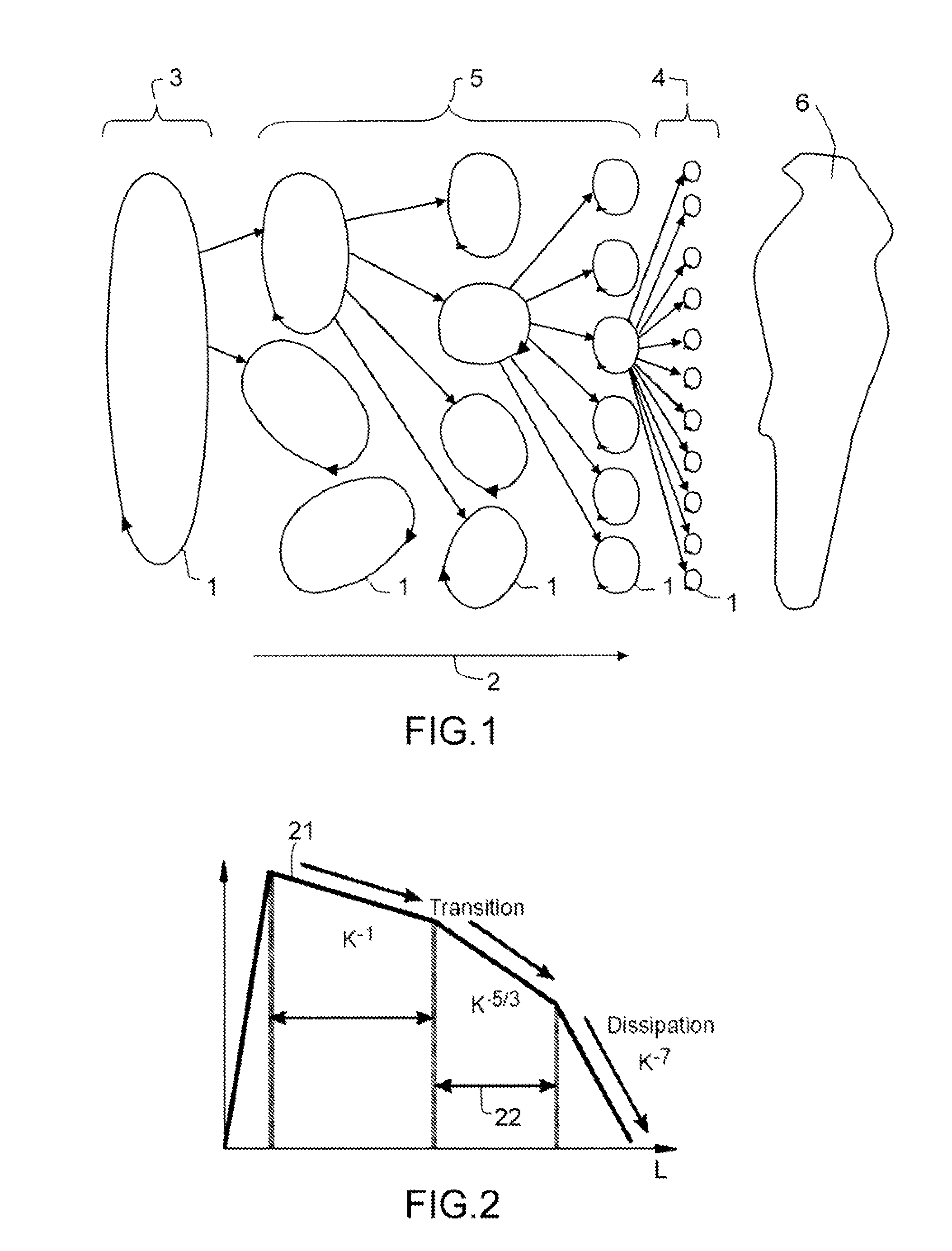
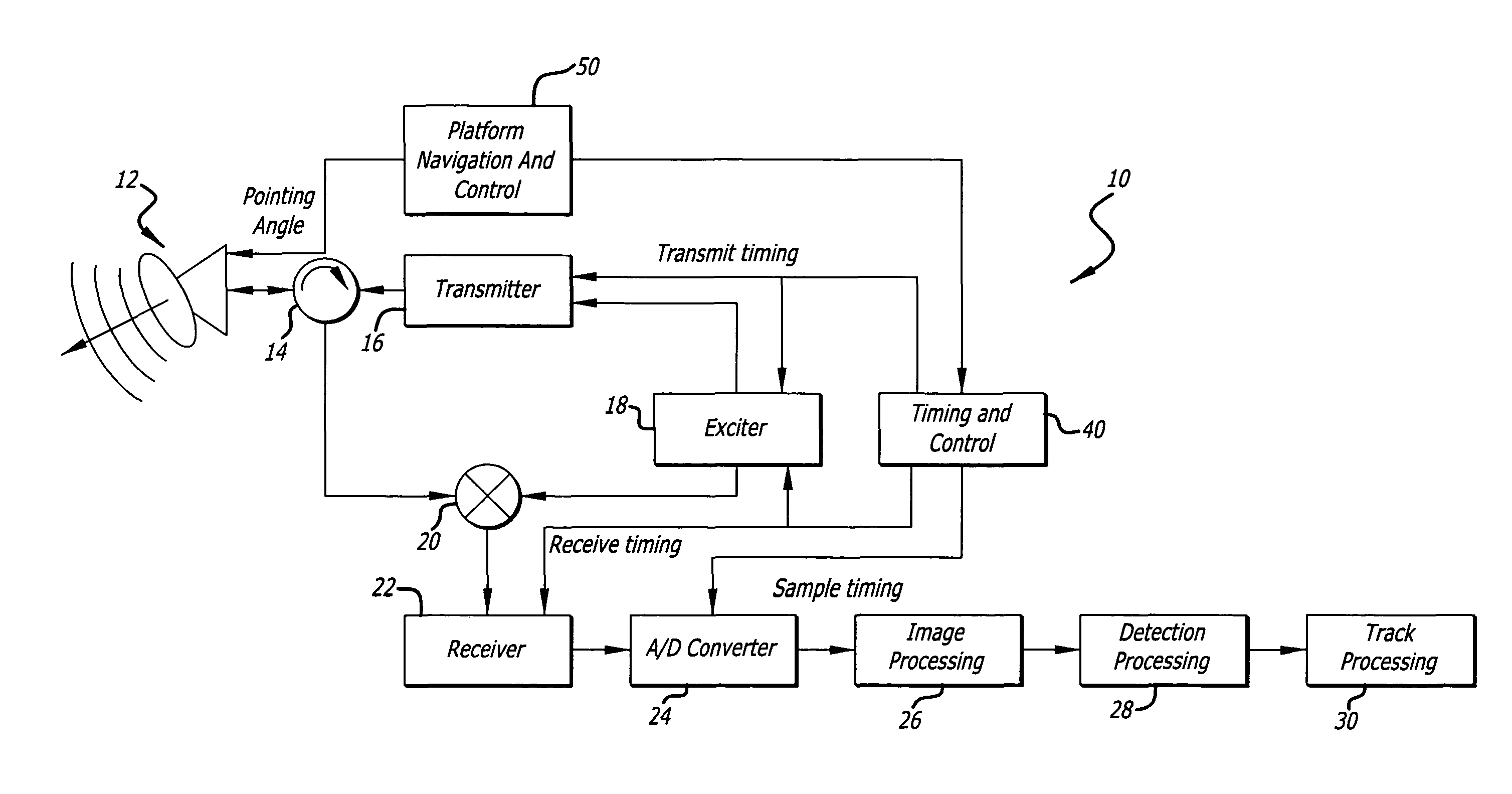
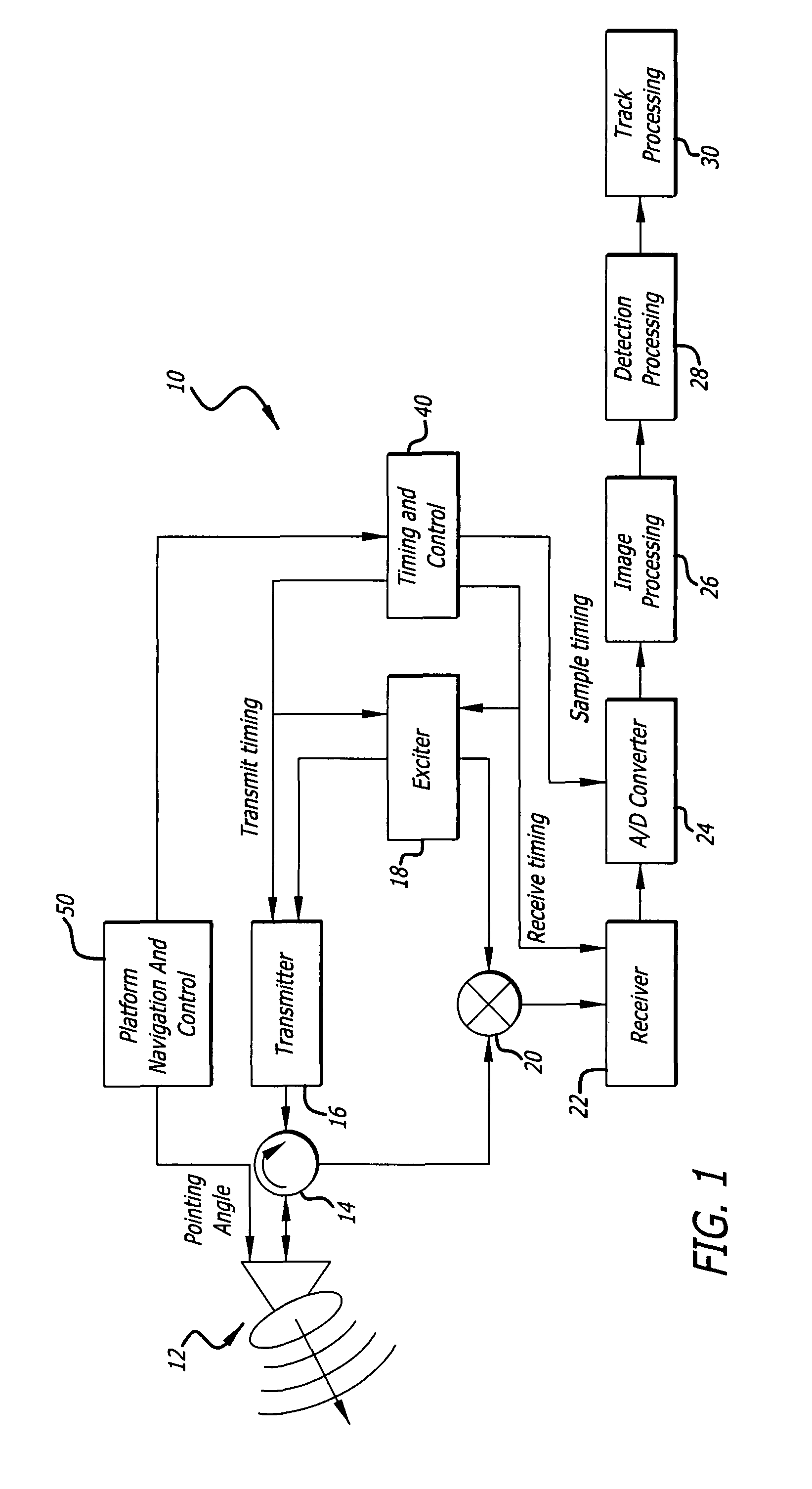
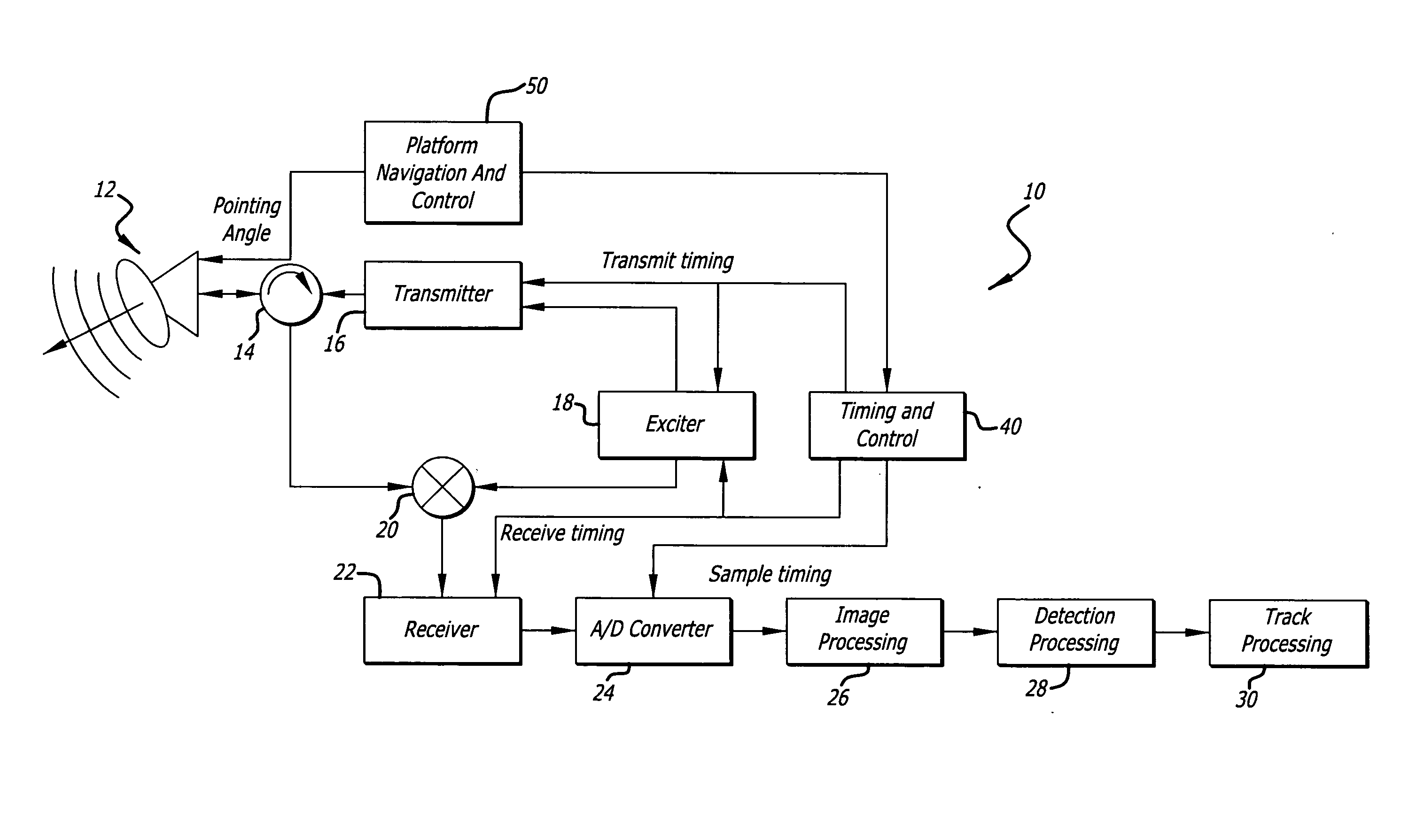
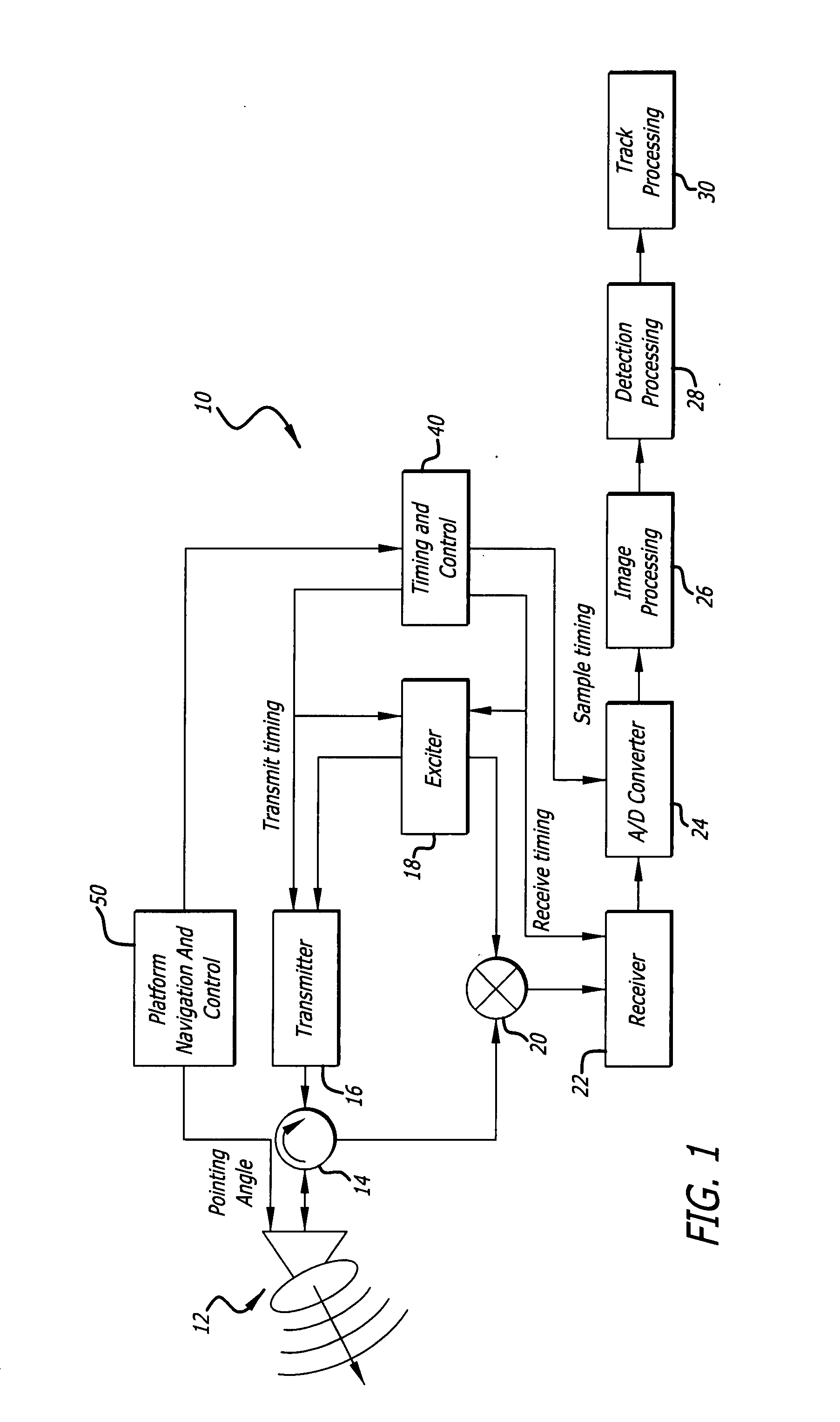
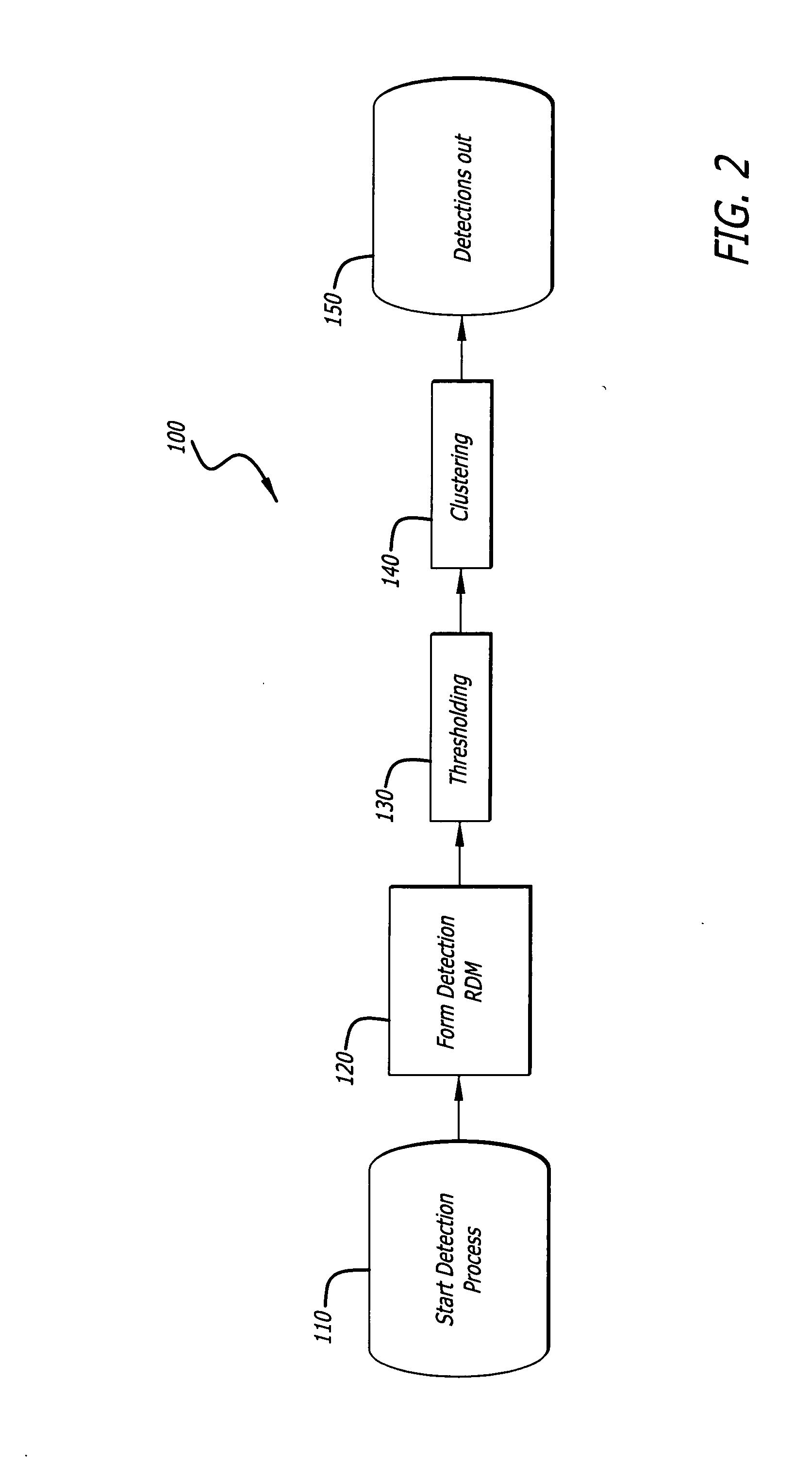
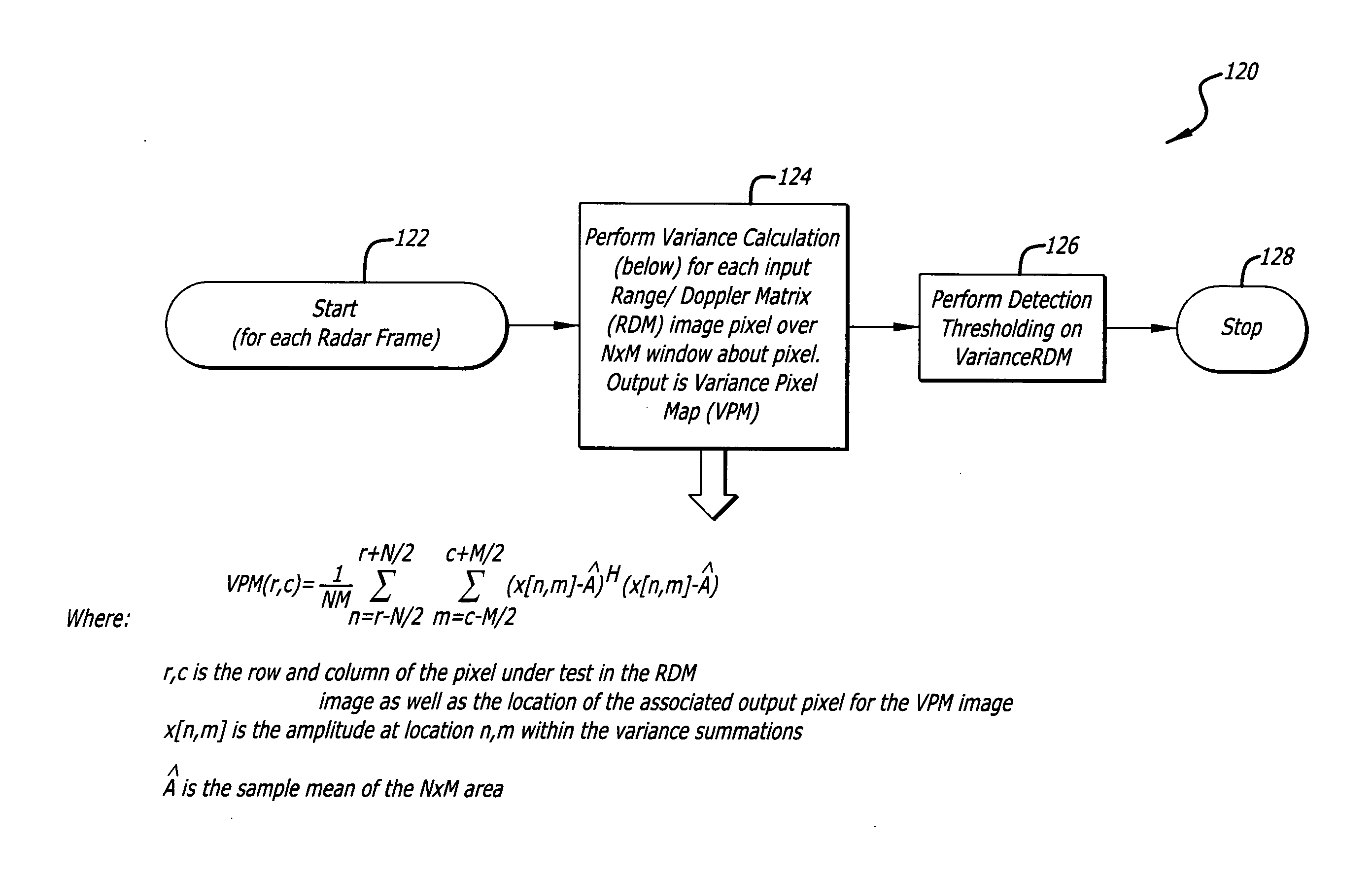
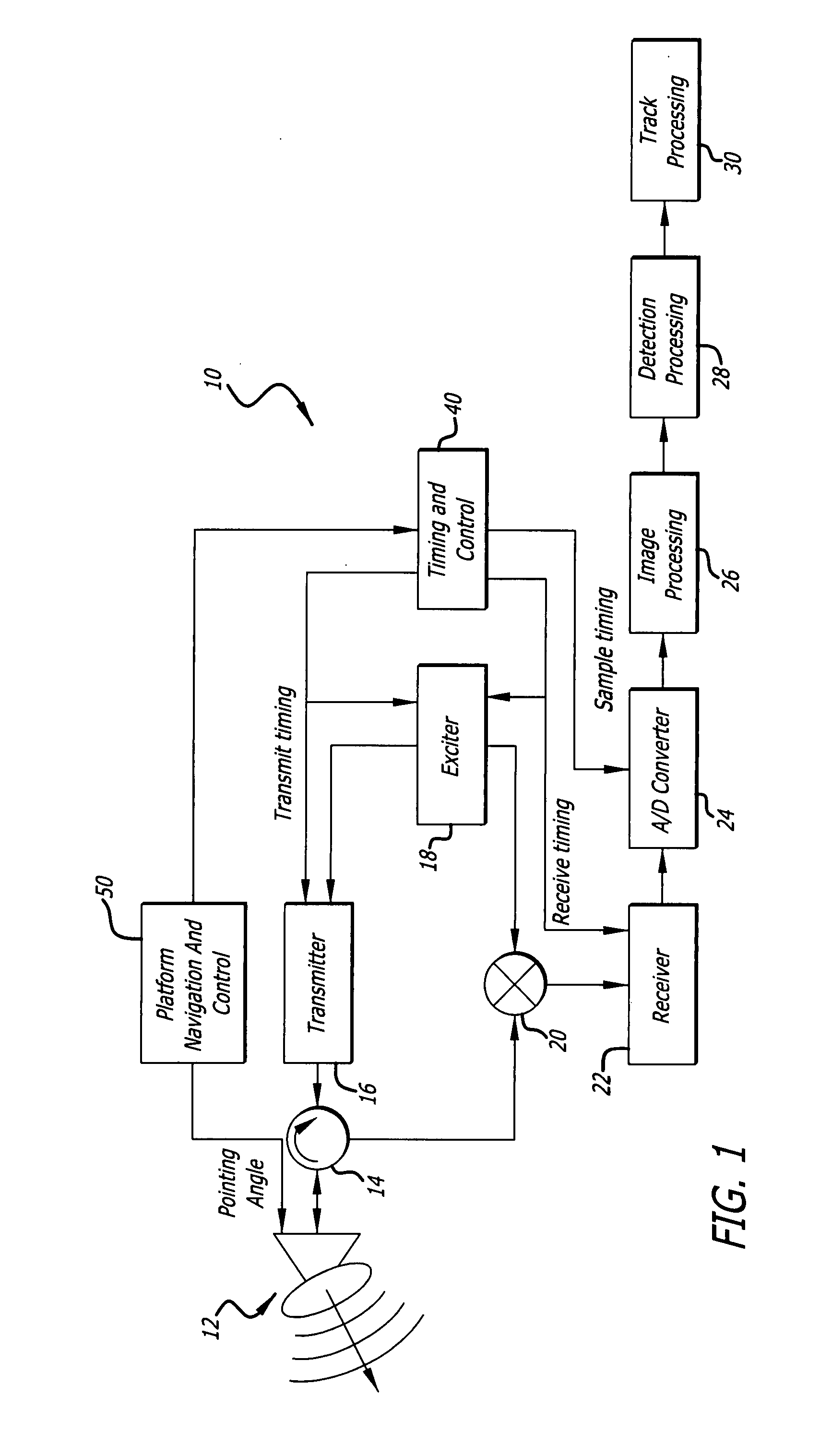
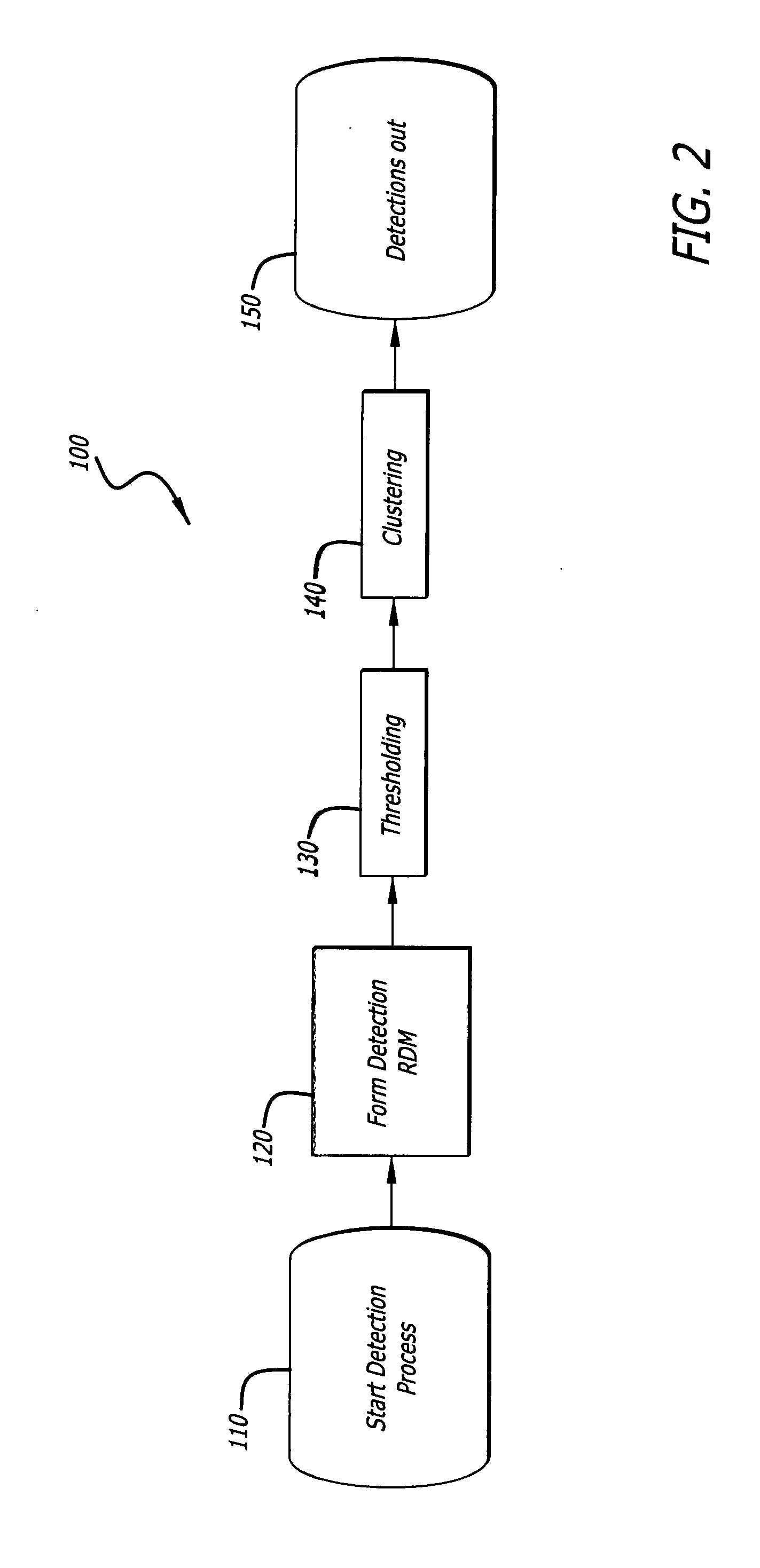
Radar imaging system and method using directional gradient magnitude second moment spatial variance detection
A detection system and method. The inventive system includes an arrangement for receiving a frame of image data; an arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation with respect to at least one pixel in said frame of image data; and an arrangement for comparing said calculated rate of change of variance with a predetermined threshold to provide output data. In the illustrative embodiment, the frame of image data includes a range / Doppler matrix of N down range samples and M cross range samples. In this embodiment, the arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation includes an arrangement for calculating a rate of change of variance over an N×M window within the range / Doppler matrix. The arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation includes an arrangement for identifying a change in a standard deviation of a small, localized sampling of cells. In accordance with the invention, the arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation outputs a rate of change of variance pixel map.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Motionless adaptive stereoscopic scene capture with tuneable liquid crystal lenses and stereoscopic auto-focusing methods
A motionless adaptive focus stereoscopic scene capture apparatus employing tunable liquid crystal lenses is provided. The apparatus includes at least two image sensors preferably fabricated as a monolithic stereo image capture component and at least two corresponding tunable liquid crystal lenses preferably fabricated as a monolithic focus adjustment component. Using a variable focus tunable liquid crystal lens at each aperture stop provides constant magnification focus control. Controlled spatial variance of a spatially variant electric field applied to the