Patents
Literature
40 results about "Core shroud" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
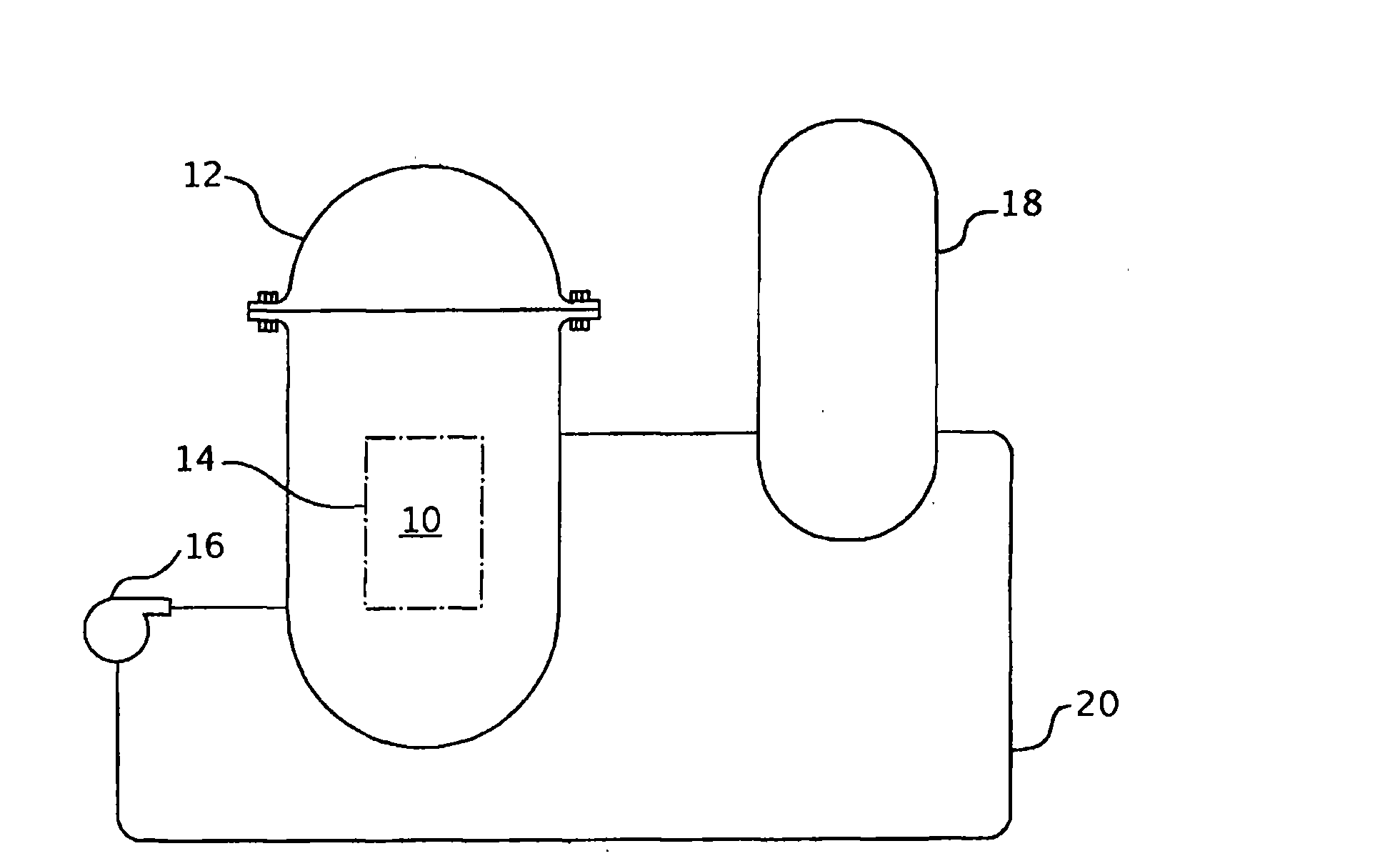
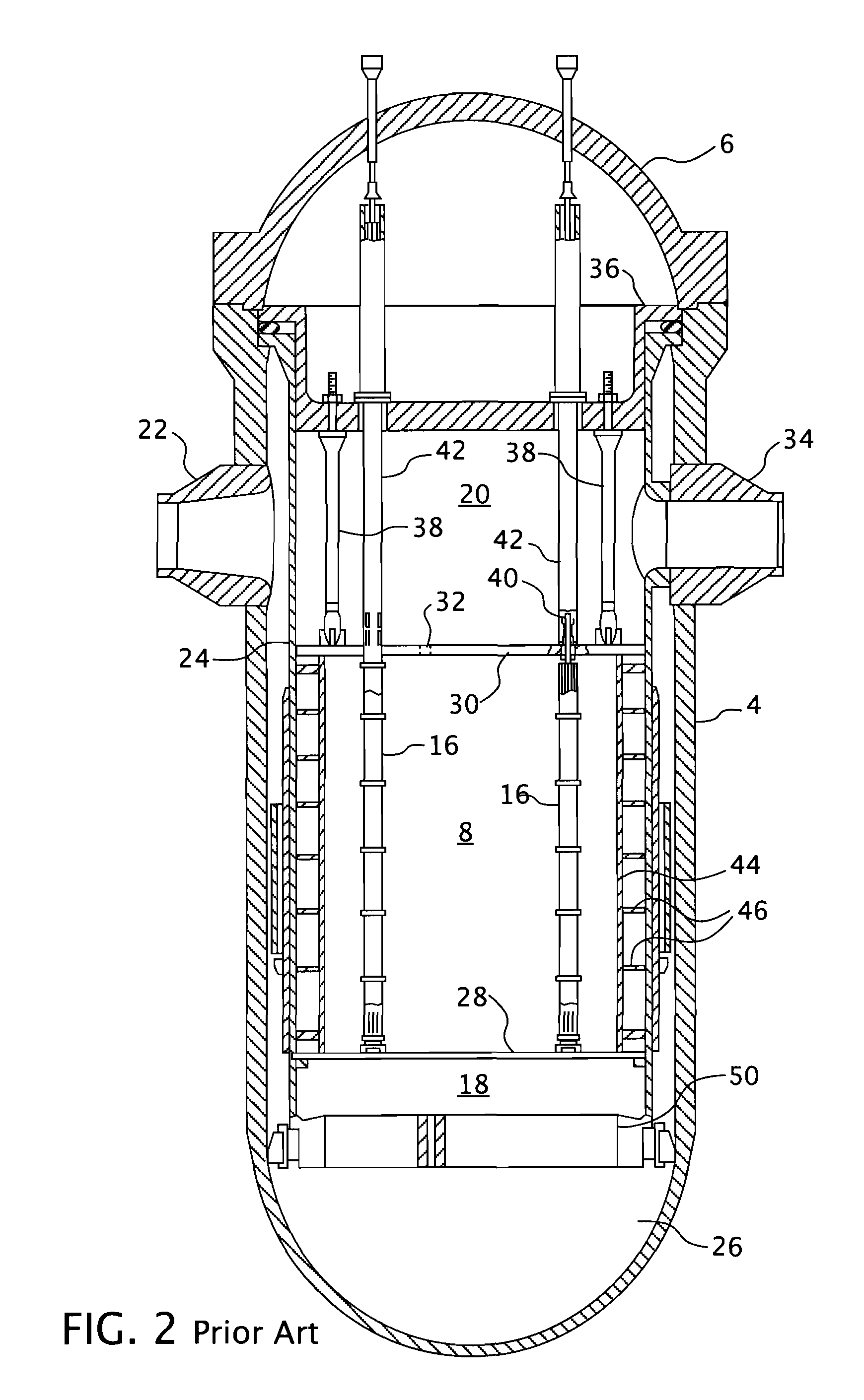
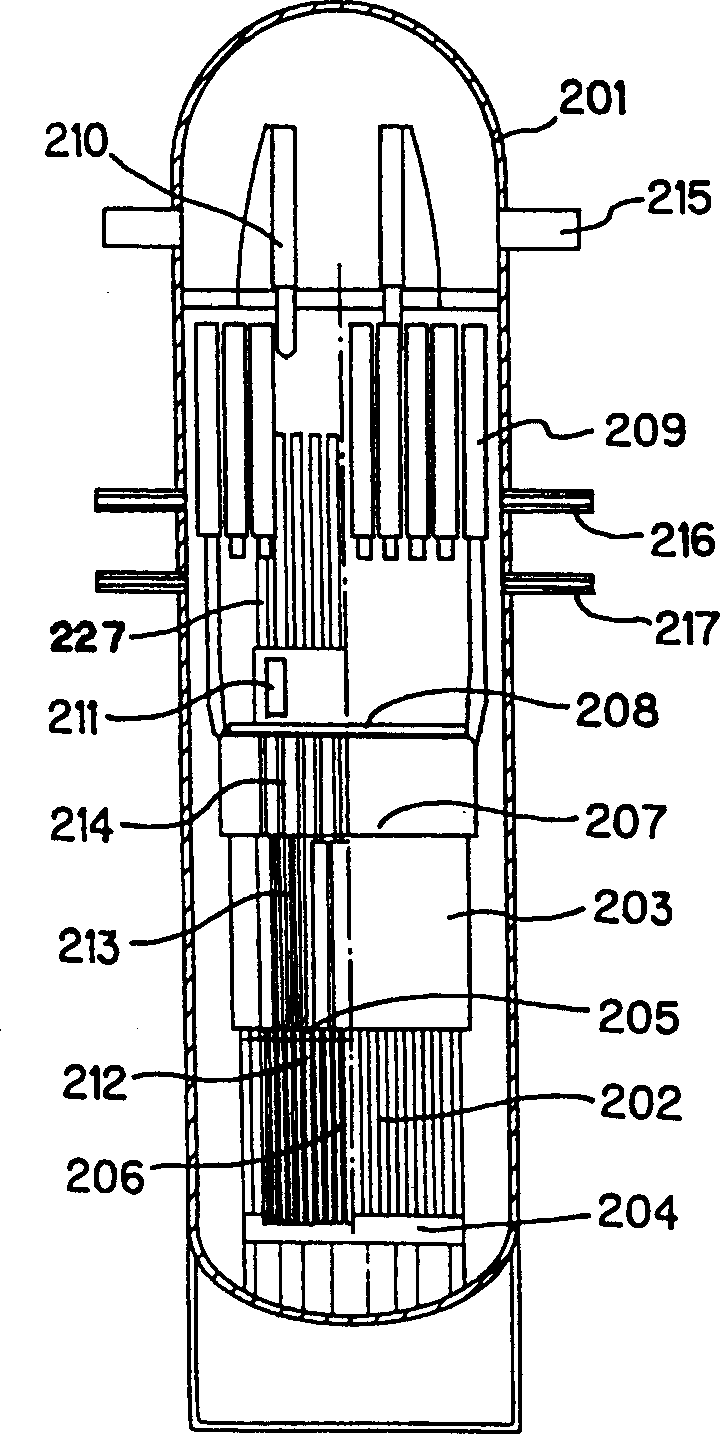
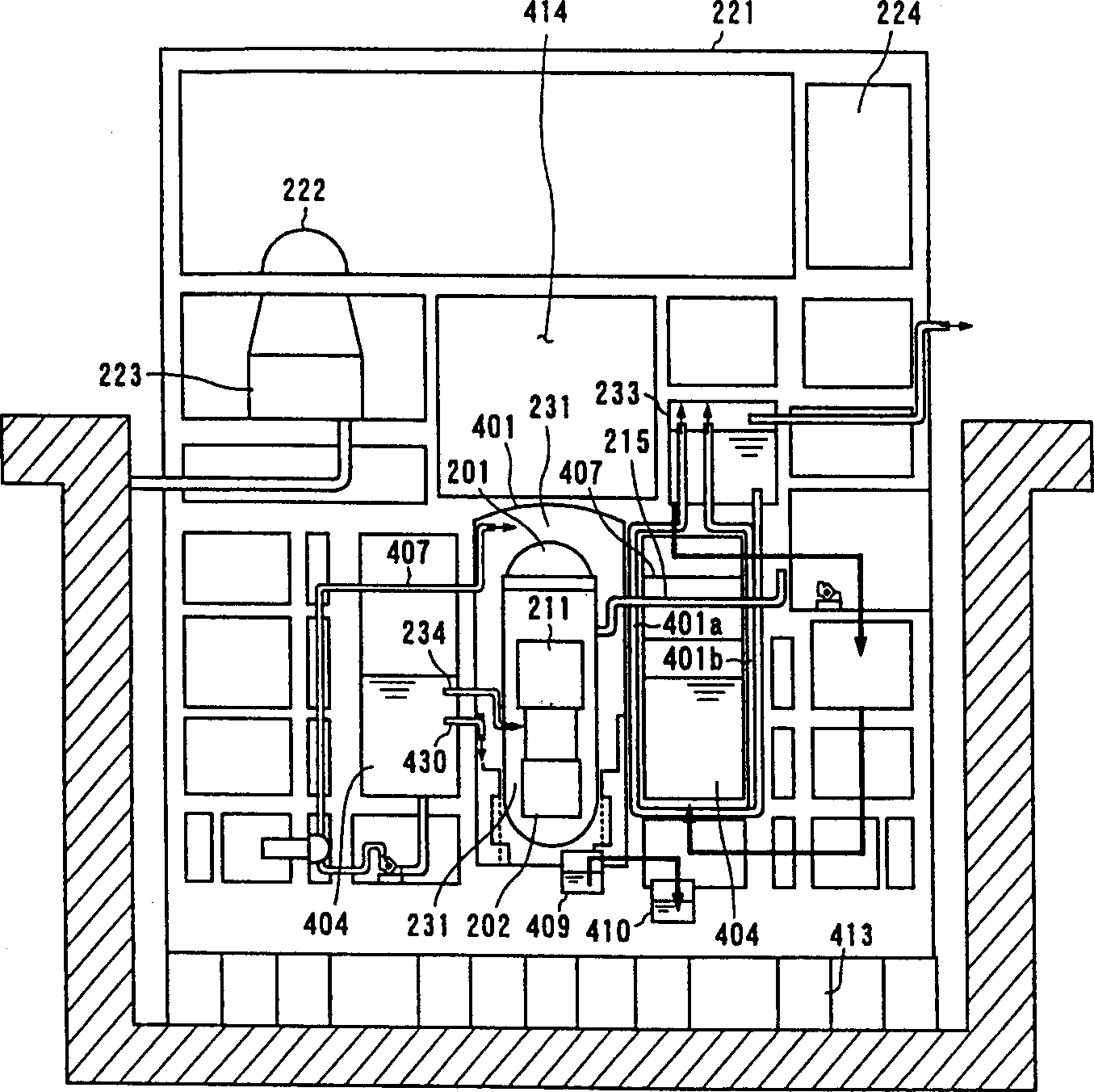
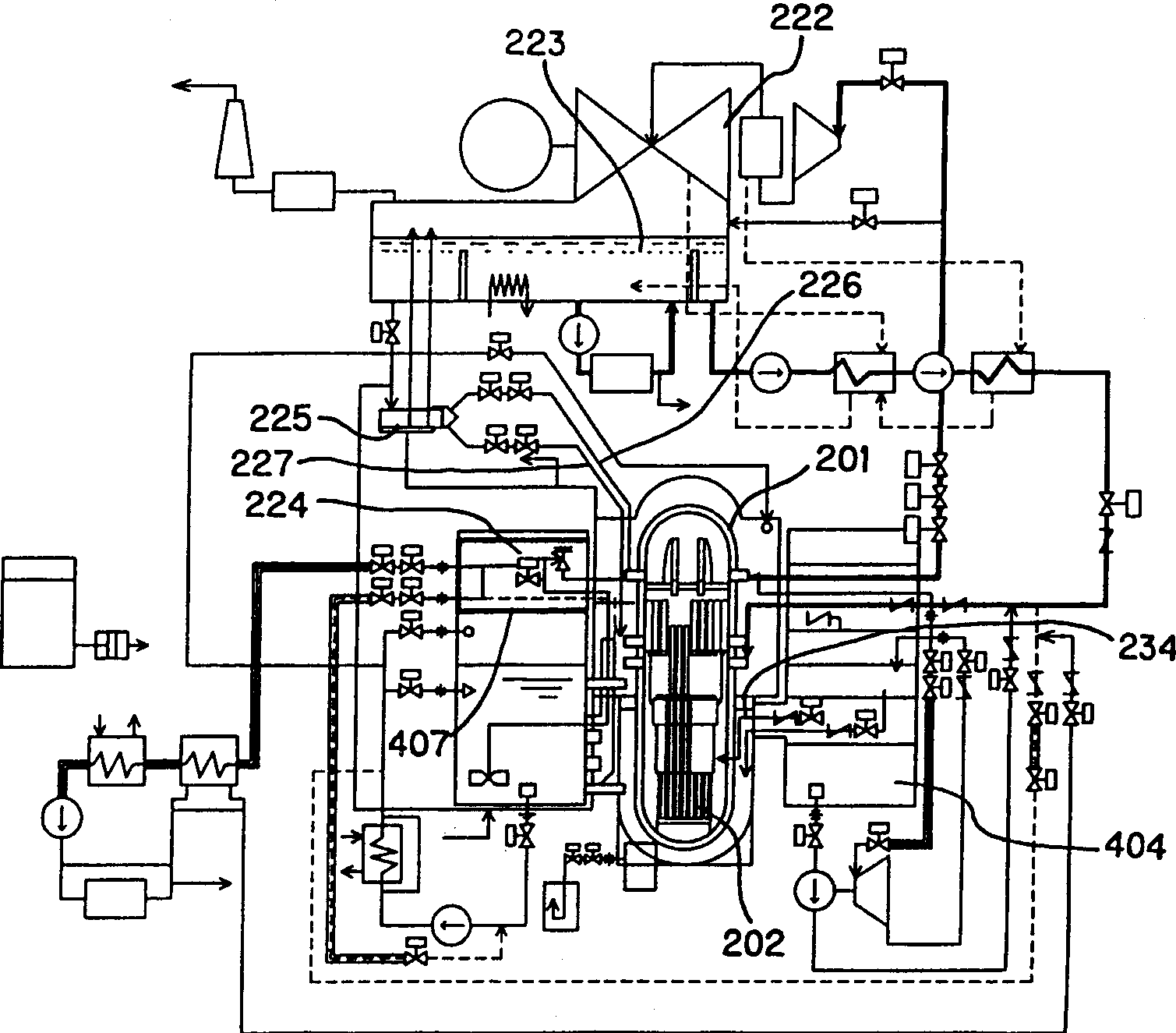
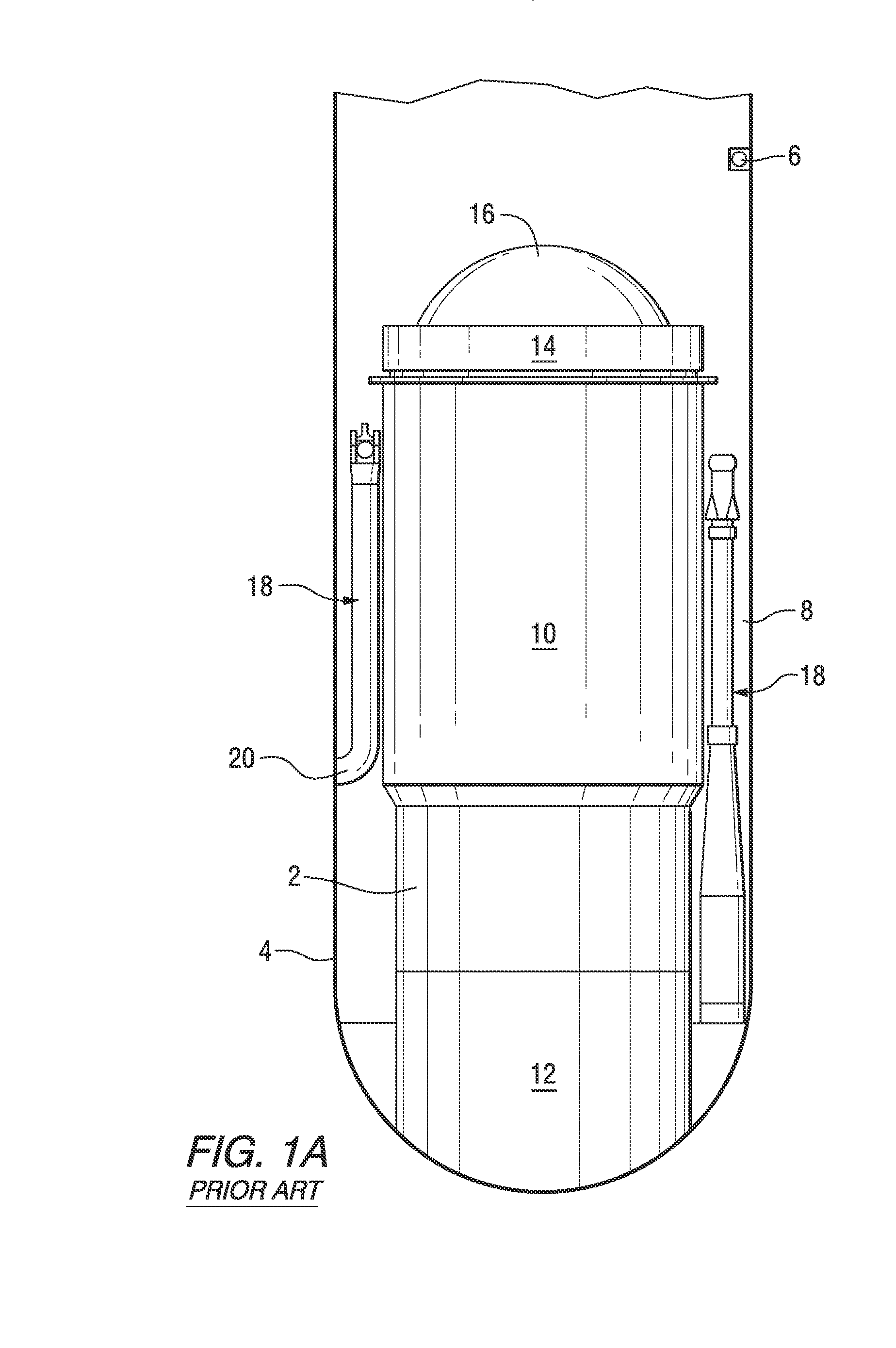
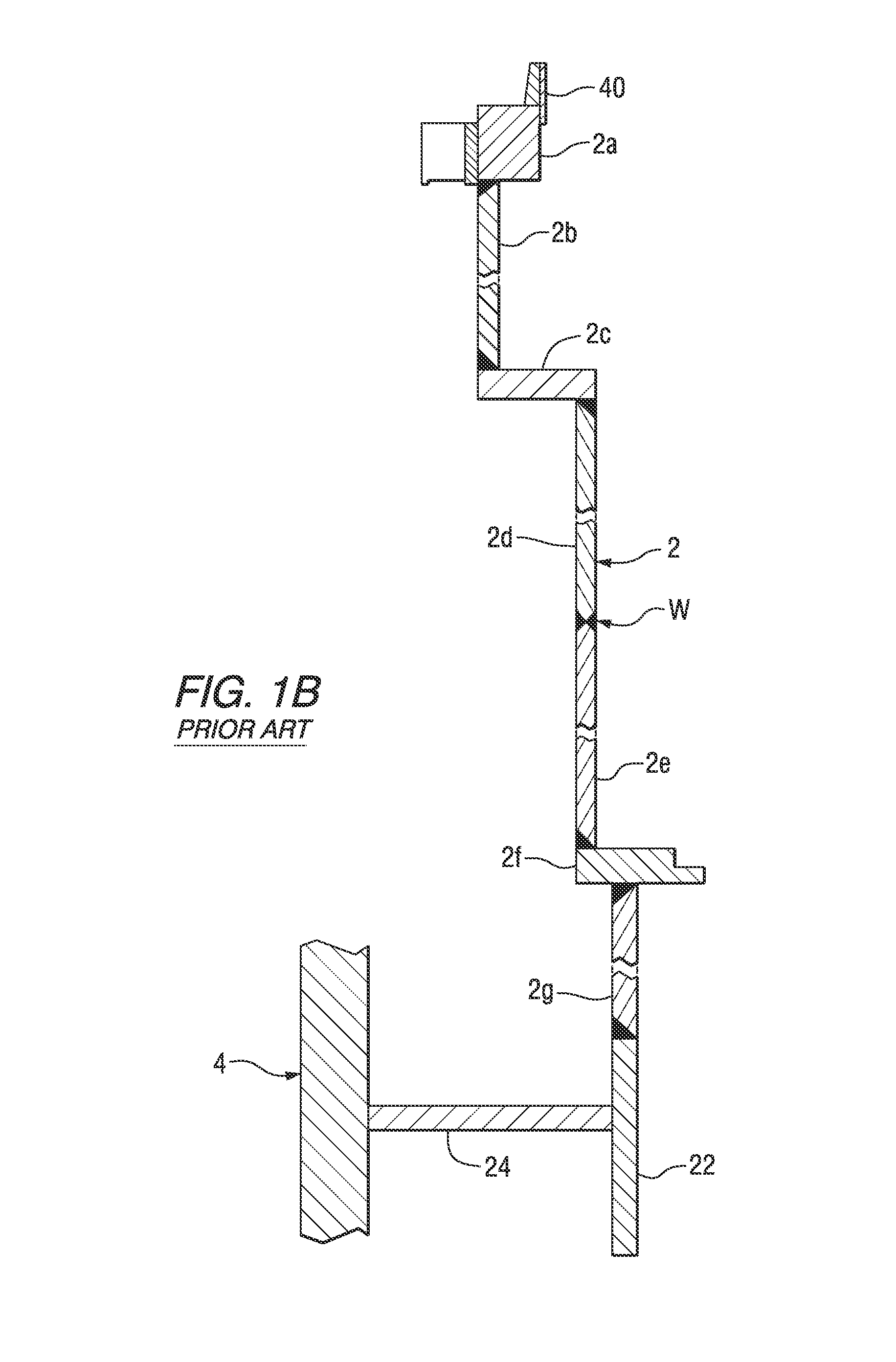
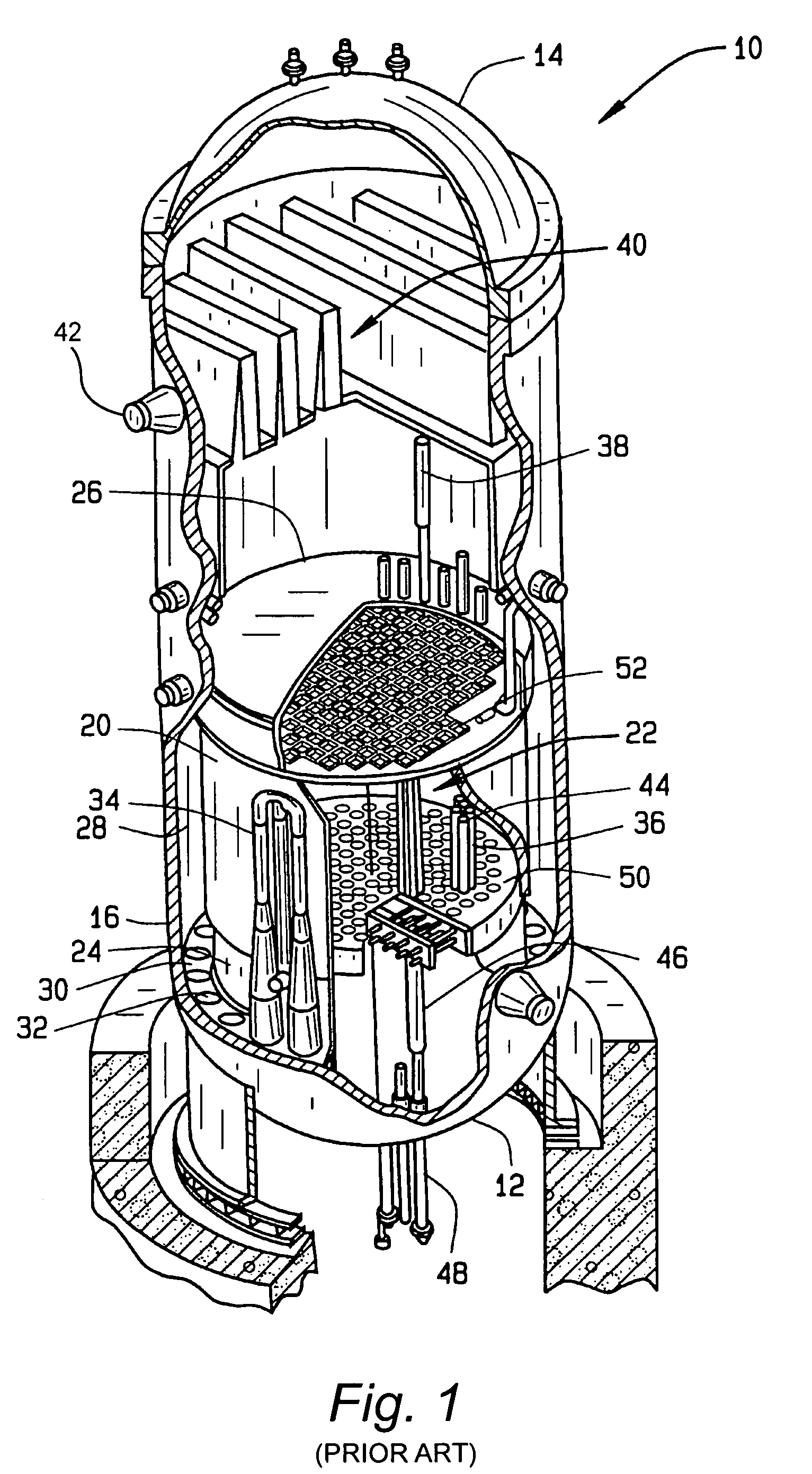
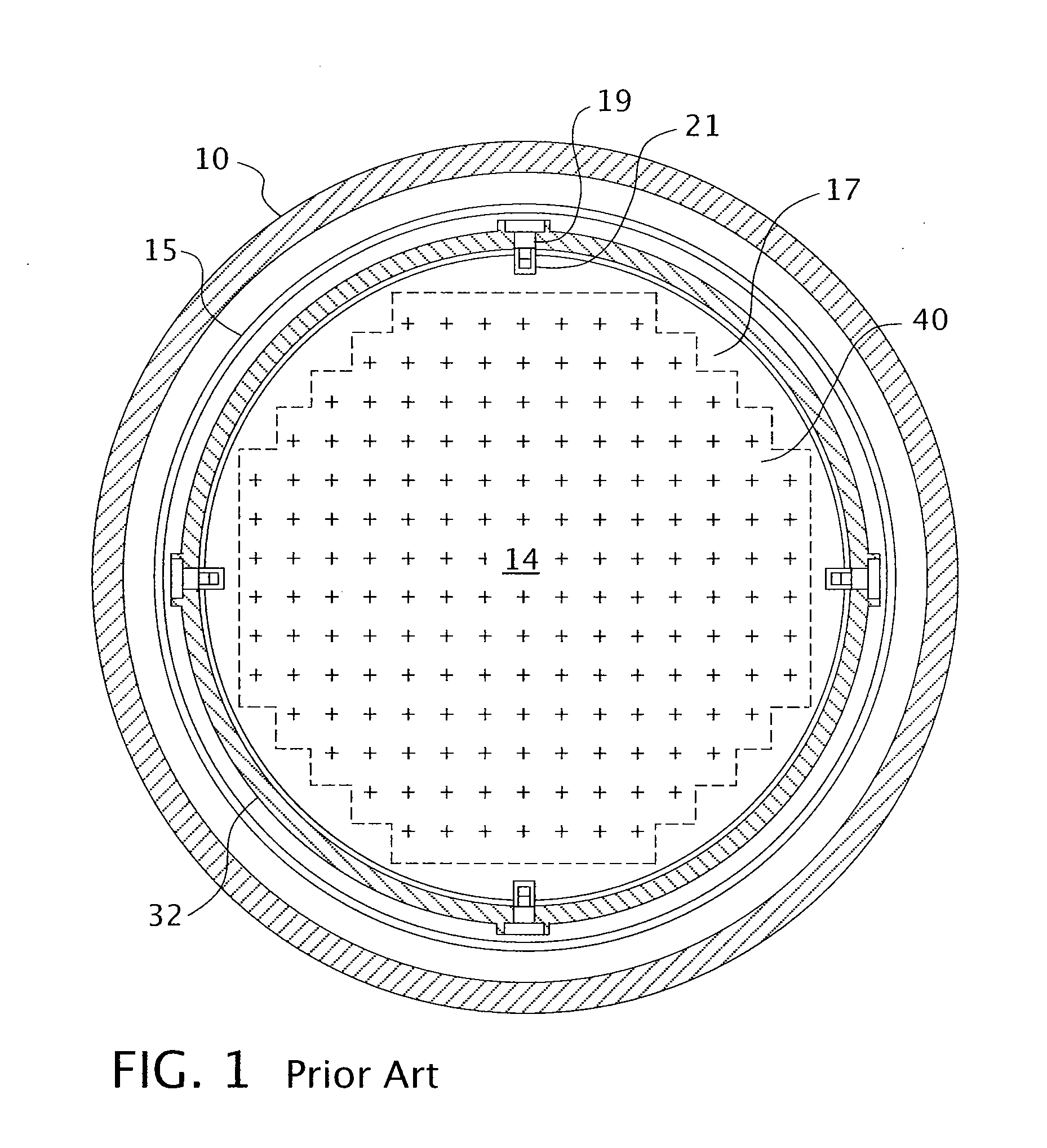
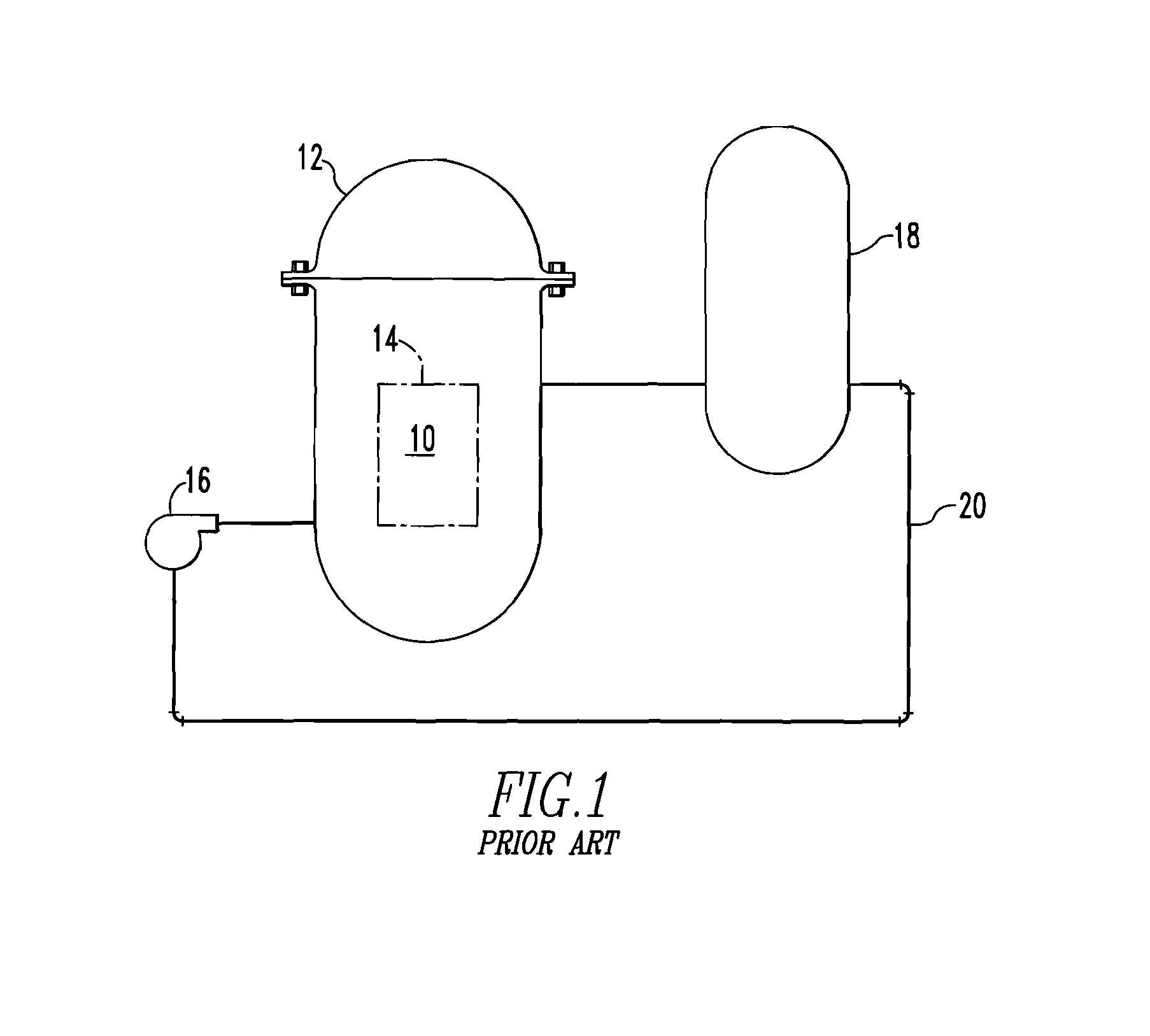
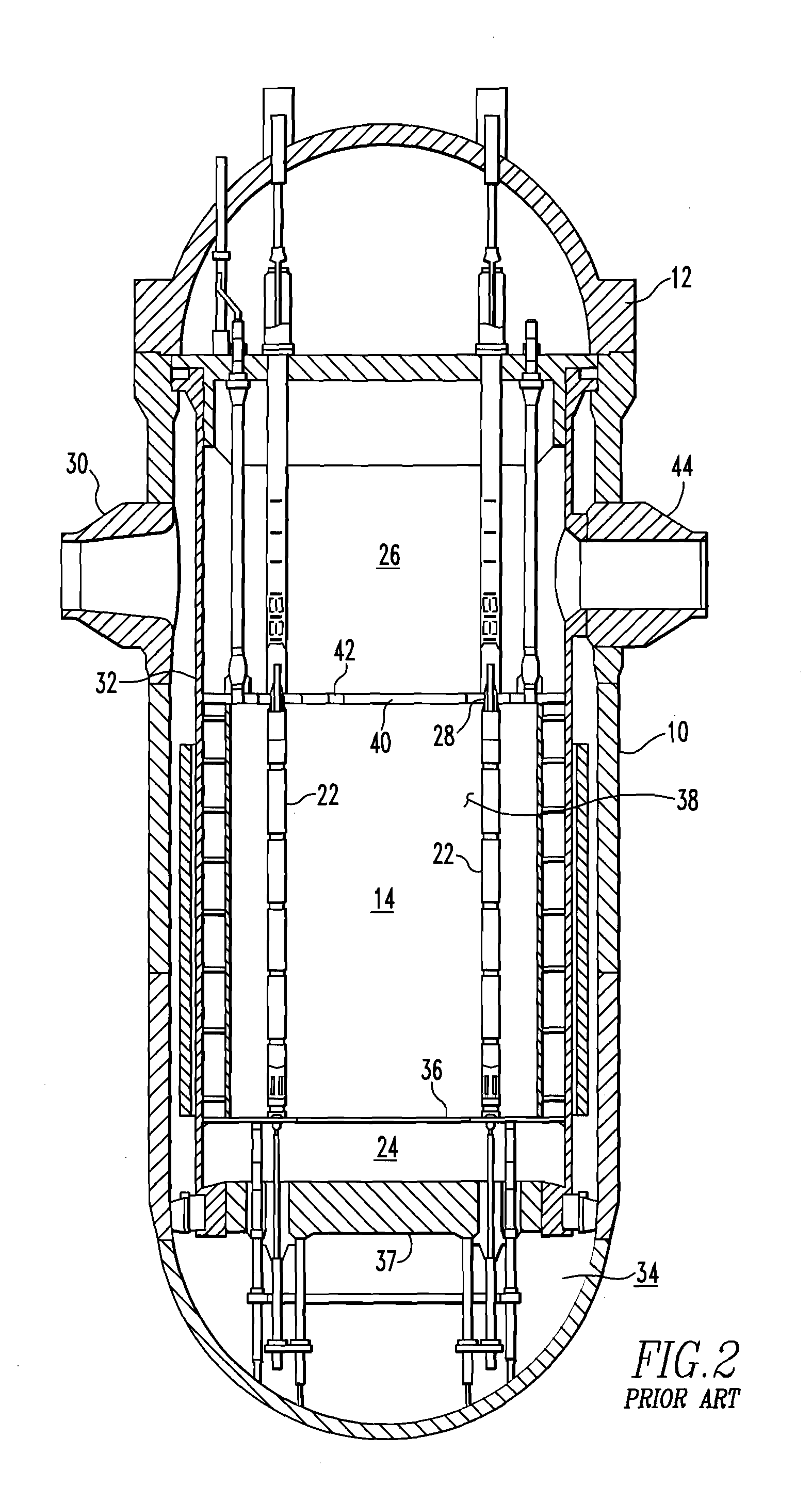
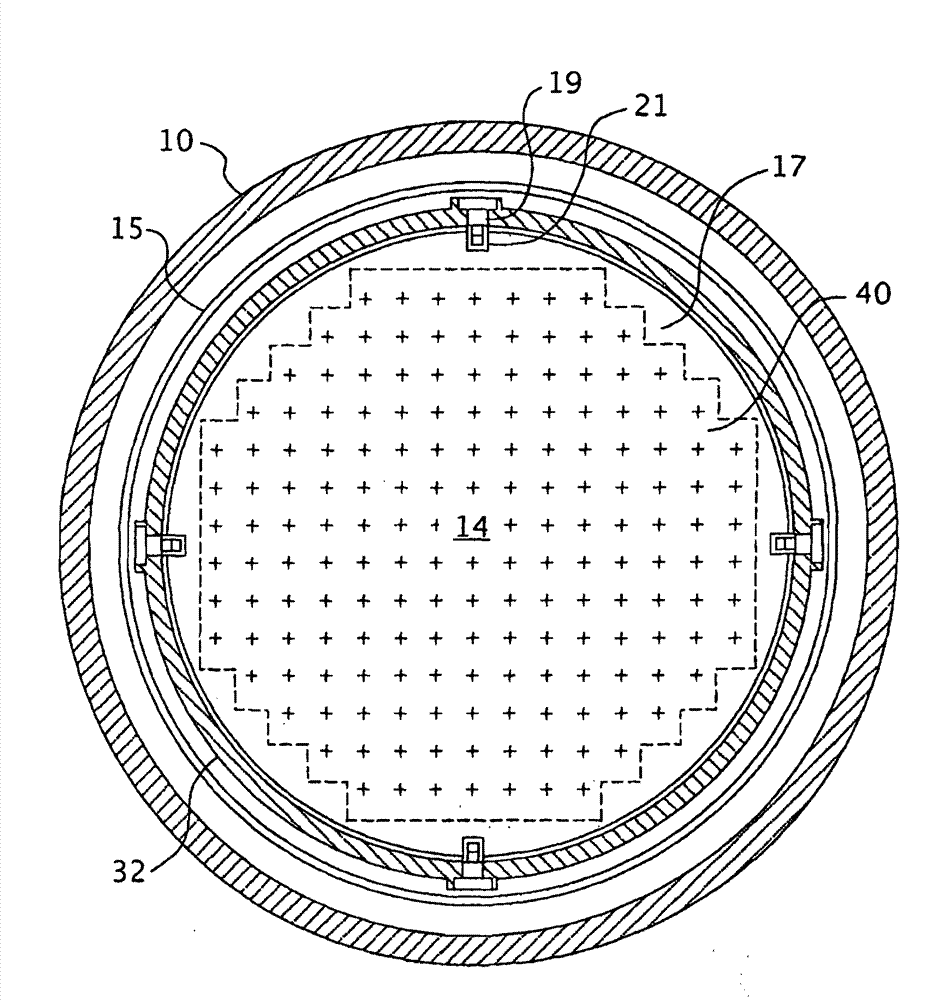
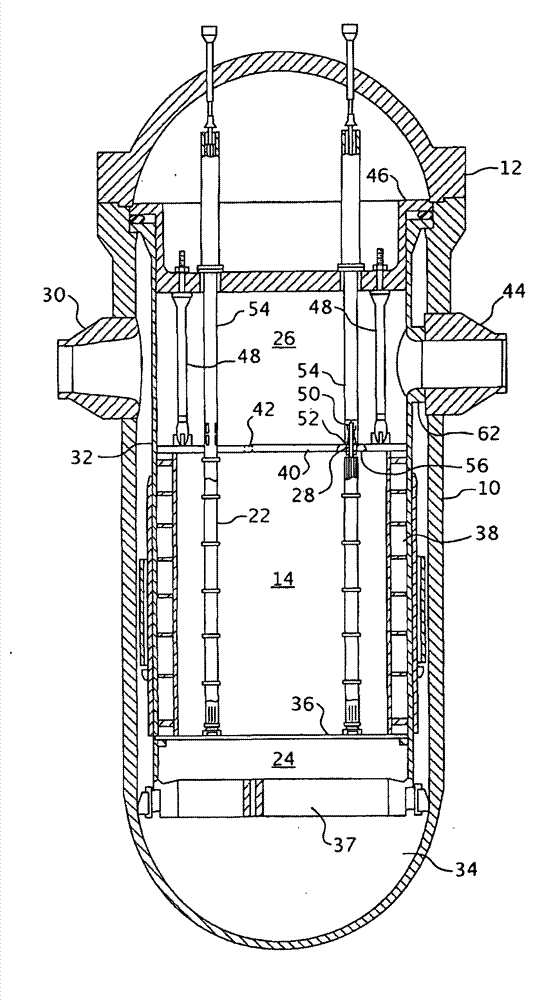
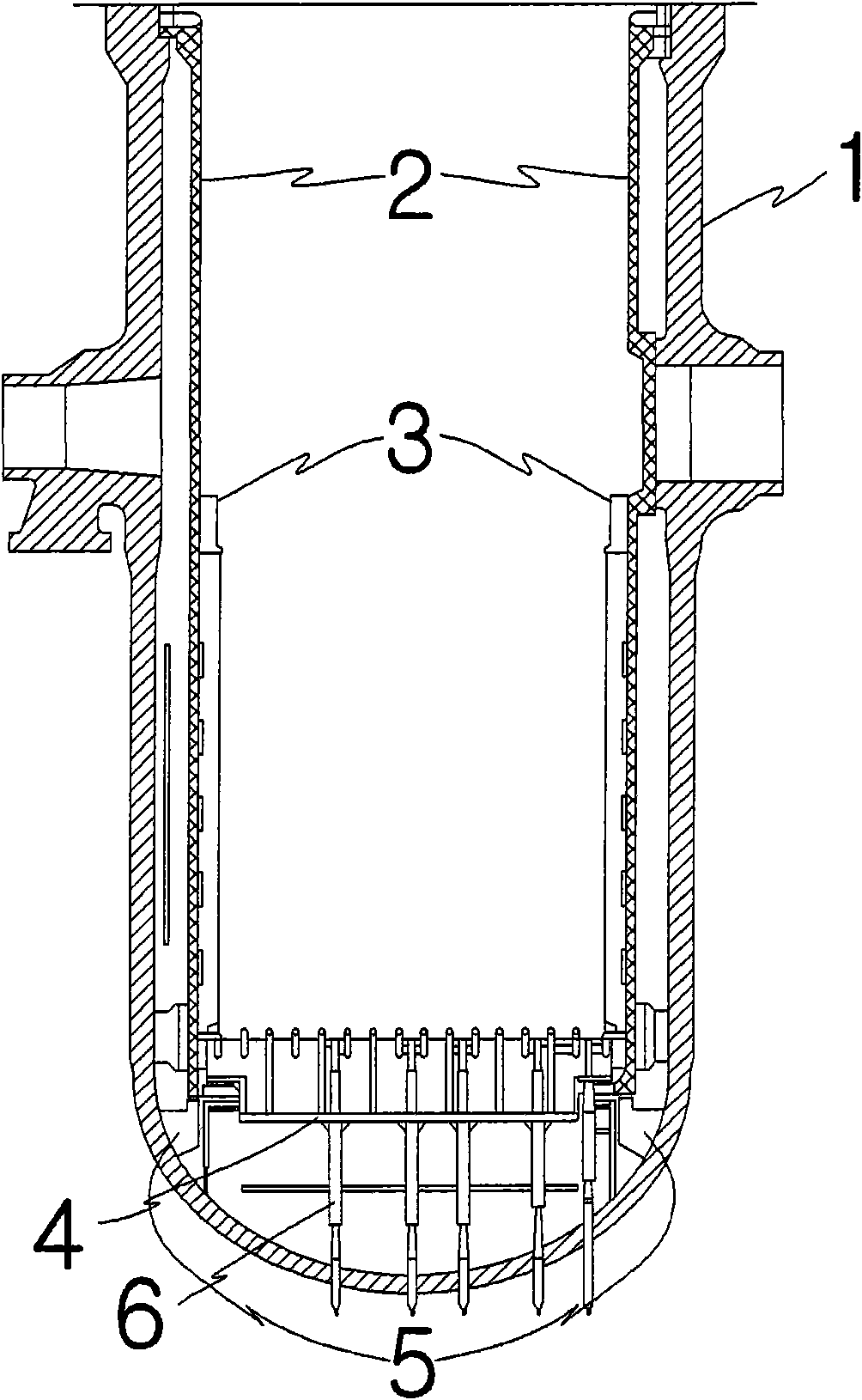
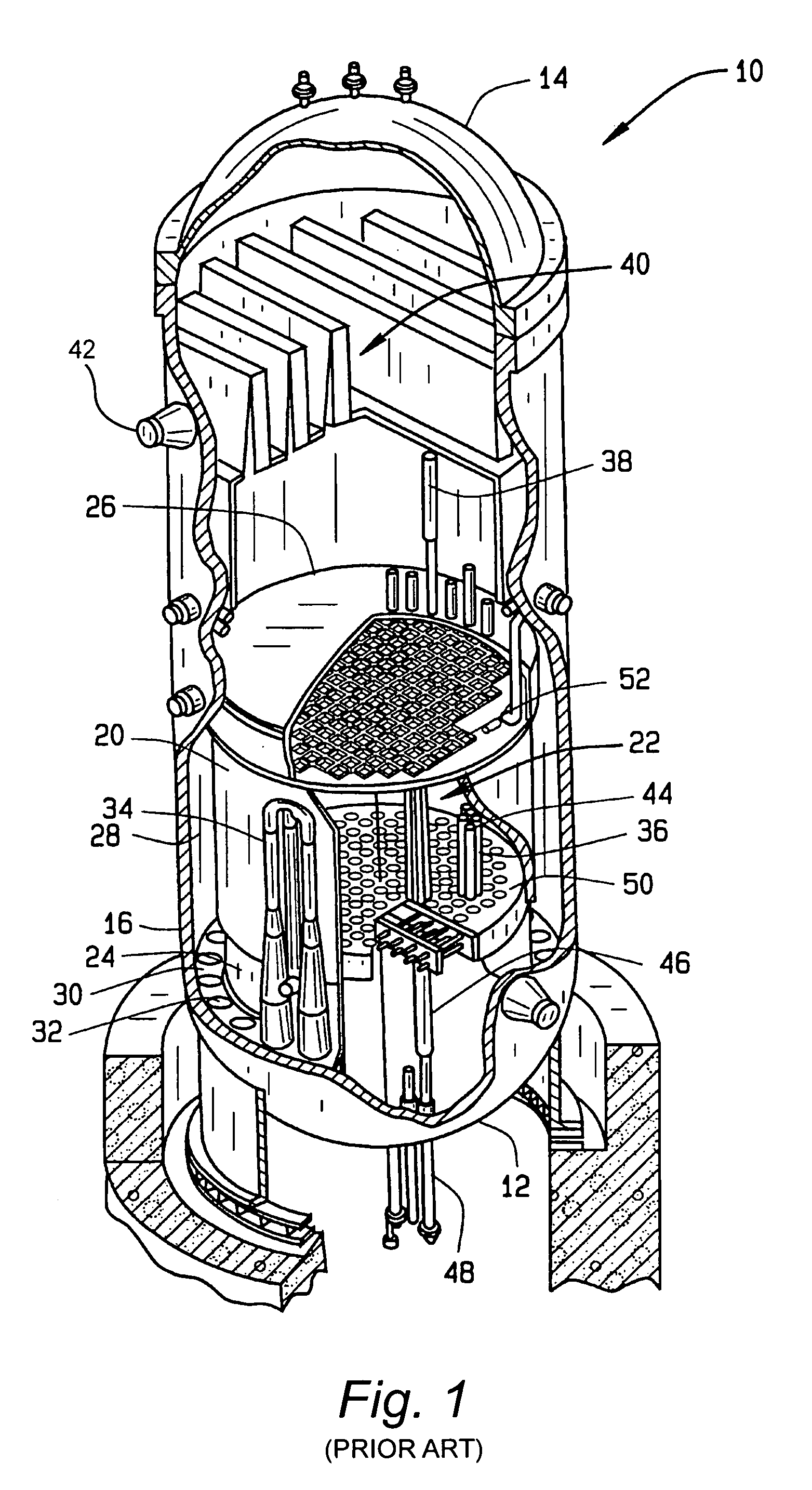
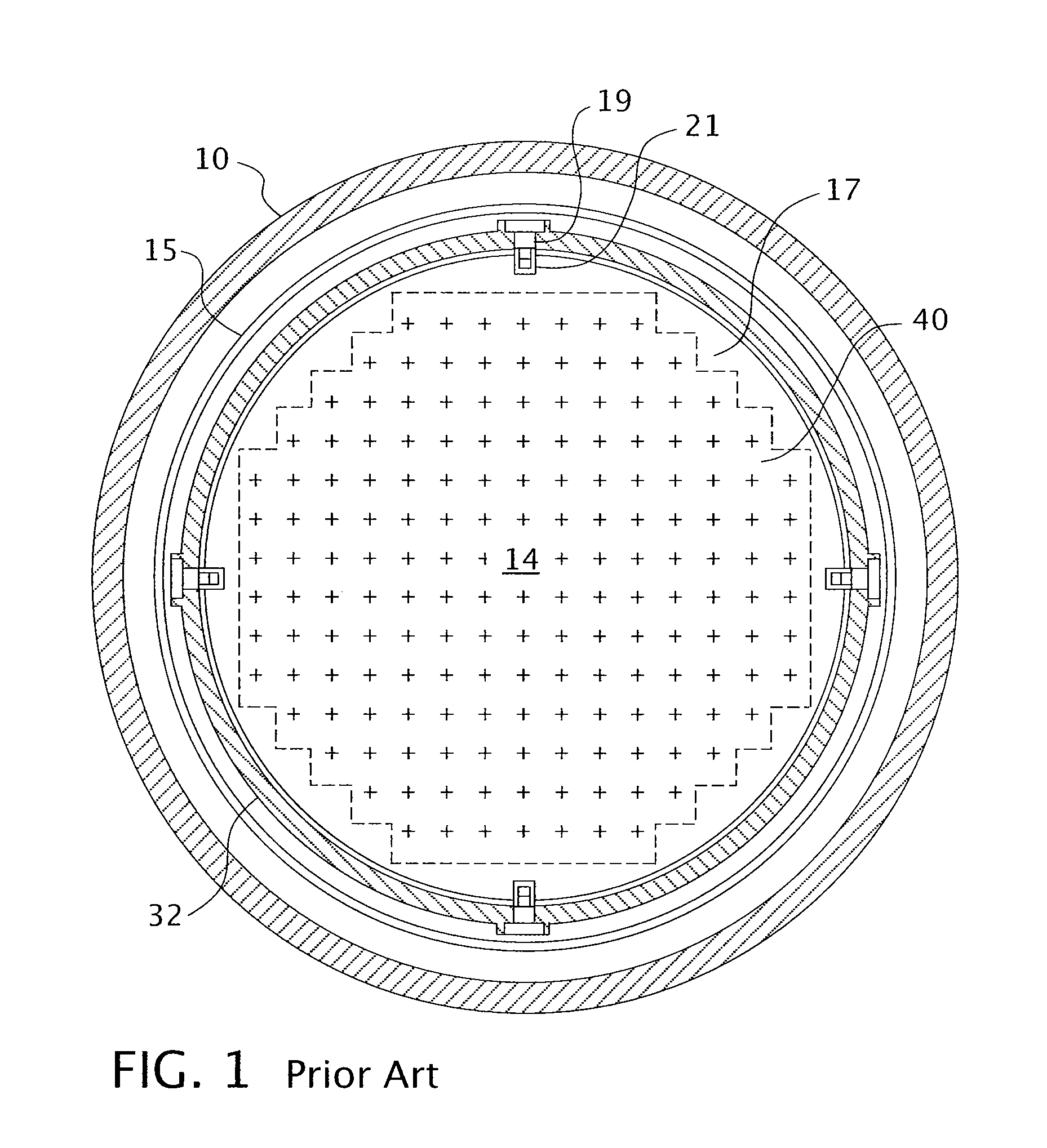
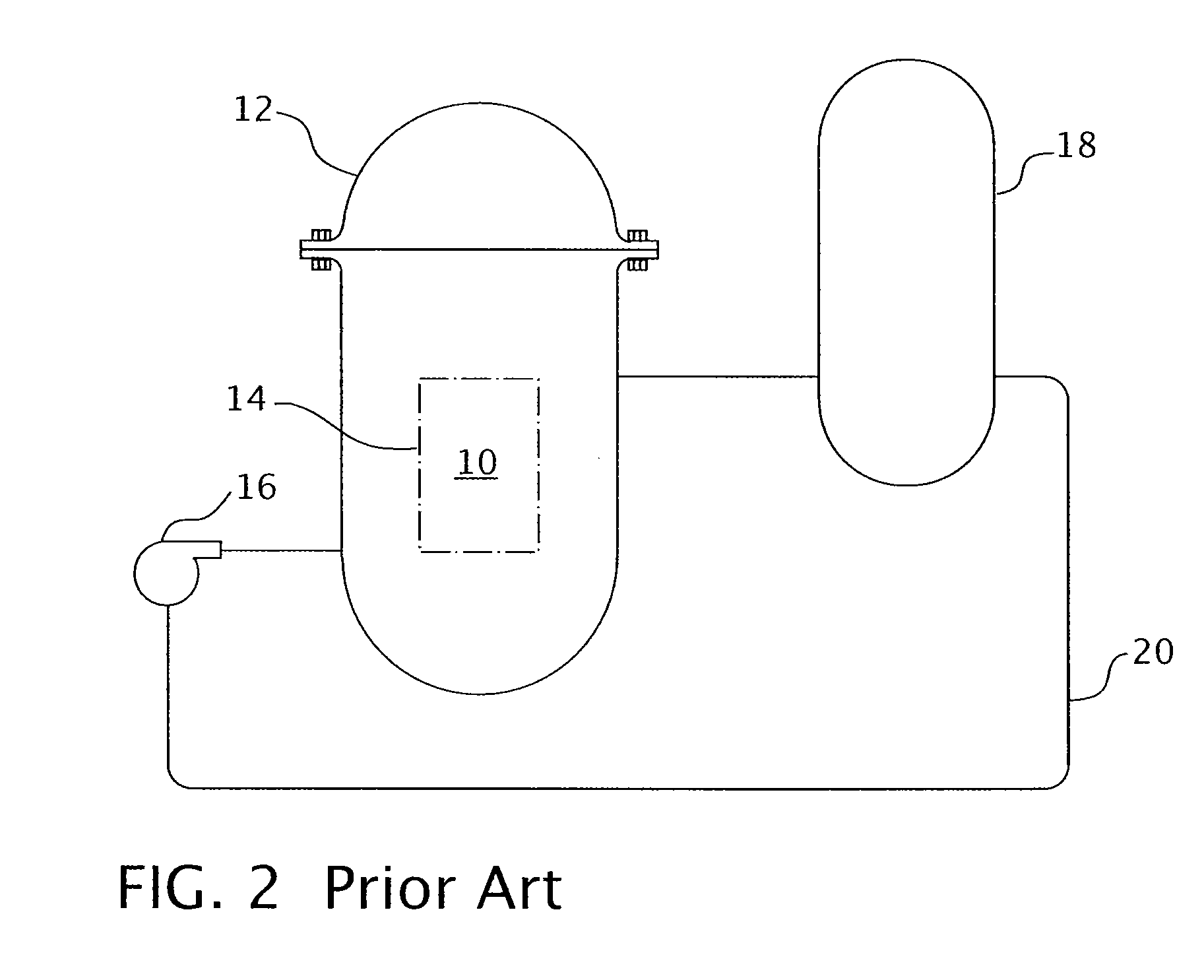
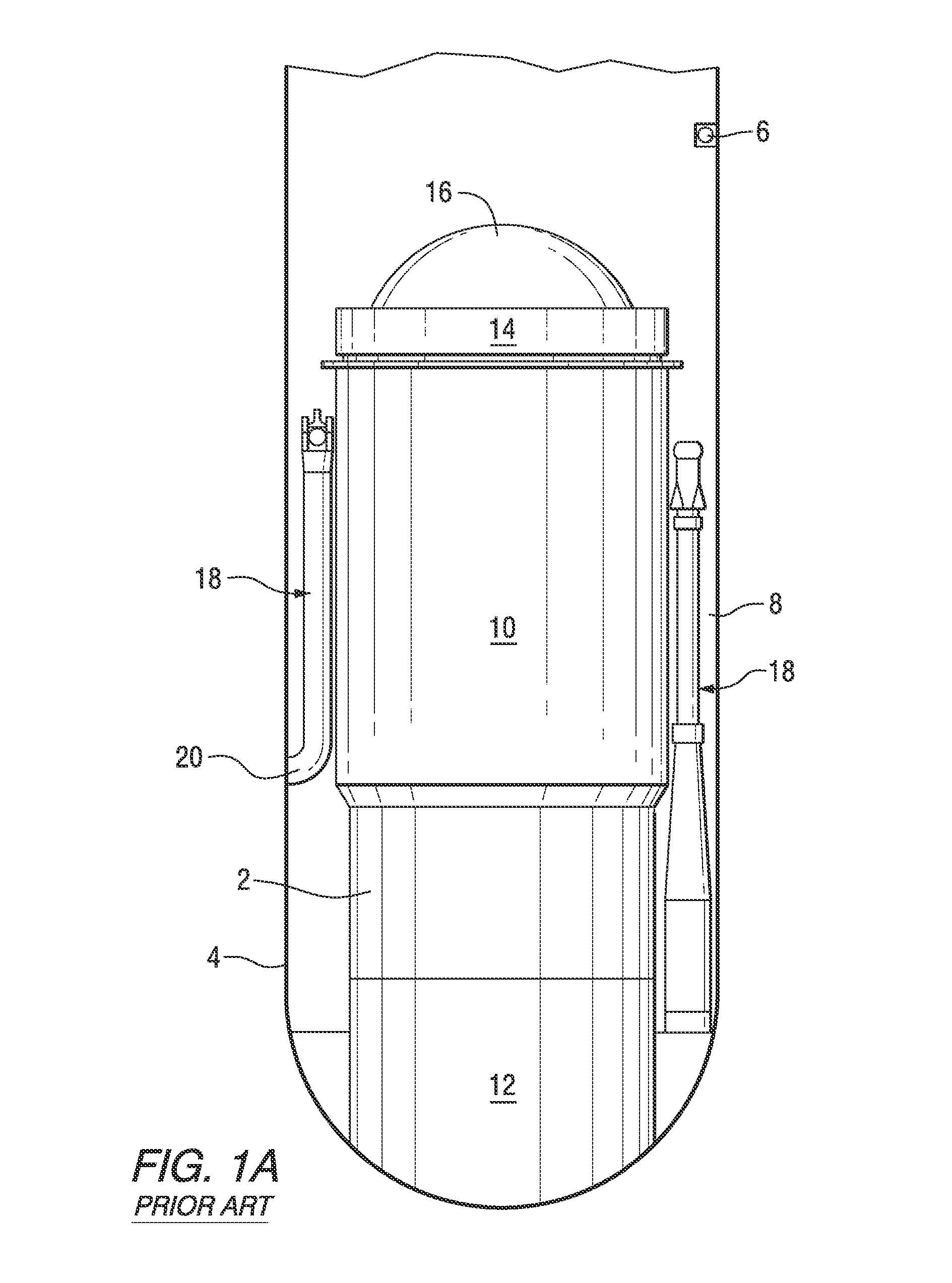
A core shroud is a stainless steel cylinder surrounding a nuclear reactor core whose main function is to direct the cooling water flow. The nuclear reactor core is where the nuclear reactions take place. Because the reactions are exothermic, cool water is needed to prevent the reactor core from melting down. The core shroud helps by directing this cool water towards the reactor core, providing stability to the nuclear reactions.
Sheath-core bicomponent fiber and its applications
InactiveUS6207276B1Ensure the necessary strengthImprove adhesionAnimal housingMachine wet endFiberPolyamide
In a core-shroud bicomponent fiber, which exhibits a core and a shroud at least partially enveloping the core, an elevated abrasion behavior, a low compaction under exposure to temperature and pressure and a high strength of the fibers is achieved by having the shroud consist of 45-98% w / w of a first polyamide having a melting point exceeding 280° C., and 2-20% w / w of a layer silicate.
Owner:EMS CHEM AG
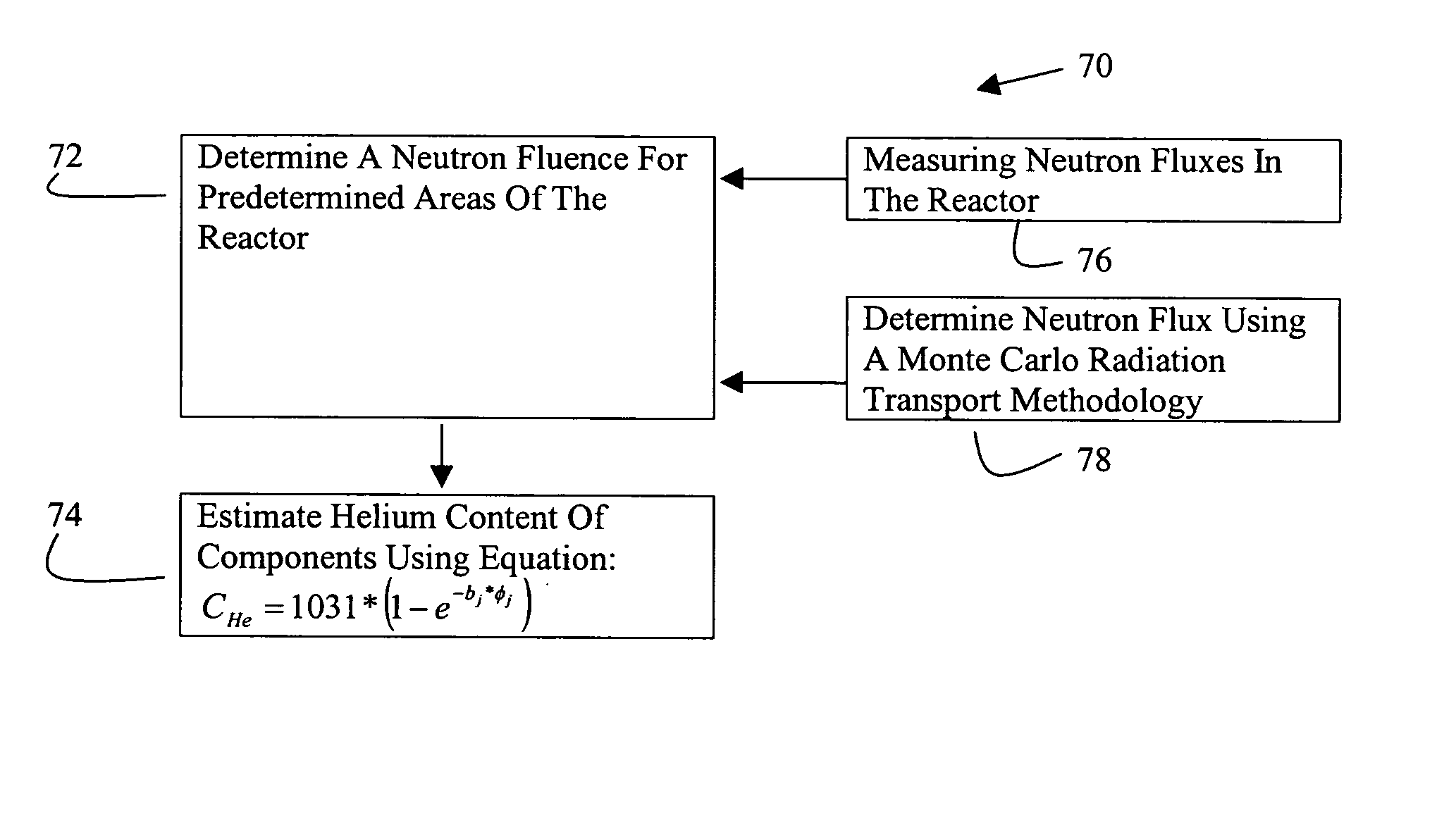
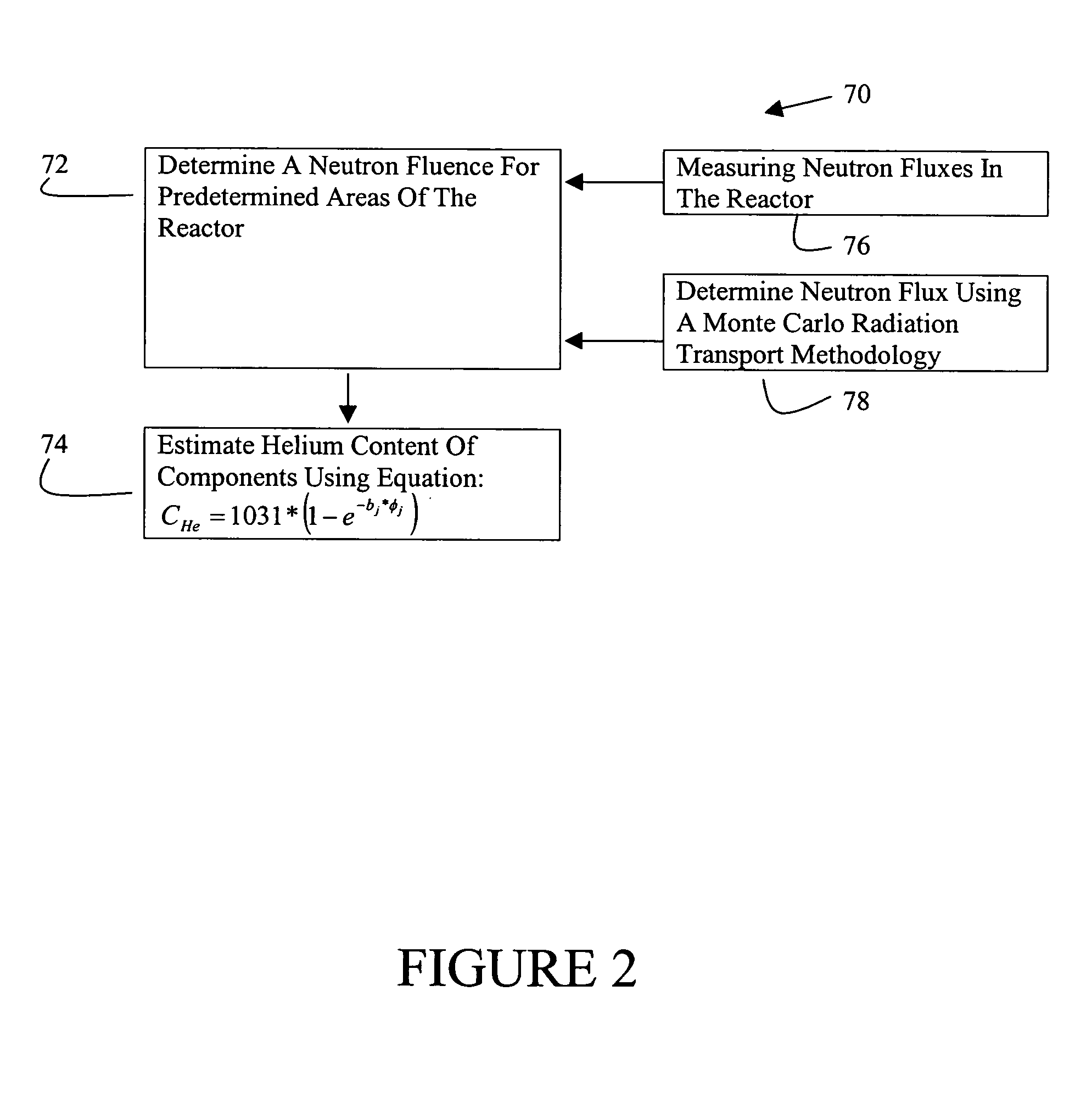
