Patents
Literature
67 results about "Memory scrubbing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
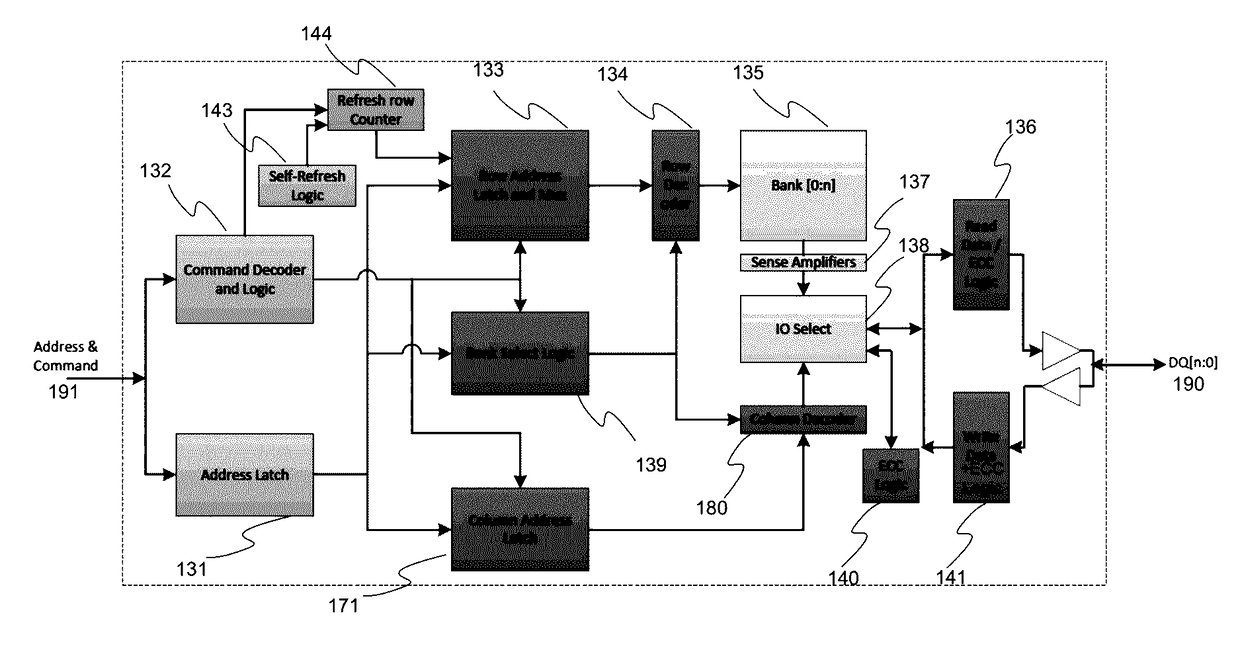
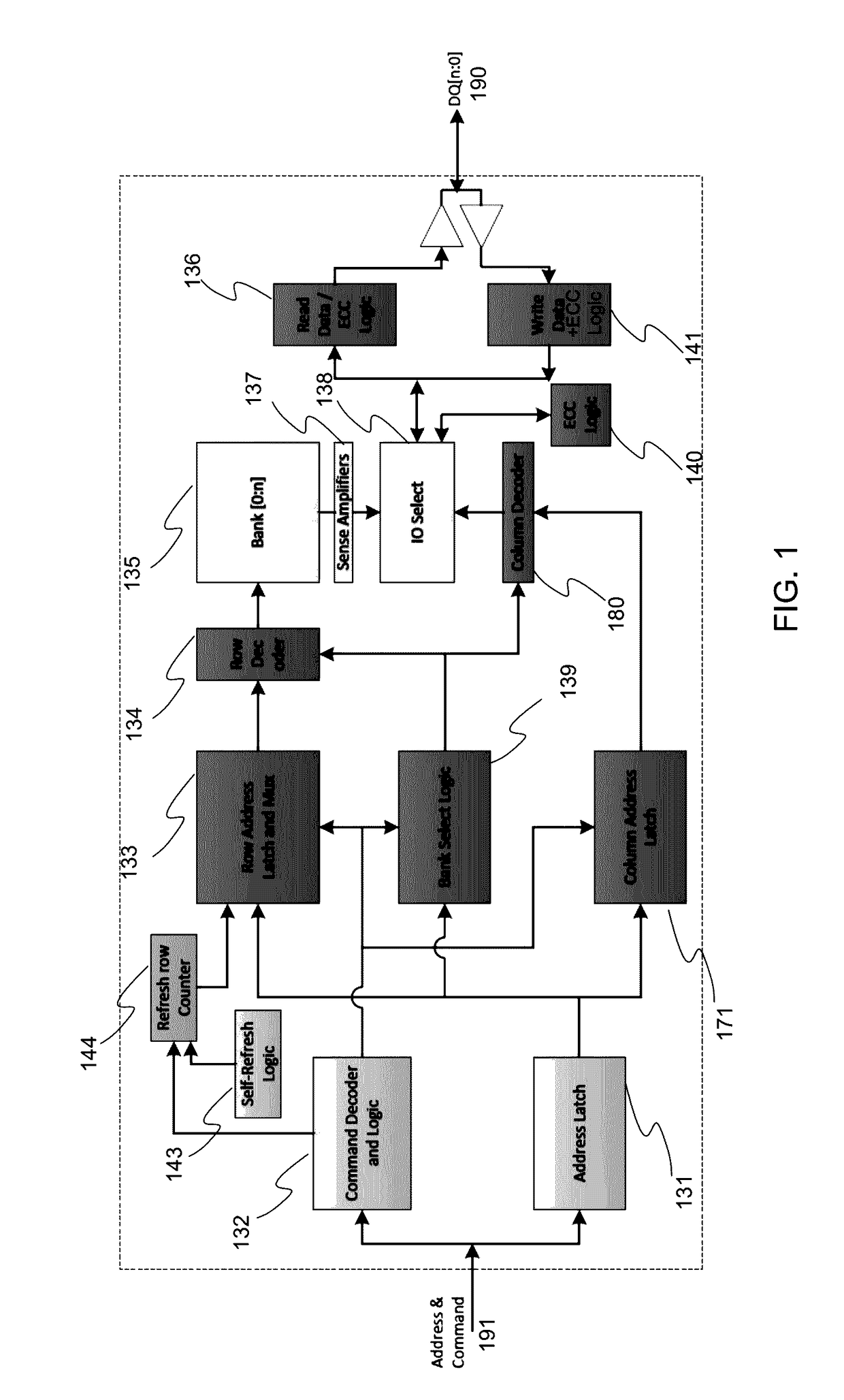
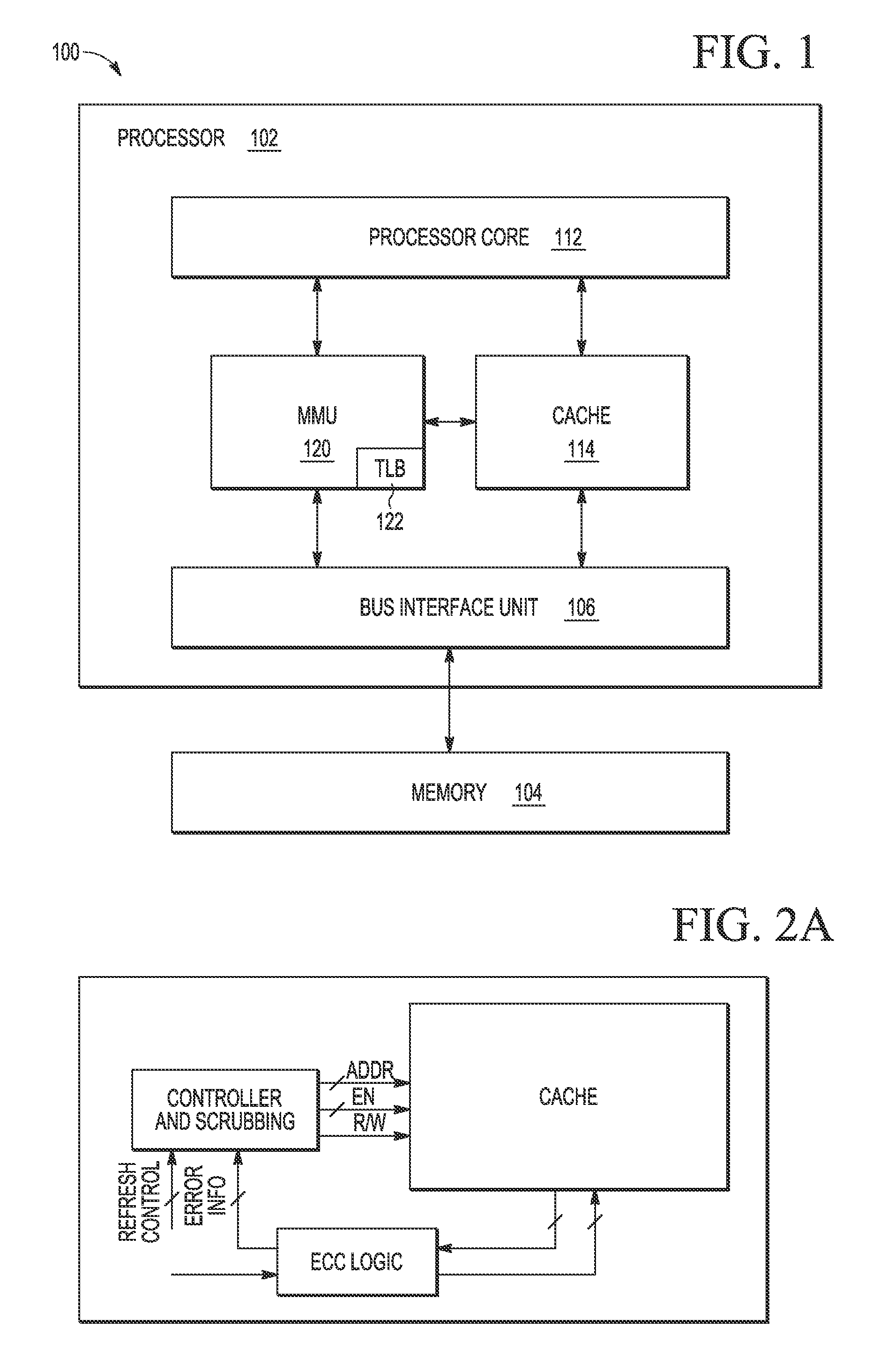
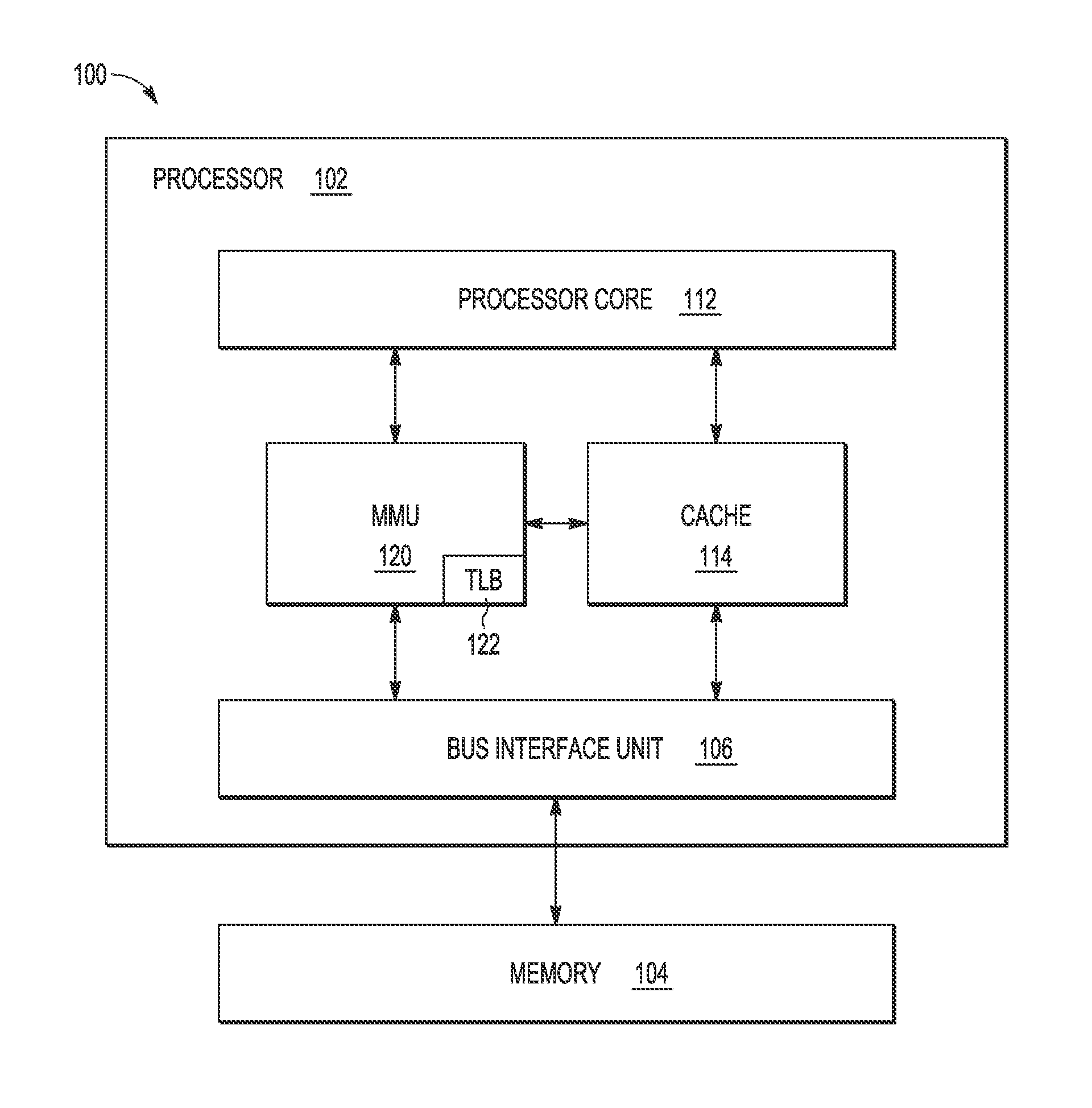
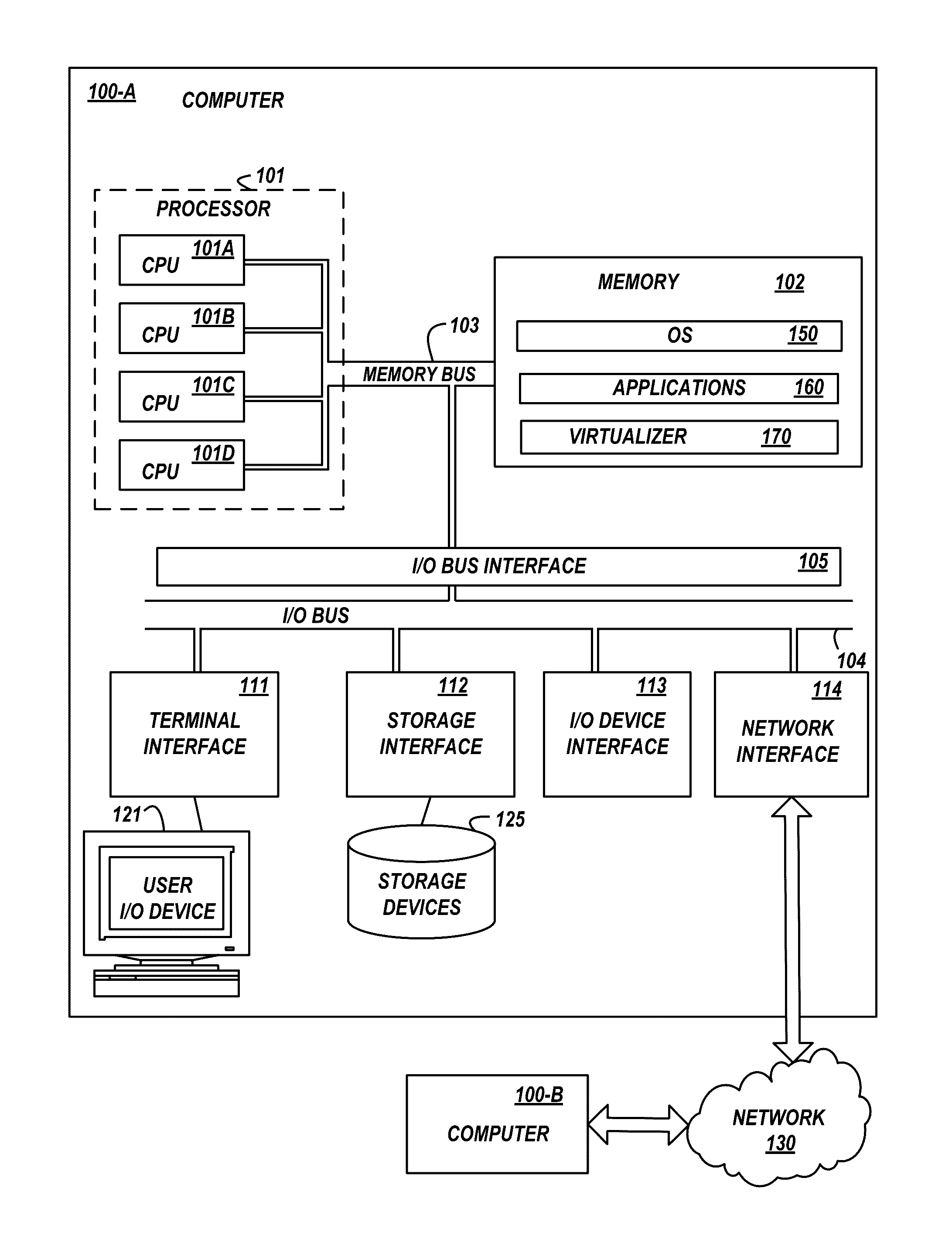
Memory scrubbing consists of reading from each computer memory location, correcting bit errors (if any) with an error-correcting code (ECC), and writing the corrected data back to the same location. Due to the high integration density of modern computer memory chips, the individual memory cell structures became small enough to be vulnerable to cosmic rays and/or alpha particle emission. The errors caused by these phenomena are called soft errors. Over 8% of DIMM modules experience at least one correctable error per year. This can be a problem for DRAM and SRAM based memories. The probability of a soft error at any individual memory bit is very small. However, together with the large amount of memory modern computers—especially servers—are equipped with, and together with extended periods of uptime, the probability of soft errors in the total memory installed is significant.
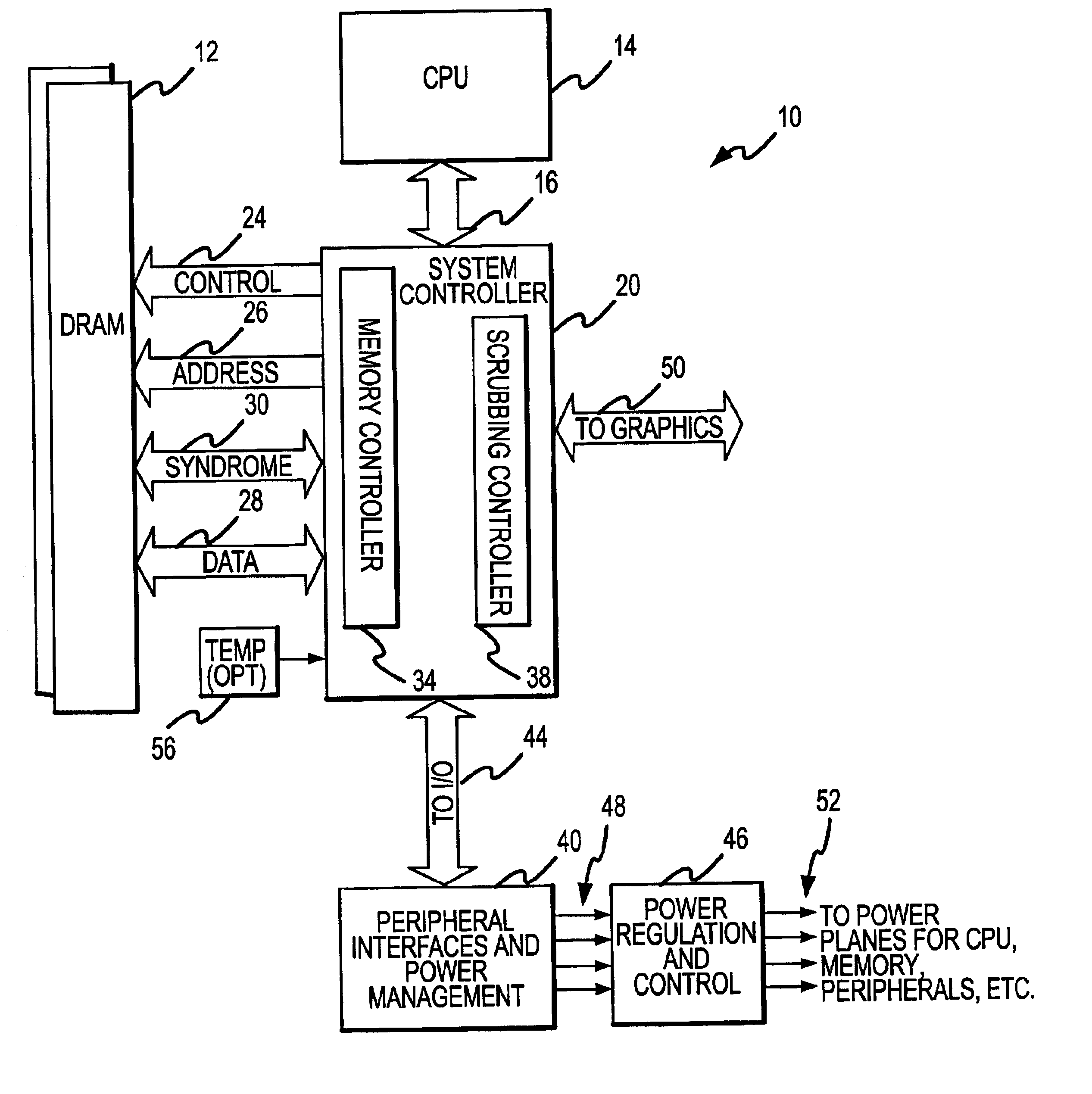
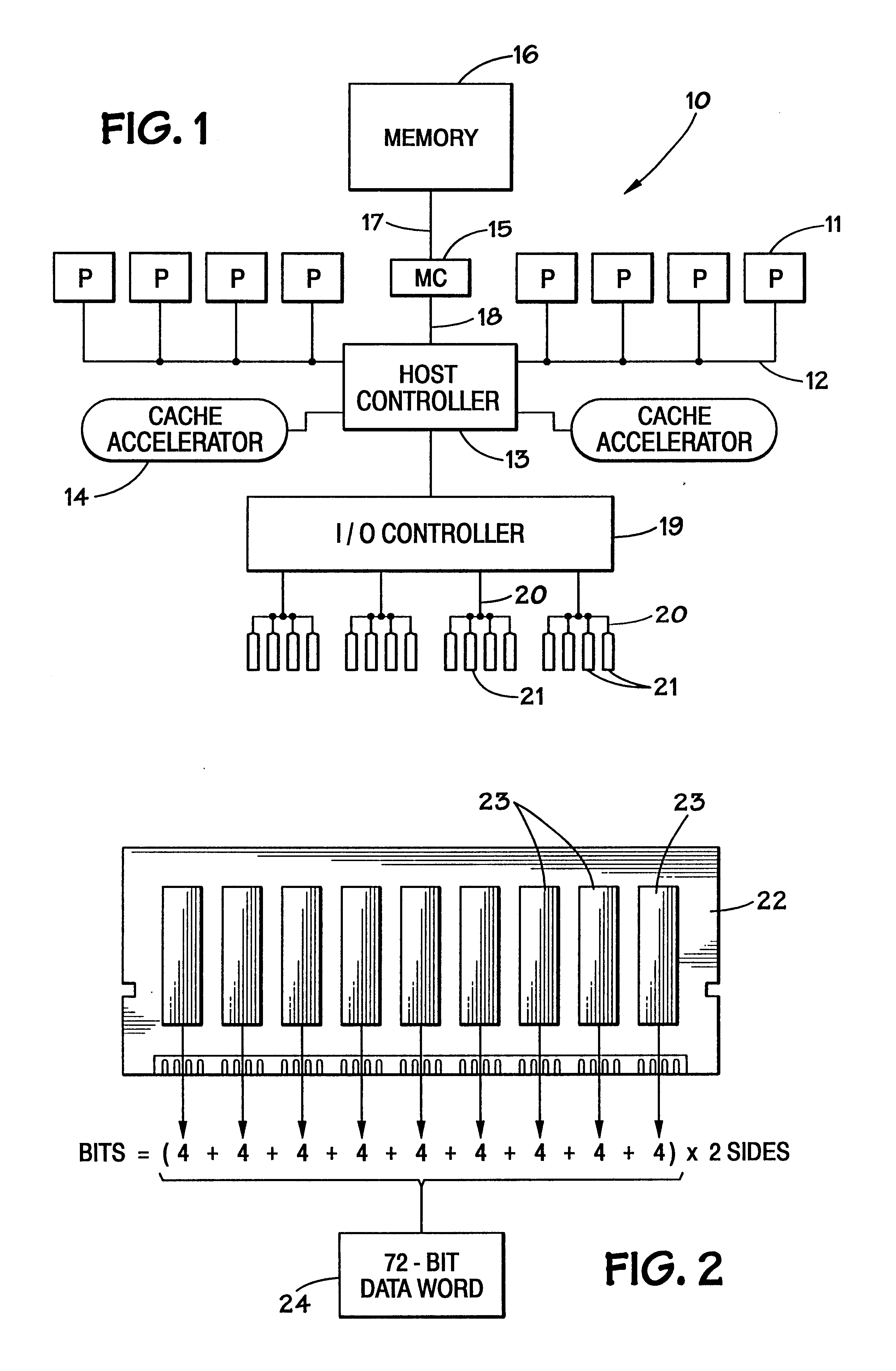
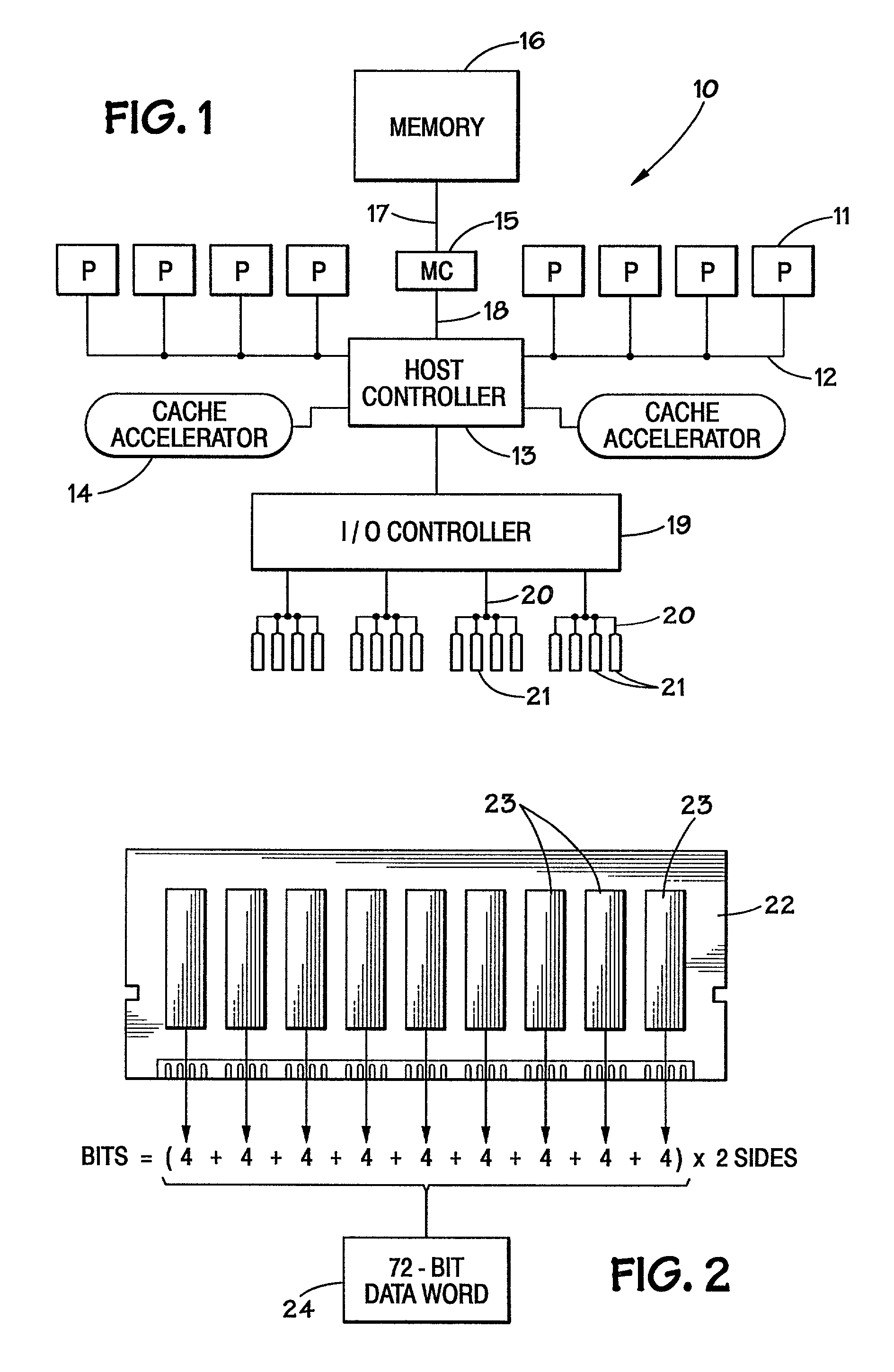
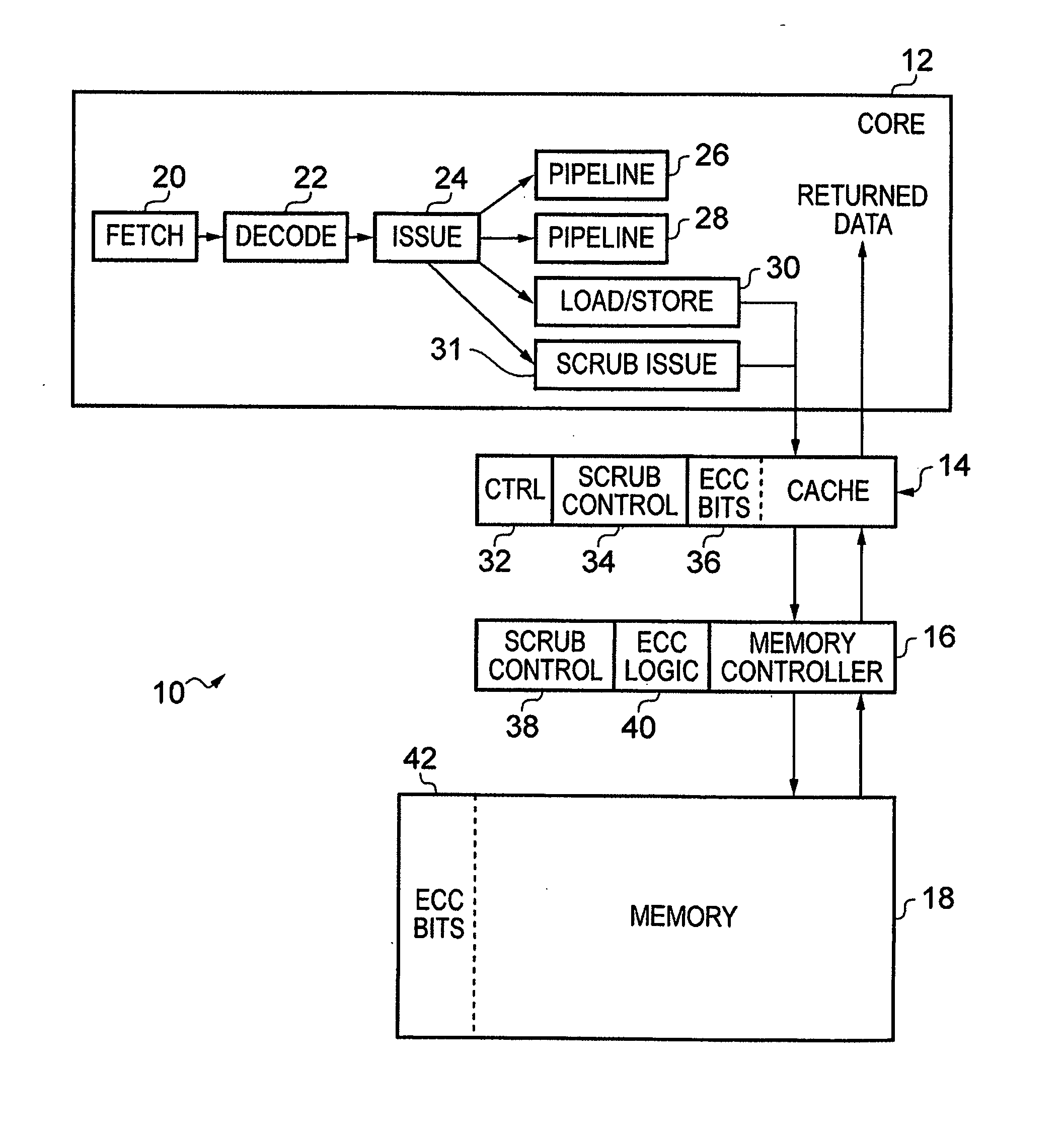
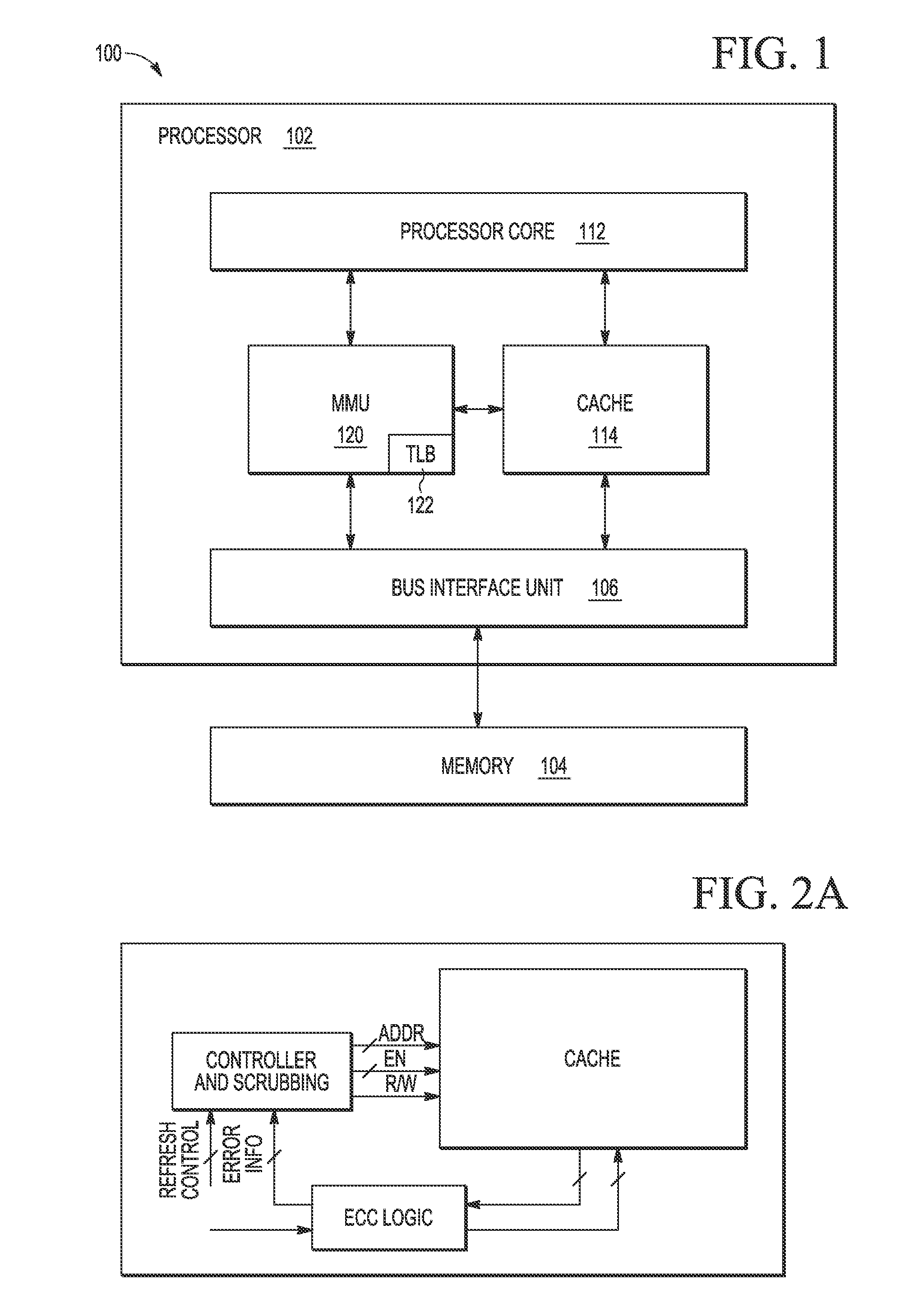
Method and system for dynamically operating memory in a power-saving error correcting mode
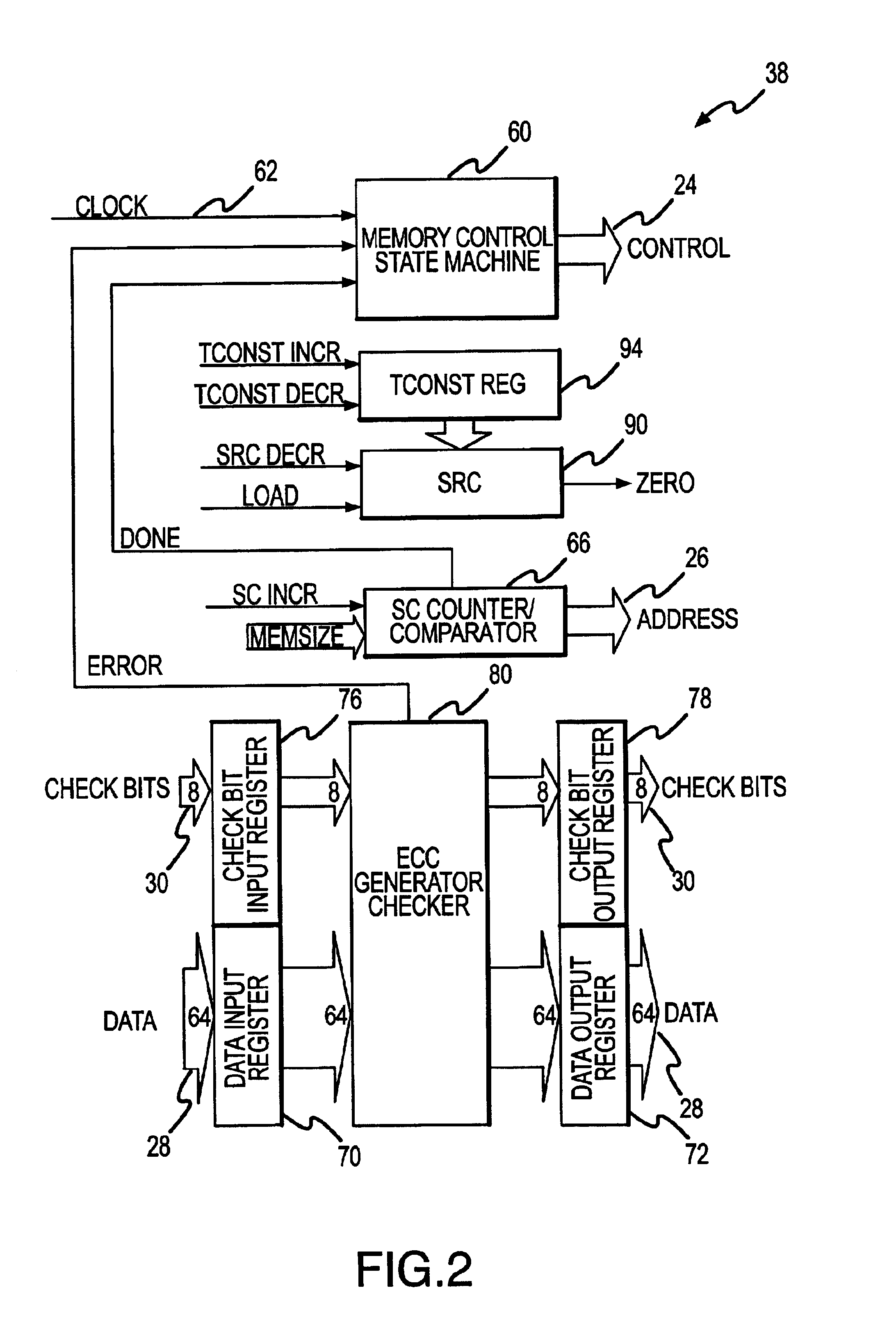
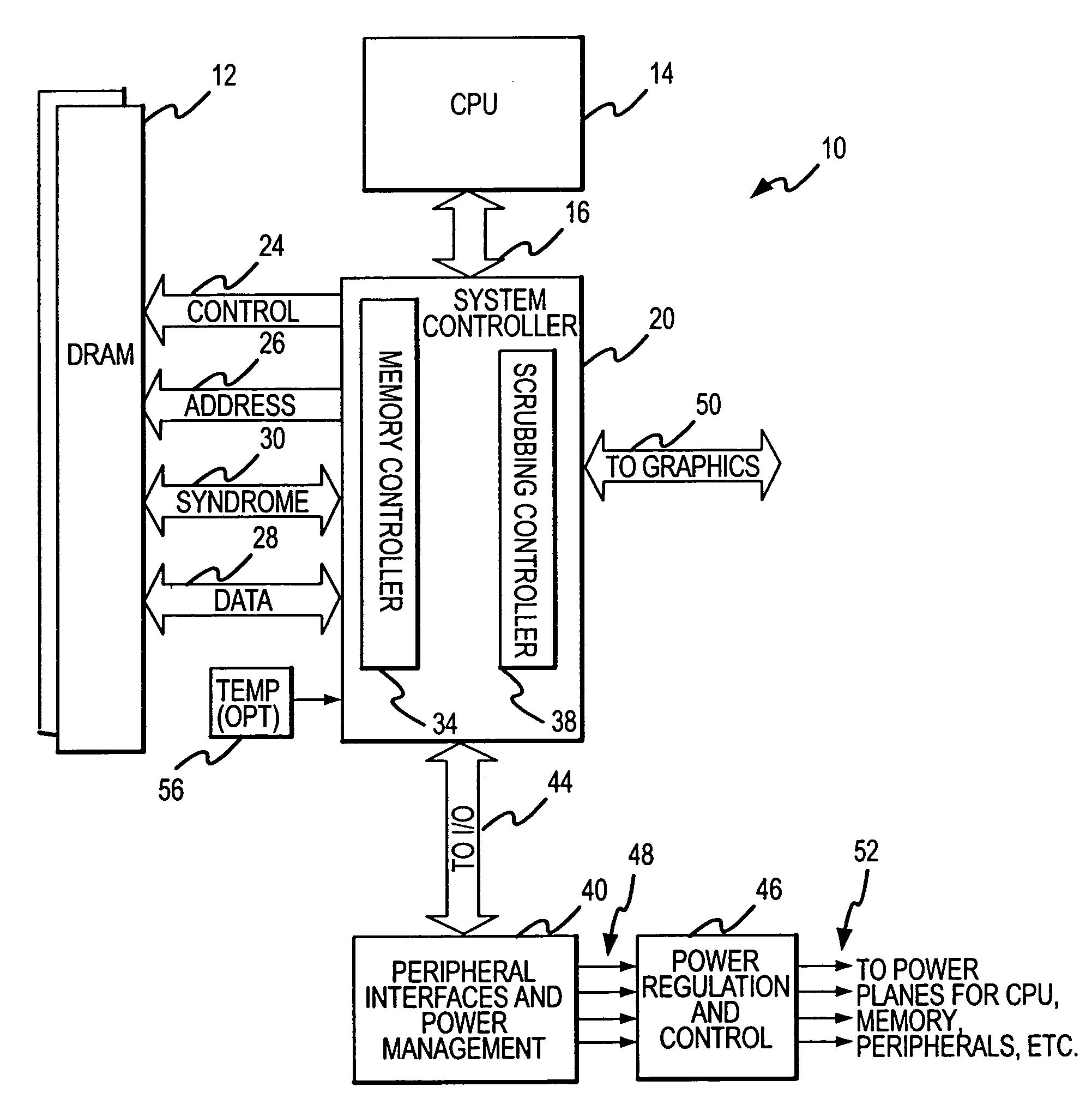
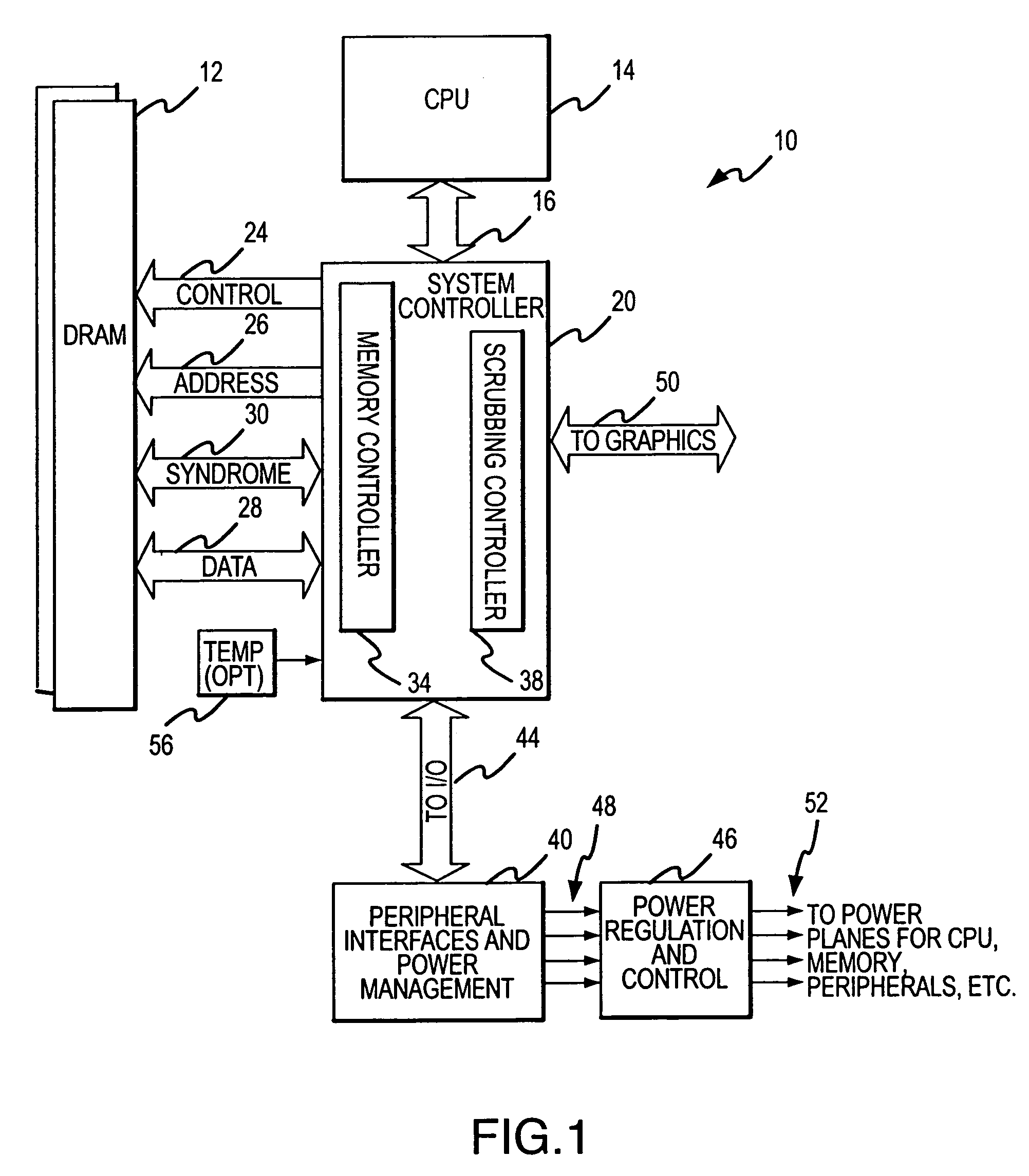
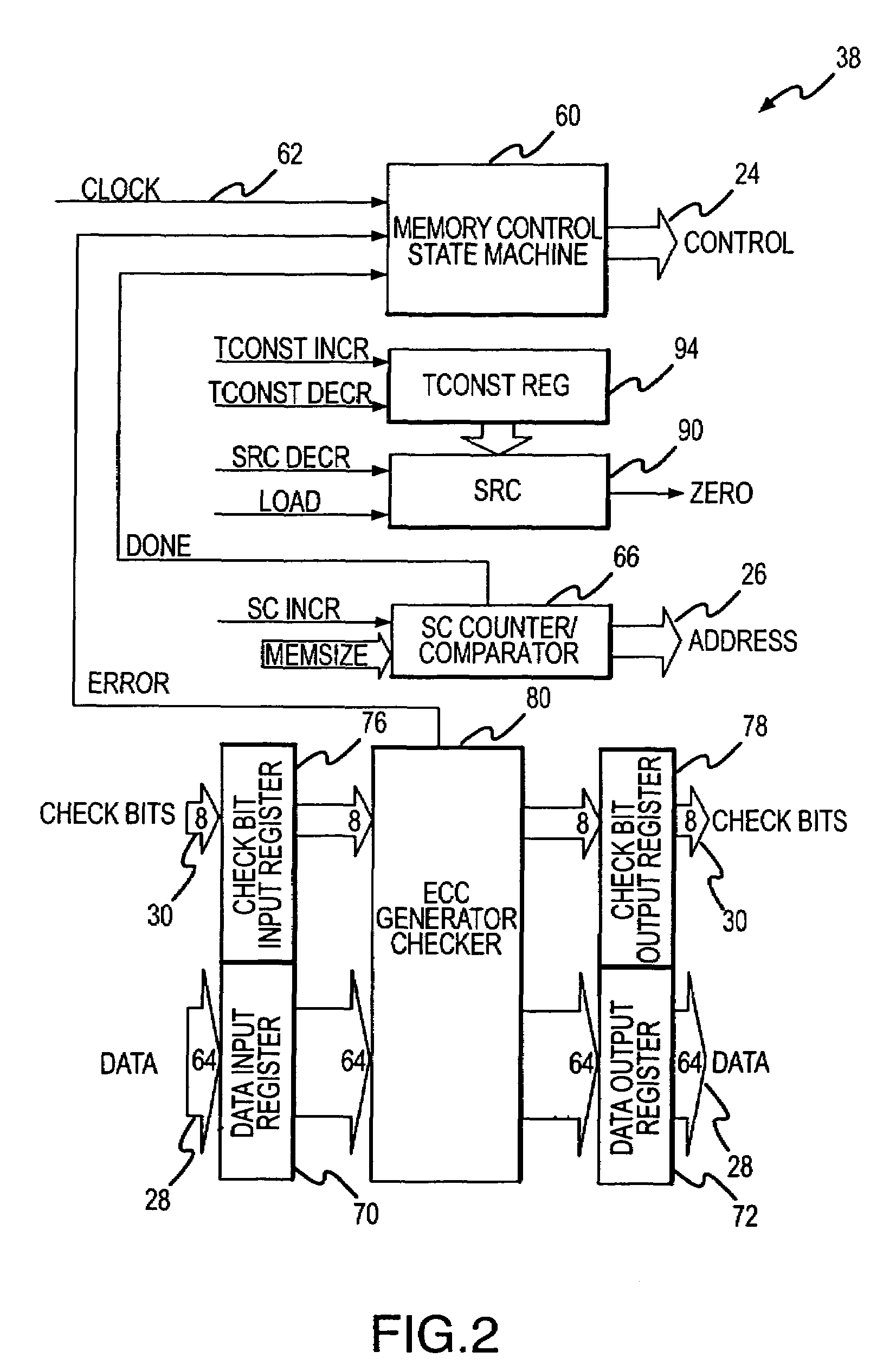
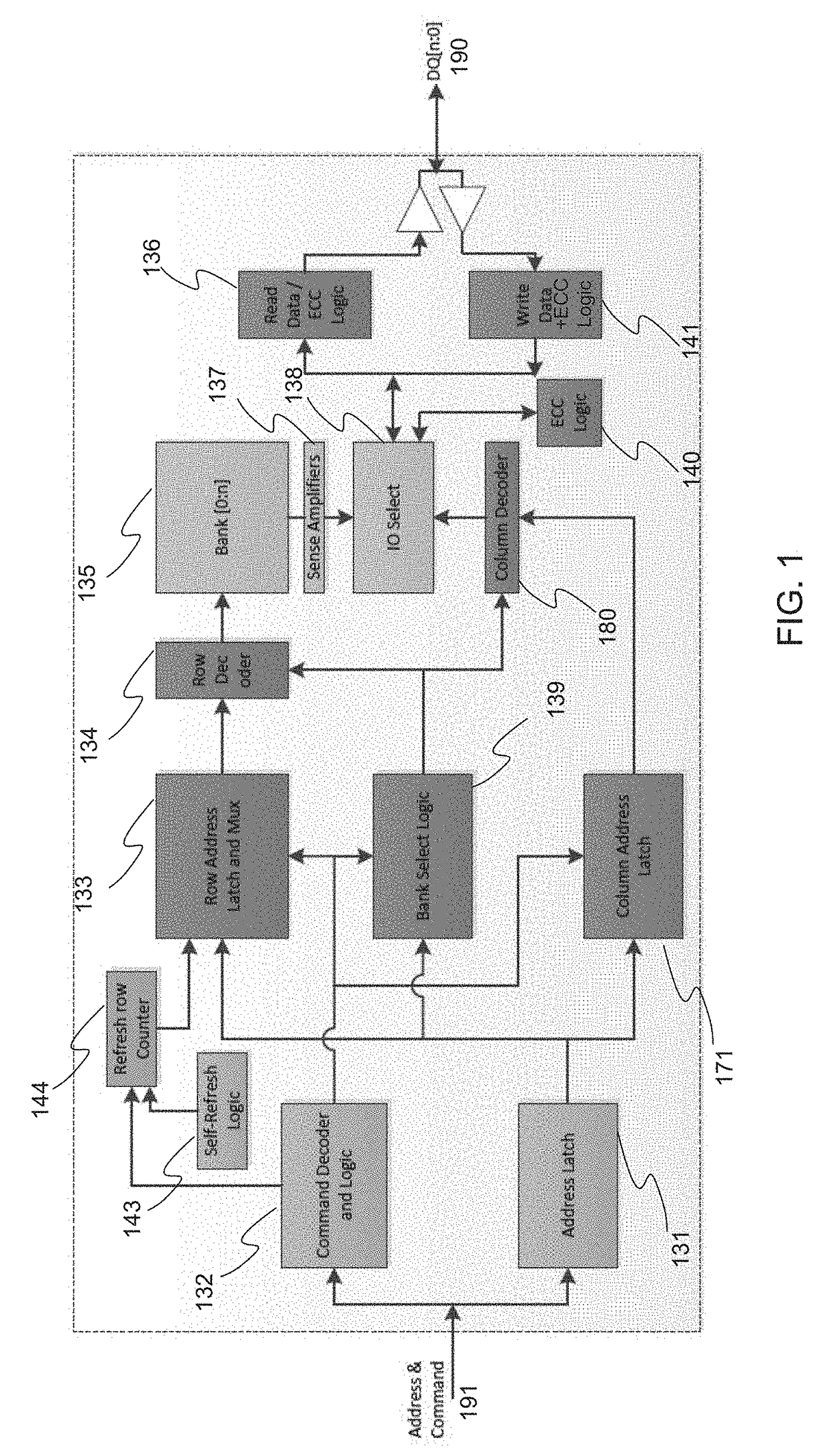
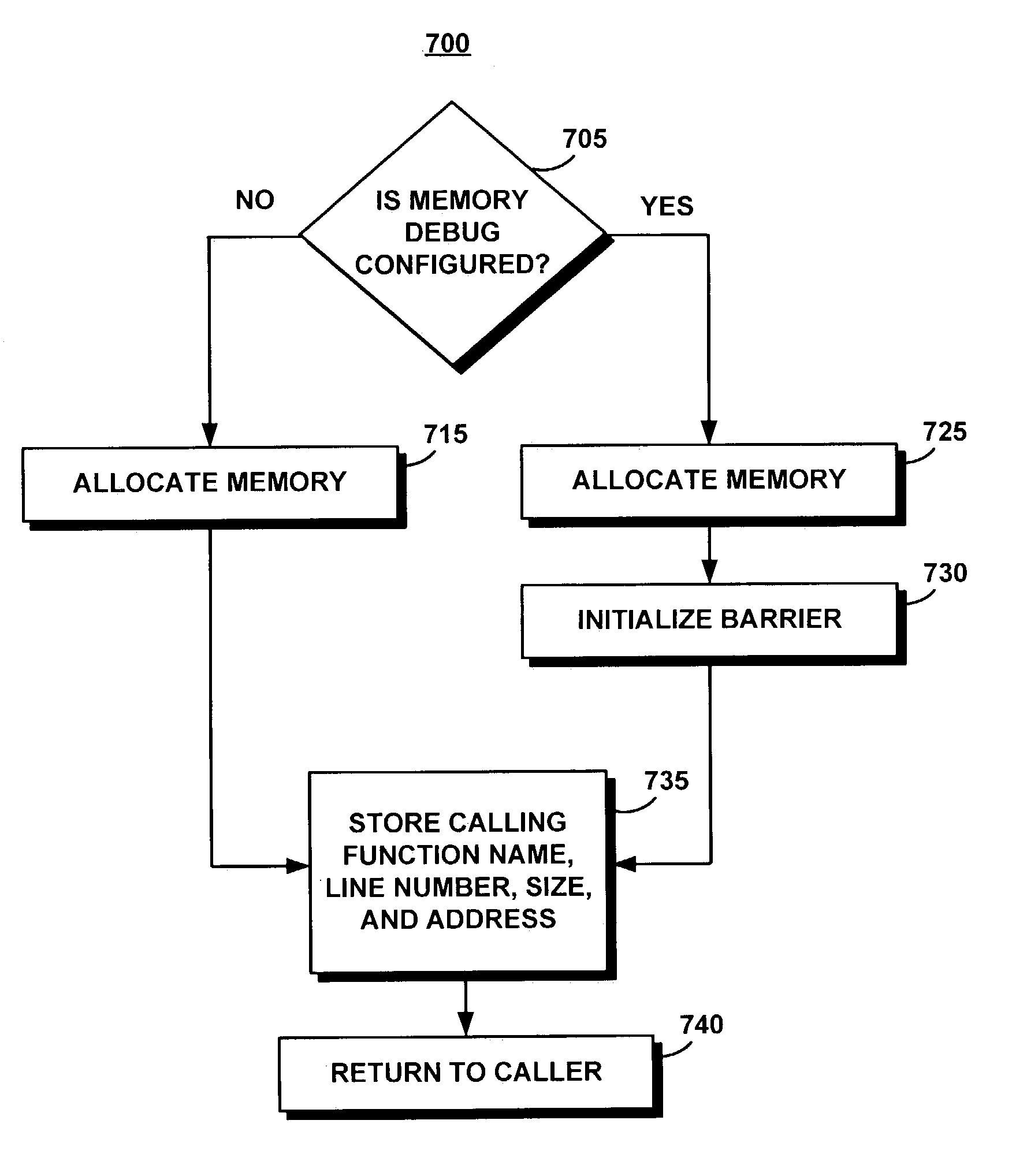
A scrubbing controller used with a DRAM stores data in an error correcting code format. The system then uses a memory control state machine and associated timer to periodically cause the DRAM to read the error correcting codes. An ECC generator / checker in the scrubbing controller then detects any errors in the read error correcting codes, and generates corrected error correcting codes that are written to the DRAM. This scrubbing procedure, by reading error correcting codes from the DRAM, inherently refreshes memory cells in the DRAM. The error correcting codes are read at rate that may allow data errors to be generated, but these errors are corrected in the memory scrubbing procedure. However, the low rate at which the error correcting codes are read results in a substantial power saving compared to refreshing the memory cells at a higher rate needed to ensure that no data errors are generated.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
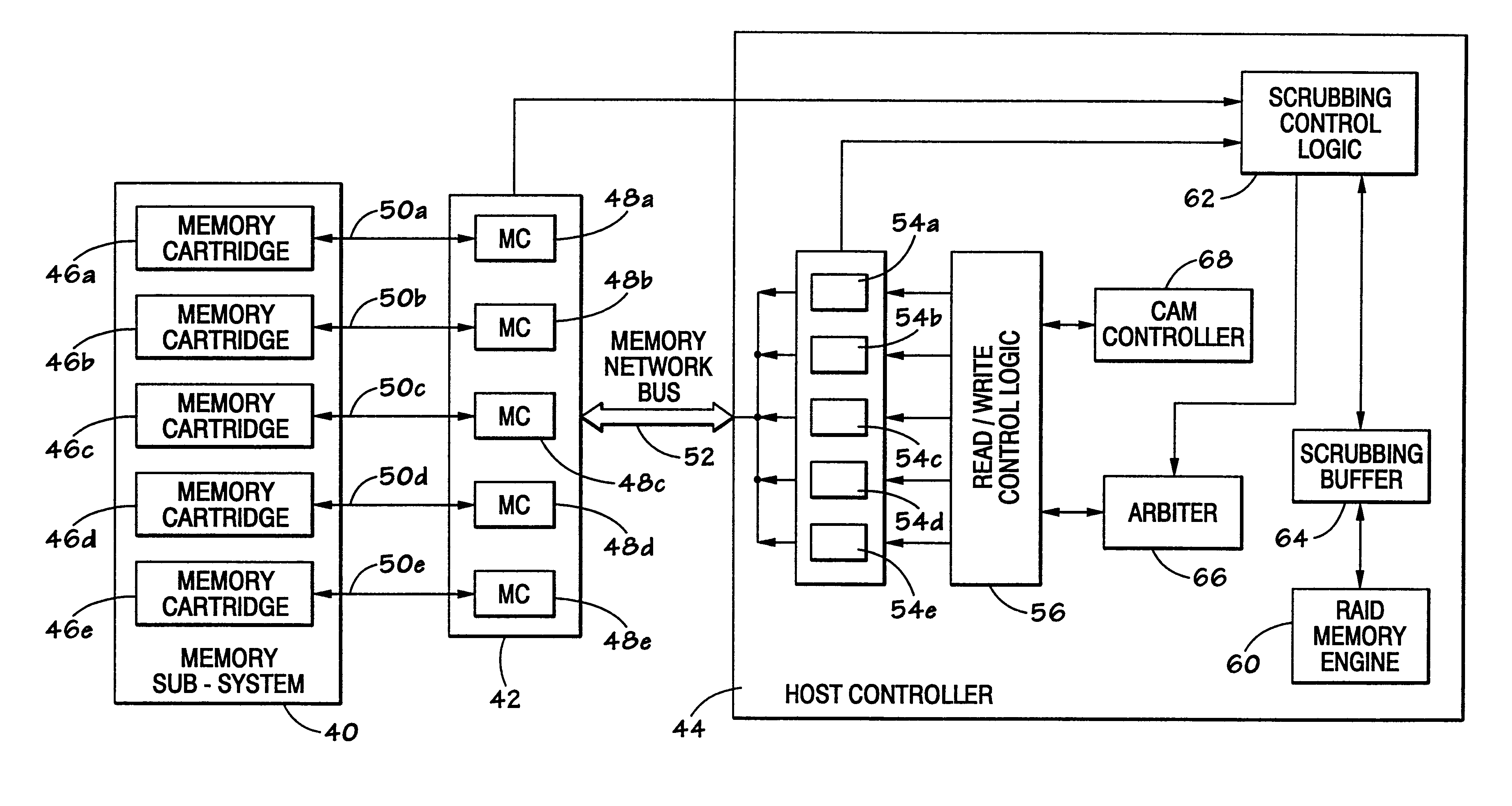
Real-time hardware memory scrubbing
A system and technique for correcting data errors in a memory device. More specifically, data errors in a memory device are corrected by scrubbing the corrupted memory device. Generally, a host controller delivers a READ command to a memory controller. The memory controller receives the request and retrieves the data from a memory sub-system. The data is delivered to the host controller. If an error is detected, a scrub command is induced through the memory controller to rewrite the corrected data through the memory sub-system. Once a scrub command is induced, an arbiter schedules the scrub in the queue. Because a significant amount of time can occur before initial read in the scrub write back to the memory, an additional controller may be used to compare all subsequent READ and WRITE commands to those scrubs scheduled in the queue. If a memory location is rewritten with new data prior to scheduled scrub corresponding to the same address location, the controller will cancel the scrub to that particular memory location.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
