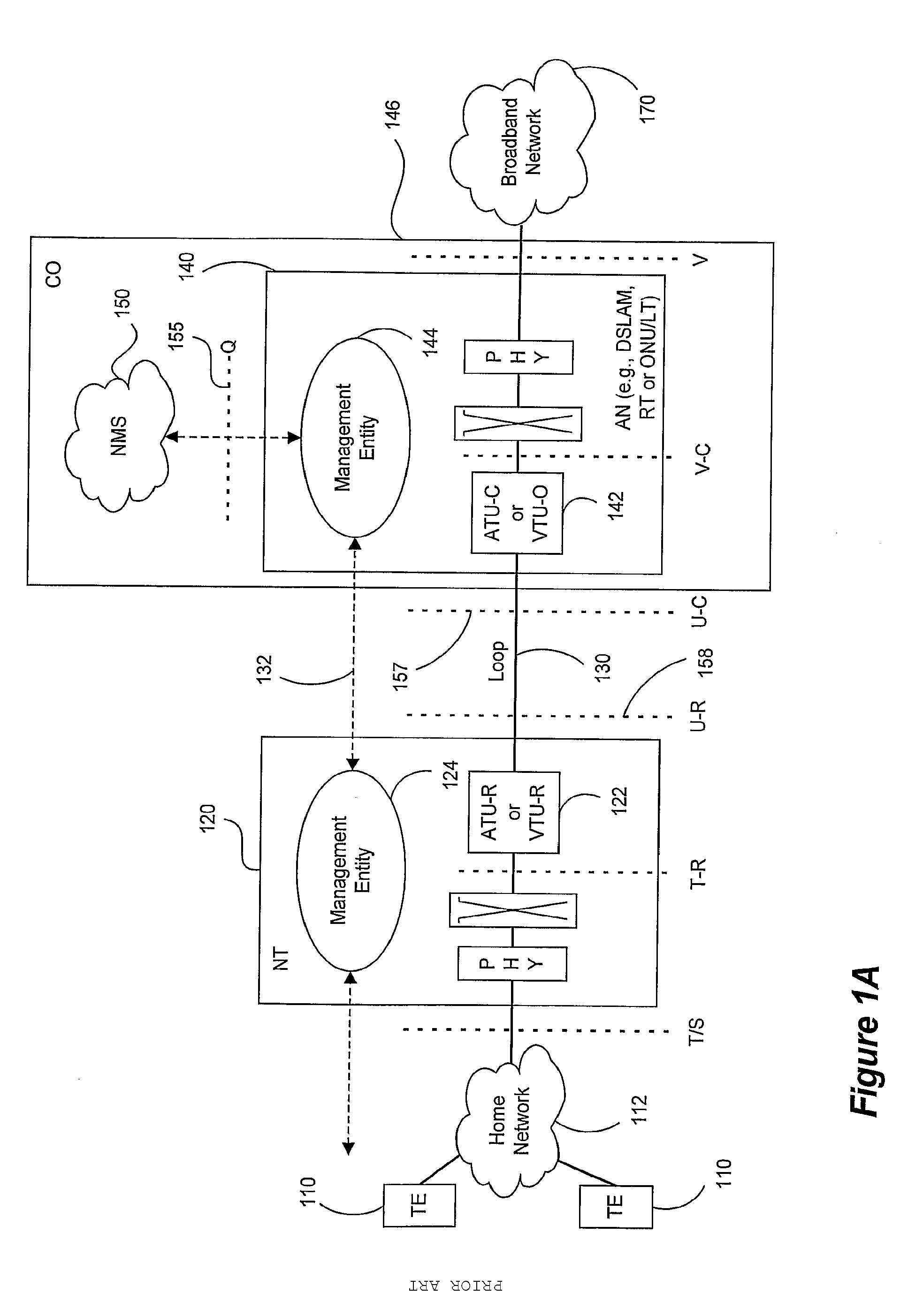
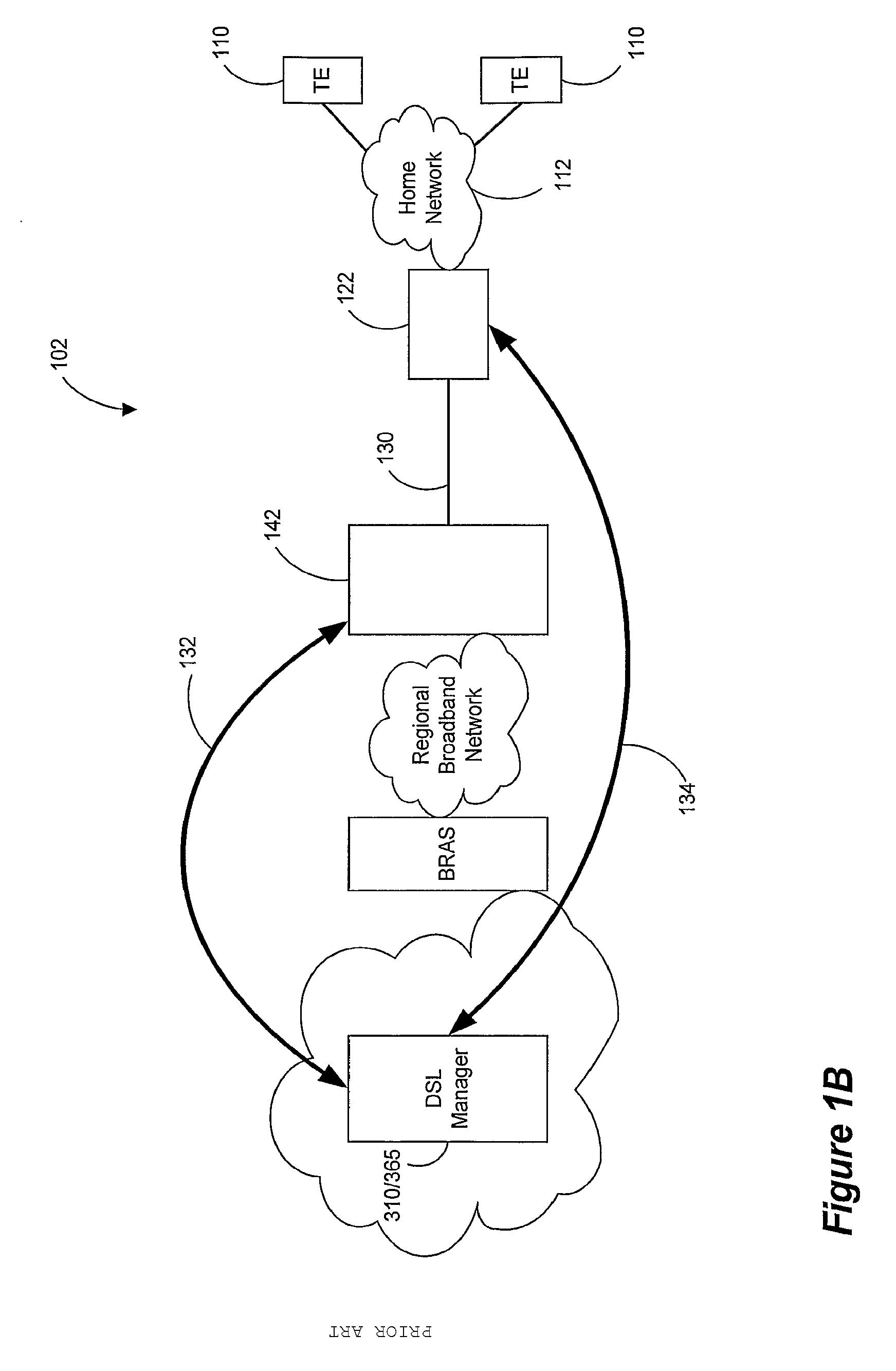
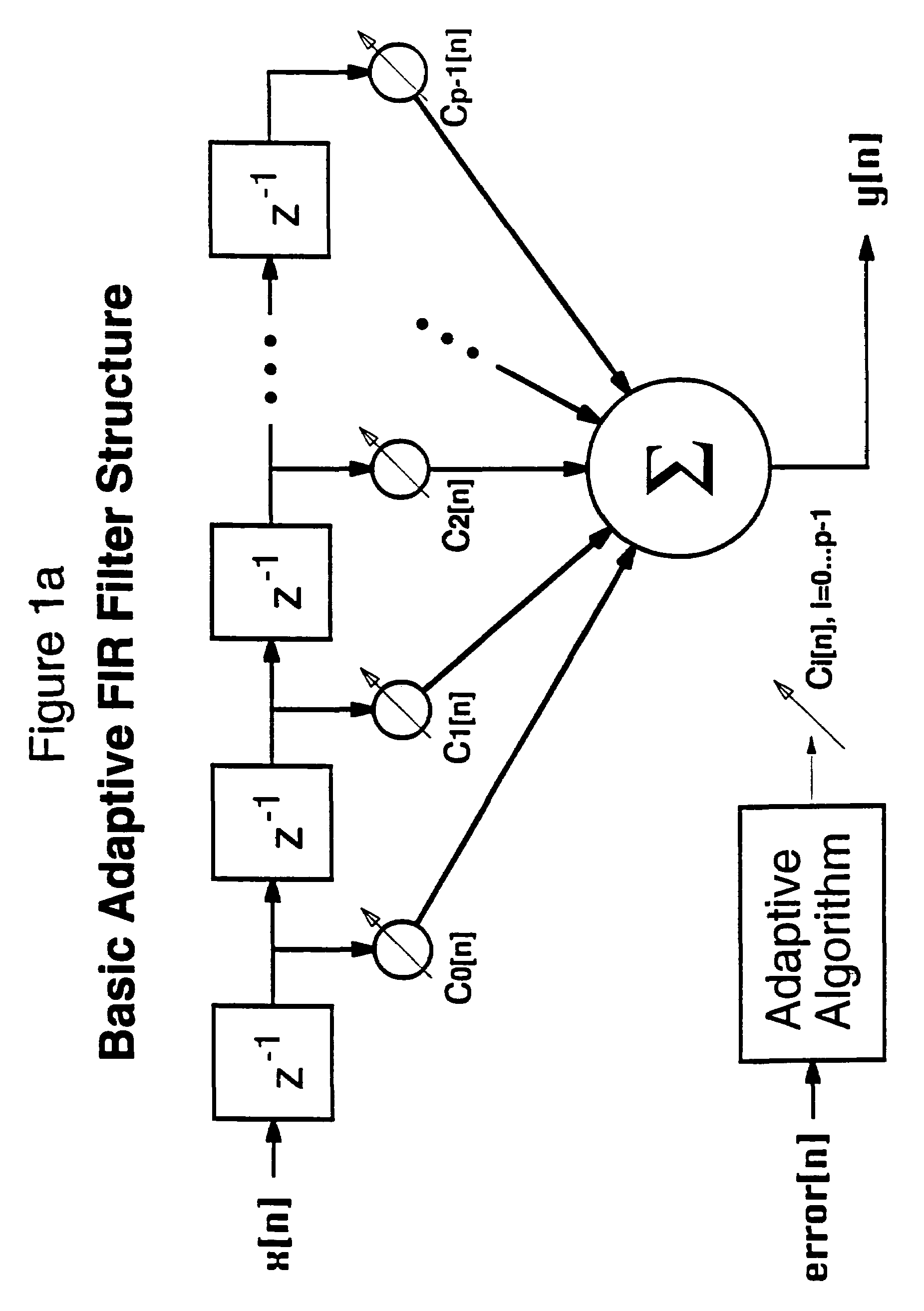
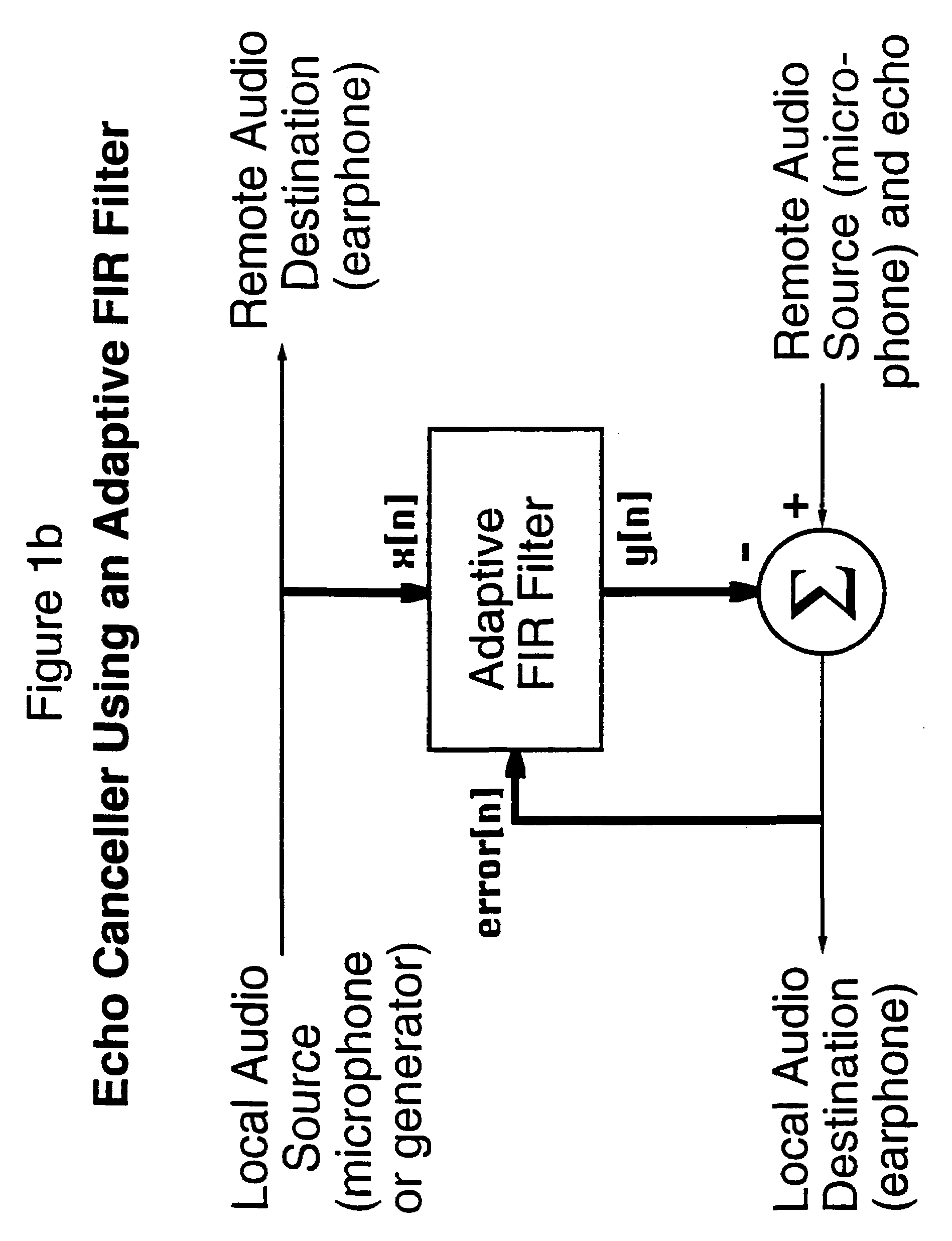
Patents
Literature
312results about "Subscriber line interface circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
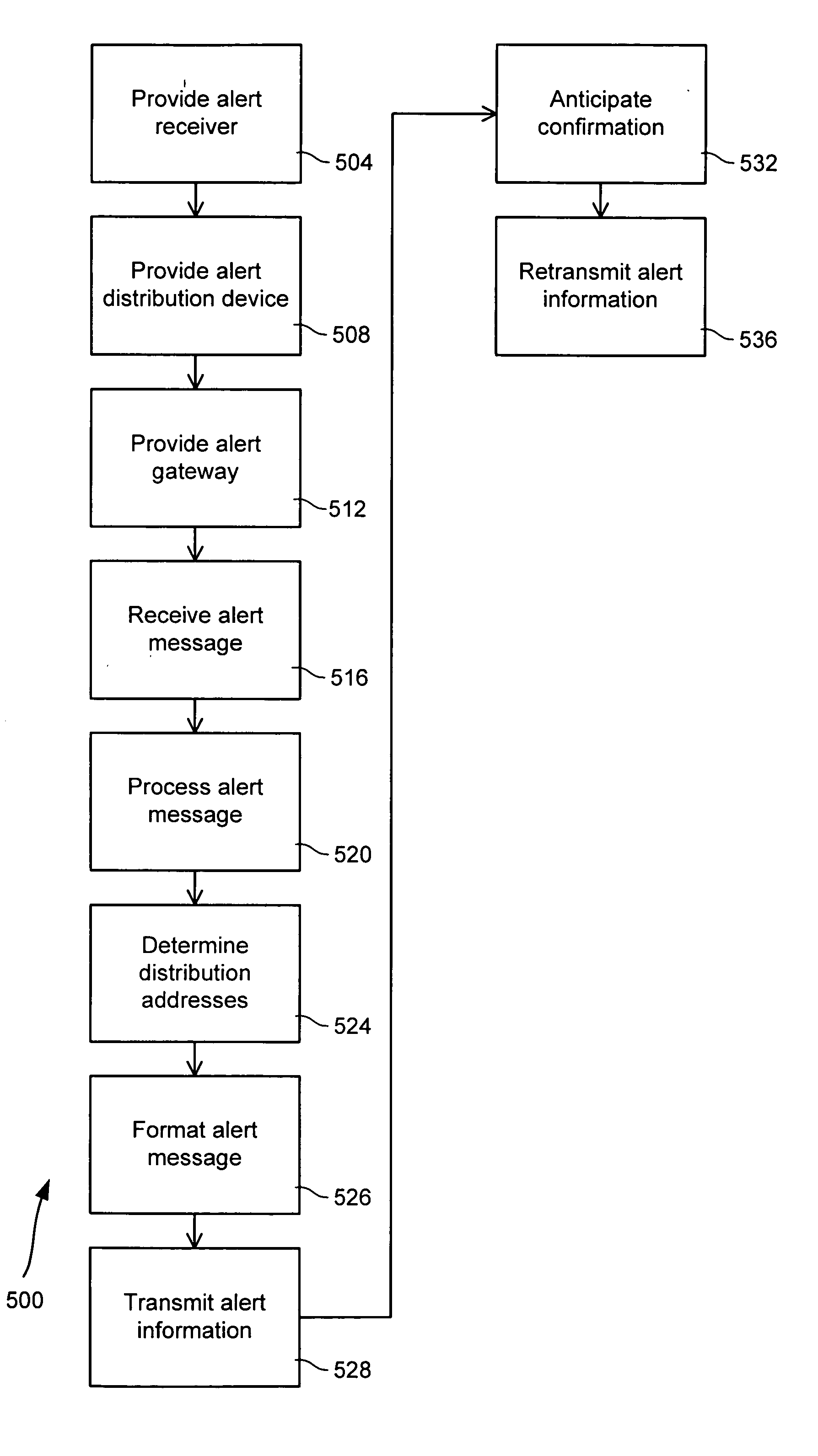
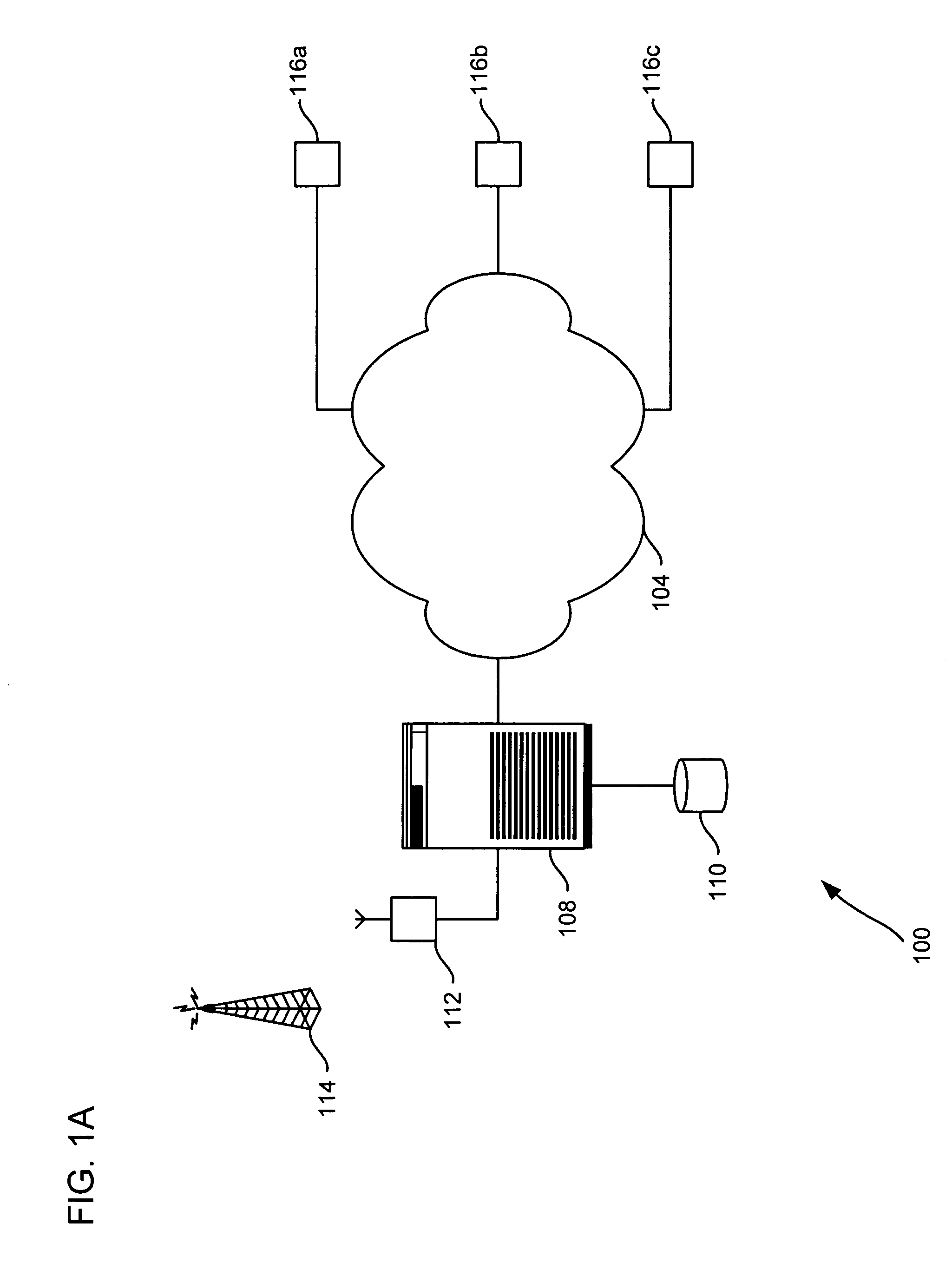
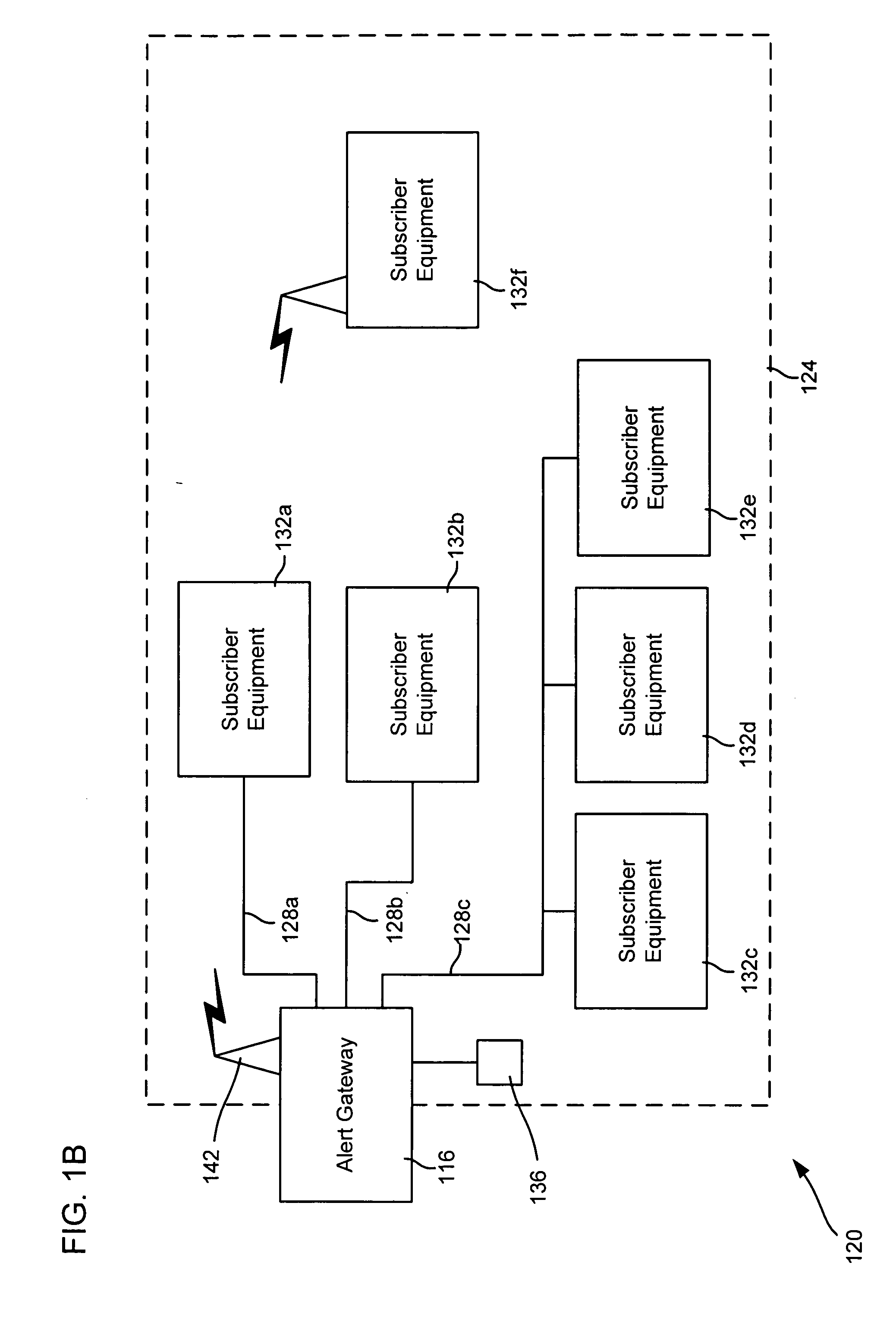
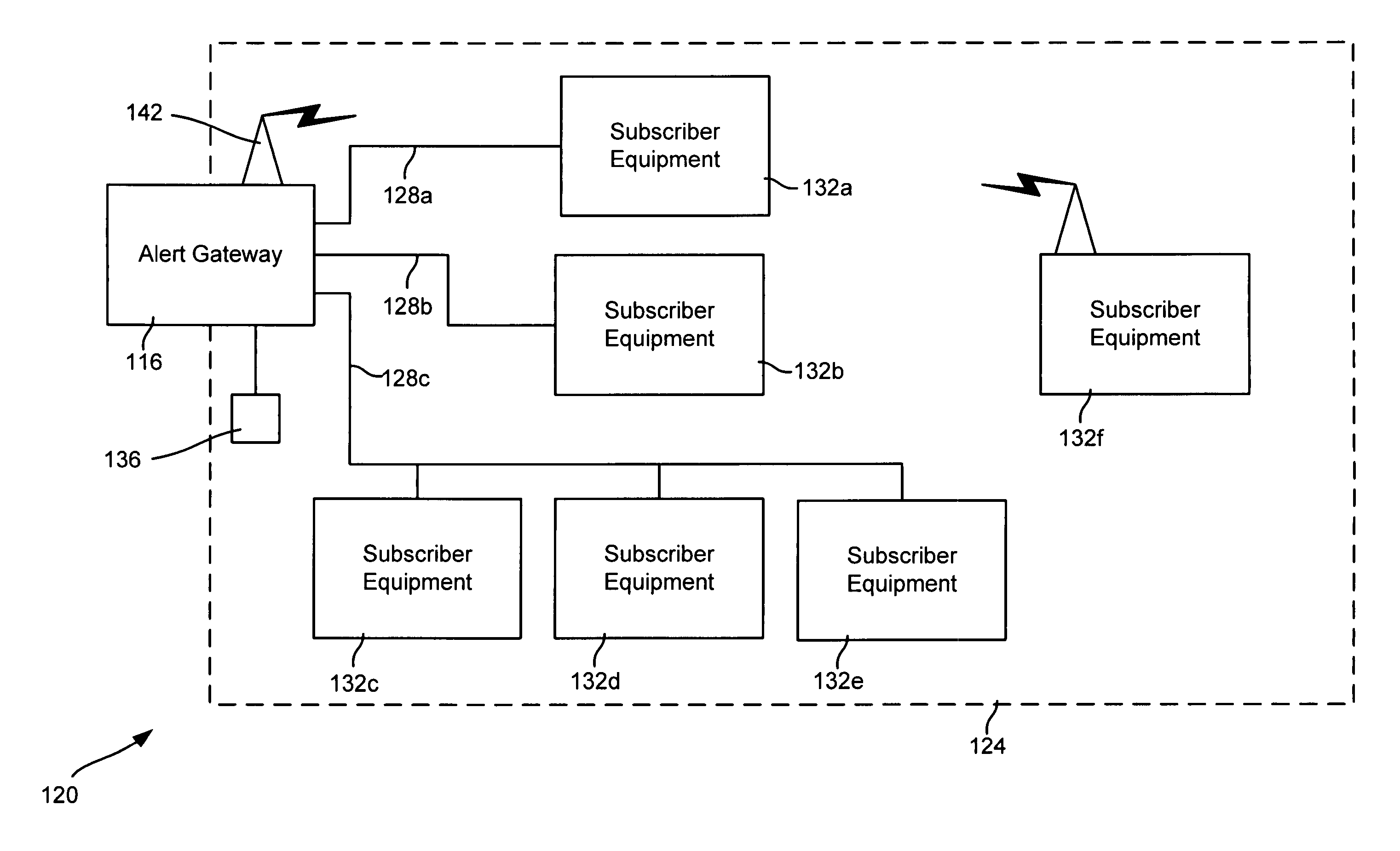
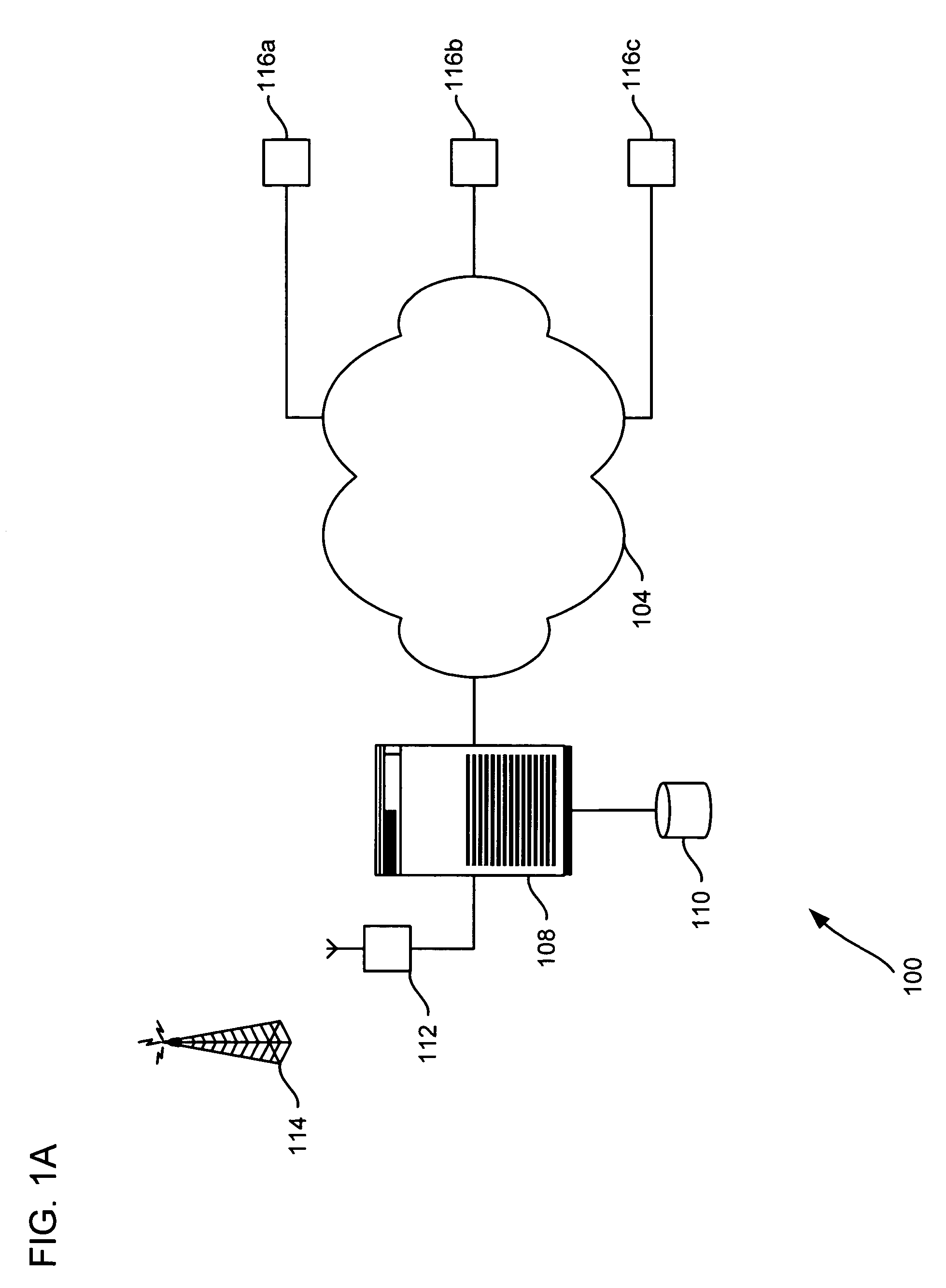
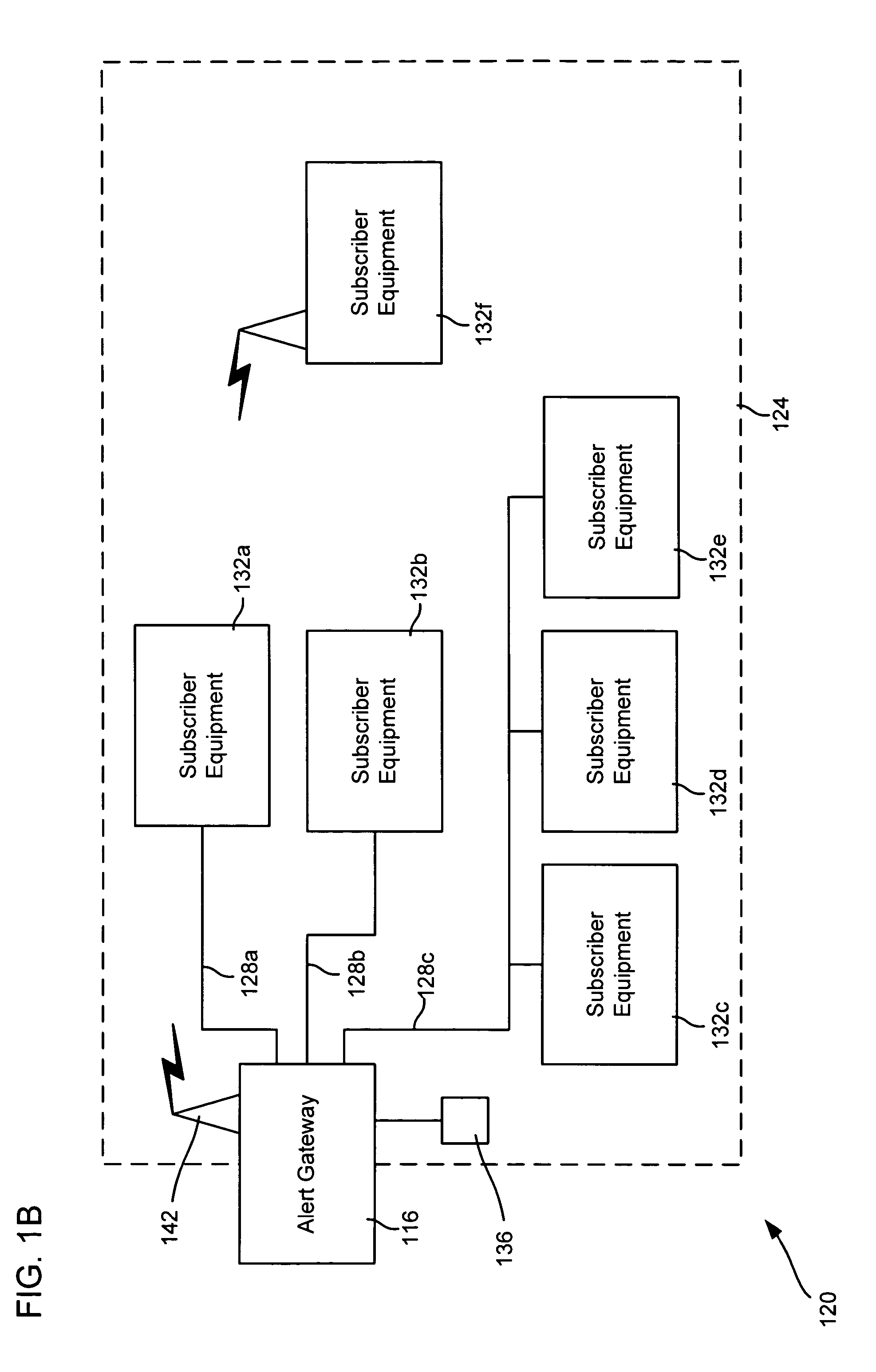
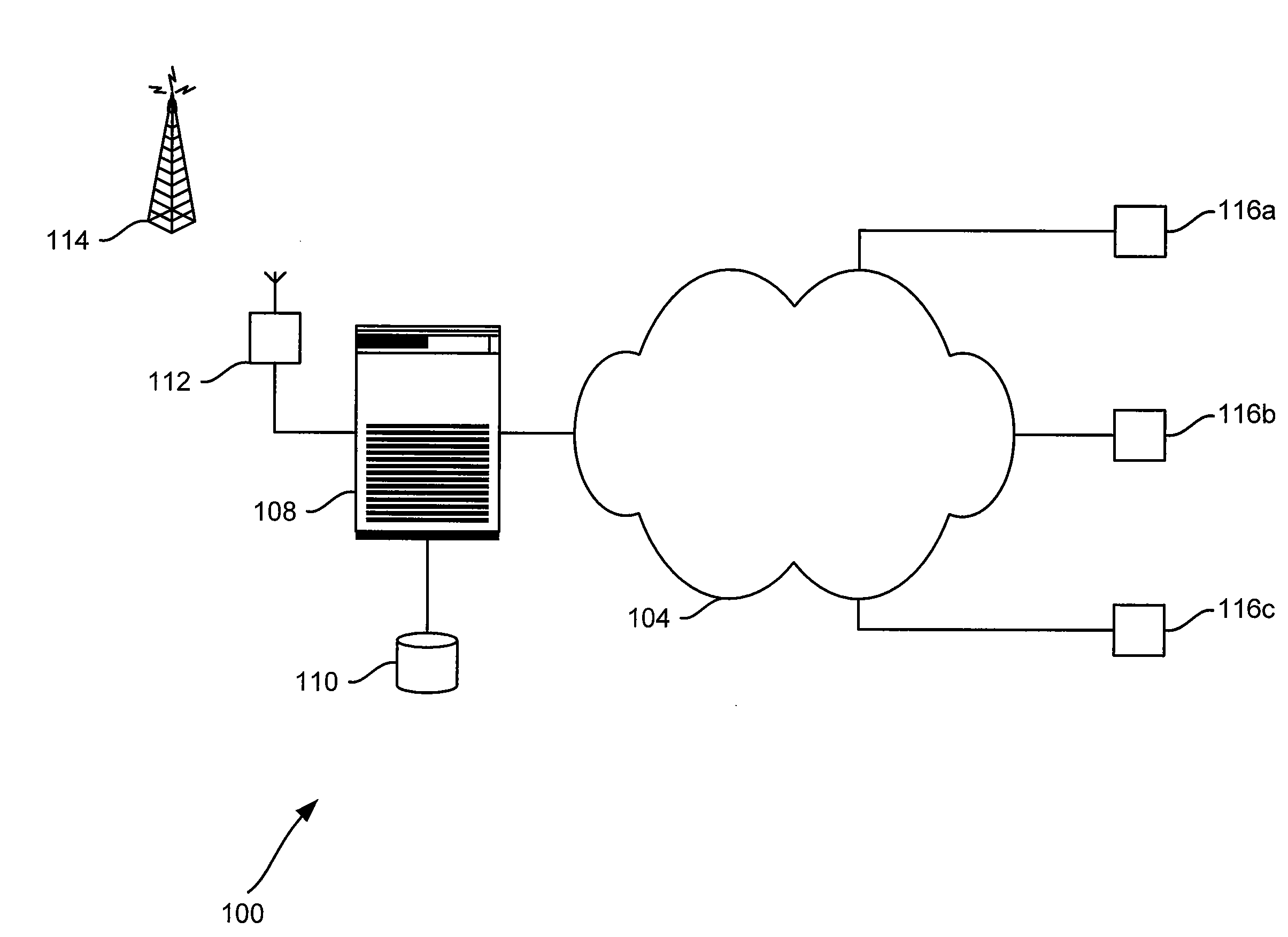
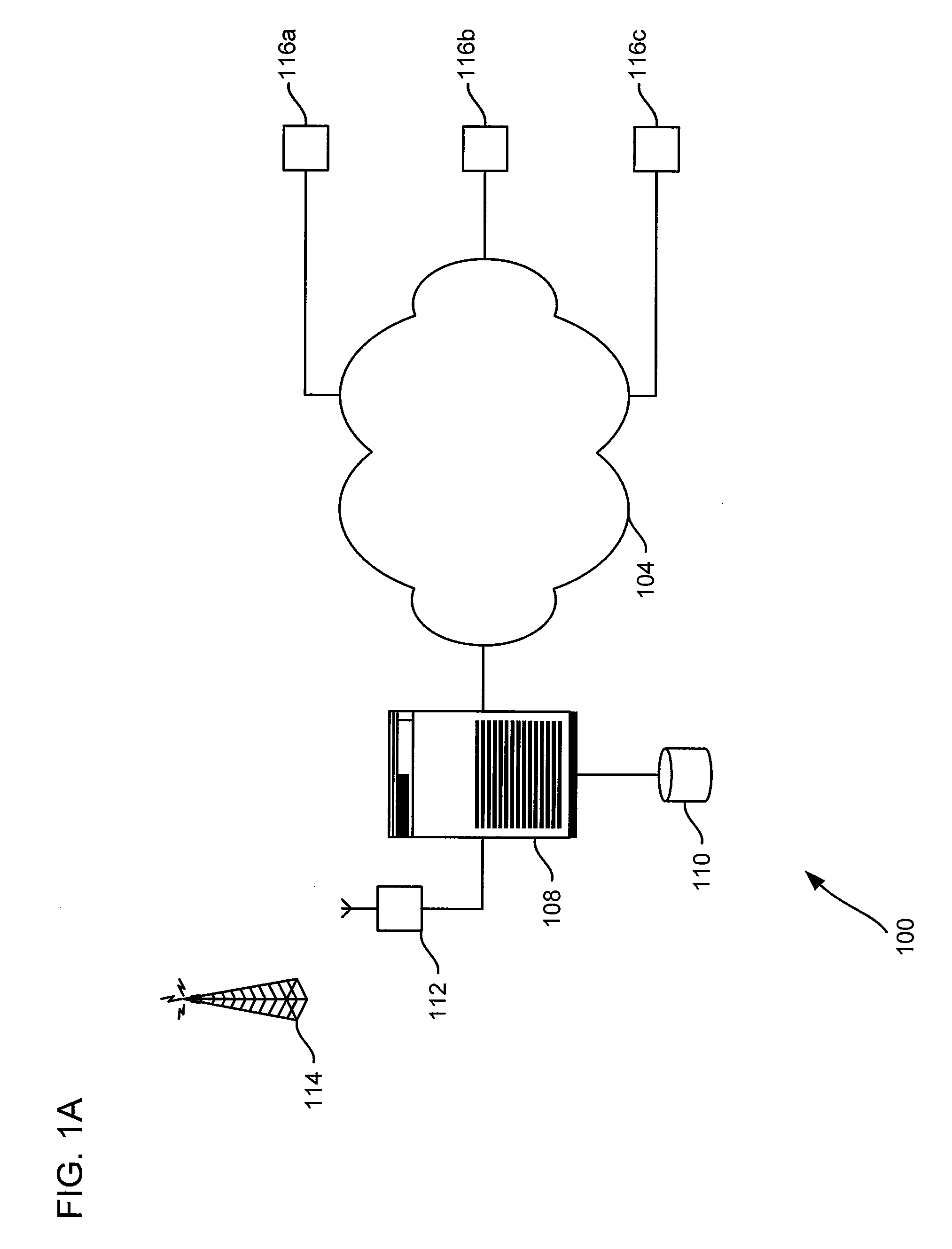
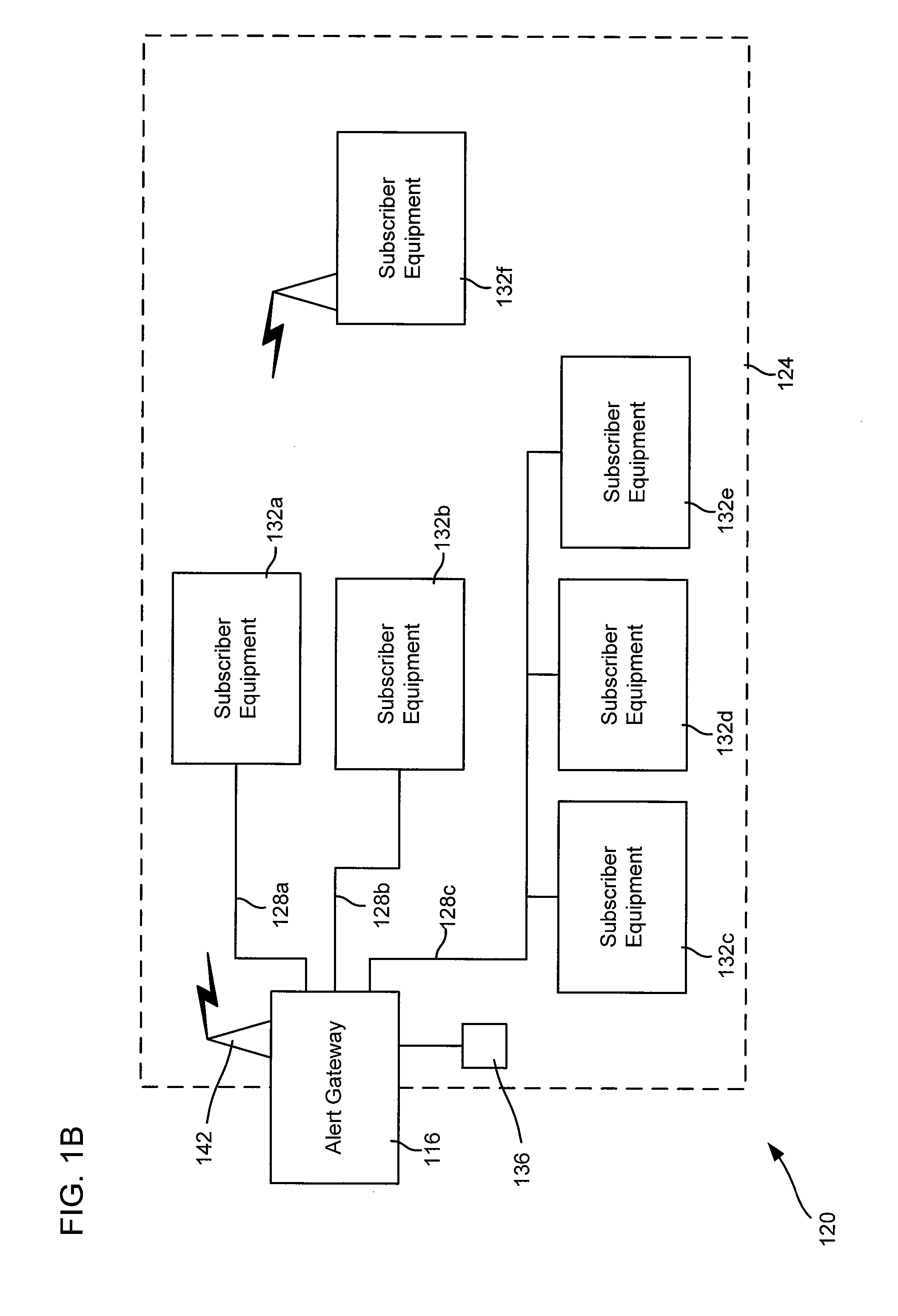
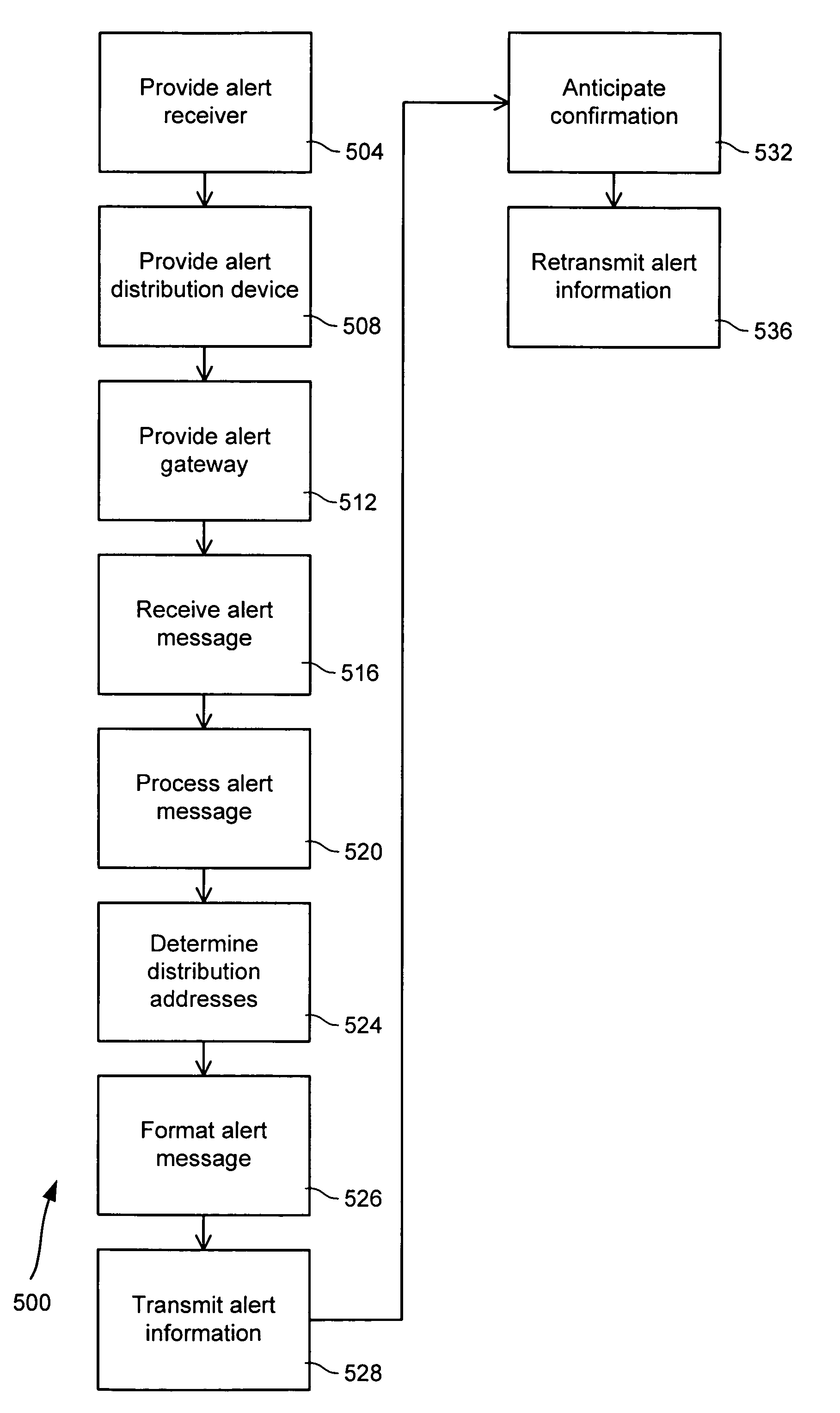
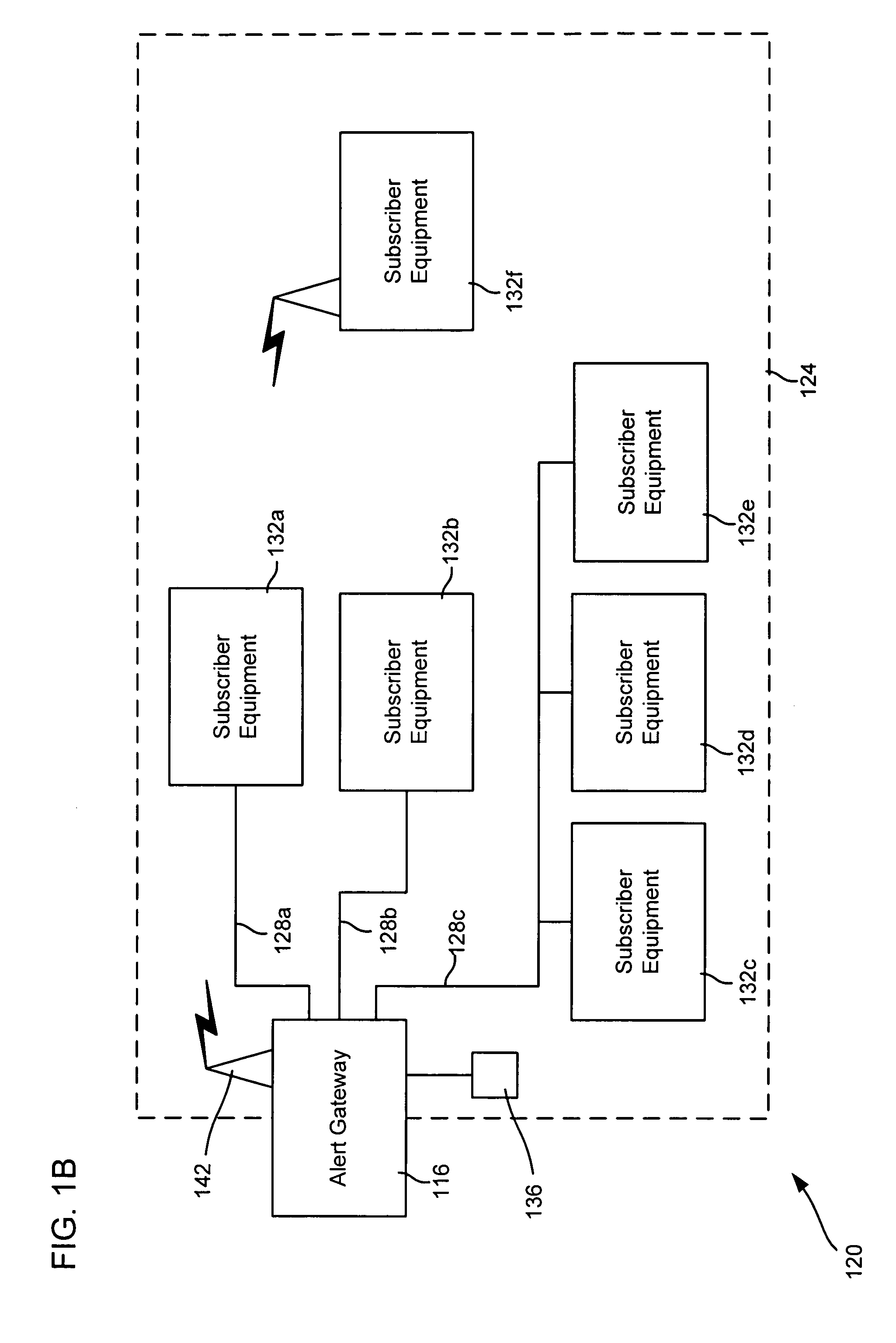
Alert gateway, systems and methods
ActiveUS20050030977A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionPublic informationReal-time computing
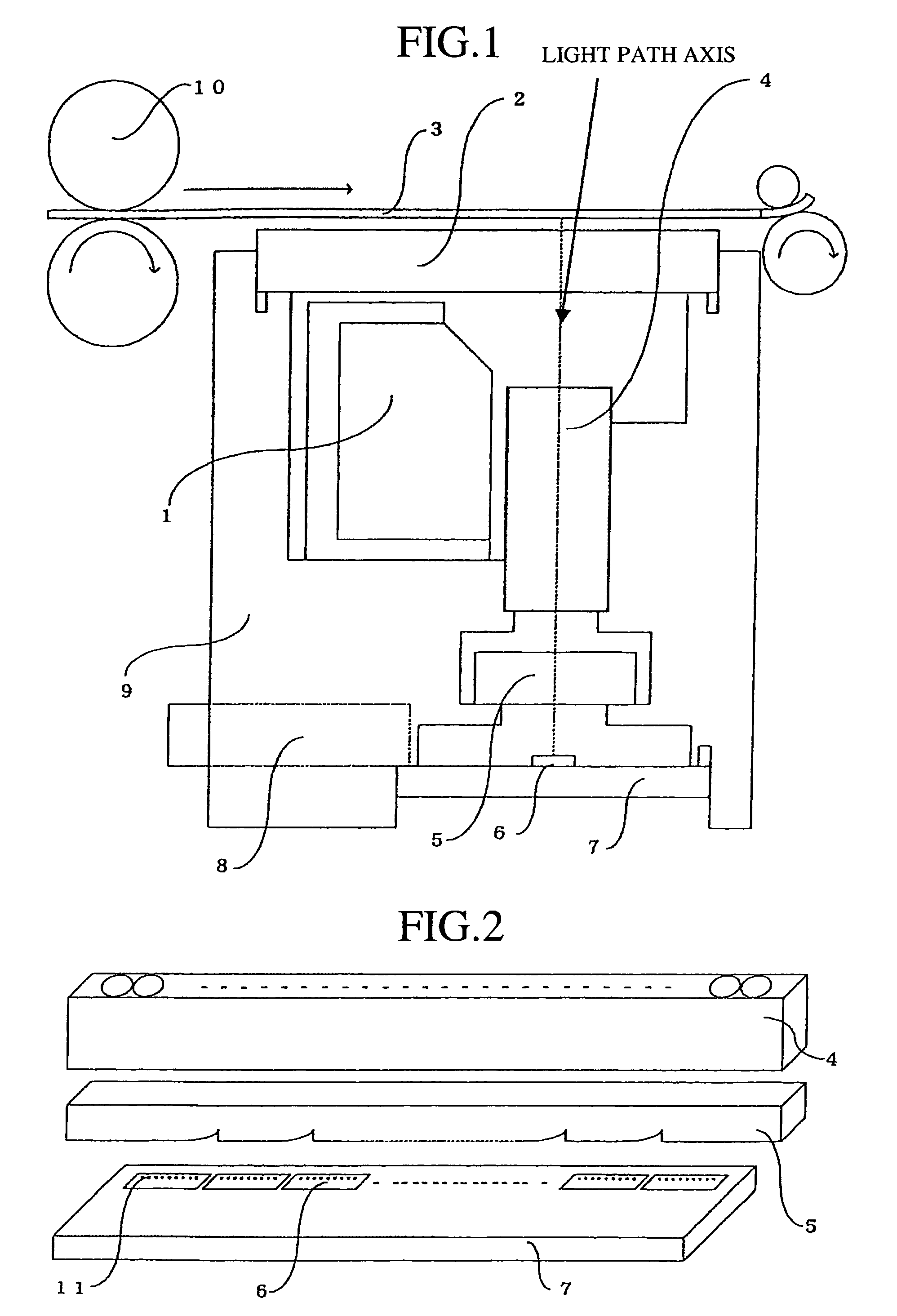
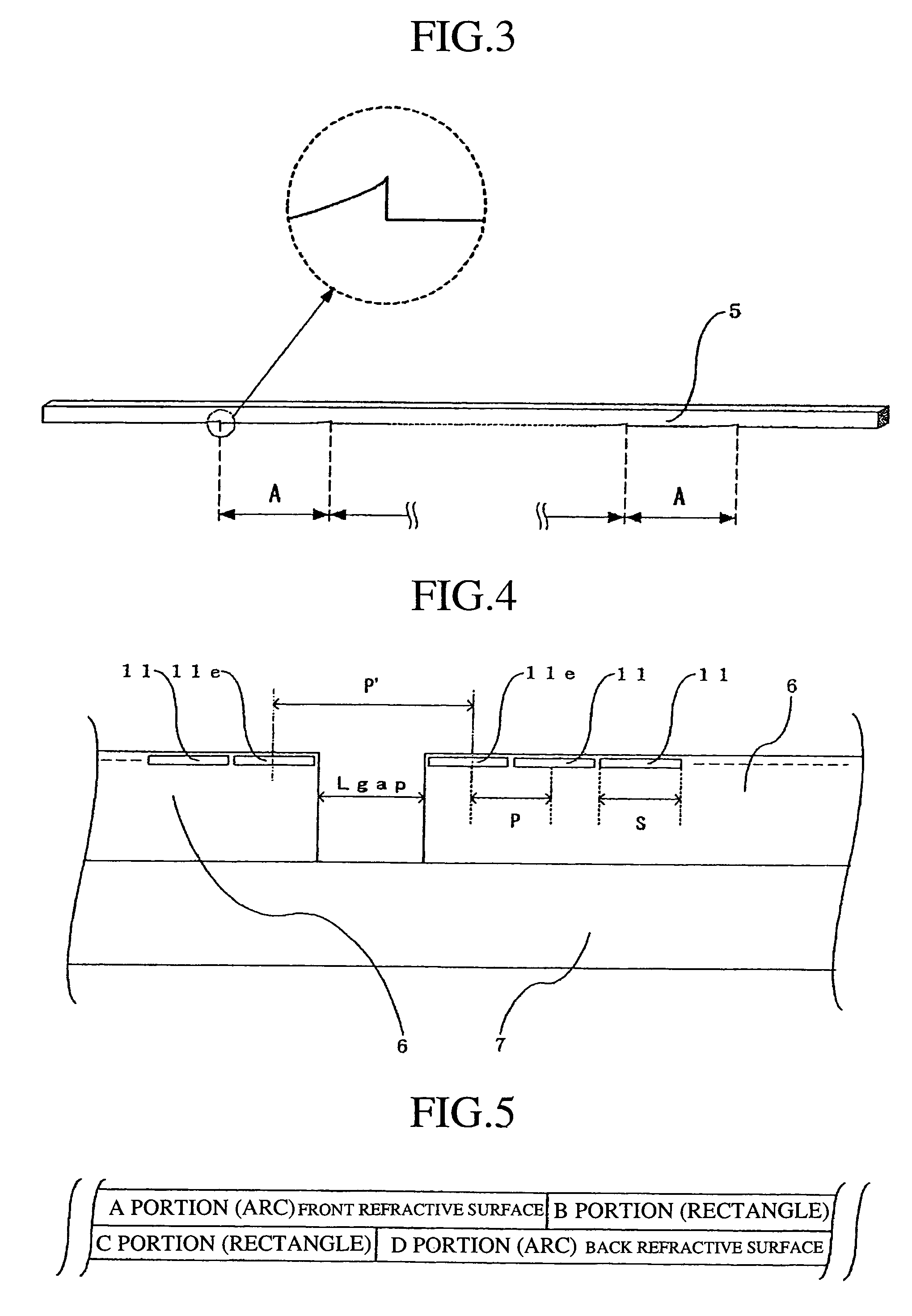
Embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for distributing urgent public information. Merely by way of example, urgent public information, such as an alert message, may be received by, inter alia, an alert gateway device. The alert message may then be distributed to a subscriber in any of a variety of ways, including by telephone, by data message (e.g., to a computer), by video message (e.g., via a television), by display on an alert notification device. In some embodiments, the alert gateway device may process the alert message and / or may determine how to provide the alert message to the subscriber.
Owner:QWEST
Methods, systems and apparatus for providing urgent public information
ActiveUS7194249B2Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionReal-time computing
Embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for distributing urgent public information. For example, one exemplary of the invention provides a method for providing an alert to a subscriber. The exemplary method comprises receiving an alert message from at least one alert source. The alert message often will be pertinent to at least one of the subscribers. The alert message can comprise an alert and associated alert information. The alert information can provide information about the alert such that the information can be analyzed determine whether a particular subscriber likely should receive the alert. Other embodiments provide systems, which can be used to perform the methods of the invention.
