Patents
Literature
1426results about "Battery overvoltage protection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
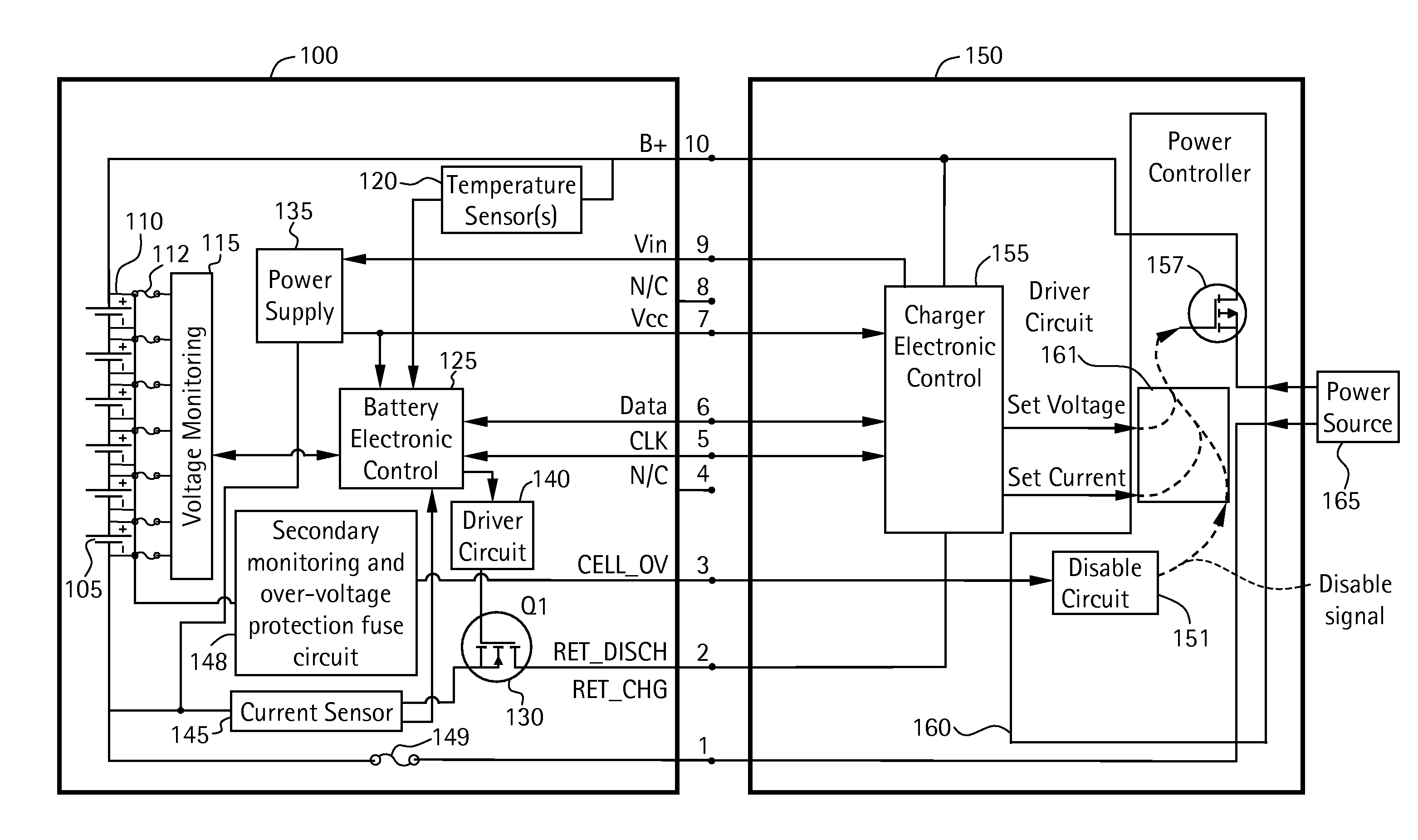
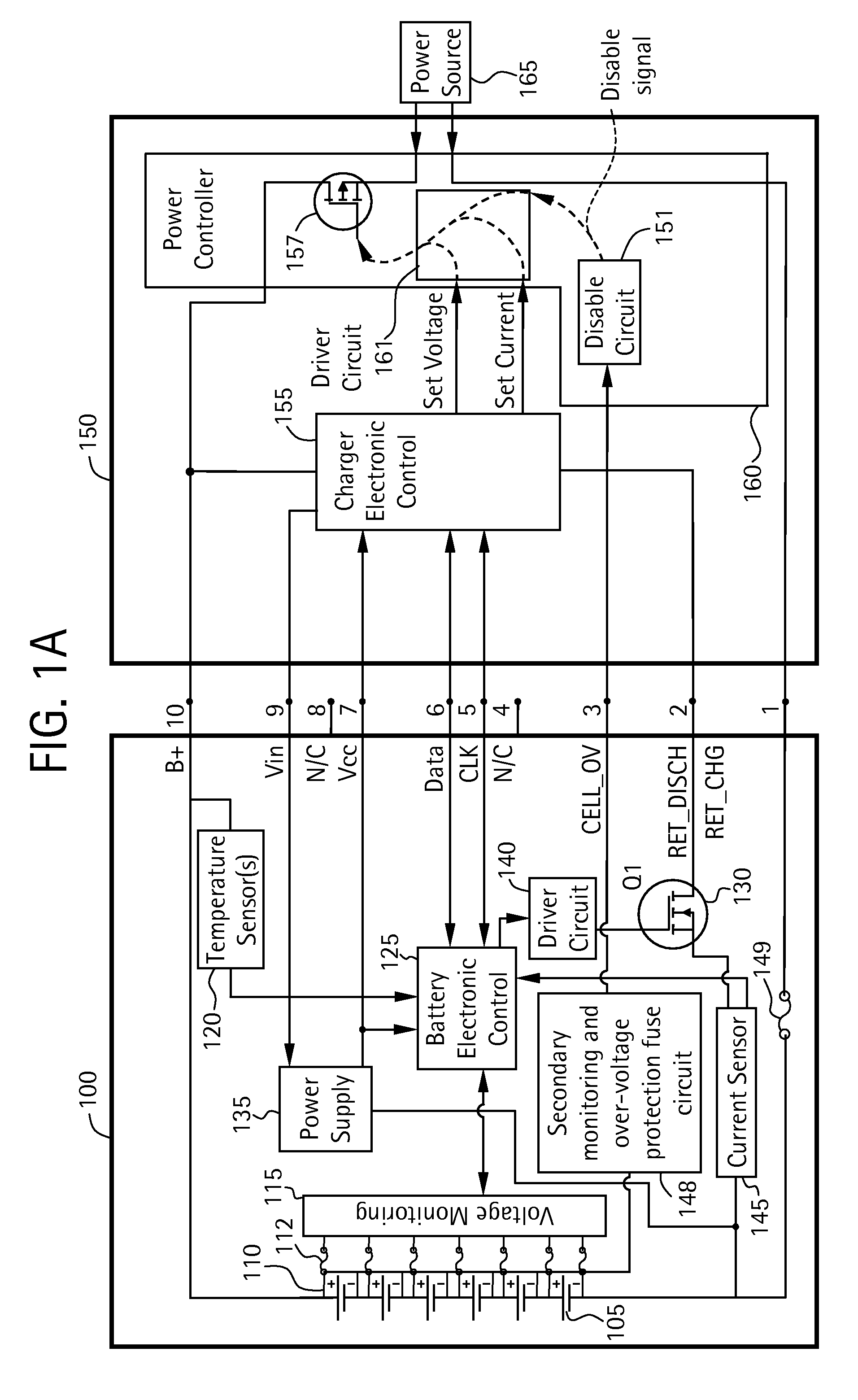
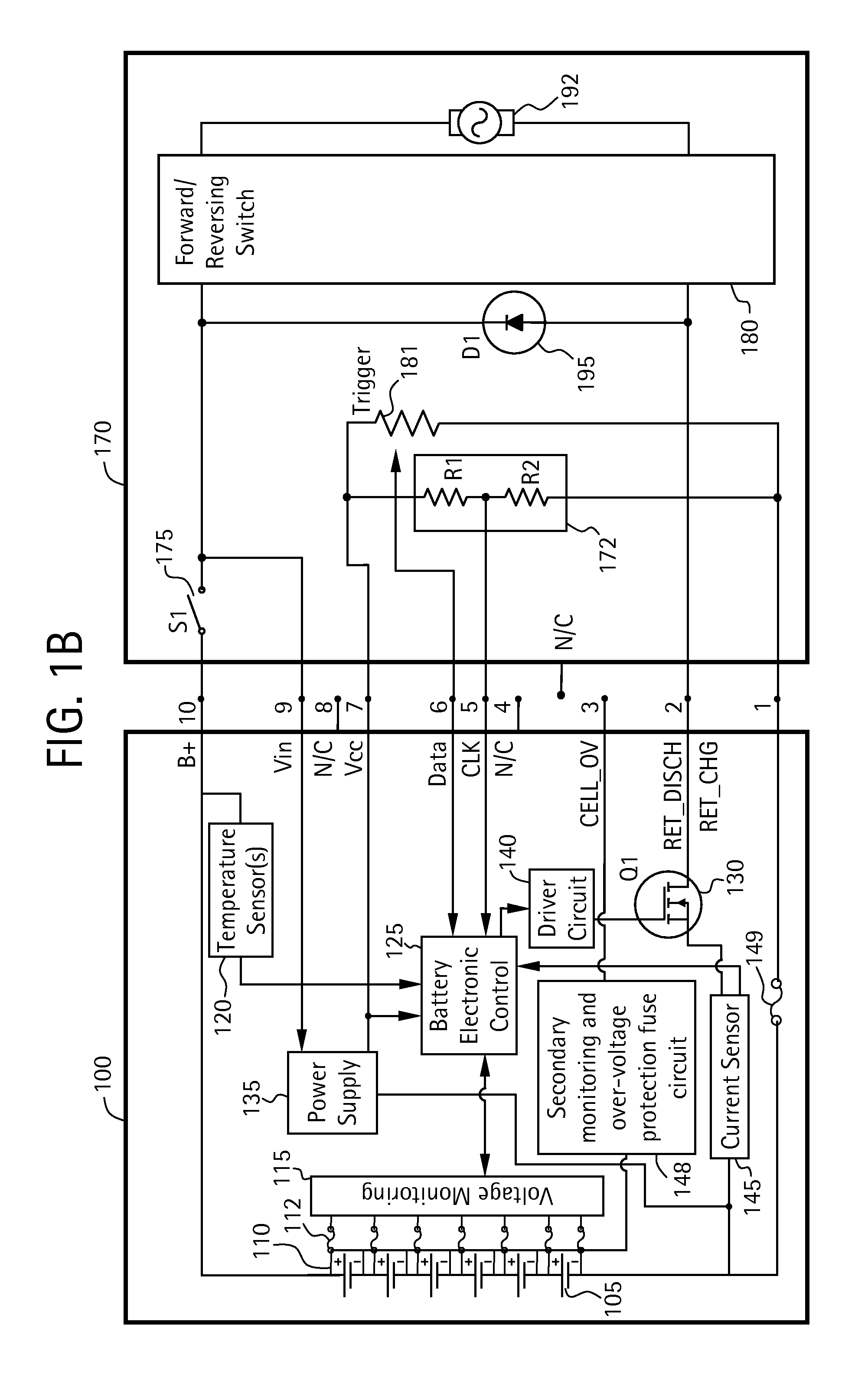
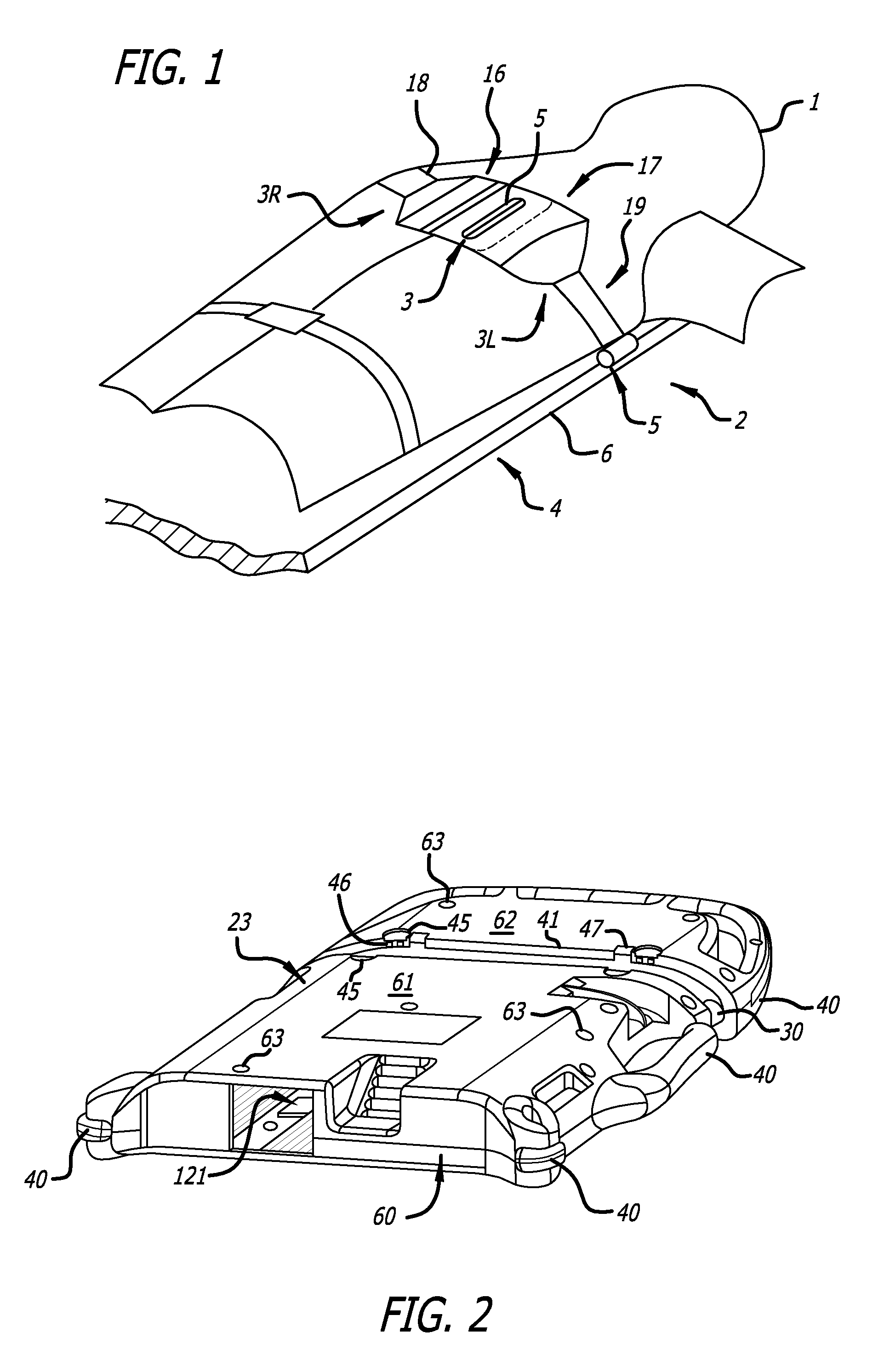
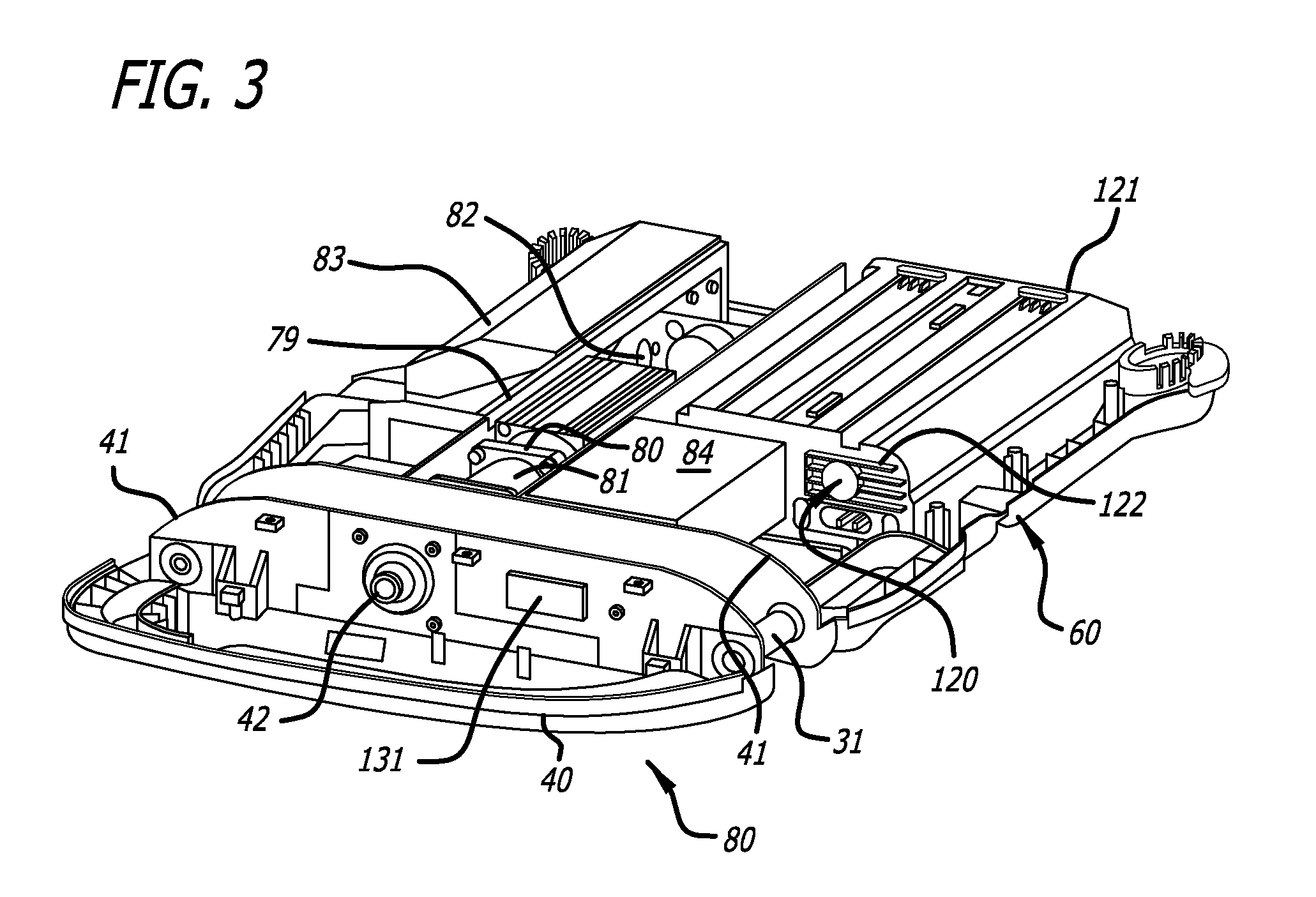
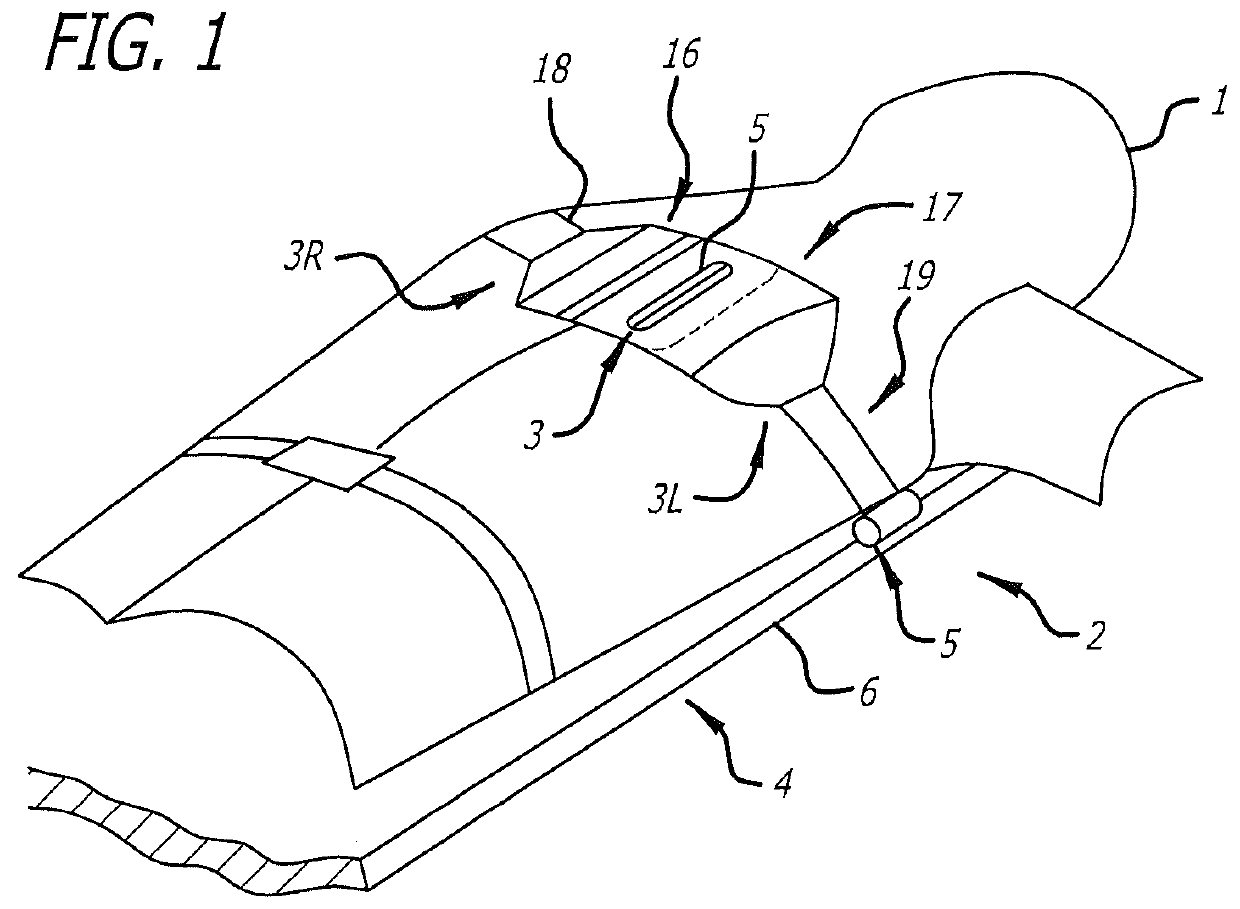
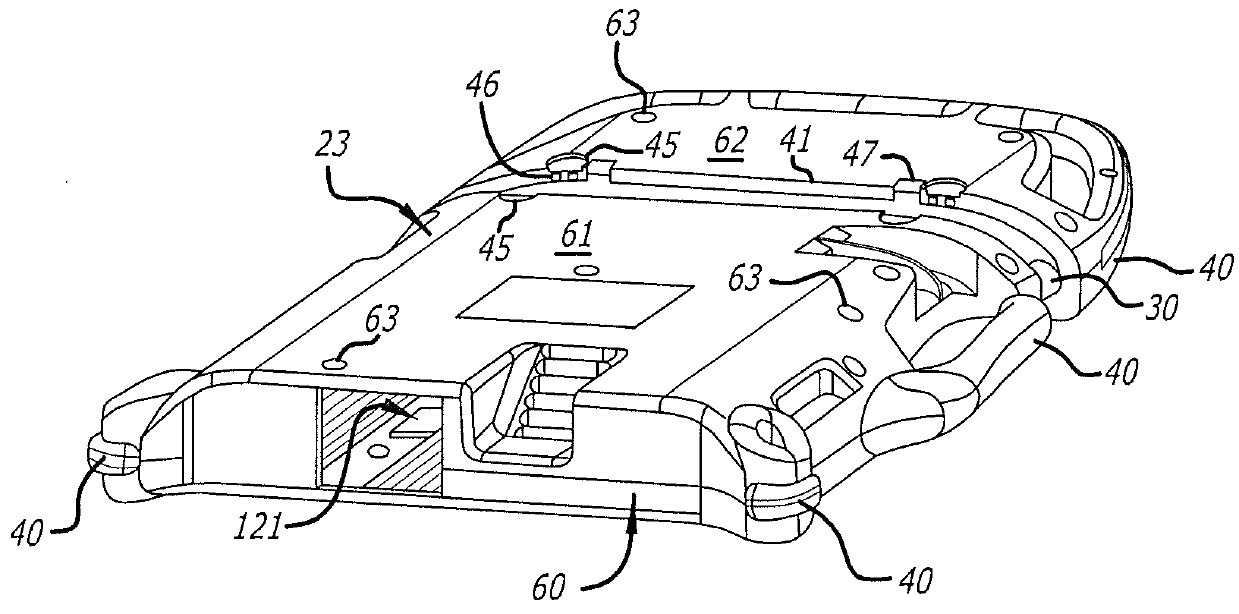
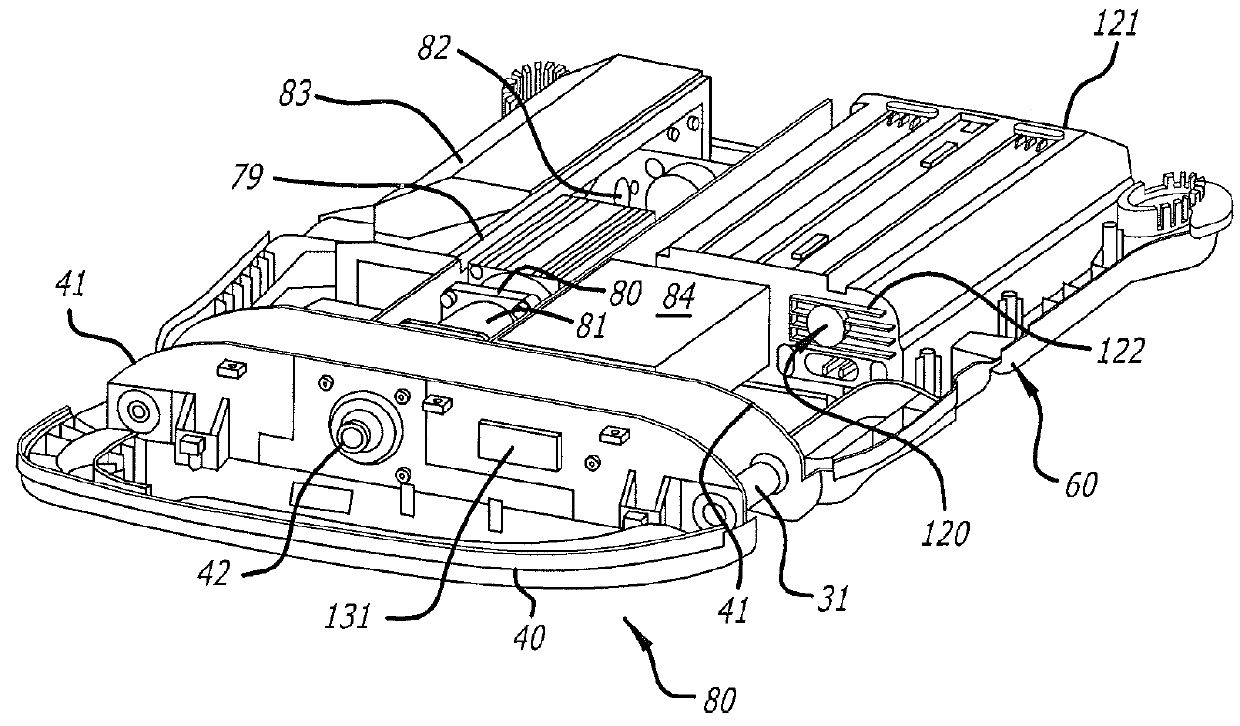
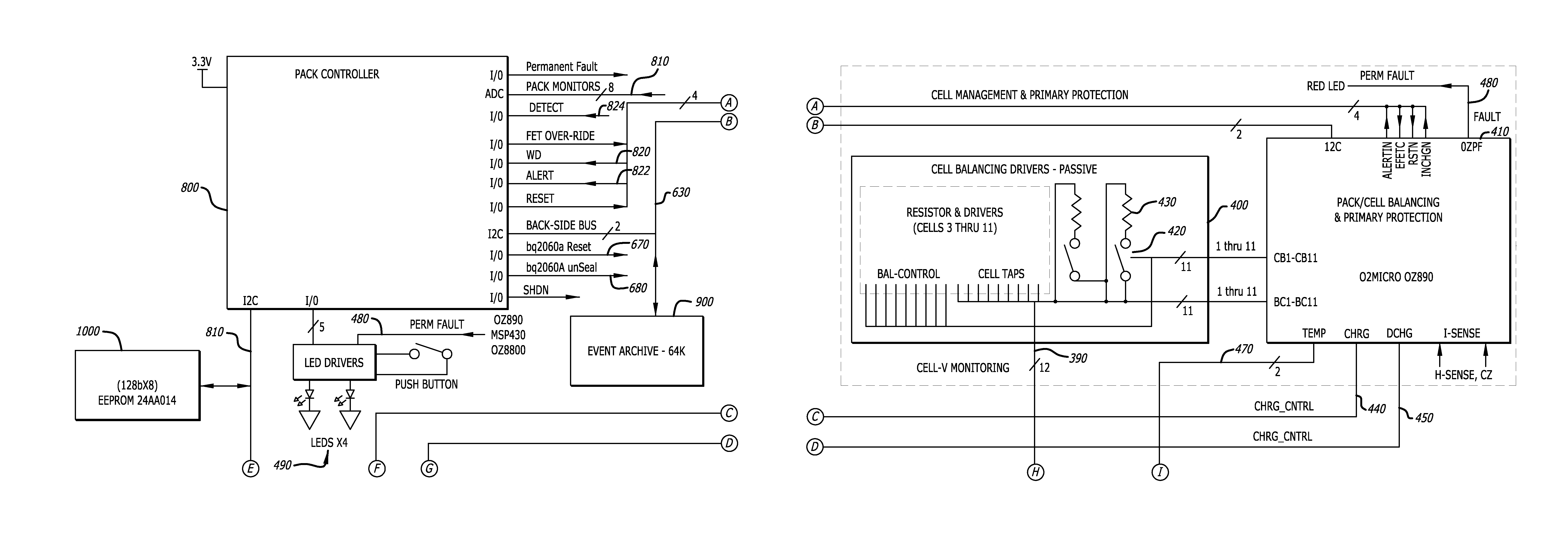
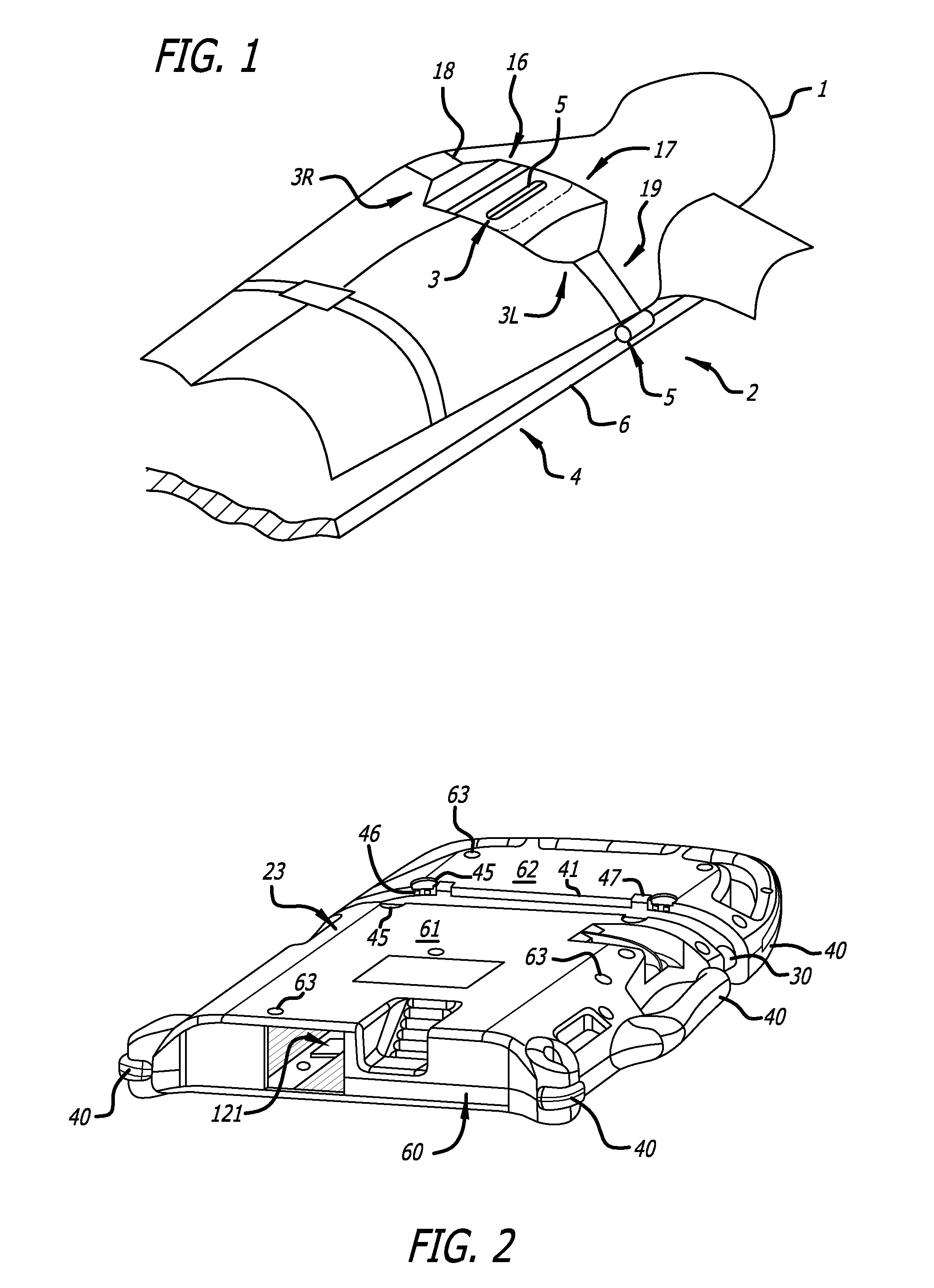
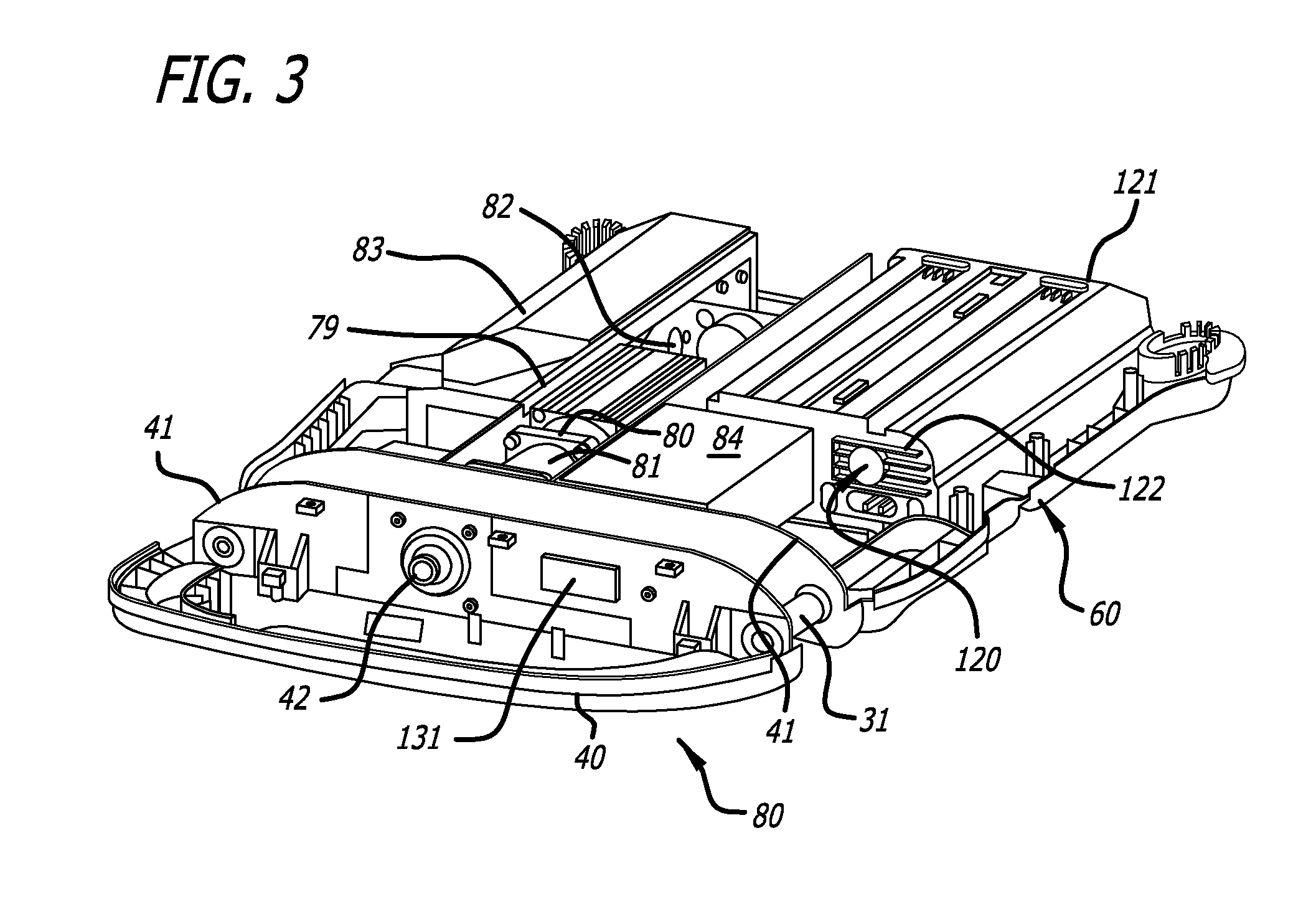
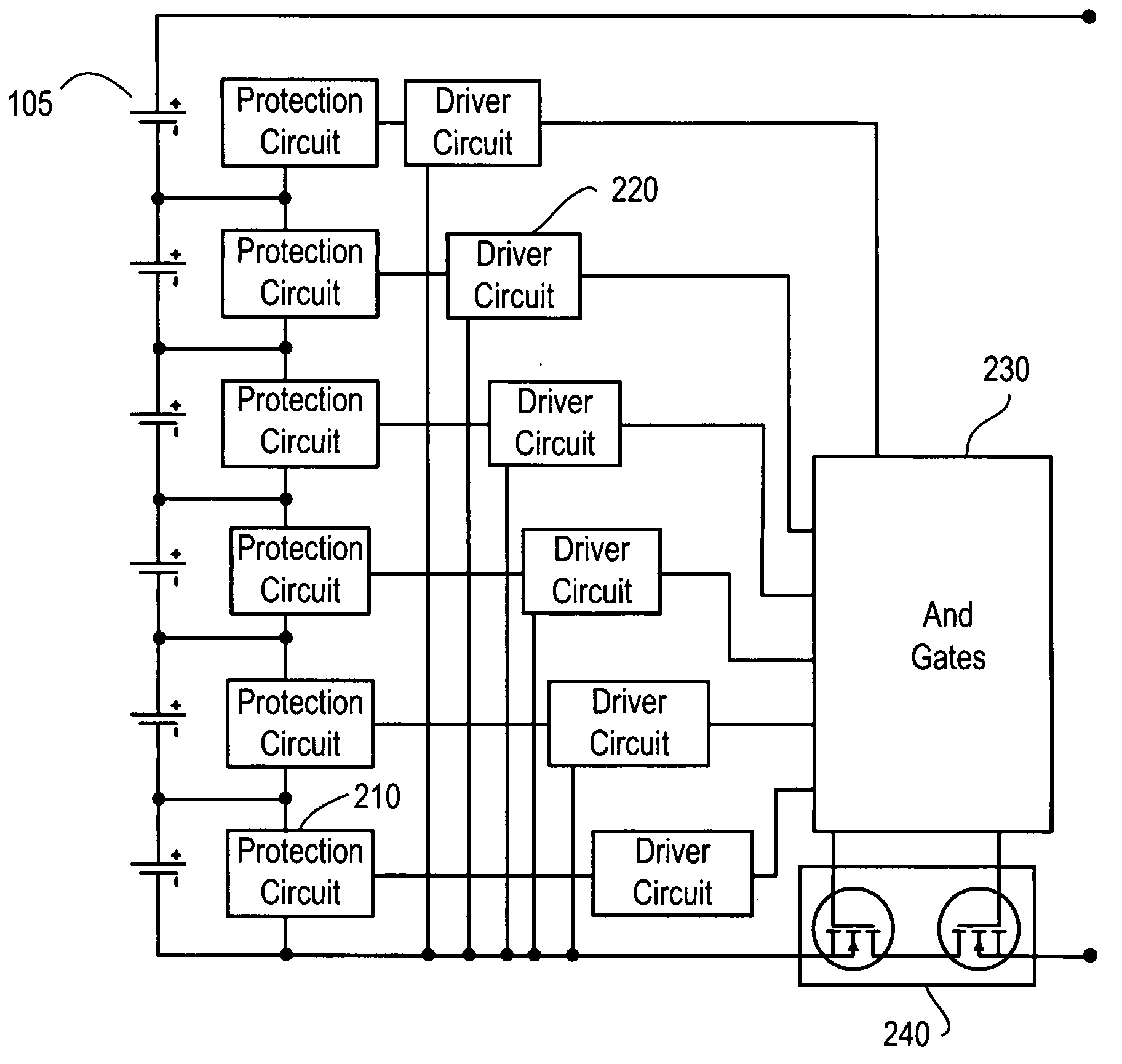
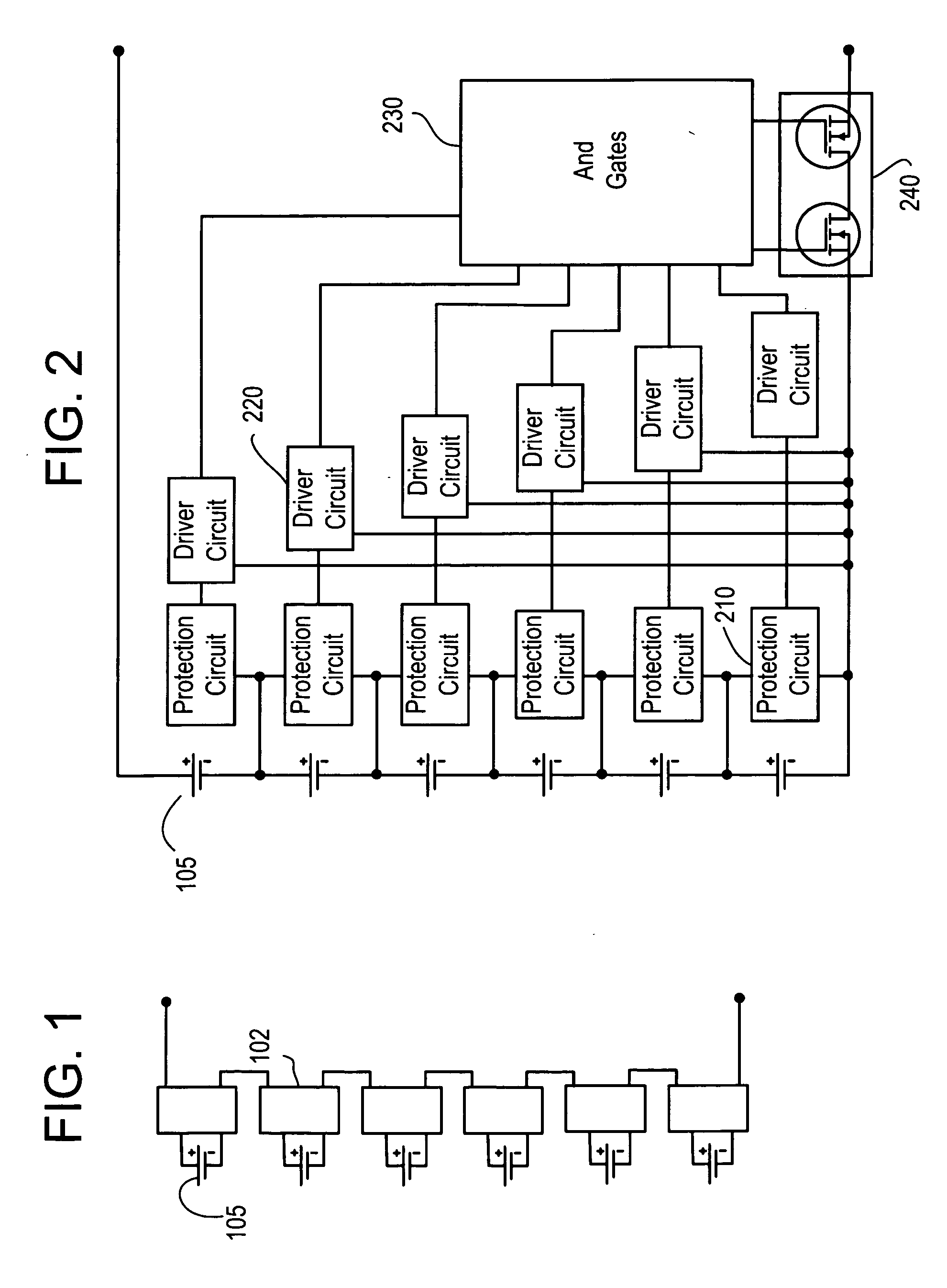
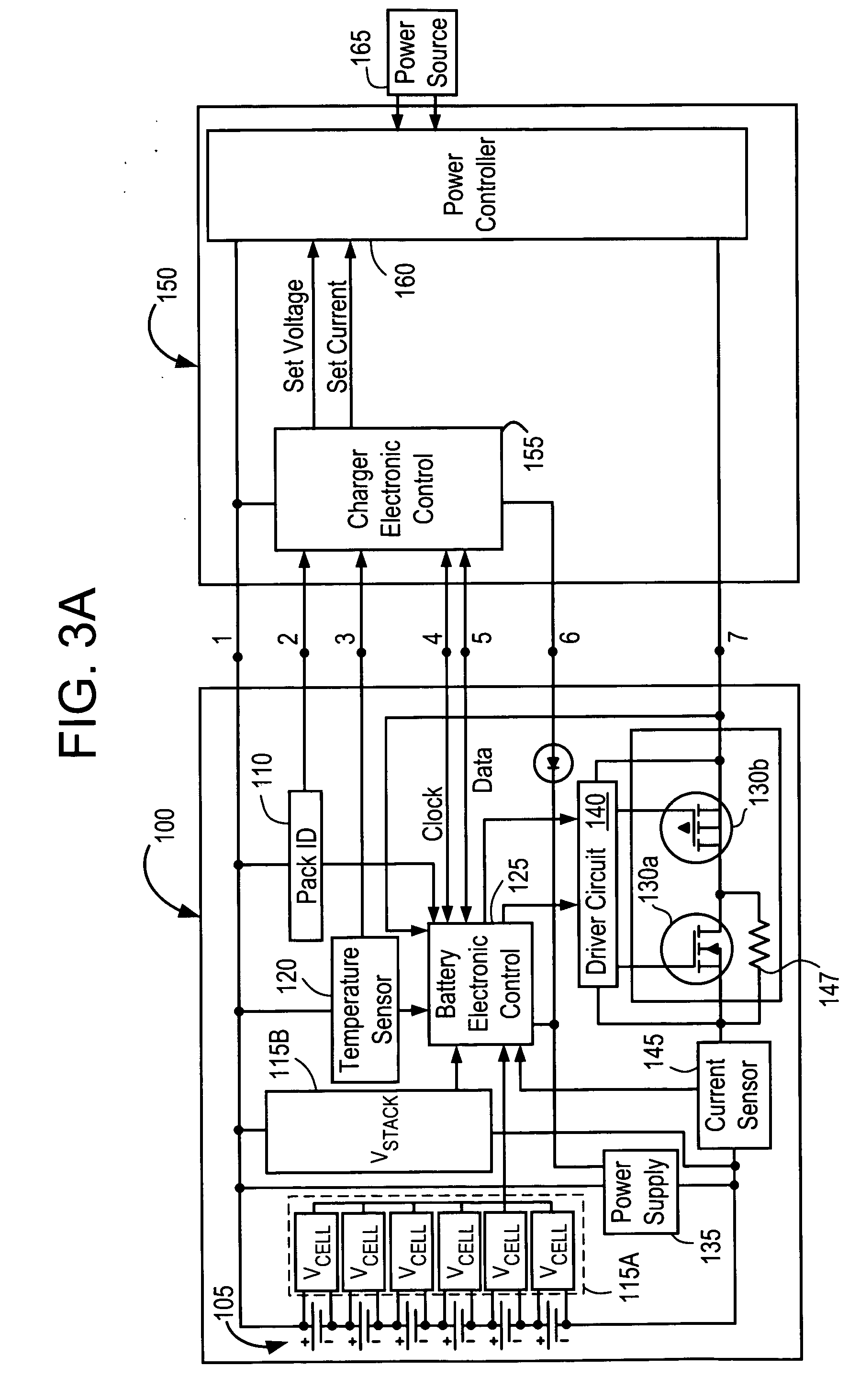
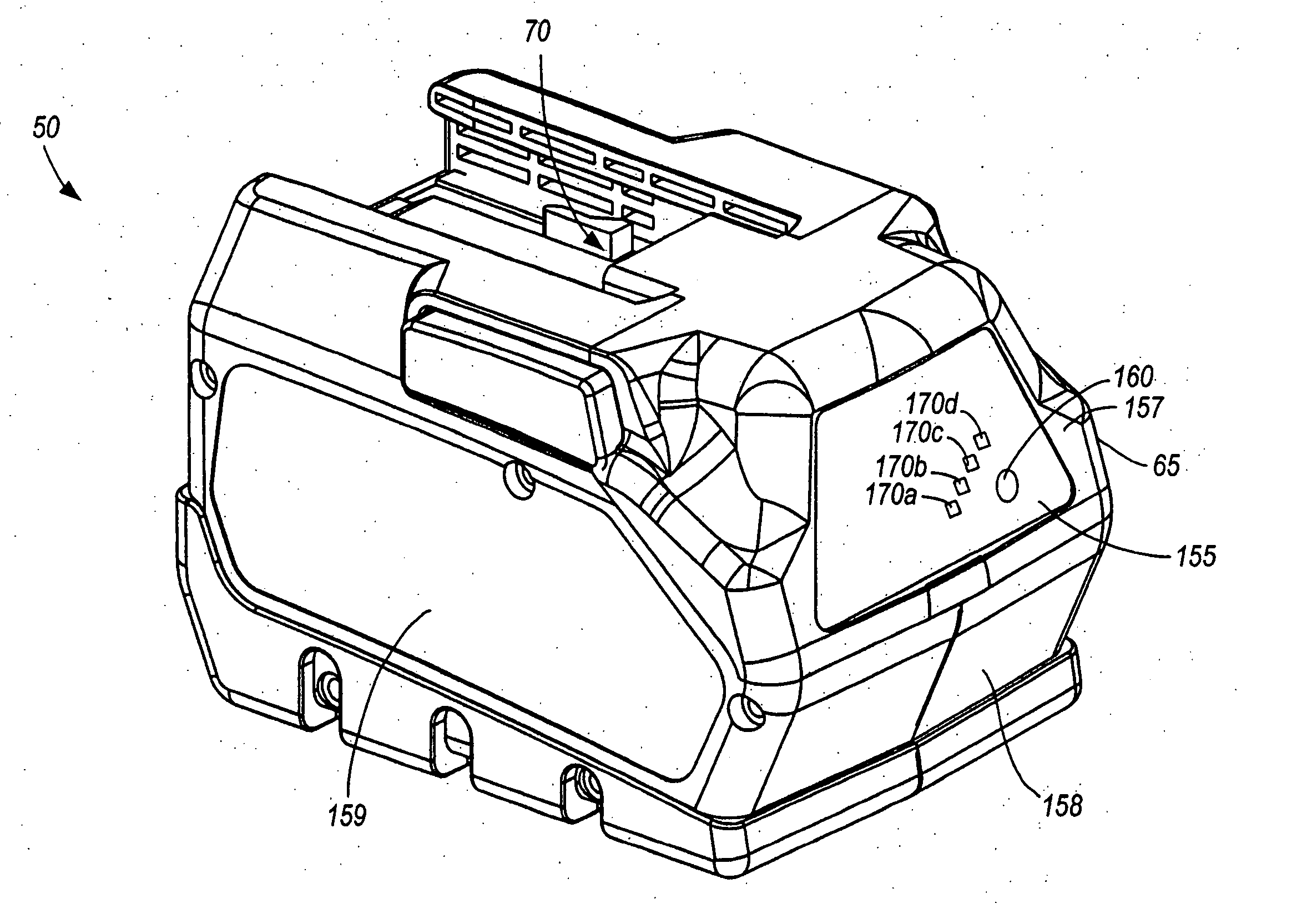
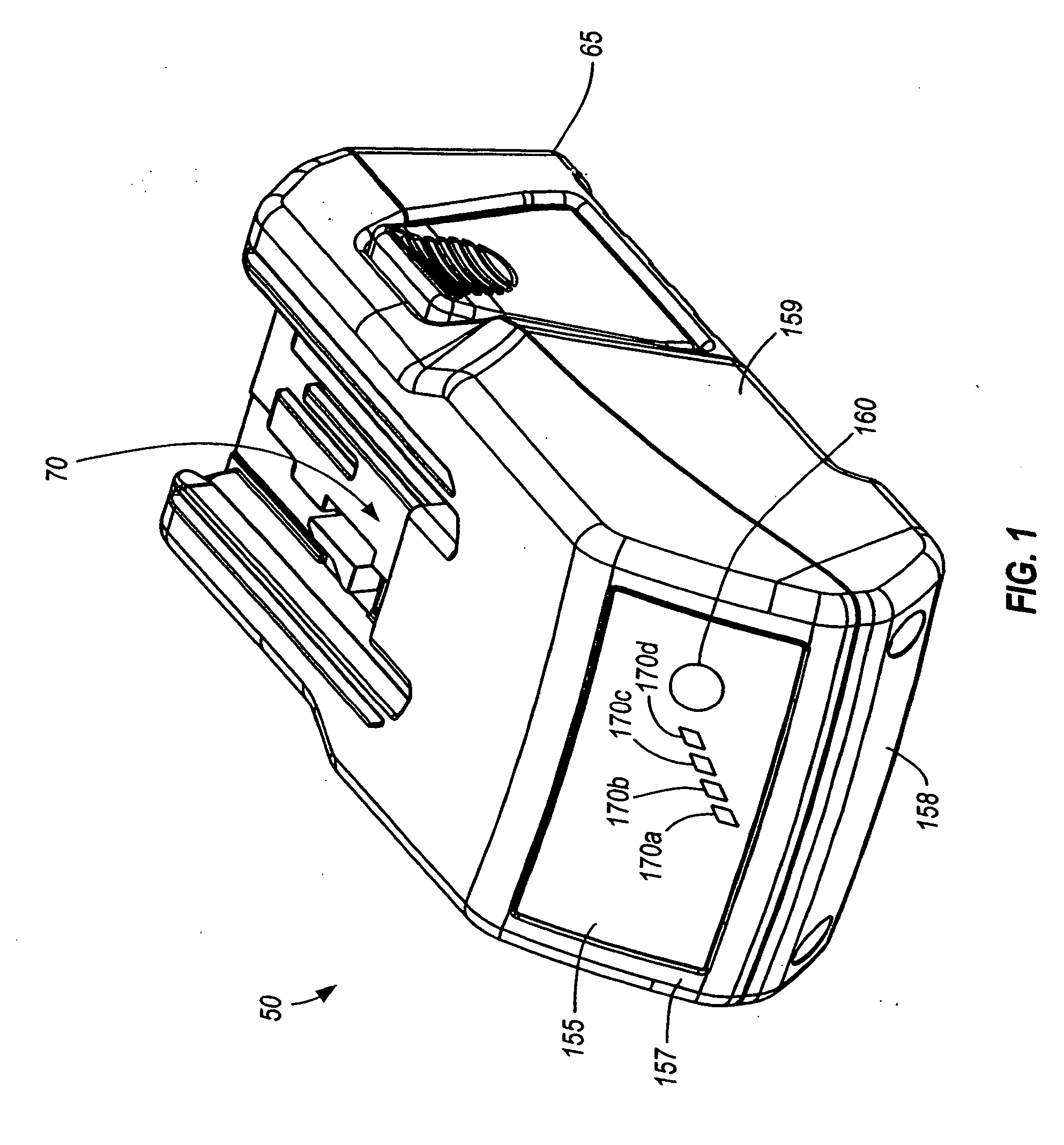
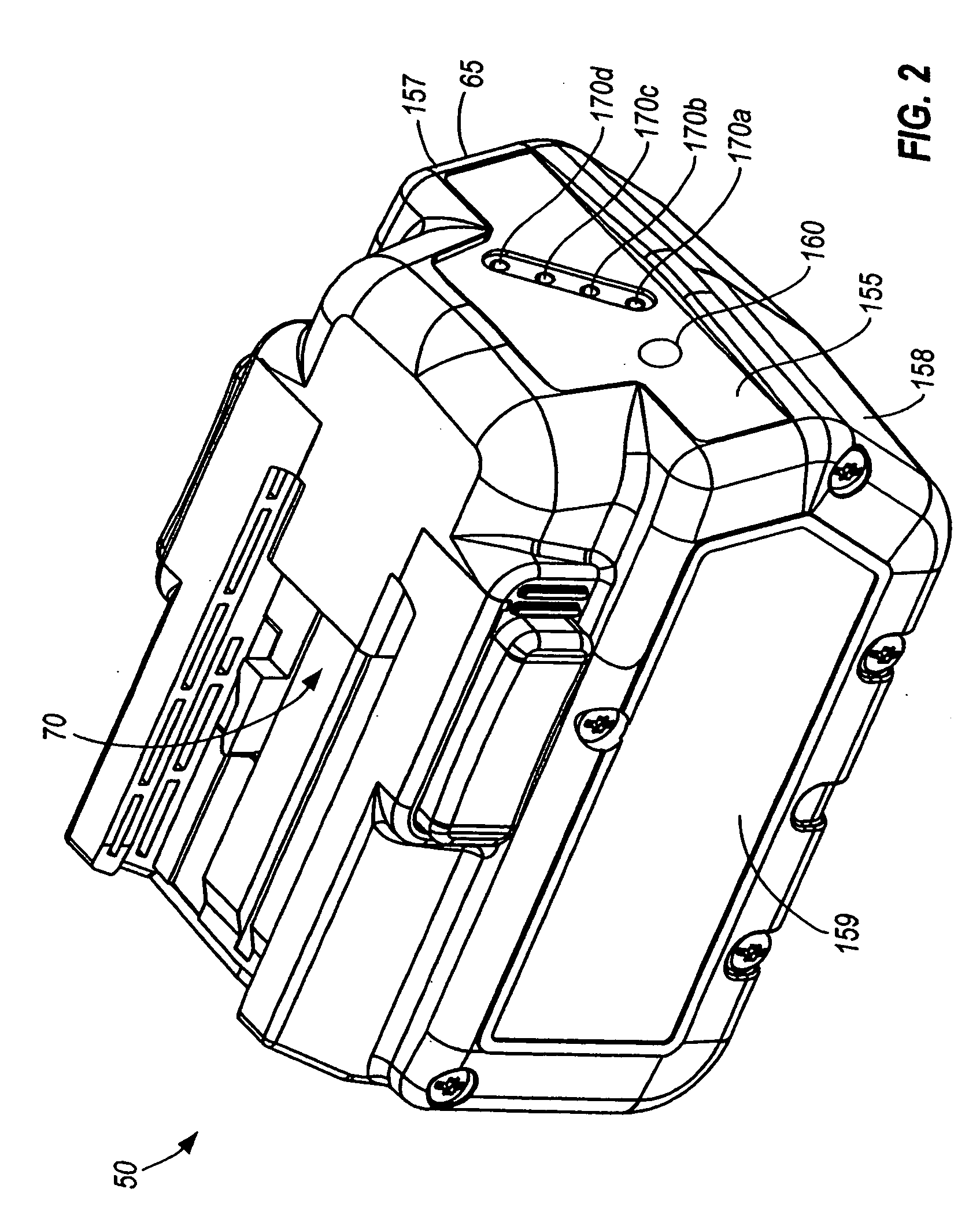
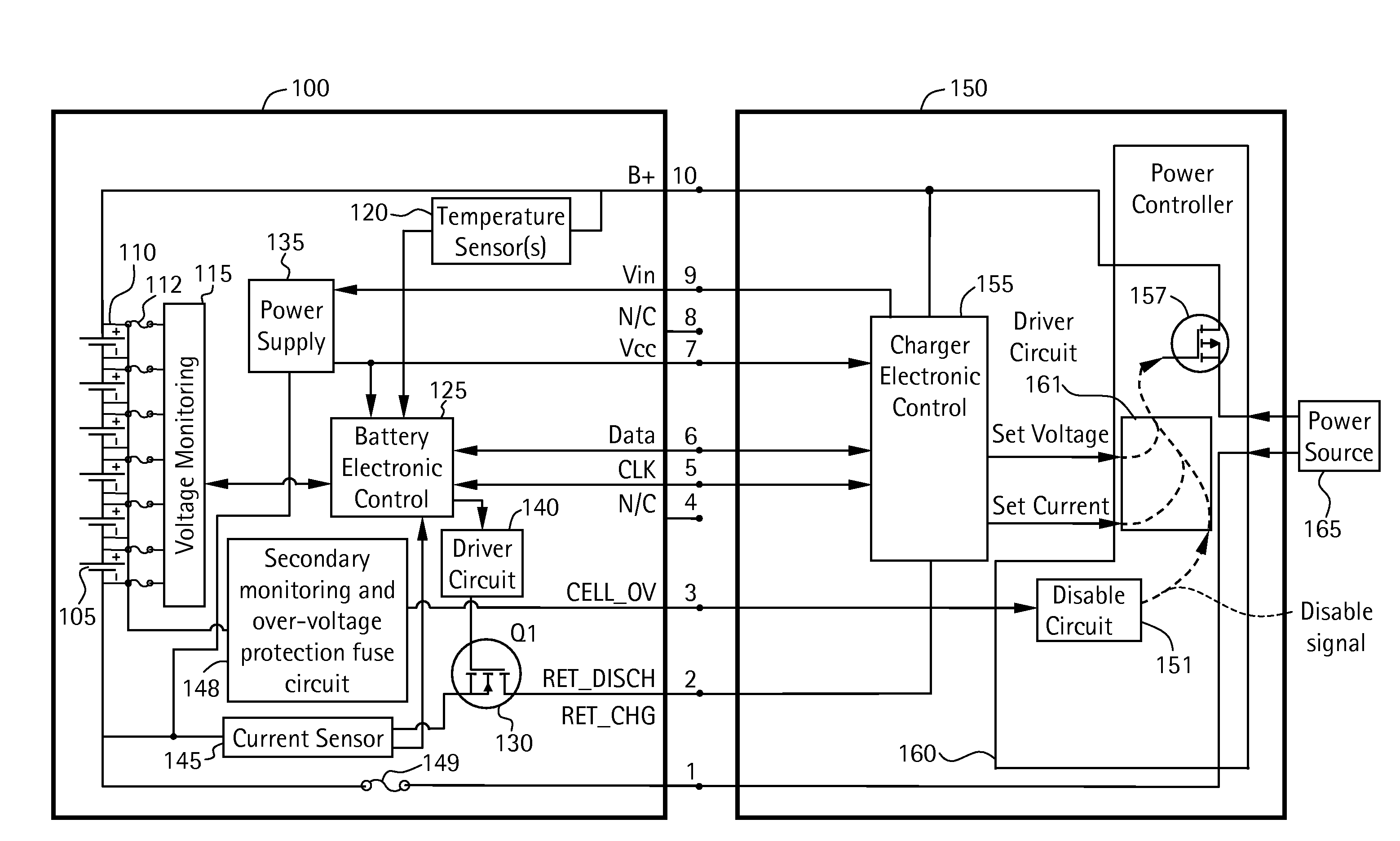
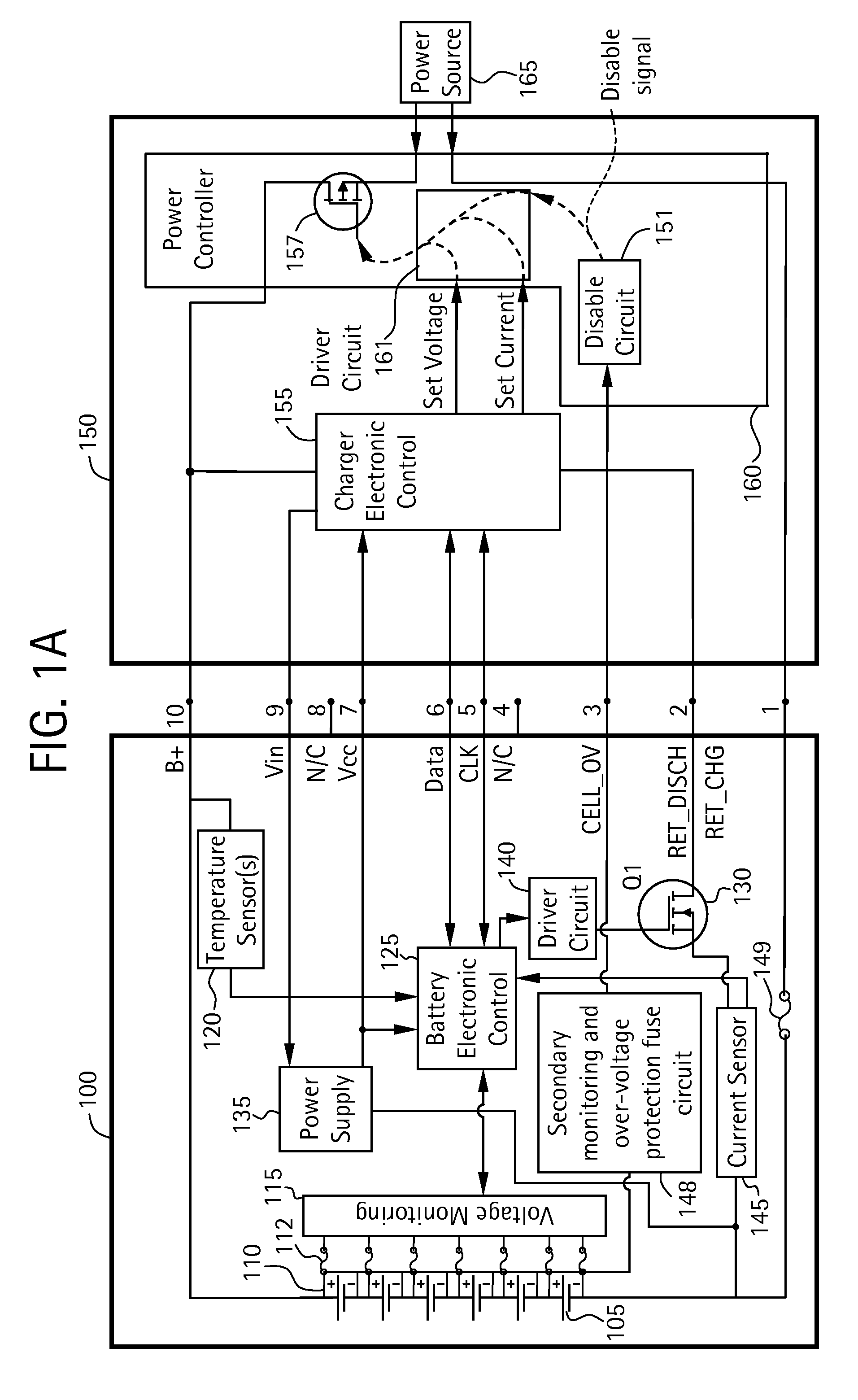
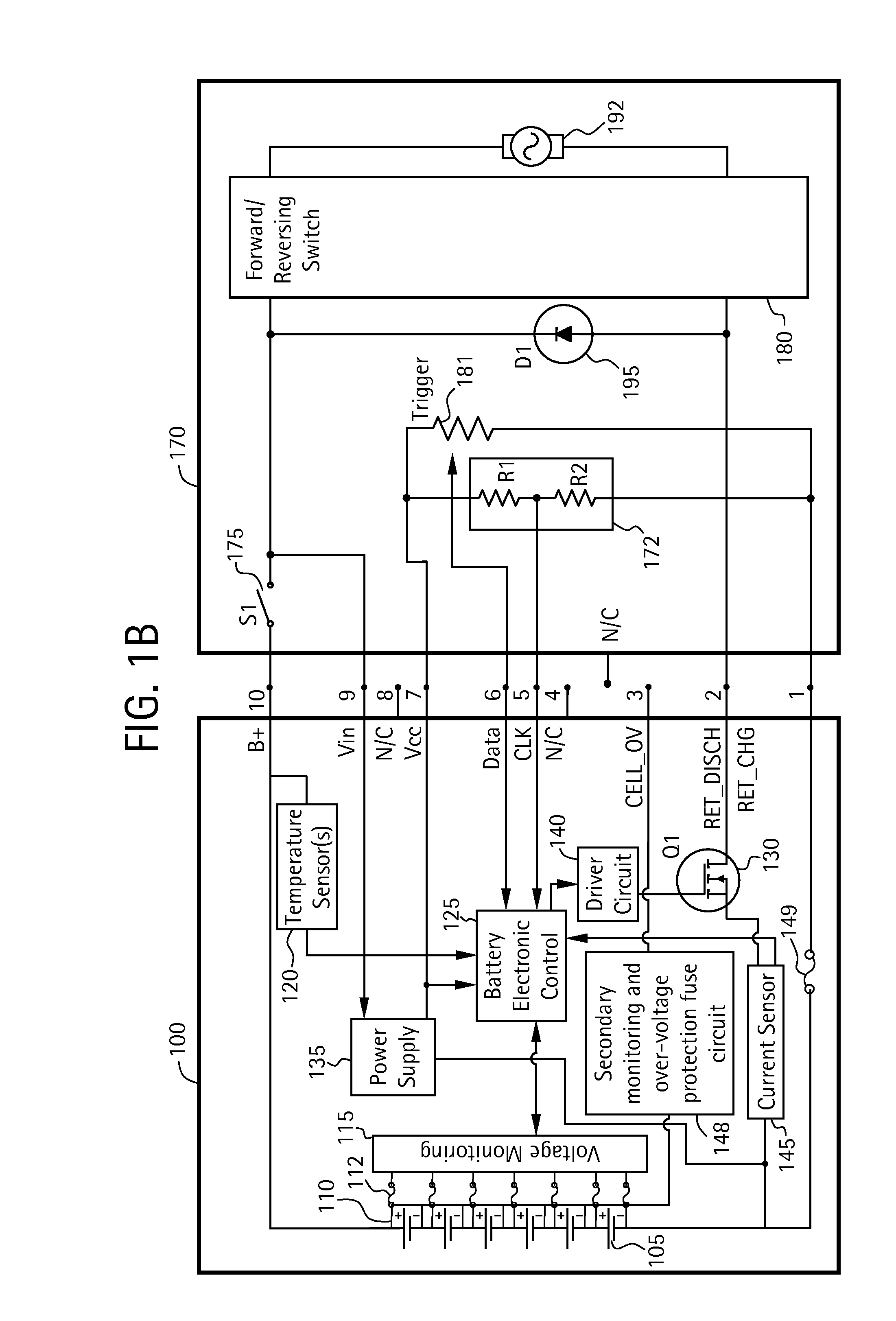
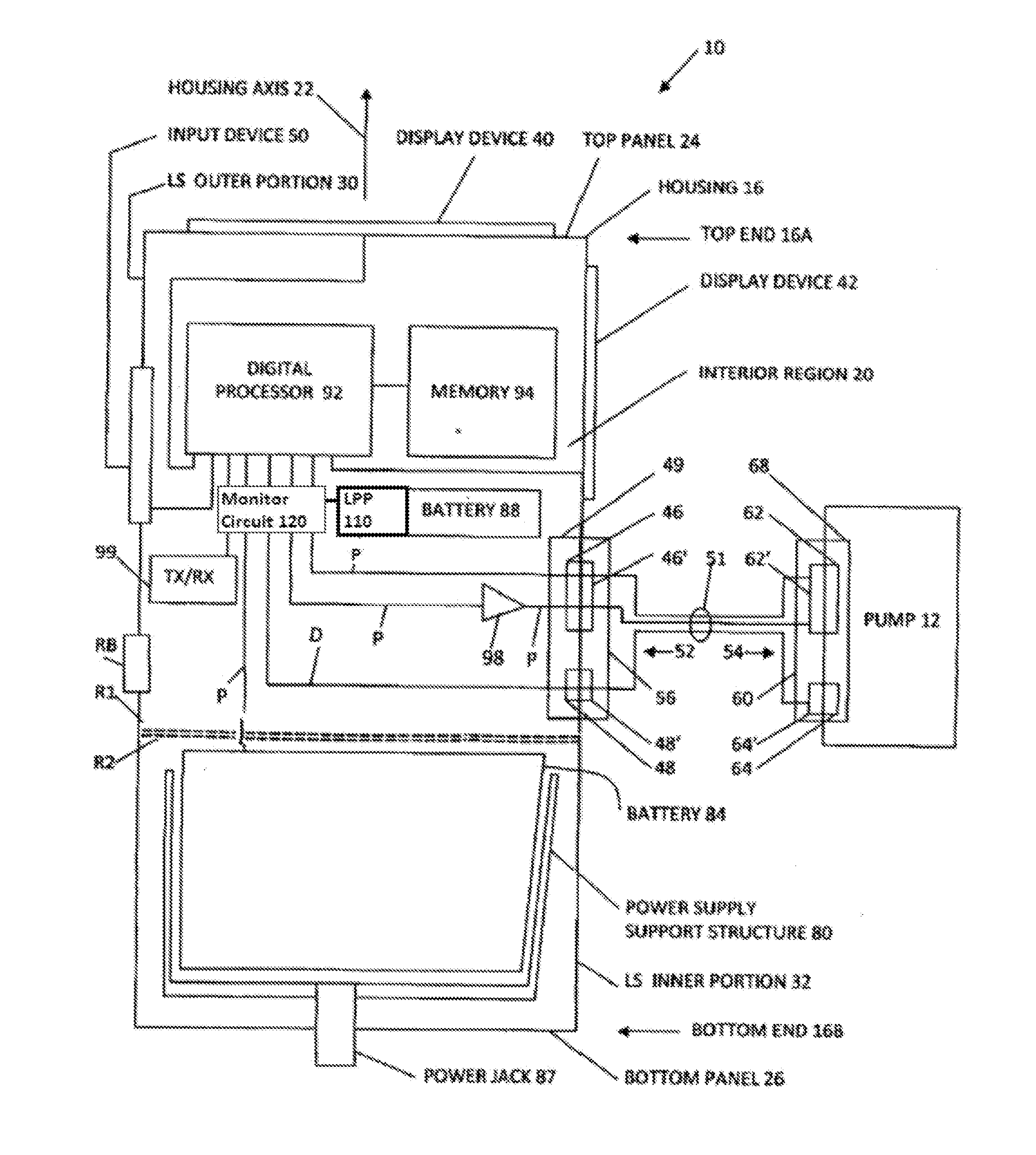
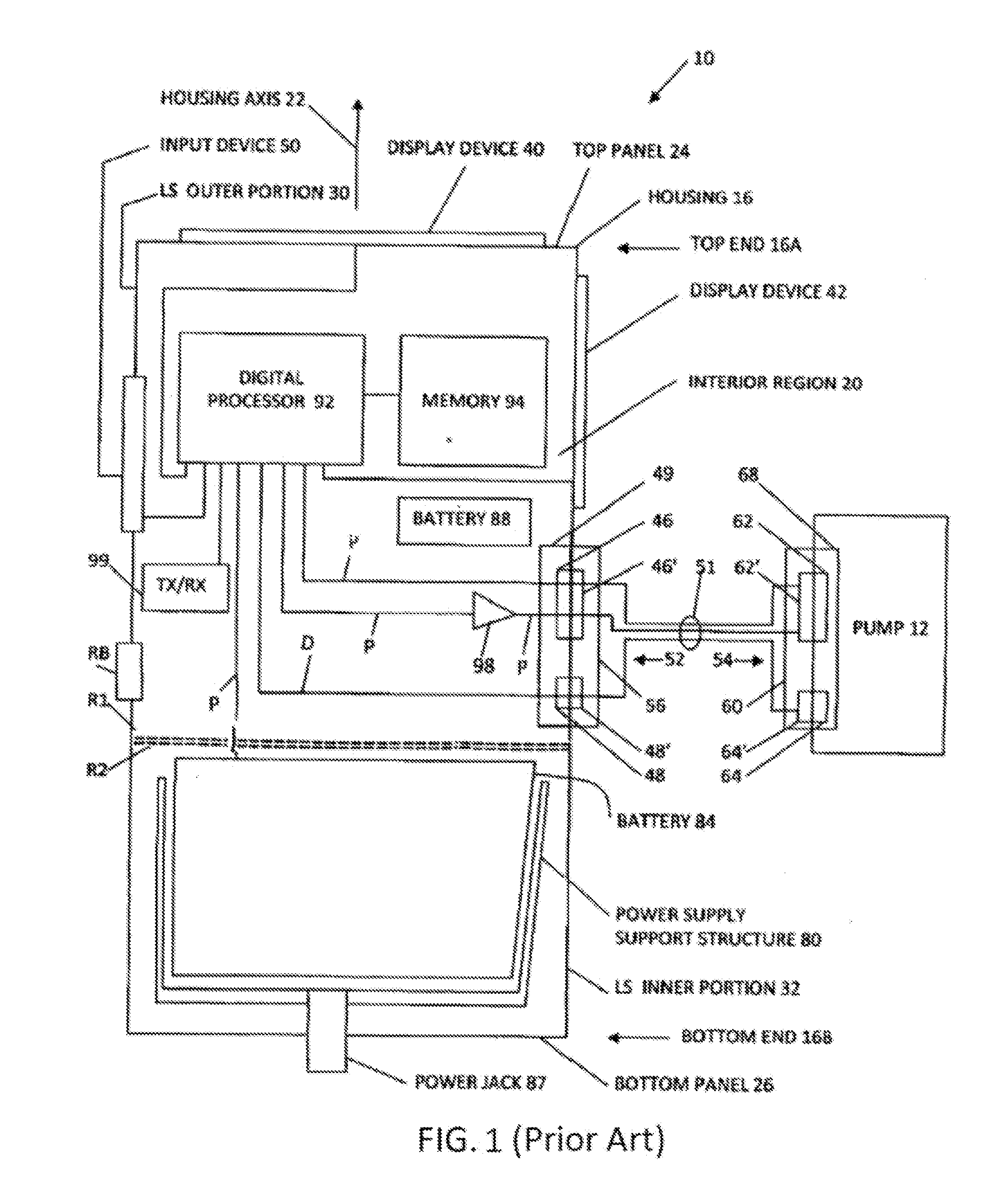
Battery pack for cordless power tools
InactiveUS7728553B2Avoid damageCircuit monitoring/indicationCharge equalisation circuitEngineeringPower tool
A battery pack which includes a battery pack electronic control circuit adapted to control an attached power tool and / or an attached charger. The battery pack includes additional protection circuits, methodologies and devices to protect against fault conditions within the pack, as the pack is operatively attached to and providing power to the power tool, and / or as the pack is operatively attached to and being charged by the charger.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
System and method for tracking and archiving battery performance data
ActiveUS9197079B2Provide reliablyEnhanced and improved operatingCircuit authenticationCircuit monitoring/indicationRechargeable cellEngineering
An intelligent rechargeable battery pack having a battery management system for monitoring and controlling the charging and discharging of the battery pack is described. The battery management system includes a memory for storing data related to the operation of the battery, and the battery management system is also configured to communicate the data related to the operation of the battery to other processors for analysis.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Viral distribution of battery management parameters
A carrier, such as a battery, that queries a memory of a charger or charging circuit, or the memory of equipment or discharging circuit powered by the battery, to determine the relative date or version of data, operating parameters and / or software on both the battery and the equipment, and either provides updated data, operating parameters and / or software to the equipment, or retrieves later dated data, operating parameters and / or software from the equipment to update the memory of the battery and / or further distribute the updated data, operating parameters and / or software to other batteries or equipment.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Battery management system for control of lithium power cells
