Patents
Literature
158 results about "Effects unit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
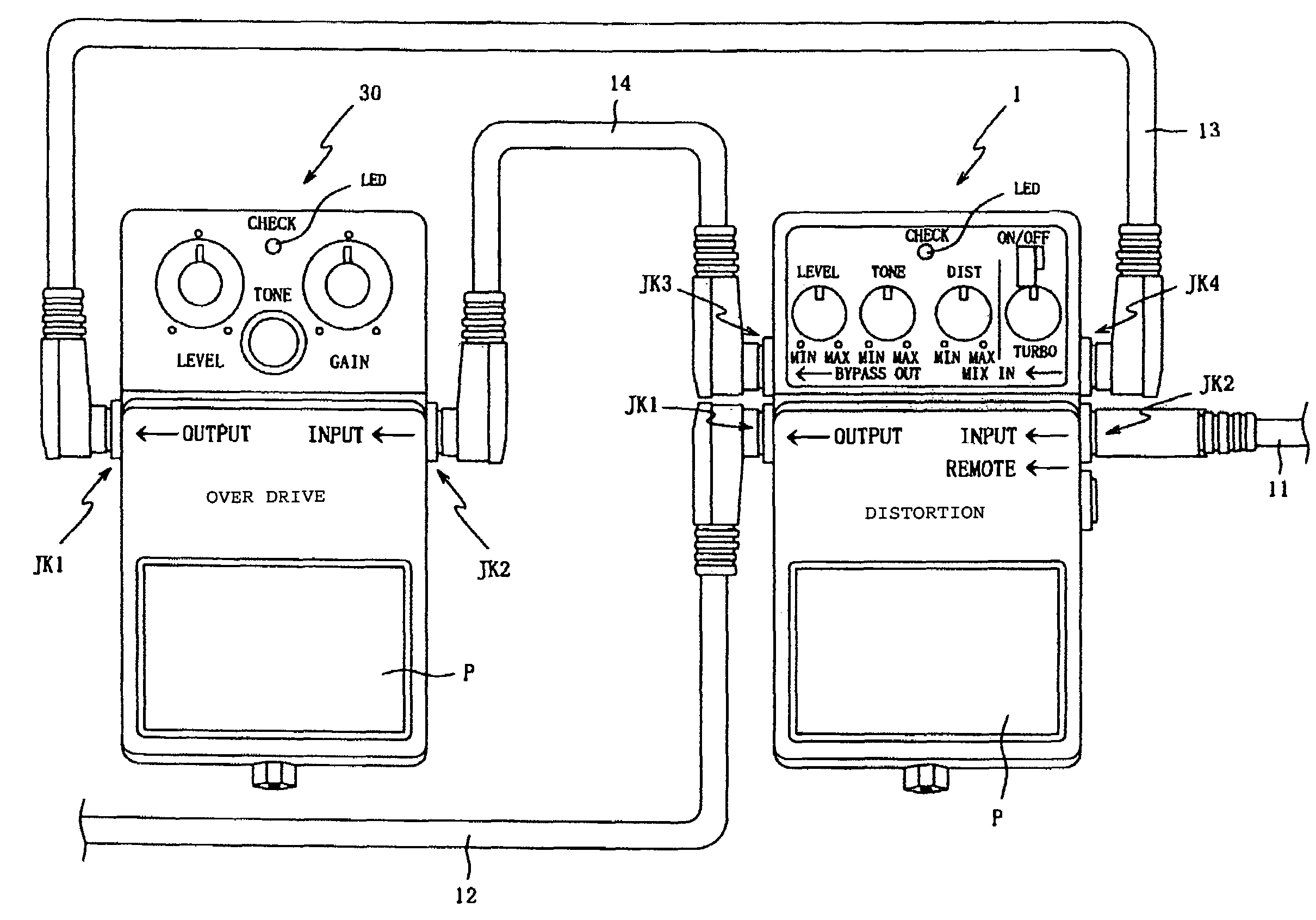
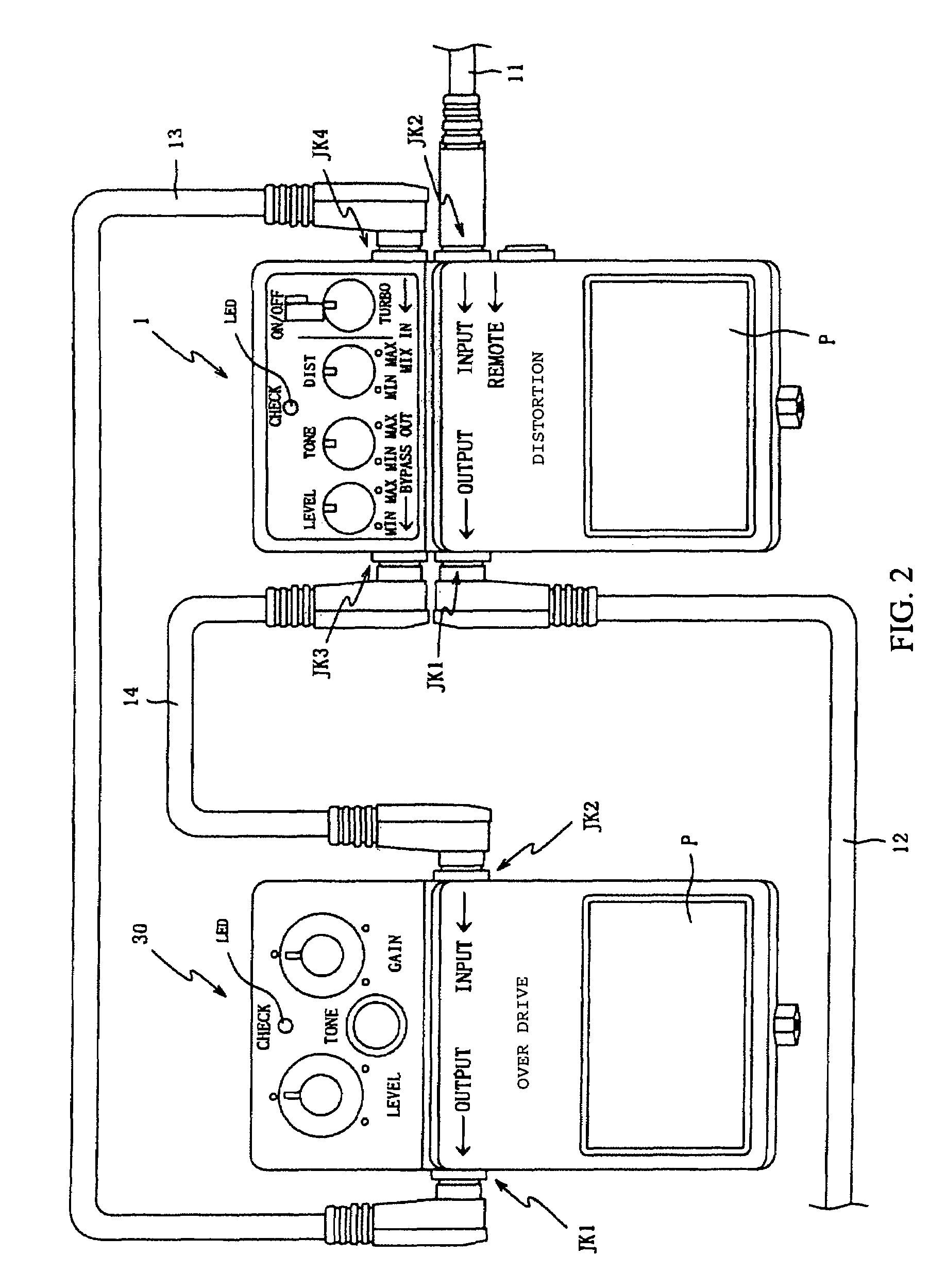
An effects unit or effects pedal is an electronic or digital device that alters the sound of a musical instrument or other audio source. Common effects include distortion/overdrive, often used with electric guitar in electric blues and rock music; dynamic effects such as volume pedals and compressors, which affect loudness; filters such as wah-wah pedals and graphic equalizers, which modify frequency ranges; modulation effects, such as chorus, flangers and phasers; pitch effects such as pitch shifters; and time effects, such as reverb and delay, which create echoing sounds and emulate the sound of different spaces.
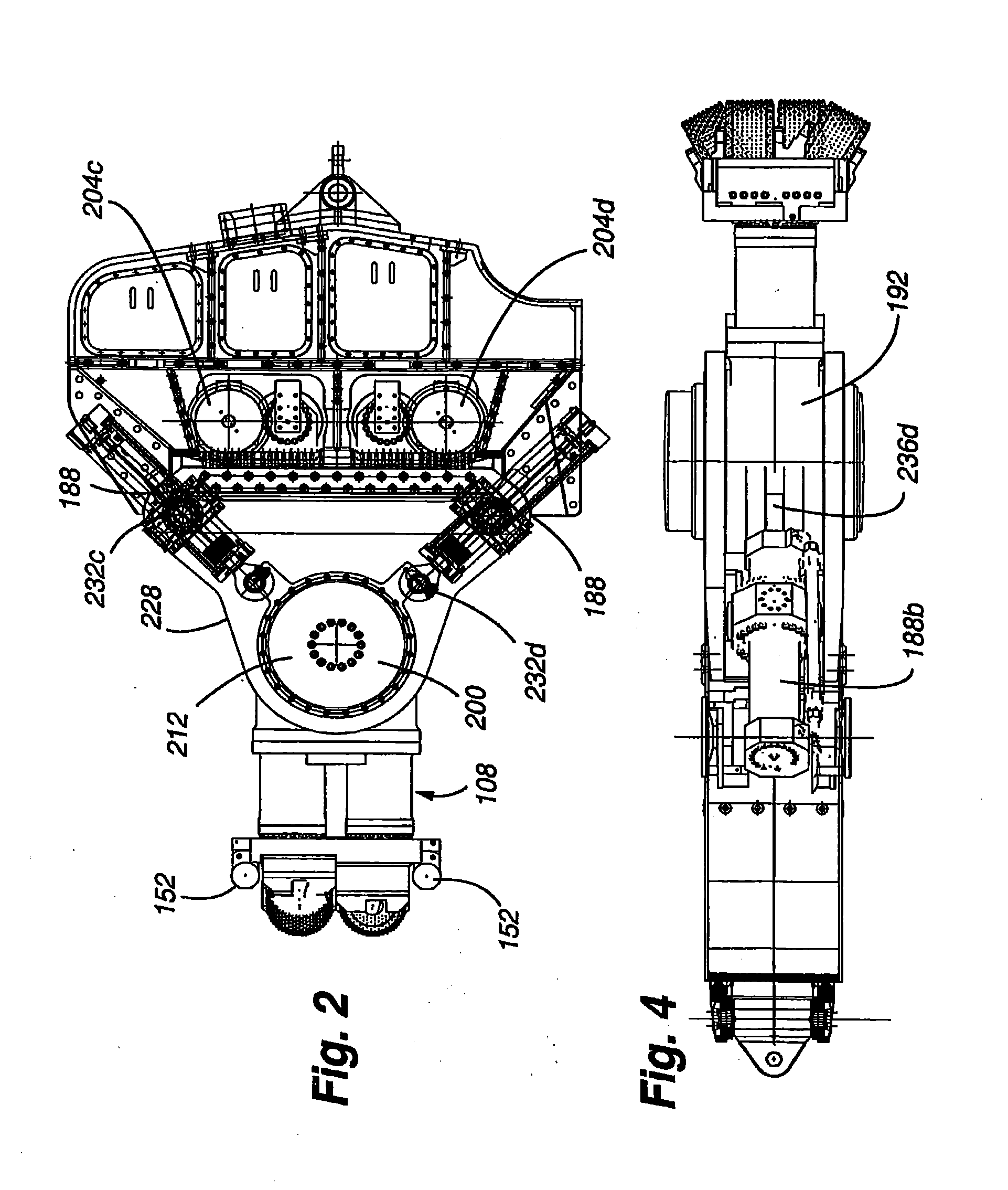
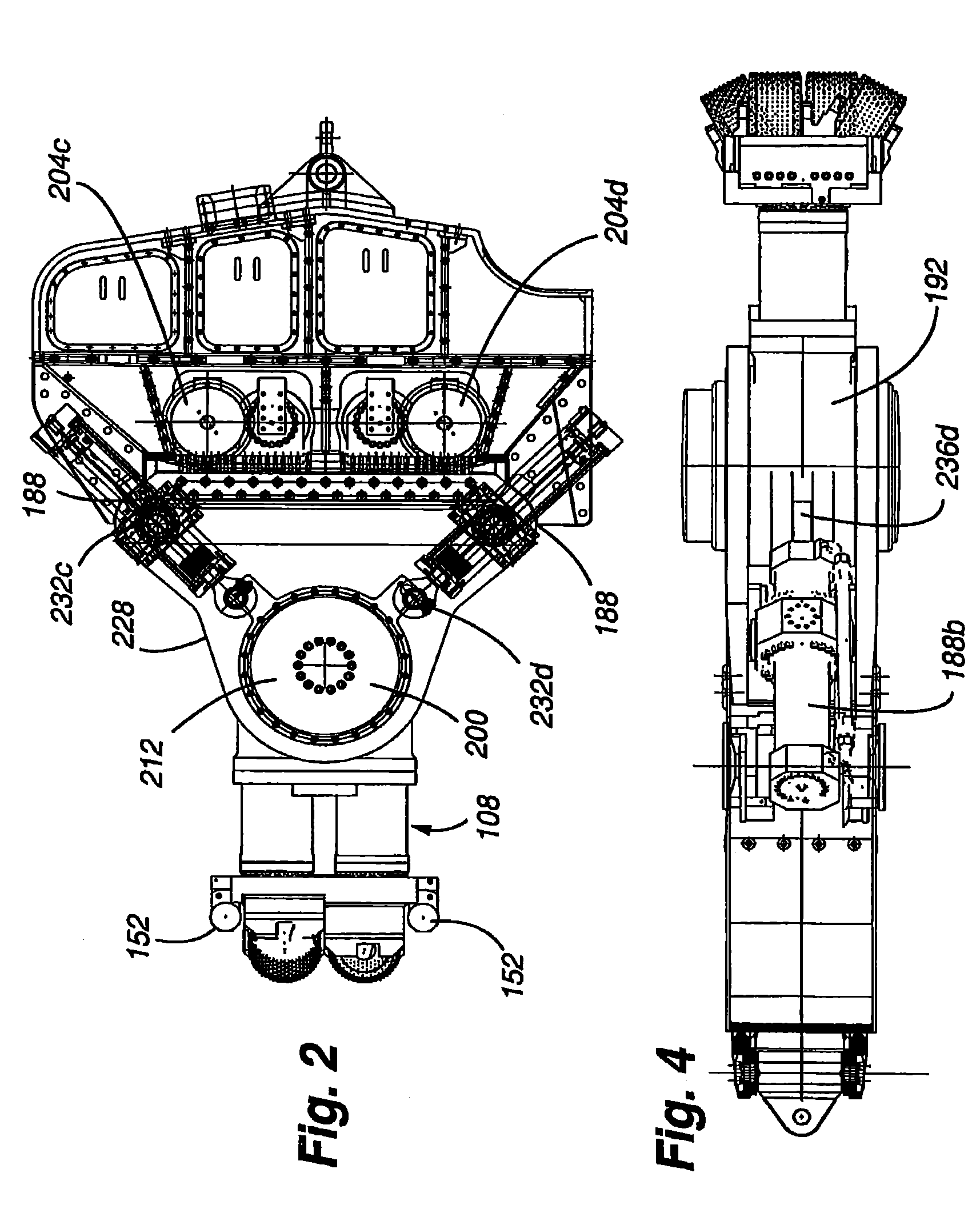
Automated excavation machine
InactiveUS7695071B2Efficiently and effectively excavatingUnderground miningSlitting machinesActuatorExcavator
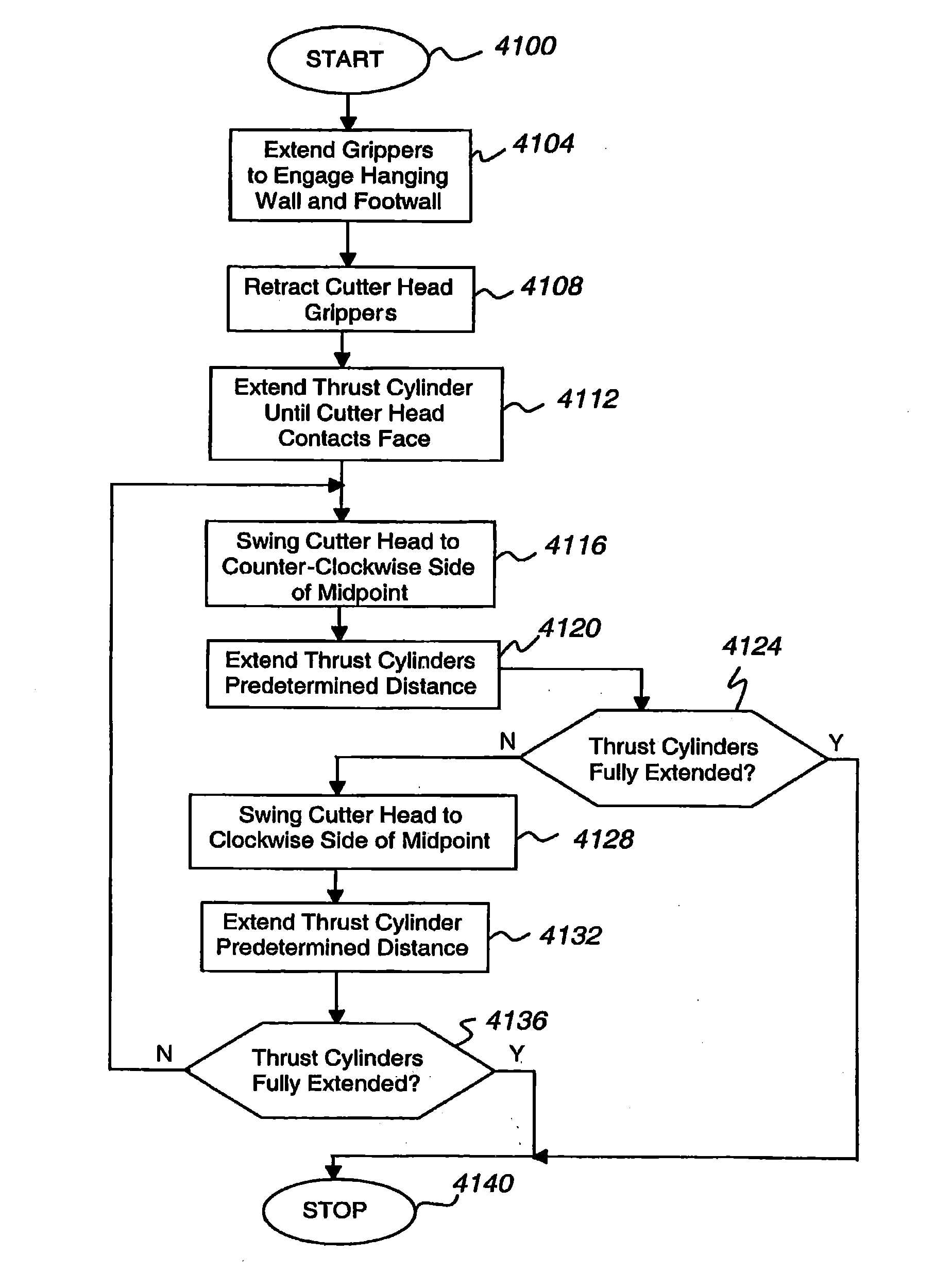
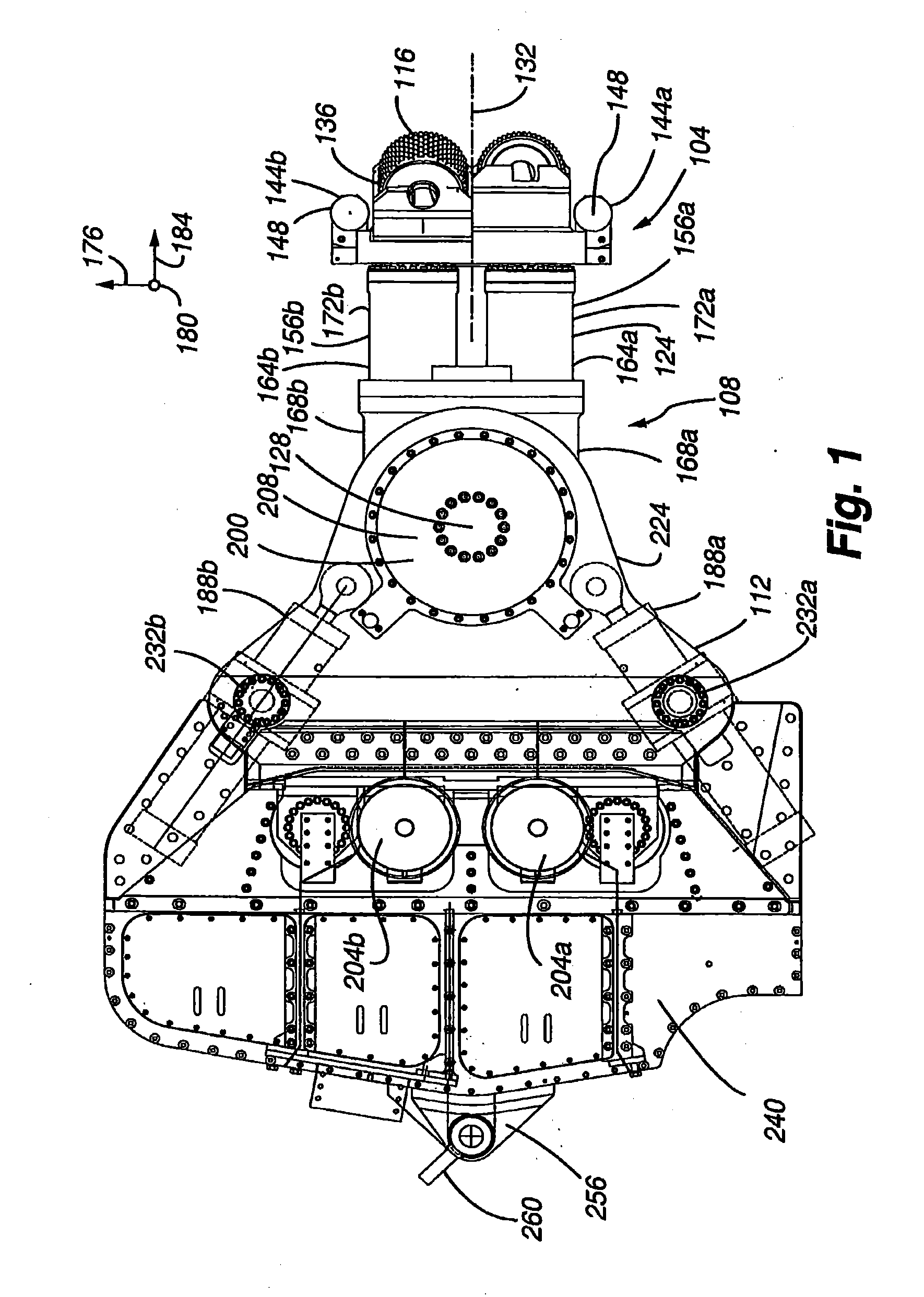
The present invention is directed to an excavator that is operable in manual and automatic modes and uses state machines to effect unit operations, rotationally offset swing actuators to rotate boom and cutter head, a fail safe hydraulic system to maintain gripper pressure in the event of a malfunction of the hydraulic system, differing position and pressure control functions in the hydraulic actuators, a kinematic module to effect pitch and roll adjustments, a cutting face profile generator to generate a profile of the excavation face, and an optimization module to realize a high degree of optimization of excavator operation.