Systems and methods for estimating helium production in shrouds of nuclear reactors
A method for estimating a helium content of the stainless steel core shroud in a boiling water nuclear reactor includes, in an exemplary embodiment, determining a neutron fluence for predetermined areas of the reactor, and estimating a helium content of the stainless steel shroud at predetermined areas of the reactor using the following equation: CHe=1031*(1−e−b<sub2>j< / sub2>*φ<sub2>j< / sub2>), where CHe is the helium concentration as atomic parts per billion of helium in the stainless steel shroud per weight parts per million of boron in the stainless steel shroud, bj is a value between about 2.50 e−21 and about 5.00 e−21, φj is fluence expressed as neutrons per square centimeter, and subscript j denotes thermal fluence or fast fluence.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
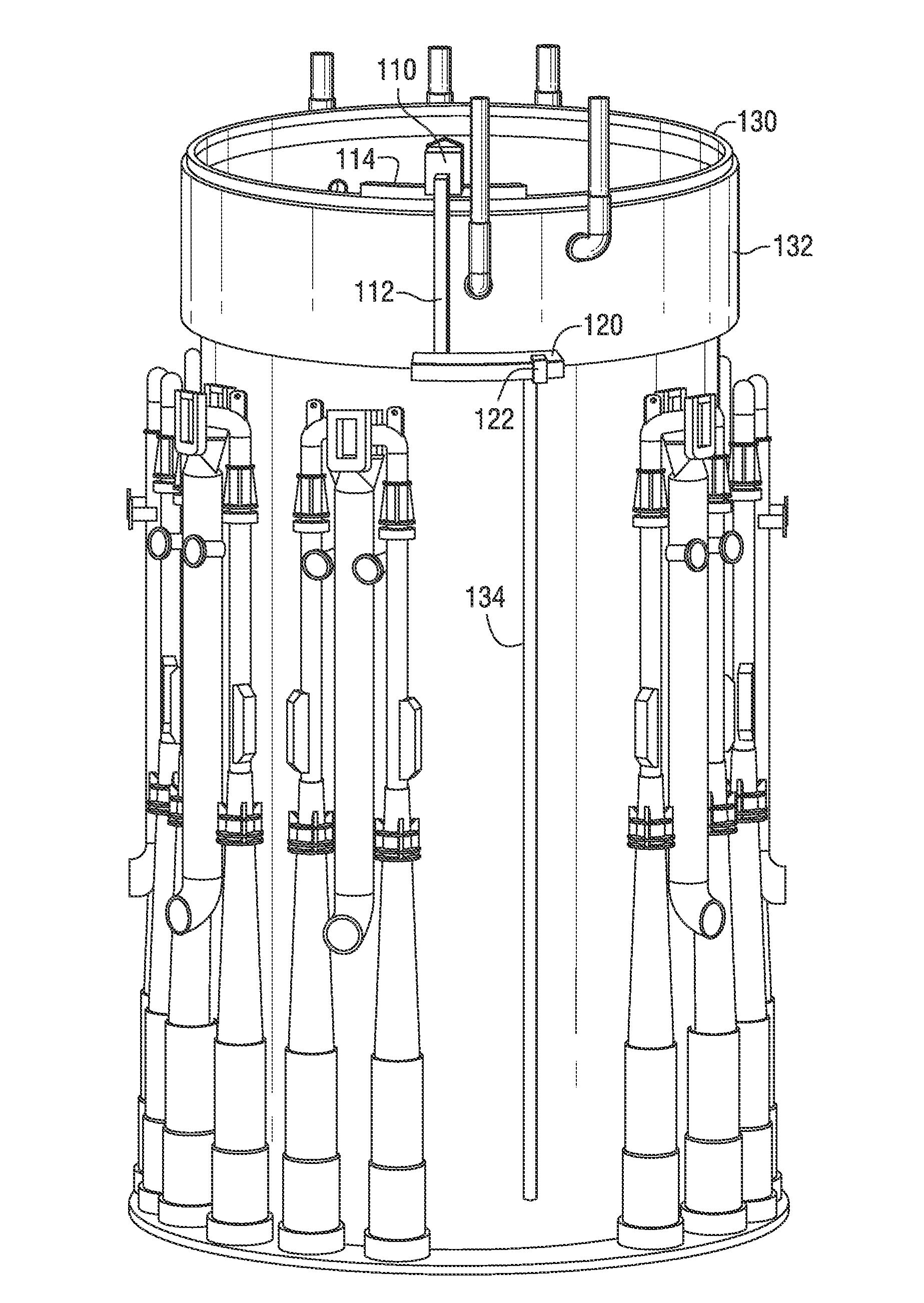
Nuclear reactor alignment plate configuration
ActiveCN101584007ANuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsFillet weldPressurized water reactor
An alignment plate that is attached to a core barrel of a pressurized water reactor and fits within slots within a top plate of a lower core shroud and upper core plate to maintain lateral alignment of the reactor internals. The alignment plate is connected to the core barrel through two vertically-spaced dowel pins that extend from the outside surface of the core barrel through a reinforcement pad and into corresponding holes in the alignment plate. Additionally, threaded fasteners are inserted around the perimeter of the reinforcement pad and into the alignment plate to further secure the alignment plate to the core barrel. A fillet weld also is deposited around the perimeter of the reinforcement pad. To accommodate thermal growth between the alignment plate and the core barrel, a gap isleft above, below and at both sides of one of the dowel pins in the alignment plate holes through which the dowel pins pass.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
