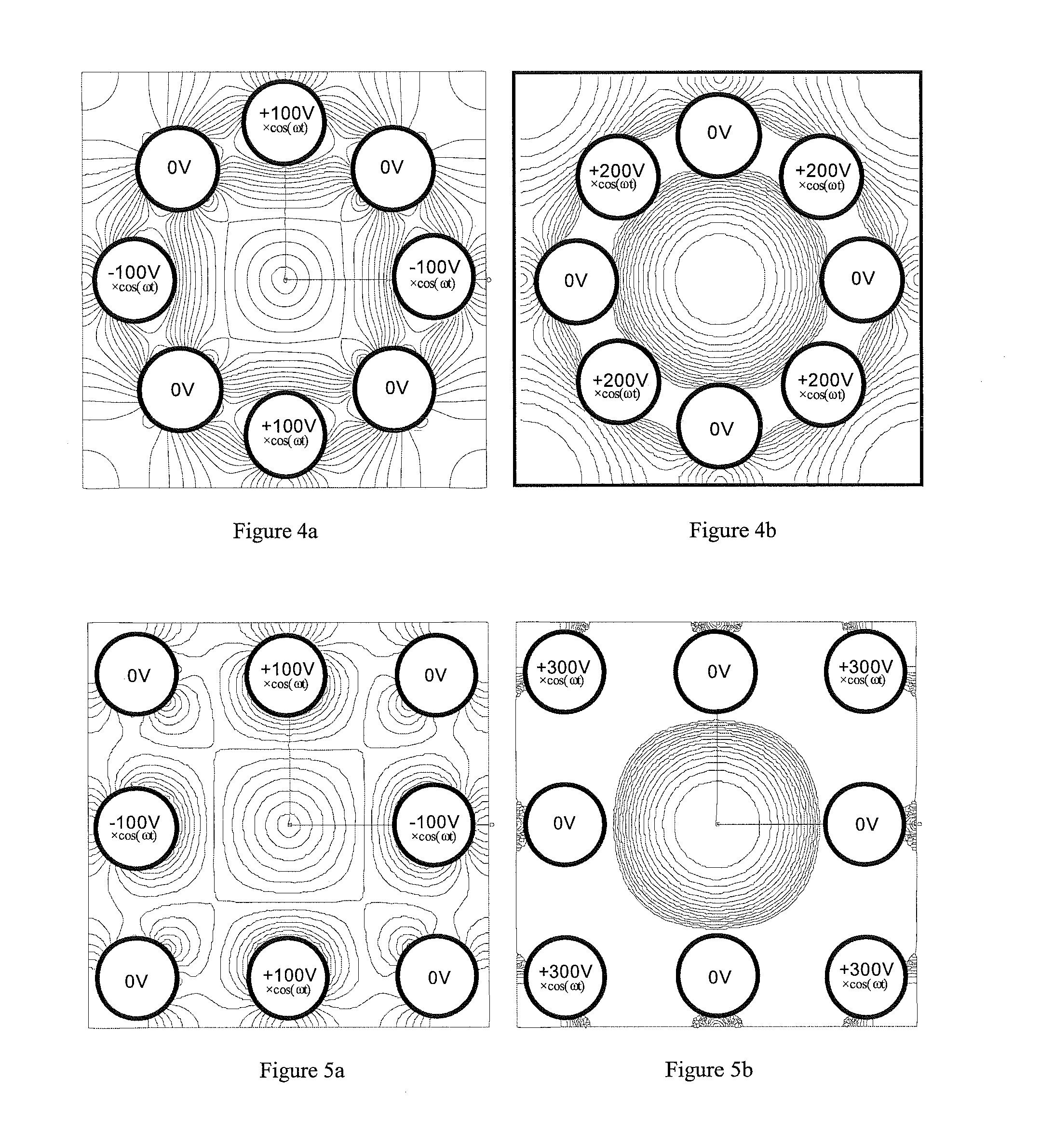
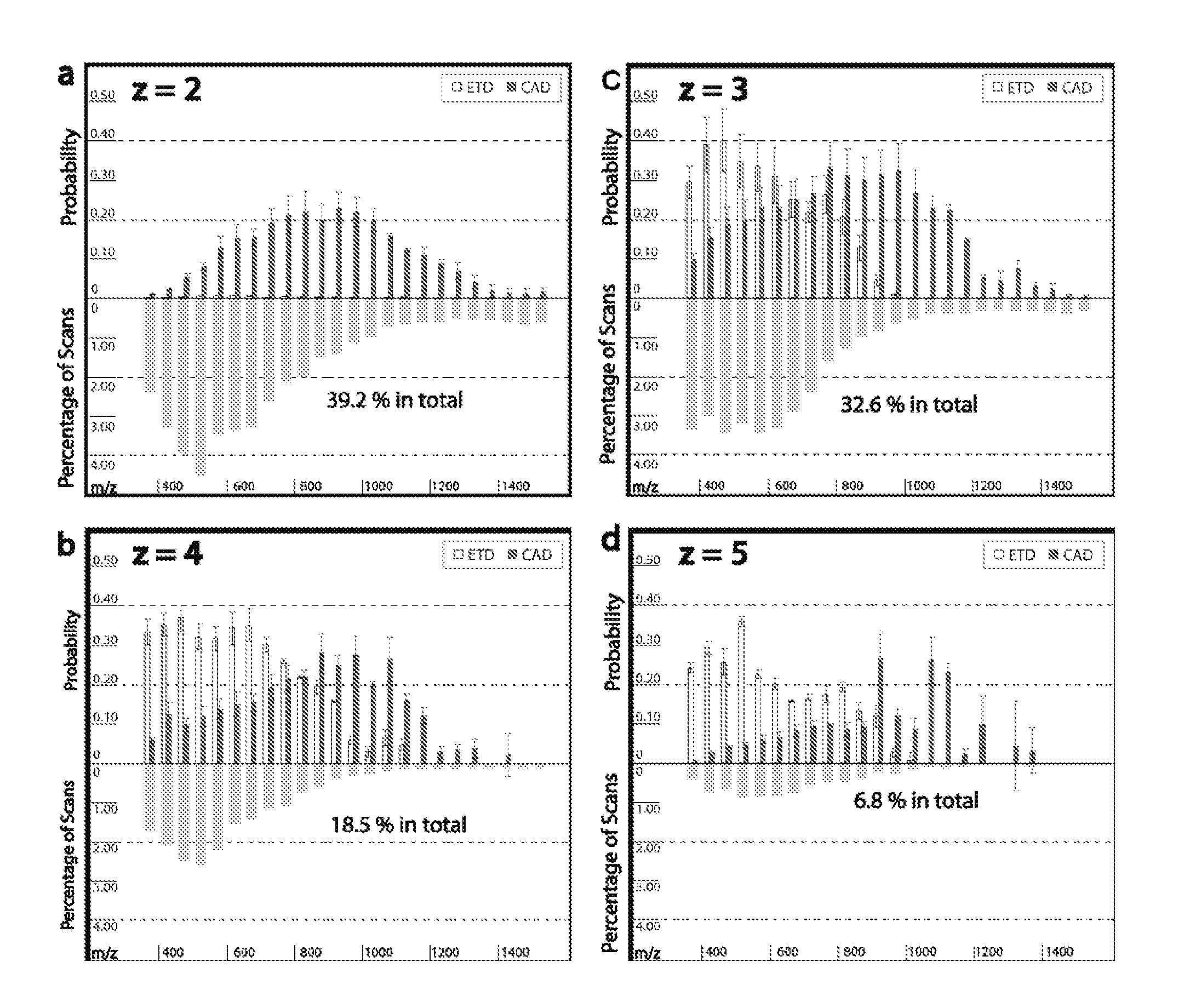
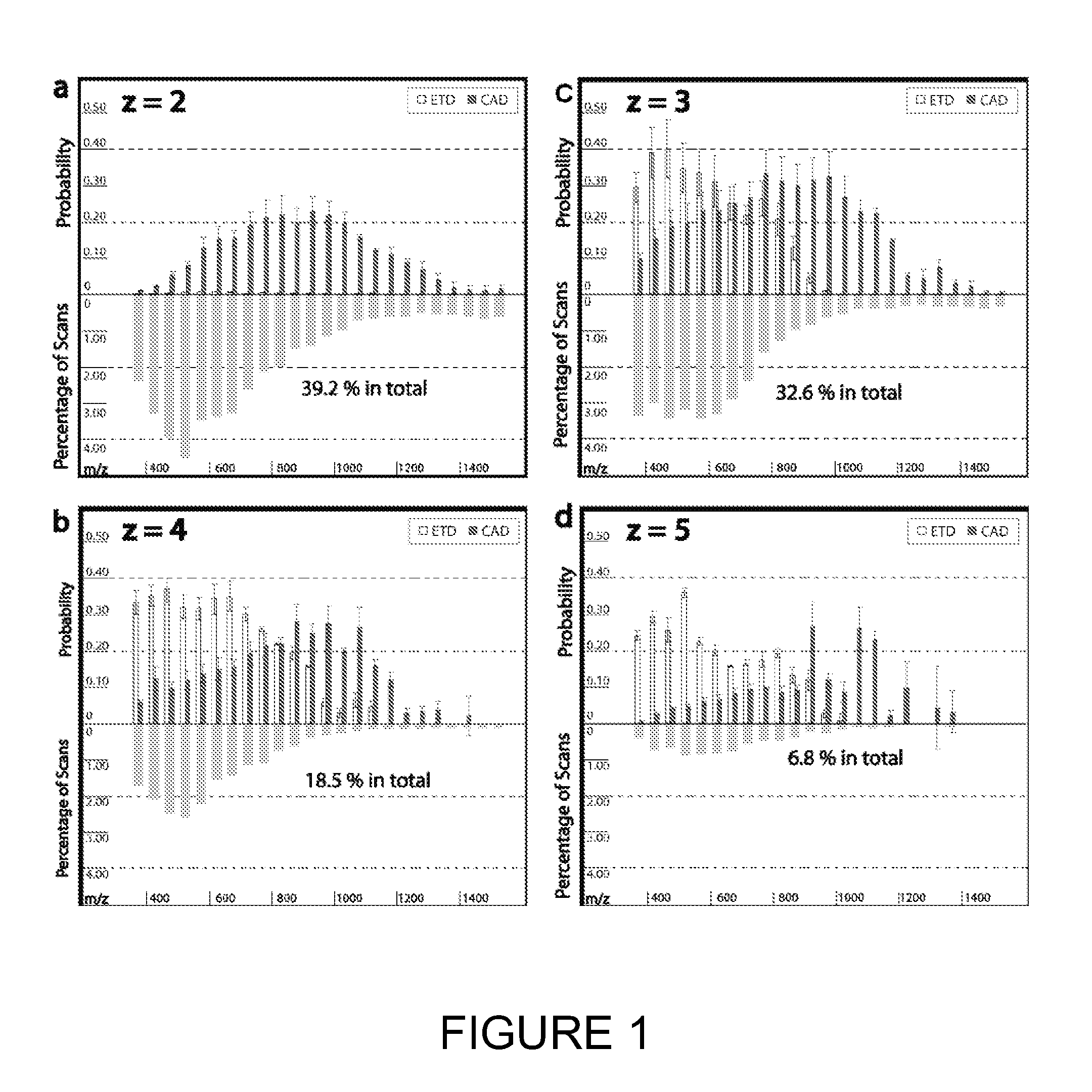
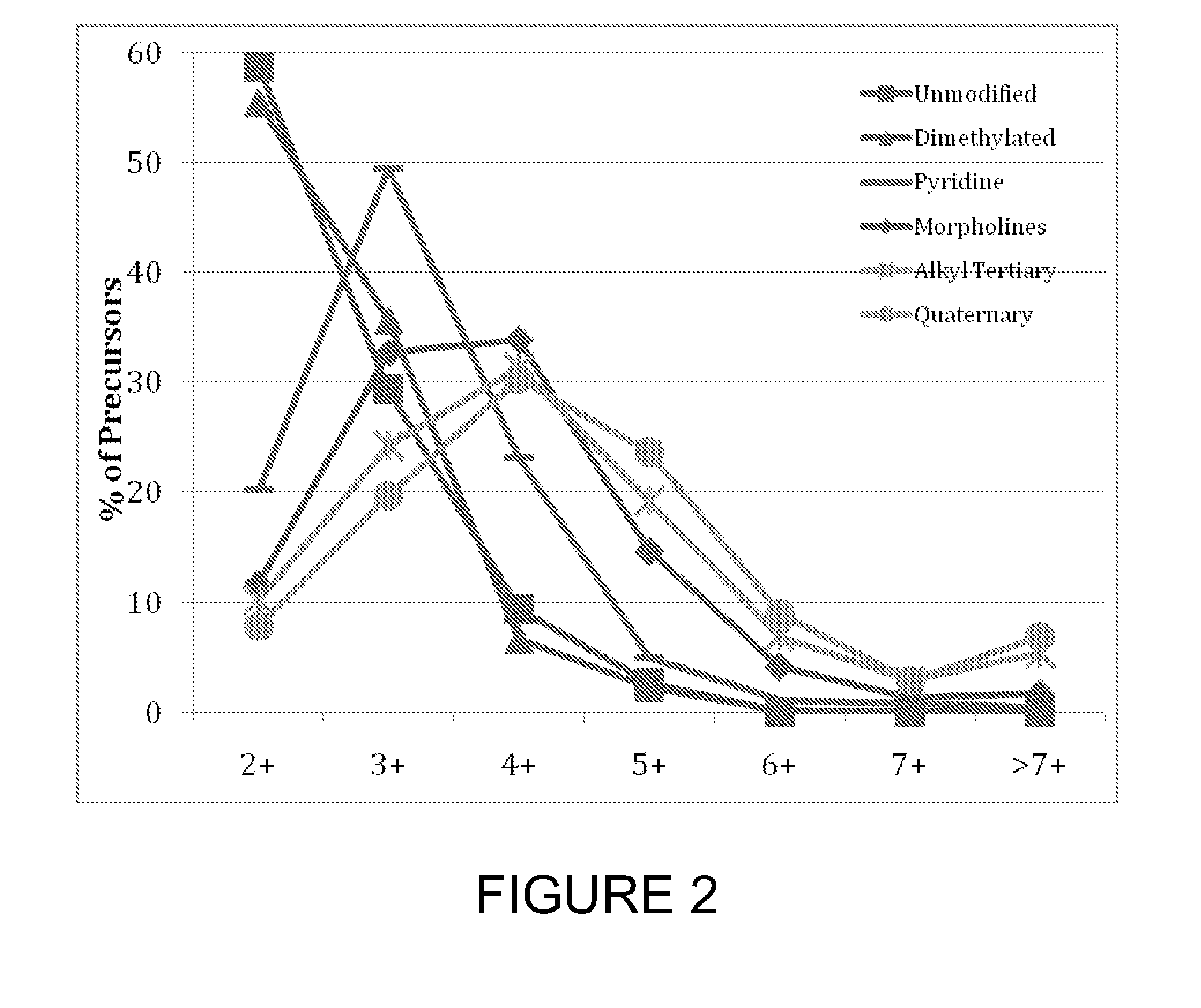
