Patents
Literature
351 results about "Event list" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
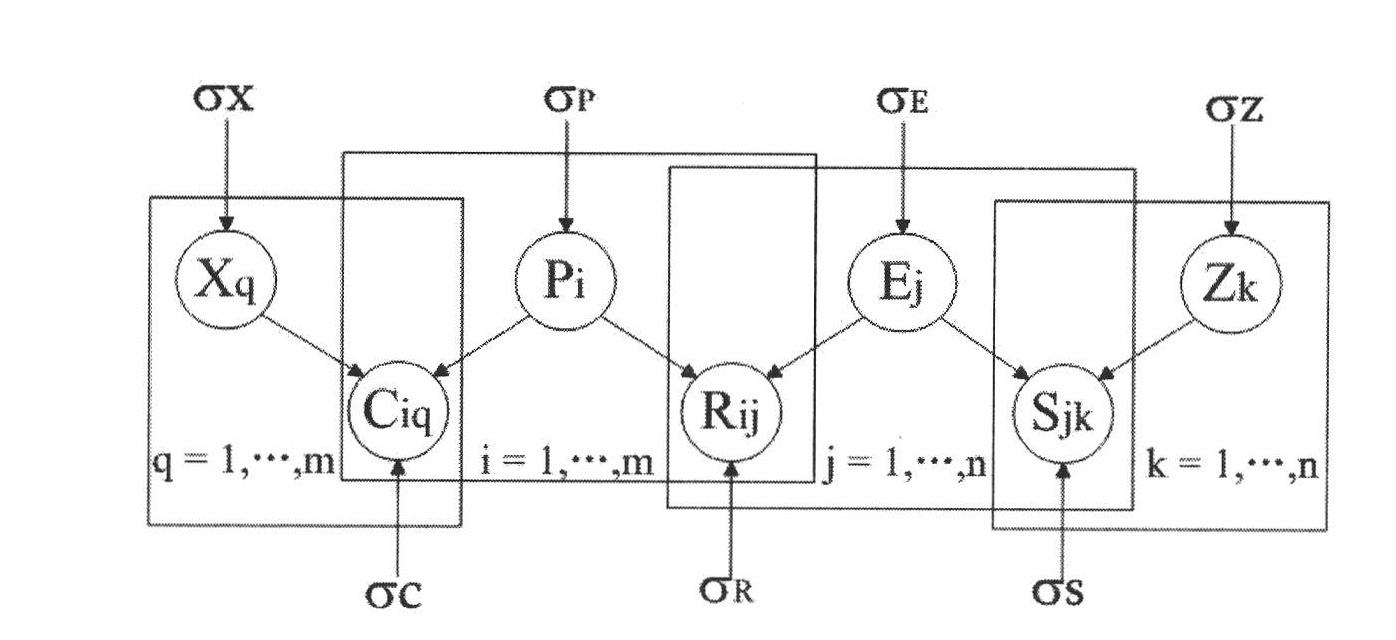
Learning system and learning method comprising an event list database
InactiveUS8290883B2Adaptable to changeImprove efficiencyDigital computer detailsMachine learningStudy methodsLearning methods
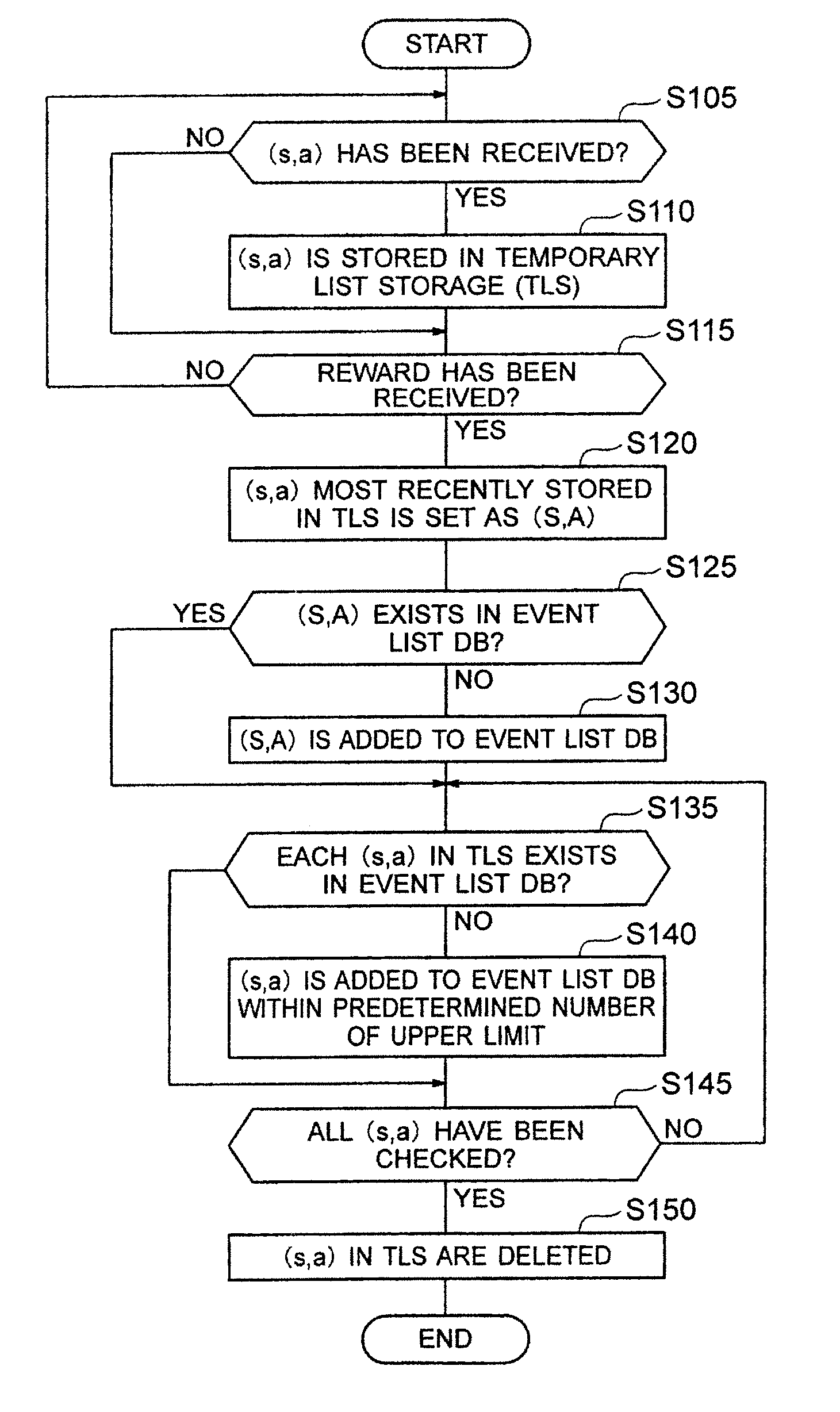
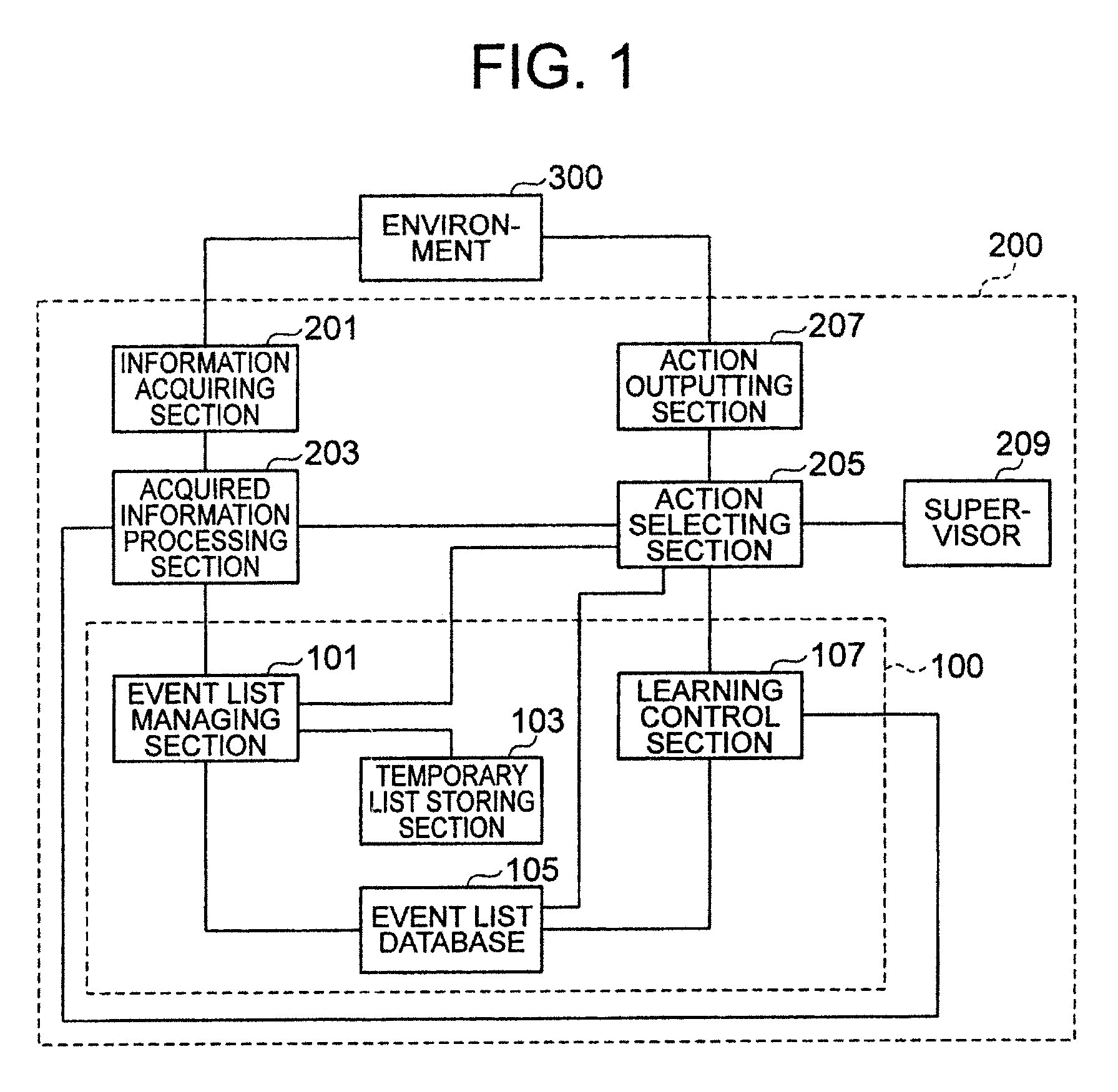
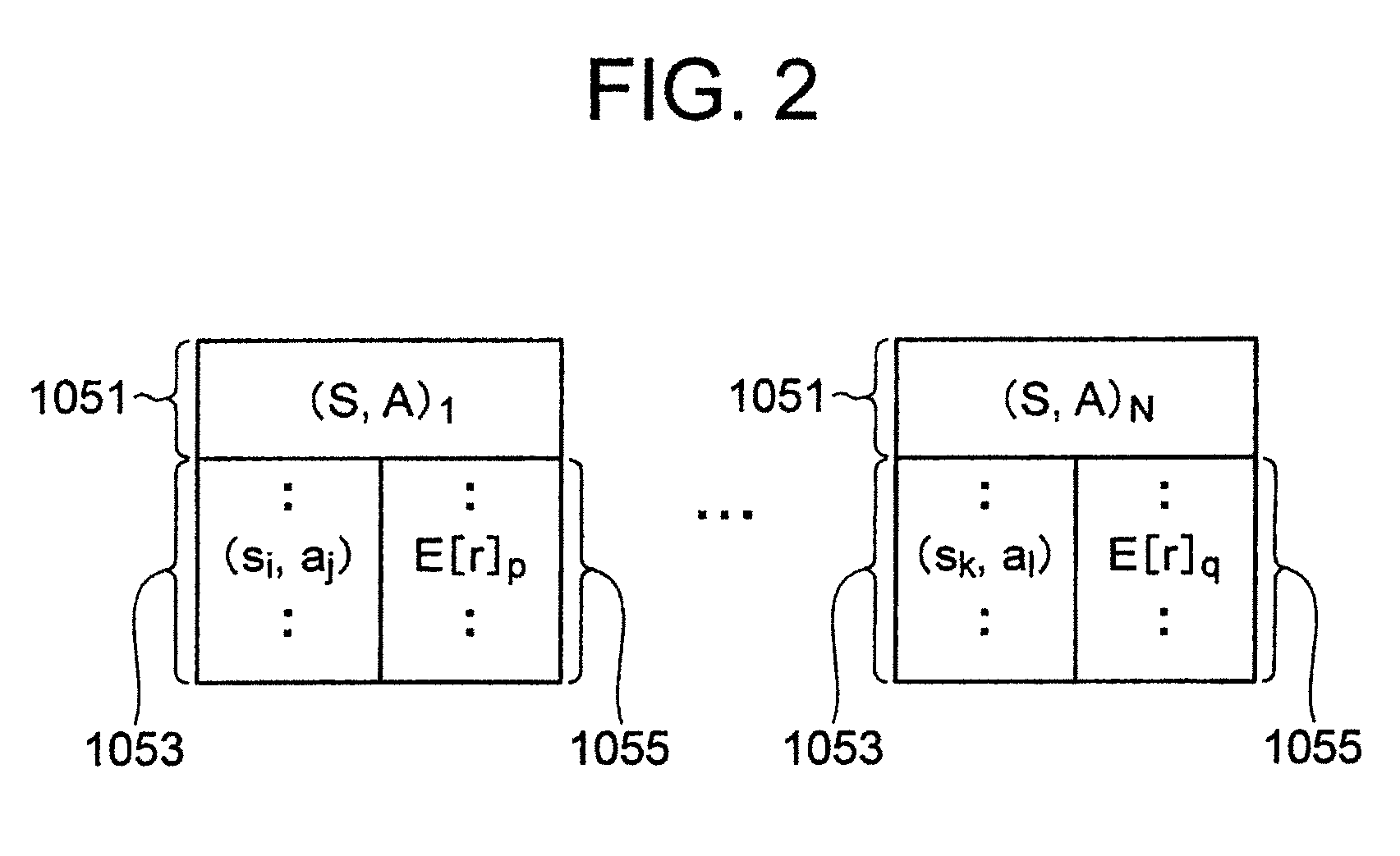
A learning system according to the present invention includes an event list database for storing a plurality of event lists, each of the event lists being a set including a series of state-action pairs which reaches a state-action pair immediately before earning a reward, an event list managing section for classifying state-action pairs into the plurality of event lists for storing, and a learning control section for updating expectation of reward of a state-action pair which is an element of each of the event lists.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
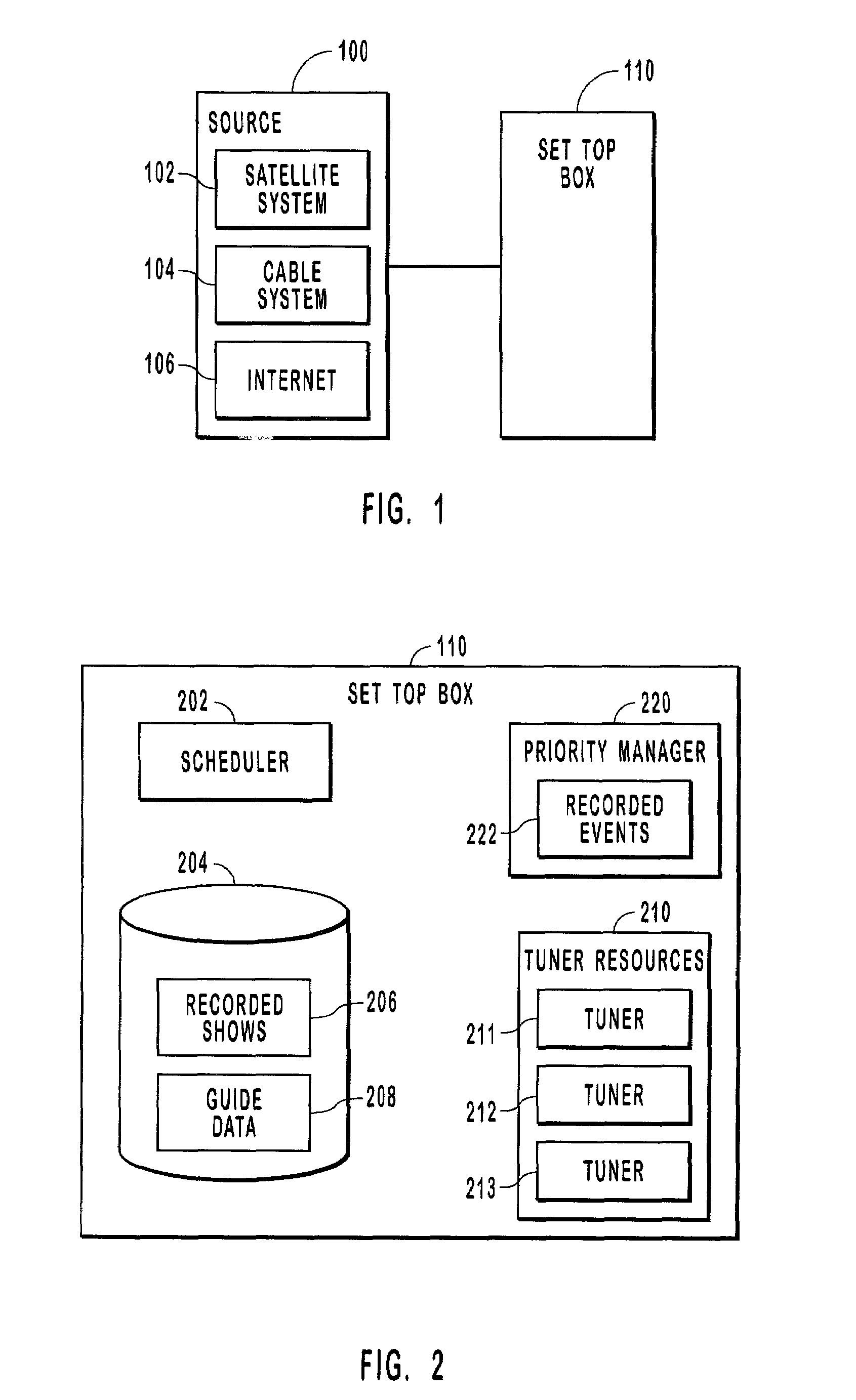
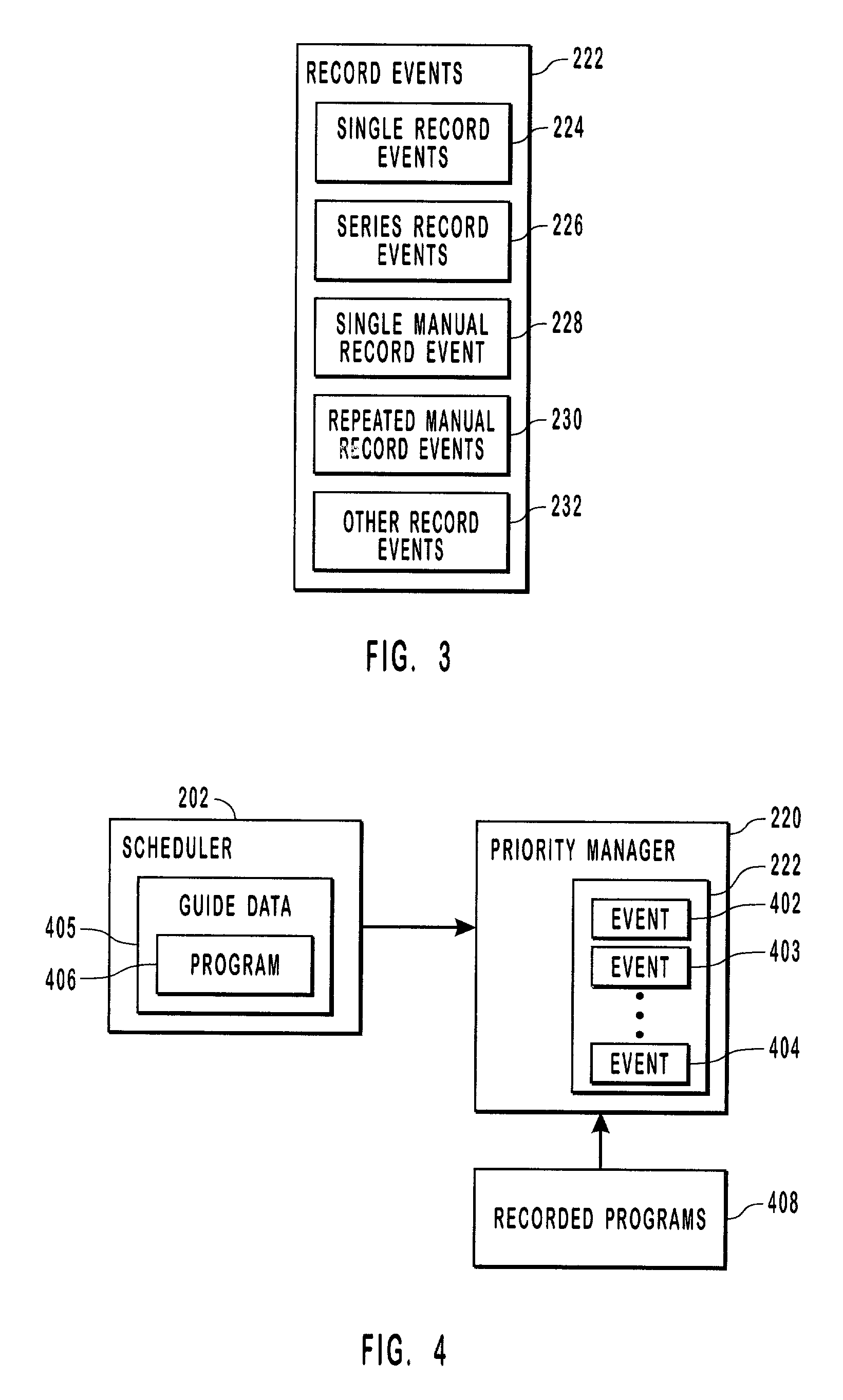
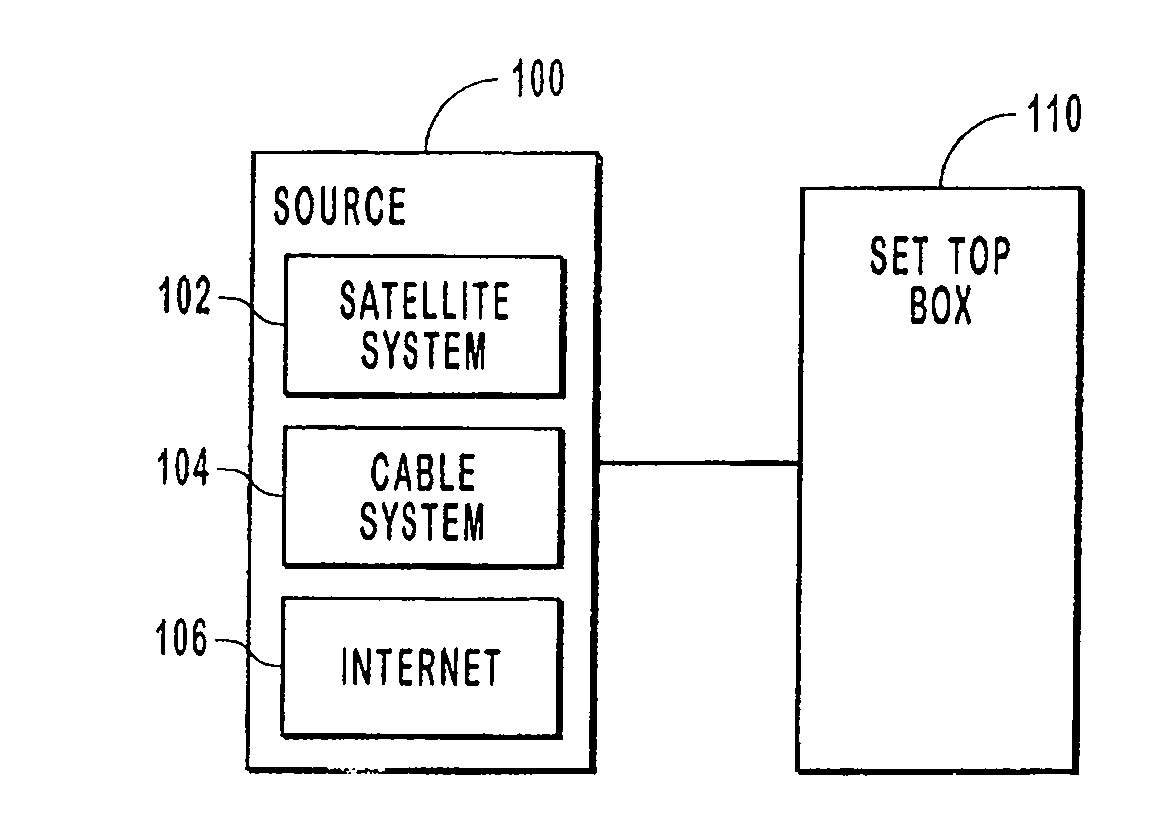
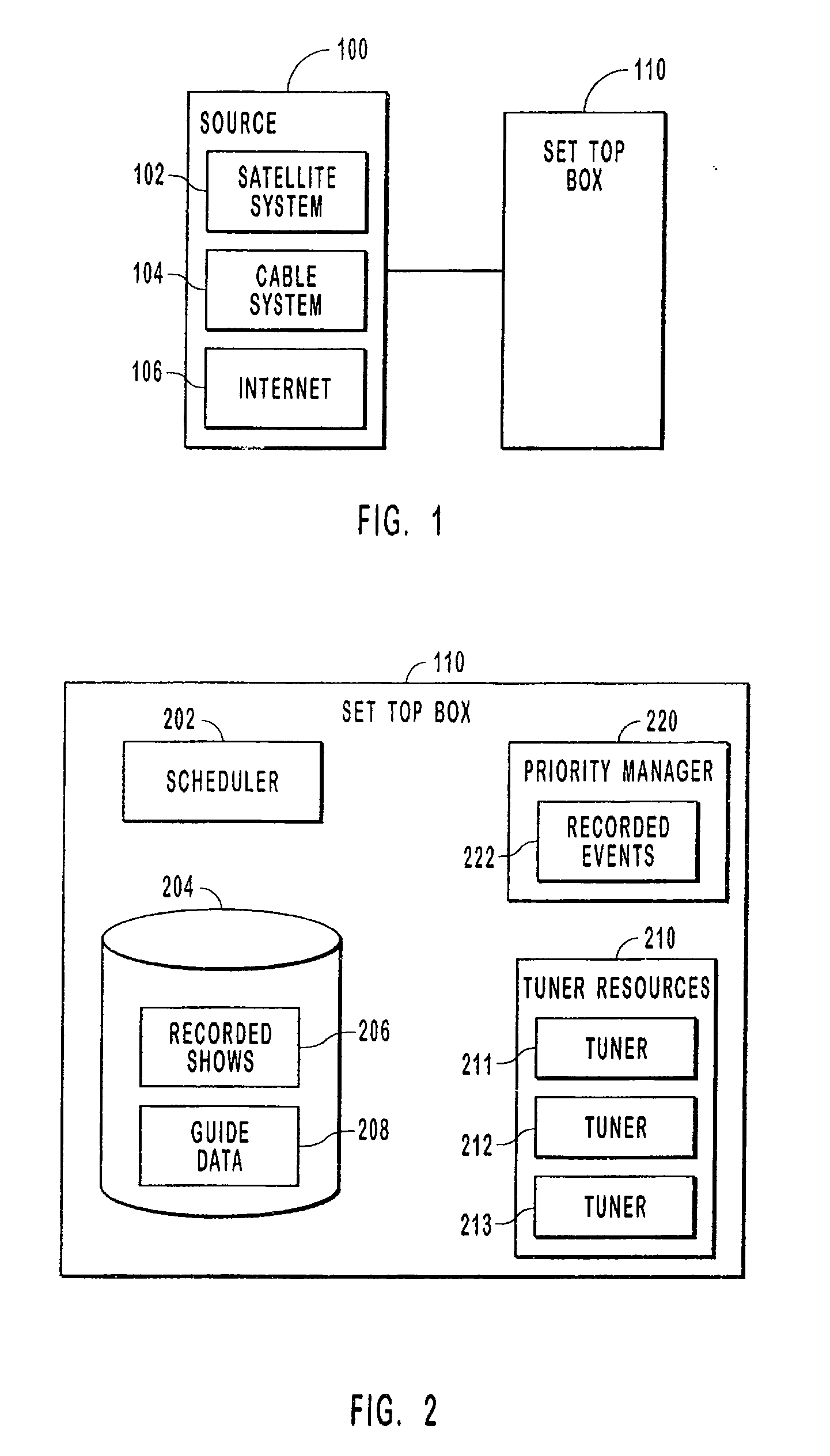
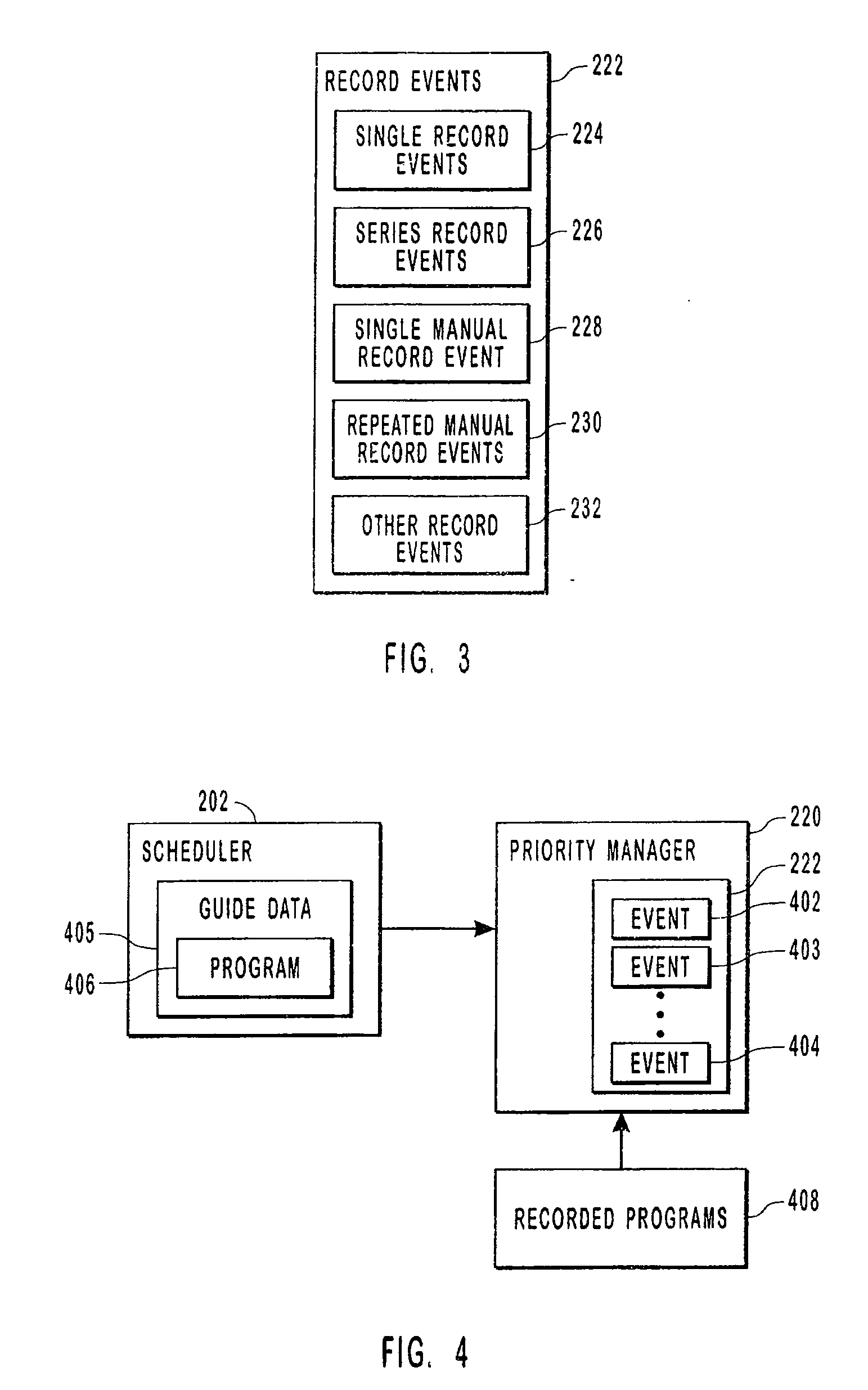
Managing record events
ActiveUS7369750B2Solve conflictsTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsComputer programReal-time computing
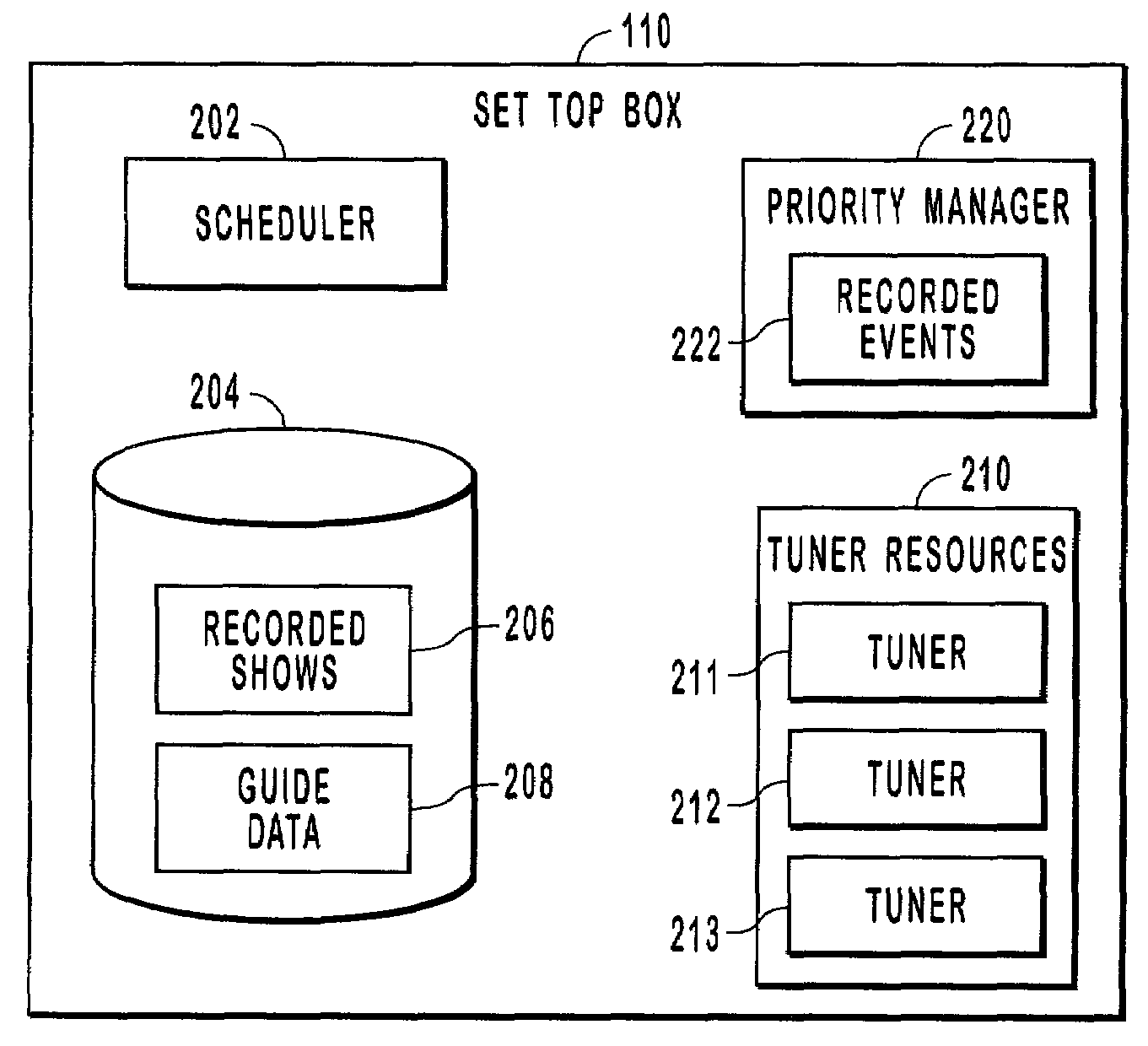
Systems, methods, and computer program products for managing and prioritizing record events. A priority manager includes an event list that lists scheduled record events. Each event in the event list has a priority that is different from the other events in the event list. If some of the events conflict, then those events with the highest priority in the event list are recorded. A user can assign priority to events when they are scheduled or at a later time. This enables event conflicts to be resolved by the user when the events are initially scheduled. When an event conflict arises later, the conflict is resolved by the priority manager according to the relative priority of the events in the event list.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
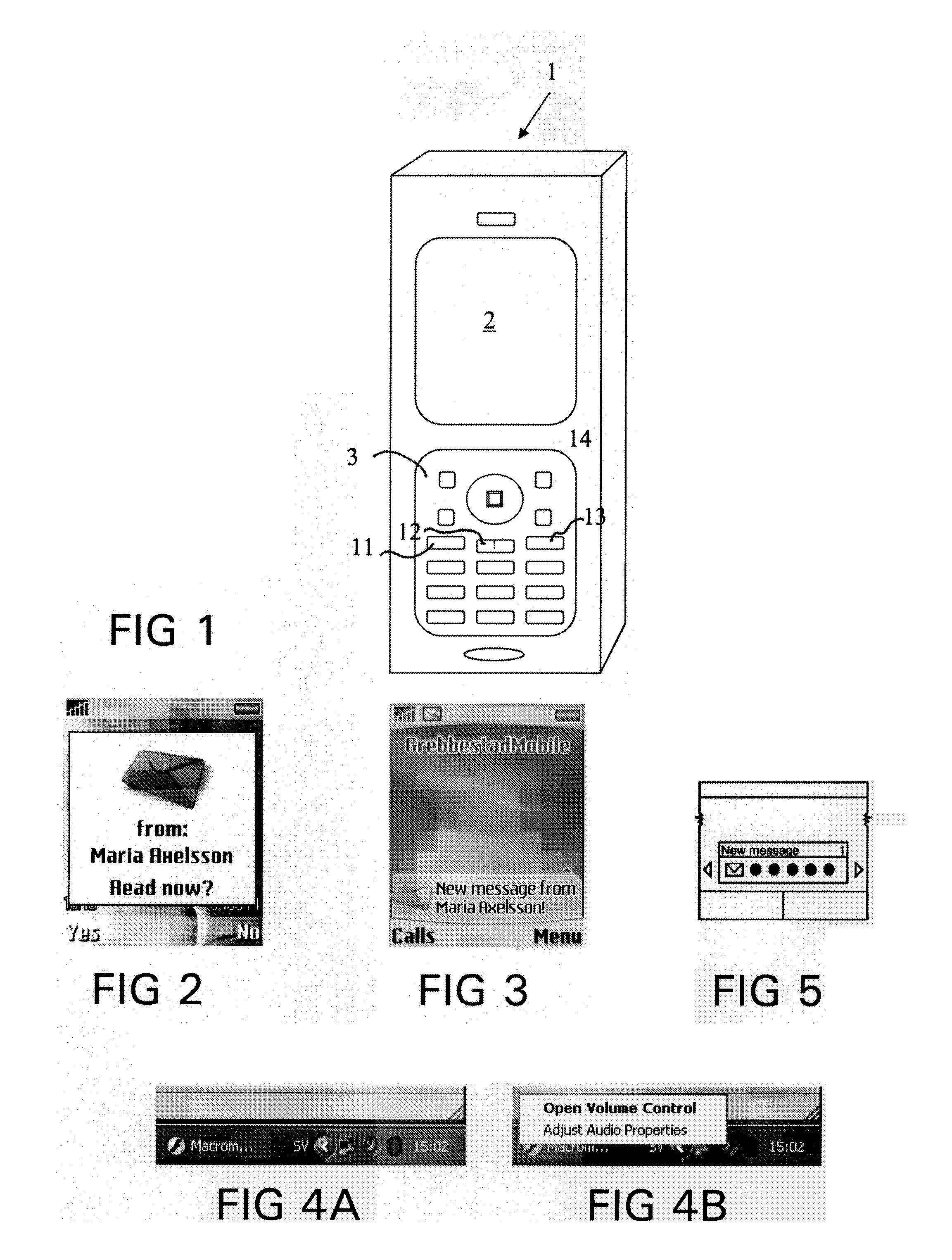
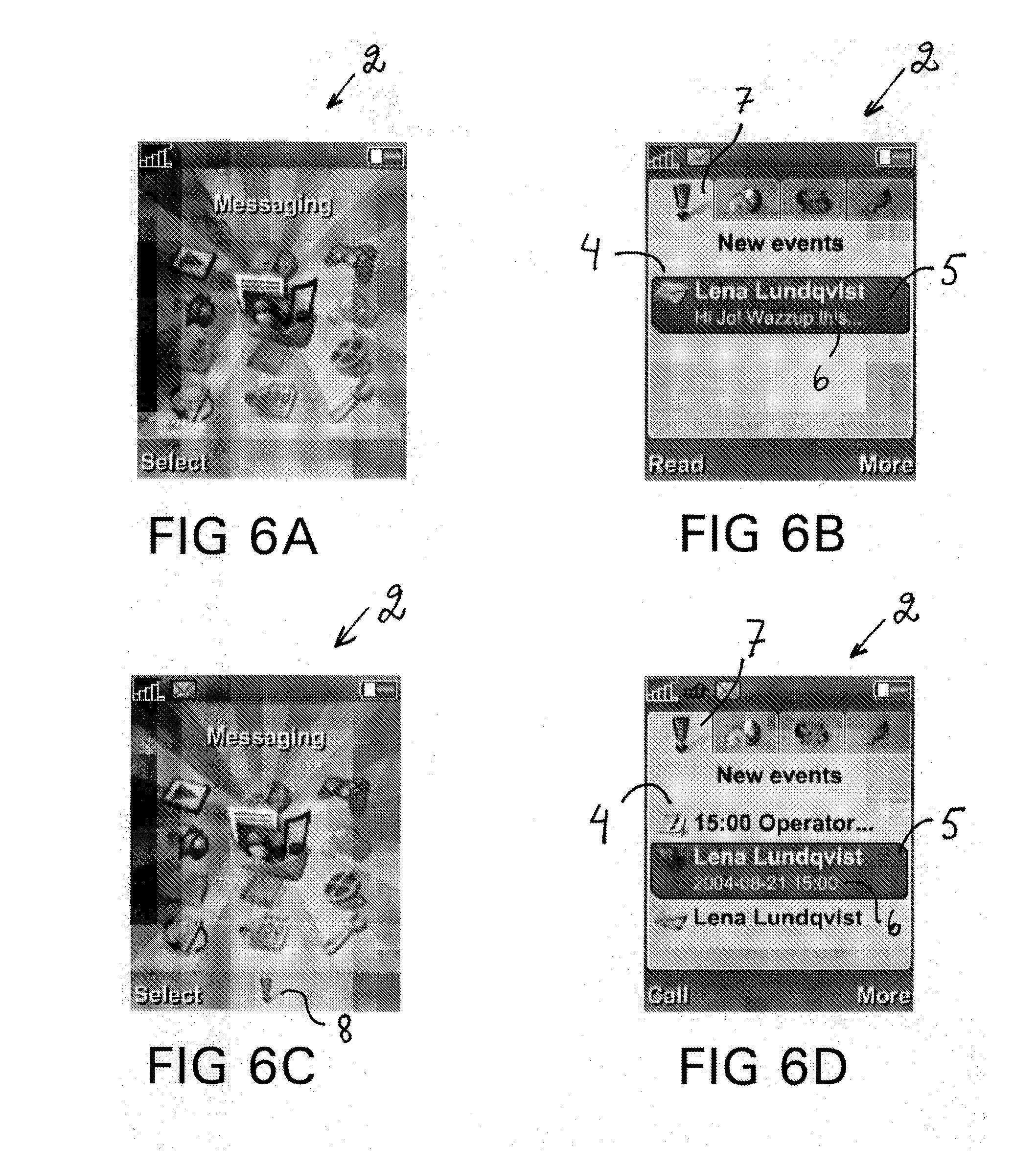
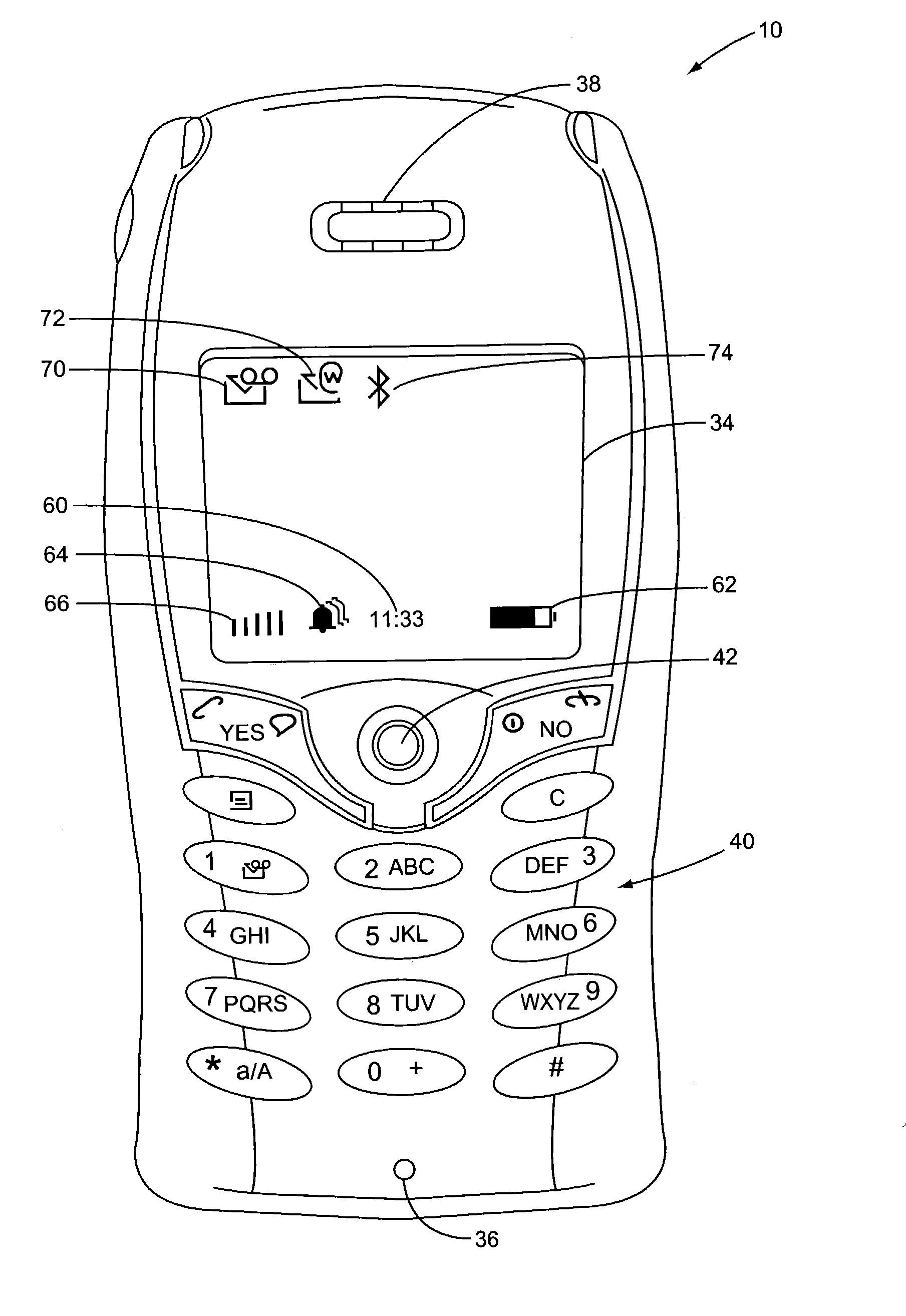
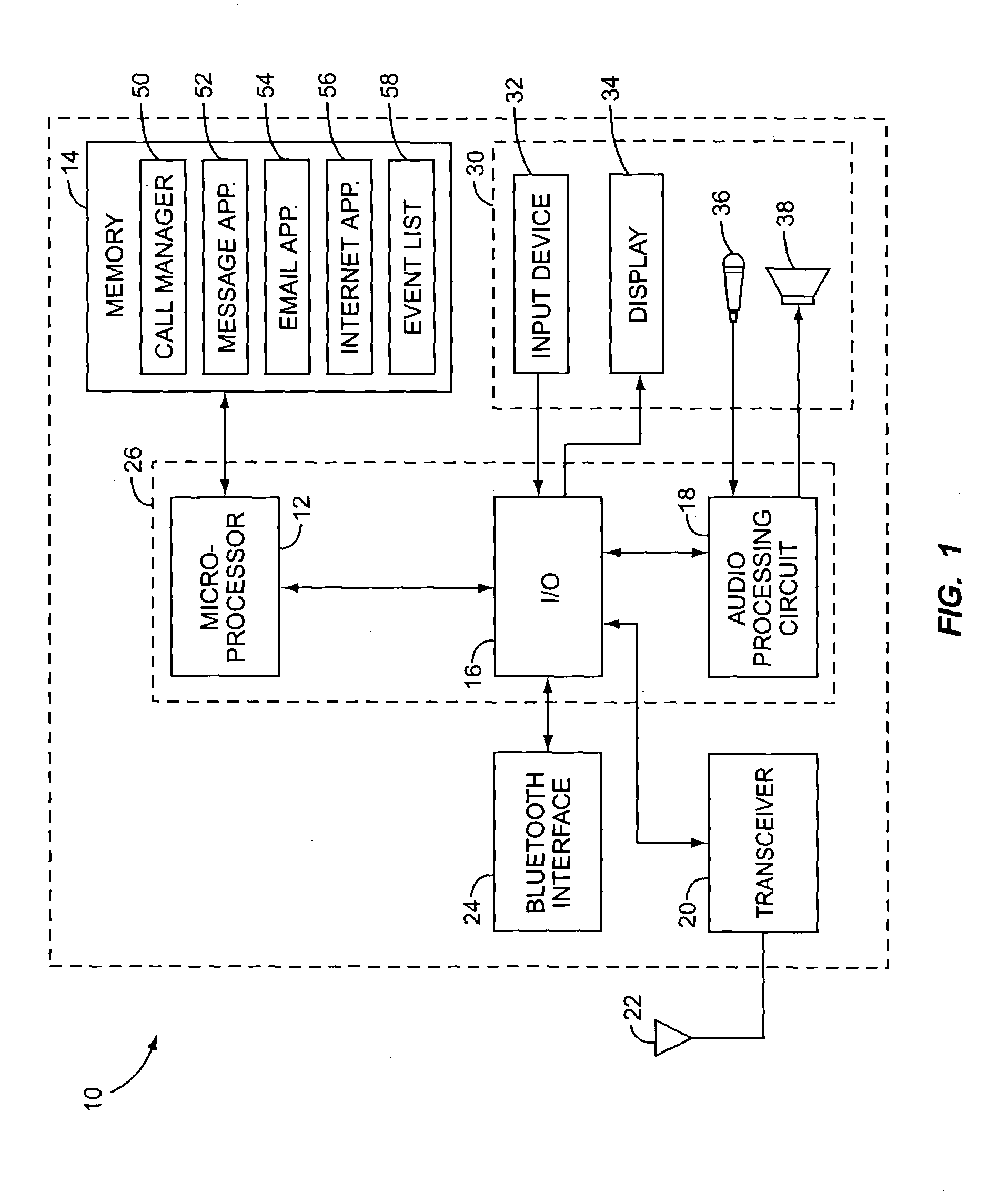
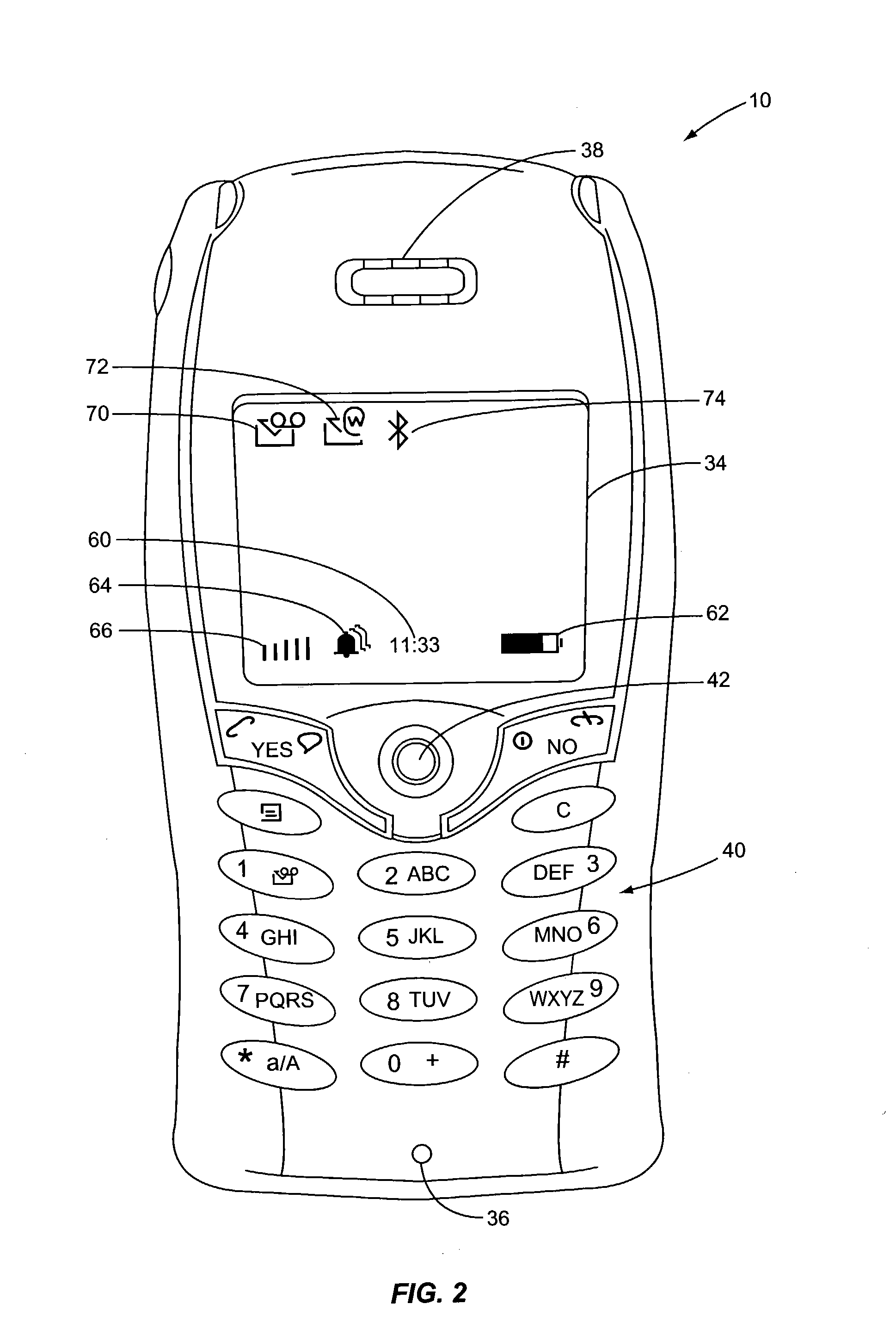
Method for Providing Alerts in a Mobile Device and Mobile Device Therefor
InactiveUS20080057910A1Raise prioritySubstation equipmentData switching networksDisplay deviceMobile device
The invention relates to a method for providing alerts in a mobile device, and more particularly a method for providing a shortcut for displaying and hiding alerts by providing an event list that is shown automatically or accessible by a shortcut button. The invention also relates to a corresponding mobile device. Thus, the invention provides a method for providing alerts in a mobile device having a display and a keypad. The method comprises the steps of: detecting an event; adding an event presentation (5) associated with the event on an event list (4); and showing the event list or a symbol (8) on the display. The event list is shown automatically for critical alerts and is accessible with one key stroke for less critical alerts. The user can choose to hide the list, also with a single key stroke, or act on an event.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Automatic generation of multimedia presentation
