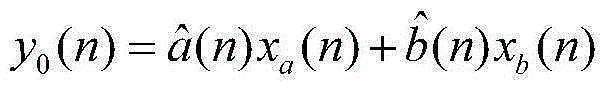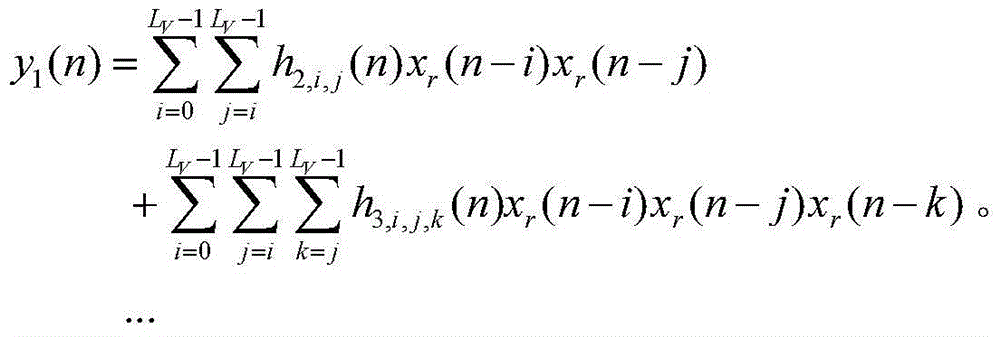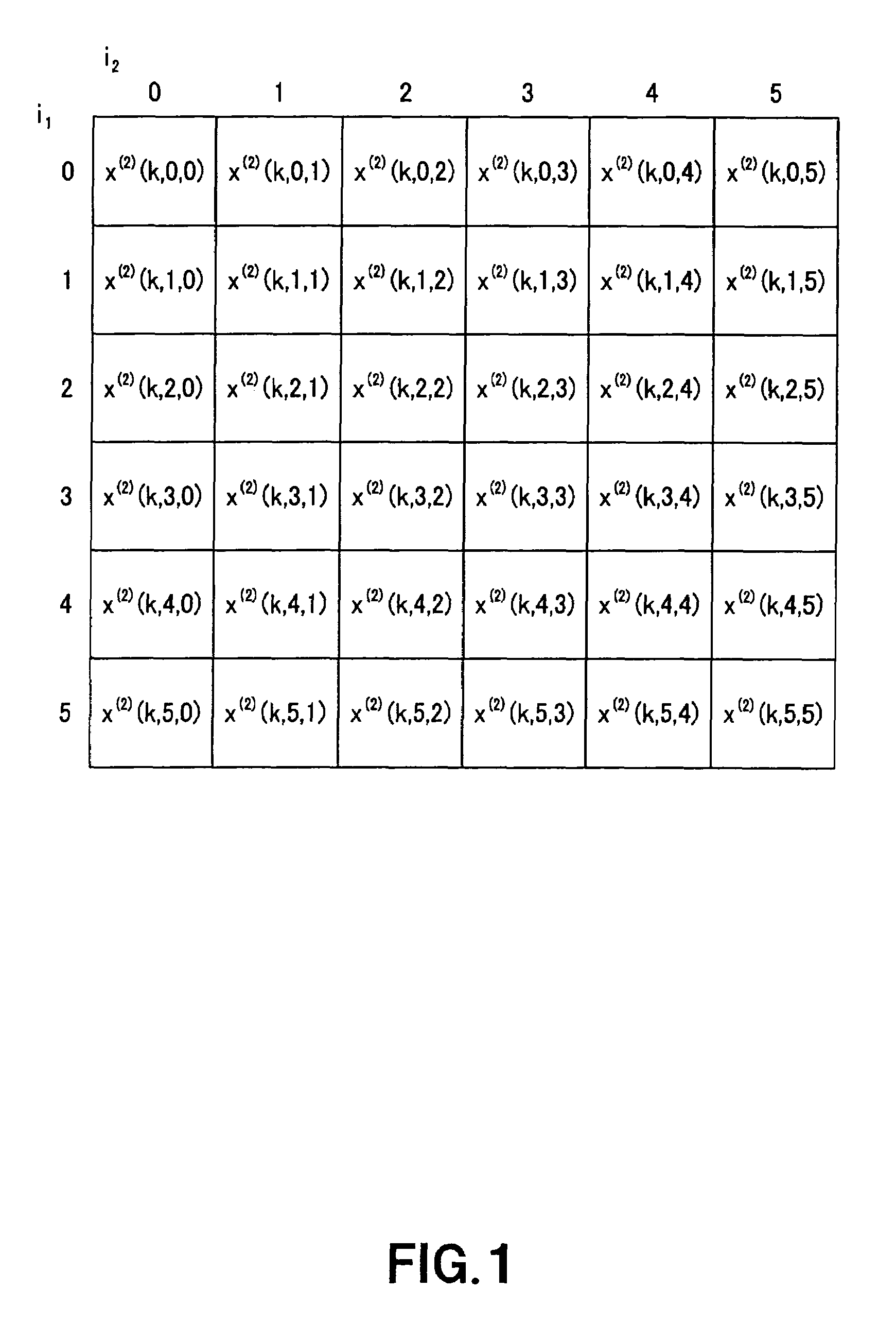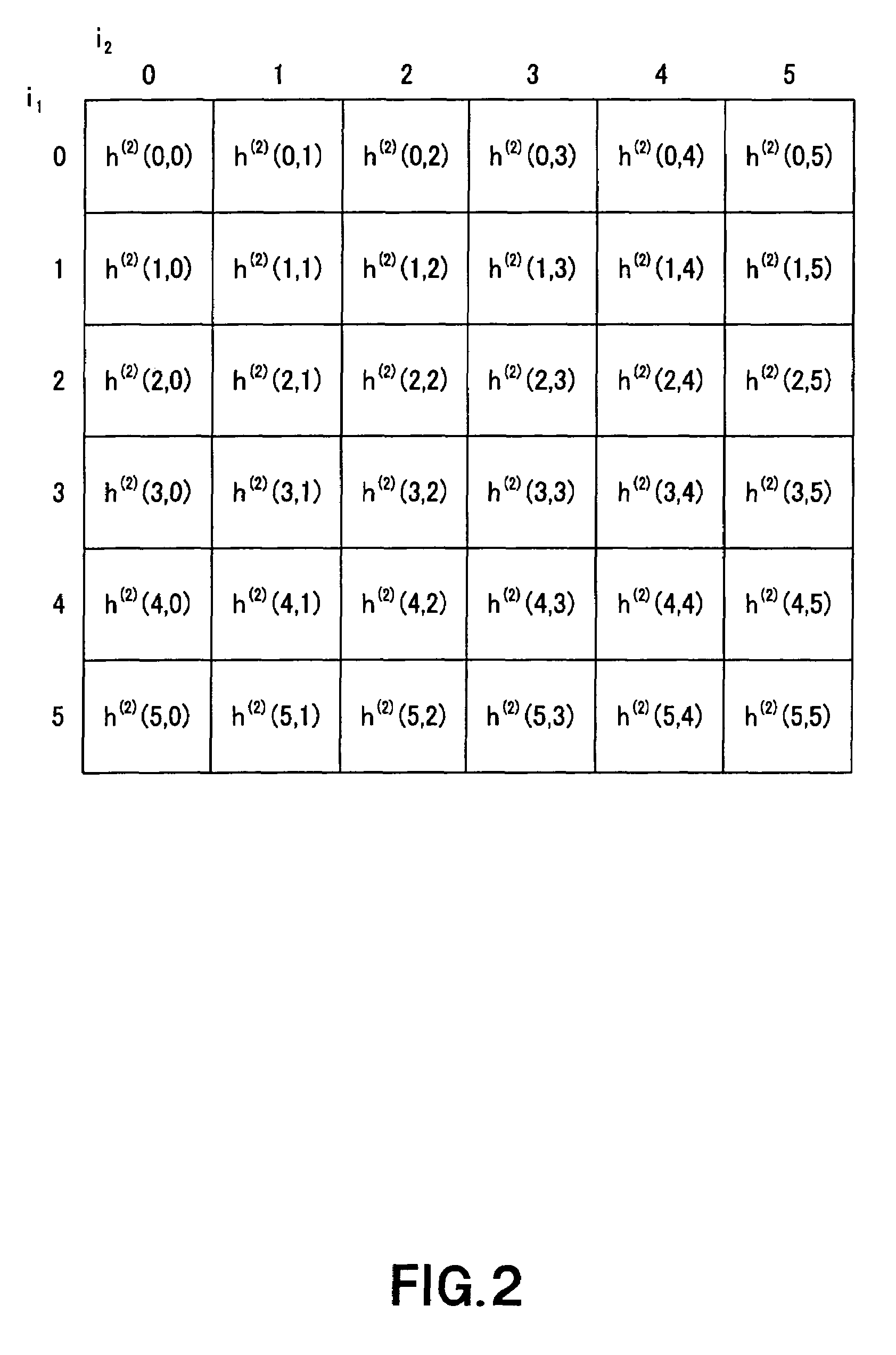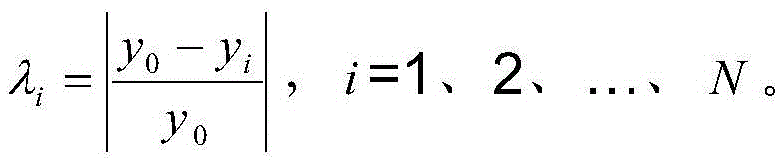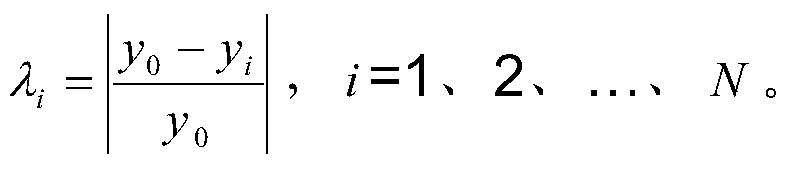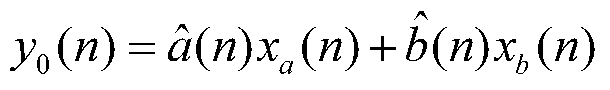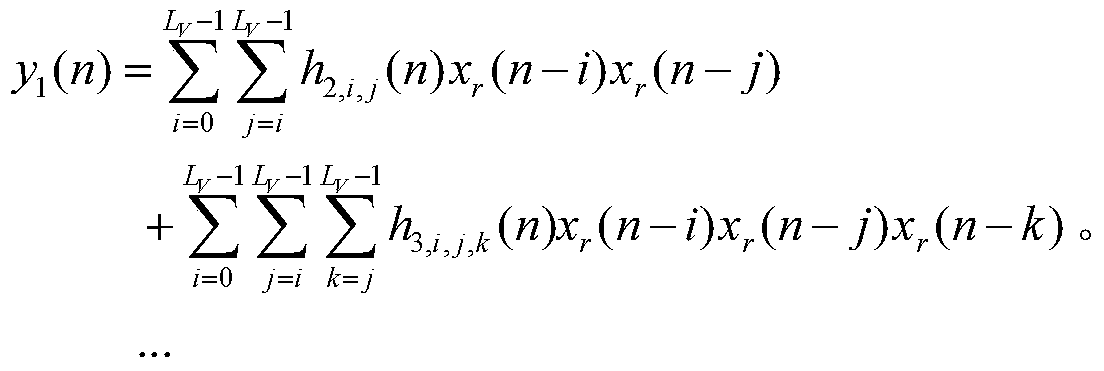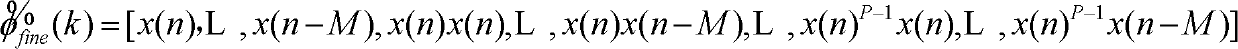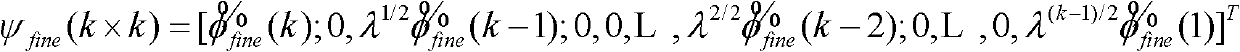Patents
Literature
30 results about "Volterra filters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
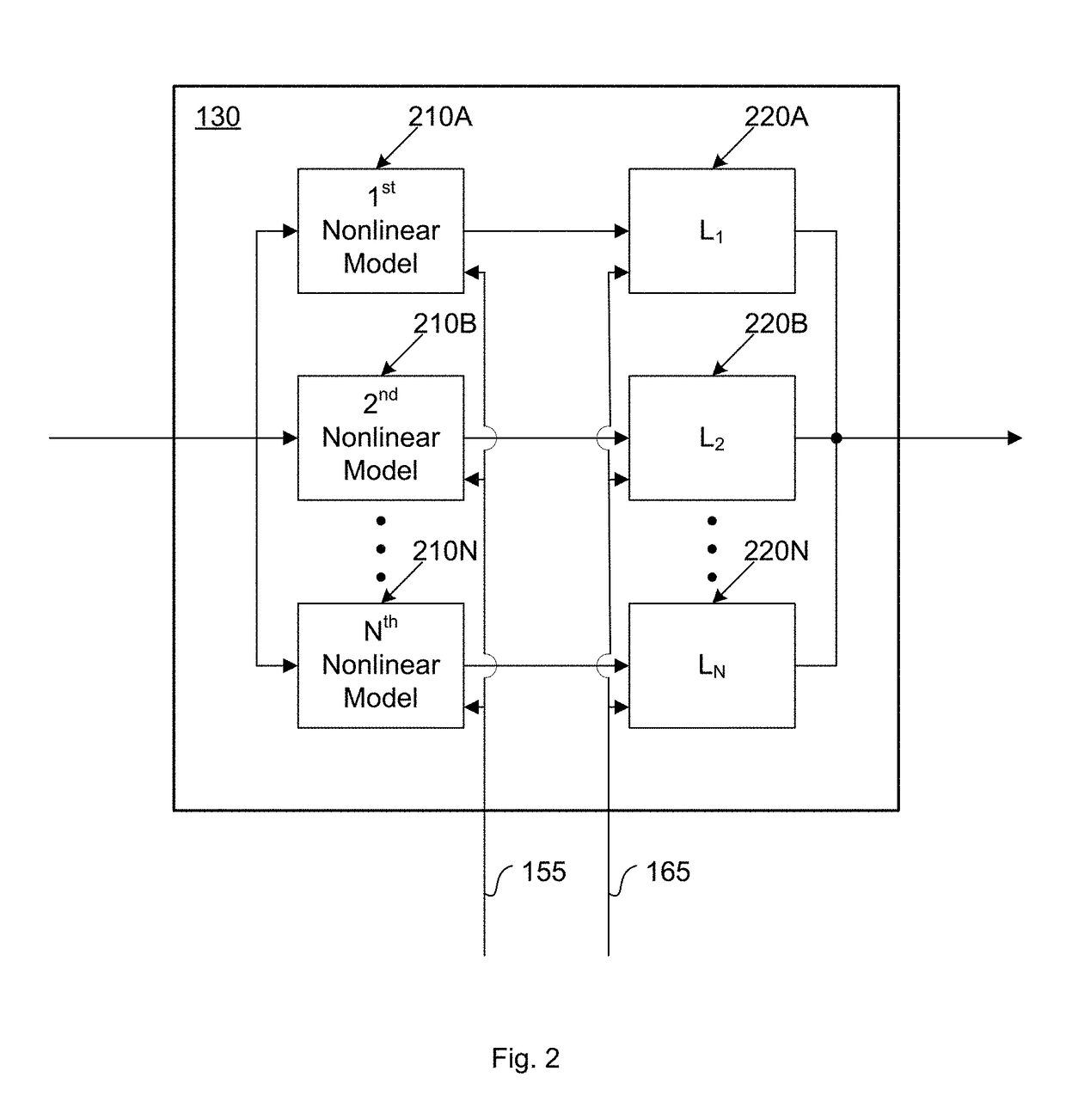
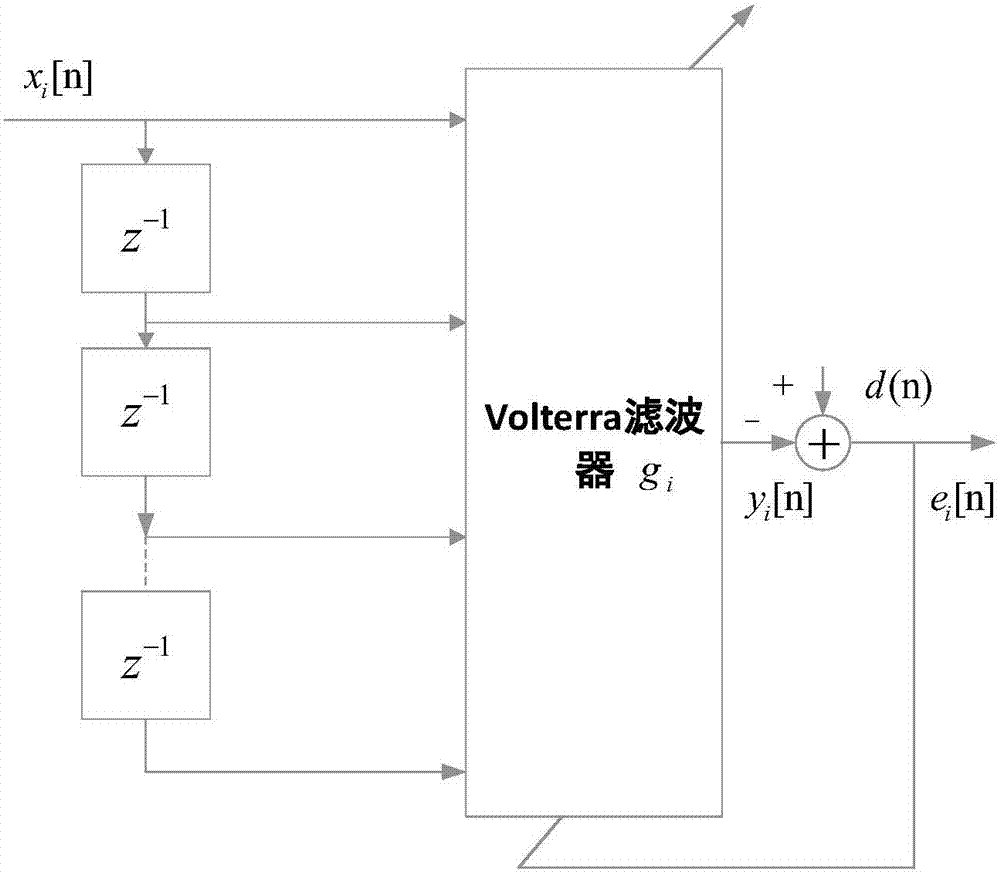
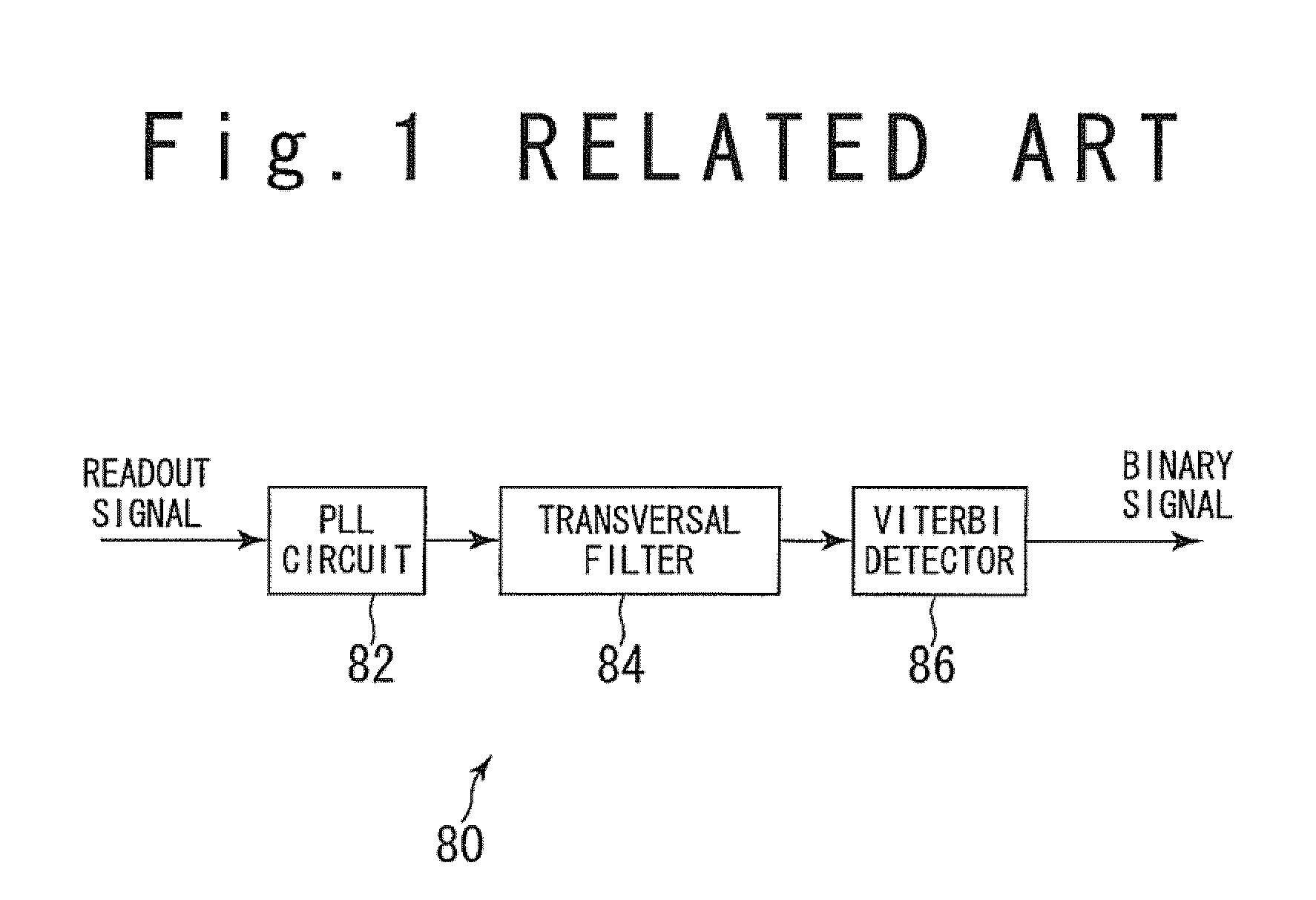
Volterra filters are generally carried out using an equivalent redundancy-removed implementation (known as triangular implementation) in which the symmetry of the kernels is exploited to reduce the total number of filter coefficients [1].
