Patents
Literature
108 results about "Compound document" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
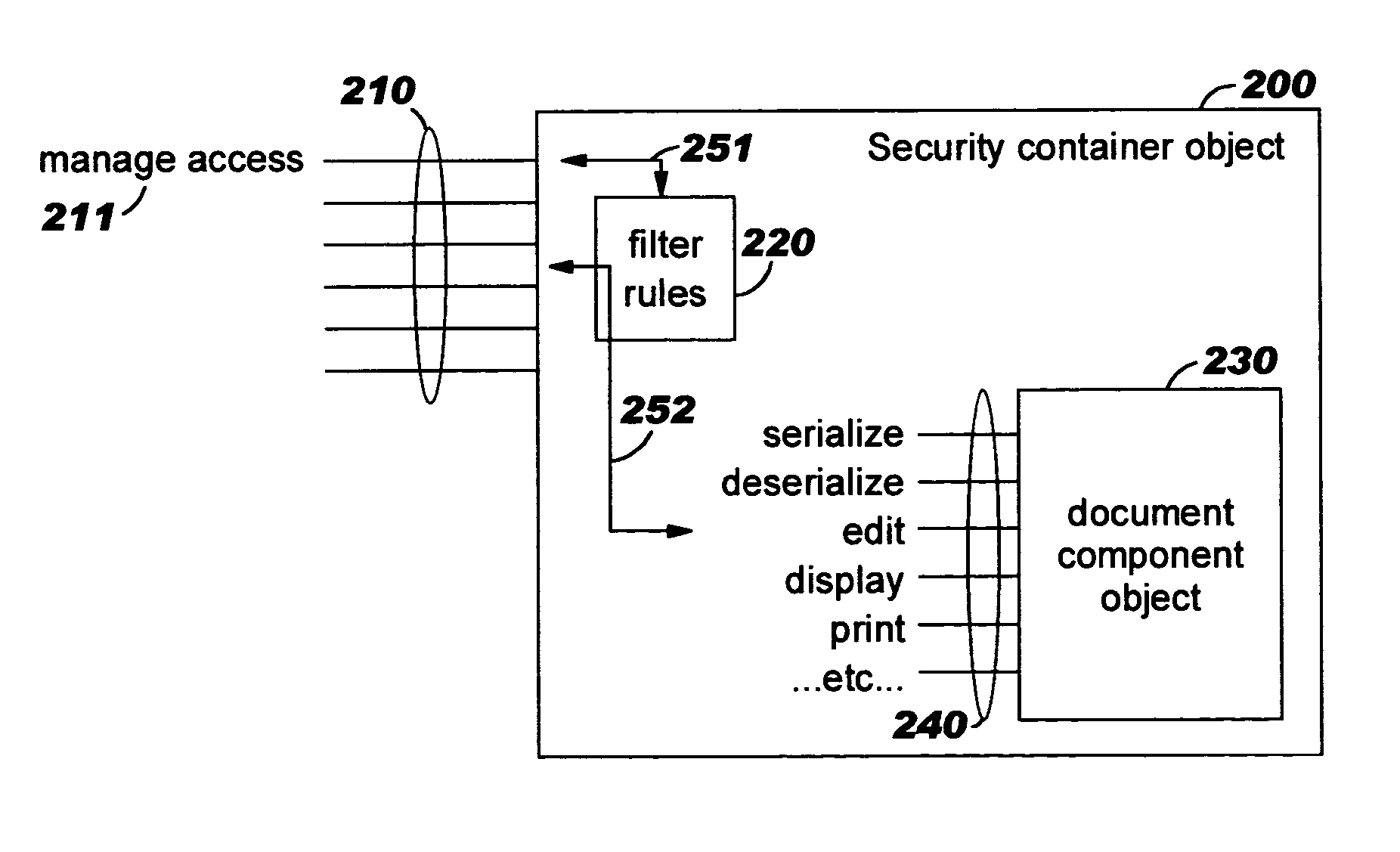
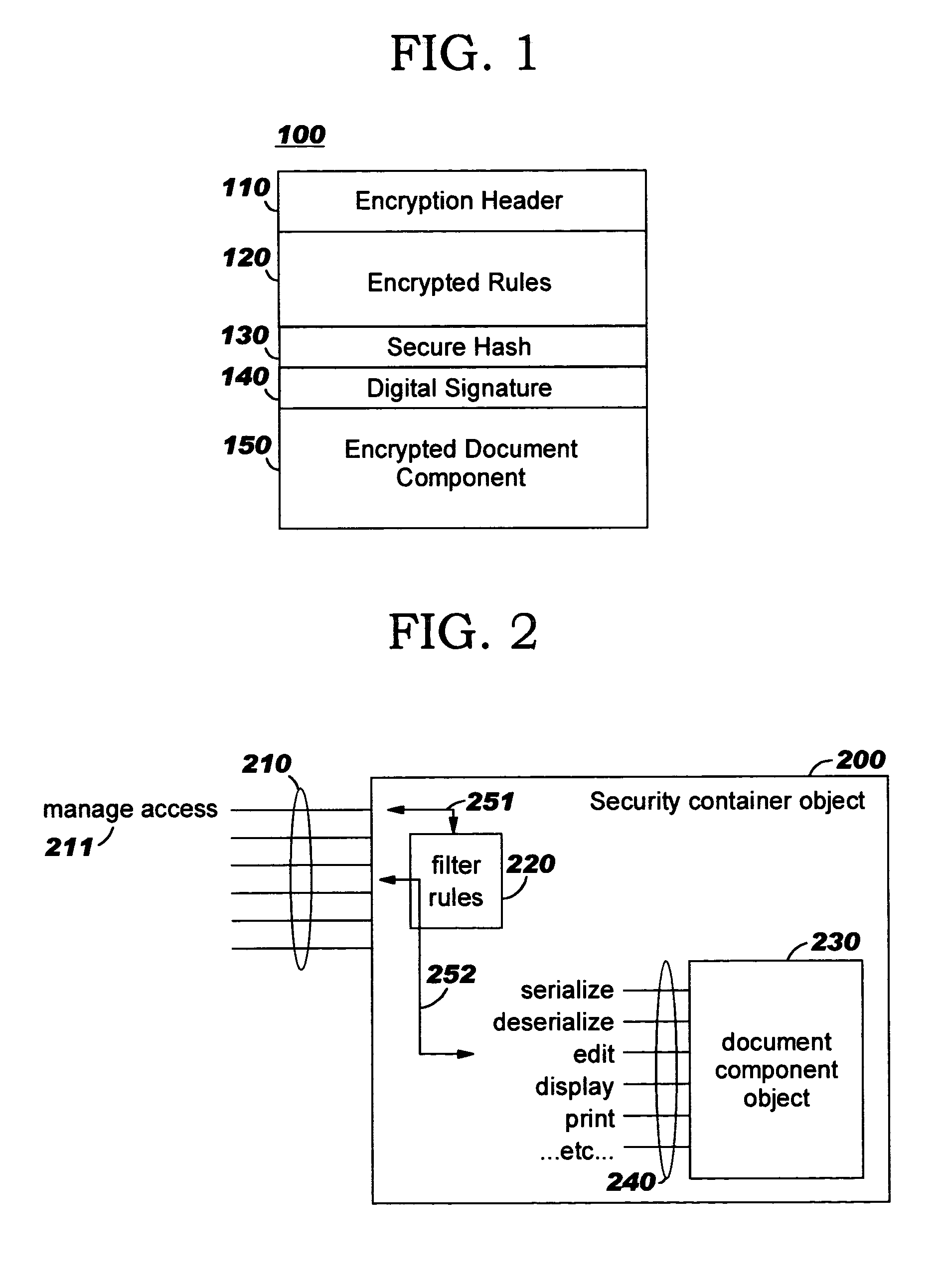
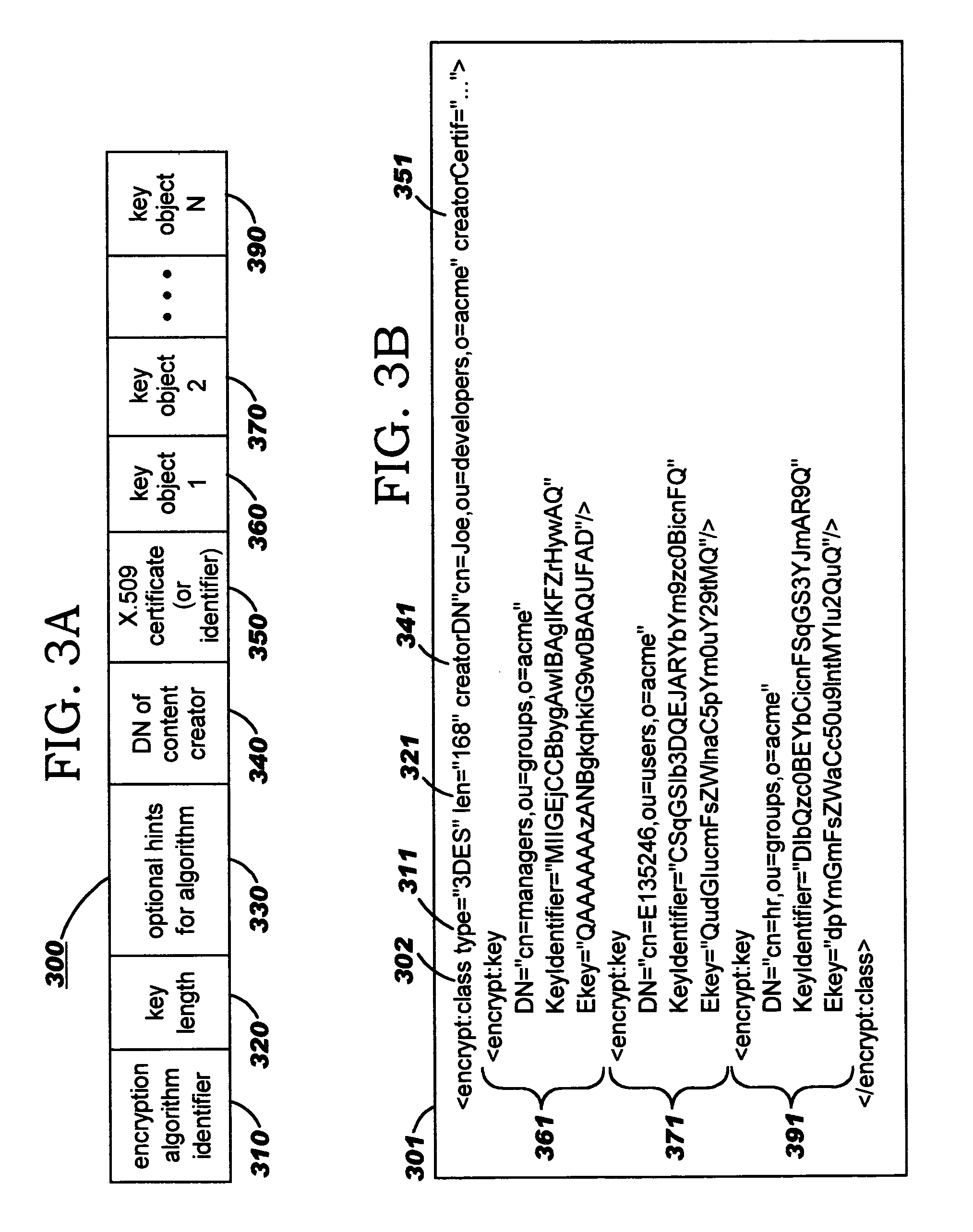
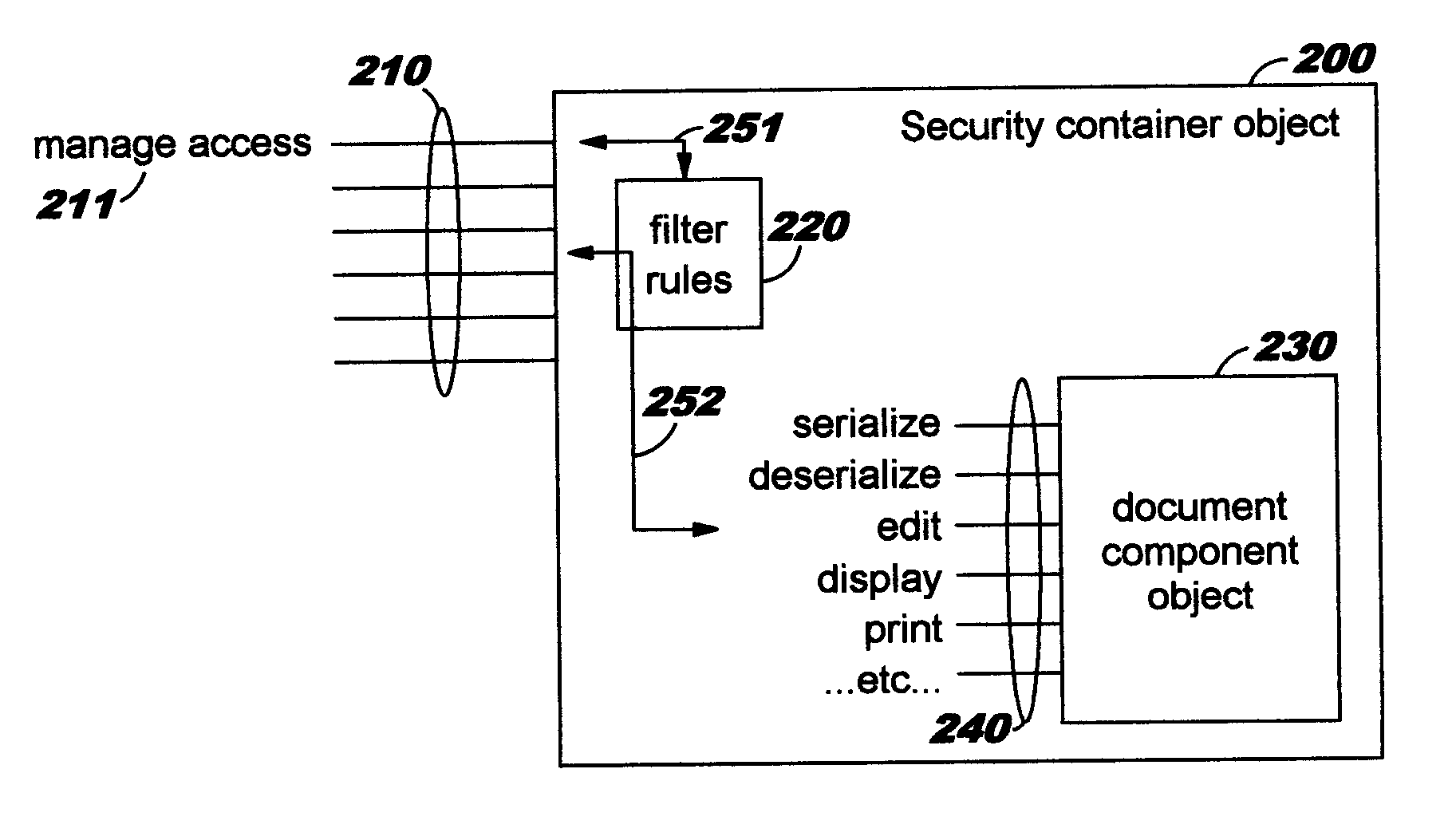
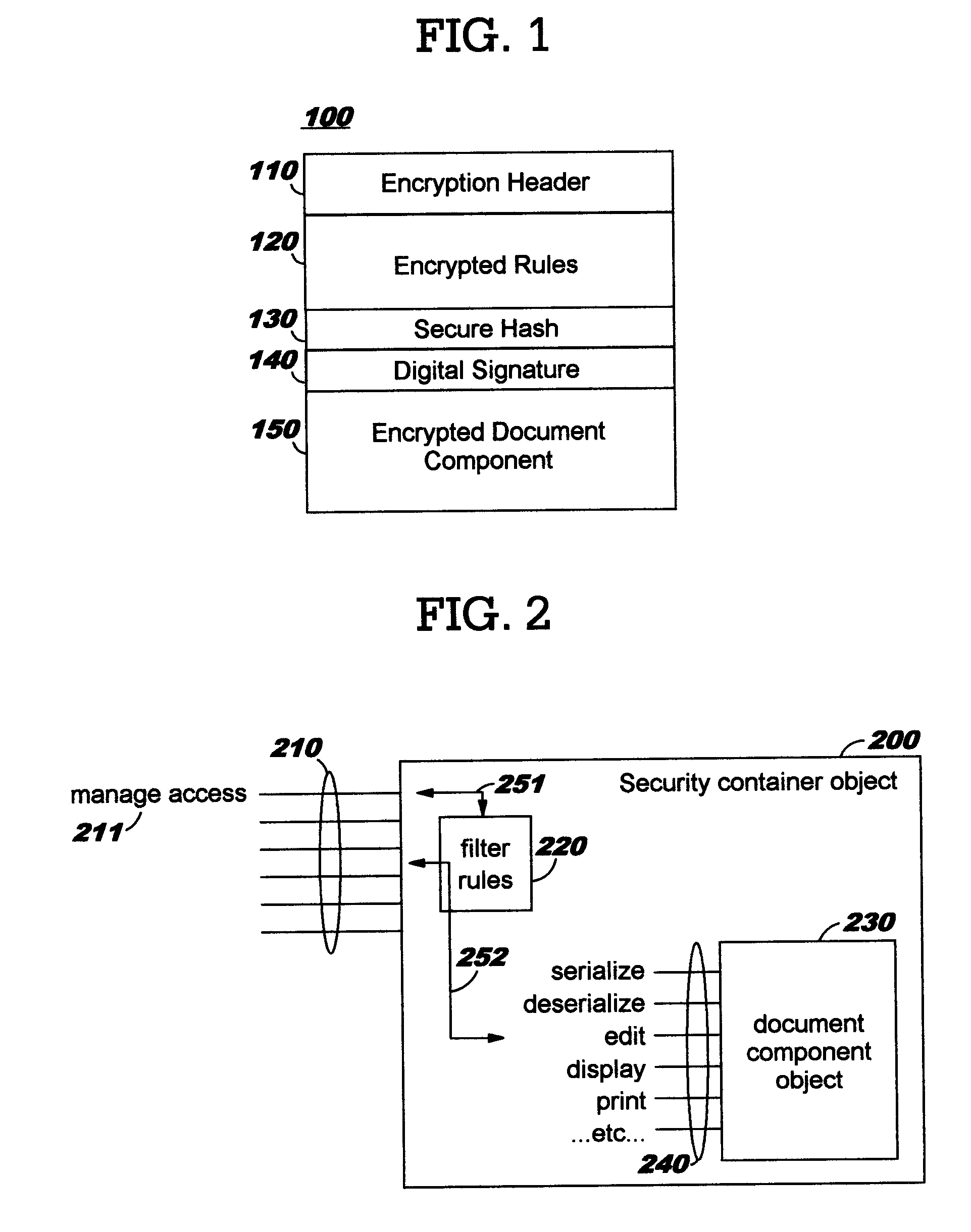
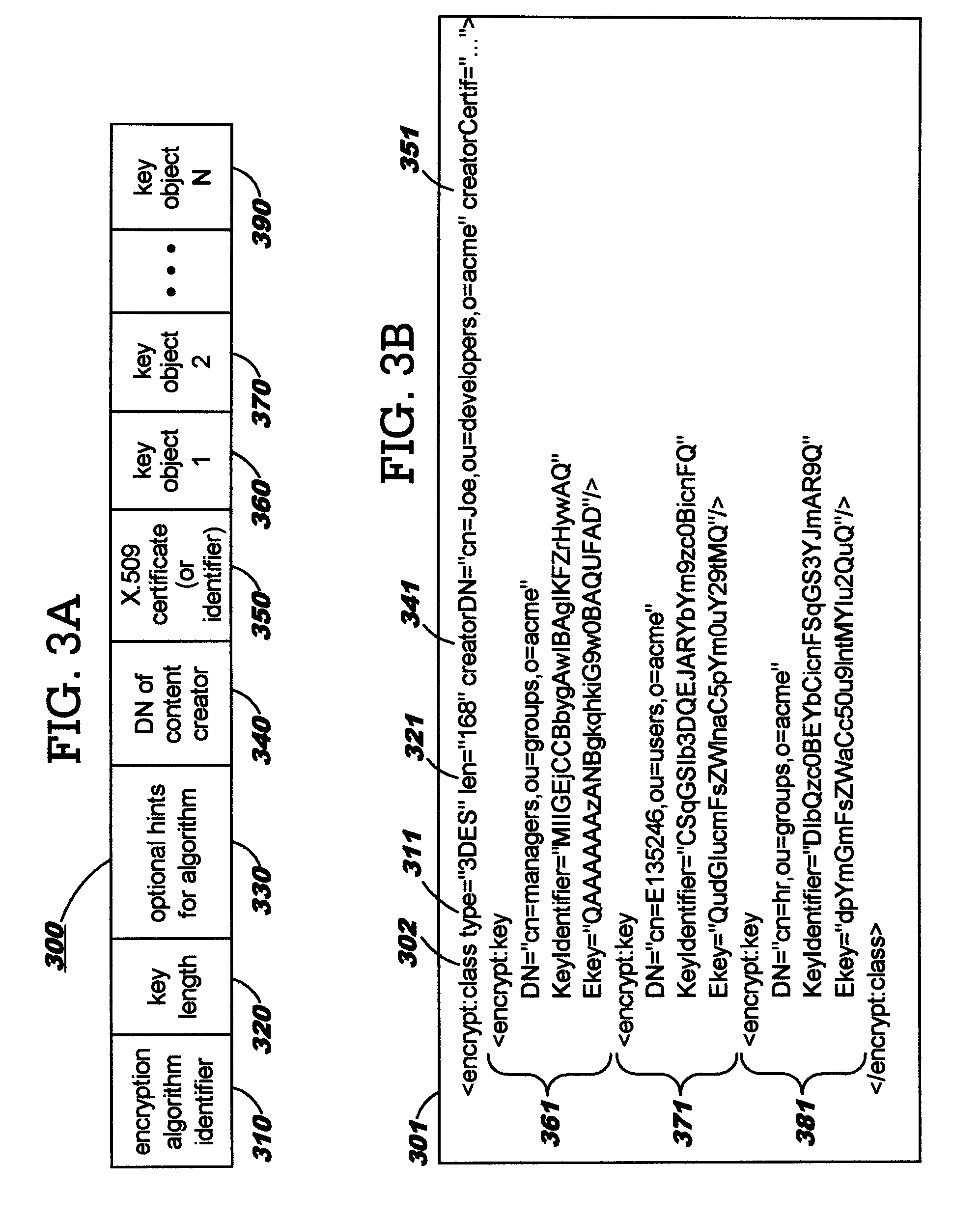
Security containers for document components
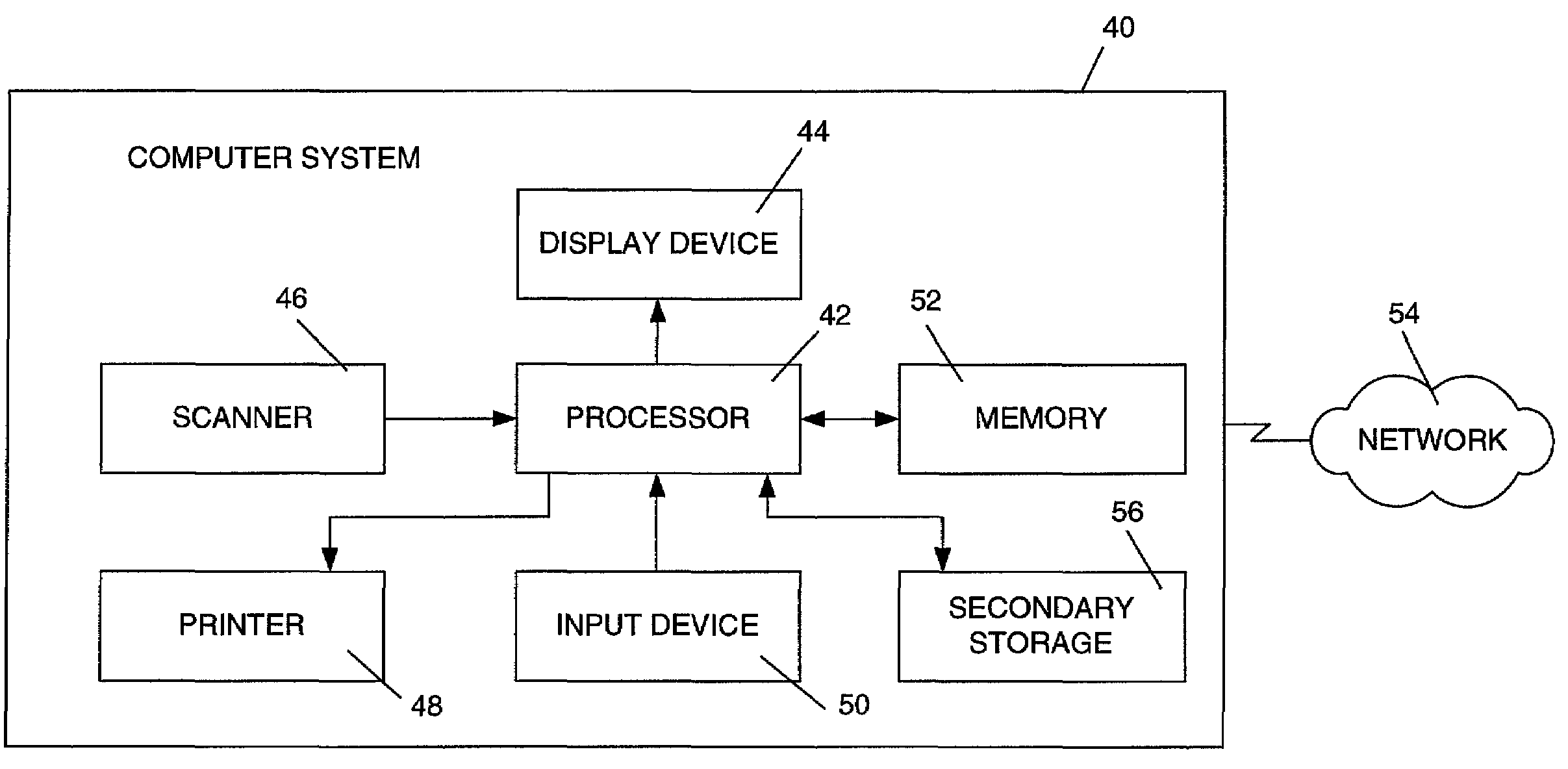
ActiveUS20050039034A1Easy to useSafe storageKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSoftware engineeringPaper document
Methods, systems, computer program products, and methods of doing business whereby document components are secured or controlled using “security containers” which encapsulate the components (and other component metadata). A “security container” encapsulates the component (i.e., content) that is to be controlled within a higher-level construct such as a compound document. The security container also contains rules for interacting with the encapsulated component, and one or more encryption keys usable for decrypting the component and rules for authorized requesters.
Owner:IBM CORP
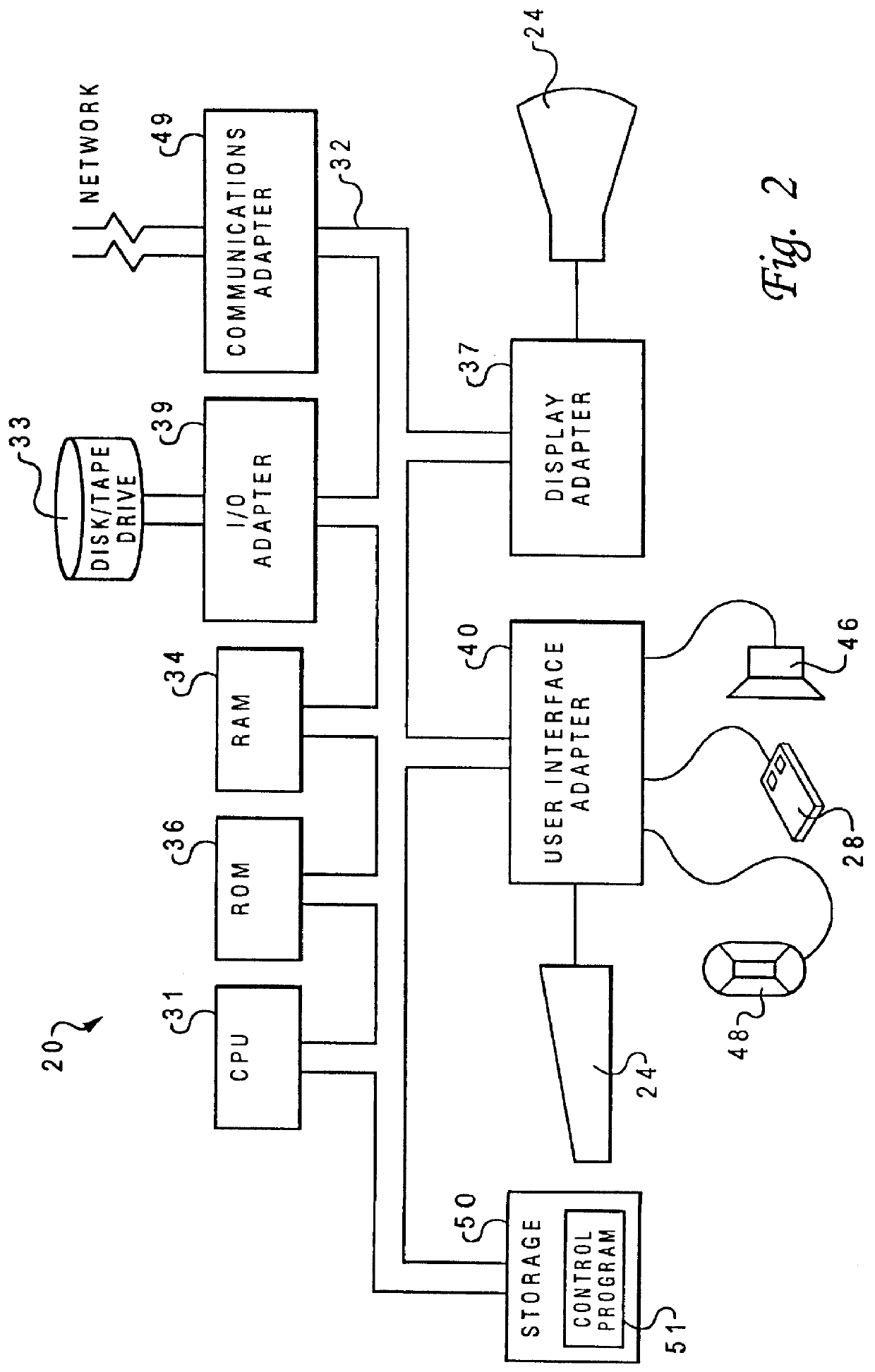
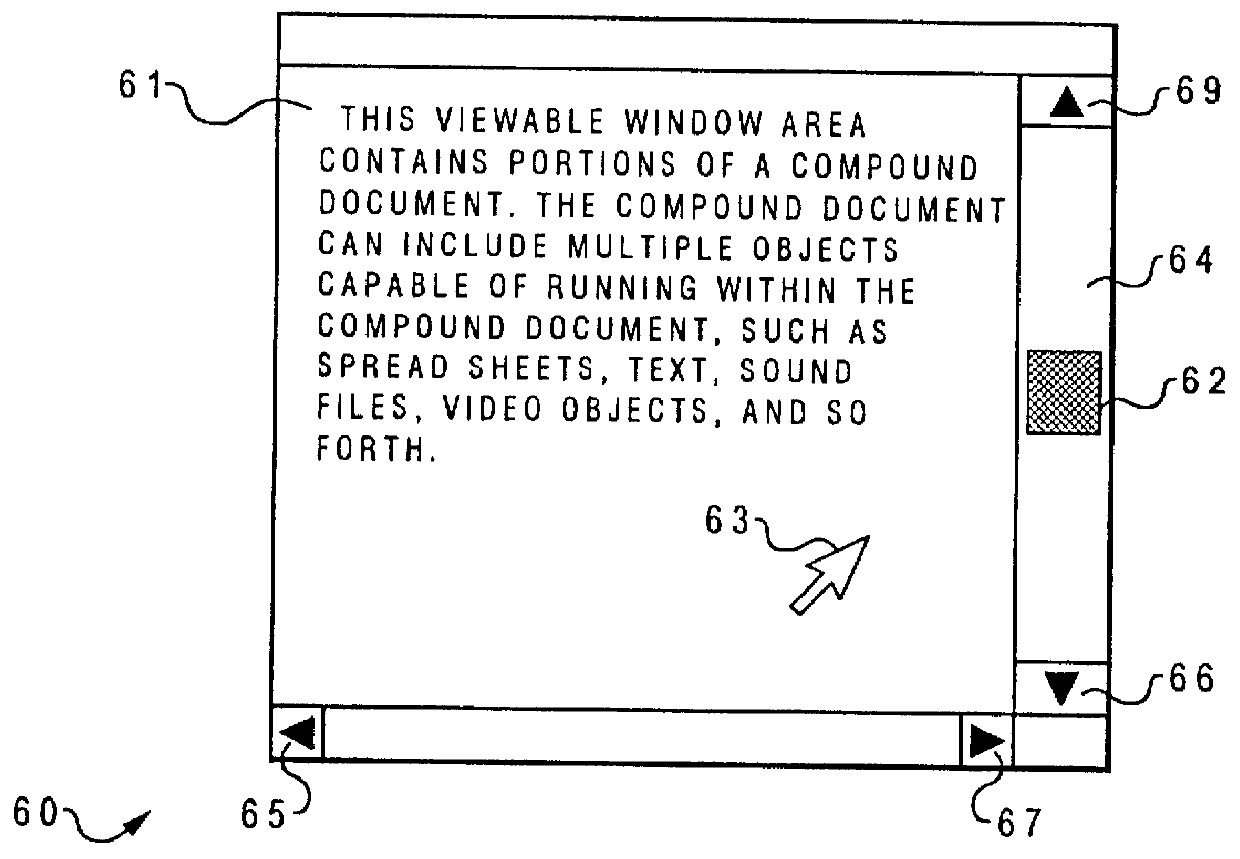
Method and system for locating and displaying the position of a cursor contained within a page of a compound document
InactiveUS6014140AData processing applicationsCathode-ray tube indicatorsData processing systemGraphics
A method and system for locating and displaying the actual position of a cursor contained within a predetermined selectable segment of a compound document within a graphical user interface environment within a data-processing system wherein only a portion of the predetermined selectable segment can be displayed at one time. In response to user input, the graphical user interface dynamically moves to the relative location of a predetermined selectable segment of a compound document wherein a cursor is located. Next, if the cursor is not located within a viewable portion of the graphical user interface, the graphical user interface automatically scrolls within the predetermined selectable segment to a relative location of the cursor within the predetermined selectable segment. Thereafter, a portion of the predetermined selectable segment wherein the cursor is located is displayed within the graphical user interface.