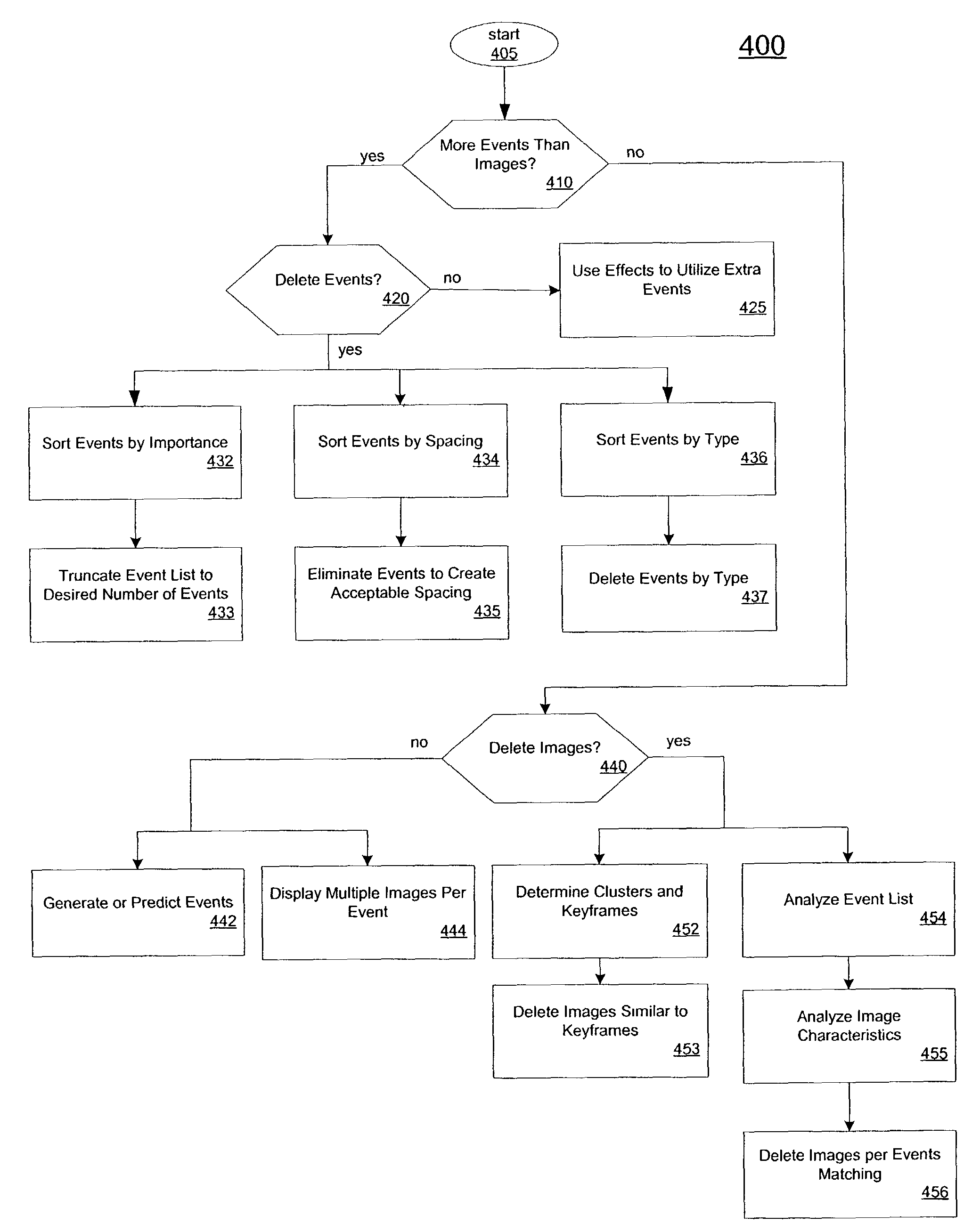
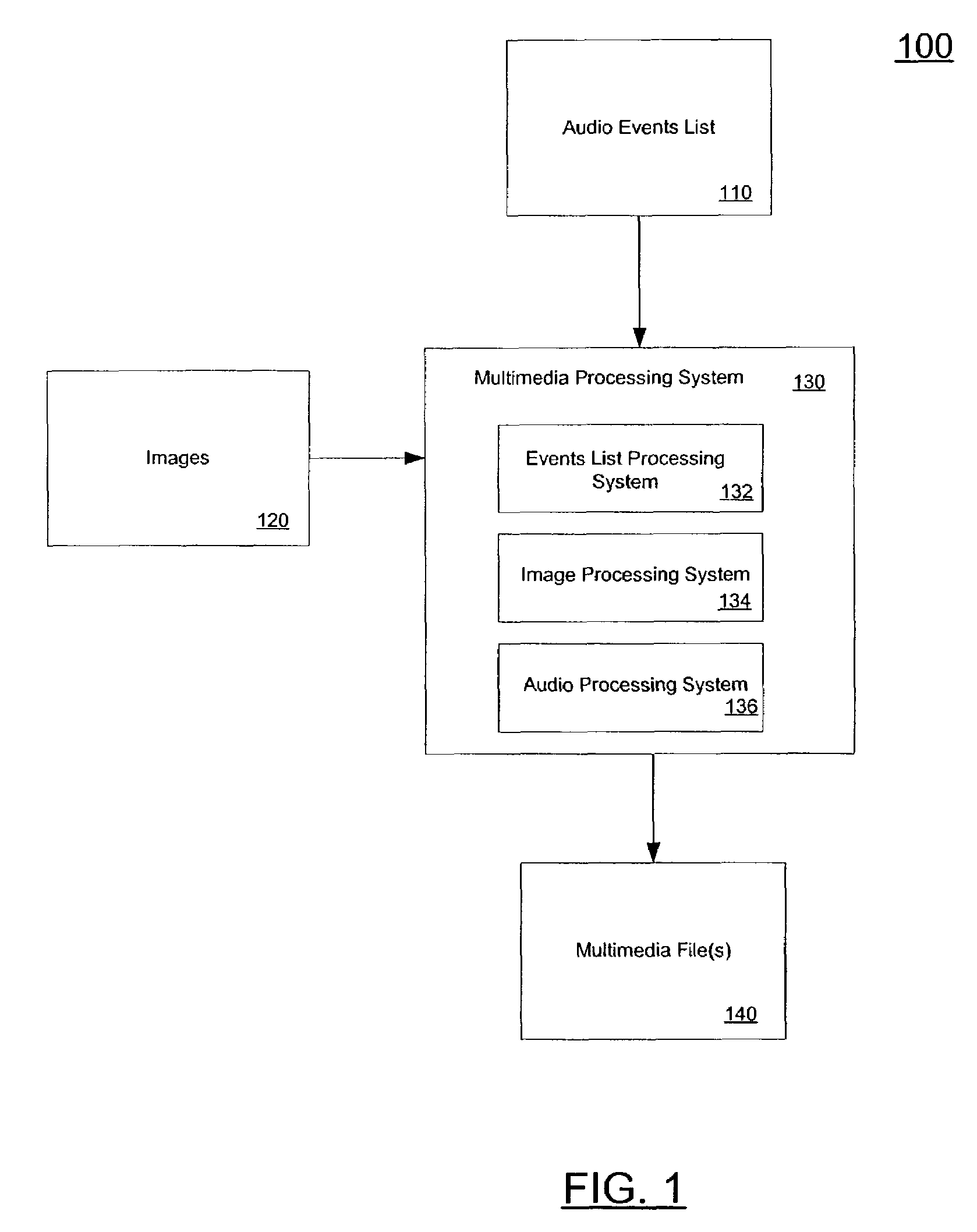
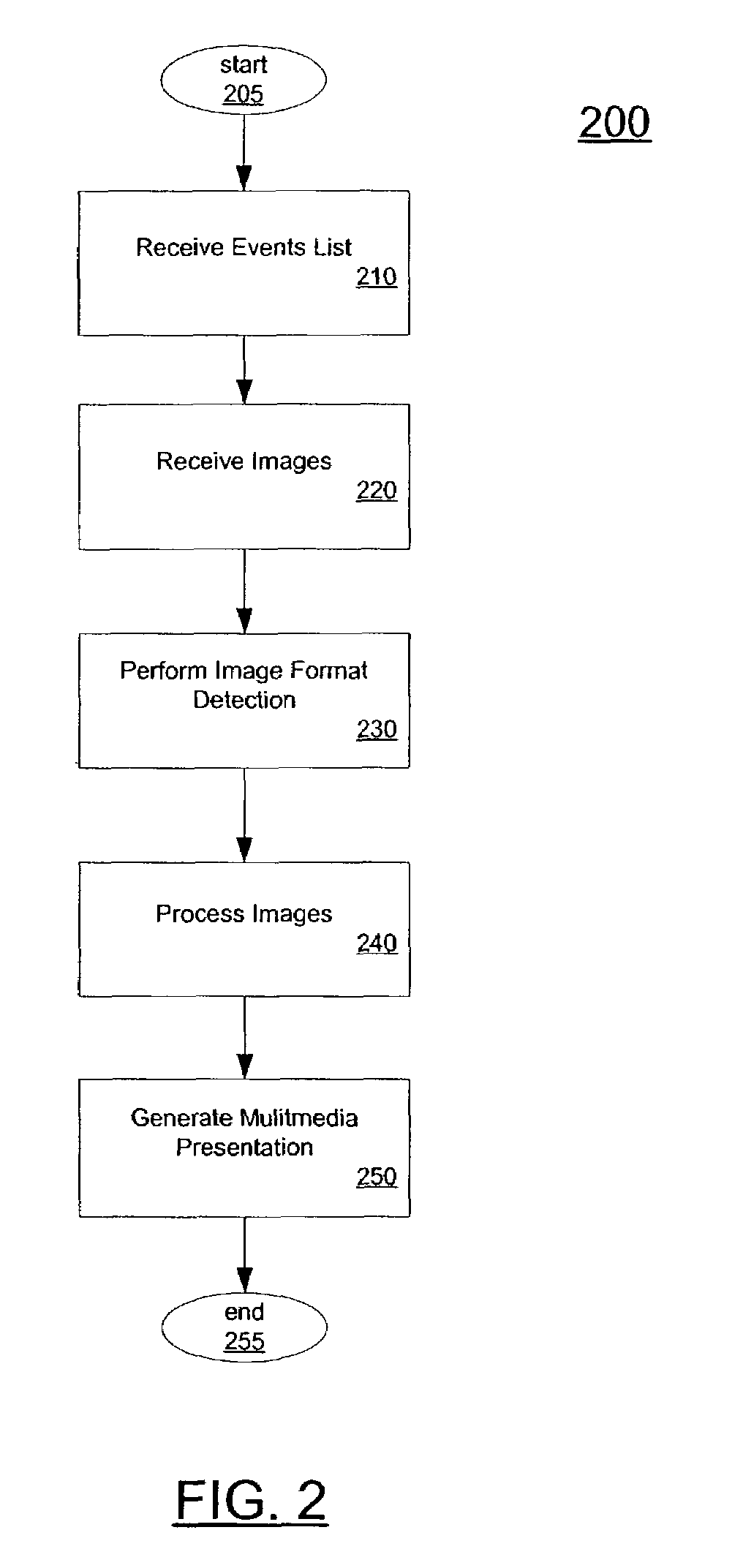
The present invention provides a system and method for automatically combining image and audio data to create a multimedia presentation. In one embodiment, audio and image data are received by the system. The audio data includes a list of events that correspond to points of interest in an audio file. The audio data may also include an audio file or audio stream. The received images are then matched to the audio file or stream using the time. In one embodiment, the events represent times within the audio file or stream at which there is a certain feature or characteristic in the audio file. The audio events list may be processed to remove, sort or predict or otherwise generate audio events. Images processing may also occur, and may include image analysis to determine image matching to the event list, deleting images, and processing images to incorporate effects. Image effects may include cropping, panning, zooming and other visual effects.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
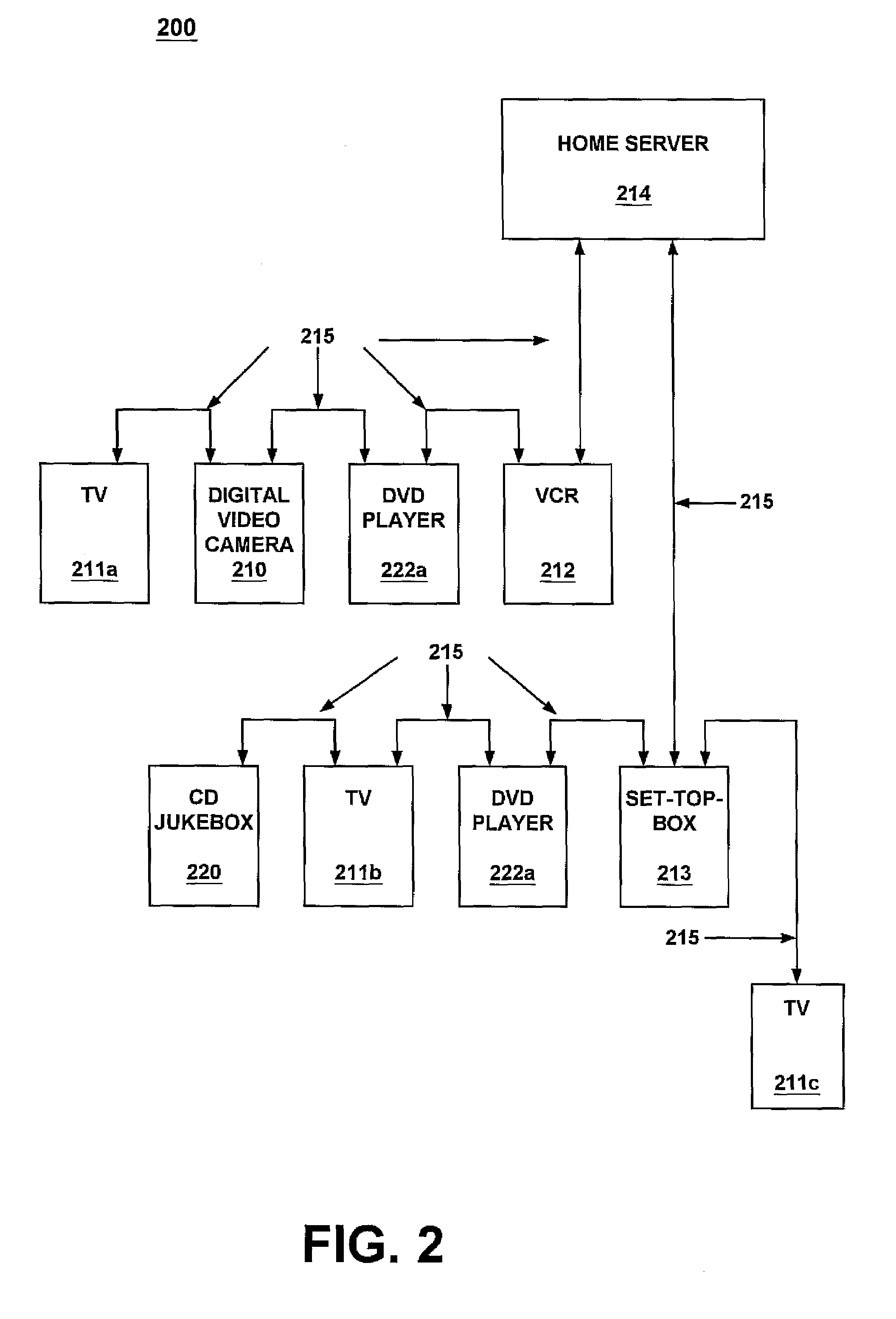
Request event manager and event lists for home and office systems and networks
InactiveUS7412538B1Multiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsNetwork activityApplication software
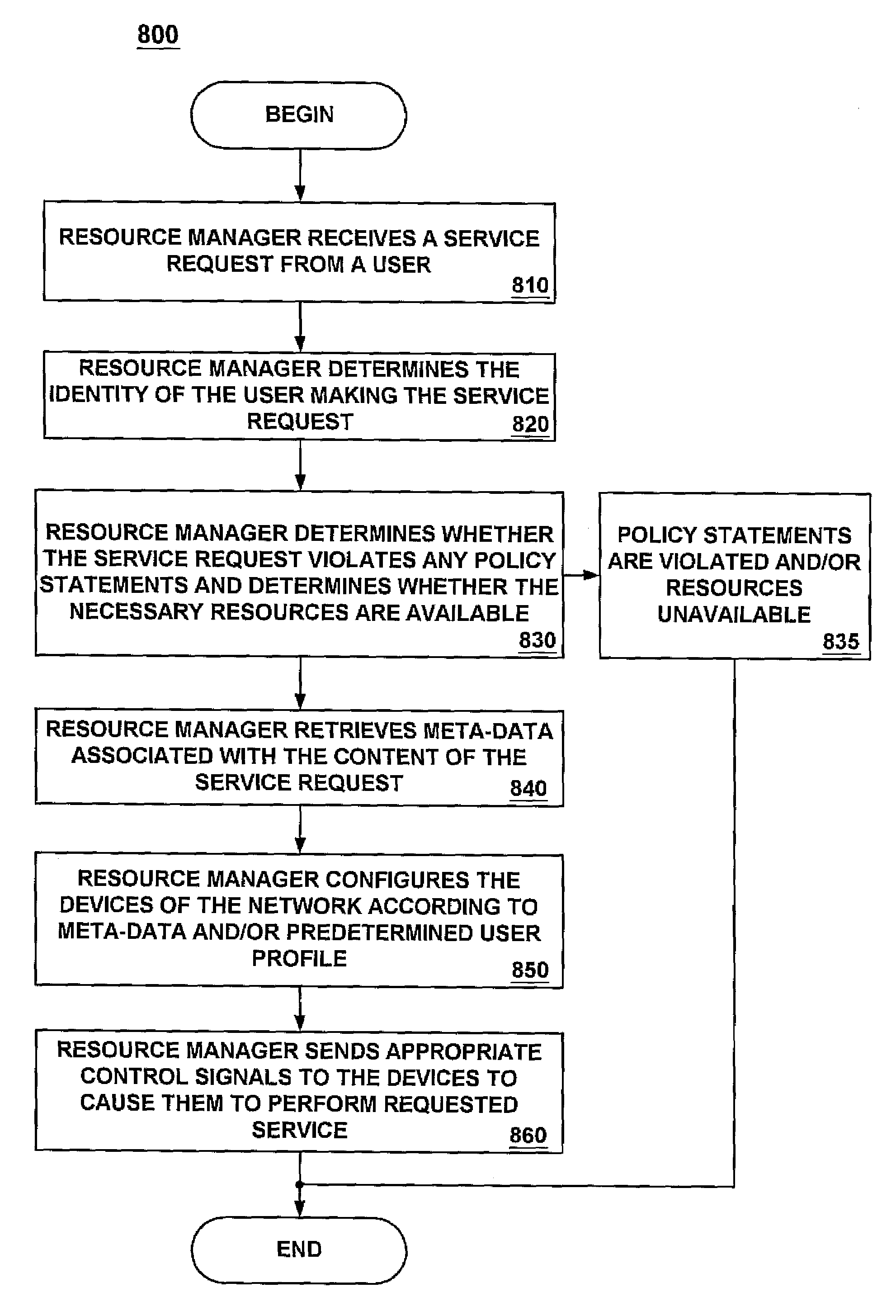
A request event manager for a network of consumer electronic devices. In one embodiment, the request event manager maintains a database of home network services, and allows the home network services to be scheduled for execution over time. Home network services herein refer to high-level abstractions of a consumer electronic device's functionalities, and also content that is available from the consumer electronic device. The request event manager of the present invention also creates and maintains a service request list (SRL) which details the service actions in a hierarchical fashion. By maintaining a database of home network services, the request event manager of the present invention allows user applications to specify and schedule concatenated or hierarchical events such that different network activity across interconnected heterogeneous consumer electronic devices can be synchronized without requiring complicated logic to be implemented. The request event manager of the present invention may be implemented as part of a middleware infrastructure for a home network, and may reside within a home server.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Event list menu for accessing menu items in a hierarchical menu
InactiveUS20050020316A1Quickly and easily accessSimple and consistentSubstation equipmentData switching networksUser inputKeyboard shortcut