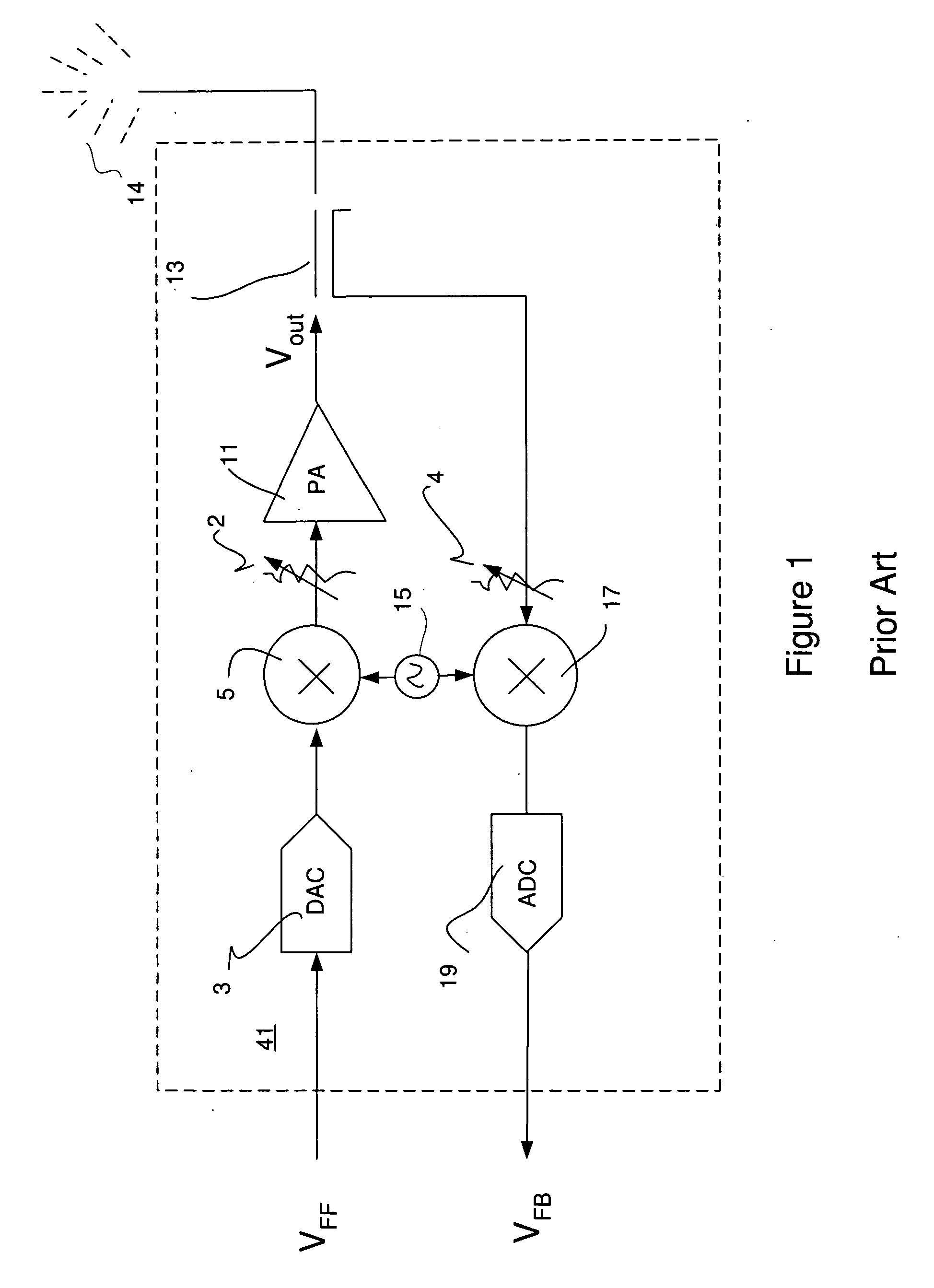
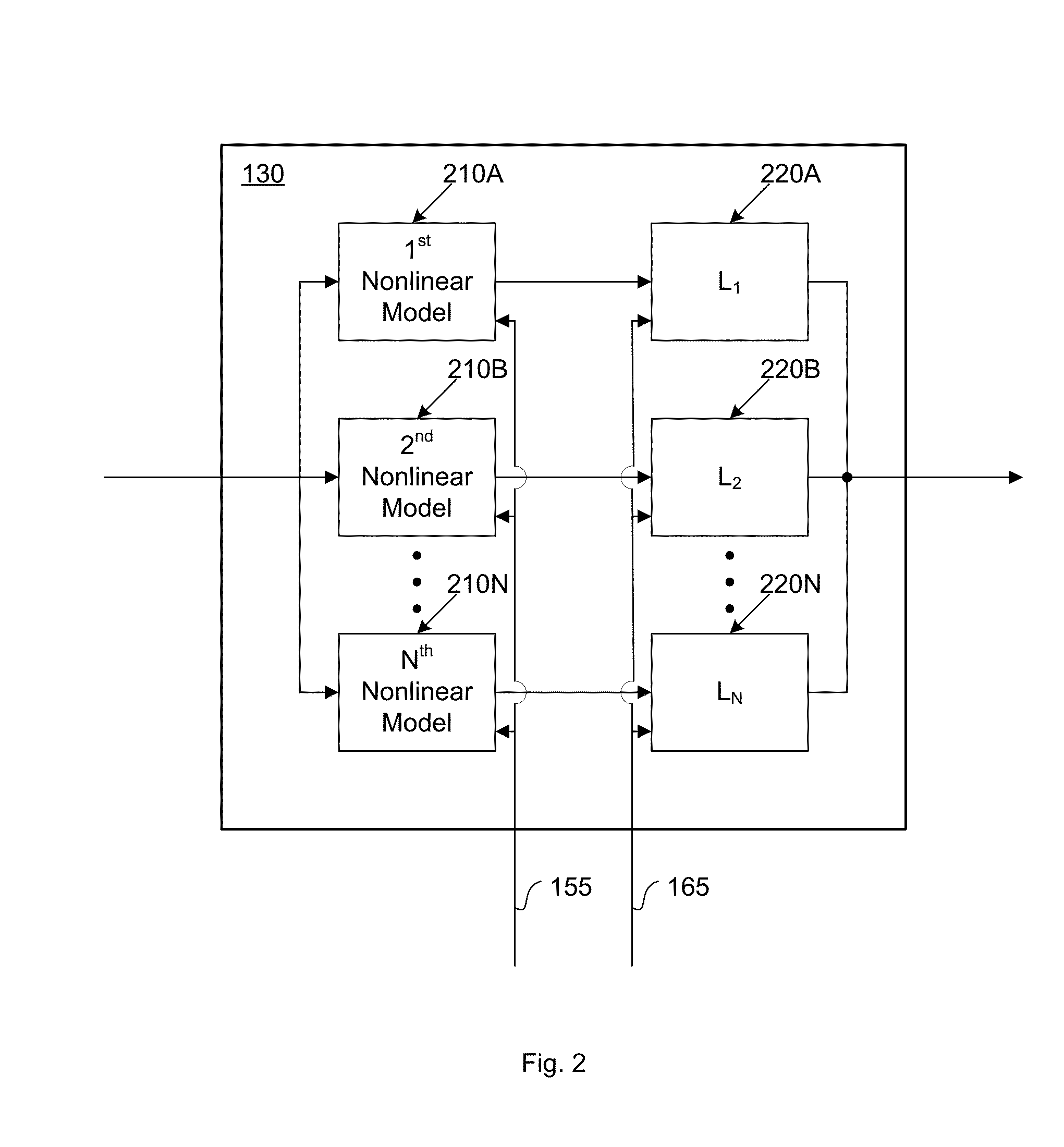
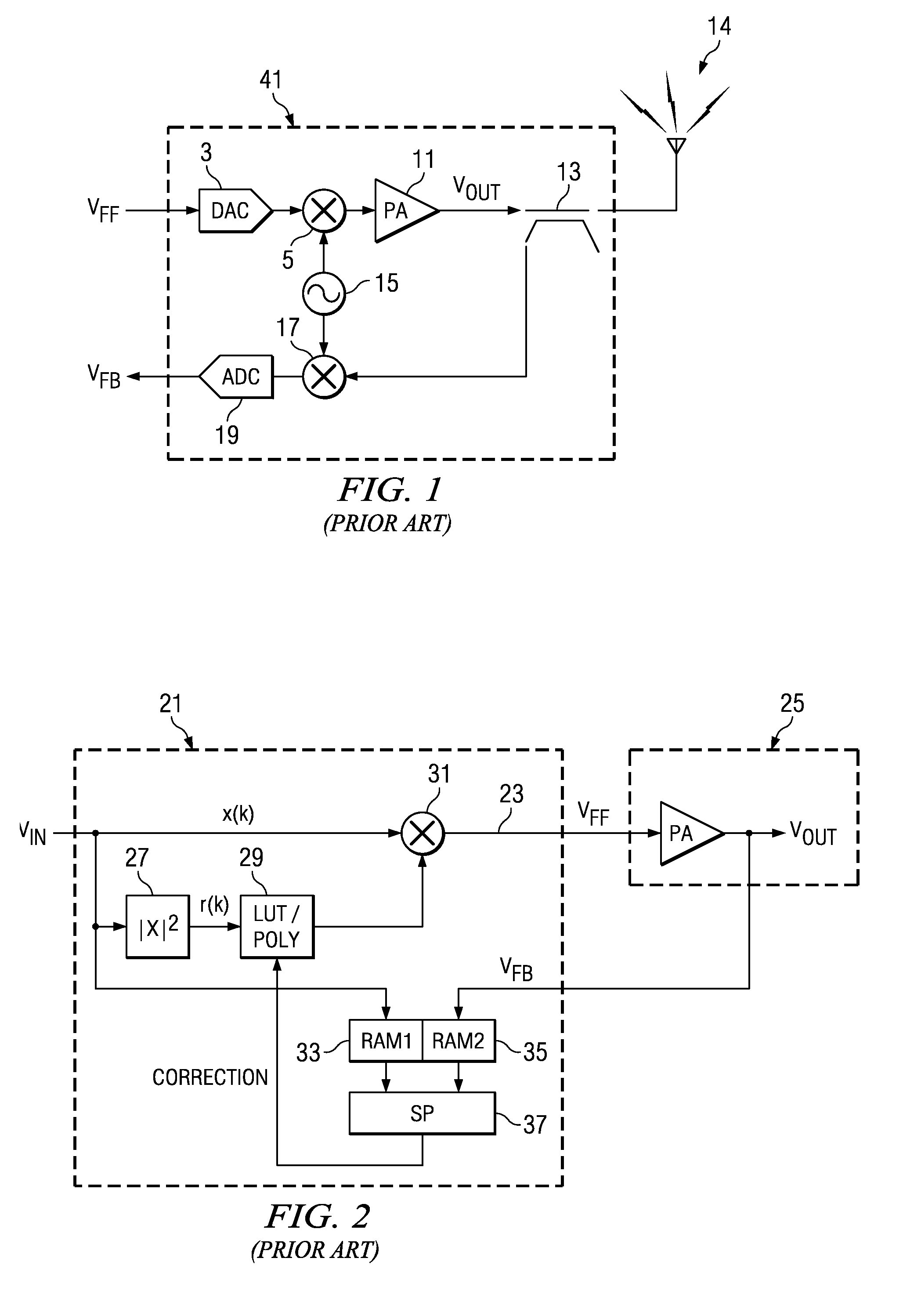
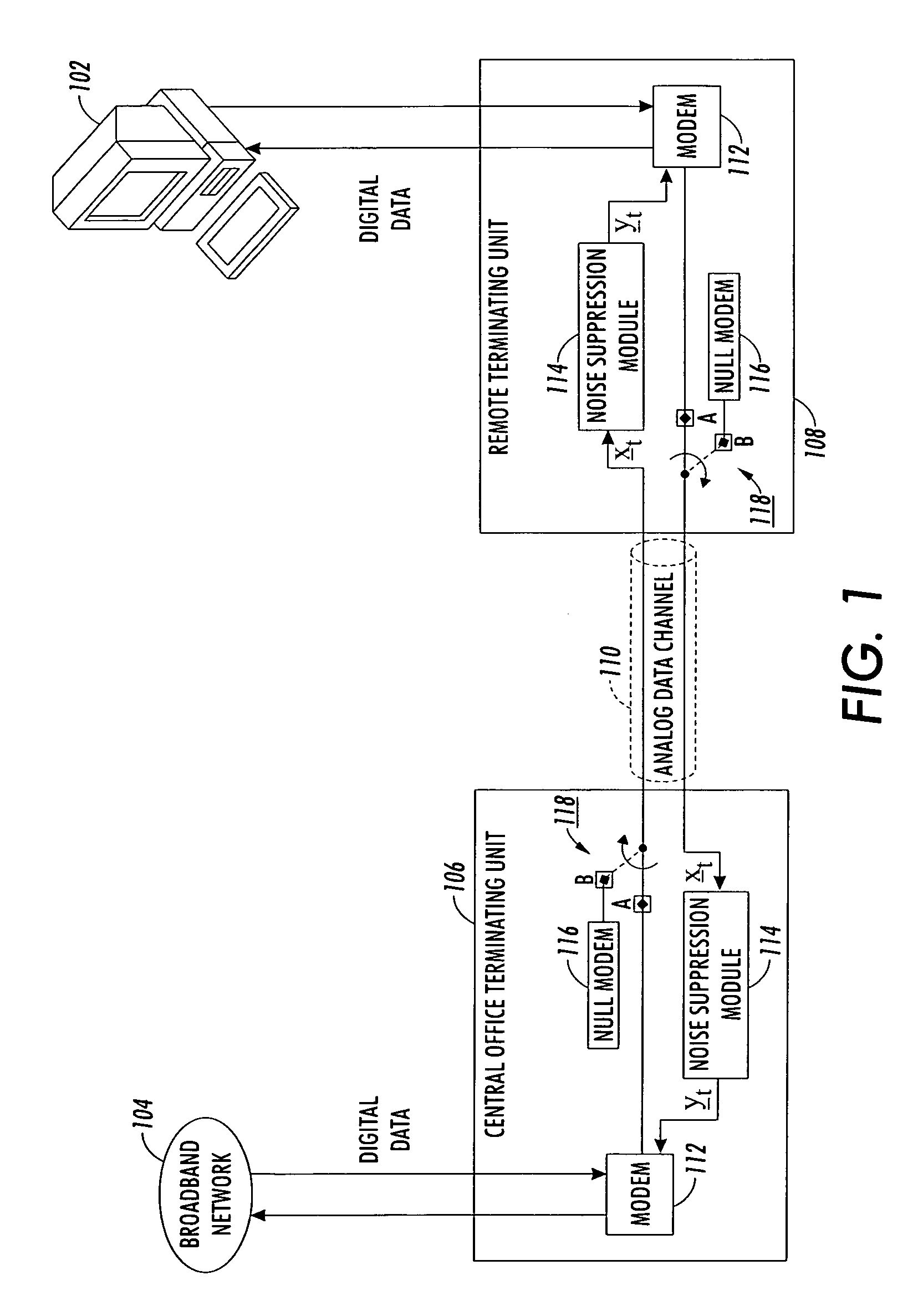
Sampled amplitude read channel employing an adaptive non-linear correction circuit for correcting non-linear distortions in a read signal
InactiveUS7012772B1Minimize complexityLow costMultiple-port networksModification of read/write signalsNonlinear distortionAsymmetric head
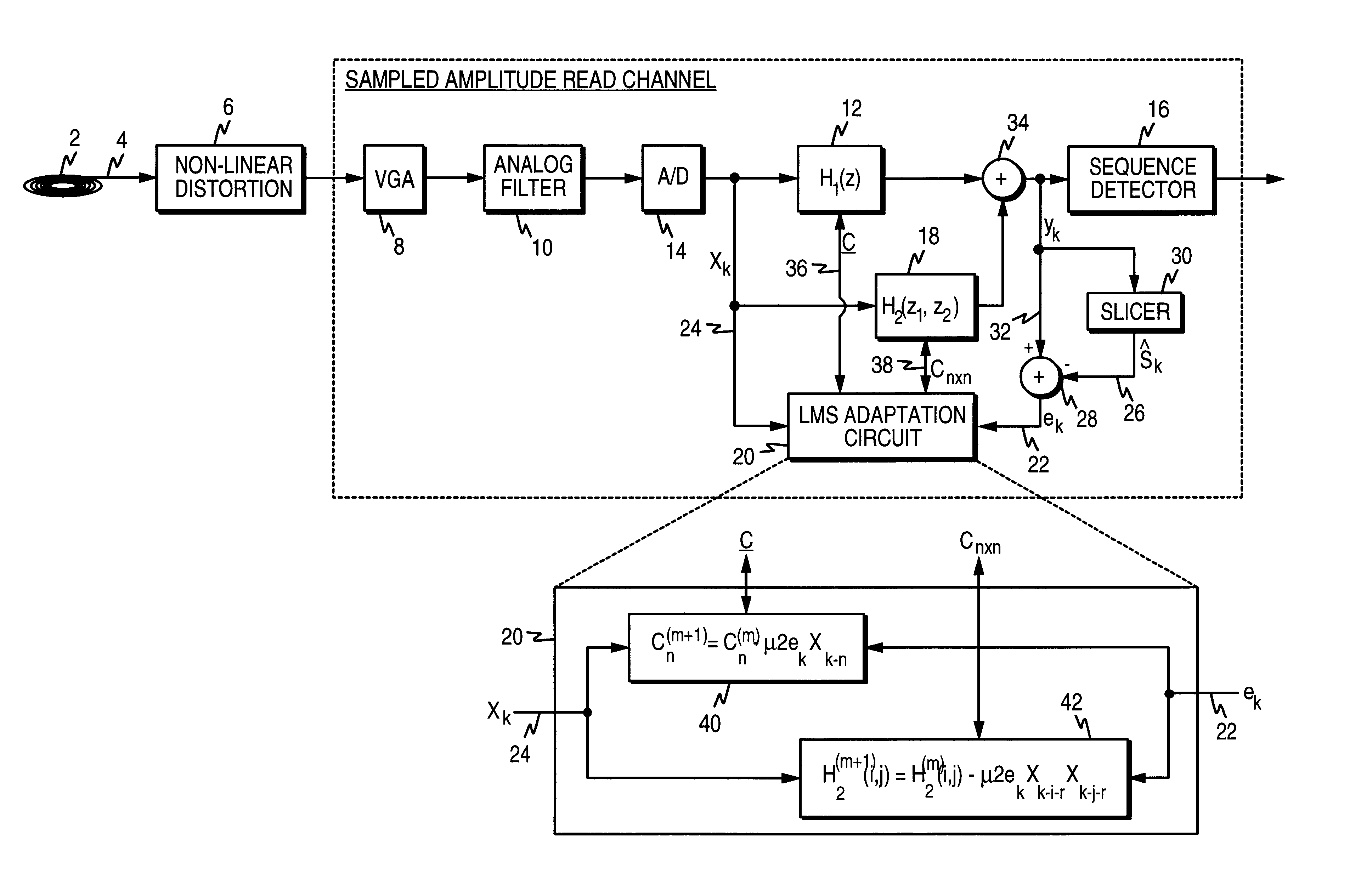
A sampled amplitude read channel is disclosed for magnetic disk storage systems comprising an adaptive non-linear correction circuit for correcting non-linear distortions in the read signal, such as asymmetry caused by the non-linear response of a magneto-resistive (MR) read head. The analog read signal is sampled and the discrete time sample values equalized into a desired partial response prior to sequence detection. The non-linear correction circuit is inserted into the read path prior to the sequence detector and adaptively tuned by a least-mean-square (LMS) adaptation circuit. In one embodiment, the non-linear correction circuit is a discrete-time Volterra filter comprising a linear response for implementing an equalizing filter, and a non-linear response for attenuating non-linear distortions in the read signal. The filter coefficients of both the linear and non-linear sections of the Volterra filter are adaptively adjusted by the LMS adaptation circuit. In an alternative embodiment, the non-linear correction circuit operates in the analog domain, prior to the sampling device, where the cost and complexity can be minimized. The analog correction circuit implements an inverse response to that of the non-linearity in the read signal, and the response is adaptively tuned using an LMS update value computed in discrete-time for a Volterra filter, without actually implementing a Volterra filter. Further, the LMS update value for the analog correction circuit can be implemented using a simple squaring circuit.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
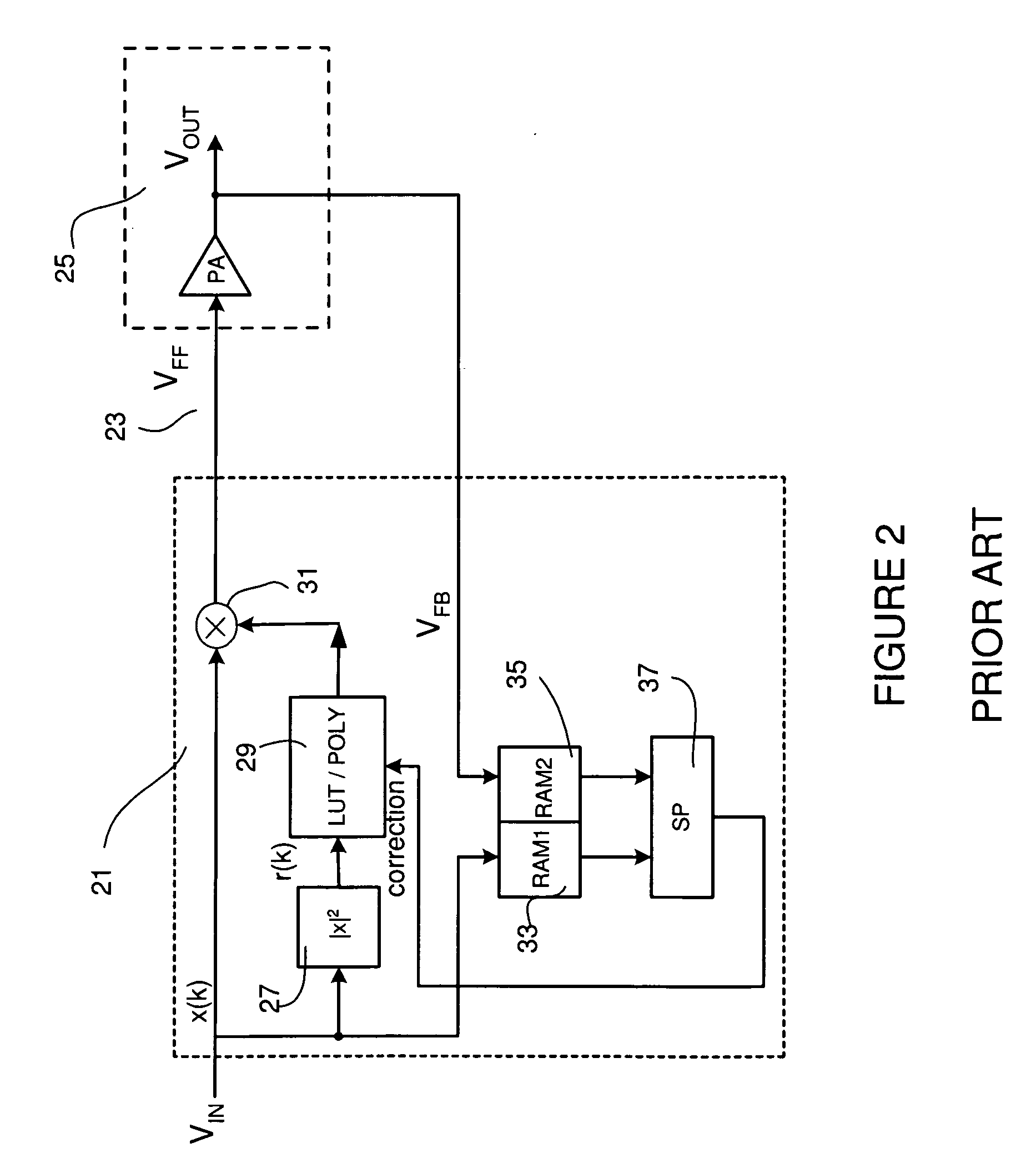
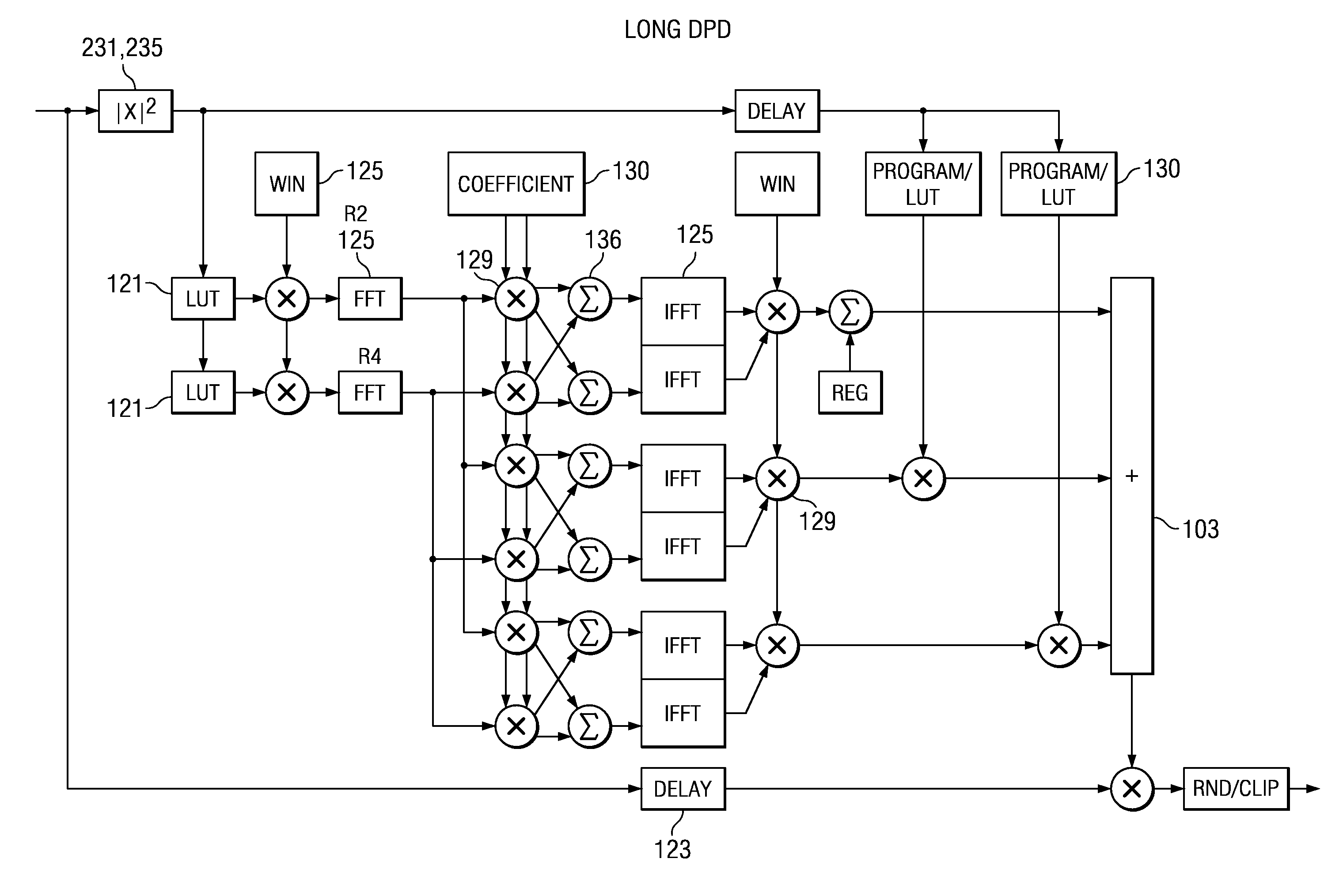
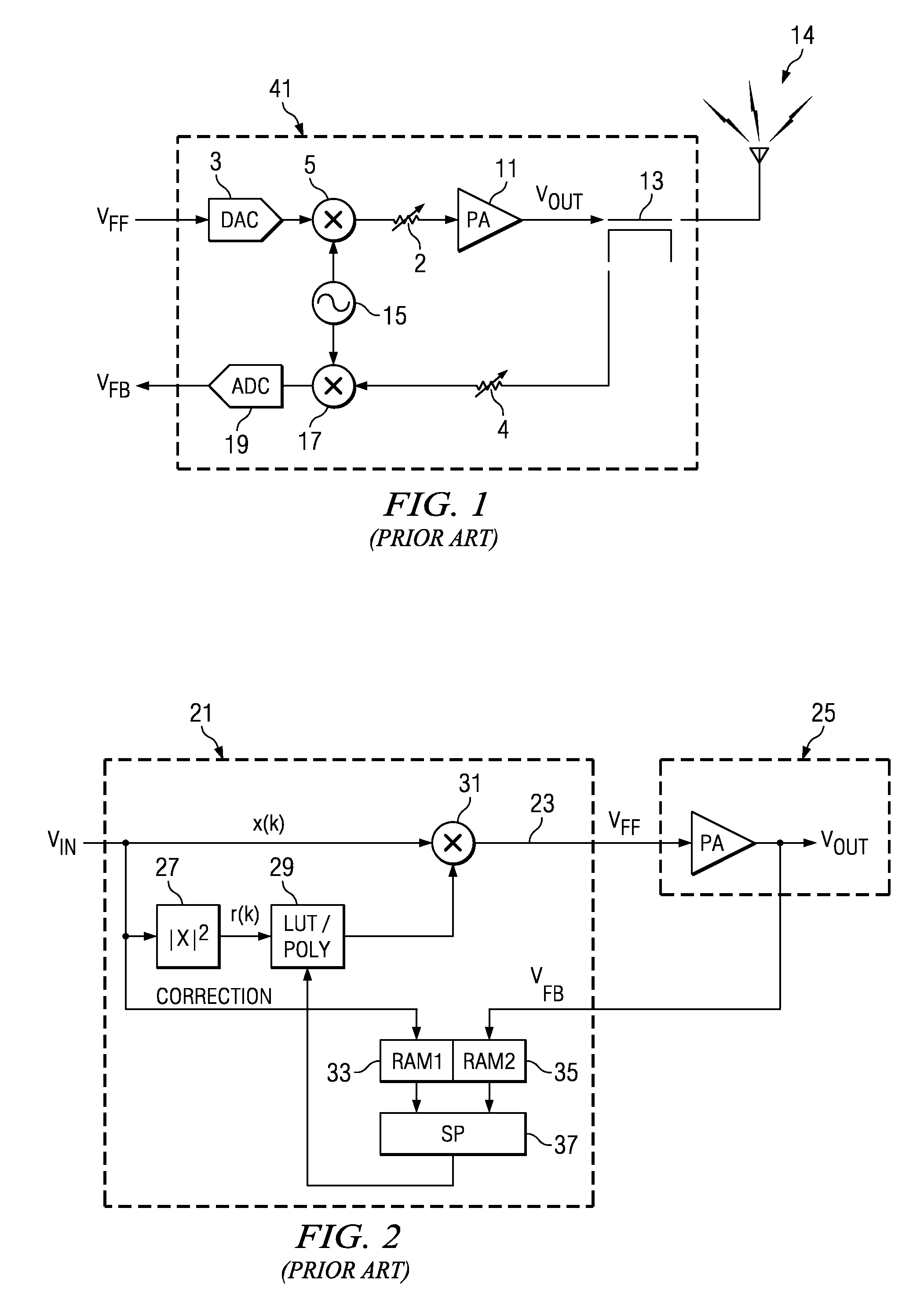
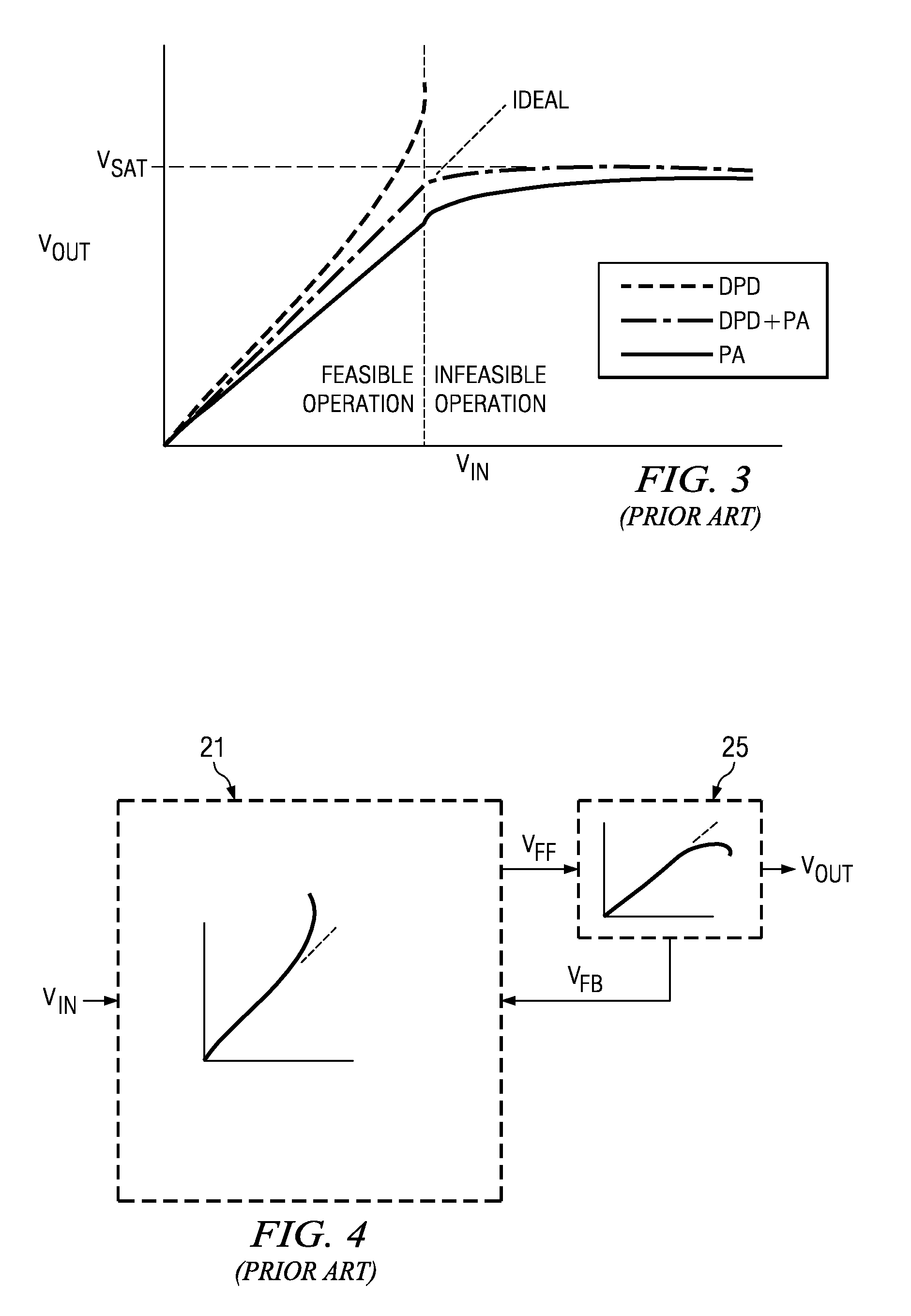
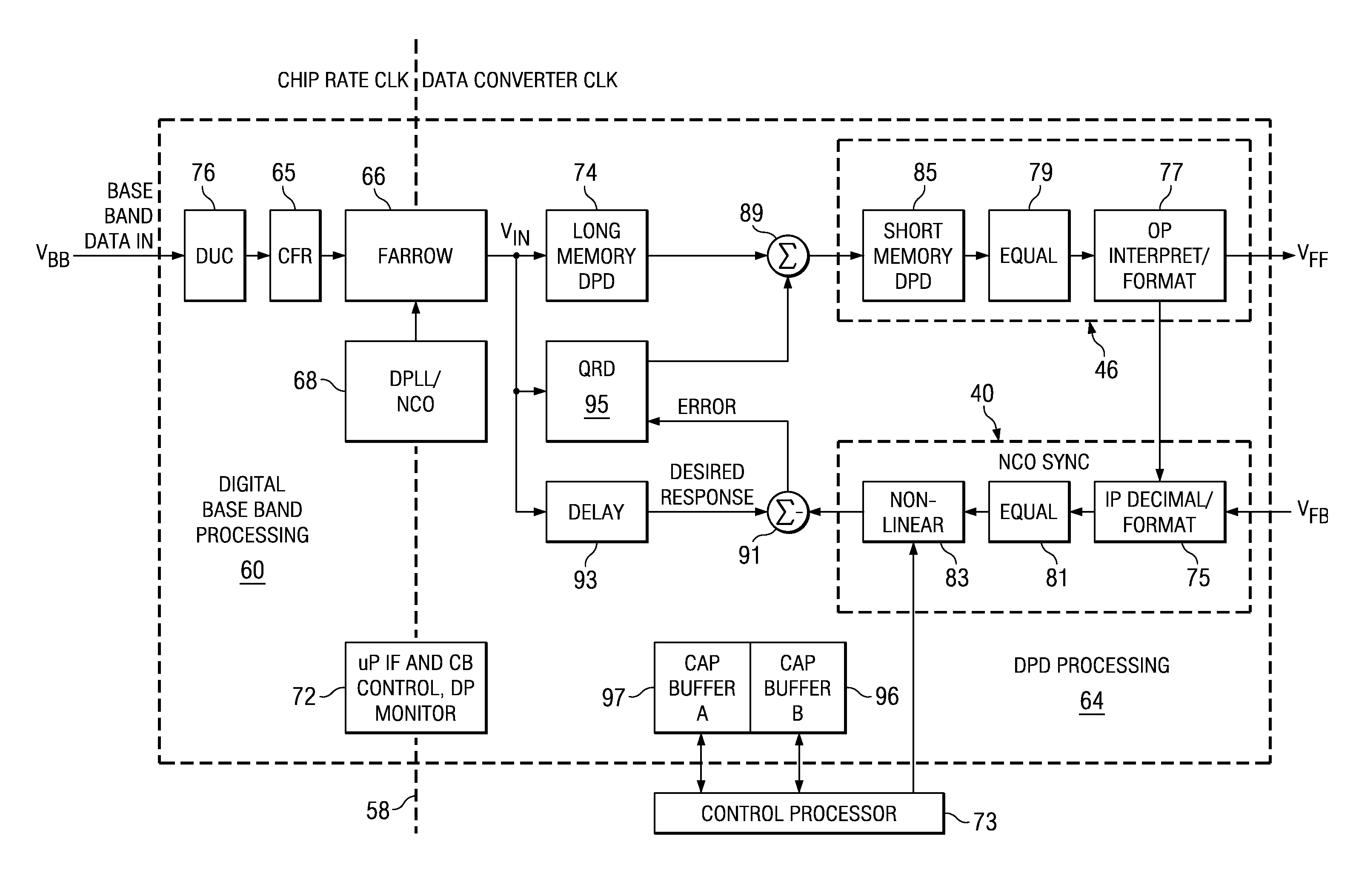
System and methods for digitally correcting a non-linear element using a digital filter for predistortion
ActiveUS20080130789A1Effective linearizationPower amplifiersMemory effect compensationEngineeringNonlinear element
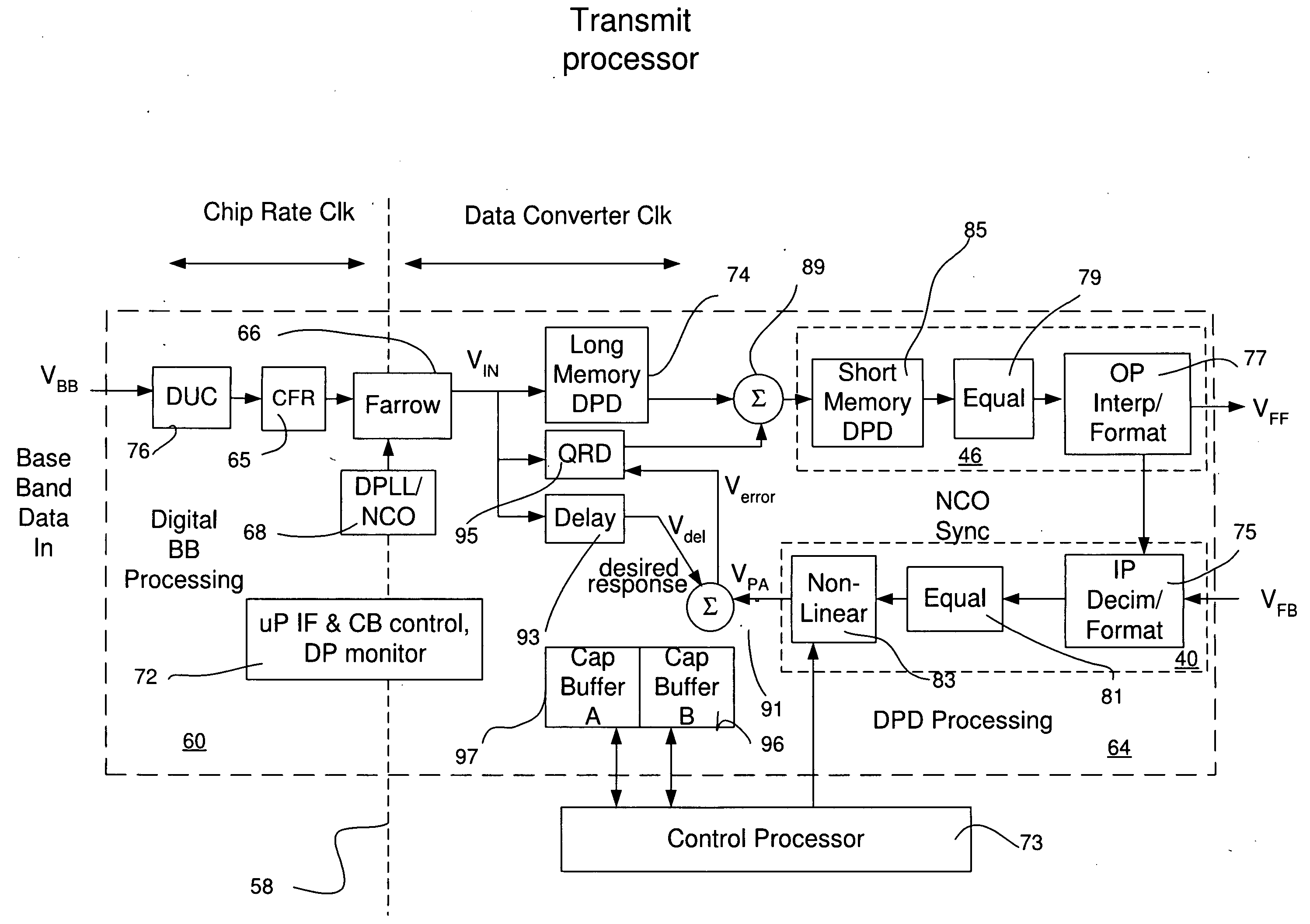
System and methods for a digital linearization of a non linear element. Digital predistortion methods and circuitry for linearizing a non-linear element that address long or “memory” effects and shorter duration effects, these two predistortion functions are operated together in an adaptive fashion with the non-linear element to provide a highly linear system. A short duration predistortion block comprises an Nth order polynomial filter coupled to a programmable linear