Owner:MIN OF NATURAL RESOURCES CANADA
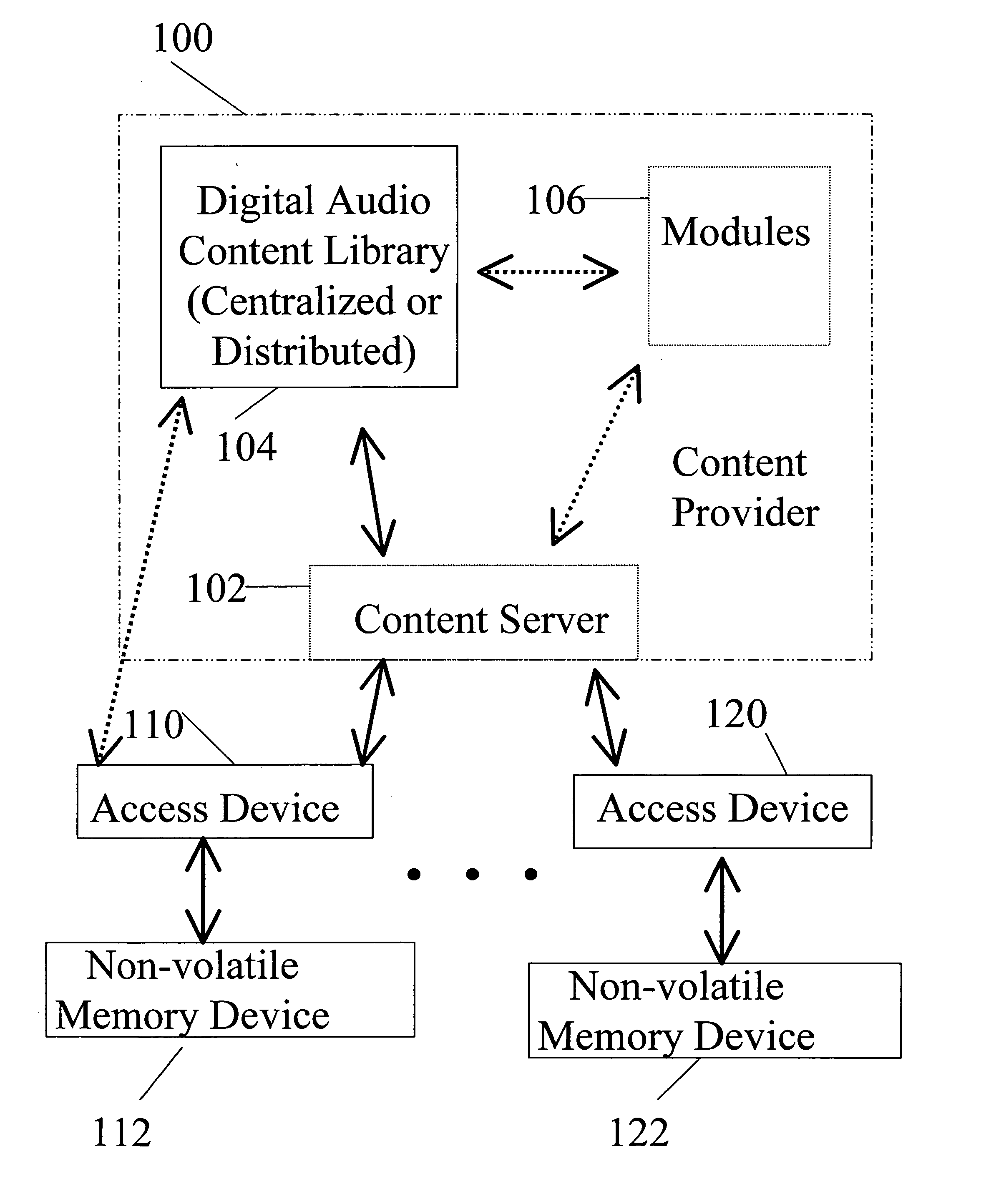
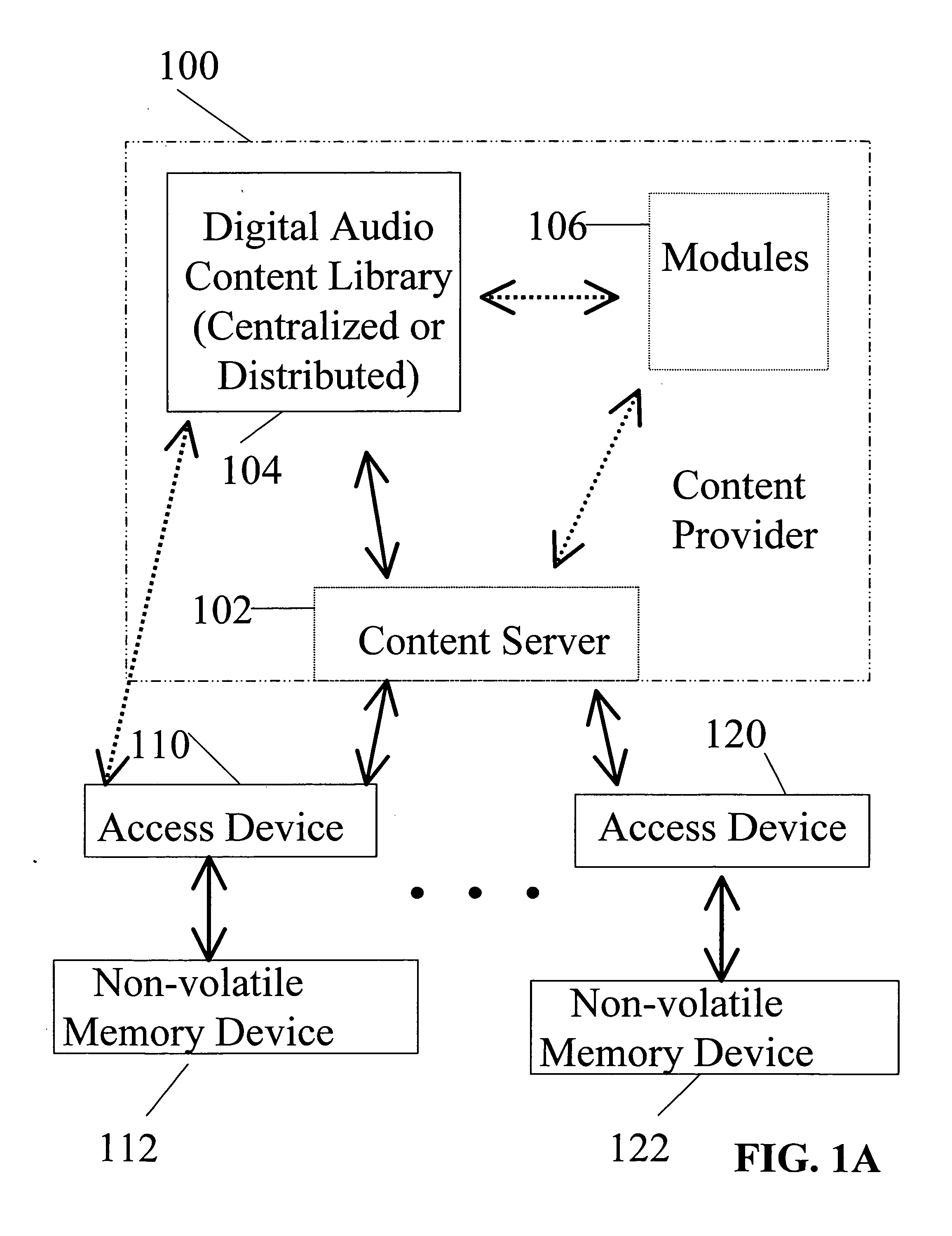
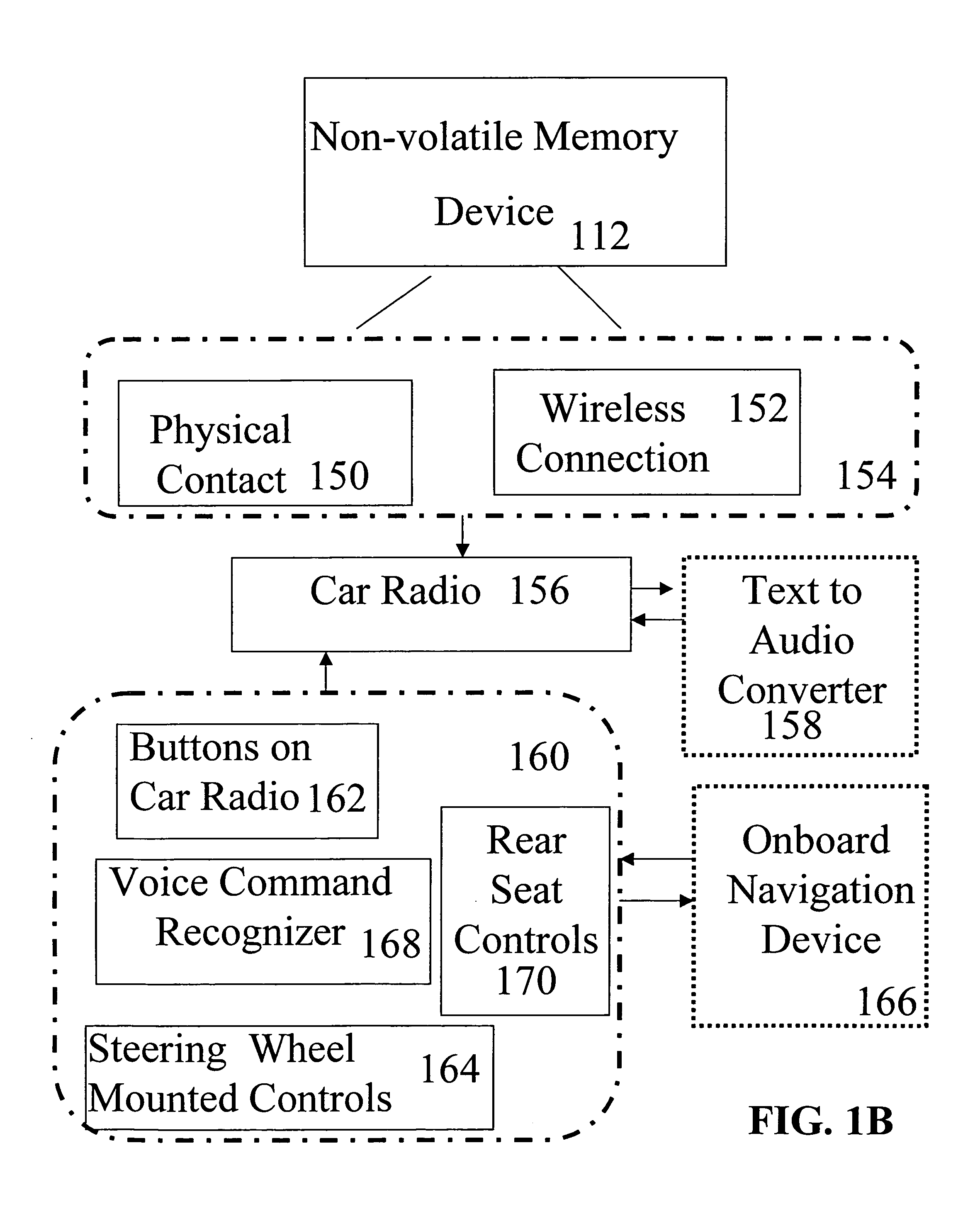
Playback of downloaded digital audio content on car radios
InactiveUS20060029109A1Metadata audio data retrievalTime-division multiplexSteering wheelEngineering
Digital audio content is delivered to a non-volatile memory device, operatively connected to a car radio mounted in a motor vehicle, and played back using a playback effecter mounted in the motor vehicle. Exemplary playback effecters include but are not limited to buttons contained within the car radio, rear seat audio controls, voice command recognizers, and playback effecters physically mounted to a steering wheel of the motor vehicle. A car radio capable of generating speech from digital text content is disclosed. According to some embodiments, digital text content is delivered to the non-volatile memory device, and played back using the car radio capable of generating speech from digital text content.
Owner:SANDISK IL
Integrated multi-format audio/video production system
InactiveUS20080030614A1Improve compatibilityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoMass storage
Owner:SCHWAB BARRY H +1
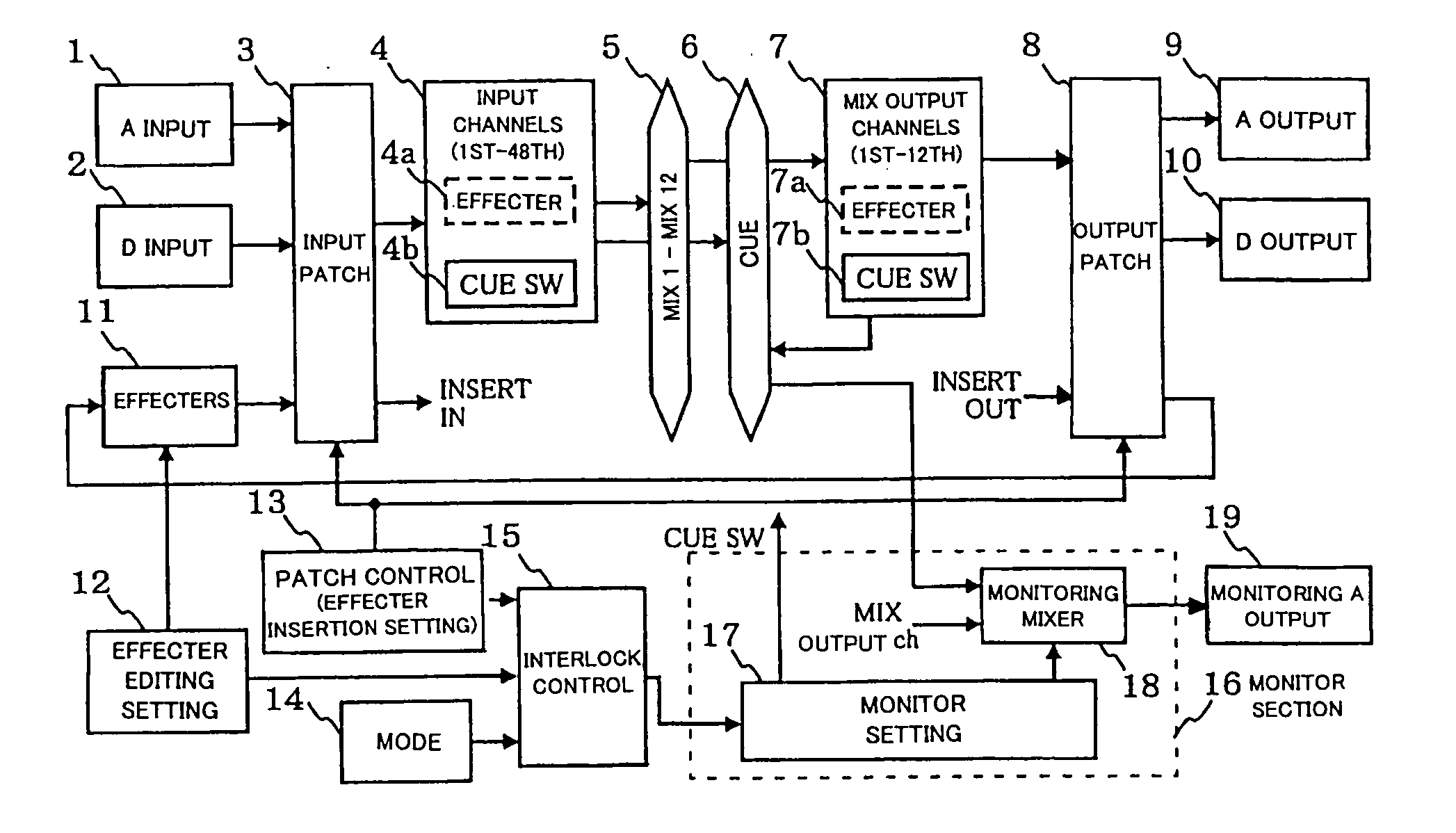
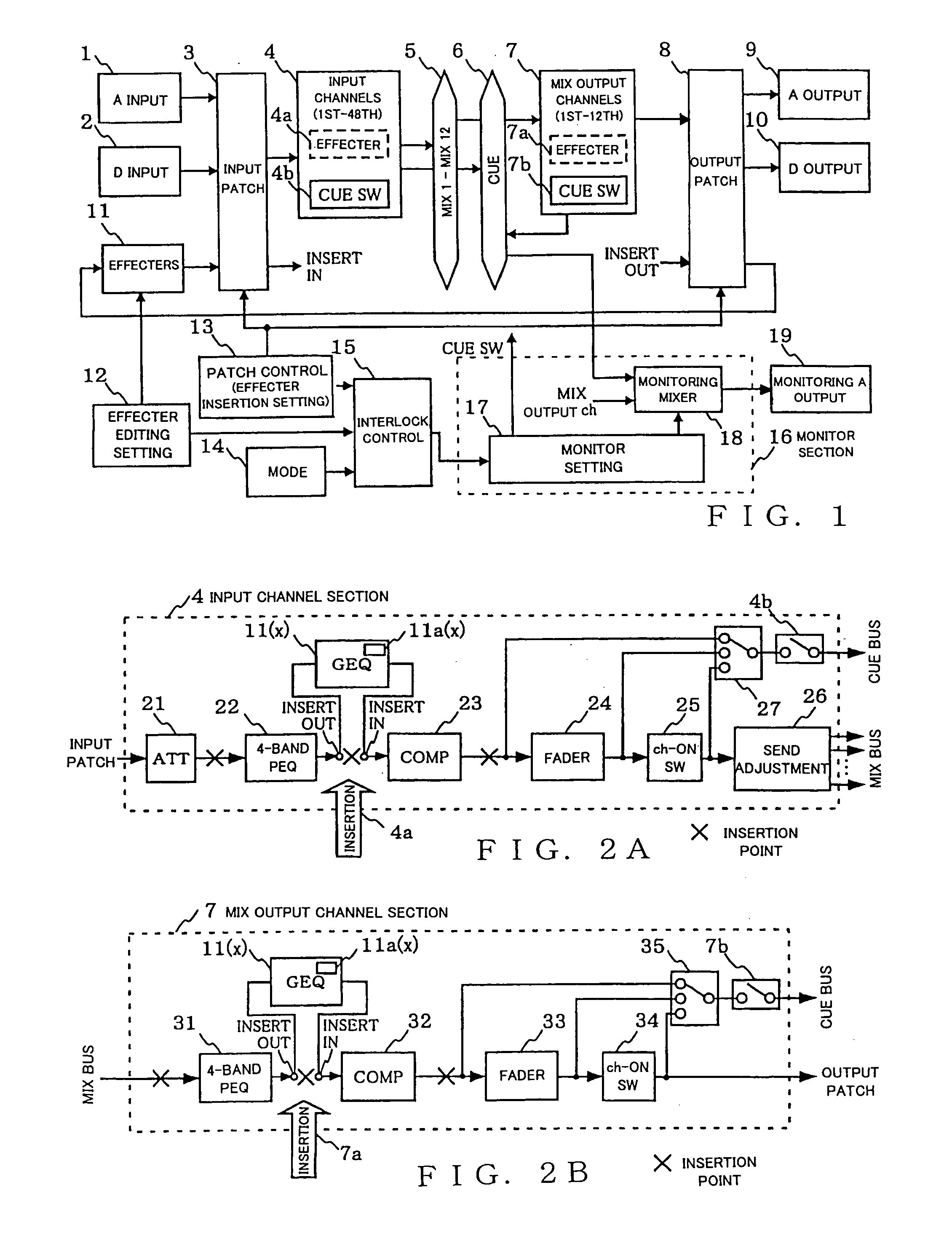
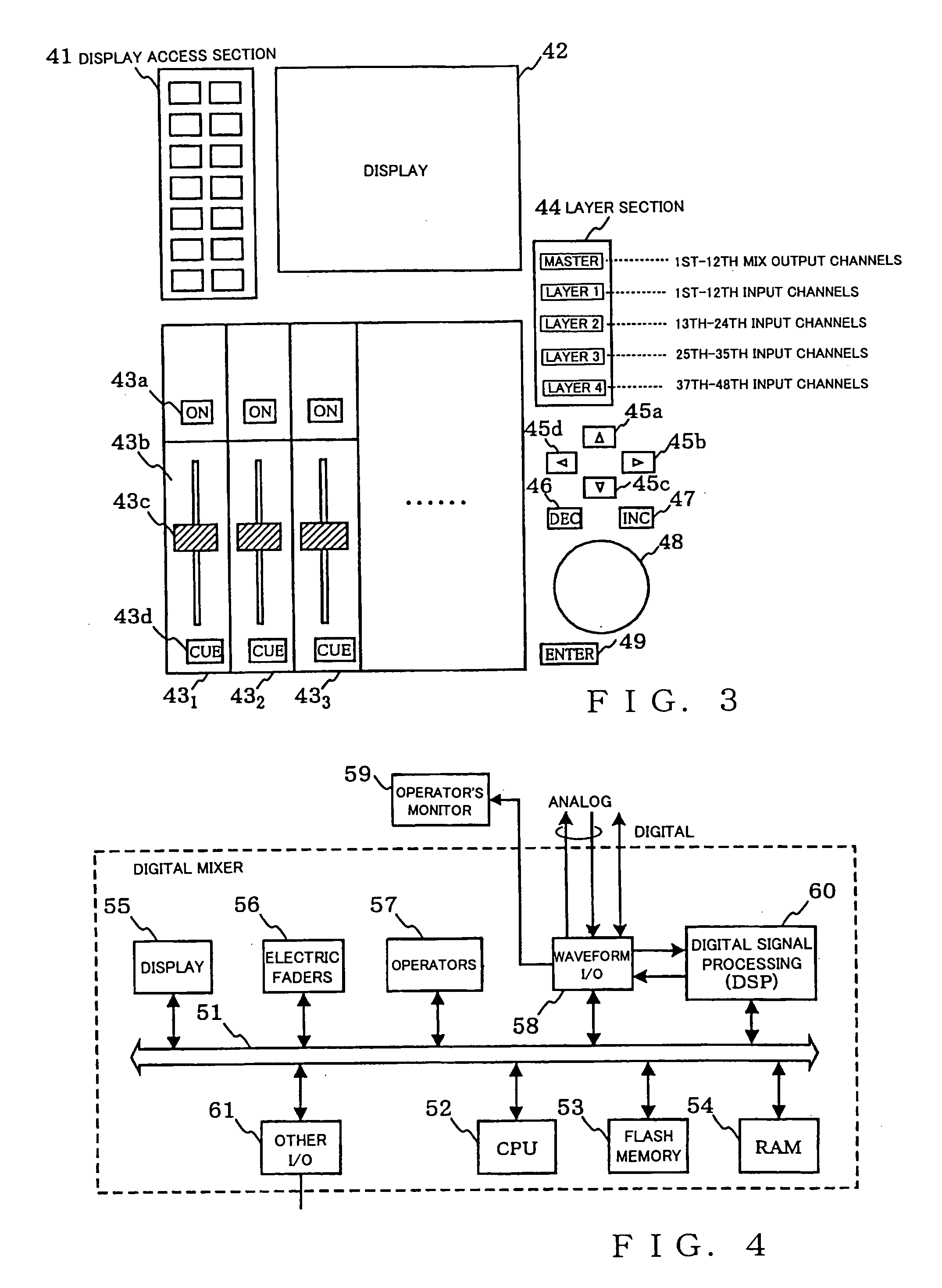
Digital mixer apparatus and editing method therefor
ActiveUS20060015198A1Operation is necessaryAvoid changeElectrophonic musical instrumentsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsEngineeringExecution control
Mixer apparatus includes: a plurality of input channels, mixing buses and output channels; a monitor section that outputs, for a monitoring purpose, signals of one or more of the channels selected in response to monitoring selecting operation; and a plurality of effecters. For each of the plurality of effecters, setting is performed to insert the effecter in a designated one of the input or output channels, to allow the inserted effecter to be used in the designated channel. The mixer also permits editing of a selected one of the effecters while causing an editing screen for the selected effecter to be displayed. When any one of the effecters has been selected for editing while the mixer is set in the interlock mode, control is performed to automatically output, for the monitoring purpose, the signal of the channel having the selected effecter inserted therein.
