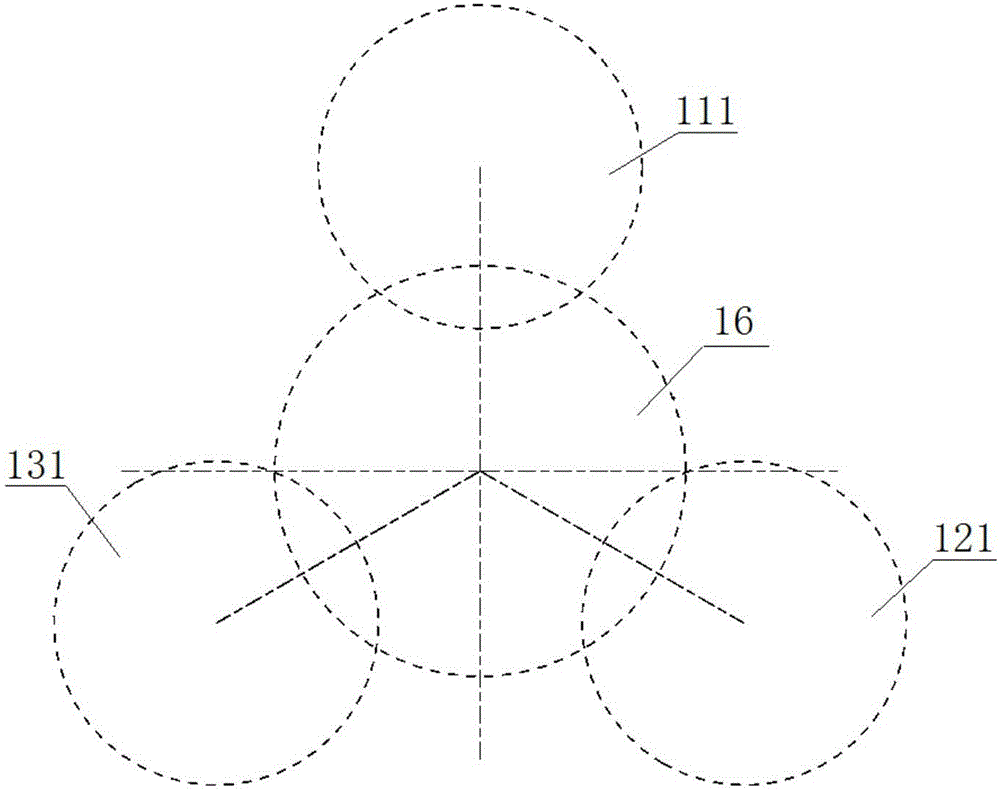Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Good torsional vibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
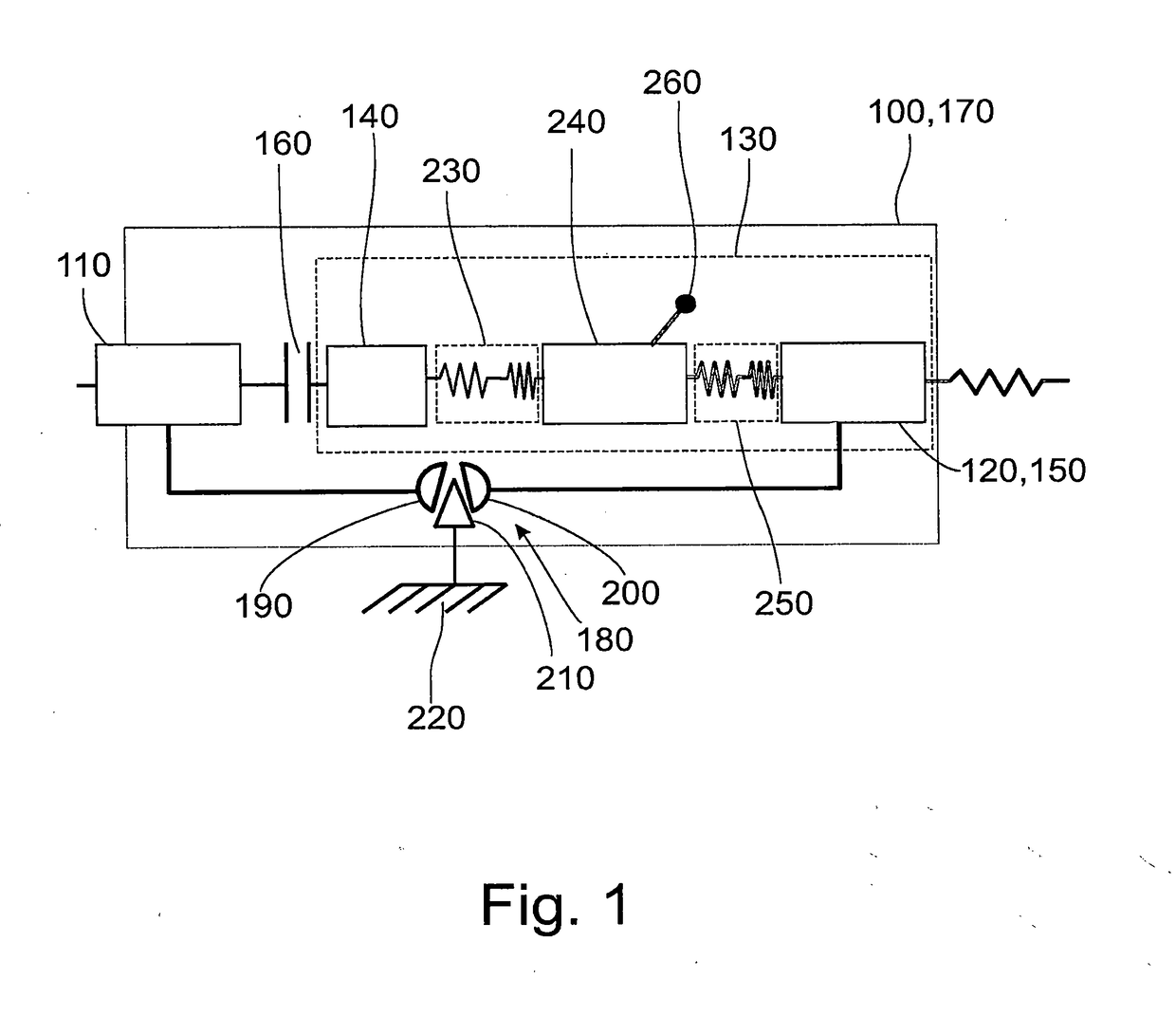
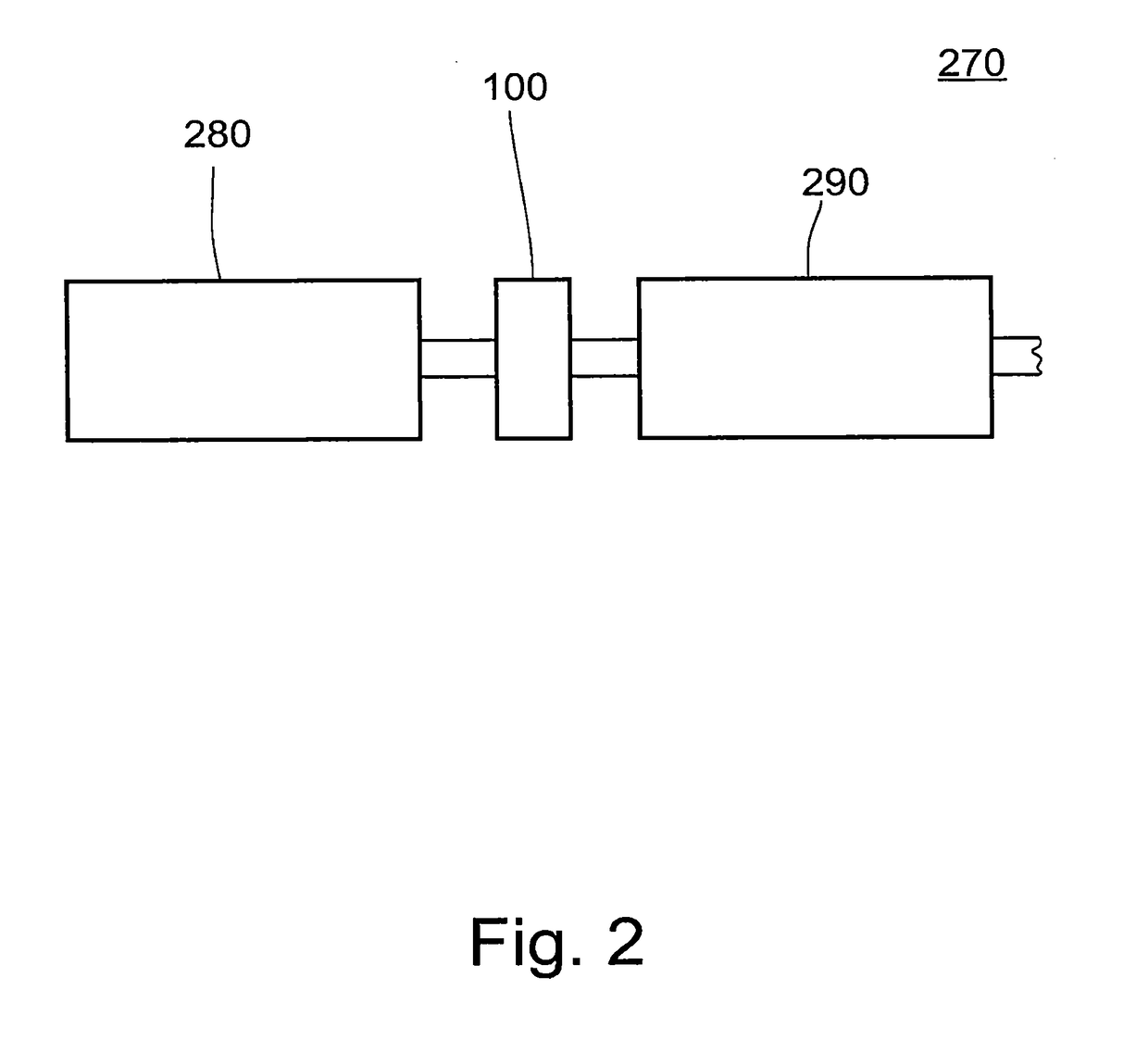
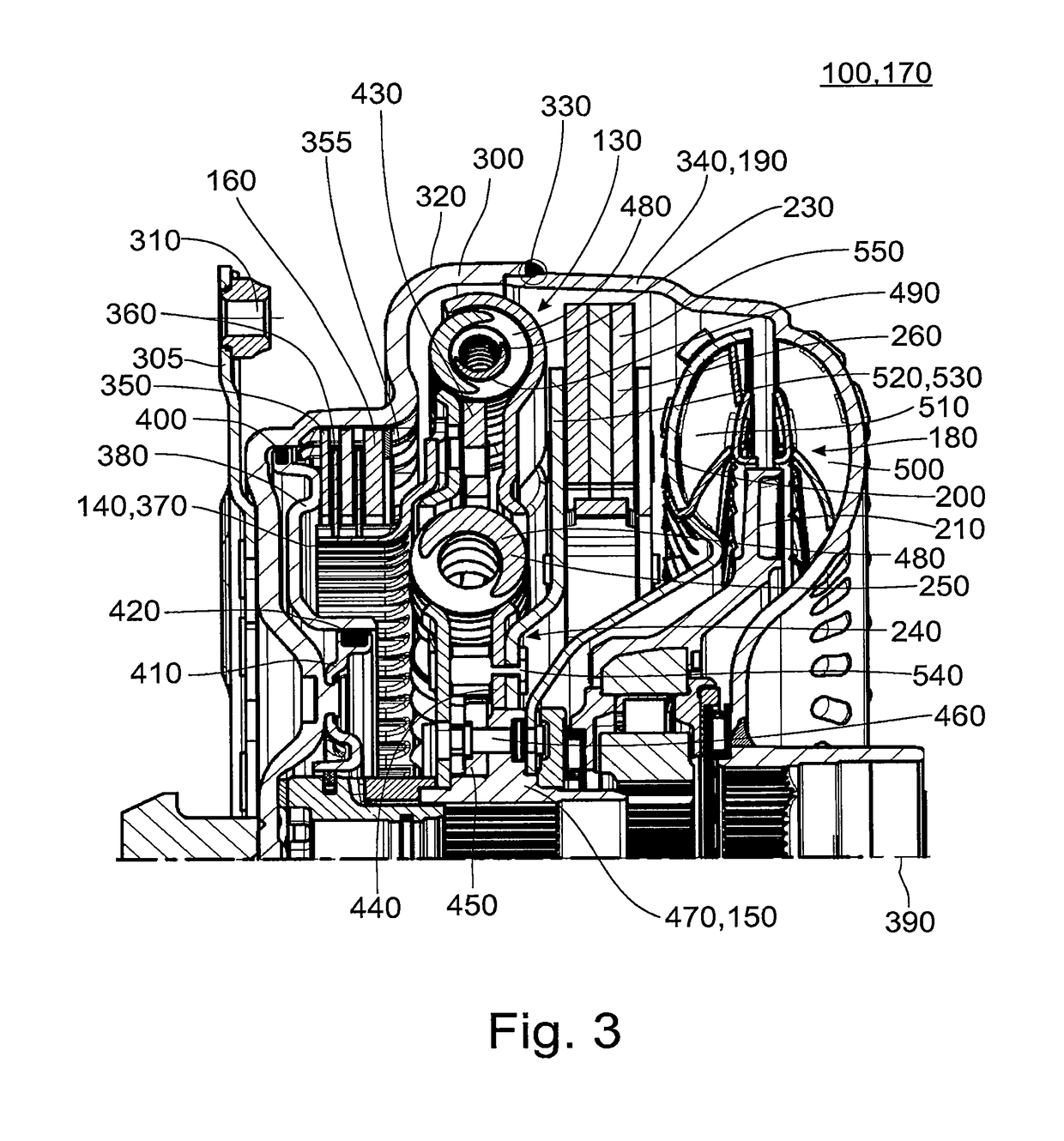
Torque transmission unit
InactiveUS6302253B1Good characteristicOptimize consumptionRotating vibration suppressionPower operated startersTorque transmissionControl theory
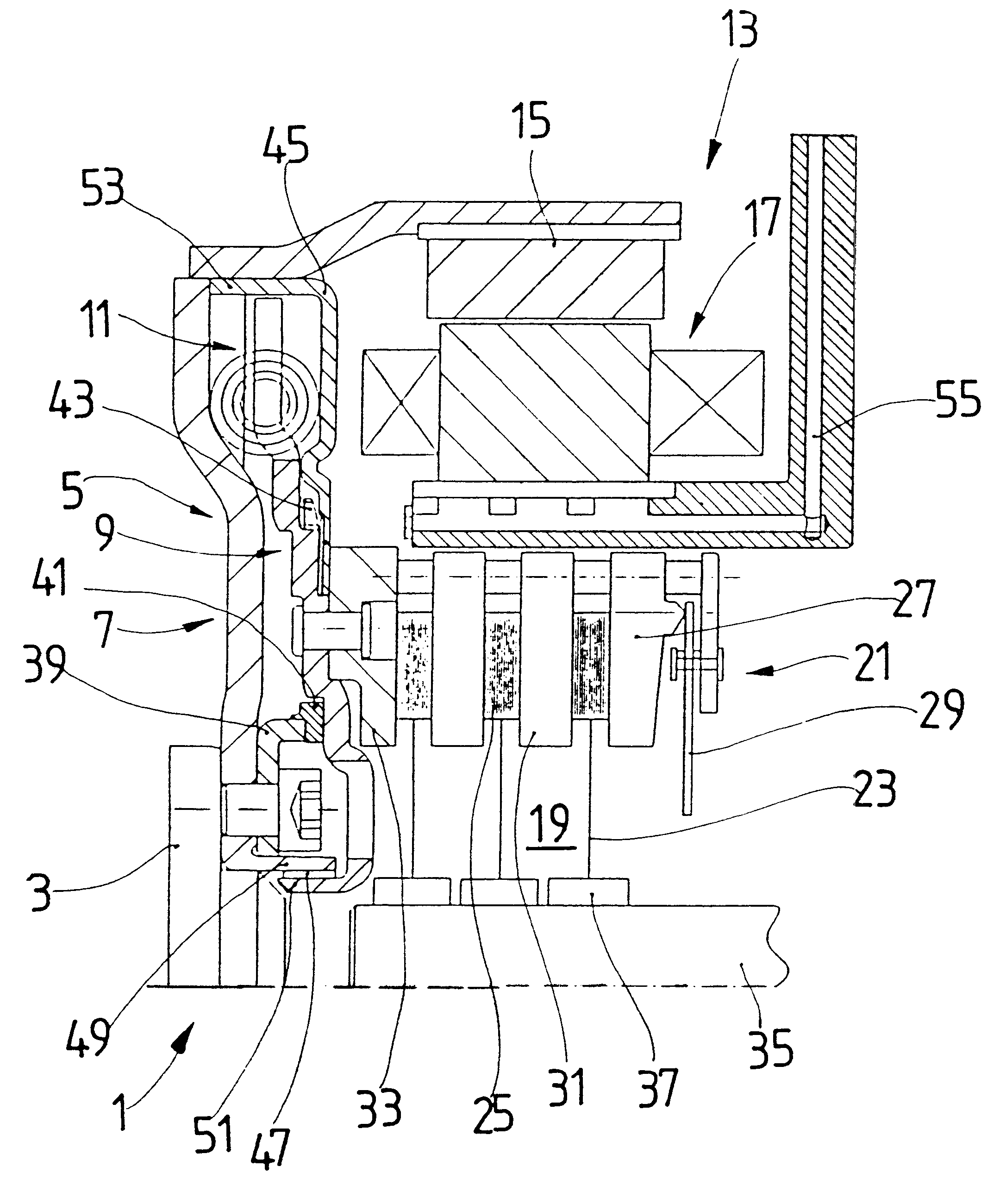
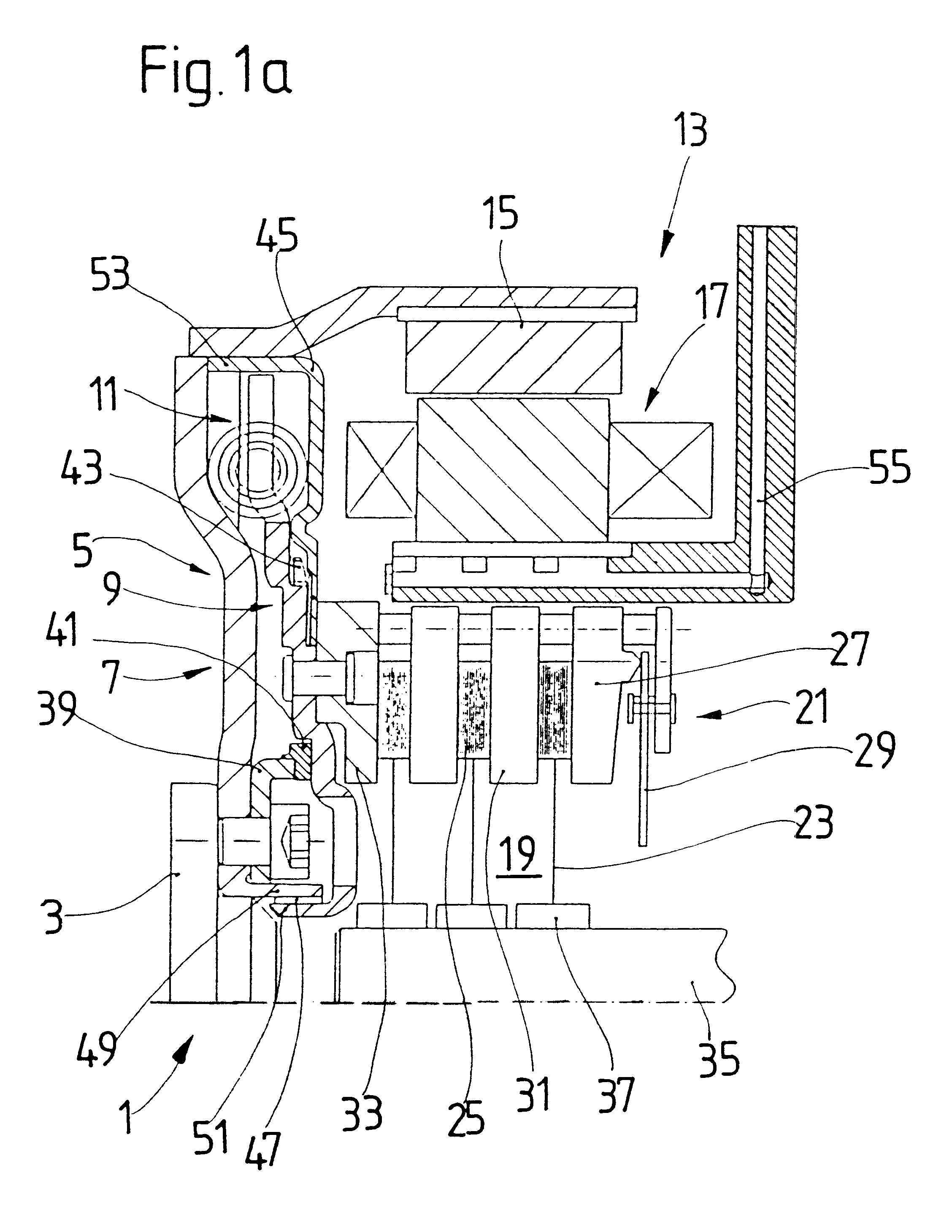
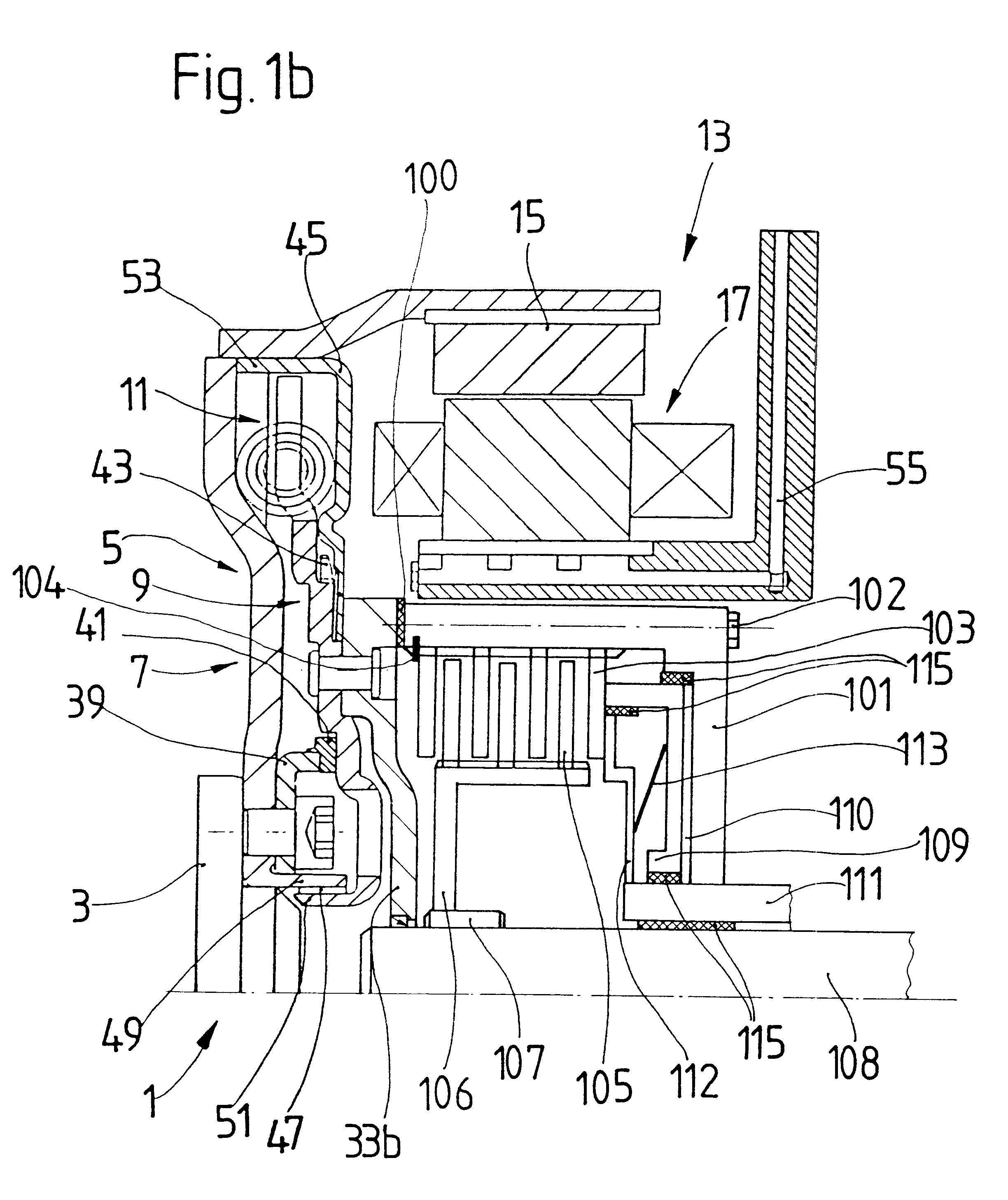
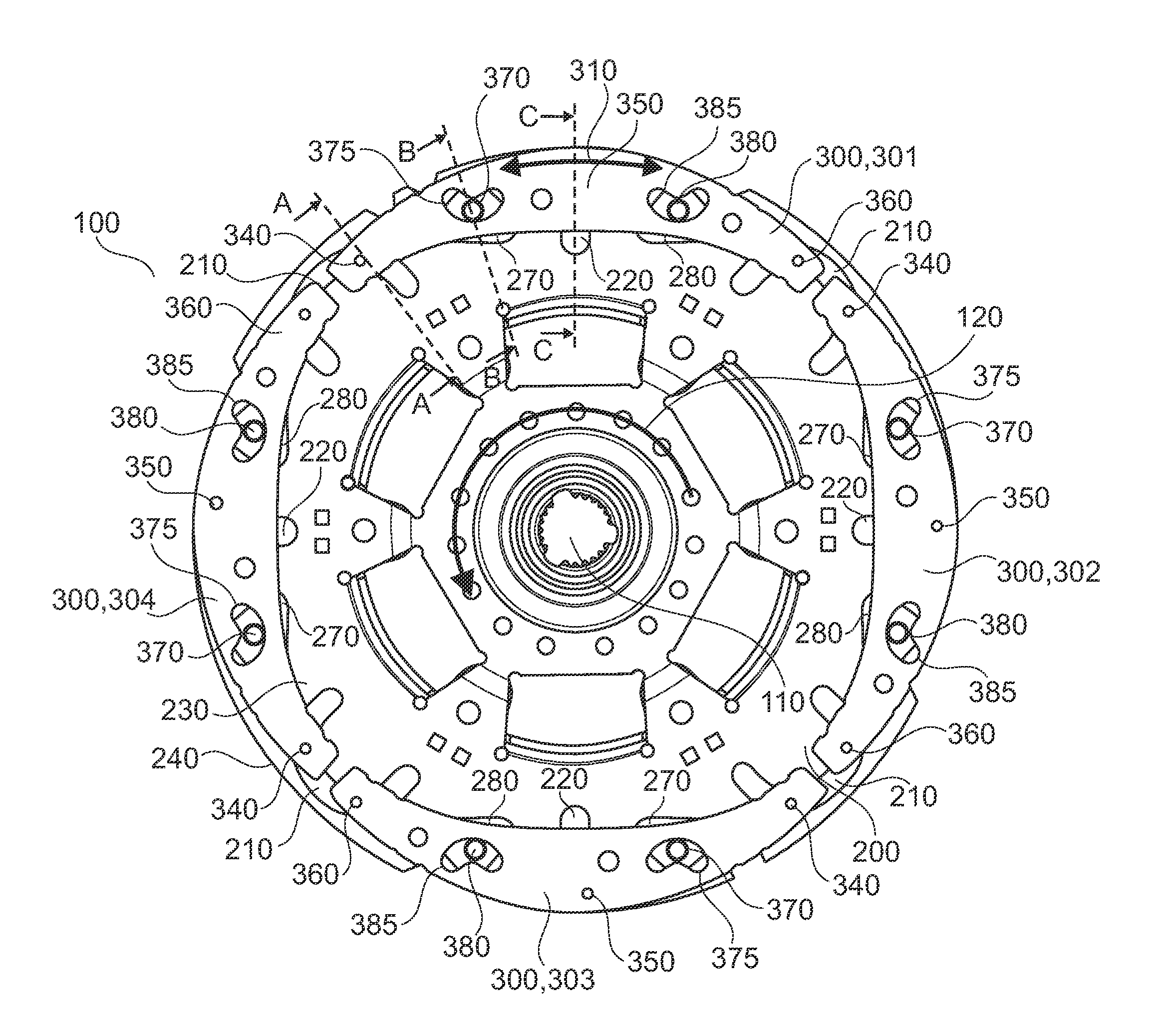
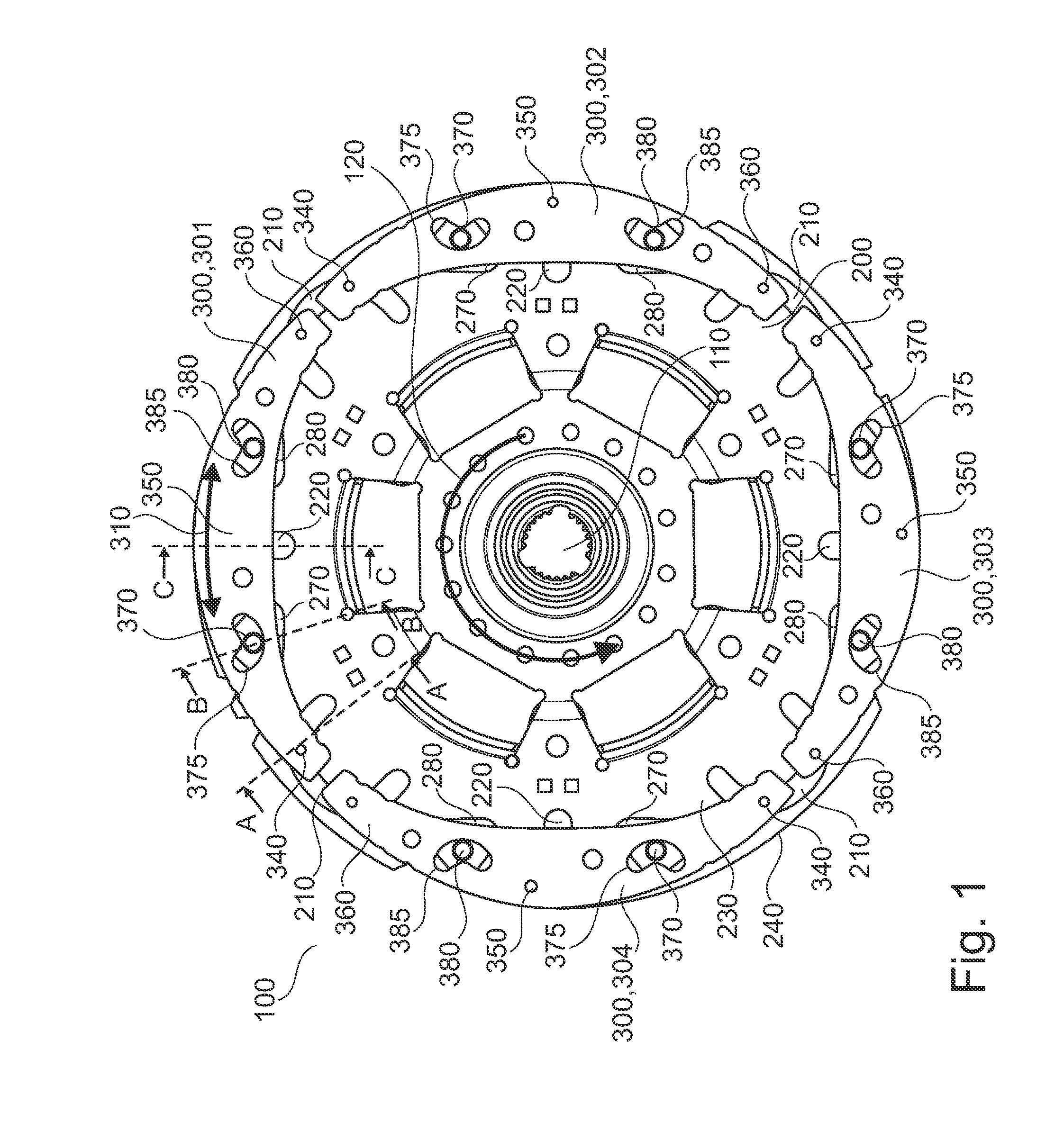
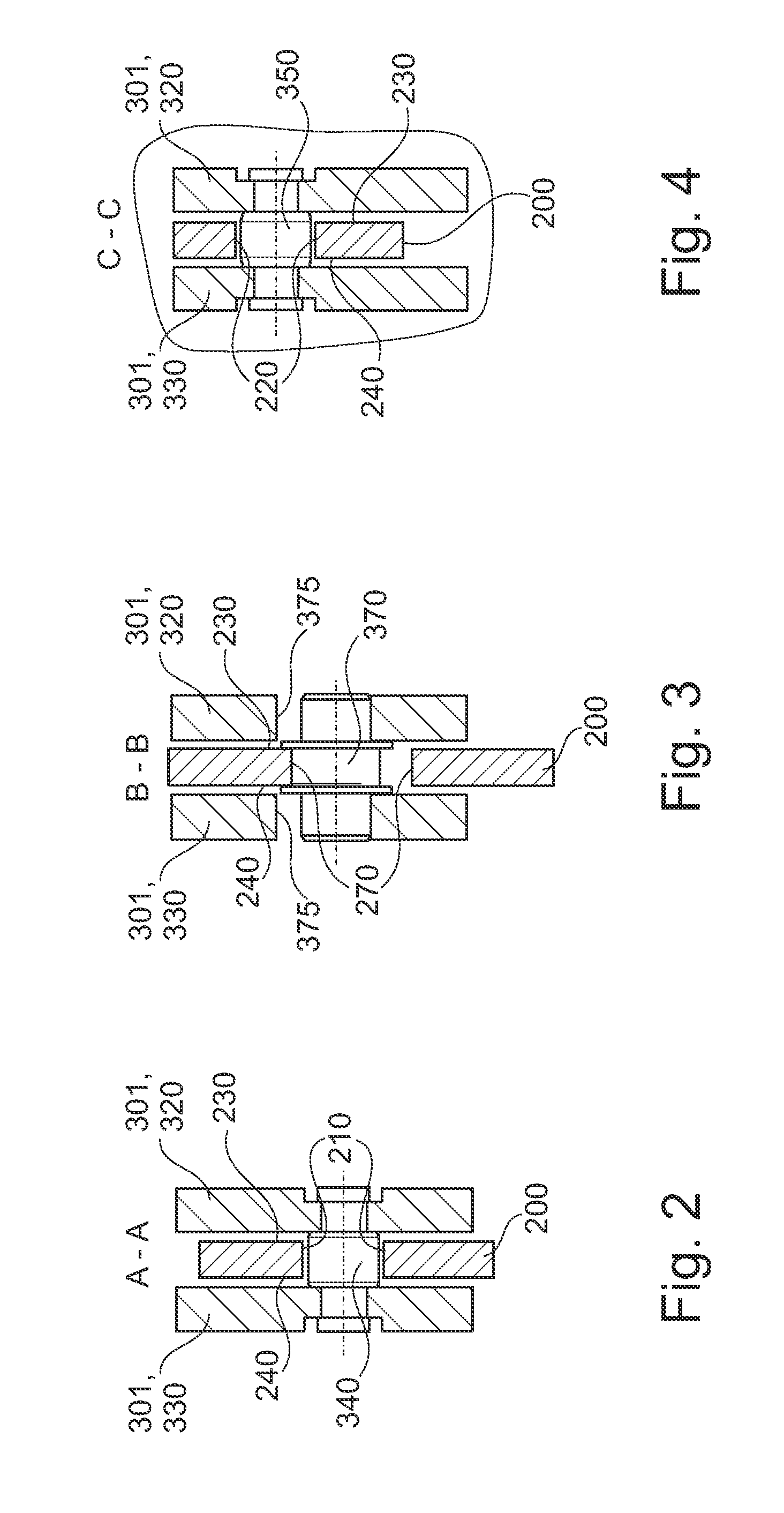
Torque transmission unit includes an input shaft and an output shaft with a torsion damping device functionally arranged between the input shaft and an output shaft. A shift clutch is also operatively arranged between the input shaft and the output shaft for selectively varying the torque transmitted from the input shaft to the output shaft. The torsion damping device has at least a primary mass and a secondary mass, the primary mass being effectively connected to the input shaft and the secondary mass being effectively connected to the output shaft. The torque transmission unit further comprises an electric machine with a stator and a rotor effectively connected to the input shaft. At least one of the shift clutch and the torsion damping device is arranged within an annular space delimited by the rotor and the stator of the electric machine.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Torsional vibration damper
ActiveUS20130233125A1Reduce rolling frictionGood damping propertiesRotating vibration suppressionFlywheelsDrivetrainEngineering
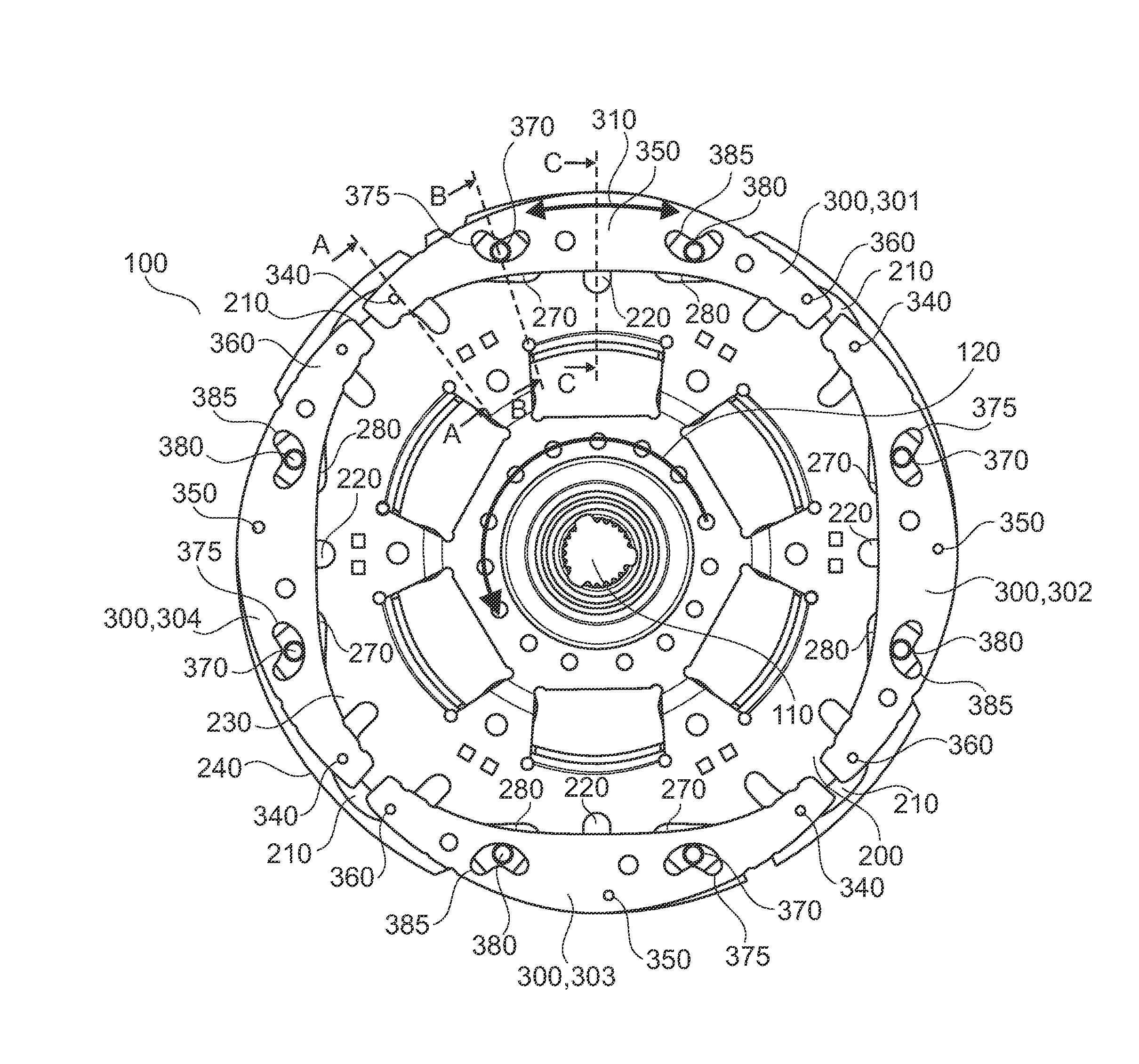
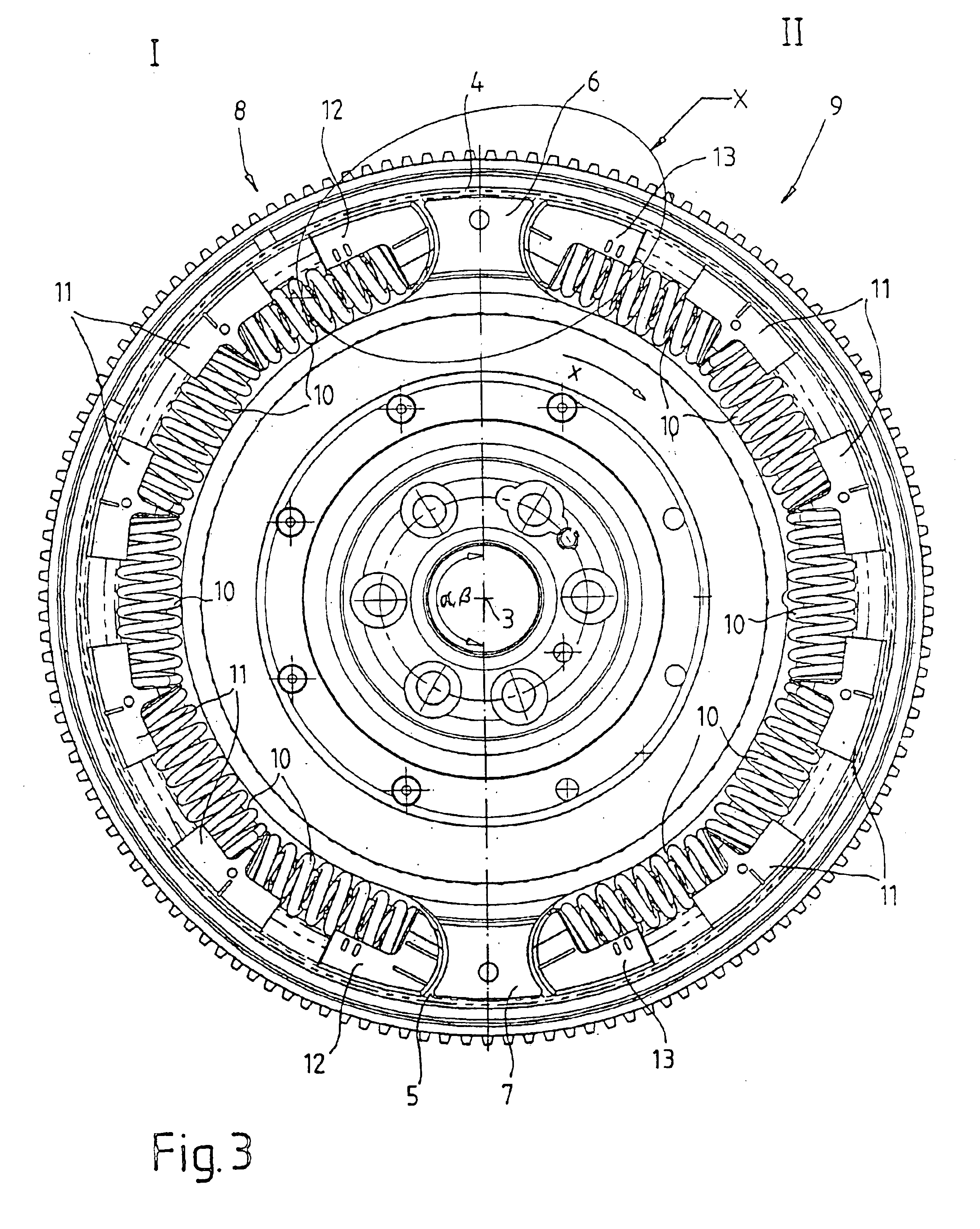
A torsional vibration damper for a drivetrain of a motor vehicle having a substantially discoidal centrifugal flange and a plurality of centrifugal pendulum-type absorbers. Each centrifugal pendulum-type absorber includes a first pendulum mass and a second pendulum mass. The first pendulum mass is arranged above a first surface of the pendulum