liquid crystal of each tunable liquid crystal lens provides optical axis shift enabling registration between stereo images. A controller implements coupled auto-focusing methods employing multiple focus scores derived from at least two camera image sensors and providing multiple tunable liquid crystal lens drive signals for synchronous focus acquisition of a three dimensional scene. Wafer manufacture provides a compact stereoscopic image capture apparatus for endoscopic surgery, optical inspection and entertainment applications.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
Probabilistic bit-rate and rate-distortion cost estimation for video coding
ActiveUS8160136B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionRate distortion
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Radar imaging system and method using gradient magnitude second moment spatial variance detection
A detection system and method. The inventive system includes an arrangement for receiving a frame of image data; an arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation with respect to at least one pixel in said frame of image data; and an arrangement for comparing said calculated rate of change of variance with a predetermined threshold to provide output data. In the illustrative embodiment, the frame of image data includes a range / Doppler matrix of N down range samples and M cross range samples. In this embodiment, the arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation includes an arrangement for calculating a rate of change of variance over an N×M window within the range / Doppler matrix. The arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation includes an arrangement for identifying a change in a standard deviation of a small, localized sampling of cells. In accordance with the invention, the arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation outputs a rate of change of variance pixel map.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Inter-frame registration and adaptive step length-based infrared image non-uniformity correction method
InactiveCN108665425AFast convergenceImprove the correction effectImage enhancementImage analysisRelative displacementSelf adaptive