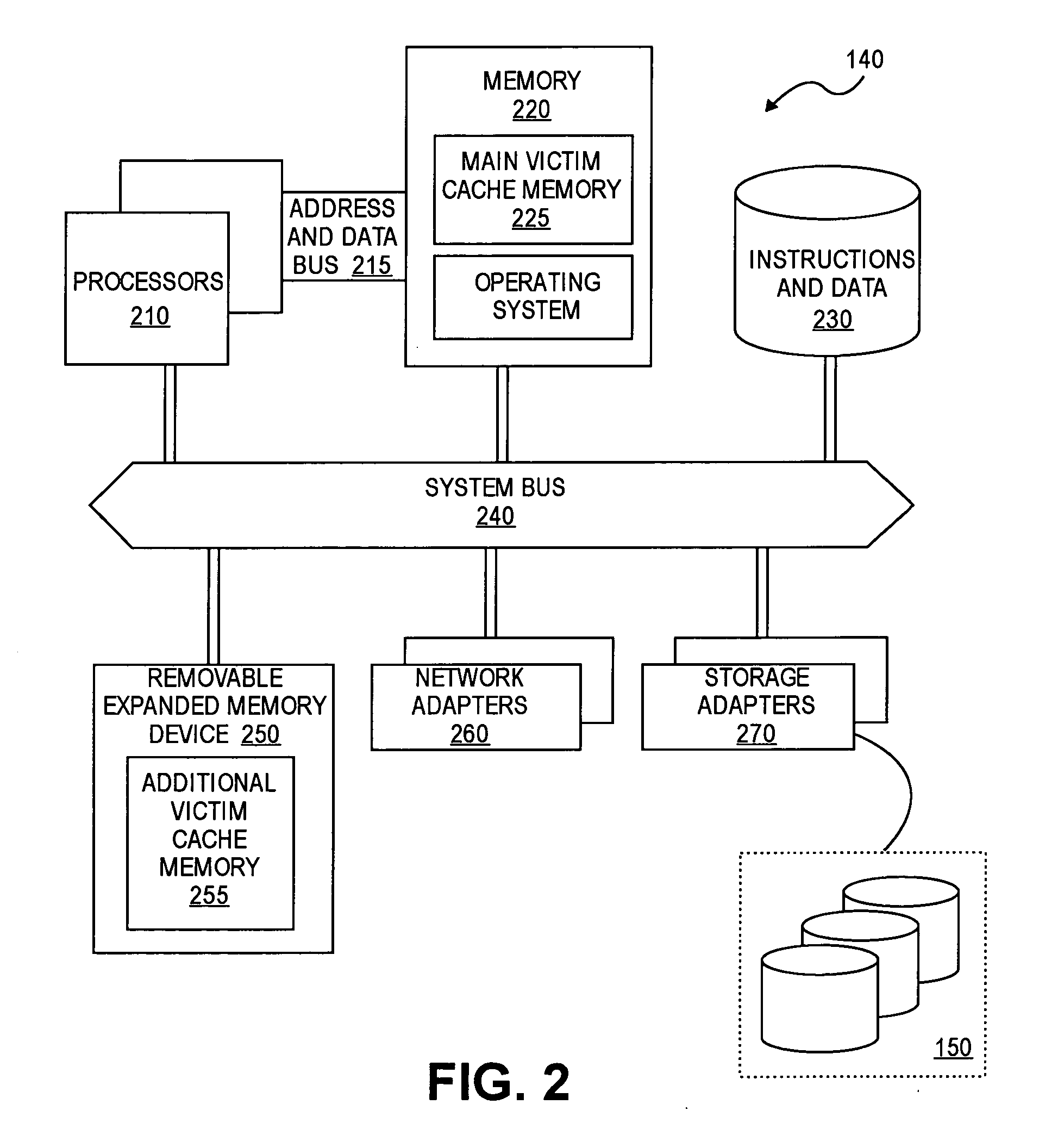
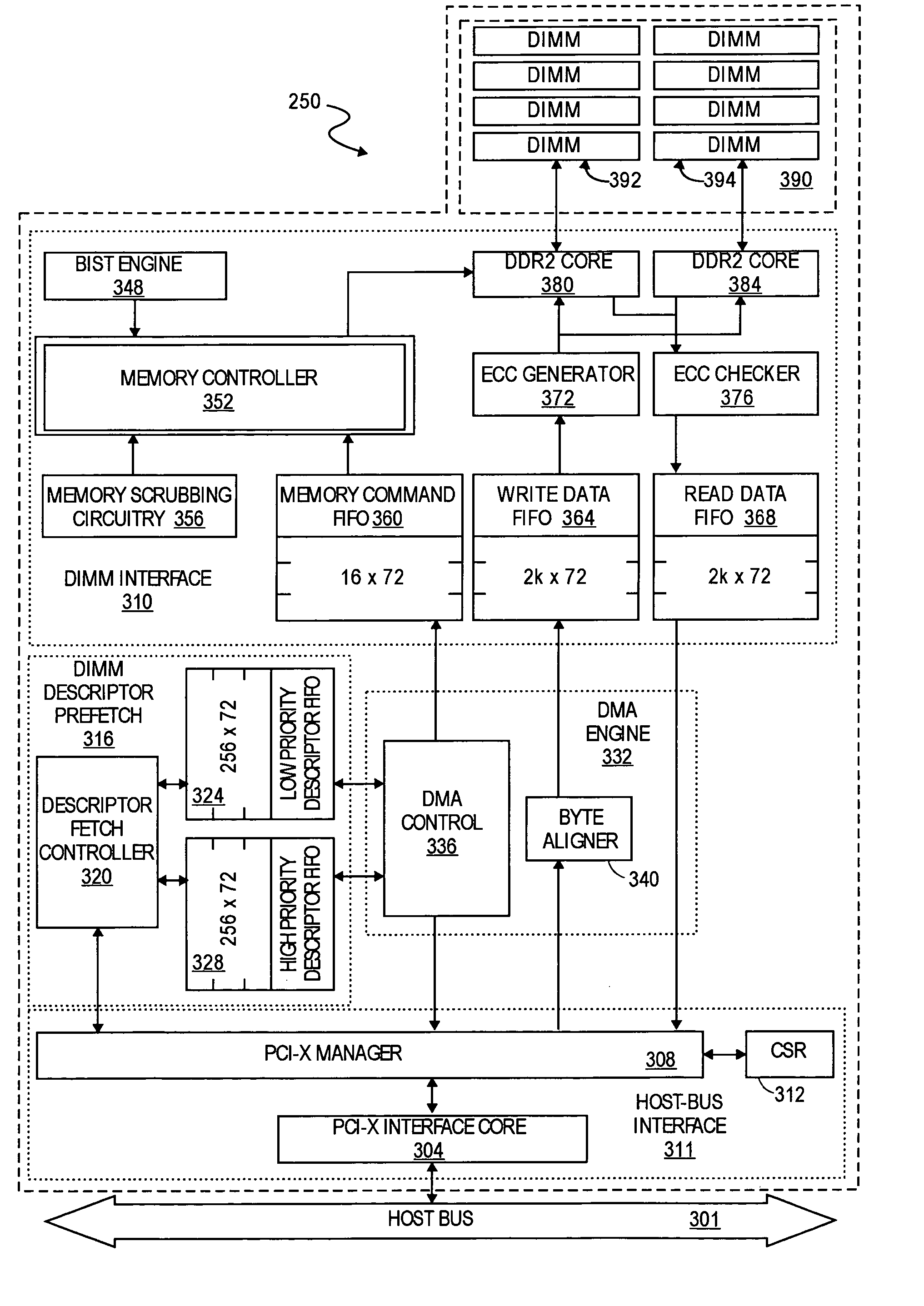
Memory scrubbing of expanded memory
Embodiments of the invention include a memory device, such as a removable expanded memory card, having a host bus interface that allows a host to access a memory of the device. The memory device also includes memory scrubbing circuitry to read data stored at addresses in the memory and to identify single-bit errors and multiple-bit errors in the data read from the memory.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
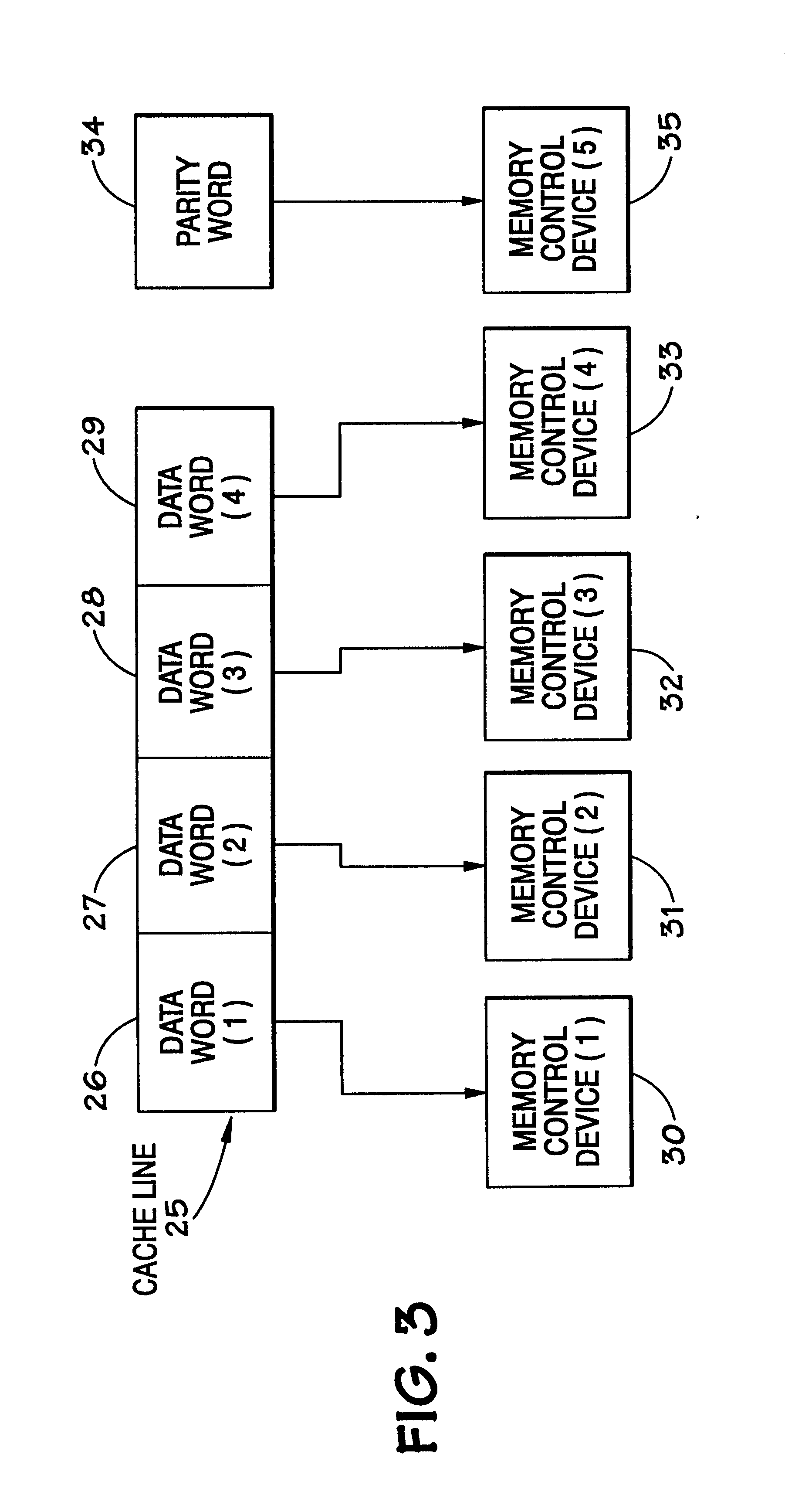
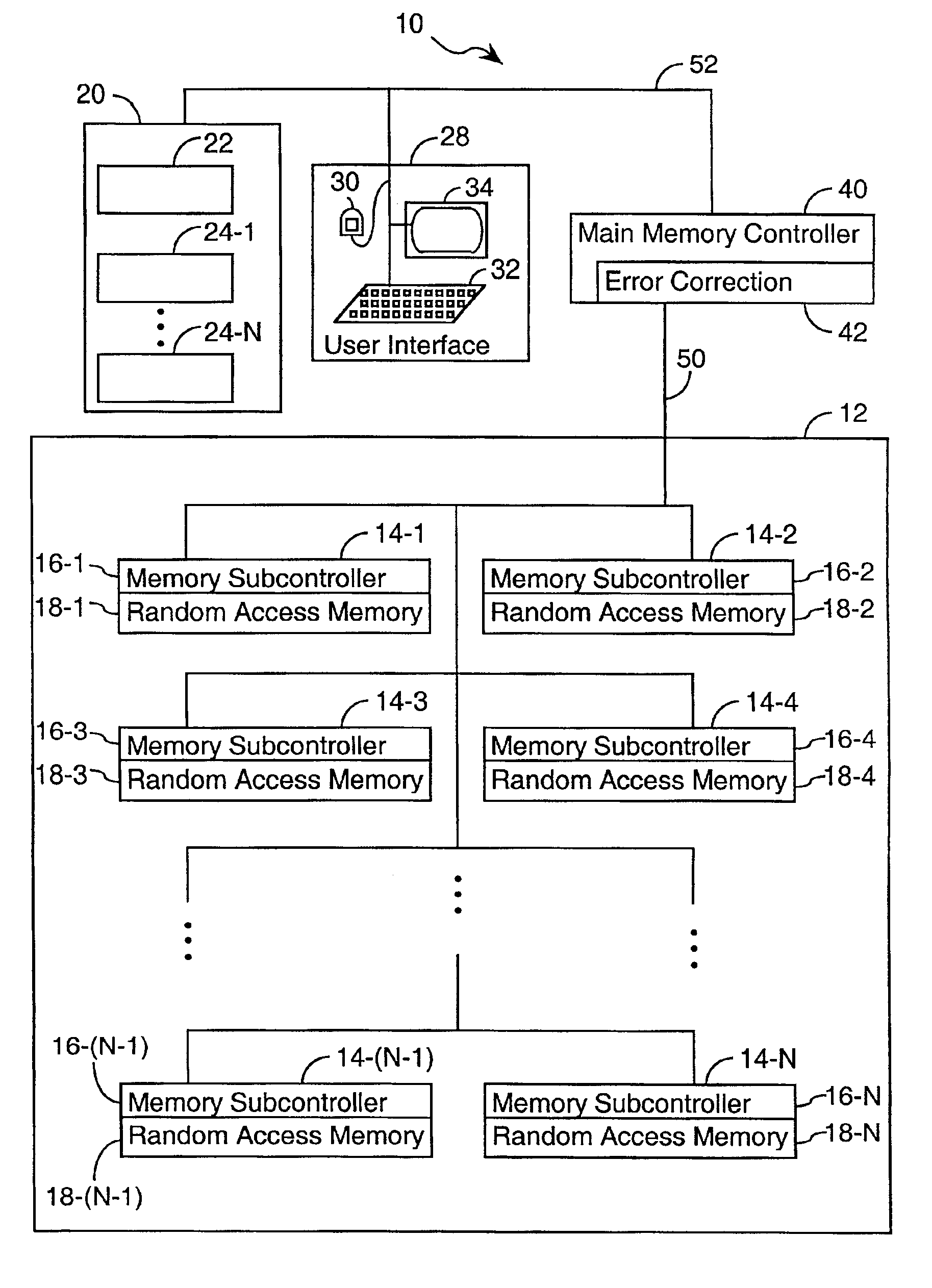
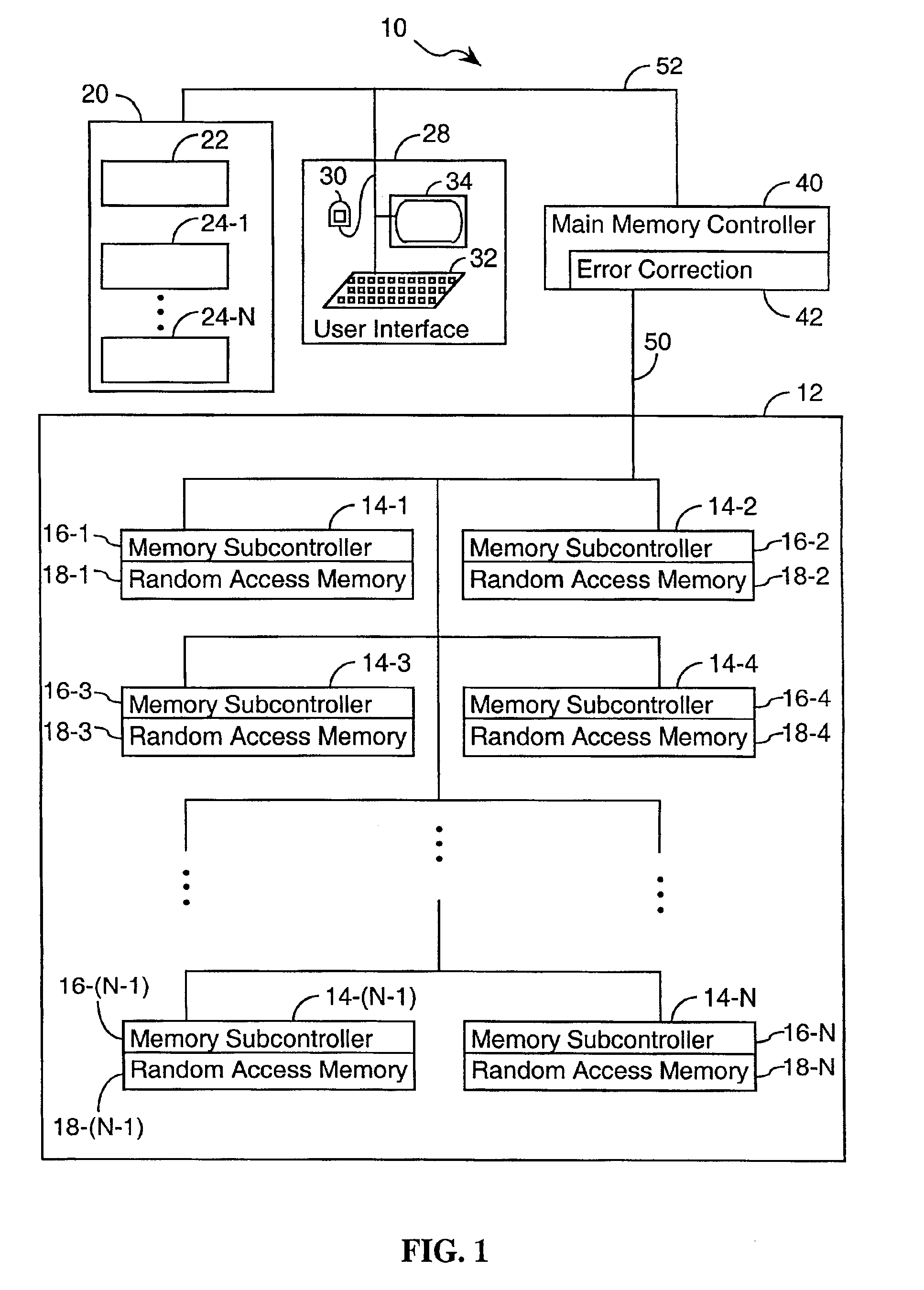
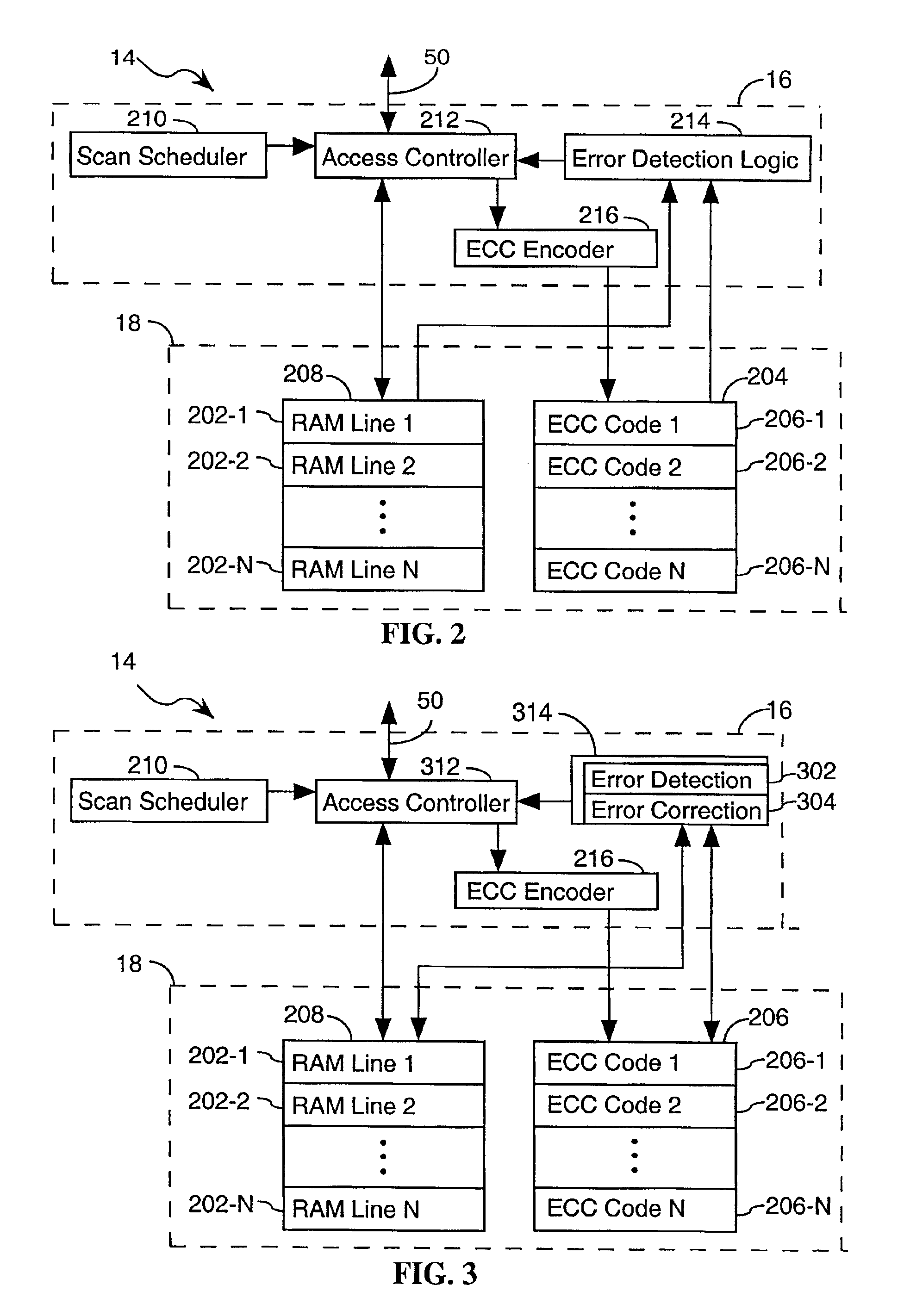
System and method for scrubbing errors in very large memories
InactiveUS6848063B2Improving memory scrubbing techniqueReduce failure rateError preventionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareMemory scrubbing
Systems and methods for improving scrubbing techniques are provided. In one aspect, the error correction code for a memory line is strengthened by reorganizing the memory line into distinct portions and providing an error code set that includes a distinct error code for each portion of the memory line. In another aspect of the invention, the scan rate is effectively increased by moving memory scrubbing functionality into the memory system and distributing it among a number of subcomponents that can operate scrubbing functions in parallel. The effective scan rate increase reduces the probability of failure for any given ECC strength.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Real-time hardware memory scrubbing
A system and technique for correcting data errors in a memory device. More specifically, data errors in a memory device are corrected by scrubbing the corrupted memory device. Generally, a host controller delivers a READ command to a memory controller. The memory controller receives the request and retrieves the data from a memory sub-system. The data is delivered to the host controller. If an error is detected, a scrub command is induced through the memory controller to rewrite the corrected data through the memory sub-system. Once a scrub command is induced, an arbiter schedules the scrub in the queue. Because a significant amount of time can occur before initial read in the scrub write back to the memory, an additional controller may be used to compare all subsequent READ and WRITE commands to those scrubs scheduled in the queue. If a memory location is rewritten with new data prior to scheduled scrub corresponding to the same address location, the controller will cancel the scrub to that particular memory location.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
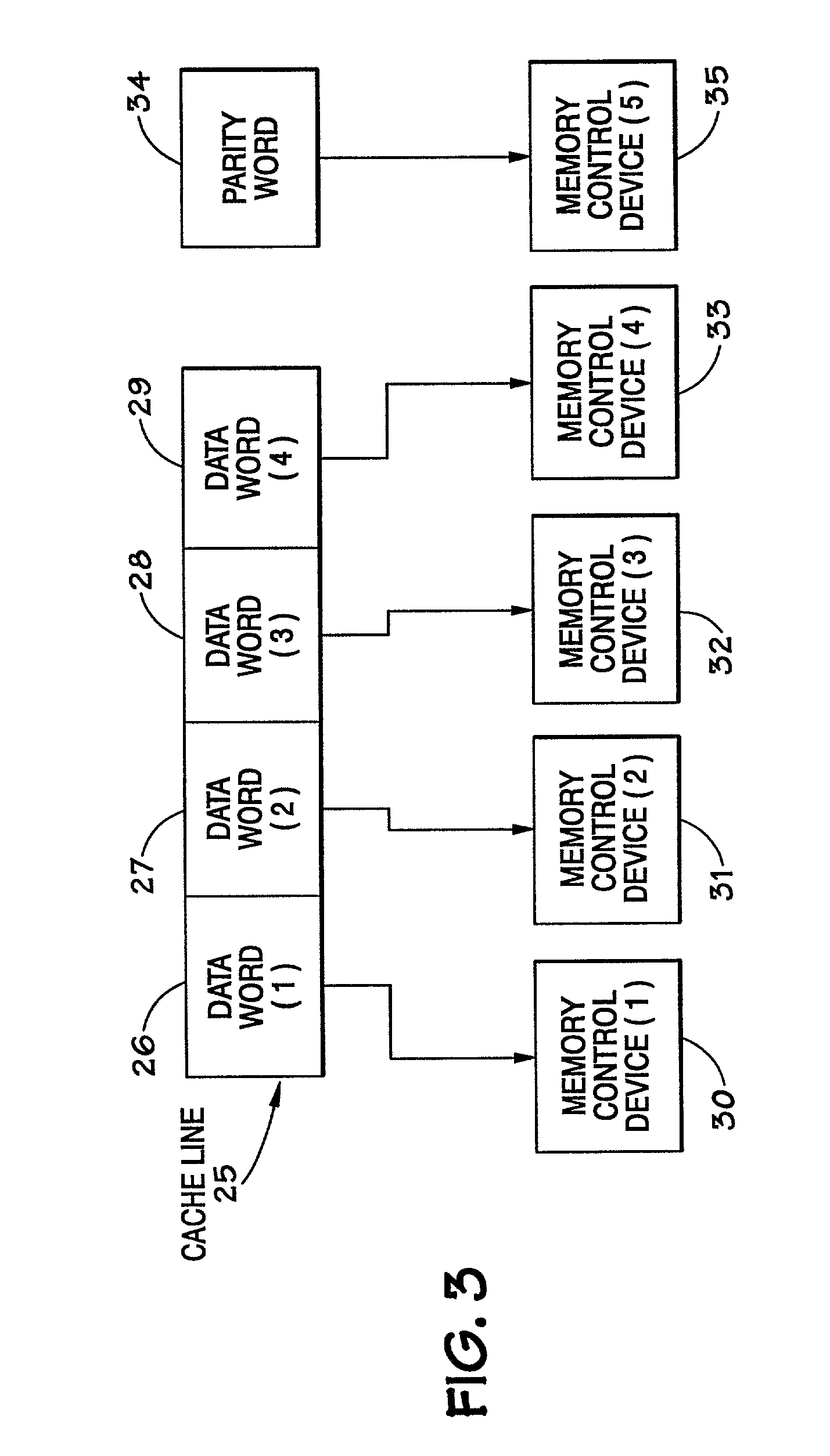
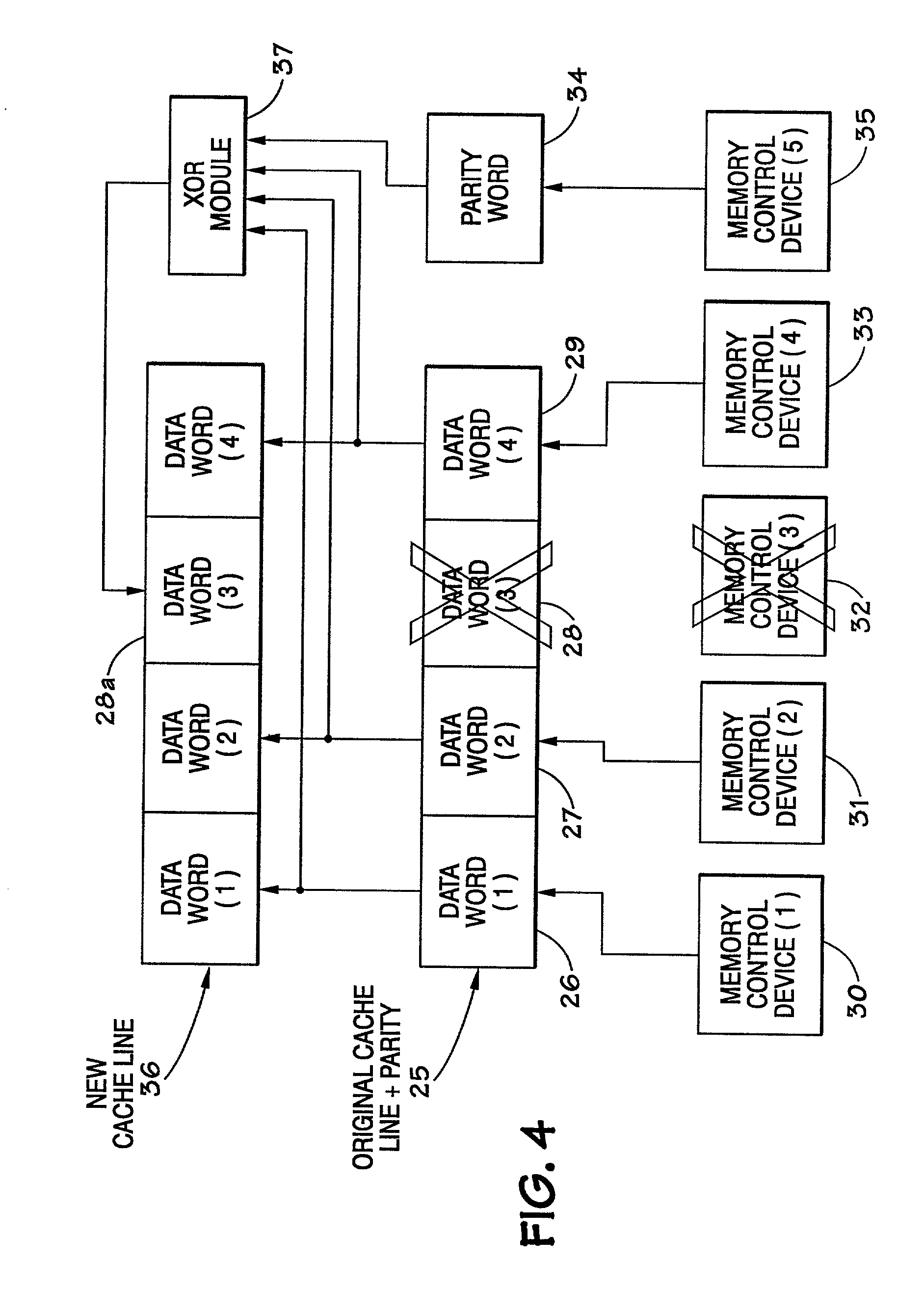
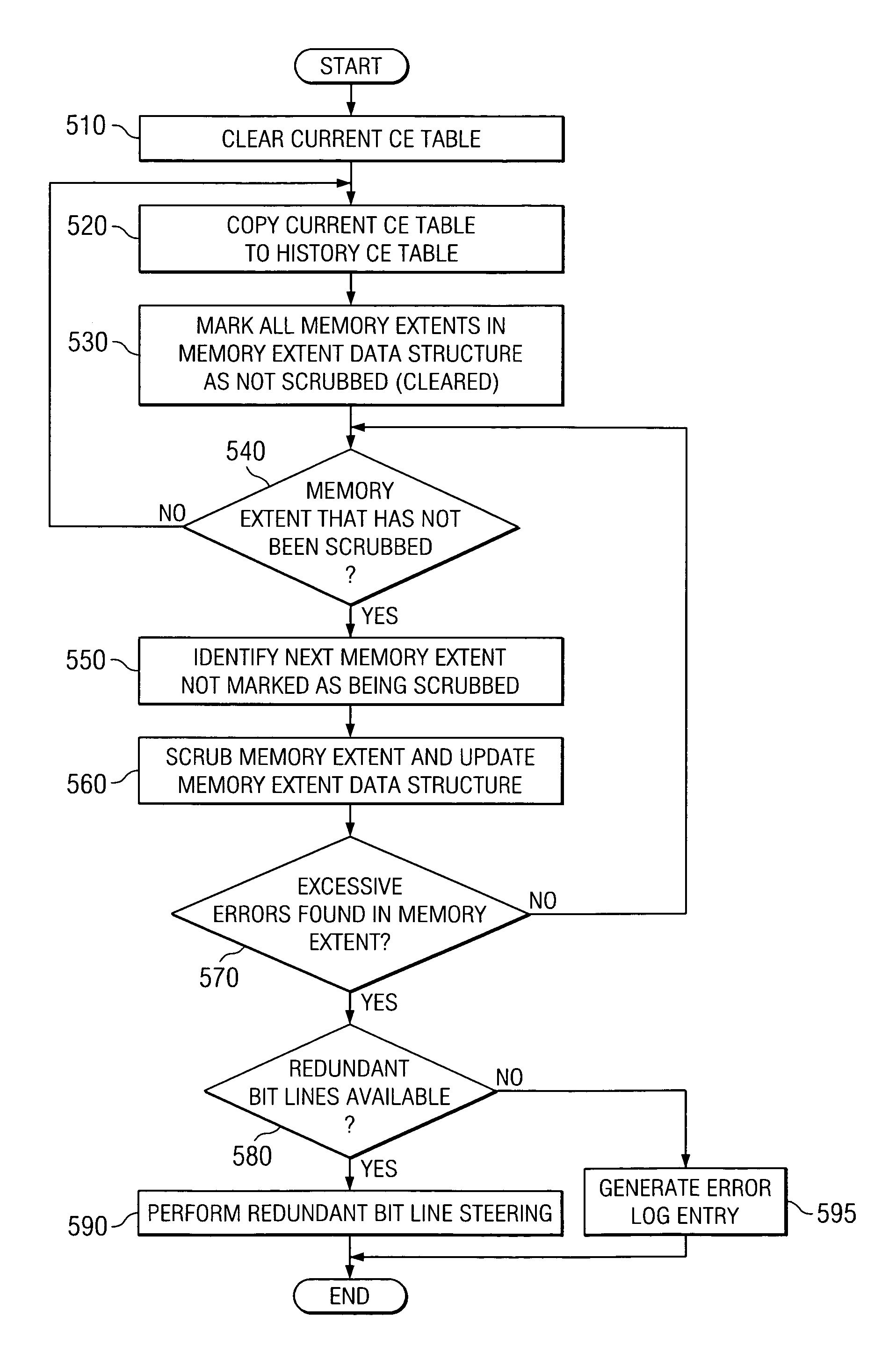
Method and apparatus for coordinating dynamic memory deallocation with a redundant bit line steering mechanism
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and apparatus for coordinating dynamic memory deallocation with a redundant bit line steering mechanism
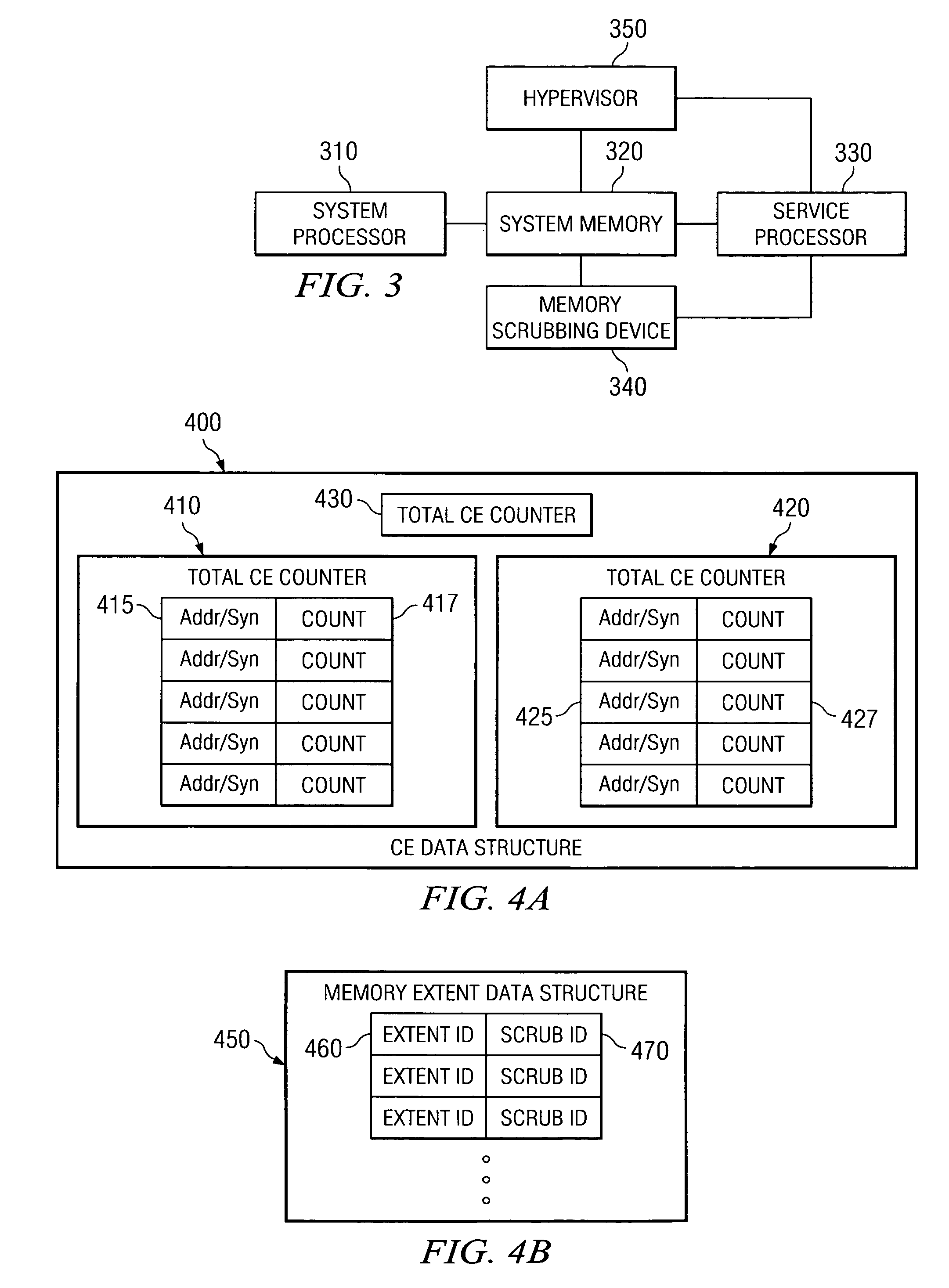
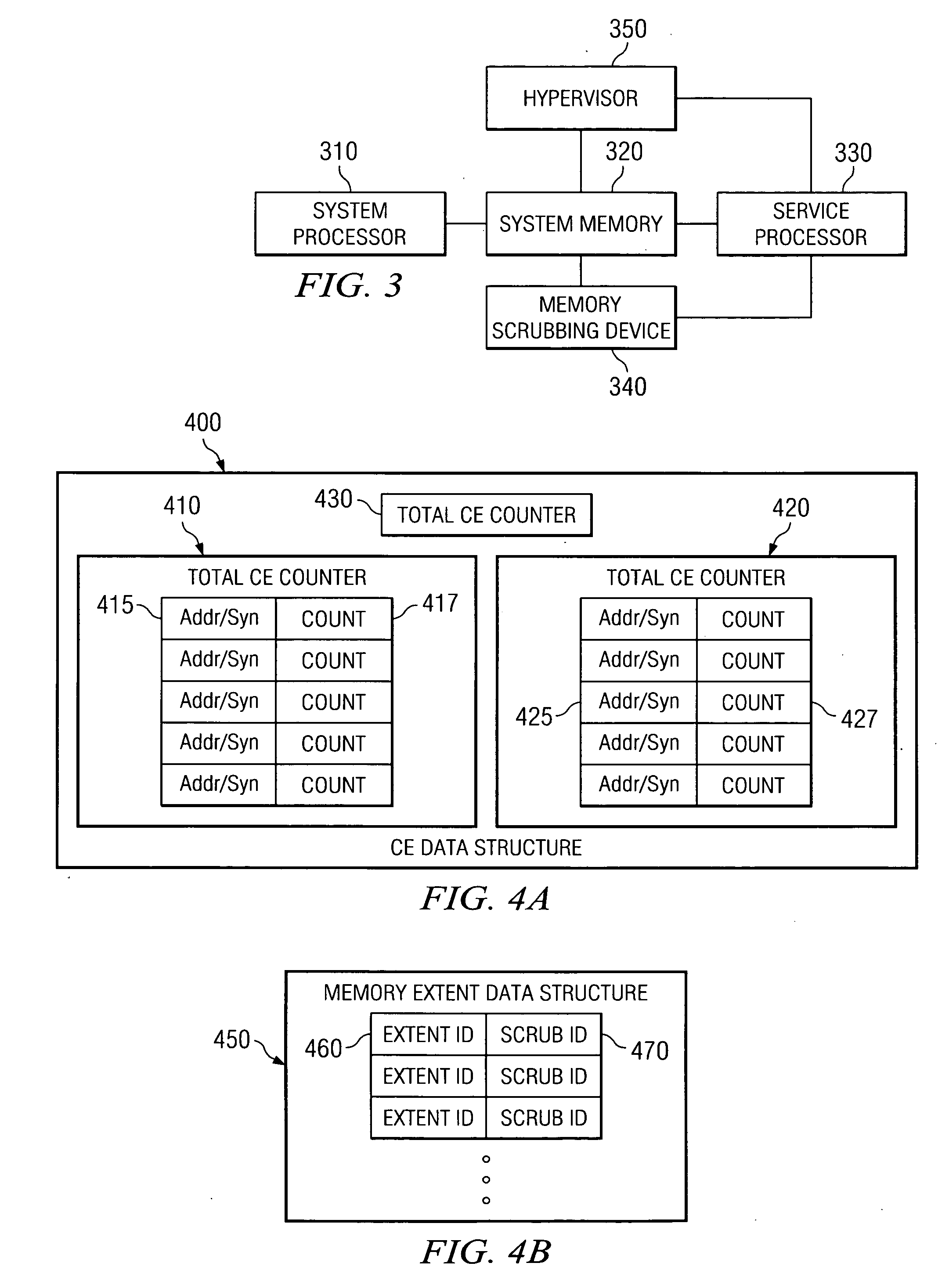
A method and apparatus for coordinating dynamic memory page deallocation with a redundant bit line steering mechanism are provided. With the method and apparatus, memory scrubbing and redundant bit line steering operations are performed in parallel with handling of notifications of runtime correctable errors. When a correctable error is encountered during runtime, and the correctable error is determined to be persistent, then dynamic memory page deallocation is requested of a hypervisor. The determination of persistence is based on a history CE table that is populated by the operation of the memory scrubbing and redundant bit line steering mechanism of a service processor. Thus, only those correctable errors that persist for longer than one memory scrubbing cycle are subject to memory page deallocation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for dynamically operating memory in a power-saving error correcting mode