Owner:IBM CORP
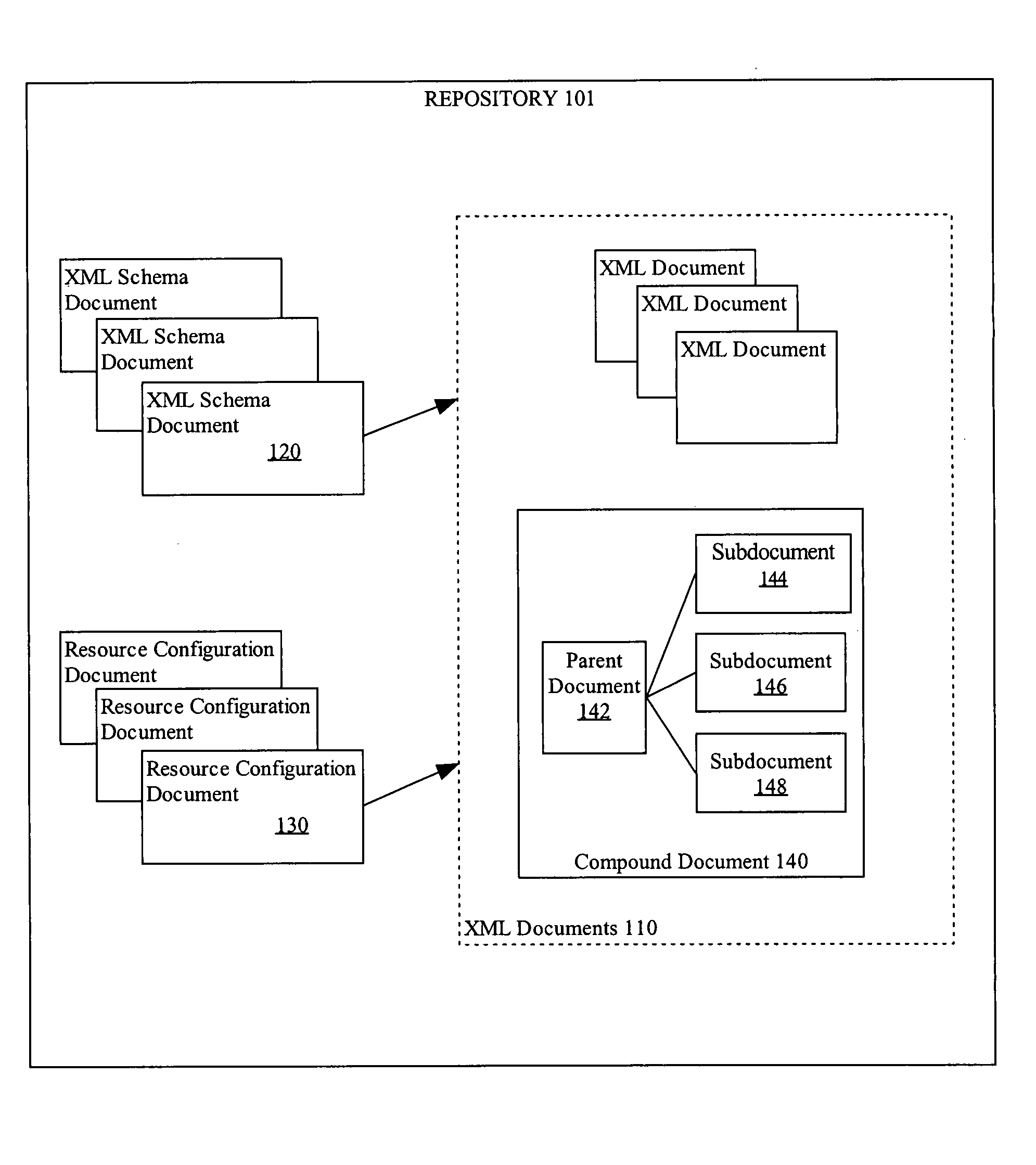
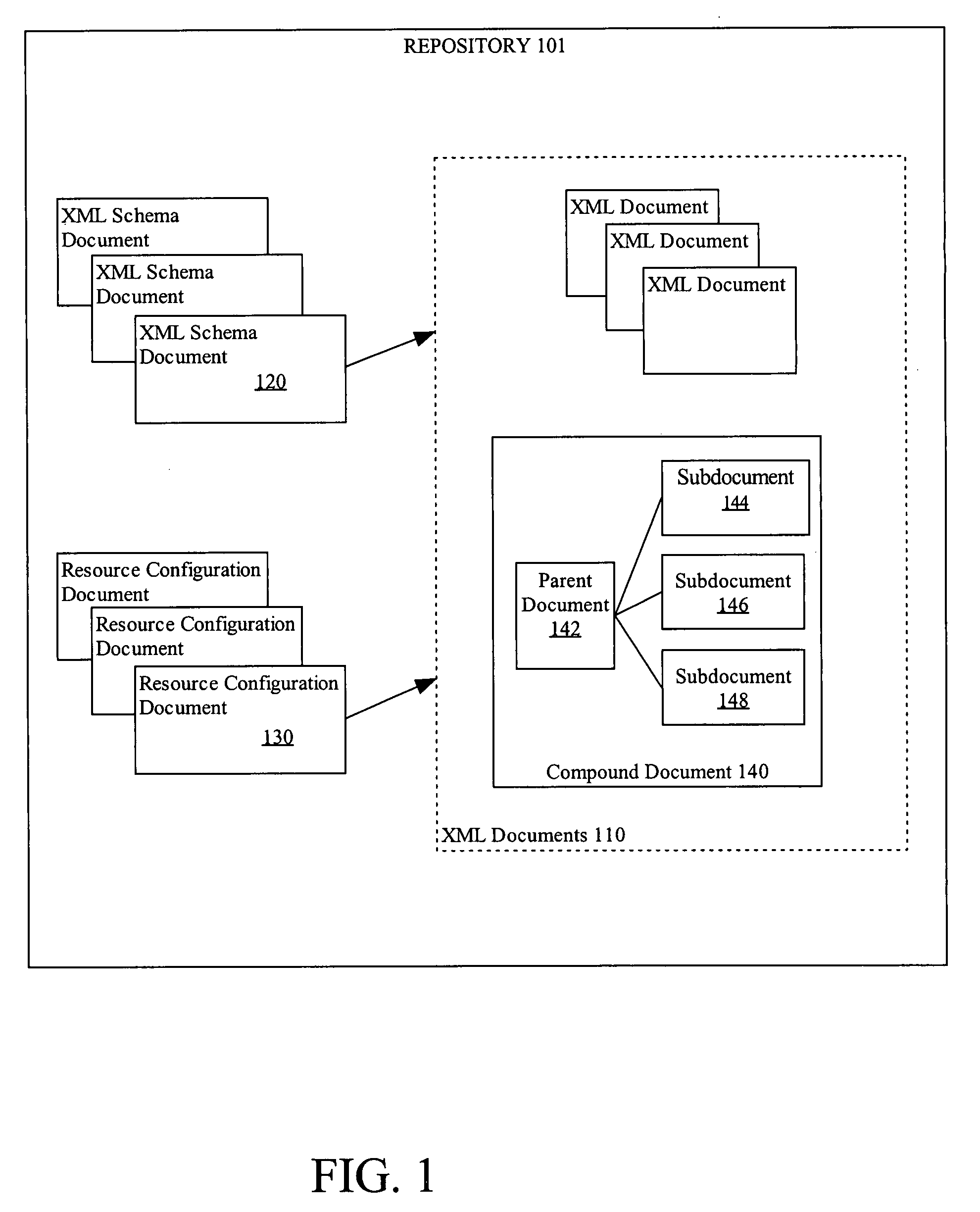
Managing compound XML documents in a repository
ActiveUS9183321B2Natural language data processingWebsite content managementGranularityDocument preparation
A declarative mechanism is used to manage large documents within a repository. The large documents are sectioned into subdocuments that are linked together by a parent document. The combination of the parent document and subdocument is referred to as a compound document. There are multiple options for configuring rules to break up a source document into a compound document and naming the subdocuments. The compound documents may be queried using statements that treat the compound document as a single XML document, or the parent document of a subdocument may be queried and treated independently. Access control and versioning can be applied at the finer granularity of the subdocument.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System, method, and computer program product for identifying multi-page documents in hypertext collections
InactiveUS20050071310A1Precise definitionBetter quality toolDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsWebIDEntry point
A system, method, and computer program product for identifying compound documents as a coherent body of hyperlinked material on a single topic as created by an author or collaborating authors, analyzing the content and structure of the compound documents and related hyperlinks, and responsively selecting a preferred entry point at which to begin processing such documents. The body of material may include the internet, an intranet, or other digital library that typically has content distributed over several separate pages or URLs, sometimes in a hierarchical directory structure. The processing may include creating at least one taxonomy, as well as searching or indexing the compound documents. The identification and analysis schemes include a observation of a number of heuristics run on component documents in the compound documents.
Owner:IBM CORP
Deploying and distributing of applications and software components
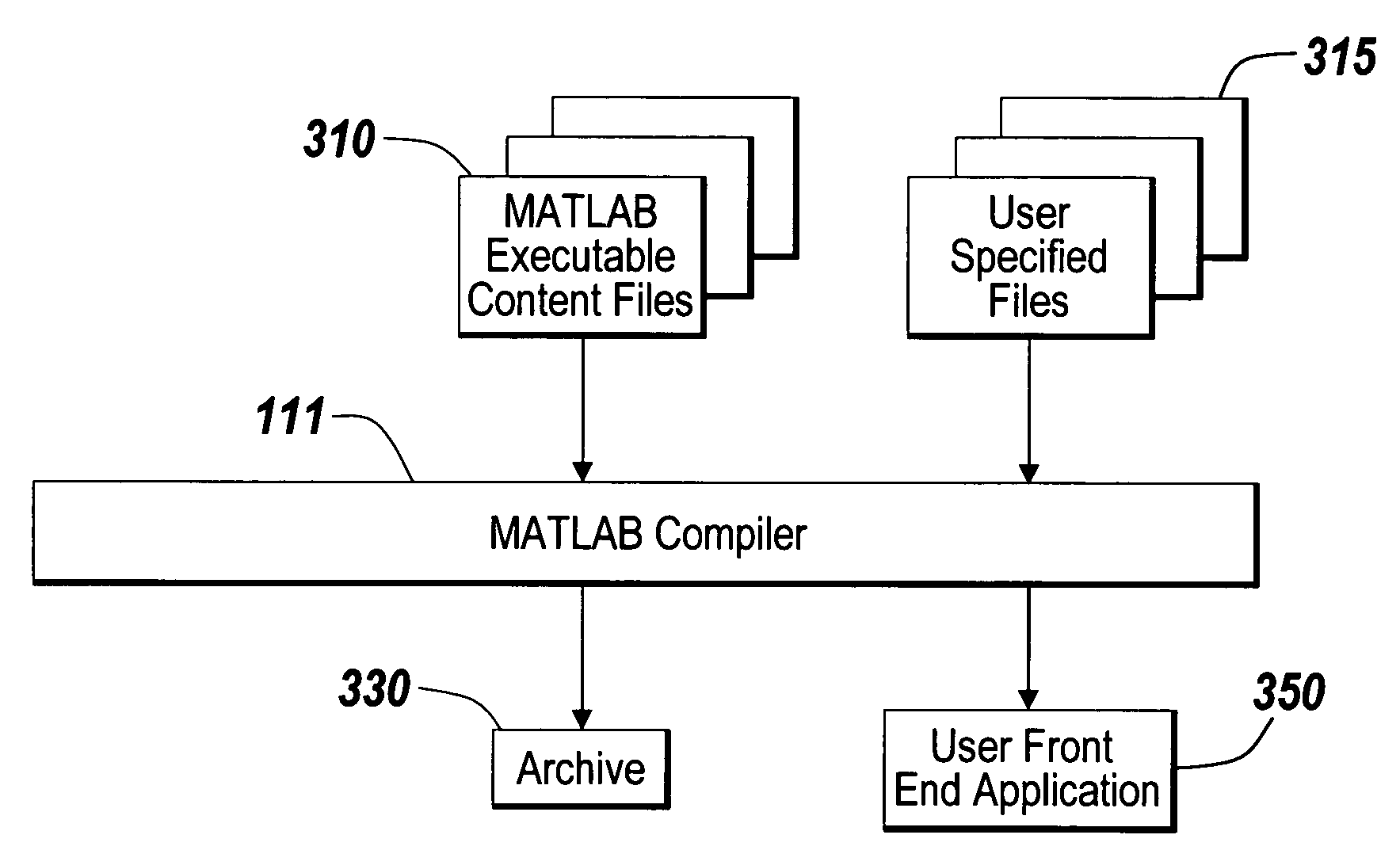
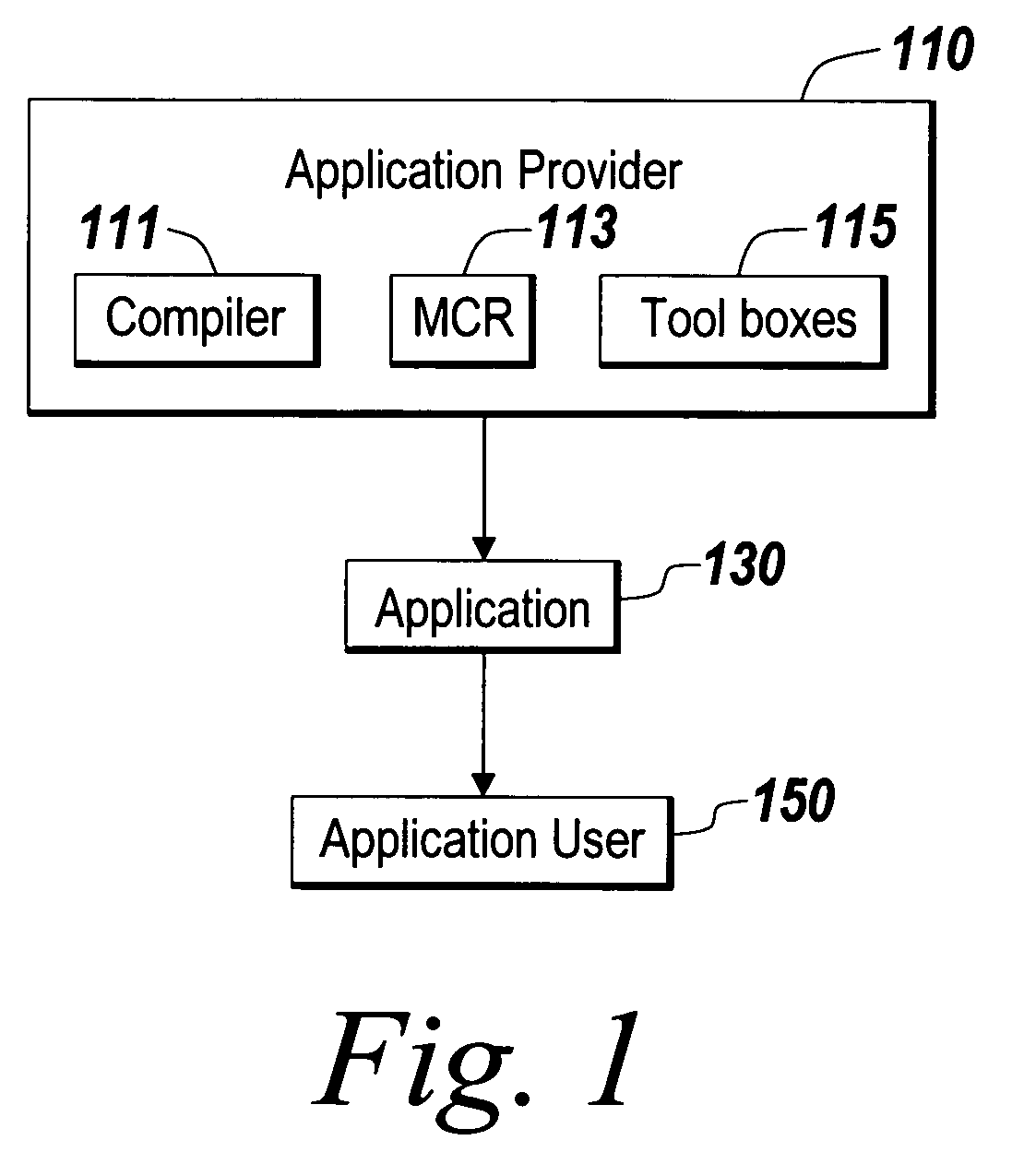
ActiveUS7685596B1Easy to controlEasy to trackFile access structuresProgram loading/initiatingVirtual file systemDirectory structure
A self-contained virtual file system is disclosed for deploying and distributing an application and / or software component. Executable files relating to the application are included in a distributable composite file. The composite file and a user front end application are deployed and distributed to an application user where the application is executed. An application provider can tag the composite file with the version information and other useful meta-data of the files for the application. The format of the composite file may support the storage of any kind of file types and associated meta-data. The composite file may contain the hierarchical directory structure of the files for the application so that the hierarchical directory structure is installed in the application user's electronic device.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Method and apparatus for segmentation of compound documents
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
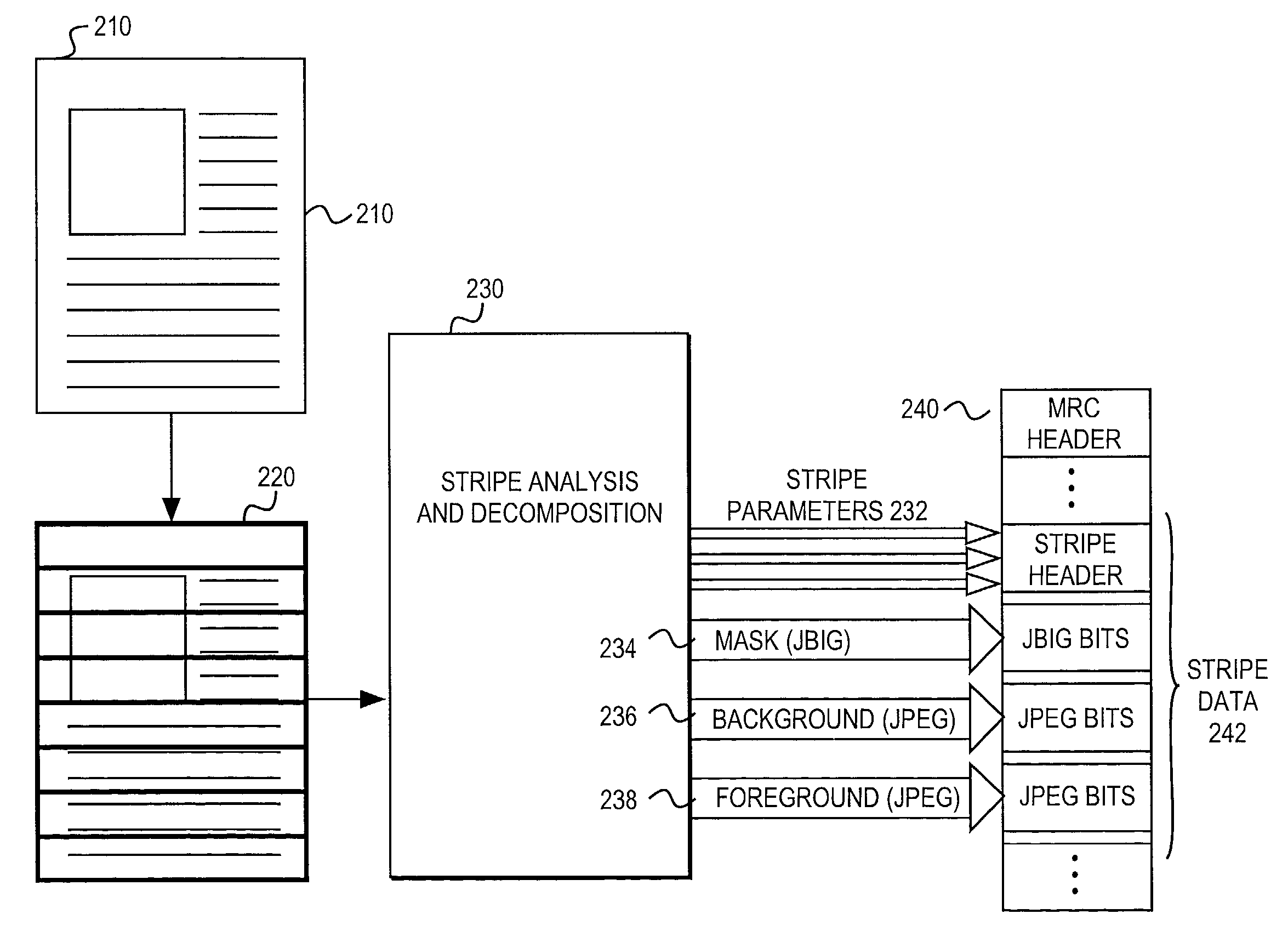
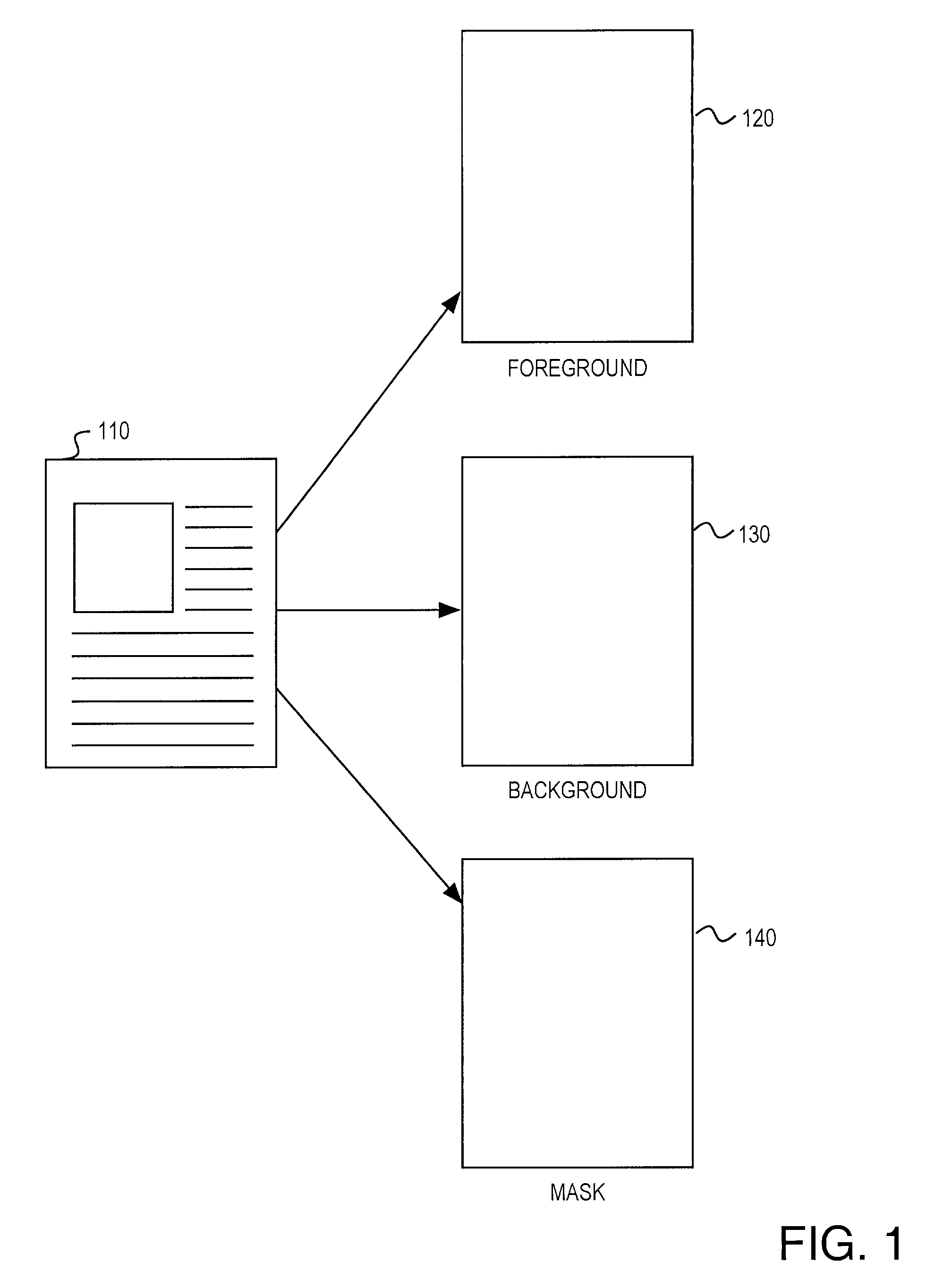
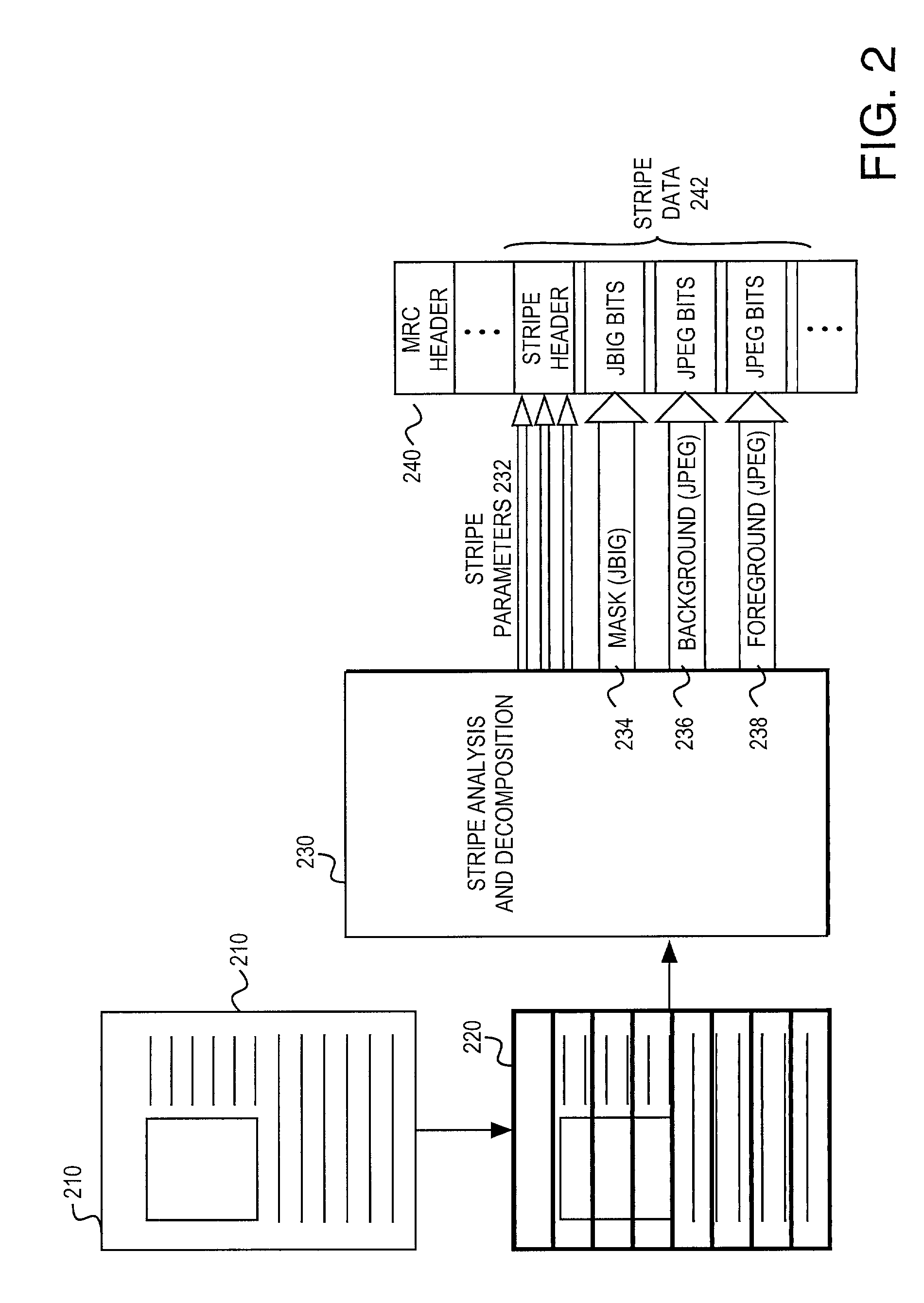
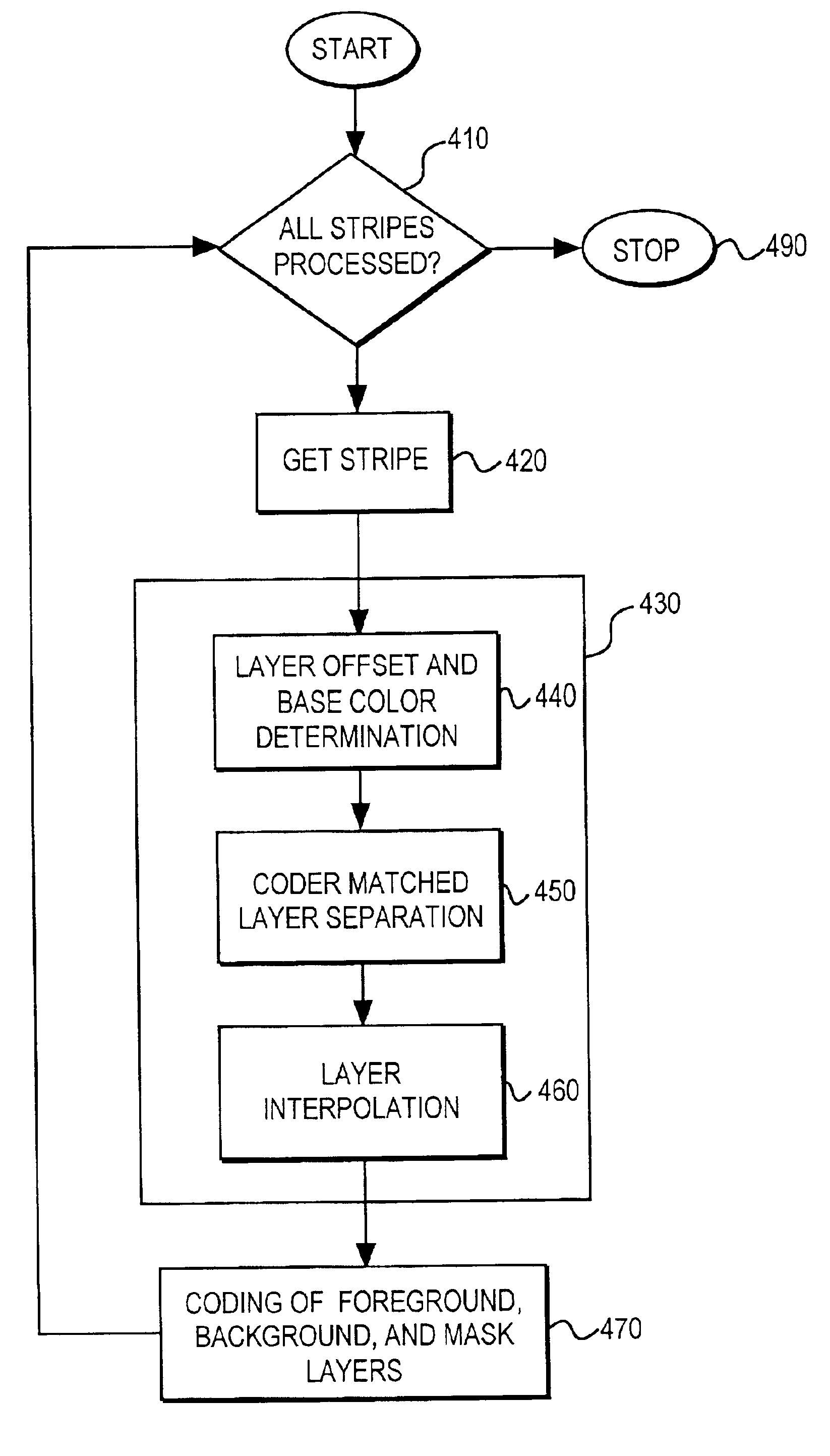
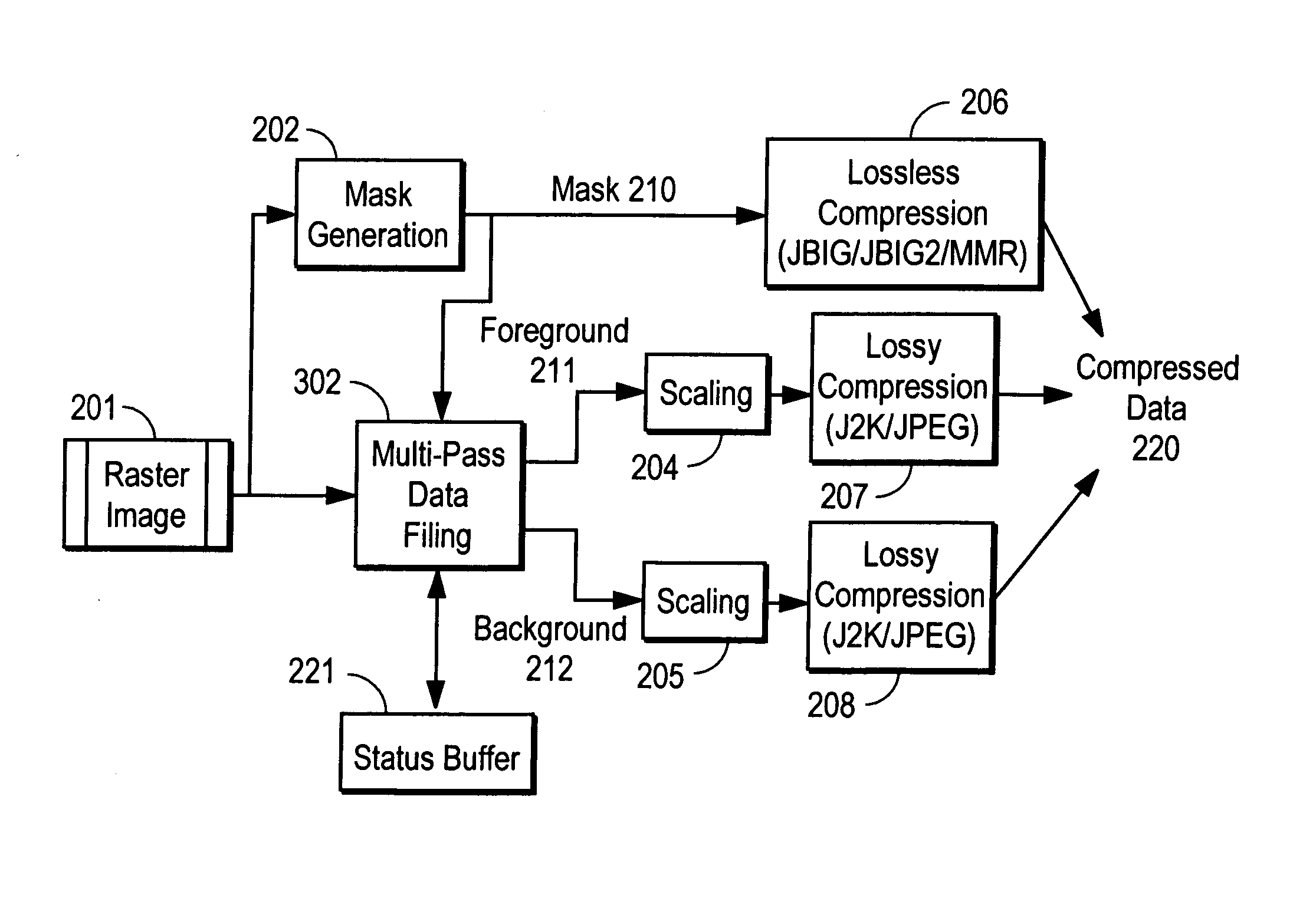
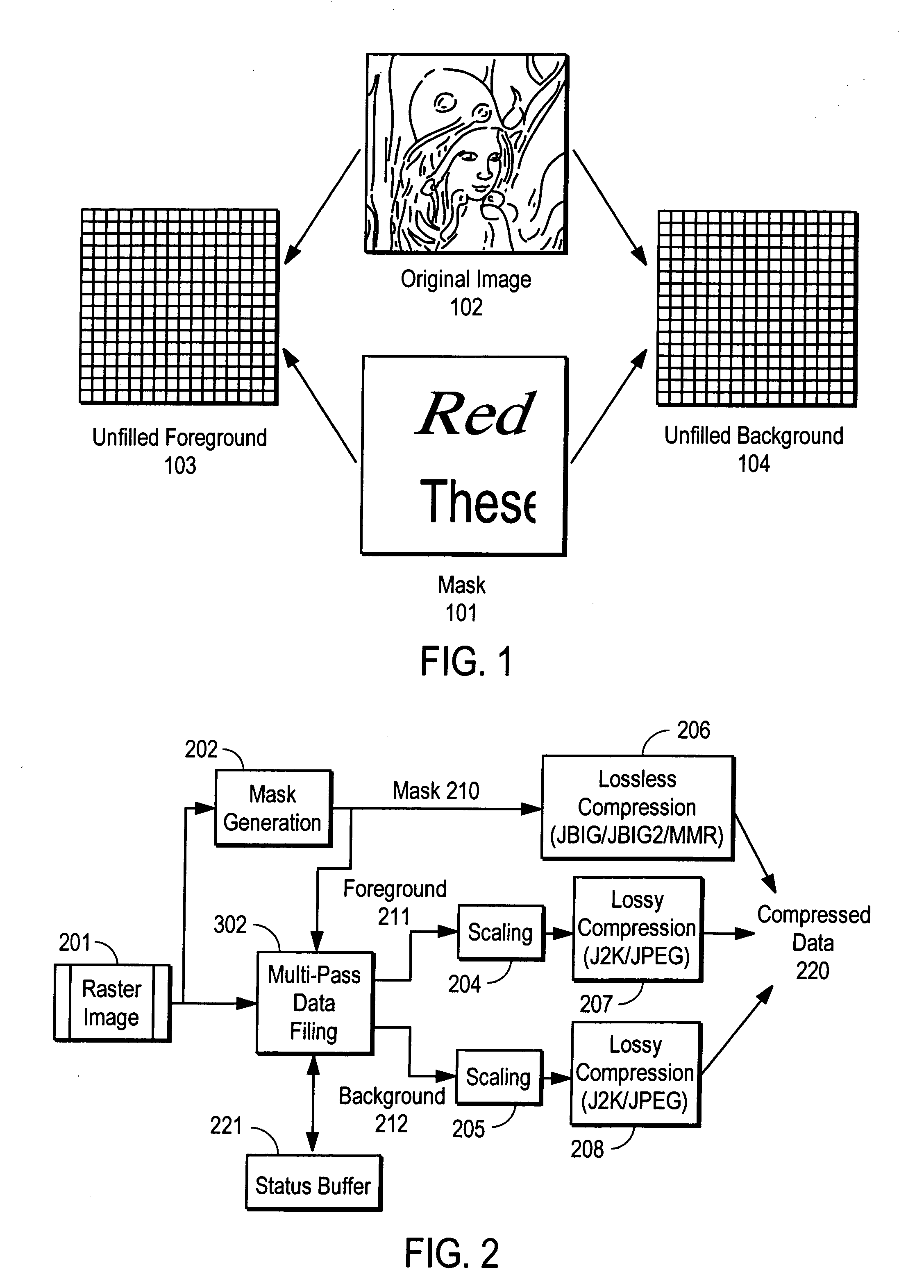
Coder matched layer separation for compression of compound documents
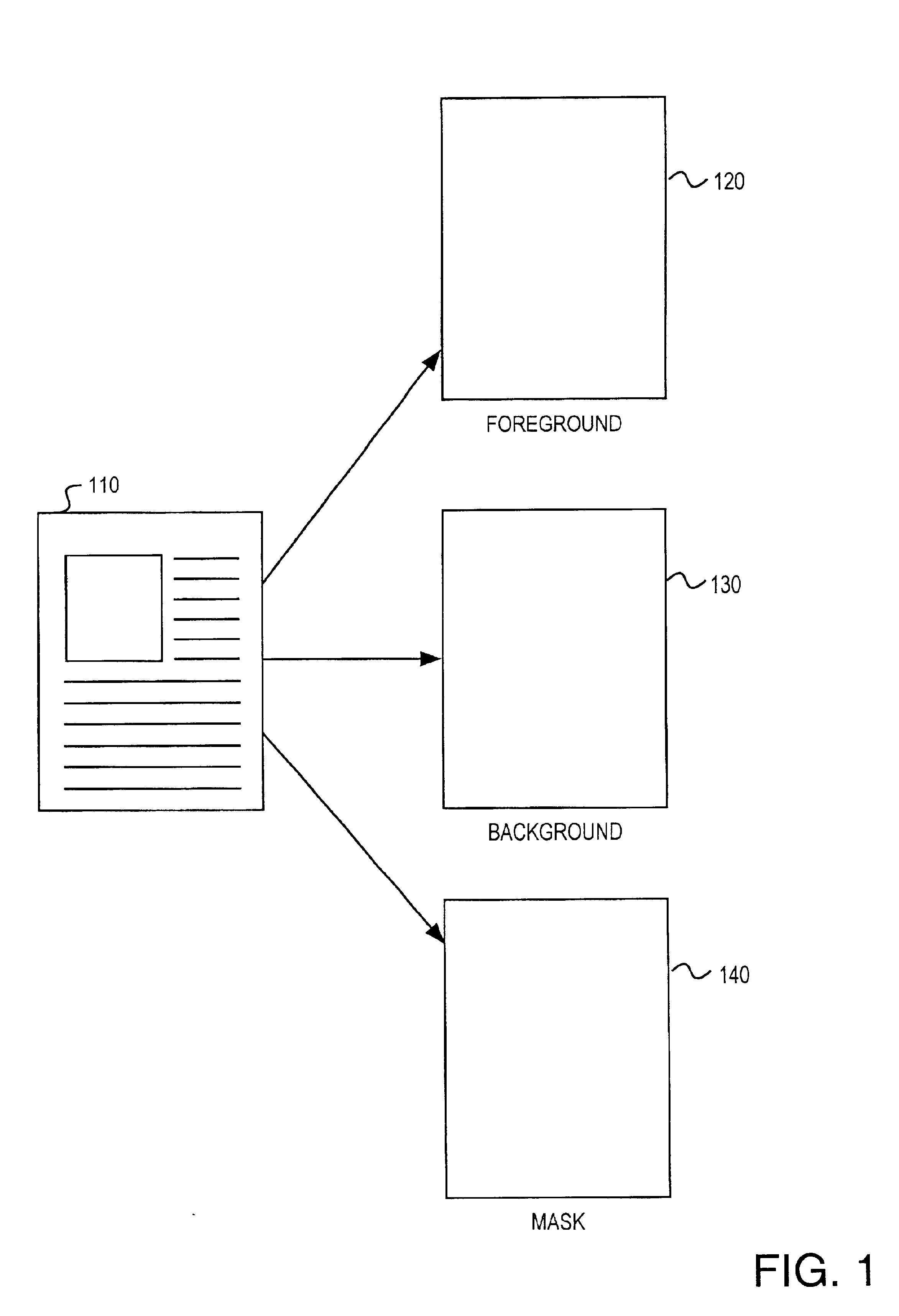
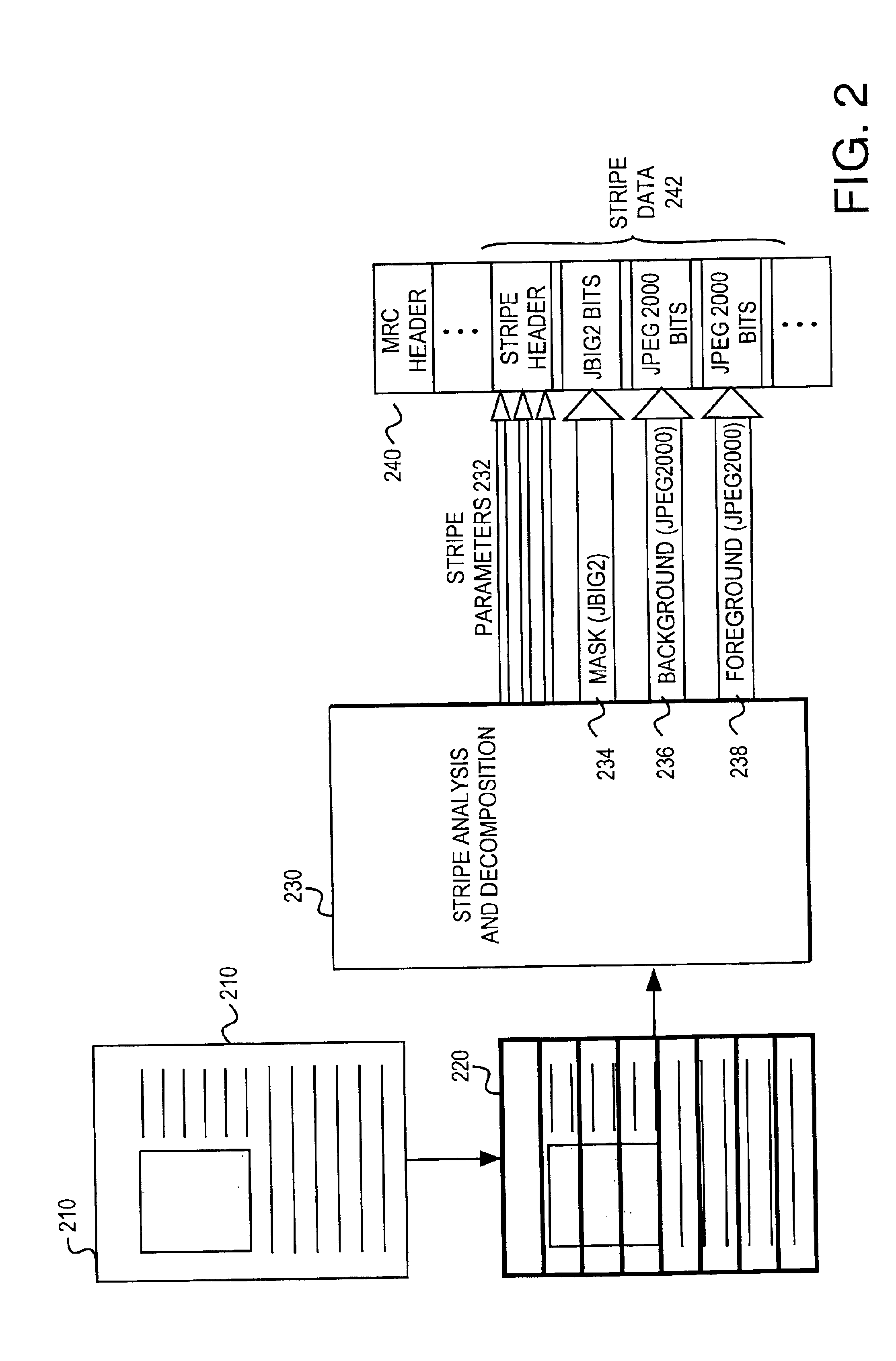
