Patents
Literature
73results about How to "Reduce lighting brightness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Image display device and image display method
InactiveUS7053881B2Rule out the possibilityImprove dynamic contrastCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDisplay devicePeak value
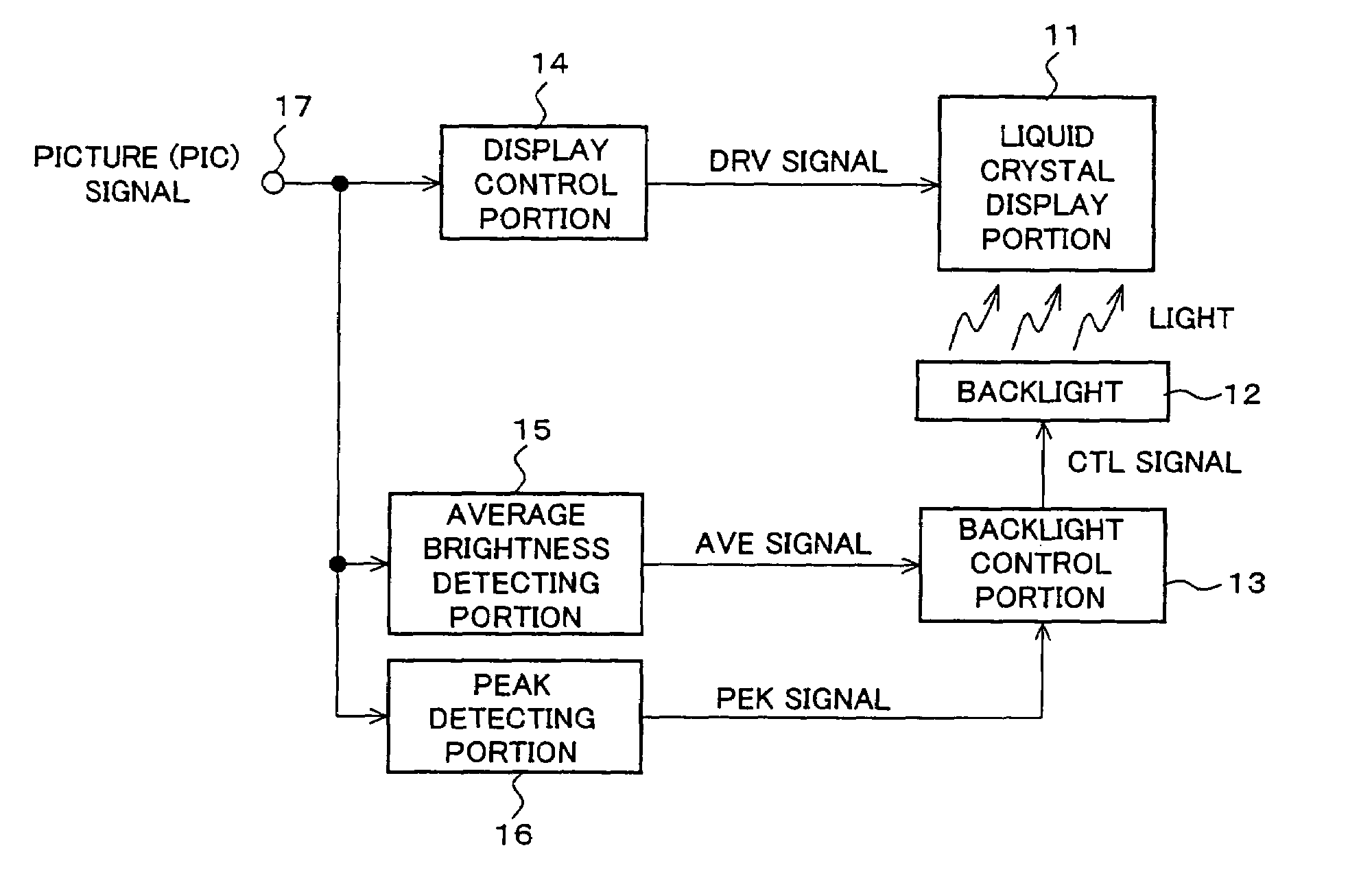
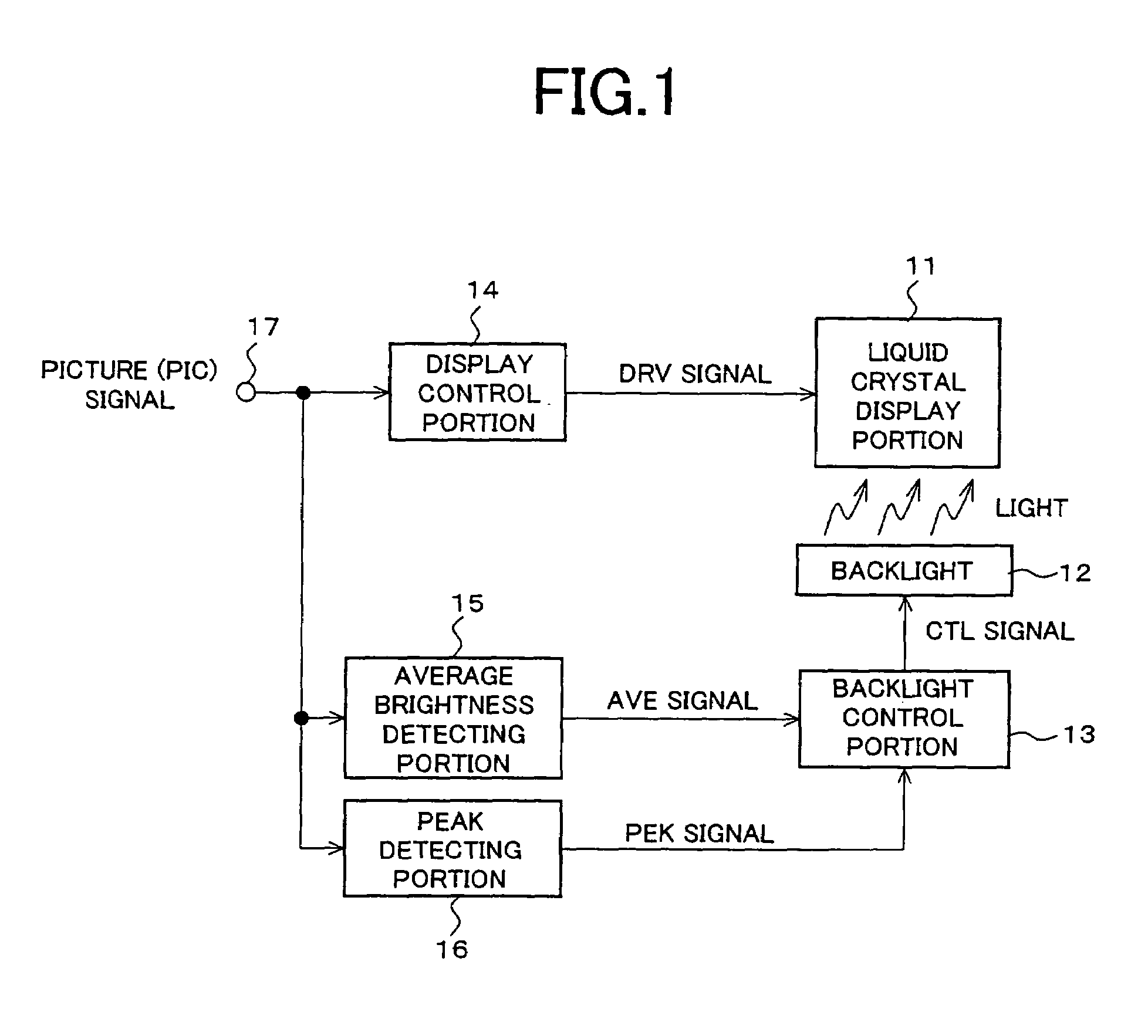
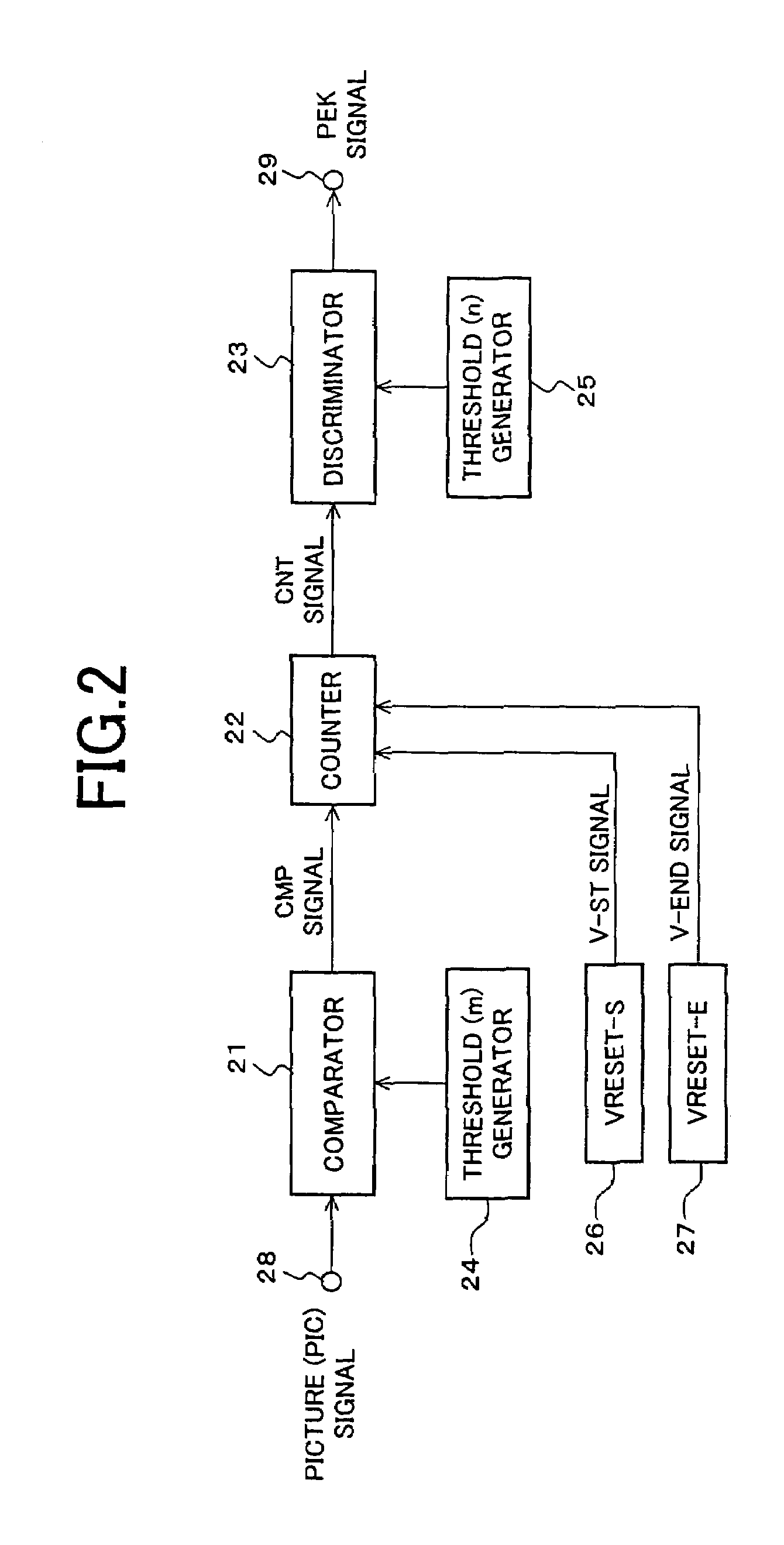
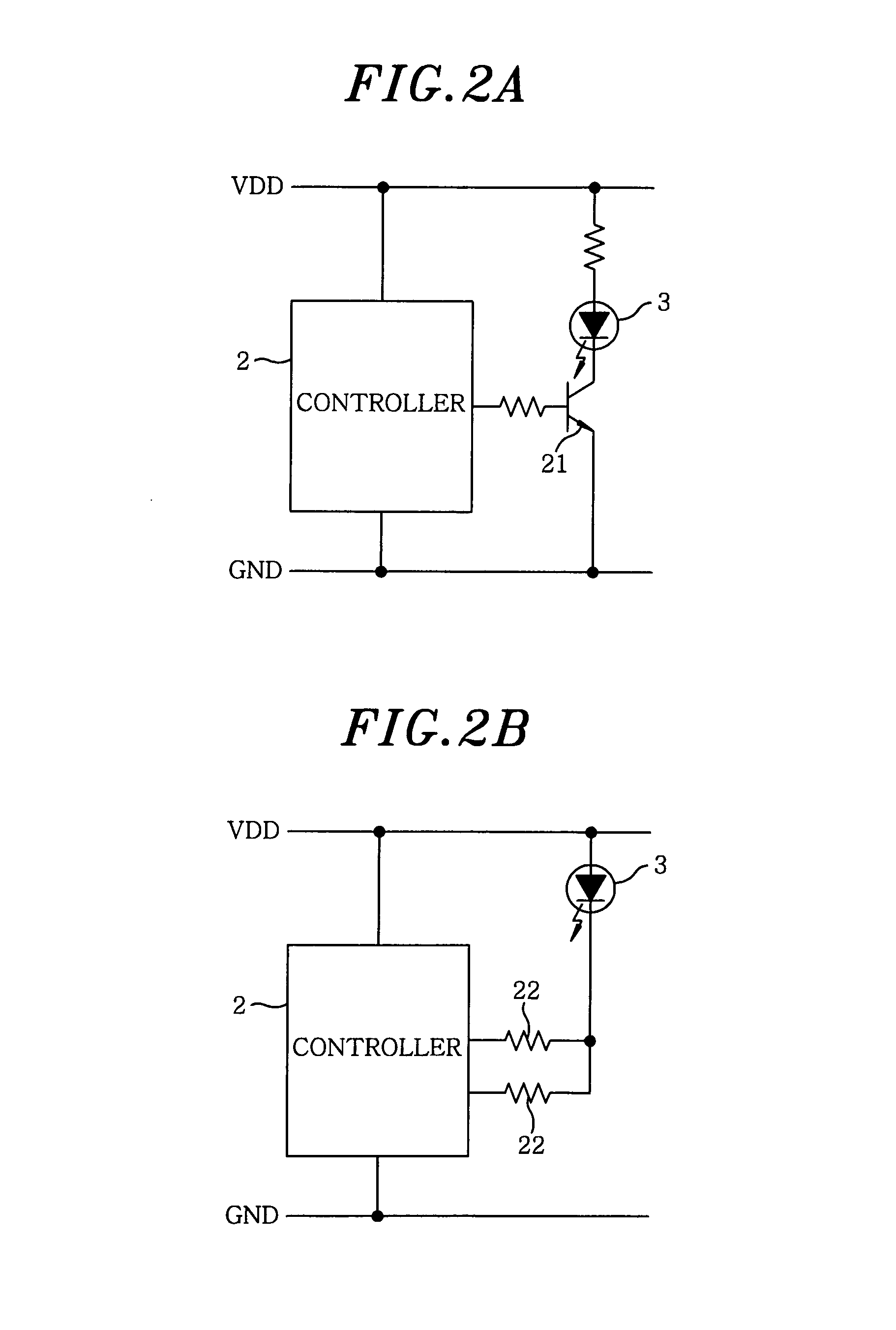
An image display device according to the present invention is capable of presenting to a viewer a high-quality lustrous video on a display screen with best screen brightness by increasing visual contrast and avoiding loss of true black elements without widening a dynamic range of a picture signal. The image display device is provided with a liquid crystal display portion (11), a display control portion (14), a backlight (12), a backlight control portion (13) and an average brightness detecting portion (15) and detects brightness of the light source in accordance with the average brightness of a picture signal to be displayed. It is further provided with a peak detecting portion (16) and corrects the control of the backlight control portion (13) in accordance with a detected peak value of a picture.
