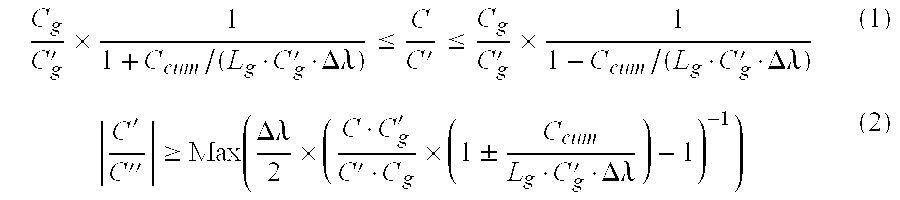Patents
Literature
122results about "Optical fibre with desired dispersion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber and communication system incorporating the same
ActiveUS6904218B2Increase the effective areaLow cutoff wavelengthOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberUltrasound attenuation
A super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber that is suitable for communicating over a wide wavelength range and that, because of its large effective area, suppresses nonlinear effects that typically result from interaction between signal channels. The effective area, Aeff, of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is equal to or greater than approximately 80 μm2 at a wavelength window around 1310 nm. The cutoff wavelength of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is less than 1310 nm. Thus, the SLA fiber of the present invention has a very large effective area and a very low cutoff wavelength. In accordance with the present invention, a variety of SLA fibers are provided that all have very large effective areas and desirable transmission properties. The large effective areas of the SLA fibers of the present invention enable nonlinear effects to be suppressed, as well as Stimulated Brillouin Scattering in analog transmission. The large effective areas also enable attenuation to be reduced. The result of suppressing nonlinear effects and reducing attenuation enable signals to be transmitted over long distances and over a broad bandwidth.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Dispersion-controlled optical fiber
ActiveUS6999667B2Low loss characteristicIncrease the areaOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive index profile
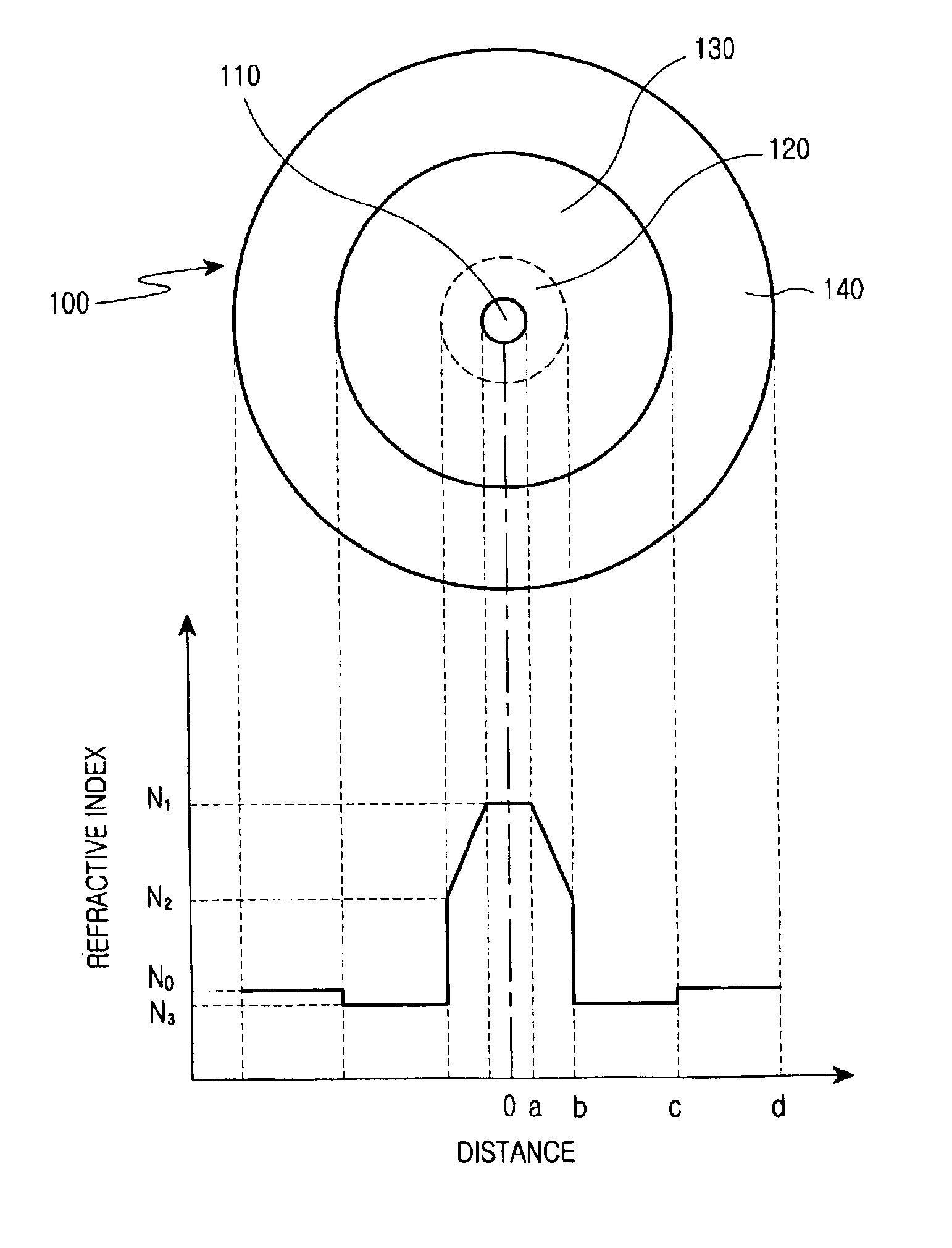
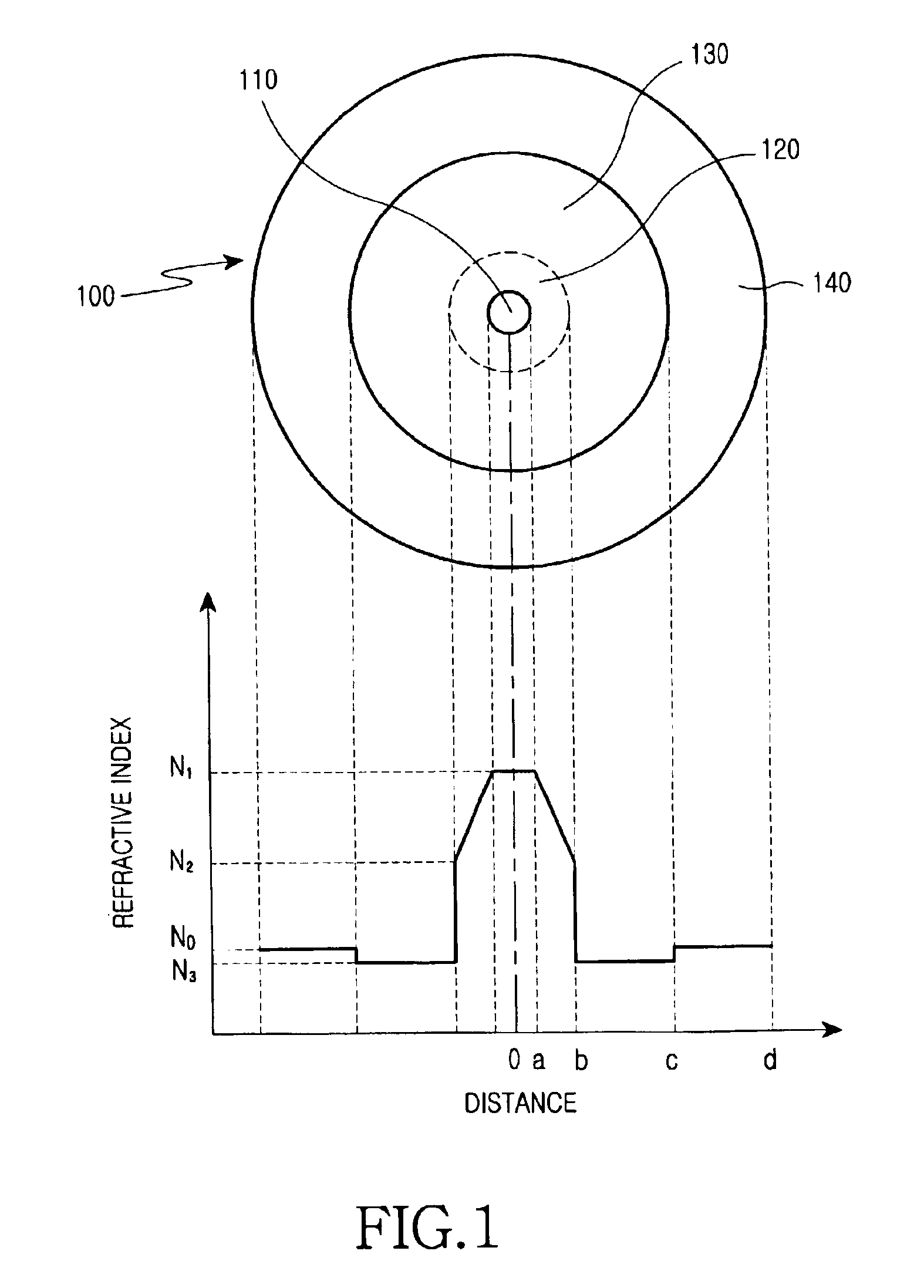
Disclosed is an optical fiber comprising a center core which forms a passageway for transmitting optical signals and has a refractive index N1, and a cladding which encloses the center core and has a refractive index N0. The optical fiber further comprises an upper core, which has a distribution of refractive indices increased starting from a refractive index N2 (>N0) at its outer circumference to the refractive index N1 at its internal circumference, and a minutely depressed refractive index region, which is interposed between said upper core and cladding and has a refractive index N3. The refractive index N3 is lower than the refractive index N0.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
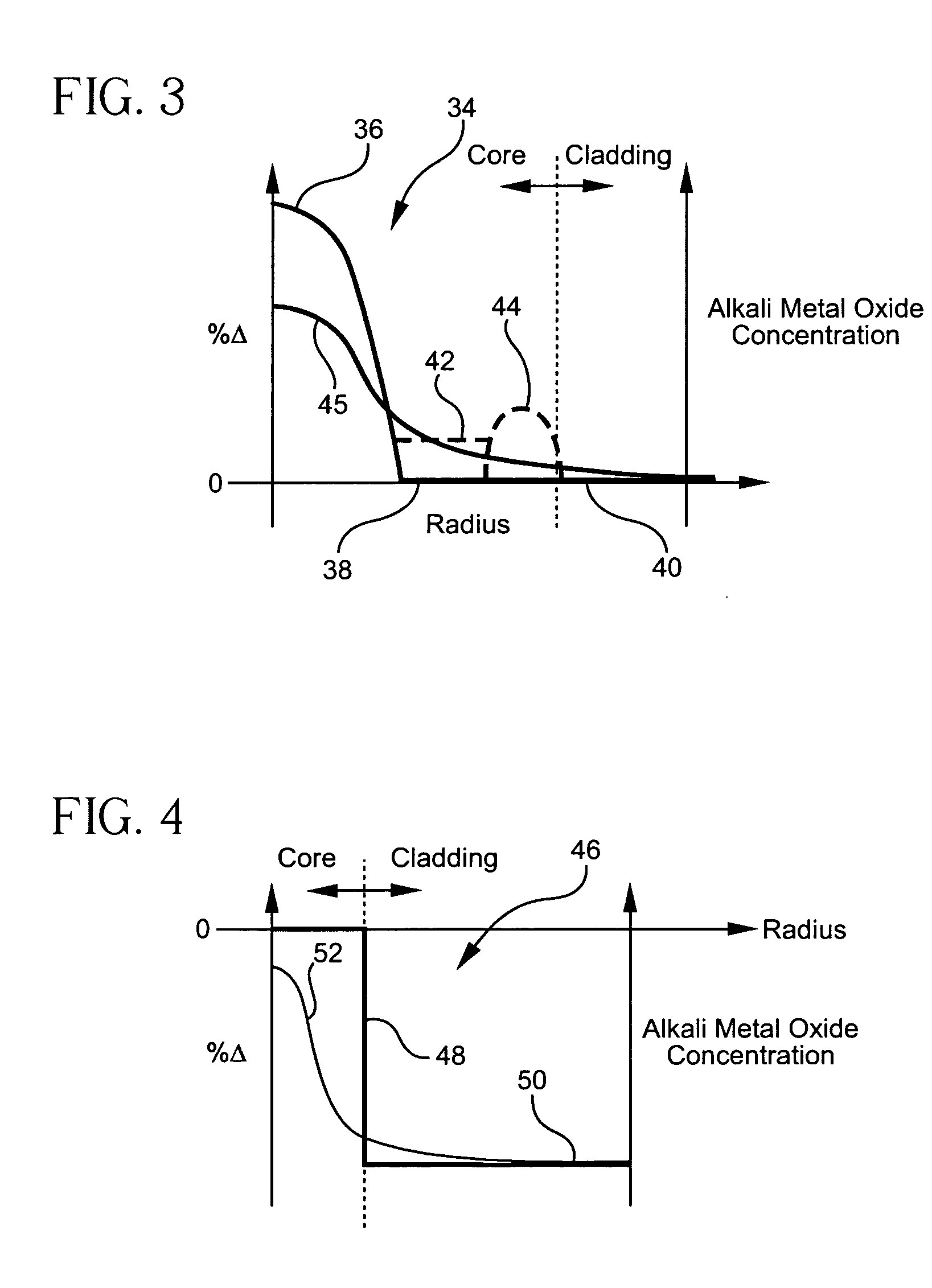
Optical fiber containing an alkali metal oxide and methods and apparatus for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20050063663A1Increase radiusReduce doping concentrationOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDopantAlkali metal oxide
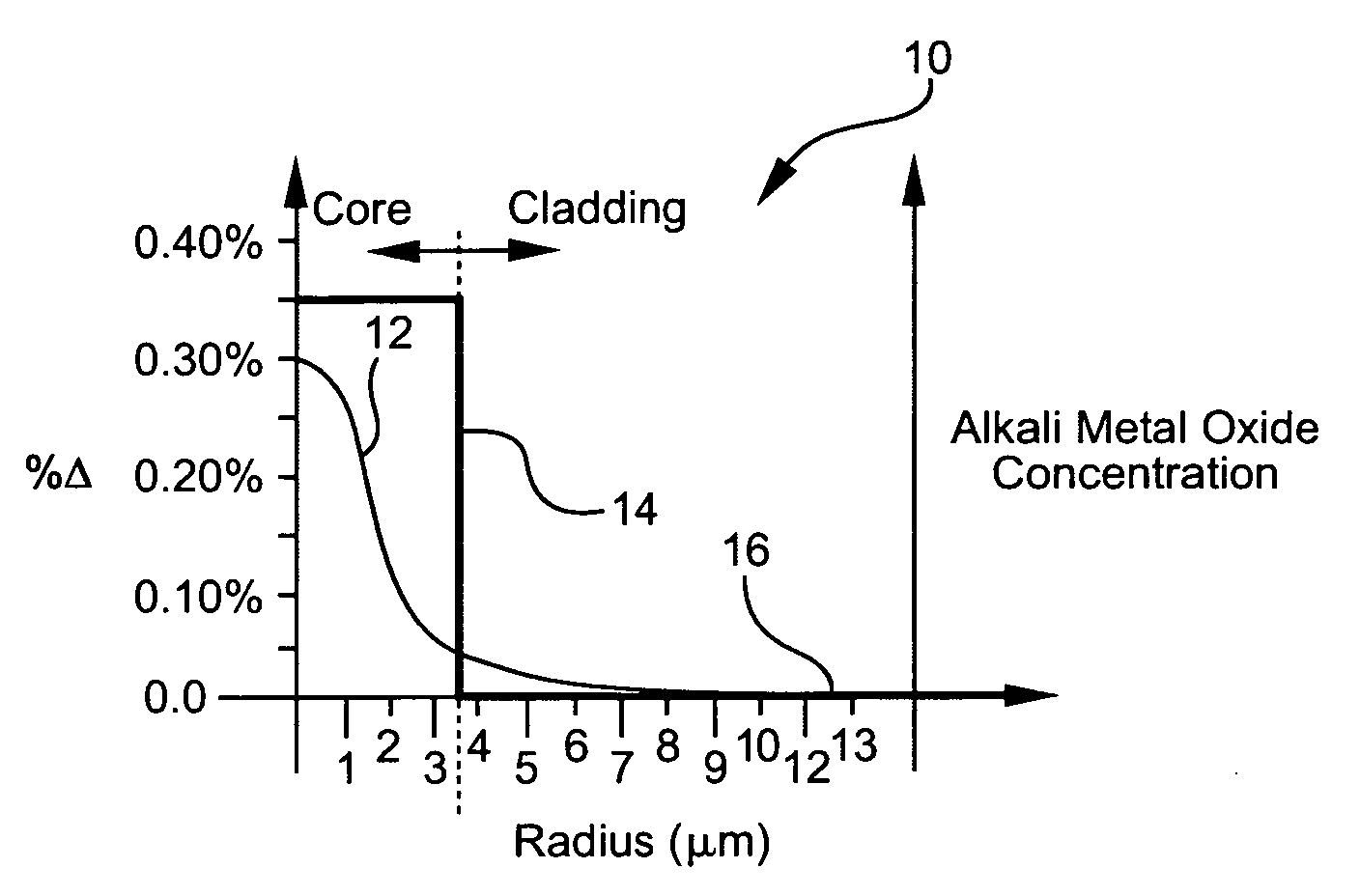
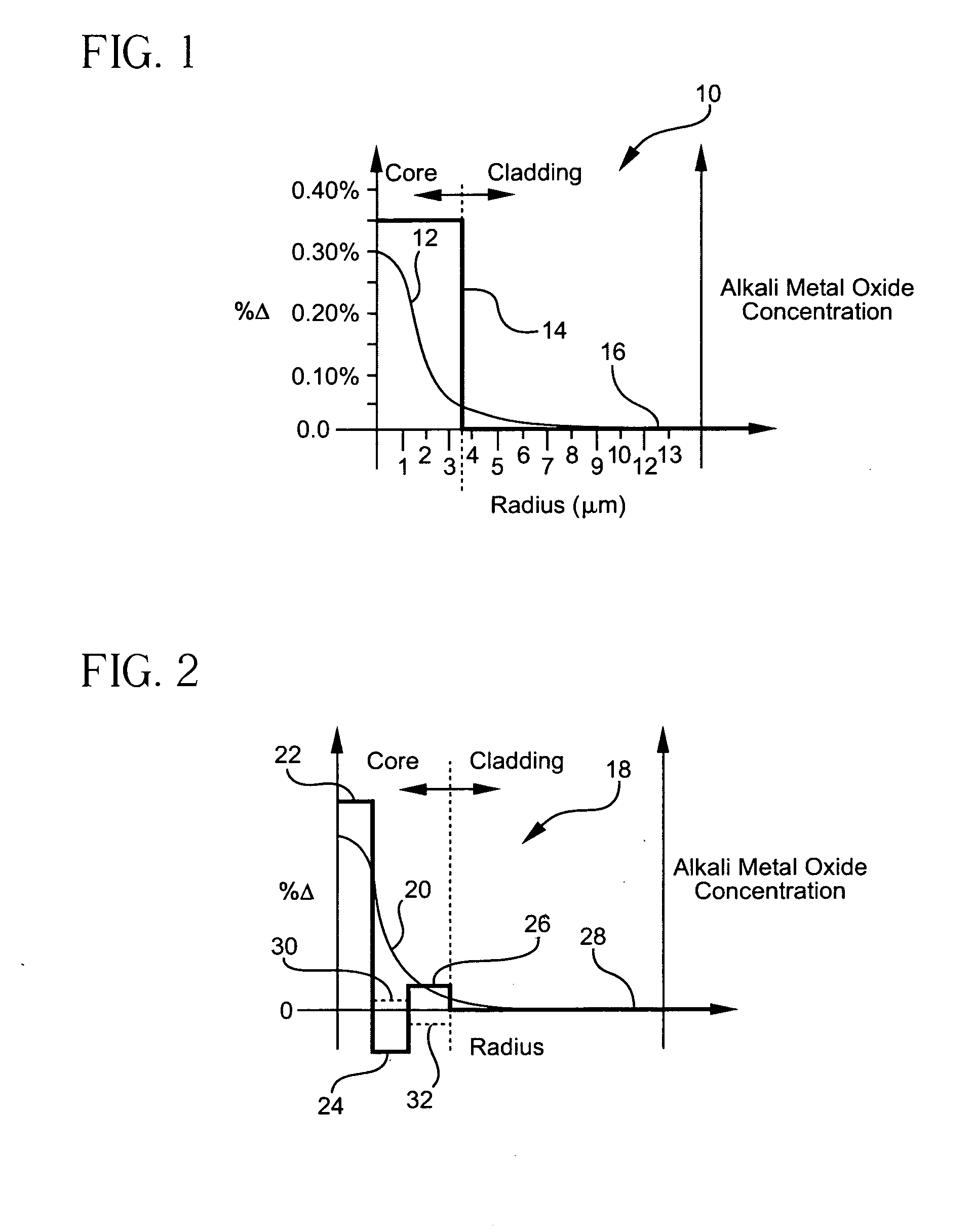
Disclosed is an optical fiber having a core with an alkali metal oxide dopant in an peak amount greater than about 0.002 wt. % and less than about 0.1 wt. %. The alkali metal oxide concentration varies with a radius of the optical fiber. By appropriately selecting the concentration of alkali metal oxide dopant in the core and the cladding, a low loss optical fiber may be obtained. Also disclosed are several methods of making the optical fiber including the steps of forming an alkali metal oxide-doped rod, and adding additional glass to form a draw perform. Preferably, the draw preform has a final outer dimension (d2), wherein an outer dimension (d1) of the rod is less than or equal to 0.06 times the final outer dimension (d2). In a preferred embodiment, the alkali metal oxide-doped rod is inserted into the centerline hole of a preform to form an assembly.
