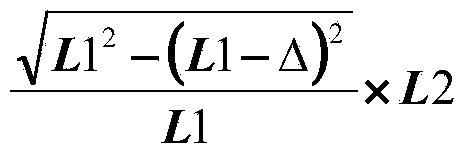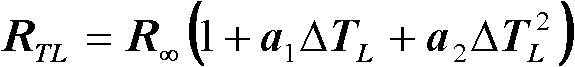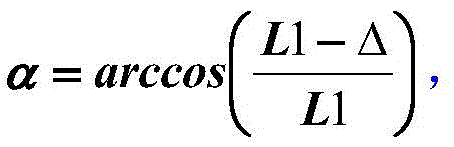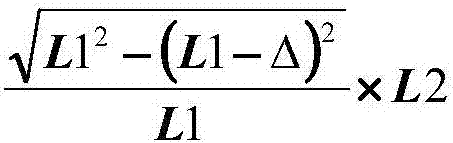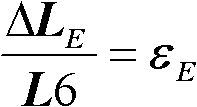Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Meet the requirements of the online test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
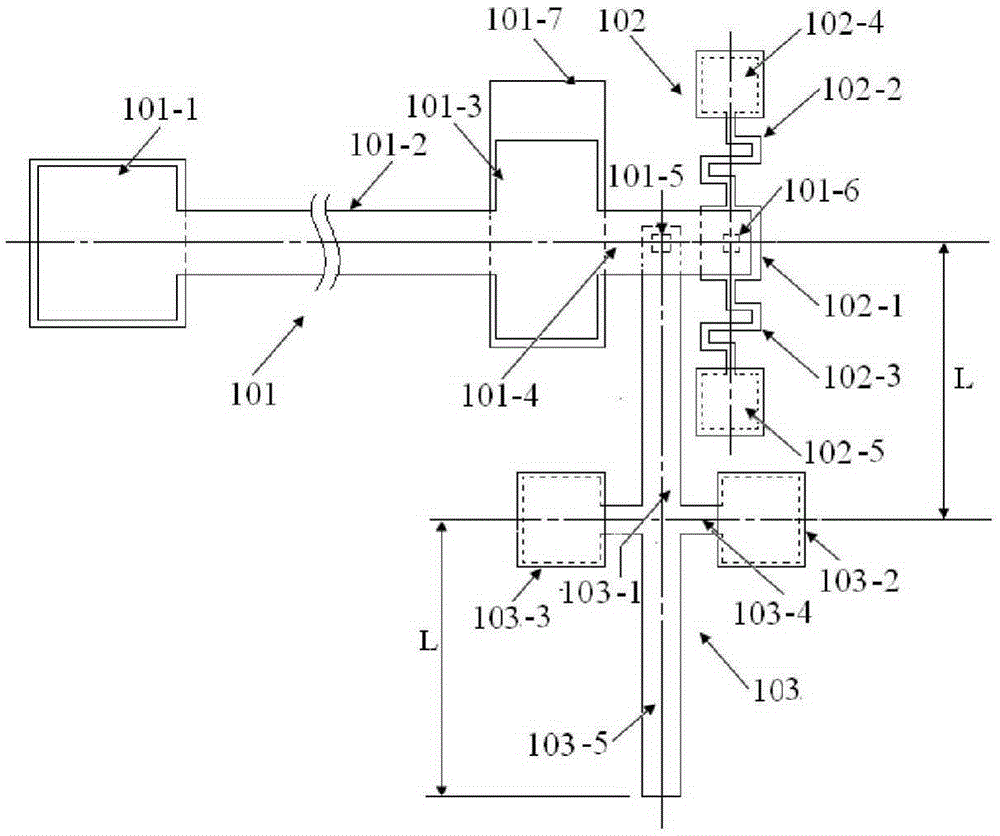
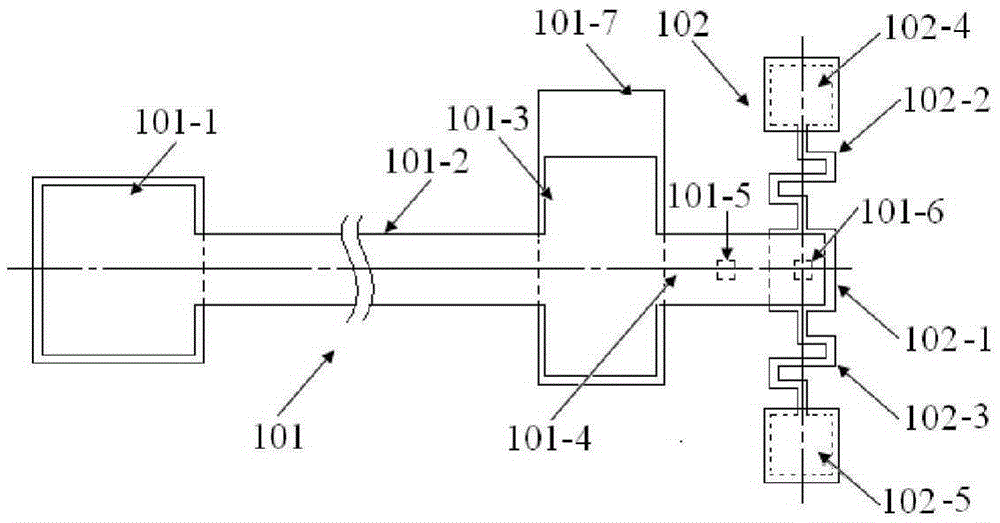
Online measurement method and measurement apparatus of residual stress of conductive thin film material
ActiveCN106248280ALower requirementEasy loadingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementElectricityYoung's modulus
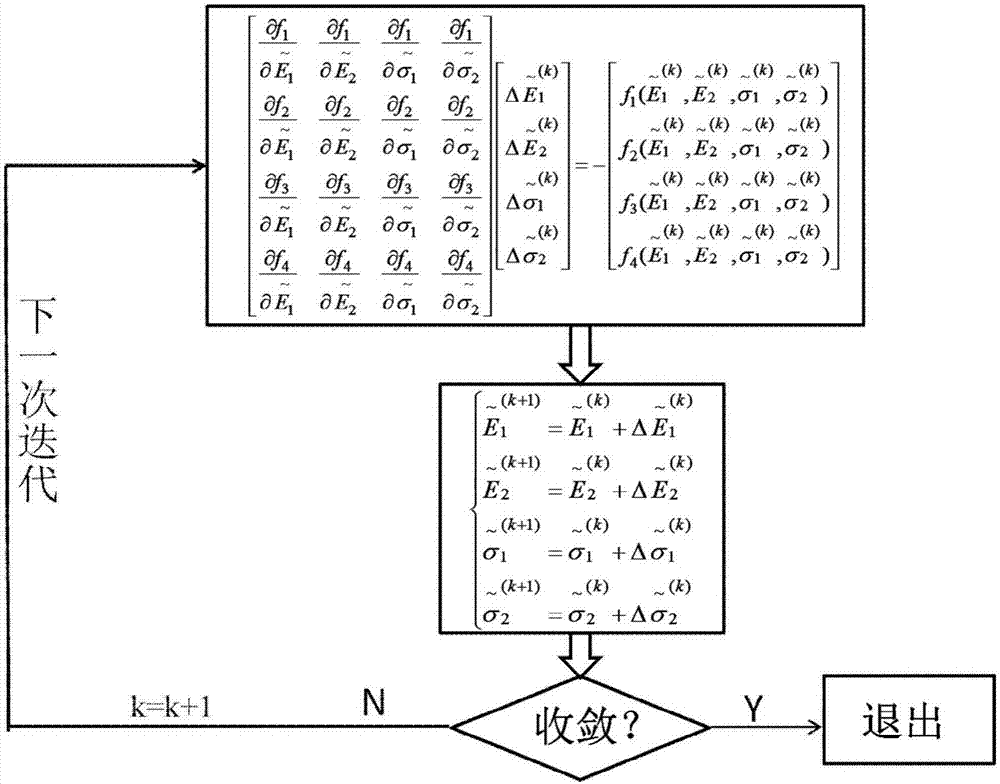
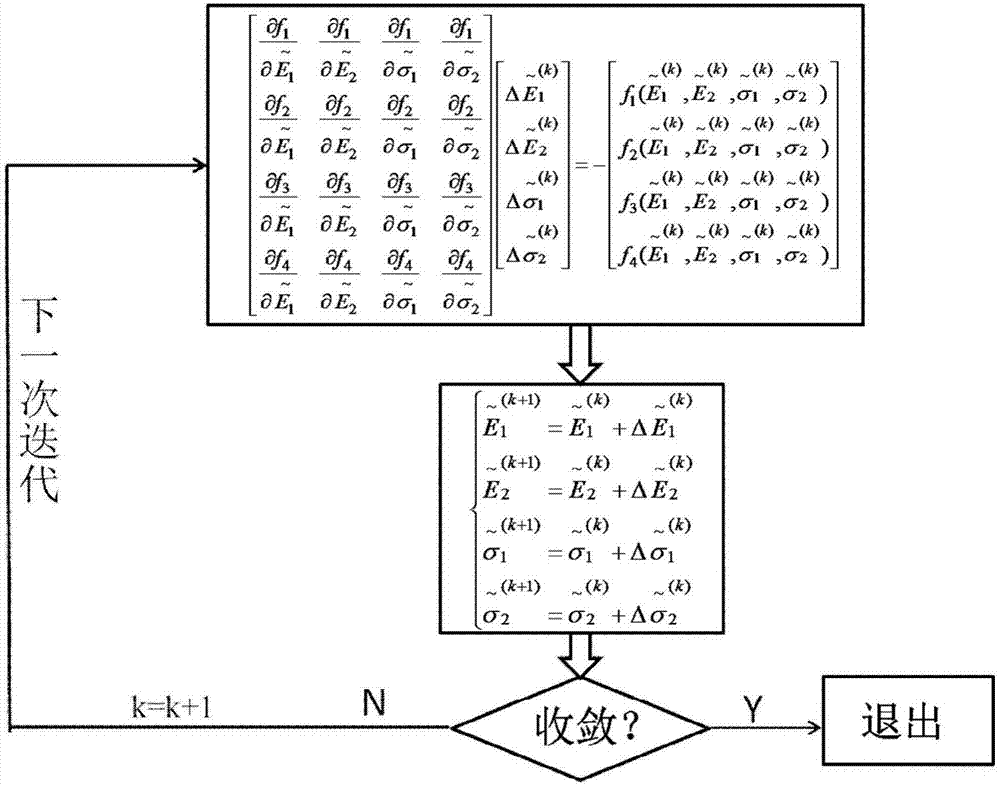
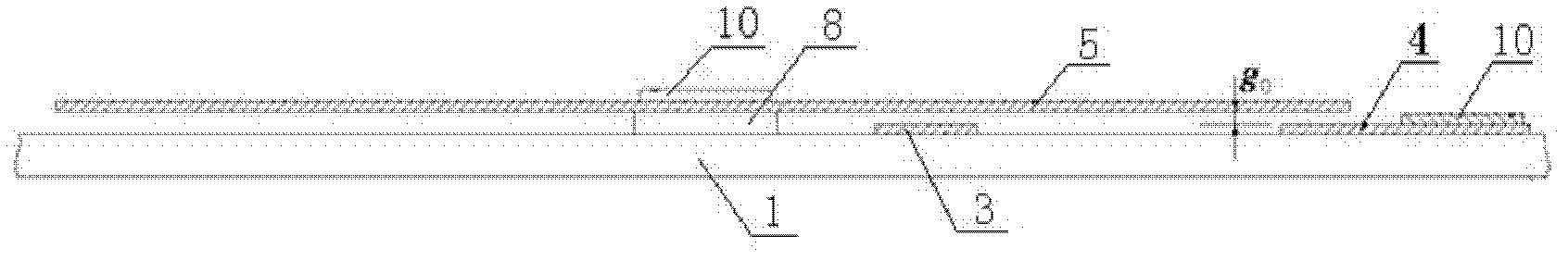
The invention brings forward an online measurement method of residual stress of a conductive thin film material, and a corresponding measurement apparatus. A measurement structure is designed by use of an electrostatic driving Pull-in principle, relevance of parameters of two measurement members is controlled through use of synchronous processing control, through limiting correlation parameters of total strain energy of the two measurement members, a partial differential equation set of the total strain energy is constrained accordingly, and values of unknown residual stress sigma 0 and a Young's modulus E of the two measurement members are obtained through a mode of solving the partial differential equation set. According to the invention, the problem of incapability of real-time measurement of the conductive thin film material under the condition of unknown material parameters, unknown residual stress size and unknown positivity and negativity (tensile stress or compression stress) is solved. The apparatus and method have the advantages of simple measurement structure, simple electric signal loading and measurement, stable calculation method and high measurement efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Double-layer thin film residual stress testing structure
InactiveCN103439031ALower requirementSimple test methodForce measurement by permanent gauge deformationCircular discCalculation methods
The invention brings forward a double-layer thin film material residual stress testing structure. A measuring unit is a first layer thin film disc structure which is supported by a circular cylinder. The surface of the first layer thin film disc is covered with another layer thin film material so that a double-layer thin film disc structure is formed. The diameter direction of the edge of the first layer thin film disc stretches out so that a straight beam is formed. The tail end of the straight beam is provided with a projection vernier. The simple double-layer thin film disc structure is adopted and the projection vernier is combined cooperatively so that residual stress of an MEMS common thin film material can be obtained. Besides, residual stress test of each layer thin film under the condition of more layers of thin film material can be popularized, and a measuring method and a calculation method of parameter extraction are quite simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and device for measuring mechanical parameters of double-end-fixed support beam based on resonant frequency
InactiveCN106932263ASolve the problem of measuring mechanical parametersLower requirementStrength propertiesOnline testClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a method for measuring mechanical parameters of a double-end-fixed support beam based on a resonant frequency. According to the method, equivalent young's modulus and equivalent residual stress of each layer of a multi-layer composite double-end-fixed support beam are obtained once by virtue of a solving equation set based on a relation between a first-order resonant frequency and parameters such as material properties and structure sizes of the multi-layer composite double-end-fixed support beam. The method can meet online test requirements of multi-layer film materials, a test structure and a calculation method are simple, and the accuracy is relatively high. The invention further discloses a device for measuring the mechanical parameters of the double-end-fixed support beam based on the resonant frequency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
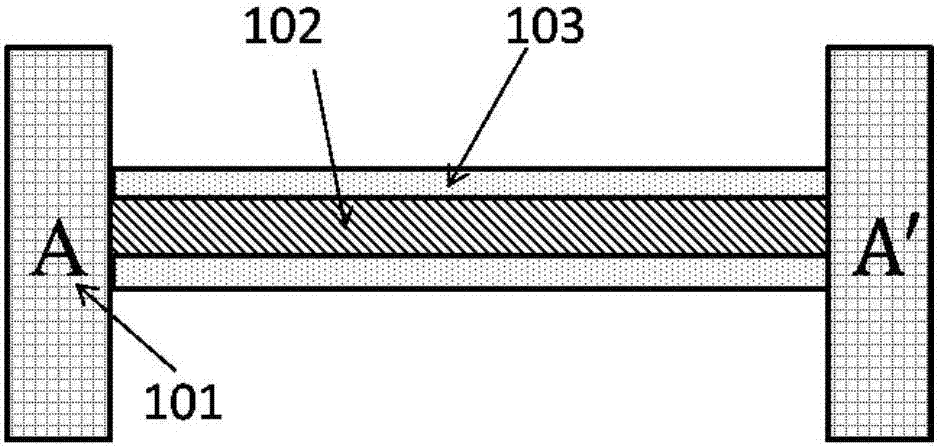
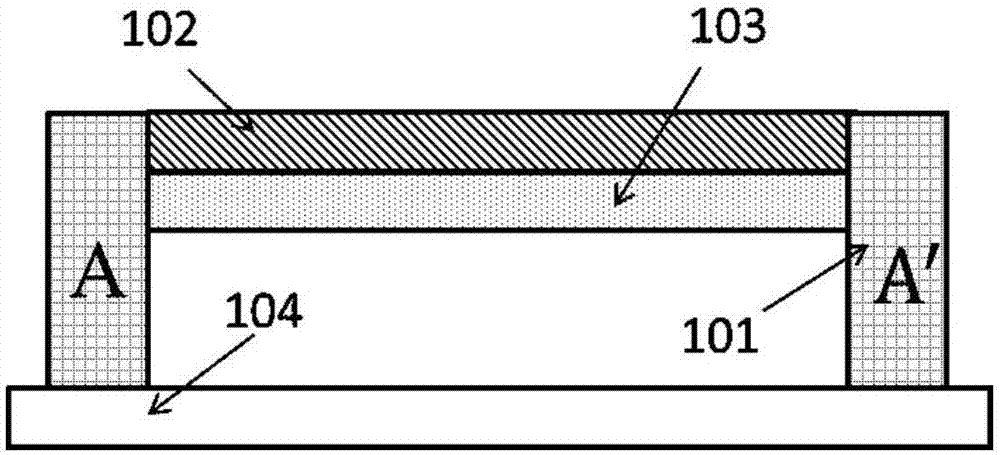
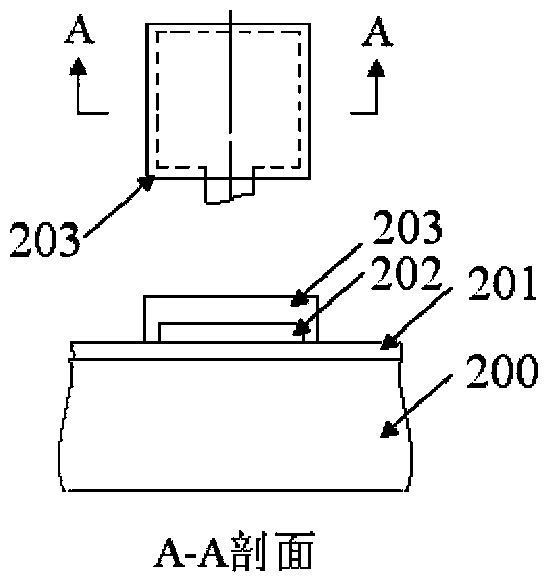
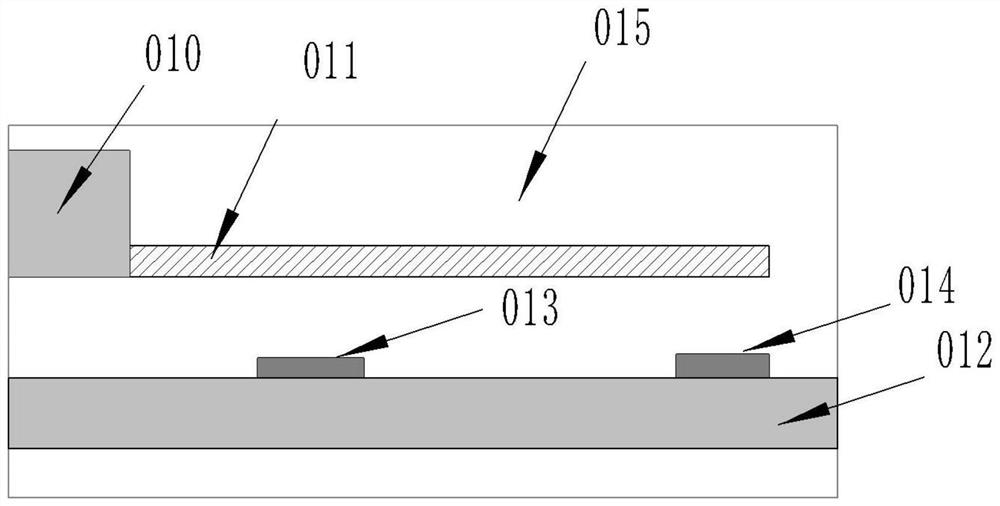
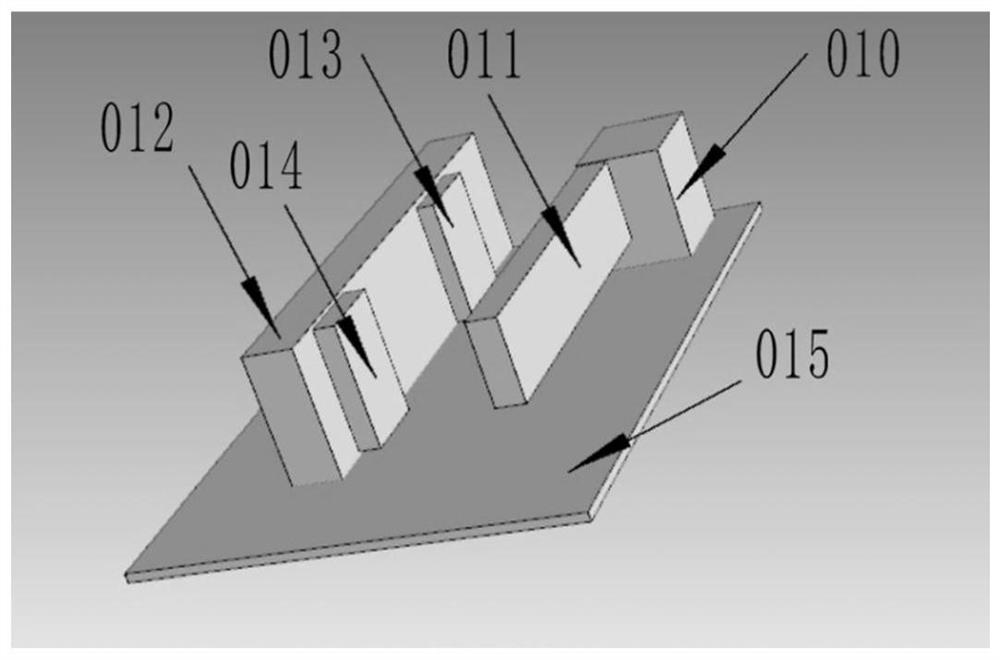
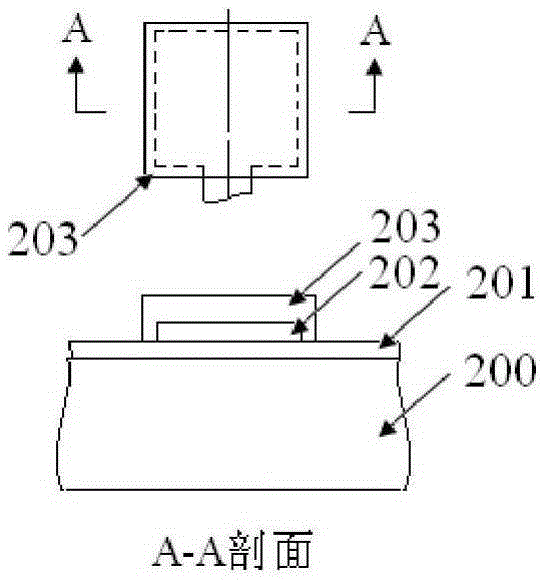
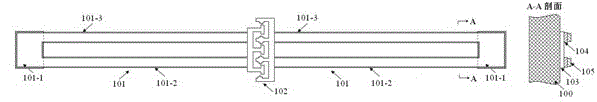
Structure and method for testing Young modulus of thin film silicon material on insulating substrate
InactiveCN104034603ASimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsMaterial strength using steady bending forcesYoung's modulusCushion
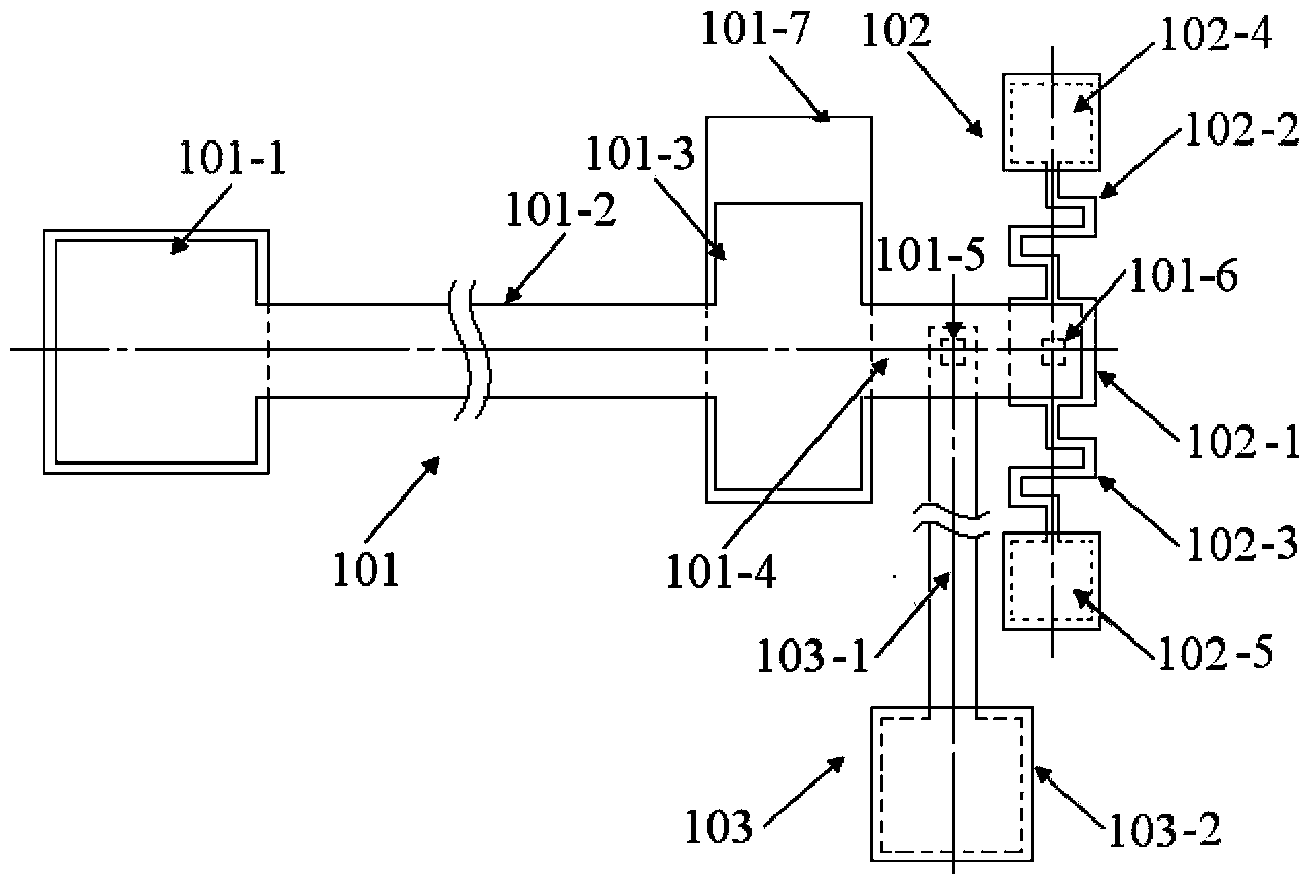
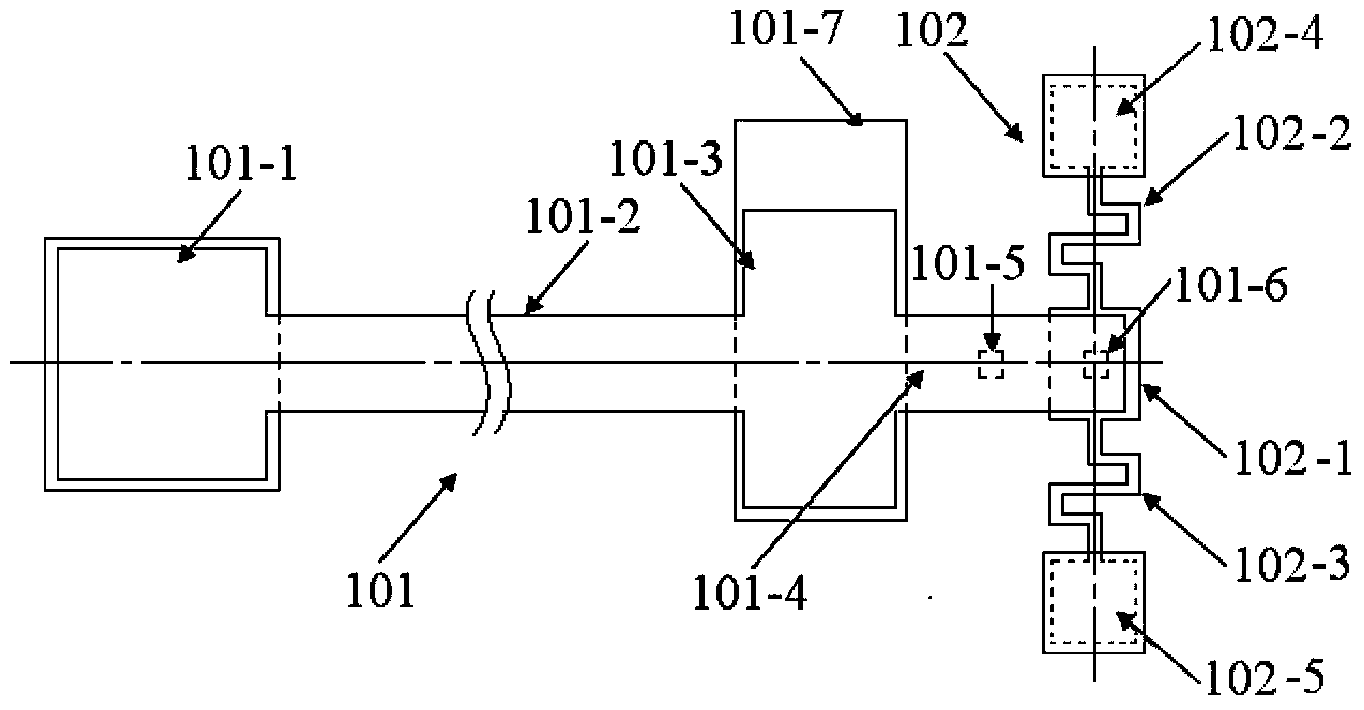
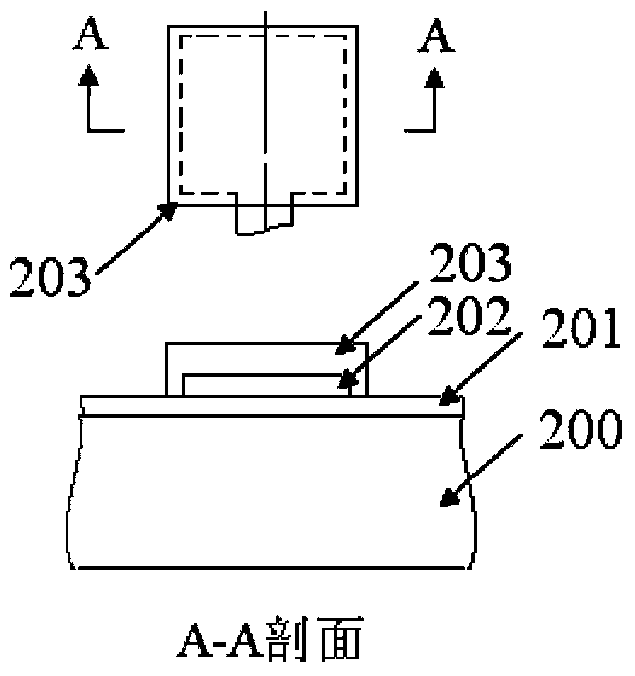
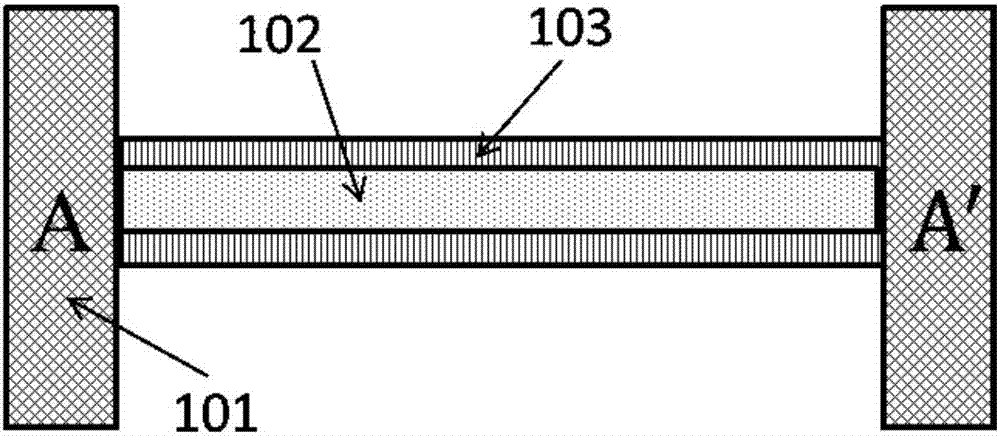
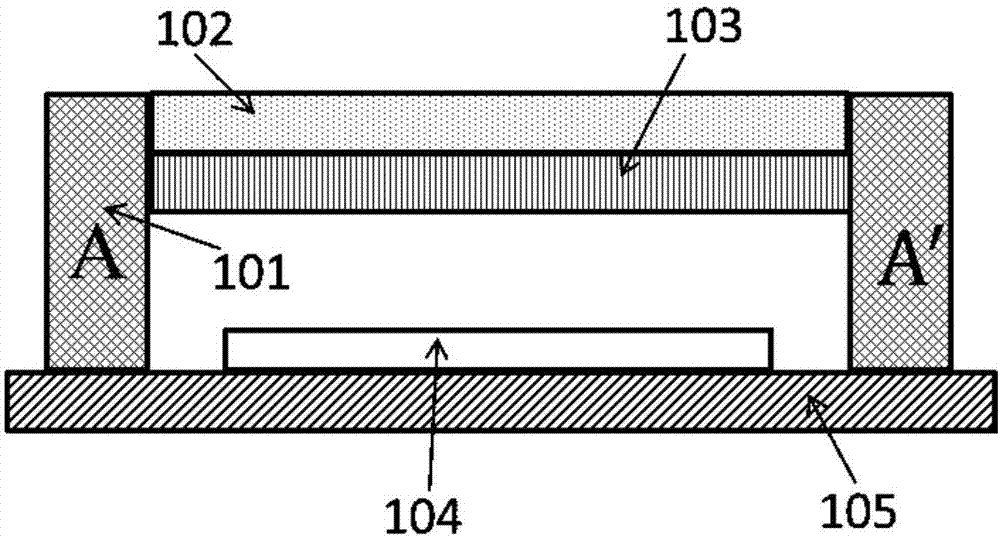
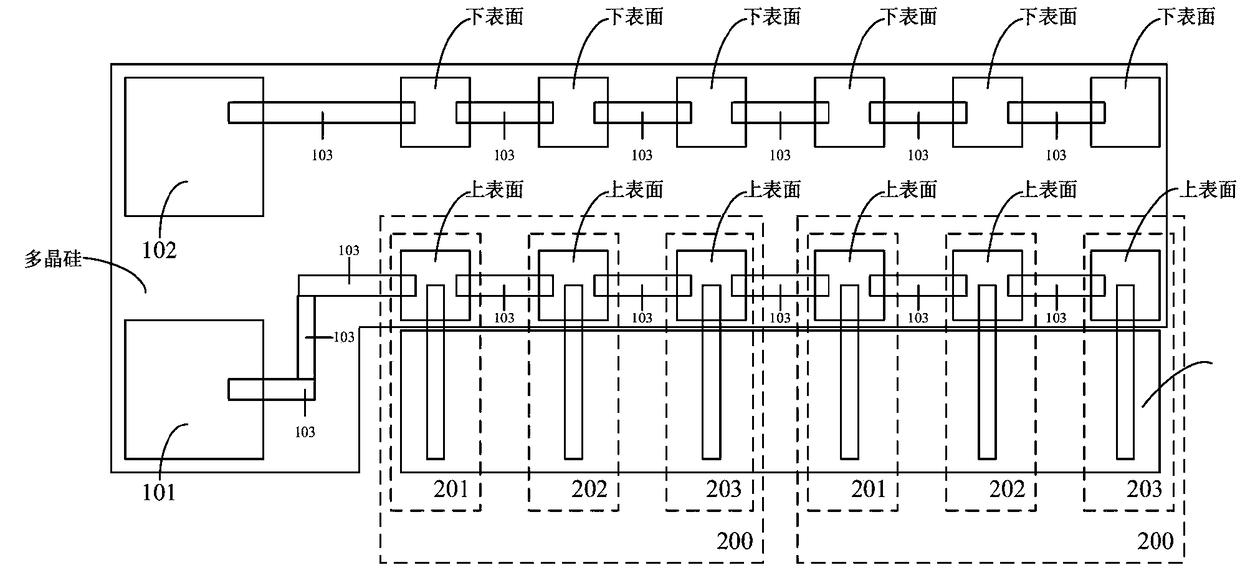
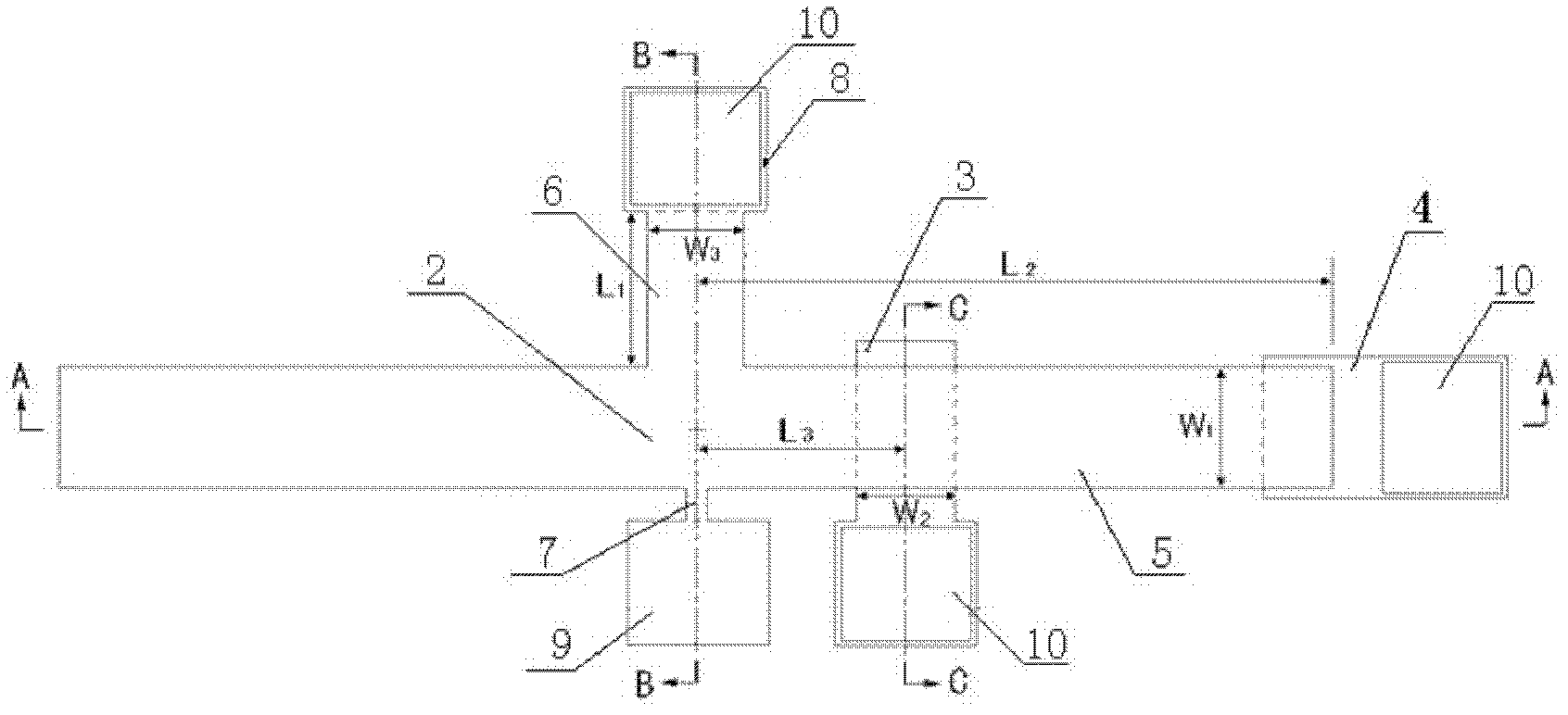
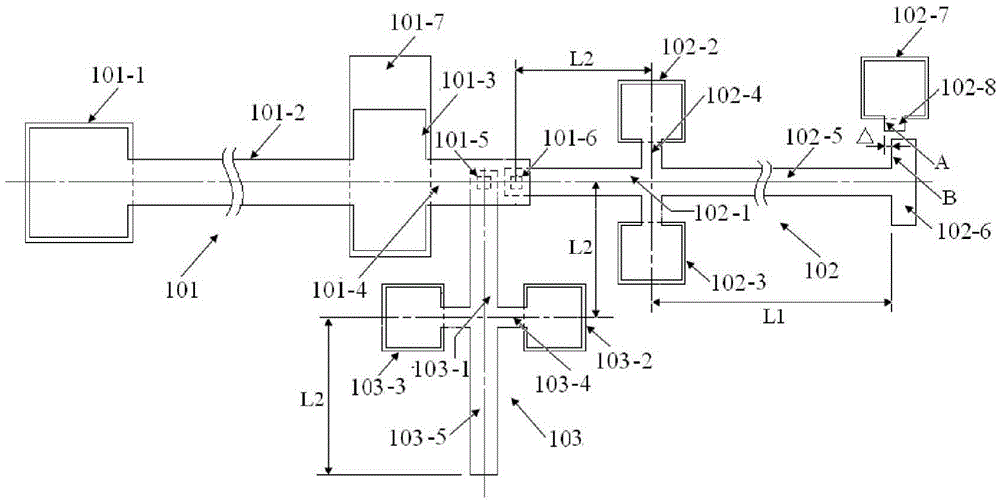
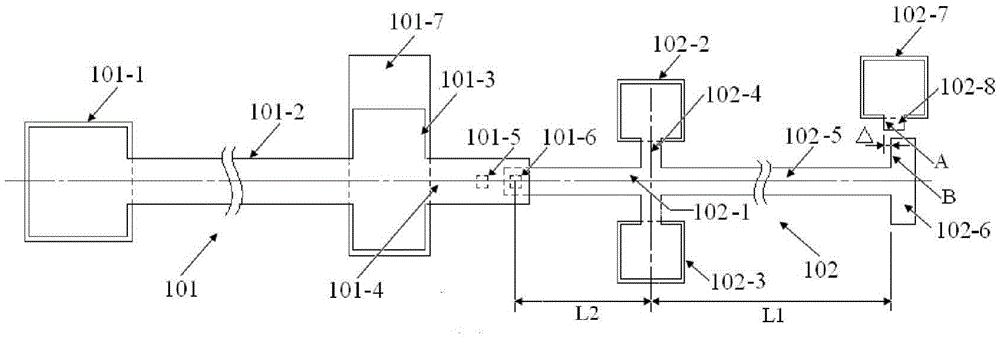
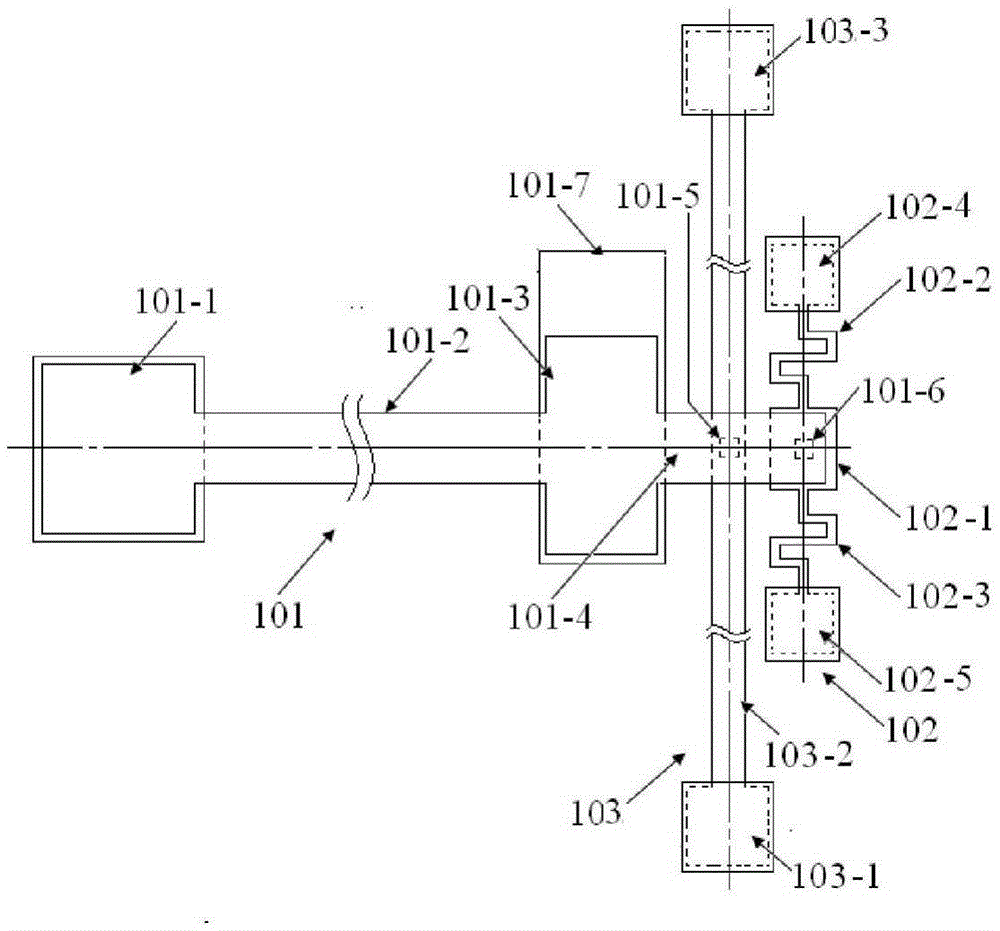
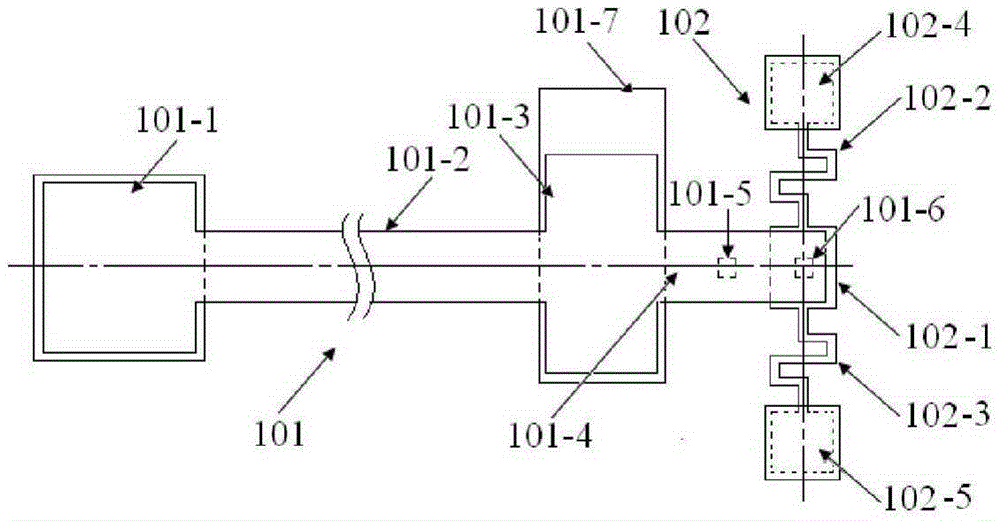
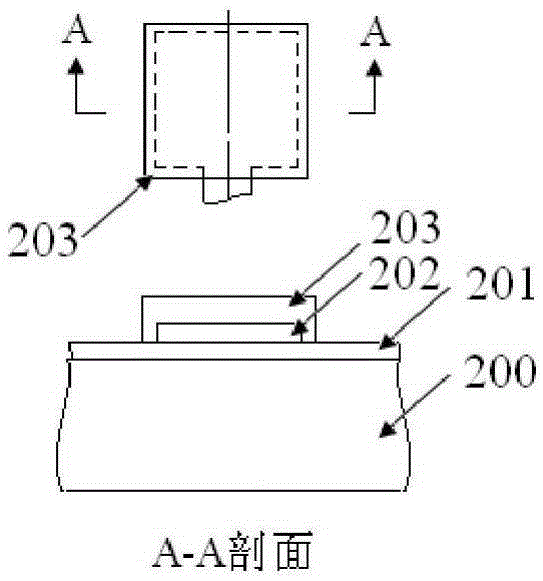
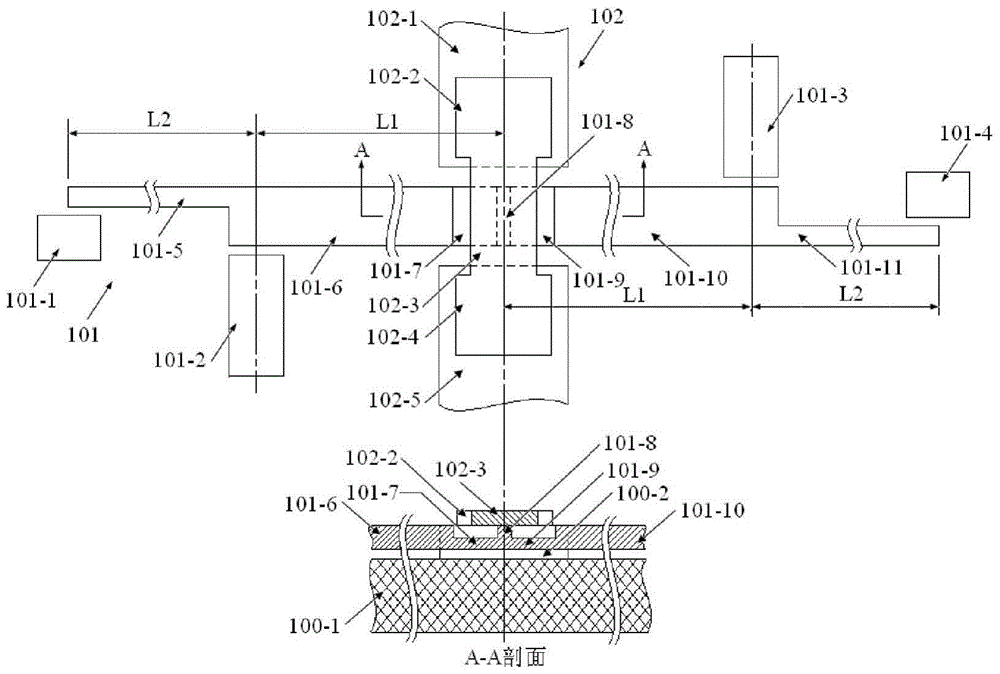
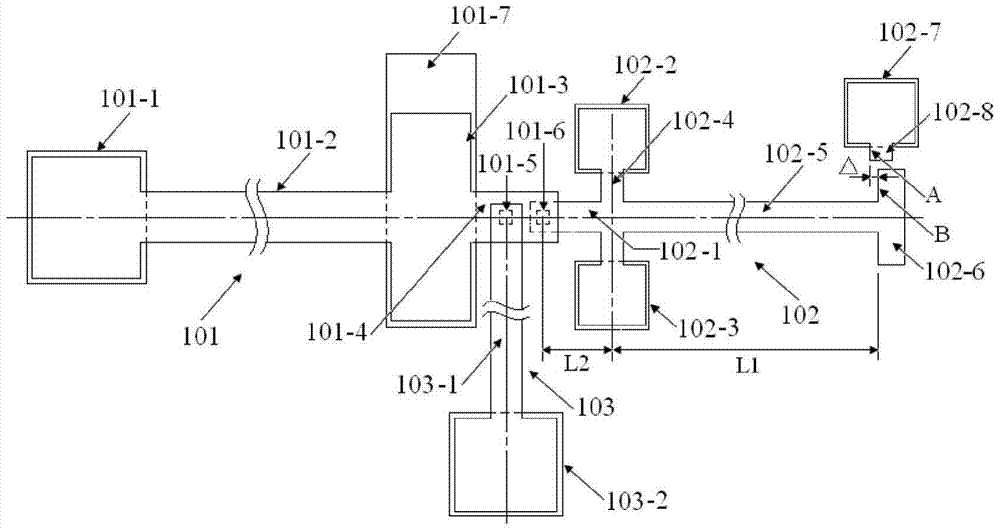
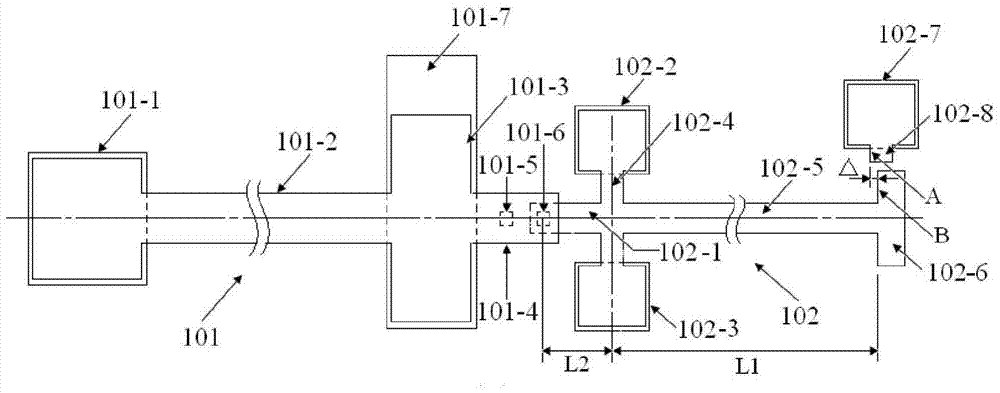
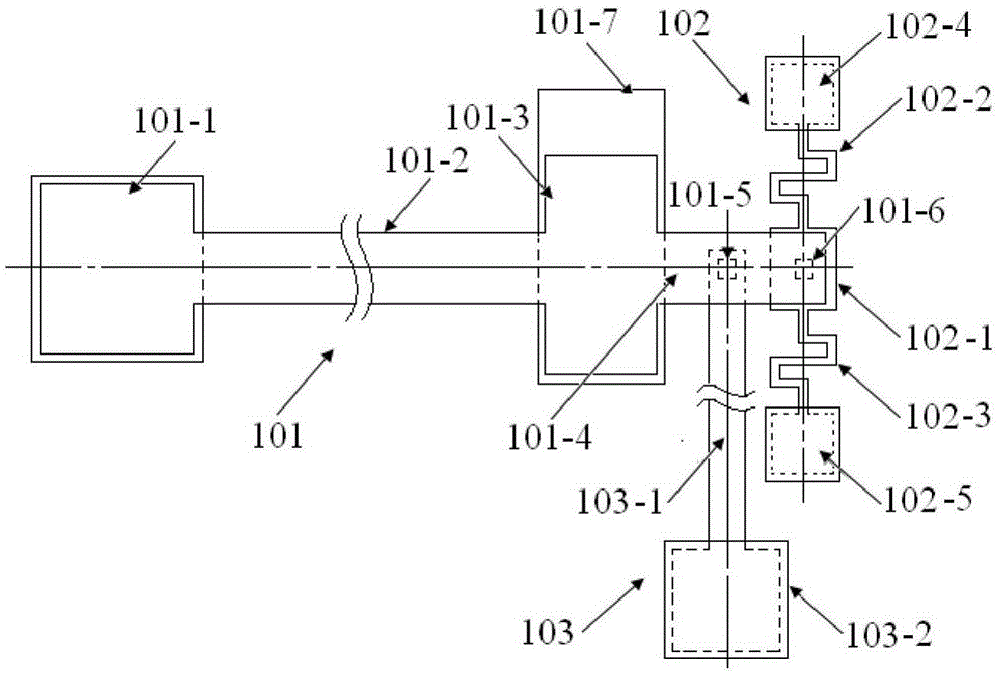
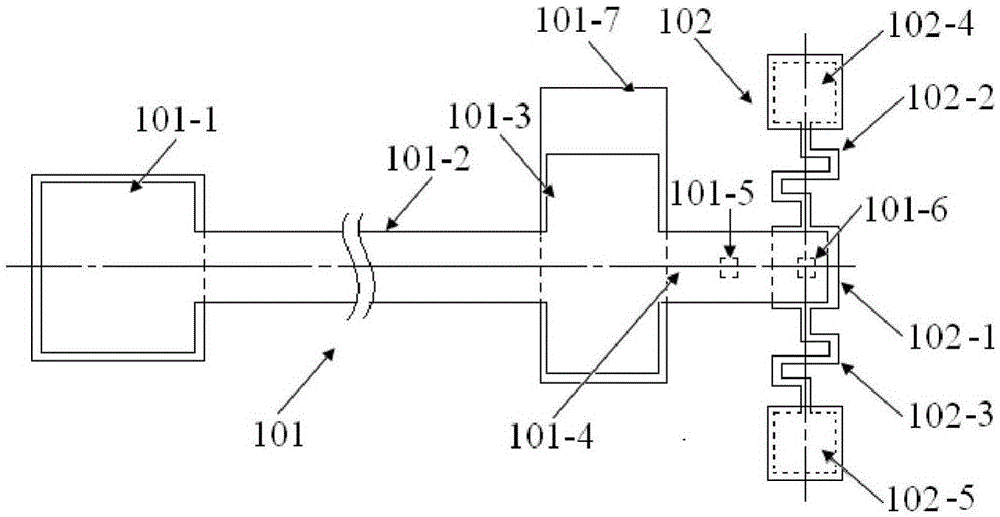
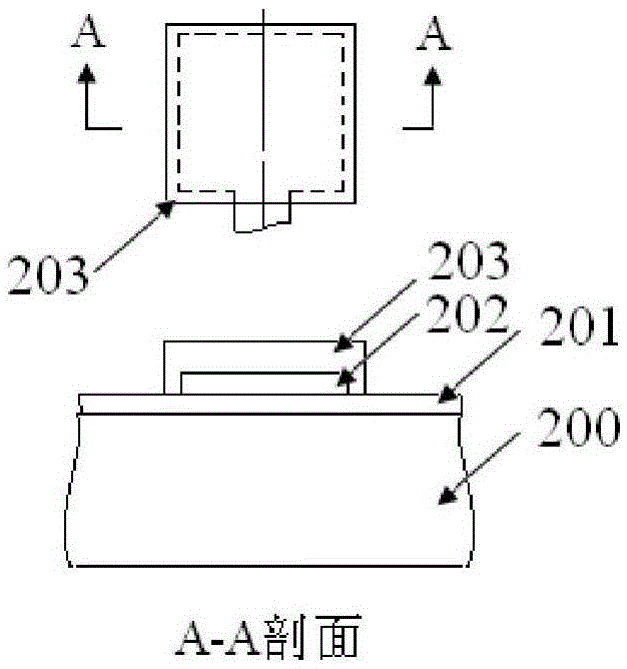
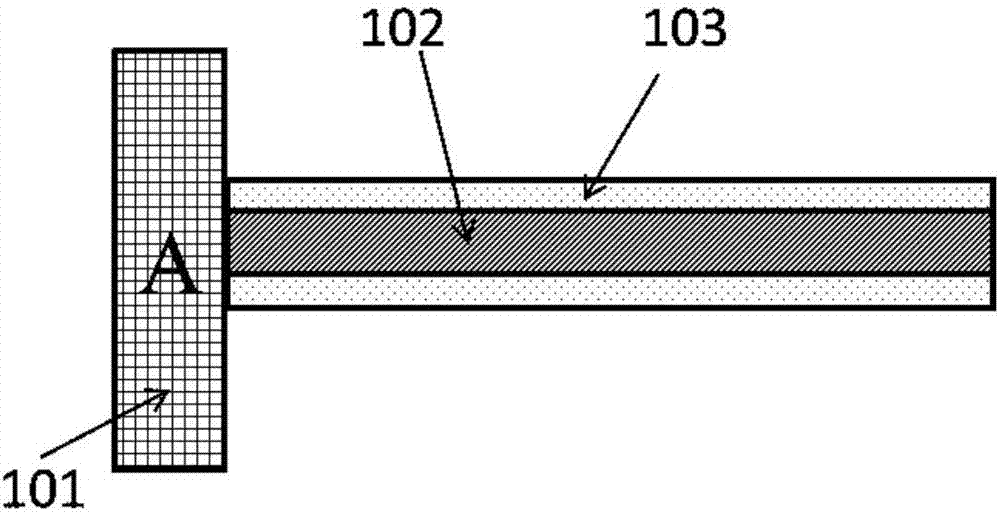
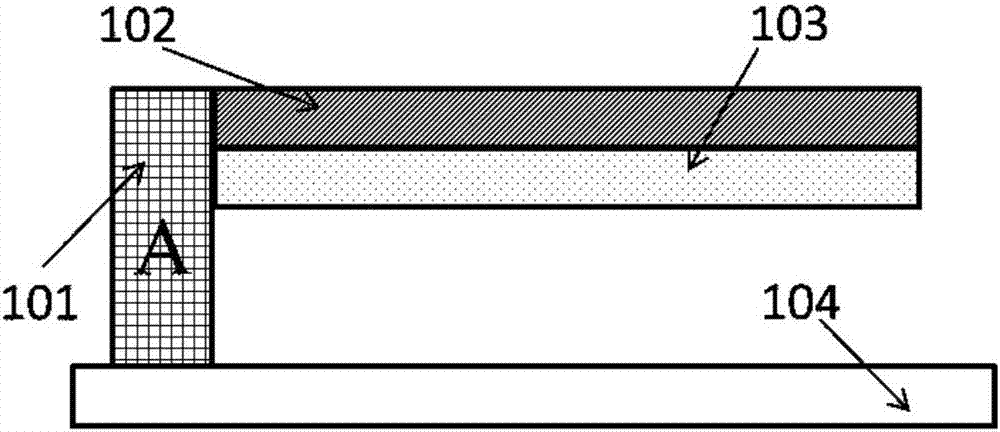