An events list menu provides quick and easy access to menus associated with desired functions or features of a mobile communication device. The mobile communication device dynamically updates the event list menu responsive to designated events and displays the event list menu responsive to user input. In one embodiment of the invention, the user may display the event list by pressing a shortcut key or a combination of keys. Each event in the event list is associated with a menu item in a hierarchical menu. The associated menu item is invoked when the user selects an event from the event list.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
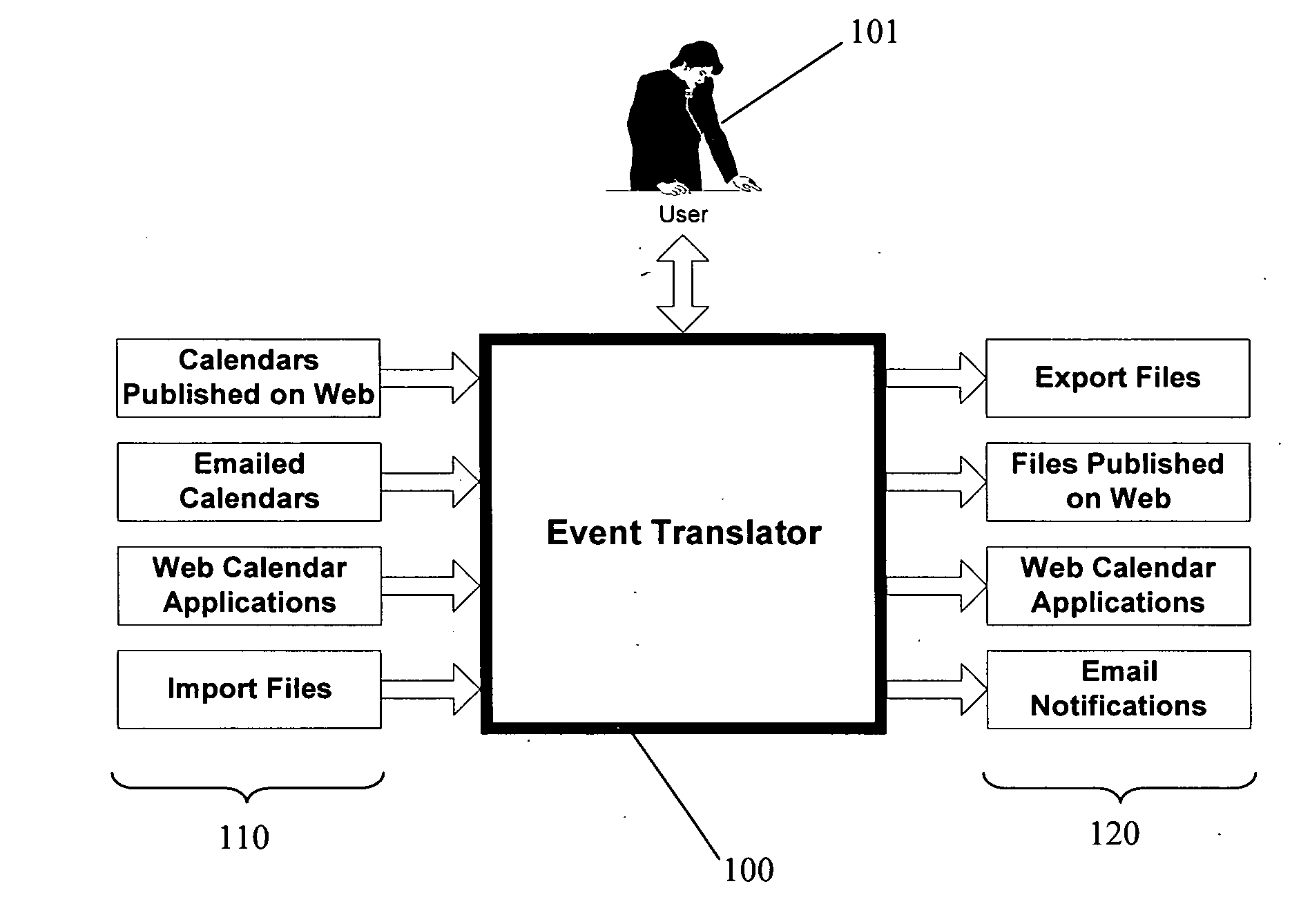
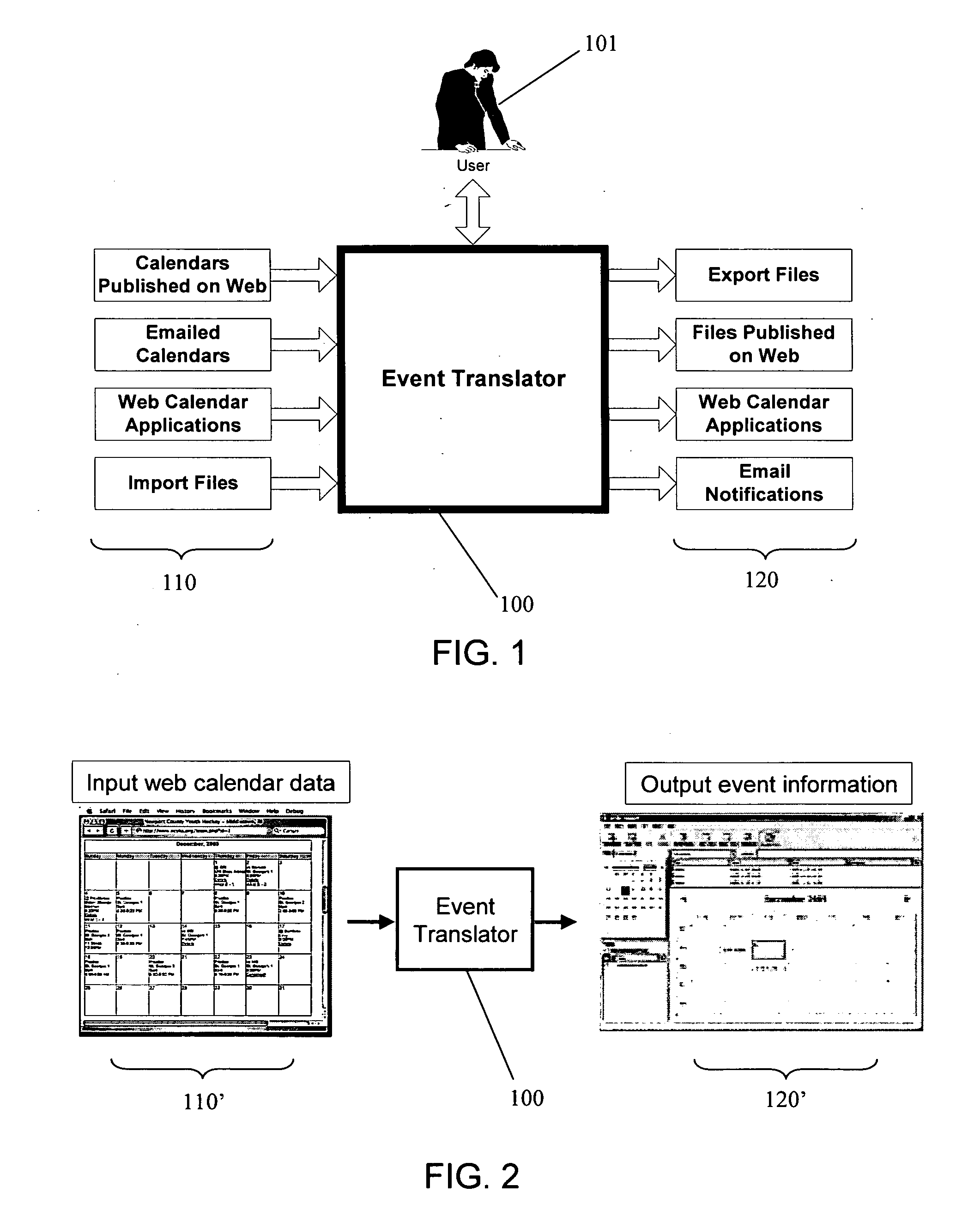
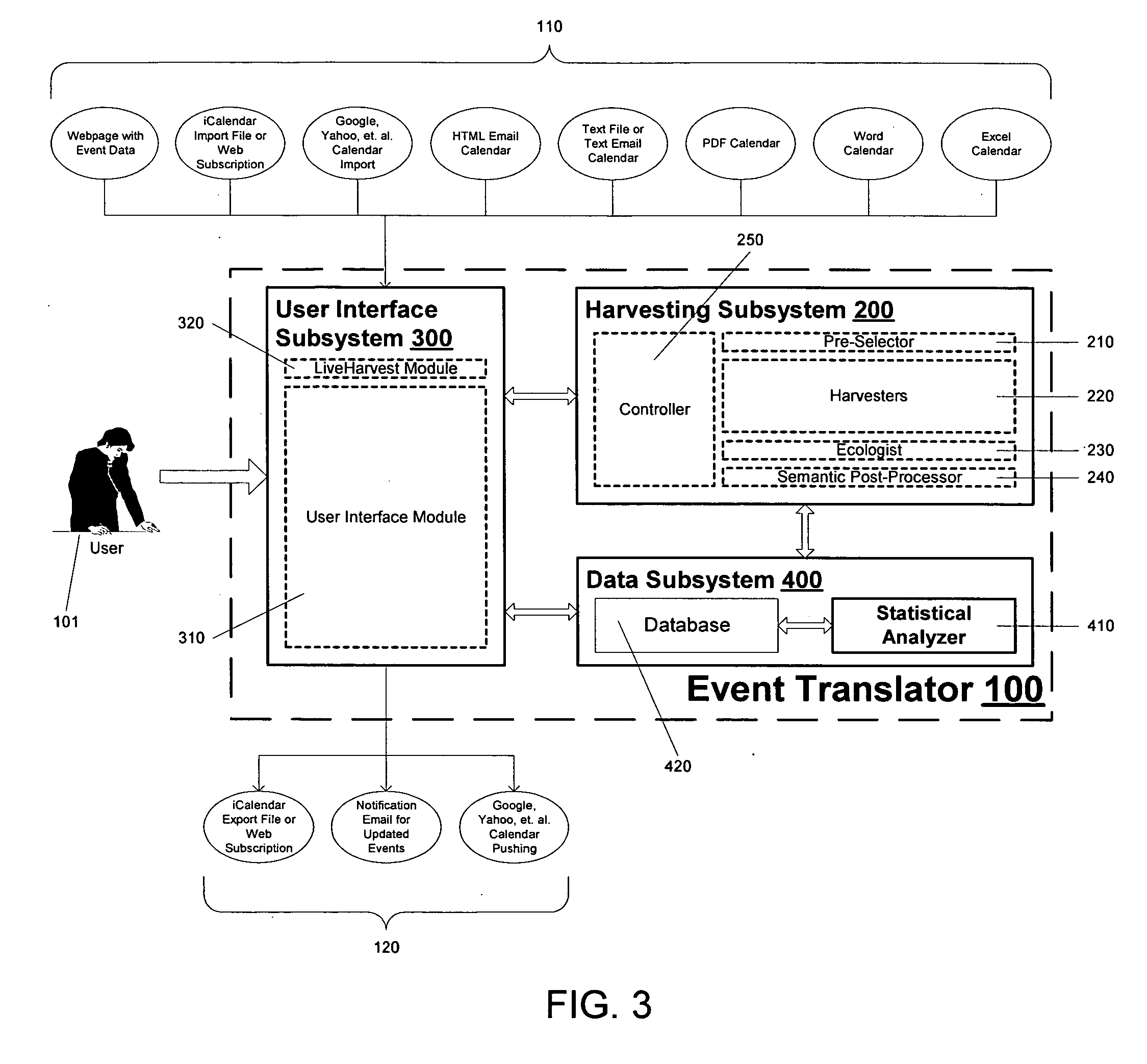
Event data translation system
InactiveUS20070220063A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData translationElectronic mail
An event translator system may perform at least three tasks: (1) extract or “harvest” date, time, description, and other information from digital files generated for human reading, such as web calendars or other event lists, emailed calendars, and imported files; (2) present the extracted event data to a user for modification, management, and monitoring; and (3) export the events to PIM software, web pages and / or application programming interfaces as appropriate file formats. The event translation system may be incorporated into a web site that is accessed by the user who enters a desired web address for event translation or otherwise transmits the digital files for translation. Alternatively, the system may be incorporated into a webpage as a browser plug-in that provides a user-selectable option to extract event information from a visited webpage. Other implementations are possible, including incorporation into desktop software, enterprise software on a server, and plug-ins for e-mail or other applications, among others.
Owner:HUNTE VADIM +1
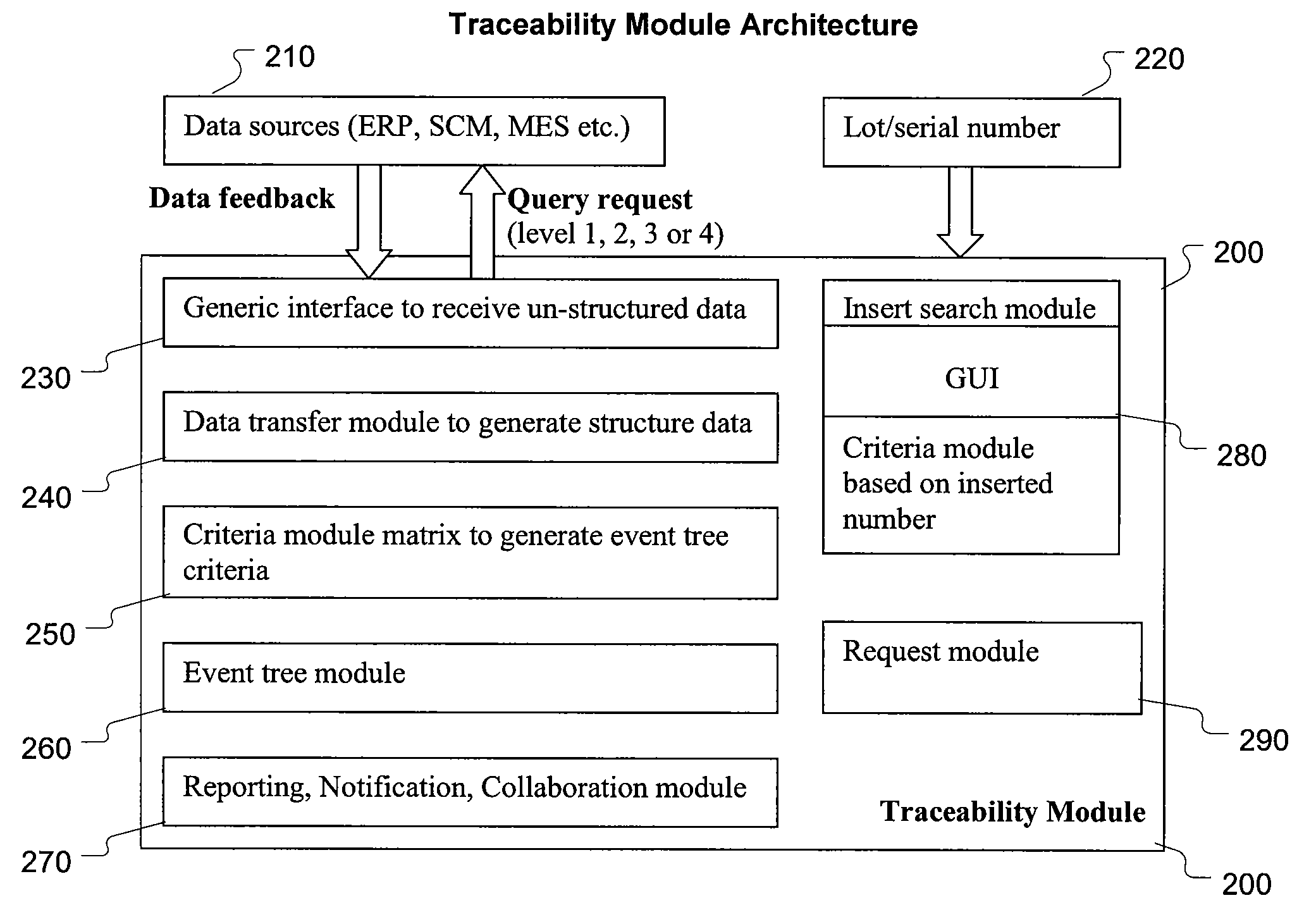
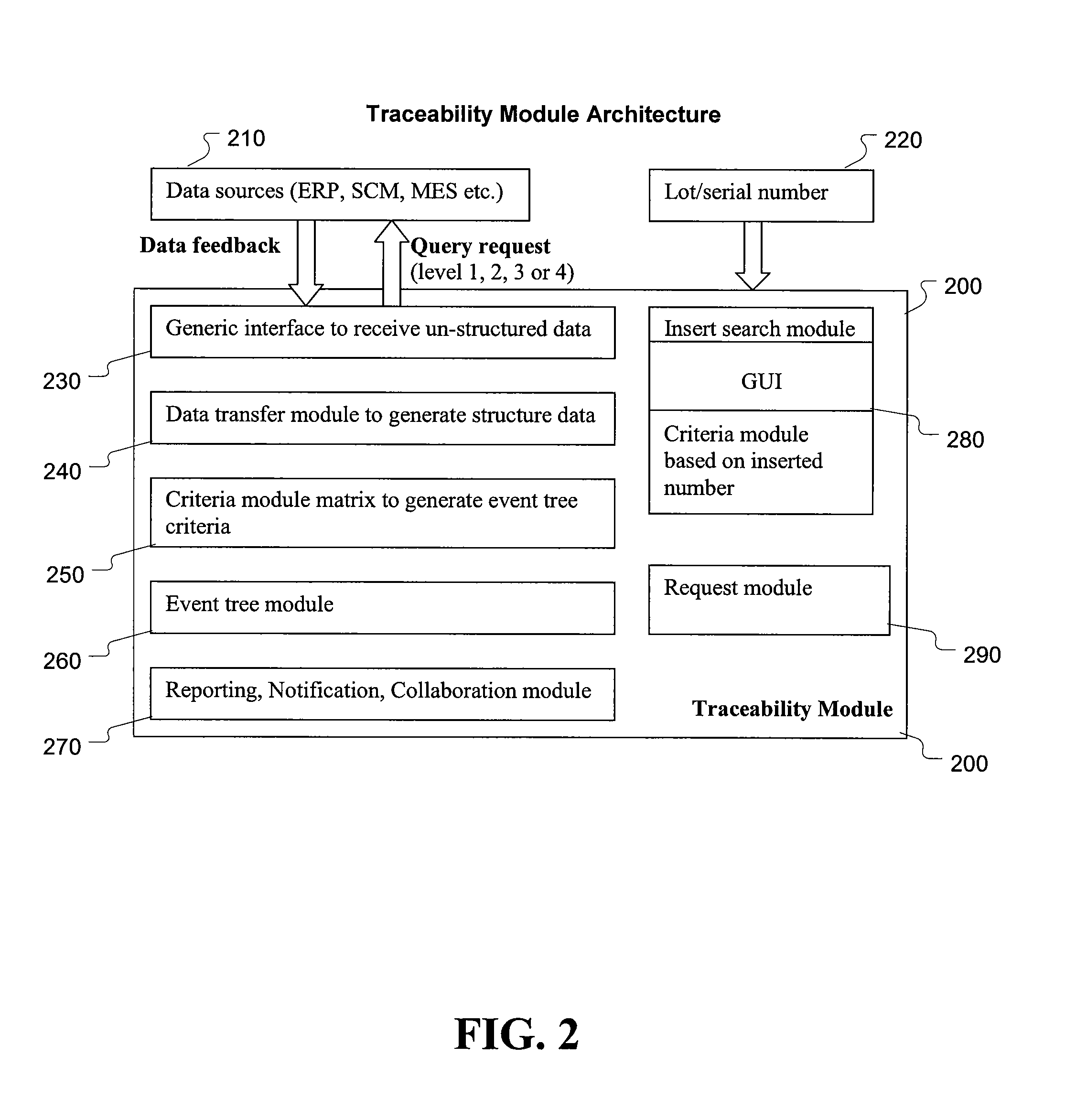
Search engine to improve product recall traceability activities
InactiveUS20090254535A1Avoid damageIncrease costWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsTime rangeHuman search engine
The present invention provides an improved method of handling product recall activities through traceability. One embodiment of the present invention involves gathering data in a multi-layered database architecture containing supply, process, test, and customer layers. The data is supplied to a traceability module which contains a search engine to link and access the data. The search engine enables a search by part number, lot number, serial number, time stamp, and date / time frame. A traceability analysis is generated from the search, allowing failure analysis of the data. This analysis is performed through an event list over the entire supply, manufacturing, and customer data, facilitating backward and forward traceability of parts and components of the parts. This failure analysis further facilitates automatic response such as automatic warning and automatic recall to manufacturers and customers.