ActiveUS9099877B2Provide reliablyEnhanced and improved operatingCharge equalisation circuitCircuit monitoring/indicationRechargeable cellEngineering
An intelligent rechargeable battery pack having a battery management system for monitoring and controlling the charging and discharging of the battery pack is described. The battery management system includes primary and secondary protection circuits for monitoring the charging and discharging of the battery. Individual battery cells forming the battery pack are connected by a main bus to a connector for connection to a battery charger or a device to be powered, and the main bus may be interrupted by a switch controlled by the battery management system to prevent damage to the battery during charging or discharging of the battery.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Protection methods, protection circuits and protective devices for secondary batteries, a power tool, charger and battery pack adapted to provide protection against fault conditions in the battery pack
InactiveUS20050077878A1Primary cell to battery groupingCharge equalisation circuitElectrical batteryEngineering
In a cordless power tool system, protection methods, circuits and devices are provided to protect against fault conditions within a battery pack that is operatively attached to a power tool or charger, so as to prevent internal or external damage to the battery pack or attached tool or charger. The exemplary methods, circuits and devices address fault conditions such as over-charge, over-discharge, over-current, over-temperature, etc.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
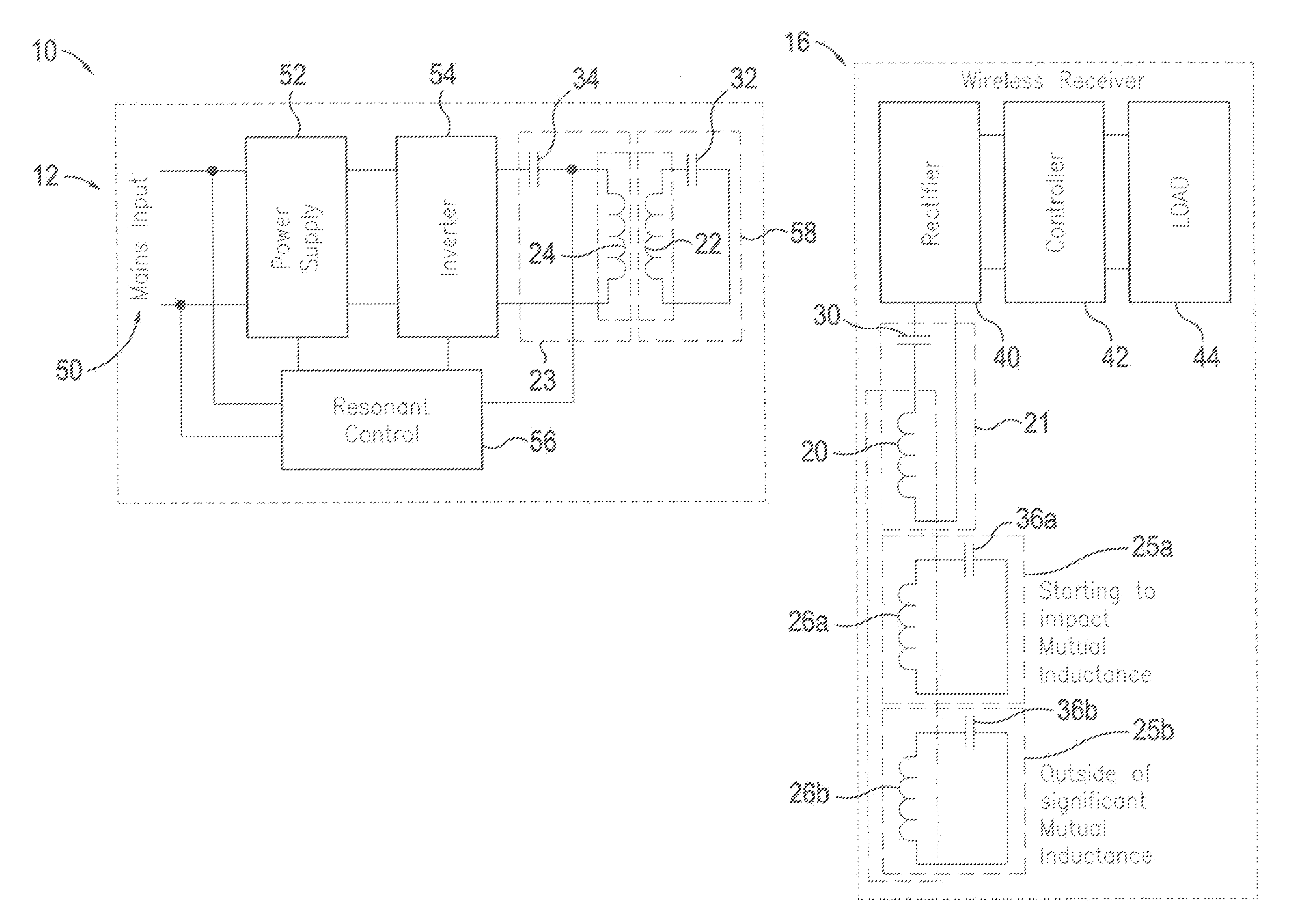
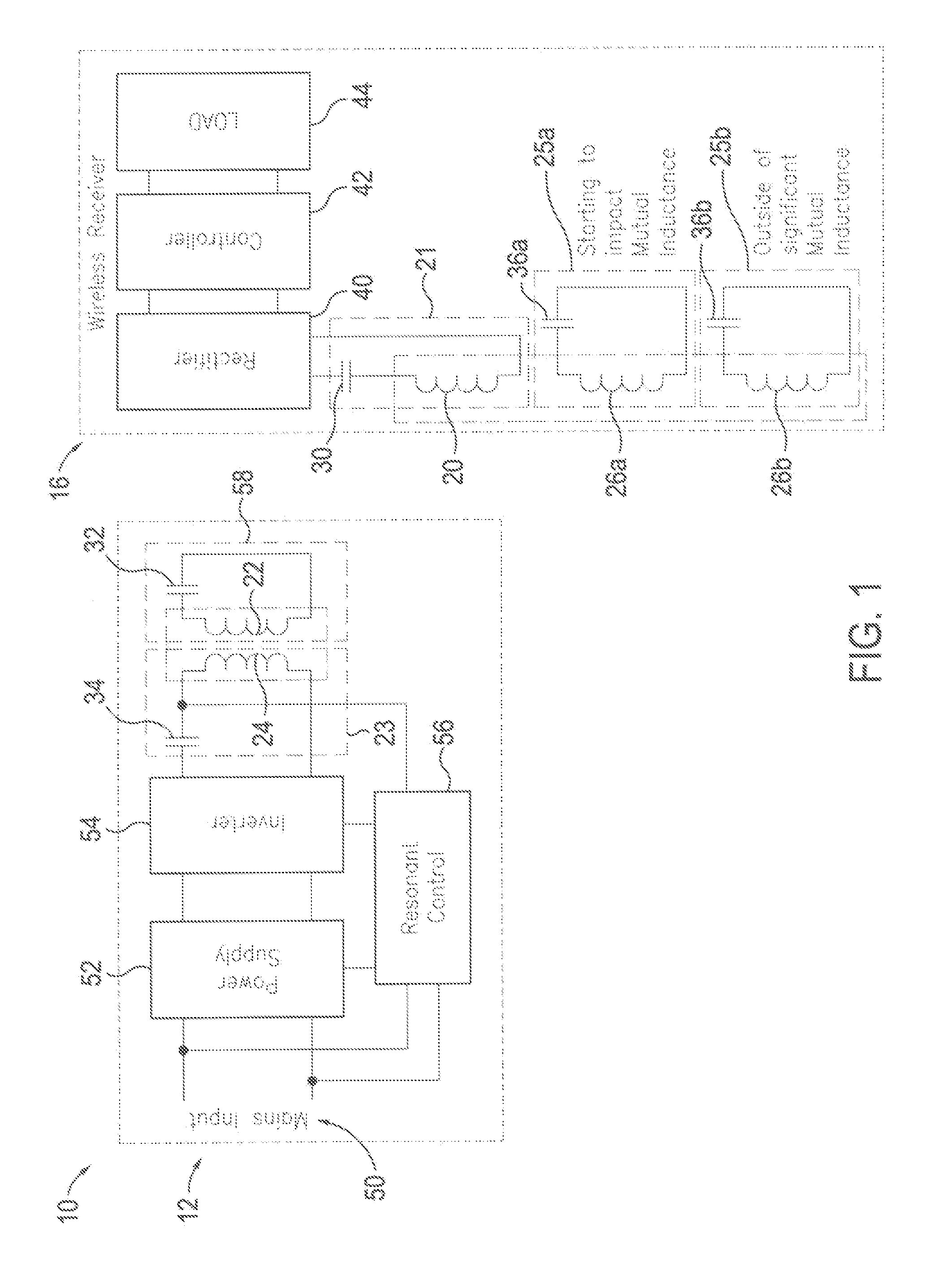
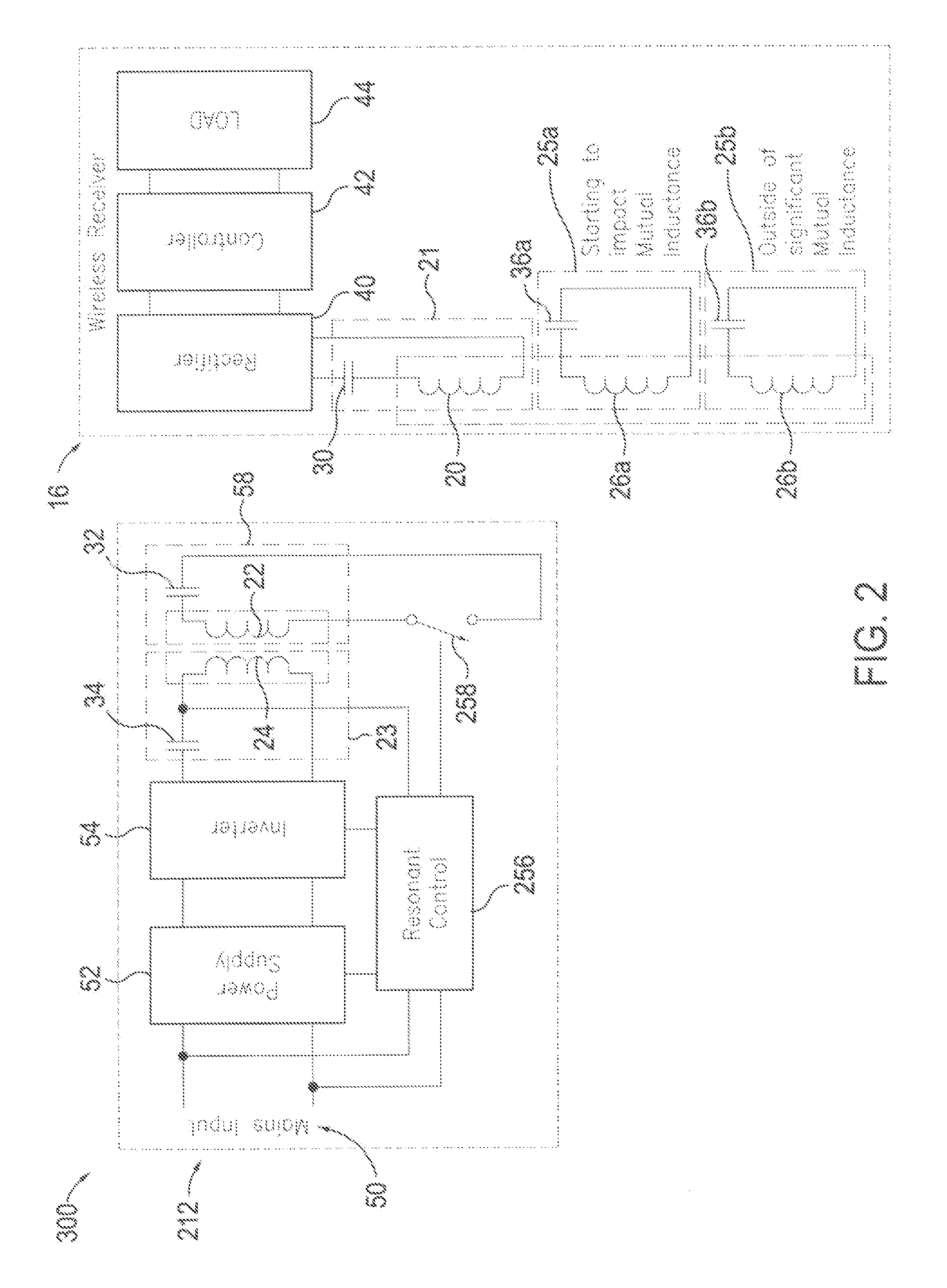
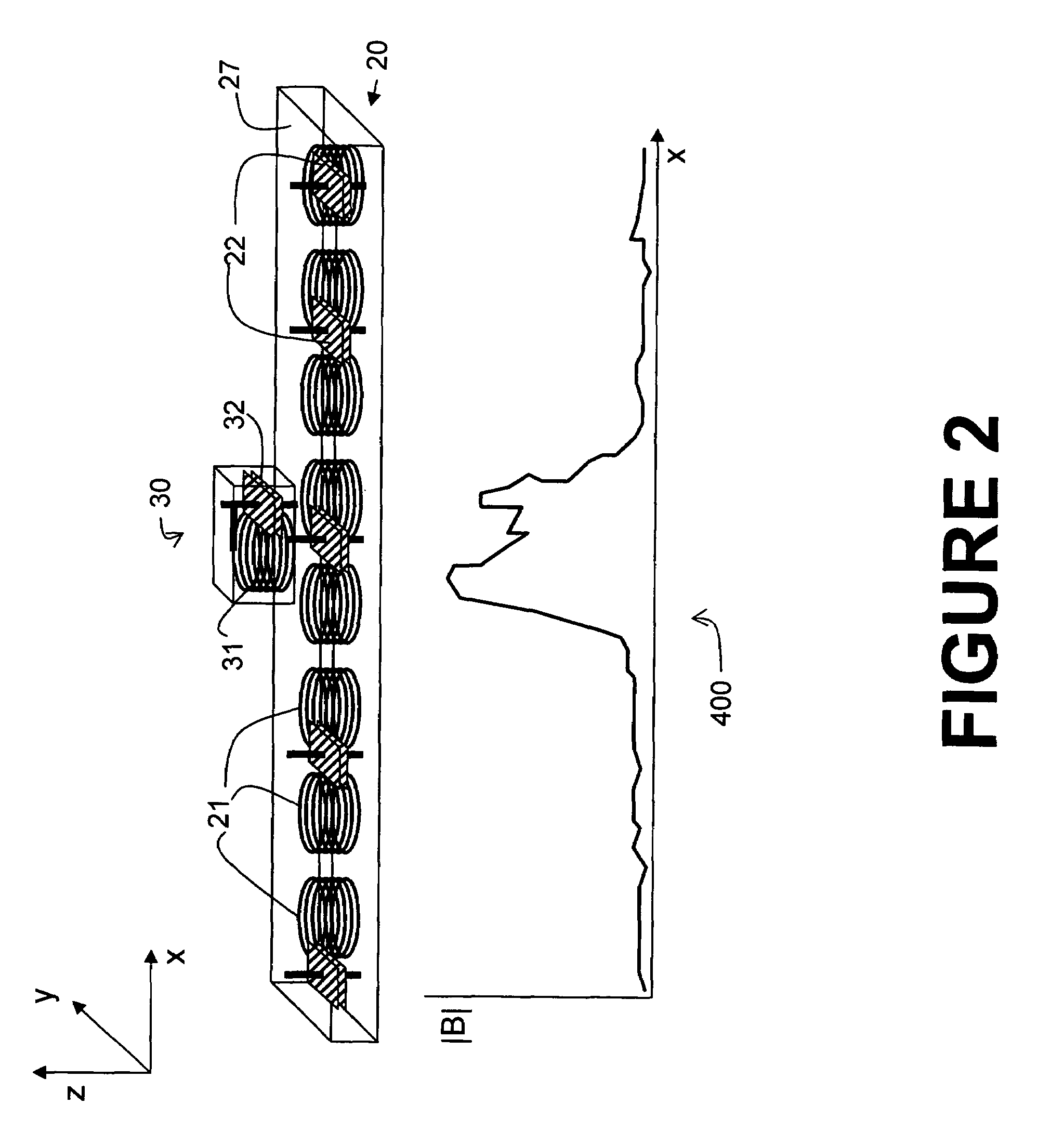
Coil configurations for inductive power transer
ActiveUS20110304216A1High power transmission efficiencyThe process is simple and effectiveNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionElectric power system
An inductive power supply system in which the receiving unit includes a secondary coil and a plurality of resonating circuits with different characteristics. Each of the resonating circuits may include a resonating coil and a resonating capacitor. The resonating coils may be inductively coupled to the secondary coil so that energy may be transferred from one or more of the resonating coils to said receiving unit. The plurality of resonating circuits are configured to provide improved power transfer efficiency or performance at different distances between the primary coil and secondary coil. The present invention may also provide a method for tuning the wireless power system including the general steps of measuring an operating characteristic in the primary unit, measuring an operating characteristic in the receiver unit and tuning one or more of the components in the primary unit and the secondary unit based on a comparison of the two measurements.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