The invention provides a structure and a method for testing Young modulus of a thin film silicon material on an insulating substrate. The structure comprises two groups of structures, wherein the first group of structures consists of a polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam (101), a thin film silicon cantilever beam (103) and a cushion plate (102) made from polycrystalline silicon; the second group of structures consists of a polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam and a cushion plate made from the polycrystalline silicon. According to the structure, units for actually testing the Young modulus of thin film silicon are the thin film silicon cantilever beams, the only difference of the two groups of structures is whether the thin film silicon cantilever beam exists, and corresponding structures and geometric dimensions of other units in the two groups of structures are completely the same. According to the method, by applying an electrostatic force, the polycrystalline silicon cantilever beams are bent downwards to press the thin film silicon cantilever beam and the cushion plates to contact with the substrate; by testing with the two groups of test structures, a force for independently driving the thin film silicon cantilever beam to be bent to reach test deflection is extracted, and the Young modulus of the thin film silicon material on the insulating substrate can be calculated by virtue of the force, the test deflection and the geometric dimensions.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Structure and method for testing Young modulus of polycrystalline silicon thin film material
InactiveCN104034574AEasy to measureSimple extraction methodStrength propertiesCantilevered beamThin membrane
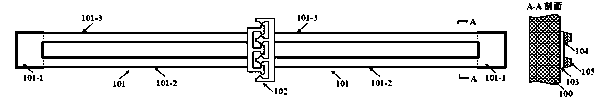
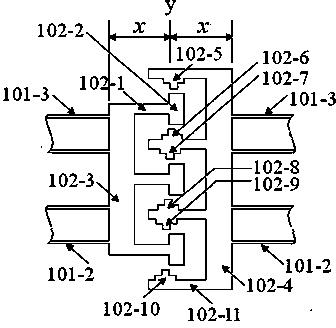
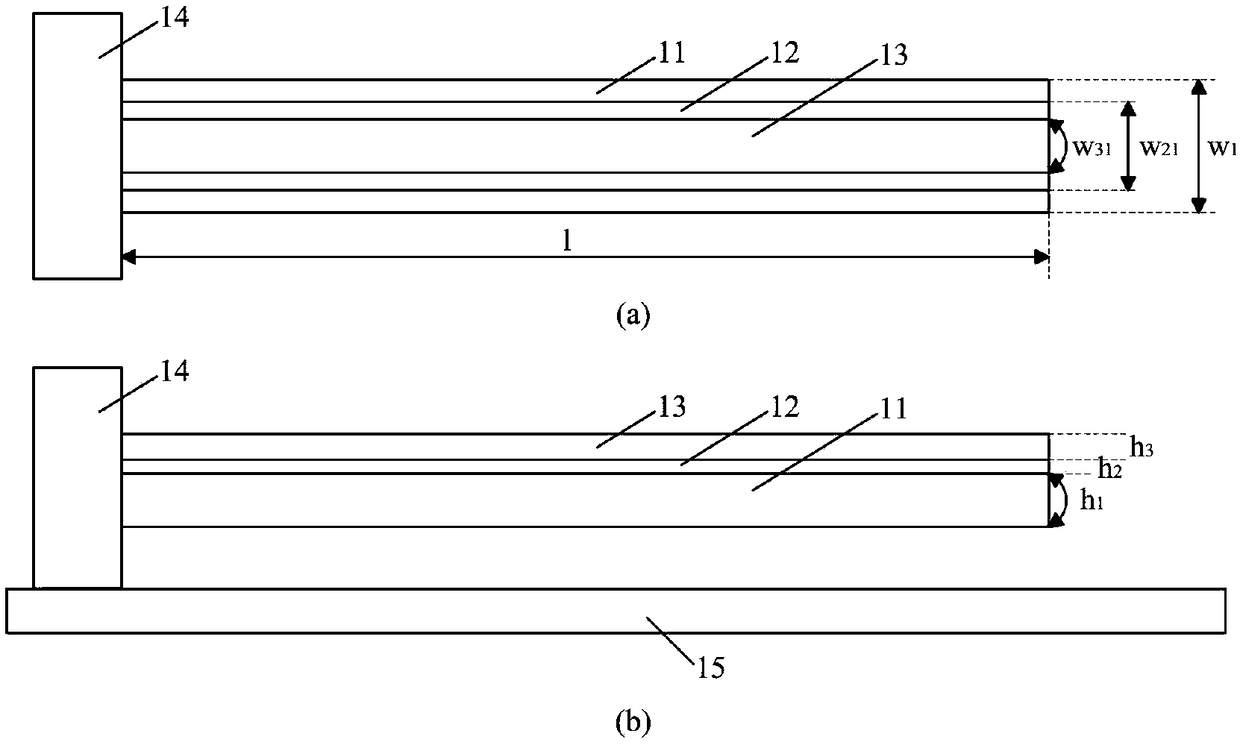
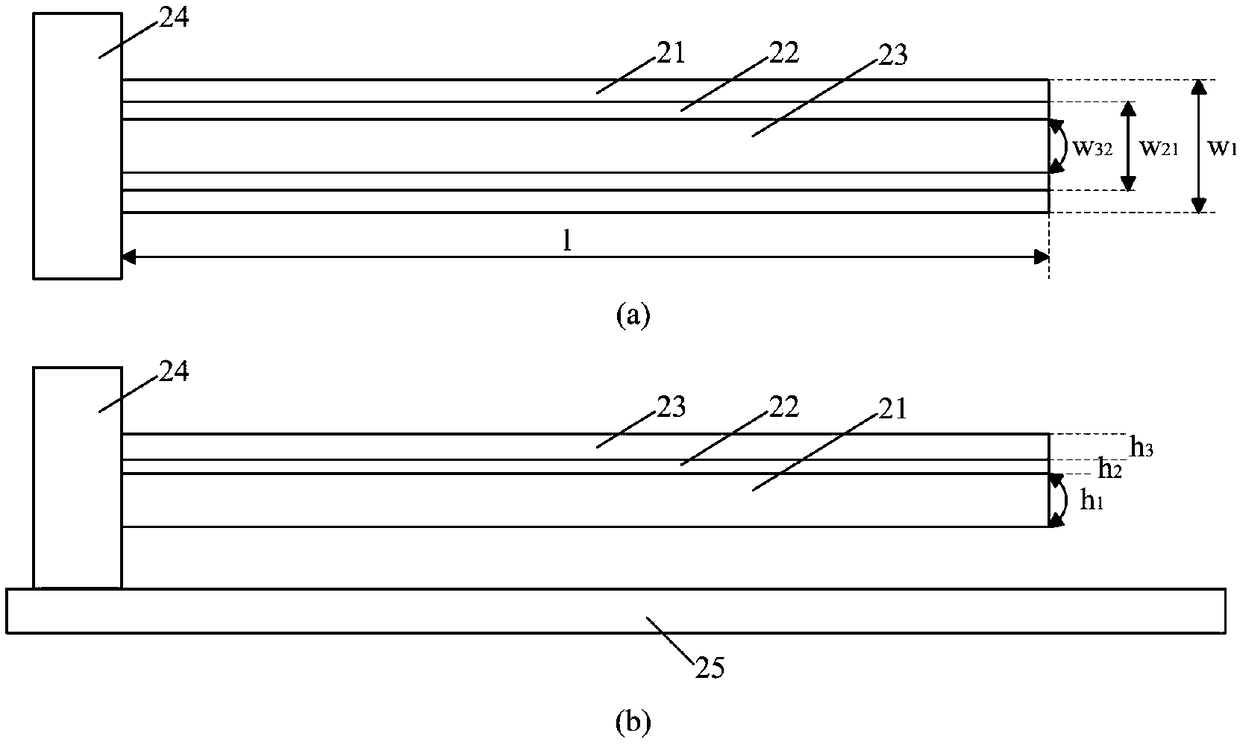
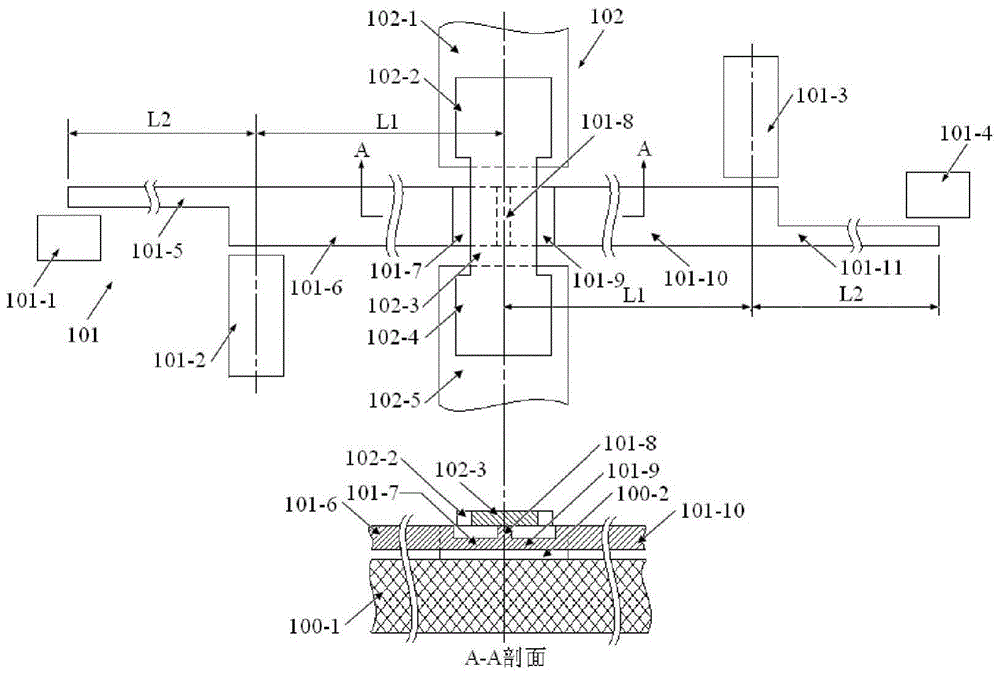
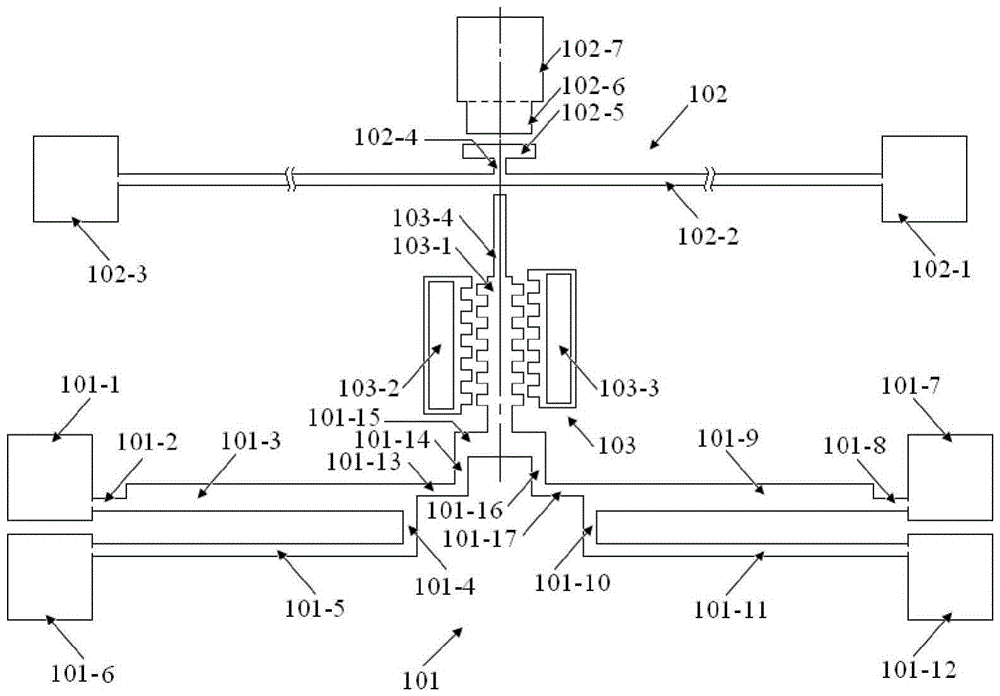
The invention provides a structure and method for testing the Young modulus of a polycrystalline silicon thin film material, which are mainly used for testing the materials of polycrystalline silicon structure layers. The testing structure comprises two structures, wherein the first structure comprises an electrostatic driven polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam (101), a first asymmetric cross beam (102) which is made from a thin film material to be tested and is provided with an alignment structure, and a second asymmetric cross beam (103) made from the thin film material to be tested; the second structure comprises the remaining structures of the first structure except the second asymmetric cross beam; the stress of the material and the deflection of deformation or bending caused because the structure is stressed usually need to be known to measure the Young modulus of the material. The bending deflection of the testing structure is controlled by designing the geometric parameters, the force borne by the Young modulus testing structure is extracted according to the principle that the same parts of the two testing structures have the same stress, and the Young modulus of the polycrystalline silicon thin film material is computed by utilizing the force and the deflection. The testing structure, the measuring method and a parameter extraction method are extremely simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and device for measuring mechanical parameters of double-layer double-clamped beam
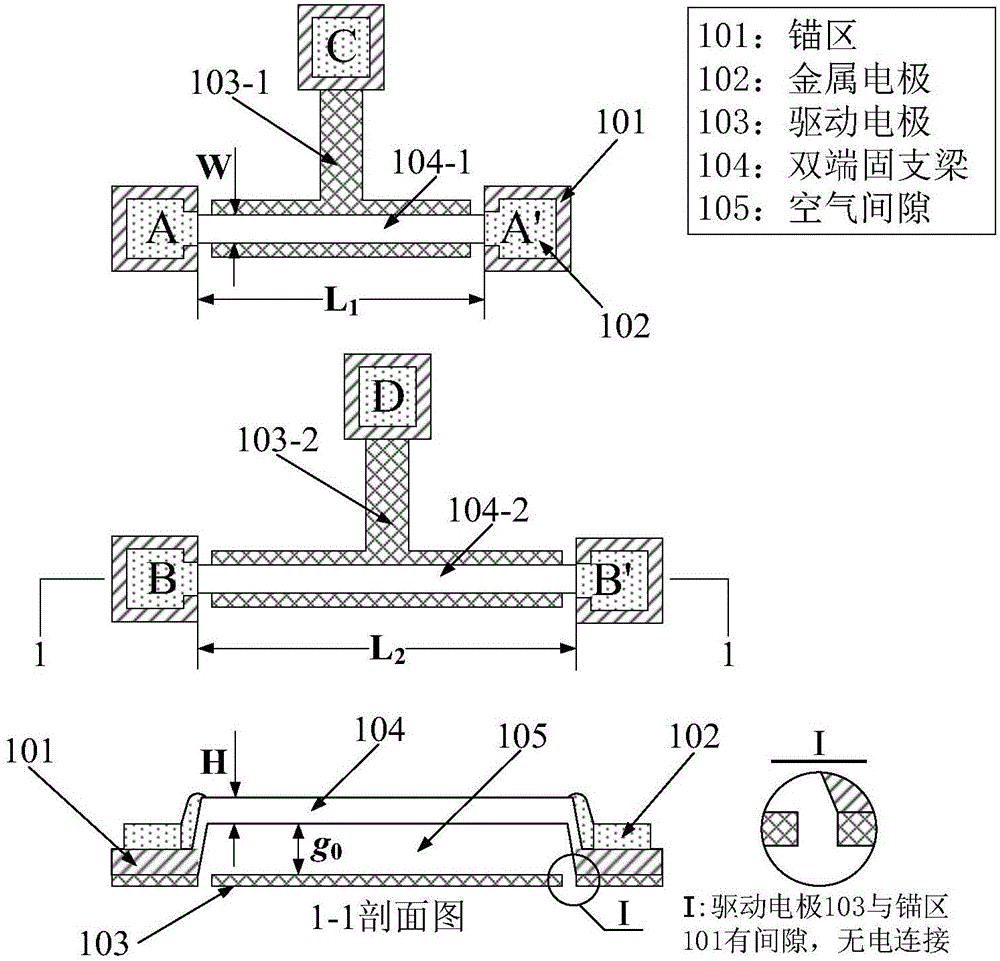
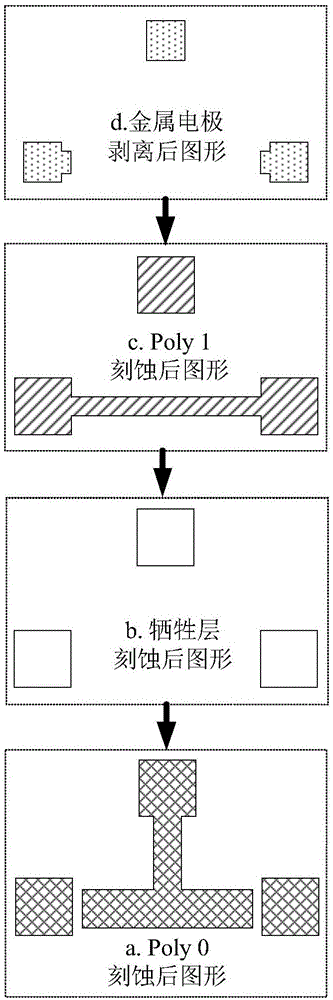
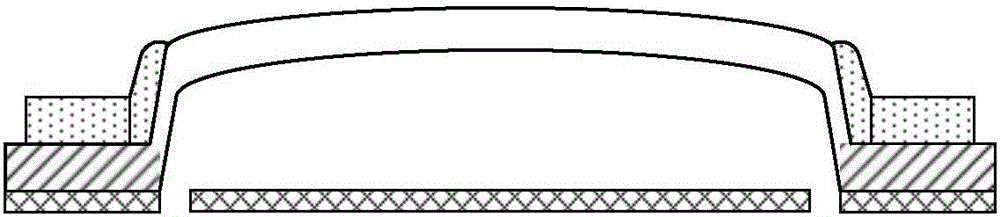
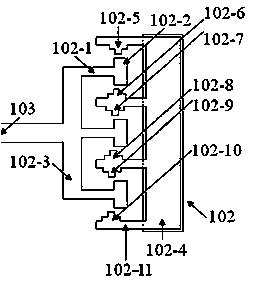
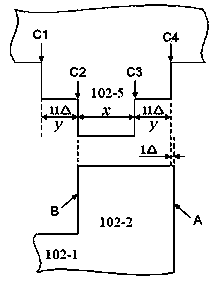
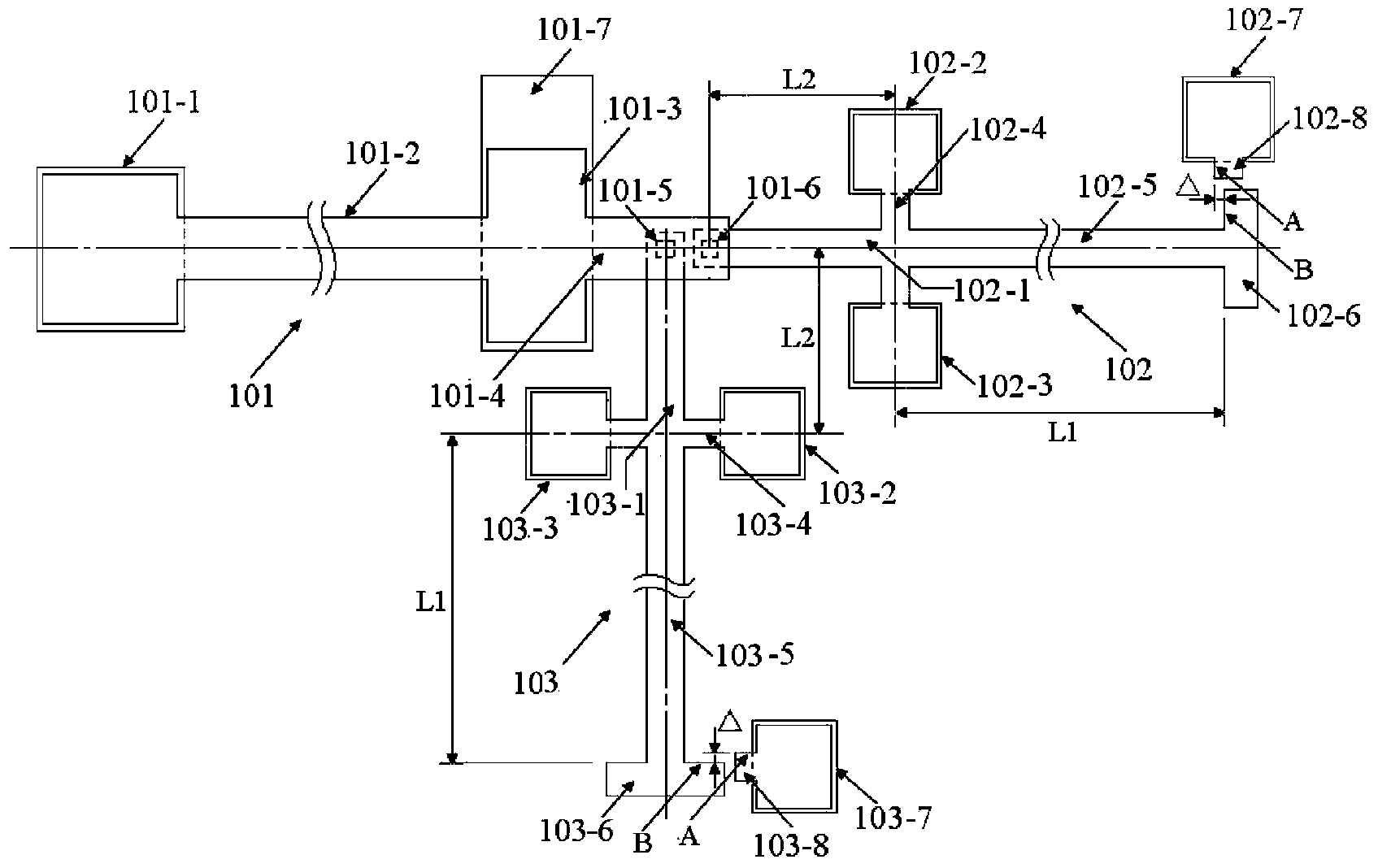
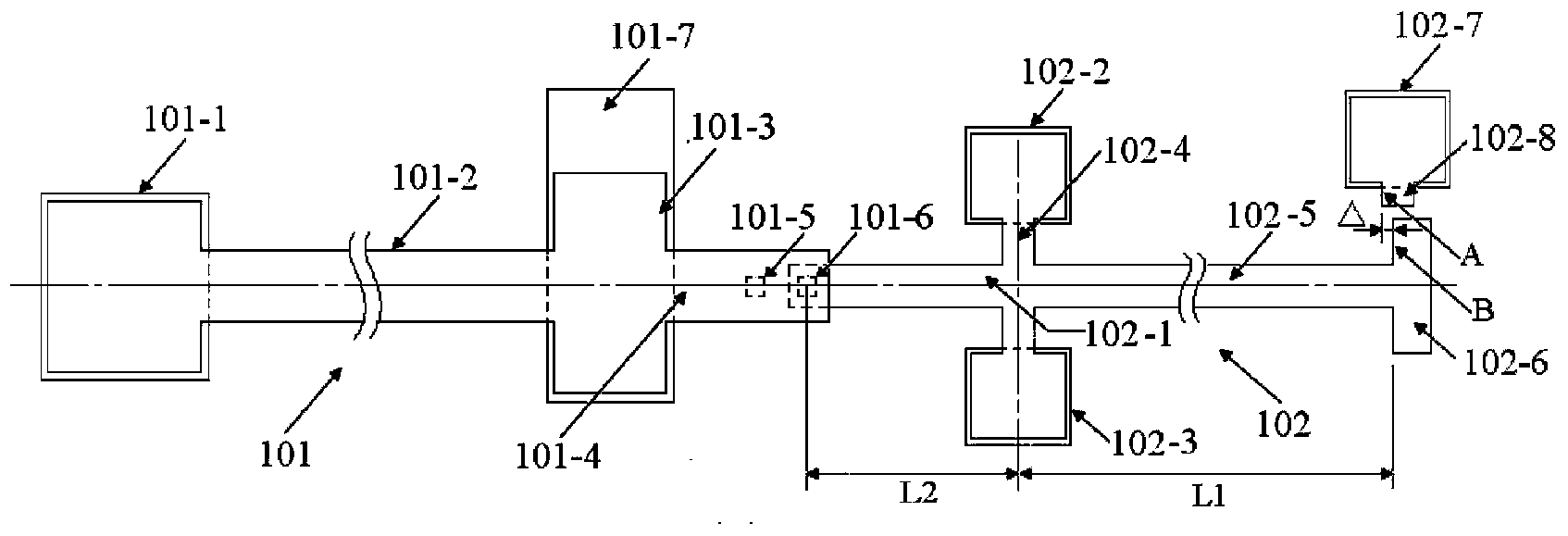
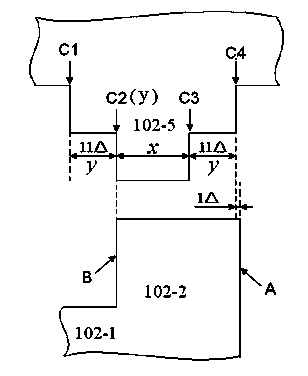
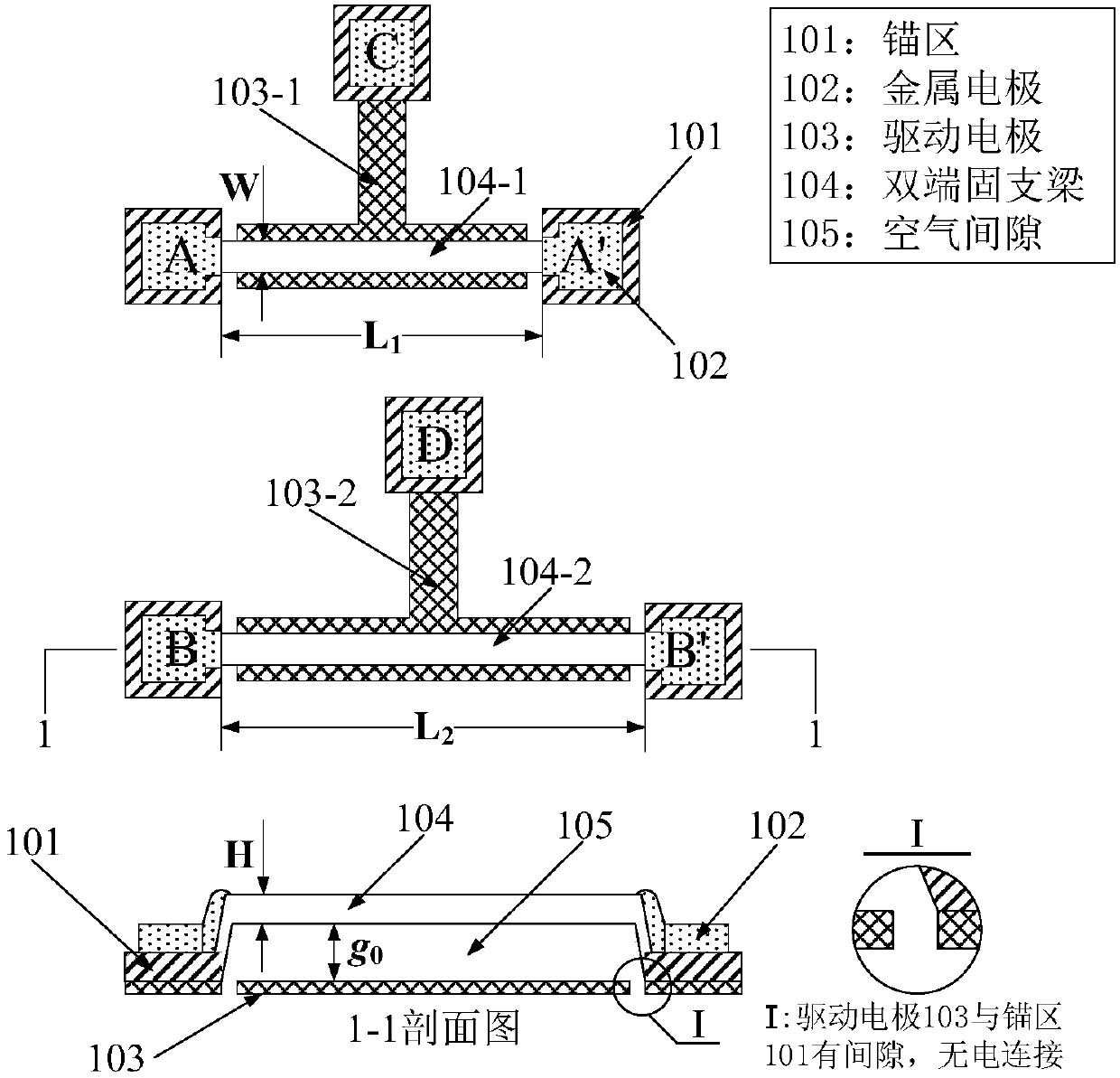
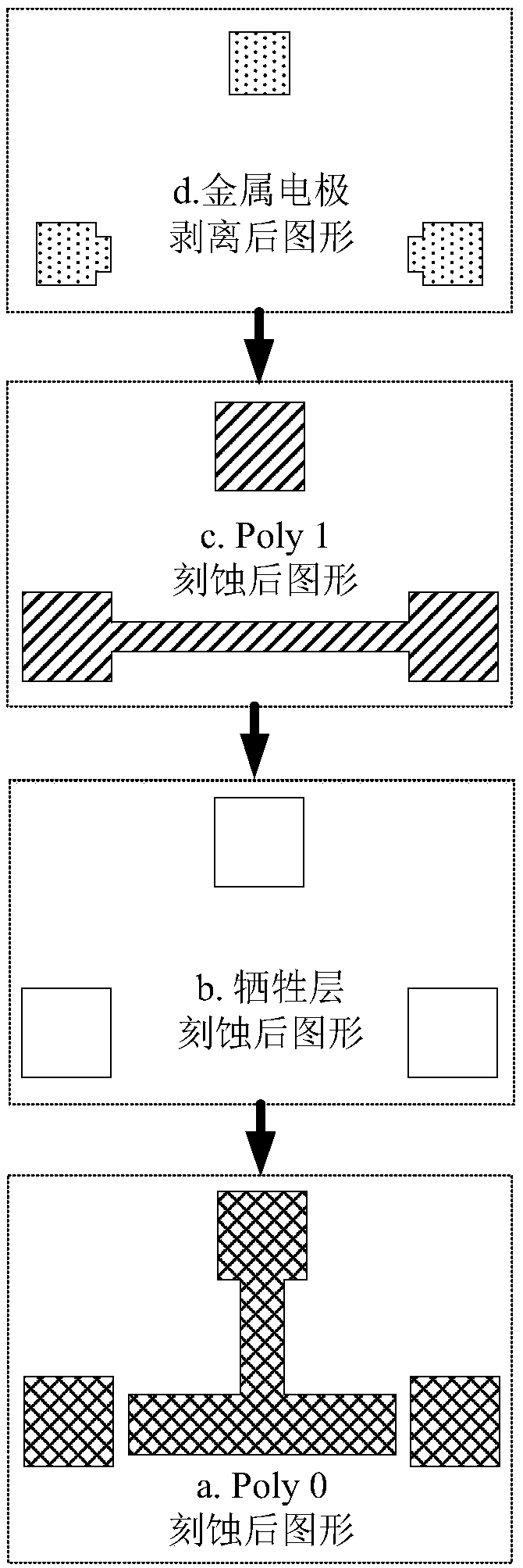
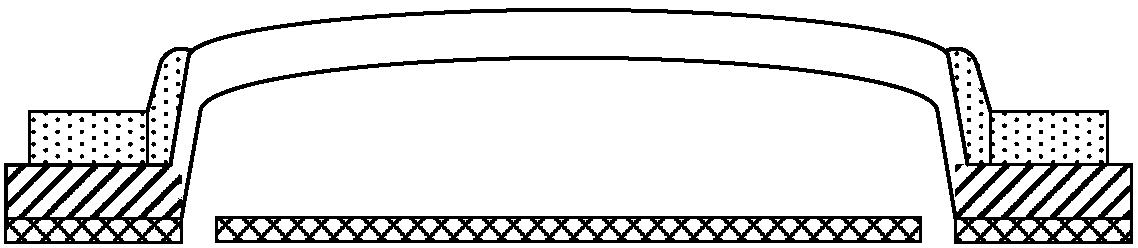
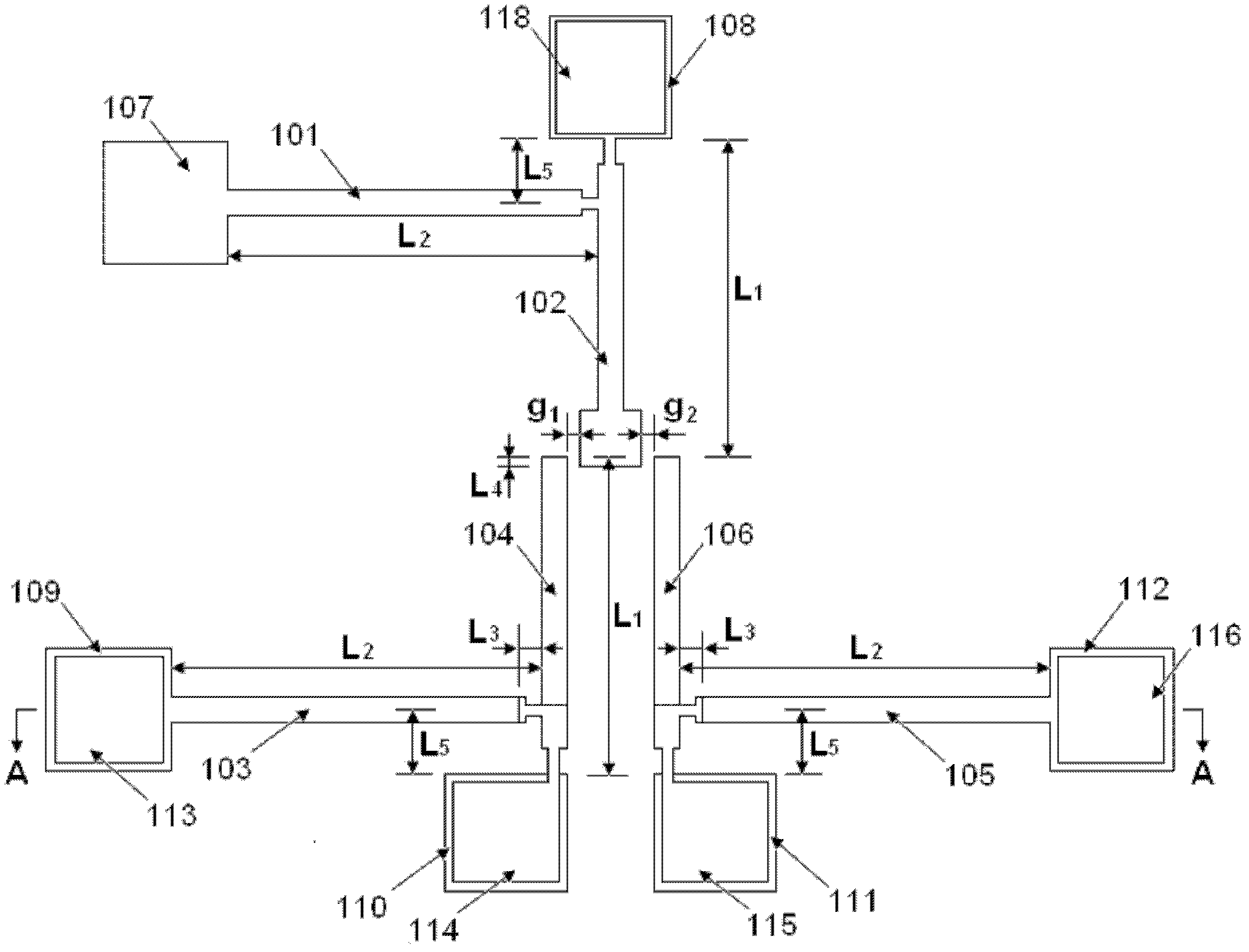
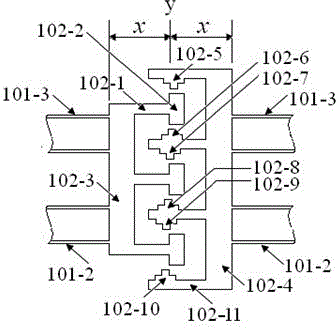
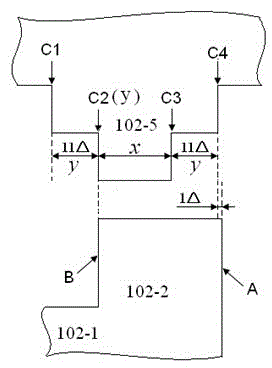
InactiveCN106996893AAccurate equivalent residual stress dataMeet the requirements of the online testStrength propertiesOnline testPull in voltage
The invention discloses a method for measuring the mechanical parameters of a double-layer double-clamped beam, which belongs to the technical field of micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) material parameter online test. According to the method, based on a pull-in voltage analysis model of upper and lower unequal-width double-layer double-clamped beams, numerical calculation is carried out by using pull-in voltage of a group of upper and lower unequal-width double-layer double-clamped beams, equivalent Young's modulus of each layer and equivalent residual stress data of each layer can be obtained more accurately at one time, which is of great significance for the production and research of MEMS. The invention also discloses a mechanical parameter measuring device for double-layer double-clamped beam.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
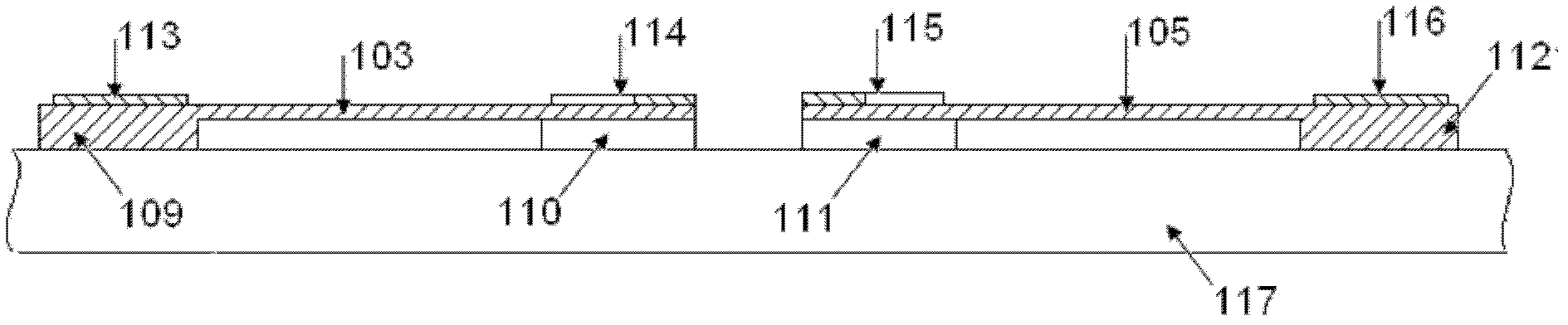
MEMS (micro electro mechanical system) double-layer film unit out-of-plane curvature testing structure
InactiveCN103411516ASimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsLeft halfFilm material