Owner:CORNING INC
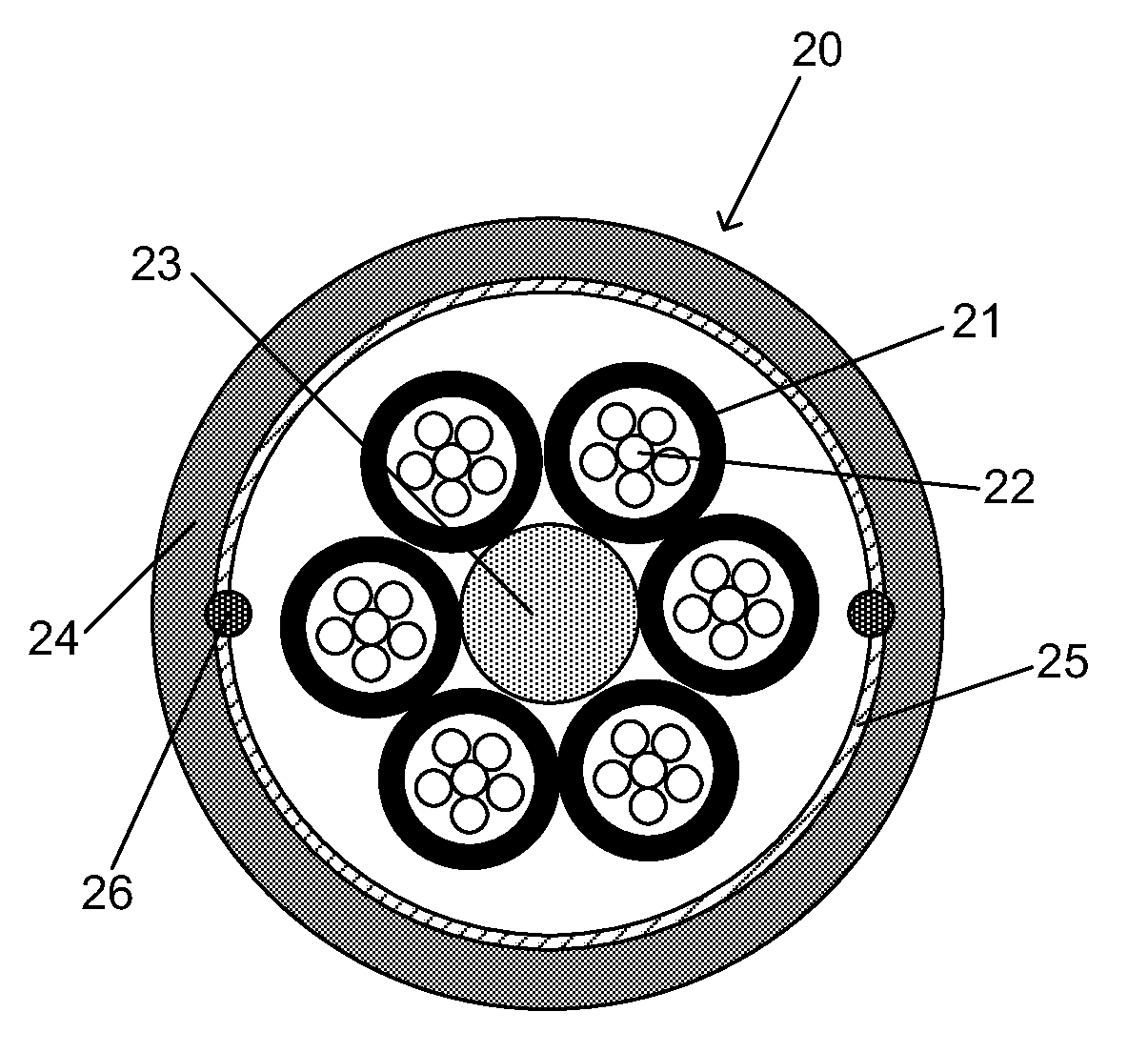
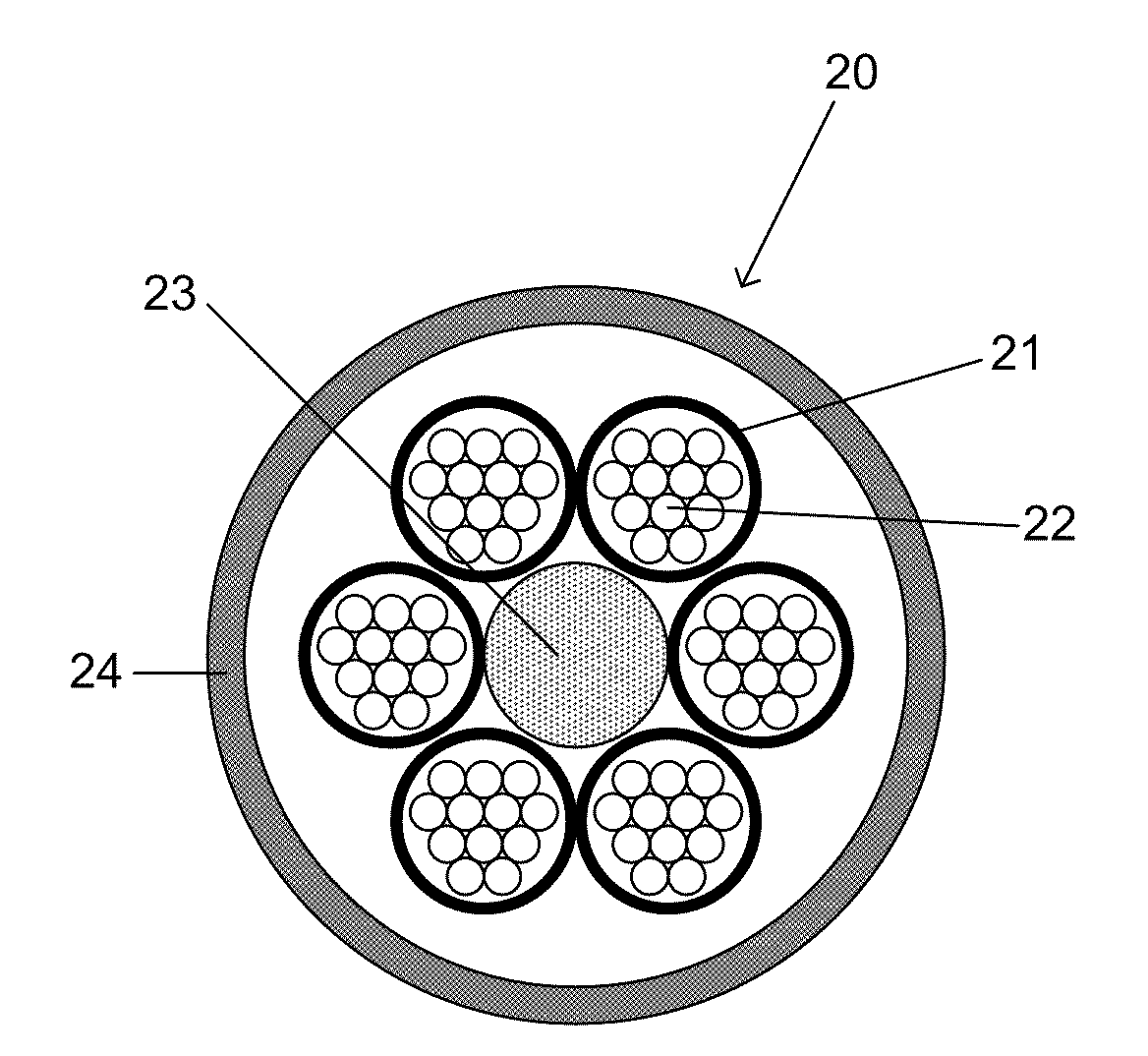
Optical-Fiber Loose Tube Cables
ActiveUS20100092140A1Improve protectionEasily matedGlass optical fibreFibre mechanical structuresGlass fiberFiber
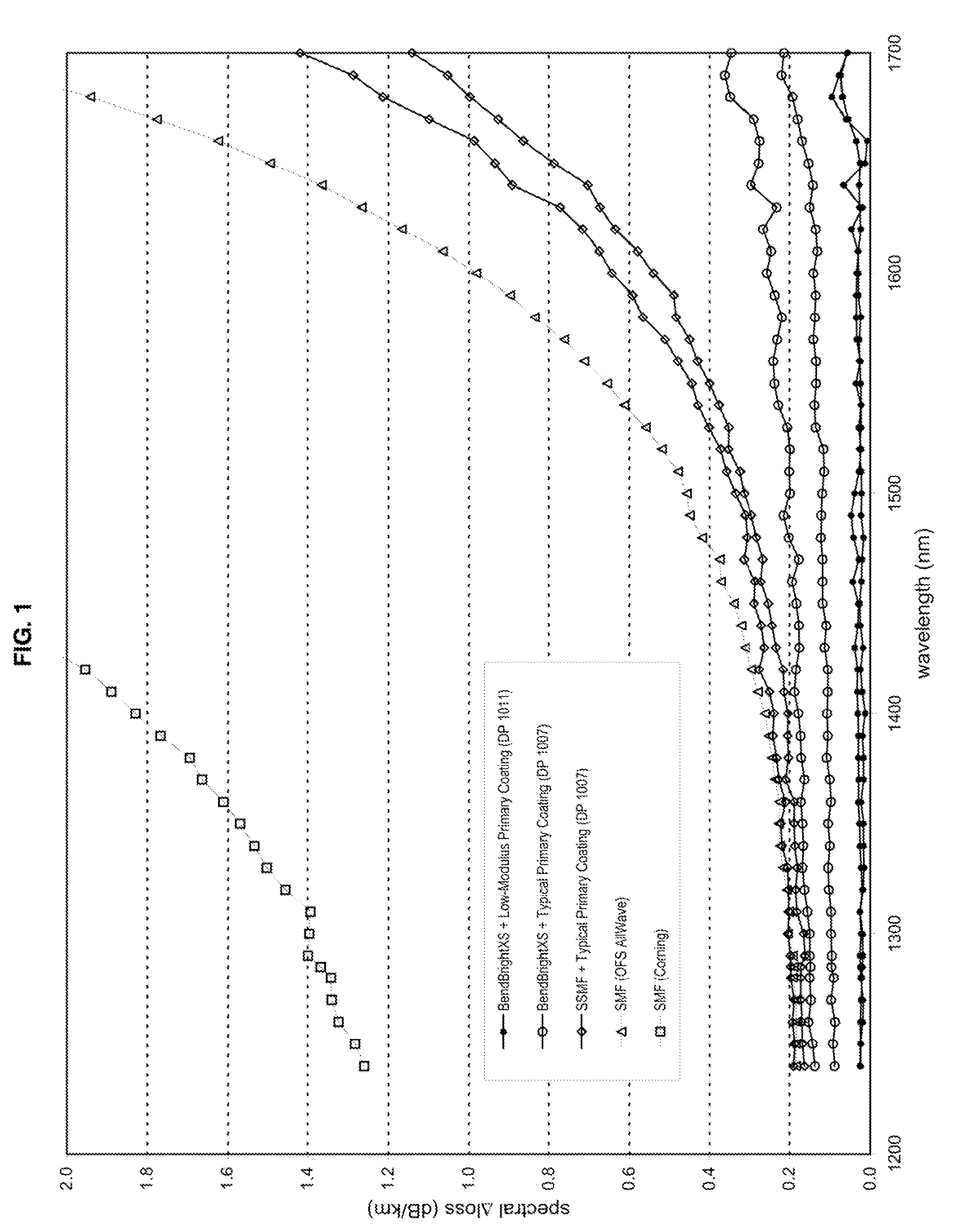
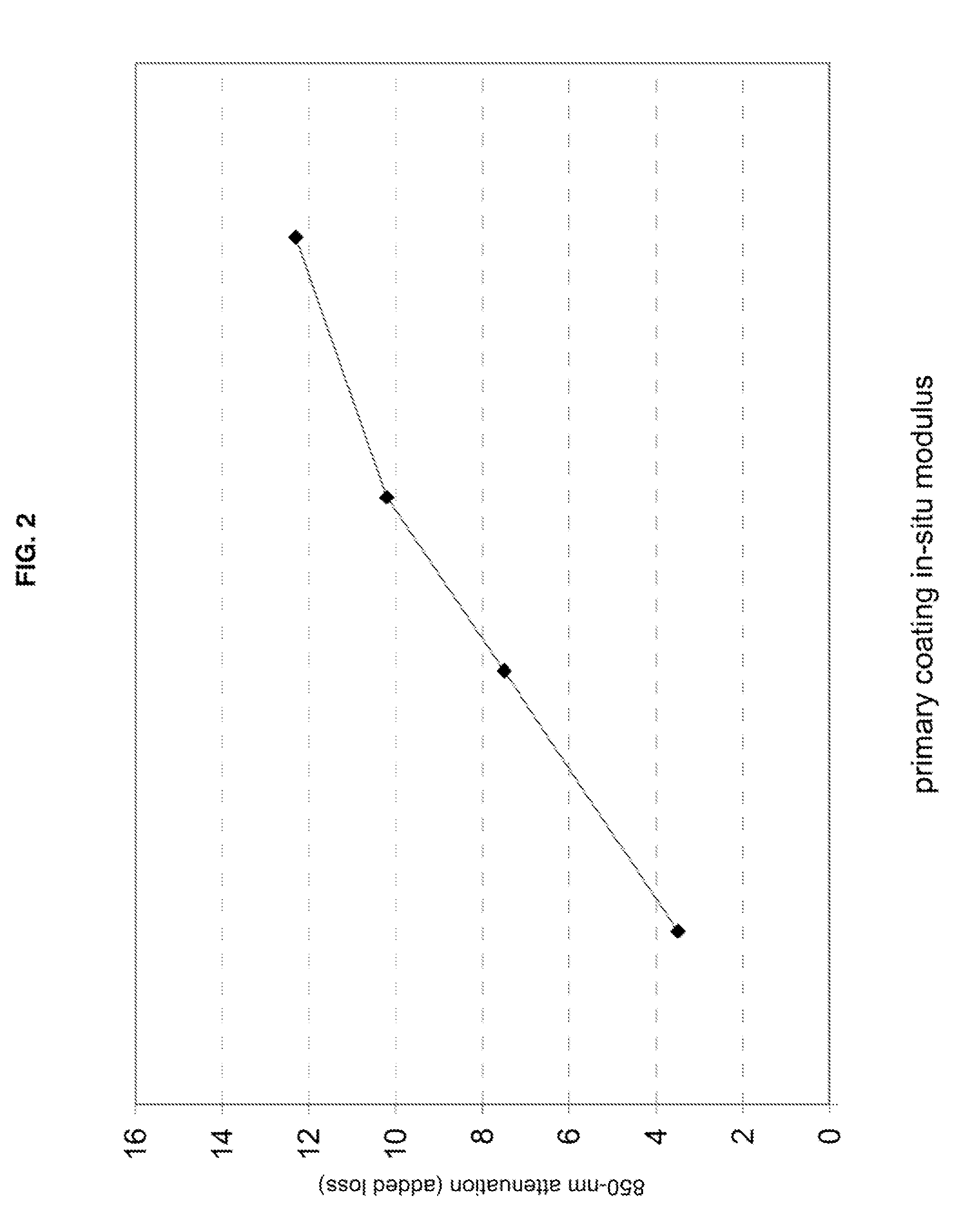
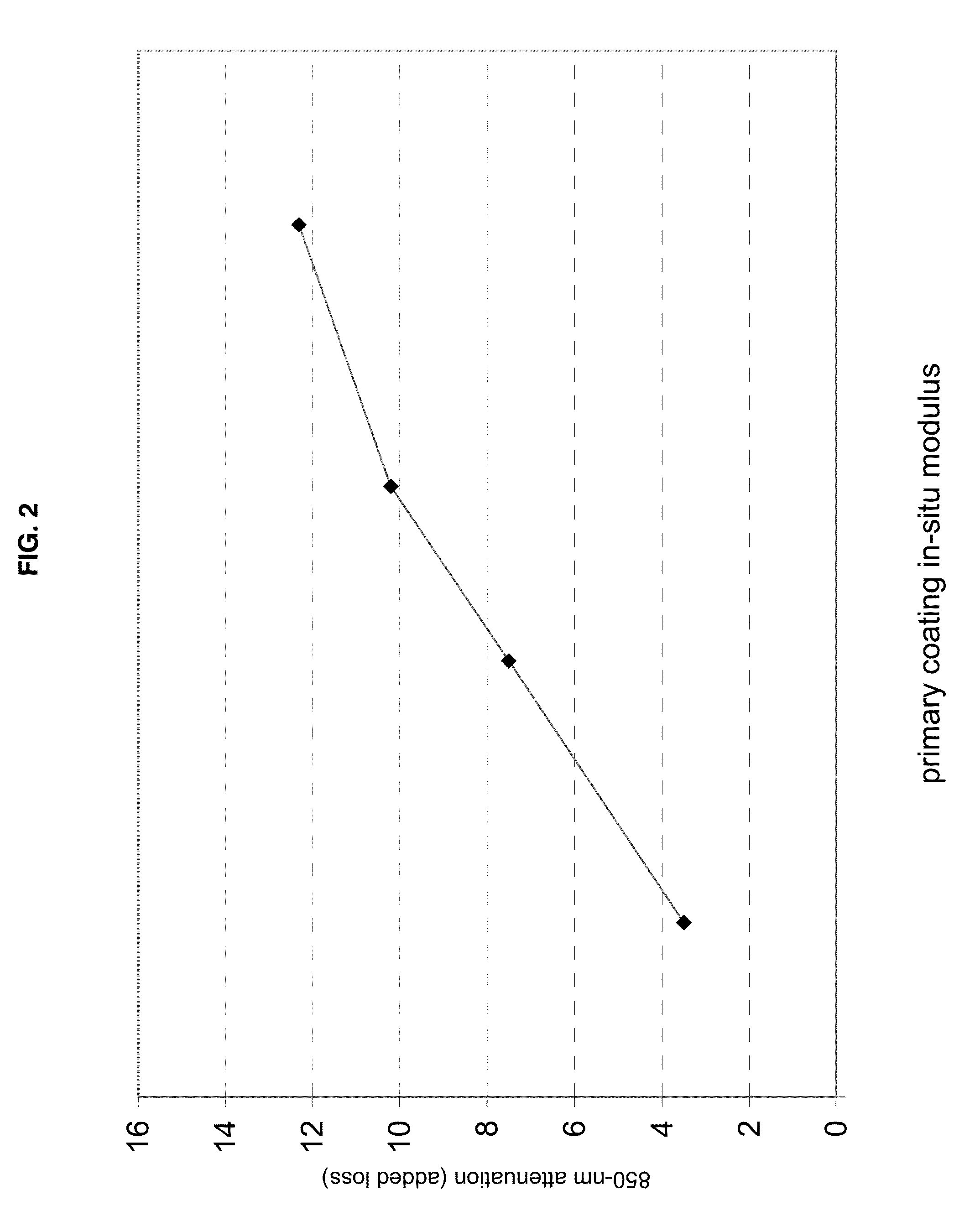
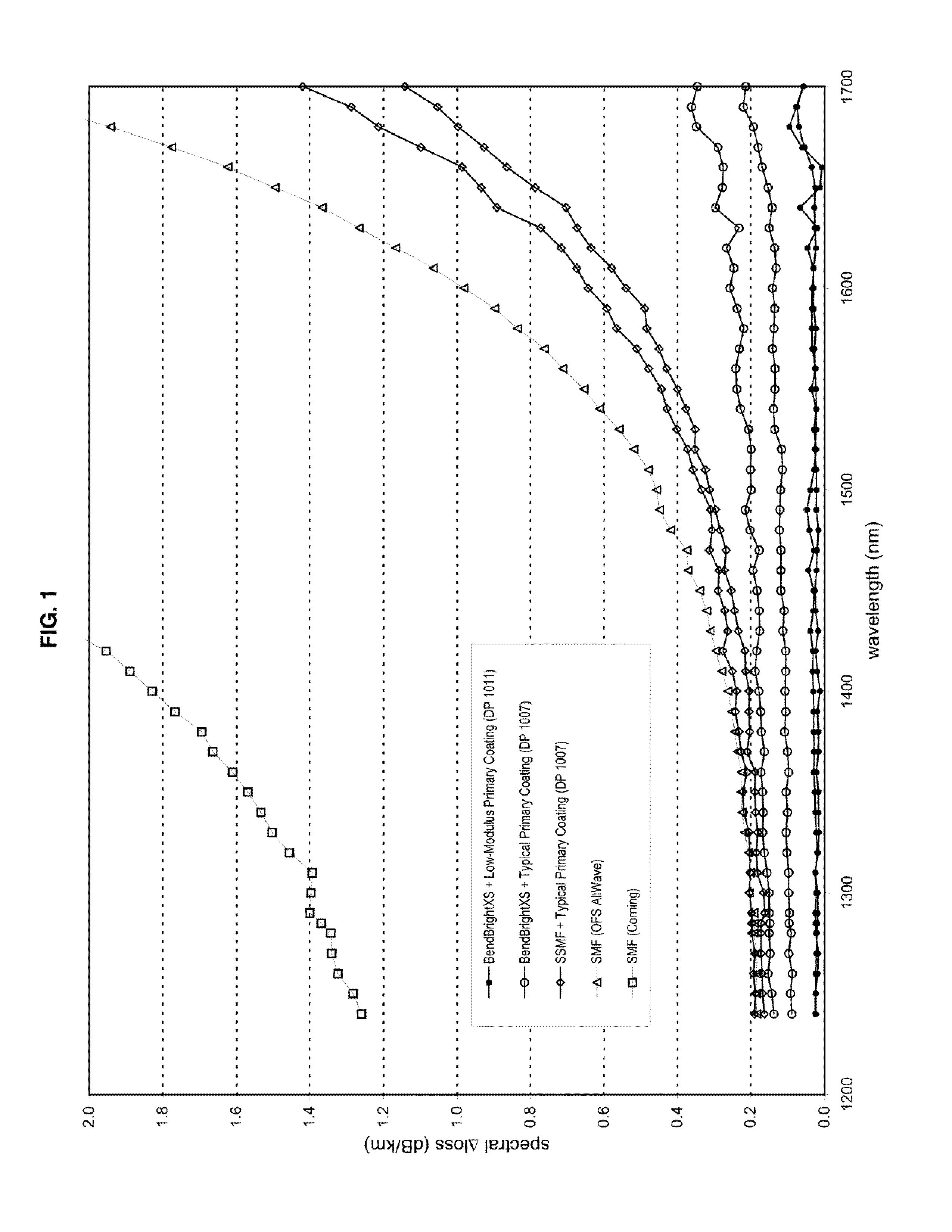
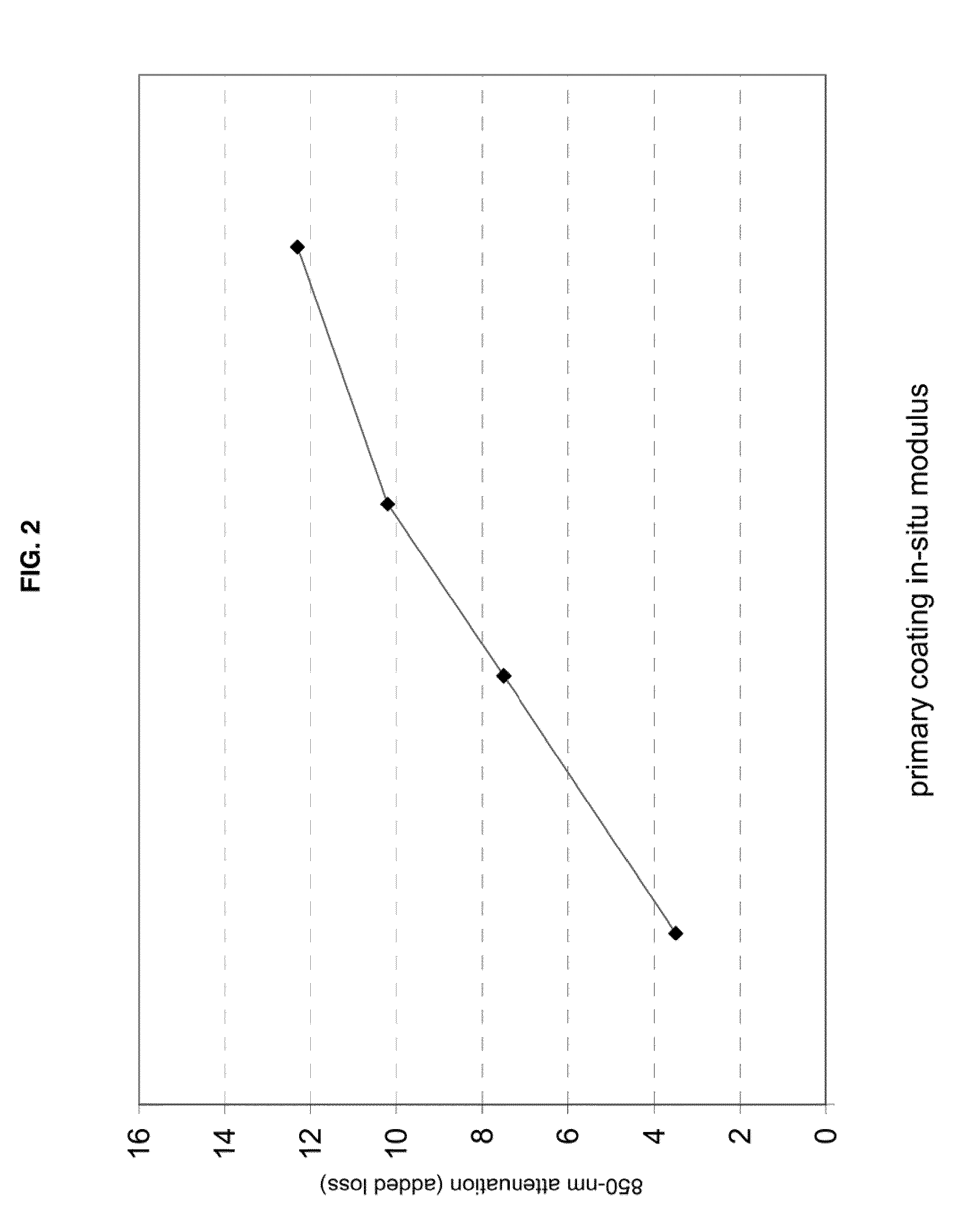
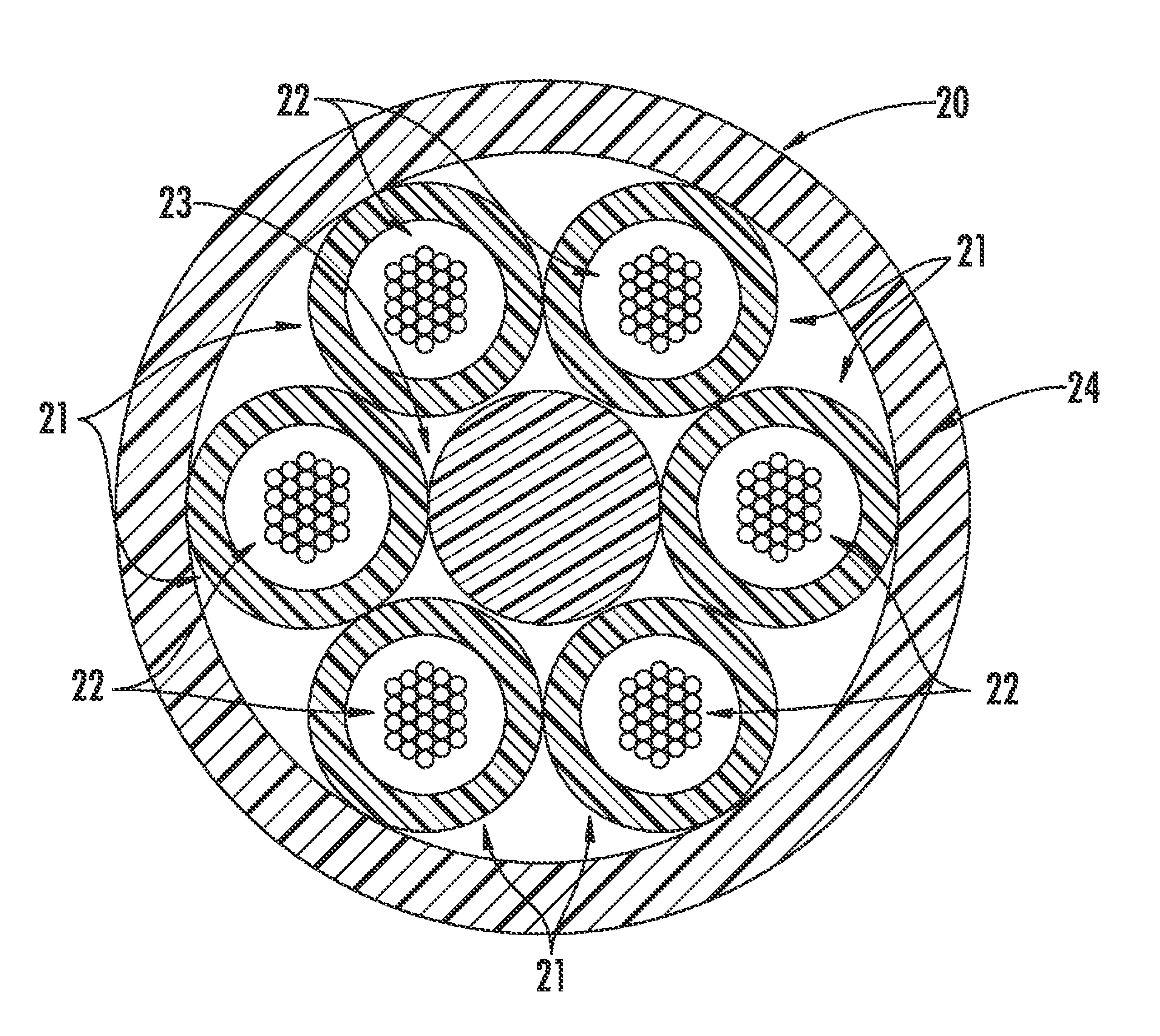
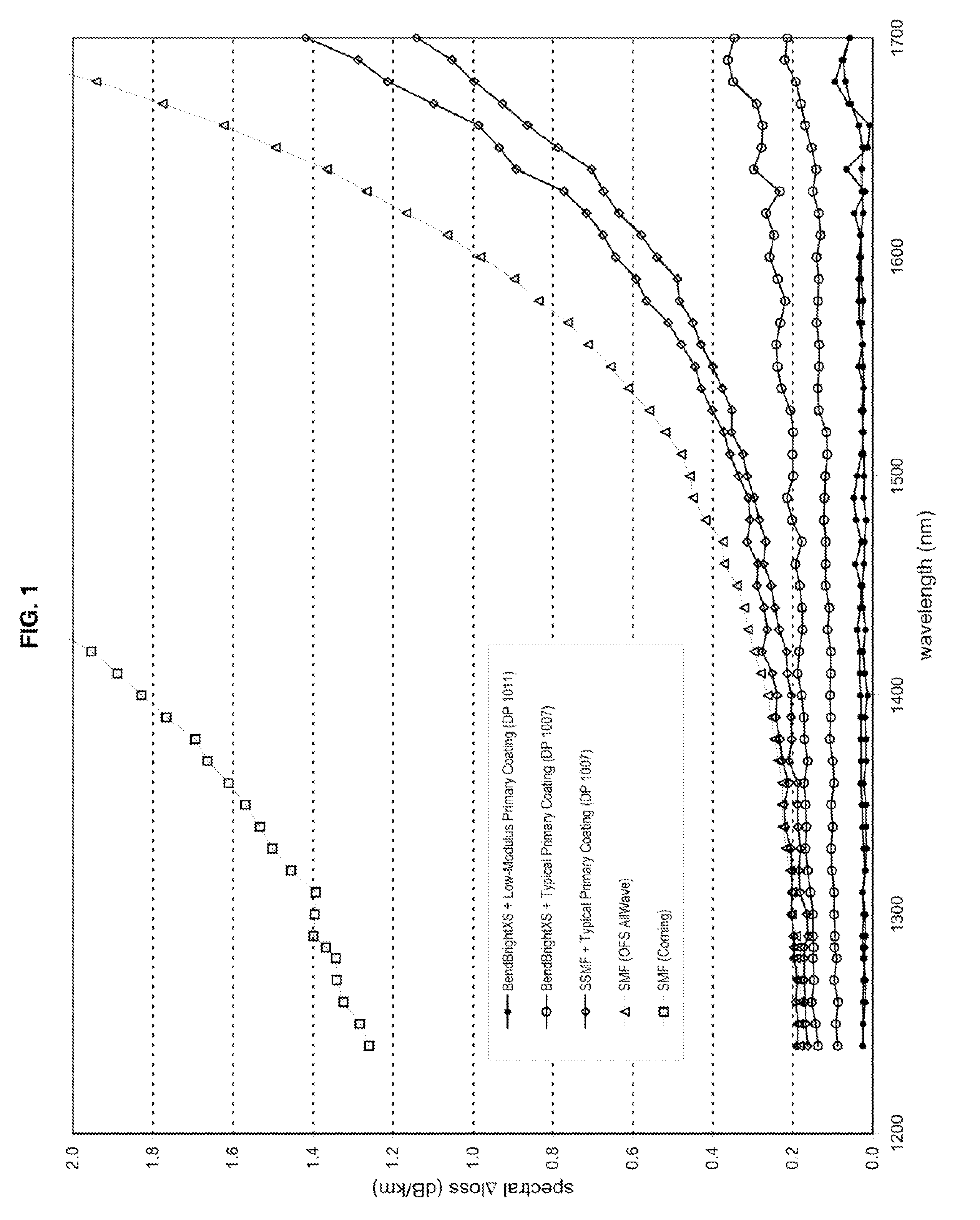
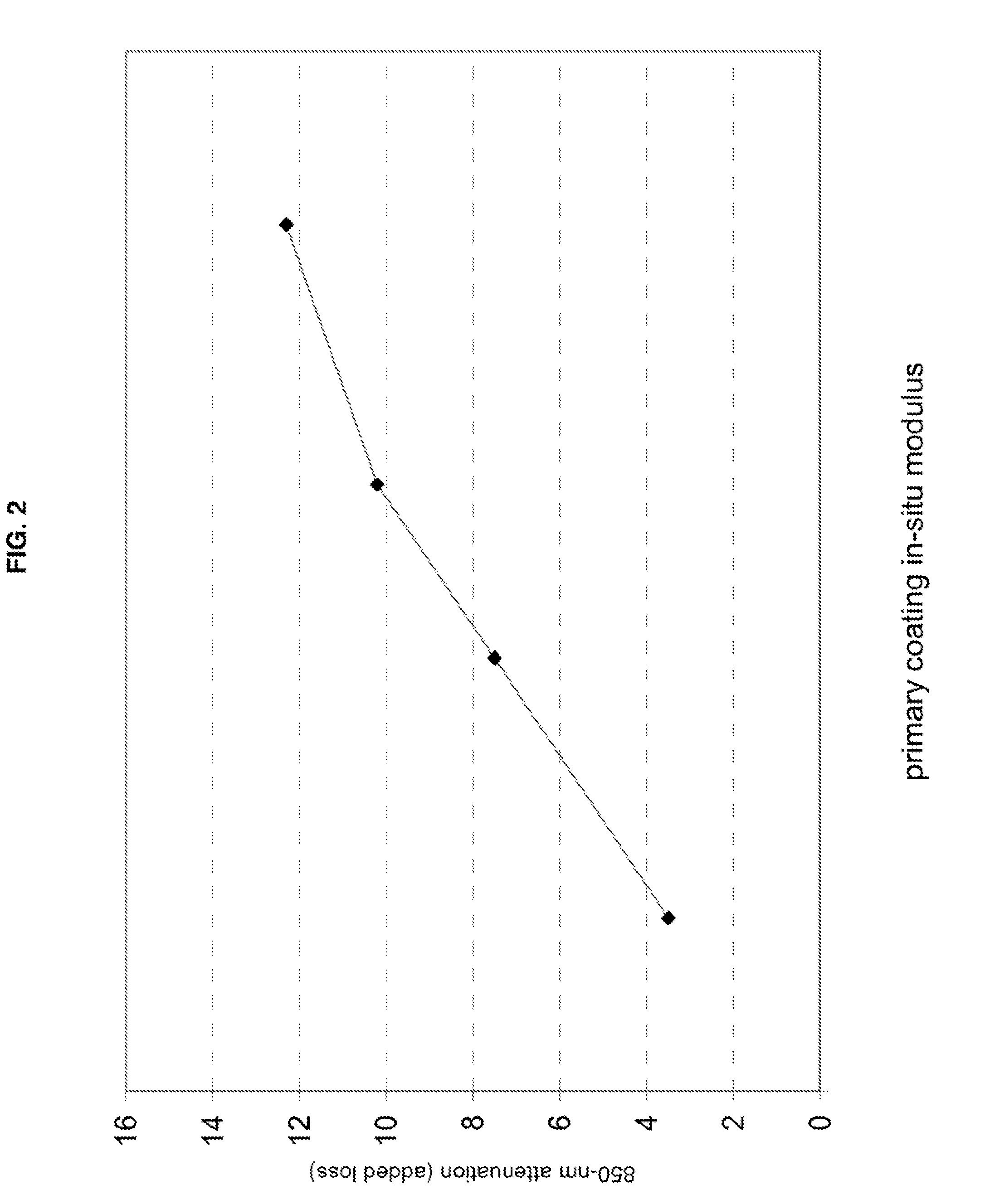
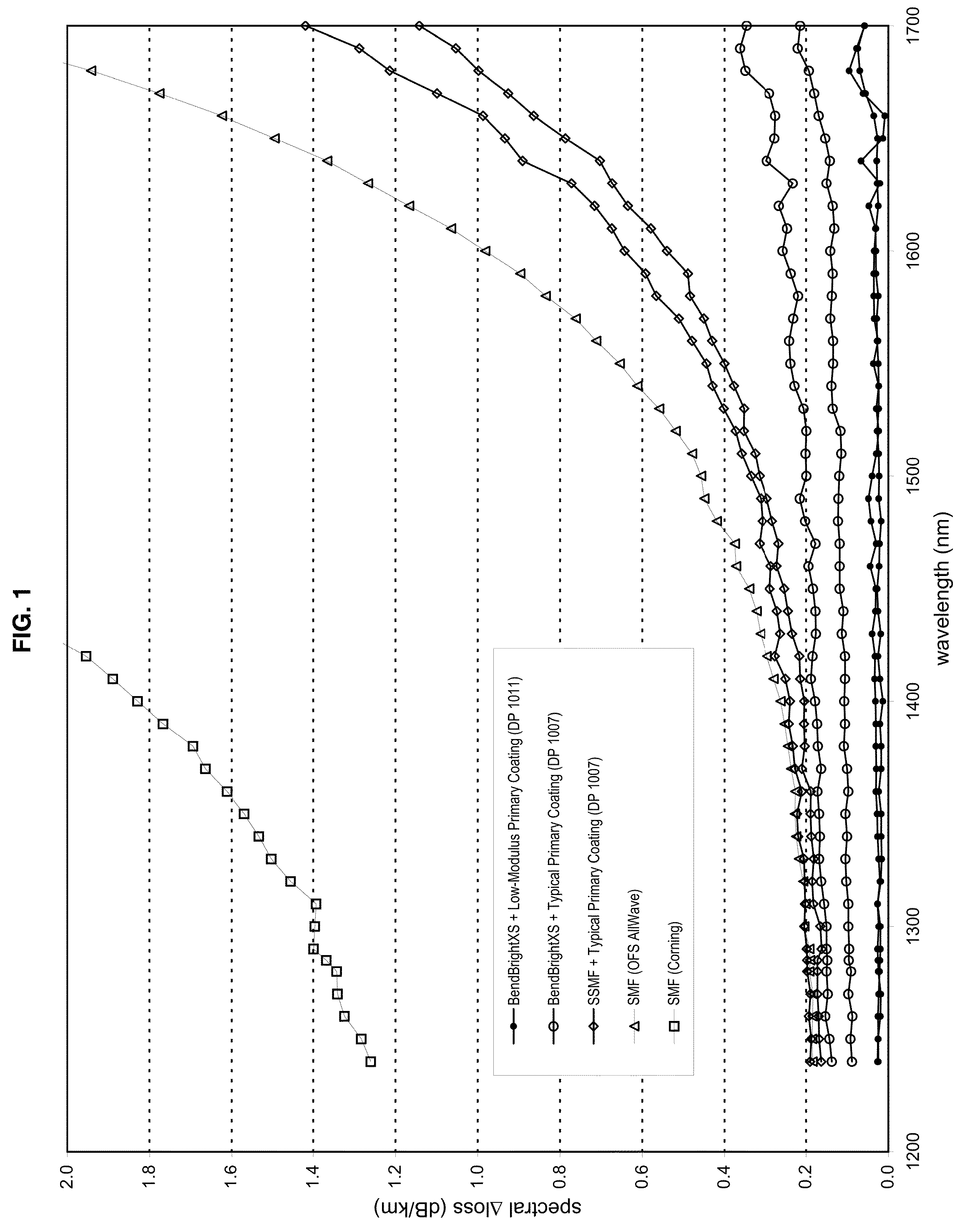
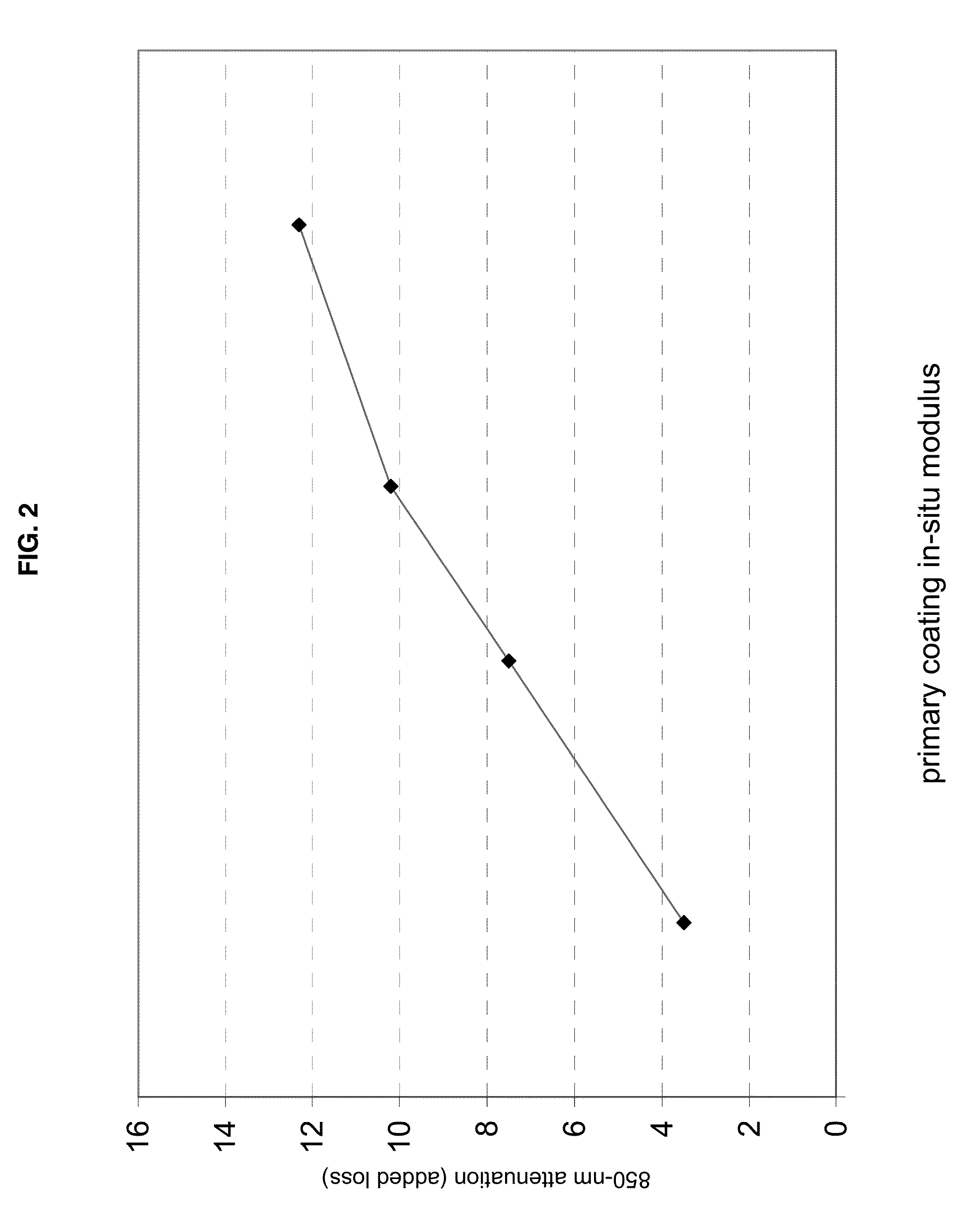
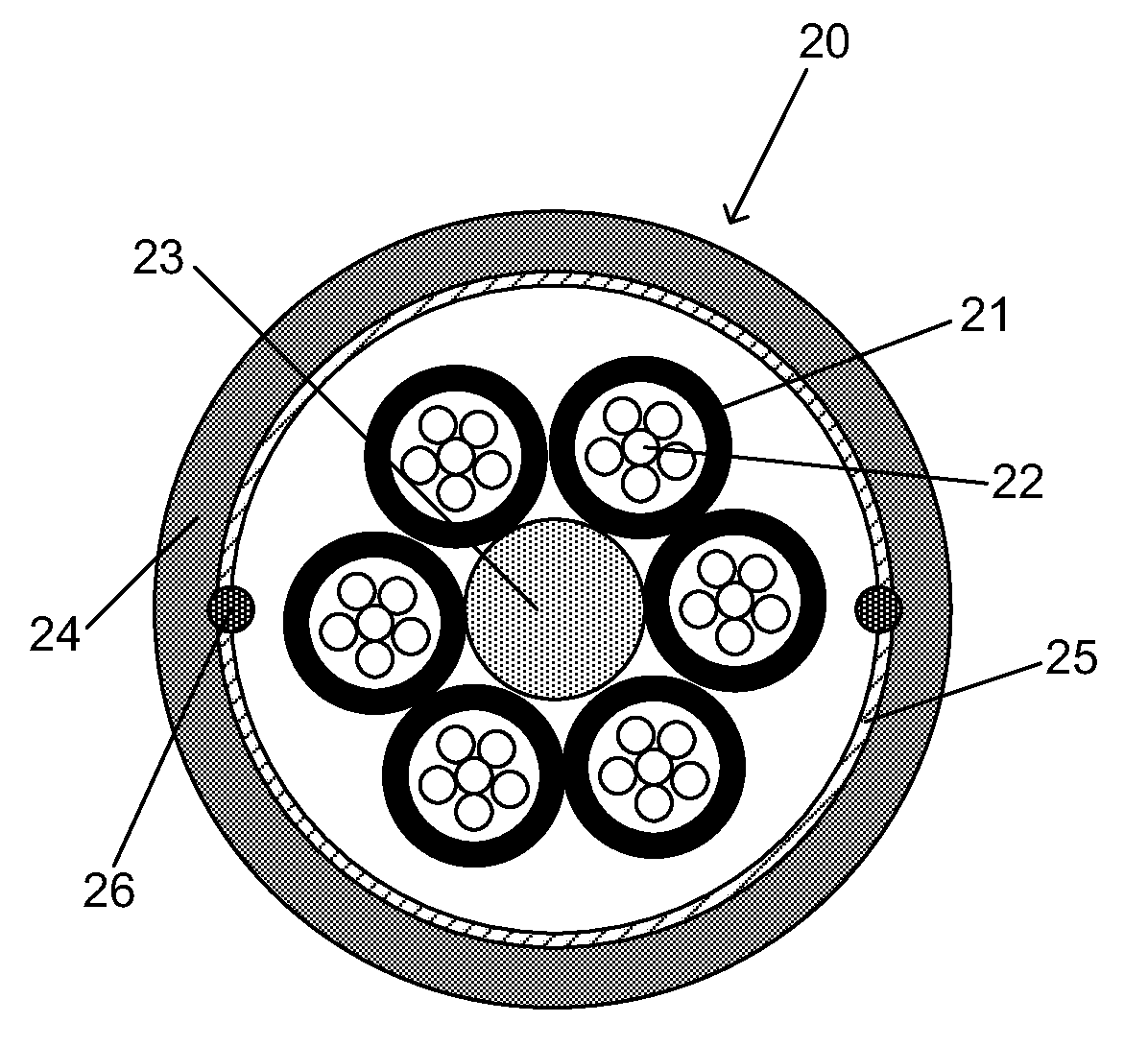
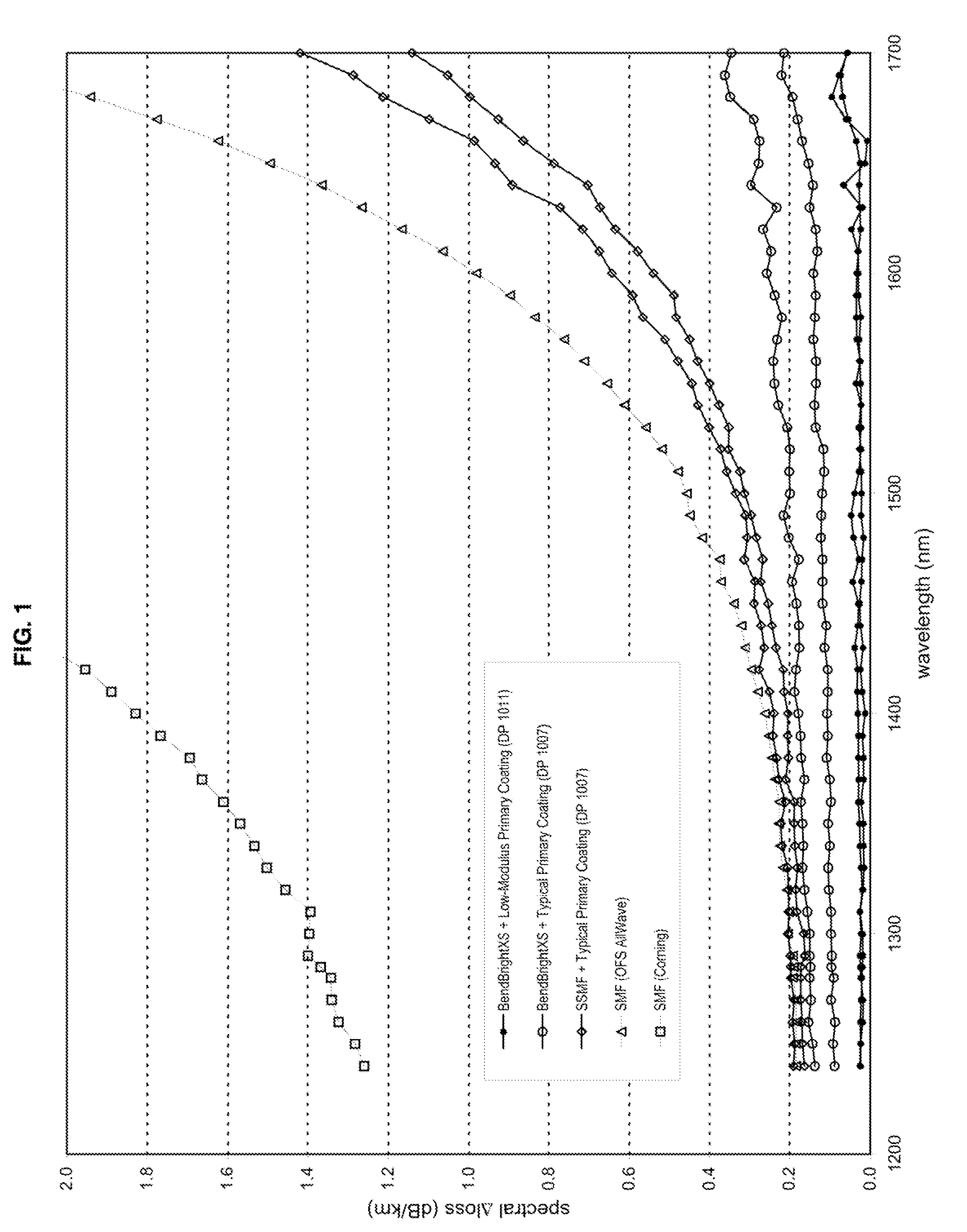
Disclosed is an improved optical fiber that employs a novel coating system. When combined with a bend-insensitive glass fiber, the novel coating system according to the present invention yields an optical fiber having exceptionally low losses.The coating system features (i) a softer primary coating with excellent low-temperature characteristics to protect against microbending in any environment and in the toughest physical situations and, optionally, (ii) a colored secondary coating possessing enhanced color strength and vividness.The improved coating system provides optical fibers that are useful in buffer tubes and cables having relatively high filling coefficients and fiber counts.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
ADSS Cables with High-Performance Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20100092138A1Improve protectionEasily matedGlass optical fibreFibre mechanical structuresGlass fiberCoating system
Disclosed is an improved optical fiber that employs a novel coating system. When combined with a bend-insensitive glass fiber, the novel coating system according to the present invention yields an optical fiber having exceptionally low losses.The coating system features (i) a softer primary coating with excellent low-temperature characteristics to protect against microbending in any environment and in the toughest physical situations and, optionally, (ii) a colored secondary coating possessing enhanced color strength and vividness.The improved coating system provides optical fibers that are useful in all-dielectric self-supporting (ADSS) cables.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Optical fiber and optical communication system including the same
InactiveUS6658190B2Increase the effective areaRestrains nonlinear optical phenomenaOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCommunications systemEngineering
The present invention relates to an optical fiber having a structure suitable for long-distance optical communications, and an optical transmission line including the same. The optical fiber in accordance with the present invention comprises a core region extending along a predetermined axis, and a cladding region disposed so as to surround the outer periphery of the core region; and, as characteristics at a wavelength of 1.55 mum, an effective area of at least 110 mum<2>, a dispersion of 18 to 23 ps / nm / km, and a dispersion slope of 0.058 to 0.066 ps / nm<2> / km.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Microbend-Resistant Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20100290781A1Improve protectionGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fiberCoating system