flange, and the second pendulum mass is arranged above a second surface of the pendulum flange. The first pendulum mass and the second pendulum mass are firmly connected to each other by means of at least two spacing bolts in each case. The pendulum flange has a plurality of cutouts in which the spacing bolts are guided. A second spacing bolt of a first centrifugal pendulum-type absorber and a first spacing bolt of a second centrifugal pendulum-type absorber are guided in at least one first cutout.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Vehicle torsional vibration control method, device and system
InactiveCN106143209AGood torsional vibrationSuppression of torsional vibrationSpeed controllerElectric energy managementElectric vehicleTransmission system
The invention discloses a vehicle torsional vibration control method, device and system. The method comprises the steps of receiving a torque signal emitted by a vehicle controller, detecting the current actual rotating speed of a vehicle and extracting a torsional vibration component of the vehicle, calculating a compensation torque signal with phase opposite to that of the torque signal according to the torsional vibration component, and conducting compensation on the torque signal according to the compensation torque signal. By the adoption of the vehicle torsional vibration control method, device and system, torsional vibration of transmission systems of electric vehicles can be reduced, and vehicle driving smoothness can be improved.
Owner:SAIC MOTOR
Spring seat and damper disk assembly
ActiveUS20080237950A1Increase stiffnessGood torsional vibrationMachine framesLiquid springsCoil springEngineering
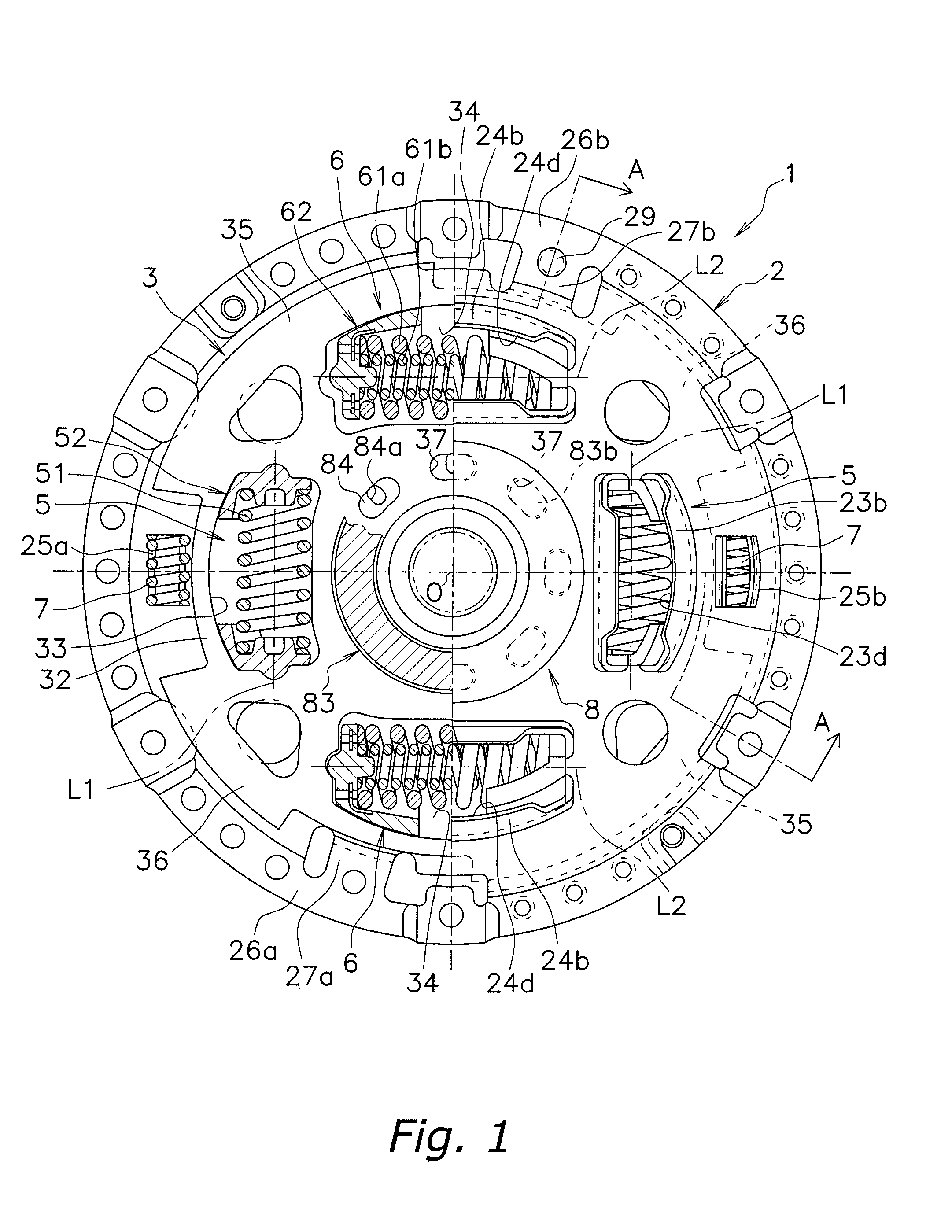
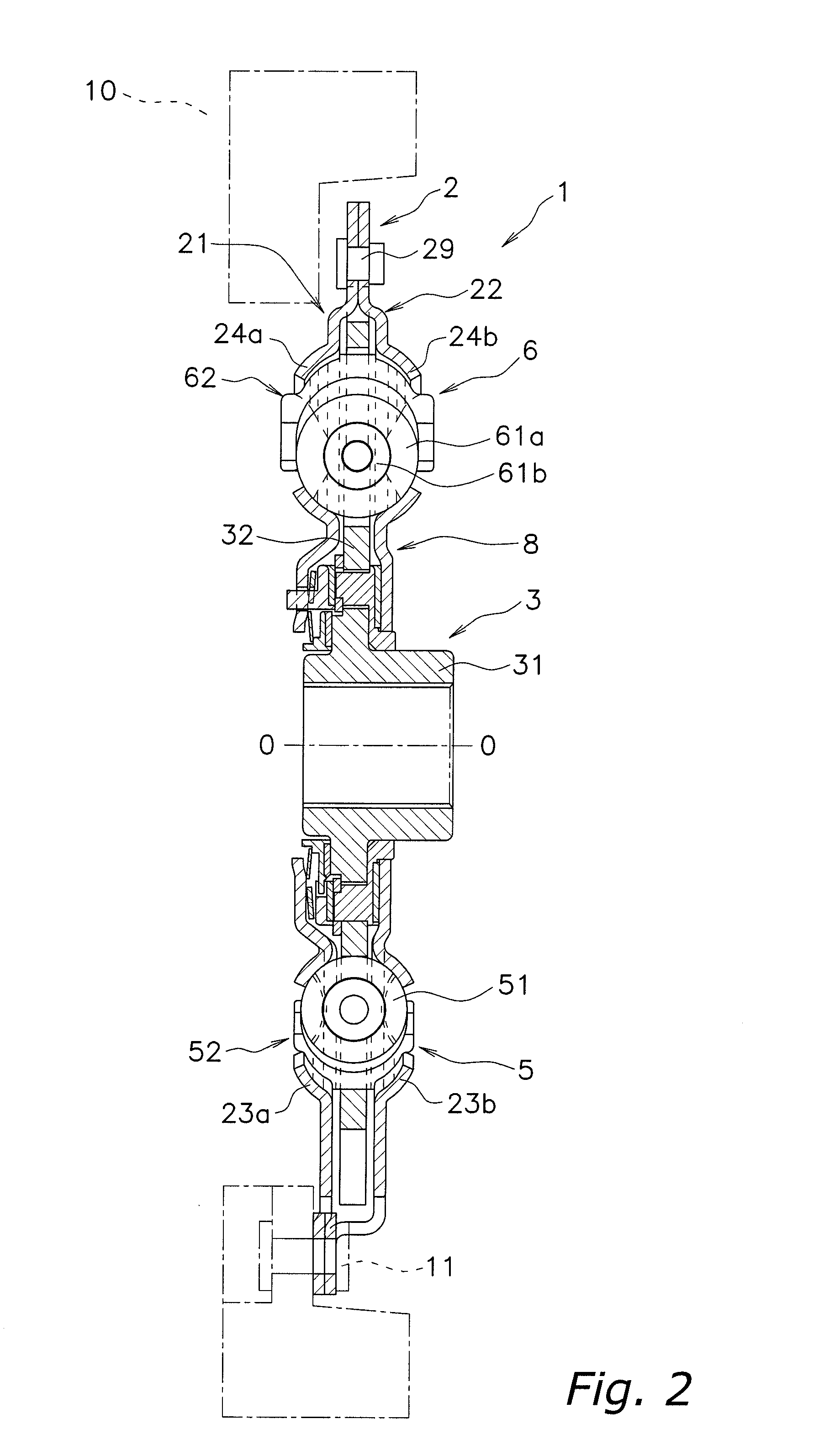
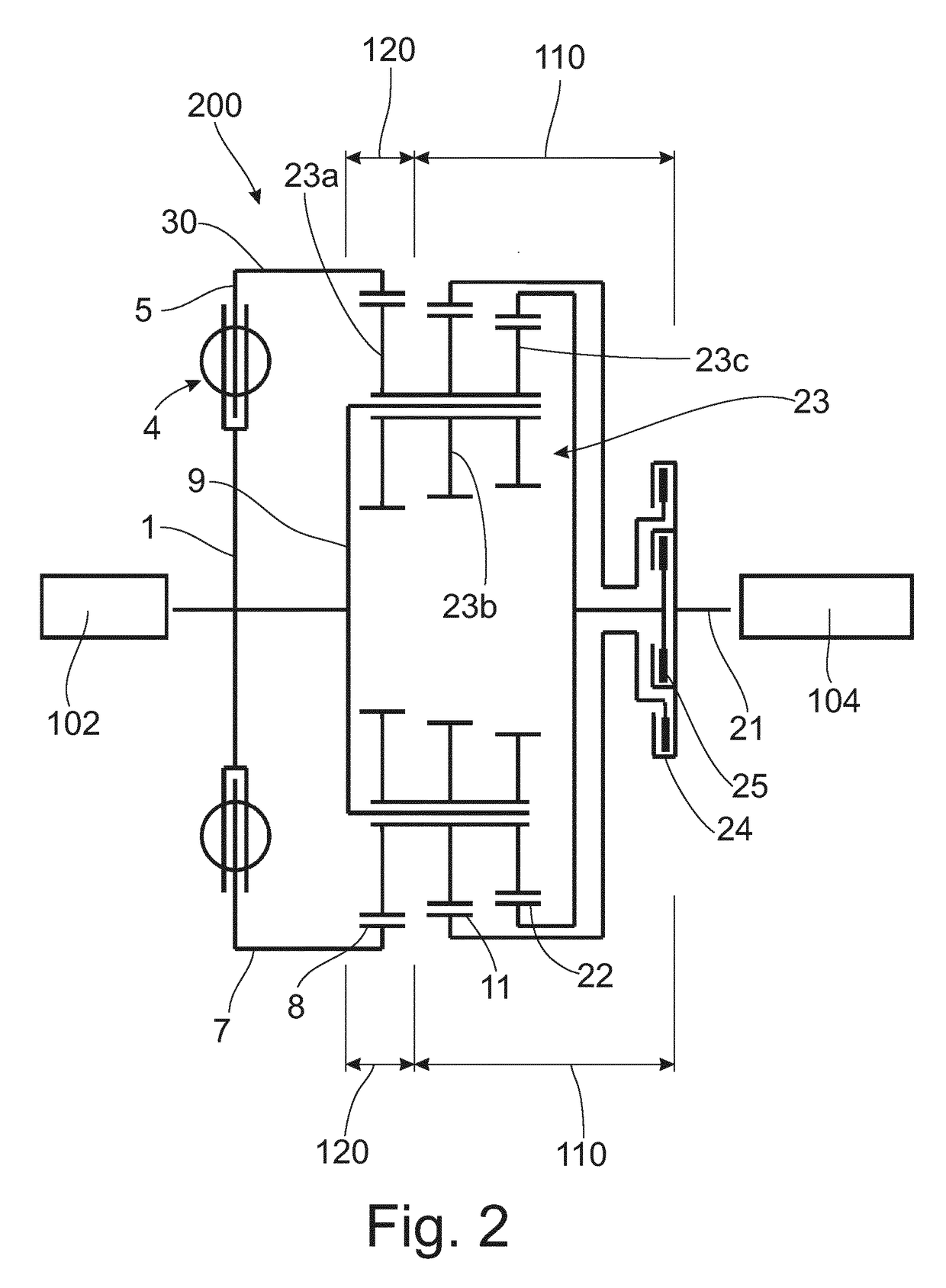
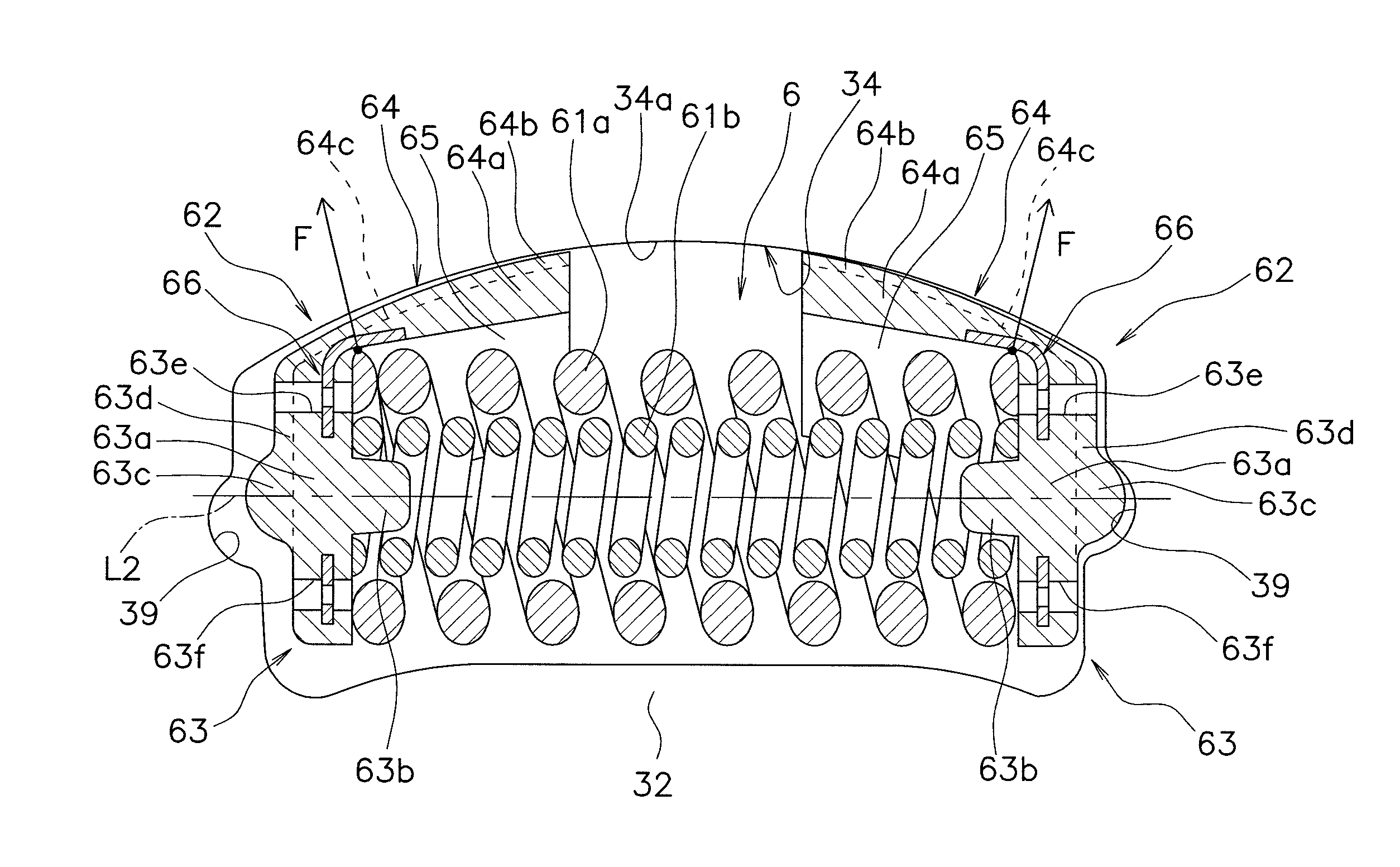
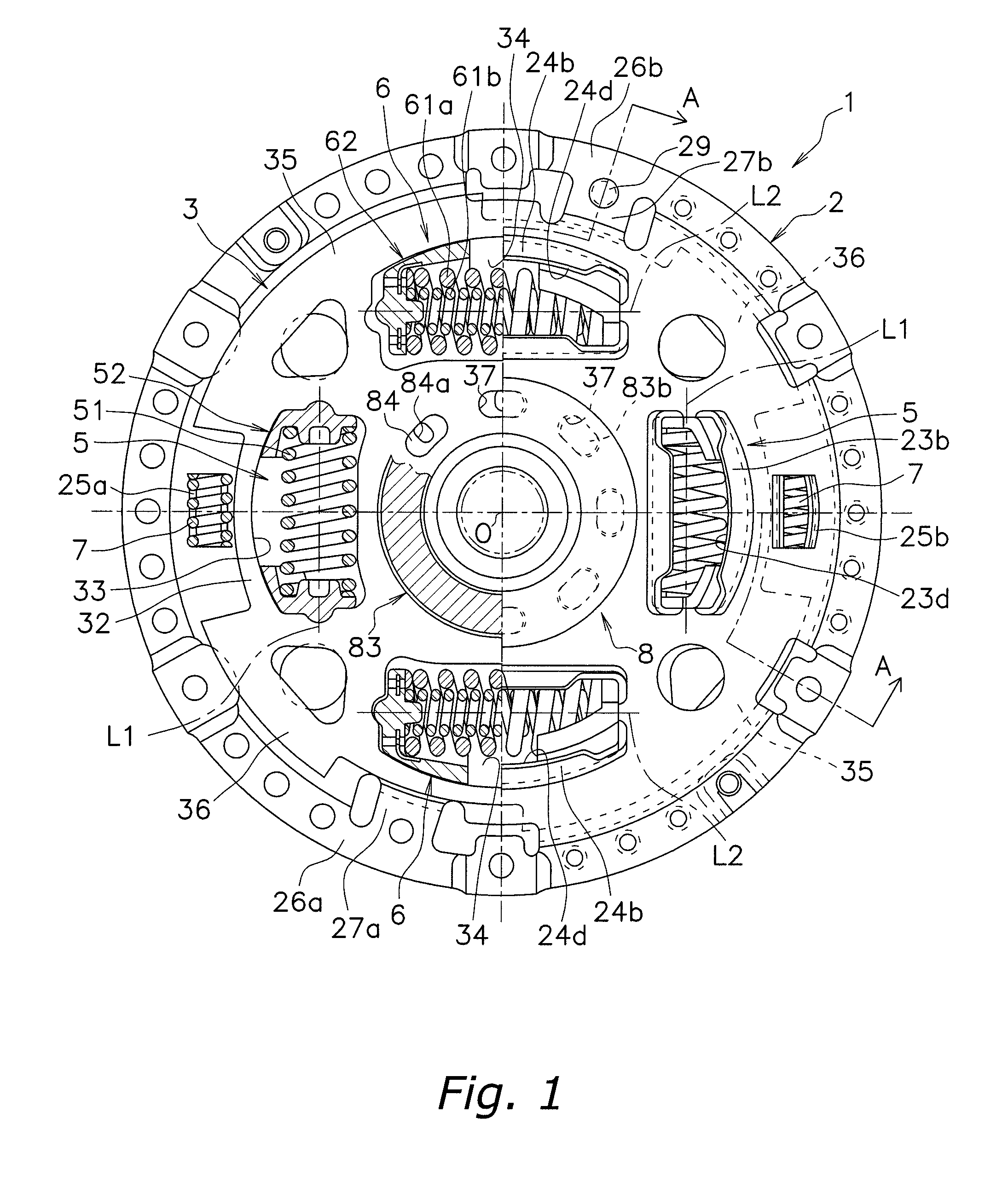
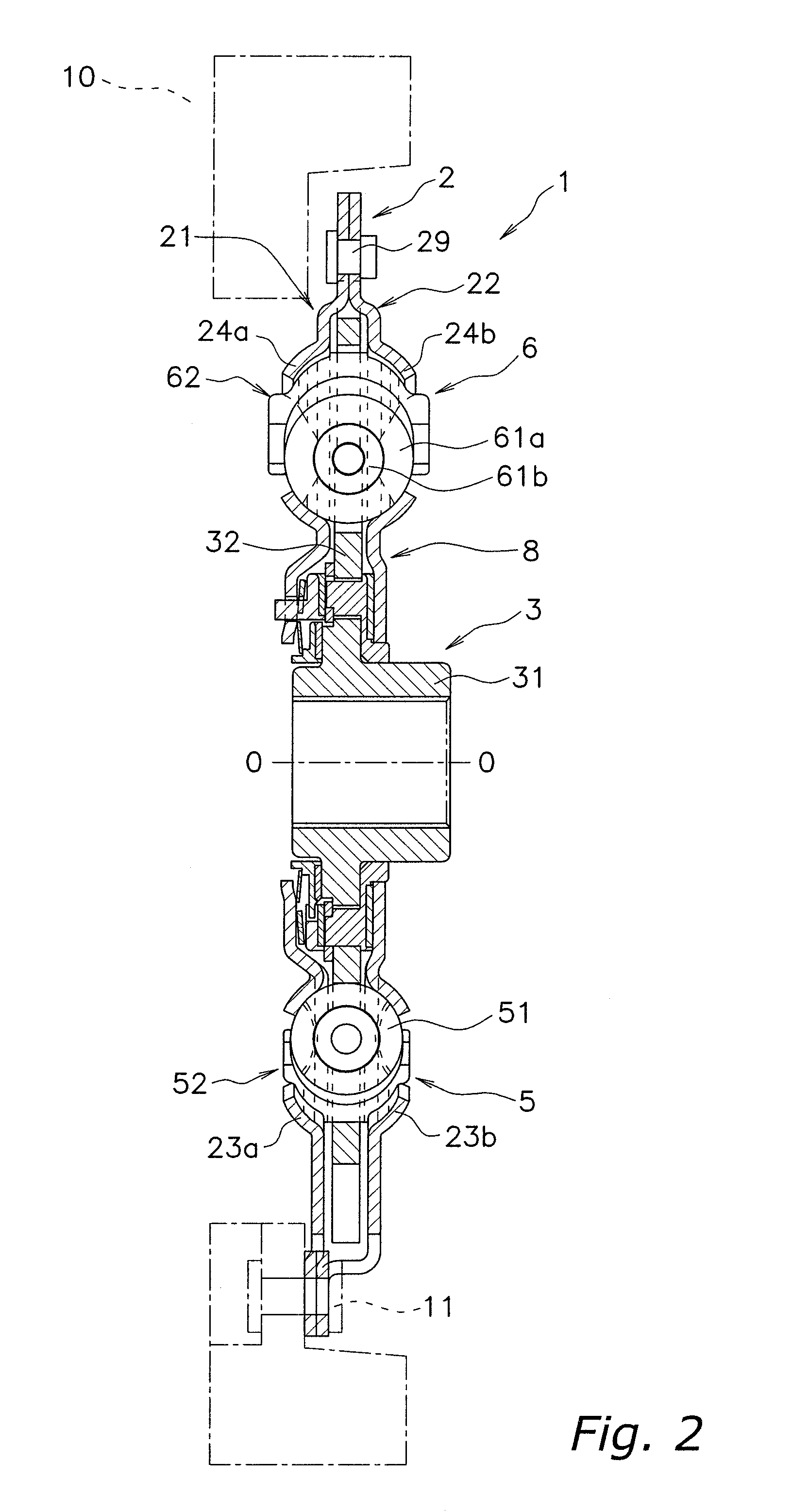
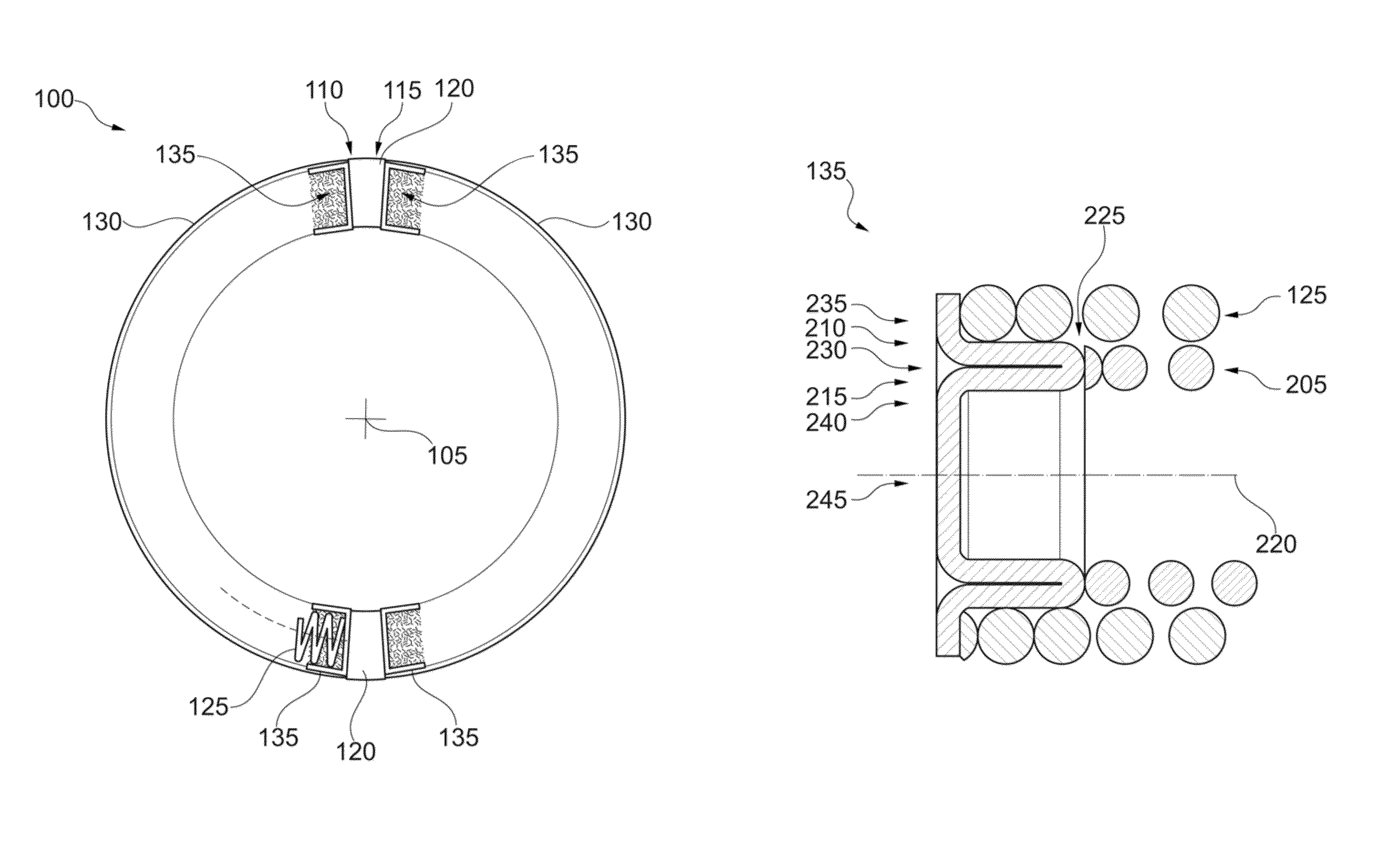
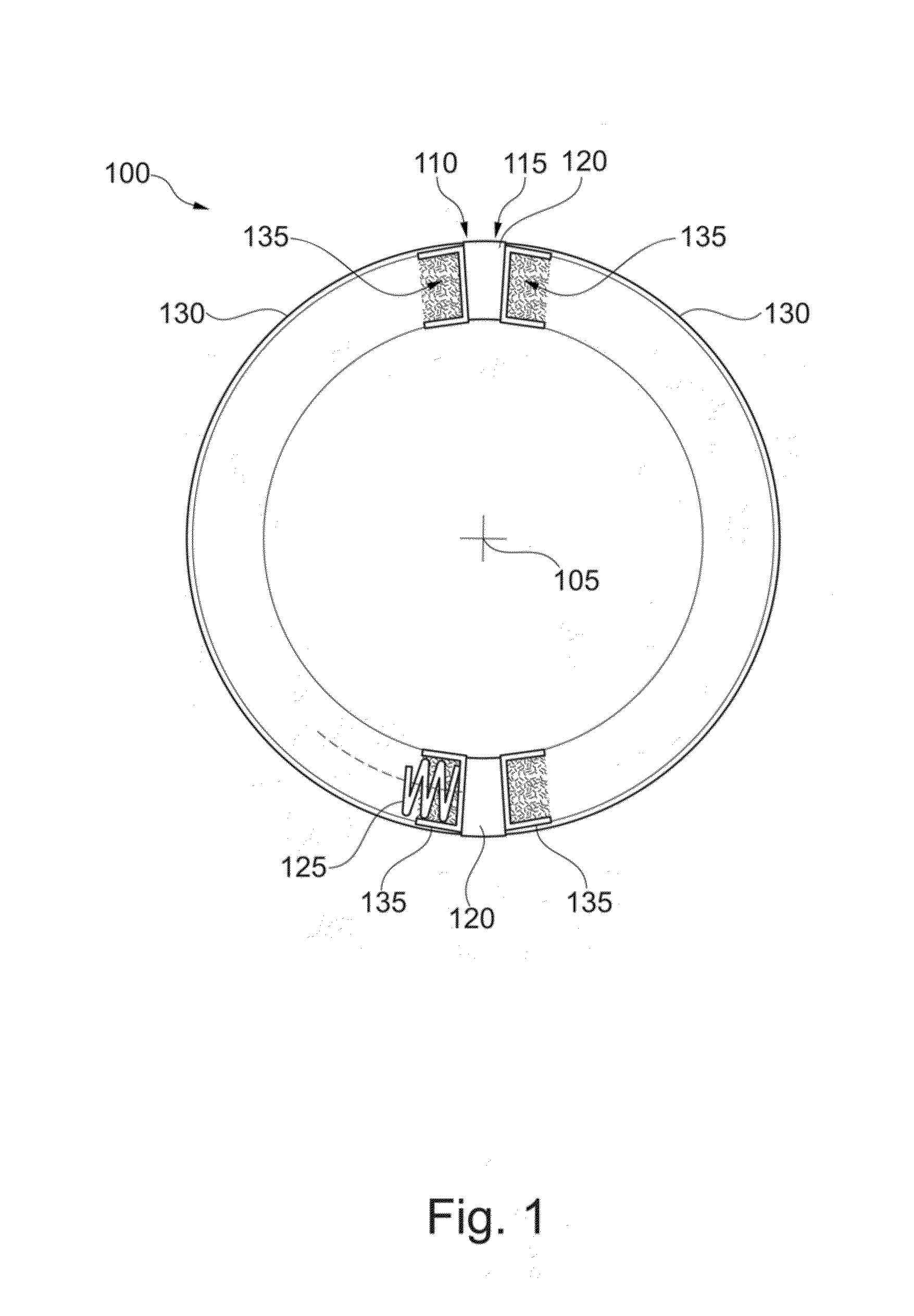
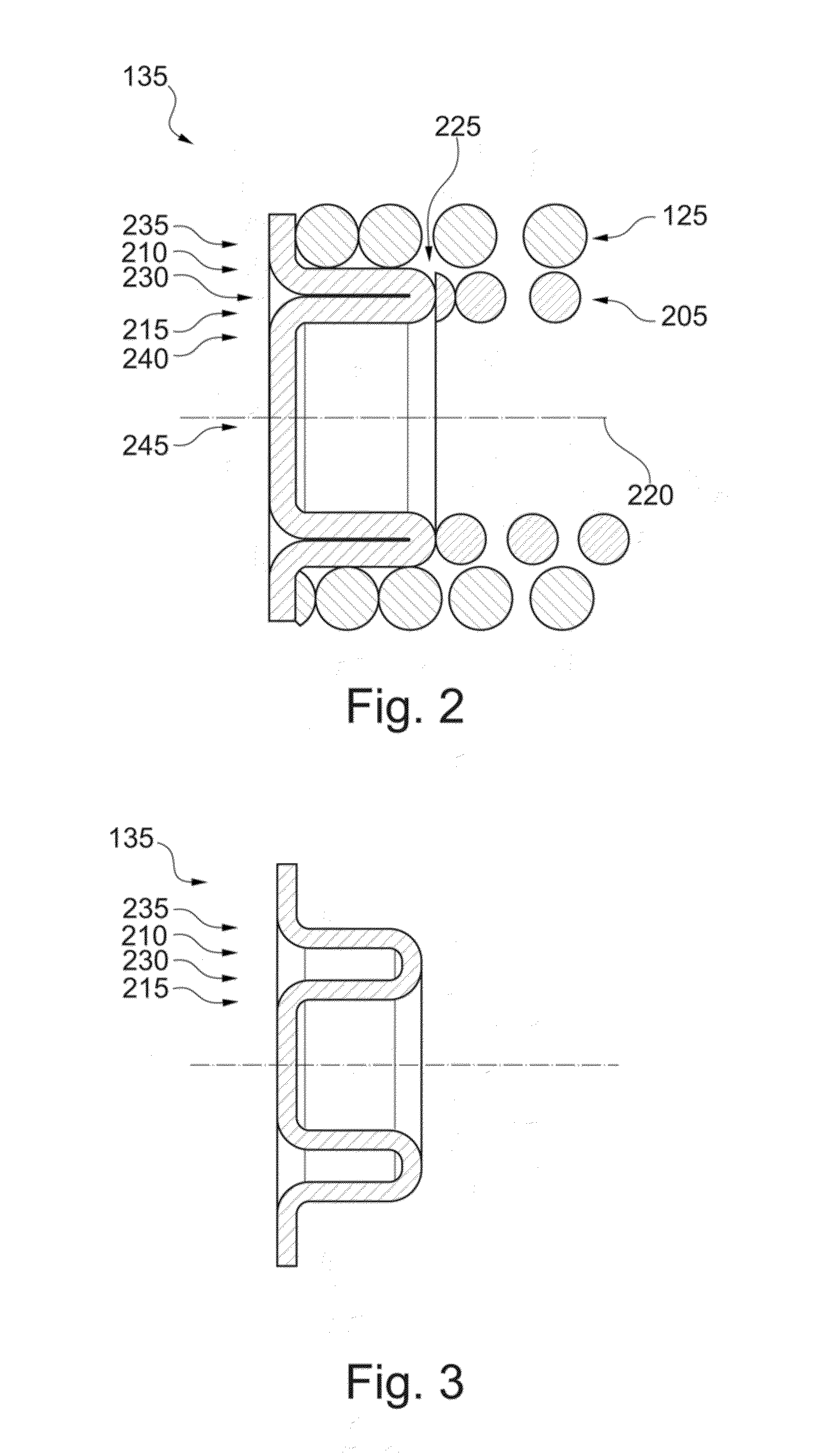
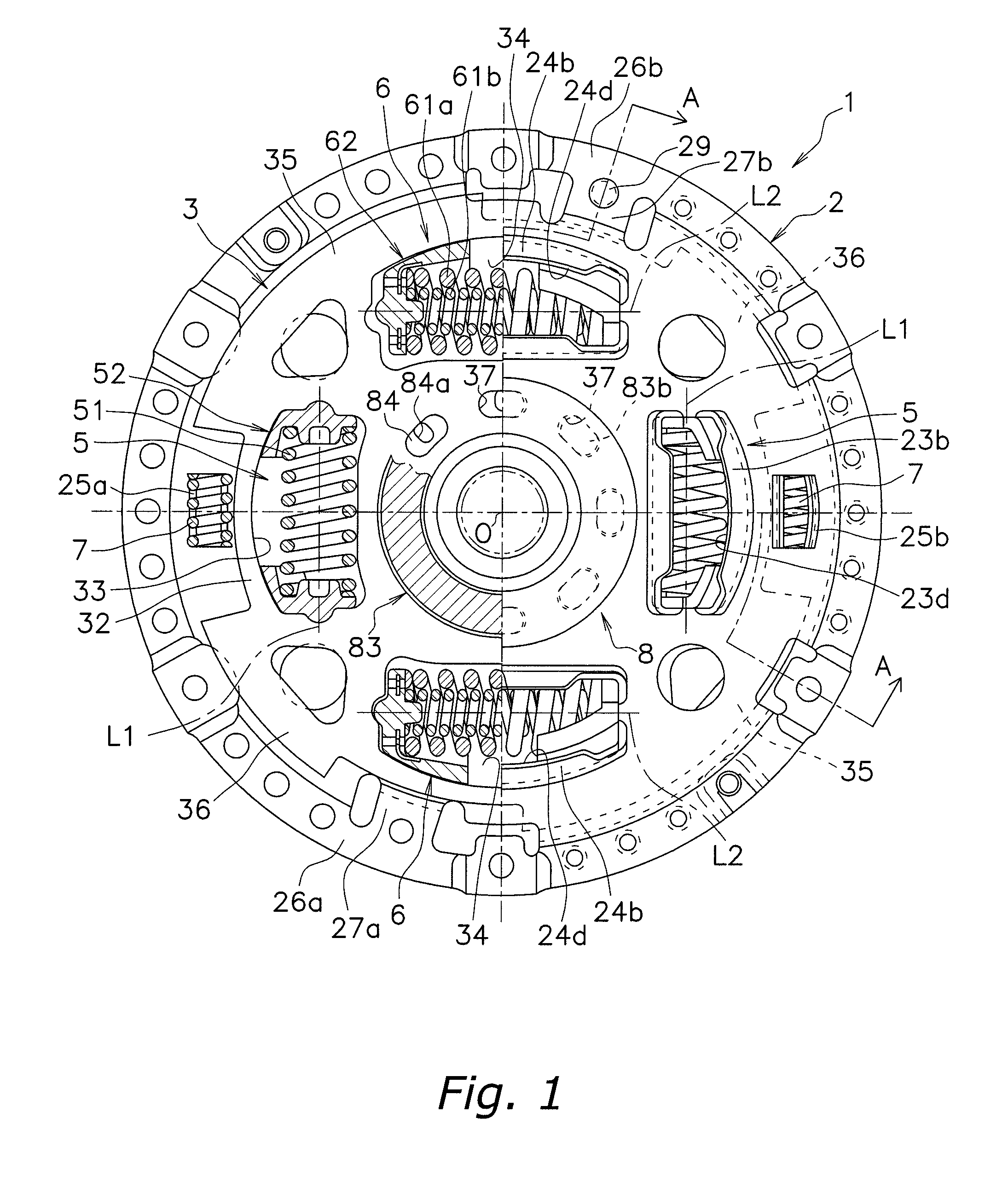
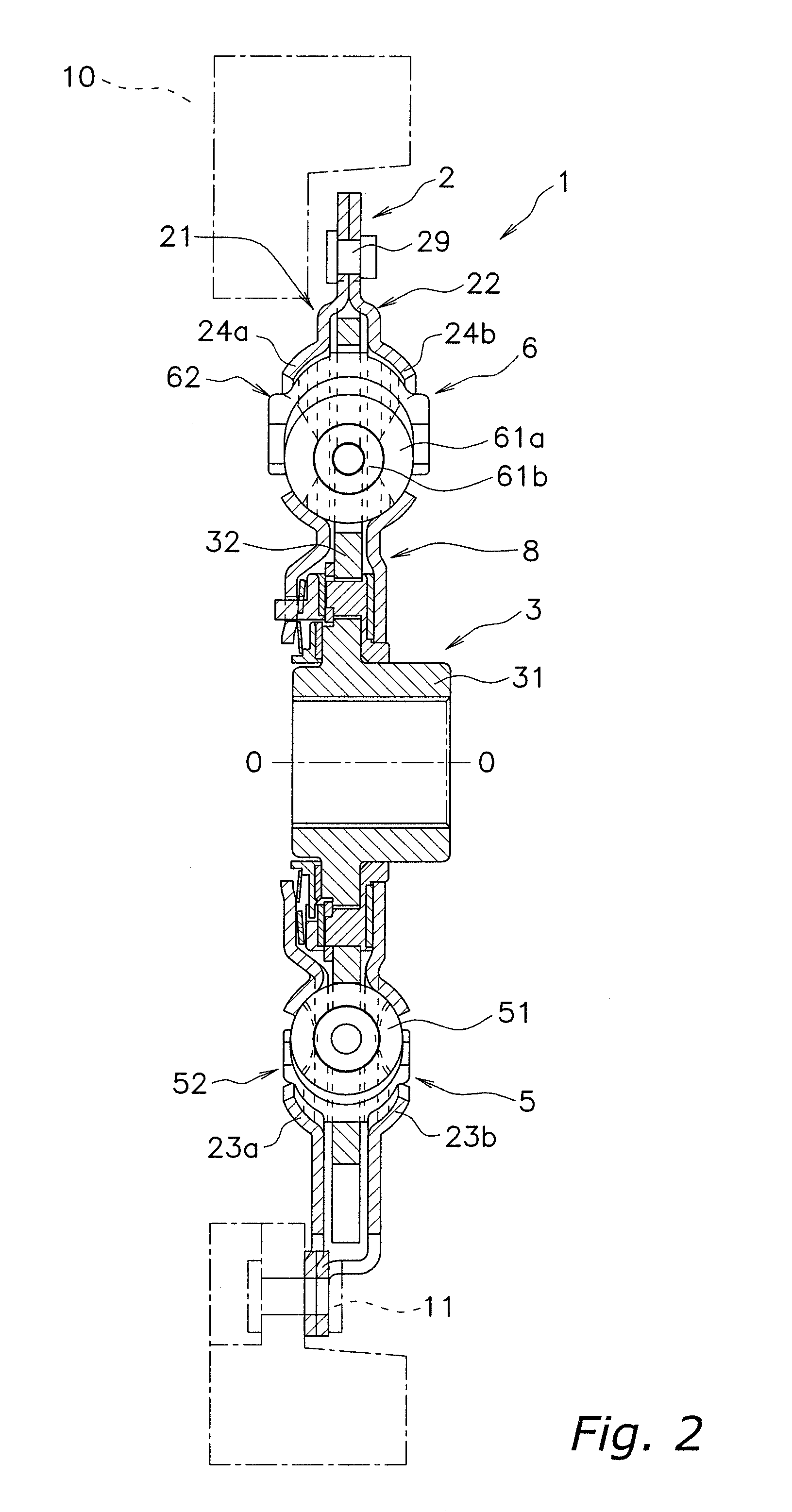
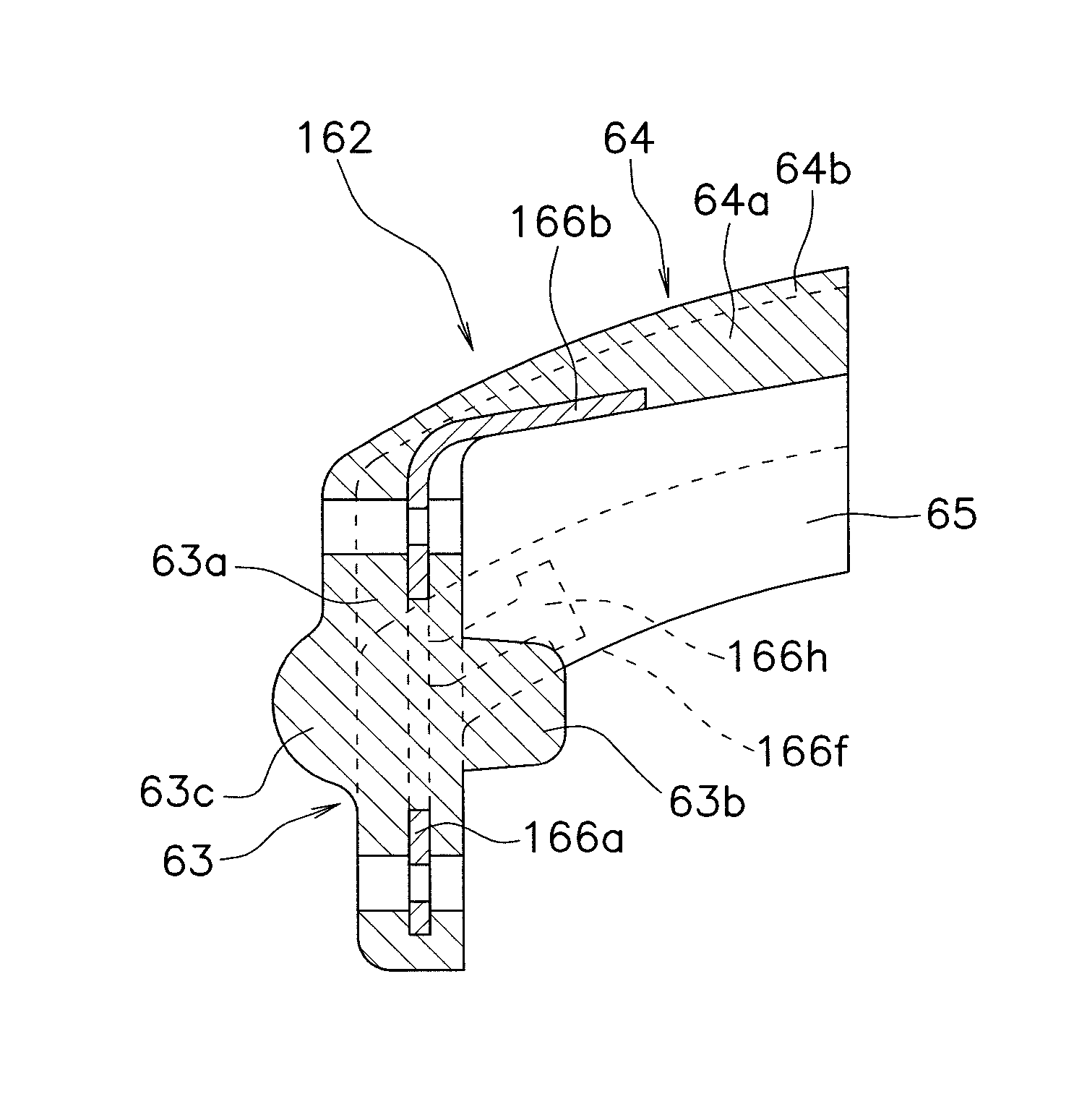
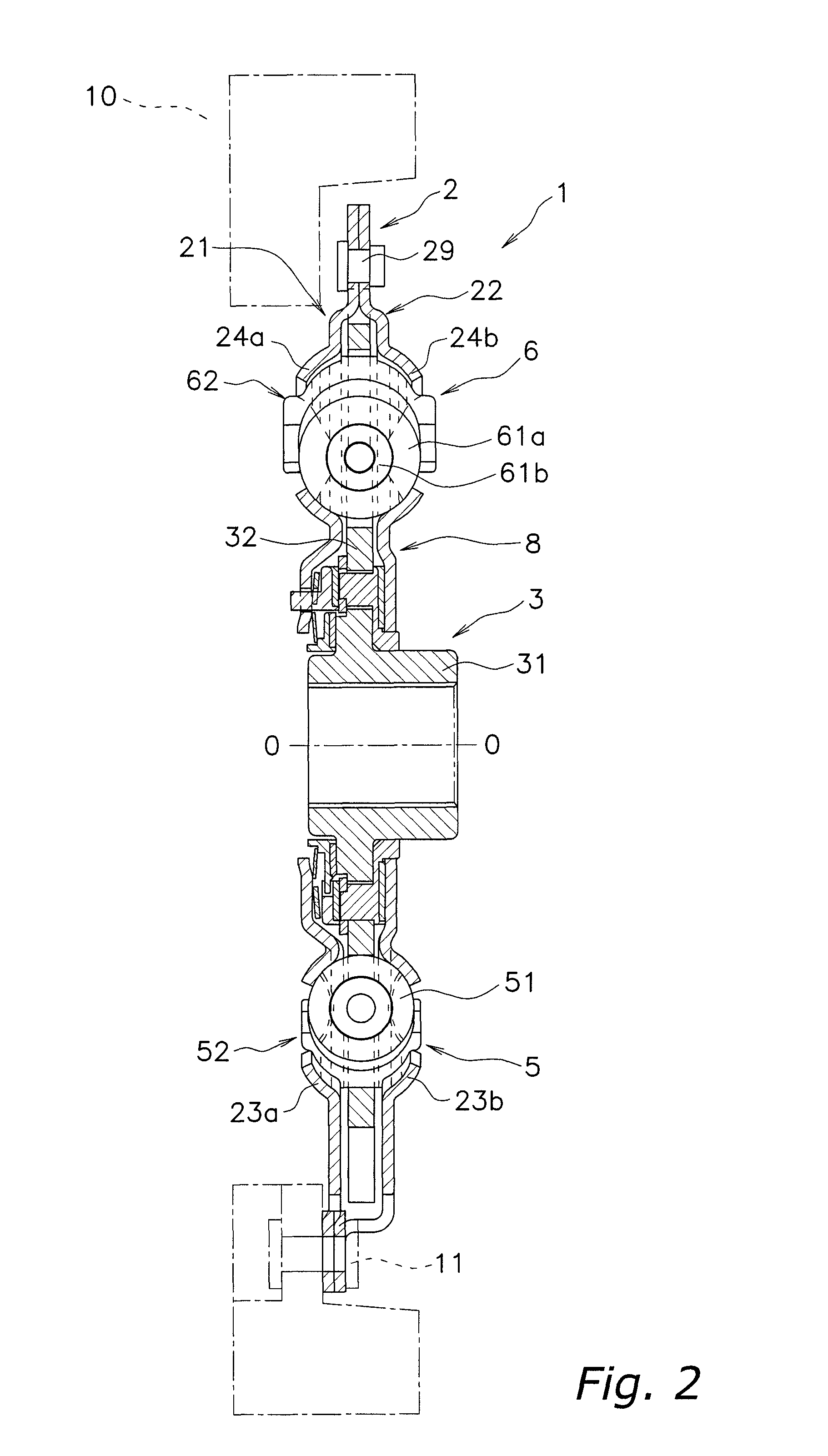
