Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Optics Simplified" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
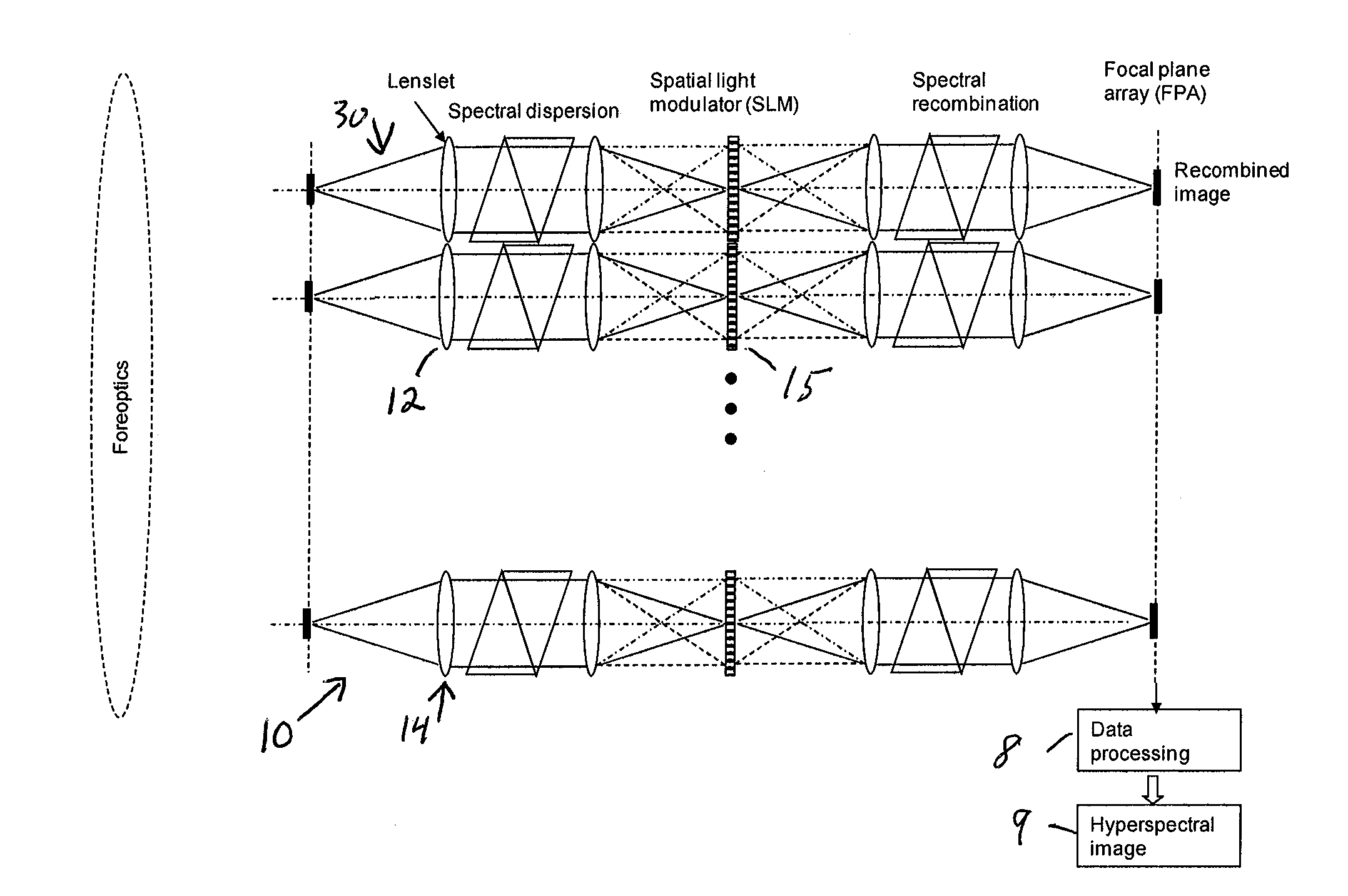
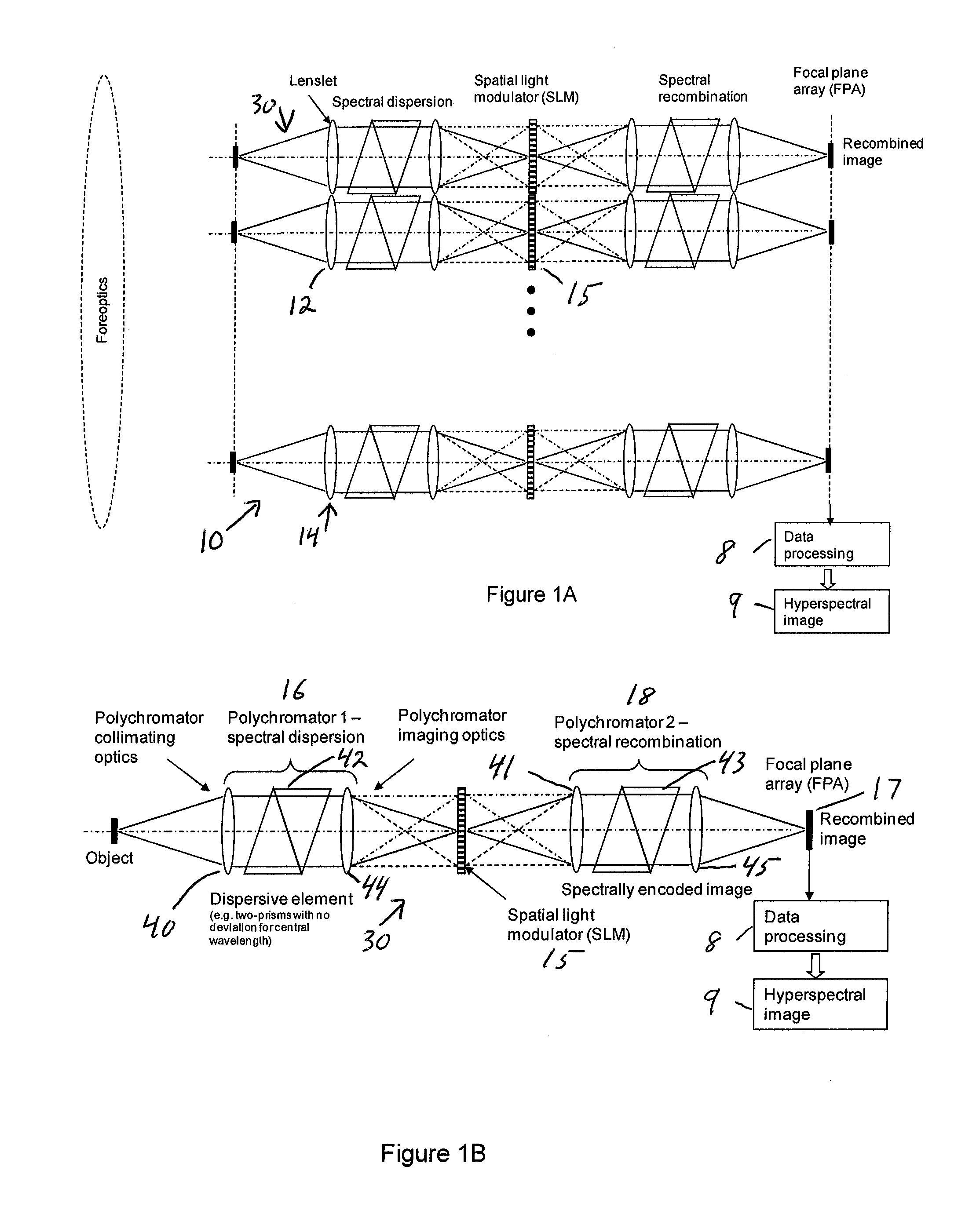
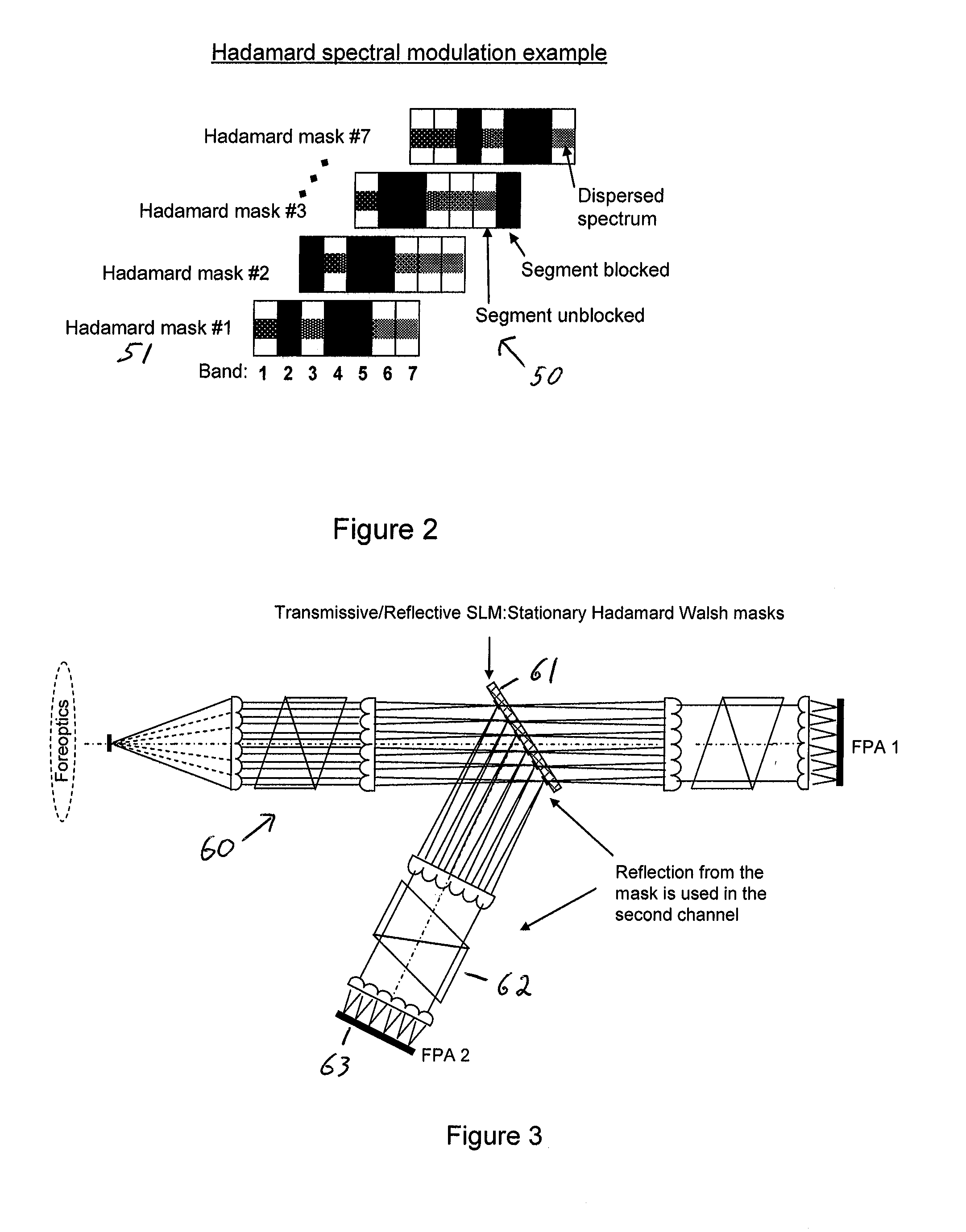
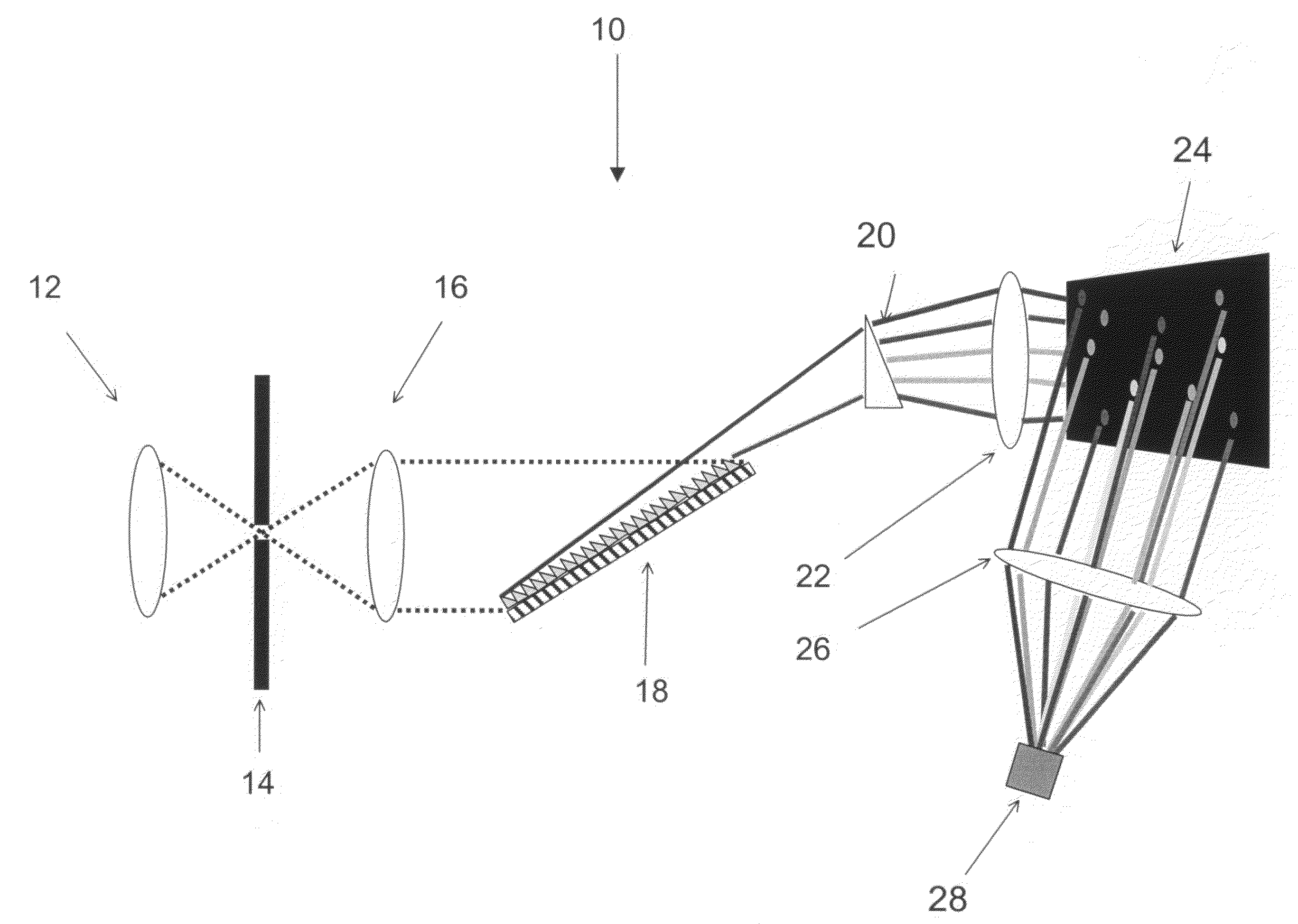
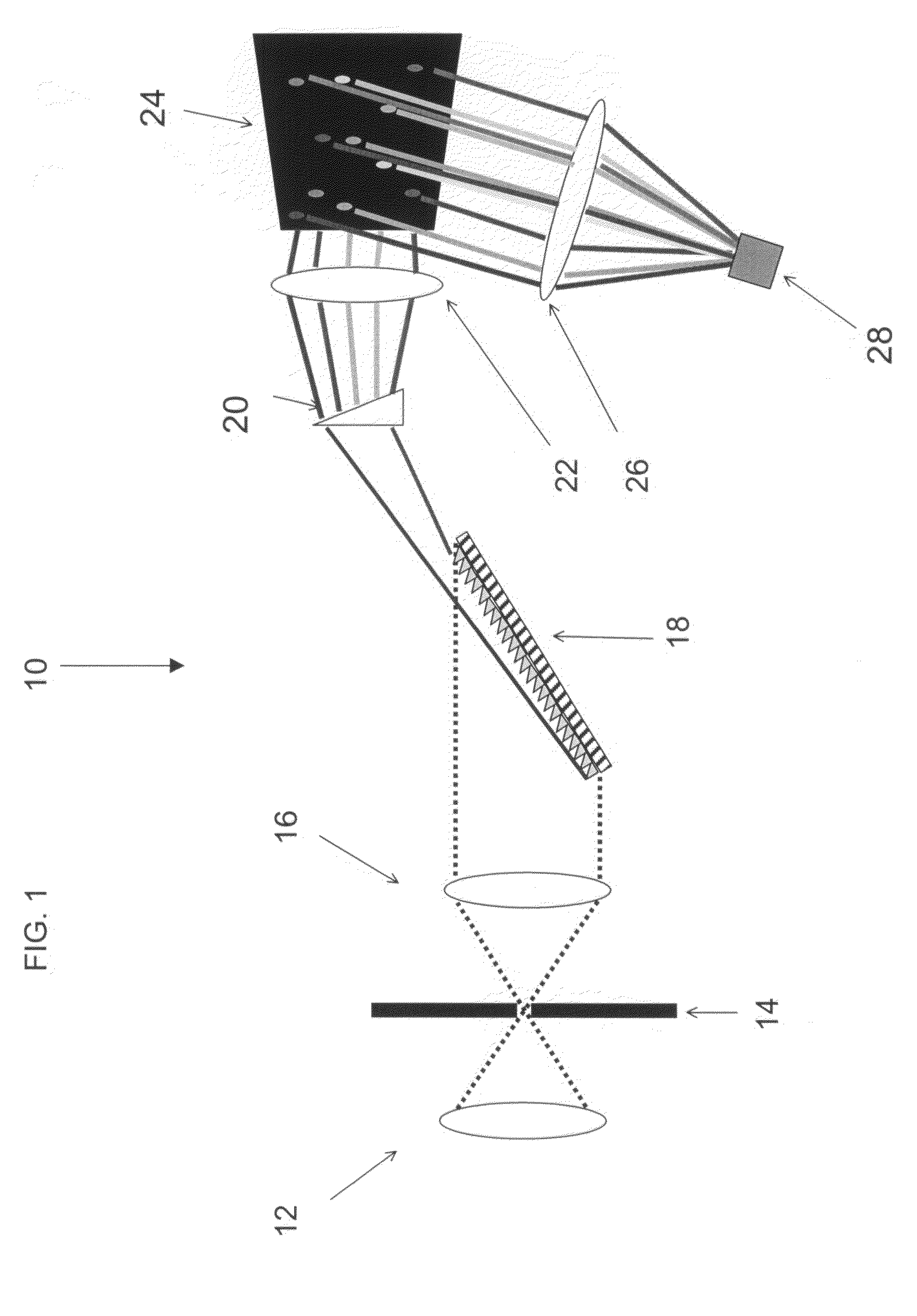
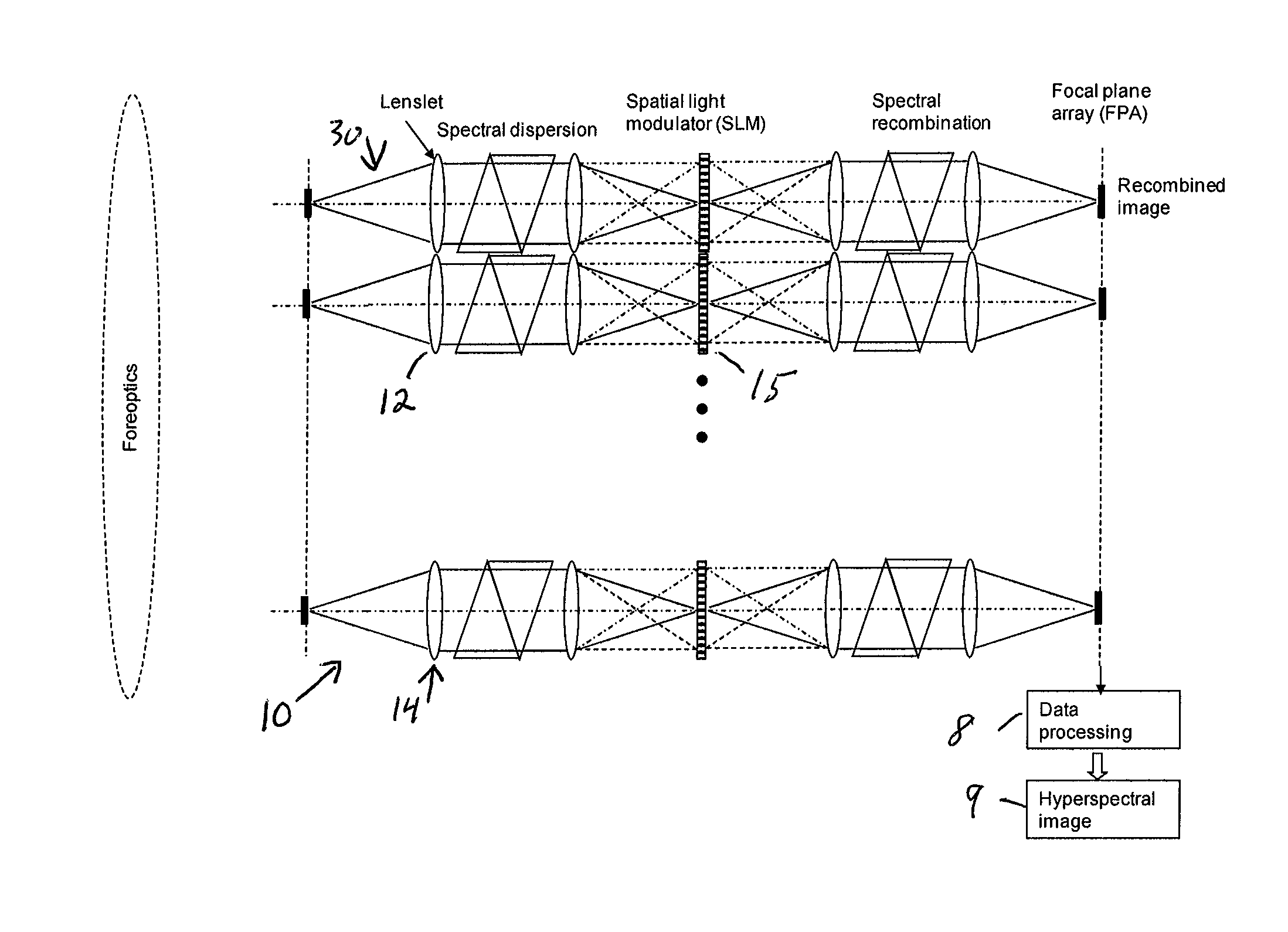
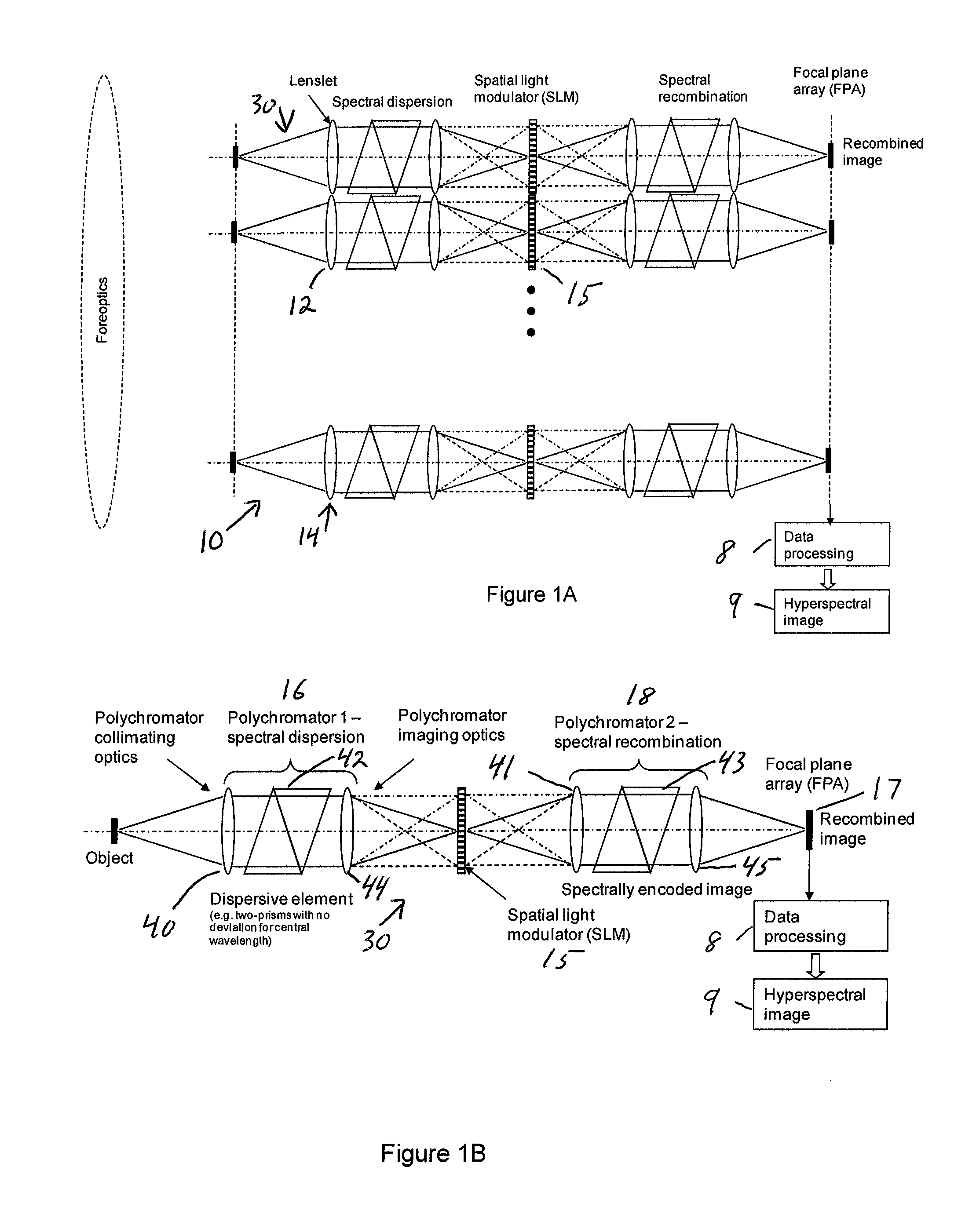
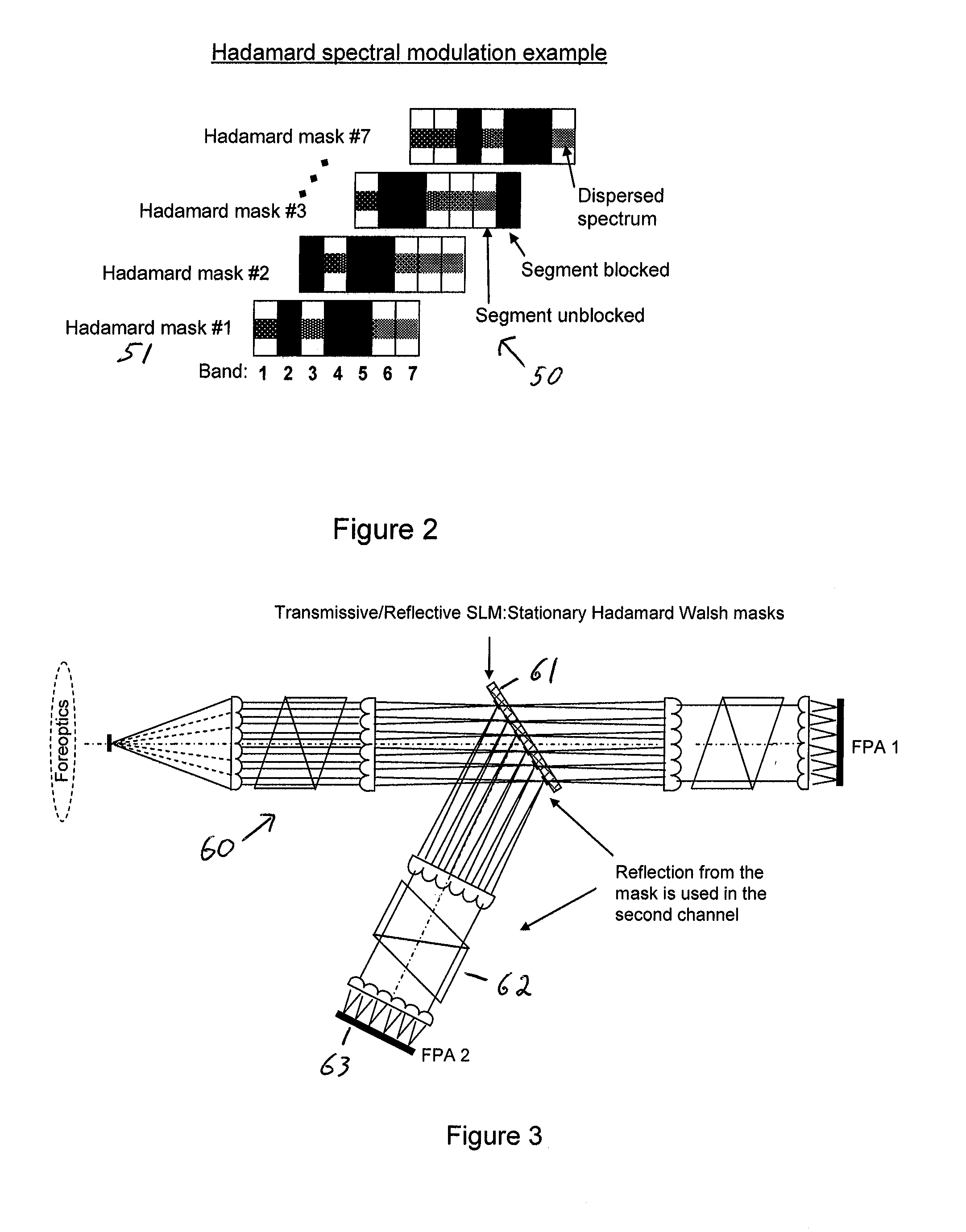
Single-Shot Spectral Imager
ActiveUS20100309467A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy to useRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using refracting elementsMultiplexingSpatial light modulator
A single-shot spectral imager or imaging system which acquires multiplexed spatial and spectral data in a single snapshot with high optical collection efficiency and with the speed limited only by the readout time of the detector circuitry. The imager uses dispersive optics together with spatial light modulators to encode a mathematical transform onto the acquired spatial-spectral data. A multitude of encoded images is recorded simultaneously on a focal plane array and subsequently decoded to produce a spectral / spatial hypercube.