Owner:QWEST
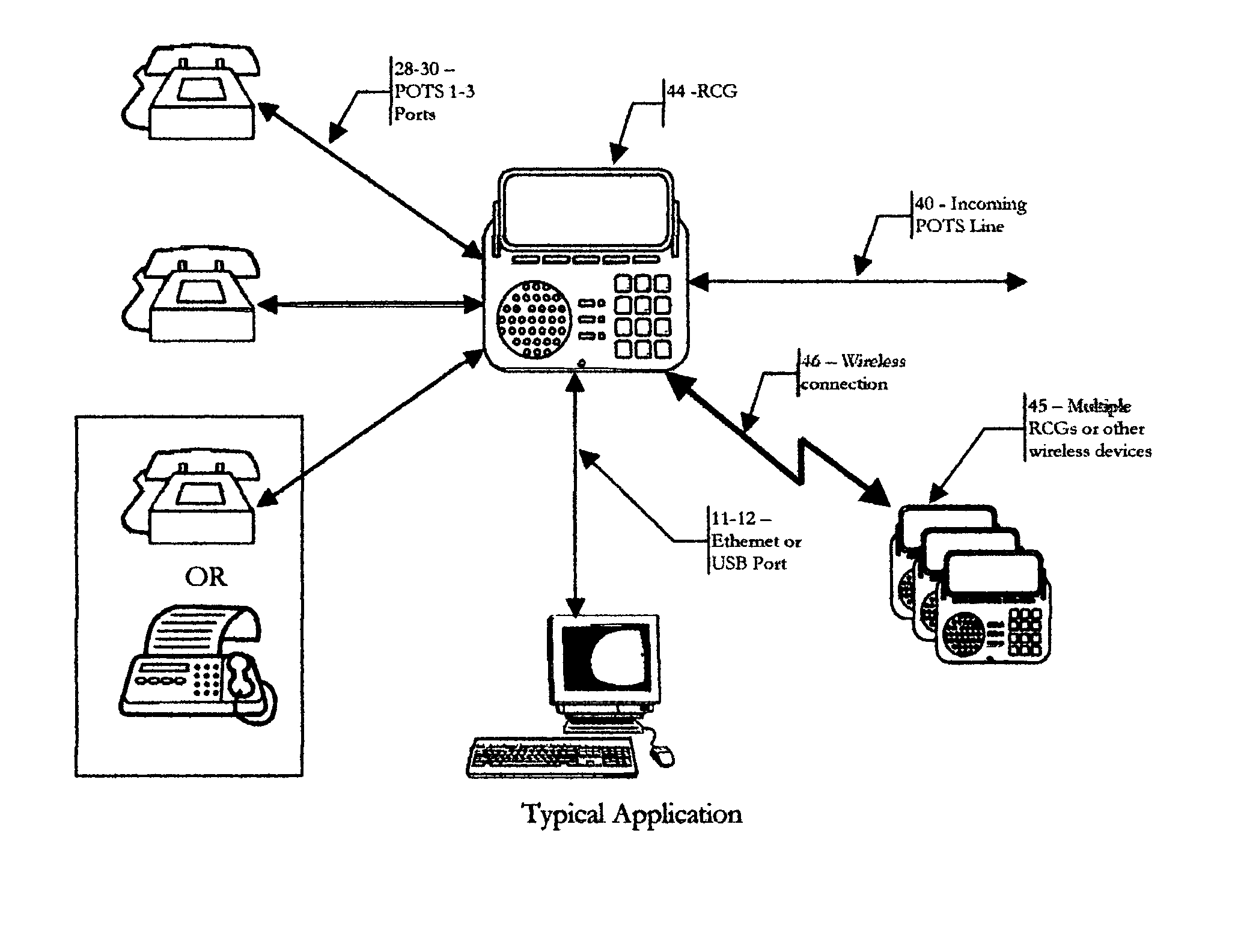
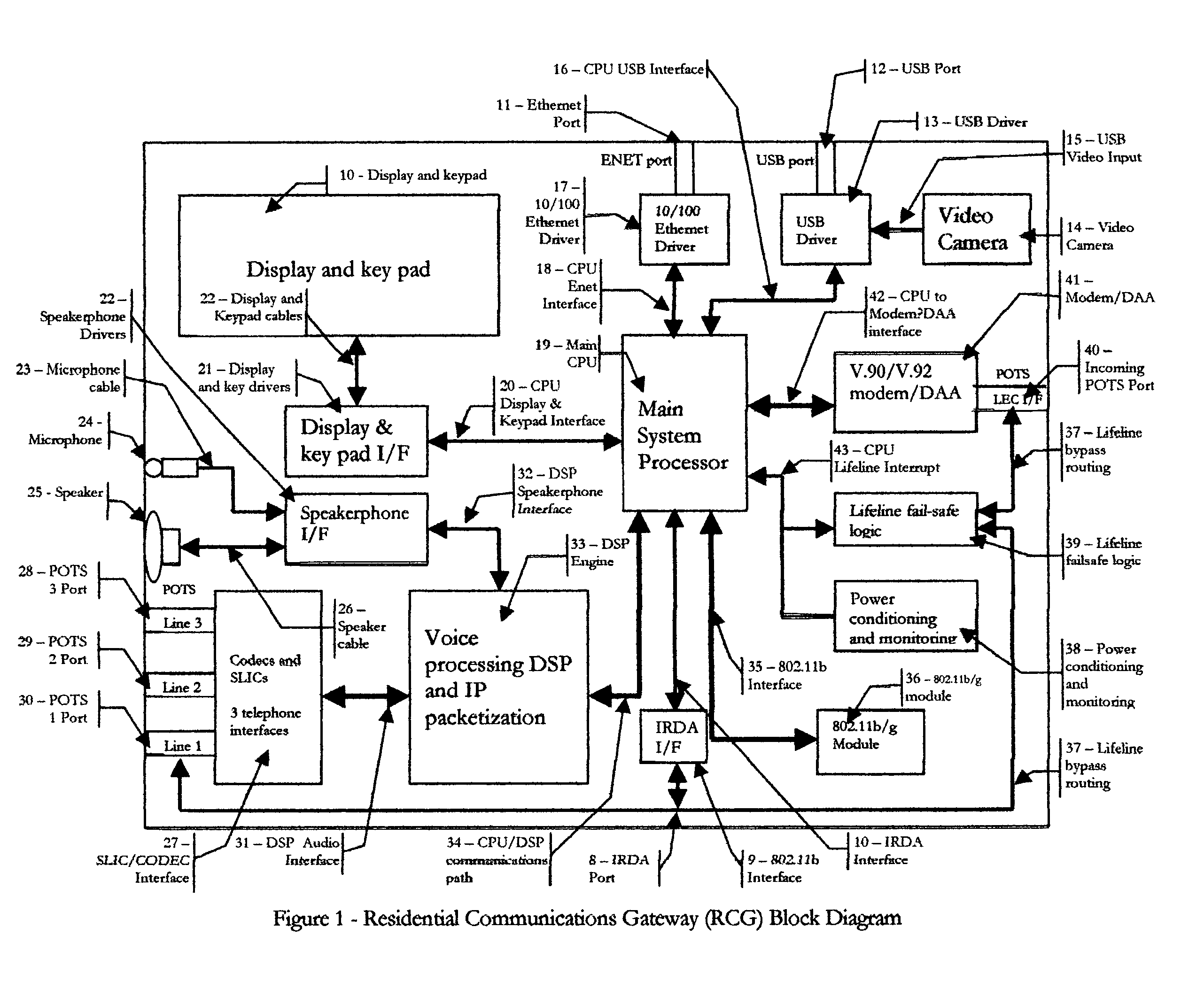
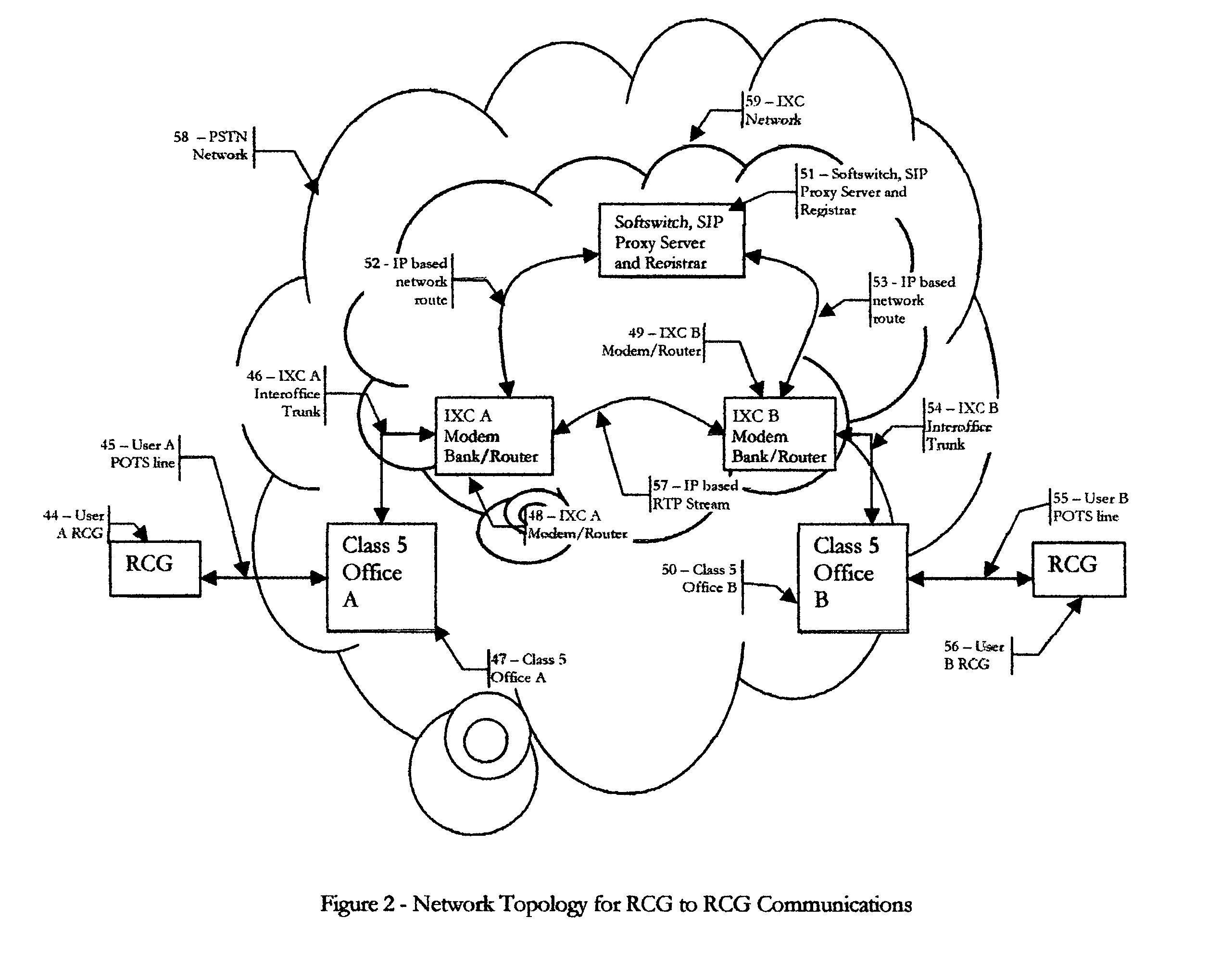
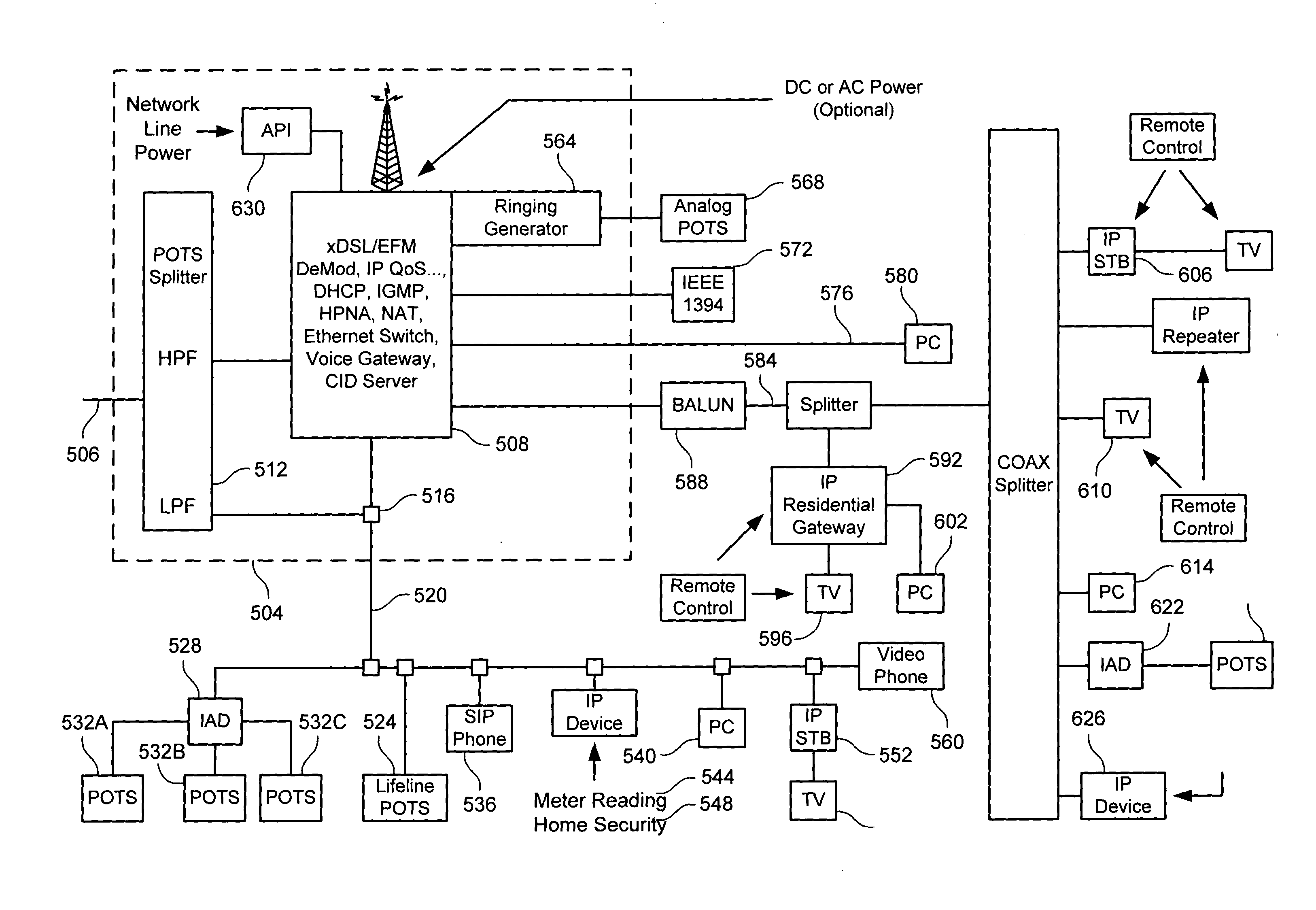
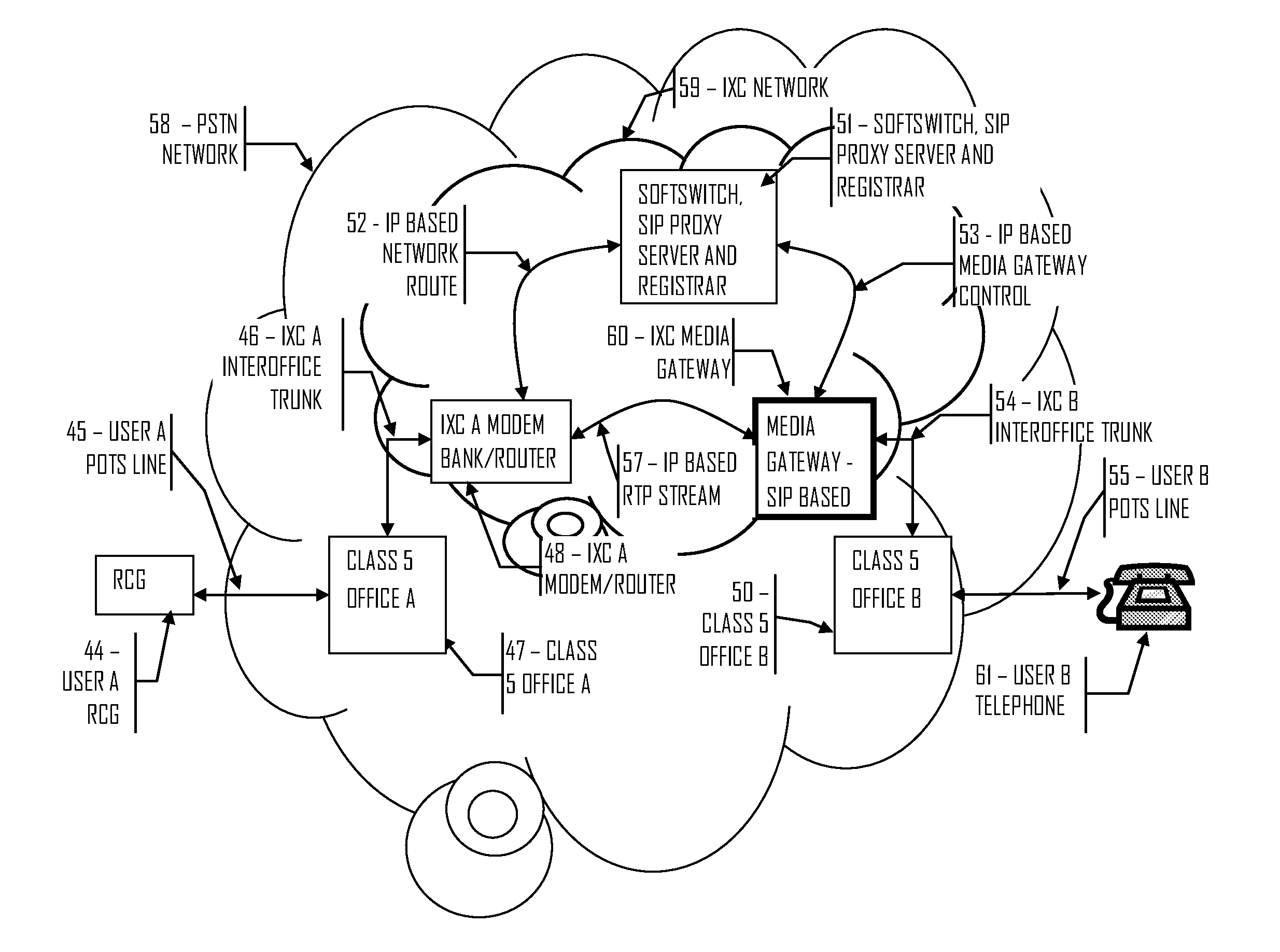
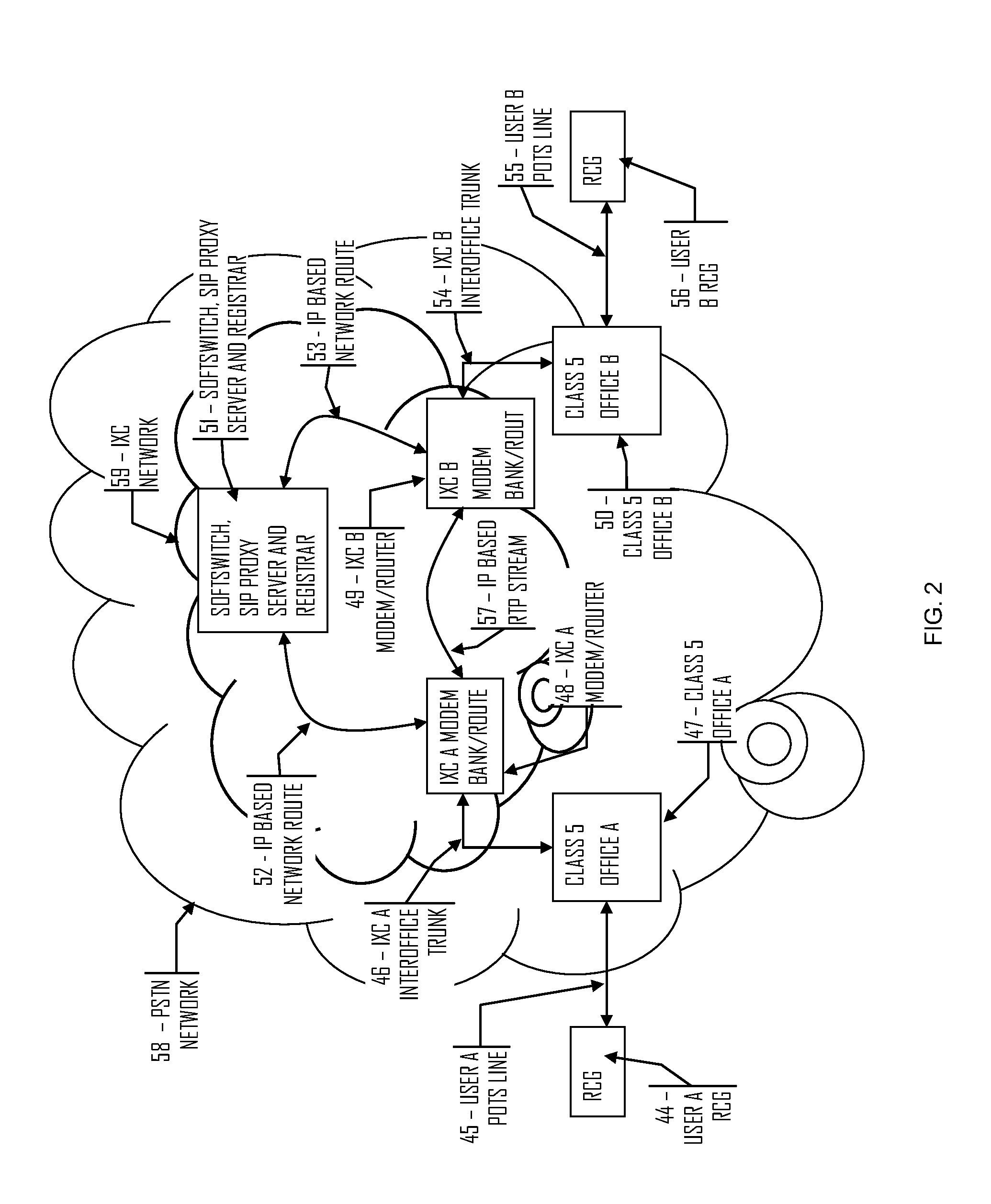
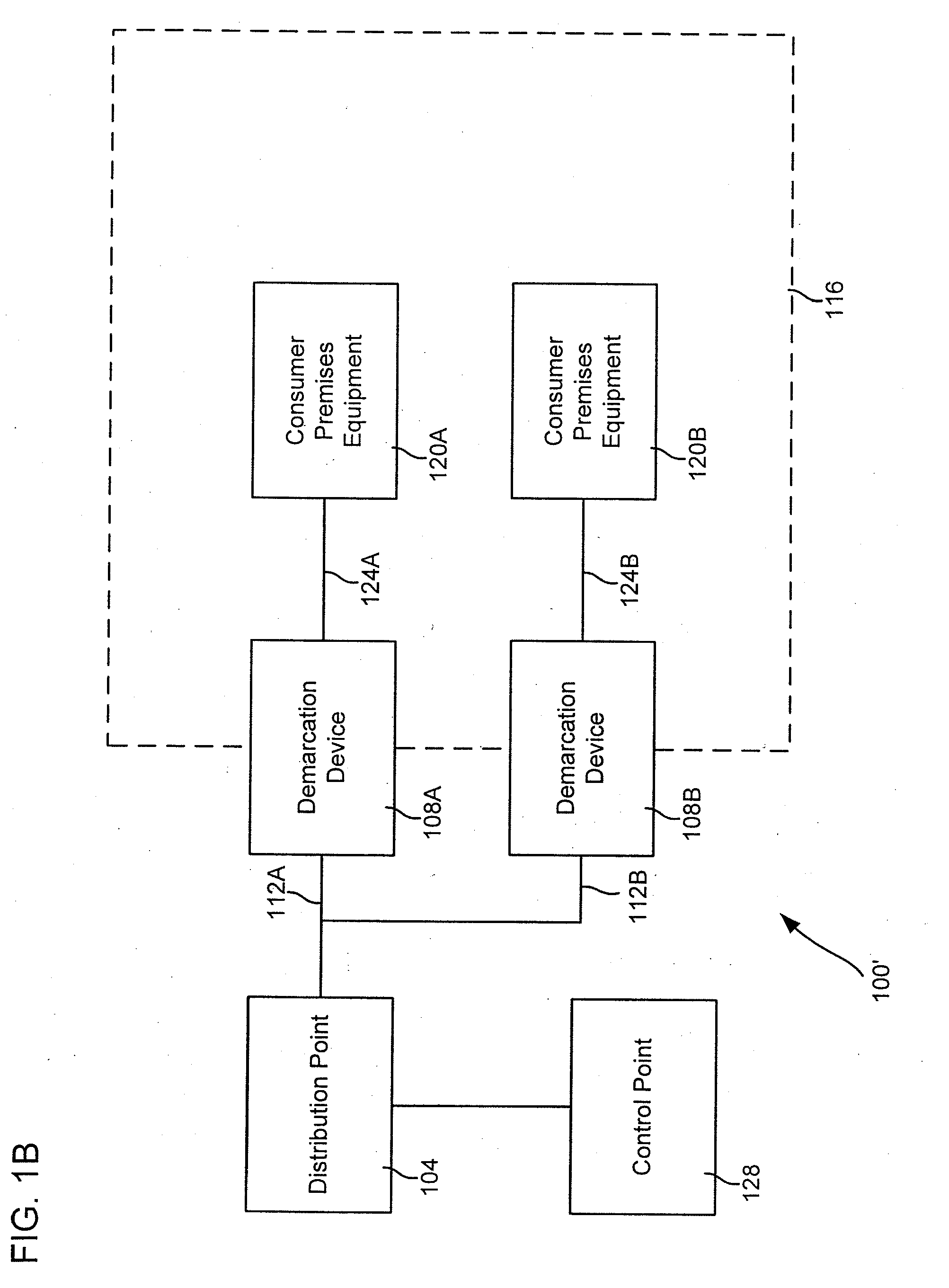
Residential communications gateway (RCG) for broadband communications over a plurality of standard POTS lines, with dynamic allocation of said bandwidth, that requires no additional equipment or modifications to the associated class 5 offices or the PSTN at large
ActiveUS20050078690A1Easy to deployEliminates tremendously expensive infrastructure costInterconnection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementResidenceEngineering
The Residential Communications Gateway (RCG) is a broadband communications device that combines all voice, data and video communications to and from a typical residence or small business for transmission over a single, or a plurality of Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) lines separately or in conjunction with, a wireless broadband backbone. The RCG does this by employing packetized data with Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technologies combined with RF communications technologies. A key consideration to the design of the RCG is that no additional or special transmission equipment must be installed at the Central Office or anywhere else in the network to enable new calling features provided by the RCG as is the case with DSL and Cable systems. By eliminating the requirement for costly infrastructure enhancements, ubiquitous high speed communications and services can be deployed to every POTS subscriber.
Owner:COMPETITIVE ACCESS SYST INC
Methods, systems and apparatus for providing video transmissions over multiple media
ActiveUS20050144645A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionService provisionVideo transmission
Various embodiments of the invention provide novel apparatus, methods and systems for providing relatively high-speed bandwidth to enable, inter alia, video transmission services over media previously unable to support such services. In accordance with certain embodiments, a device located at the telecommunication service provider can logically couple two or more physical media to provide a single, consolidated source of bandwidth, which can be used to transmit data, which can represent a video signal. In accordance with other embodiments, a device located at the subscriber's location can be used to receive the data from each of the two physical media and recreate the video signal from the data, such that the video signal can be transmitted to a display device, such as a television, monitor, etc.
Owner:QWEST
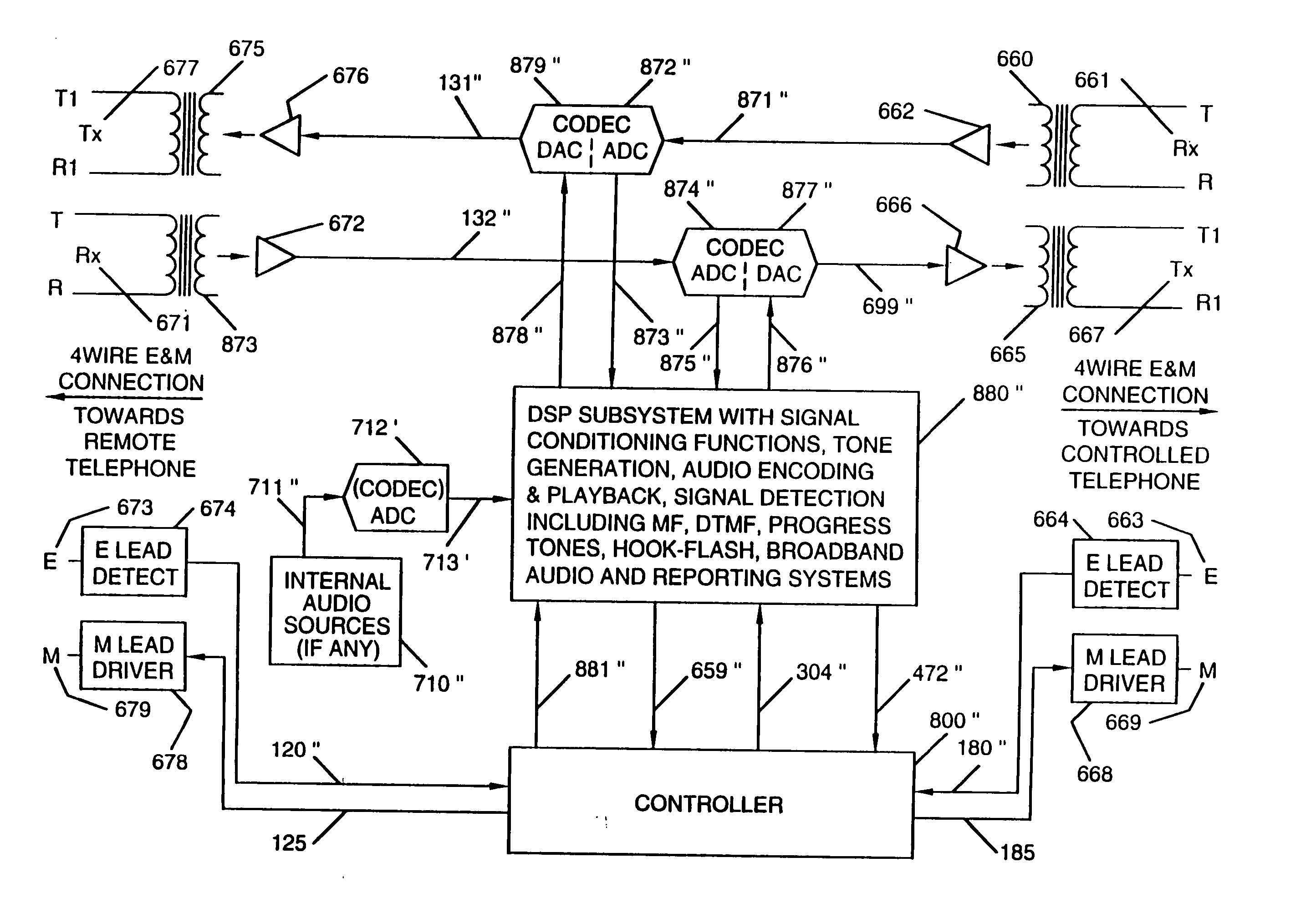
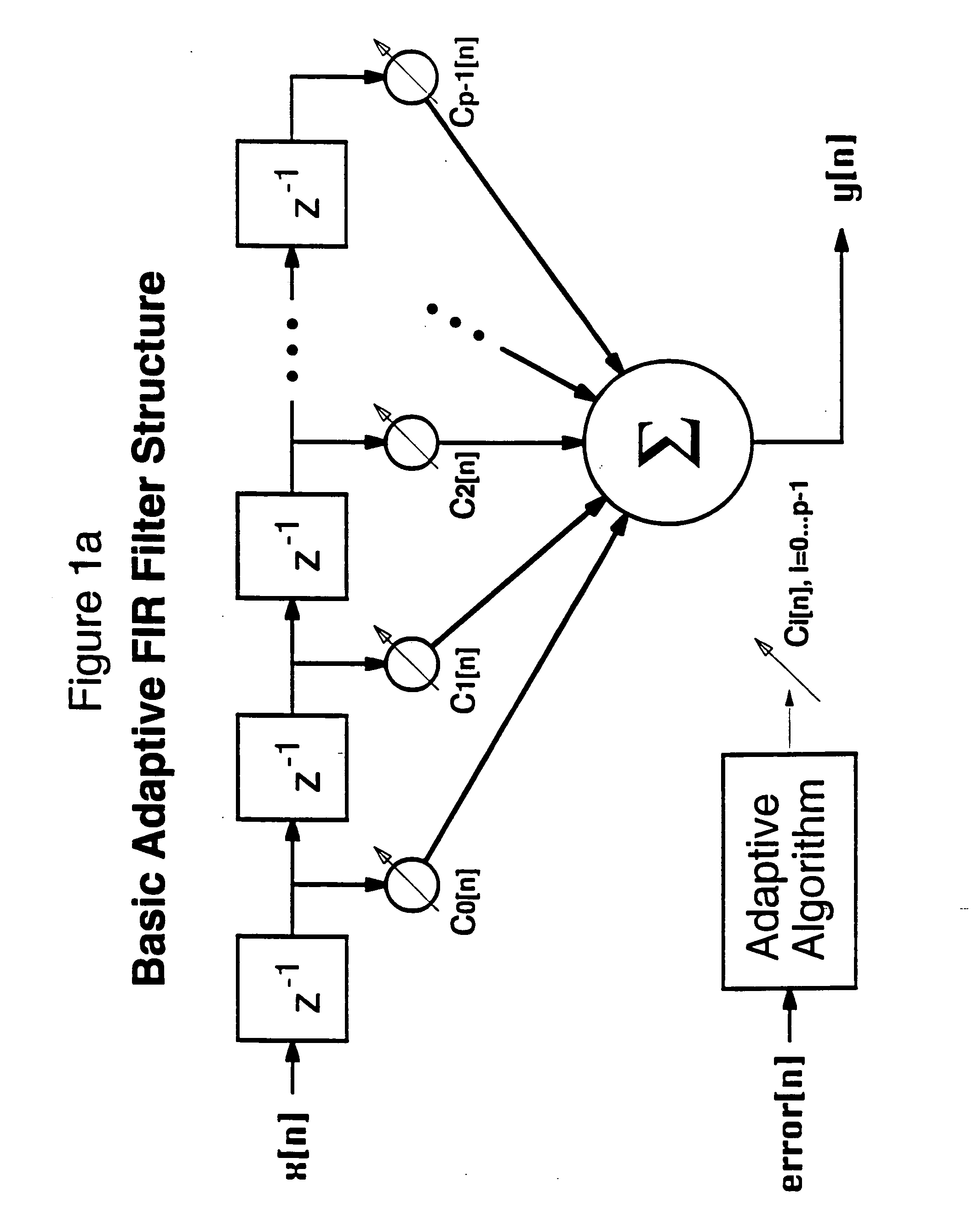
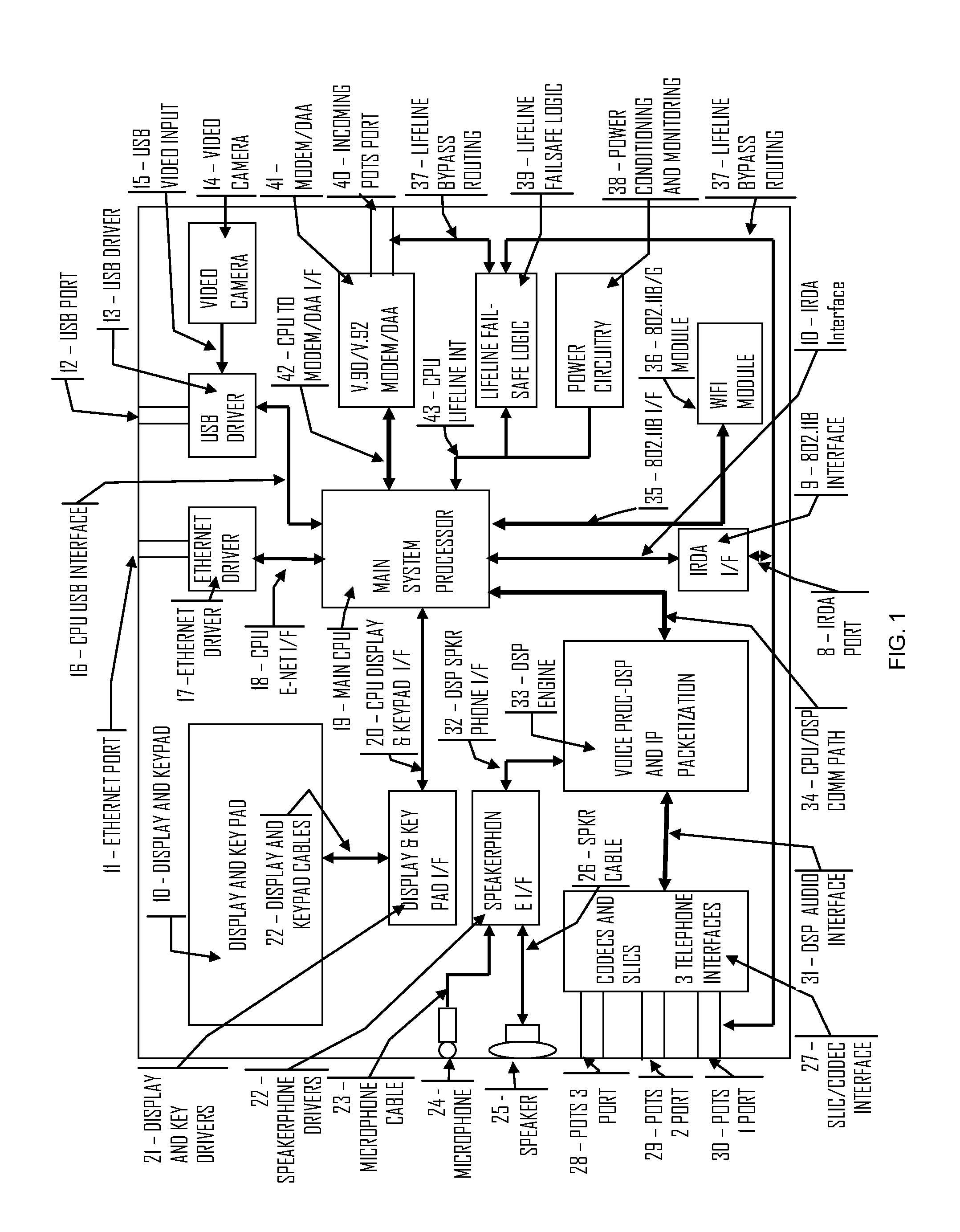
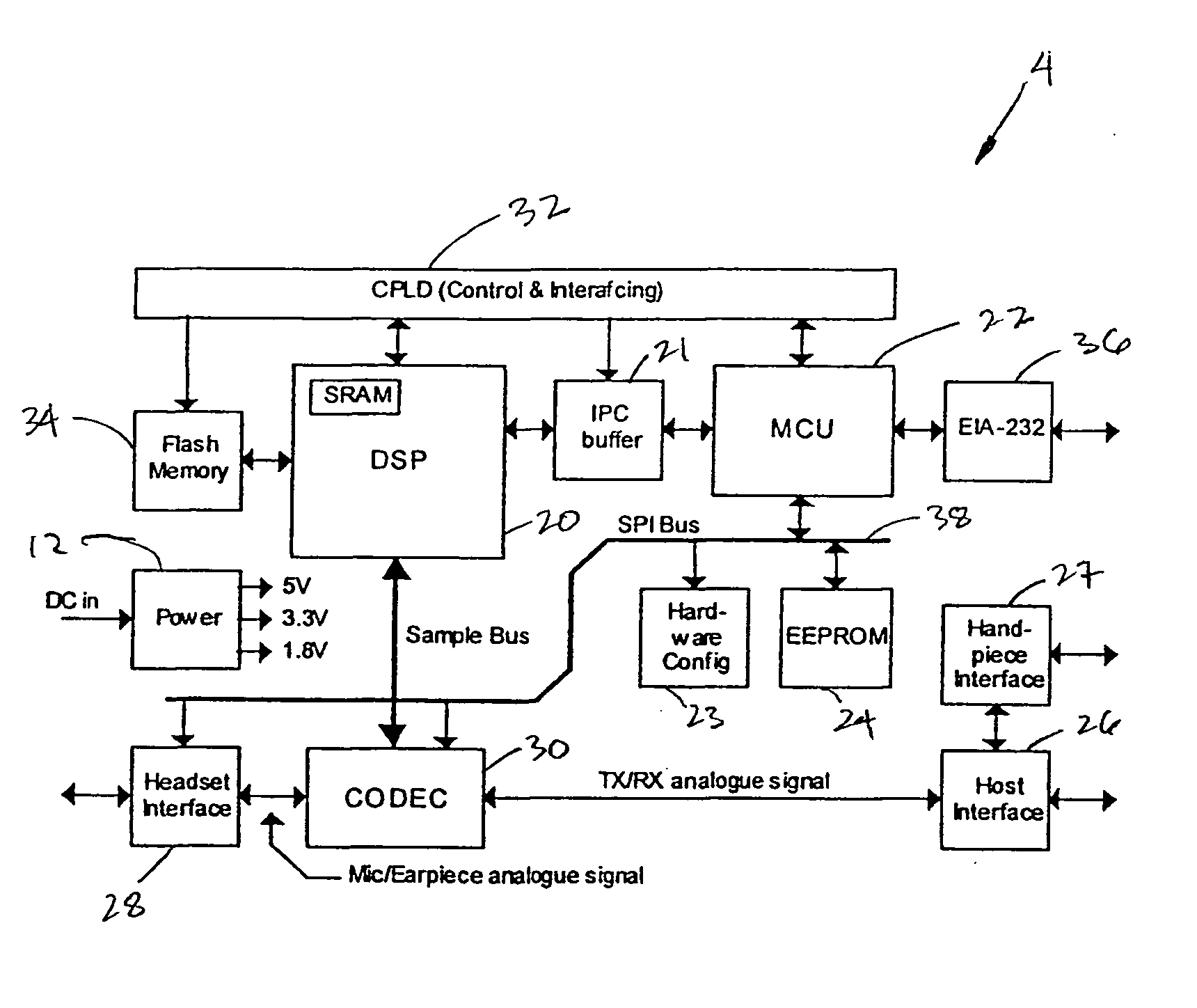
Digital signal processing system and method for a telephony interface apparatus
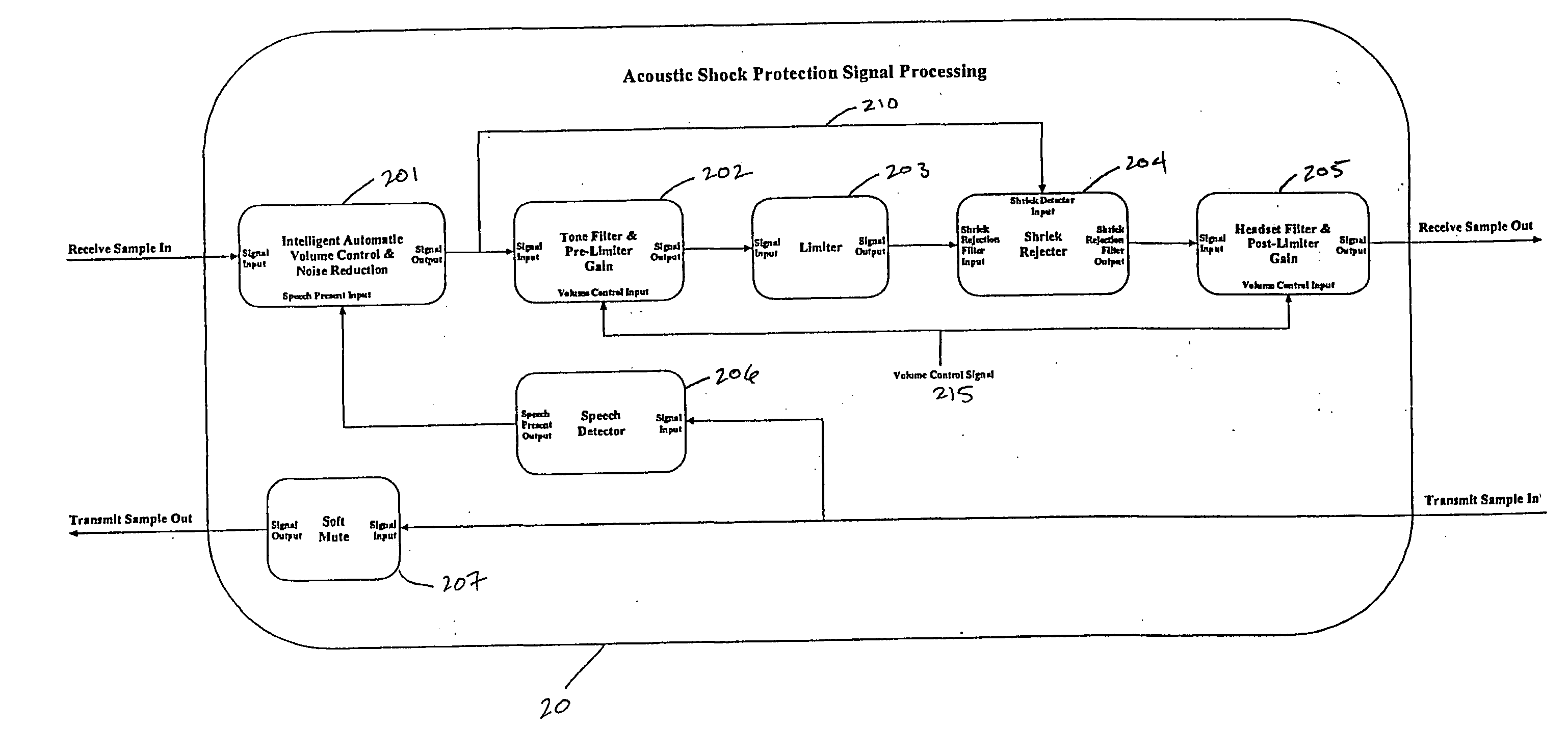
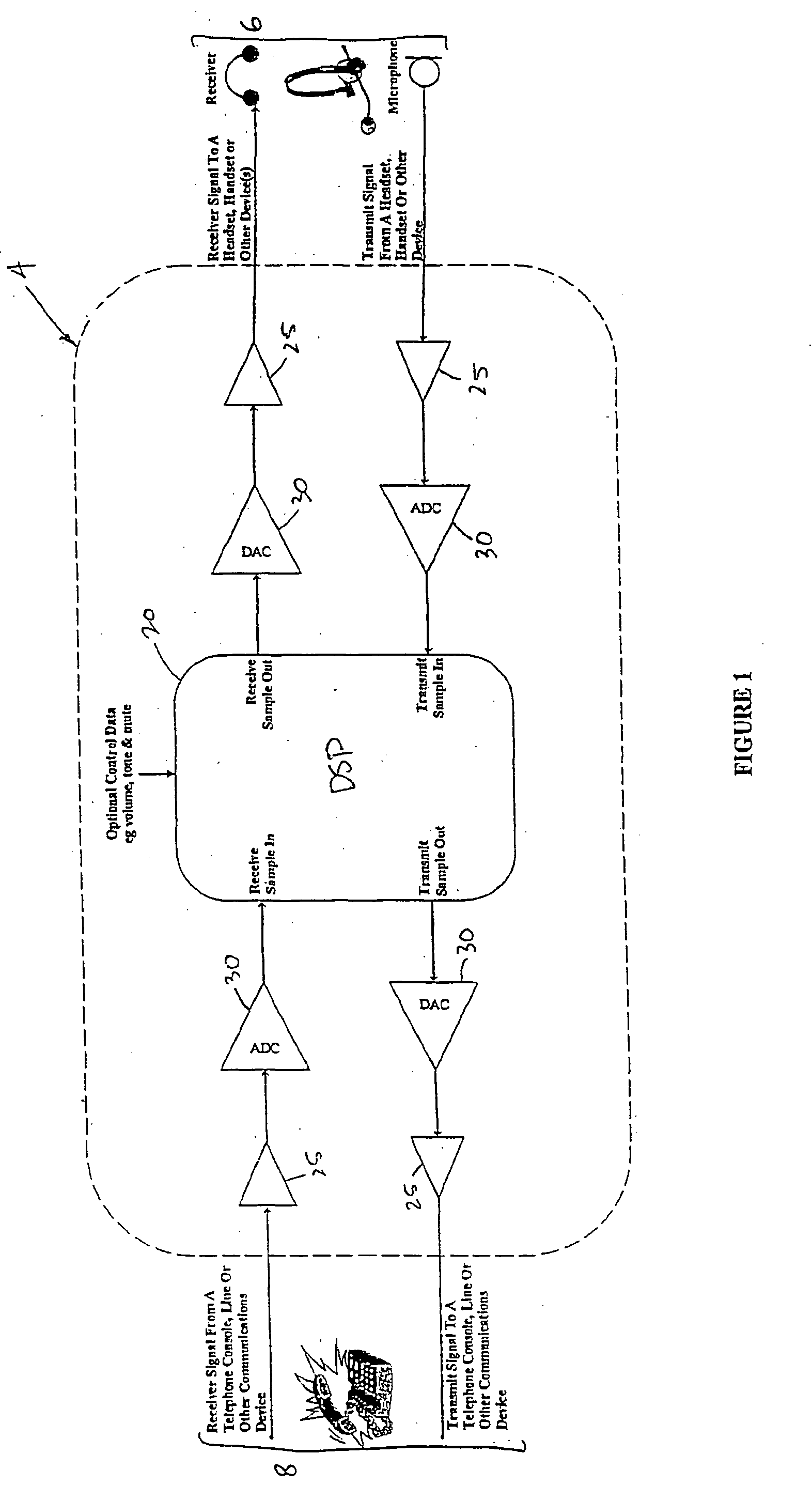
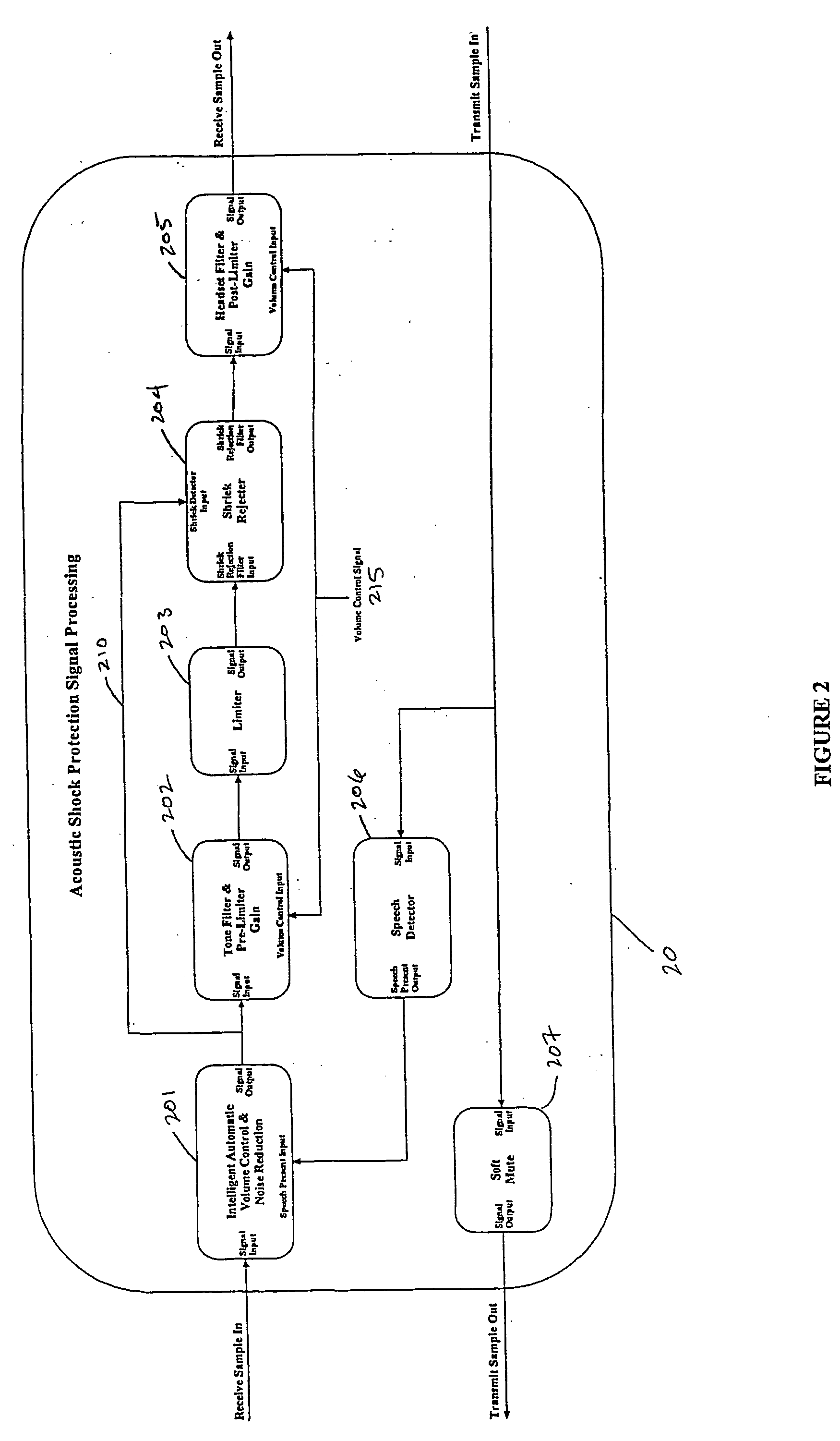
InactiveUS20050018862A1Lower Level RequirementsLess-dangerous to operatorSpeech amplifier applicationsSubstation speech amplifiersDigital signal processingAudio frequency
A signal processing method including the steps of: receiving a first audio signal; detecting the presence of one or more shrieks within an audible frequency range of said audio signal; creating one or more filters to selectively attenuate the respective one or more shrieks within the audible frequency range; filtering the audio signal using the one or more filters; and transmitting the filtered audio signal to an audio telephone device.
