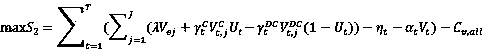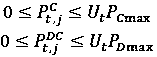Patents
Literature
43 results about "Vehicle-to-grid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
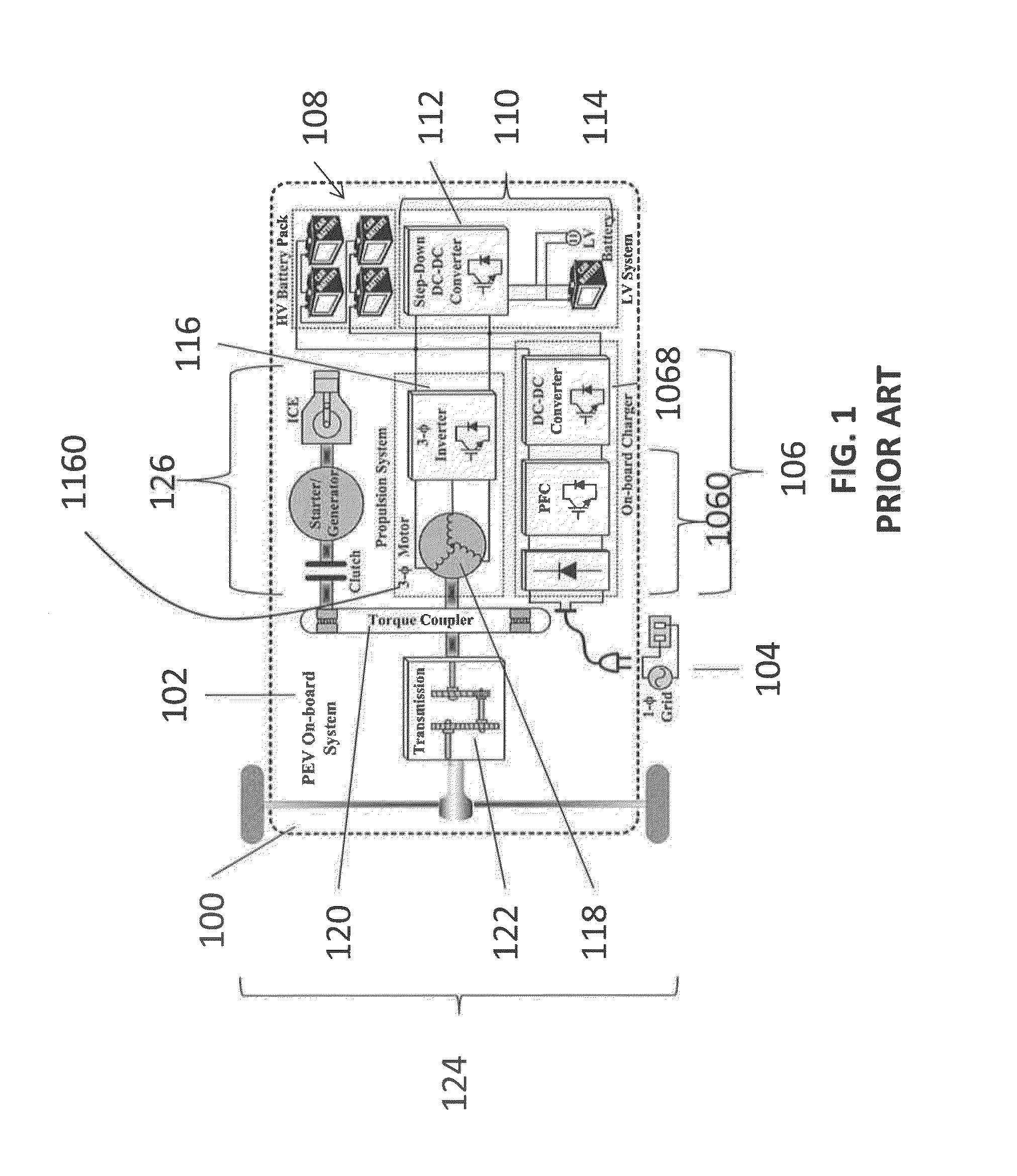
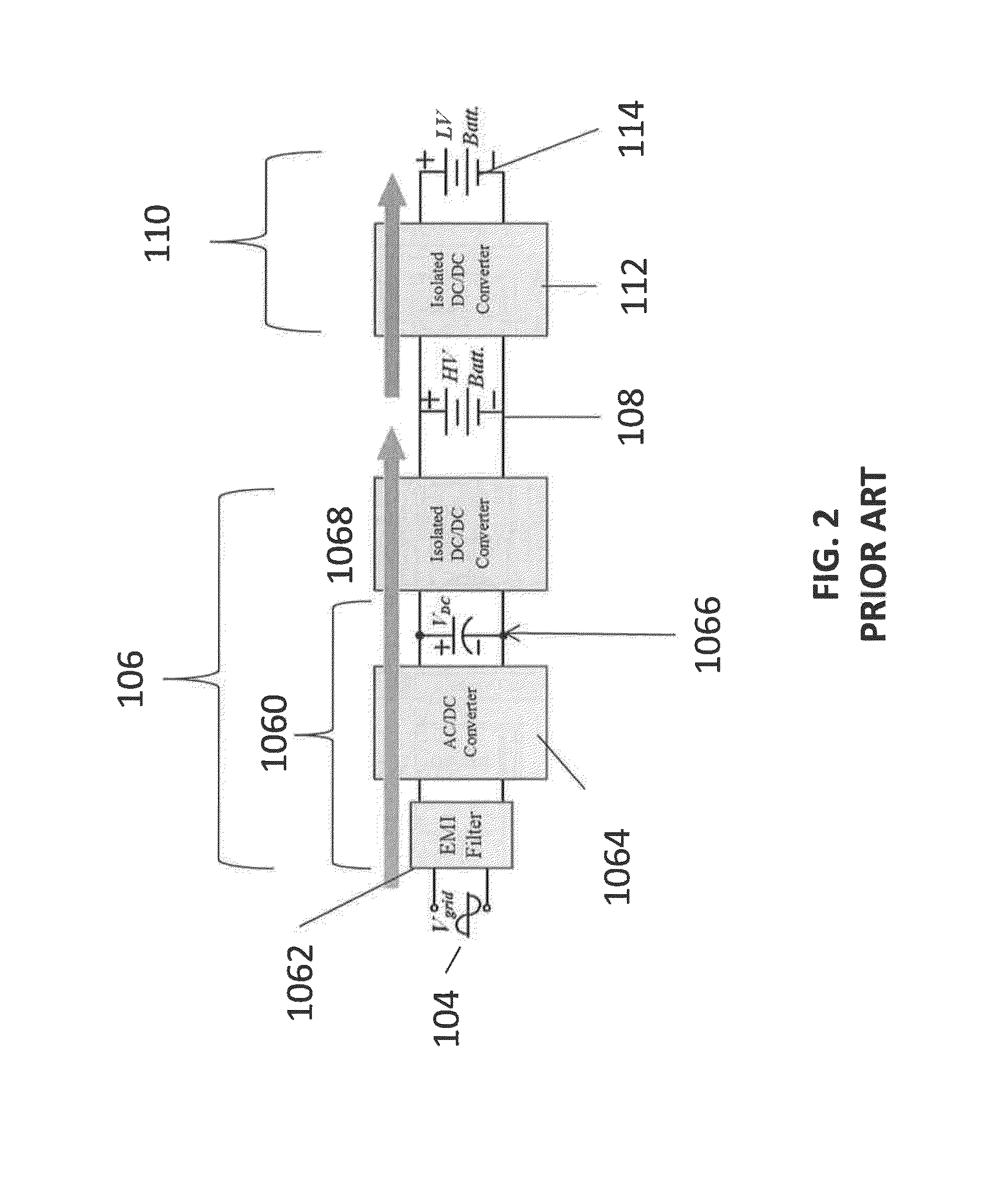
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) describes a system in which plug-in electric vehicles, such as battery electric vehicles (BEV), plug-in hybrids (PHEV) or hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEV), communicate with the power grid to sell demand response services by either returning electricity to the grid or by throttling their charging rate. V2G storage capabilities can also enable EVs to store and discharge electricity generated from renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, with output that fluctuates depending on weather and time of day.
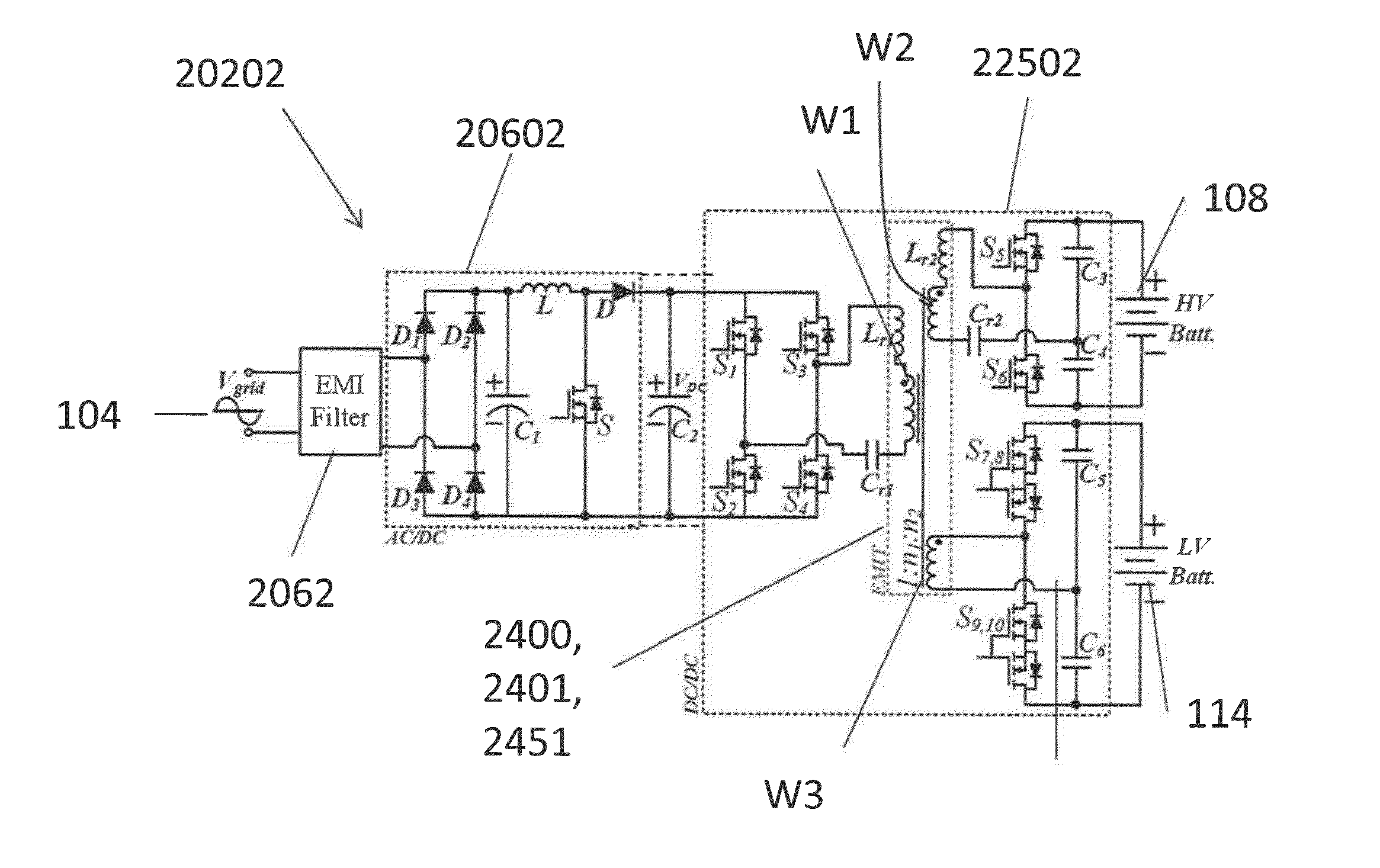
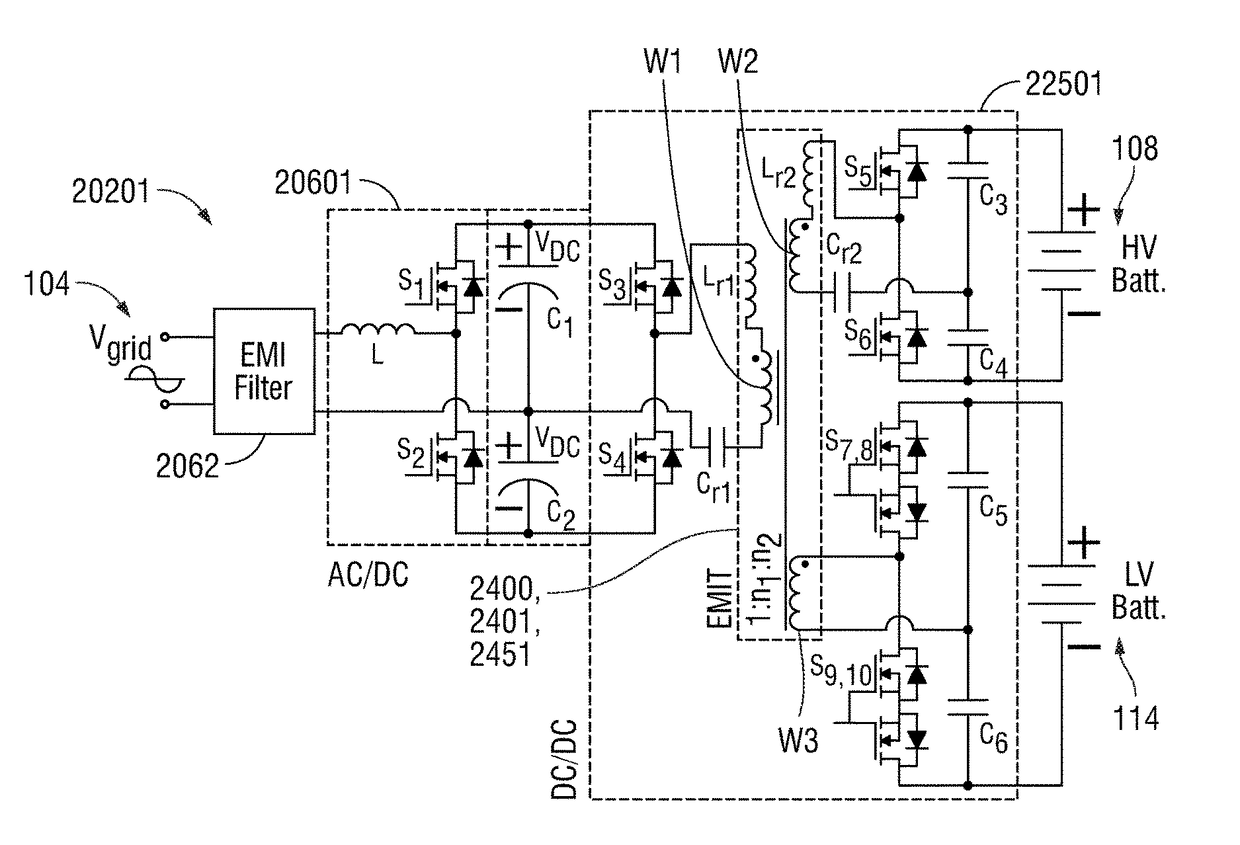
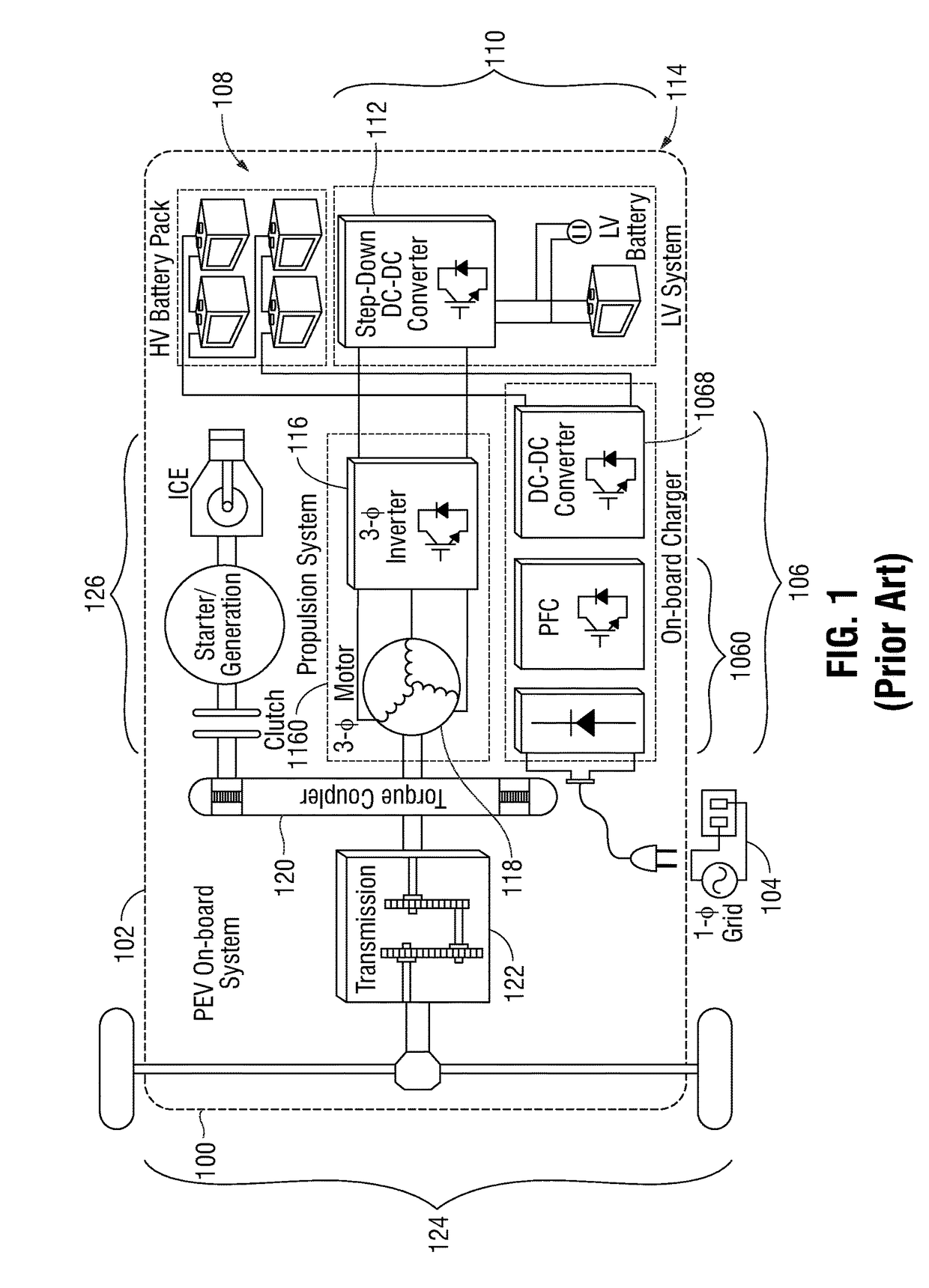
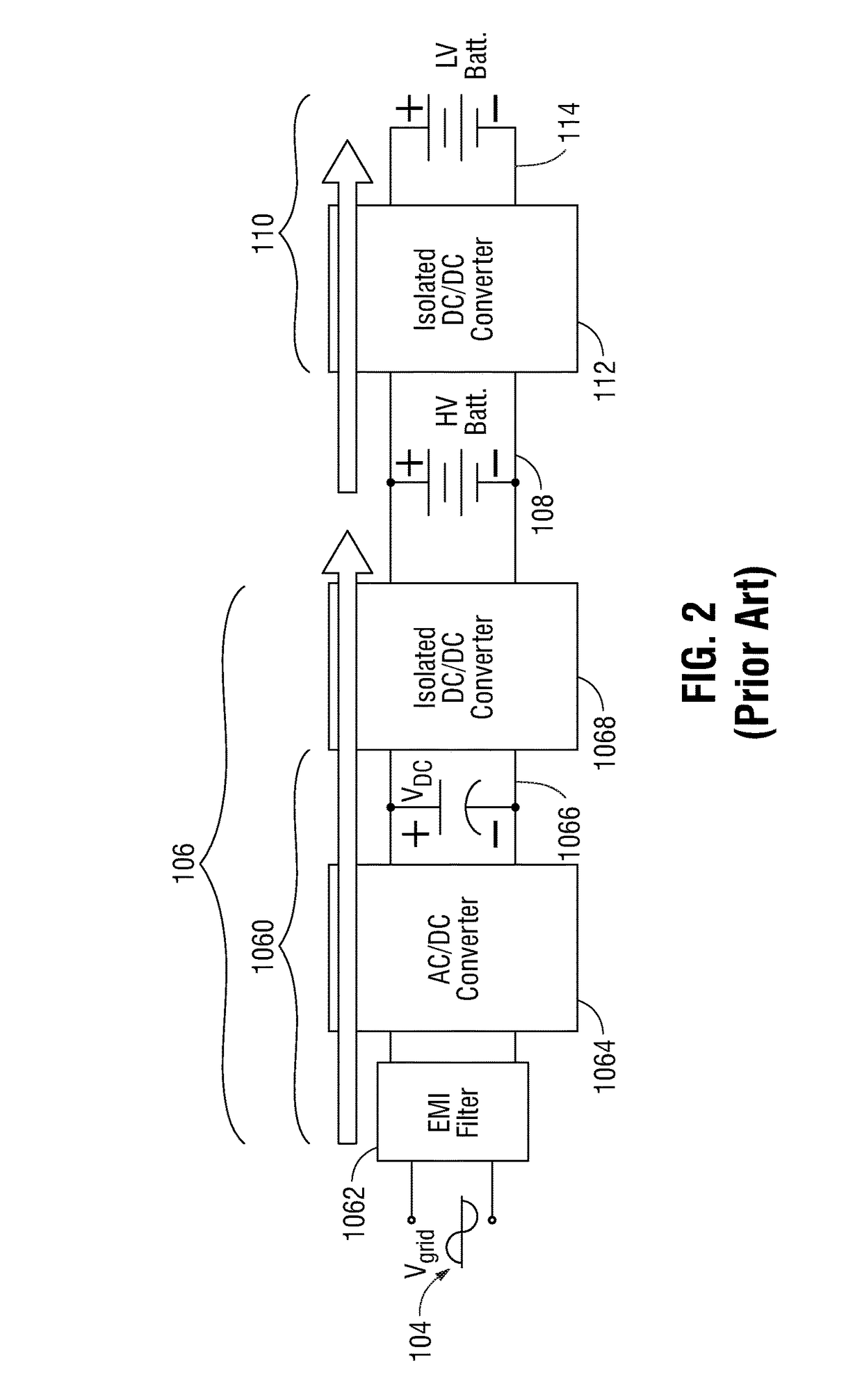
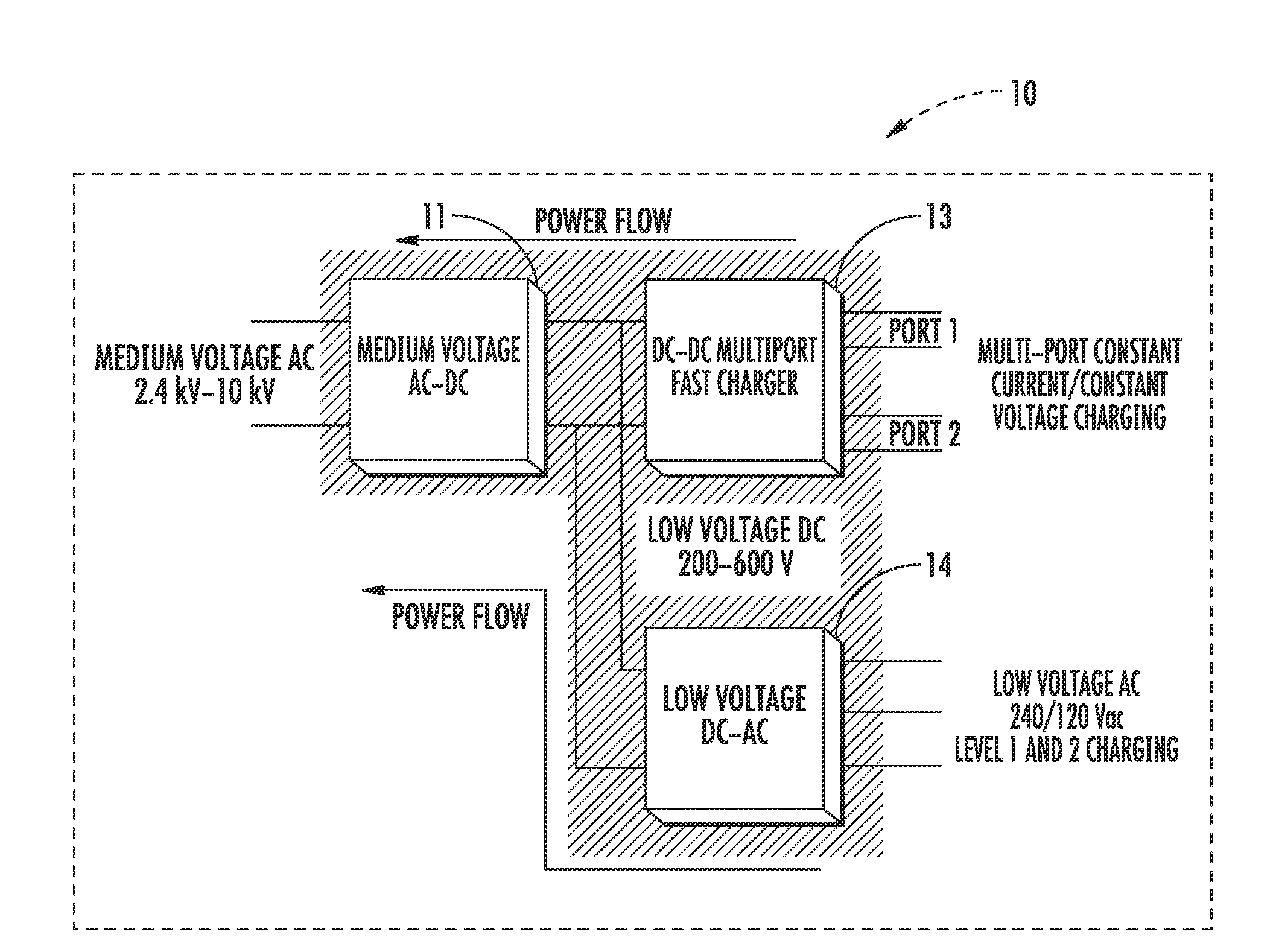
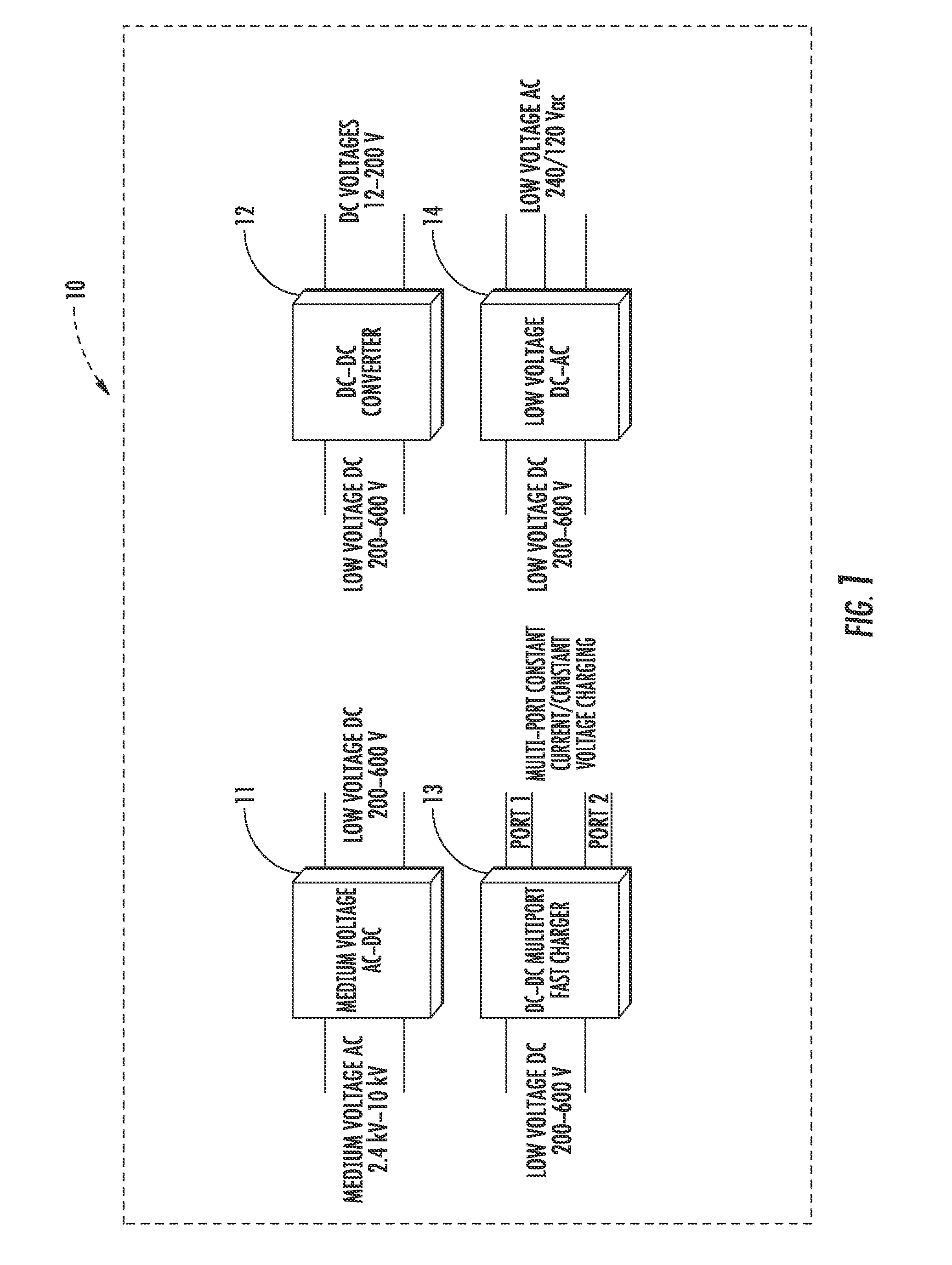
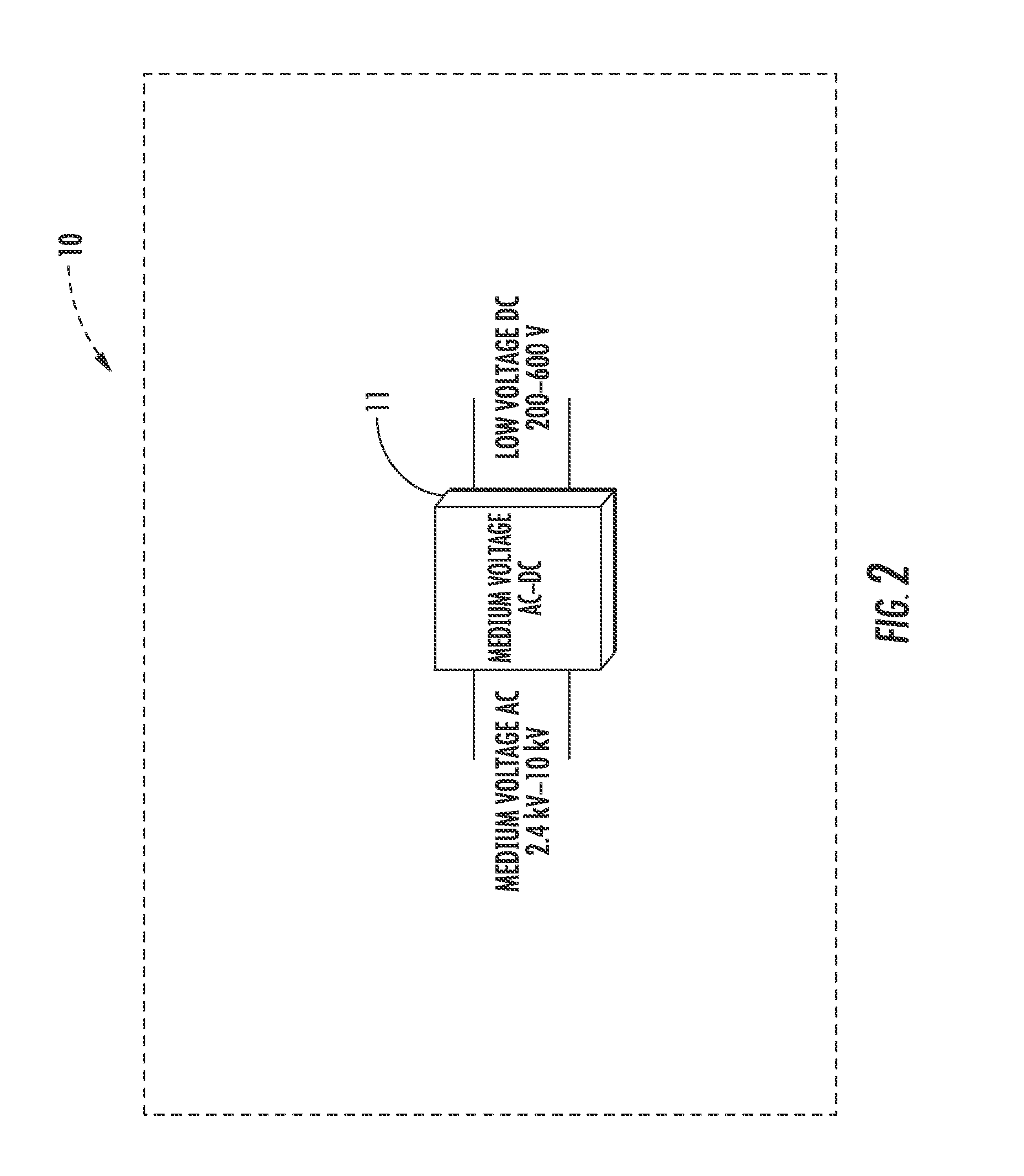
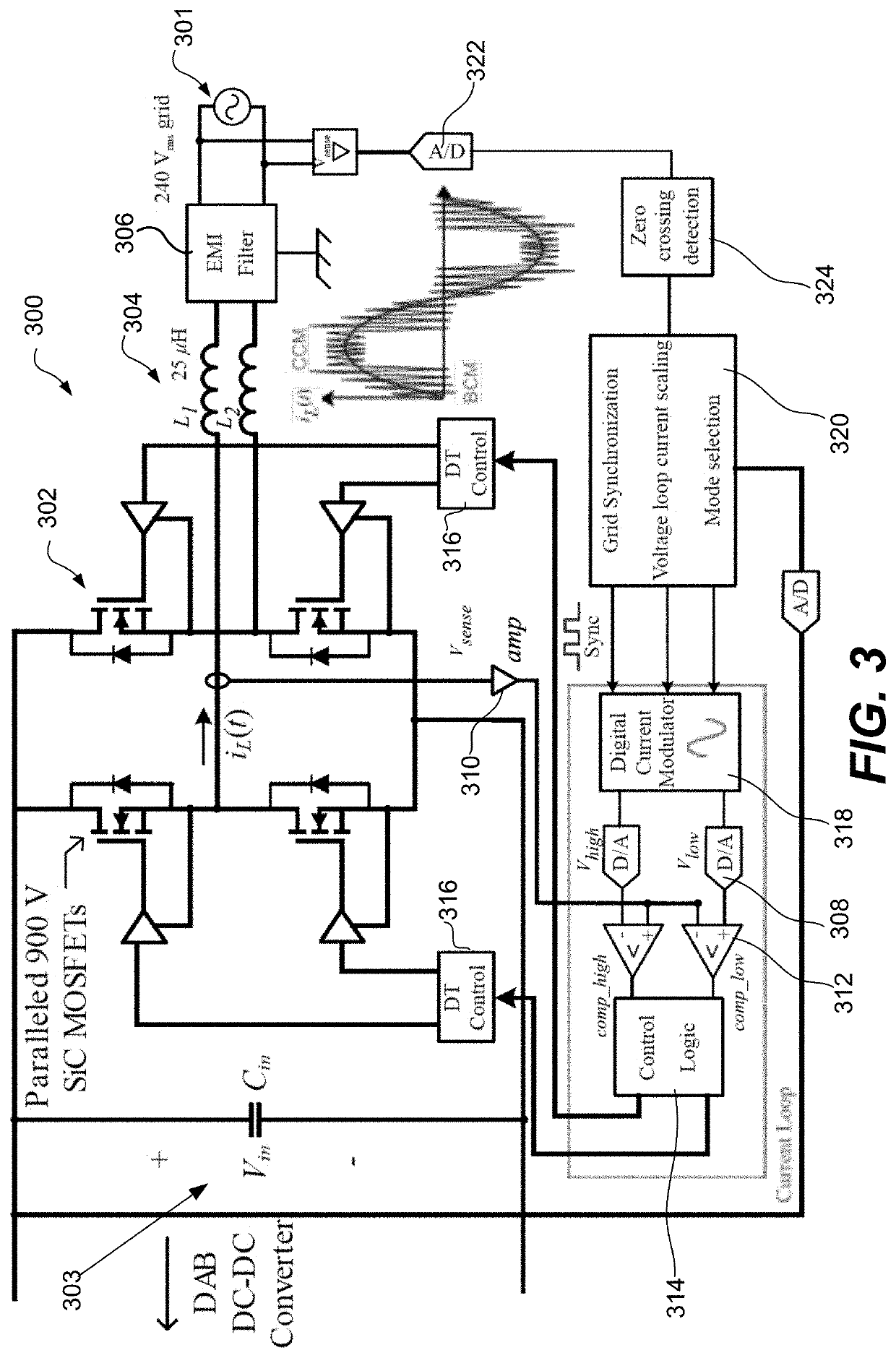
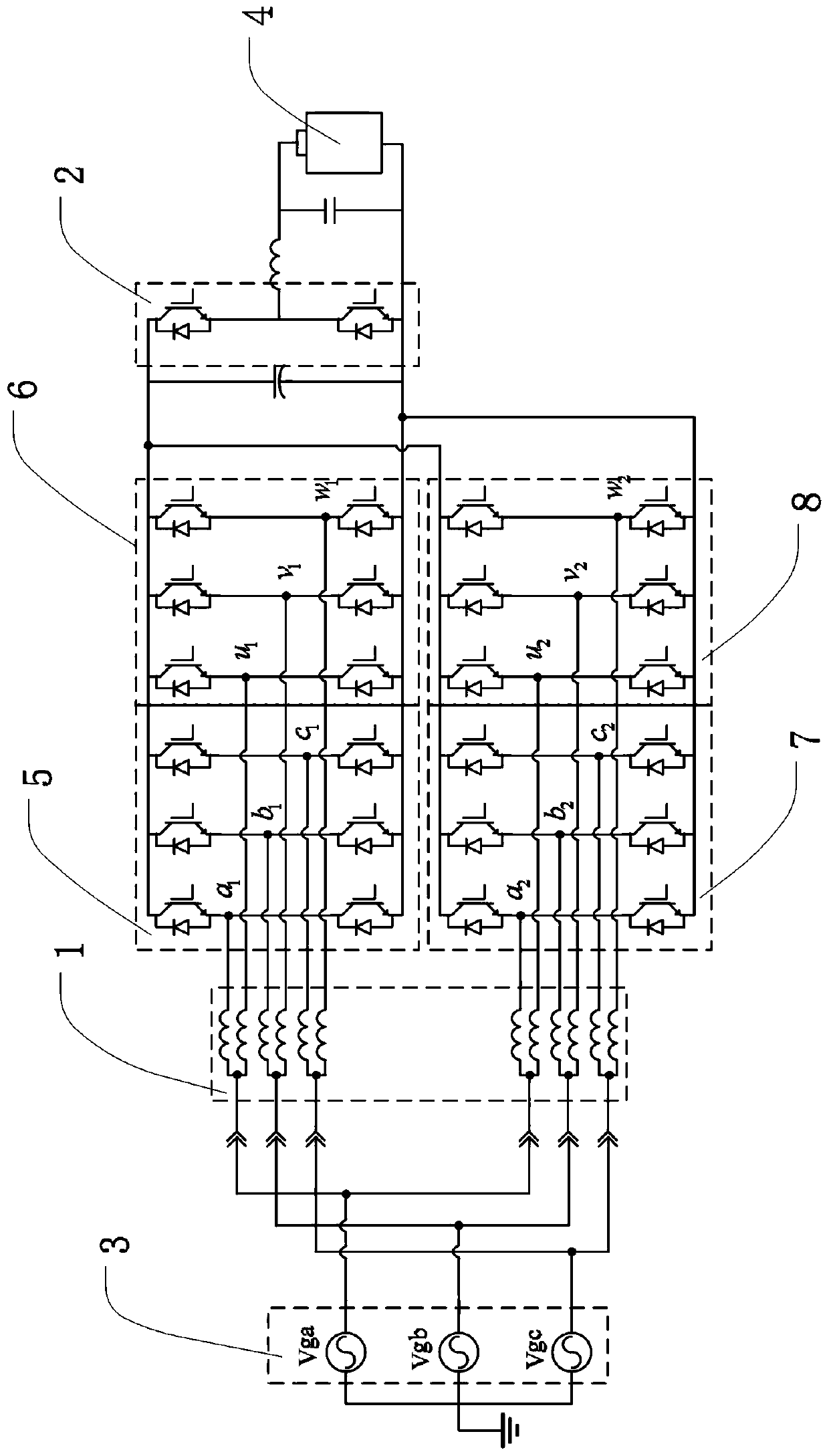
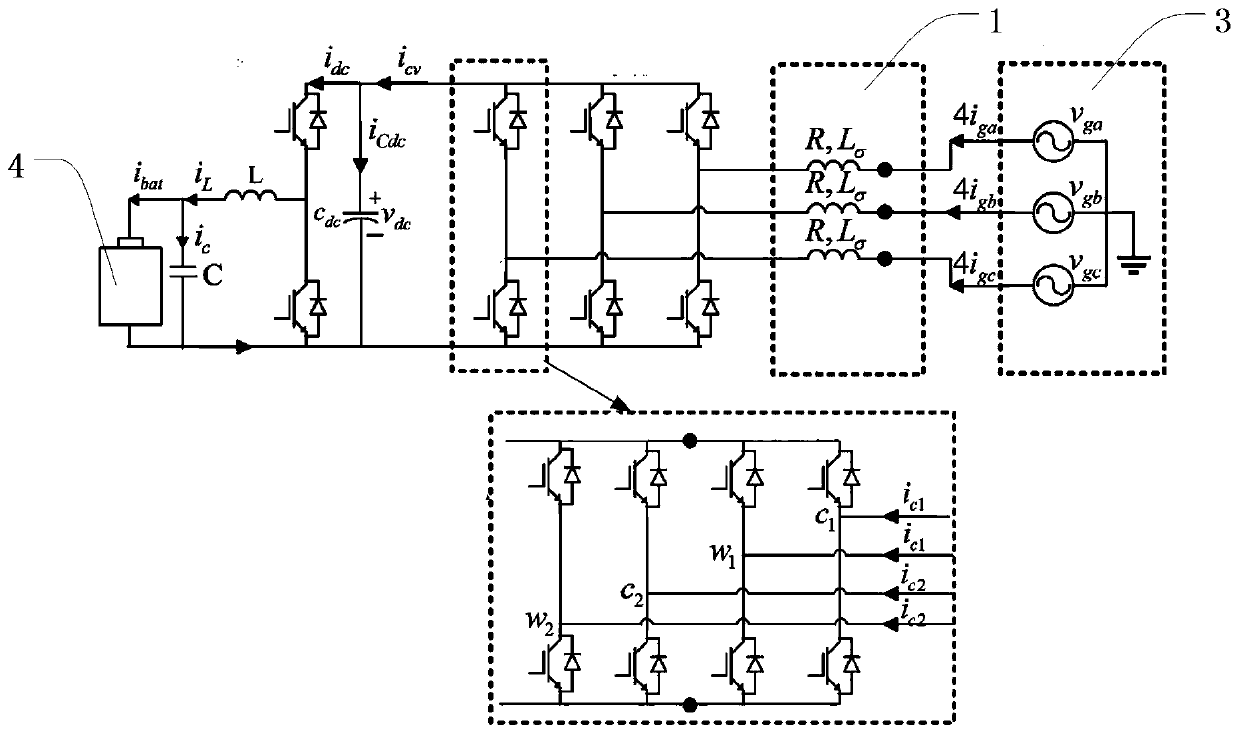
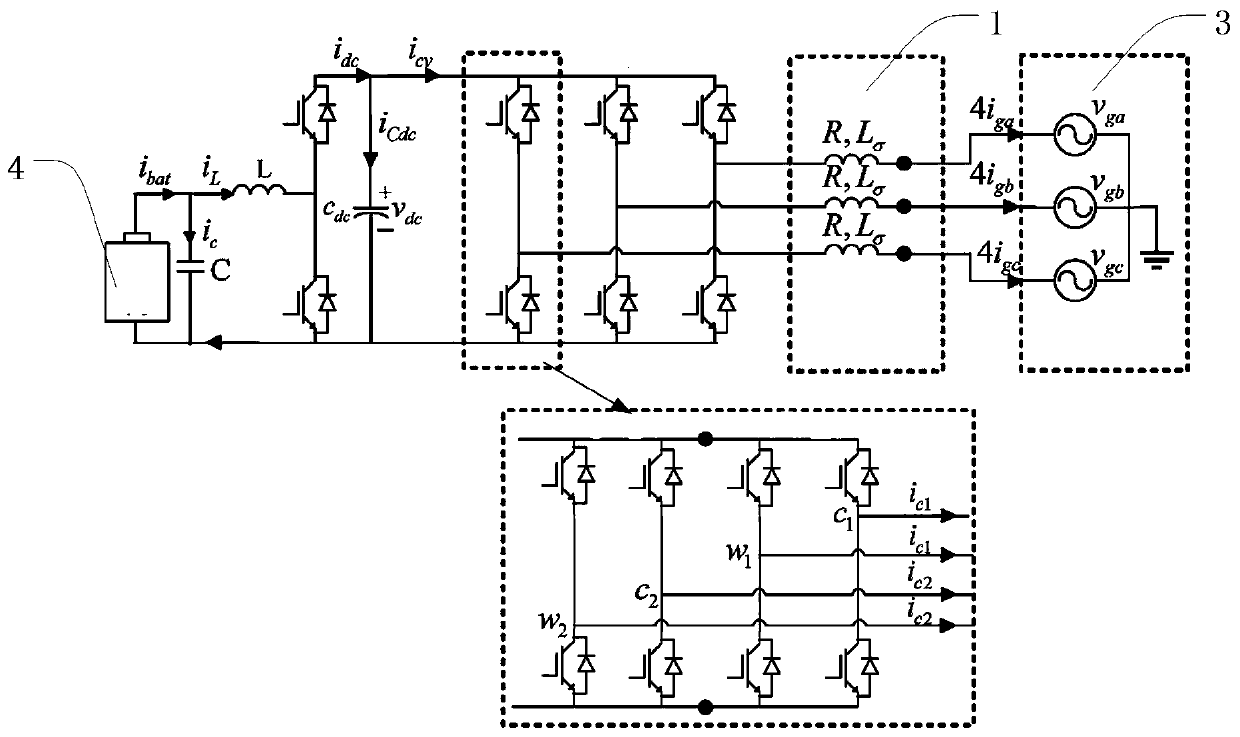
An integrated dual-output grid-to-vehicle (G2V) and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) onboard charger for plug-in electric vehicles
ActiveUS20160016479A1Improve power densitySmall sizeTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresElectrical batteryLow voltage
An integrated and isolated onboard charger for plug-in electric vehicles, includes an ac-dc converter and a dual-output dc-dc resonant converter, for both HV traction batteries and LV loads. In addition, the integrated and isolated onboard charger may be configured as unidirectional or bidirectional, and is capable of delivering power from HV traction batteries to the grid for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications. To increase the power density of the converter, the dual-output DC-DC resonant converter may combine magnetic components of resonant networks into a single three-winding electromagnetically integrated transformer (EMIT). The resonant converter may be configured as a half-bridge topology with split capacitors as the resonant network components to further reduce the size of converter. The integrated charger may be configured for various operating modes, including grid to vehicle (G2V), vehicle to grid (V2G) and high voltage to low voltage, HV-to-LV (H2L) charging.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
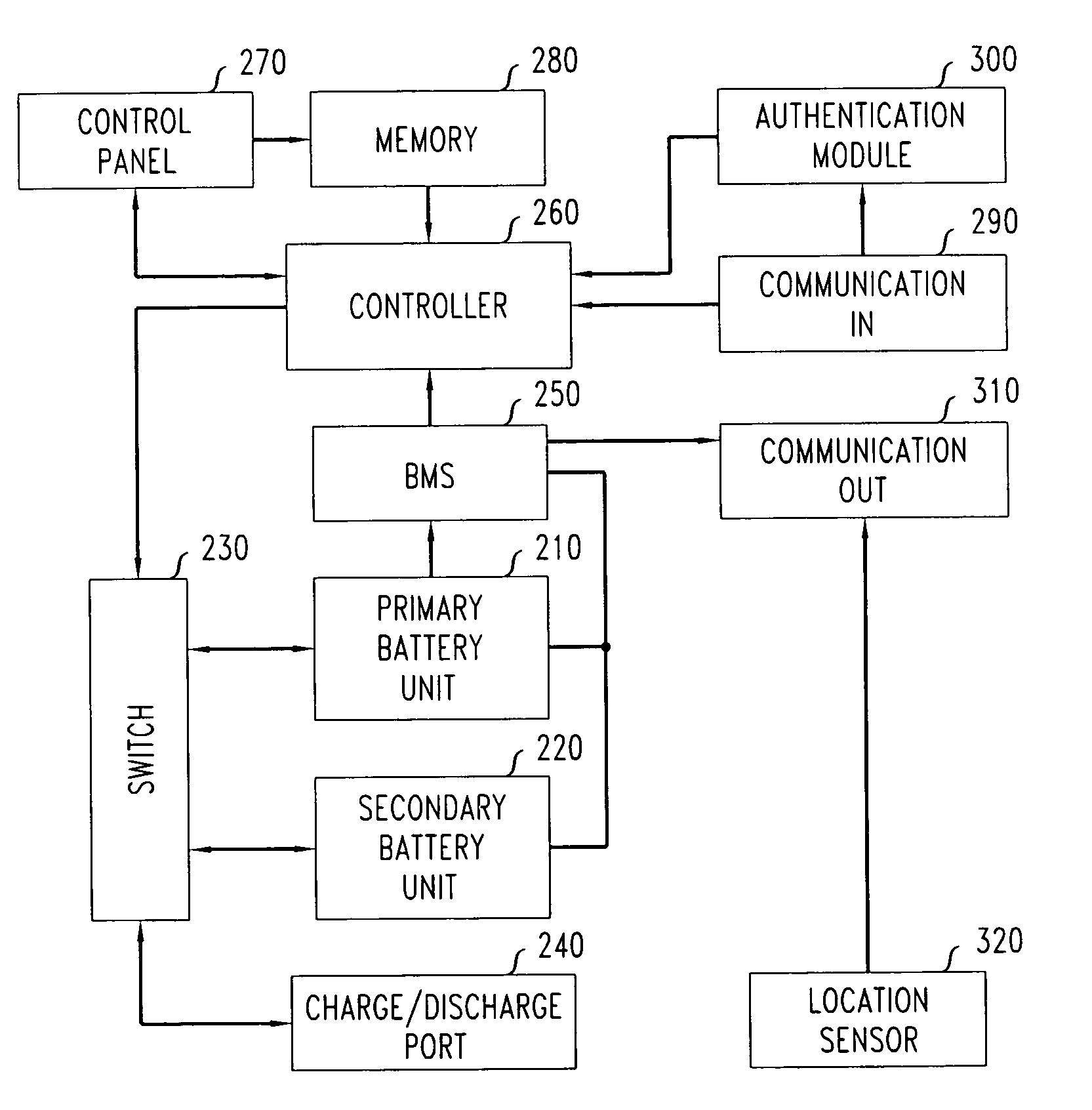
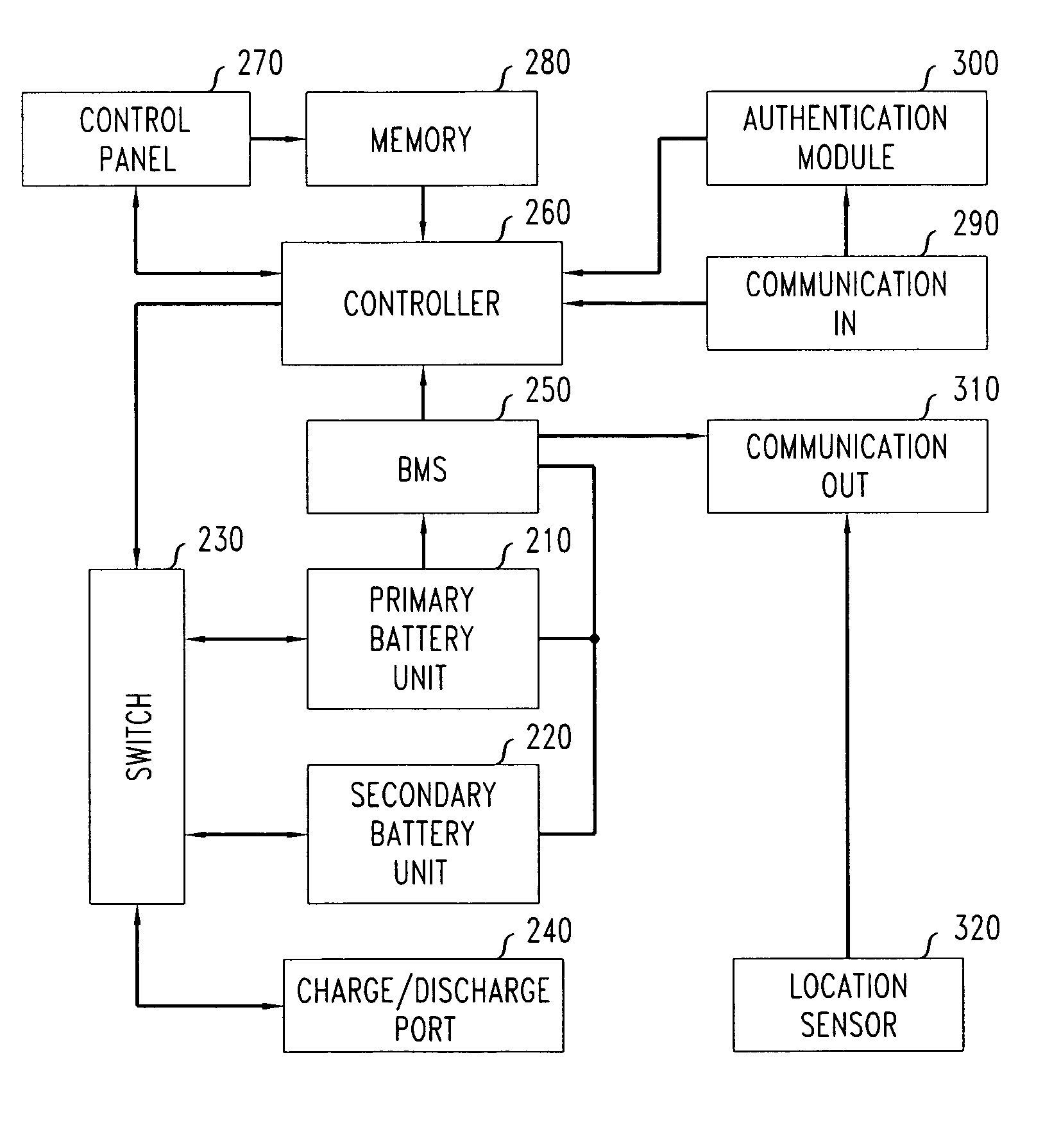
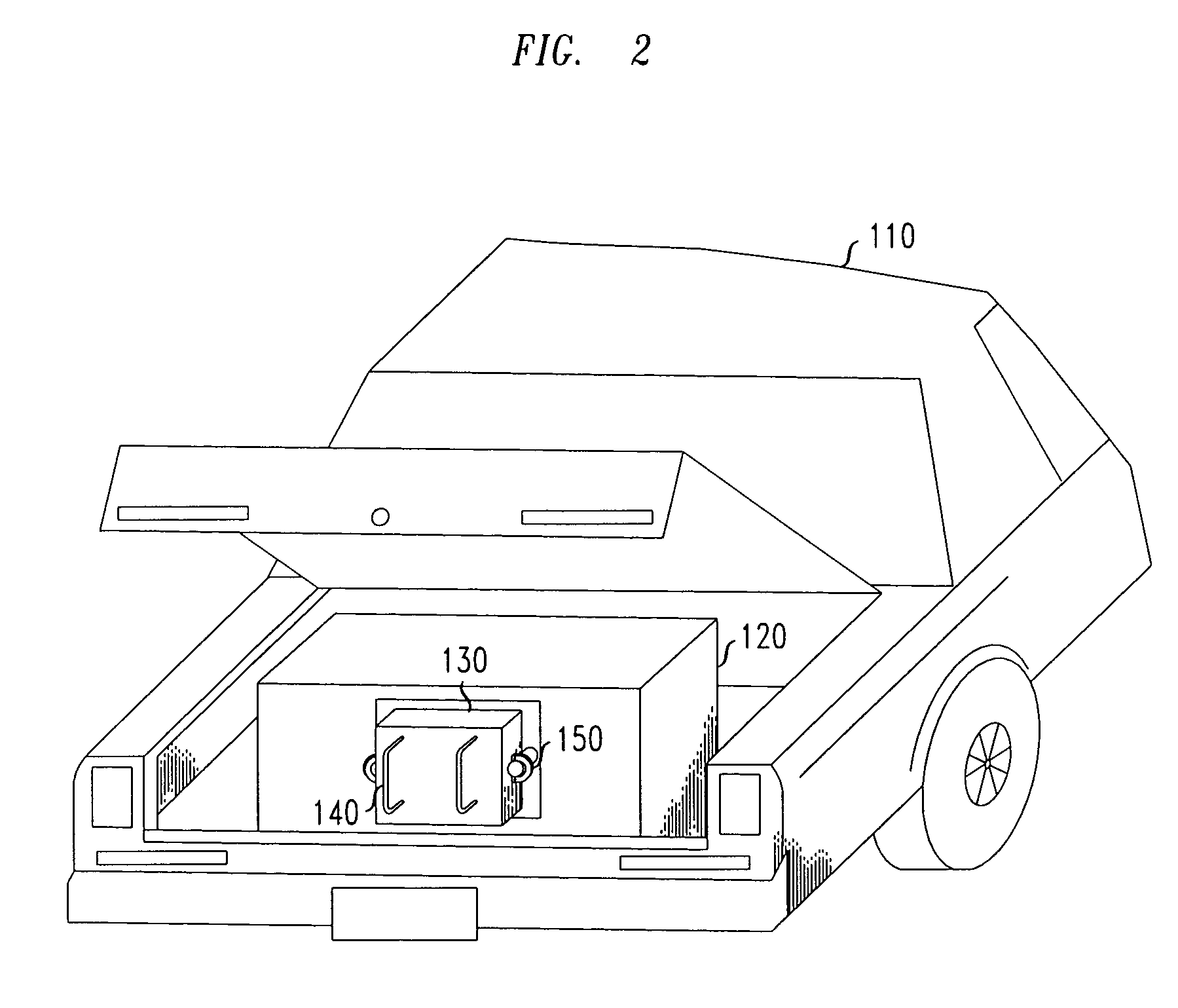
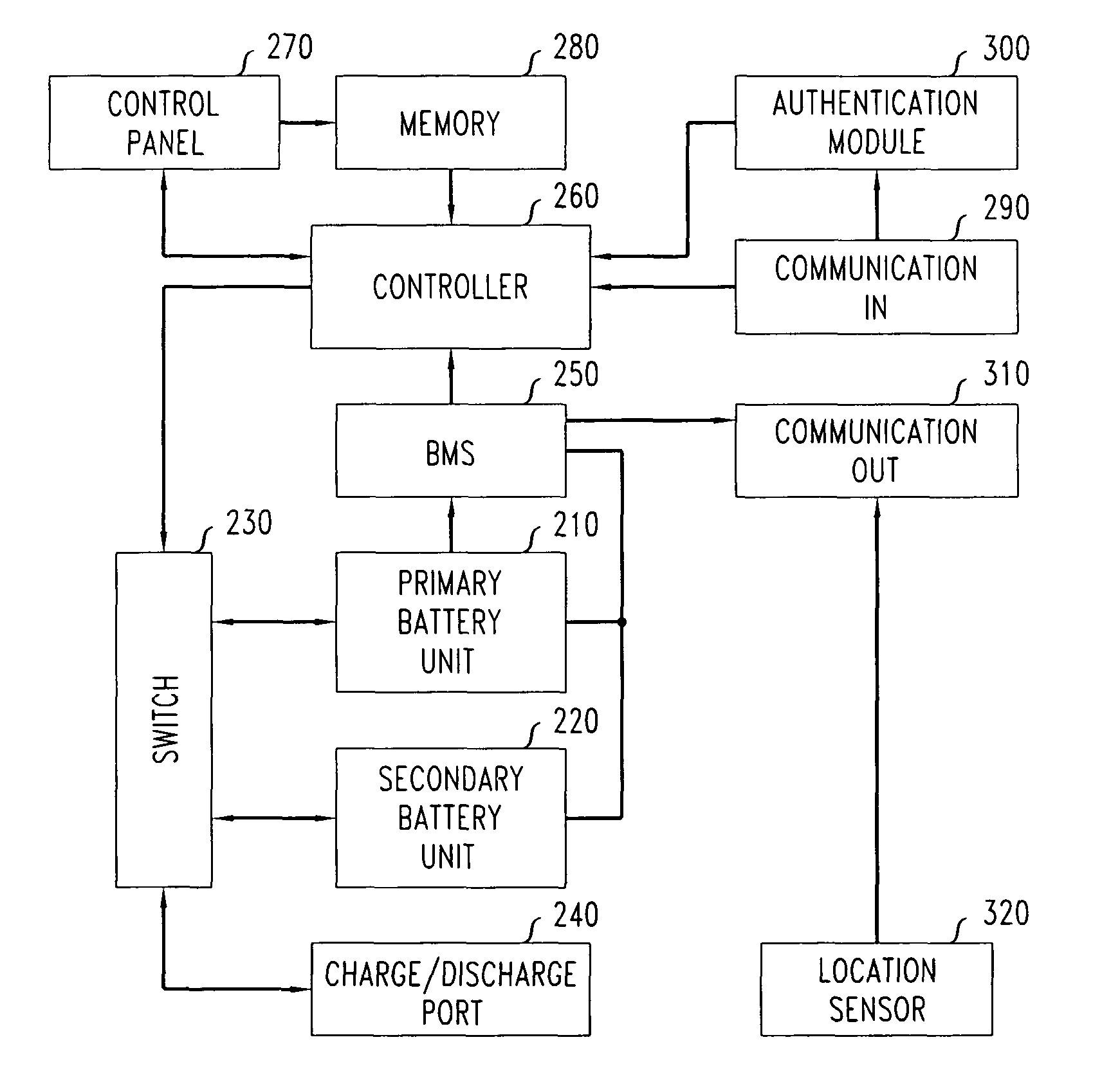
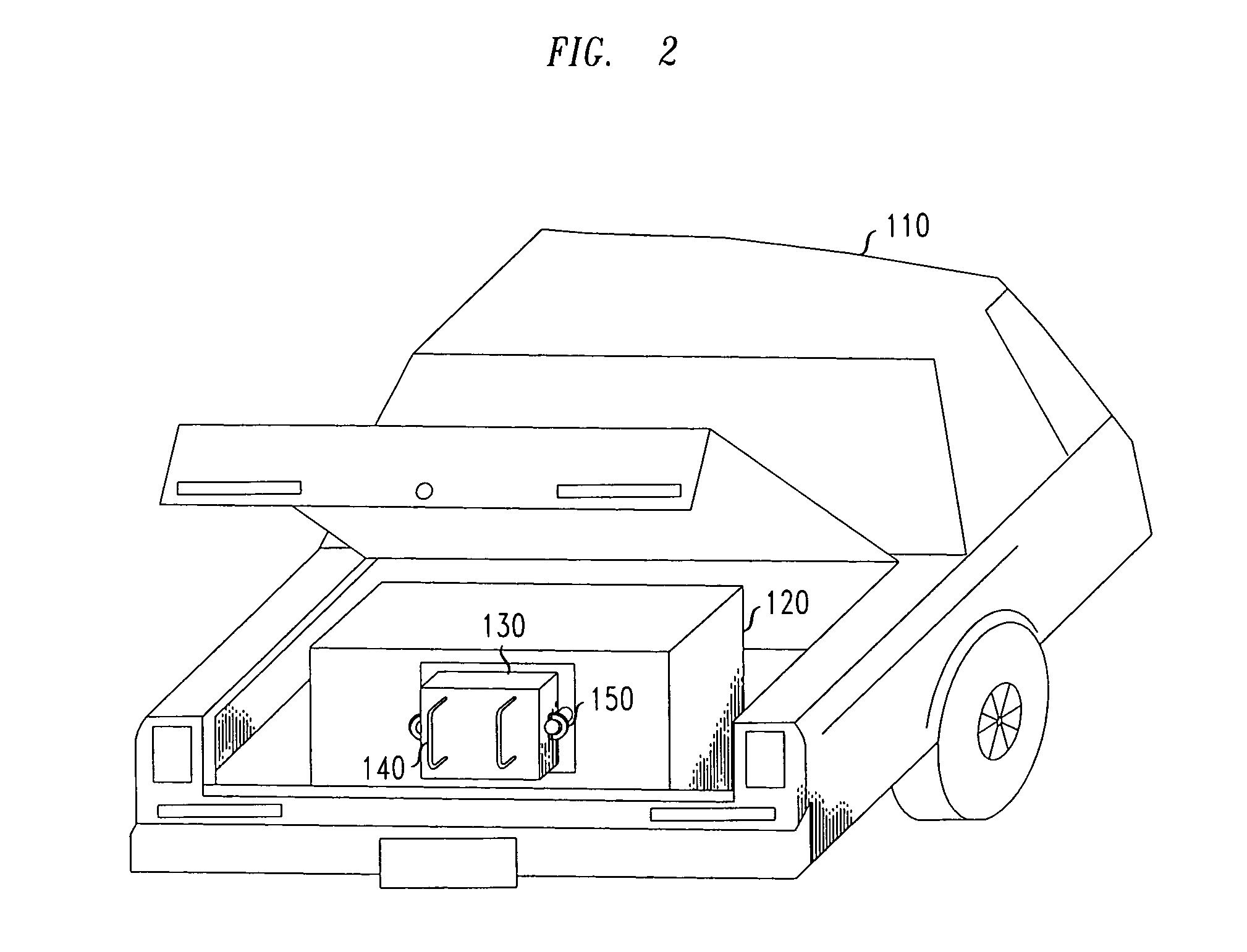
Method and apparatus of stored energy management in battery powered vehicles
A secondary battery and charging system are provided within an electric car or other electric drive vehicle. The secondary battery may, e.g., be owned by the electric utility. The battery is removable and can be charged and discharged independently of the primary car battery system. The utility can use the secondary battery to implement vehicle-to-grid functionality.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G)-technology-based vehicle-mounted charging and discharging device and control method thereof
InactiveCN102163856AImprove transmission efficiencyZero steady-state error elimination effect is goodBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionHysteresisControl manner