Owner:SPECTRAL SCI
Spectrometers using 2-dimensional microelectromechanical digital micromirror devices
InactiveUS20080174777A1Low costSpeed up the time required for analysisEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryGratingSpectroscopy
Echelle gratings and microelectromechanical system (MEMS) digital micromirror device (DMD) detectors are used to provide rapid, small, and highly sensitive spectrometers. The new spectrometers are particularly useful for laser induced breakdown and Raman spectroscopy, but could generally be used with any form of emission spectroscopy. The new spectrometers have particular applicability in the detection of improvised explosive devices.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
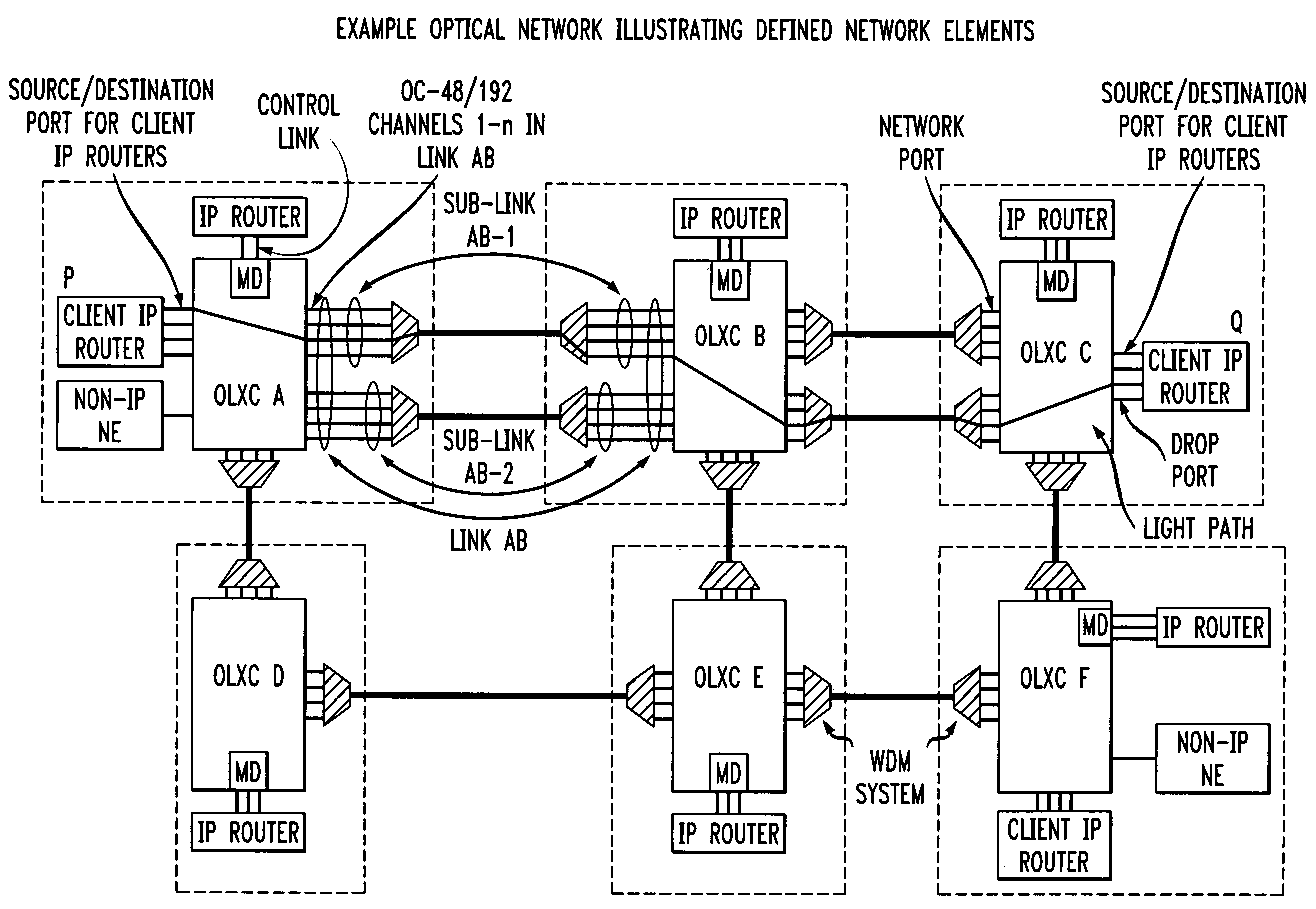
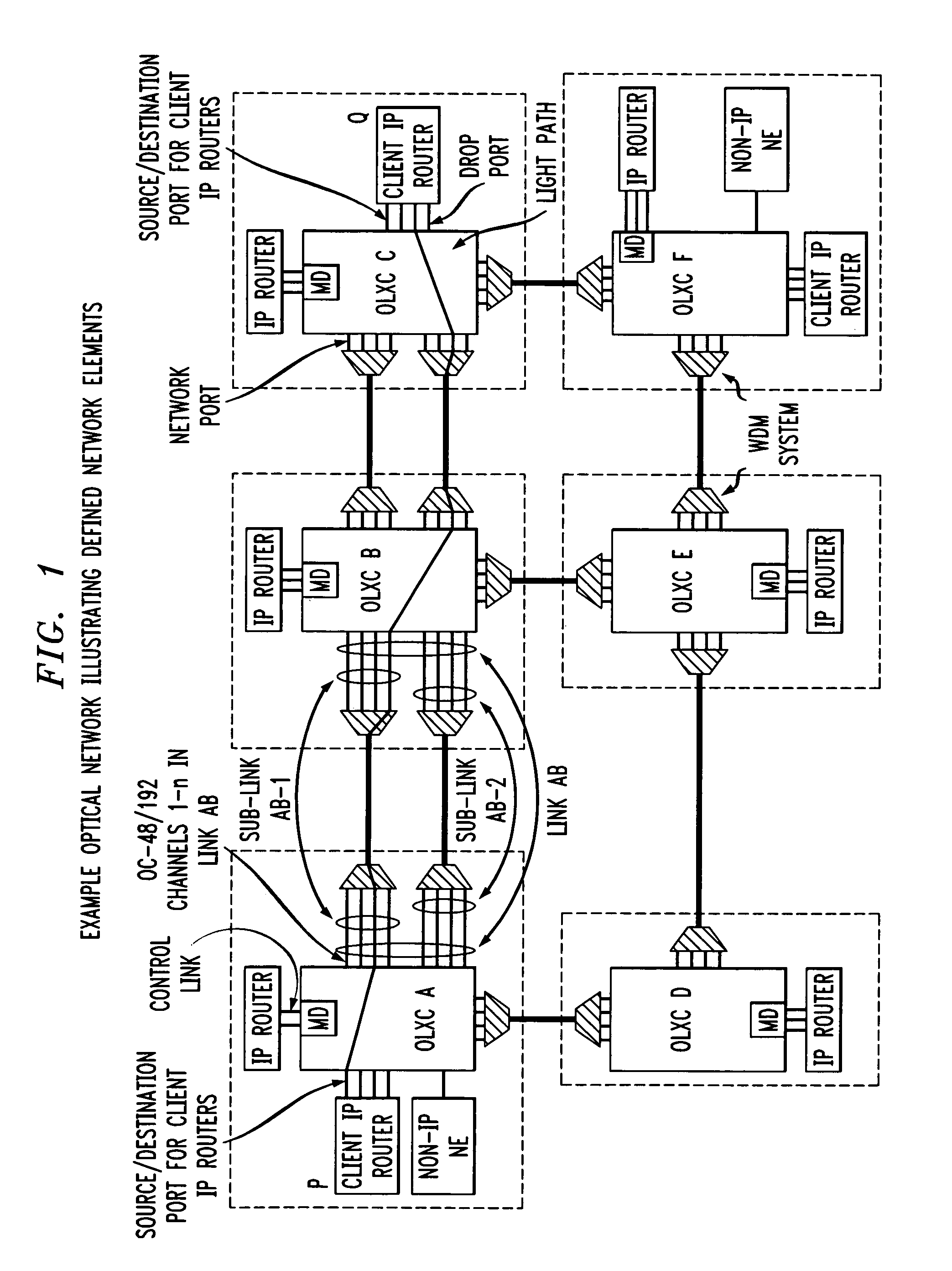
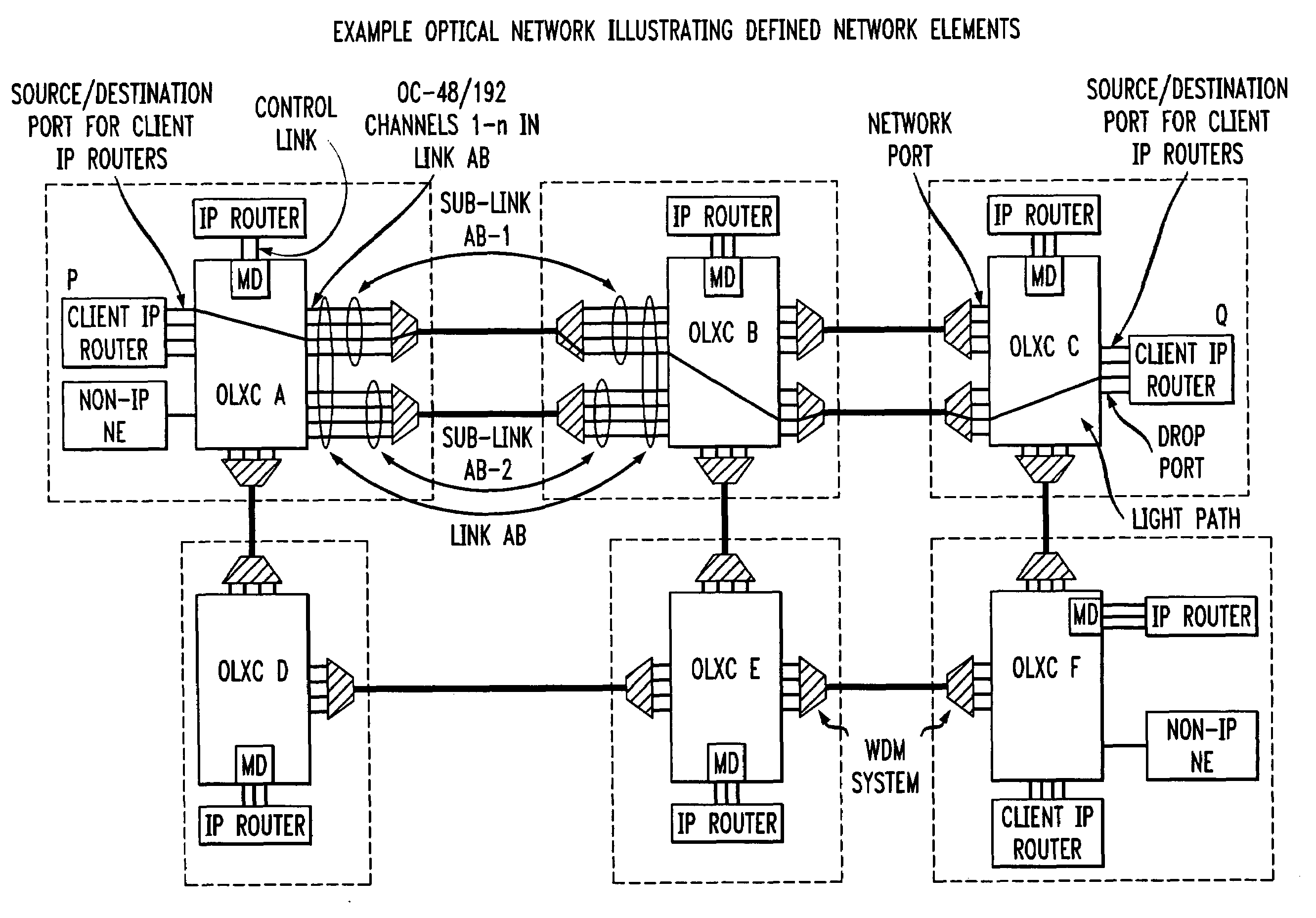
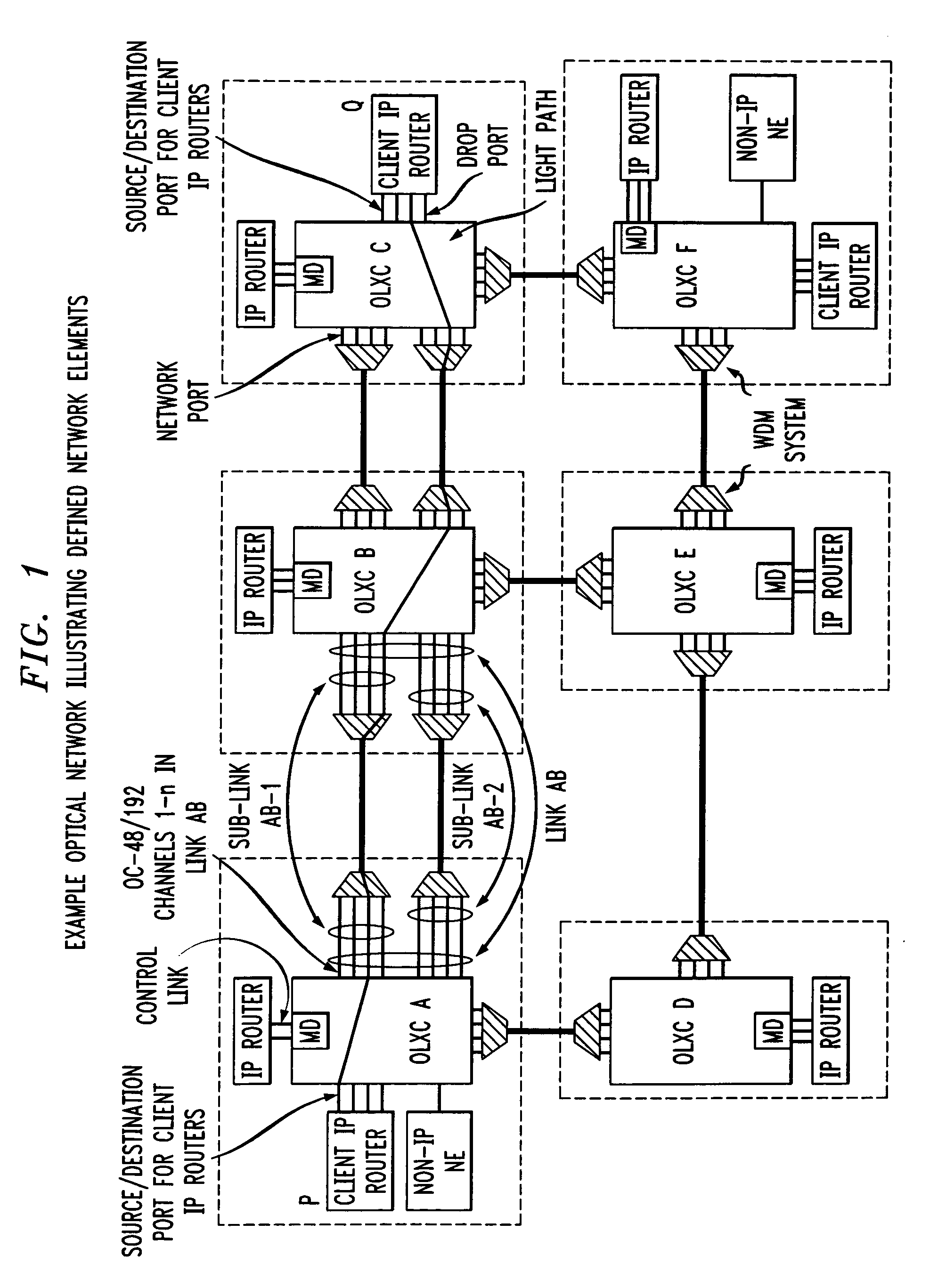
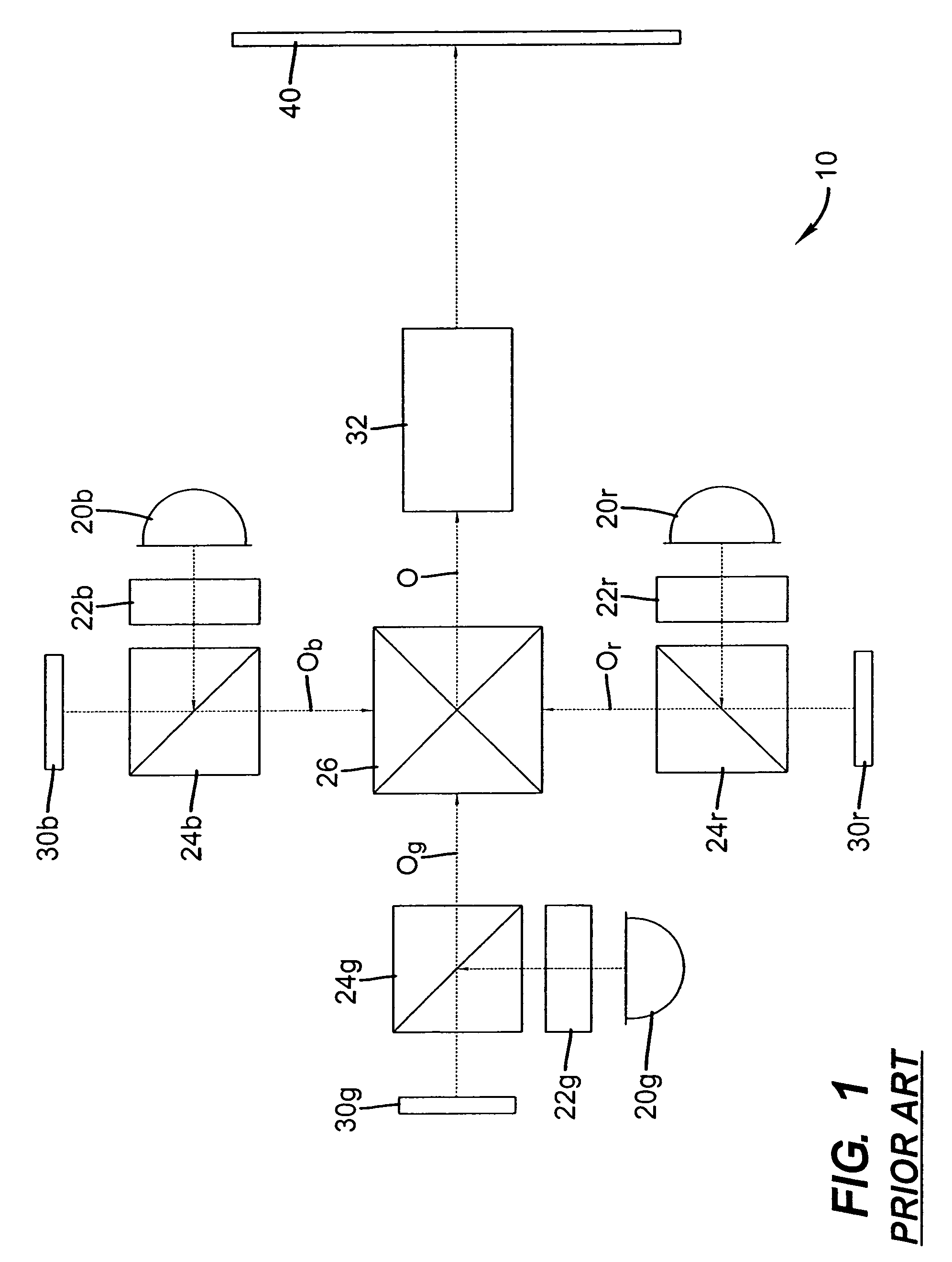
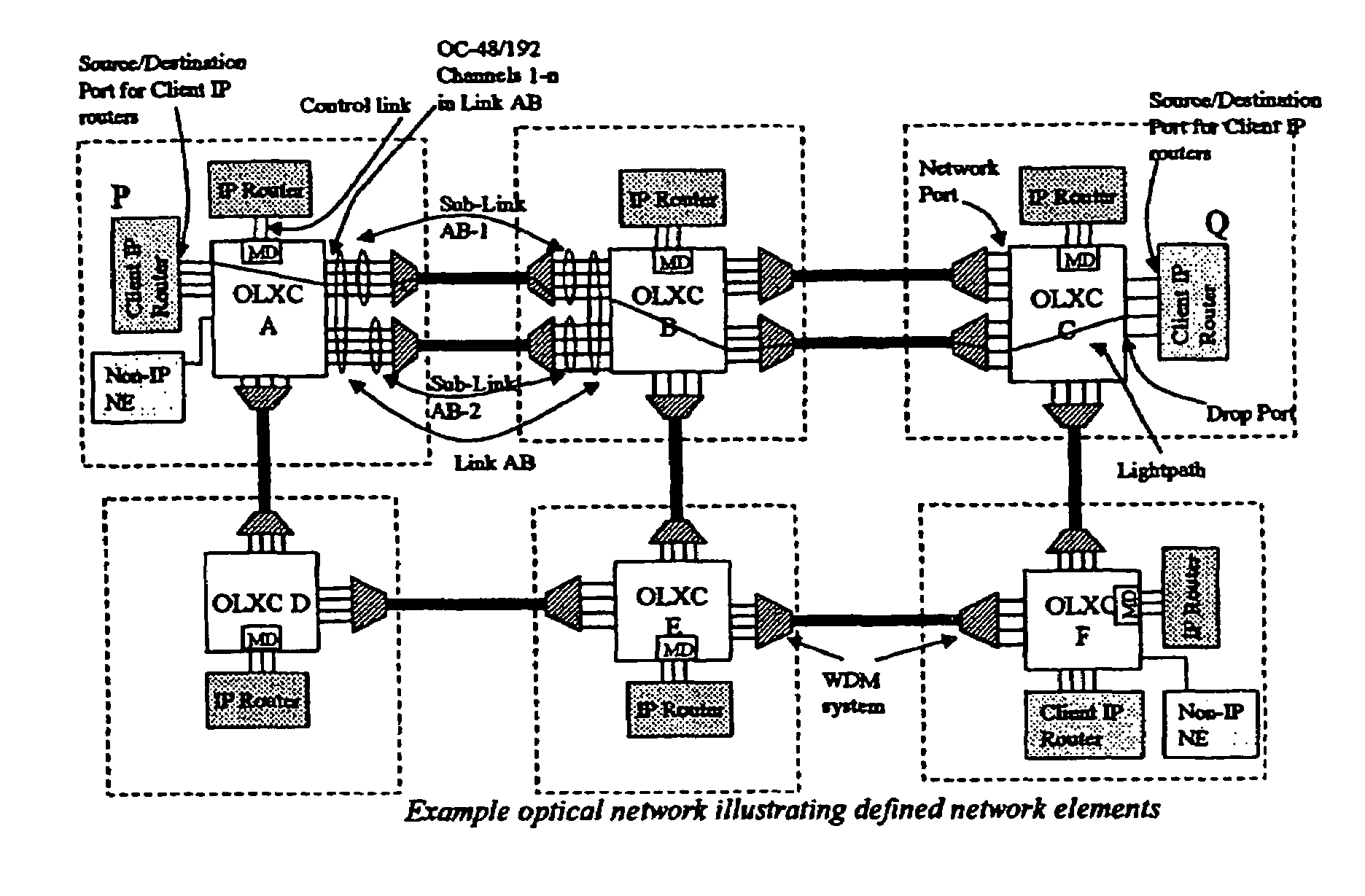
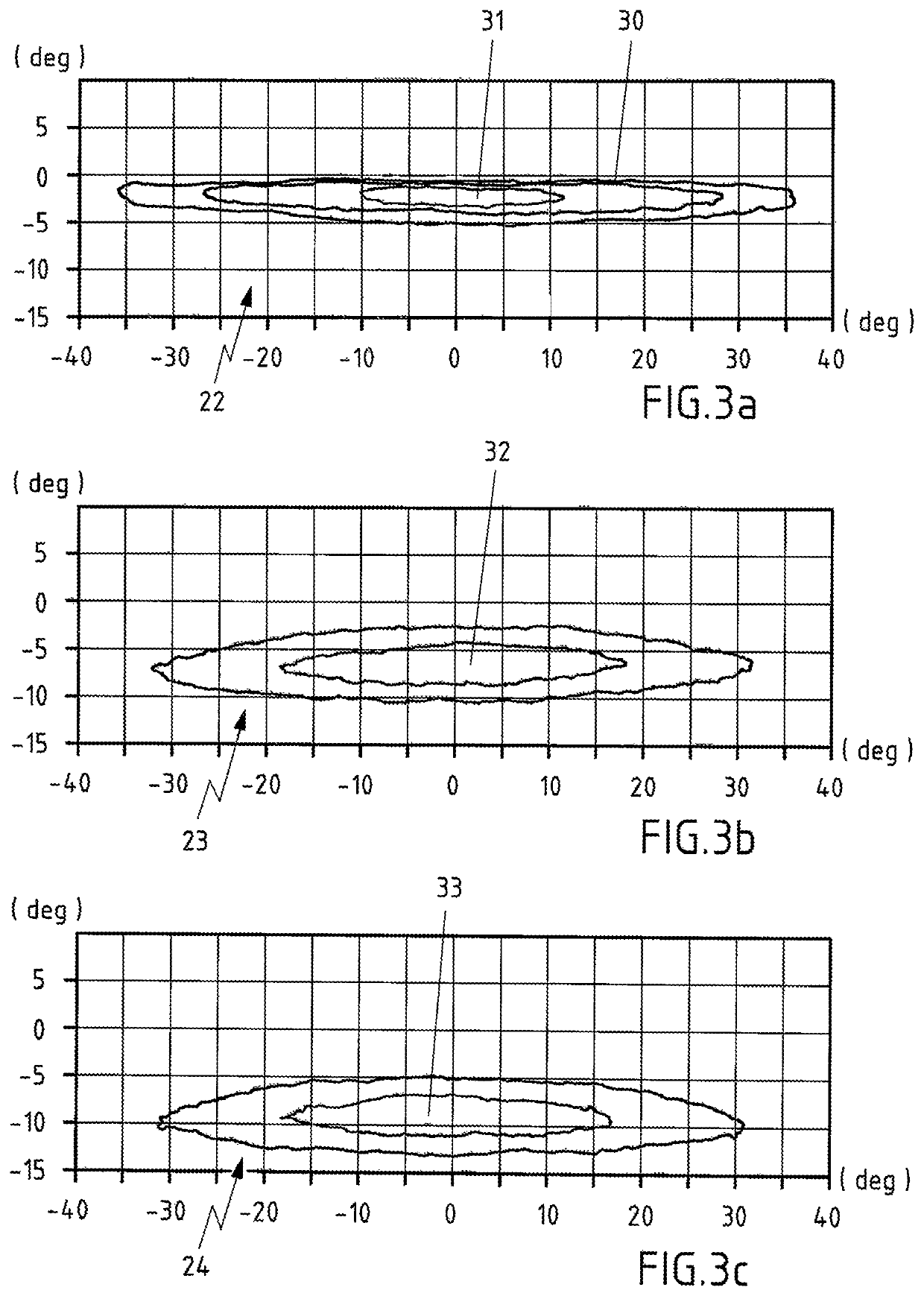
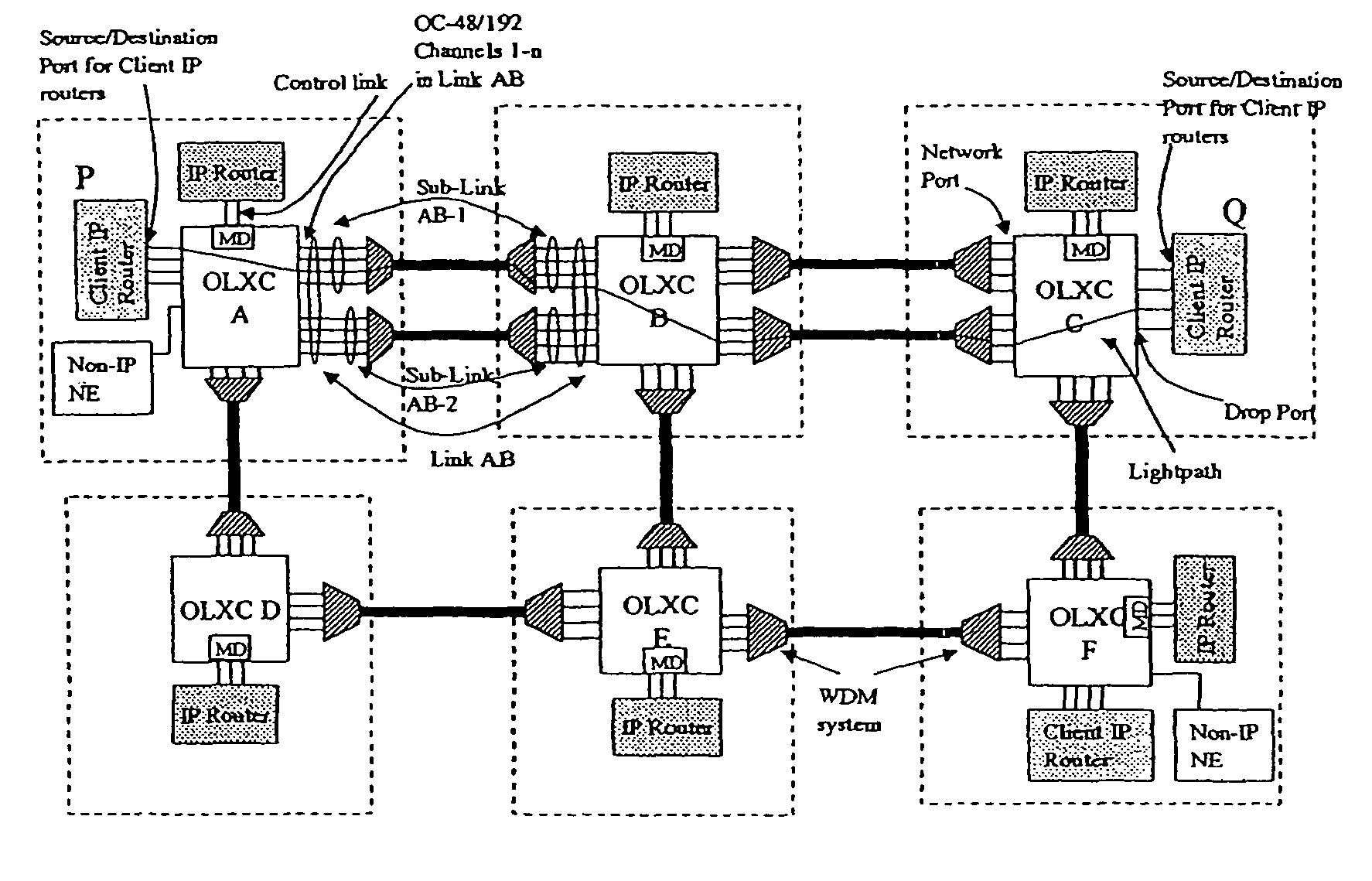
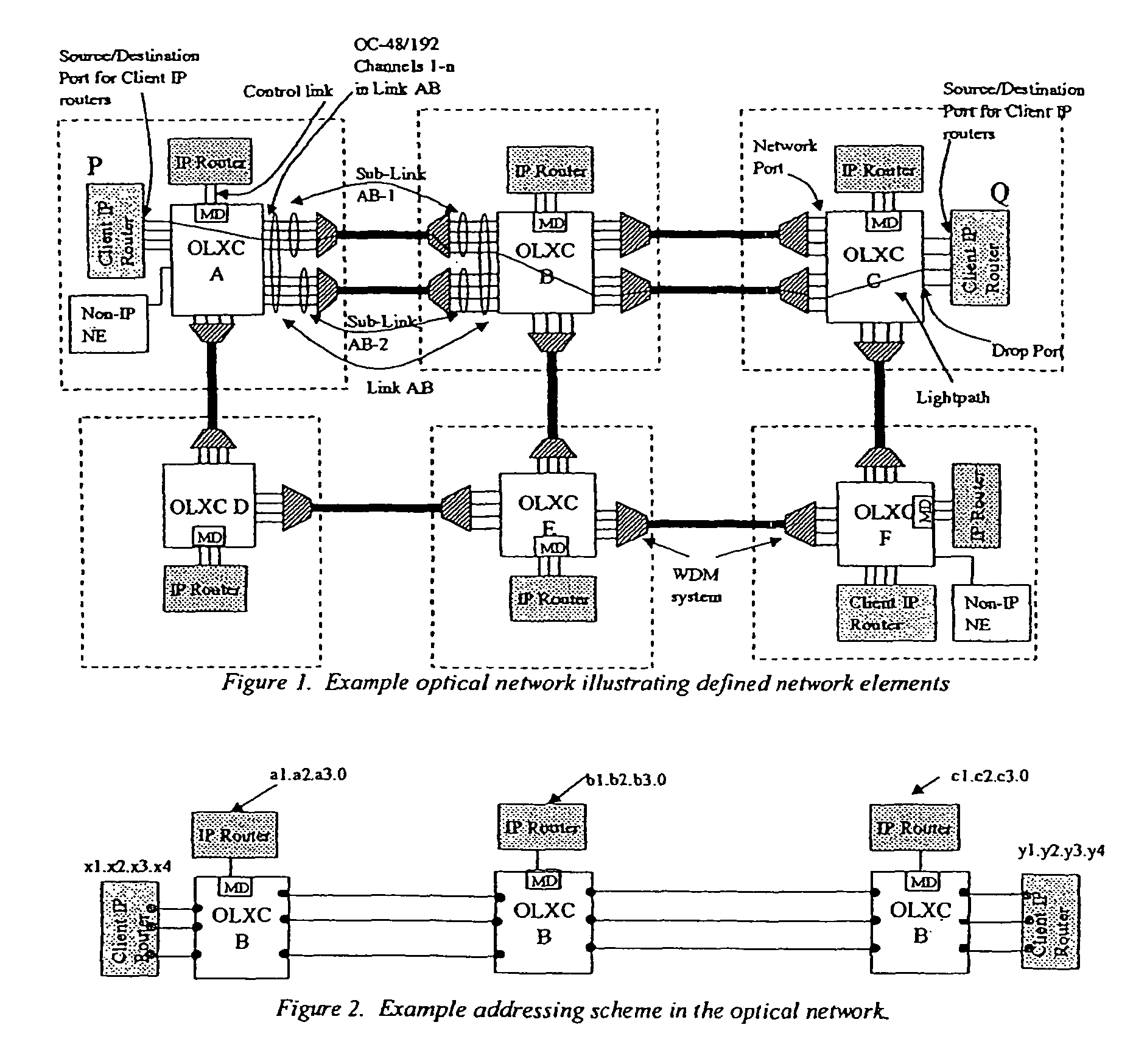
Control of optical connections in an optical network
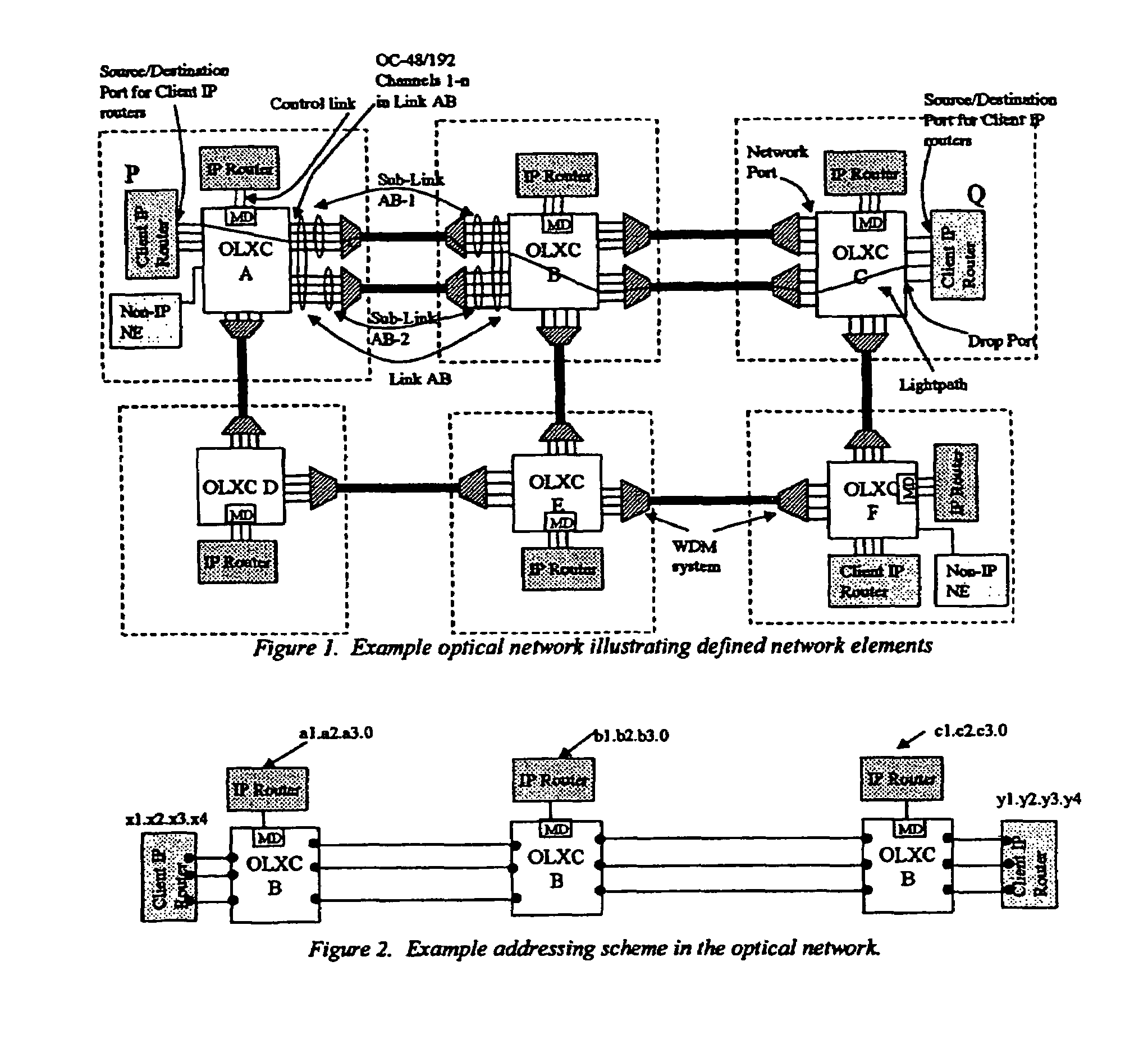
InactiveUS7039009B2Effective recoveryOptics SimplifiedLaser detailsError preventionOptical mesh networkOptical path
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Control of optical connections in an optical network
InactiveUS7031299B2Optics SimplifiedEnhance layeringMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer networkOptical network unit