Owner:IBM CORP
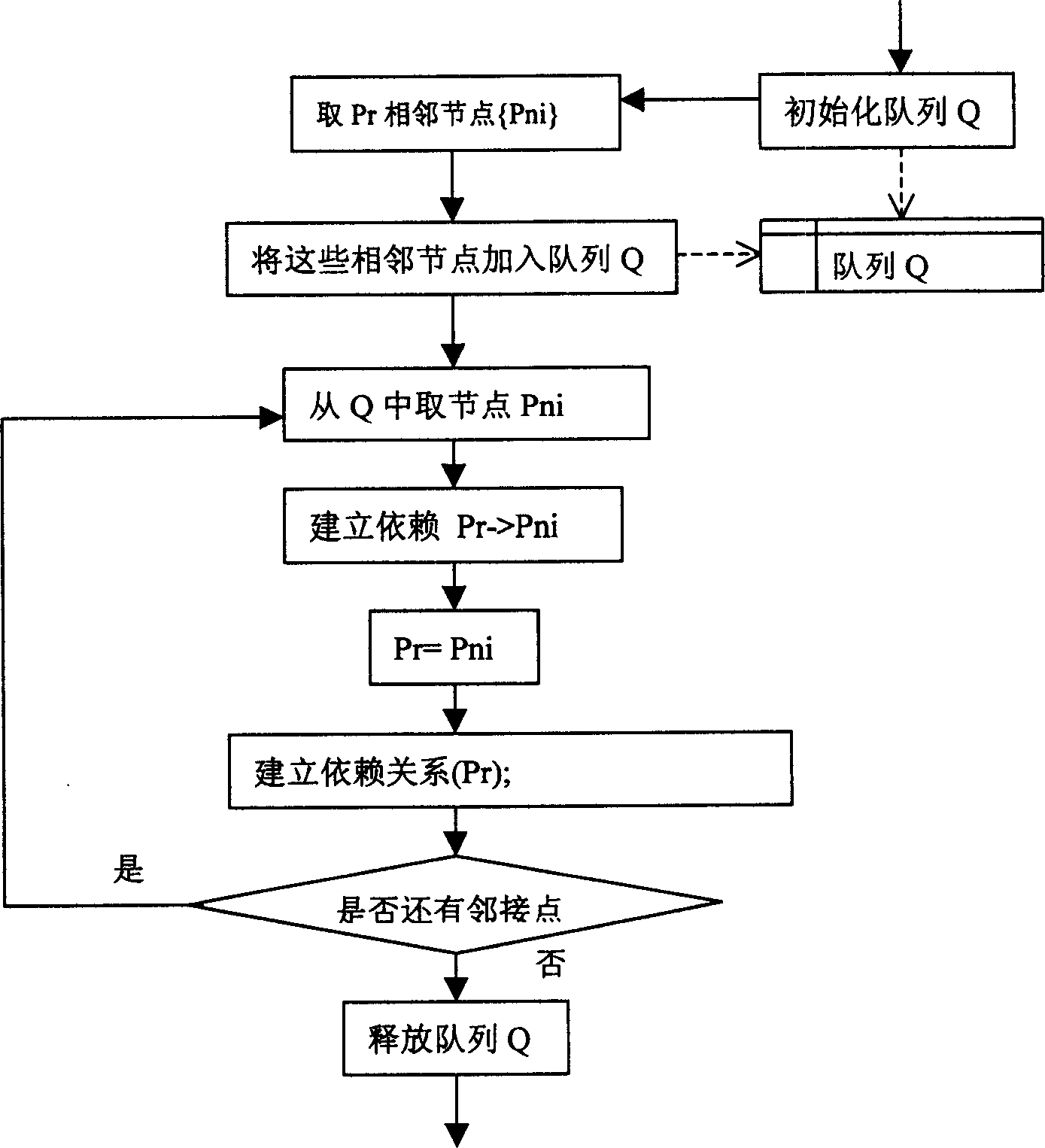
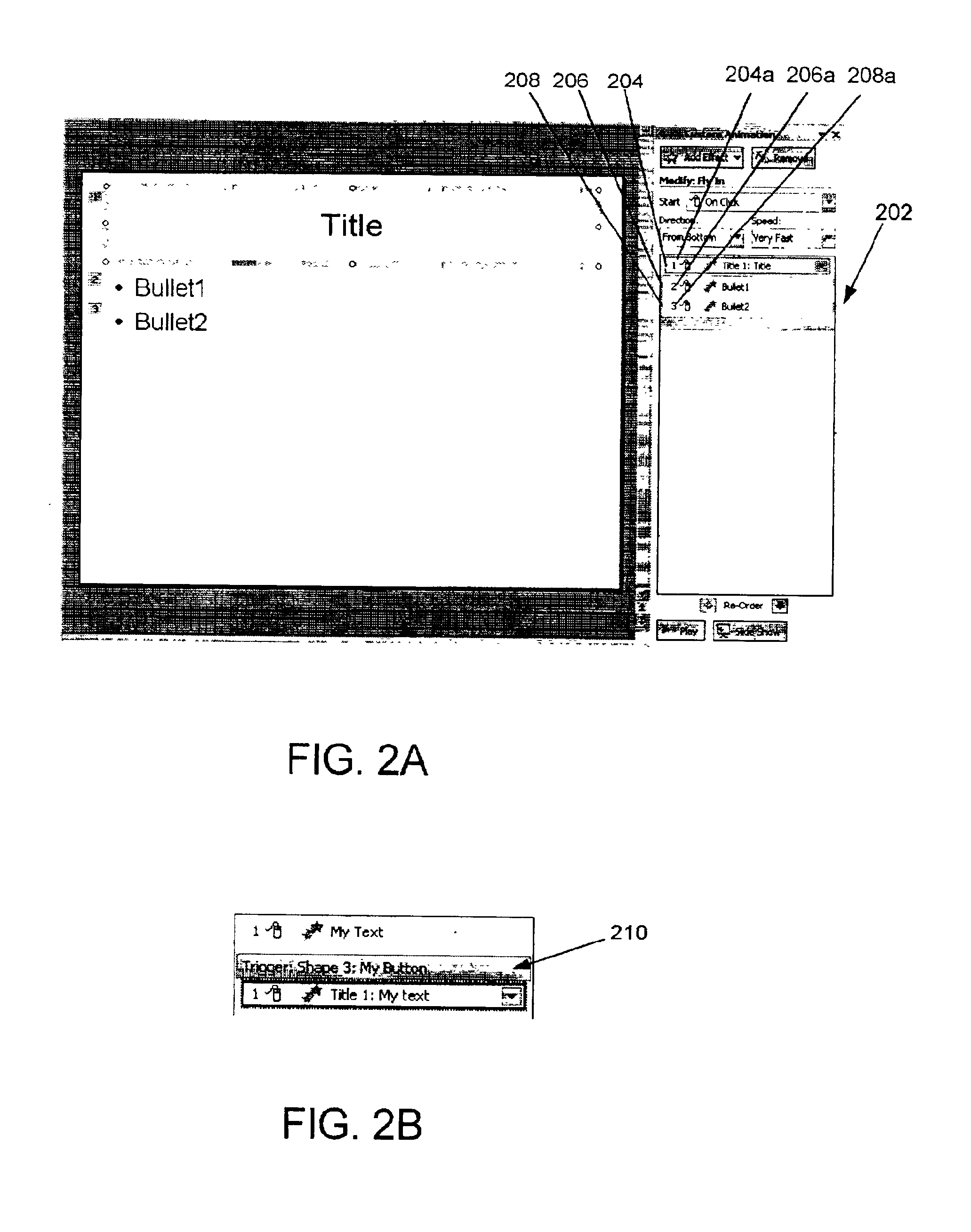
Integrated timeline and logically-related list view
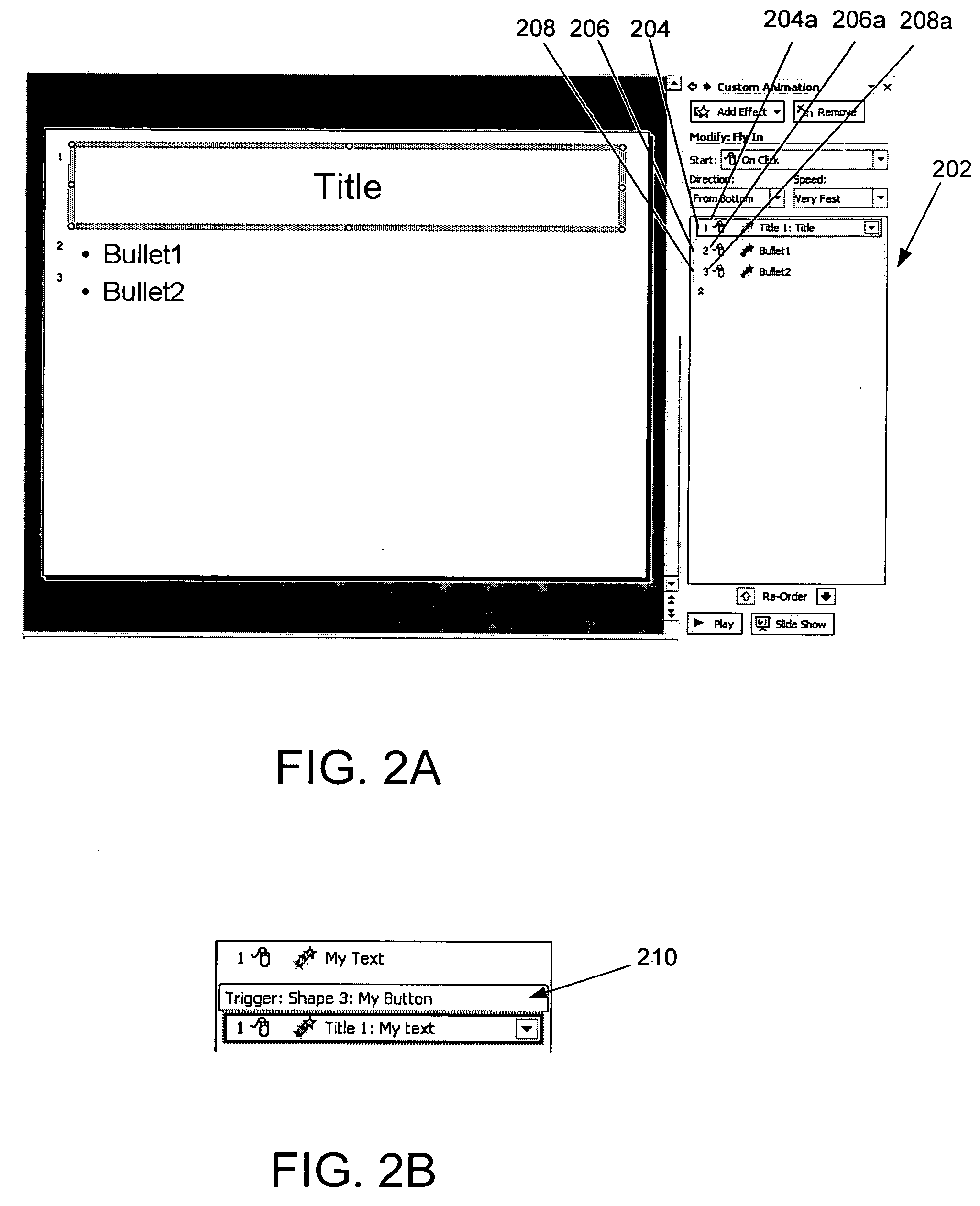
InactiveUS20050097471A1Less screen real estateMore discoverableRecording carrier detailsRecord information storageGraphicsAnimation
A system and method for graphically showing the order and timing of elements in a presentation program or other software. The sequence of events is shown in an event list, a list of events in sequence order, each event being associated with an event timeline bar and correlated with a universal timeline, in the editing window of an electronic presentation or other software that deals with the scheduling of events. In one embodiment, each item in the list represents an individual animation effect. Elements of the event list are logically related to each other and these logical relationships may be used in assisting a user to build a sequence of events (e.g., an animation sequence).
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Taking distance images
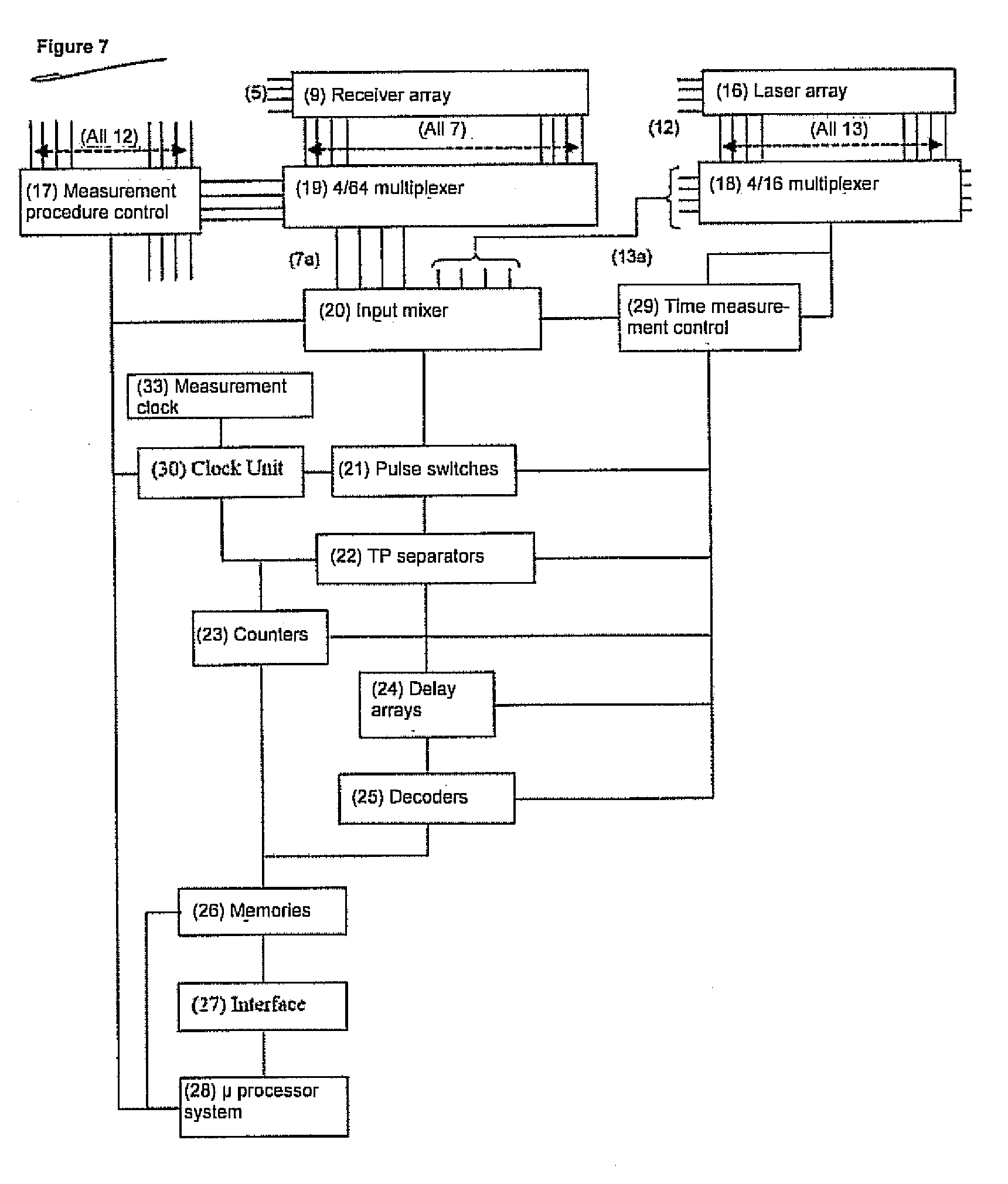
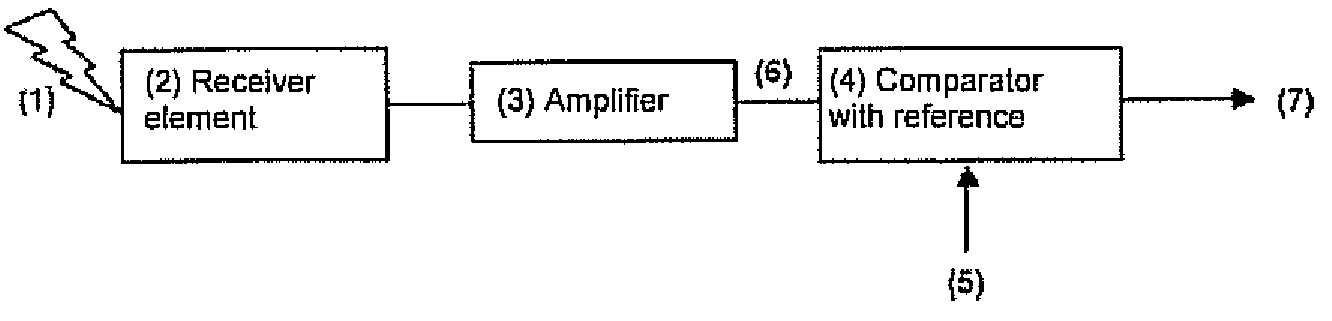
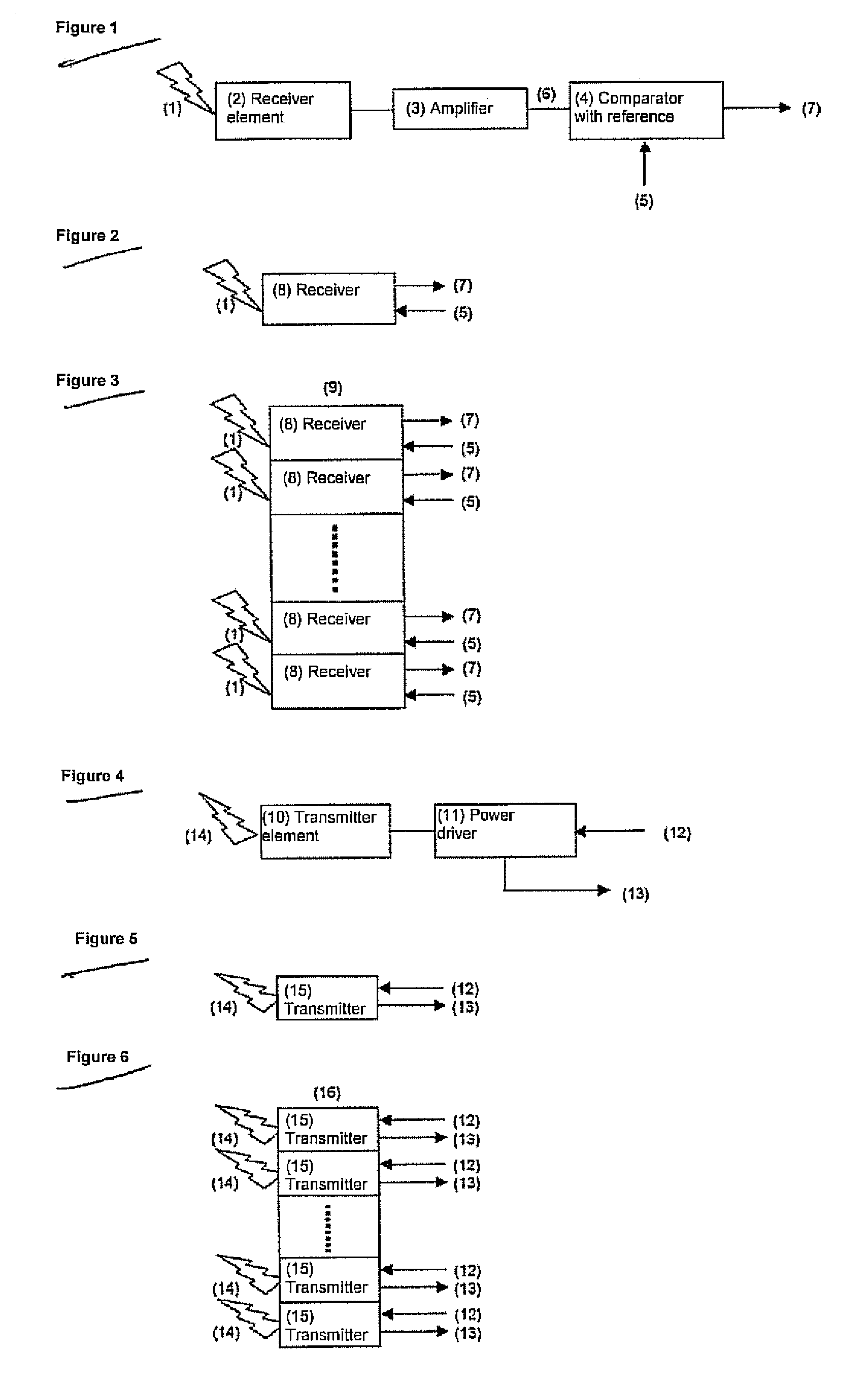
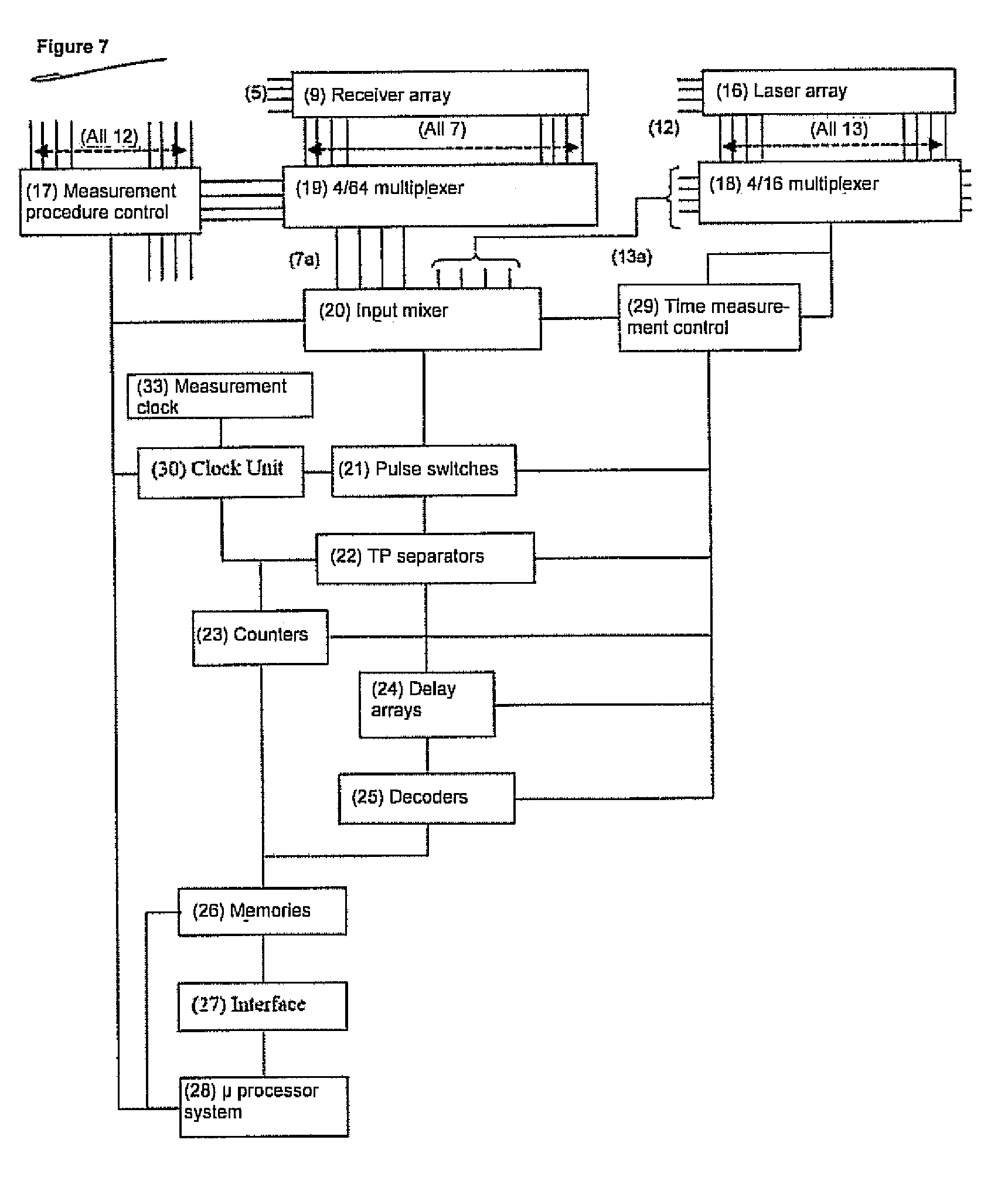
ActiveUS20080186470A1High sensitivityAvoid mistakesOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationTime informationElectromagnetic radiation
The invention relates to a method for the taking of a large number of distance images comprising distance picture elements, wherein electromagnetic radiation is transmitted in each case in the form of transmission pulses using a plurality of transmitters arranged in an array for each distance image to be taken and reflected echo pulses are detected using a plurality of receivers arranged in an array, with the respective distances of objects at which the transmission pulses are reflected and forming a distance picture element being measured by determining the pulse time of flight, wherein a plurality of individual measurements are carried out using a time measuring device connected after the receiver array for each distance image to be taken, in which individual measurements a respective pulse chain is processed which includes a logical start pulse derived from the respective transmission pulse and at least one logical receiver pulse formed from an echo pulse or a noise pulse, wherein the logical receiver pulses are each generated by means of at least one reference of the receiver, the reference being broken through by the underlying echo pulses or noise pulses, with an exceeding of the reference forming the positive flank of the receiver pulse defining an up event and a falling below of the reference forming the negative flank of the receiver pulse defining a down event, wherein, for each distance image to be taken, the associated pulse chains are formed in that the start pulses and the associated receiver pulses are each combined at the right time, the pulse chains formed in this manner are distributed over an array of time measuring channels formed by the time measuring device in accordance with a pre-settable measurement procedure, and, for each time measuring channel, the time durations are determined which, in each case with reference to a point in time before the start pulse, pass until a receiver pulse in that, for each up event and / or for each down event, at least the respective clock pulses are counted which are made available by a central clock at a known frequency, and the counter results are stored as an event list in an arrangement taking account of their respective time information, and wherein the stored event lists of all time measuring channels are read out and evaluated in order to convert the respective time information contained in the event lists into distance values corresponding to the distance picture elements.
Owner:TRIPLE IN HLDG
Multi-epoch method for saving and exporting file system events
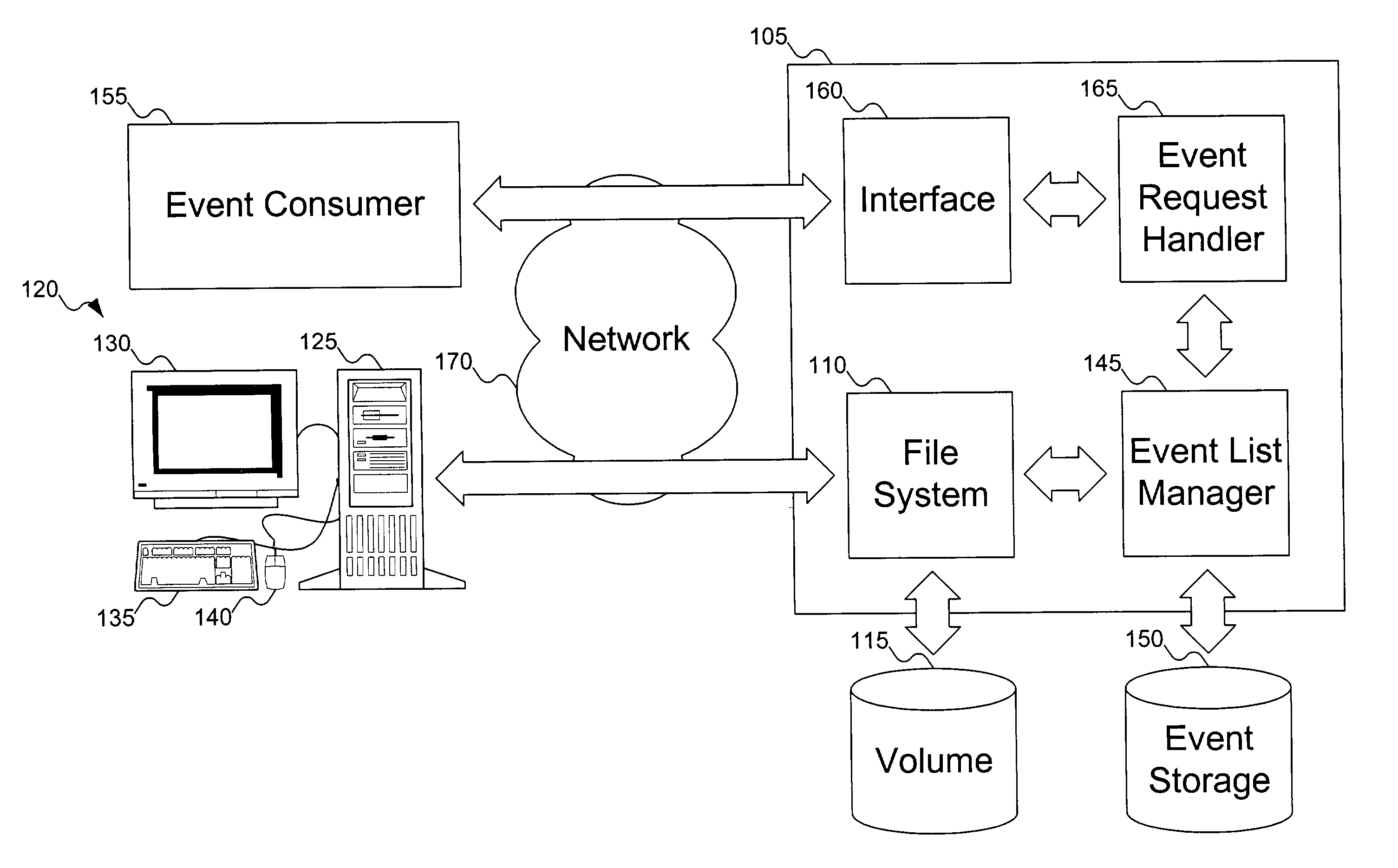
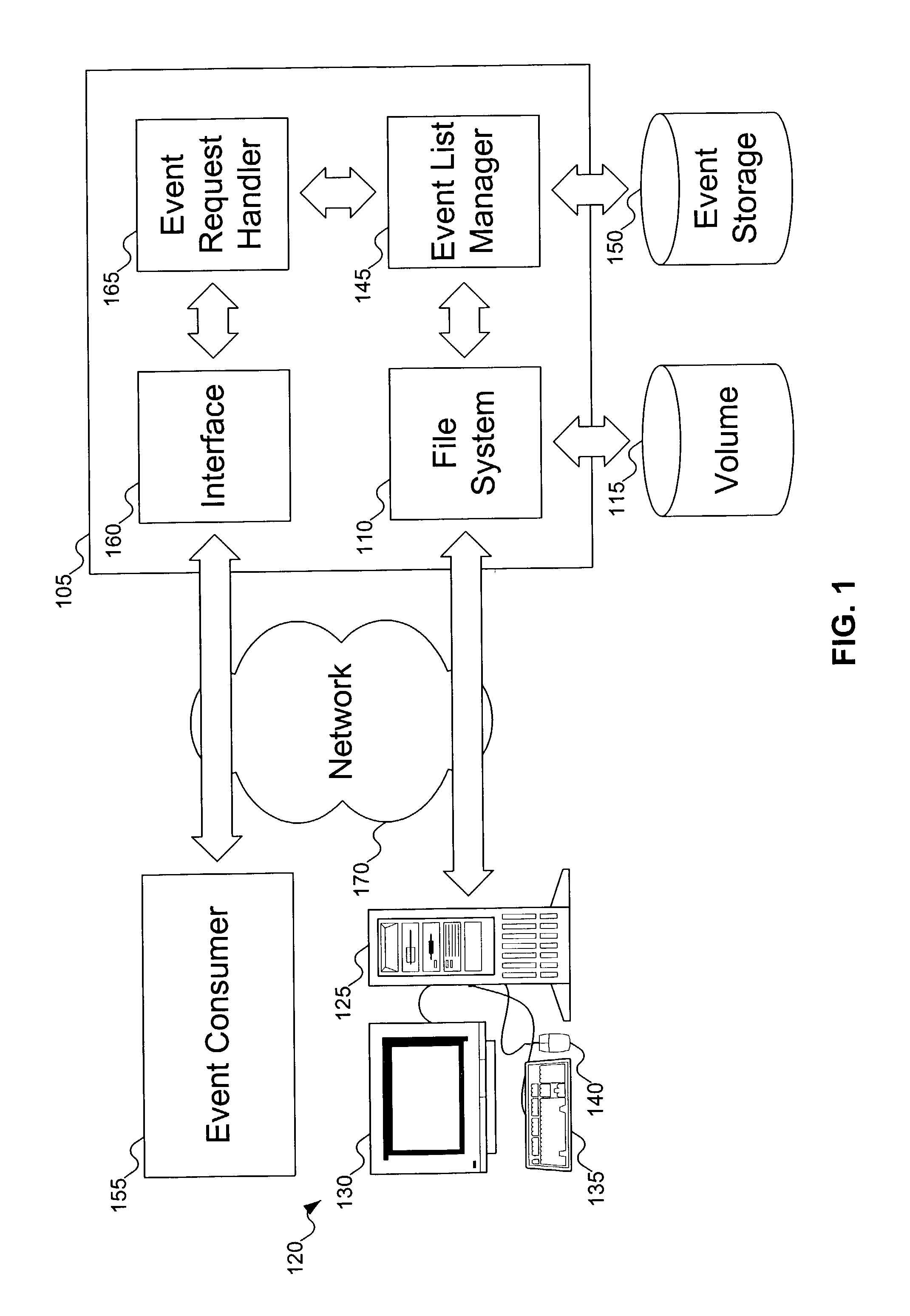
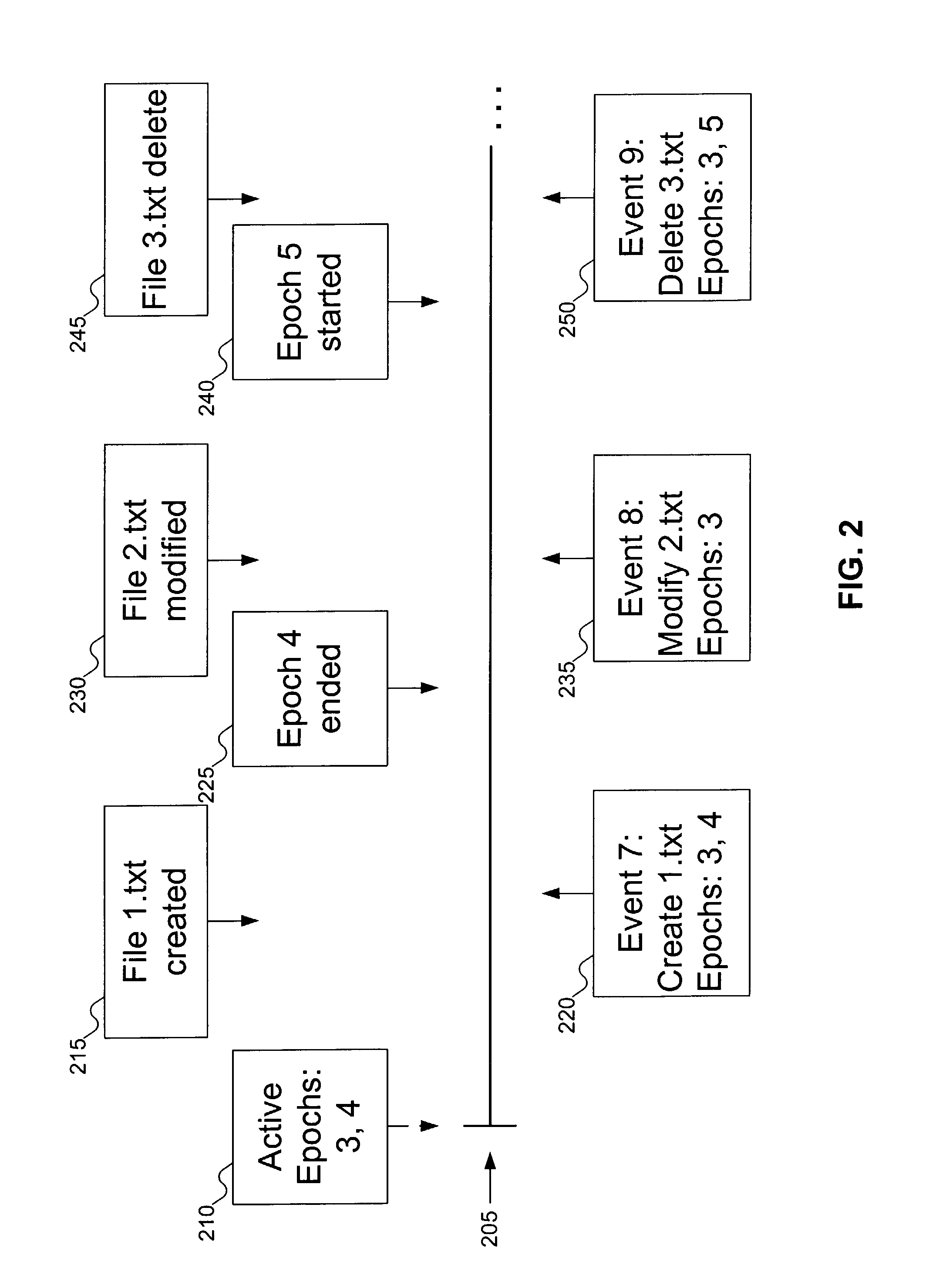
InactiveUS7653645B1Data processing applicationsError detection/correctionFile systemDistributed computing
As things happen on a volume, the file system forwards events to an event list manager. The event list manager stores the events and associates them with epochs that were active at the time the event occurred. Event consumers can independently declare epochs at any time. When event consumers end an epoch, they can request events that occurred during the epoch, which are reported to the event consumer using the event list manager.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