Methods for decomposing compound documents for mixed raster content representation are provided. A method for decomposing an image includes the step of decomposing the image into a plurality of stripes. Each stripe is decomposed into foreground, background, and mask layers. The layers are interpolated to modify values of irrelevant pixels in order to achieve more efficient compression. The layers may subsequently be compressed with a coder.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Security Containers for Document Components
InactiveUS20080215897A1Easy to useSafe storageKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsSoftware engineeringDocumentation
Methods, systems, computer program products, and methods of doing business whereby document components are secured or controlled using “security containers” which encapsulate the components (and other component metadata). A “security container” encapsulates the component (i.e., content) that is to be controlled within a higher-level construct such as a compound document. The security container also contains rules for interacting with the encapsulated component, and one or more encryption keys usable for decrypting the component and rules for authorized requesters.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
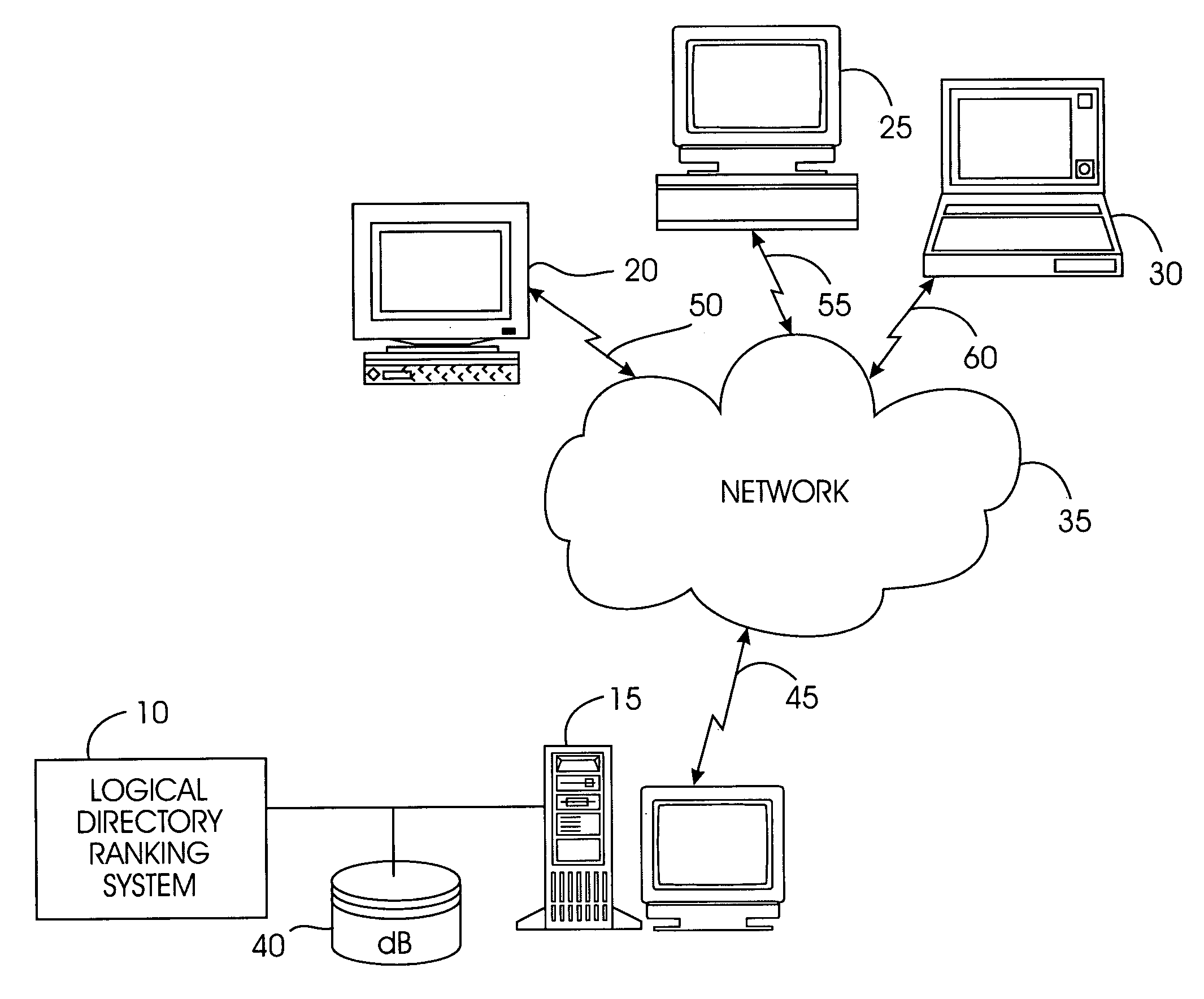
System and method for ranking logical directories
InactiveUS20050256887A1Reduce computationReduce the amount of dataData processing applicationsWeb data indexingGranularityPaper document
A logical directory ranking system ranks documents or web pages utilizing logical directories. From the hierarchical structure represented in a URL string, URLs can often be grouped into “compound documents” that represent a single unit of information. Such compound documents tend to comprise URLs that agree up to a last delimiter such as a forward slash ( / ). The present system groups together compound documents as a single information node with one or more leaves, constructing a logical directory graph. URLs can be grouped at a level of granularity below an individual directory. For example, the URLs may be grouped together on the basis of hostname, domain, or any level of the hierarchy of the URLs. Edges in the logical directory graph are formed by links between the logical directories. Edges have weights corresponding to the number of links between logical directories. Nodes have weights corresponding to the number of web pages or leaves represented by a node. A ranking level is determined for each node as a function of the node weight and the edge weight. The ranking level is then applied to each URL that the node represents.
Owner:IBM CORP
Coder matched layer separation and interpolation for compression of compound documents
InactiveUS6941024B2Efficient compressionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionBackground imageCompound document
A method of preparing an image for efficient wavelet transform compression includes the steps of separating the image into foreground and background image layers, and a mask layer. A smoothing filter is applied to interpolate irrelevant pixel values in the foreground and background layers for coder efficiency. The irrelevant pixel values are interpolated as a function of relevant pixels and causal irrelevant pixels within the smoothing filter window.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
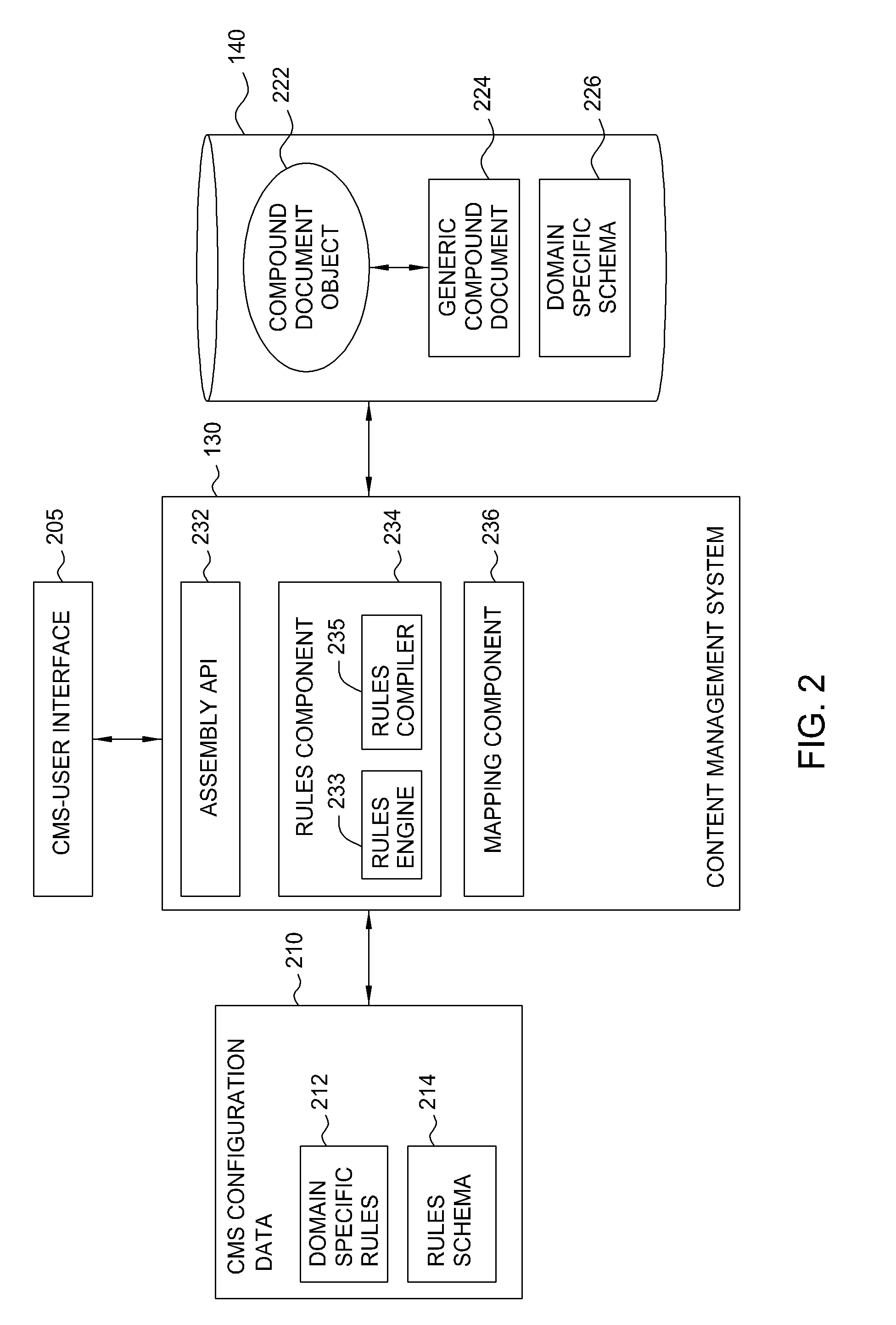
Method and system for compound document assembly with domain-specific rules processing and generic schema mapping
InactiveUS20080005138A1Efficient solutionData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalSchema mappingXML schema
Method, system, and article of manufacture for assembling a compound document according to a collection of domain-specific rules. For example, a content management system (CMS) may be configured to process the domain-specific compound document according to domain-specific schema and rules (e.g., an XML schema and DTD), while at the same time, maintaining the compound document in a generic form according to a generic schema for a compound document format used by the CMS.