A method for lightpath provisioning in a reconfigurable optical network that comprises the steps of naming each network addressable element in the reconfigurable optical network, determining current resources therein, determining current topology therein, requesting establishment of a lightpath, and allocating the lightpath. A system for lightpath provisioning in a reconfigurable optical network is also provided, comprising means for naming each network addressable element in the reconfigurable optical network, means for determining current topology in the reconfigurable optical network, means for determining current resources in the reconfigurable optical network, means for requesting establishment of a lightpath, means for allocating the lightpath and means for removing the lightpath upon completion.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
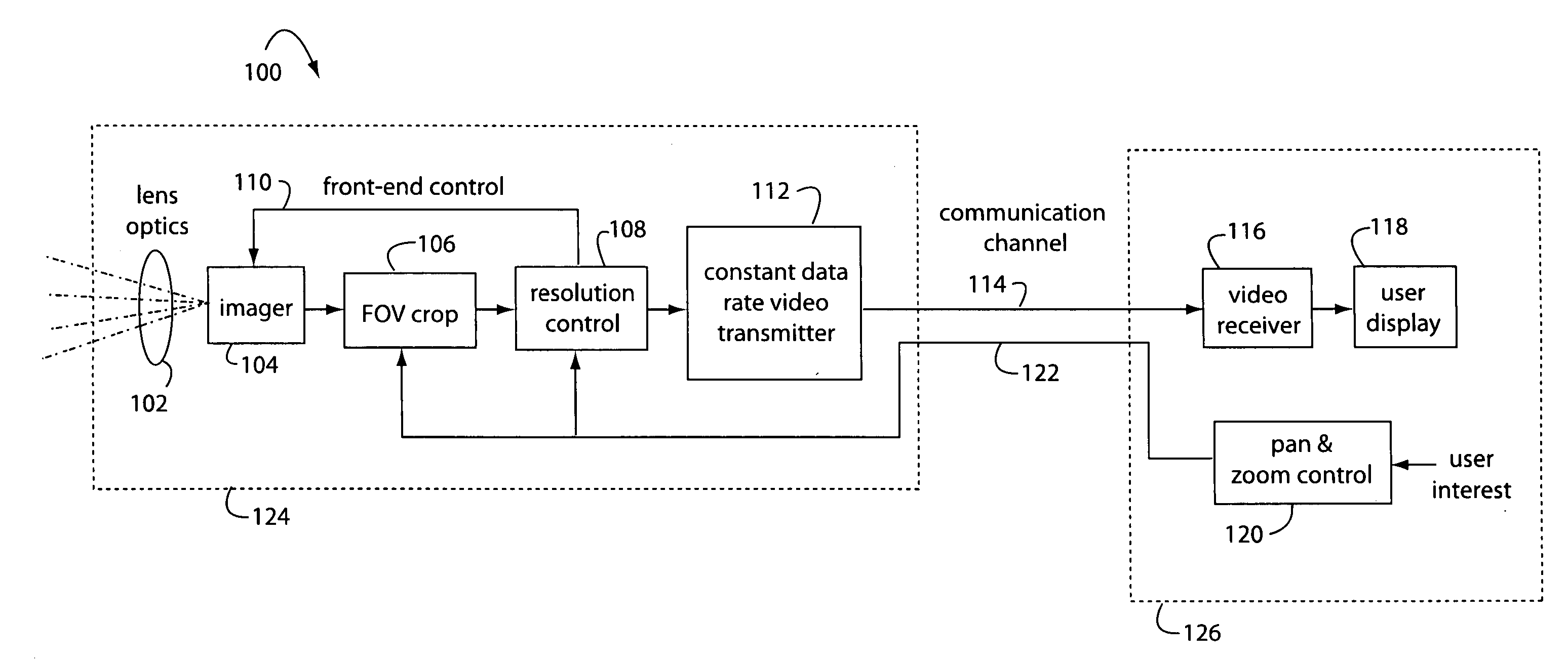
Resolution proportional digital zoom
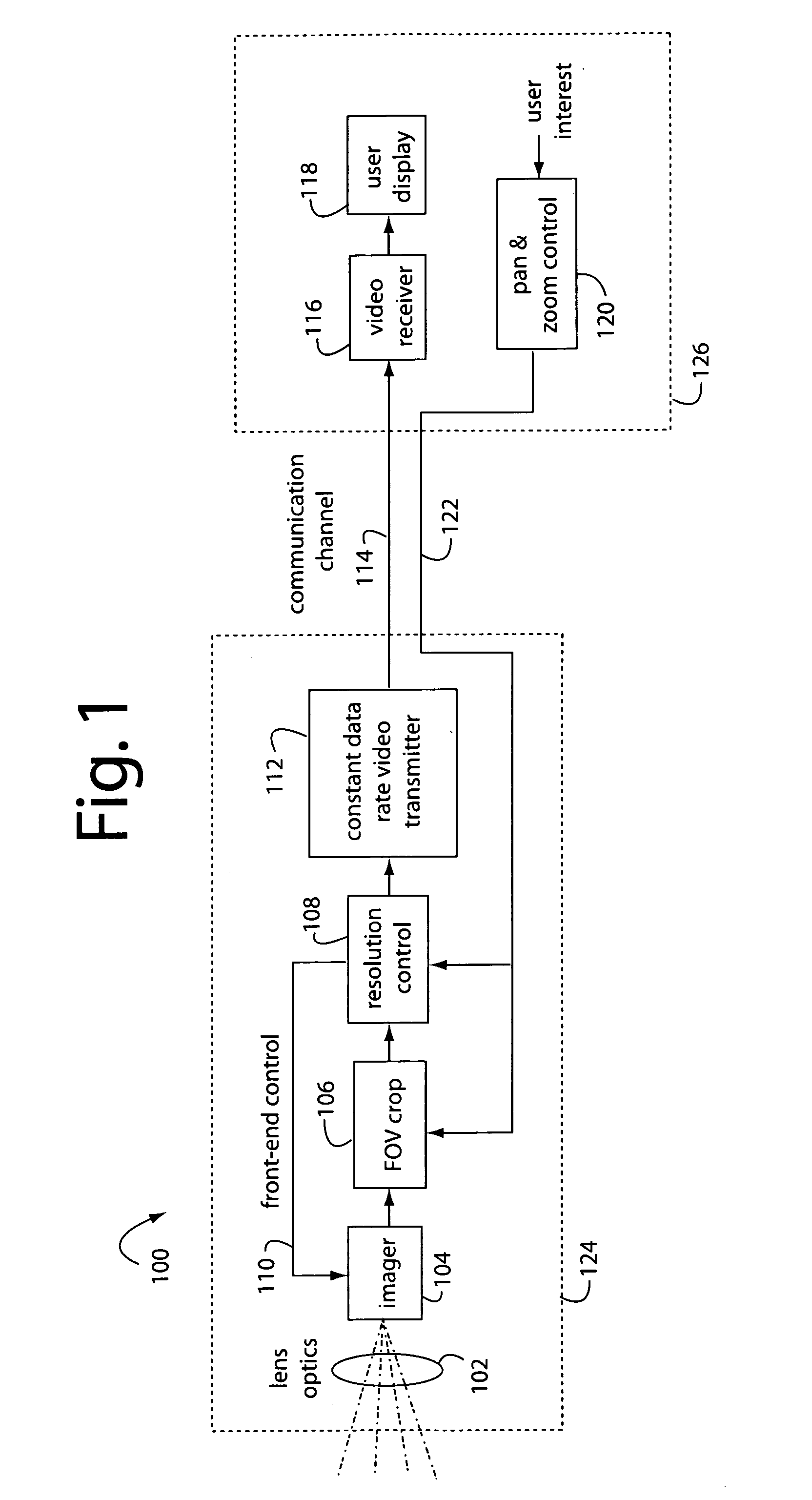
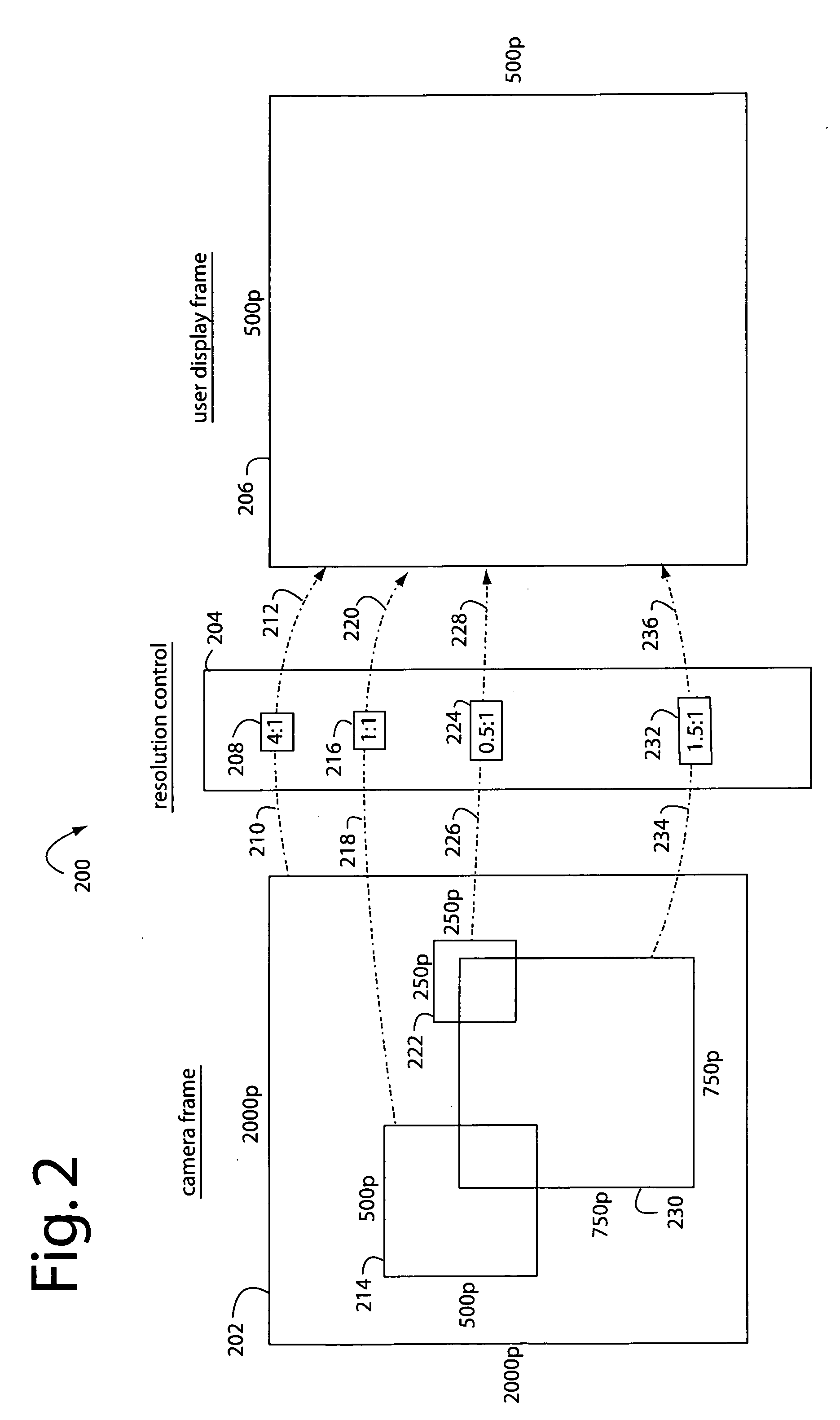
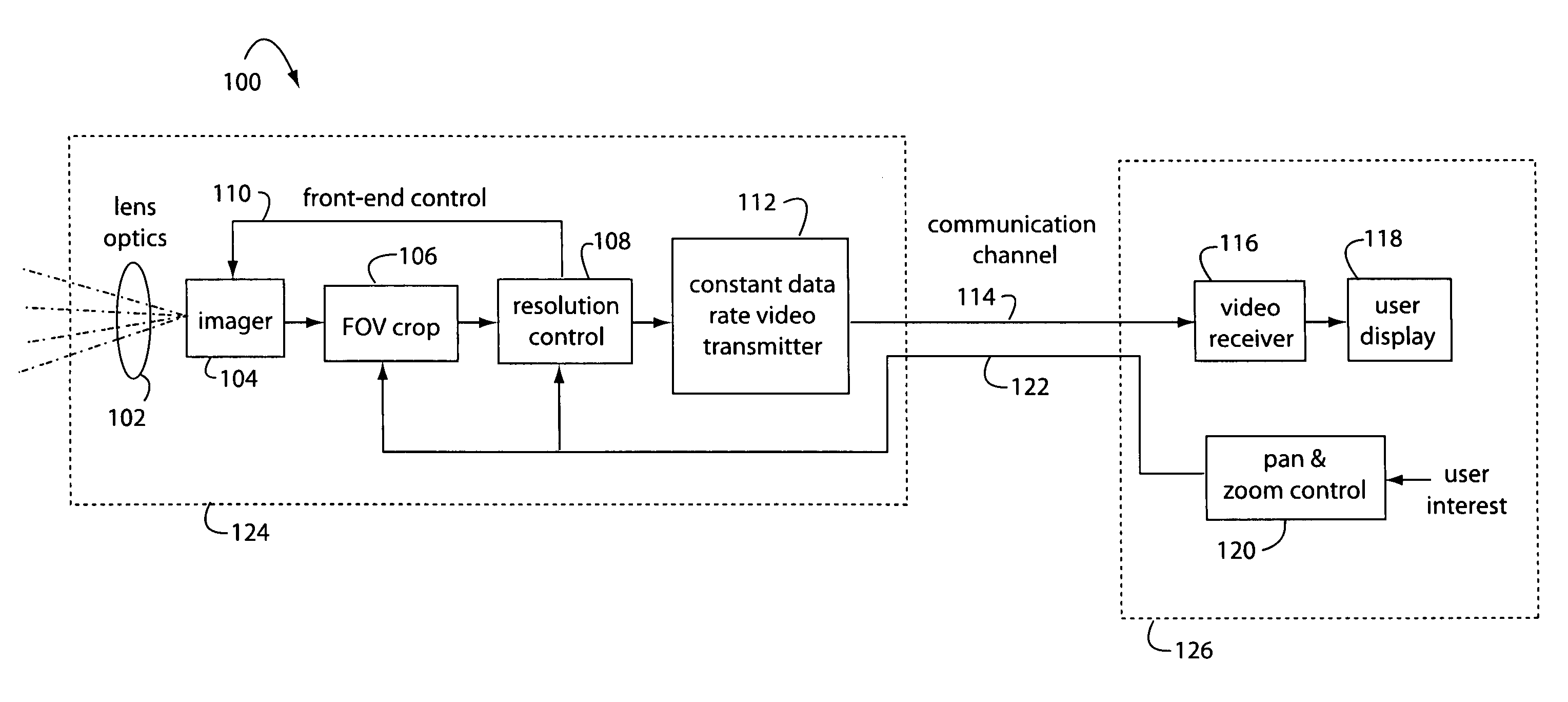
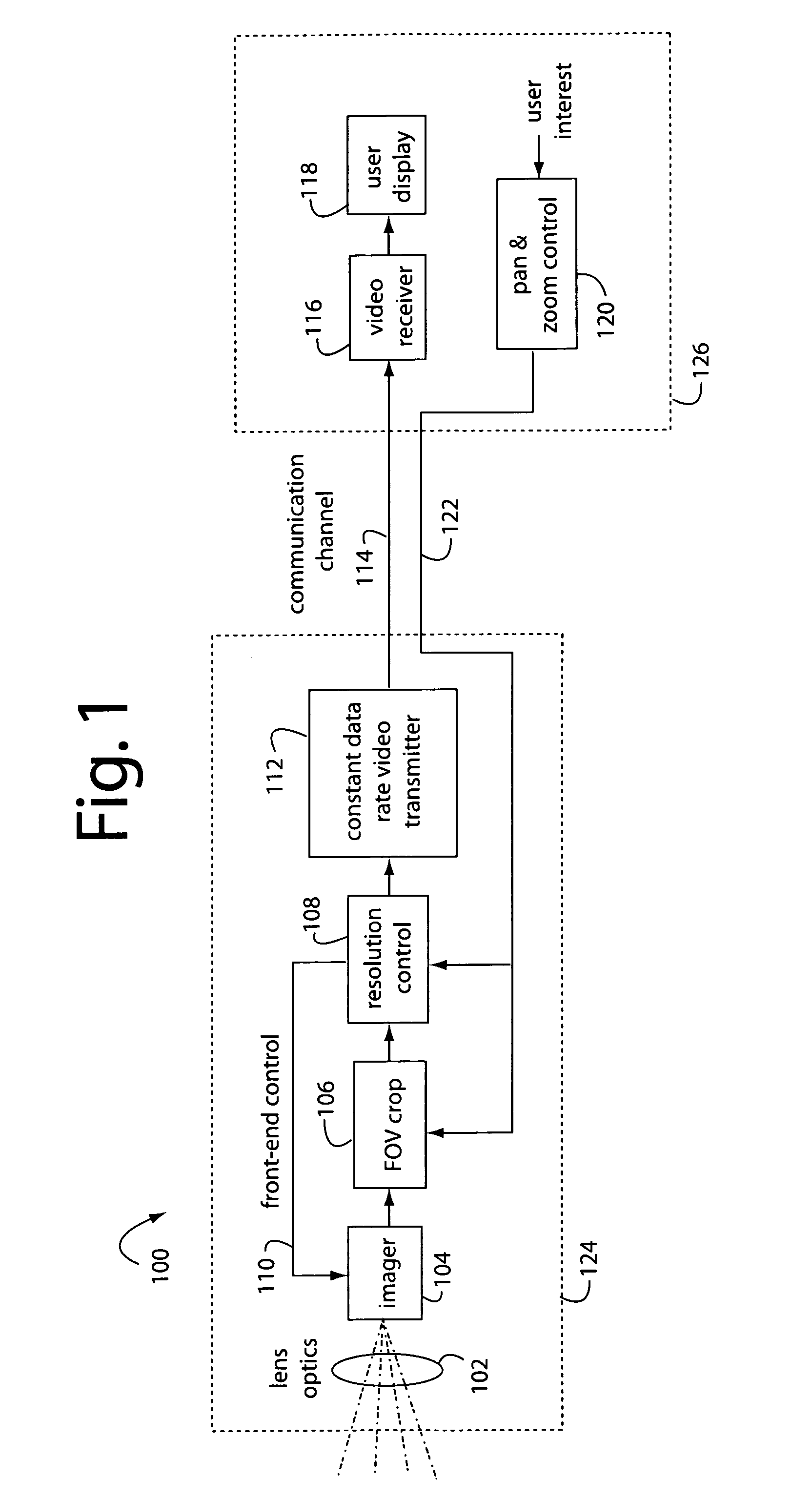
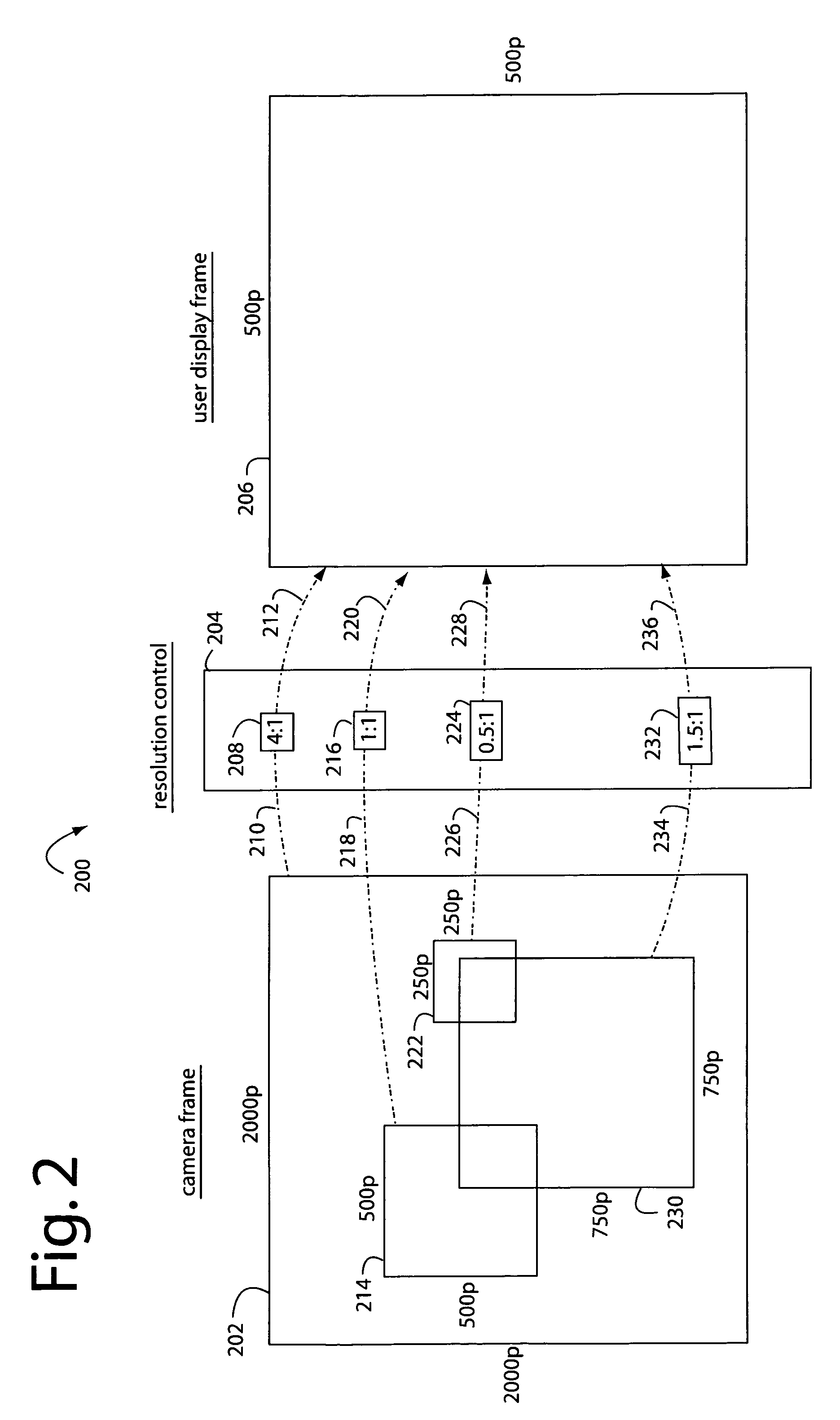
InactiveUS20070229680A1Simple opticOptics SimplifiedTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationCamera lensImage resolution
A resolution proportional digital zoom system comprises a CCD imaging device with over a million pixels resolution. A standard fixed-1X optical lens is fitted to the imager. A communication channel with a limited bandwidth is used to transmit video. Such bandwidth is substantially less than the imager's full resolution times its frame rate. A user is provided with controls to pan and zoom within the imager's field of view. The pixel resolution is proportionally controlled such that video output data rate on the communication channel is optimal and held within maximum limits at any pan / zoom setting.