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Electron-capture dissociation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
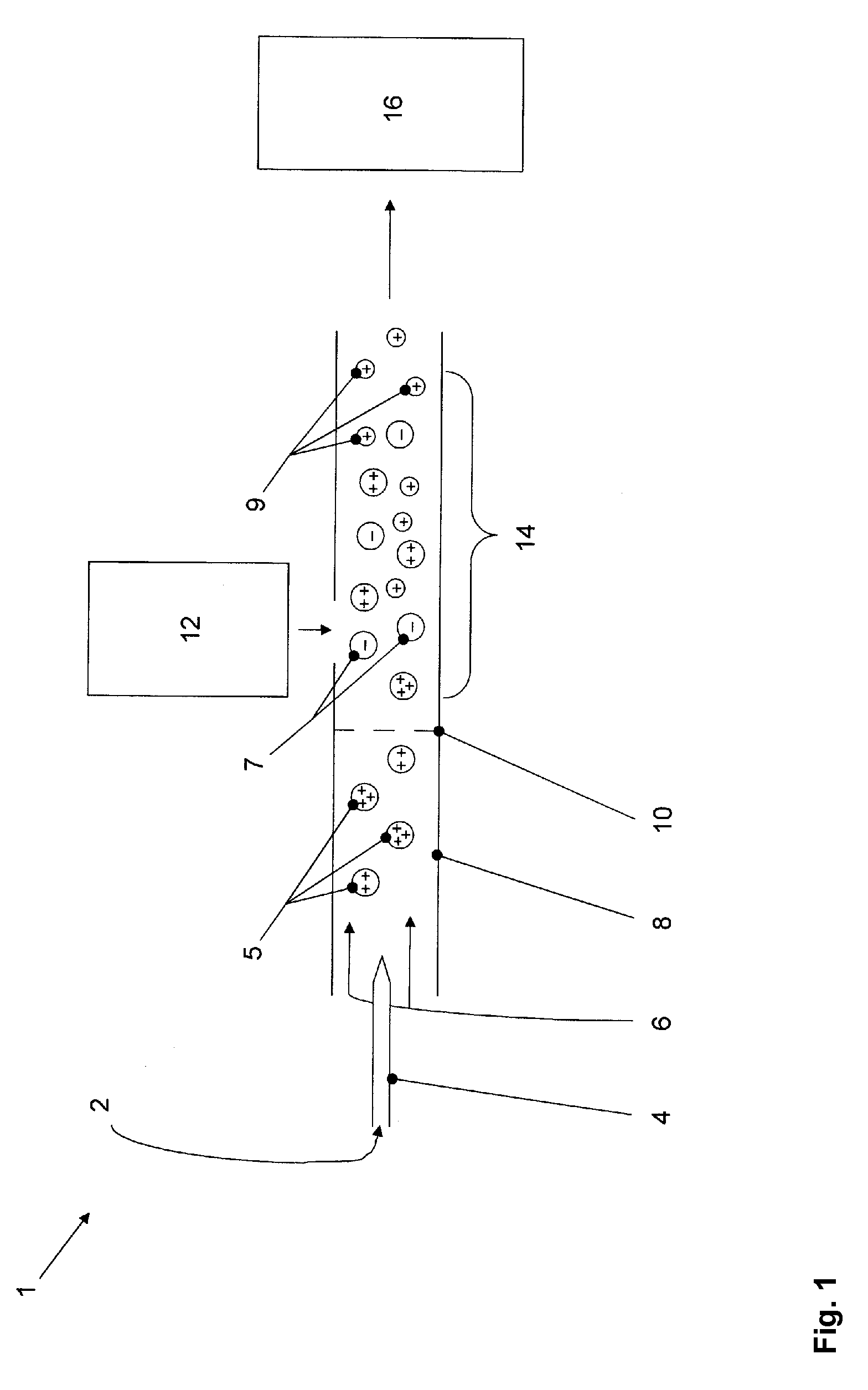
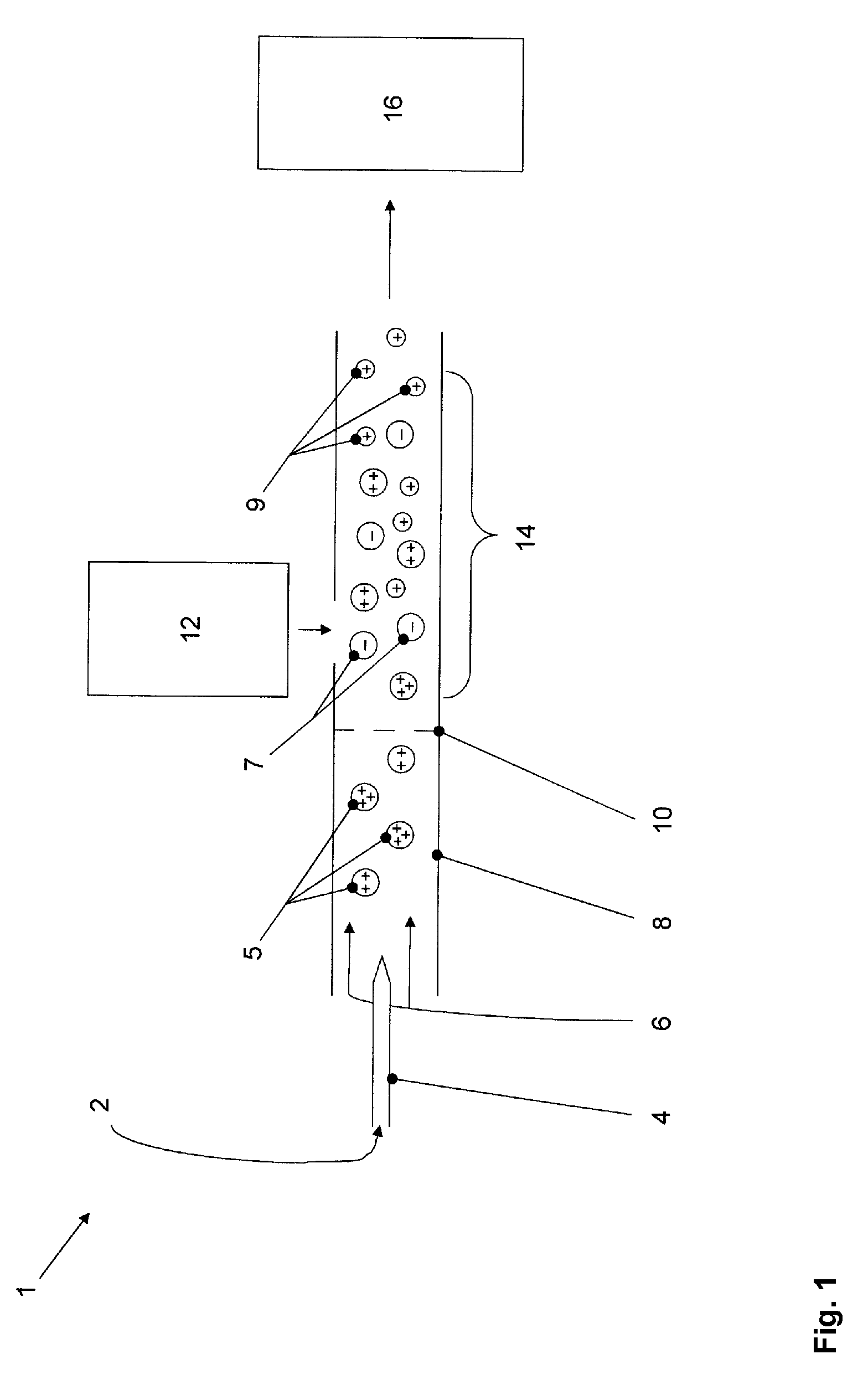