The invention provides an MEMS (micro electro mechanical system) double-layer film unit out-of-plane curvature testing structure. A measuring unit consists of two double-layer film portal structures and an error measuring cursor, wherein the two double-layer film portal structures are left and right double-layer film portal structures in opposite arrangement, the error measuring cursor consists of a left part and a right part, the double-layer film portal structures consist of an anchor region and two straight beams and are formed through overlapping an upper layer film material and a lower layer film material, one end of the straight beam is connected with the anchor region, the other end of the straight beam of the left double-layer film portal structure is connected with the straight beam of the left half part of the error measuring cursor, and the other end of the straight beam of the right double-layer film portal structure is connected with the straight beam of the right half part of the error measuring cursor. The simple double-layer film portal structure is utilized, in addition, the error measuring cursor is matched, the out-of-plane curvature of double-layer films formed by the MEMS common-use film materials can be obtained, in addition, the structure can be popularized to the testing under the condition of film materials with more layers, and a measuring method and a parameter extraction calculation method are very simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Structure and testing method for testing Poisson ratio of thin-film silicon material on insulating substrate
InactiveCN104034575ASimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsStrength propertiesYoung's modulusUnit structure
The invention relates to a structure and a method for testing the Poisson ratio of a thin-film silicon material positioned on an insulating substrate. The testing structure comprises two groups of structures, wherein the first group of structure comprises a polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam (101), a thin-film silicon rood beam (103) and a backing plate (102) made from thin-film silicon; the second group of structure comprises the polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam and the backing plate made from the thin-film silicon; a unit which actually measures the Poisson ratio of the thin-film silicon is the thin-film silicon rood beam (103), the difference of the two groups of structures is whether the thin-film silicon rood beam (103) is included or not, and other corresponding unit structures and geometric dimensions in the two groups of structures are completely same. According to the testing structure, the polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam is downwards bent by applying electrostatic force to downwards press the thin-film silicon rood beam and the backing plate so as to contact with the insulating substrate; the force needed for independently driving the thin-film silicon rood beam (103) to be turned to a testing angle is extracted through the testing of the two groups of structures, and the Poisson ratio of the thin-film silicon material on the insulating substrate can be calculated through the force, the testing angle, Young modulus and the geometric dimension.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
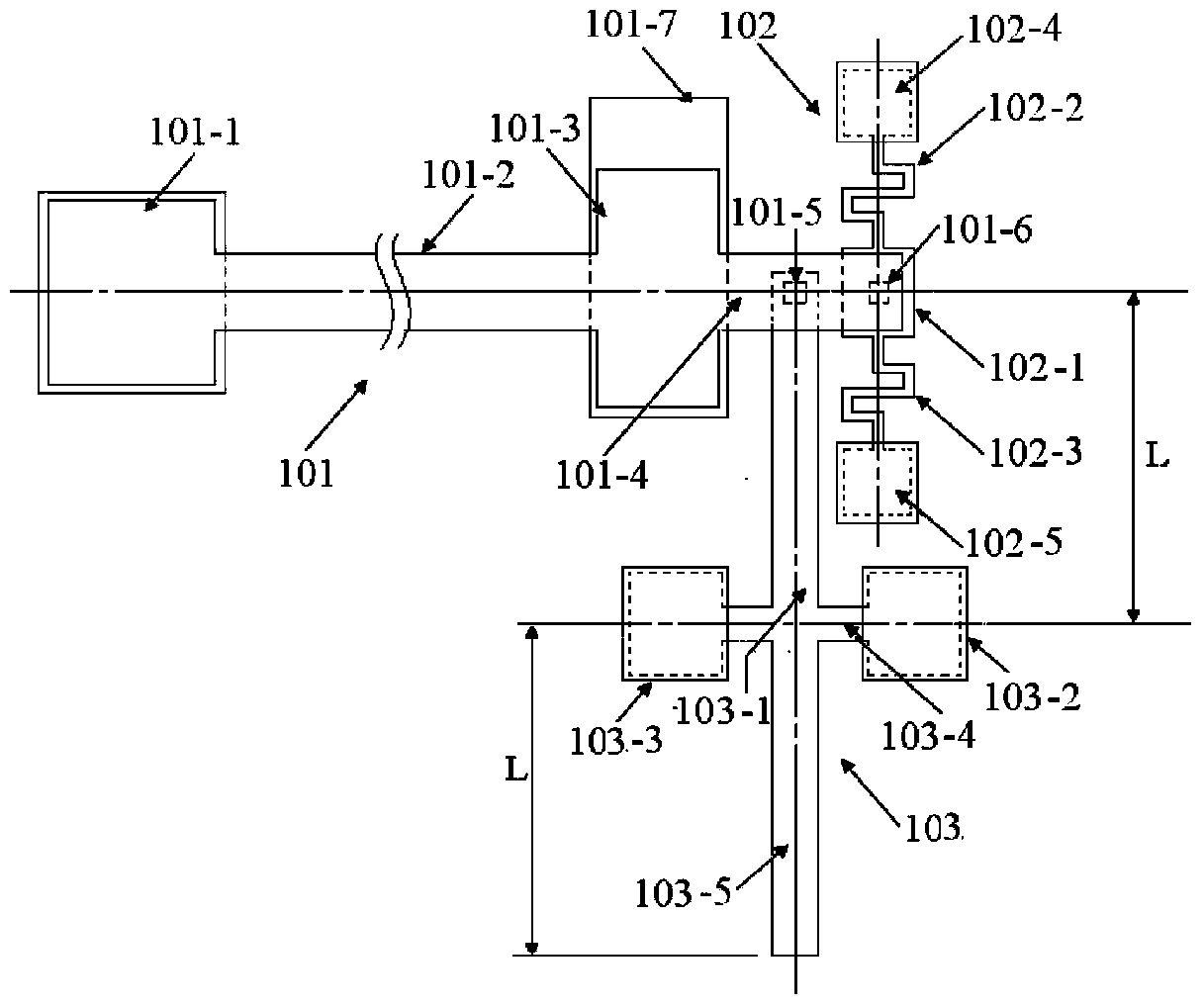
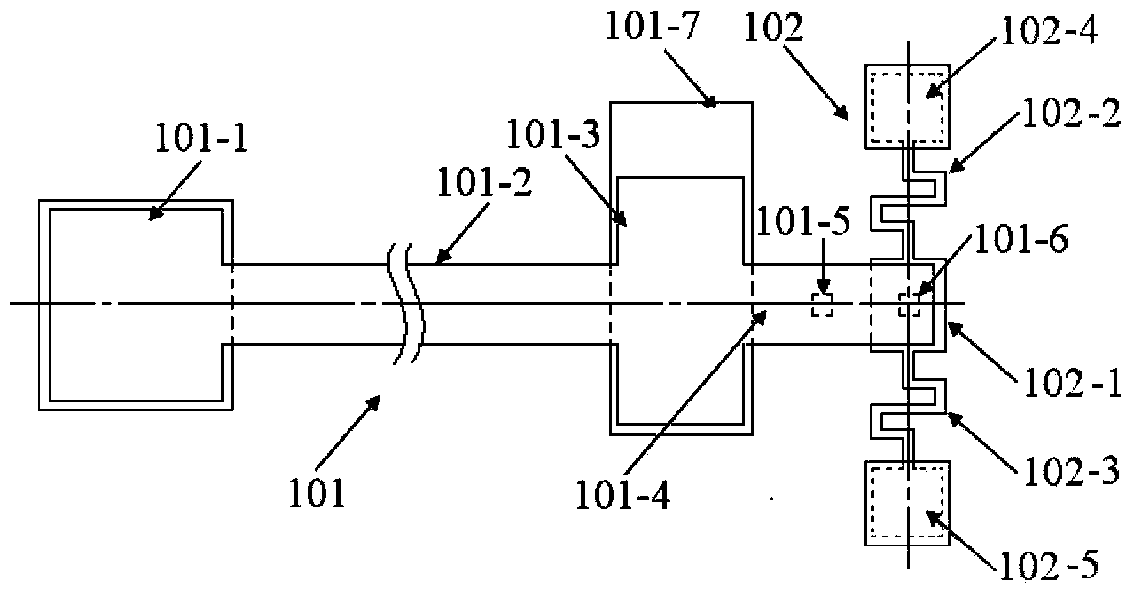
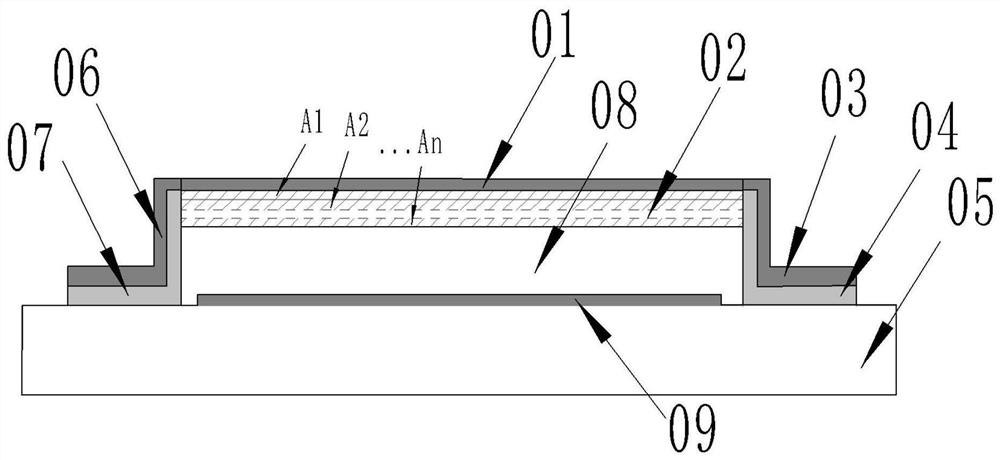
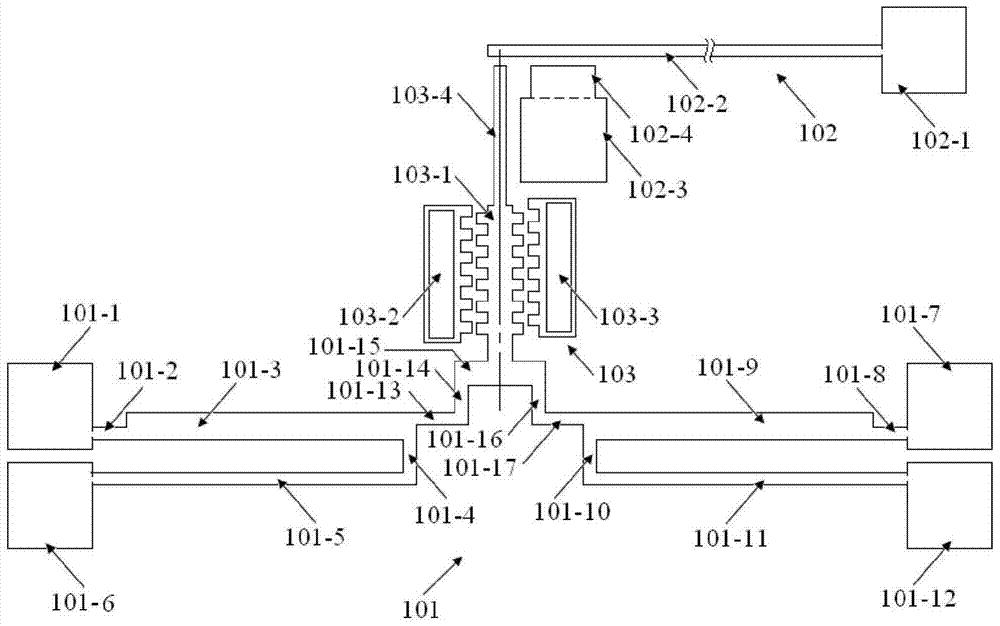
Multi-layer film residual stress and Young modulus on-line test structure for micro-manufacturing and on-line extraction method
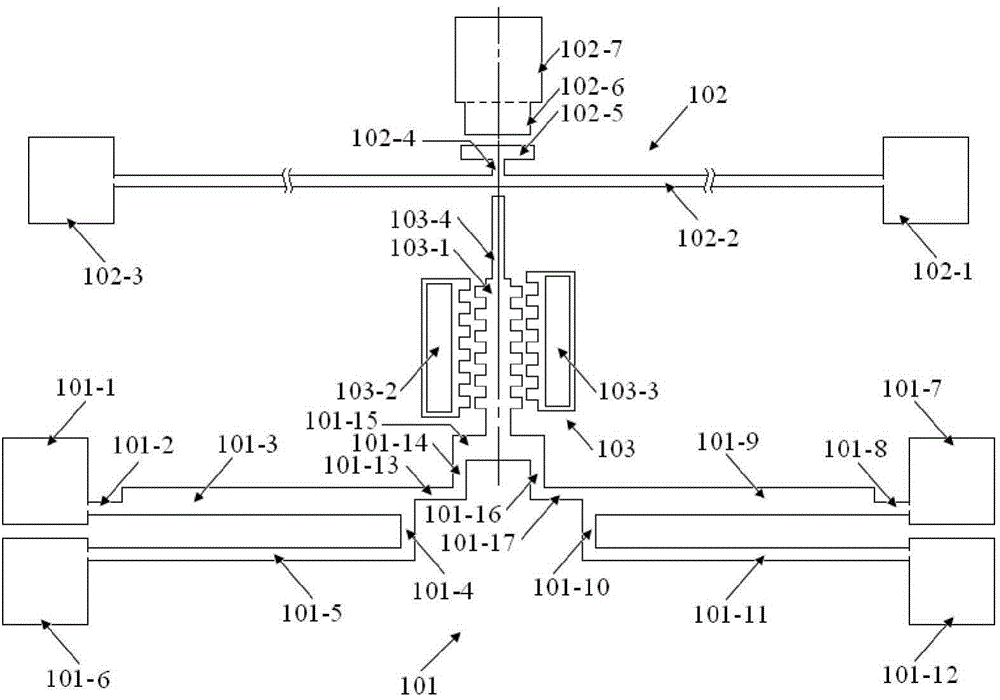
ActiveCN112129347ALower requirementMeet the requirements of the online testMeasurement devicesDecorative surface effectsCantilevered beamMicro fabrication
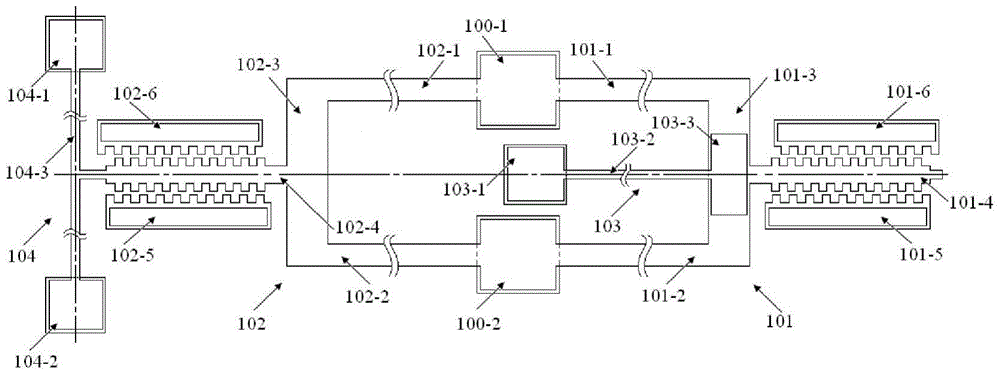
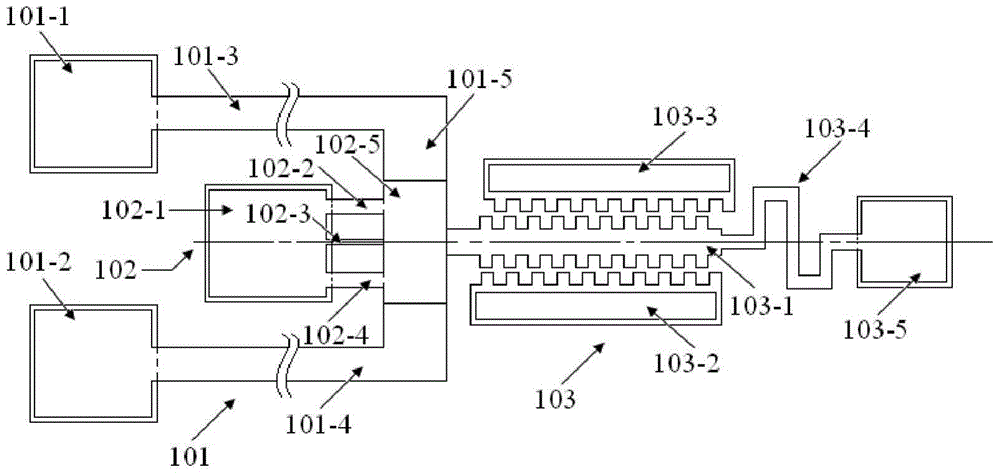
The invention belongs to the technical field of micro electro mechanical systems, and discloses an on-line test structure for Young modulus of a single-layer film and for micro-manufacturing, an on-line test structure for multi-layer film residual stress and Young modulus and an on-line extraction method. The Young modulus test structure of the single-layer film is composed of a set of transversely-pulled cantilever beam structures made of different film materials and contact electrodes. The transversely-pulled cantilever beam structures comprise single-layer films serving as upper electrodesand driving electrodes serving as lower electrodes. The Young modulus and residual stress test structure of the multi-layer film comprises top metal electrodes, multi-layer two-end clamped beam structures and bottom electrodes. As for the multi-layer two-end clamped beam structures of a group of test structures, two-end clamped beams are connected with a substrate through reinforcing anchor areas.The pull-in voltage of each test structure is measured by using electrostatic drive. The contact voltage and the pull-in voltage are sent into an extraction program for calculation to obtain the residual stress and the Young modulus of each layer of film. The testing method is simple, and can meet the precision requirement of on-line testing of a process line.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Metal film material Young modulus test structure
InactiveCN104568585ASimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFilm materialTest structure
The invention provides a metal film material Young modulus test structure. The test structure comprises five parts, namely a first heat swelling power source with a micrometer vernier, a second heat swelling power source with a micrometer vernier, a metal part to be stretched, a double-end fixed support beam and an anchoring area for loading drive current. Both the heat swelling power source with the micrometer vernier and the double-end fixed support beam are made of a polycrystalline silicon material with known Young modulus and residual stress. The metal film material Young modulus test structure can be used for measuring the Young modulus of a metal film and also can be used for measuring the residual stress of the metal, the breaking strength and the Young modulus close to the breaking by controlling the test process.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