Owner:PULNIX AMERICA
Projection display system using polarized light
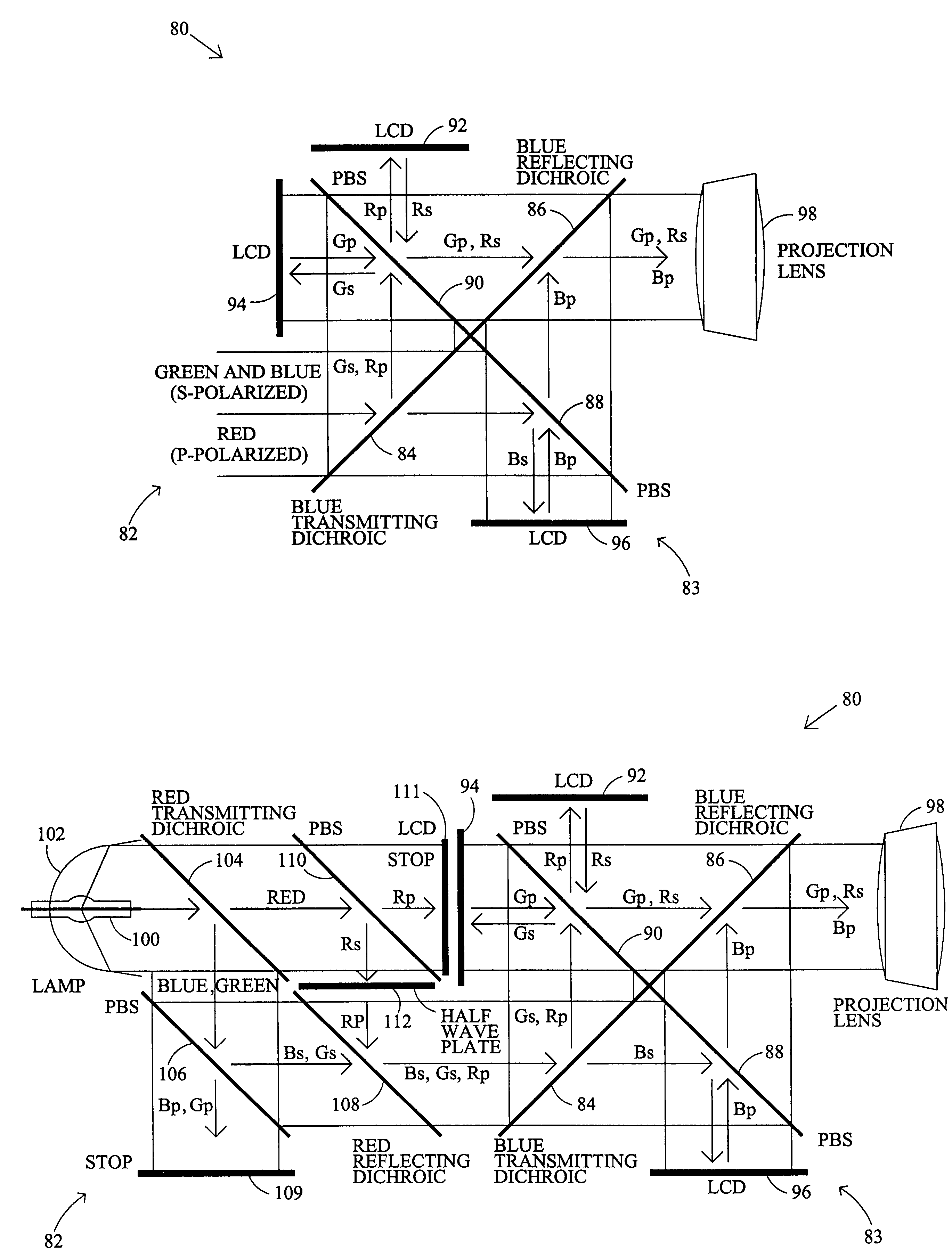
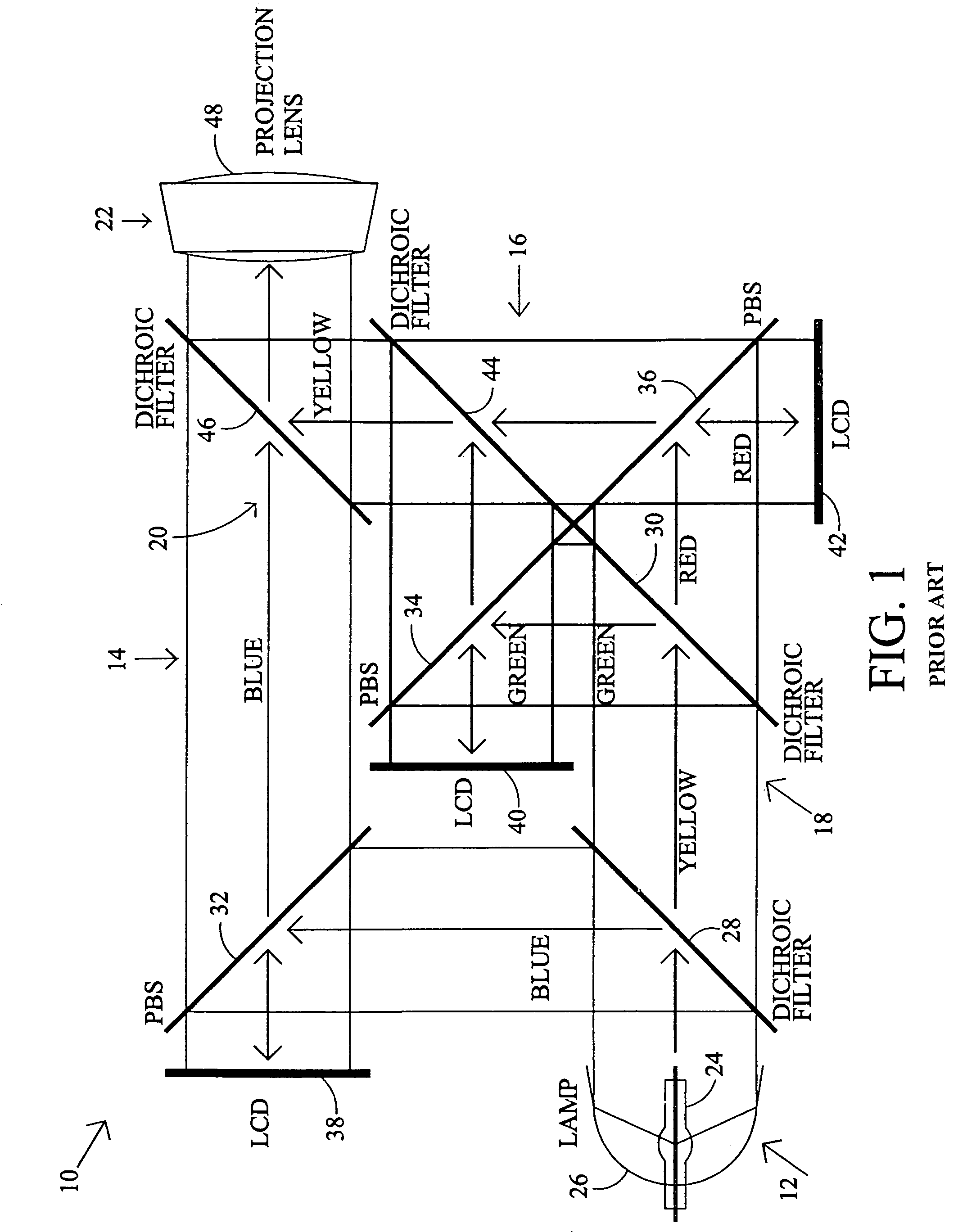
InactiveUS6995917B1Small distanceReduce manufacturing costTelevision system detailsProjectorsLight beamProjection system
A projection display system using polarized light comprises a light source for generating a light beam having at least two light components, wherein the light components are polarized and at least one of the light components is polarized differently than another of the light components. The projection display system has a projection system having a plurality of polarized light modulators, each modulator generating a light-component-specific image associated with one of the light components. The projection display system also has a projection lens for projecting an image combined from the light-component-specific images from the modulators. The present invention also provides a polarization converter for use with a light source that generates a light beam having at least two light components. The polarization converter comprises an optics array capable of separating the light beam into at least one light component having a polarization that is different than another light component.
Owner:SHARP KK
Image-recording device for a printing form, having an array of VCSEL light sources
InactiveUS20020129723A1Advantageous beam propertyLong system service lifeLaser detailsDuplicating/marking methodsImage recordingLight beam
A device for recording images on a printing form, including an array of light sources and imaging optics for generating (n.times.m) imaging spots on a printing form, which is distinguished by the array of light sources including an array of mutually independently controllable VCSEL light sources. One specific imaging spot may be formed on the printing form by combining the light emitted by a subarray of the VCSEL light sources. Due to the advantageous beam properties of VCSEL light sources, such as the small divergence and negligible astigmatism, the device for recording images on printing forms is especially advantageous for use in a printing-form imaging unit or in a print unit.
Owner:HEIDELBERGER DRUCKMASCHINEN AG
Advanced illumination system for use in microlithography
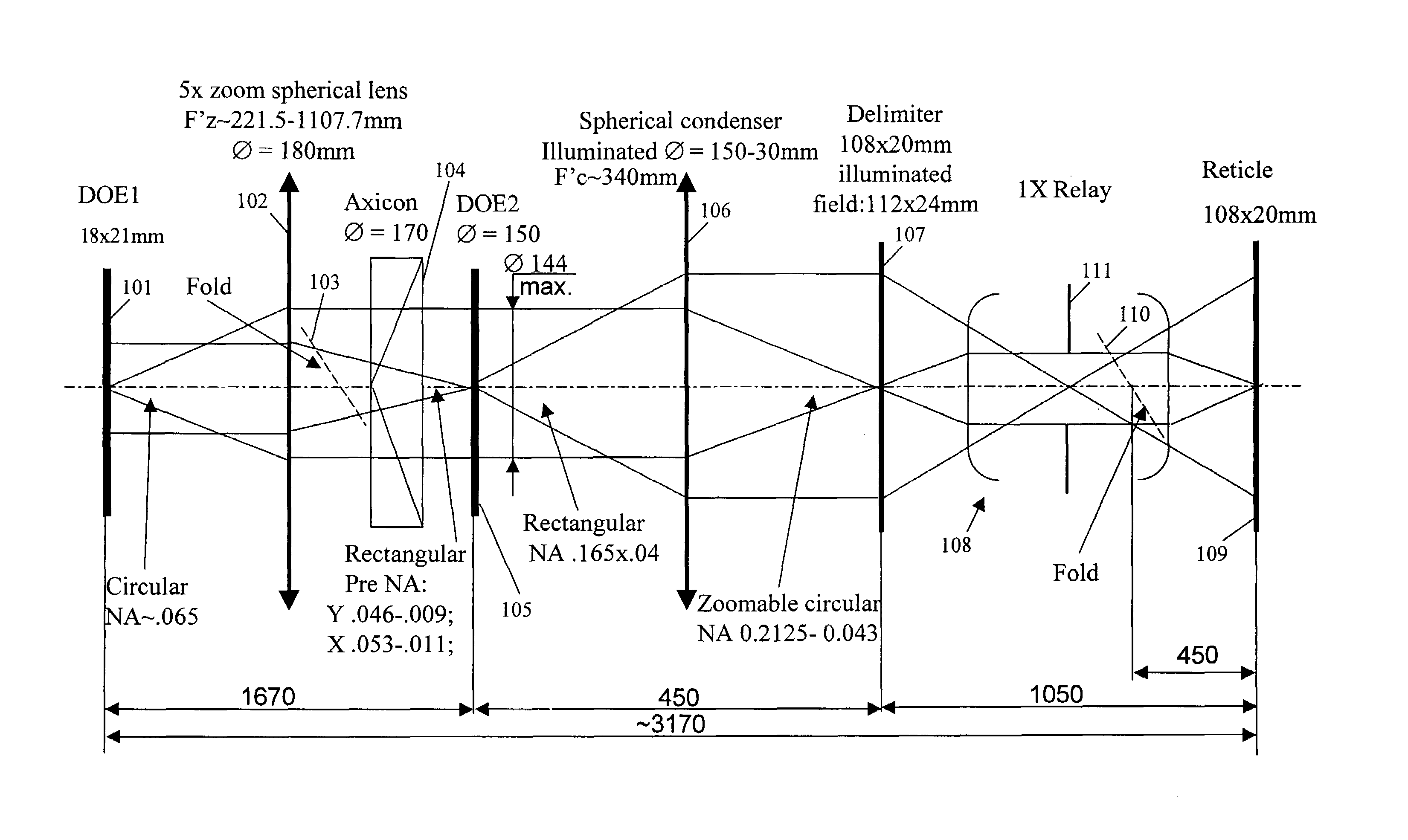
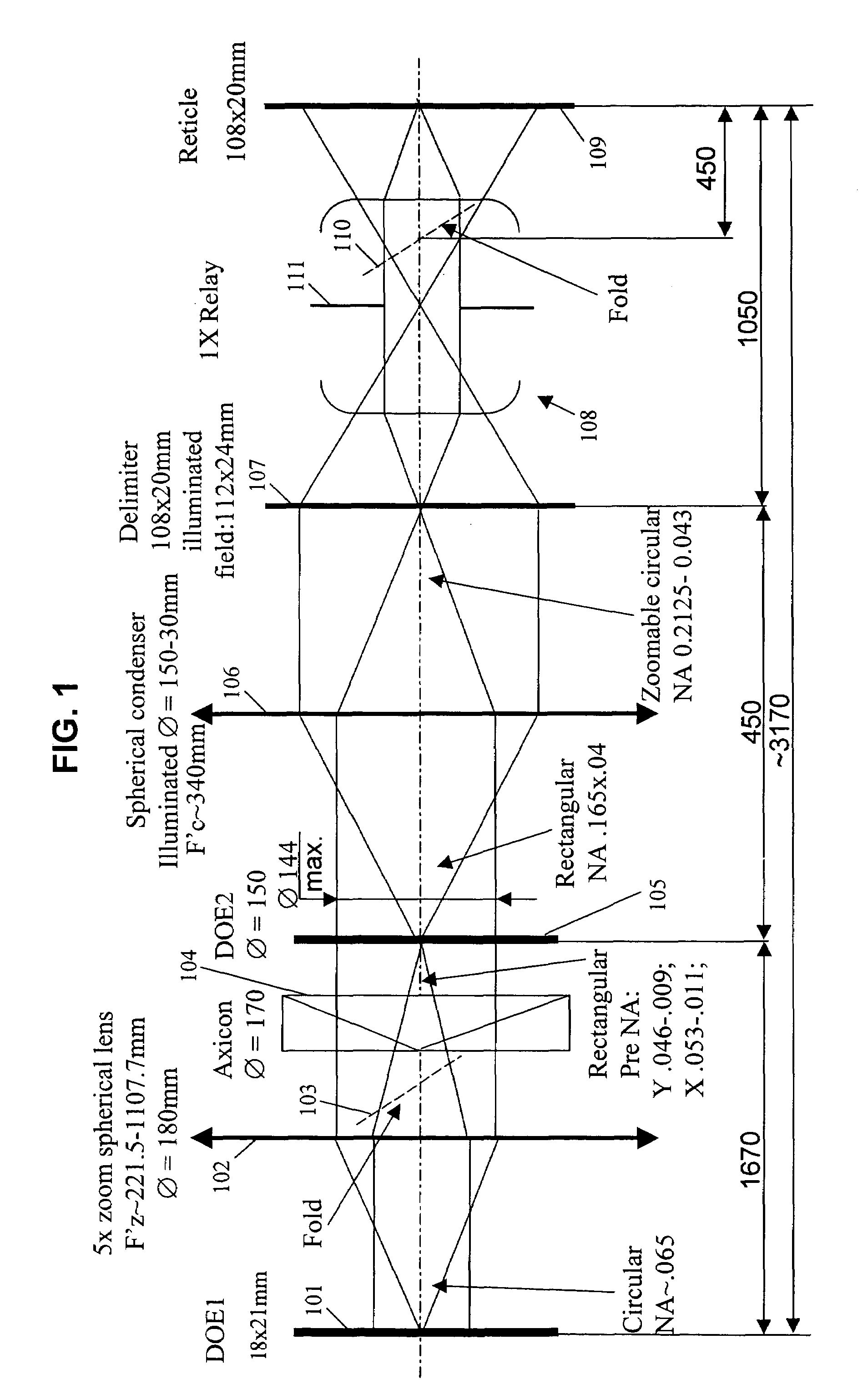
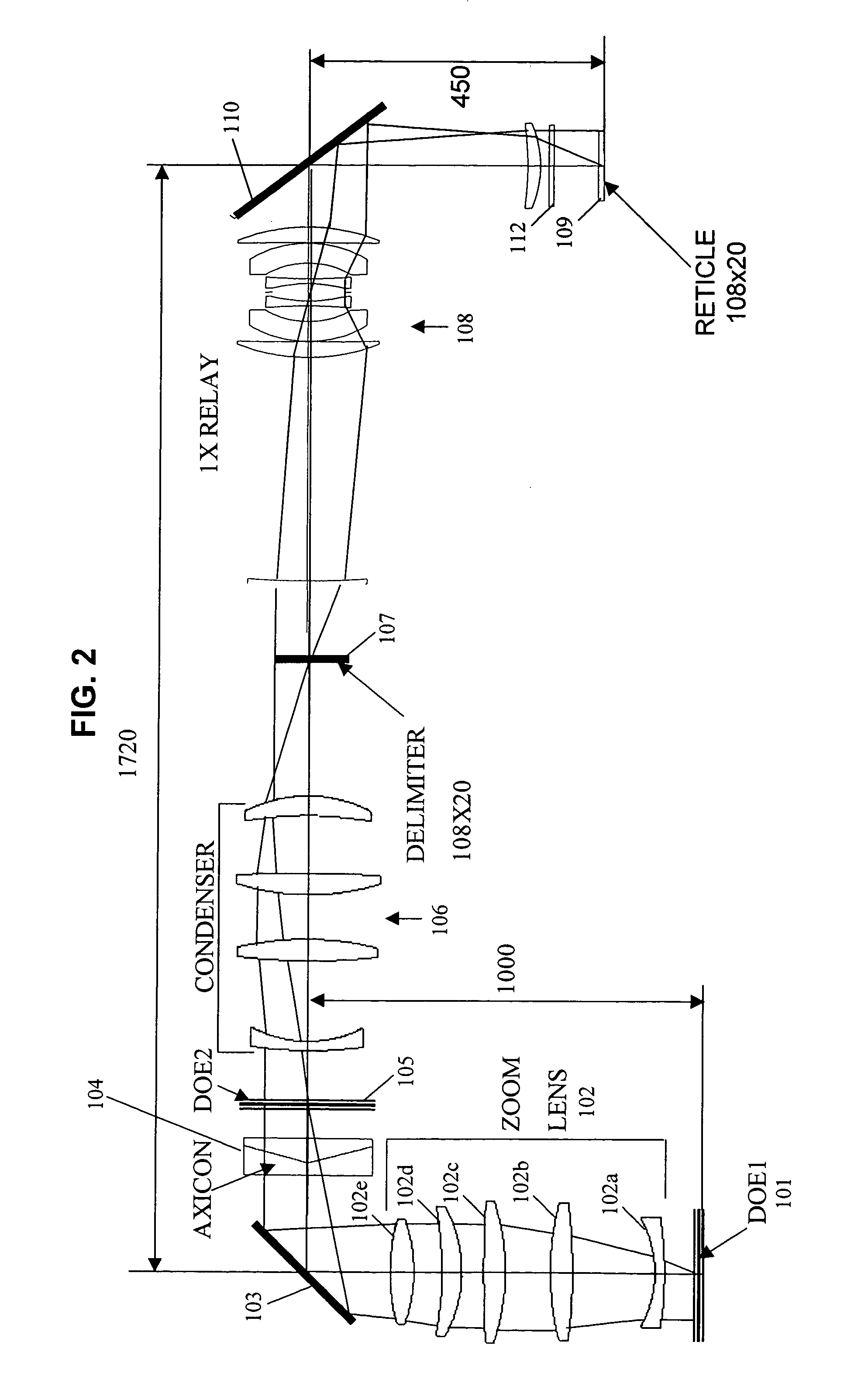
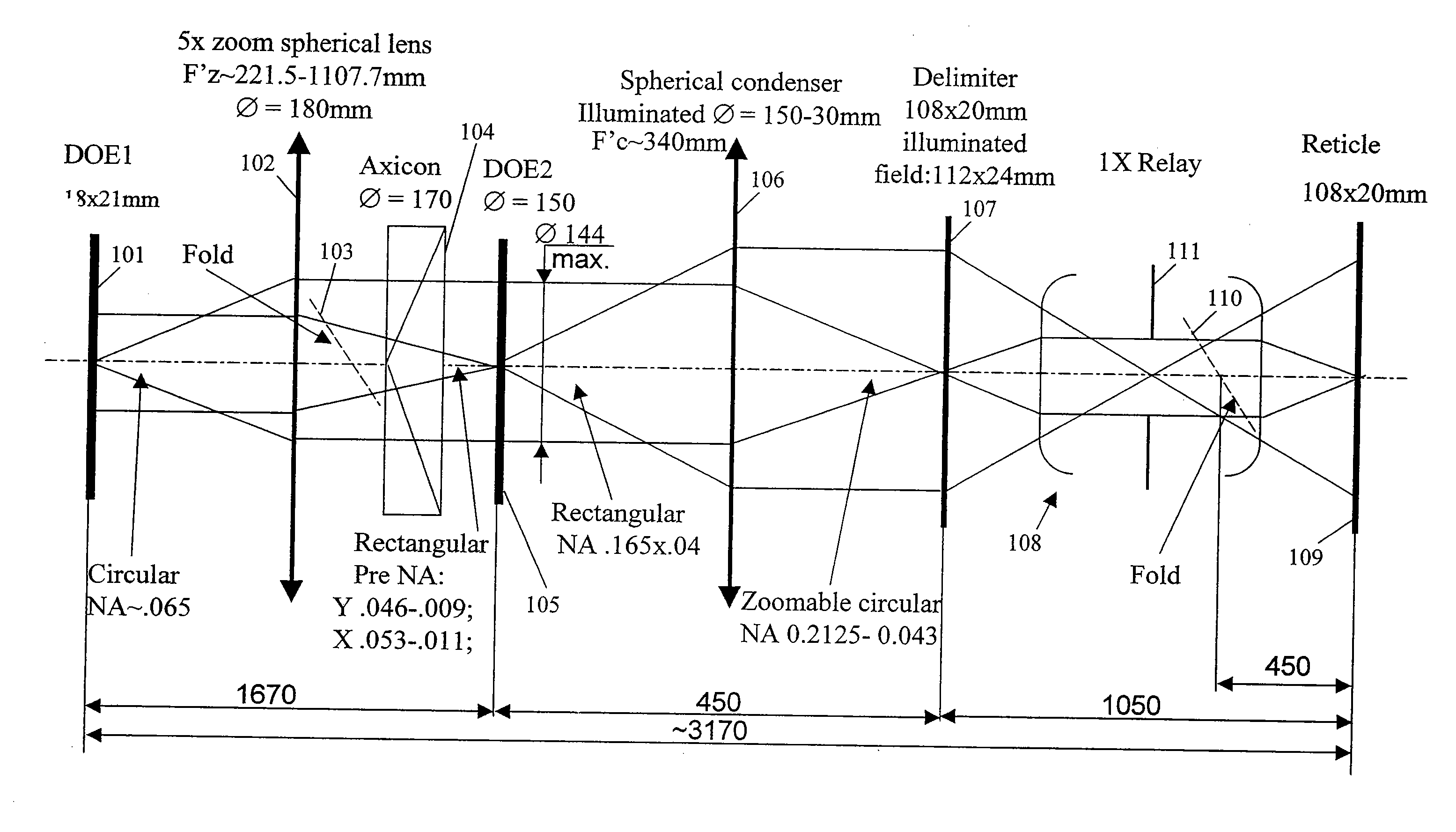
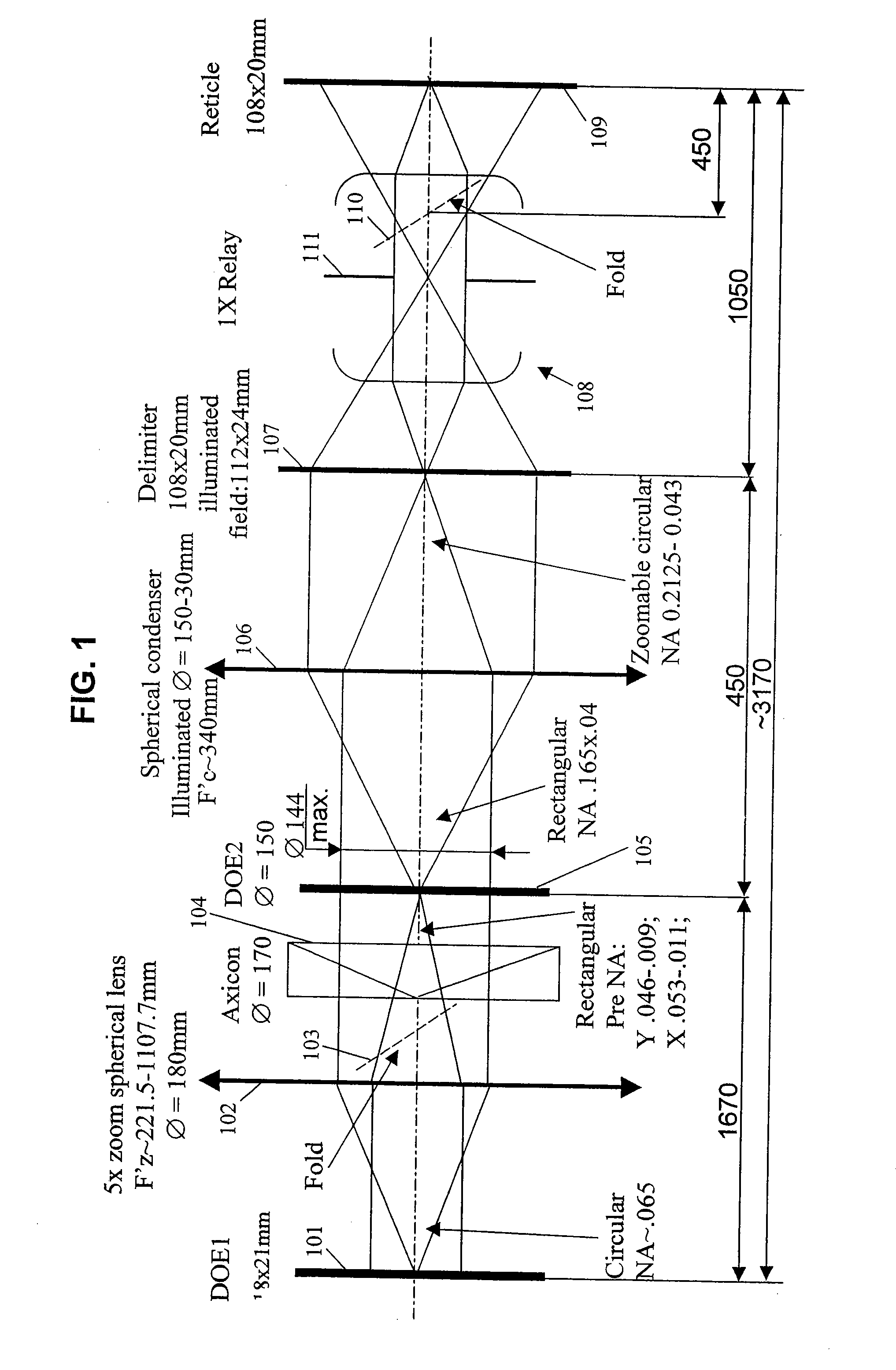
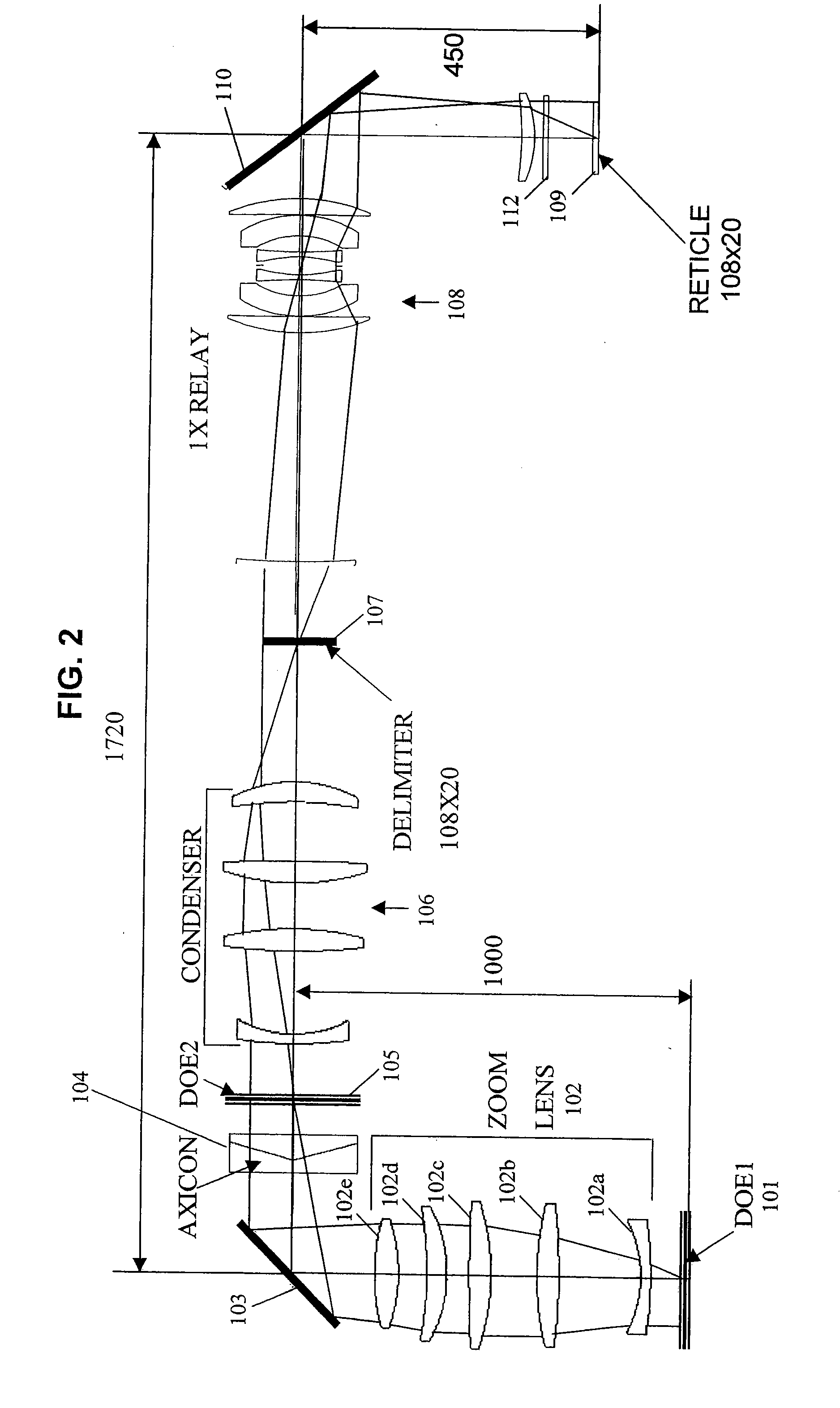
InactiveUS7187430B2Continuous changeOptics SimplifiedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansLighting systemReticle
A system for microlithography comprises an illumination source; an illumination optical system including, in order from an objective side, (a) a first diffractive optical element that receives illumination from the illumination source, (b) a zoom lens, (c) a second diffractive optical element, (d) a condenser lens, (e) a relay lens, and (f) a reticle, and a projection optical system for imaging the reticle onto a substrate, wherein the system for microlithography provides a zoomable numerical aperture.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
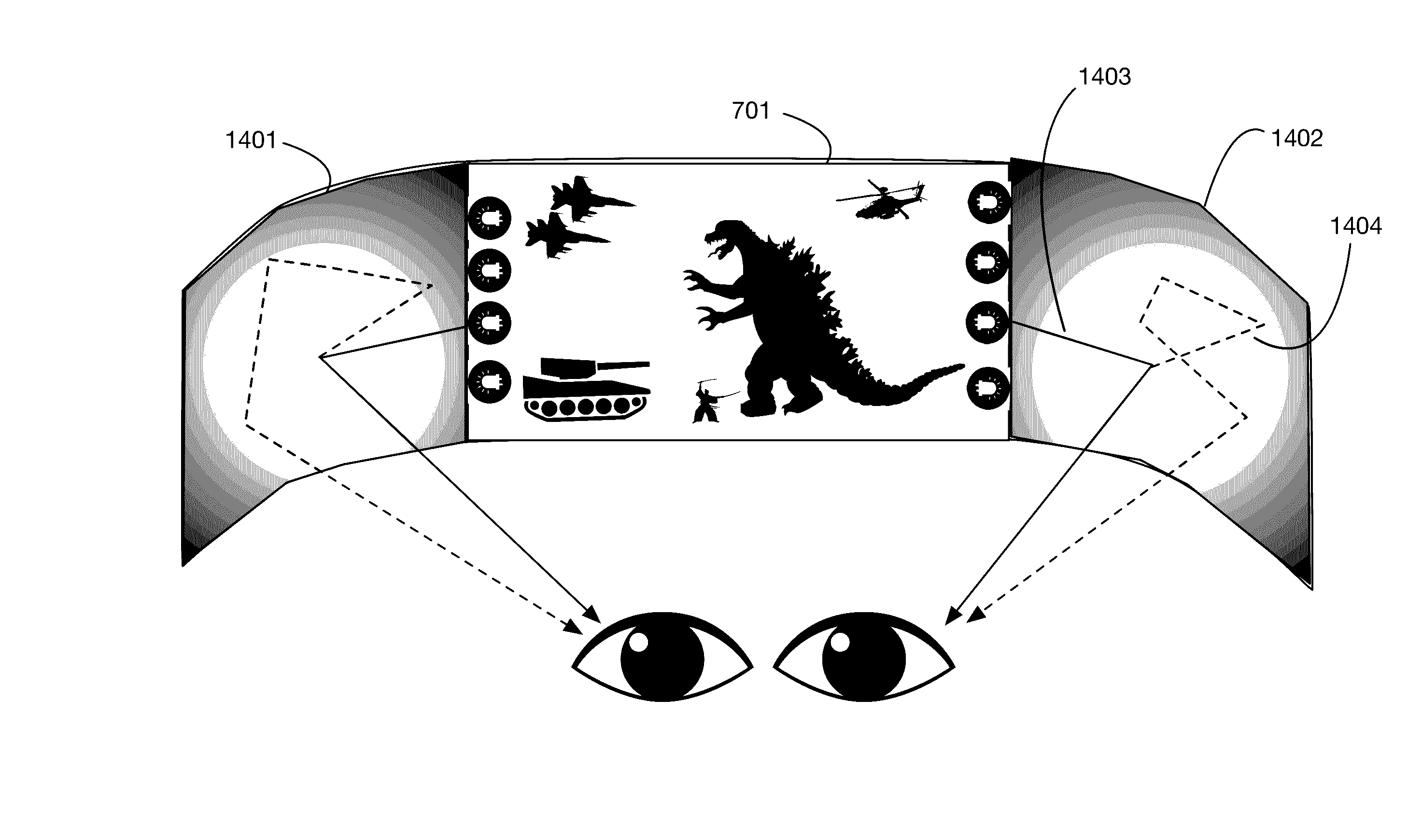
Wide field-of-view head mounted display system