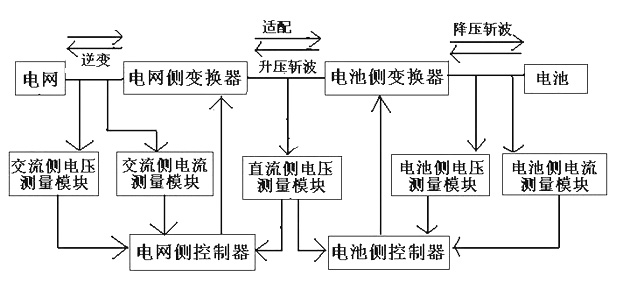
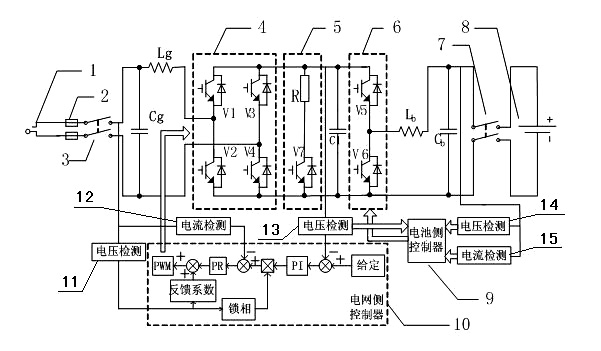
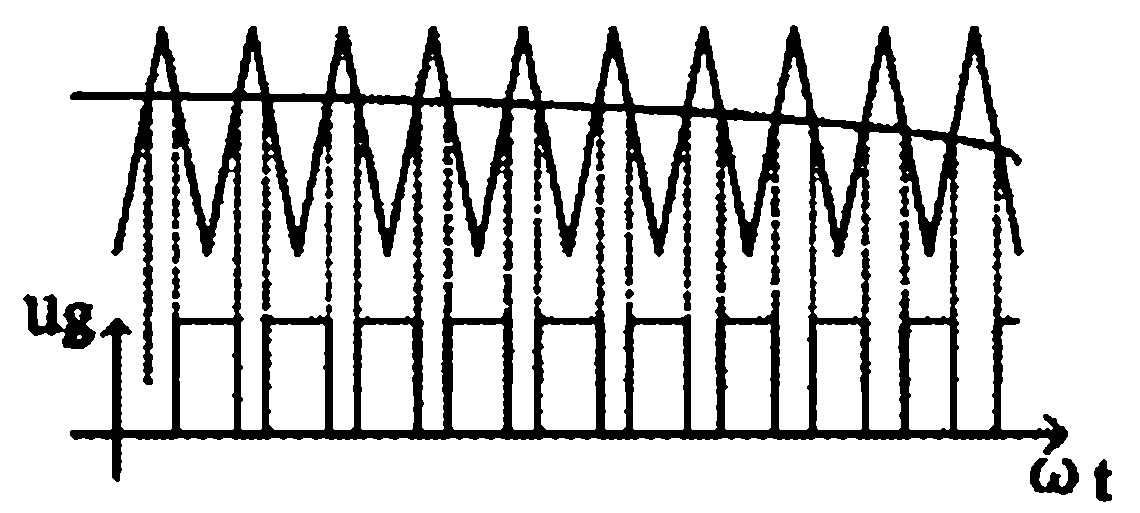
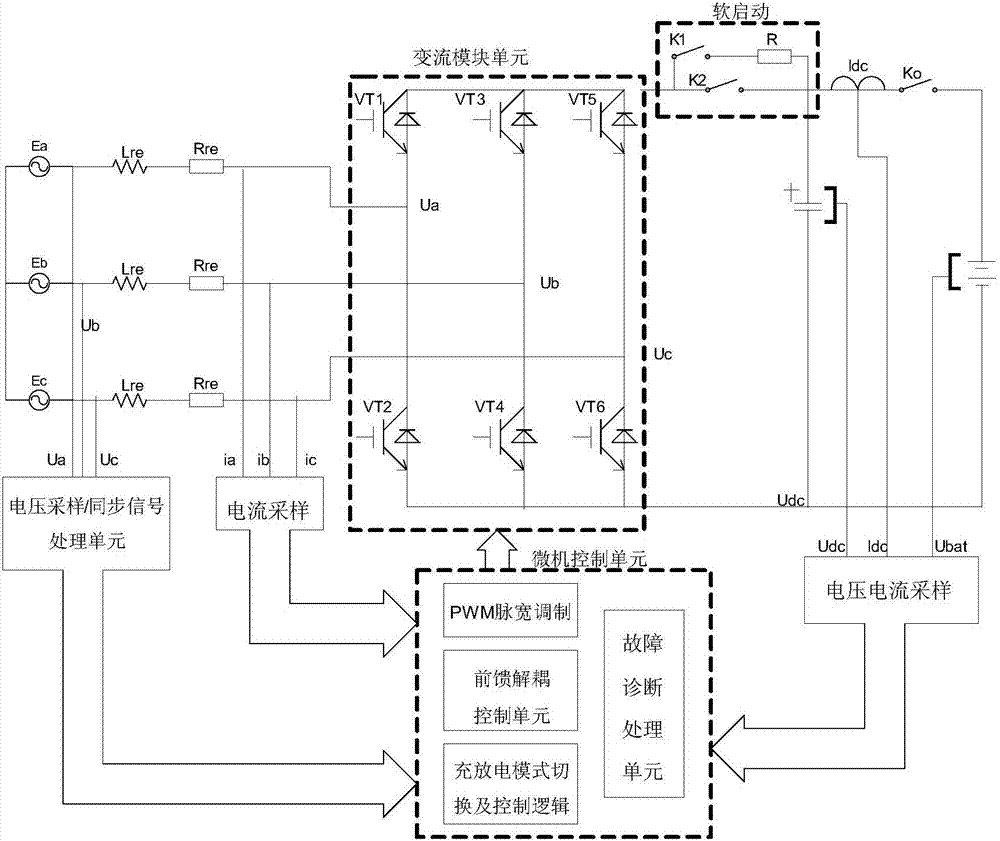
The invention relates to a vehicle-to-grid (V2G)-technology-based vehicle-mounted charging and discharging device and a control method thereof. The device comprises a power supply input part, a battery, a power grid side controller, a power grid side converter, a battery side controller and a battery side converter, wherein the power supply input part, the power grid side converter and the battery side converter are connected with the battery in turn; the battery side controller adopts a hysteresis loop comparison control mode and compares voltage and current amount which is detected in real time with the set value, and a duty ratio of the battery side converter is subjected to hysteresis loop output control, so that Boost chopped wave conversion during constant current, constant voltage charging and grid connection is realized; and the power grid side controller adopts a double closed loop control mode of a voltage outer ring and a current inner ring to realize charging adaptation and grid-connected inversion of the power grid side converter. The device overcomes the defects that the traditional bidirectional converter circuit is complex in structure, high in cost and low in efficiency in the V2G technology, and the requirement of operating the same circuit in two working modes is met.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and apparatus of stored energy management in battery powered vehicles
A secondary battery and charging system are provided within an electric car or other electric drive vehicle. The secondary battery may, e.g., be owned by the electric utility. The battery is removeable and can be charged and discharged independently of the primary car battery system. The utility can use the secondary battery to implement vehicle-to-grid functionality.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and apparatus of stored energy management in battery powered vehicles
A secondary battery and charging system are provided within an electric car or other electric drive vehicle. The secondary battery may, e.g., be owned by the electric utility. The battery is removable and can be charged and discharged independently of the primary car battery system. The utility can use the secondary battery to implement vehicle-to-grid functionality.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Integrated dual-output grid-to-vehicle (G2V) and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) onboard charger for plug-in electric vehicles
ActiveUS9931951B2Improve power densitySmall sizeInductancesVehicular energy storageElectrical batteryLow voltage
An integrated and isolated onboard charger for plug-in electric vehicles, includes an ac-dc converter and a dual-output dc-dc resonant converter, for both HV traction batteries and LV loads. In addition, the integrated and isolated onboard charger may be configured as unidirectional or bidirectional, and is capable of delivering power from HV traction batteries to the grid for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications. To increase the power density of the converter, the dual-output DC-DC resonant converter may combine magnetic components of resonant networks into a single three-winding electromagnetically integrated transformer (EMIT). The resonant converter may be configured as a half-bridge topology with split capacitors as the resonant network components to further reduce the size of converter. The integrated charger may be configured for various operating modes, including grid to vehicle (G2V), vehicle to grid (V2G) and high voltage to low voltage, HV-to-LV (H2L) charging.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