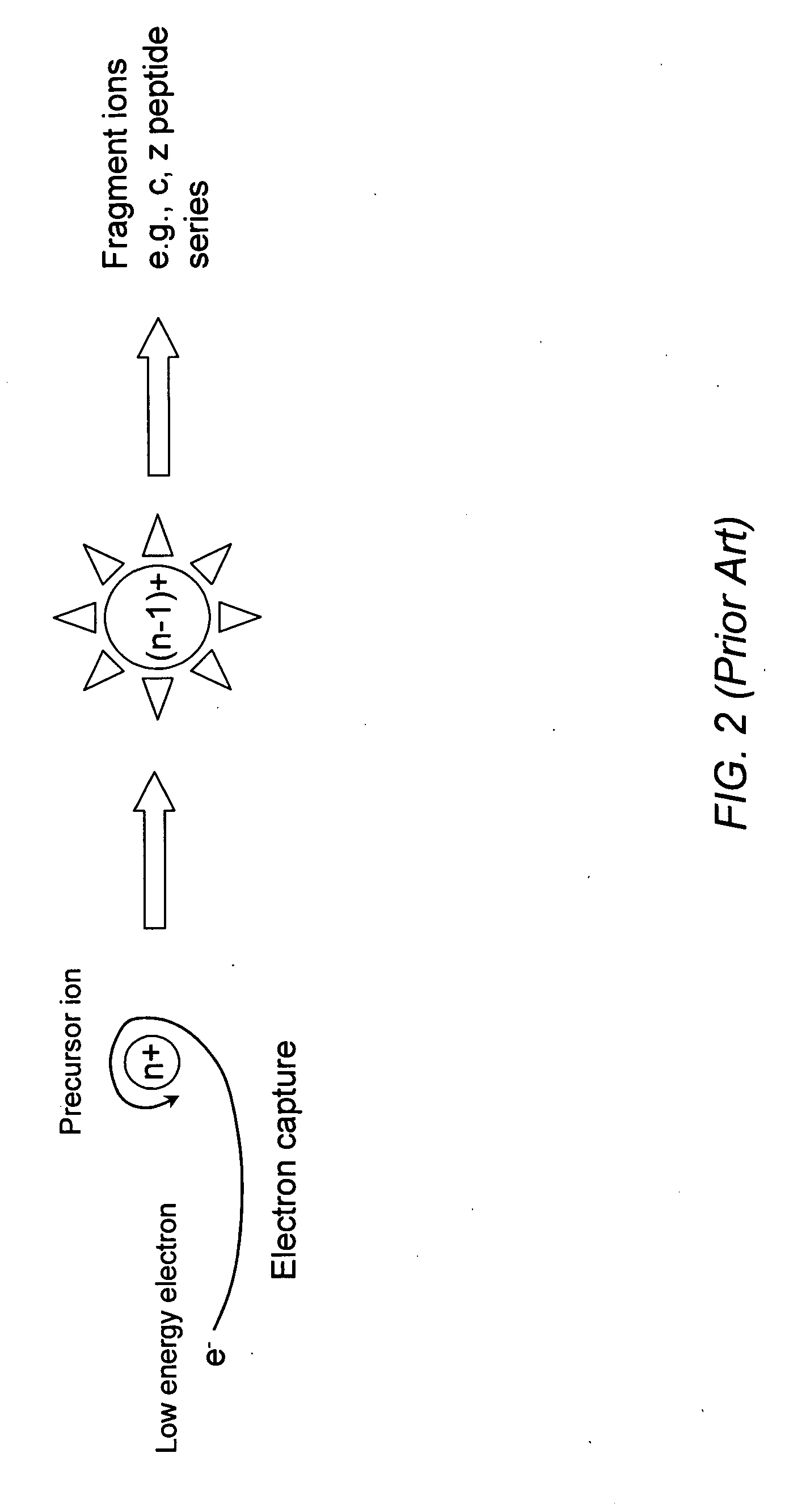
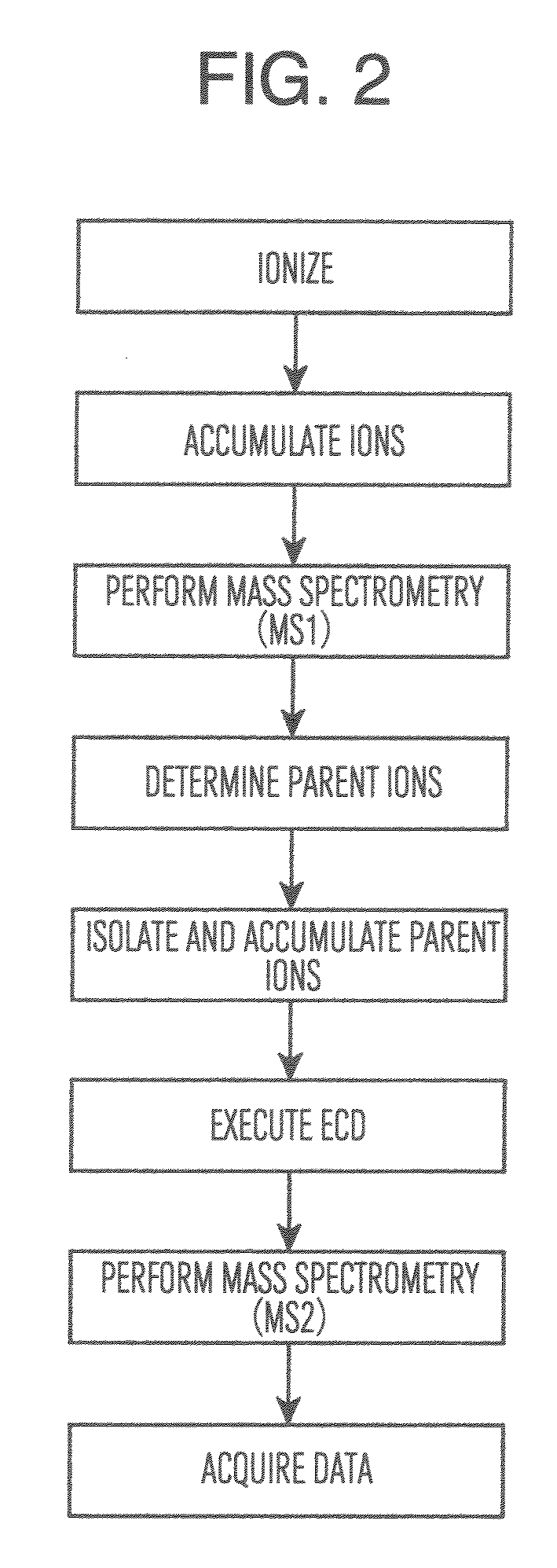
Electron-capture dissociation (ECD) is a method of fragmenting gas-phase ions for