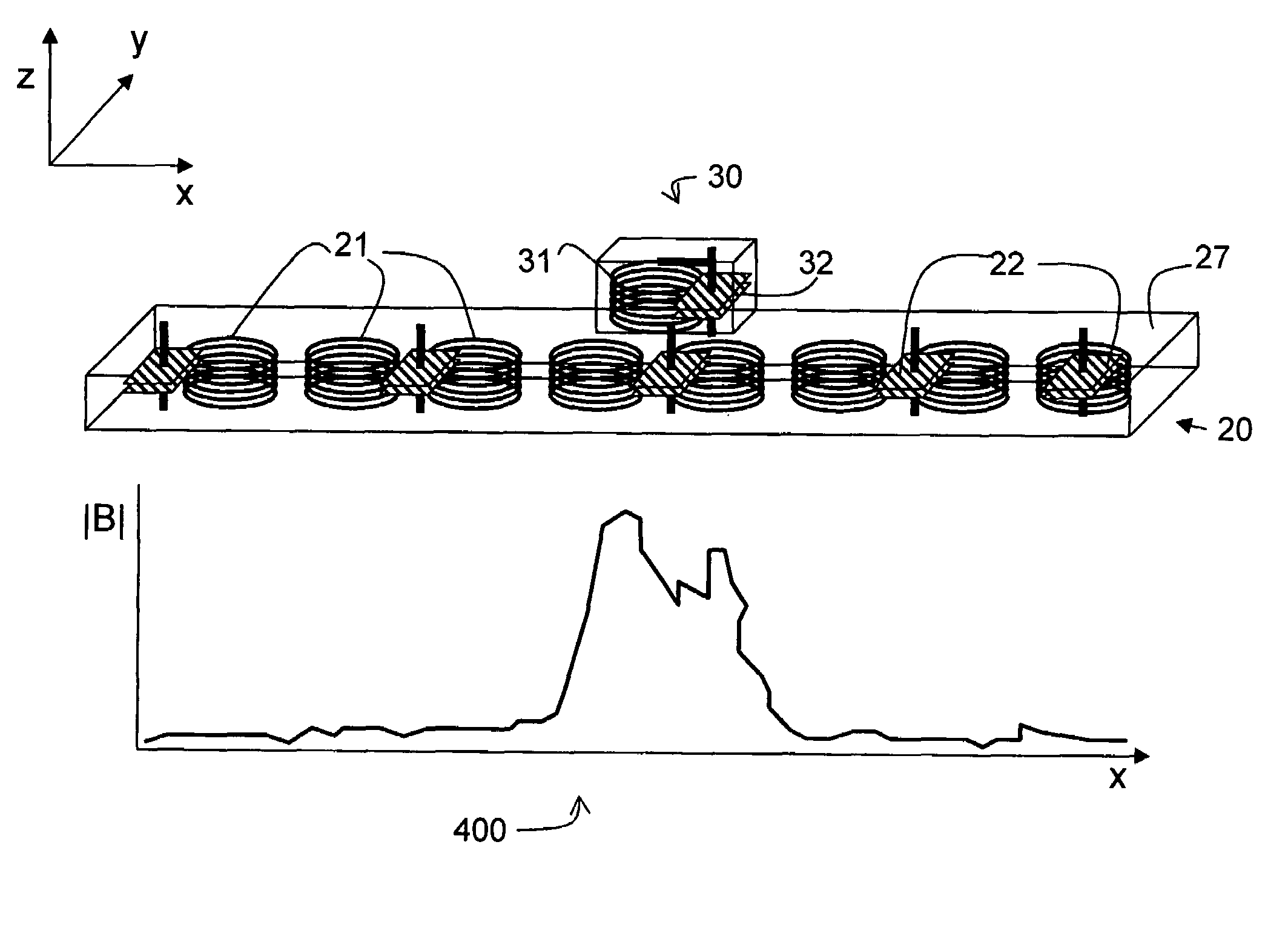
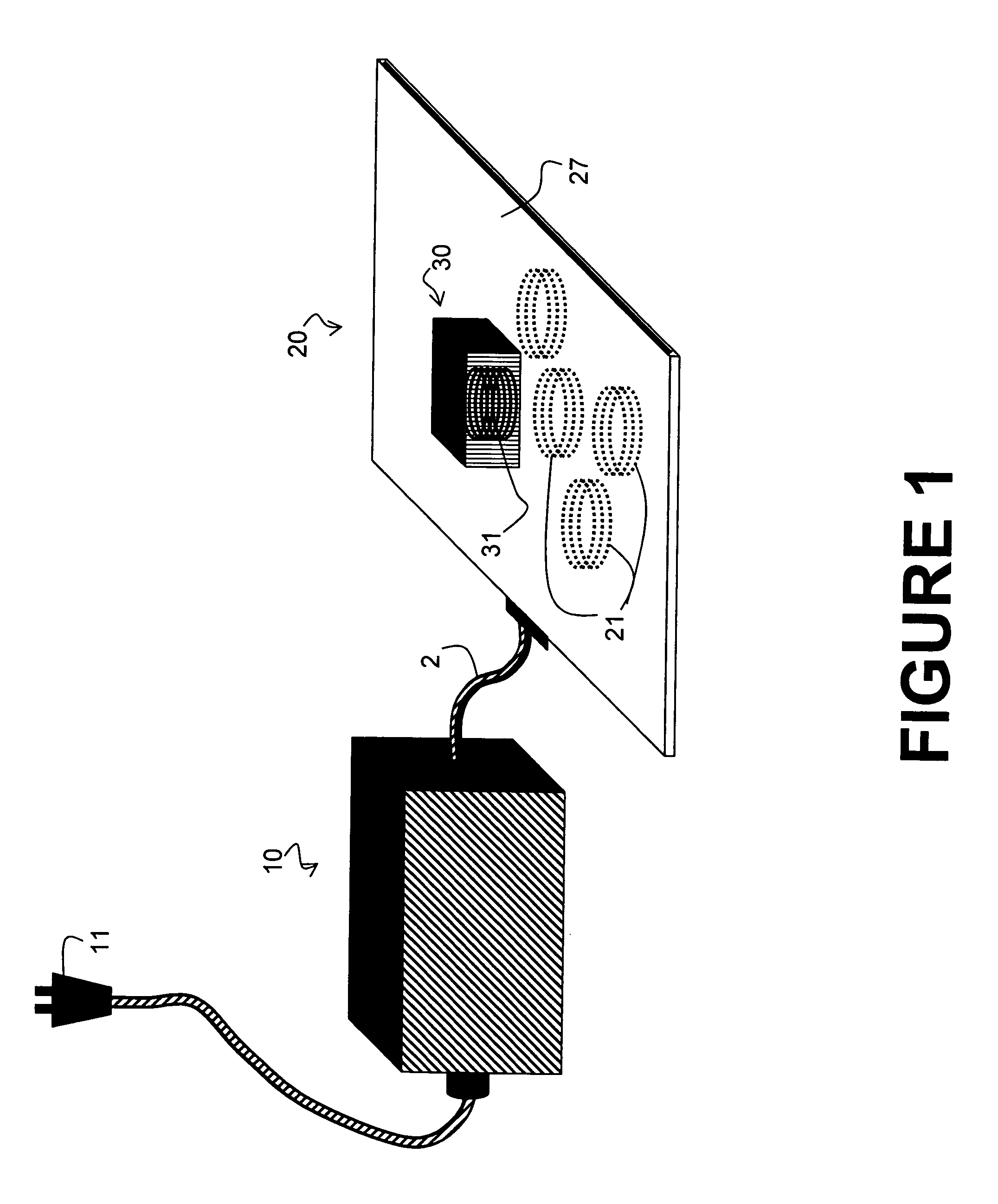
System and method for selective transfer of radio frequency power
InactiveUS7521890B2Improve toleranceSufficient powerSecondary cellsElectric switchesHigh frequency powerRadio frequency
A system and method is provided for the inductive transfer of electric power between a substantially flat primary surface and a multitude of secondary devices in such a way that the power transfer is localized to the vicinities of individual device coils. The contact free power transfer does not require precise physical alignment between the primary surface and the secondary device and can allow the secondary device or devices to be placed anywhere and in arbitrary orientation with respect to the primary surface. Such power transfer is realized without the need of complex high frequency power switching network to turn the individual primary coils on or off and is completely scalable to almost arbitrary size. The local anti-resonance architecture of the primary device will block primary current from flowing when no secondary device or devices are in proximity to the local RF power network. The presence of a tuned secondary device detunes the local anti-resonance on the primary surface; thereby enable the RF power to be transferred from the local primary coils to the secondary device. The uniformity of the inductive coupling between the active primary surface and the secondary devices is improved with a novel multi-pole driving technique which produces an apparent traveling wave pattern across the primary surface.
Owner:MOBILEWISE
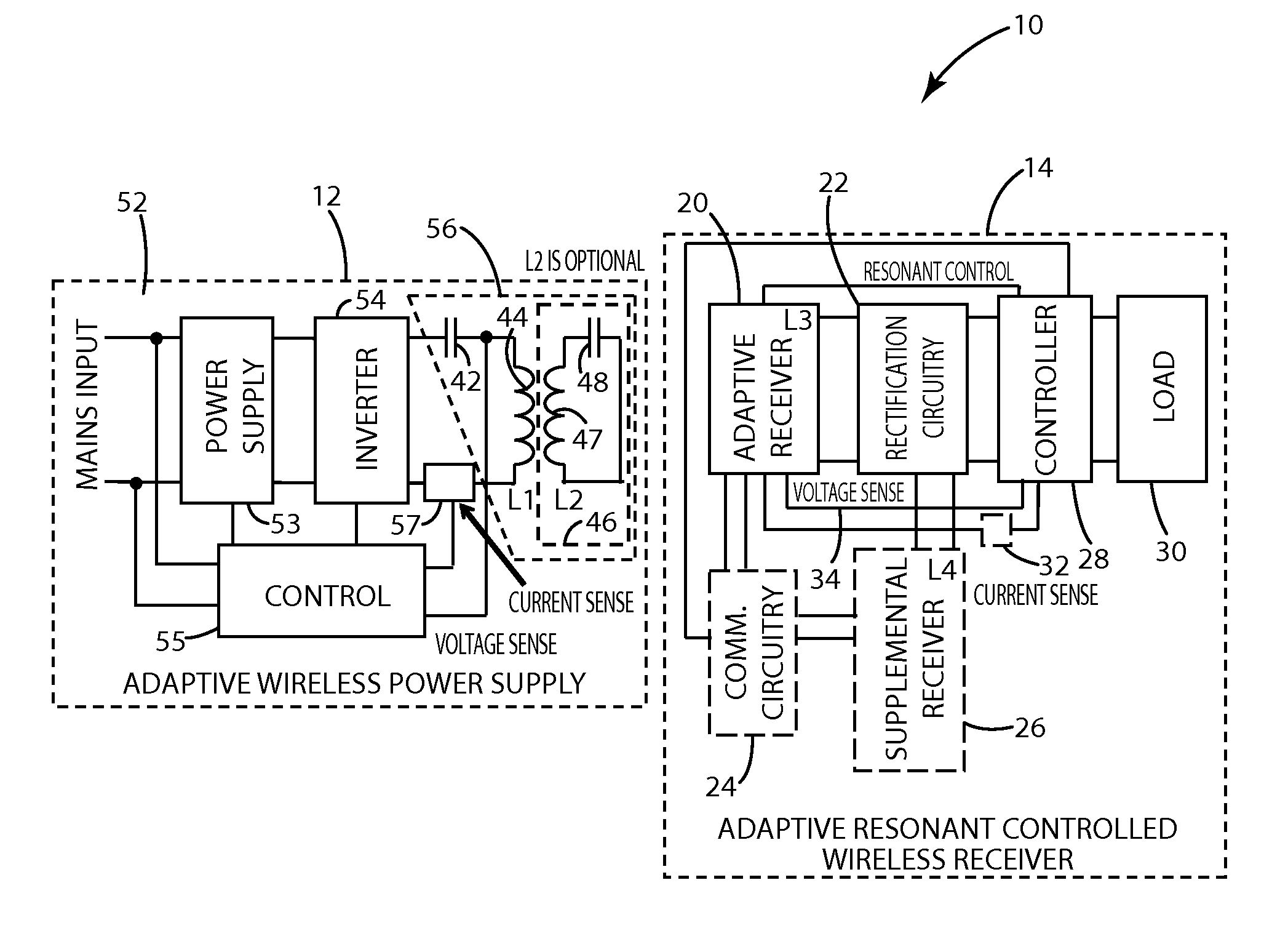
Wireless power control
ActiveUS20150207333A1Improve powerHigh power transmission efficiencyElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersResonanceEngineering
A remote device in accordance with the present invention includes an adaptive power receiver that receives wireless power from the wireless power supply by induction. The adaptive power receiver may be switched among two or more modes of operation, including, for example, a high-Q mode and a low-Q mode. By controlling the switching between modes, the amount of energy received by the adaptive receiver may be controlled. This control is a form of adaptive resonance control or Q control.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
Contact-less power supply, contact-less charger systems and method for charging rechargeable battery cell
ActiveUS20090033280A1Effectively transmits induced electromotive forceReduce energy wasteNear-field transmissionTransformersCoil arrayRechargeable cell
The present invention relates to a contact-less power supply magnetically coupled to a battery device having a receiving coil therein, for contact-less charging the battery device, the contact-less power supply having a sending coil array including a plurality of sending coils for inducing a charging power to the receiving coil; and a driving means for detecting a sending coil magnetically coupled to the receiving coil and selectively driving only the detected sending coil.