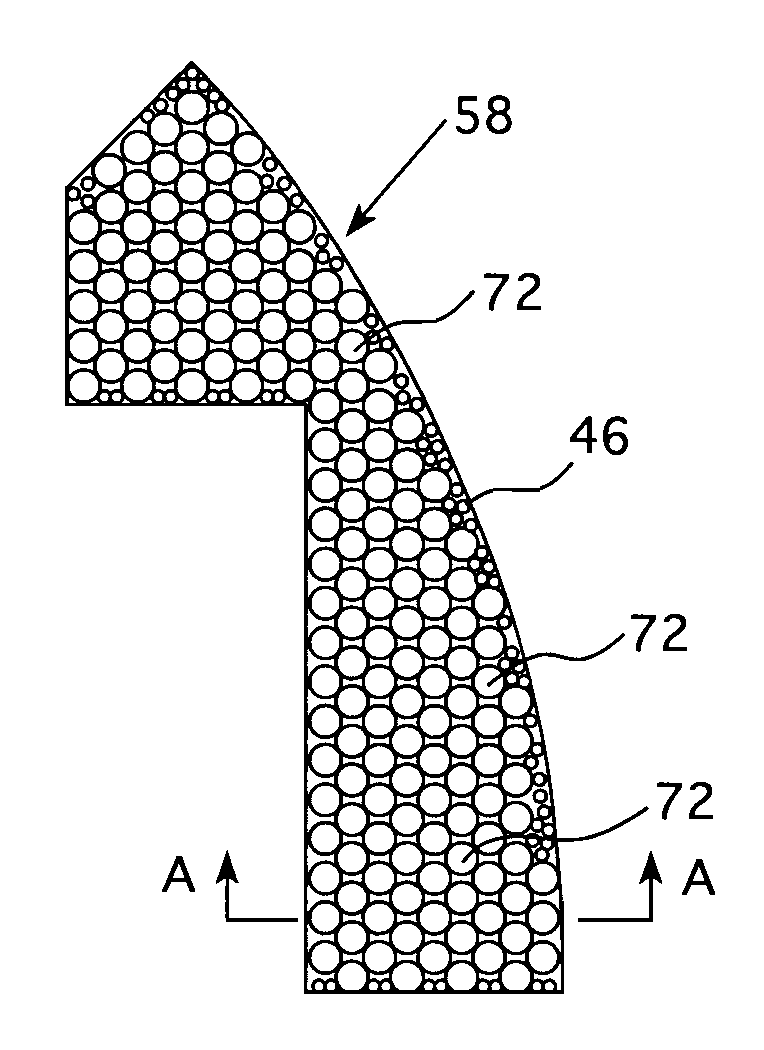
Heavy radial neutron reflector for pressurized water reactors
A heavy radial neutron reflector for a pressurized water reactor that employs elongated lengths of round bar stock closely packed in either a triangular or rectangular array extending between former plates of a core shroud between the core barrel and the baffle plates which outline the periphery of the reactor core and are formed in axial and circumferential modules. Flow channels are formed in the long gaps between the adjacent round bar stock that communicates cooling water that enters through the core barrel at the top of the shroud and flows down through openings in the former plates to the bottom of the neutron reflector where it exits through a lower baffle orifice to join other cooling water flowing up through the lower core support plate.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
BWR type nuclear power generator and construction method
InactiveCN1351353AStrong natural circulationImprove economyNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsReactor pressure vesselNuclear power
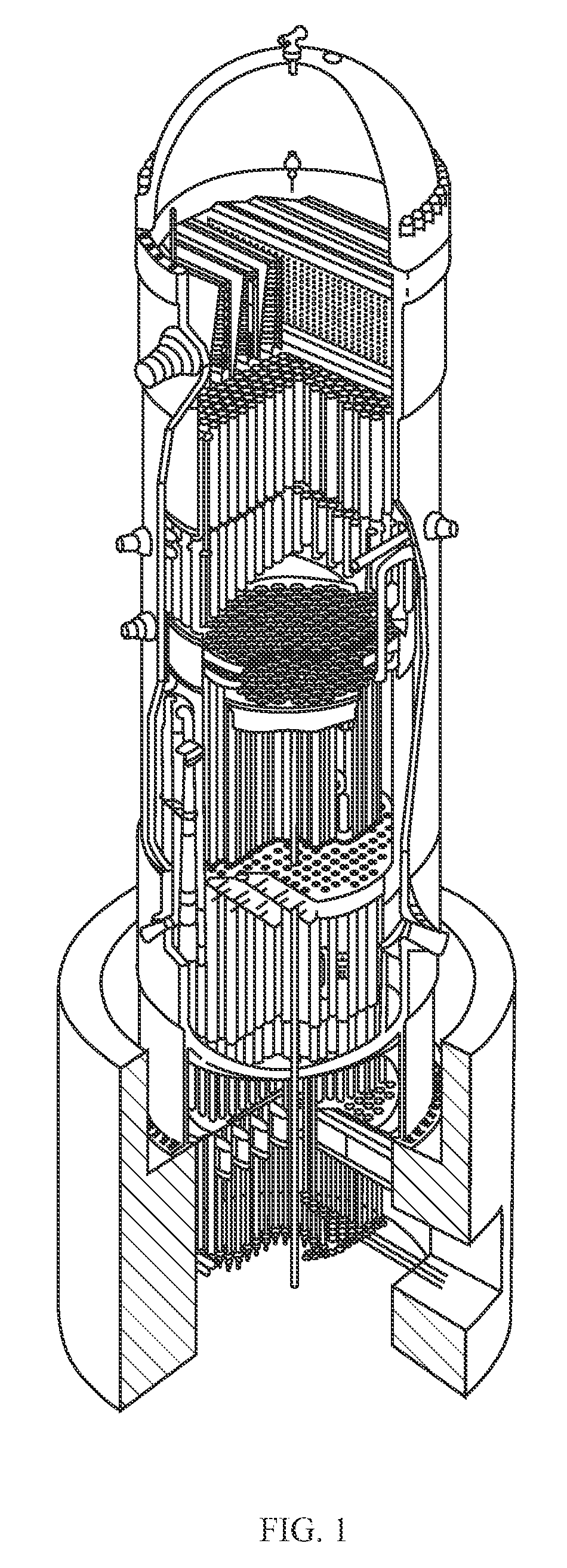
The present invention provides a boiling water reactor nuclear power plant in which a reactor core support plate, upper grid plate, and a reactor core consisting of fuel assemblies supported by these plates are provided in the inner base portion of a nuclear reactor pressure vessel. Control rod guide tubes and a reactor core shroud are positioned over the upper grid plate, and a control rod drive mechanism is provided further above same, whereby the control rods can be inserted from above the reactor core, and natural circulation of cooling water inside the reactor can be achieved by means of a chimney effect of the control rod guide tubes. According to the above structure, there can be provided a compact and economical nuclear power plant.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