Owner:SHARP KK
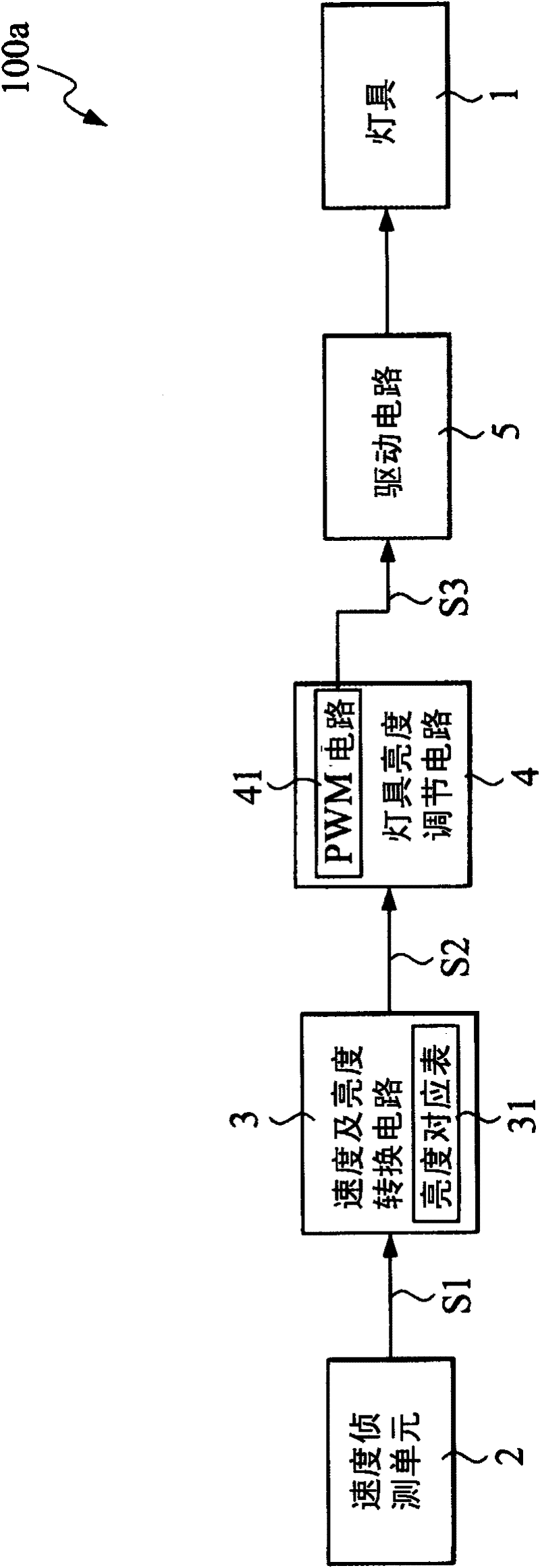
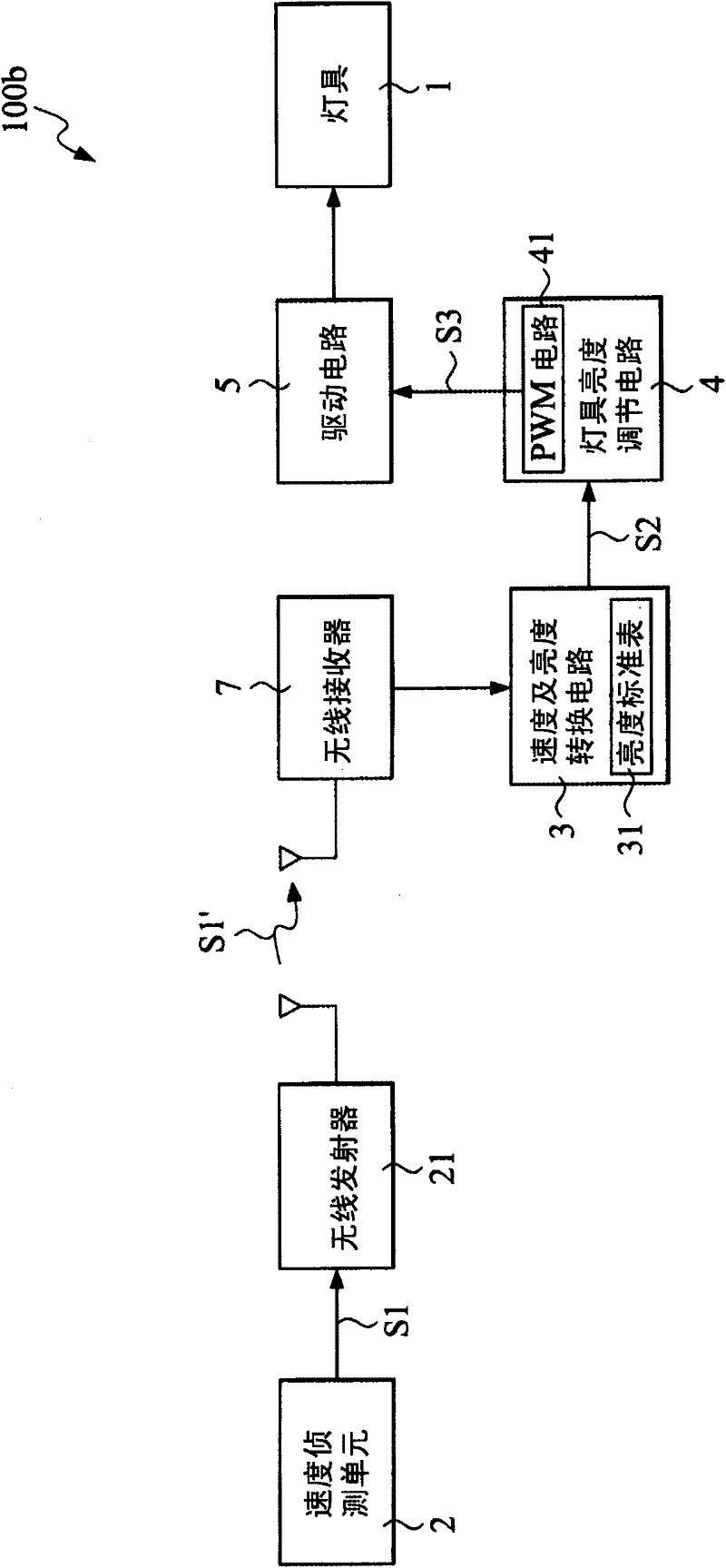
Control circuit of controlling the illumination brightness of bicycle according to bicycle speed
InactiveCN102209412ASolve the problem that you must operate by hand to adjust the state of the lampAvoid accidentsElectric light circuit arrangementControl circuitDriving circuit
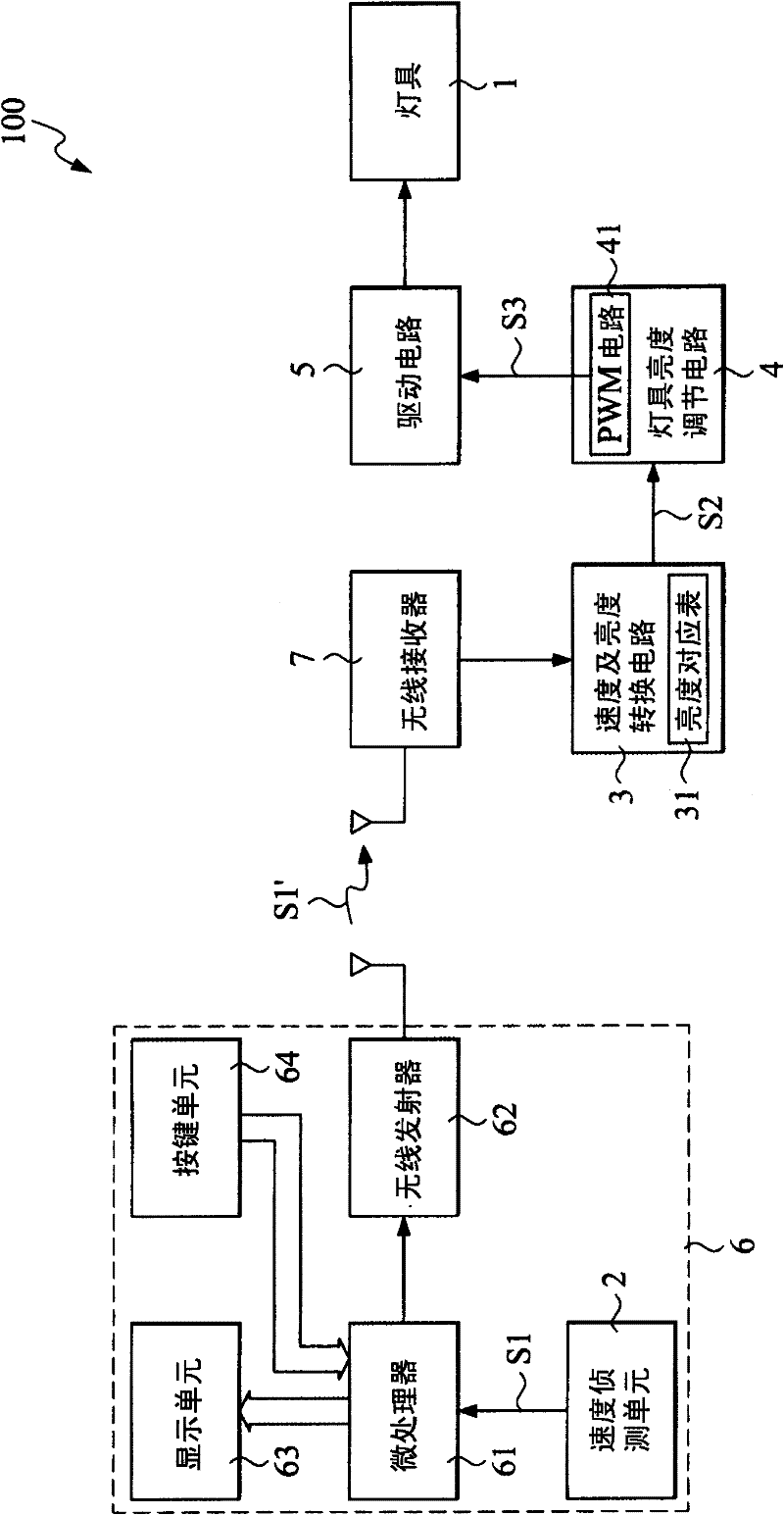
The invention provides a control circuit of controlling the illumination brightness of a bicycle according to the bicycle speed. Through detecting the running speed of a bicycle, the illumination state of a lamp on the bicycle is controlled. The control circuit comprises a speed detection unit, a speed and brightness converting circuit, a lamp brightness adjusting circuit and a drive circuit. The speed detection unit is used for detecting the speed of the running bicycle and producing a speed signal. The speed and brightness converting circuit connects the speed detection unit and generates a conversion signal according to the speed signal. The lamp brightness adjusting circuit connects the speed and brightness converting circuit and produces a brightness adjusting signal according to the conversion signal. The drive circuit connects the speed and brightness converting circuit and adjusts the brightness of the lamp according to the brightness adjusting signal.
Owner:BION
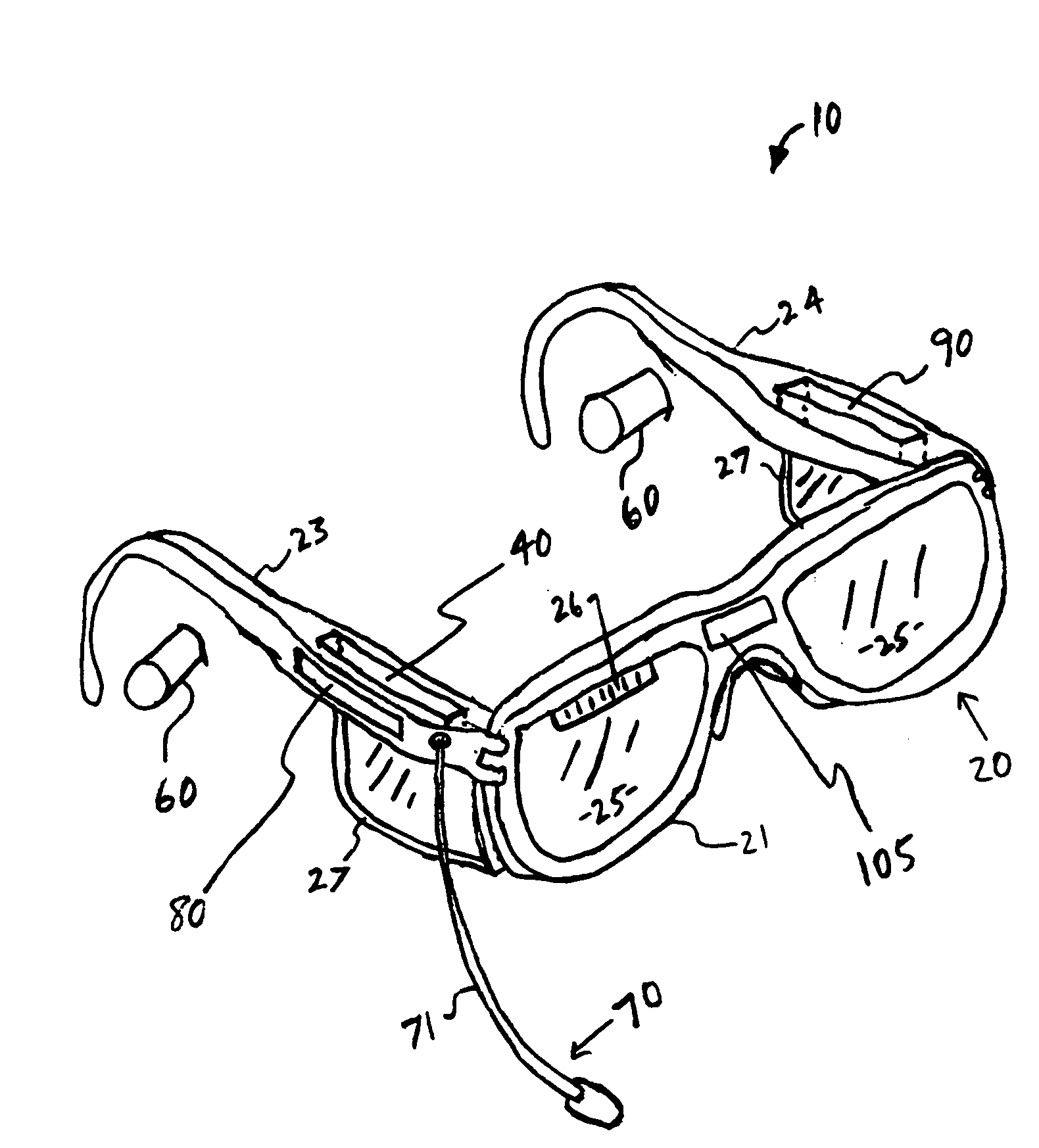
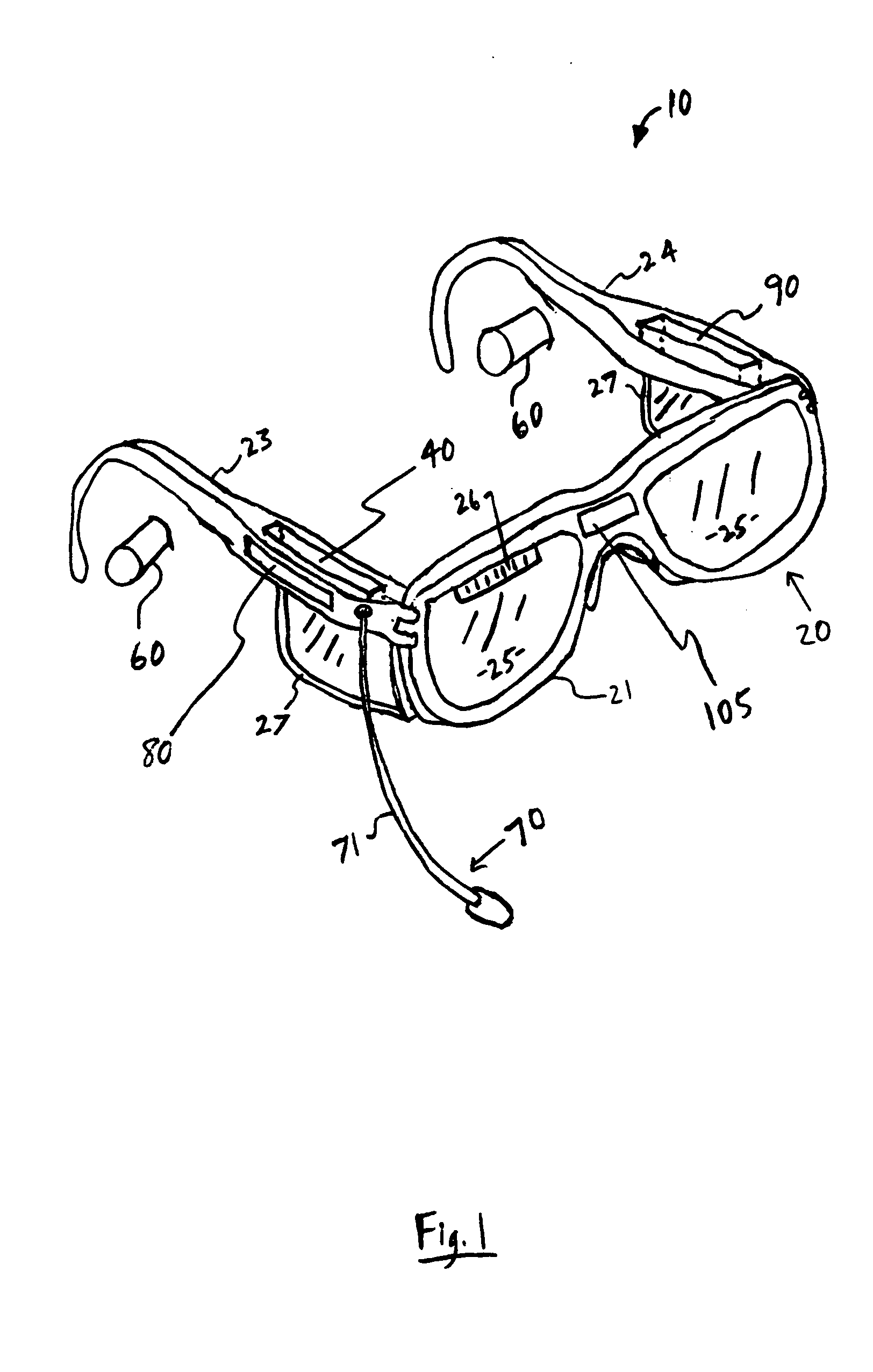
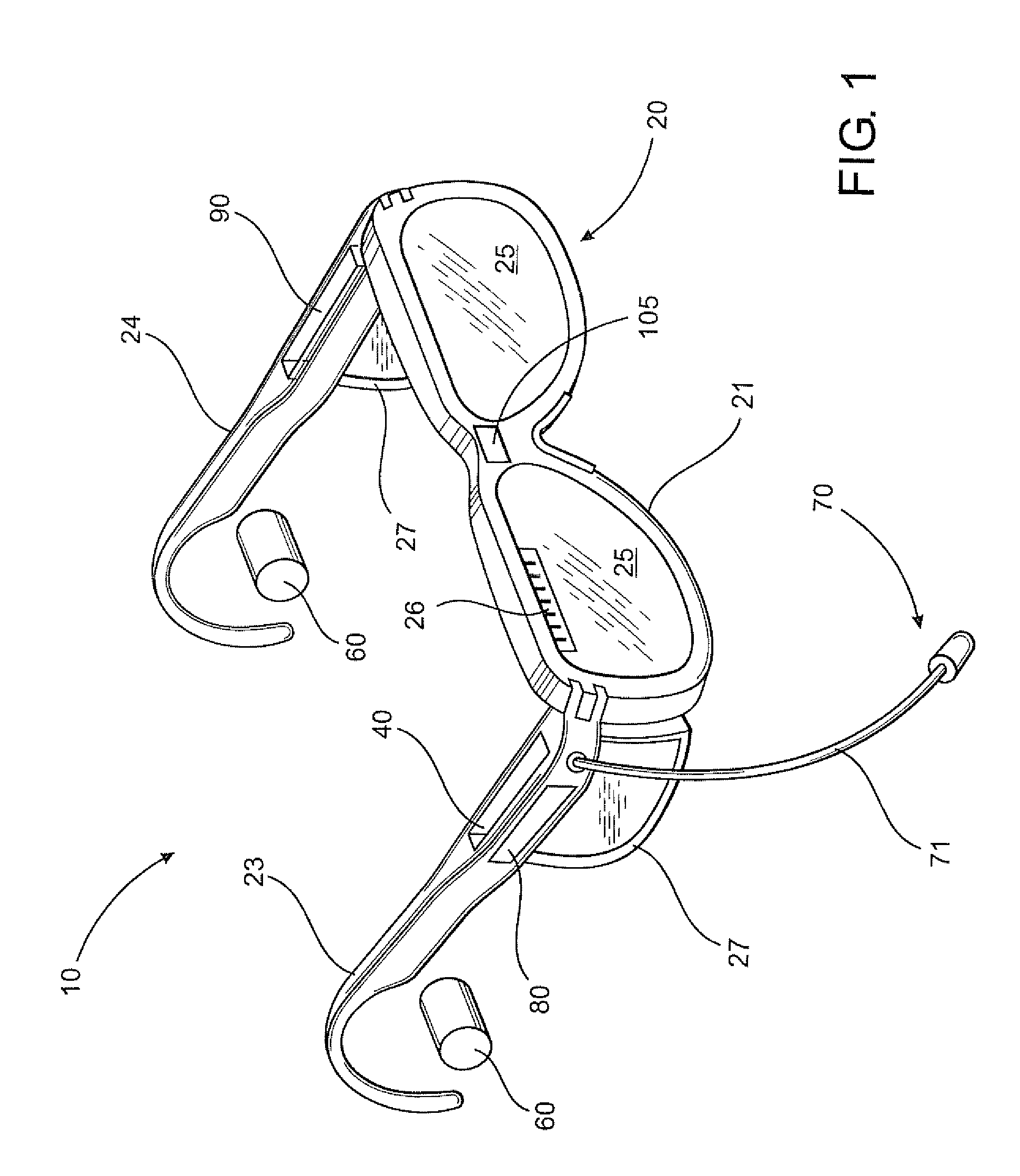
Communication eyewear assembly
InactiveUS20100061579A1Facilitate communicationIncrease heightMicrophonesNon-optical adjunctsEyewearEngineering
A frame assembly is worn by a wearer to maintain at least one substantially transparent eye panel in a generally shielding position in front of the wearer's eyes. A processor receives an incoming audio signal and wirelessly transmits the incoming audio signal to at least one earpiece which audibly communicates the incoming audio signal to the wearer. An outbound microphone assembly picks up an outbound audio signal from the wearer and transmits the outbound audio signal to the processor which further transmits the outbound signal to a remote recipient. An ambient microphone assembly picks up an ambient audio signal and transmits the ambient audio signal to the processor. The processor is structured to enhance the incoming audio signal and / or the outbound audio signal based on the ambient audio signal. The processor is also structured to transmit a voice component of the ambient audio signal to the earpiece. A camera assembly picks up an outbound visual signal and transmits the outbound video signal to the processor which further transmits the outbound video signal to a remote recipient. A display assembly displays to the wearer an incoming visual signal received by the processor.