Owner:IBM CORP
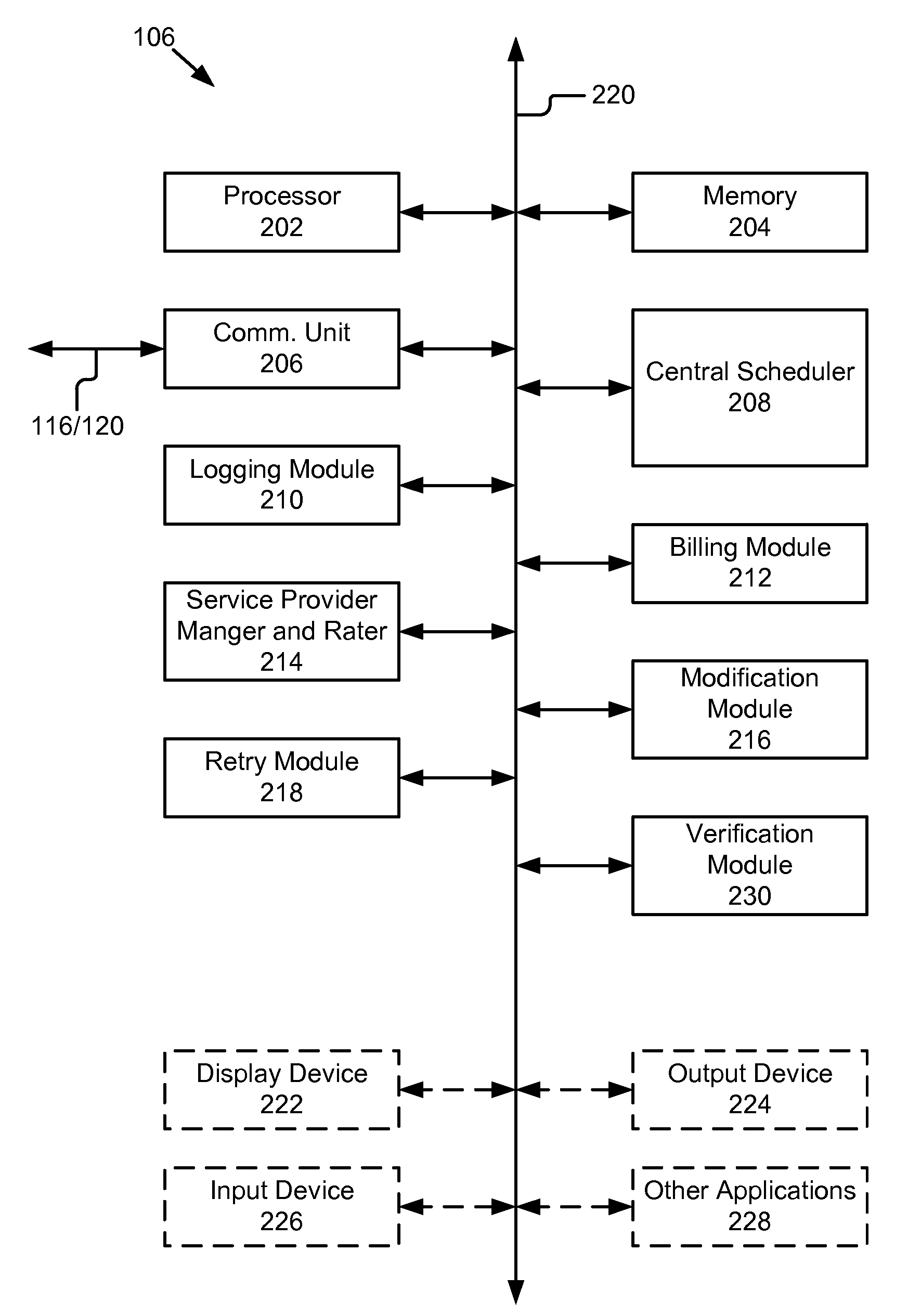
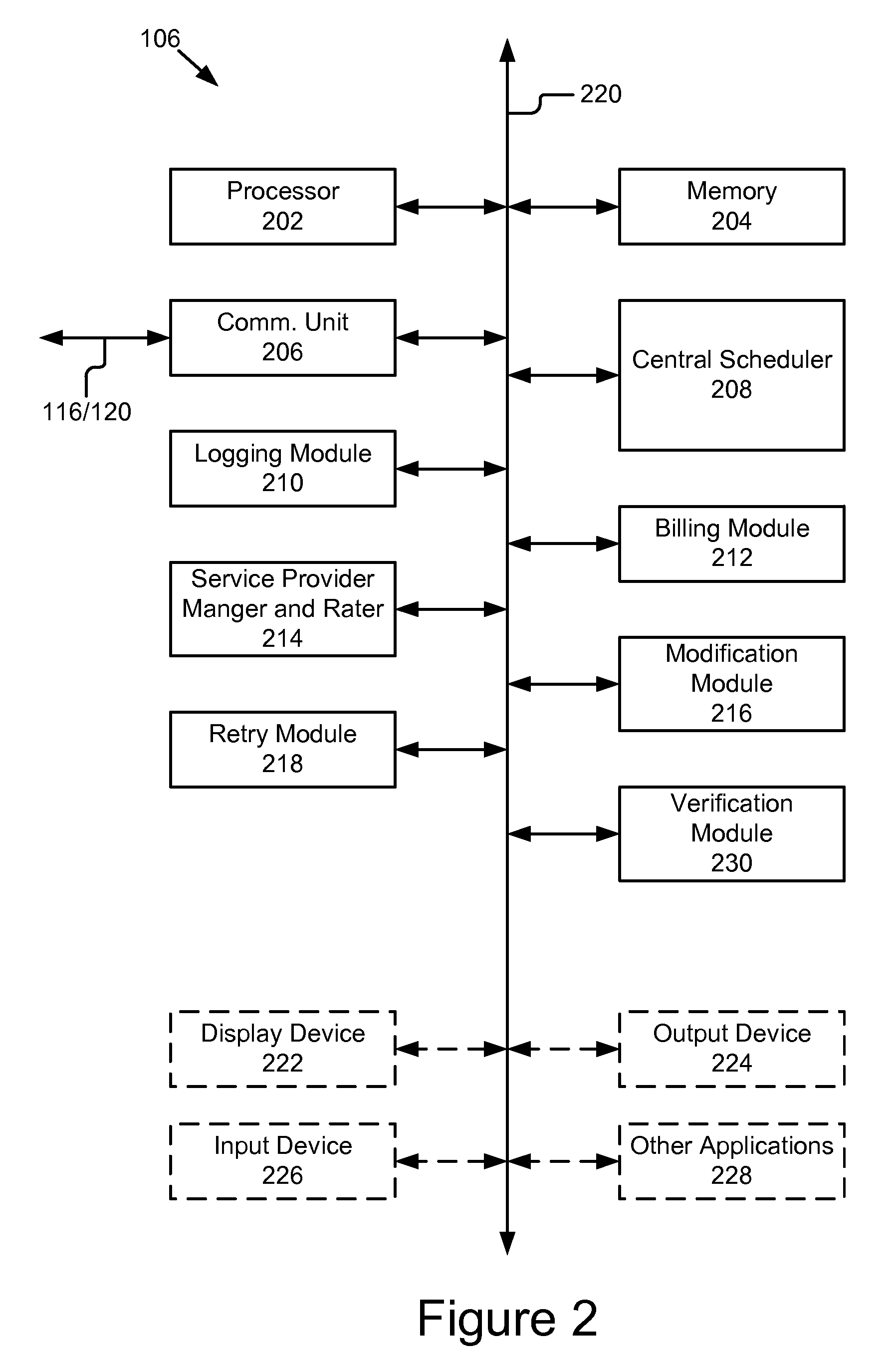
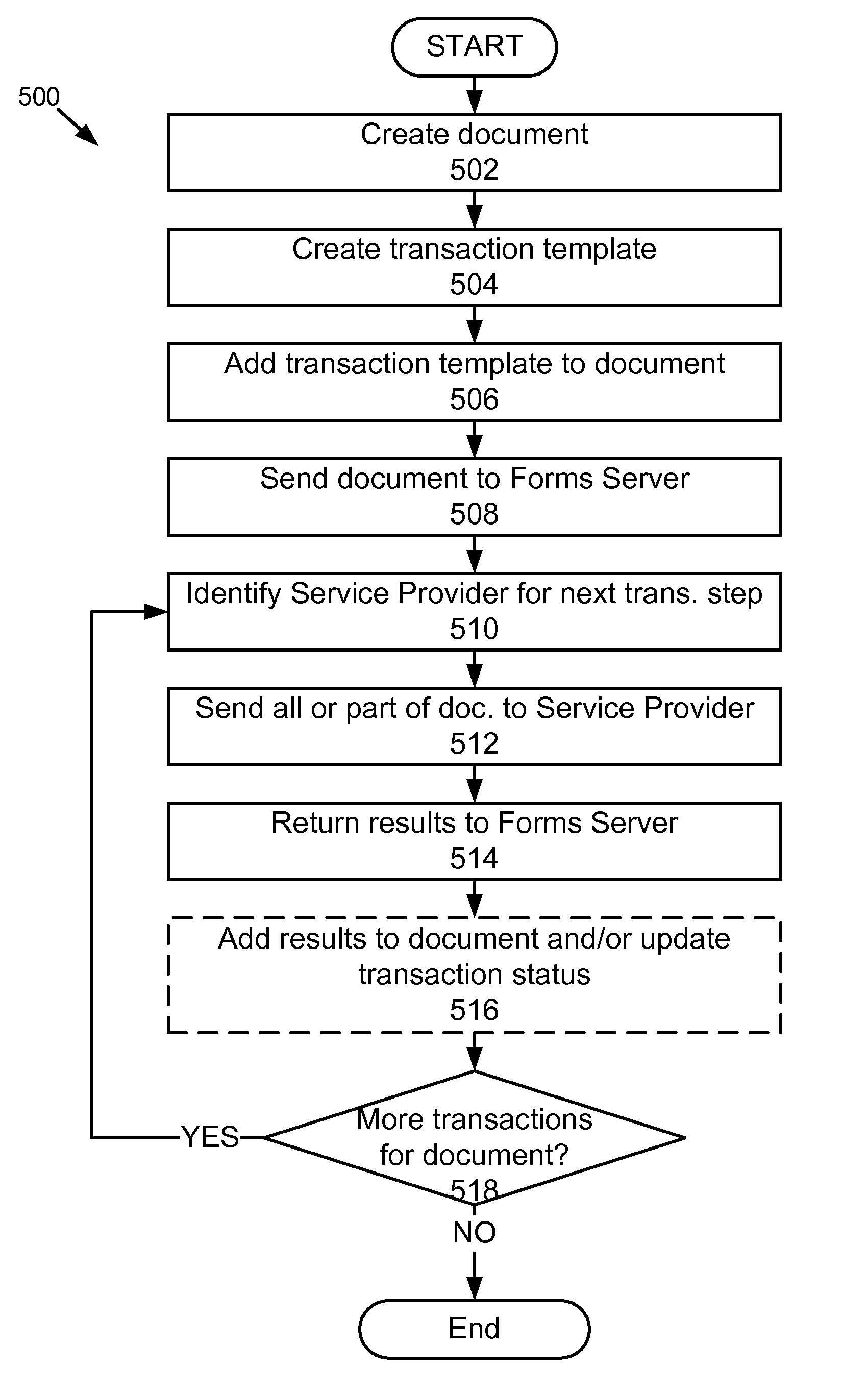
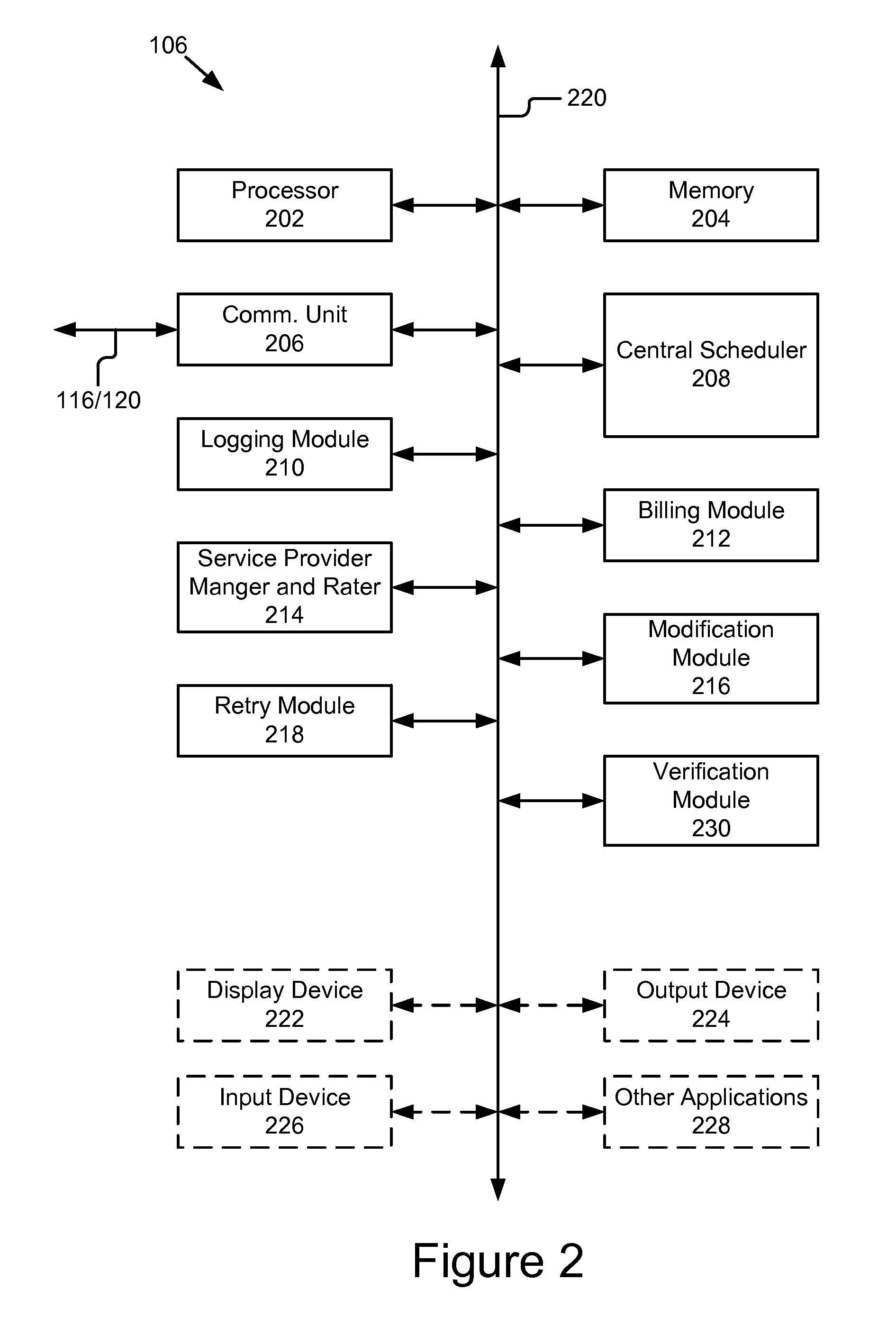
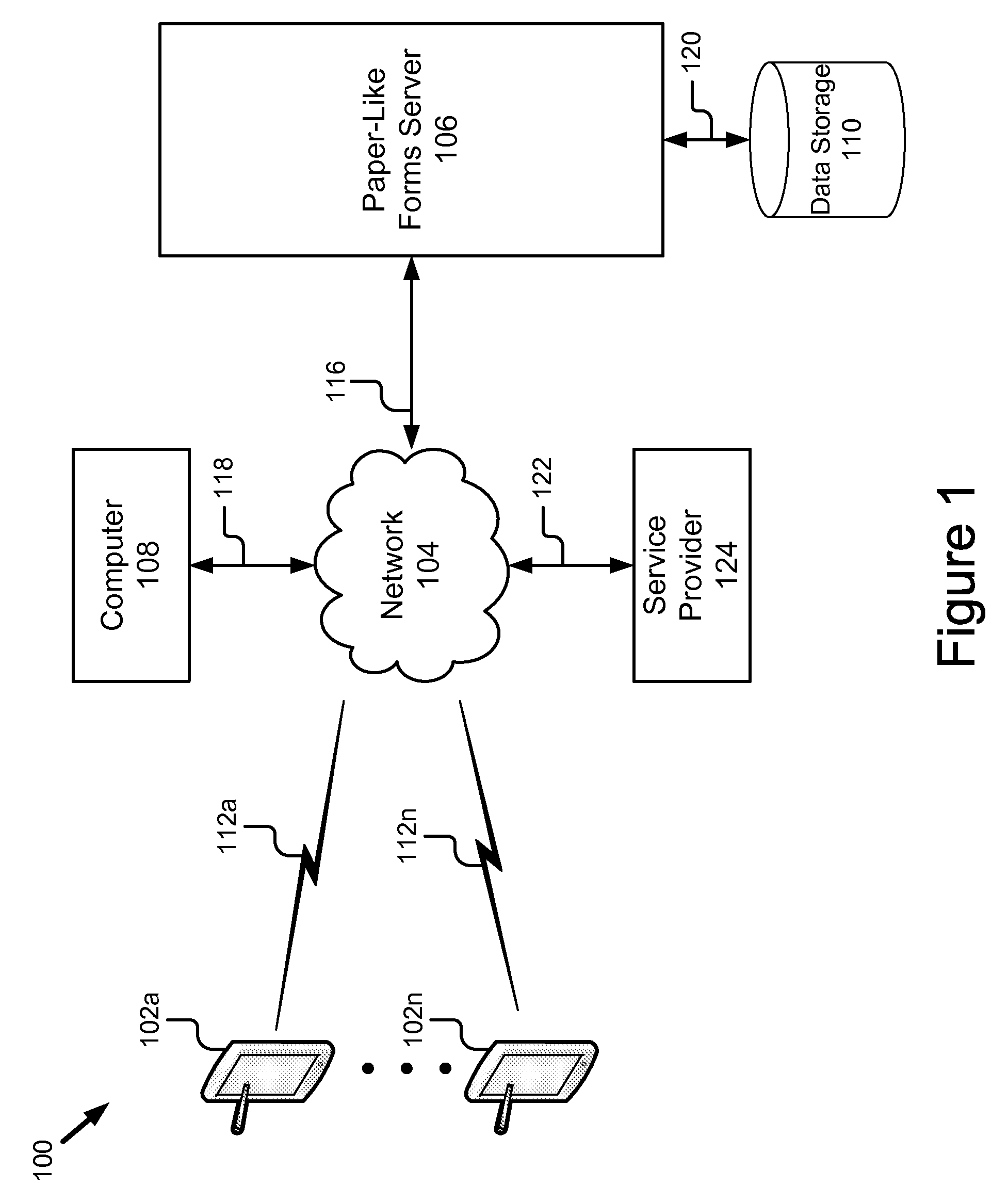
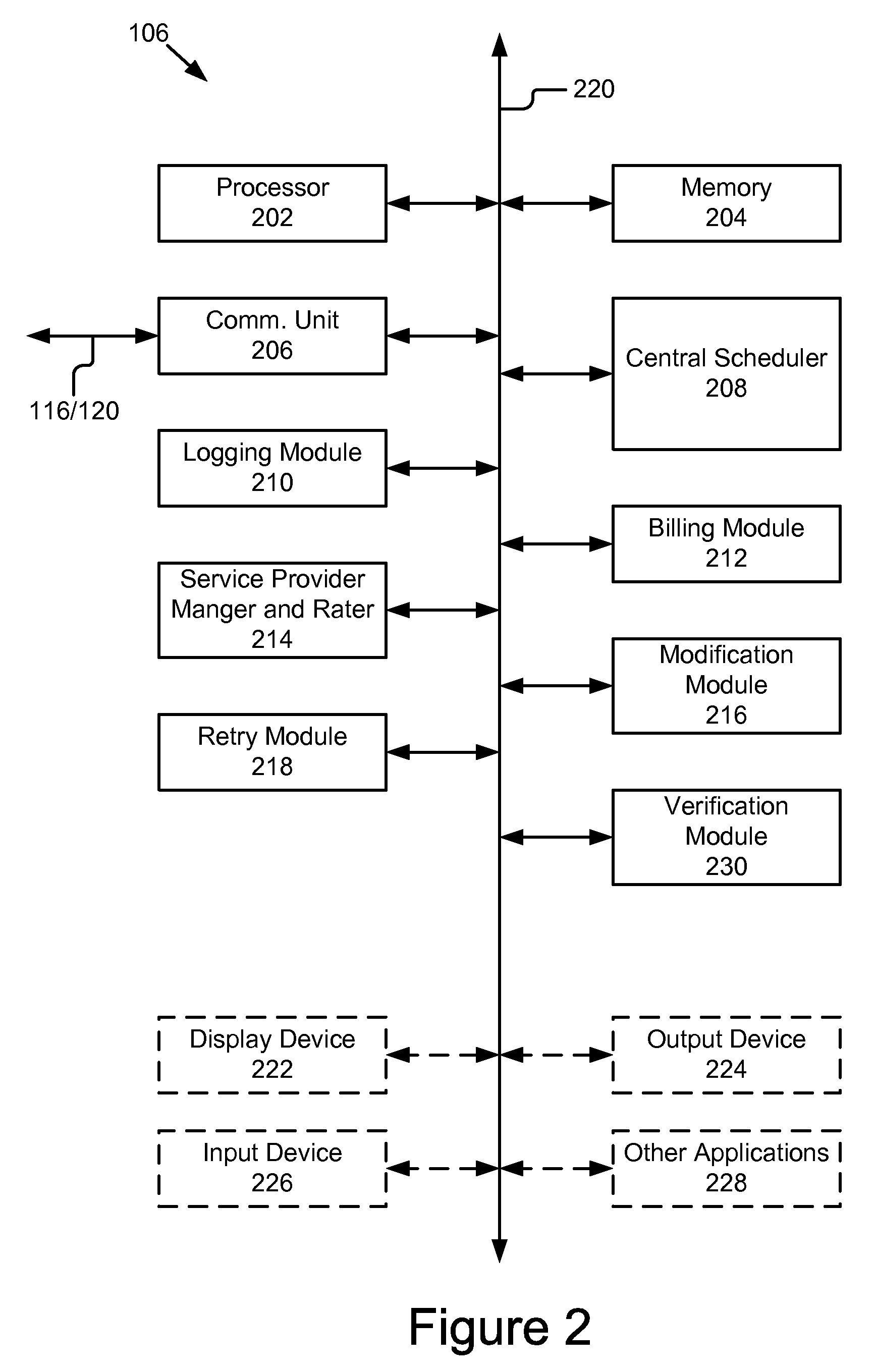
Multi-provider forms processing system with retry upon failure
ActiveUS20110060622A1Complete banking machinesDigital data processing detailsForm processingDocumentation
A multi-provider forms processing system with retry upon failure comprises: a plurality of portable computing devices, a plurality of service providers and a paper-like forms server coupled by a network. The paper-like forms server performs the scheduling, routing, logging, verification and billing for the paper-like processing of compound documents. The paper-like forms server comprises a central schedule, a retry module and a billing module. The multi-provider forms processing system is advantageous because it monitors for failure of transactions, automatically issues a retry or replacement transactions and adjusts the billing for the failed transaction. In particular, the central scheduler tracks and determines when transaction failures occur, and based on these failures revises the billing to users and credits to service providers. The central scheduler also monitors the logs for completion as well as restarts, attempts, failure, reworked and re-performed transaction steps and modifies the bills accordingly.
Owner:RICOH KK
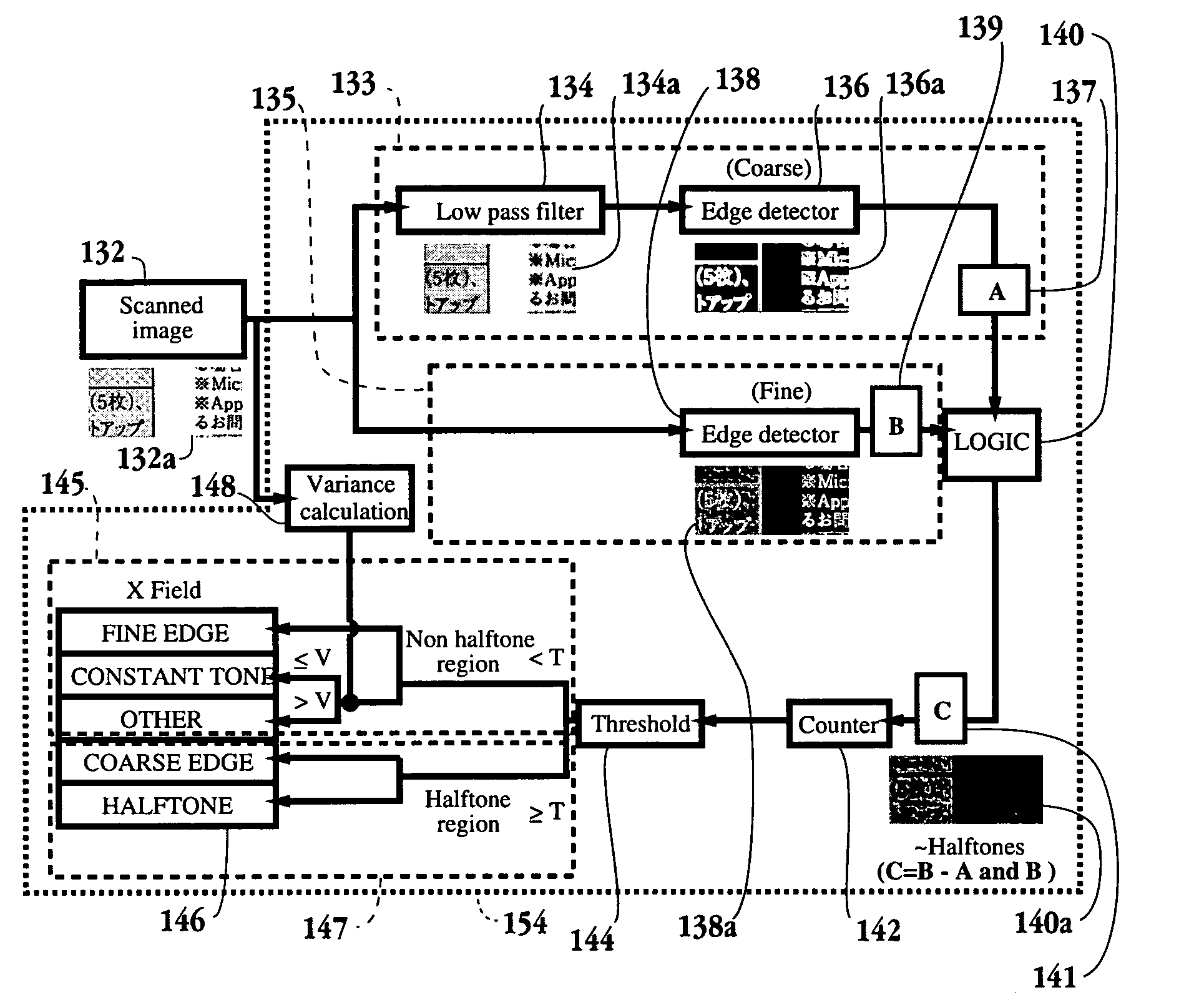
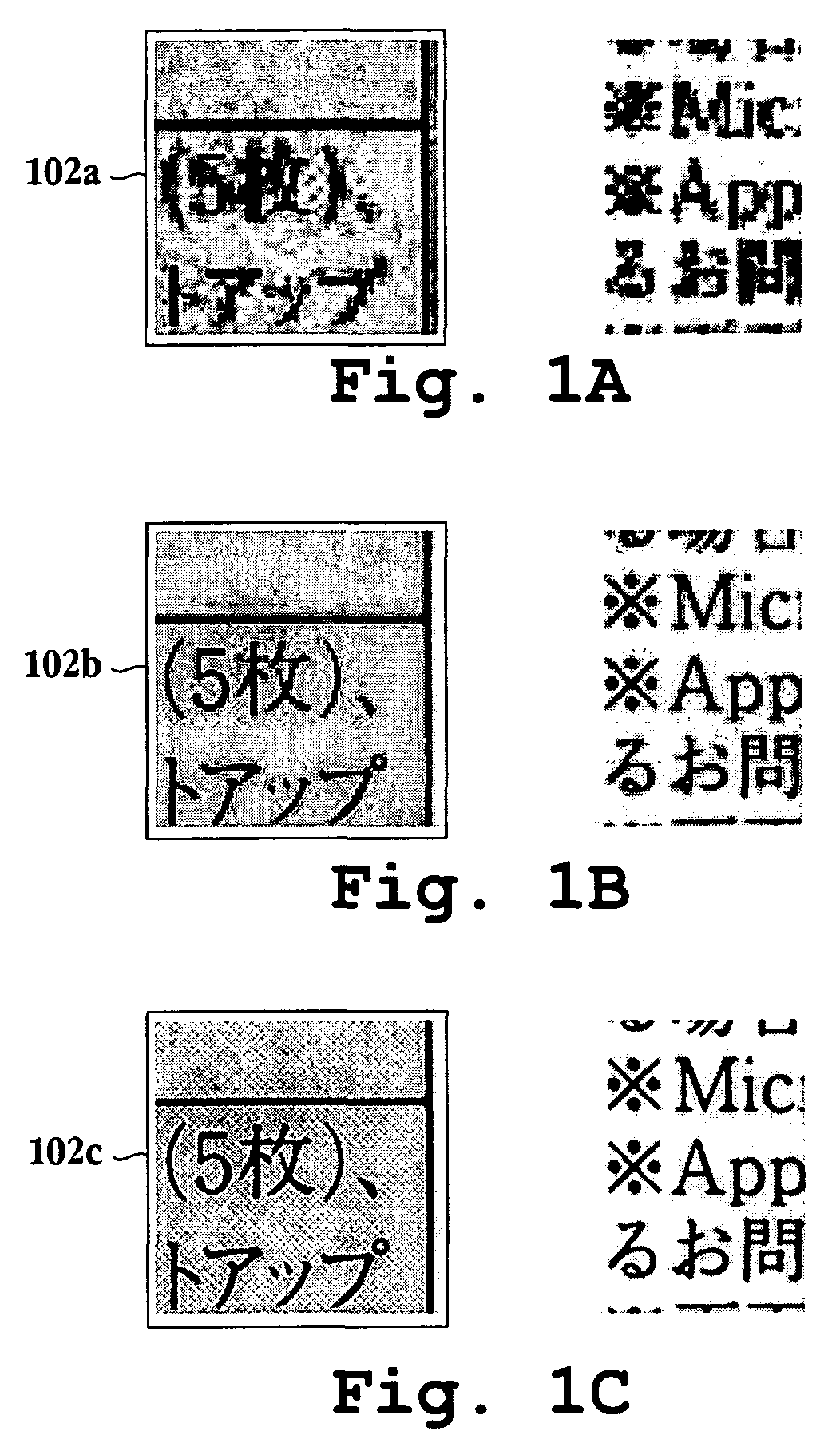
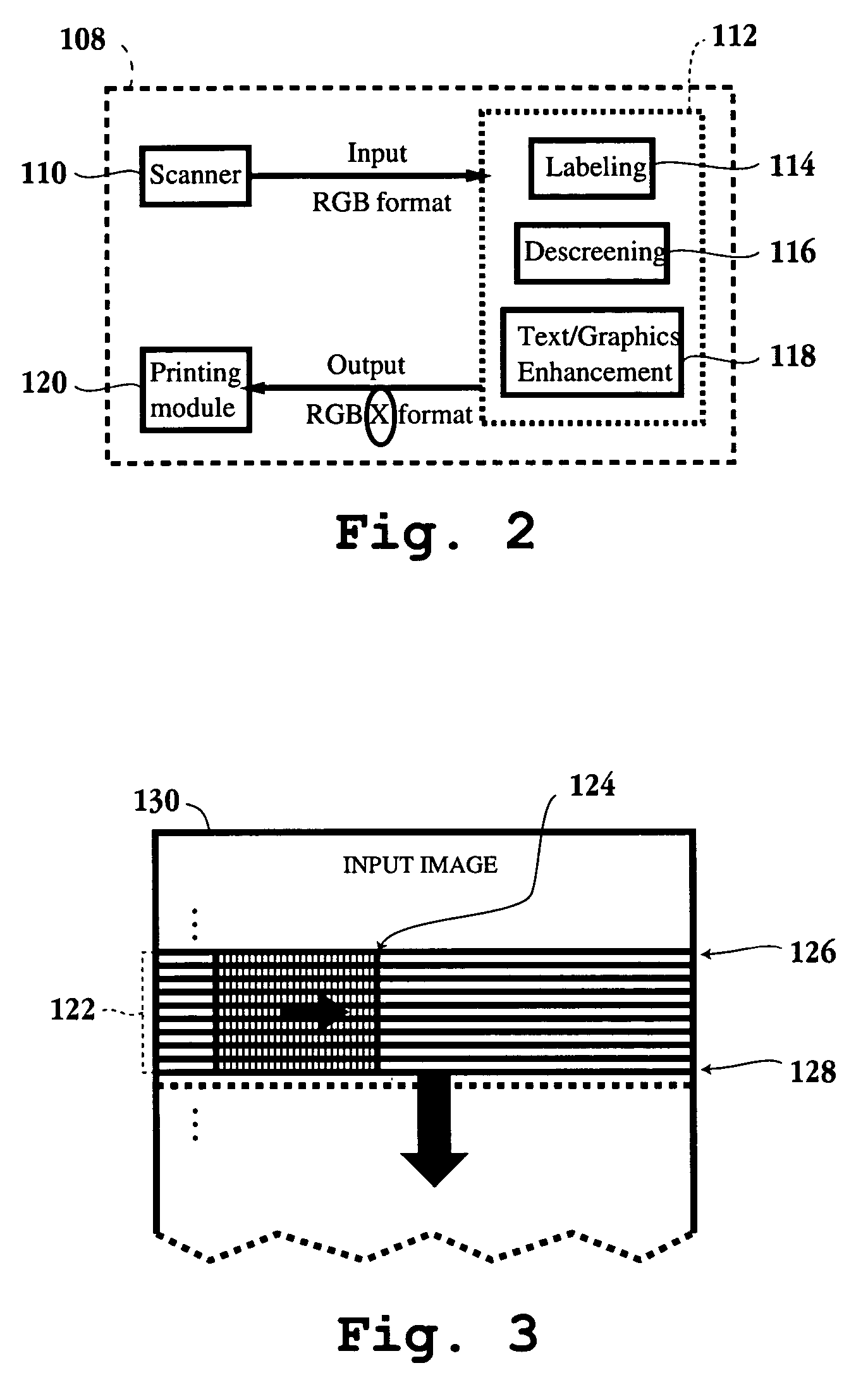
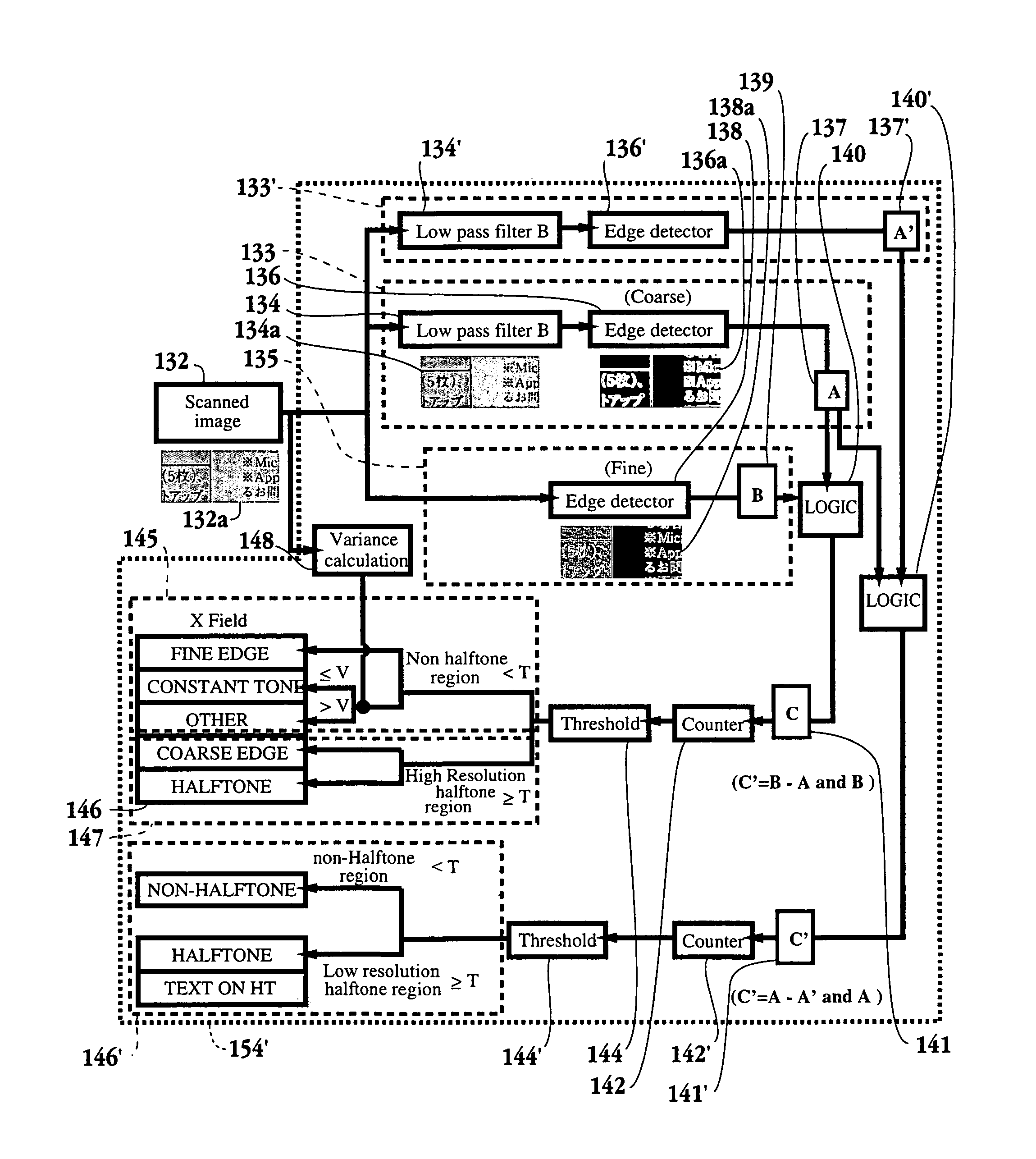
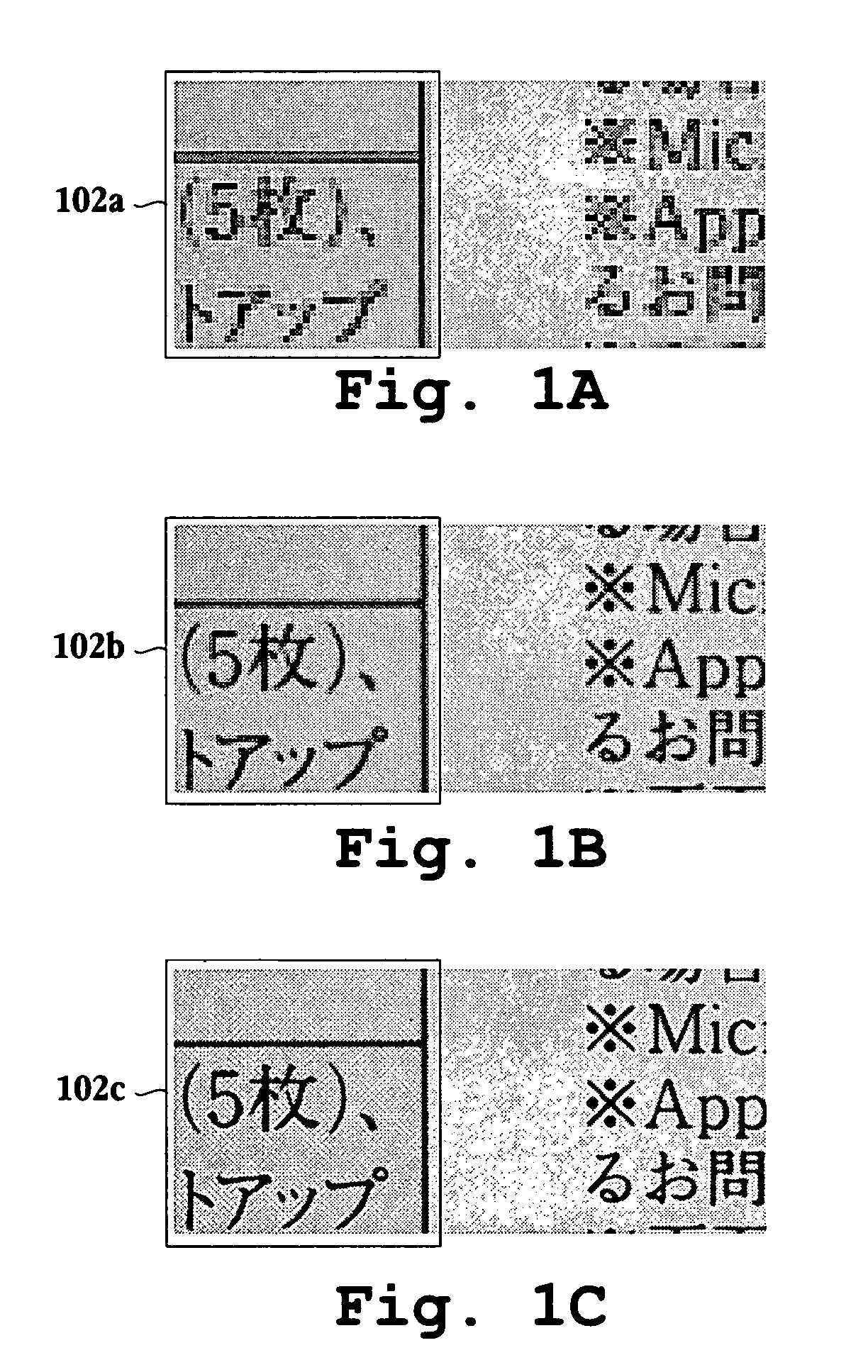
Method and apparatus for segmentation of compound documents having low resolution halftones
A method for segmenting a compound document for enhancement during replication of the compound document is provided. The method initiates with filtering data representing a portion of the compound document through a filter associated with a first resolution. Then, the data representing the portion of the compound document is filtered through a filter associated with a second resolution. Next, edges are detected on both, an output of the filter associated with the first resolution and an output of the filter associated with the second resolution. Then, data representing detected edges from both outputs are combined. Next, it is determined whether a pixel corresponding to the data representing the detected edges is over a halftone region. Methods for labeling digital image data and labeling and enhancing documents defined through digital data, as well as associated computer readable medium embodiments are provided. An image replication device and an integrated circuit configured to segment and enhance image data associated with a compound document are also provided.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
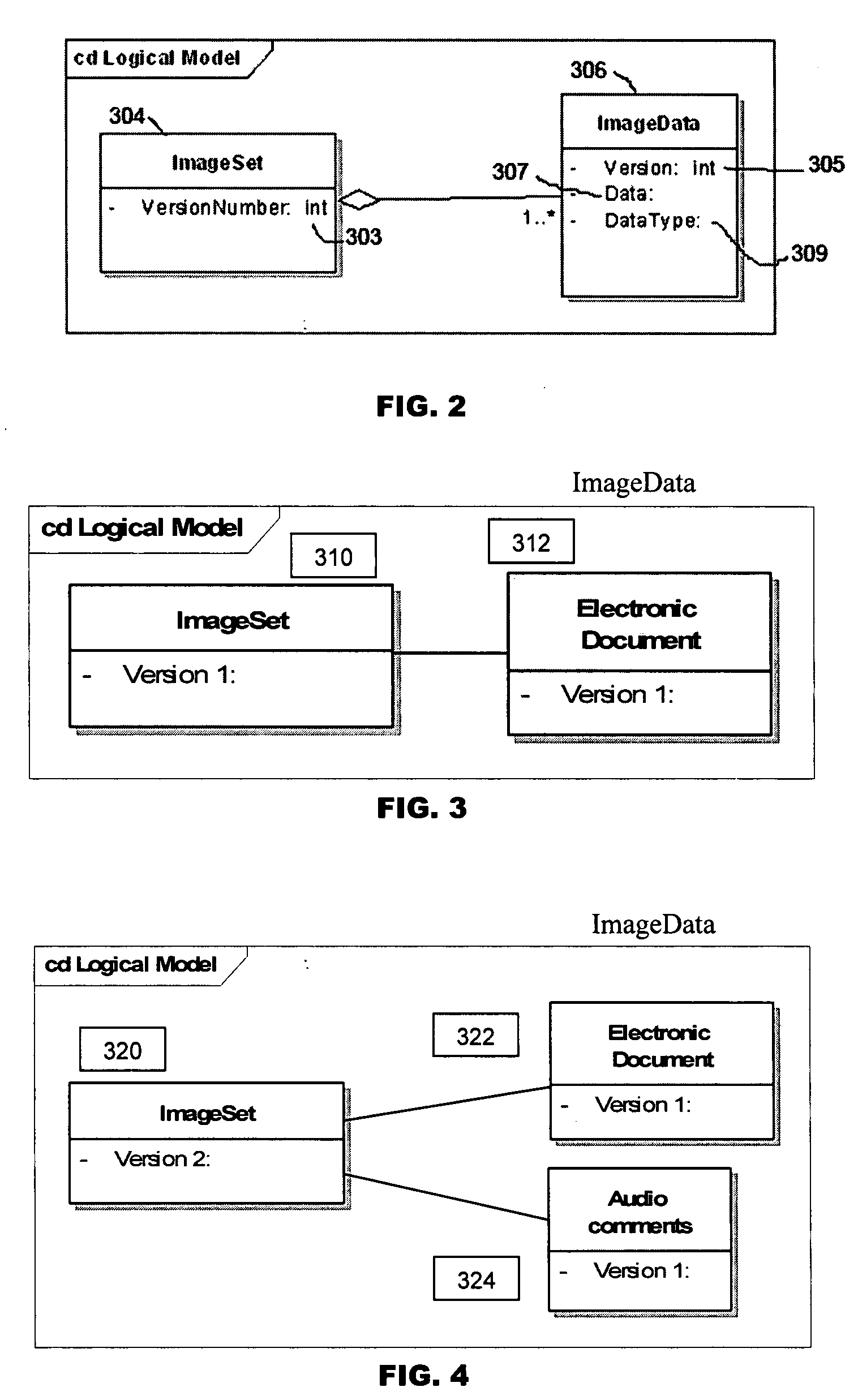
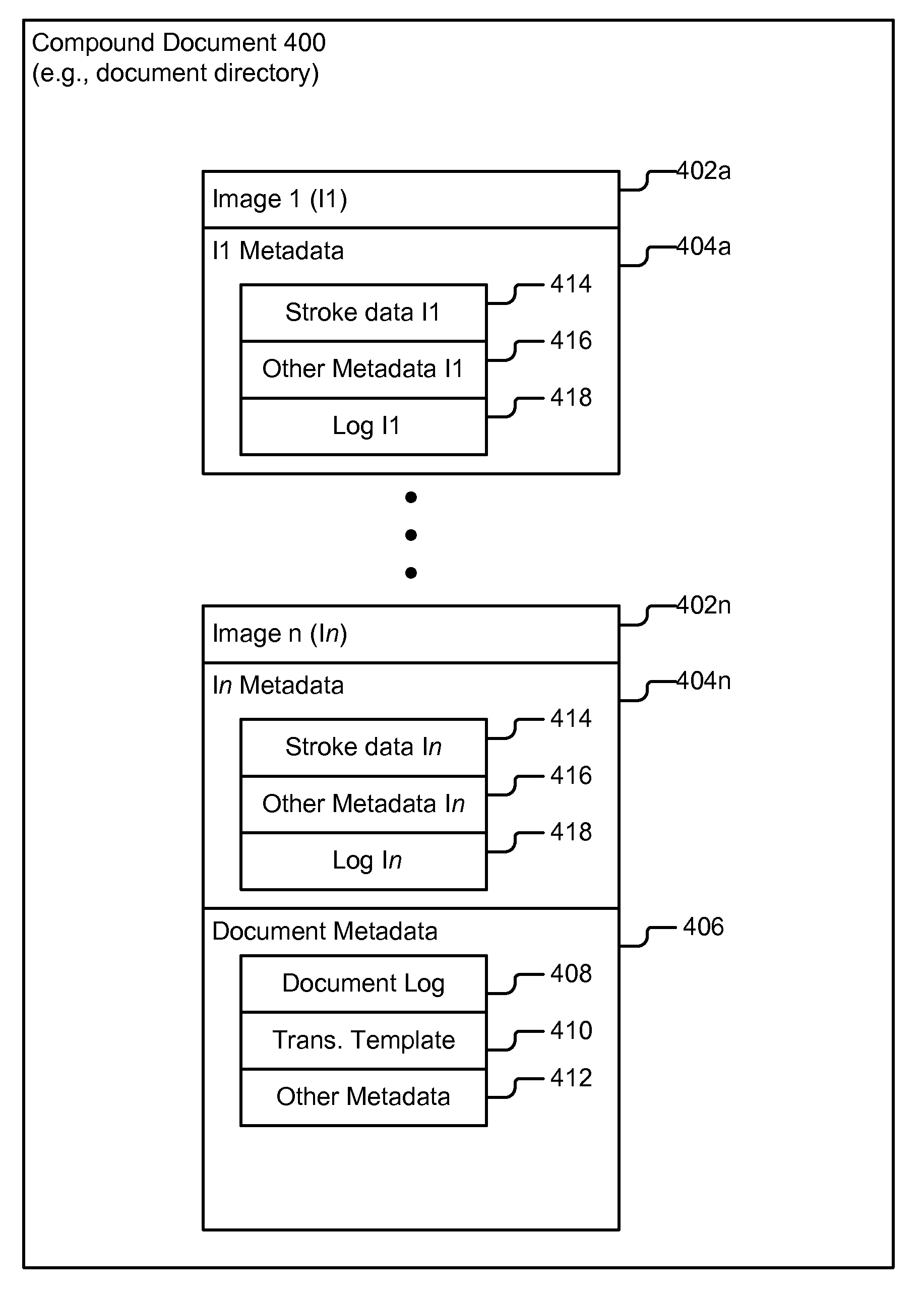
Method, system, and computer-readable medium to provide version management of documents in a file management system