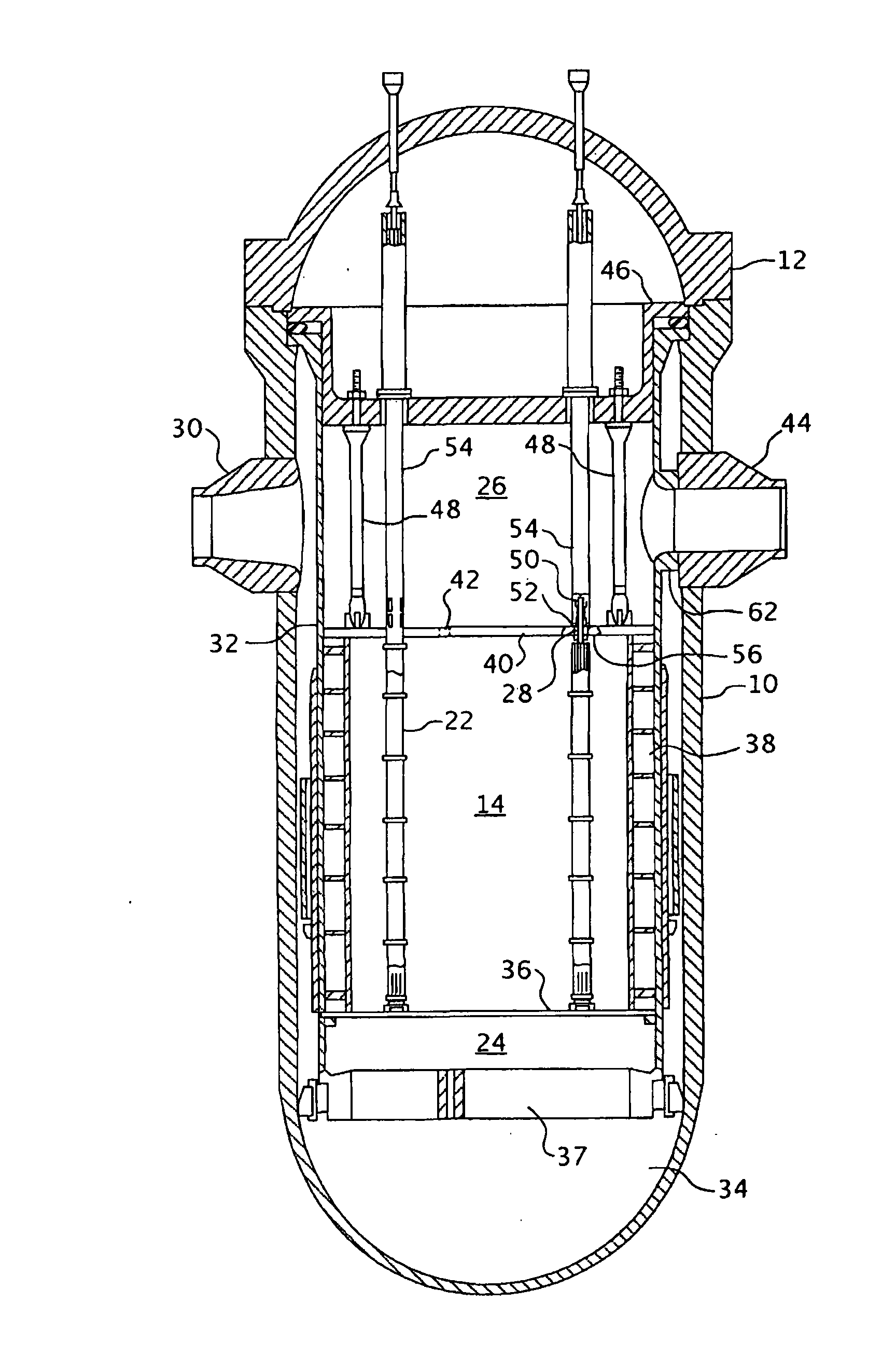
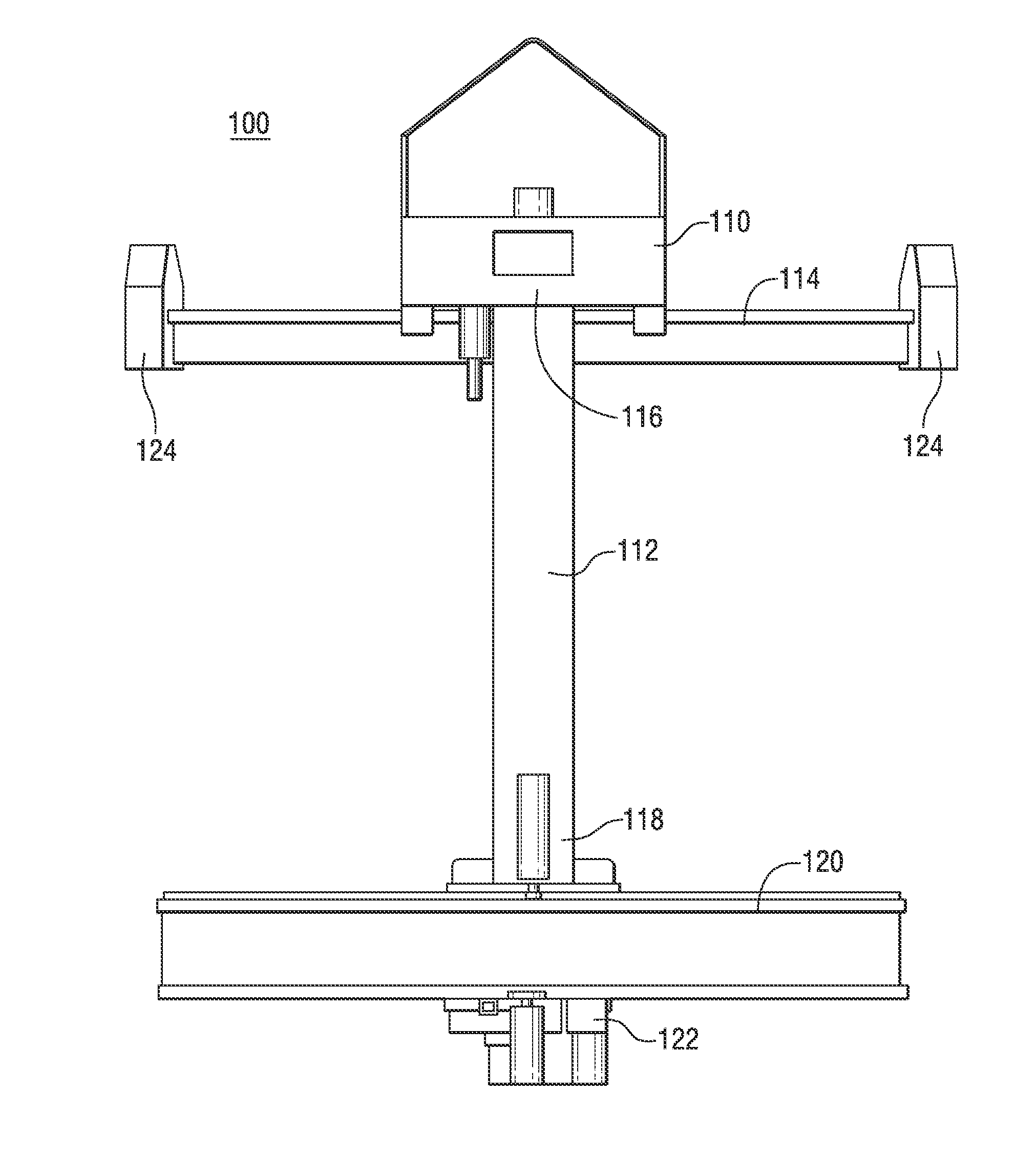
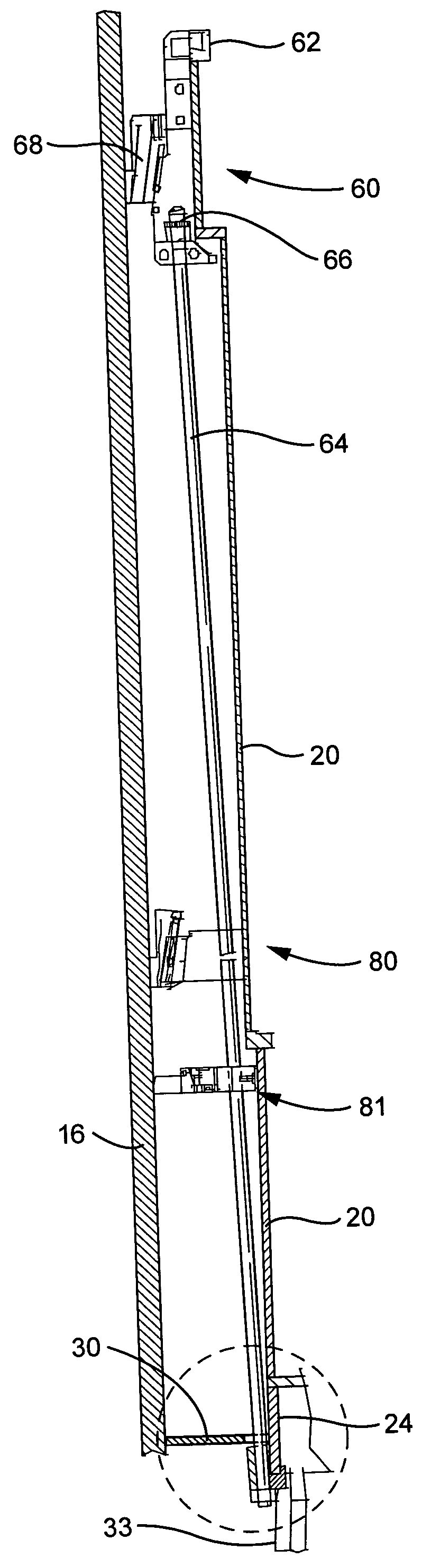
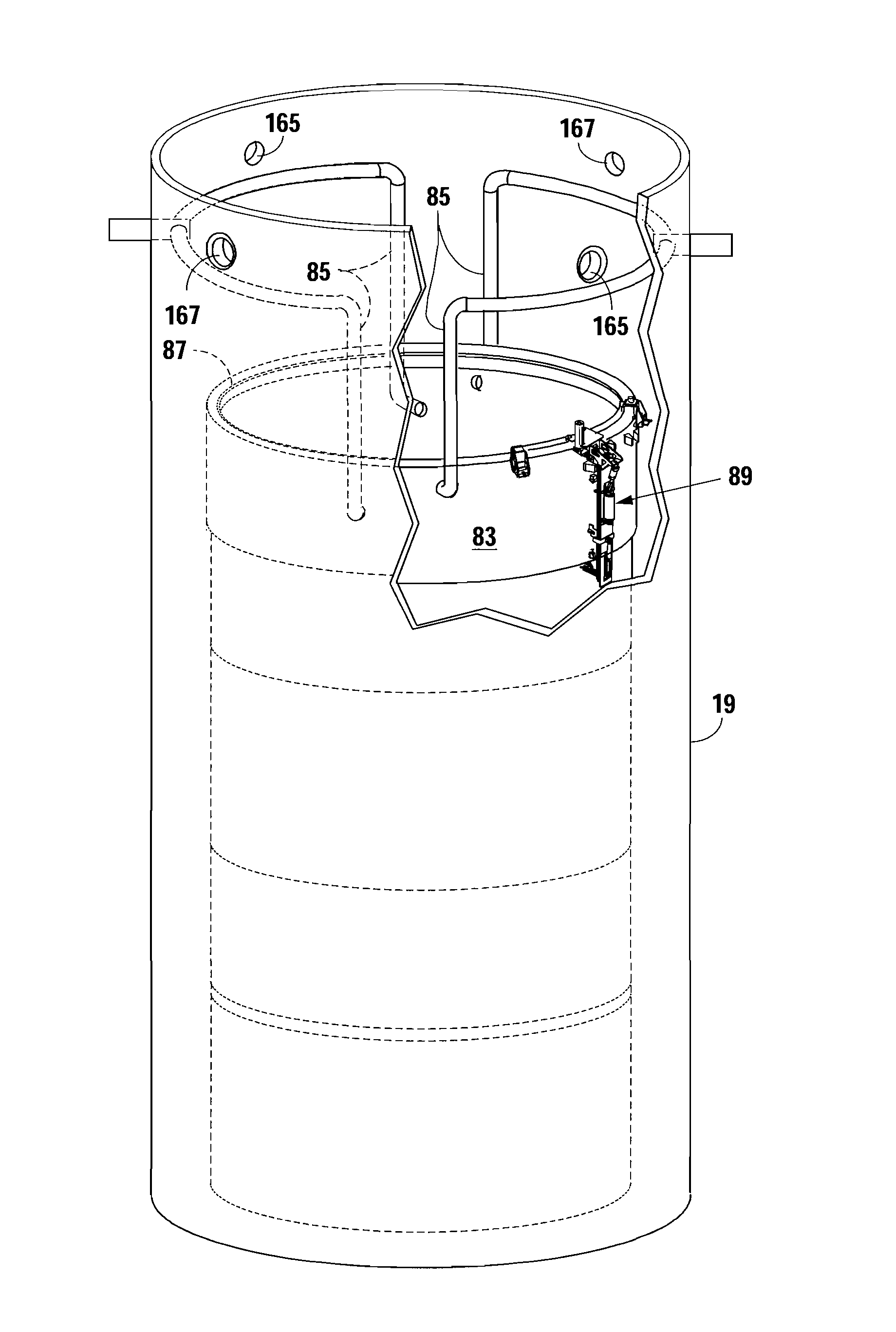
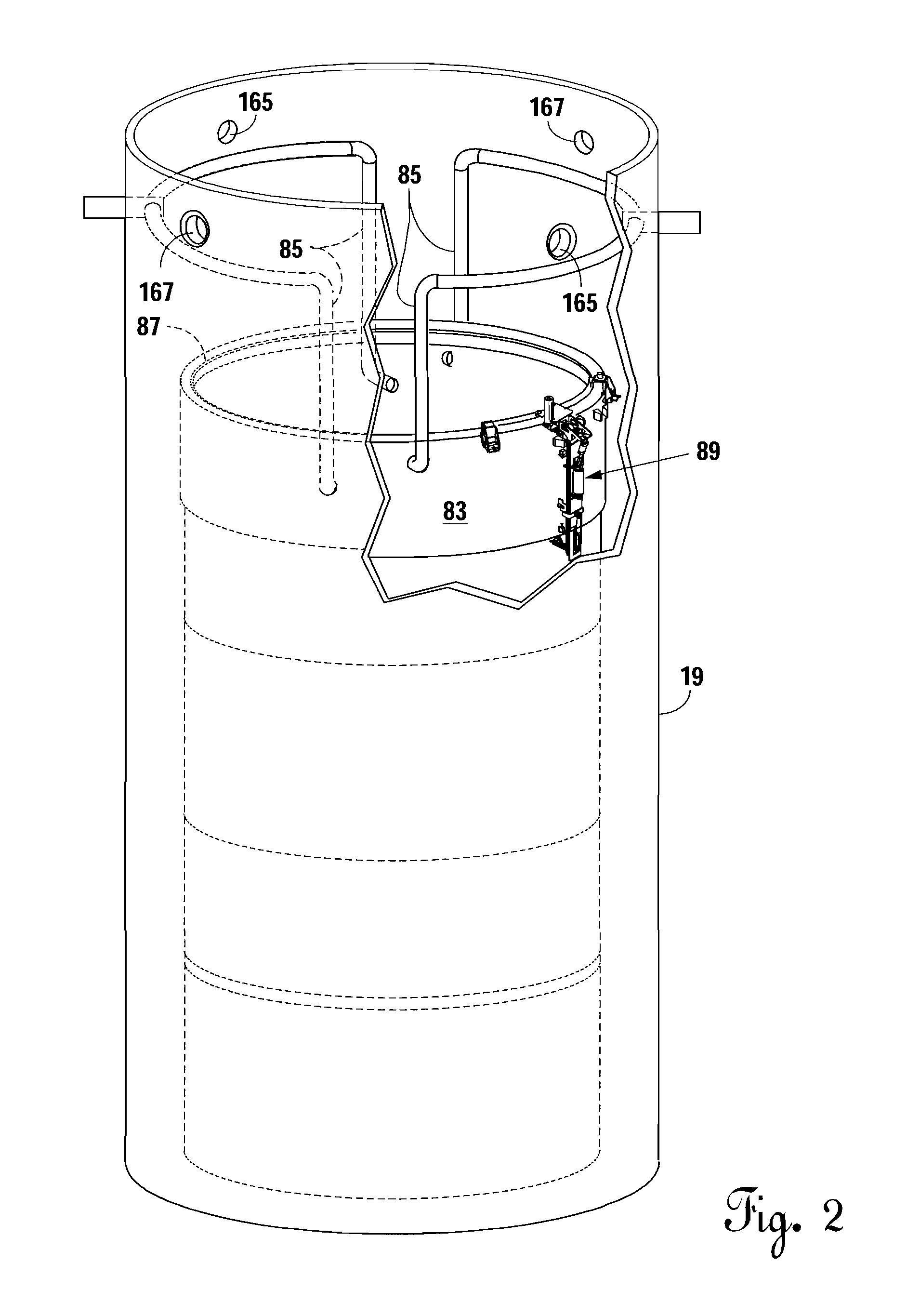
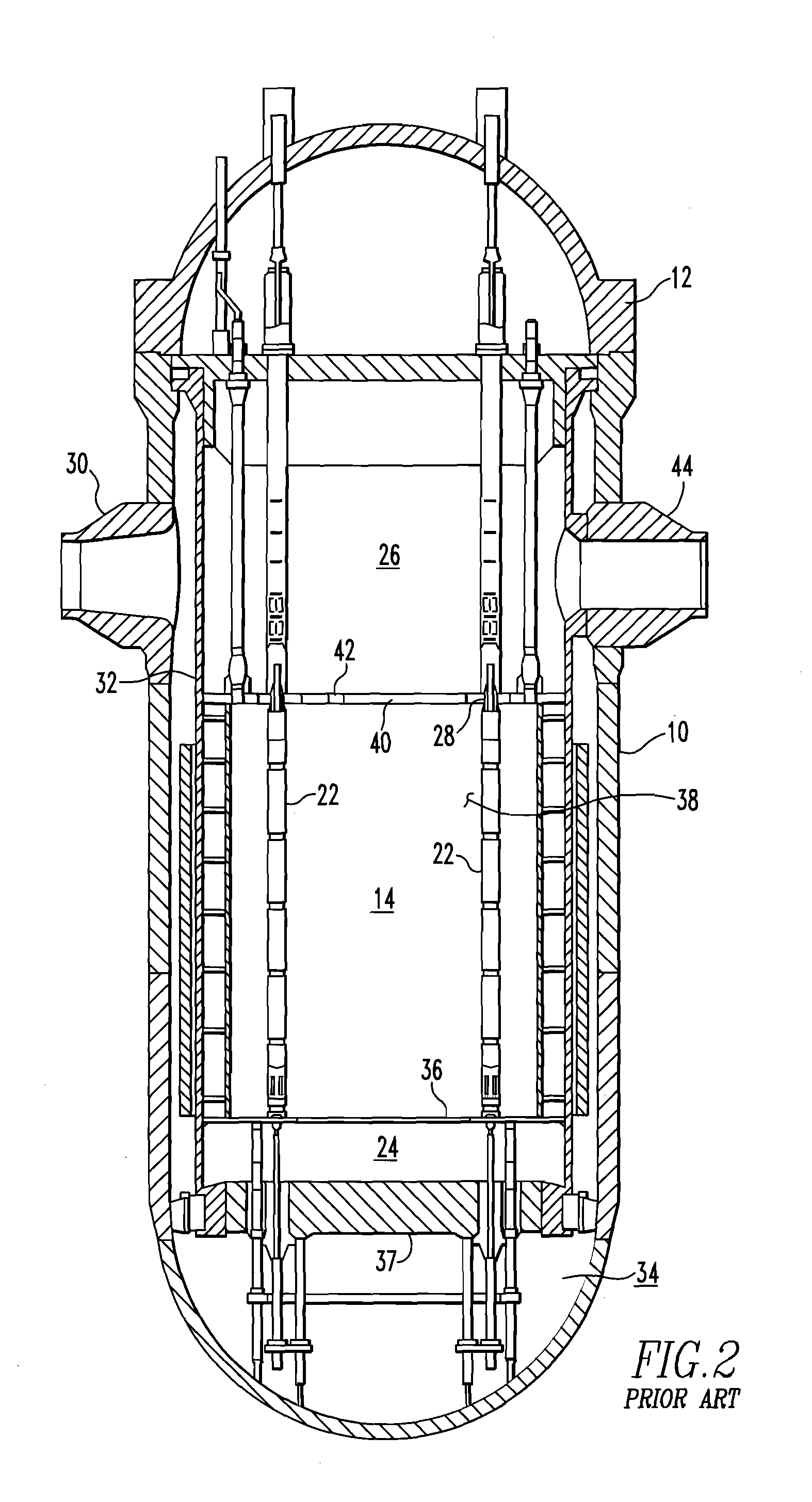
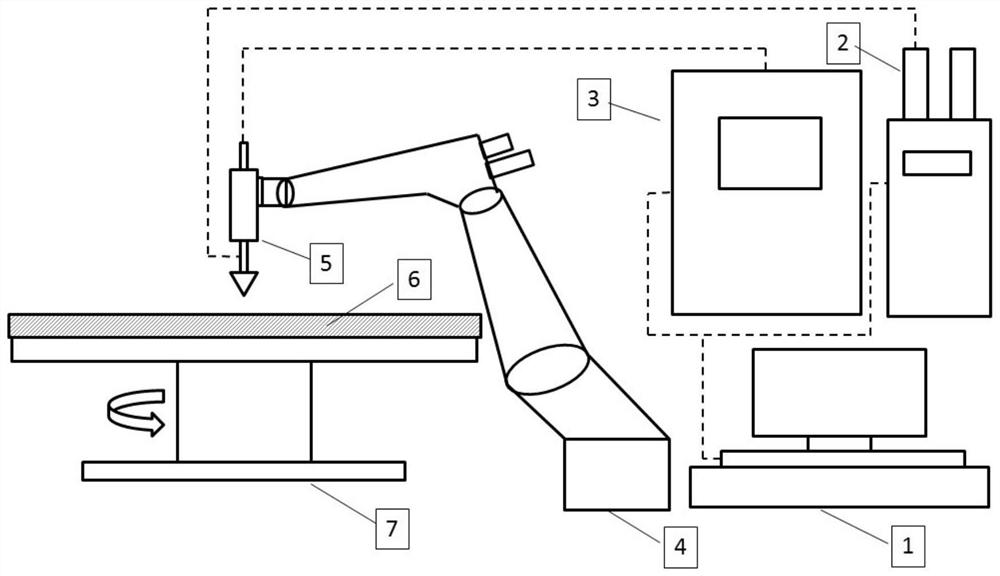
Apparatus and method to inspect, modify, or repair nuclear reactor core shrouds
ActiveUS20140098922A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactor coreReactor pressure vessel
This invention generally concerns robotic systems and is particularly concerned with improved apparatus and methods for remotely inspecting, modifying or repairing a core shroud in a nuclear reactor. The apparatus of the invention includes a partial upper track which horizontally movable along the core shroud, a head and frame assembly which is horizontally movable along the partial upper track, a lower track which is connected to the head and frame assembly and is horizontally movable along the core shroud, and a carriage and arm assembly which extends downward into an annulus formed by the reactor pressure vessel and the core shroud, wherein the arm includes at least one sensor for inspecting the core shroud.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Method and apparatus of inspecting the upper core shroud of a nuclear reactor vessel
A method and apparatus for inspecting the upper portion of a core shroud of a nuclear power plant is provided. The upper shroud scanner mounts on an arcuic section of a steam dam of the core shroud and moves back and forth there along. A vertical arm with transducers thereon extend down from a Y-car portion of the upper shroud scanner. Transducers adjacent the core shroud emit and receive an ultrasonic sound to inspect for flaws and defects in the core shroud.