Owner:LS CABLE & SYST LTD
Method of determining battery power limits for an energy storage system of a hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS20050077867A1Improve robustnessOvercome deficienciesHybrid vehiclesCircuit monitoring/indicationPower flowElectrical battery
A method of providing closed-loop control of power flowing into and out of an energy storage system (ESS), wherein the ESS comprises a battery is provided. The method may be implemented as a computer control algorithm for determining the charge and discharge limits for the ESS in a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV), wherein the ESS comprises a battery pack or array. The method comprises determining charge and discharge power limits during each of a plurality of control loops, comparing these limits during each of the plurality of control loops, and providing a charge power limit output and a discharge power limit output for use in a subsequent control loop which are based upon the charge power limit and the discharge power limit. The charge power limit output and discharge power limit output are set equal to the discharge power limit and charge power limit, respectively, when the discharge power limit is greater than the charge power limit; and are selected from the group consisting of the charge power limit, the discharge power limit and zero when the discharge power limit is less than or equal to the charge power limit.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Apparatus and method for wireless charging
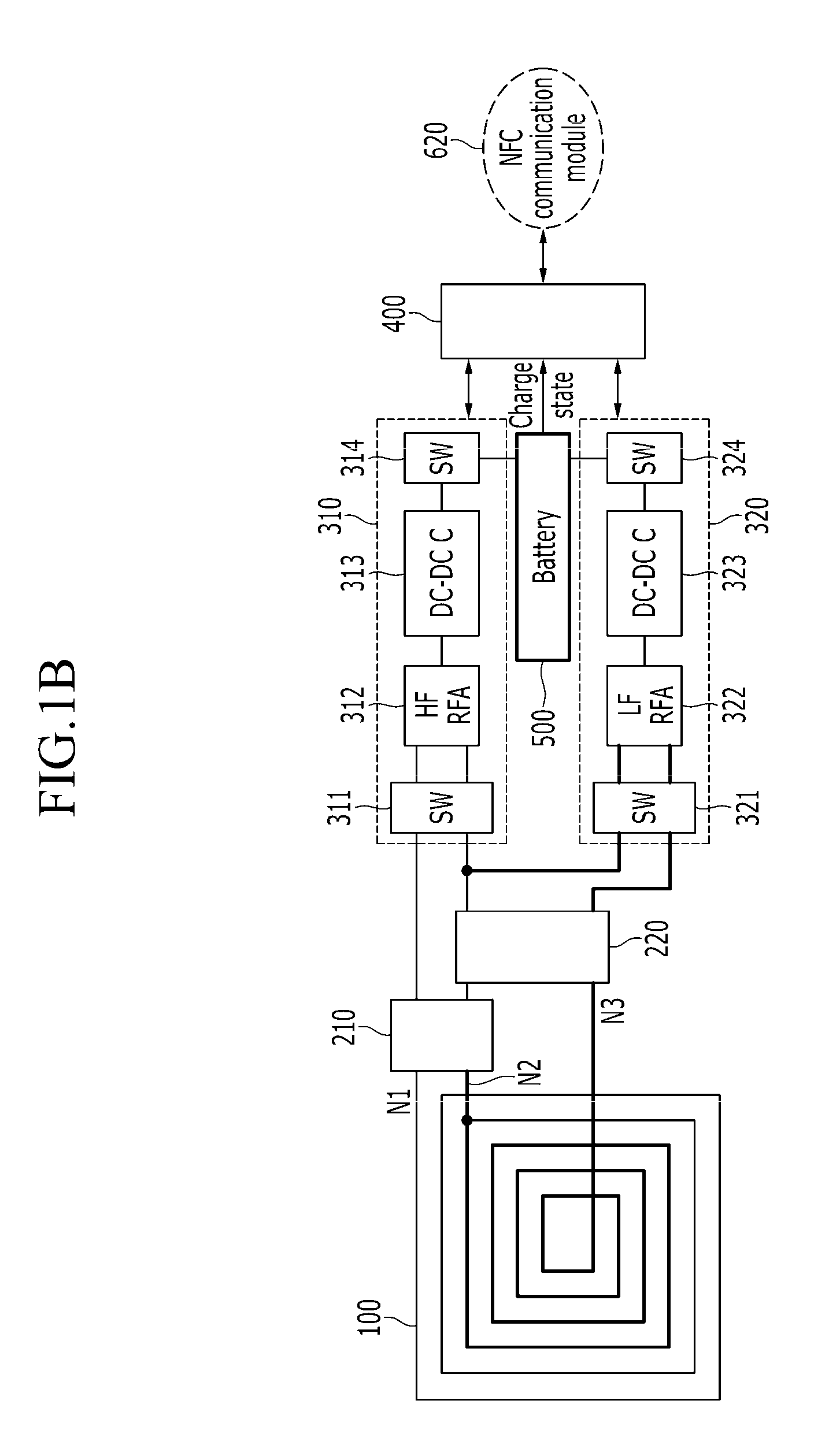
A wireless charging apparatus is provided. The wireless charging apparatus includes: an antenna that receives electrical waves; at least two charging power generators that generate charging power for charging a battery using the electrical waves received through the antenna; and a controller that senses a frequency of the electrical waves received through the antenna and that activates one of the at least two charging power generators according to a sensed result.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
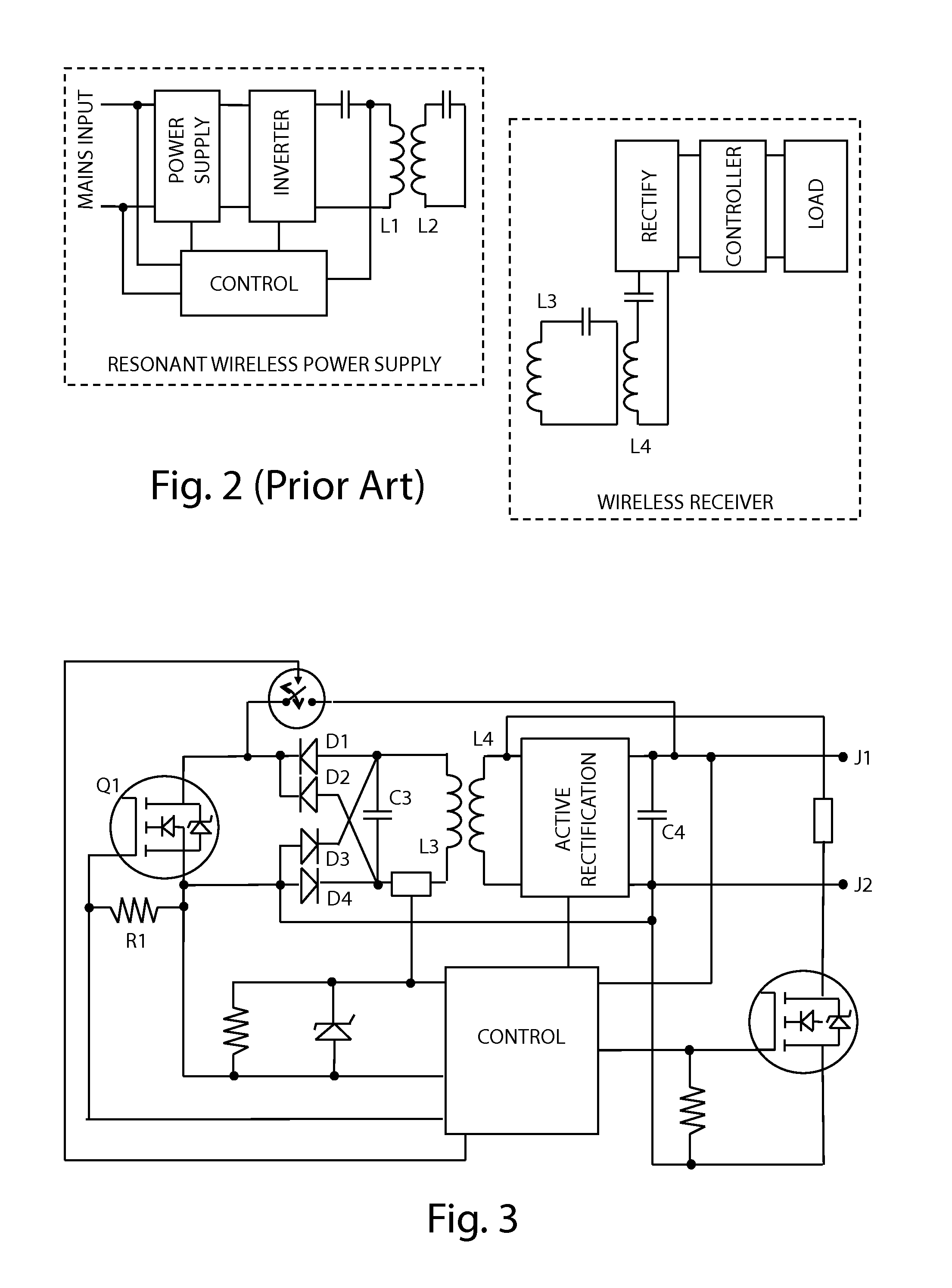
Method and apparatus for contactless power transfer
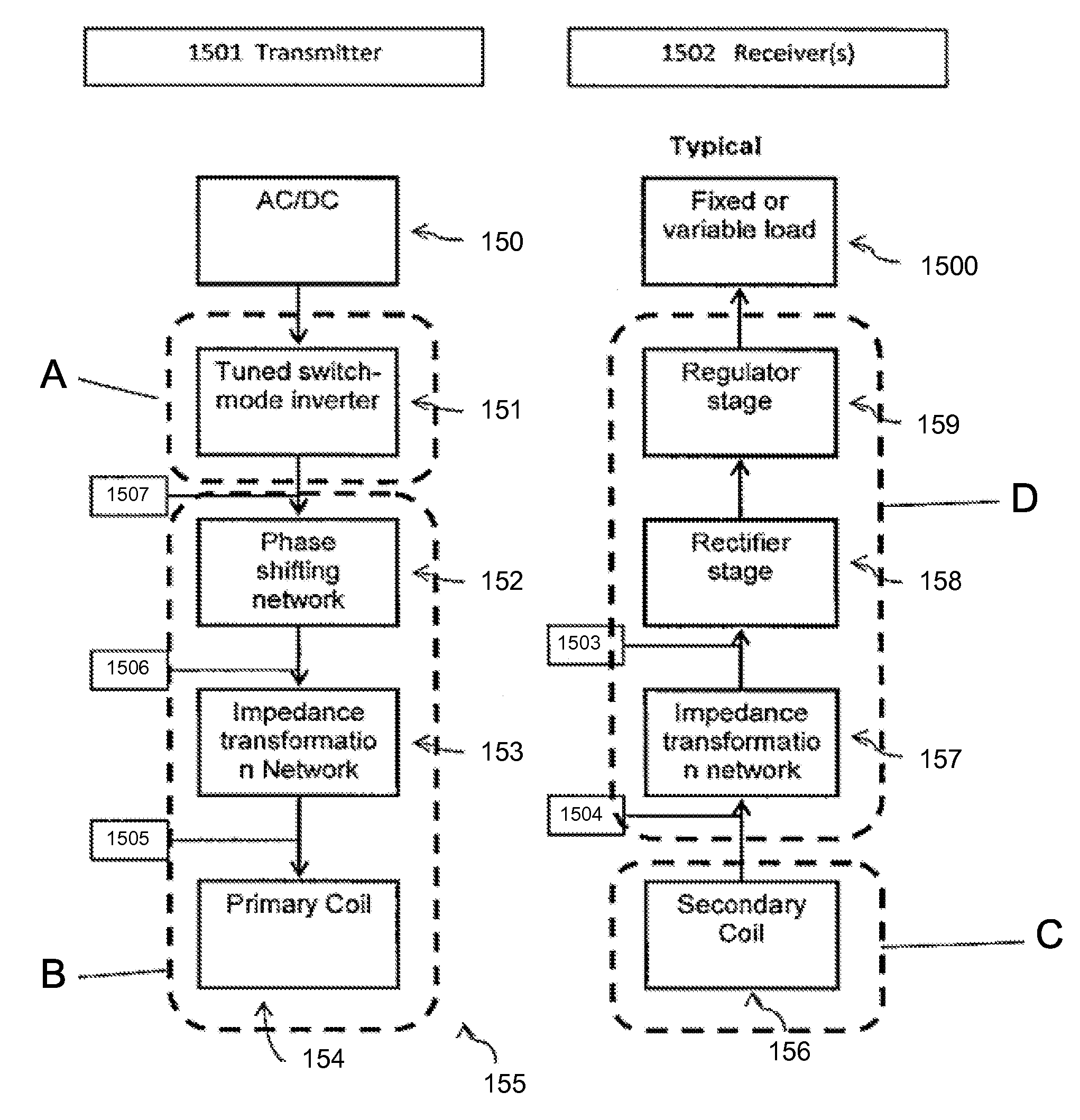
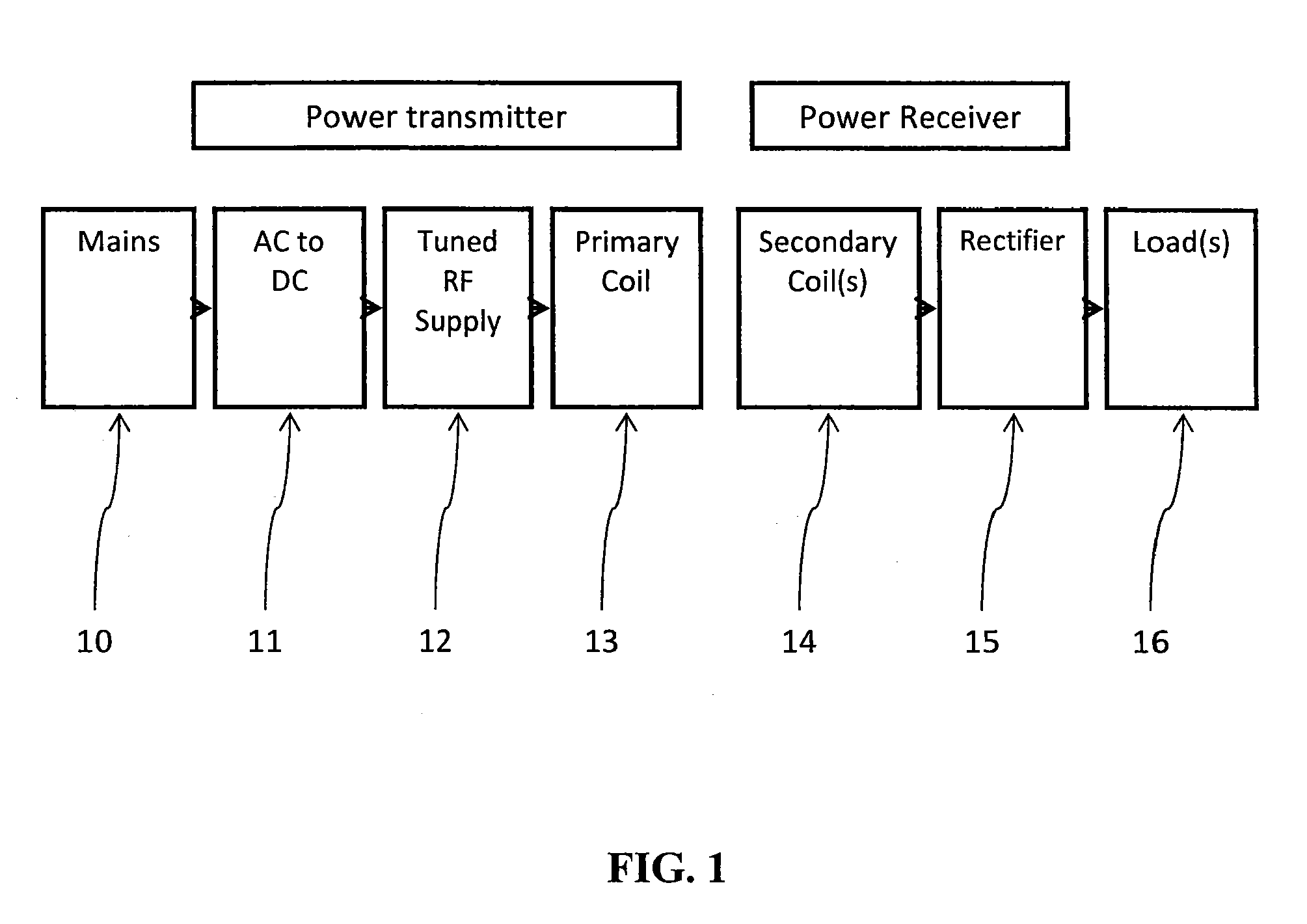
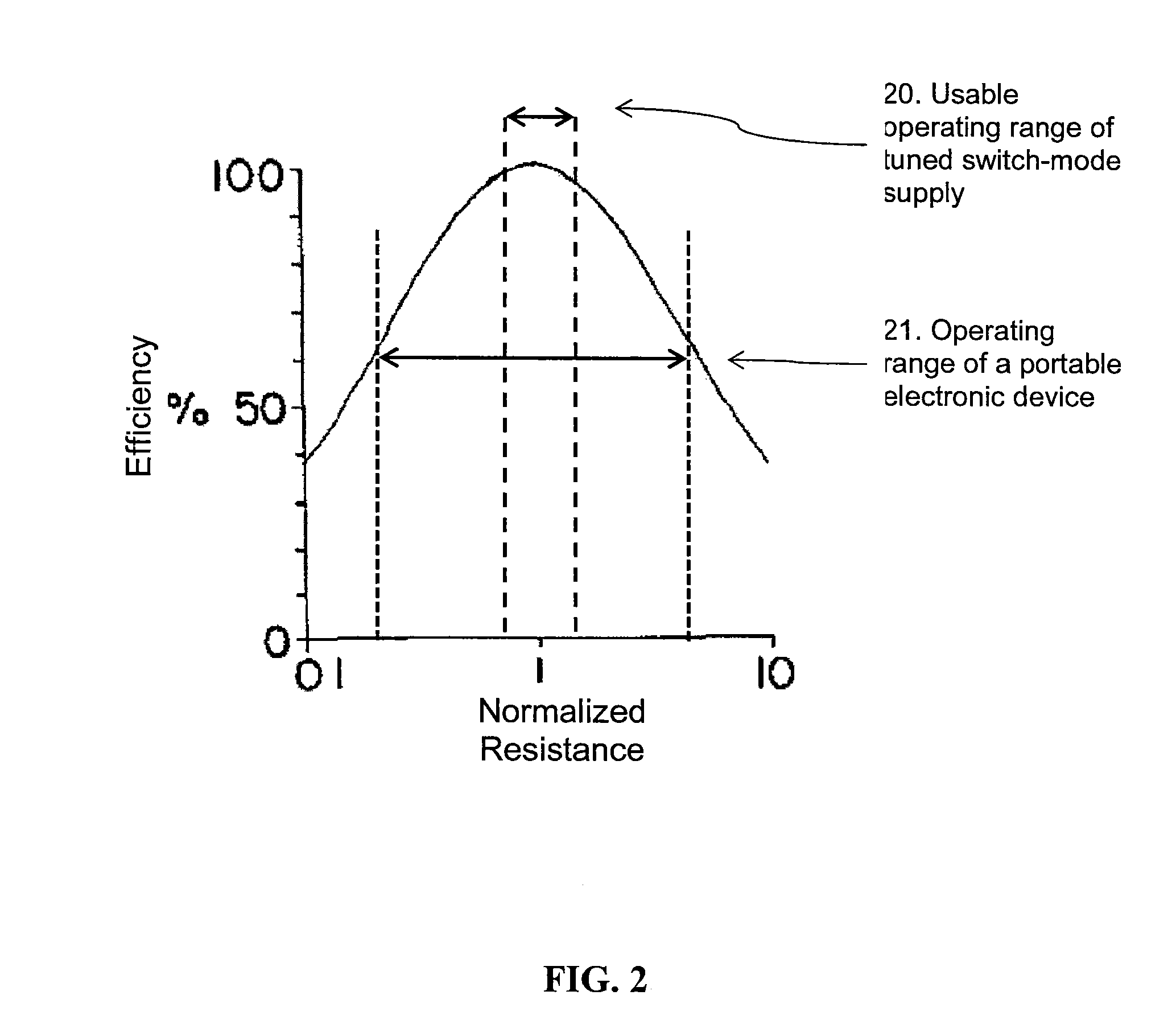
ActiveUS8674551B2Improve system performanceEasy to controlCircuit monitoring/indicationTransformersElectric power transmissionEngineering
Embodiments of the subject invention pertain to a method and apparatus for contactless power transfer. A specific embodiment relates to an impedance transformation network, a new class of load network for application to a contactless power system. Embodiments of the impedance transformation network enable a contactless power system to operate without encountering the common problems of: 1) over-voltage and / or under-voltage conditions; 2) over-power and / or under-power conditions; 3) power oscillations; and 4) high heat dissipation.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and system for battery protection
ActiveUS20060091858A1Solution to short lifeSevere impactCharge equalisation circuitCell electrodesElectric powerBattery pack
A method of conducting an operation including a battery. The battery includes a cell having a voltage. Power is transferable between the cell and the electrical device. A controller is operable to control a function of the battery pack. The controller is also operable with a voltage at least one of equal to and greater than an operating voltage threshold. The cell is operable to selectively supply voltage to the controller. The method includes the act of enabling the controller to operate when the voltage supplied by the cell is below the operating voltage threshold.
Owner:MILWAUKEE ELECTRIC TOOL CORP
Systems and methods for wireless power transfer
InactiveUS20080116847A1Relax requirementsEasy to customizeTransformersTransformers/inductances circuitsEngineeringMagnetic amplifier
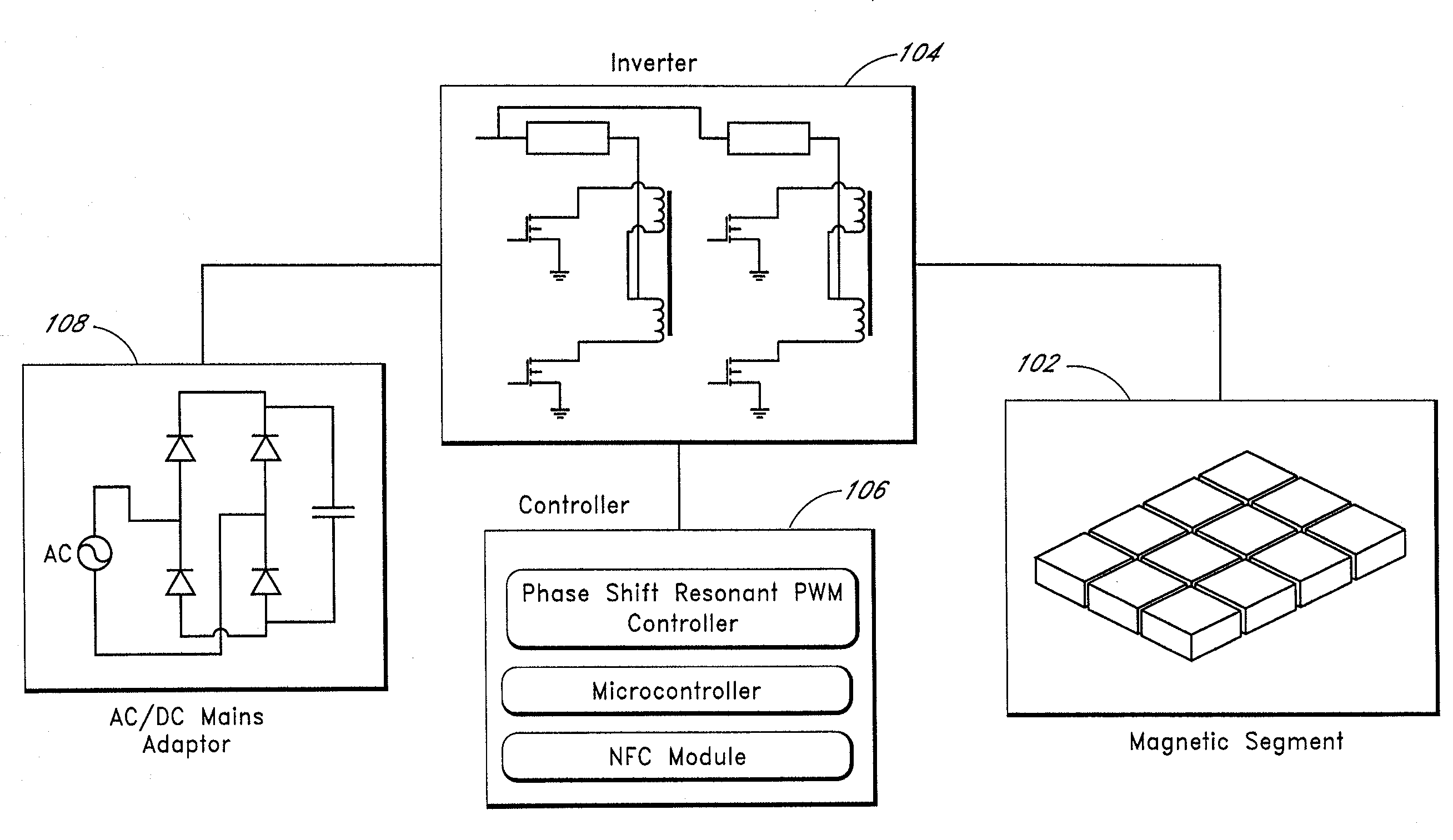
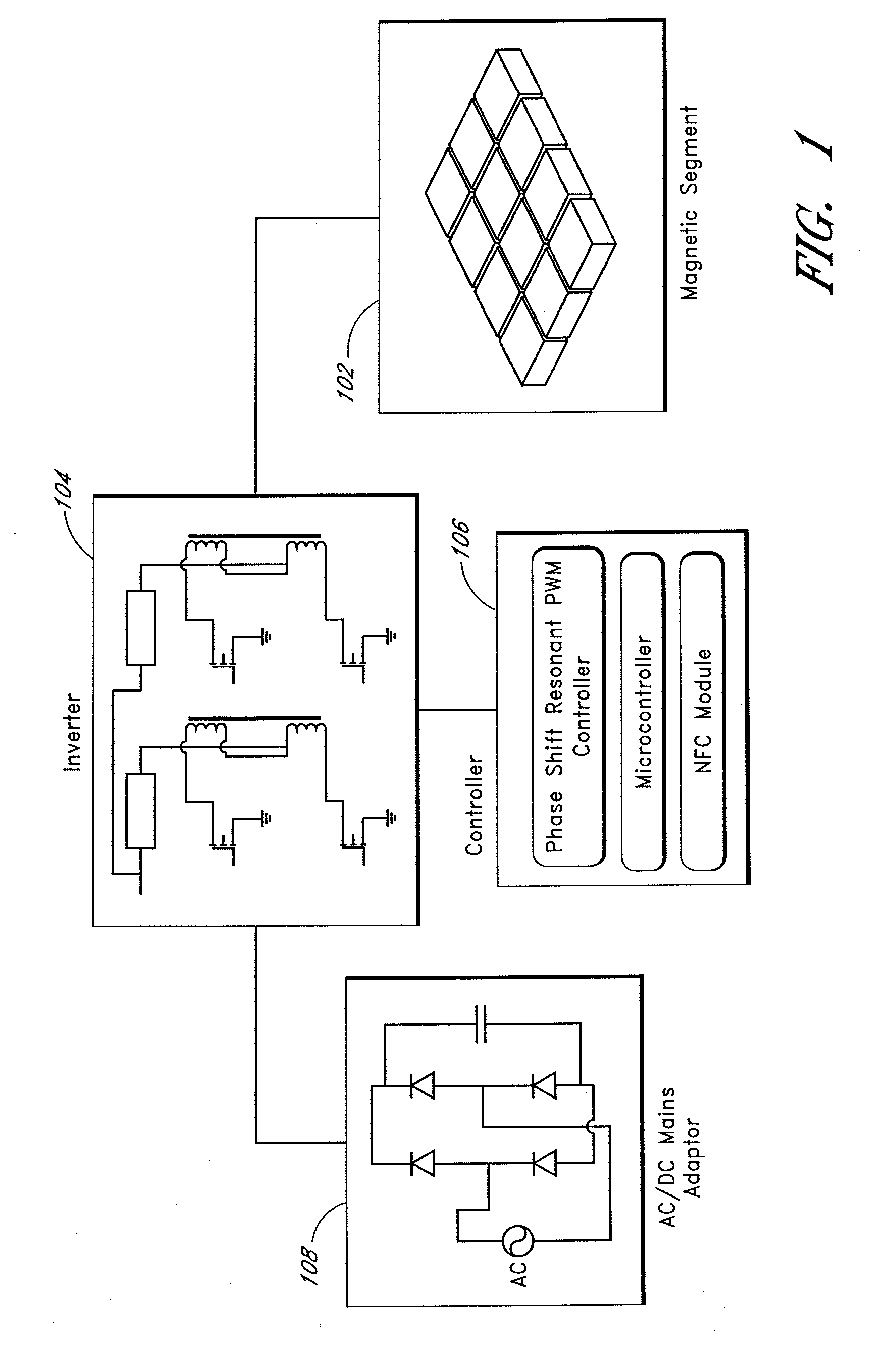
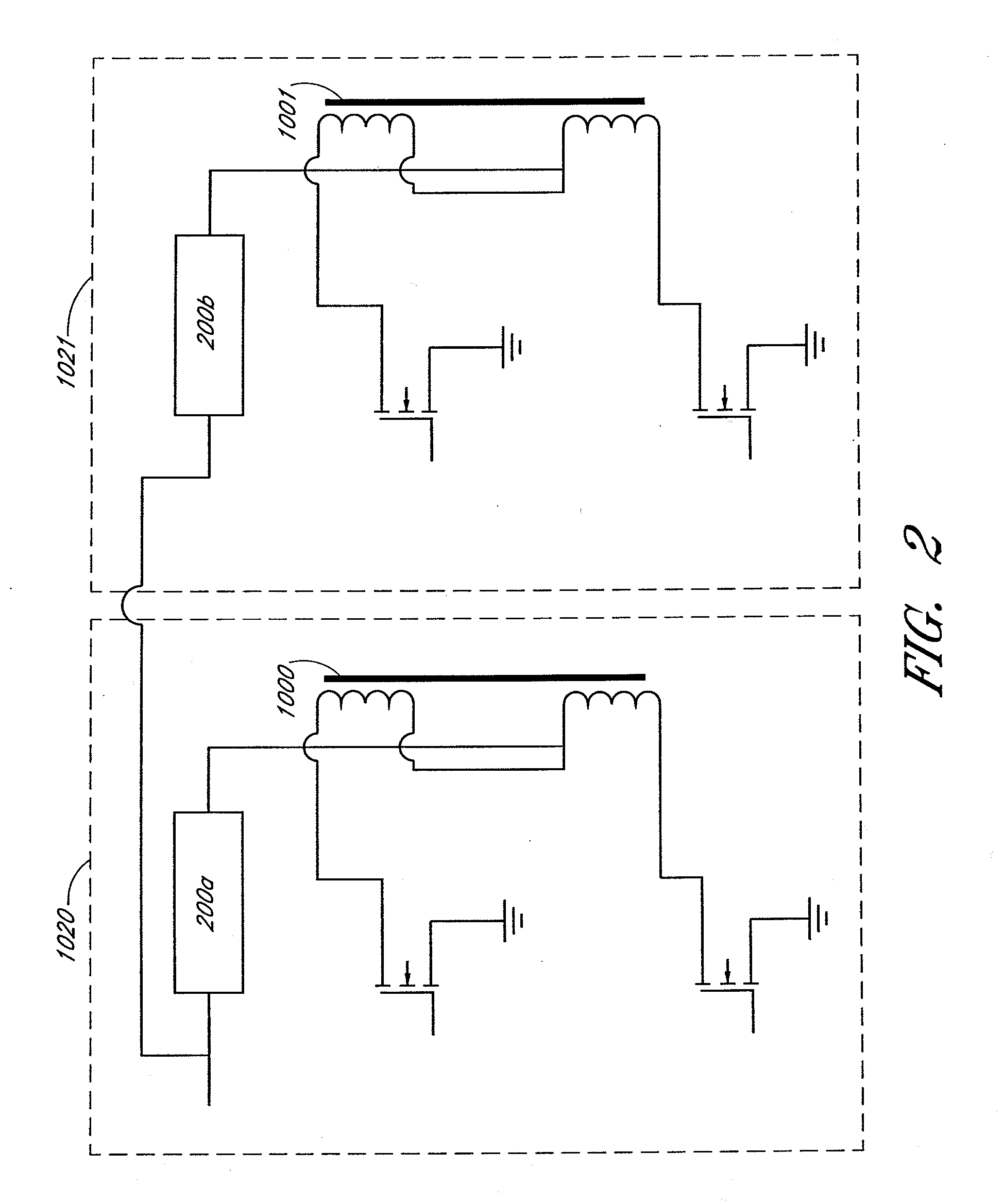
Systems and methods for wireless power transfer are disclosed. Primary windings generate magnetic fields which are inductively coupled to secondary windings to transfer power in a wireless manner. One embodiment includes a plurality of tiles of magnetic cores and windings for the primary windings. The tiles can be arranged in a magnetic segment with windings of tiles being orthogonal with respect to windings of adjacent tiles. For example, a winding of a first tile can be horizontal, and windings of adjacent tiles can be vertical. One embodiment further groups these magnetic segments into larger entities, wherein each magnetic segment can be independently activated. One embodiment includes a magnetic amplifier or an electronic device for secondary side control of power. This permits multiple devices to be powered or charged to be able to regulate power or charging independently from one another.