Disclosed is an improved, single-mode optical fiber possessing a novel coating system. When combined with a bend-insensitive glass fiber, the novel coating system according to the present invention yields an optical fiber having exceptionally low losses.The coating system features (i) a softer primary coating with excellent low-temperature characteristics to protect against microbending in any environment and in the toughest physical situations and, optionally, (ii) a colored secondary coating possessing enhanced color strength and vividness. The secondary coating provides improved ribbon characteristics for structures that are robust, yet easily entered (i.e., separated and stripped).The optional dual coating is specifically balanced for superior heat stripping in fiber ribbons, with virtually no residue left behind on the glass. This facilitates fast splicing and terminations. The improved coating system provides optical fibers that offer significant advantages for deployment in most, if not all, fiber-to-the-premises (FTTx) systems.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Reduced-diameter, easy-access loose tube cable
ActiveUS8031997B2Improve protectionEasily matedGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fiberCoating system
Disclosed is an improved optical fiber that employs a novel coating system. When combined with a bend-insensitive glass fiber, the novel coating system according to the present invention yields an optical fiber having exceptionally low losses. The coating system features (i) a softer primary coating with excellent low-temperature characteristics to protect against microbending in any environment and in the toughest physical situations and, optionally, (ii) a colored secondary coating possessing enhanced color strength and vividness. The improved coating system provides optical fibers that are useful in relatively thin-walled, low-modulus buffer tubes (i.e., “flextubes”) that can be readily accessed without special tools.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Optical-fiber loose tube cables
ActiveUS8041167B2Improve protectionEasily matedGlass optical fibreFibre mechanical structuresGlass fiberFiber
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Microbend-resistant optical fiber
ActiveUS8145027B2Improve protectionGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fiberCoating system
Disclosed is an improved, single-mode optical fiber possessing a novel coating system. When combined with a bend-insensitive glass fiber, the novel coating system according to the present invention yields an optical fiber having exceptionally low losses.The coating system features (i) a softer primary coating with excellent low-temperature characteristics to protect against microbending in any environment and in the toughest physical situations and, optionally, (ii) a colored secondary coating possessing enhanced color strength and vividness. The secondary coating provides improved ribbon characteristics for structures that are robust, yet easily entered (i.e., separated and stripped).The optional dual coating is specifically balanced for superior heat stripping in fiber ribbons, with virtually no residue left behind on the glass. This facilitates fast splicing and terminations. The improved coating system provides optical fibers that offer significant advantages for deployment in most, if not all, fiber-to-the-premises (FTTx) systems.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
ADSS cables with high-performance optical fiber
ActiveUS8165439B2Improve protectionEasily matedGlass optical fibreFibre mechanical structuresGlass fiberCoating system
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Dispersion-compensating optical fiber, and, optical transmission line and dispersion-compensating module respectively including the same
InactiveUS6477306B2Improve scalabilityAvoid it happening againOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingLength waveDispersion compensation