structure elucidation of peptides and proteins in tandem mass spectrometry. It is one of the most widely used techniques for activation and dissociation of mass selected precursor ion in MS/MS. It involves the direct introduction of low-energy electrons to trapped gas-phase ions.
Fragmentation methods for mass spectrometry
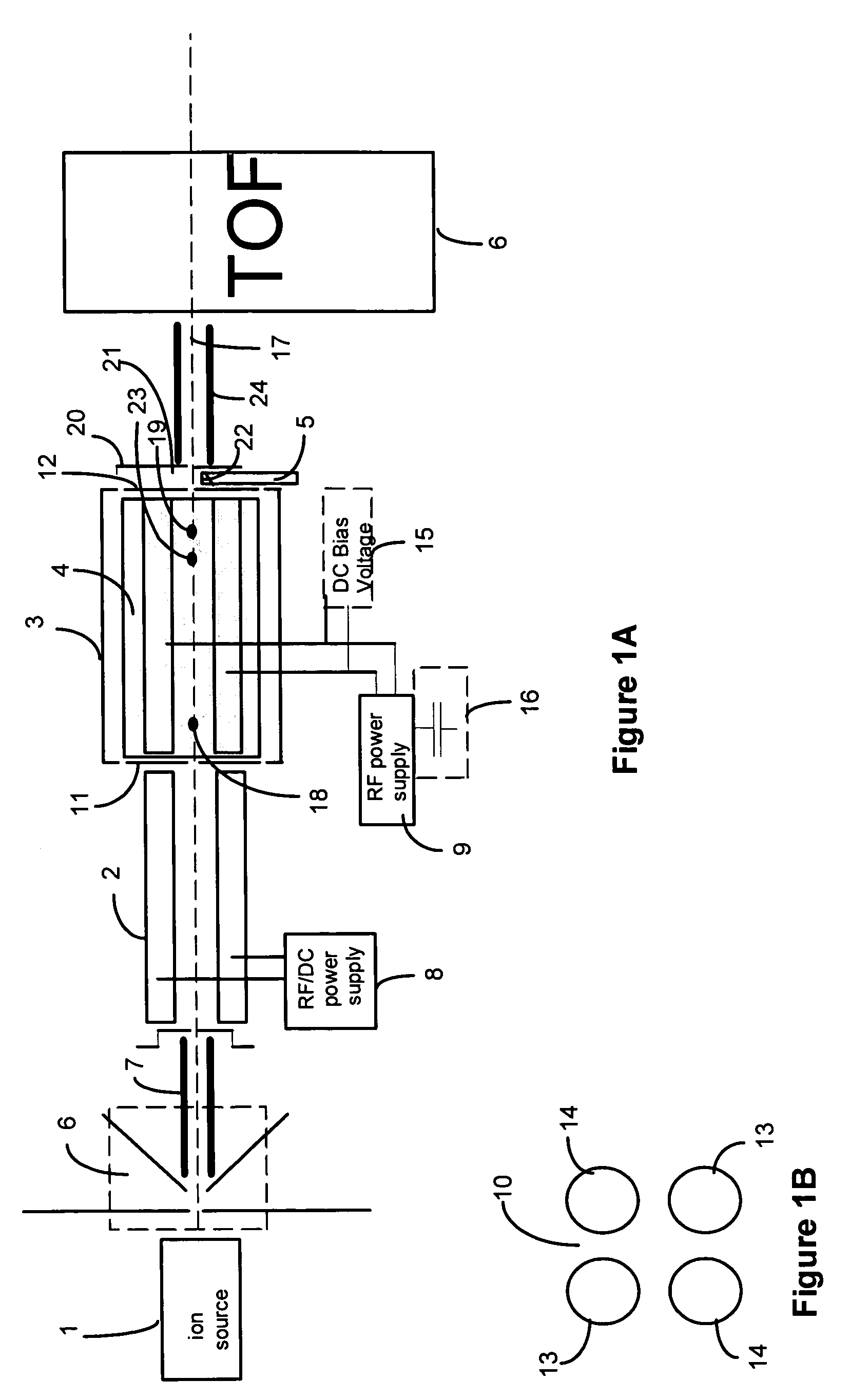