The invention discloses an inter-frame registration and adaptive step length-based infrared image non-uniformity correction method. The method comprises the steps of firstly calculating normalized cross-power spectrums of original infrared images, with non-uniformity, of an nth frame and an (n-1)th frame, and obtaining horizontal relative displacements and vertical relative displacements of the original infrared images, with the non-uniformity, of the nth frame and the (n-1)th frame; secondly calculating out a spatial variance and a time variance of each pixel of the original infrared image, with non-uniformity, of the nth frame, calculating an adaptive iterative step length of each pixel of the original infrared image, with non-uniformity, of the nth frame by utilizing the obtained spatial variance and time variance, and updating a gain correction coefficient and a bias correction coefficient by using the iterative step length; and finally performing non-uniformity correction on the pixels of an overlapping region of the original infrared images, with the non-uniformity, of the nth frame and the (n-1)th frame.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Radar imaging system and method using directional gradient magnitude second moment spatial variance detection
A detection system and method. The inventive system includes an arrangement for receiving a frame of image data; an arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation with respect to at least one pixel in said frame of image data; and an arrangement for comparing said calculated rate of change of variance with a predetermined threshold to provide output data. In the illustrative embodiment, the frame of image data includes a range / Doppler matrix of N down range samples and M cross range samples. In this embodiment, the arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation includes an arrangement for calculating a rate of change of variance over an N×M window within the range / Doppler matrix. The arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation includes an arrangement for identifying a change in a standard deviation of a small, localized sampling of cells. In accordance with the invention, the arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation outputs a rate of change of variance pixel map.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