Owner:HEAR WORKS PTY LTD
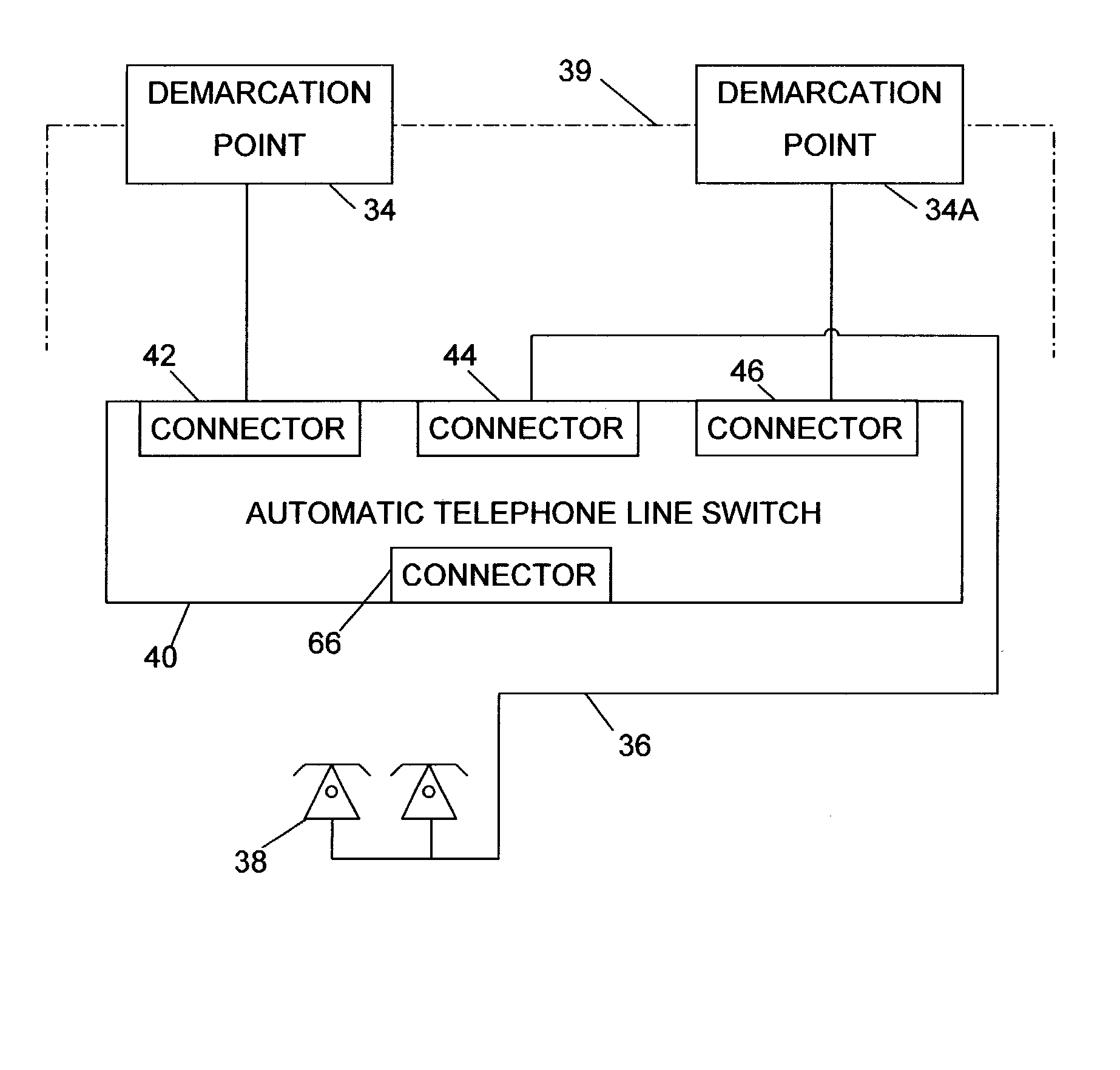
Automatic telephone line switch
InactiveUS20050117732A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSubstations coupling interface circuitsSignal onAmpere
An apparatus (40) and method for switching a customer-premises telephone line (36) between a plurality of local telephone networks (35). The local telephone networks may have different electrical and operational characteristics. Using less than 100 micro-amperes of current from the telephone networks, the apparatus (40) requires no external power and performs its tasks without interfering with the normal operation of the telephone networks including test equipment, terminal equipment, data transmission on the telephone line and test equipment. The method involves monitoring electrical signals on both local telephone networks (35) and using this information to assign a weight to each network. The customer-premises telephone line (36) is switched to the telephone network having the highest weight. The advantages are the elimination of a service call by a technician to manually switch the customer premises telephone line (36), equal access by both service providers to the switch and a seamless interface to the telephone networks.
Owner:ARPIN CLAUDE
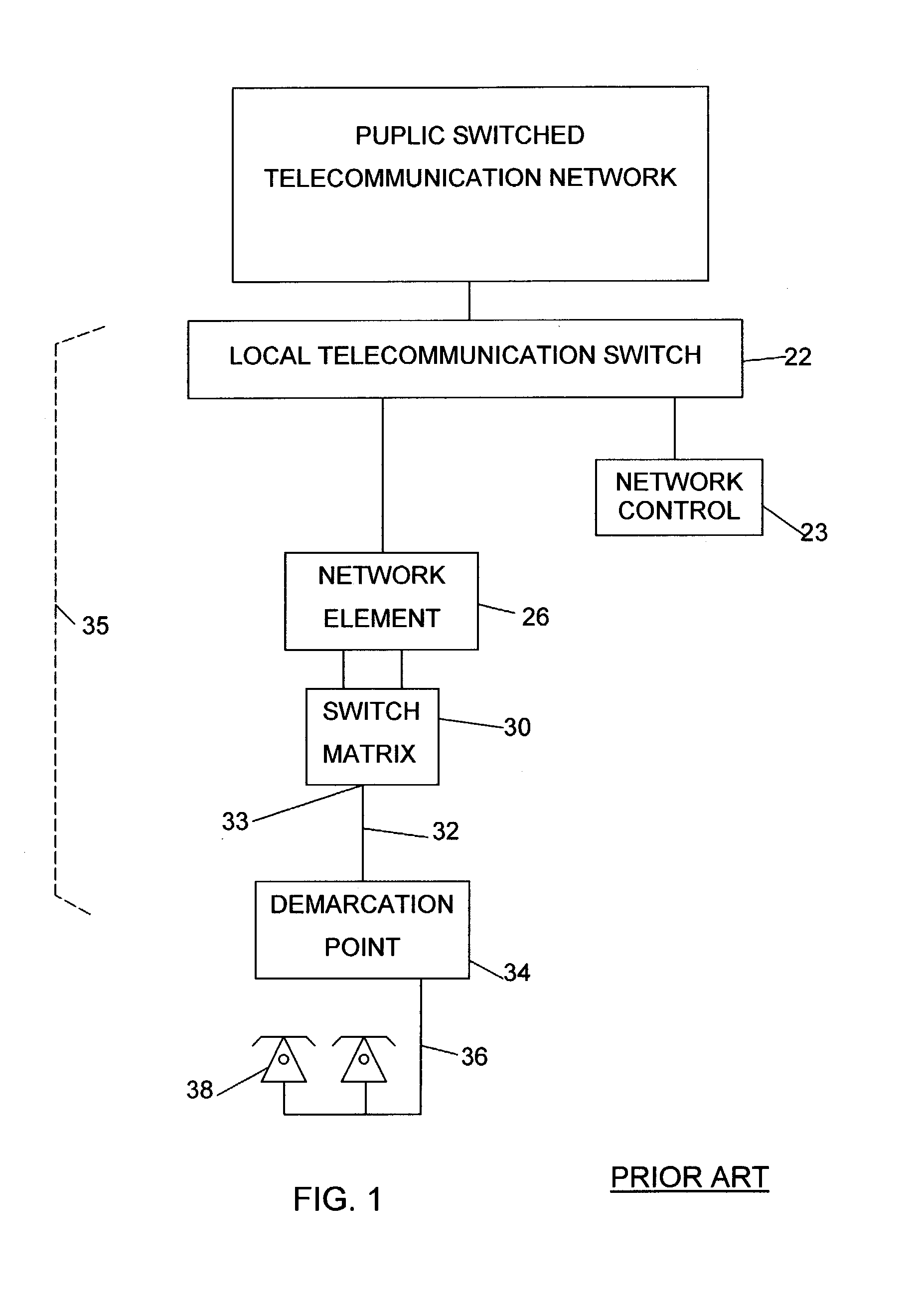
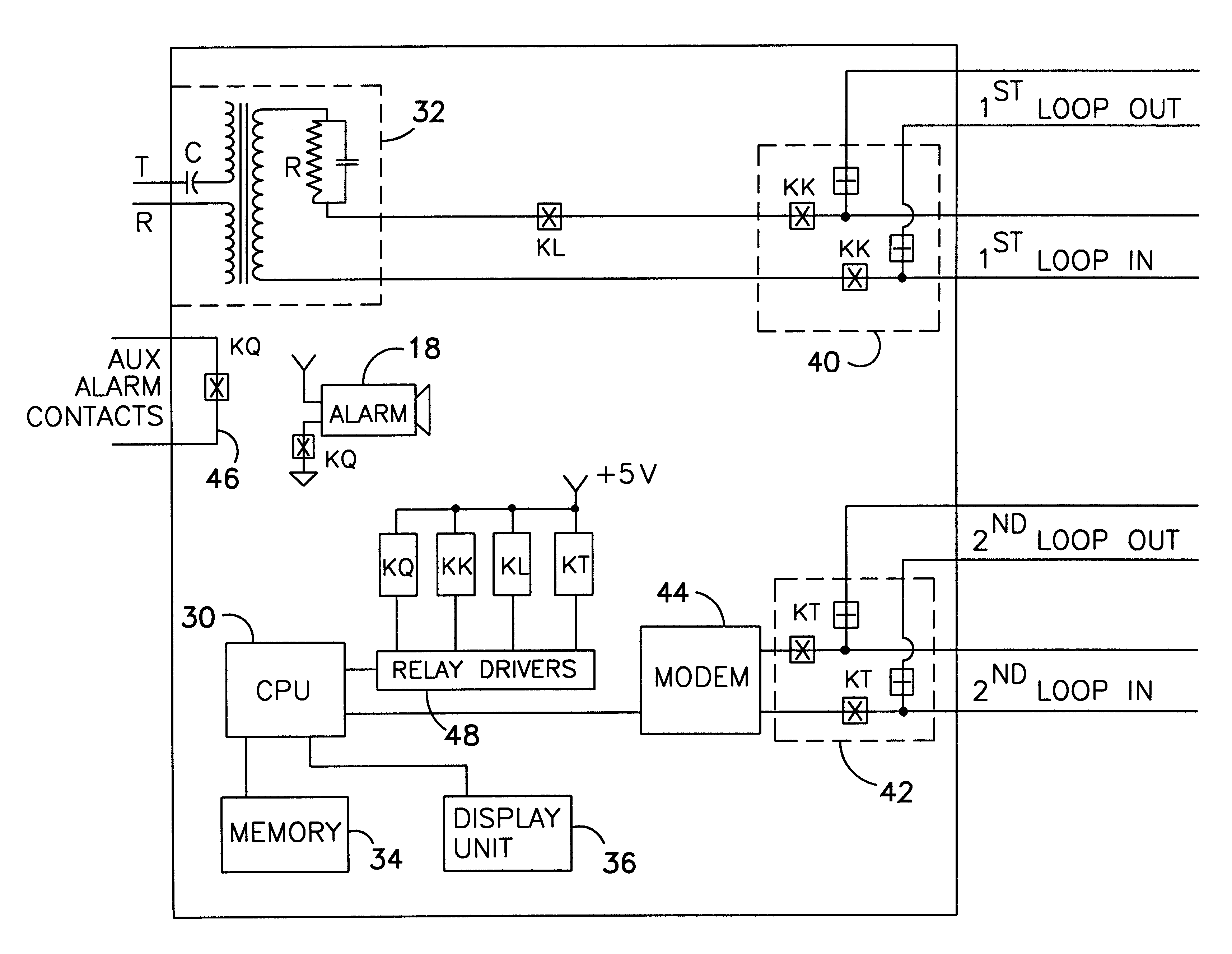
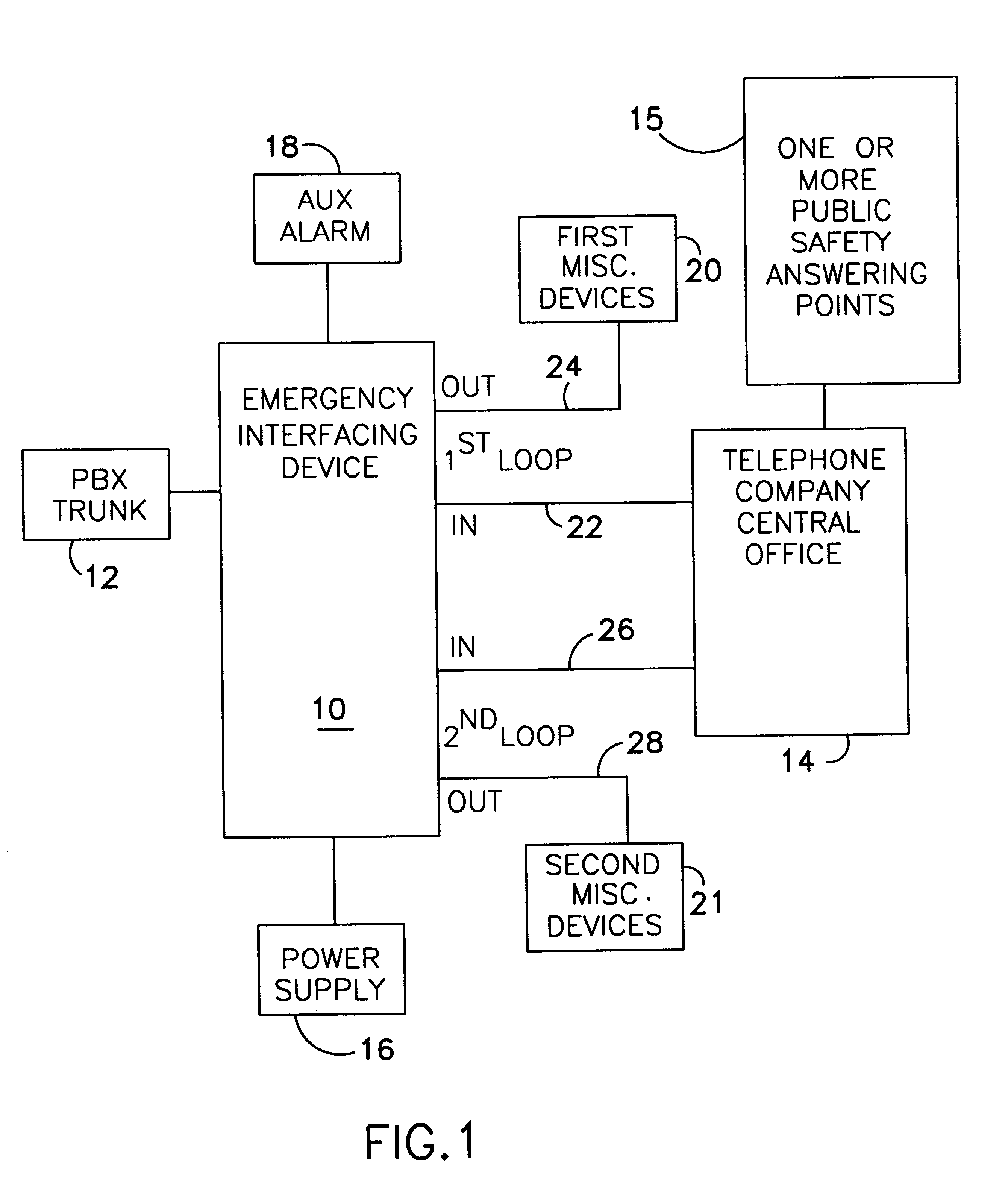
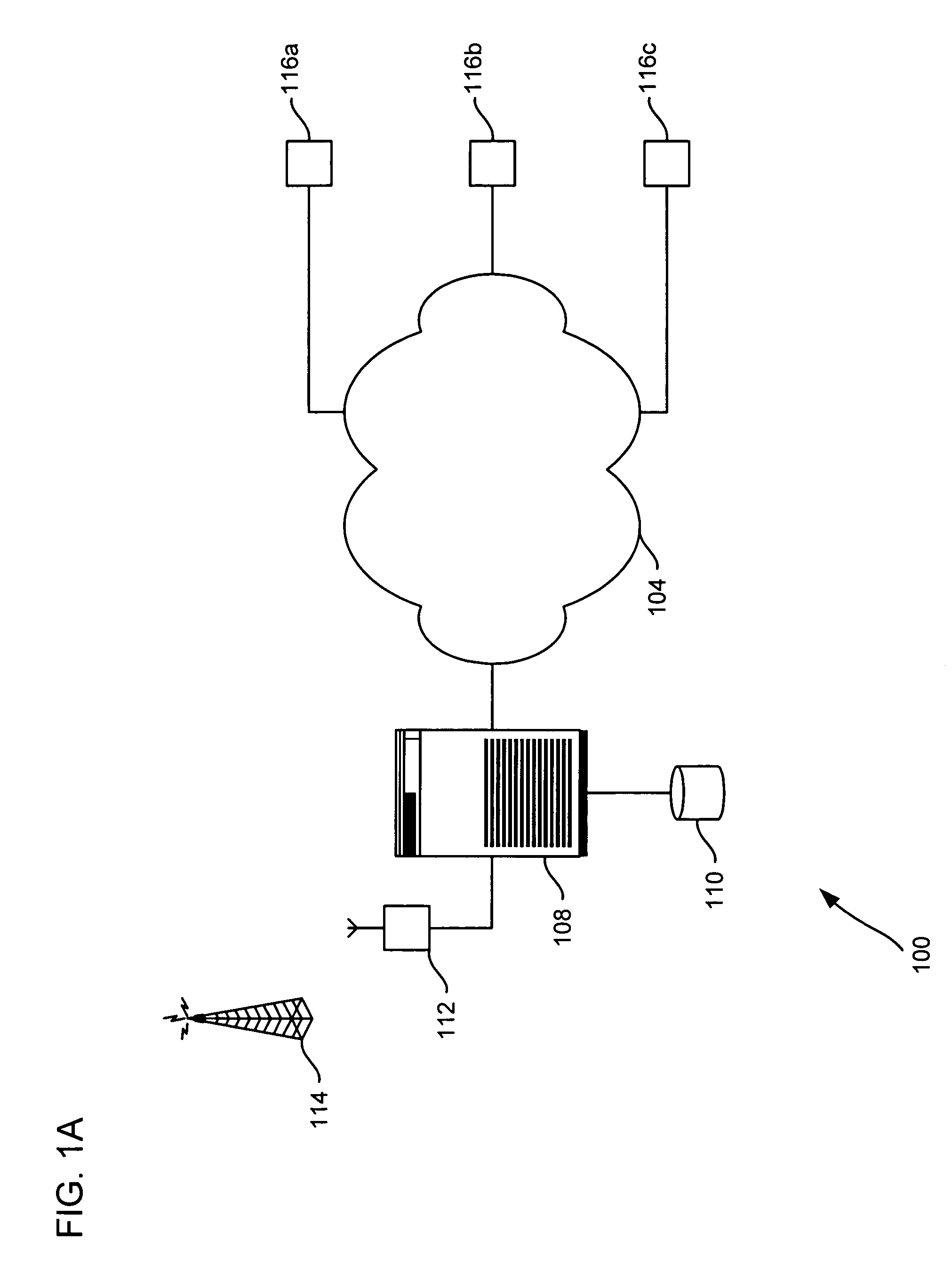
Interfacing device to be used with a telephone system terminal for transmitting extended station information to a public safety answering point
InactiveUS6266397B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersBranch exchangeEmergency situations
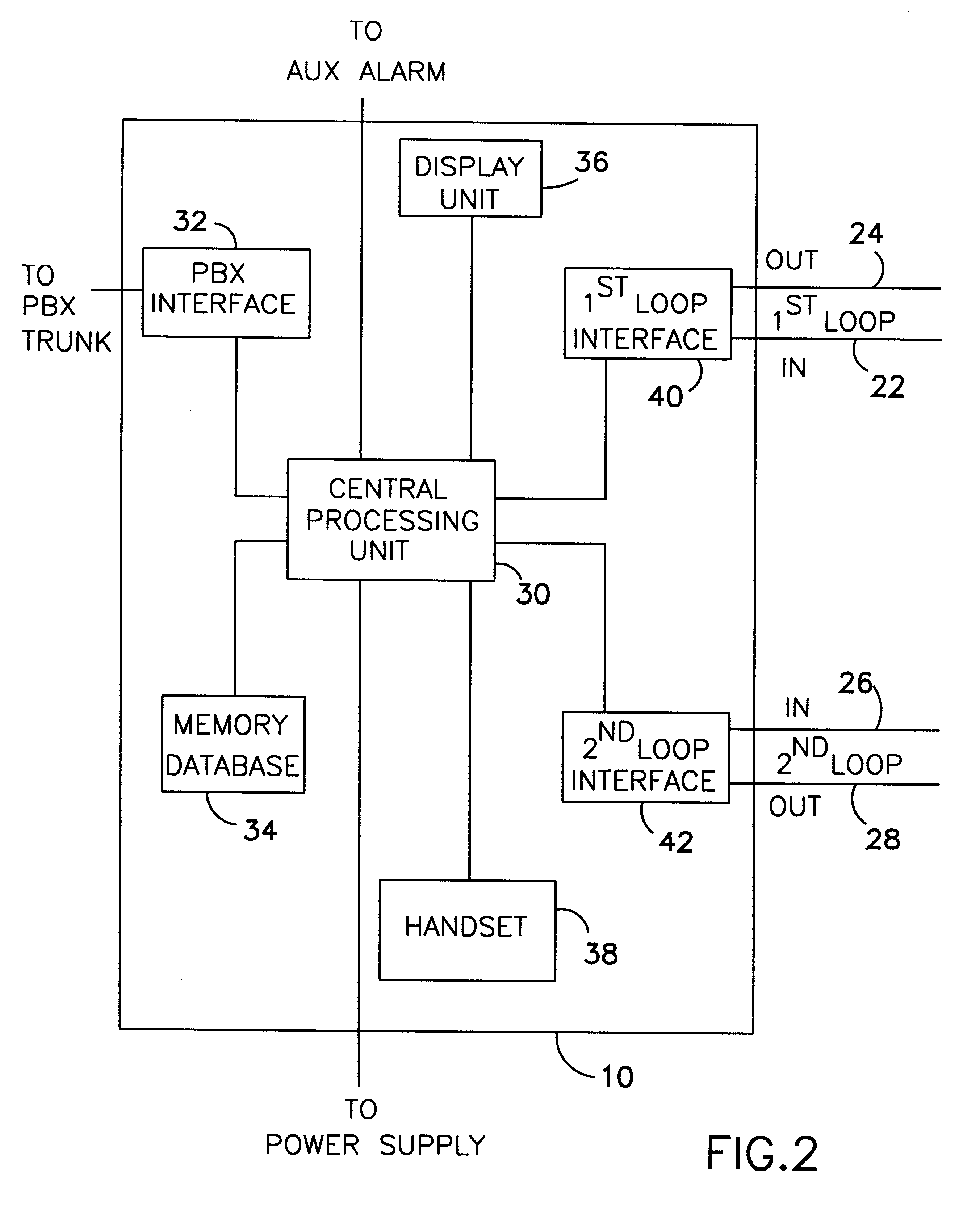
A method or apparatus to be used with a telephone system, such as a private branch exchange (PBX) trunk, for transmitting extended station information to an emergency call handling center, such as a public safety answering point (PSAP). The apparatus has a central processing unit (CPU) which is connected a PBX interface, a memory database, a first loop interface, and a second loop interface. The PBX interface is connected to the PBX trunk and receives an emergency call from a specified station which initiated the emergency call. The memory database stores information on the plurality of extension stations within a facility. The first loop interface is connected to the PSAP. The second loop interface is also connected to the PSAP. The CPU connects the audio of the emergency call to the first loop interface which in turn transmits the audio to the PSAP. The CPU searches the memory database for information about the specified station which initiated the emergency call, whereby the CPU sends extended station information to the PSAP over the second loop interface while maintaining contact between the specified station which initiated the emergency phone call and the PSAP.