Owner:ENERGY TELECOM
Optical Fiber Combiner and Method of Manufacturing Thereof
InactiveUS20090154881A1Reduce lighting brightnessReduce light lossOptical articlesCoupling light guidesEngineeringFiber coupling
Owner:CORELASE
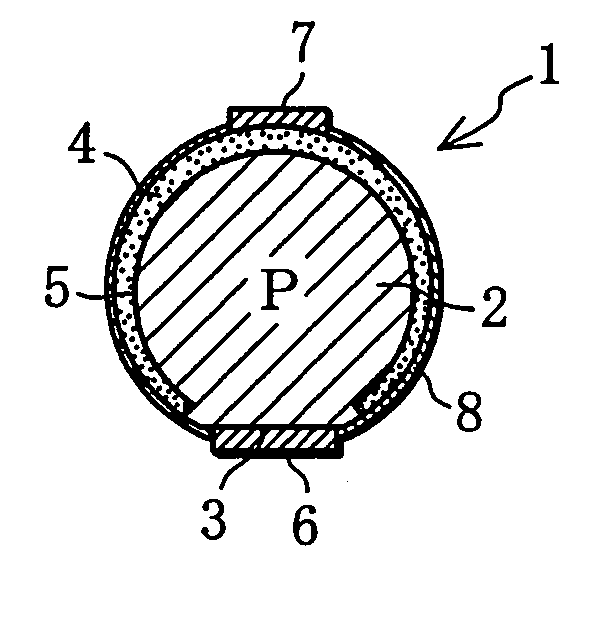
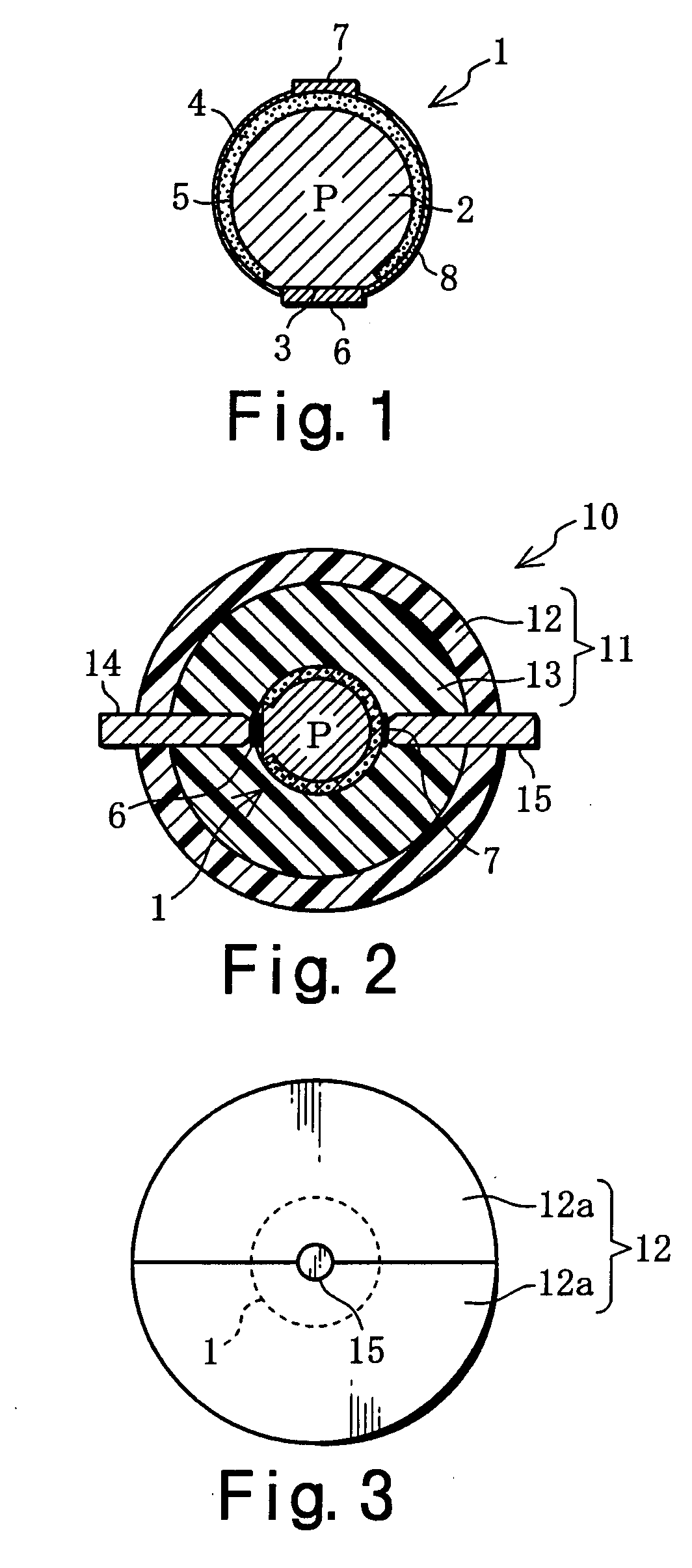
Light receiving or emitting semiconductor apparatus
InactiveUS7109528B2Reduce lighting brightnessIncrease in sizeSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar cell
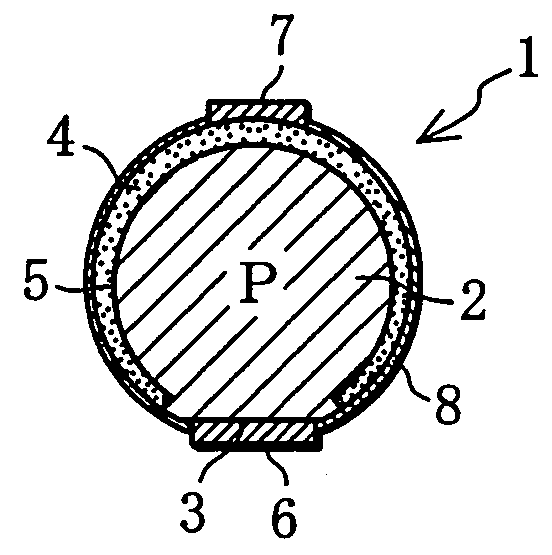
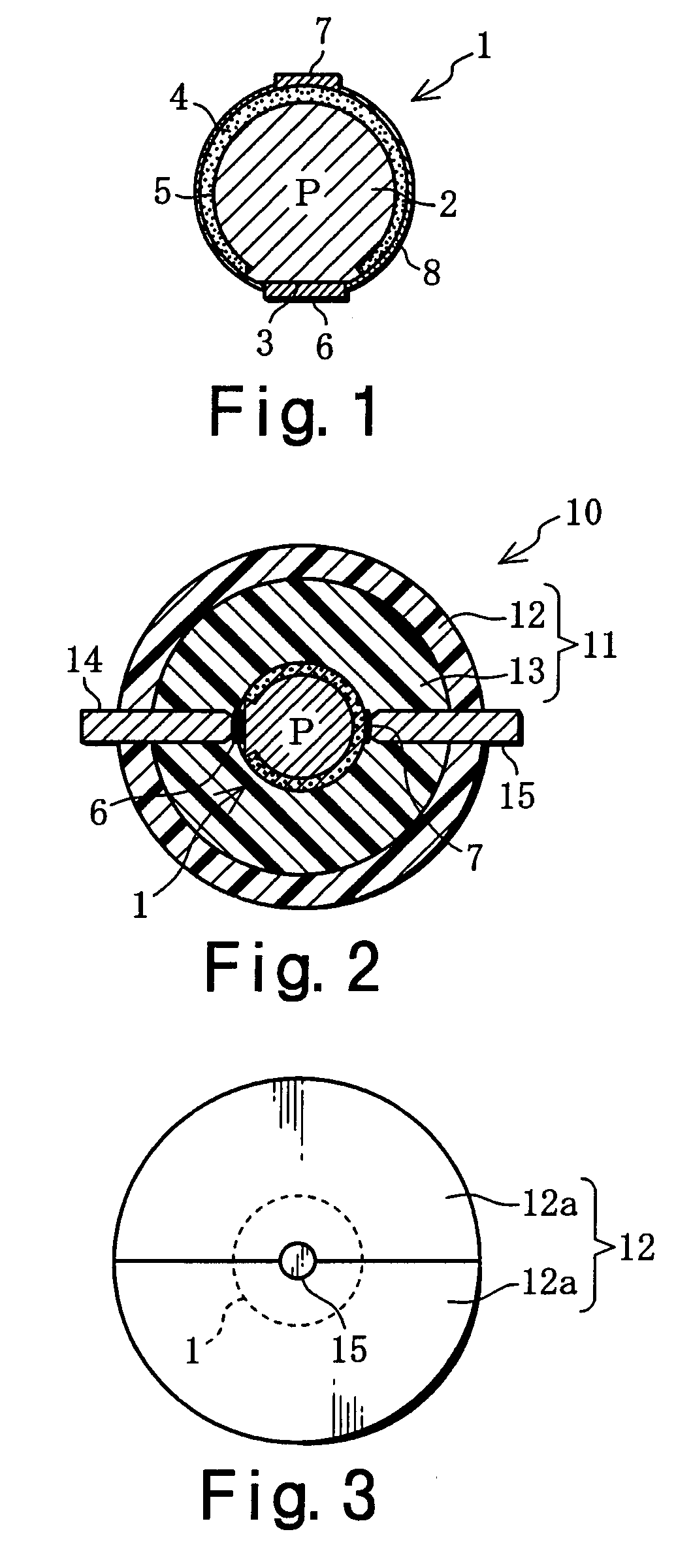
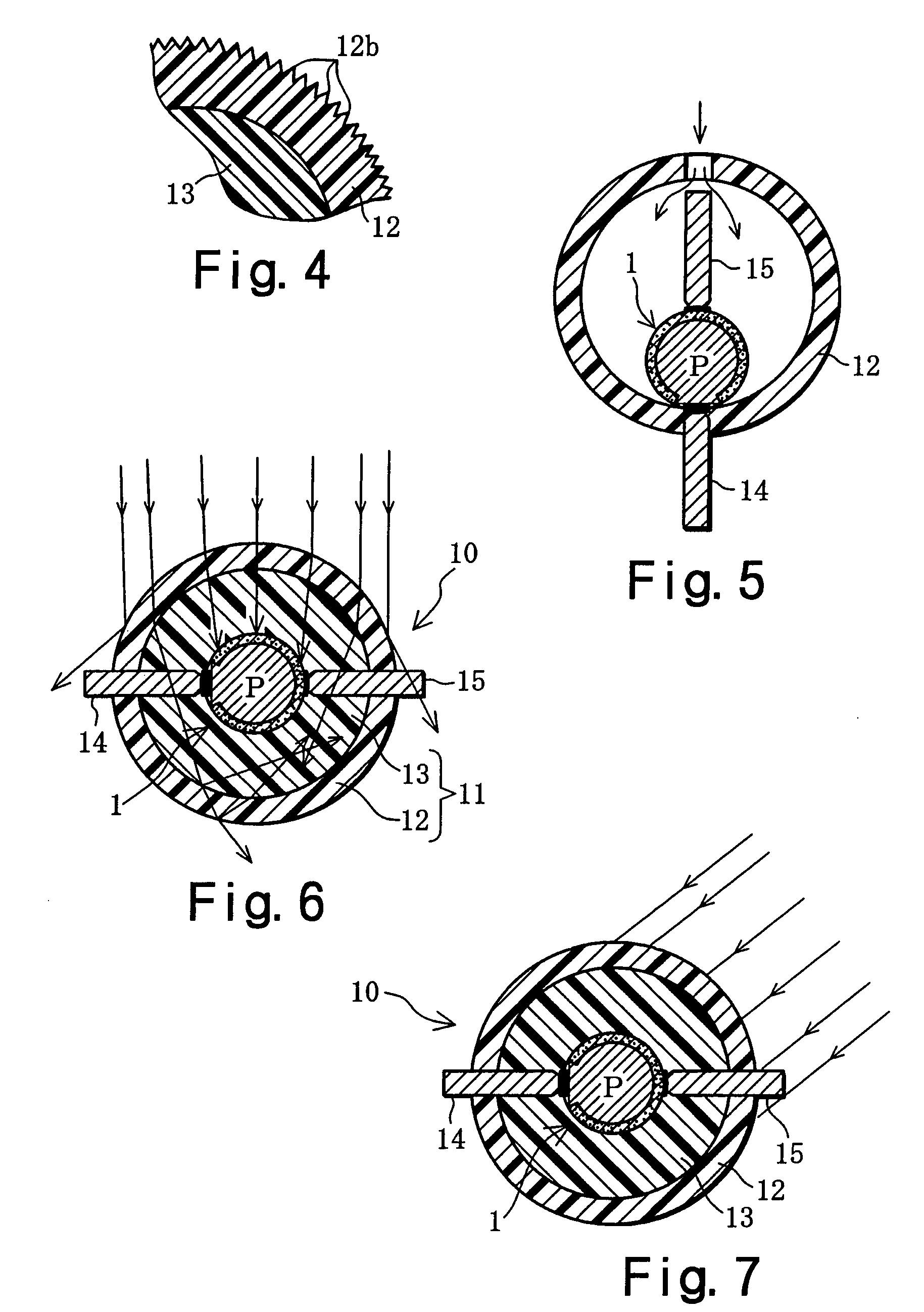
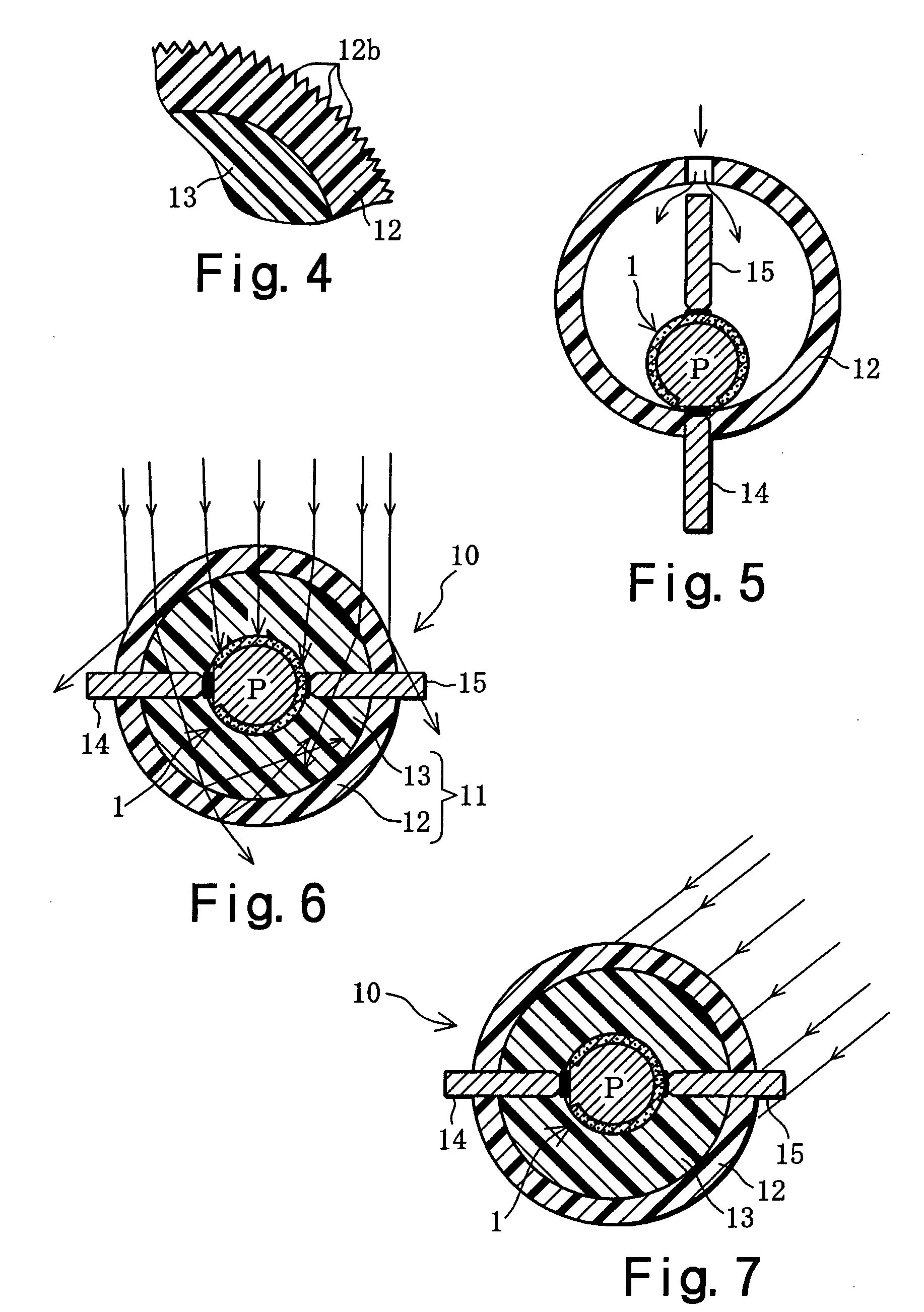
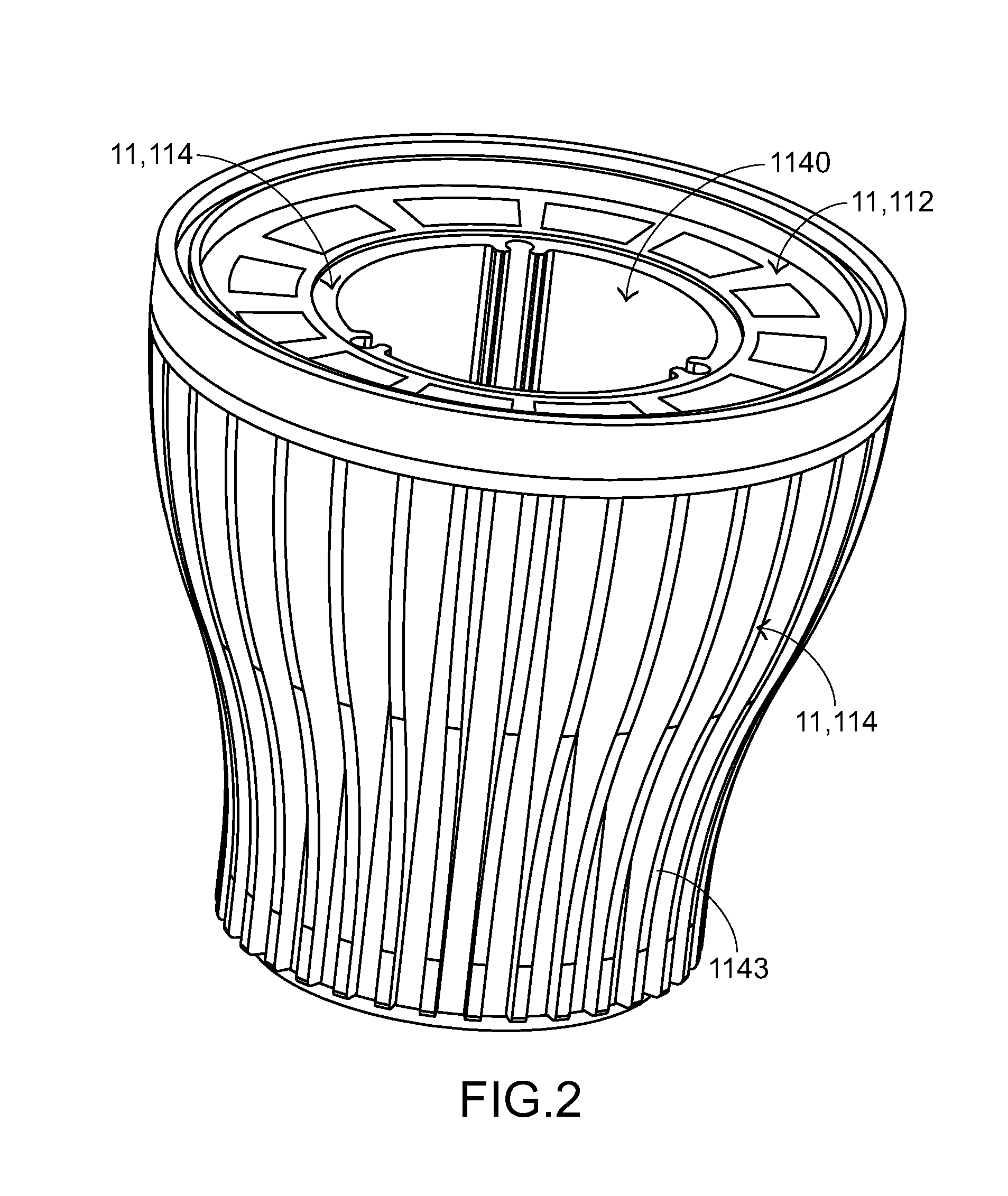
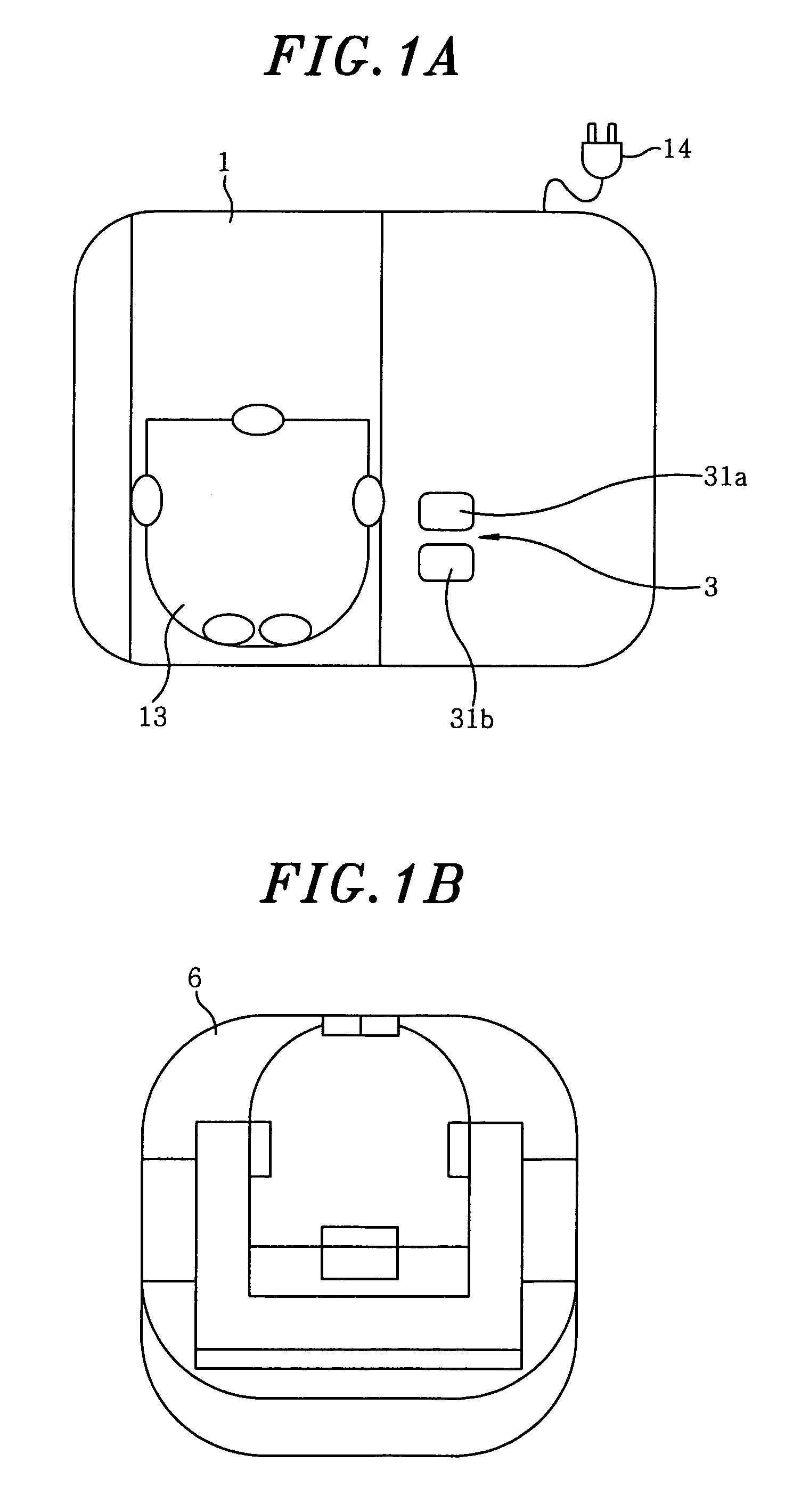
With a solar ball 10 serving as a light-receiving semiconductor apparatus, the outer surface of a spherical solar cell 1 is covered with a light-transmitting outer shell member 11, and electrode members 14, 15 are connected to electrodes 6, 7 of the solar cell 1. The outer shell member 11 comprises a capsule 12 produced by bonding together two halves, and a filler 13 that is packed inside this capsule and cured. A solar panel can be configured such that a plurality of the solar balls 10 are arrayed in a matrix and connected in parallel and in series, or a solar panel can be configured such that a multiplicity of spherical solar cells 1 are arrayed in a matrix and covered with a transparent outer shell member. A solar string in the form of a rod or cord can be configured such that a plurality of the solar cells 1 are arrayed in columns and connected in parallel, and then covered with a transparent outer shell member. Since the outer shell member 11 condenses light, the light-receiving area of the solar cell 1 can be expanded. Also discussed is a light-emitting semiconductor apparatus in which a spherical semiconductor device with a light-emitting function, rather than the solar cell 1, is covered with an outer shell member.
Owner:SPHELAR POWER
Battery powered LED lamp
InactiveUS7481554B2Preventing thermal runawayReduce voltageNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceElectrical batteryLow voltage
Owner:ANDERSON GARY
Portable electronic device with touch screen
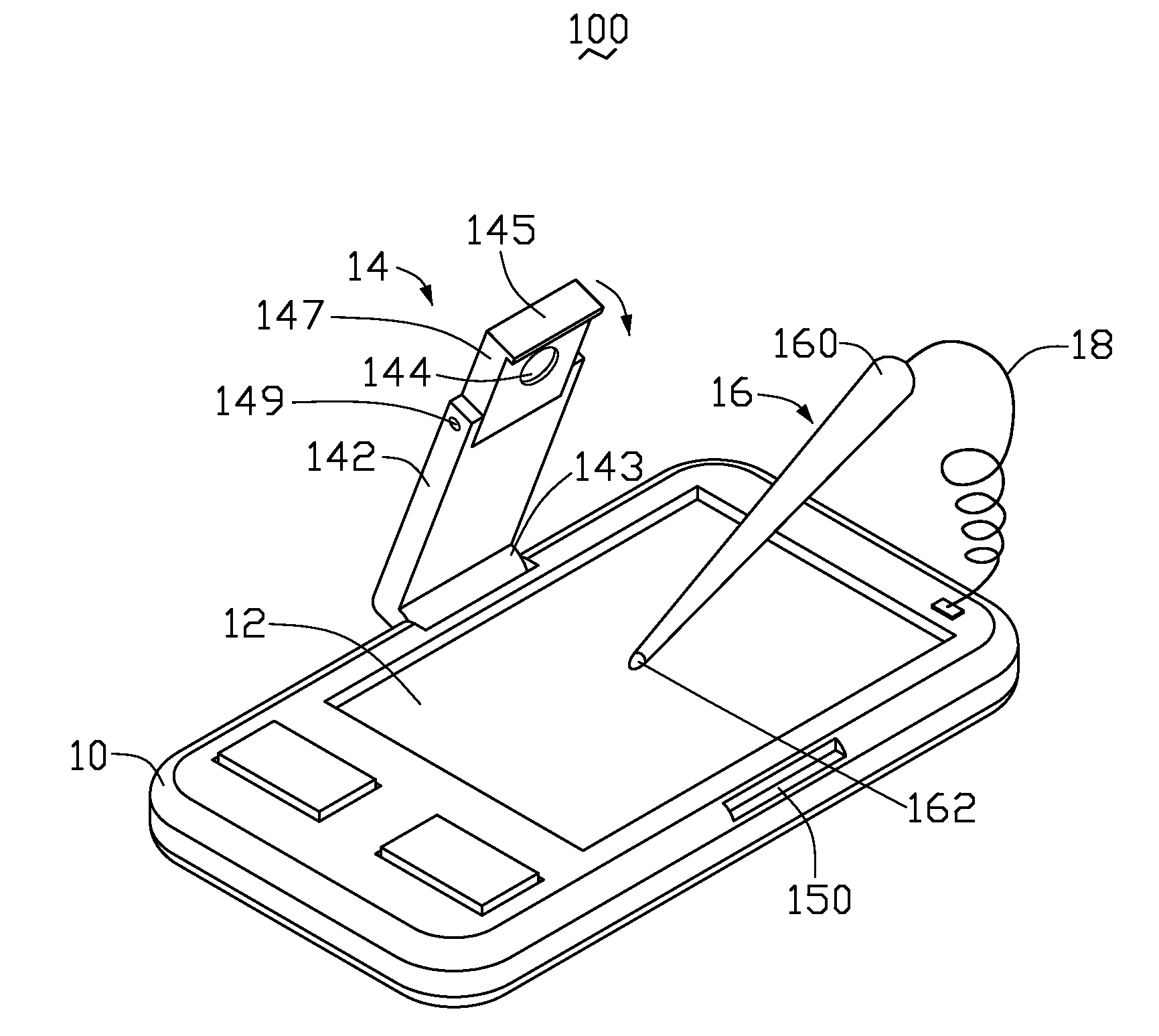
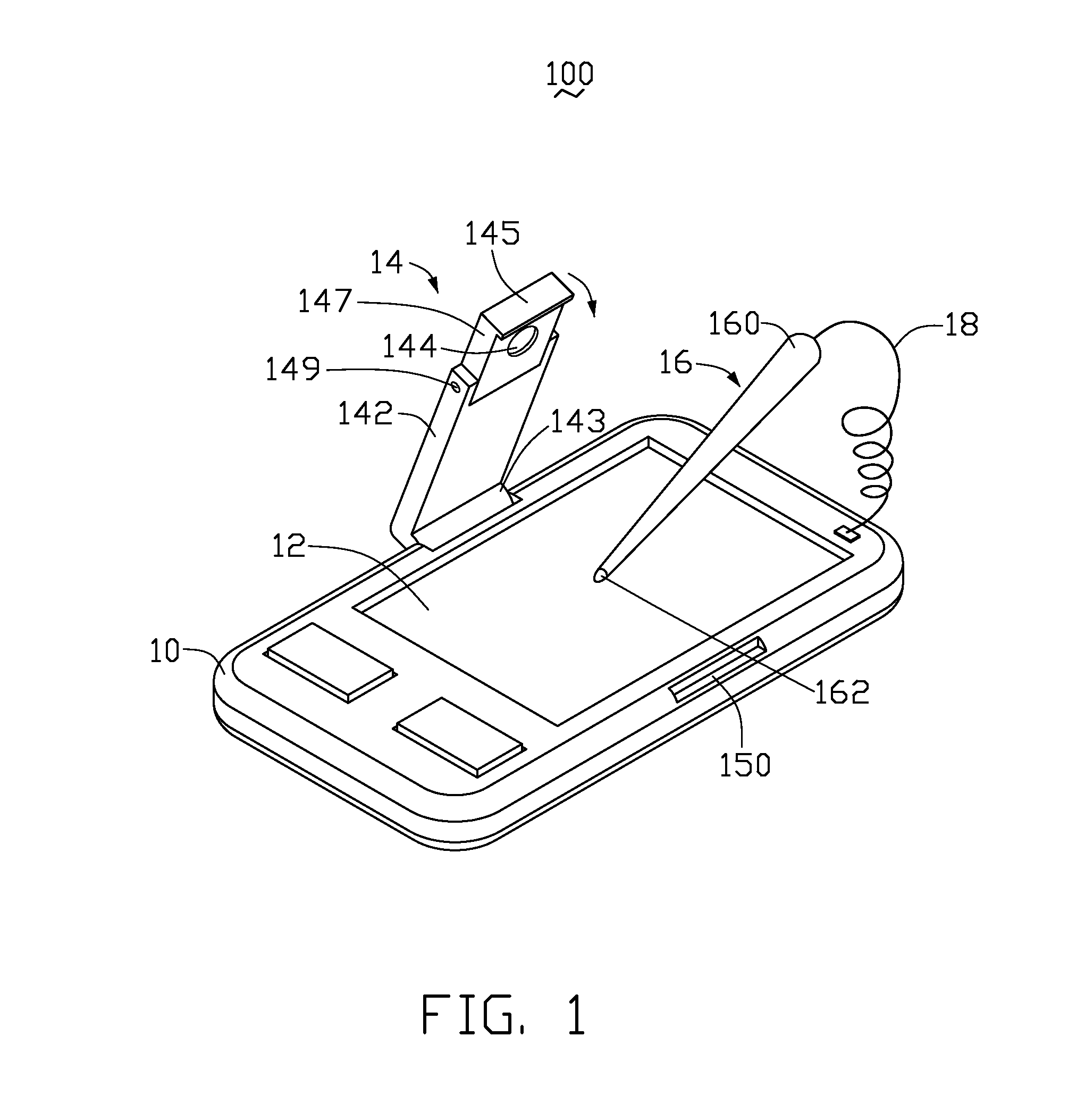
InactiveUS20080278462A1Reduce lighting brightnessDigital data processing detailsInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Light spot
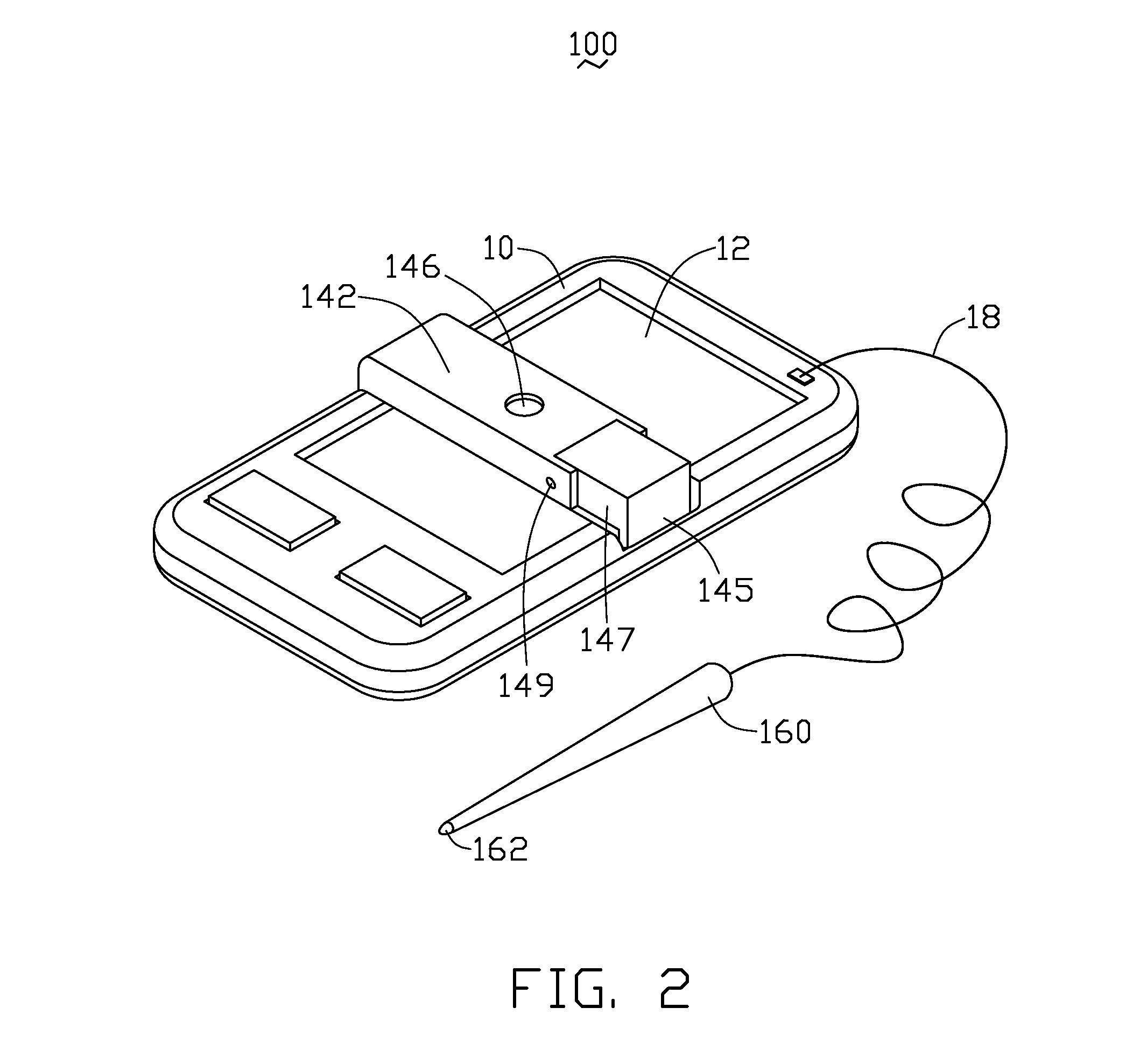