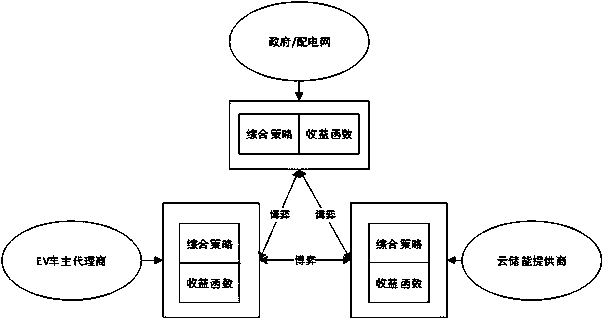
Electric car and cloud energy storage economic scheduling method based on dynamic non-cooperative game
ActiveCN108596464AIncrease flexibilityImprove intelligenceInternal combustion piston enginesResourcesMulti objective optimization algorithmPower grid
The invention puts forward an electric car and cloud energy storage economic scheduling method based on a dynamic non-cooperative game. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) establishingan electric car agent economic optimization scheduling model; (2) establishing a three-party non-cooperative game model; and (3) adopting particle swarm optimization to solve the above model, and determining a final Nash equilibrium point. By use of the method, the concept of V2G (Vehicle-to-grid) and a cloud storage retailer is imported for inhibiting the volatility influence of intermittent energy power generation, an electric car can be used as a load and also can be used as an energy storage characteristic, and electric energy grid-generation commercial operation is realized on a premise that the own requirement of the EV car owner is met, and therefore, the maximum car owner benefits are pursed; and meanwhile, since a cloud energy storage retailer and the EV car owner agent has economic conflicts, on the basis of a non-cooperative game theory, solving is carried out so as to achieve the maximum car owner benefits. Compared with subjectivity that a solution set obtained by a traditional multi-objective optimization algorithm is decided and selected by an administrator, the method disclosed by the invention imports a game theory to improve the flexibility and the intelligence ofelectric energy utilization.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
V2G (Vehicle-to-grid) AC-DC mixed micro grid power supply system and structure
ActiveCN105914799ASolve construction problemsSolve charging problemsAc-dc network circuit arrangementsOperational costsElectrical battery
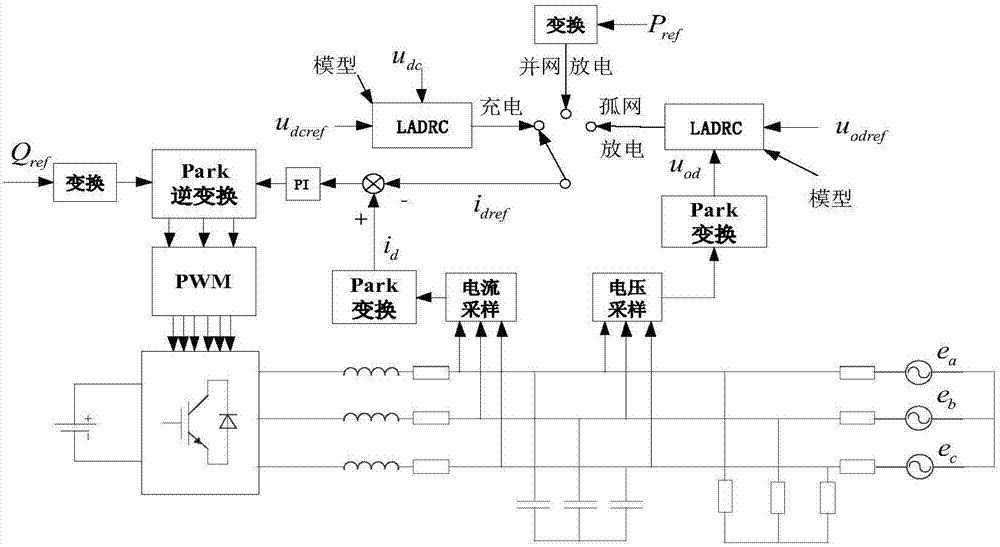
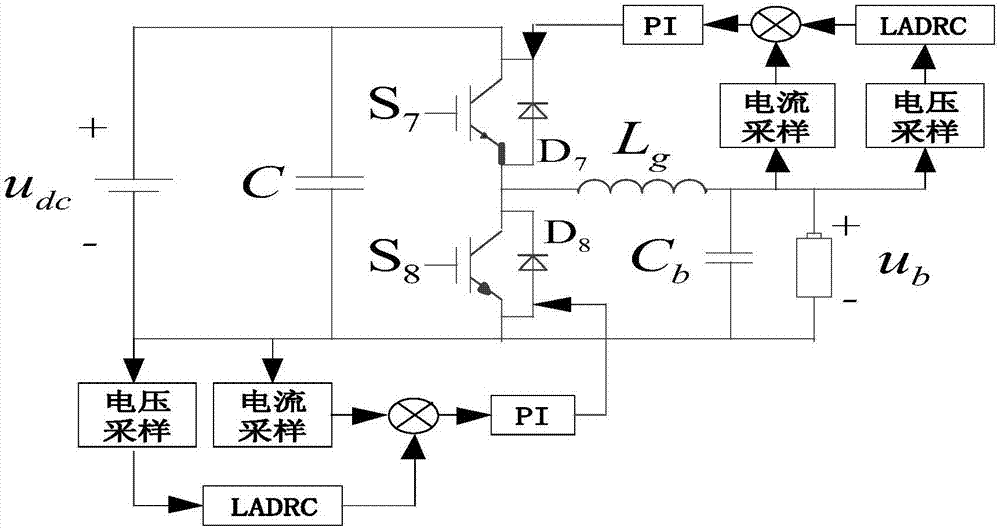
The invention relates to a V2G (Vehicle-to-grid) AC-DC mixed micro grid power supply system and structure, which comprise a DC micro grid and an AC micro grid wherein the DC micro grid includes DC buses, distributed type DC power supply apparatuses, DC energy storing apparatuses, DC charging piles, and changed cell DC charging and discharging apparatuses. The distributed type DC power supply apparatuses, the DC energy storing apparatuses, the DC charging piles, and the changed cell DC charging and discharging apparatuses are connected to the DC buses through their own current transformers. The AC micro grid comprises AC buses and AC power grid connection apparatuses in connection to the AC buses through their own current transformers. The AC buses are connected to the DC buses through the DC-AC current transformers in the micro grid. The AC power grid connection apparatuses are connected to a larger power grid. According to the invention, the system and structure can effectively reduce the processing work in photovoltaic inversion and charging pile rectification, lower the construction costs and operation costs, ease the pressure of a power grid by making an electric vehicle cell a mobile type energy storage apparatus, increase the stability and reliability of a power grid and cut down the operation costs for a power system.