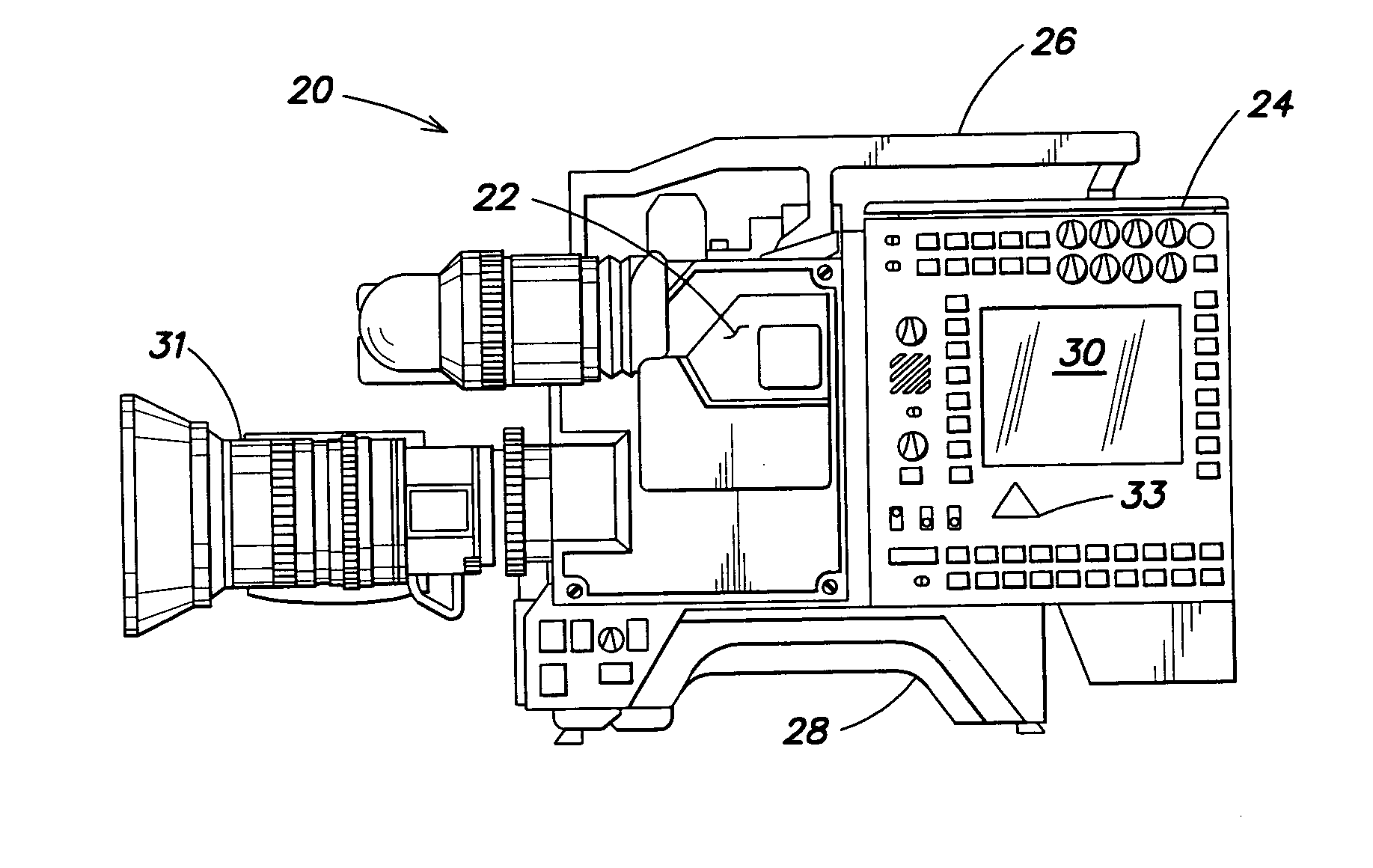
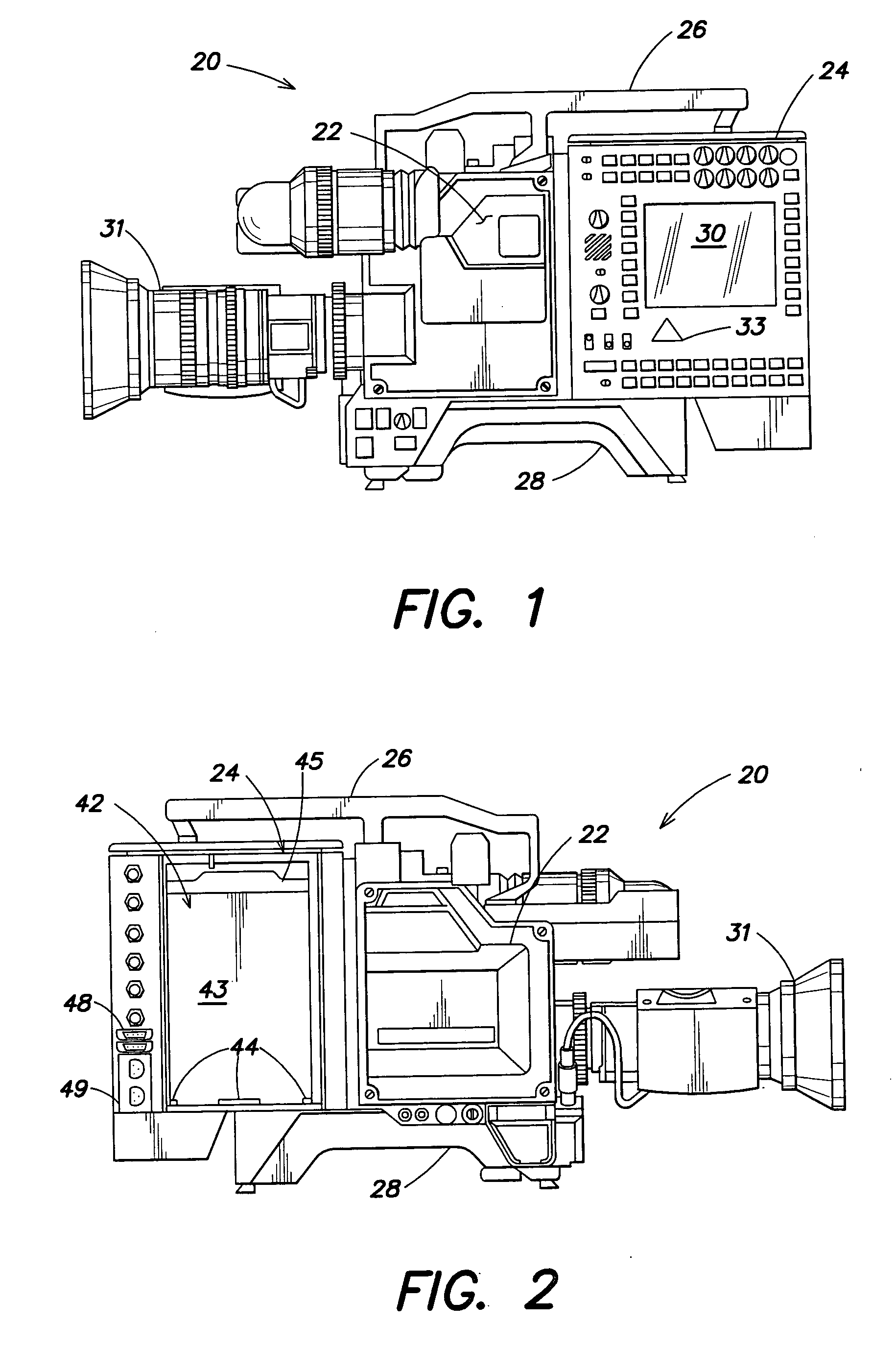
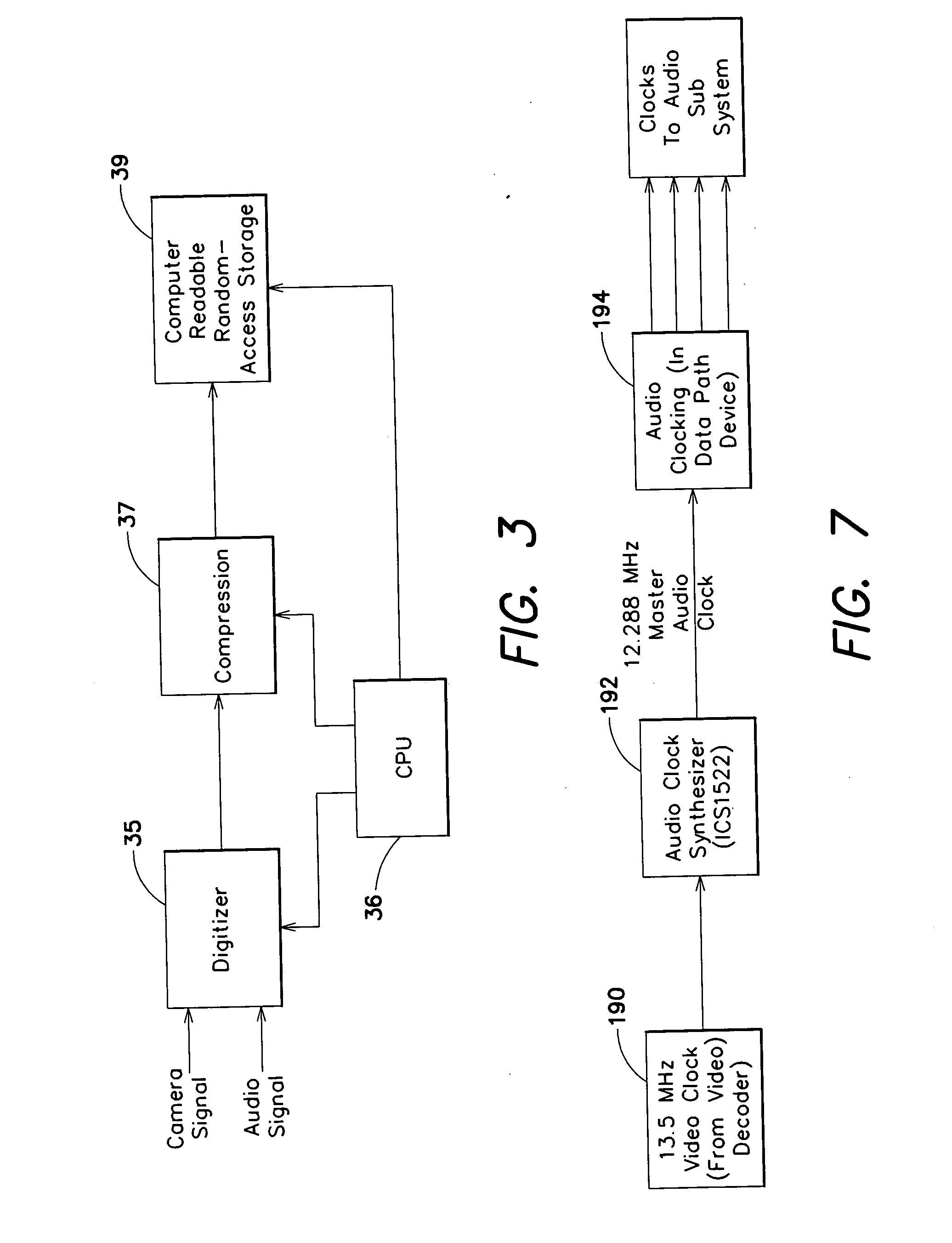
Combined editing system and digital moving picture recording system
InactiveUS20050053352A1Shorten the timeSignificant competitive advantageTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersGraphicsGraphical user interface
A moving picture recording device includes a random-access, computer-readable and writable storage medium to provide non-linear access to recorded clips. The device provides digital capture of both video and audio information. Multiple data paths are provided to allow recording to and playback from the storage medium. Lists are maintained to manage recorded clips and edited events. An outtake list of deleted clips is also maintained. An event list includes a list of video events including clips from the storage medium as well as other video sources including a camera or external video. With switching circuitry, recorded clips can be viewed during editing while live images are output to a program output. An editing interface includes dedicated keys for performing standard recording functions as well as a display with associated input keys having adaptive functions. The textual display indicates the function currently associated with the input key. This display provides a simple interface for editing video without a mouse or other external input device or complex graphical user interface. The interface also may allow a user to input a value, stored as an attribute of a clip, that represents the merit of the clip. These attributes may be used to rank and / or select clips.
Owner:AVID TECHNOLOGY
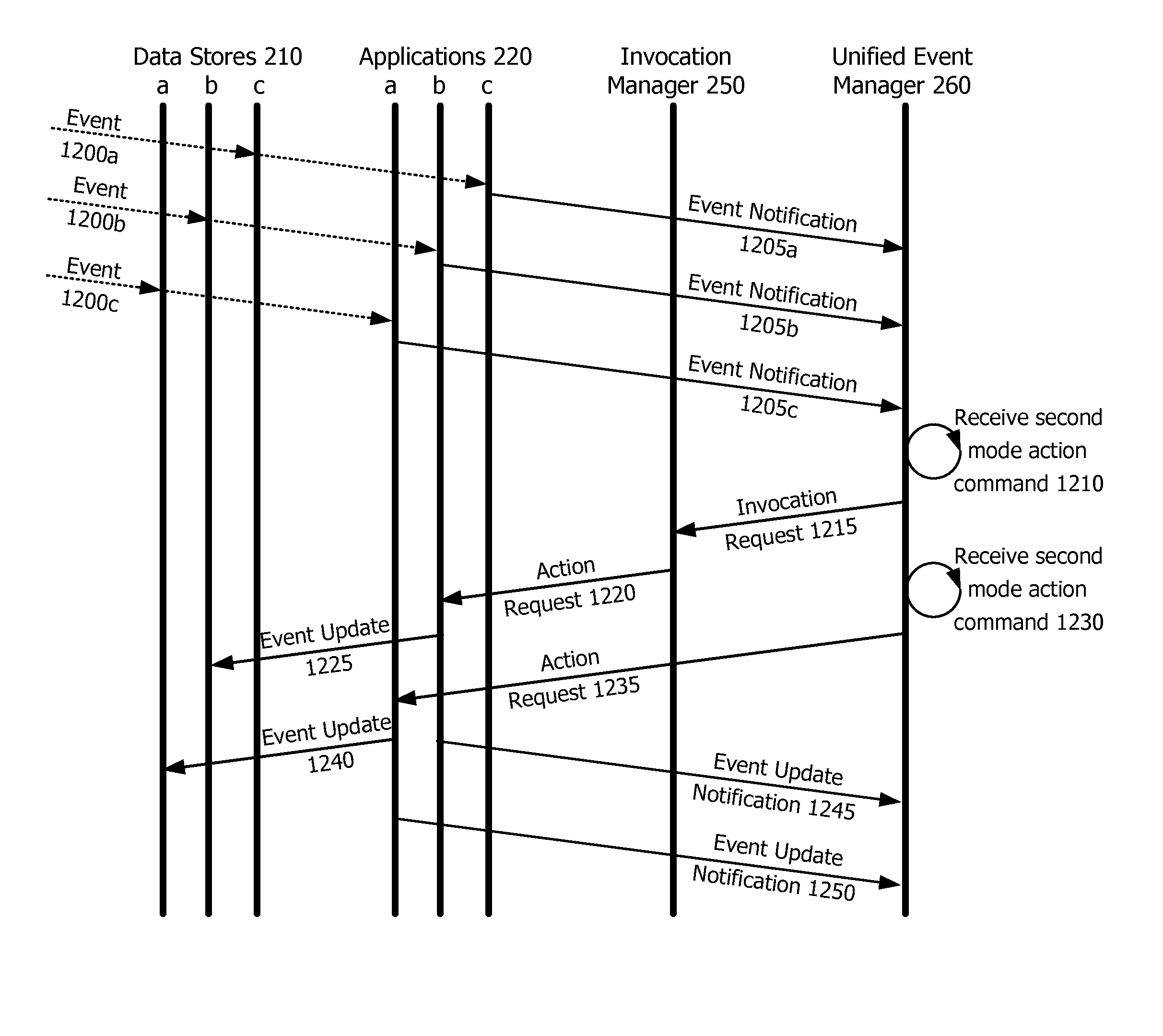
System, method and device-readable medium for communication event interaction within a unified event view
ActiveUS20160028875A1Efficient managementHeavy relianceSubstation equipmentInput/output processes for data processingMode selectionComputer science
A method, electronic device, and device-readable medium are provided for implementing quick actions or additional actions in a unified inbox context. A number of communication event listings are displayed in either a first mode or a second mode. In the first mode, at least one user interface element for invoking a first operation is displayed for each communication event listing. In the second mode, at least one other user interface element for invoking a further operation is included in the communication event listing in addition to a user interface element for invoking the first operation. The user can selectively invoke the second mode from the first mode.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Network failure real-time relativity analysing method and system
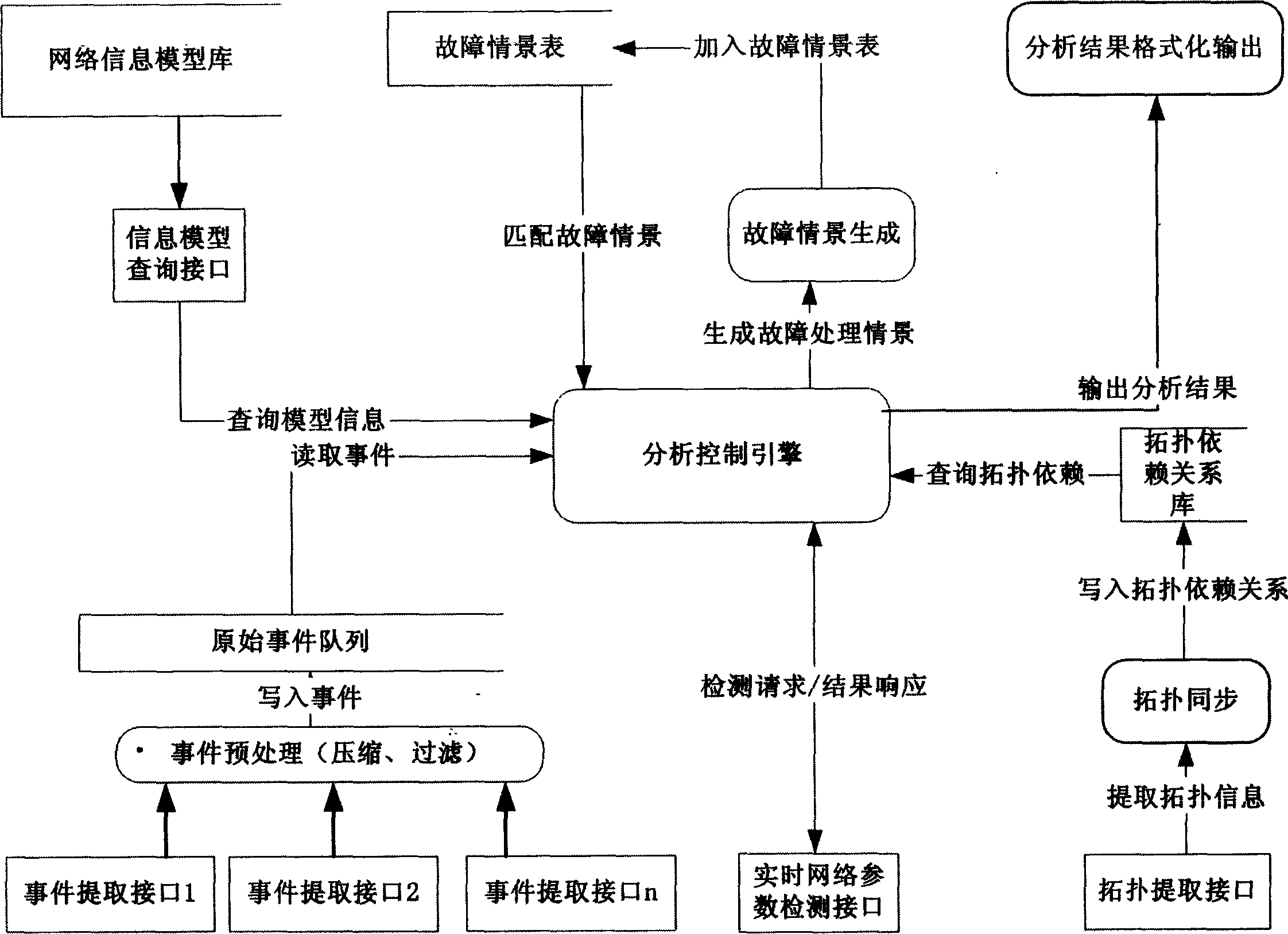
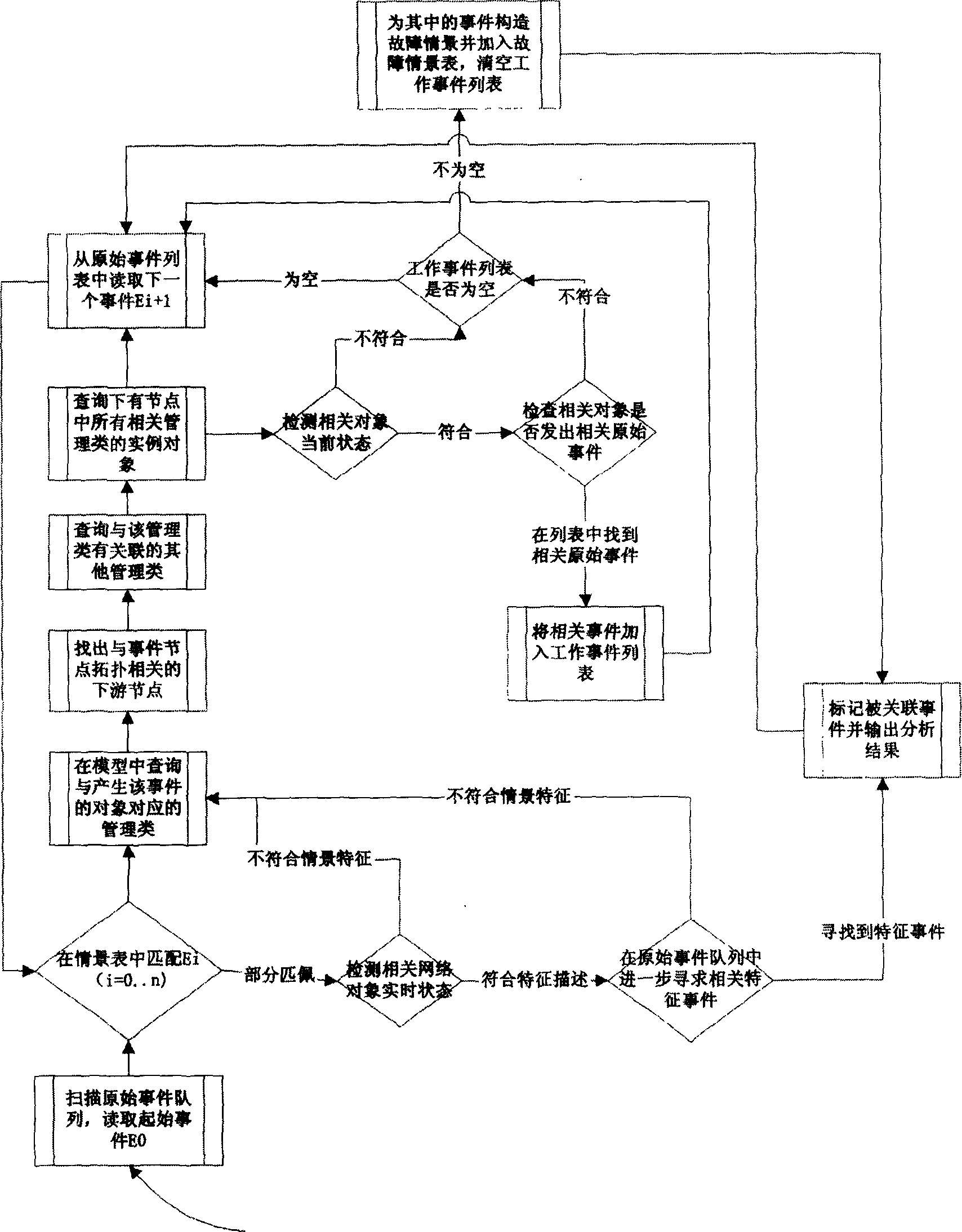
InactiveCN1529455AAvoid Correlation AnalysisEfficient identificationData switching networksTopology informationEvent level
Information of failure events from various network devices and service objects is written into original event list. Correlation analysis is carried out for events read by analyzing and controlling engine from the original event list according to levels of original event and selection of classes. The dynamic analytical algorithm synthetically handles information in each area such as scene of historical fault analysis, dynamic performance parameters of network, dynamic topology information and time character of event etc. comparing with prior art, the invention overcomes disadvantages of overlooking information of dynamic network state, dependent on preset rule and lack of auto study ability etc. The invented method provides effective correlation analysis, fault reason analysis and location in real time when storm of network fault happens.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH SERVICE
Integrated timeline and logically-related list view
InactiveUS6904561B1Easy to createEasy to editSpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsAnimation
A system and method for graphically showing the order and timing of elements in a presentation program or other software. The sequence of events is shown in an event list, a list of events in sequence order, each event being associated with an event timeline bar and correlated with a universal timeline, in the editing window of an electronic presentation or other software that deals with the scheduling of events. In one embodiment, each item in the list represents an individual animation effect. Elements of the event list are logically related to each other and these logical relationships may be used in assisting a user to build a sequence of events (e.g., an animation sequence).