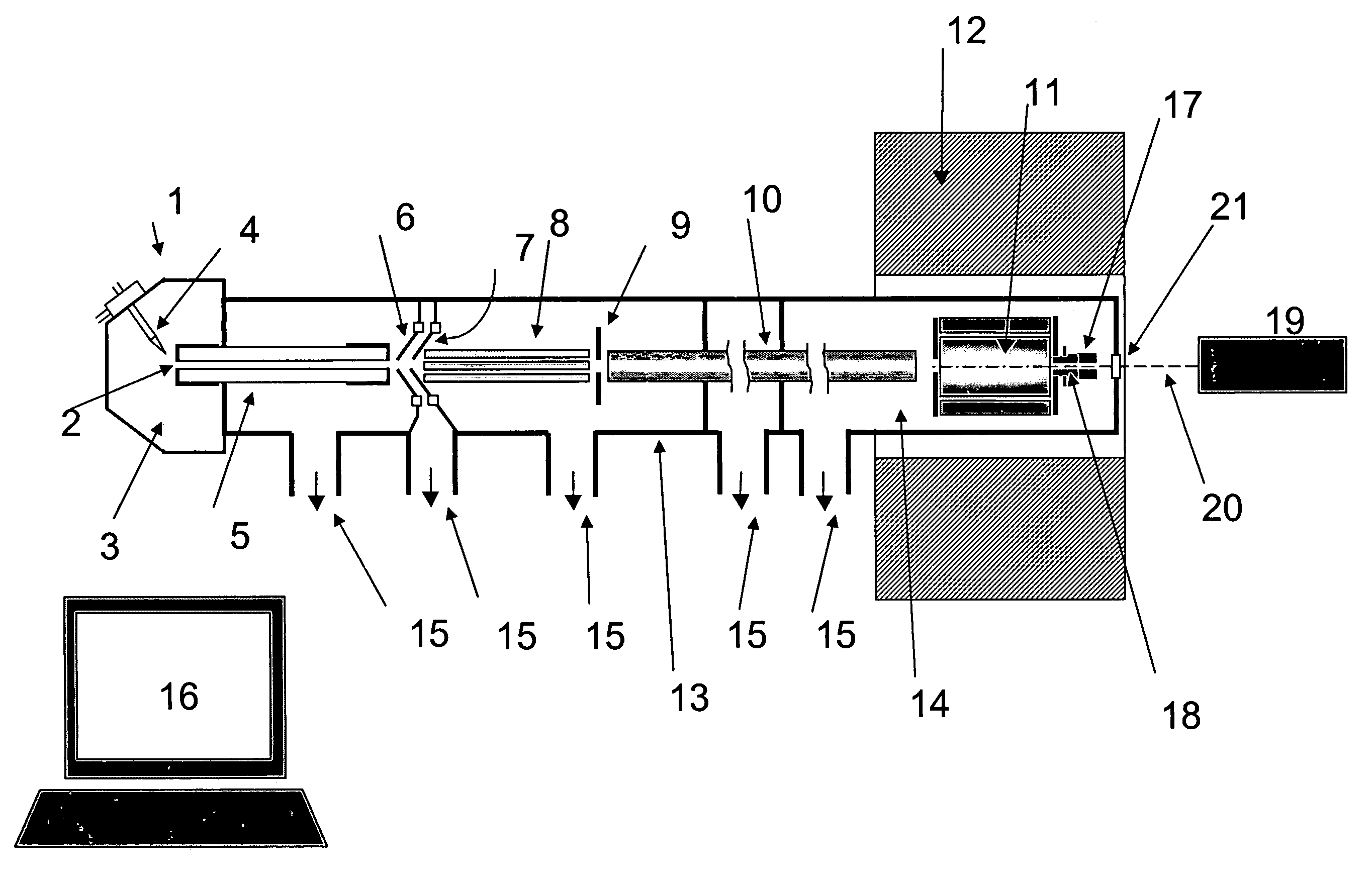
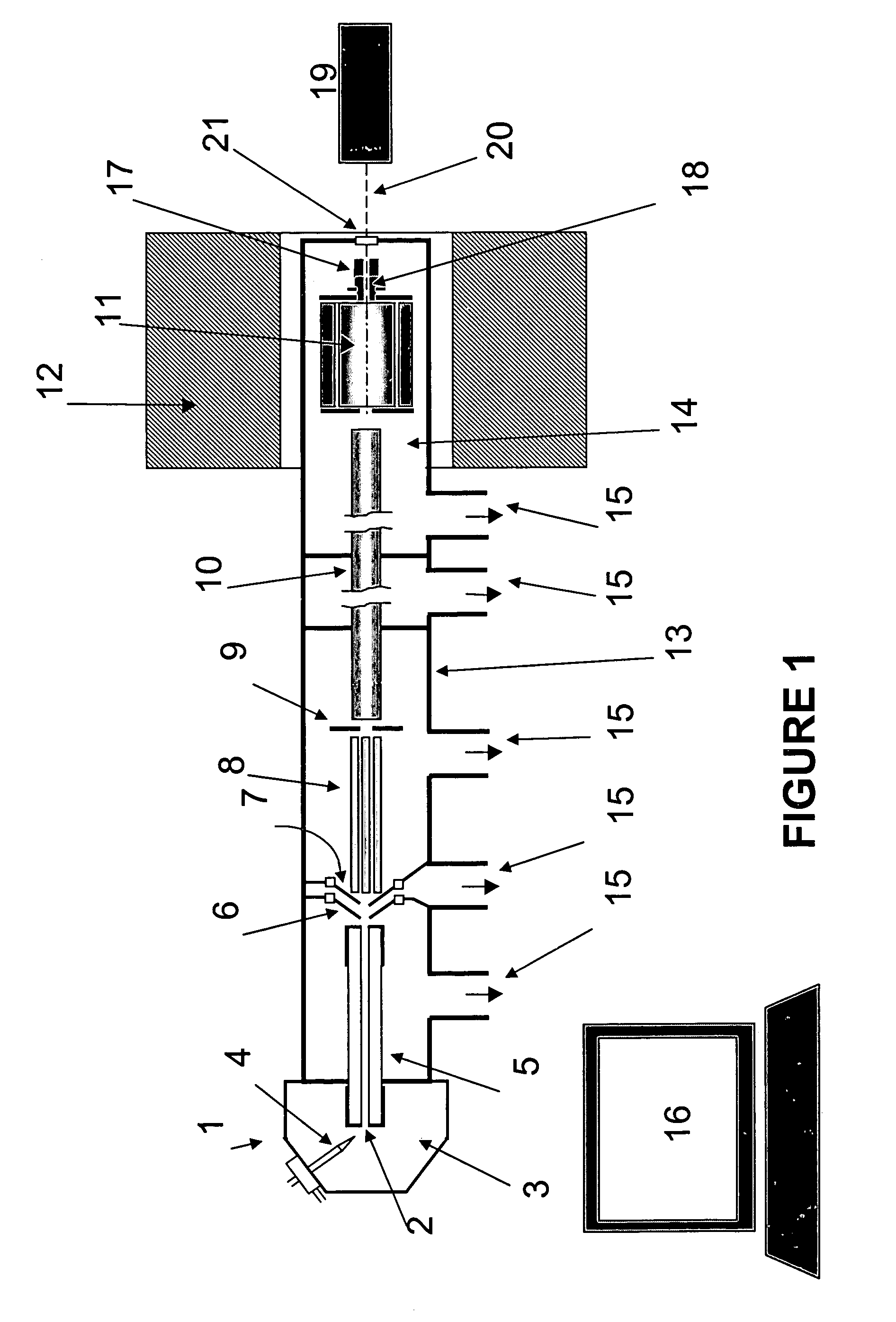
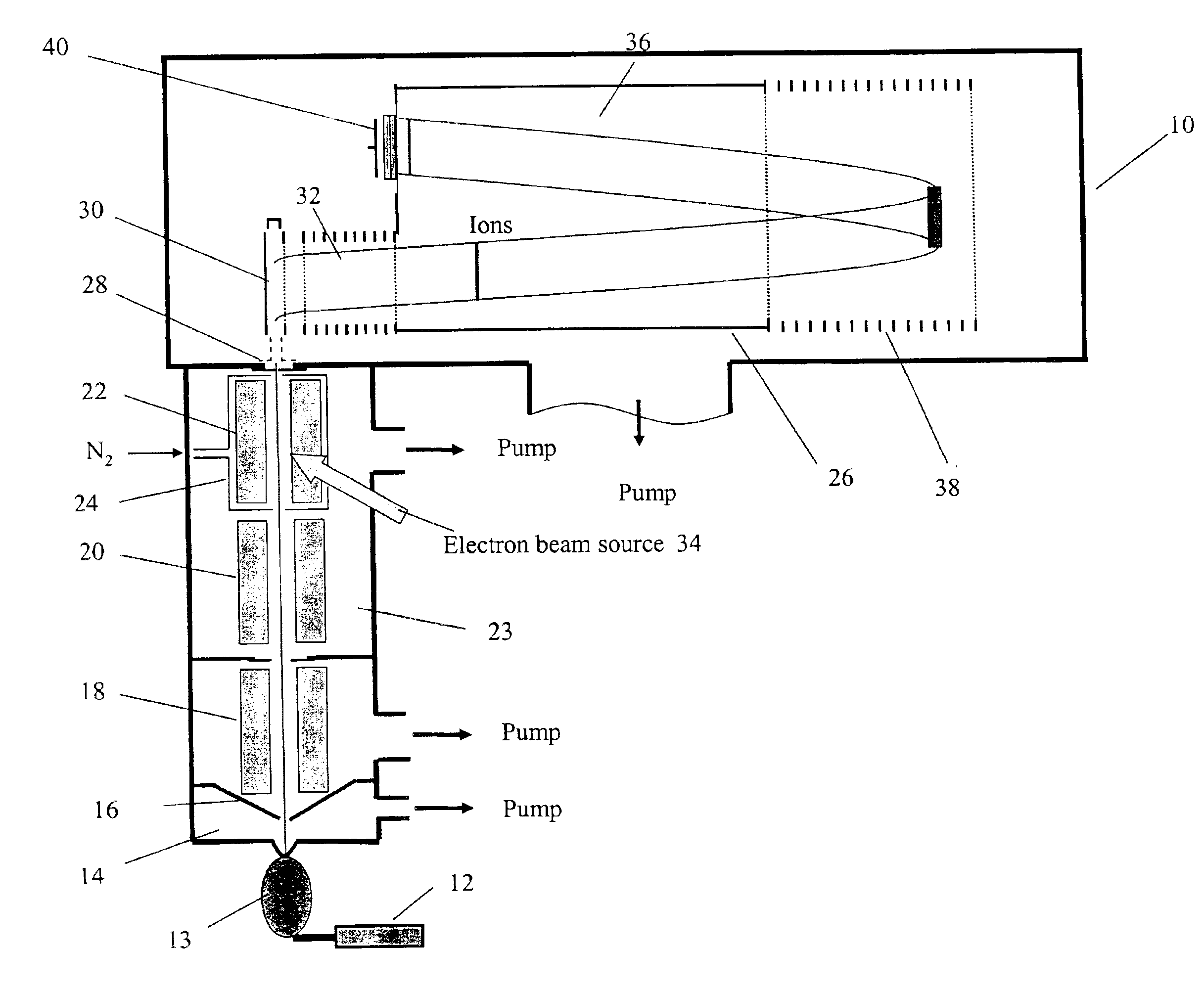
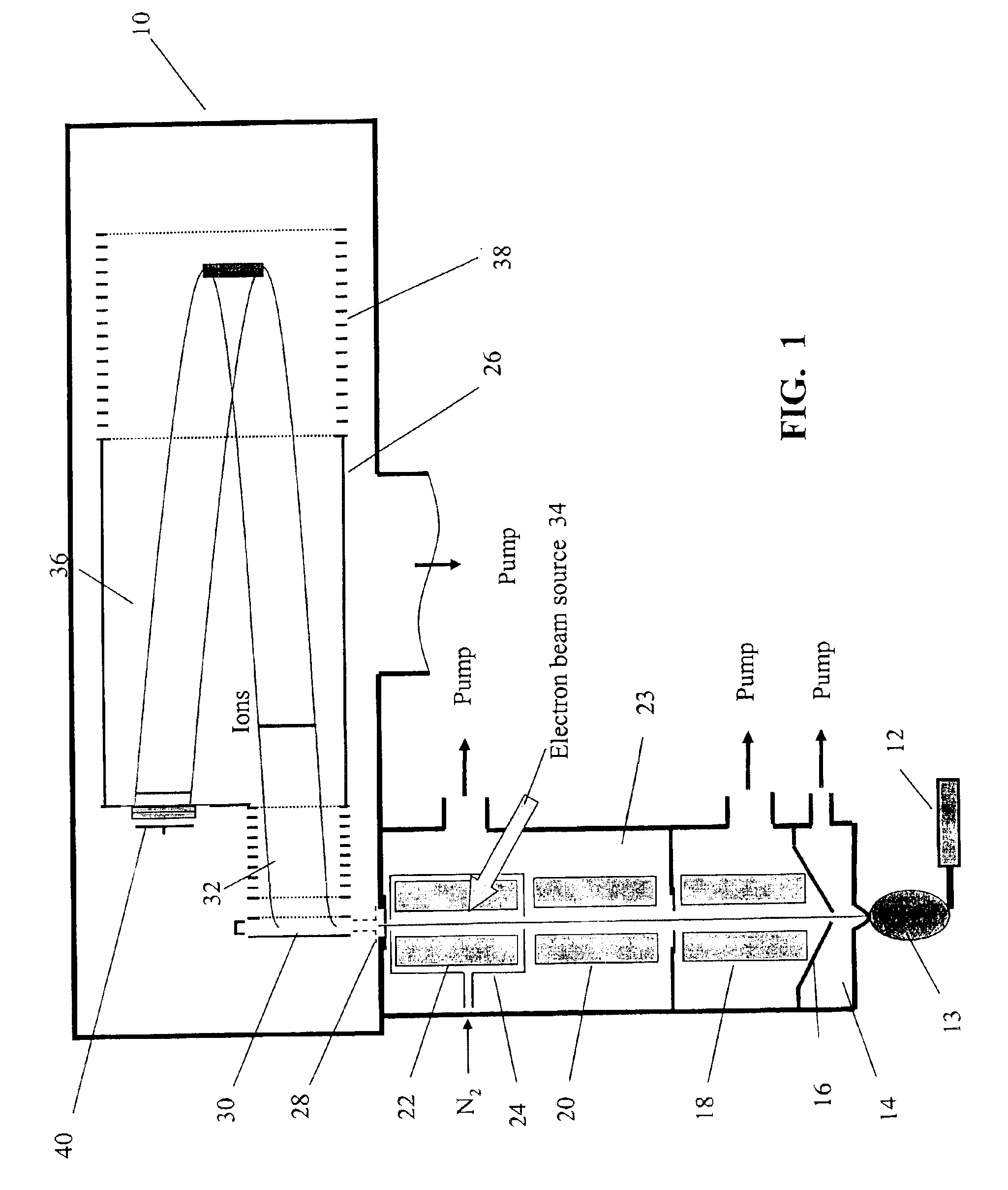