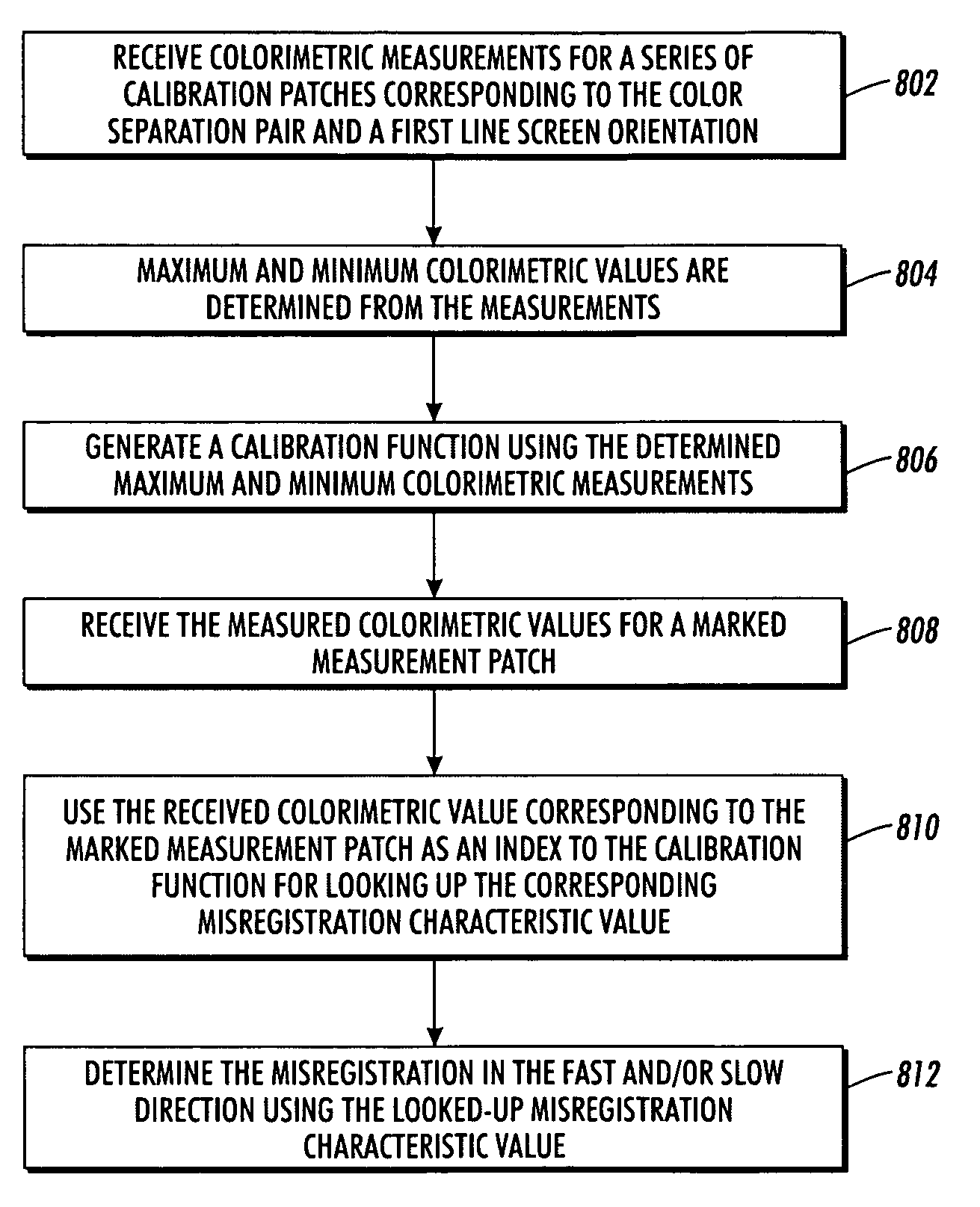
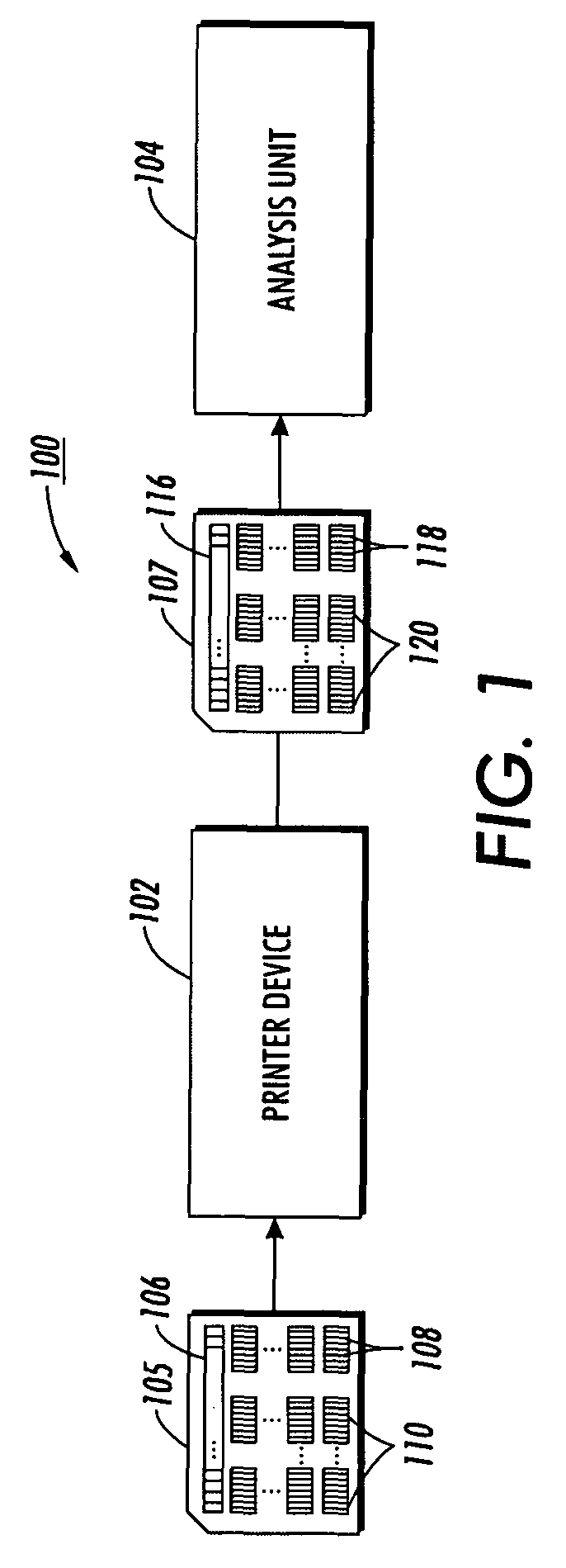
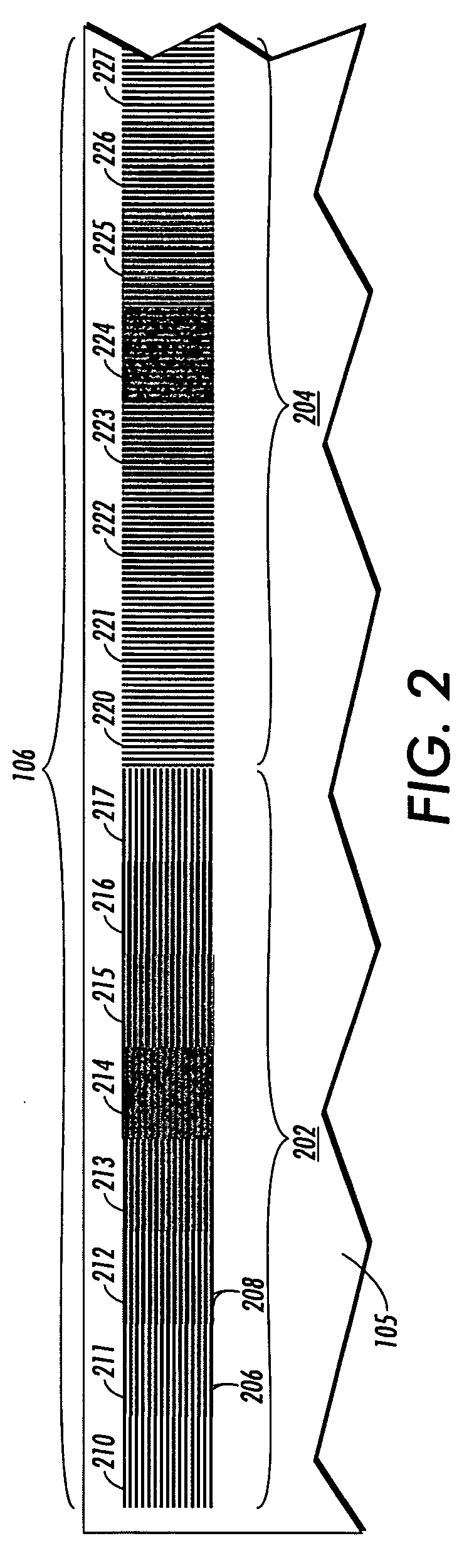
System and method for characterizing spatial variance of color separation misregistration
InactiveUS7894109B2Image enhancementDigitally marking record carriersComputer scienceCalibration function
A method is provided for characterizing color separation misregistration of a printer device, the method including receiving from the printer device an output image having marked calibration patches having a variety of color separation configurations, each using a first and second color separation, and a marked measurement patch having a predetermined color separation configuration. Measured colorimetric values are received corresponding to the calibration patches and the marked measurement patch, and a characteristic of a curve associated with the measured colorimetric values corresponding to the calibration patches is determined. A calibration function is generated based on the determined characteristic of the curve, providing expected colorimetric values for the predetermined color separation configuration as related to a misregistration characteristic value. A misregistration characteristic value is determined from the calibration function that corresponds to the measured colorimetric value of the marked measurement patch for characterizing misregistration between the first and second color separations.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and system for block noise reduction
InactiveUS8254462B2Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionVertical edge
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method for characterizing an atmospheric turbulence using representative parameters measured by radar
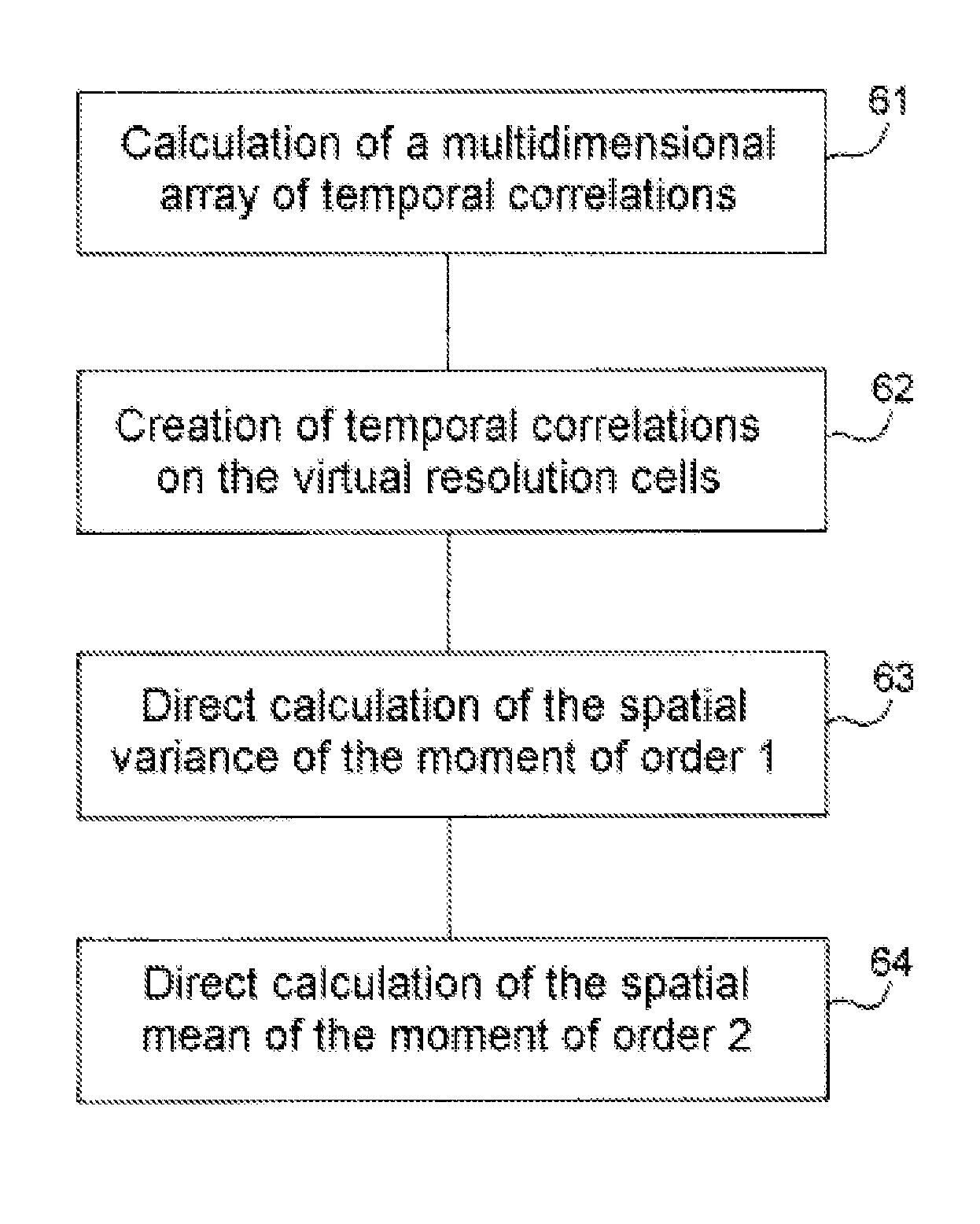
The present invention relates to a method for characterizing an atmospheric turbulence by representative parameters measured by a radar. The emission beam of the radar carried by an aircraft scanning the zone of the turbulence, a measured parameter being the total variance of the velocity of the turbulence σU, this total variance at a point x0 inside