Second spring seats 62 each have a first support component 63, a second support component 64, and a reinforcing plate 66. The first support component 63 supports the ends of second coil spring 61a in the rotational direction. The second support component 64 extends in the rotational direction from the first support component 63 and supports the end of the second spring 61a in the radial direction. At least part of the reinforcing plate 66 is embedded in at least one of the first and second support components 63 and 64. The reinforcing plate 66 directly or indirectly supports the end of the second spring 61a along with the first and second support components 63 and 64.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
Torsional vibration damper, especially a dual-mass flywheel
InactiveUS6962533B2Easy to useGood torsional vibrationClutchesYielding couplingRotational axisEngineering
Owner:ZF SACHS AG
Tuned massed damper device
ActiveCN107060125AImproved torsional and bending vibration characteristicsReduce impact damageProtective buildings/sheltersShock proofingFlexural vibrationTuned mass damper
The invention belongs to the field of tuned massed dampers, and specifically is a tuned massed damper device. The tuned massed damper device comprises a mounting frame, a damping system, a horizontal sliding system and a vertical swinging system, wherein the damping system and the horizontal sliding system are arranged in the mounting frame, and the vertical swinging system is suspended below the horizontal sliding system; the horizontal sliding system comprises a first mass block, and the first mass block is mounted on the mounting frame in a mode that the mass block can move in the length direction of the mounting frame; the damping system comprises two dampers, the two dampers are arranged at the two sides, in the length direction of the mounting frame, of the first mass block symmetrically and correspondingly, one end of each damper is connected to the first mass block, and the other end of each mass block is connected to the corresponding edge, in the width direction, of the mounting frame; and the vertical swinging system comprises a second mass