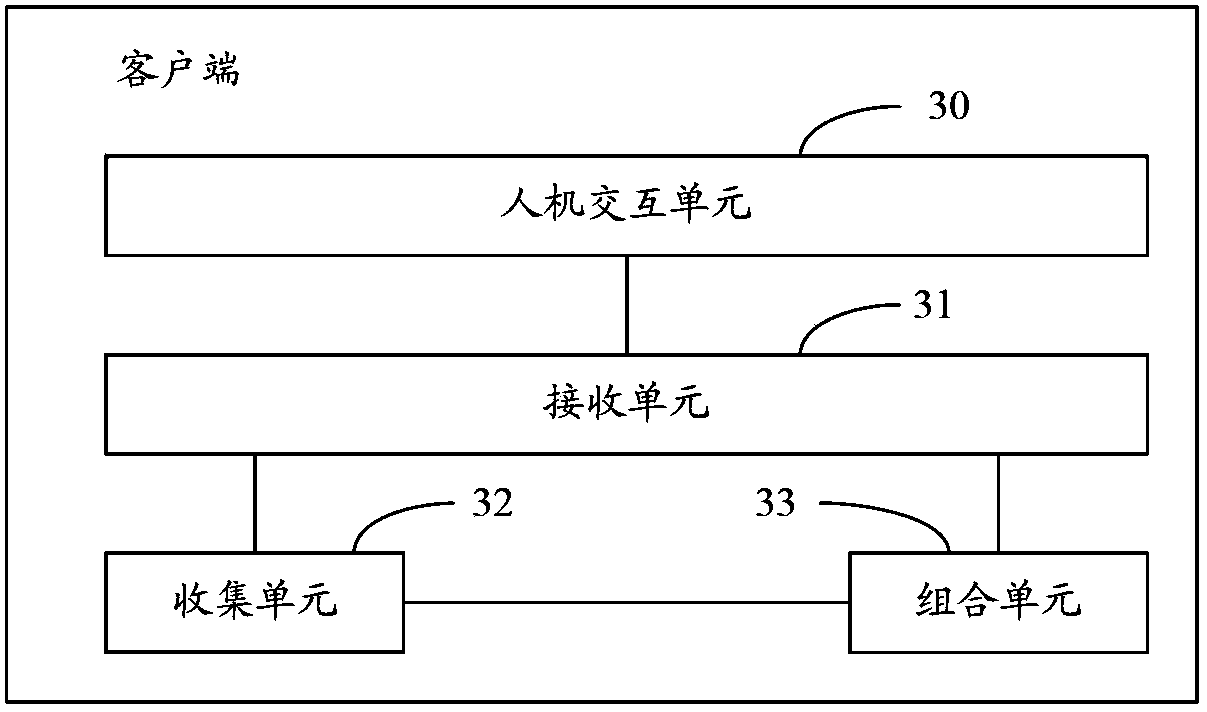
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
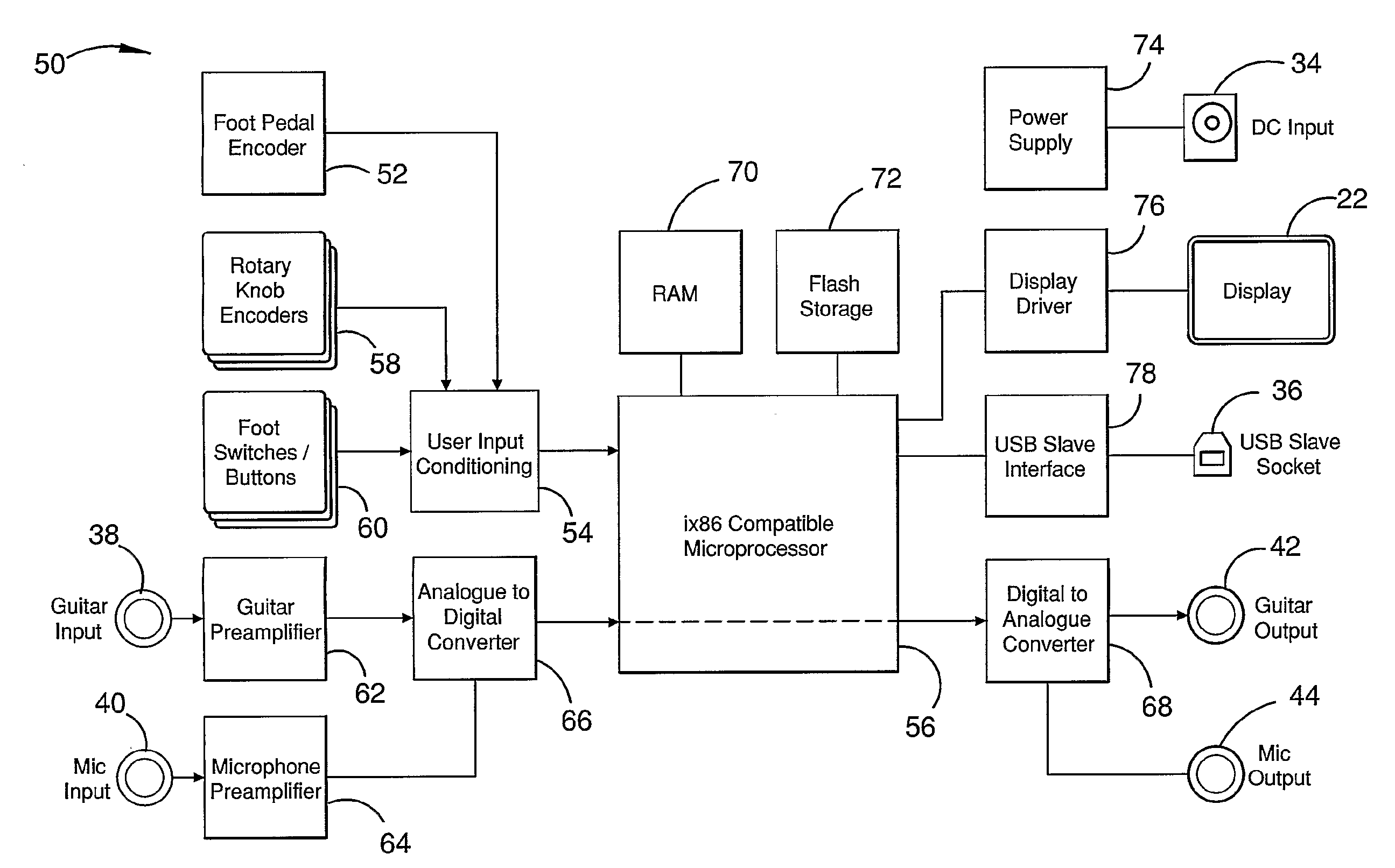
Foot-Operated Audio Effects Device
InactiveUS20100269670A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsLinear/angular speed measurementMass storageAudio frequency
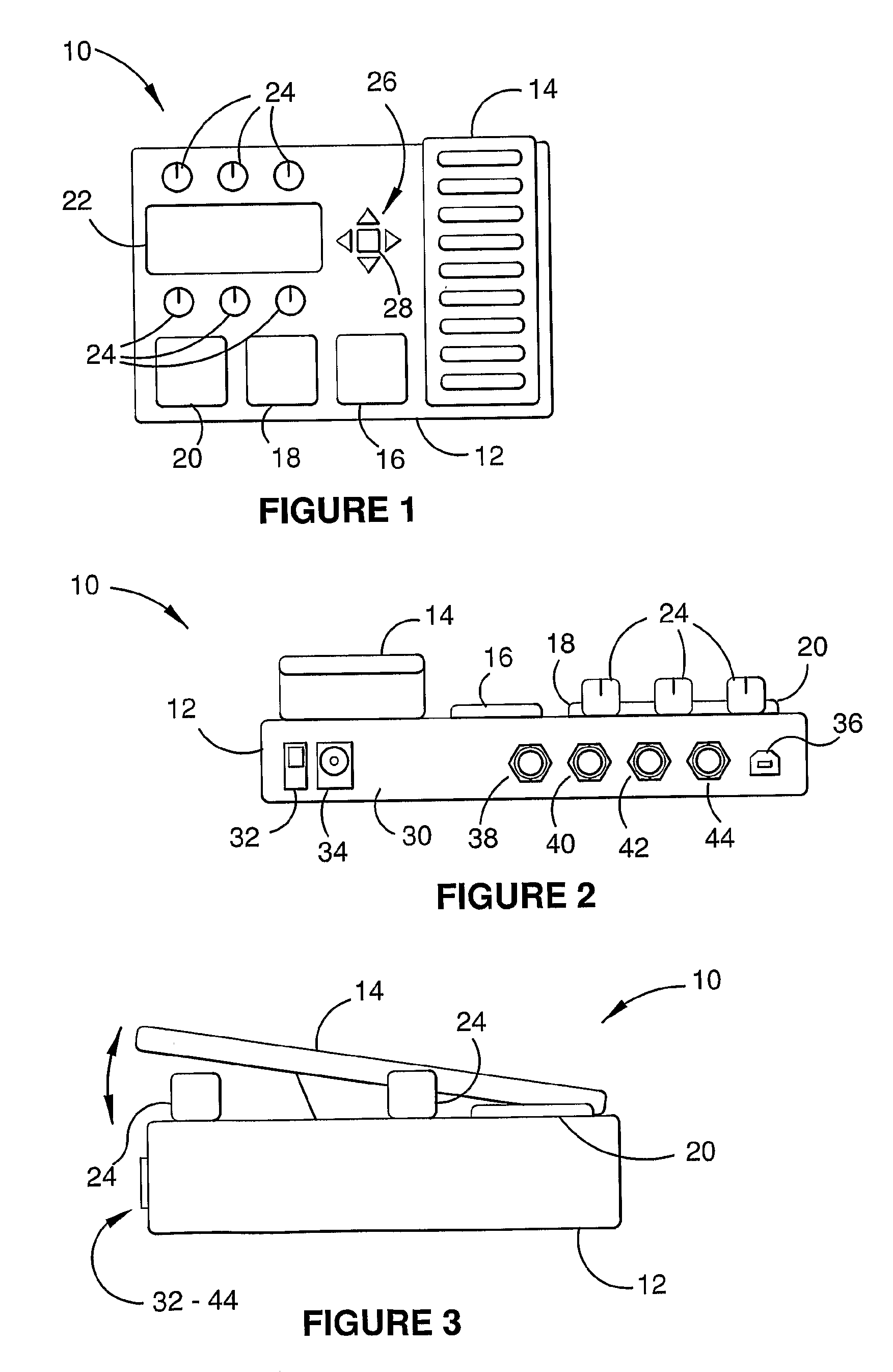
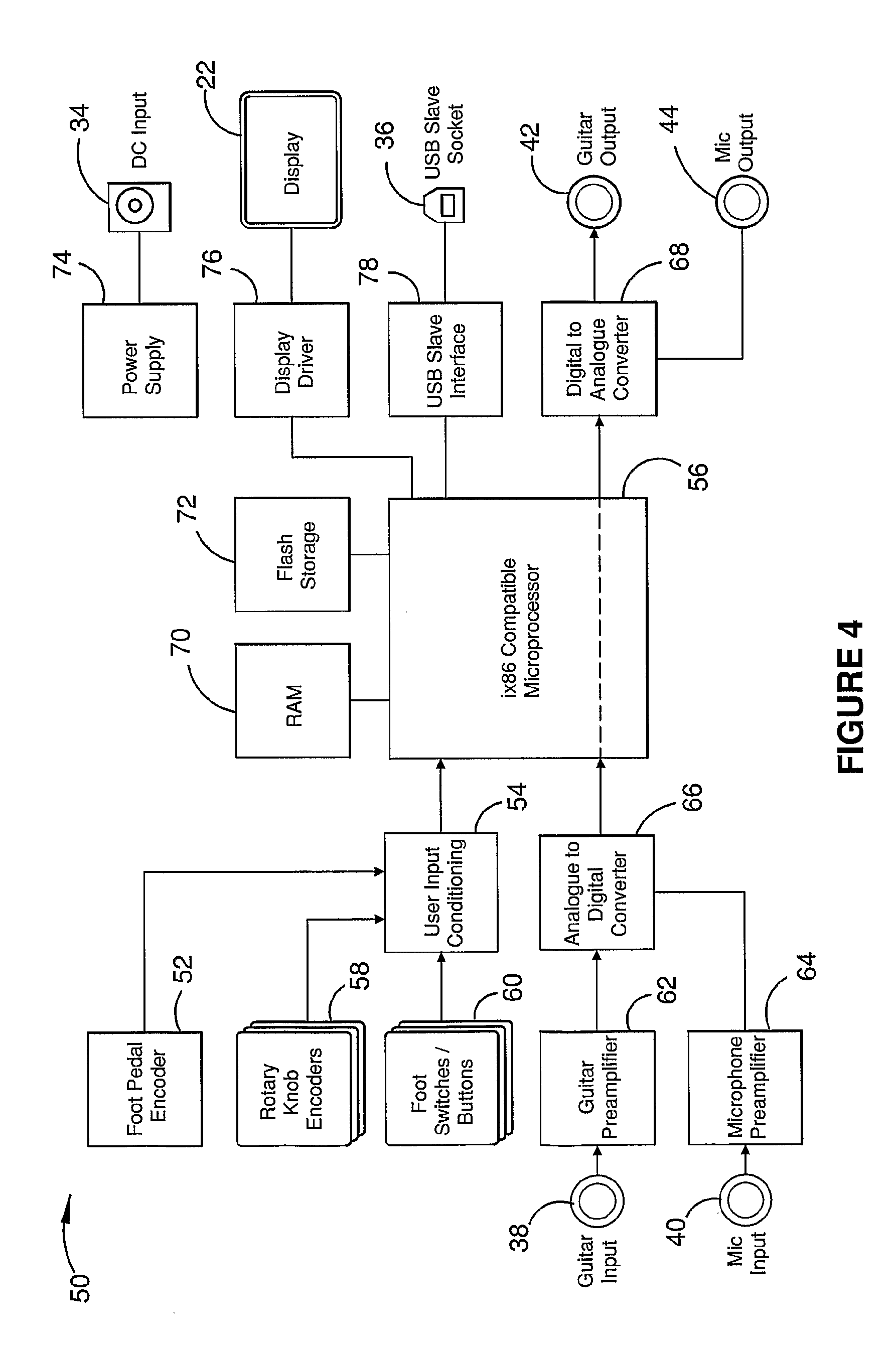
A foot-operated audio effects device (10) receives, stores and operates at least one software audio effect plug-in (86). At least two of the audio effect plug-in (86) may be designed to operate under different operating systems. The device (10) may receive multiple audio input streams (38, 40). Users can control at least one parameter of the audio effect plug-ins (86). The device (10) may include a mass storage device (72) which stores audio which has been generated within the device (10). In use, the device (10) may be connected to a computer (110) and software audio effect plug-ins (86) transferred to and stored in the device (10). The computer (110) may be used to configure parameters of the audio effect plug-in (86). Those parameters may be stored within the computer (110).
Owner:VFX SYST
Displaying device and method thereof
ActiveUS8388165B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsLighting elementsDisplay deviceComputer science
Owner:ZHANG YUDONG
Method for performing virtual makeup by using computer program and makeup simulation program
InactiveCN102184108APrecise positioningReduce participationSpecific program execution arrangementsComputer graphics (images)Computer module
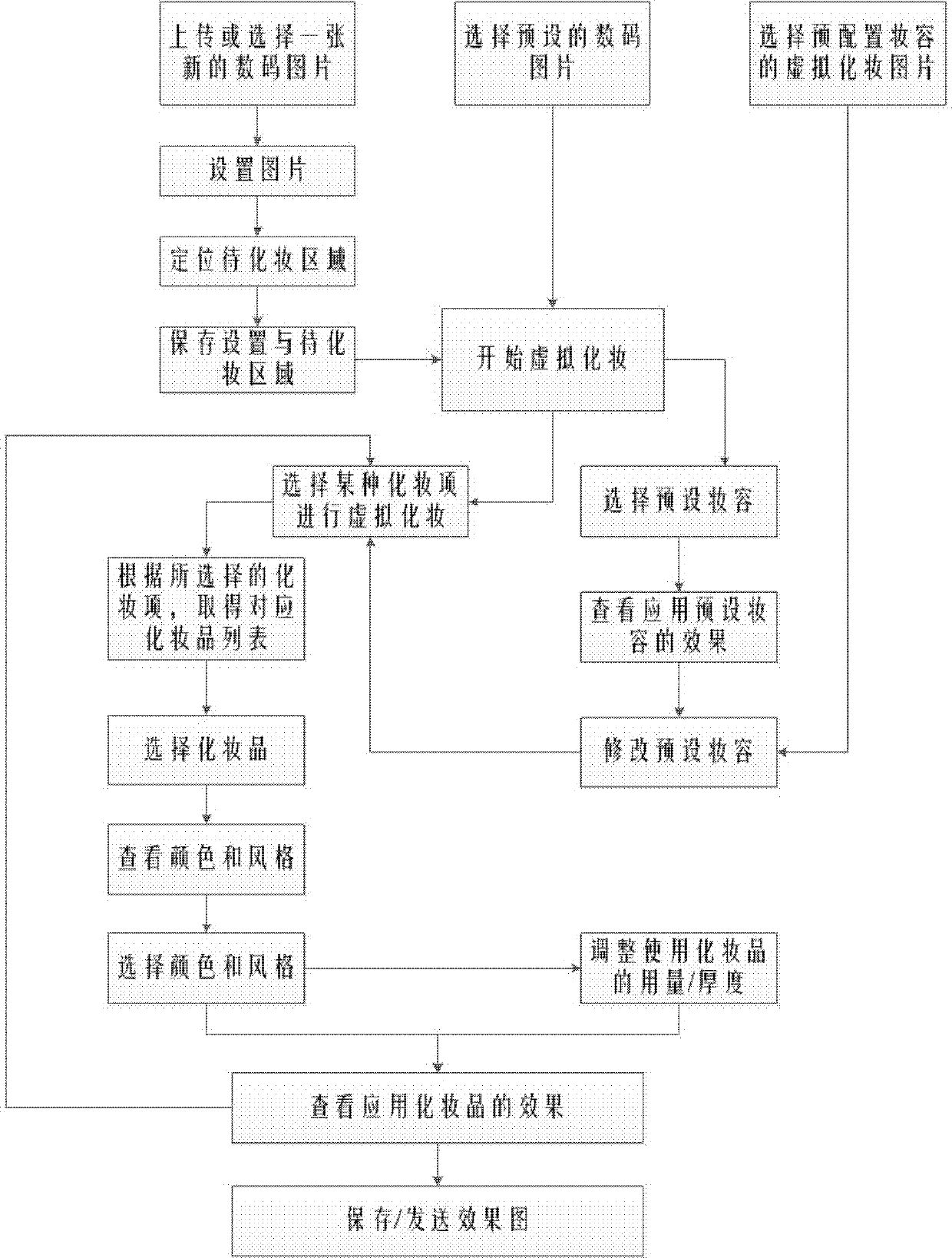
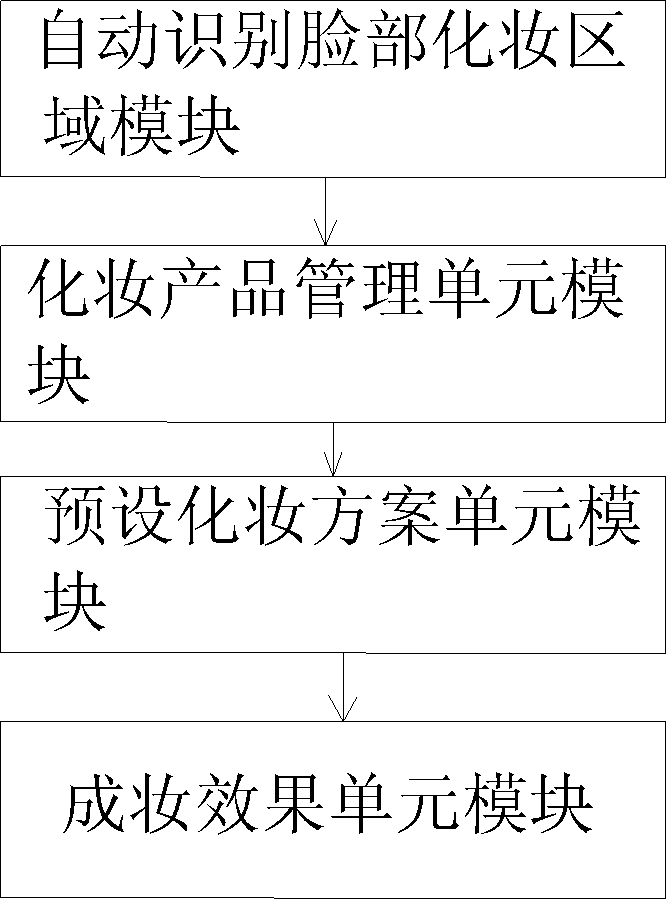
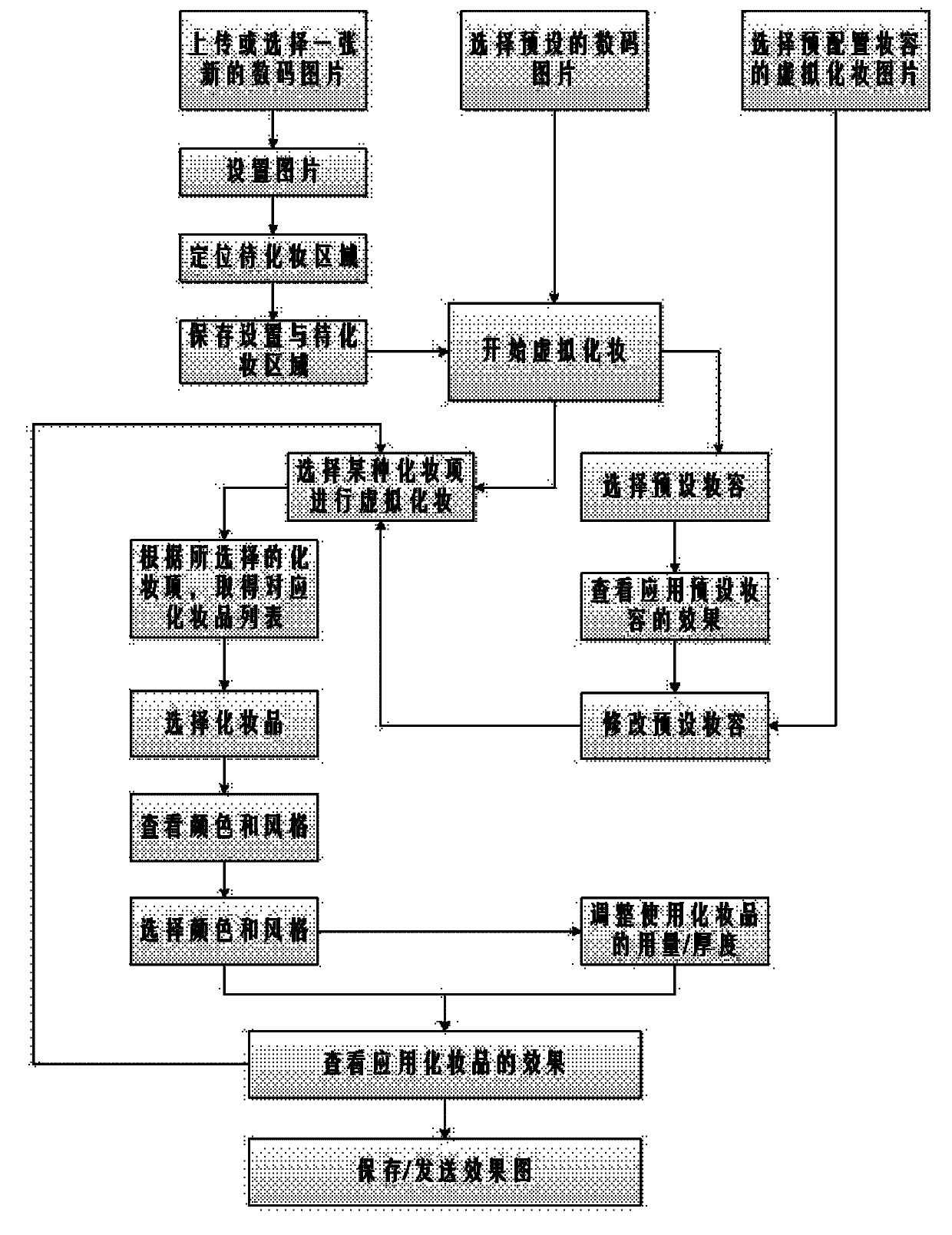
The invention discloses a method for performing virtual makeup by using a computer program and a makeup simulation program. The makeup method comprises the following steps of: 1, uploading or selecting a preset digital picture to be made up in a computer; 2, after finishing selection of the digital picture to be made up, positioning an area to be made up, starting a module which is arranged in the computer and used for automatically recognizing areas to be made up on the face, selecting the area to be made up, and storing the area to be made up; and 3, uploading or selecting a makeup picture with a makeup model from the computer, and performing virtual makeup on the digital picture to be made up through the makeup simulation program in the computer. The simulation program comprises a module for automatically recognizing areas to be made up on the face, a makeup product management unit module, a preset makeup scheme unit module and a makeup effect unit module.
Owner:JIANGTIAN NETWORKS CHENGDU
Wireless karaoke microphone headset
InactiveCN106028208AImprove sharing effectImprove the karaoke experienceEarpiece/earphone mechanical/electrical switchesTransducer circuitsEngineeringHeadphones
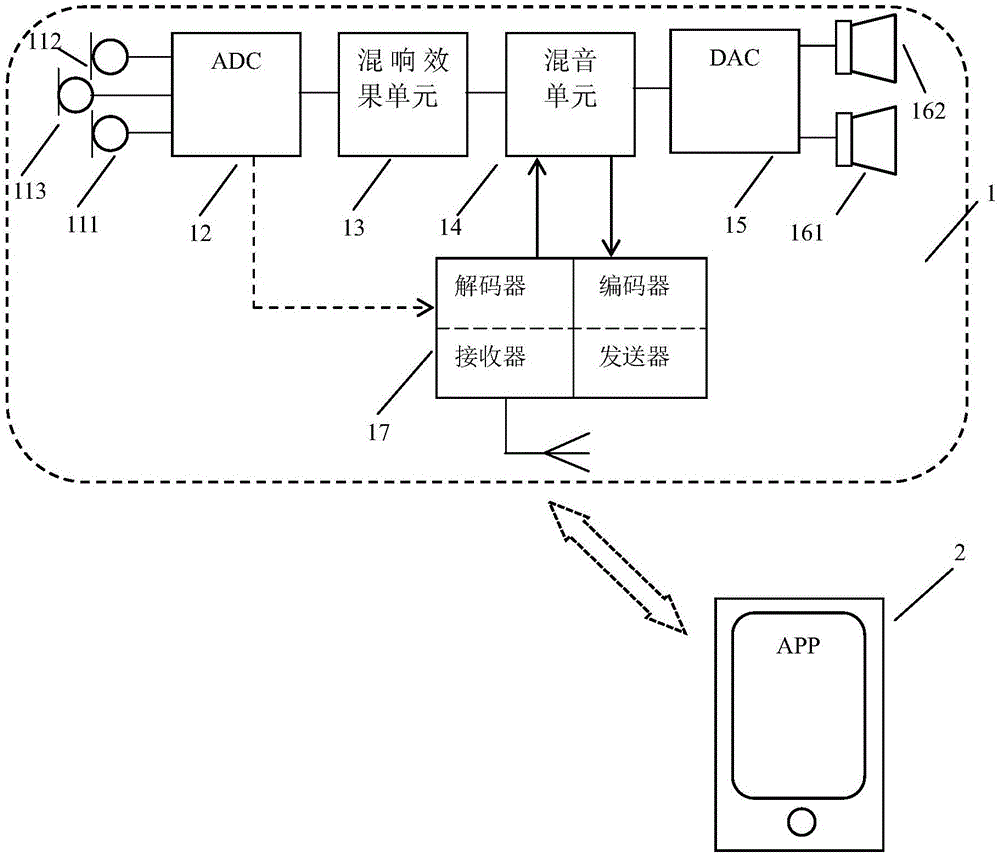
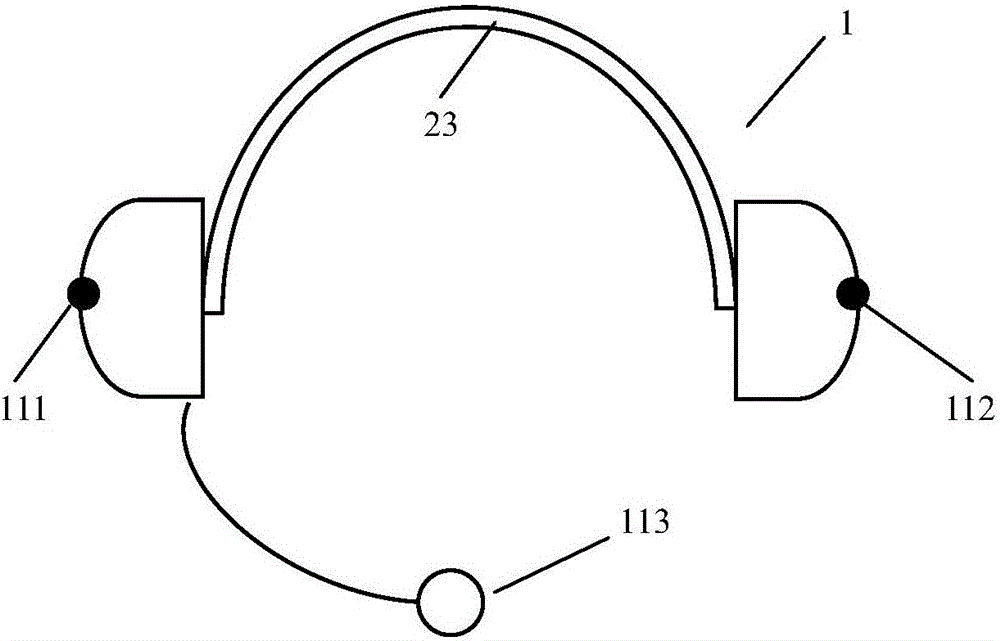
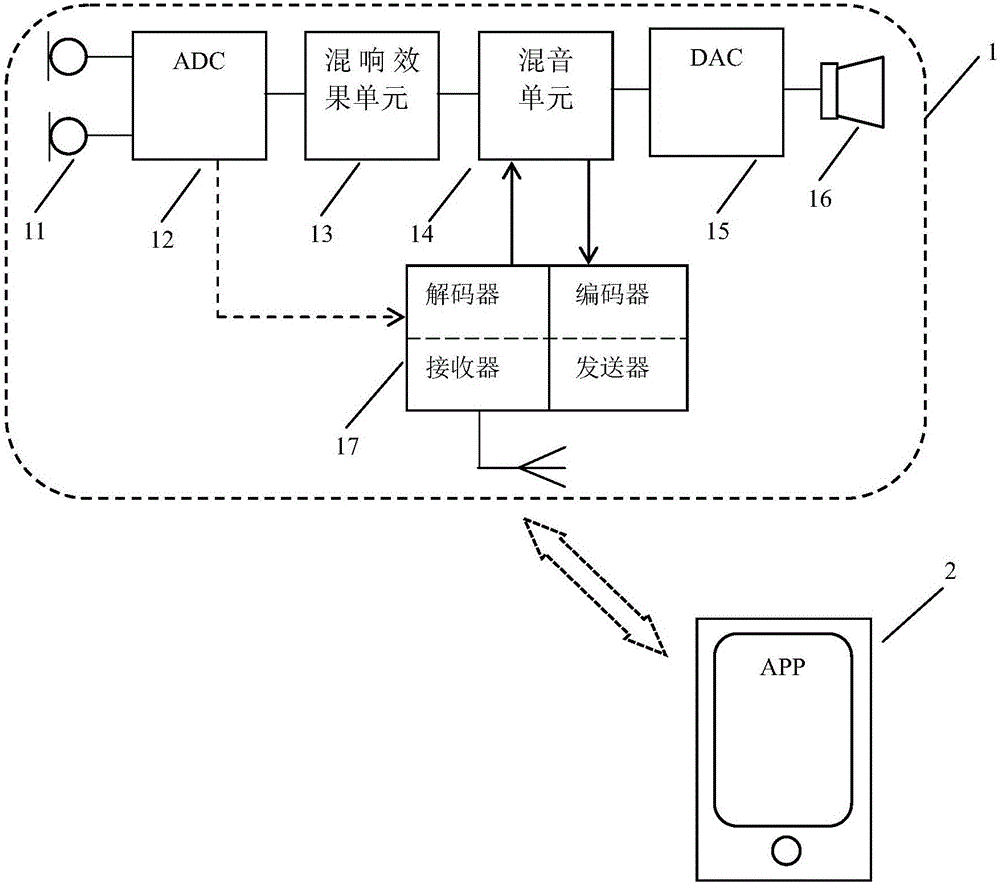
The invention discloses a wireless karaoke microphone headset which comprises a left microphone, a right microphone, an ADC (analog-to-digital converter), a reverberation effect unit, a sound mixing unit, a DAC (Digital To Analog Converter), a left loudspeaker, a right loudspeaker and a wireless connection unit which are positioned at auricular positions when a user wears the headset. Voice signals picked up by the left and right microphones enter the reverberation effect unit after being subjected to analog-to-digital conversion by the ADC; after carrying out reverberation effect processing on the digital voice signals, the reverberation effect unit sends the digital voice signals to the sound mixing unit; the wireless connection unit receives a music accompaniment signal sent by a mobile terminal and sends the music accompaniment signal to the sound mixing unit; the sound mixing unit mixes the voice signals with the music accompaniment signal and sends a mixed signal to the DAC; after digital-to-analog conversion, sound is output to the user by the left and right loudspeakers; and the headset can send the sound mixed signal, the voice signals or a holographic sound field signal to the mobile terminal in a Bluetooth manner. By the wireless karaoke microphone headset disclosed by the invention, karaoke experience of the user and sharing capacity of high-quality sound an be effectively promoted.