InactiveUS20070244935A1Metadata multimedia retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsMultiuser systemEngineering
A method, system, and computer-readable medium to provide version management of a compound document in a document management system where the compound document includes multiple component files. The method comprises assigning a version number to the compound document, enabling a user to index the version number according to a change in any one of the component files, assigning a respective component version number to respective component files, enabling a user to index the component file version number according to changes therein, maintaining a record of component version numbers associated with each version of the compound document, and retrieving a version of a compound document by retrieving the associated versions of the component files. The method may be implemented in a multi-user system over a LAN or WAN network, and component files may be stored on a central networked file server as images accessible by the multiple users.
Owner:VERTAFORE
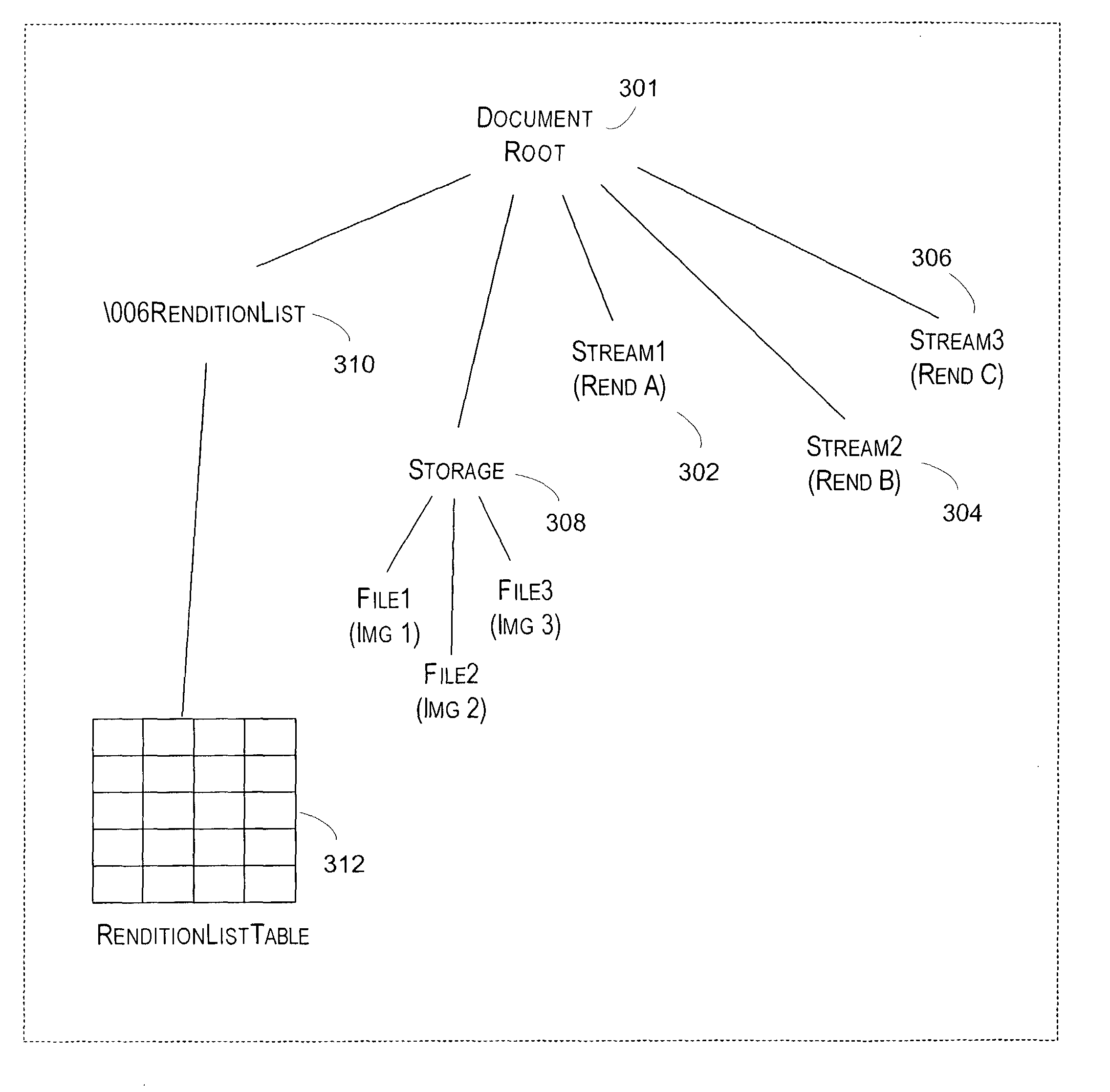
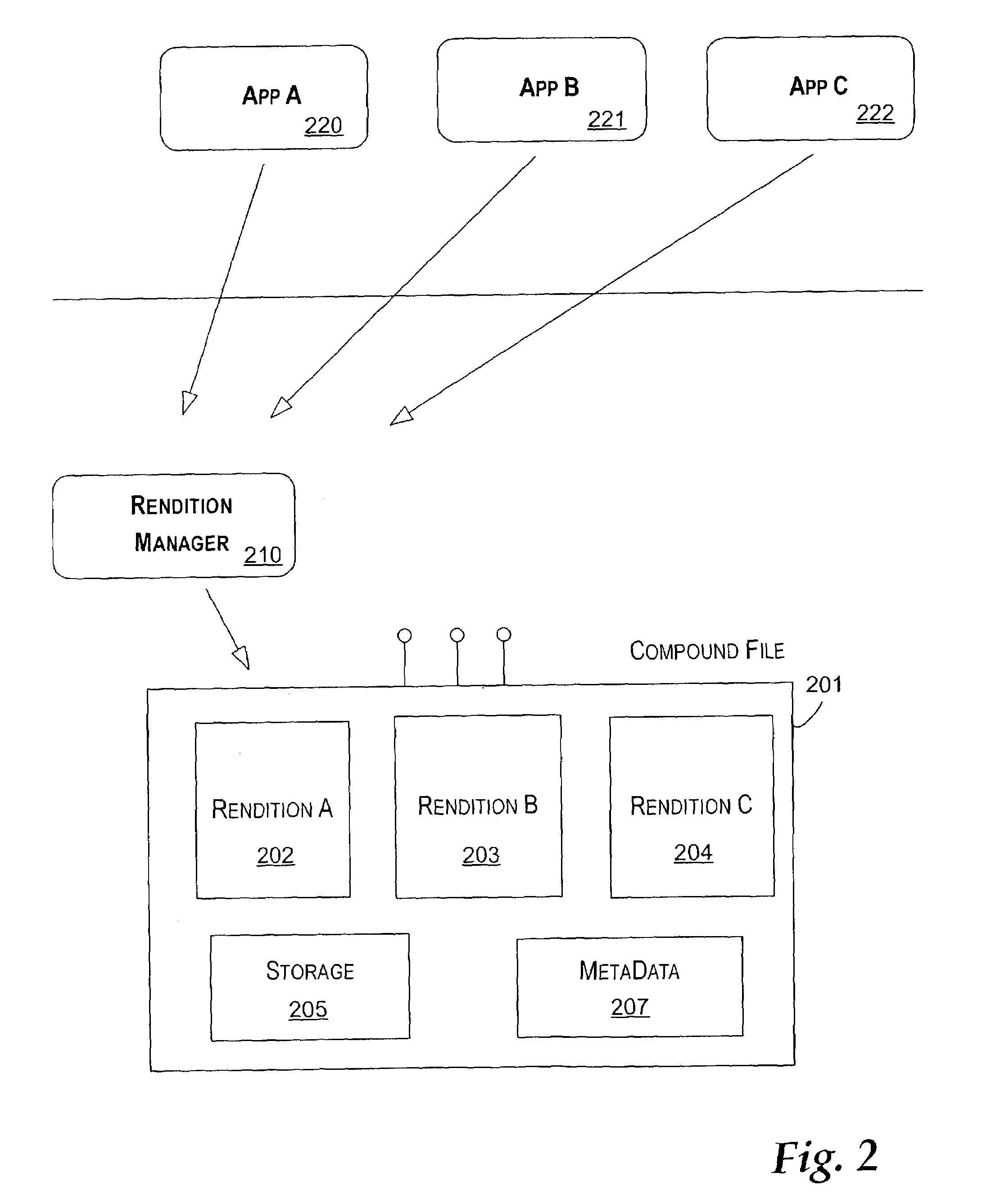
System and method for providing multiple renditions of document content
ActiveUS7213035B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDocumentation procedureApplication software
Described is a mechanism for providing a single file that includes multiple representations of the same document content. Each of the representations may be optimized to provide a superior presentation for a particular device or application. The mechanism of the invention is preferably based on a compound file format that allows multiple renditions of the same content to be stored in a single document. Meta information is included within the single document that describes each of the multiple renditions together with any supporting files that may be used with those renditions. The inventors have determined that the Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) compound file format is especially well suited to implementations of the invention.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
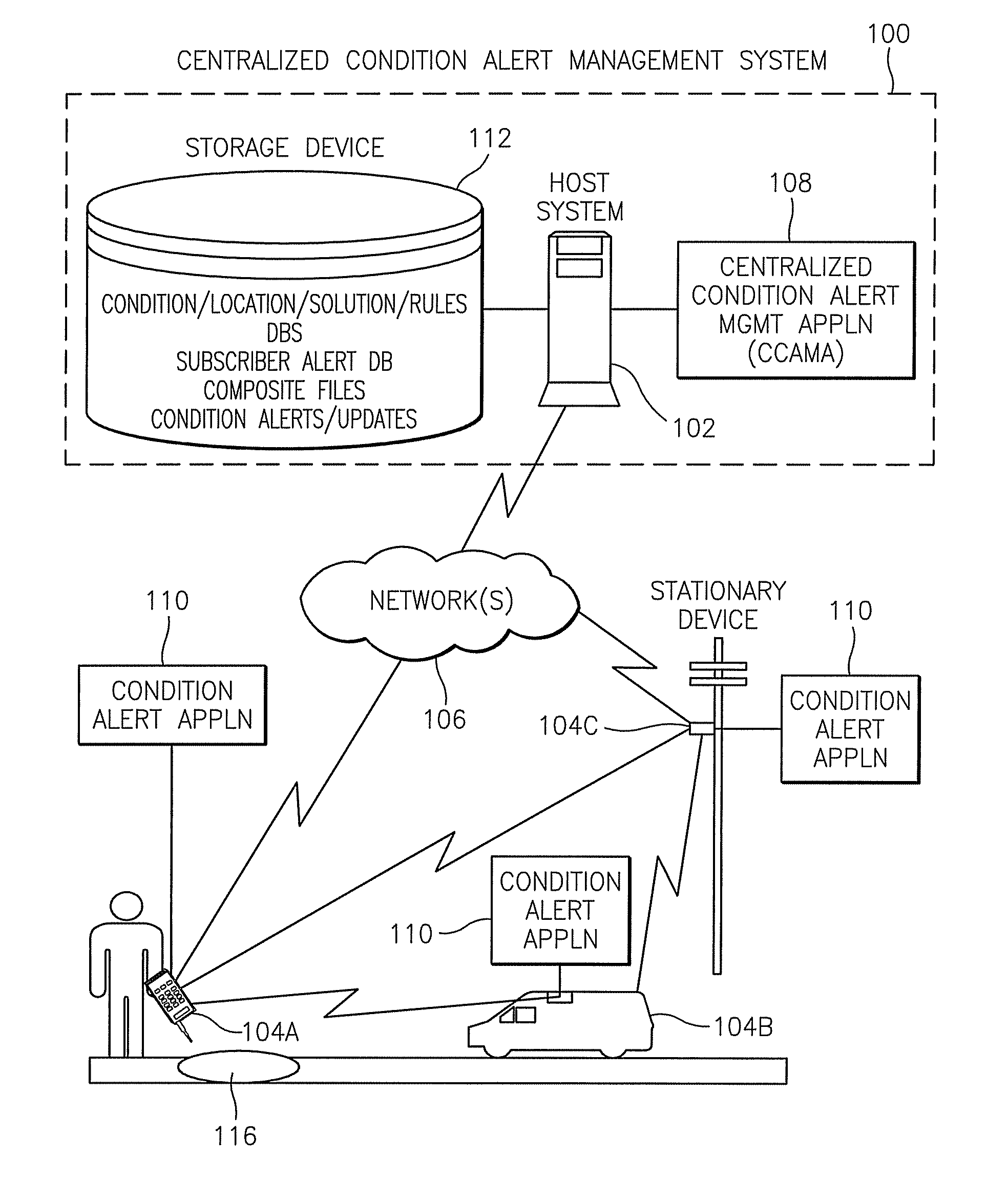
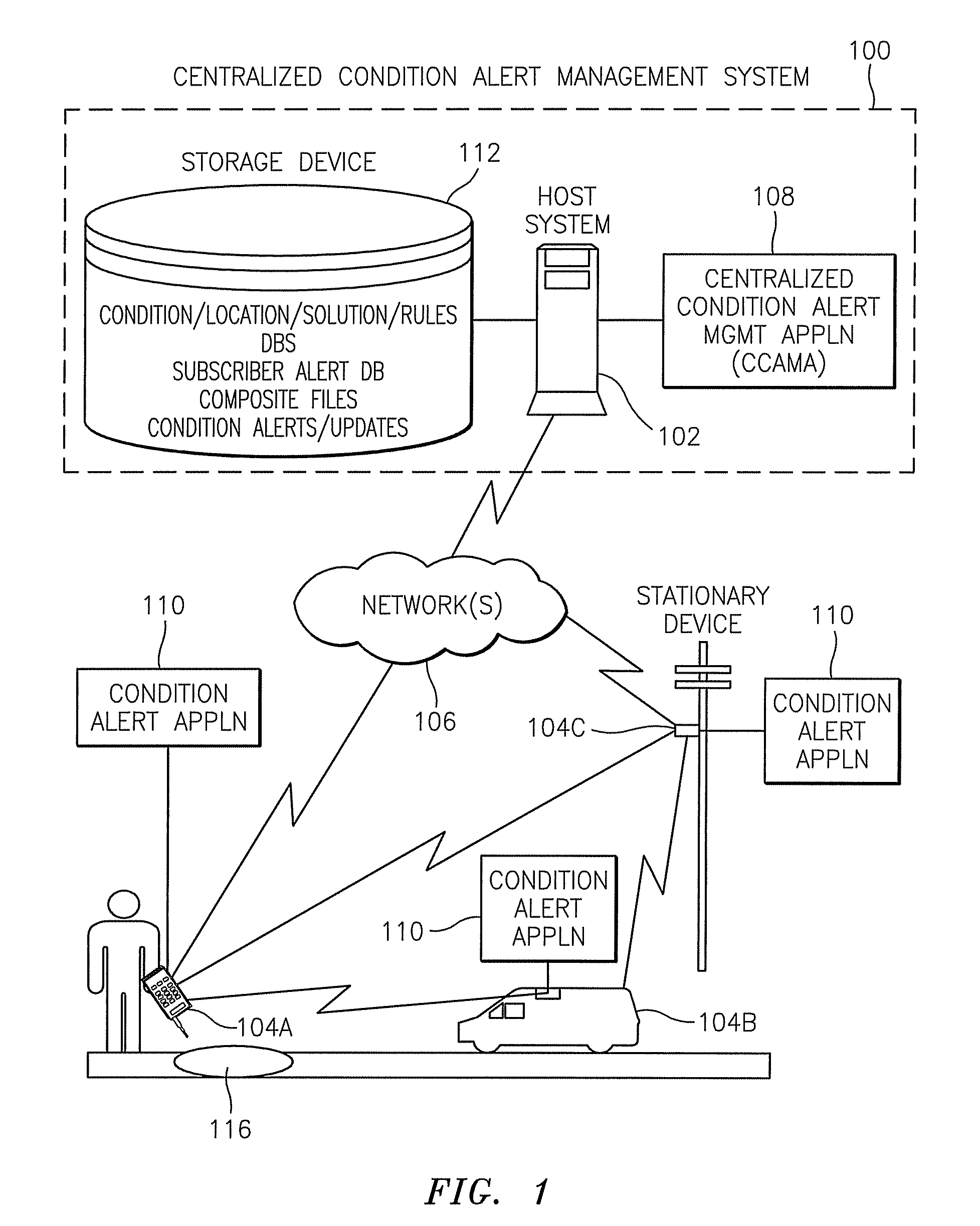
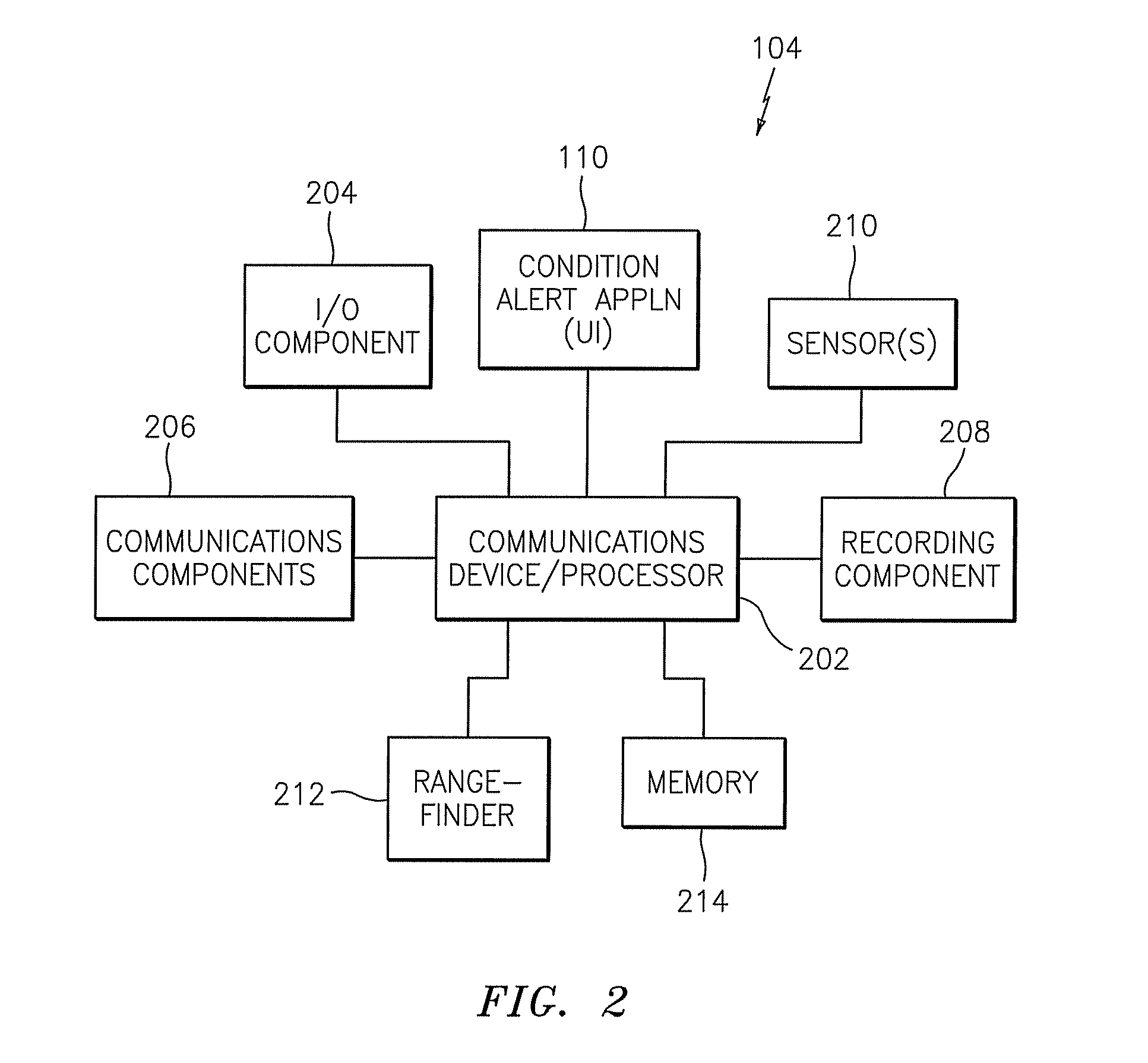
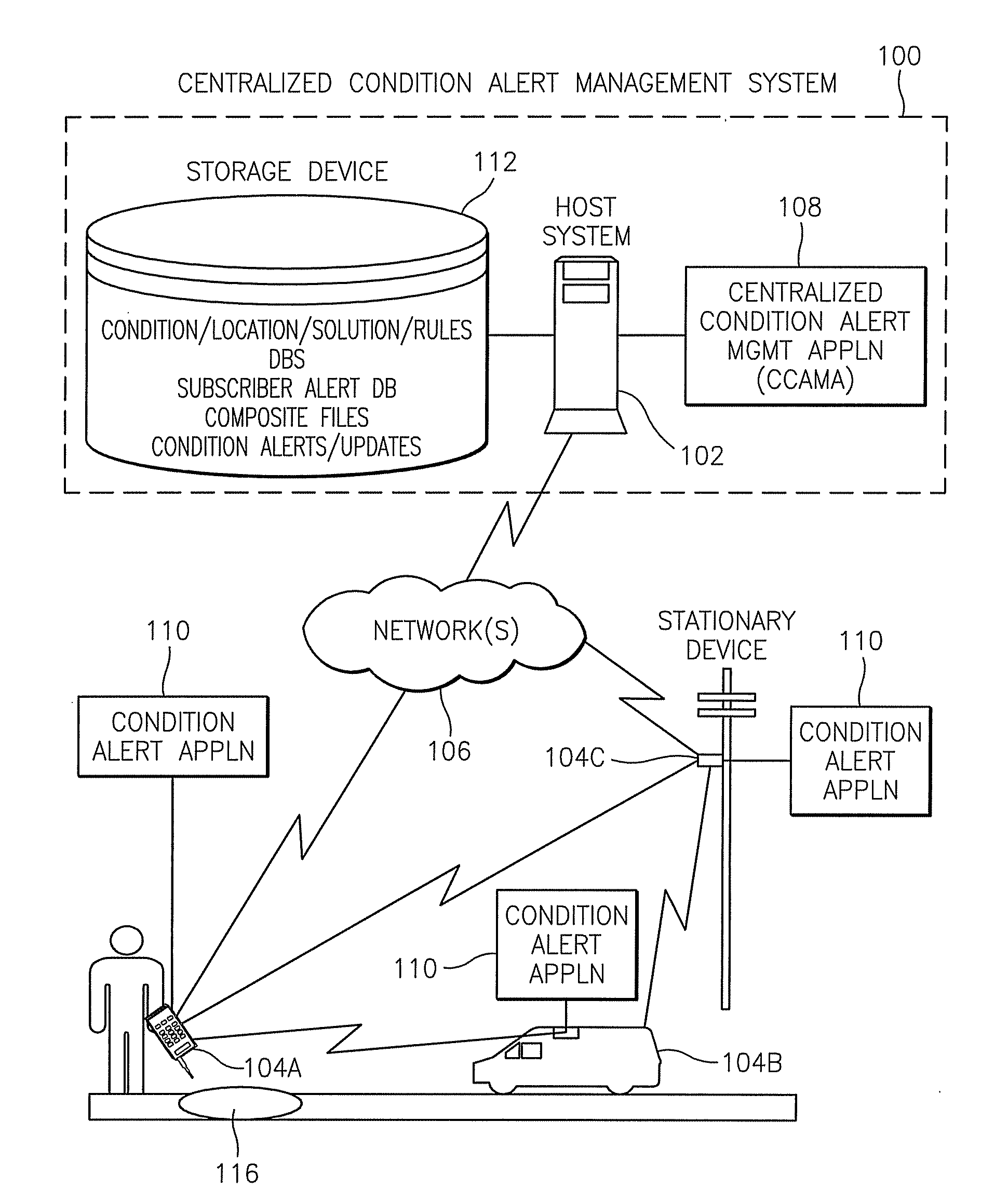
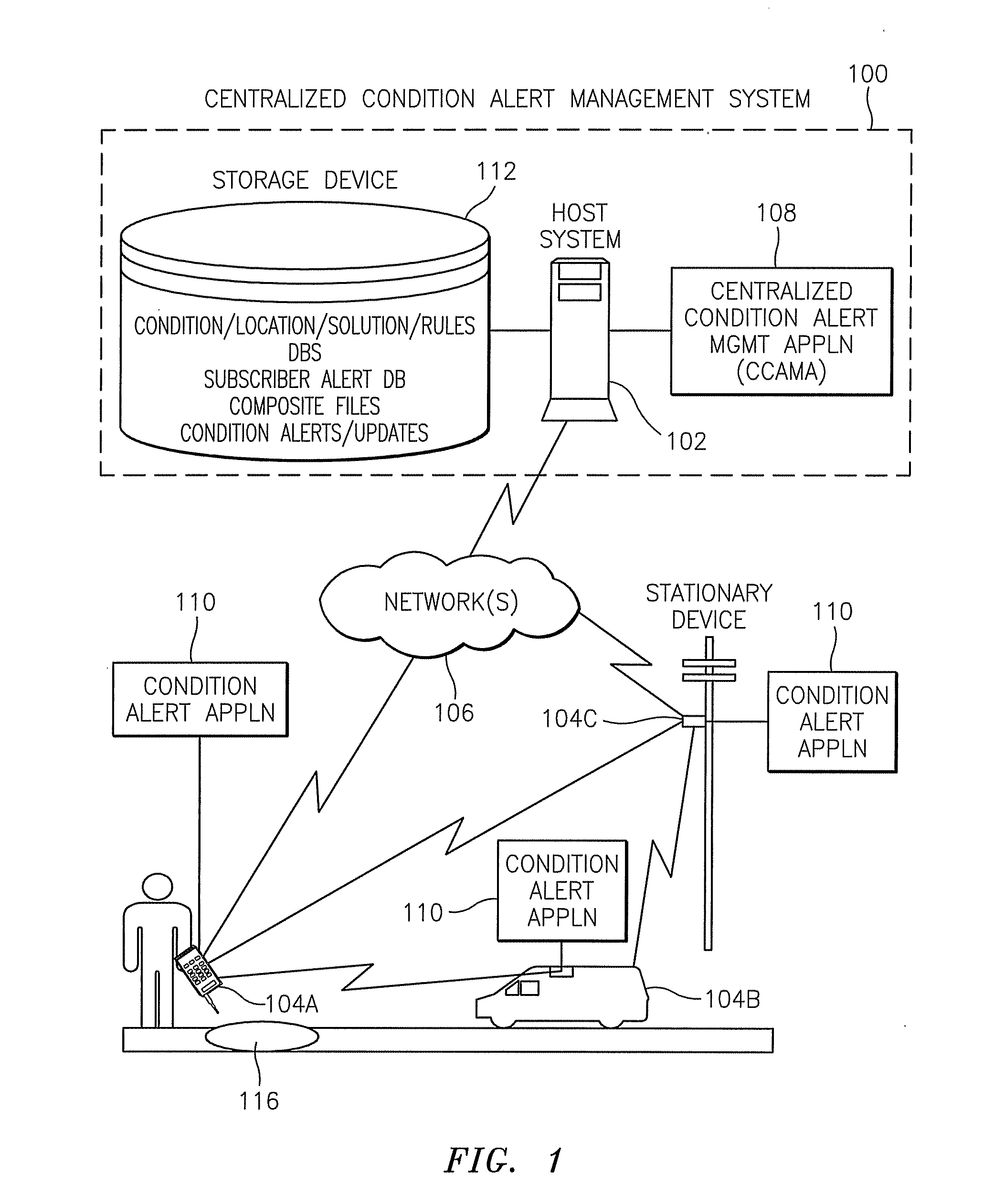
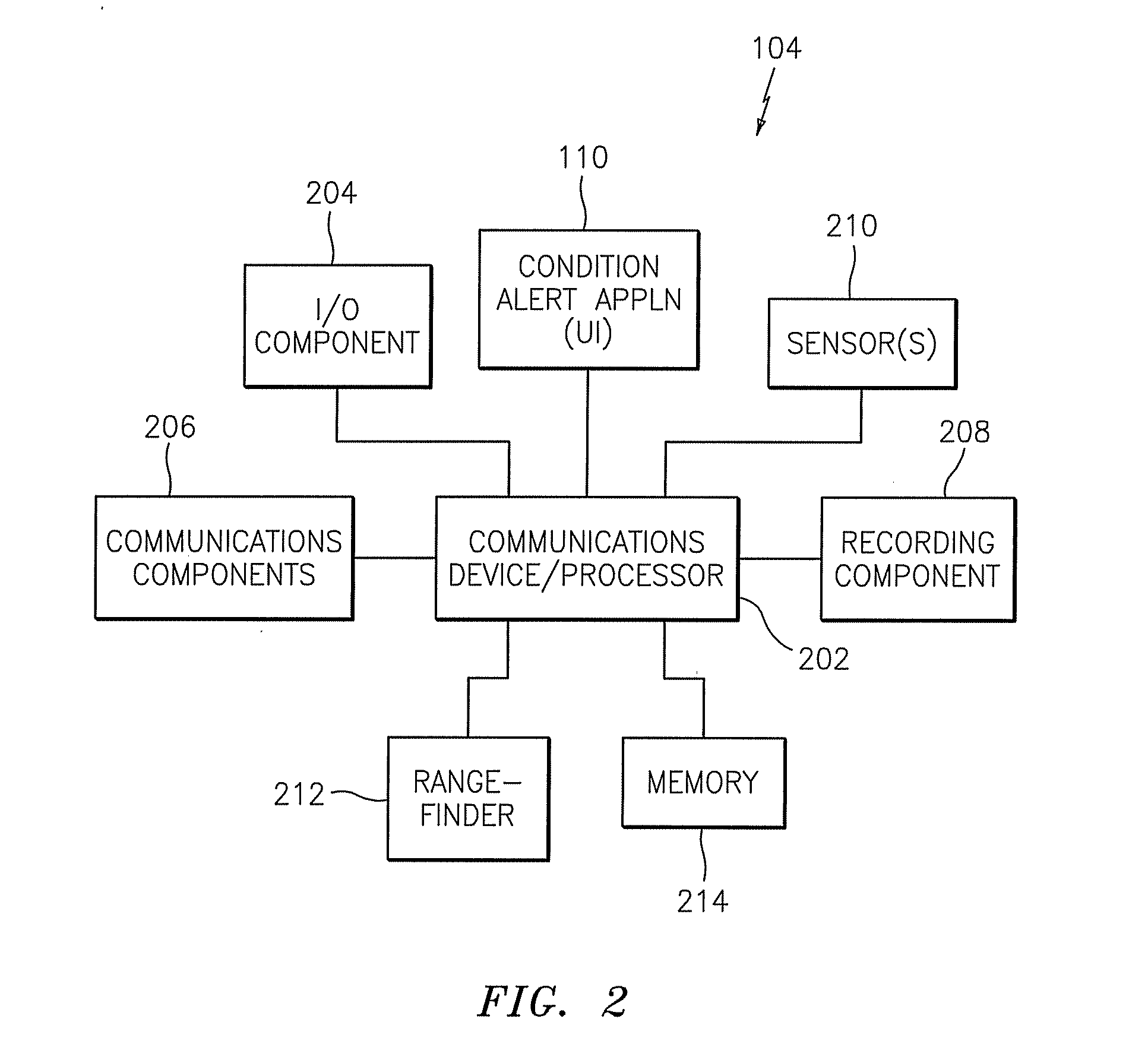
Methods, systems, devices, and computer program products for implementing condition alert services
ActiveUS8428856B2Analogue computers for vehiclesArrangements for variable traffic instructionsCompound documentCommunication device
Methods, systems, devices, and computer program products for implementing condition alert services are provided. A method includes receiving information elements from a source that identify a condition, aggregating the information elements from the source with information elements from other sources that identify the same condition, and creating a composite file that includes the aggregated information elements representing each of the sources. The method also includes generating a condition alert from the composite file and transmitting the condition alert to a recipient communications device.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I LP