the turbulence is the sum of the spatial variance of the spectral moment of order 1 of the signals received by the radar Var[M1({right arrow over (x)})] and of the spatial mean of the spectral moment of order 2 of the signals received Mean[M2({right arrow over (x)})], the moments being distributed as a vector {right arrow over (x)} sweeping an atmospheric domain around the point x0. The invention applies notably in respect of meteorological radars fitted to aircraft such as airliners for example.
Owner:THALES SA
Radar imaging system and method using second moment spatial variance
A detection system and method. The inventive system includes an arrangement for receiving a frame of image data; an arrangement for performing a variance calculation with respect to at least one pixel in the frame of image data; and an arrangement for comparing the calculated variance with a predetermined threshold to provide output data. In the illustrative embodiment, the frame of image data includes a range / Doppler matrix of N down range samples and M cross range samples. In this embodiment, the arrangement for performing a variance calculation includes an arrangement for calculating a variance over an N×M window within the range / Doppler matrix. The arrangement for performing a variance calculation includes an arrangement for identifying a change in a standard deviation of a small, localized sampling of cells. In accordance with the invention, the arrangement for performing a variance calculation outputs a variance pixel map.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
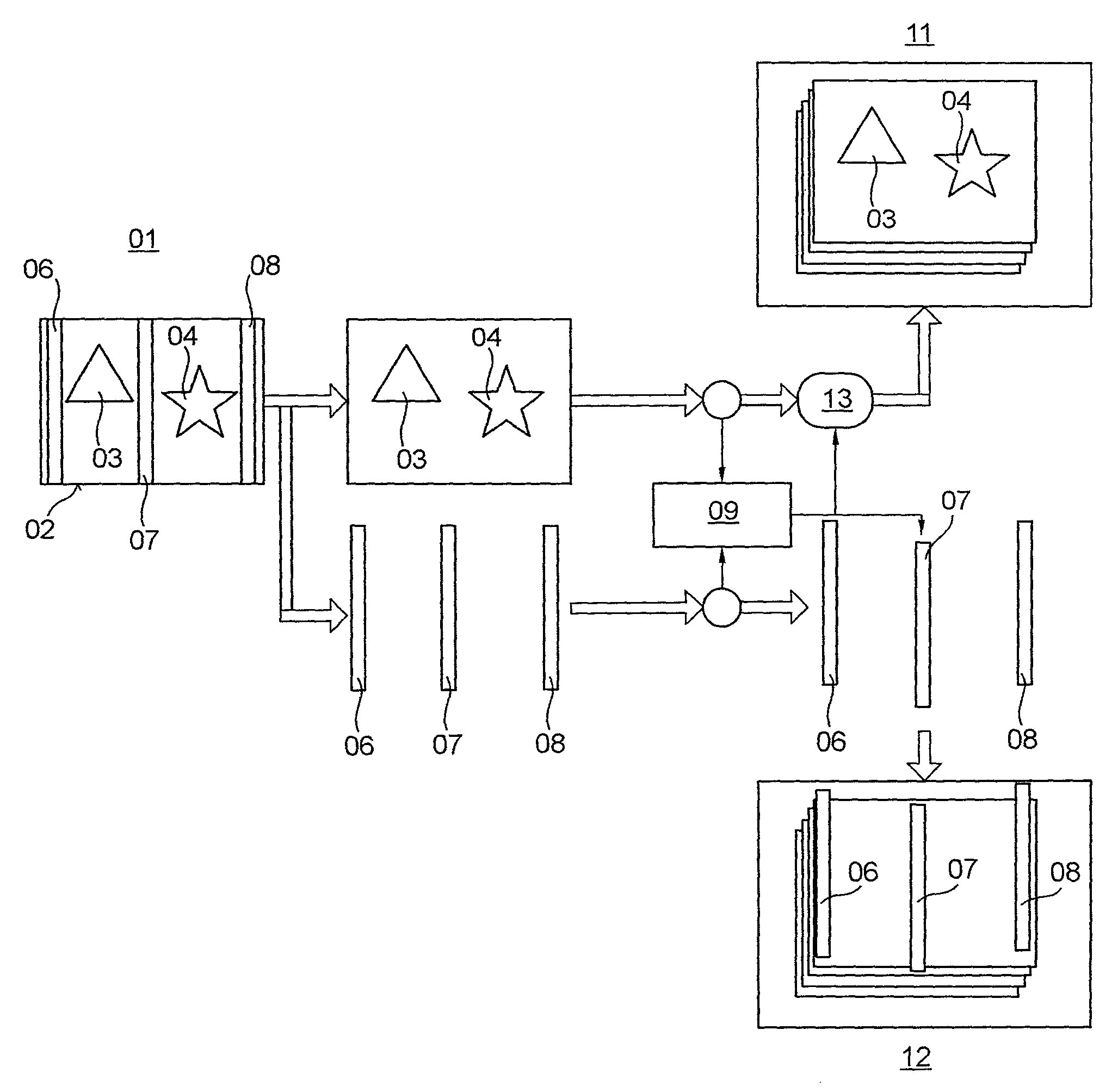
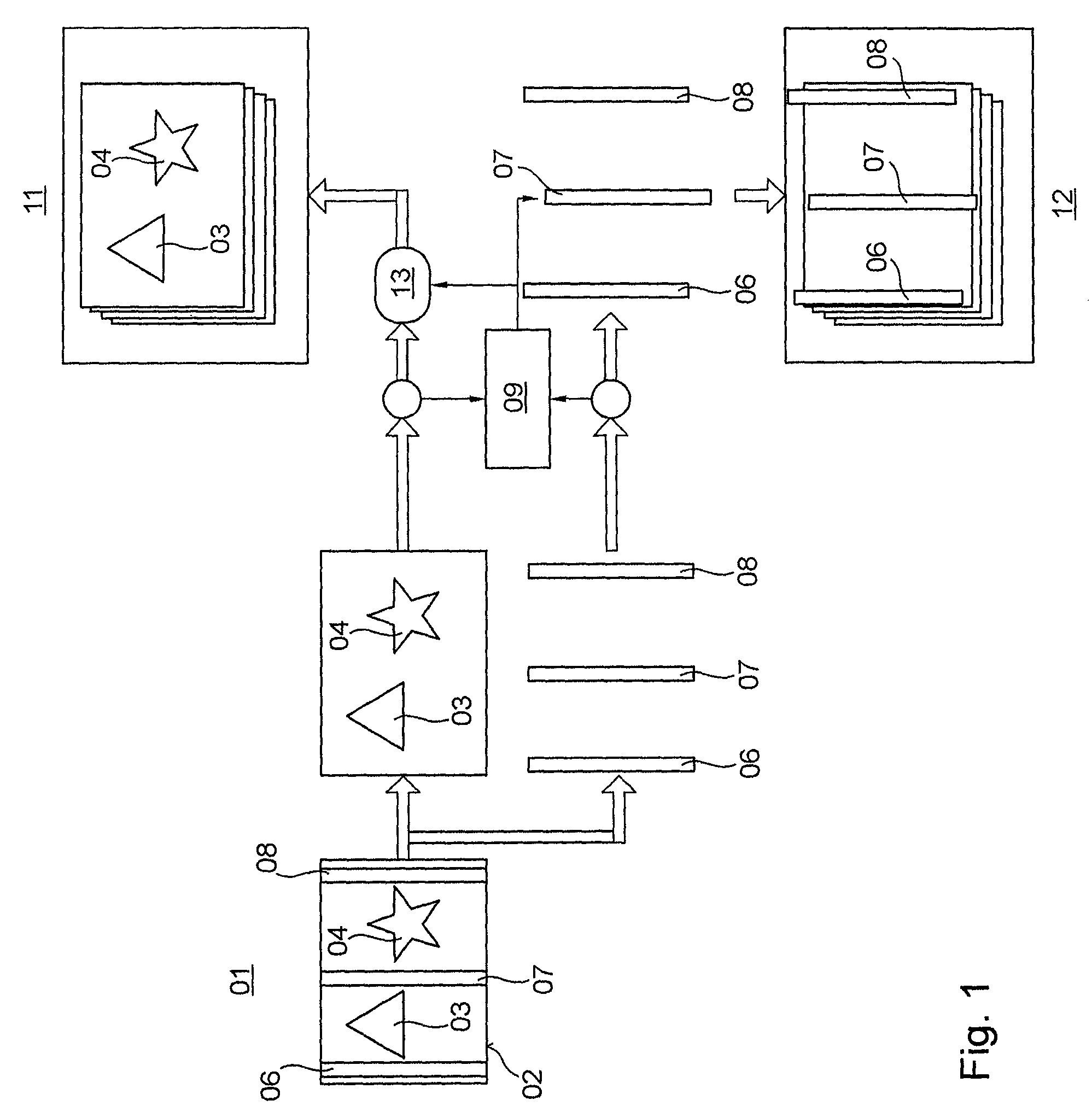
Method for inspecting at least one copy of a printed product
A method is used for inspecting at least one copy of a printed product. At least one element, which is spatially constant with respect to a fixed reference point and at least one element which is spatially variant with respect to the same fixed reference point are reliably inspected by reference image data being used for a desired-actual value comparison of the at least one spatially variant element. The reference image data takes account of the variable position of the at least one element; i.e. the spatial variance thereof.