Owner:BIO AIM TECH HLDG
High voltage power line multi-sensor system
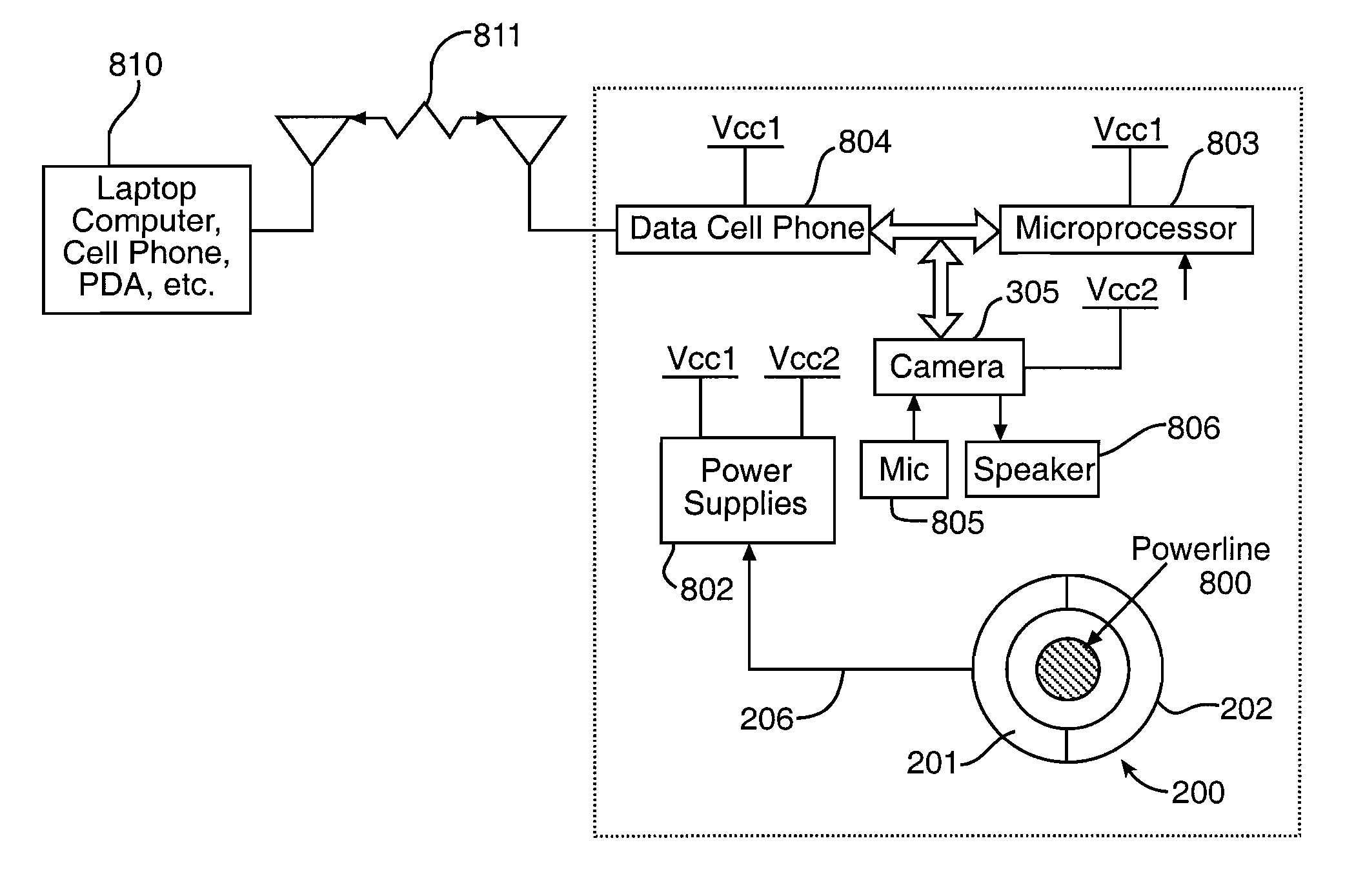
InactiveUS8767071B1Limited powerOvercome problemsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringHigh pressure
A multi-sensor system can be attached to a high voltage power line, draw power from the power line inductively, and convert the power to lower voltages and direct currents for operating cameras, sensors, a processor, and communications equipment that provide persistent intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance capabilities. The multi-sensor system can detect and track targets in detection regions and transmit such detection data and other data from the camera and sensors to a remote operator who can initiate response actions and send control instructions to the multi-sensor system from the remote location.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Battery charger and method of charging a battery
InactiveUS6963186B2Quickly and conveniently chargeSmall sizeCircuit monitoring/indicationSecondary cells charging/dischargingOn boardCopper foil
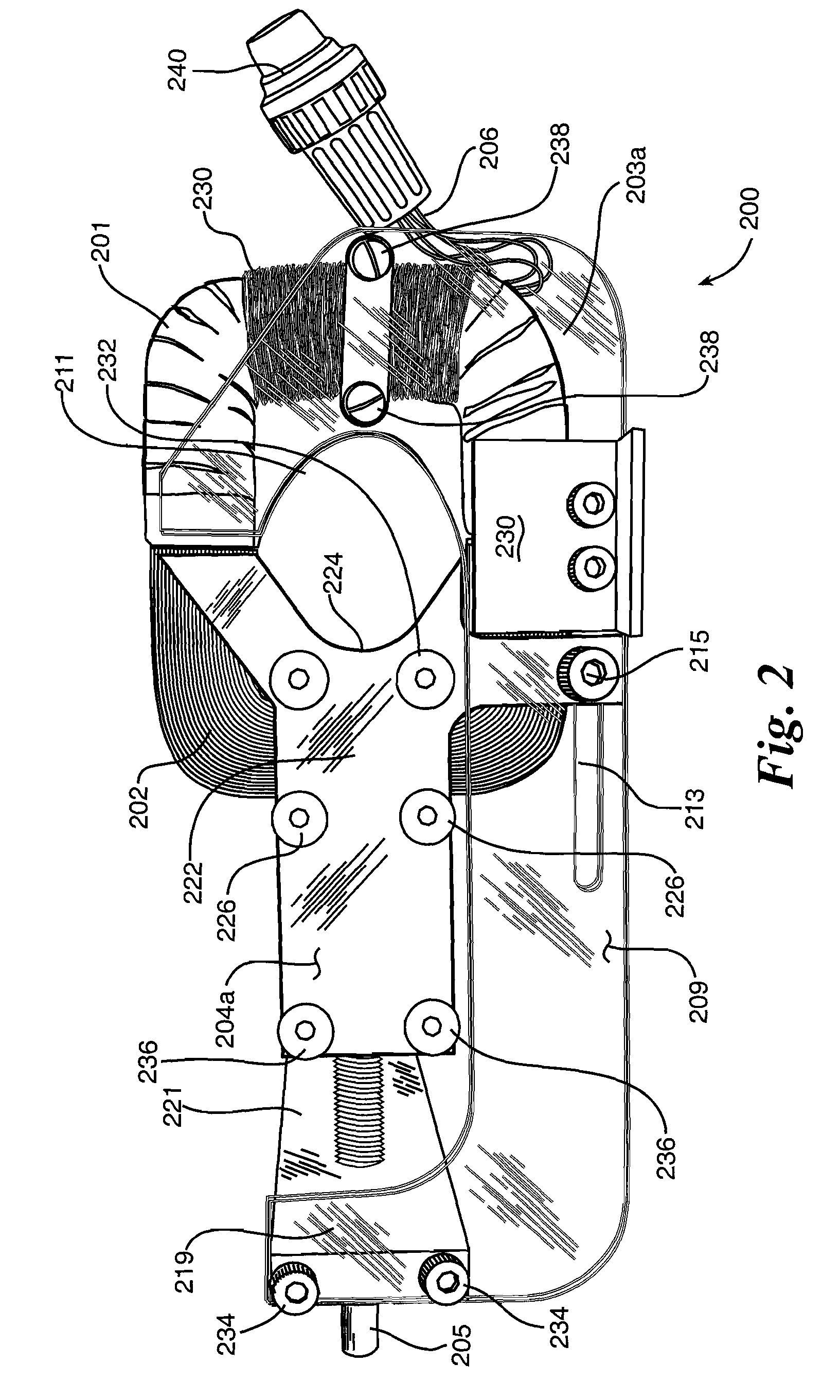
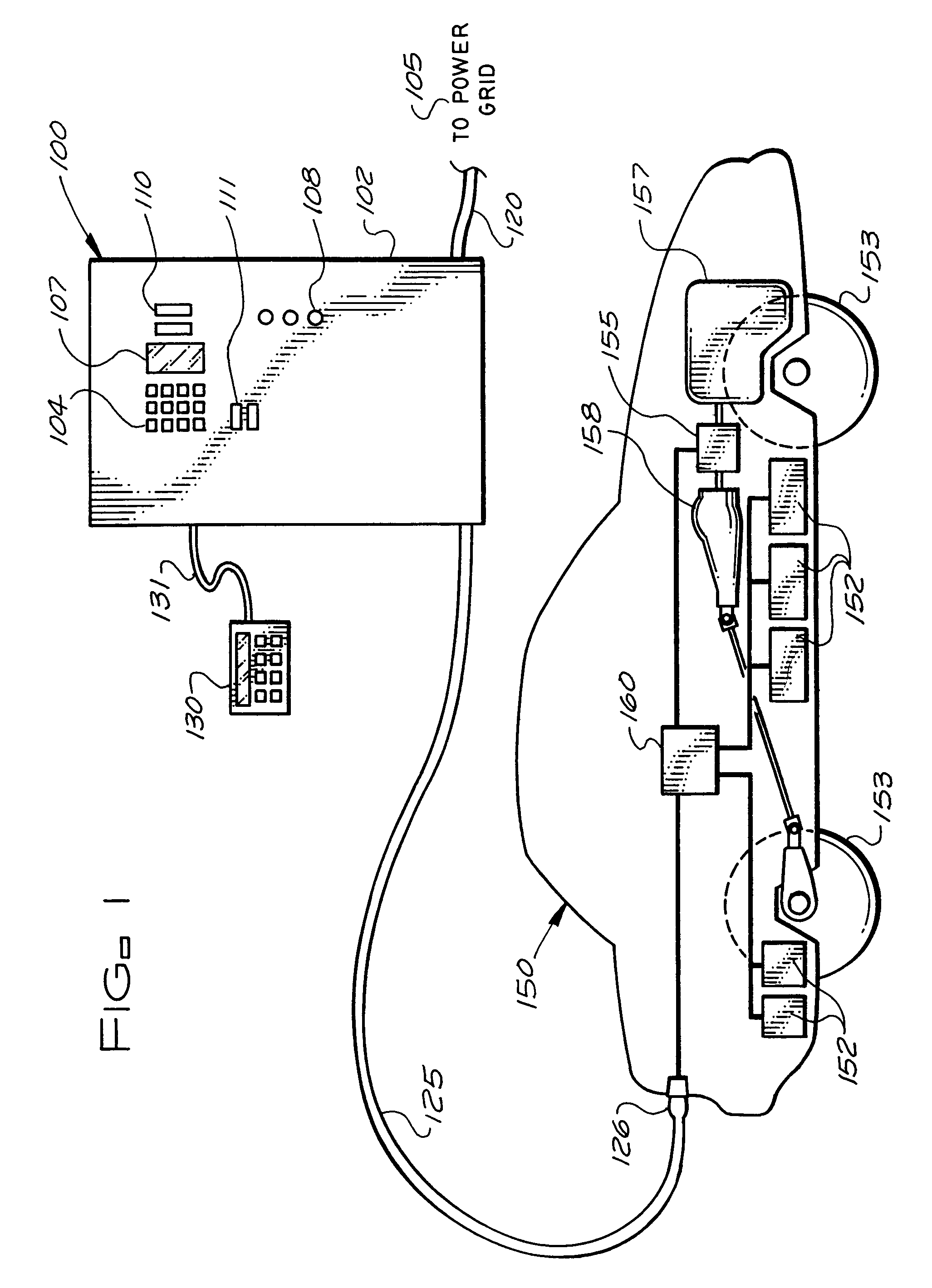
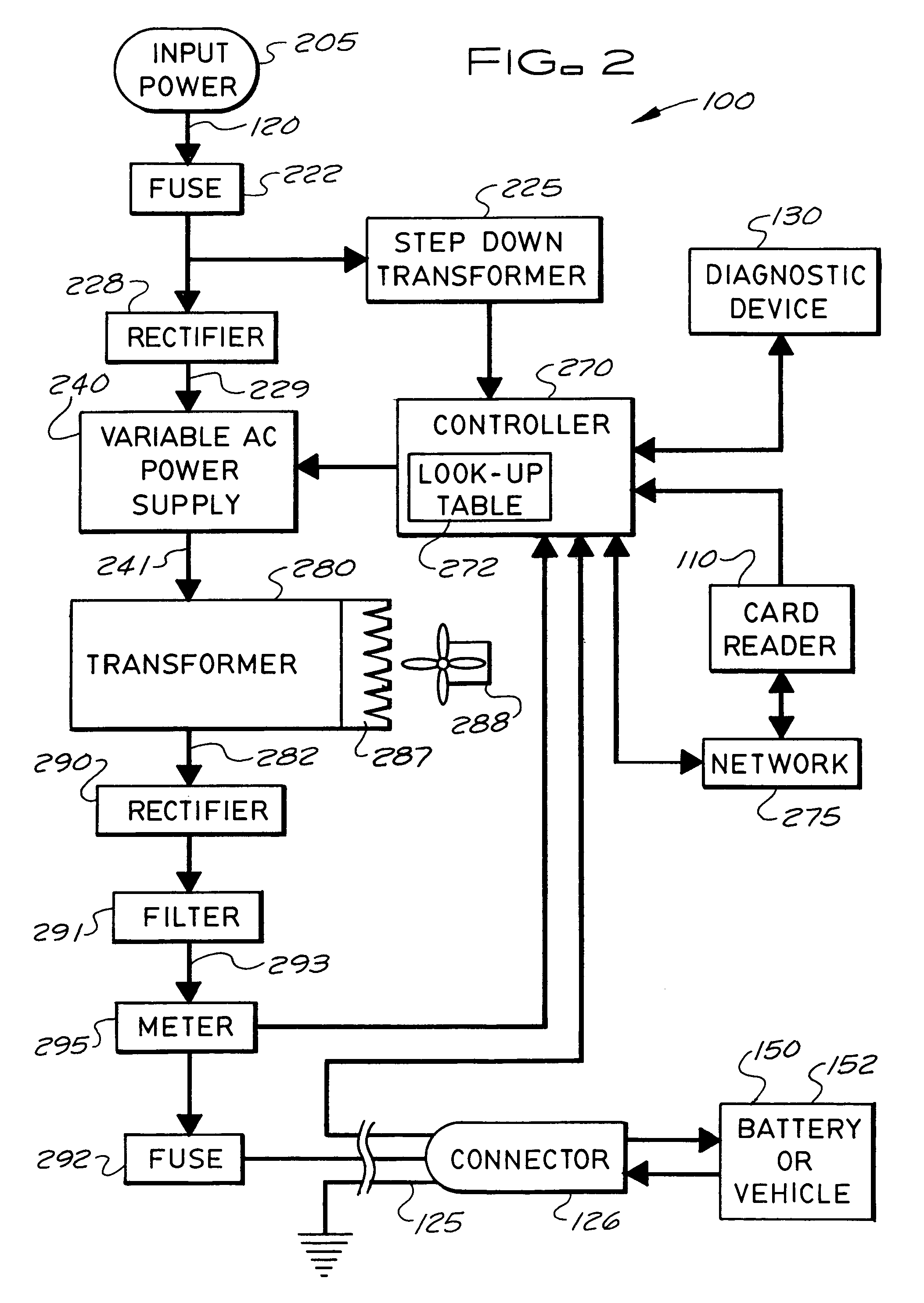
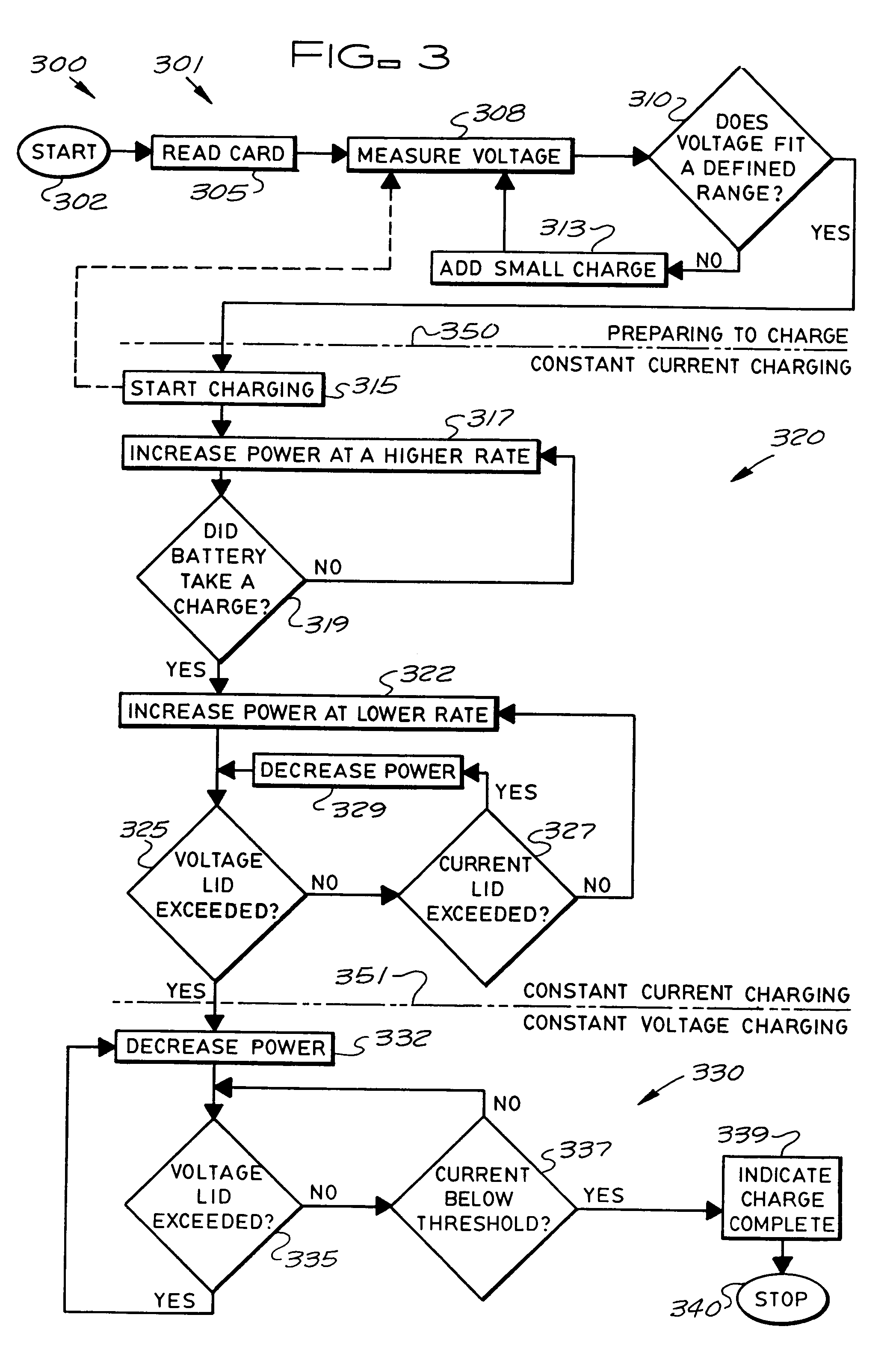
Stationary and on-board battery chargers, methods of charging batteries, electric-vehicle chargers, and vehicles with chargers, including electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles. Chargers may automatically charge at the correct battery voltage for various types of batteries. Chargers have variable AC power supplies controlled by digital controllers, isolation transformers, and rectifiers. Transformers may be foil-type, and may have copper foil. Power supplies may be variable-frequency generators and the controllers may control the frequency. Electric vehicle chargers may have card readers, and vehicles may have batteries and a charger. Methods of charging include identifying the battery type and gradually increasing the charging at different rates of increase while monitoring charging voltage, charging current, or both, until a current lid is reached. Charging may occur at constant current and then at constant voltage.
Owner:ARIZONA PUBLIC SERVICE
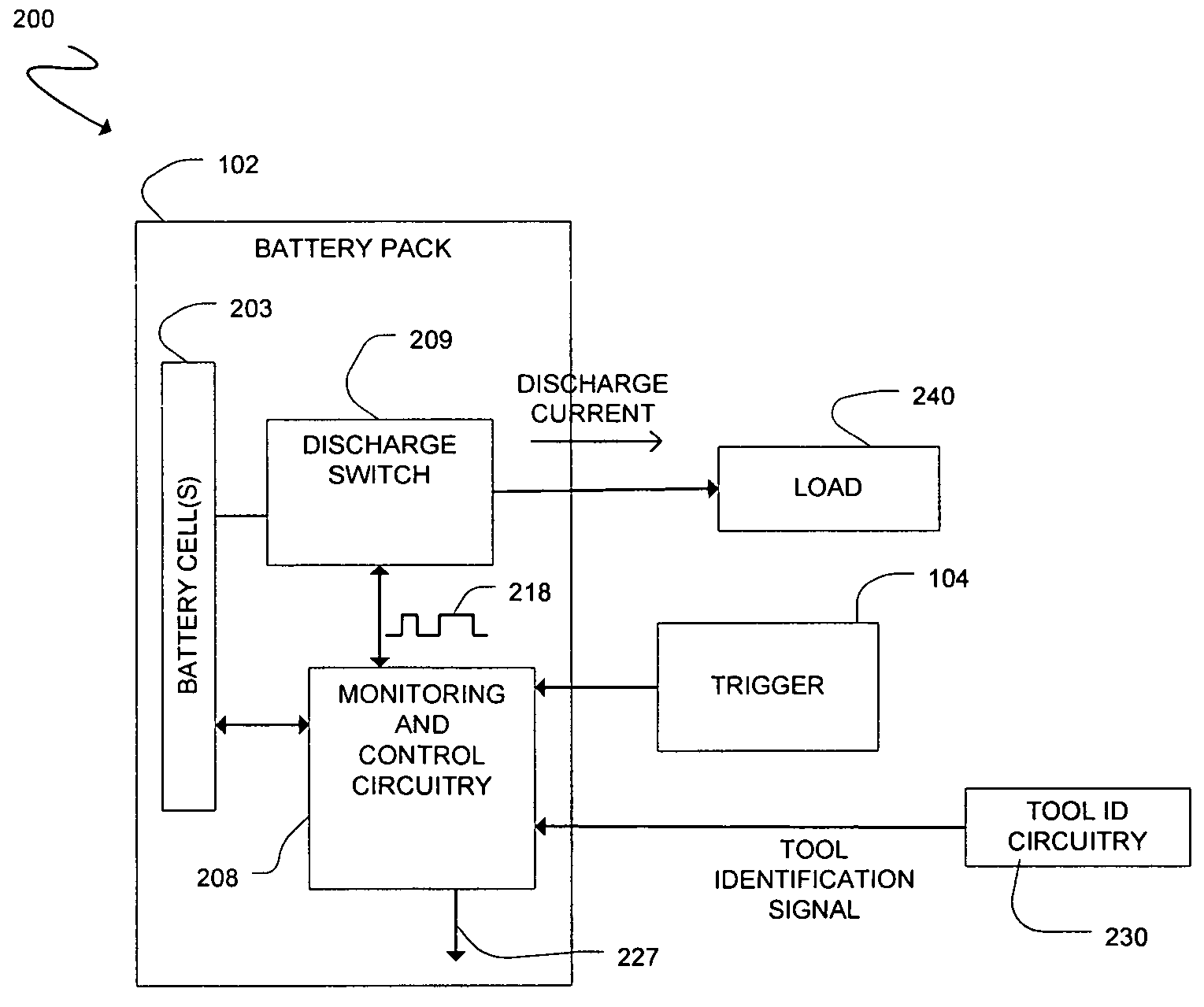
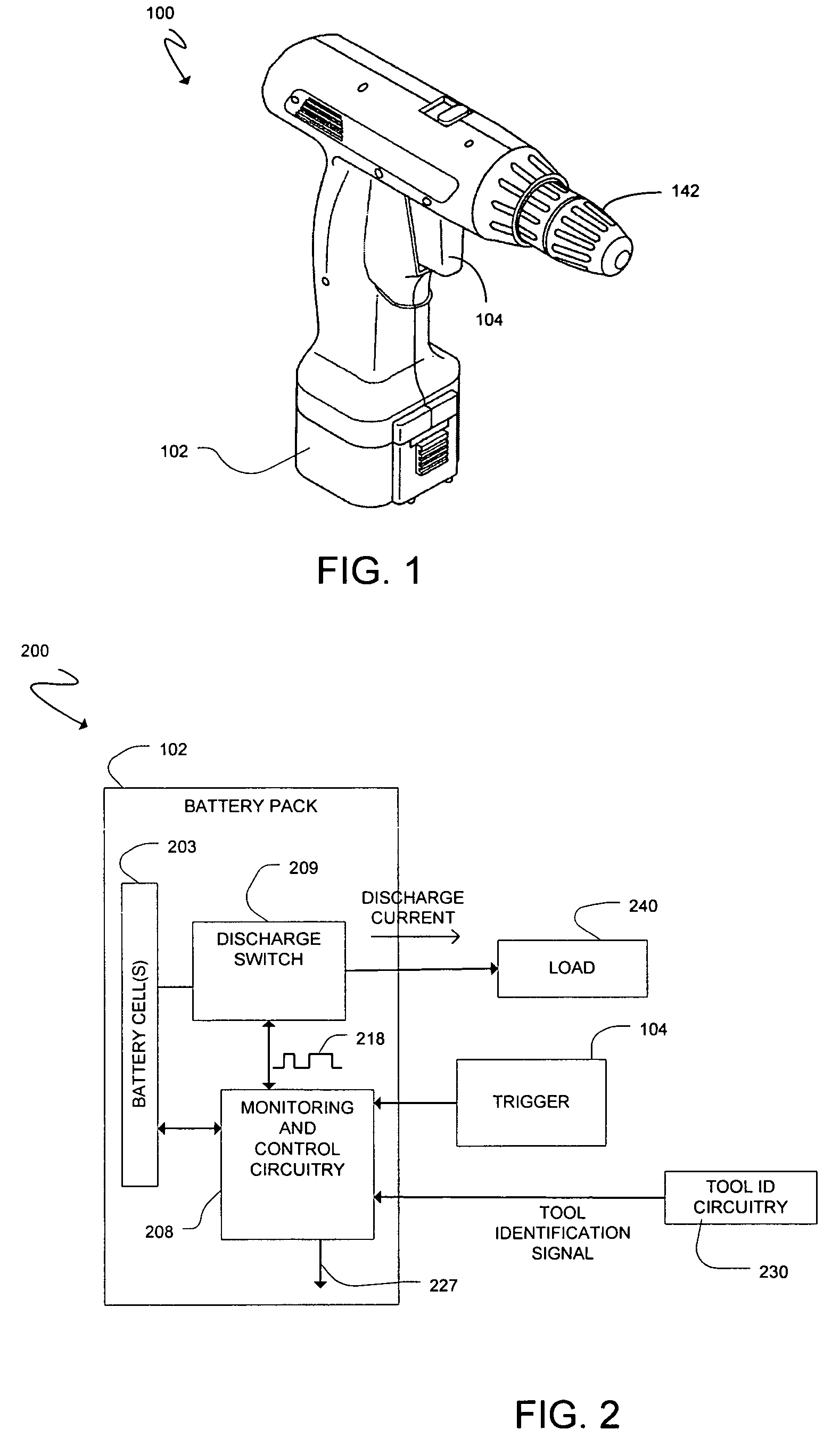
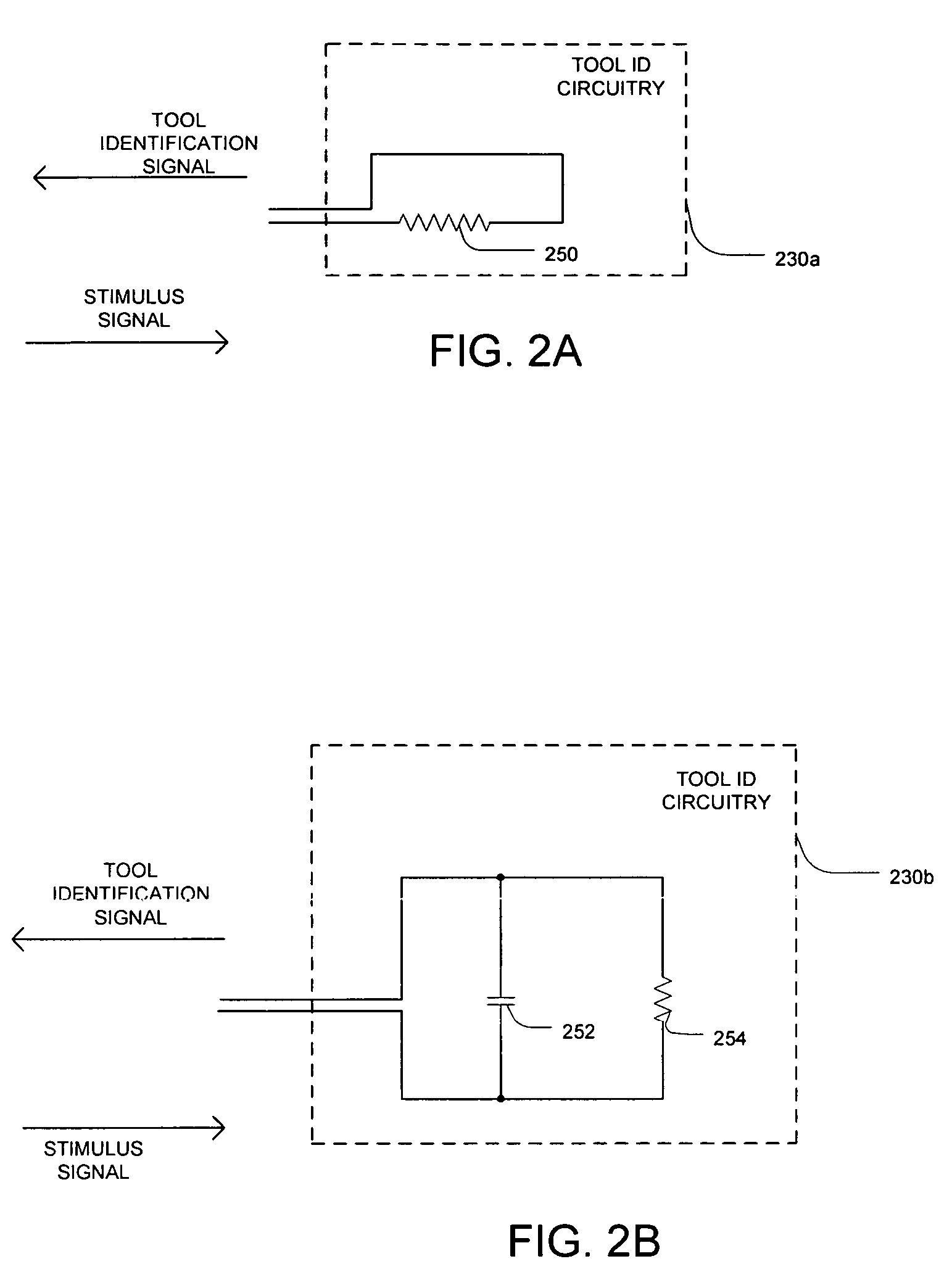
Cordless power tool with tool identification circuitry
ActiveUS7119516B2Electric motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringPower tool
A cordless power tool may include tool identification circuitry to provide a tool identification signal to a battery pack. The tool identification signal may be representative of data particular to the cordless power tool. A method may include coupling a battery pack to a cordless power tool, and providing a tool identification signal to the battery pack from the cordless power tool once the battery pack is coupled to the cordless power tool, the tool identification signal representative of data particular to the cordless power tool.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
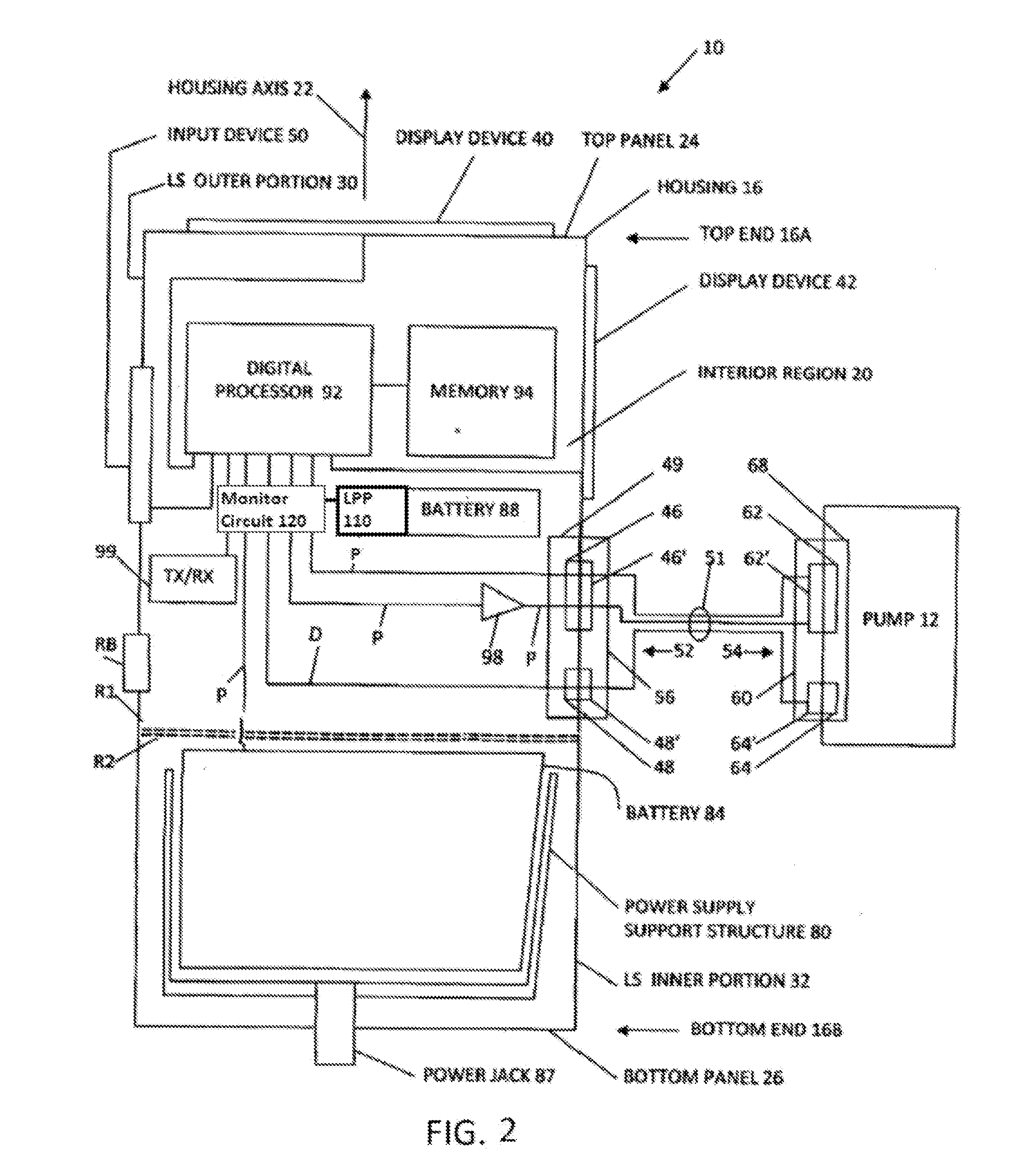
Battery pack for cordless power tools
InactiveUS20080238370A1Avoid damageCharge equalisation circuitCircuit monitoring/indicationEngineeringPower tool
A battery pack which includes a battery pack electronic control circuit adapted to control an attached power tool and / or an attached charger. The battery pack includes additional protection circuits, methodologies and devices to protect against fault conditions within the pack, as the pack is operatively attached to and providing power to the power tool, and / or as the pack is operatively attached to and being charged by the charger.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
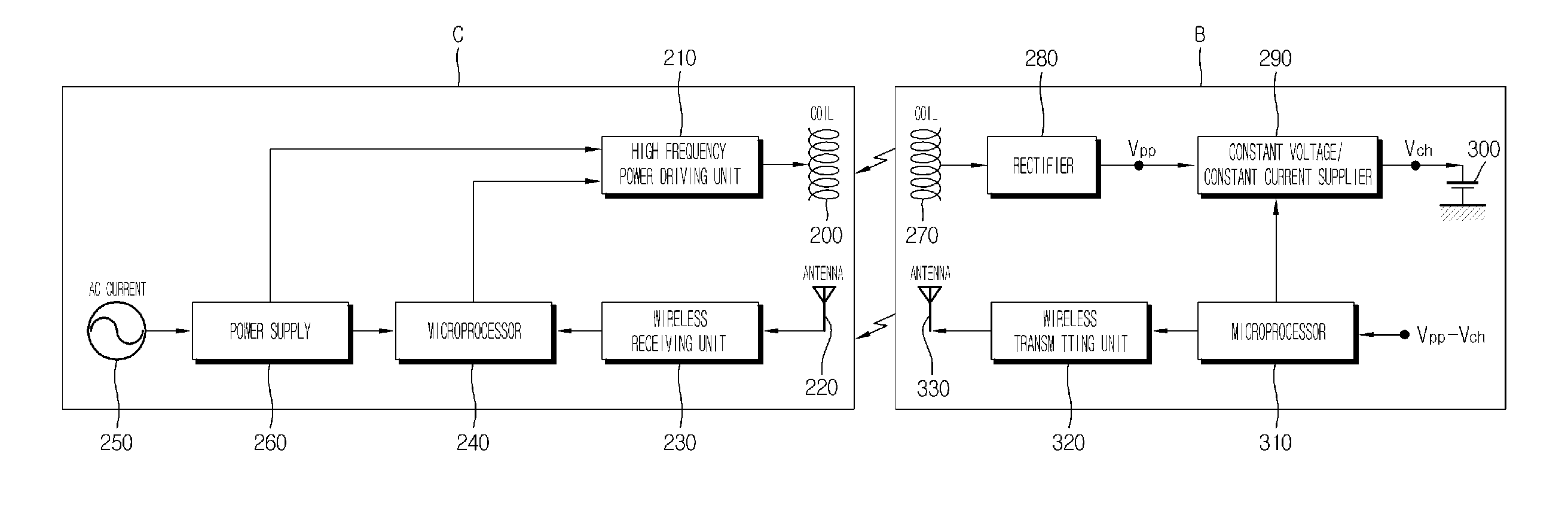
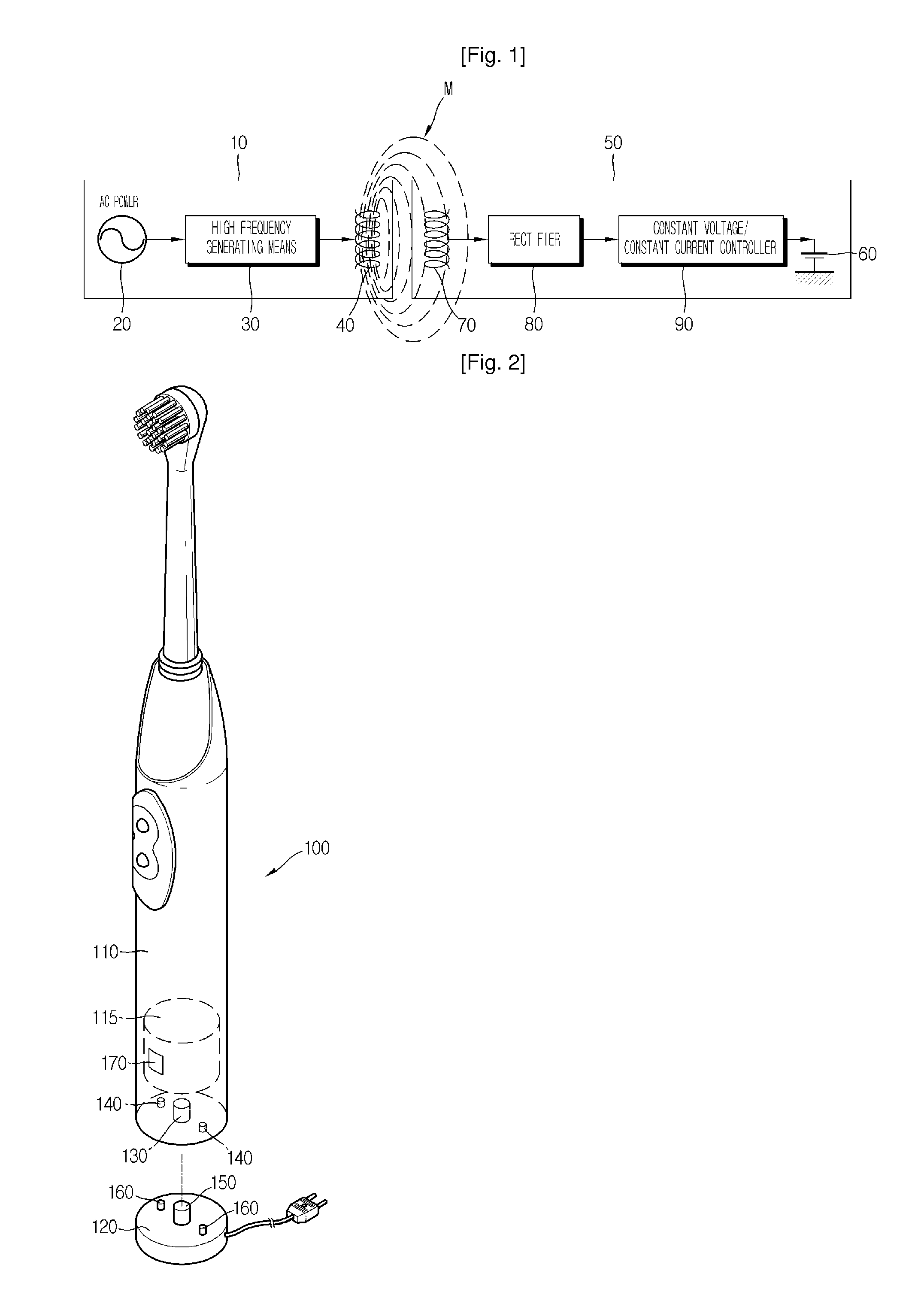
Contact-Less Chargeable Battery and Charging Device, Battery Charging Set, and Charging Control Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080303479A1Avoid internal damageAc-dc conversion without reversalCircuit monitoring/indicationBattery chargeRechargeable cell
The present invention relates to a wireless charger for a mobile communication terminal, which allows charging a plurality of batteries in a conveniently way without any terminal connection of the batteries to chargers for various mobile communication terminals such as a cellular phone and PDA and also allows intercepting electromagnetic waves while the charger is used, by means of Faraday's law.The wireless charger of the present invention includes a charger body having an electromagnetic wave intercepting means; a charging pad received in the charger body; and at least one battery that is to be charged by means of induced electromotive force generated by the charging pad, wherein the charger body includes a power supply means, a housing having a receiver for receiving the charging pad and connected to the power supply means, and a cover hinged to the housing.