InactiveUS6919562B1Shorten speedMinimizing velocityIsotope separationMass spectrometersMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
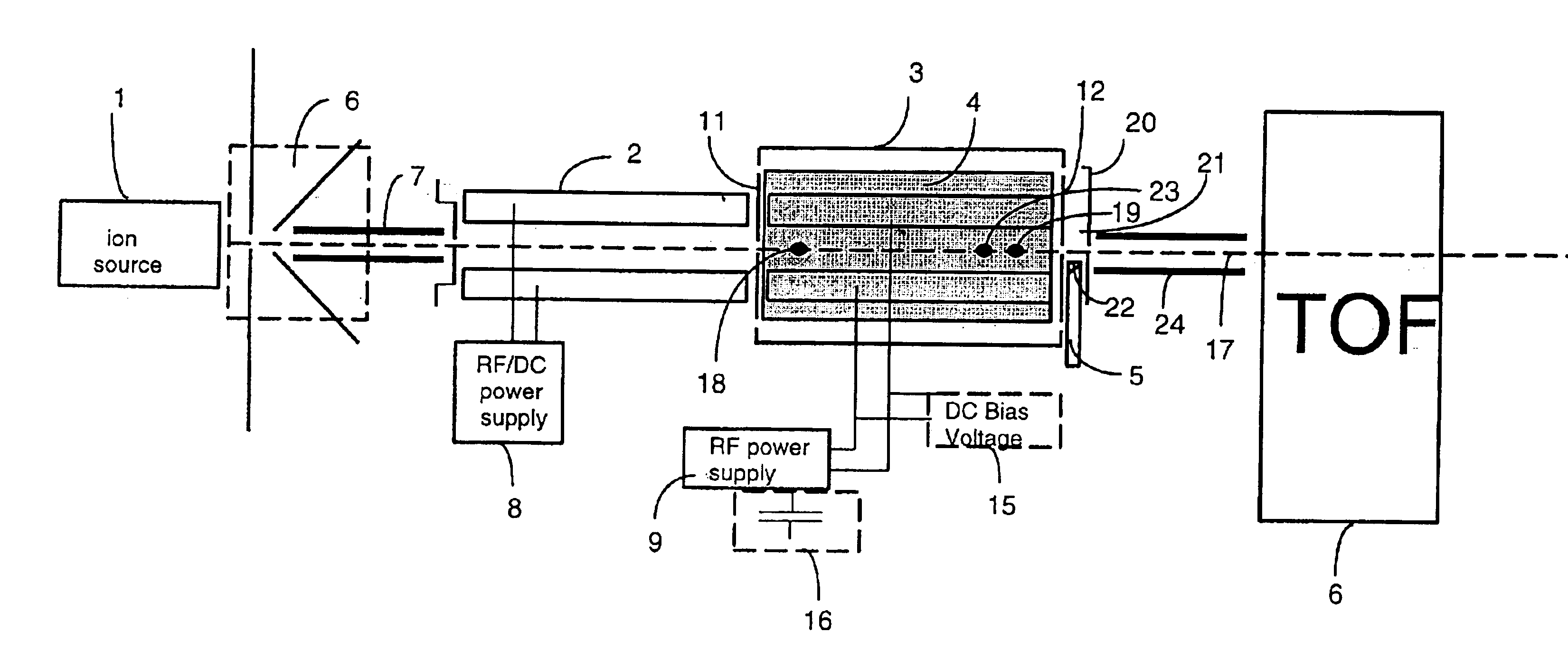
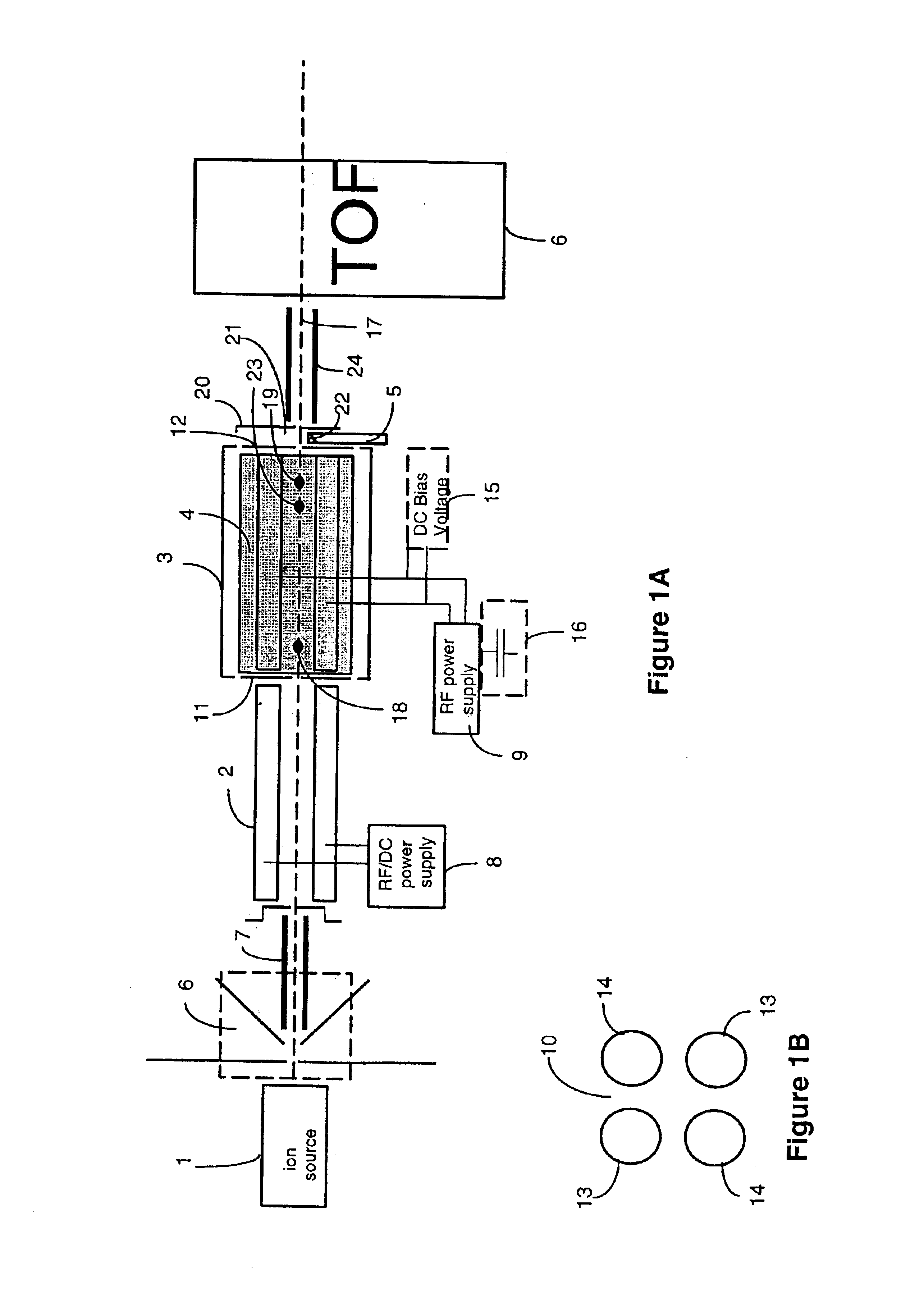
