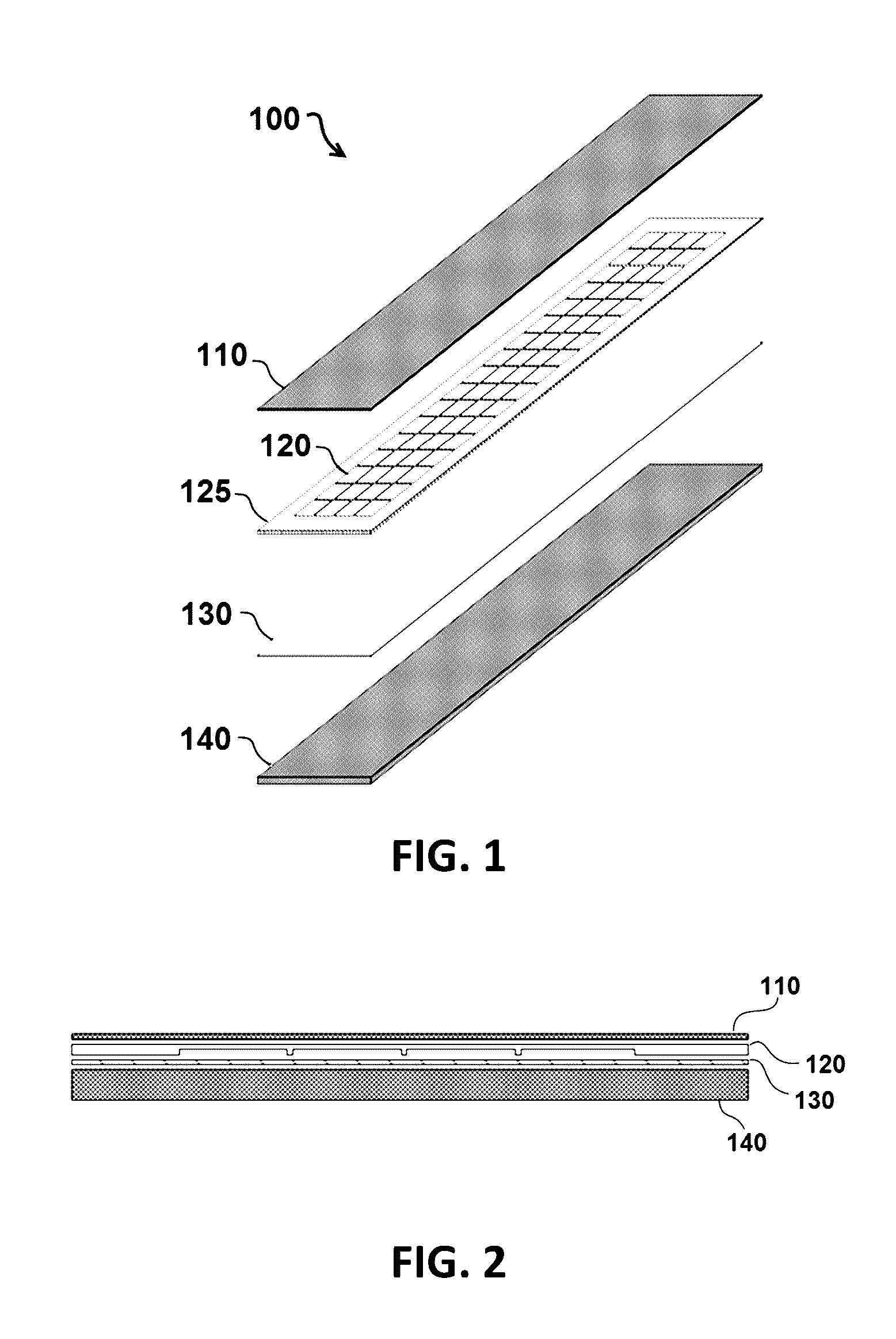
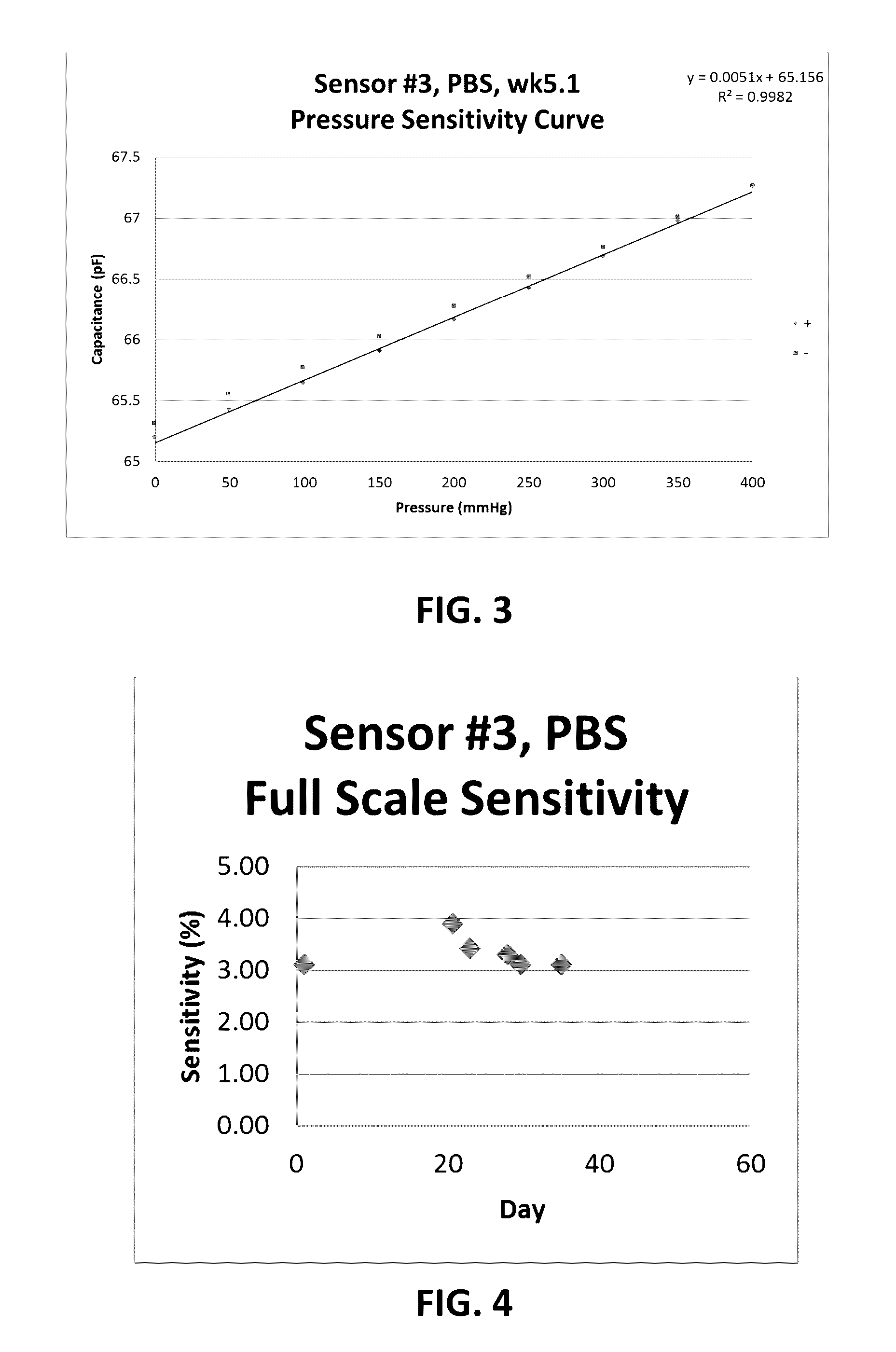
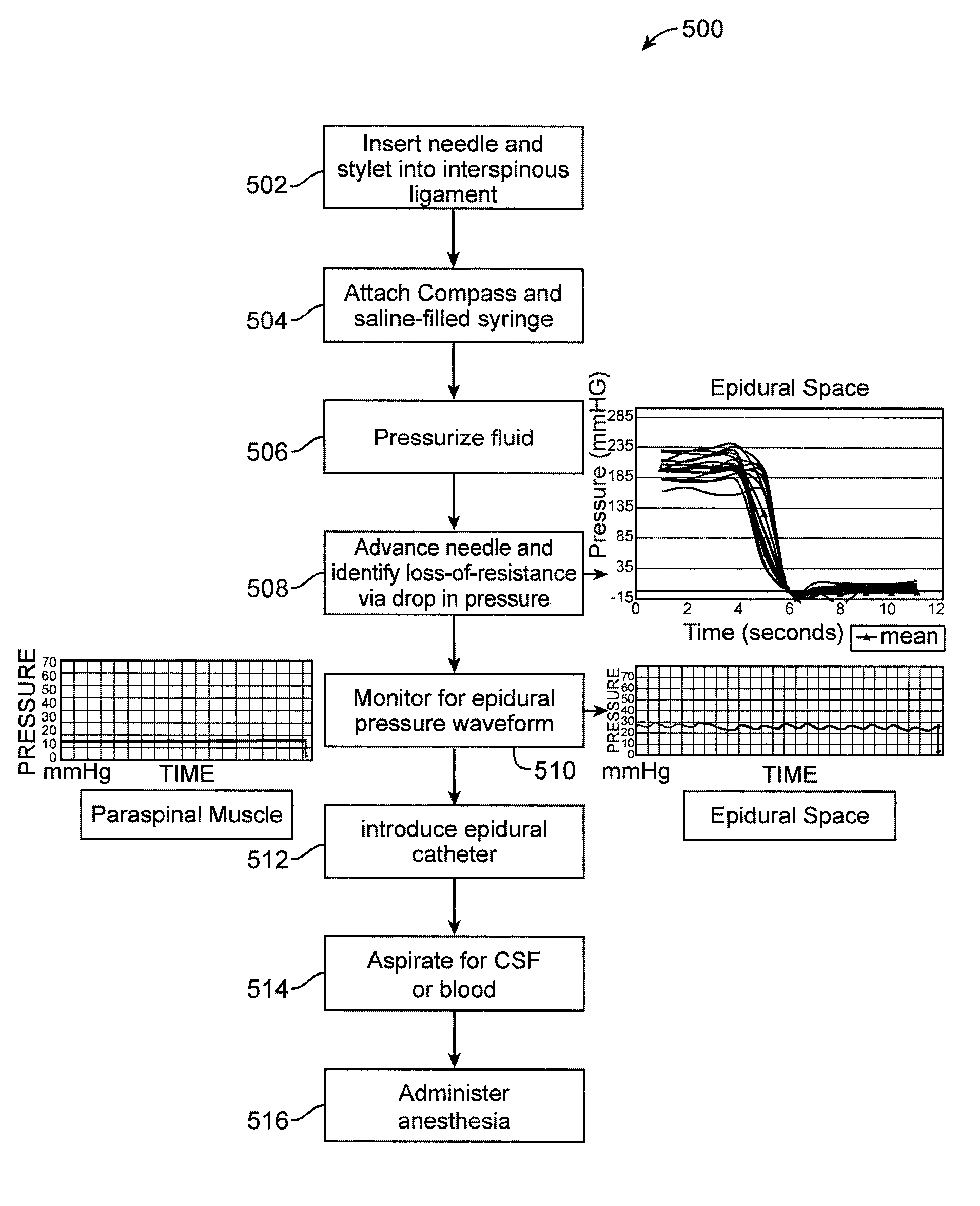
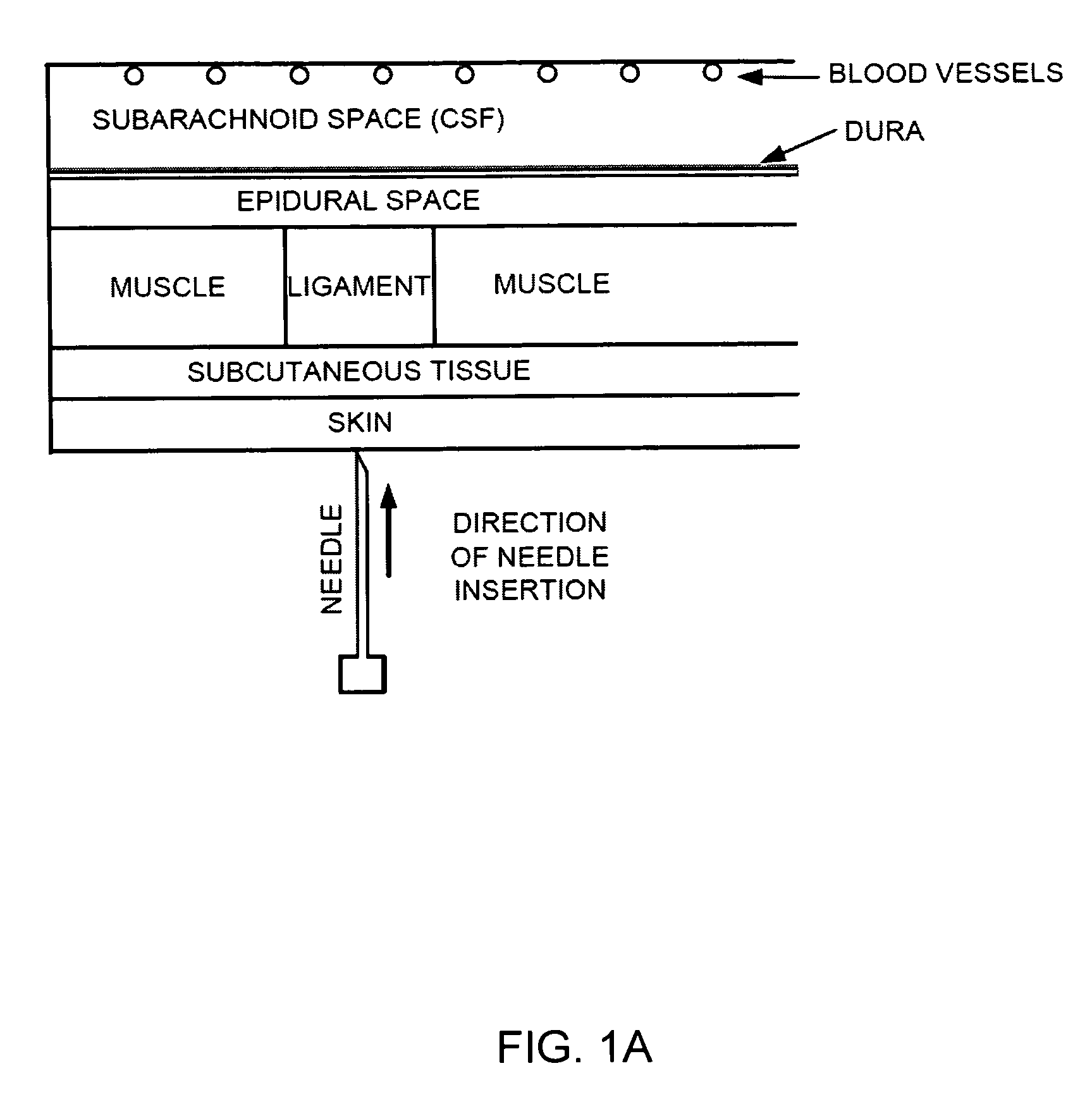
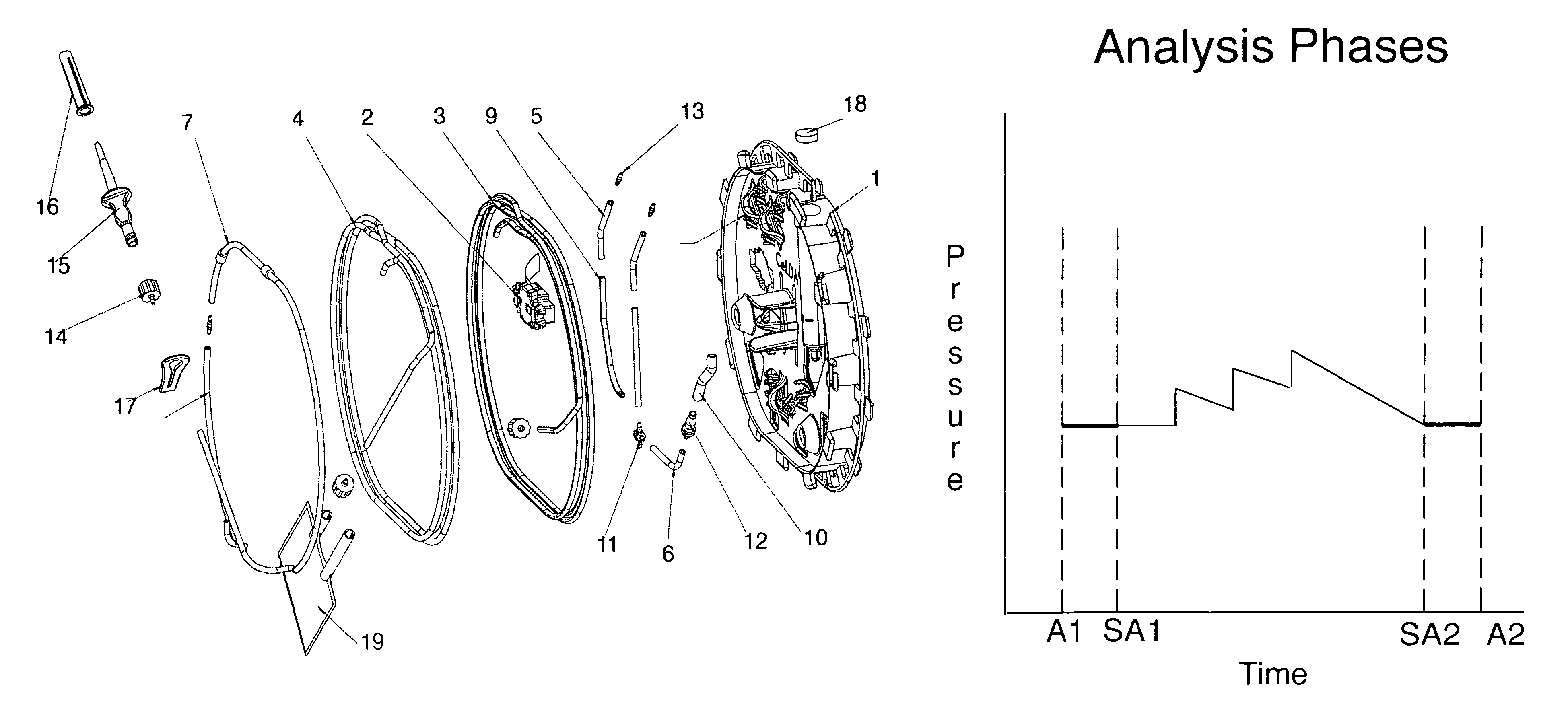
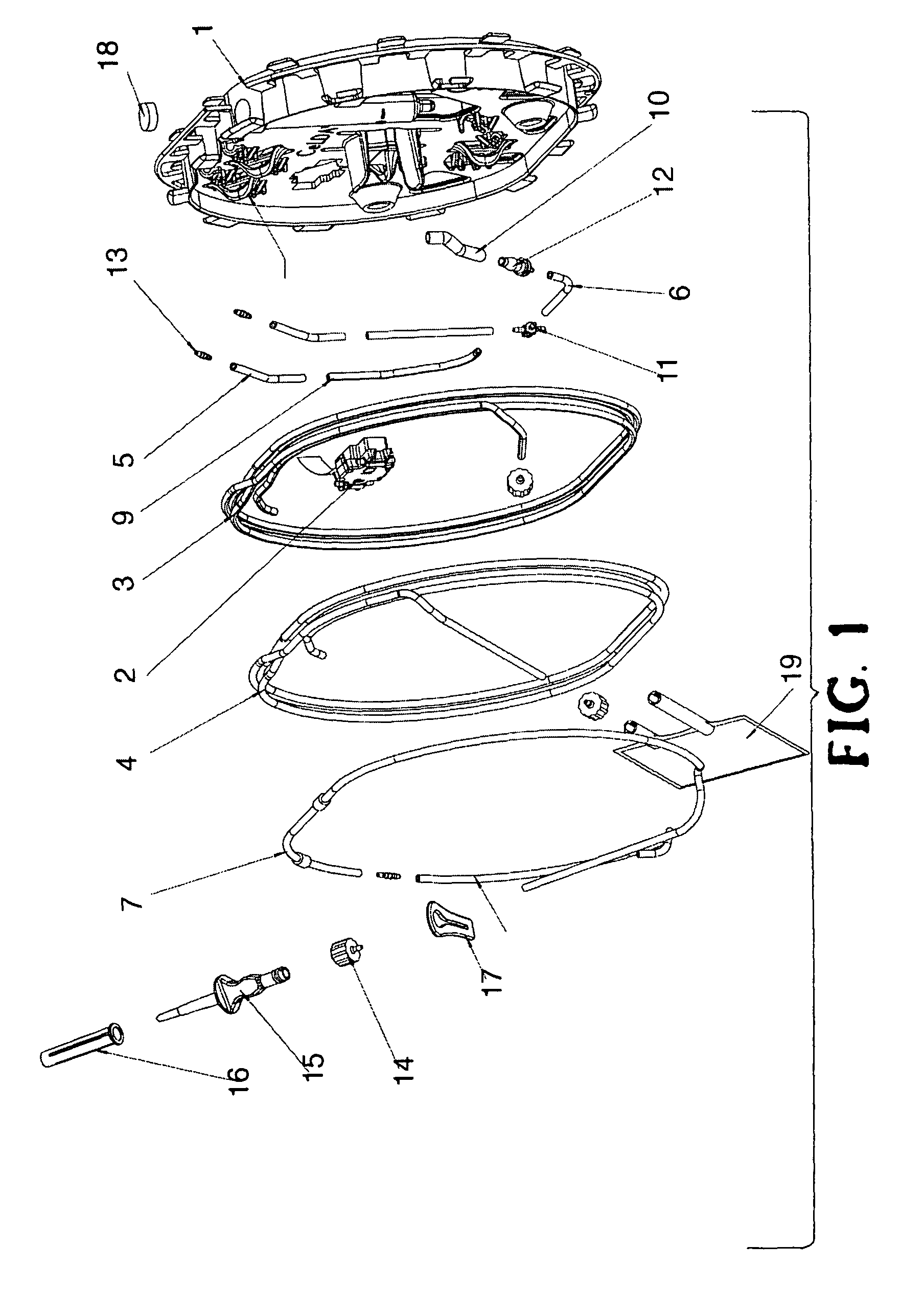
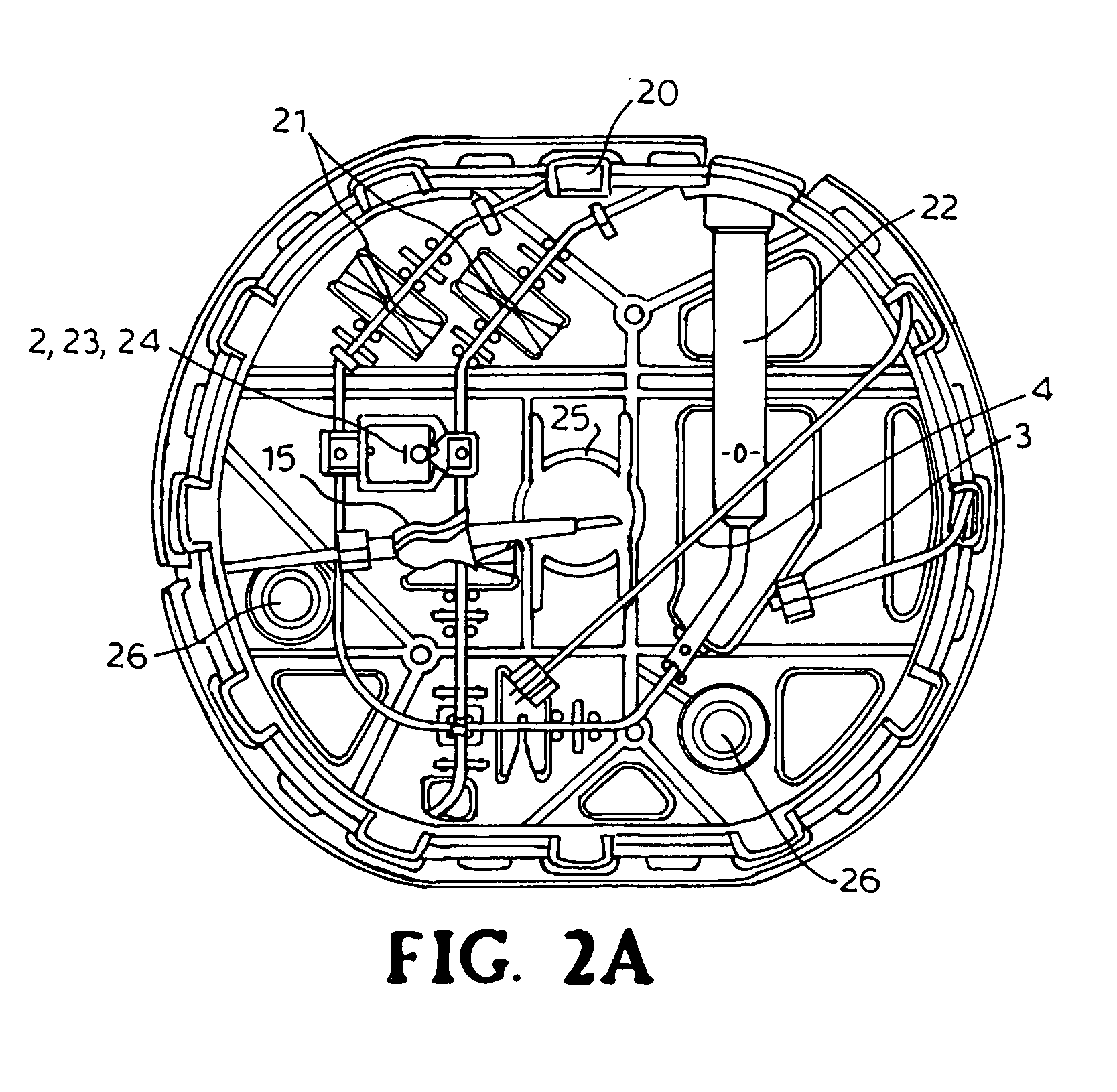
Patents
Literature
120results about "Spinal fluid pressure measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
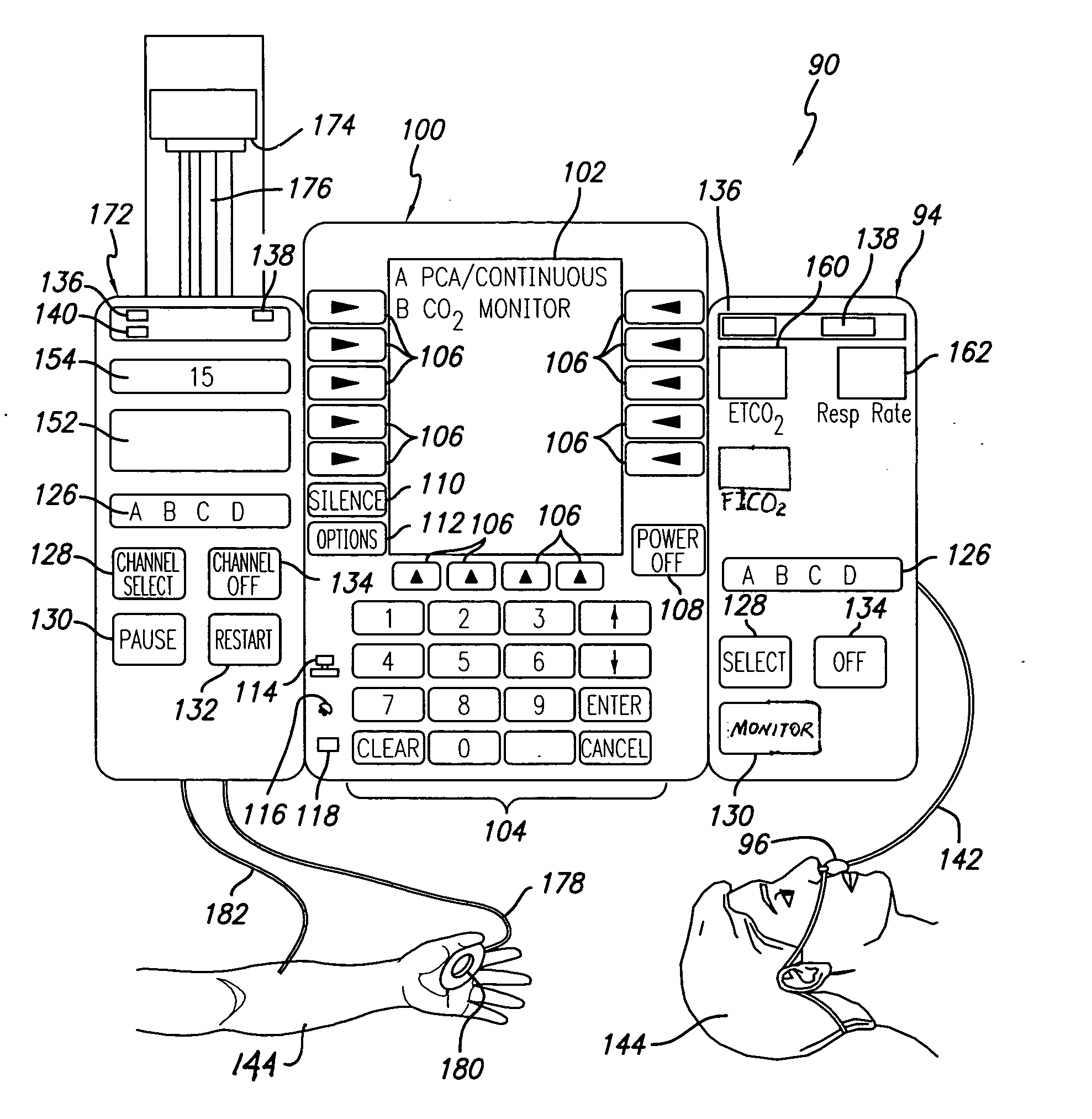
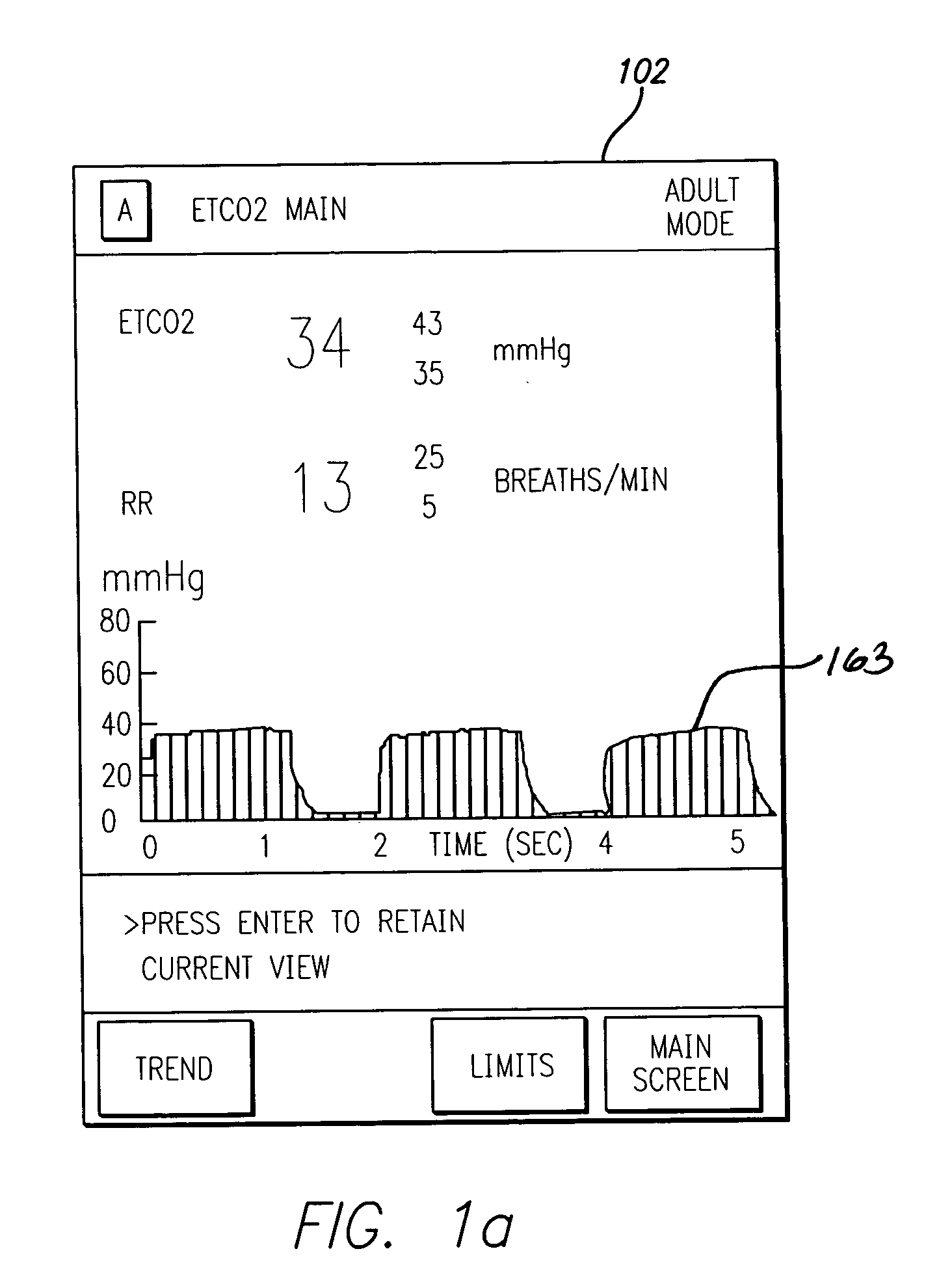
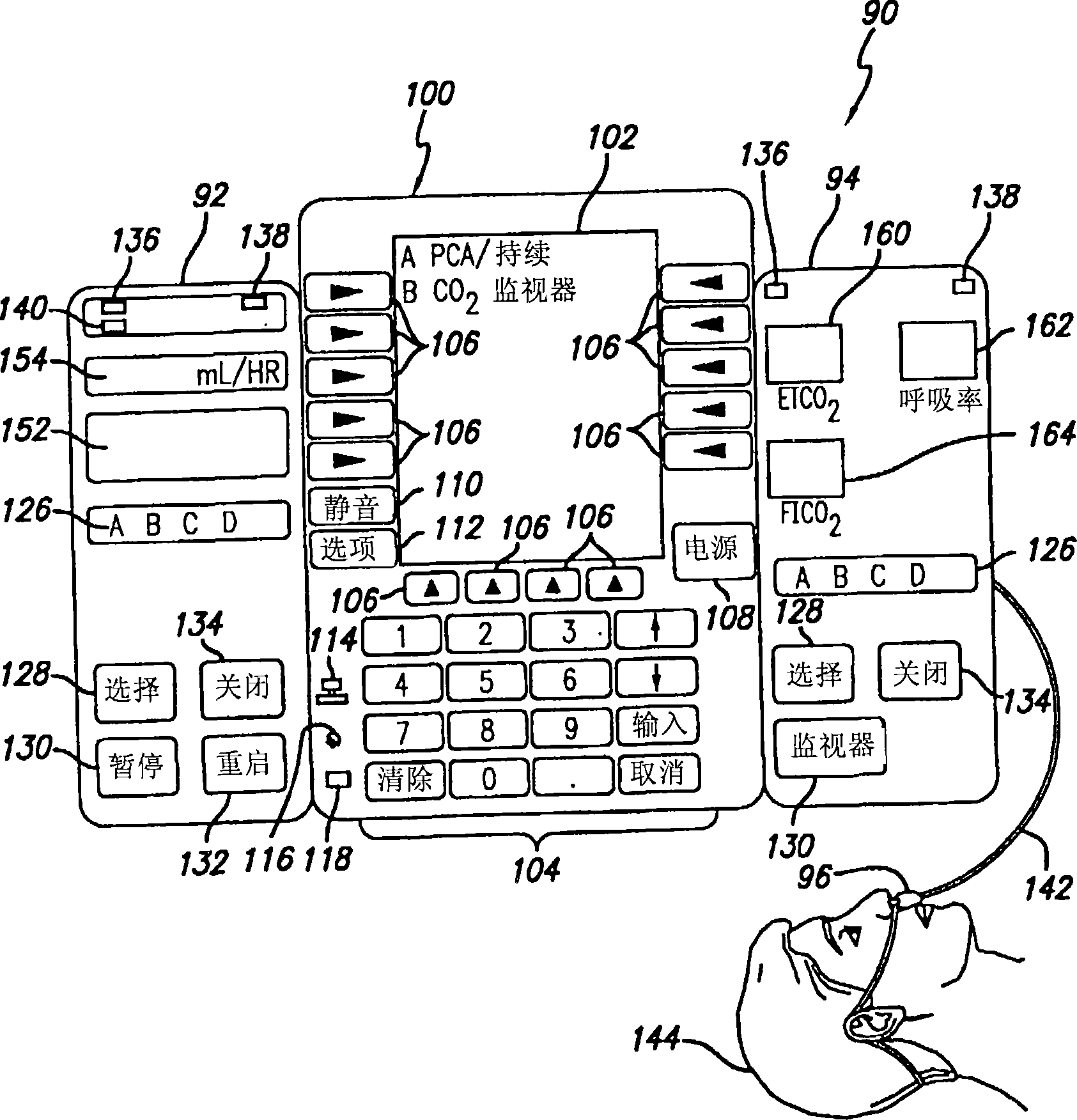
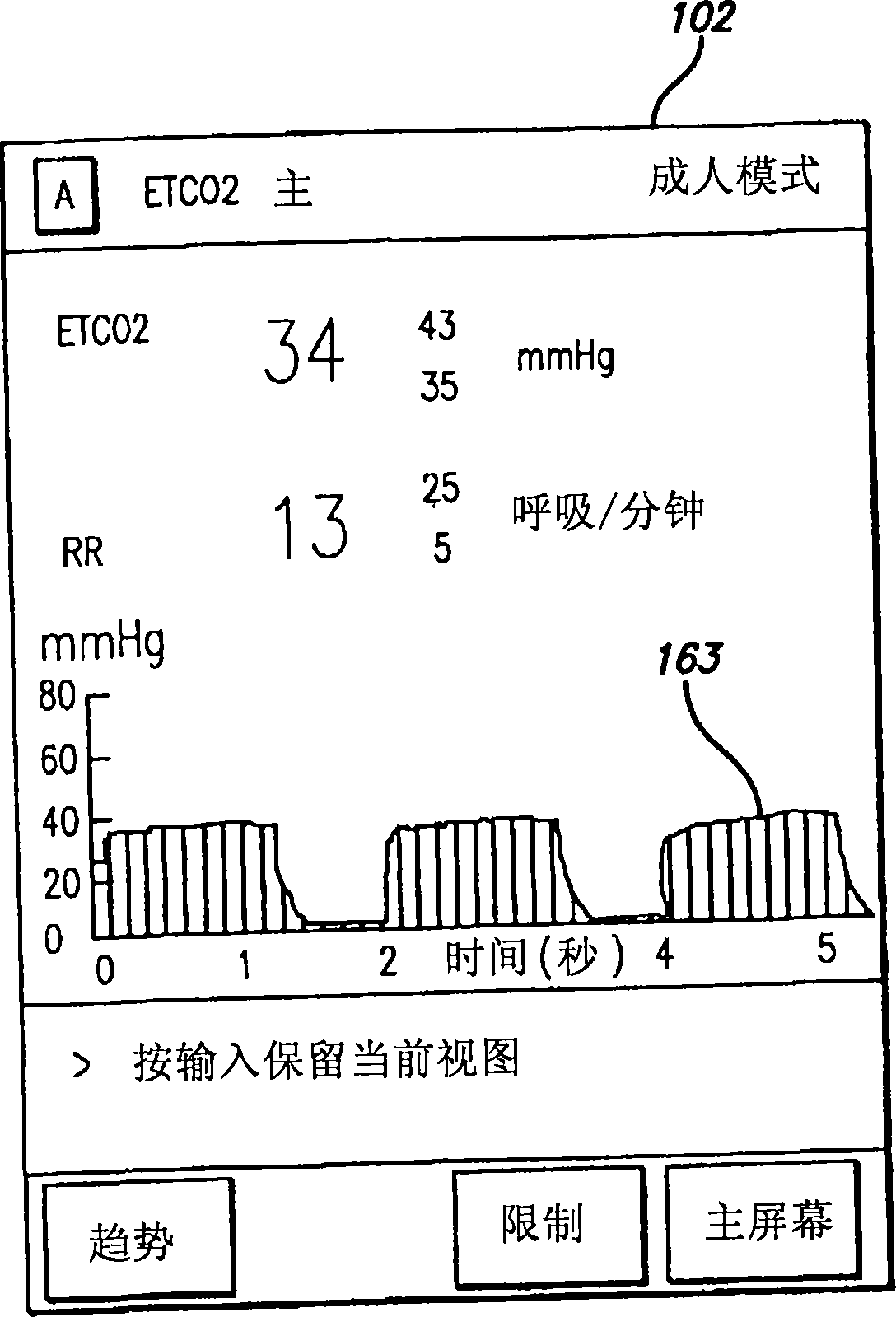
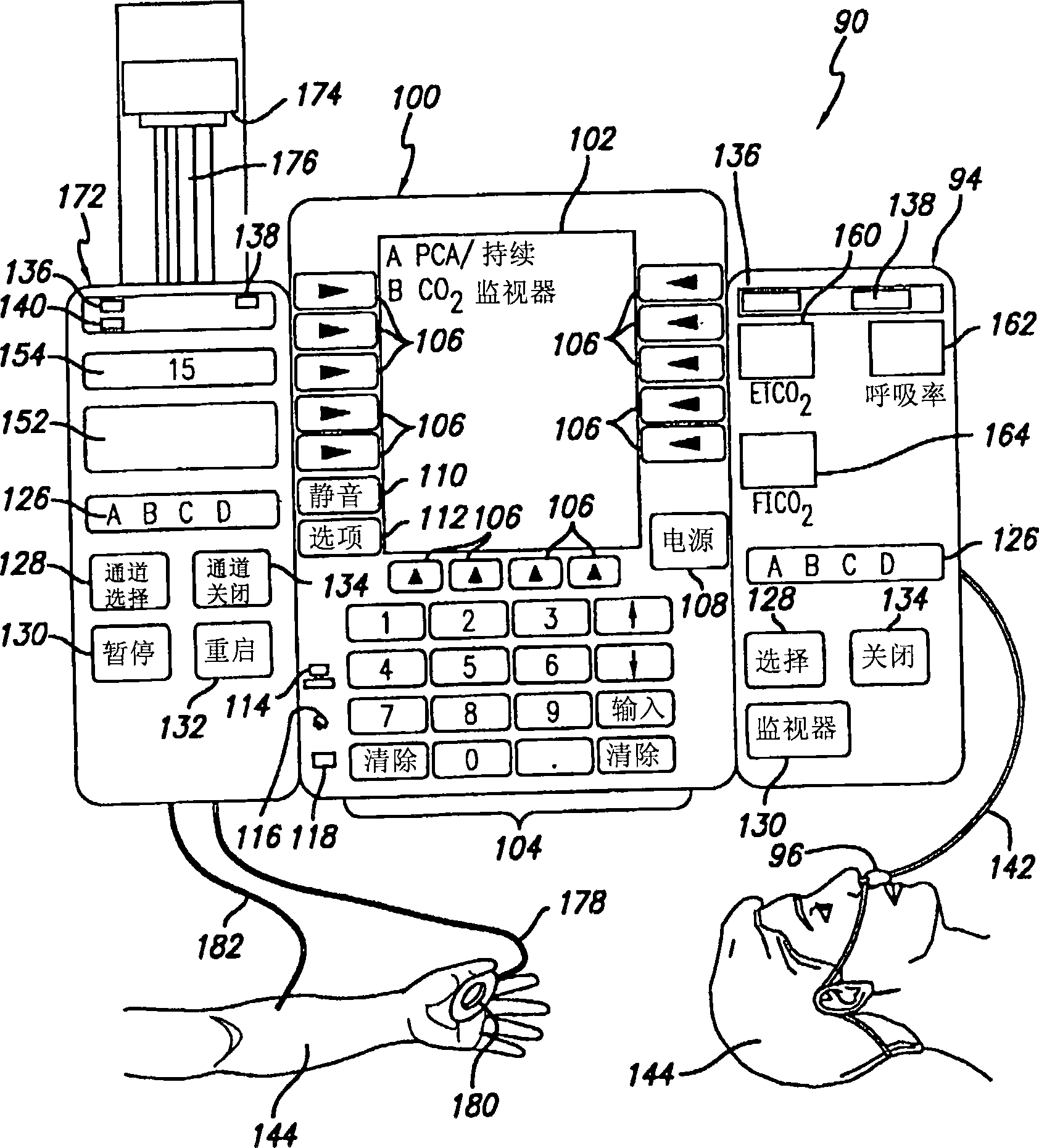
Patient-controlled analgesia with patient monitoring system and method
A patient care system in which a physiological parameter of a patient is monitored while the patient self-administers analgesic. A display presents a trend of the patient's physiological parameter along with the time of self-administration of the analgesic (“PCA”—patient controlled analgesic) such that the effect of the analgesic on the physiological parameter can be seen over selectable time periods. The physiological parameter may be ETCO2 or SpO2 or other. Also included is a drug library having acceptable pumping parameters as well as other PCA specific data. Should the operator program a pumping parameter that is outside an acceptable range, or should the patient attempt to self-administer more analgesic than the acceptable range permits, or should a patient's physiological parameter change during infusion such that a pumping parameter becomes outside an acceptable range, an indication of such will be given and action, such as stopping the pump, will be taken.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
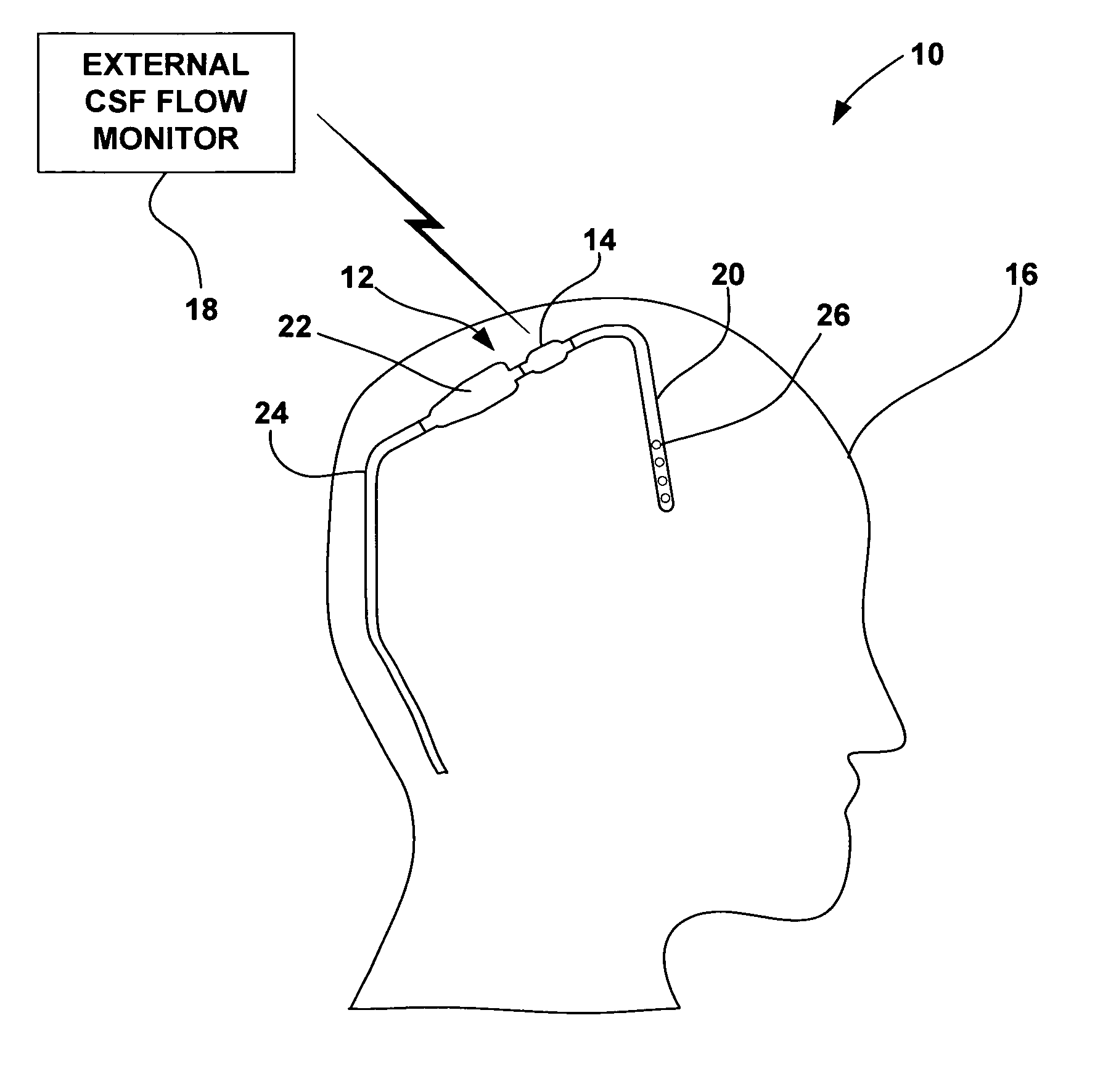
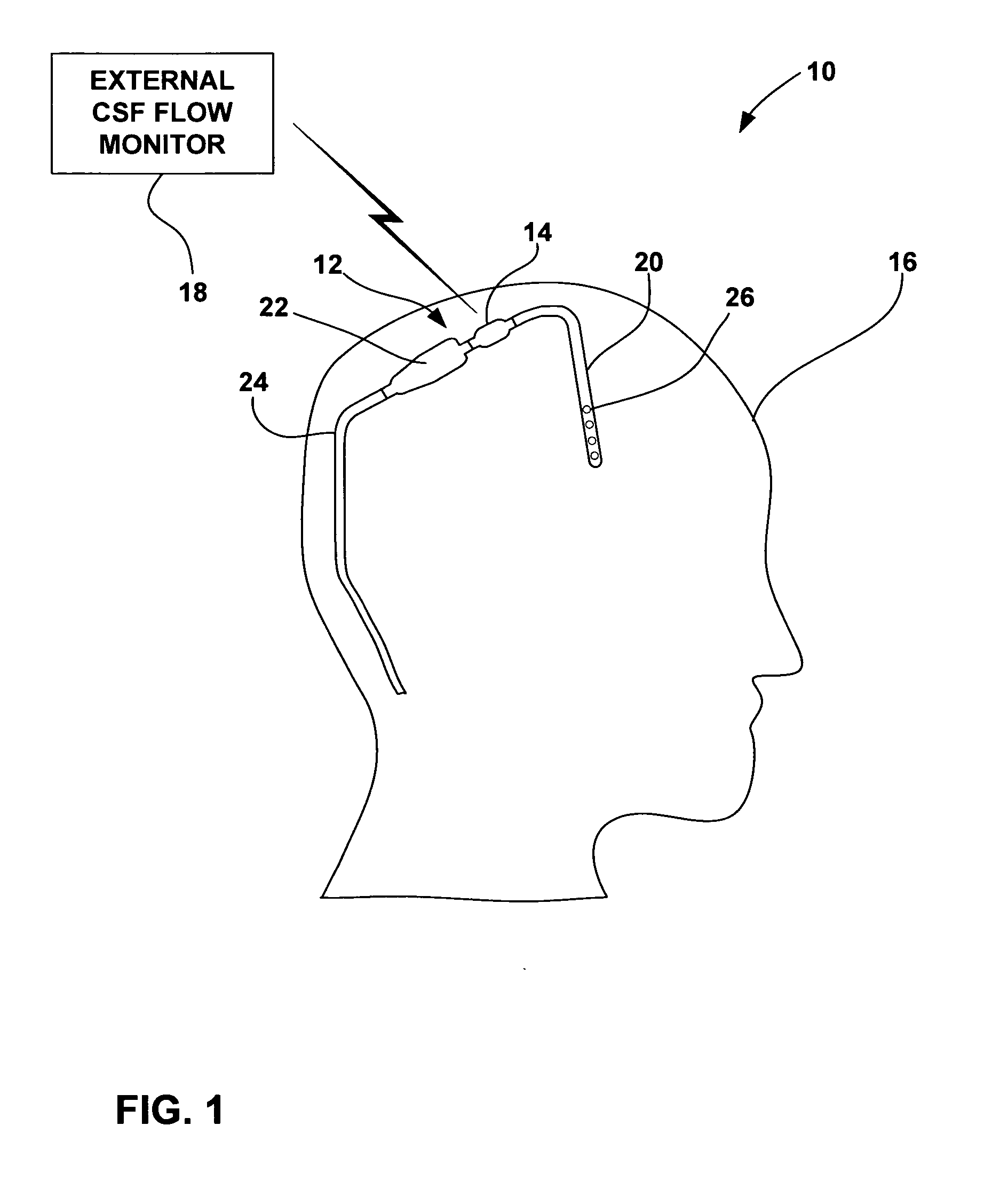
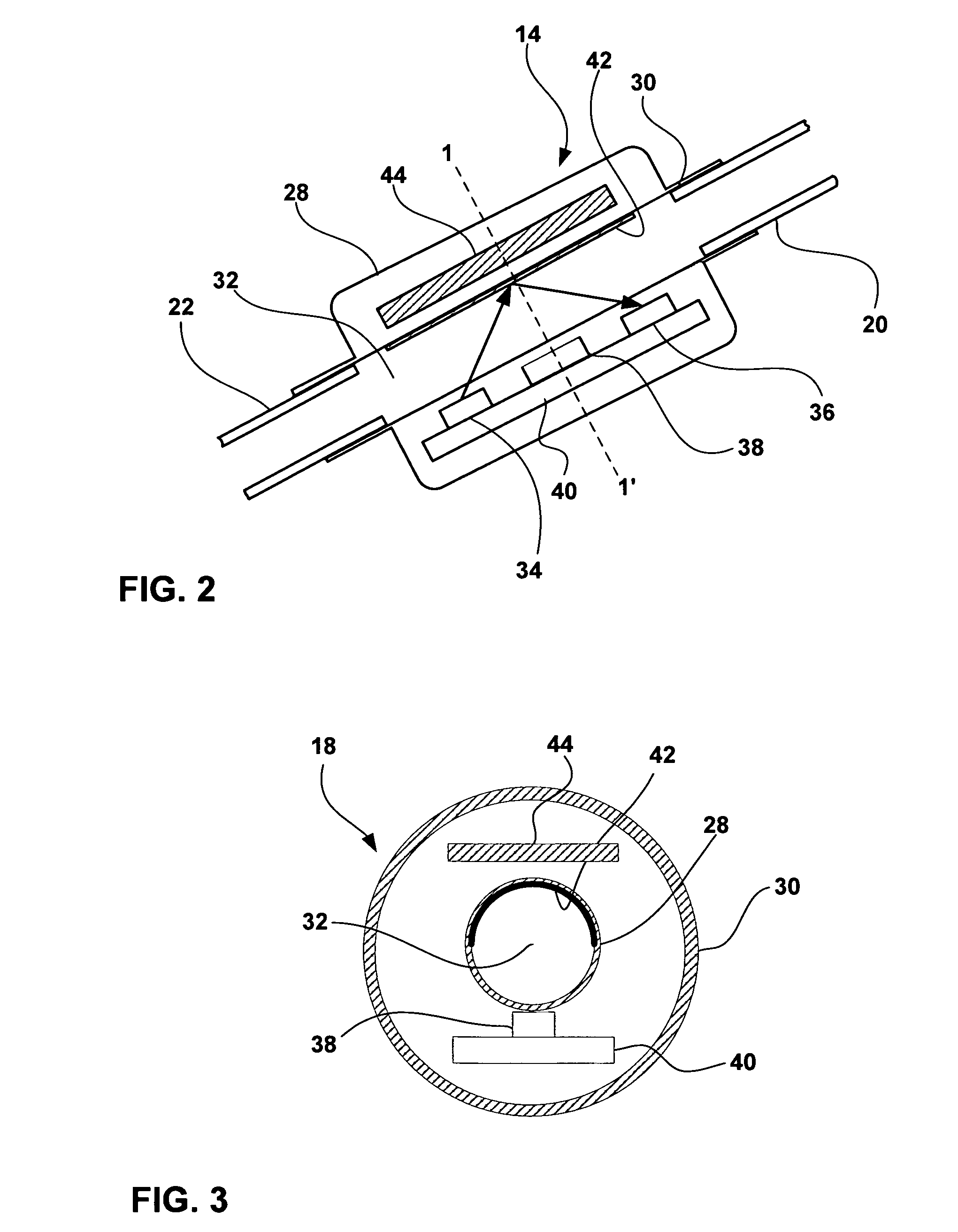
Cerebral spinal fluid flow sensing device
InactiveUS20060020239A1Evaluate performance of ventricular shuntEnsure correct executionWound drainsEndoradiosondesFlow transducerCsf shunt
The disclosure is directed to an implantable device for sensing CSF flow through an implantable ventricular shunt. The sensing device is implanted with the CSF shunt, and includes a flow sensor to sense flow rate or shunt blockage. The sensing device is either placed within or adjacent to the fluid path through the shunt. The sensing device transmits the sensed