Owner:STONER DAVID M
Self-installable and portable voice telecommunication service
InactiveUS6847704B1Telephone data network interconnectionsSpecial service for subscribersVoice communicationIp address
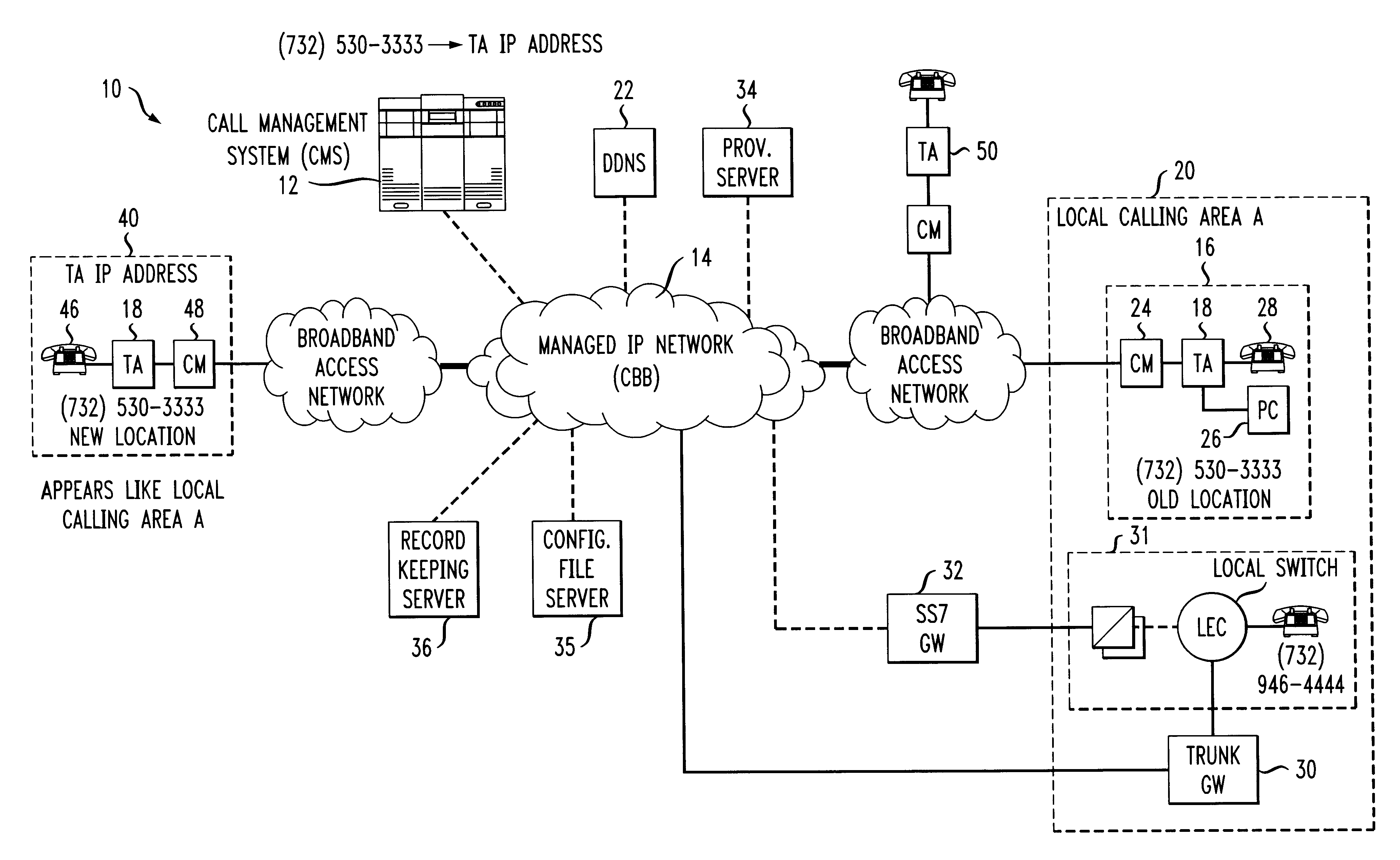
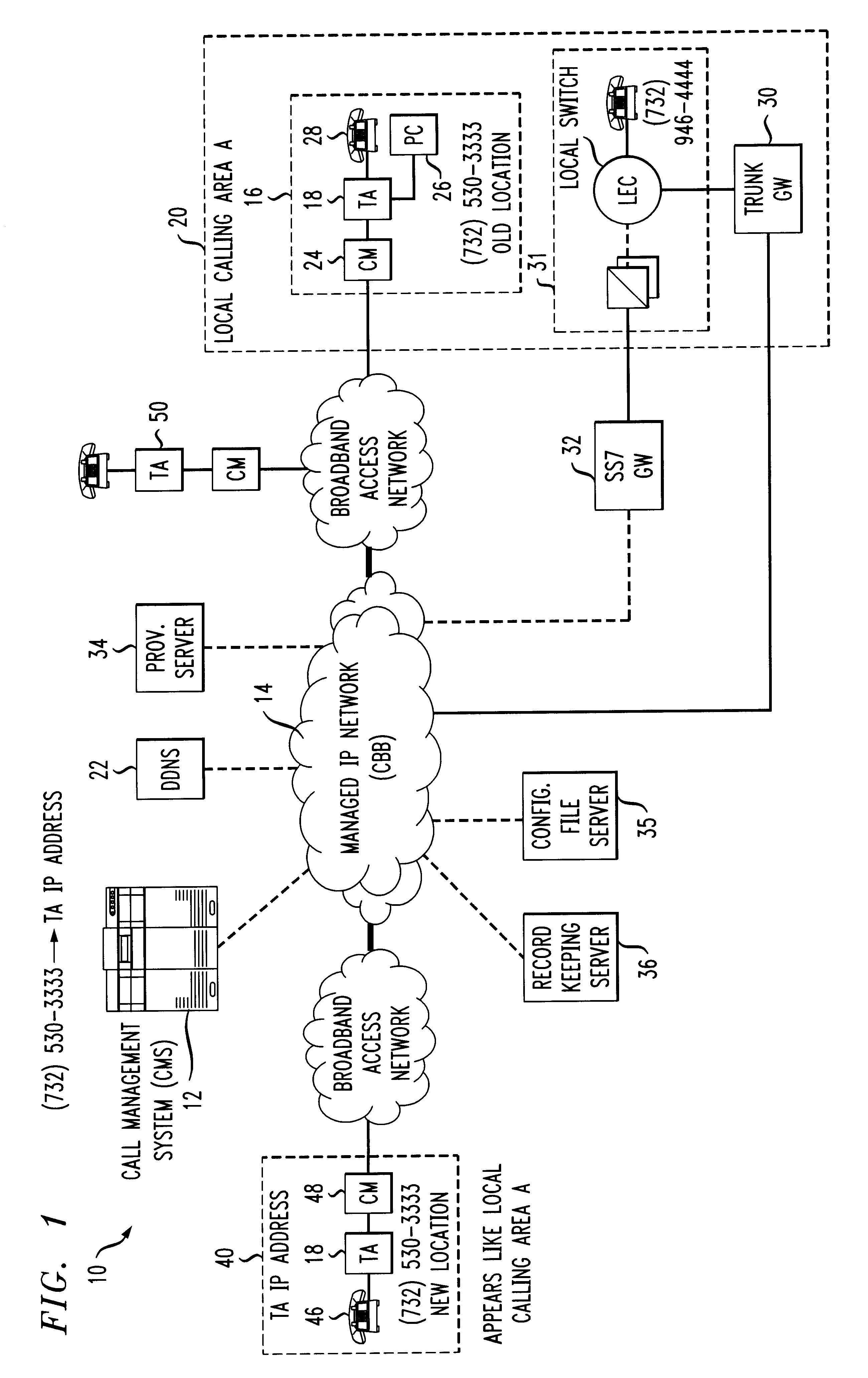
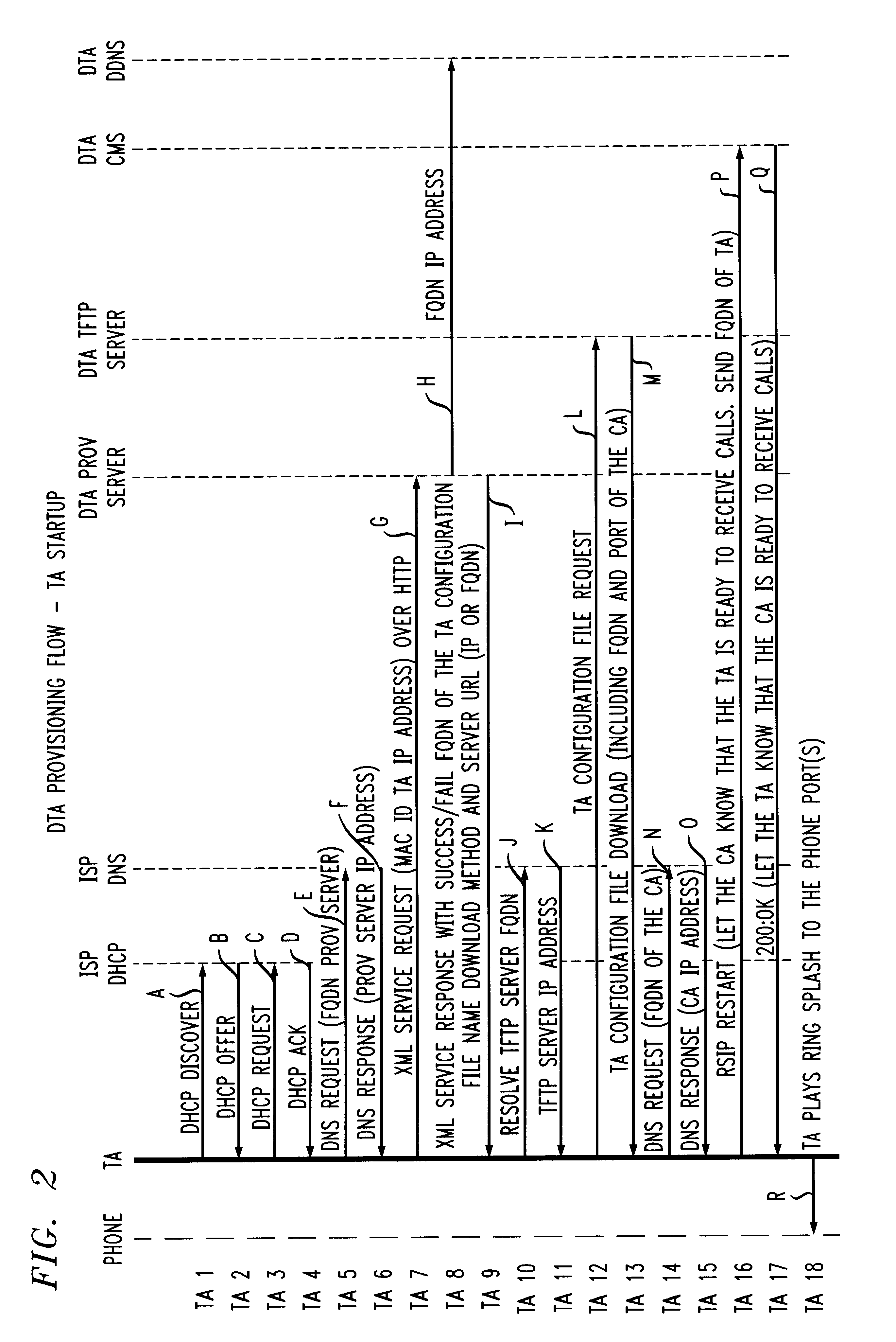
An architecture and technique for creating self-installable and portable telephony (dial tone) service that can be moved between any two locations that has access to both a voice communication network and a data network. A telephony adapter is used as a subscriber premises device that is connected between a conventional telephone set and both a voice network and a data network. A provisioning server communicates with the telephony adapter through the data network and maintains a record of the subscriber's local telephone number and IP address of the telephony adapter. As the subscriber moves from one location to another, the telephony adapter (once turned “on”) will communicate with the provisioning server and re-establish phone service, always using the same local phone number of the subscriber.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
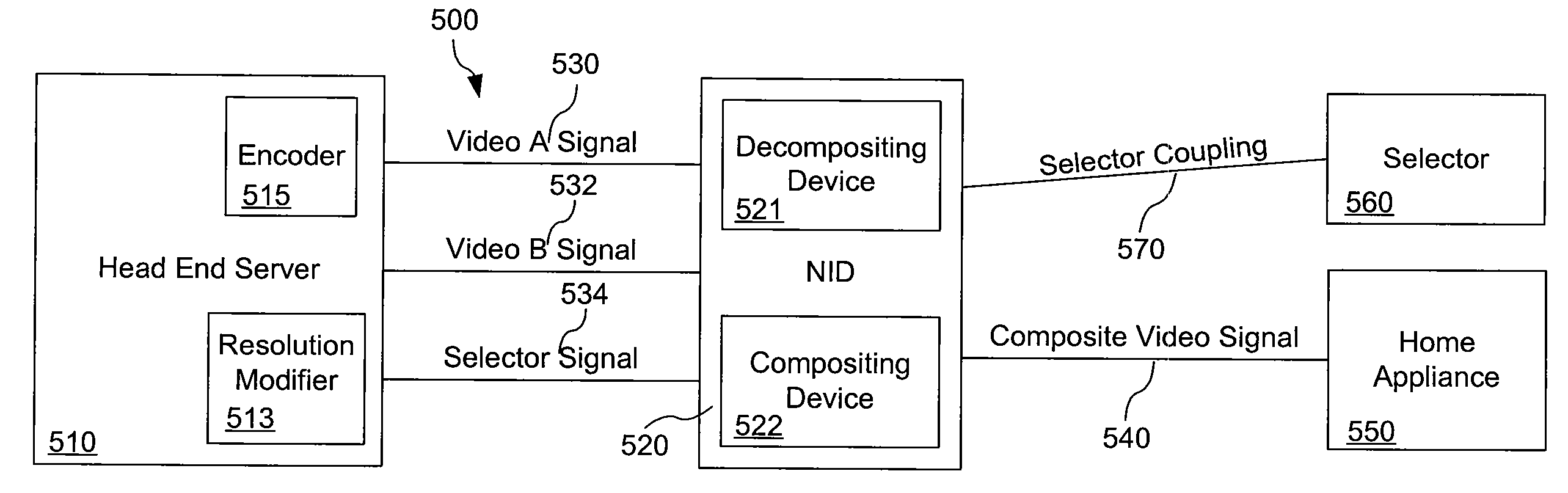
Systems and methods for delivering picture-in-picture signals at diverse compressions and bandwidths
ActiveUS20050052578A1Reduce in quantityTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionData signalComputer science
T Systems and methods for providing picture-in-picture, or other multi-picture displays. Some of the systems include two or more video and / or data signals that are coupled to a transmission device. In addition, a selector signal is coupled to the transmission device. The transmission device also includes a video output that, based at least in part on the selector signal, provides a derivative of one of the video and / or data signals at a first compression and bandwidth, and the other video and / or data signal at a second compression and bandwidth. Various of the methods include utilize the systems to transmit two or more video outputs based at least in part on a selector signal.
Owner:QWEST
Adaptive margin and band control
ActiveUS20110051906A1Transmission path divisionSubstation equipmentDigital subscriber lineFrequency spectrum
Configuration or otherwise controlling parameters of a Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) system related to power, band usage and margin is based on collected operational data. Operational data are collected from at least one DSL system operating under a known configuration and / or a profile. A target profile is selected based on binder-level information. The collected operational data is analyzed and conditions for changing the DSL system configuration to the target profile are evaluated, including any applicable transition rules pertaining to changing profiles. If the conditions hold, then the DSL system is instructed to operate with the target profile. Binder-level information can include deployment point information, topology information, and / or crosstalk coupling information. The controlled parameters may have values that are chosen using one or more spectrum balancing methods. Such spectrum balancing methods may be executed infrequently, and may make use of all binder-level information that is available.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
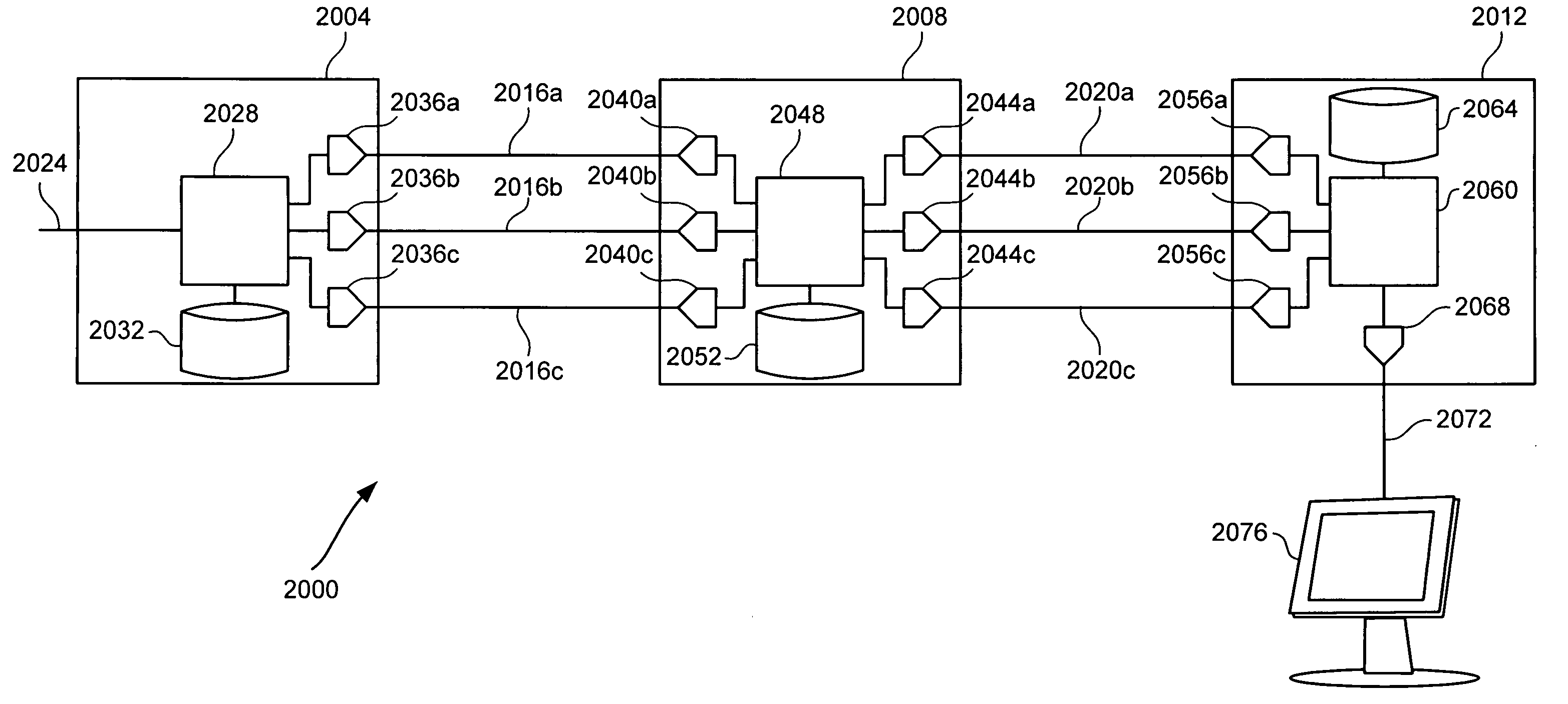
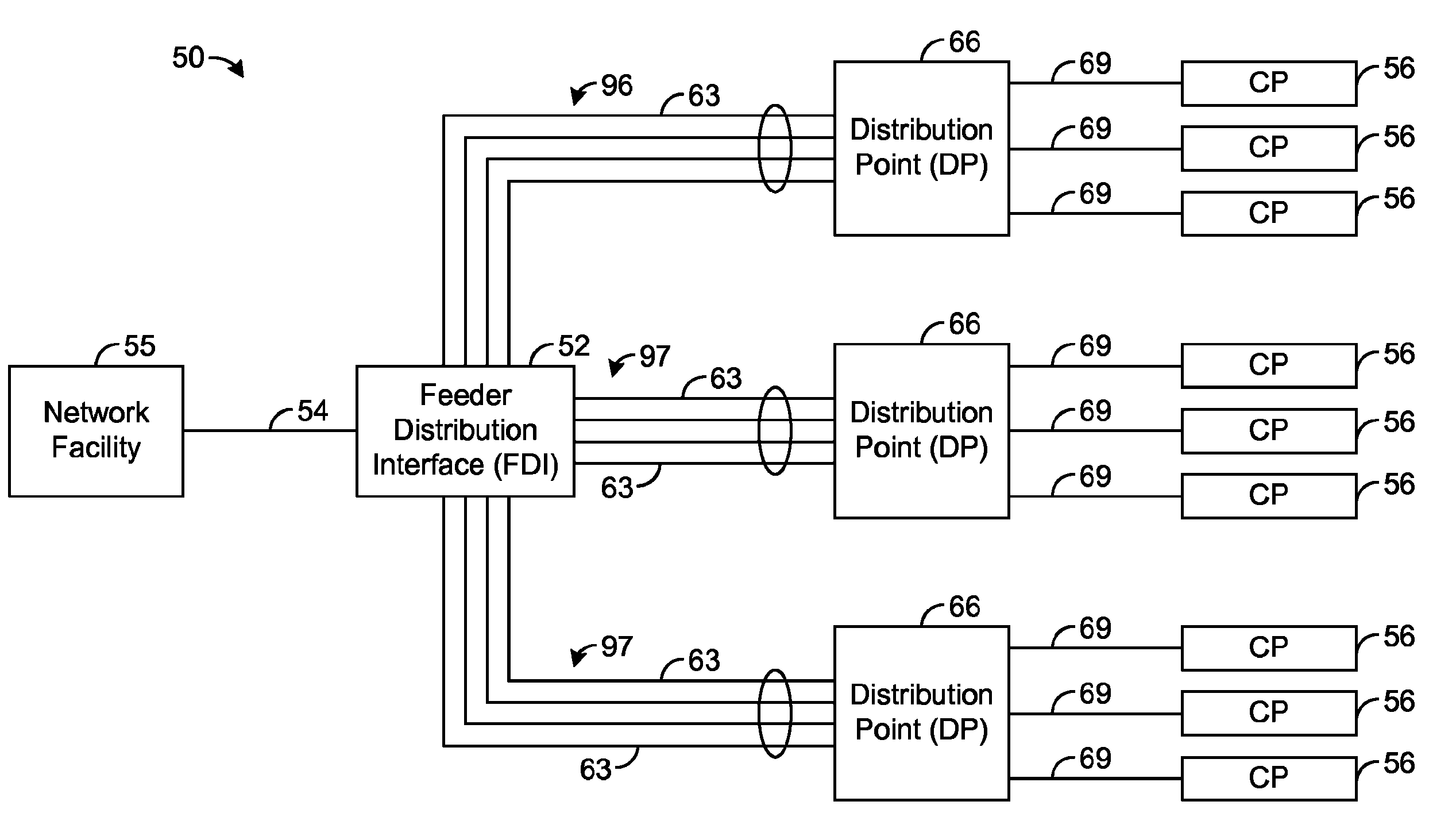
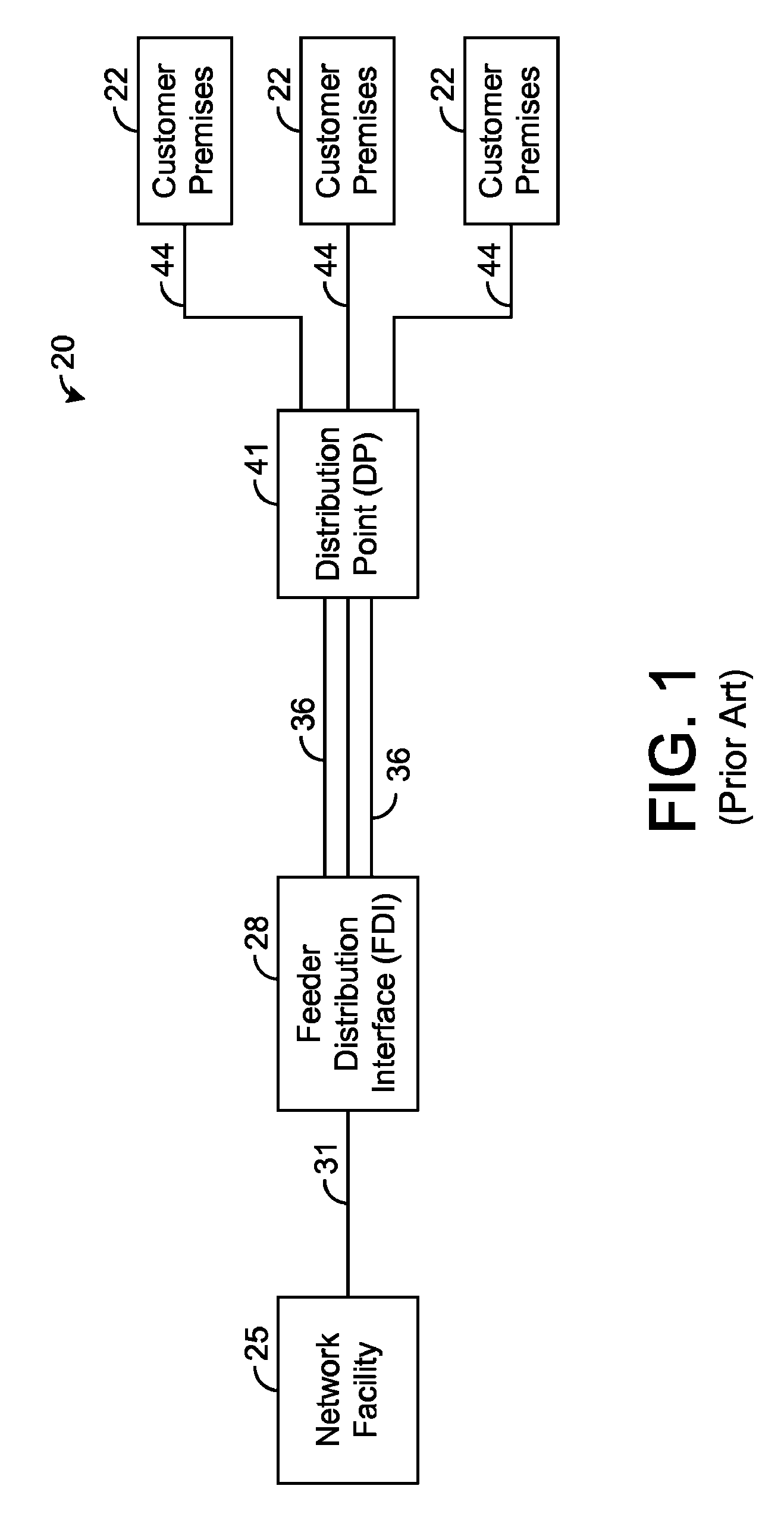
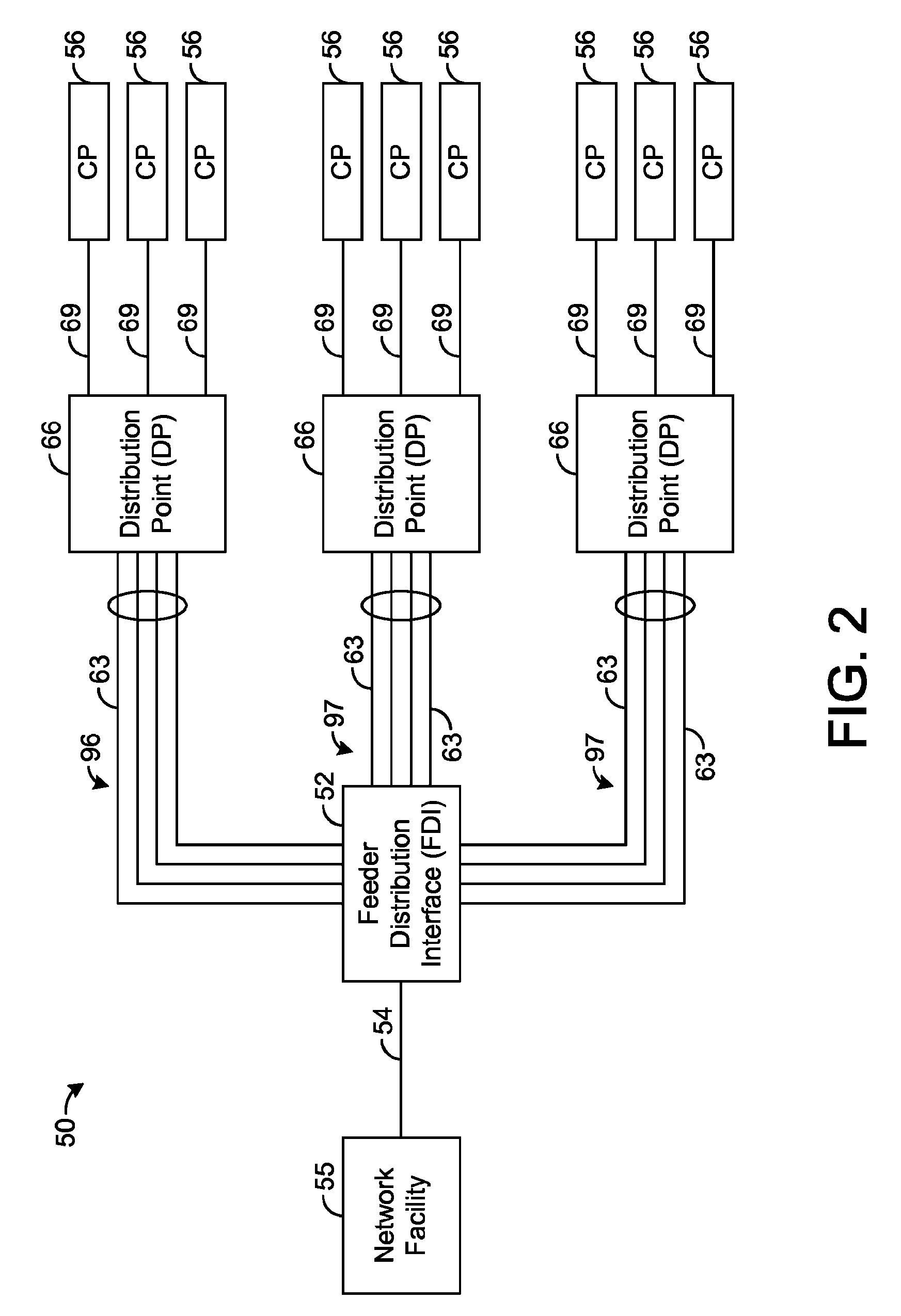
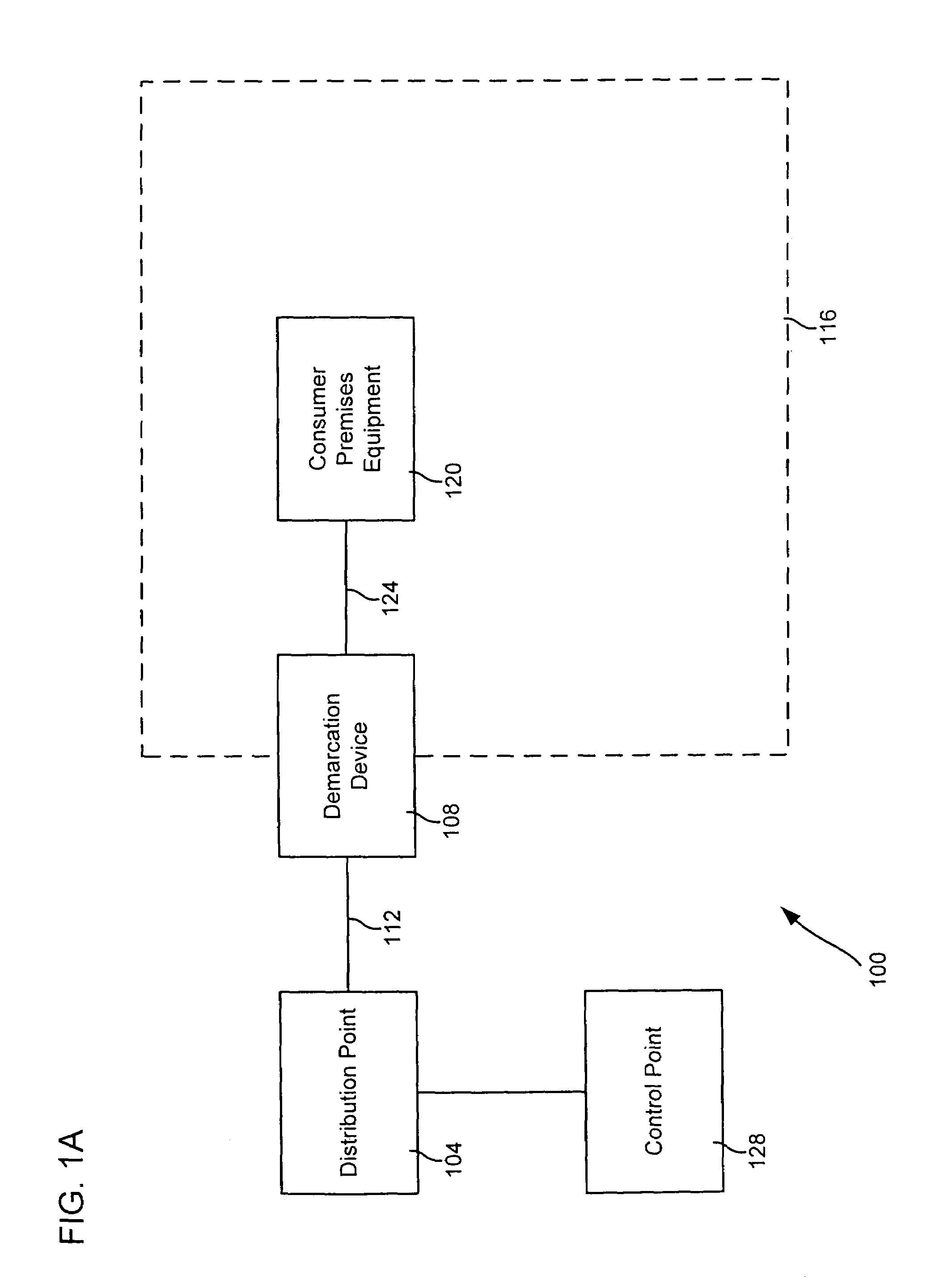
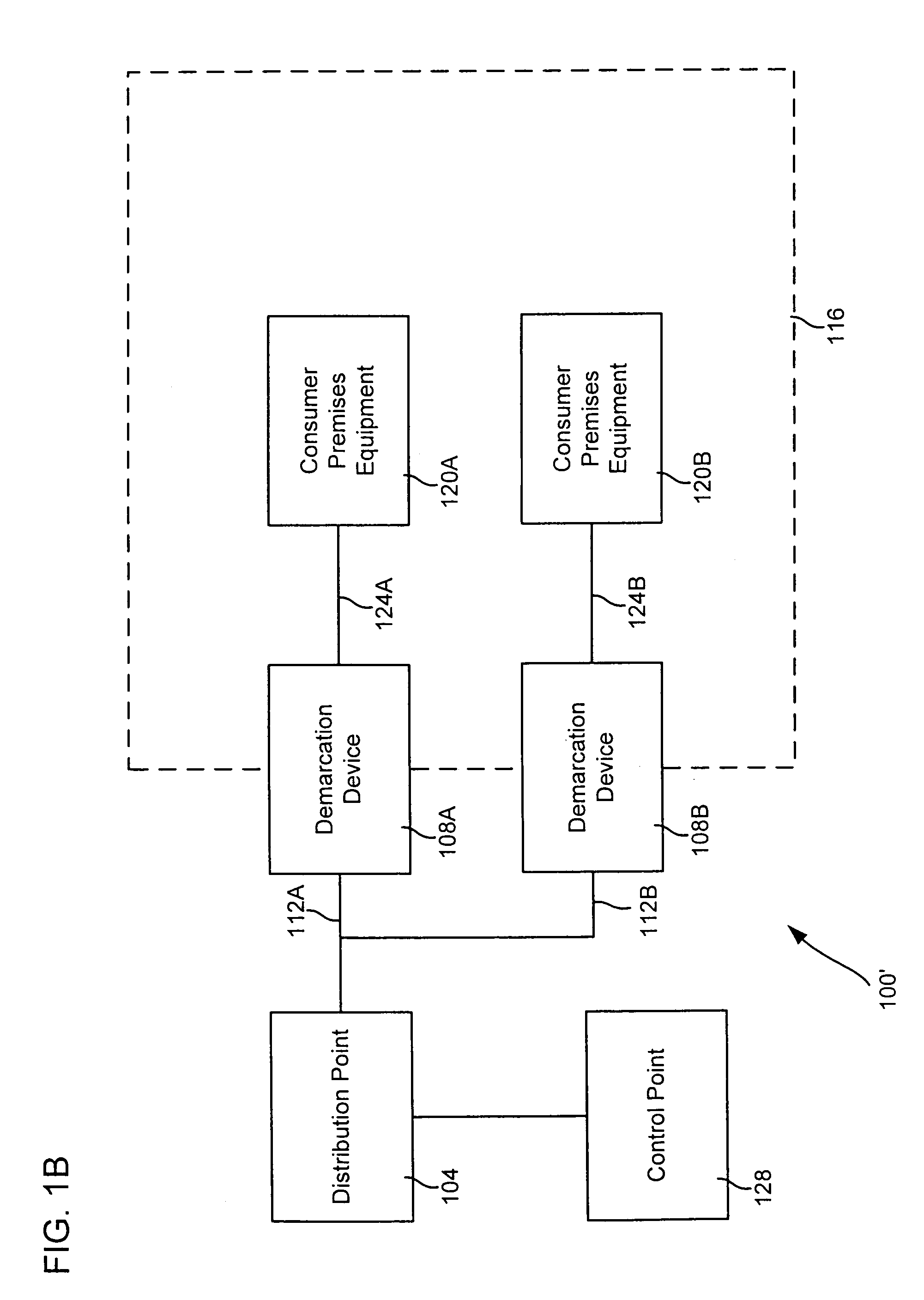
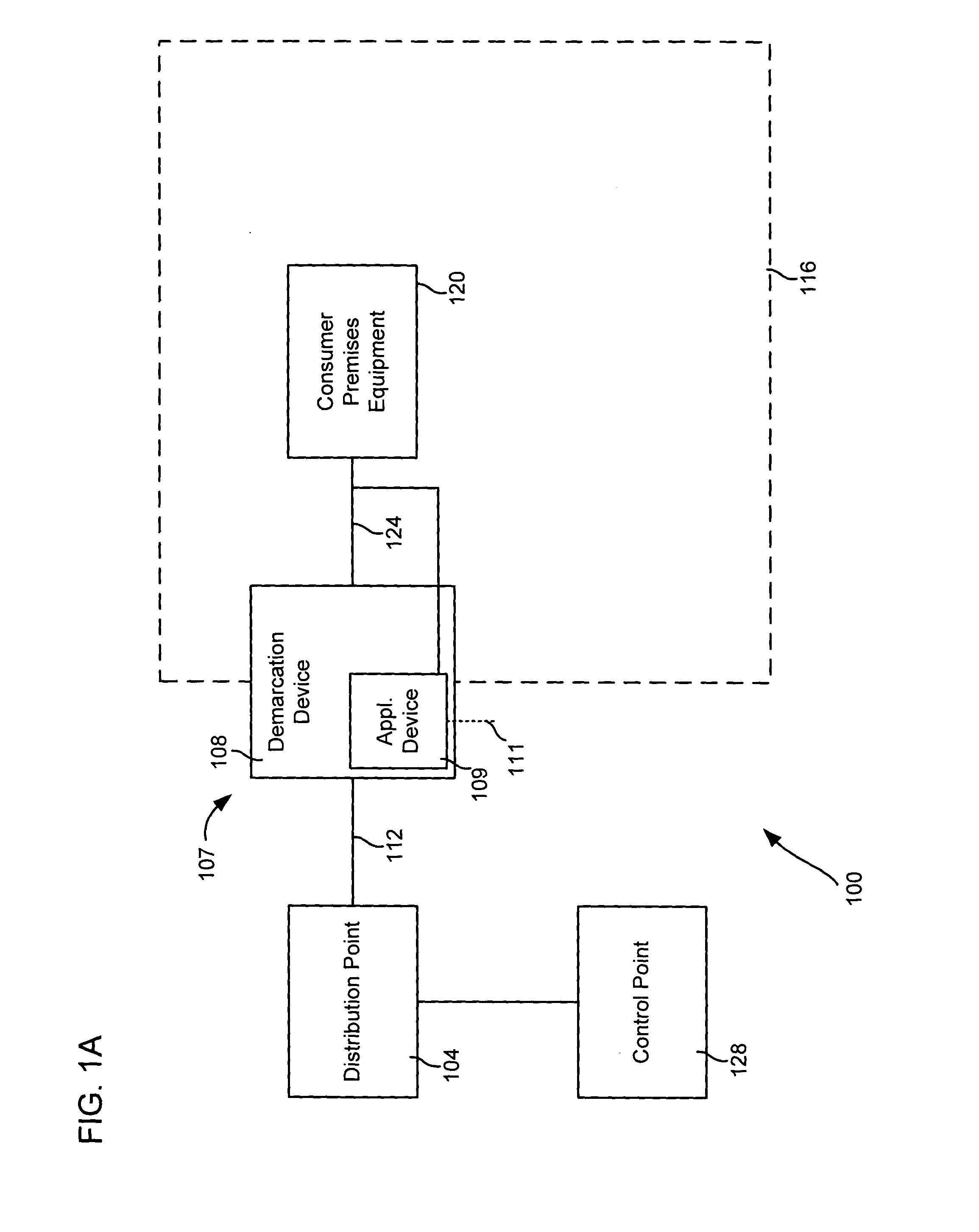
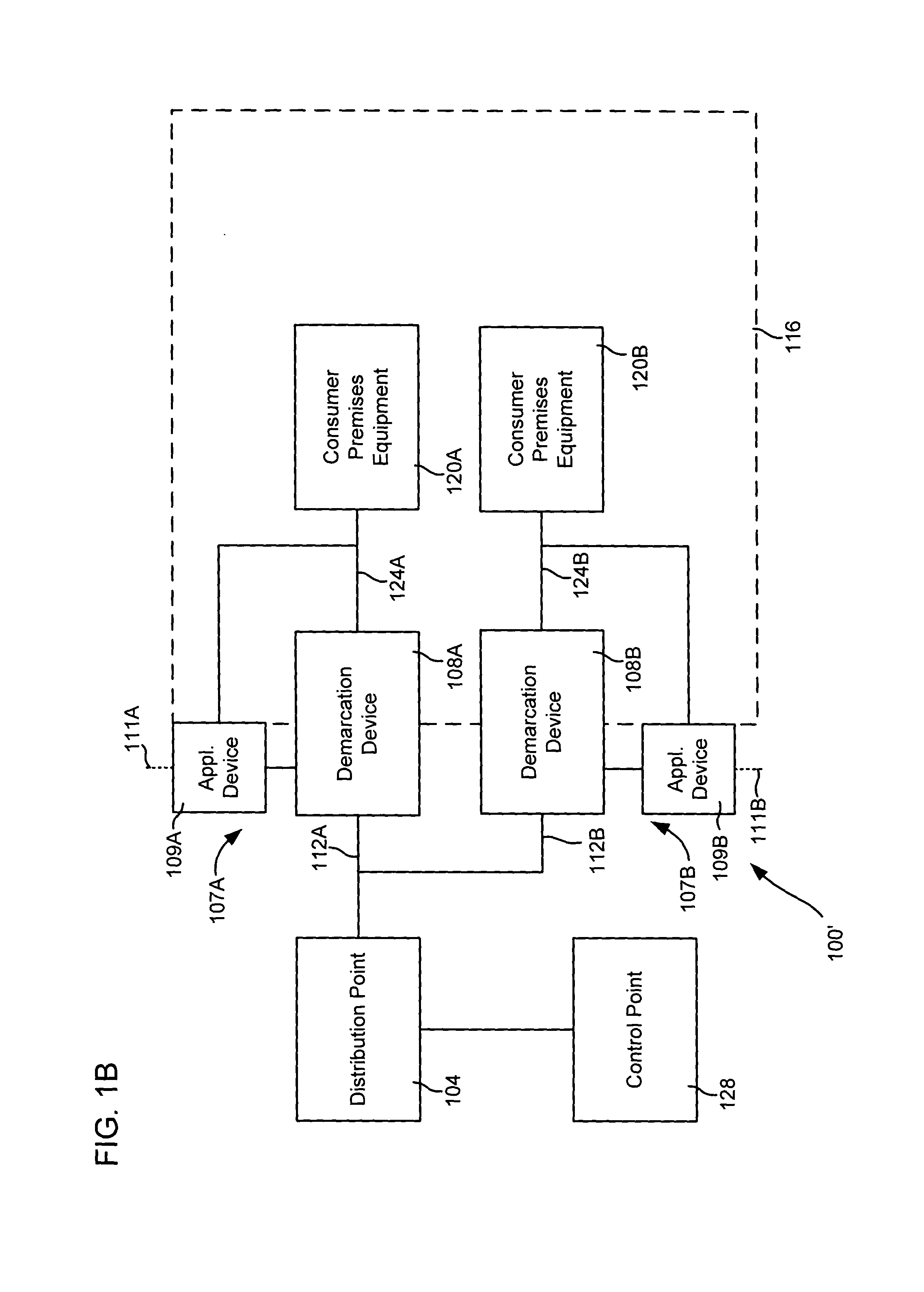
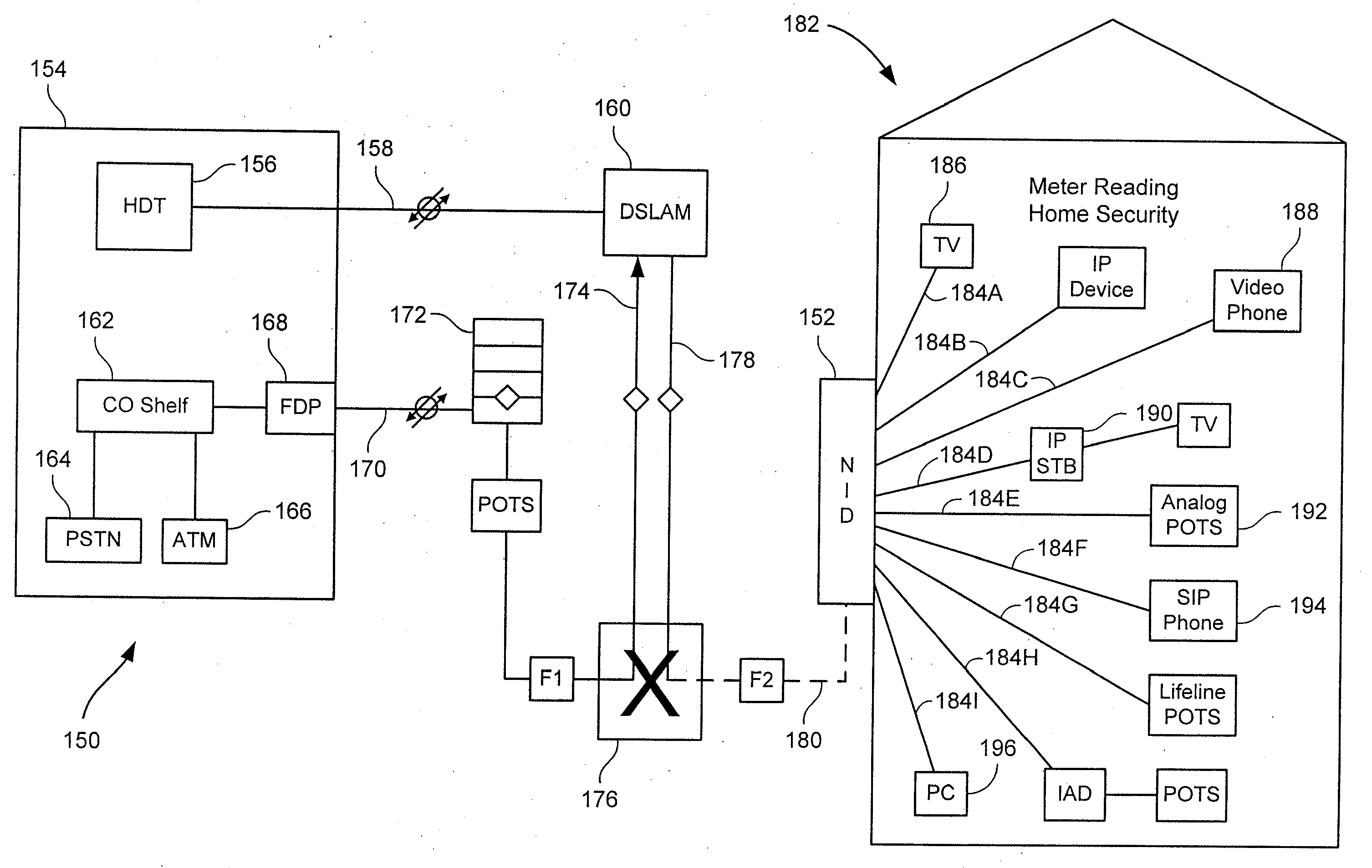
Systems and methods for communicating with multiple distribution points of a network
The present disclosure generally pertains to systems and methods for communicating data. In one exemplary embodiment, a system has a high-speed channel, such as an optical fiber, between a network facility, such as a central office (CO), and a first intermediate point between the network facility and a plurality of customer premises (CP). Digital communication links, such as DSL links, are used to carry data between the first intermediate point, such as a feeder distribution interface (FDI), and a second intermediate point, such as the Distribution Point (DP). Non-shared links may then carry the data from the second intermediate point to the CPs. The links between the two intermediate points are bonded to create a high-speed, shared data channel that permits peak data rates much greater than what would be achievable without bonding. In some embodiments, multicast data flows may be prioritized and transmitted across a set of connections to each of the intermediate points. In addition, it is possible to power components at the intermediate points from one or more of the CPs.