Owner:BEIJING SAIBIN TECH
Automated Excavation Machine
InactiveUS20100109417A1Efficiently and effectively excavatingDisloding machinesUnderground miningEngineeringActuator
The present invention is directed to an excavator that is operable in manual and automatic modes and uses state machines to effect unit operations, rotationally offset swing actuators to rotate boom and cutter head, a fail safe hydraulic system to maintain gripper pressure in the event of a malfunction of the hydraulic system, differing position and pressure control functions in the hydraulic actuators, a kinematic module to effect pitch and roll adjustments, a cutting face profile generator to generate a profile of the excavation face, and an optimization module to realize a high degree of optimization of excavator operation.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN IN RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NATURAL RESOURCES CANADA
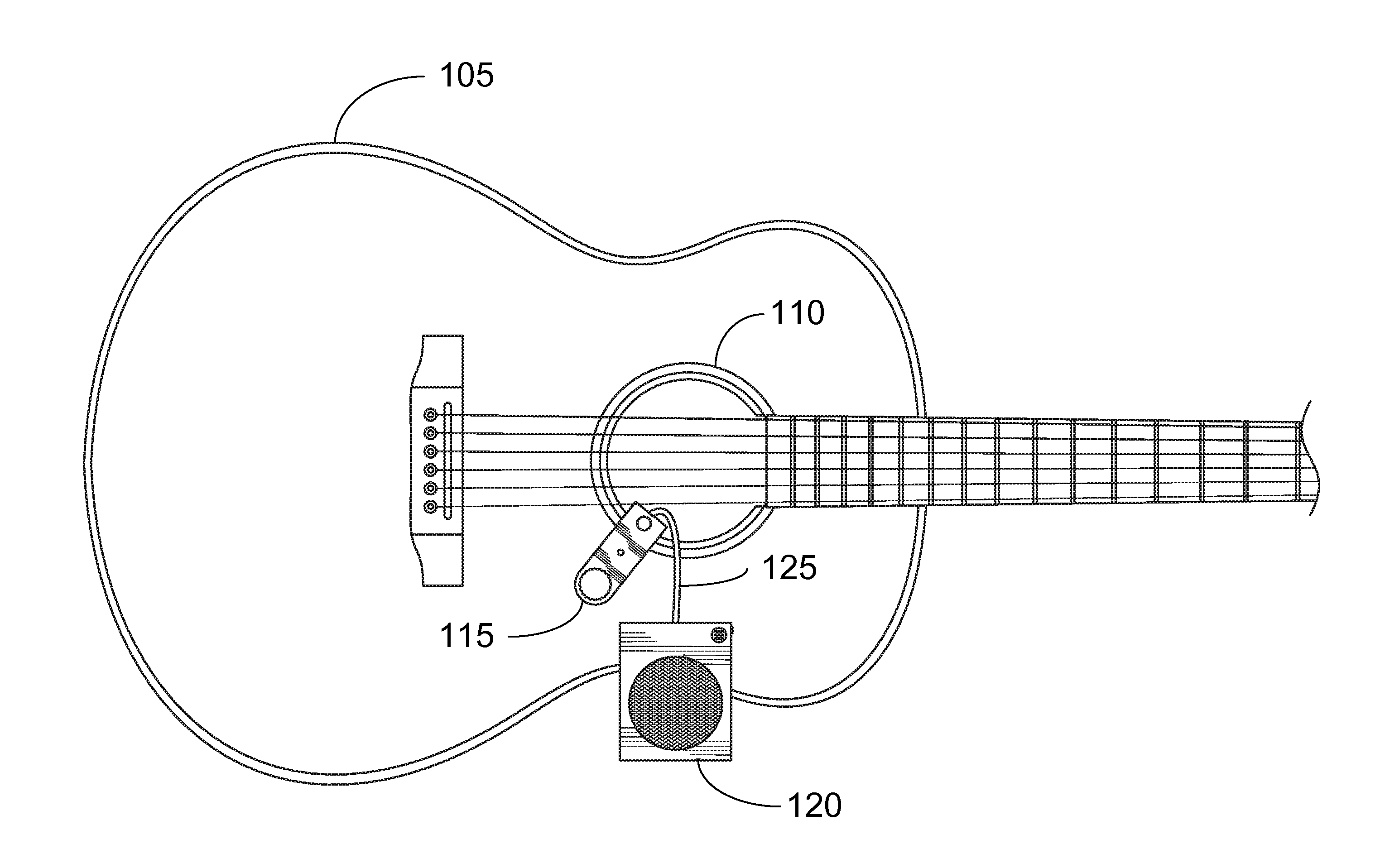
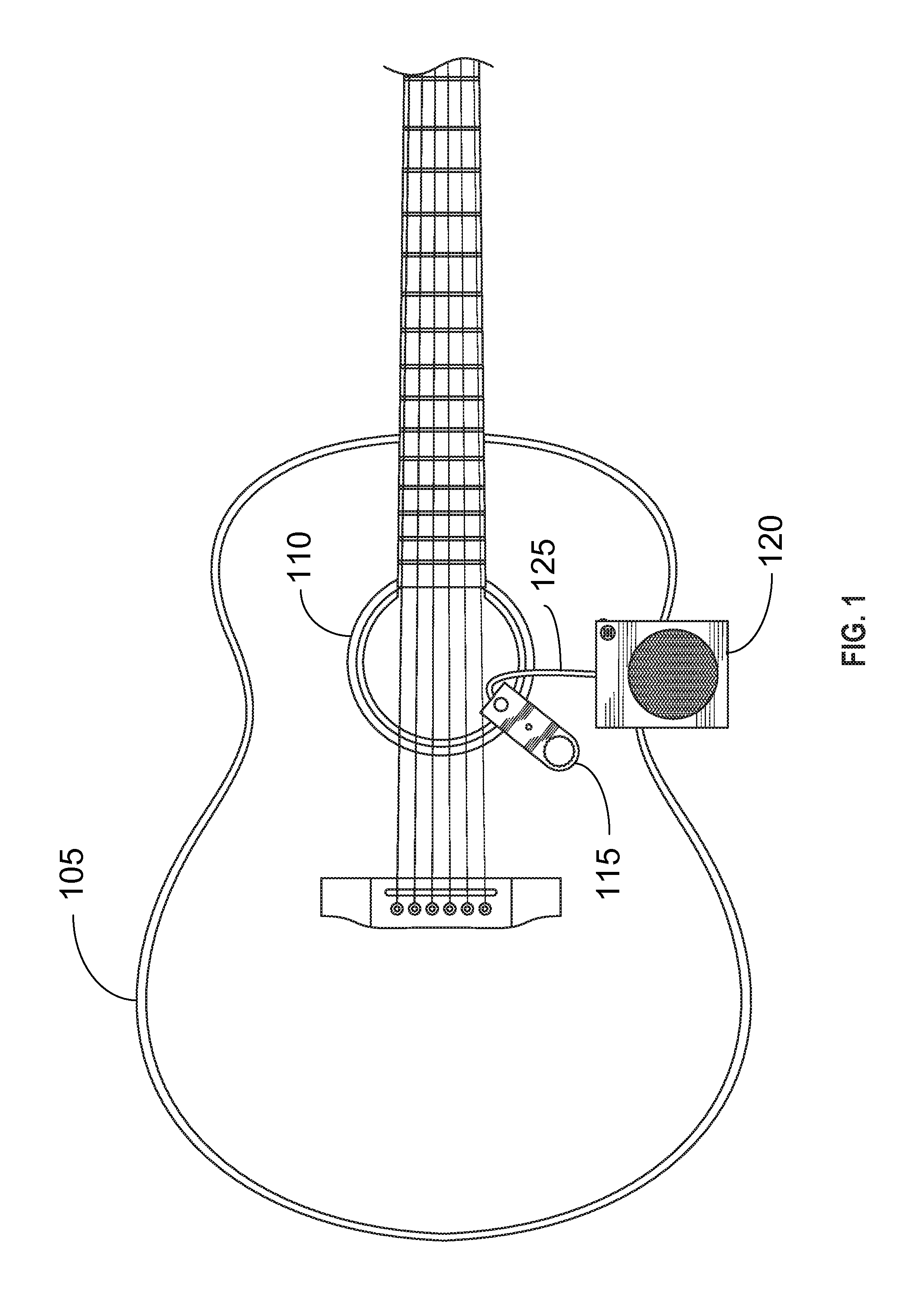
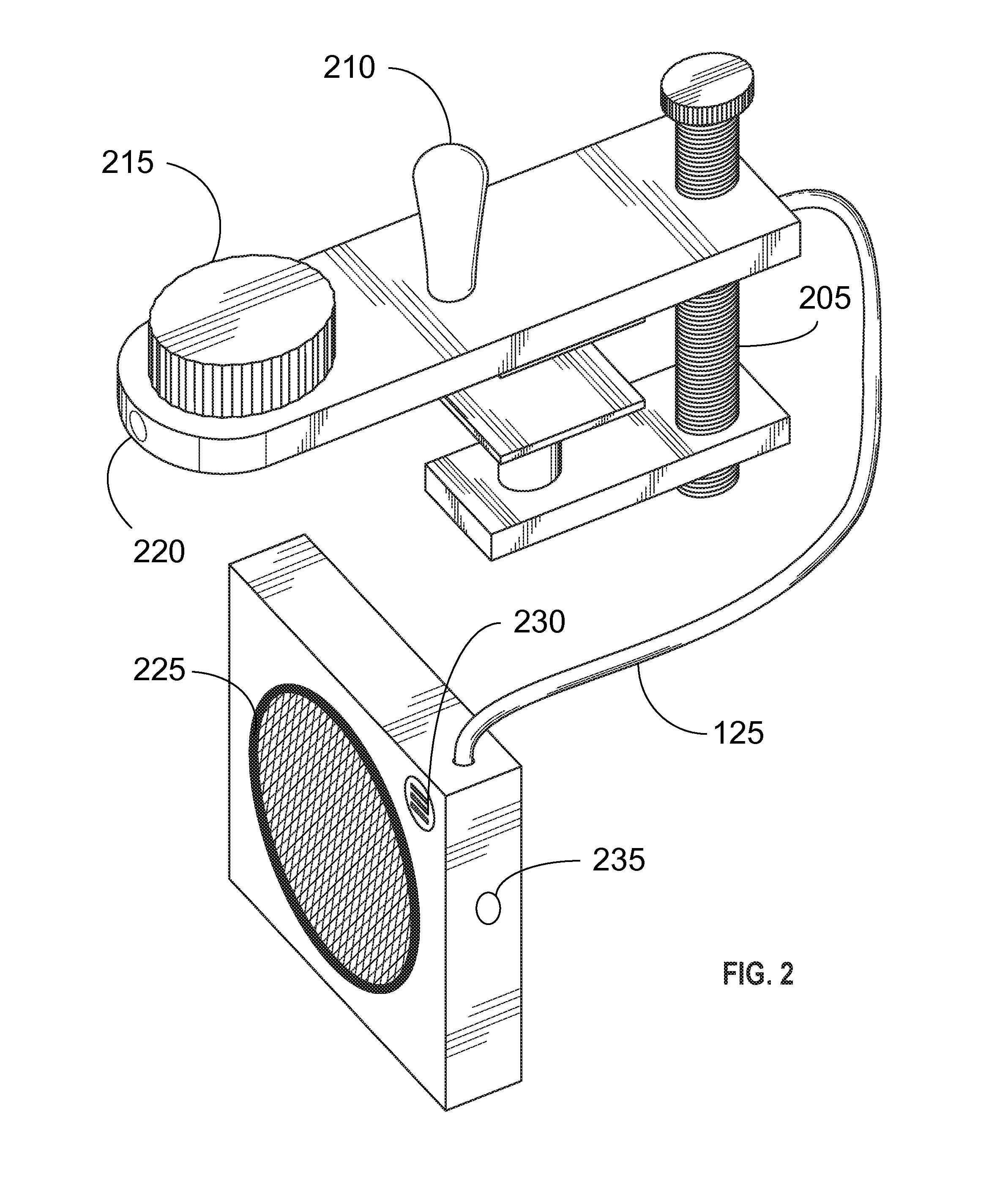
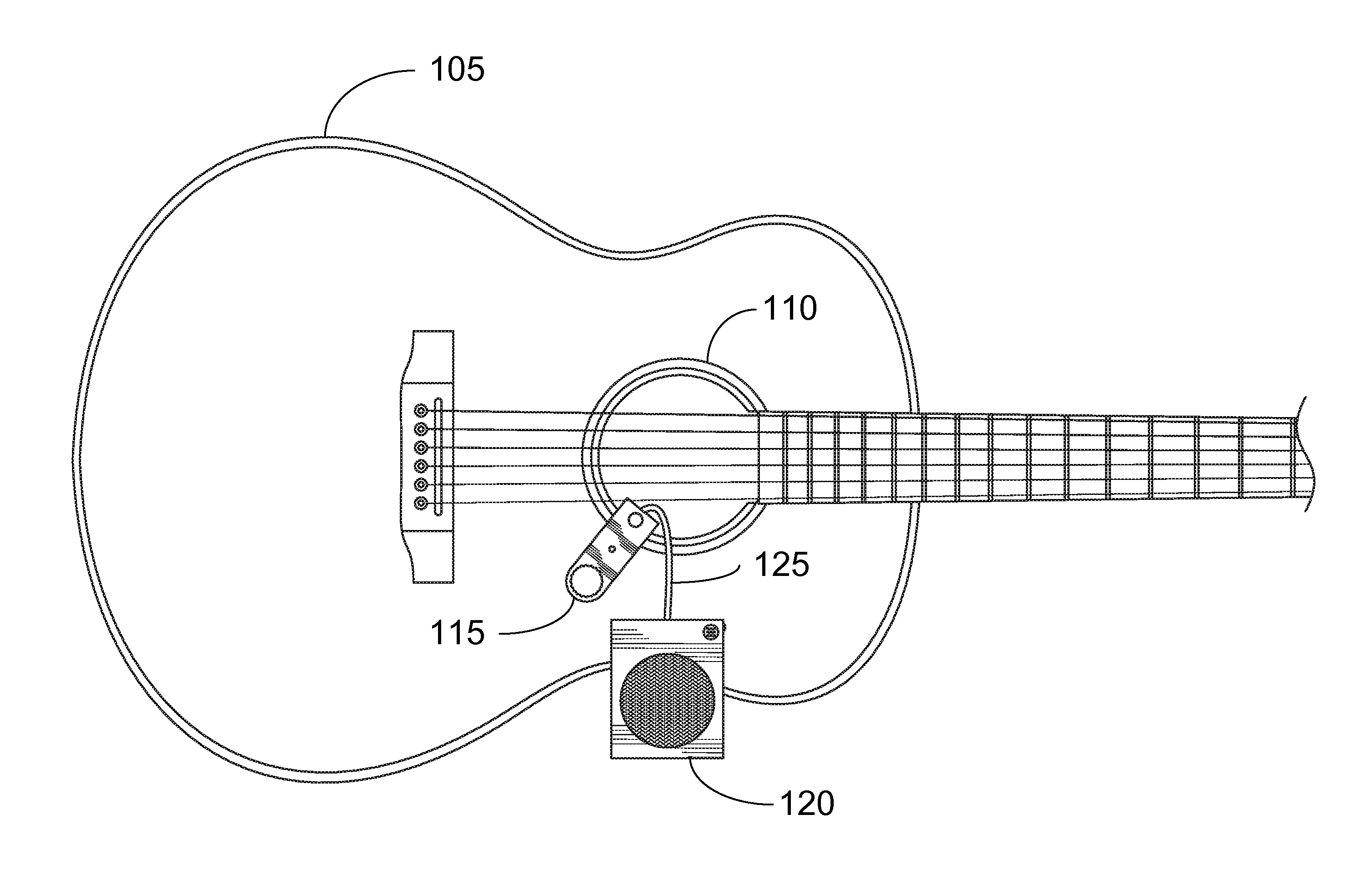
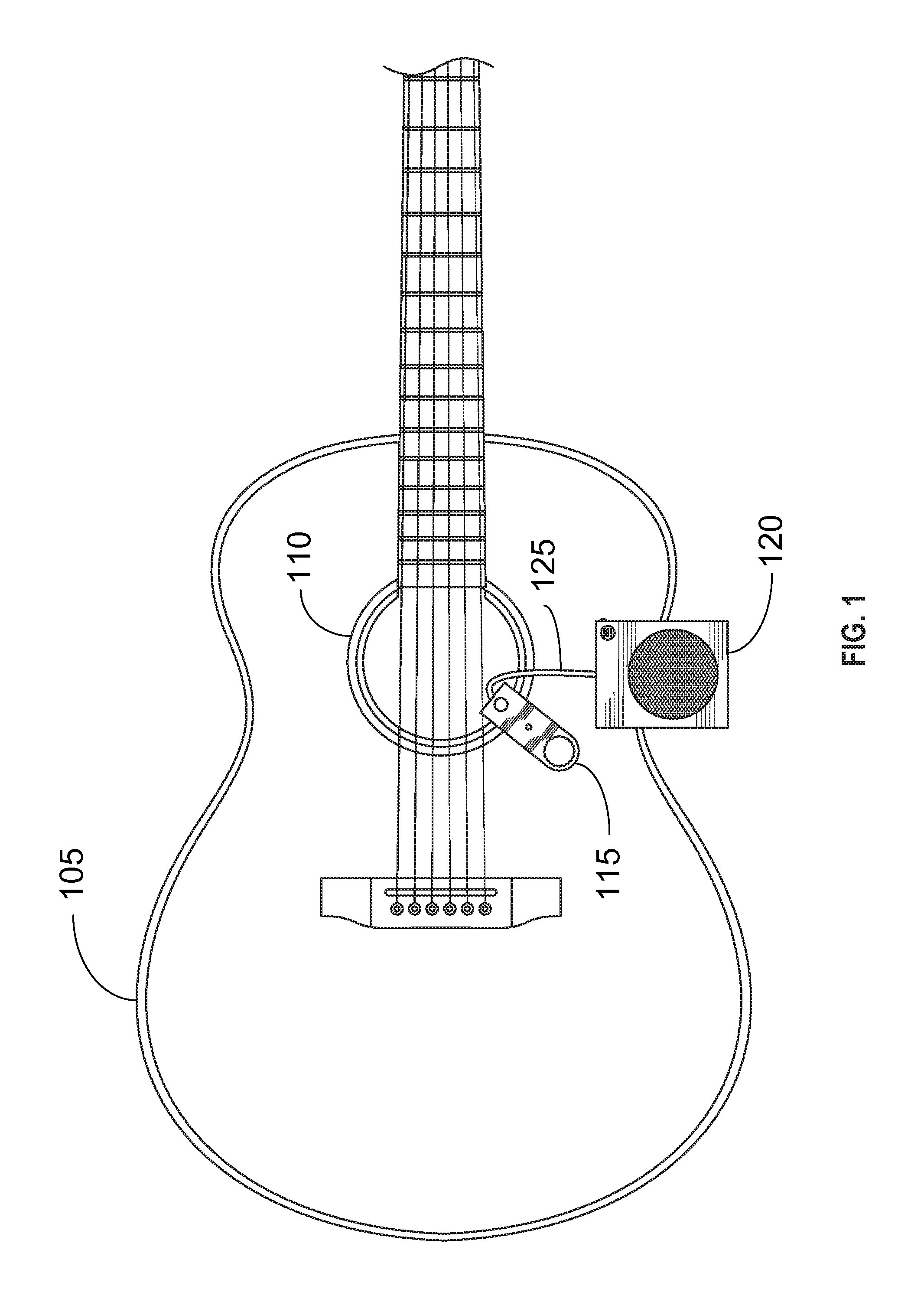
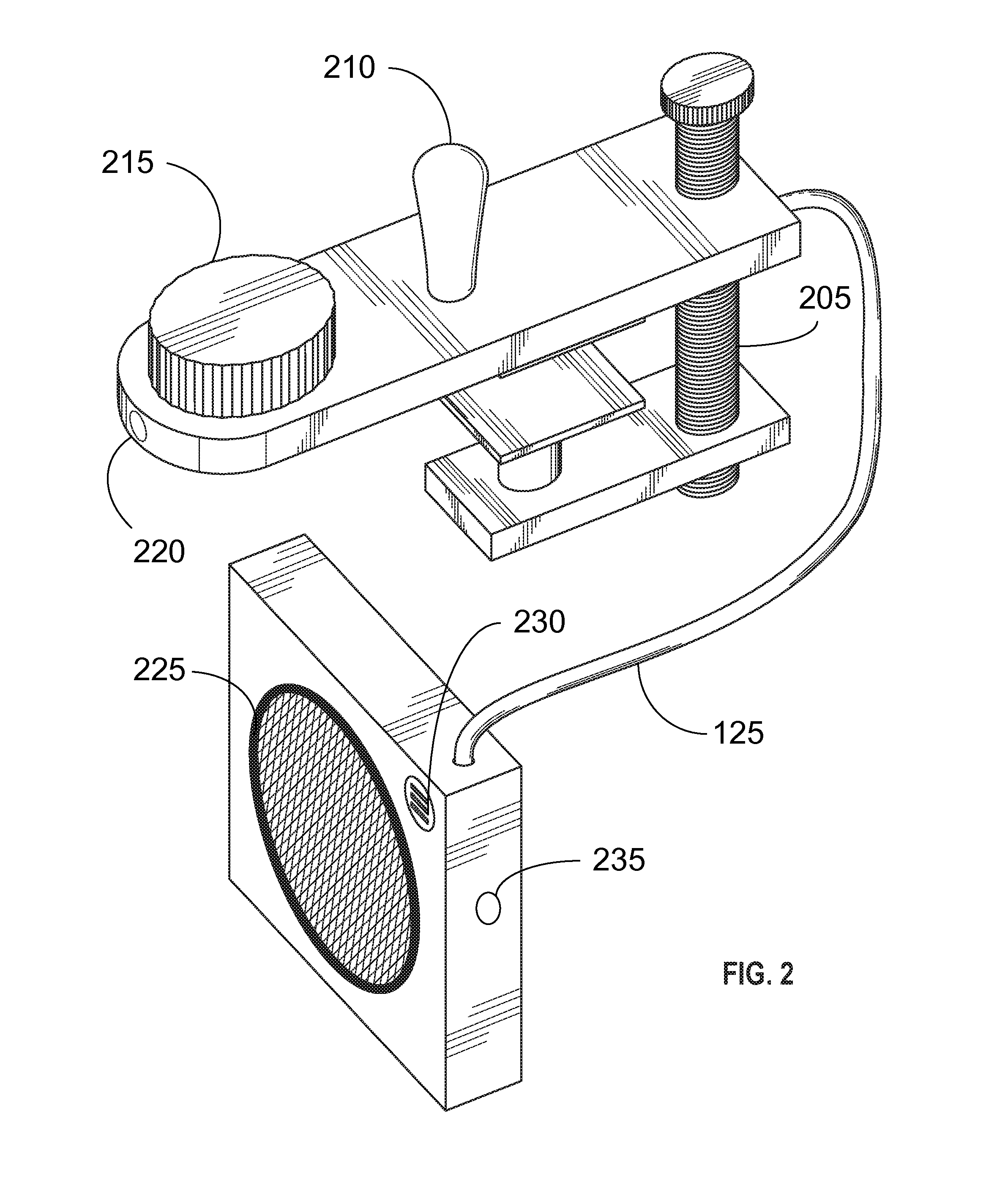
Portable Recording, Looping, and Playback System for Acoustic Instruments
Embodiments of the present invention provide an electronic looping, recording, and playback apparatus. The apparatus may comprise a clamp, enabling the apparatus to be positioned in or on an acoustic instrument, such as an acoustic guitar. The clamp may be used to attach the apparatus to a portion of the acoustic instrument. The apparatus may further comprise, but not be limited to, for example, a speaker, a rechargeable battery, a microphone, a volume knob, an LED indicator light, a switch, and a processing module. The switch may be used to activate the electronic recording, looping, and playback system, much like a pedal in a stompbox configuration.
Owner:INTELLITERRAN
Wireless karaoke microphone
InactiveCN106210943AImprove the karaoke experienceImprove sharing effectMouthpiece/microphone attachmentsEngineeringBluetooth
The invention provides a wireless karaoke microphone which comprises a microphone body, an analog-digital conversion (ADC) unit, a reverb effect unit, a sound mixing unit, a digital-analog conversion (DAC) unit, a monitoring playback unit and a wireless connection unit, and is characterized in that a voice signal collected by the microphone body enters the reverb effect unit after being subjected to analog-digital conversion of the ADC, the digitalized voice signal is sent to the sound mixing unit after being subjected to reverb effect processing by the reverb effect unit, the wireless connection unit receives a music accompaniment signal sent by a mobile terminal and sends the signal to the sound mixing unit, the sound mixing unit mixes the voice signal with the music accompaniment signal and sends a sound mixed signal to the DAC, sound is output to a user by the monitoring playback unit after the sound mixed signal is subjected to digital-analog conversion, and the microphone can send the sound mixed signal or the voice signal to the mobile terminal in a Bluetooth manner. According to the wireless karaoke microphone, the karaoke experience of the user and sharing capacity of high-quality sound can be effectively improved.