block, and the second mass block is mounted below the first mass block in an extensible swinging mode. According to the tuned massed damper device, the purposes that torsional vibration and flexural vibration of a power transmission tower are controlled simultaneously and wind-vibration of the power transmission tower in every direction is reduced can be achieved simultaneously.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Lightweight design method of high-torsional-rigidity drive shaft
ActiveCN103807281AImprove comfortIncreased torsional stiffnessYielding couplingShaftsDrive shaftTorsional vibration
The invention provides a lightweight design method of a high-torsional-rigidity drive shaft. The lightweight design method of the high-torsional-rigidity drive shaft comprises the following steps: designing a drive shaft into a hollow rotary forging shaft, calculating the maximal outer diameters of two performance constraint sections of the drive shaft, and simplifying the drive shaft into a three-section-type stepped shaft, wherein the relatively small maximal outer diameter of two performance constraint sections as the two-end-section outer diameter; designing the intermediate section outer diameter with the aim that the outer diameter of the intermediate section is maximized by combining the outer peripheral rotation space of the intermediate section of the drive shaft according to the constraint condition that the outer diameter of the intermediate section of the drive shaft is not greater than twice of the outer diameter of the sections at two ends; and designing the inner diameter and the weight losing ratio of each section of the three-section-type stepped shaft according to the allowable torque intensity value of raw materials of the rotary forging shaft and the required torque intensity improvement ratio. Compared with a solid shaft in the prior art, according to the method, the torque rigidity of the drive shaft can be improved by 60% approximately, and meanwhile the weight can be lost by 20%, so that the horizontal finished automobile control stability is improved with the minimum cost; the torque vibration of a drive system is improved; the vehicle comfort is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI GKN DRIVE SYST