Owner:IIA NUCLEAR SERVICES INC
Repair apparatus for a nuclear reactor shroud
InactiveUS7649970B2Nuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Nuclear reactor internals alignment configuration
An alignment system that employs jacking block assemblies and alignment posts around the periphery of the top plate of a nuclear reactor lower internals core shroud to align an upper core plate with the lower internals and the core shroud with the core barrel. The distal ends of the alignment posts are chamfered and are closely received within notches machined in the upper core plate at spaced locations around the outer circumference of the upper core plate. The jacking block assemblies are used to center the core shroud in the core barrel and the alignment posts assure the proper orientation of the upper core plate. The alignment posts may alternately be formed in the upper core plate and the notches may be formed in top plate.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Method and apparatus of inspecting the upper core shroud of a nuclear reactor vessel
A method and apparatus for inspecting the upper portion of a core shroud of a nuclear power plant is provided. The upper shroud scanner mounts on an arcuic section of a steam dam of the core shroud and moves back and forth there along. A vertical arm with transducers thereon extend down from a Y-car portion of the upper shroud scanner. Transducers adjacent the core shroud emit and receive an ultrasonic sound to inspect for flaws and defects in the core shroud.
Owner:IIA NUCLEAR SERVICES INC
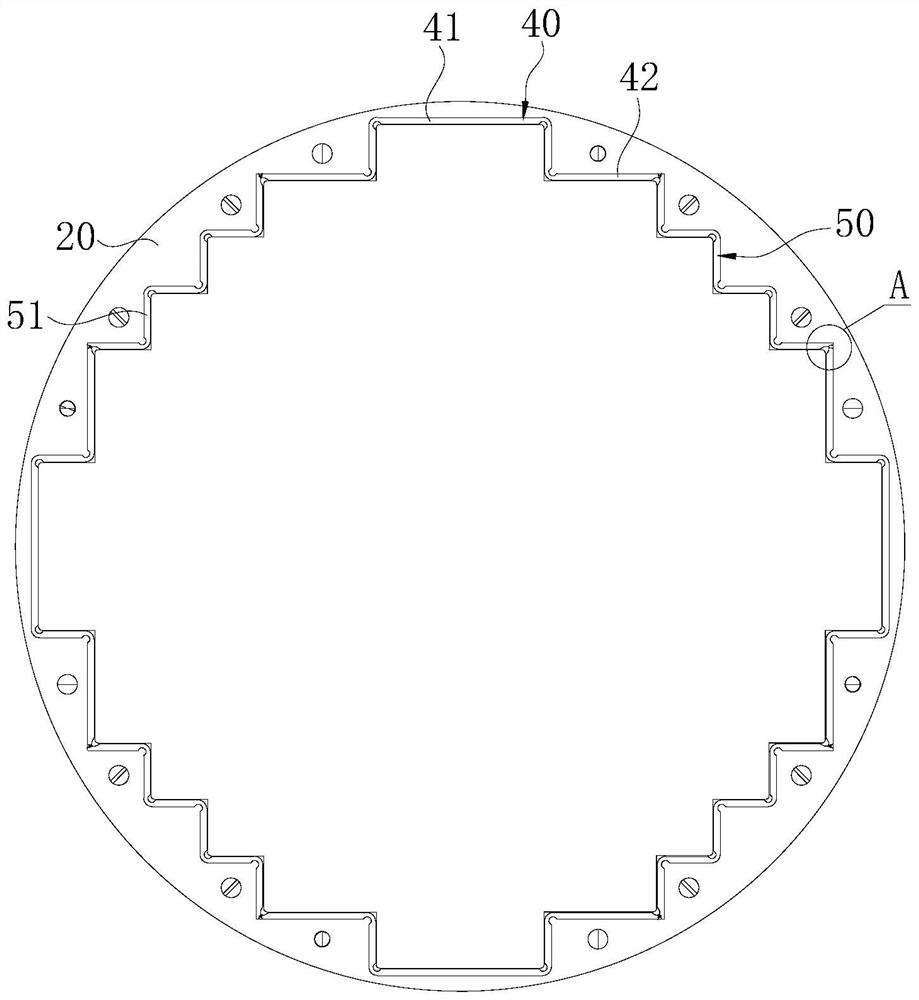
Reactor core shroud assembly welding clamping device and clamping and welding method
PendingCN107520537AImprove stabilityEasy to adjustLaser beam welding apparatusNuclear engineeringChange positions
The invention belongs to the technical field of manufacturing and machining of internal components of nuclear power reactors, and discloses a reactor core shroud assembly welding clamping device. The device comprises an inner supporting assembly, an outer hoop assembly and a roller assembly, wherein the inner supporting assembly comprises a plurality of inner supports connected together; each inner support is provided with a positioning layer and jacking layers; the supporting assembly is arranged inside a reactor core shroud assembly; the outer hoop assembly comprises a plurality of outer hoops; universal jacking pieces are arranged on each outer hoop; the outer hoop assembly is arranged on the periphery of the reactor core shroud assembly; the jacking layers of the inner supporting assembly and the universal jacking pieces of the outer hoop assembly are used for fixing a reactor core shroud into an integral part; the roller assembly comprises rollers and a roller frame; the rollers are arranged at the two ends of the reactor core shroud; and the roller assembly enables the reactor core shroud to rotate and change positions on the roller frame. The invention further discloses a clamping and welding method. According to the reactor core shroud assembly welding clamping device and the clamping and welding method, repeated welding can be carried out on the reactor core shroud through one-time clamping, and enough rigid support is provided for deformation after welding.
Owner:上海第一机床厂有限公司
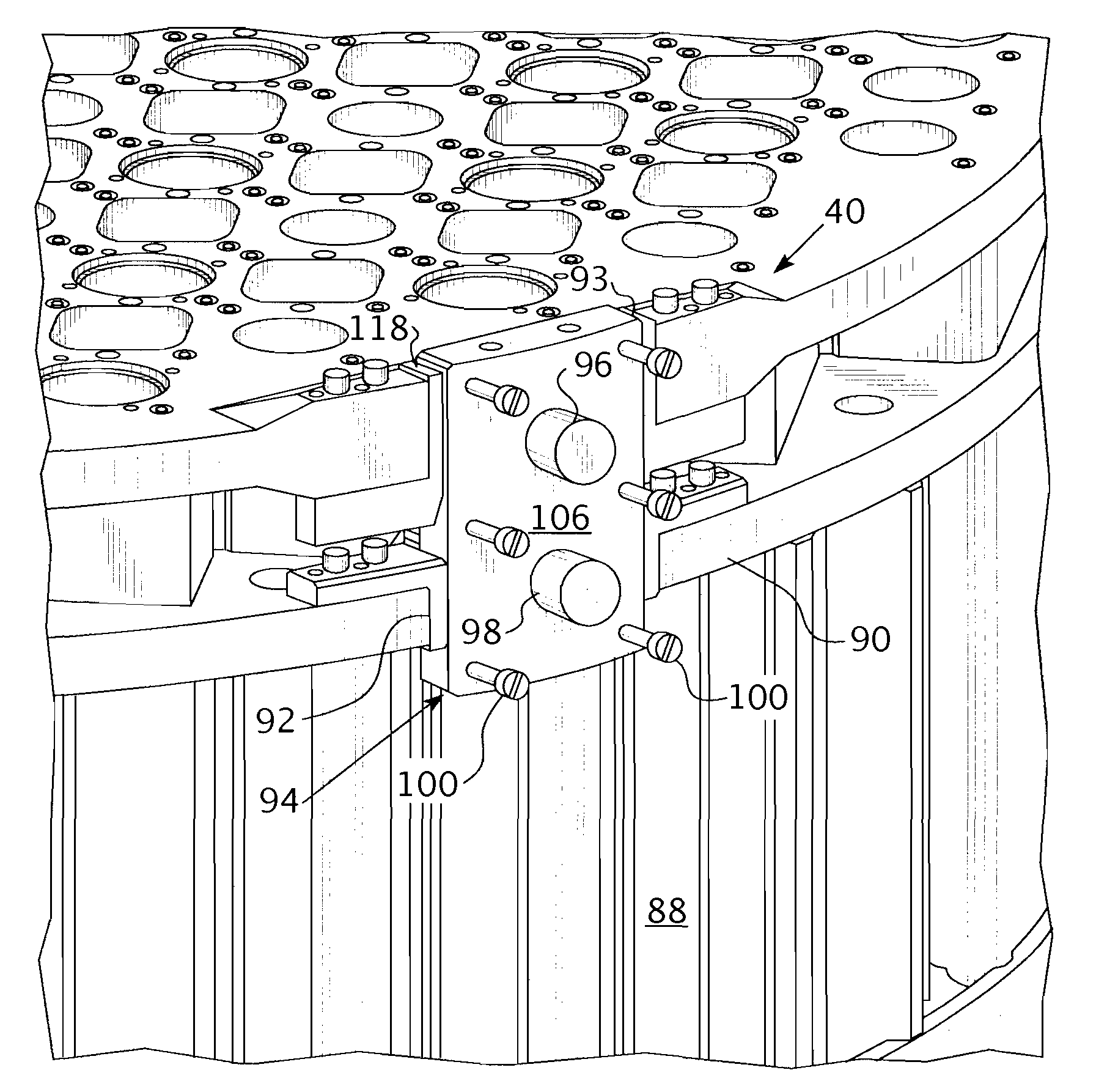
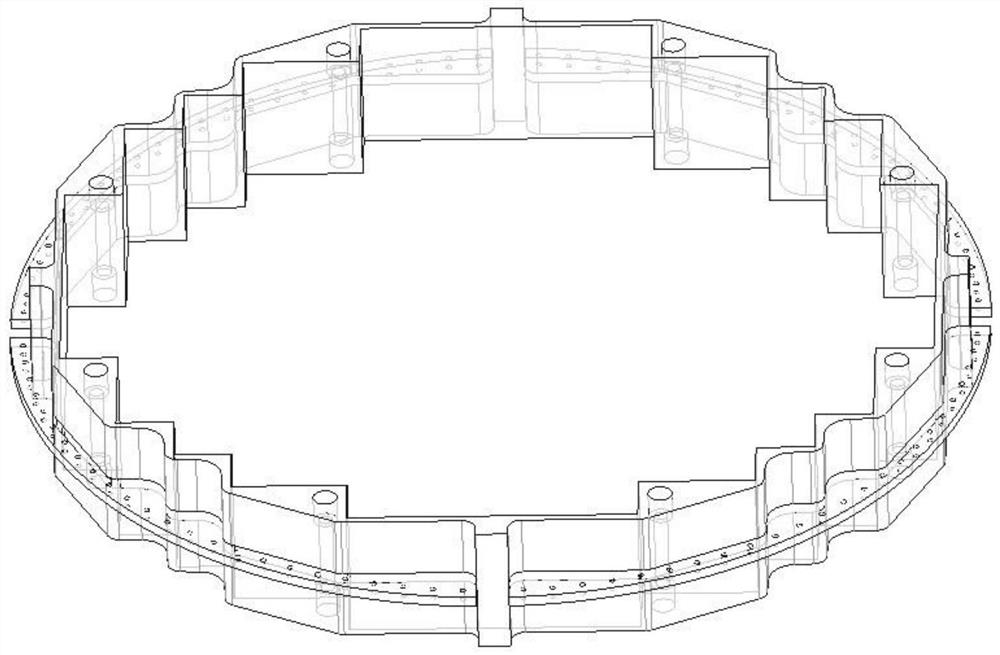
Core shroud corner joints
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Nuclear reactor alignment plate configuration
ActiveCN101584007BNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsFillet weldPressurized water reactor
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Apparatus and method for automatically and remotely measuring the internal gap of a reactor