A portable electronic device with a simulation touch screen includes a main body, a display screen, a stylus, a camera unit and a processing unit. The display screen is mounted on the main body. The stylus is used for controlling movement of a cursor on the display screen. The stylus has a light source for generating a light spot on the display screen. The stylus is configured for controlling movement of a cursor on the display screen. The camera unit is electrically connected with the main body and faces the display screen. The camera unit is configured for capturing images of the display screen and the light spot thereon. The processing unit is mounted in the main body and electronically coupled to the camera unit.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Surface light source device
InactiveUS20120020078A1Improve directionalityIncrease the light areaNon-electric lightingPlanar light sourcesDiffusionLight beam
A surface light source device includes a number of light sources, a first prism sheet and a second prism sheet. The light sources are distributed on a bottom plate of a housing. The first prism sheet and the second prism sheet are arranged above the light sources in that order. The light sources and the first prism sheets are spaced by a first predefined distance, and the first prism sheets and the second prism sheets are spaced by a second predefined distance. The light emitting surface of the first prism sheet includes a number of first diffusion structures, and the light emitting surface of the second prism sheet includes a number of second diffusion structures. Light beams emitted by the light sources are substantially diffused after passing through the first prism sheet and the second prism sheet and become surface light beams.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
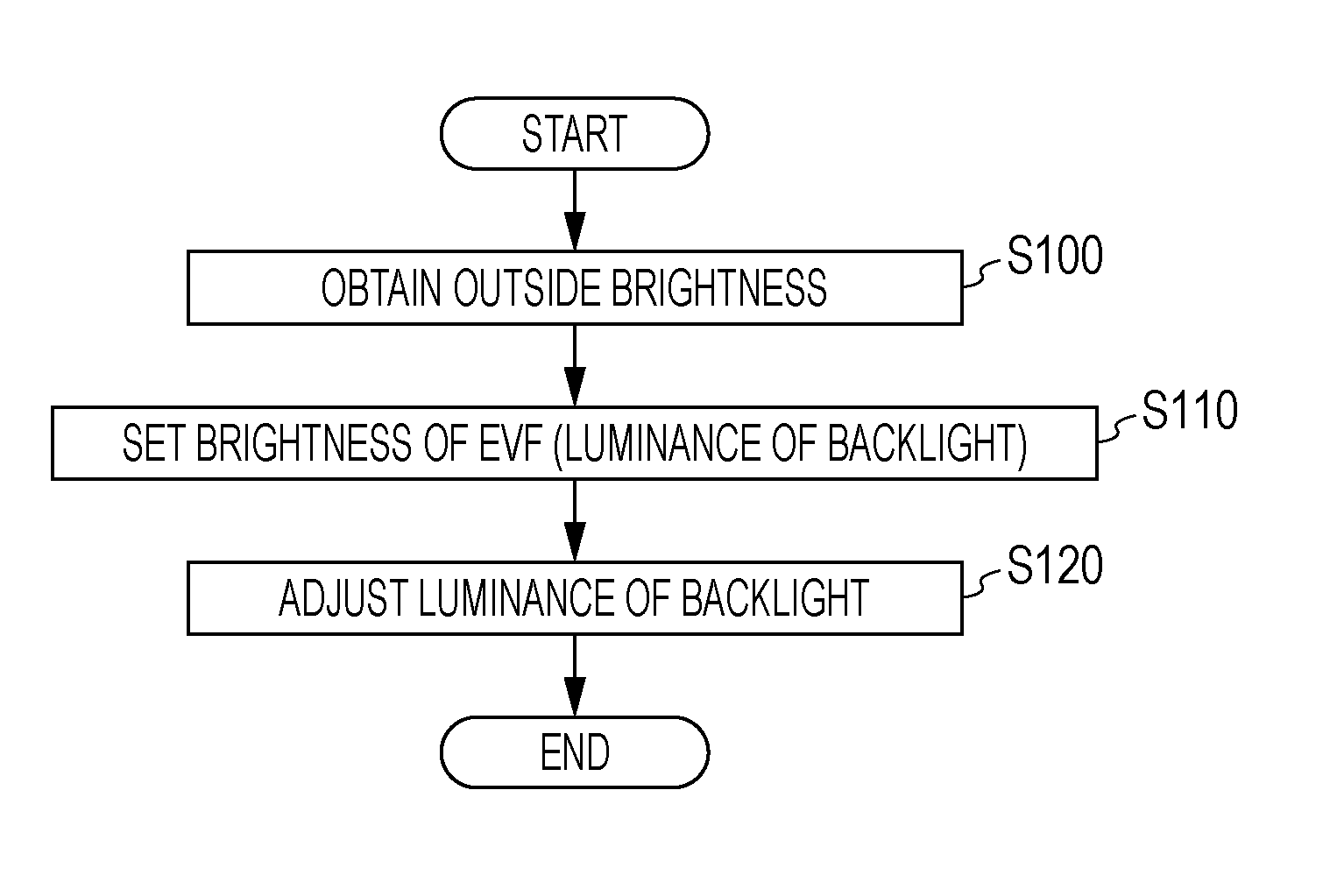
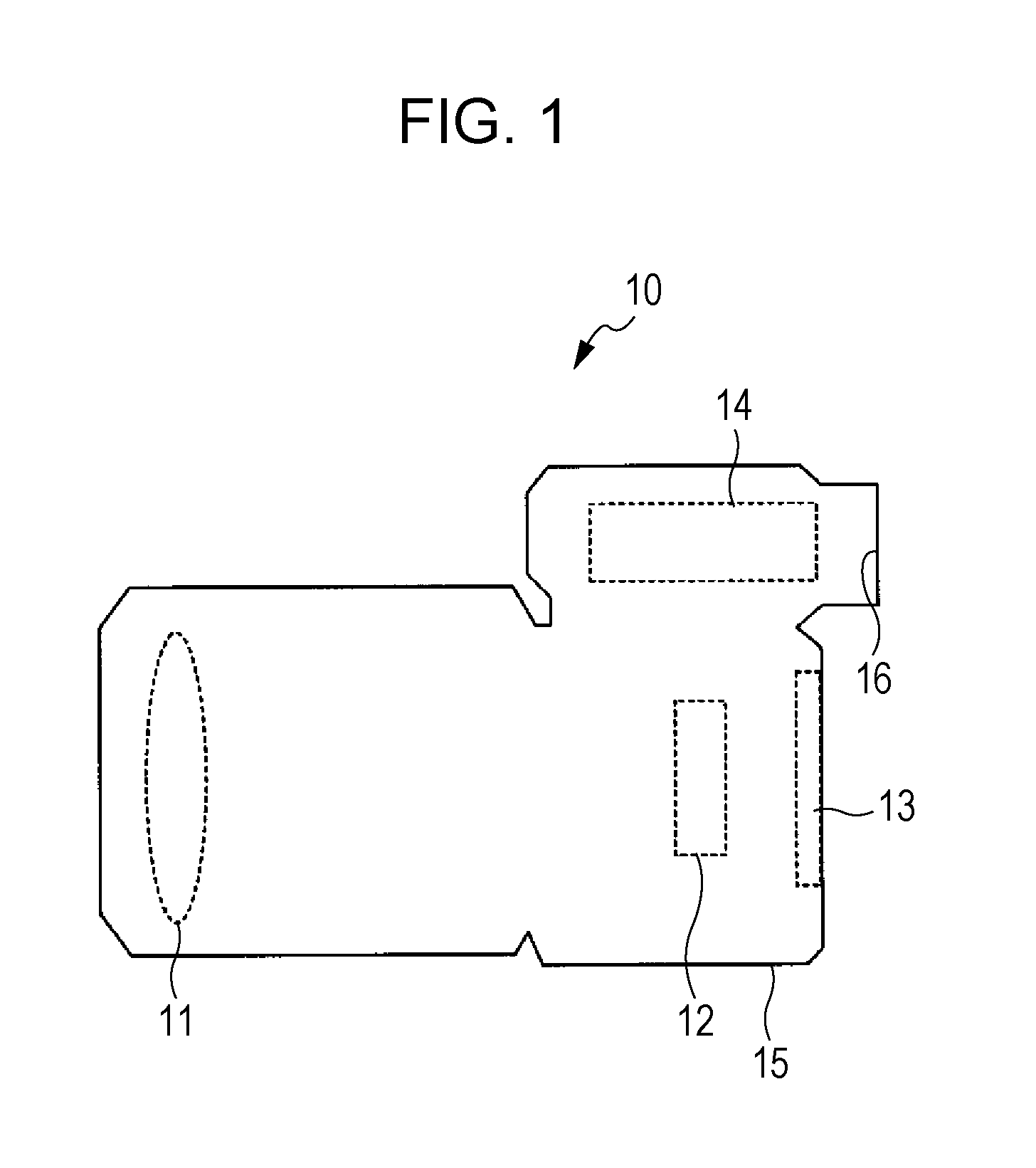
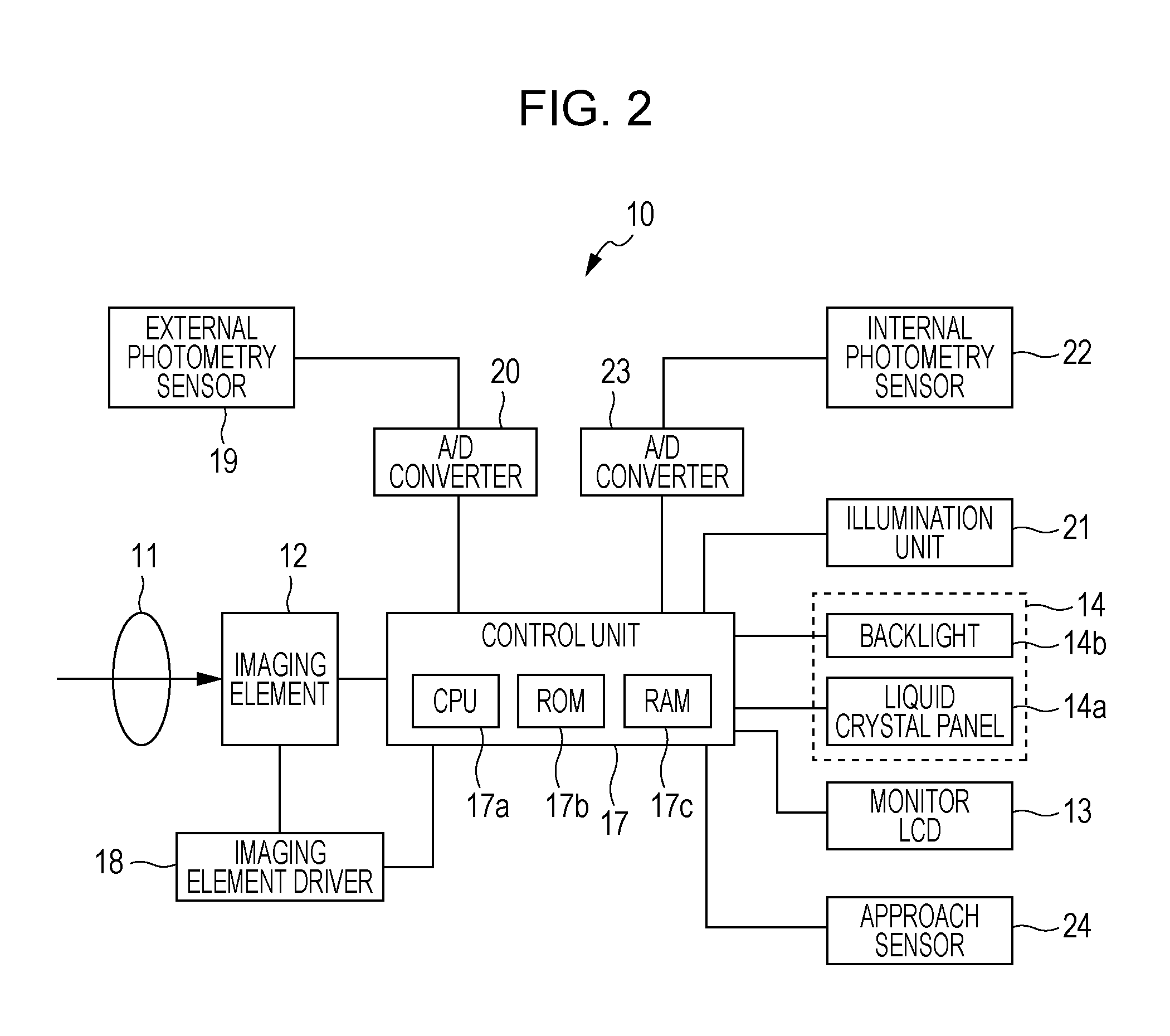
Image display device, brightness control method and brightness control program
ActiveUS20110200318A1Reducing and eliminating disorientationReduce lighting brightnessTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceComputer science
An image display device includes a display unit that is installed inside a finder window provided in a housing and displays images, an illumination unit that illuminates a space inside the finder window, an obtaining unit that obtains brightness of an outside of the housing, and a control unit that when the brightness obtained by the obtaining unit is a first brightness, sets the brightness of the illumination unit to a second brightness, and when the brightness obtained by the obtaining unit is a third brightness brighter than the first brightness, sets the brightness of the illumination unit to a fourth brightness brighter than the second brightness.