Data filling technique for compound document compression
InactiveUS20080050023A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationData fillingCompound document
Owner:RICOH KK
Methods, systems, devices, and computer program products for implementing condition alert services
ActiveUS20090109020A1Analogue computers for vehiclesArrangements for variable traffic instructionsCompound documentCommunication device
Methods, systems, devices, and computer program products for implementing condition alert services are provided. A method includes receiving information elements from a source that identify a condition, aggregating the information elements from the source with information elements from other sources that identify the same condition, and creating a composite file that includes the aggregated information elements representing each of the sources. The method also includes generating a condition alert from the composite file and transmitting the condition alert to a recipient communications device.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Method and system for displaying a plurality of discrete files in a compound file
InactiveUS7644366B1Quickly and easily navigateReadily apparentMulti-dimensional databasesSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method for managing and displaying related information in a graphical user interface includes storing each of a plurality of related datasets in a discrete file. A compound file is stored linking the discrete data files to each other. A common window for the combined file is displayed in the graphical user interface. A discrete window for each discrete file is displayed within the common window.
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
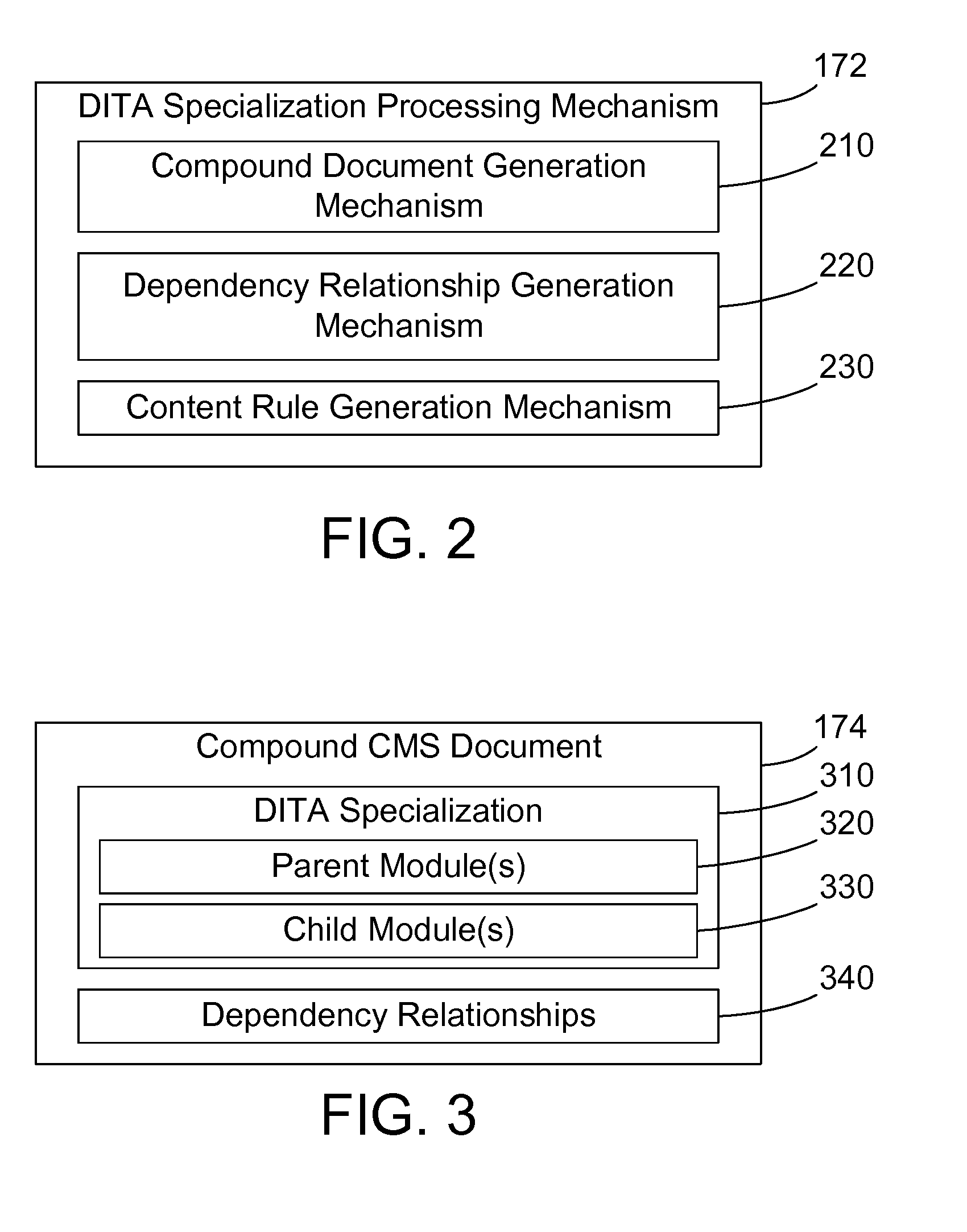
Document specialization processing in a content management system
InactiveUS20090193036A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsDocument preparationDocumentation
A content management system (CMS) provides a DITA specialization processing mechanism that provides the full functions of a content management system across the full functionality of the DITA architecture. A DITA specialization is used to generate an import descriptor that describes how to import the DITA specialization, which may include required modules, stylesheets, catalogs, and content rules into the repository of a content management system. When the DITA specialization is imported into the repository, a compound document is created with appropriate parent / child links. Dependency relationships between modules in the compound document are then created. In addition, new XML content rules for the DITA specialization may be automatically generated from existing content rules.