flow rate to an external monitoring device by wireless telemetry. The sensing device may be integrally formed as part of the shunt, or clamped onto a portion of the shunt, in which case the sensing device may be resusable. An external monitor receives the transmitted flow signal and presents information based on the flow signal. The sensing device may be inductively powered or include its own power supply.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Portable medical imaging system
ActiveUS20170215827A1Expand field of viewComputerised tomographsTomographyMedical imagingEngineering
Medical imaging devices, systems, and methods thereof. The medical imaging system may include a movable station and a gantry. The movable station includes a gantry mount rotatably attached to the gantry. The gantry includes an outer C-arm slidably mounted to and operable to slide relative to the gantry mount, an inner C-arm slidably coupled to the outer C-arm and, an imaging signal transmitter and sensor attached to the C-arms. The two C-arms work together to provide a full 360 degree rotation of the imaging signal transmitter. In embodiment, the imaging signal transmitter and imaging sensor are offset from a center axis of the medical imaging system such that the portable medical imaging system is operable to capture an enlarged field of view.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Systems, methods, and devices for facilitating access to target anatomical sites or environments
ActiveUS20110060229A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGuide needlesDistal portionBiomedical engineering
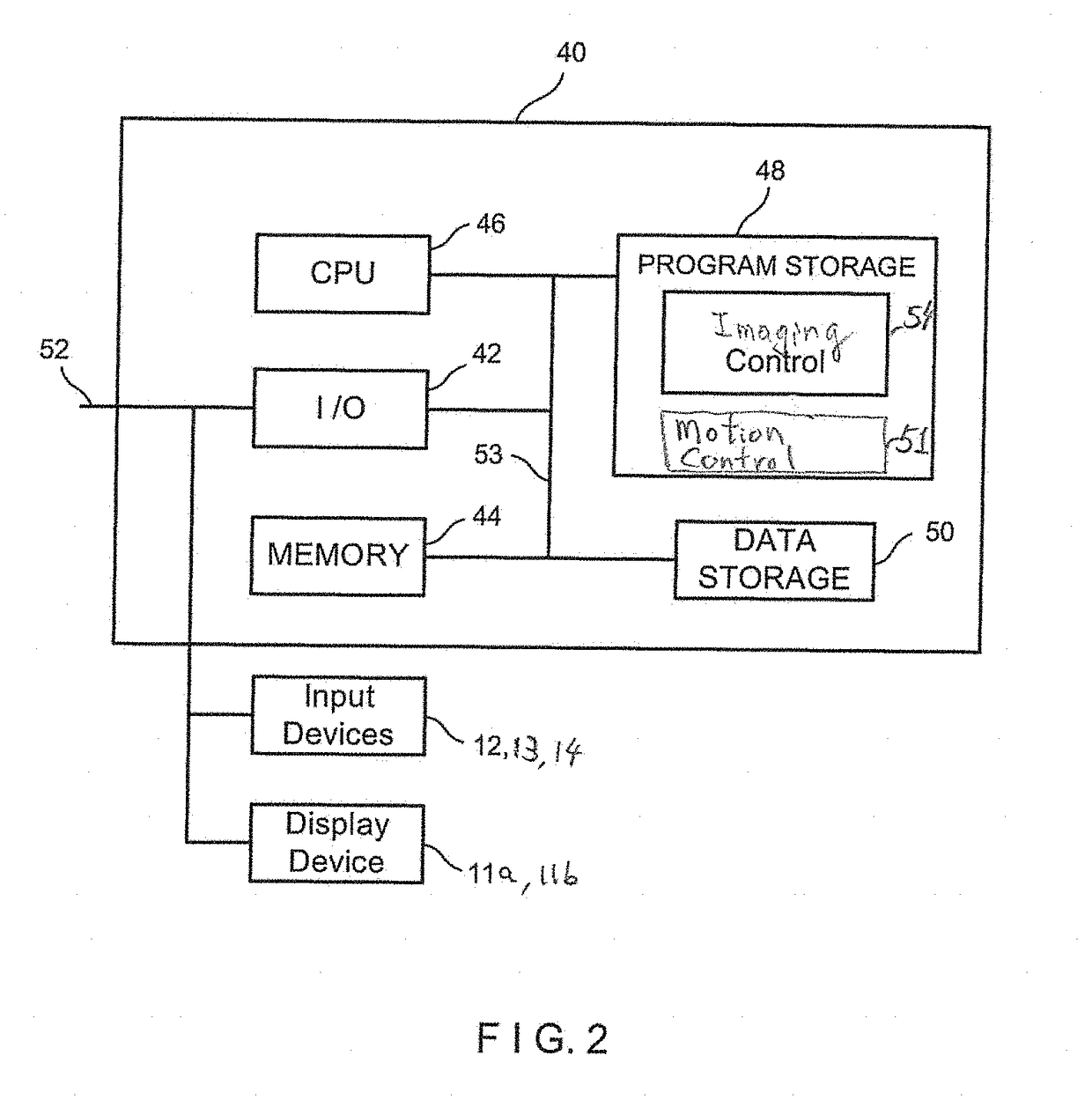
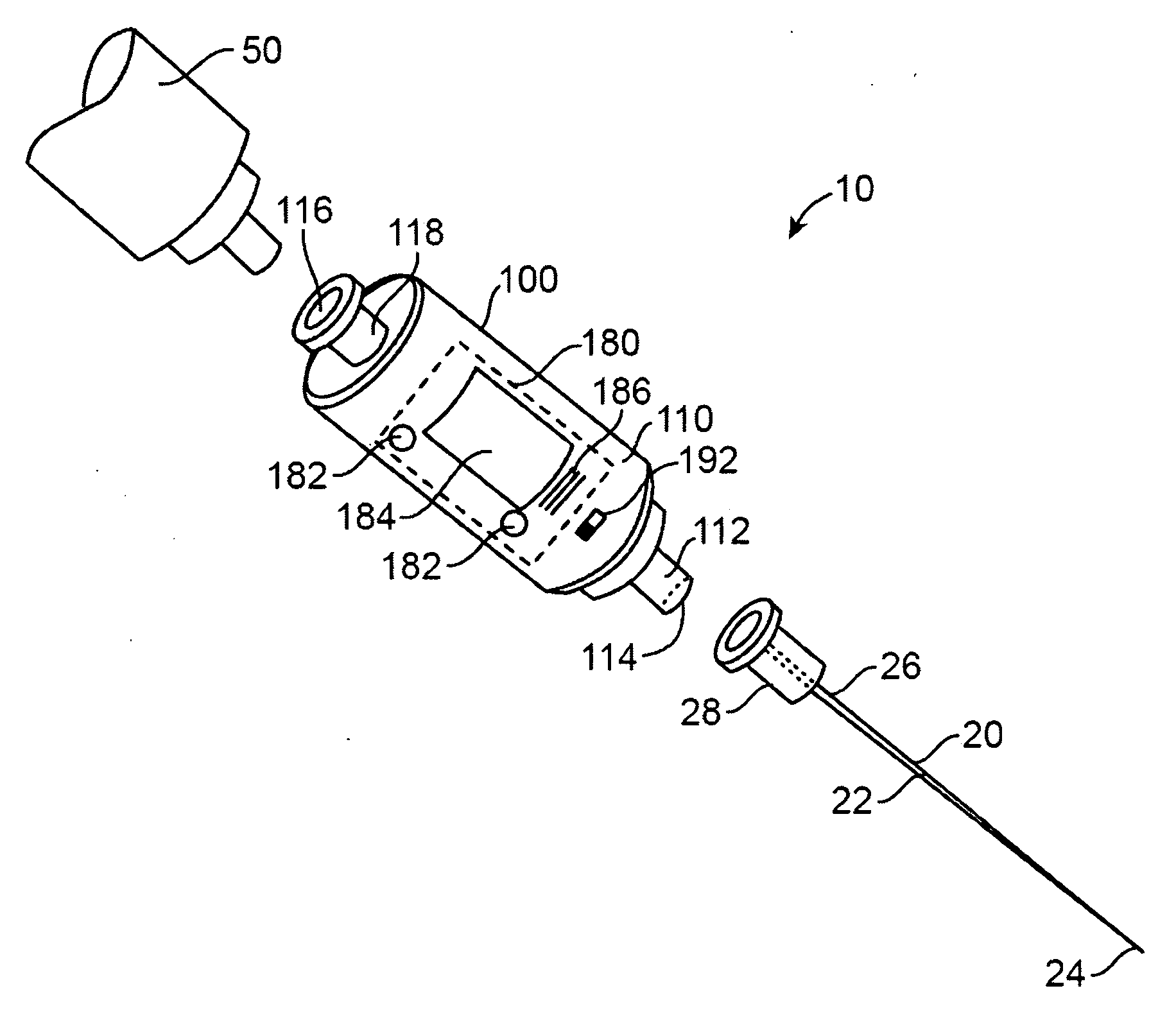
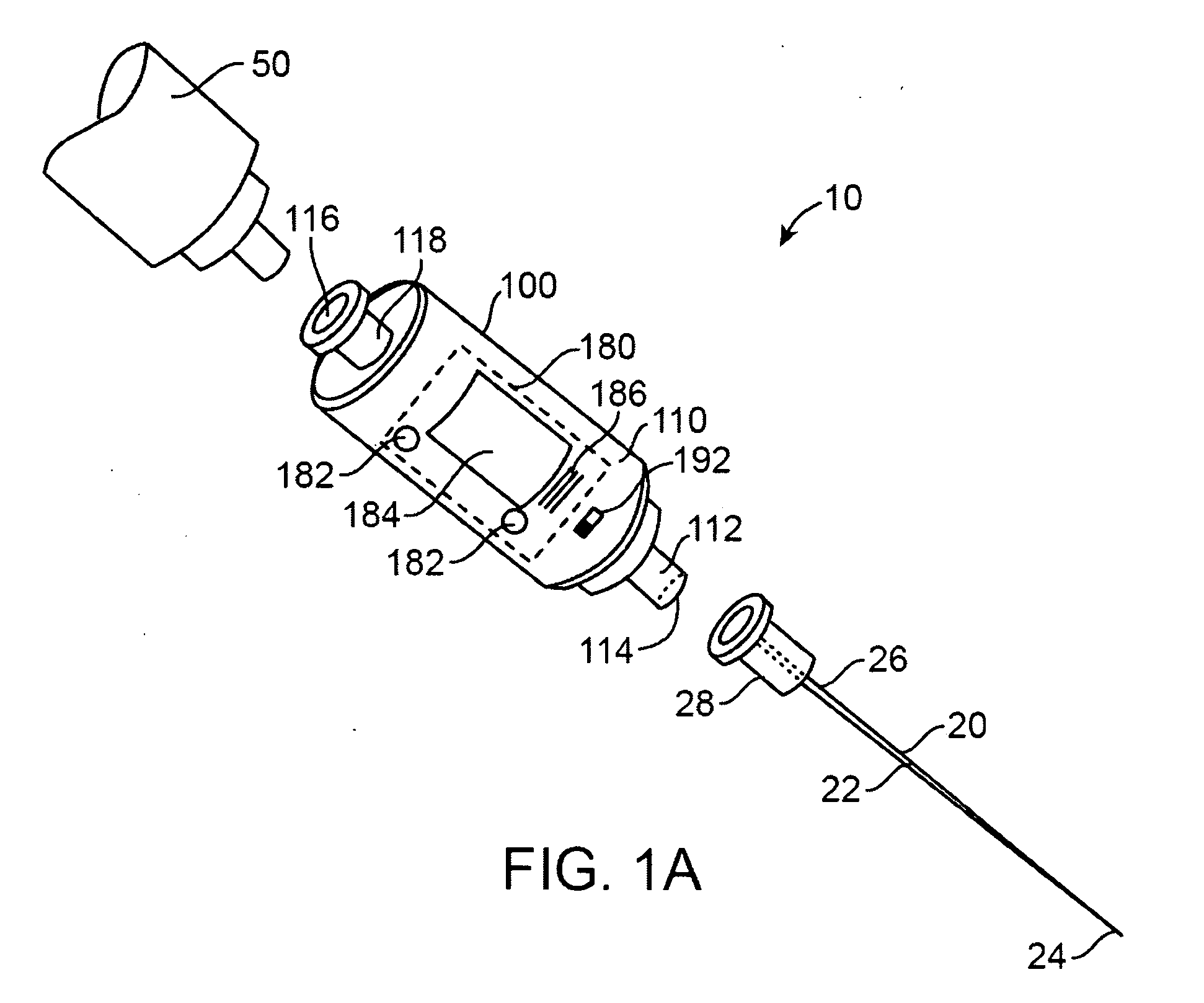
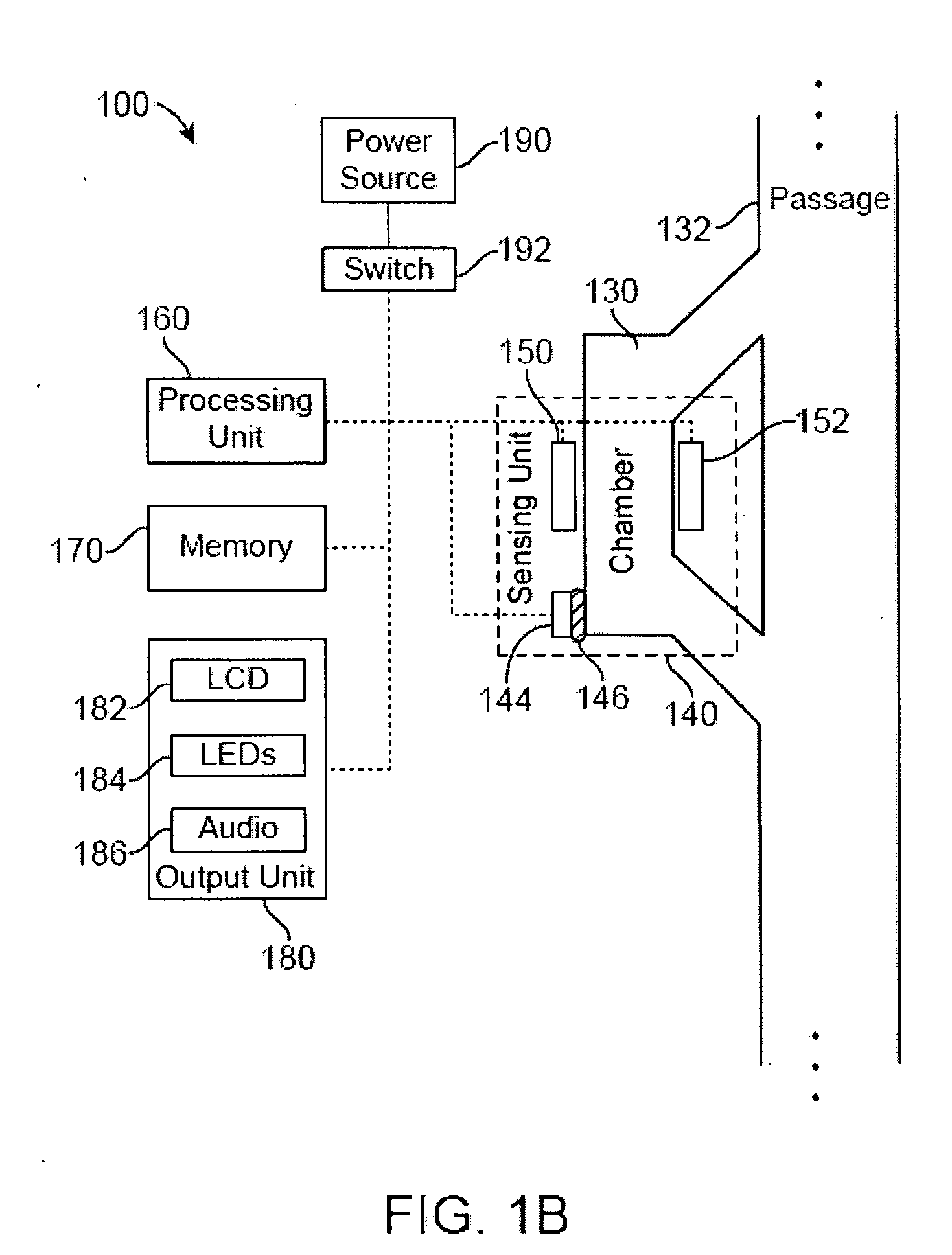
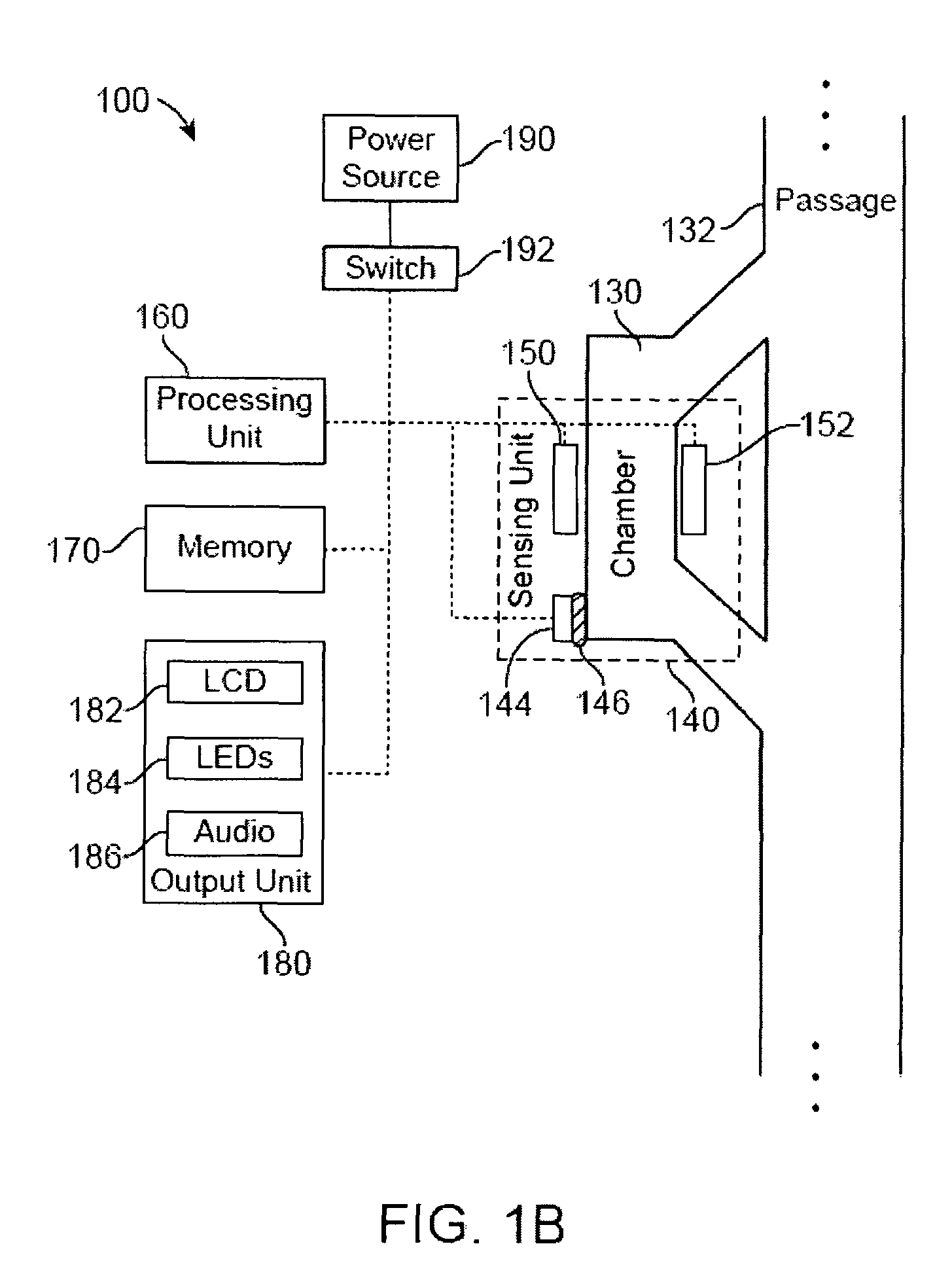
Methods and structures for detecting a physiologic parameter of a target anatomical environment. The device including a housing with a distal portion first port couplable to a probe and a proximal portion; and a sensing unit, a processing unit, and an output unit carried by the housing, the output unit configured to output a reporting signal based on the determined physiologic parameter value such as pressure; the sensing unit, processing unit, and output unit being disposed substantially between the first port and the proximal portion of the housing.