A scrubbing controller used with a DRAM stores data in an error correcting code format. The system then uses a memory control state machine and associated timer to periodically cause the DRAM to read the error correcting codes. An ECC generator / checker in the scrubbing controller then detects any errors in the read error correcting codes, and generates corrected error correcting codes that are written to the DRAM. This scrubbing procedure, by reading error correcting codes from the DRAM, inherently refreshes memory cells in the DRAM. The error correcting codes are read at rate that may allow data errors to be generated, but these errors are corrected in the memory scrubbing procedure. However, the low rate at which the error correcting codes are read results in a substantial power saving compared to refreshing the memory cells at a higher rate needed to ensure that no data errors are generated.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Memory scrubbing of expanded memory
Embodiments of the invention include a memory device, such as a removable expanded memory card, having a host bus interface that allows a host to access a memory of the device. The memory device also includes memory scrubbing circuitry to read data stored at addresses in the memory and to identify single-bit errors and multiple-bit errors in the data read from the memory.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
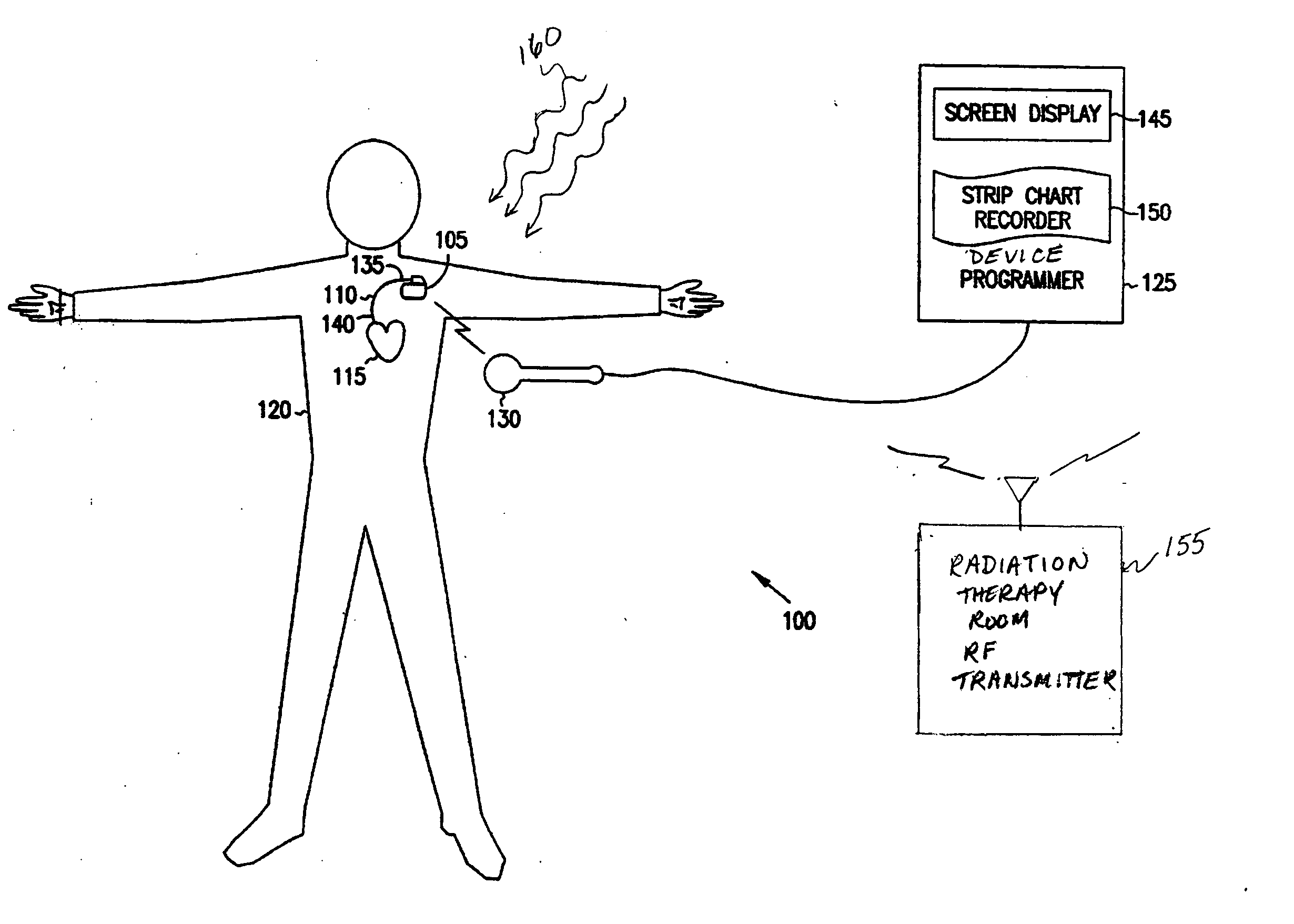
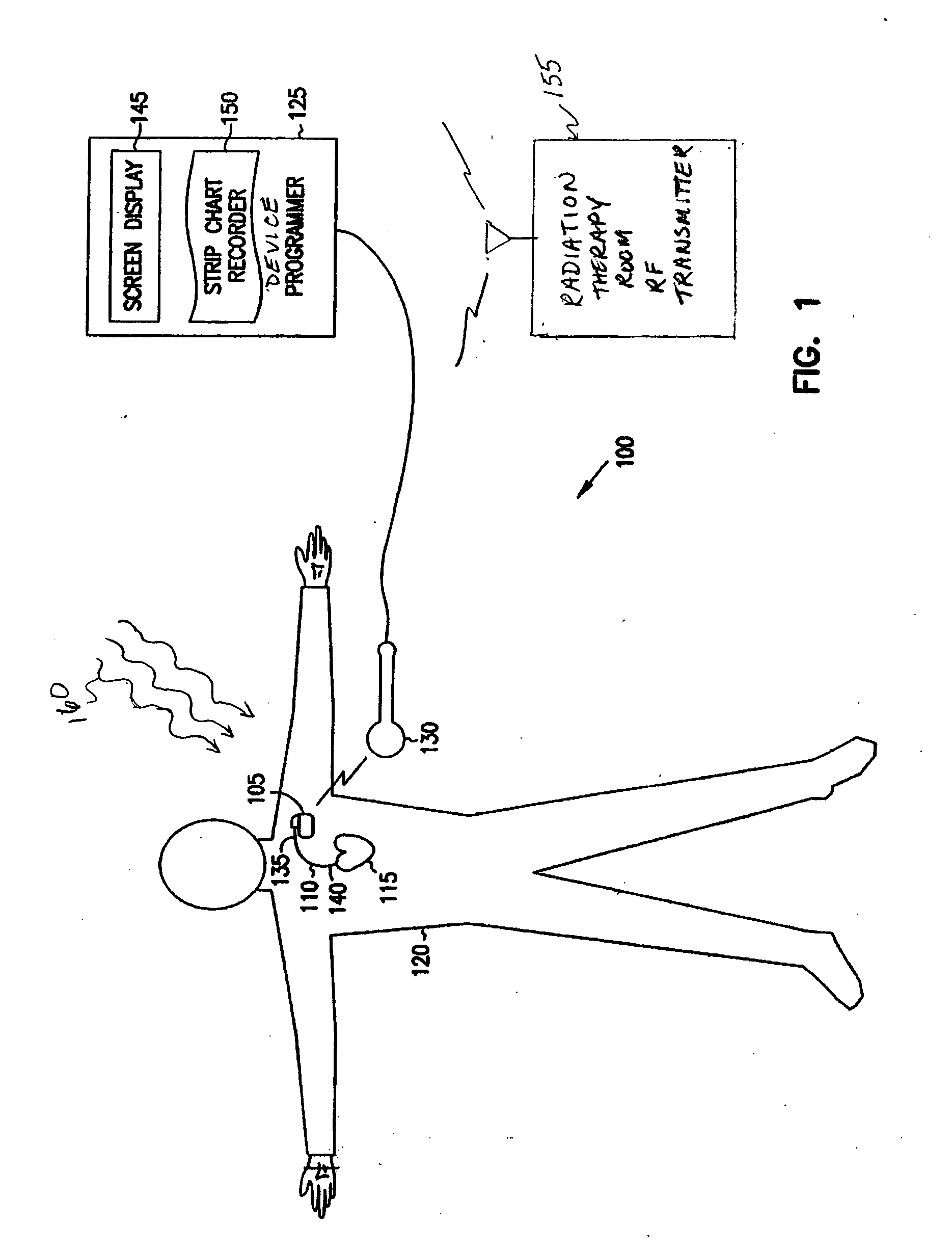
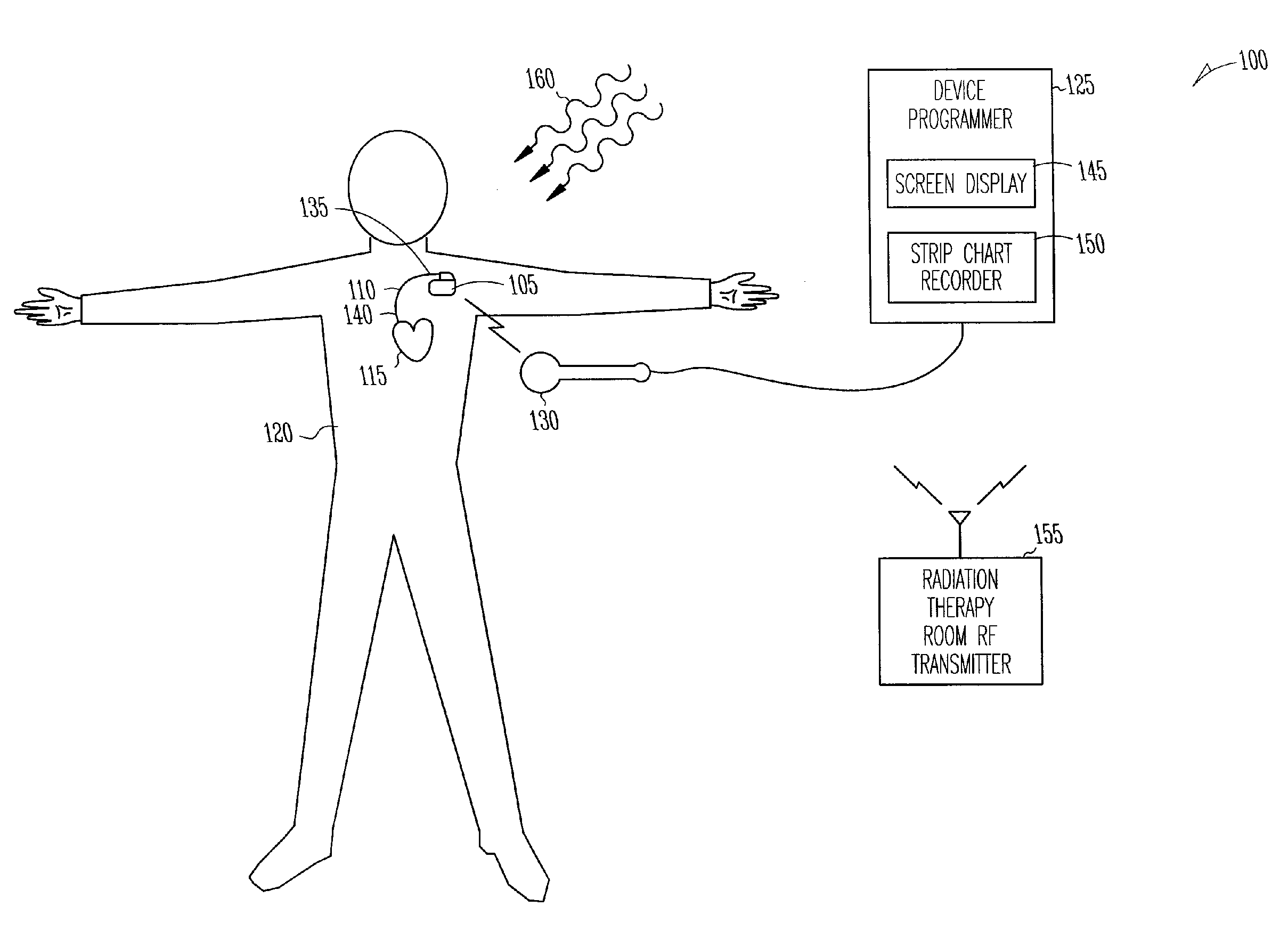
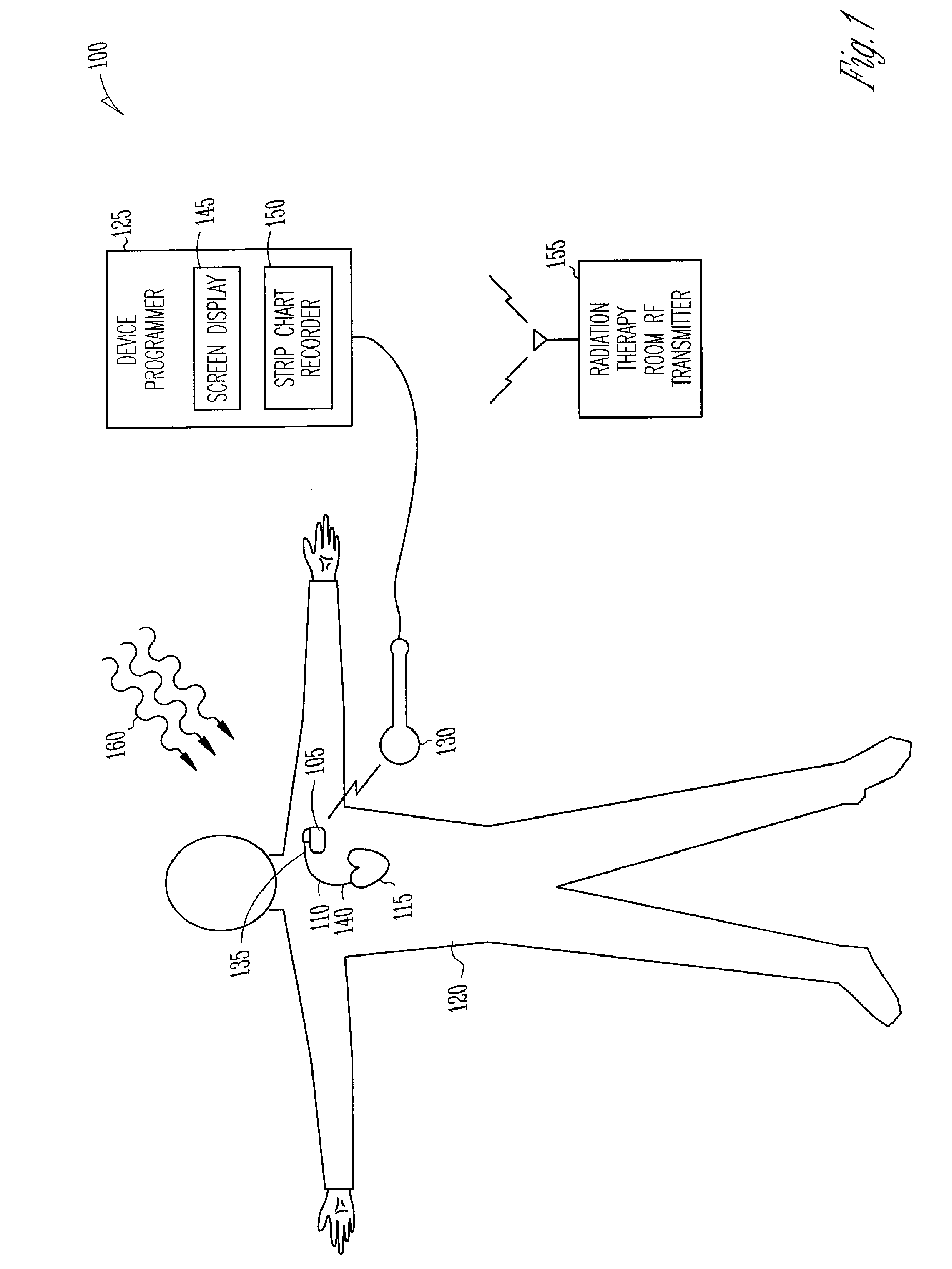
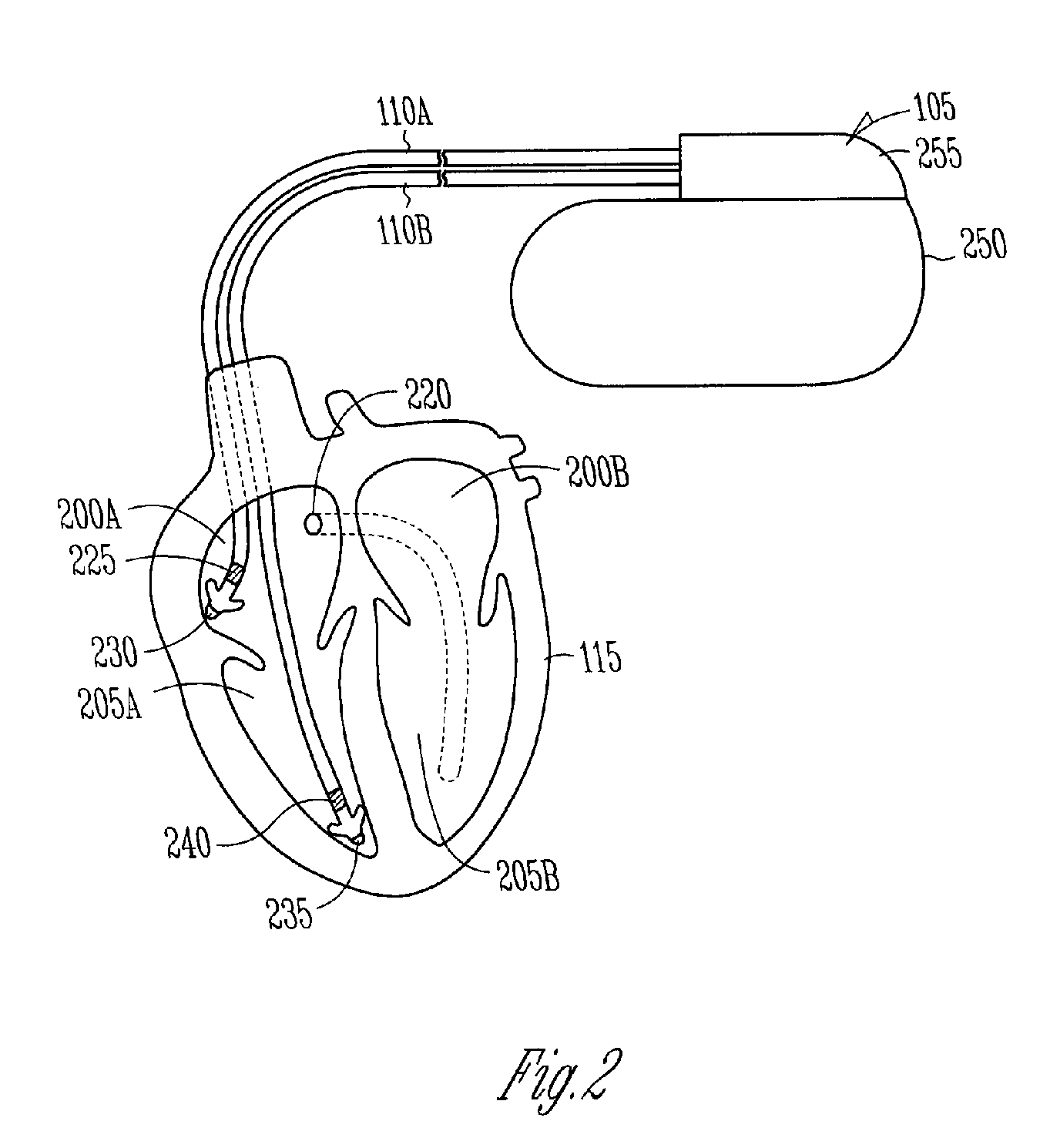
System and method for recovery from memory errors in a medical device
InactiveUS20050216063A1Improve errorIncrease ratingsElectrotherapyNon-redundant fault processingMemory scrubbingHigh energy
A system comprising an implantable medical device that comprises at least one electrical input to receive sensed electrical activity of a heart of a patient, a memory, and a controller circuit. The controller circuit is coupled to the electrical input and memory and is operable to enter a memory scrubbing mode that increases a rate of detecting and correcting single bit errors in the memory when the controller circuit determines the implantable device is in a high-energy radiation environment.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and method for recovery from memory errors in a medical device
InactiveUS20080103542A1Improve errorIncrease ratingsElectrotherapyNon-redundant fault processingElectricityHigh energy
A system comprising an implantable medical device that comprises at least one electrical input to receive sensed electrical activity of a heart of a patient, a memory, and a controller circuit. The controller circuit is coupled to the electrical input and memory and is operable to enter a memory scrubbing mode that increases a rate of detecting and correcting single bit errors in the memory when the controller circuit determines the implantable device is in a high-energy radiation environment.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
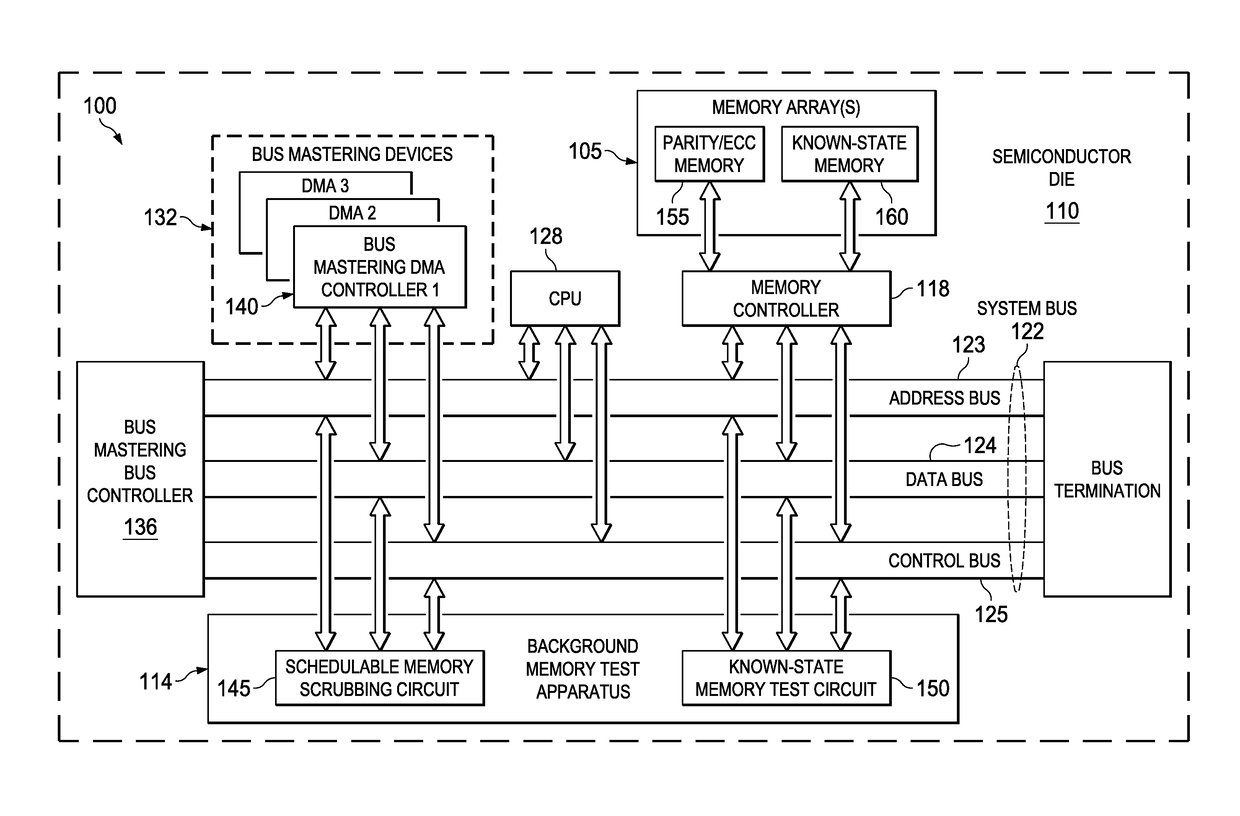
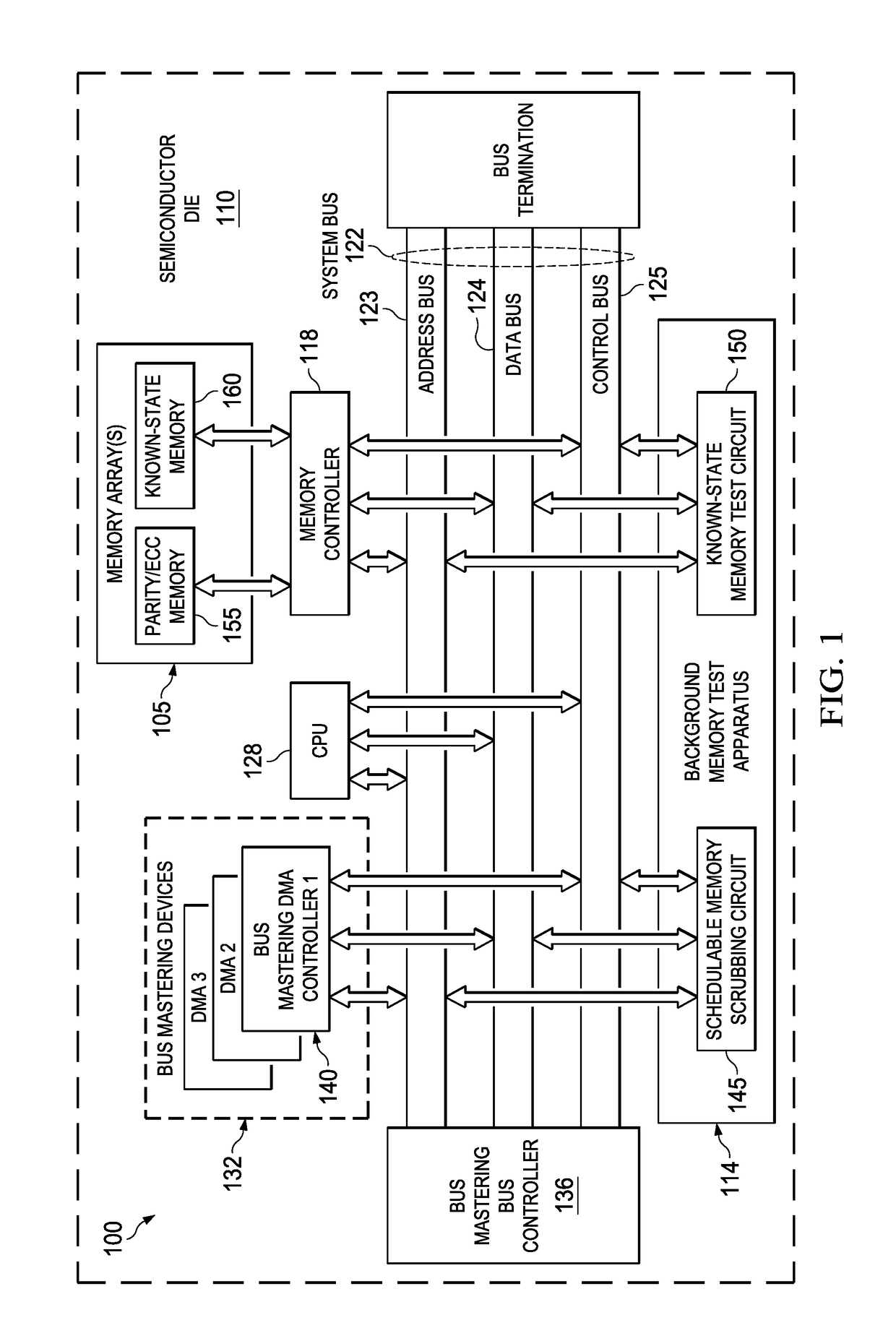
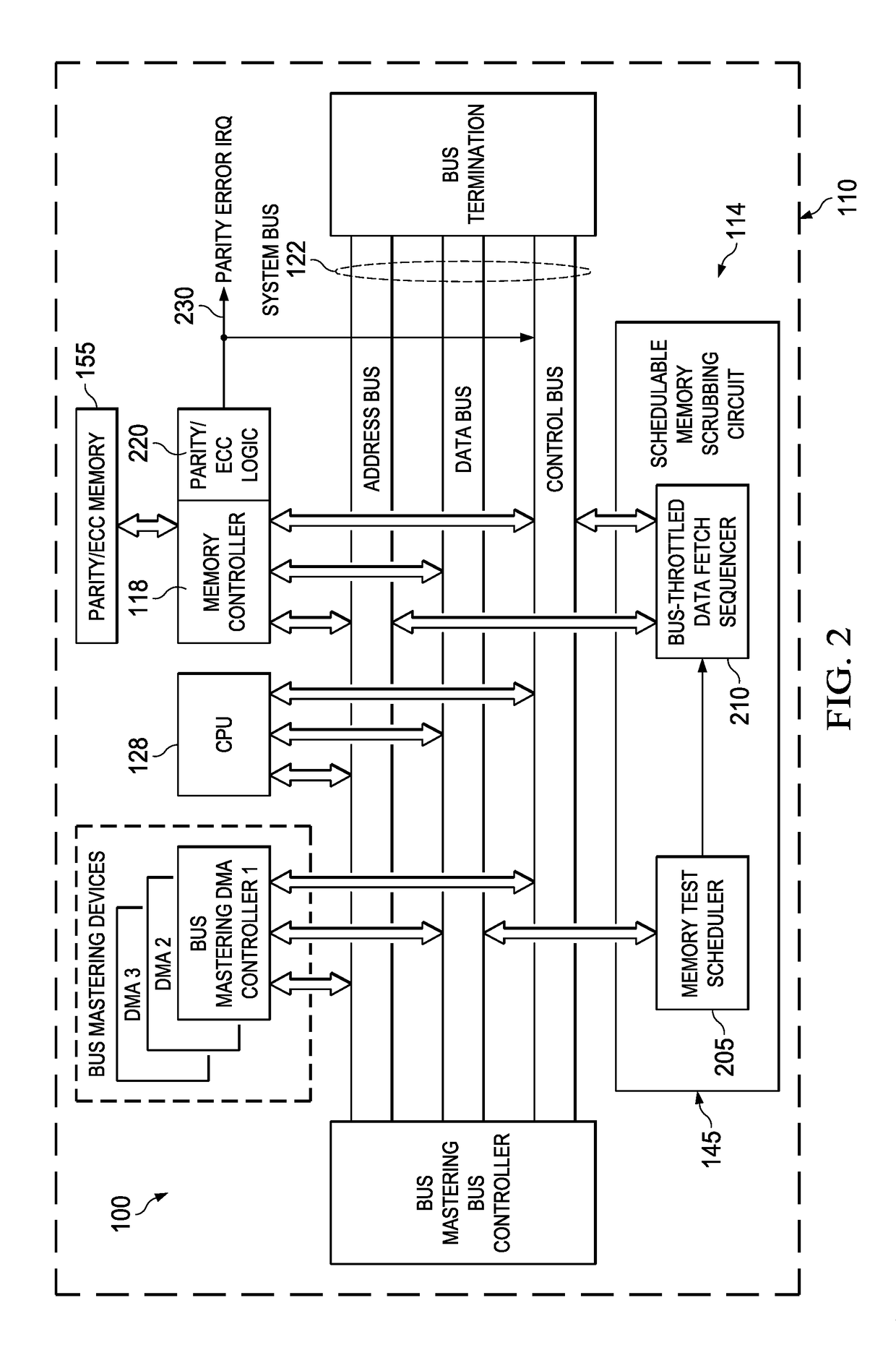
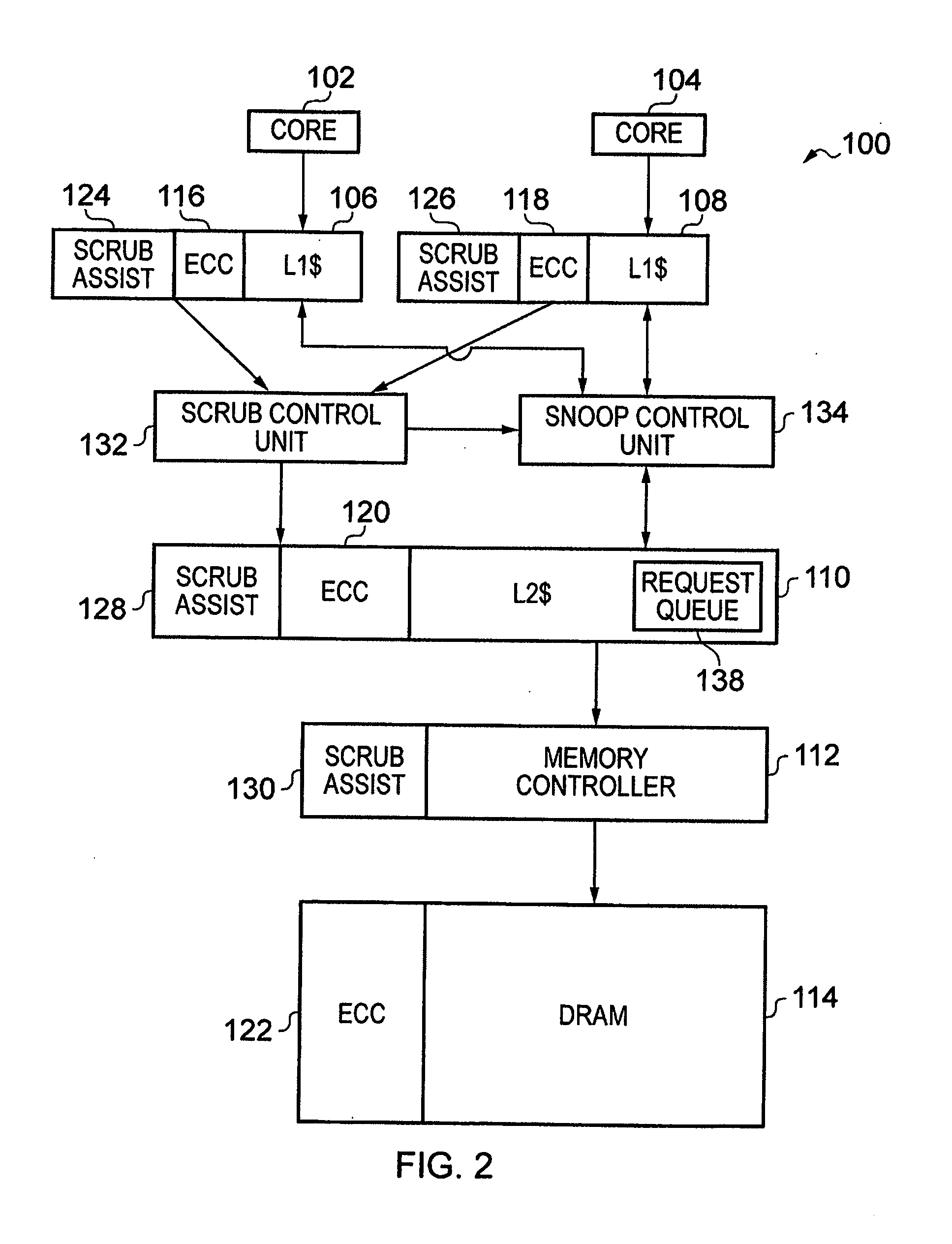