Owner:ADTRAN
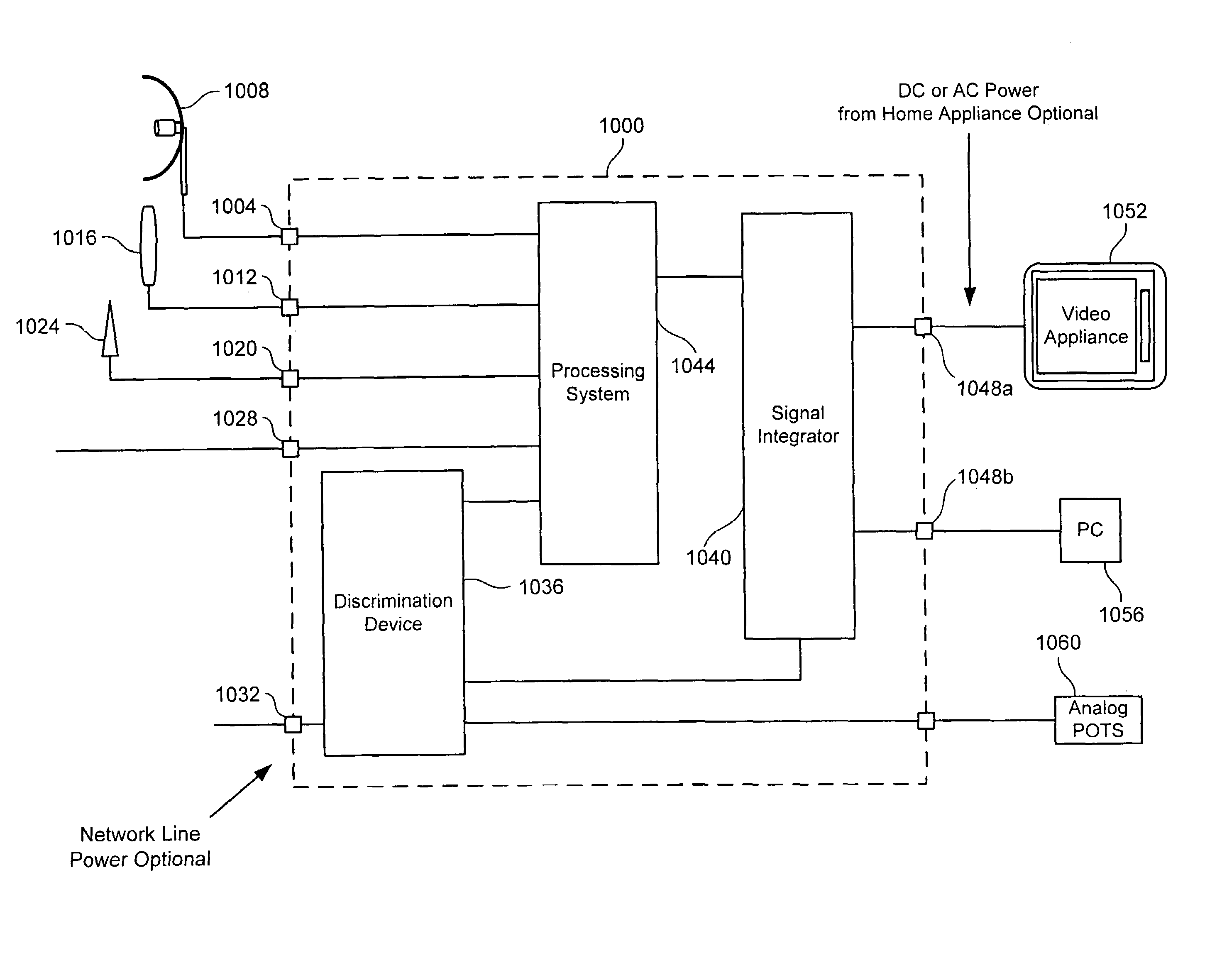
Fiber optic internet protocol network interface device and methods and systems for using the same
ActiveUS7099443B2Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionFiberNetwork interface device
A network interface device located at a customer's premises includes an external interface that receives a plurality of telecommunication services via a fiber optic connection from a telecommunication service provider. The services are received using Internet Protocol. The network interface device also includes at least two distinct internal interfaces that distribute the plurality of telecommunication services to at least two distinct internal transport media. The network interface device also includes a processor that is programmed to receive combined signals comprising the telecommunication services from the external interface, process the combined signals into separate signals representative of distinct telecommunication services, and map each of the separate signals to separate ones of the at least two distinct internal interfaces for distribution at the customer's premises via the internal transport media.
Owner:QWEST
Communication System for VOIP Using an Internet Protocol Converter
ActiveUS20100091764A1Improve permeabilitySpecial service for subscribersNetwork connectionsCommunications systemTTEthernet
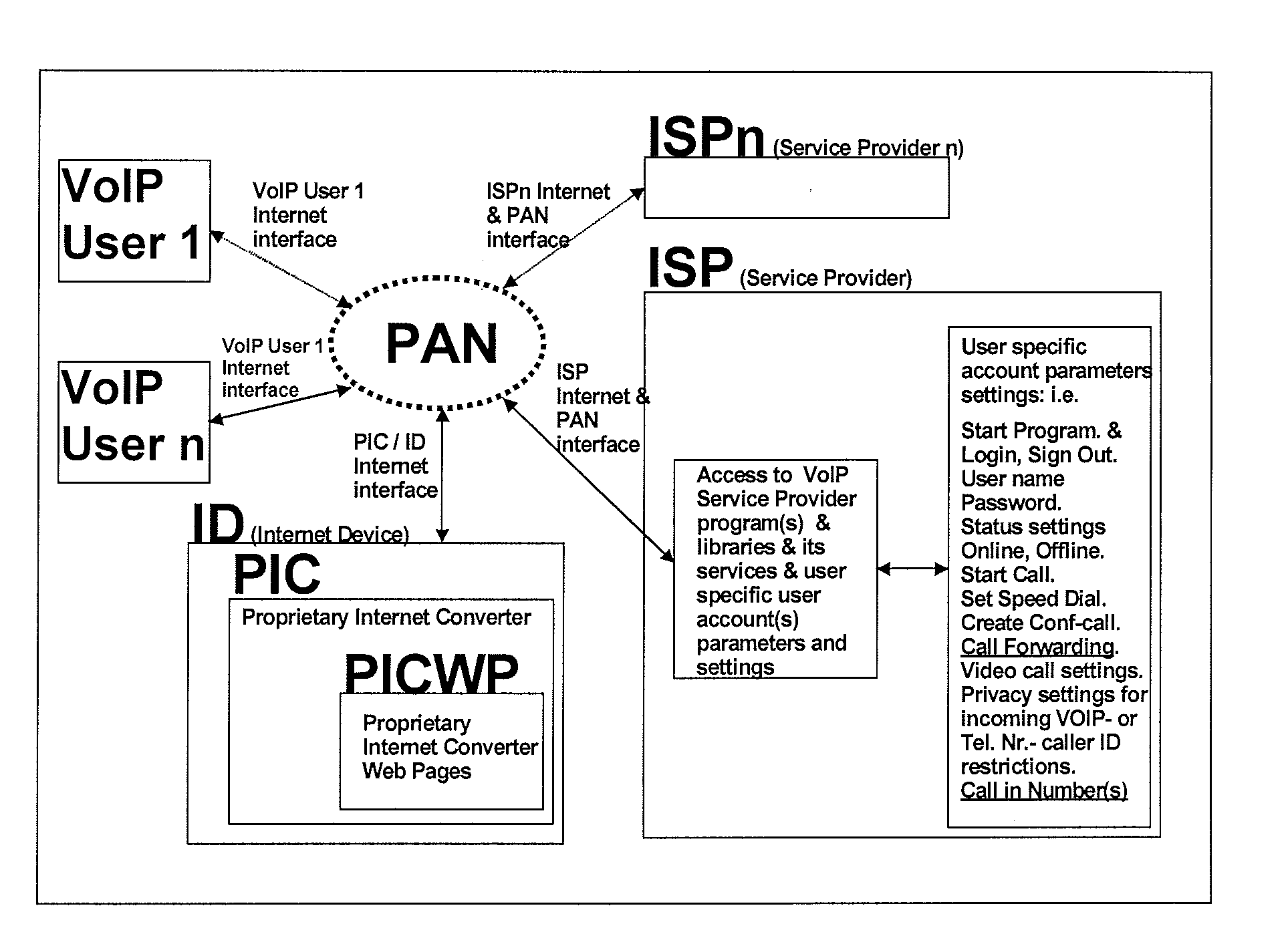
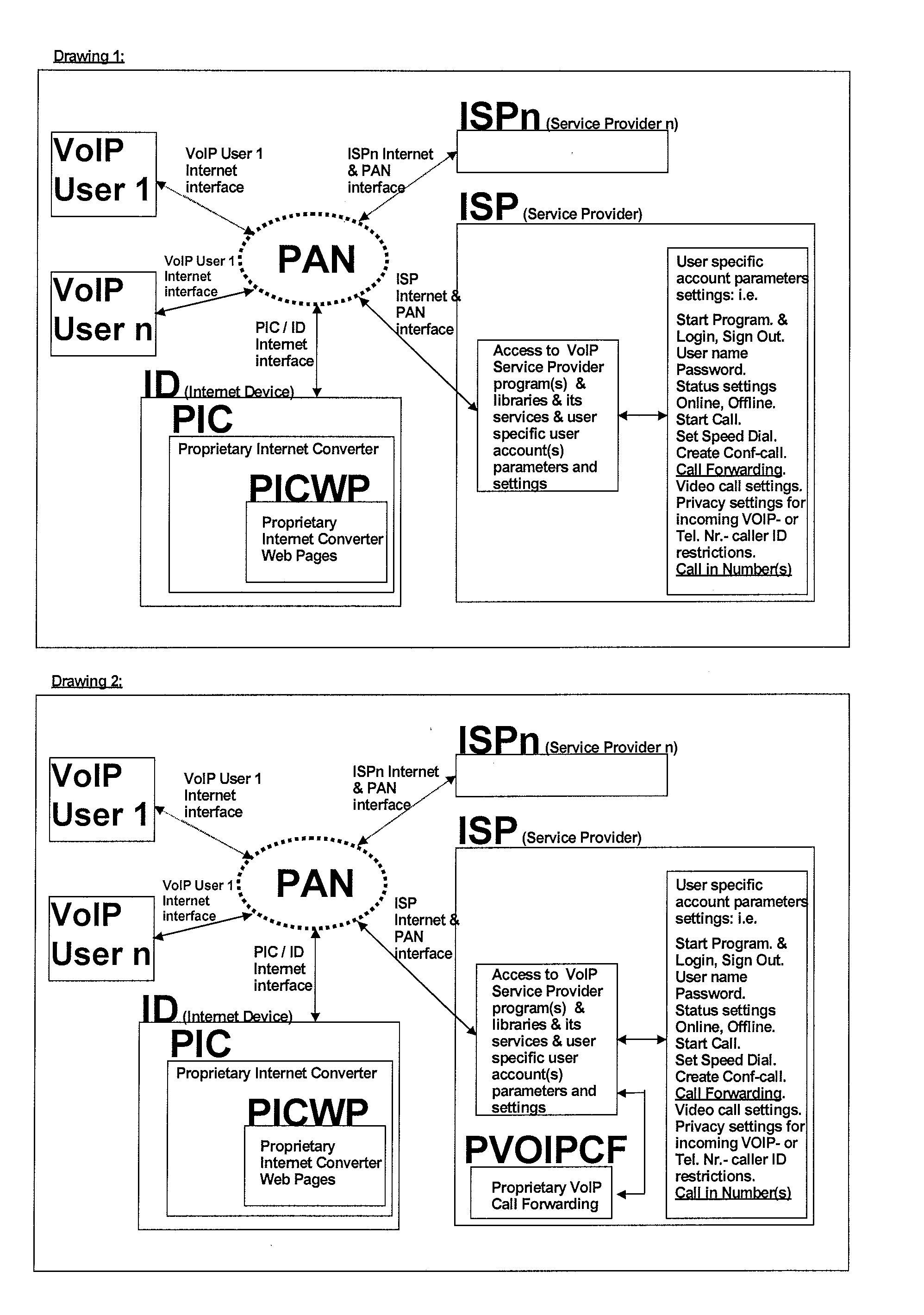
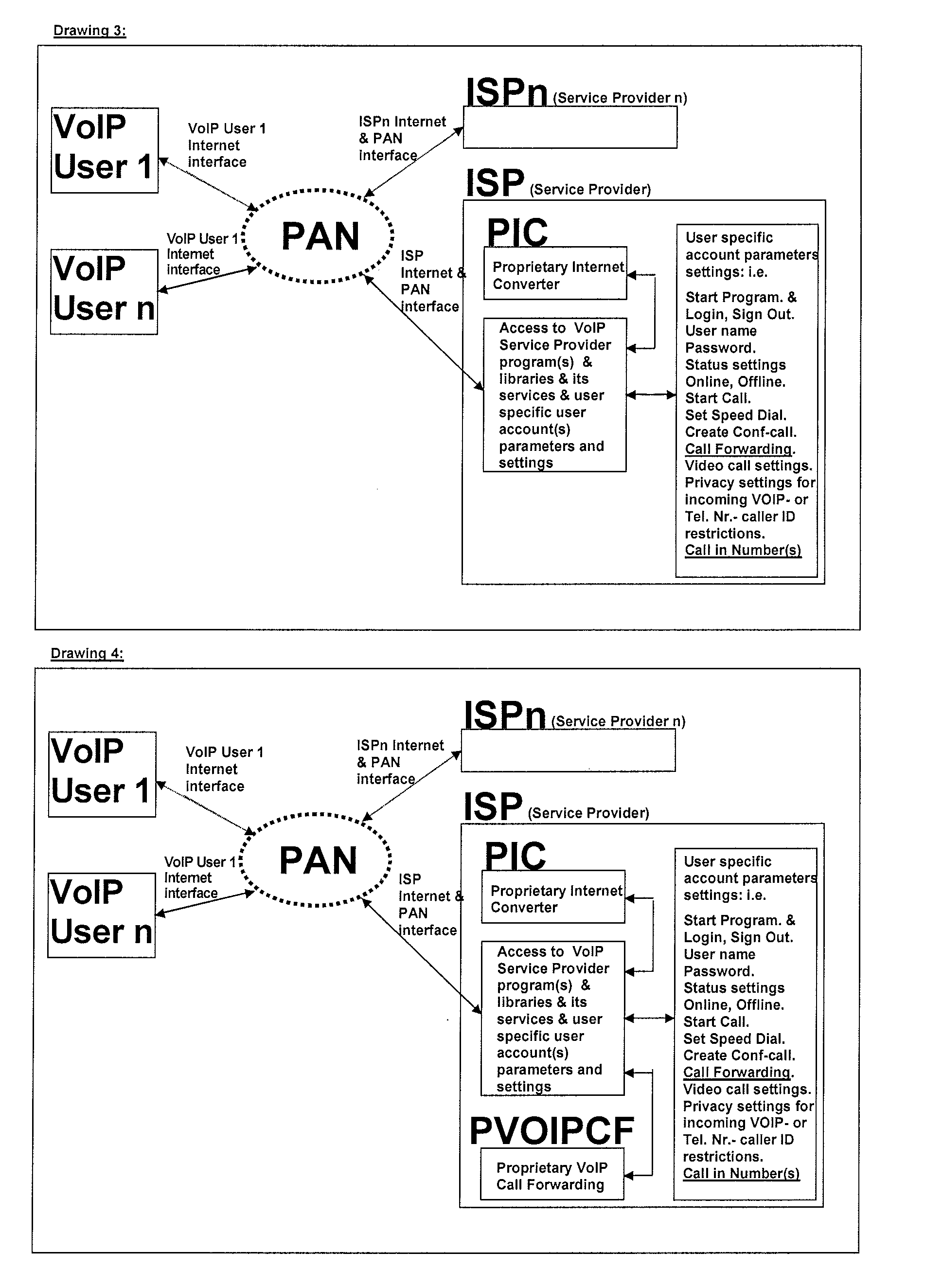
A proprietary internet converter (PIC) is disclosed, which allows a calling party end-user device with internet access such as a mobile telephone, to initiate voice communication with a called party VoIP (Voice Over Internet protocol) end-user device. The ID (Internet Device with a built-in PIC) converts the protocols used by the calling party end-user device so that the switch that routes calls to the called party VoIP end-user device understands instructions sent from the calling party end-user device. The switch has a call forwarding function. The calling party gives the calling party user name (e.g. ISP user name / contact or VoIP user name / contact) to the PIC over the internet. The PIC then sets call forwarding function on the switch, for that particular calling party, so that an incoming call from the calling party is automatically forwarded to the ISP user or VoIP user defined by the calling party.
Owner:SHOO 533 +1
Method and apparatus for detecting a secondary destination of a telephone call based on changes in the telephone signal path
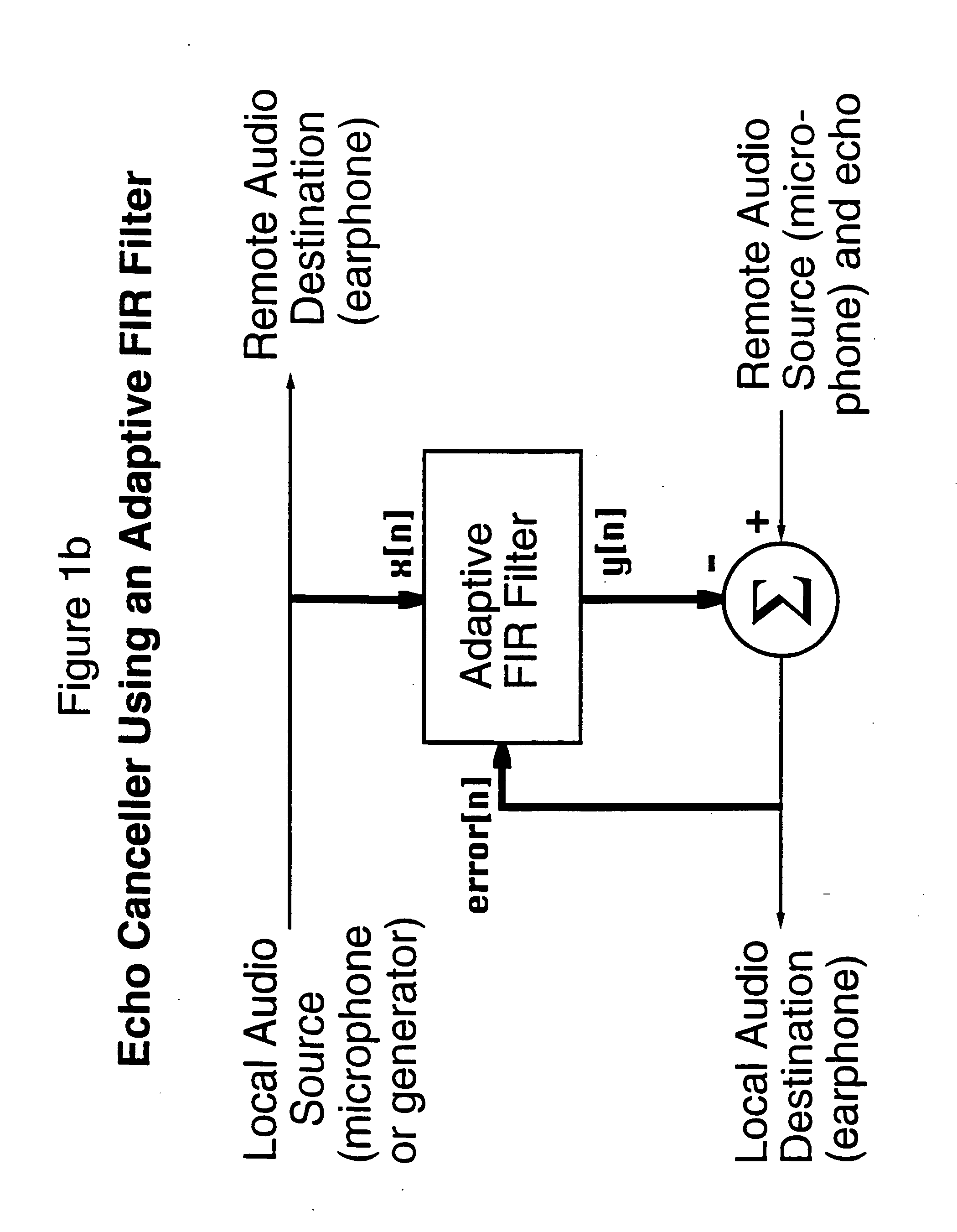
InactiveUS20050014491A1Improve reliabilitySuitable for useTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpecial service for subscribersBiological activationComputer science
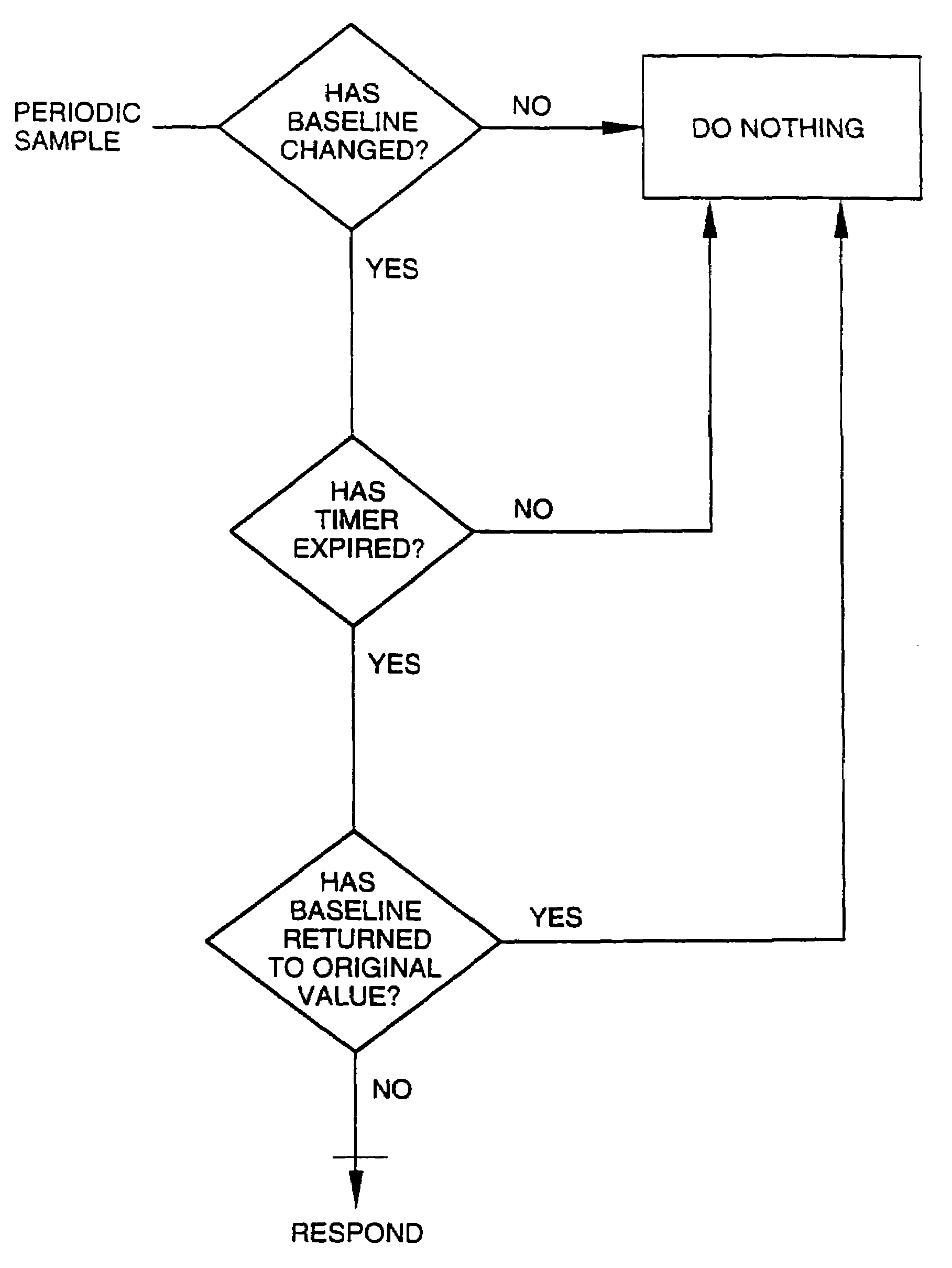
A method and apparatus for detecting whether a remote party has added a secondary telephone destination to a telephone call, for example through the activation of three-way calling service, conference calling or two lining bridging, by identifying an echo characteristic to the telephone connection between the local and the remote telephone and monitoring the echo characteristic to determine whether there is a significant change. The addition of a secondary telephone destination can be verified by continuing to monitor the echo characteristic to determine whether it has returned to its original value.
Owner:SECURUS TECH
DOCSIS network interface device and methods and systems for using the same
InactiveUS7239698B2Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionNetwork interface deviceTransport medium
A network interface device located at a customer's premises includes an external interface that receives a plurality of telecommunication services via a coaxial connection from a telecommunication service provider. The services are received using Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifications. The network interface device also includes at least two distinct internal interfaces that distribute the plurality of telecommunication services to at least two distinct internal transport media. The network interface device also includes a processor the is programmed to receive combined signals comprising the telecommunication services from the external interface, process the combined signals into separate signals representative of distinct telecommunication services, and map each of the separate signals to separate ones of the at least two distinct internal interfaces for distribution at the customer's premises via the internal transport media.