InactiveUS9454010B1Reduce manufacturing costSimple geometryCathode-ray tube indicatorsEye diagnosticsFresnel lensWide area
A display system for a head mounted device that provides a wide field-of-view image to the user. The system may use a pair of displays angled relative to one another, and a lens or lenses between the displays and the user's eyes to generate a wide field-of-view image. Lenses may be for example gradient index lenses, Fresnel lenses, or holographic optical elements in order to provide significant and complex bending of light across the field of view with relatively thin lenses. The system may provide lower resolution images at the periphery of the user's field of view, using for example light emitting elements at the periphery that are directed by the lens or lenses towards the outside edges of the field of view.
Owner:KAYA DYNAMICS LLC
Miniaturized opto-electronic magnifying system
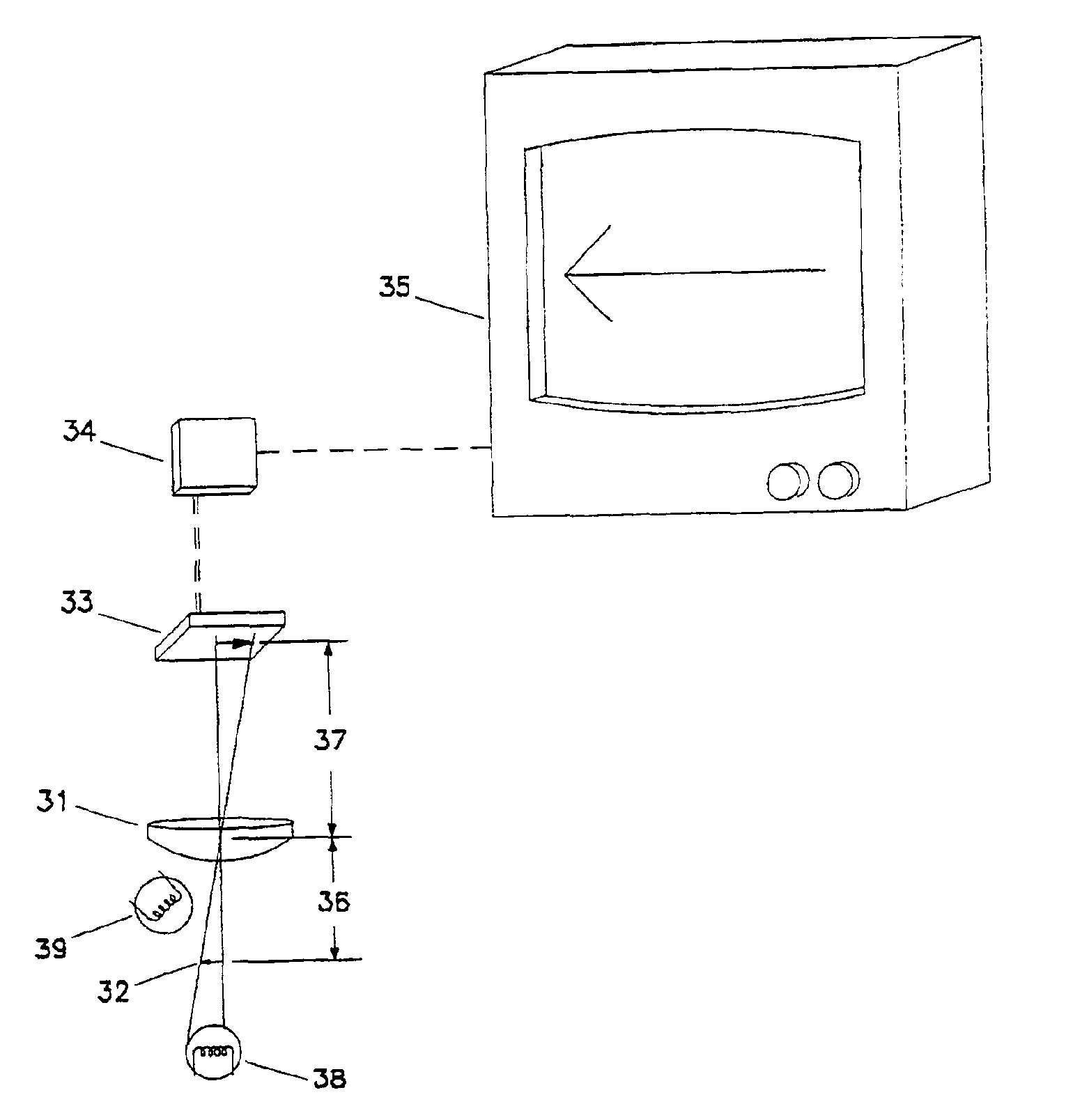
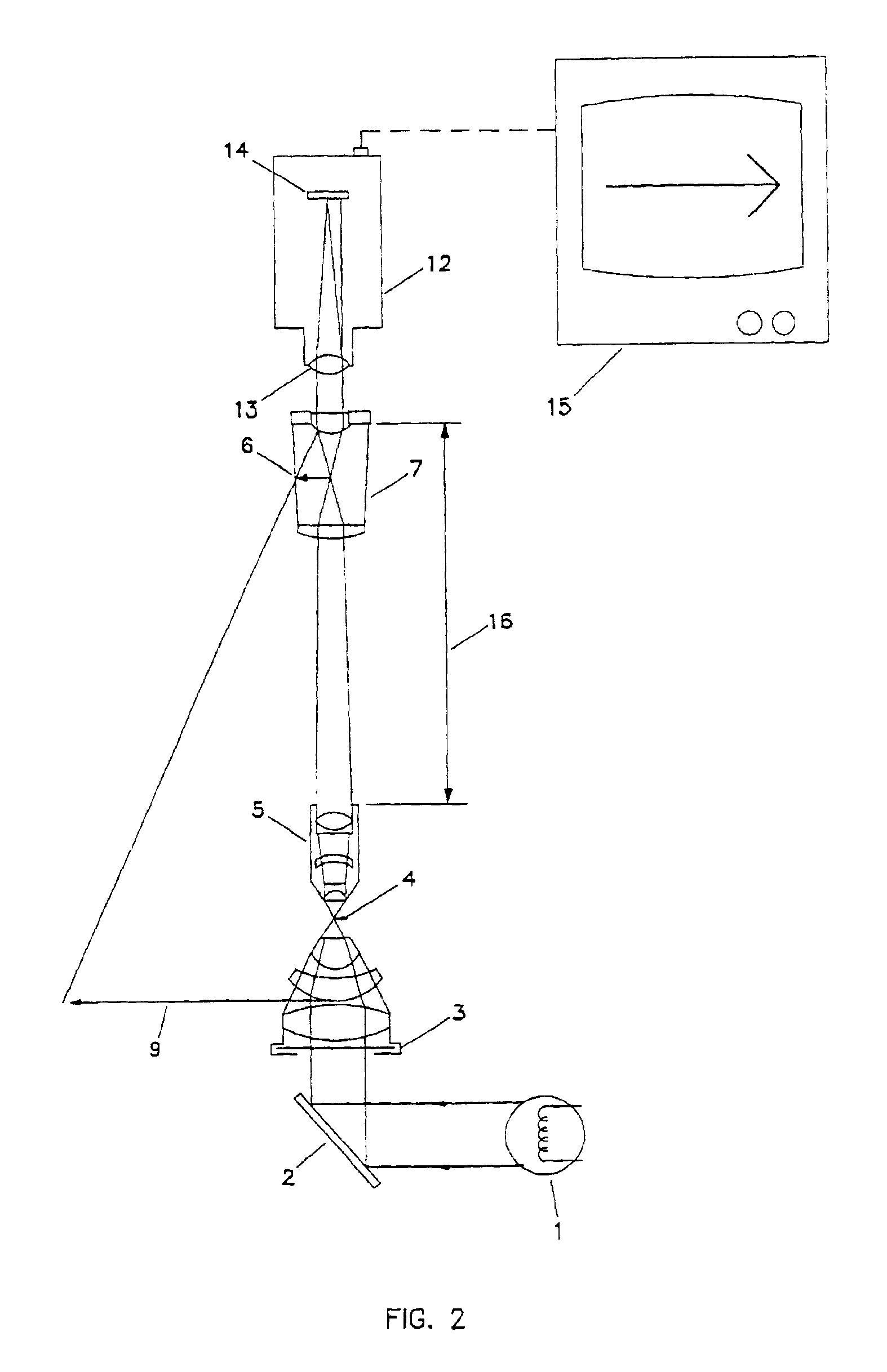
InactiveUS6907390B1Low costSignificant comprehensive benefitsMicroscopesAnalogue computers for heat flowAudio power amplifierPhotovoltaic detectors
An opto-electronic image magnifying system. The magnifiying system includes: a light source (38, 39) which illuminates an object to be viewed; a miniaturized opto-electronic magnifier module (MOM), made of a lens (31) and a photodetector array (32), which receives the light from the illuminated object; an electronic circuit (34) which receives the signal from the MOM; a video-monitor (35) which receives the magnified signal from the electronic circuit and displays the image. The opto-electronic image magnifying system allows for small objects or features of small objects to be observed in which historically compound microscopes or specialized optical viewing systems were required to observe the small objects.
Owner:SMITHS DETECTION
High luminance display apparatus using LCD panel
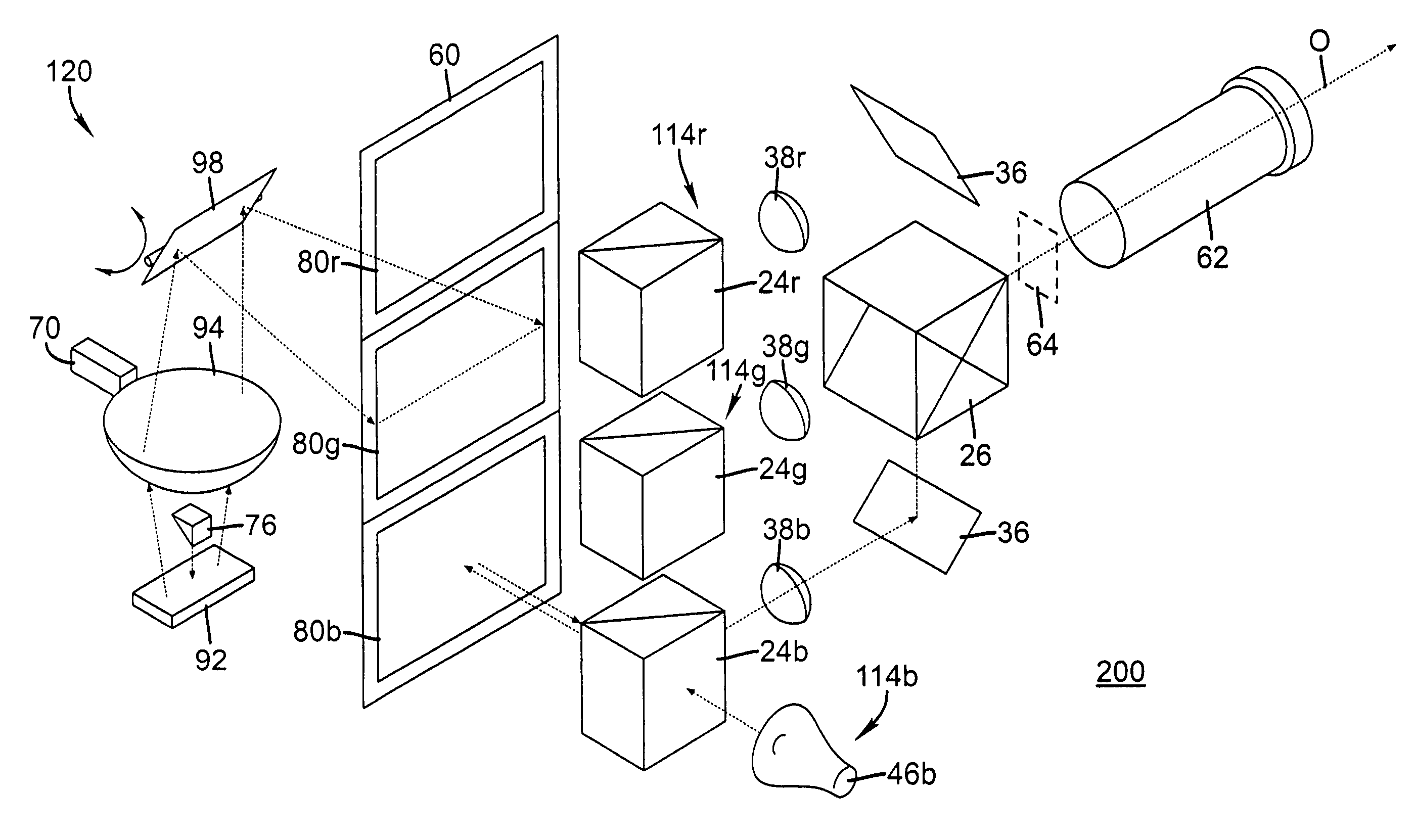
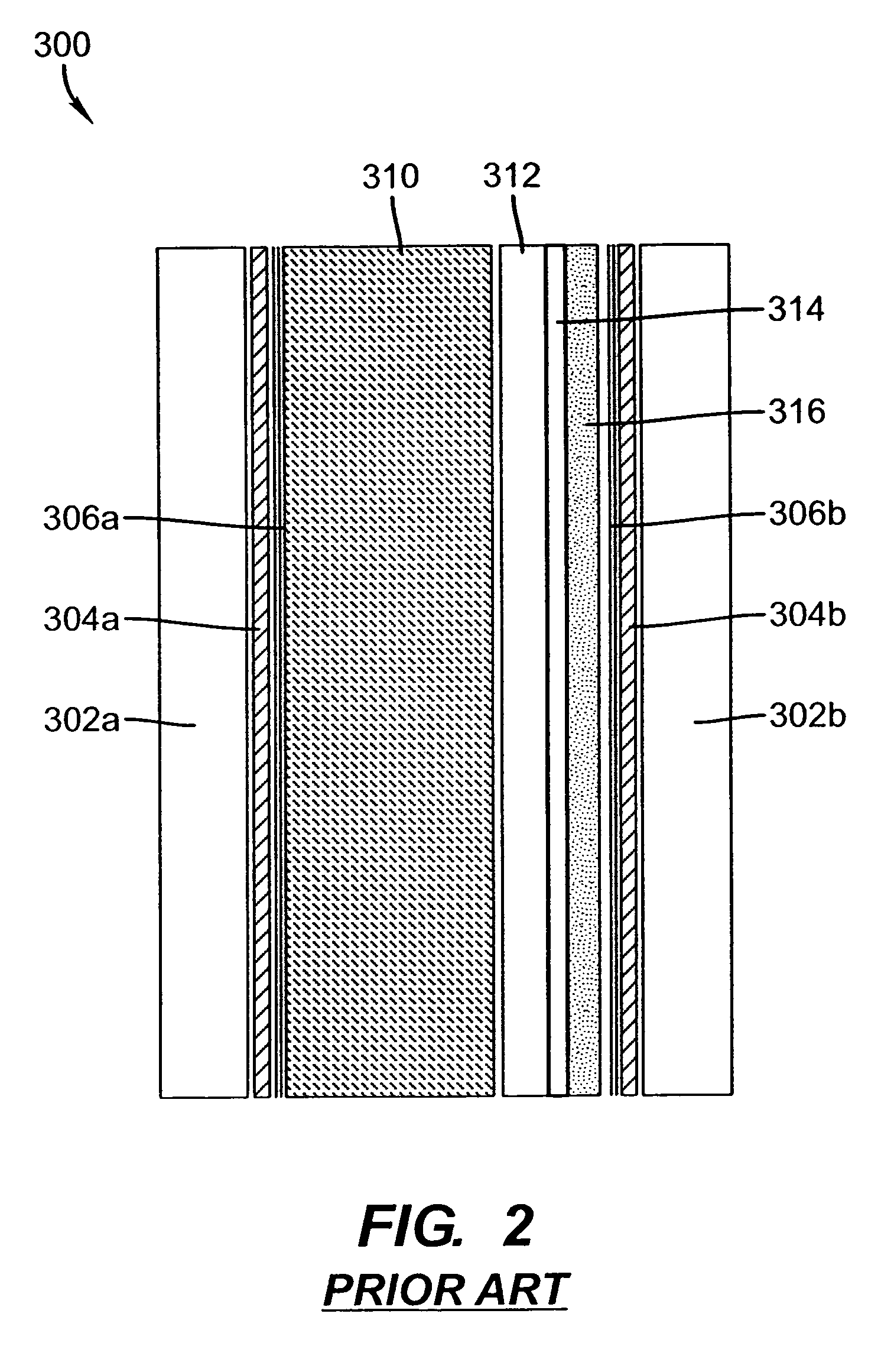
InactiveUS7621641B1Increase brightnessOptics SimplifiedTelevision system detailsProjectorsGratingLight beam
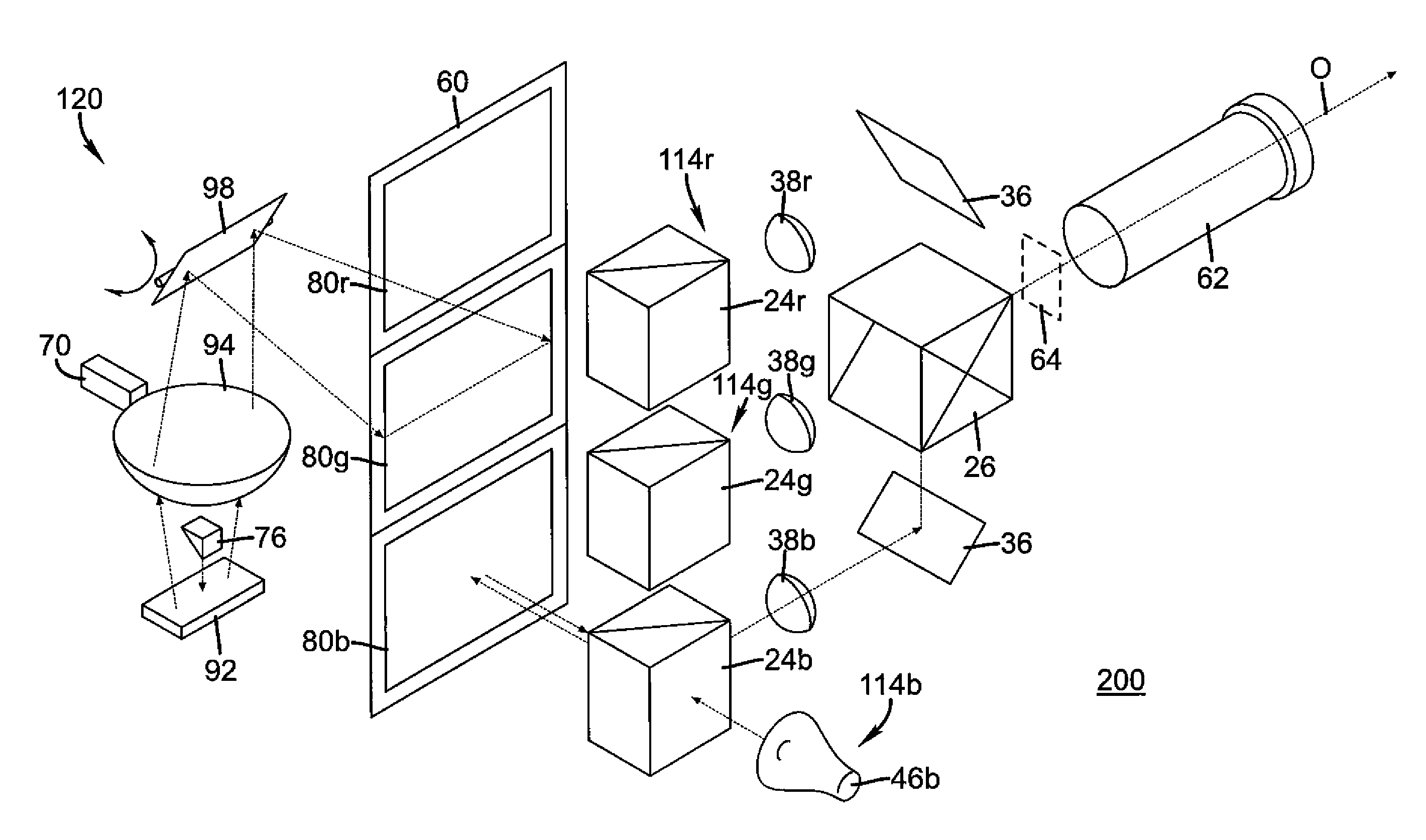
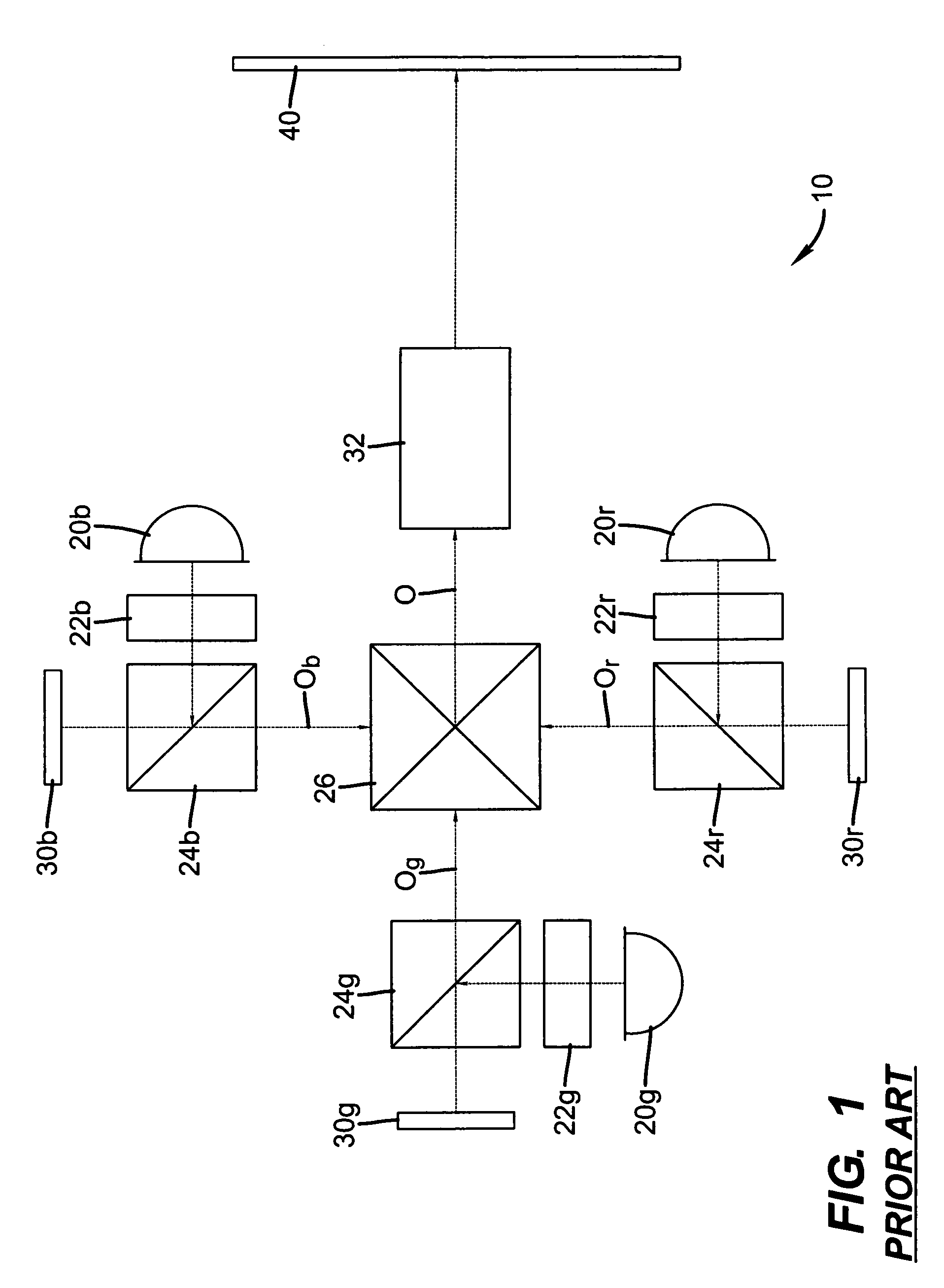
A projection apparatus (10) has an LC modulator panel (60) with photoresponsive layer, segmented into at least first, second, and third portions, each spatially separated. An image writing section (120) forms a first, second, or third image within the corresponding portion of the LC modulator panel by scanning successive lines of image writing light to energize the photoresponsive layer (316). The image writing section has at least one grating electromechanical system for modulating incident emission from a narrow-band light source (70) by providing diffracted and non-diffracted orders and a scanning element for directing a line of light thus formed toward the LC modulator panel to energize the photoresponsive layer. An illumination section (130) directs first, second, and third illumination beams for modulation by the respective portions of the LC modulator panel. A polarizing beamsplitter (24r, 24g, 24b), associated with each portion, polarizes and directs the illumination beams toward the LC modulator panel and directs modulated light toward a projection lens (62).