ActiveCN102017009AShort construction periodGuaranteed reliabilityNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactorMeasurement device
Owner:KOREA HYDRO & NUCLEAR POWER CO LTD
Fast flux shield and method of reducing fast neutron fluence at a core shroud of a boiling water reactor using the same
A boiling water reactor core according to an example embodiment may include a core shroud and a plurality of fuel bundles within the core shroud. A plurality of shielding bundles are arranged as a fast flux shield between the plurality of fuel bundles and the core shroud. The plurality of shielding bundles include a metal hydride as a neutron moderator.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Core shroud corner joints
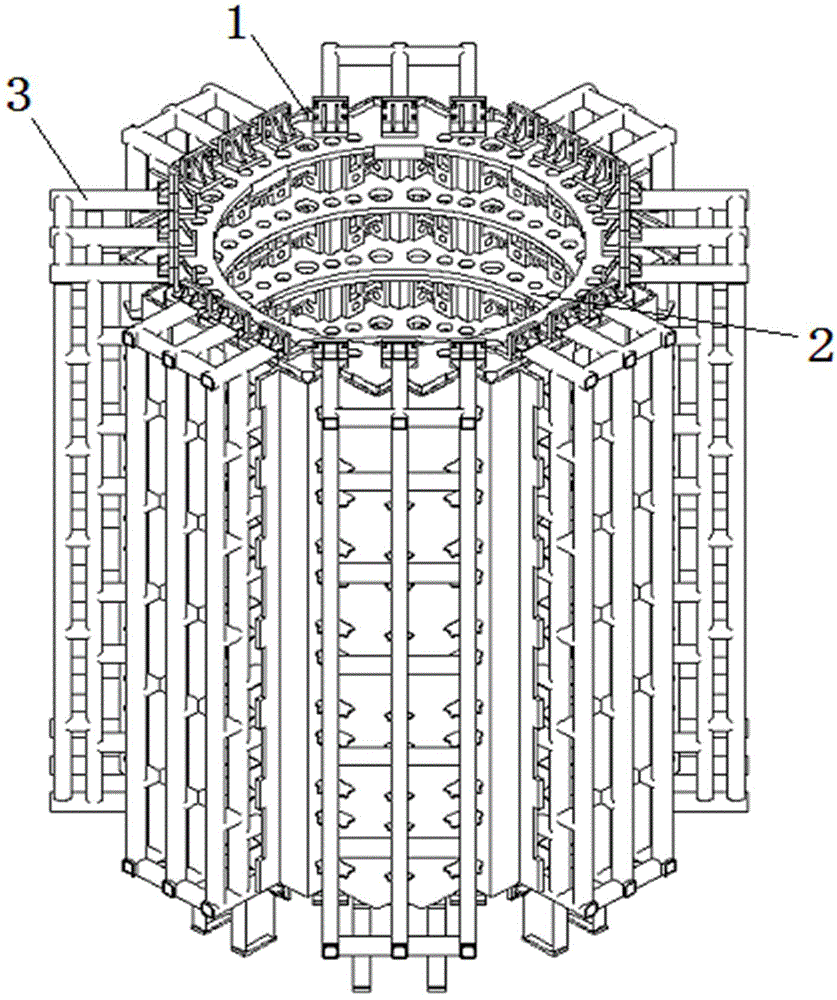
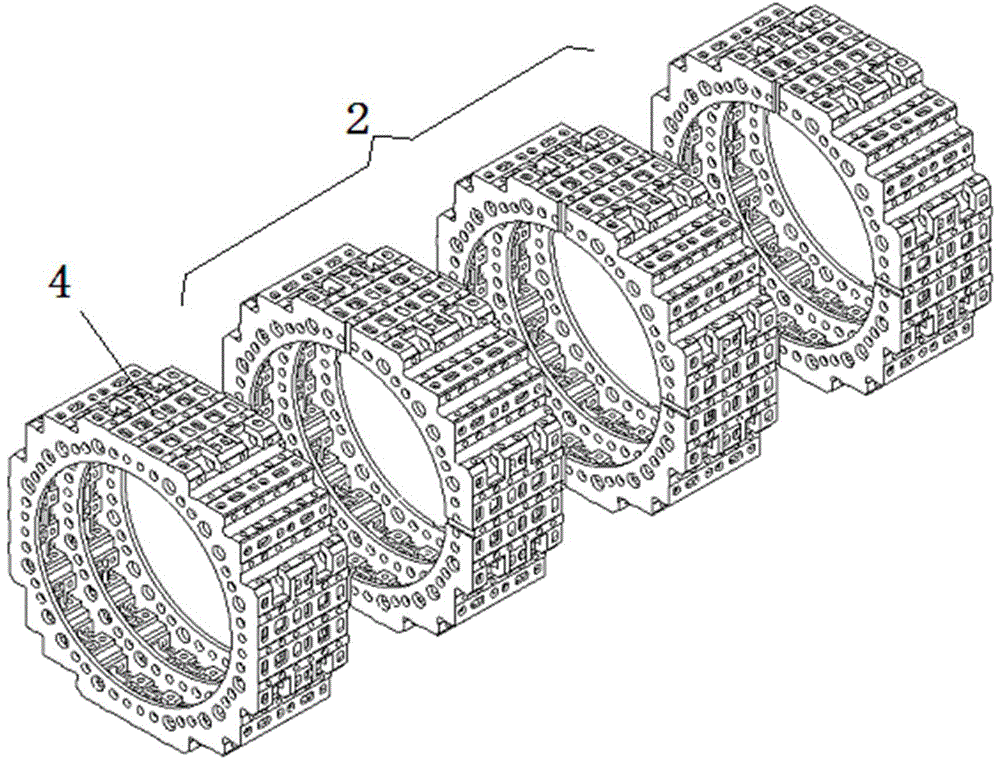
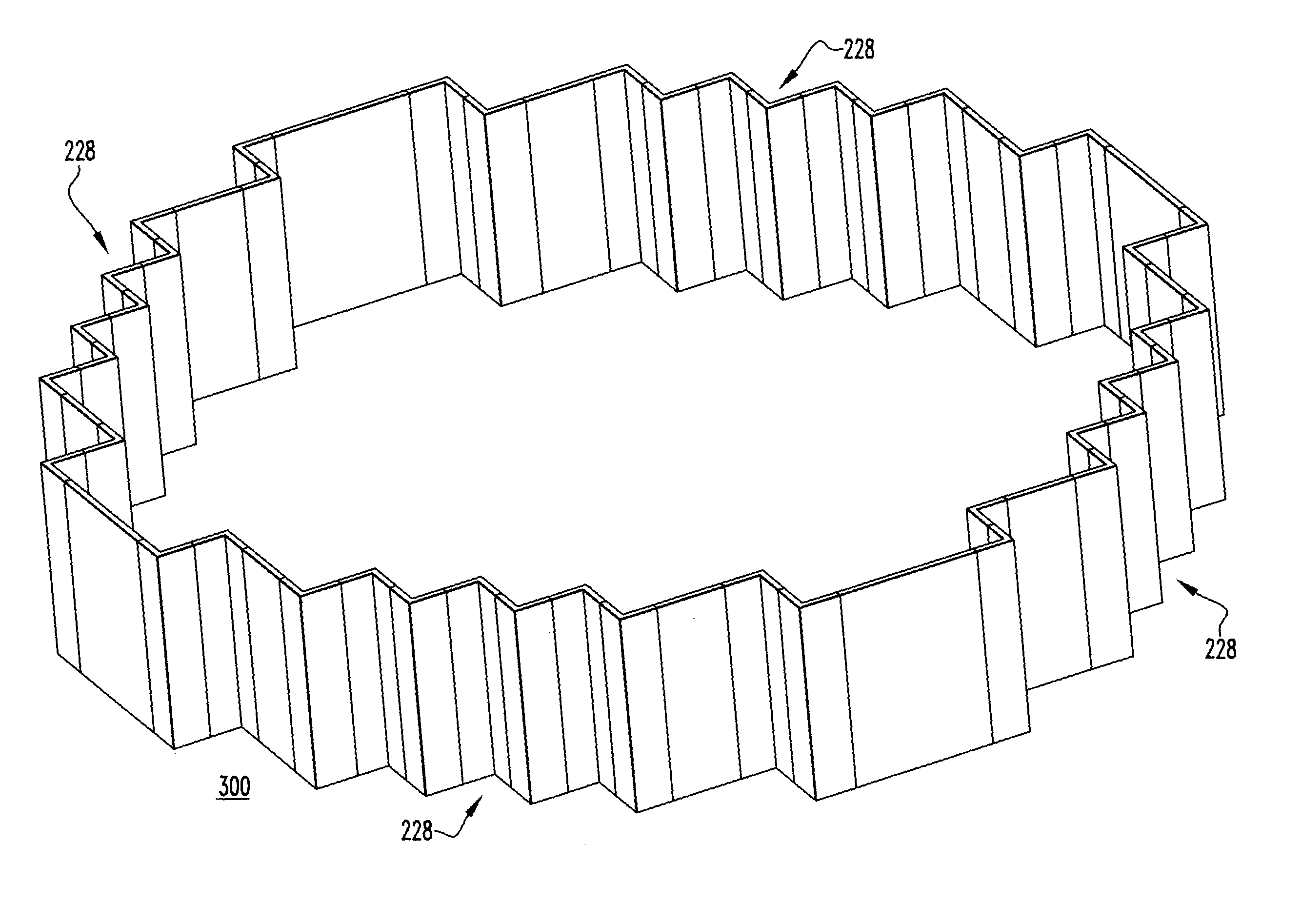
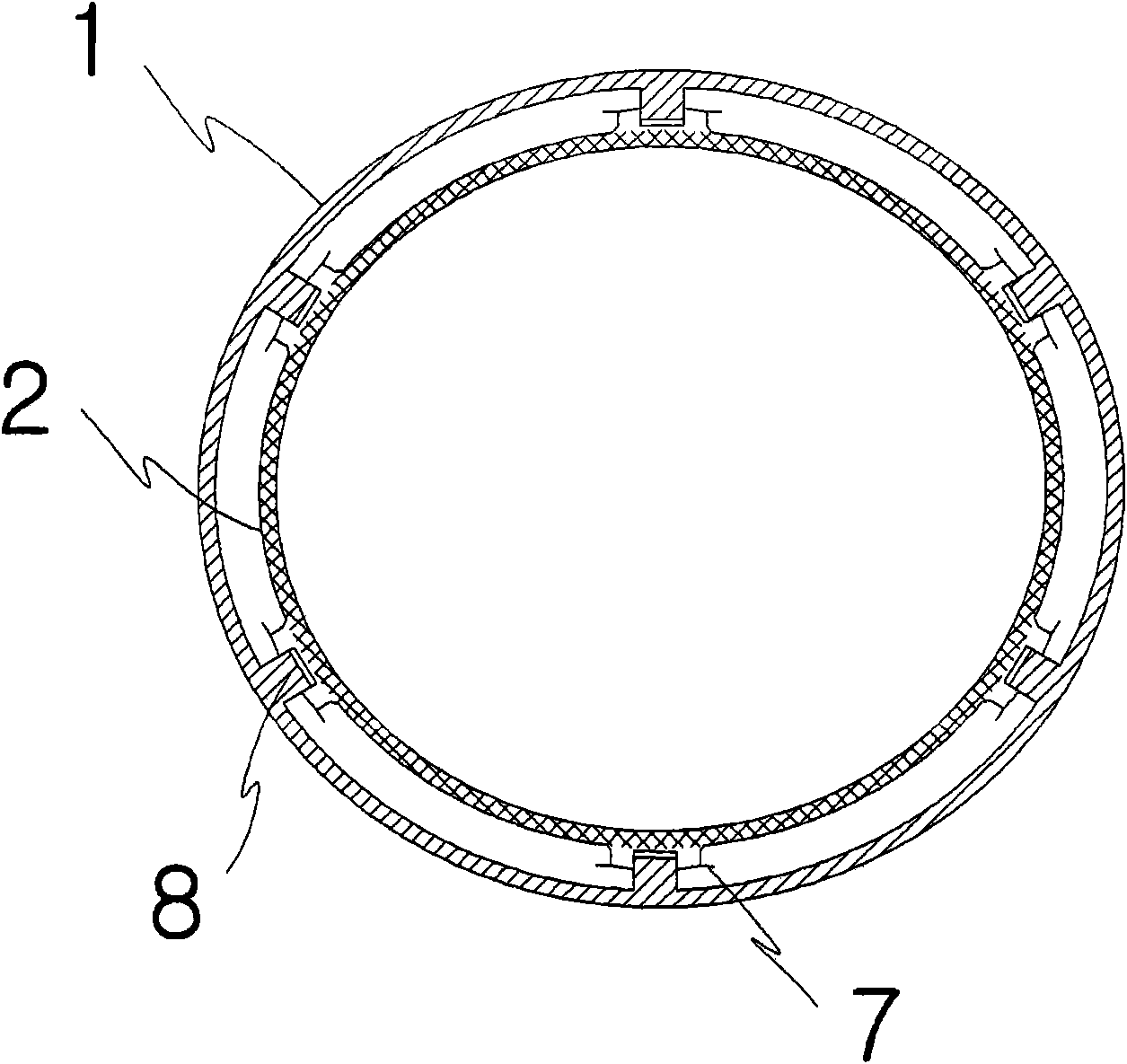
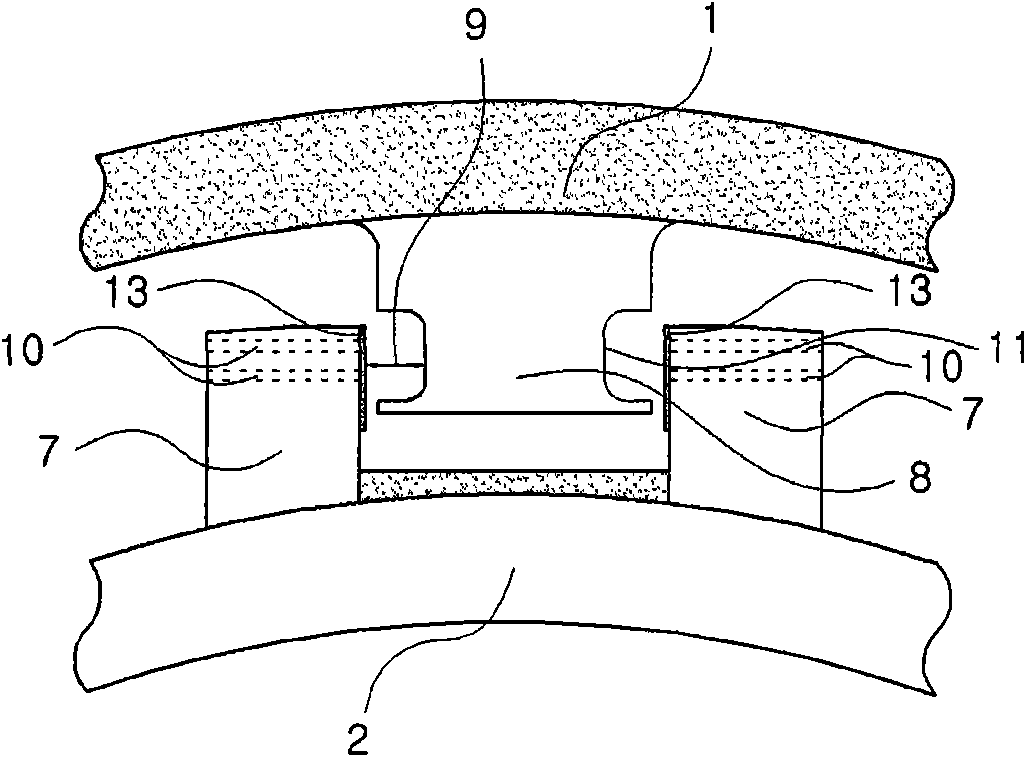
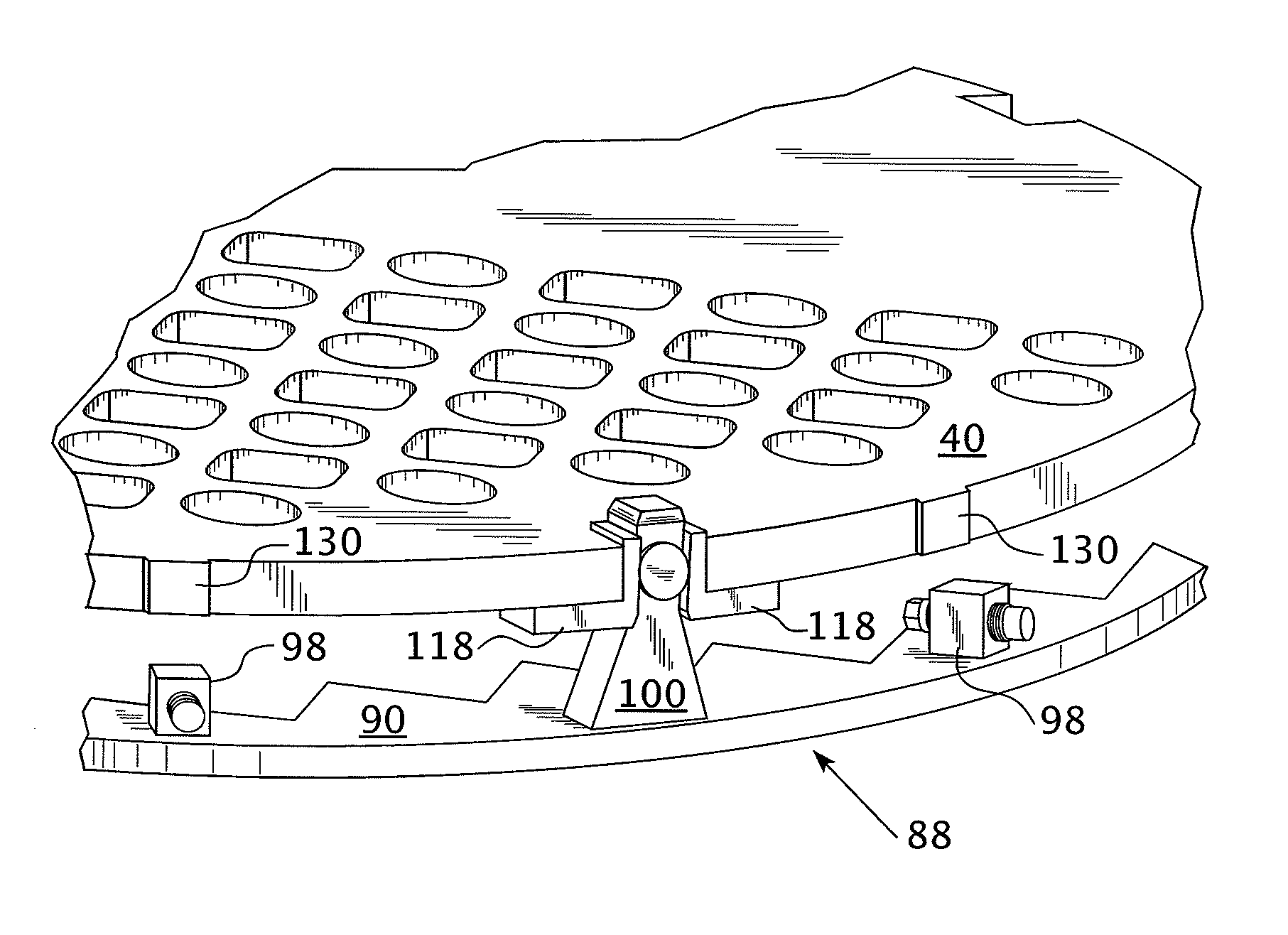
A core shroud is provided, which includes a number of planar members, a number of unitary corners, and a number of subassemblies each comprising a combination of the planar members and the unitary corners. Each unitary corner comprises a unitary extrusion including a first planar portion and a second planar portion disposed perpendicularly with respect to the first planar portion. At least one of the subassemblies comprises a plurality of the unitary corners disposed side-by-side in an alternating opposing relationship. A plurality of the subassemblies can be combined to form a quarter perimeter segment of the core shroud. Four quarter perimeter segments join together to form the core shroud.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
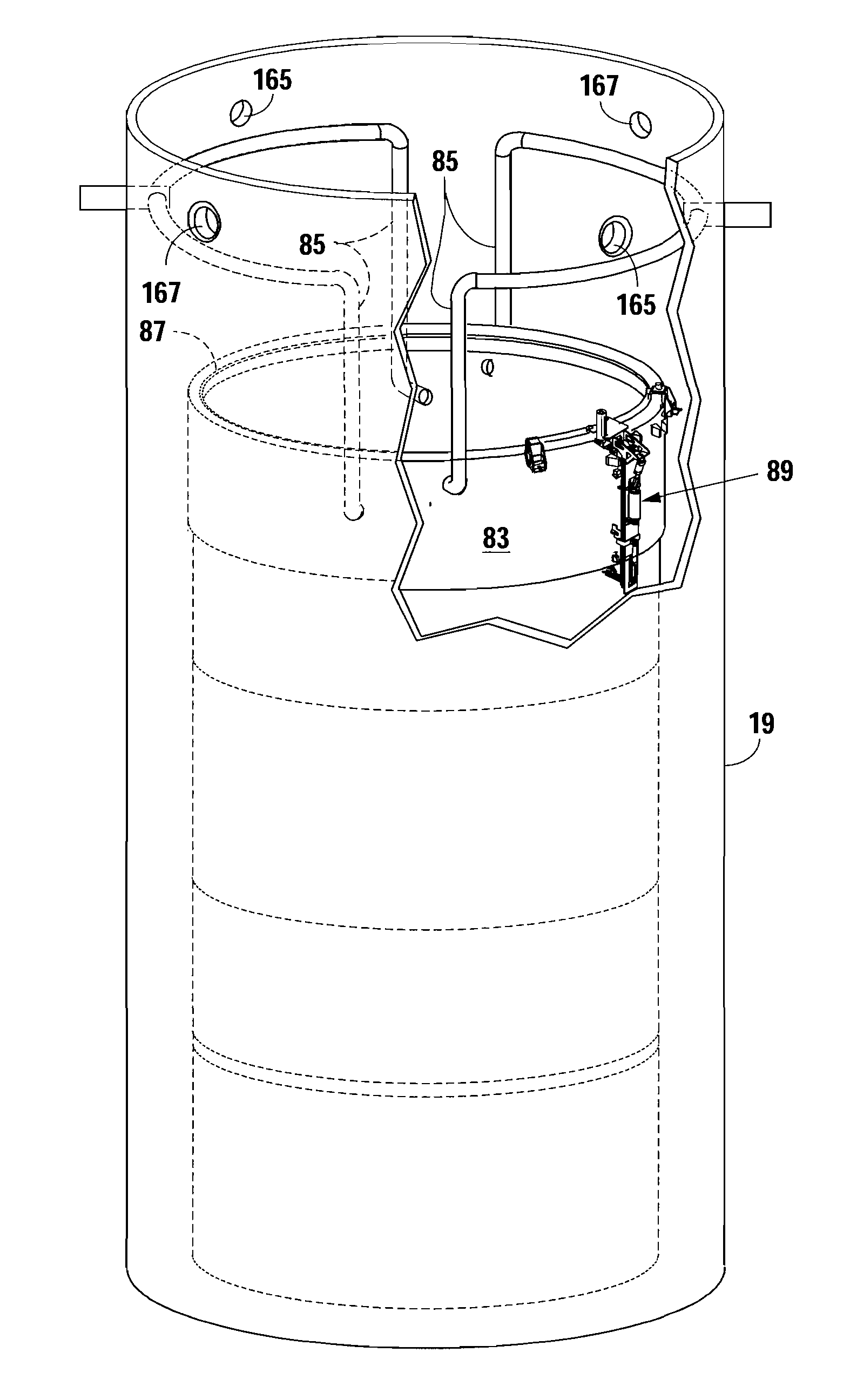
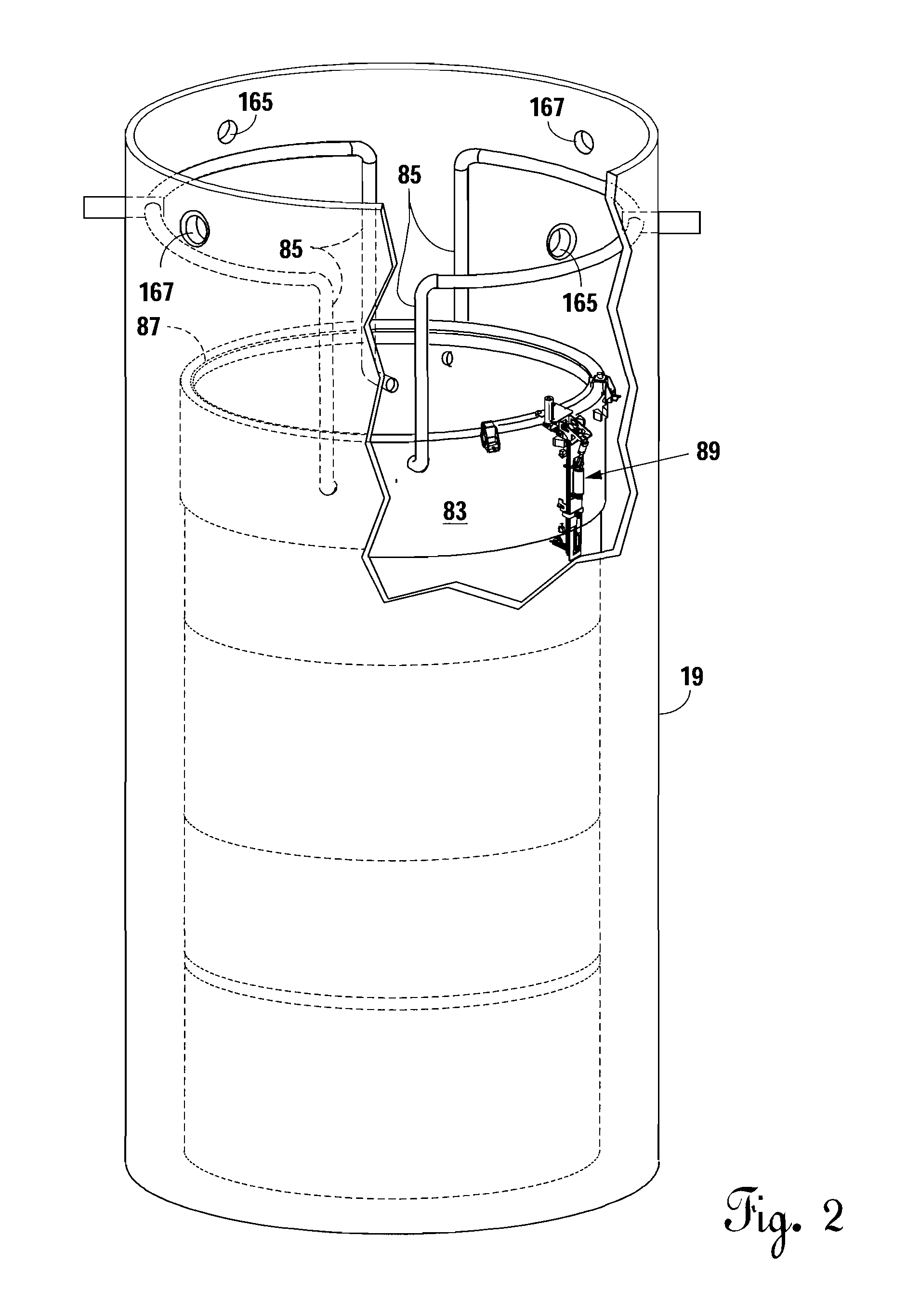
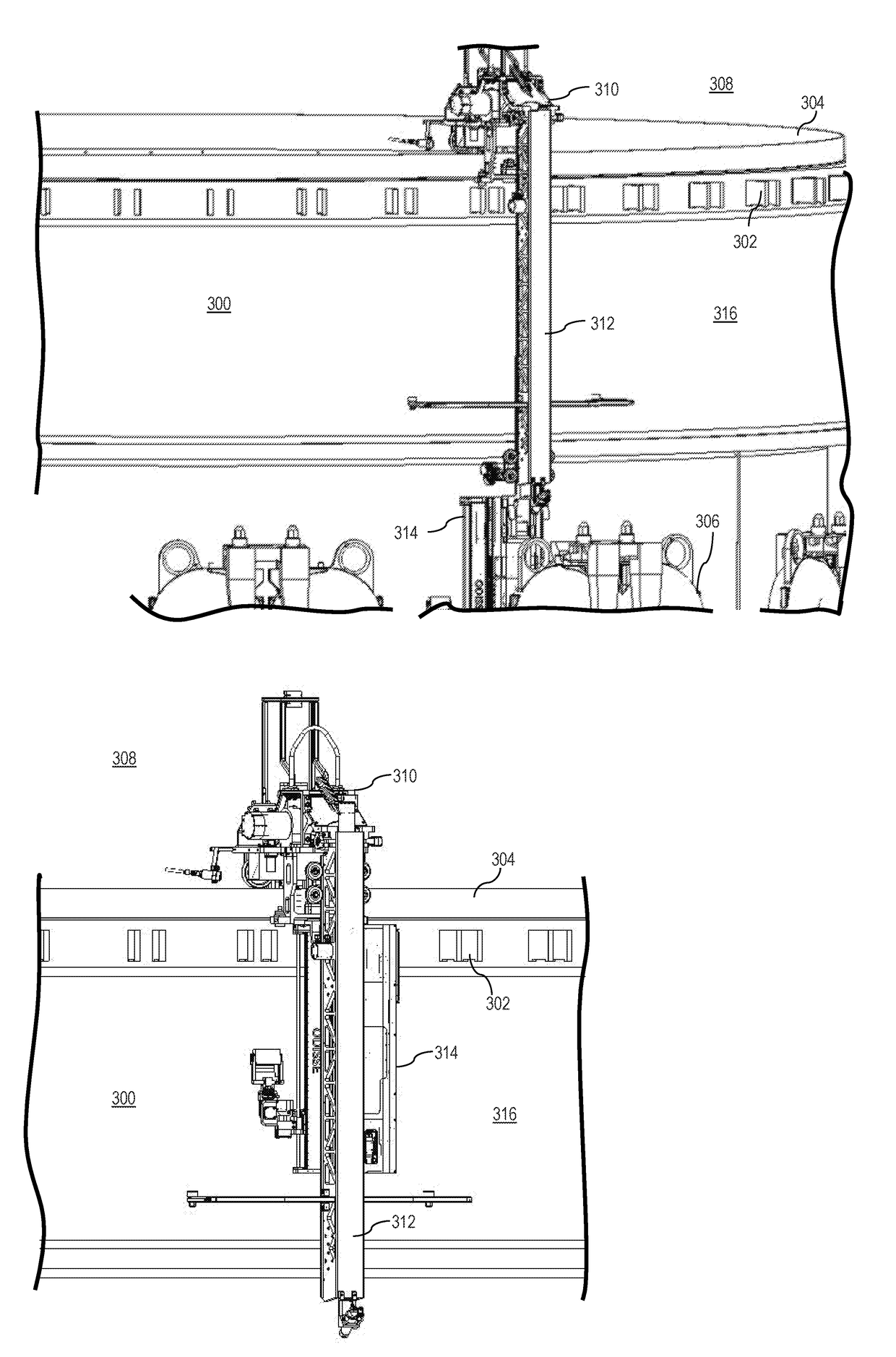
Remotely operated vehicles, systems, and methods for inspecting core shrouds
ActiveUS20180053572A1Programme-controlled manipulatorMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringRemotely operated vehicle
A remotely operated vehicle (ROV) for inspecting a core shroud having an outer surface may include: a body configured to be operatively connected to a tether; and / or a sensor, configured to be operatively connected to the body, and configured to provide inspection information of the shroud. The tether may be configured to provide vertical position information for the ROV relative to the outer surface. A system for inspecting a core shroud may include: a trolley; an arm; the tether; and / or the ROV. The arm may be configured to be operatively connected to the trolley. The ROV may be configured to be operatively connected to the arm via the tether. A method for inspecting a core shroud may include: installing a system for inspecting the shroud on the shroud; driving the system horizontally around the shroud; and / or using a sensor of the system to inspect the shroud.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Boiling water reactor core shroud head bolt retainer tool
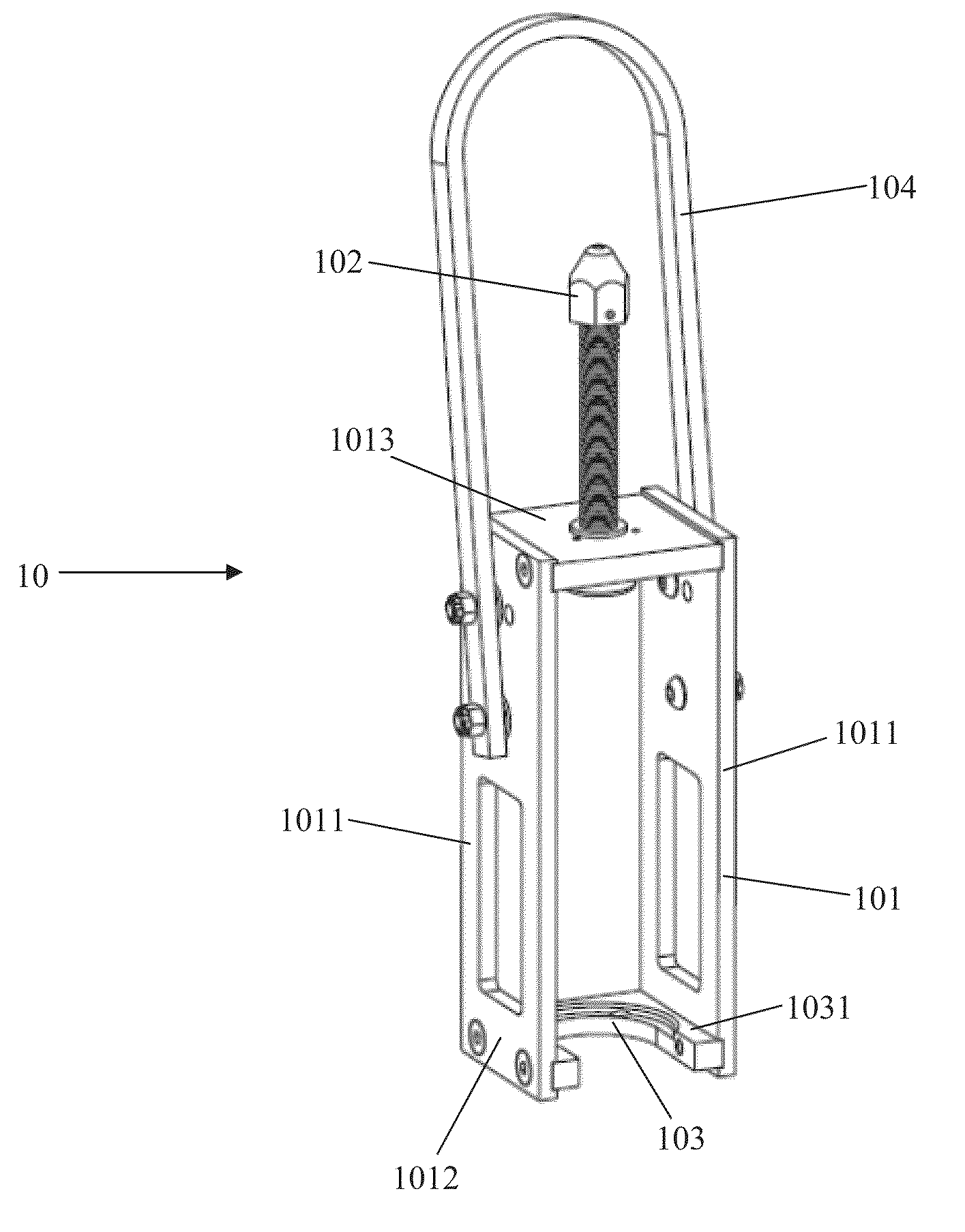
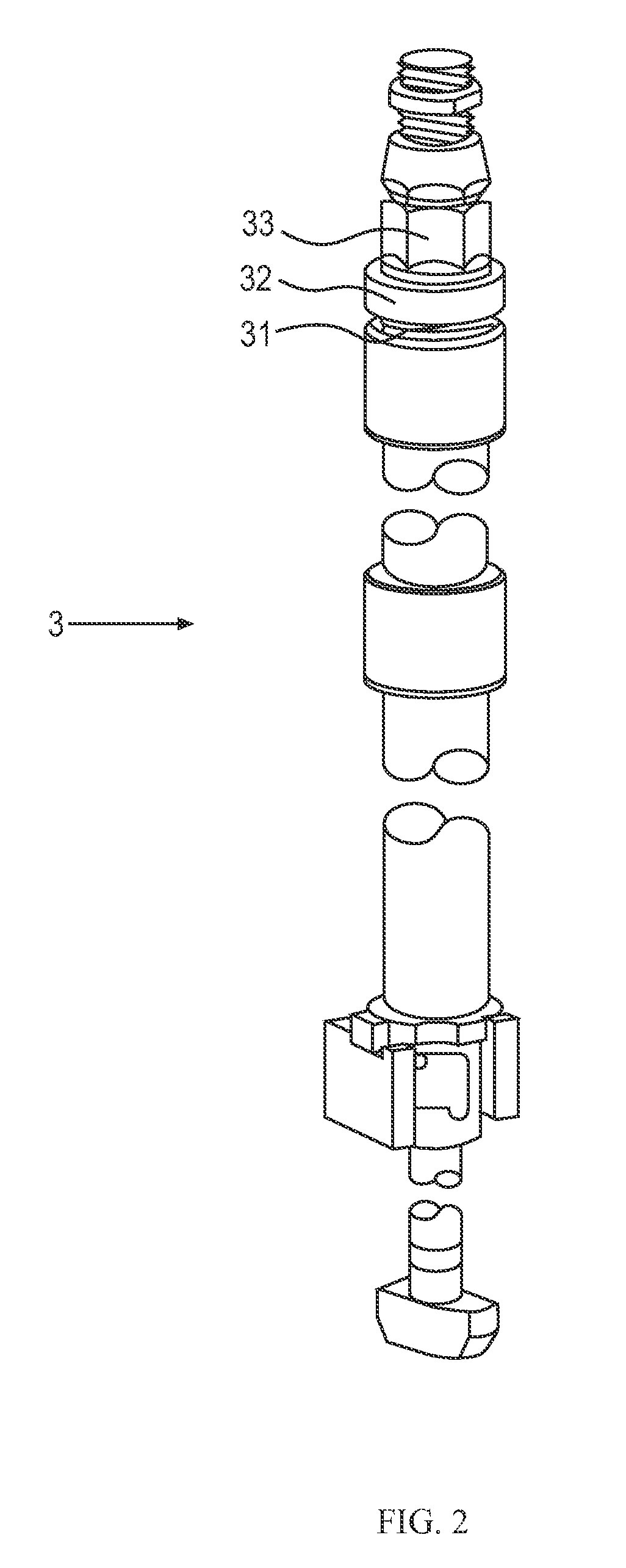
The inventive tool is designed to ensure proper plant operation position of the core shroud head bolt assemblies of a boiling water nuclear reactor. The tool exerts an upward pulling force on stuck retainers to return them to the locking position around the nut. The tool includes a frame, an engagement member, and a collar. The engagement member is lowered toward and end of the bolt until it comes into contact therewith. Further movement of the engagement member causes the frame and collar to move upward, lifting the retainer and extending the spring.