Owner:QWEST
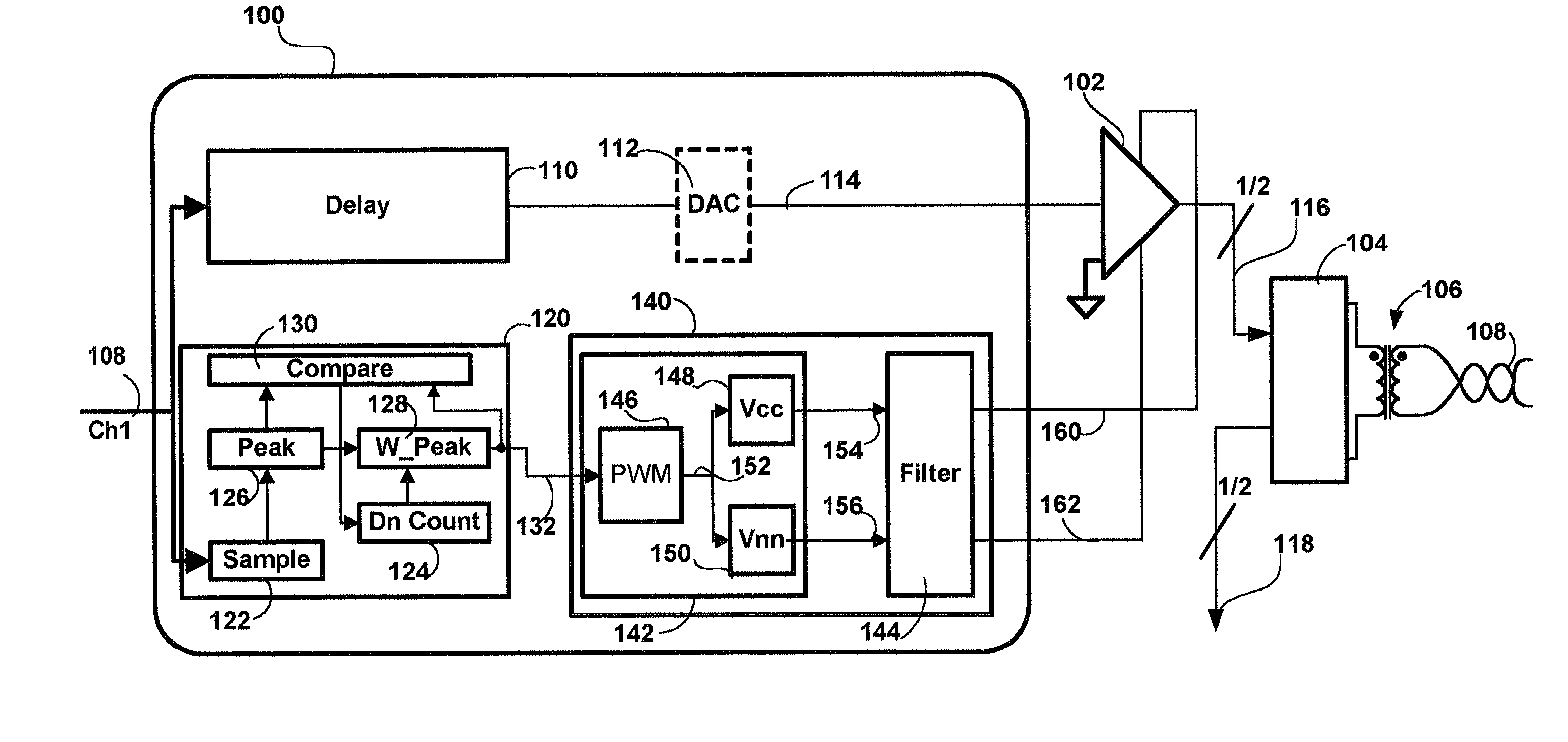
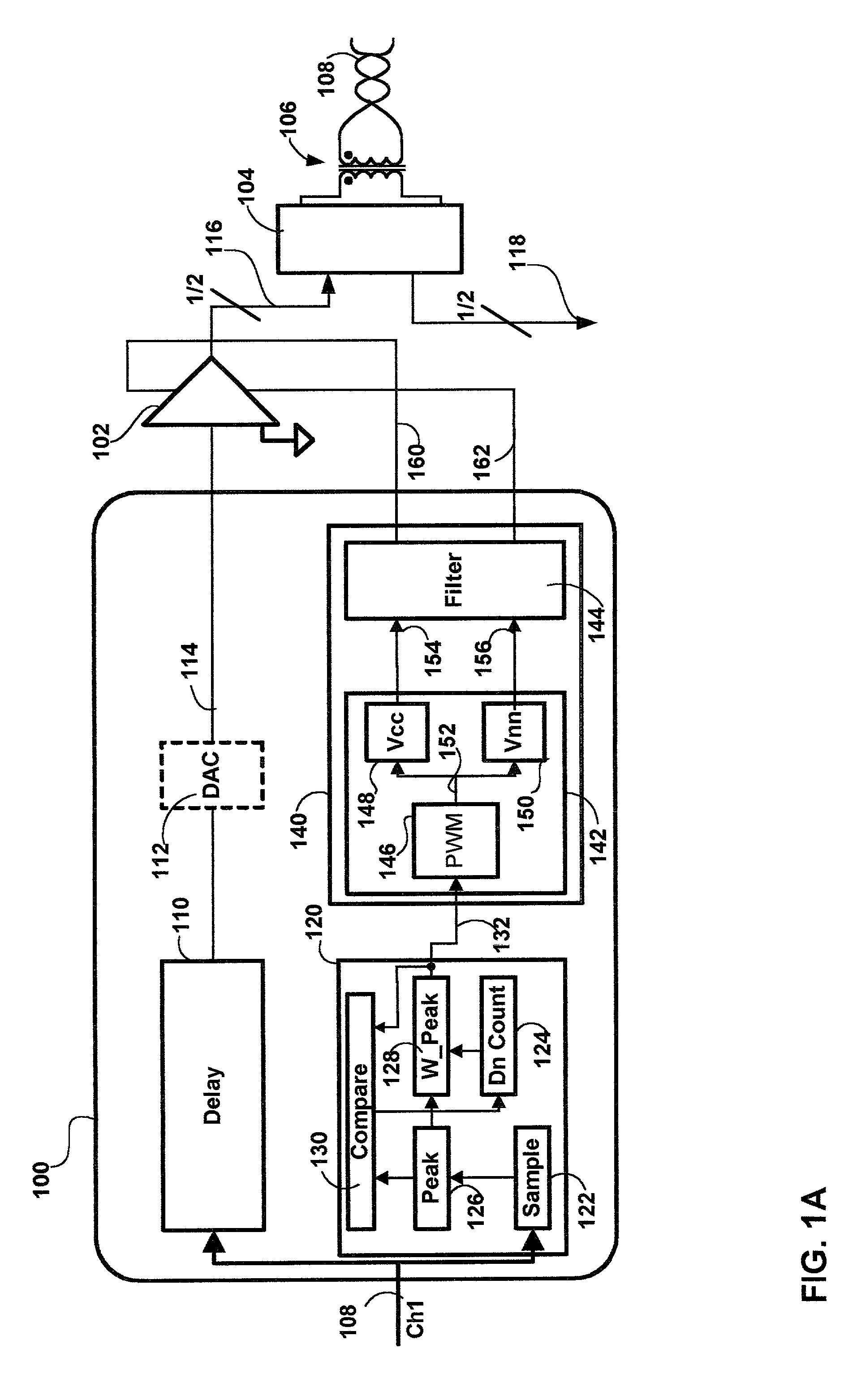
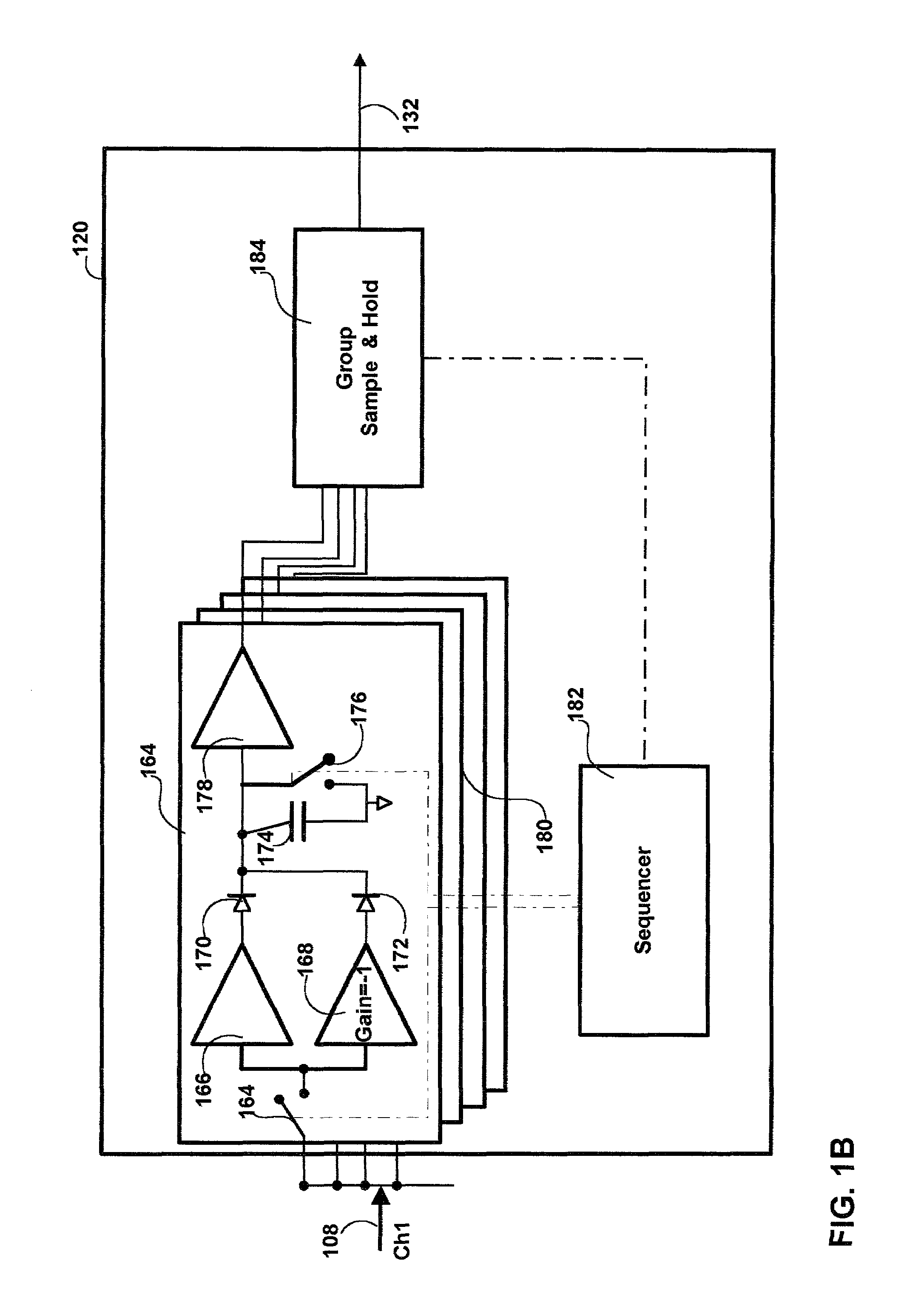
Method and apparatus for a high efficiency line driver
InactiveUS6987851B1Improve efficiencyMinimum power consumptionInterconnection arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierControl signal
A high efficiency line driver is disclosed. The line driver may be applied with equal advantage in wired and wireless communication media to amplify data signals with a minimum of power consumption. In an embodiment of the invention a line driver is disclosed which includes: at least one amplifier, a delay element, a control signal generator and a generator. The at least one amplifier includes at least one bias supply, a signal input and a signal output. The delay element accepts as an input the data signal and delays delivery of the data signal to the at least one line amplifier for amplification. The generator is responsive to a control signal to generate varying voltage levels corresponding thereto on the at least one bias supply of the at least one amplifier. The control signal generator is responsive to the input data signal to detect peaks therein and to generate the control signal corresponding thereto in advance of delivery of the data signal to the amplifier.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Broadband communications device
ActiveUS20100098058A1Easy to deployExpand the CLECs customer base quicklyInterconnection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementTTEthernetResidence
Owner:COMPETITIVE ACCESS SYST INC
Method and apparatus for handling voice and data signals
A method and apparatus is provided for impedance matching for an apparatus capable of supporting voice and data. The method includes receiving an input signal having at least one of a voice component, data component, and DC component, and filtering at least a portion of the data component and DC component of the input signal to provide a filtered signal. The method further includes adjusting an input impedance of the apparatus to a first preselected value for the voice band in response to the filtered signal and adjusting the input impedance of the first apparatus from the first preselected value to a second preselected value. The method includes adjusting at least one of a magnitude and phase of the filtered signal to adjust the input impedance to a third value.
Owner:MICROSEMI SEMICON U S
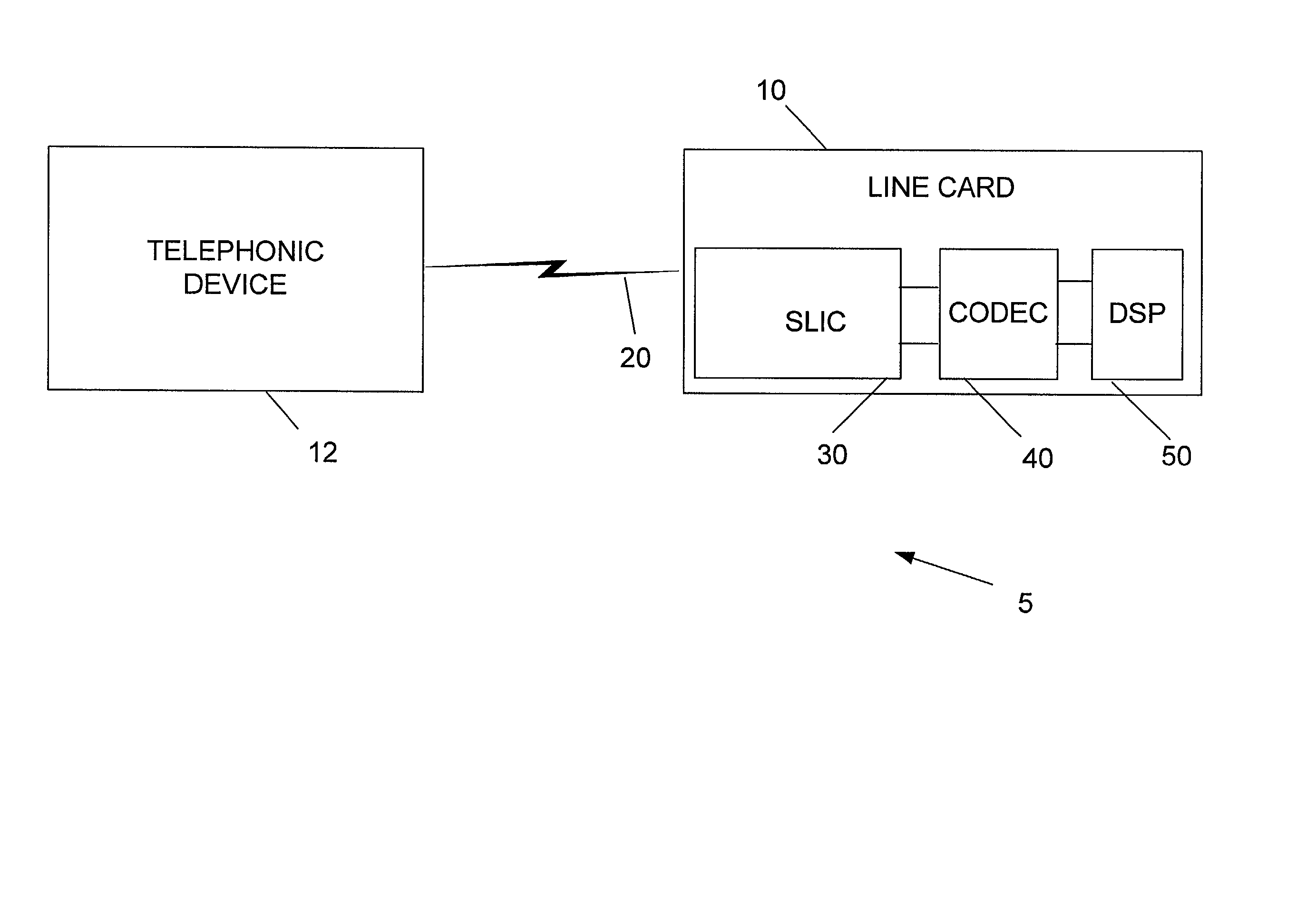
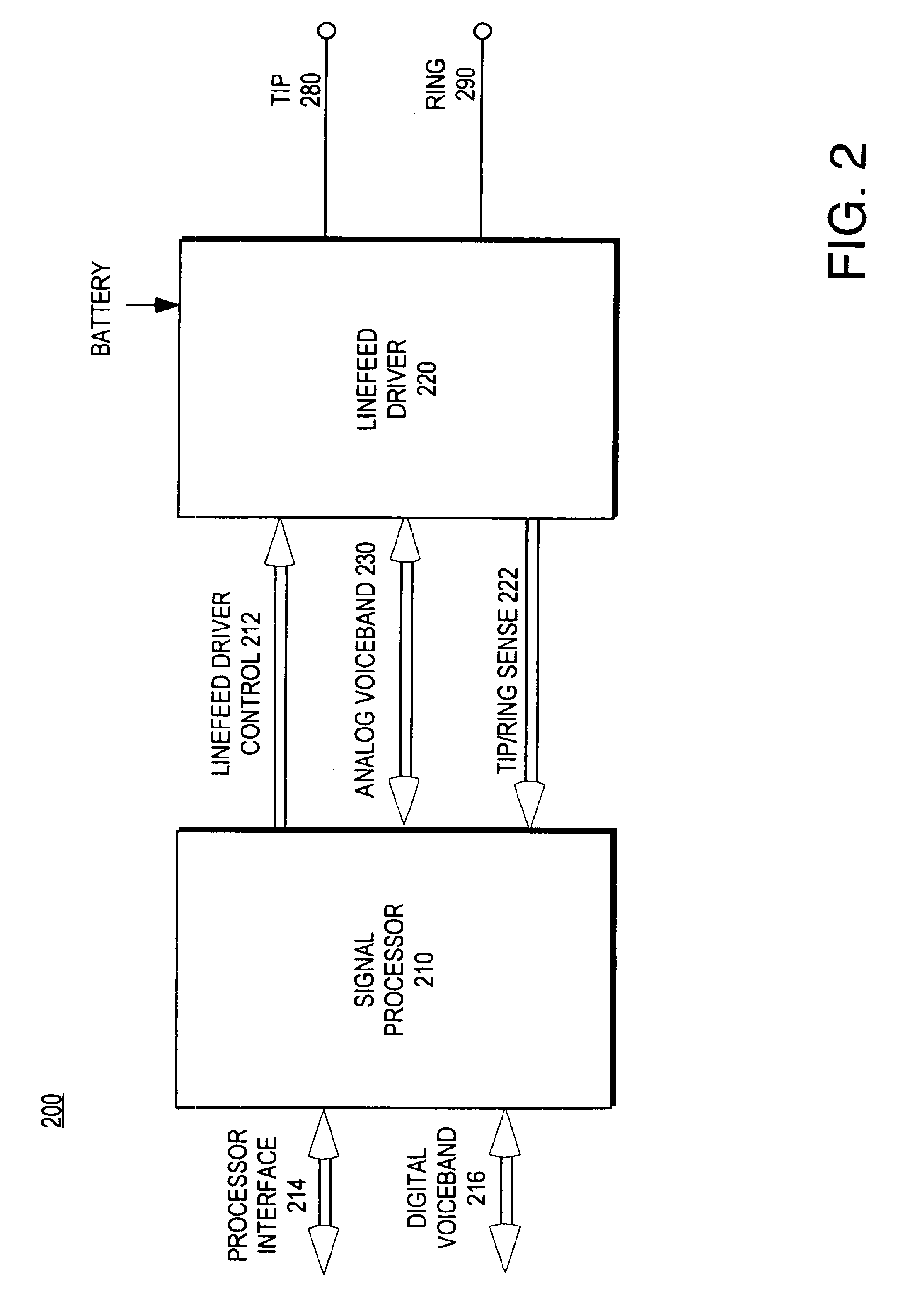
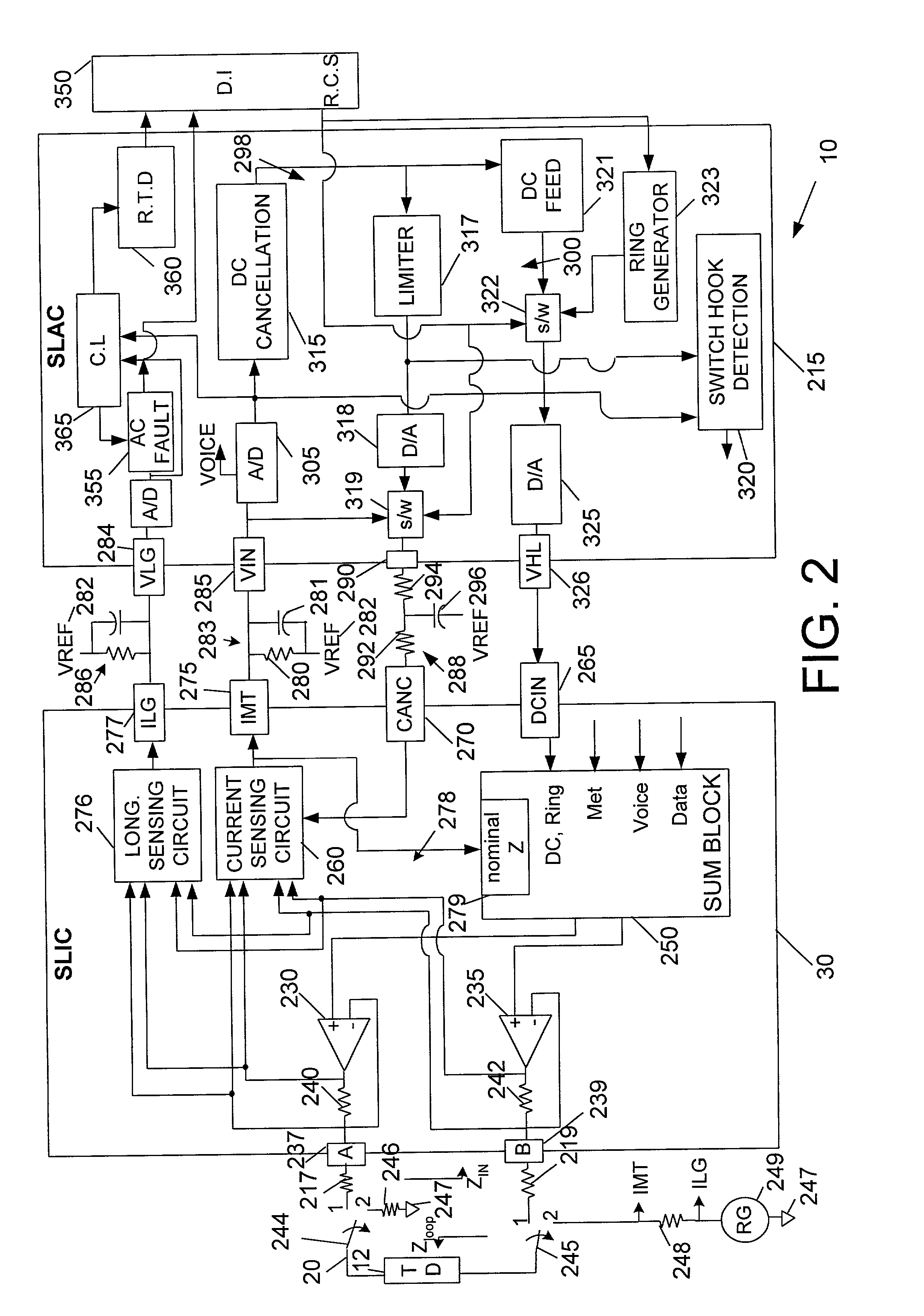
Subscriber line interface circuitry
InactiveUS6934384B1Interconnection arrangementsSubstations coupling interface circuitsLoop controlControl signal
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Systems and methods for delivering picture-in-picture signals at diverse compressions and bandwidths
ActiveUS7187418B2Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionData signalComputer science
Owner:QWEST
Methods, Systems and Apparatus for Providing Urgent Public Information
InactiveUS20070129053A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionPublic informationReal-time computing
Owner:QWEST
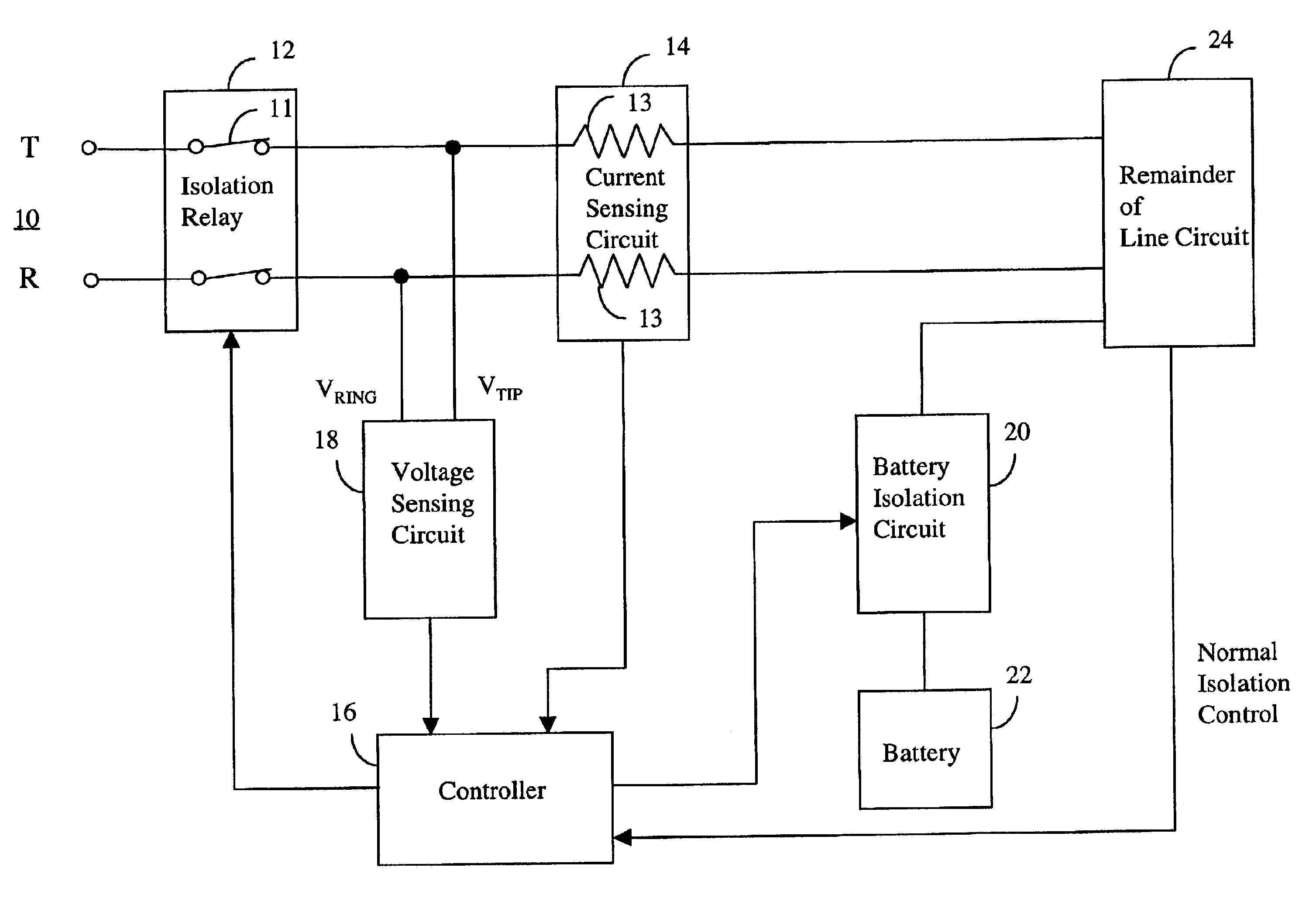
Voltage and protection arrangement for a telephone subscriber line interface circuit
InactiveUS6885745B1Guaranteed uptimeImproved voltage and current protection arrangementInterconnection arrangementsCurrent supply arrangementsEngineeringShort duration
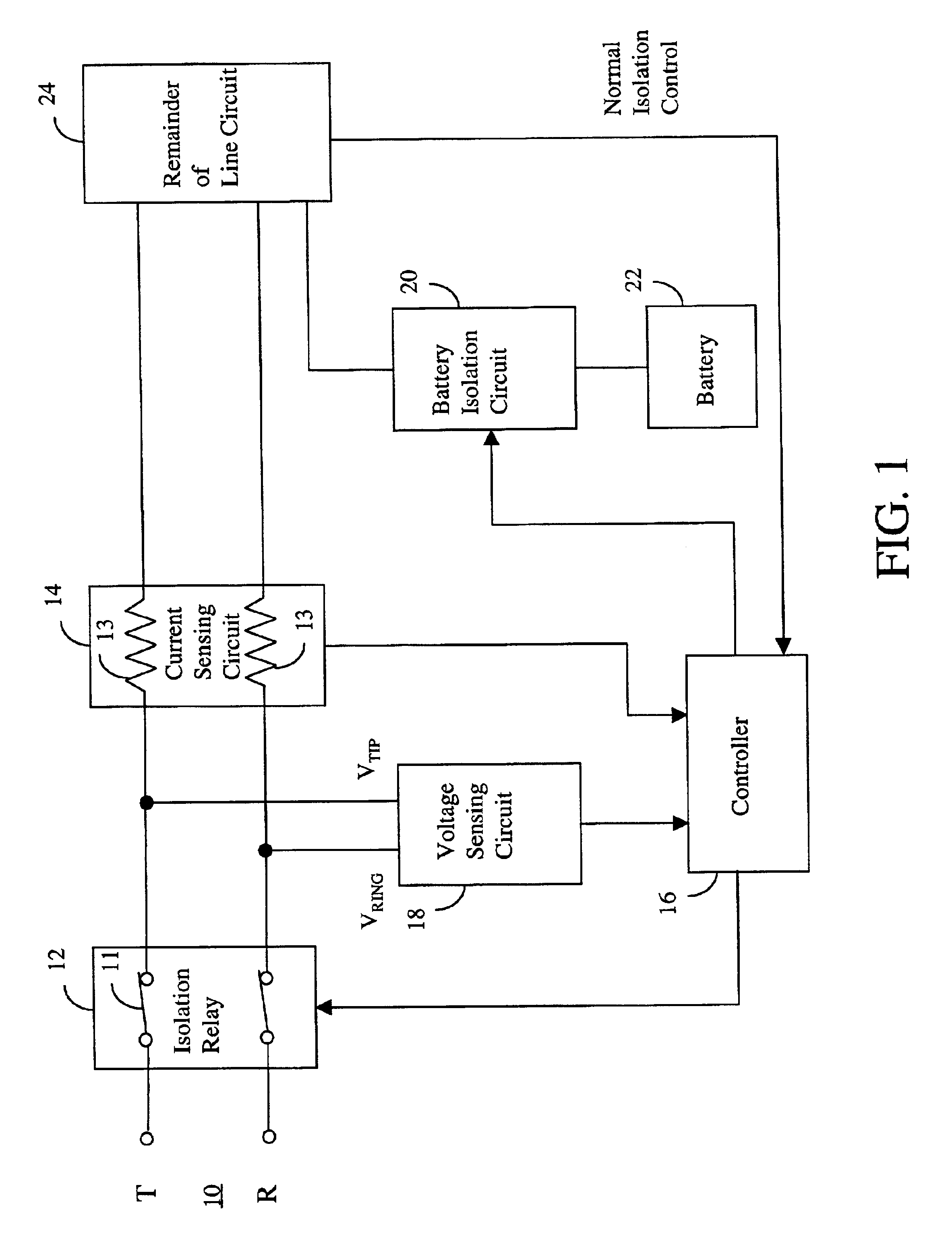
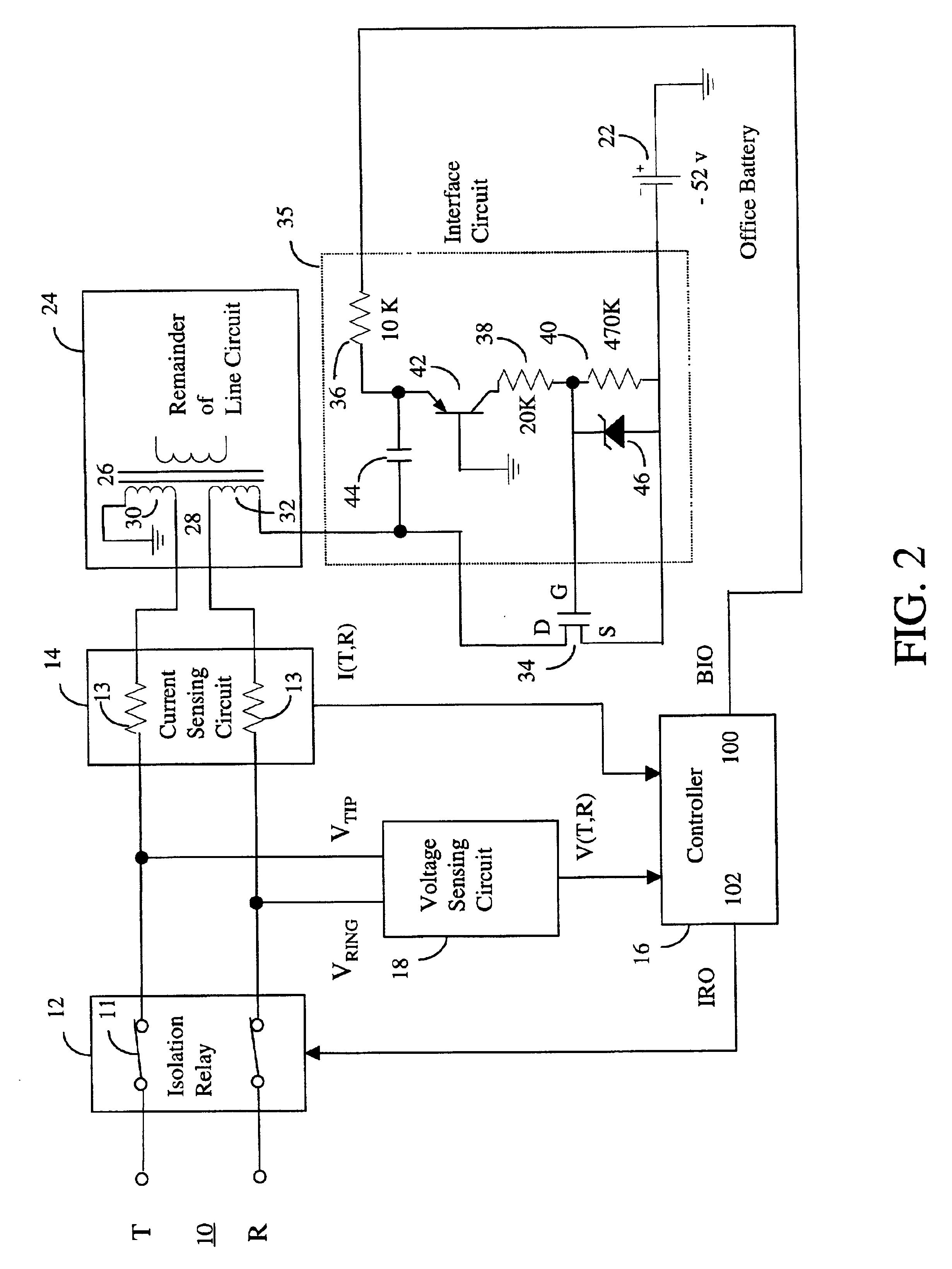
A protection arrangement for a telephone subscriber line interface circuit is disclosed. The arrangement is particularly useful for protecting an electronic telephone set from over-voltage and over-current fault conditions. The arrangement provides a FET that operates in saturation mode to connect an office battery to the subscriber line under normal operation. The FET also provides isolation capabilities for protecting the line circuit from an over-current condition on the subscriber line. Over-voltage protection is provided by way of an isolation relay between the line circuit and the subscriber line. Both the FET and isolation relay are operated by a controller that uses timers in the methods of over-voltage and over-current protection that it performs. A further capability of the arrangement is that it resets itself after the fault condition has ended. This feature is particularly useful in the case of fault conditions of short duration.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
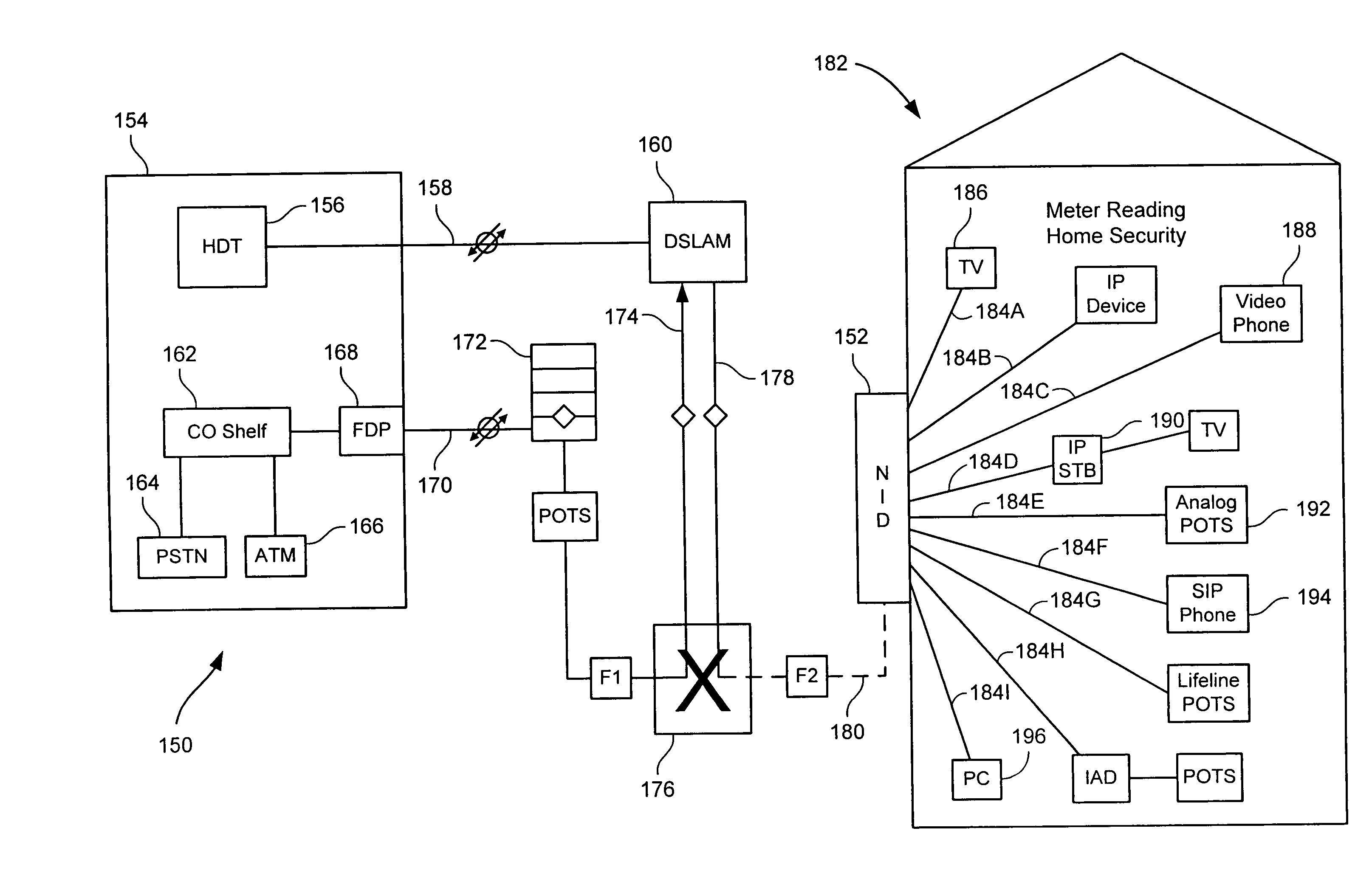
Transmitting utility usage data via a network interface device
ActiveUS20090212971A1Television system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsDigital subscriber lineModem device
Tools and techniques for transmitting utility usage data. In some cases, the tools receive utility usage data provided by a utility meter and transmit that data for reception by a utility provider. In particular cases, the utility usage data may be received at a network interface device. The network interface device might, in some instances, include a broadband modem, such as a digital subscriber line modem, which can be used to transmit the utility usage data to the utility provider.
Owner:QWEST
Method and apparatus for detecting line card threshold
ActiveUS20020118819A1Interconnection arrangementsSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsLine cardEngineering
A method and apparatus is provided. The method includes transmitting a signal having an AC component to a subscriber line and receiving at least a portion of the transmitted signal from the subscriber line. The method includes determining at least a portion of a period of the AC component of the received signal, and performing a function of a line card in response to determining at least the portion of the period of the AC component. The apparatus includes circuitry that is capable of transmitting a signal having at least one of an AC component and a DC component to a subscriber line, and receiving at least a portion of the transmitted signal from the subscriber line. The apparatus includes a filter and computation logic. The filter is capable of filtering the DC component from the received signal. The computation logic is capable of determining a value proportional to a power of the AC component of the received signal over at least a portion of a period of the AC component. The apparatus further includes logic capable of performing a function of a line card in response to determining the value proportional to the power of the AC component.