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multiple-level graphics processing with animation interval generation
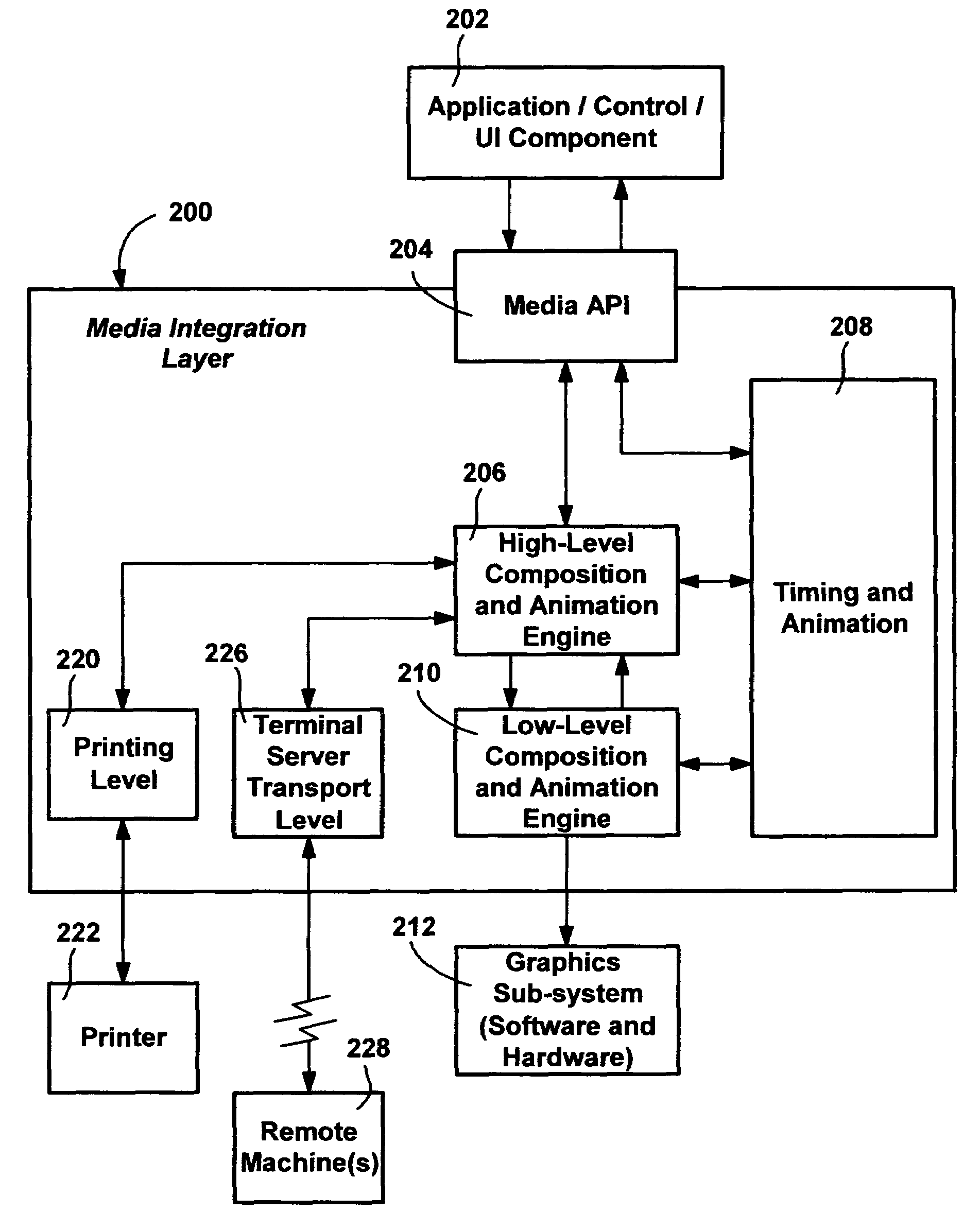
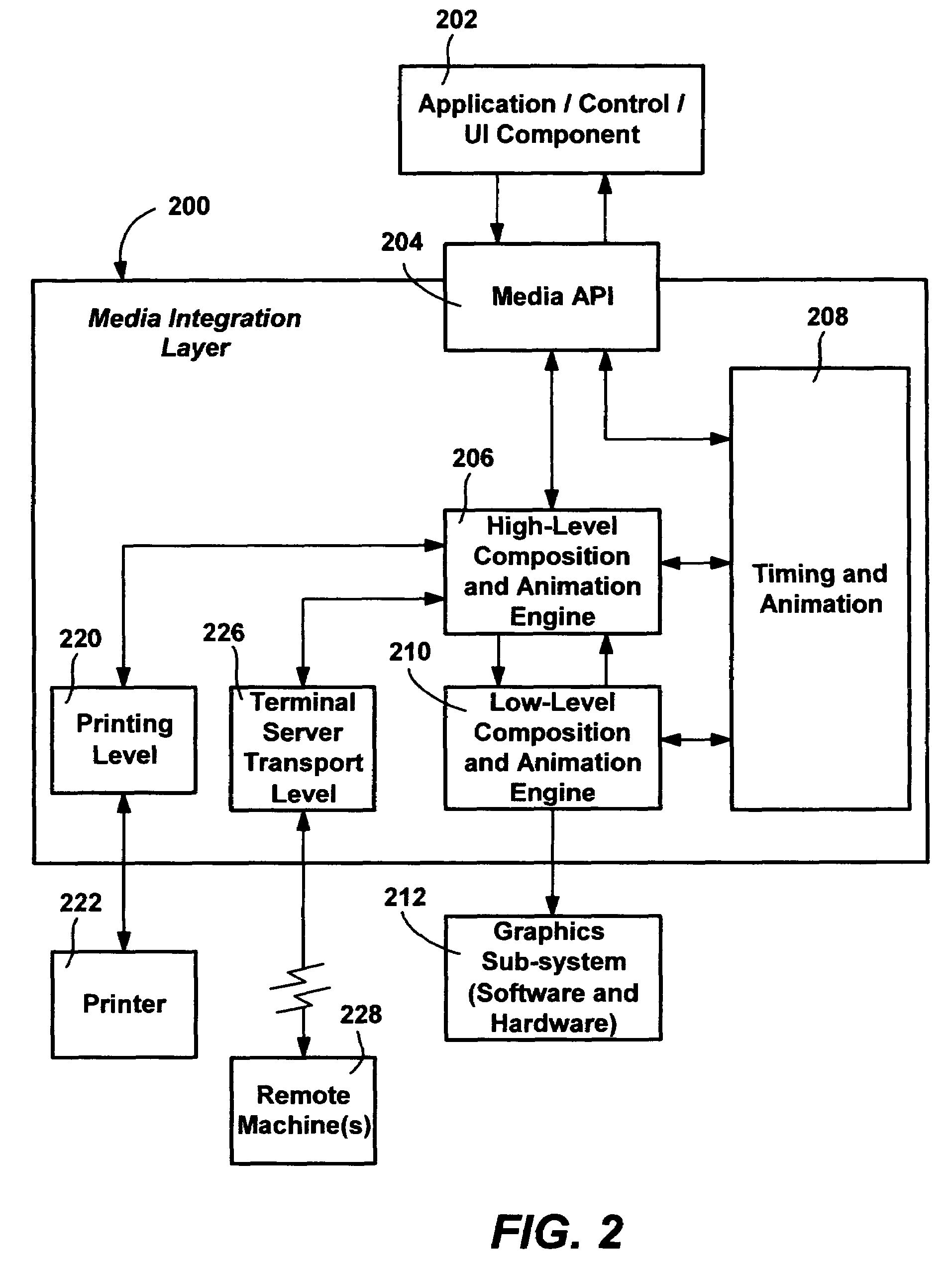
Described is a method and system in which timing intervals are generated from clock properties, and used to interpolate values for smooth animation. A high-level component maintains a set of clocks related to animated objects and / or linear media in a scene graphs. The clocks correspond to clock properties received from an application program. The clocks are processed into event lists at the higher level, from which timing interval data is generated and passed to a low-level component. The low-level component, which generally operates at a faster rate than the high-level component, uses the timing interval data to rapidly calculate current values for an animated object. Interaction, such as to pause an animation or resume a paused animation, causes the high-level component to re-compute the event list and regenerate new animation intervals for affected clocks. The new animation intervals are passed and used by the lower-level component.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
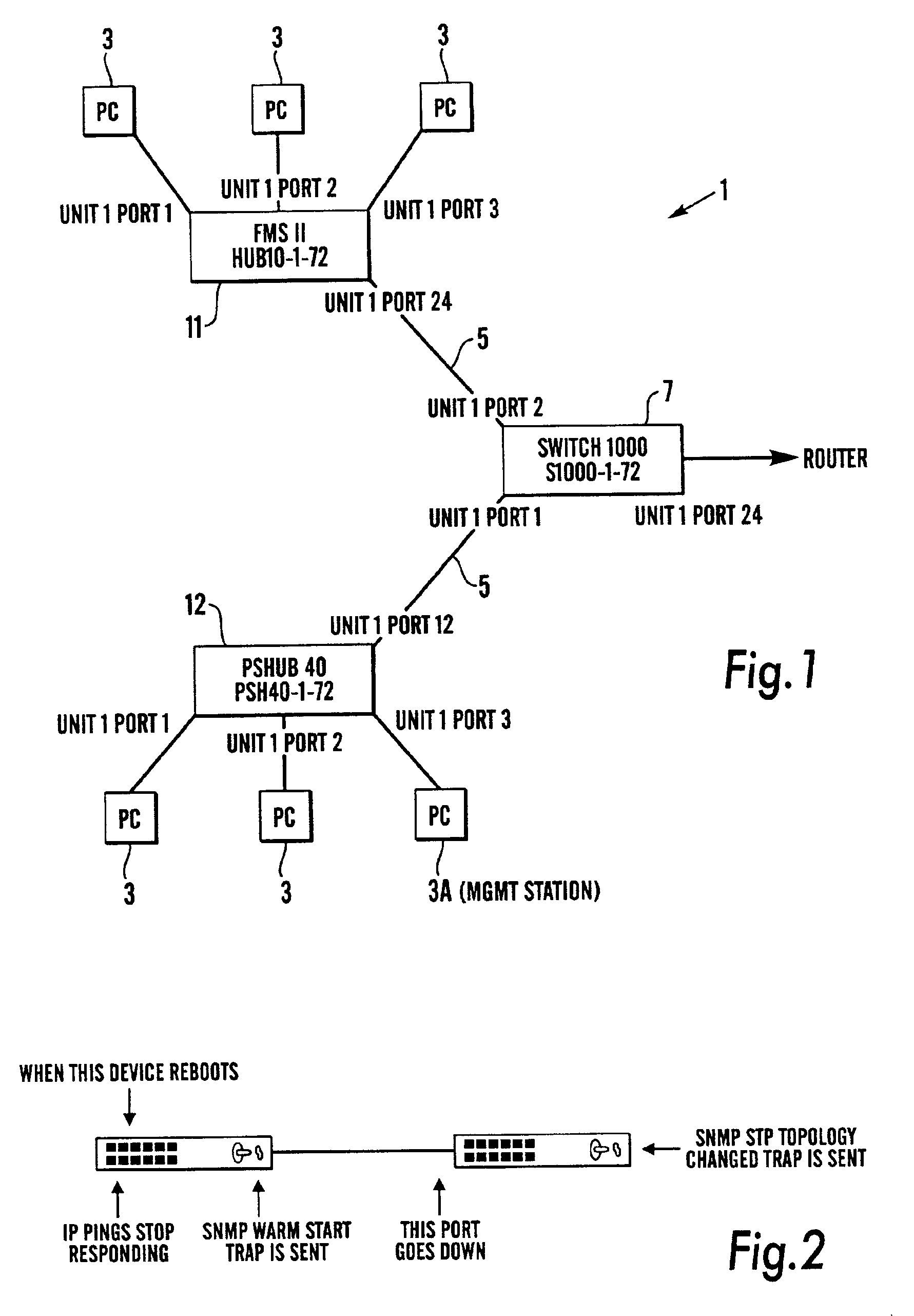
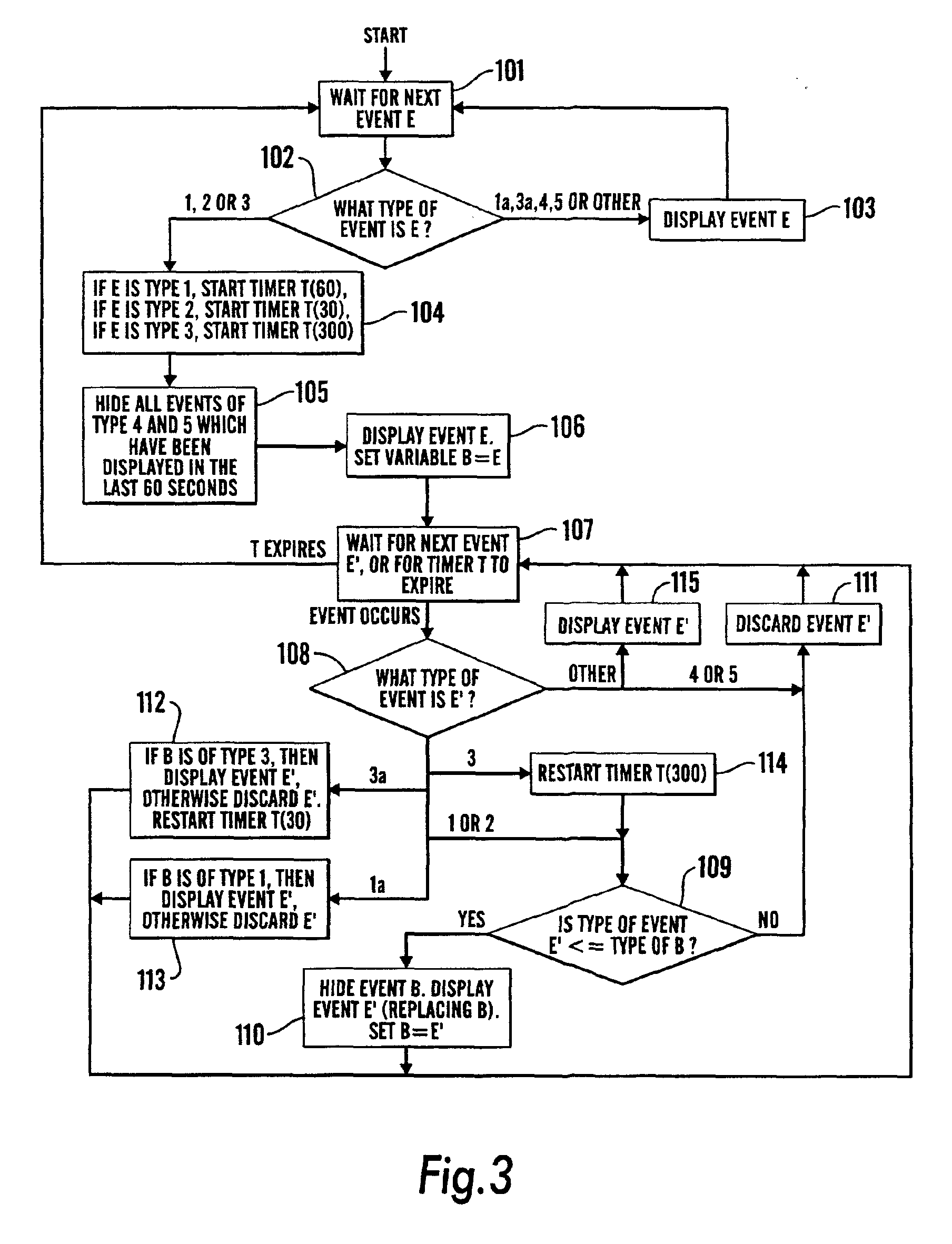
Network management apparatus and method for processing events associated with device reboot
ActiveUS7016955B2Reduce in quantityDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork management applicationNetwork management
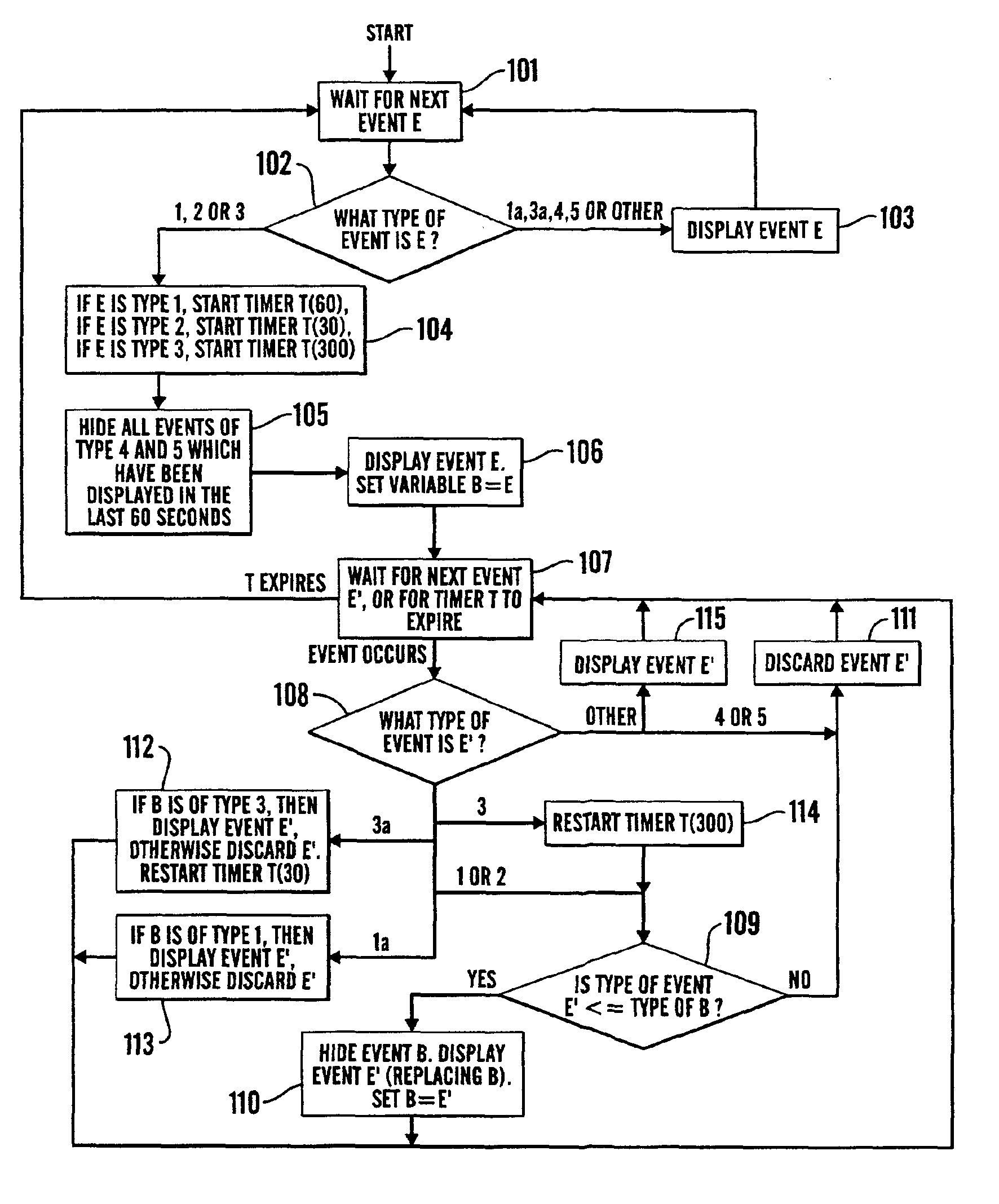
A network management apparatus and method reduces the number of events presented in an event list to a user. In particular, the apparatus and method reduces the number of events, which are generated during the monitoring of a network and may be due to rebooting of a device on the network, presented to the user by determining, upon receiving an event relating to a device, whether a more significant event already appears in the event list relating to the device, and if so, preventing the received event from being presented in the event list to the user.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
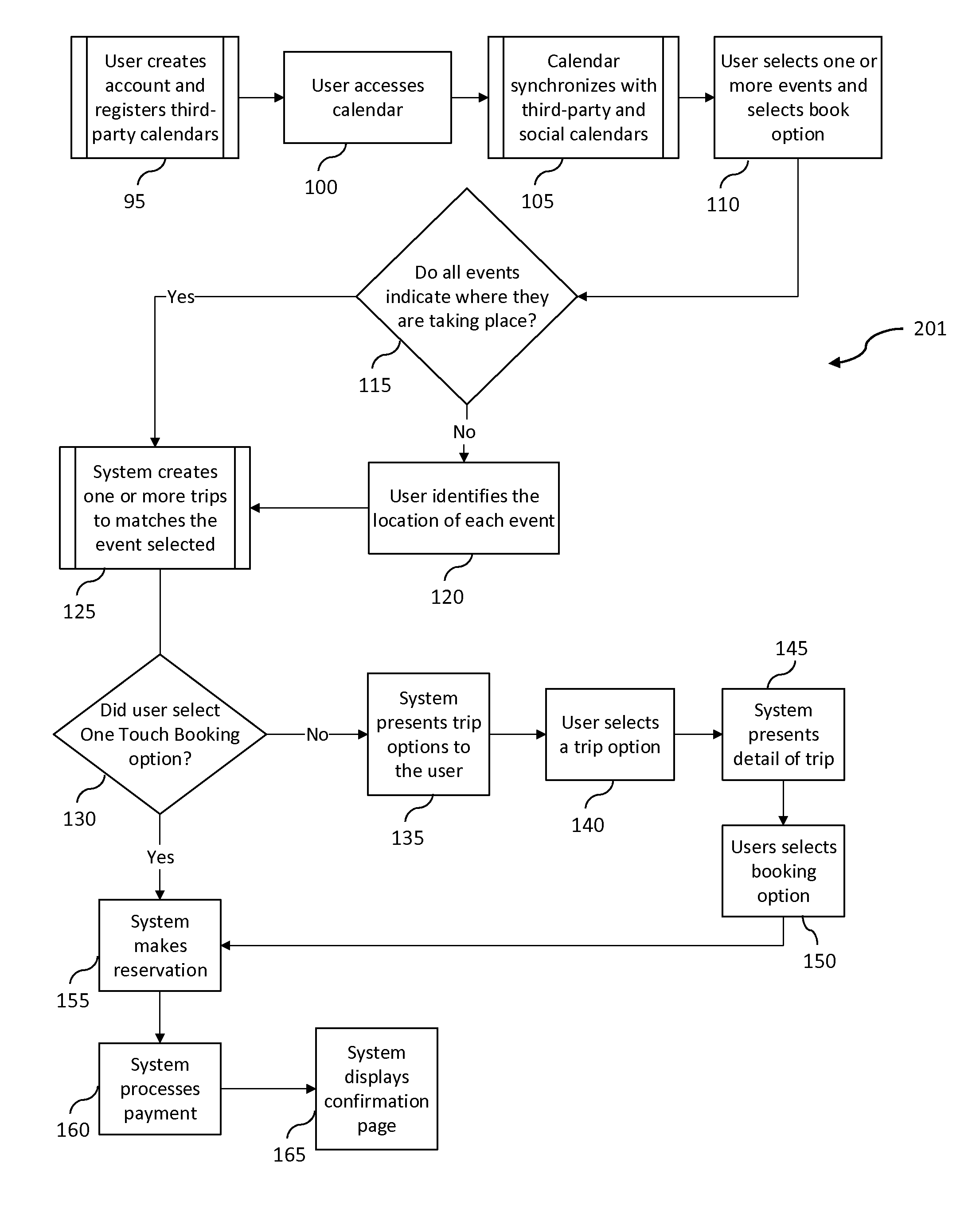
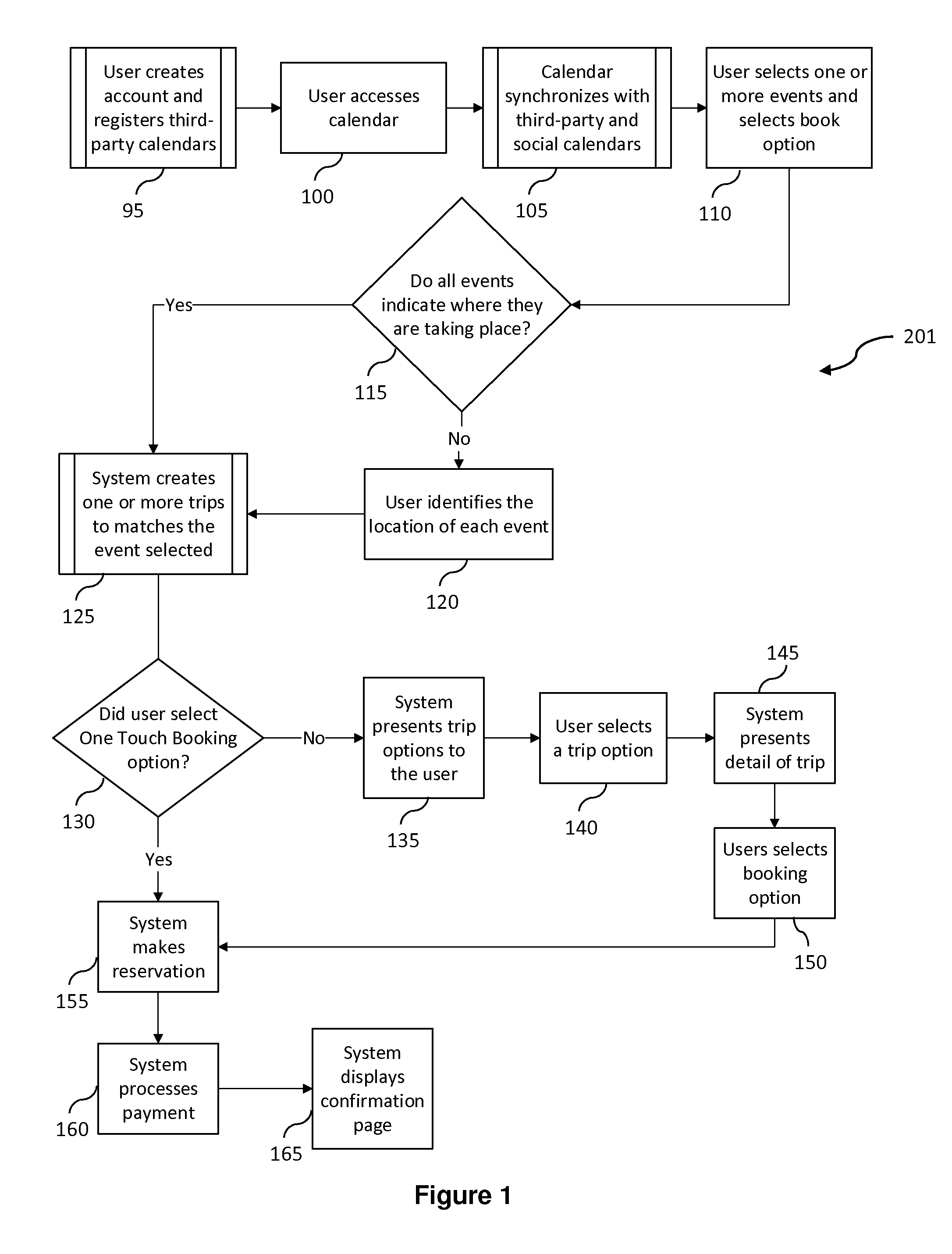
Method, compupter program, and system for planning, reserving, and purchasing travel accommodations from calendar events
The present invention is directed to a method, computer program, and system for automating the planning, reserving, and purchasing of travel accommodations based on calendar events of a user. A user's event list is created on an application server, which may comprise synchronizing a calendar in at least one embodiment, and a user's booking request is received at the application server for a selected event in the event list. Additional information is then retrieved by an event booking component, and along with the received user's booking request, allows the event booking component to generate at least one travel plan for the user. The travel plan is then reviewed and selected by the user, and then fulfilled by the application server.
Owner:PARKJOCKEY GLOBAL INC
Methods and apparatus for enabling/disabling calling forwarding service
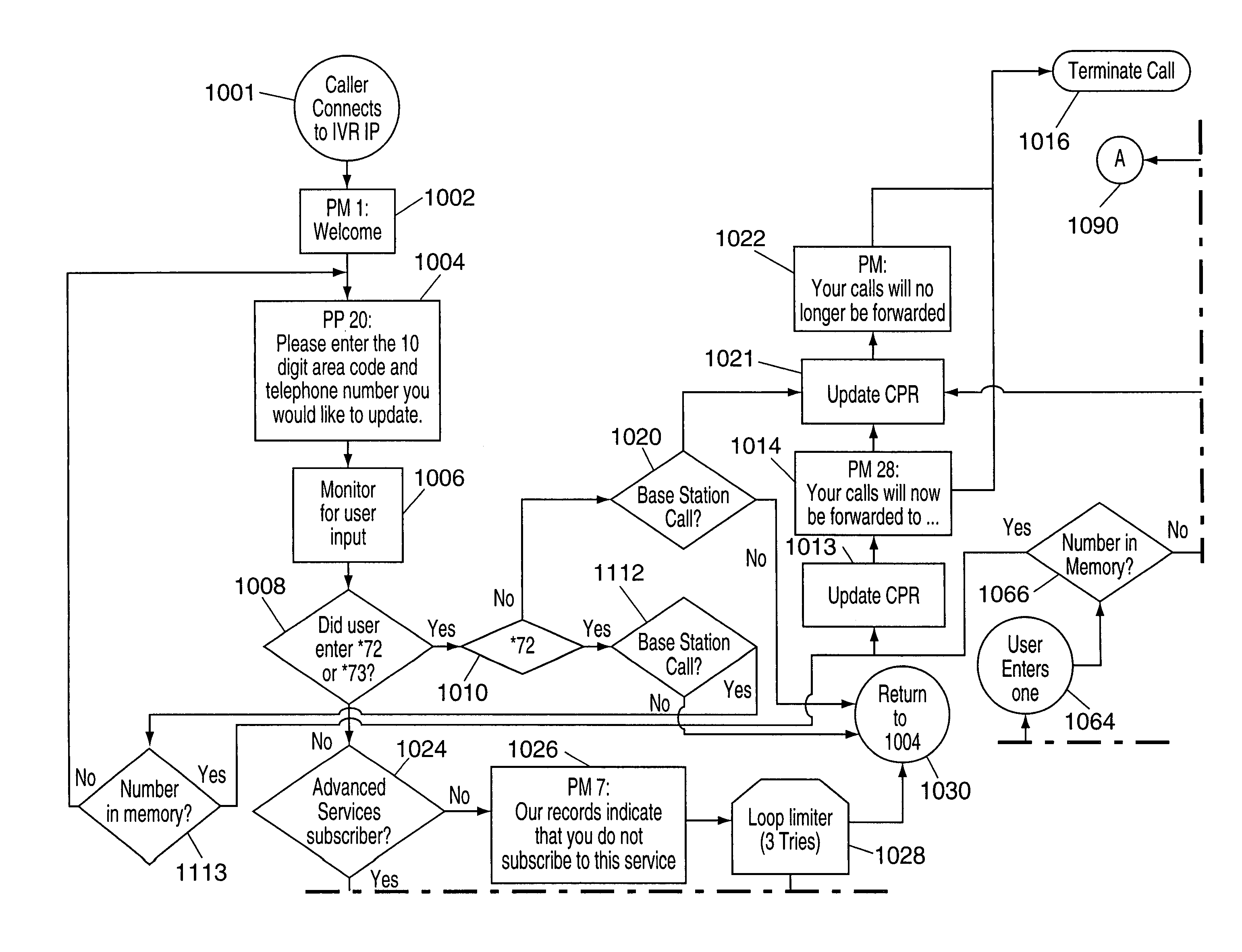
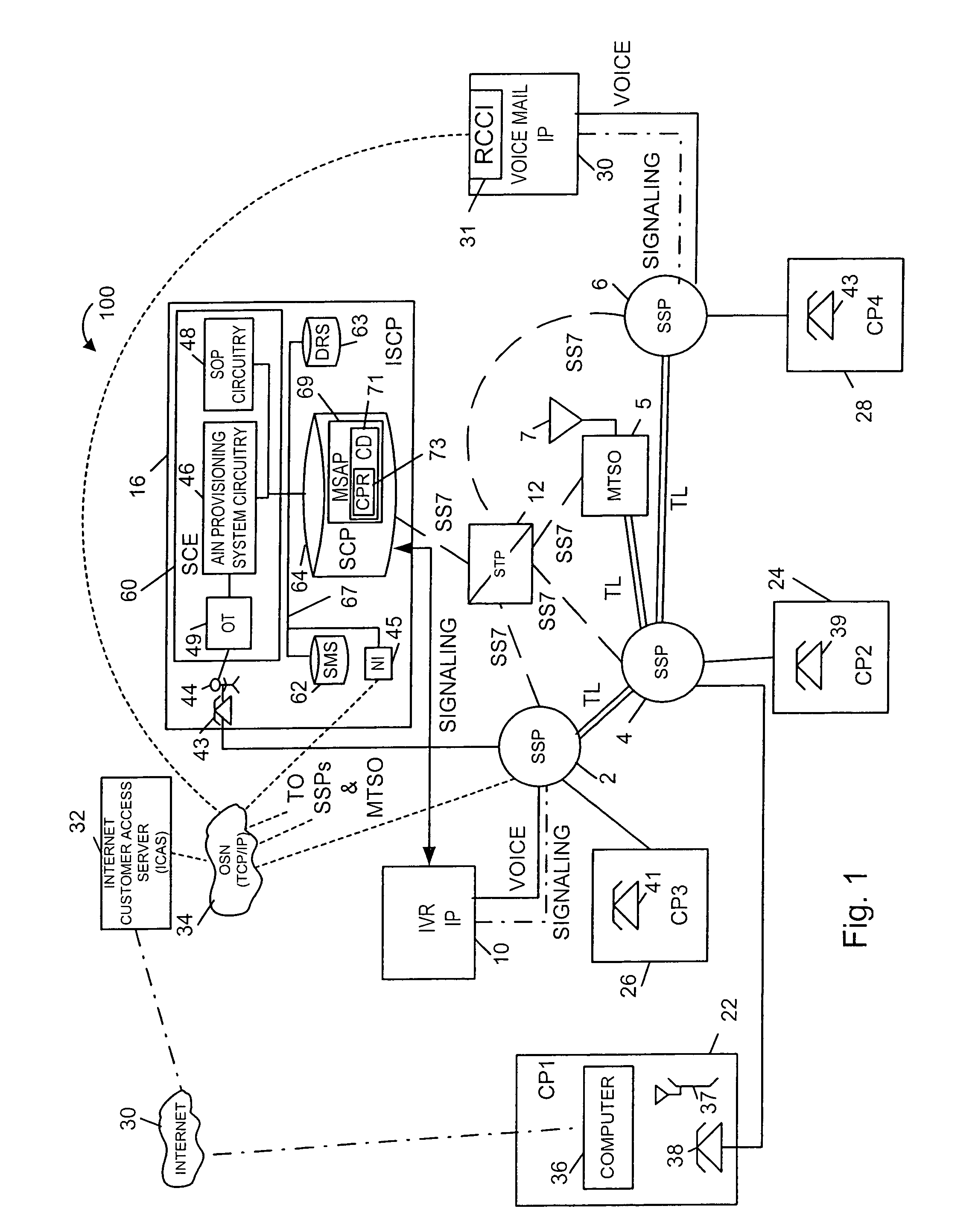
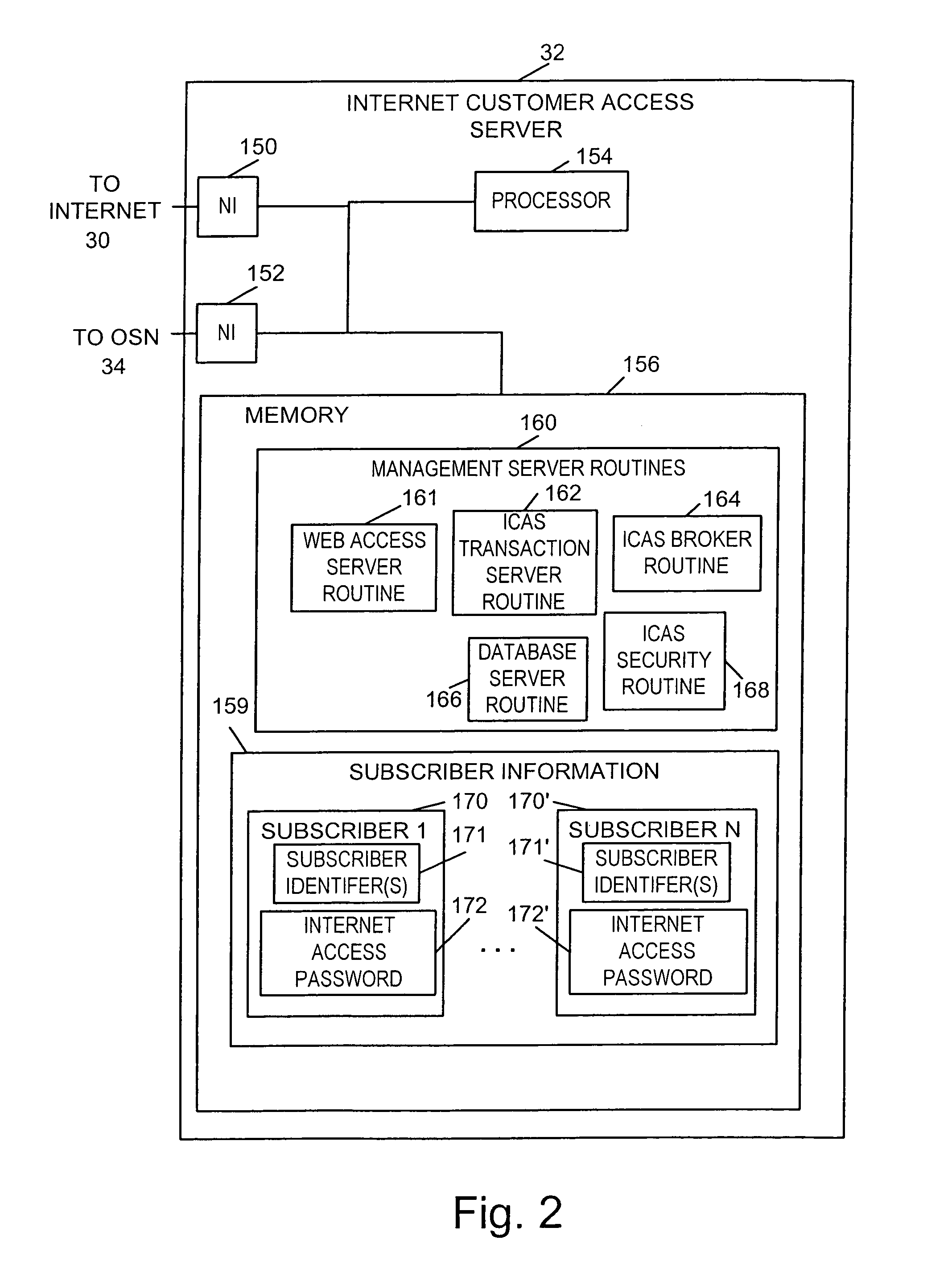
InactiveUS7050558B1Easy maintenanceService is limitedIntelligent networksInterconnection arrangementsSelective callingService control
Methods and apparatus for implementing call forwarding services using AIN techniques and next event list messages are described. Methods of notifying a subscriber of a call forwarded using AIN techniques are also described. In accordance with one feature of the present invention, a subscriber is allowed to set the number of rings which are allowed to occur prior to a call being forwarded. The number of rings, e.g., the ring count, is stored as part of a customer's call processing record (CPR) which is used by a service control point (SCP) to implement the call forwarding service. The ring count information may be updated via the Internet or via a dial-up telephone connection. Call forwarding customers are provided with a distinctive ring, e.g., a ring shorter than an ordinary telephone ring, to notify them when a call is being forwarded. Distinctive rings may be used to distinguish between different forwarding services. For example a different ring may be used for forwarding to voice mail than for selective call forwarding or follow-me call forwarding. The distinctive ring may be implemented by using an SCP to instruct a telephone switch to provide any one of a plurality of different rings which are supported by the telephone switch or by simply causing the subscribers phone to ring for different periods of time which are shorter than a normal ring.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC +1