Owner:ADVANCED INTERCONNECT SYST LTD
Communication eyewear assembly
InactiveUS8243973B2Facilitate communicationPermit hands-free multimedia wireless communicationMicrophonesNon-optical adjunctsEyewearEngineering
Owner:ENERGY TELECOM
Light receiving or emitting semiconductor apparatus
InactiveUS20050121683A1Reduce lighting brightnessIncrease in sizeSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationDevice materialEngineering
With a solar ball 10 serving as a light-receiving semiconductor apparatus, the outer surface of a spherical solar cell 1 is covered with a light-transmitting outer shell member 11, and electrode members 14, 15 are connected to electrodes 6, 7 of the solar cell 1. The outer shell member 11 comprises a capsule 12 produced by bonding together two halves, and a filler 13 that is packed inside this capsule and cured. A solar panel can be configured such that a plurality of the solar balls 10 are arrayed in a matrix and connected in parallel and in series, or a solar panel can be configured such that a multiplicity of spherical solar cells 1 are arrayed in a matrix and covered with a transparent outer shell member. A solar string in the form of a rod or cord can be configured such that a plurality of the solar cells 1 are arrayed in columns and connected in parallel, and then covered with a transparent outer shell member. Since the outer shell member 11 condenses light, the light-receiving area of the solar cell 1 can be expanded. Also discussed is a light-emitting semiconductor apparatus in which a spherical semiconductor device with a light-emitting function, rather than the solar cell 1, is covered with an outer shell member.
Owner:SPHELAR POWER
Battery powered LED lamp
InactiveUS20070058365A1Reduce voltageMaximum amount of brightnessNon-electric lightingLighting support devicesLow voltageElectrical battery
A battery powered LED lamp including an array of high-performance LEDs disposed in a lightweight directionally oriented shade. Converting electronics are provided which may include a step-down DC voltage switching regulator for converting a higher voltage of the battery power source to a lower voltage required to drive the LEDs at greater than 90% efficiency. The converting electronics may also include an LED current monitoring circuit for preventing thermal runaway of the LEDs and for reliably operating the LEDs near their maximum rating so to provide the maximum amount of brightness from the LED array and maximum battery life.