The invention is directed to a dispersion-compensating optical fiber which can compensate for the chromatic dispersion and dispersion slope of a non-zero dispersion-shifted optical fiber by a short length. The dispersion-shifted optical fiber constitutes an optical transmission line together with a dispersion-compensating optical fiber fusion-spliced thereto. The dispersion-compensating optical fiber has, at a wavelength of 1550 nm, a chromatic dispersion DDCF of -40 ps / nm / km or less and a ratio (DDCF / SDCF) of dispersion slope SDCF to the chromatic dispersion DDCF of 0.005 / nm or more.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Compensating fiber for cumulated chromatic dispersion and chromatic dispersion slope
InactiveUS7440662B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingMultimode transmissionFiberLength wave
A multimode fiber having an index profile such that, for a propagation mode other than the fundamental mode and at a wavelength of 1550 nm, the fiber presents a positive chromatic dispersion greater than or equal to 50 ps / run / km, a positive chromatic dispersion slope and a figure of merit (FOM) greater than or equal to 200 ps / run / dB.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
High performance dispersion compensating optical fibers and manufacturing method for the same
ActiveUS6925239B2Eigen attenuation of the optical fiber can be decreasedImprove optical efficiencyOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass reforming apparatusEngineeringSilicon dioxide
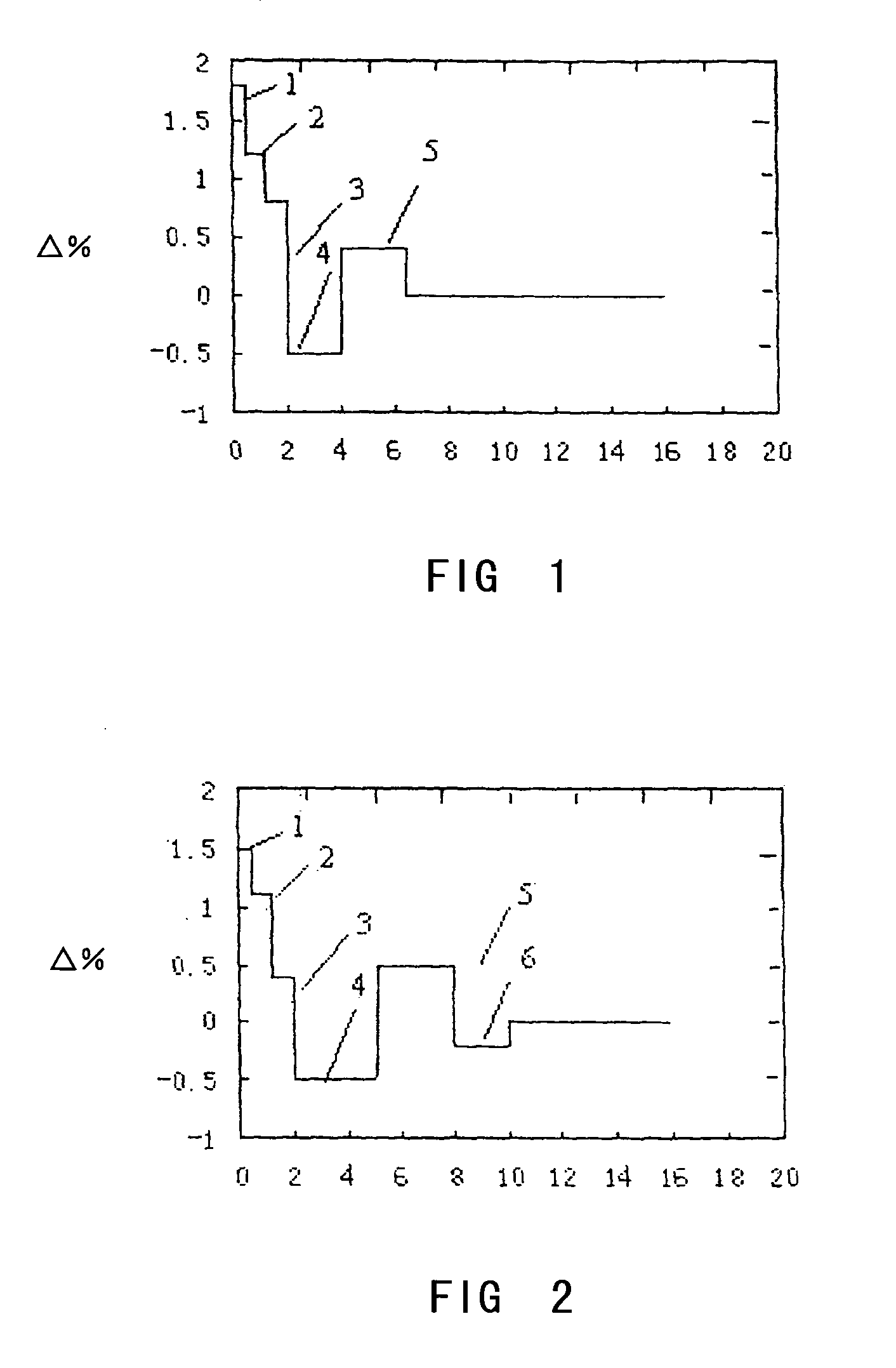
A high performance dispersion compensating optical fiber is provided. In one embodiment, the optical fiber includes a core layer and a cladding layer surrounding the core layer. The core layer includes five core sublayers wherein the □% of the first core sublayer is positive, and the □% of at least one of the other core sublayers is negative, the radius ranges of the respective core sublayers beginning outwardly from the first core sublayer are 0.6 to 0.8 μm, 1.0 to 1.2 μm, 1.6 to 2.0 μm, 5.0 to 6.0 μm, and 7.0 to 8.0 μm, respectively; the ranges of □% of the respective sublayers beginning outwardly from the first core sublayer are about 1.8 to 2.1%, 1.2 to 1.4%, 0.6 to 1%, −0.4 to −0.6% and 0.2 to 0.4%, and the cladding layer is a pure Silicon Dioxide glass layer.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Dispersion compensated optical fiber transmission system and module including micro-structured optical fiber
InactiveUS6993228B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesEngineeringOptical fiber transmission
Disclosed is an optical transmission system and module which includes a negative dispersion, dispersion compensating optical fiber coupled to a micro-structured optical fiber (such as band gap fiber, photonic crystal fiber or holey fiber) for compensating for the accumulated dispersion in a transmission fiber. The optical transmission system and module in accordance with the invention provides substantially equal compensation of total dispersion over an operating wavelength band, reduced overall system length, and lower insertion loss.
Owner:CORNING INC
Dispersion-managed cable for raman-assisted transmission
InactiveUS6943935B2Reduce power lossGlass making apparatusLaser using scattering effectsFiberEngineering
An apparatus for transporting an optical signal is provided. The apparatus includes sections of optical fiber span with at least one section negative dispersion, negative slope fiber positioned at a distance from the output. A pump light emitting device optically coupled to the optical fiber span near the output is provided for generating an amplification signal.
Owner:CORNING INC
Dispersion-managed cable for raman-assisted transmission
An apparatus for transporting an optical signal is provided. The apparatus includes sections of optical fiber span with at least one section negative dispersion, negative slope fiber positioned at a distance from the output. A pump light emitting device optically coupled to the optical fiber span near the output is provided for generating an amplification signal.