equalizer. The Nth order filter includes programmable non-linearities and variable delay taps. The Nth order filter may be configured to implement a non-sequential or a sequential ordered polynomial. The equalizer may, in a preferred embodiment, include circuitry for equalizing imbalances between real and complex signal values. The Nth order filter may implement a compound Volterra filter. The combined system of the predistortion circuitry and a non-linear element has a linear input-output signal response. Methods for initializing, parameterizing and adapting the system are disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
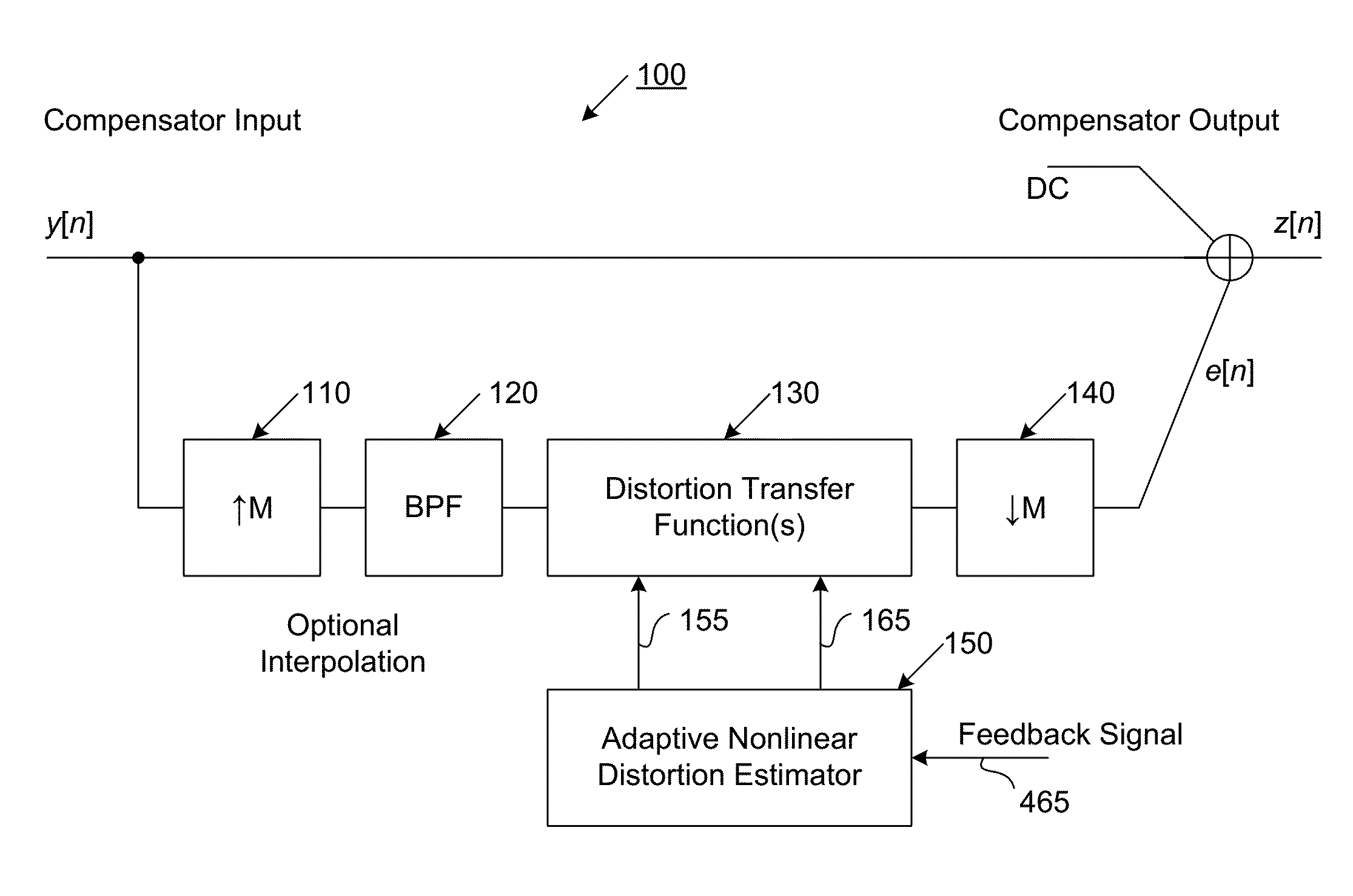
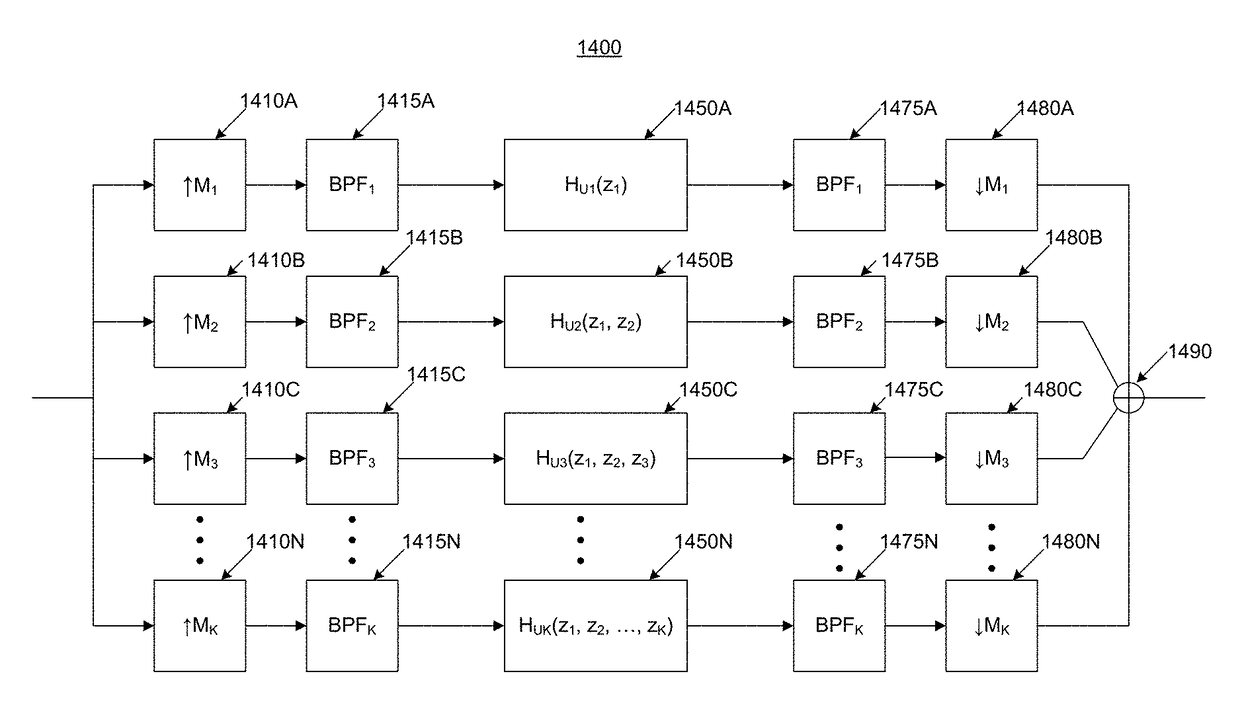
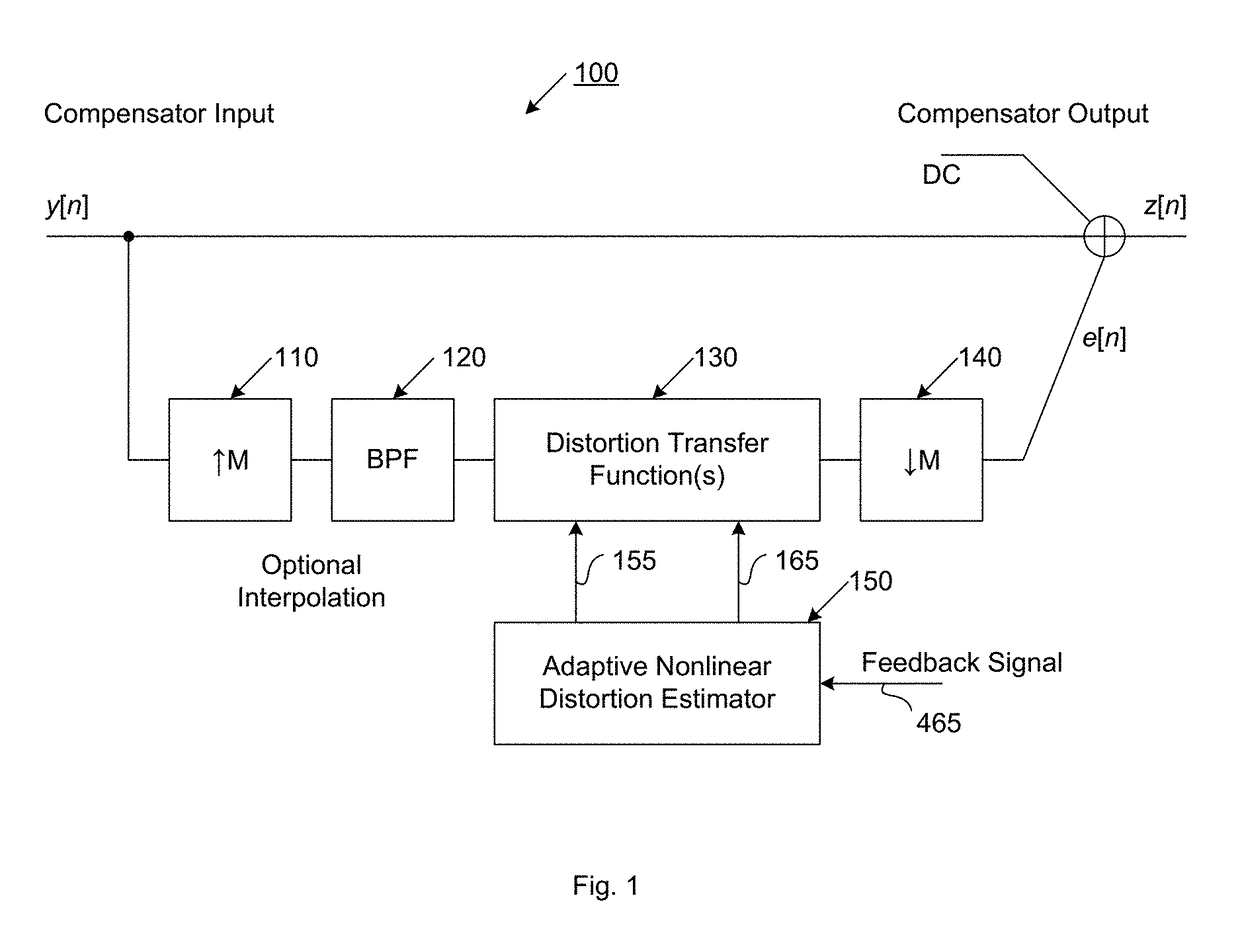
Compensator for removing nonlinear distortion
ActiveUS20160191020A1Easy to processReduce complexityChannel dividing arrangementsElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionComputation complexity
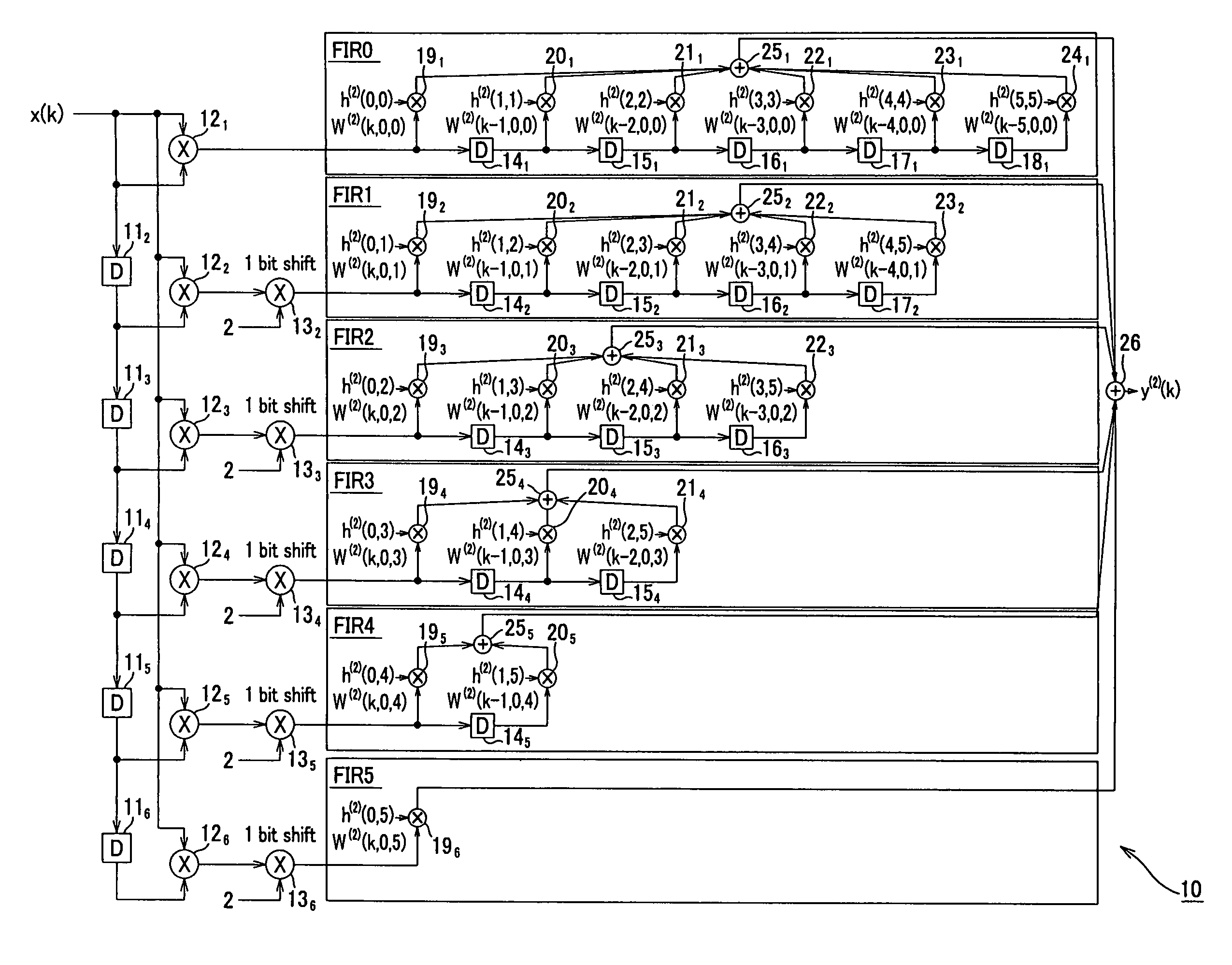
The present invention is a computationally-efficient compensator for removing nonlinear distortion. The compensator operates in a digital post-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as analog-to-digital converters and RF receiver electronics. The compensator also operates in a digital pre-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as digital-to-analog converters, RF power amplifiers, and RF transmitter electronics. The compensator effectively removes nonlinear distortion in these systems in a computationally efficient hardware or software implementation by using one or more factored multi-rate Volterra filters. Volterra filters are efficiently factored into parallel FIR filters and only the filters with energy above a prescribed threshold are actually implemented, which significantly reduces the complexity while still providing accurate results. For extremely wideband applications, the multi-rate Volterra filters are implemented in a demultiplexed polyphase configuration which performs the filtering in parallel at a significantly reduced data rate. The compensator is calibrated with an algorithm that iteratively subtracts an error signal to converge to an effective compensation signal. The algorithm is repeated for a multiplicity of calibration signals, and the results are used with harmonic probing to accurately estimate the Volterra filter kernels. The compensator improves linearization processing performance while significantly reducing the computational complexity compared to a traditional nonlinear compensator.
Owner:LINEARITY LLC
Volterra filters for enhancement of contours in images
Enhancement of contours in images that are noisy or otherwise corrupted is important in medical imaging, scanning for weapons detection, and many other fields. Here, the Curve Indicator Random Field (CIRF) is used as a model of uncorrupted images of contours for constructing linear, quadratic and cubic Volterra filters involving a number of adjustable parameters.