Owner:JAMES M PIGOTT
Drug infusion with pressure sensing and non-continuous flow for identification of and injection into fluid-filled anatomic spaces
ActiveUS20140012226A1Accurately and reproducibly administerLimit amount of pain and tissue damageAnaesthesiaInfusion syringesMedicinePharmaceutical drug
An automatic injection apparatus uses non-continuous fluid-flow of drugs to identify an intended injection site and includes a drive mechanism, a sensor and a controller for establishing fluid flow and pressure and preventing fluid flow until the pressure drops below a predetermined threshold. The pressure threshold is determined based on an internal pressure generated during an injection and more fluid will not flow until it drops below a predetermined pressure. An injection is performed to establish an initial pressure threshhold and then to stop the fluid flow into a patient until the pressure drops below a predetermined pressure which allows fluid flow to resume, thus identifying a fluid filled tissue space. The initial pressure threshold is used as a control parameter to a microprocessor below which controls the rate of injection. Fluid flows below certain pressures are also used to identify a specific location within the body during injections.
Owner:MILESTONE SCIENTIFIC INC
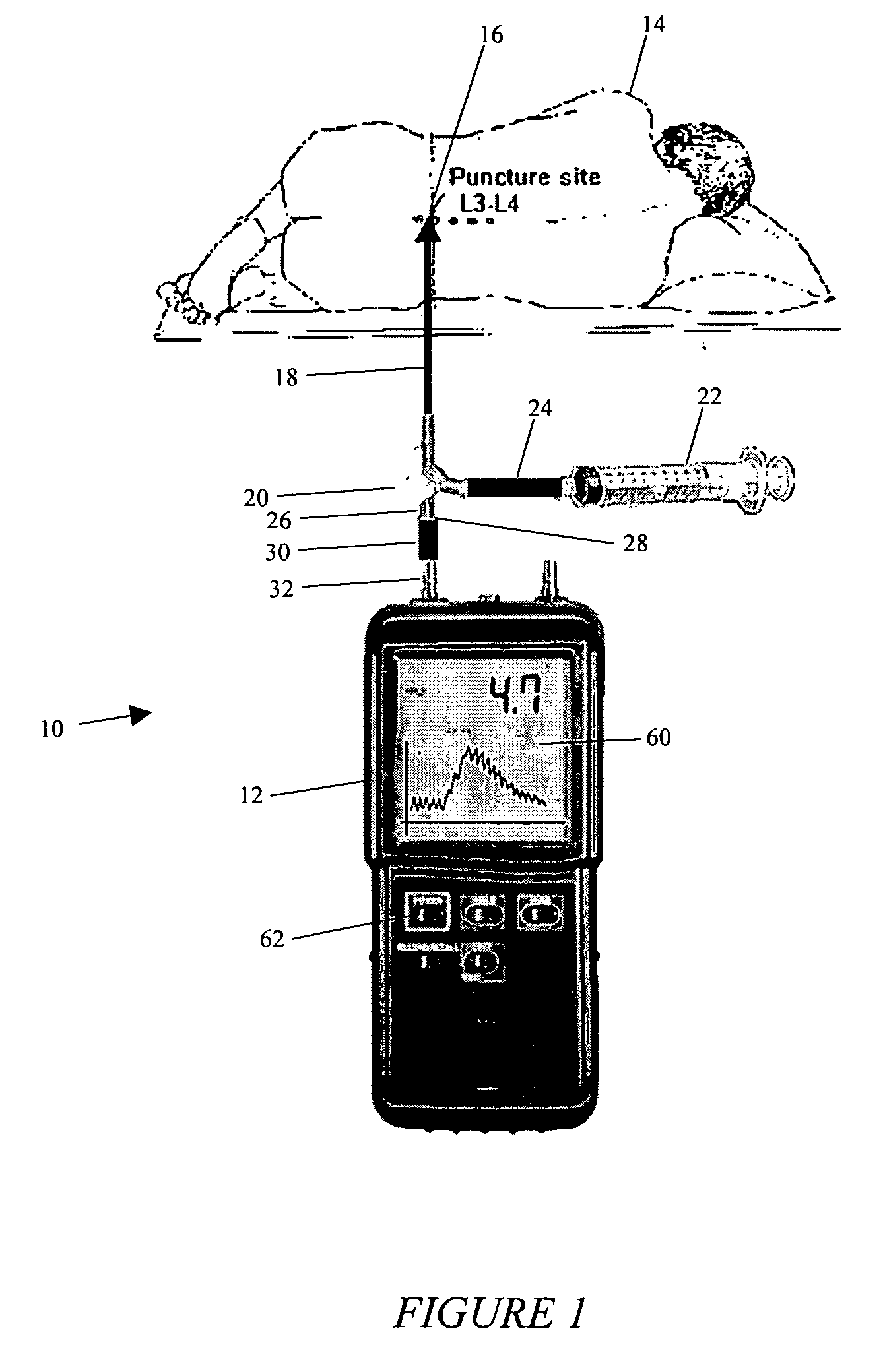
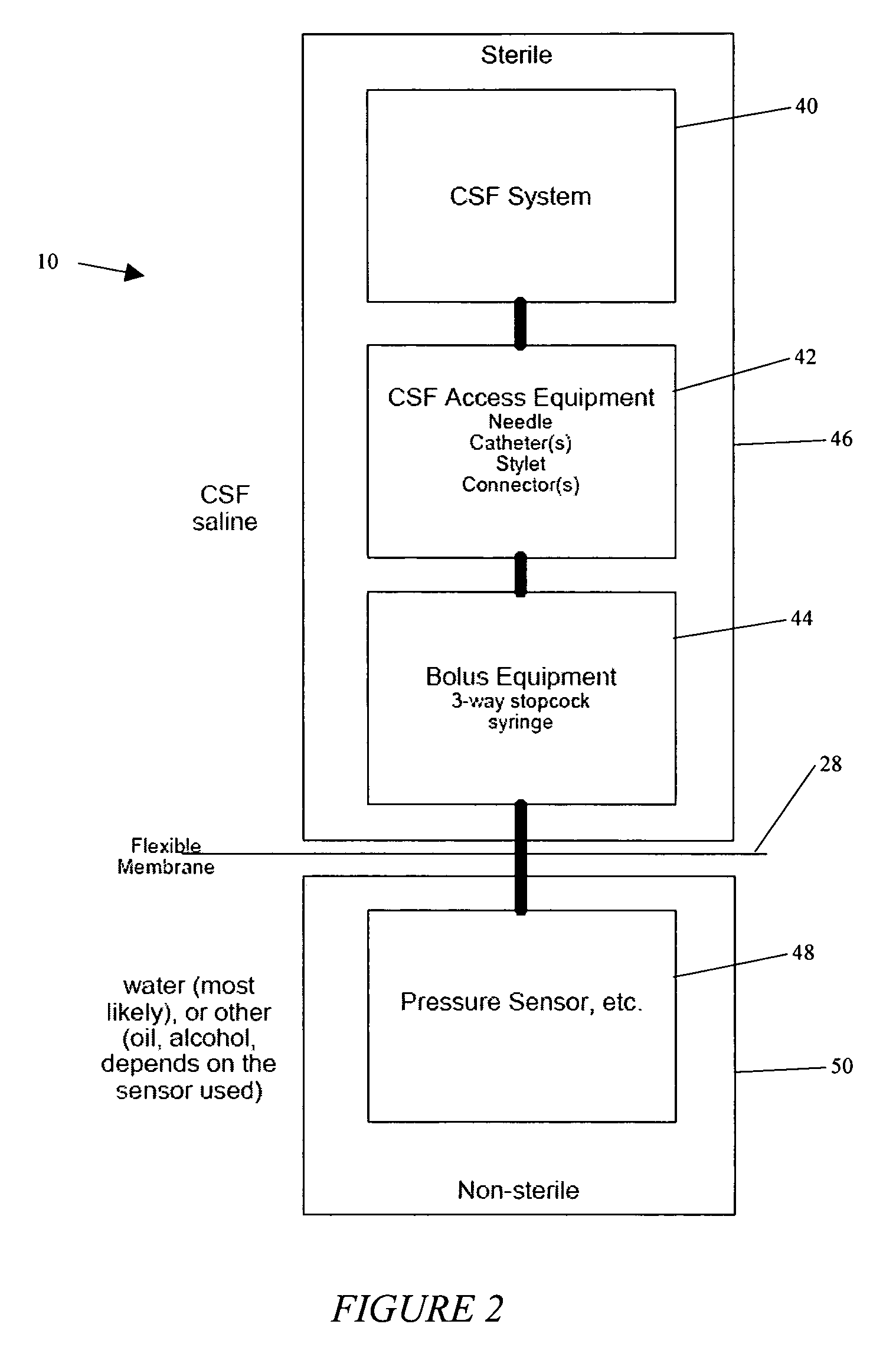
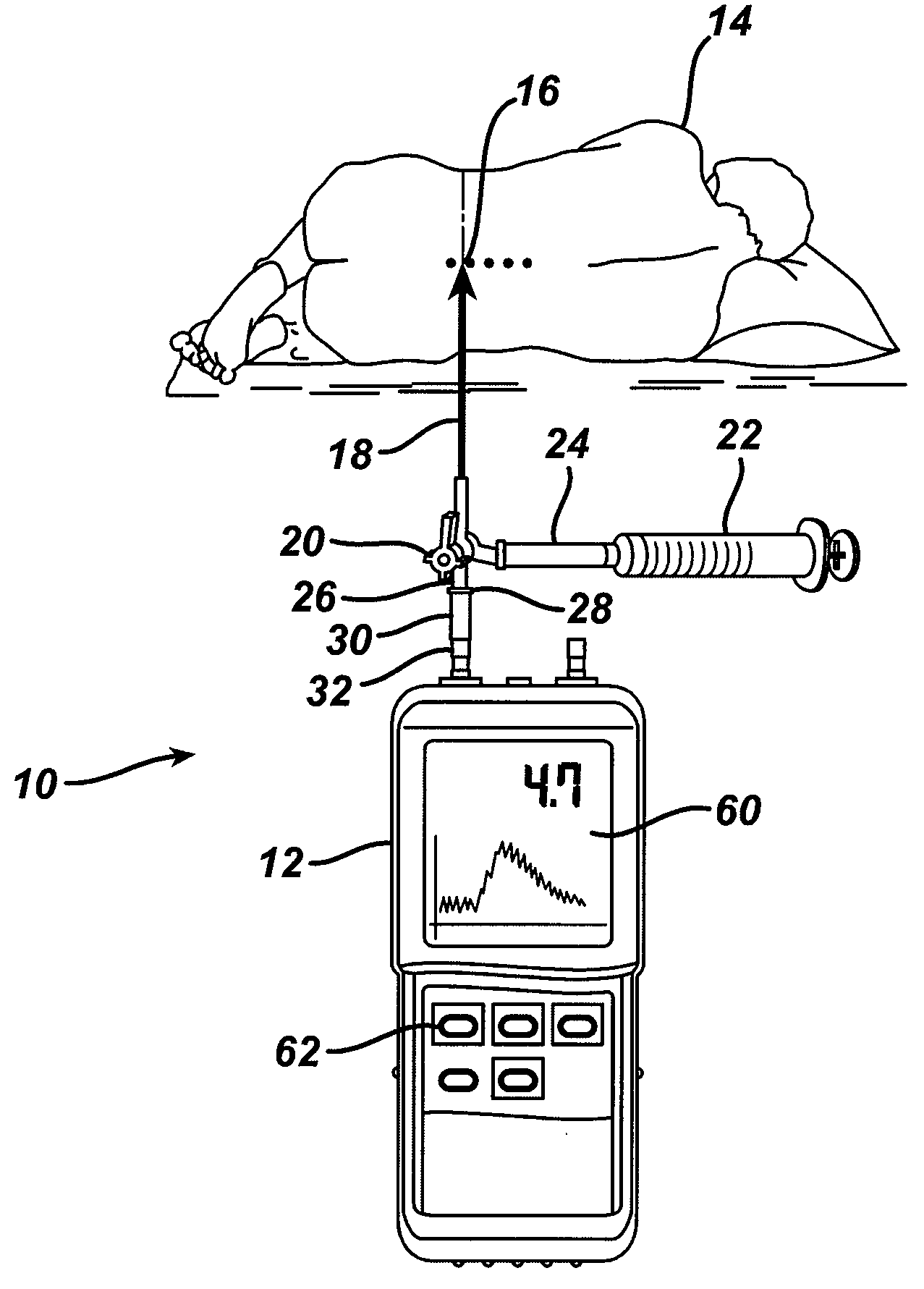
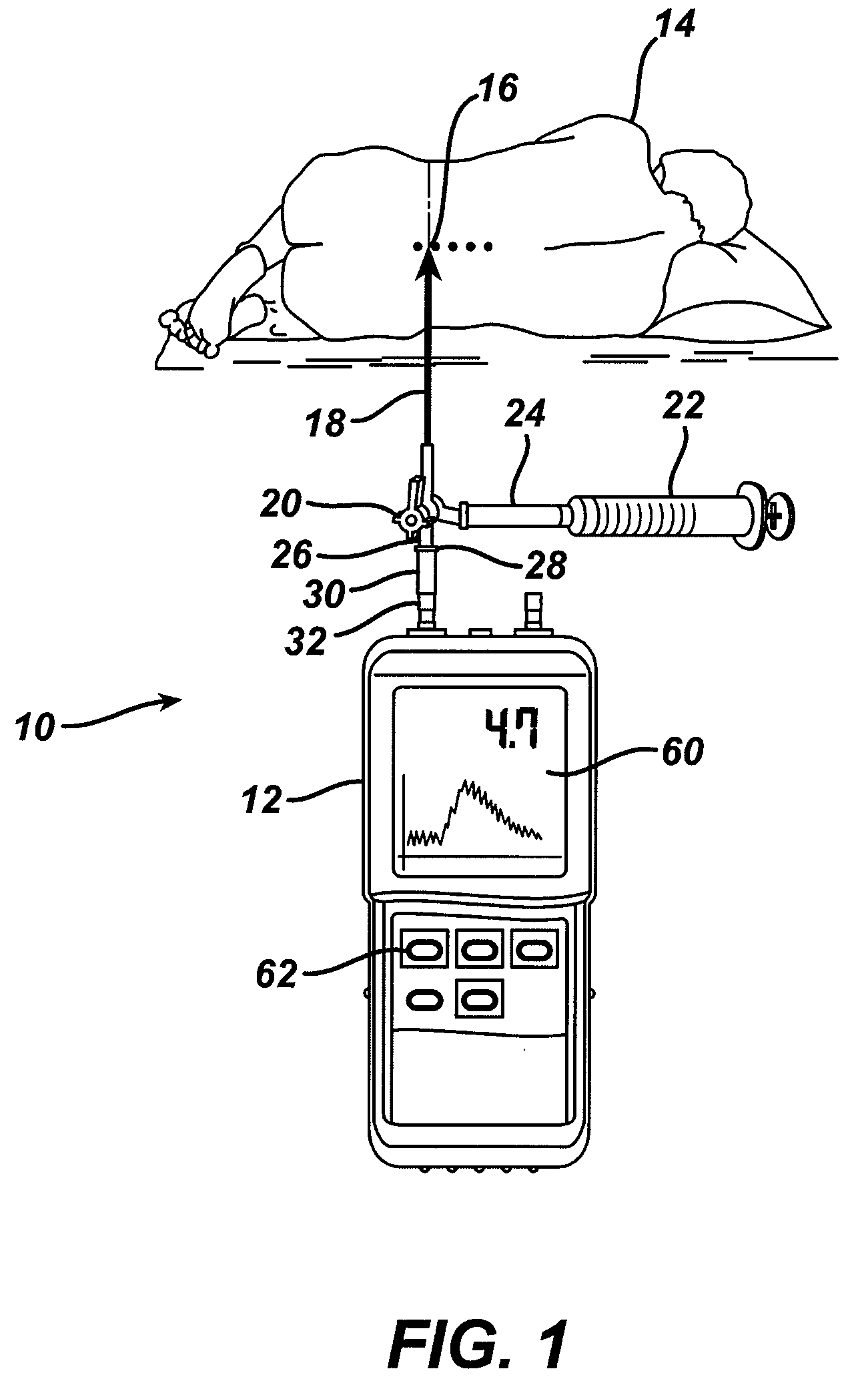
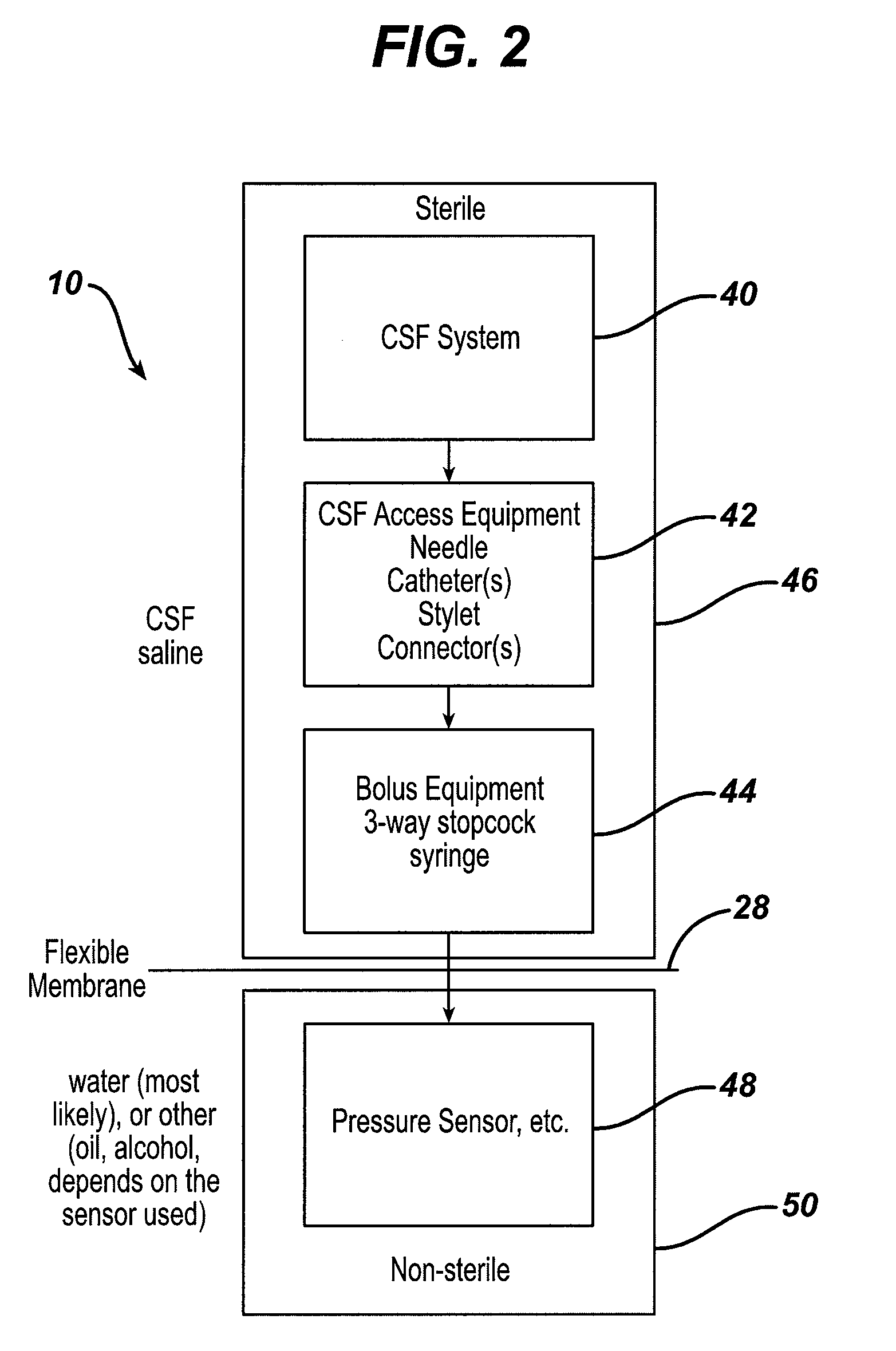
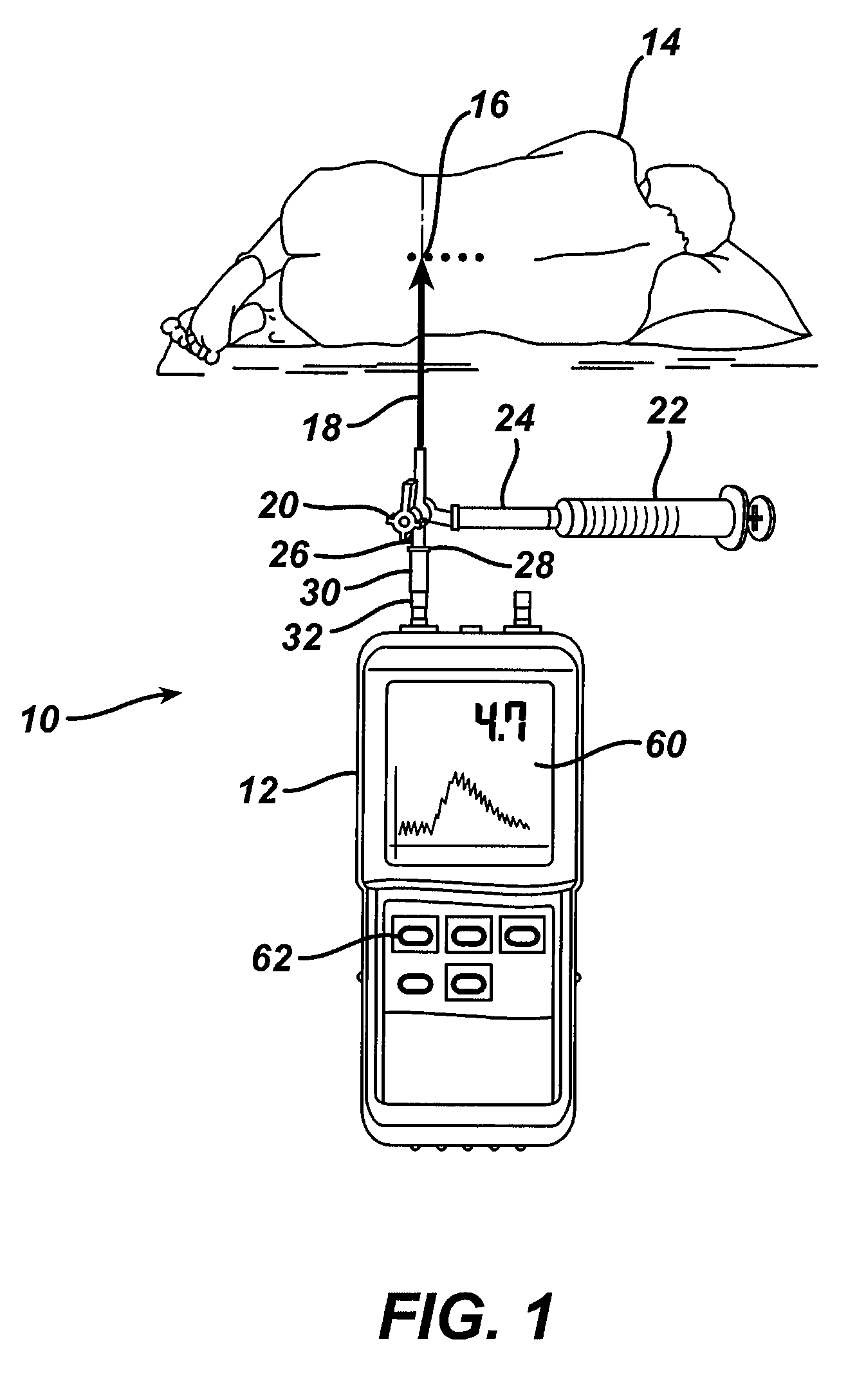
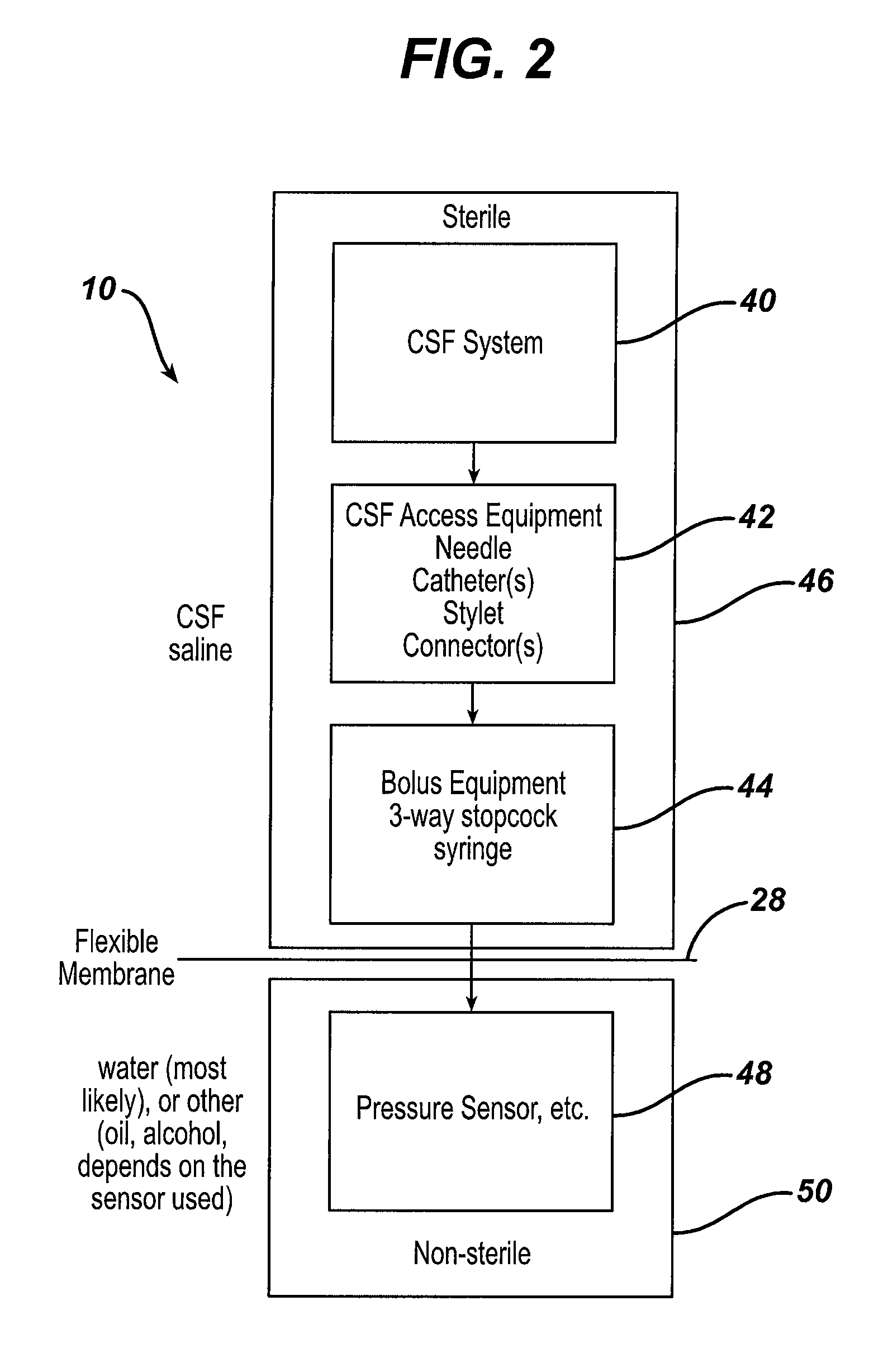
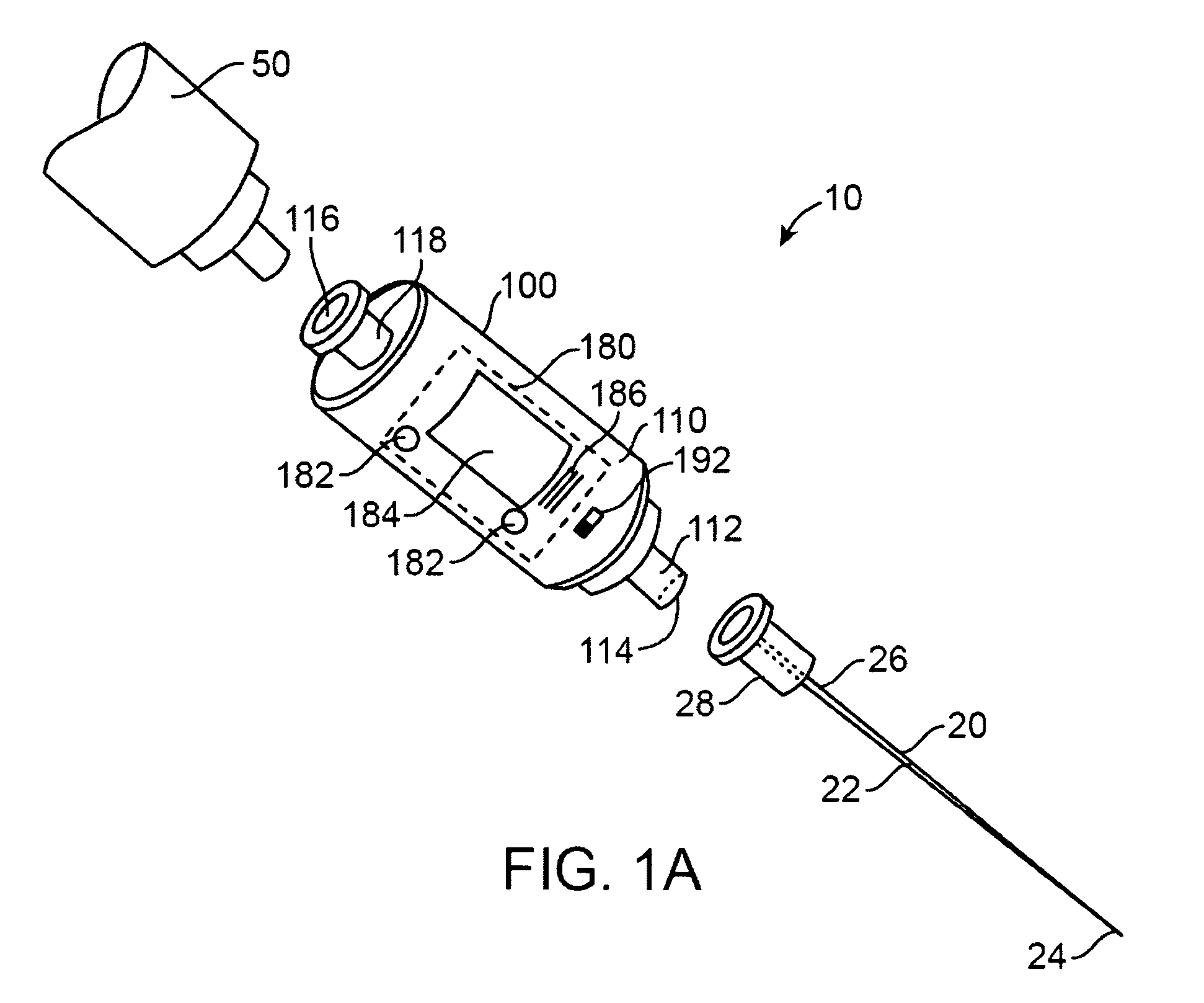
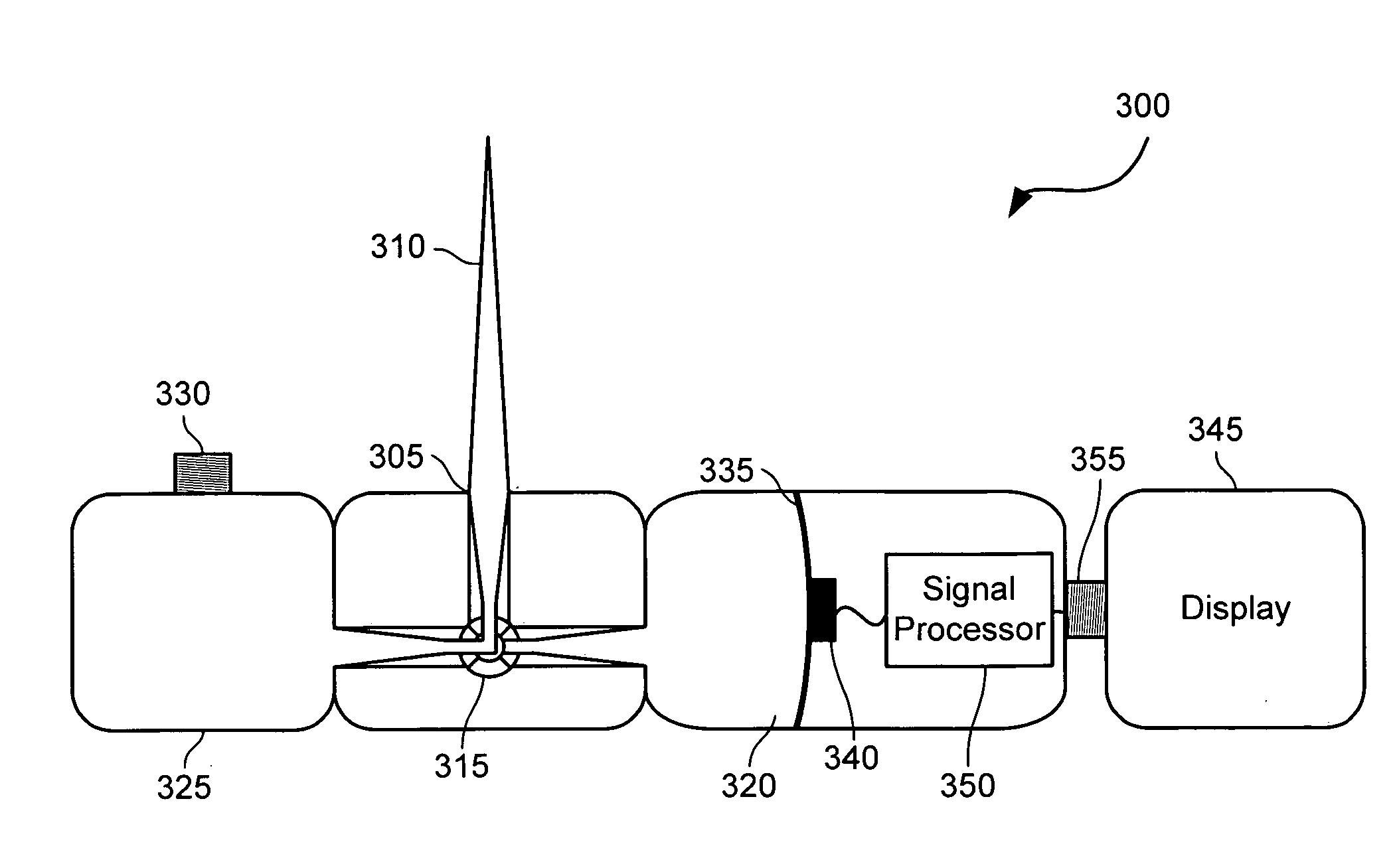
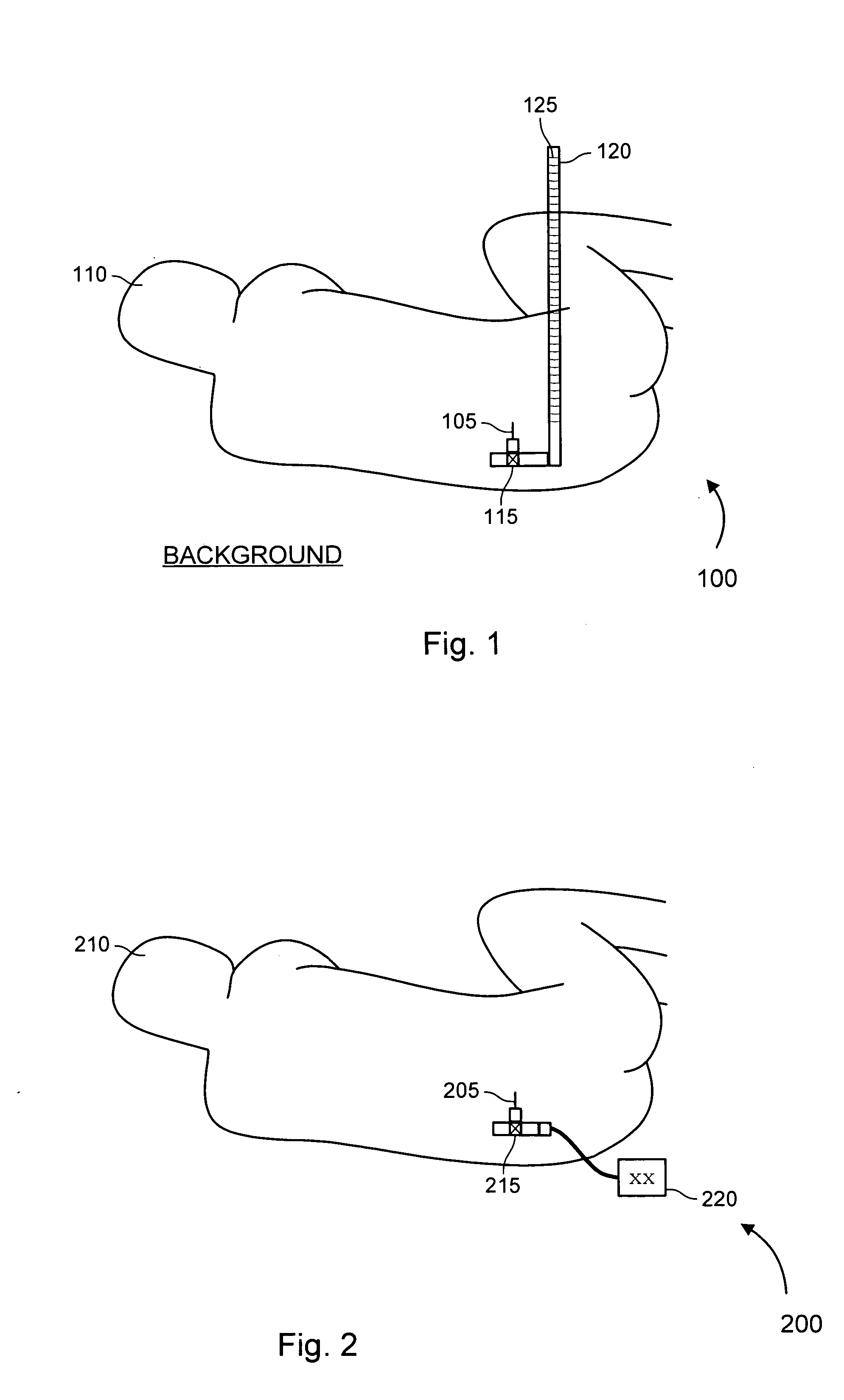
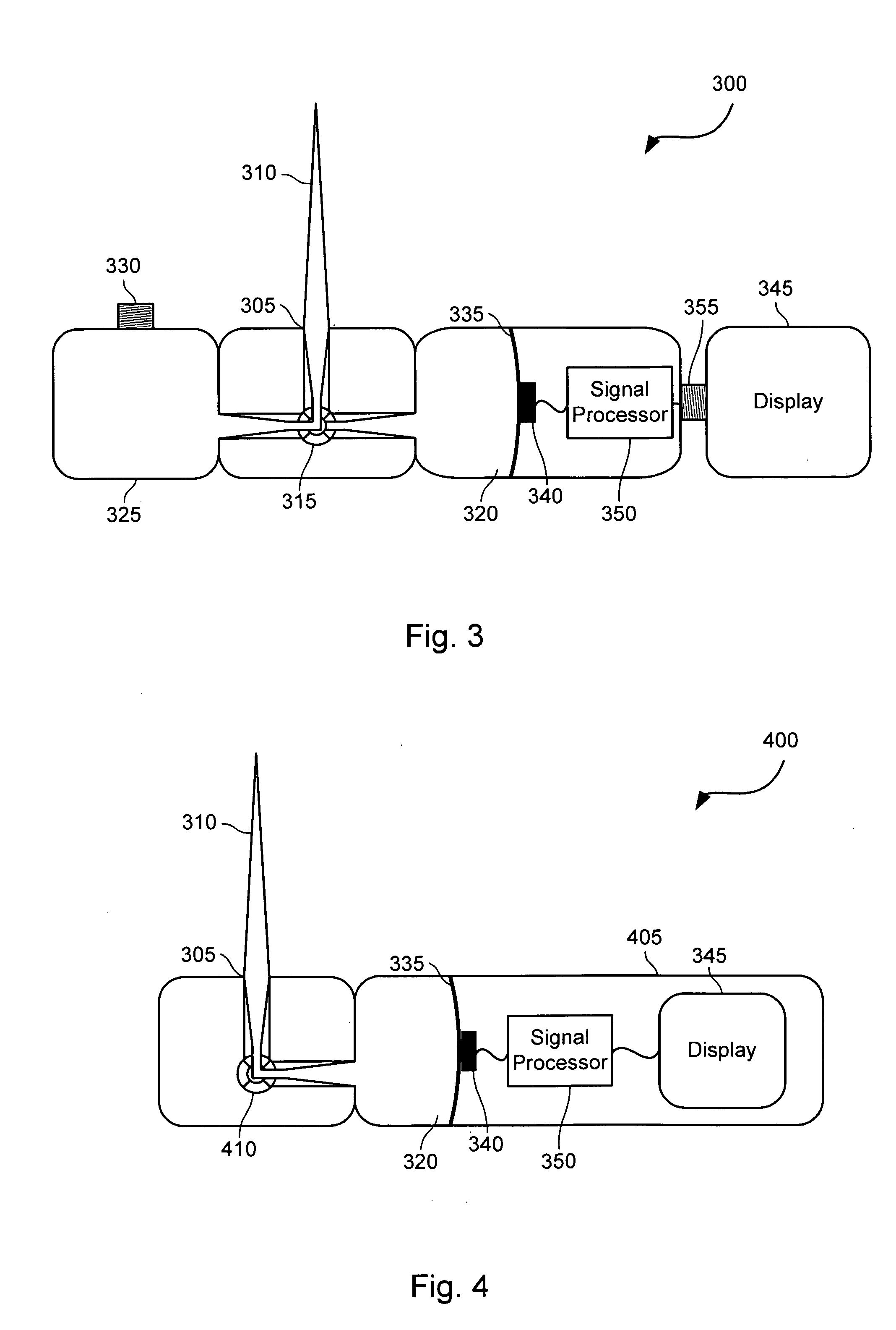
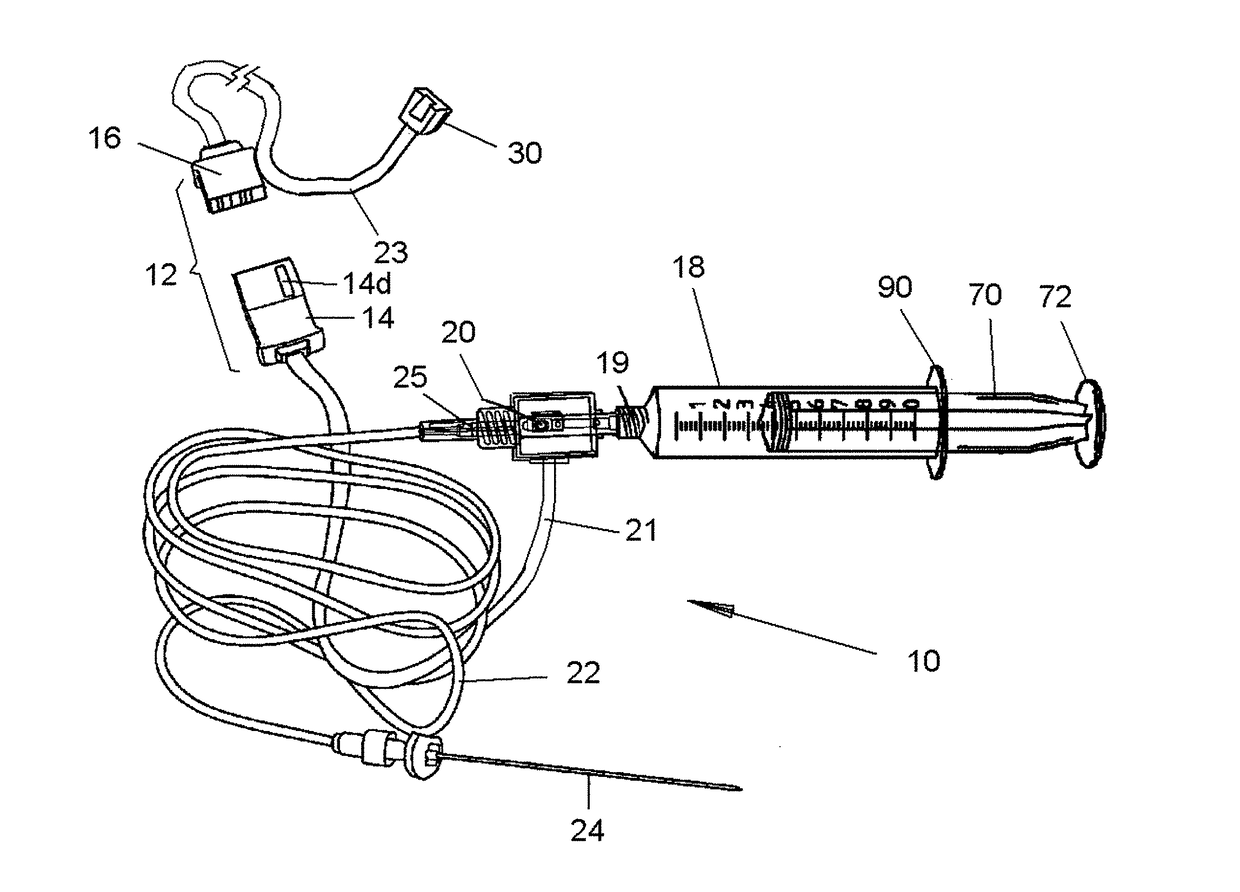
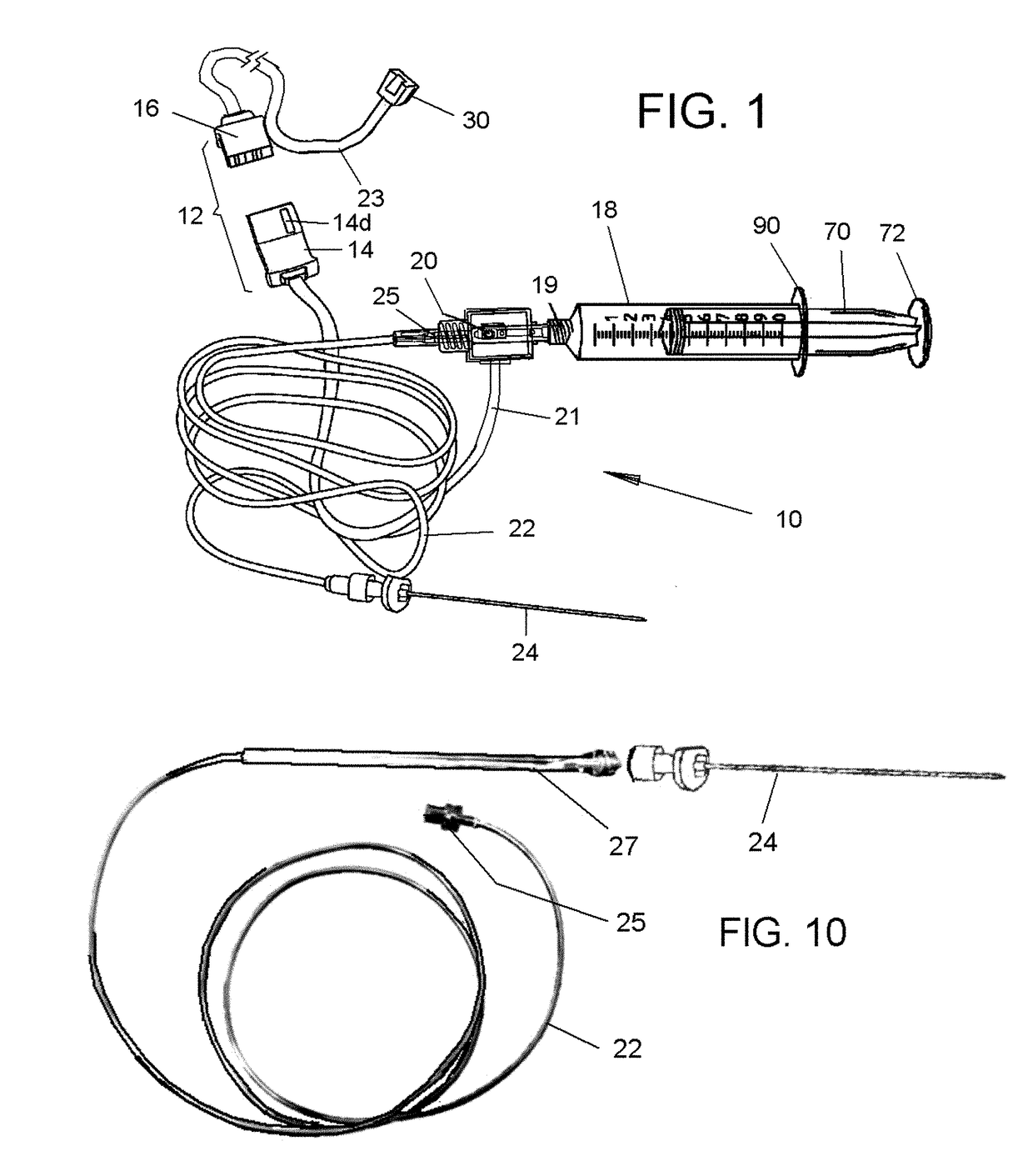
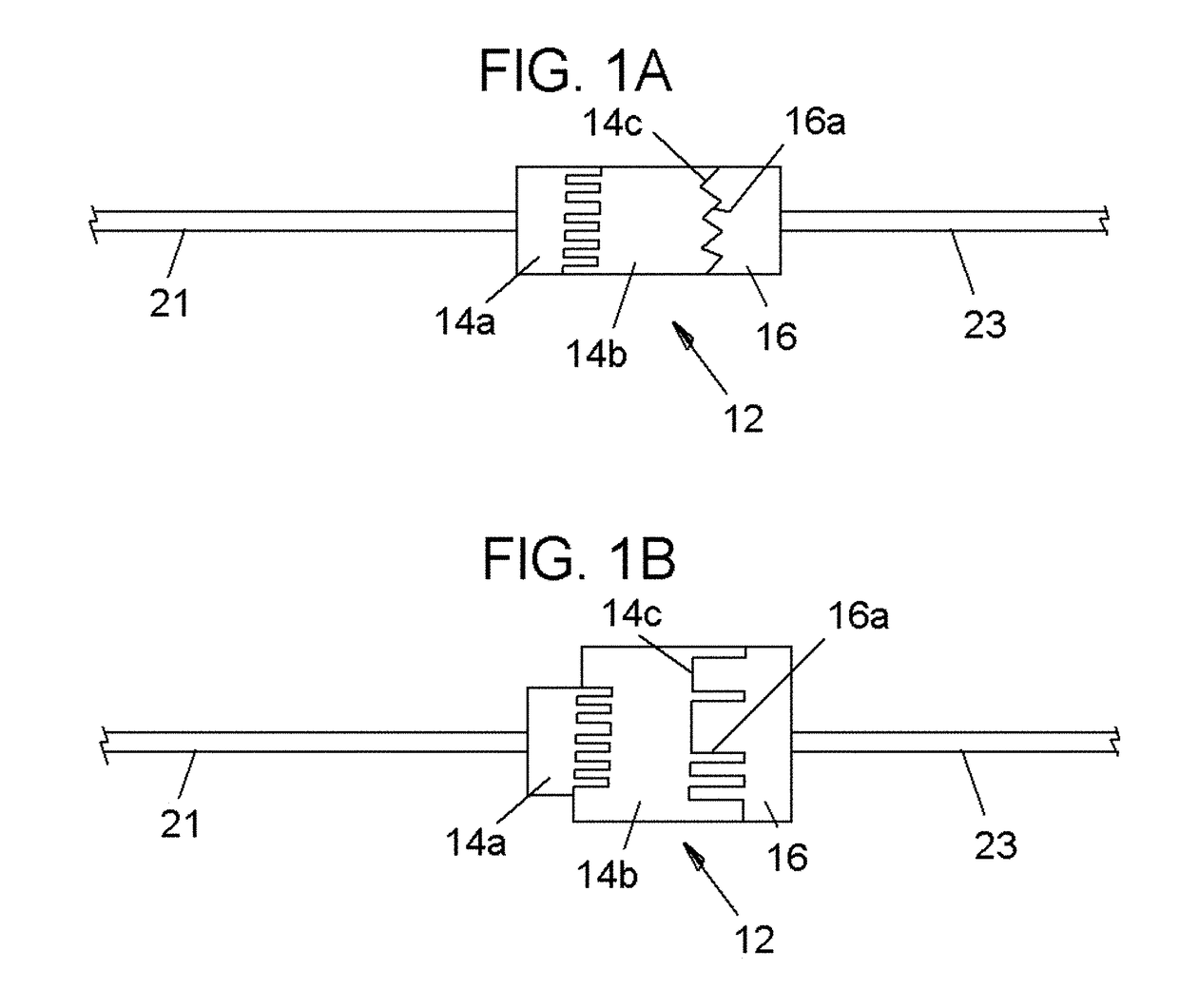
System and method for measuring the pressure of a fluid system within a patient