Owner:CORNING INC
Dispersion-compensating optical fiber, and, optical transmission line and dispersion-compensating module respectively including the same
InactiveUS20010033724A1Improve scalabilityAvoid it happening againOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingLength waveDispersion compensation
The invention is directed to a dispersion-compensating optical fiber which can compensate for the chromatic dispersion and dispersion slope of a non-zero dispersion-shifted optical fiber by a short length. The dispersion-shifted optical fiber constitutes an optical transmission line together with a dispersion-compensating optical fiber fusion-spliced thereto. The dispersion-compensating optical fiber has, at a wavelength of 1550 nm, a chromatic dispersion DDCF of -40 ps / nm / km or less and a ratio (DDCF / SDCF) of dispersion slope SDCF to the chromatic dispersion DDCF of 0.005 / nm or more.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Optical fiber and optical device using the same
ActiveUS20070053641A1Easy to adjust dispersion characteristicReduce the valueLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingZero-dispersion wavelengthComputational physics
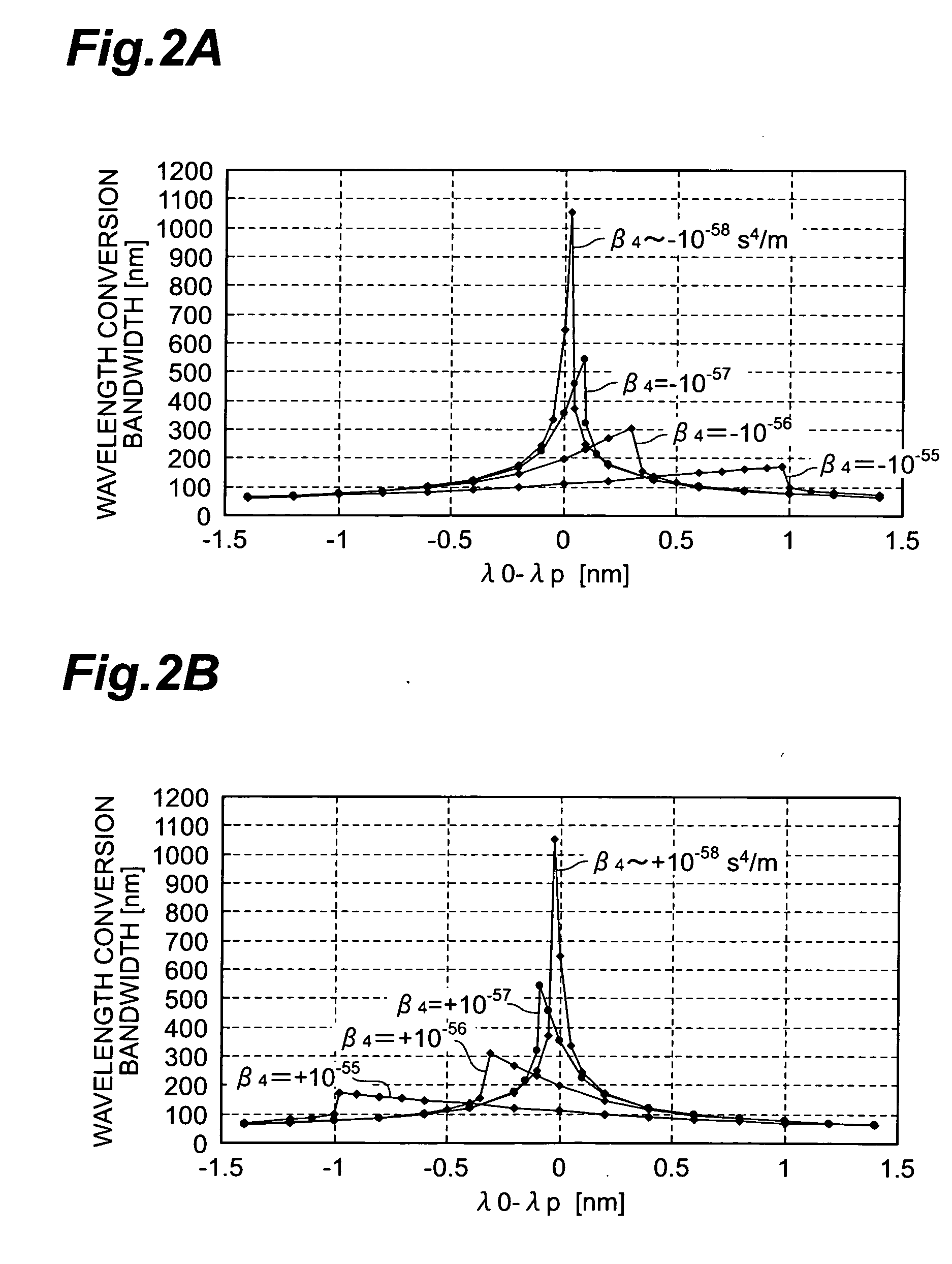
There is disclosed an optical fiber wherein an absolute value of the fourth order dispersion β4 of fourth derivative β4 of propagation constant β with respect to angular frequency ω at a mean zero dispersion wavelength λ0 in an overall length is not more than 5×10−56 s4 / m and wherein a fluctuation of a zero dispersion wavelength along a longitudinal direction is not more than ±0.6 nm.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Optical fiber
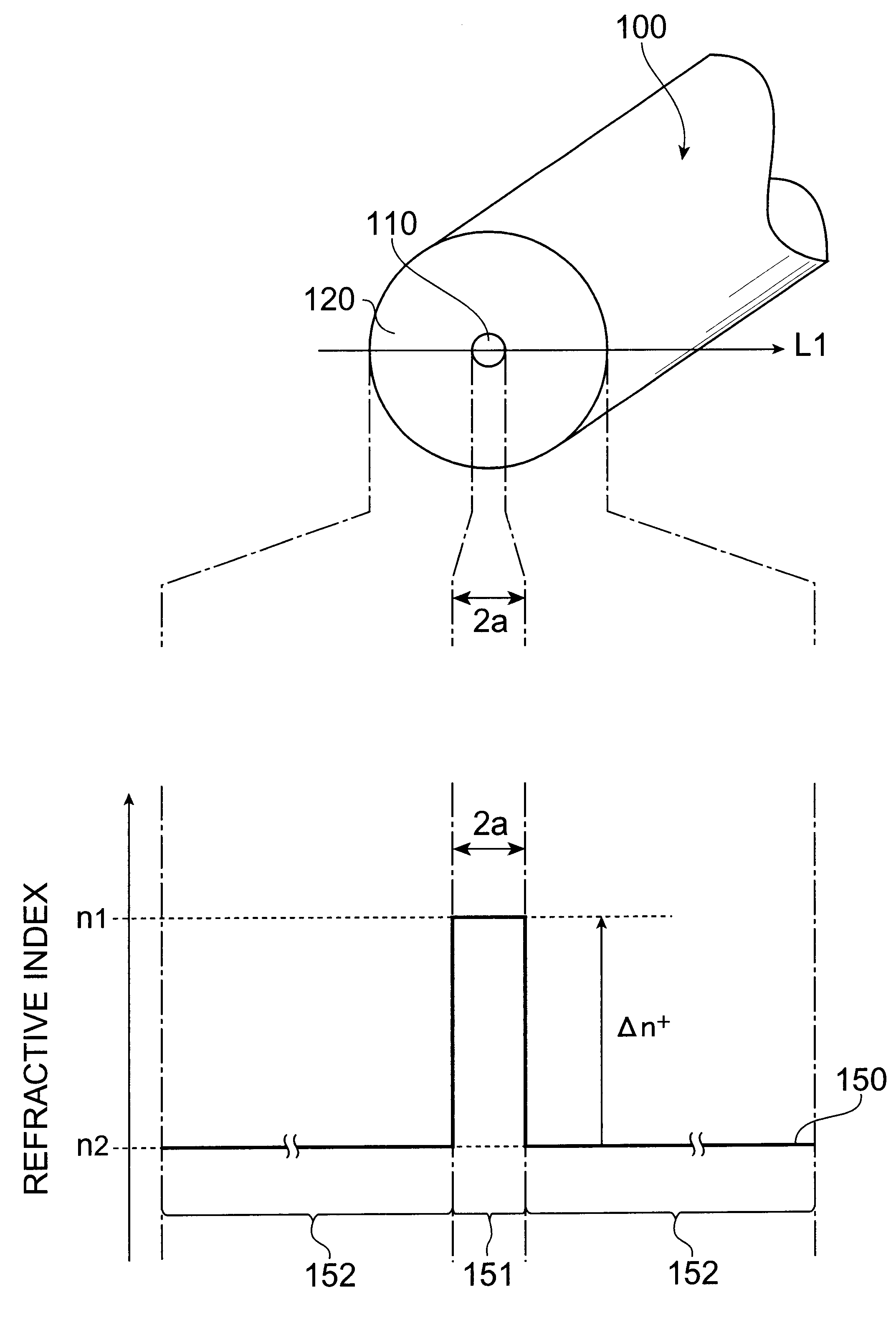
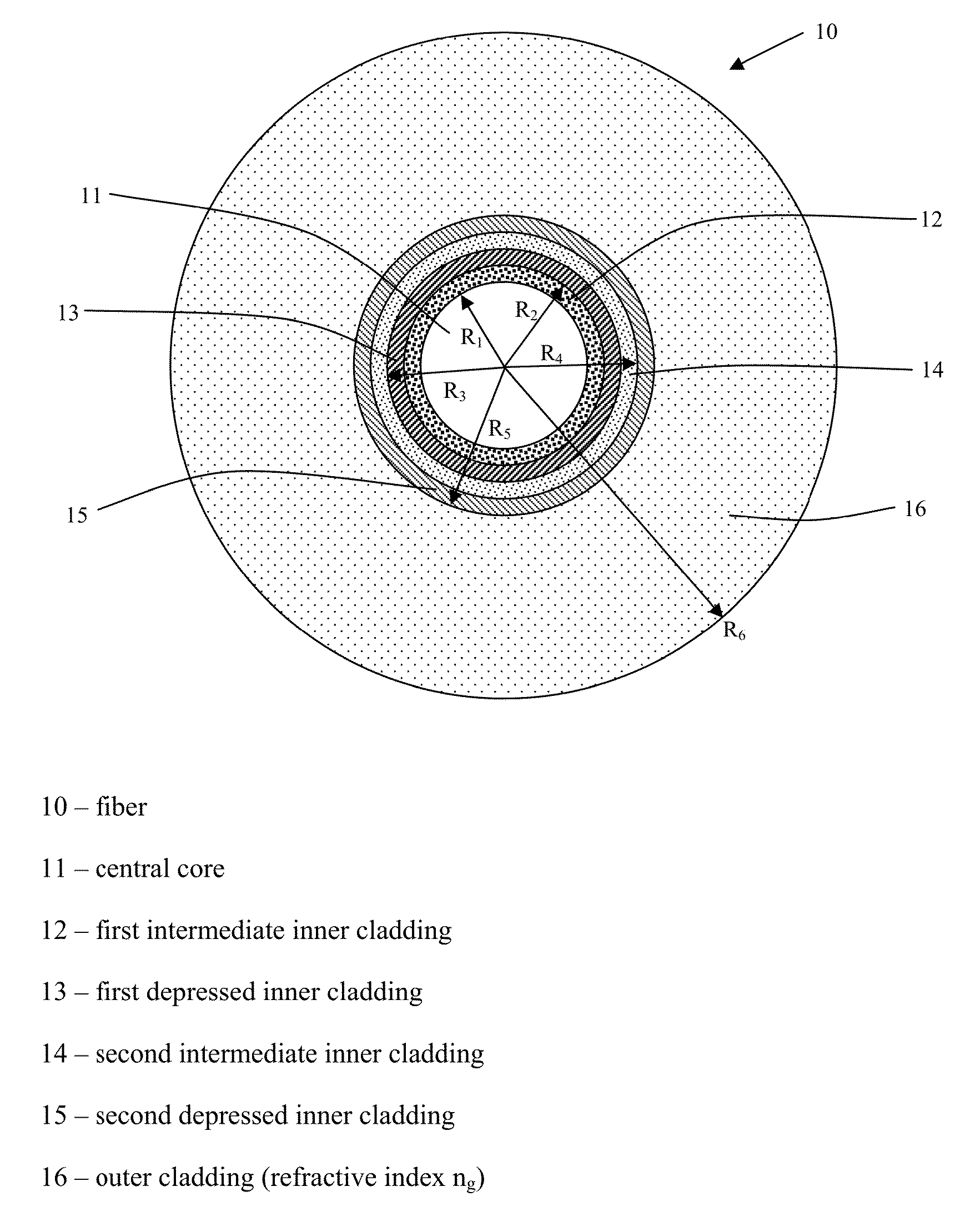
InactiveUS20010055455A1Lowering of the bending lossLower the bending lossOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexOptical fiber cable
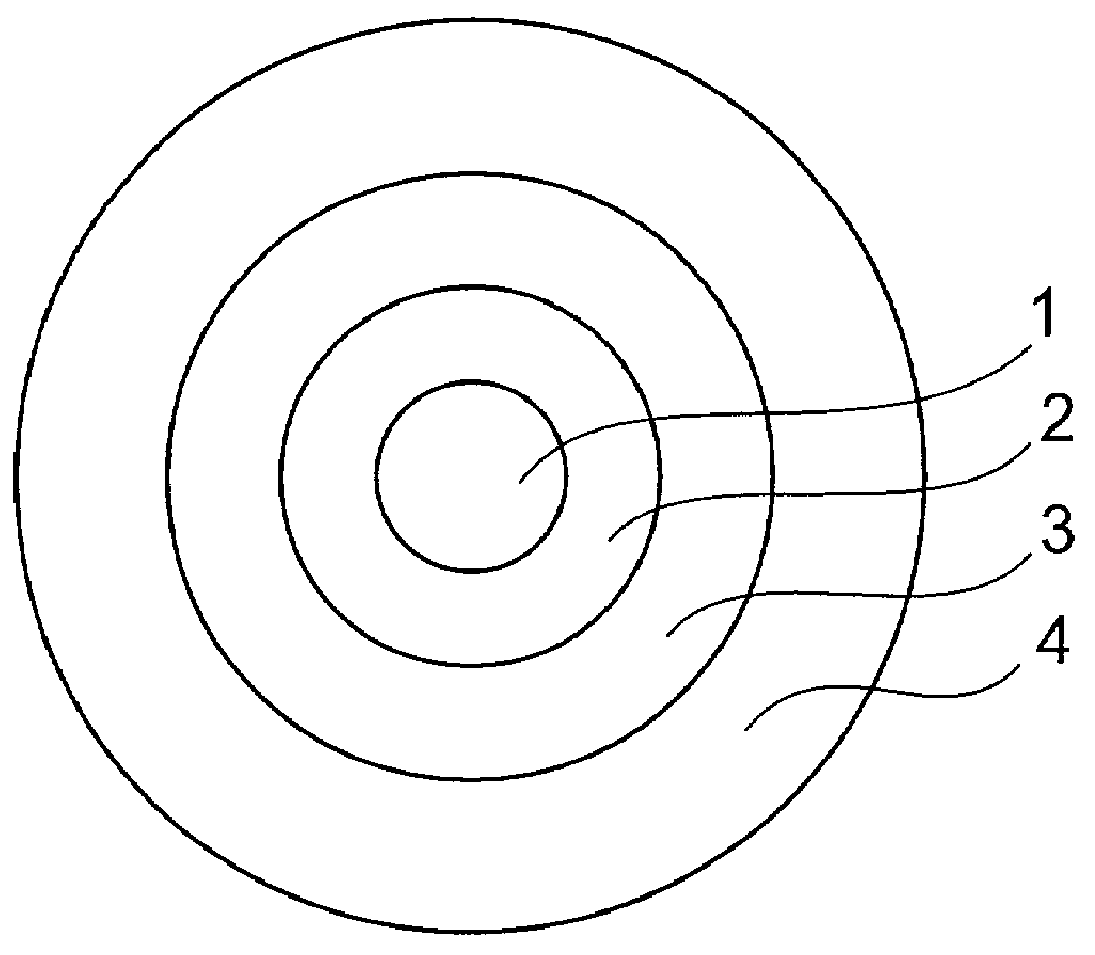
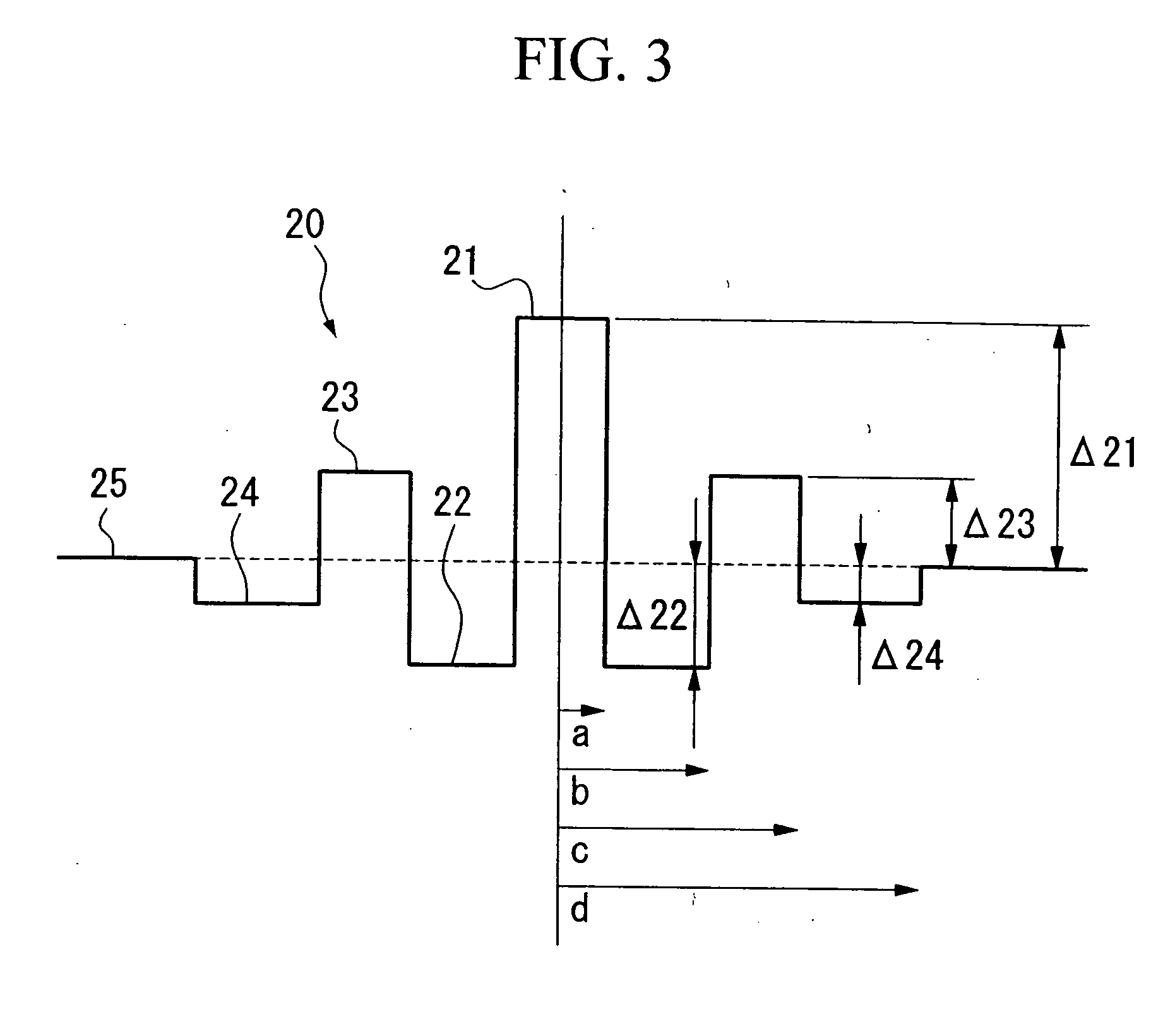
In an optical fiber including a core region and cladding regions of not less than three layers which surround the core region in order, at least one of the cladding regions has lower mean refractive index than both adjacent regions, and at least one cladding region is provided with a plurality of sub medium regions each having a refractive index lower than a main medium constituting this cladding region.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Dispersion-compensating optical fiber and hybrid transmission line
InactiveUS20040234219A1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideDispersion compensationWavelength range
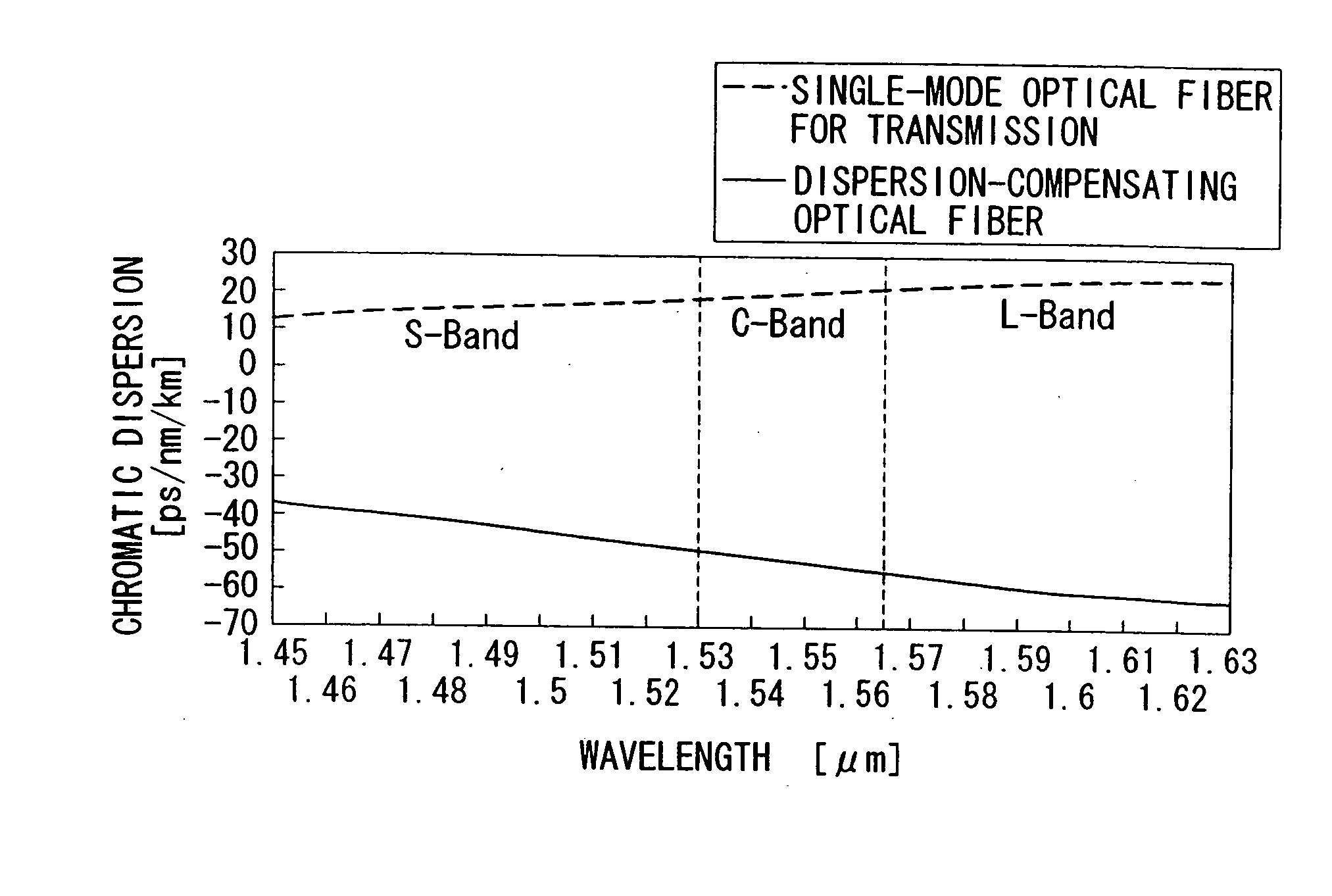
In order to provide a dispersion-compensating optical fiber able to be applied over a broad wavelength band, having a large effective area, and as a result, suppressing the occurrence of non-linear effects, the present invention comprises a dispersion-compensating optical fiber that compensates chromatic dispersion of a 1.3 mum single-mode optical fiber over the entire wavelength range of 1.53-1.63 mum characterized in that, chromatic dispersion at a wavelength of 1.55 mum is -50 ps / nm / km or less, the dispersion slope is negative over the entire wavelength range of 1.53-1.63 mum, a cutoff wavelength is provided at which there is substantially single-mode propagation, bending loss is 30 dB / m or less, effective area is 20 mum<2 >or more, and the absolute value of chromatic dispersion during compensation of the chromatic dispersion of a 1.3 mum single-mode optical fiber serving as the target of compensation is 0.5 ps / nm / km or less.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Optical transmission line
InactiveUS20020012509A1High strengthReduce non-linearityOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesNonlinear phenomenaWaveform distortion
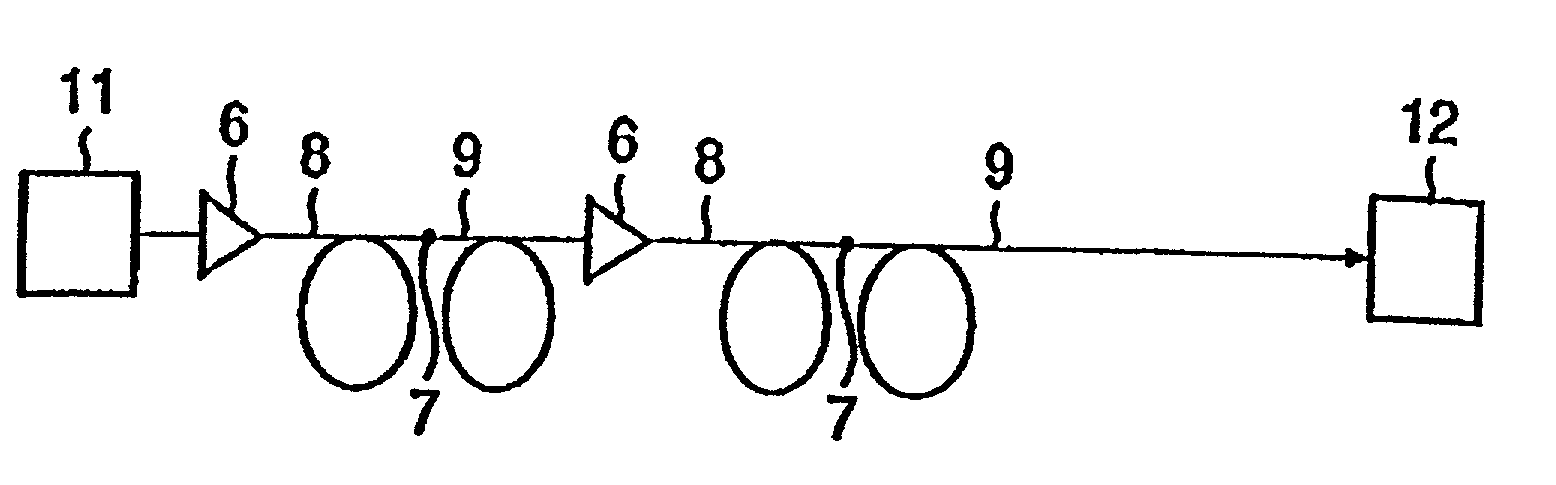