Owner:KOENIG & BAUER AG
Radar imaging system and method using gradient magnitude second moment spatial variance detection
A detection system and method. The inventive system includes an arrangement for receiving a frame of image data; an arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation with respect to at least one pixel in said frame of image data; and an arrangement for comparing said calculated rate of change of variance with a predetermined threshold to provide output data. In the illustrative embodiment, the frame of image data includes a range / Doppler matrix of N down range samples and M cross range samples. In this embodiment, the arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation includes an arrangement for calculating a rate of change of variance over an N×M window within the range / Doppler matrix. The arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation includes an arrangement for identifying a change in a standard deviation of a small, localized sampling of cells. In accordance with the invention, the arrangement for performing a rate of change of variance calculation outputs a rate of change of variance pixel map.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Tissue Sample Analysis
ActiveUS20180317818A1Improve insightsGood removal effectDiagnostics using spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsTumour tissueAnalyte
Method and instrument for analysing a tissue sample. Localized concentrations of an analyte are measured at a plurality of spaced apart locations around a controlled depth. Spatial variance of the analyte is calculated based on the measured analyte concentrations. The procedure is repeated while varying the controlled depth to obtain the spatial variance as a function of depth. Tissue at a particular depth may be evaluated as tumour tissue when the spatial variance is below the threshold. For example, a section distance is calculated between the tissue surface and a depth where the measured spatial variance crosses a predetermined threshold variance. Feedback can be provided based on a comparison between a calculated section distance and a pre-set minimum section margin.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
Component frame enhancement for spatial compounding in ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS9081097B2Character and pattern recognitionAcoustic wave reradiationAnatomical structuresUltrasound imaging
Steered spatial compounding is provided in ultrasound imaging. Component frames of data associated with different spatial response are processed to identify different sources of signals. Matched filtering and / or spatial variance with erosion distinguish between sources of signals, such as distinguishing between (1) anatomical structure and (2) soft tissue and / or noise. The locations in the patient are segmented by the source of signals and different compounding is applied for the different sources.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Motionless adaptive stereoscopic scene capture with tuneable liquid crystal lenses and stereoscopic auto-focusing methods