Background memory test apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20170133106A1Increase probabilityImpact system throughputCode conversionStatic storageError processingMemory scrubbing
A schedulable memory scrubbing circuit and / or a known-state memory test circuit (collectively, background memory test apparatus (“BGMTA”)) are located on-chip with an integrated computing system. The BGMTA operates in parallel with a system CPU but shares a system bus with the CPU. The BGMTA sequentially reads one word at a time from a block of memory to be tested during system bus idle cycles. The schedulable memory scrubbing circuit embodiment tests on-chip parity / ECC memory arrays using memory controller-implemented parity or ECC error detection to trigger error handling interrupts. The known-state memory test circuit embodiment performs CRC calculations on known-state memory arrays as each data word is read sequentially. A final resulting CRC calculation value is compared to a known CRC value for the block, sometimes referred to as a “golden CRC.” If the two CRC values differ, a CRC error interrupt is triggered for servicing by the CPU.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Memory scrubbing
ActiveUS20120254698A1Ensure reliabilityReduce participationError correction/detection using block codesStatic storageMemory scrubbingProbable Case
A data processing apparatus is provided which comprises a processor unit configured to perform data processing operations in response to a sequence of instructions and a storage unit configured to store data values for access by the processor unit when performing its data processing operations. Redundant error control data is stored in association with the data values, the redundant error control data enabling identification of an error in the data values. The data processing apparatus also comprises a data scrubbing unit configured to perform a data scrubbing process on at least a subset of the data values, the data scrubbing process comprising determining with reference to the redundant error control data if an error is present in that subset of data values and, where possible, correcting that error with reference to the redundant error control data. The data scrubbing unit is configured to receive a scrub transaction issued within said data processing apparatus, and to perform the data scrubbing process upon receipt of the scrub transaction.
Owner:ARM LTD
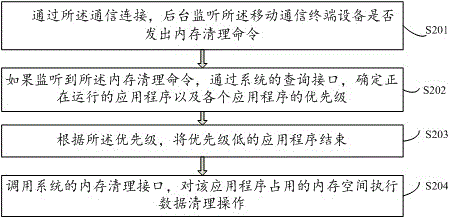
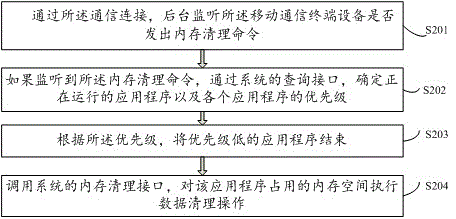
Memory cleaning method and device for video playback equipment
InactiveCN103607643AFriendly operation interfaceAvoid occupyingSelective content distributionComputer hardwareTerminal equipment
The invention relates to the field of memories and provides a memory cleaning method and a memory cleaning device for video playback equipment. The video playback equipment is in communication connection with mobile communication terminal equipment in advance on the side of the mobile communication terminal equipment. The method comprises the following steps: providing a user operation entrance in a user interface of the mobile communication terminal equipment; receiving a request for cleaning the memory of the video playback equipment transmitted by a user through the user operation entrance; transmitting a memory cleaning command to the video playback equipment through the communication connection, so that the video playback equipment executes the memory cleaning operation according to the memory cleaning command. According to the method, a phenomenon that lots of memory space is occupied by unimportant programs is avoided, and the operating speed of the whole system is improved.
Owner:LE SHI ZHI ZIN ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY (TIANJIN) LTD
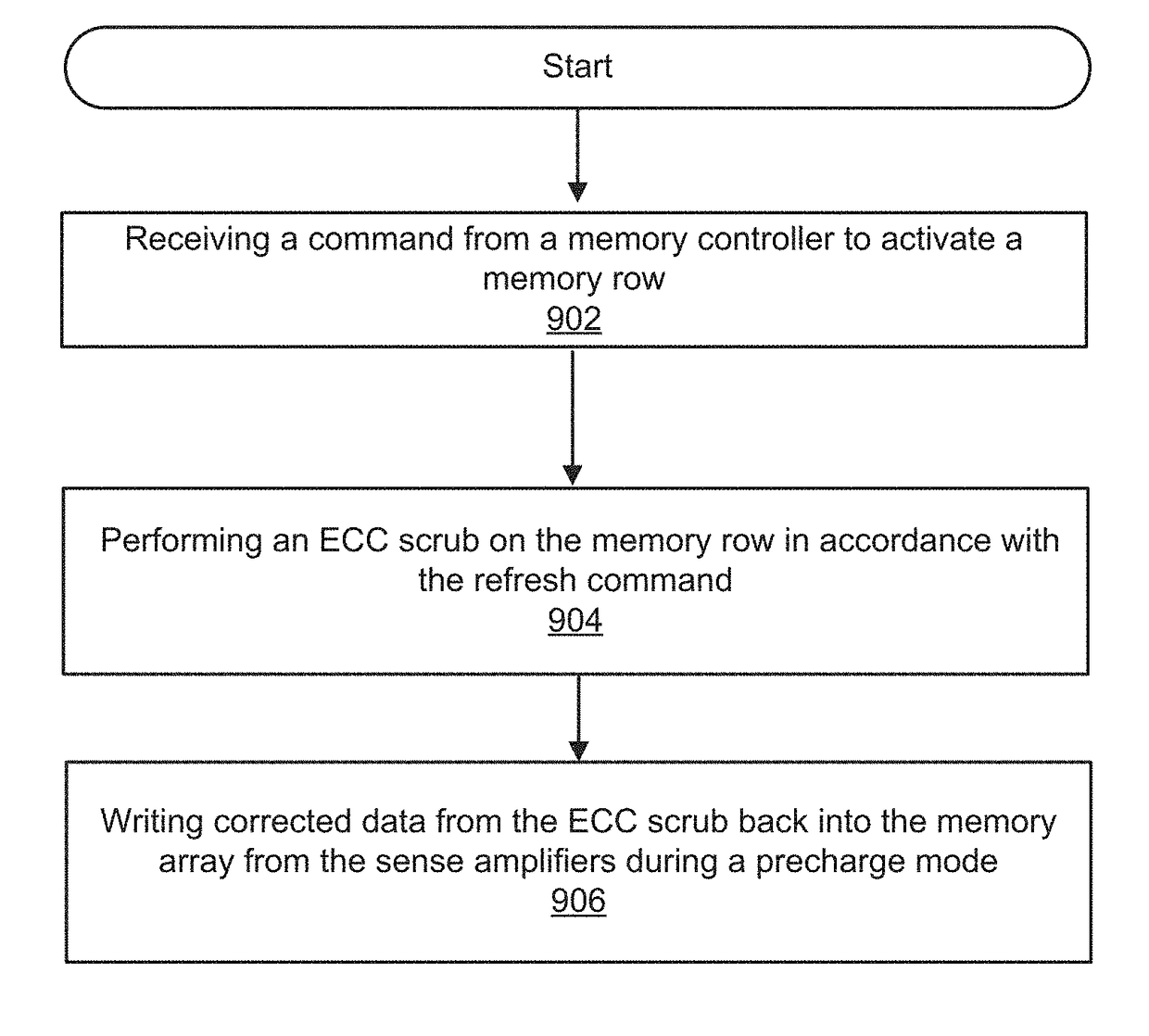