Managing record events
InactiveUS20080196065A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsComputer scienceComputer program
Systems, methods, and computer program products for managing and prioritizing record events. A priority manager includes an event list that lists scheduled record events. Each event in the event list has a priority that is different from the other events in the event list. If some of the events conflict, such as when a tuning resource is lost and unavailable, then those events with the highest priority in the event list are recorded. A user can assign priority to events when they are scheduled or at a later time. This enables event conflicts to be resolved by the user when the events are initially scheduled. When an event conflict arises later, the conflict is resolved by the priority manager according to the relative priority of the events in the event list.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
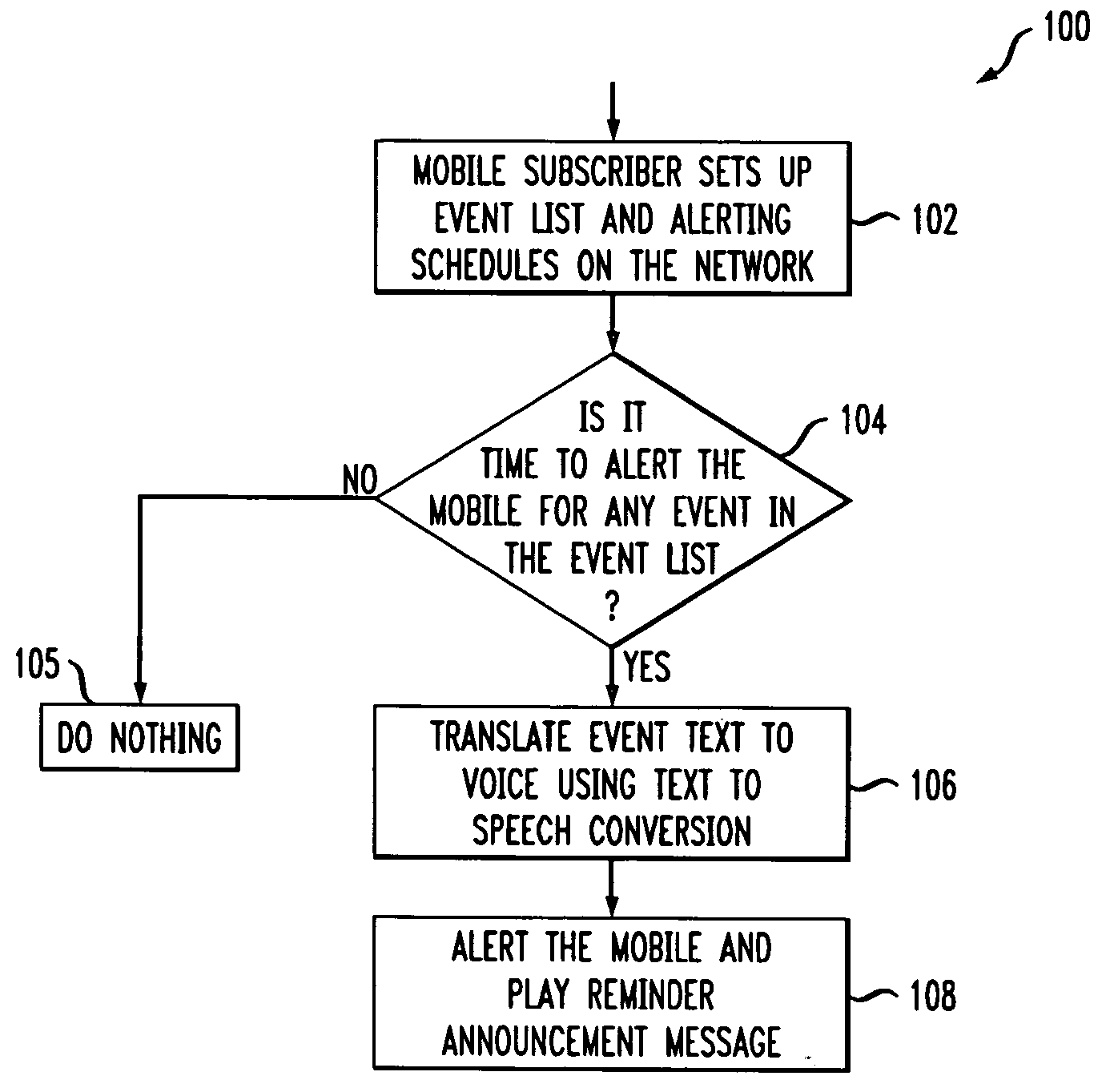
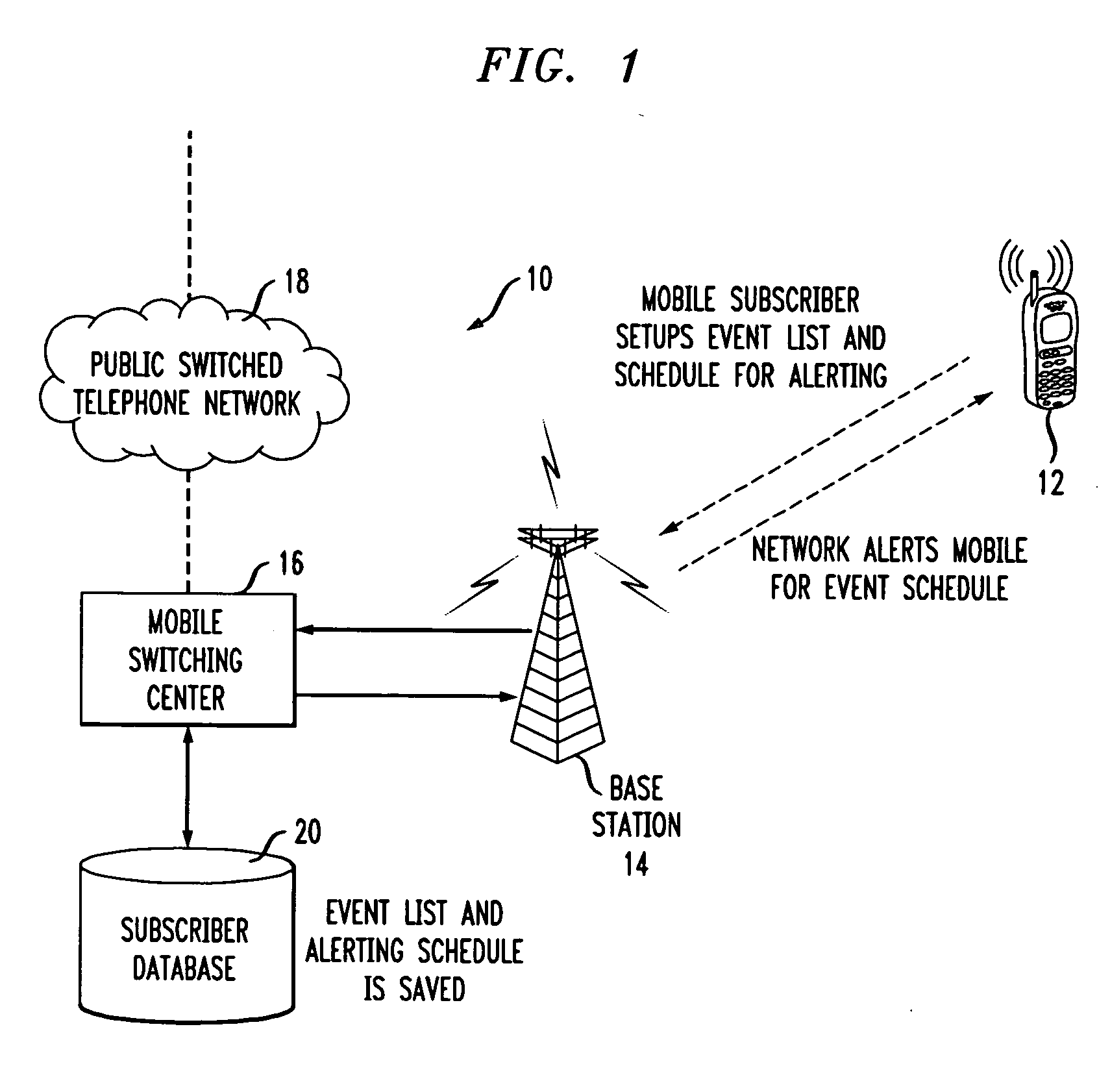
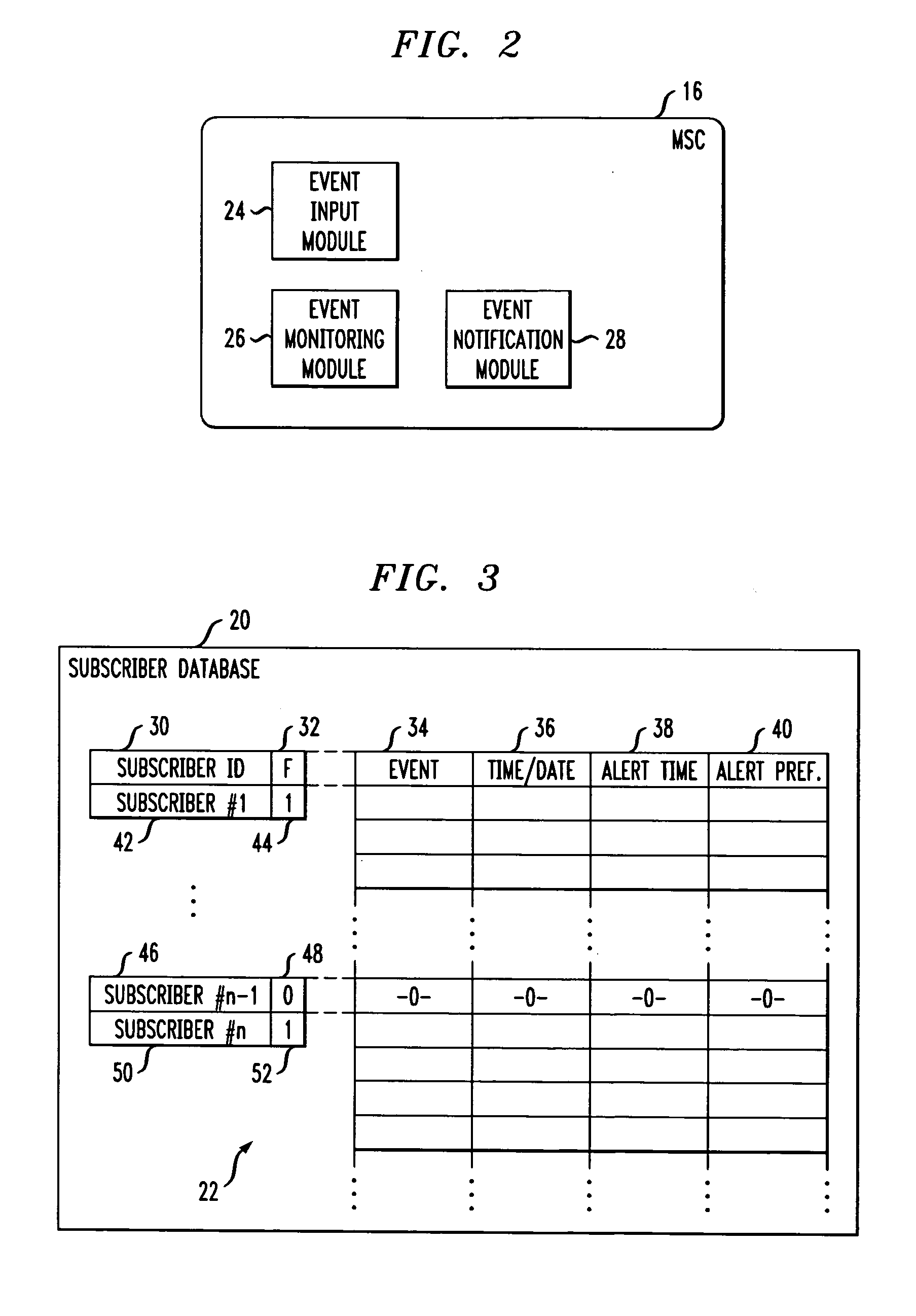
Method and apparatus for network initiated event reminder alerting
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for network initiated event reminder alerting. More particularly, the invention is directed to a system to provide network components that initiate an event reminder call prior to an upcoming event to alert a mobile subscriber of the event such as an appointment or a meeting. The network supports the provisioning of a user defined event list and corresponding reminder data for alerting the subscriber prior to each event. The network monitors the event schedule and takes appropriate action.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method and apparatus for generating an event log
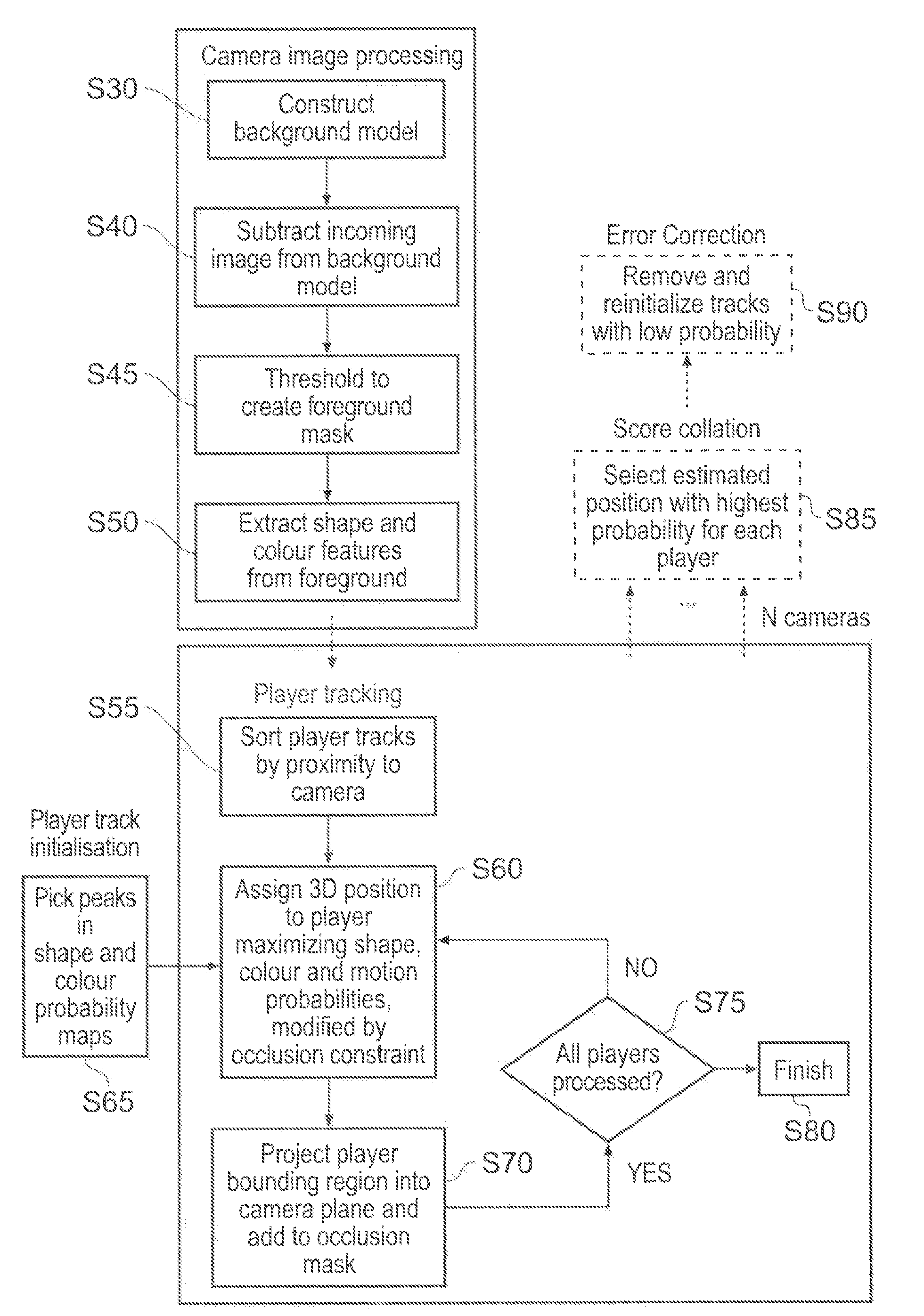
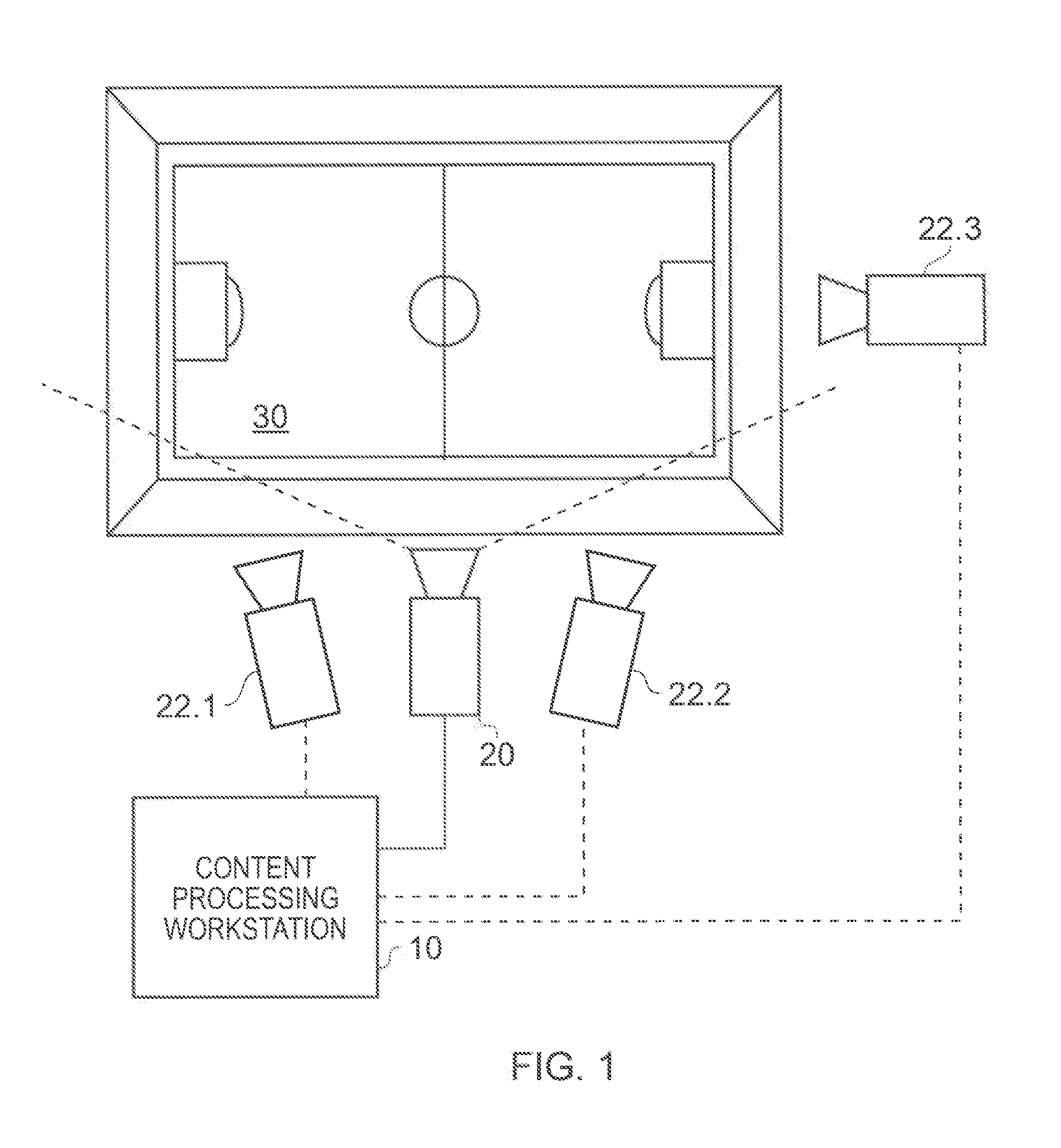
ActiveUS20100026801A1Improving D simulationLow costImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer graphics (images)Imaging Feature
A method of generating an event log of game events associated with elements in a sporting event. The method includes tracking, within a sequence of video images, image features which correspond to respective elements in the sporting event and selecting, from the tracked image features, a first image feature which corresponds to one of the elements so as to designate that element as a selected element. The method further includes selecting a game event from an event list of possible game events for association with the selected element, and associating the selected game event with the selected element so as to generate the event log.
Owner:SONY CORP
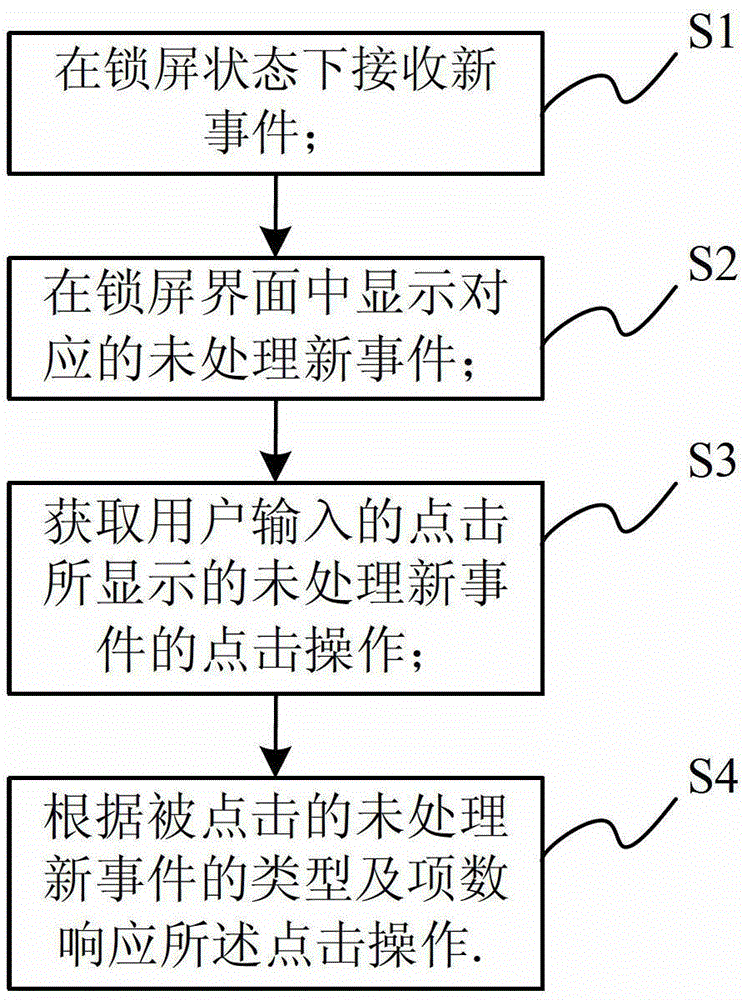
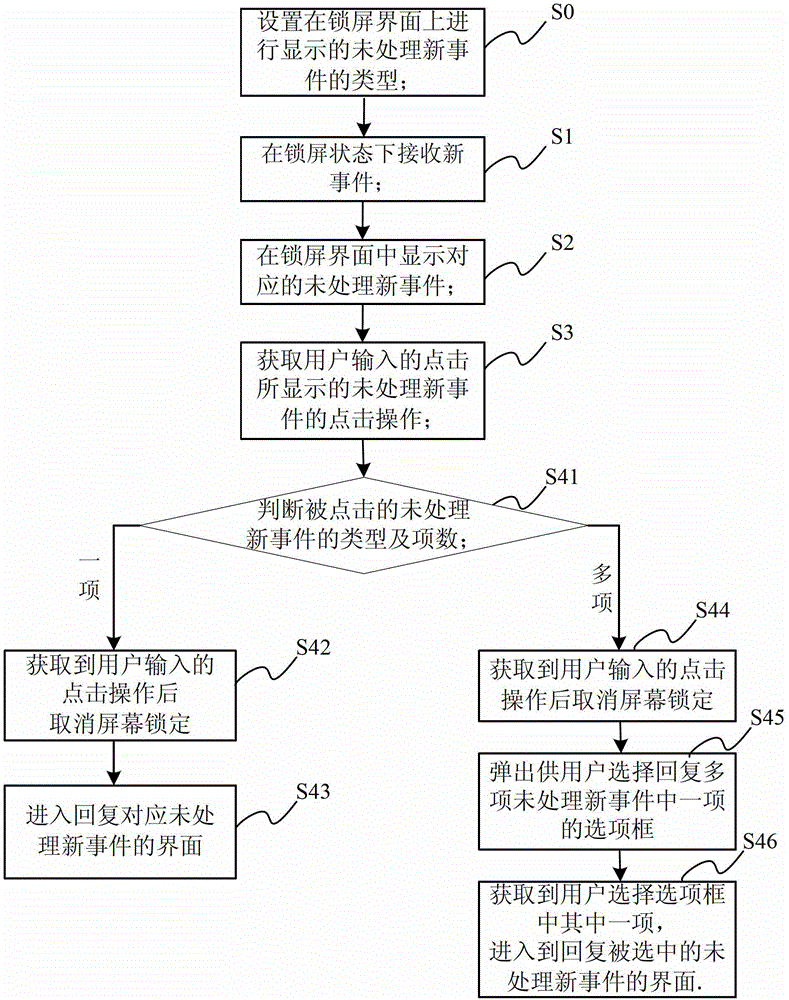
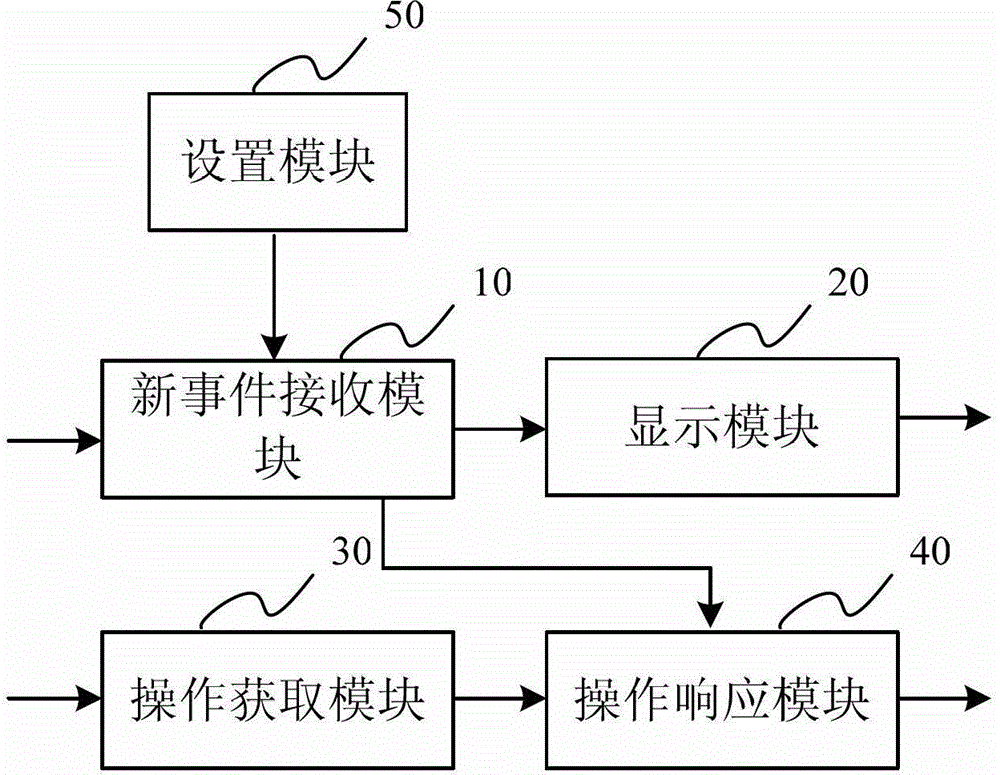
Screen lock operation method, screen lock operation device and mobile terminal
ActiveCN102946495AImprove experienceEasy to operateSubstation equipmentInput/output processes for data processingElectricityUser input
The invention relates to a screen lock operation method, a screen lock operation device and a mobile terminal. The method includes the steps: receiving new events in a screen-lock state; displaying corresponding unprocessed new events in a screen lock; and obtaining clicking operation for the unprocessed new events displayed by clicking outputted by a user, and responding the clicking operation according to types and the number of terms of the clicked unprocessed new events. The unprocessed new events are directly replied or an unprocessed new event list needing selection is popped up by responding the clicking operation of the user, so that the user can know the unprocessed new events in the screen-lock state and can directly process the new events, operation is more convenient and faster, better user experience can be provided, and electricity can be saved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Taking distance images
ActiveUS7787105B2High sensitivityFast measurement speedOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationTime informationElectromagnetic radiation
A system and method for the taking of a large number of distance images having distance picture elements. Electromagnetic radiation is transmitted in the form of transmission pulses at objects, and reflected echo pulses are detected. Measurements are made by determining the pulse time of flight of the distances of objects which respectively form a distance picture element and at which the transmission pulses are reflected. A time measuring device carries out a plurality of associated individual measurements for each distance image to be taken. Stored event lists of all time measuring channels are read out and evaluated in order to convert the respective time information contained in the event lists into distance values corresponding to the distance picture elements.