A motionless adaptive focus stereoscopic scene capture apparatus employing tuneable liquid crystal lenses is provided. The apparatus includes at least two image sensors preferably fabricated as a monolithic stereo image capture component and at least two corresponding tuneable liquid crystal lenses preferably fabricated as a monolithic focus adjustment component. Using a variable focus tuneable liquid crystal lens at each aperture stop provides constant magnification focus control. Controlled spatial variance of a spatially variant electric field applied to the liquid crystal of each tuneable liquid crystal lens provides optical axis shift enabling registration between stereo images. A controller implements coupled auto-focusing methods employing multiple focus scores derived from at least two camera image sensors and providing multiple tuneable liquid crystal lens drive signals for synchronous focus acquisition of a three dimensional scene. Wafer manufacture provides a compact stereoscopic image capture apparatus for endoscopic surgery, optical inspection and entertainment applications.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
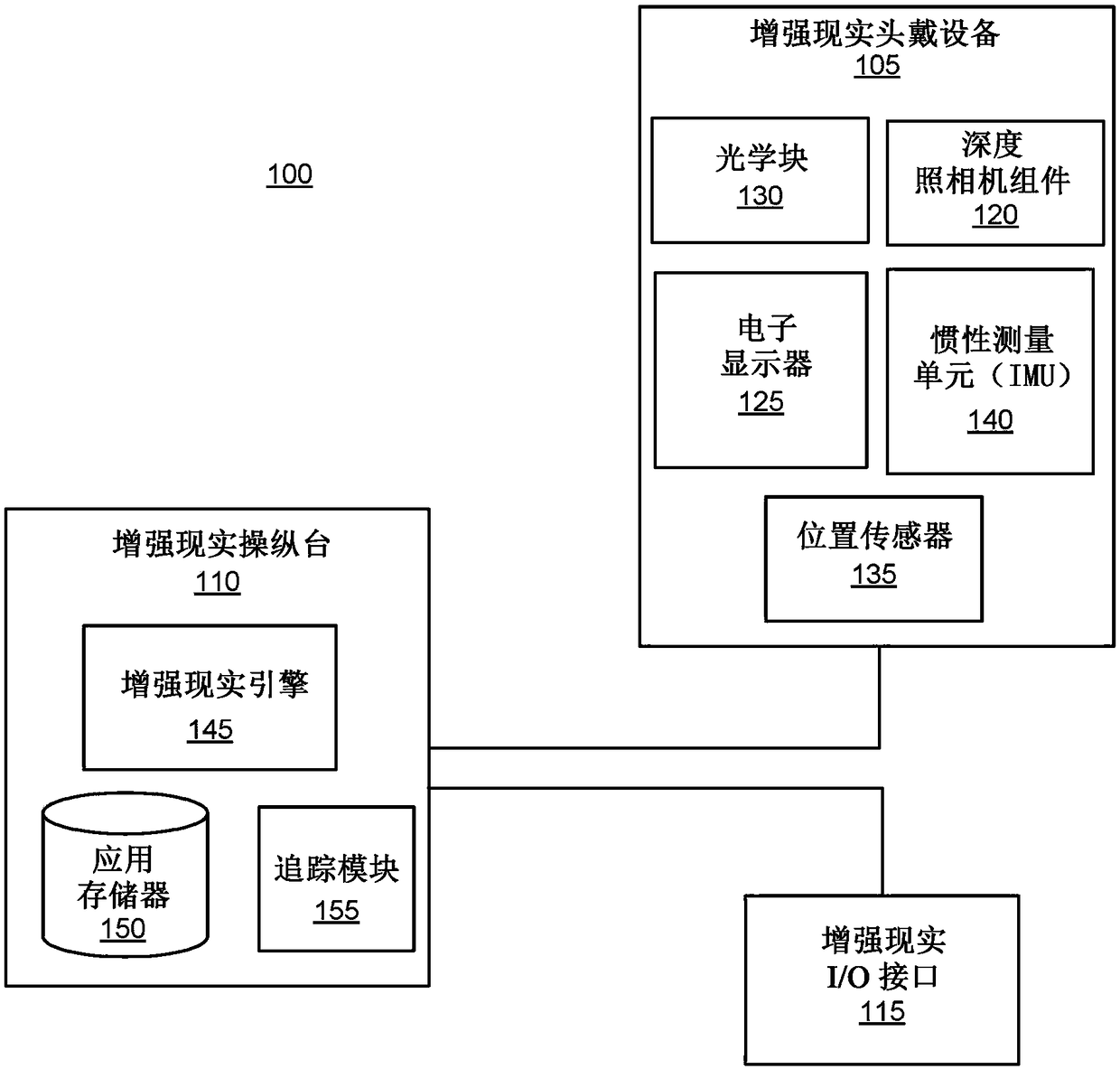
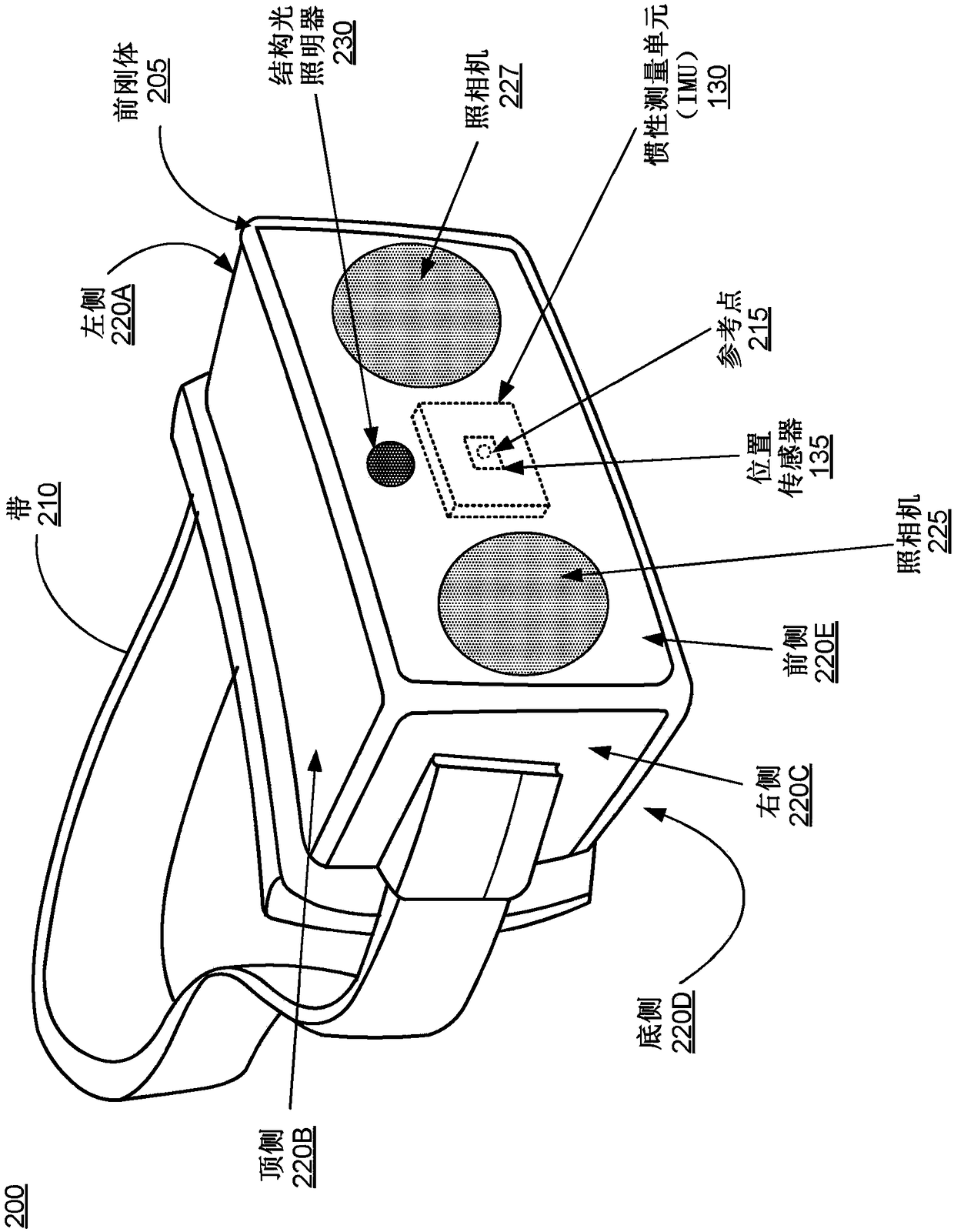
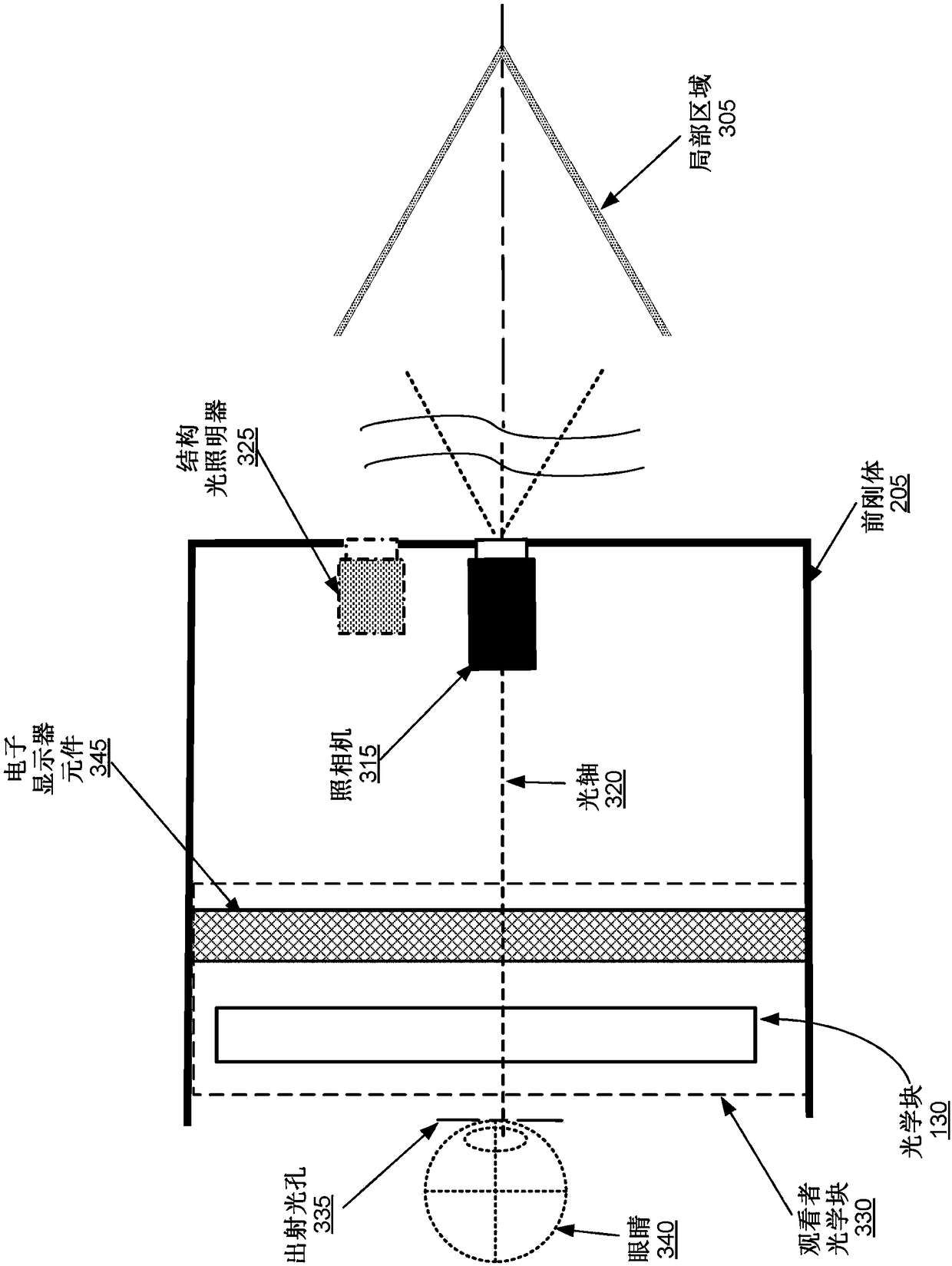
Depth mapping with a head mounted display using stereo cameras and structured light
A an augmented reality (AR) headset includes a depth camera assembly that combines stereo imaging with structured light (SL) to generate depth information for an area of interest. The depth camera assembly includes at least two image capture devices and a SL illuminator and determines an imaging mode based on a signal to noise ratio or spatial variance of images captured by one or more of the cameras. Different imaging modes correspond to different operation of one or more image capture devices and the SL illuminator. The depth camera assembly includes different ranges of signal to noise ratios that each correspond to an imaging mode, and the depth camera assembly configures the image capture devices and the SL illuminator based on an imaging mode associated with a range of signal to noiseratios including the signal to noise ratio of a captured image.
Owner:CTRL LABS CORP
Radar imaging system and method using second moment spatial variance
A detection system and method. The inventive system includes an arrangement for receiving a frame of image data; an arrangement for performing a variance calculation with respect to at least one pixel in the frame of image data; and an arrangement for comparing the calculated variance with a predetermined threshold to provide output data. In the illustrative embodiment, the frame of image data includes a range / Doppler matrix of N down range samples and M cross range samples. In this embodiment, the arrangement for performing a variance calculation includes an arrangement for calculating a variance over an N×M window within the range / Doppler matrix. The arrangement for performing a variance calculation includes an arrangement for identifying a change in a standard deviation of a small, localized sampling of cells. In accordance with the invention, the arrangement for performing a variance calculation outputs a variance pixel map.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Motion detection for interlaced video
Motion detection in interlaced video fields, as useful in de-interlacing, includes spatial-temporal maximum filtering, temporal IIR filtering dependent upon spatial-temporal variance, and spatial variance dependent moving-still interpolation blending factor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