Owner:BEIJING SAIBIN TECH
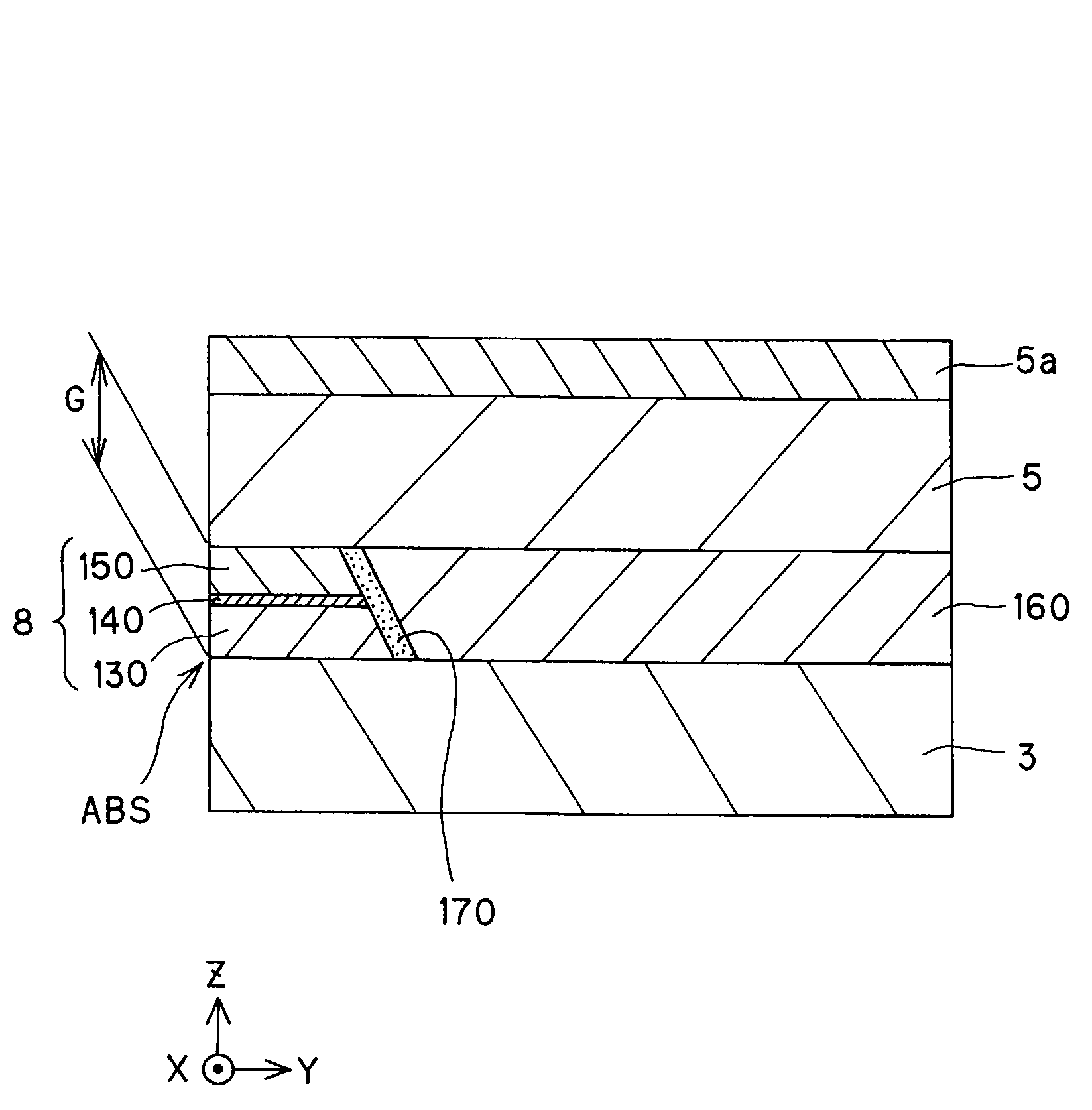
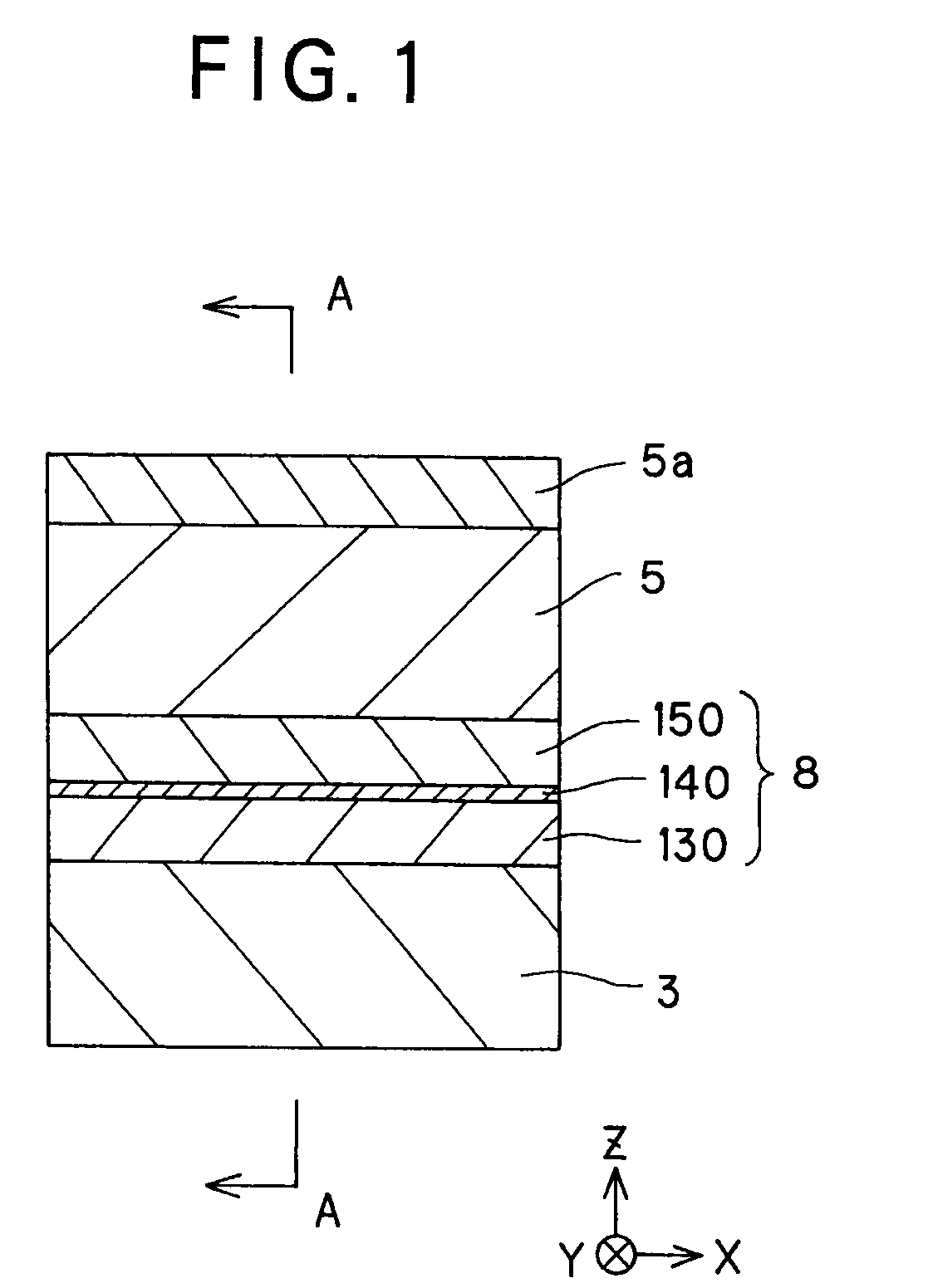
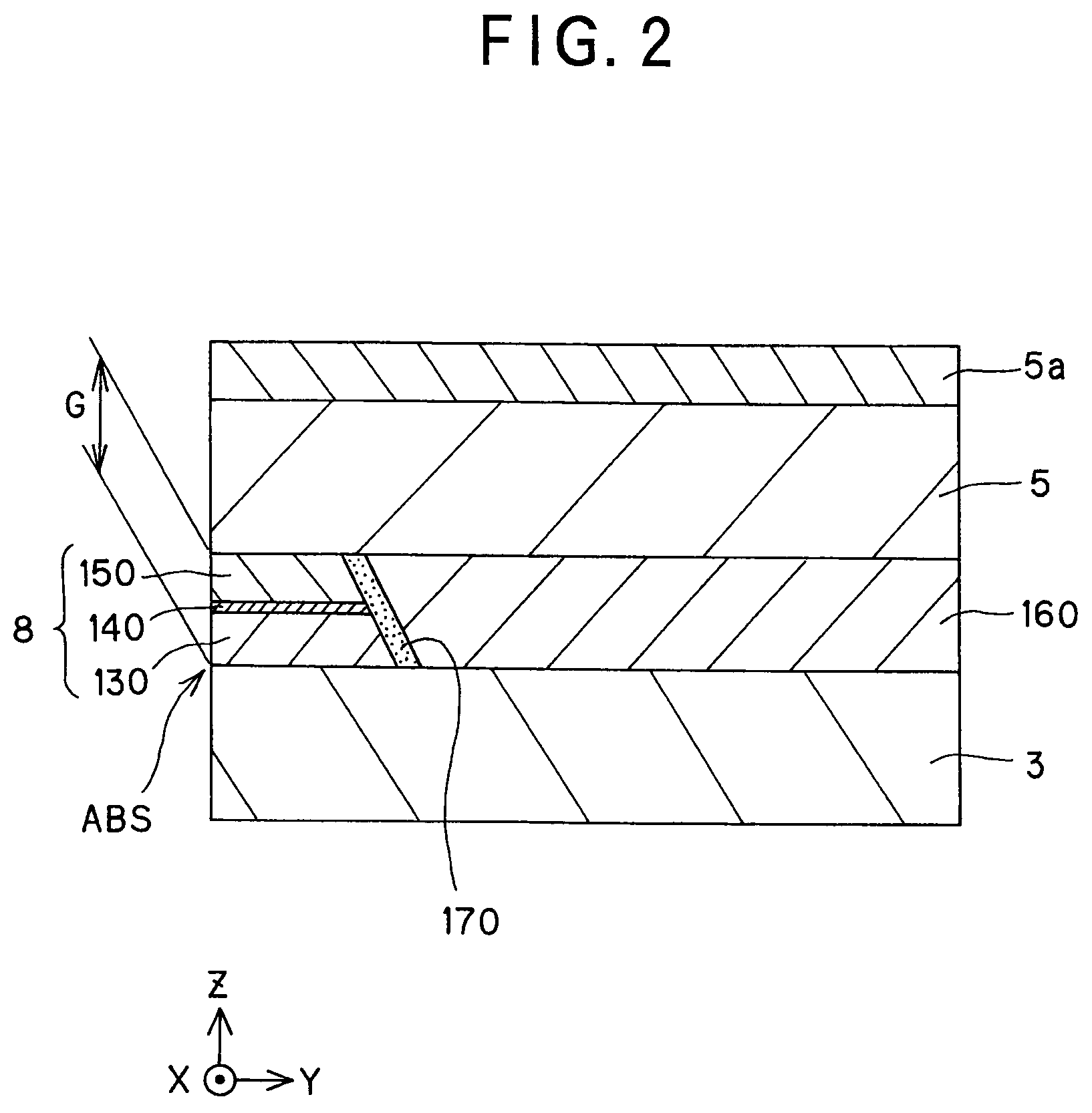
Magneto-resistive effect device of the cpp structure and magnetic disk system
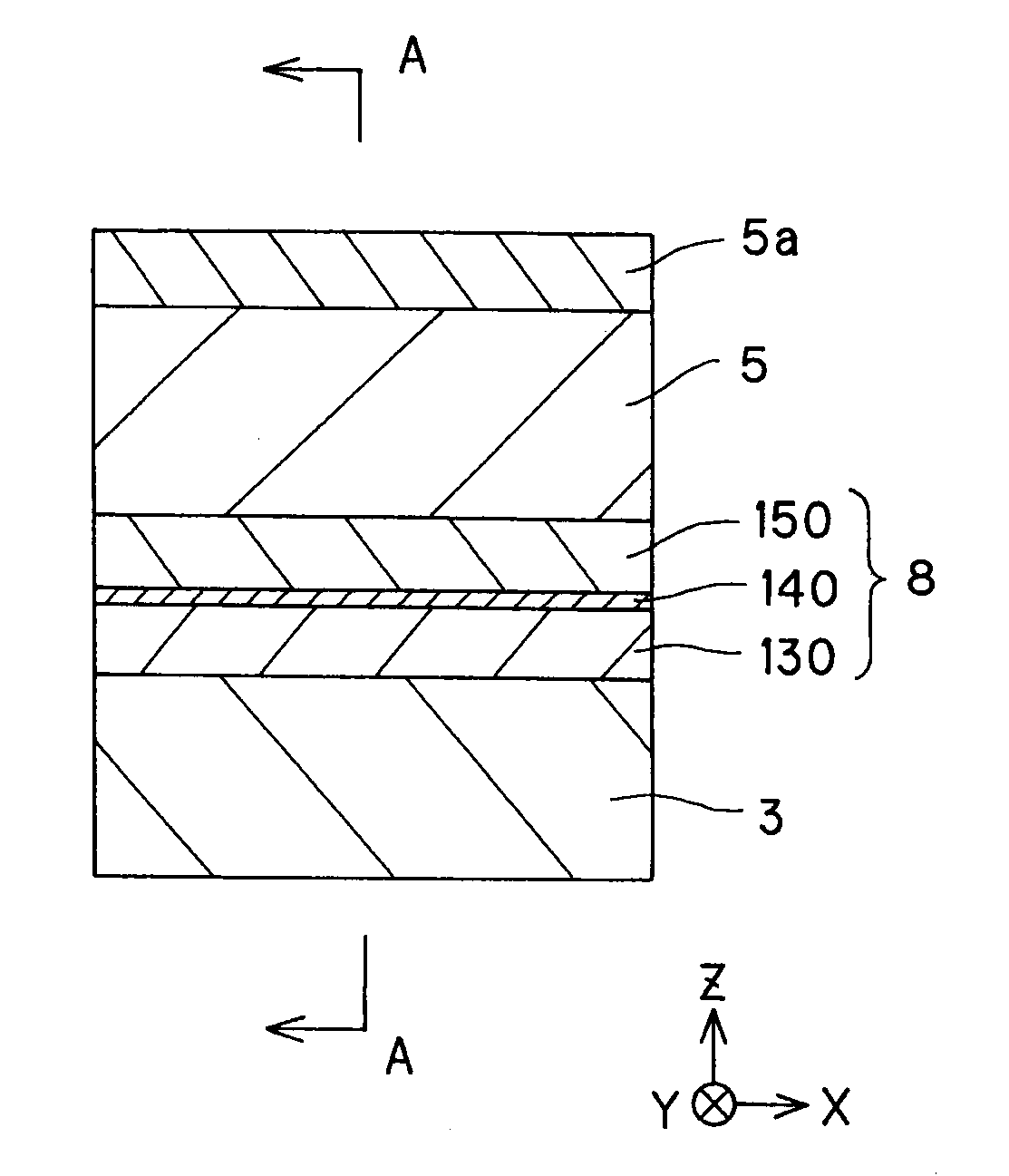
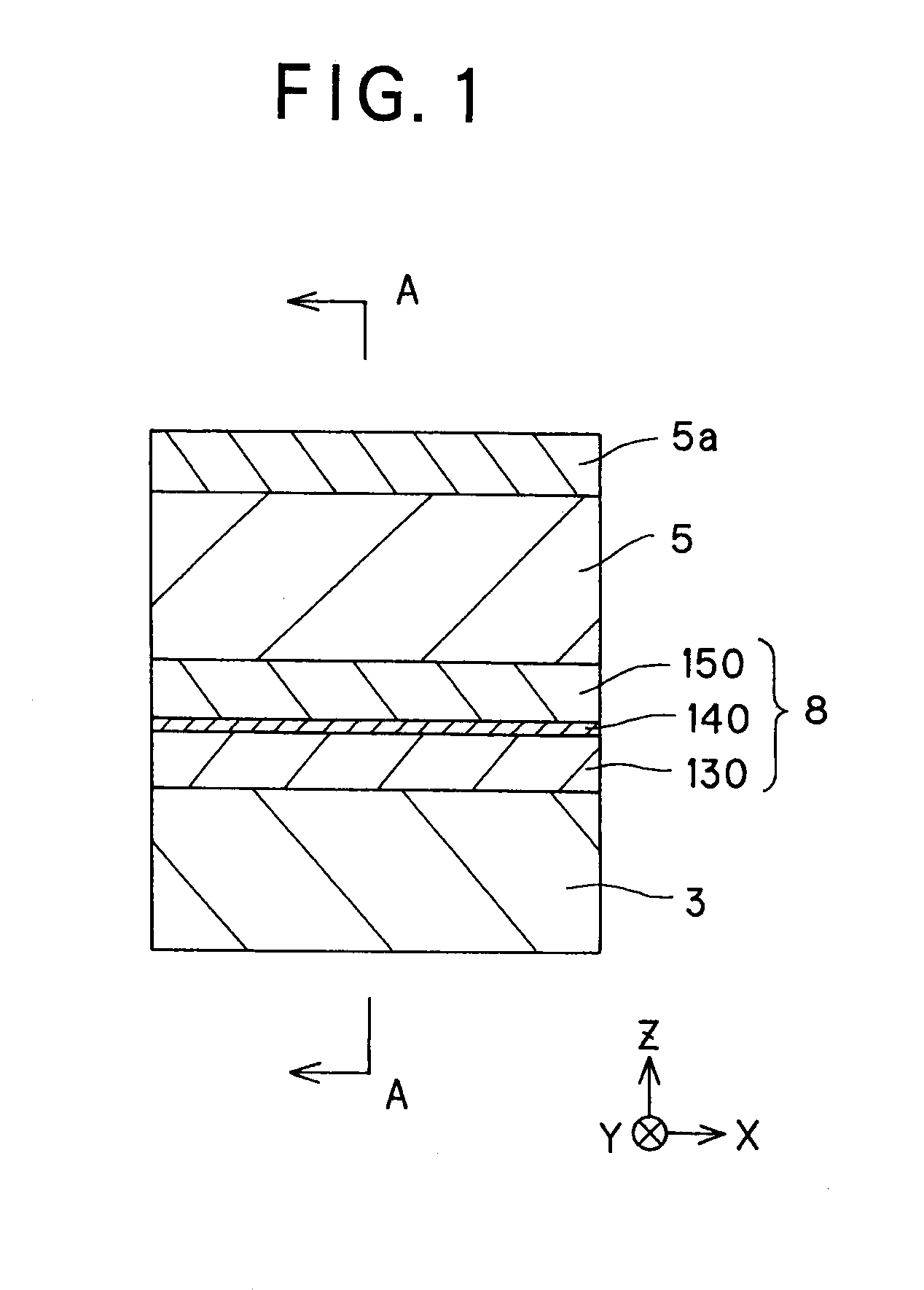
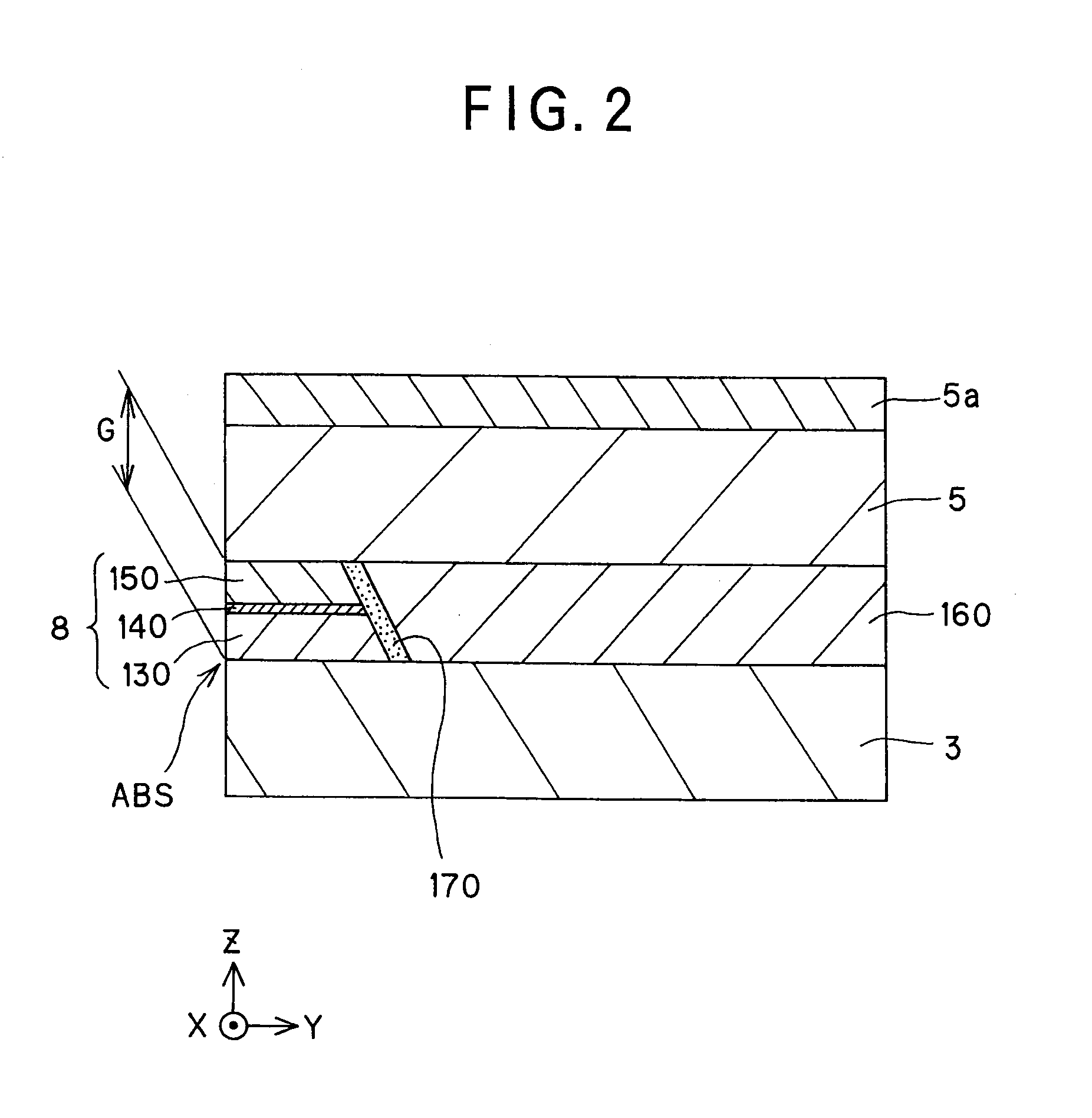
The invention provides a magneto-resistive effect device of the CPP (current perpendicular to plane) structure, comprising a magneto-resistive effect unit, and an upper shield layer and a lower shield layer located with that magneto-resistive effect unit sandwiched between them, with a sense current applied in a stacking direction, wherein the magneto-resistive effect unit comprises a nonmagnetic metal intermediate layer, and a first ferromagnetic layer and a second ferromagnetic layer stacked and formed with that nonmagnetic metal intermediate layer sandwiched between them, wherein the first ferromagnetic layer and said second ferromagnetic layer are exchange coupled via the nonmagnetic metal intermediate layer such that where there is no bias magnetic field applied as yet, their magnetizations are anti-parallel with each other, and at least one of the upper shield layer and the lower shield layer has an inclined magnetization structure with its magnetization inclining with respect to a track width direction, so that by the magnetization of that inclined magnetization structure, a bias magnetic field can be applied to the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer. It is thus possible to obtain a magneto-resistive effect device of improved reliability that enables a structure capable of having a narrowed read gap (the gap between the upper shield and the lower shield) to be adopted to meet the recently demanded ultra-high recording density, allows a stable bias magnetic field to be applied in simple structure, and obtain a stable magneto-resistive effect change.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Portable recording, looping, and playback system for acoustic instruments
Embodiments of the present invention provide an electronic looping, recording, and playback apparatus. The apparatus may comprise a clamp, enabling the apparatus to be positioned in or on an acoustic instrument, such as an acoustic guitar. The clamp may be used to attach the apparatus to a portion of the acoustic instrument. The apparatus may further comprise, but not be limited to, for example, a speaker, a rechargeable battery, a microphone, a volume knob, an LED indicator light, a switch, and a processing module. The switch may be used to activate the electronic recording, looping, and playback system, much like a pedal in a stompbox configuration.