Owner:IBM CORP
Previewing a compound document
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
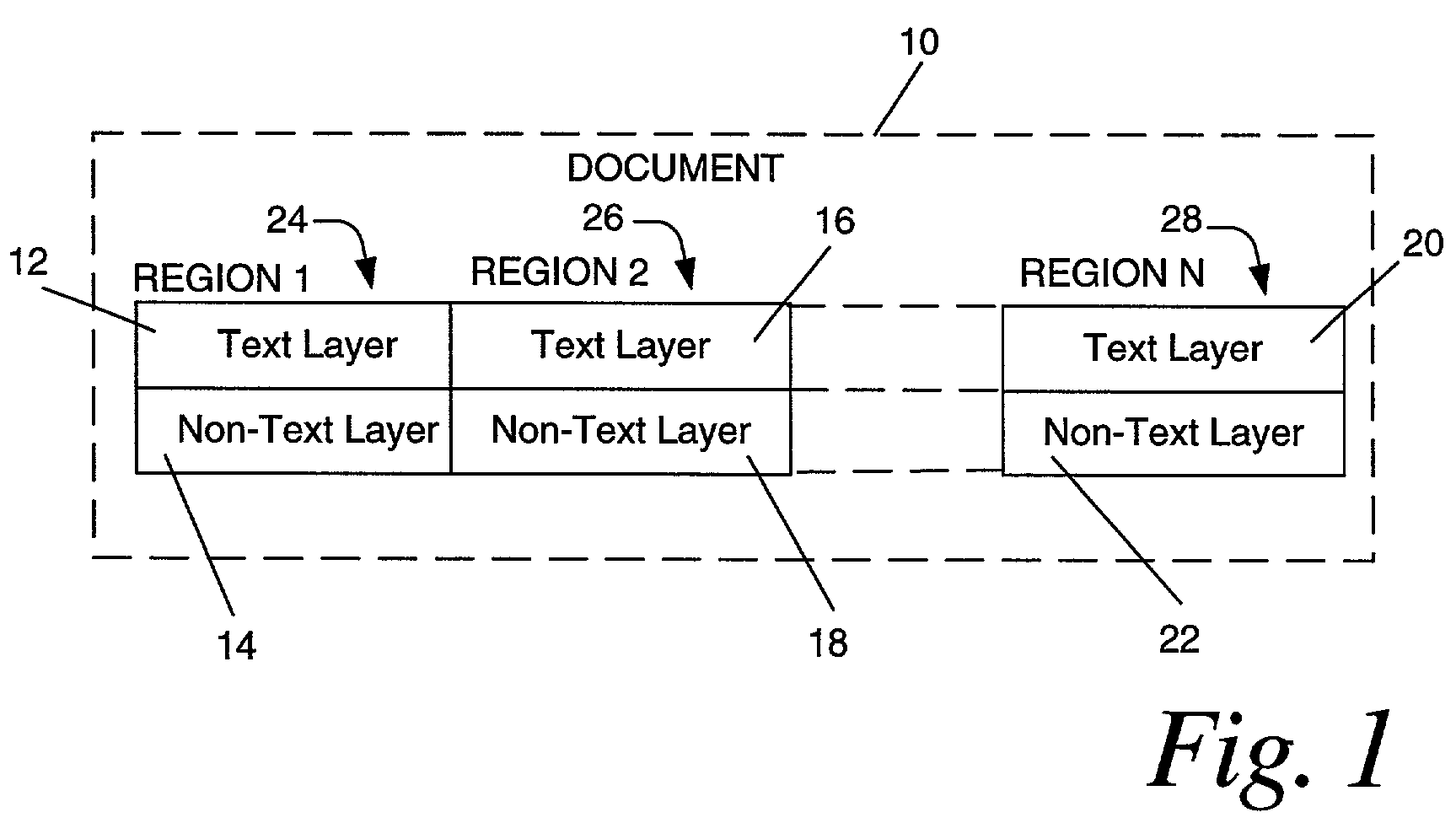
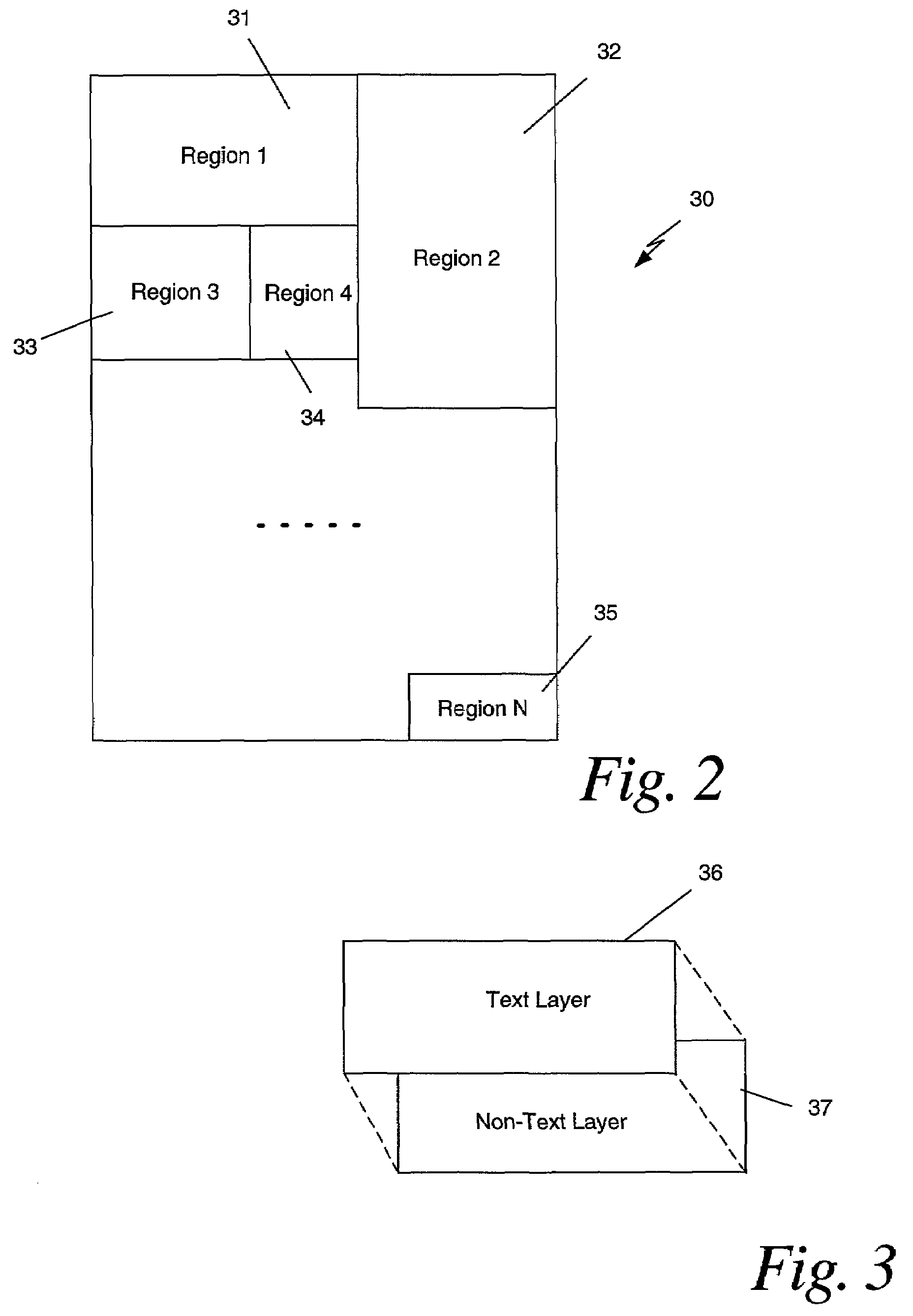
Compound document image compression using multi-region two layer format
Two layer formatting of documents for compatibility with two layer formatting schemes while maintaining color information and edge sharpness for text. A document is divided into multiple regions based upon bodies of text having the same color. A text layer and a non-text layer are specified for each region. The text layer includes a text color along with binary values for each pixel to specify whether to use the text color or a background color. The non-text layer includes a red-green-blue value for each pixel to specify its color for both image or non-text information including the background color for the bodies of text. The text layer is compressed using a lossless compression method and the non-text layer is compressed using a lossy compression method.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Electronic document signature protecting method and system
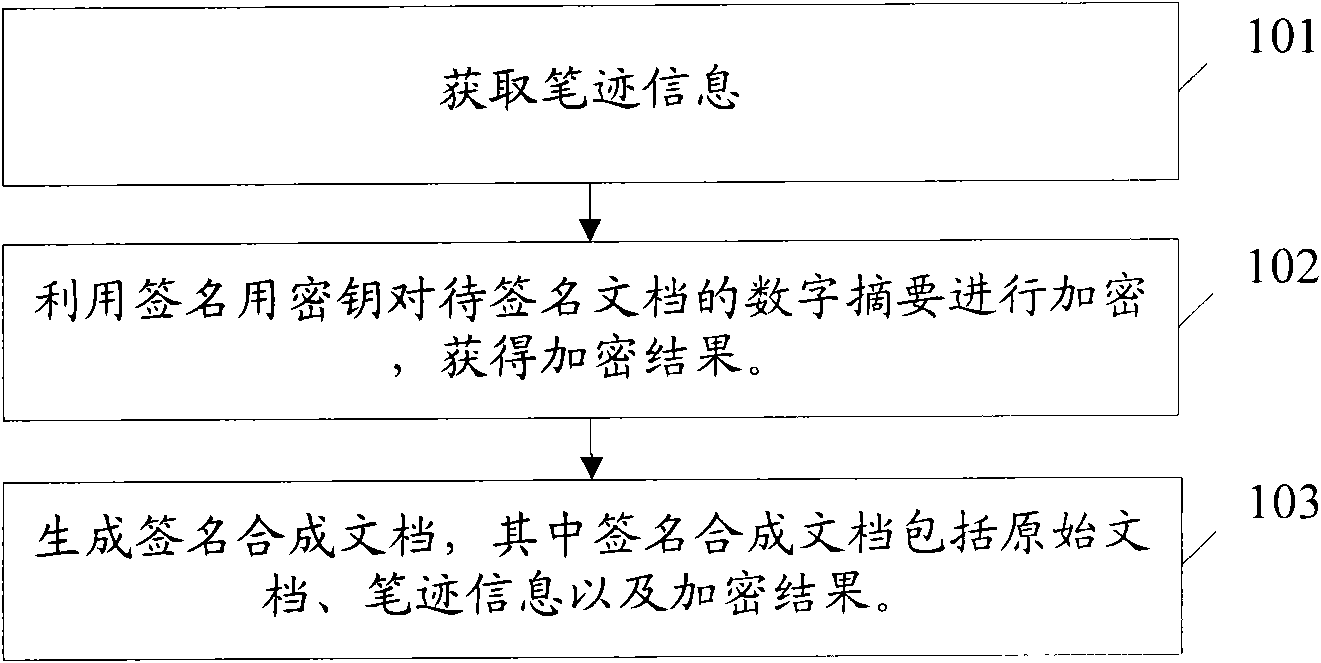
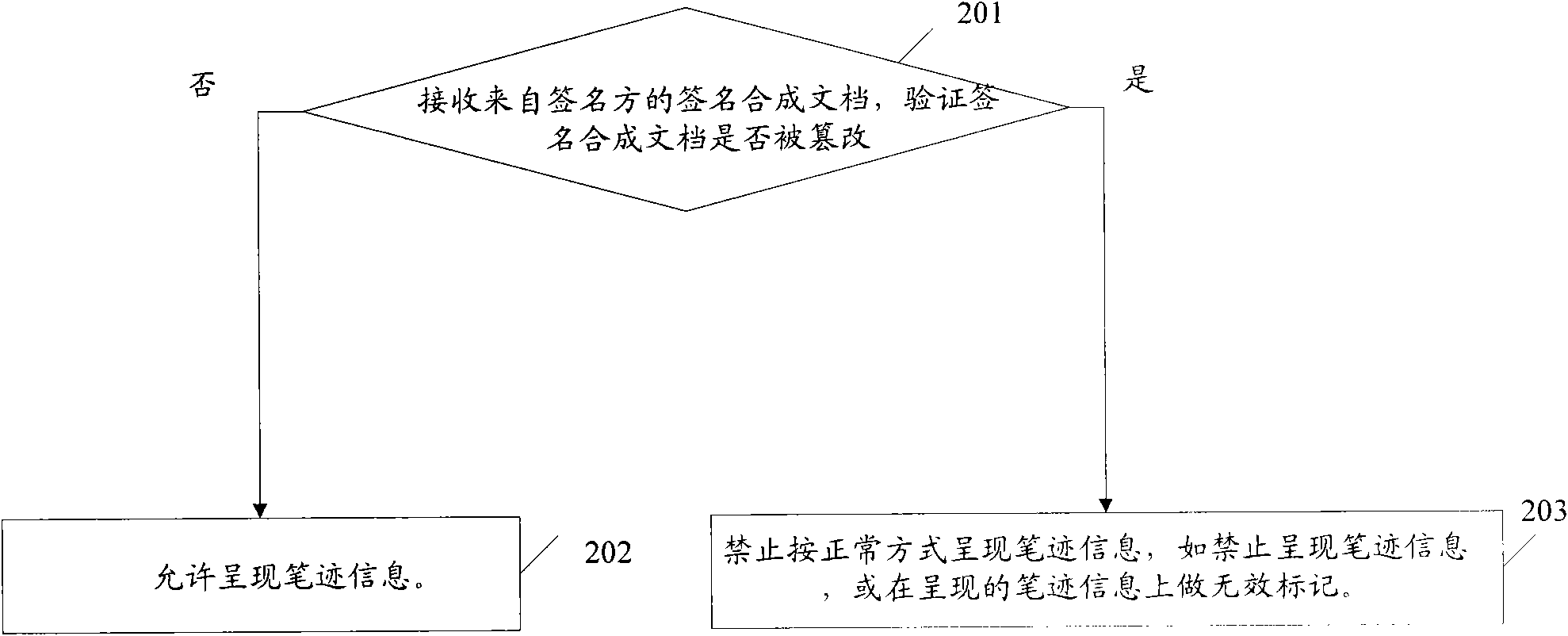
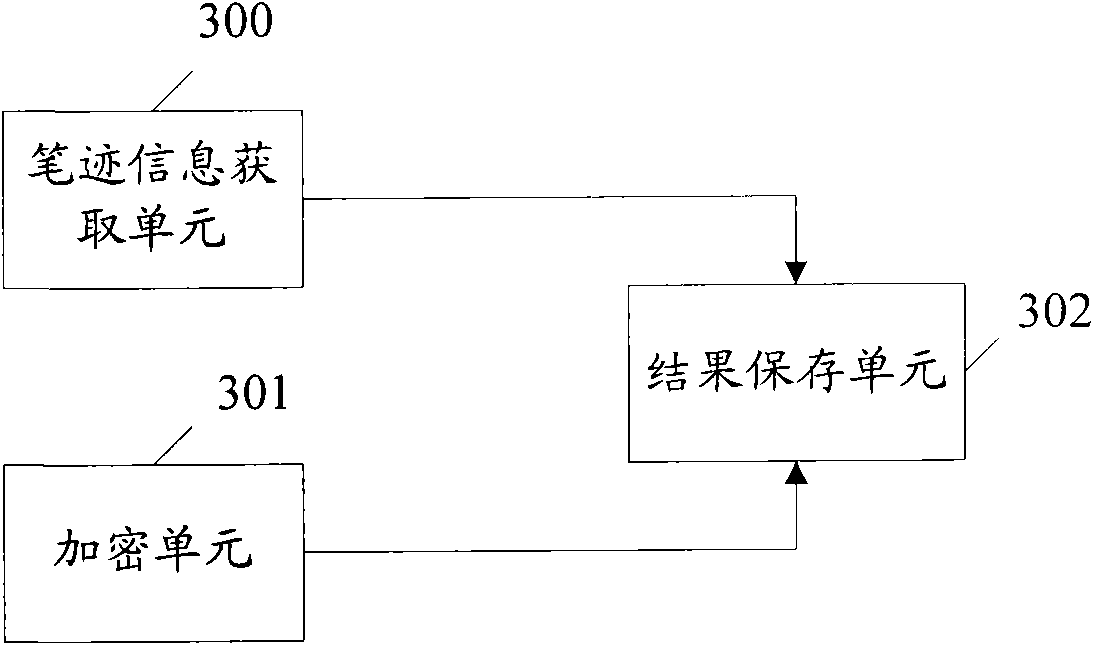
ActiveCN101789067AProtection securityIntegrity guaranteedDigital data protectionGraph readingHandwritingElectronic document
The invention discloses an electronic document signature protecting method which comprises the following steps of: acquiring handwriting information of a signer; encrypting the digital summary of a document to be signed by utilizing at least one key for signing to acquire an encryption result, wherein the signed document comprises an original document; and generating a signature compound document which comprises handwriting information, the signed document and the encryption result. The invention also discloses an electronic document signature protecting system. Under the condition that special preset processes (manufacture and confirmation processes) are not needed, the method and the system can be used for confirming the safety of the document and are visual and convenient.
Owner:北京书生电子技术有限公司
Multi-provider forms processing system with quality of service
A multi-provider forms processing system with a quality of service rating includes a plurality of portable computing devices, a plurality of service providers and a paper-like forms server coupled by a network. The paper-like forms server comprises a central scheduler and service provider manager and rater. The multi-provider forms processing system provides ratings for the service providers that are used in selection of services providers and processing of compound documents. In particular, the central scheduler tracks and determines where transaction failures occur, and based on these failures provides a quality of service rating for each service provider. The central scheduler also monitors the logs for completion as well as restarts, attempts, failure, reworked and re-performed transaction steps and provides ratings that can be reviewed by a user in selecting a service provider or automatically by a selection module.
Owner:RICOH KK
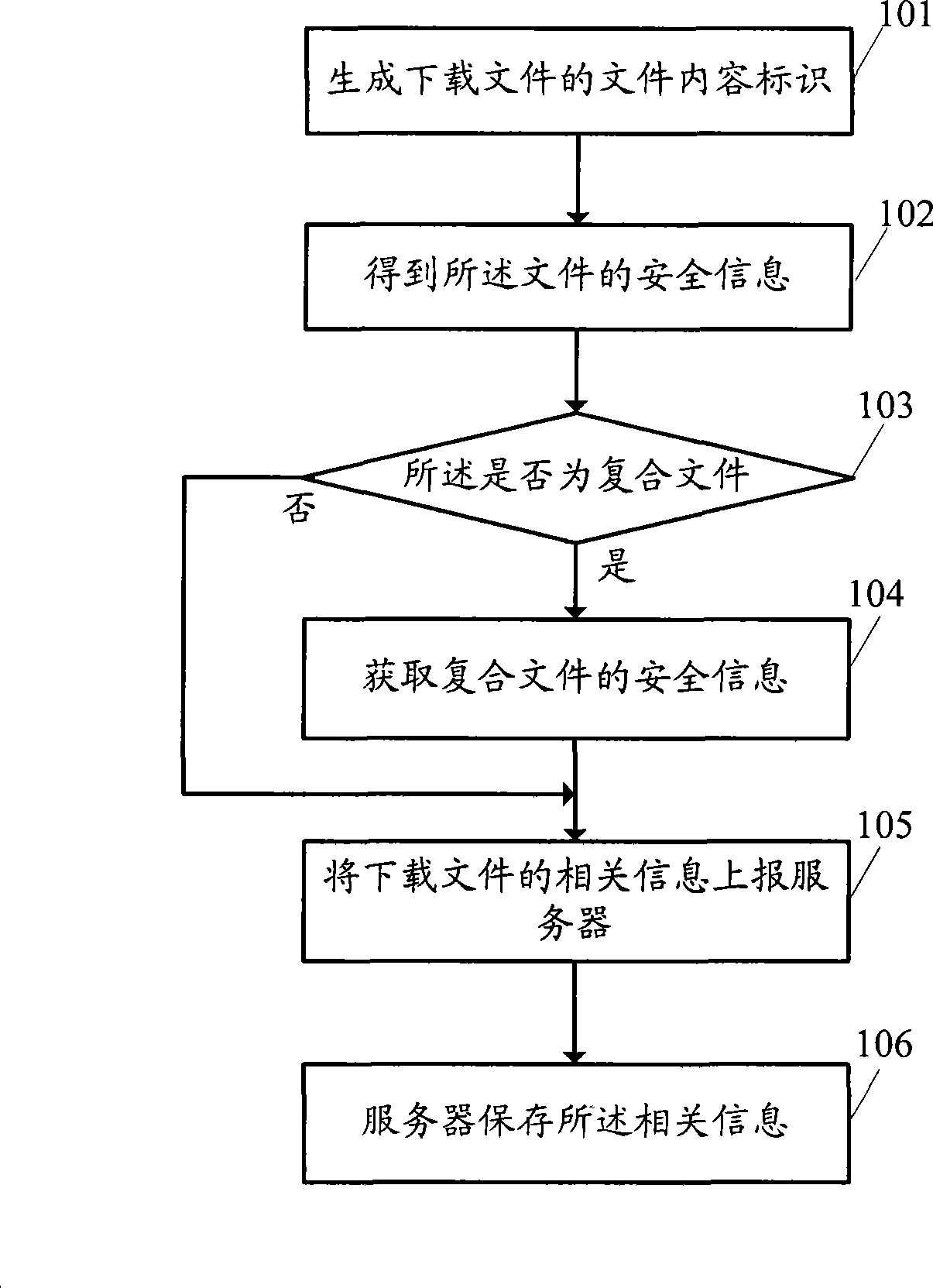
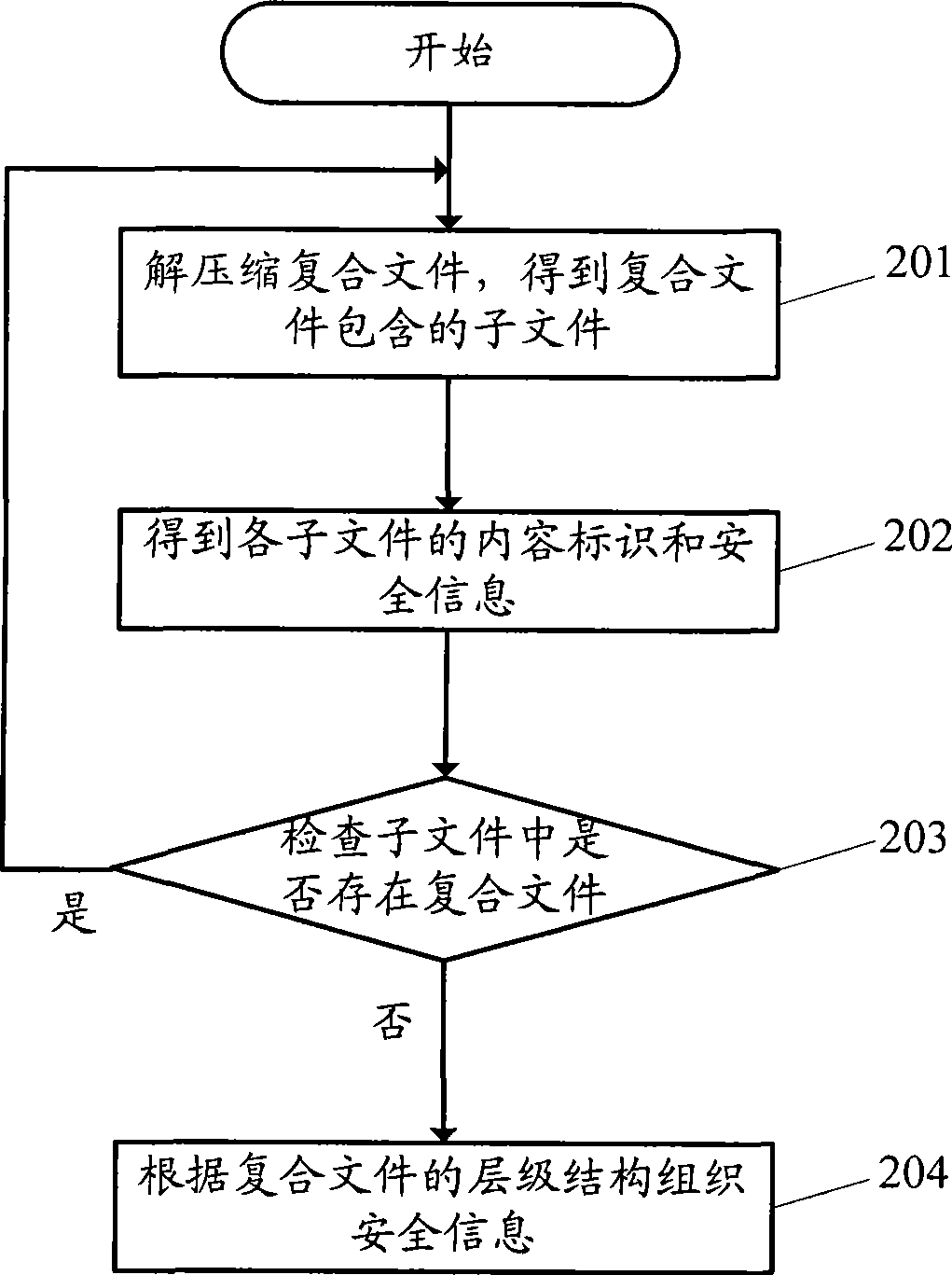
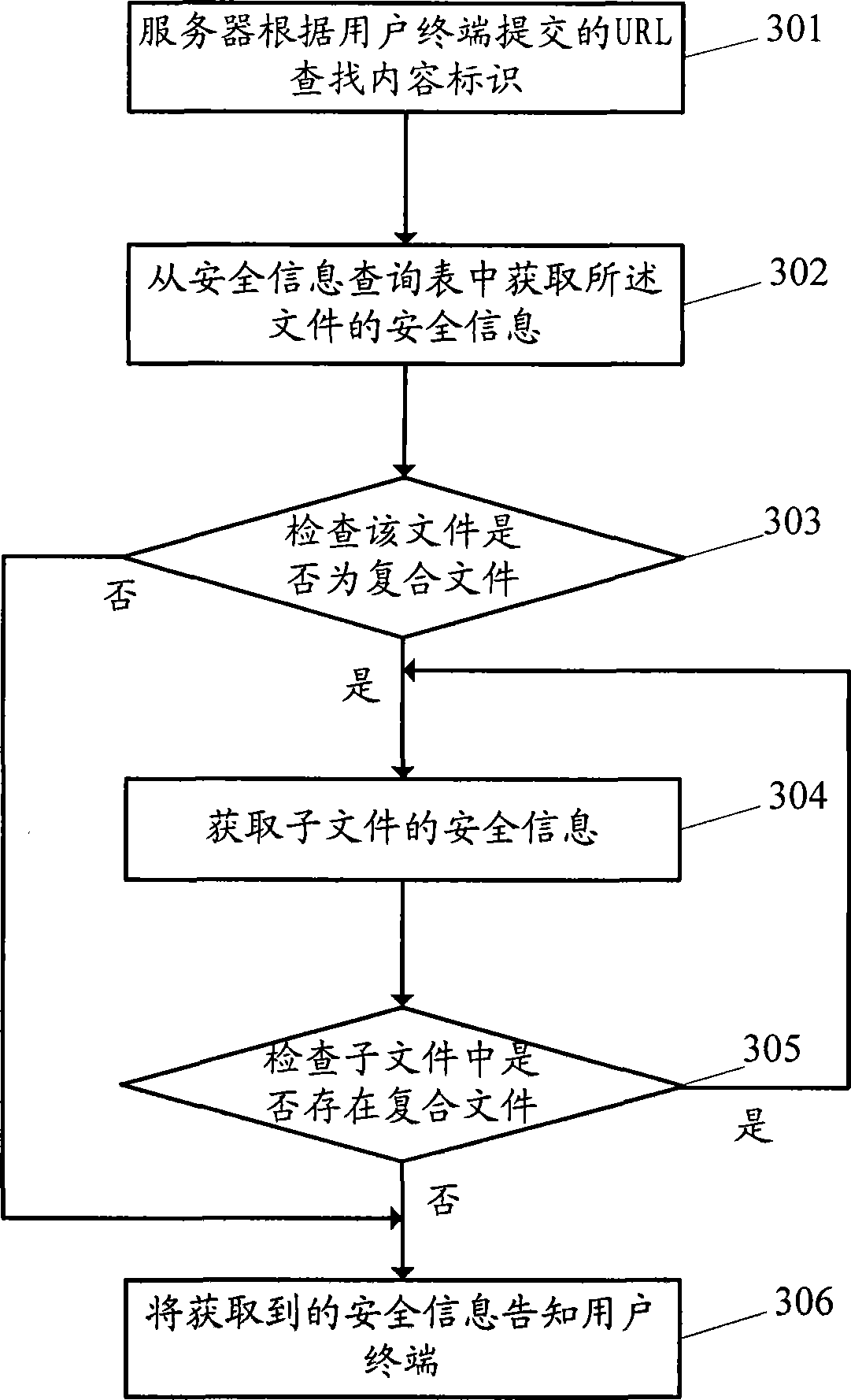
Method for providing file security information and security information processing system
InactiveCN101447006AOvercoming the problem of security informationOvercome the problem of providing only part of the file security informationComputer security arrangementsTransmissionInformation processingComputer terminal
The invention discloses a method for downloading a file and a system thereof, and aim at solving the problem that security information provision is incomplete in the prior art. A method for providing the security information comprises the following steps: a server terminal receives a uniform resource locator submitted by a user terminal at file downloading, obtains a content identification of the file according to the uniform resource locator, then acquires the security information of the file according to the content identification, and finds out the security information of a subfile which is contained in a composite file according to the content identification when the file is the composite file, and finally provides the security information of the file and the security information of the subfile to the user terminal. The scheme provided by the invention can help a user to acquire the security information of all files before downloading the files.
Owner:SHENZHEN THUNDER NETWORK TECH
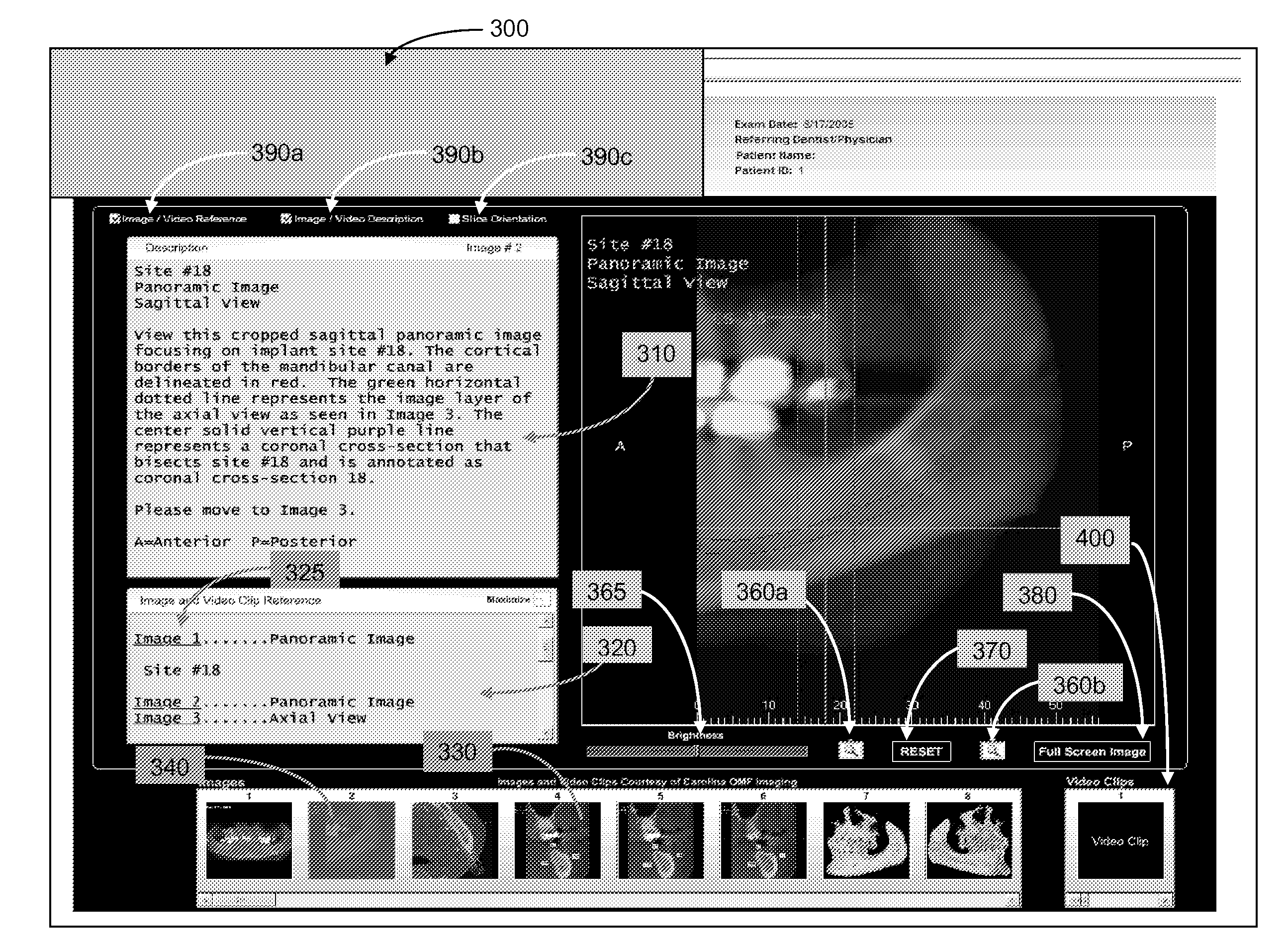
Method for forming and distributing a composite file including a dental image and associated diagnosis
A method of providing dental-related imaging data of a patient to a dental practitioner is provided, the dental-related imaging data being obtained by a third party imaging provider at a third-party imaging provider site using a three-dimensional digital imaging device. Three-dimensional image data of the maxillofacial complex of the patient is obtained with the imaging device and analyzed to form a diagnosis. A two-dimensional image associated with the diagnosis is formed from the three-dimensional image data, and the two-dimensional image and diagnosis are combined into a composite file as part of the dental-related imaging data. The dental-related imaging data is stored in encrypted read-only format executable by a standard multi-media player and made available to the dental provider in a secure arrangement. The composite file is thereby selectively viewable by the dental provider for determining an appropriate treatment for the patient. Associated methods and apparatuses are also provided.
Owner:HOWERTON JR WILLIAM BRUCE
Method and system for embedding user assistance in documents utilizing markup languages
A document creation application, compound document format, and method for providing user assistance in a compound document are described. The compound documents are formed using a markup language and include both non-volatile text and user selected and / or input data. The compound documents also include embedded user assistance triggers, or links, at specific terms, concepts or user input areas which dynamically link a user to appropriate user assistance information in the document creation application. The method describes embedding user assistance links in compound documents to allow users to dynamically link to topic specific user assistance information.