Owner:BEIJING BEIBIAN MICRO GRID TECH
Charge-discharge-storage integrated station control method based on improved V2G and priority scheduling
ActiveCN107634532ARandom Load Fluctuation SuppressionFix security issuesFlexible AC transmissionAc network load balancingLower limitElectrical battery
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
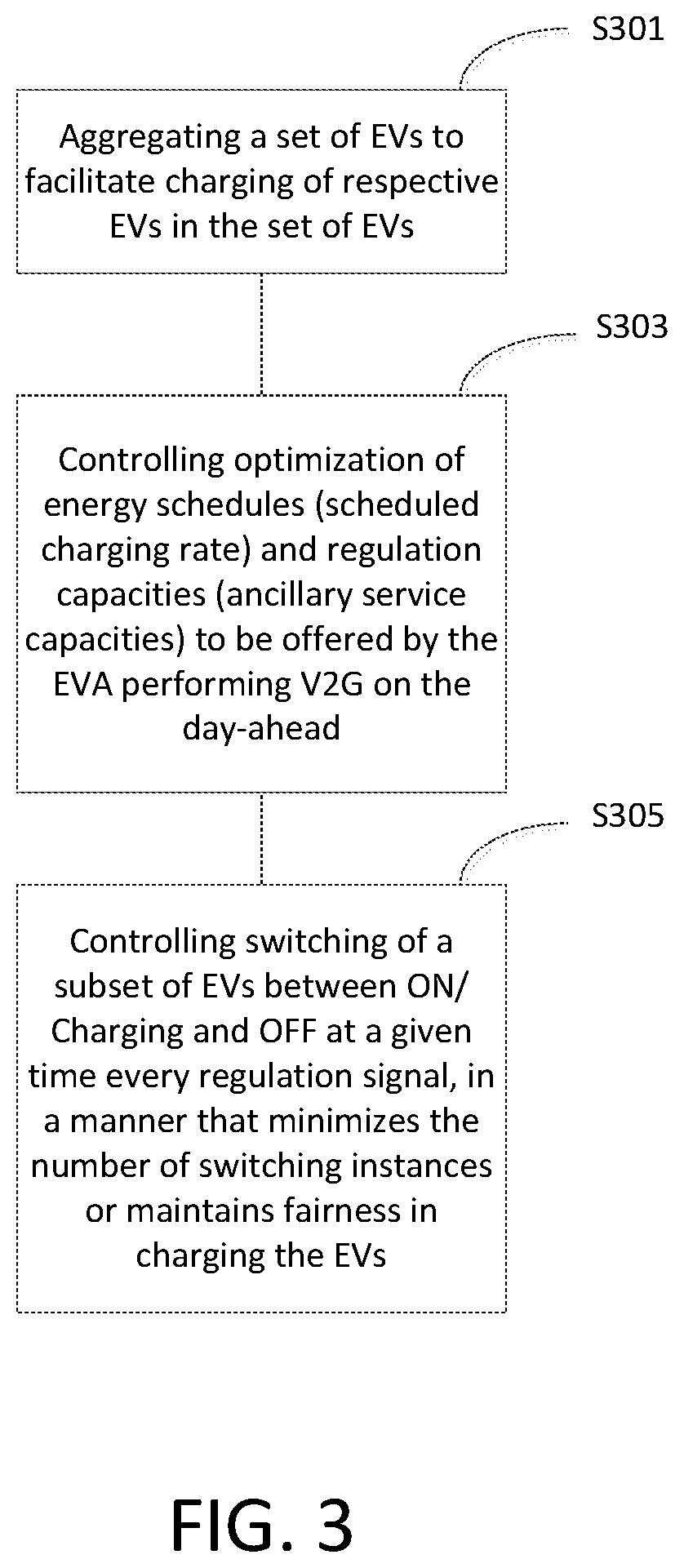
Optimal dispatch of electric vehicles performing v2g regulation
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
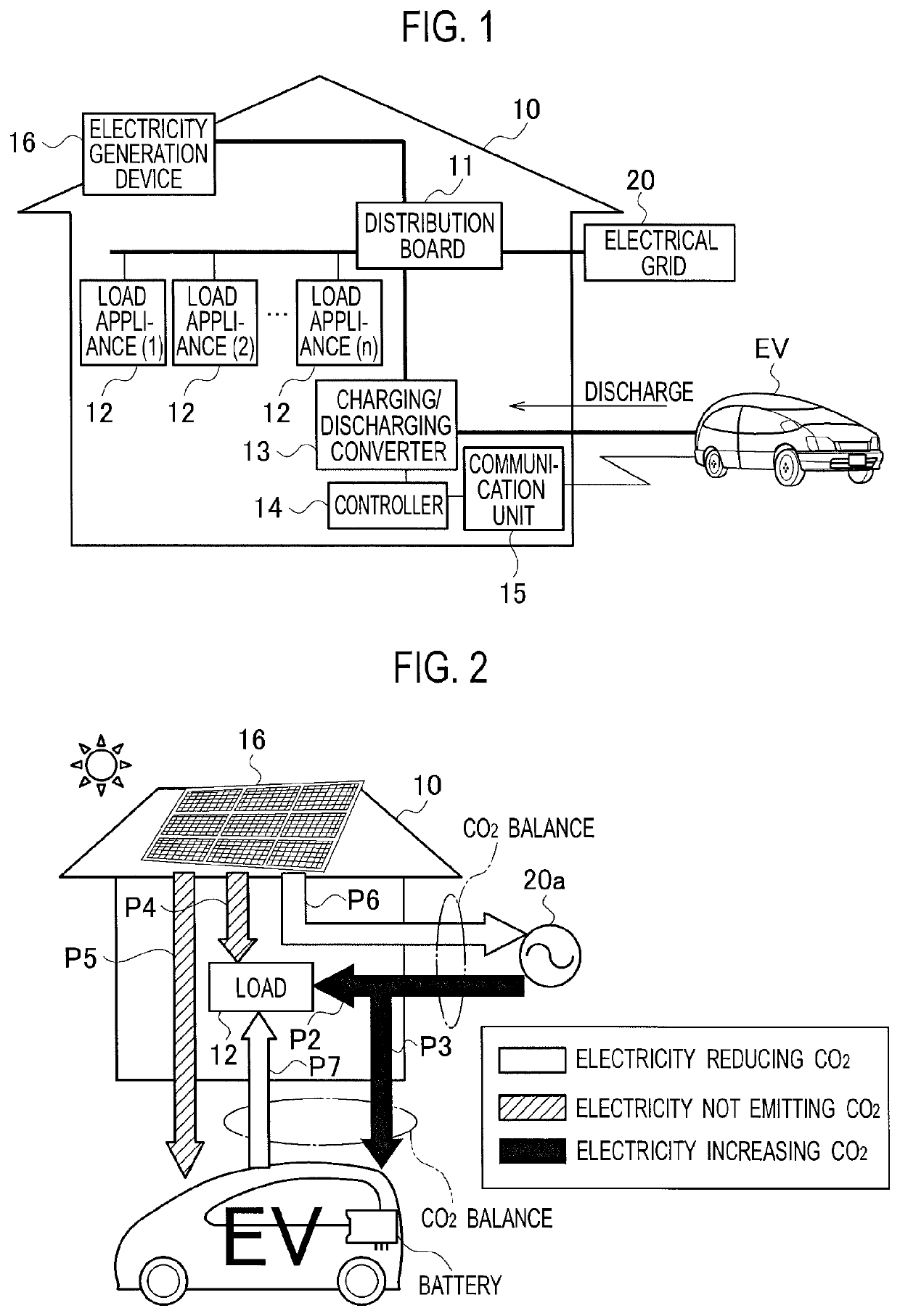
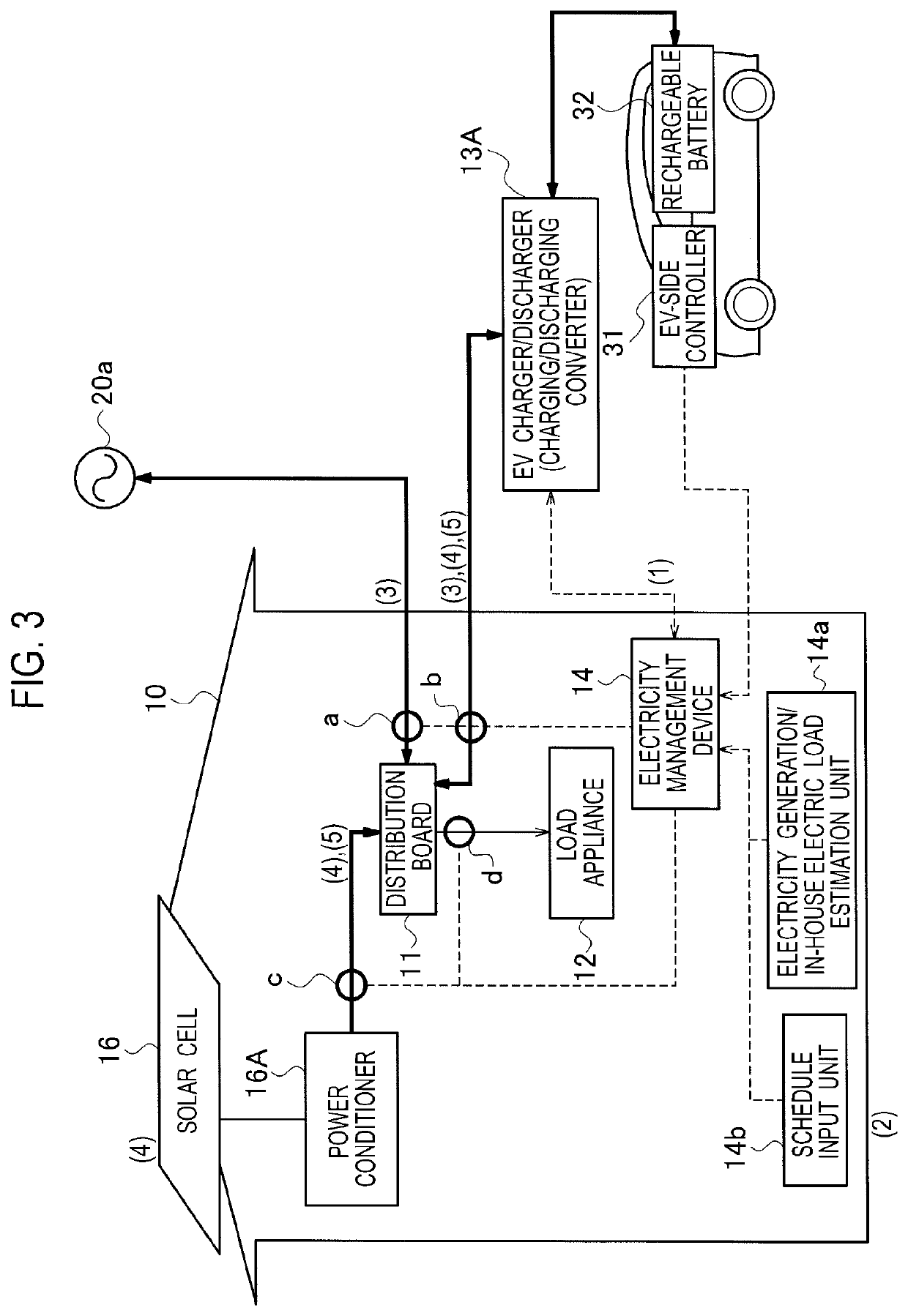
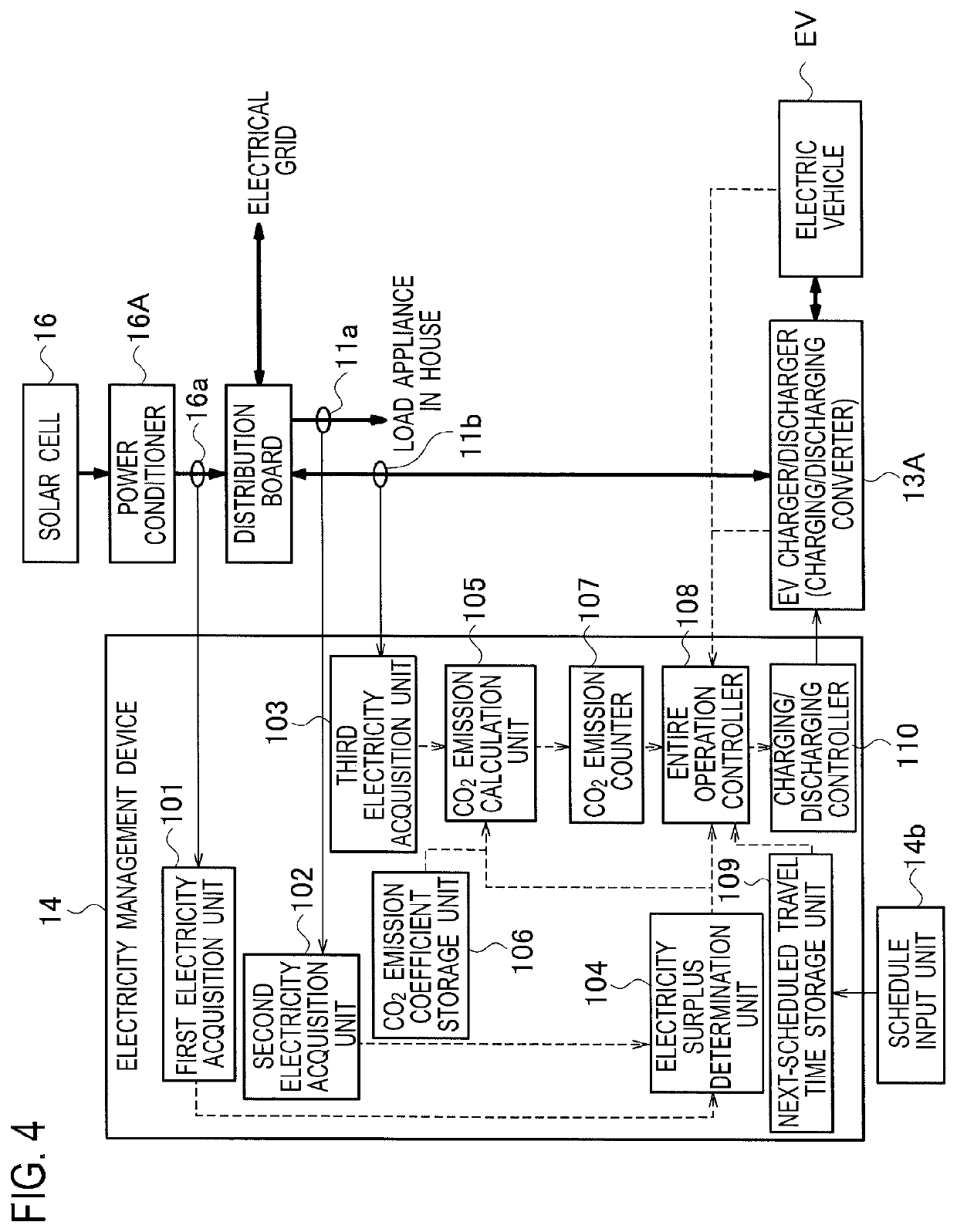
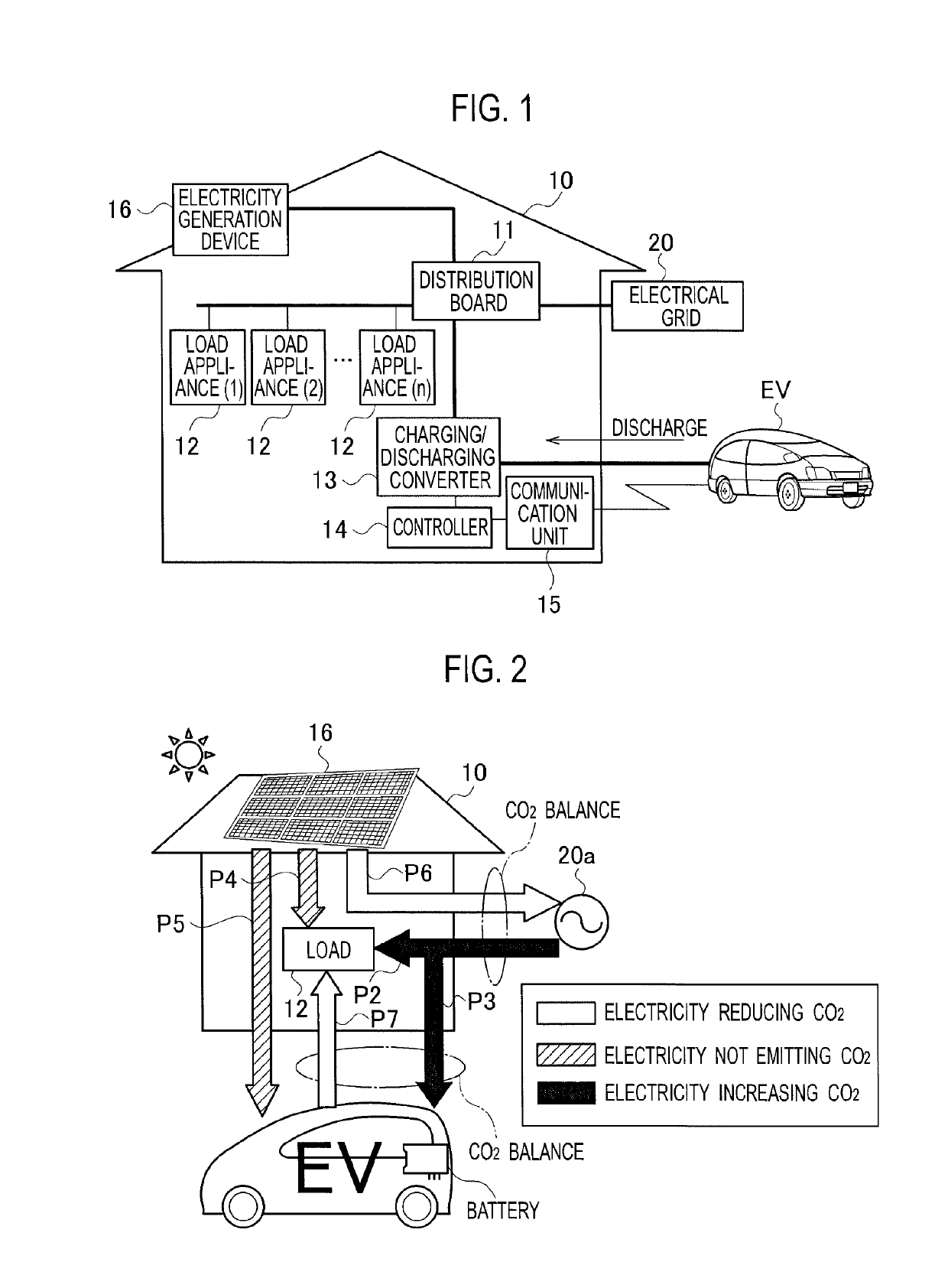
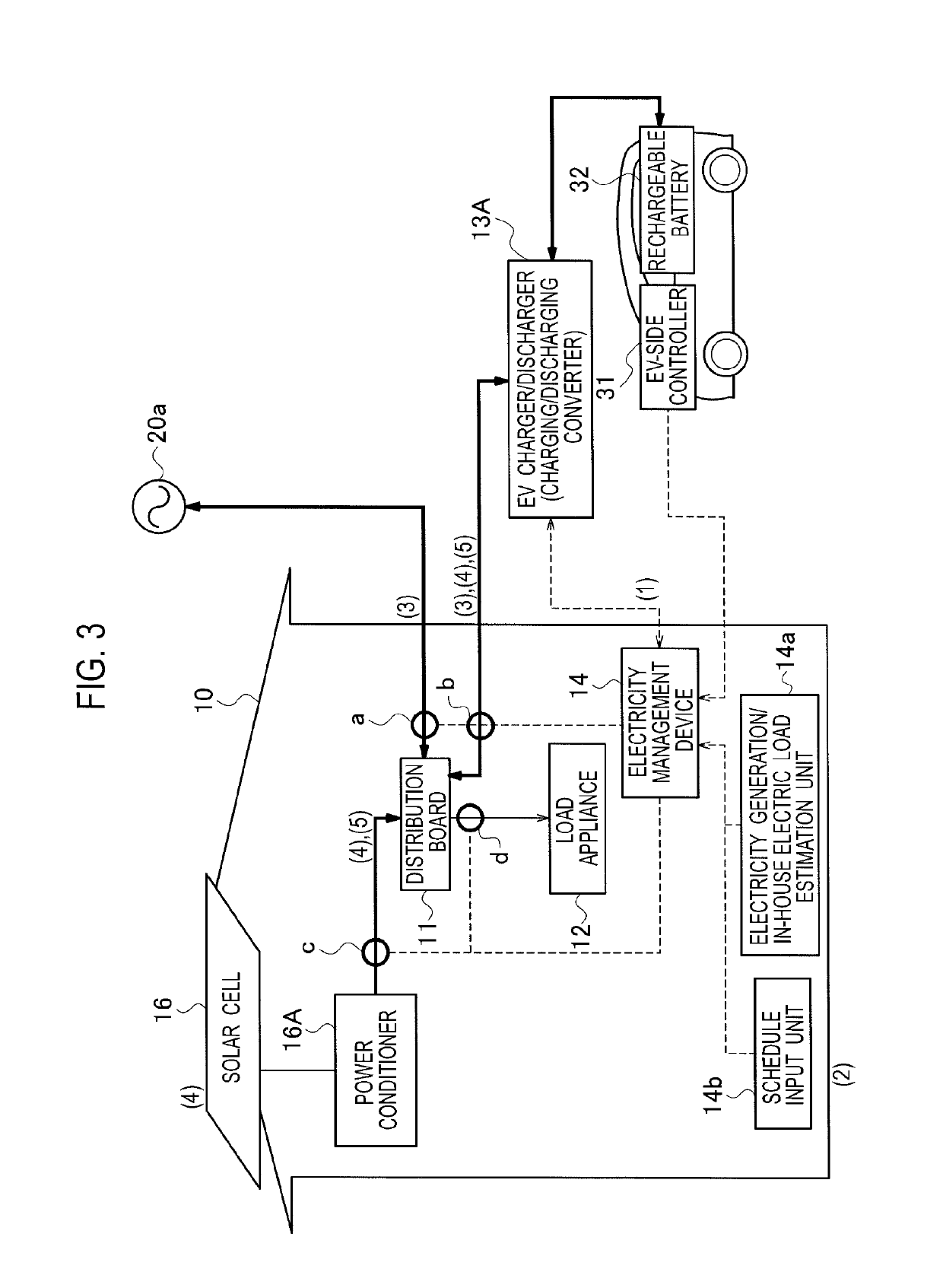
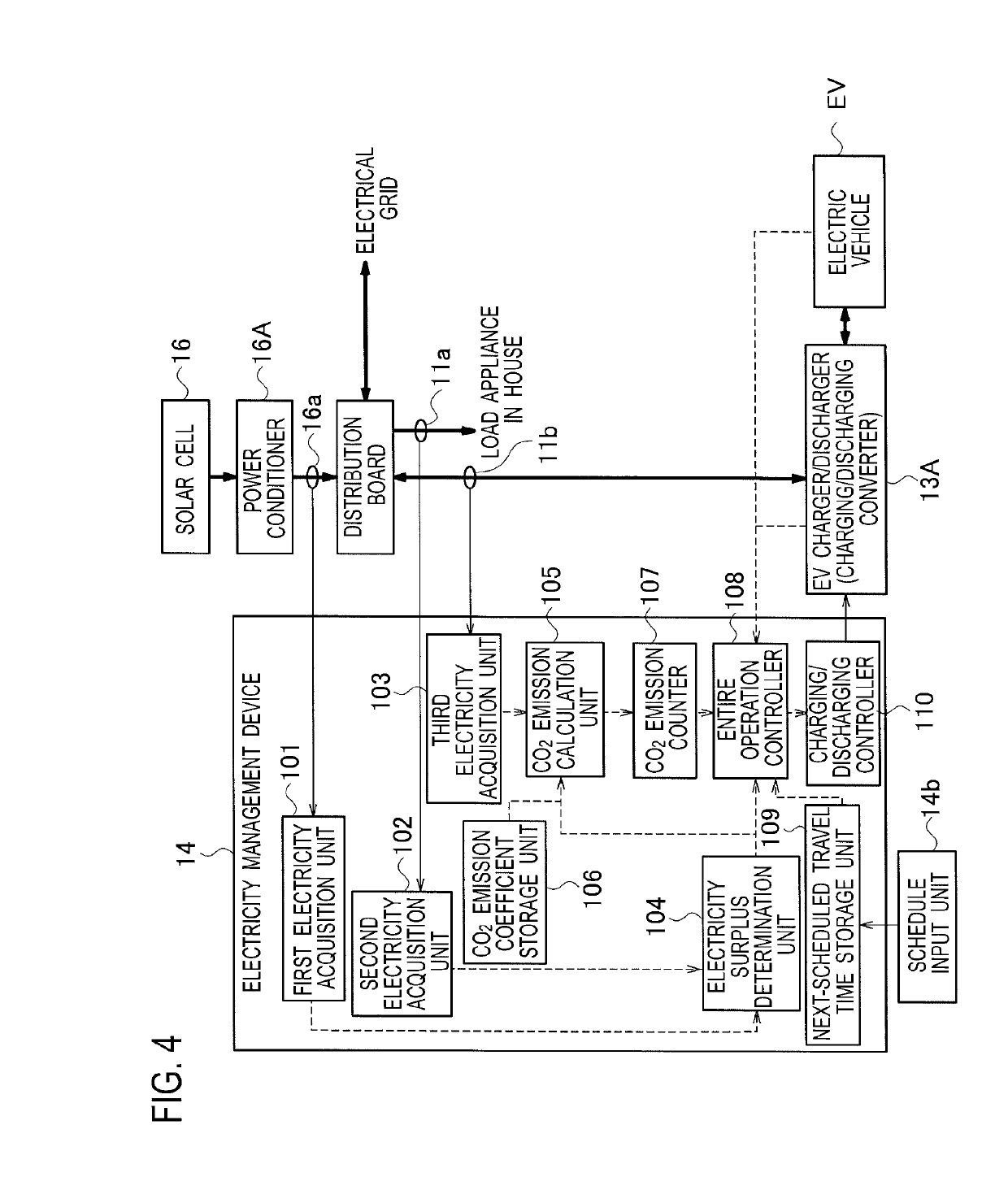
Electricity management device, electricity management method, and electricity distribution system inside a house with electricity generating device, utility grid connection, and electric vehicle containing a rechargeable battery in a vehicle-to-grid connection with counter device
ActiveUS20190366871A1Increase valueReduce the valueCharging stationsPower network operation systems integrationRechargeable cellPower grid
A electricity management device increases a counter value as an electric vehicle is charged from grid power that is supplied from an electrical grid, retains the counter value when the electric vehicle is charged from electricity generated by an electricity generation device, and reduces the counter value as electricity in the electric vehicle is discharged to a distribution board.