Owner:TRIPLE IN HLDG
Method for detecting abnormity of OpenStack cloud platform
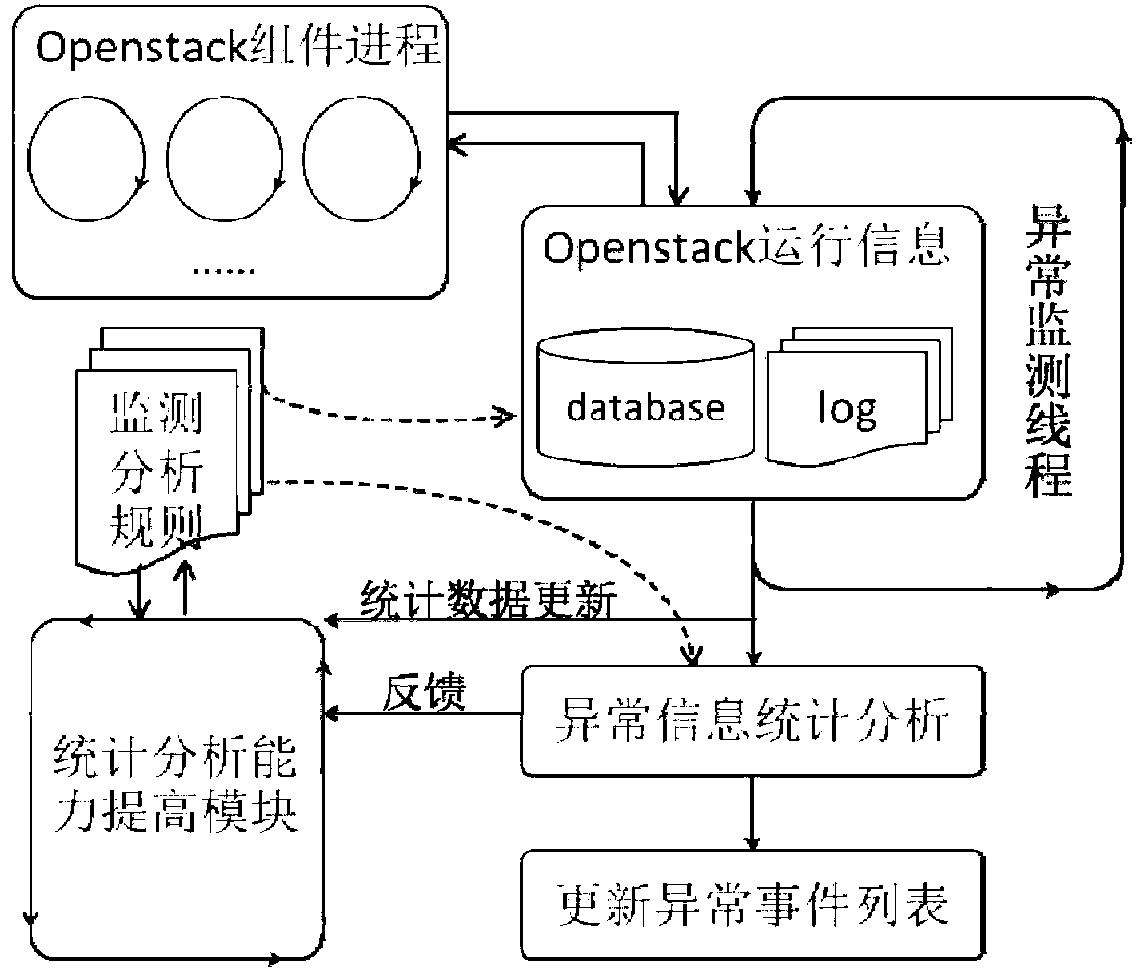
InactiveCN103227734AEasy to detectComplete expertiseData switching networksData miningCloud computing
The invention discloses a method for detecting abnormity of an OpenStack cloud platform. The method comprises the following steps that (1), an abnormity monitoring and analyzing rule is defined, wherein the monitoring and analyzing rule is a basis for locating and extracting abnormity information, and extracting an abnormity event; (2), the abnormity information is located, wherein operation information of OpenStack comprises description of a resource situation, a running state and an abnormity situation of an infrastructure service of a cloud computing platform; (3), the abnormity information is extracted; the abnormity information in the operation information is extracted and converted into a self-defining format; (4); the abnormity information is counted and analyzed, and a final abnormity event is obtained; and (5), an abnormity event list is updated. The method has the advantages that the method can conveniently and quickly detect common explicit abnormity information and implicit abnormity information of the OpenStack, and a manual participation degree can be reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Computer aided newsmaker retrieval method based on multimedia analysis
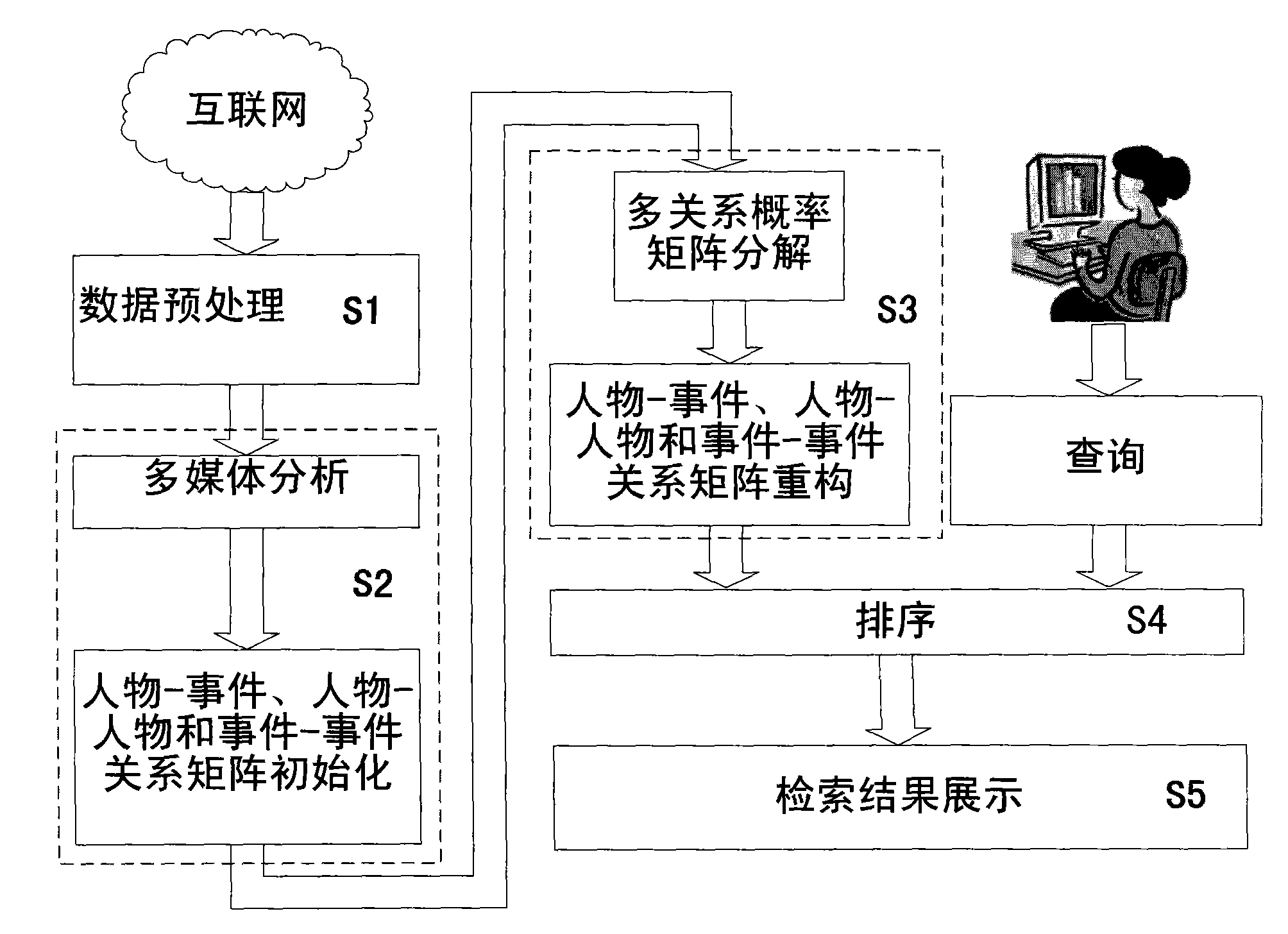
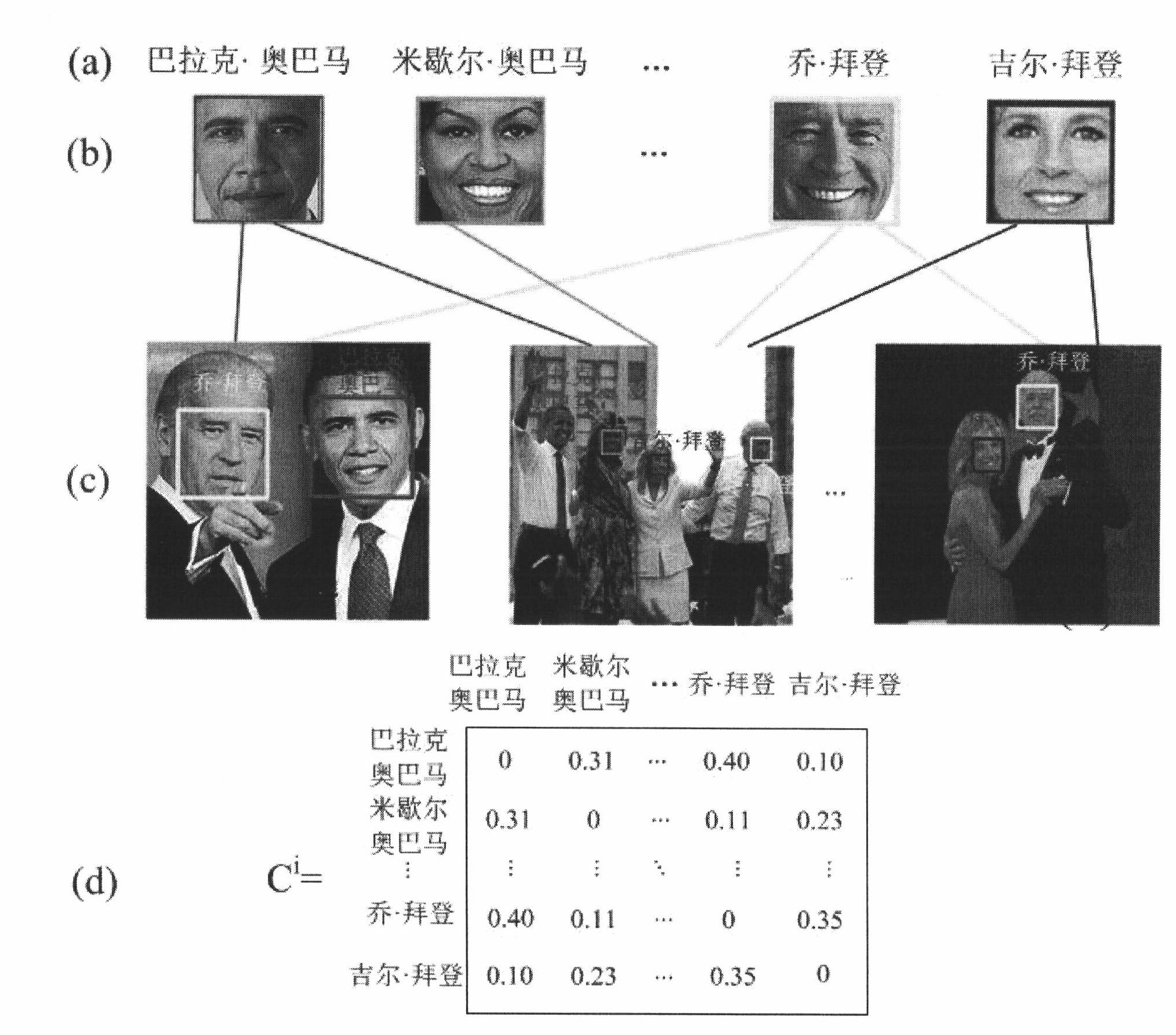
InactiveCN102024056AVivid understandingReliable initial character-character relationshipsSpecial data processing applicationsComputer-aidedComputer aid
The invention relates to a computer aided newsmaker retrieval method based on multimedia analysis. The method comprises the following steps: data preprocessing is performed on a news picture; the multimodality fusion figure relation is initialized; event relation is initialized, a multi-relation probability matrix decomposition model is provided, the potential relations are mined, the correlations between the newsmakers and news events and the query keyword are sorted according to the query keyword submitted by a user and the reconstructed relations; and a result browsing interface is retrieved, namely the name of a person which is submitted to a computer by the user, is used as the retrieval keyword, a relation view using the query person as the center and a related news event list view are provided, and the retrieval result is fed back to the user.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Asynchronous network application program processing method
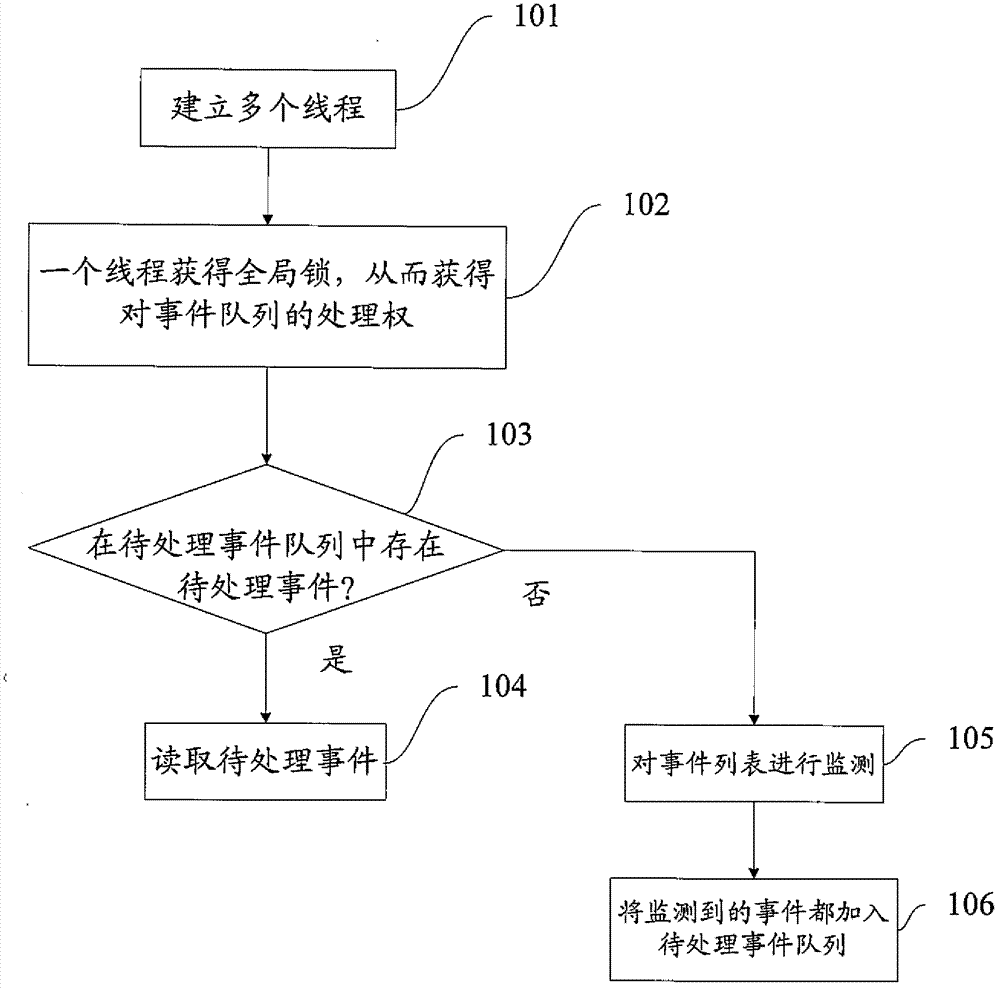
ActiveCN103092682AThe processing algorithm is simpleEasy to manageMultiprogramming arrangementsAsynchronous networkApplication software
The invention discloses an asynchronous network application program processing method. The method includes: establishing multiple threads, wherein each thread has a same operating logic; obtaining a global lock by one of the threads to obtain processing right to event queues; inquiring a to-be-processed event queue by the thread having the event queue processing right, and when to-be-processed events exist in the to-be-processed event queue, reading a to-be-processed event by the thread for processing the to-be-processed event; and when the to-be-processed event queue has no to-be-processed events, monitoring an event list by the thread, and when events are monitored by the thread, adding the events into the to-be-processed event queue. By establishing multiple equivalent threads and lock competing logics to the global lock among the multiple threads, compactness and efficiency in management of the multiple threads are realized, and software and hardware resources are saved; and by performing timeout processing through a compact thread model, a lightweight timer mechanism and a safe and efficient asynchronous information mechanism are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DAHUA TECH CO LTD
Wearable device and method, based on intelligent terminal, for intelligently displaying important information of user
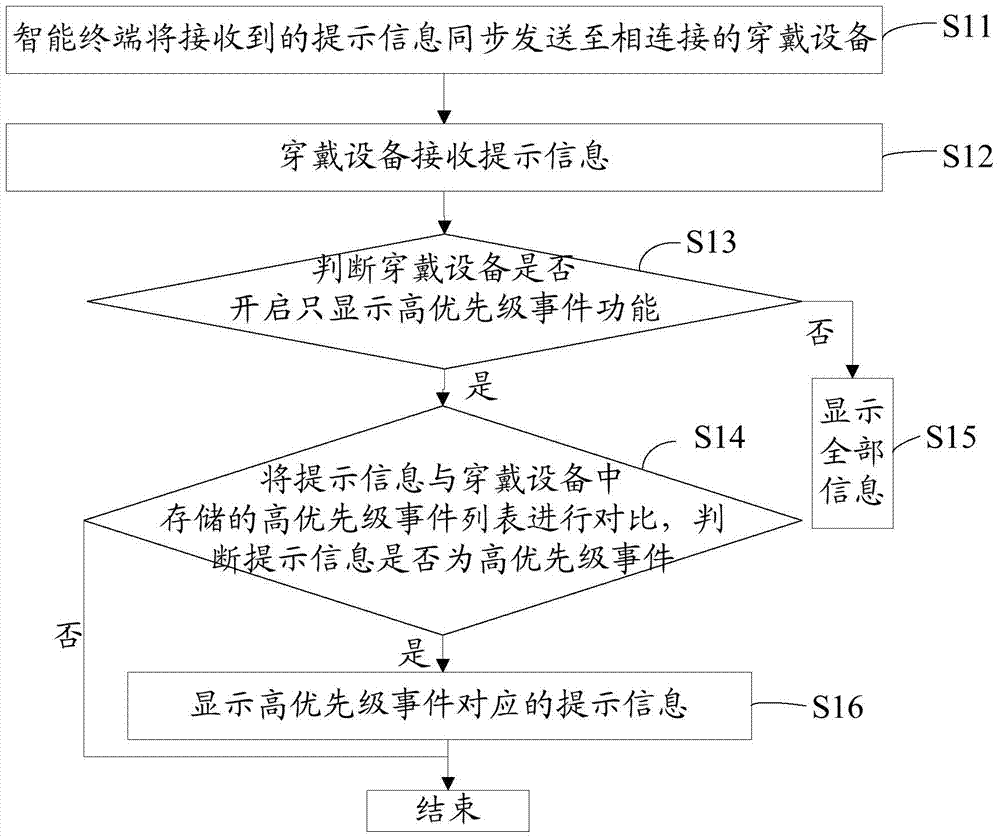
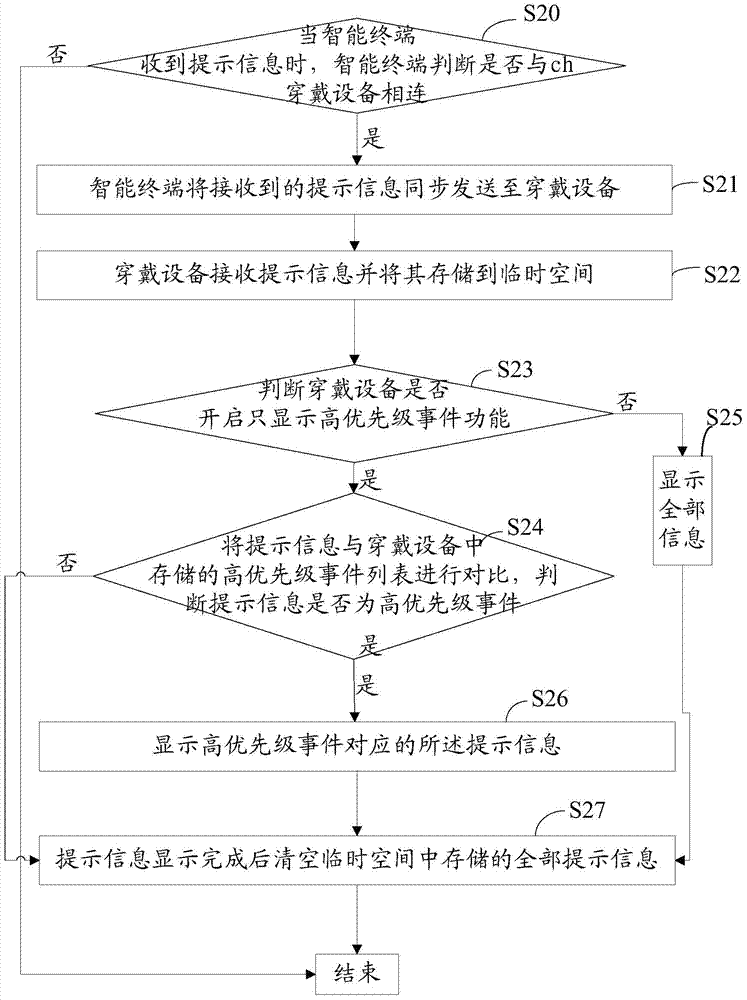
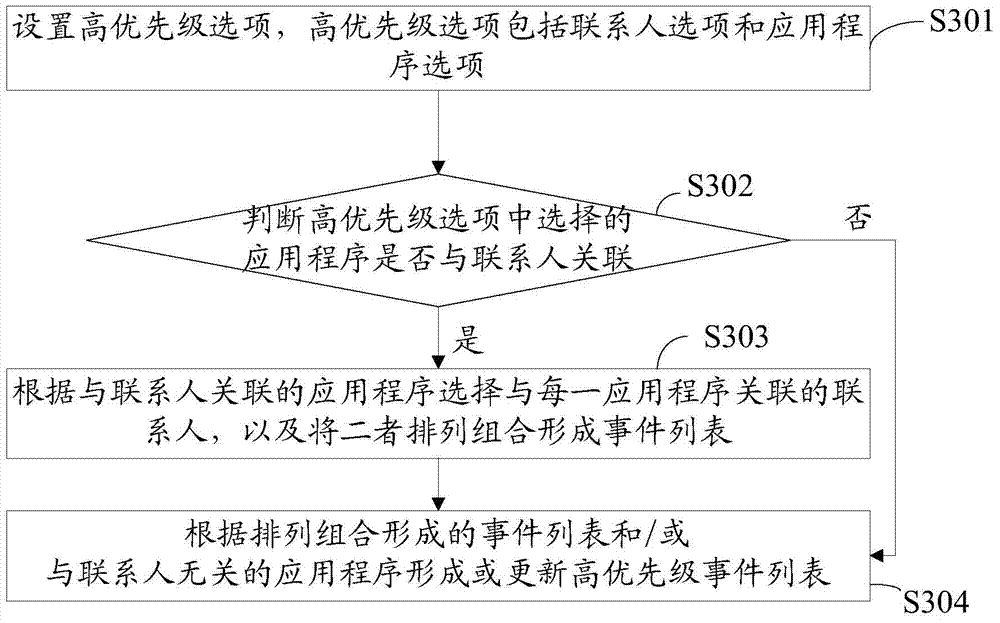
InactiveCN104853037AQuick ViewFree from harassmentSubstation equipmentWireless commuication servicesComputer hardwareEvent list
The invention discloses a method, based on an intelligent terminal, for intelligently displaying important information of a user. The method includes the steps of sending synchronously received prompt information by an intelligent terminal to a wearable device; receiving the prompt information by the wearable device; determining whether only the high priority event function of the wearable device is started; comparing the prompt information with a high priority event list stored in the wearable device if only the high priority event function of the wearable device is started, and determining whether the prompt information is a high priority event; and displaying on the wearable device the prompt information corresponding to the high priority event when only the high priority event function is started or displaying all of the prompt information when only the high priority event function is not started. The wearable device can automatically filter prompt information for a user so as to only display the important and high priority prompt information that is cared by the user.
Owner:HUIZHOU TCL MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Network alarm event processing method and device
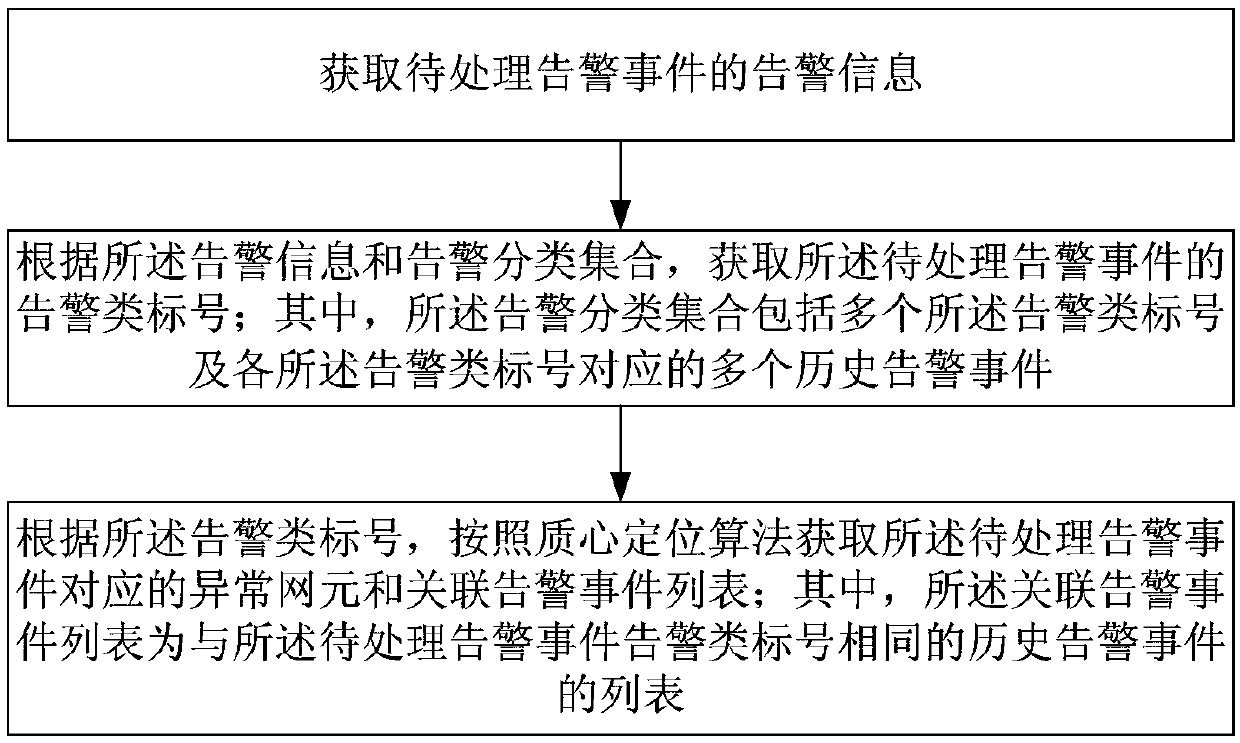
ActiveCN108737147AImprove processing efficiencyData switching networksReal-time computingNetwork element
The embodiment of the invention provides a network alarm event processing method and a network alarm event processing device. The method comprises the steps of acquiring alarm information of an alarmevent to be processed; according to the alarm information and an alarm classification set, acquiring an alarm type mark number of the alarm event to be processed, wherein the alarm classification setcomprises the multiple alarm type mark numbers and multiple historical alarm events corresponding to each alarm type mark number; and according to the alarm type mark number, acquiring an abnormal network element corresponding to the alarm event to be processed and an associated alarm event list according to a centroid positioning algorithm, wherein the associated alarm event list is the list of the historical alarm events having the same alarm type mark number with the alarm event to be processed. The device is used for executing the abovementioned method. According to the method and device provided by the invention, the processing efficiency of the network alarm event is improved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP GUANGDONG CO LTD +1
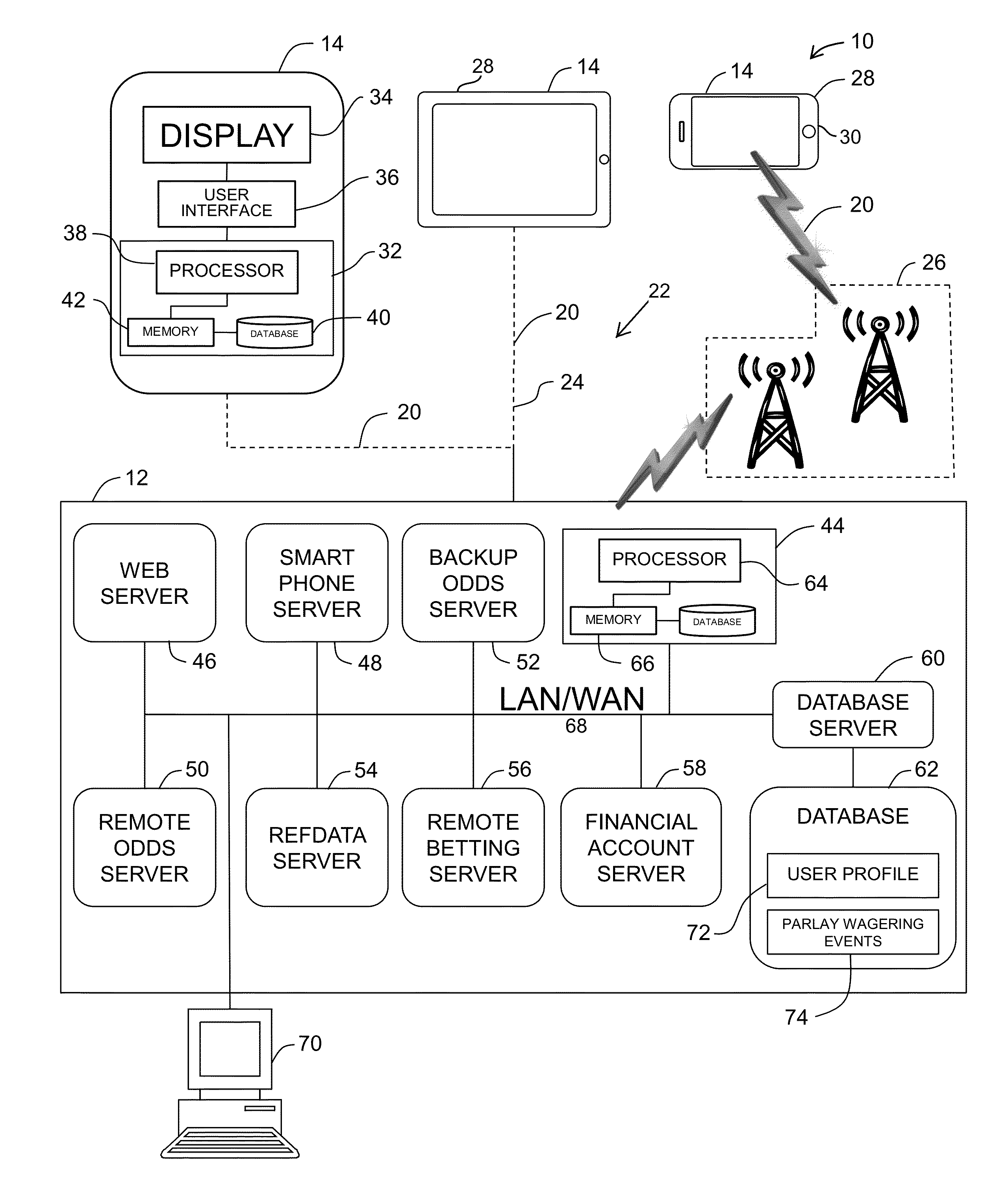
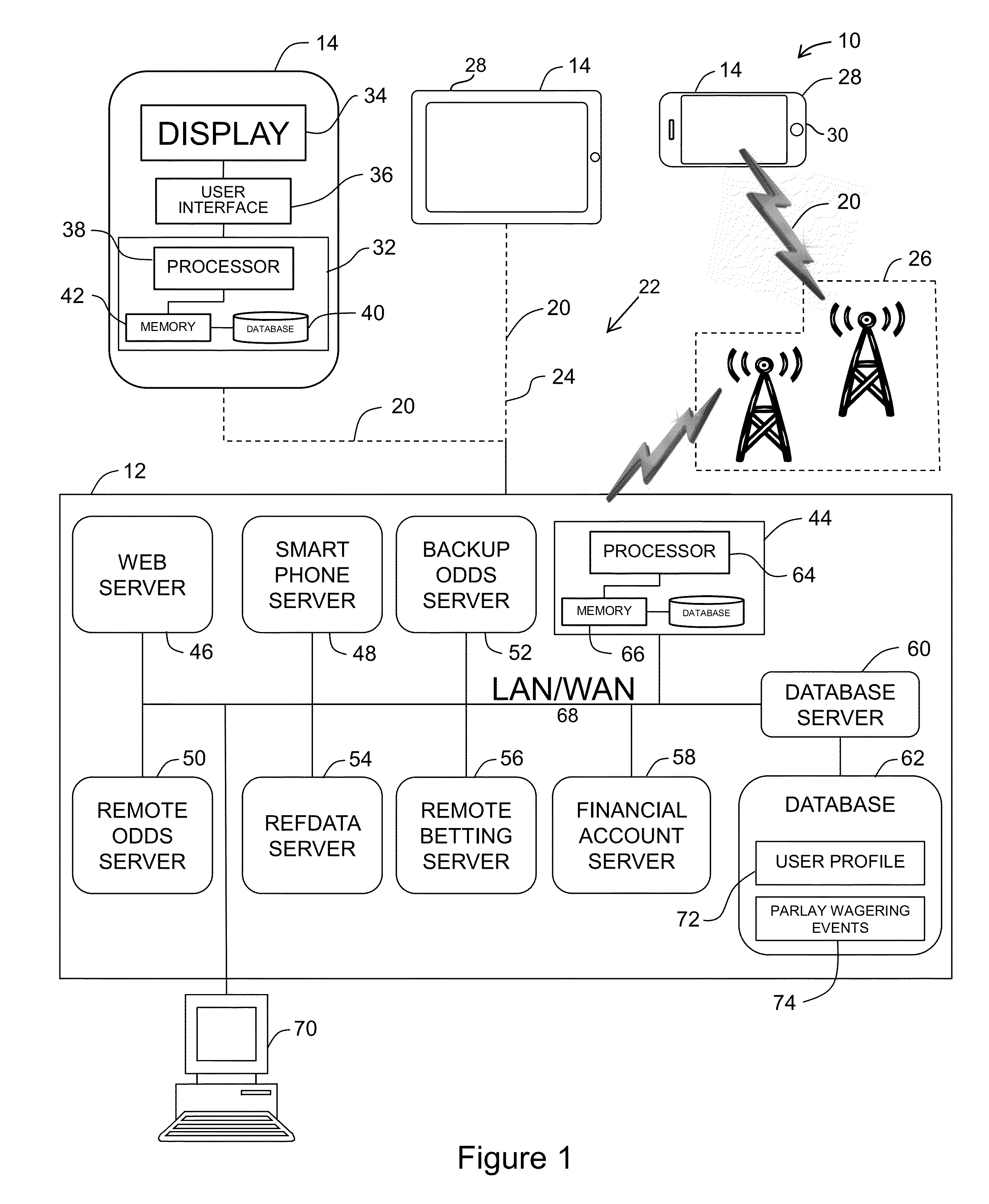
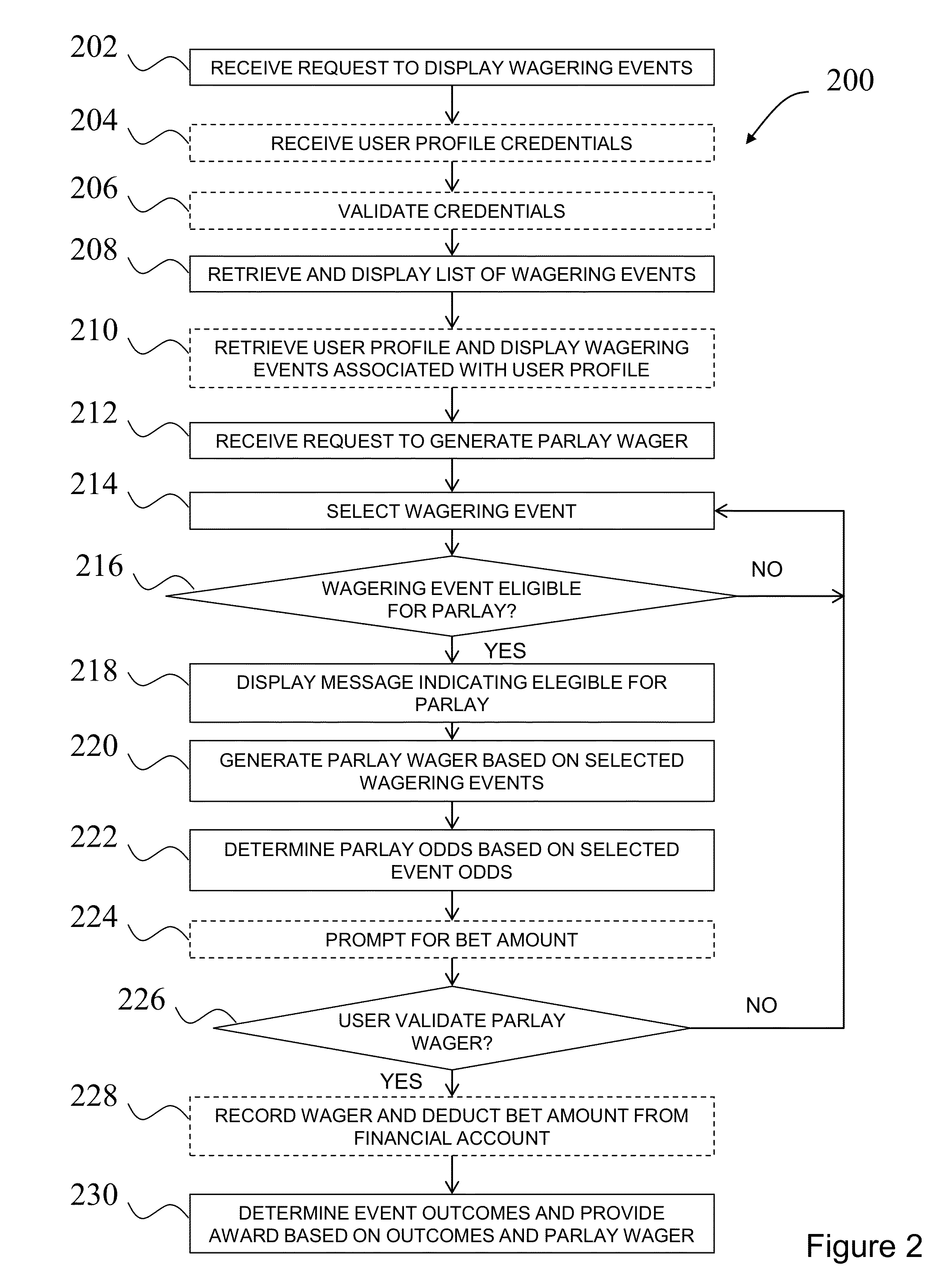
System and method for allowing users to place parlay wagers via mobile computing devices
InactiveUS20130217475A1Apparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesMobile deviceComputer science
A method of allowing a user to place a parlay wager via a mobile computing device is described herein. The method includes receiving, from the mobile computing device, a request to display information associated with a plurality of wagering events, and retrieving, from a database, an event list including a plurality of wagering events and displaying the list of wagering events on the mobile computing device. The method also includes receiving a request to generate a parlay wager, selecting a first wagering event and a second wagering event, and generating a parlay wager based on the selected first and second wagering events. The method also includes determining the outcome of each of the first and second wagering events, and providing an award to the user determined as a function of the first and second wagering event outcomes and the generated parlay wager.
Owner:ONEWORKS IP HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com