Owner:INT DOCUMENT SERVICES INC
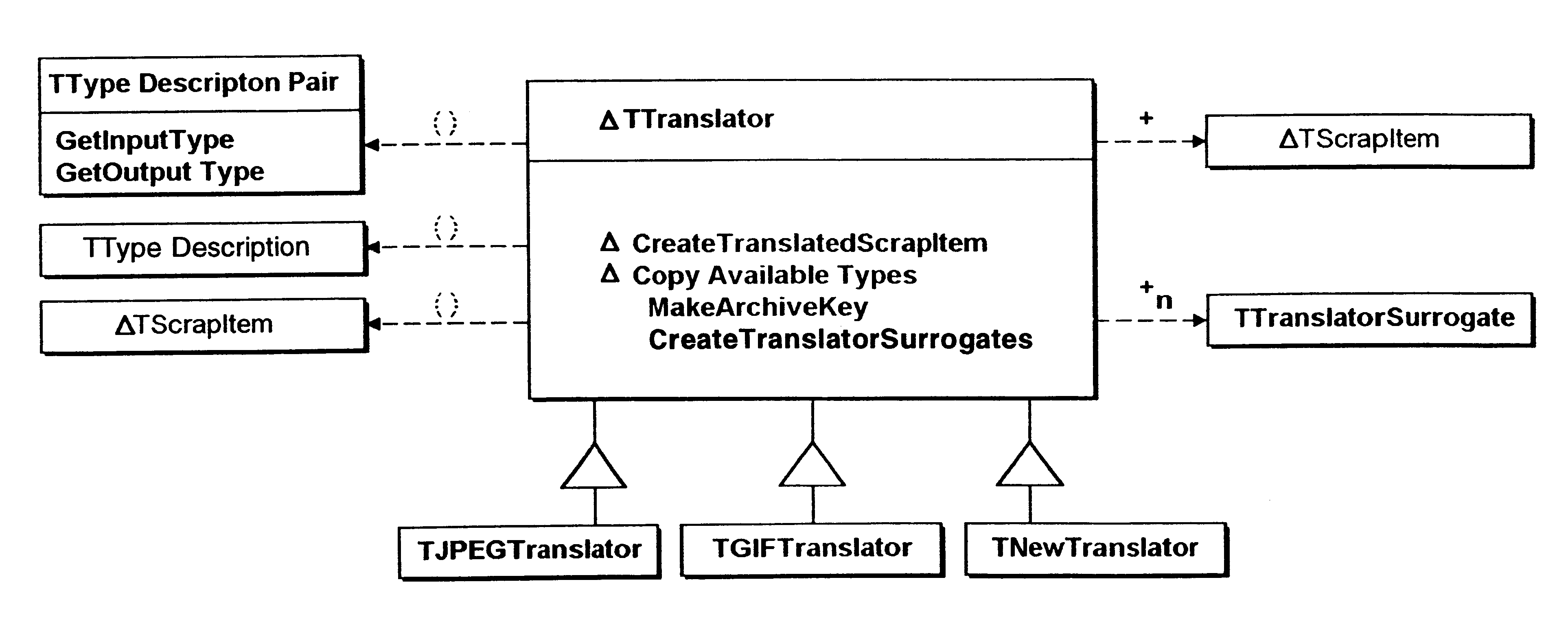
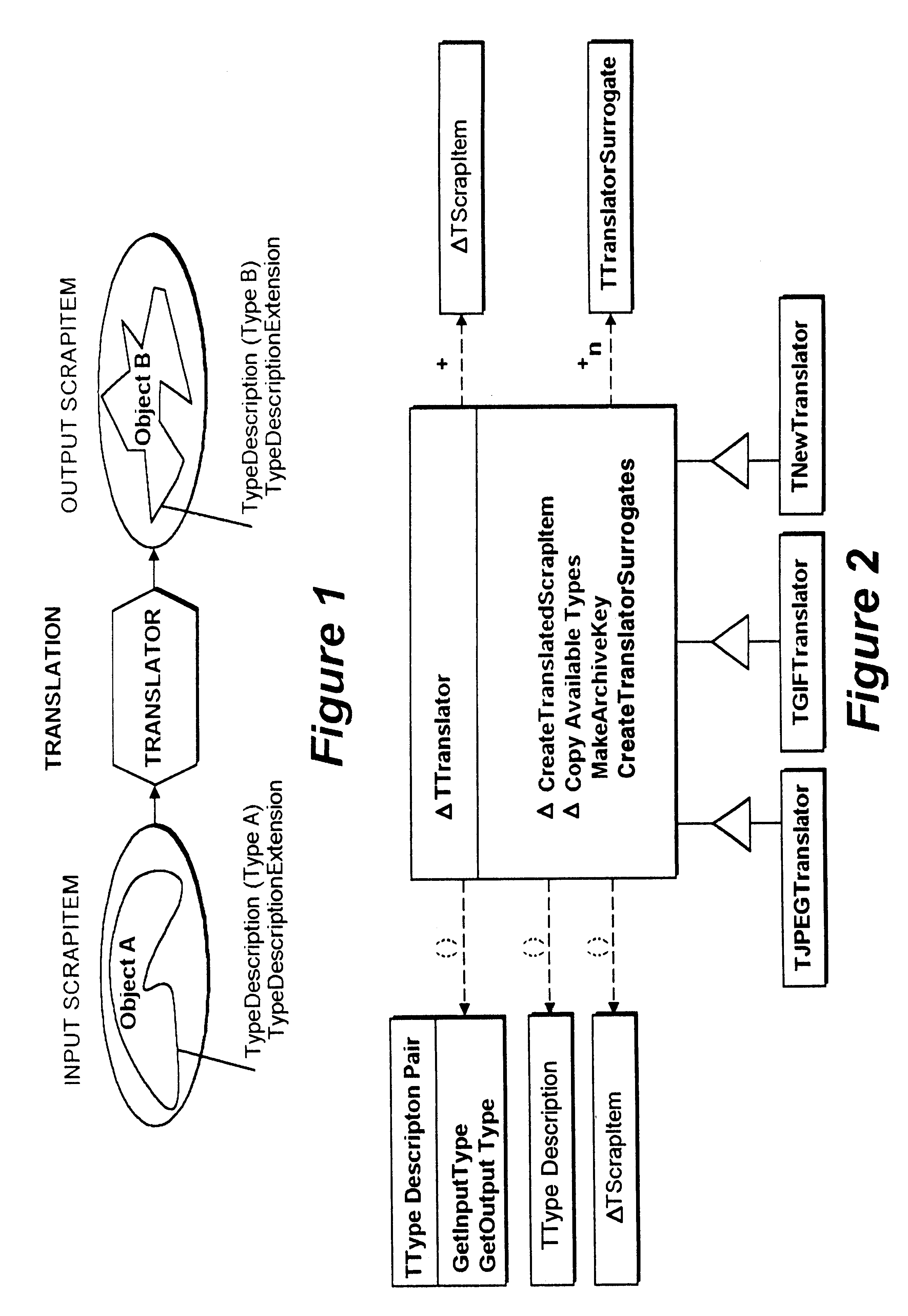
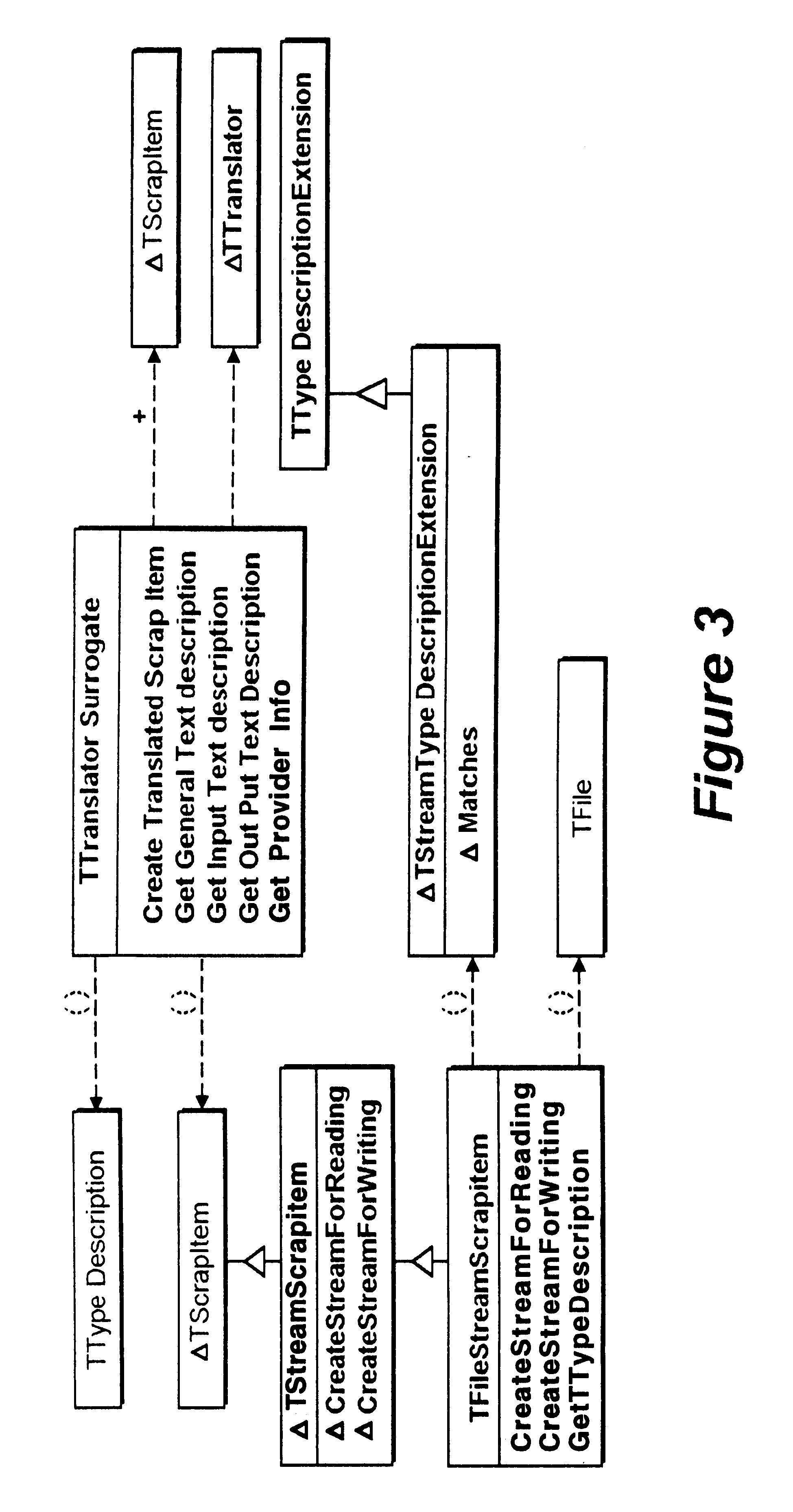
Object oriented translation framework method, apparatus, and program
InactiveUS6253205B1More securityData processing applicationsSpecific program execution arrangementsClient-sideDocumentation
The invention is a translation framework which performs data conversions in an object oriented environment from clipboards, drag, and drop tend entire files and entire objects into compound documents. There are three primary classes: the translator, the translator surrogates, and the translation query. Translators are heavy objects that may include the translator's shared library and supporting libraries. The framework uses light weight surrogate translators as stand-ins for translators. The surrogates do not pull in the translators unless there is a request to do an actual translation. When a translation is requested, the translator must be streamed into the address space of the repeating client. Clients desiring a document object be translated for inclusion in a compound document interact with the framework by using queries to access a translation surrogate.
Owner:APPLE INC
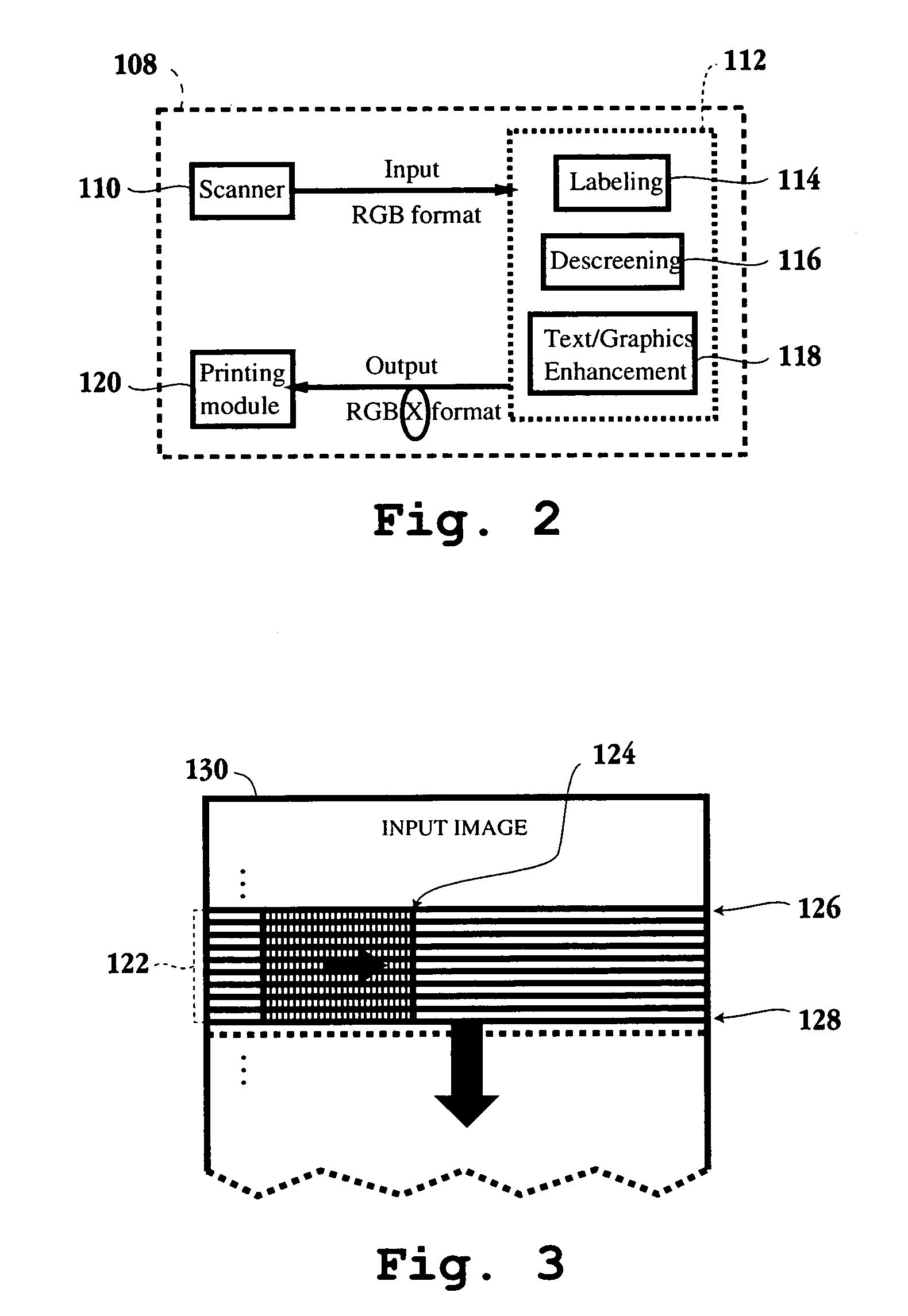
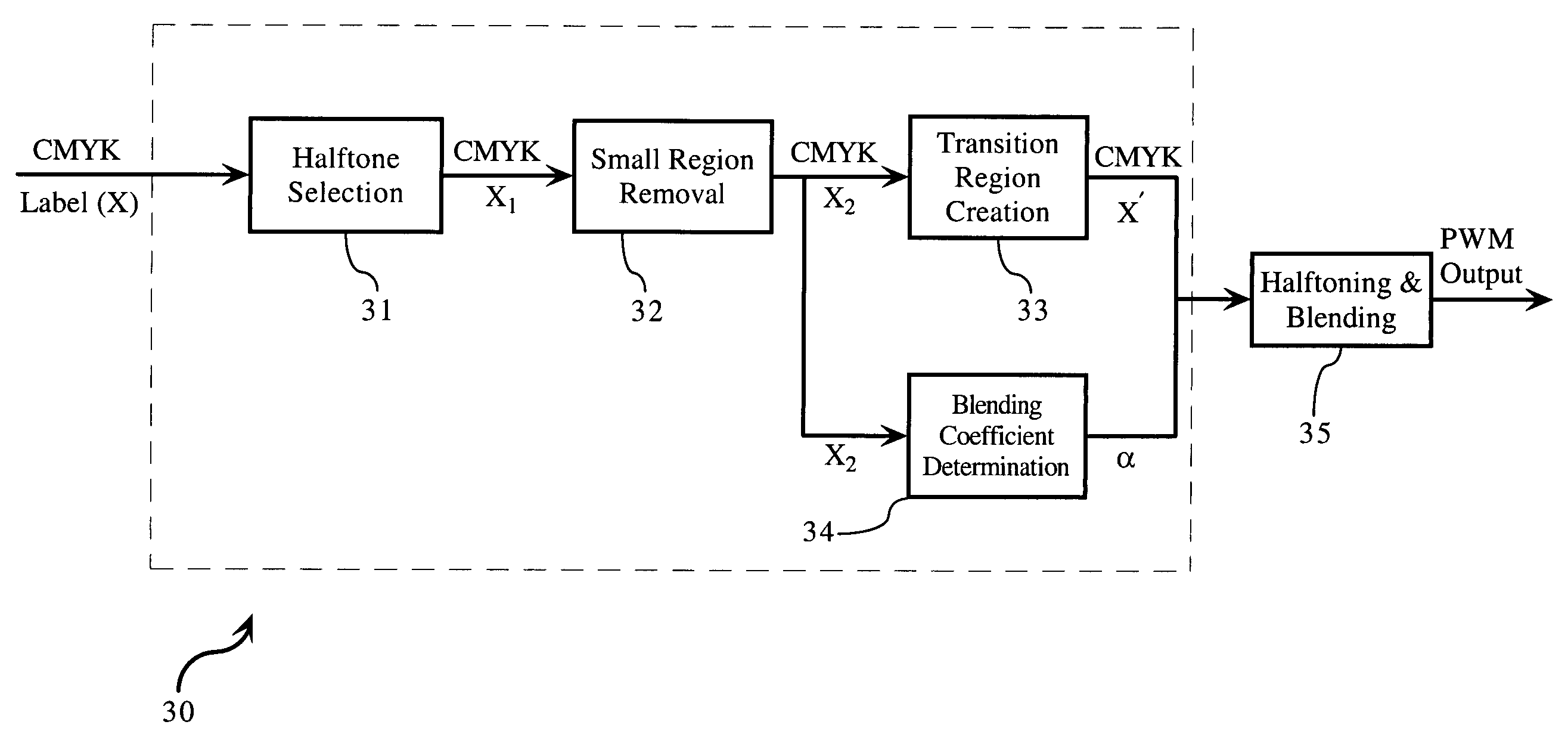
Adaptive halftone scheme to preserve image smoothness and sharpness by utilizing X-label
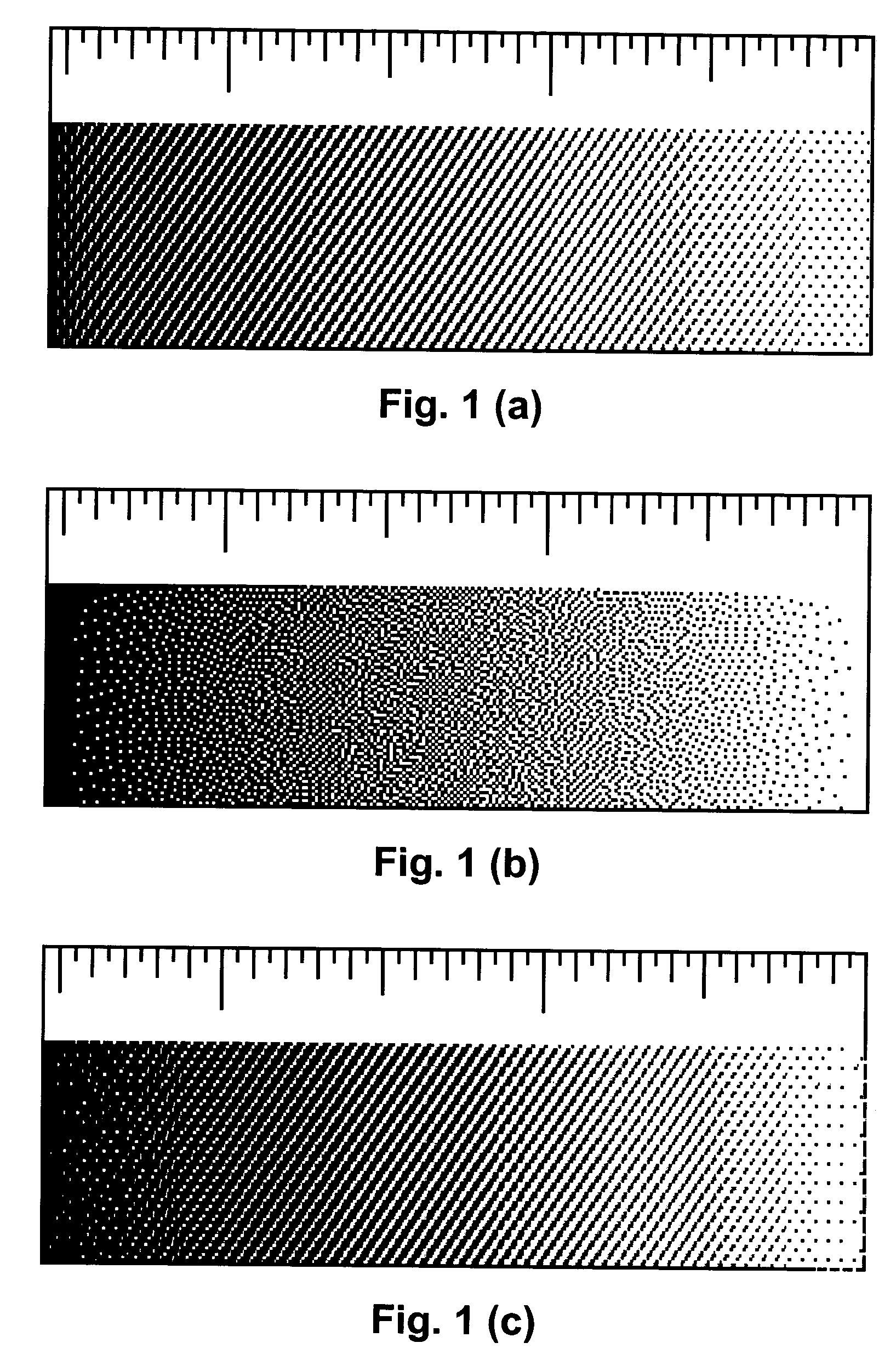
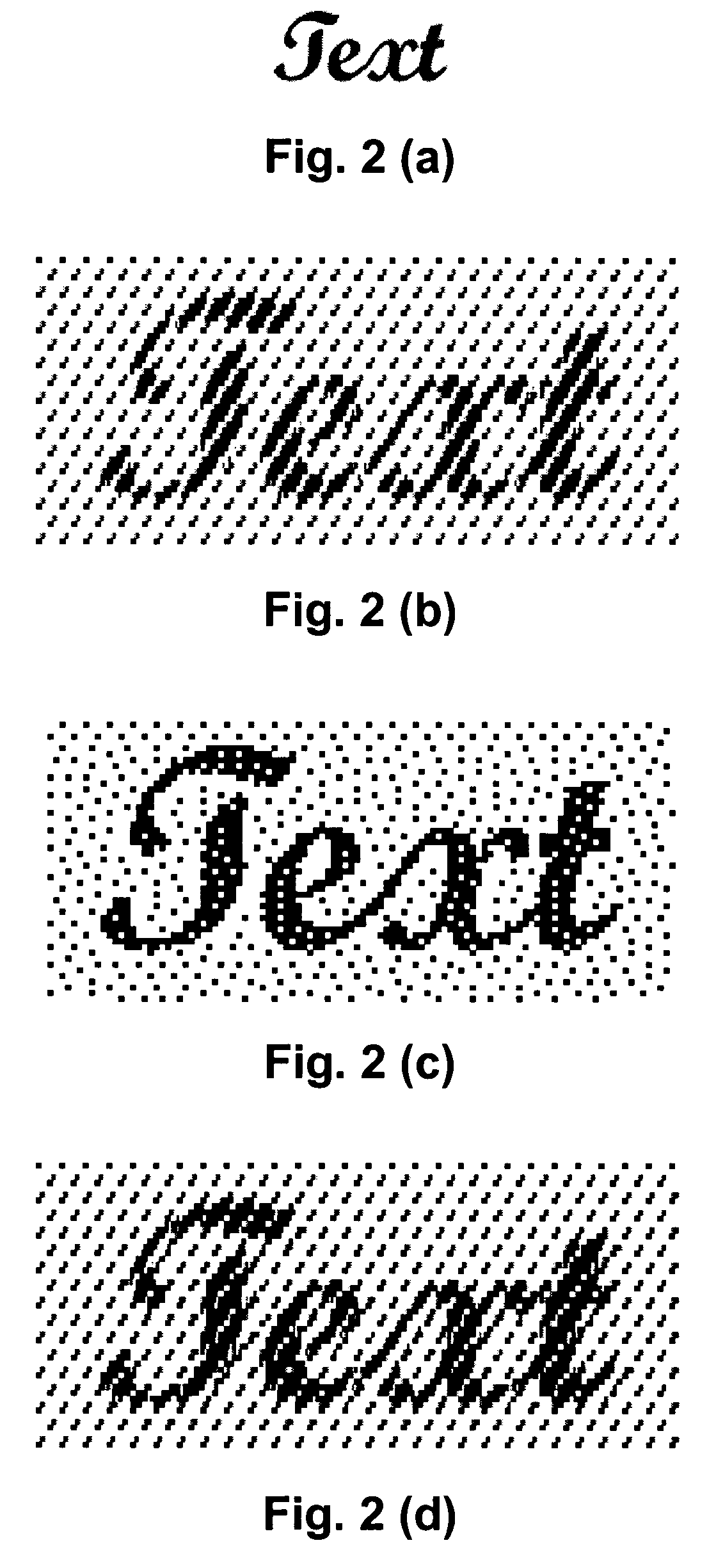
InactiveUS20050030586A1Improve visual appearancePreserving edge sharpnessImage enhancementVisual presentationCompound documentPaper document
An adaptive halftone scheme is applied to a compound document to smooth the rendering while preserving edge sharpness. The adaptive halftone scheme involves identifying document regions as either smooth, edge or texture. Each identified region is then processed as follows. Wherever a smooth region is adjacent to an edge region and wherever a smooth region is adjacent to a texture region, create a transition region in a portion of that smooth region bordering that other region and apply a blend of a screening halftone technique (SCN) and an error diffusion with screening halftone technique (EDSCN) to that transition region, apply SCN to the remainder of that smooth region, apply ED to that other region if it is an edge region, and apply either EDSCN or SCN if it is texture region.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
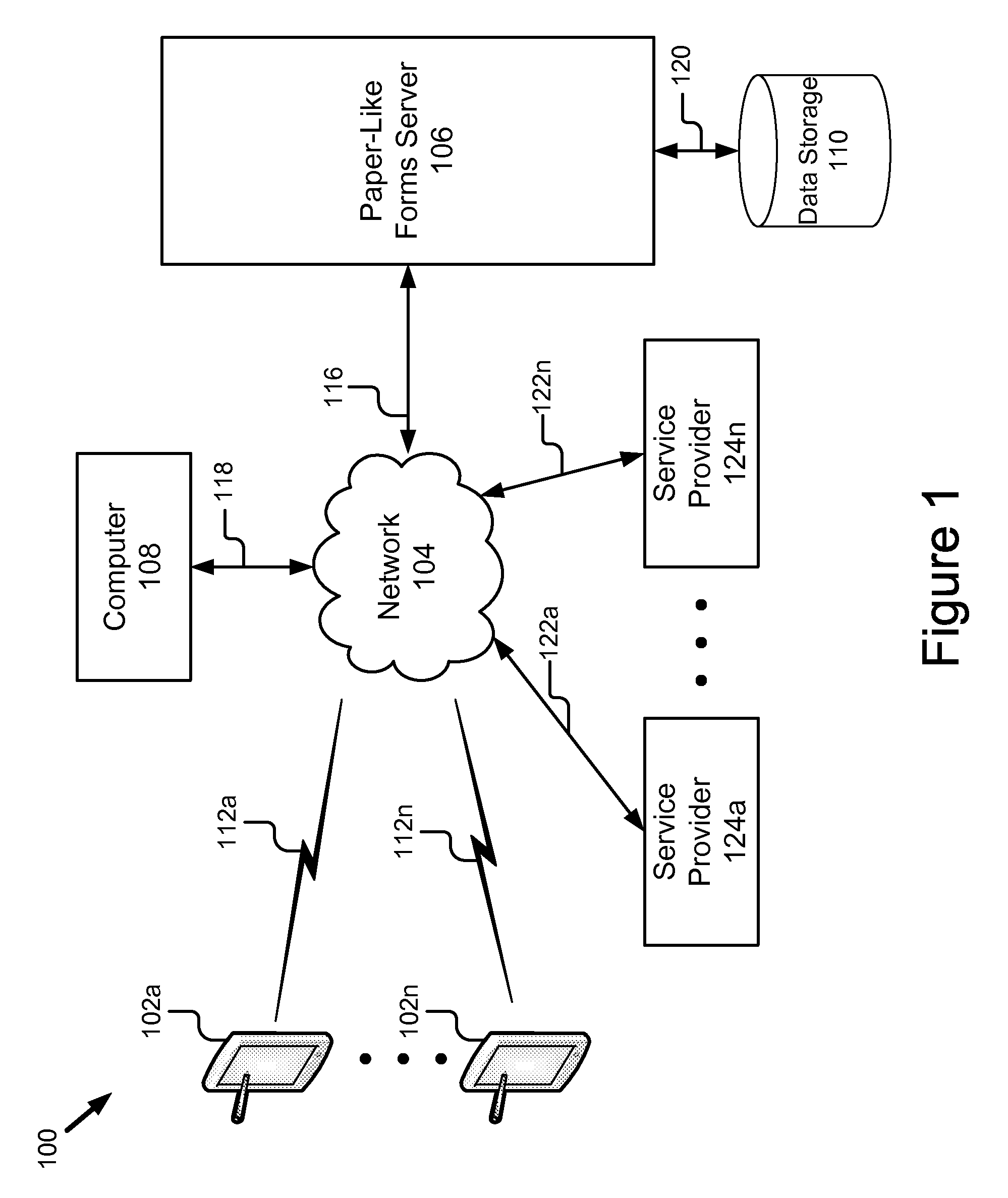
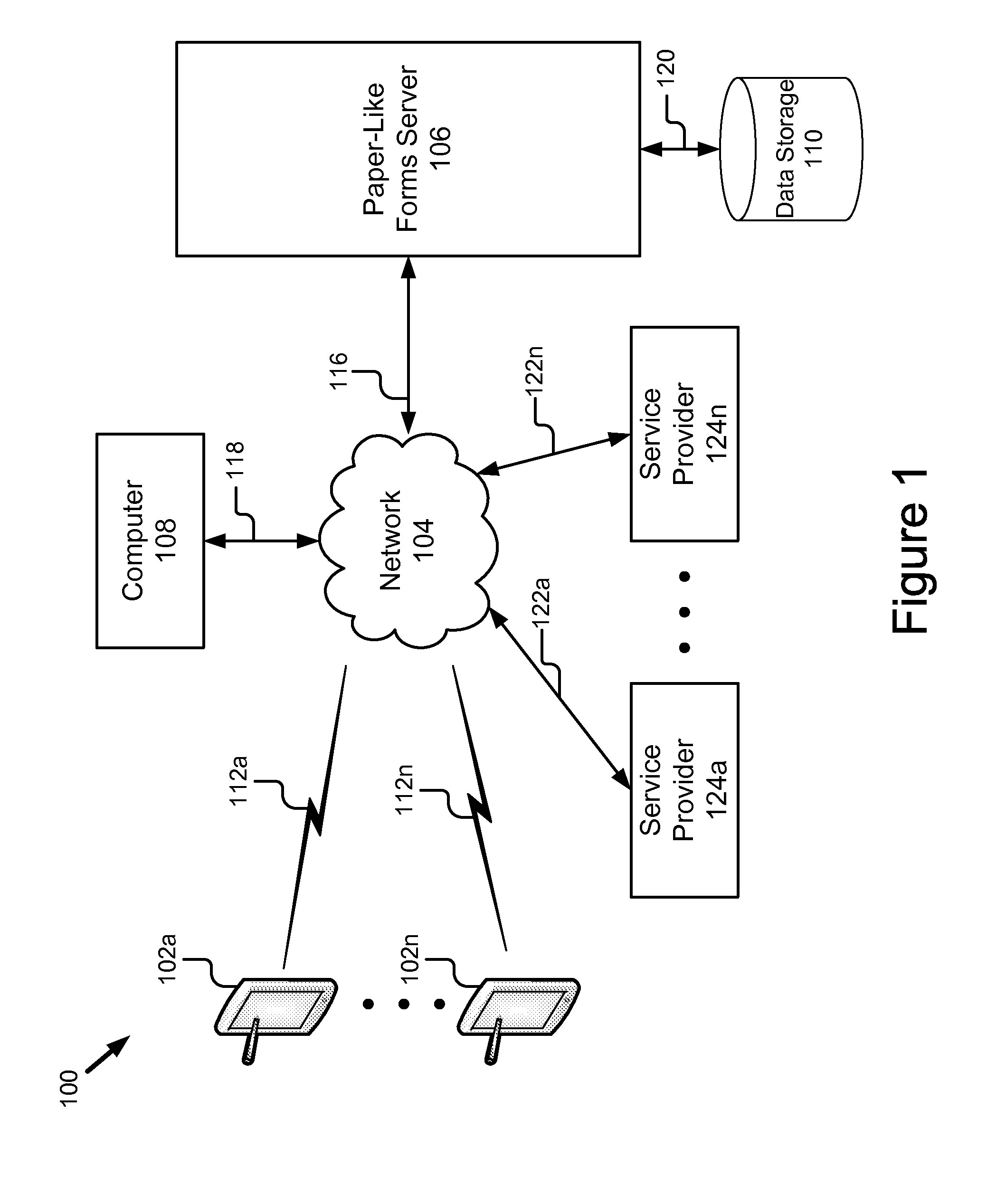
Paper-like forms processing system & method
ActiveUS20110060981A1Overcome deficienciesMinimal modificationOffice automationSpecial data processing applicationsDocumentation procedureForm processing
A system for paper-like forms processing includes a plurality of portable computing devices coupled by a network to a paper-like forms server. The portable computing devices are adapted to receive images (e.g., compound documents / forms), add stroke annotations to the received images, and send the annotated received images or the stoke annotations themselves to the paper-like forms server. The paper-like forms server comprises a central scheduler and a logging module. The paper-like forms server processes compound documents as paper like forms and sends input to and receives results from service providers to perform various types of paper like processing on the compound document. The paper-like forms server performs the scheduling, routing, logging, verification and billing for the paper-like processing of compound documents. The central scheduler also stores results from service providers for later retrieval.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com