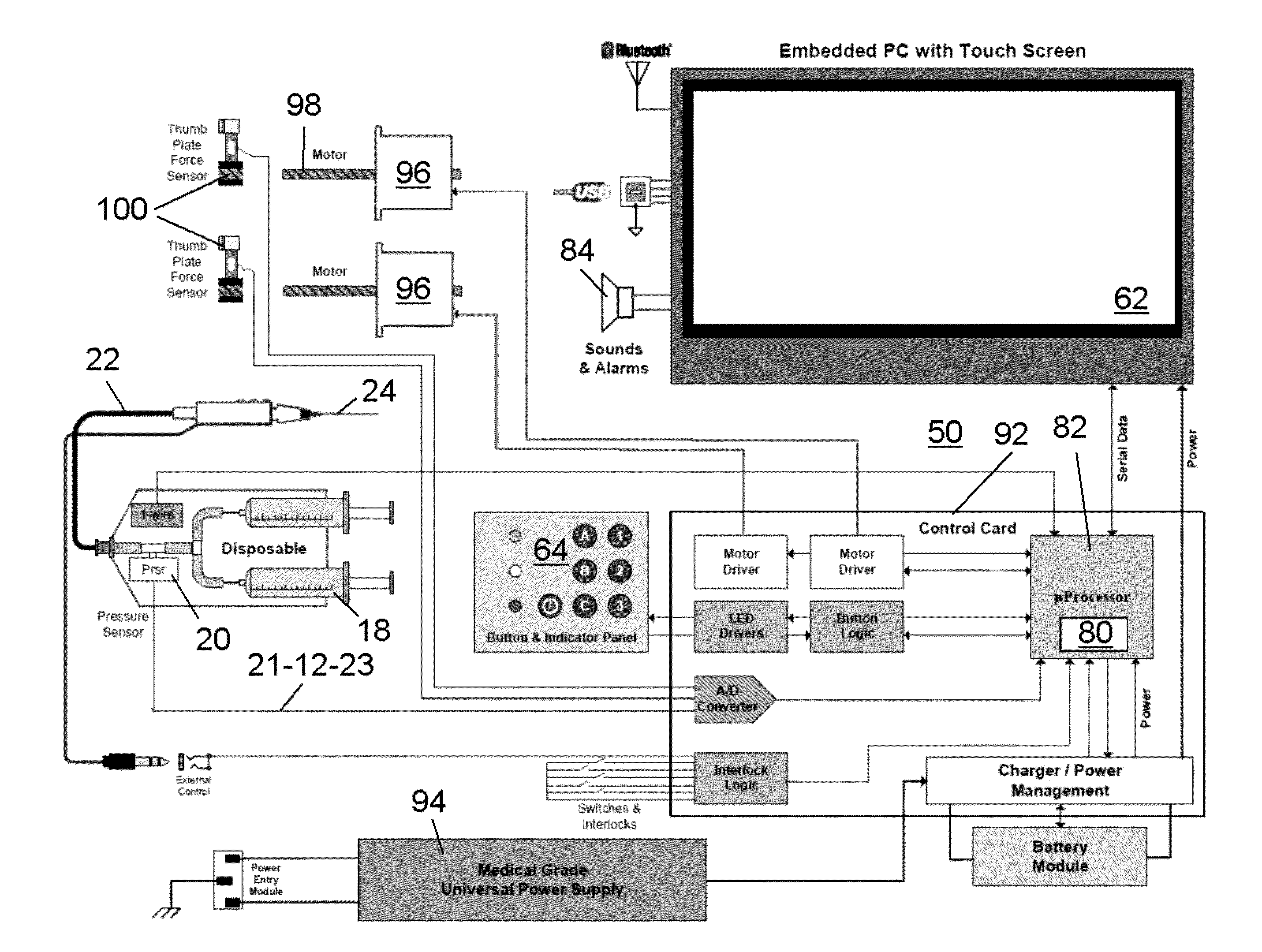
A pressure sensing apparatus has a pressure sensor component that includes a pressure sensing port, a pressure sensor for sensing a pressure of a fluid in the pressure sensing port, and a digital processor communicating with the pressure sensor for performing calculations involving fluid pressures sensed. The pressure sensing apparatus further includes a first chamber in fluid contact with the pressure sensing port, a second chamber fluidically connectable with a patient's cerebrospinal fluid system, and a membrane located between the first and second chambers so as to transmit fluid pressure from the second chamber to the first chamber.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
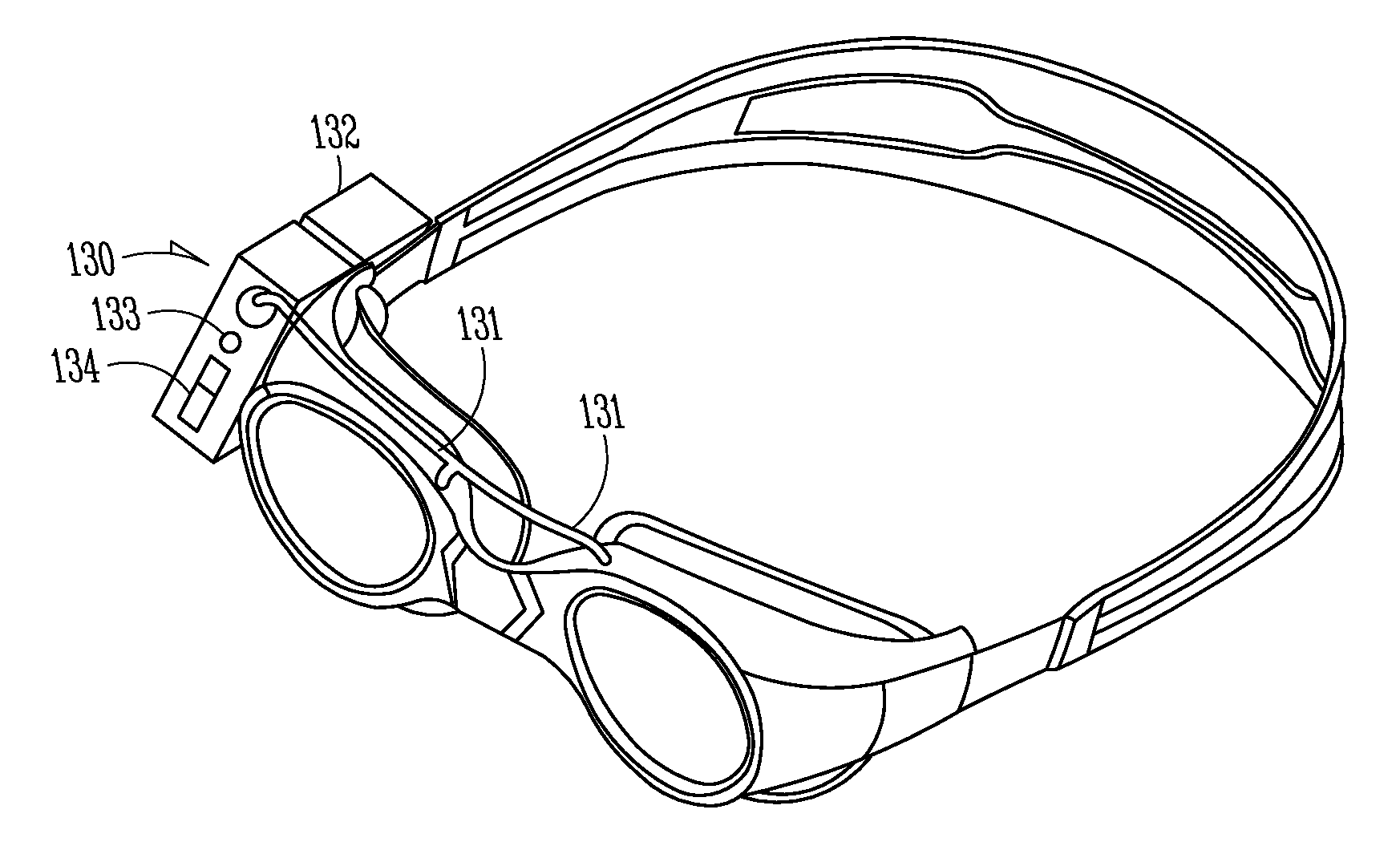
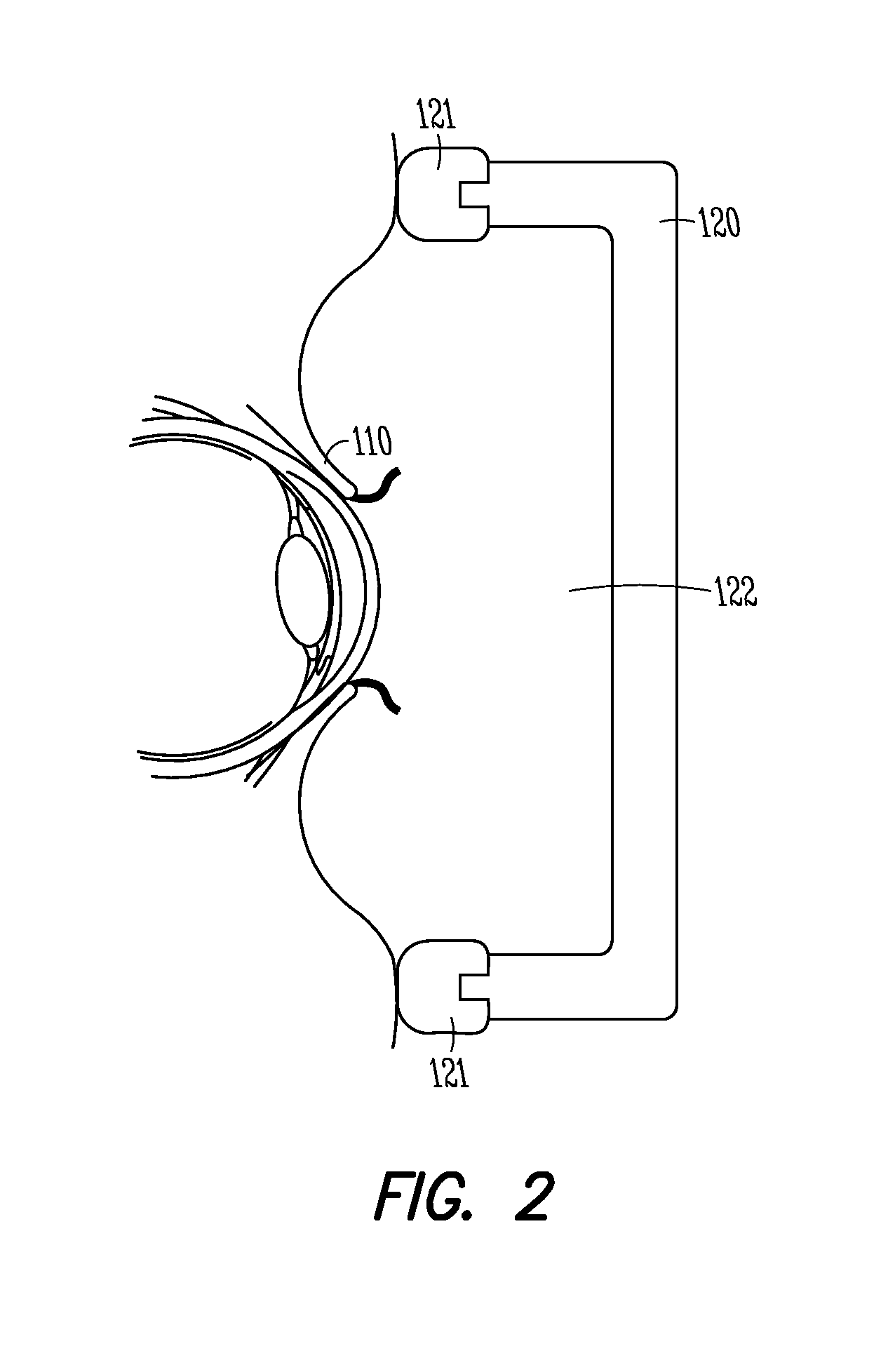
Intraocular pressure modification
ActiveUS20130238015A1Easy to createMinimize timeGogglesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesIIH - Idiopathic intracranial hypertensionHigh intraocular pressure
Assemblies and methods for modifying an intraocular pressure of a patient's one or both eyes are disclosed. The assemblies and methods can be used to treat, inhibit, or prevent ocular conditions such as glaucoma, high intraocular pressure, optic disc edema, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, zero-gravity induced papilledema, and other optic pressure related conditions. An assembly can include a goggle including at least one cavity, a pump in fluid communication with the at least one cavity, and a control mechanism. The control mechanism can be operatively coupled to the pump and can maintain a target pressure or target pressure range in the at least one cavity, which, when the assembly is worn by a patient, is the area between a patient's eye(s) and wall surfaces of the goggle. Controlling the pressure over the outer surfaces of the patient's eye(s) can drive a desired change in the intraocular pressure of the eye(s).