Owner:LS CABLE & SYST LTD
Non-contact power supply system
ActiveUS20100270867A1Suppressing waste of powerImprove signal transmission reliabilityMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionElectric power transmissionHigh frequency power
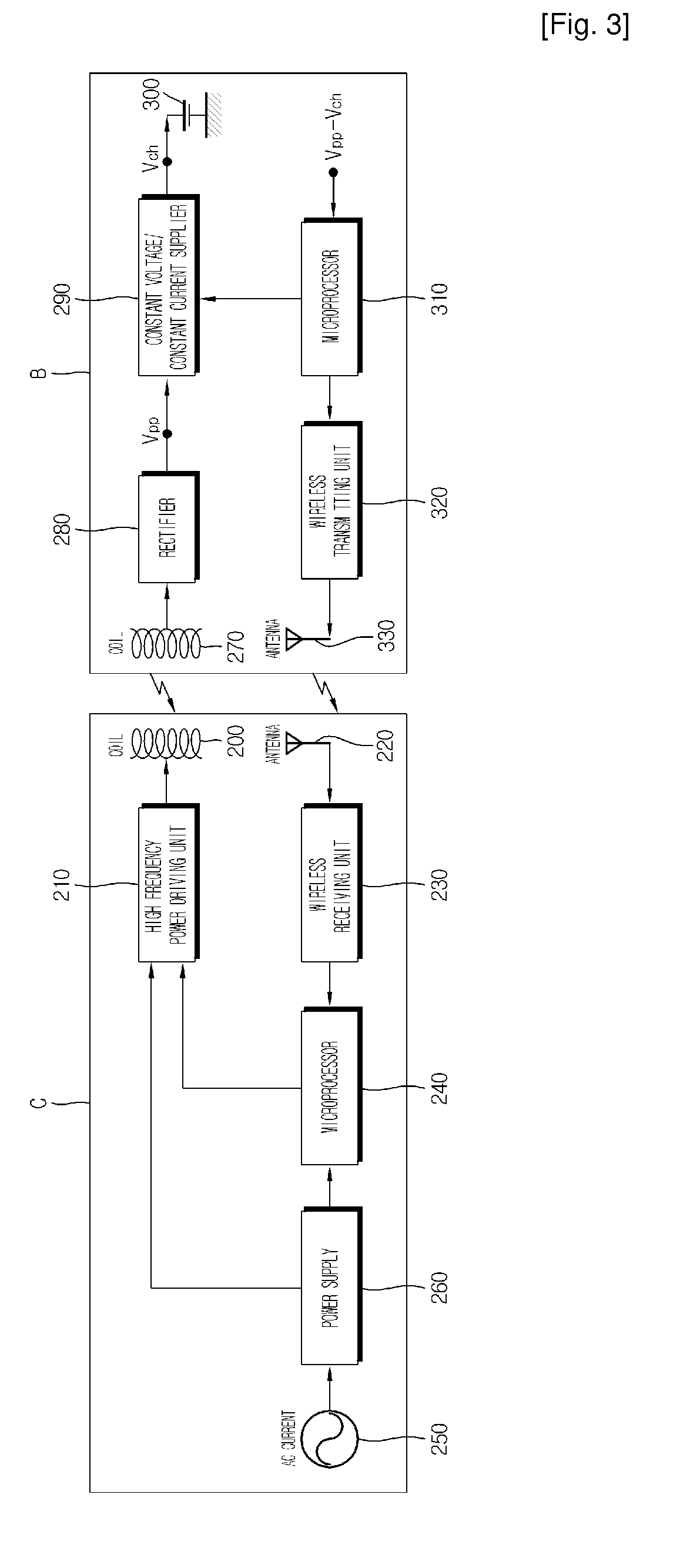
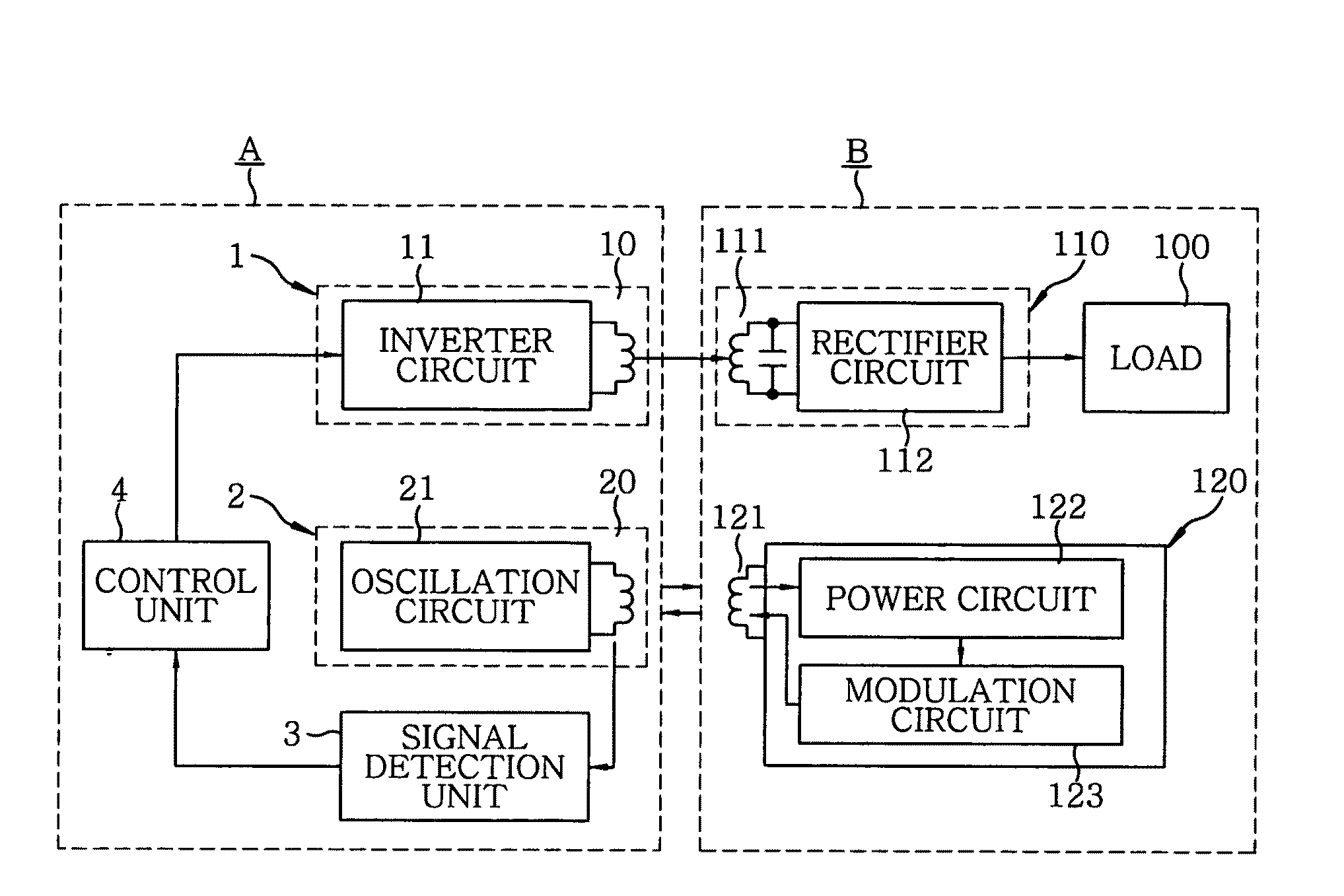
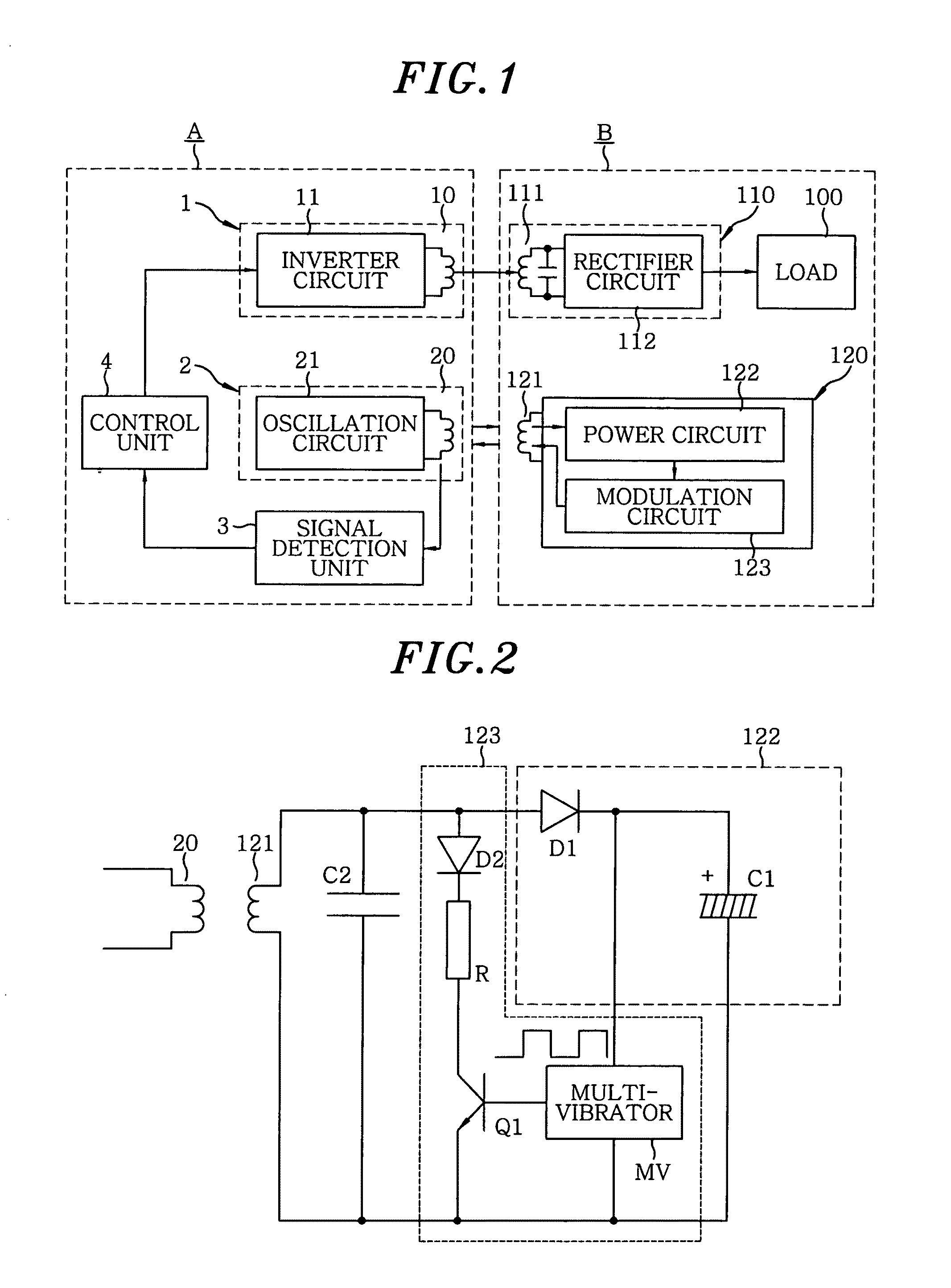
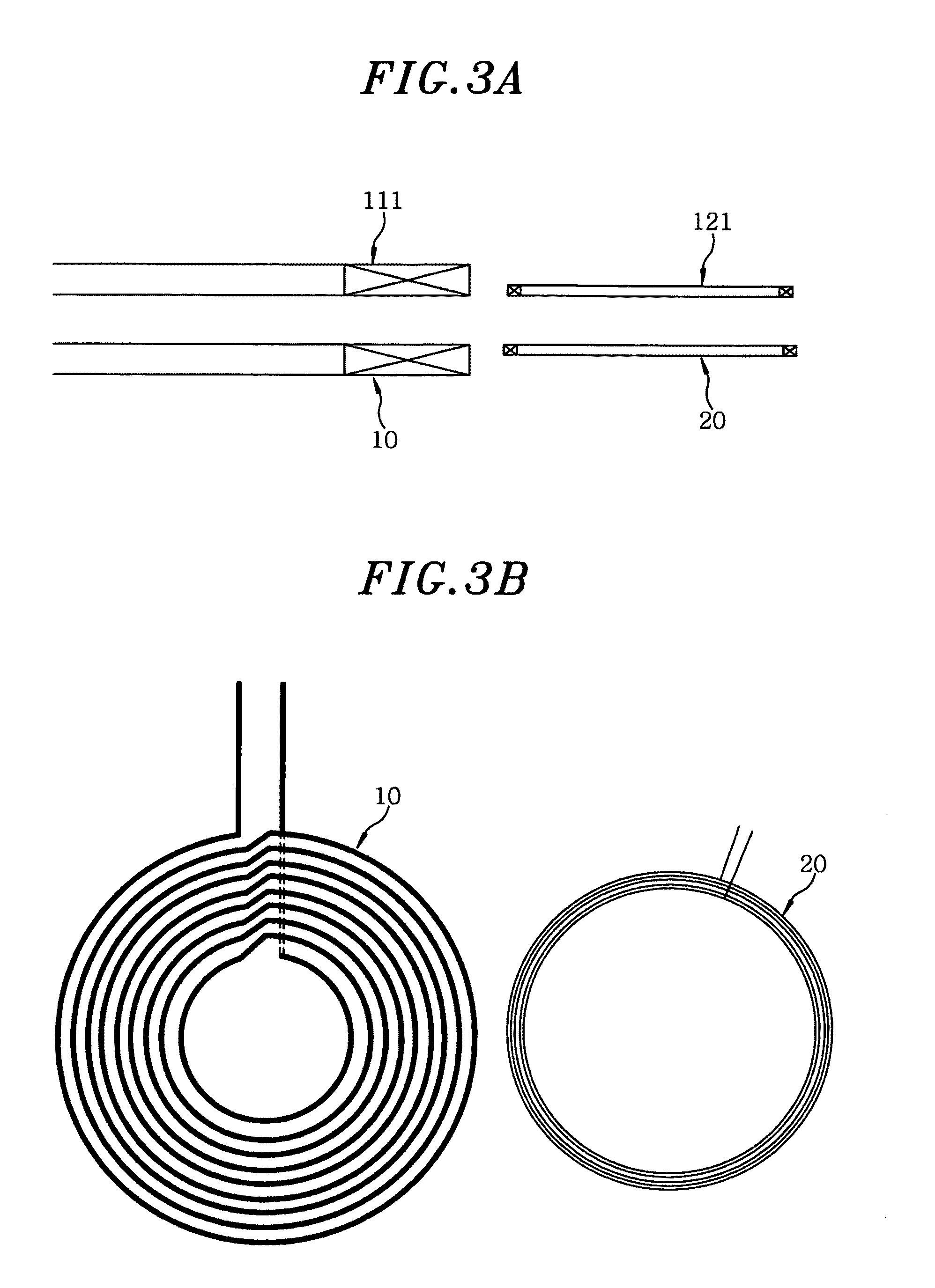
A non-contact power supply system includes a power supply device for transmitting high frequency power and a load device which receives the high frequency power in a non-contact mode by electromagnetic induction to supply it to a load. The power supply device includes a power transmission unit having a primary power coil and an inverter circuit, an inquiry unit having at least one primary signal coil and an oscillation circuit, a signal detection unit and a control unit. The load device includes a power reception unit having a secondary power coil magnetically coupled to the primary power coil and a power conversion unit, a secondary signal coil magnetically coupled to the primary signal coil, and a response unit which is operated by electromotive force induced in the secondary signal coil. The control unit stops power transmission when no signal is detected and executes power transmission which a signal is detected.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Low-power battery pack with safety system
InactiveUS20130314047A1Low powerFull gauging capabilityCircuit monitoring/indicationDigital data processing detailsPower batteryElectrical battery
The present application is directed toward a method and system for conserving battery power in low power systems. According to one aspect of the invention, a battery with a low power processor is used to shut off the monitor circuit that determines the charge remaining on a battery. Periodically, the low power processor will wake-up and power on the monitor circuit to determine the remaining charge of the battery. According to another aspect of the invention, there is a safety override circuit. The safety override circuit is a fail-safe that allows charge to flow from the battery when there is a fault with the low power processor, for example if the low power processor fails to wake-up.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
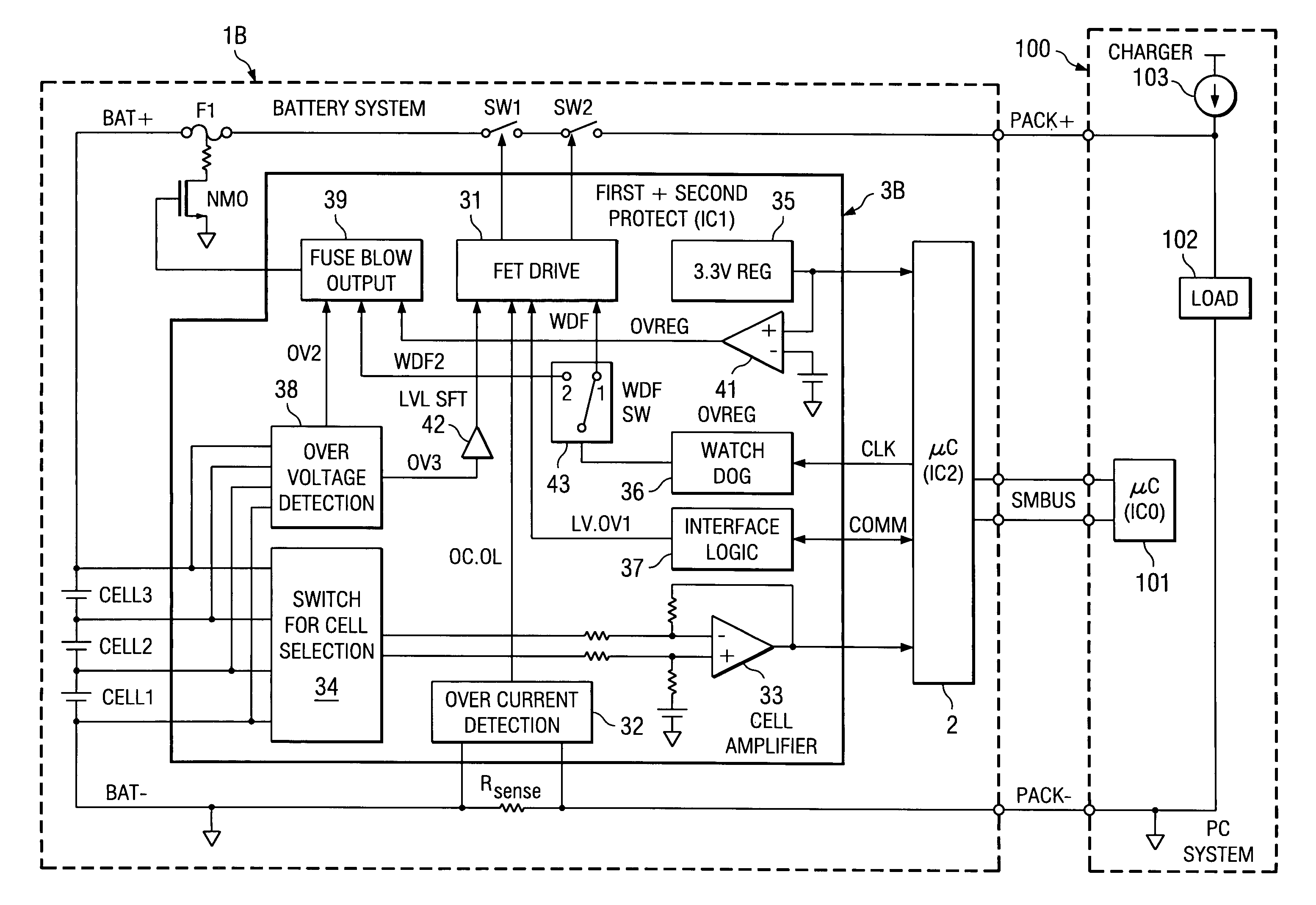
Battery protection circuit
ActiveUS6992463B2Cells structural combinationBattery overcharge protectionBattery systemBattery cell
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
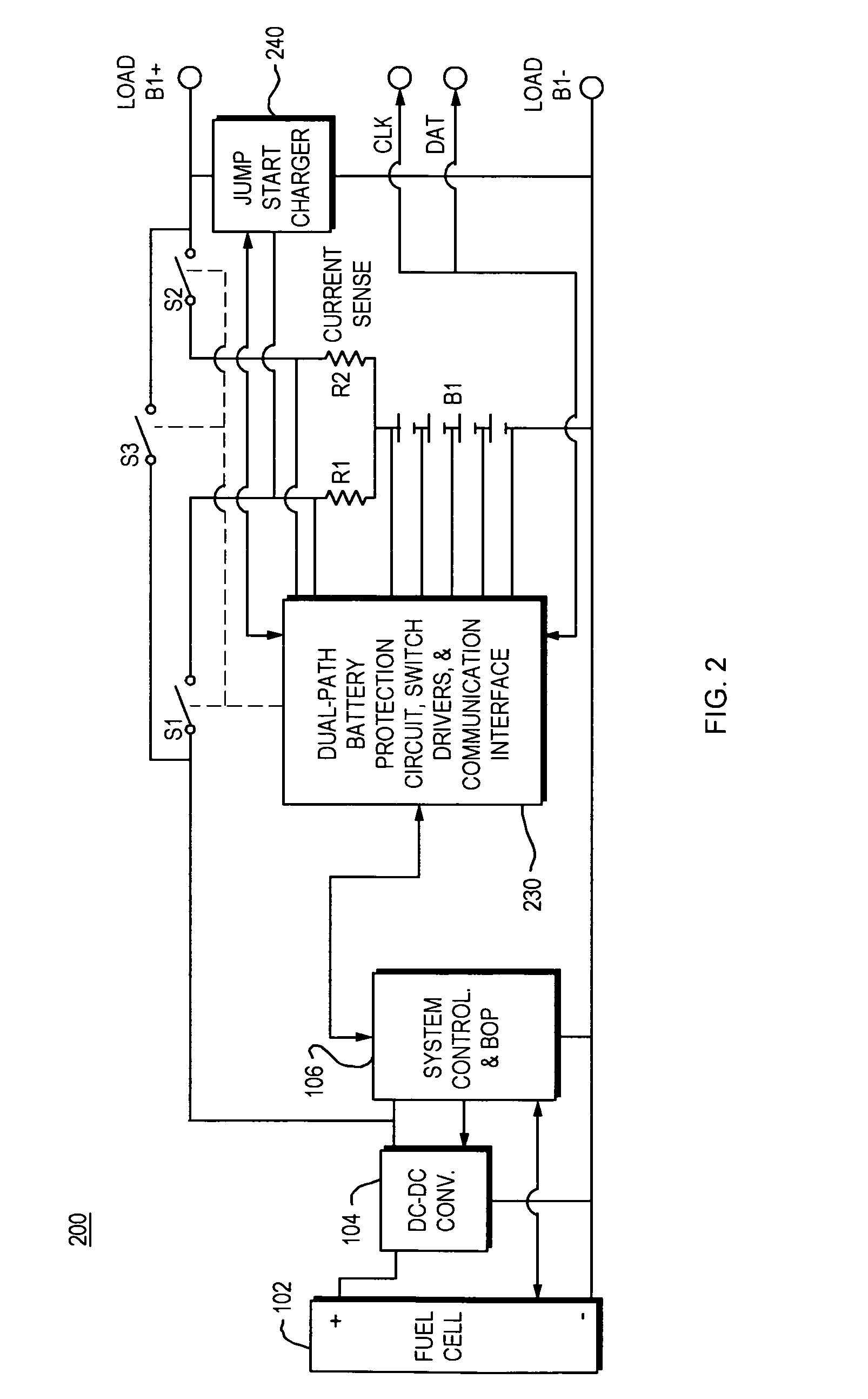
Fuel cell based rechargable power pack system and associated methods for controlling same
InactiveUS20070190369A1Primary cell to battery groupingCharge equalisation circuitDc dc converterFuel cells
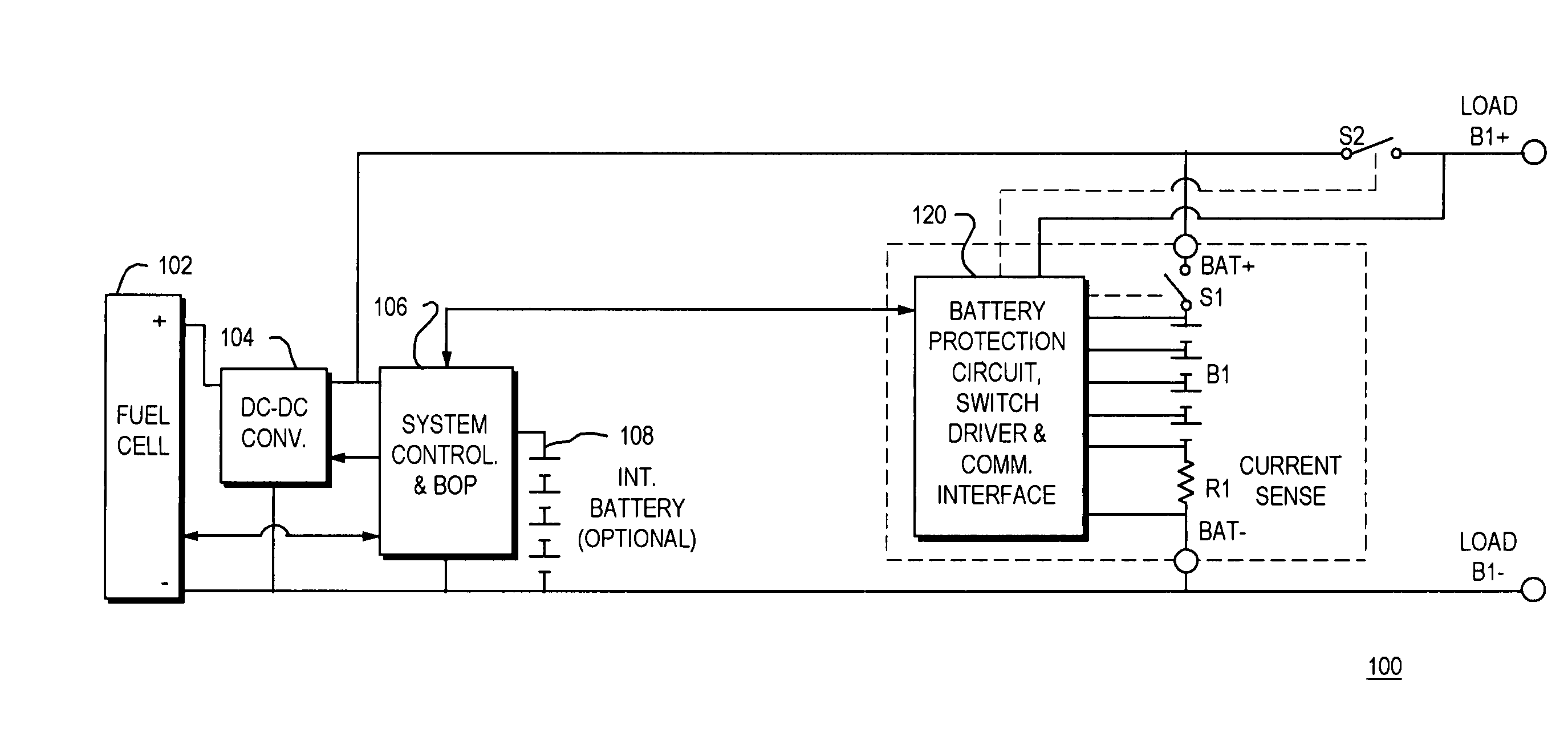
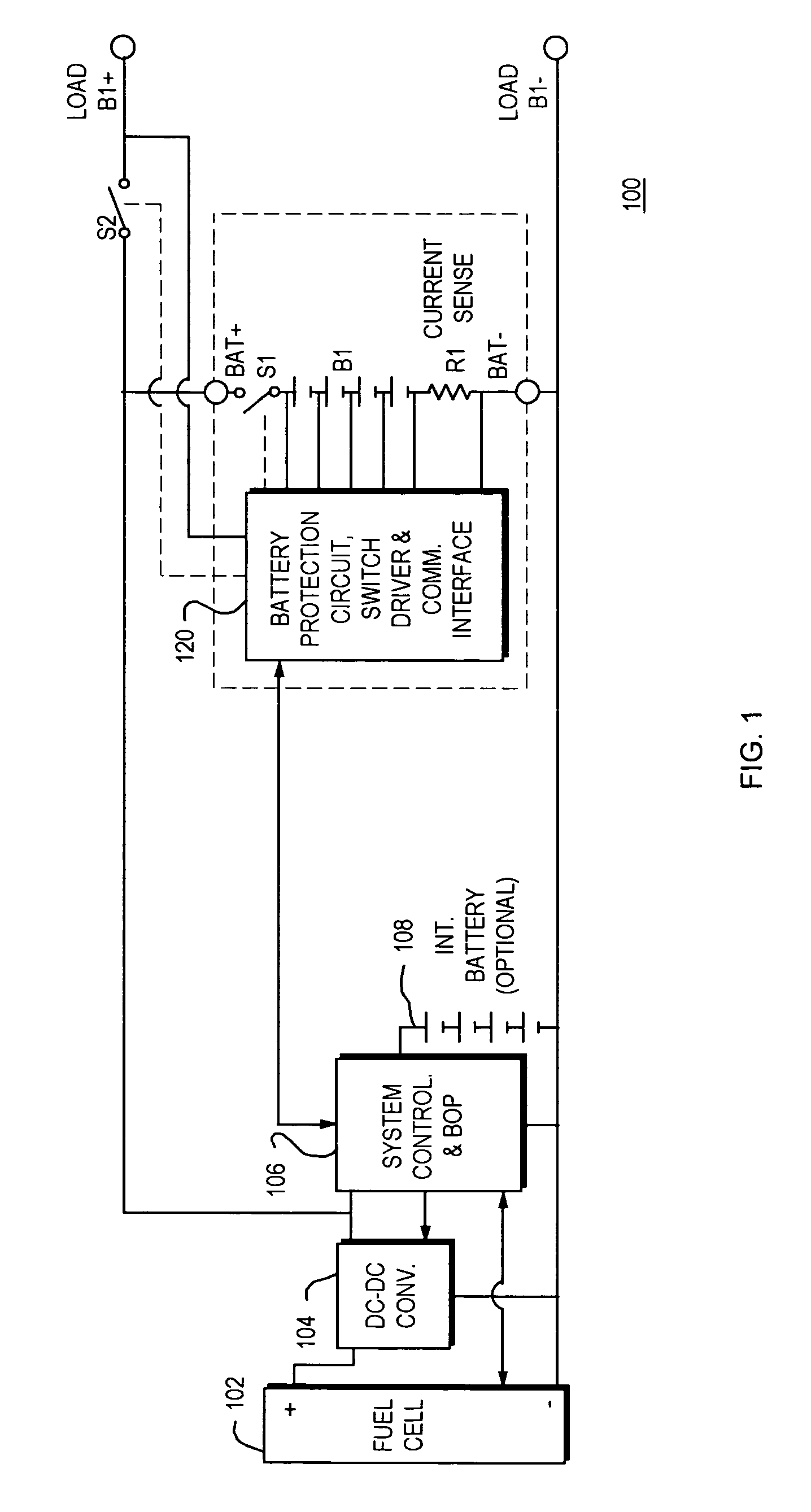
A power pack system for charging a set of isolated batteries is provided. In an illustrative embodiment of the invention, a single fuel cell, a single DC-DC converter and a single system controller device comprises the power-generation side of the power pack. A set of switches is used to connect the power-generation side of the Power pack to one of the isolated batteries in the power pack, thereby recharging that particular battery in the battery power pack set. A battery protection and powerpath control device communicates with the system controller to determine which switches are to be closed depending upon which battery requires recharging. During normal operation the switches will follow the direction from the system controller. If a fault is detected by the battery protection circuit, the protection circuit will take priority and turn off the appropriate switch(es).
Owner:MTI MICROFUEL CELLS
Method and system for battery protection
InactiveUS7589500B2Solution to short lifeSevere impactCharge equalisation circuitCell electrodesEngineeringElectric power
A method of conducting an operation including a battery. The battery includes a cell having a voltage. Power is transferable between the cell and the electrical device. A controller is operable to control a function of the battery pack. The controller is also operable with a voltage at least one of equal to and greater than an operating voltage threshold. The cell is operable to selectively supply voltage to the controller. The method includes the act of enabling the controller to operate when the voltage supplied by the cell is below the operating voltage threshold.