Owner:AUGUST JONAS
System and methods for digitally correcting a non-linear element using a digital filter for predistortion
ActiveUS7773692B2Effective linearizationPower amplifiersMemory effect compensationNonlinear elementVolterra filters
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for digitally correcting a non-linear element
ActiveUS7822146B2Effective linearizationModulated-carrier systemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceEngineeringNonlinear element
System and methods for a digital linearization of a non-linear element. Preferred embodiments provide digital predistortion methods and circuitry that addresses long or “memory” effects and separately shorter duration effects, these two predistortion functions are operated together in an adaptive fashion with a non-linear element to provide a highly linear system. A long predistortion block comprises a plurality of configurable parallel coupled memory blocks, each further comprising a programmable nonlinearity, variable delays, digital filters, and signal combiners. These parallel blocks are selectively configured to provide a parallel filter, a Hammerstein filter and a compound Volterra filter. The parallel coupled memory blocks include programmable parameters that enable real time adaptation of the predistortion; the delay elements also include variable delays. The combined system of the predistortion circuitry and a non-linear element has a linear input-output signal response. Methods for initializing, parameterizing and adapting the system are disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
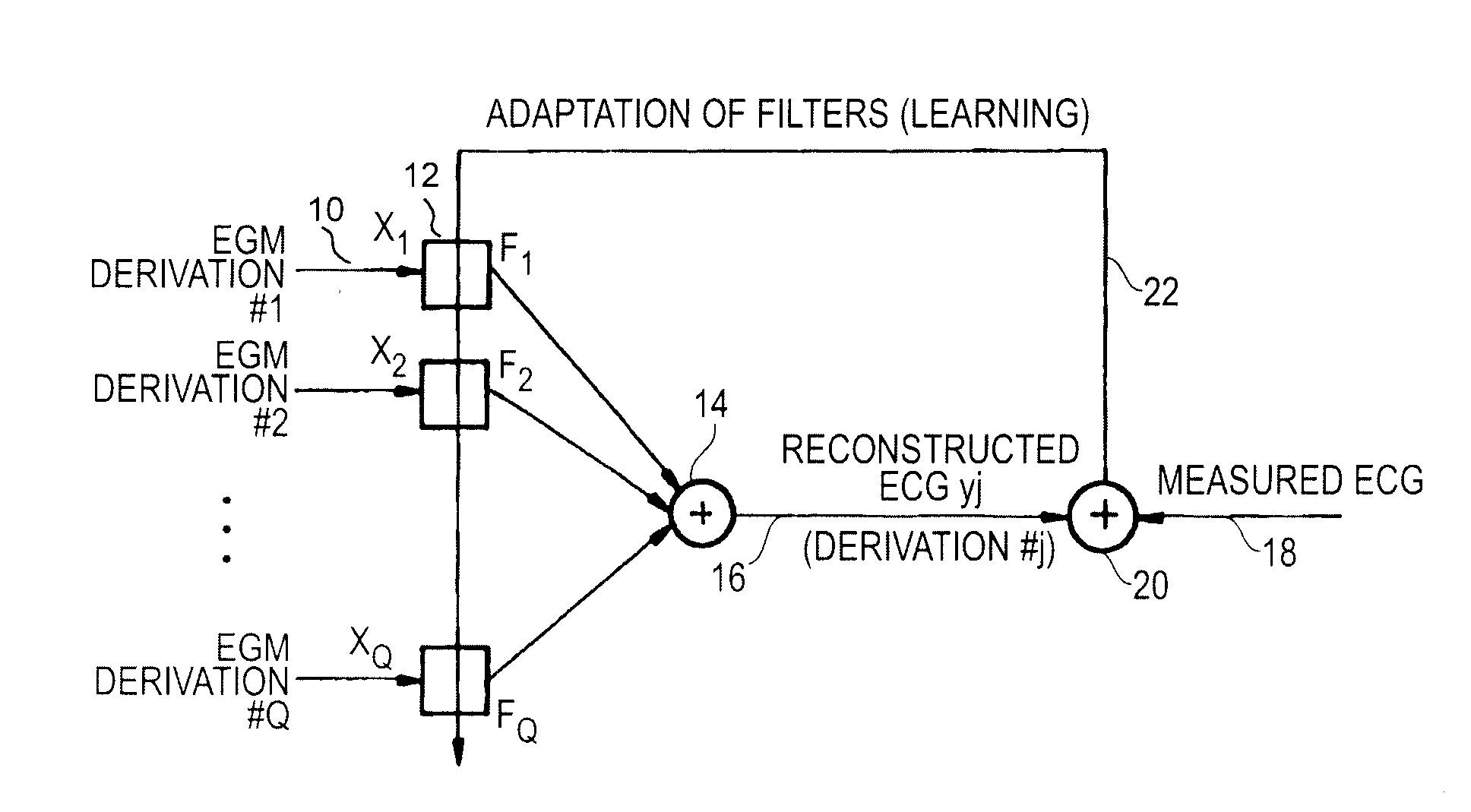
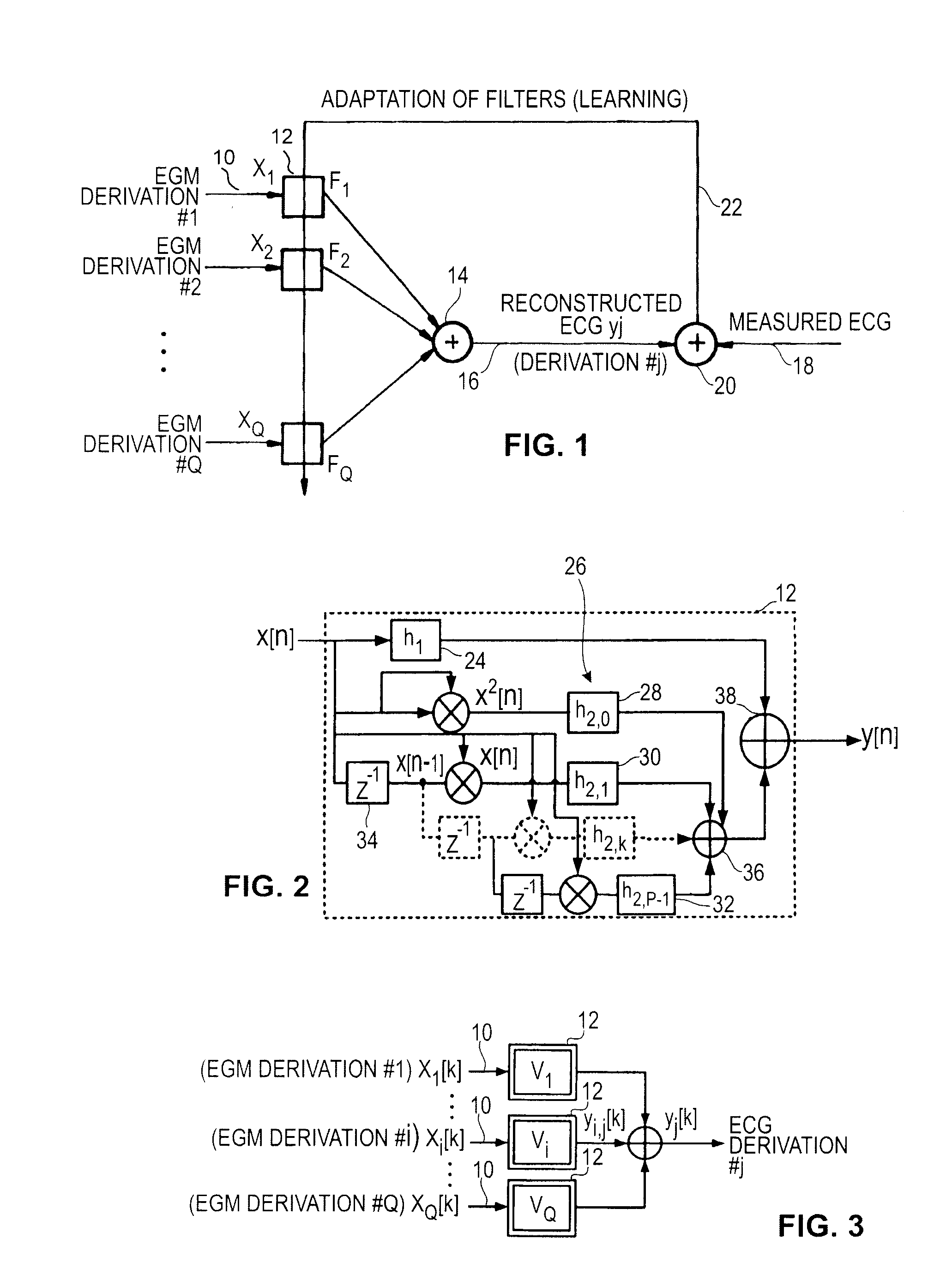
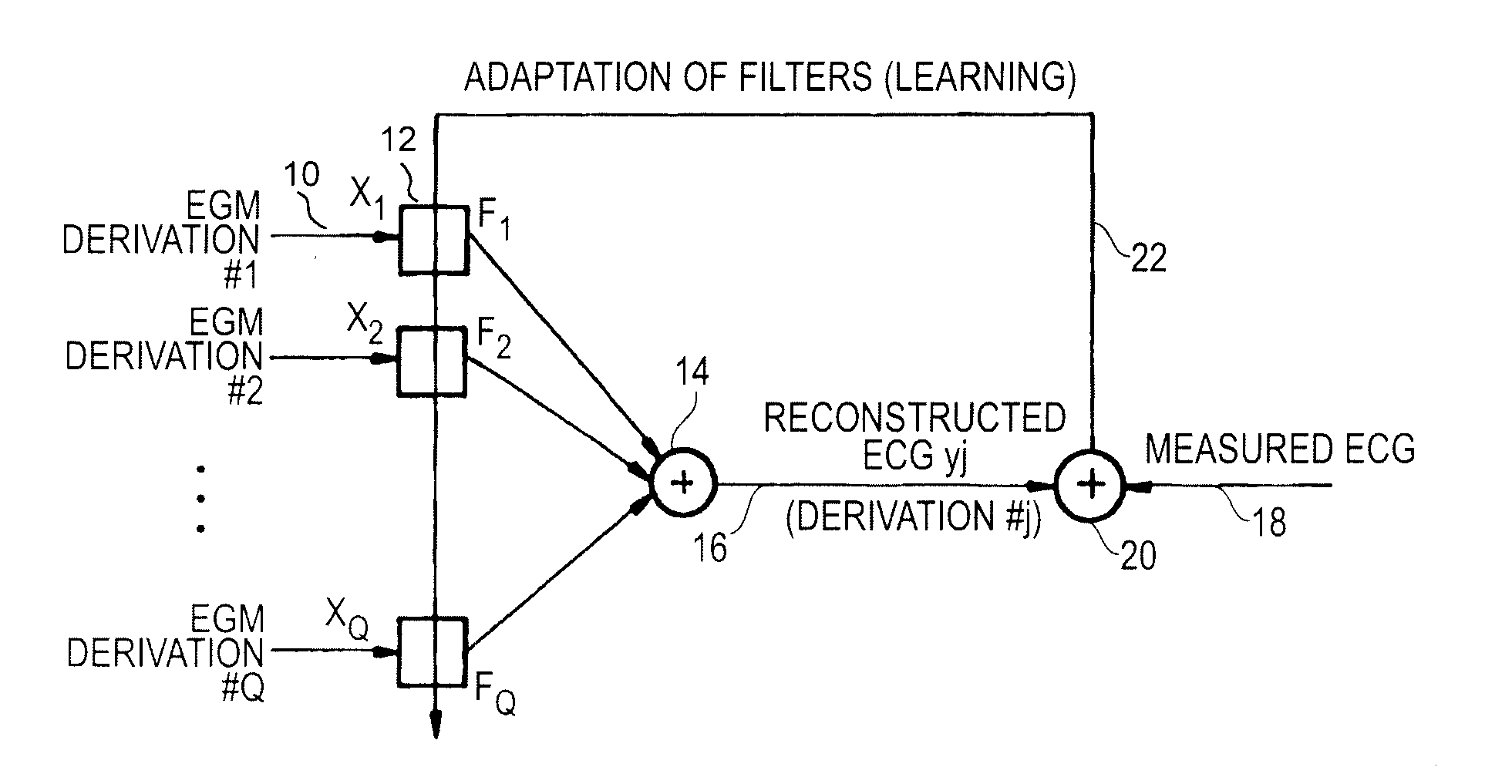
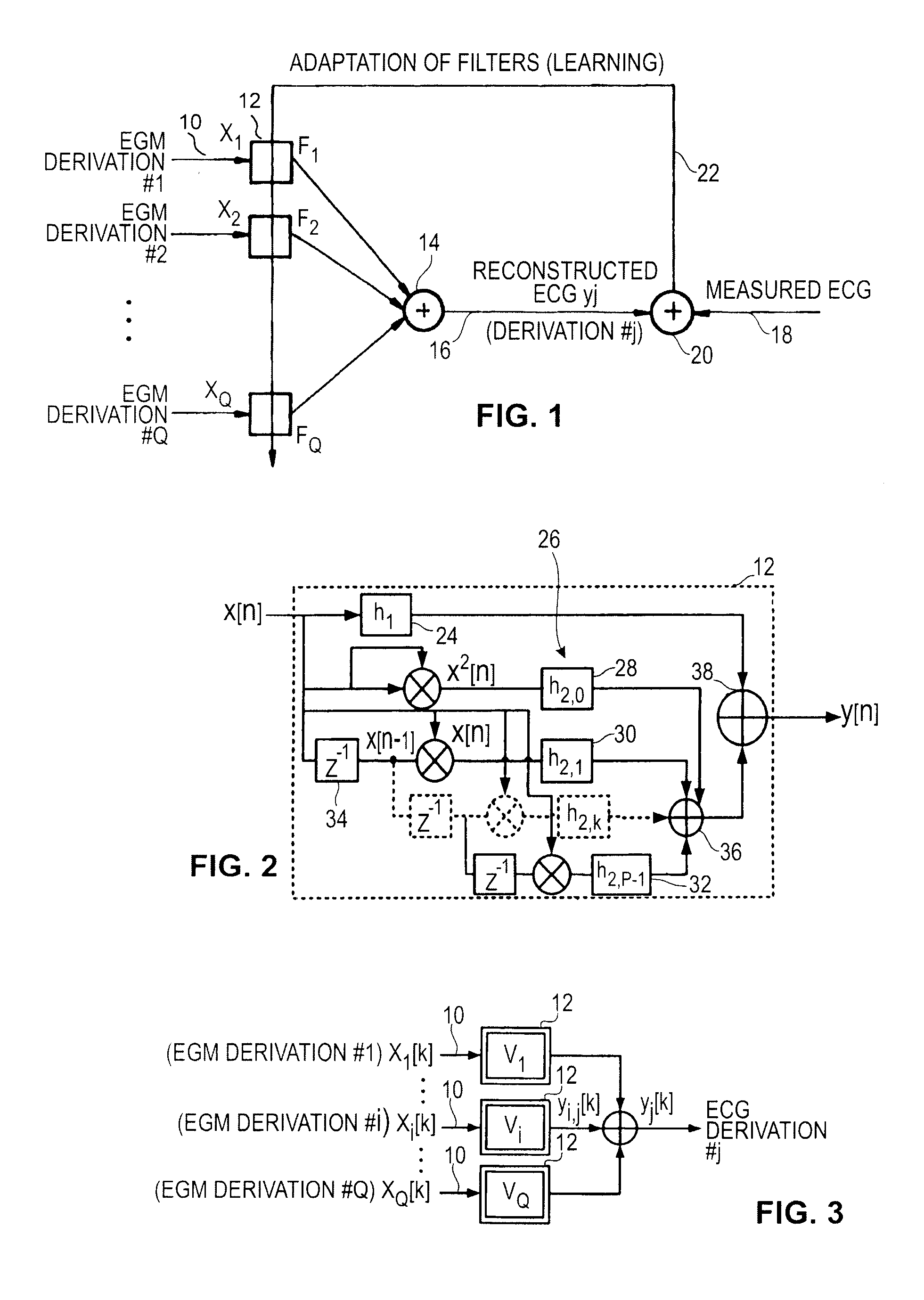
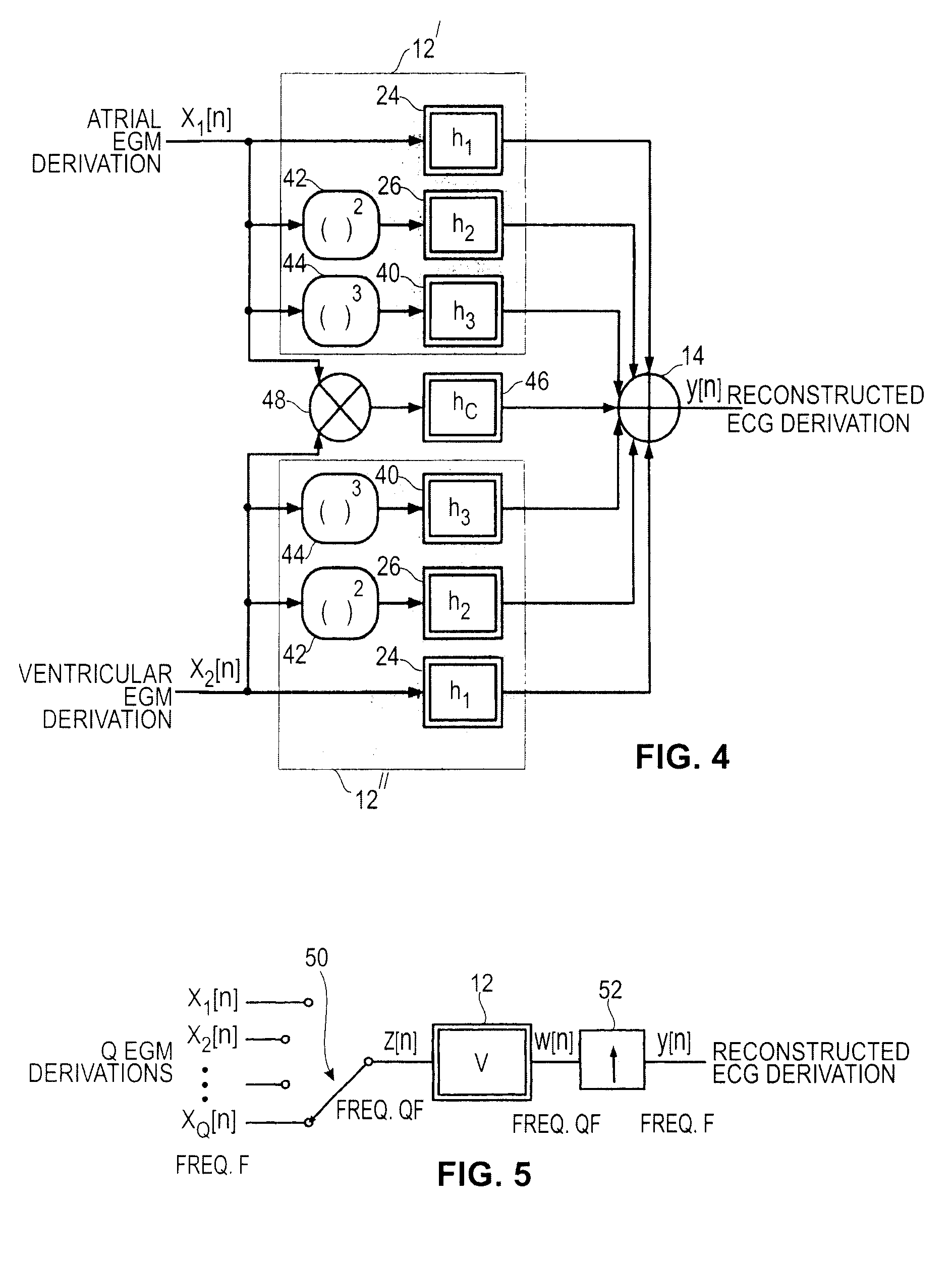
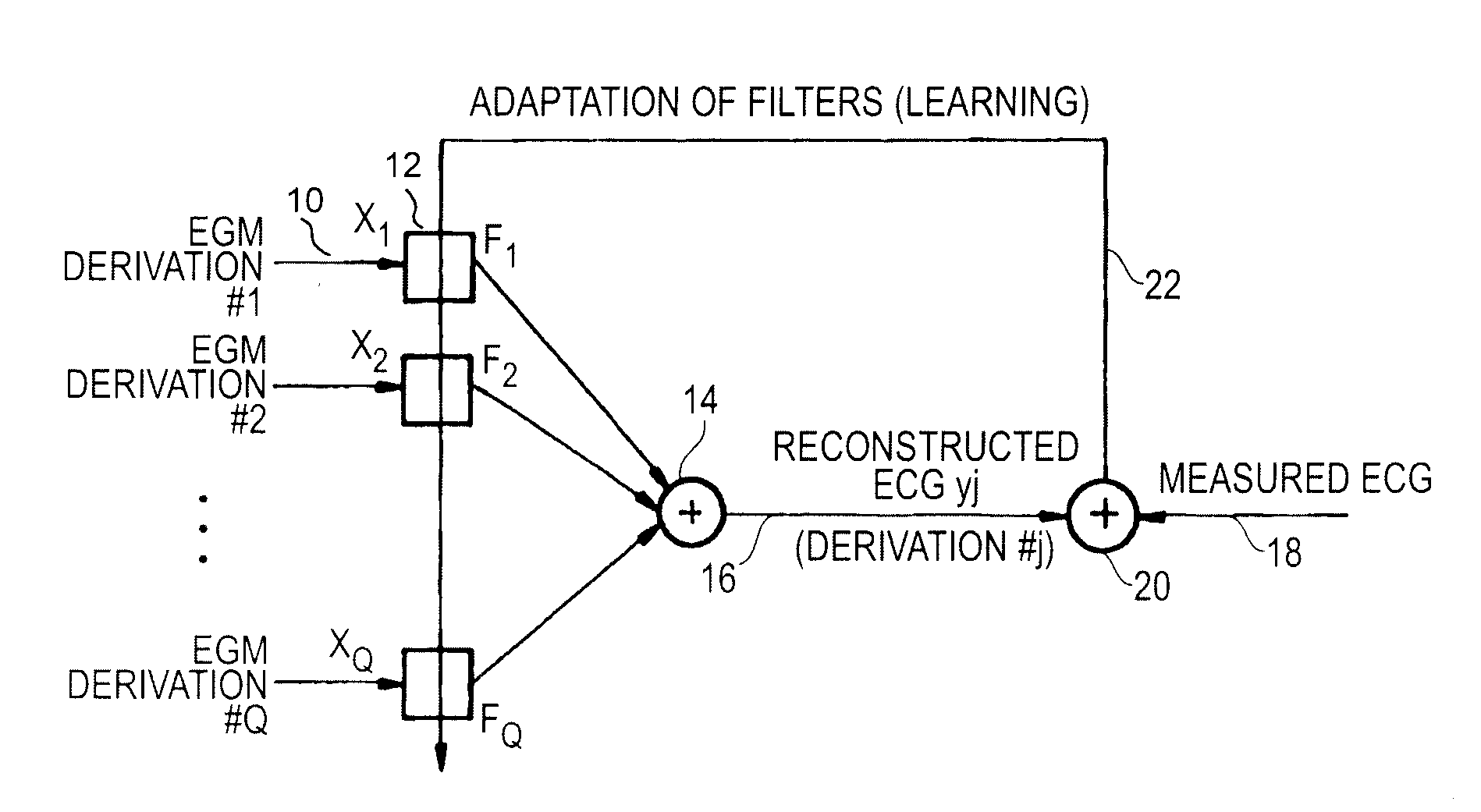
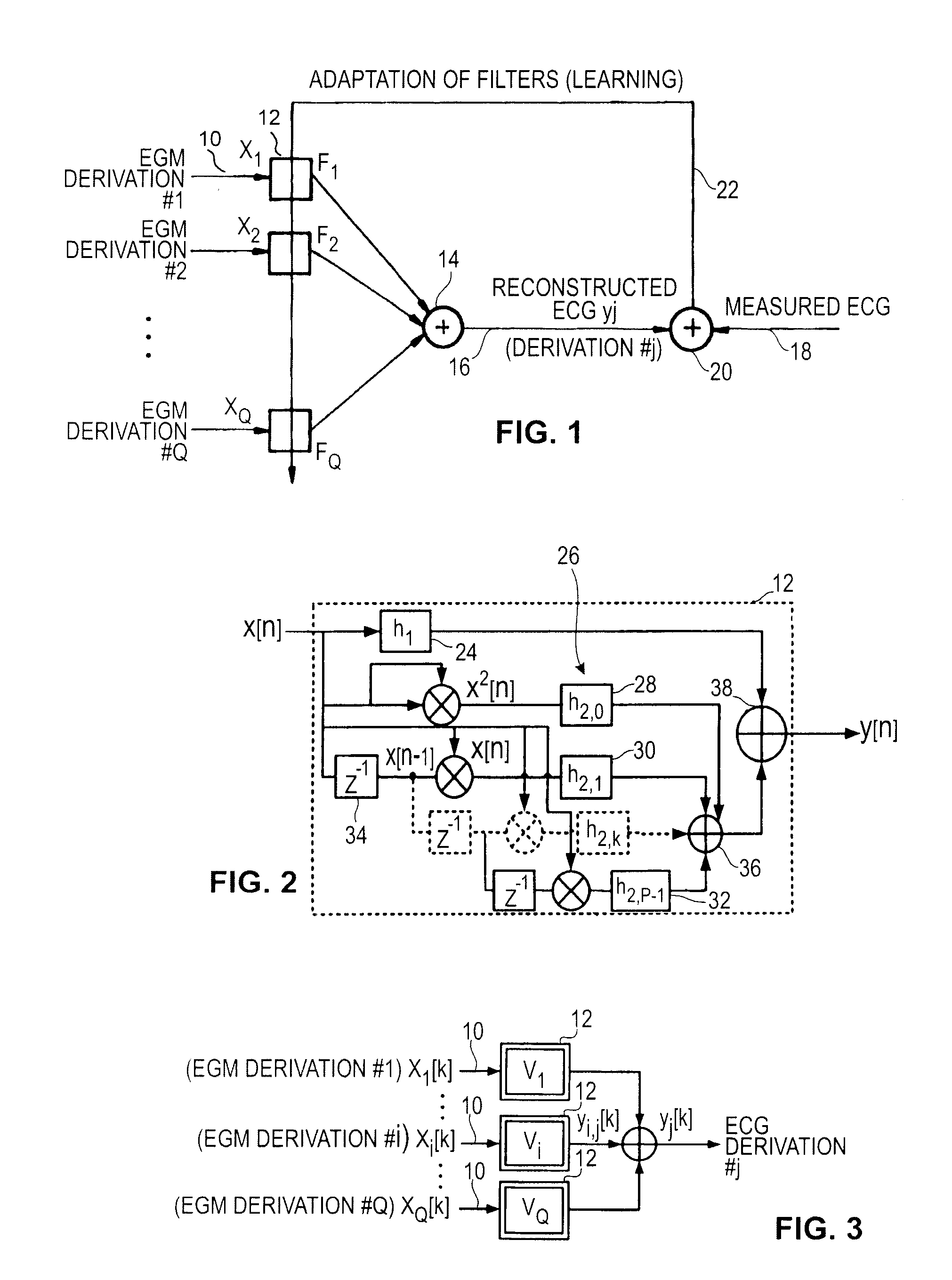
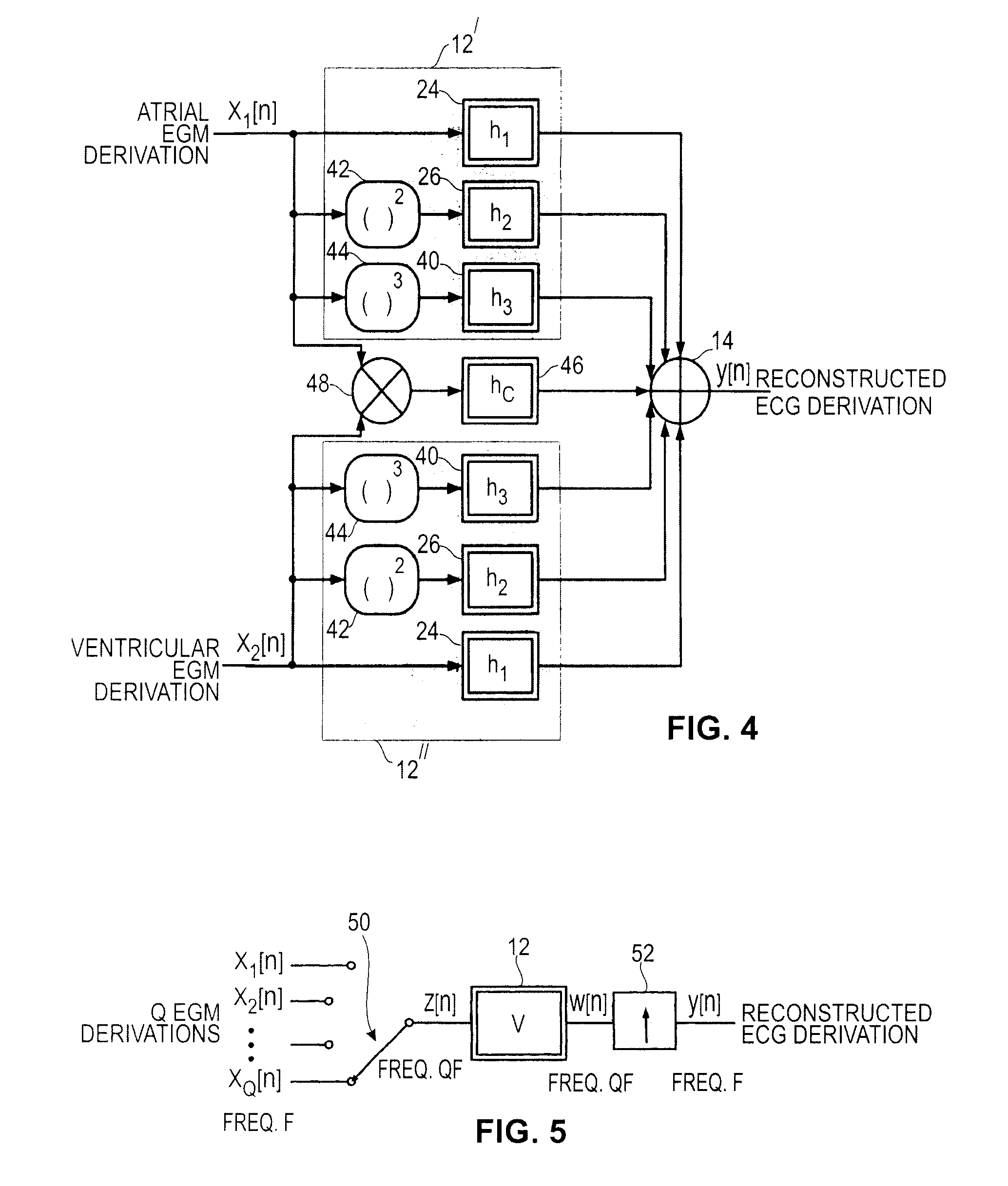
Non-linear filtering for the reconstruction of a surface Electrocardiogram from an endocardial electrogram
InactiveUS20100249623A1Quality improvementElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsEcg signalLinear filter
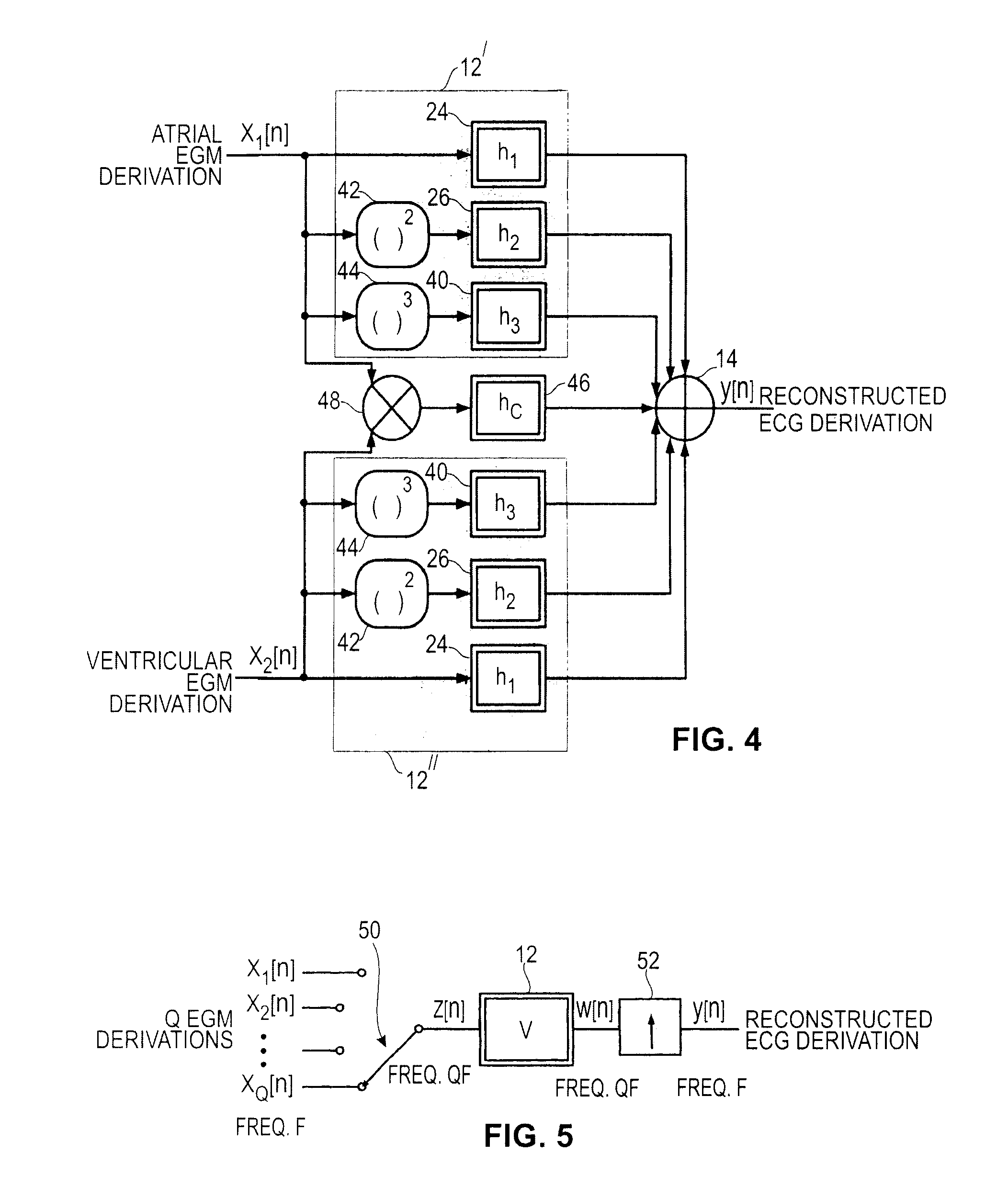
An active medical device using non-linear filtering for the reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram (ECG) from an endocardial electrogram (EGM) is disclosed. The device for the reconstruction of the surface ECG comprises: a plurality of inputs, receiving a corresponding plurality of EGM signals from endocardial or epicardial electrogram (x1[n], x2[n]) each collected on a respective EGM derivation of a plurality of EGM derivations, and at least one output delivering a reconstructed surface ECG electrocardiogram signal (y[n]), related to an ECG derivation, and a non-linear digital filter (12′, 12′, 14) with a transfer function that determines the reconstructed ECG signal based on said plurality of input EGM signals. The non-linear digital filter includes a Volterra filter type (12, 12′, 12″) whose transfer function includes a linear term (h1) and at least one quadratic (h2) and / or cubic (h3) term(s).