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Peripheral field-of-view illumination system for a head mounted display
ActiveUS20170038588A1Reduce manufacturing costSimple geometryLighting support devicesGeometric image transformationImage resolutionDisplay device
A display system for a head mounted device that illuminates the peripheral regions of the user's field of view to enhance an immersive experience. The system may use peripheral light emitters to the left and right of one or more central displays. Peripheral light emitters may provide lower resolution images, or only with vertical resolution, corresponding to the user's lower resolution vision in these peripheral regions. Reflective surfaces and lenses may be used to direct peripheral light into desired shapes and patterns. Rendering of peripheral light colors and intensities at each peripheral pixel may use approximations for improved performance since users may not be sensitive to precise color values in the peripheral regions.
Owner:KAYA DYNAMICS LLC
Control of optical connections in an optical network
InactiveUS7742395B1Optics SimplifiedEffective recoveryError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsOptical network unitComputer science
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
High luminance display apparatus using LCD panel
InactiveUS7559654B1Increase brightnessOptics SimplifiedTelevision system detailsProjectorsGratingLight beam
A projection apparatus (10) has an LC modulator panel (60) with photoresponsive layer (316), segmented into a first, second, and third portion, each spatially separated. An image writing section (120) forms a first, second, or third image within the corresponding portion of the LC modulator panel by scanning successive lines of image writing light to energize the photoresponsive layer. The image writing section has at least one grating electromechanical system for modulating a narrow-band light source (70) by providing diffracted and non-diffracted orders and a scanning element (98) for directing a line of light toward the LC modulator panel to energize the photoresponsive layer. An illumination section (130) directs the illumination beams for modulation by the LC modulator panel. Polarizing beamsplitter (24r, 24g, 24b), polarize and direct the illumination beams toward the LC modulator panel and directs modulated light toward projection lens (32).
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
New dual color laser device
ActiveCN106067653AOvercoming the problem of uneven modulation frequency stabilitySimple structureLaser detailsGratingGuide tube
The invention discloses a new dual color laser device which helps overcome a problem that rotation speed of an optical grating in a laser device of the prior art is not uniform enough for ensuring stability of laser device modulation frequency. The new dual color laser device comprises two discharge glass tubes each including a discharge cathode, a discharge anode, an air inlet opening, an extraction opening, a cathode harmonic resonance cavity adjusting device, an anode output adjusting device and working gas; the cathode harmonic resonance cavity adjusting device comprising: a cathode cavity head inner ring, a cathode cavity head outer ring, a cathode cavity head sealing gland, a directional guide tube, a corrugated tube, a stepped shaft and a reflecting mirror device positioned on an end, close to the cathode cavity head inner ring, of the stepped shaft. According to the new dual color laser device, via an adjusting structure designed at a reflecting mirror end of the laser device, resonance of a laser device harmonic resonance cavity can be caused, power of the laser device can be enabled to reach an ideal value to ensure that frequency change of two laser devices which run synchronously can generate a difference frequency signal of a controlled MHz, and a rotating optical grating can be replaced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Resolution proportional digital zoom
InactiveUS7746391B2Optics SimplifiedTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationCamera lensDigital zoom
A resolution proportional digital zoom system comprises a CCD imaging device with over a million pixels resolution. A standard fixed-1X optical lens is fitted to the imager. A communication channel with a limited bandwidth is used to transmit video. Such bandwidth is substantially less than the imager's full resolution times its frame rate. A user is provided with controls to pan and zoom within the imager's field of view. The pixel resolution is proportionally controlled such that video output data rate on the communication channel is optimal and held within maximum limits at any pan / zoom setting.
Owner:PULNIX AMERICA
System and method for resolving spatial orientation using intelligent optical selectivity
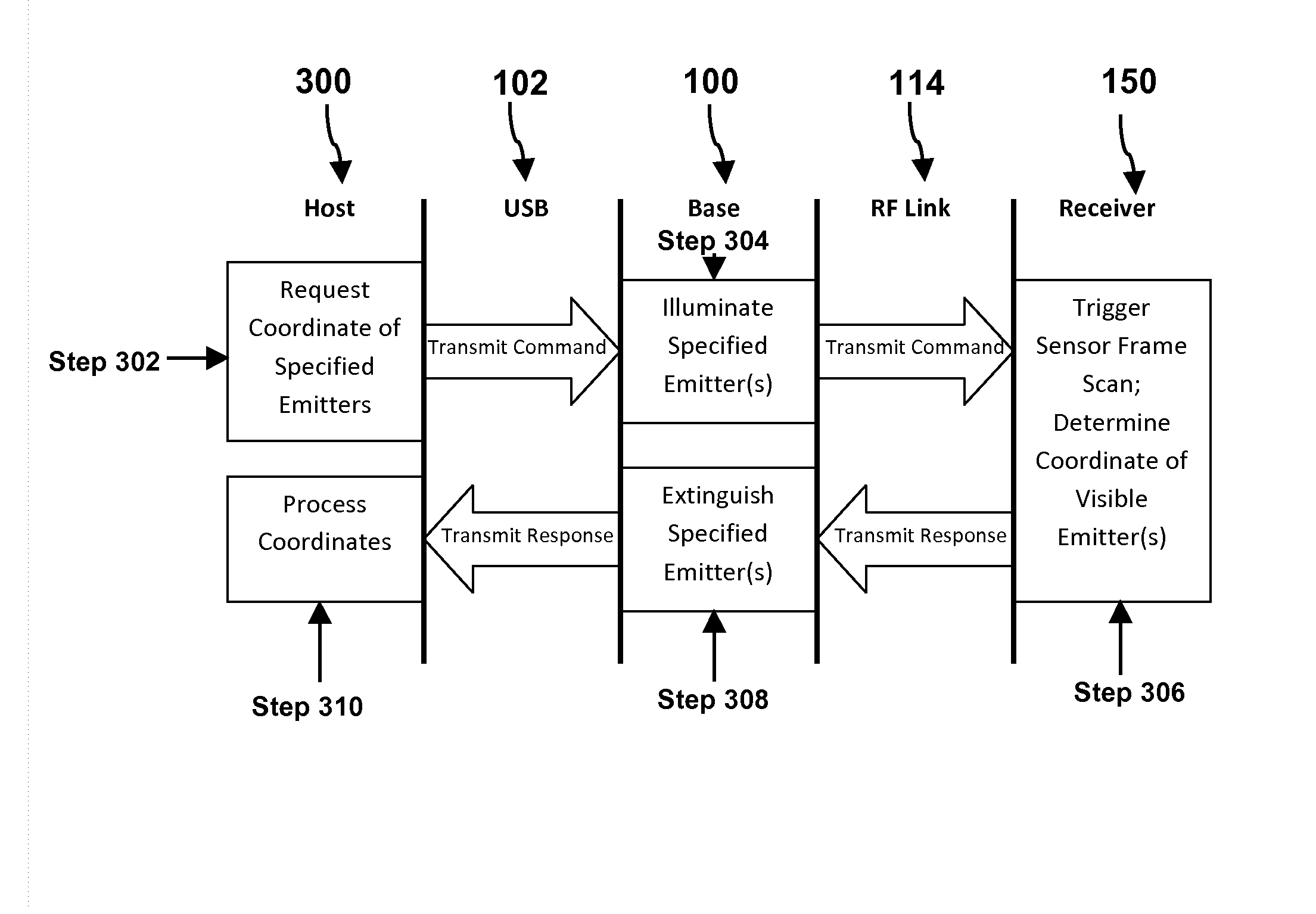
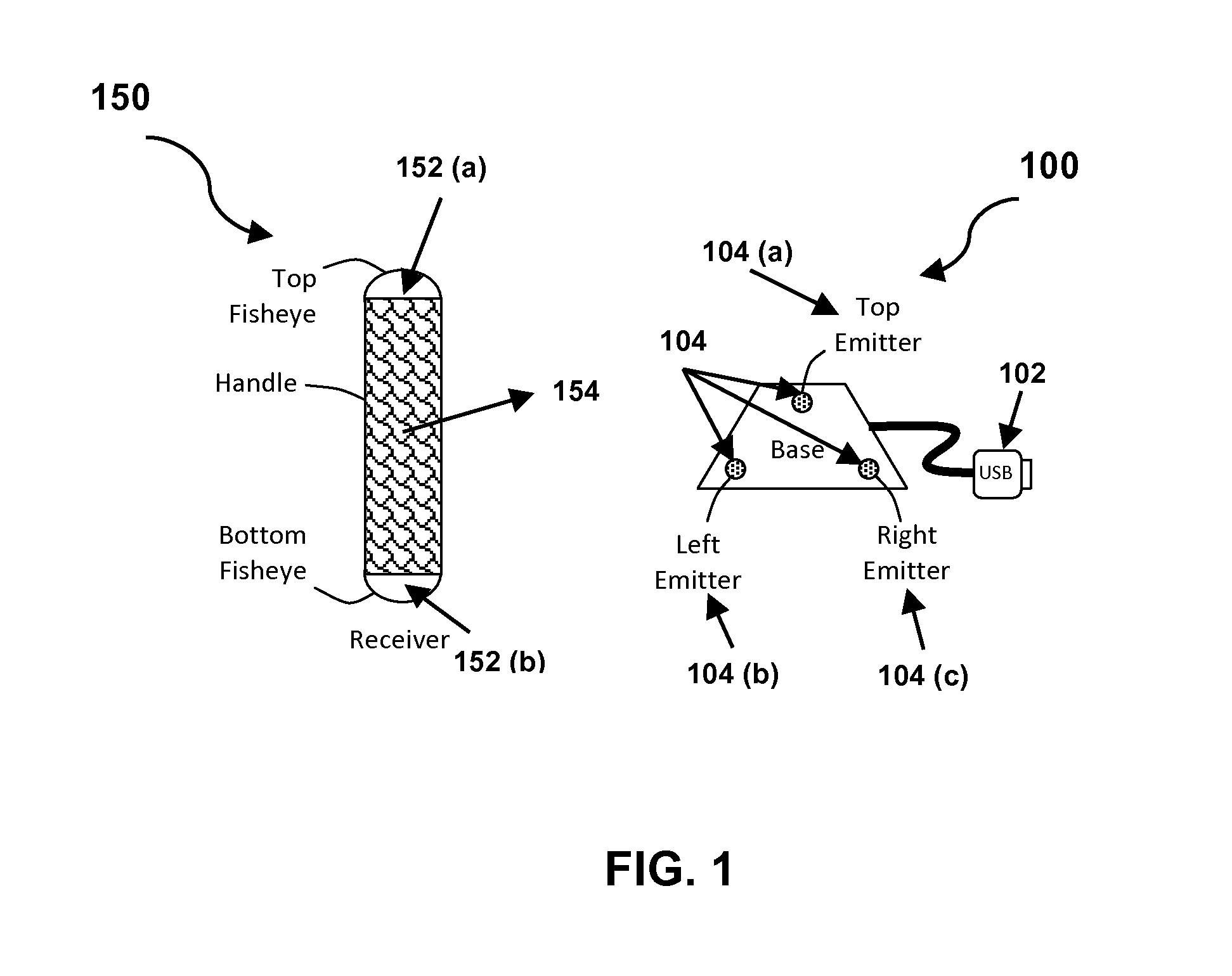
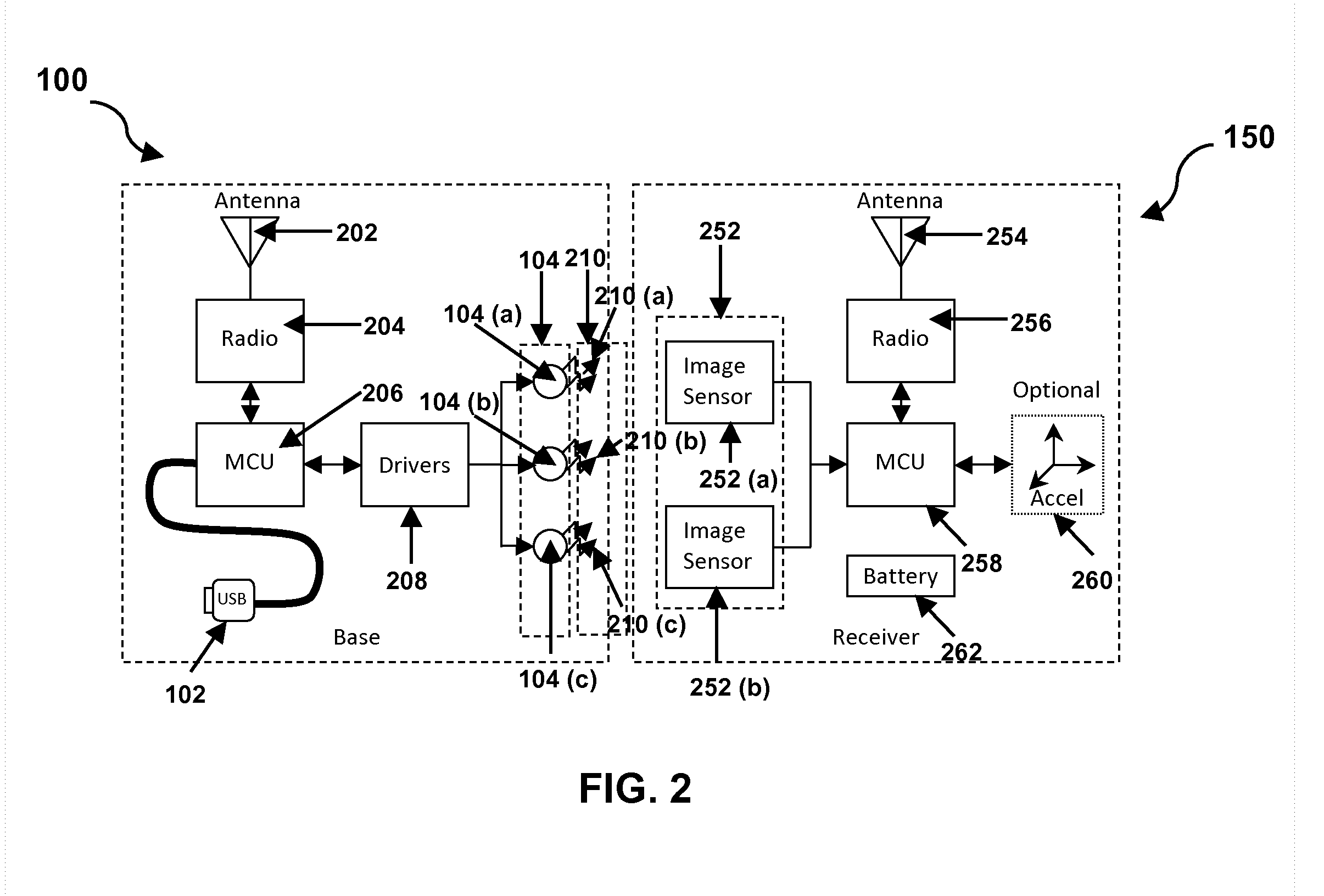
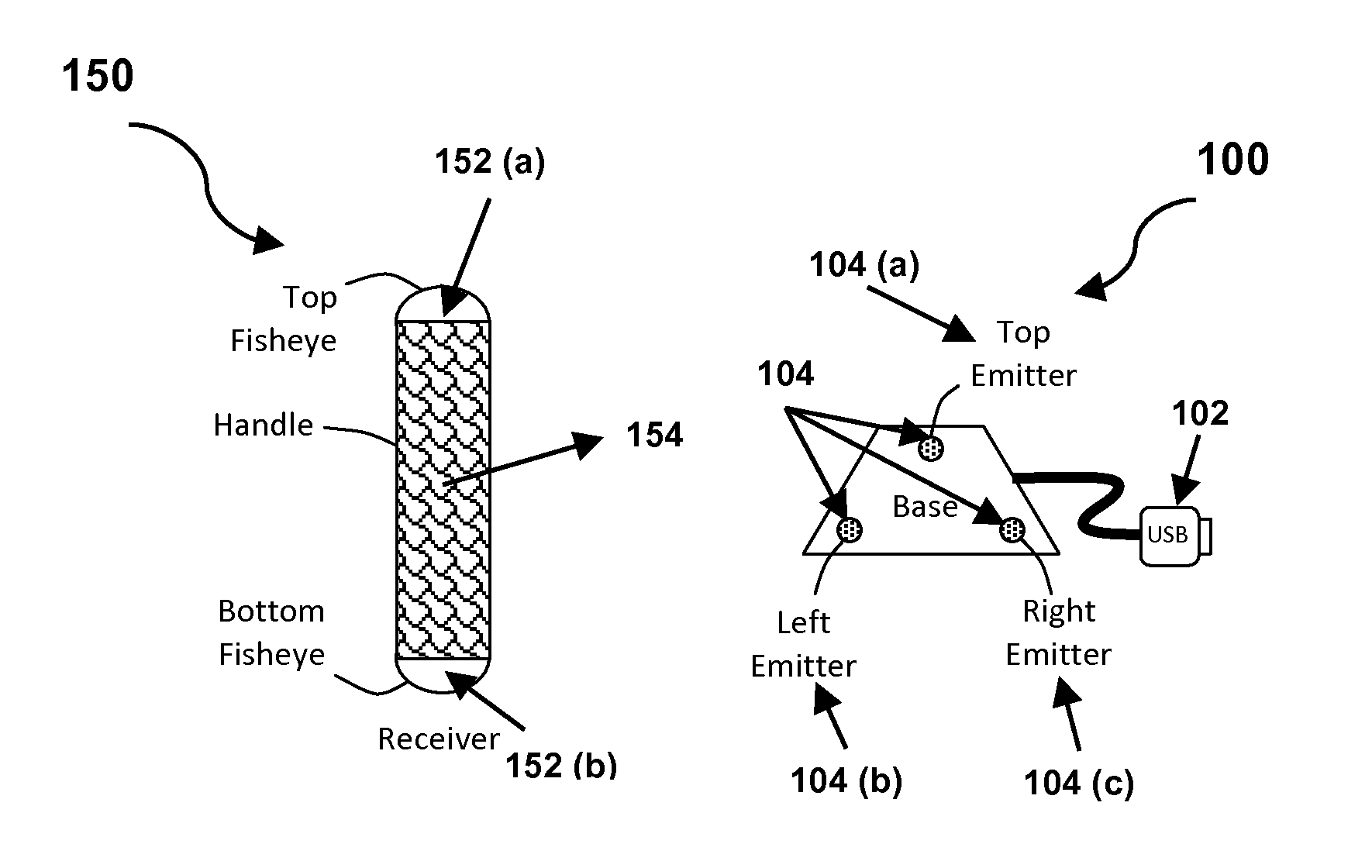
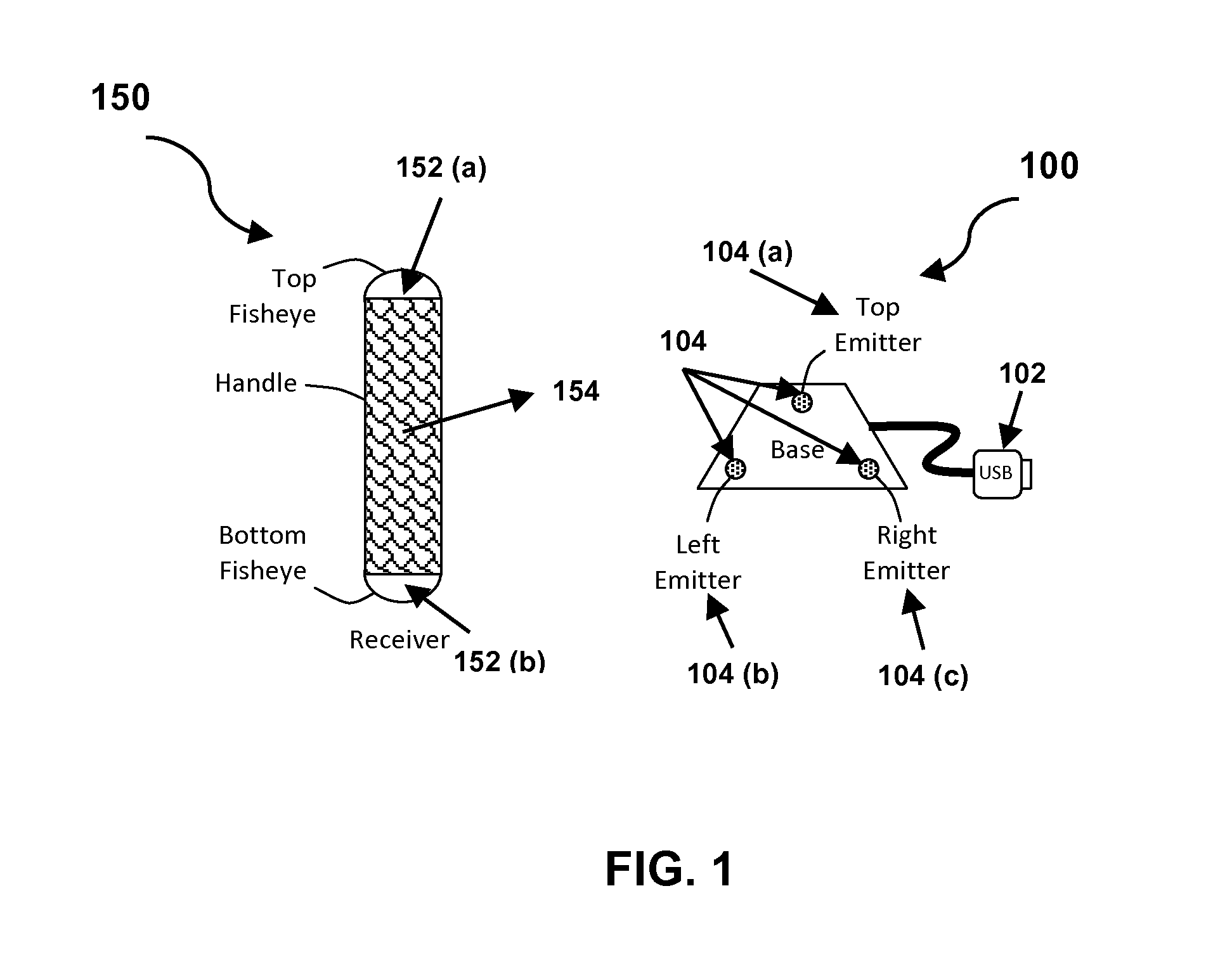
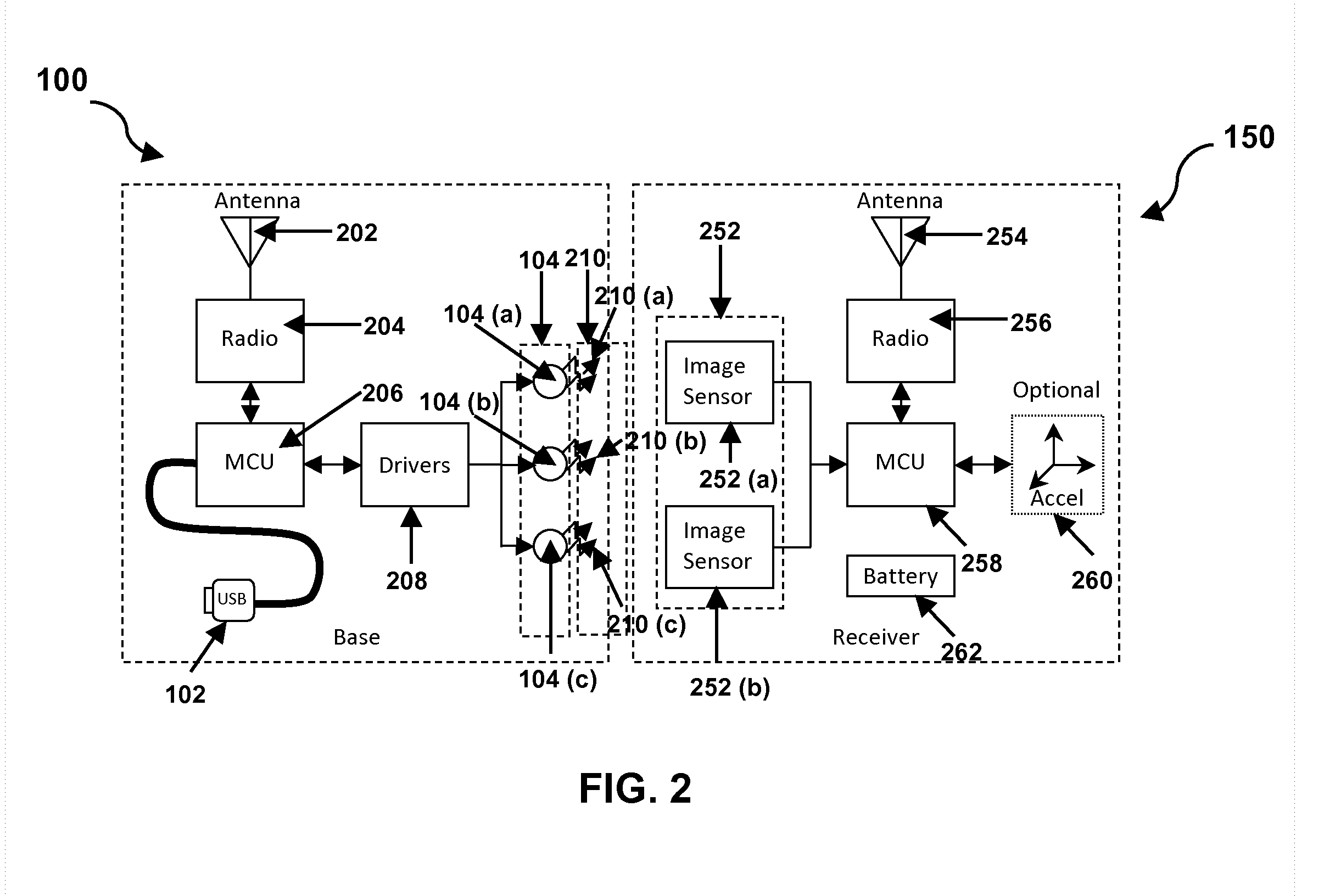
InactiveUS8428394B2Increase speedSimple circuitPosition fixationCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial OrientationsAccelerometer
The present invention provides a method and system for resolving complete free space orientation of an active receiving device at high speed using simple optics, trigonometry, simple circuitry, and using minimal processing power. The rapid triangulation of distance from the emitters, as well as resolution of rotational orientation, are determined by changing the contrast level in an infrared spectrum and by using wide angle lenses with greater than 180 degree hemispherical viewing angles. Furthermore, the system consists of an optional accelerometer, resident on the receiver, to dynamically adjust the image sensor frame rate.