Owner:ANDERSON GARY
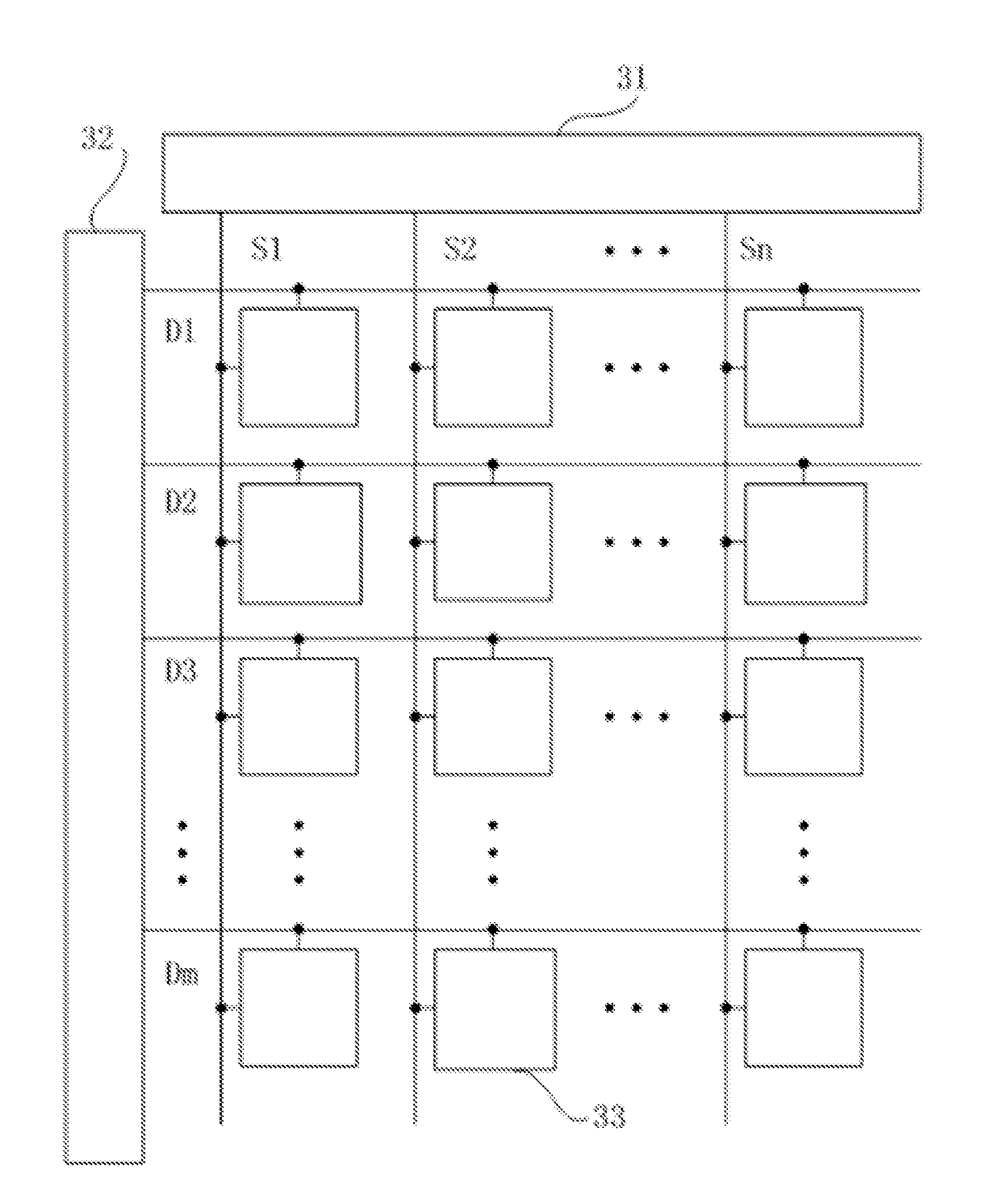
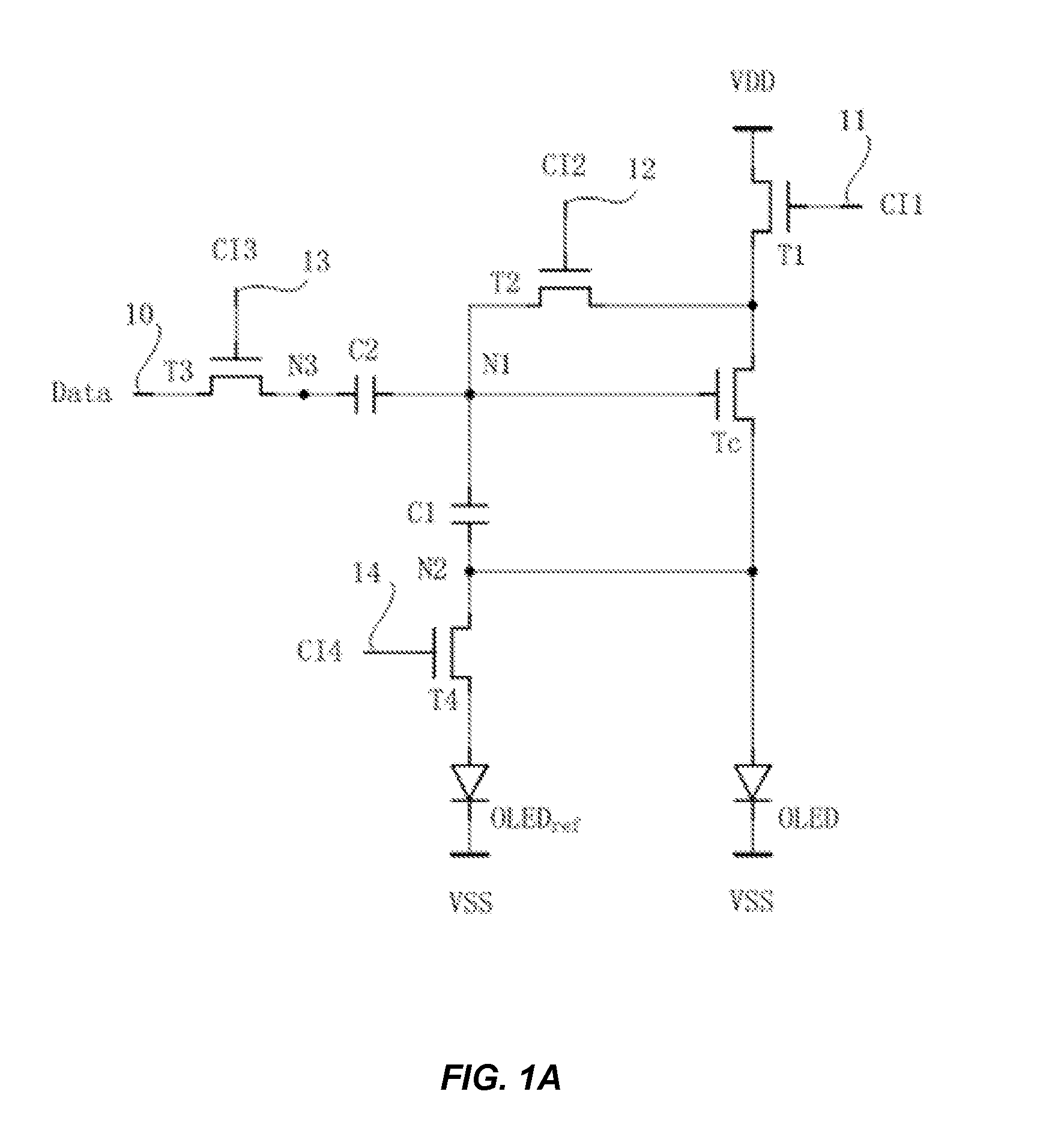
Organic light emitting display device, pixel circuit of the same and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20150310806A1Service life of the organic light emitting display device is further shortened.Reduce lighting brightnessStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceHemt circuits
An organic light emitting display device, a pixel circuit of the organic light emitting display device and a method of driving the same are disclosed. The pixel circuit comprises a driving transistor, a first transistor, a second transistor, a third transistor, a fourth transistor, a first capacitor, a second capacitor, a light emitting diode and a compensating diode. The degradation of the light emitting diode is compensated by the compensating diode. Since the degradation phenomena of the light emitting diode is compensated by the compensating diode, the light emitting diode is able to maintain an effective and normal brightness while using the same driving voltage, thereby ensuring higher display quality of images and scenes of the organic light emitting display device.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
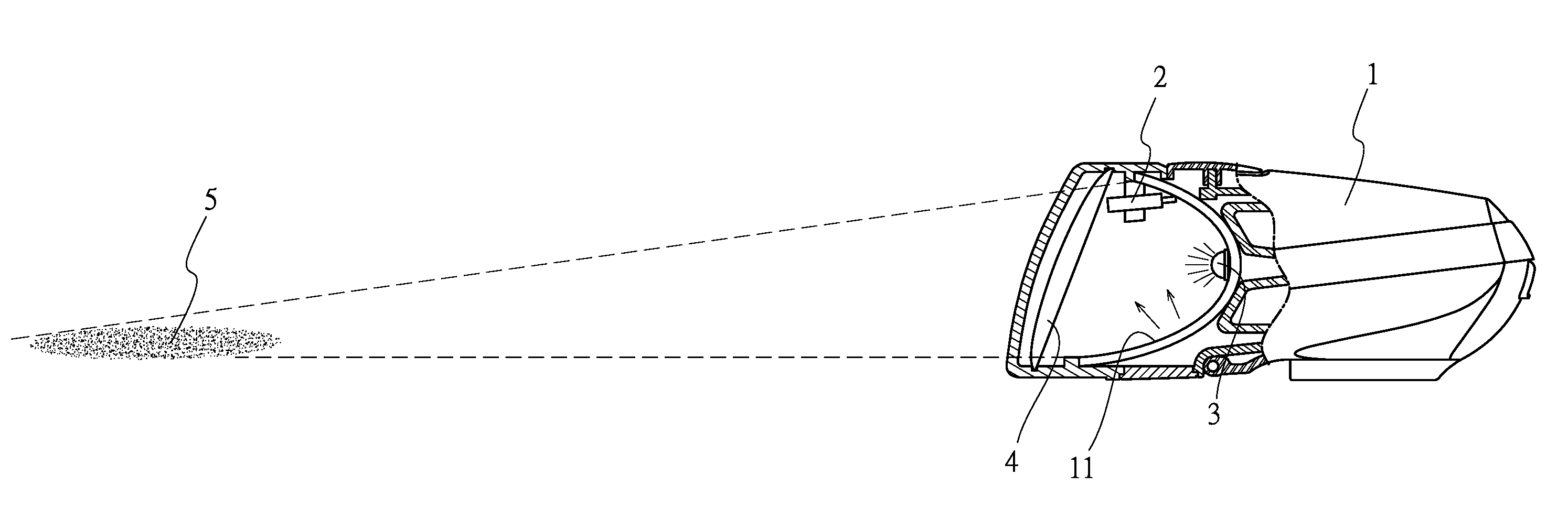
Smart lighting device for vehicle
InactiveUS20160360593A1Save powerFew or no effectsElectrical apparatusOptical signalIntelligent lightingOptoelectronics
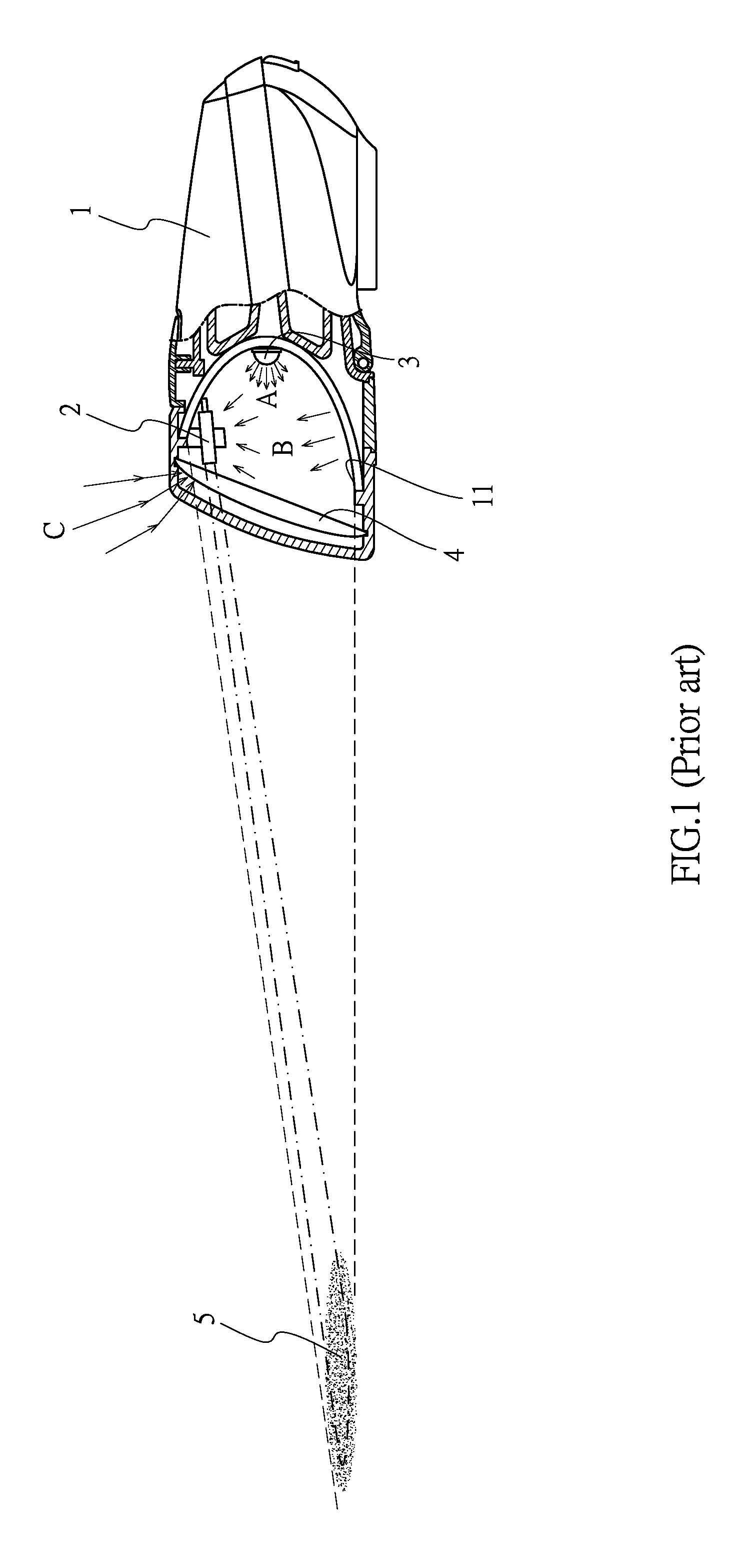
A smart lighting device for vehicle is disclosed and comprises a light body, a light collection unit, a lightening unit, and light focusing glass. An output current of the pulse-width modulation unit is zero while the light collection unit is collecting the ambient light brightness, even the lightening unit is not lightened, so that there is not any light brightness in the light body and then the ambient light brightness of the light projection area is accurately detected while the light collection unit is collecting the ambient light brightness of the light projection area.
Owner:LEE IN OK
Surface light source device
InactiveUS20120020079A1Improve directionalityIncrease the light areaPlanar light sourcesNon-electric lightingLight beamOptoelectronics
A surface light source device includes a number of light sources, a first prism sheet and a second prism sheet. The light sources are distributed on a bottom plate of a housing. The first prism sheet and the second prism sheet are arranged above the light sources in that order. The light sources and the first prism sheets are spaced by a first predefined distance, and the first prism sheets and the second prism sheets are spaced by a second predefined distance. The light emitting surface of the first prism sheet includes a number of substantially parallel elongated protrusions, and the light emitting surface of the second prism sheet includes a number of elongated V-shaped ridge structures extending along different directions. Light beams emitted by the light sources are substantially diffused after passing through the first and the second prism sheet and become surface light beams.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Optically controlled lighting device and control method thereof
InactiveUS20180084622A1Drawback can be obviatedReduce lighting brightnessElectrical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsPersistence of visionEffect light
An optically controlled lighting group includes a plurality of optically controlled lighting devices, each of which includes a lighting main body, a dimming time controller and an optical detector. The light source is turned on during an on period corresponding to an on dimming signal, and the light source is turned off during an off period corresponding to the off dimming signal. If the ambient light intensity detected by the optical detector is different from a predetermined value, the light source is controlled by the dimming time controller. The light sources of the optically controlled lighting devices are sequentially and alternately enabled to illuminate at specified time intervals, and each of the specified time interval is shorter than the time period for producing persistence of vision.
Owner:LIVINGSTYLE ENTERPRISES LTD
Street lamp control method based on ZigBee
InactiveCN104486875AAvoid wastingTimely investigationElectric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesElectricityRemote control
The invention discloses a street lamp control method based on ZigBee, and belongs to the technical field of street lamp control. According to the method, a voltage sensor, a current sensor, an air pressure sensor, a temperature sensor and a human body heat release infrared sensor are arranged in a lamp cavity of each LED (light emitting diode) street lamp, and data of the work state of each LED street is collected; whether a lamp bulb reaches the service life or not is judged; whether each lamp bulb has a fault or not is judged; the illuminating brightness of each street lamp is dynamically regulated. A clock chip is arranged in a remote control center, and the on-off state of the street lamps in a ZigBee network is controlled. The street lamp control method has the advantages that the condition of the street lamps in the ZigBee network can be monitored in real time, in addition, the work state of the street lamps is controlled, the electricity consumption can be greatly reduced, the street lamps with the fault can be repaired in time, and a user is reminded to replace the lamps in time.