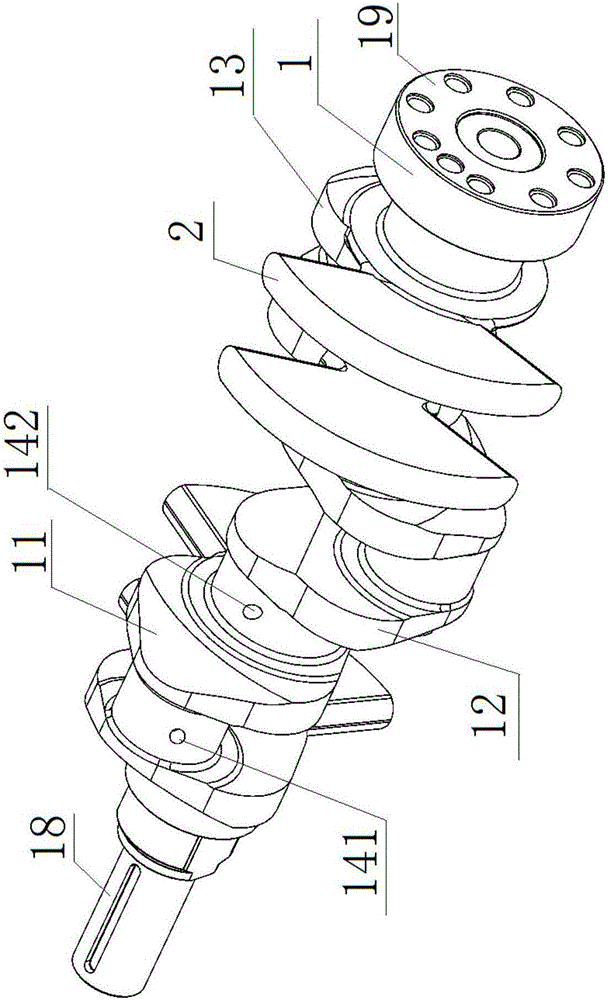
Crankshaft structure of straight-eight engine
InactiveCN106065898AReduce torsional vibration amplitudeReduce internal torqueCrankshaftsInertia force compensationFiring orderEngineering
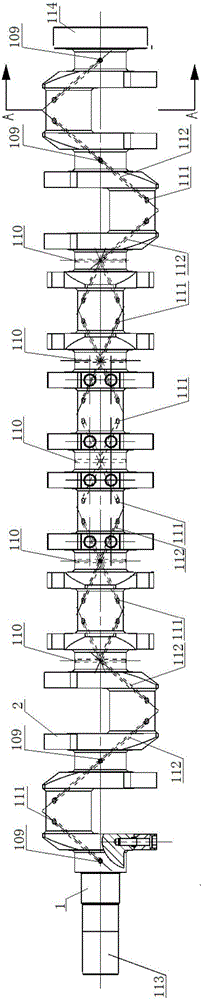
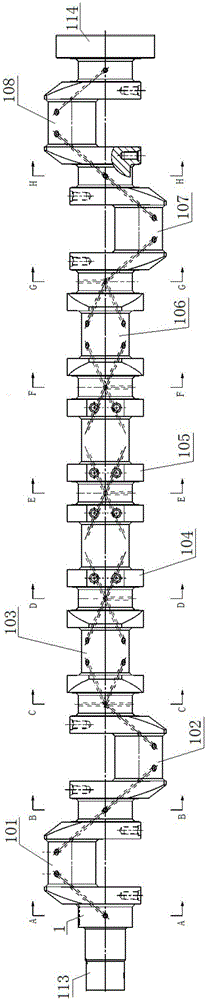
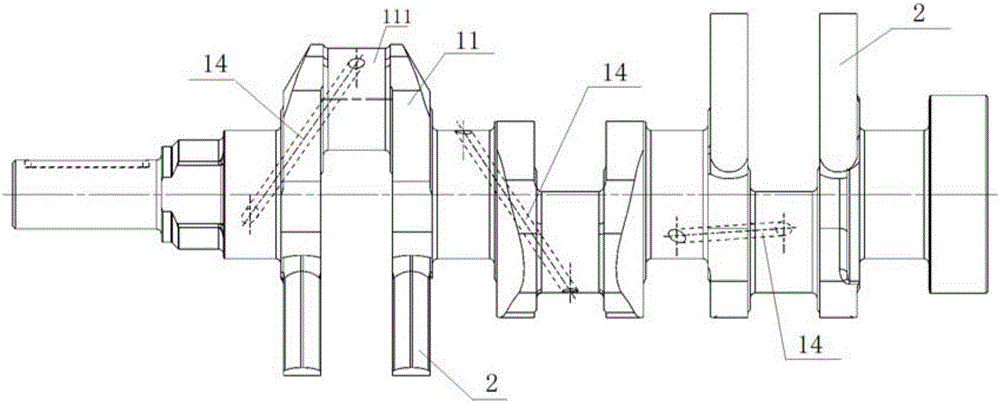
The invention discloses a crankshaft structure of a straight-eight engine. The two ends of a crankshaft are the free end and the power output end. A first crank throw, a second crank throw, a third crank throw, a fourth crank throw, a fifth crank throw, a sixth crank throw, a seventh crank throw and an eighth crank throw are arranged in sequence from the free end to the power output end. Projections from the free end to the power end are the projections of the first crank throw and the eighth crank throw which are mutually parallel, the projections of the third crank throw and the sixth crank throw which are mutually parallel, the projections of the second crank throw and the seventh crank throw which are mutually parallel and the projections of the fourth crank throw and the fifth crank throw which are mutually parallel in sequence in the clockwise direction. The firing order of the crankshaft is the first crank throw, the fifth crank throw, the seventh crank throw, the third crank throw, the eighth crank throw, the fourth crank throw, the second crank throw and the sixth crank throw. The firing order of the crankshaft structure is beneficial for lowering the torsional vibration amplitude of a crankshaft system and improving the strength and the torsional vibration resistance of the crankshaft.
Owner:GUANGXI YUCHAI MASCH CO LTD
Torsional vibration damper and torsional vibration damping method
InactiveUS9797470B2Easy to eliminateReduce violationsRotating vibration suppressionToothed gearingsPhase shiftedTorque regulation
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Spring seat and damper disk assembly
ActiveUS20080237955A1Better torsional vibration attenuationIncrease stiffnessVibration suppression adjustmentsWound springsEngineeringCoil spring