Owner:SORIN CRM
Direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method of virtual two-order array extension
InactiveCN107092007AEstimate performance impactImproved estimated resolution capabilitiesRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsComputation complexityWireless transmission
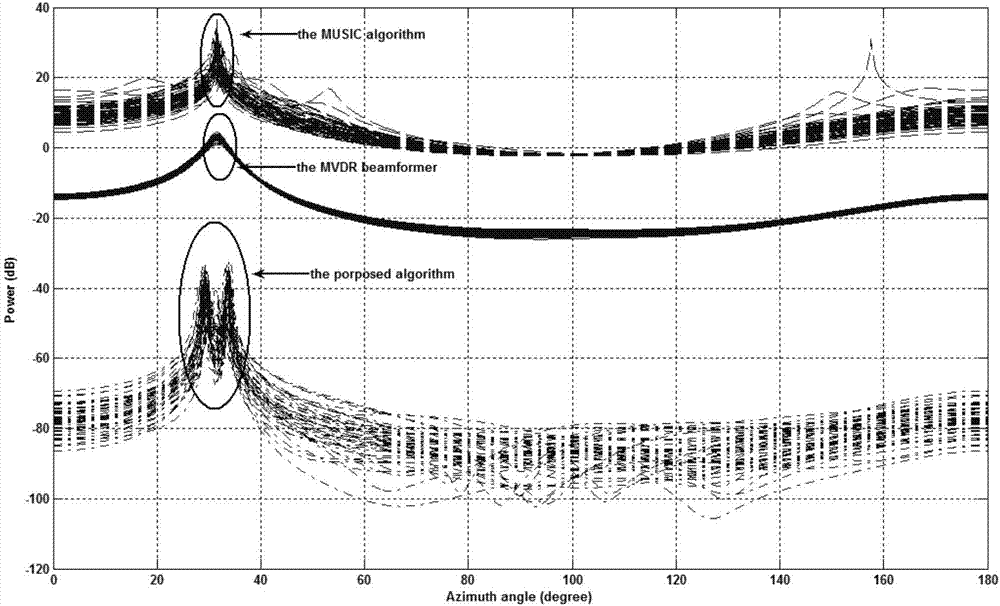
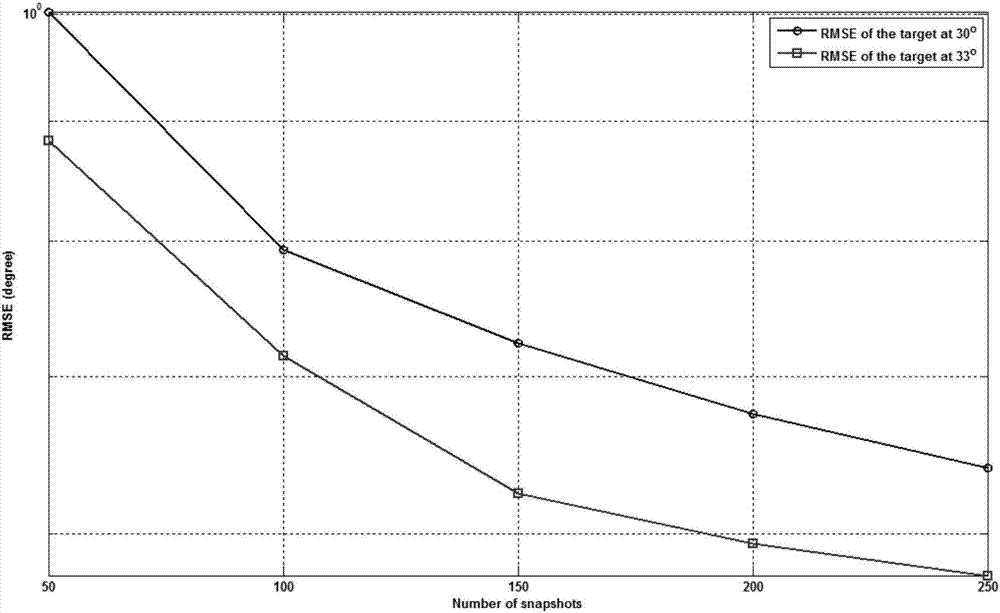
The invention discloses a direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method of virtual two-order array extension, belonging to the processing category of receiving an antenna array signal of a wireless transmission signal. In particular, the method is a method that a steering vector is constructed to be a virtual Volterra filter structure and the beamforming technology and the Lagrange multiplier method technology are combined to carry out direction of arrival (DOA) estimation. The steering vector is constructed to be the virtual Volterra filter structure and the beamforming technology and the Lagrange multiplier method technology are combined to carry out direction of arrival (DOA) estimation. According to the algorithm, the DOA estimation under the condition of an unknown number of signal sources can be realized and does not rely on subspace decomposition. The influence of the wrong estimation of the number of the signal sources on the performance of DOA estimation is avoided, the DOA estimation resolution ability is improved, and the computational complexity is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
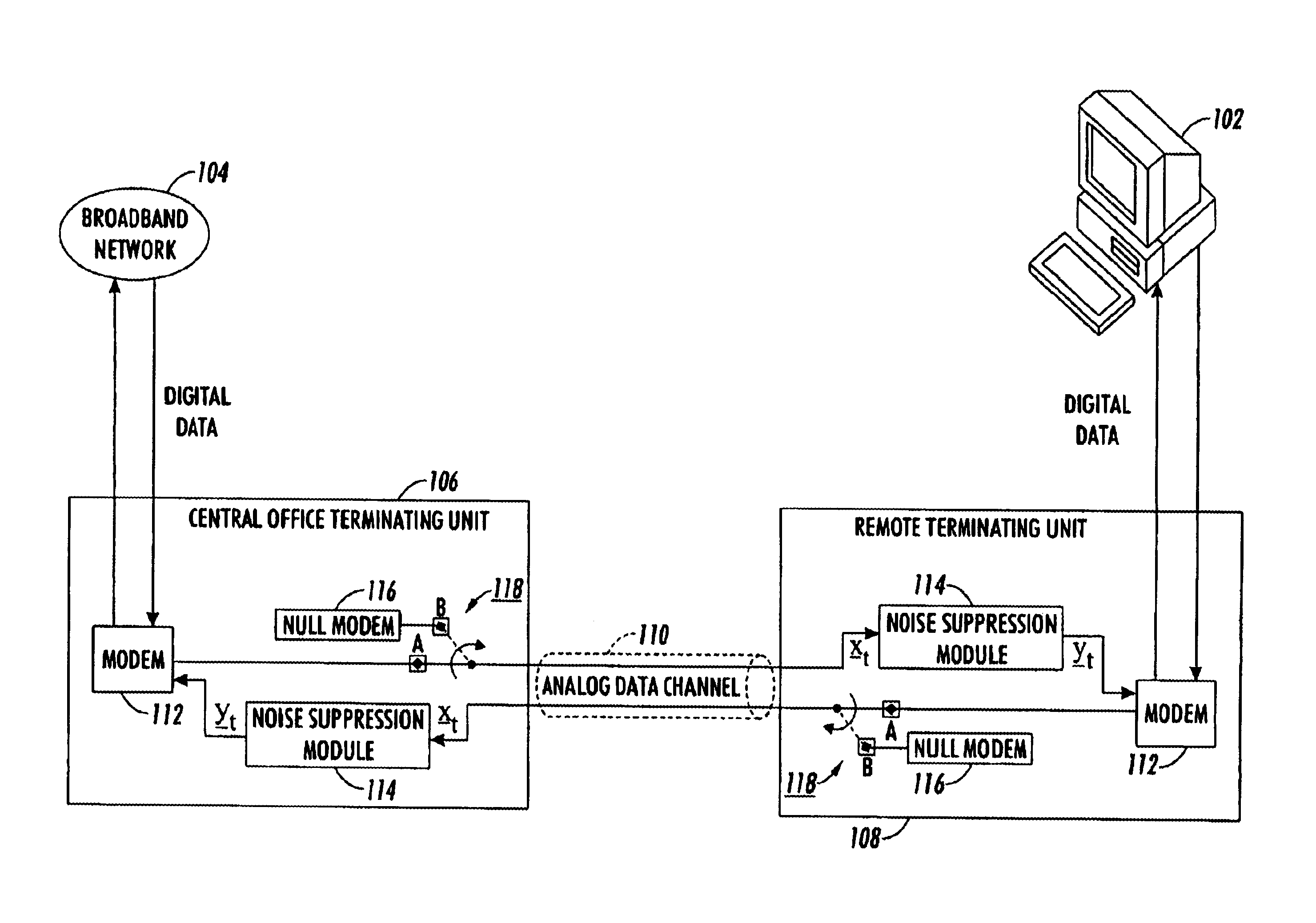
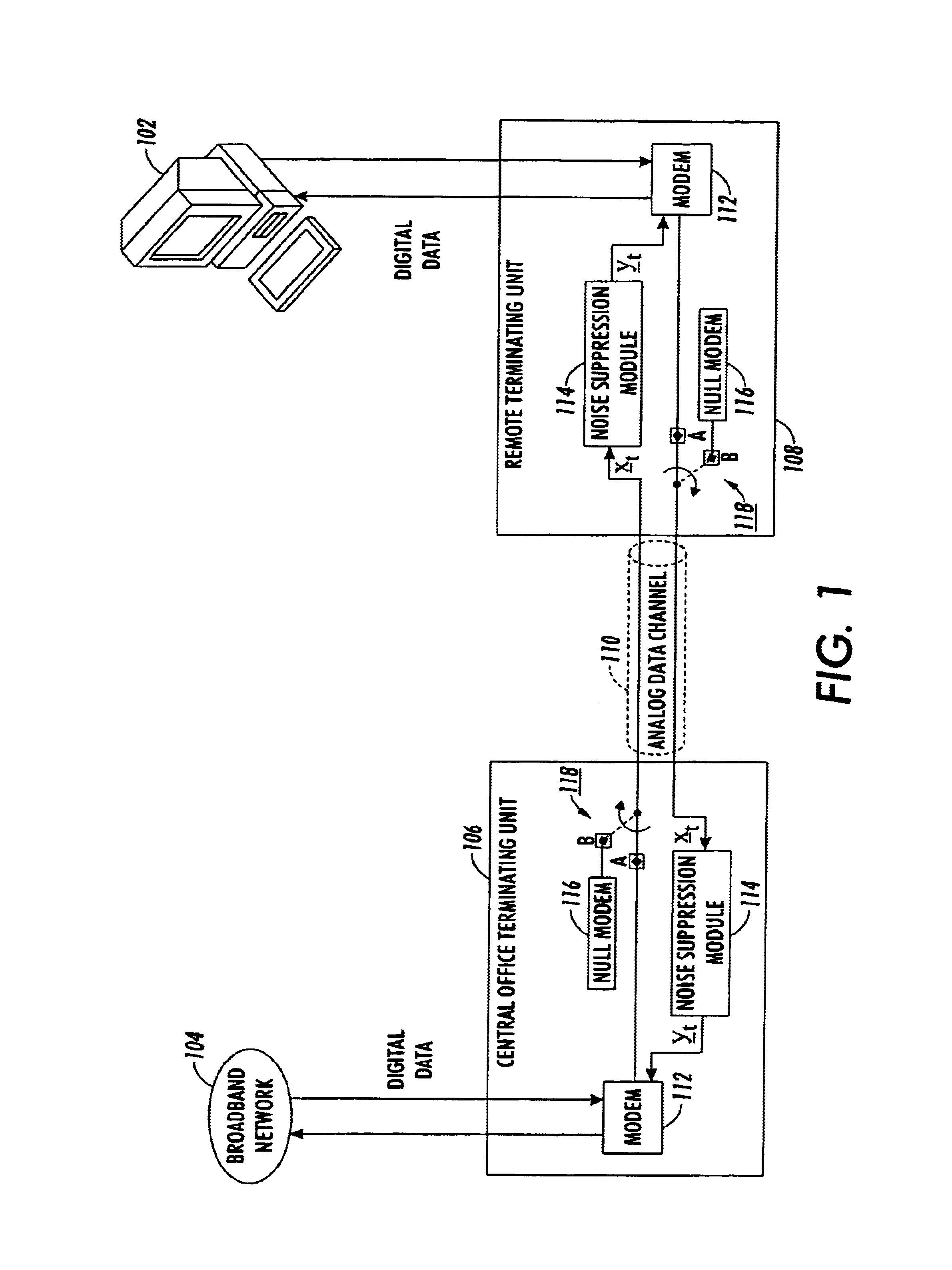
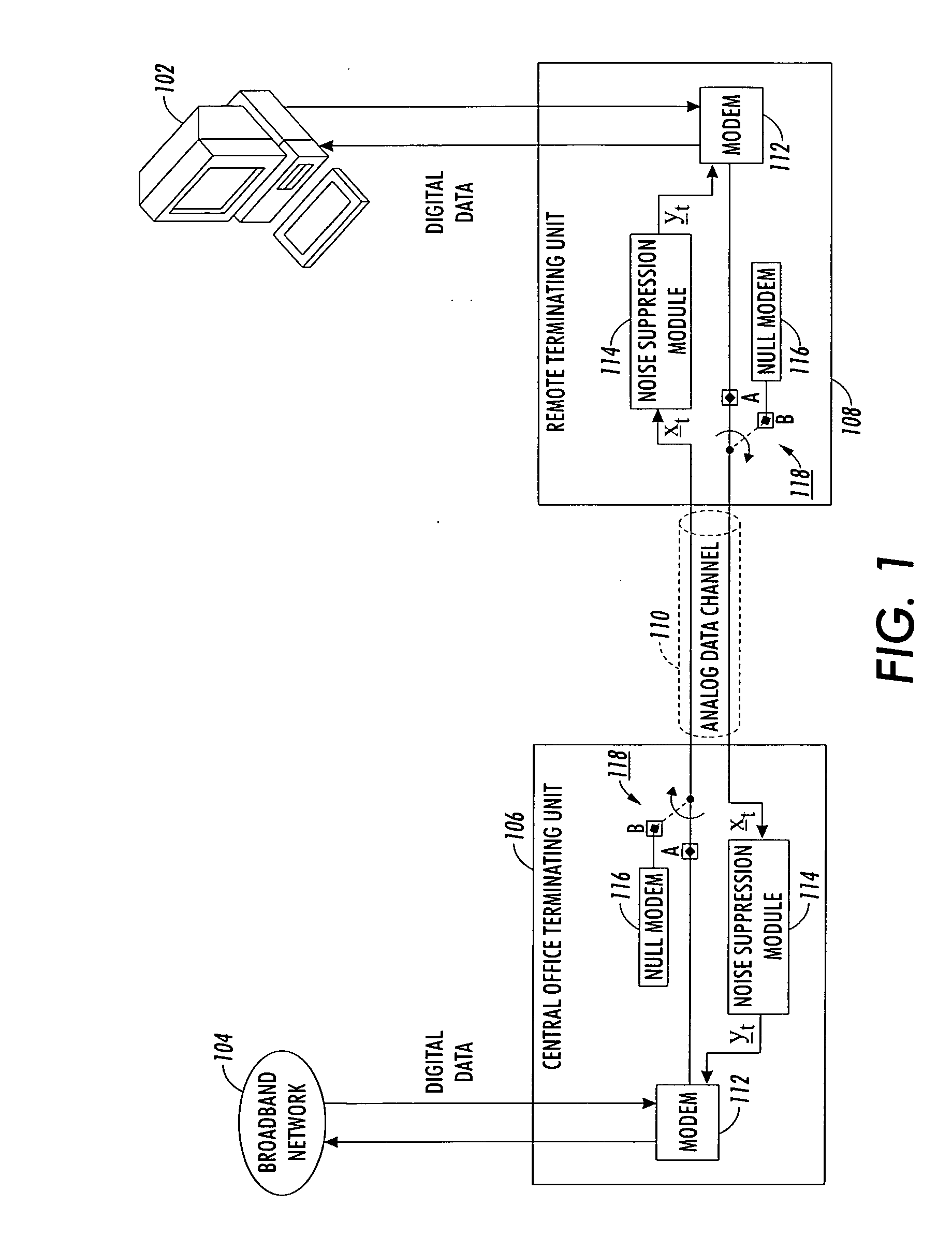
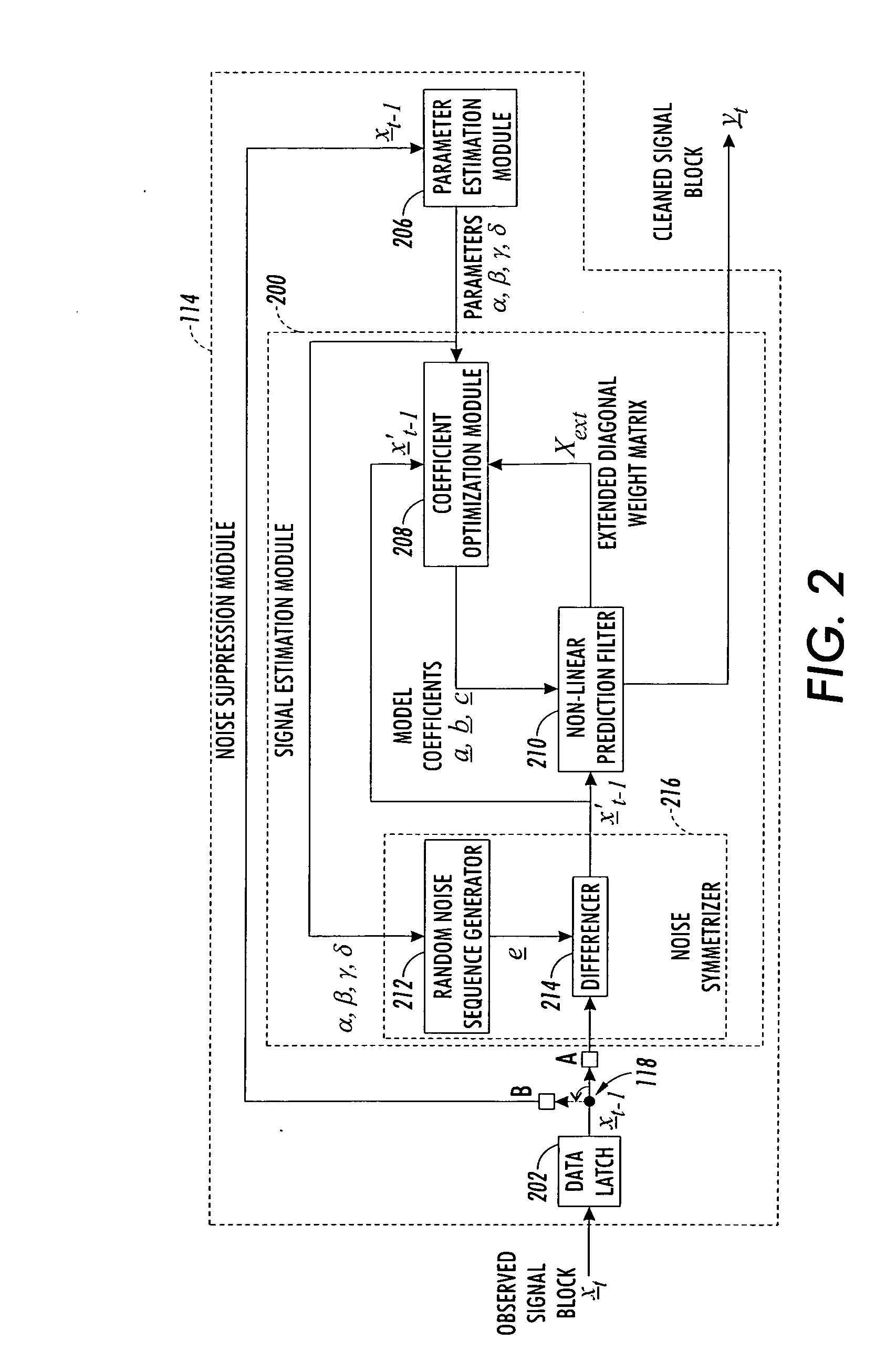
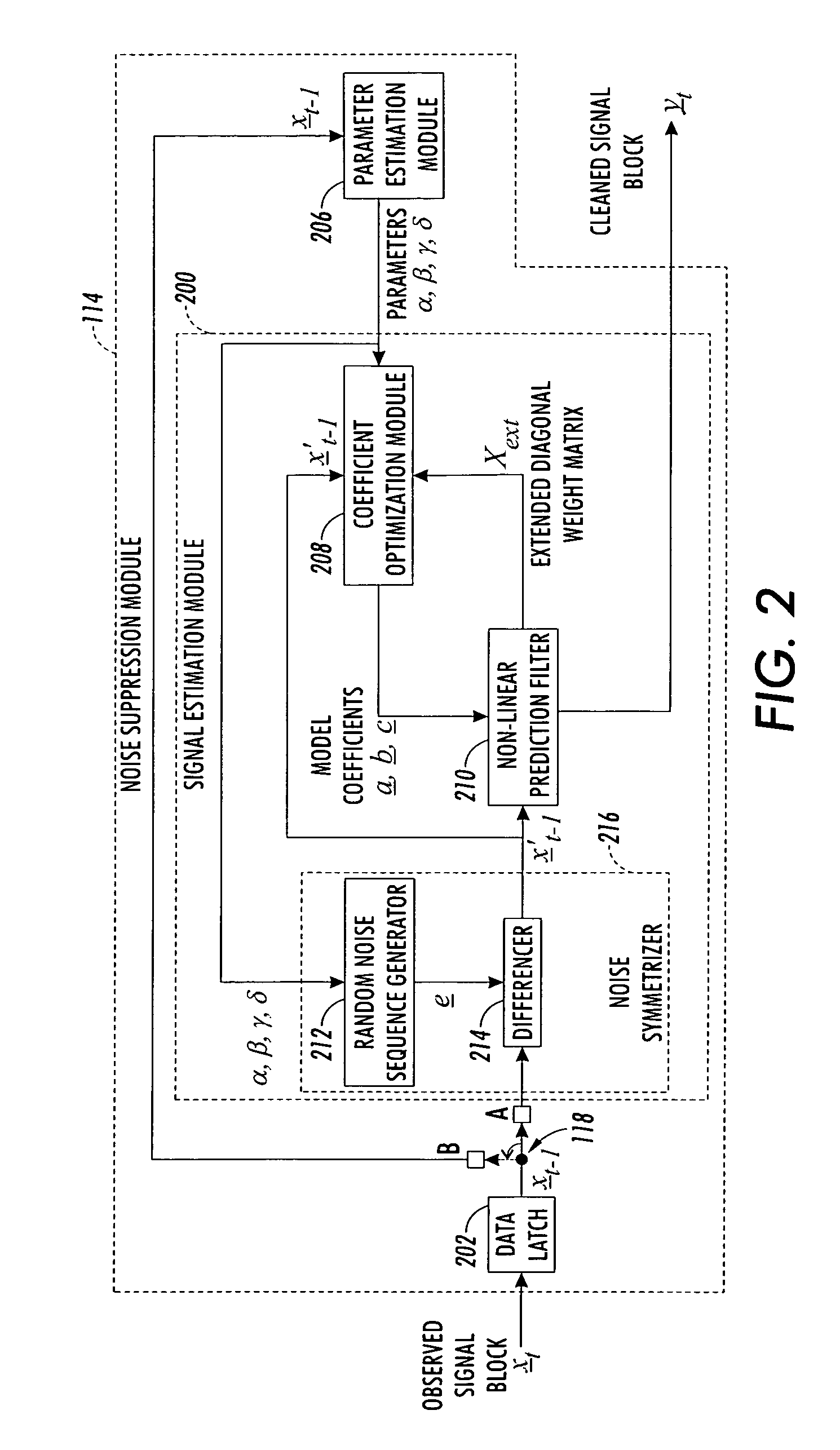
Method and apparatus for reducing impulse noise in a signal processing system
InactiveUS6944304B1Reducing impulse noise corruptingTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTransmission noise suppressionHandling systemVolterra filters
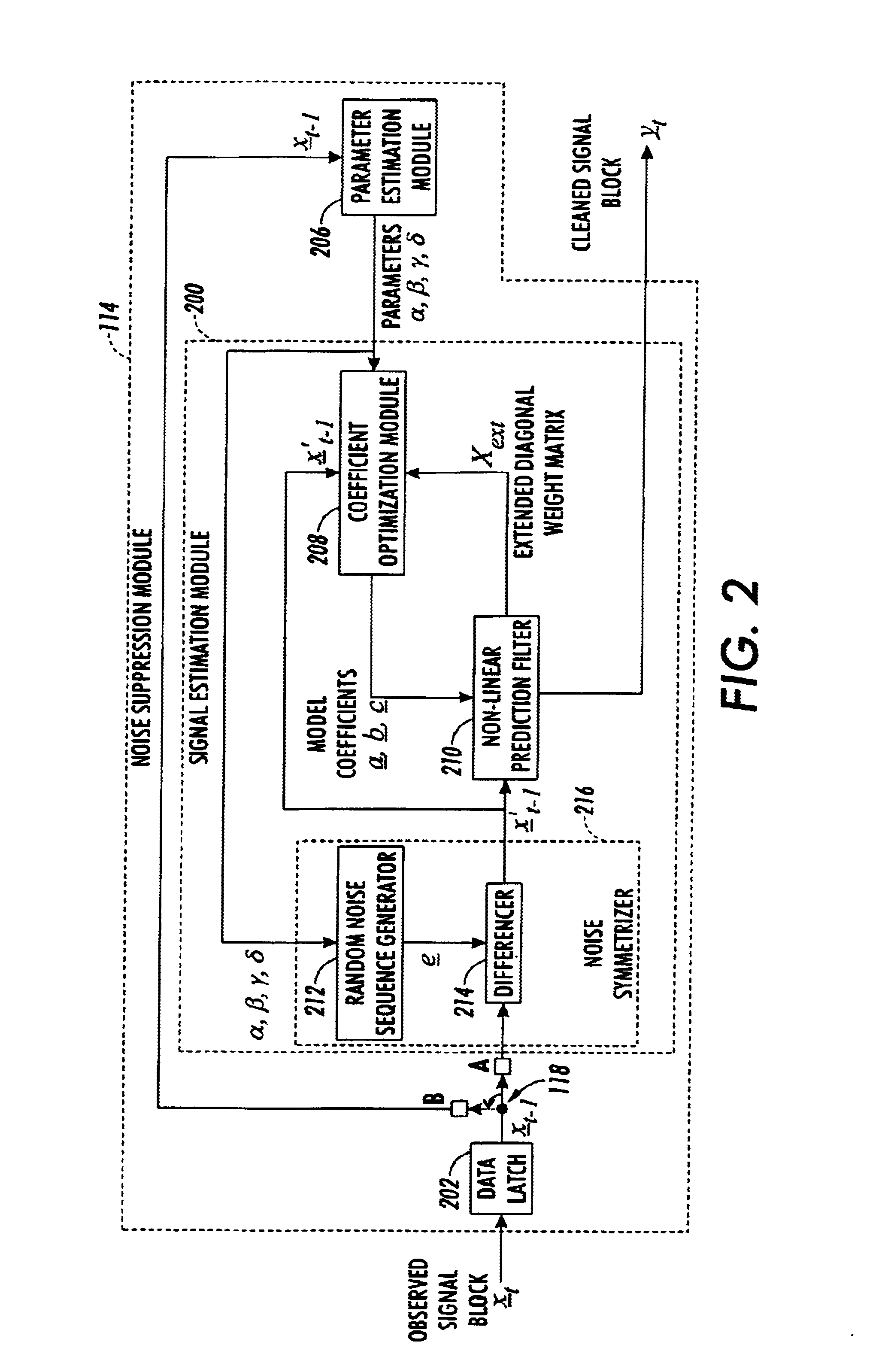
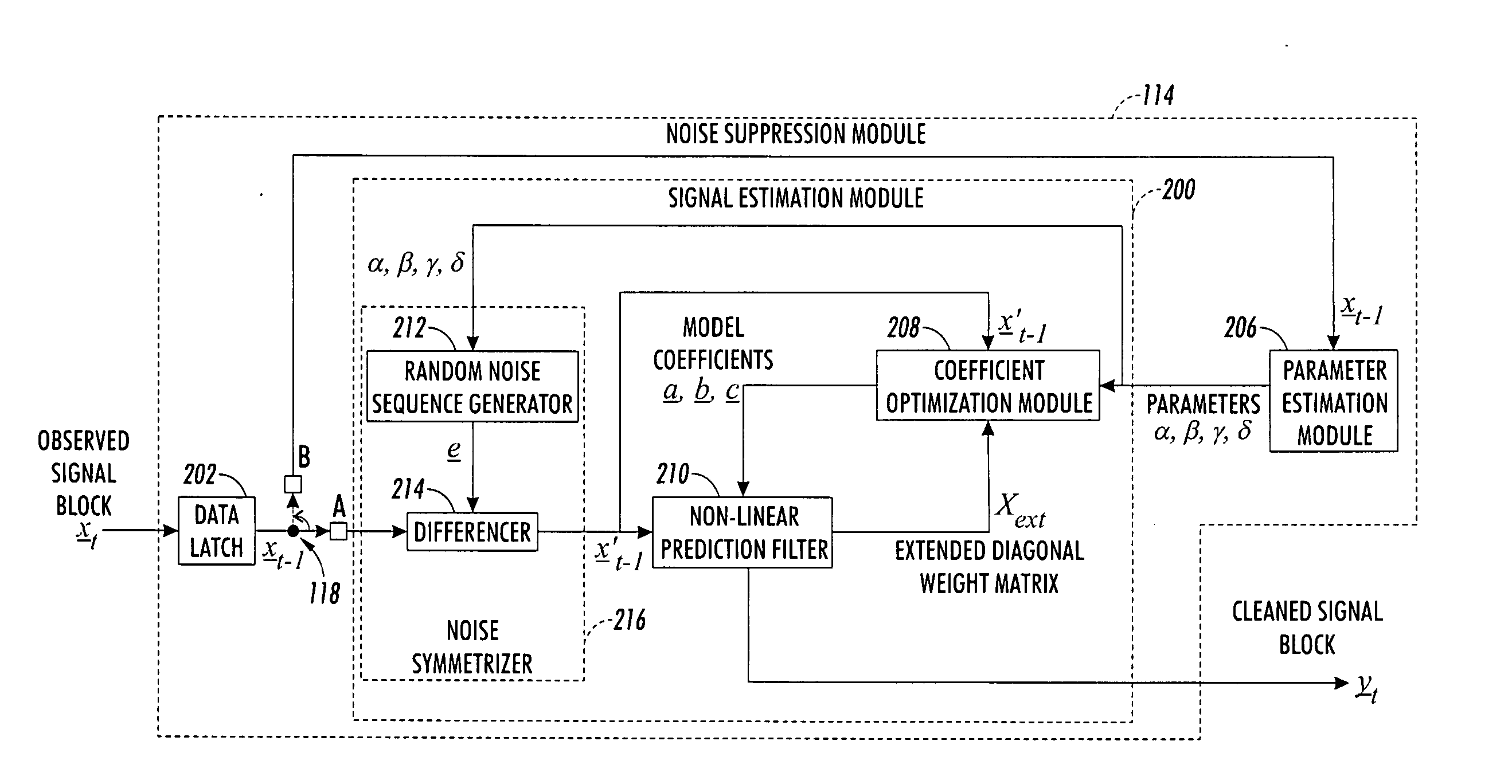
An observed signal that is corrupted with impulse noise is recorded in a signal processing system of an image processing system or a digital subscriber line (xDSL). The observed signal that is recorded by the signal processing system includes a noise component and data component. The signal processing system estimates the parameters of an alpha-stable distribution using a modified iteratively reweighted least squares (IRLS) technique. The estimated parameters define a probability density function that is used to model the noise component of the observed signal. Once the parameters of the alpha-stable distribution are estimated, the signal processing system uses them to estimate model coefficients of a non-linear prediction filter such as a Volterra filter. Using the model coefficients, the non-linear prediction filter estimates the data component of the observed signal.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and apparatus for reducing impulse noise in a signal processing system
InactiveUS20050058302A1Reducing impulse noise corruptingTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTransmission noise suppressionHandling systemIteratively reweighted least squares
An observed signal that is corrupted with impulse noise is recorded in a signal processing system of an image processing system or a digital subscriber line (xDSL). The observed signal that is recorded by the signal processing system includes a noise component and data component. The signal processing system estimates the parameters of an alpha-stable distribution using a modified iteratively reweighted least squares (IRLS) technique. The estimated parameters define a probability density function that is used to model the noise component of the observed signal. Once the parameters of the alpha-stable distribution are estimated, the signal processing system uses them to estimate model coefficients of a non-linear prediction filter such as a Volterra filter. Using the model coefficients, the non-linear prediction filter estimates the data component of the observed signal.