Owner:PANASONIC INTPROP MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Modular reconfigurable medium voltage transformer for data centers, volt/var control, ac and DC charging, and vehicle-to-grid applications
A modular reconfigurable medium voltage transformer configured for data centers, VOLT / VAR control, AC and DC charging, and vehicle-to-grid applications is disclosed. The modular reconfigurable transformer includes a plurality of modules configured to be connected to or disconnected from each other to provide multiple transformer configurations. Each of the modules are configured for bi-directional or uni-directional power flow to allow the transformer to provide power from a power source to an application or from the application back to the power source
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST INC
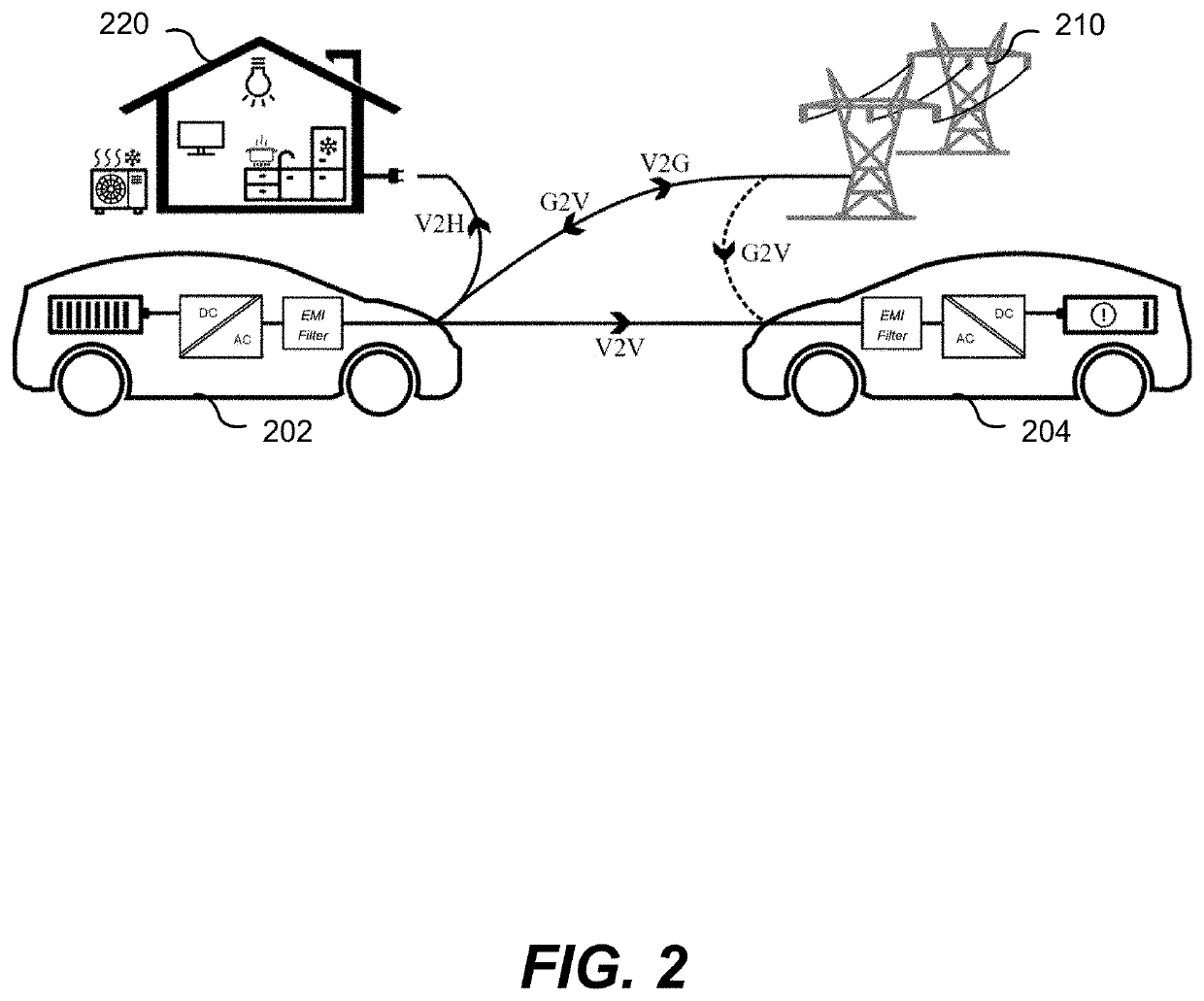
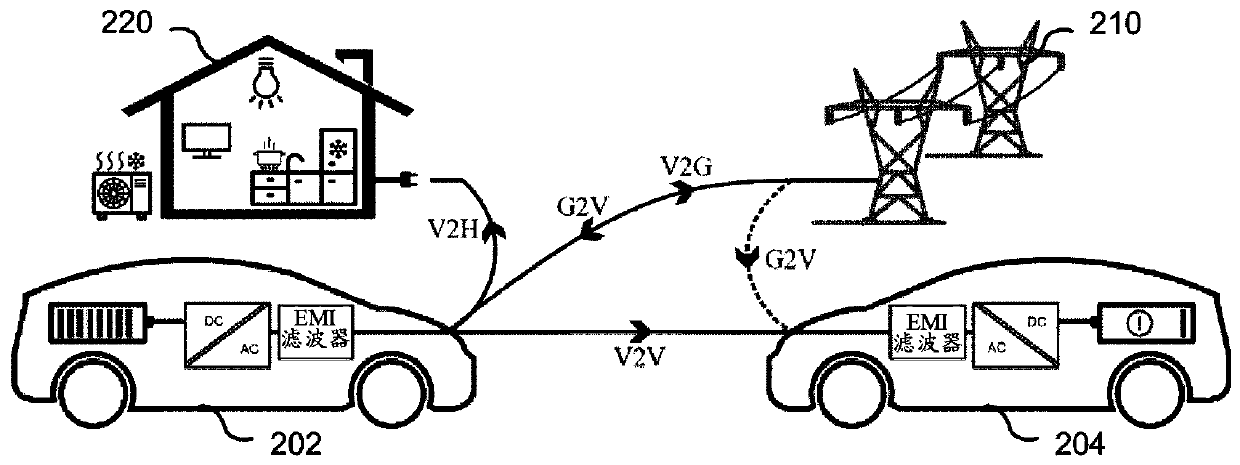
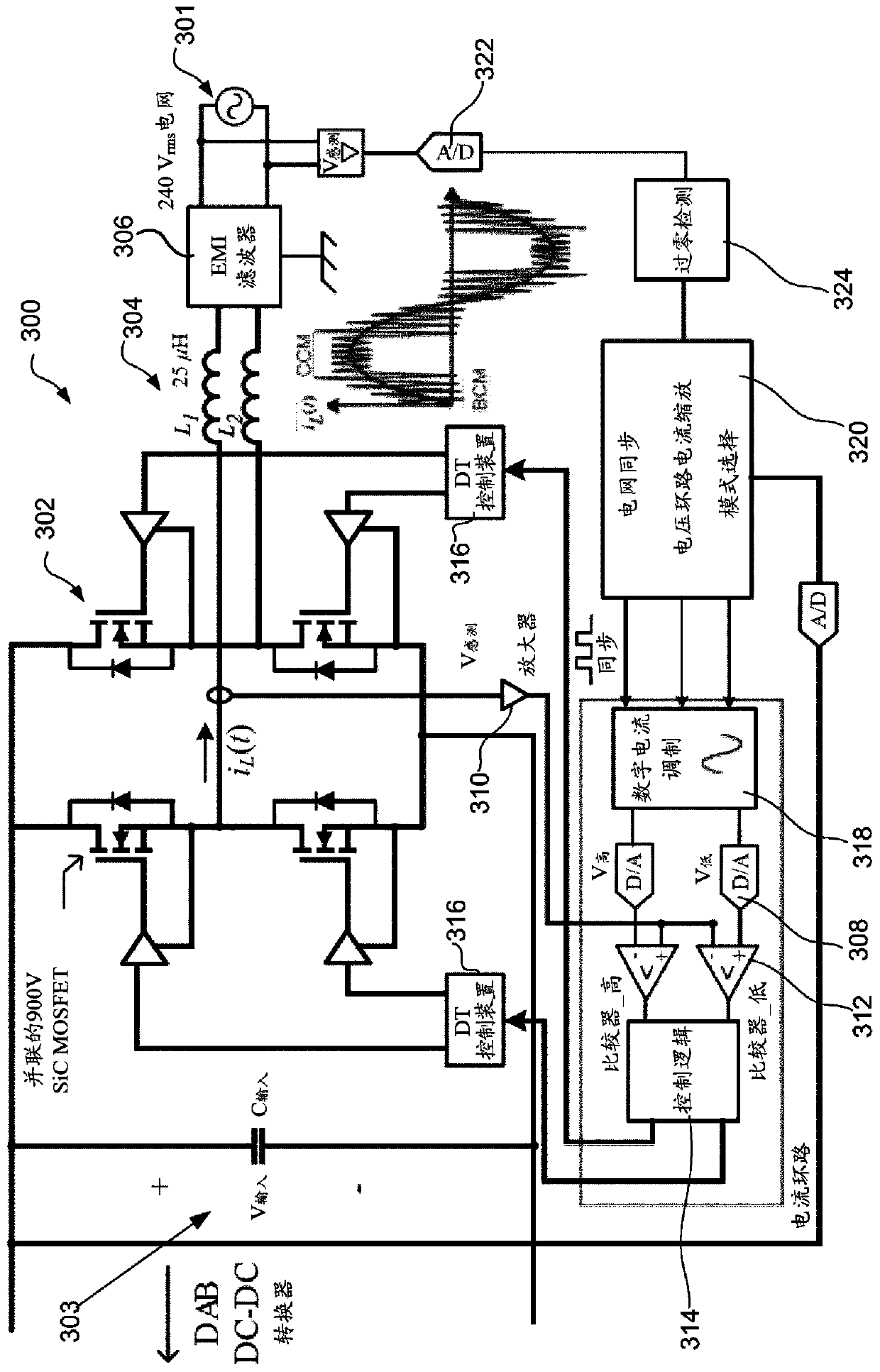
Electric vehicle power-hub and operating modes thereof
ActiveUS20210061125A1Improve efficiencyHigh transferCharging stationsAc-dc conversionCurrent mode controlPower grid
A power-hub for an electric vehicle and operating modes thereof are disclosed herein. The disclosed power-hub is designed to operate in the Vehicle-to Grid (V2G), Grid-to-Vehicle (G2V), Vehicle-to-Home (V2H), and Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) operating modes. When operating in the V2V mode, the power-hub is configured to allow for sending DC power through a conventional AC power port, with all the associated ratings and constraints from the AC design, in order to achieve higher power transfer and efficiency for V2V operation. A digital Hysteretic Current Mode Control (HCMC) scheme is disclosed and the efficiency and loss distribution of four operating modes are disclosed for the power-hub: 1) DC-AC Boundary Conduction Mode (BCM), 2) DC-AC Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM) / BCM hybrid, 3) DC-DC BCM, and 4) DC-DC CCM. A low-frequency commutation scheme is also disclosed that allows for reducing the peak junction temperature.
Owner:HAVELAAR CANADA IND R & D LAB LTD +1
Electric automobile charging and discharging control method based on active disturbance rejection controller
InactiveCN107272445AImprove robustnessOvercome the shortcoming of large overshootCharging stationsSimulator controlElectricityControl system
The invention relates to an electric automobile charging and discharging control method based on an active disturbance rejection controller and belongs to the Vehicle to Grid (V2G) technology and power electronic technology field. The method comprises steps that step A, an electric vehicle charging and discharging model is constructed; step B, the active disturbance rejection controller is summarized; step C, an AC / DC and DC / DC mathematics model in a bidirectional charging and discharging system is established, and the active disturbance rejection controller is established according to the two-stage system model of the charging and discharging system; and step D, simulation analysis is carried out. The method is advantaged in that 1, a problem of relatively large overshooting of a common PID control system can be solved, and influence of parameter time varying on system decoupling performance and contradiction between rapidity and stationarity existing in a control system are effectively solved; and 2, the active disturbance rejection controller is not dependent on a specific mathematics model of a controlled system and further has relatively strong anti-interference capability for internal and external interference, the active disturbance rejection controller is proved to have relatively good robustness for uncertainty of the model and measurement noise according to the simulation result, and relatively good dynamic performance is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Electricity management device, electricity management method, and electricity distribution system inside a house with electricity generating device, utility grid connection, and electric vehicle containing a rechargeable battery in a vehicle-to-grid connection with counter device
ActiveUS10406927B2Increase valueReduce the valueCharging stationsPower network operation systems integrationElectrical batteryPower grid
A electricity management device increases a counter value as an electric vehicle is charged from grid power that is supplied from an electrical grid, retains the counter value when the electric vehicle is charged from electricity generated by an electricity generation device, and reduces the counter value as electricity in the electric vehicle is discharged to a distribution board.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
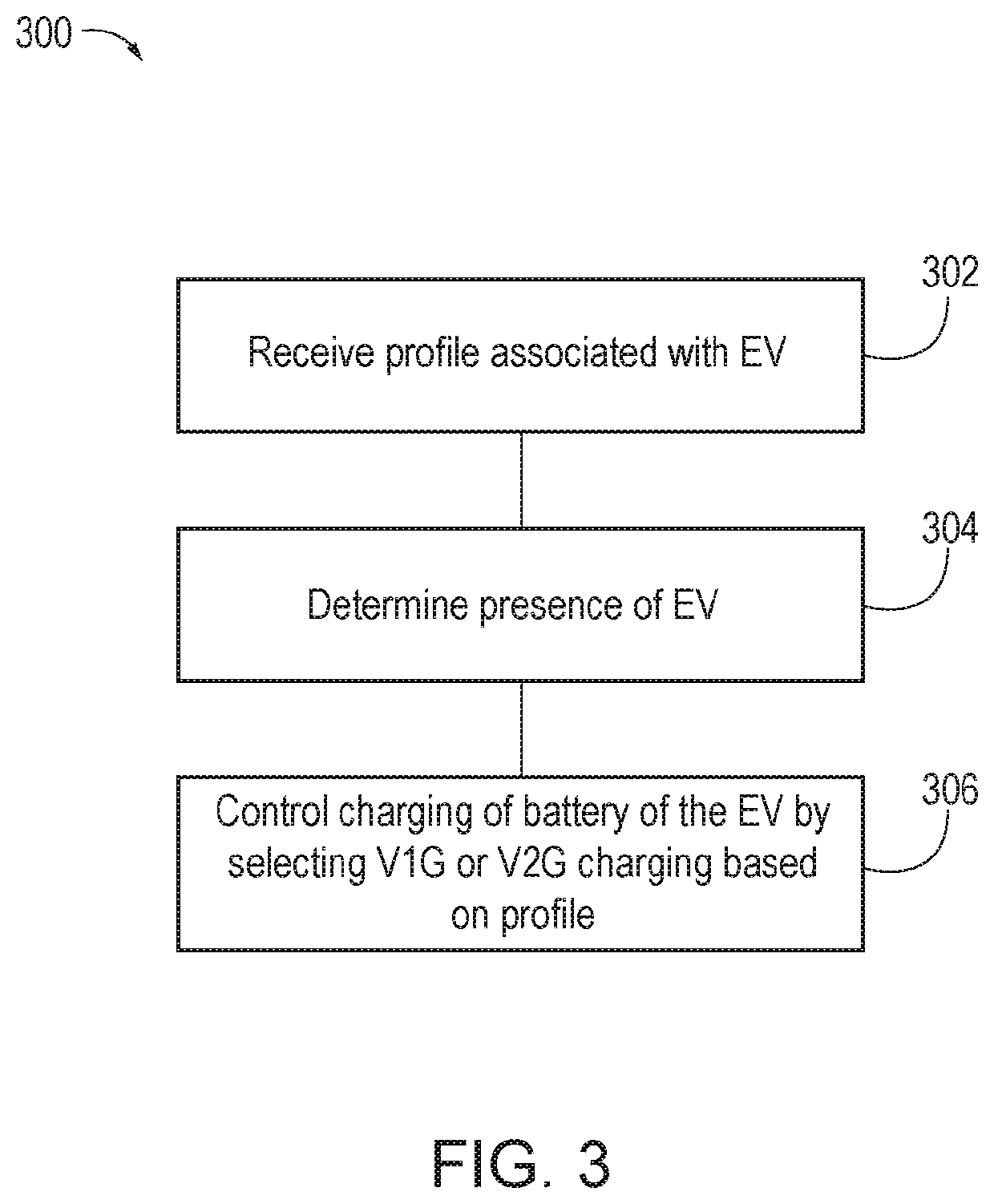
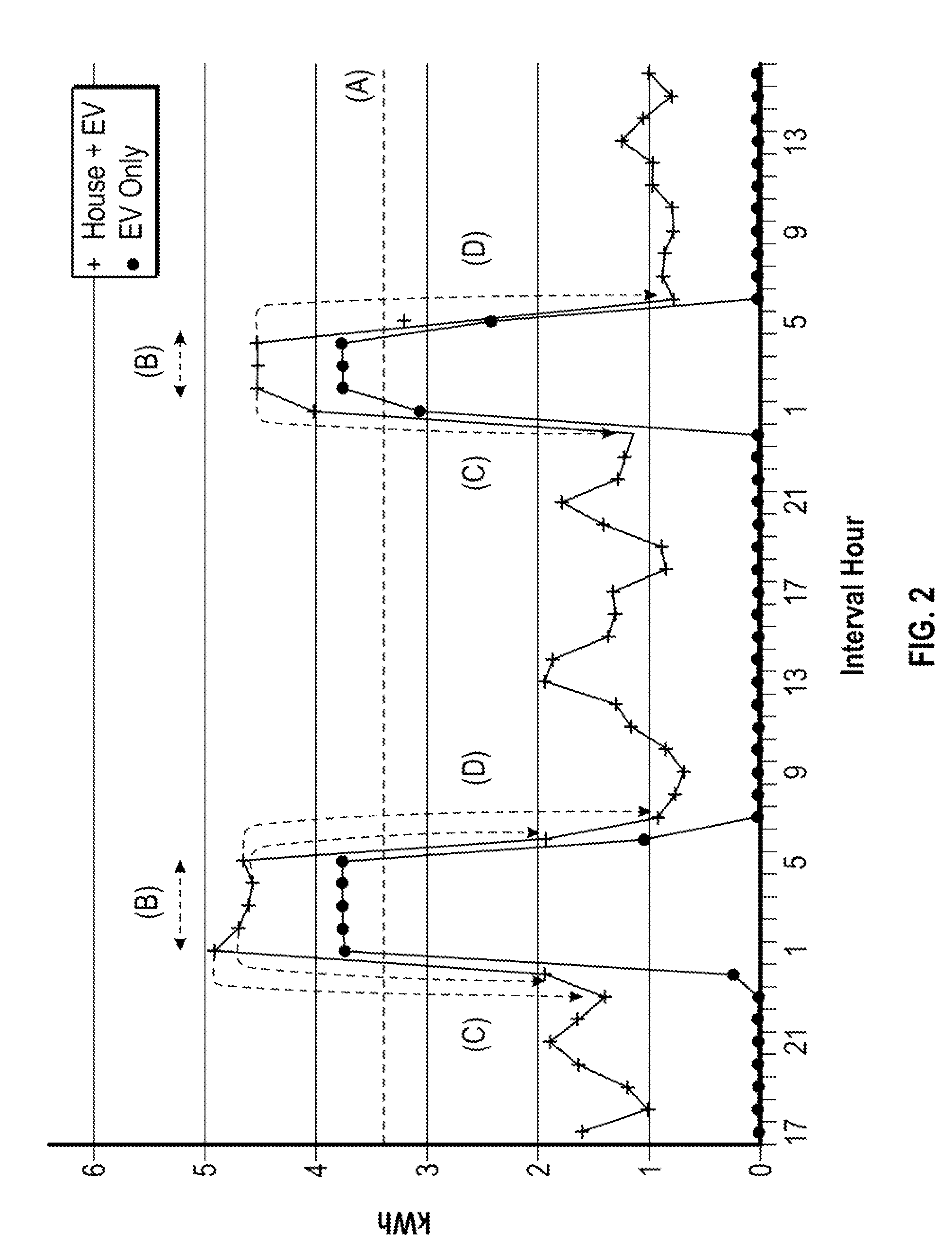
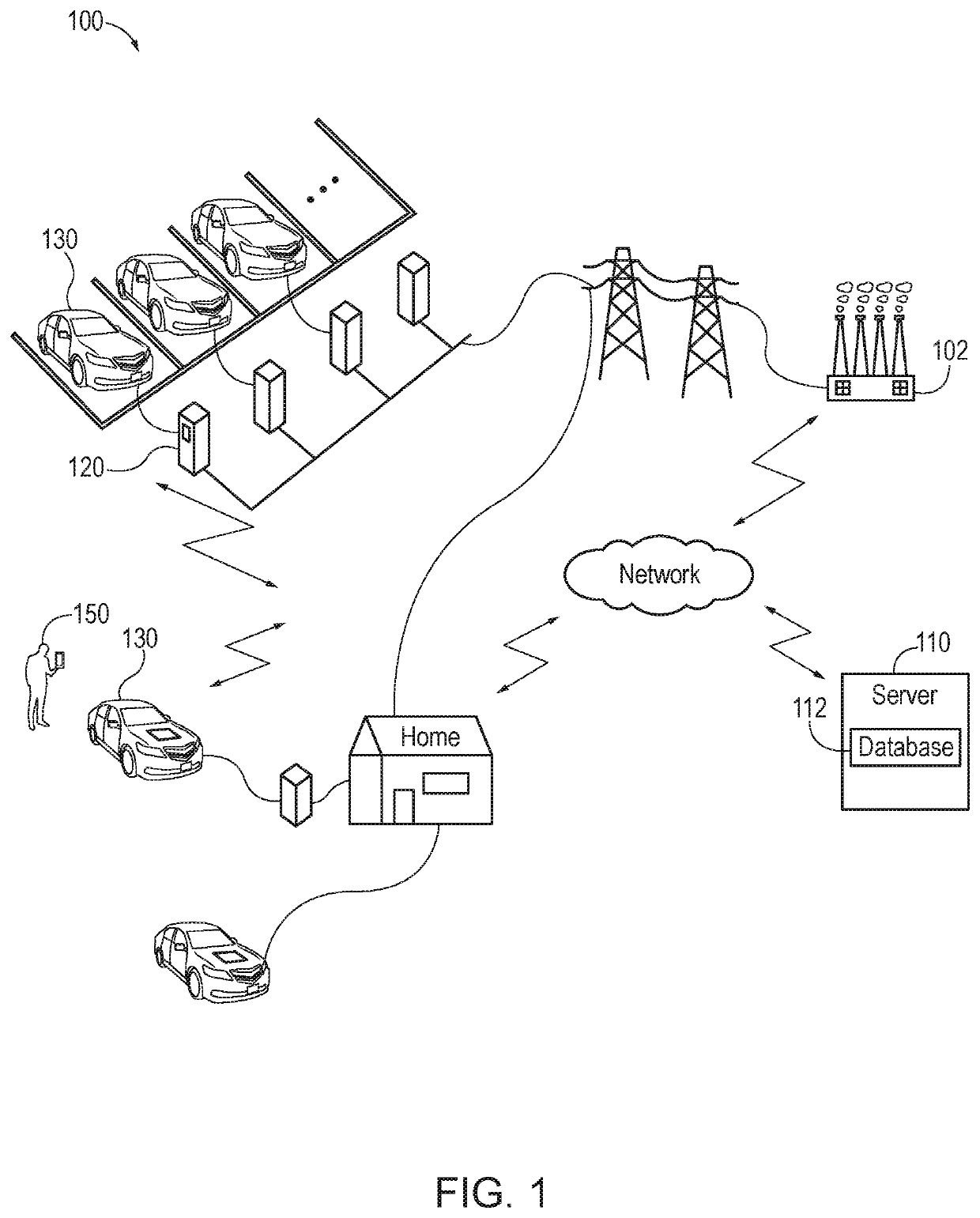
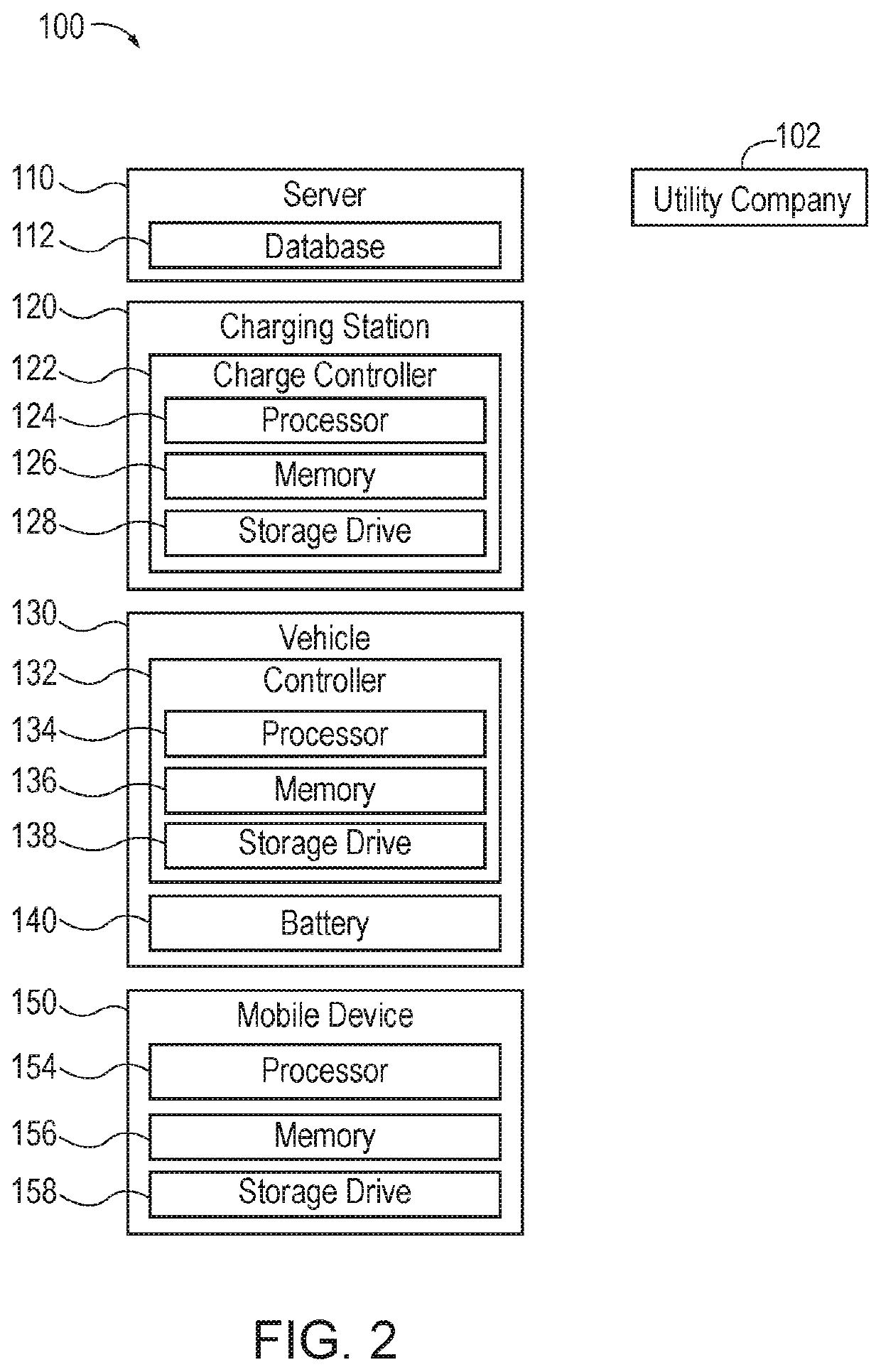
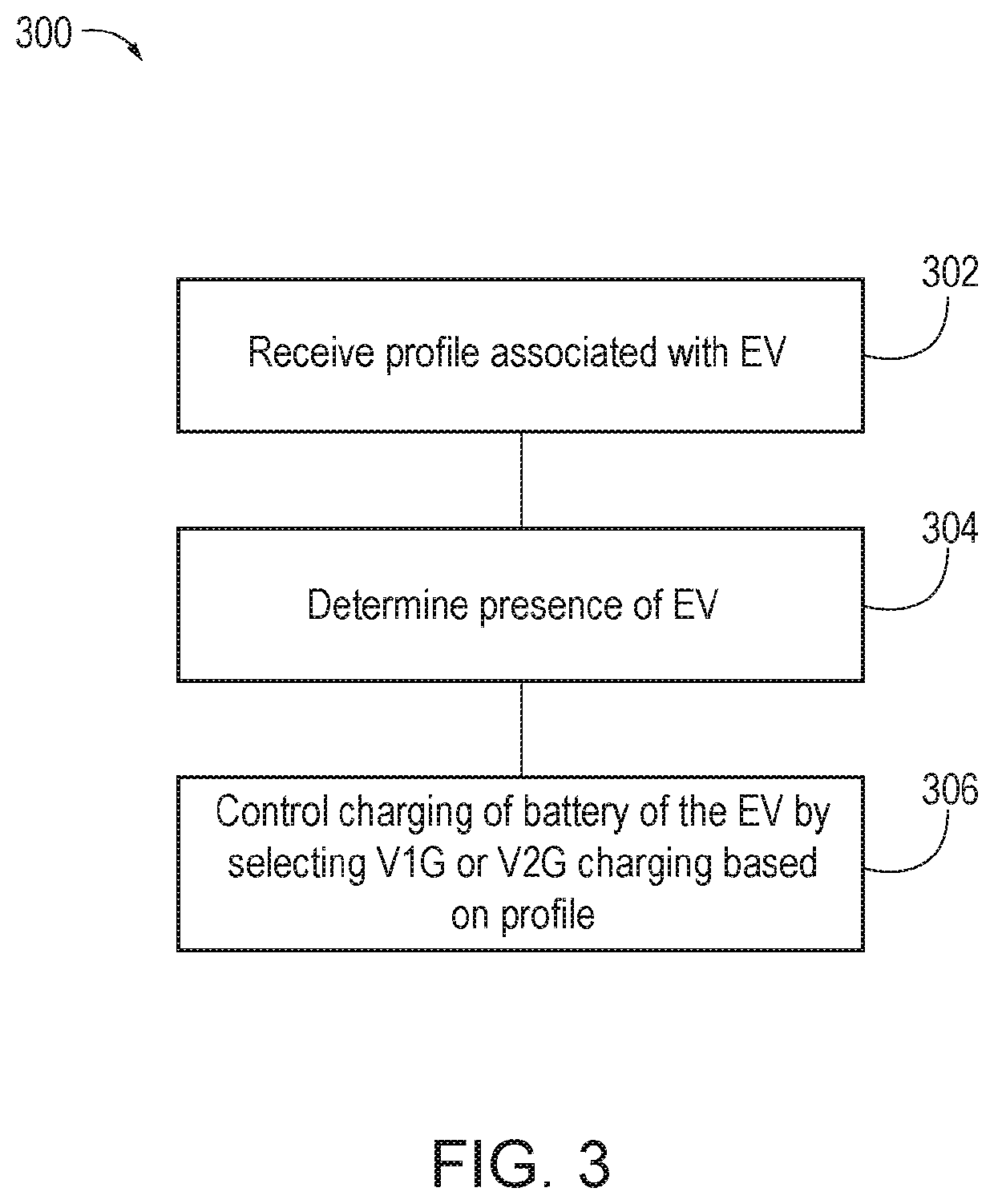
V1g or v2g selection
ActiveUS20210094437A1Charging stationsSelective ac load connection arrangementsPower flowElectrical battery
According to one aspect, a charging station or a system for adjustment of electric vehicle (EV) charging timing, power, or location in coordination with the electrical grid (V1G) or vehicle to grid bidirectional power flow (V2G) selection may include a memory, a processor, and a charge controller or controller. The memory may receive a profile associated with an electric vehicle (EV). The profile may be indicative of a V1G / V2G charging schedule preference for the EV. The processor may determine a presence of the EV and the charge controller may control charging of a battery of the EV by selecting V1G or V2G based on the profile and in accordance with the V1G / V2G charging schedule preference.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
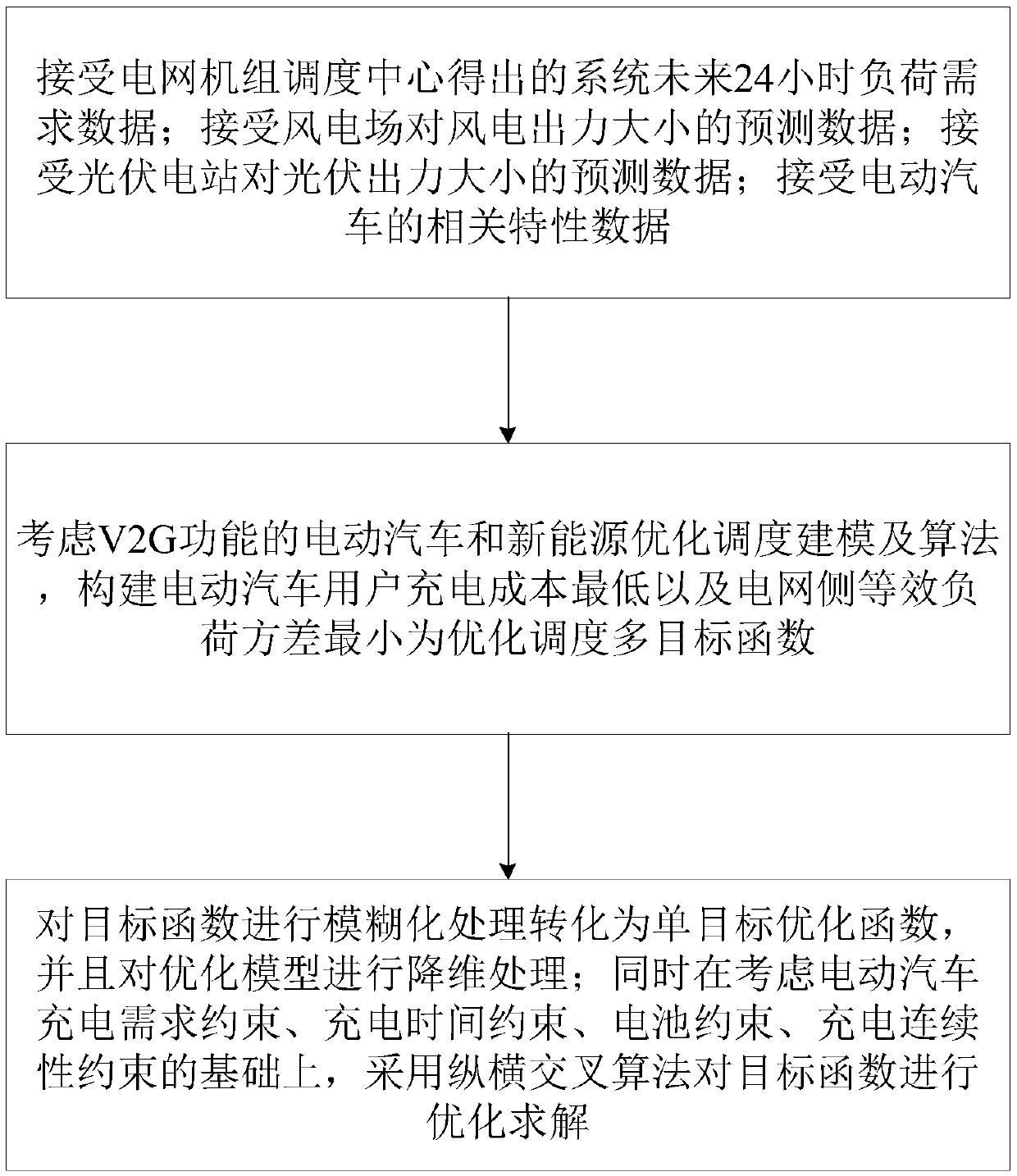
Electric vehicle and new energy scheduling optimization modeling and algorithm considering Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) function
InactiveCN108921331AReduce electricity costsOptimal scheduling strategyForecastingSystems intergating technologiesElectricityNew energy