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
Torsional vibration damper with arc spring and end cap
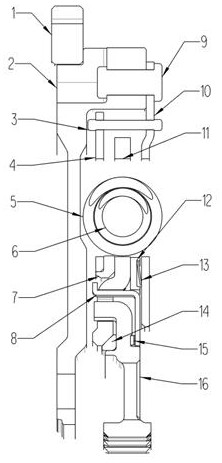
InactiveUS8863892B2Produced economicallyGood torsional vibrationRotating vibration suppressionSpringsMetal sheetTorsional vibration
An end cap for an arc spring in a torsional vibration damper having a cylindrical section for engaging with the arc spring and a radial section at one end of the cylindrical section for engaging with an input or output side of the torsional vibration damper, the end cap being producible by shaping from a metal sheet. A torsional vibration damper for elastic transmission of torque between an input side and an output side including the described end cap for transmission of force between one of the sides and the arc spring.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Spring seat and damper disk assembly
ActiveUS8021234B2Increase stiffnessGood torsional vibrationVibration suppression adjustmentsWound springsCoil springEngineering
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
Crankshaft structure of V-shaped 16-cylinder engine
The invention discloses a crankshaft structure of a V-shaped 16-cylinder engine. Two ends of a crankshaft are respectively a free end and a power output end; a first crank throw, a second crank throw, a third crank throw, a fourth crank throw, a fifth crank throw, a sixth crank throw, a seventh crank throw and an eighth crank throw are arranged from the free end to the power output end in sequence; horizontal first oil ways are respectively formed in main bearing journals on two sides of a first connecting rod journal and an eighth connecting rod journal; the first oil ways are perpendicular to the center axes of the main bearing journals; and vertical second oil ways are respectively formed in main bearing journals on two sides of a third connecting rod journal, a fourth connecting rod journal, a fifth connecting rod journal and a sixth connecting rod journal. The oil way arrangement is convenient for machining; main bearings and connecting rod bearings can be fully lubricated; and the lubricating effect of journal bearings is improved.