An optical transmission line according to the present invention is an optical transmission line which is able to control both the waveform distortion due to the non-linearity phenomenon and the waveform distortion due to dispersion. The optical transmission line is formed by connecting, in series, the first optical fiber (8), of which the dispersion value in the set wavelength band within the 1.5 mum wavelength band is 6 to 14 ps / nm / km, and the second optical fiber (9), of which the dispersion value in said set wavelength band is -14 to -6 ps / nm / km. The dispersion slopes of the first optical fiber (8) and the second optical fiber (9) are of mutually opposite symbols. Light transmitted from an optical transmitter (11) enters the first optical fiber (8) and light which has been transmitted through the first optical fiber (8) enters the second optical fiber (9). The absolute value of the dispersion in the 1.5 mum wavelength band of each of the optical fibers (8) and (9) is set to be 6 ps / nm / km or more so as to control the four light wave mixture and said absolute value is set to be 14 ps / nm / km or less so as to control a local dispersion, in order to set at approximately zero, for the entire optical transmission line, both the dispersion value and the dispersion slope in said set wavelength band.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Optical fiber, optical transmission line, and optical communications system
ActiveUS6917743B2Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCommunications systemEngineering
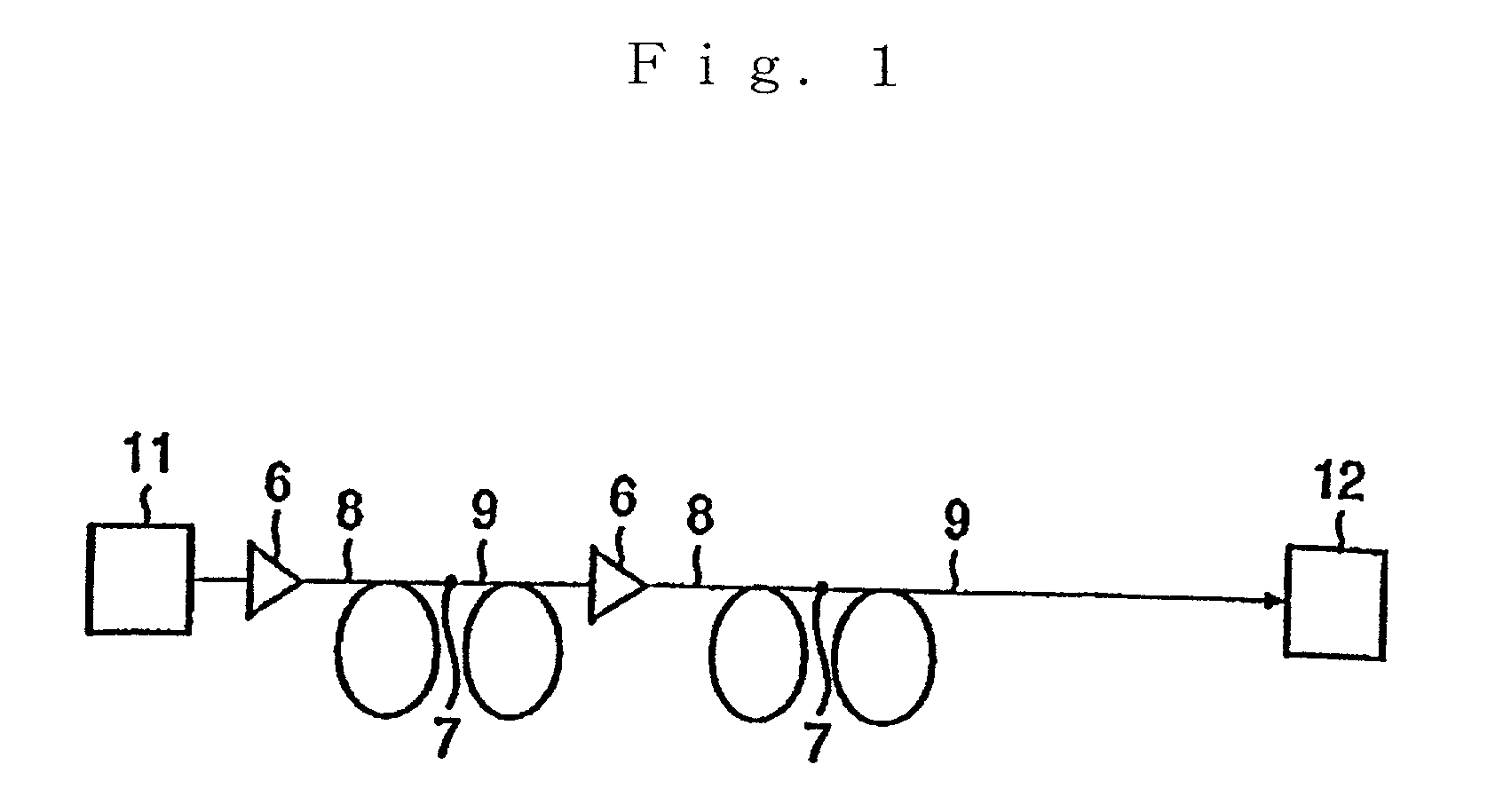
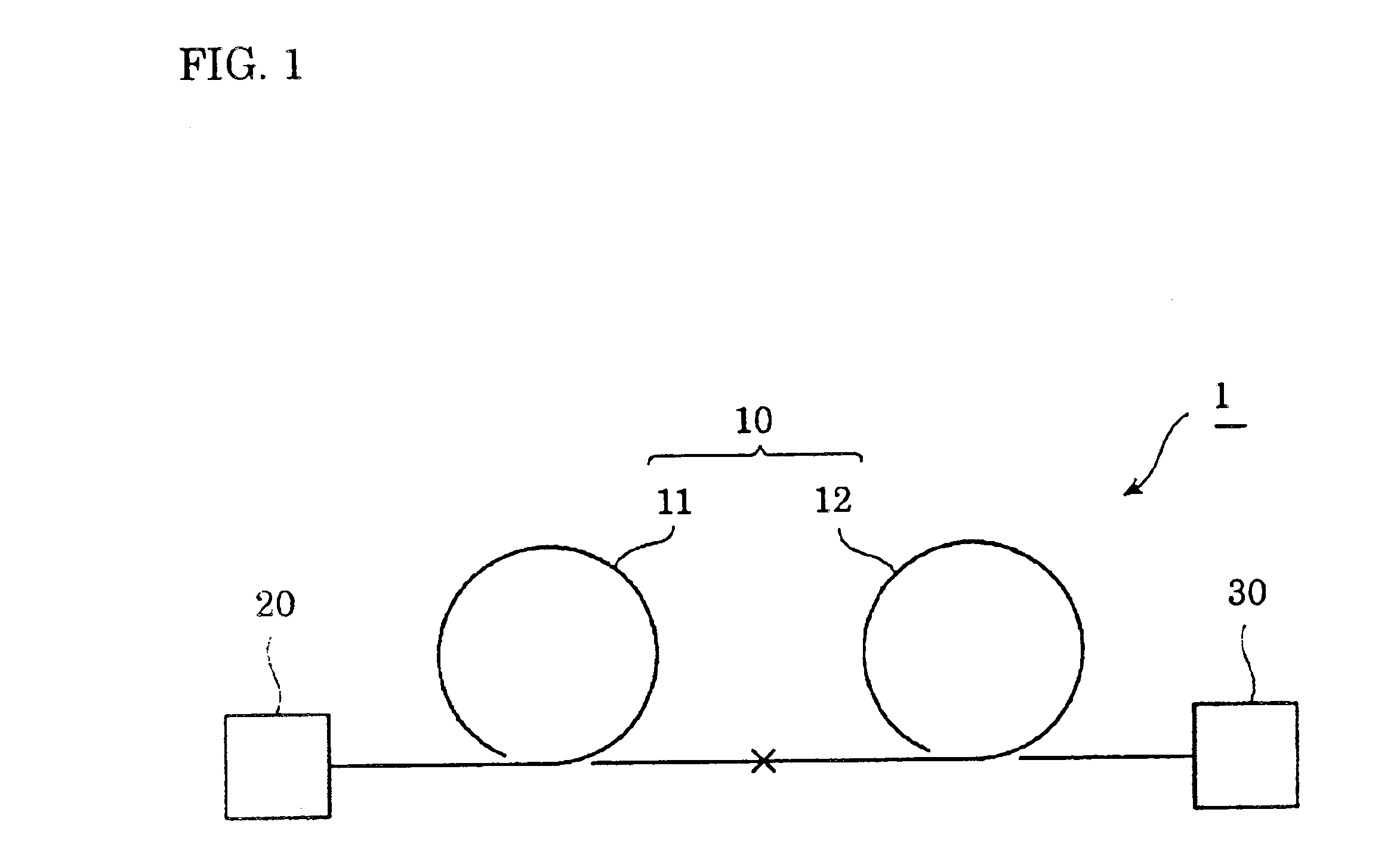
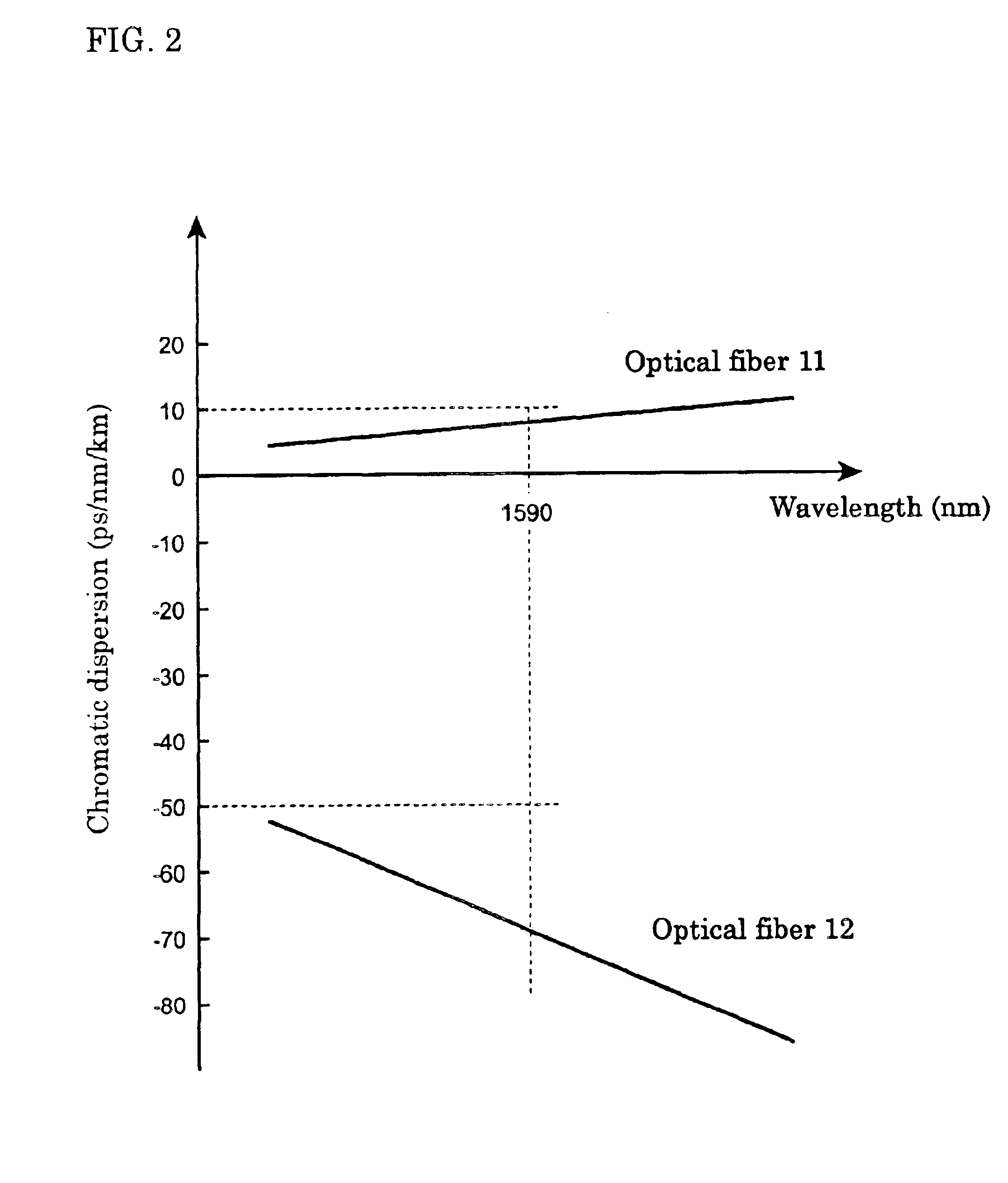
An optical fiber capable of compensating in the L-band both the chromatic dispersion and dispersion slope of a positive-dispersion optical fiber, an optical transmission line incorporating the optical fiber, and an optical communications system incorporating the optical transmission line. An optical communications system 1 comprises an optical transmission line 10, an optical transmitter 20, and an optical receiver 30. The optical transmission line 10 comprises an optical fiber 11 and an optical fiber 12 that are mutually fusion-spliced. The optical fiber 12 has at a wavelength of 1,590 nm a chromatic dispersion, D2, and a dispersion slope, S2, that satisfy the formulae −200 ps / nm / km≦D2≦−50 ps / nm / km, and 0.009 / nm≦S2 / D2.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Fiber for compensating chromatic dispersion of a monomode fiber in band S
InactiveUS20020067903A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexLength wave
A chromatic dispersion-compensating fiber adapted to compensate the chromatic dispersion of a step index monomode fiber in band S presents chromatic dispersion of less than -40 ps / (nm.km) around 1475 nm, chromatic dispersion slope of less than -0.16 ps / (nm2.km), and an effective area greater than or equal to 14 mum2 around said wavelength value. The fiber is monomode at 1475 nm. The fiber can present a rectangle profile with a buried trench and a ring. It serves to compensate chromatic dispersion and chromatic dispersion slope for transmission systems in band S using a step index monomode fiber as the line fiber.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Dispersion compensated optical fiber transmission system and module including micro-structured optical fiber
InactiveUS20050036752A1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesEngineeringHoley fiber
Disclosed is an optical transmission system and module which includes a negative dispersion, dispersion compensating optical fiber coupled to a micro-structured optical fiber (such as band gap fiber, photonic crystal fiber or holey fiber) for compensating for the accumulated dispersion in a transmission fiber. The optical transmission system and module in accordance with the invention provides substantially equal compensation of total dispersion over an operating wavelength band, reduced overall system length, and lower insertion loss.