The invention discloses an electric vehicle and new energy scheduling optimization modeling and algorithm considering a Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) function. An electric power system containing an electricvehicle capable of being connected into a network, wind power and solar energy serves as a study object, a scheduling method considering the V2G function is constructed and aims to simultaneously lower system load fluctuation and the charging cost of an electric vehicle user, through fuzzy processing of multiple targets, a to-be-solved problem is converted into a single target optimization problem, a latest vertical and horizontal cross optimization algorithm is applied to conduct solving, and an optimal scheduling scheme is obtained.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Electric vehicle power-hub and operating modes thereof
A power-hub for an electric vehicle and operating modes thereof are disclosed herein. The disclosed power-hub is designed to operate in the Vehicle-to Grid (V2G), Grid-to-Vehicle (G2V), Vehicle-to-Home (V2H), and Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) operating modes. When operating in the V2V mode, the power-hub is configured to allow for sending DC power through a conventional AC power port, with all the associated ratings and constraints from the AC design, in order to achieve higher power transfer and efficiency for V2V operation. A digital Hysteretic Current Mode Control (HCMC) scheme is disclosed andthe efficiency and loss distribution of four operating modes are disclosed for the power-hub: 1 ) DC-AC Boundary Conduction Mode (BCM), 2) DC-AC Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM) / BCM hybrid, 3) DC-DC BCM, and 4) DC-DC CCM. A low-frequency commutation scheme is also disclosed that allows for reducing the peak junction temperature.
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO +1
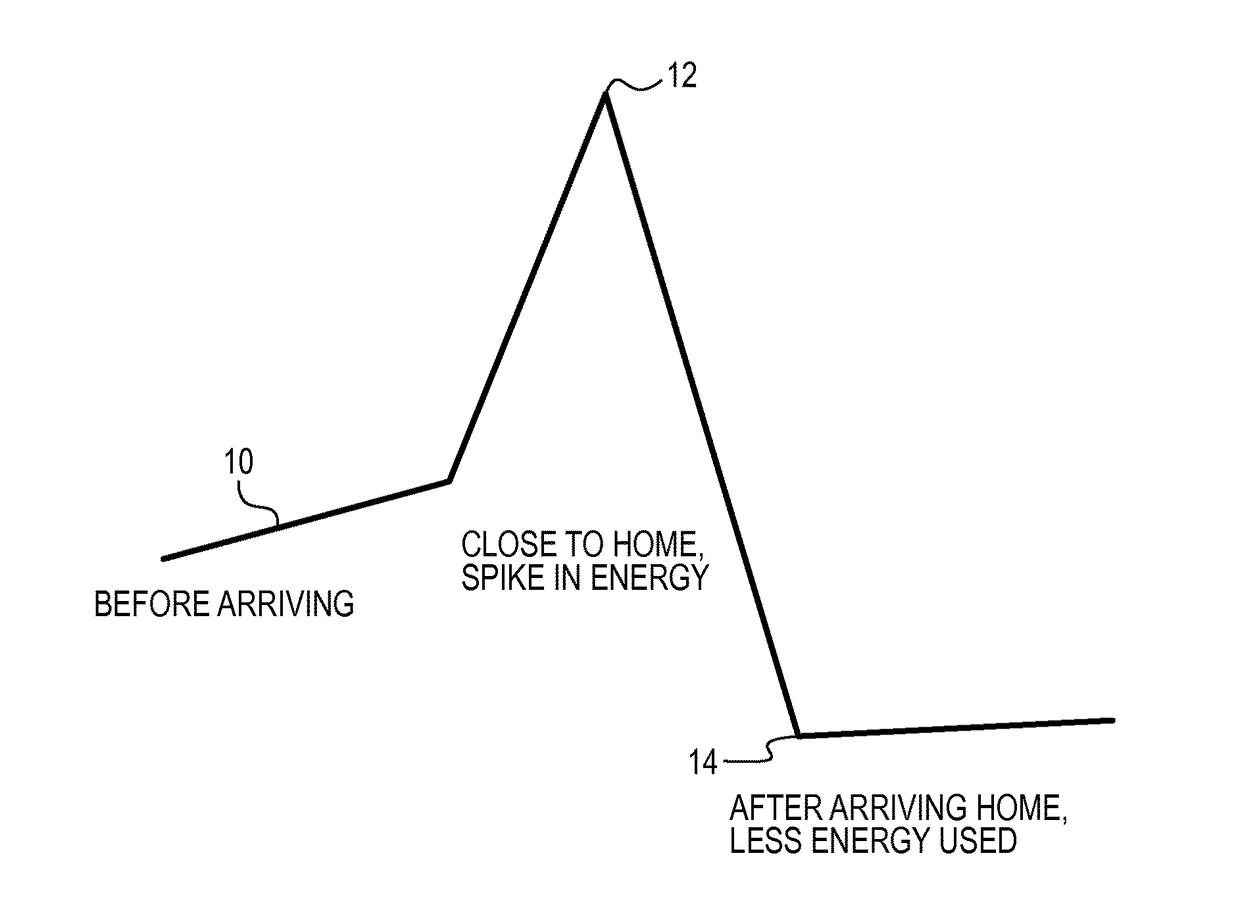
System and method for cooperatively operating a smart thermostat and vehicle to grid automobile
A system and method of managing the operation of a remotely controllable control unit for an appliance in a building during peak power demand hours with an application on a mobile device further in communication with a vehicle having a rechargeable battery capable of providing power to a power grid is disclosed. The application determines a state-of-charge of the rechargeable battery in the vehicle, and determines a location of the vehicle and whether the vehicle is within a threshold distance to the building. The building is preconditioned using the appliance to a preferred state if the vehicle is within the threshold distance to the building. When the vehicle arrives at the building, it is electrically connected to the power grid to provide electricity from the rechargeable battery to the power grid to replace the power used during the preconditioning.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method for detection of plug-in electric vehicle charging via interrogation of smart meter data
ActiveUS9156368B2Improve accuracyFast chargingCharging stationsElectric devicesUtility industryEngineering
A method and application that utilizes a signal processing algorithm is provided for detecting plug-in electric vehicle charging events through interrogation of smart meter data. The method is a form of non-invasive load monitoring that allows the utility to track plug-in electric vehicle charging events in real time or over extended periods. These parameters are suitably flexible so as to accommodate diverse electric vehicle technologies and a range of electric vehicle owners' charging habits. Application of the method facilitates the integration of electric vehicles into utilities' electrical grids, protection of the utilities' assets, geographic mapping of electric vehicle owners and charging events, managed charging through communication between the utility and the vehicle or owner, managed charging through the offer of time of use rates for electric vehicle owners, and an enabling technology to accompany other Smart Grid functions such as Vehicle-to-Grid distributed energy storage.
Owner:SAN DIEGO GAS & ELECTRIC COMPANY
V1G or V2G selection
ActiveUS11173804B2Charging stationsSelective ac load connection arrangementsPower flowElectrical battery
According to one aspect, a charging station or a system for adjustment of electric vehicle (EV) charging timing, power, or location in coordination with the electrical grid (V1G) or vehicle to grid bidirectional power flow (V2G) selection may include a memory, a processor, and a charge controller or controller. The memory may receive a profile associated with an electric vehicle (EV). The profile may be indicative of a V1G / V2G charging schedule preference for the EV. The processor may determine a presence of the EV and the charge controller may control charging of a battery of the EV by selecting V1G or V2G based on the profile and in accordance with the V1G / V2G charging schedule preference.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
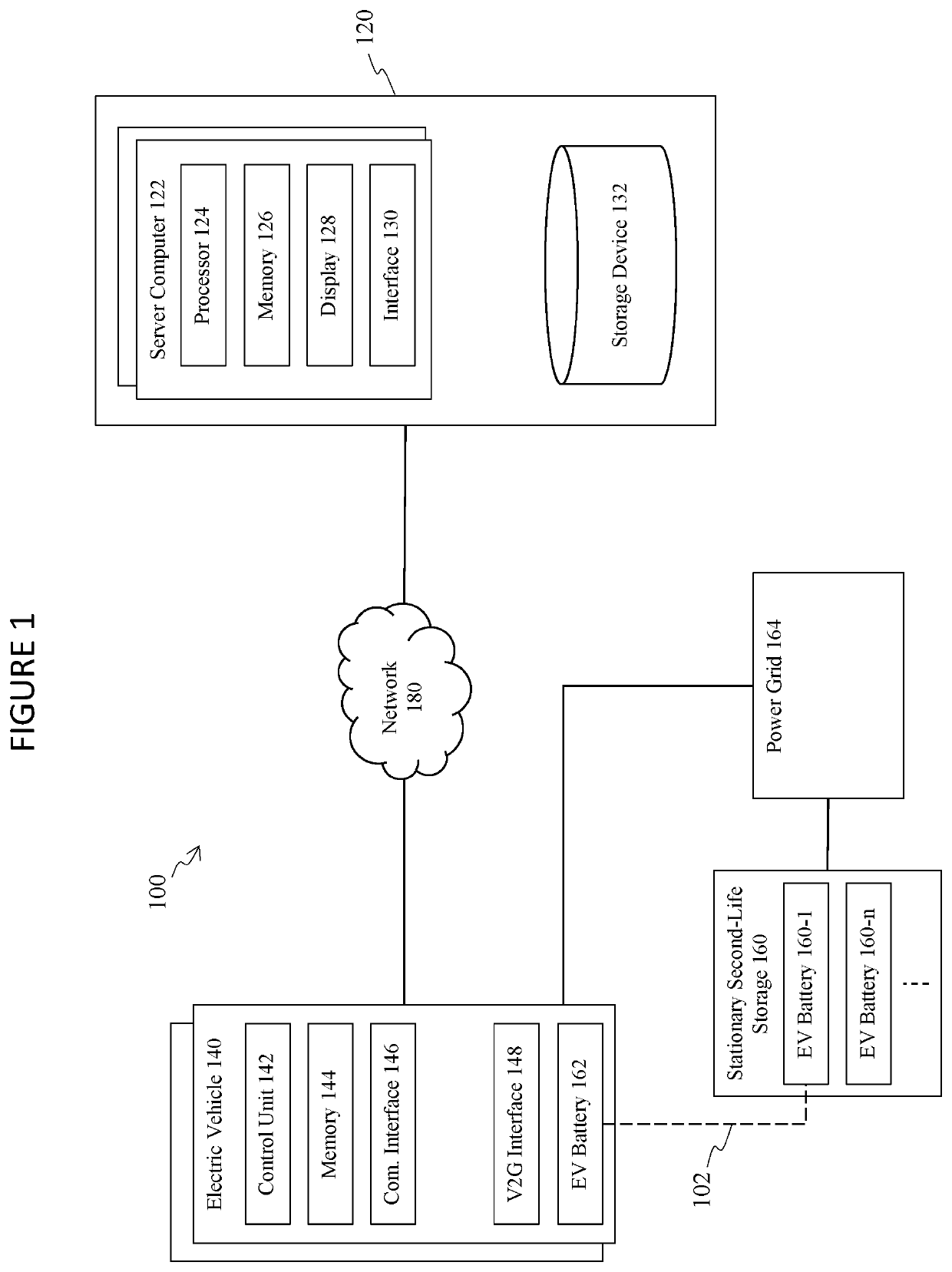
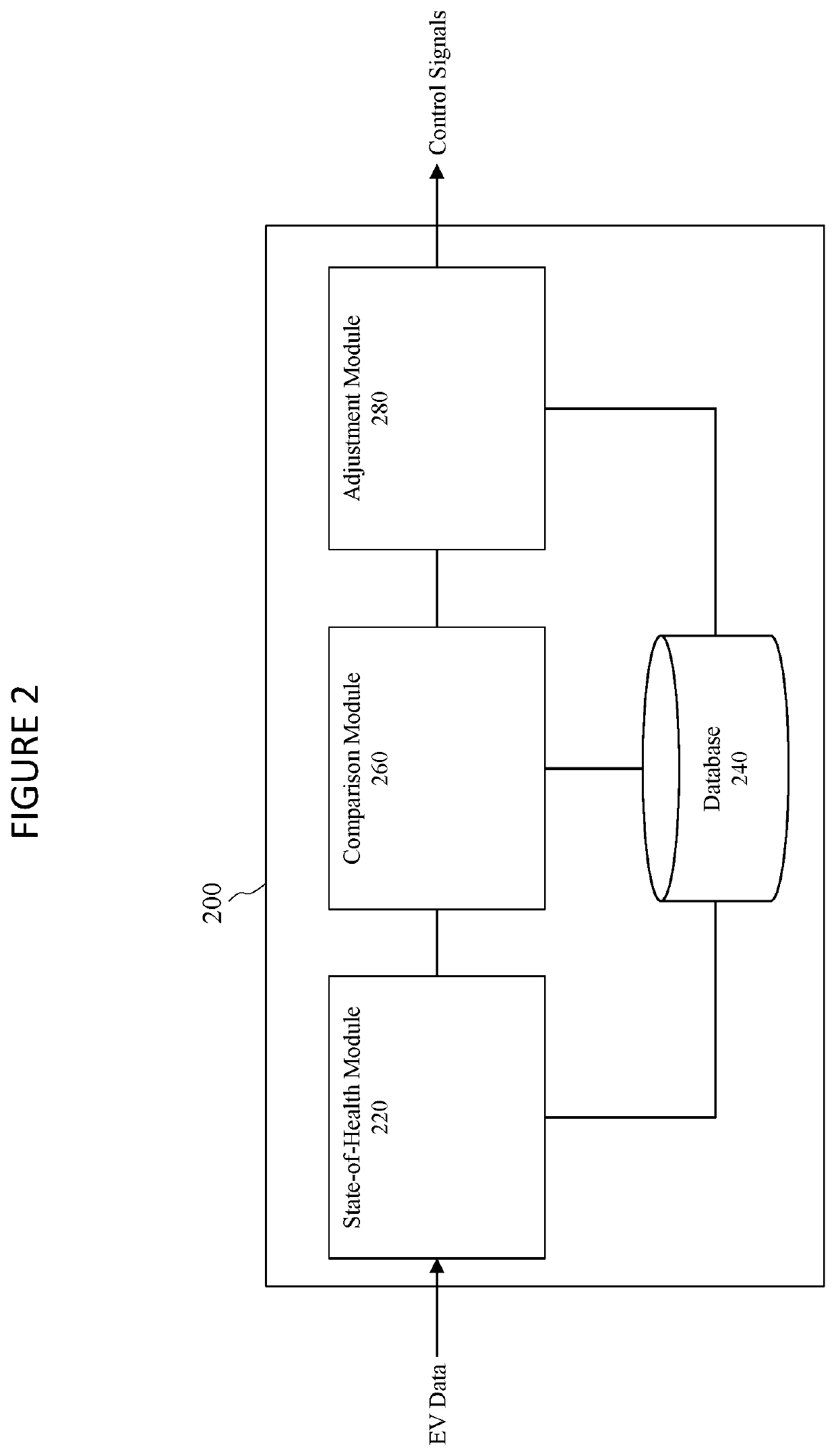
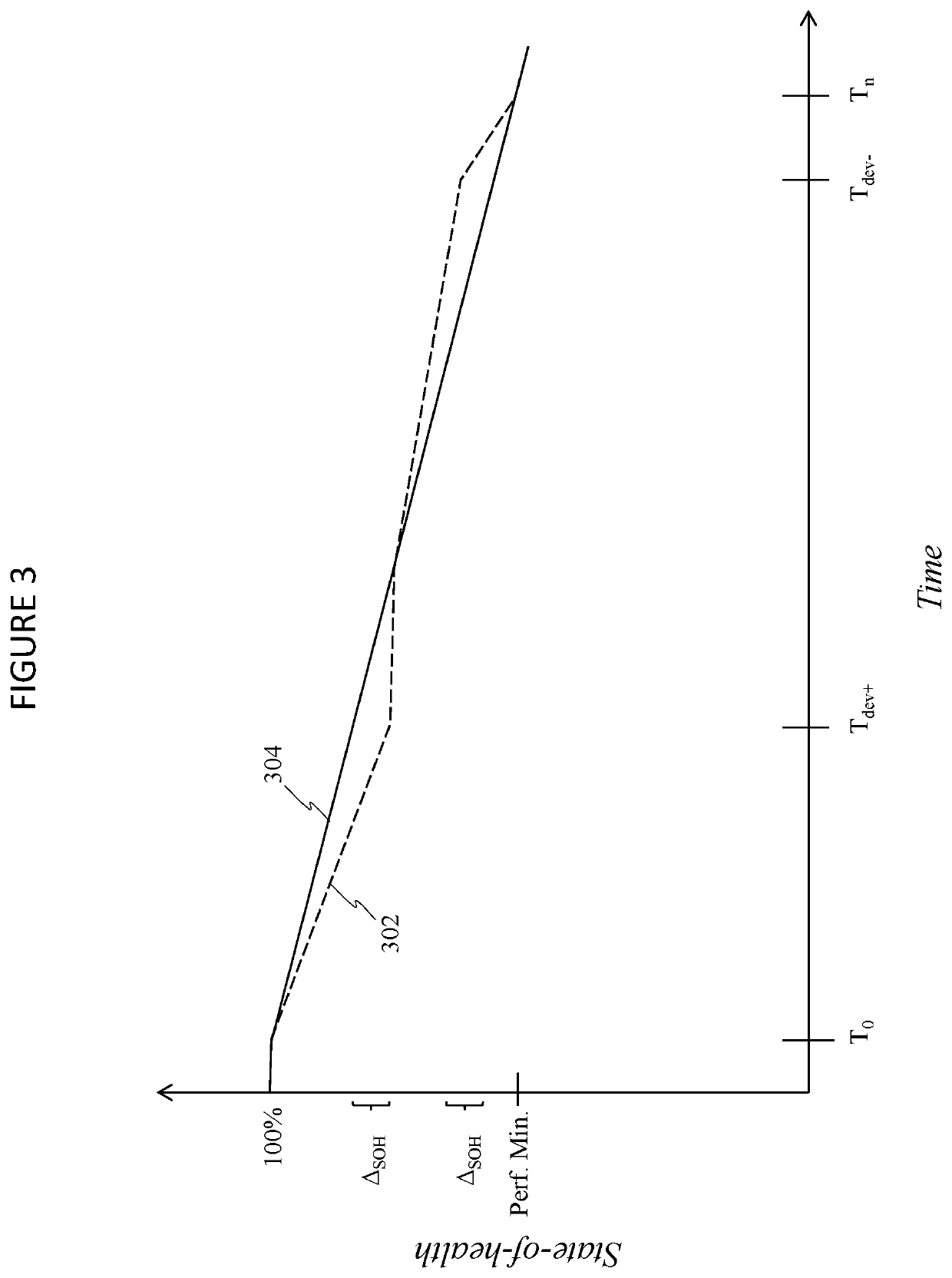
Systems and method for EV battery second-life management
ActiveUS10752128B1Easy to participateAvoid wastingElectric powerElectric vehicle charging technologyElectrical batteryPower exchange
A system for managing second-lives of a plurality of electric vehicle (EV) batteries includes a plurality of electric vehicles and a stationary second-life unit. Each electric vehicle includes at least one of the plurality of EV batteries during a first-life of each respective EV battery, in which each respective EV battery is utilized to power a respective one of the plurality of electric vehicles. Each of the plurality of electric vehicles is configured for bi-directional electric power exchange with a power grid via a vehicle-to-grid interface. The stationary second-life unit includes each of the plurality of EV batteries during a second-life of each respective EV battery. The stationary second-life unit is configured for bi-directional power exchange with the power grid. A state-of-health of each of the plurality of EV batteries is individually controlled, during the first-life of each respective EV battery, such that the plurality of EV batteries each have substantially similar states-of-health at a start of the second-life of each respective EV battery.