Owner:GUANGXI YUCHAI MASCH CO LTD
Torsional vibration damper
ActiveUS10533650B2Improve vibration damping effectIncreased Design FreedomRotating vibration suppressionFluid gearingsFluid couplingGear wheel
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Torsional vibration damper and manufacturing method thereof
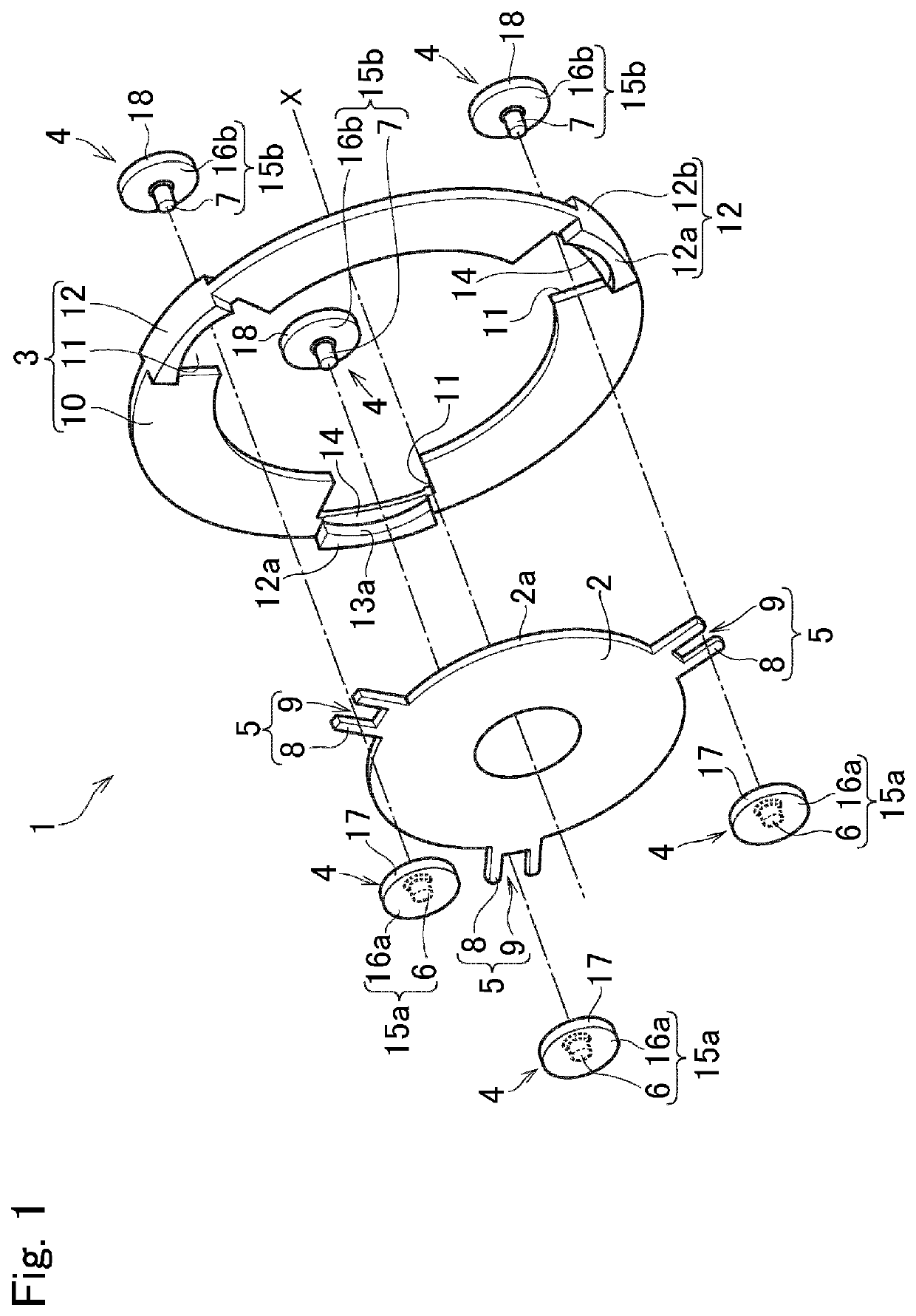
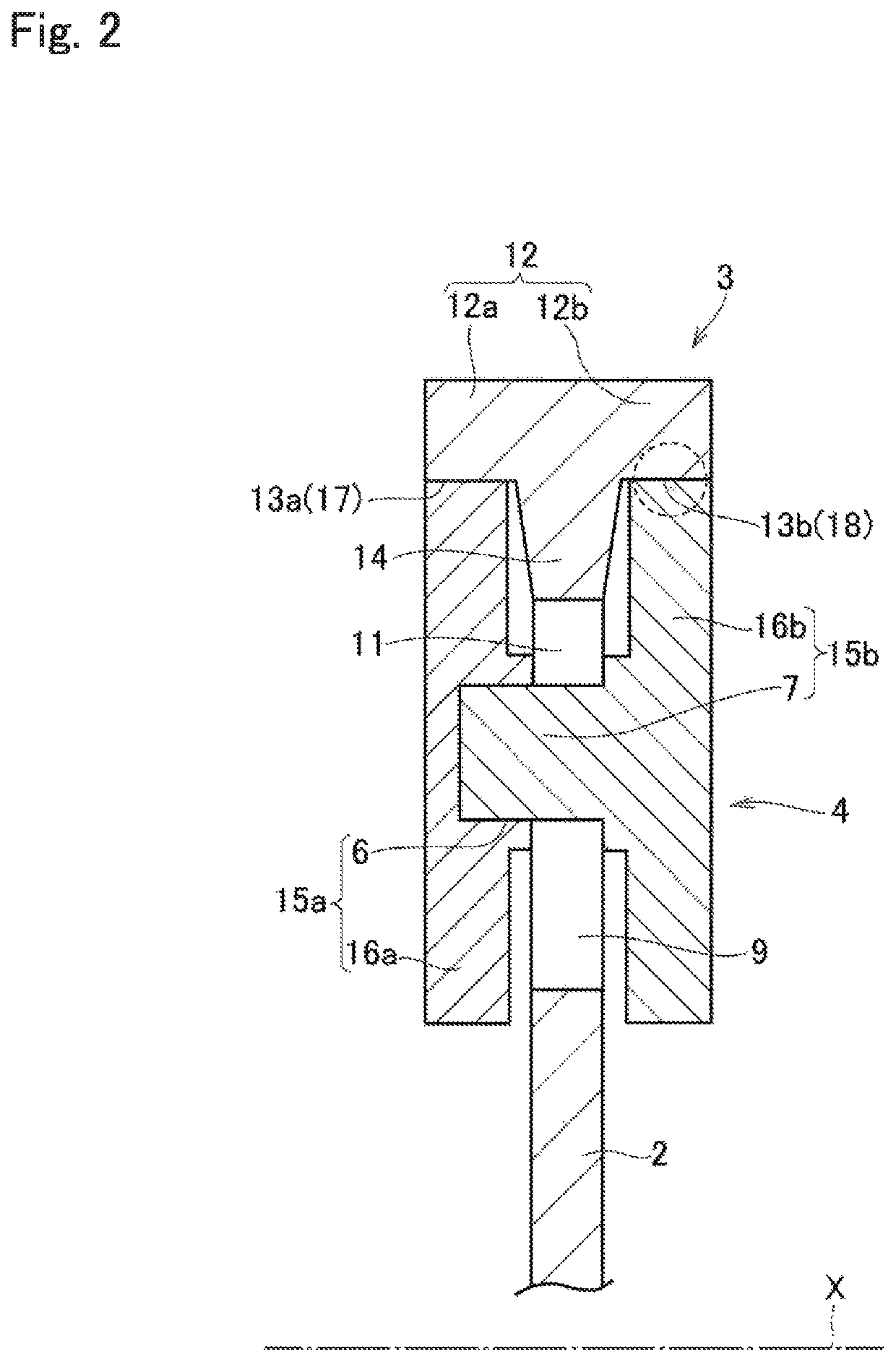
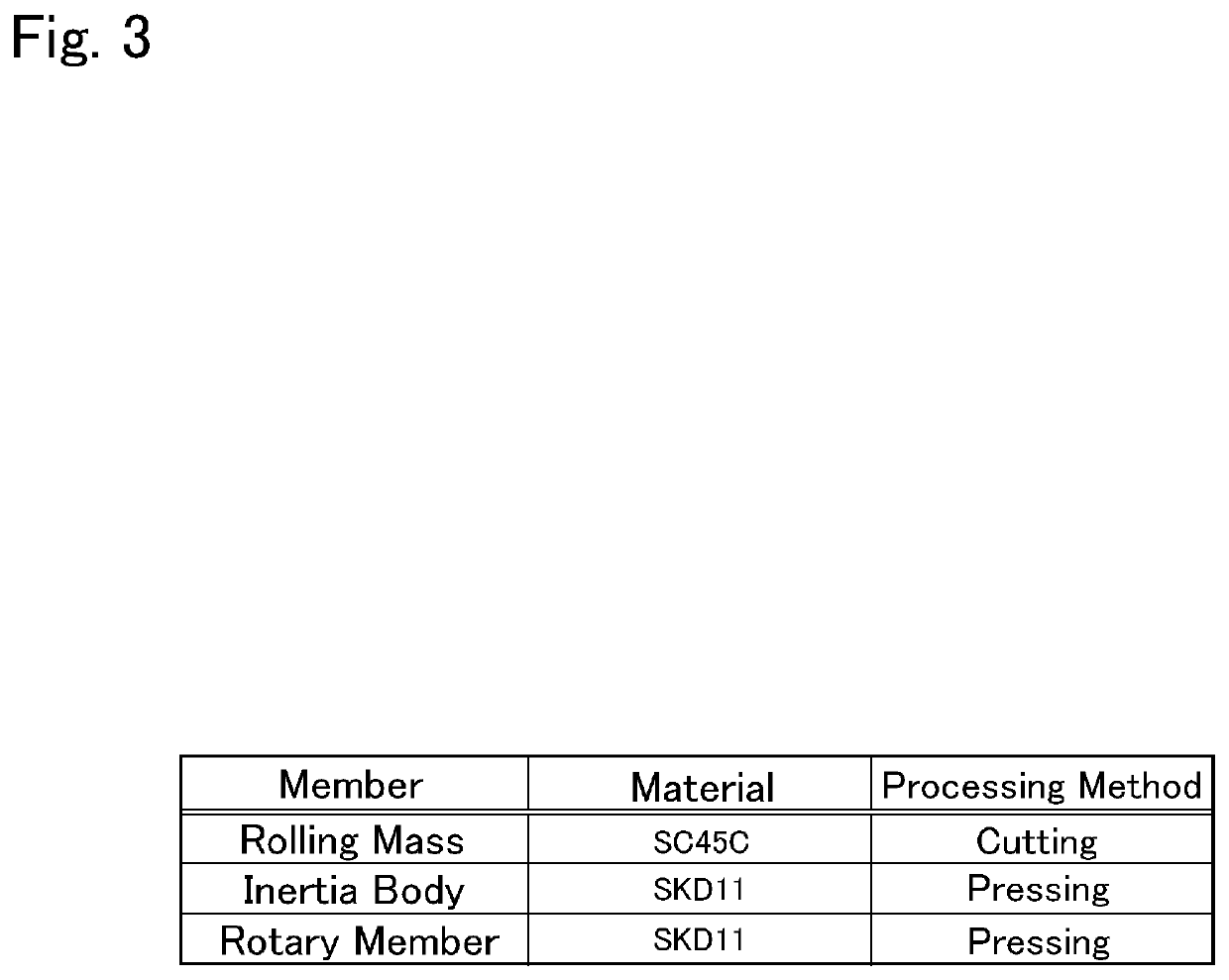
ActiveUS10816058B2Improve vibration damping effectGood torsional vibrationRotating vibration suppressionSpringsClassical mechanicsTorsional vibration
A torsional vibration damper in which a vibration damping performance is enhanced without increasing a manufacturing cost. A torsional vibration damper damps torsional vibrations by a relative rotation between a rotary member and an inertia body. Hardness of the contact surface of any one of the inertia body and a rolling mass is harder than the contact surface of the other one. Smoothness of the contact surface of any one of the inertia body and the rolling mass is smoother than the contact surface of the other one.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Crankshaft structure of V-shaped six-cylinder engine
InactiveCN106015305AMiniaturizationReduce torsional vibration amplitudeCrankshaftsEngine componentsFiring orderEngineering
The invention discloses a crankshaft structure of a V-shaped six-cylinder engine. Two ends of the crankshaft are a free end and a power output end, projection is carried out along a direction from the free end to the power output end, a first toggle, a second toggle and a third toggle are sequentially arranged along the clockwise direction, an included angle between the first toggle and the second toggle is 120DEG, an included angle between the second toggle and the third toggle is 120DEG, and the firing order of the crankshaft is 1-2-3. The firing order is in favor of reducing the torsional vibration amplitude of a crankshaft system and improving the strength, the torsional oscillation and the strength of the crankshaft.
Owner:GUANGXI YUCHAI MASCH CO LTD
Spring seat and damper disk assembly
ActiveUS8029370B2Increase stiffnessGood torsional vibrationMachine framesLiquid springsCoil springEngineering
Second spring seats 62 each have a first support component 63, a second support component 64, and a reinforcing plate 66. The first support component 63 supports the ends of second coil spring 61a in the rotational direction. The second support component 64 extends in the rotational direction from the first support component 63 and supports the end of the second spring 61a in the radial direction. At least part of the reinforcing plate 66 is embedded in at least one of the first and second support components 63 and 64. The reinforcing plate 66 directly or indirectly supports the end of the second spring 61a along with the first and second support components 63 and 64.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
Flywheel shock absorber integrating multi-stage variable damping
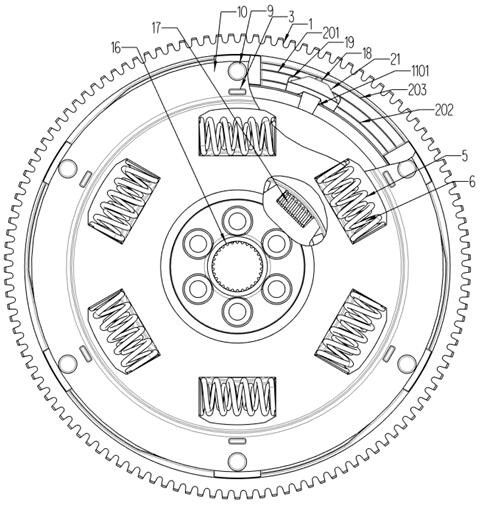
PendingCN111734783AGood torsional vibrationIncrease dampingVibration dampersSpringsEngineeringFlywheel
The invention discloses a flywheel shock absorber integrating multi-stage variable damping. The absorber comprises a flywheel sub-assembly, a shock absorber sub-assembly and a multi-stage variable damping sub-assembly. A flywheel outer ring of the flywheel sub-assembly is provided with a plurality of step damping friction pairs which are radially arranged, a variable damping friction pair and a variable damping control surface. The multi-stage variable damping sub-assembly is assembled to realize step damping and local variable damping at the same time. The invention has the advantages that the step damping and the variable damping are realized by a set of multi-stage variable damping sub-assemblies, the structure is compact, and the space is saved.
Owner:华域动力总成部件系统(上海)有限公司
Full-rotary device
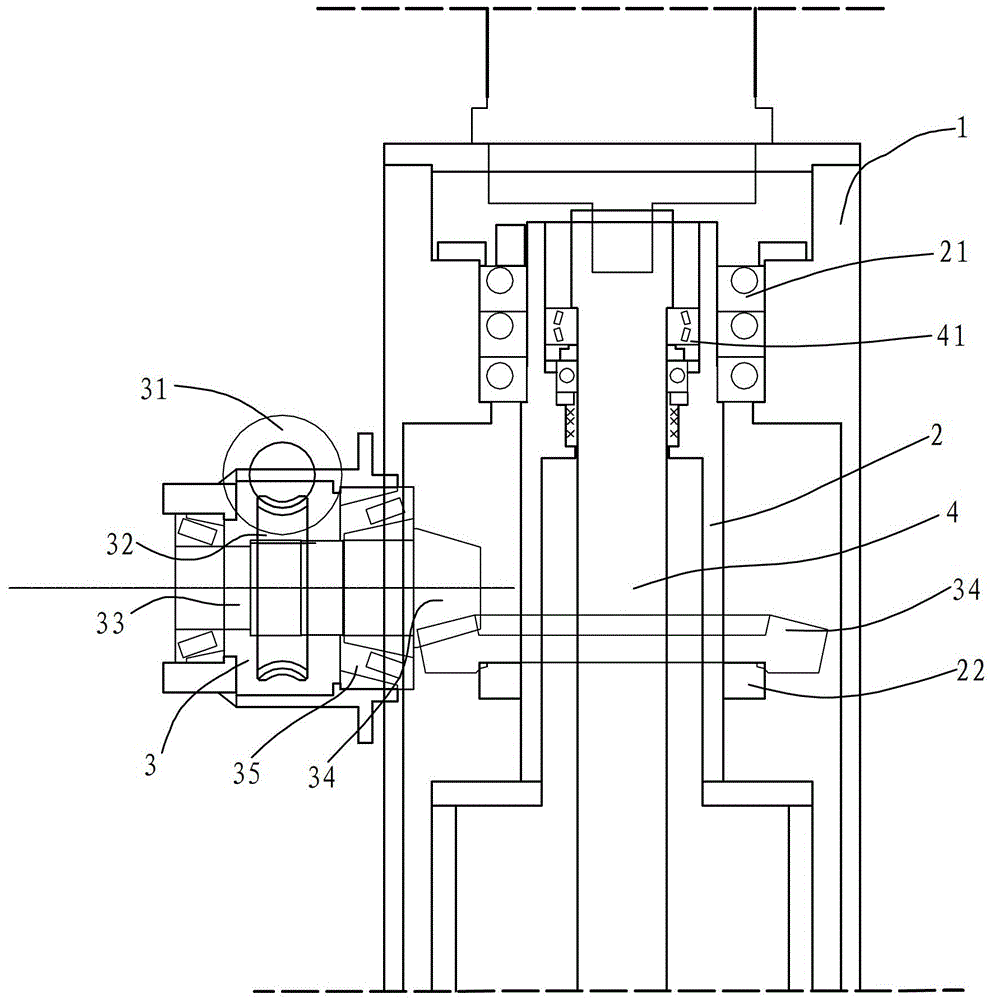
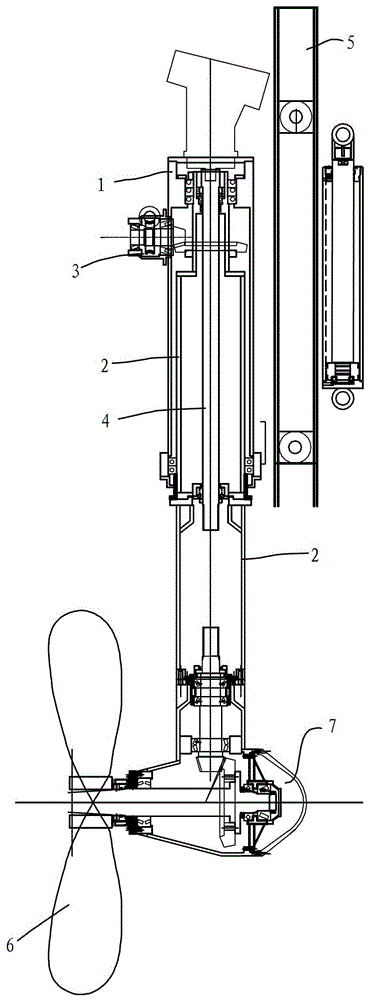
InactiveCN103043200ASimple structureResistant to torsional vibrationSteering ruddersPropulsive elementsDrive shaftEngineering
The invention discloses a full-rotary device. The full-rotary device is characterized by comprising a support sleeve, a rotary sleeve and a rotary transmission unit, wherein the rotary sleeve is in a hollow cylindrical shape, movably installed in the support sleeve, and can rotate around the axis; a drive shaft of an oar penetrates through the rotary sleeve and can rotate around the axis in the rotary sleeve; the rotary transmission unit comprises a set of worm and worm wheel and a set of sector gears, the worm and the worm wheel are installed on the support sleeve, one sector gear is mounted on a worm wheel shaft, the other sector gear is fixedly sleeved on the rotary sleeve, and the two sector gears are in engagement transmission; and the worm drives the worm wheel which drives the sector gear on the worm wheel shaft to rotate so as to drive the sector gear on the rotary sleeve to rotate. The full-rotary device has the advantages of being simple in structure, good in torsional vibration and rotary vibration resistance, reliable in performances and low in production and maintenance costs.
Owner:舟山海川船舶机械有限公司
Torsional vibration damper
ActiveUS20160290434A1Suppress torsional vibrationGood torsional vibrationRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingTorsional vibrationControl theory
A torsional vibration damper having enhanced vibration damping performance is provided. The torsional vibration damper comprises: a vacant area existing between an outer circumference of the sun gear and an inner circumference of the ring gear outside of a revolving range of the planetary gears revolved as a result of relative rotation between the sun and the ring gear; and a mass increasing portion that is formed on the rotary member other than an input element and an output element within the vacant area in such a manner as to protrude from the rotary member.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Torsional vibration damper with arc spring and end cap
InactiveUS20140014435A1Reduce the overall diameterSecurely holdSpringsSprings/dampers manufactureMetal sheetTorsional vibration
An end cap for an arc spring in a torsional vibration damper having a cylindrical section for engaging with the arc spring and a radial section at one end of the cylindrical section for engaging with an input or output side of the torsional vibration damper, the end cap being producible by shaping from a metal sheet. A torsional vibration damper for elastic transmission of torque between an input side and an output side including the described end cap for transmission of force between one of the sides and the arc spring.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Torsional vibration damper
ActiveUS9261165B2Good torsional vibrationPrevents annoying development of noiseRotating vibration suppressionFlywheelsDrivetrainEngineering
A torsional vibration damper for a drivetrain of a motor vehicle having a substantially discoidal centrifugal flange and a plurality of centrifugal pendulum-type absorbers. Each centrifugal pendulum-type absorber includes a first pendulum mass and a second pendulum mass. The first pendulum mass is arranged above a first surface of the pendulum flange, and the second pendulum mass is arranged above a second surface of the pendulum flange. The first pendulum mass and the second pendulum mass are firmly connected to each other by means of at least two spacing bolts in each case. The pendulum flange has a plurality of cutouts in which the spacing bolts are guided. A second spacing bolt of a first centrifugal pendulum-type absorber and a first spacing bolt of a second centrifugal pendulum-type absorber are guided in at least one first cutout.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Torsional vibration damper
ActiveUS9903439B2Improve performanceImprove vibration damping effectRotating vibration suppressionToothed gearingsTorsional vibrationControl theory
A torsional vibration damper having enhanced vibration damping performance is provided. The torsional vibration damper comprises: a vacant area existing between an outer circumference of the sun gear and an inner circumference of the ring gear outside of a revolving range of the planetary gears revolved as a result of relative rotation between the sun and the ring gear; and a mass increasing portion that is formed on the rotary member other than an input element and an output element within the vacant area in such a manner as to protrude from the rotary member.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Crankshaft structure of V-shaped eight-cylinder engine
InactiveCN106246708AReduce internal torqueImprove dynamic balance rateCrankshaftsEngine componentsEngineeringCrankshaft
The invention discloses a crankshaft structure of V-shaped eight-cylinder engine. Two ends of a crankshaft are a free end and a power output end respectively, a first crank, a second crank, a third crank and a fourth crank are sequentially arranged from the free end to the power output end, every crank arm of the crankshaft is symmetric to a plane formed by the center axis of a corresponding rod journal and the center axis of the crankshaft, the lower end of each of the crank arms of the crank and the fourth crank is provided with an arc-shaped first balancing weight , and an included angle between the center axis of the balancing weight and the center axis of the corresponding crank arm is 0-45 DEG. The design of the crank arms and the balancing weights is in favor of realizing light weight the crankshaft, reducing the internal moment of the crankshaft and improving the dynamic balancing rate of the crankshaft.