Owner:INTELLITERRAN
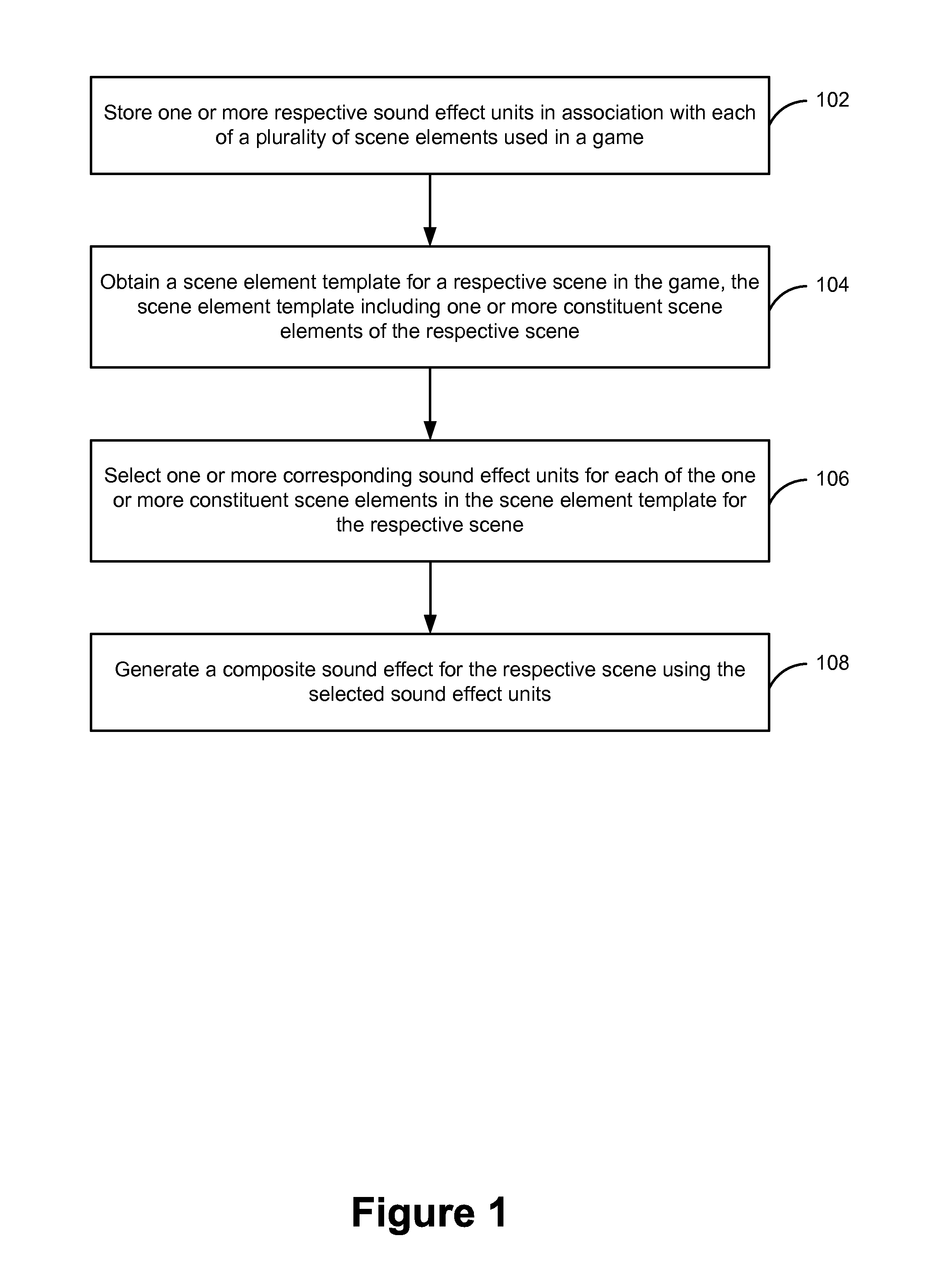
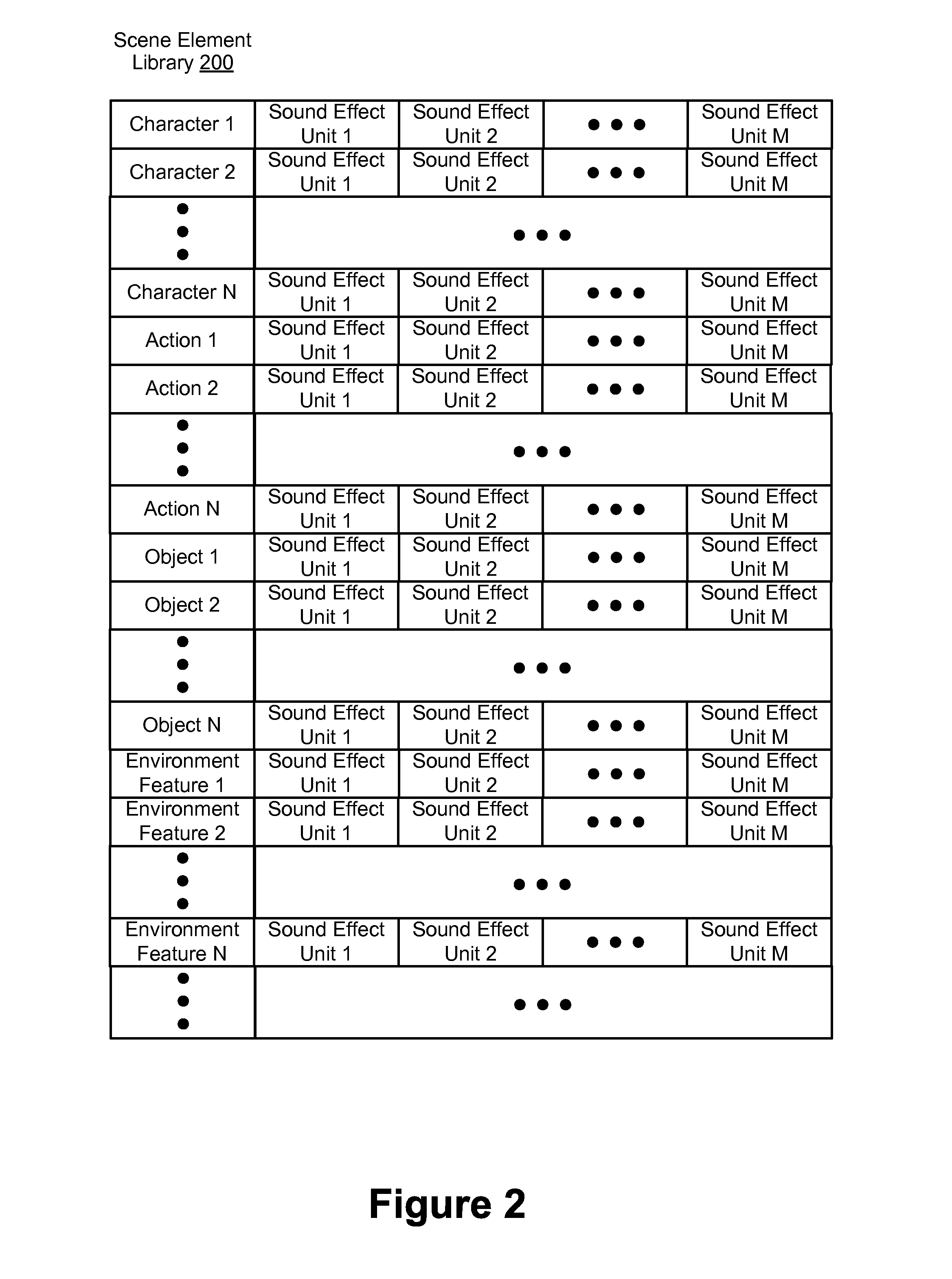
Method and device for generating sounds effects for a game
ActiveUS20140235347A1Video gamesSpecial data processing applicationsElectric equipmentComputer science
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
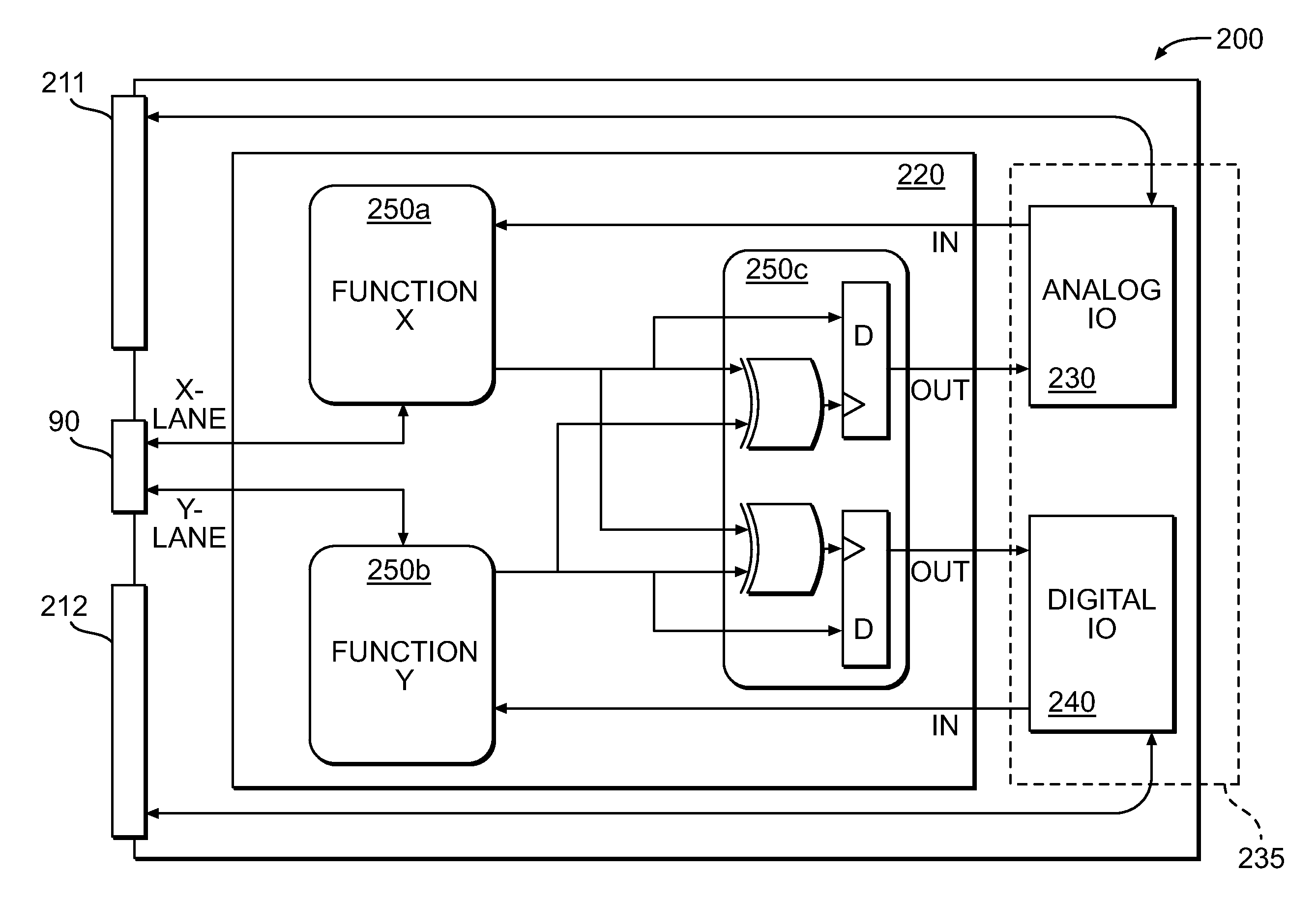
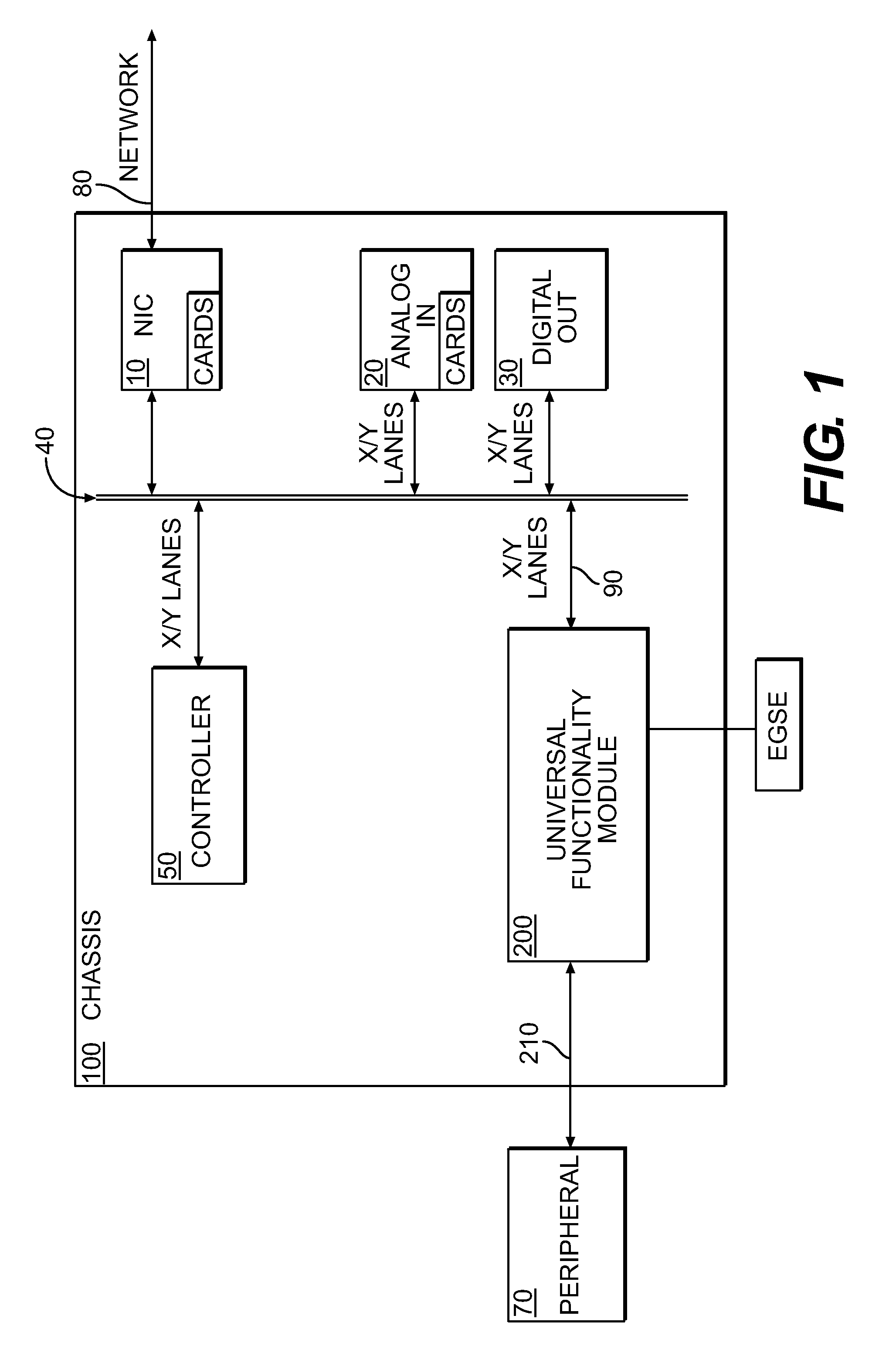
Universal functionality module
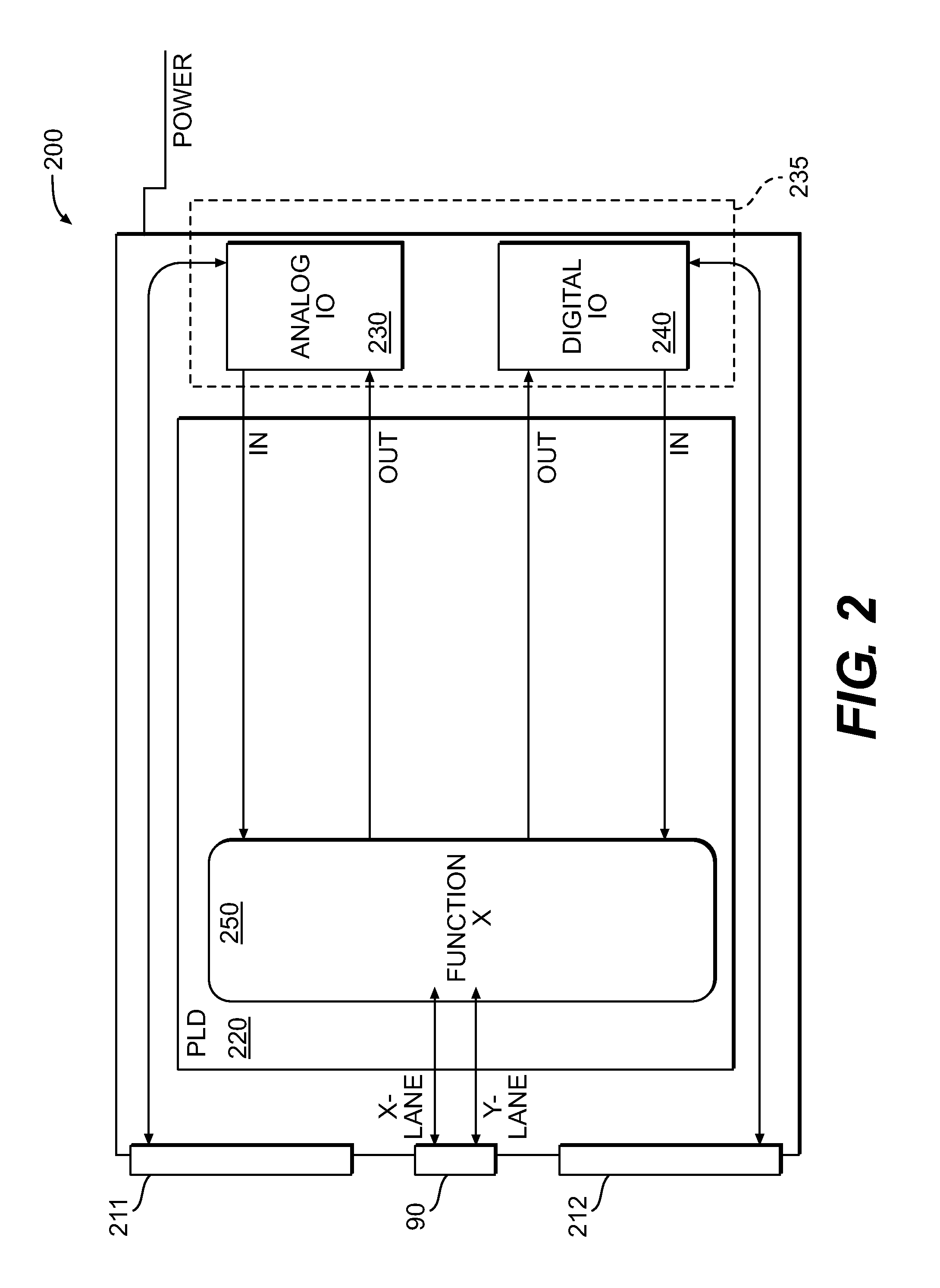
ActiveUS20120068733A1Solid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsProgrammable logic deviceActuator
Methods and apparatus are provided for a Universal functionality Module (UFM). The apparatus comprises a programmable logic device (PLD) configured to be reprogrammed in real time and a means for universally interfacing the PLD with any effectuator device. The UFM loads a startup personality bit stream from a boot memory, which allows it to read a pin configuration associated with a effectuator device. The UFM receives a function personality associated with the pin configuration, writes the function personality to programmable logic device, and initiates the function personality.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Game sound effect generating method and client
ActiveCN103893971AEnhance the music experienceSound input/outputVideo gamesComputer graphics (images)Client
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Effect system
ActiveUS7525038B2Easy to switchElectrophonic musical instrumentsLinear/angular speed measurementEngineeringMode switch
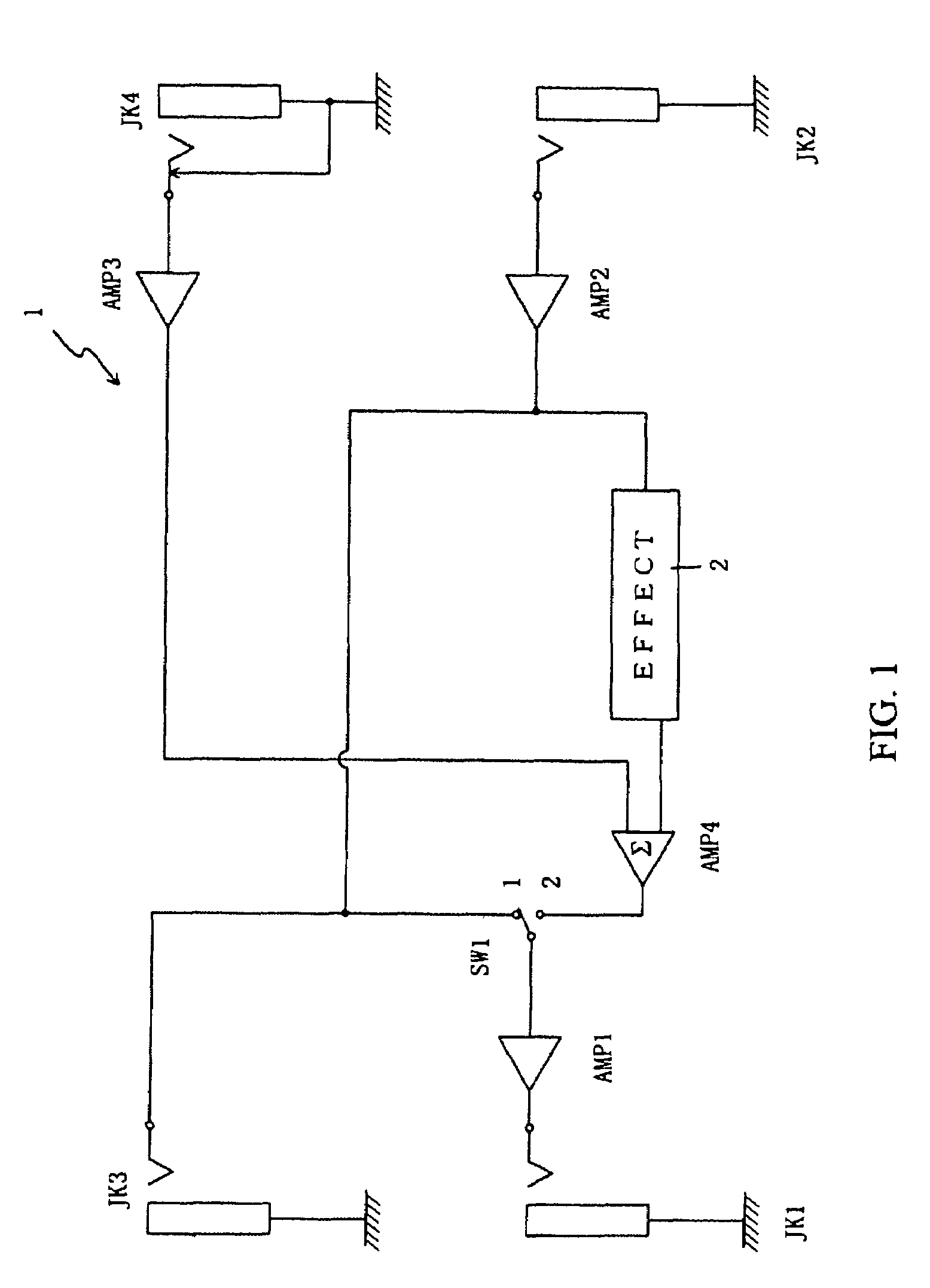
The disclosure presented here involves an effect device that can easily connect with other effect devices in parallel. A preferred embodiment of this device is equipped with a number of components including an effect add means that adds effects, a mixing means that mixes the musical signals, a mode switching means that configures the operation from parallel mode to serial mode, and a phase reversal means that reverses the phase of the musical sound signals. Various combinations using the above means are possible and are presented in this disclosure. The output terminal outputs the musical sound signals that were selected, mixed, and or treated by the enabled features of the underlying embodiments.
Owner:ROLAND CORP
Magneto-resistive effect device of the CPP structure and magnetic disk system
The invention provides a magneto-resistive effect device of the CPP (current perpendicular to plane) structure, comprising a magneto-resistive effect unit, and an upper shield layer and a lower shield layer located with that magneto-resistive effect unit sandwiched between them, with a sense current applied in a stacking direction, wherein the magneto-resistive effect unit comprises a nonmagnetic metal intermediate layer, and a first ferromagnetic layer and a second ferromagnetic layer stacked and formed with that nonmagnetic metal intermediate layer sandwiched between them, wherein the first ferromagnetic layer and said second ferromagnetic layer are exchange coupled via the nonmagnetic metal intermediate layer such that where there is no bias magnetic field applied as yet, their magnetizations are anti-parallel with each other, and at least one of the upper shield layer and the lower shield layer has an inclined magnetization structure with its magnetization inclining with respect to a track width direction, so that by the magnetization of that inclined magnetization structure, a bias magnetic field can be applied to the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer. It is thus possible to obtain a magneto-resistive effect device of improved reliability that enables a structure capable of having a narrowed read gap (the gap between the upper shield and the lower shield) to be adopted to meet the recently demanded ultra-high recording density, allows a stable bias magnetic field to be applied in simple structure, and obtain a stable magneto-resistive effect change.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
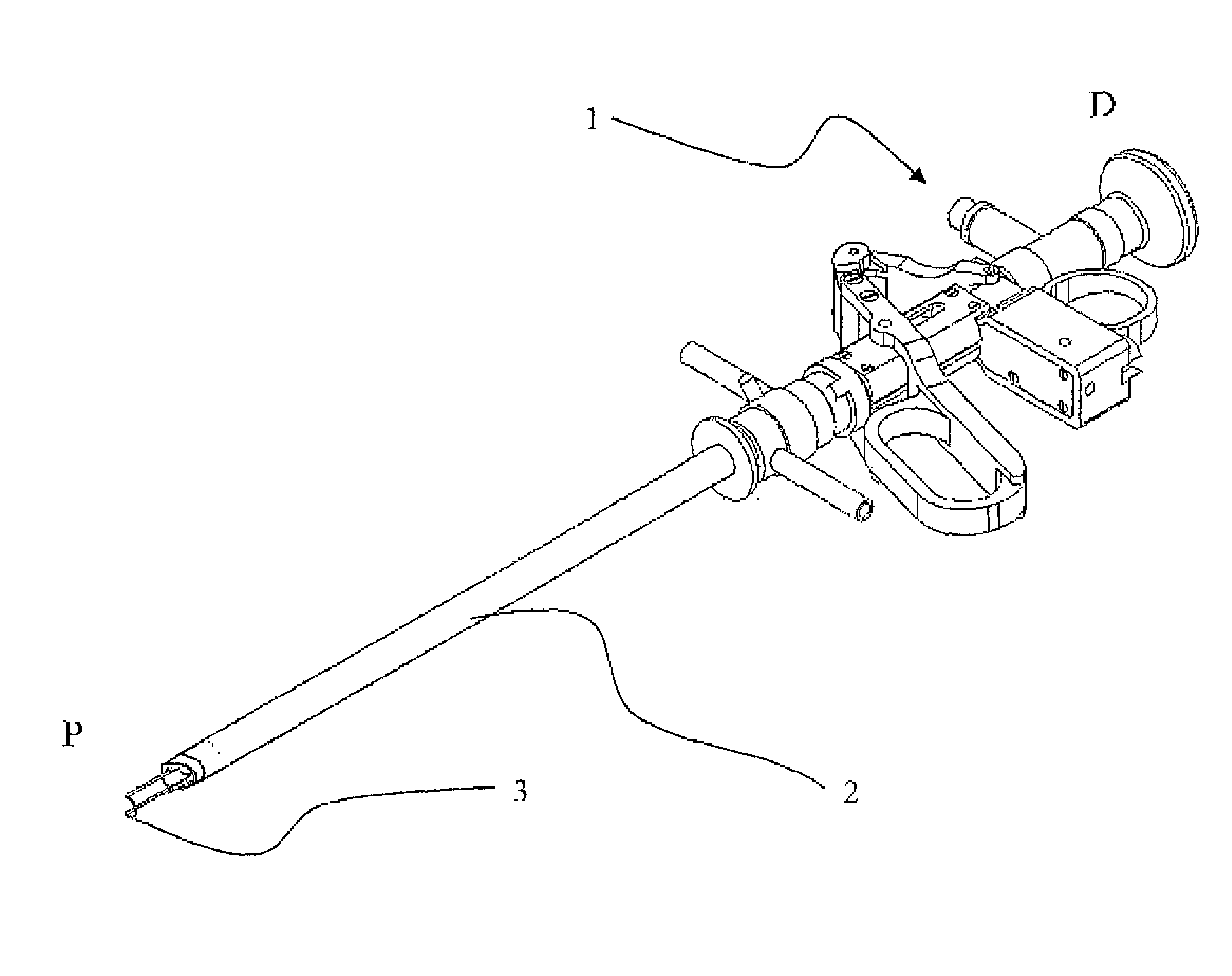
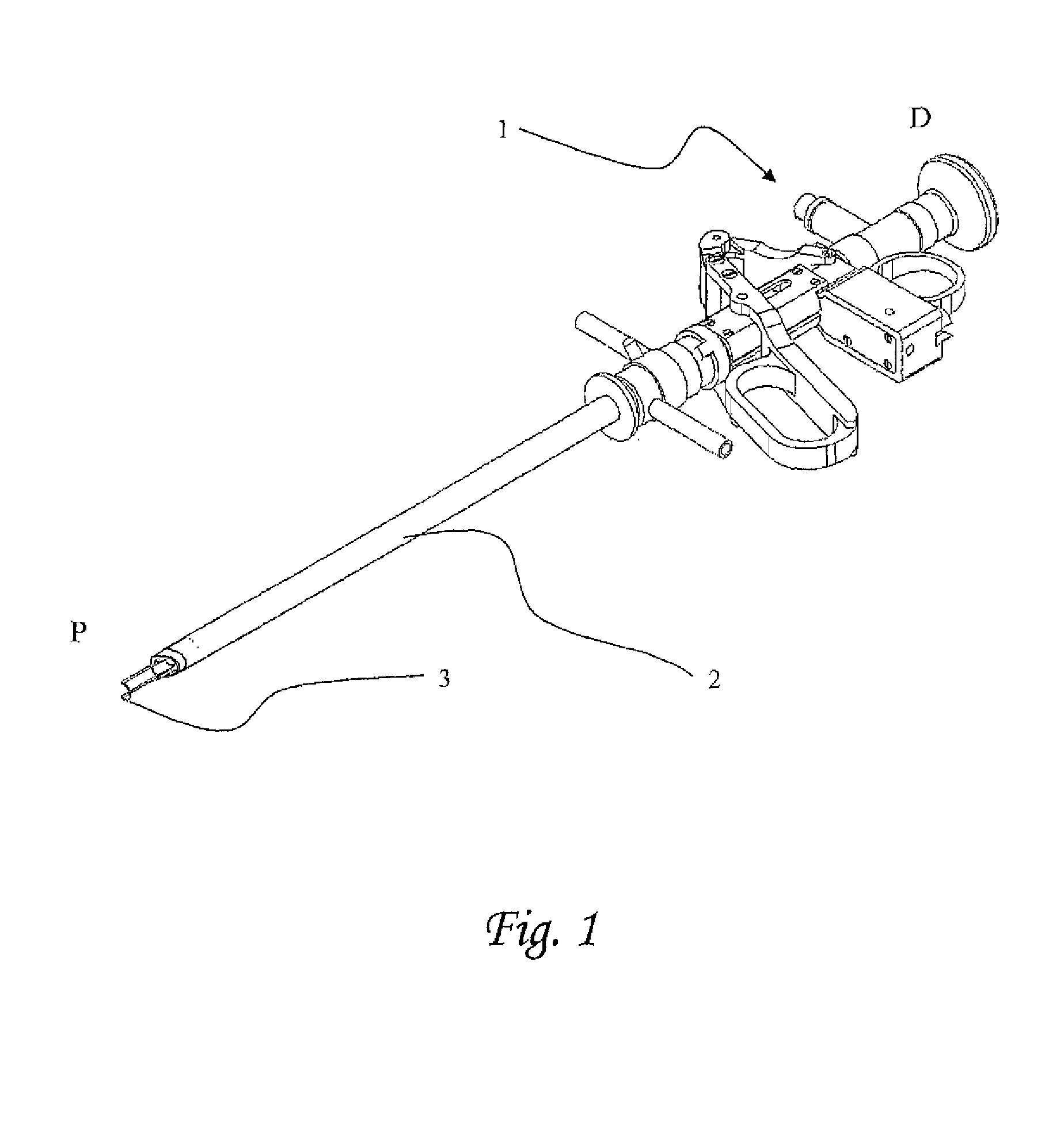
Rotational/linear converter for medical device
The present invention discloses a surgical equipment, having a proximal portion and a distal portion at least reversibly or temporarily interconnected along a main longitudinal axis (shaft P:D); said proximal portion is insertable into a body cavity, and having at least one manoeuvrable effecter; said effecter is adapted to be either manoeuvred linearly along said axis (linear effecter) or to be manoeuvred rotationally around said axis (rotational effecter); said distal portion comprising a handset located outside the body; said handset is adapted to manoeuvre said effecter with either a linear motion along said axis (linear handset) or a rotational motion around said axis (rotational handset); said effecter comprising a proximal effecting means and a distal converter; said converter translates either linear motion to rotational motion or rotational motion to linear motion; so as said rotational effecter is adaptable to a linear handset, and vice versa, a linear effecter is adaptable to a rotational handset.