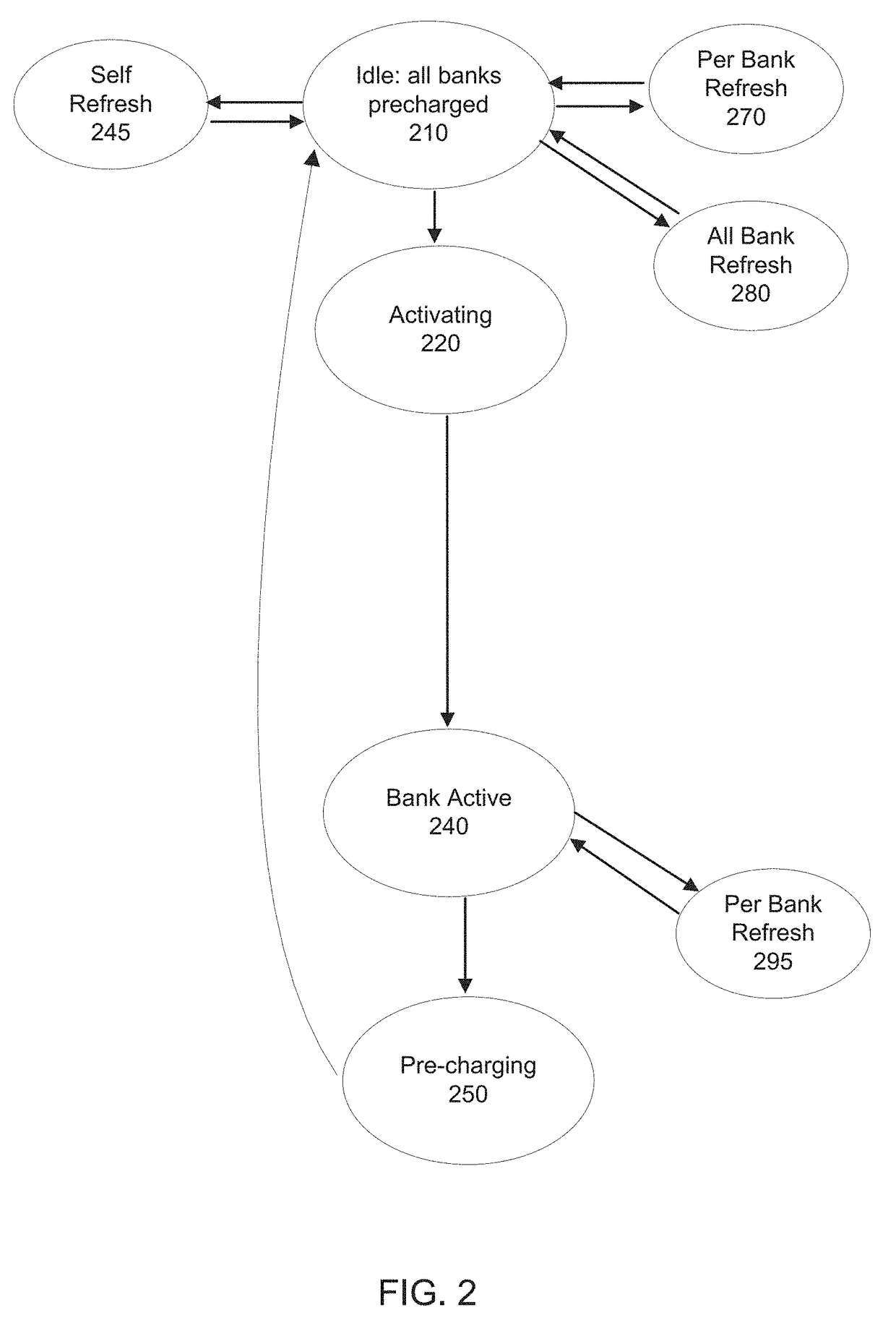
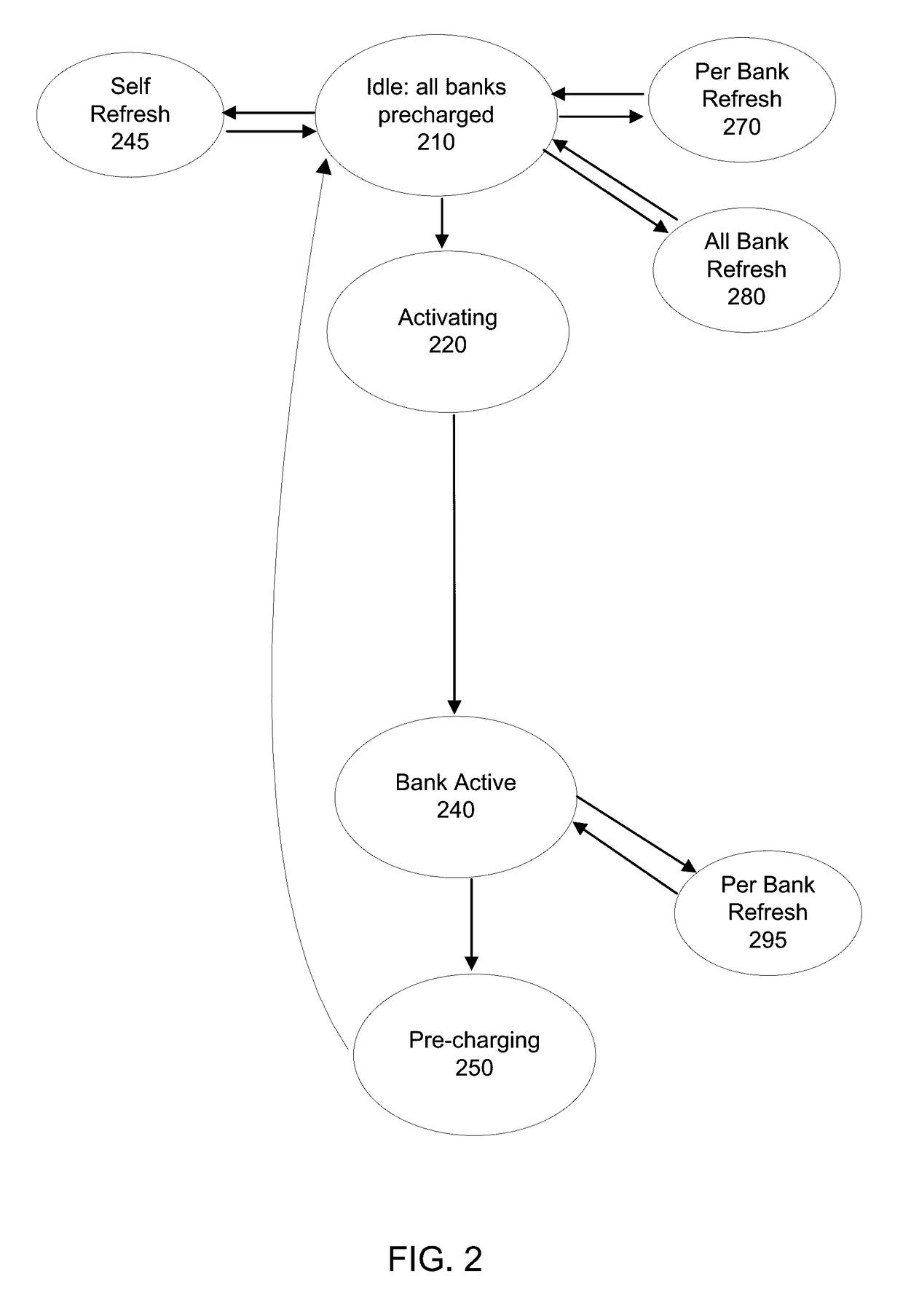
Method for memory scrub of DRAM with internal error correcting code (ECC) bits during either memory activate and/or precharge operation
ActiveUS9823964B2Improve the correction effectLong-term operational reliabilityInput/output to record carriersDigital storageComputer architectureDram memory
A method for updating a DRAM memory array is disclosed. The method comprises: a) receiving a command from a memory controller to initiate an active cycle for activating a memory row in a DRAM memory array; b) performing an Error Correction Code (ECC) scrub on the memory row prior to reading data from the memory row into sense amplifiers in the DRAM memory array in accordance with the command to activate; c) activating the memory row; and d) writing corrected data following the ECC scrub back into memory from the sense amplifiers during a pre-charge cycle of the DRAM memory array.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method for memory scrub of dram with internal error correcting code (ECC) bits during either memory activate and/or precharge operation
ActiveUS20170161144A1Improve the correction effectIncrease elasticityInput/output to record carriersDigital storageComputer architectureDram memory
A method for updating a DRAM memory array is disclosed. The method comprises: a) receiving a command from a memory controller to initiate an active cycle for activating a memory row in a DRAM memory array; b) performing an Error Correction Code (ECC) scrub on the memory row prior to reading data from the memory row into sense amplifiers in the DRAM memory array in accordance with the command to activate; c) activating the memory row; and d) writing corrected data following the ECC scrub back into memory from the sense amplifiers during a pre-charge cycle of the DRAM memory array.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Memory management method and device and mobile terminal
InactiveCN105893152ANo action requiredAutomate processingResource allocationMemory management unitEffective management
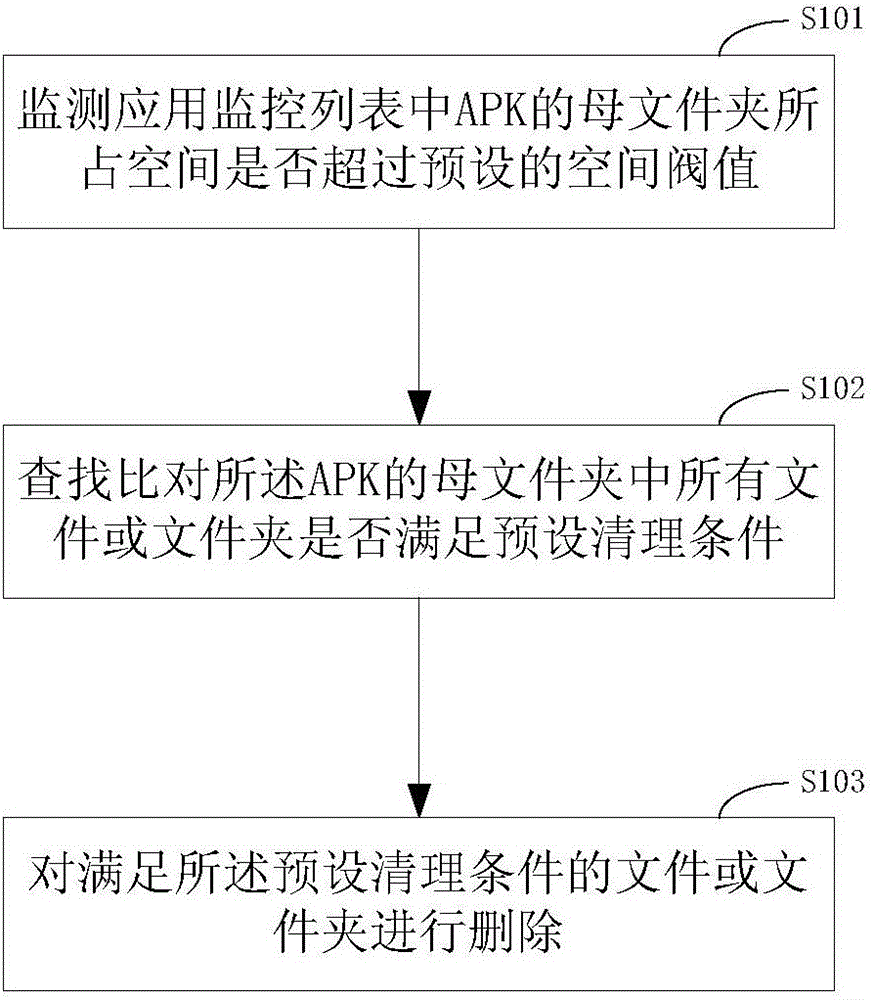
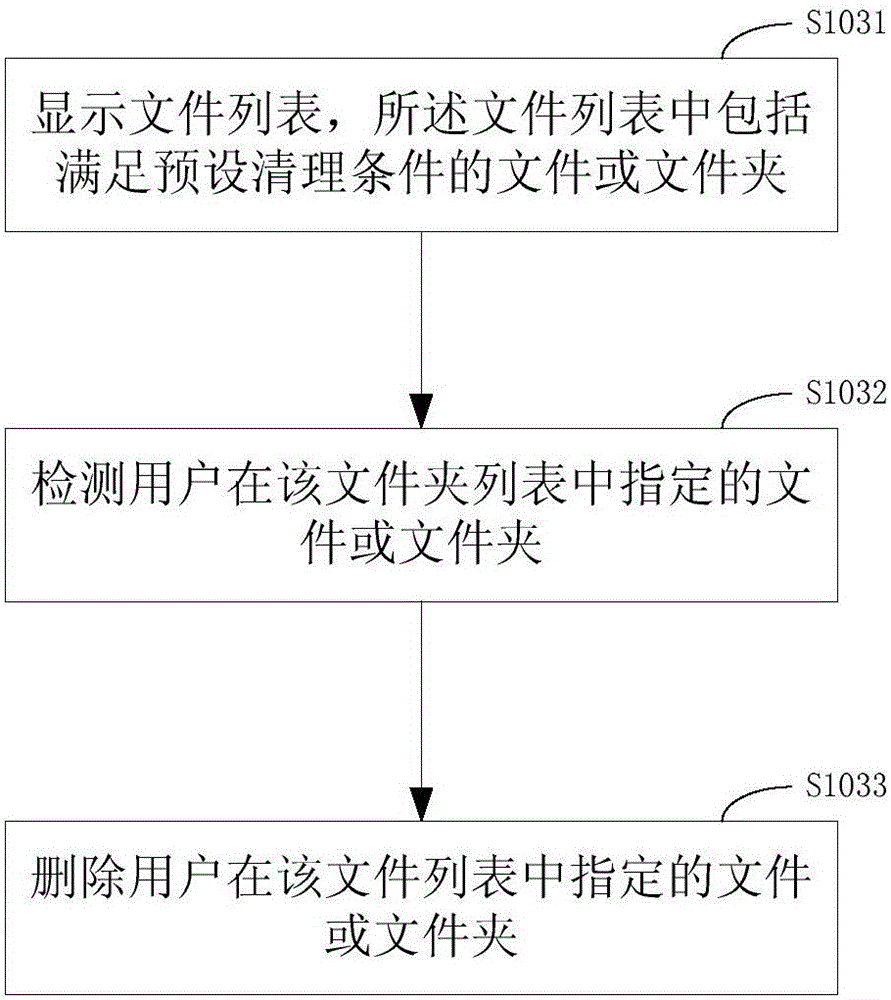
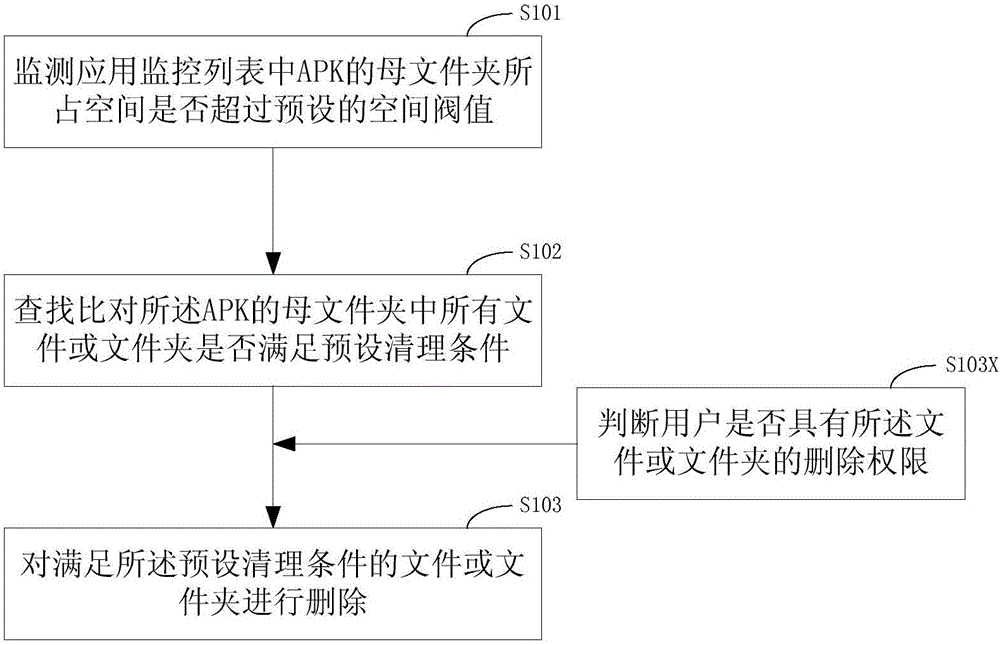
The invention discloses a memory management method and device and a mobile terminal. The method comprises the following steps that a monitoring application monitors the space occupied by an APK mother folder in a list exceeds the preset space threshold value or not, and if yes, the operation is transferred to the next step; whether all files or folders in the APK mother folder meet the preset clearing conditions or not are searched and compared; the files or folders meeting the preset clearing conditions are deleted. According to the memory management method and device and the mobile terminal, the files are deleted based on the maximum occupation space of the limited APK folder and according to time attributes, automatic processing of memory management is achieved, when the preset upper limit is reached, part of early-stage useless files which are not systematically functional are deleted, and it can be guaranteed that the memory occupied certain APKs do not get larger and larger as time goes; effective memory management is achieved, files occupying the memory are cleared in time, efficient smooth operation of a system is guaranteed, and use experience of an operating terminal of a user is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
System and method for detecting memory management programming errors
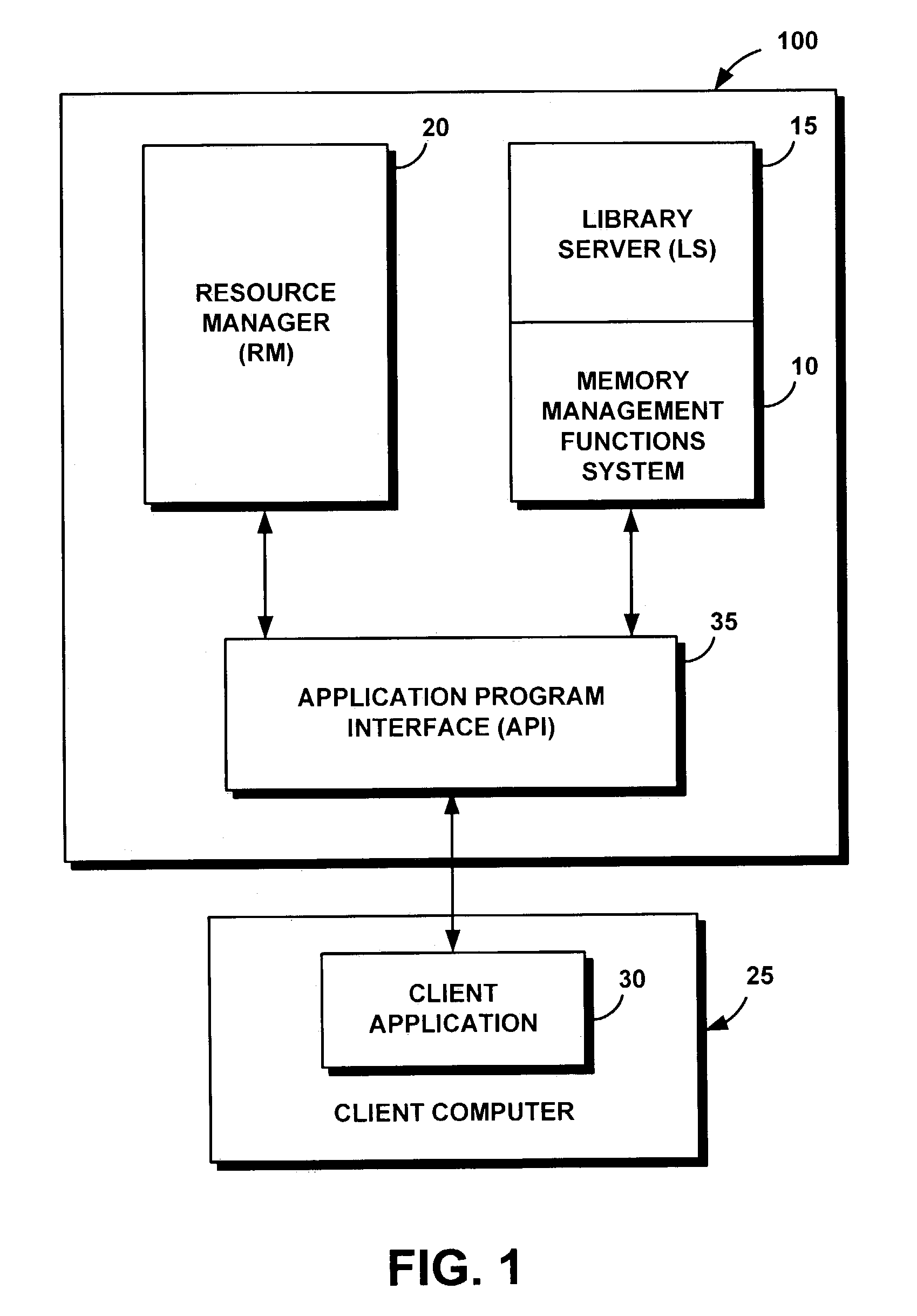
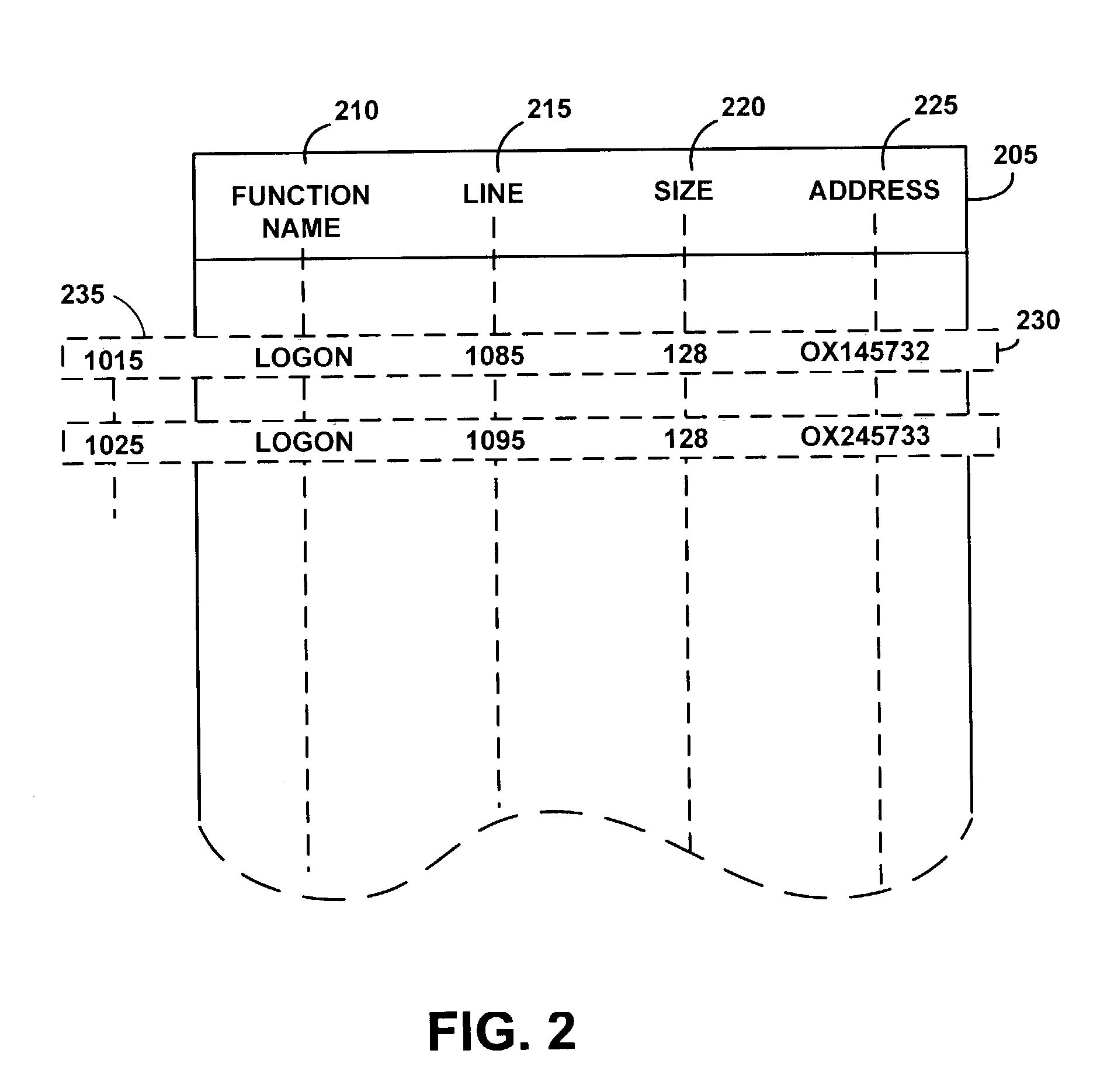
InactiveUS7096339B2Improve performanceReduce processing timeNon-redundant fault processingMemory systemsStored procedureMemory leak