Owner:BERDAHL JOHN
System and Method for Measuring the Pressure of a Fluid System Within a Patient
A pressure sensing apparatus has a pressure sensor component that includes a pressure sensing port, a pressure sensor for sensing a pressure of a fluid in the pressure sensing port, and a digital processor communicating with the pressure sensor for performing calculations involving fluid pressures sensed. The pressure sensing apparatus further includes a first chamber in fluid contact with the pressure sensing port, a second chamber fluidically connectable with a patient's cerebrospinal fluid system, and a membrane located between the first and second chambers so as to transmit fluid pressure from the second chamber to the first chamber.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
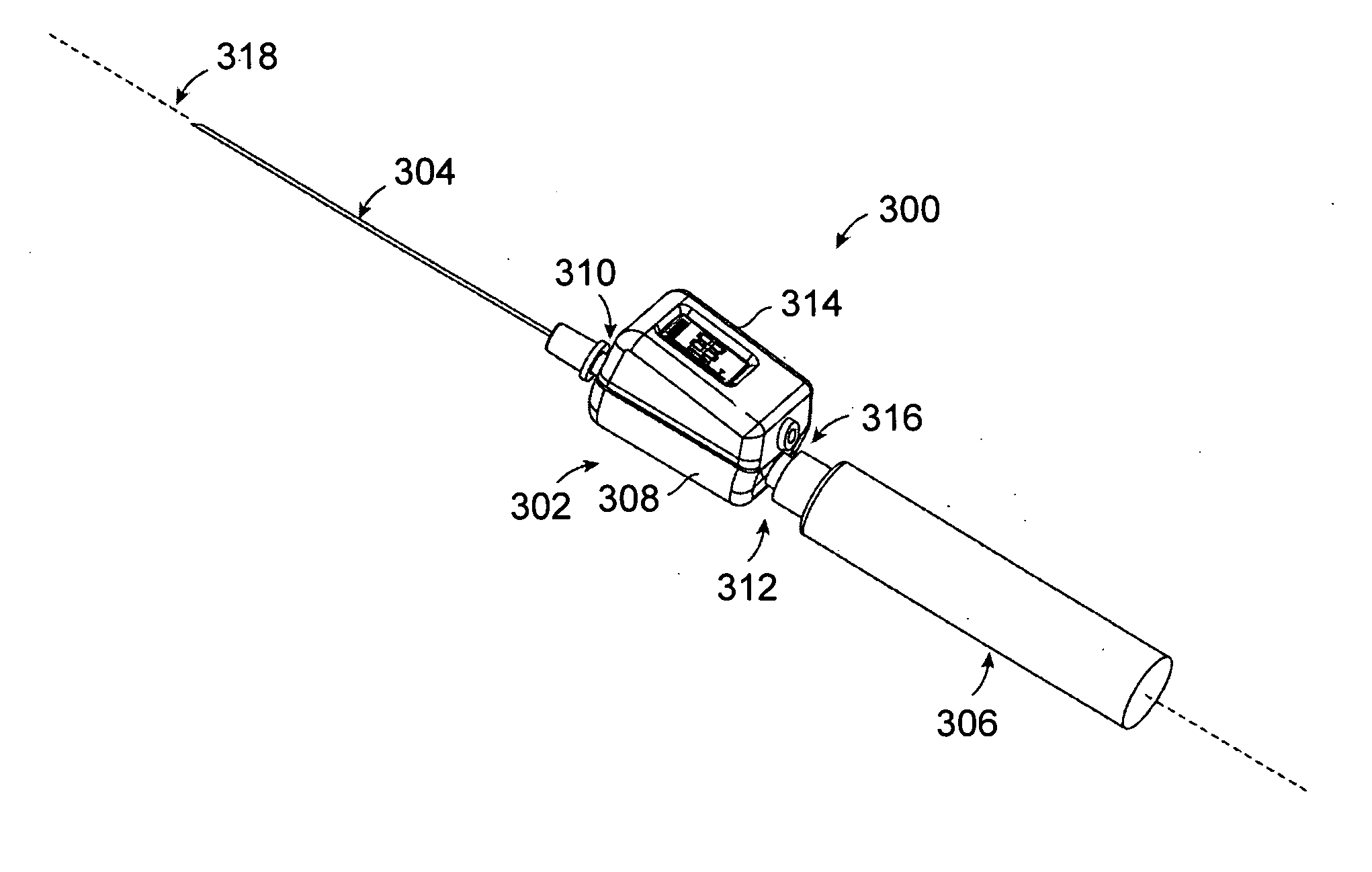
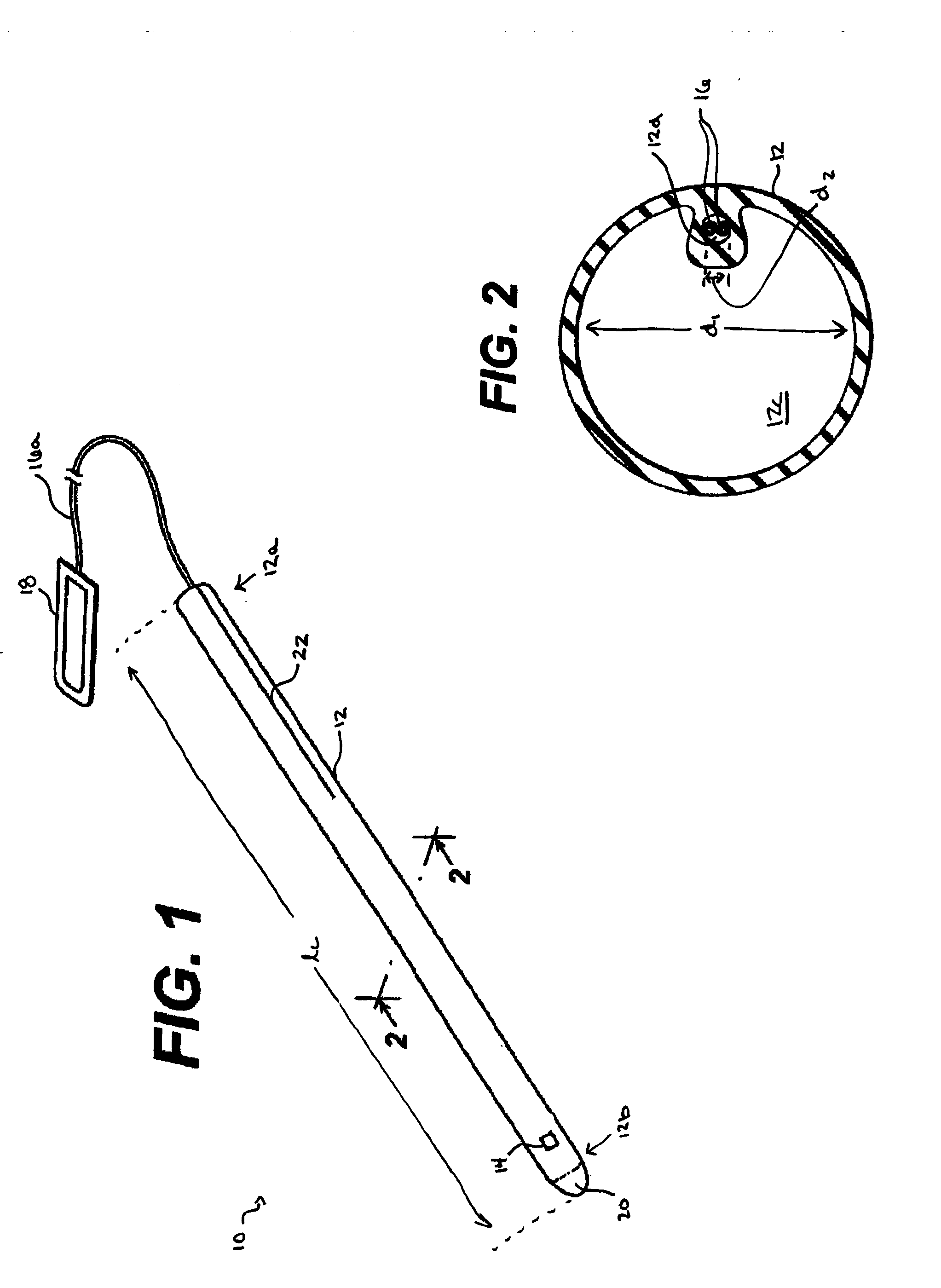
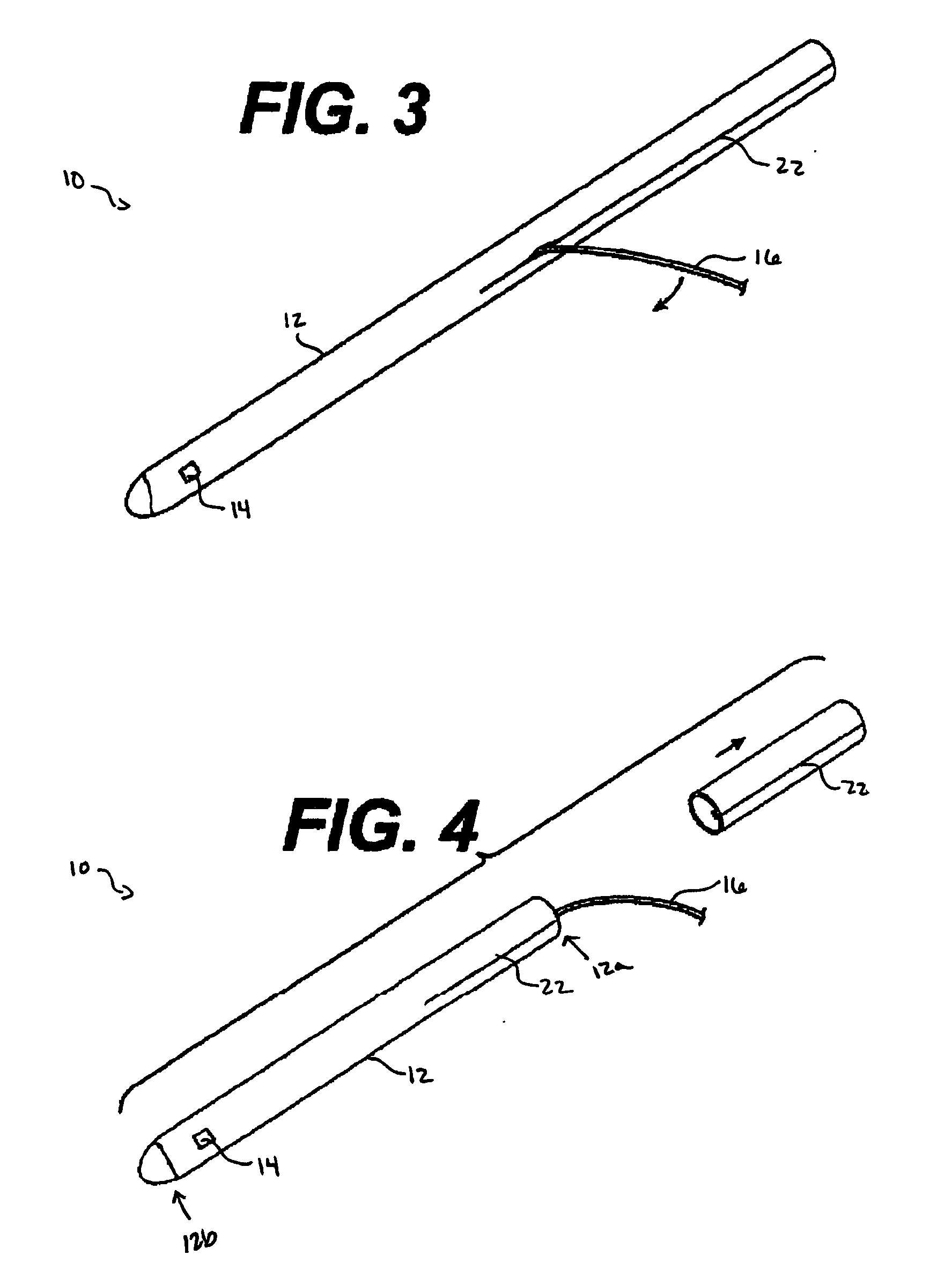
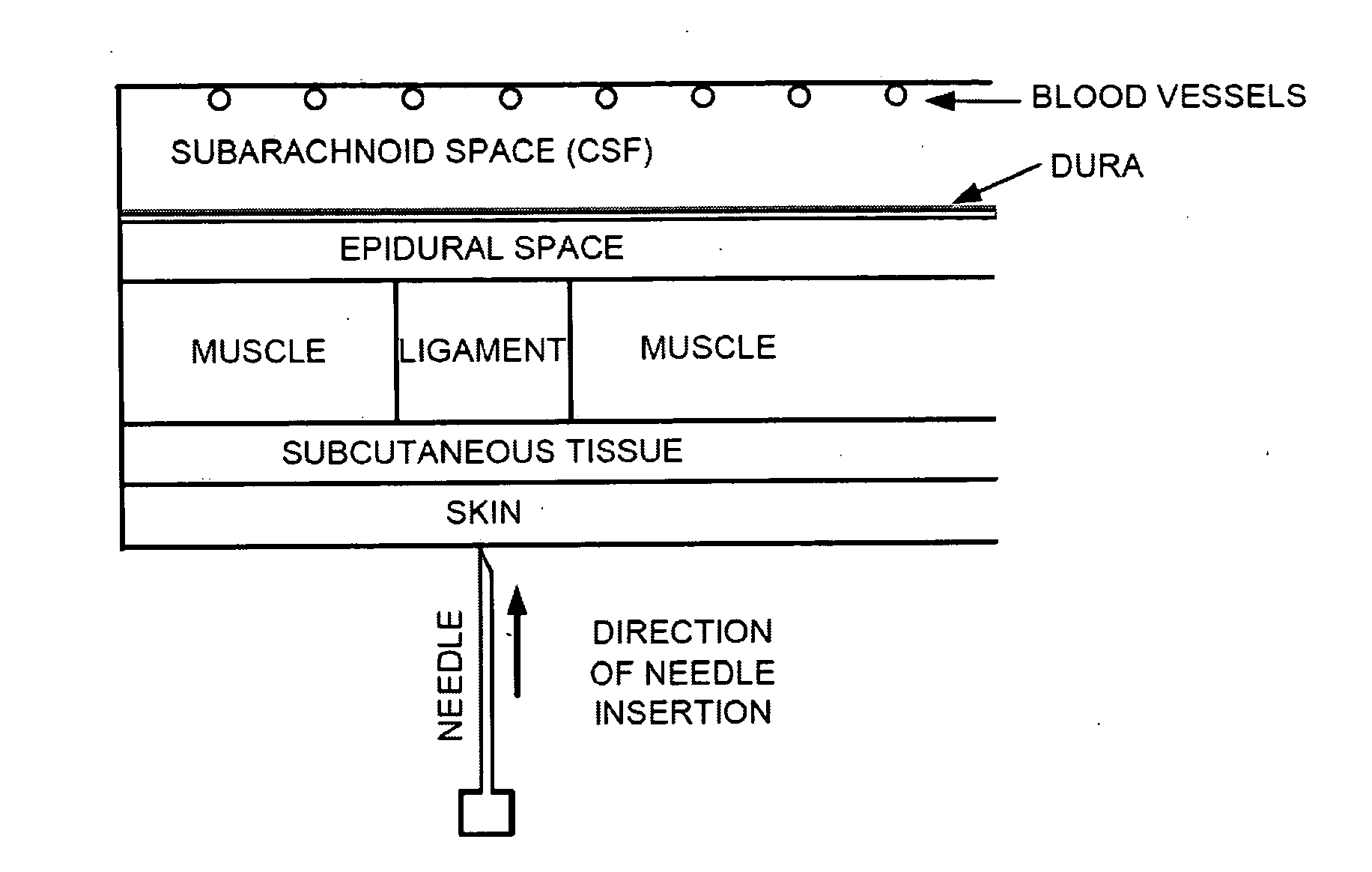
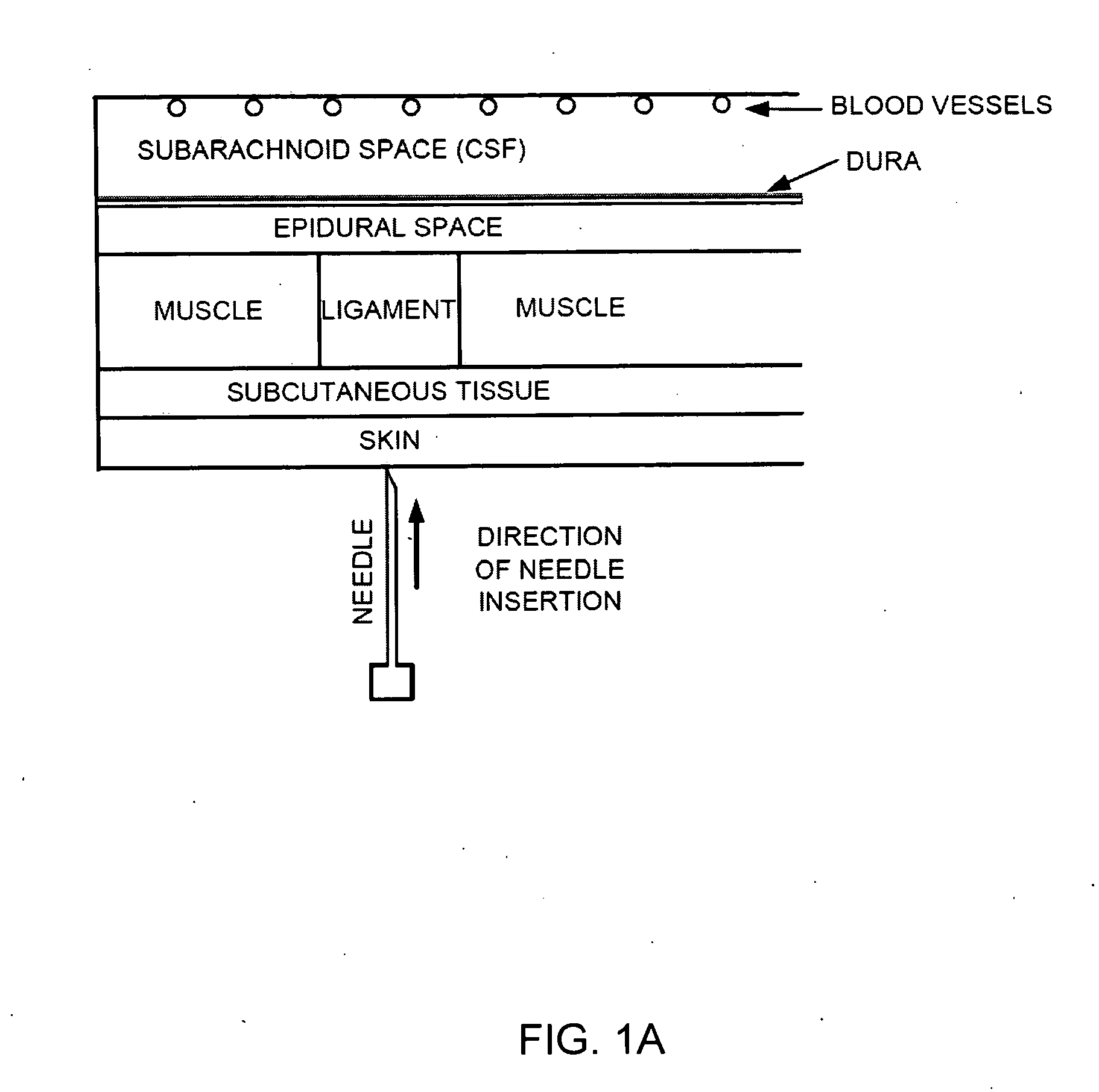
Spinal canal access and probe positioning, devices and methods
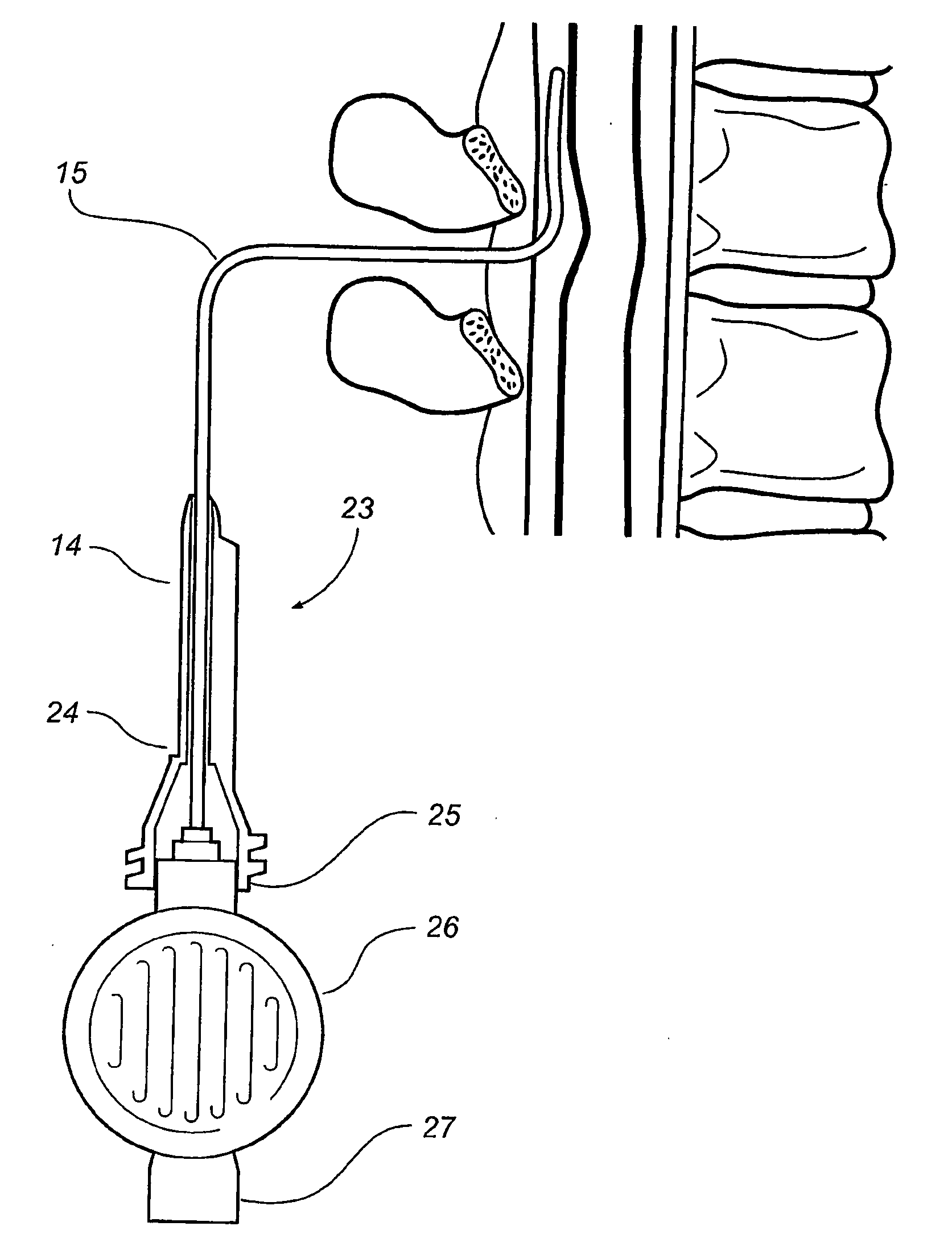
Methods and devices for detecting positioning of a probe in a tissue of a patient. A method can include providing a detection device; advancing a device coupled probe through the tissue of the patient and toward the patient's spinal canal; detecting a change in pressure about the distal portion of the coupled probe during advancing, where the detected pressure change indicates probe positioning in the patient's spinal canal; outputting the detected pressure change or indication of probe positioning to a visual display.
Owner:JAMES M PIGOTT
System and method for measuring the pressure of a fluid system within a patient
A pressure sensing apparatus has a pressure sensor component that includes a pressure sensing port, a pressure sensor for sensing a pressure of a fluid in the pressure sensing port, and a digital processor communicating with the pressure sensor for performing calculations involving fluid pressures sensed. The pressure sensing apparatus further includes a first chamber in fluid contact with the pressure sensing port, a second chamber fluidically connectable with a patient's cerebrospinal fluid system, and a membrane located between the first and second chambers so as to transmit fluid pressure from the second chamber to the first chamber.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
Systems, methods, and devices for facilitating access to target anatomical sites or environments
ActiveUS8926525B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGuide needlesDistal portionBiomedical engineering
Methods and structures for detecting a physiologic parameter of a target anatomical environment. The device including a housing with a distal portion first port couplable to a probe and a proximal portion; and a sensing unit, a processing unit, and an output unit carried by the housing, the output unit configured to output a reporting signal based on the determined physiologic parameter value such as pressure; the sensing unit, processing unit, and output unit being disposed substantially between the first port and the proximal portion of the housing.
Owner:JAMES M PIGOTT
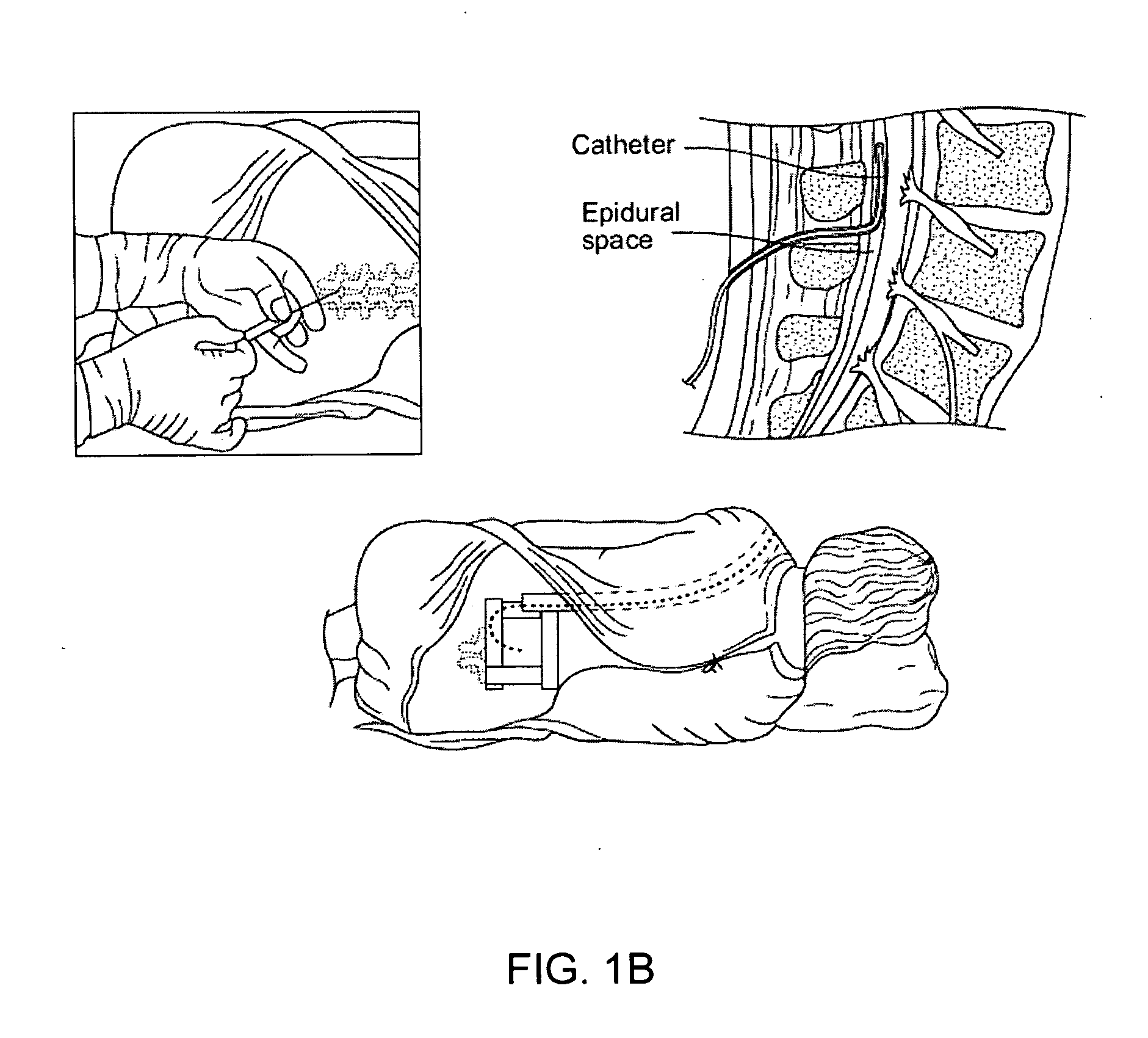
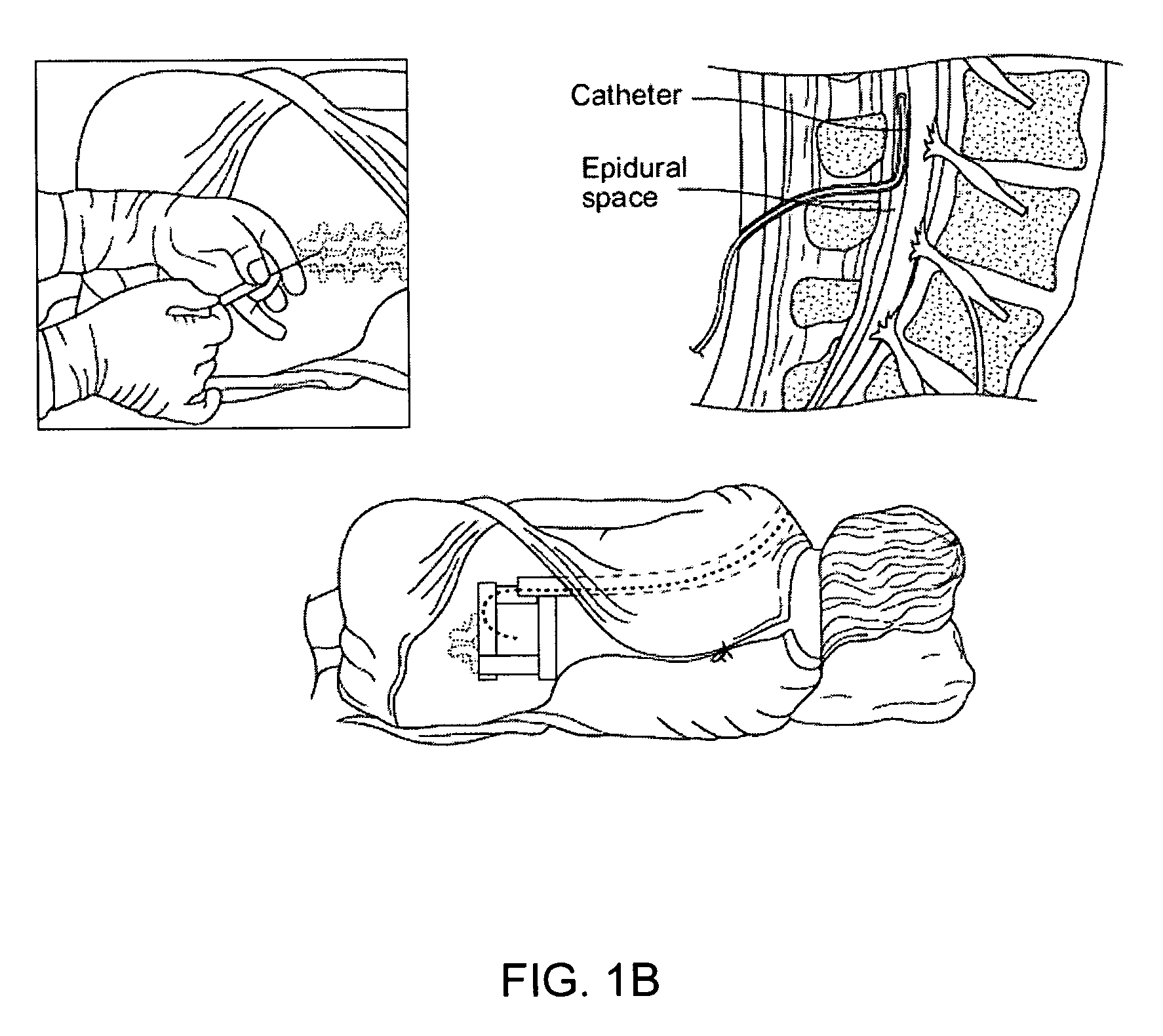
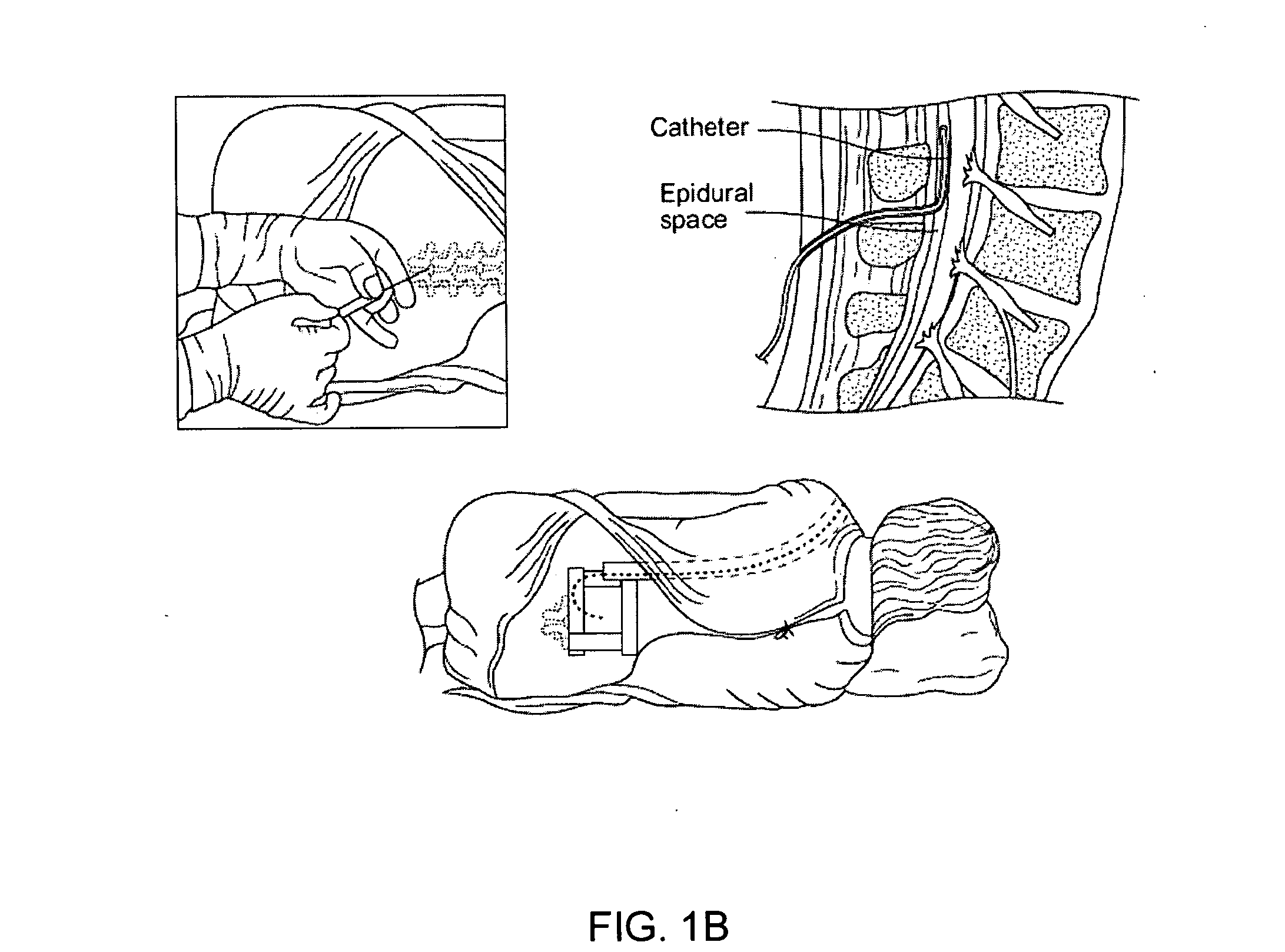
Epidural administration systems
InactiveUS20090157044A1Easy to identifyEnhance detection of movementAnaesthesiaInfusion syringesLoss of resistanceMedicine
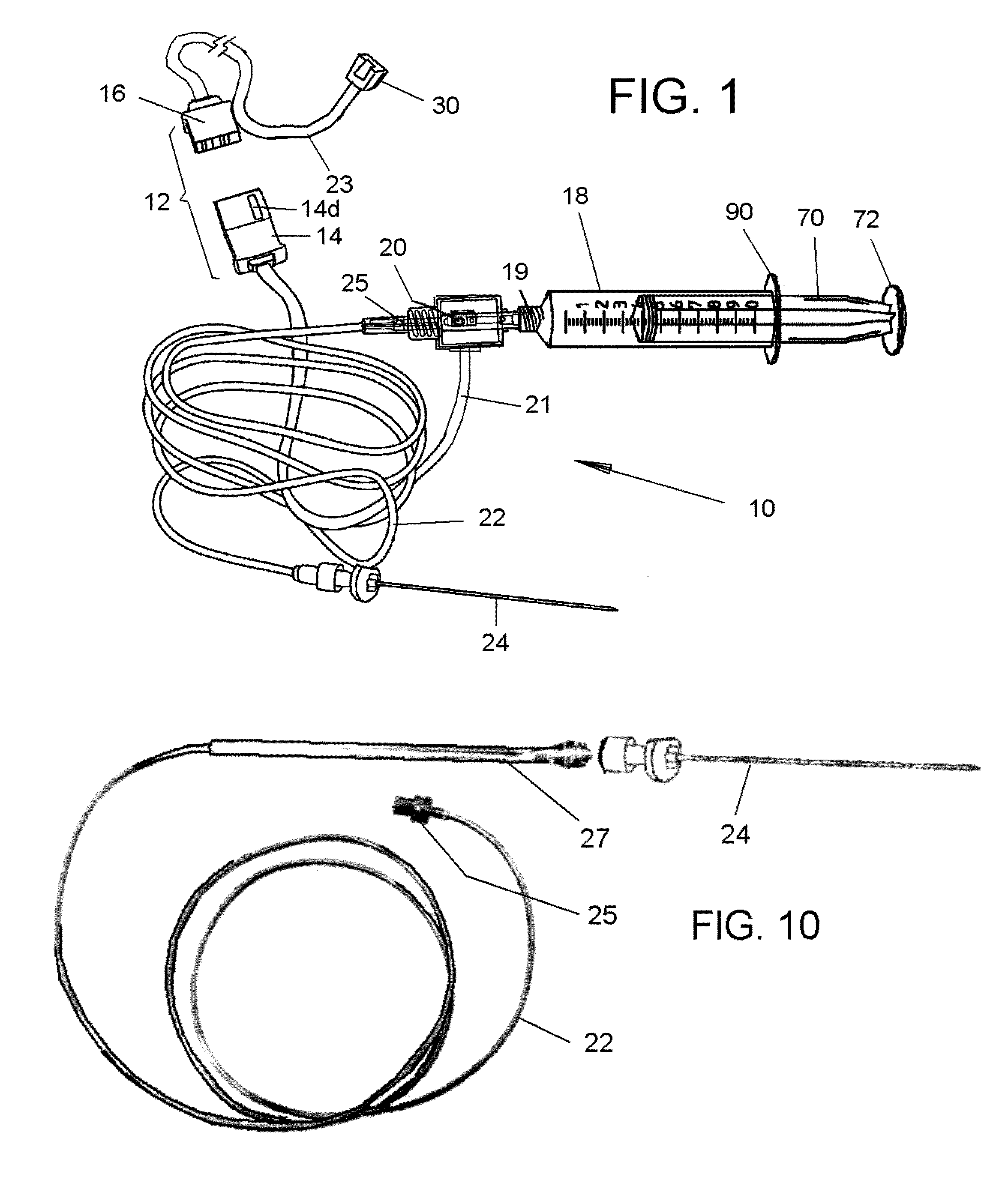
The invention relates to improved equipment for the administrations of epidural anaesthetic and to novel methods of administration using the same. Improvements include a needle configured for reduced incidence of post dural puncture headaches, an improved sensitivity loss of resistance syringe and a novel cannula which in one form readily facilitates combined spinal epidural anaesthesia (CSE). Also includes is a catheter having a pre-assembled injection hub and connection means to optionally retain a cannula that is withdrawn over the catheter.