Owner:ROEI MEDICAL TECH LTD
Action toy and movable member
An action toy includes a toy body including four mounting units, four function switches removably mounted to the four mounting units, detection means disposed in the toy body, where the detection means detects that each of the function switches is mounted to one of the mounting units, a dramatic effect unit disposed in the toy body, where the dramatic effect unit creates a dramatic effect using light or sound, and a control unit disposed in the toy body. When the detection means detects that one of the function switch is attached to the toy body, the control unit causes the dramatic effect unit to create a first dramatic effect. When a push button unit is operated, the control unit causes the dramatic effect unit to create a second dramatic effect.
Owner:BANDAI CO LTD
Sound effect circuit and processing method
ActiveUS20090169026A1Suppresses noise generationIncrease in circuit sizeGain controlDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlAudio frequencyComputer science
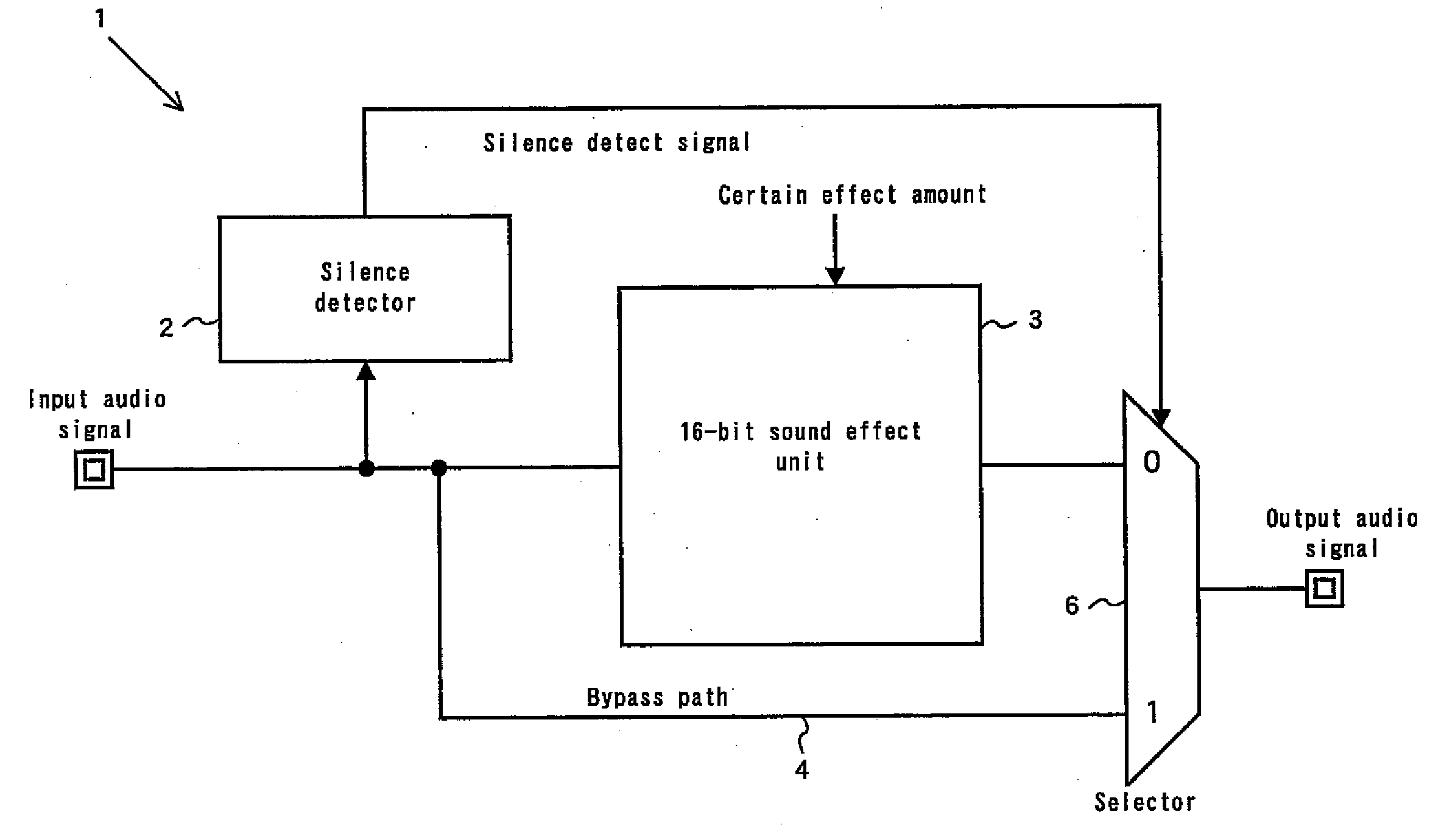
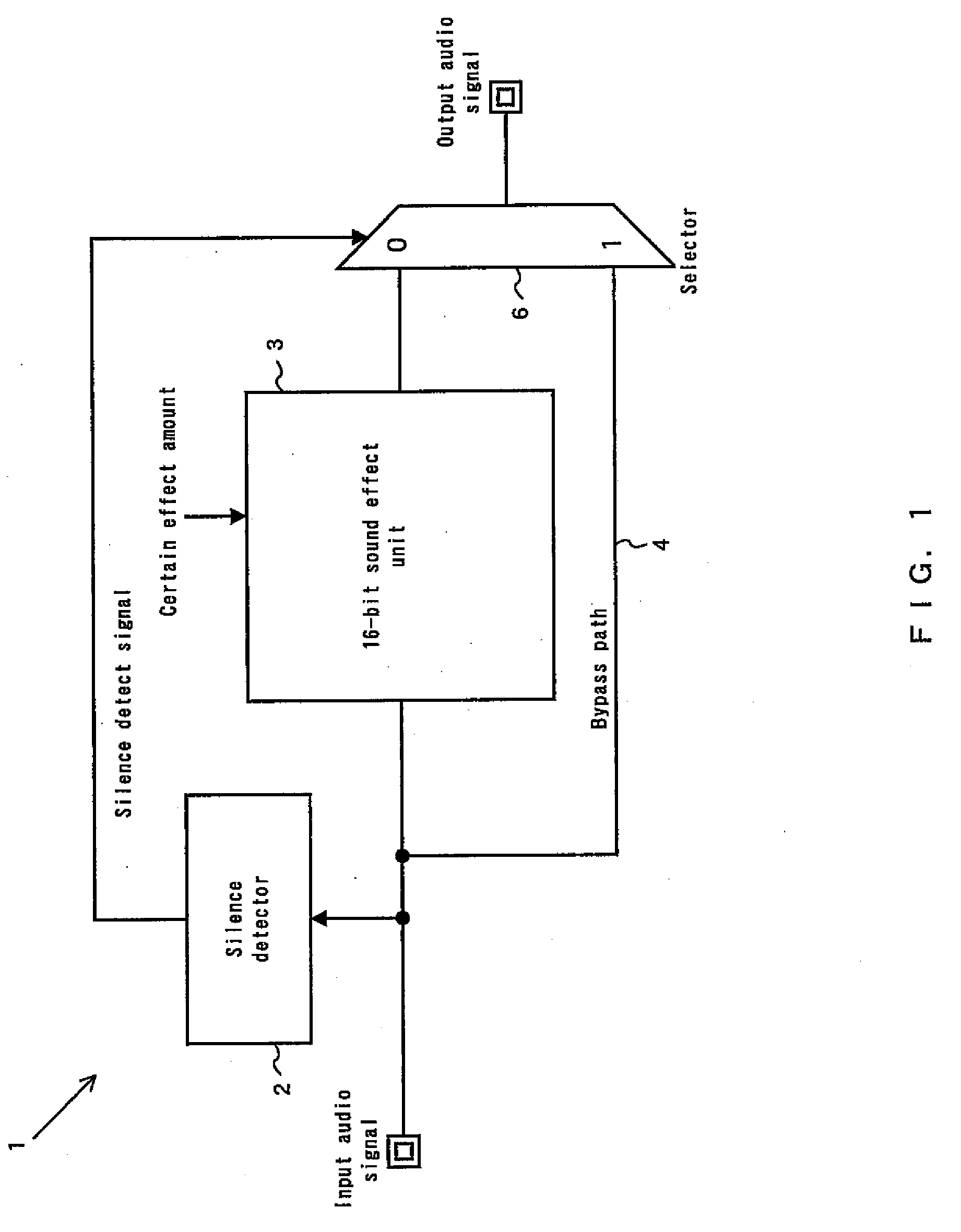
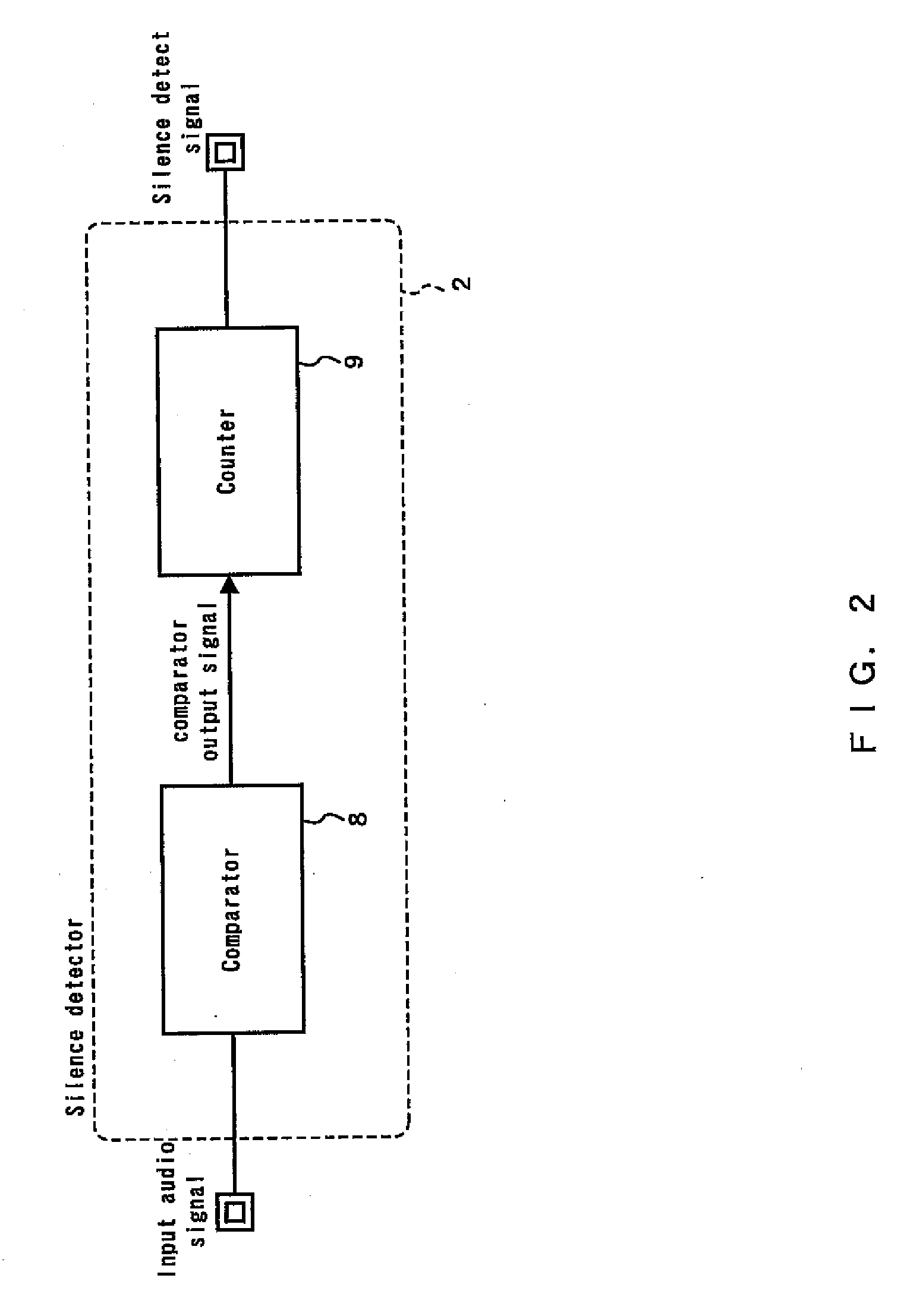
A sound effect circuit and processing method are disclosed. An input audio signal is input to a digital sound effect unit, an output signal is generated and output with a sound effect in accordance with an effect amount of a certain value from the input audio signal using the digital sound effect unit, the input audio signal is also input to a silence state detection unit, a silence detect signal is generated and output when detecting that the current state of the input audio signal is a silence state using the silence state detection unit, the output signal is input to a sound effect amount control unit, and an output audio signal is output using the sound effect amount control unit, wherein the sound effect amount control unit changes the effect amount to be smaller than the certain value when the silence detect signal is generated.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Magneto-resistive effect device of the cpp type, and magnetic disk system
The invention provides a magneto-resistive effect device of a CPP (current perpendicular to plane) structure, comprising a magneto-resistive effect unit, and a first shield layer and a second shield layer located and formed such that the magneto-resistive effect unit is sandwiched between them, with a sense current applied in a stacking direction, characterized in that: said magneto-resistive effect unit comprises a non-magnetic intermediate layer, and a first ferromagnetic layer and a second ferromagnetic layer stacked and formed such that said nonmagnetic intermediate layer is interposed between them, wherein: said first shield layer, and said second shield layer is controlled by magnetization direction control means in terms of magnetization direction, and said first ferromagnetic layer, and said second ferromagnetic layer receives action such that there is an antiparallel magnetization state created, in which mutual magnetizations are in opposite directions, under influences of magnetic actions of said first shield layer and said second shield layer. It is thus possible to achieve an antiparallel magnetization state for two ferromagnetic layers with simple structure yet without being restricted by the material and specific structure of an intermediate film interposed between the two ferromagnetic layers.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Automated excavation machine
InactiveUS8016363B2Efficiently and effectively excavatingDisloding machinesUnderground miningActuatorExcavator
The present invention is directed to an excavator that is operable in manual and automatic modes and uses state machines to effect unit operations, rotationally offset swing actuators to rotate boom and cutter head, a fail safe hydraulic system to maintain gripper pressure in the event of a malfunction of the hydraulic system, differing position and pressure control functions in the hydraulic actuators, a kinematic module to effect pitch and roll adjustments, a cutting face profile generator to generate a profile of the excavation face, and an optimization module to realize a high degree of optimization of excavator operation.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN IN RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NATURAL RESOURCES CANADA
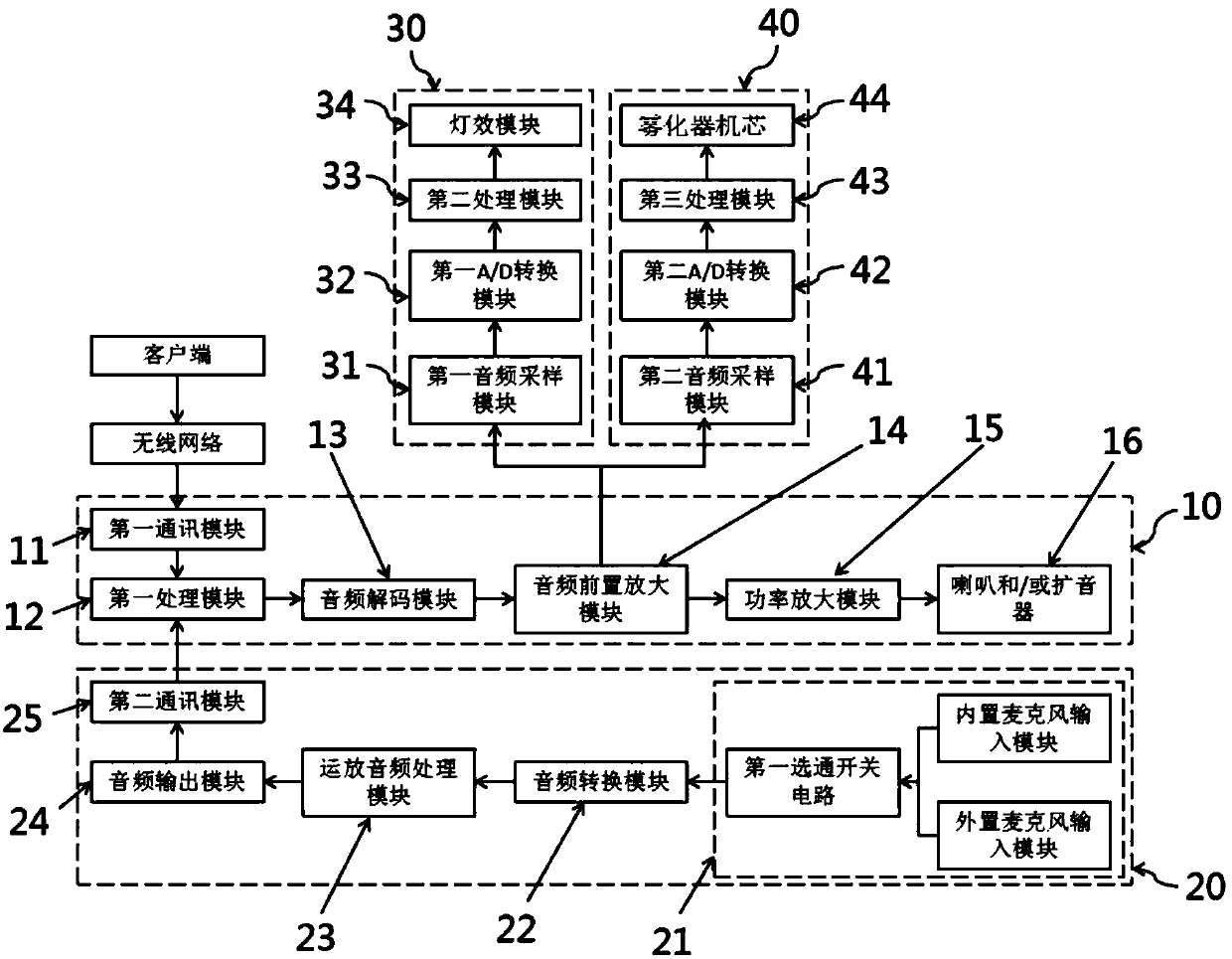
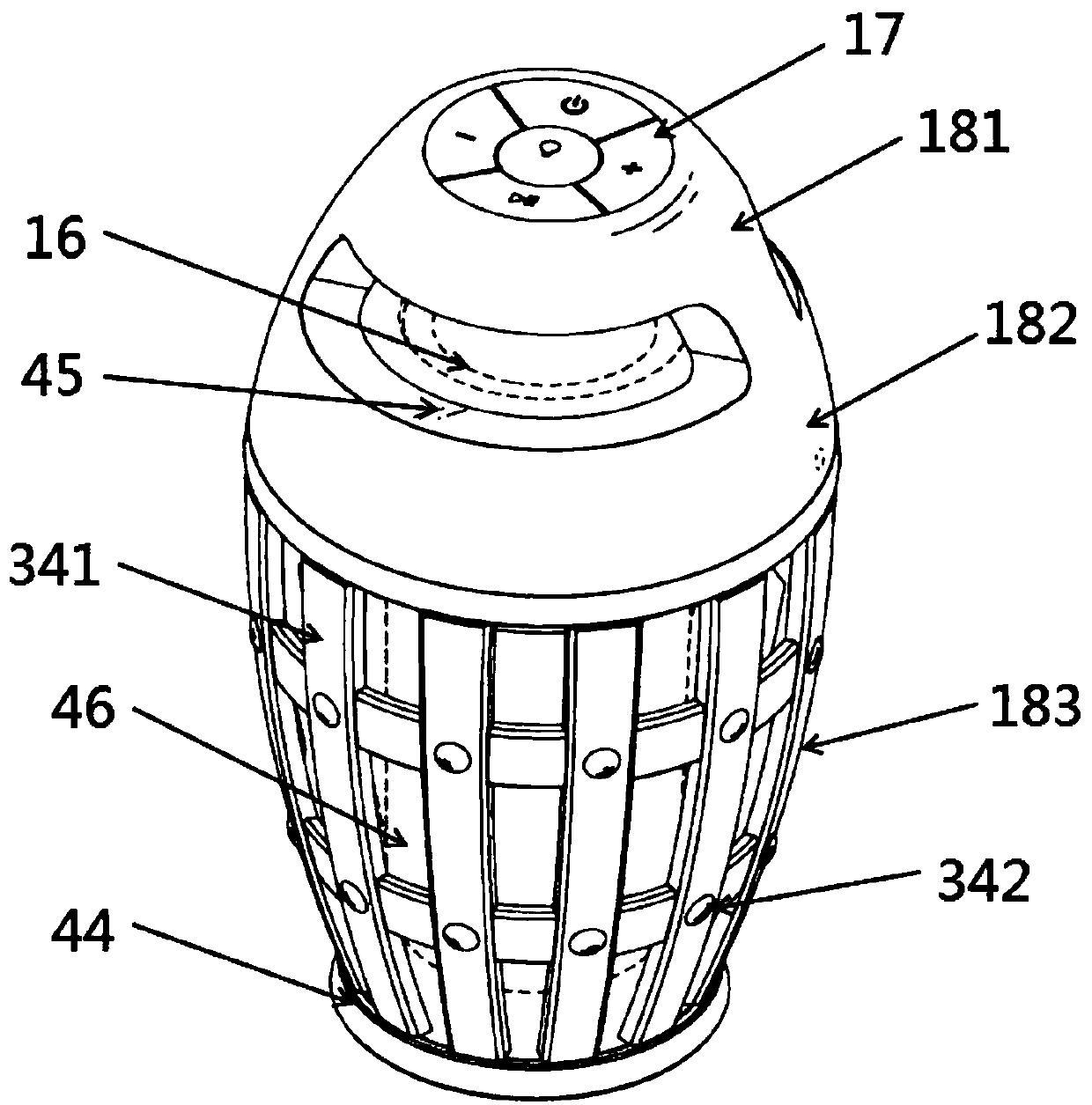
Multifunctional sound box equipment
PendingCN108055609AObvious beneficial effectImprove performance experienceFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsEffect lightEngineering
The invention provides multifunctional sound box equipment. The multifunctional sound box equipment comprises a wireless sound box unit, a lighting effect unit, a microphone unit, and a power supply unit; the wireless sound box unit comprises a box body, a horn and / or a loudspeaker; the microphone unit comprises a microphone, an audio conversion module, an operational amplifier audio processing module, an audio output module, and a second communication module electrically connected in order; the lighting effect unit comprises a first audio sampling module, a first A / D conversion module, a second processing module and a lighting effect module electrically connected in order. A microphone unit is connected through the wireless technology so as to form portable loud-speaking equipment; the lighting effect unit is arranged in the sound box to drive multiple groups of LED lamps to combine different visual effects according to the audio; a spray unit is arranged in the sound box to realize ahumidifier function capable of regulating and controlling the range more convenient and more extensively while enhancing the effect experience of the sound box.