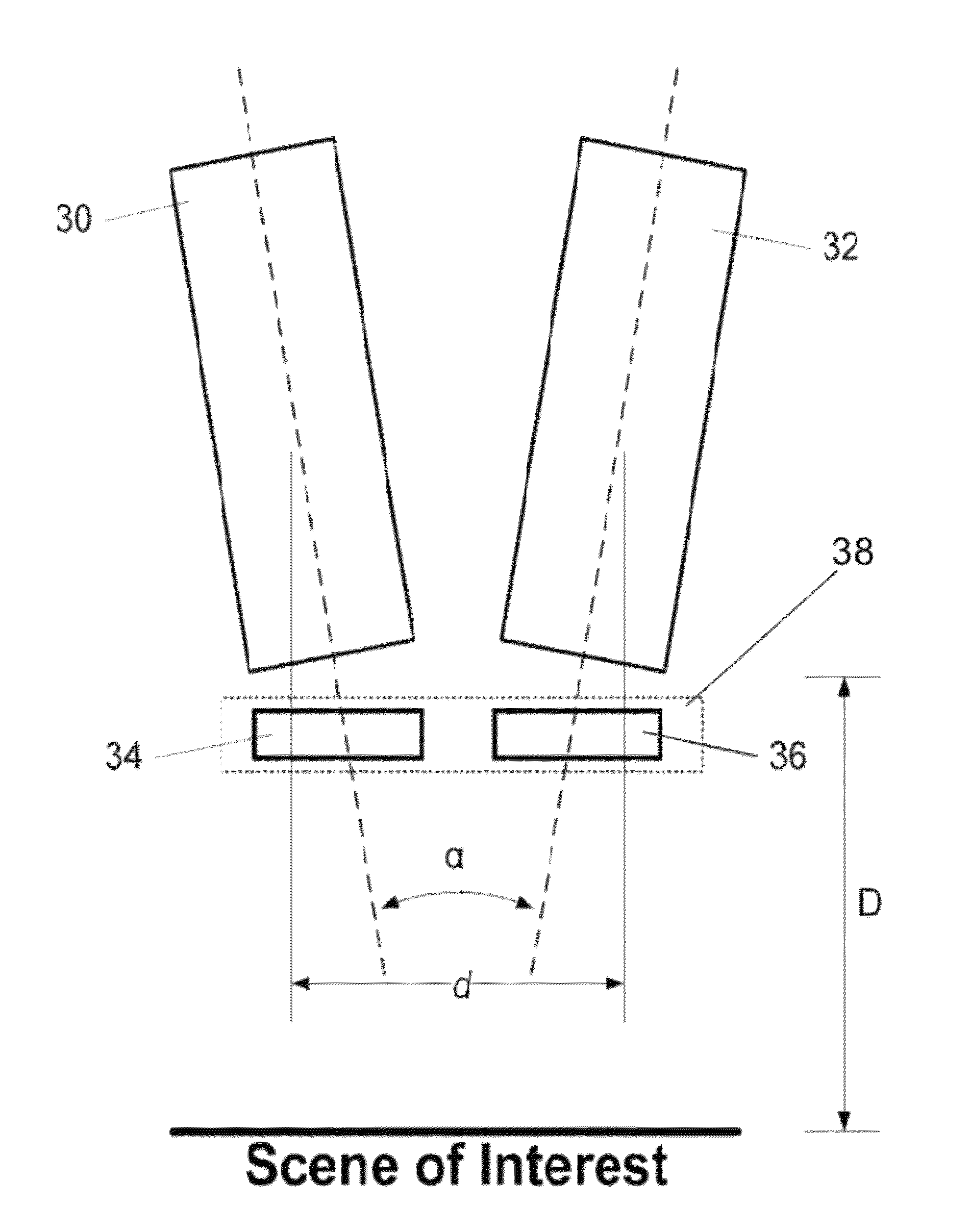
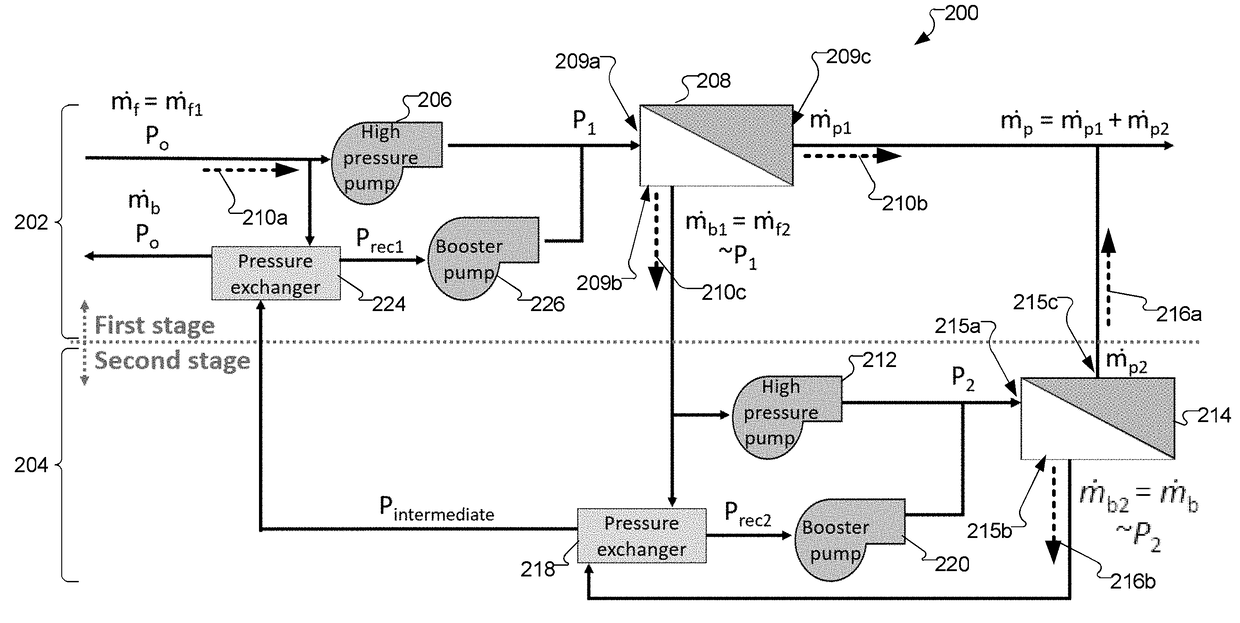
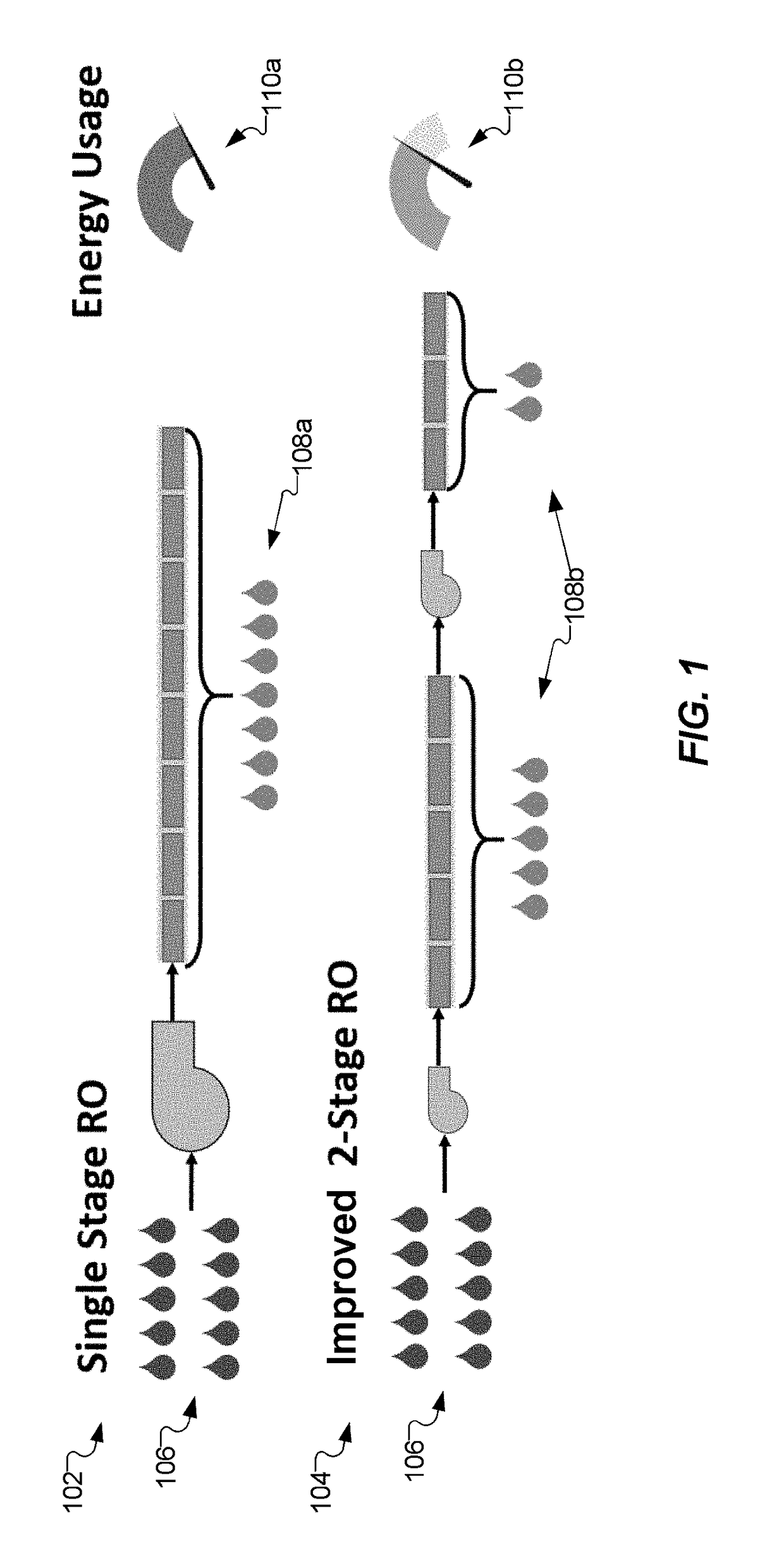
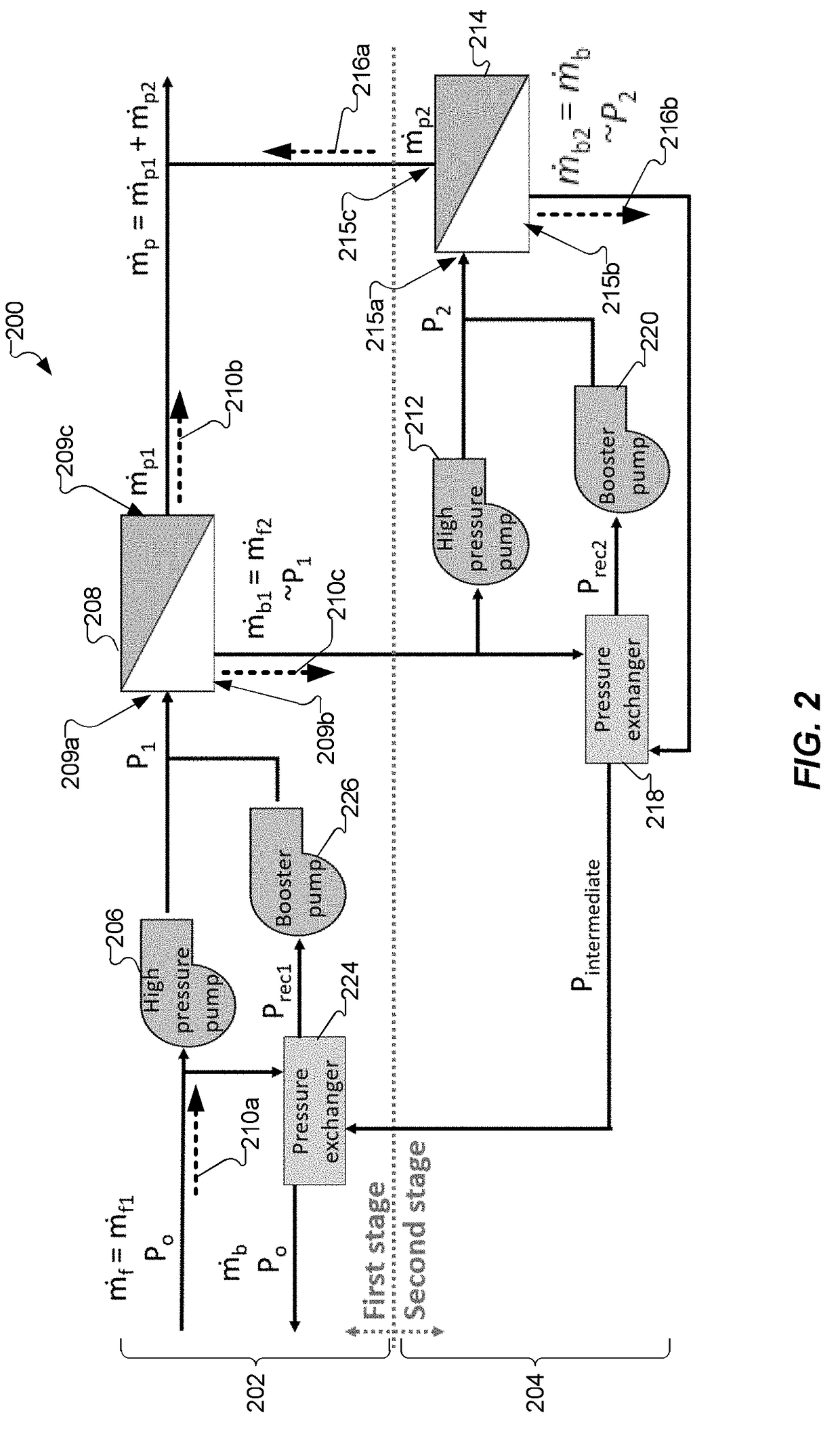
Multi-Stage Reverse Osmosis Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20170320016A1Space minimizationWaste water treatment from quariesMembranesReverse osmosisPressure exchanger
Improved reverse osmosis (RO) systems include at least first and second stages wherein each stage has at least one RO membrane, each stage has a feed stream inlet, a permeate stream outlet, and a concentrate stream outlet, the feed stream inlet of the second stage is coupled to the concentrate stream outlet of the first stage, the second pressure is greater than the first pressure, and pressure exchangers associated with each of the first and second stages are configured to recover energy from the second stage concentrate stream. The systems include M reverse osmosis membranes in the first stage and N reverse osmosis membranes in the second stage, wherein M≧N. The first pressure and second pressure are configured so that spatial variance in flux of the first stage permeate stream relative to flux of the second stage permeate stream is minimized.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for inspecting at least one copy of a printed product
Owner:KOENIG & BAUER AG
Spectral doppler detection
ActiveCN107550516ABlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionFrequency spectrumDoppler imaging
In spectral pulsed wave Doppler imaging, spatial variance in signal and / or noise are reduced by combination of multiple spectra with at least partially decorrelated noise. Rather than requiring oversampling in time, the multiple spectra for one Doppler gate are created from different spatial signals. The Doppler gate is divided into sub-gates, the beamformed sample locations in the Doppler gate are grouped into two or more groups using any selection criterion, and / or different receive apertures are used to simultaneously sample the Doppler gate. Spectra for the gate are estimated from the samples with the different spatial content and then combined.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method for identifying stochastic information of heterogeneous materials
A method for identifying stochastic information of a heterogeneous material utilizes physical loading measurements that are input into a global optimization process. The optimization process executes, in parallel, a force-driven non-linear finite element simulation and a displacement-driven finite element simulation of a constitutive model of the heterogeneous material. The constitutive models model the spatially varying random material properties (i.e. stochastic properties) using the Karhunen-Loeve expansion, thereby introducing the stochastic parameters, including spatial mean, spatial variance, and correlation length for example into the models. Stress and strain values for both the force-driven and displacement driven finite element analyzes are input into an objective function, whereupon the finite element simulations are updated after each iteration of the optimization process is performed until the objective function is minimized to a desired level. This results in the identification of optimized stochastic parameters associated with the heterogeneous material under investigation.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com