Owner:BAYERISCHE MOTOREN WERKE AG
Vehicle-mounted integrated charger based on six-phase open winding motor driving system
ActiveCN110838750AGuaranteed to be stillImprove reliabilityBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsBattery chargeElectric machine
The invention discloses a vehicle-mounted integrated charger based on a six-phase open winding motor driving system, which relates to a vehicle-mounted integrated charger, so as to overcome the problems that an electric vehicle motor can rotate and the charging power is low when an existing integrated charger is in a charging mode and a V2G mode. The integrated charger comprises a six-phase open-winding motor, a DC / AC power converter and a DC / DC converter. When the vehicle-mounted integrated charger works in a charging mode, electric energy outputted by grid-side three-phase power is inputtedto a storage battery to be charged through the six-phase open winding motor, the DC / AC power converter and the DC / DC converter in sequence to charge the storage battery; and when the vehicle-mounted integrated charger works in a V2G mode from a vehicle to a power grid, electric energy outputted by the storage battery is inputted to grid-side three-phase power through the DC / DC converter, the DC / ACpower converter and the six-phase open-winding motor in sequence, and the electric energy is fed back to the grid-side three-phase power.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
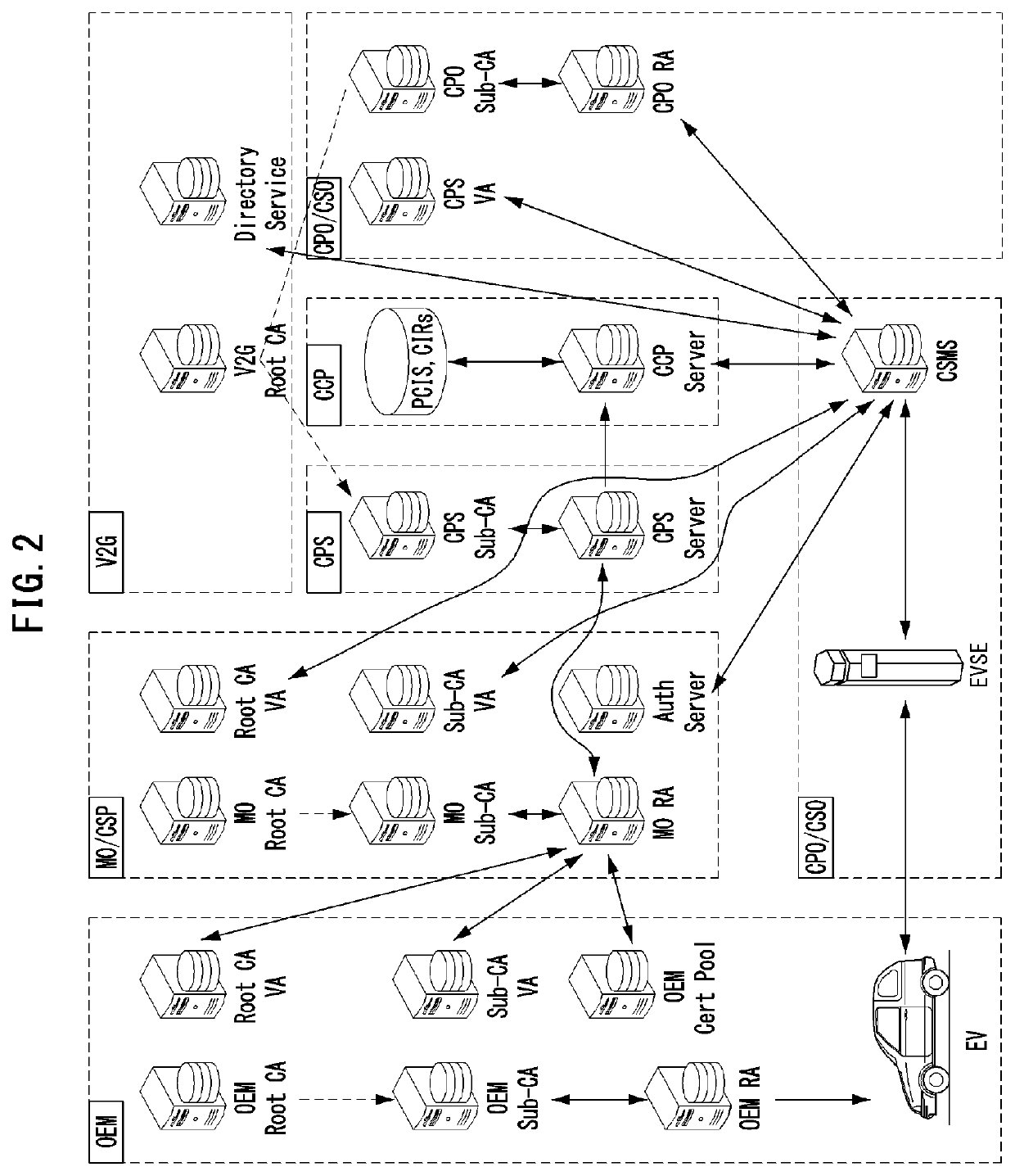
Method and apparatus for automatically authenticating electric vehicle charging user based on blockchain
PendingUS20220069602A1Efficiently support use caseSimple processCircuit authenticationUser identity/authority verificationEngineeringElectric network
A method and apparatus are configured to automatically authenticate an electric vehicle (EV) charging user based on blockchain. A vehicle-to-grid (V2G) operator generates a smart contract for a specific EV or an EV user on a blockchain, and a mobility operator (MO) or a charge point operator acquire an access control authority to the blockchain. The EV user provides an authentication identifier to the MO. The MO generates an account identifier based on the authentication identifier, generates a contract on the blockchain based on the authentication identifier, the account identifier, an expiration date of the account identifier, and the activity status of the account identifier, and transmits contract information including the account identifier corresponding to the authentication identifier, the expiration date of the account identifier, and the activity status of the account identifier to the EV user.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +2
System and method for cooperatively operating a smart thermostat and vehicle to grid automobile
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Intelligent grid electric power injection system and method based on V2G (vehicle-to-grid)
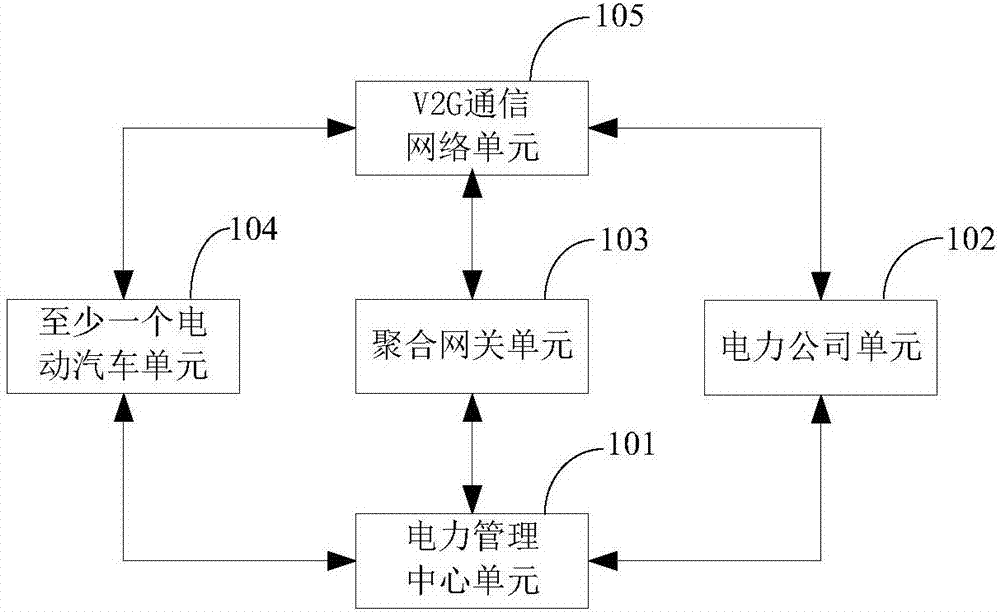
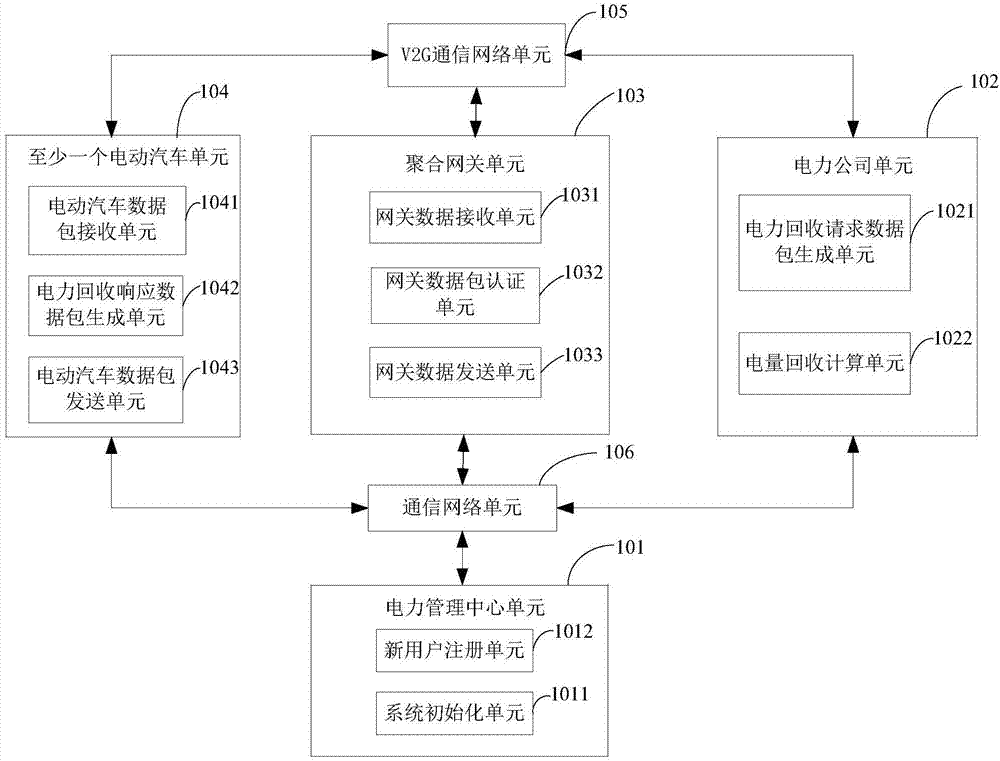
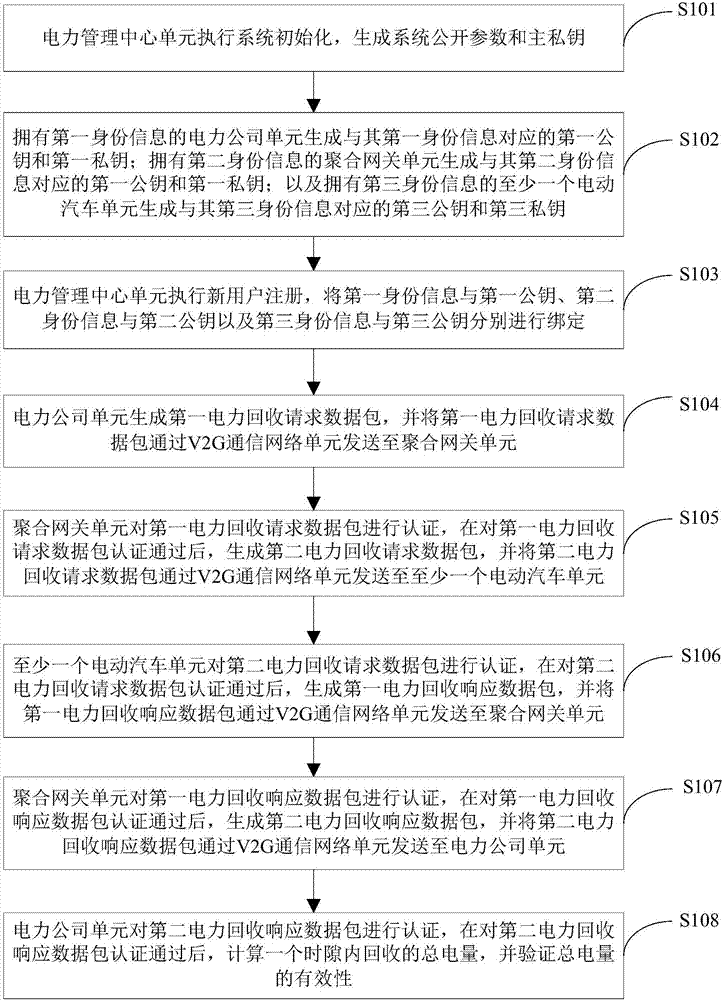
ActiveCN107571768APrivacy protectionImprove energy efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationElectric vehicle charging technologyElectricityNetwork packet
The invention provides an intelligent grid electric power injection system and method based on a V2G (vehicle-to-grid). The system comprises an electric power management center unit, an electric powercompany unit, an aggregation gateway unit, at least one electric automobile unit and a V2G communication network unit, the electric power management center unit executes system initialization and newuser registration, the electric power company unit generates a first electric power recovery request packet, and / or analyzes and calculates total electricity of time slot recovery and verifies effectiveness of the total electricity, the aggregation gateway unit generates a second electric power recovery request packet, and / or generates a second electric power recovery response packet, the electric automobile units generate a first electric power recovery response packet, and the V2G communication network unit is used for communication and / or electric energy transfer between the electric powercompany unit and the aggregation gateway unit and among the aggregation gateway unit and the electric automobile units. According to the intelligent grid electric power injection system and method based on the V2G, energy utilization rate is increased by the aid of the advantages of an internet of vehicles and an intelligent grid, privacies of users are protected, and the system has excellent popularization and application prospects.
Owner:西安旭尧网络科技股份有限公司
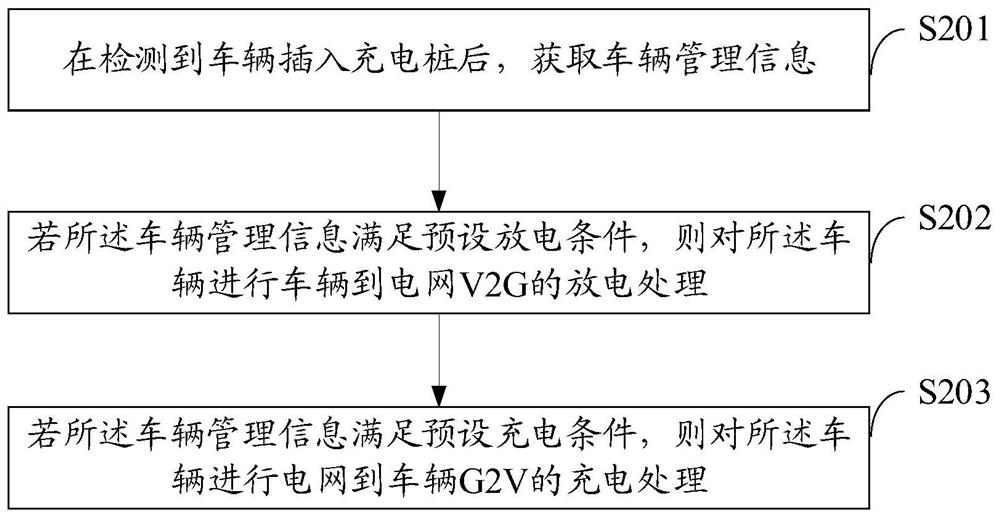
Charging and discharging management method based on Internet of Vehicles, terminal equipment and medium
ActiveCN113619443ARealize charge and discharge managementSolving Charging AnxietyCharging stationsAc network load balancingTerminal equipmentPower grid
The invention discloses a charging and discharging management method based on the Internet of Vehicles, terminal equipment and a medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining vehicle management information after detecting that a vehicle is inserted into a charging pile; if the vehicle management information meets a preset discharge condition, carrying out discharge processing from the vehicle to a power grid V2G on the vehicle; and if the vehicle management information meets the preset charging condition, carrying out charging processing from a power grid to a vehicle G2V on the vehicle. According to the invention, the technical problems in the prior art that the charging peak period is easily caused and the reverse power supply of the vehicle is not considered can be solved.