Owner:XEROX CORP
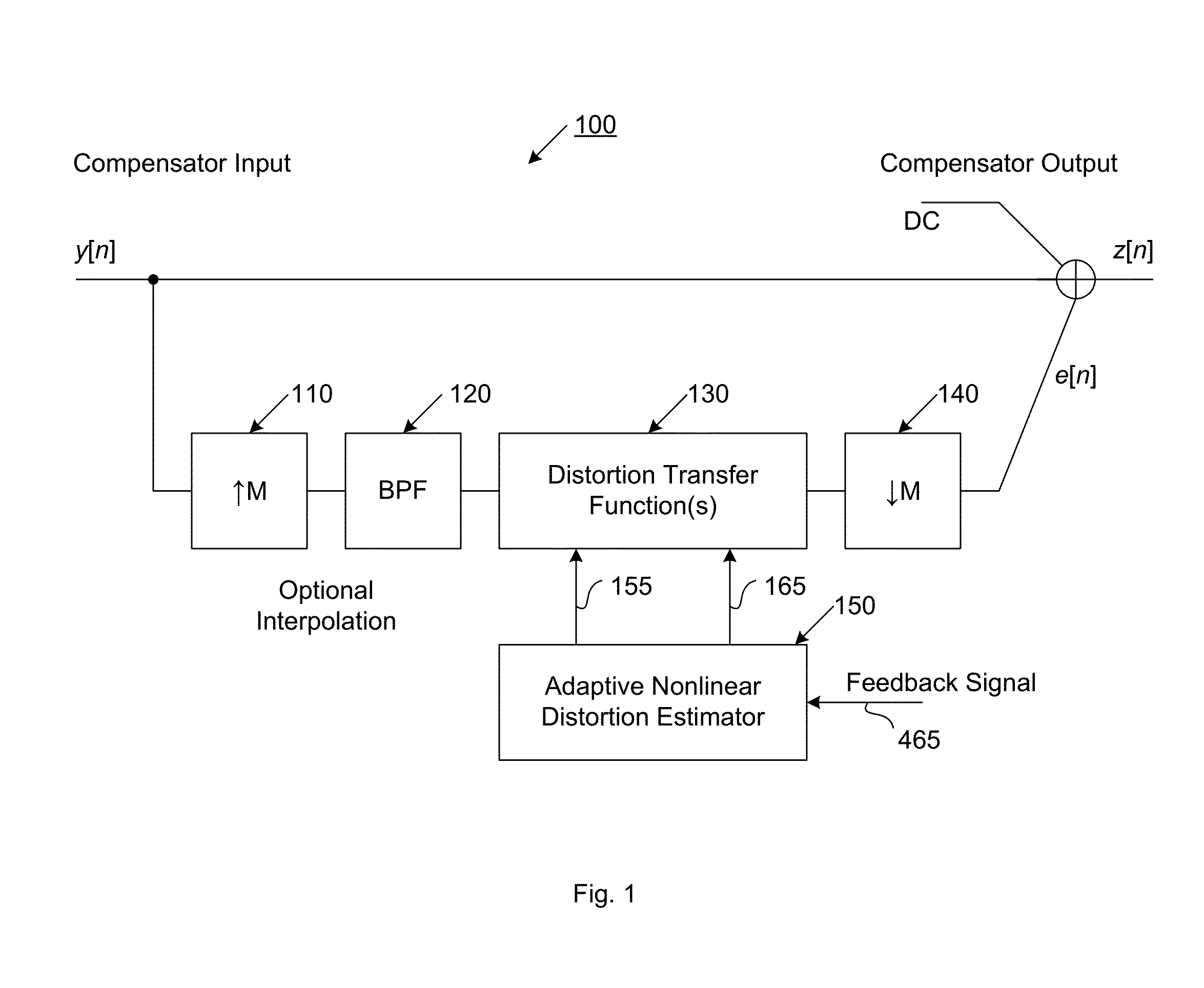
Compensator for removing nonlinear distortion
ActiveUS9705477B2Easy to processReduce complexityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionChannel dividing arrangementsNonlinear distortionComputation complexity
The present invention is a computationally-efficient compensator for removing nonlinear distortion. The compensator operates in a digital post-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as analog-to-digital converters and RF receiver electronics. The compensator also operates in a digital pre-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as digital-to-analog converters, RF power amplifiers, and RF transmitter electronics. The compensator effectively removes nonlinear distortion in these systems in a computationally efficient hardware or software implementation by using one or more factored multi-rate Volterra filters. Volterra filters are efficiently factored into parallel FIR filters and only the filters with energy above a prescribed threshold are actually implemented, which significantly reduces the complexity while still providing accurate results. For extremely wideband applications, the multi-rate Volterra filters are implemented in a demultiplexed polyphase configuration which performs the filtering in parallel at a significantly reduced data rate. The compensator is calibrated with an algorithm that iteratively subtracts an error signal to converge to an effective compensation signal. The algorithm is repeated for a multiplicity of calibration signals, and the results are used with harmonic probing to accurately estimate the Volterra filter kernels. The compensator improves linearization processing performance while significantly reducing the computational complexity compared to a traditional nonlinear compensator.
Owner:LINEARITY LLC
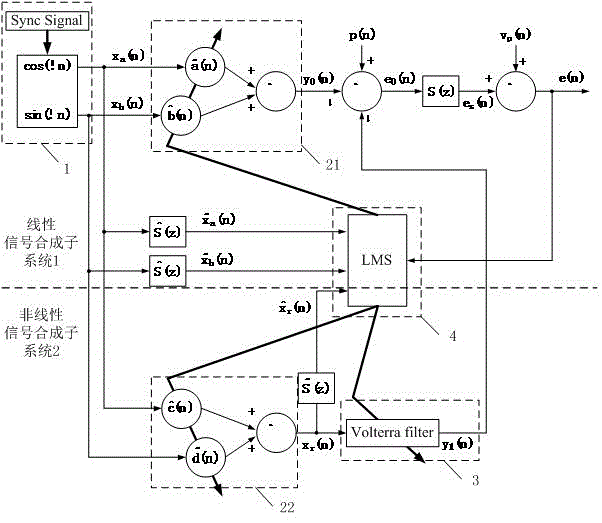
Nonlinear narrowband active noise control method based on Volterra filter
InactiveCN104575512AReduce narrowband noiseEasy to implementSpeech analysisNoise controlNonlinear filter
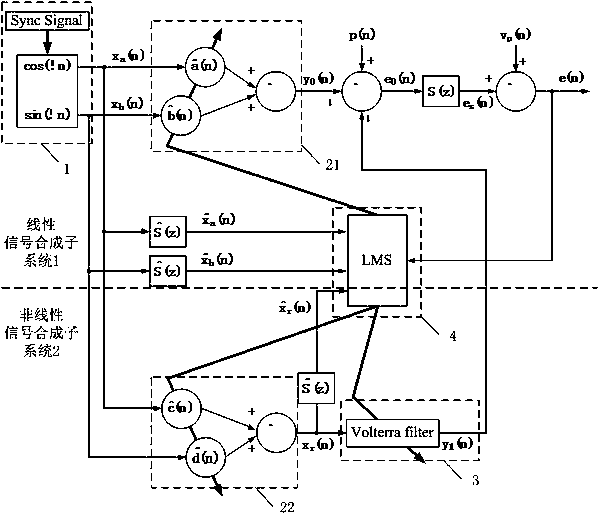
The invention provides a nonlinear narrowband active noise control method based on a Volterra filter and aimed at a situation that higher harmonic noise is generated after a narrowband noise source is distorted nonlinearly. A linear signal synthesis subsystem (1), a nonlinear signal synthesis subsystem (2), a reference signal generation module and a least mean square algorithm module are used in the method; a reference signal in the method is generated by a synchronous signal generator based on a source noise frequency obtained by a non-acoustic sensor; one part of a secondary source is synthesized through a linear combiner, the other part of the secondary source is synthesized through another linear combiner and the nonlinear Volterra filter, and when primary source noise is distorted nonlinearly, a fundamental component and a higher harmonic component are independently inhibited by a linear filter and the nonlinear Volterra filter respectively. According to the nonlinear narrowband active noise control method, the nonlinearly distorted narrowband noise can be effectively inhibited, and the influence of nonlinearity on system performance can be easily analyzed due to an independent working structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
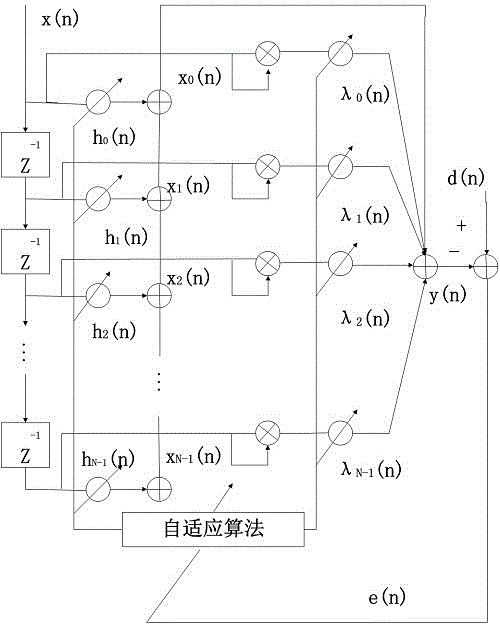
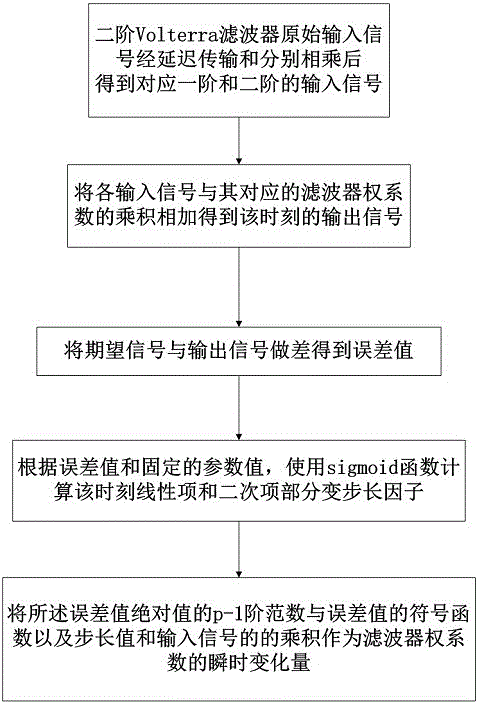
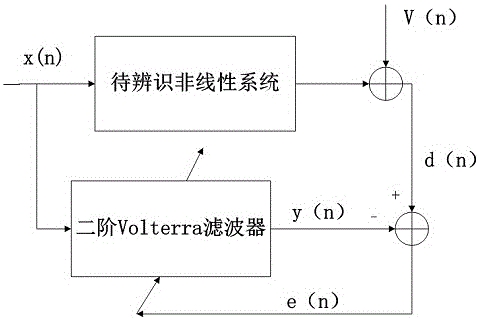
Variable step size VLMP filtering algorithm based on sigmoid function and application thereof
InactiveCN106411290ASmall steady state errorFast convergenceDigital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsDigital signal processingNonlinear filter
The invention belongs to the technical field of digital signal processing, and specifically relates to a variable step size VLMP (adaptive Volterra least mean P norm) algorithm and an application thereof in noise reduction of engines. The variable step size VLMP algorithm provided by the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, updating a step size factor by using a sigmoid function, and then performing iterative update on a first-order weight coefficient and a second-order weight coefficient, therefore a relatively small steady state error can be acquired; and constructing a nonlinear filter by employing the variable step size VLMP algorithm, using engine noise as a noise signal, identifying a kernel of a Volterra filter, and performing noise reduction processing on the engine noise while identifying and optimizing the kernel so as to achieve the objectives of filtering Gaussian noise and pulse noise contained in the engine noise and to maximally reduce the engine noise. The variable step size VLMP algorithm has the advantages of high instantaneity and good tracking performance.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
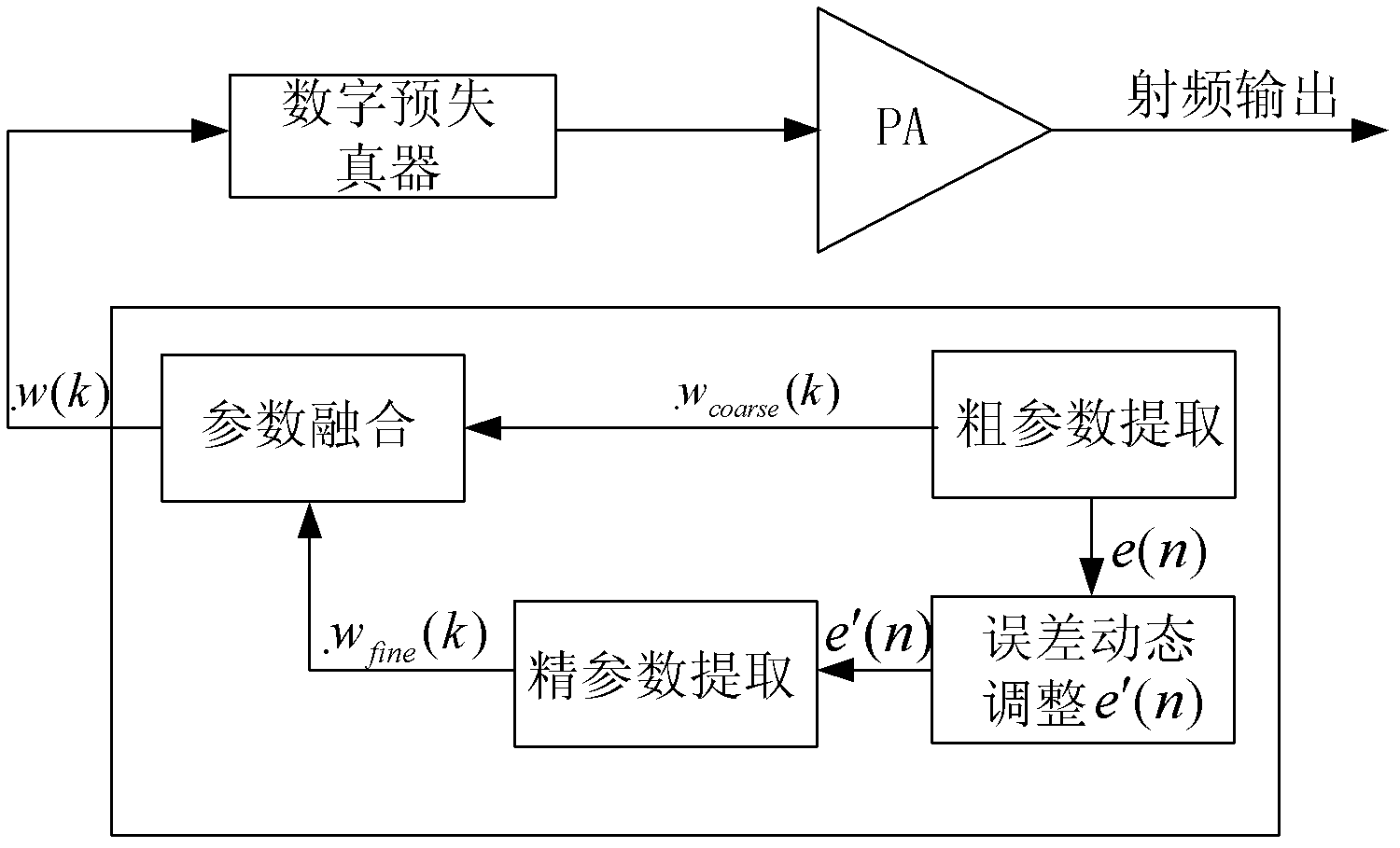
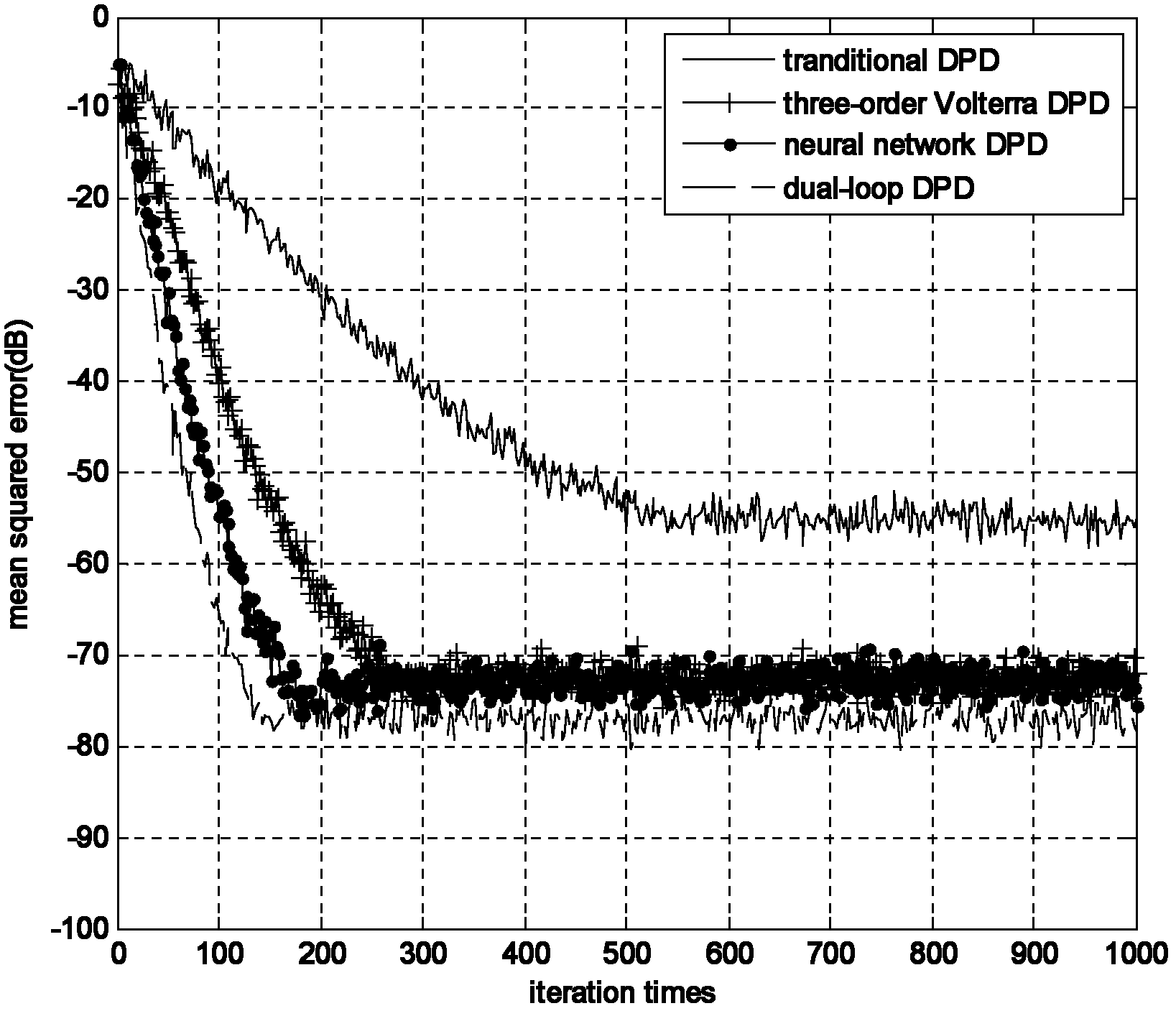
Volterra-filtering-based power amplifier pre-distortion method for double-loop feedback model
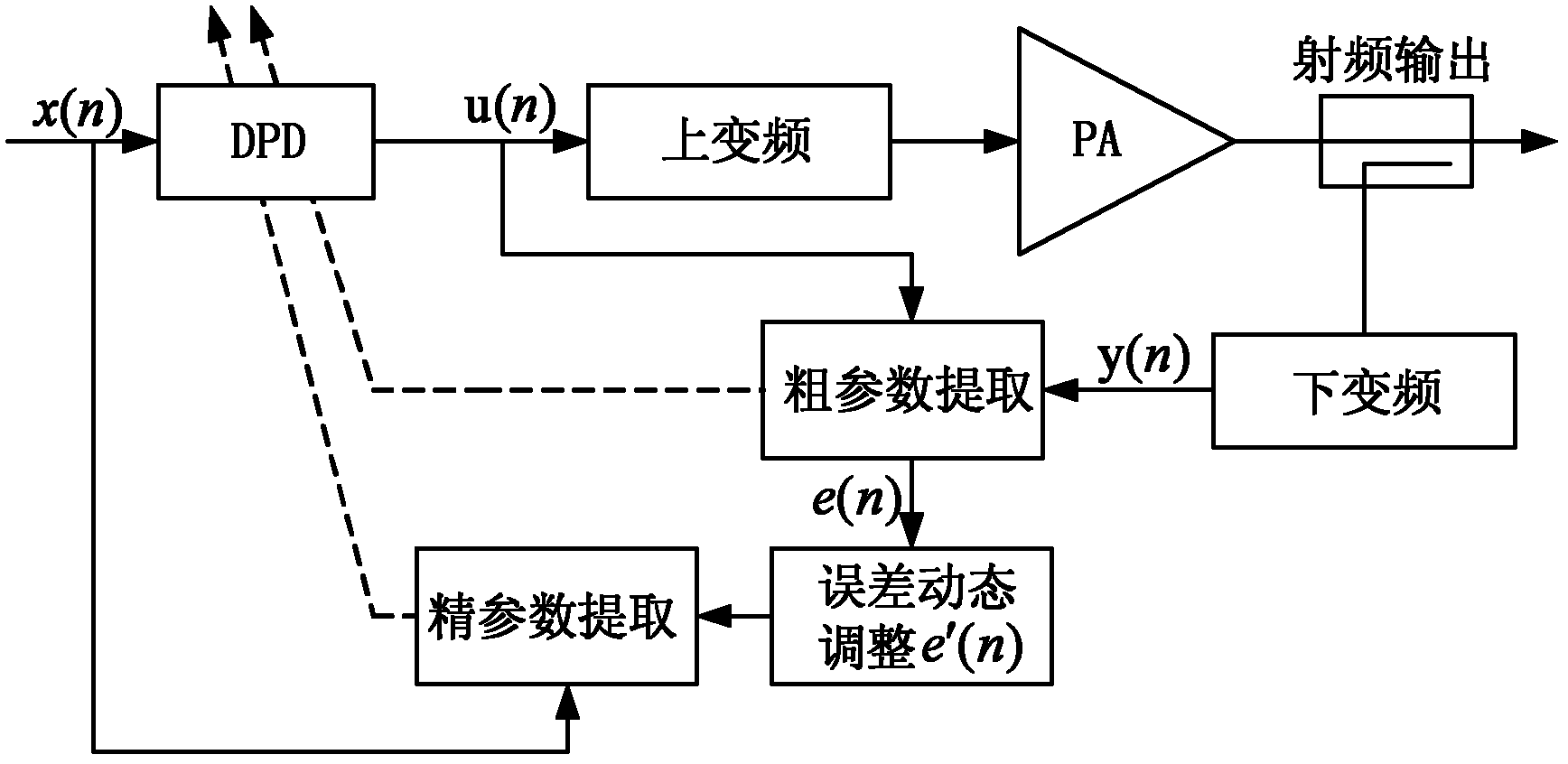
InactiveCN102624338ASmall amount of calculationFast convergenceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAdaptive networkMemory effectAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a Volterra-filtering-based power amplifier pre-distortion method for a double-loop feedback model. The method mainly comprises the three parts of pre-distortion crude parameter vector extraction, error regulation and pre-distorter fine parameter vector extraction, and specifically comprises the following steps of: performing down-conversion output and pre-distorter output by adopting a first-order dynamic truncation Volterra filtering structure to obtain a pre-distortion crude parameter vector in the pre-distortion crude parameter vector extraction; dynamically regulating an error vector caused by the pre-distortion crude parameter vector according to an average criterion; combining a regulated error vector which serves as an expected signal and a base-band input signal, and obtaining a pre-distorter fine parameter vector by adopting the first-order dynamic truncation Volterra filtering structure; and correcting the crude parameter vector by utilizing the fine parameter vector to obtain a final pre-distorter parameter vector. The problems of slow adaptive convergence, great pre-distortion parameter calculation amount, complexity in implementation, incapability of effectively compensating the complex memory effect of a power amplifier in high-speed communication, and the like of the conventional pre-distortion method are solved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Multinomial adaptive active noise cancellation method based on Laguerre structure
InactiveCN102724152ALess input lengthReduce computational complexityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksNonlinear filterComputation complexity
The invention discloses a multinomial adaptive active noise cancellation method based on a Laguerre structure. The method comprises: a Laguerre time delay unit having the characteristics of an IIR (infinite impulse response) filter is used for replacing a time delay unit Z-1 in a Volterra filter, output by virtue of a laguerre time delay node is taken as input of a non-linear filter based on bounded constrain product coupling Volterra approximate structure, characteristic convergence conditions can be effectively improved, the system stability is guaranteed, the computation complexity is low, hardware is easy to realize; and an LMS (least mean square) adaptive algorithm with input signal and instant error normalized is adopted for adjusting filtering parameters, the input length of a filter can be further reduced while a non-linear adaptive filter is guaranteed to be stable, and the convergence rate is improved; especially under the condition that strong non-linear distortion exists, good anti-noise capacity is shown, so that the method is beneficial to popularization and application of an adaptive multinomial filter.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
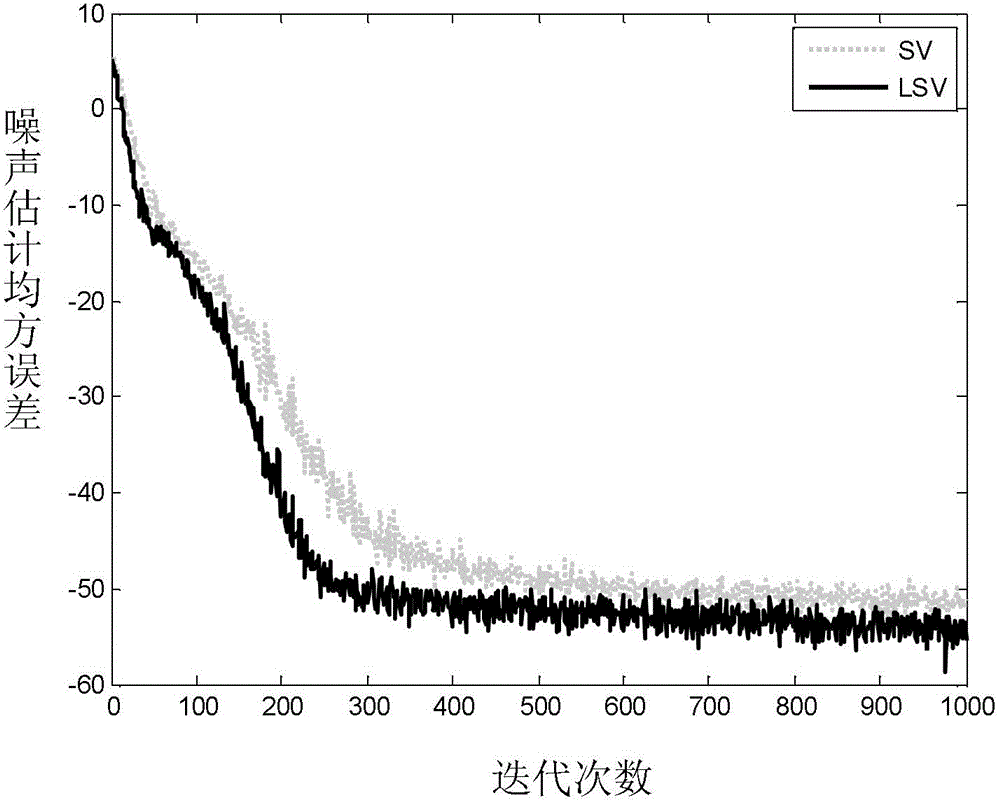
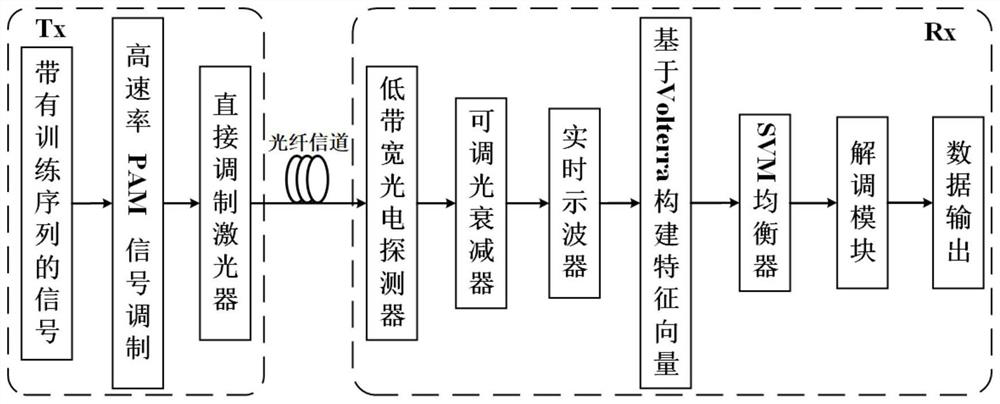
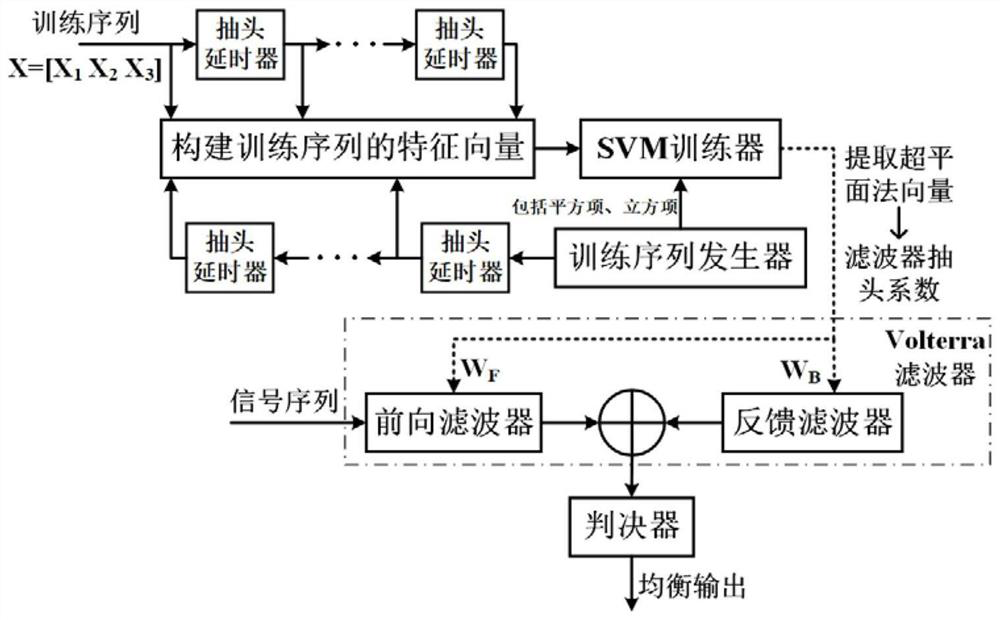
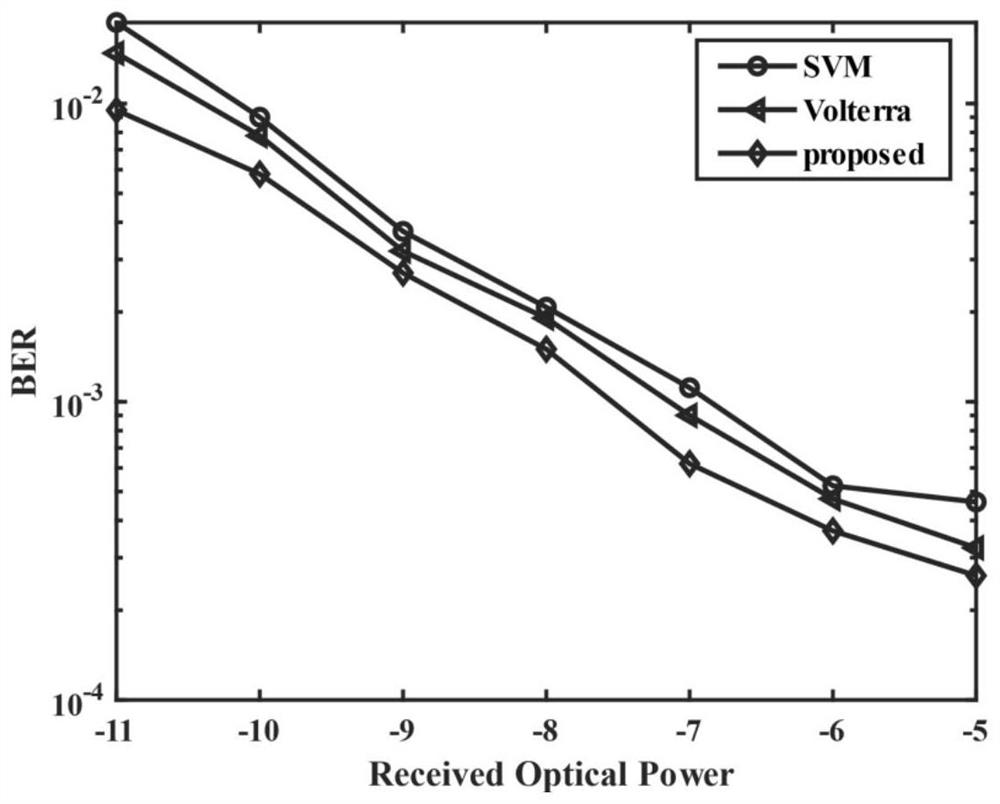
An SVM training-based weight coefficient migration improved Volterra filter equalization method
PendingCN112598072AAvoid time costReduce computational complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionDistortion/dispersion eliminationComputation complexityEqualization
The invention relates to an SVM training-based weight coefficient migration improved Volterra filter equalization method, which comprises the following steps: S1, demodulating an optical signal transmitted by an optical fiber, and extracting a training sequence from a received signal of a receiving end; s2, constructing a feature vector for the training sequence according to the structure of the Volterra filter, and constructing a training set; s3, inputting the training set into an SVM trainer, and obtaining an optimal hyperplane through calculation; s4, extracting a normal vector of the optimal hyperplane as a weight coefficient, and migrating the weight coefficient to a Volterra filter as a tap coefficient; and S5, inputting a signal sequence to be detected into the Volterra filter in the S4, and judging the output of the Volterra filter to realize channel equalization. According to the invention, the normal vector of the optimal hyperplane is migrated to the Volterra filter, the tap coefficient of the filter does not need to be updated by an adaptive algorithm, and the calculation complexity is reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Non-linear filtering for the reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram from an endocardial electrogram
An active medical device using non-linear filtering for the reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram (ECG) from an endocardial electrogram (EGM) is disclosed. The device for the reconstruction of the surface ECG comprises: a plurality of inputs, receiving a corresponding plurality of EGM signals from endocardial or epicardial electrogram (x1[n], x2[n]), each collected on a respective EGM derivation of a plurality of EGM derivations, and at least one output delivering a reconstructed surface ECG electrocardiogram signal (y[n]), related to an ECG derivation, and a non-linear digital filter (12′, 12′, 14) with a transfer function that determines the reconstructed ECG signal based on said plurality of input EGM signals. The non-linear digital filter includes a Volterra filter type (12, 12′, 12″) whose transfer function includes a linear term (h1) and at least one quadratic (h2) and / or cubic (h3) term(s).