Owner:GUANGXI YUCHAI MASCH CO LTD
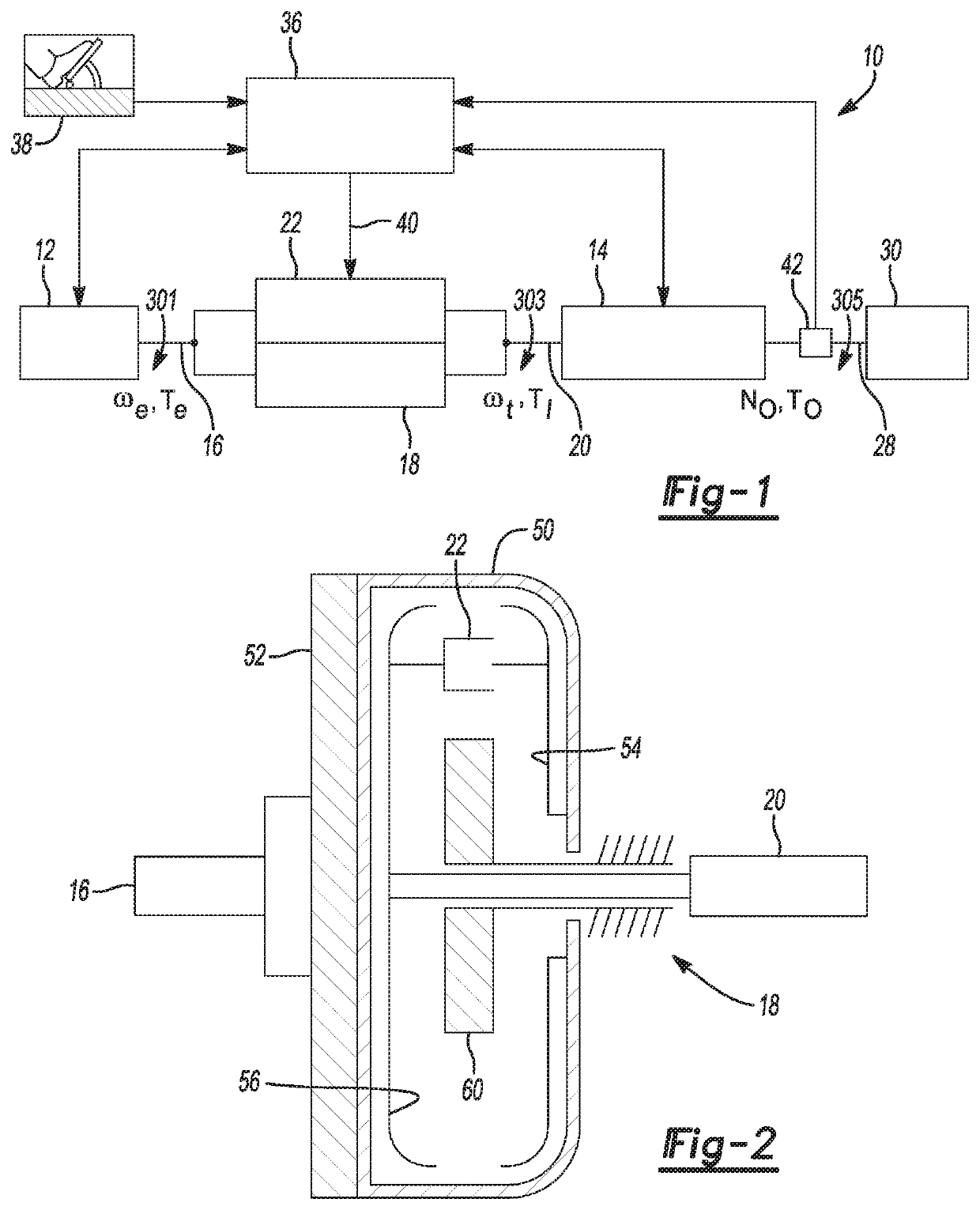
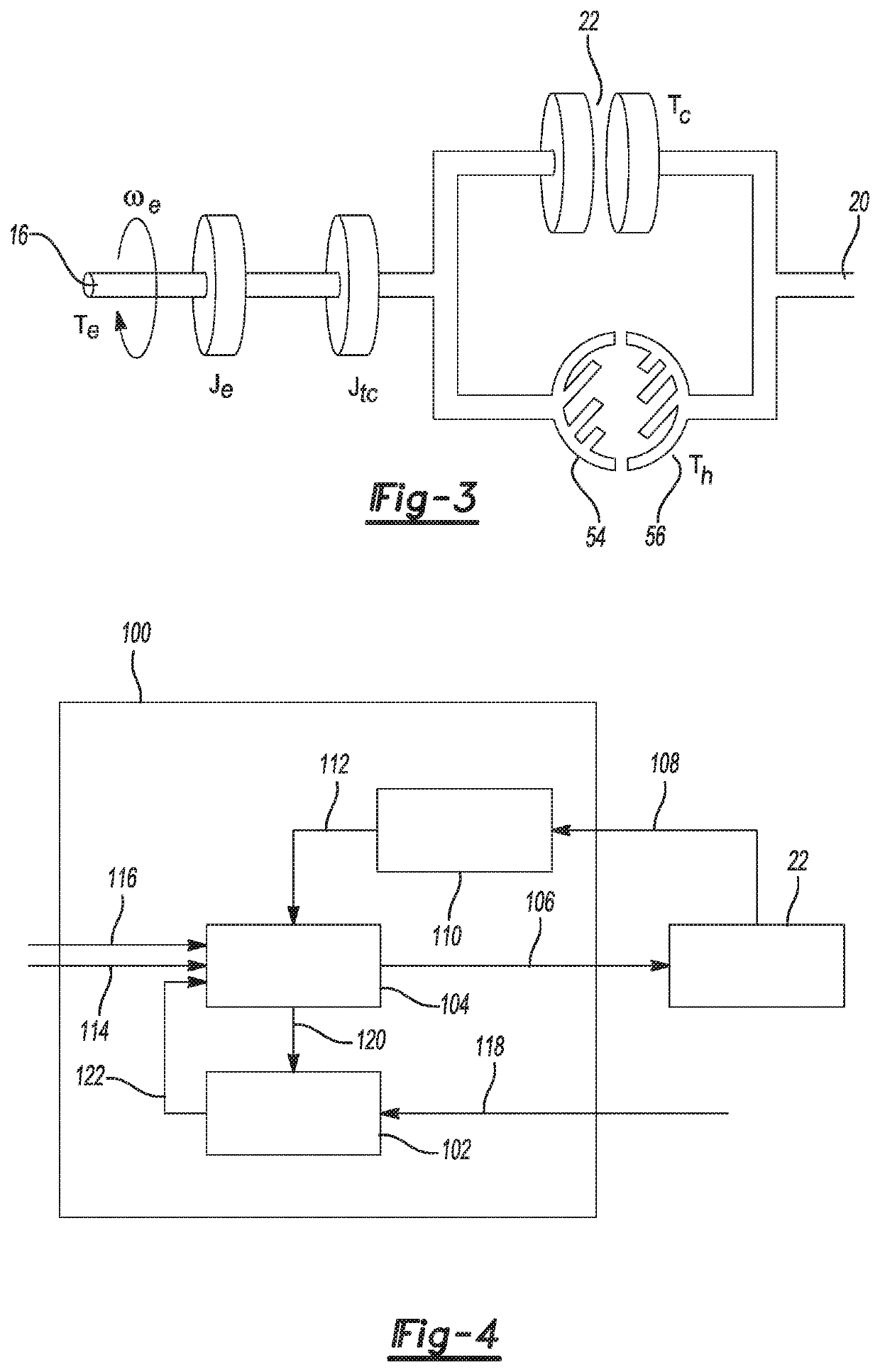
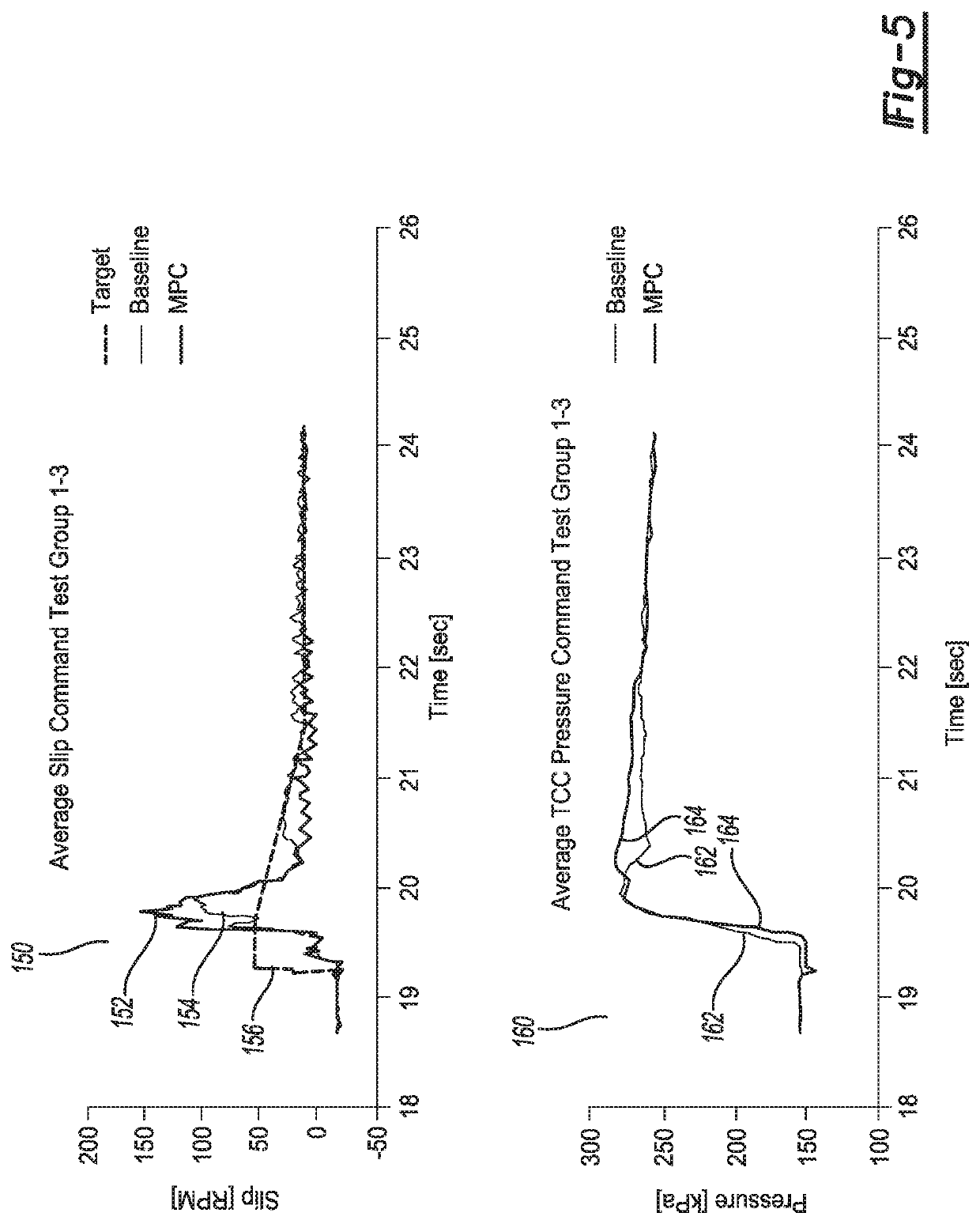
Model predictive control of torque converter clutch slip
ActiveUS20200256459A1Increase valueSmooth changeGearing controlFluid gearingsControl systemPredictive controller
A control system to control slip of a torque converter clutch includes a clutch plant model configured to predict a value of a parameter that relates to torque converter clutch slip as a function of clutch plant model inputs comprising commanded clutch pressure and of torque from the torque generative device. The control system also includes a model predictive controller configured to receive signals that allow determination of a desired value of the parameter that relates to torque converter clutch slip and a predicted value of the parameter that relates to torque converter clutch slip, receive a signal representing reported torque of the torque generative device, identify an optimal commanded clutch pressure value that will result in an optimal value of an objective function based on the clutch plant model, and provide a command signal to an actuator effective to control commanded clutch pressure to the torque converter clutch.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Torsional Vibration Damper And Start-Up Element
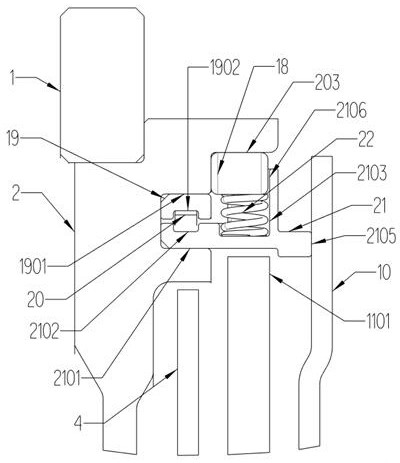
InactiveUS20170284475A1Increase dampingInhibit abrupt back-couplingYielding couplingSpringsTorsional vibrationTransition point
A torsional vibration damper has an input, an output and an intermediate mass arranged therebetween, a first plurality of spring elements coupled between the input and the intermediate mass that form a first stage, a second plurality of spring elements coupled between the intermediate mass and the output that form a second stage of the torsional vibration damper, at least one damper mass to damp the vibration component of the rotational movement. The first stage of the torsional vibration damper has a progressive first characteristic with at least one transition point. The second stage of the torsional vibration damper has a progressive, second characteristic with at least one transition point. All of the transition points of the first characteristic and the second characteristic are spaced apart from one another with respect to torque.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Crankshaft structure of in-line three-cylinder engine
InactiveCN106015303AReduce torsional vibration amplitudeImprove strengthCrankshaftsInertia force compensationFiring orderEngineering
The invention discloses a crankshaft structure of an in-line three-cylinder engine. Two ends of the crankshaft are a free end and a power output end, projection is carried out along a direction from the free end to the power output end, a first toggle, a second toggle and a third toggle are sequentially arranged along the clockwise direction, an included angle between the first toggle and the second toggle and between the second toggle and the third toggle is 120DEG, and the firing order of the crankshaft is 1-2-3. The firing order is in favor of reducing the torsional vibration amplitude of a crankshaft system and improving the strength, the torsional oscillation and the strength of the crankshaft.
Owner:GUANGXI YUCHAI MASCH CO LTD
Turbine torsional vibration damper, and converter and torque transmission device
ActiveUS10180176B2Good torsional vibrationImproved simple torsional vibration damperRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingDrivetrainTorque transmission
A turbine torsional vibration damper, in particular a simple torsional vibration damper, for a vehicle, preferably for a drivetrain of a motor vehicle, having a damper part for introducing a torque into the turbine torsional vibration damper and a damper part for extracting the torque from the torsional vibration damper, wherein a pendulum mass flange of a centrifugal pendulum device is rigidly coupled mechanically with a damper part of the turbine torsional vibration damper. A converter or a torque transmission device for a vehicle, in particular for a drivetrain of a motor vehicle, wherein the converter or torque transmission device has a turbine torsional vibration damper according to the invention.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Full-turn paddle rudder
InactiveCN103112577BSimple structureImprove performanceSteering by propulsive elementsPropulsive elementsDrive shaftGear wheel
The invention discloses a full rotary type oar-rudder which comprises a support sleeve, a rotary system, and a power propulsion system. The support sleeve is fixedly mounted on a ship body. The rotary system comprises a rotary sleeve, a worm and worm wheel transmission case, and a group of conical gears. The power propulsion system comprises a motor, a drive shaft, propellers, and a gear case body. The full rotary type screw-rudder is reasonable in structure, direct input of motor power and the drive shaft is realized through a way of combination of an oar and an rudder, and the propellers can rotate around the vertical axis in any direction of 360 degrees. A full rage of maximum thrust and efficiency can be obtained through controlling and pushing each rotary angle of the propellers, and maneuverability and agility of a ship can be greatly improved.
Owner:舟山海川船舶机械有限公司
azimuth device
InactiveCN103043200BSimple structureResistant to torsional vibrationSteering ruddersPropulsive elementsDrive shaftEngineering
The invention discloses a full-rotary device. The full-rotary device is characterized by comprising a support sleeve, a rotary sleeve and a rotary transmission unit, wherein the rotary sleeve is in a hollow cylindrical shape, movably installed in the support sleeve, and can rotate around the axis; a drive shaft of an oar penetrates through the rotary sleeve and can rotate around the axis in the rotary sleeve; the rotary transmission unit comprises a set of worm and worm wheel and a set of sector gears, the worm and the worm wheel are installed on the support sleeve, one sector gear is mounted on a worm wheel shaft, the other sector gear is fixedly sleeved on the rotary sleeve, and the two sector gears are in engagement transmission; and the worm drives the worm wheel which drives the sector gear on the worm wheel shaft to rotate so as to drive the sector gear on the rotary sleeve to rotate. The full-rotary device has the advantages of being simple in structure, good in torsional vibration and rotary vibration resistance, reliable in performances and low in production and maintenance costs.
Owner:舟山海川船舶机械有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com