Owner:CORNING INC
High figure of merit dispersion compensating fiber for standard single mode fiber and transmission system utilizing same
InactiveUS20050063655A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingEngineeringFigure of merit
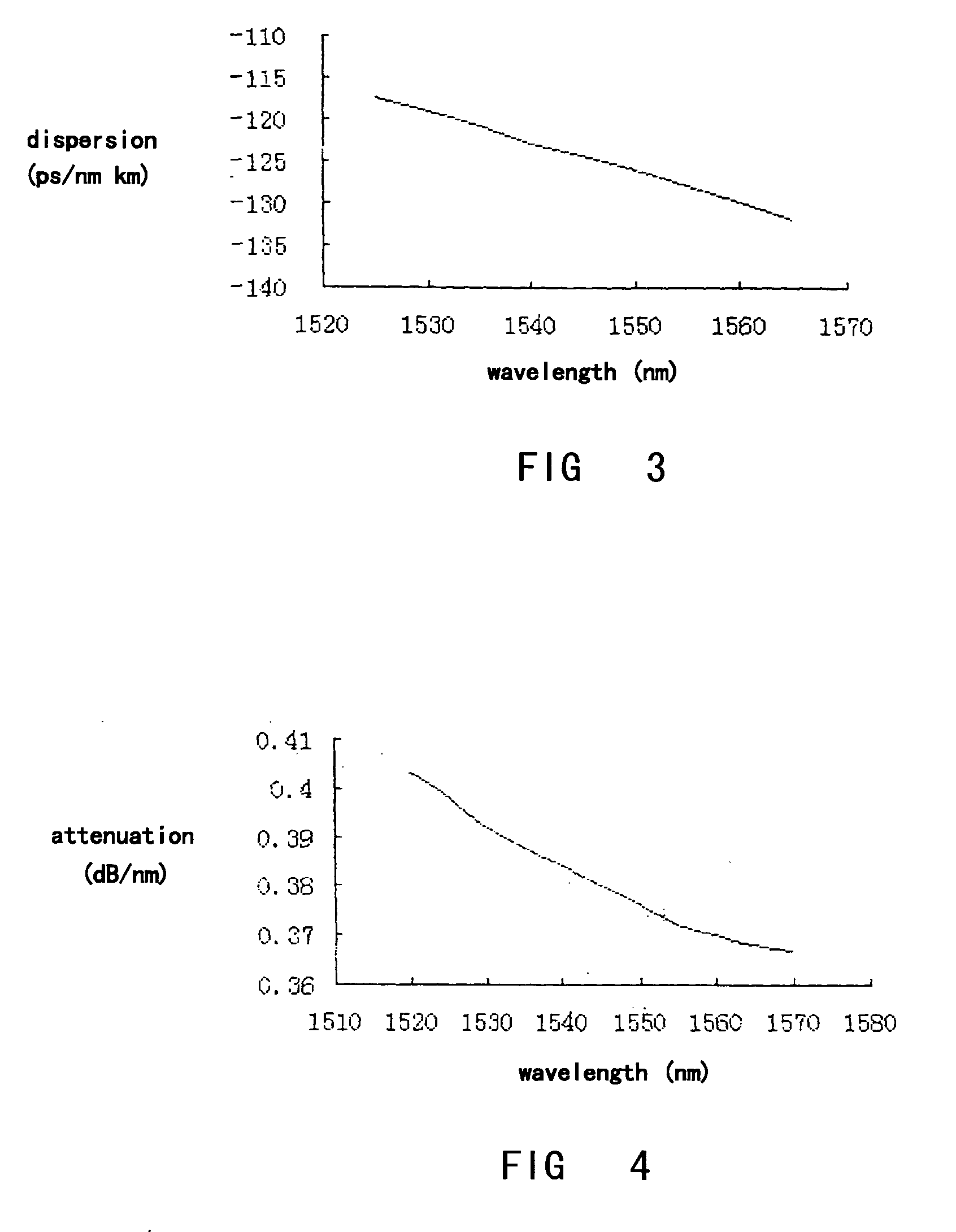
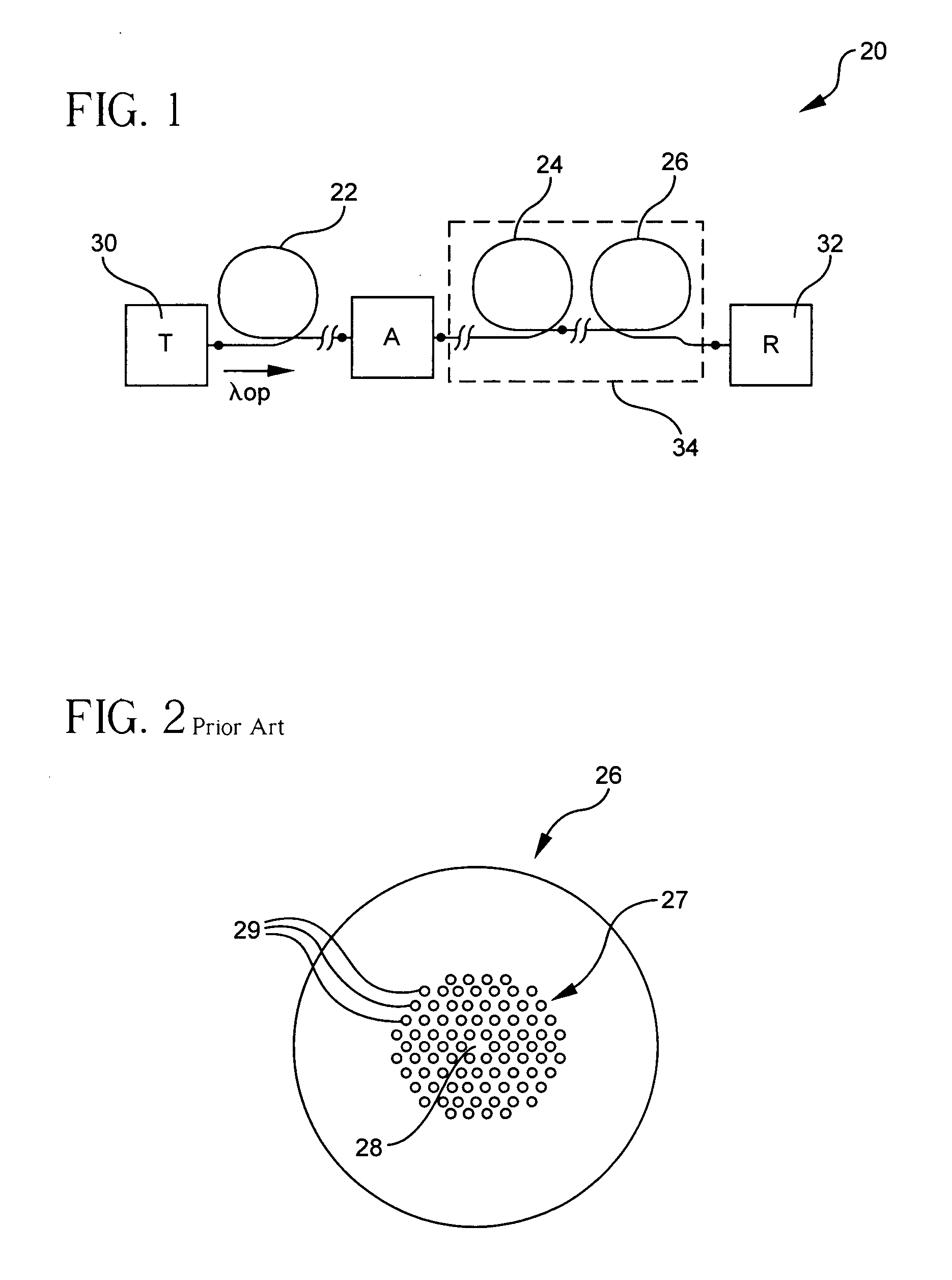
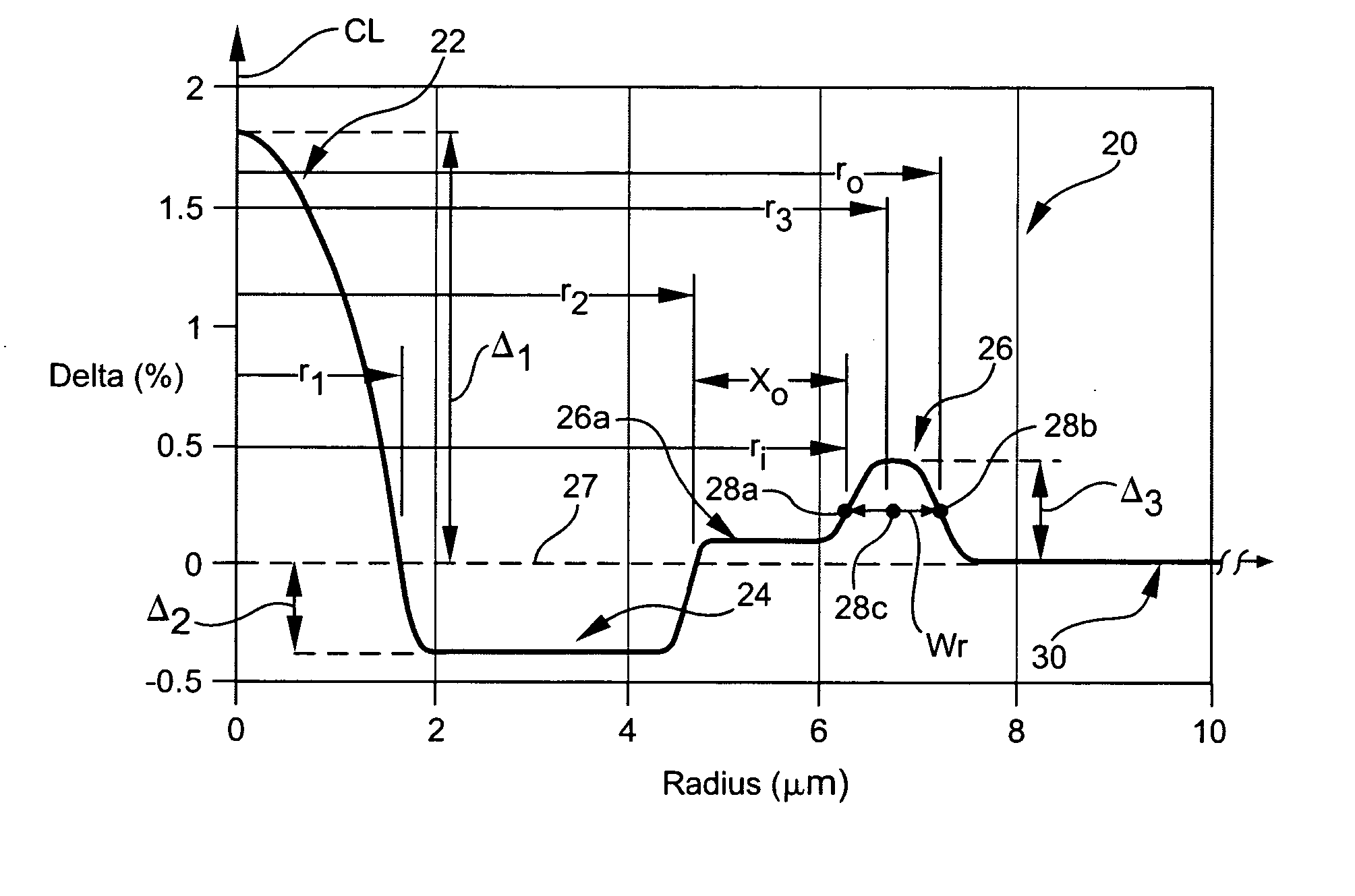
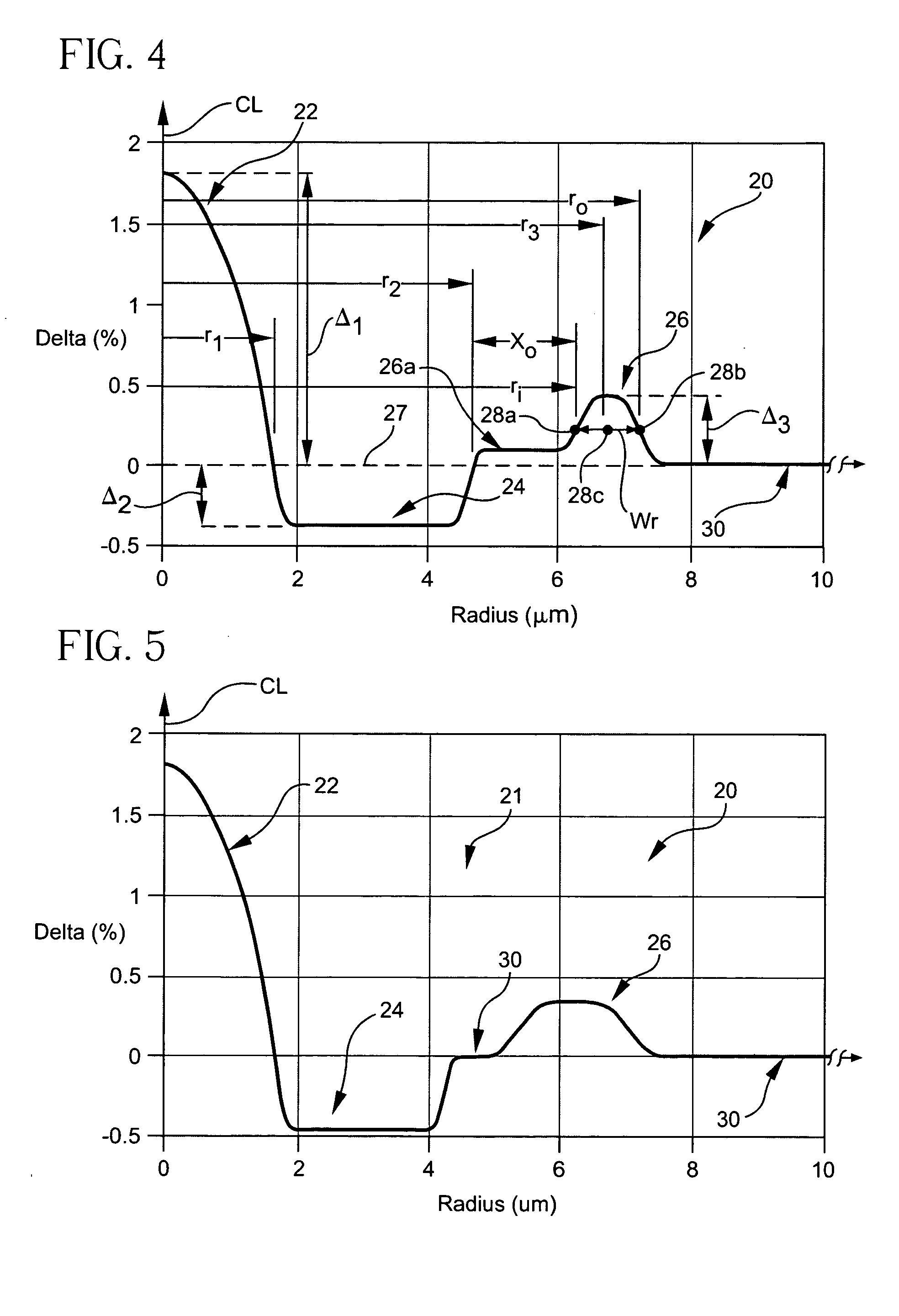
A dispersion compensating optical fiber that includes a segmented core having a central core segment, a moat segment, and a ring segment wherein the ring segment is preferably offset from the moat outer radius, r2, by a ring offset, Xo, greater than 0.4 μm. The refractive index profile is selected to provide a total dispersion at 1550 nm of between about −120 and −145 ps / nm / km, and a total dispersion slope at 1550 nm of between about −0.36 and −0.56 ps / nm2 / km. The refractive index profile is preferably further selected to provide a kappa, defined as the total dispersion at 1550 nm divided by the dispersion slope at 1550 nm, of between about 250 and 320 nm. Optical transmission systems including the present invention dispersion compensating optical fiber which have residual dispersion less than ± 15 ps / nm per 100 km of standard single mode transmission fiber are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Microstructured optical fiber
InactiveUS6859598B2Large chromatic dispersionIncrease the areaOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexMicrostructured optical fiber
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Chromatic dispersion compensation in an optical fiber transmission system, and a compensation fiber
InactiveUS6574407B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWavelength-division multiplex systemsBroadband transmissionDispersion compensation
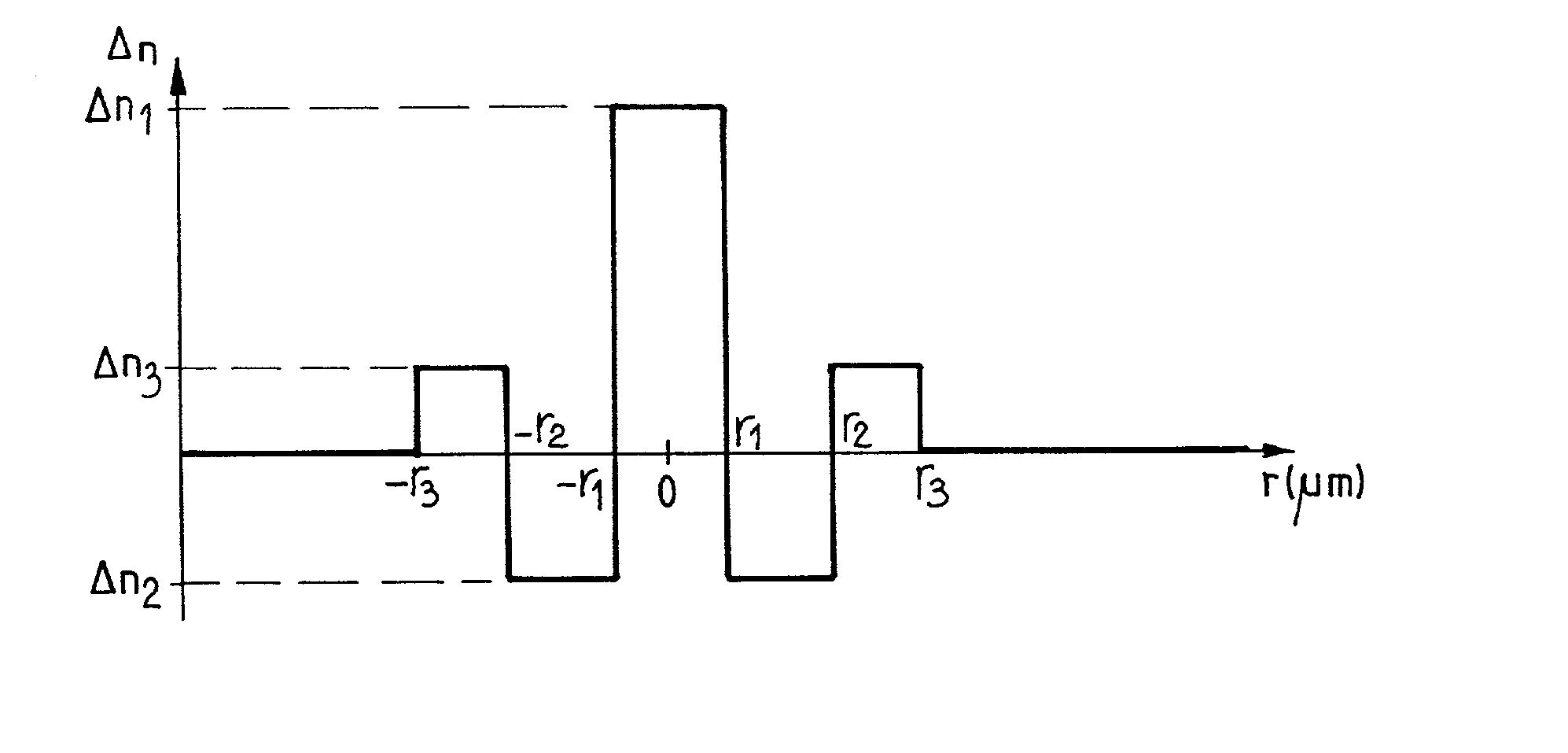
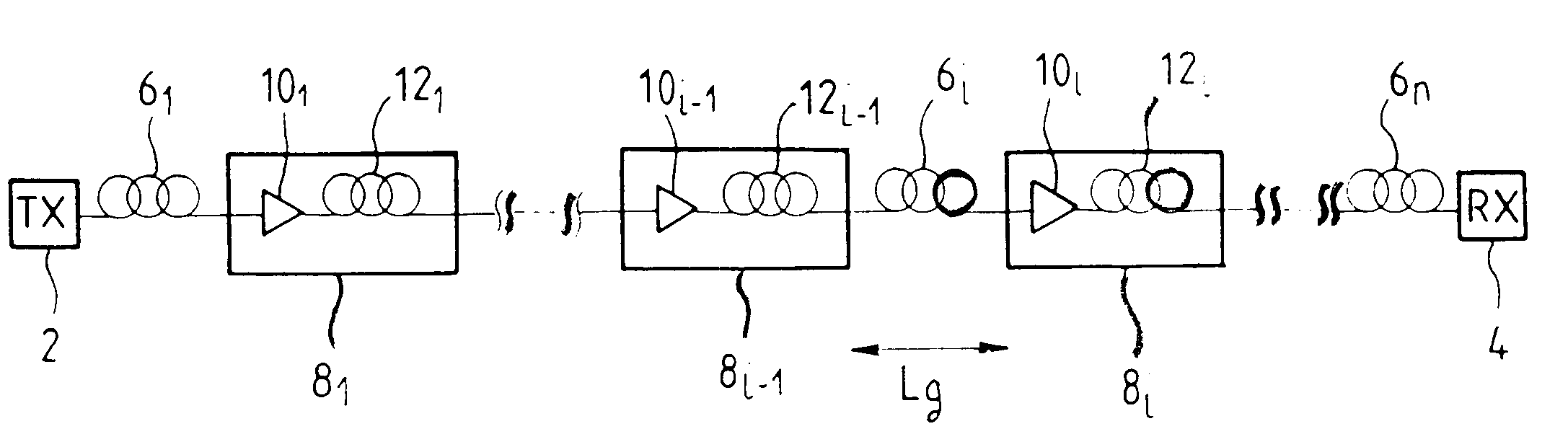
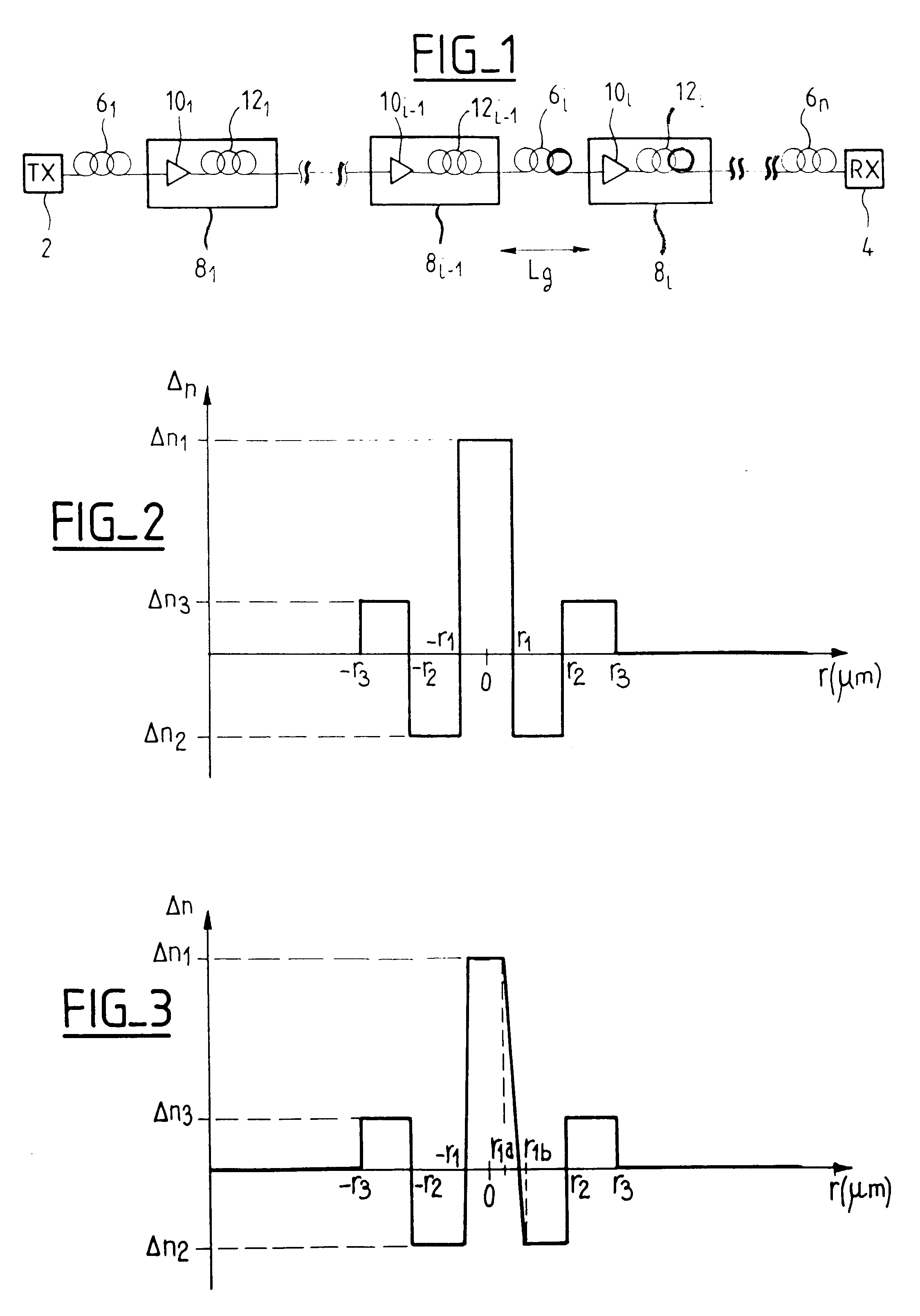
The invention proposes providing an optical fiber transmission system with a dispersion compensating fiber 12l to 12n to compensate the chromatic dispersion and chromatic dispersion slope of the line fiber 6l to 6n; the dispersion compensating fiber satisfies the following criteria:where C, C' et C'' are the chromatic dispersion, the chromatic dispersion slope and the first derivative of the chromatic dispersion slope of the dispersion compensating fiber, Cg and C'g are the chromatic dispersion and the chromatic dispersion slope of the line fiber, Ccum is the upper limit of the modulus of the cumulative chromatic dispersion in the transmission system, Lg is the length of a line fiber section, and DELTAlambd is half the bandwidth of the transmission system.The invention also proposes optical fibers verifying the above criteria and suitable for compensating the chromatic dispersion of step index or dispersion shifted line fiber.The proposed criteria compensate chromatic dispersion and chromatic dispersion slope in wideband transmission systems, e.g. in C band and L band transmission systems, for wavelengths from 1530 to 1620 nm.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Dispersion compensating fiber and dispersion compensating fiber module