On-line measurement method and measurement device for residual stress of conductive thin film material
ActiveCN106248280BLower requirementEasy loadingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementElectricityMeasurement device
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Structure for testing residual stress on thick film silicon material on insulating substrate
ActiveCN104568272ASimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementMicrometerYoung's modulus
The invention provides a structure for testing the residual stress on a thick film silicon material on an insulating substrate. The structure is used for testing the residual stress on the thick film silicon material on the insulating substrate. The structure is composed of a relative electric heating driving unit, a flexibility measuring unit with a micrometer vernier, and a fixed supporting beam unit driven by static electricity. The relative electric heating driving unit is perpendicularly connected with the flexibility measuring unit with the micrometer vernier. The flexibility measuring unit is measured through the vernier. The micrometer vernier is driven by the relative electric heating driving unit to move. The force acting face acting on a fixed supporting beam is reduced through an H-shaped structure at the center of the fixed supporting beam. When static electricity is loaded, the fixed supporting beam is transversely bent, and the flexibility value is measured through the flexibility measuring unit under a certain voltage. The residual stress is calculated through the static electricity, the bending flexibility and the geometric size and Young modulus of the fixed supporting beam. The testing structure, a measuring method and a parameter extracting method are extremely simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Film material lateral piezoelectric coefficient testing model based on multi-layer cantilever beam and method thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of material parameter on-line testing for a micro electromechanical system, and provides a film material lateral piezoelectric coefficient testing model based on a multi-layer cantilever beam and a method thereof. The testing model consists of three cantilever beams which have nonlinear correlation between middle layer and top layer width combination, wherein the materials, the thicknesses, and the lengths of the bottom layer, the middle layer, and the top layer of the three cantilever beams are exactly the same. The testing method comprises the steps of: firstly measuring the first-order resonance frequency of each cantilever beam; extracting the Young modulus of each layer of material of each cantilever beam based on a resonant frequency method; measuring the tip displacement of any one cantilever beam based on an inverse piezoelectric effect method; and finally, analyzing to obtain the transverse piezoelectric coefficient d31 of the filmmaterial used in the middle layer of the cantilever beams based on an energy method. According to the film material lateral piezoelectric coefficient testing model based on the multi-layer cantileverbeam and the method thereof, the testing model is simple; the machining process can be synchronous with the MEMS; no special machining requirements are needed; the testing method is low in solution complexity, small in calculation amount, and easy to operate; the testing process has repeatability, stability, and high efficiency; and the method meets online testing requirements.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Thick-film silicon material poisson ratio test structure on insulation substrate
InactiveCN104596864ASimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsMaterial strength using steady torsional forcesSpecific testClassical mechanics
The invention provides a thick-film silicon material poisson ratio test structure on an insulation substrate, which is used for measuring a poisson ratio of a thick-film silicon material on an insulation substrate. The test structure consists of two parts, i.e. a polycrystalline silicon clamped beam for suspending a torsion structure and the torsion structure. The torsion structure consists of an electrostatic-driven torsion rod, a left limiting structure and a right limiting structure. The center of the torsion rod is a torsion beam, and the upper end surface of the torsion beam is connected to the center position of the polycrystalline silicon clamped beam to form a suspension-torsion structure. The torsion rod is driven by an electrostatic force to make torsion motion by adopting the torsion beam as an axis. The torsion angle is controlled by utilizing a stop structure to form a specific test angle. The poisson ratio of the thick-film silicon material can be calculated by virtue of the length, the width and the thickness of the torsion beam, the Young modulus of the thick-film silicon material and the applied electrostatic force. The test structure, a measuring method and a parameter extraction method are very simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
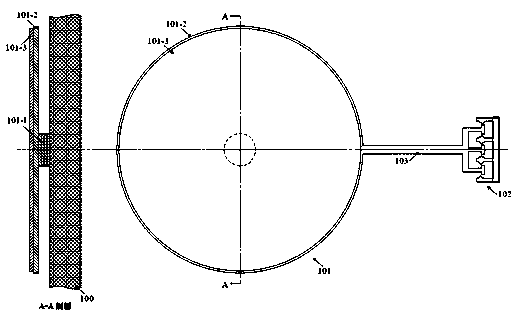
On-line testing structure for polycrystalline silicon material residual stress
InactiveCN102565143BImpact meetsEasy loadingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementApparatus for force/torque/work measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceOnline test