A memory management functions system enables an efficient memory management programming errors. The system includes a server code that reports detailed trace data showing memory management calls; memory that was allocated but not freed; memory requested to be freed that was not allocated; corrupted memory immediately following the allocated space; and incorrect exit from a stored procedure that bypasses reporting and memory cleanup. In addition, the present system frees on exit, memory leaks or memories that were allocated but not explicitly freed earlier. These features allow a programmer to more readily easily detect and debug memory management errors within their program code.
Owner:IBM CORP
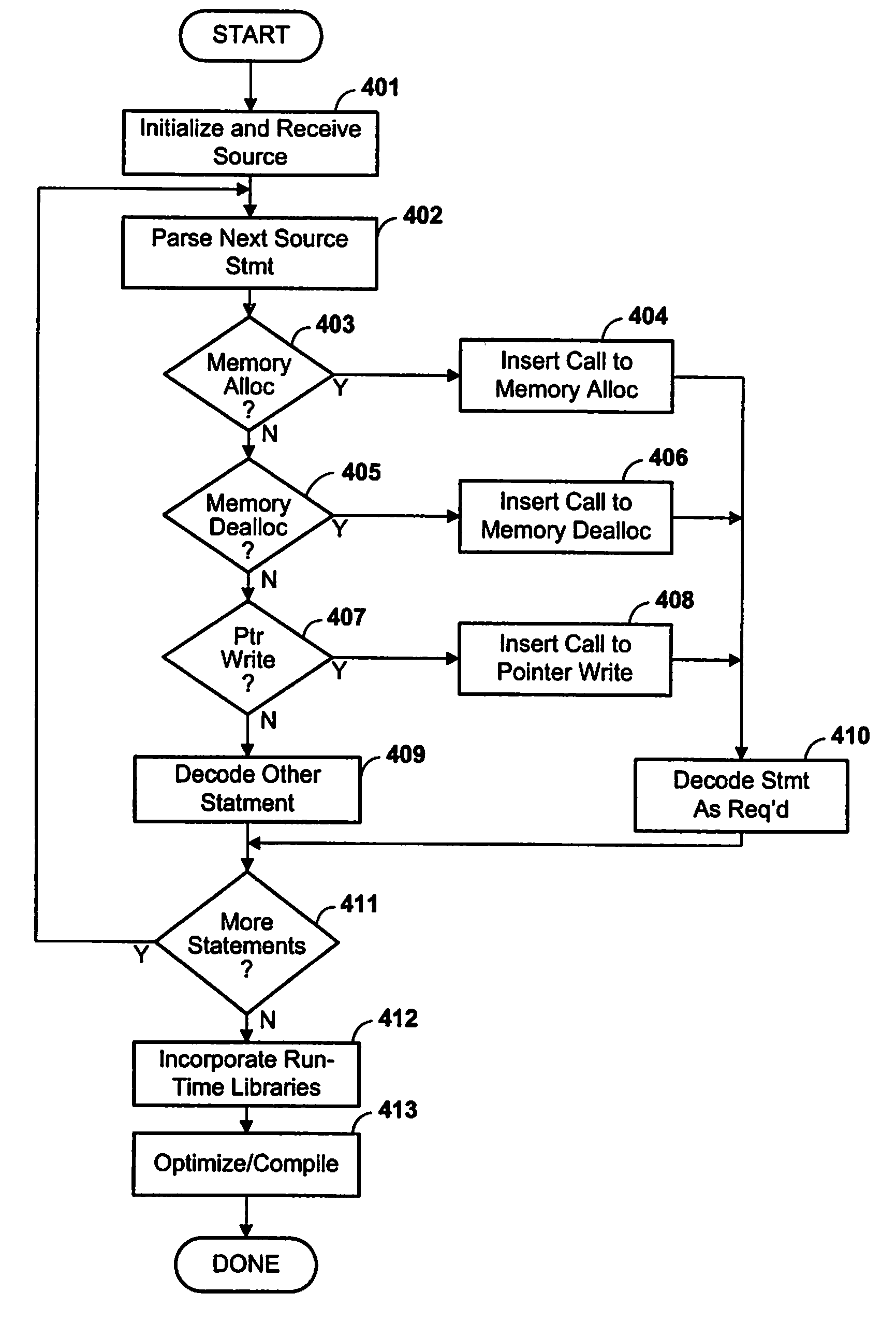
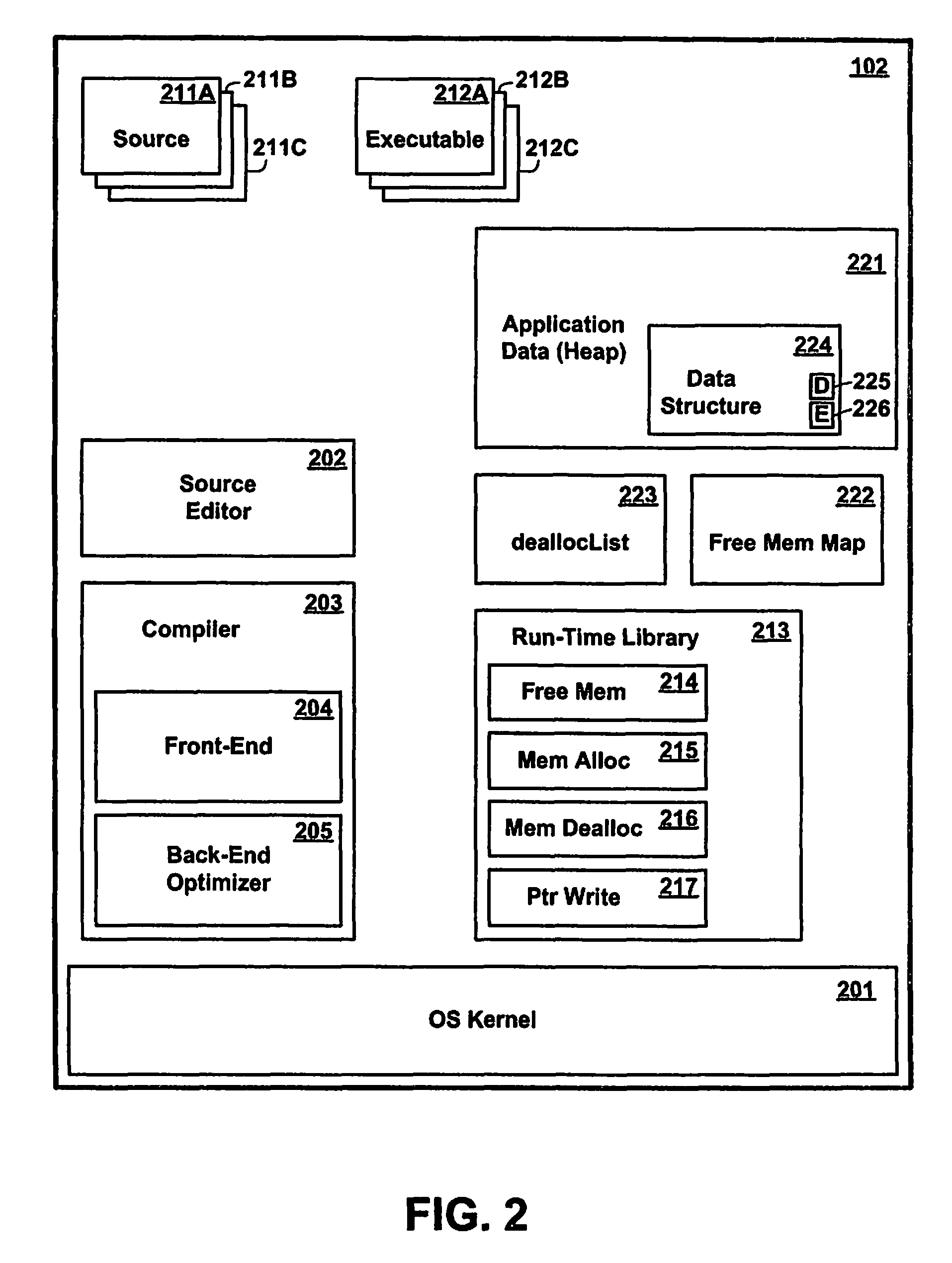
Method and apparatus for re-using memory allocated for data structures used by software processes
ActiveUS8255887B2Error proneEasy to findProgram controlMemory systemsParallel computingMemory scrubbing
A memory management mechanism requires data structures to be explicitly deallocated in the programming code, but deallocation does not immediately make the memory available for reuse. Before a deallocated memory region can be reused, memory is scanned for pointers to the deallocated region, and any such pointer is set to null. The deallocated memory is then available for reuse. Preferably, deallocated memory regions are accumulated, and an asynchronous memory cleaning process periodically scans memory to nullify the pointers. In order to prevent previously scanned memory becoming contaminated with a dangling pointer before the scan is finished, any write to a pointer is checked to verify that the applicable target address has not been deallocated.
Owner:IBM CORP
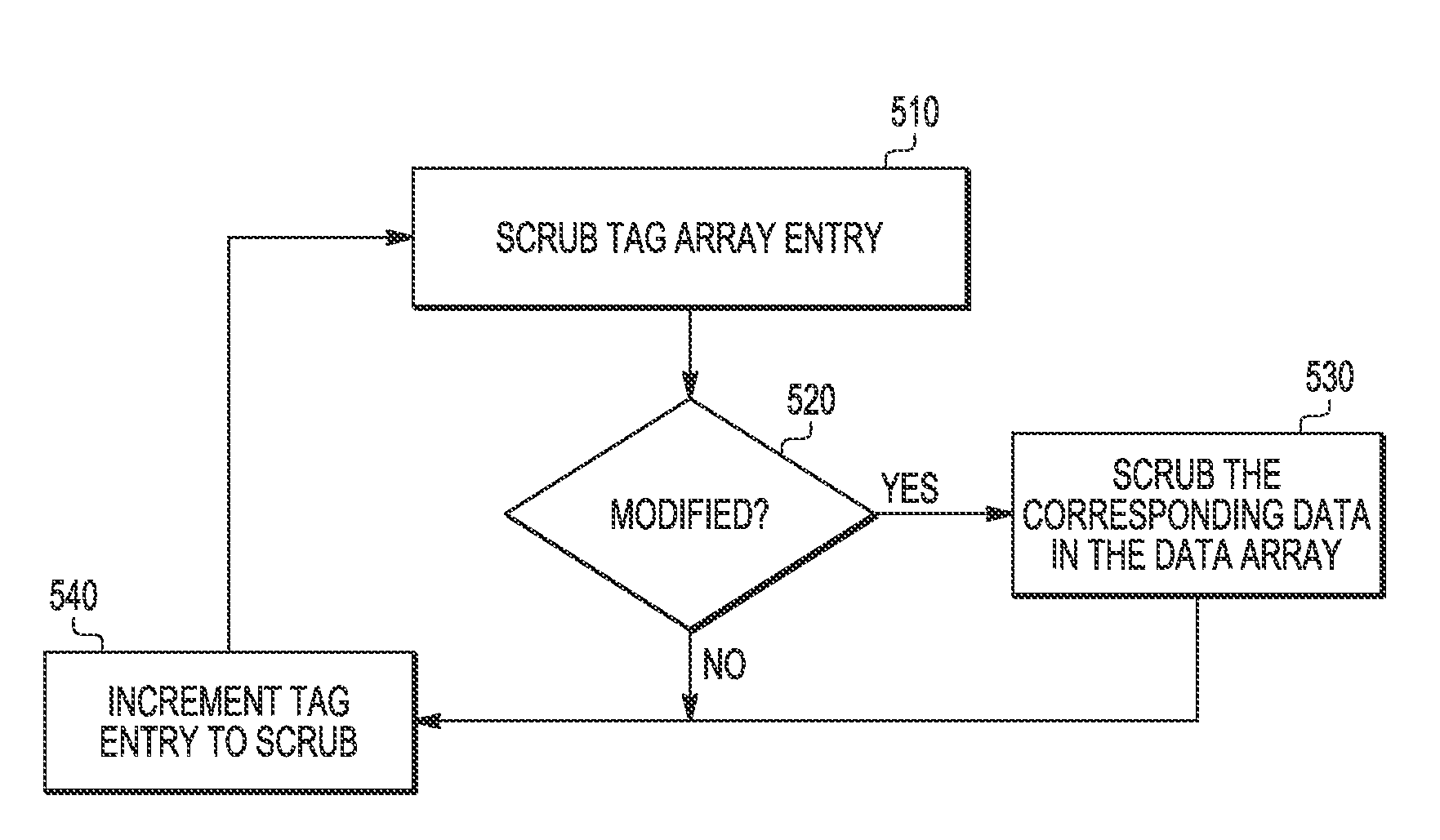
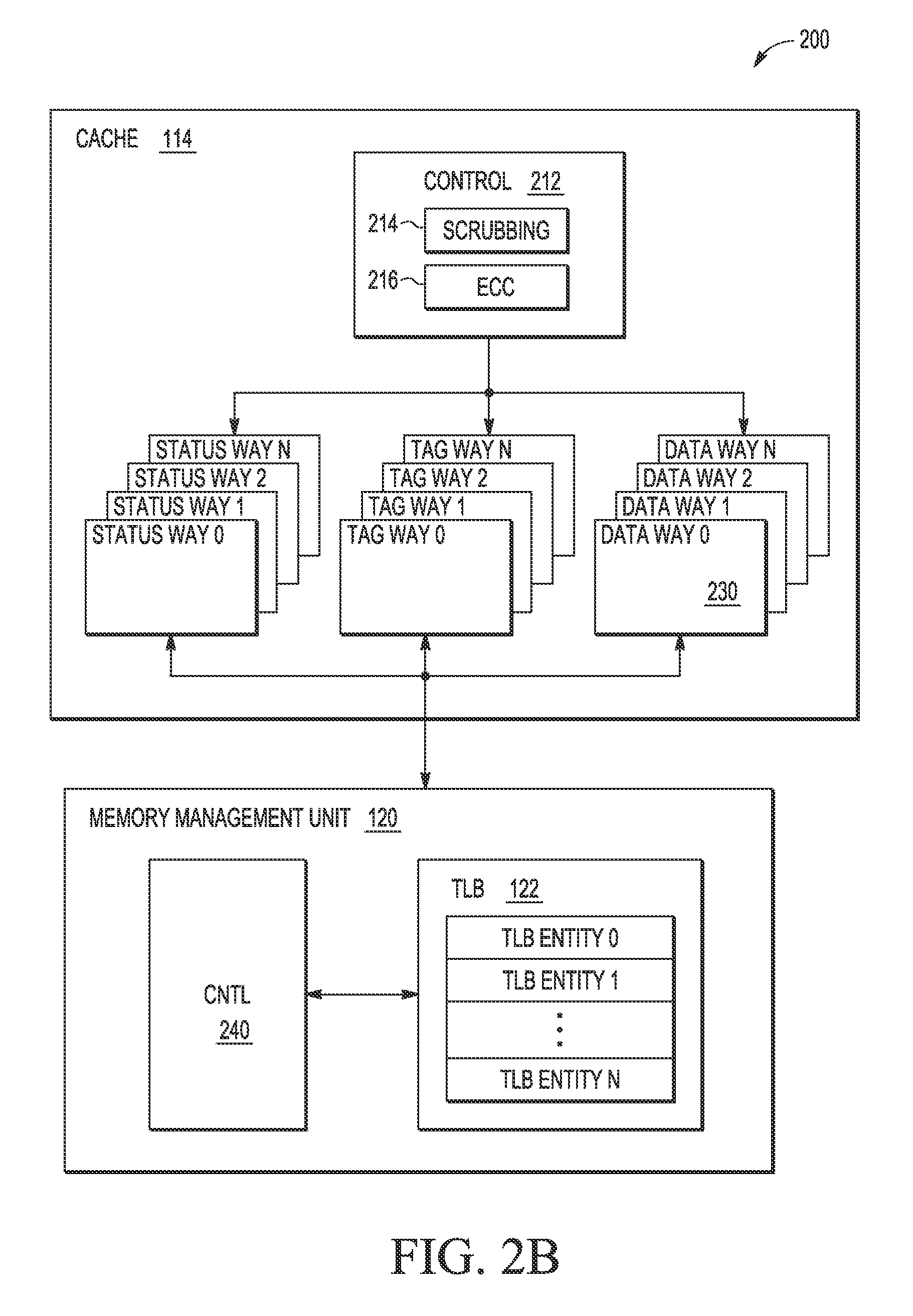
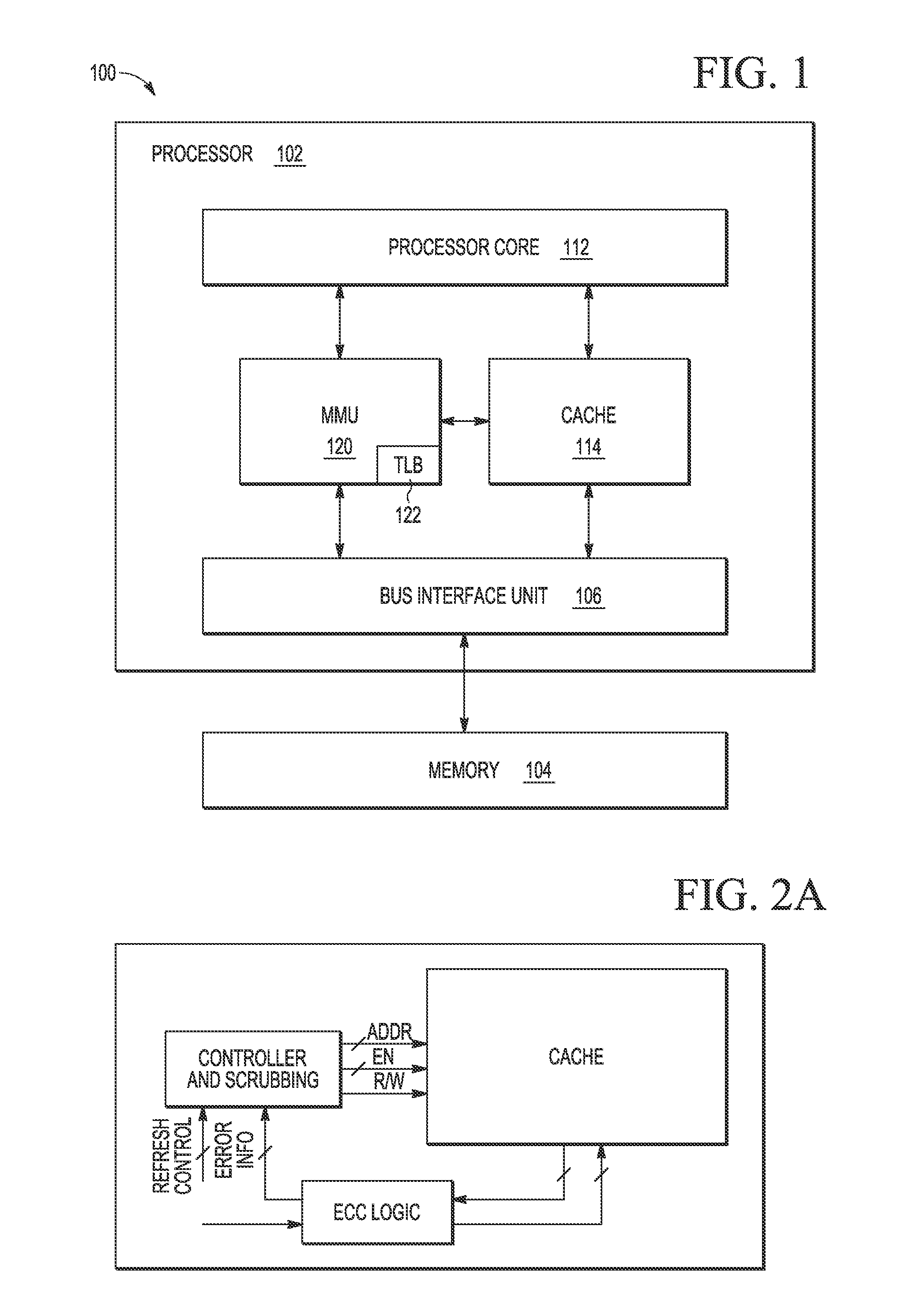
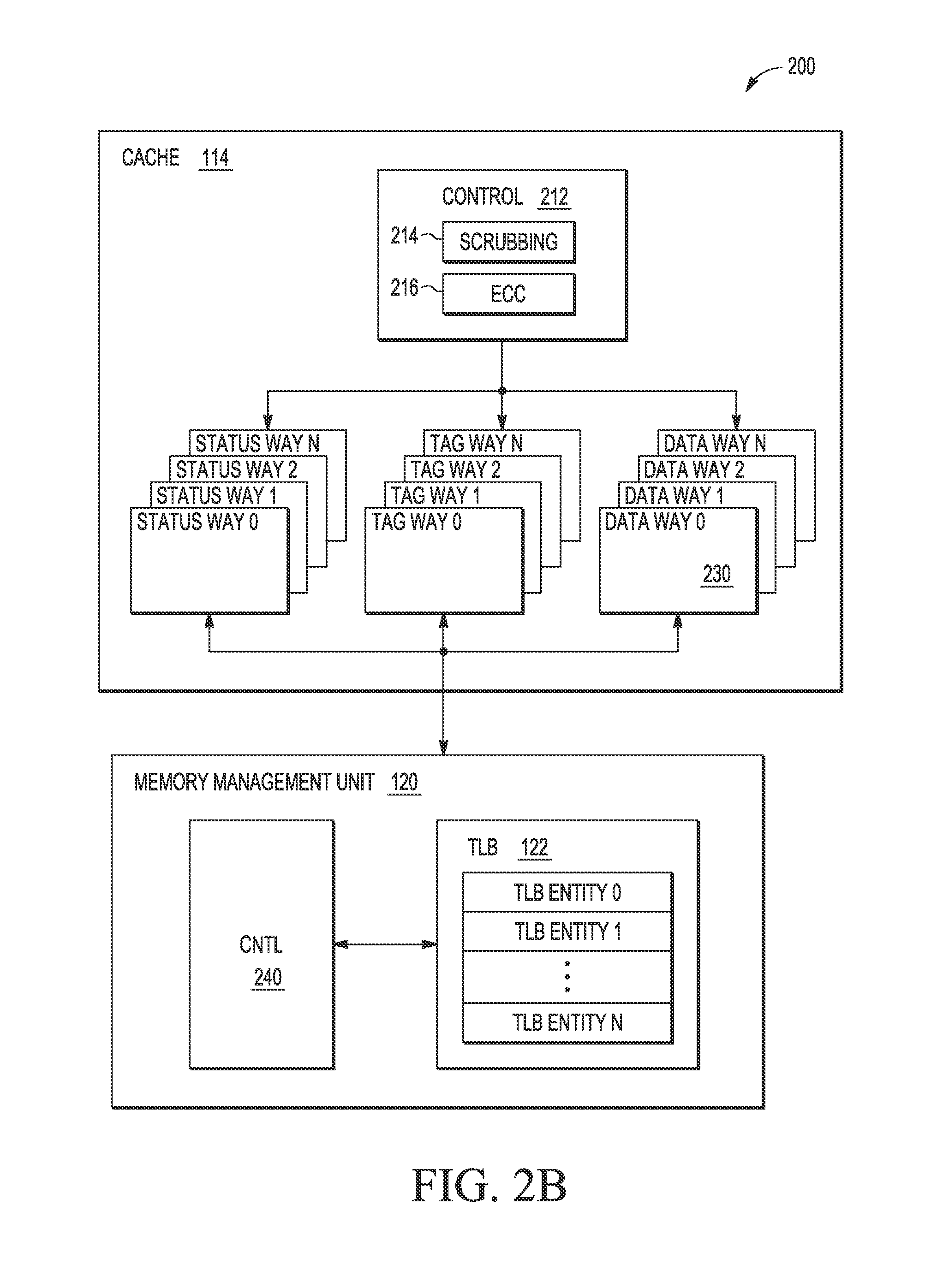
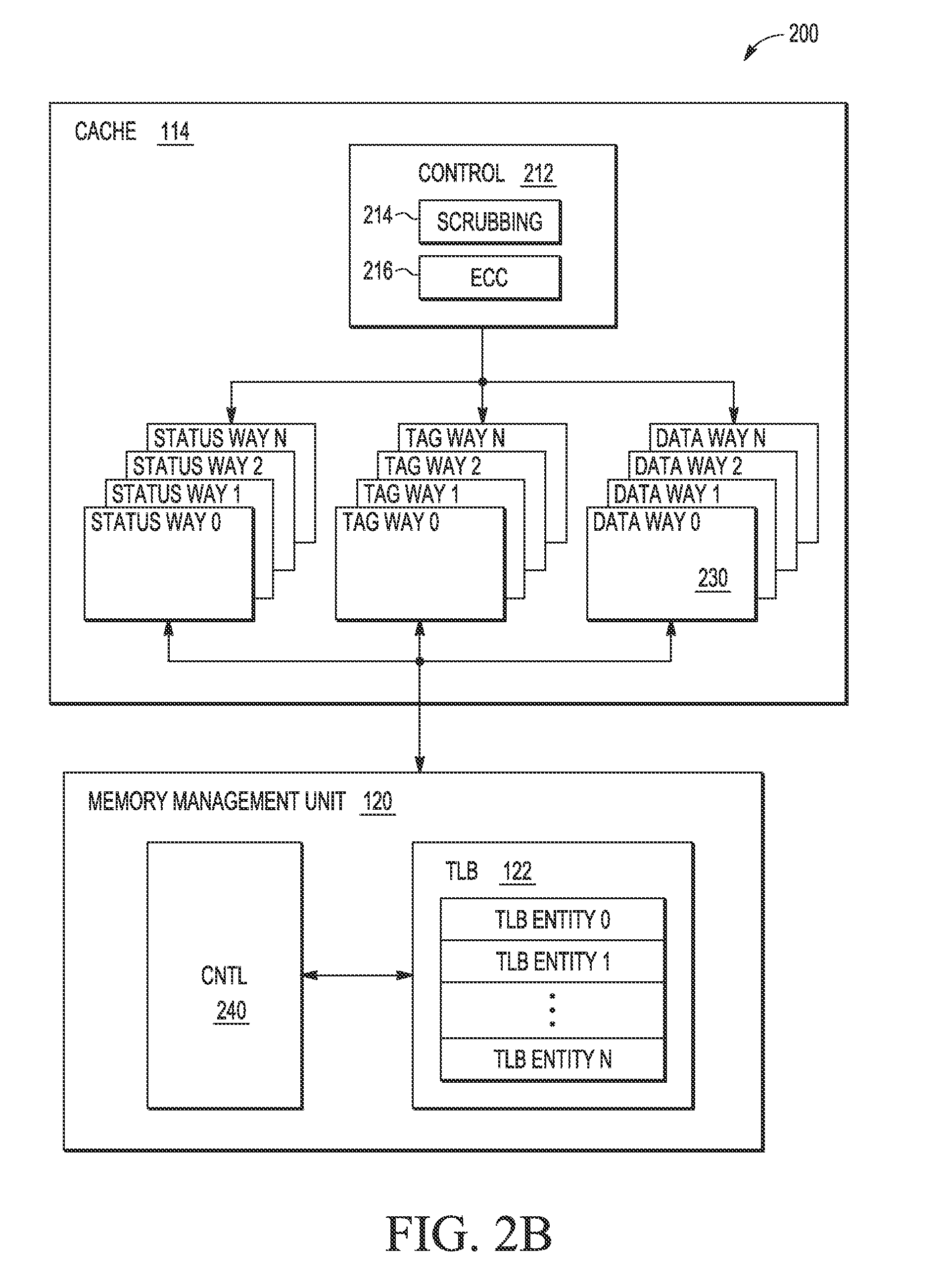
Data type dependent memory scrubbing
ActiveUS9081693B2Energy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData integrityMemory scrubbing
A method for controlling a memory scrubbing rate based on content of the status bit of a tag array of a cache memory. More specifically, the tag array of a cache memory is scrubbed at smaller interval than the scrubbing rate of the storage arrays of the cache. This increased scrubbing rate is in appreciation for the importance of maintaining integrity of tag data. Based on the content of the status bit of the tag array which indicates modified, the corresponding data entry in the cache storage array is scrubbed accordingly. If the modified bit is set, then the entry in the storage array is scrubbed after processing the tag entry. If the modified bit is not set, then the storage array is scrubbed at a predetermined scrubbing interval.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Data Type Dependent Memory Scrubbing
ActiveUS20140052931A1Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory scrubbingTerm memory
A method for controlling a memory scrubbing rate based on content of the status bit of a tag array of a cache memory. More specifically, the tag array of a cache memory is scrubbed at smaller interval than the scrubbing rate of the storage arrays of the cache. This increased scrubbing rate is in appreciation for the importance of maintaining integrity of tag data. Based on the content of the status bit of the tag array which indicates modified, the corresponding data entry in the cache storage array is scrubbed accordingly. If the modified bit is set, then the entry in the storage array is scrubbed after processing the tag entry. If the modified bit is not set, then the storage array is scrubbed at a predetermined scrubbing interval.