Owner:KRIETER MARCUS
Microwindow device
InactiveUS20120086999A1Optics SimplifiedMore compact in sizeSemiconductor devicesOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorFill factor
The present invention provides a transmissive Spatial Light Modulator with fast response speed and higher brightness using micro-windows having switching transistors on said window so that the fill factor of light transferring area can be maximized. Conventional systems have transistors out of windows which substantially reduce the area to pass incoming light, because transistors are usually opaque and block light transmission. Transmissive Spatial Light Modulator requires simpler and smaller optics than reflective Spatial Light Modulator.
Owner:ISHII FUSAO
Systems and methods for handheld projection displays
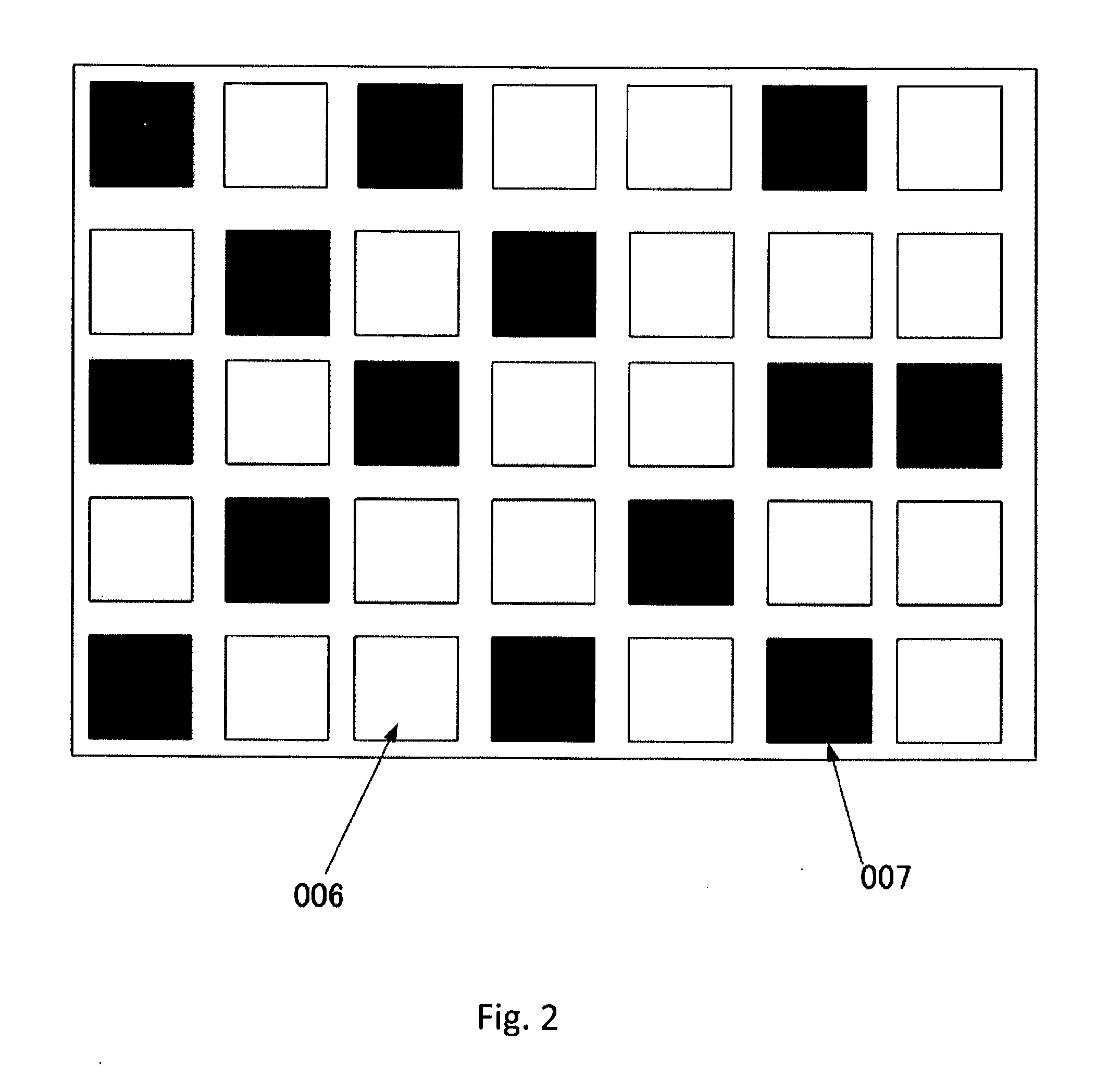
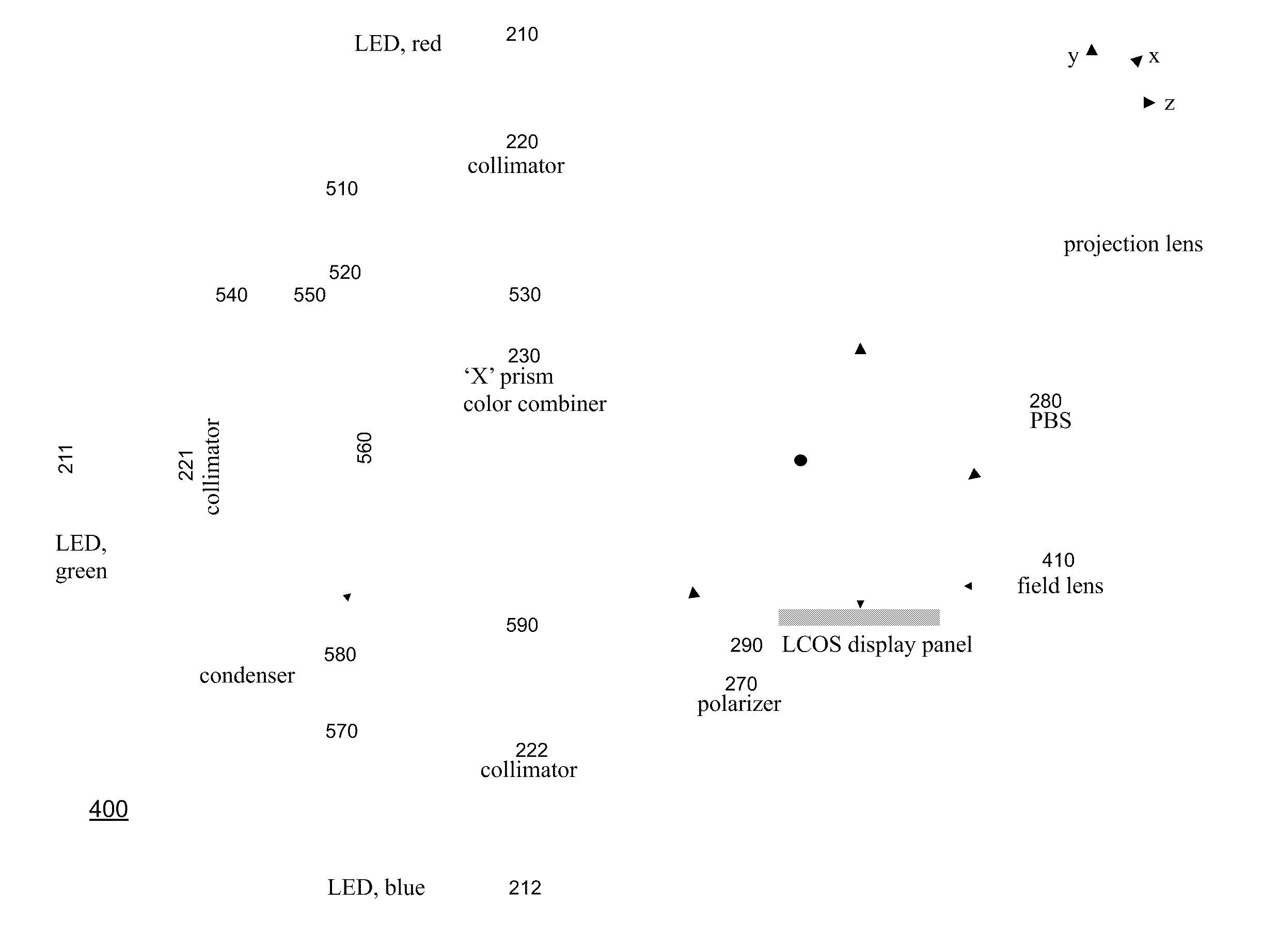
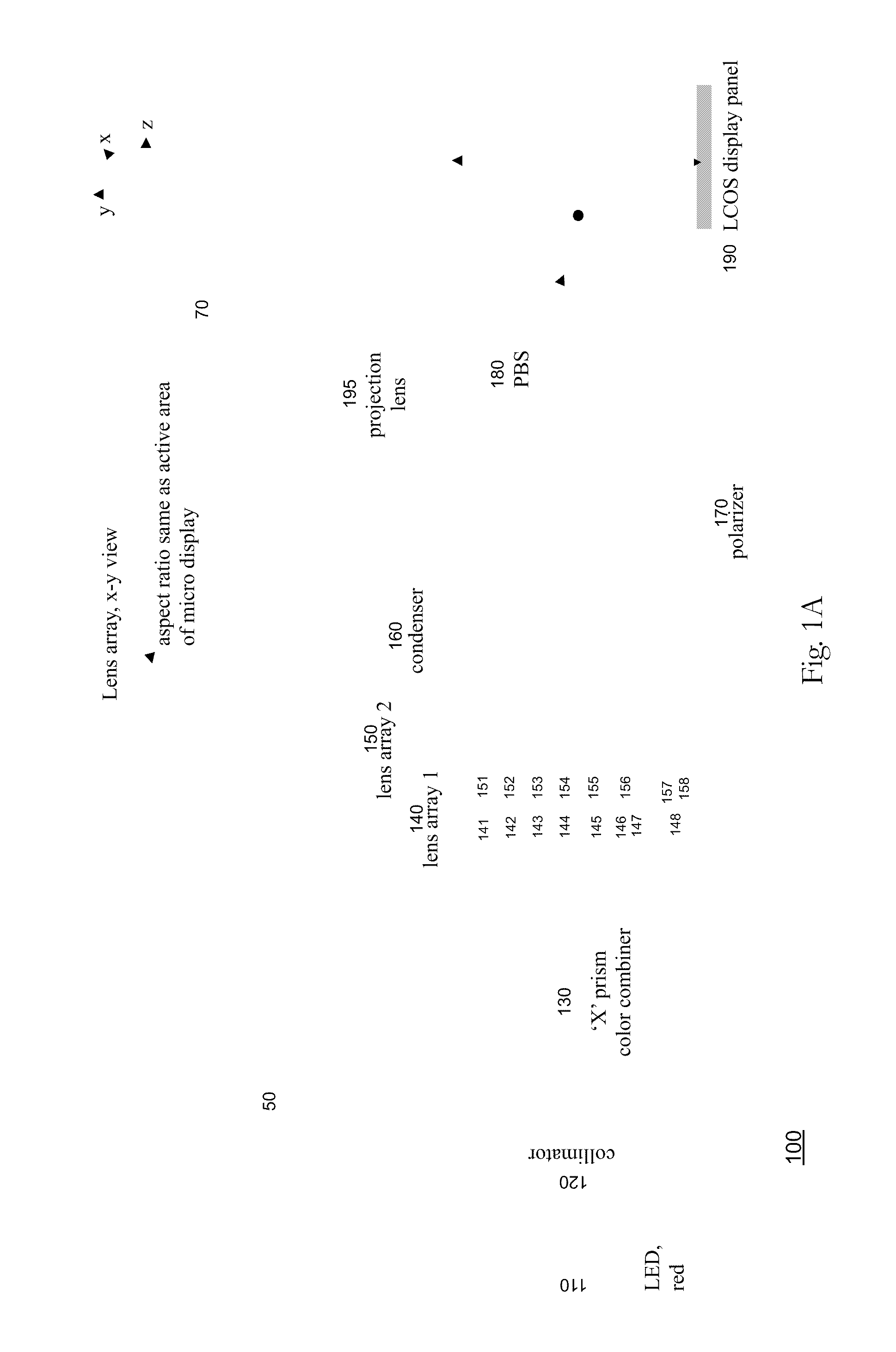
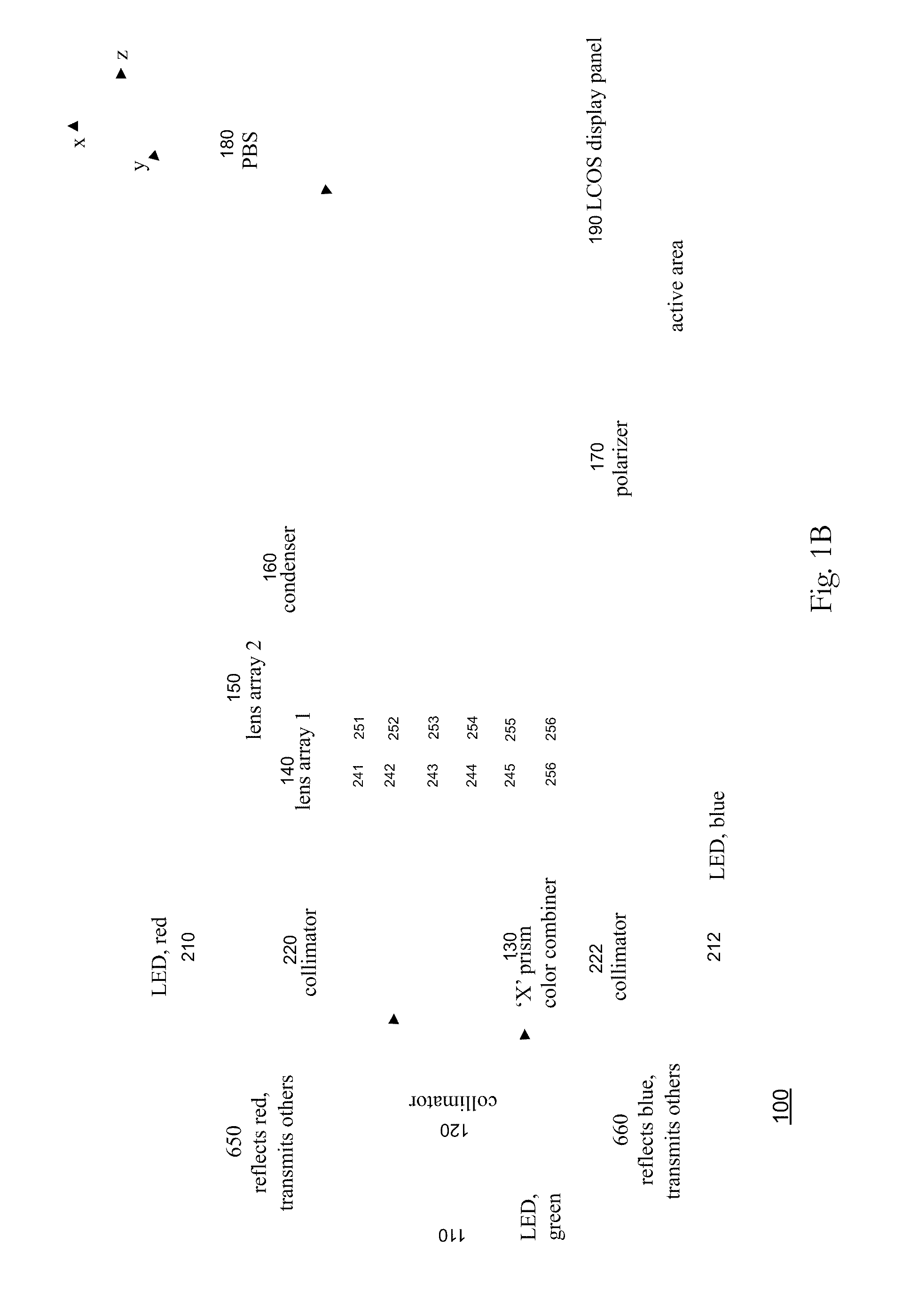
Systems and methods are described employing a first lens array and a second lens array that are separated by one focal length that receives a plurality of colors signals from an X-prism and transmits to a condenser for overlapping lenslet images onto a display panel, such as a LCOS or LCD display panel. The first lens array includes a plurality of lenslets where each lenslet in the first lens array corresponds with each lenslet in a plurality of lenslets in the second lens array. The lenslets can be either refractive, defractive, or a combination of refractive and defractive.
Owner:PHOTONEDGE
System and method for resolving spatial orientation using intelligent optical selectivity
InactiveUS20110293182A1Increase speedSimple circuitPosition fixationCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial OrientationsAccelerometer
The present invention provides a method and system for resolving complete free space orientation of an active receiving device at high speed using simple optics, trigonometry, simple circuitry, and using minimal processing power. The rapid triangulation of distance from the emitters, as well as resolution of rotational orientation, are determined by changing the contrast level in an infrared spectrum and by using wide angle lenses with greater than 180 degree hemispherical viewing angles. Furthermore, the system consists of an optional accelerometer, resident on the receiver, to dynamically adjust the image sensor frame rate.
Owner:KRIETER MARCUS
Lighting device for vehicles having a micro-optical array including at least a first subarray and a second subarray with different partial light distributions
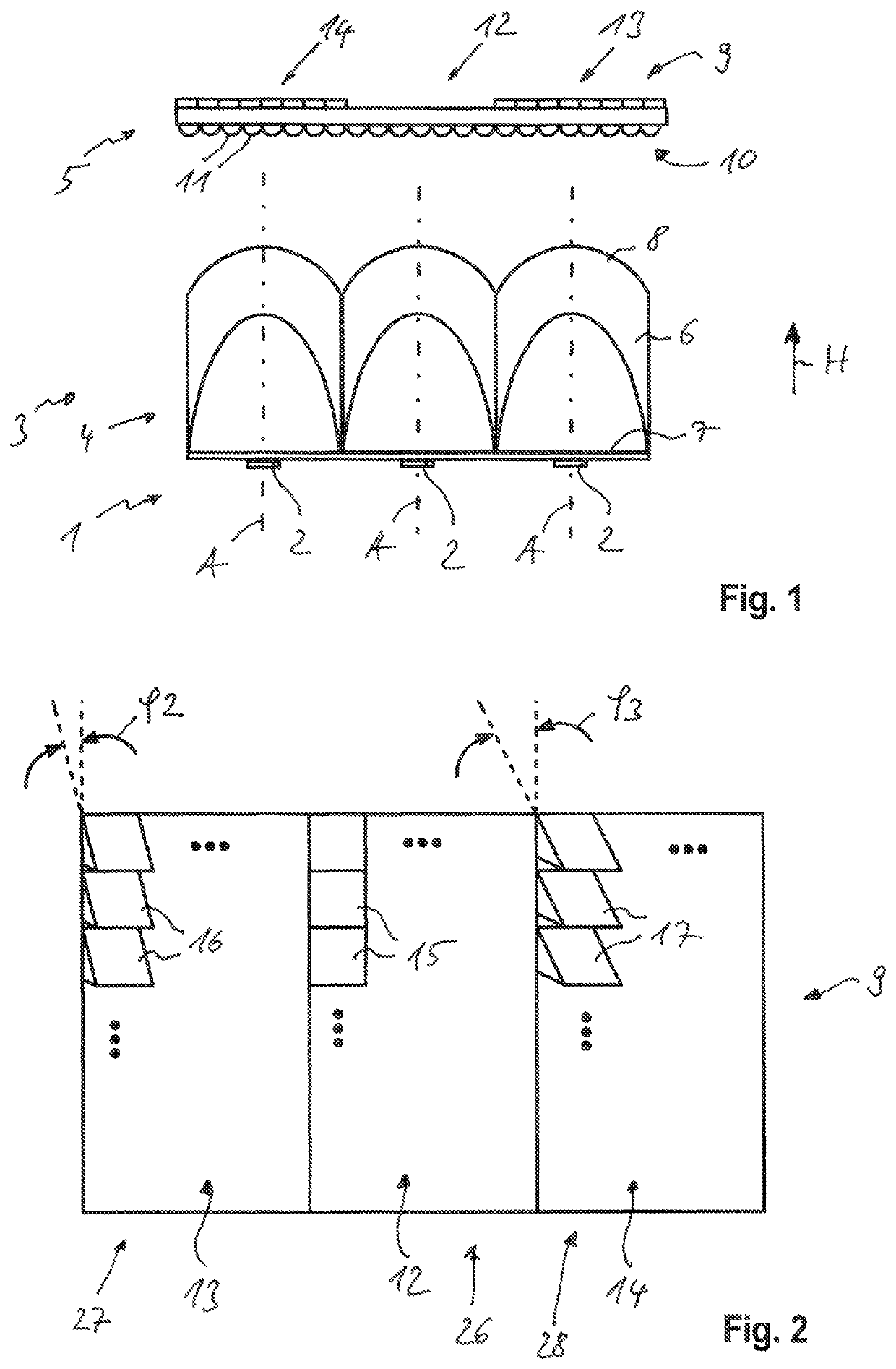
ActiveUS10718483B2Reduce the overall heightSmall heightVehicle headlampsLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:HELLA KG HUECK & CO
Control of optical connections in an optical network
InactiveUS7920484B1Optics SimplifiedEnhance layeringMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer networkEngineering
A method for lightpath provisioning in a reconfigurable optical network that comprises the steps of naming each network addressable element in the reconfigurable optical network, determining current resources therein, determining current topology therein, requesting establishment of a lightpath, and allocating the lightpath. A system for lightpath provisioning in a reconfigurable optical network is also provided, which includes naming each network addressable element in the reconfigurable optical network, determining current topology in the reconfigurable optical network, determining current resources in the reconfigurable optical network, requesting establishment of a lightpath, allocating the lightpath and removing the lightpath upon completion.
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
Advanced Illumination System for Use in Microlithography
InactiveUS20070146674A1Continuous changeOptics SimplifiedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLighting systemNumerical aperture
A system for microlithography comprises an illumination source; an illumination optical system including, in order from an objective side, (a) a first diffractive optical element that receives illumination from the illumination source, (b) a zoom lens, (c) a second diffractive optical element, (d) a condenser lens, (e) a relay lens, and (f) a reticle, and a projection optical system for imaging the reticle onto a substrate, wherein the system for microlithography provides a zoomable numerical aperture.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Single-shot spectral imager
ActiveUS8351031B2Easy to useImprove efficiencyRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using refracting elementsMultiplexingSpatial light modulator
A single-shot spectral imager or imaging system which acquires multiplexed spatial and spectral data in a single snapshot with high optical collection efficiency and with the speed limited only by the readout time of the detector circuitry. The imager uses dispersive optics together with spatial light modulators to encode a mathematical transform onto the acquired spatial-spectral data. A multitude of encoded images is recorded simultaneously on a focal plane array and subsequently decoded to produce a spectral / spatial hypercube.
Owner:SPECTRAL SCI
Lighting device for vehicles
ActiveUS20190301699A1Reduce the overall heightSave installation spaceVehicle headlampsLighting and heating apparatusOptoelectronicsLight source
A lighting device for vehicles having a light source unit containing a number of light sources, having an optical unit that is arranged in front of the light source unit in the primary direction of emission for generating a predetermined light distribution, wherein the optical unit has a micro-optical array with a multiplicity of micro-optical elements arranged in a matrix, wherein a first subarray of the micro-optical array is designed without optics to form a first partial light distribution with a light / dark boundary and with a luminance maximum in a region close to the light / dark boundary, in that at least a second subarray of the micro-optical array has such micro-optical elements. A second partial light distribution is formed below the first partial light distribution in the vertical direction. The light distribution is formed by superimposing the first partial light distribution and the additional partial light distribution.