An online test structure for the residual stress of a polycrystalline silicon material, comprising three deflecting pointers of polycrystalline silicon having substantially the same structure, the three deflecting pointers of polycrystalline silicon being arranged in a delta shape with all pointers pointing to the centre. Each deflecting pointer comprises a horizontal driving beam (101, 103, 105), a pointer (102, 104, 106) perpendicular to the driving beam (101, 103, 105), and two anchoring regions fixed on a substrate, the two anchoring regions (107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112) fixing one end of the driving beam (101, 103, 105) and one end of the pointer (102, 104, 106) respectively. By controlling the initial direction of deflection of the pointer under the action of the residual stress, the maintenance and change in distance can effectively reflect the amount and properties of the residual stress. During testing, heat driving is utilised, and the measured parameters are the electrical resistance of the front and rear driving beams for heat driving. The measurement and calculation do not require a thermal expansion co-efficient, avoiding the effect of errors in the measurement results during online testing of the thermal expansion co-efficient.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
On-line test structure for polycrystalline silicon Poisson ratio
InactiveCN102589965BLow test equipment requirementsSimple test methodStrength propertiesStrength of materialsLower pole
The invention discloses an on-line test structure for polycrystalline silicon Poisson ratio. The on-line test structure comprises an insulating substrate, an asymmetric polycrystalline cross beam, a first polycrystalline lower pole plate and a second polycrystalline lower pole plate, wherein the asymmetric polycrystalline cross beam is deflected in an electrostatic driving mode, so Poisson ratio parameters of a polycrystalline material are obtained according to a geometrical relationship and a material mechanics principle. The test structure rotates under the action of electrostatic force which is generated through excitation voltage, a maximum torsion angle becomes known quantity through structural design, and the Poisson ratio of the polycrystalline material is computed according to a measurement value of the excitation voltage when the test structure reaches the maximum torsion angle and unknown structure geometric parameters and physical parameters. Therefore, requirements for test equipment are low, a test method is simple, and the test process and test parameter values are stable. During synchronization of the polycrystalline silicon preparation process and the manufacturing process of a subsequent micro electro mechanical system (MEMS), special processing requirements are eliminated, and requirements for on-line test are completely met.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Measuring Structure and Method for Poisson's Ratio of Thin Film Material
InactiveCN104034583BEasy to measureSimple test methodMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCantilevered beamStructure extraction
The present invention proposes a test structure and method for the Poisson's ratio of a film material. In the test structure, the first group of structures includes an electrostatically driven polysilicon cantilever beam (101), a non-conductive beam with an alignment structure made of the film material to be tested. Symmetrical cross beams (102), symmetrical cross beams (103) made by the film material to be tested; the second group of structures is the remaining structure after the first group of structures remove the symmetrical cross beams; the symmetrical cross beams are formed by the second anchorage area (103- 2), the third anchorage area (103-3), the horizontal short beam (103-4), the upper semi-vertical long beam (103-1) and the lower semi-vertical long beam (103-5). The loading driving part is separated from the Poisson's ratio test structure made of the film material to be tested. The test torsion angle of the Poisson's ratio test structure is controlled by geometric parameter design, and the Poisson's ratio is extracted by the principle that the same part of the two test structures is under the same force. The force on the test structure is calculated using the force and torsion angle to obtain the Poisson's ratio of the film material to be tested.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Test Structure for Residual Stress of Thin Film Silicon Material on Insulating Substrate
InactiveCN104034604BSimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsForce measurementMaterial strength using steady bending forcesYoung's modulusUnit structure
The invention provides a structure and method for testing the residual stress of a thin film silicon material on an insulating substrate. The testing structure comprises two structures, wherein the first structure is formed by a polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam, a thin film silicon double-end clamped beam and a base plate made from thin film silicon; the second structure is formed by a polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam and a base plate made from thin film silicon; the unit which actually measures the residual stress of thin film silicon is the thin film silicon double-end clamped beam; the difference of the two structures only lies in whether the structures comprise the thin film silicon double-end clamped beam; other corresponding unit structures in the two structures and the geometric dimensions are identical; the electrostatic force is applied to bend down the polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam and then press down the thin film silicon double-end clamped beam and the base plate to come into contact with the substrate; the force needed to individually drive the thin film silicon double-end clamped beam to achieve the testing deflection is extracted through testing of the two testing structures; the residual stress of the thin film silicon material on the insulating substrate can be computed according to the force, the testing deflection, the Young modulus and the geometric dimensions. The testing structure, the measuring method and a parameter extraction method are extremely simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Metal thin film material Young's modulus test structure