Owner:AREVA INC
Nuclear reactor alignment plate configuration
ActiveUS20090296877A1Avoid large gapsNuclear energy generationContainmentFillet weldPressurized water reactor
An alignment plate that is attached to a core barrel of a pressurized water reactor and fits within slots within a top plate of a lower core shroud and upper core plate to maintain lateral alignment of the reactor internals. The alignment plate is connected to the core barrel through two vertically-spaced dowel pins that extend from the outside surface of the core barrel through a reinforcement pad and into corresponding holes in the alignment plate. Additionally, threaded fasteners are inserted around the perimeter of the reinforcement pad and into the alignment plate to further secure the alignment plate to the core barrel. A fillet weld also is deposited around the perimeter of the reinforcement pad. To accommodate thermal growth between the alignment plate and the core barrel, a gap is left above, below and at both sides of one of the dowel pins in the alignment plate holes through which the dowel pins pass.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
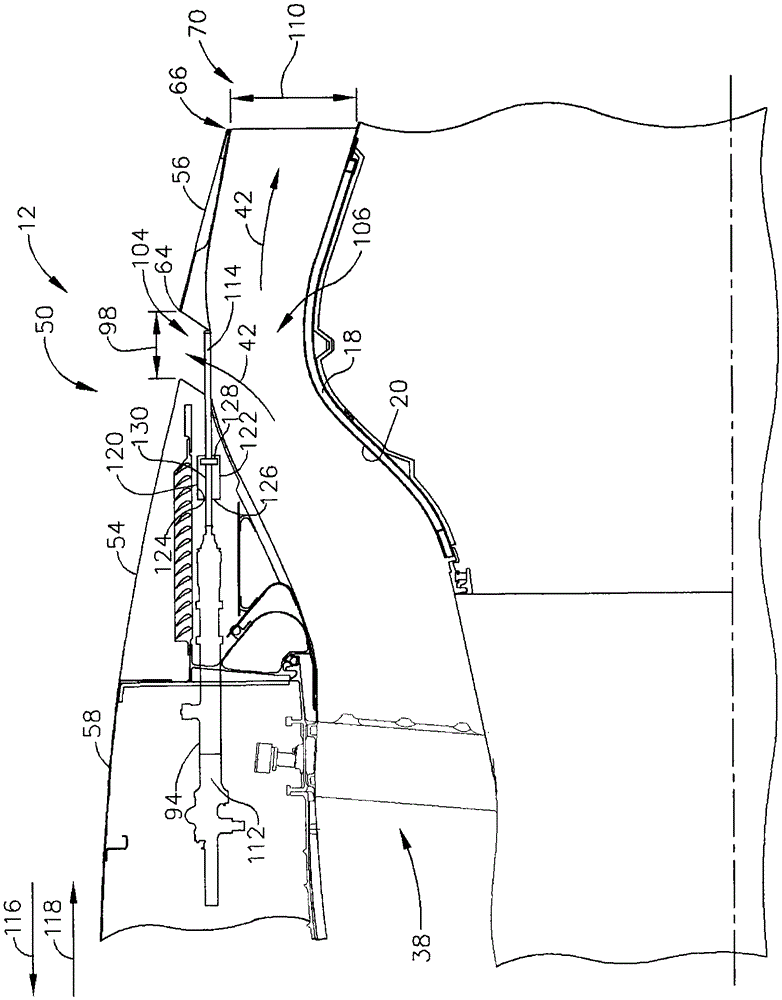
Systems and methods of operating a thrust reverser for a turbofan propulsion system
The present invention relates to systems and methods of operating thrust reversers for turbofan propulsion systems. A thrust reverser assembly for a turbofan engine assembly is provided. The engine assembly includes a core gas turbine engine; a core shroud surrounding the core gas turbine engine; and a nacelle positioned radially outside the core shroud to define a fan nozzle duct between the core shroud and a portion of the nacelle, the nacelle including a stationary shroud. The thrust reverser assembly includes: a first translating cowl slidably coupled to the nacelle, the first translating cowl being positionable relative to the fixed cowl; a second translating cowl slidably coupled to the nacelle such that the first translating cowl is between the shield and the second translating shield, the second translating shield being positionable relative to the first translating shield; a positioning assembly coupled to the first translating shield; and operatively coupled to the second translating shield for selectively moving the second translating shield An actuator assembly configured to engage the positioning assembly to selectively move the first translating shield.
Owner:伍德沃德HRT公司
Repair apparatus for a nuclear reactor shroud
InactiveUS20070030942A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsNuclear reactorArchitectural engineering
The tie rod repair apparatus includes a tie rod secured at its upper end to the shroud flange at the top of the shroud. The lower end of the tie rod passes through an opening in the shroud support plate without imposing a load on the plate. The lower end of the tie rod is anchored to the lower end of the core shroud support cylinder such that the compressive load path exerted by the tie rod to restrain the cracked shroud passes directly through the shroud support cylinder and the assembly of shroud cylinders bypassing the shroud support plate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Nuclear reactor internals alignment configuration
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
A metal reactor internals suitable for spherical fuel and high temperature coolant
ActiveCN111341467AAvoid displacementEasy to manufactureNuclear energy generationShieldingGraphitePhysics
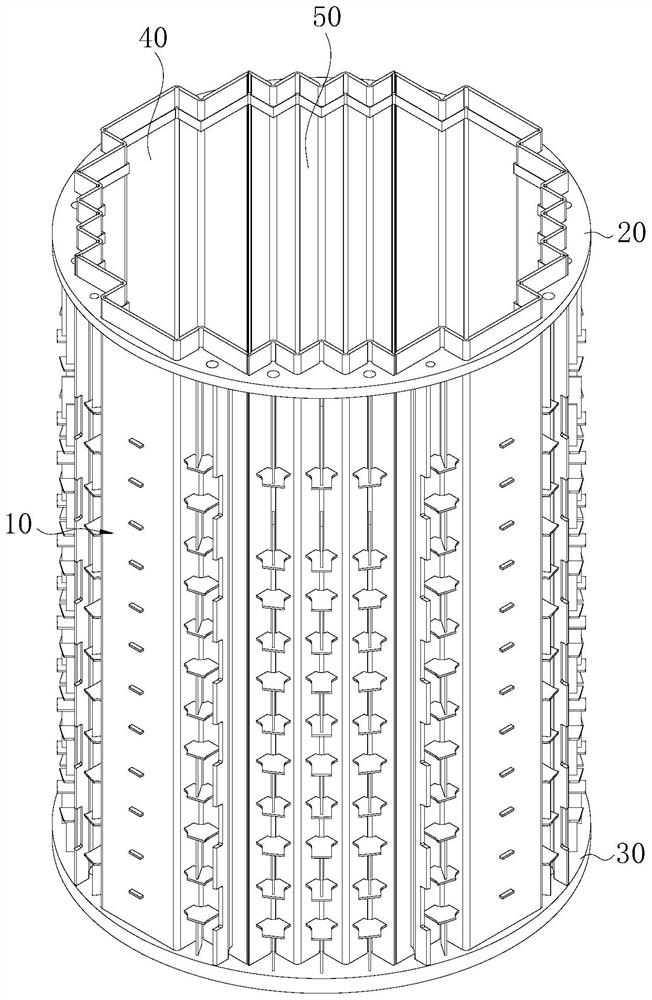
The invention discloses a metal reactor internal suitable for spherical fuel and a high-temperature coolant. The reactor core comprises an upper shroud assembly arranged at the upper part and a reactor core shroud assembly arranged below an upper shroud part, the upper shroud assembly is detachably connected with the reactor core shroud assembly; an axial positioning device for axially limiting the upper-layer graphite is arranged below a pressing plate in the upper shroud assembly; the reactor core shroud assembly comprises a reactor core shroud, the inner wall of the reactor core shroud is provided with two or more circumferential limiting layers arranged in parallel up and down in the axial direction, each circumferential limiting layer is composed of a plurality of circumferential limiting parts arranged in the circumferential direction of the inner wall of the reactor core shroud, and the two or more circumferential limiting layers limit graphite arranged in the reactor core shroud in the circumferential direction. According to the invention, the graphite part arranged in the metal part can be contained and positioned by the metal part, and the problem of displacement betweenthe metal part and the graphite part caused by temperature change is prevented.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Nuclear power plant head package mobile cable bridge apparatus
PendingCN105932612AReduce lifting weightMitigate the risk of lifting the integrated roof assembly structureElectrical apparatusCable trayEngineering
The invention provides a nuclear power plant head package mobile cable bridge apparatus which includes: an integrated head package assembly which is provided with a core shroud thereon; the side of the core shroud is provided with a cable connection board and a cable arrangement platform; the cable arrangement platform is intended for assignment and fixing of cables at the side of the core shroud and also positioning of nuclear and non-nuclear cables on the head package; the side of the core shroud is also provided with a first cable socket connector; the first cable socket connector is fixed to the cable connection board. The nuclear power plant head package mobile cable bridge apparatus is also provided with a second cable socket connector which is configured to be mounted or dismounted in cooperation with the first socket connector. The nuclear power plant head package mobile cable bridge apparatus is arranged on the integrated head package assembly and a civil engineering plane through track arrangement. During material changing, part of the track is dismounted through moving the cable bridge apparatus, so that hoisting weight of the integrated head package assembly is reduced and the risk of lifting the integrated head package assembly structure is mitigated.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
A novel nature cycle cooling lead-based fast reactor
ActiveCN108520786AImprove securityImprove economyNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementInterior spaceNuclear engineering
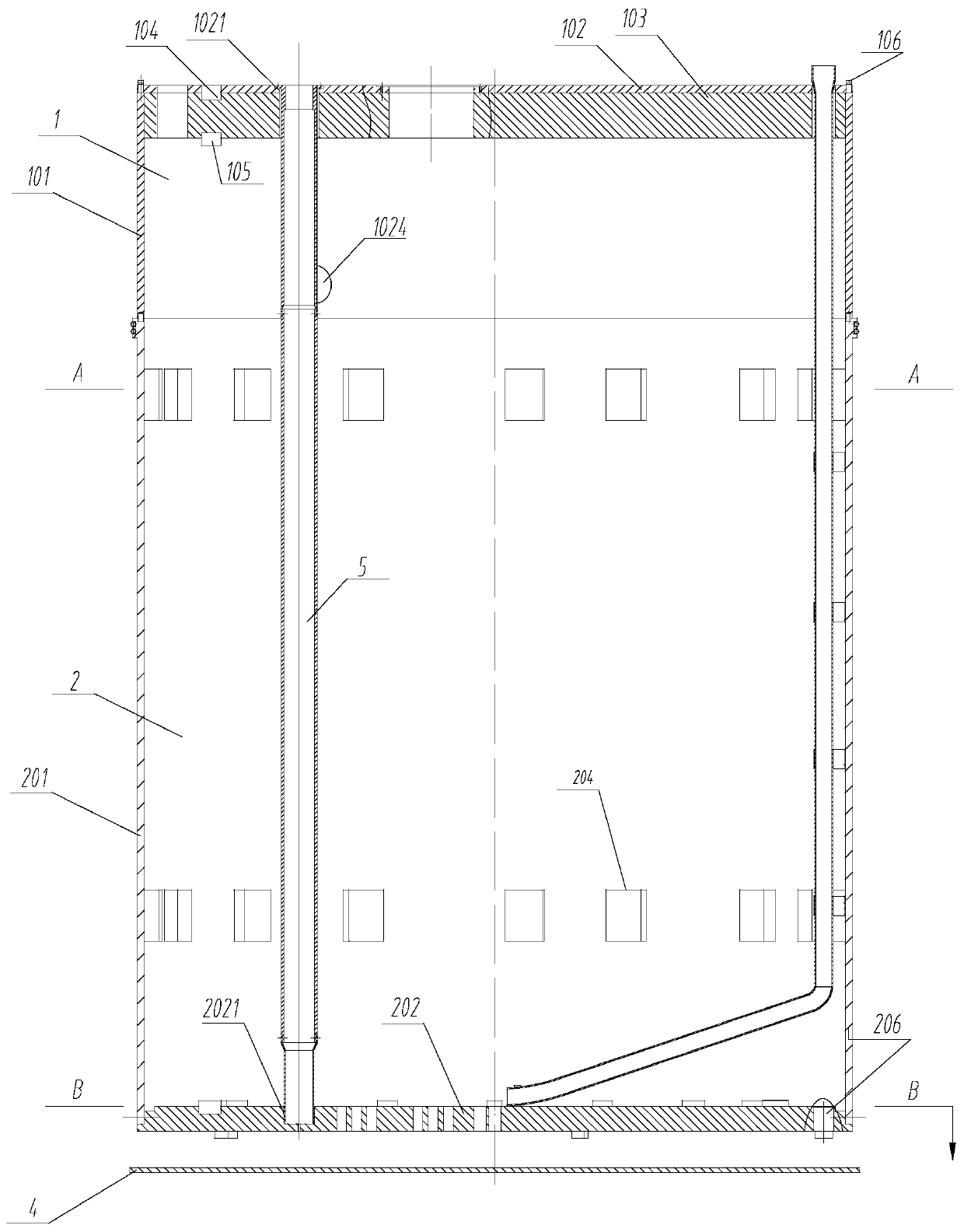
The invention discloses a novel nature cycle cooling lead-based fast reactor. The novel nature cycle cooling lead-based fast reactor at least includes: a core, a main container, a core shroud, a heatpool, a cool pool, a main heat exchanger and a reactor top cover. The main container is a circular column metal container, the two ends of the main container are sealed; the core shroud is arranged inthe main container, the inner space of the main container is divided into the heat pool and cool pool; at least one part of the core shroud has a circular column metal plate with a taper curved surface, the core is arranged at the bottom of the heat pool of the main container, the height difference is existed between the core and the main heat exchanger, the main heat exchanger is connected withthe heat pool and cool pool, and the nature circulation canal of the cooling agent is formed by the main heat exchanger, cool pool and heat pool. The nature cycle capability of the first loop coolingagent can be enhanced, and the security and economy of the nature cycle cooling lead-based fast reactor are effectively improved.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +3
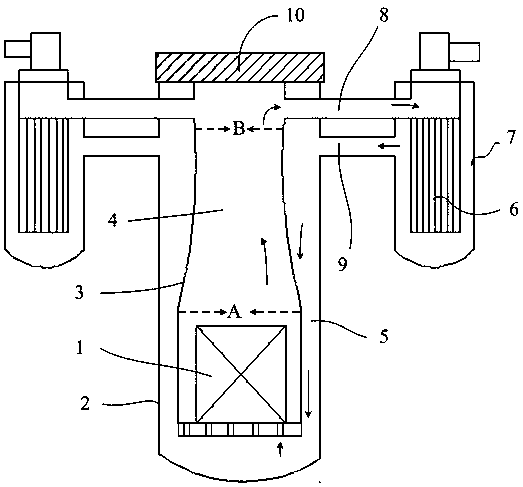
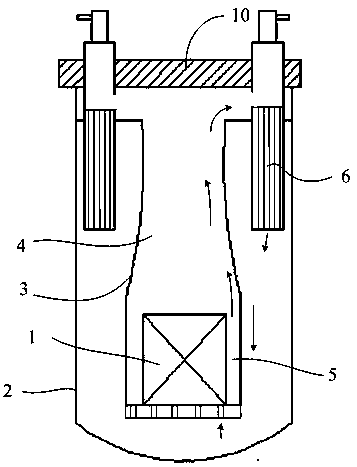
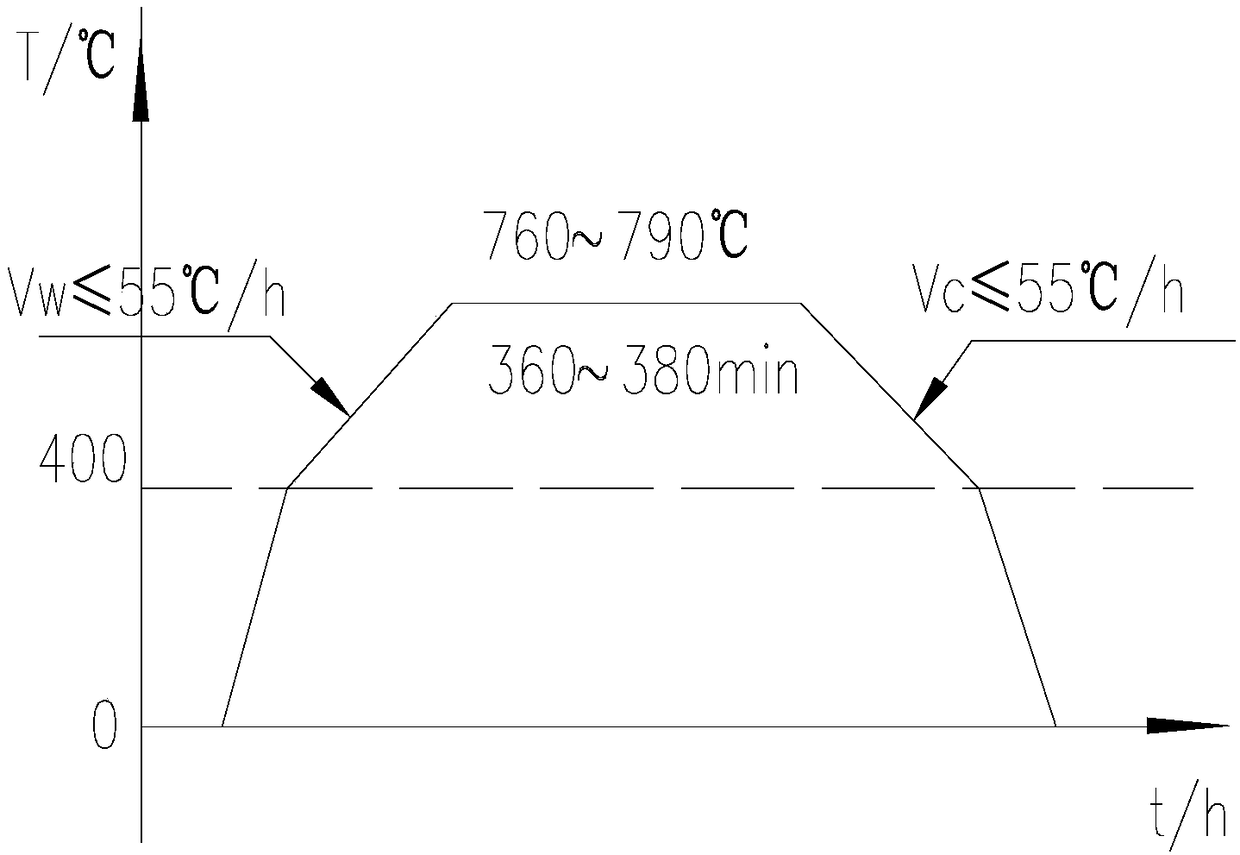
Heat treatment method of thorium-based fused salt main container and core shroud
ActiveCN109306402AMeet manufacturing requirementsGuaranteed accuracy requirementsFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesIsolation effectSize change
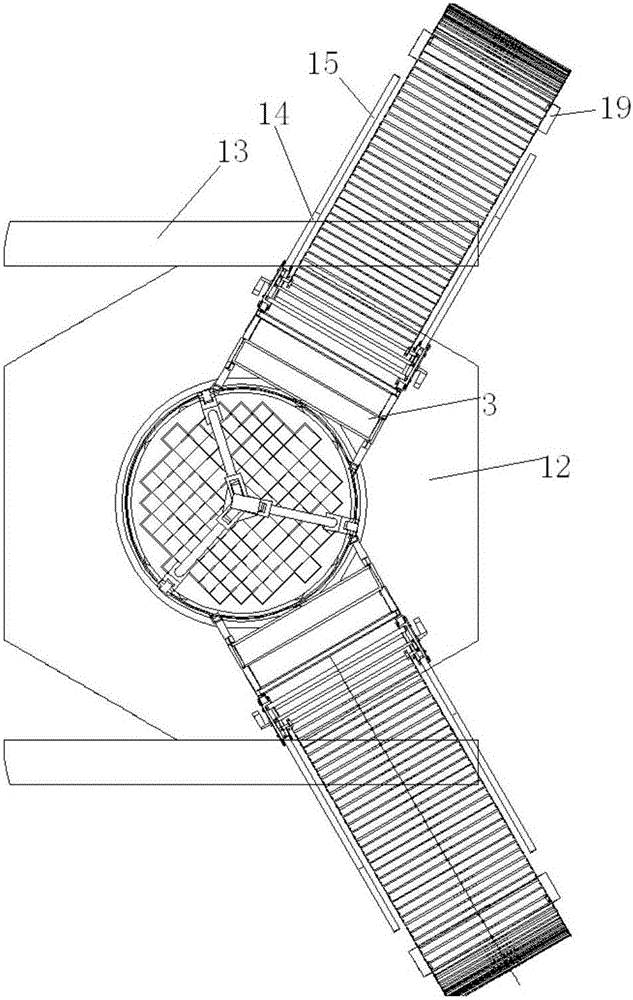
The invention discloses a heat treatment method of a thorium-based fused salt main container and a core shroud. The method comprises the following steps of S1, heat treatment of the main container, specifically, the main container is of a vertical structure to be subjected to heat treatment, a bottom board is a carbon steel or low-alloy steel thick board and horizontally arranged on a furnace bodybearing point inside the furnace, and a placement plane of the main controller is provided; and S2, heat treatment of the core shroud, specifically, the core shroud is of a vertical structure to be subjected to heat treatment, the bottom board and a partition board are horizontally arranged on the furnace body bearing point inside the furnace, and a placement plane and an isolation effect of thecore shroud are provided. By the adoption of the heat treatment method of the thorium-based fused salt main container and the core shroud, the precision requirements for size changes in the heat treatment process of equipment can be effectively ensured, the heat treatment cost is reduced, the equipment which is subjected to heat treatment and is good in performance, stable in quality and high in precision is obtained, the manufacturing requirements of the thorium-based fused salt main container and the core shroud are met, and the service life of the equipment is prolonged.