Owner:NXP USA INC
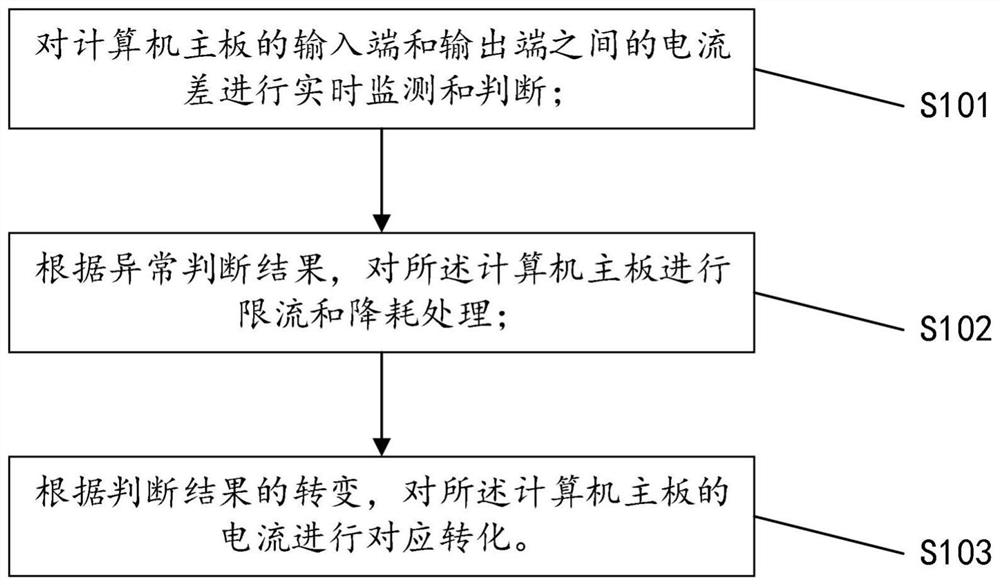
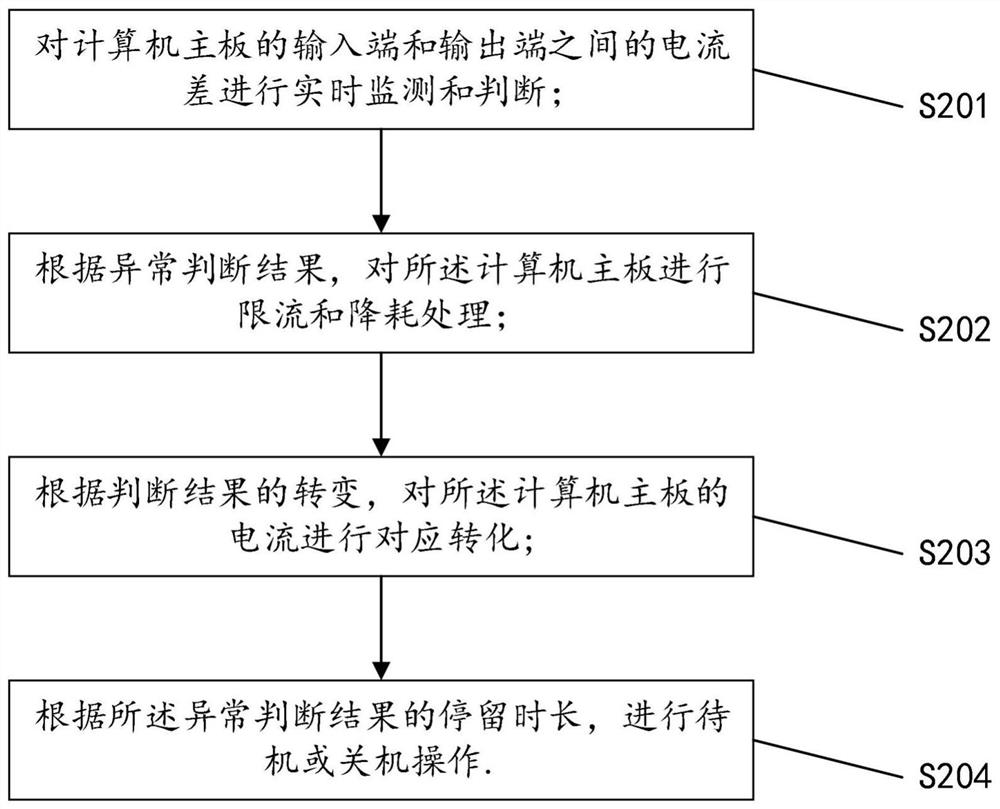
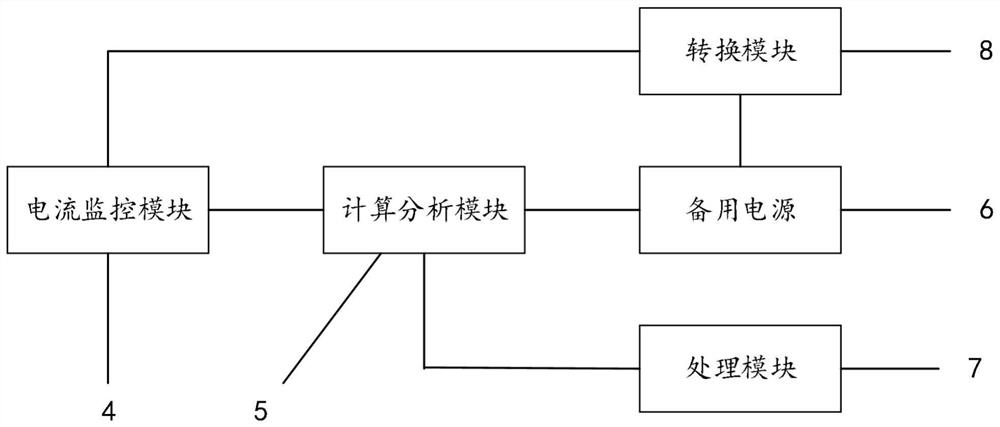
Control method, circuit and system for reducing standby power consumption of computer mainboard
ActiveCN111984108AReduce standby power consumptionReduce power consumptionPower supply for data processingComputer hardwareStandby power
The invention discloses a control method, circuit and system for reducing standby power consumption of a computer mainboard. The system comprises a processor, a user interface and a memory, and the control circuit comprises a current monitoring module, a calculation and analysis module, a standby power supply and a processing module. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, monitoring acurrent input end and a current output end of a computer mainboard in real time, performing calculation and analysis according to the monitored current values, when an abnormal judgment result is output, changing current input of the computer mainboard, closing operation of a program connected with the computer mainboard, performing memory cleaning and backup on the computer mainboard, and adjusting the brightness of a display screen or closing the display screen. The current input of the computer mainboard can be converted in real time according to the output judgment result, so that the standby state of the computer mainboard can be conveniently controlled, and the standby power consumption of the computer mainboard can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN ITZR TECH
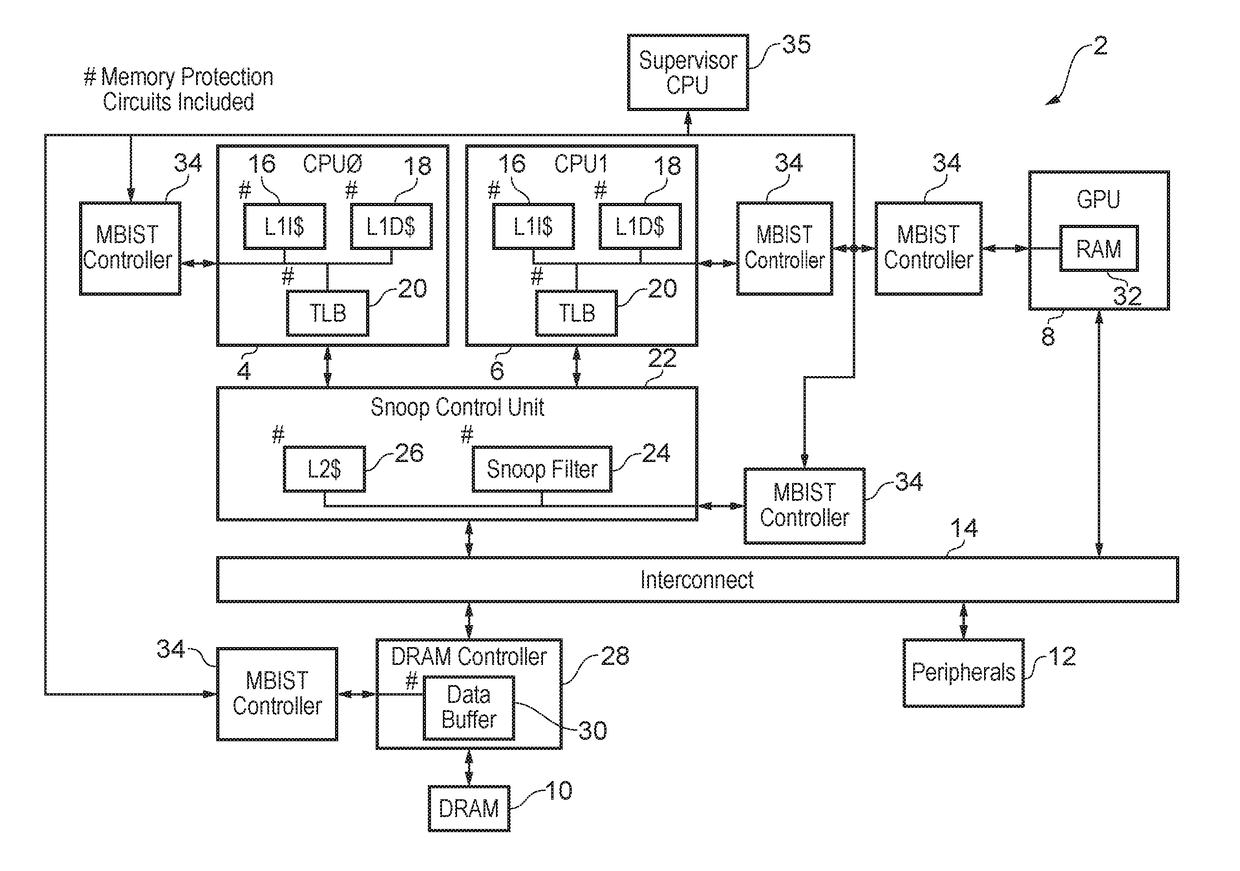
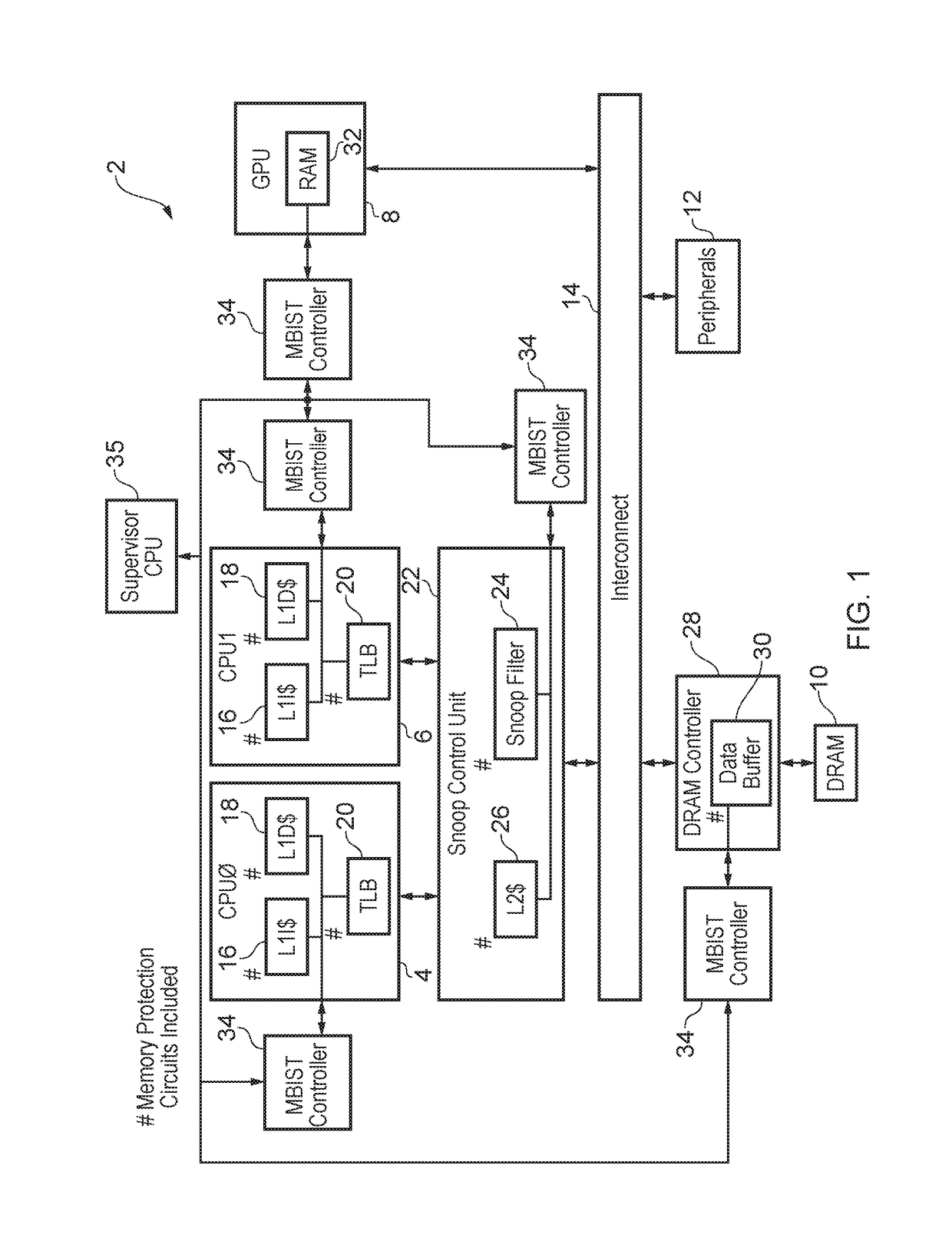
Memory protection circuitry testing and memory scrubbing using memory built-in self-test
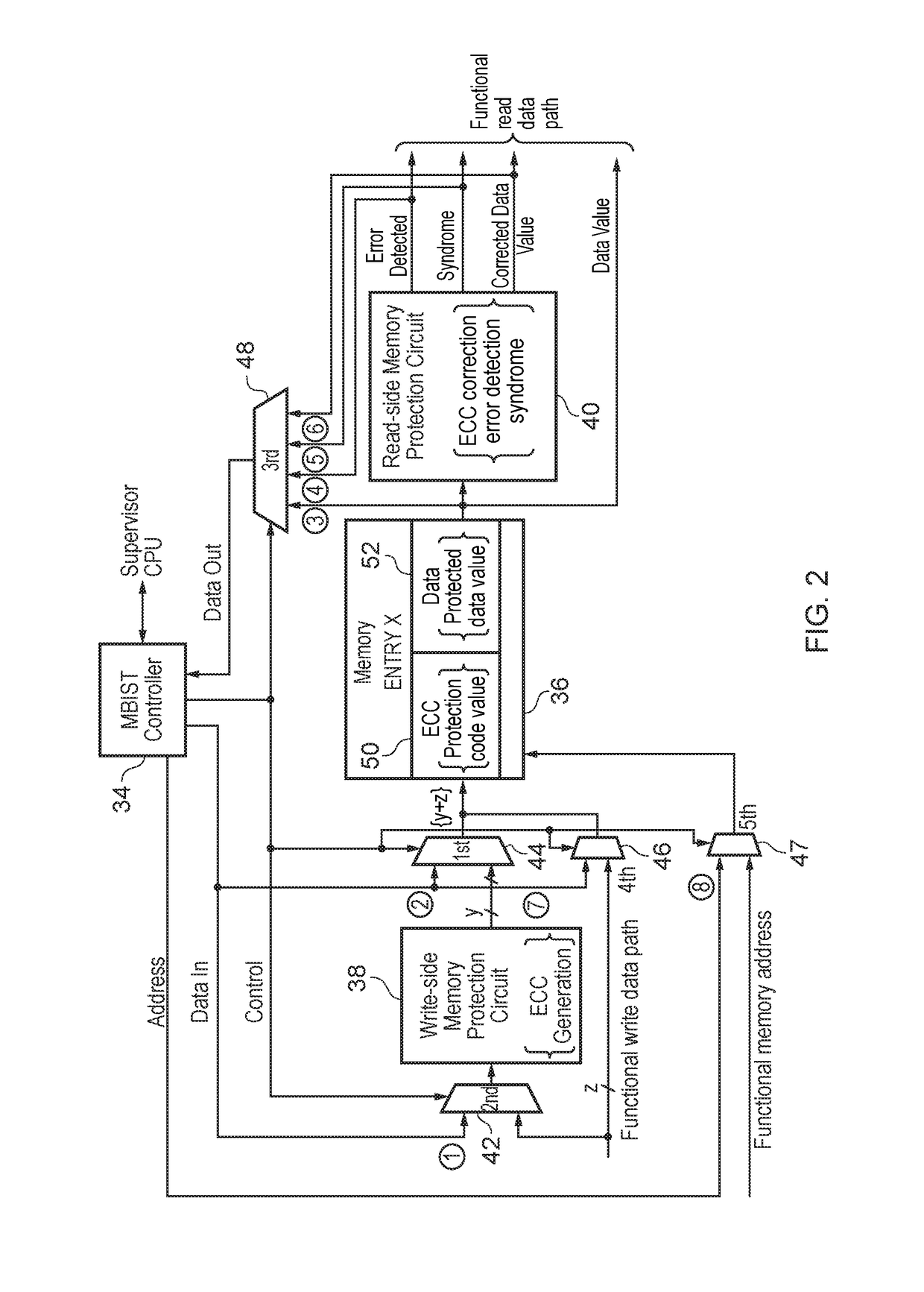
ActiveUS9984766B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationElectrical testingComputer hardwareMemory scrubbing
A data processing apparatus includes a memory and memory protection circuitry for providing an operational path to the memory during operational use of the memory. A memory built-in self-test controller 34 performs built-in self-test operations upon the memory using either an indirect test access path to the memory via the memory protection circuitry or a direct test access path to the memory which bypasses the memory protection circuitry. Thus, the correct operation of the memory protection circuitry itself can be tested in addition to the correct operation of the memory.