Owner:SUZHOU OUBORI AUTOMATION TECH
Shading plate assembly, control method and control device thereof and vehicle
PendingCN111591111AAuto adjust discolorationColor change real-time automatic adjustmentInput/output for user-computer interactionAntiglare equipmentInformation controlTarget control
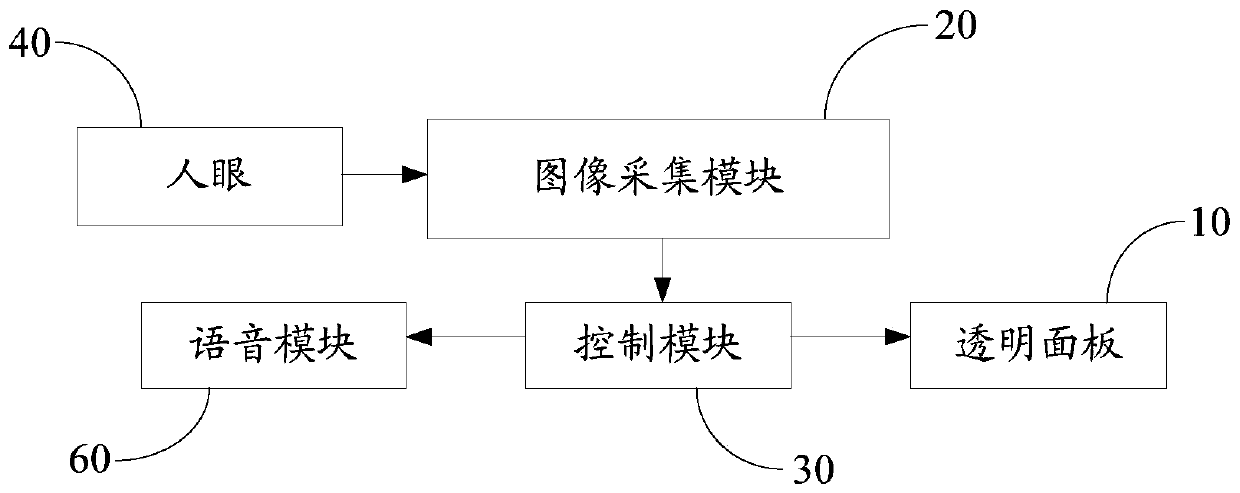
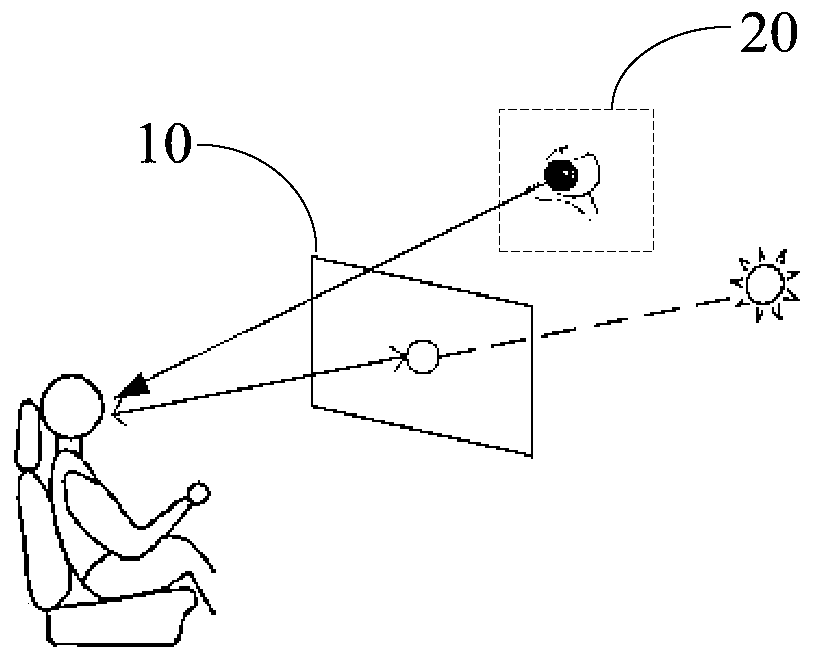
The invention provides a shading plate assembly, a control method and a control device thereof and a vehicle, which relate to the technical field of shading, and can avoid the problems of darkening ofan exterior scene and worsening of a visual field while solving the problem of visual dizziness of human eyes caused by direct sunlight in the driving process of the vehicle. An image acquisition module in the shading plate assembly is used for acquiring image information of a transparent panel and human eyes; a control module is used for determining target position information of fixation pointsof human eyes positioned on the transparent panel according to the image information, and determining a target control area, corresponding to the target position information, on the transparent panel; a detection module is used for detecting corresponding optical information when light penetrates through the target control area and is emitted to human eyes; and the control module is also used foradjusting the light transmission degree of the transparent panel in the target control area according to the optical information, so that the optical information is within a preset range. The shadingplate assembly provided by the invention is used for shading.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Luminaire reflector with light-modifying flange
ActiveUS7850342B2Reduce lighting brightnessLess noticeableSpectral modifiersRefractorsEngineeringDome shape
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
Lens, light emitting device and backlight module
InactiveCN106287570AImprove light uniformityReduce lighting brightnessPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsMean squareLight emitting device
The invention provides a light incoming surface and a light emitting surface, which are located on the two sides away from each other of the lens and are symmetric with respect to the central axis of the lens. The light incoming surface and the light emitting surface are located in the same coordinate system. The light incoming surface meets a formula 1 (shown in the description), wherein C1 is the curvature of the light incoming surface, r1 is the distance between the center of the lens and the intersecting point between the light incoming surface and the radius perpendicular to the central axis of the lens, u1 is the normalized radius of the light incoming surface, am is the non-spherical coefficient, and Qm is an m polynomial representing that the sum of the am in the formula 1 is equal to the sum of the mean square root of the slope of the light incoming surface. The light emitting surface meets a formula 2 (shown in the description), wherein C2 is the curvature of the light emitting surface, r2 is the distance between the center of the lens and the intersecting point between the light emitting surface and the radius perpendicular to the central axis of the lens, u2 is the normalized radius of the light emitting surface, am is the non-spherical coefficient, Qm is an m polynomial representing that the sum of the am in the formula 2 is equal to the sum of the mean square root of the slope of the light emitting surface.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Lighting device, display device and television receiver
InactiveUS20100182514A1Reduce in quantityLow costTelevision system detailsNon-electric lightingLight reflexTelevision receivers
Owner:SHARP KK
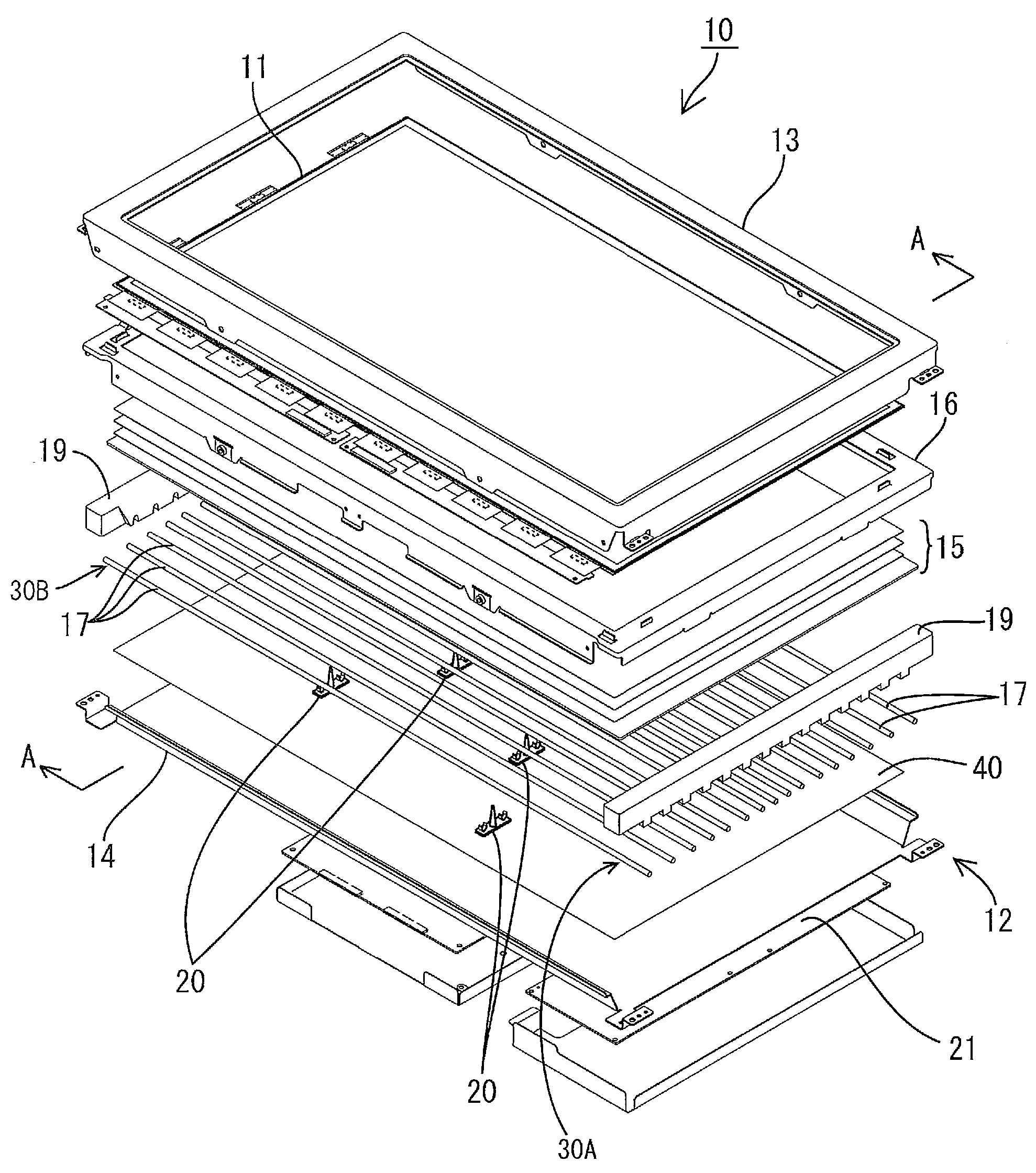
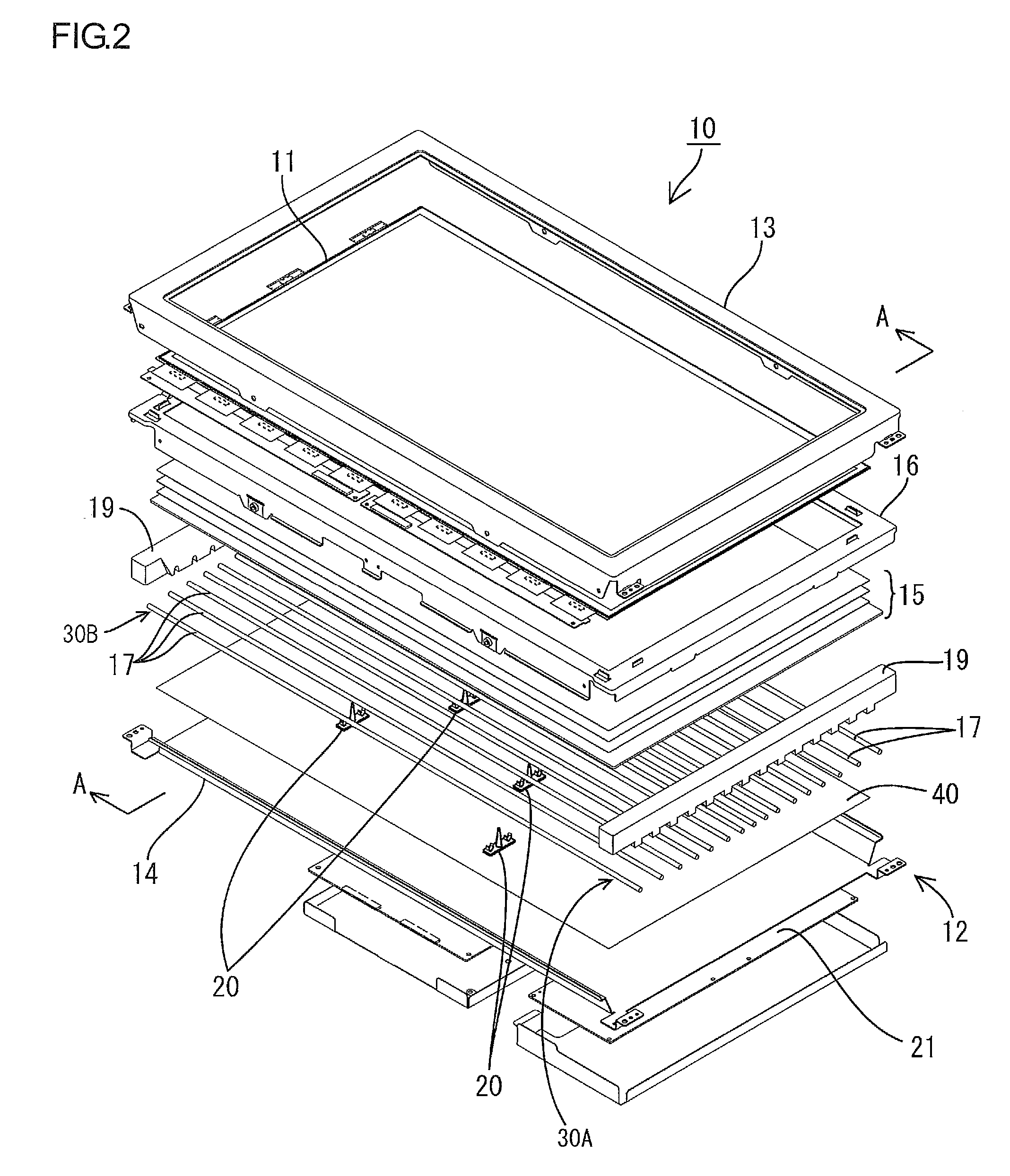
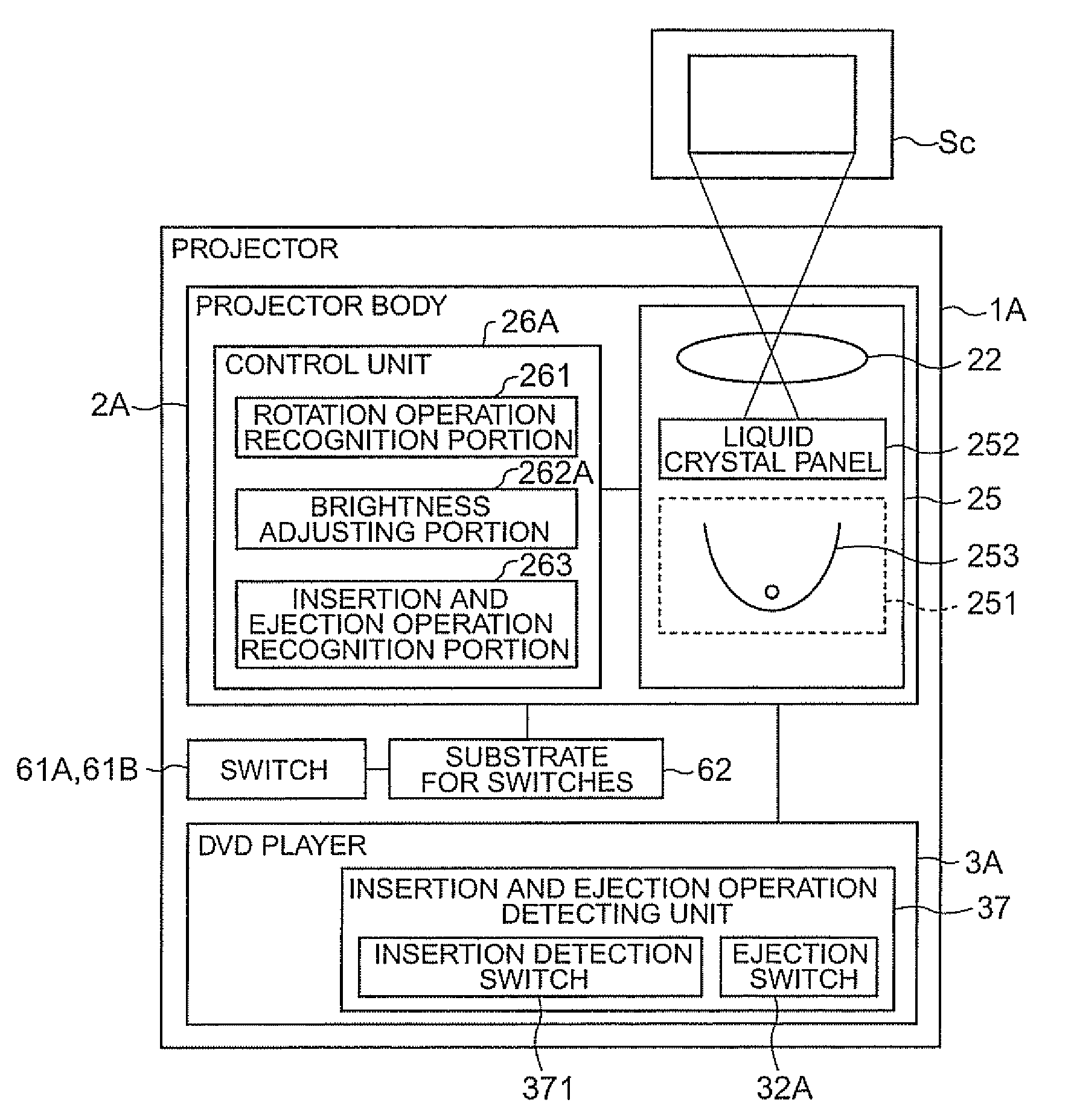
Projector and brightness adjusting method
InactiveUS20090015800A1Comfortable to useReduce lighting brightnessTelevision system detailsPrintersOutput deviceComputer science
A projector includes: a projector body, which has a light modulating device that modulates light emitted from a light source according to input image information to thereby form an optical image and a projection optical device that projects the formed optical image in an enlarged manner; an image output device that outputs the image information to the projector body; a connection mechanism for connecting the projector body and the image output device with each other such that the projector body and the image output device can rotate relative to each other; a rotation operation detecting unit that detects a relative rotation operation of the projector body and the image output device; and a control unit that controls the projector body and the rotation operation detecting unit. The control unit includes: a rotation operation recognition portion that recognizes whether or not the projector body and the image output device are in a relative rotation operation state on the basis of a detection result of the rotation operation detecting unit; and a brightness adjusting portion that adjusts the brightness of light emitted from the projection optical device when the rotation operation recognition portion has recognized that the projector body and the image output device are in the relative rotation operation state.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optically controlled lighting device and control method thereof
InactiveUS20150156849A1Save electricityReduce lighting brightnessElectric circuit arrangementsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsPersistence of visionEngineering
An optically controlled lighting device and a control method thereof are provided. The optically controlled lighting device includes a lighting main body, a dimming time controller and an optical detector. The control method includes the following steps. In a step (a), the lighting main body, including a controlling circuit and a light source, the dimming time controller and the optical detector are provided. In a step (b), the dimming time controller is enabled to respectively generate an on / off dimming signal, and the light source is respectively turned on / turned off during an on / off period respectively corresponding to the on / off dimming signal, wherein the off period is shorter than the time period for producing persistence of vision. In a step (c), an ambient light intensity is detected by the optical detector during the off period, the brightness of the light source is increased or decreased or the light source is turned off.