Owner:MILWAUKEE ELECTRIC TOOL CORP
Implantable power management system
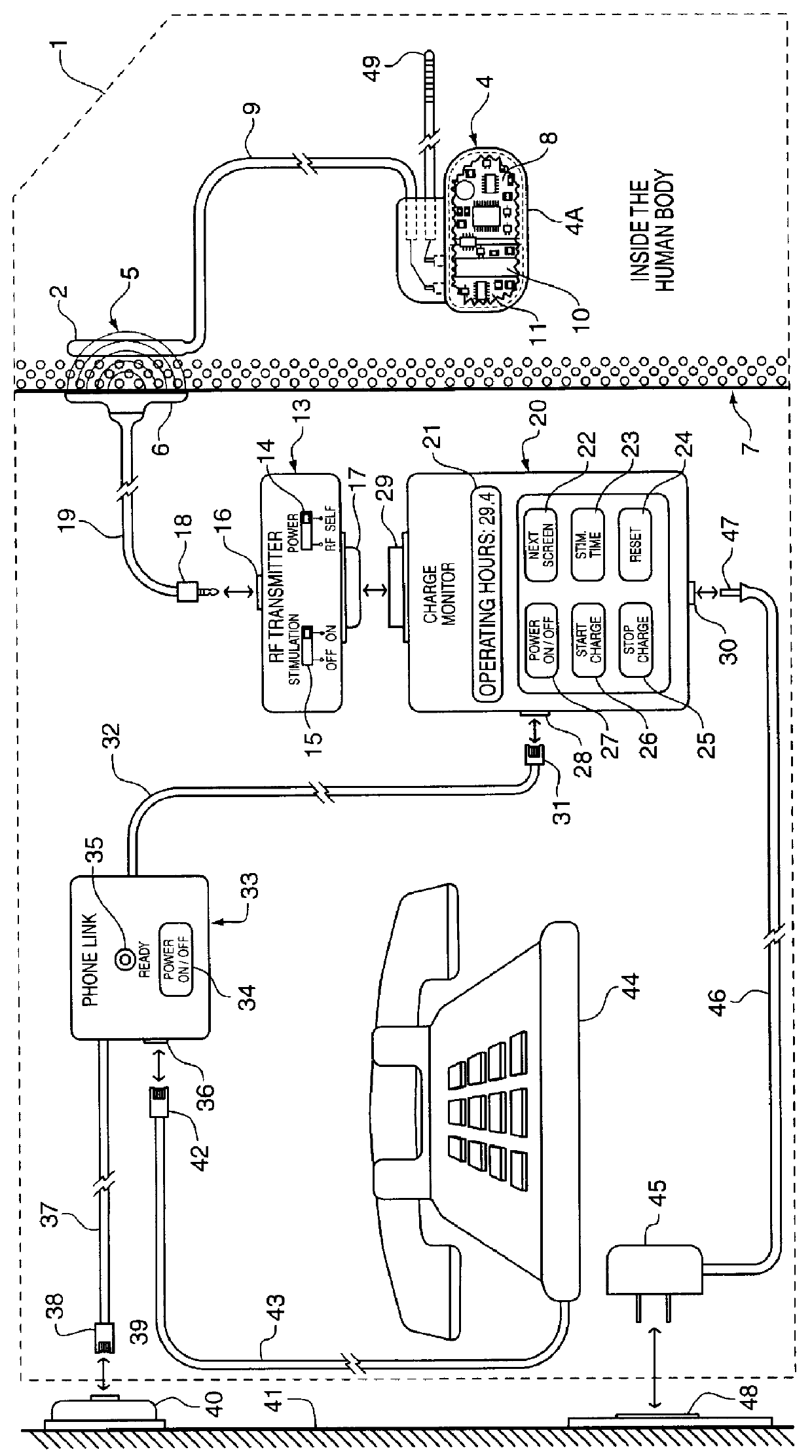
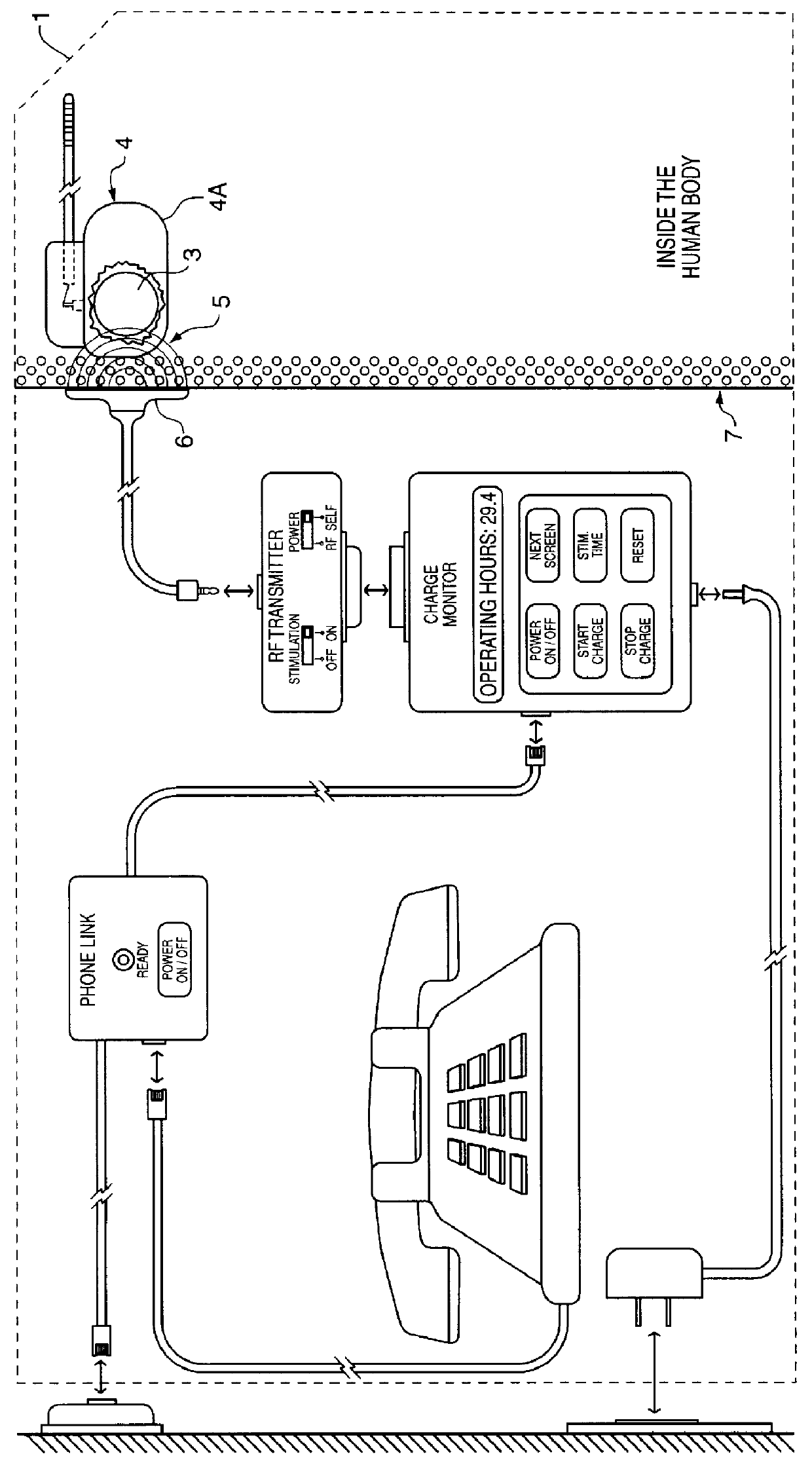
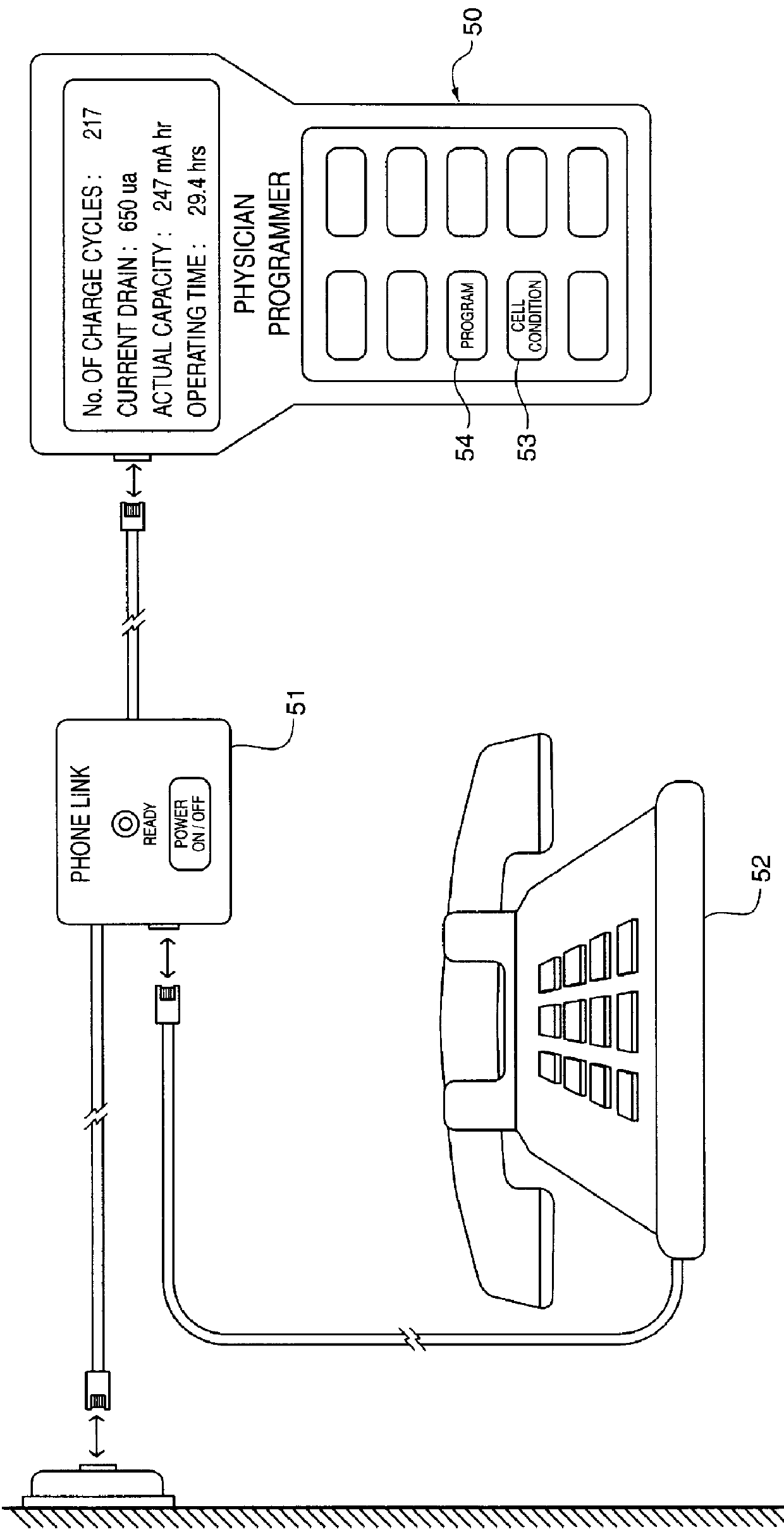
InactiveUS6166518AAccurately calculate and displayIncrease energy densityElectromagnetic wave systemHeart stimulatorsLow voltageElectric power
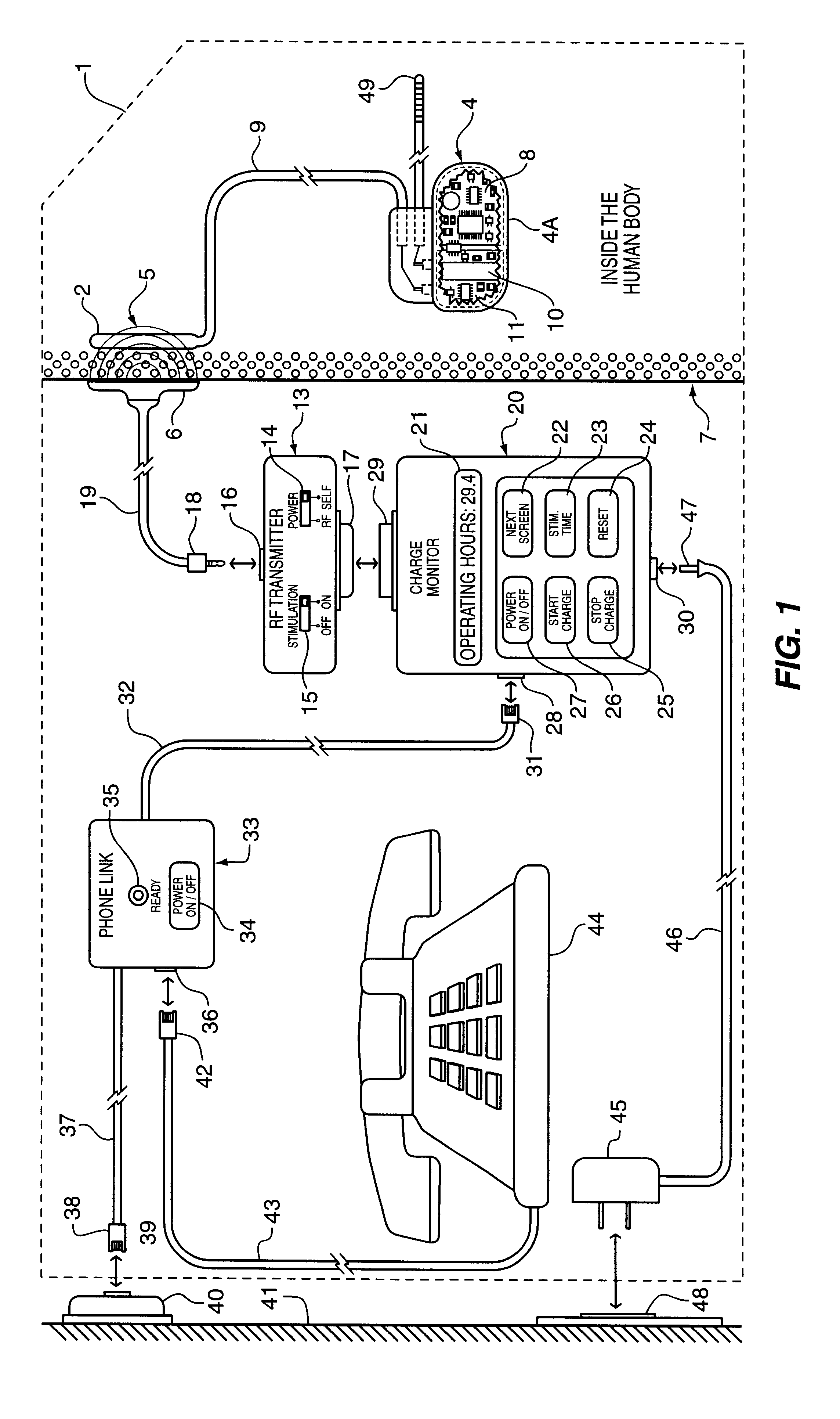
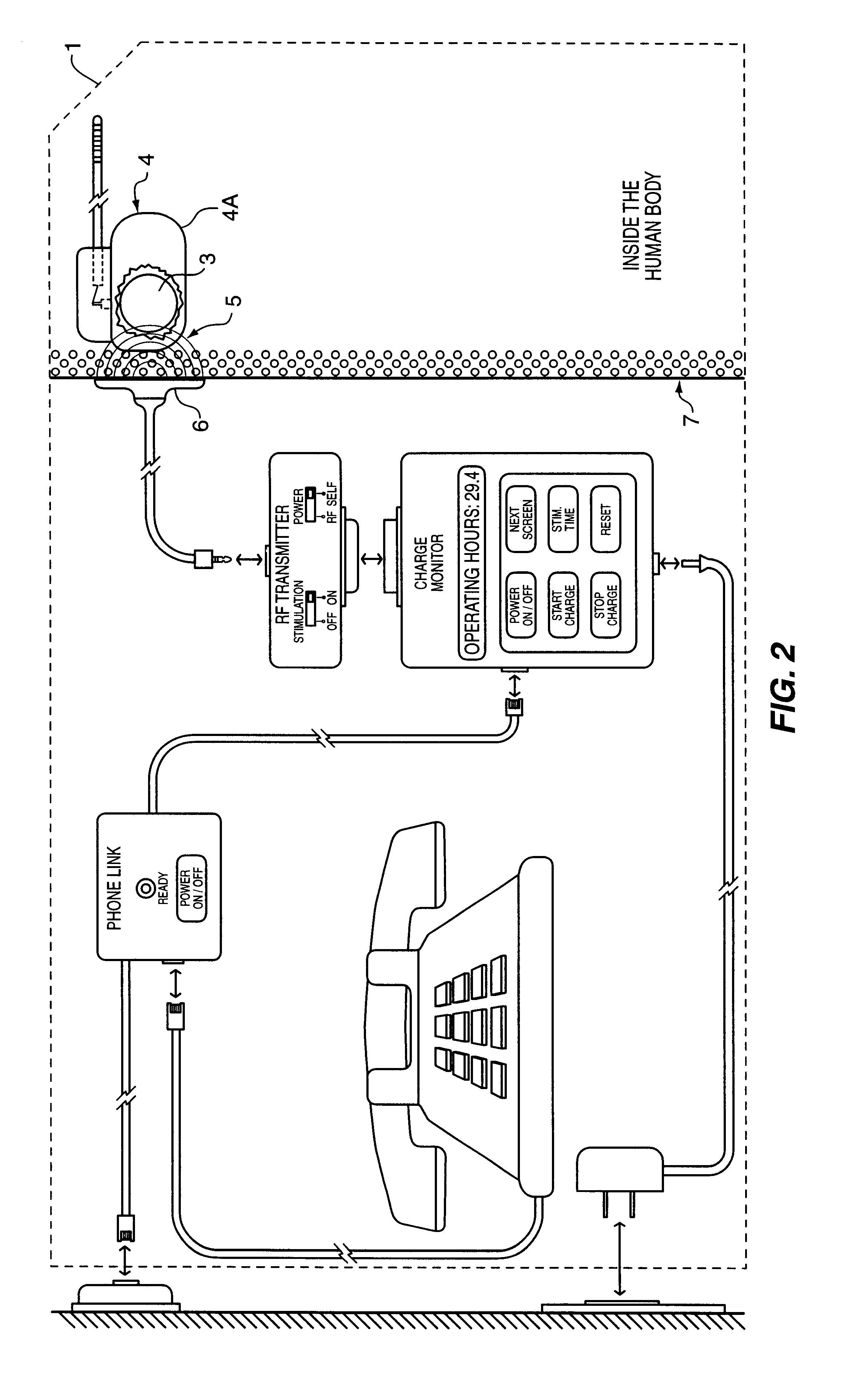
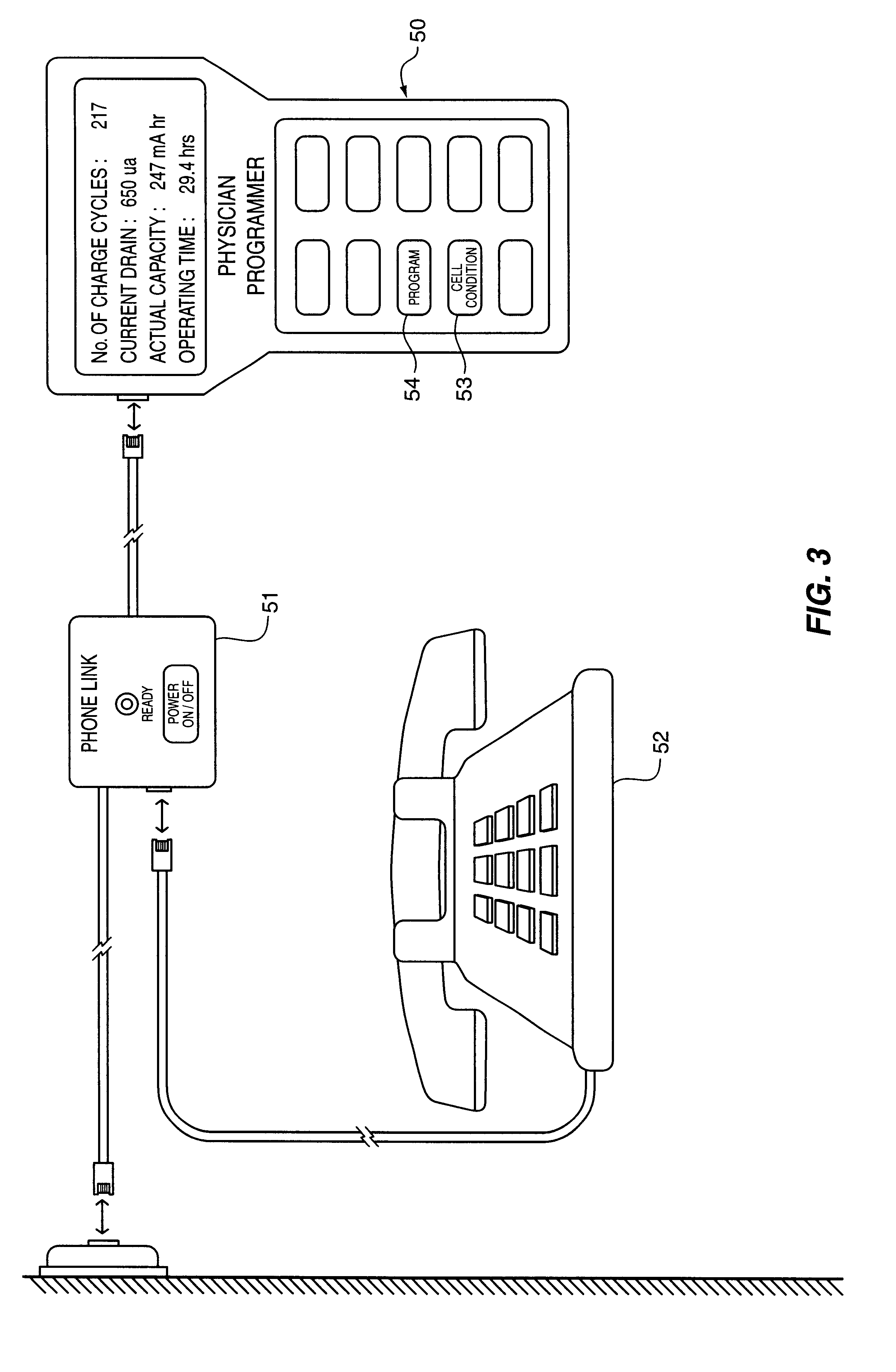
The method and system for managing power supplied from a charging circuit to a power source in an implantable medical device comprises the steps of and circuitry for: measuring the current drain of the medical device; measuring the elapsed time since the last full charge of a power source of the device; calculating the actual capacity of the power source (corrected for fade) based on the variable of current drain and the variable of elapsed time; calculating the operating time based on the variable of current drain and the variable of the actual capacity of the power source; measuring the voltage of the power source; signaling the medical device when the power source voltage has reached a certain low value which requires disconnection from the power source; disconnecting, during discharging, the power source from the medical device upon the power source reaching a certain low voltage in order to prevent deep discharging of the power source and subsequent damage; precisely limiting the charging voltage to the power source in order to prevent overcharging beyond safe limits; disconnecting, during charging, the power source from the charging circuit upon the power source reaching a certain high voltage in order to prevent overcharging of the power source and subsequent damage; sensing when the electromagnetic waves being transmitted by an RF transmitter / charger induce a voltage level above a certain value at an RF receiver of the implanted power management system; reconnecting power supply inputs of the medical device to the power source upon sensing this induced high voltage level; monitoring the temperature of the power source during charging and discharging; disconnecting the charging circuitry from the power source if the temperature of the power source raises above a certain level during charging; reconnecting the charging circuitry to the power source when the temperature of the power source drops below a certain low value during charging; disconnecting the implanted medical device from the power source if the temperature of the power source raises above a certain level during discharging; and, reconnecting the medical device to the power source when the temperature of the power source drops below a certain low value during discharging.
Owner:EXONIX
Wireless power system for portable devices under rotational misalignment
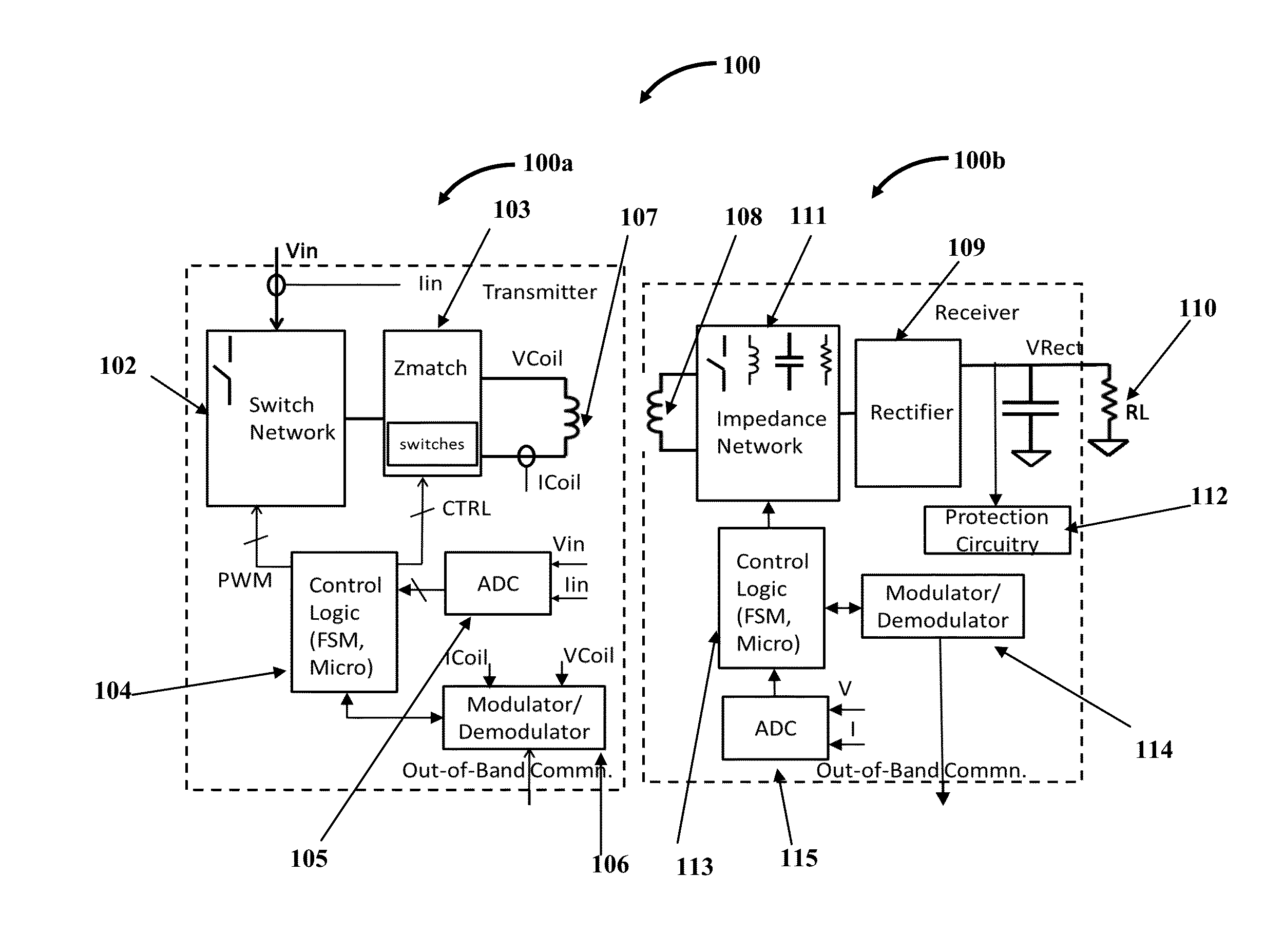
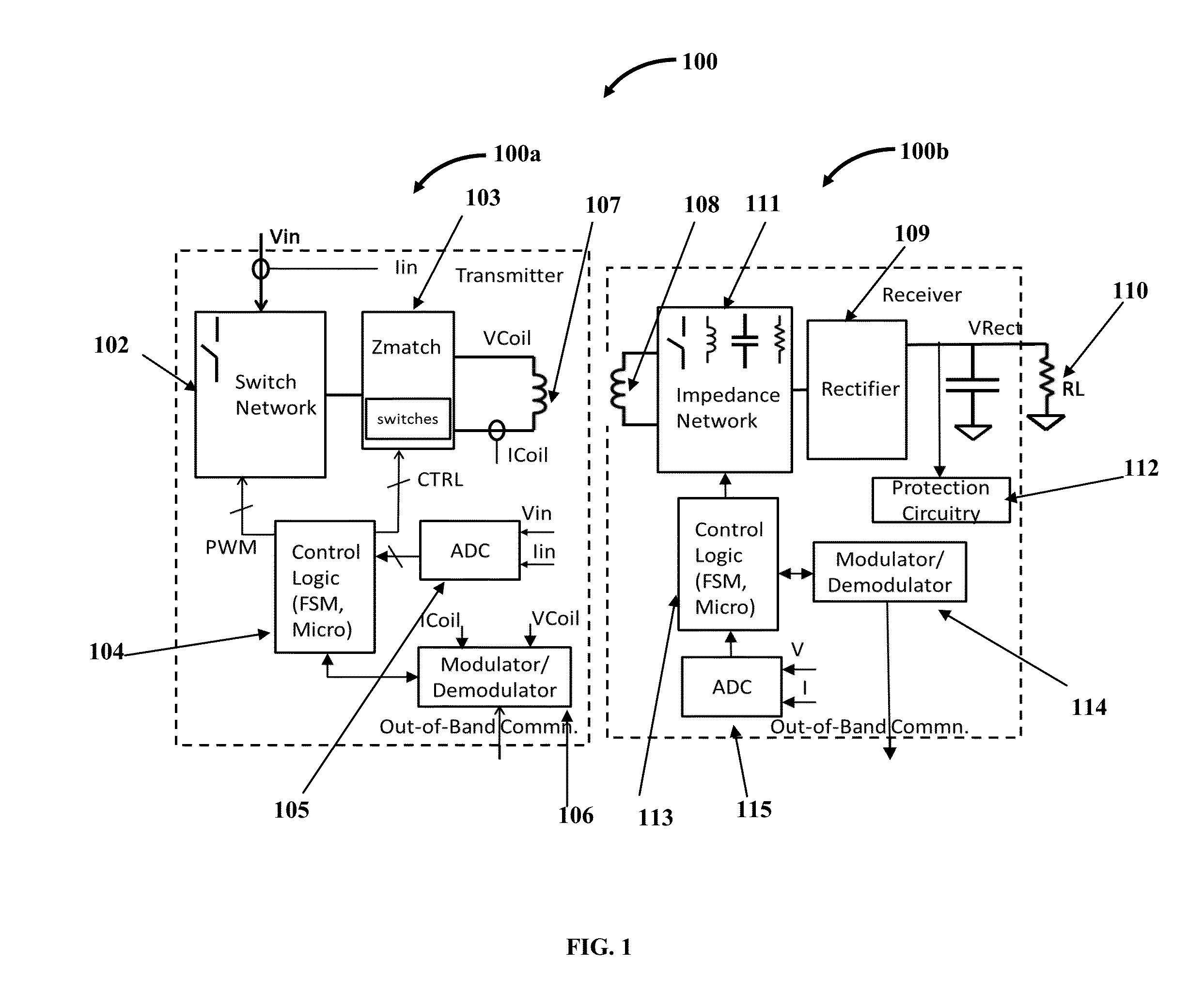
InactiveUS20150372493A1Avoid security issuesEfficient detectionTransformersTransformers/inductances circuitsElectric power transmissionElectricity
A wireless power transmitter (WPT) including a first, second, third circuit and a transmit coil for wirelessly delivering power to a wireless power receiver (WPR) including a receiver coil, rectifier, impedance network, protection circuitry, control logic, modulator / demodulator and ADC is provided. A method that enables WPT and WPR to deliver the required power to the WPR's downstream load in planar, orthogonal and intermediate modes of WPR placement on WPT is provided. The WPR is integrated into the strap / frame or in the vital area of the device. To avoid a heated metal object safety issue, the WPT implements a metal object detect algorithm to detect metal objects and terminate transmission of power. To protect their circuitry from induced voltage spikes in excess of acceptable levels, the WPR includes a simple protection circuitry that naturally turns on and siphons out the excess power when the acceptable threshold levels are exceeded.