Owner:NOVODURAL
Methods and apparatus for measuring pressures in bodily fluids
Owner:101 ASSOCS
Trimmable sensing catheter
An implantable fluid management device is provided that includes a catheter having at least one wire running therethrough and coupled to a sensor disposed at a distal portion of the catheter. At least a portion of the wire is removably coupled to the catheter to allow a length of the catheter to be selectively adjusted, thereby providing a trimmable sensing catheter. The device can be used for a variety of medical procedures, but in an exemplary embodiment the device is a ventricular catheter that is used to drain CSF from a patient's ventricles.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
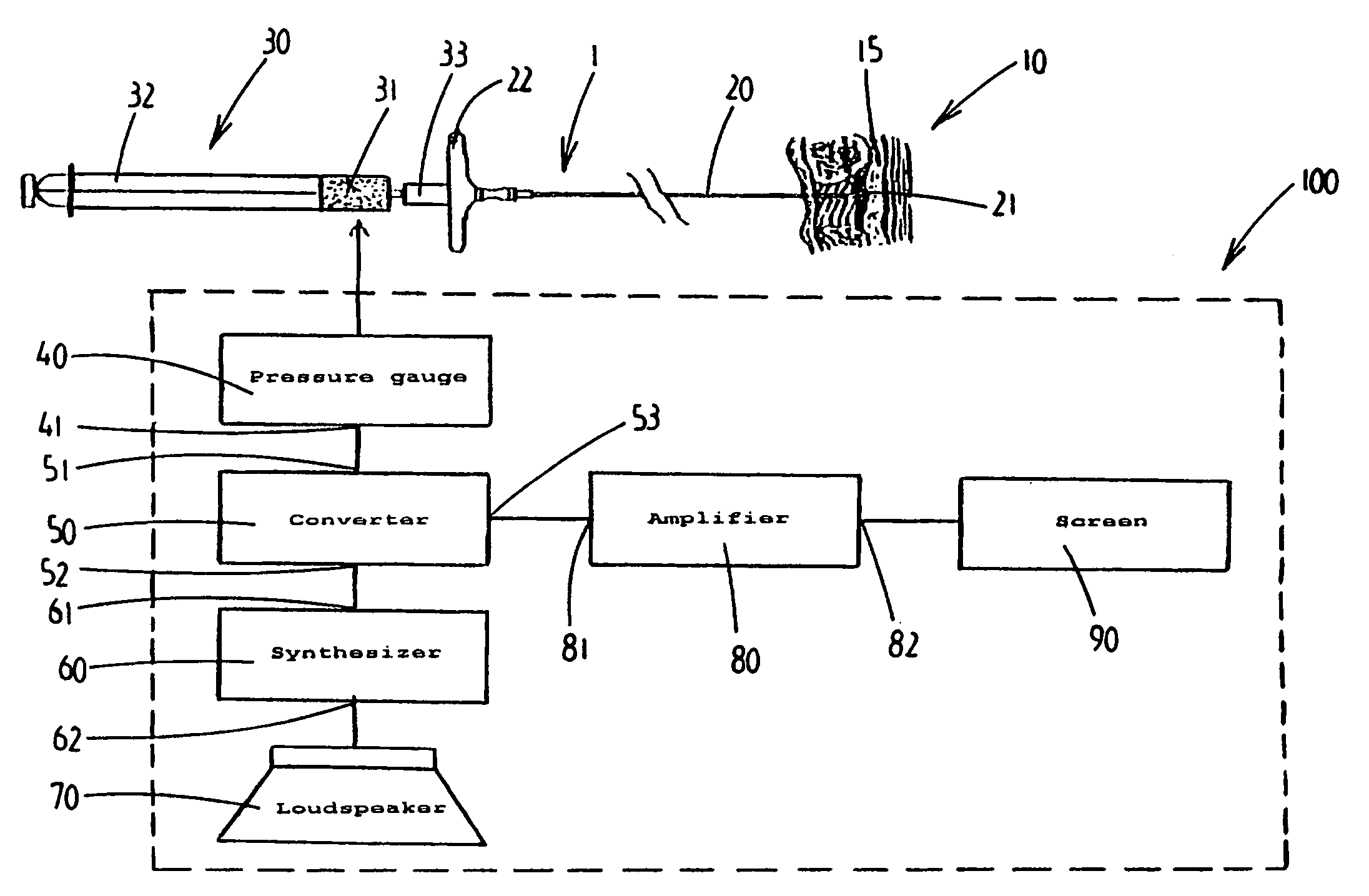
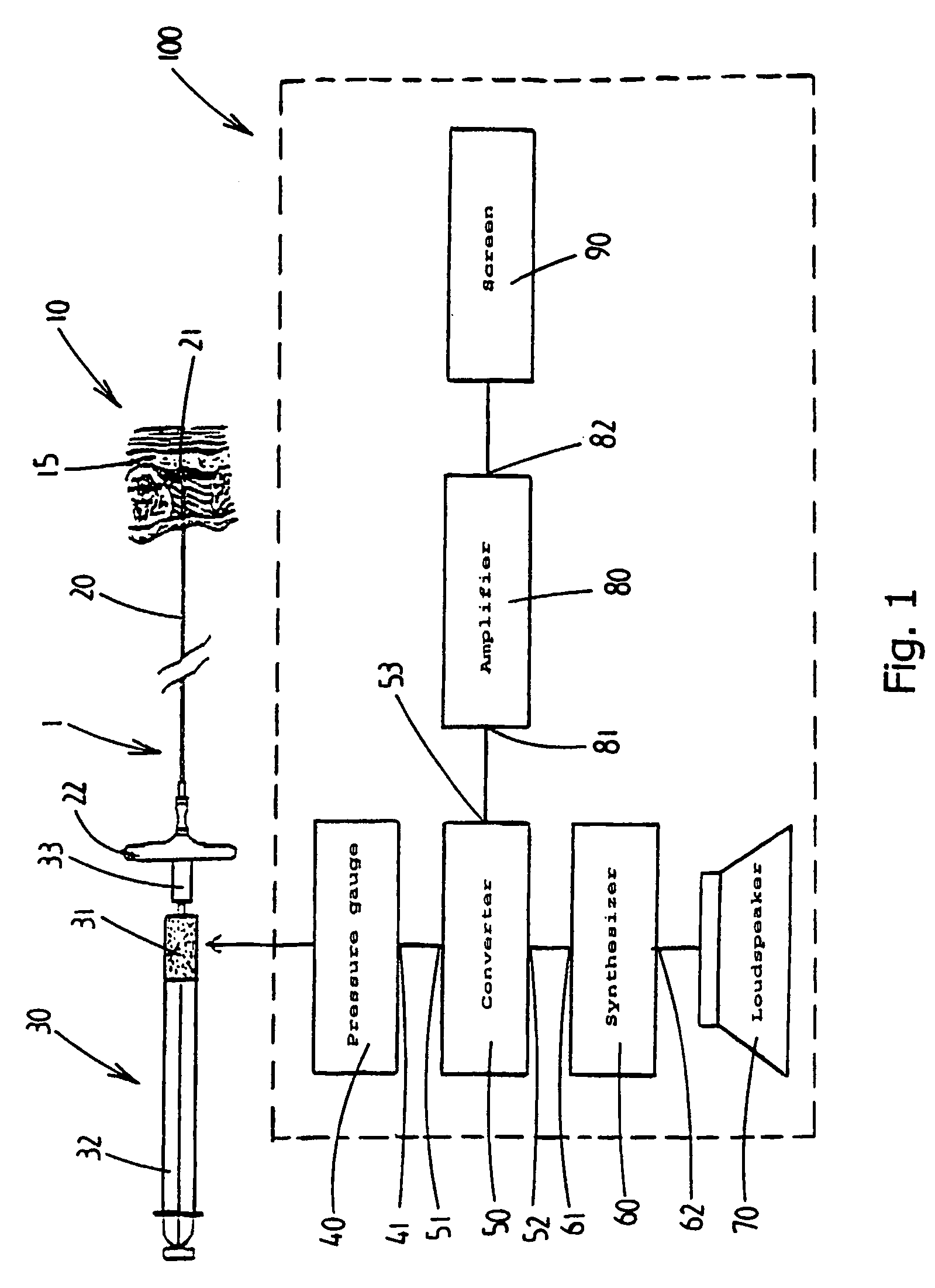
Device and method for locating anatomical cavity in a body
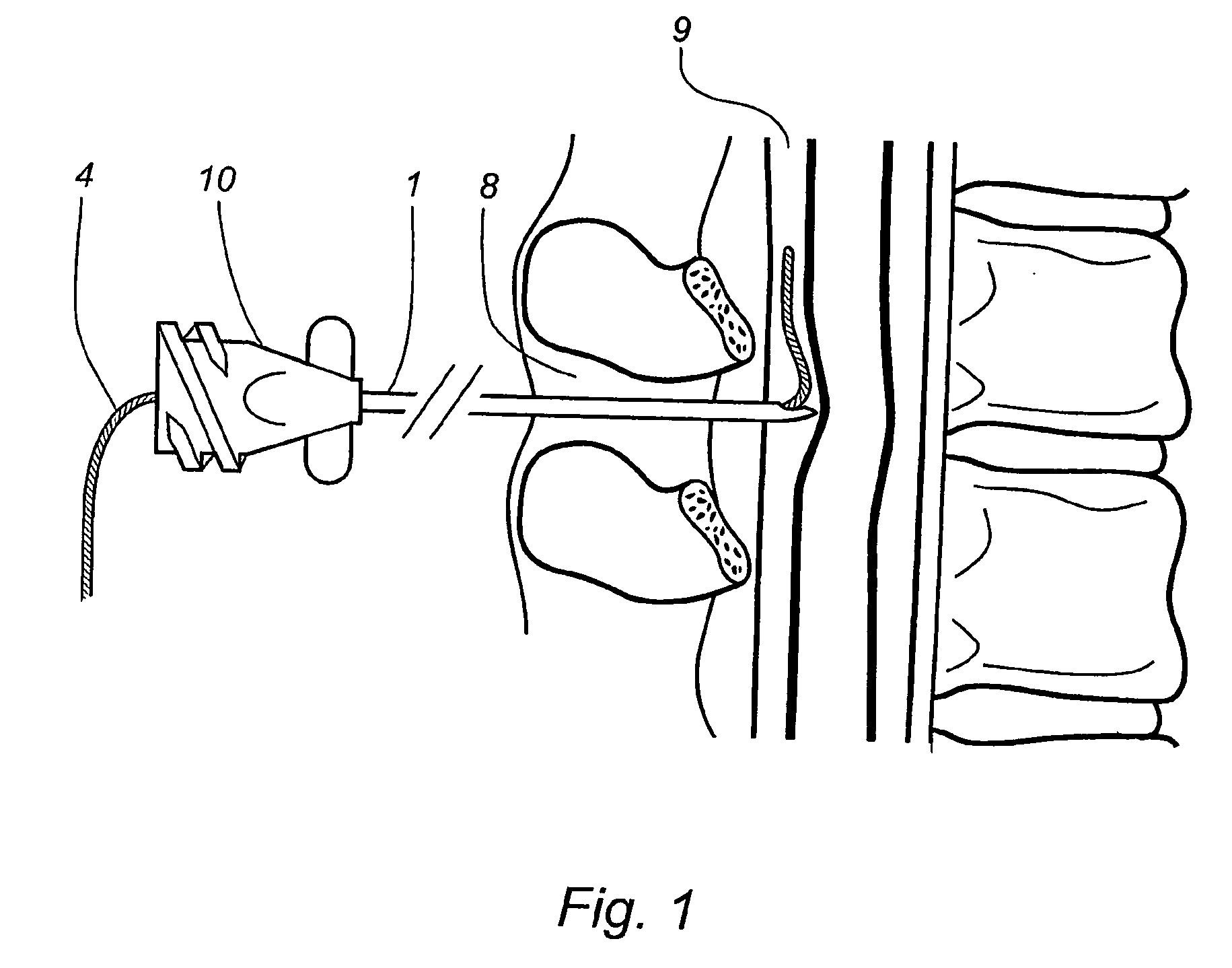
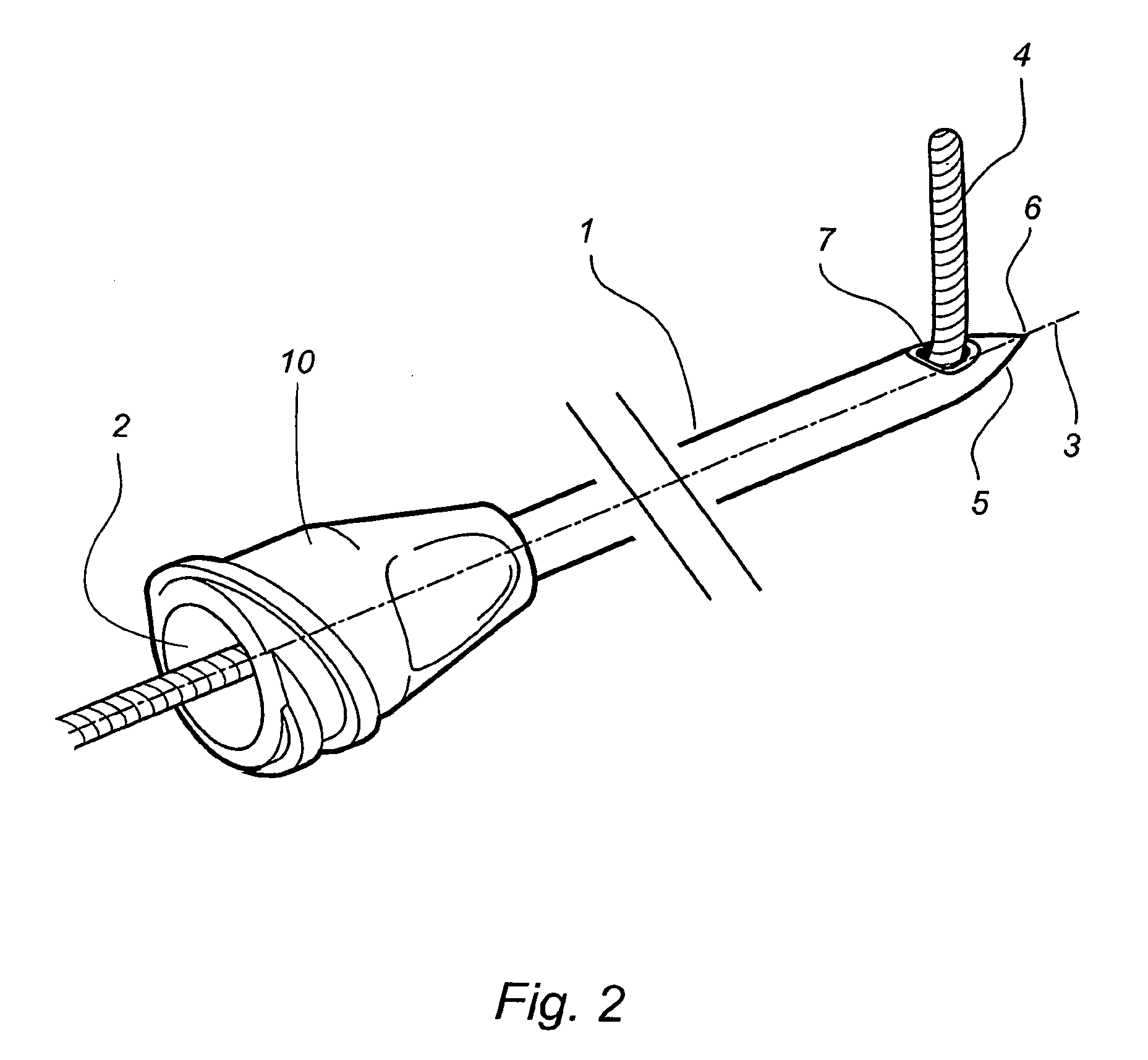
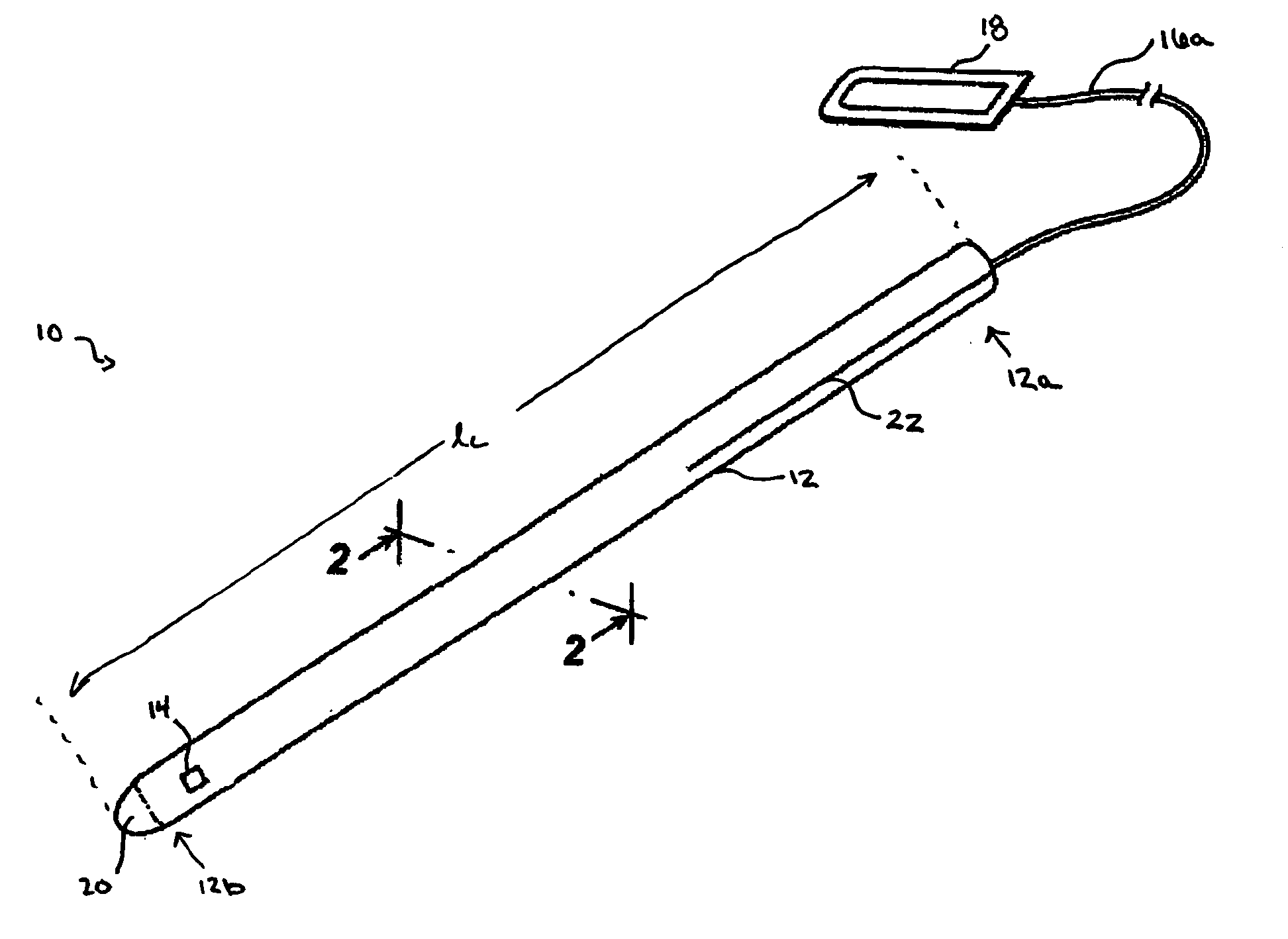
ActiveUS7922689B2Limiting introductionForce can be exertedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesEngineeringPressure measurement
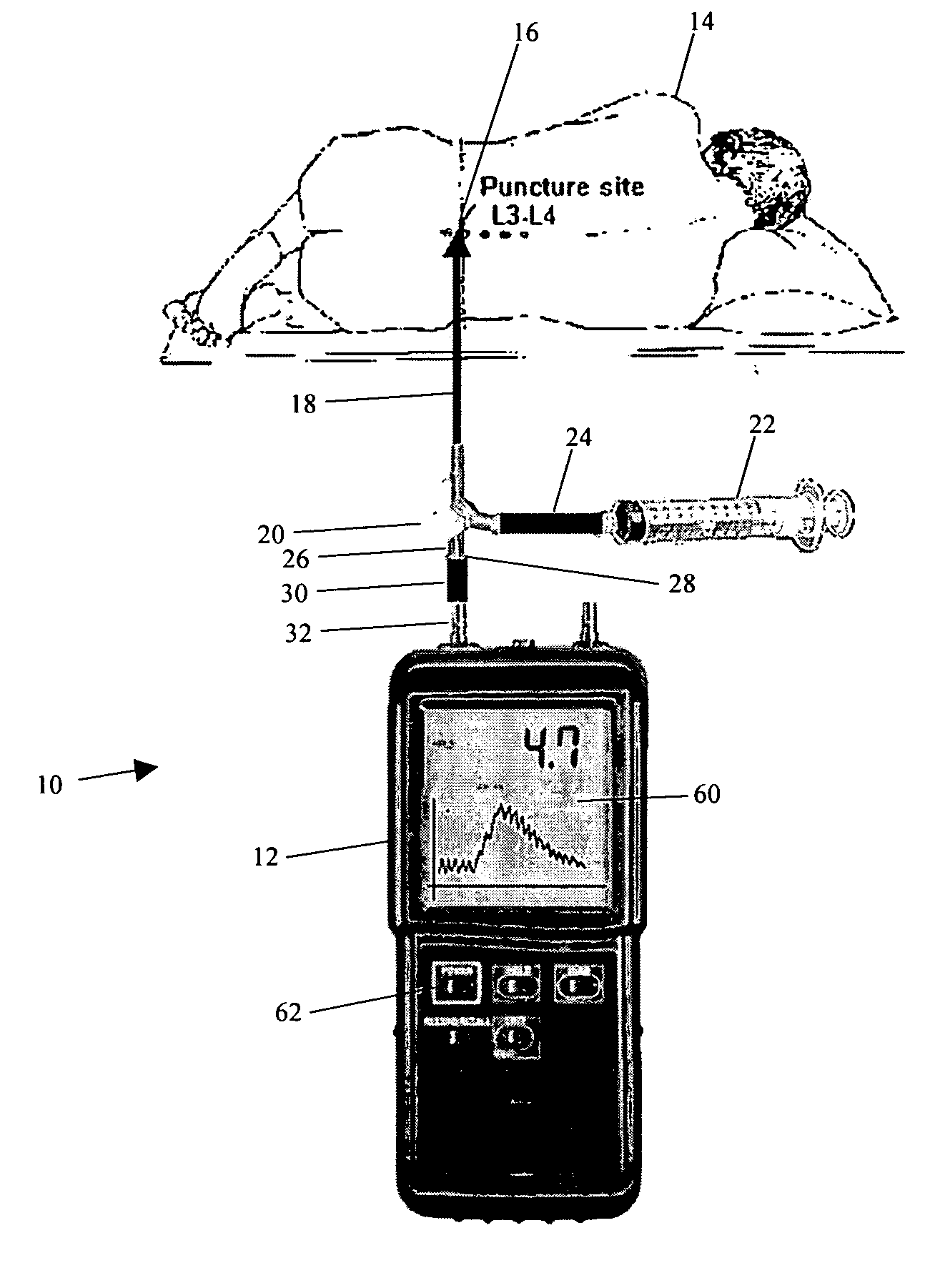
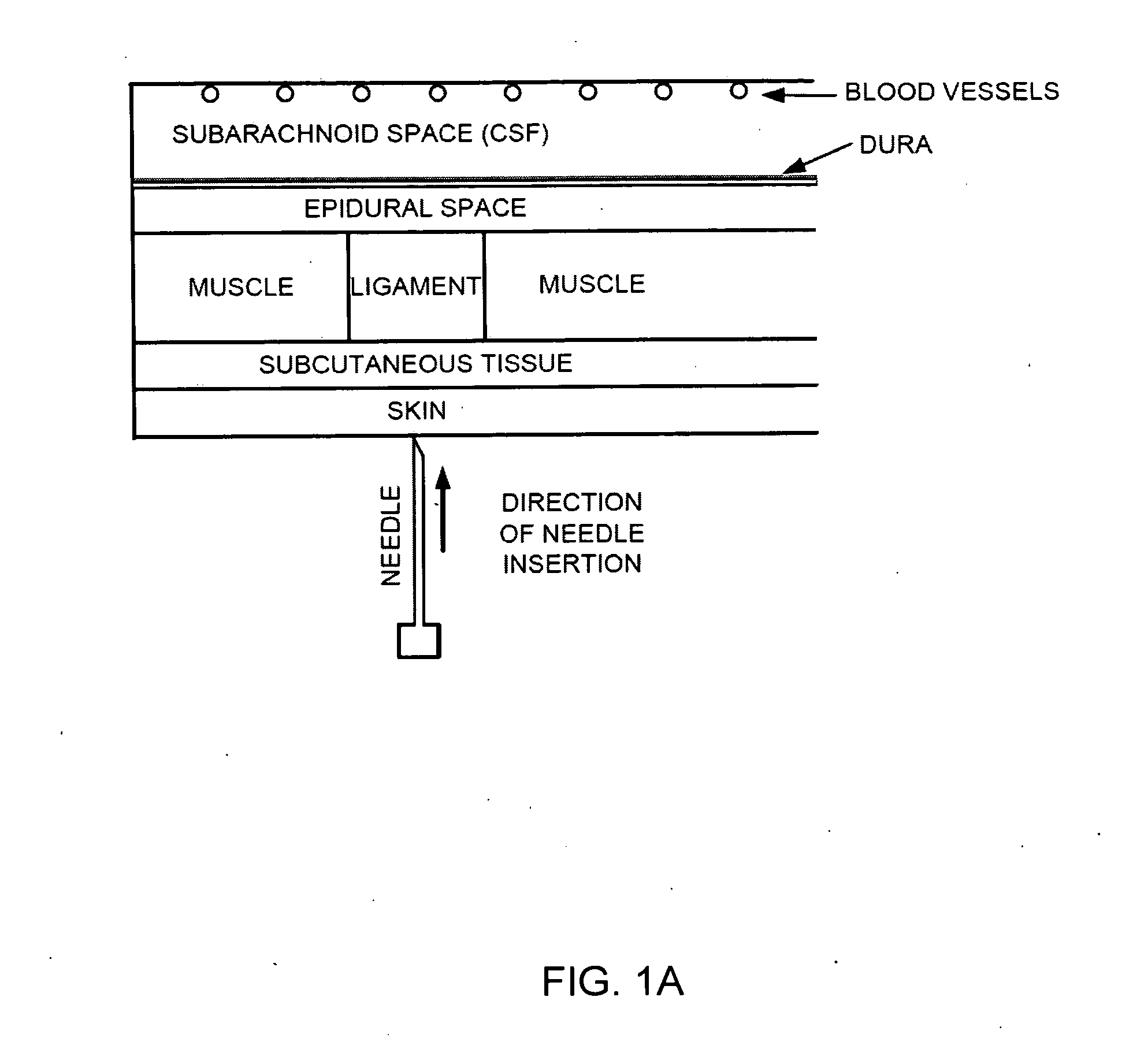
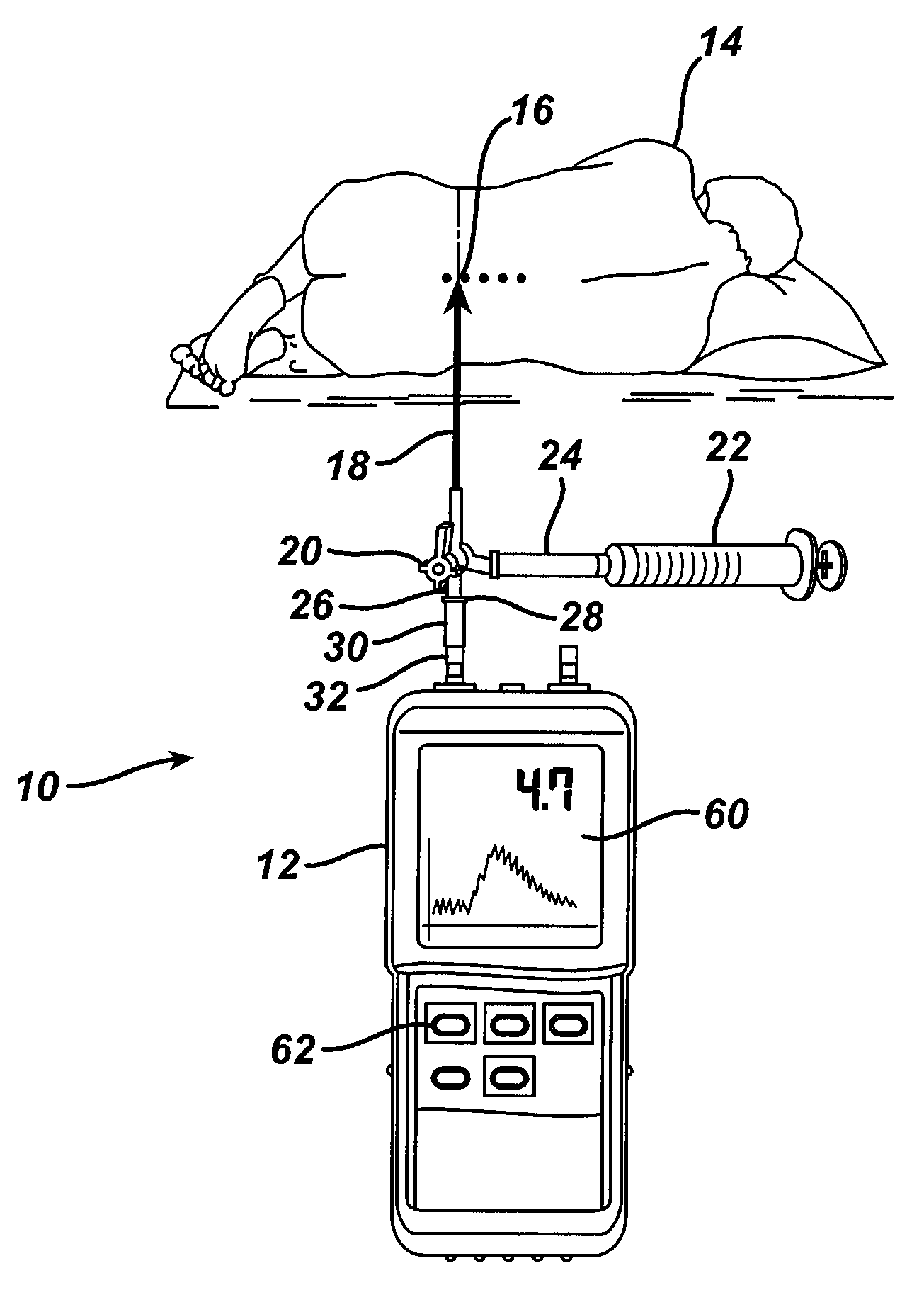
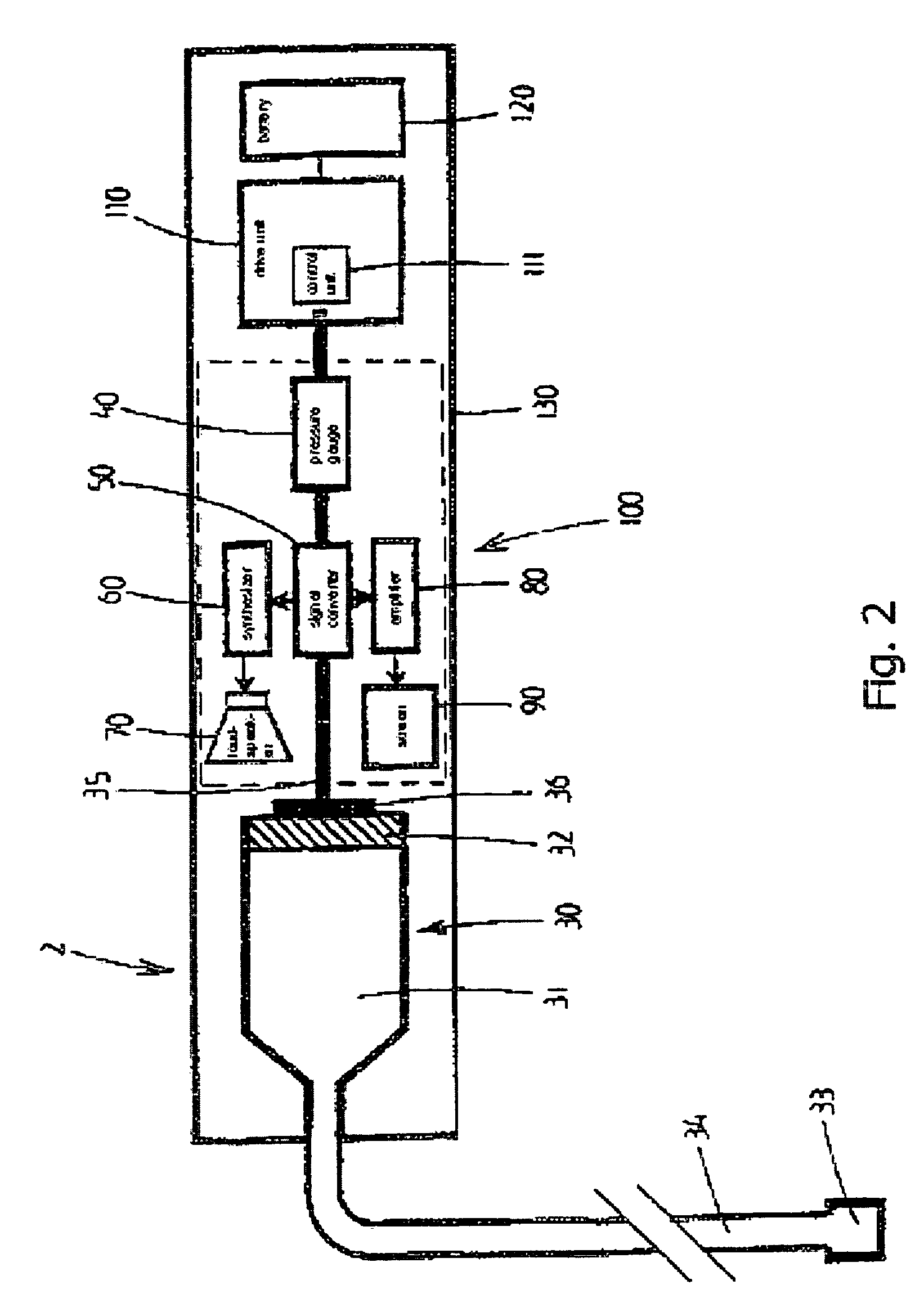
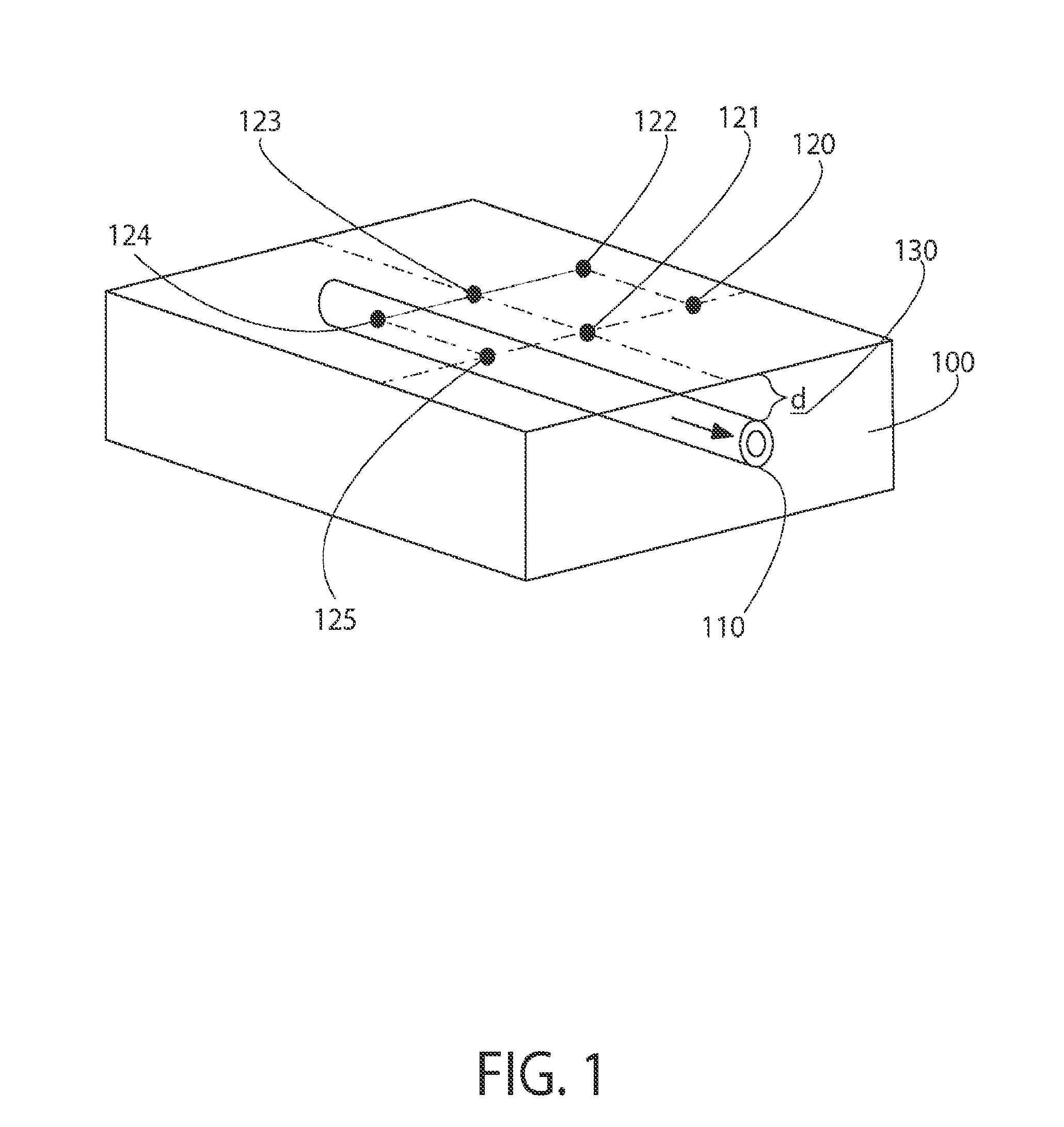
A device (1) is designed for locating a region which is situated in a body (10). The device has a fluid-filled reservoir (30) which is closed off in a sealed manner by a displaceable plunger (32) and is connected to a hollow puncture needle (20). To measure the pressure prevailing in the fluid, the device has a pressure gauge (40). A signal converter (50) is used to convert a continuous pressure-measurement signal provided by the pressure gauge (40) into a form which is suitable for further processing. A synthesizer (60) is designed to process the converted pressure-measurement signal into a continuous sound signal which is representative of the pressure. If, during a displacement of the puncture needle (20), a needle point (21) reaches the anatomical cavity (15), the result is a readily perceptible change in the sound signal. The device records the pressure-measurement signal over the course of time.