Owner:SORIN CRM
Signal processing device and method, and signal decoding device and method
InactiveUS7711042B2Reduce in quantityReduce circuit sizeMultiple-port networksModification of read/write signalsVolterra filtersComputer science
A second-order Volterra filter has a quadratic section including a plurality of multiplication units that multiply a first input signal with a second input signal. One of the multiplication units employs a signal not delayed from the first input signal, as the second input signal. A remaining one of the multiplication units employs a signal delayed a preset time from the first input signal, as the second input signal. The one of the multiplication units includes a multiplier that multiplies the signal output from the one of the multiplication units and a signal output from each of one or more delay units, each with a preset coefficient. A step gain parameter for updating each preset coefficient of a multiplier of the remaining one of the multiplication units is twice a step gain parameter for updating each preset coefficient of the multiplier of the one of the multiplication units.
Owner:SONY CORP
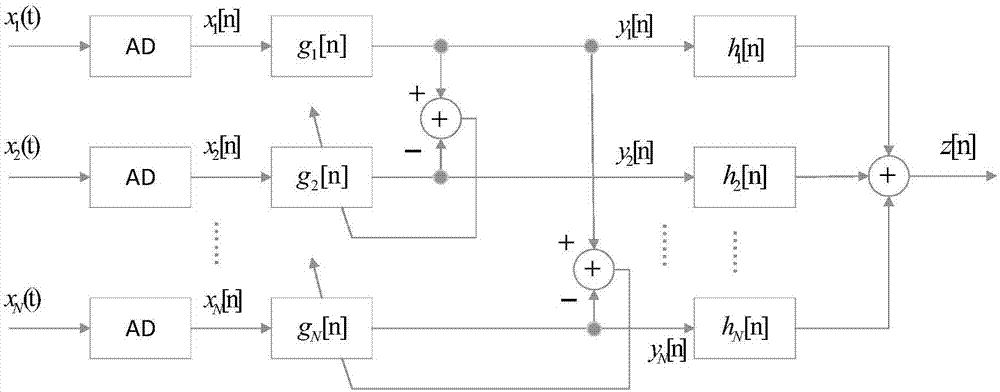
Microphone array channel mismatch calibration method based on Volterra filters
InactiveCN106973353AQuality improvementImprove performanceElectrical apparatusEngineeringMinimum mean square error
The invention relates to a microphone array channel mismatch calibration method based on Volterra filters. The method comprises the steps of S1, carrying out AD conversion on output signals of microphones; S2, establishing a Volterra filter for the output signal of each microphone, and carrying out parameter adjustment on the Volterra filters of the output signals of the microphones through utilization of a minimum mean square error algorithm, and inputting the output signals of the microphones into the corresponding Volterra filters for filter calibration; and S3, inputting the output signals after the filter calibration into a beam former, thereby obtaining a single sound signal.
Owner:SYSU CMU SHUNDE INT JOINT RES INST +1
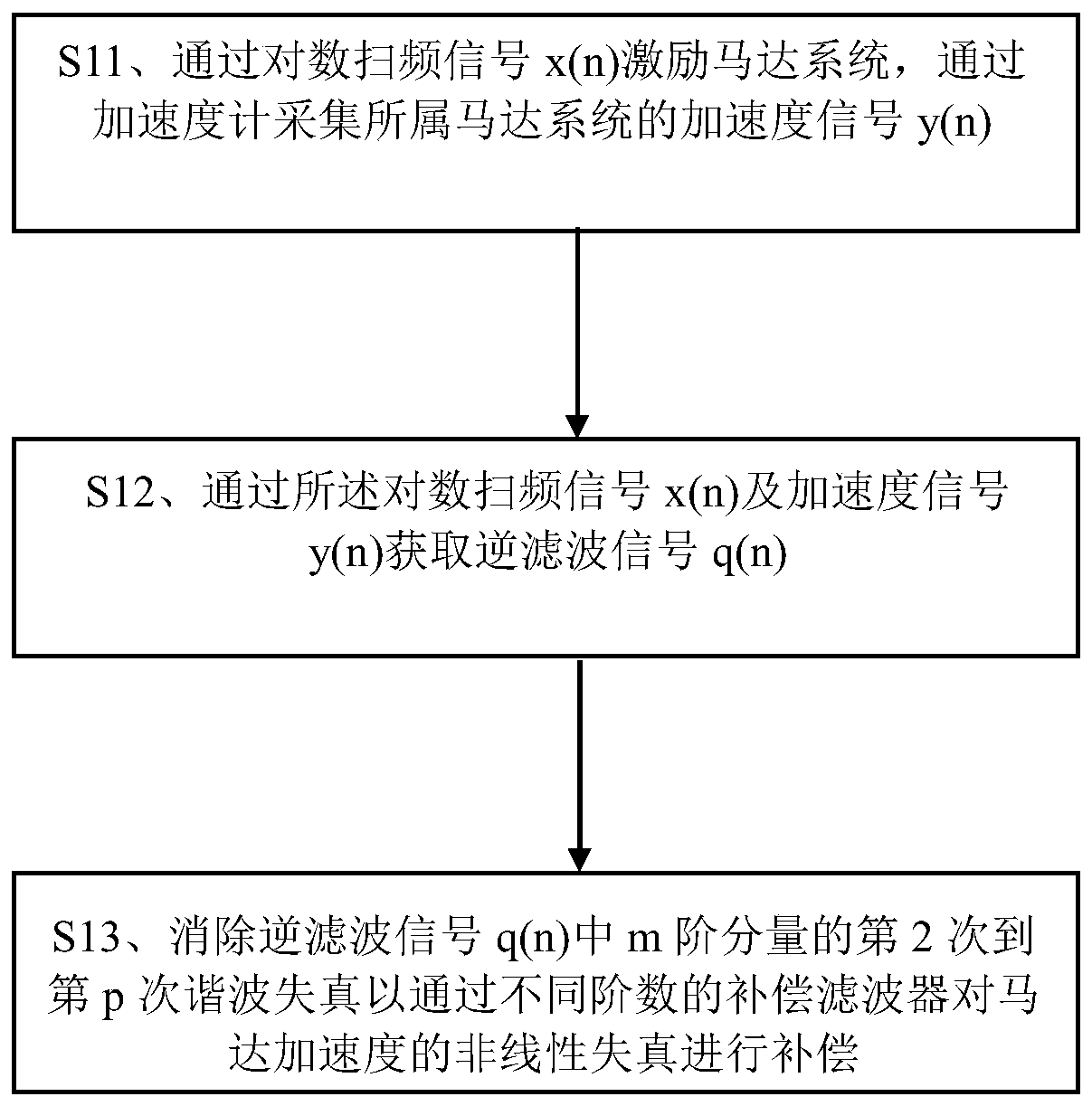
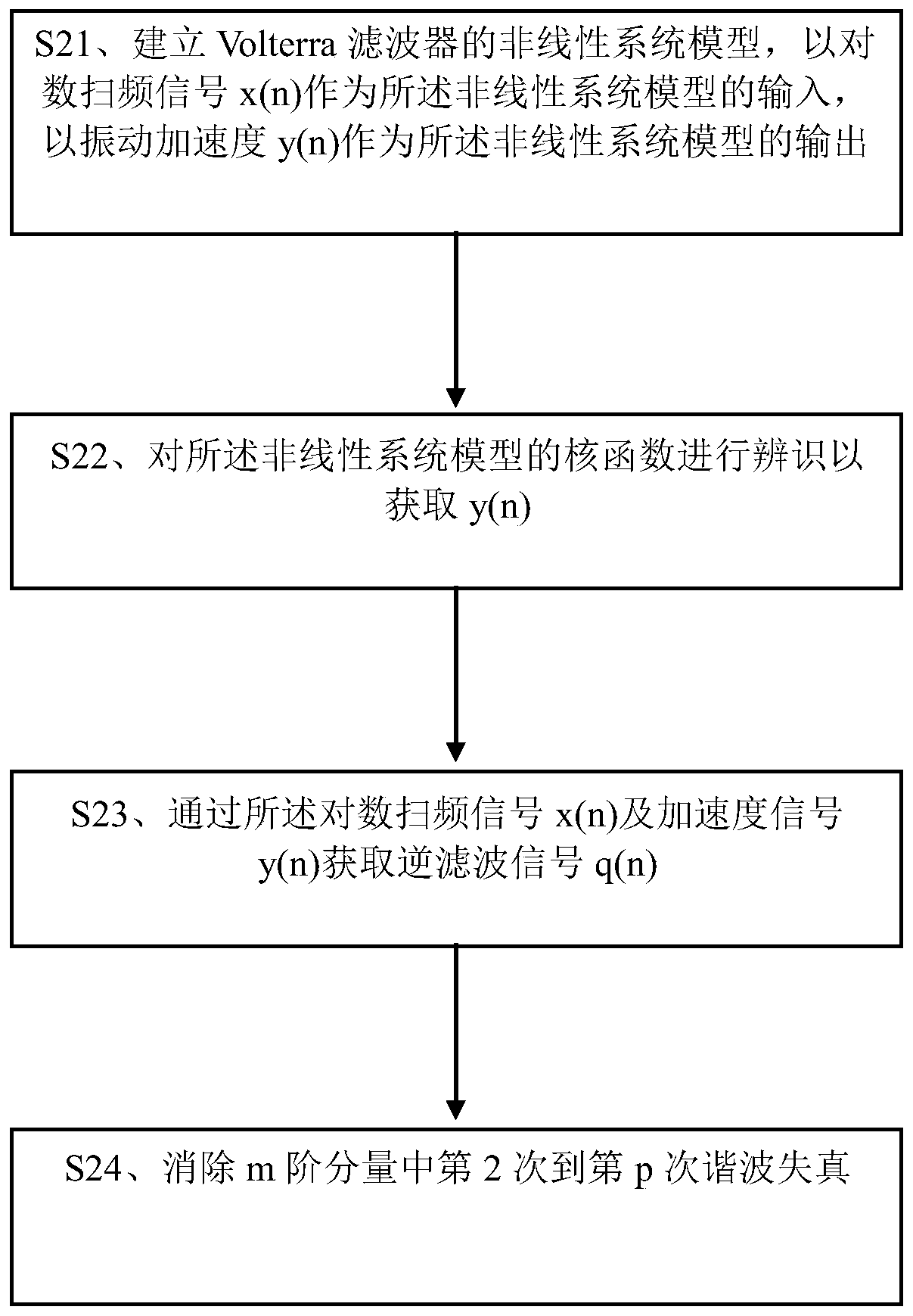
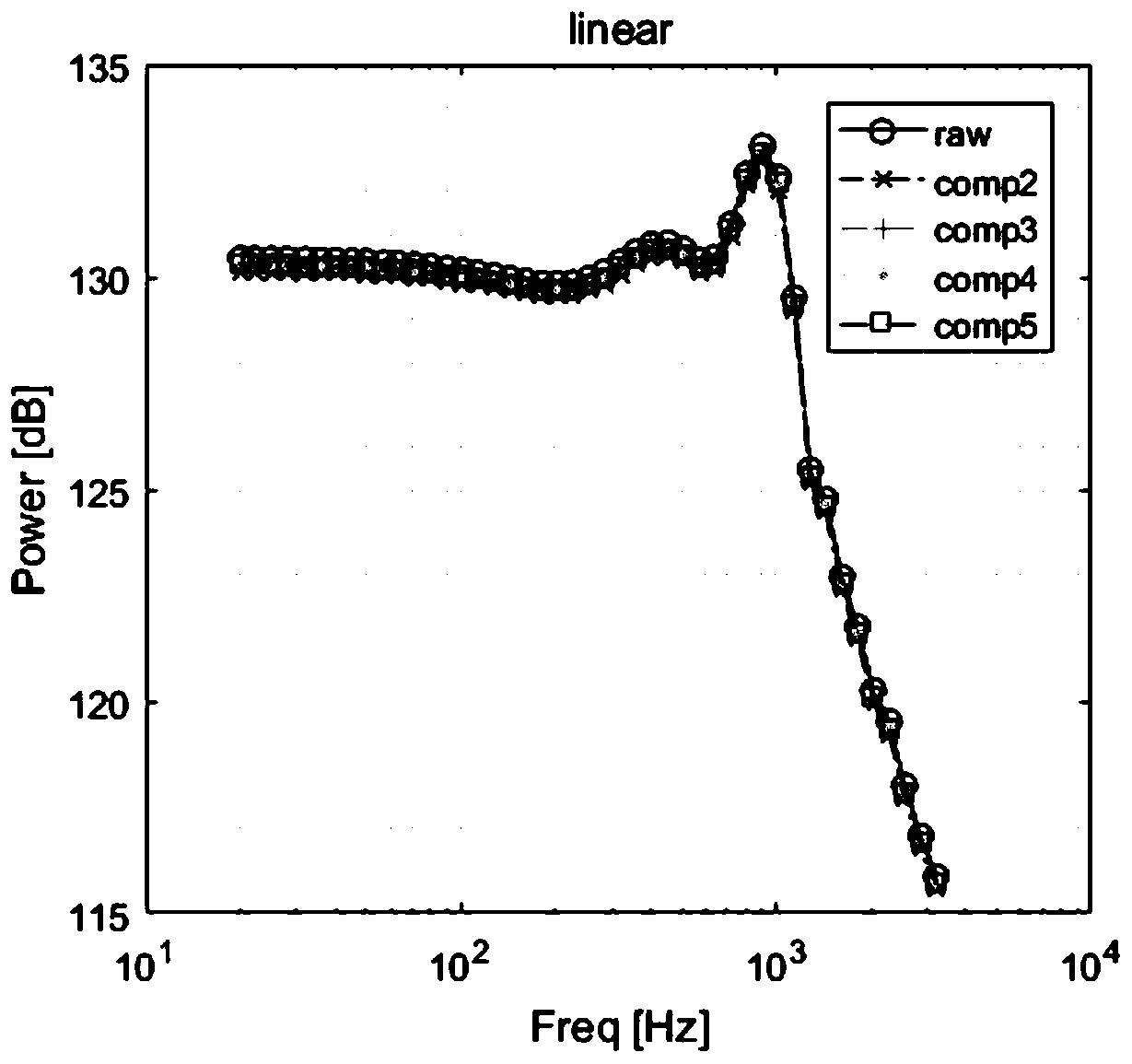
Motor nonlinear distortion compensation method and device and computer readable storage medium
The invention discloses a motor nonlinear distortion compensation method and device and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps of: exciting a motor system through a logarithm sweep signal x (n), and collecting the acceleration signal y (n) of the motor system through an accelerometer; obtaining an inverse filtering signal q (n) through the logarithm swept-frequency signal x (n) and the acceleration signal y (n); and eliminating the second to p-th harmonic distortion of the m-order component in the inverse filtering signal q (n) so as to compensate the nonlinear distortion of the acceleration of a motor through compensation filters with different orders. The motor system is used as a black box, and the nonlinear distortion of the nonlinear system model of the Volterra filter is numerically compensated, so that the nonlinear distortion compensation can be performed on the premise of not knowing a physical model.
Owner:AAC TECH PTE LTD
Non-linear filtering for the reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram from an endocardial electrogram
An active medical device using non-linear filtering for the reconstruction of a surface electrocardiogram (ECG) from an endocardial electrogram (EGM) is disclosed. The device for the reconstruction of the surface ECG comprises: a plurality of inputs, receiving a corresponding plurality of EGM signals from endocardial or epicardial electrogram (x1[n], x2[n]), each collected on a respective EGM derivation of a plurality of EGM derivations, and at least one output delivering a reconstructed surface ECG electrocardiogram signal (y[n]), related to an ECG derivation, and a non-linear digital filter (12′, 12′, 14) with a transfer function that determines the reconstructed ECG signal based on said plurality of input EGM signals. The non-linear digital filter includes a Volterra filter type (12, 12′, 12″) whose transfer function includes a linear term (h1) and at least one quadratic (h2) and / or cubic (h3) term(s).
Owner:SORIN CRM
Method and apparatus for reducing impulse noise in a signal processing system
InactiveUS7024005B2Transmitter/receiver shaping networksTransmission noise suppressionHandling systemVolterra filters
An observed signal that is corrupted with impulse noise is recorded in a signal processing system of an image processing system or a digital subscriber line (xDSL). The observed signal that is recorded by the signal processing system includes a noise component and data component. The signal processing system estimates the parameters of an alpha-stable distribution using a modified iteratively reweighted least squares (IRLS) technique. The estimated parameters define a probability density function that is used to model the noise component of the observed signal. Once the parameters of the alpha-stable distribution are estimated, the signal processing system uses them to estimate model coefficients of a non-linear prediction filter such as a Volterra filter. Using the model coefficients, the non-linear prediction filter estimates the data component of the observed signal.