Owner:NANJING BAOSE
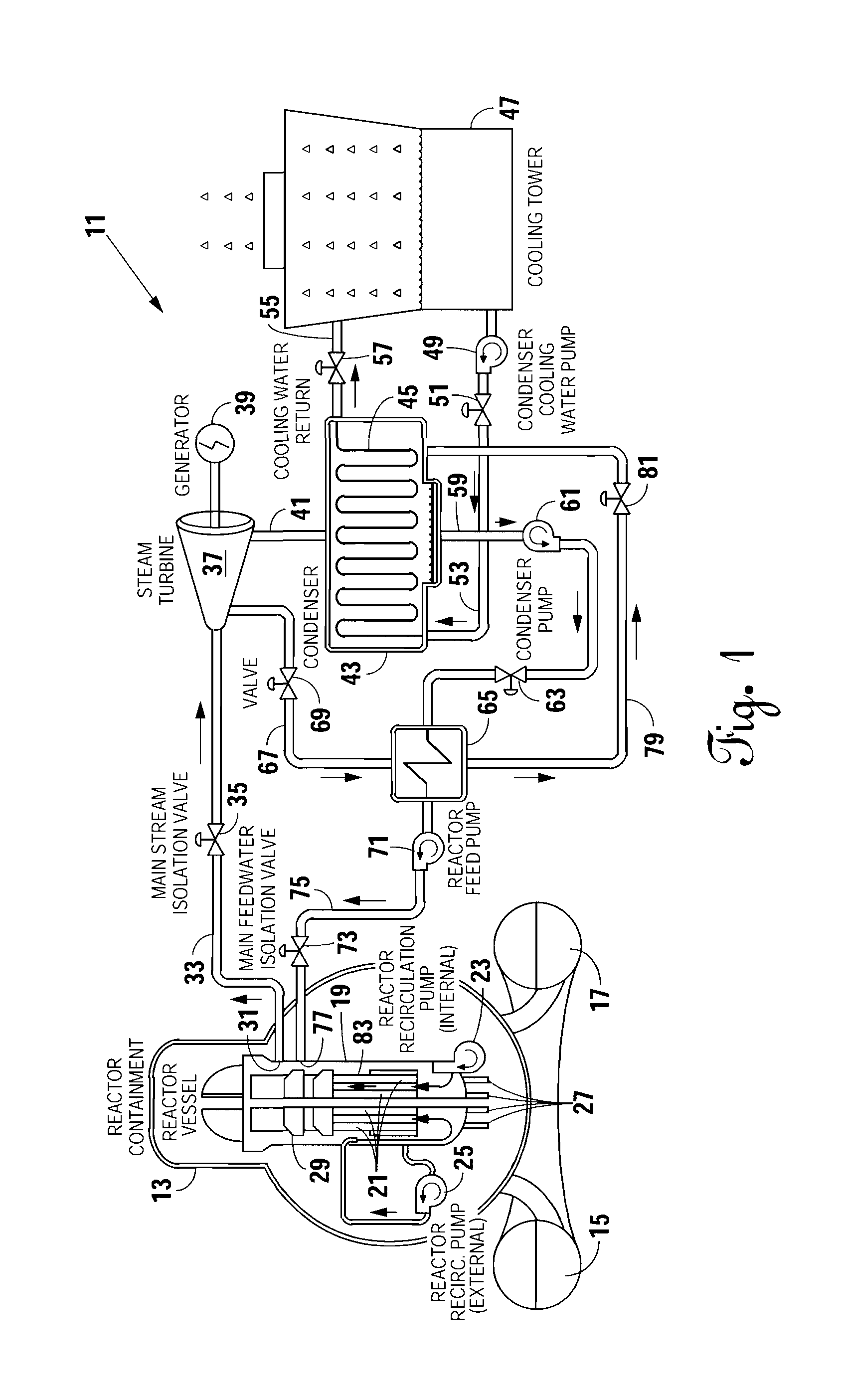
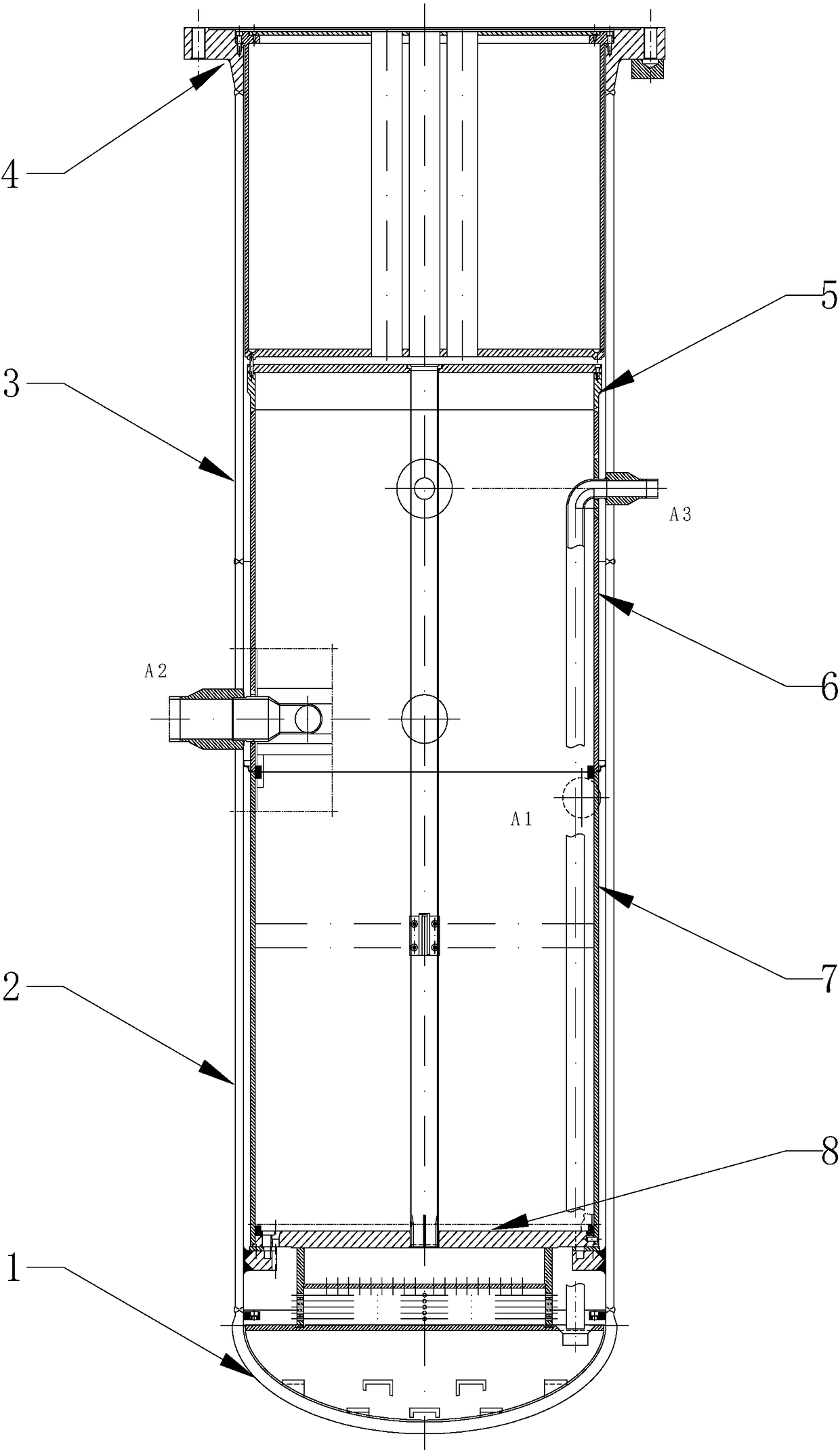
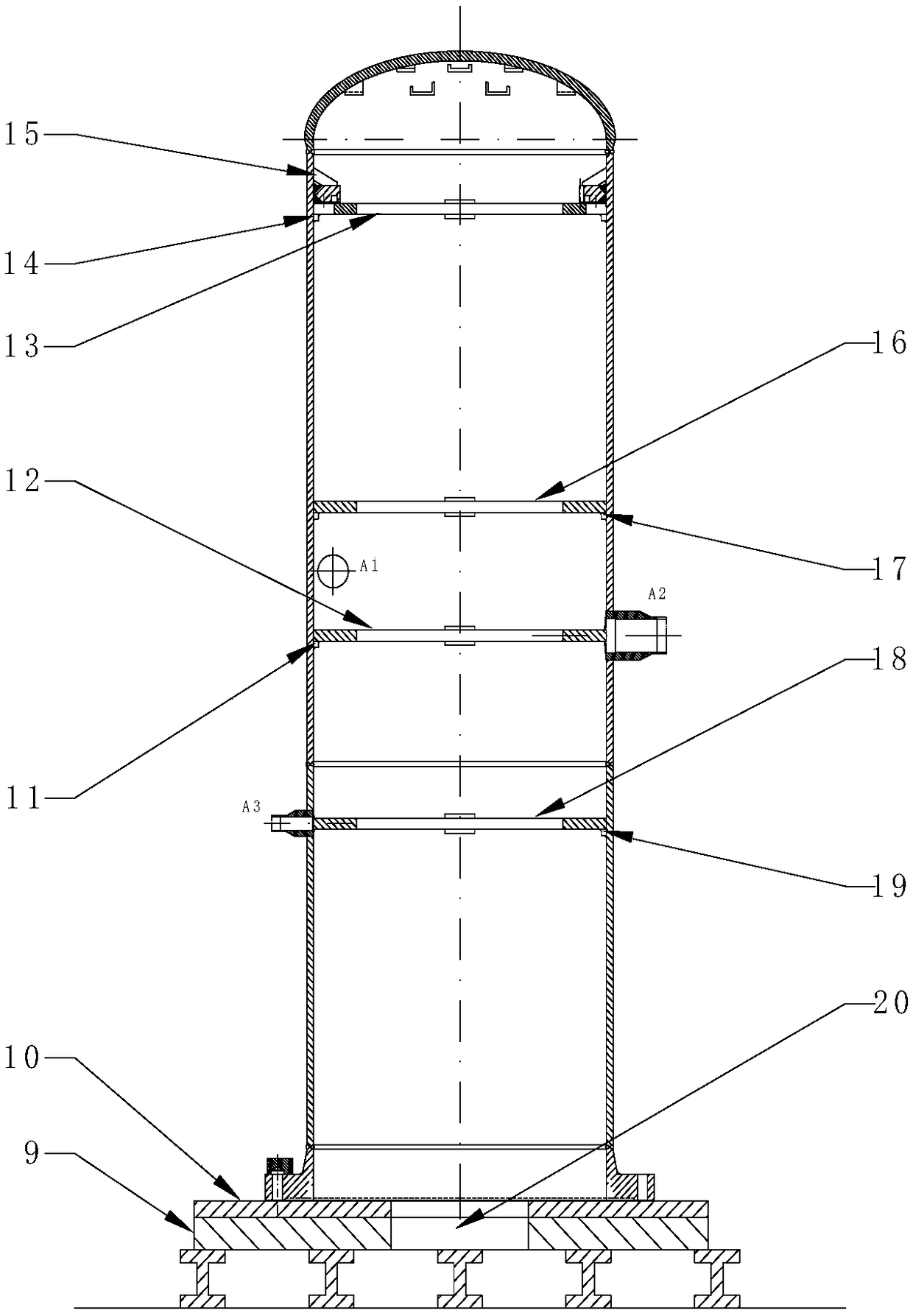
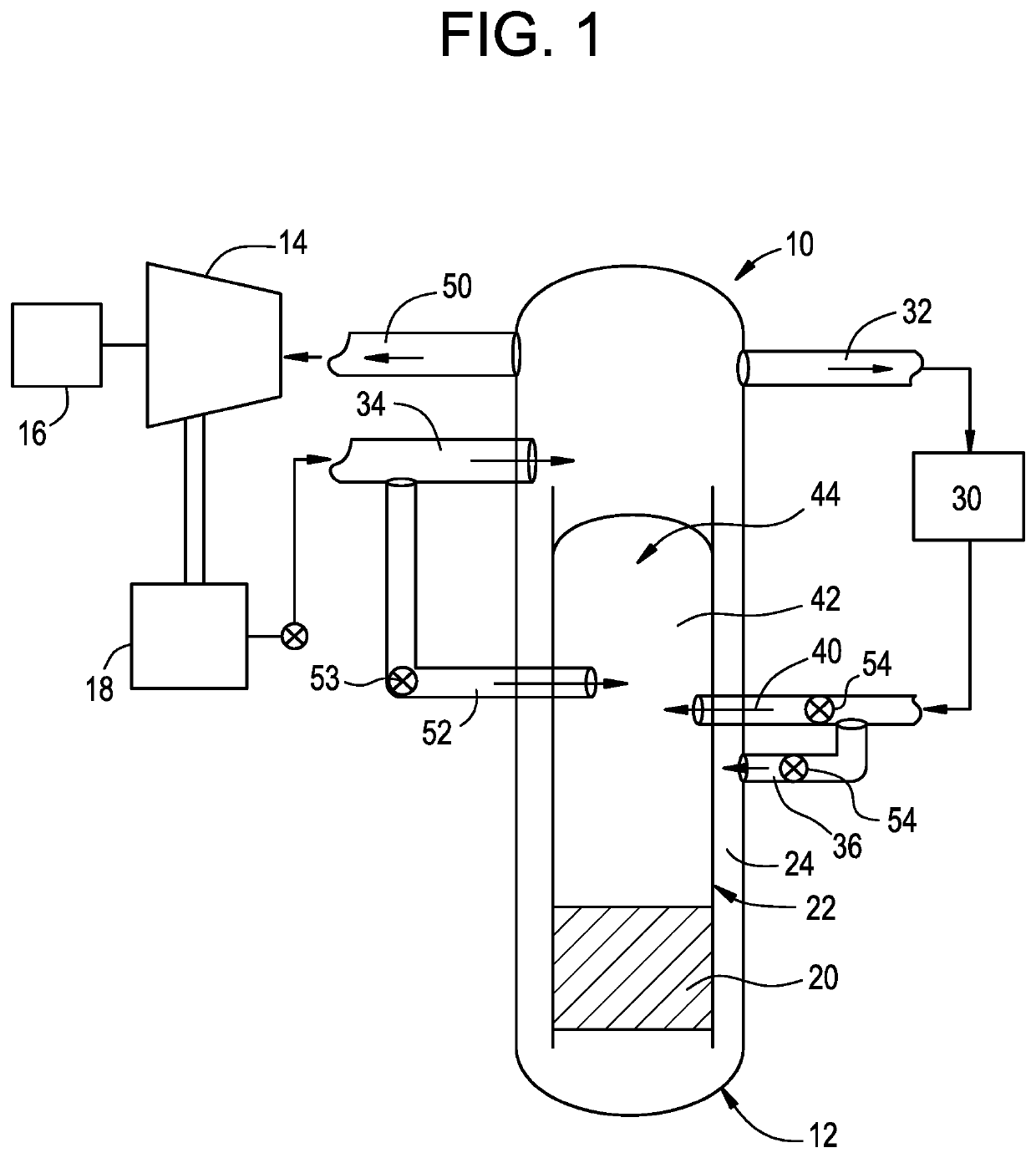
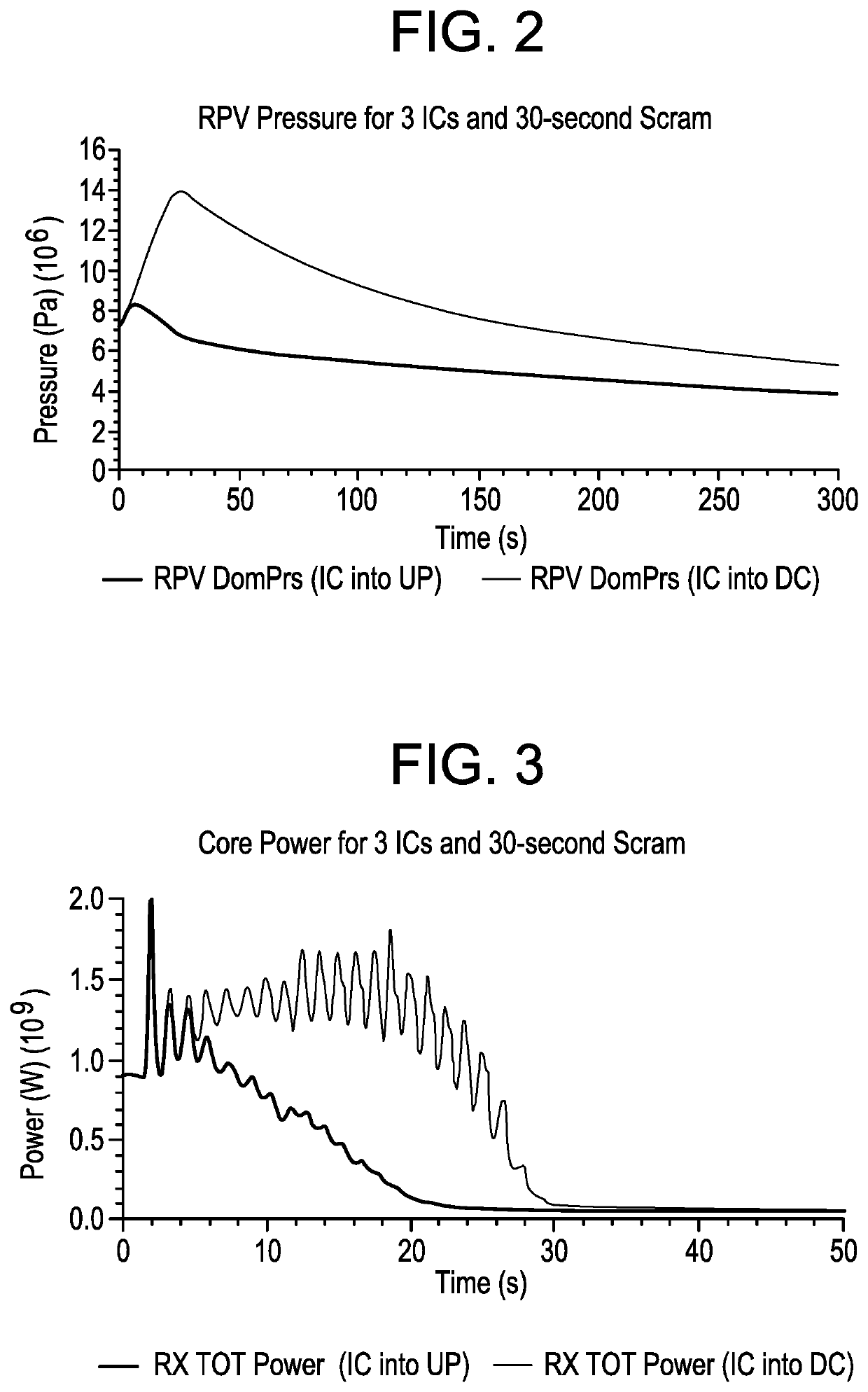
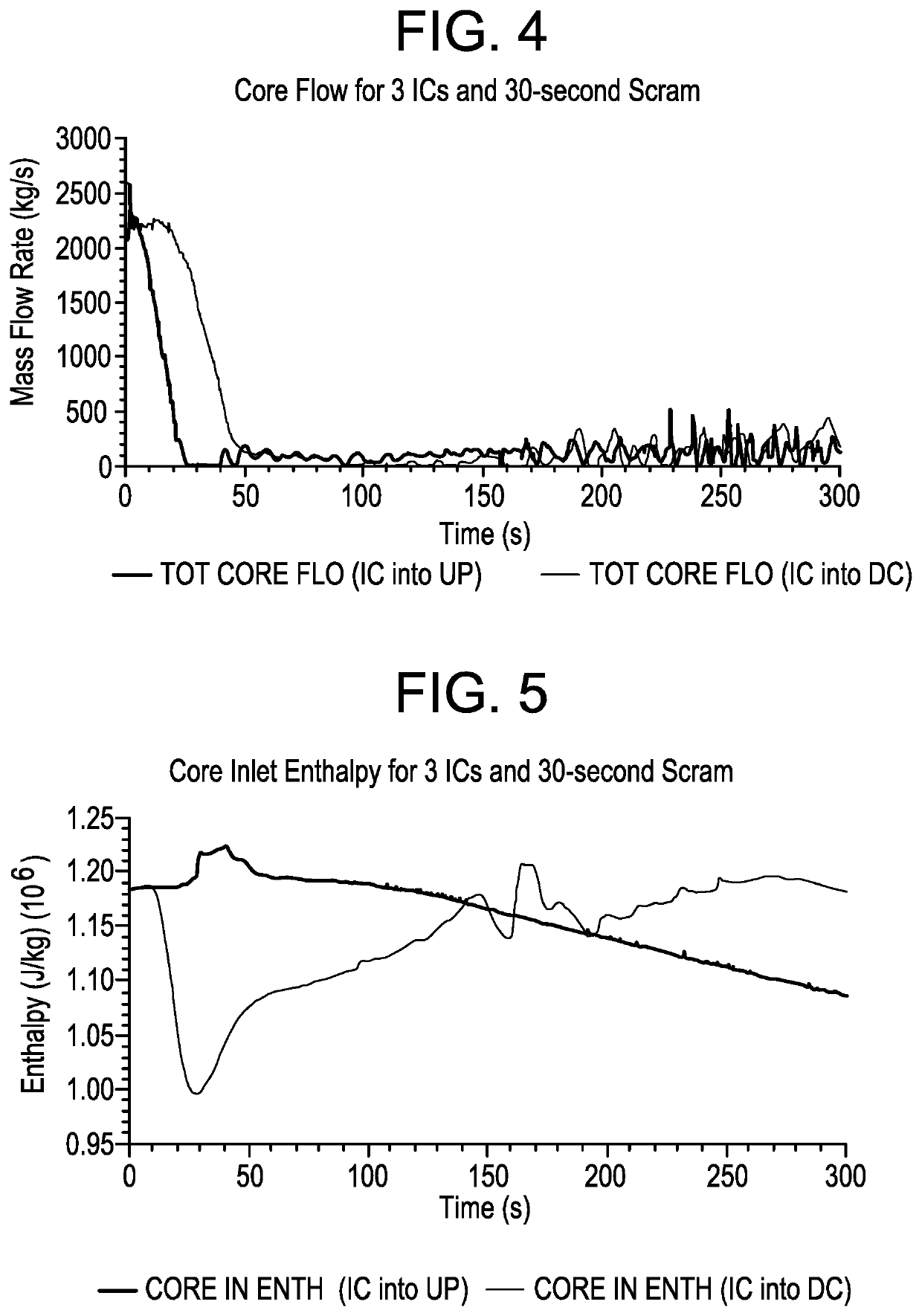
Use of isolation condenser and/or feedwater to limit core flow, core power, and pressure in a boiling water reactor
ActiveUS11139087B2Reduced effectivenessImprove efficiencyPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationReactor pressure vesselSteam line
A method and apparatus of limiting power of a boiling water nuclear reactor system includes a reactor pressure vessel, a reactor core disposed in the reactor pressure vessel, a core shroud surrounding the reactor core, a downcomer region disposed between an inner surface of the reactor pressure vessel and the core shroud, a steam line connected to an upper end of the reactor pressure vessel and a condenser system that receives steam from the reactor pressure vessel. A portion of the condenser system condensate is returned to the reactor pressure vessel of the boiling water reactor inside the core barrel above the core rather than into the downcomer. Returning the condensate in this way increases the effectiveness of an isolation condenser system or if the condensate is a portion of the feedwater from the main condenser it provides an effective means to regulate core flow and core power.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Preparation method of ultra-large integral stainless steel reactor core shroud member of nuclear power station
ActiveCN113976913AExcellent forming mechanical propertiesIncrease profitAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyNuclear engineeringNuclear power
The invention discloses a preparation method of an ultra-large integral stainless steel reactor core shroud member of a nuclear power plant, which comprises the following steps of: establishing a three-dimensional model of an ultra-large integral stainless steel reactor core shroud member of a nuclear power plant, and segmenting, blocking and layering the model in the axial direction; machining a stainless steel reactor core shroud structure layer by layer through the laser cladding forming technology, so as to complete machining of one stainless steel reactor core shroud structure; machining stainless steel reactor core shroud structures one by one, so as to complete machining of one section of stainless steel reactor core shroud structures; machining stainless steel reactor core shroud structures section by section, so as to complete machining of the stainless steel reactor core shroud structure on one side; and machining a second-side stainless steel reactor core shroud structure on the symmetric surface of a substrate forming the stainless steel reactor core shroud structure on one side, and finally forming an ultra-large integral stainless steel reactor core shroud structure of a nuclear power station. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, the reactor core shroud structure with excellent mechanical properties is integrally formed through a laser cladding forming technology, the material utilization rate is high, and the machining period is short.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Apparatus and method to inspect, modify, or repair nuclear reactor core shrouds
This invention generally concerns robotic systems and is particularly concerned with improved apparatus and methods for remotely inspecting, modifying or repairing a core shroud in a nuclear reactor. The apparatus of the invention includes a partial upper track which horizontally movable along the core shroud, a head and frame assembly which is horizontally movable along the partial upper track, a lower track which is connected to the head and frame assembly and is horizontally movable along the core shroud, and a carriage and arm assembly which extends downward into an annulus formed by the reactor pressure vessel and the core shroud, wherein the arm includes at least one sensor for inspecting the core shroud.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Welding method of reactor core shroud assembly
InactiveCN114273759AReduce welding costsStable and meet welding precision requirementsWelding accessoriesButt jointWeld seam
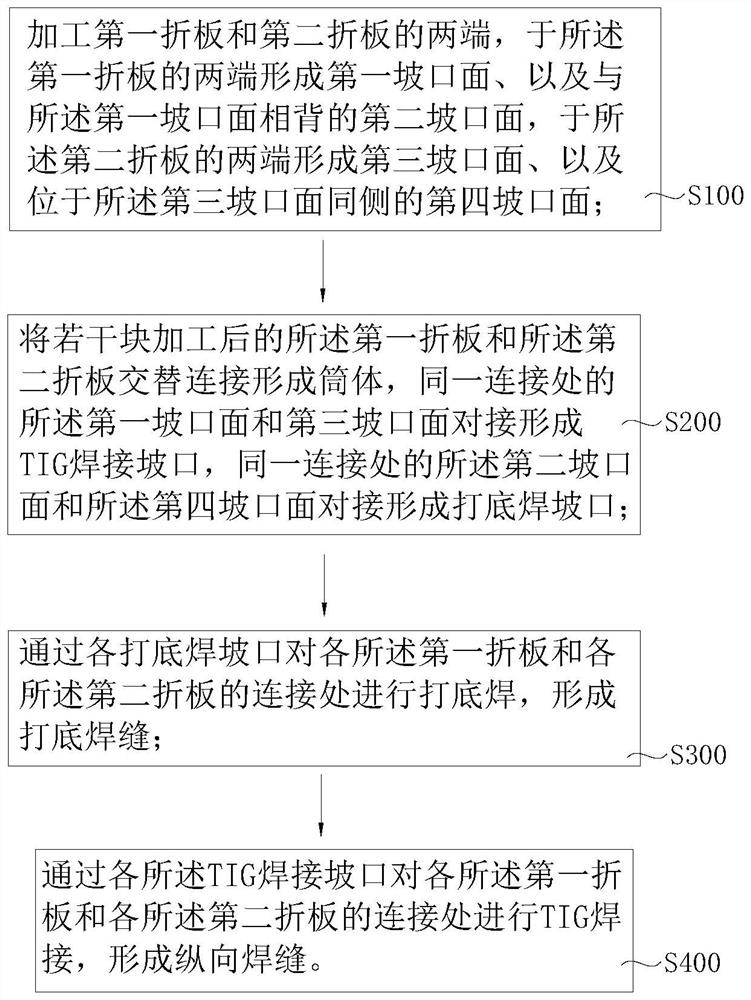
The invention relates to the technical field of welding processes, in particular to a welding method of a reactor core shroud assembly, which comprises the following steps: forming a first groove surface and a second groove surface at two ends of a first folded plate, forming a third groove surface and a fourth groove surface at two ends of a second folded plate, and alternately connecting a plurality of processed first folded plates and second folded plates to form a barrel; due to the fact that the second groove face and the fourth groove face at the same connecting position are in butt joint to form the backing welding groove, the first groove face and the third groove face are in butt joint to form the TIG welding groove, the backing welding groove can be used for backing welding of the first folded plate and the second folded plate, and the premise is provided for the first folded plate and the second folded plate to achieve stability and meet the welding precision requirement through TIG welding. By means of TIG welding of the longitudinal weld joints, automatic welding of the longitudinal weld joints of the reactor core shroud assembly can be achieved, the welding efficiency is guaranteed, and meanwhile the welding cost of the reactor core shroud assembly can be effectively reduced.
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRIC WUHAN NUCLEAR EQUIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com