Owner:HELLA KG HUECK & CO
Inspection apparatus
InactiveUS8542354B2Improve throughputHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionCatoptricsFourier transform on finite groups
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
High-energy laser system intercepting a target and method thereof
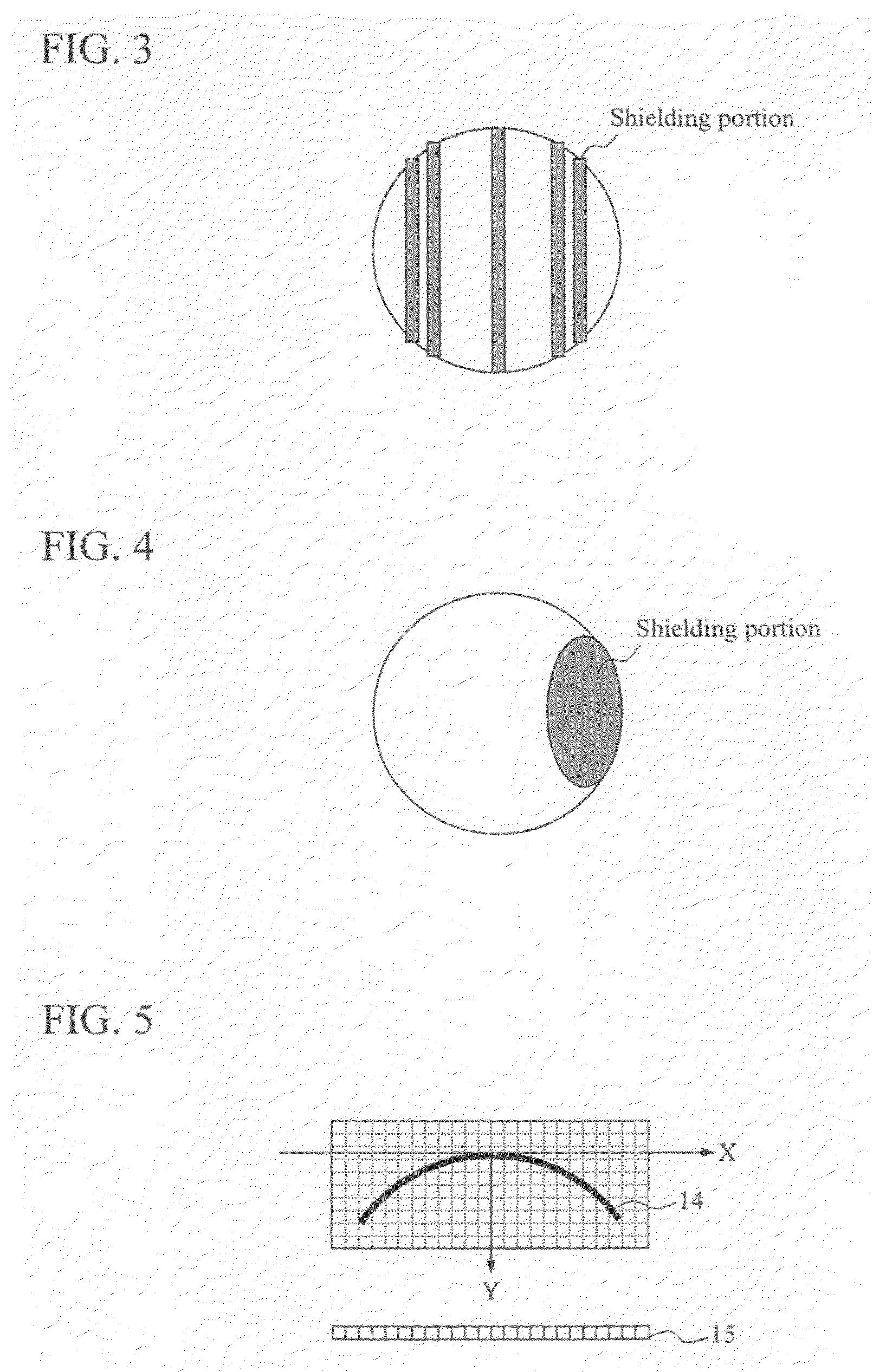
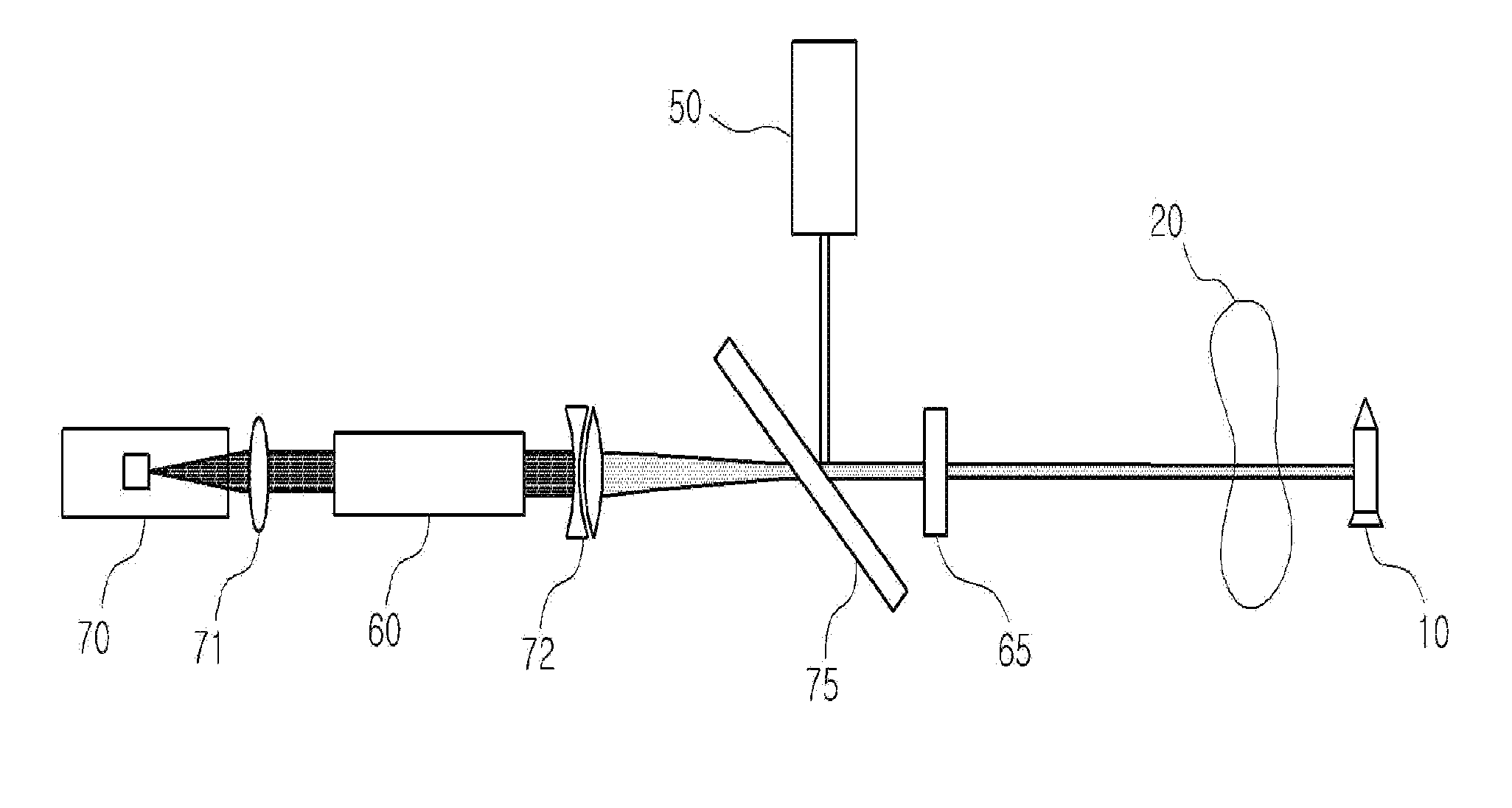
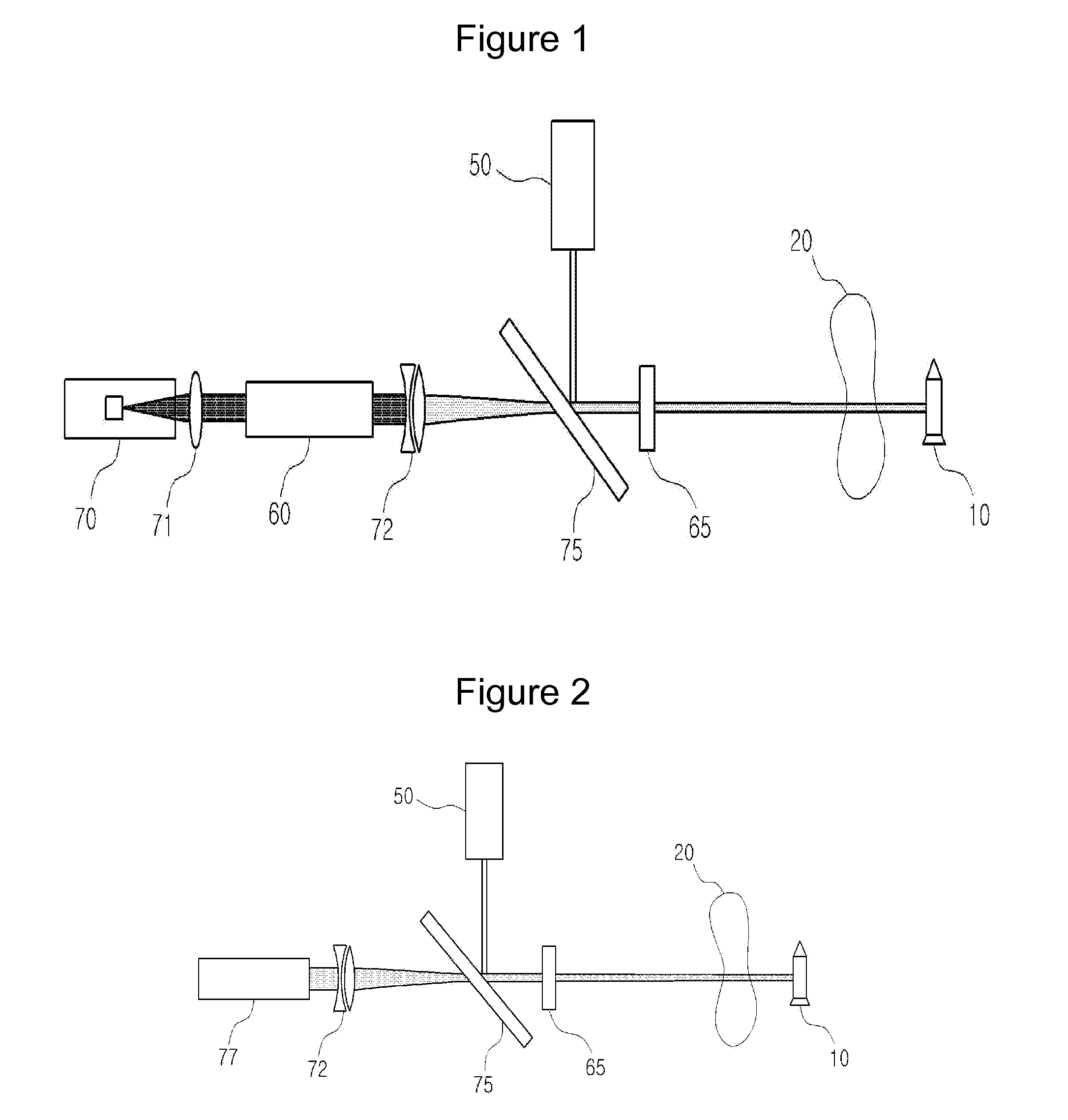
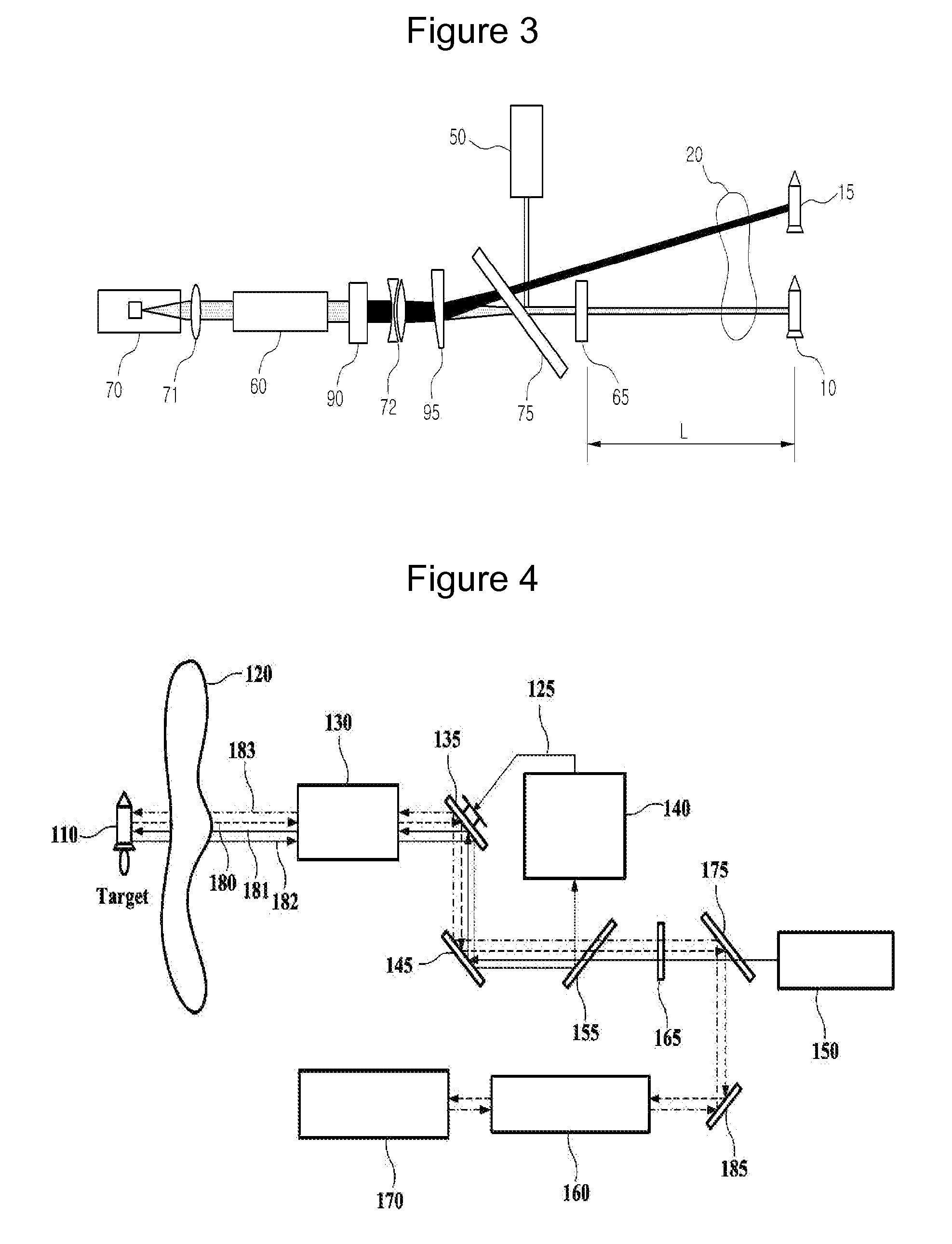
ActiveUS9074853B2Control speedOptics SimplifiedDevices using optical meansWeapons typesOptoelectronicsHigh energy laser
A high-energy laser system intercepting a target using a phase conjugate mirror includes a laser oscillator which generates a laser beam irradiated to the target, a light amplifier which receives the laser beam irradiated to and reflected by the target so as to amplify it, a phase conjugate mirror which reflects the amplified laser beam. And the laser beam that is reflected by the phase conjugate mirror is amplified again in the light amplifier, and then irradiated to the target so as to intercept the target.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
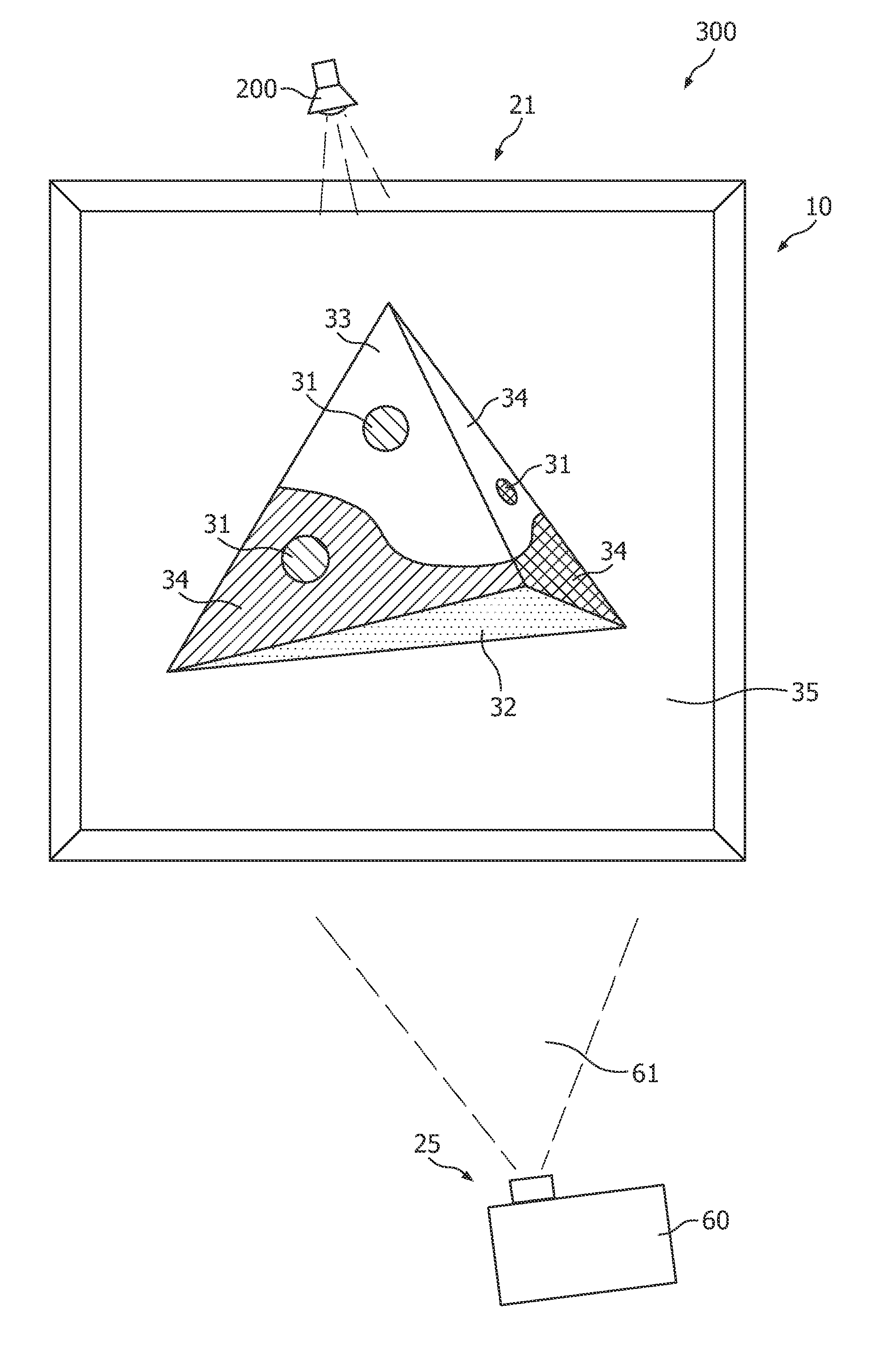
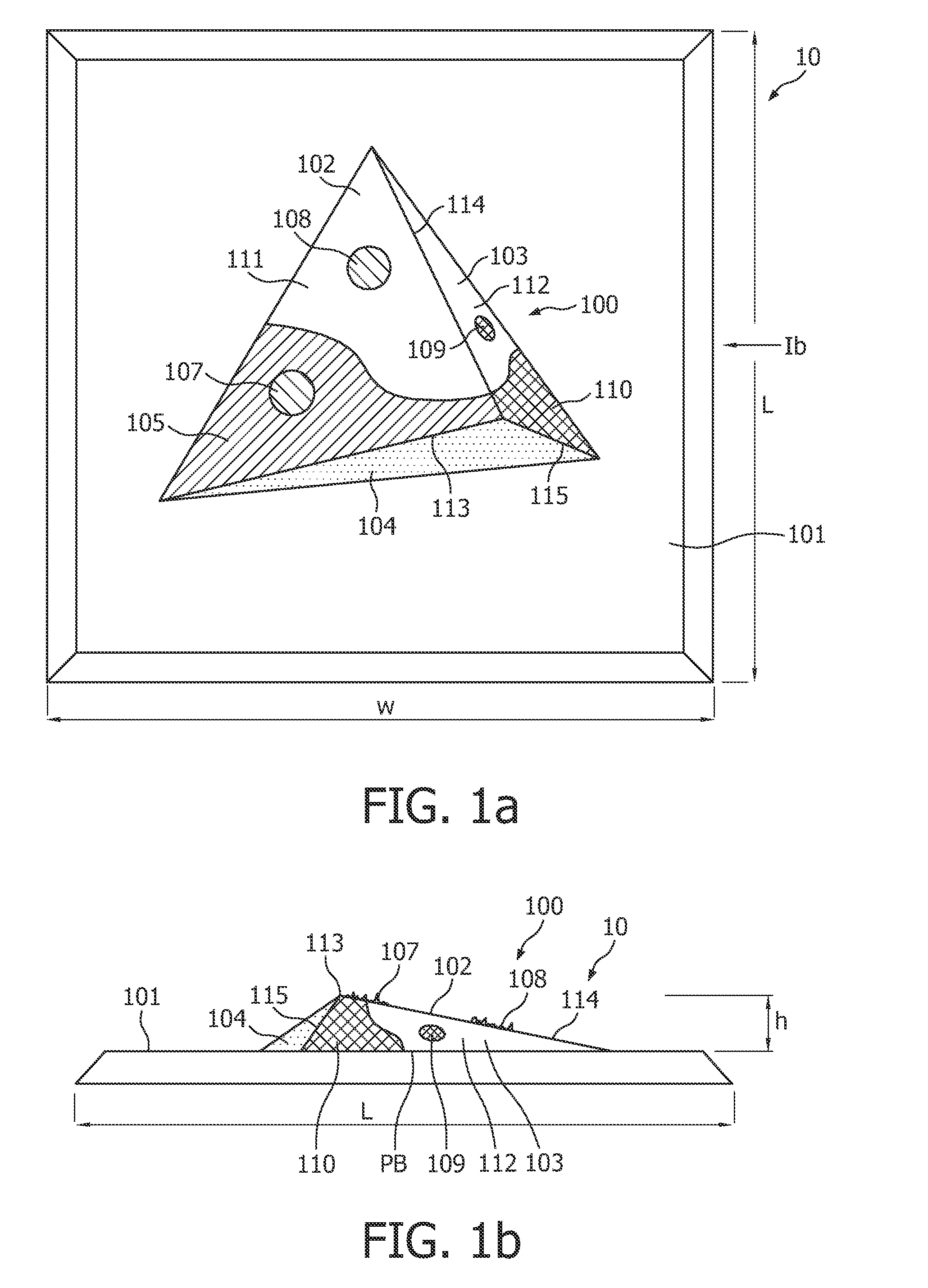
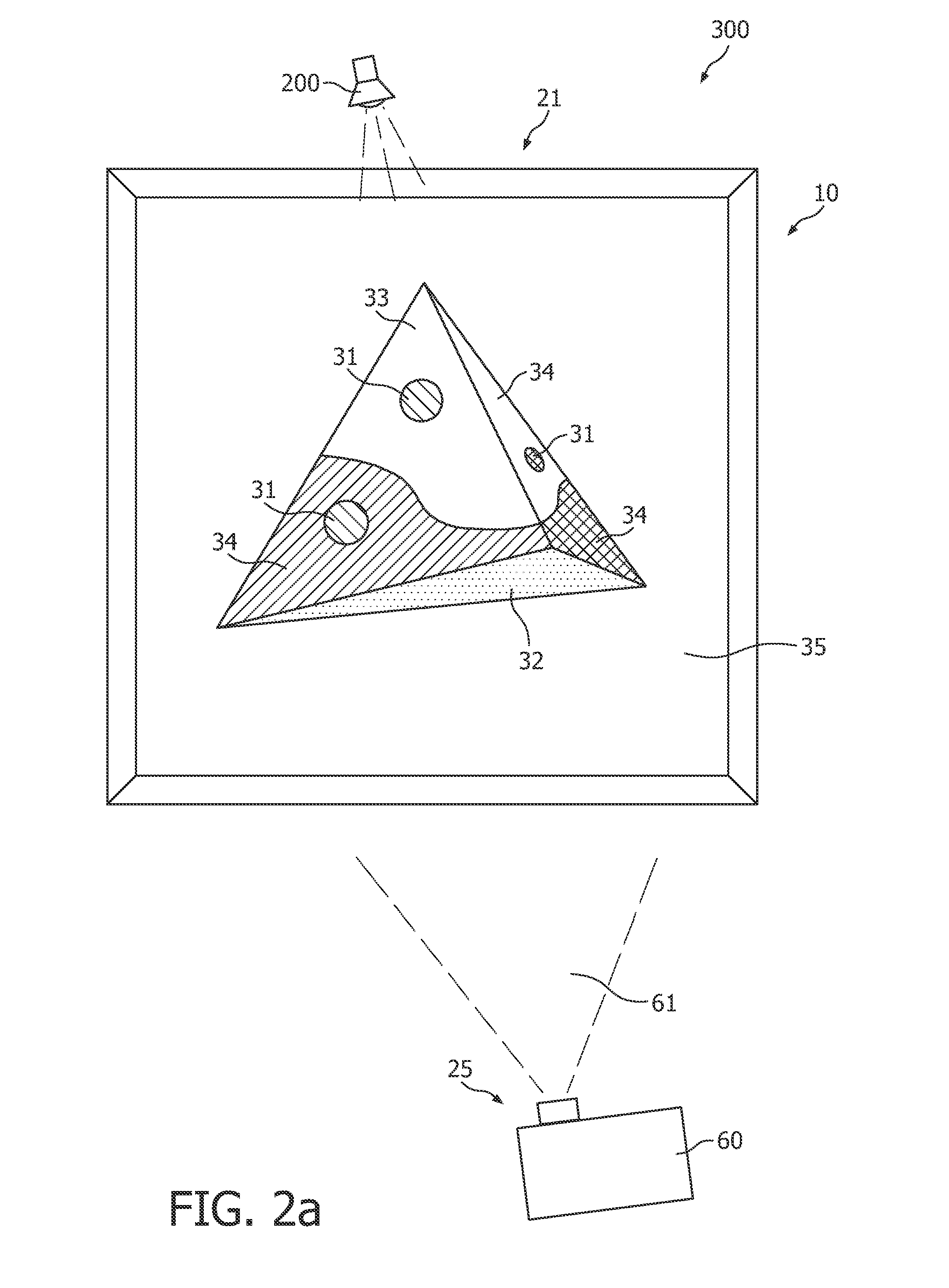
Method of illuminating a 3D object with a modified 2D image of the 3D object by means of a projector, and projector suitable for performing such a method
InactiveUS8619131B2Easy to createEasy to implementProjectorsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Radiology
The invention provides a method of illuminating a 3D object 10 with a modified 2D image of the 3D object 10. Further, the invention provides a dedicated projector 40 for performing this method. This projector 40 further comprises an image sensor 60 to capture a 2D image of the object, which may, after modification into the modified 2D image, be projected by the projector 40 on the 3D object 10.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
A New Two-color Laser
The invention discloses a new dual color laser device which helps overcome a problem that rotation speed of an optical grating in a laser device of the prior art is not uniform enough for ensuring stability of laser device modulation frequency. The new dual color laser device comprises two discharge glass tubes each including a discharge cathode, a discharge anode, an air inlet opening, an extraction opening, a cathode harmonic resonance cavity adjusting device, an anode output adjusting device and working gas; the cathode harmonic resonance cavity adjusting device comprising: a cathode cavity head inner ring, a cathode cavity head outer ring, a cathode cavity head sealing gland, a directional guide tube, a corrugated tube, a stepped shaft and a reflecting mirror device positioned on an end, close to the cathode cavity head inner ring, of the stepped shaft. According to the new dual color laser device, via an adjusting structure designed at a reflecting mirror end of the laser device, resonance of a laser device harmonic resonance cavity can be caused, power of the laser device can be enabled to reach an ideal value to ensure that frequency change of two laser devices which run synchronously can generate a difference frequency signal of a controlled MHz, and a rotating optical grating can be replaced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Microwindow device
InactiveUS8654435B2Fast and bright transmissive display configurationOptics SimplifiedNon-linear opticsSemiconductor devicesSpatial light modulatorFill factor
The present invention provides a transmissive Spatial Light Modulator with fast response speed and higher brightness using micro-windows having switching transistors on said window so that the fill factor of light transferring area can be maximized. Conventional systems have transistors out of windows which substantially reduce the area to pass incoming light, because transistors are usually opaque and block light transmission. Transmissive Spatial Light Modulator requires simpler and smaller optics than reflective Spatial Light Modulator.
Owner:ISHII FUSAO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com