Owner:ARM LTD
Method and device for automatically cleaning memory, electronic equipment and storage medium
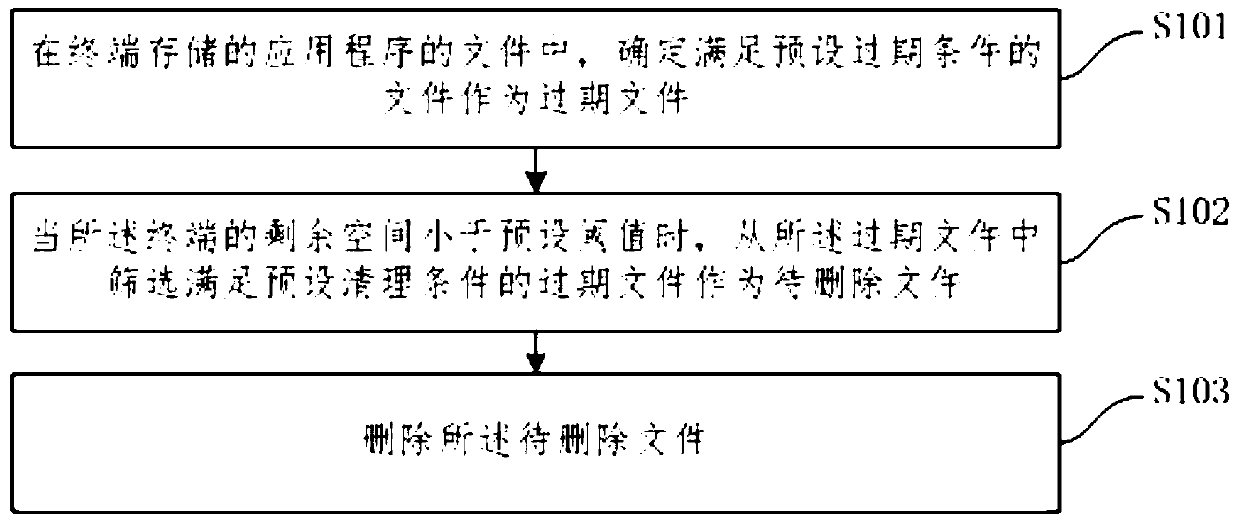
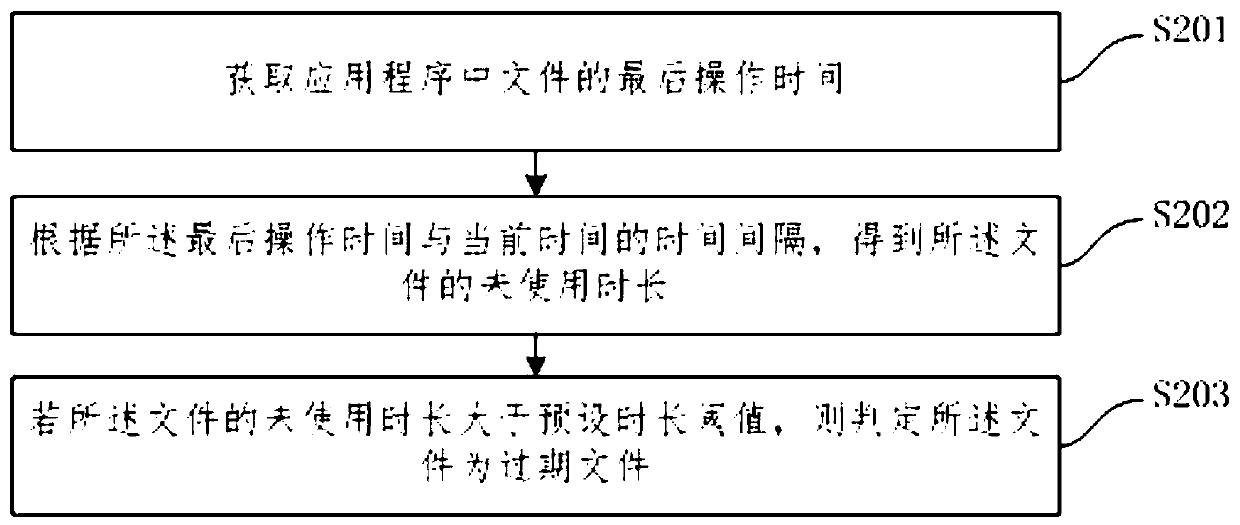
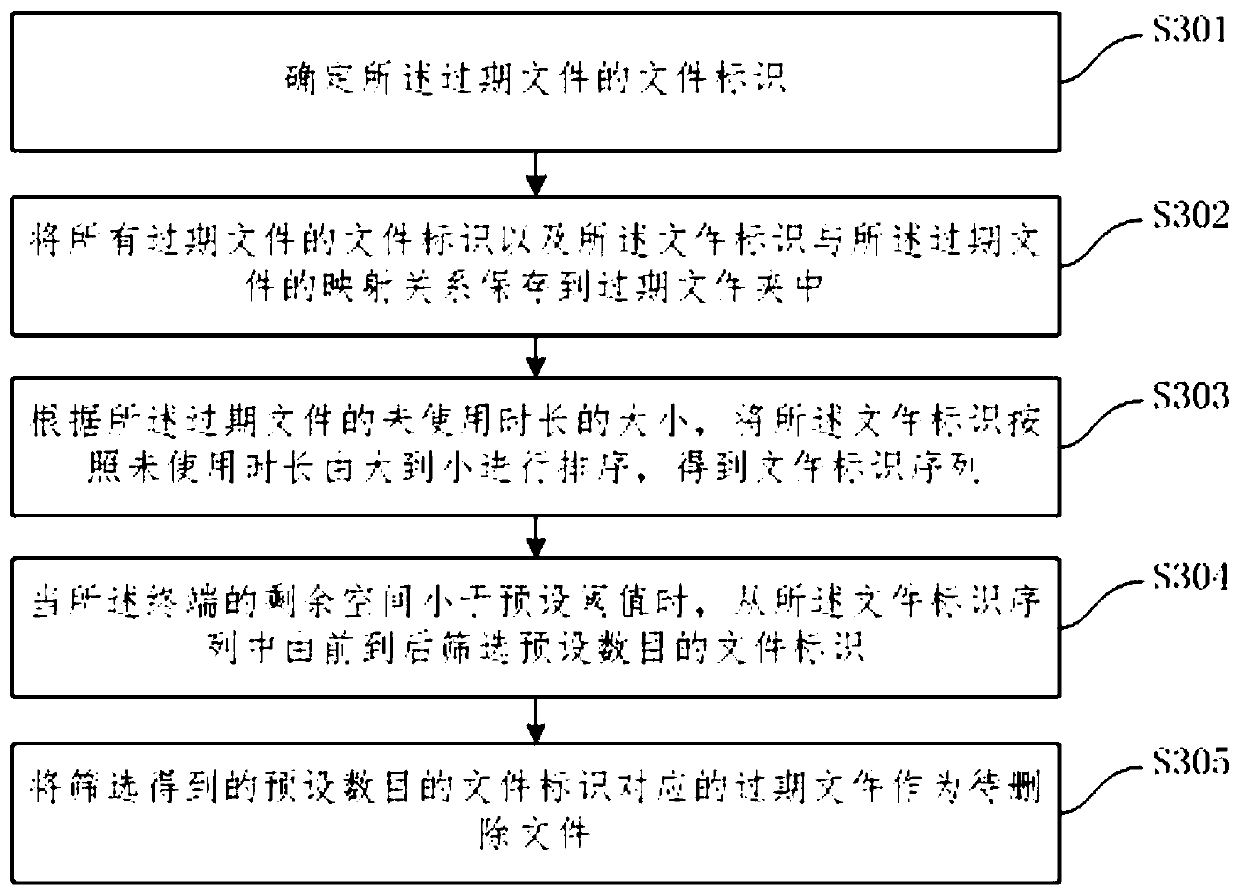
InactiveCN110737604AReduce stepsImprove cleaning efficiencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile/folder operationsComputer hardwareMemory scrubbing
The invention relates to a method and device for automatically cleaning memory, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: determining a file meeting a preset expiration condition as an expiration file in files of an application stored in a terminal; when the residual space of the terminal is smaller than a preset threshold value, screening out an expired file meeting a preset cleaning condition from the expired files as a to-be-deleted file; and deleting the to-be-deleted file. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the file meeting the condition is used as the expired file; deleting the to-be-deleted files in the expired files when the residual space of the terminal is smaller than a preset threshold value; compared with the priorart that a user needs to manually delete the files, the method has the advantages that the expired files are searched out firstly, and then the unnecessary files are automatically deleted when the residual space of the terminal is insufficient, so that the memory can be automatically cleaned, other memory cleaning software does not need to be downloaded, the operation process of the user is reduced, and the memory cleaning efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING QIYI CENTURY SCI & TECH CO LTD
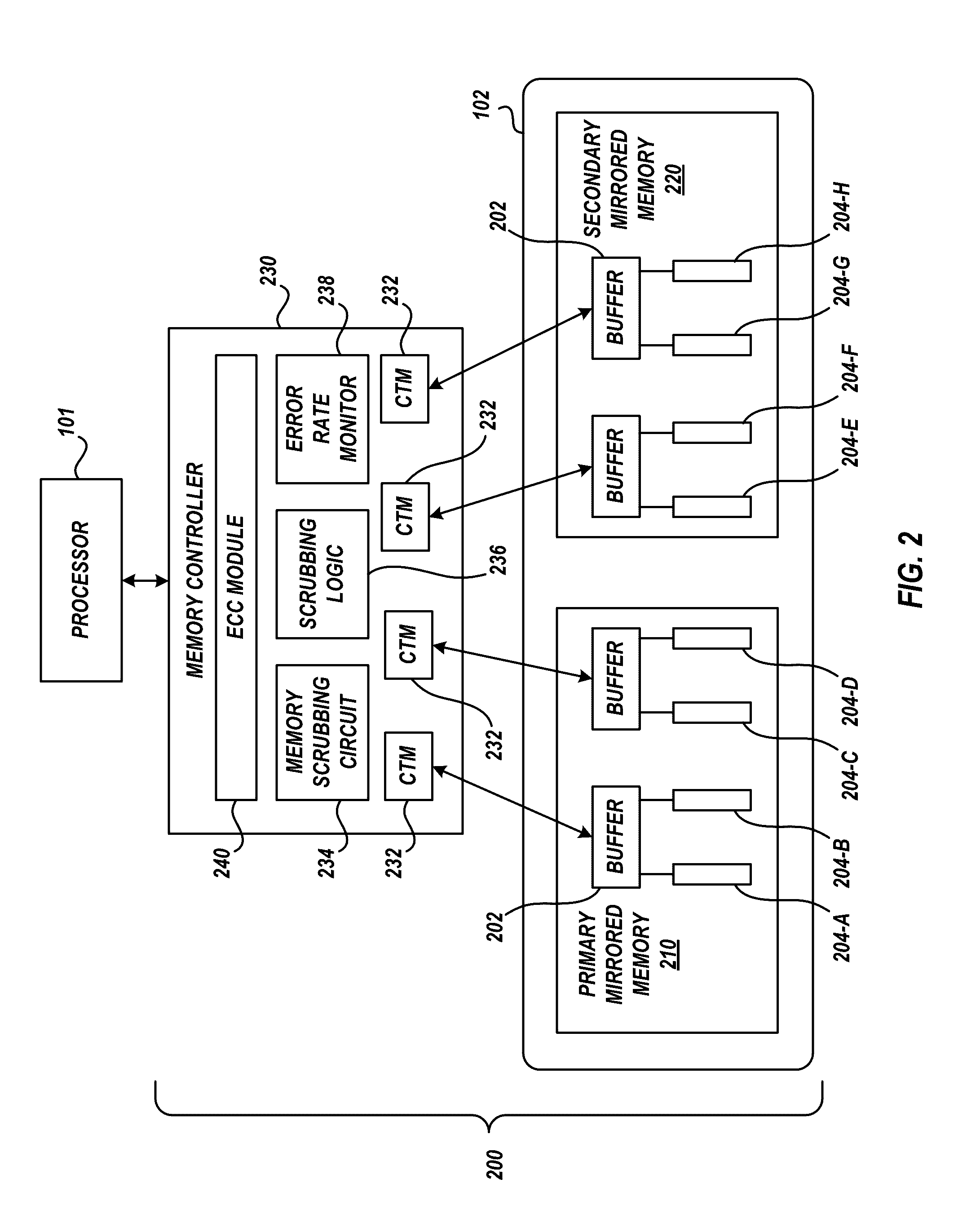
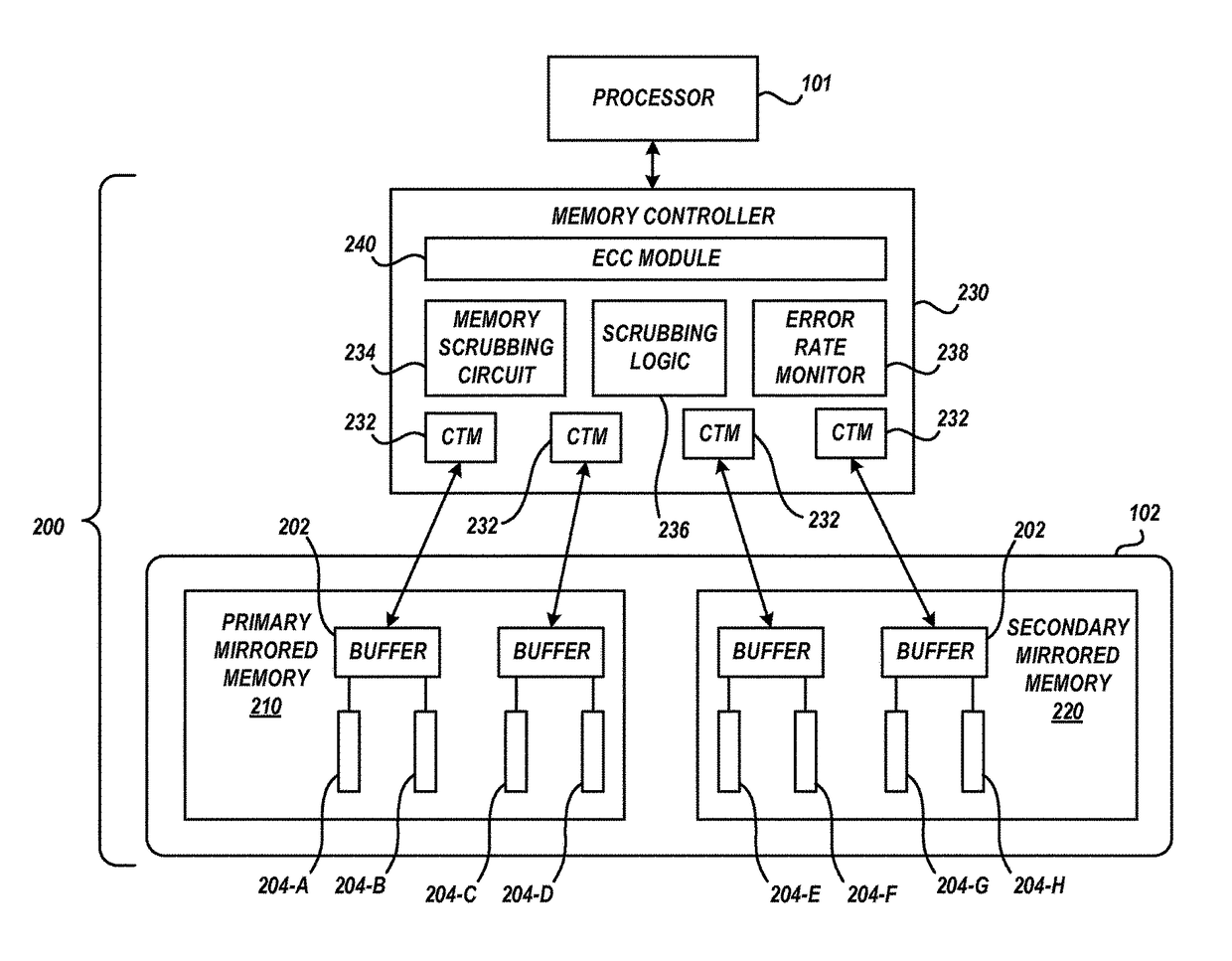
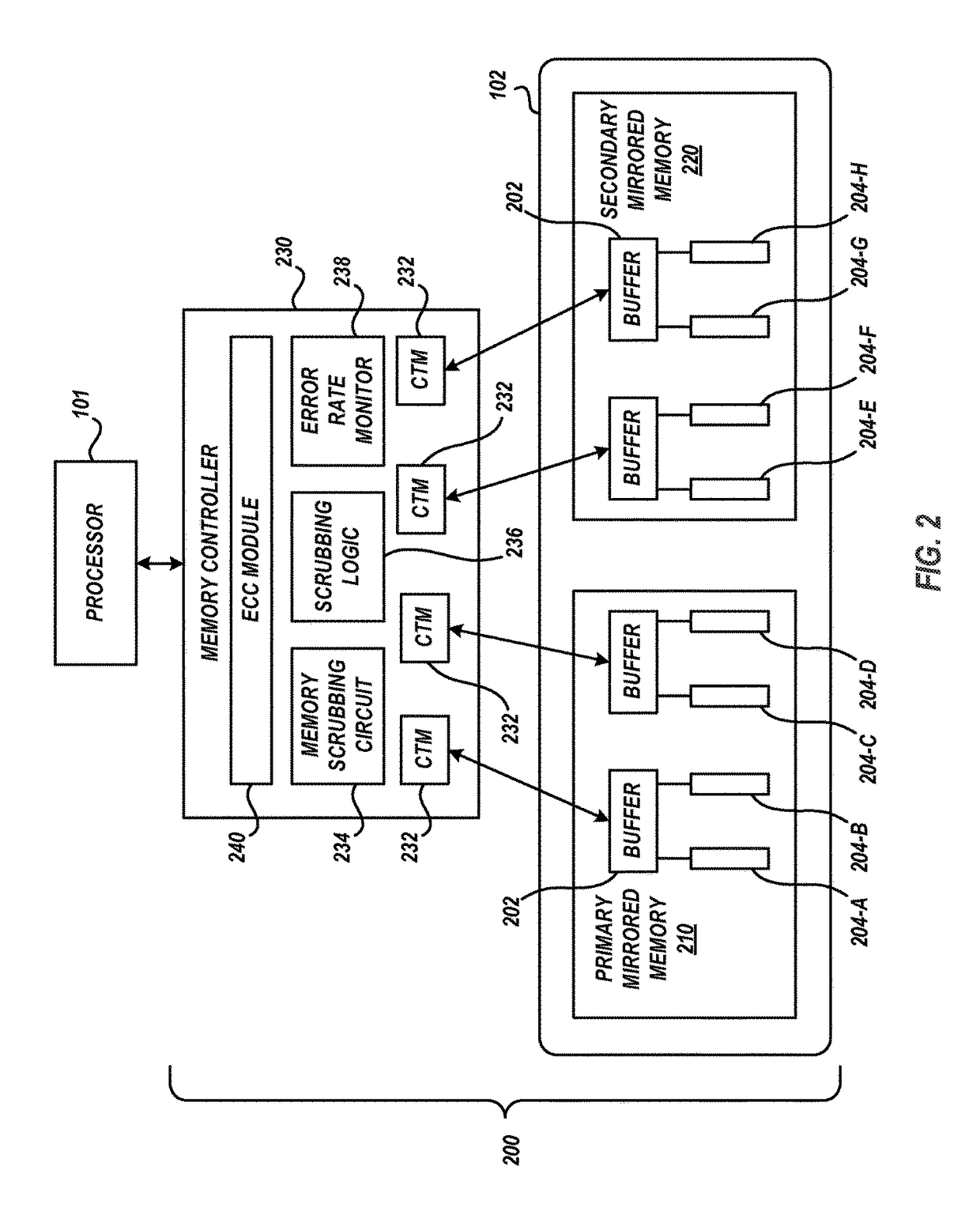
Memory scrubbing in a mirrored memory system to reduce system power consumption
ActiveUS20170031754A1Reduce power consumptionReduce probabilityInput/output to record carriersStatic storageComputer hardwareMemory scrubbing
Mirrored memory scrubbing is optimized to reduce system power consumption and increase system performance. A memory scrub operation scrubs a first portion of the mirrored memory to detect and correct soft errors. The scrub rate of a second portion of the mirrored memory is eliminated, minimized, or reduced, relative to the scrub rate of the first portion. The reduced scrub operation preserves power consumed in association with scrubbing the second portion.
Owner:IBM CORP
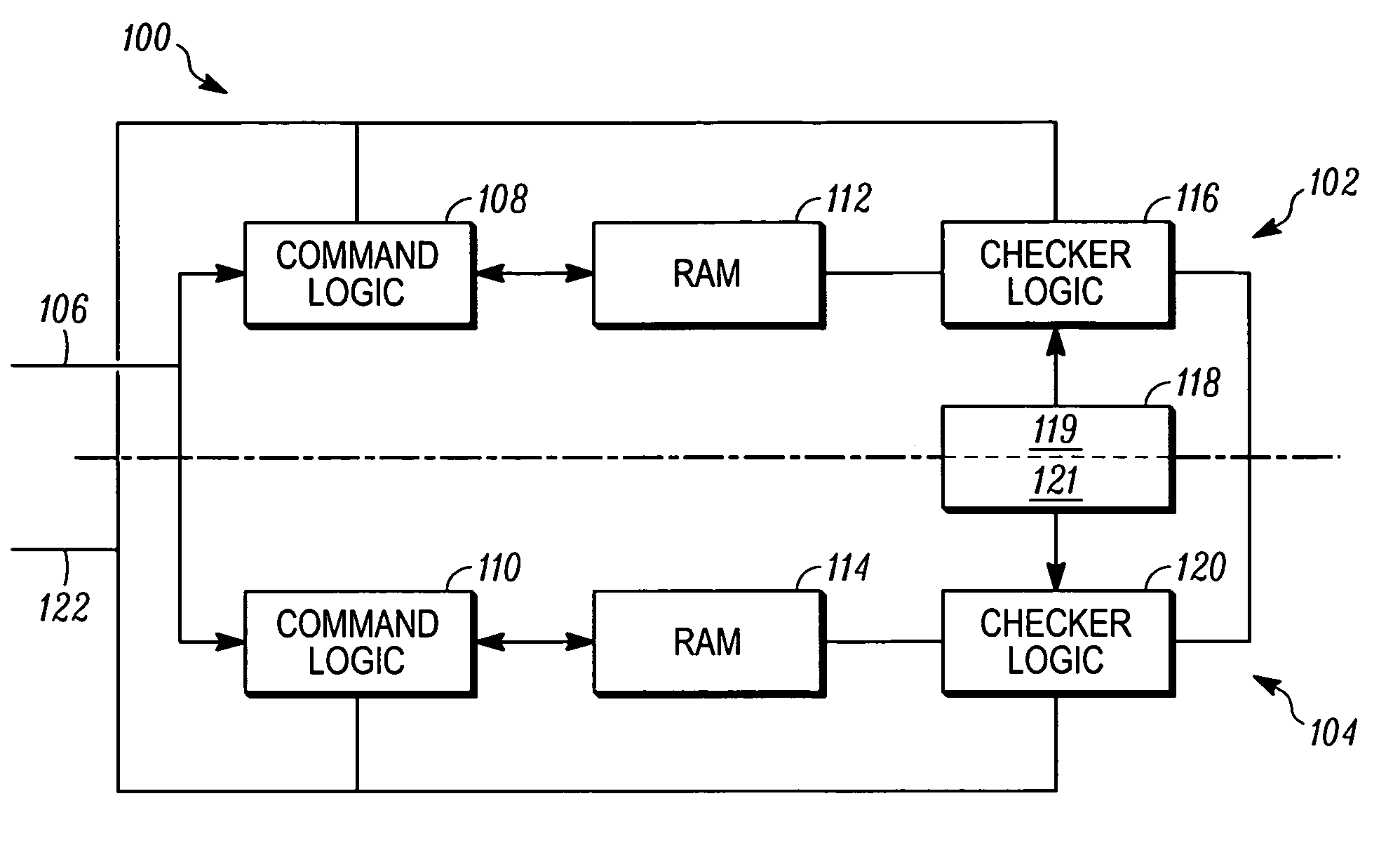
Method and apparatus for latent fault memory scrub in memory intensive computer hardware
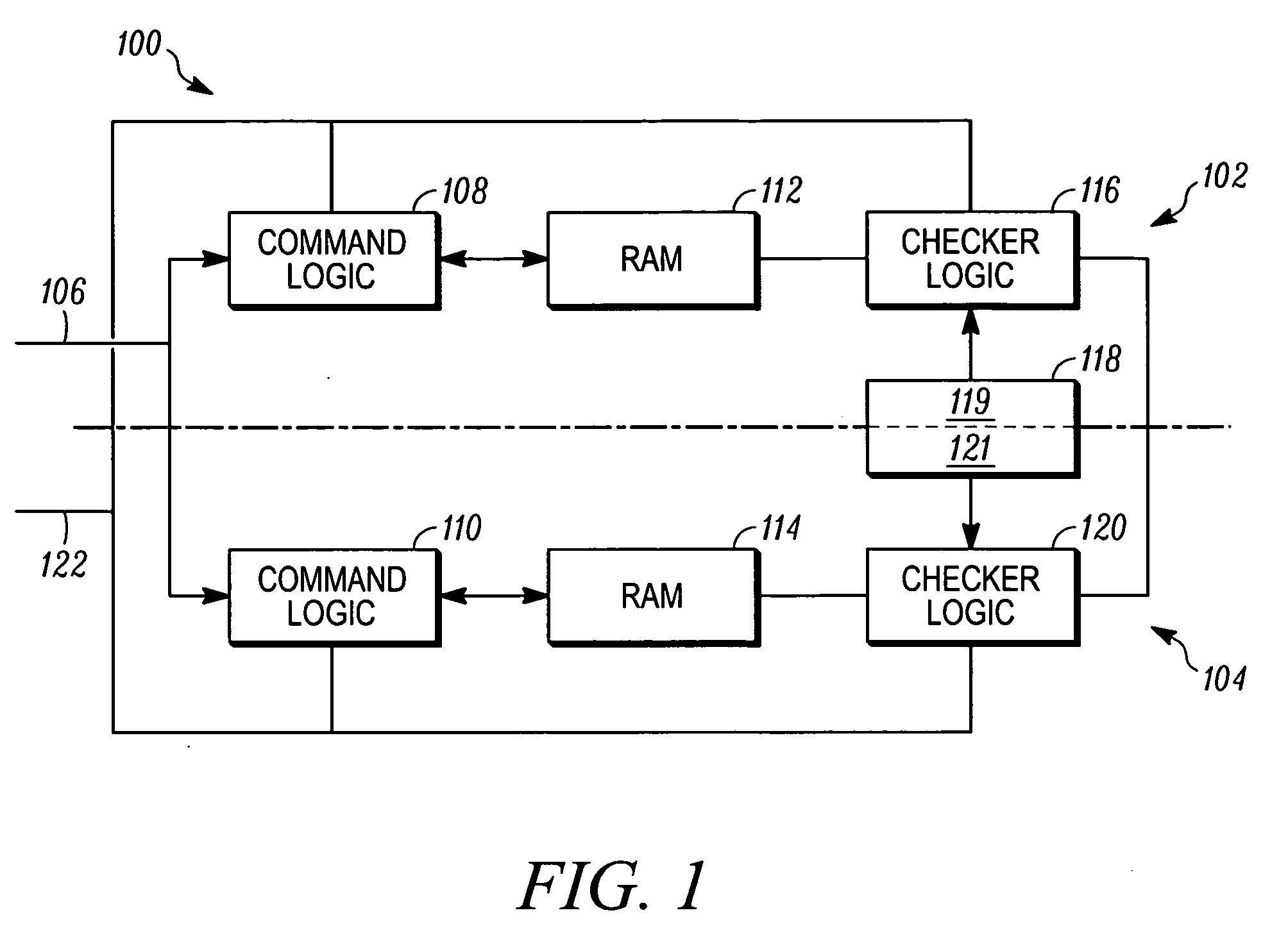
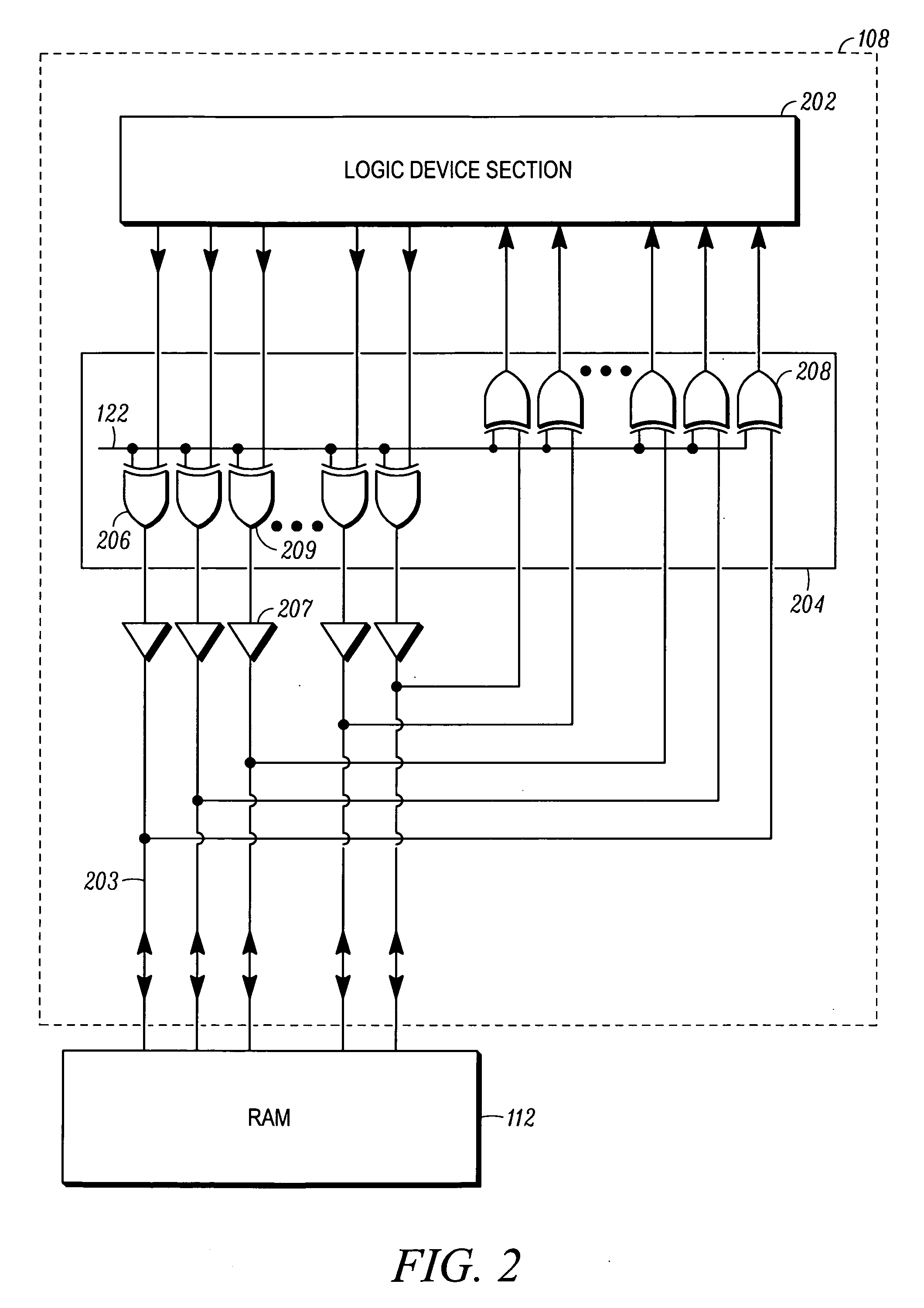
InactiveUS20080002513A1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionComputer hardwareComputer architecture
A method for operating a memory checker in a command monitoring architecture comprising at least two processing lanes comprises a first step of receiving a command to activate a first test mode. The first test mode comprises an initial step of inverting data read from a memory and inverting data written to the memory. Next, it is determined if there is a match between data associated with a first processing lane and retrieved by a second checker logic associated with a second processing lane and with data associated with a second processing lane and retrieved by a first checker logic associated with the first processing lane. A failure in the memory is determined if there is no match.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Application aware memory patrol scrubbing techniques
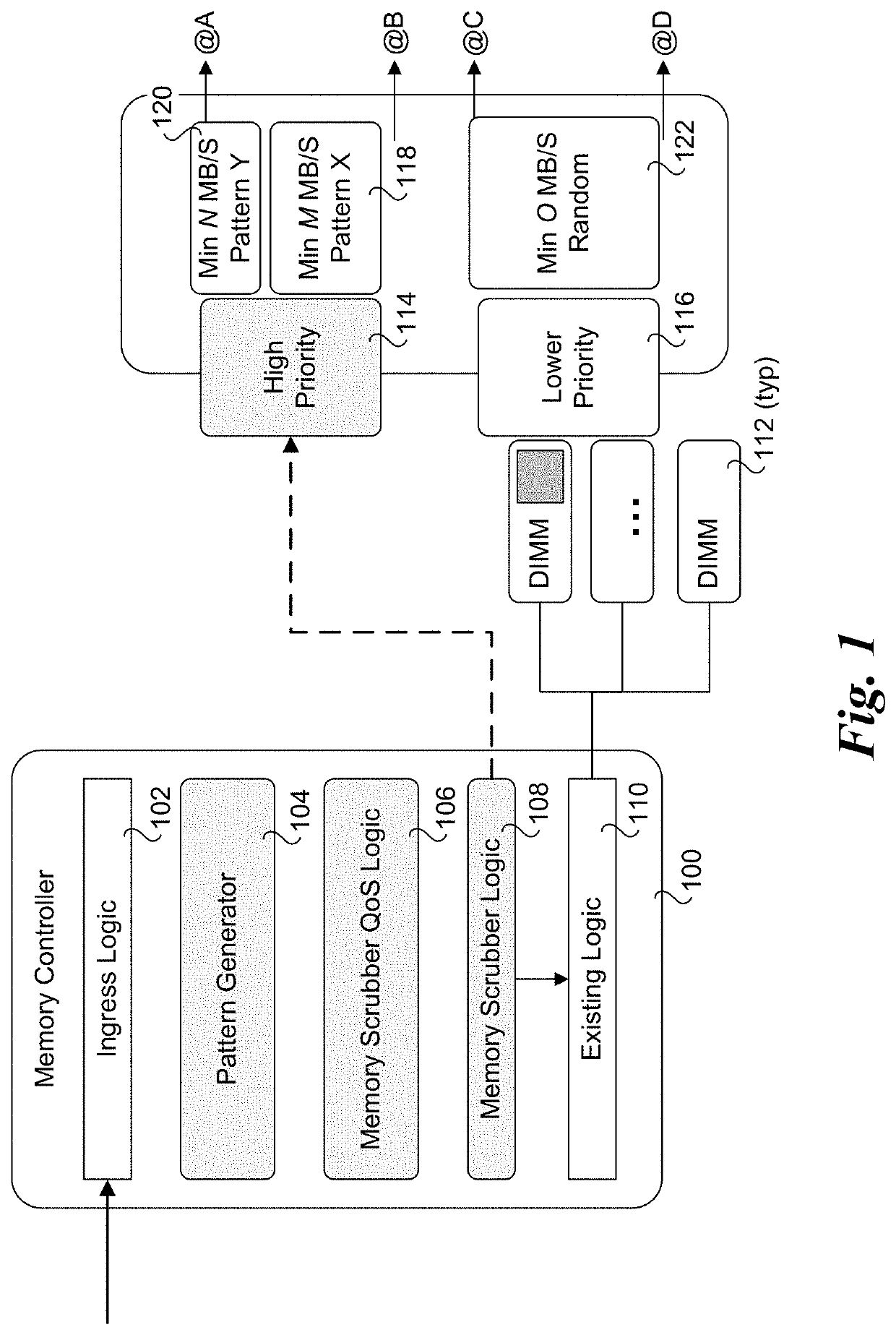
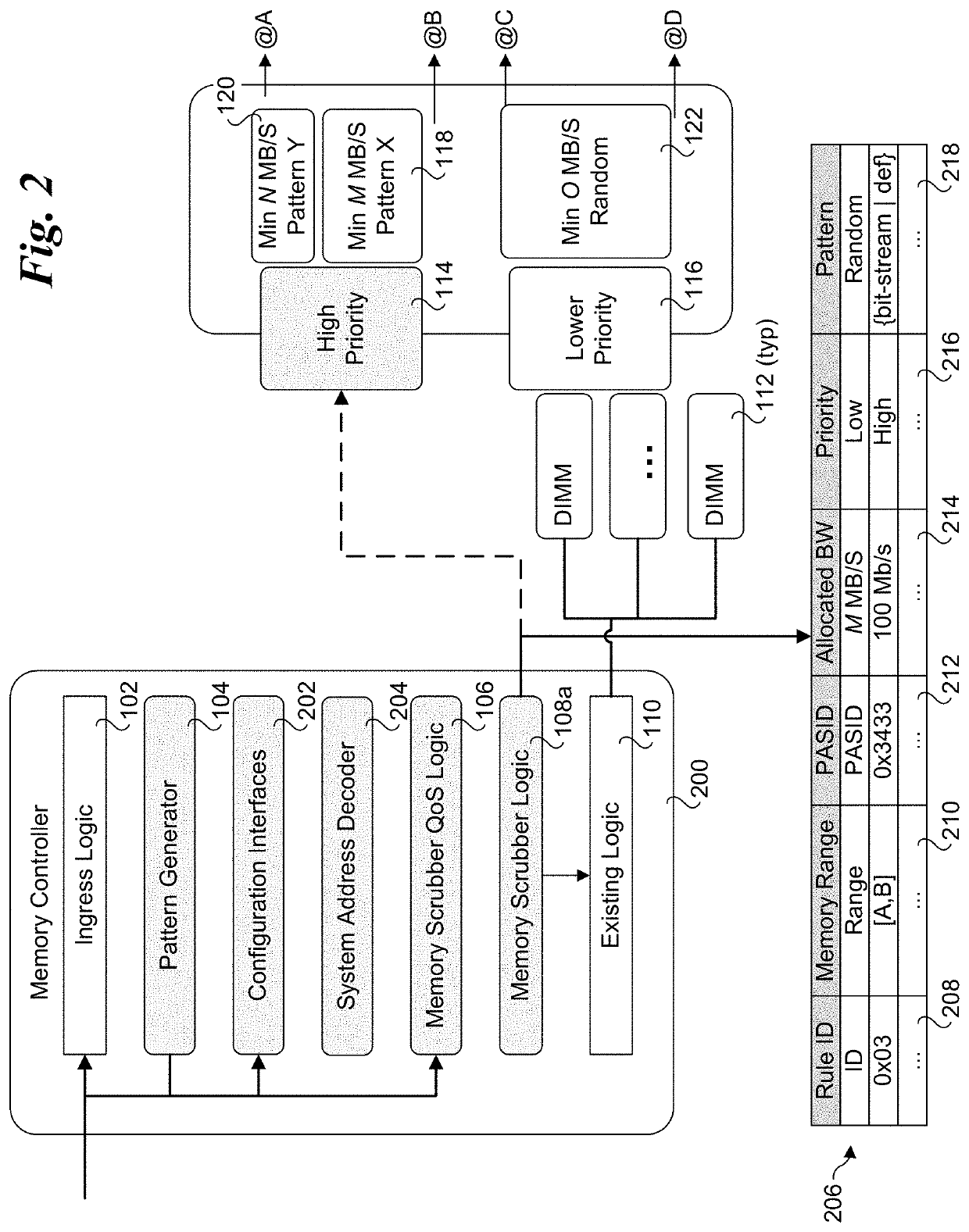
PendingUS20210318929A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationResource allocationQos quality of serviceVirtualization
Methods and apparatus for application aware memory patrol scrubbing techniques. The method may be performed on a computing system including one or more memory devices and running multiple applications with associated processes. The computer system may be implemented in a multi-tenant environment, where virtual instances of physical resources provided by the system are allocated to separate tenants, such as through virtualization schemes employing virtual machines or containers. Quality of Service (QoS) scrubbing logic and novel interfaces are provided to enable memory scrubbing QoS policies to be applied at the tenant, application, and / or process level. This QoS policies may include memory ranges for which specific policies are applied, as well as bandwidth allocations for performing scrubbing operations. A pattern generator is also provided for generating scrubbing patterns based on observed or predicted memory access patterns and / or predefined patterns.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Track flow data-oriented continuous range query method and system
PendingCN113742536AReduce the number of intersection judgmentsReduce the number of dataOther databases indexingOther databases queryingMemory scrubbingTerm memory
The invention provides a track flow data-oriented continuous range query method and system. The system comprises a position information sending module, an index module and a query module. According to the invention, an index module is improved firstly, it can be guaranteed that track points are rapidly inserted according to the spatial positions and the time sequence of the track points, and ID-time range query and spatial range query of tracks are supported. Thirdly, a query module is improved, an internal and external memory combined query mechanism is adopted, and the number of times of spatial intersection judgment and the number of times of data needing to be retrieved are reduced to the maximum extent; and furthermore, an index module and a query module are supplemented, so that the query accuracy can be ensured under the condition that the query is changed. Finally, a memory cleaning module is further included, when the number of query times and the number of concurrent queries are increased, a result set is reduced, and the memory burden is relieved. According to the invention, under the condition of ensuring real-time updating of data, time range query and space range query are realized at the same time, and the efficiency of continuous range query is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Memory scrubbing in a mirrored memory system to reduce system power consumption
InactiveUS9864653B2Reduce power consumptionReduce probabilityInput/output to record carriersStatic storageMemory scrubbingParallel computing
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Selective memory scrubbing based on data type
ActiveUS9081719B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingMemory scrubbing
A method for minimizing soft error rates within caches by controlling a memory scrubbing rate selectively for a cache memory at an individual bank level. More specifically, the disclosure relates to maintaining a predetermined sequence and process of storing all modified information of a cache in a subset of ways of the cache, based upon for example, a state of a modified indication within status information of a cache line. A cache controller includes a memory scrubbing controller which is programmed to scrub the subset of the ways with the modified information at a smaller interval (i.e., more frequently) compared to the rest of the ways with clean information (i.e., information where the information stored within the main memory is coherent with the information stored within the cache).
Owner:NXP USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com