InactiveCN104568585BYoung's modulus test method is simpleSimple test methodMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesYoung's modulusEngineering
The invention provides a metal film material Young modulus test structure. The test structure comprises five parts, namely a first heat swelling power source with a micrometer vernier, a second heat swelling power source with a micrometer vernier, a metal part to be stretched, a double-end fixed support beam and an anchoring area for loading drive current. Both the heat swelling power source with the micrometer vernier and the double-end fixed support beam are made of a polycrystalline silicon material with known Young modulus and residual stress. The metal film material Young modulus test structure can be used for measuring the Young modulus of a metal film and also can be used for measuring the residual stress of the metal, the breaking strength and the Young modulus close to the breaking by controlling the test process.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Measuring structure and method for Poisson's ratio of thin film silicon material on insulating substrate
InactiveCN104034575BSimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsStrength propertiesYoung's modulusUnit structure
The invention relates to a structure and a method for testing the Poisson ratio of a thin-film silicon material positioned on an insulating substrate. The testing structure comprises two groups of structures, wherein the first group of structure comprises a polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam (101), a thin-film silicon rood beam (103) and a backing plate (102) made from thin-film silicon; the second group of structure comprises the polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam and the backing plate made from the thin-film silicon; a unit which actually measures the Poisson ratio of the thin-film silicon is the thin-film silicon rood beam (103), the difference of the two groups of structures is whether the thin-film silicon rood beam (103) is included or not, and other corresponding unit structures and geometric dimensions in the two groups of structures are completely same. According to the testing structure, the polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam is downwards bent by applying electrostatic force to downwards press the thin-film silicon rood beam and the backing plate so as to contact with the insulating substrate; the force needed for independently driving the thin-film silicon rood beam (103) to be turned to a testing angle is extracted through the testing of the two groups of structures, and the Poisson ratio of the thin-film silicon material on the insulating substrate can be calculated through the force, the testing angle, Young modulus and the geometric dimension.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Test structure for Young's modulus of thick-film silicon material on insulating substrate
ActiveCN104568606BSimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsMaterial strength using steady bending forcesTransverse planeYoung's modulus
The invention provides a testing structure for the Young's modulus of the thick-film silicon material on the insulating substrate, which is used for measuring the Young's modulus of the thick-film silicon material on the insulating substrate. The test structure consists of three parts: a relative electrothermal drive unit; a stopper unit with a micrometer vernier; and an electrostatically driven cantilever beam unit. The opposite type electrothermal driving unit is vertically connected with the stopper unit with micrometer vernier. The electrostatic force is used to drive the cantilever beam to perform in-plane lateral bending motion. The stopper structure is used to control the amount of bending and to prevent measurement instability caused by snap-in. The movement of the stop structure is realized by the thermal expansion driving structure, and the movement amount of the stop structure is measured by the vernier. In order to prevent the inaccurate position measurement caused by process errors, two position measurement methods are used, that is, the first thermally driven stopper structure touches the cantilever beam, reads the cursor position, and then reduces the drive current to generate a small gap. This gap is recorded by the vernier as the final bending deflection.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Test Structure of Poisson's Ratio of Thick Film Silicon Material on Insulating Substrate
InactiveCN104596864BSimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsMaterial strength using steady torsional forcesSpecific testClassical mechanics