Owner:WIPQTUS
Safety method, device and system for an energy storage device
InactiveUS6531847B1Draining rapidly and safely remaining stored energy in a batteryPrimary cell maintainance/servicingSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
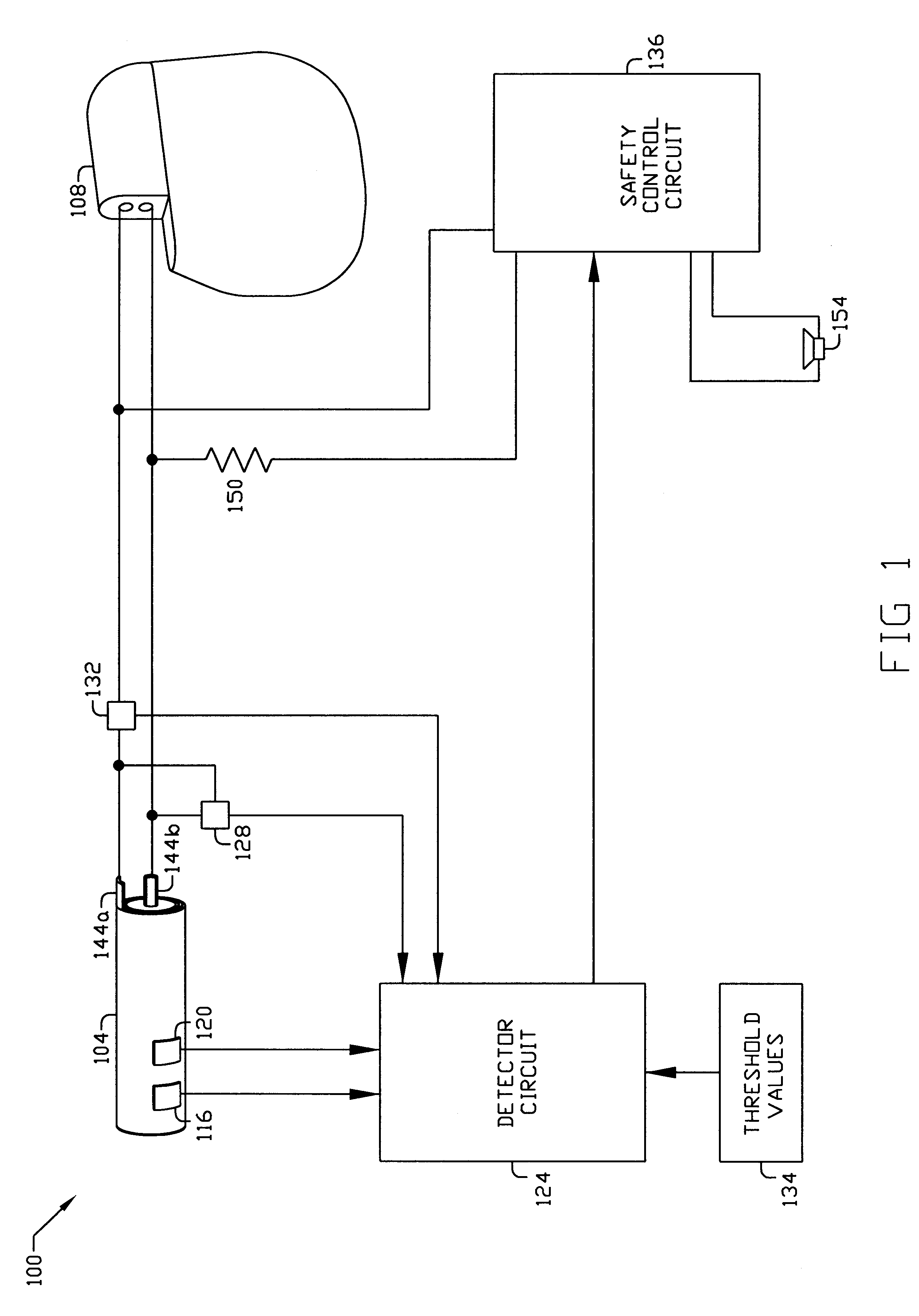
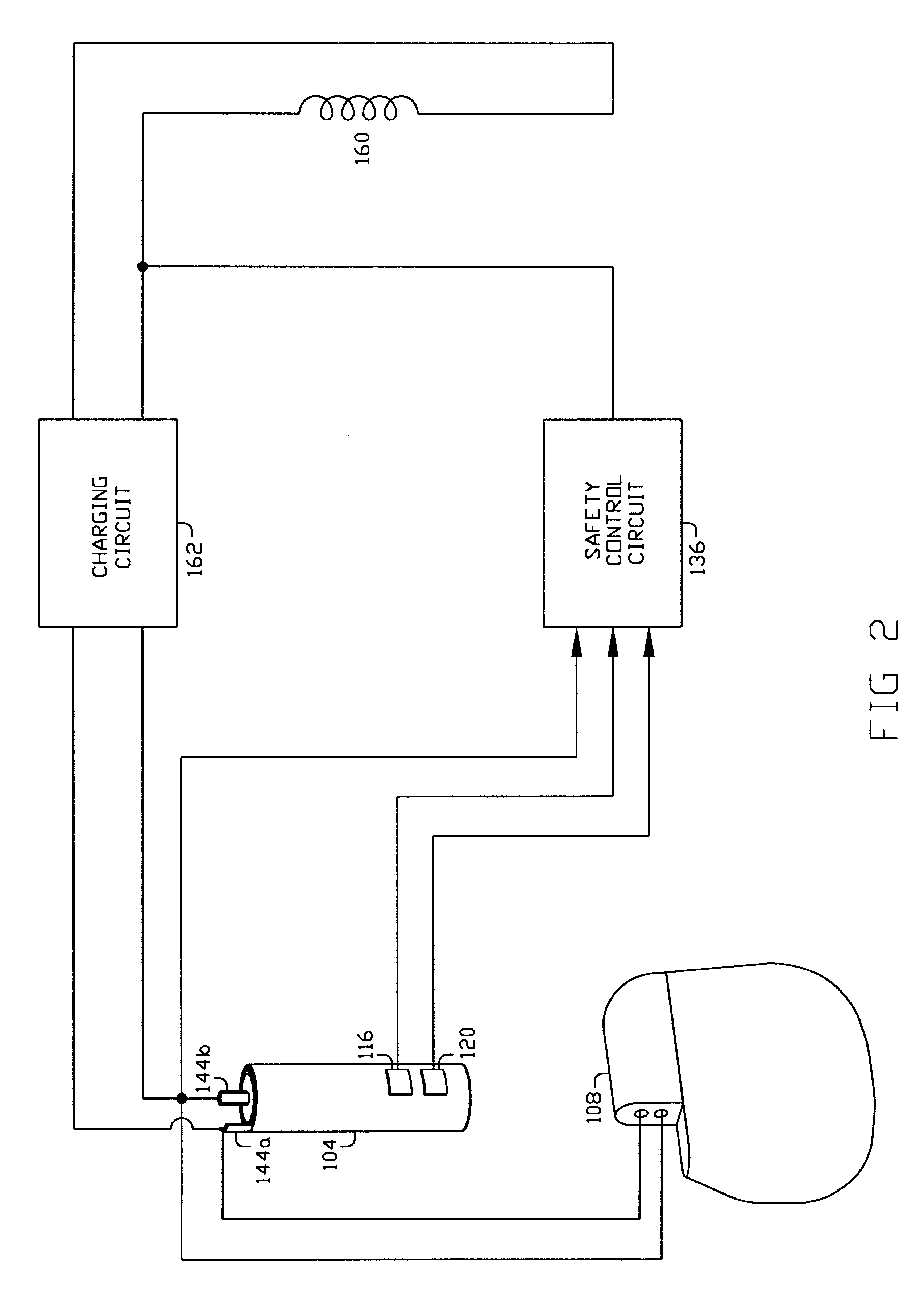
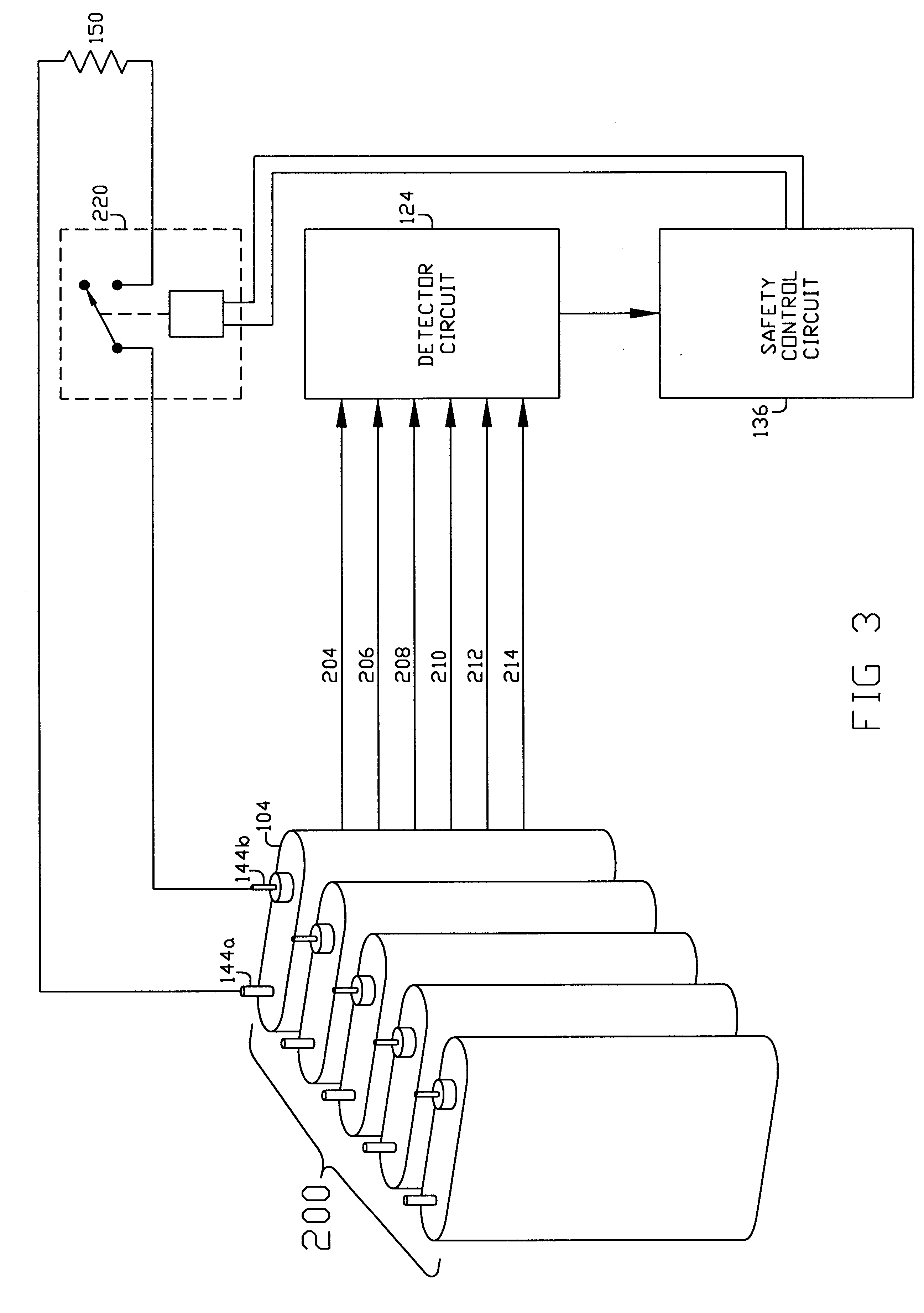
A method, device and system is disclosed for rapidly and safely discharging remaining energy stored in an electrochemical battery 104 in the event of an internal short circuit or other fault. In its best mode of implementation, if a sensor 116 detects one or more parameters such as battery temperature 204 or pressure 206, exceeding a predetermined threshold value 334, the terminals 144 of the battery or cell are intentionally short-circuited external to the battery through a low or near zero resistance load 150 which rapidly drains energy from the battery 104. The rate energy is drained via the external discharge load 150 may be controlled with an electronic circuit 136 responsive to factors such as state of charge and battery temperature. Devices such as piezoelectric and Peltier devices 300, may also be used as emergency energy discharge loads.
Owner:QUALLION
Implantable power management system
InactiveUS6278258B1Accurately calculate and displayIncrease energy densityElectromagnetic wave systemSecondary cellsLow voltageElectric power
The method and system for managing power supplied from a charging circuit to a power source in an implantable medical device comprises the steps of and circuitry for: measuring the current drain of the medical device; measuring the elapsed time since the last full charge of a power source of the device; calculating the actual capacity of the power source (corrected for fade) based on the variable of current drain and the variable of elapsed time; calculating the operating time based on the variable of current drain and the variable of the actual capacity of the power source; measuring the voltage of the power source; signaling the medical device when the power source voltage has reached a certain low value which requires disconnection from the power source; disconnecting, during discharging, the power source from the medical device upon the power source reaching a certain low voltage in order to prevent deep discharging of the power source and subsequent damage; precisely limiting the charging voltage to the power source in order to prevent overcharging beyond safe limits; disconnecting, during charging, the power source from the charging circuit upon the power source reaching a certain high voltage in order to prevent overcharging of the power source and subsequent damage; sensing when the electromagnetic waves being transmitted by an RF transmitter / charger induce a voltage level above a certain value at an RF receiver of the implanted power management system; reconnecting power supply inputs of the medical device to the power source upon sensing this induced high voltage level; monitoring the temperature of the power source during charging and discharging; disconnecting the charging circuitry from the power source if the temperature of the power source raises above a certain level during charging; reconnecting the charging circuitry to the power source when the temperature of the power source drops below a certain low value during charging; disconnecting the implanted medical device from the power source if the temperature of the power source raises above a certain level during discharging; and, reconnecting the medical device to the power source when the temperature of the power source drops below a certain low value during discharging.
Owner:EXONIX
Battery protection circuit
ActiveUS20050242779A1High protection levelCells structural combinationBattery overcharge protectionBattery systemBattery cell
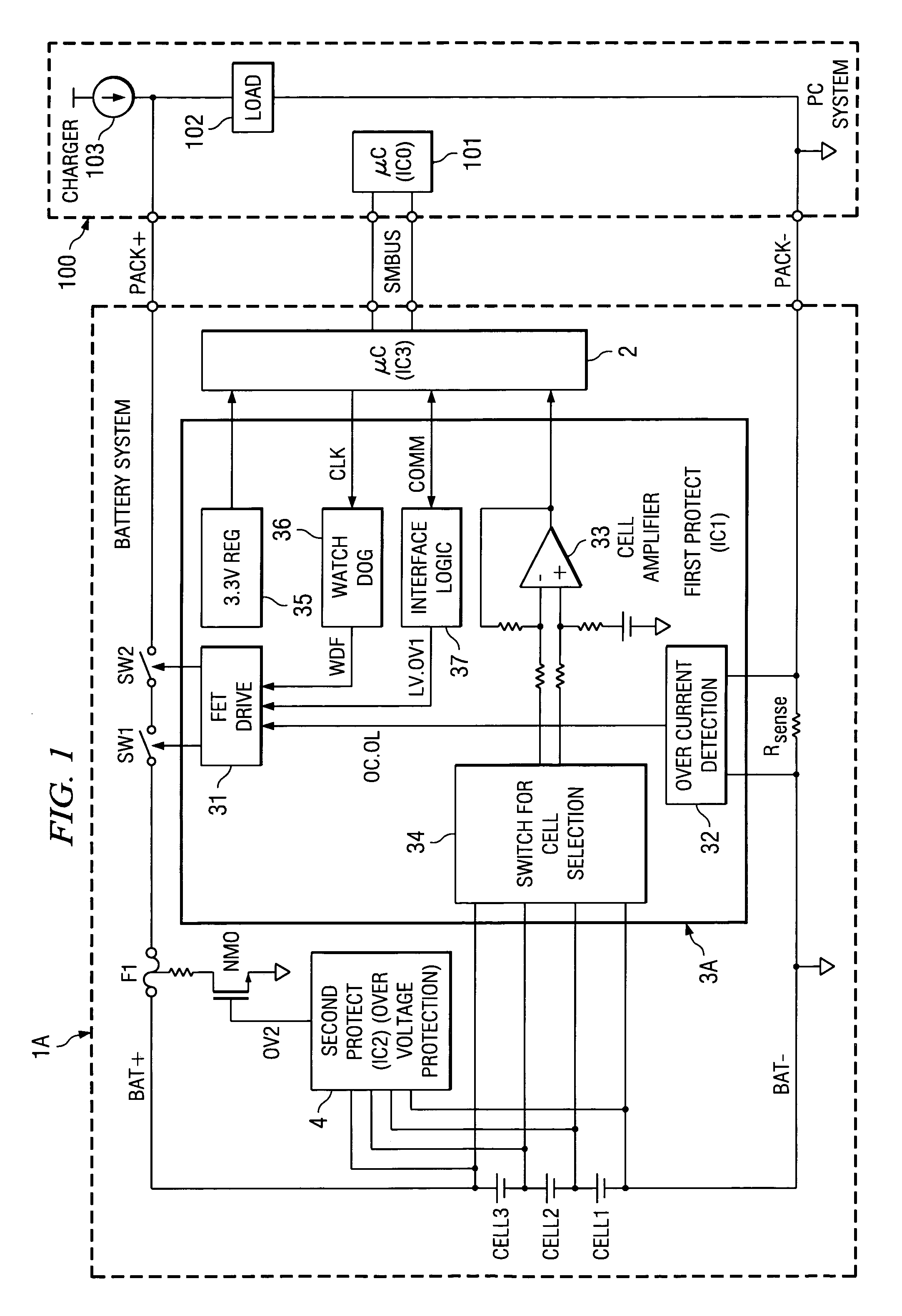
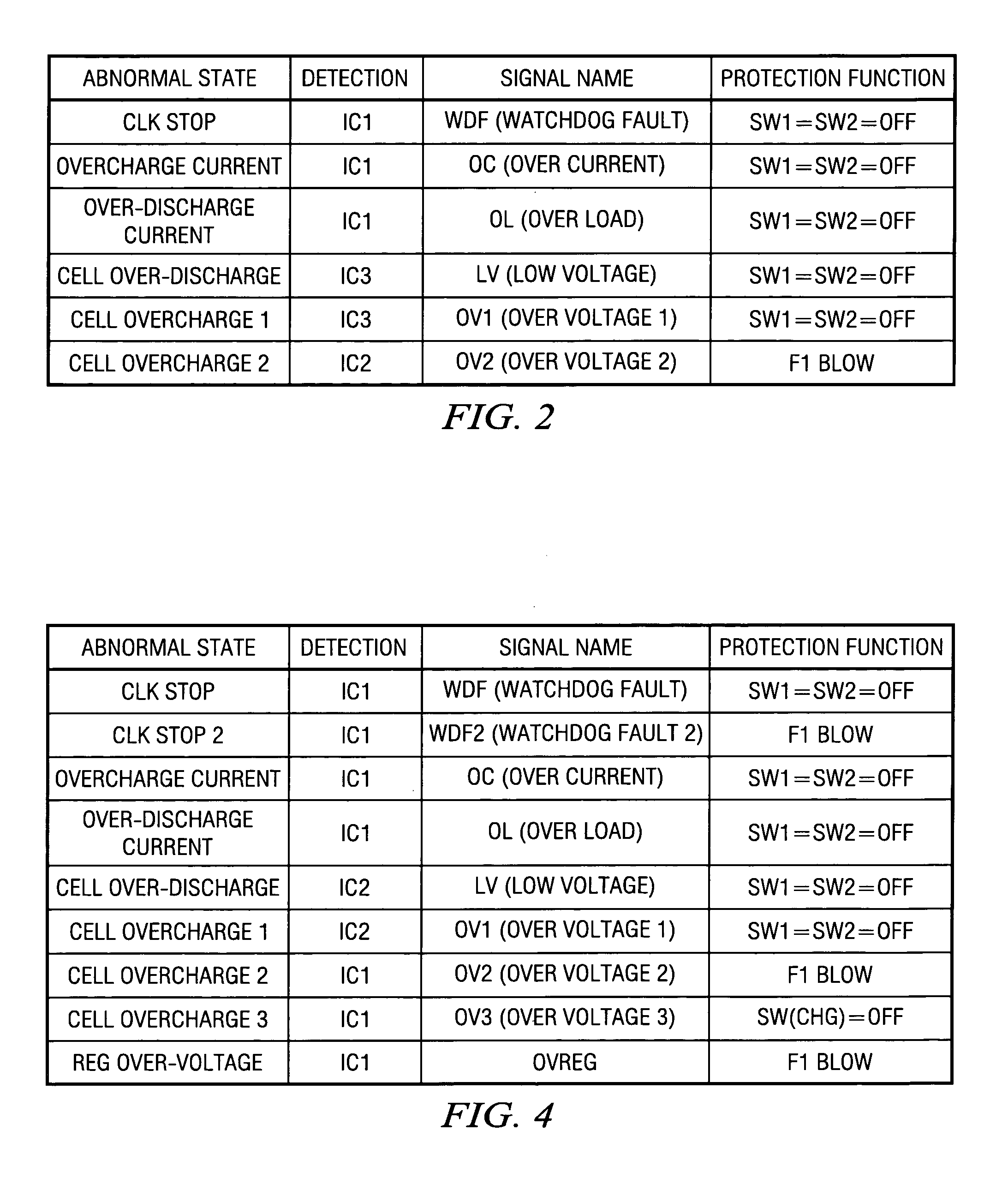
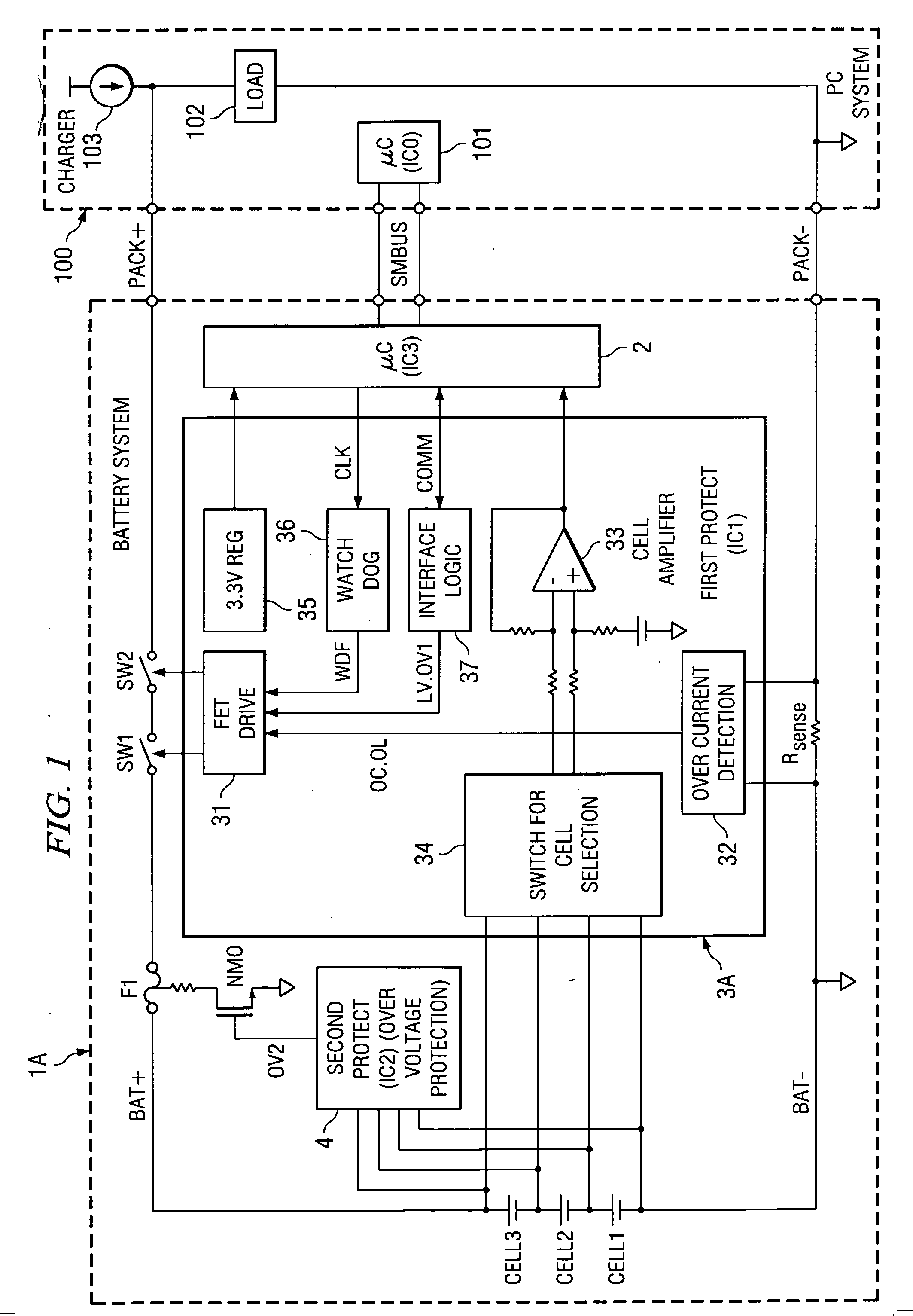
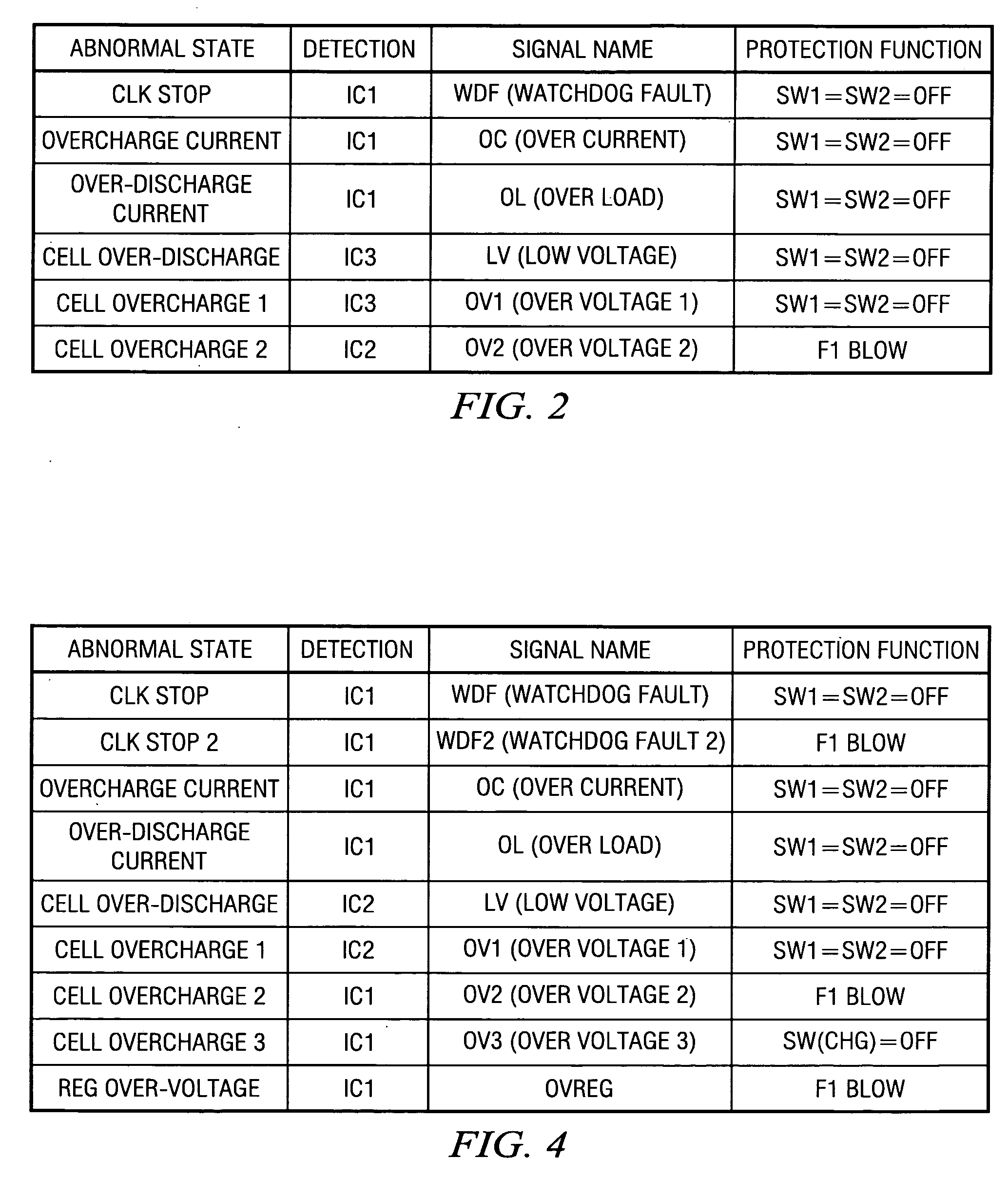
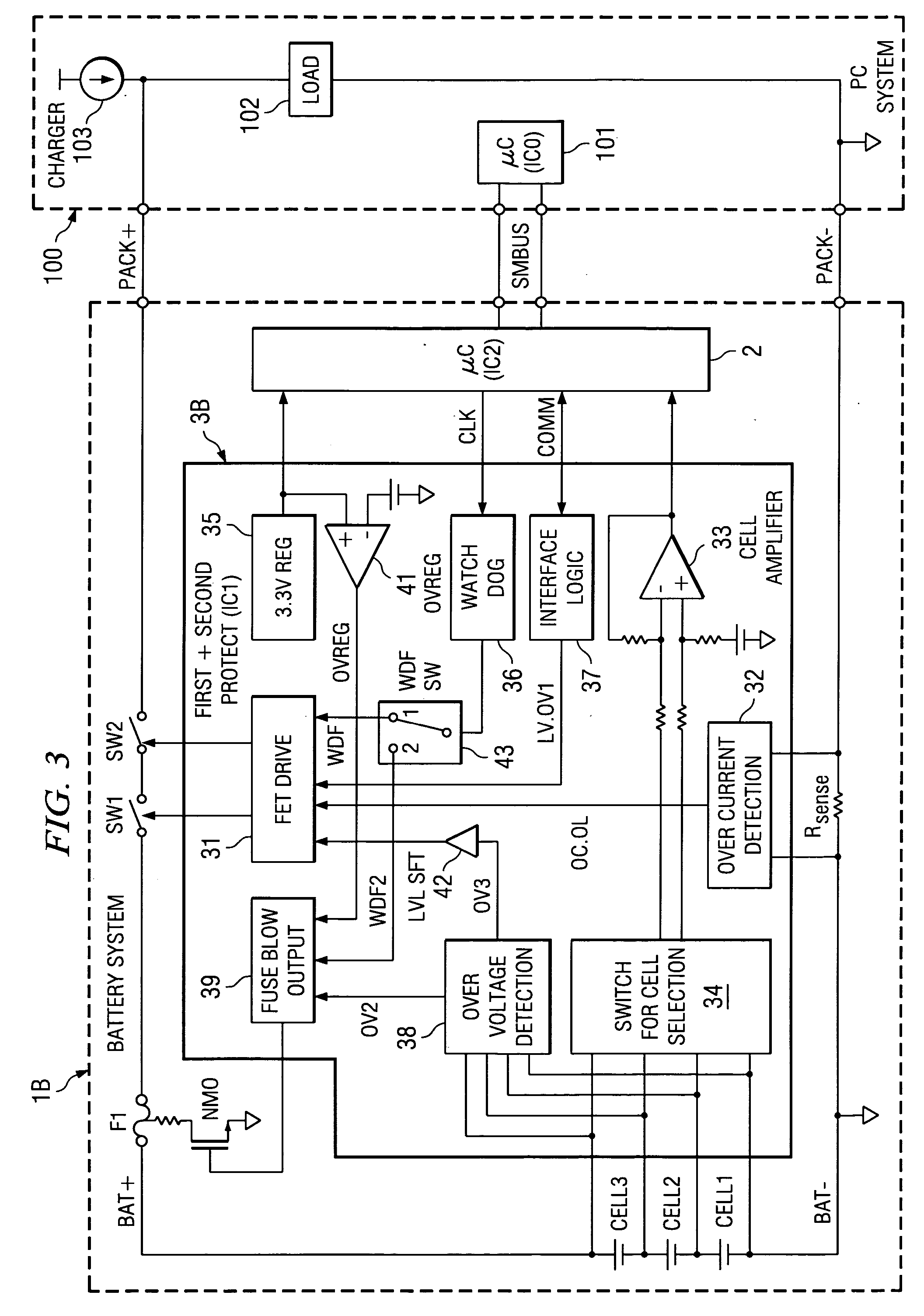
A protection of battery system having battery cells Cell1˜Cell3, FET switches SW1, SW2 that are connected to the high-side path and control on / off state of the path, as well as fuse F1 for cutting said path, primary protection circuits 31˜34 that detect abnormalities in charging / discharging of the battery cells and turn the FET switches off, and secondary protecting controller 38 that detect abnormalities in charging / discharging of the battery cells and controls the operation of fuse F1. Secondary protecting controller 38 controls fuse F1 if there is no tendency to a decrease in abnormalities after a prescribed period of time after control of the FET switch.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
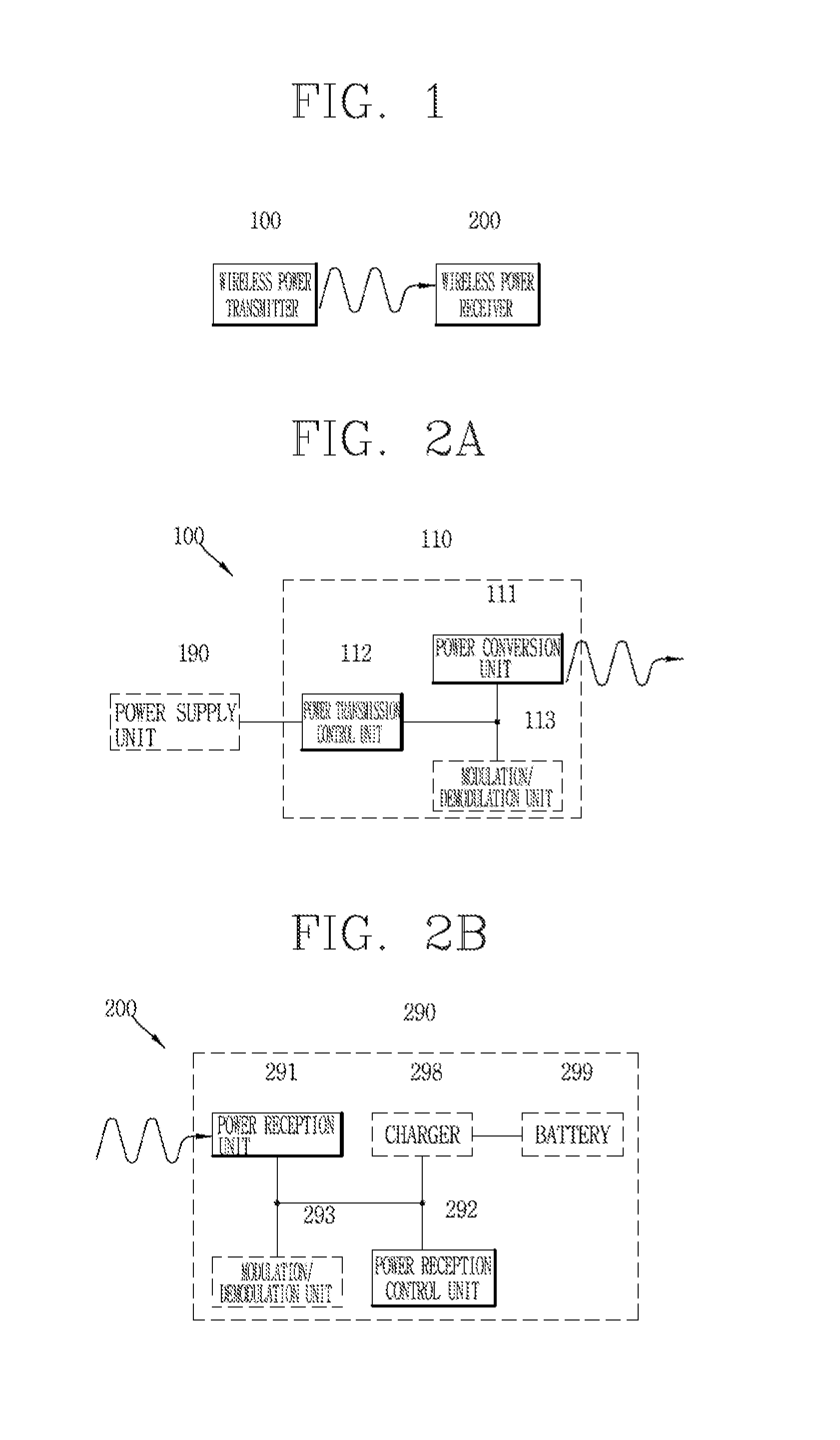
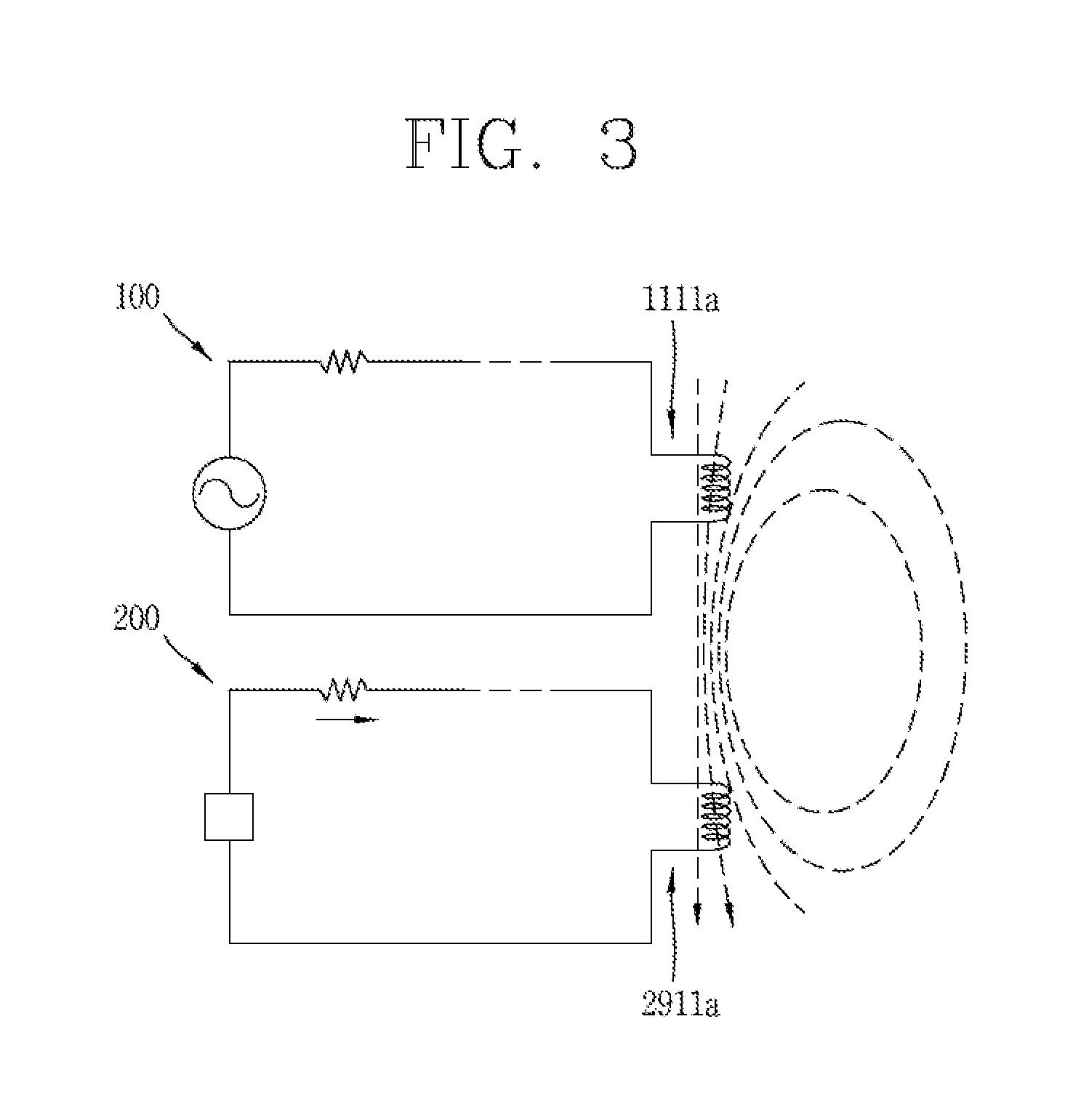
Wireless power transfer method, wireless power transmitter and wireless charging system
ActiveUS20140354223A1Increase freedomCircuit authenticationNear-field transmissionElectricityElectric power transmission
The present disclosure relates to a wireless power transfer method, a wireless power transmitter and a wireless charging system in a wireless power transfer field. That is, a wireless power transmitter configured to transfer power to a wireless power receiver in a wireless manner includes a power transfer unit configured to transmit power to the wireless power receiver in the wireless manner, a circuit unit having a plurality of capacitors electrically connected to the power transfer unit, and configured to support each of a plurality of frequencies by changing the electric connection of the capacitors, and a controller configured to detect a communication standard that the wireless power receiver supports, and control the electric connection of the capacitors such that the circuit unit operates at a frequency corresponding to the detected communication standard.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com