Owner:APAD OCTROOI
Diagnostic algorithms for a csf physiologic controller
InactiveUS20050020962A1Overcomes shortcomingOvercome limitationsWound drainsIntravenous devicesIntensive care medicineMicroprocessor
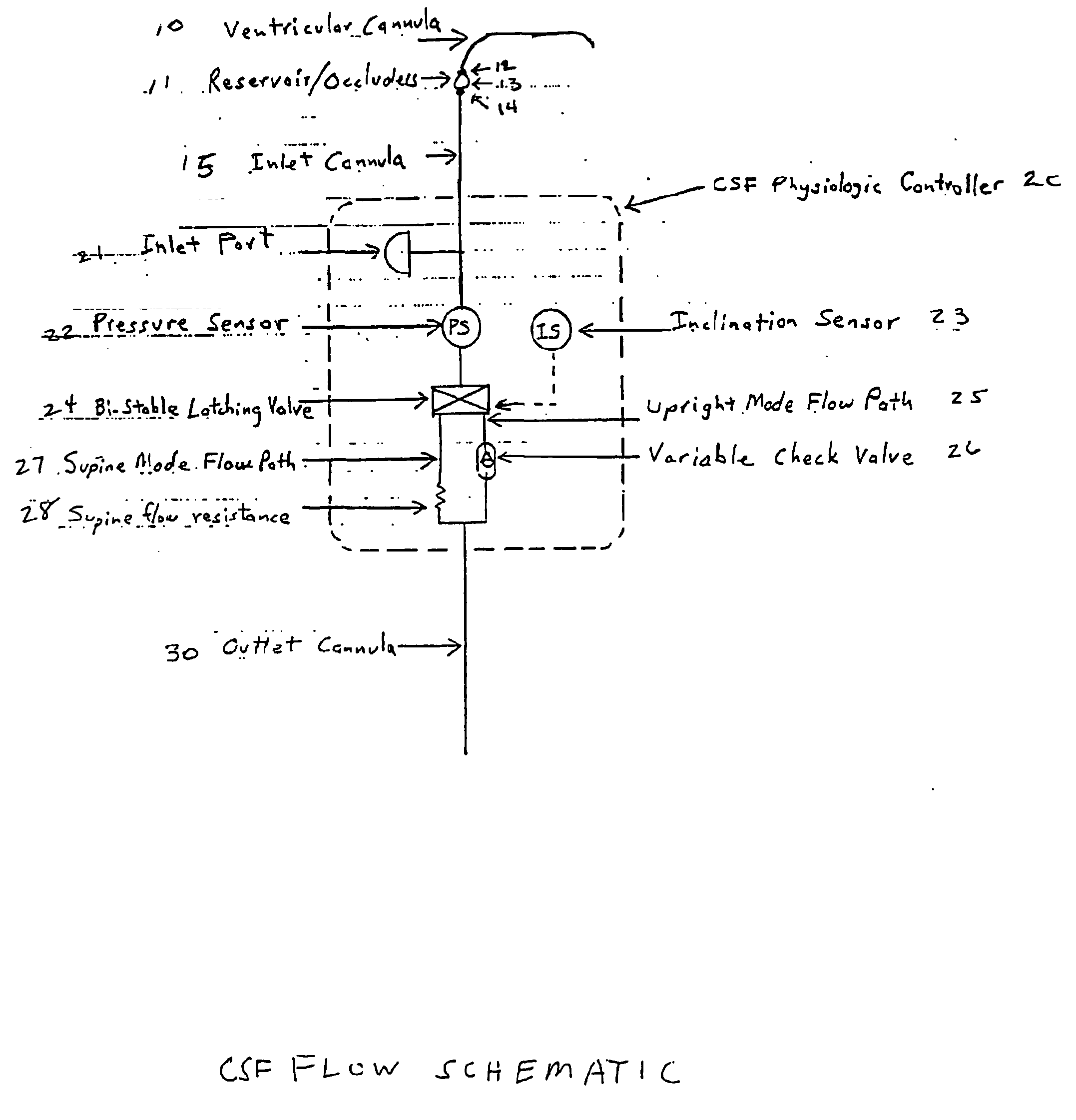
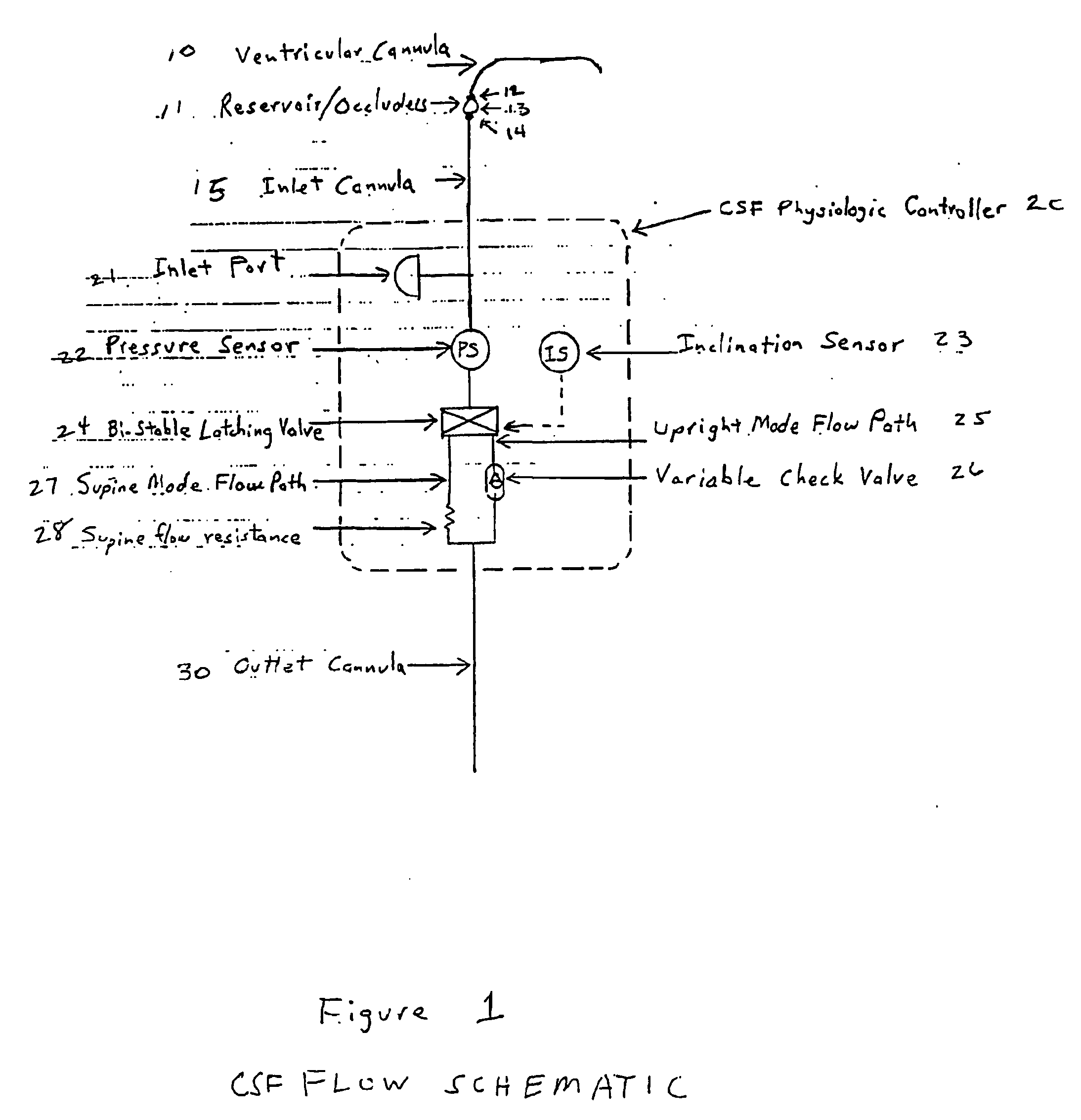
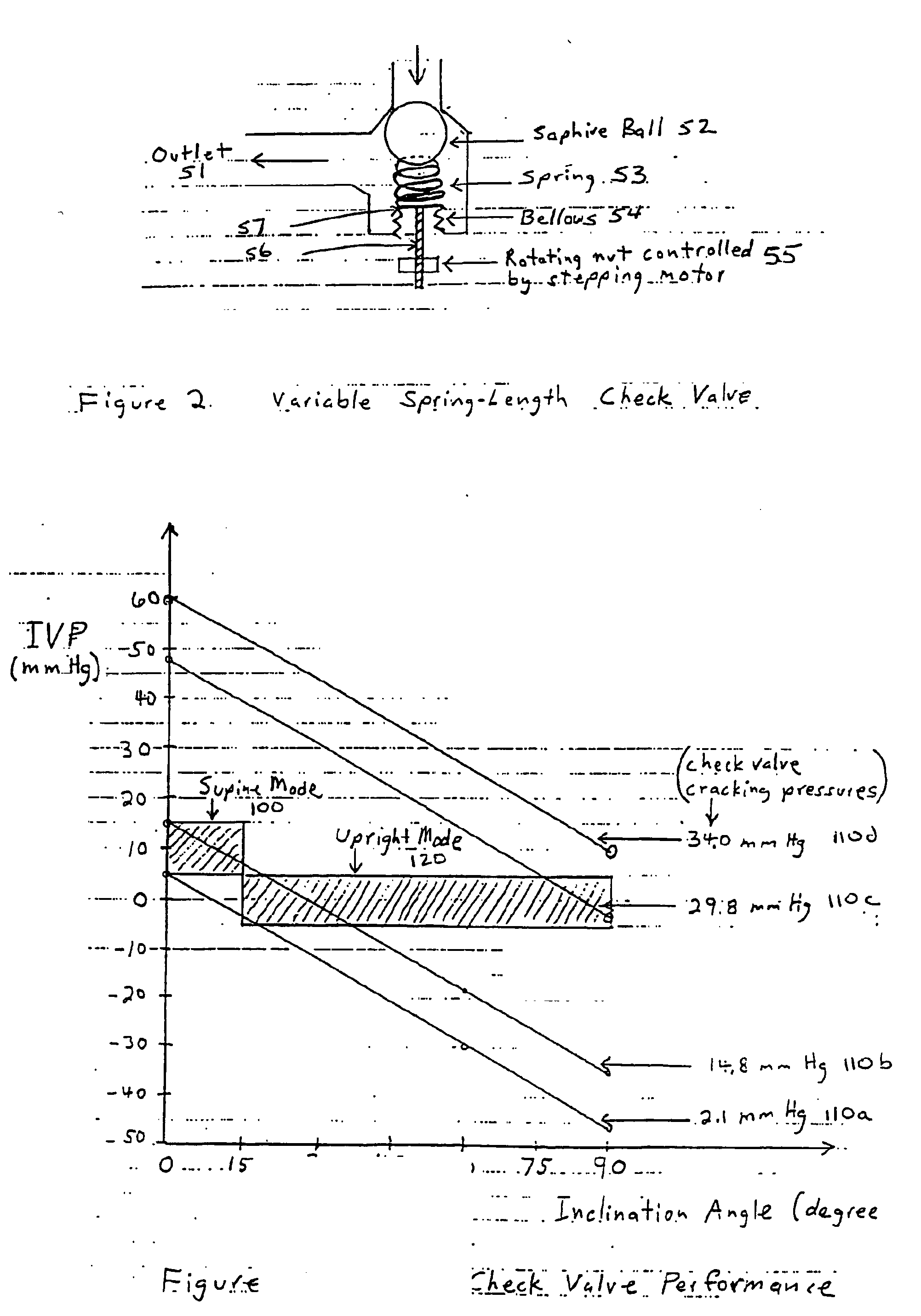
The Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Physiologic Controller is an implantable active battery-operated device that is microprocessor controlled via algorithms stored in its memory. The controller also contains numerous diagnostic features, which enable the physician to monitor the operation of the system, as well as several key patient parameters non-invasively, by performing a set of algorithms.
Owner:KUCHTA JOHN
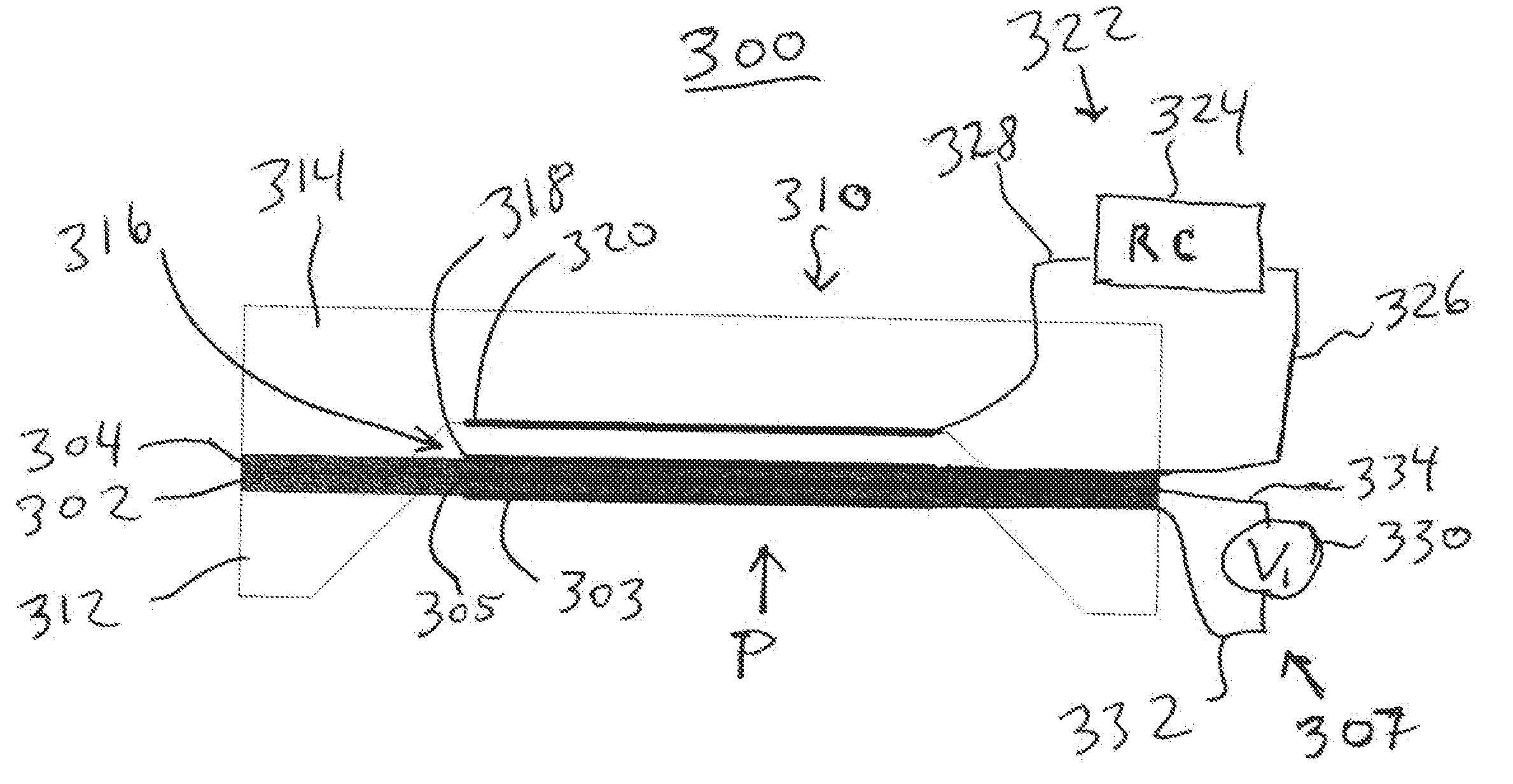
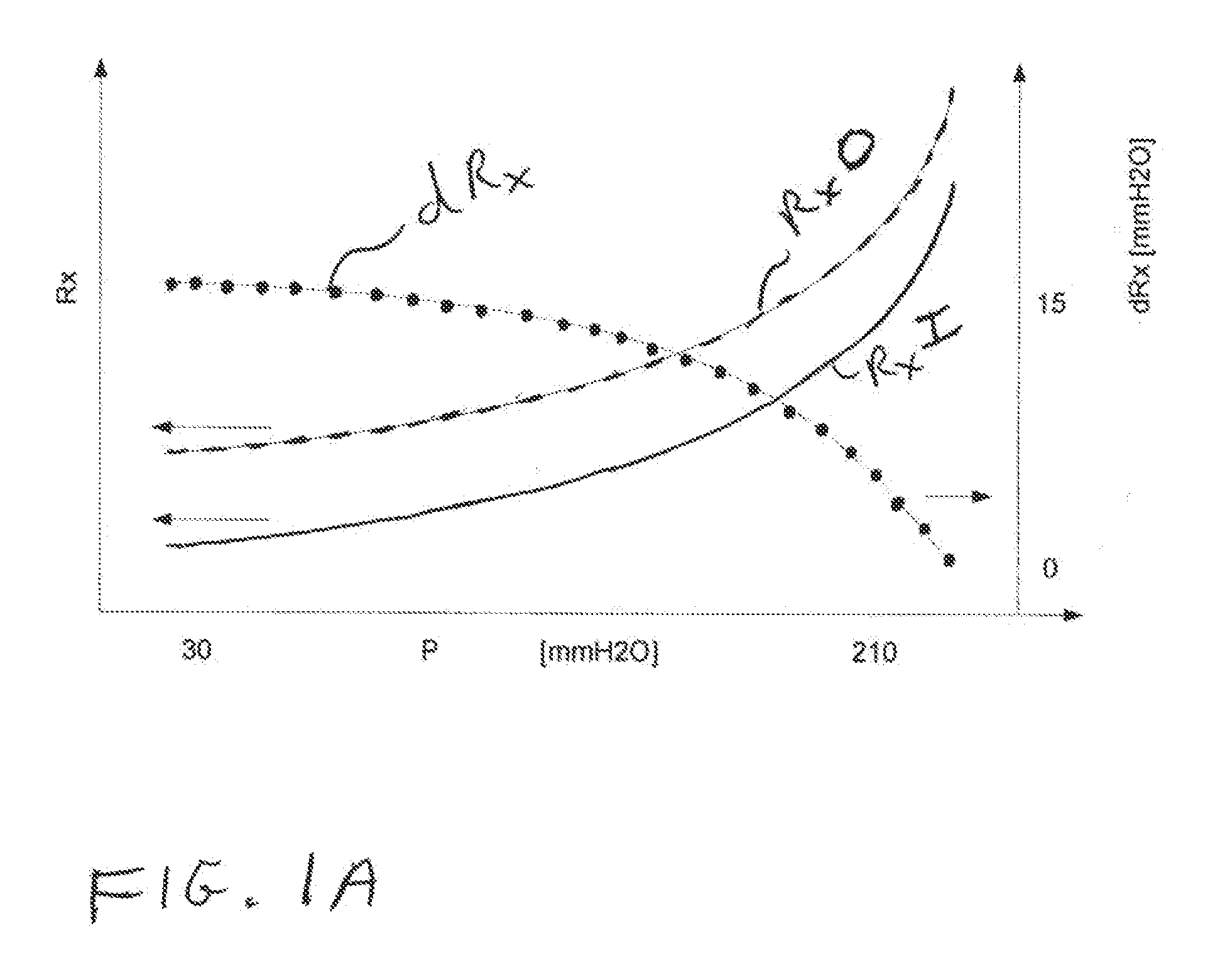
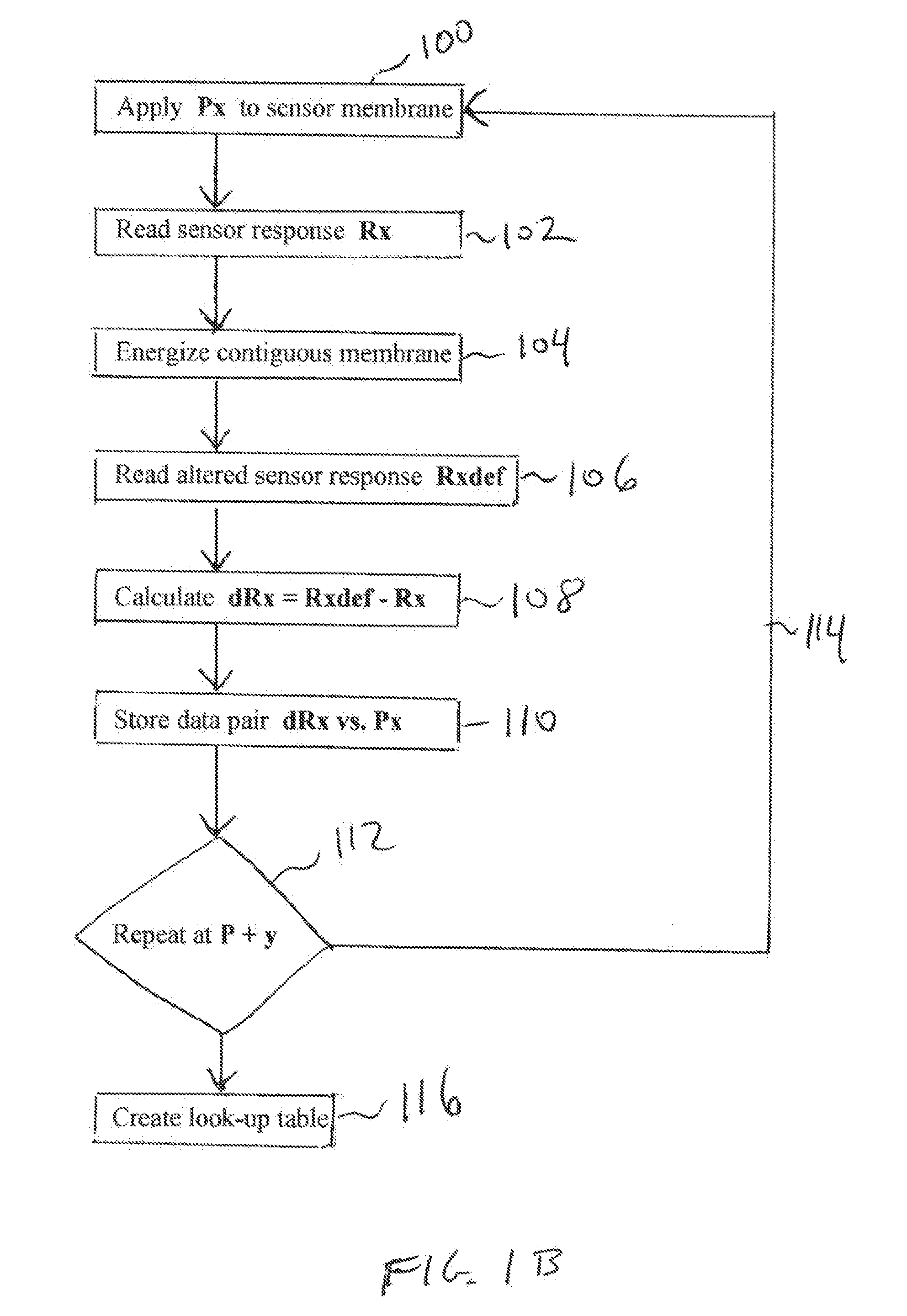
In situ offset compensation for pressure sensors
ActiveUS20110040206A1Accurate correctionShorten the timeFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationIntracranial pressure measurementBiomedical engineeringPressure sensor
A pressure sensor having a substrate and a first, deformable membrane, partially supported by the substrate, which generates a first sensor reading when deformed by pressure. A second membrane is contiguous to the first membrane. When the second membrane is energized, it deforms the first membrane to alter the first sensor reading.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
Devices and methods for parameter measurement
InactiveUS20160302729A1Restore visionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesMicrometerEngineering
A thin-film, diaphragm based device is disclosed which can be used to perform an array of sensing and actuating operations where a very thin profile is desired, such as in millimeter, micrometer, or nanometer tight spaces.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Spinal canal access and probe positioning, devices and methods
Methods and devices for detecting positioning of a probe in a tissue of a patient. A method can include providing a detection device; advancing a device coupled probe through the tissue of the patient and toward the patient's spinal canal; detecting a change in pressure about the distal portion of the coupled probe during advancing, where the detected pressure change indicates probe positioning in the patient's spinal canal; outputting the detected pressure change or indication of probe positioning to a visual display.
Owner:JAMES M PIGOTT
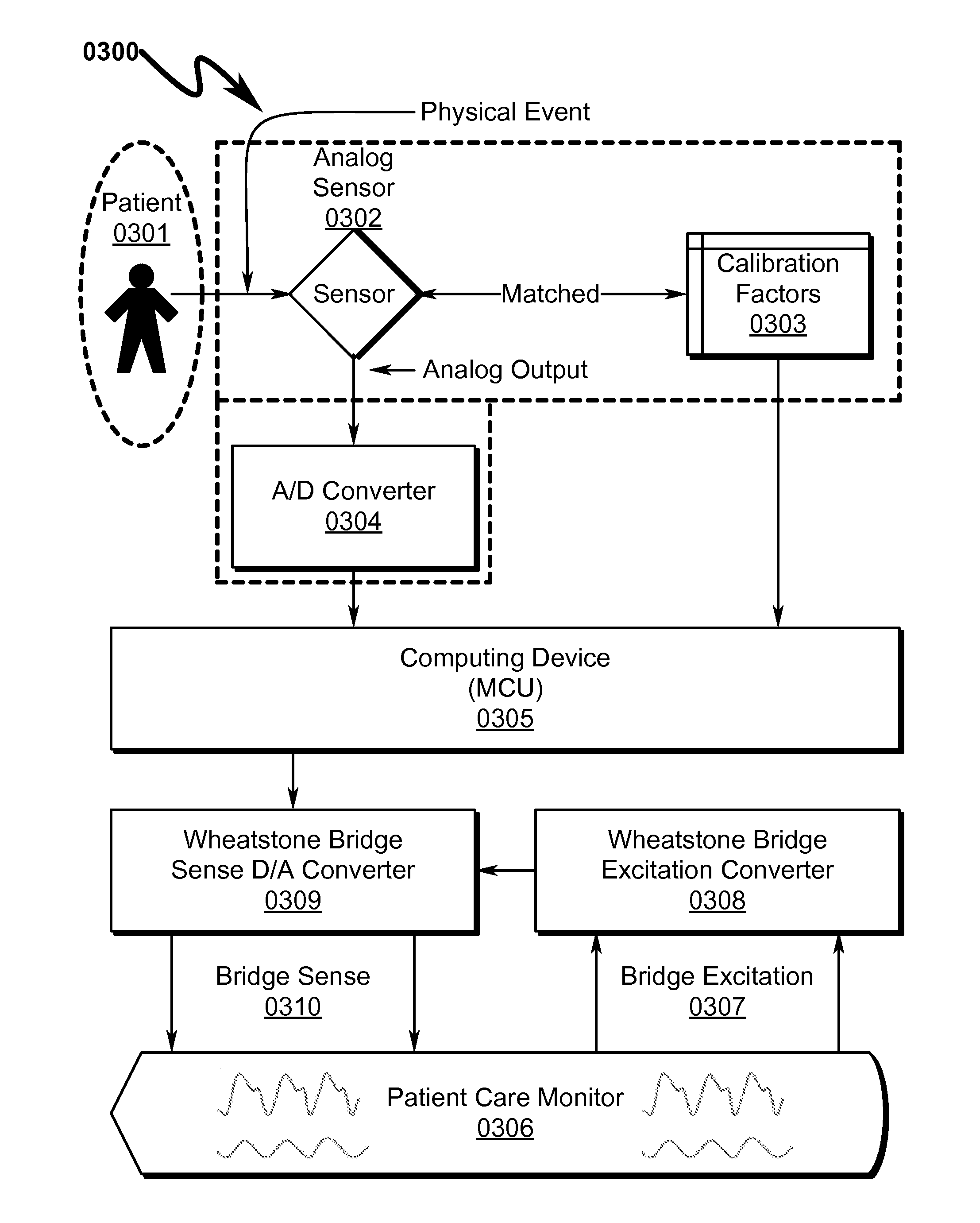
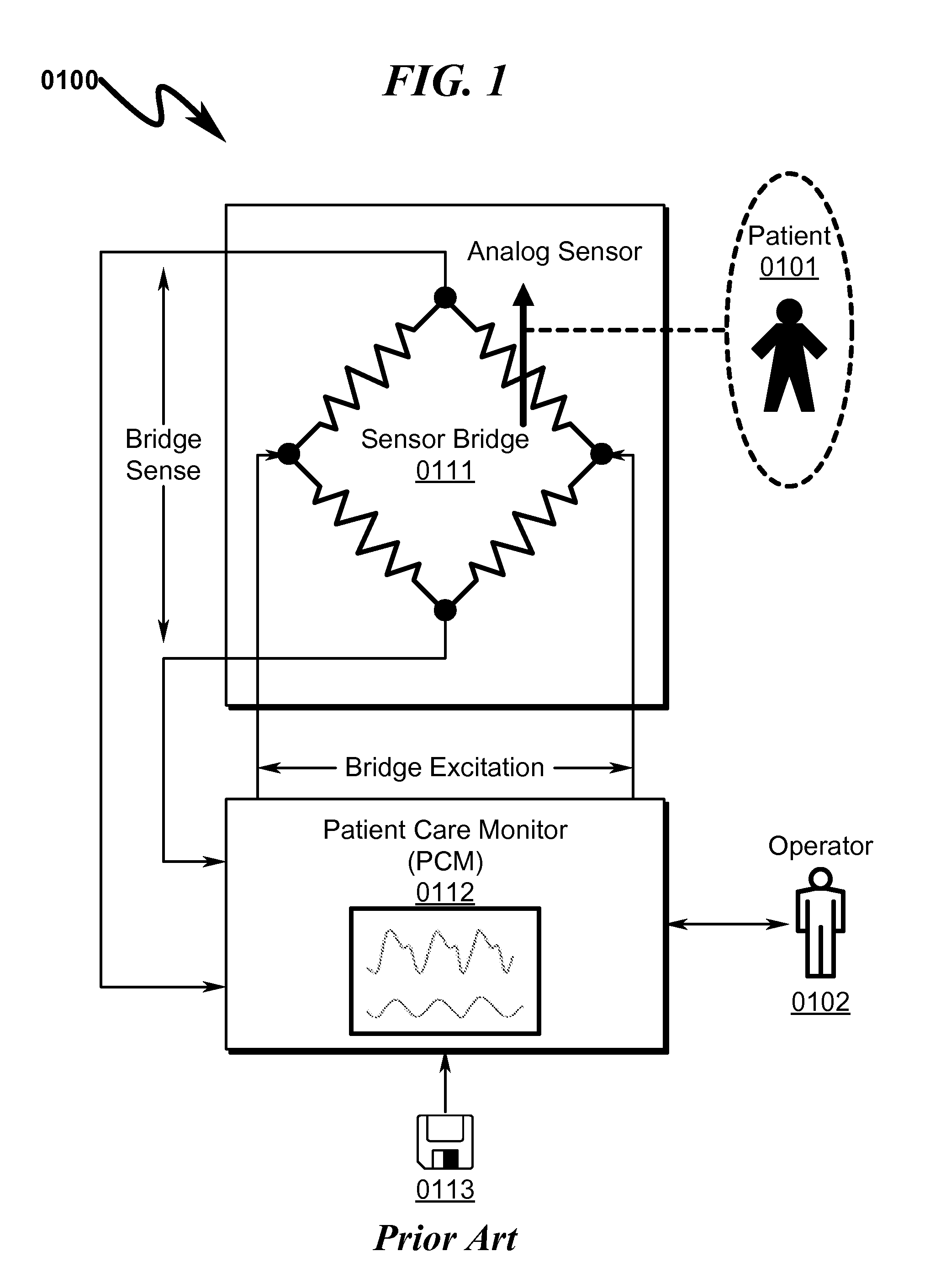
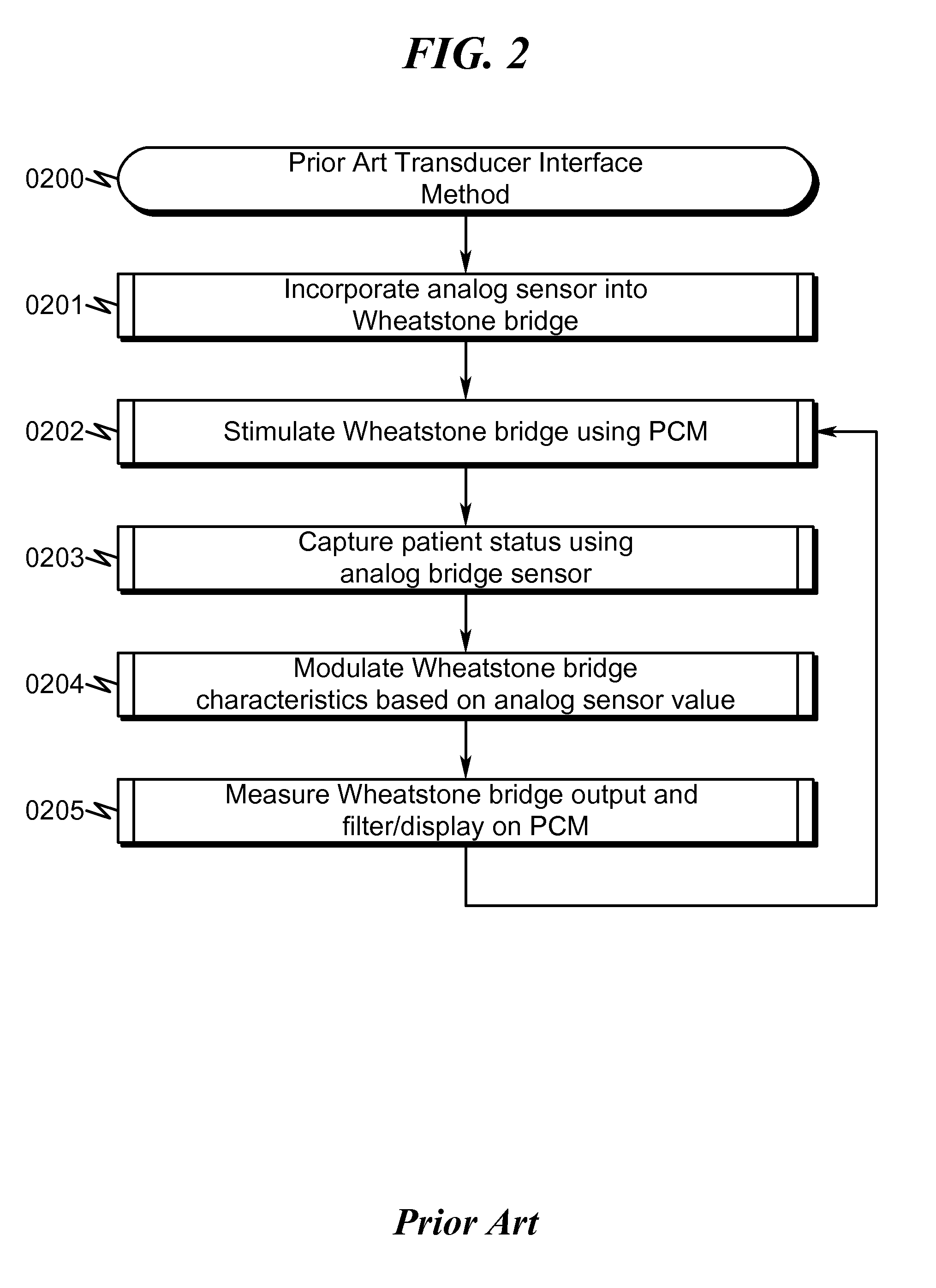
Transducer interface system and method
ActiveUS20140024956A1Diagnostic signal processingFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsFiberTransducer
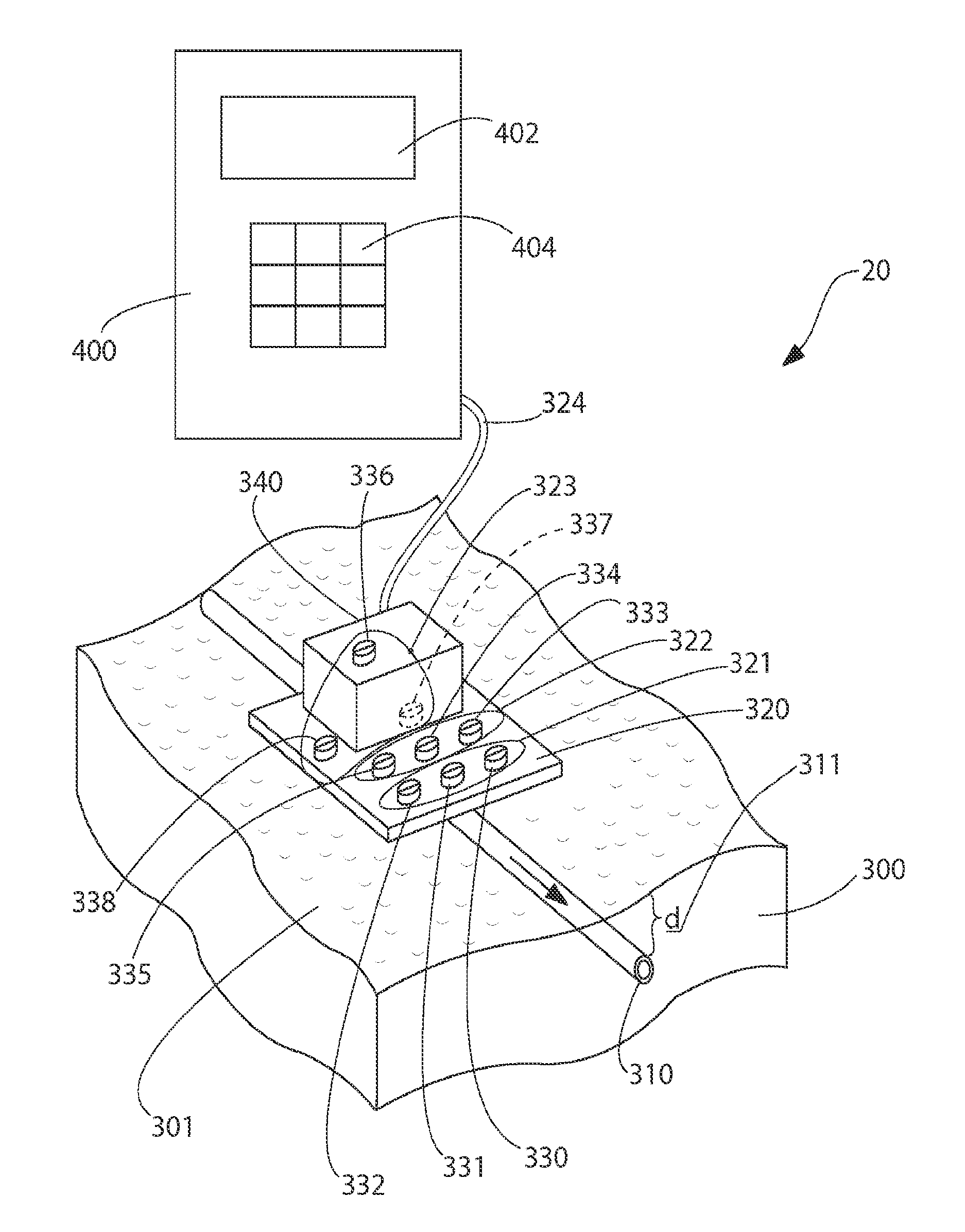
A transducer interface system / method allowing conversion from an analog sensor input to a standardized analog output interface is disclosed. In some preferred embodiments the system / method permits a fiber optic pressure sensor to be interfaced to a standard patient care monitor (PCM) system using standardized Wheatstone Bridge analog interface inputs. Within this context the Wheatstone Bridge sensed output is defined by stimulus from the PCM and modulation of bridge element values by the conditioned output of an analog pressure sensor. The use of analog-to-digital-to-analog conversion in this transducer interface permits retrofitting of PCM devices having analog Wheatstone Bridge inputs with advanced patient monitoring sensors without the need for specialized modifications to the baseline PCM data collection framework. Methods disclosed herein include techniques to connect arbitrary types / numbers of analog sensors to traditional PCM systems without the need for PCM system hardware / software modifications.