Owner:MICROSEMI SEMICON U S
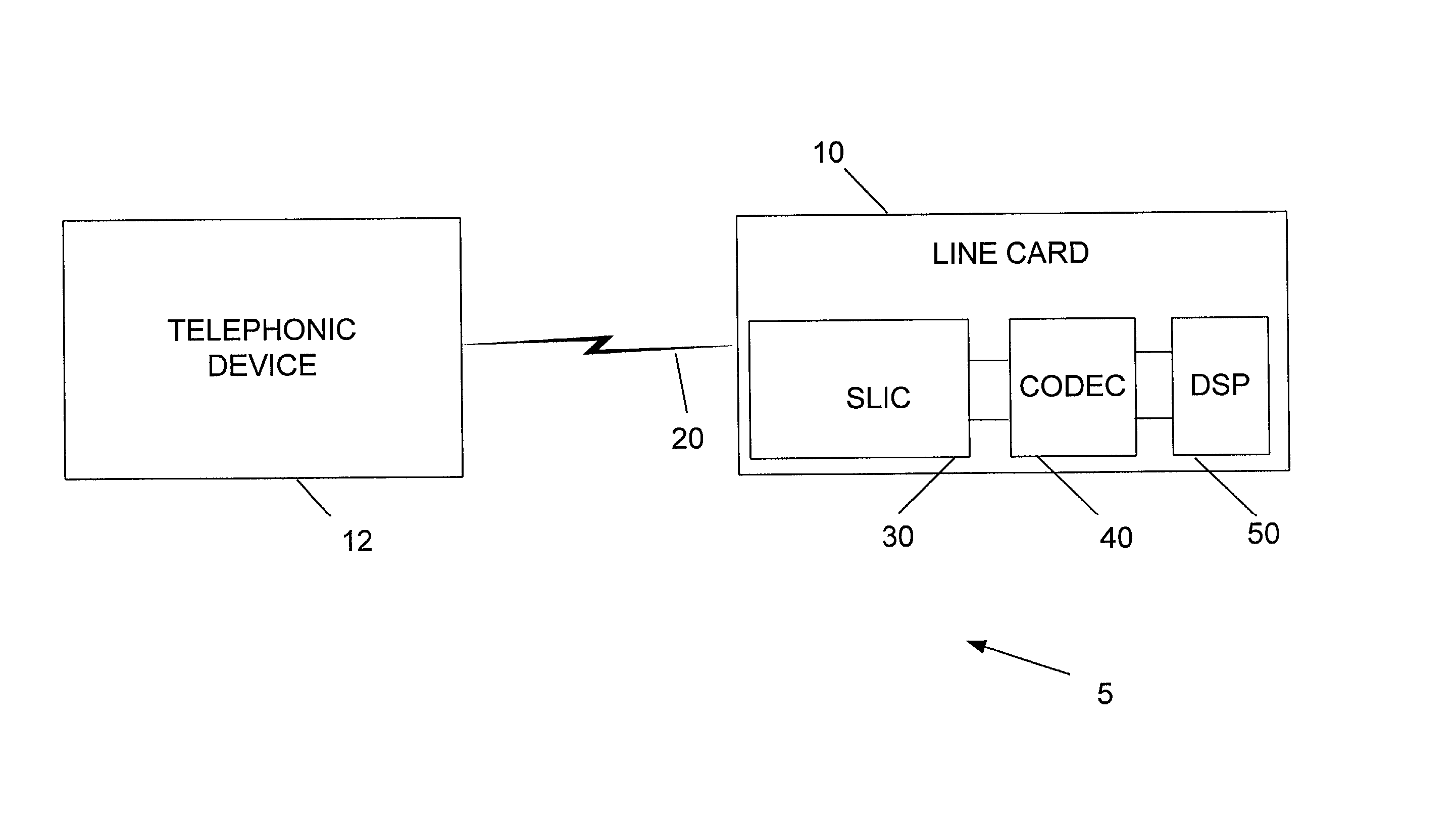
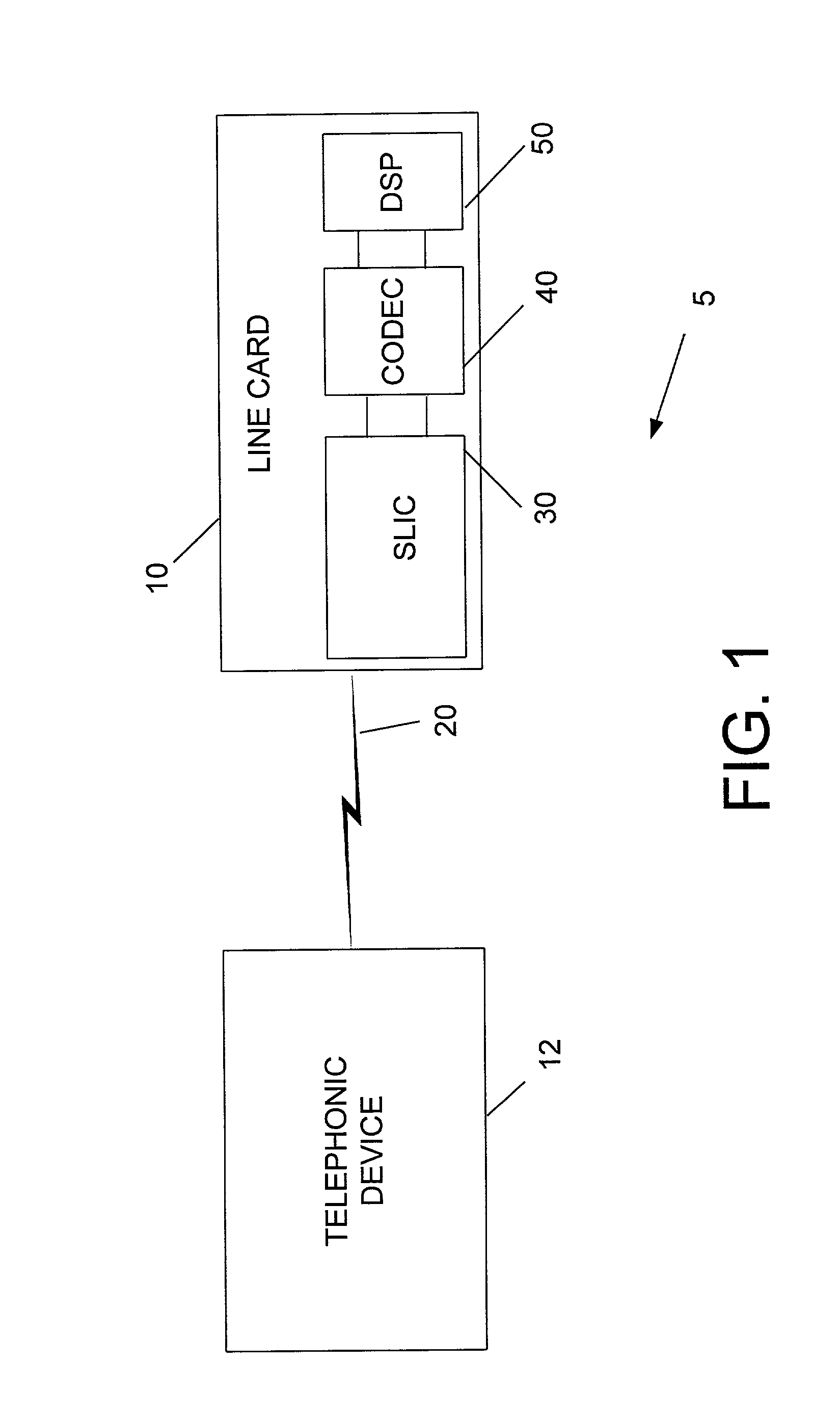
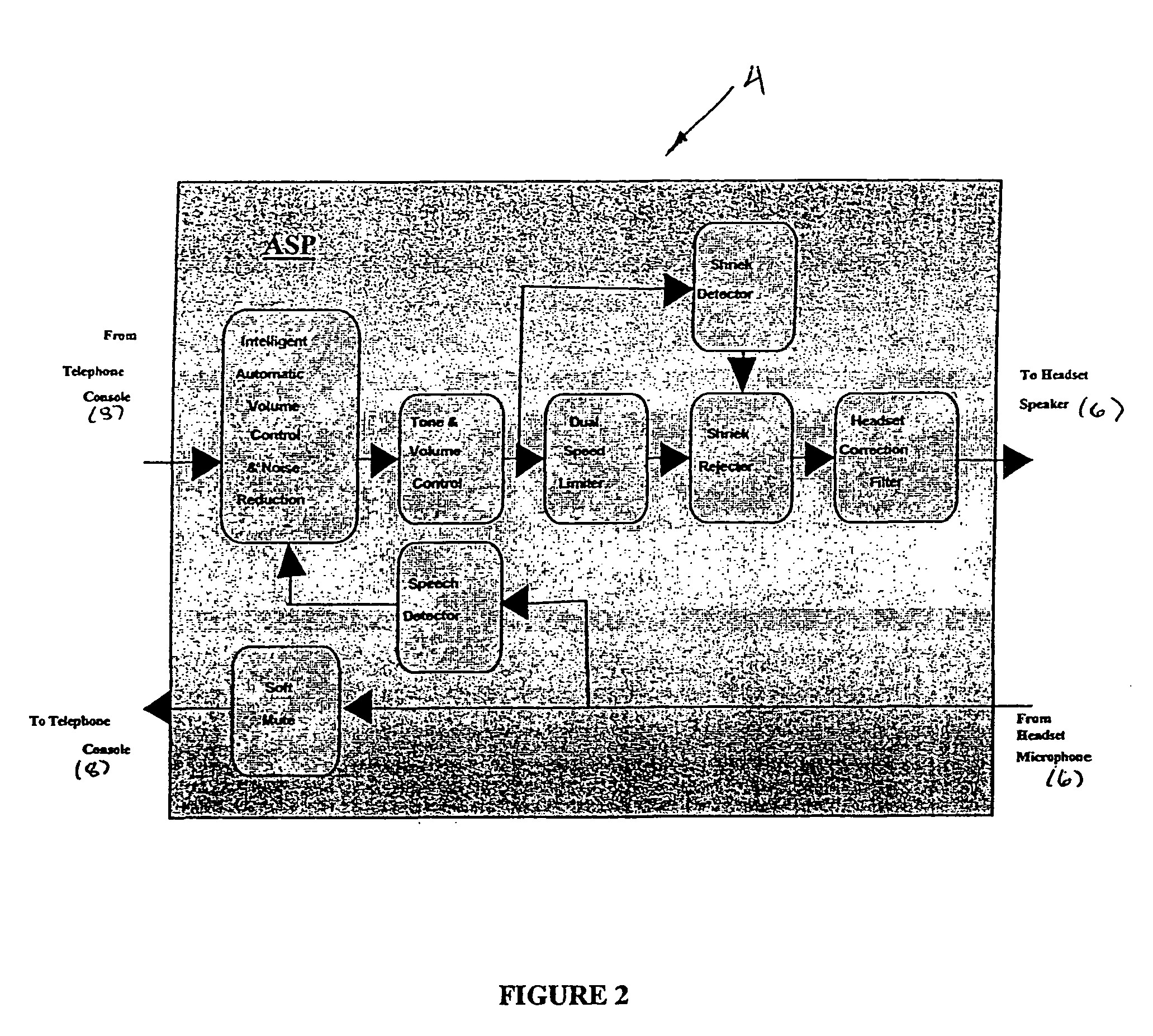
Telephony interface apparatus
InactiveUS20050105717A1Interconnection arrangementsSpeech amplifier applicationsHeadphonesEmbedded system
A telephony interface apparatus adapted to interface between a telephony device and a headset, the apparatus including: control means for controlling functions of the apparatus; function selection means coupled to the control means for selecting one of the functions; a rotationally movable dial coupled to the control means for selecting a setting of a selected function by movement of the dial; and digital display means for displaying the setting.
Owner:TELSTRA CORPORATION LIMITD +1
Image sensor
InactiveUS6969838B2Improve fidelityPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision system scanning detailsSemiconductor chipBoundary region
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Alert gateway, systems and methods
ActiveUS8050281B2Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionCable televisionReal-time computing
Embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for distributing urgent public information. Merely by way of example, urgent public information, such as an alert message, may be received by, inter alia, an alert gateway device. The alert message may then be distributed to a subscriber in any of a variety of ways, including by telephone, by data message (e.g., to a computer), by video message (e.g., via a television), by display on an alert notification device. In some embodiments, the alert gateway device may process the alert message and / or may determine how to provide the alert message to the subscriber.
Owner:QWEST
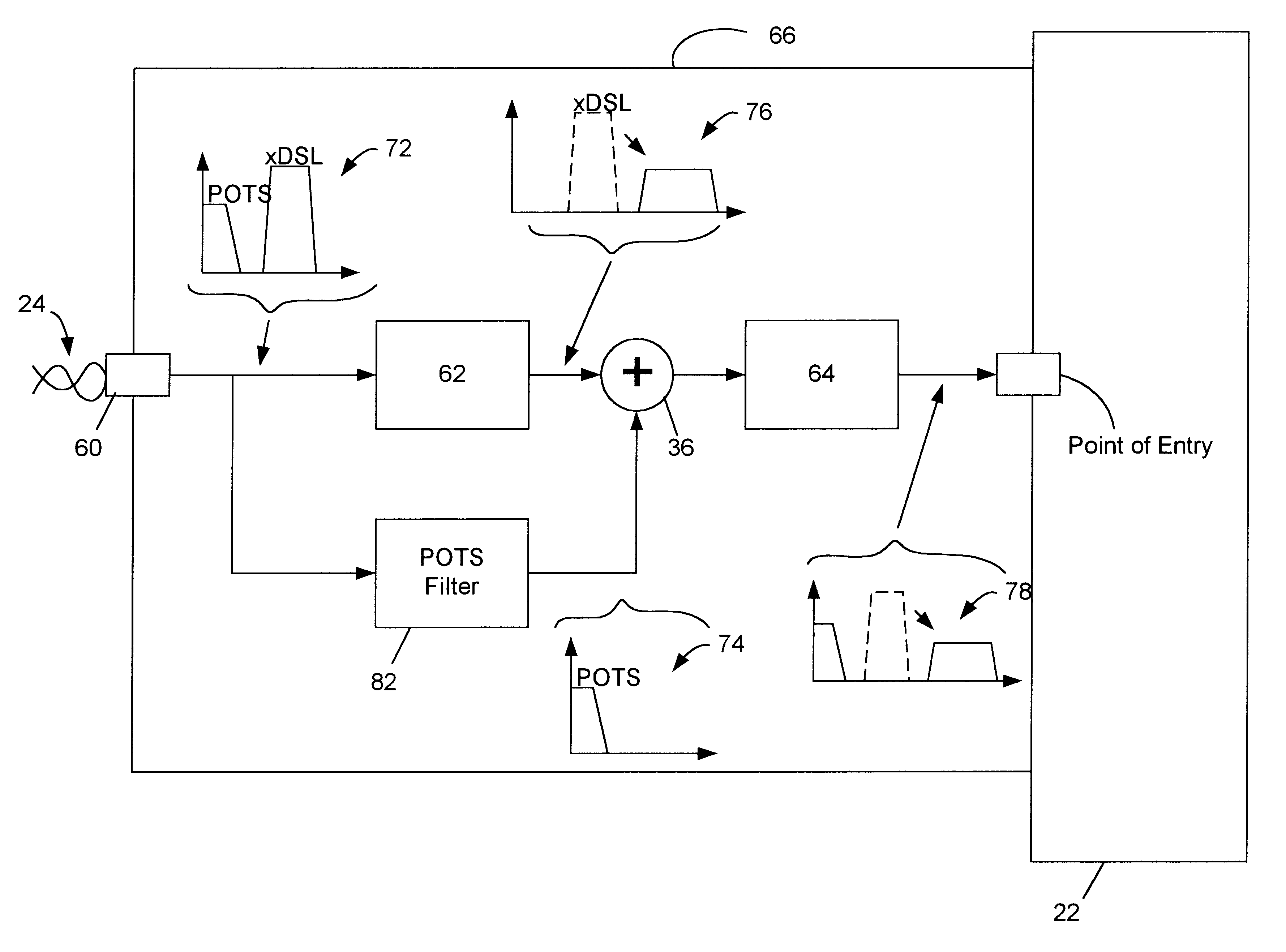
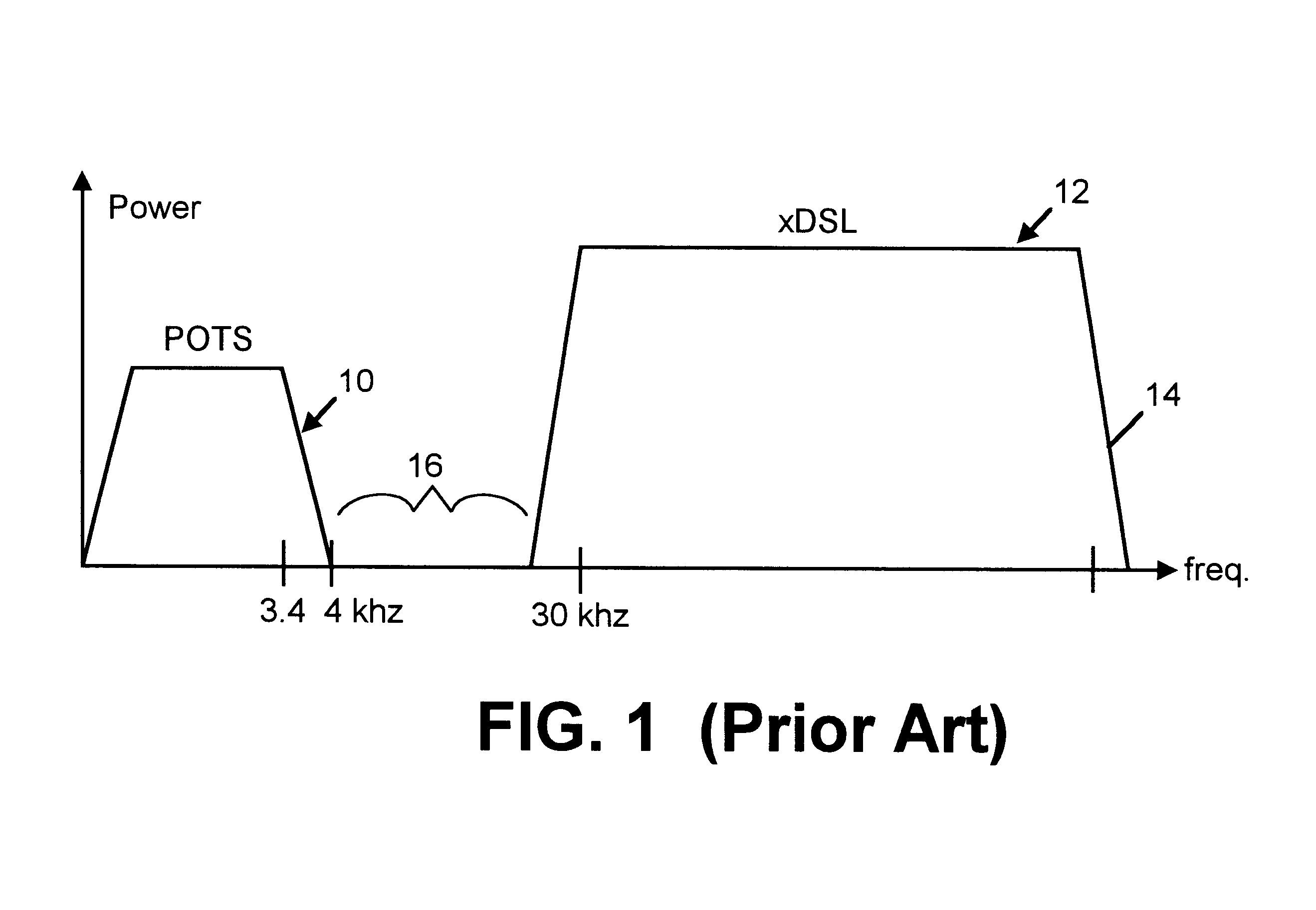
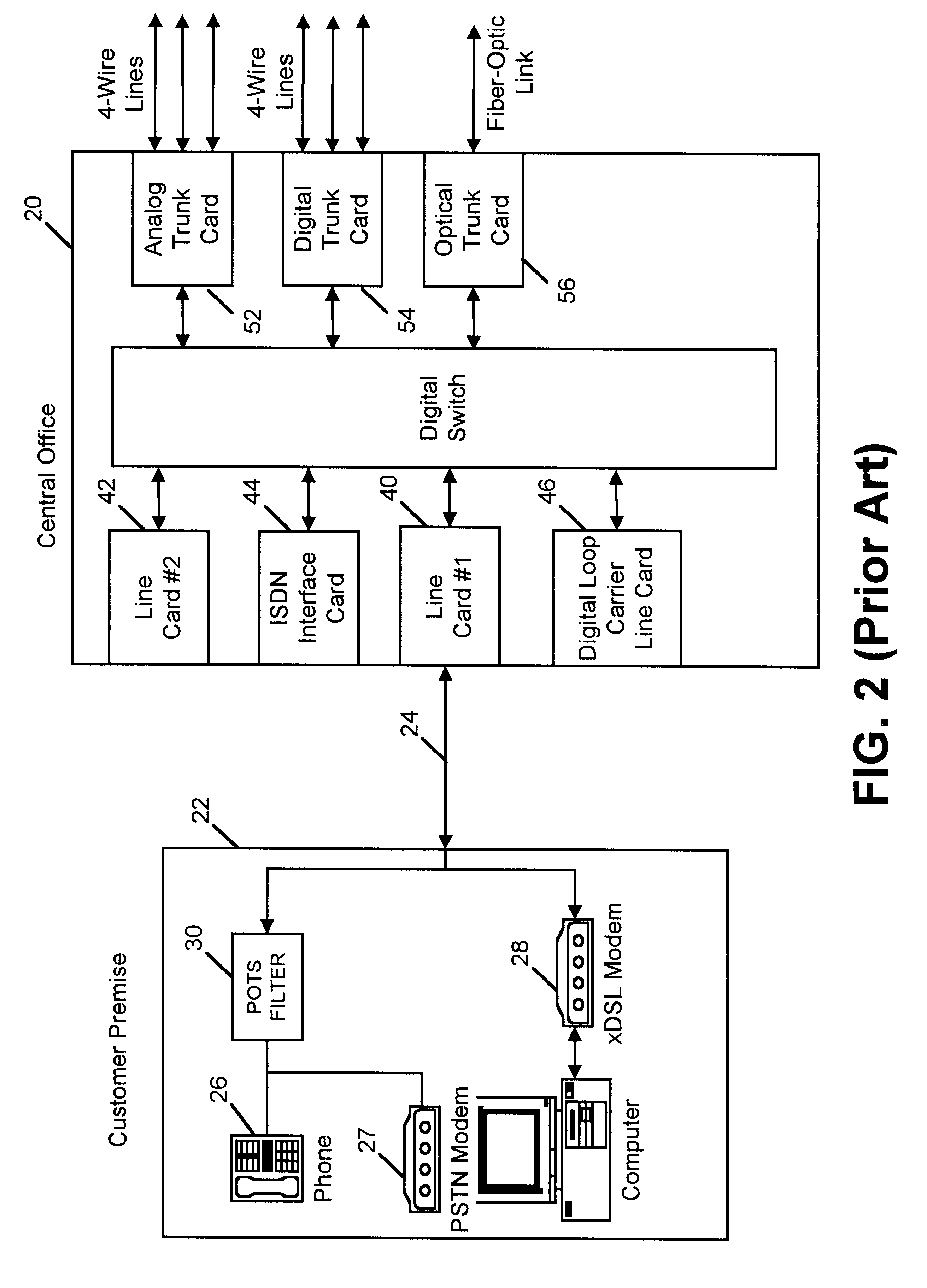
Apparatus for facilitating combined POTS and xDSL services at a customer premises
InactiveUS6466588B1Reduce the amplitudeMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsLow-pass filterSignal on
In accordance with one aspect of the invention, an apparatus is provided for facilitating combined xDSL and POTS communication across a two wire pair. The apparatus includes a first communication port for communication with a central office across a two wire pair, and a second communication port for communication with a customer premises across a two wire pair. A splitter, or tap, is disposed at the first communication port for splitting a combined xDSL and POTS signal into a first and second signal path. A low pass filter is disposed in the first signal path for filtering the xDSL signal from the combined signal in the first signal path, leaving only the low-frequency (POTS frequency) signals. A circuit is disposed in the second signal path that is configured to filter the POTS signal from the combined signal, leaving only the xDSL signal. The circuit is further configured to terminate the xDSL signal and regenerate it at a lower amplitude and higher frequency than the original xDSL signal of the combined signal. Finally, an adder is configured to combine the POTS signal on the first path with the regenerated xDSL signal on the second path, and output the result to the second communication port (for entry into the customer premises).
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Interrupt mechanism using TDM serial interface
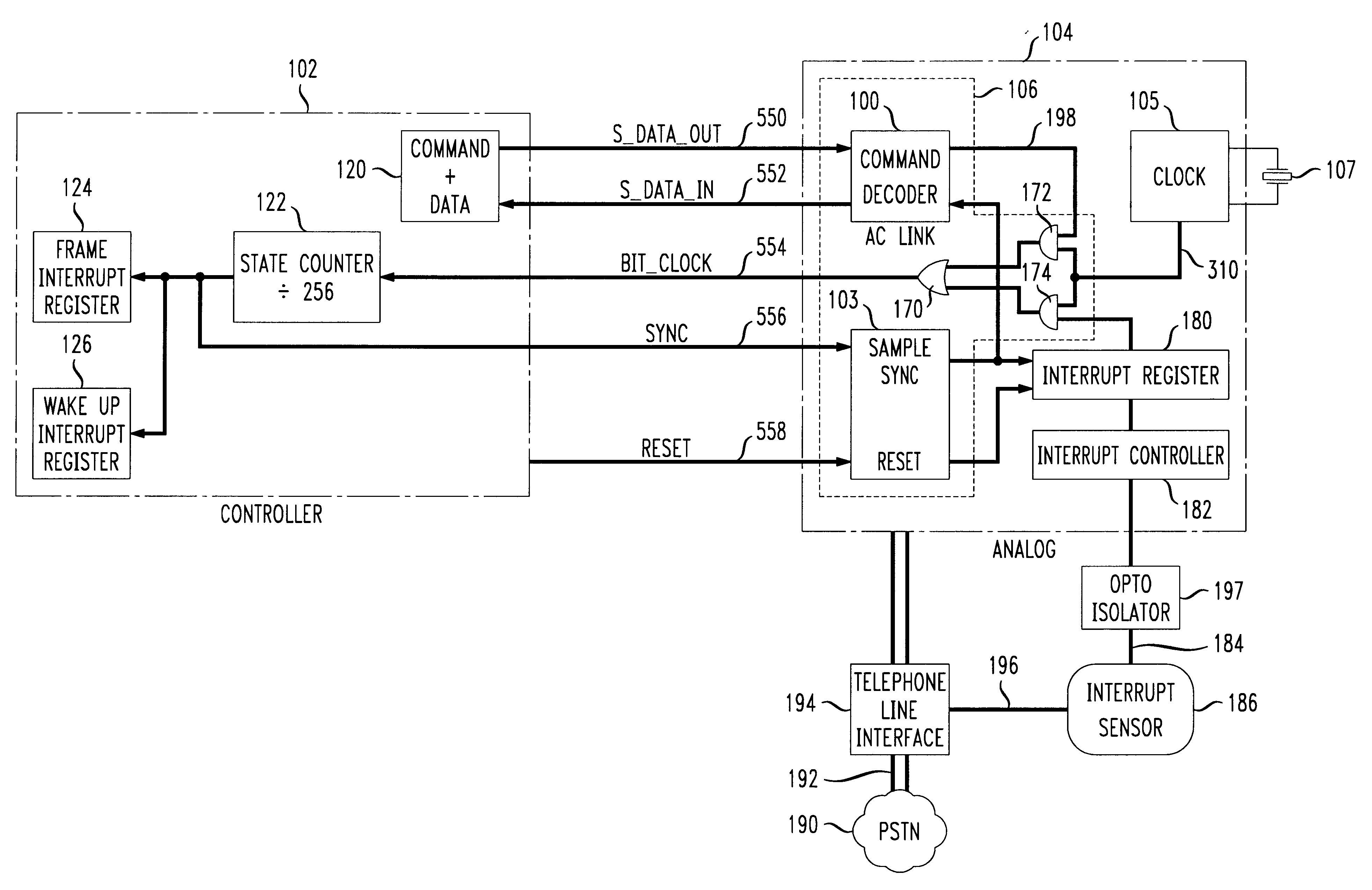
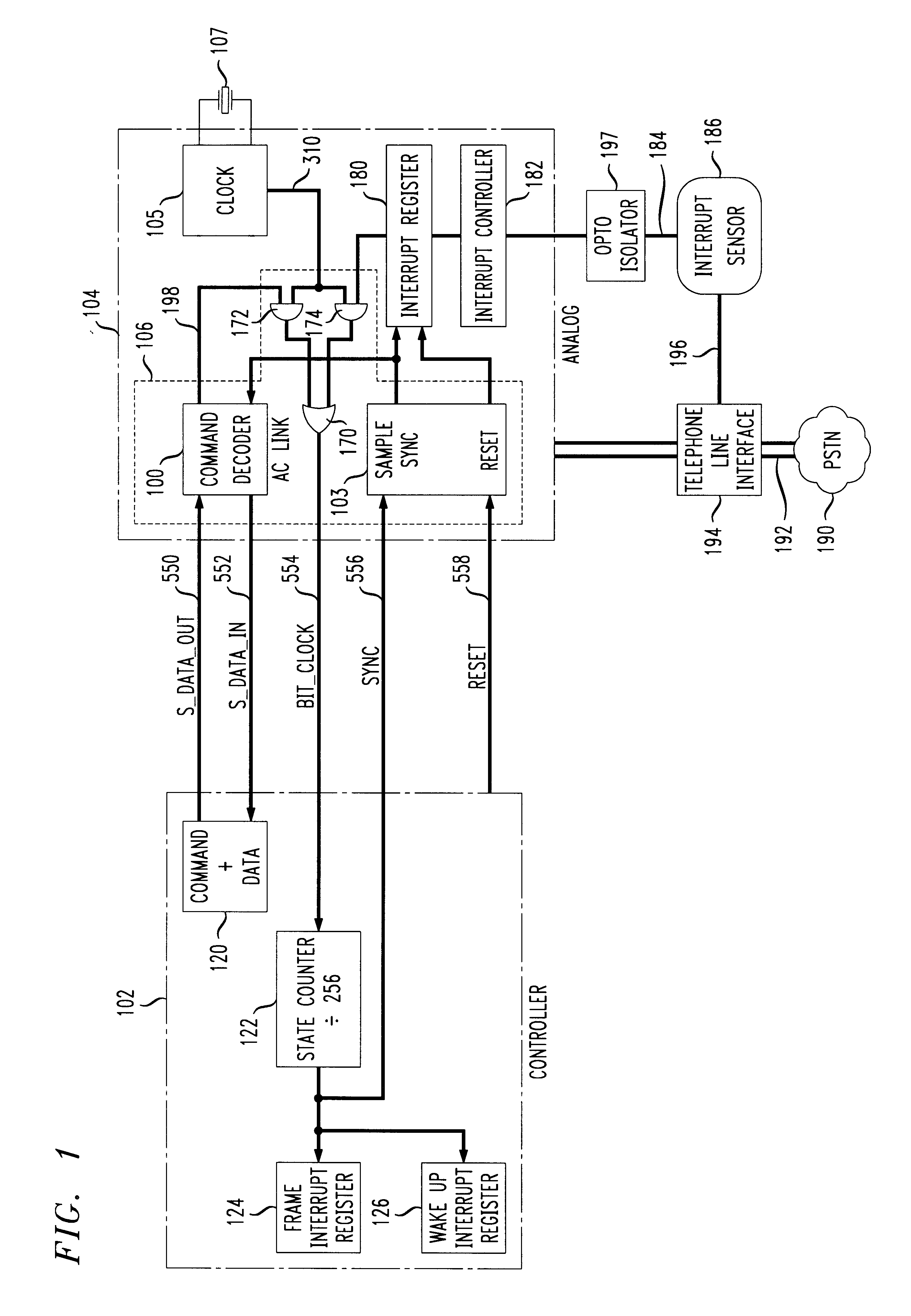
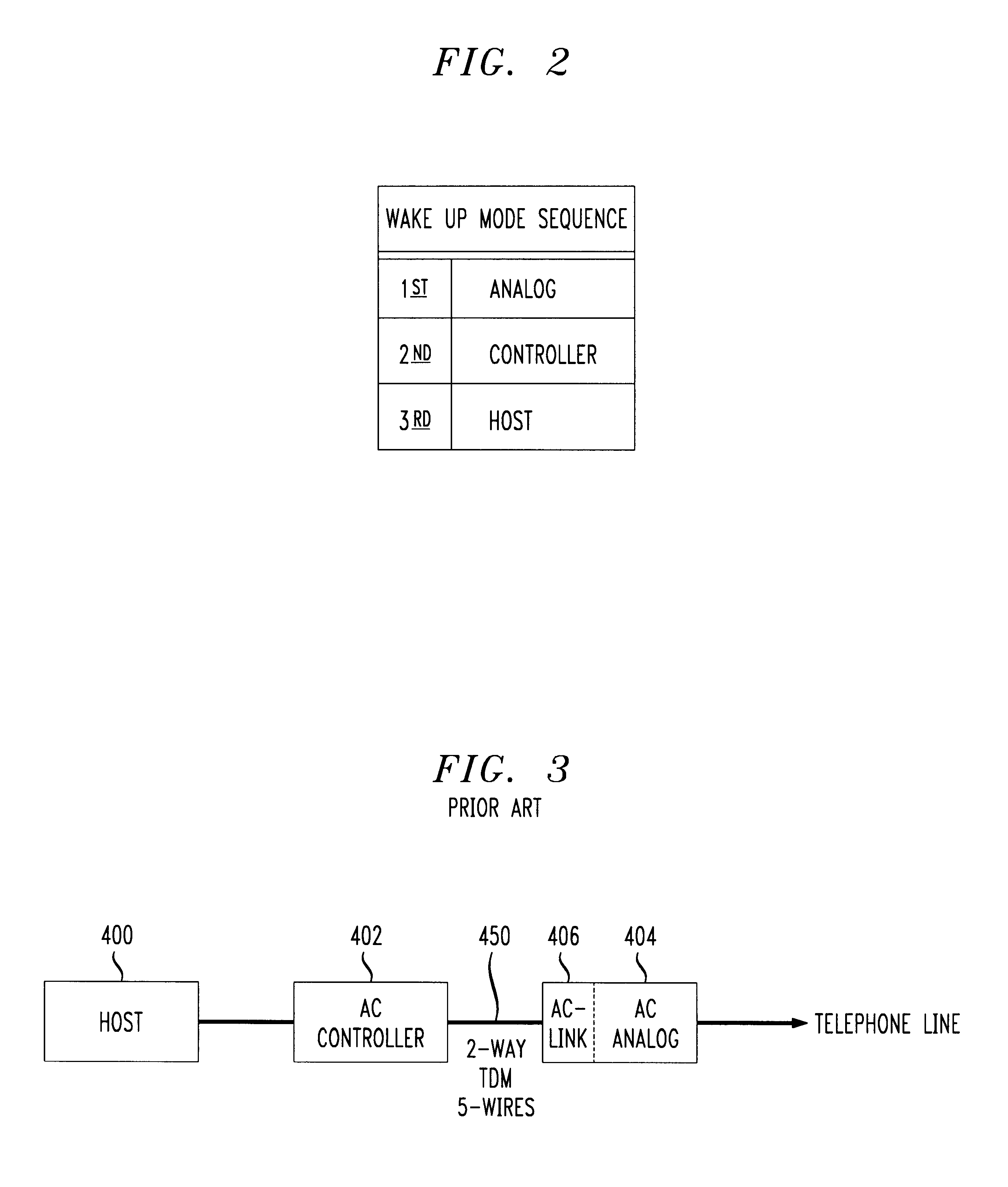
An improvement to split-architecture audio codecs such as those defined by the Audio Codec '97 specification (AC '97) includes an interrupt mechanism which allows an event at an analog peripheral device such as an incoming call to be sensed by the AC analog sub-system and initiate a wake up procedure in the split-architecture audio codec system. The interrupt mechanism includes a masked interrupt register which is responsive to an interrupt signal from an audio source, such as a ring detect from an incoming telephone line. Either the AC controller sub-system or the peripheral analog device via the AC analog sub-system can initiate a wake up procedure. The AC controller sub-system includes a static divide by 256 counter responsive to a bit clock signal. The bit clock signal is sensed at the AC controller sub-system to determine an operating mode. Upon detection of at least 256 bit clock cycles after a predetermined minimum time for the AC analog sub-system to be in a halted or sleep mode, a wake up interrupt register is enabled in the AC controller sub-system. The interrupt sensor is opto-coupled to the AC analog sub-system, and the interrupt signal from the interrupt sensor is communicated to the AC controller sub-system via the five-wire TDM serial bus between the AC analog sub-system and the AC controller sub-system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and apparatus for detecting a secondary destination of a telephone call based on changes in the telephone signal path
InactiveUS7136471B2Suitable for useImprove reliabilityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpecial service for subscribersBiological activationTeleconference
Owner:SECURUS TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com