Owner:DONGFENG MOTOR GRP
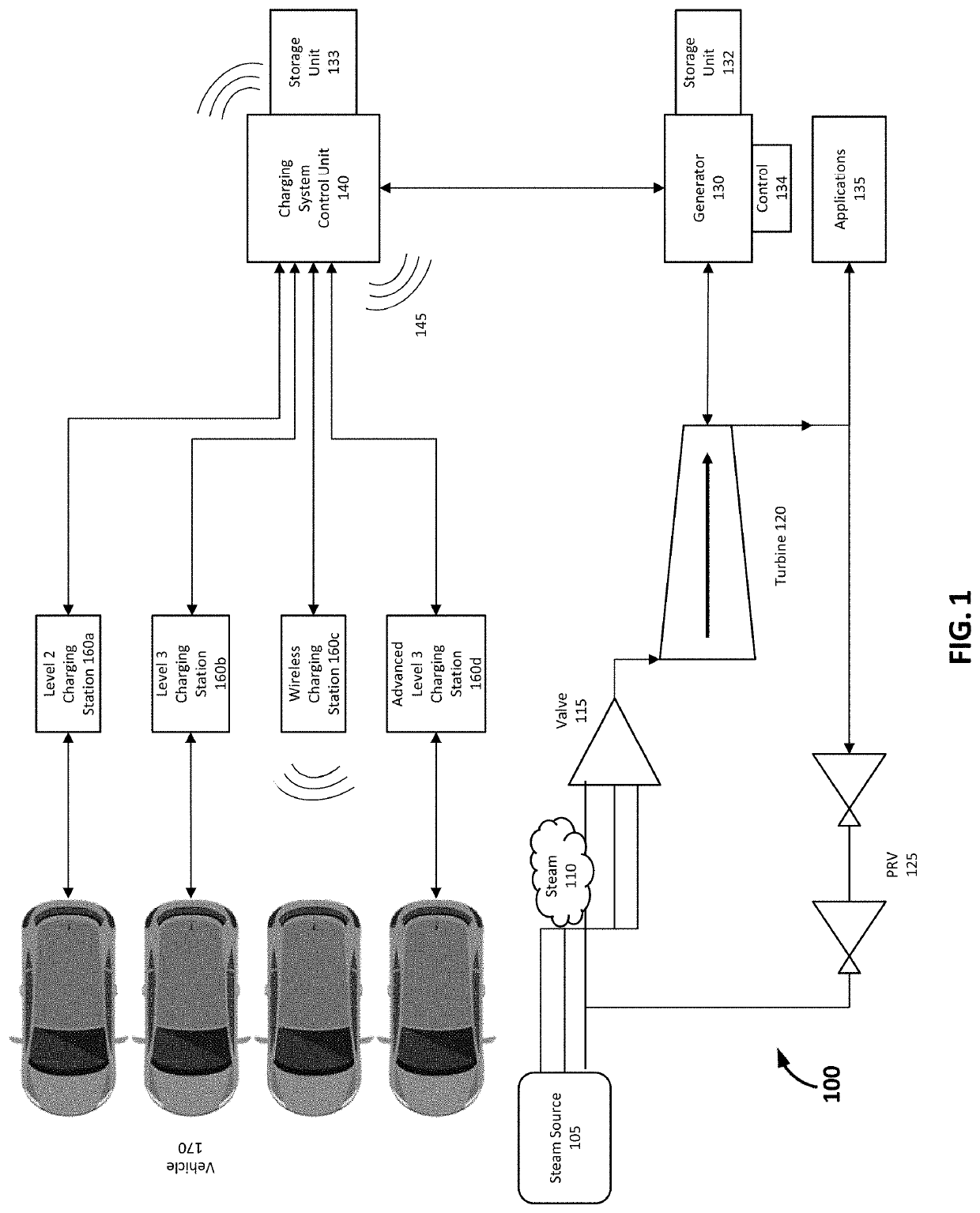
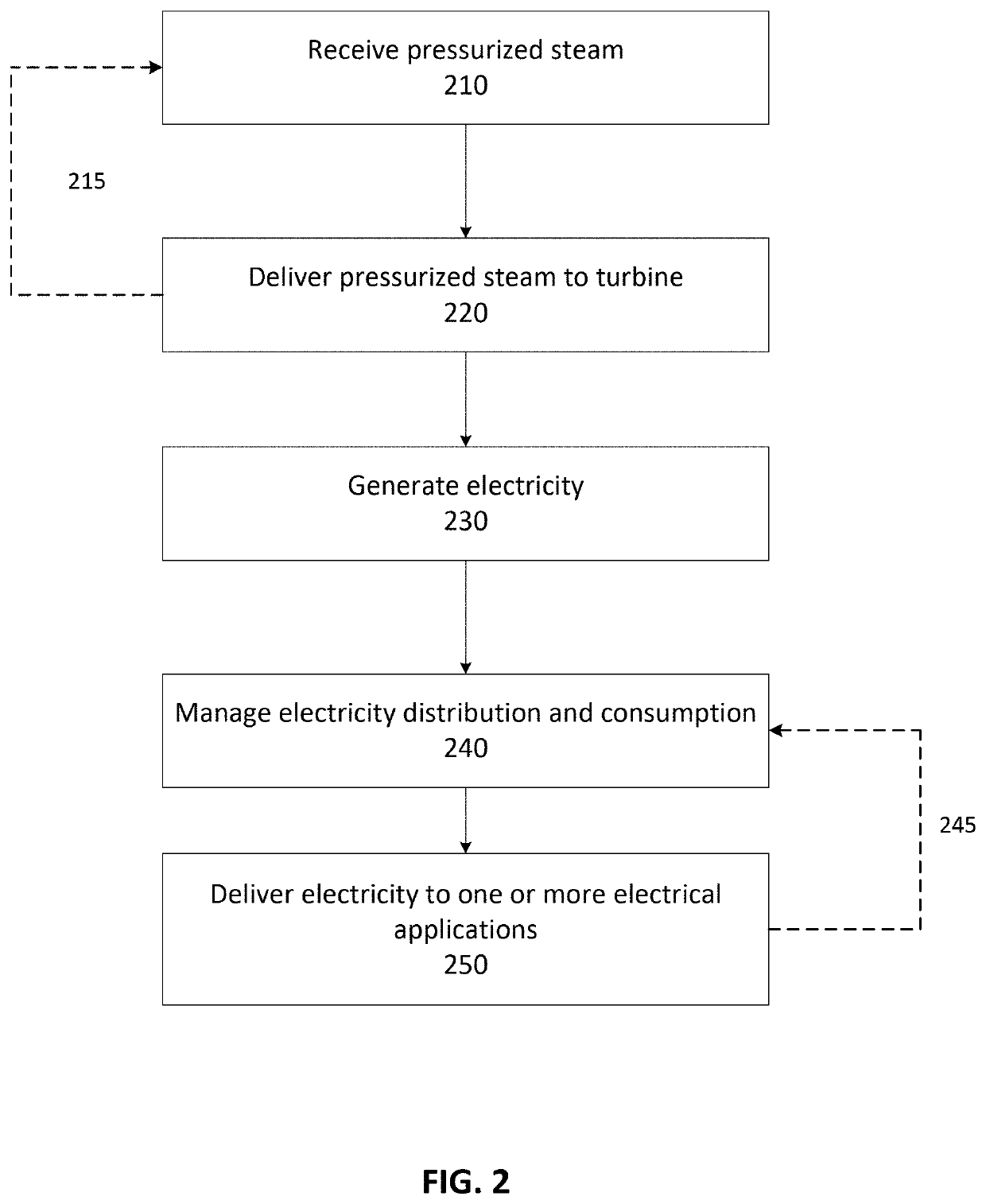
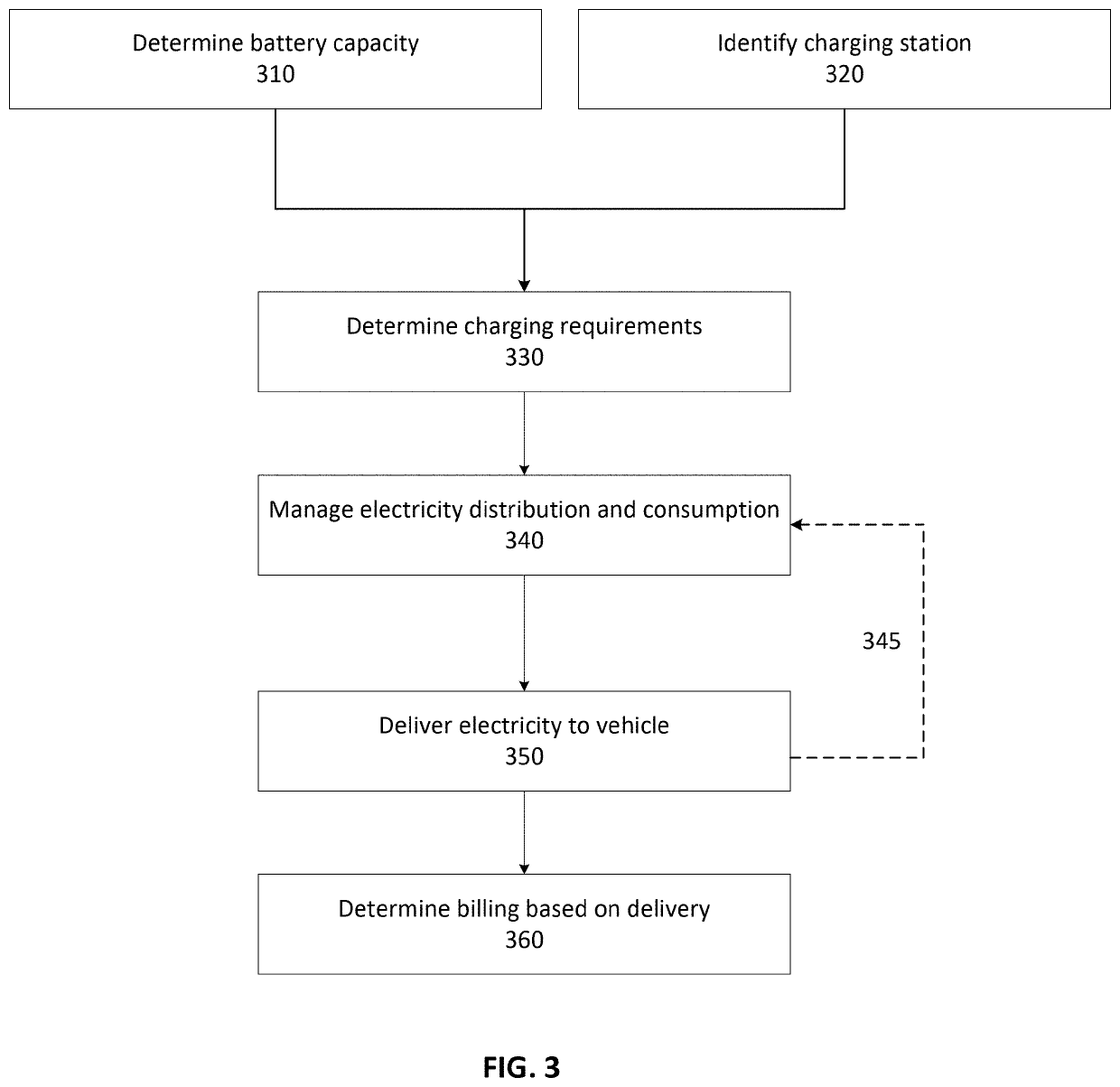
Steam Powered Green Energy Electric Vehicle Charging System
InactiveUS20200156487A1Reduce dependenceCharging stationsElectric powerElectrical batteryElectric cars
Systems and methods for utilizing steam powered “green energy” for an electric charging system for charging electric vehicles are disclosed. A control unit may manage the electricity generation and delivery to a high voltage charging station, e.g., 480+V. A steam source may provide pressurized steam to a turbine and generator to generate electricity, or store it for later in a storage unit, for delivery to the charging station. The control unit may assist in regulating the flow of the pressurized steam through one or more valves. The control unit may also be in communication with, at least, the generator and charging station to identify charging requirements, manage electricity distribution and consumption, deliver electricity to the charging station, and determine billing based on delivery. Generated electricity may be “stored” in the batteries of an electric vehicle when the batteries are charged, and then later, the vehicle's batteries may be utilized in a “vehicle-to-grid” system whereby the electrical power in the vehicle's batteries is supplied, e.g., through a home Level 2 charging station with vehicle-to-grid technology, to the electrical grid.
Owner:NADER RIZGAR
Universal battery pack, electric vehicle powertrain design and battery swapping network with battery health management
PendingUS20220289067A1Improve accuracyGood precisionBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsCommunication interfaceElectrical battery
A Universal Battery Pack (UBP), electric vehicle powertrain design and battery swapping network with battery health management enabling a user of an electric vehicle to access data such as state of health monitoring to enable advanced interface with the electricity grid to address challenges in the adoption of electric vehicles which include cost, range anxiety, charging time and infrastructure, and impacts of vehicle to grid (V2G) operations. The electric vehicle powertrain design is equipped with swapping capability, the modular swappable battery packs, battery storage apparatus, and the bidirectional charging systems. The present invention discloses a method for monitoring, assessing and controlling the battery pack and charger, and the communication interface between the systems and the electricity grid and across the battery swapping network. The present invention provides a cost-effective way of adopting electrification, reducing strain on the electricity grid during peak periods and extending the life of electric vehicle batteries.
Owner:ADEGBOHUN FEYIJIMI
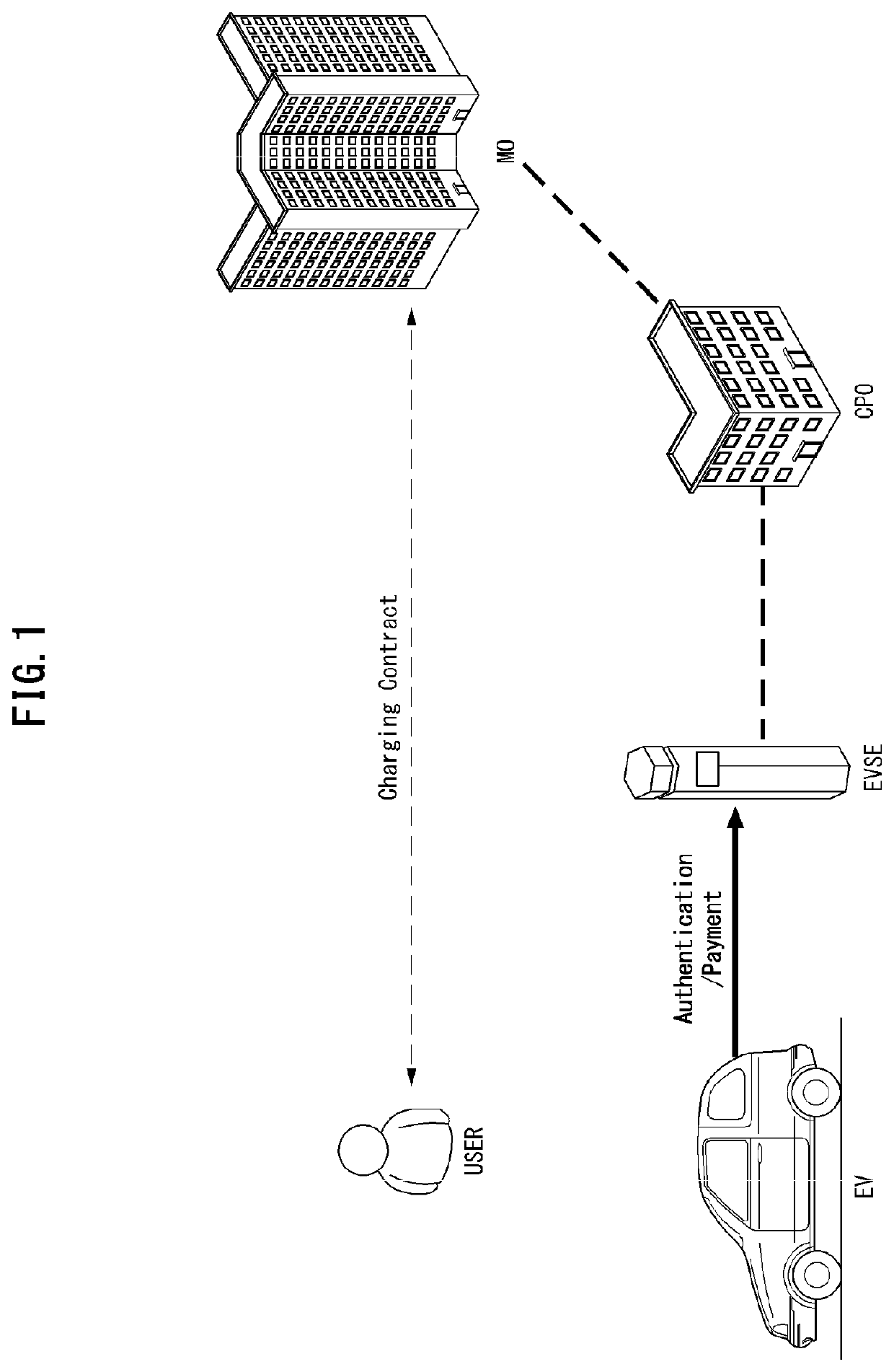
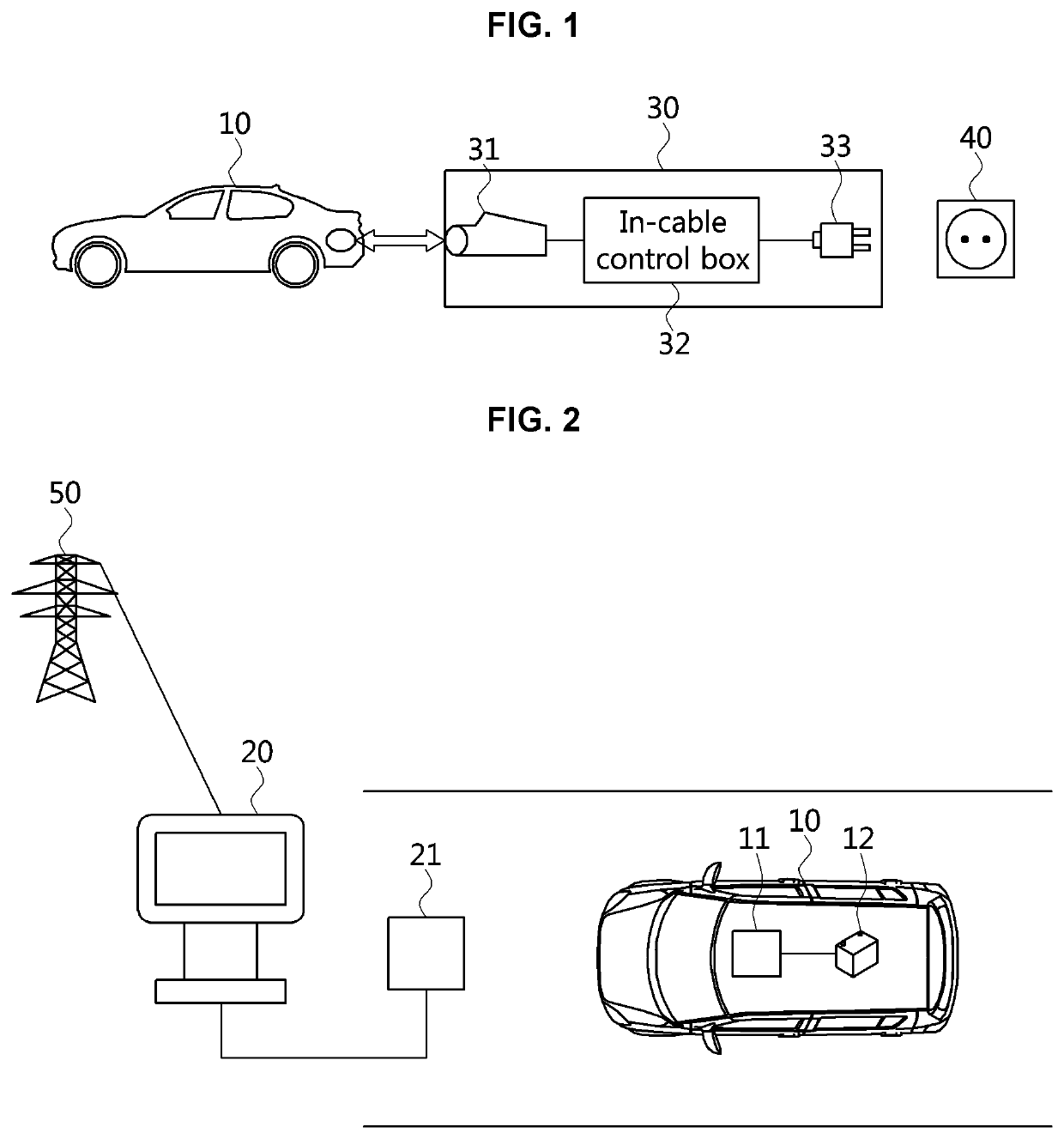
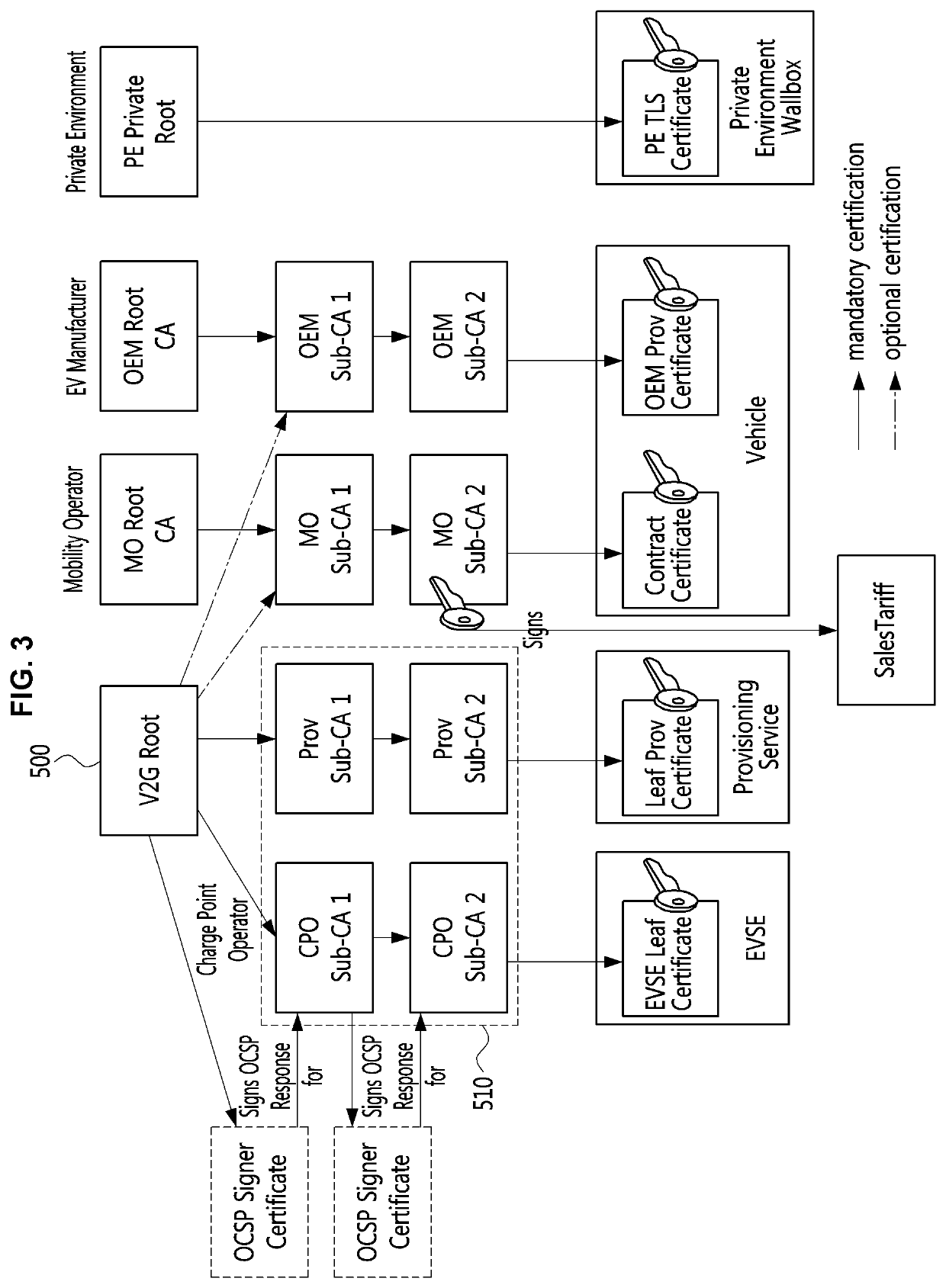
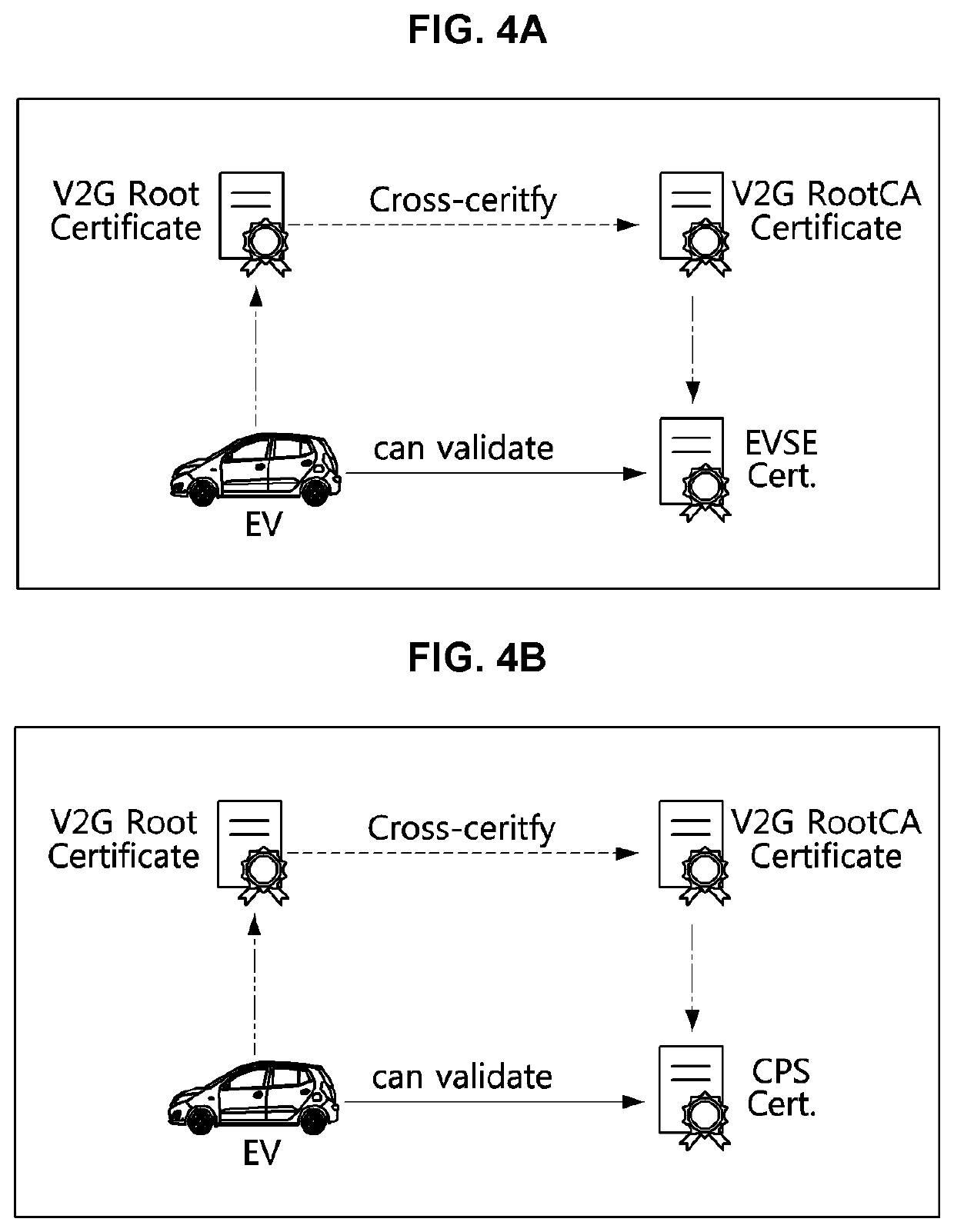
Cross-certificate method and device for electric vehicle charging
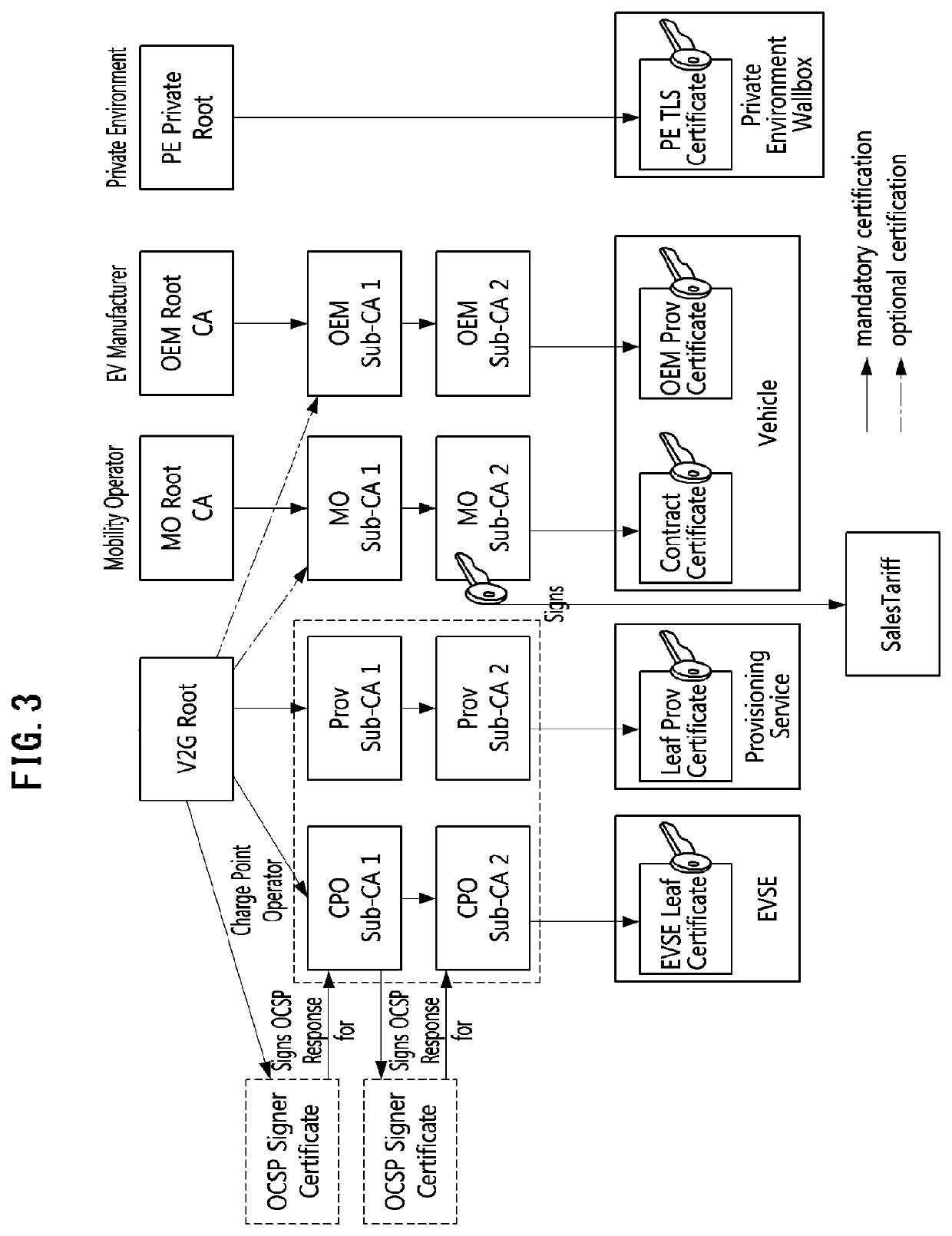
PendingUS20220158851A1Flexible managementKey distribution for secure communicationCharging stationsRoot certificatePower grid
A cross-certificate method is performed by an electric vehicle (EV) for being supplied with power from electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) associated with a charging point operator (CPO) having established a trust relationship with a first vehicle to grid (V2G) root certificate authority (rootCA) and a second V2G root certificate authority. The cross-certificate method may include steps of: requesting charging from the electric vehicle supply equipment; receiving, from the electric vehicle supply equipment, a certificate chain held by the electric vehicle supply equipment; and verifying whether or not a last certificate of the certificate chain has been signed by the second V2G root certificate authority, wherein the last certificate of the certificate chain can be a cross-certificate issued by the second V2G root certificate authority.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com