Owner:XEROX CORP
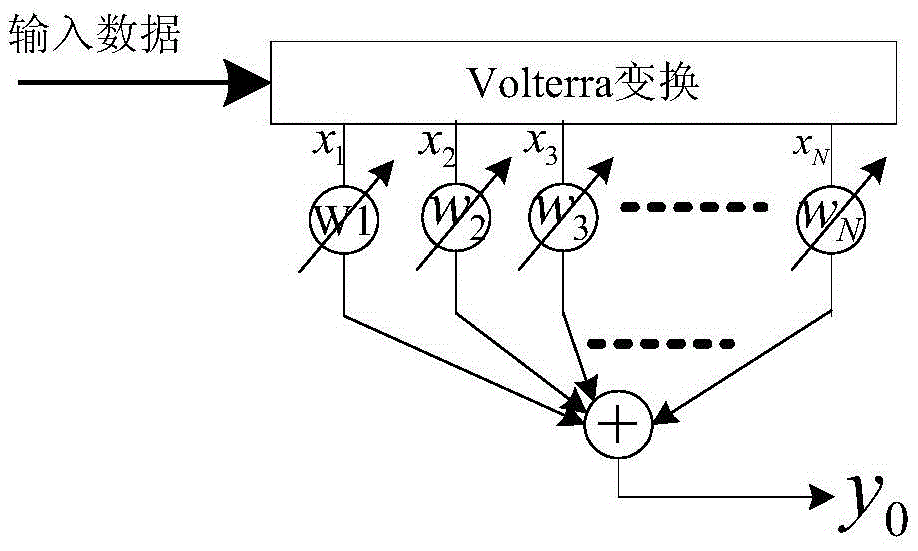
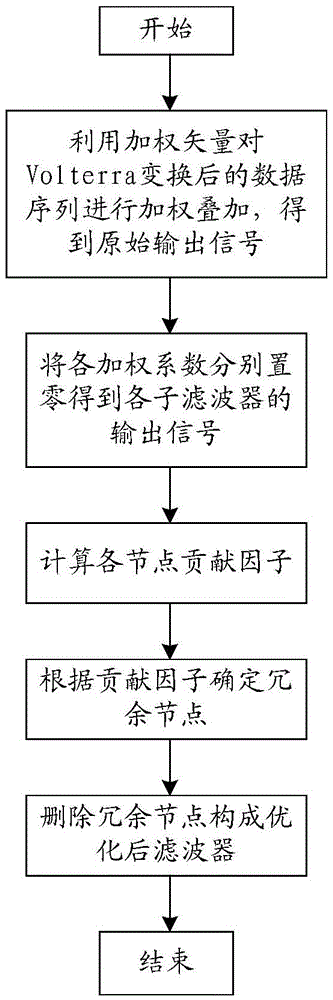
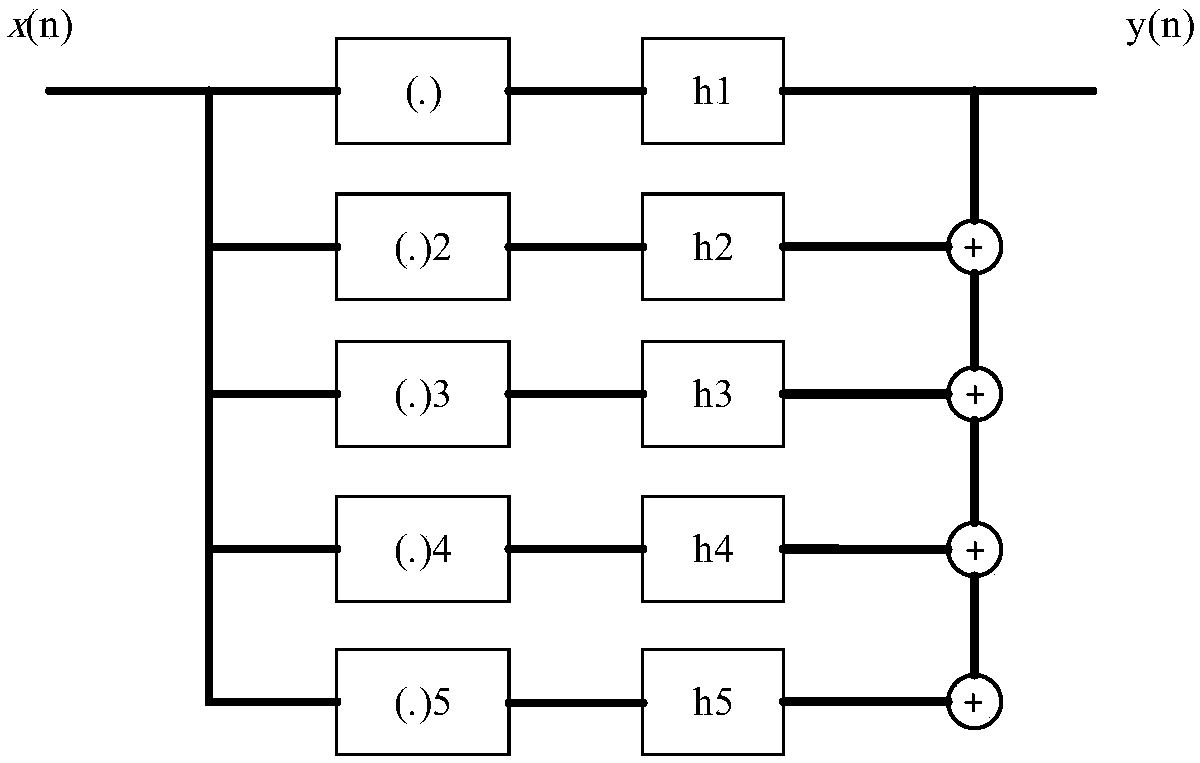
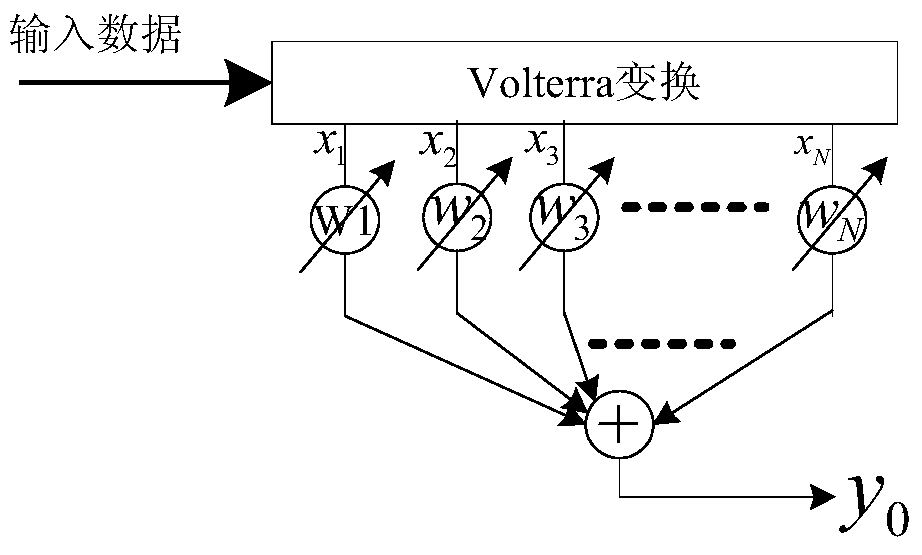
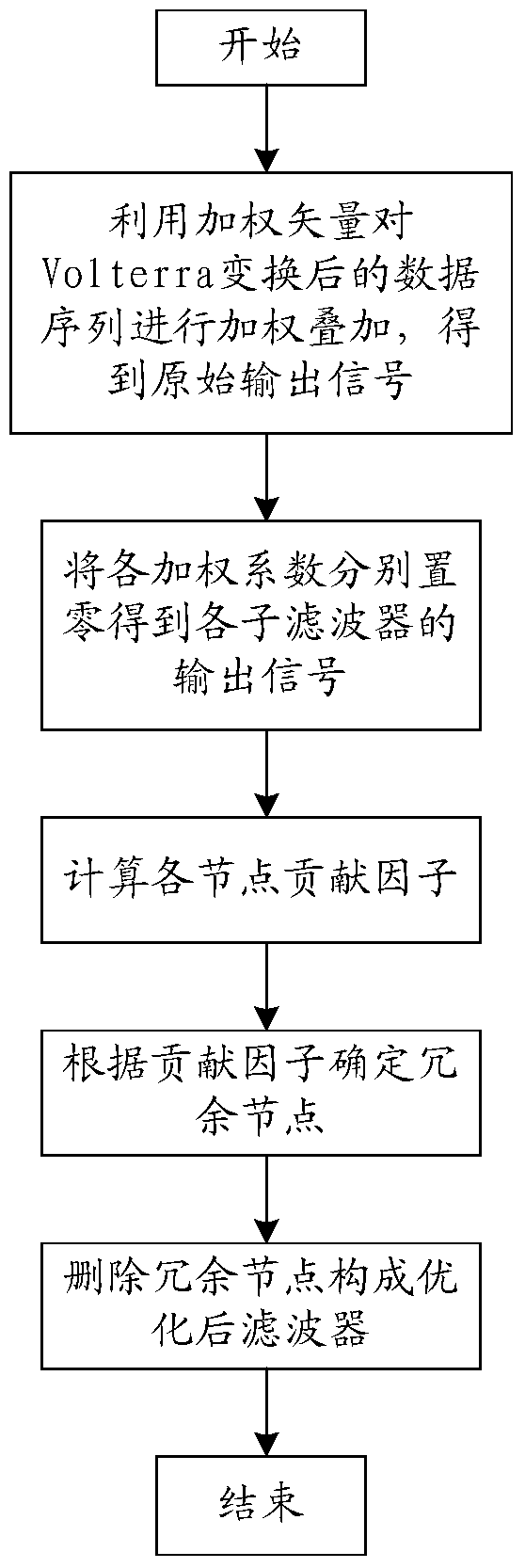
Non-linear Volterra filtering optimization method based on contribution factor
ActiveCN105610408ASmall amount of calculationImprove the possibility of engineering realizationDigital technique networkNODALAlgorithm
The invention discloses a non-linear Volterra filtering optimization method based on a contribution factor, and the method comprises the steps: 1, obtaining an original output signal of a non-linear Volterra filter; 2, setting the weighting coefficient of each node of the non-linear Volterra filter as zero, forming sub-filters, and obtaining an output signal of each sub-filter; 3, calculating the contribution factor of each node according to the output signal and the original output signal of each sub-filter; 4, comparing the contribution factor of each node with a set threshold value delta, and determining the optimal weighting coefficient of the non-linear Volterra filter; 5, forming an optimized filter according to the optimal weighting coefficient. The method aims at a problem that a conventional non-linear Volterra filtering method is large in calculation burden, proposes a method for searching and deleting the redundant nodes according to the attribution of each node to the corresponding output signal, deletes the redundant nodes with the minimum contribution to the output result under the condition that the filtering performance is not affected, can further reduce the calculation amount, and reduces the occupied resource of engineering implementation.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Information readout device and information readout method
InactiveUS20100097910A1Preventing circuit and device from being complicatedAvoid serious complicationsTelevision system detailsModification of read/write signalsEqualizationComputer science
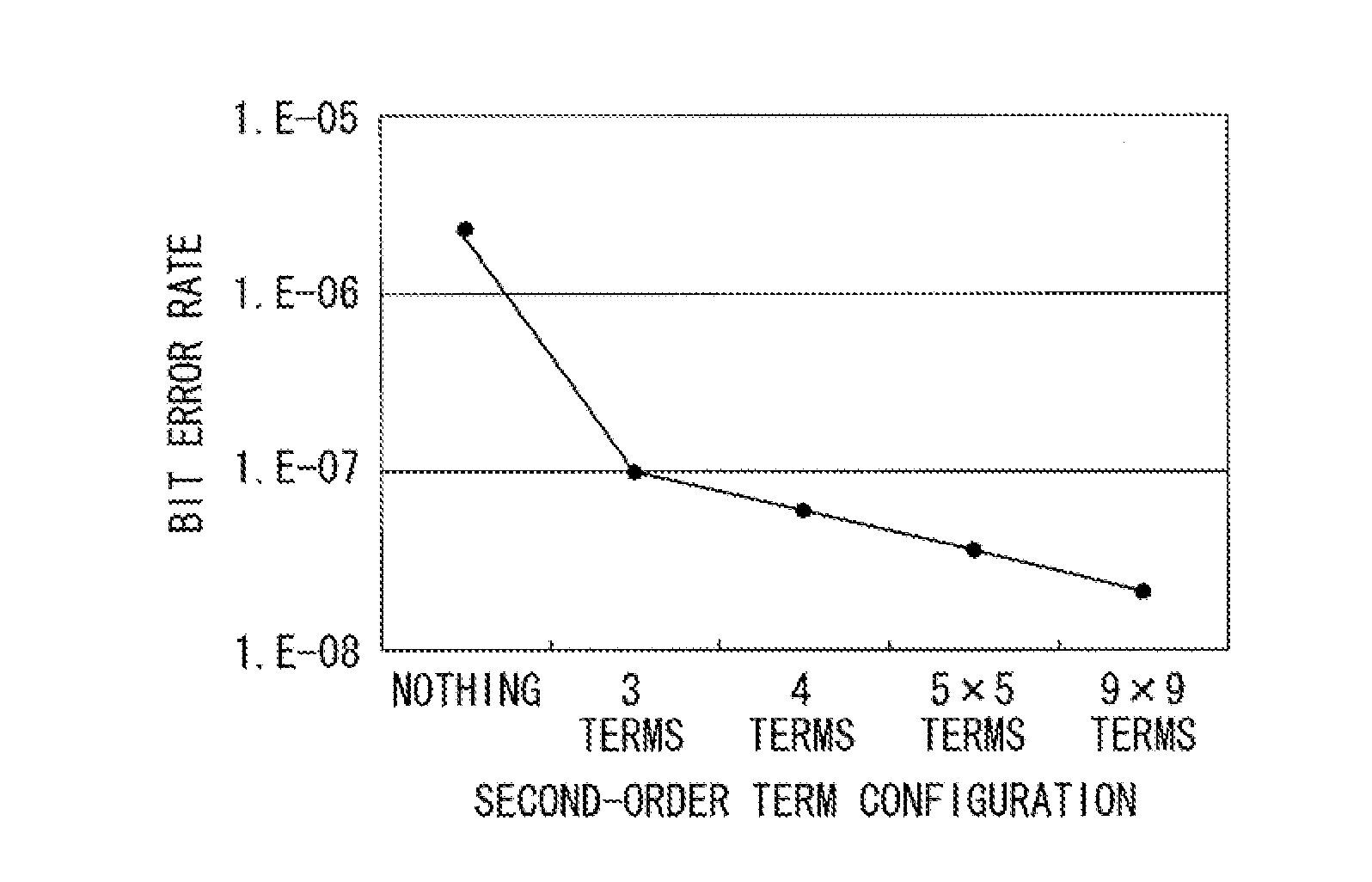
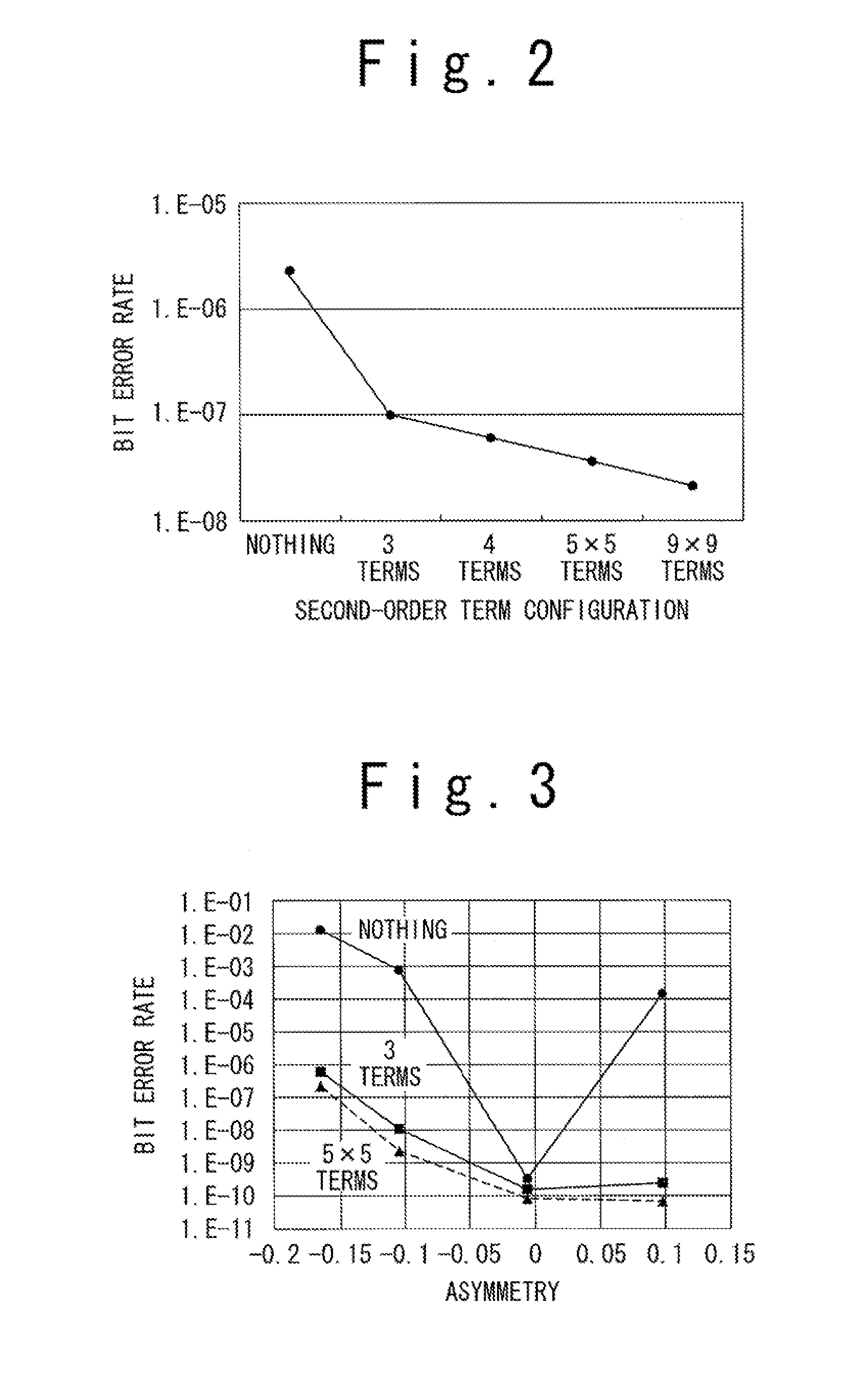
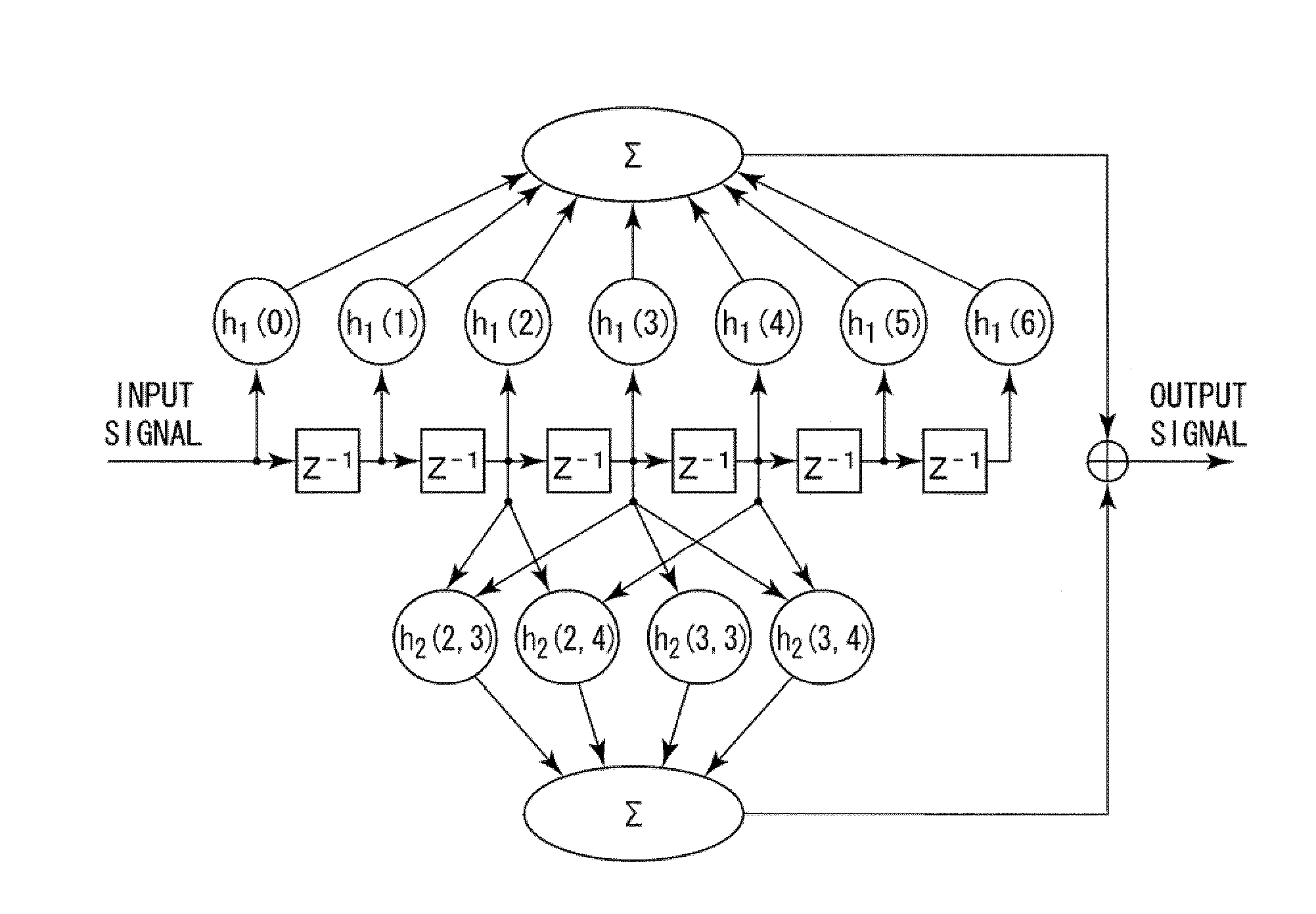
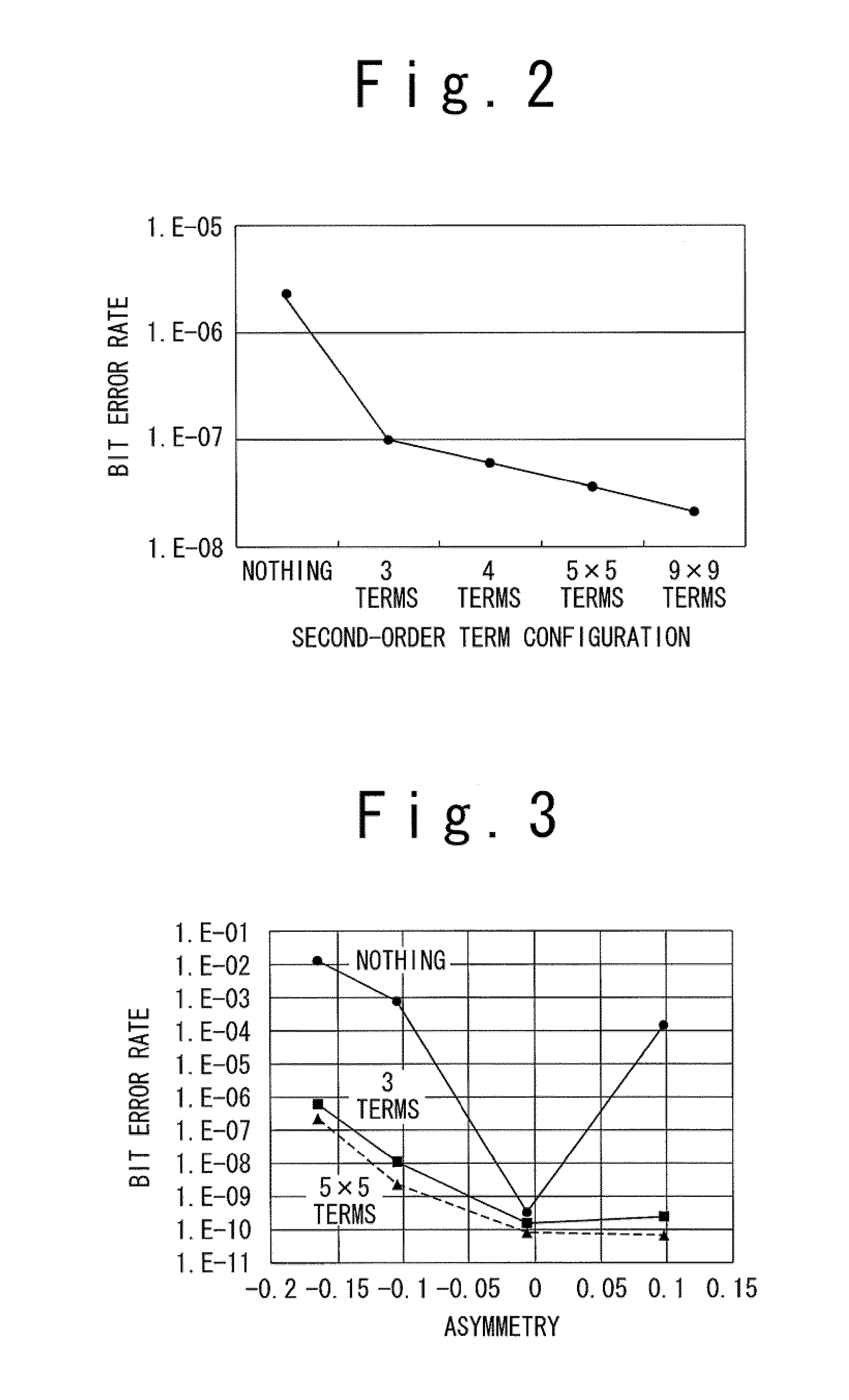
An information readout device includes an equalizer and a maximum likelihood detector. The equalizer includes a second-order Volterra filter, and equalizes a readout signal read out from an information recording medium to a predetermined characteristic to output the equalization signal. The maximum likelihood detector outputs a binary signal through maximum likelihood detection based on the equalization signal. By limiting the number of second-order terms of the second-order Volterra filter to three terms or four terms, a nonlinear component can be effectively corrected.
Owner:NEC CORP
Information readout device and information readout method
InactiveUS8331208B2Preventing circuit and device from being complicatedAvoid serious complicationsTelevision system detailsModification of read/write signalsEqualizationComputer science
An information readout device includes an equalizer and a maximum likelihood detector. The equalizer includes a second-order Volterra filter, and equalizes a readout signal read out from an information recording medium to a predetermined characteristic to output the equalization signal. The maximum likelihood detector outputs a binary signal through maximum likelihood detection based on the equalization signal. By limiting the number of second-order terms of the second-order Volterra filter to three terms or four terms, a nonlinear component can be effectively corrected.
Owner:NEC CORP
A method and system for audible evaluation of sound quality of nonlinear audio system
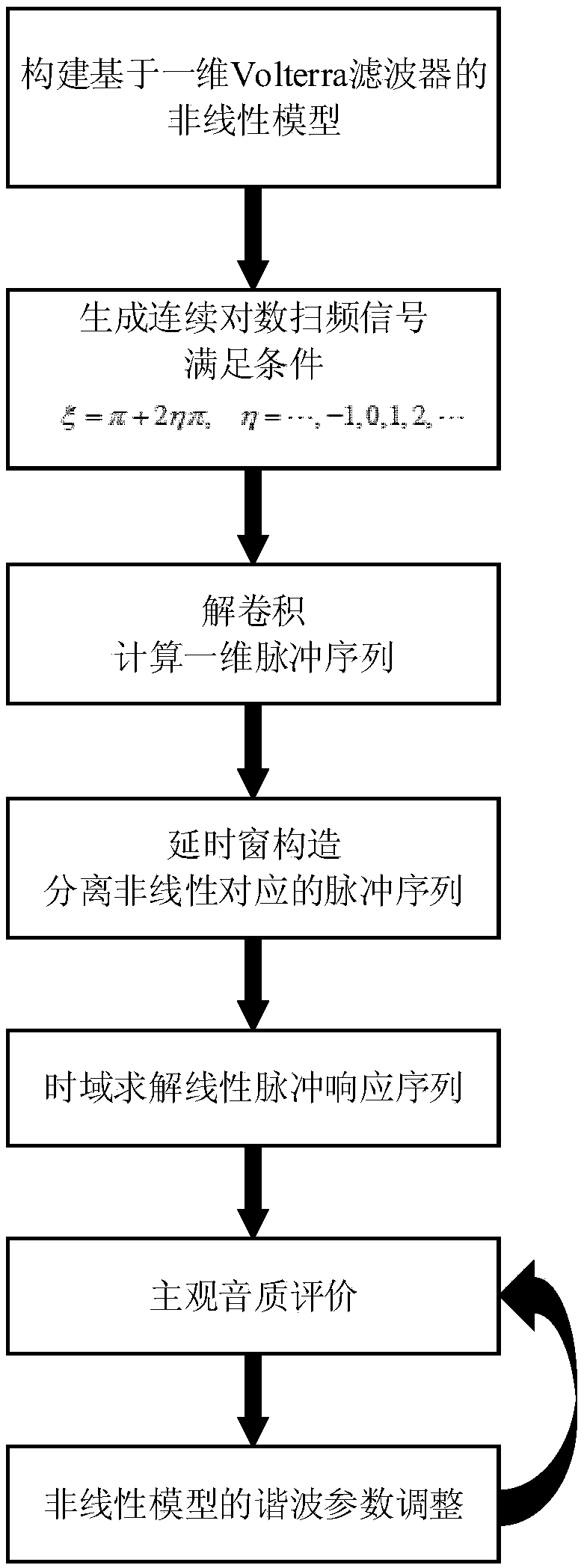
ActiveCN106255027BThe impulse response is accurately obtainedWill not introduce errorElectrical apparatusAuralizationPhase difference
The invention discloses a tone quality auralization evaluation method and system of a non-linear audio system. A one-dimensional Volterra filter parameter is solved by a time domain, so that a problem of inaccurate auralization model estimation of the non-linear system due to a phase difference in frequency domain solution in the prior art can be solved. The method comprises: S1, constructing a non-linear model based on a one-dimensional Volterra filter to simulate a non-linear response of a non-linear audio system; S2, identifying a kernel function parameter of the one-dimensional Volterra filter; S3, feeding an audio testing signal to the established non-linear model and evaluating the one quality of an output result; and S4, according to the evaluation result of the S3, adjusting a parameter of the non-linear model, returning to the S3, evaluating the tone quality improvement situation after adjustment, and carrying out steps in circles until finding an optimal non-linear model parameter.
Owner:SUZHOU SONAVOX ELECTRONICS
A Nonlinear Volterra Filter Optimization Method Based on Contribution Factor
ActiveCN105610408BSmall amount of calculationImprove the possibility of engineering realizationDigital technique networkAlgorithmVolterra filters
The invention discloses a non-linear Volterra filtering optimization method based on a contribution factor, and the method comprises the steps: 1, obtaining an original output signal of a non-linear Volterra filter; 2, setting the weighting coefficient of each node of the non-linear Volterra filter as zero, forming sub-filters, and obtaining an output signal of each sub-filter; 3, calculating the contribution factor of each node according to the output signal and the original output signal of each sub-filter; 4, comparing the contribution factor of each node with a set threshold value delta, and determining the optimal weighting coefficient of the non-linear Volterra filter; 5, forming an optimized filter according to the optimal weighting coefficient. The method aims at a problem that a conventional non-linear Volterra filtering method is large in calculation burden, proposes a method for searching and deleting the redundant nodes according to the attribution of each node to the corresponding output signal, deletes the redundant nodes with the minimum contribution to the output result under the condition that the filtering performance is not affected, can further reduce the calculation amount, and reduces the occupied resource of engineering implementation.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Nonlinear Narrowband Active Noise Control Method Based on Volterra Filter
InactiveCN104575512BReduce narrowband noiseEasy to implementSpeech analysisNoise controlNonlinear filter
The invention provides a nonlinear narrowband active noise control method based on a Volterra filter and aimed at a situation that higher harmonic noise is generated after a narrowband noise source is distorted nonlinearly. A linear signal synthesis subsystem (1), a nonlinear signal synthesis subsystem (2), a reference signal generation module and a least mean square algorithm module are used in the method; a reference signal in the method is generated by a synchronous signal generator based on a source noise frequency obtained by a non-acoustic sensor; one part of a secondary source is synthesized through a linear combiner, the other part of the secondary source is synthesized through another linear combiner and the nonlinear Volterra filter, and when primary source noise is distorted nonlinearly, a fundamental component and a higher harmonic component are independently inhibited by a linear filter and the nonlinear Volterra filter respectively. According to the nonlinear narrowband active noise control method, the nonlinearly distorted narrowband noise can be effectively inhibited, and the influence of nonlinearity on system performance can be easily analyzed due to an independent working structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Polynomial Adaptive Active Noise Cancellation Method Based on Laguerre Structure
InactiveCN102724152BLess input lengthReduce computational complexityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksNonlinear filterComputation complexity
The invention discloses a multinomial adaptive active noise cancellation method based on a Laguerre structure. The method comprises: a Laguerre time delay unit having the characteristics of an IIR (infinite impulse response) filter is used for replacing a time delay unit Z-1 in a Volterra filter, output by virtue of a laguerre time delay node is taken as input of a non-linear filter based on bounded constrain product coupling Volterra approximate structure, characteristic convergence conditions can be effectively improved, the system stability is guaranteed, the computation complexity is low, hardware is easy to realize; and an LMS (least mean square) adaptive algorithm with input signal and instant error normalized is adopted for adjusting filtering parameters, the input length of a filter can be further reduced while a non-linear adaptive filter is guaranteed to be stable, and the convergence rate is improved; especially under the condition that strong non-linear distortion exists, good anti-noise capacity is shown, so that the method is beneficial to popularization and application of an adaptive multinomial filter.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Volterra-filtering-based power amplifier pre-distortion method for double-loop feedback model
InactiveCN102624338BSmall amount of calculationFast convergenceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAdaptive networkAudio power amplifierMemory effect
The invention discloses a Volterra-filtering-based power amplifier pre-distortion method for a double-loop feedback model. The method mainly comprises the three parts of pre-distortion crude parameter vector extraction, error regulation and pre-distorter fine parameter vector extraction, and specifically comprises the following steps of: performing down-conversion output and pre-distorter output by adopting a first-order dynamic truncation Volterra filtering structure to obtain a pre-distortion crude parameter vector in the pre-distortion crude parameter vector extraction; dynamically regulating an error vector caused by the pre-distortion crude parameter vector according to an average criterion; combining a regulated error vector which serves as an expected signal and a base-band input signal, and obtaining a pre-distorter fine parameter vector by adopting the first-order dynamic truncation Volterra filtering structure; and correcting the crude parameter vector by utilizing the fine parameter vector to obtain a final pre-distorter parameter vector. The problems of slow adaptive convergence, great pre-distortion parameter calculation amount, complexity in implementation, incapability of effectively compensating the complex memory effect of a power amplifier in high-speed communication, and the like of the conventional pre-distortion method are solved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com