The invention provides a thick-film silicon material poisson ratio test structure on an insulation substrate, which is used for measuring a poisson ratio of a thick-film silicon material on an insulation substrate. The test structure consists of two parts, i.e. a polycrystalline silicon clamped beam for suspending a torsion structure and the torsion structure. The torsion structure consists of an electrostatic-driven torsion rod, a left limiting structure and a right limiting structure. The center of the torsion rod is a torsion beam, and the upper end surface of the torsion beam is connected to the center position of the polycrystalline silicon clamped beam to form a suspension-torsion structure. The torsion rod is driven by an electrostatic force to make torsion motion by adopting the torsion beam as an axis. The torsion angle is controlled by utilizing a stop structure to form a specific test angle. The poisson ratio of the thick-film silicon material can be calculated by virtue of the length, the width and the thickness of the torsion beam, the Young modulus of the thick-film silicon material and the applied electrostatic force. The test structure, a measuring method and a parameter extraction method are very simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Test Structure for Residual Stress of Thick Film Silicon Material on Insulating Substrate
ActiveCN104568272BSimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementMicrometerYoung's modulus
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
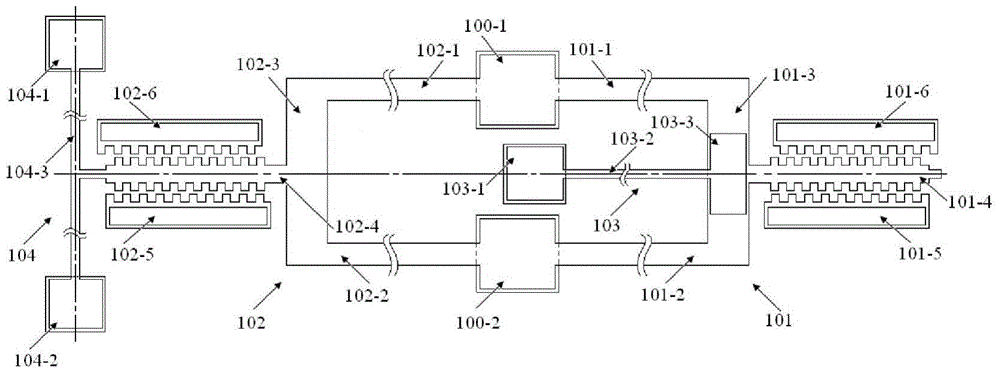
An on-line test system for the airtightness of high-voltage wiring harnesses for vehicles
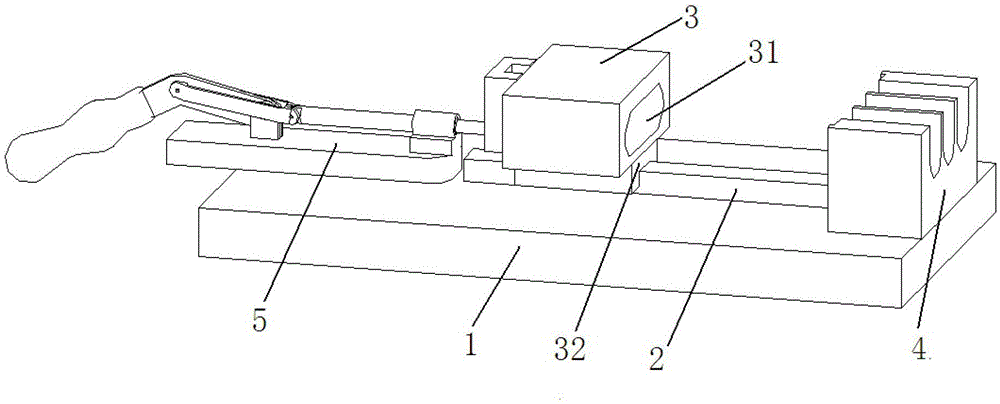
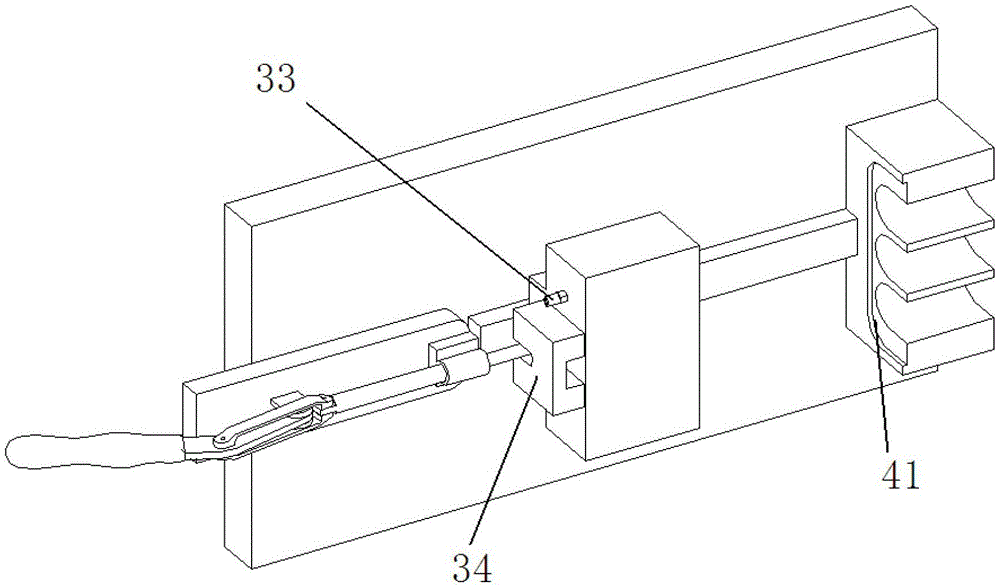
ActiveCN103308261BFast and accurate sealingTest accurateMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention provides a high-pressure wire harness leakproofness on-line testing system for vehicles. The high-pressure wire harness leakproofness on-line testing system comprises a fast detection clamp and a leakproofness detector, wherein the fast detection clamp comprises a base, a linear guide rail, a leakproof base, a leakproofness supporting base and a toggle clamp. The linear guide rail, the leakproofness supporting base and the toggle clamp are arranged on the base, the leakproofness supporting base and the toggle clamp are arranged at two ends of the linear guide rail respectively, the leakproof base is arranged on the linear guide rail and connected with the toggle clamp, an air pipe fast connector is arranged on the leakproof base and connected with the leakproofness detector through the air pipe fast connector, and the leakproofness detector can be a proper leakproofness detector sold in the market. The high-pressure wire harness leakproofness on-line testing system can effectively detect leakage rate of high-pressure wire harnesses, improves relevance ratio of bad products, greatly reduces testing time and totally meets on-line testing requirements.
Owner:AUTO KABEL TAICANG HARDNESS
Test Structure for Breaking Strength of Thin Film Materials
InactiveCN104568586BThe breaking strength test method is simpleSimple test methodMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesBreaking strengthElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a structure for testing the breaking strength of a film material, and the structure can be used for testing the breaking strength of a conductive film material and an insulating film material. According to the structure disclosed by the invention, a force loading and driving part and a breaking strength testing structure which is made from a to-be-tested film material are layered and are laminated and connected by a combination area. The tensile elongation is measured by a vernier structure. For preventing the condition that the actual tensile elongation cannot be measured when the testing structure is snapped, a buffering beam and a damping spring arranged in parallel are adopted for preventing overshoot. The testing structure, a measurement method and a parameter extraction method disclosed by the invention are quite simple and can be used for testing the breaking strength of various film materials such as conductors / insulators.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Young's modulus test structure and method of film material
ActiveCN104034584BEasy to measureSimple test methodMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesClassical mechanicsDesign control
The invention provides a Young modulus testing structure and method for a thin film material. The testing structure is composed of two sets of structures, wherein in the first set of the structure, a cantilever beam (103) manufactured by the thin film material to be detected is composed of an anchor region (103-2) and a long beam (103-1) which are connected; the long beam (103-1) is vertical to a polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam (101); the free end of the long beam (103-1) is located below a left first convex point (101-5) of the polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam (101); a loading driving part of a force is separated from the Young modulus testing structure manufactured by the thin film material to be detected; the bending deflection of the testing structure is controlled through a geometrical parameter design; the force applied to the Young modulus testing structure is extracted by virtue of a principle that the same parts of the two sets of the testing structures have the same stress; the Young modulus of the thin film material to be detected is calculated through the force and the deflection. The testing structure, a measurement method and a calculation method for parameter extraction are very simple and have wide adaptability, and can be used for testing the Young modulus of a conductive or insulating thin film material.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Measuring structure and method for Young's modulus of thin film silicon material on insulating substrate