Owner:LIVINGSTYLE ENTERPRISES
Novel light guide plate
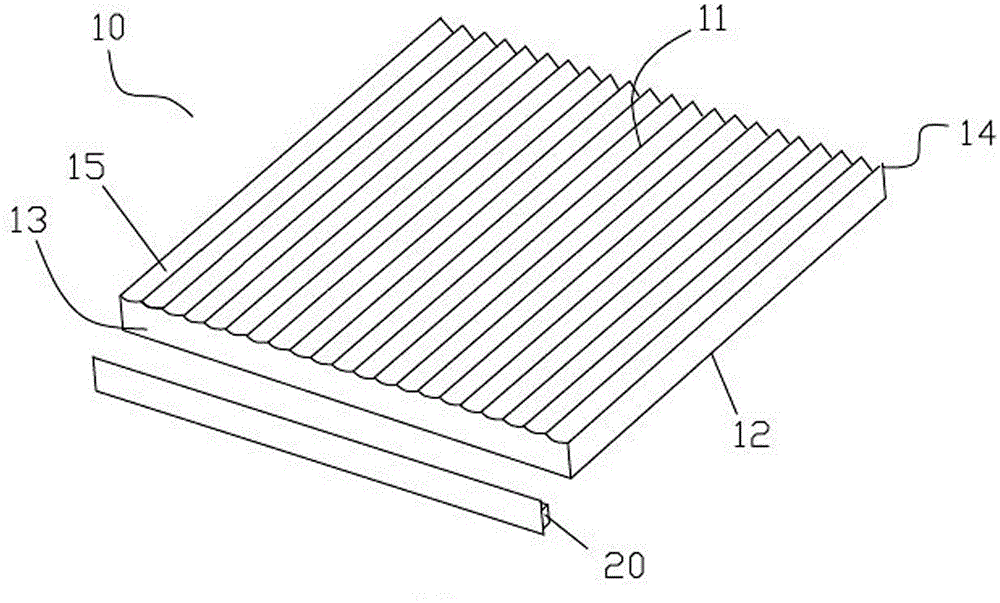
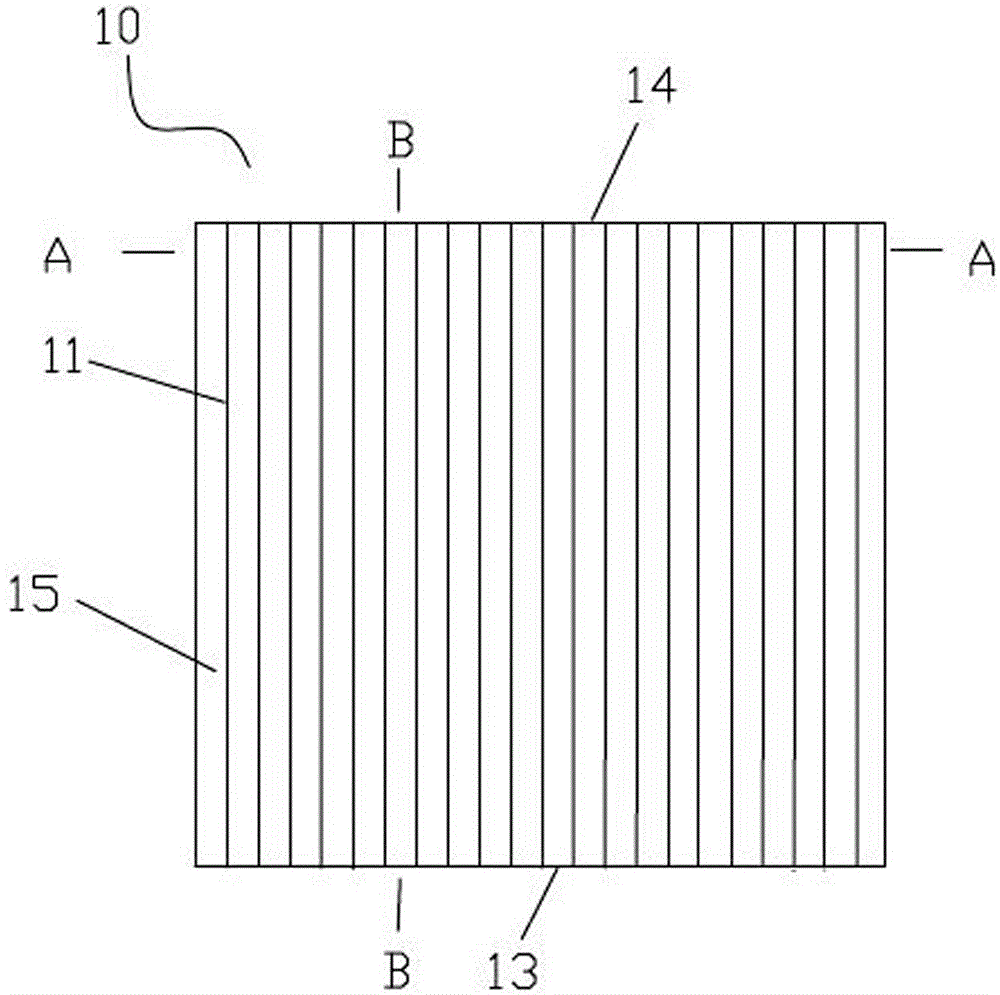
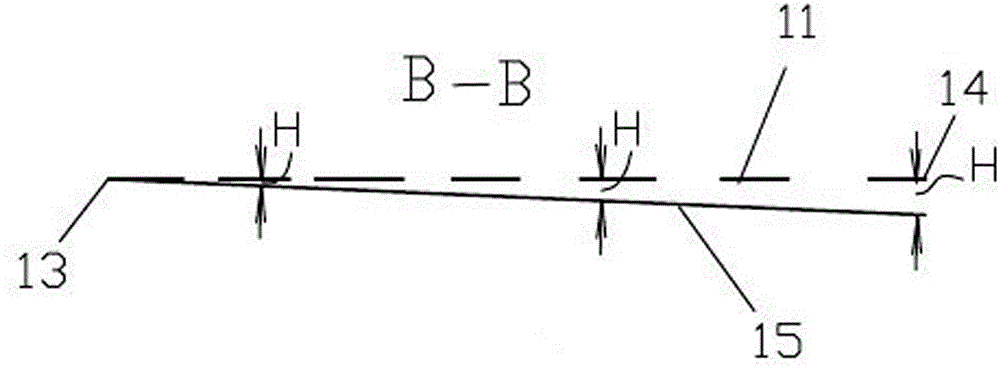
InactiveCN104459870AImprove and improve uniformityReduce lighting brightnessMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceLight guideOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a backlight source light guide plate, in particular to a novel light guide plate. The novel light guide plate comprises a light emergent surface and a light reflecting surface arranged oppositely, and a common end of the light emergent surface and the light reflecting surface is a light incident surface where light of a light source is emitted to the light guide plate; the end surface opposite to the light incident surface is the rear end surface; a plurality of grooves are formed in the light emergent surface and throughout from the light incident surface to the rear end surface, and all the grooves are arranged in parallel; the depth of the grooves at the light incident surface is smallest, the depth of the grooves at the rear end surface is largest, and the bottom of each groove is a slop getting deep from the light incident surface to the rear end surface. The novel light guide plate can improve the uniformity of outlet light of a weak light source after the light is guided by the light guide plate, and the light will be emitted in a dispersed mode gradually after entering the light guide plate instead of concentrating at the front end of the light guide plate to be emitted, so that the outlet light brightness near the rear end of the light guide plate is basically consistent with that near the front end. The novel light guide plate is particularly suitable for guiding the light of an LED primary color lamp and an OLED with low penetrating capacity.
Owner:东莞市现代精工实业有限公司
Multi-purpose flat plate lamp
InactiveCN103162138AReduce lighting brightnessEffective optical distance increasePoint-like light sourceElectric lightingColor rendering indexLight guide
The invention discloses a multi-purpose flat plate lamp. The multi-purpose flat plate lamp comprises a lamp bead installment layer, a diffusion plate, a printed light-guiding plate and a reflective sheet, wherein the lamp bead installment layer, the diffusion plate, the printed light-guiding plate and the reflective sheet are sequentially arranged in an overlapped mode. The reflective sheet is attached to the bottom of the printed light-guiding plate, and optical membrane capable of ensuring that permeated delaying light becomes soft is overlapped between the diffusion plate and the printed light-guiding plate. Compared with the prior art, because the optical membrane is additionally arranged on the multi-purpose flat plate lamp on the basis of the structure of an ordinary flat plate lamp, luminance brightness of a light source is dropped, but the effective light distance is increased to ensure that light effect is guaranteed within the distance, and meanwhile color rendering indexes are increased. Furthermore, because a heat dissipation body is arranged on an aluminum frame of the multi-purpose flat plate lamp, service life of a power source is prolonged and light weakening of a light-emitting diode (LED) light bead is delayed.
Owner:杭州益久来文化创意科技有限公司
Charger
InactiveUS8633824B2Reduce power consumptionReduce lighting brightnessCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingEngineeringElectric power
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
3D (three dimensional) display device and phase delay piece thereof
InactiveCN102636834AReduce lighting brightnessImprove image crosstalkPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsOptical axisDisplay device
The invention discloses a 3D (three dimensional) display device and a phase delay piece of the 3D display device. The phase delay piece is arranged on an external surface of a polaroid and comprises multiple first phase delay unit lines, multiple second phase delay unit lines and non-phase delay unit lines, wherein the second-phase delay unit lines and the first phase delay unit lines are arranged in a staggering manner, each non-phase delay unit line is arranged between the adjacent first phase delay unit lines and second phase delay unit line; an optical axis of the non-phase delay unit lines are vertical or parallel to a penetrating shaft of the polaroid; and according to the non-phase delay unit lines, the brightness of juncture of a phase delay region can be weakened, and further improve image interference caused by the attaching and the shifting of the phase delay piece can be improved.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Surface light source device
InactiveUS8454206B2Easy to useReduce pollutionNon-electric lightingLight source combinationsPrismOptoelectronics
A surface light source device includes a lamp post, a number of light sources distributed in rows on the side surfaces of the lamp post, and a number of first prism sheets and second prism sheets arranged around the lamp post in that order. Each of the first prism sheets and the second prism sheets includes a light incident surface and a light exit surface opposite to the light incident surface. Each of the light exit surfaces includes a number of substantially parallel elongated protrusions, and the longitudinal directions of the elongated protrusions of the first prism sheet and the second prism sheet are substantially perpendicular to each other. The first prism sheets and the lamp post are approximately spaced by a first predefined distance, and the second prism sheets and the first prism sheets are approximately spaced by a second predefined distance.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Surface light source device
InactiveUS20120020069A1Easy to useReduce pollutionNon-electric lightingLight source combinationsPrismOptoelectronics
A surface light source device includes a lamp post, a number of light sources distributed in rows on the side surfaces of the lamp post, and a number of first prism sheets and second prism sheets arranged around the lamp post in that order. Each of the first prism sheets and the second prism sheets includes a light incident surface and a light exit surface opposite to the light incident surface. Each of the light exit surfaces includes a number of substantially parallel elongated protrusions, and the longitudinal directions of the elongated protrusions of the first prism sheet and the second prism sheet are substantially perpendicular to each other. The first prism sheets and the lamp post are approximately spaced by a first predefined distance, and the second prism sheets and the first prism sheets are approximately spaced by a second predefined distance.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
System and method for projecting an image and display using said system
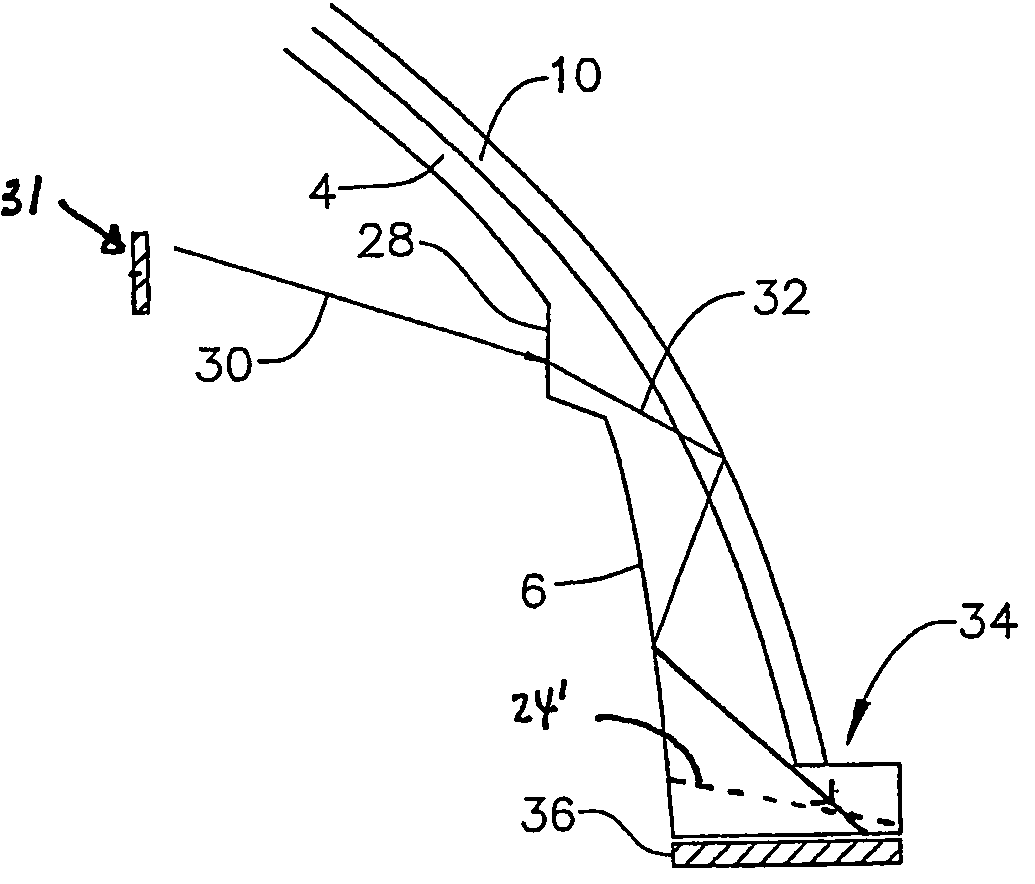
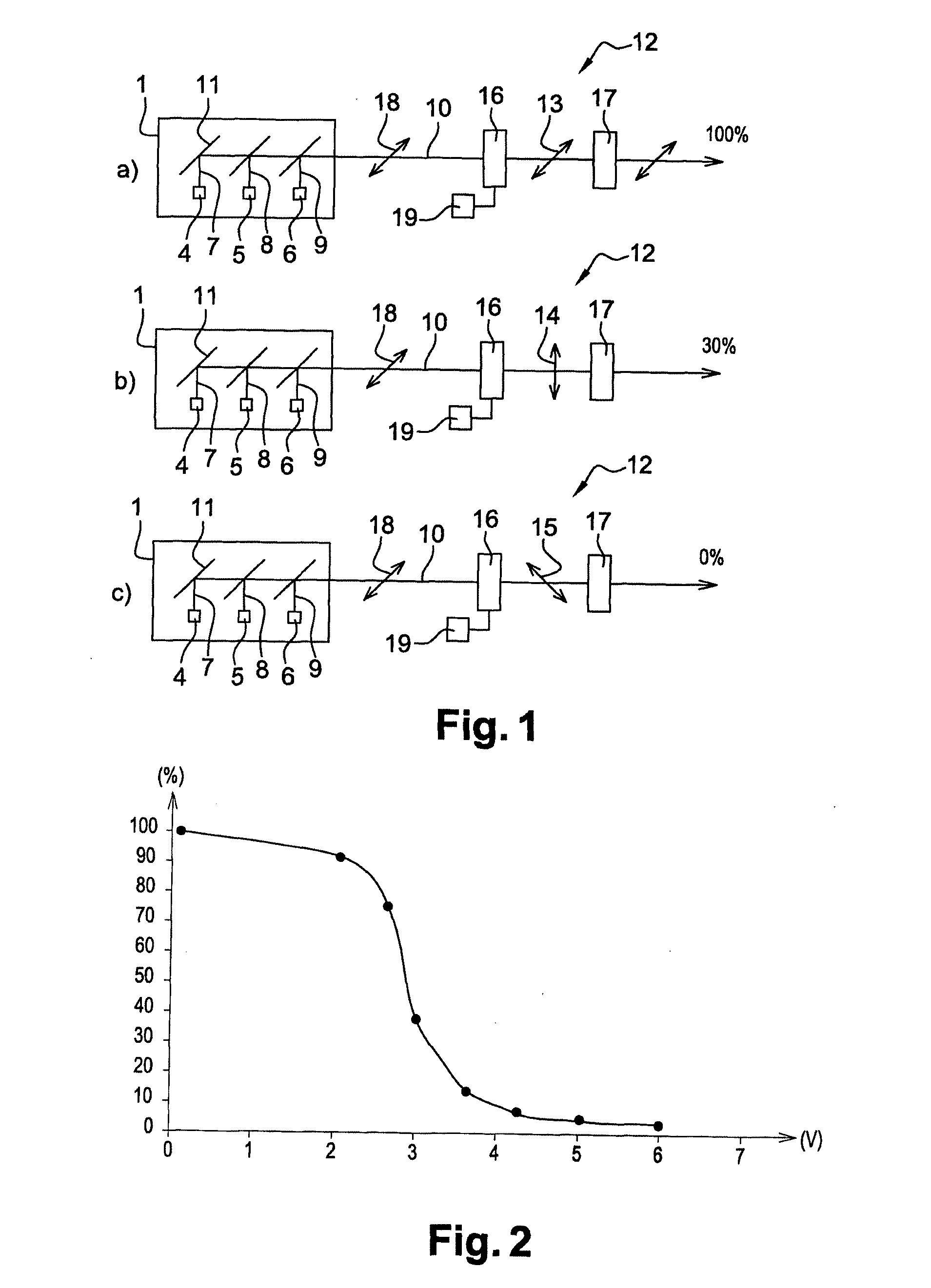
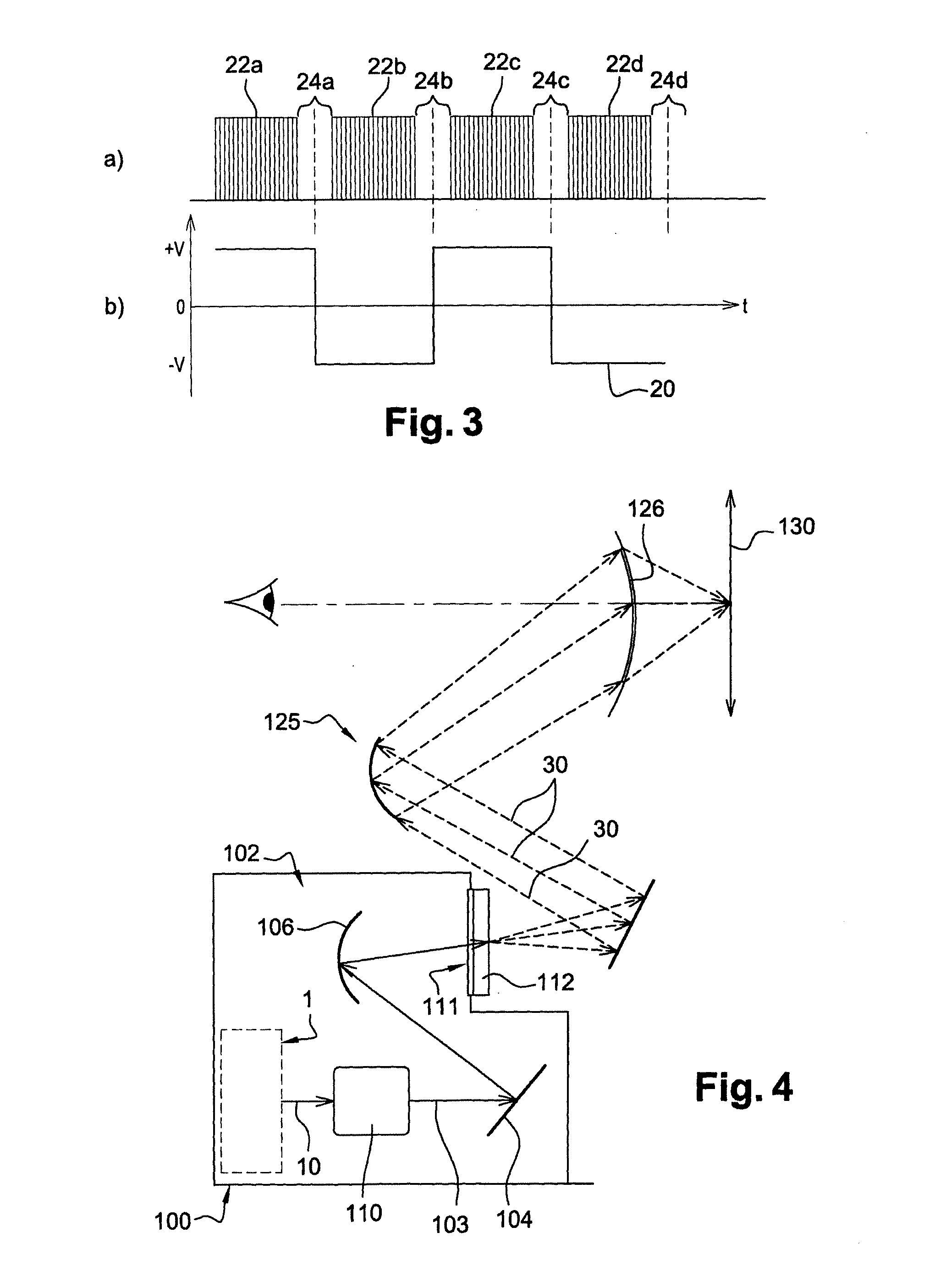
ActiveUS20170023788A1Reduce lighting brightnessProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesLight beamConsecutive frame
The invention relates to an image-projection system which comprises a device (1) for emitting a light beam (10) and means for forming an image from said light beam (10), said image being broken down into frames projected consecutively by said system. The system comprises means (12) for dimming the light beam (10) comprising a liquid crystal cell (16), capable of being controlled by an alternating signal between two voltage levels, said alternating signal being generated by a signal generator (19), said signal generator (19) switching said alternating signal from one voltage level to the other between the projections of two consecutive frames of the image.
Owner:VALEO COMFORT & DRIVING ASSISTANCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com