Owner:ENDOPHYS HLDG
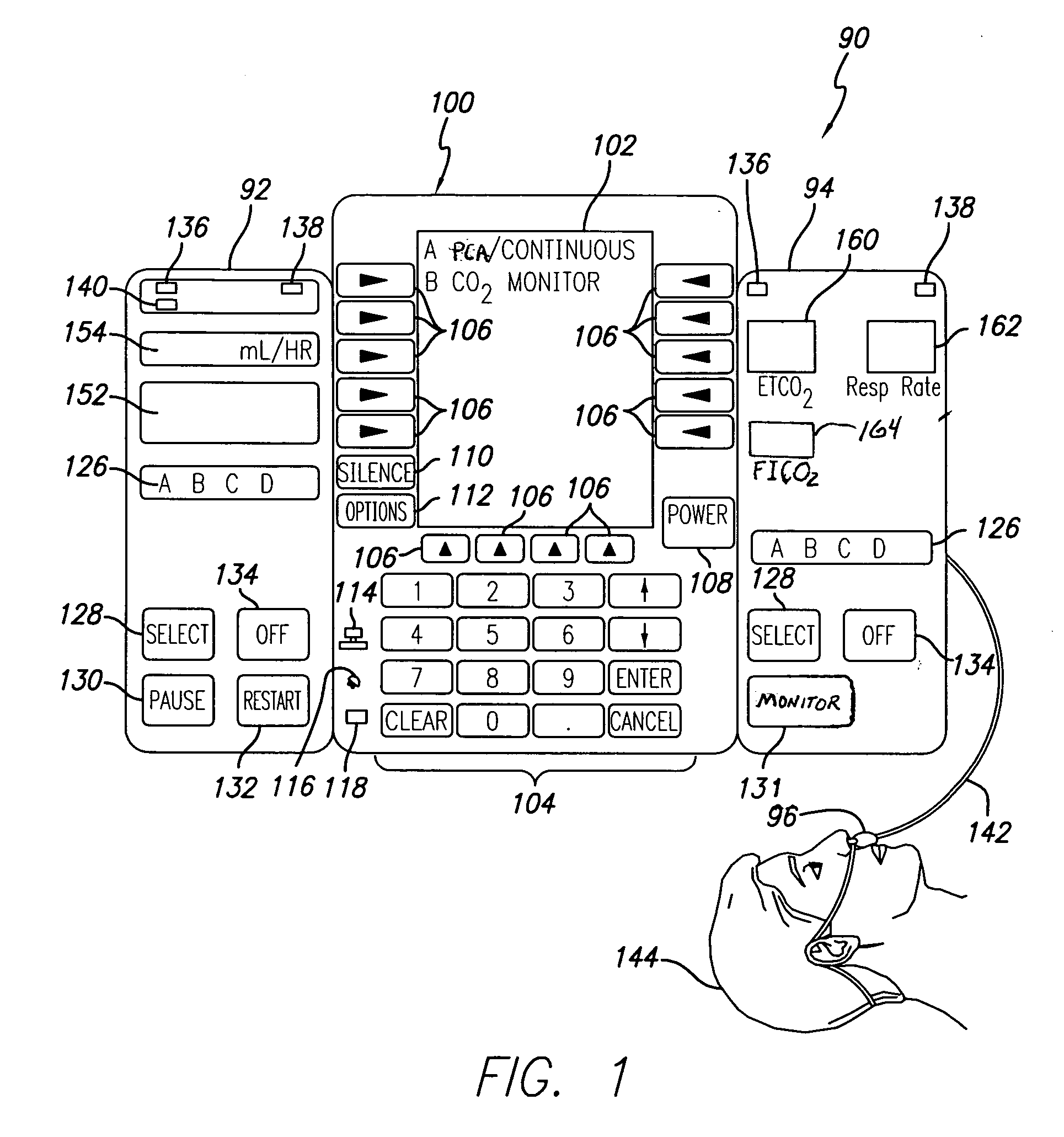
Patient-controlled analgesia with patient monitoring system and method
A patient care system in which a physiological parameter of a patient is monitored while the patient self-administers analgesic. A display presents a trend of the patient's physiological parameter along with the time of self-administration of the analgesic (''PCA''-patient controlled analgesic) such that the effect of the analgesic on the physiological parameter can be seen over selectable time periods. The physiological parameter may be ETCO2 or SpO2 or other. Also included is a drug library having acceptable pumping parameters that is outside an acceptable range, or should the patient attempt to self-administer more analgesic than the acceptable range permits, or should a patient's physiological parameter change during infusion such that a pumping parameter becomes outside an accept able range, an indication of such will be given and action, such as stopping the pump, will be taken.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
Spinal canal access and probe positioning, devices and methods
Methods and devices for detecting positioning of a probe in a tissue of a patient. A method can include providing a detection device; advancing a device coupled probe through the tissue of the patient and toward the patient's spinal canal; detecting a change in pressure about the distal portion of the coupled probe during advancing, where the detected pressure change indicates probe positioning in the patient's spinal canal; outputting the detected pressure change or indication of probe positioning to a visual display.
Owner:MEDLINE IND LP
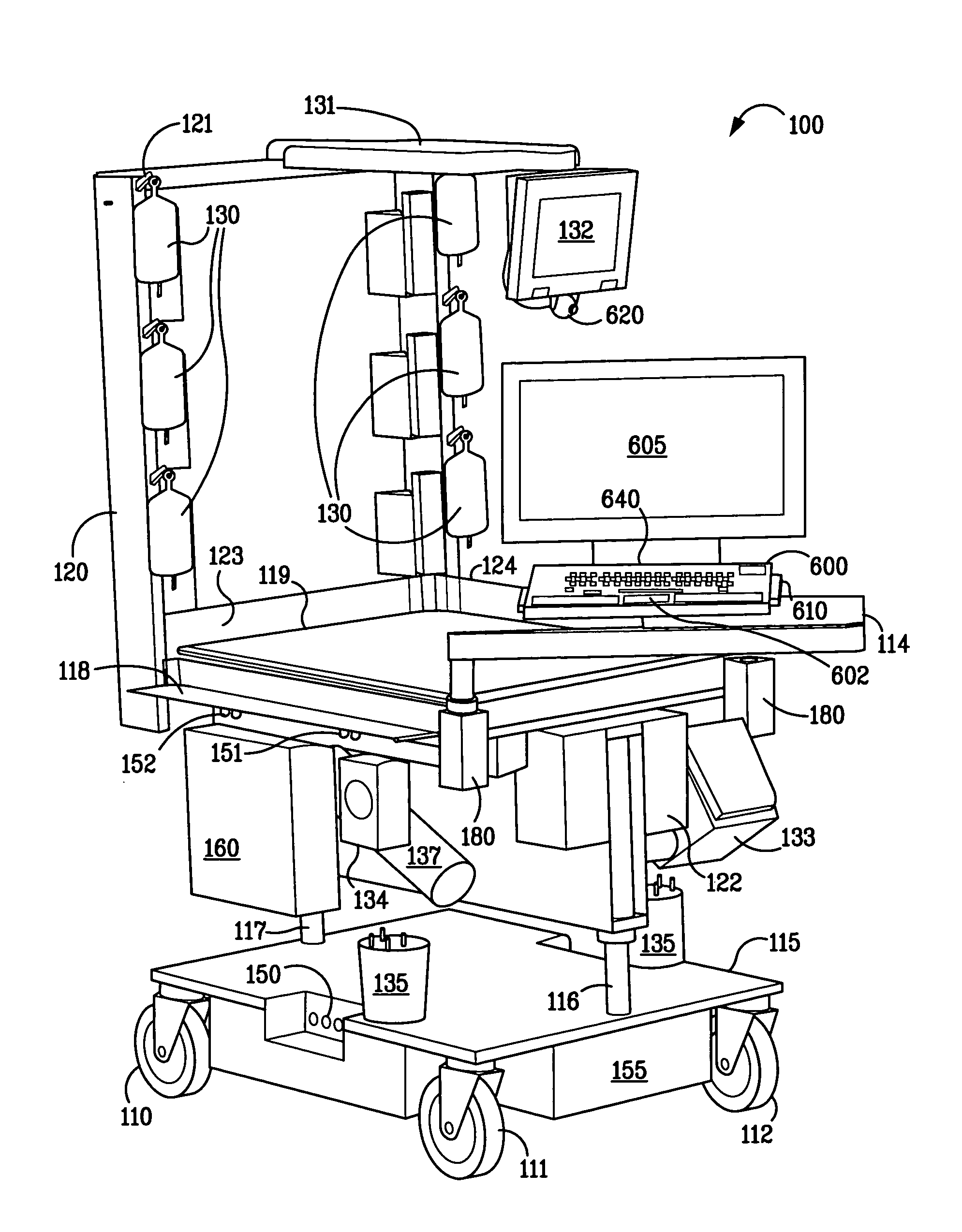
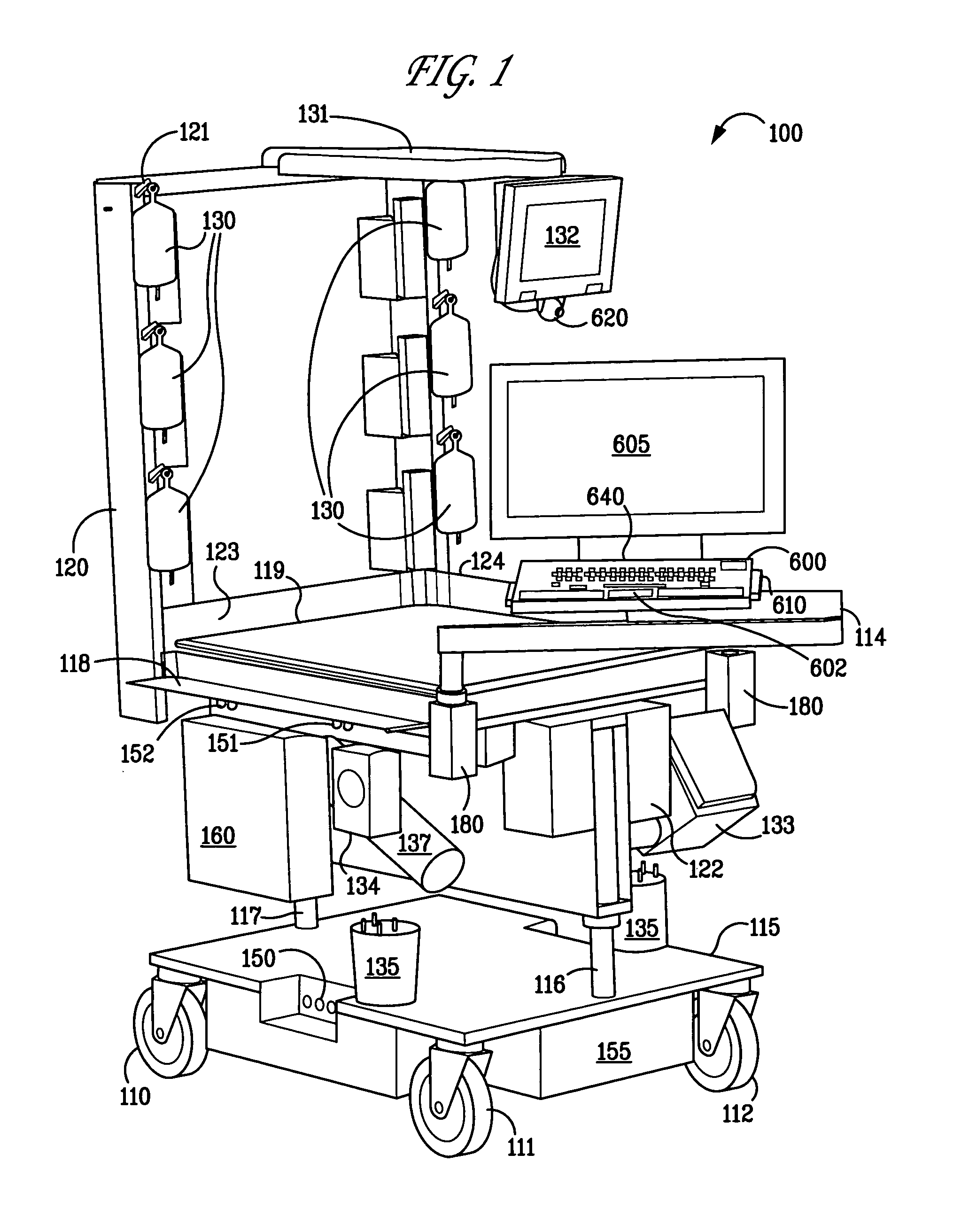
Integrated point-of-care systems and methods
ActiveUS8005686B2Enhance provider decision makingAvoid mistakesDrug and medicationsMedical devicesPoint of careDevice Monitor
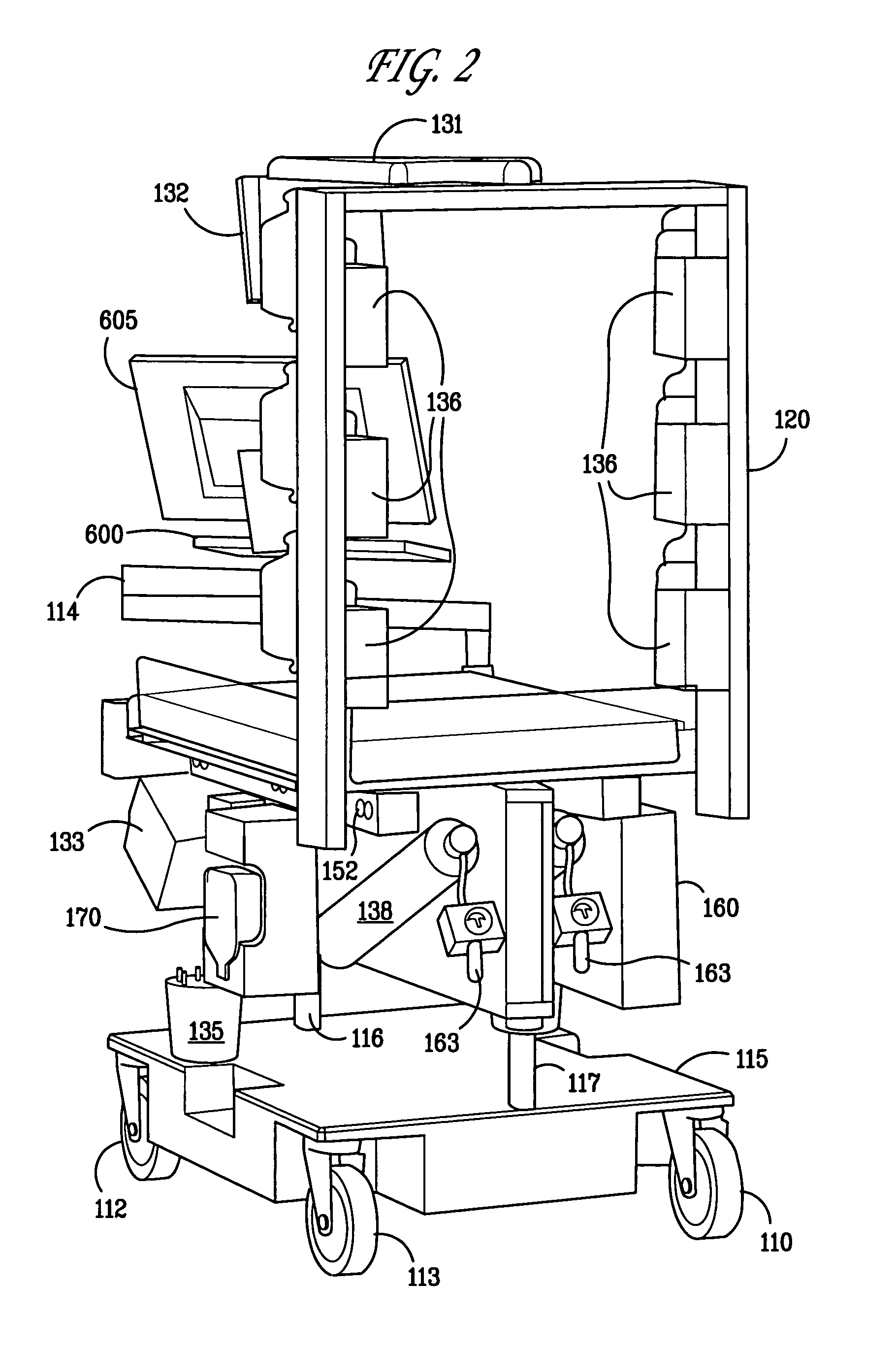
An integrated point-of-care system includes a medical monitoring device, a medical care device, a computing system, and a structure. The medical monitoring device monitors patient information for a patient. The medical care device provides medical care to the patient. The computing system receives patient information from the medical monitoring device and transmits control instructions to the medical care device to control the medical care to the patient. The computing system also exchanges data with a central data respository through a communication network. The structure supports the patient, the medical monitoring device, the medical care device, and the computing system. The structure can also transport the patient, the medical monitoring device, the medical care device, and the computing system together.
Owner:SMITH BAIRD M
Real time CSF flow measurement system & method
InactiveUS20130109998A1Remove effectVolume/mass flow measurementWound drainsTemperature responseData acquisition
A system for measuring quantitative CSF flow in shunt tubing implanted under the skin. The system includes an array of thermosensors clustered in three sections, cooling device, placed on the skin surface and an associated data acquisition and analysis device. Two sensor sections are placed over the shunt on the skin and measure real time temperature responses related to CSF movement. One array placed adjacent the cooling device collects data on thermal properties of skin including skin thermal condictivity, specific heat, diffusivity, perfusion, and thermal inertia. The method involves assessing thermal properties of skin and measuring CSF flow in shunt tubing. The method is useful for shunt patency assessment, CSF valve adjustment procedures and CSF flow measurements related to CSF over drainage. Alternatively, only one section of sensors need be used when determining relative CSF flow, without the need to determine thermal skin properties and by applying the cooling device continuously.
Owner:SHUNTCHECK
Devices and methods for monitoring and delivering therapeutics to the spinal cord
This invention is a continuous monitor of the spinal cord and brain microenvironment in injury and disease that also allows therapeutic interventions. It utilizes a multiport catheter that contains a transducer at the tip for monitoring spinal physiological parameters and also allows via additional ports for sampling and exchange of spinal fluid, as well as drug delivery to the central nervous system. This invention allows for more precise therapeutic interventions in spinal cord and brain injury and disease.
Owner:RADOJICIC MILAN
Fully automated method of measuring and regulating cerebrospinal fluid parameters using disposable tube-set
A method and device for measuring and regulating pressure and flow in the spinal canal, in order to characterize individual patient's cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) dynamics. A unique disposable tube-set plate, with computer regulated automated solenoids is used to control flow pressure and the location of a small pressure sensor allows for fully automatic control of the analysis process.
Owner:LIKVOR
Biopsy-free detection and staging of cancer using a virtual staging score
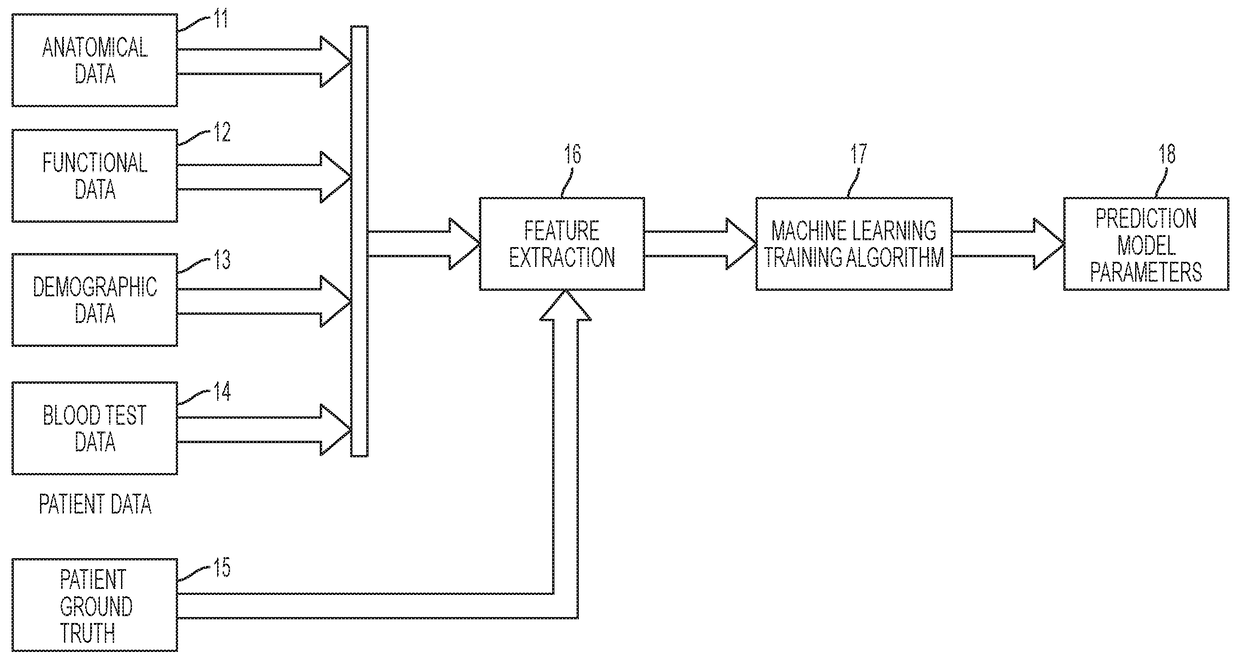
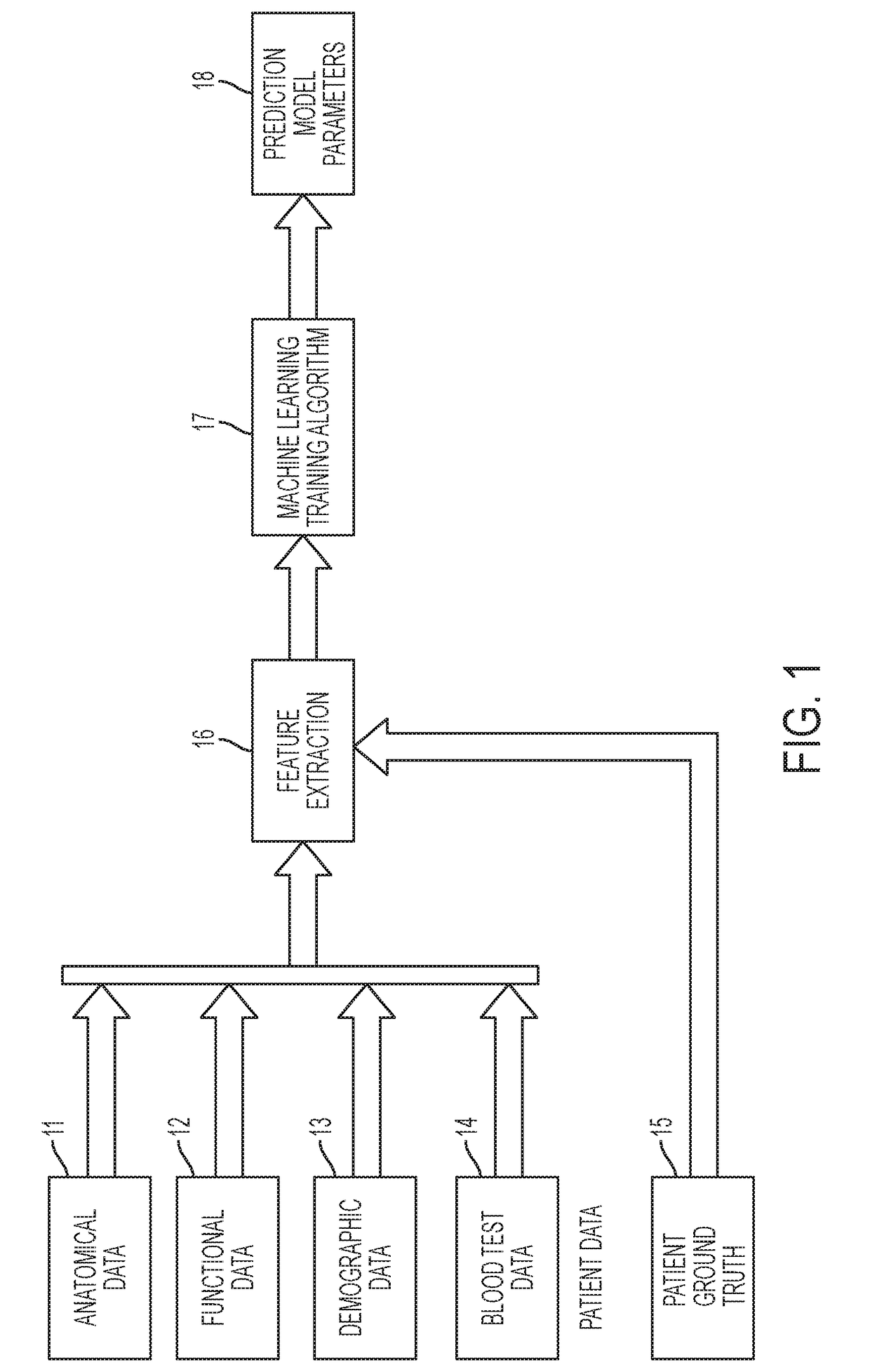
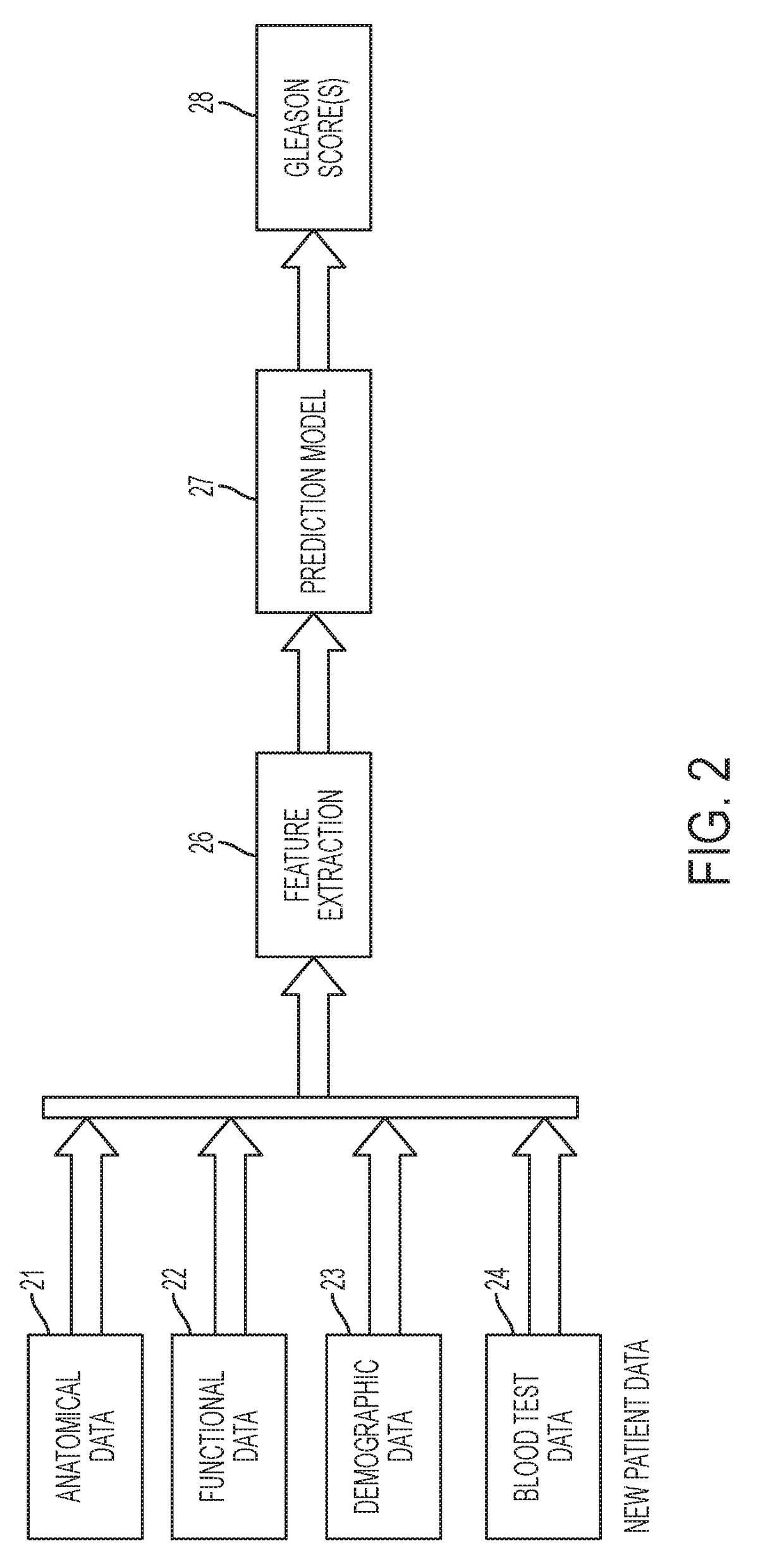
ActiveUS20170116387A1EliminateMortality rate is decreasedImage enhancementImage analysisBlood testPatient demographics
A method for predicting a cancer staging score from medical image data includes receiving patient data for a plurality of patients, where patient data for each of the plurality of patients includes one or more of an image volume of a suspected tumor in an organ, blood test data, demographic data, and ground truth tumor staging scores for the suspected tumor in the organ, extracting features from the patient data, and using the features extracted from the patient data to train a classifier to predict a cancer staging score for a new patient from one or more of an image volume of a suspected tumor in the organ, patient blood test data and patient demographic data of that new patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
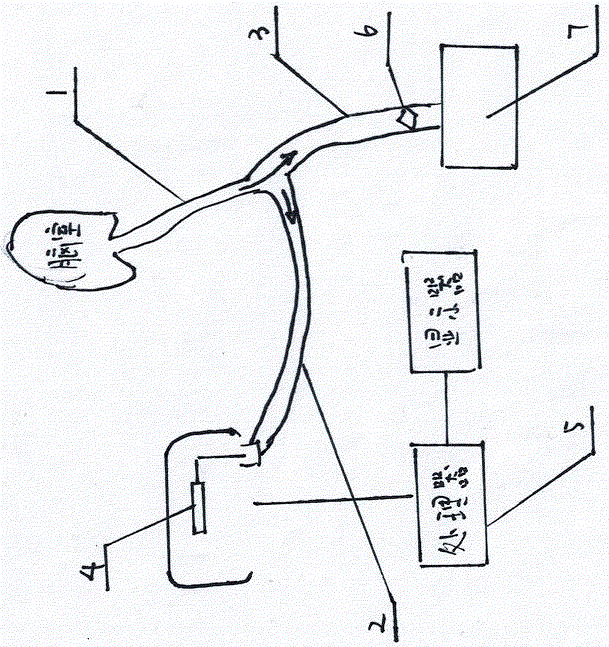
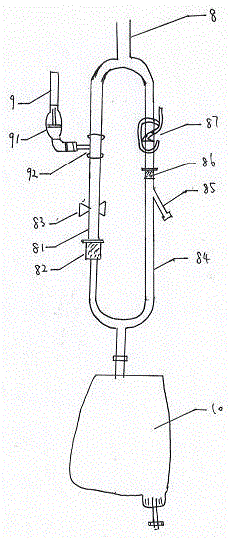
Cerebrospinal fluid drainage device and intracranial pressure monitoring system
InactiveCN105641758AAvoid backflow) phenomenonPrevent backflowWound drainsMedical devicesAirbagControl valves
The invention provides a cerebrospinal fluid drainage device and an intracranial pressure monitoring system. The cerebrospinal fluid drainage device comprises a cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube and a drainage bag used for collecting fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube, a guide tube used for being connected with a pressure sensor is communicated on the cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube, a first control valve is arranged at a position, between the guide tube and the drainage bag, of the cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube, and a buffering airbag is arranged at a position, close to a joint of the guide tube and the cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube, of the guide tube. Through the buffering airbag arranged on the guide tube, cerebrospinal fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube can be effectively avoided being sucked back into the guide tube, so that failing of the pressure sensor caused by the fact that the cerebrospinal fluid flows back to the pressure sensor can be effectively prevented, accuracy of intracranial pressure detected by the pressure sensor is guaranteed, the pressure sensor is prevented from being polluted by the cerebrospinal fluid, and cross infection caused by reuse of the sensor is avoided.
Owner:王学建
Pressure sensing devices
ActiveCN1879555ADirect pressure measurementWound drainsFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsPressure senseEngineering
A pressure sensing catheter having a pressure sensor and an antenna that is coupled to the pressure sensor, e.g., by a connector, are provided. The pressure sensor can be adapted to measure a pressure surrounding the catheter, and the antenna can be adapted to telemetrically communicate the measured pressure to an external device. In an exemplary embodiment, the antenna, pressure sensor, and / or connector are hermetically sealed, e.g., by the catheter and / or a coating, to prevent the antenna, pressure sensor, and connector from coming into contact with fluid, thereby allowing the catheter to be permanently implanted or otherwise used for long term use. Exemplary methods for manufacturing and using pressure sensing catheters are also provided.
Owner:瑞士英特格拉生命科学有限公司
Disposable assembly for drug infusion with pressure sensing for identification of and injection into fluid-filled anatomic spaces
ActiveUS20180064870A1Accurately and reproducibly administerLimit amount of pain and tissue damageAnaesthesiaDrug and medicationsDrugs infusionPressure sense
Owner:MILESTONE SCIENTIFIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com