InactiveCN104034603BSimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsMaterial strength using steady bending forcesYoung's modulusCushion
The invention provides a structure and a method for testing Young modulus of a thin film silicon material on an insulating substrate. The structure comprises two groups of structures, wherein the first group of structures consists of a polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam (101), a thin film silicon cantilever beam (103) and a cushion plate (102) made from polycrystalline silicon; the second group of structures consists of a polycrystalline silicon cantilever beam and a cushion plate made from the polycrystalline silicon. According to the structure, units for actually testing the Young modulus of thin film silicon are the thin film silicon cantilever beams, the only difference of the two groups of structures is whether the thin film silicon cantilever beam exists, and corresponding structures and geometric dimensions of other units in the two groups of structures are completely the same. According to the method, by applying an electrostatic force, the polycrystalline silicon cantilever beams are bent downwards to press the thin film silicon cantilever beam and the cushion plates to contact with the substrate; by testing with the two groups of test structures, a force for independently driving the thin film silicon cantilever beam to be bent to reach test deflection is extracted, and the Young modulus of the thin film silicon material on the insulating substrate can be calculated by virtue of the force, the test deflection and the geometric dimensions.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
On-line test structure and test method for breaking strength of polycrystalline silicon
InactiveCN102590282BSimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsMaterial resistanceThermal expansionIn-circuit test
The invention discloses an on-line test structure and an on-line test method for breaking strength of polycrystalline silicon. The method comprises the following steps of: performing simple current excitation on a test structure, measuring related resistance, substituting a related resistance value obtained through measurement into a calculation formula, and eliminating a thermal expansion coefficient by using a plurality of calculation equations to obtain the breaking strength of the polycrystalline silicon finally. The test method is simple, test equipment has low requirements, the machining process of the test structure is synchronous with a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS), special processing requirements are avoided, the requirement of on-line test is met, simple mathematical equations are adopted for calculation, test and calculation processes are stable, and output results are reliable.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Micro-electromechanical double-layer thin-film cell out-of-plane bending curvature test structure
InactiveCN103411516BSimple test methodLow test equipment requirementsMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsLeft halfEngineering
The invention provides an MEMS (micro electro mechanical system) double-layer film unit out-of-plane curvature testing structure. A measuring unit consists of two double-layer film portal structures and an error measuring cursor, wherein the two double-layer film portal structures are left and right double-layer film portal structures in opposite arrangement, the error measuring cursor consists of a left part and a right part, the double-layer film portal structures consist of an anchor region and two straight beams and are formed through overlapping an upper layer film material and a lower layer film material, one end of the straight beam is connected with the anchor region, the other end of the straight beam of the left double-layer film portal structure is connected with the straight beam of the left half part of the error measuring cursor, and the other end of the straight beam of the right double-layer film portal structure is connected with the straight beam of the right half part of the error measuring cursor. The simple double-layer film portal structure is utilized, in addition, the error measuring cursor is matched, the out-of-plane curvature of double-layer films formed by the MEMS common-use film materials can be obtained, in addition, the structure can be popularized to the testing under the condition of film materials with more layers, and a measuring method and a parameter extraction calculation method are very simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Resonant frequency based composite cantilever beam mechanical parameter measurement method and device
InactiveCN107246991ASolve the problem of measuring mechanical parametersSimple test methodTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPhysicsMeasurement device
The invention discloses a resonant frequency based composite cantilever beam mechanical parameter measurement method. The method is based on the relationship between first-order resonant frequency of a multilayer composite double-end cantilever beam, material properties, structure size and other parameters, and utilizes the form of solving equations to acquire an equivalent Young's modulus of each layer in the multilayer composite cantilever beam at one time. The invention also discloses a resonant frequency based composite cantilever beam mechanical parameter measurement device. The method and device provided by the invention can satisfy on-line testing of the multilayer composite cantilever beam's Young's modulus, and have the characteristics of simple testing structure and calculation method, and higher accuracy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com