InactiveUS6937805B2Good effectReduce connection lossOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRelative refractive indexNon-zero dispersion-shifted fiber
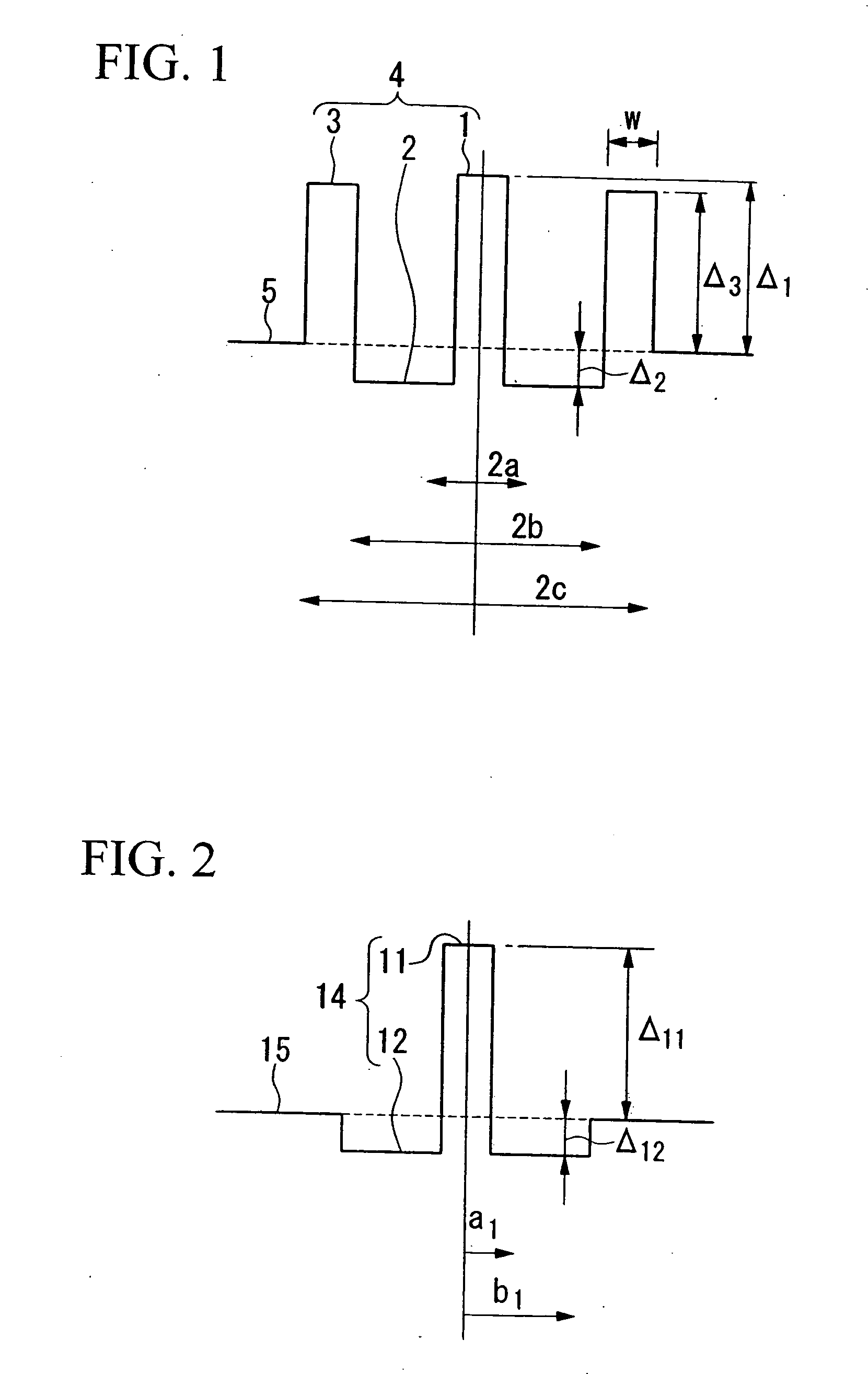
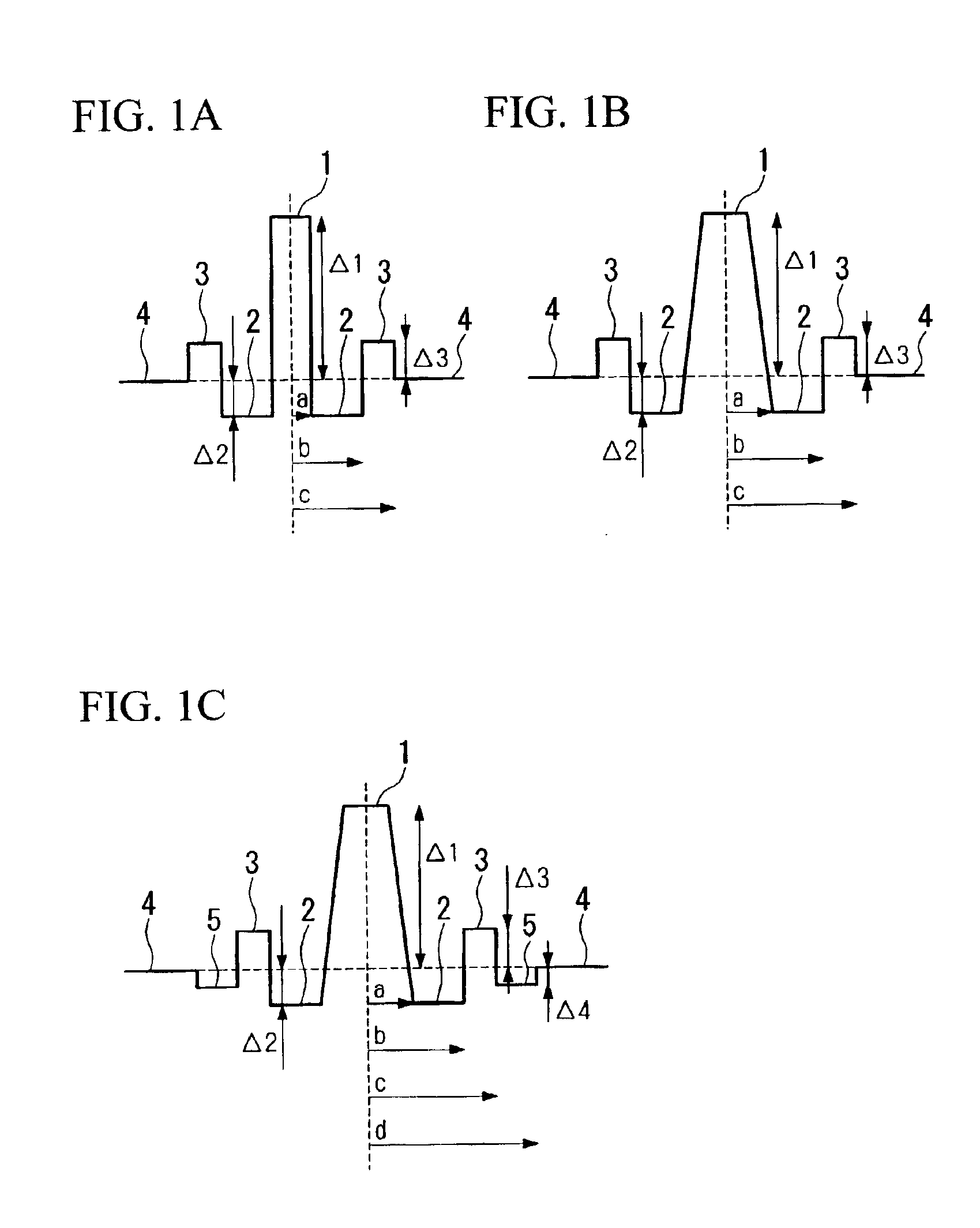
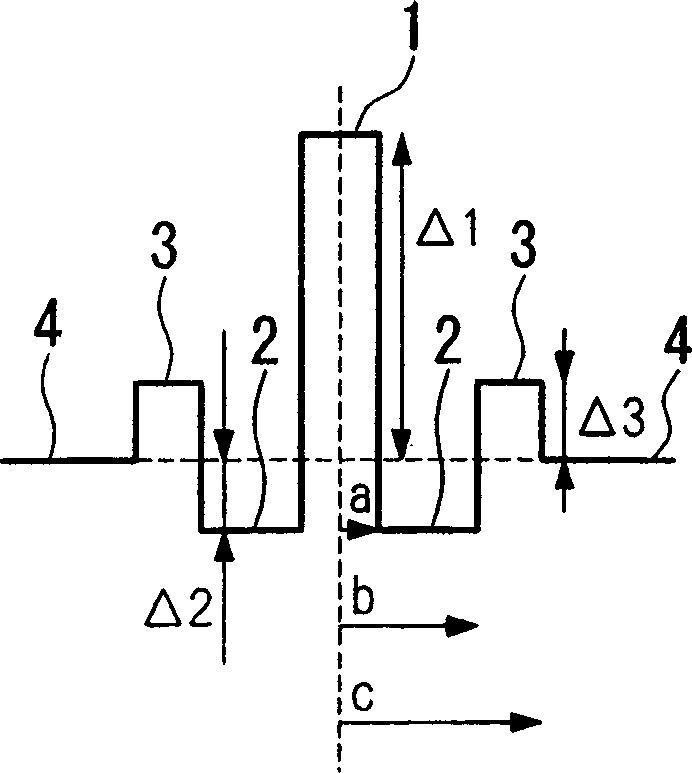
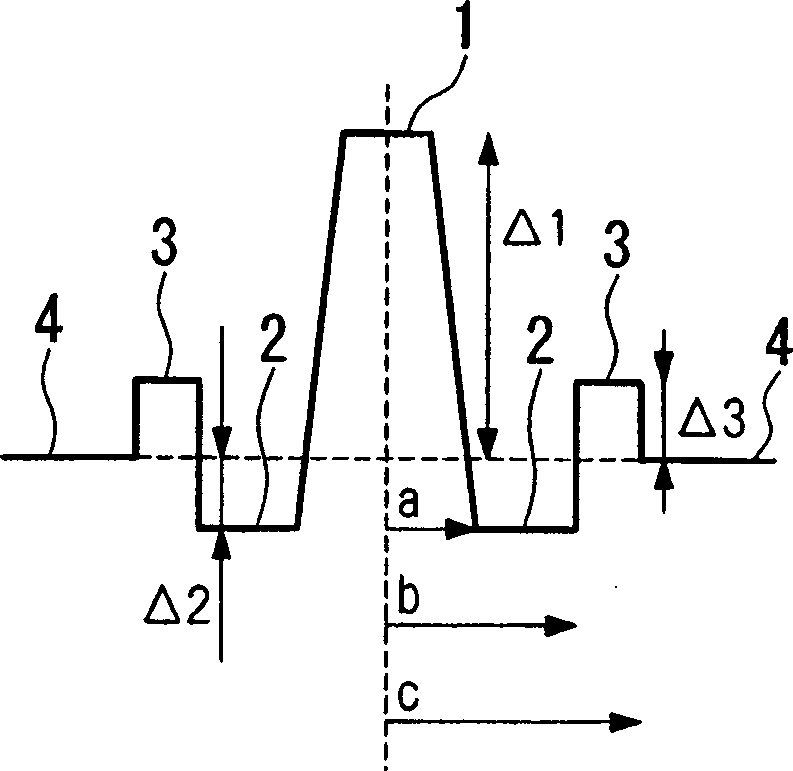
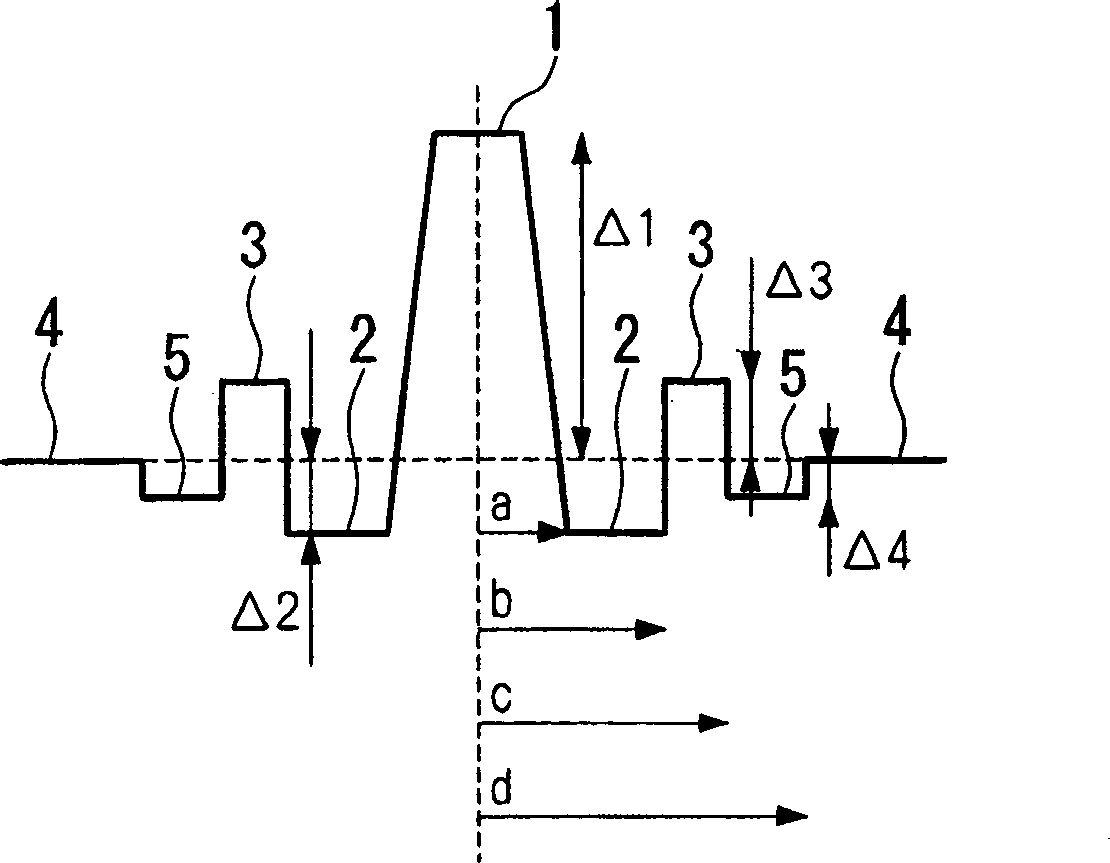
A dispersion compensating fiber, which has a negative dispersion slope with a large absolute value while maintaining the absolute value of the chromatic dispersion, and which has sufficient dispersion slope compensation properties even for the non-zero dispersion shifted optical fiber requiring a large RDS for dispersion compensation. In this dispersion compensating fiber, the radius of a ring core region is set in a range from 6.7 μm to 10.7 μm, the radius ratio of a depressed core region relative to a central core region is set in a range from 2.0 to 3.0, and the radius ratio of the ring core region relative to the depressed core region is set in a range from 1.3 to 2.0, the relative refractive index difference of the central core region relative to the cladding is set in a range from +1.00% to +1.80%, the relative refractive index difference of the depressed core region relative to the cladding is set in a range from −1.20% to −1.50%, and the relative refractive index difference of the ring core region relative to the cladding is set in a range from +0.20% to +0.50%.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Dispersion compensated optical fibre and dispersion compensated optical fibre module
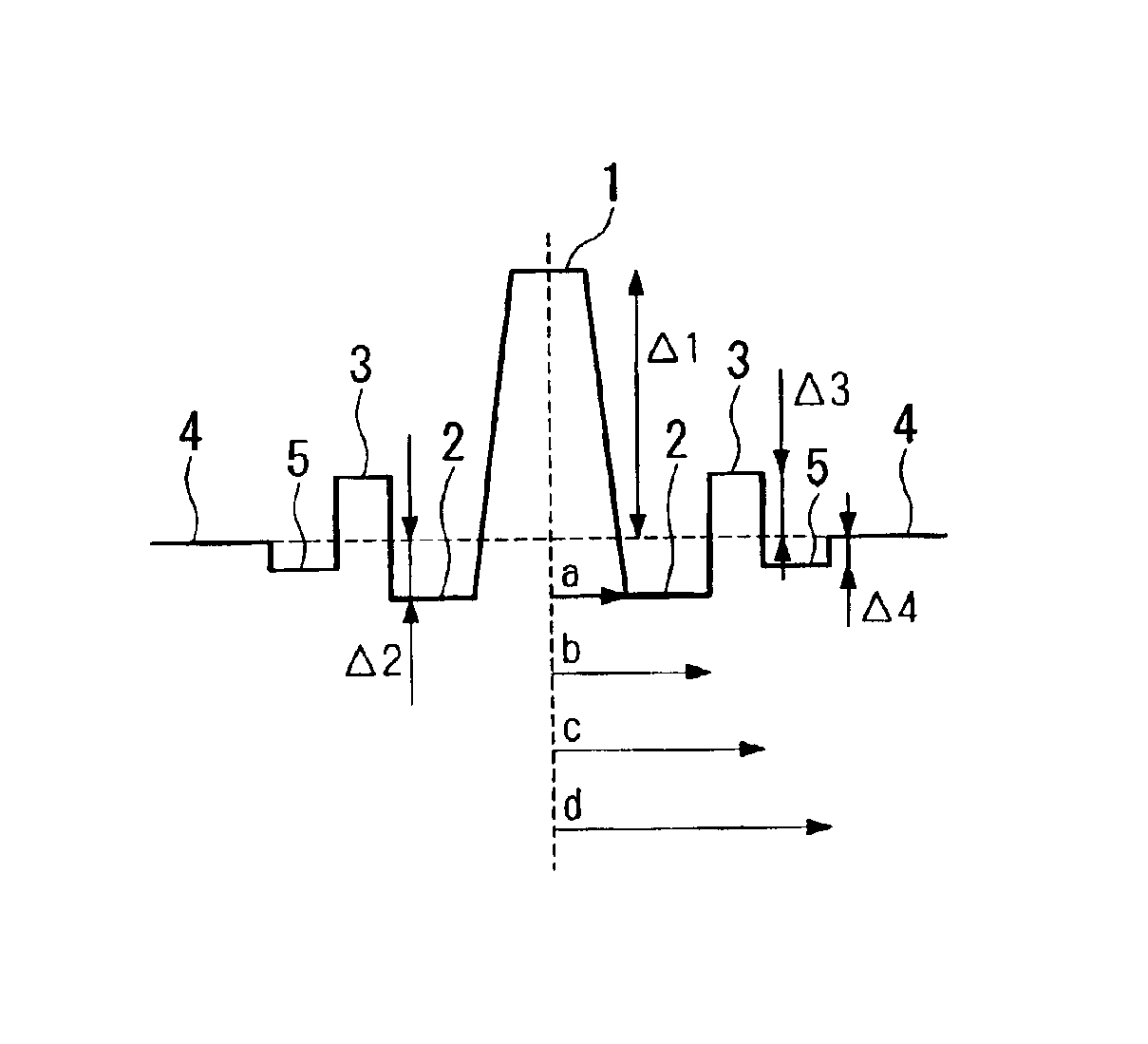
InactiveCN1414404AAvoid misalignmentOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingElectromagnetic transmissionRelative refractive indexNon-zero dispersion-shifted fiber
A dispersion compensating fiber, which has a negative dispersion slope with a large absolute value while maintaining the absolute value of the chromatic dispersion, and which has sufficient dispersion slope compensation properties even for the non-zero dispersion shifted optical fiber requiring a large RDS for dispersion compensation. In this dispersion compensating fiber, the radius of a ring core region (3) is set in a range from 6.7 mu m to 10.7 mu m, the radius ratio of a depressed core region (2) relative to a central core region (1) is set in a range from 2.0 to 3.0, and the radius ratio of the ring core region (3) relative to the depressed core region (2) is set in a range from 1.3 to 2.0, the relative refractive index difference of the central core region (1) relative to the cladding (4) is set in a range from +1.00% to +1.80%, the relative refractive index difference of the depressed core region (2) relative to the cladding (4) is set in a range from -1.20% to -1.50%, and the relative refractive index difference of the ring core region (3) relative to the cladding (4) is set in a range from +0.20% to +0.50%.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com