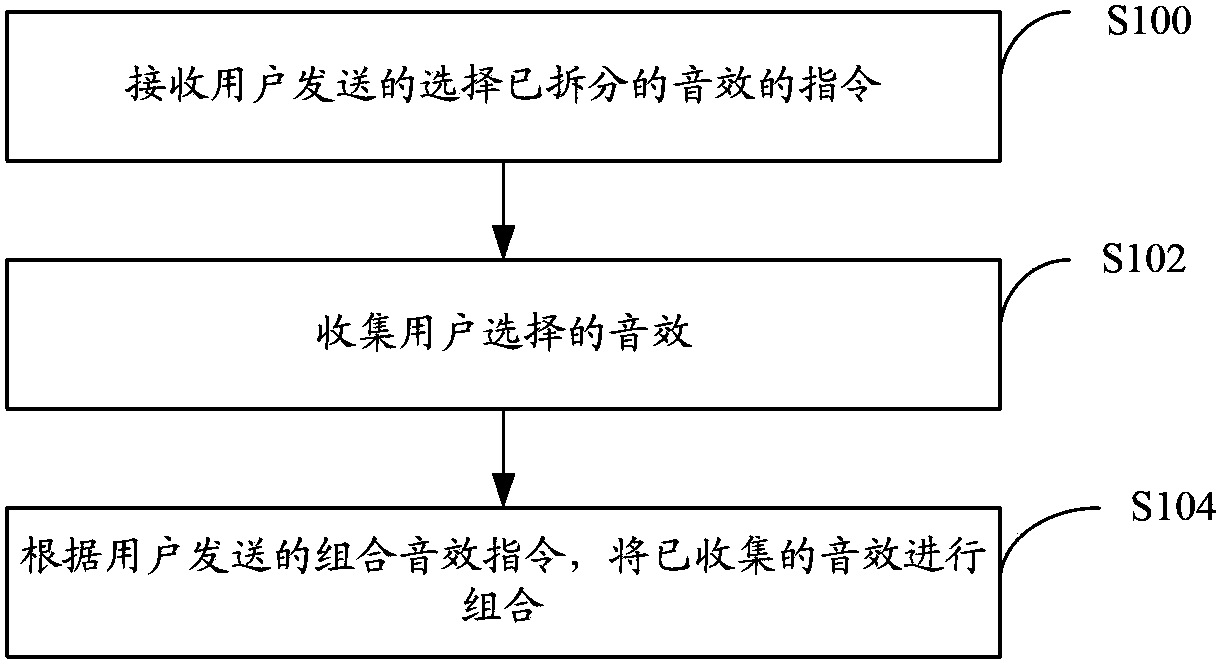
Owner:刘冬来
Apparatus for waking up a device
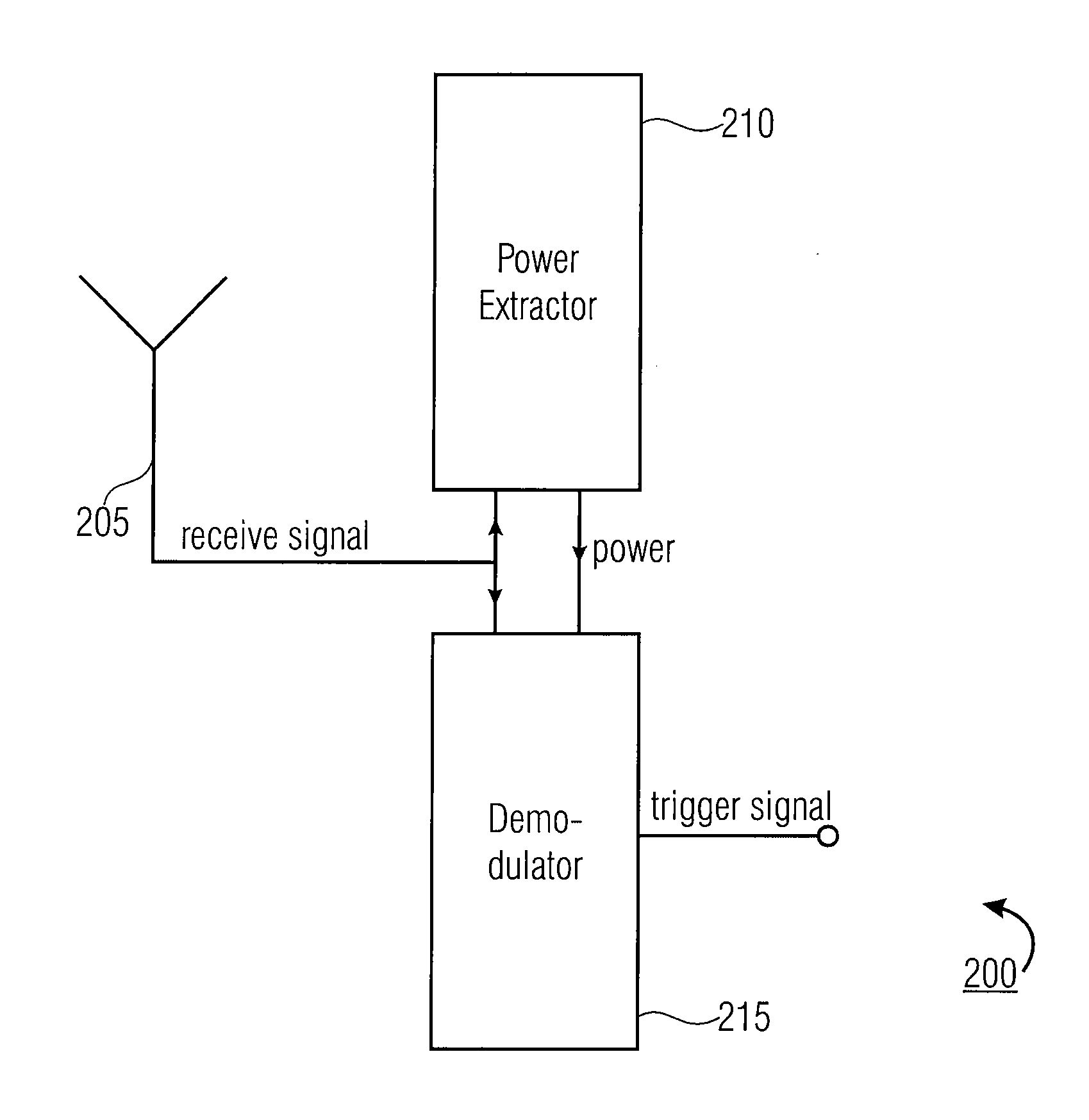
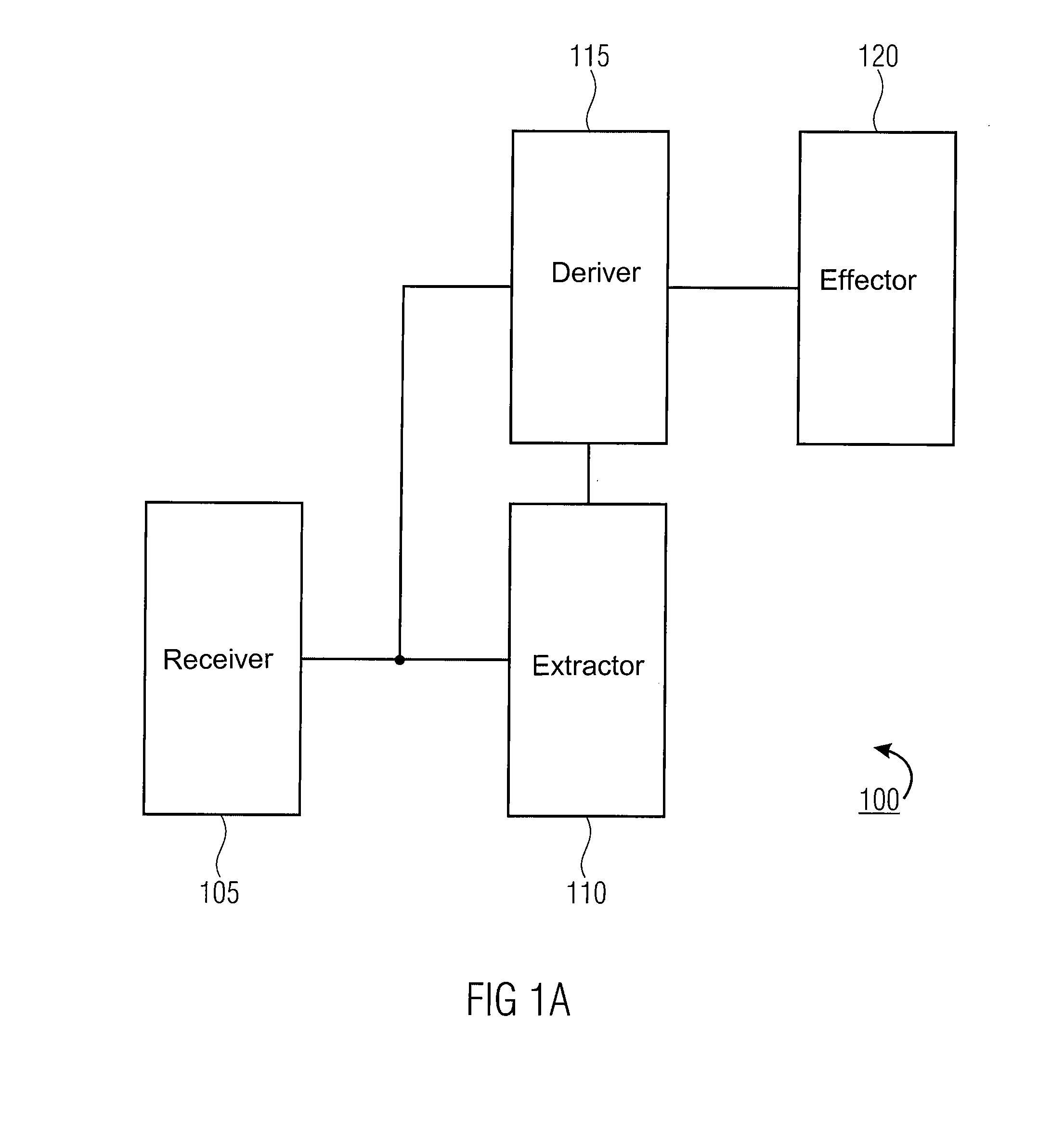
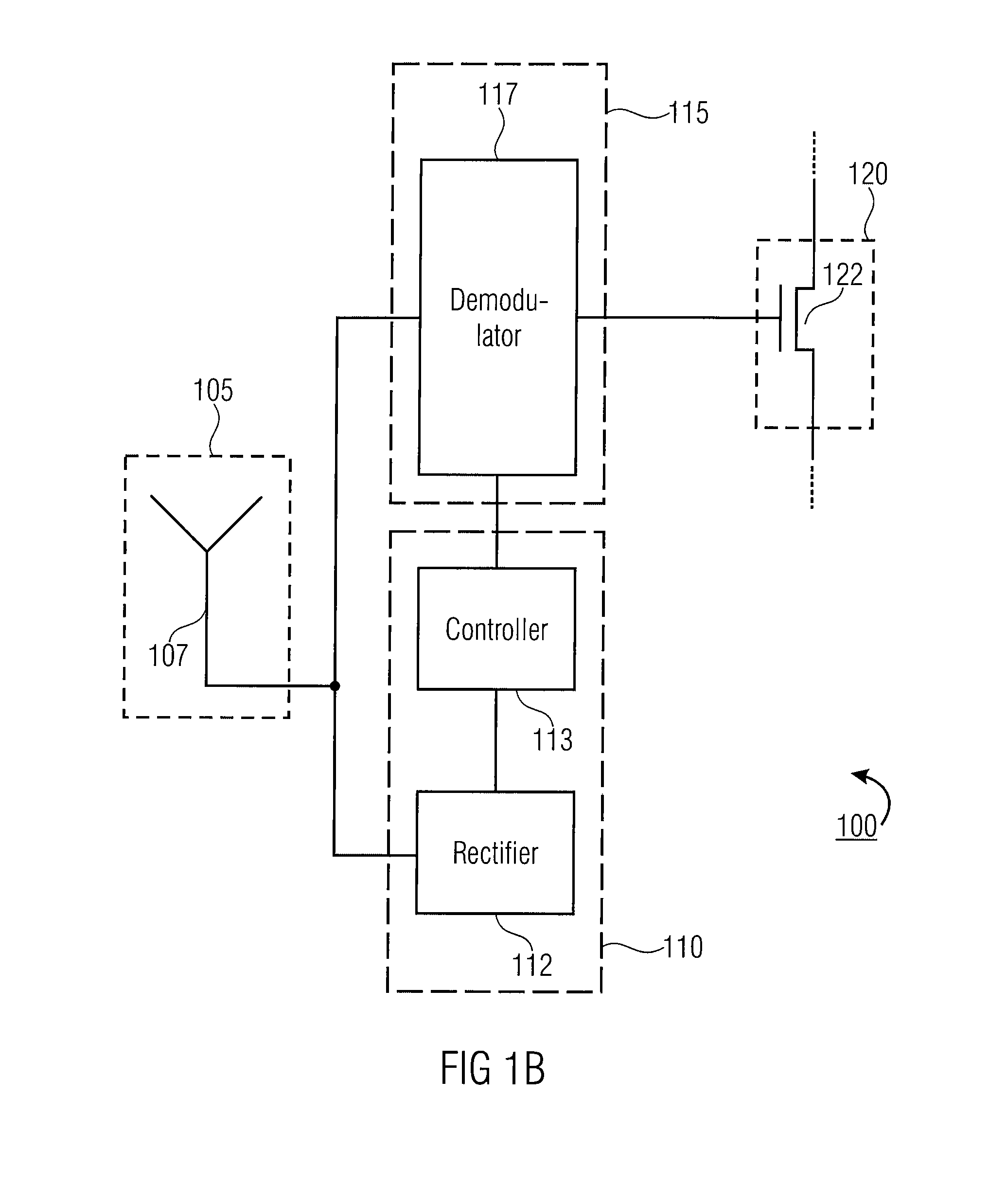
InactiveUS20090031147A1Electromagnetic wave systemVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringEffects unit
Apparatus for waking up a device having a power supply. The apparatus includes a receiver configured to receive a receive signal and an extractor configured to extract power from the receive signal. The apparatus further includes a deriver configured to derive wake up information from the receive signal, which is powered by the extracted power. Furthermore, the apparatus includes an effecter configured to effect a connection of the device to the power supply if the deriver derives the wake up information.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Sound effect device and manufacturing method therefor
The invention discloses a sound effect device and a manufacturing method therefor, and the device comprises at least one installation housing; and at least one sound effect unit. The sound effect unit comprises at least one main vibration loudspeaker, at least one auxiliary vibration loudspeaker, and at least one passive vibrator, wherein the main vibration loudspeaker and the auxiliary vibration loudspeaker are arranged in opposite directions, and the main vibration loudspeaker, the auxiliary vibration loudspeaker and the passive vibrator share one vibration cavity. When the main vibration loudspeaker and the auxiliary vibration loudspeaker respond to the input of an audio signal and vibrates to generate a sound effect, the passive vibrator is driven to vibrate to generate an auxiliary sound effect. The device is convenient to carry and store, and is good in sound quality and effect.
Owner:NINGBO SHENGYA ELECTRONICS
Guitar effector module, and multi-type guitar effector using same
ActiveUS20160275928A1Easy to transportEasy to storeElectrophonic musical instrumentsEngineeringGuitar
A guitar effector module includes: a component circuit board in which an analog guitar effector circuit is formed; a module case in which a knob for adjusting a sound by a circuit is mounted, and the component circuit board is installed therein; and a circuit connection unit, in which a circuit input unit, a circuit output unit, and a circuit power supply unit with respect to the circuit are formed, which is electrically connected with the component circuit board, and is installed on an external side of the module case.
Owner:LEE SEUNG JAE
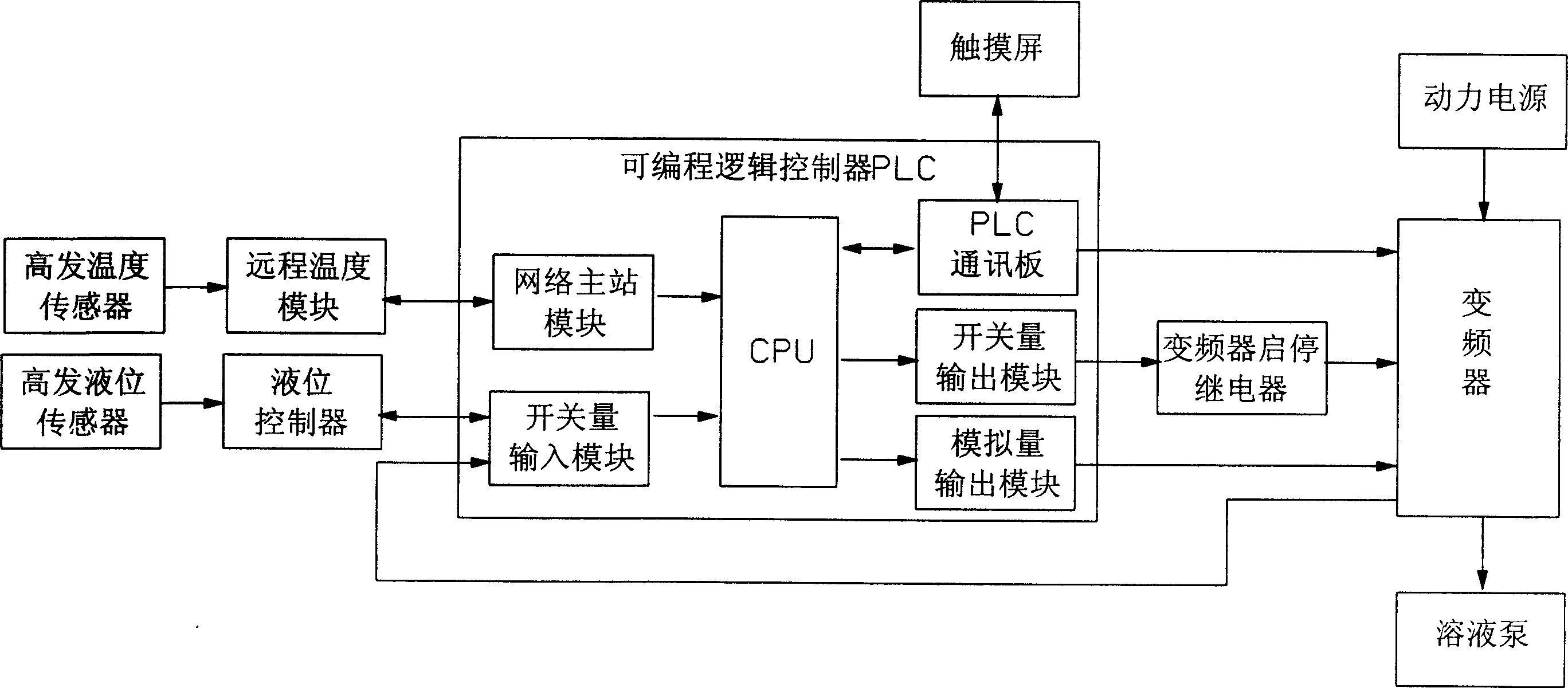
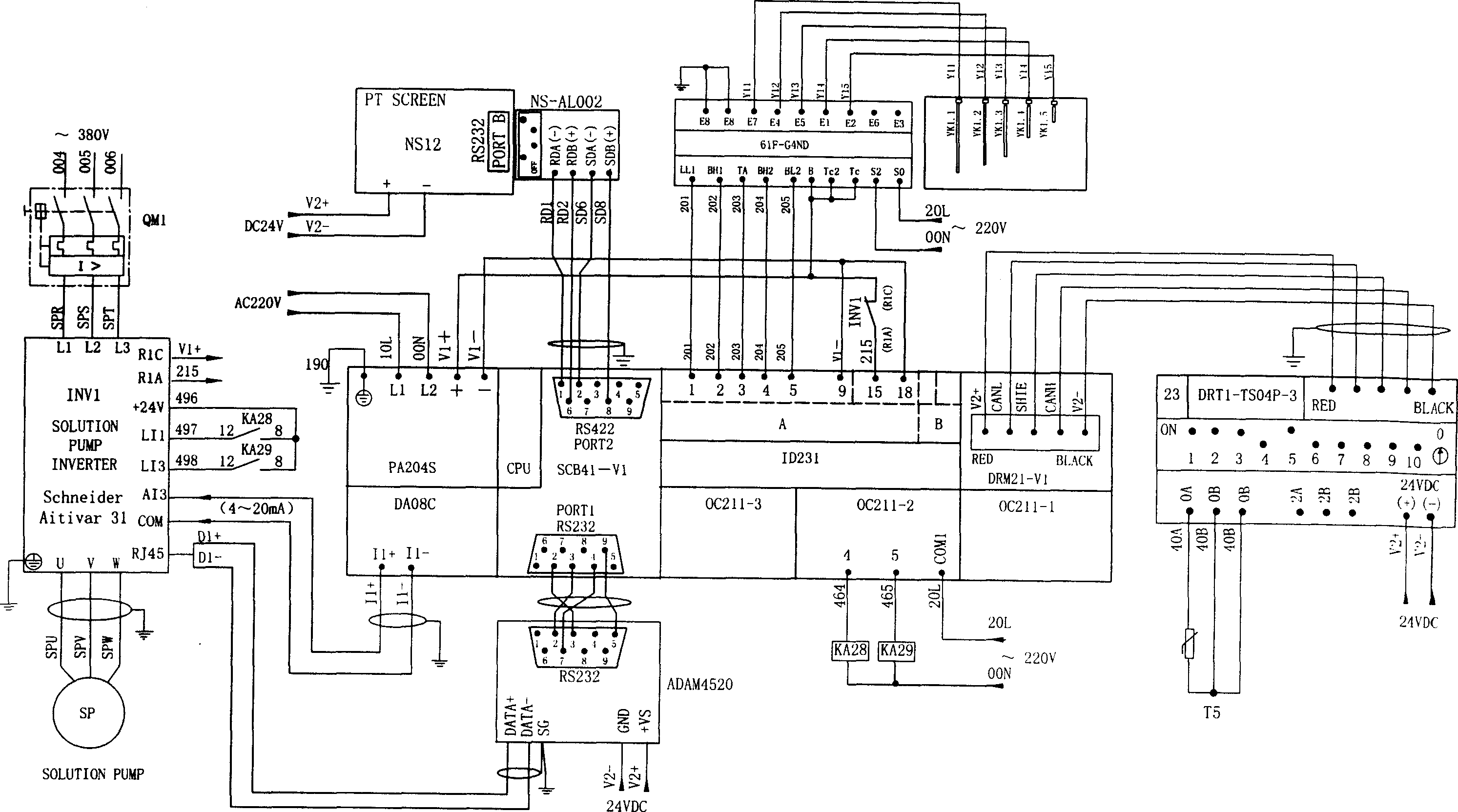
Lithium bromide absorption cold-warm water unit-double-effect machine high-generation level control method and device
InactiveCN1815113AGuaranteed uptimeRun accuratelyClimate change adaptationEnergy efficient heating/coolingInformation processingWarm water
Present invention discloses a lithium bromide absorption type cold-warm water assembly-double effect unit high transmission liquid level control method and device. It contains plurality of liquid level sensors, high transmission temperature sensor, liquid level controllerú¼ programmable logic controller PLC, long-distance temperature module, PLC primary station module, solution pump frequency converter. Said invention adopts advanced programmable logic controller PLC information processing technology information processing technology and converter technique with accuracy controlling, high intellectualization, small liquid level undulation, steady operation of the unit, to raise whole set quality and technical performance.
Owner:张跃
Effects and controller pedal board
A pedal board apparatus includes a single-tier, a double-tier, and a triple-tier variant, wherein each tier includes a deck having a top surface and an opposing bottom surface. Each deck is bound by a first sidewall and a second sidewall. Each sidewall comprises a plurality of ports providing ingress and egress for cables and / or connectors. Each deck has an incline wherein the first sidewall has a greater height than the second sidewall, and each intermediate sidewall has a height greater than the second sidewall. The apparatus may include at least one handle disposed along the deck.
Owner:OBRIEN GREGORY
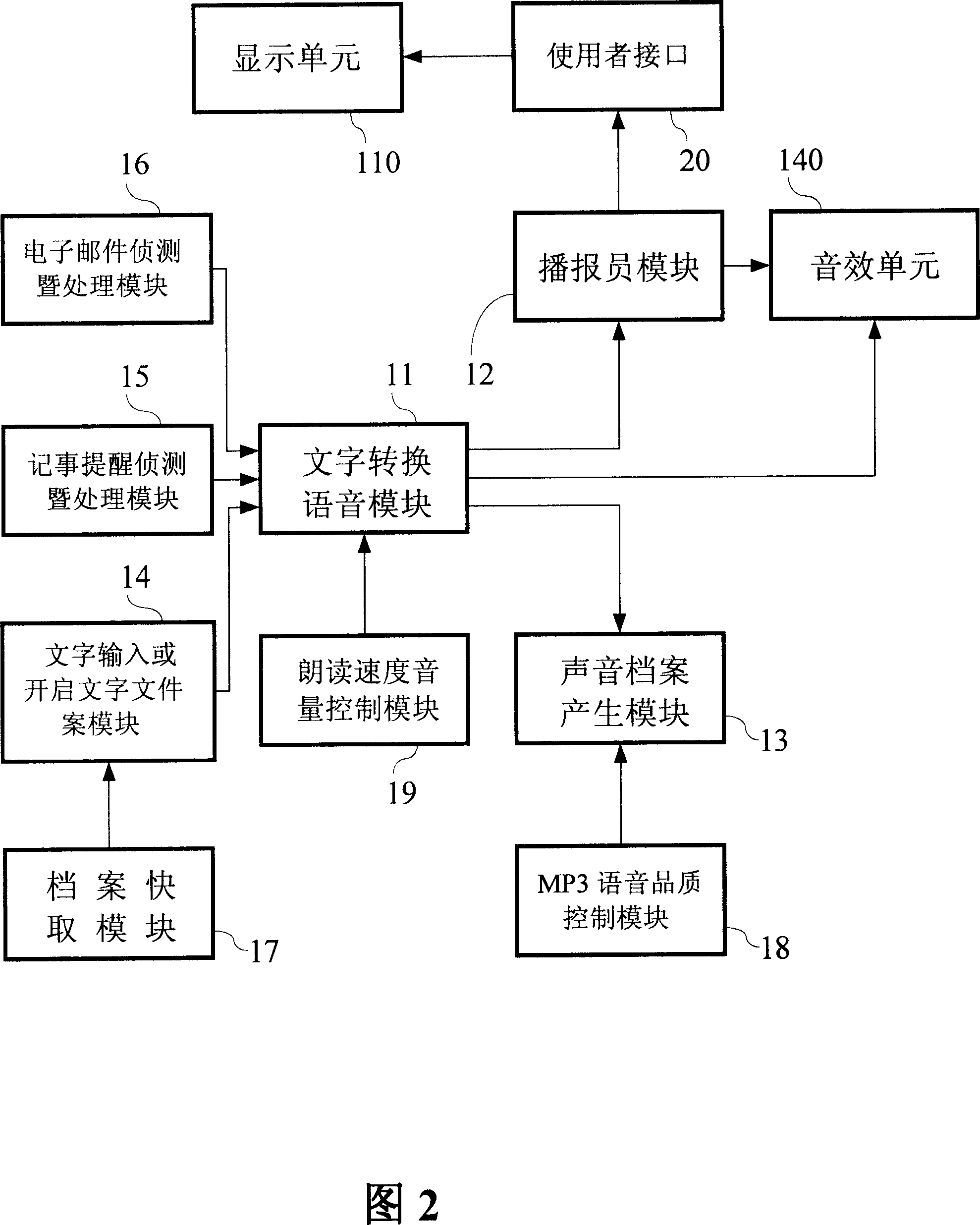
E-mail auxiliary and words-to-voice system
InactiveCN1991817AOffice automationSpecial data processing applicationsTransformation of textOperation mode
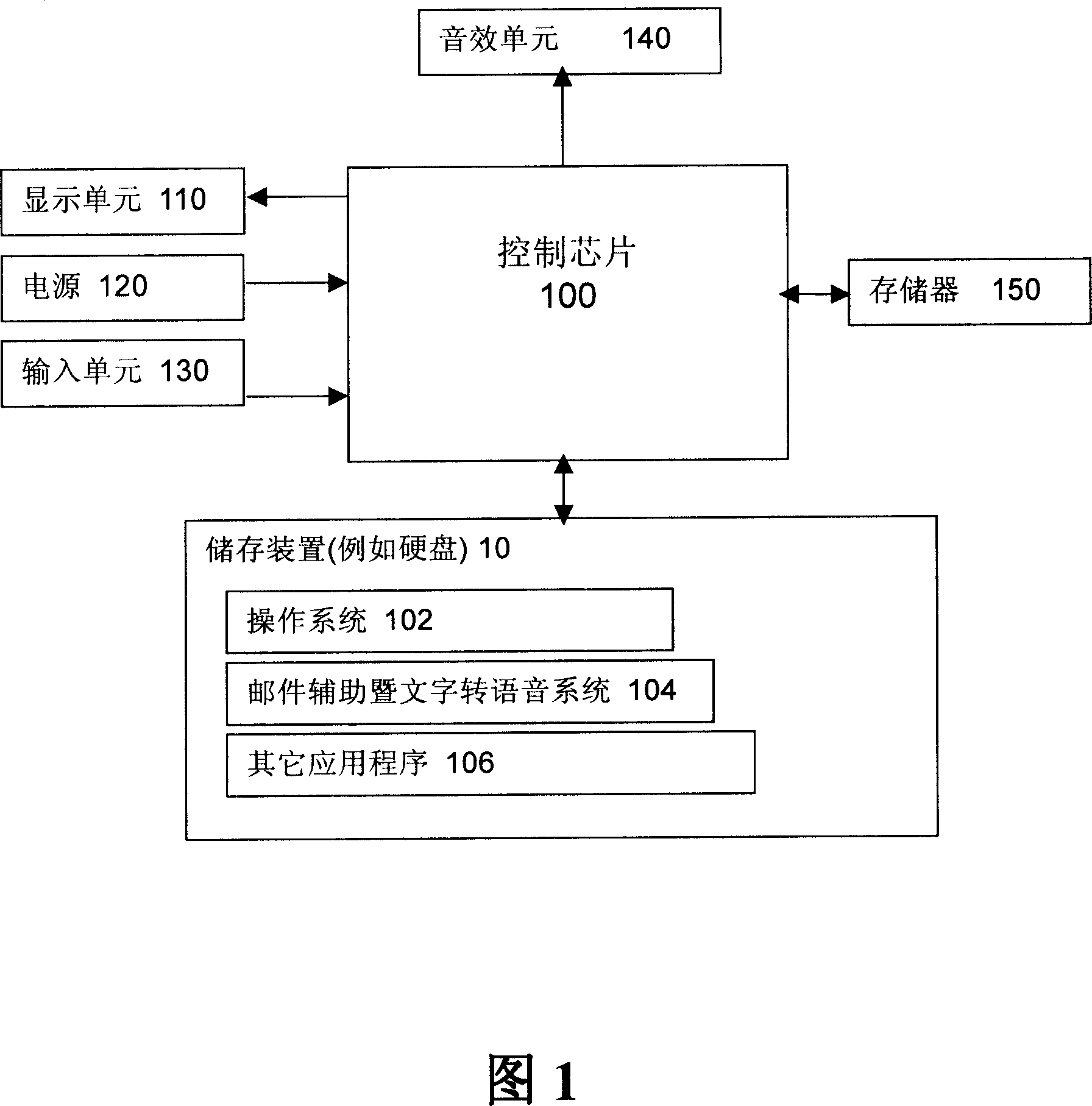
The invention provides an E-mail aided word to voice system which at least possesses two operation modes, that is broadcaster mode and direct word to voice mode, user can switch as his will. When the broadcaster mode is selected, the input words can be recited by a virtual figure, the other hand, if the direct word to voice mode is selected, the input words can be transferred to voice and output by the sound effect unit directly, user can stores it as voice file of wav / MP3 format for later listening. The system in the invention mainly includes control chip, storing device which possesses at least one function module and input unit.
Owner:罗兆鑫
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com