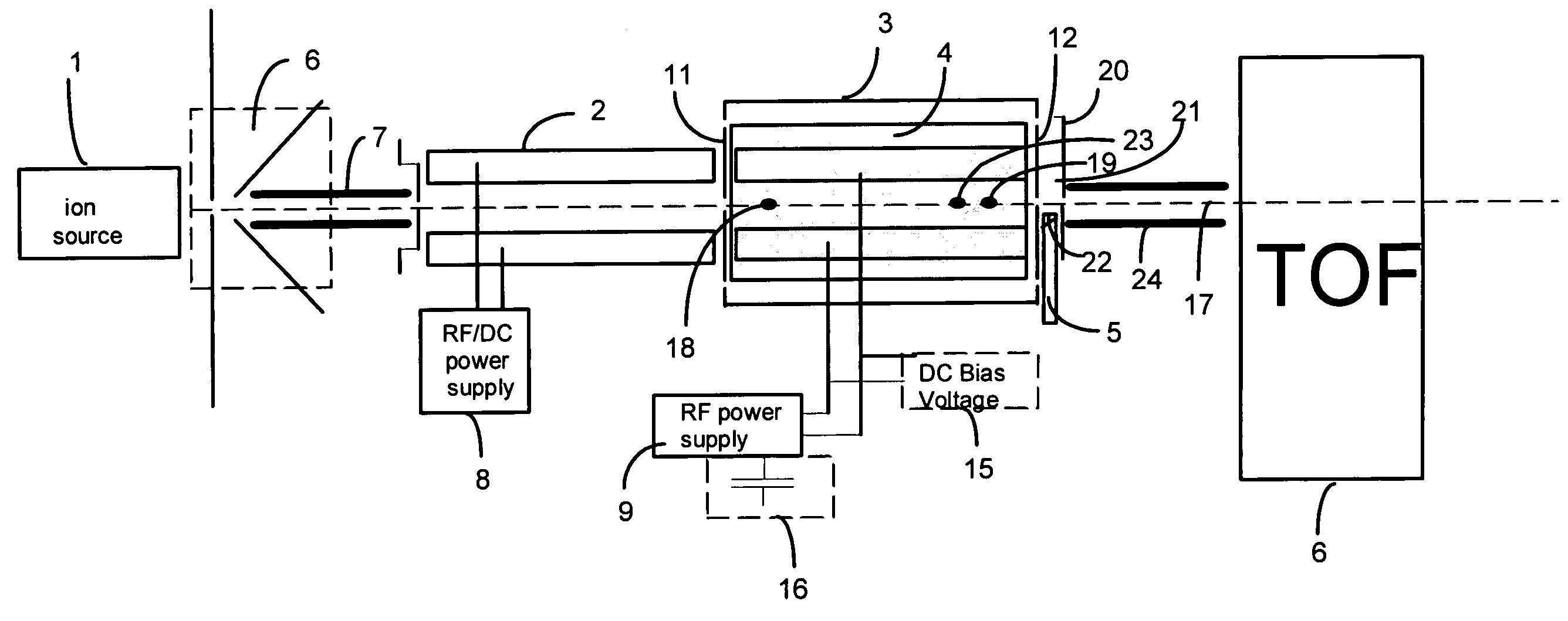
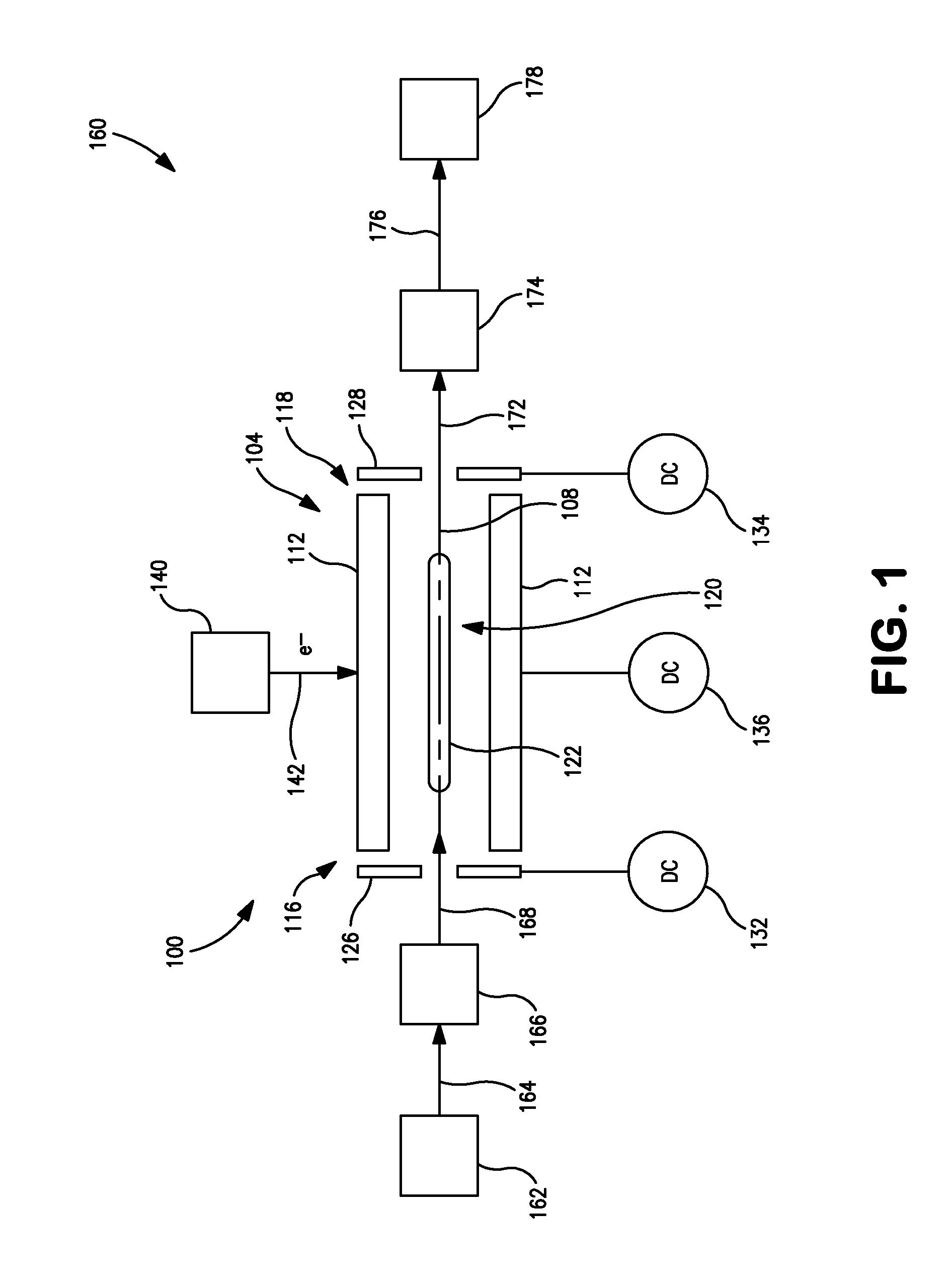
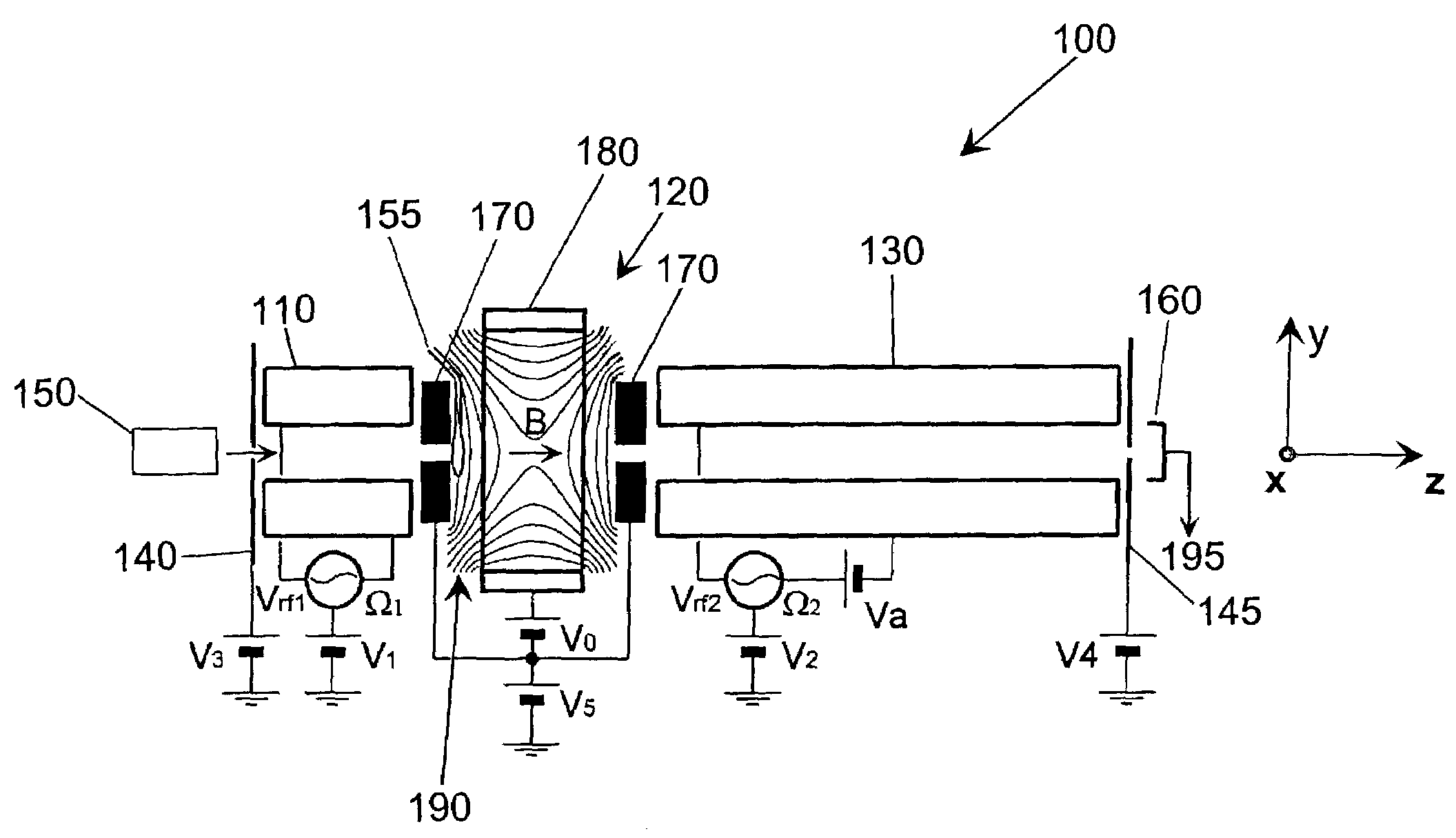
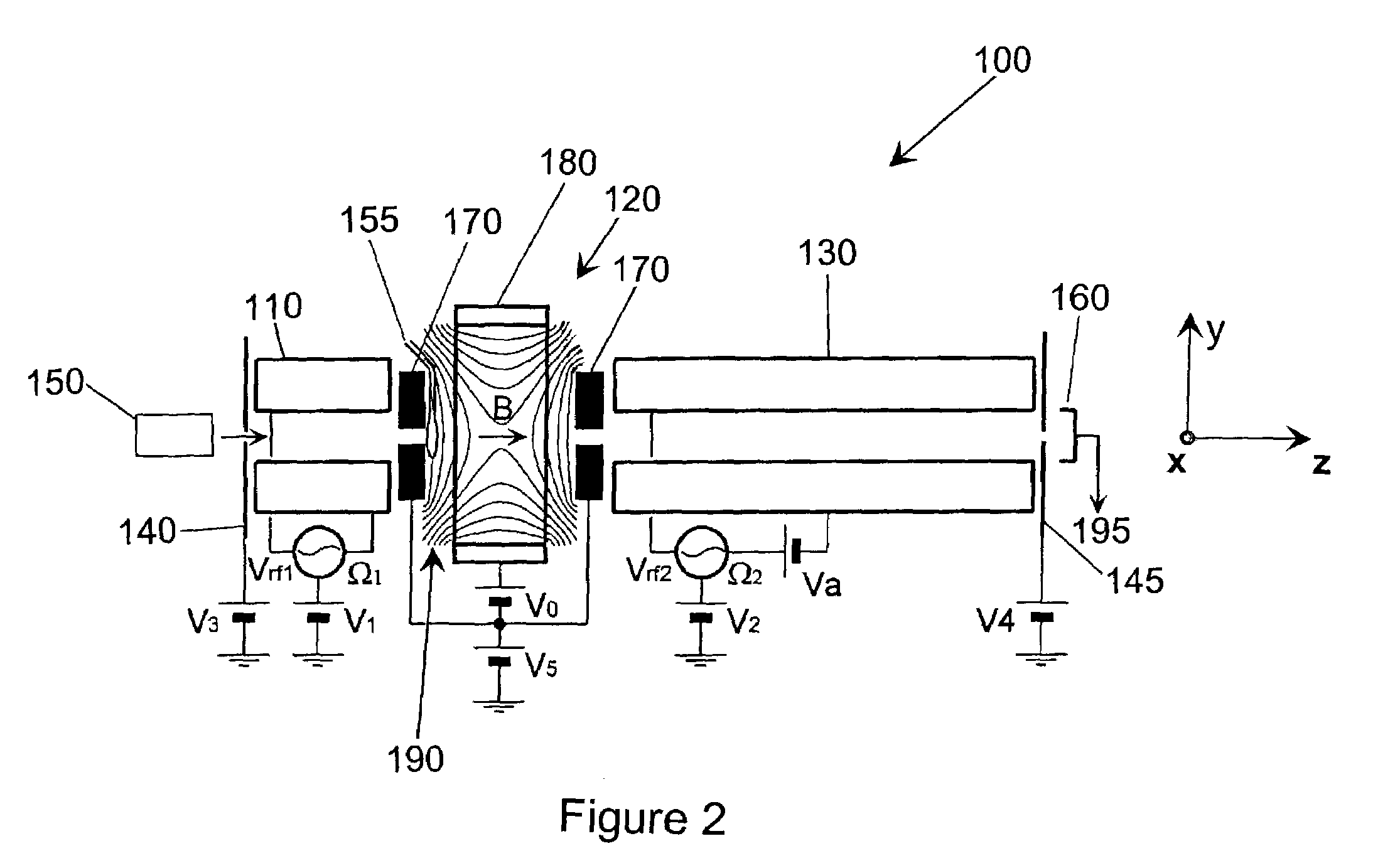
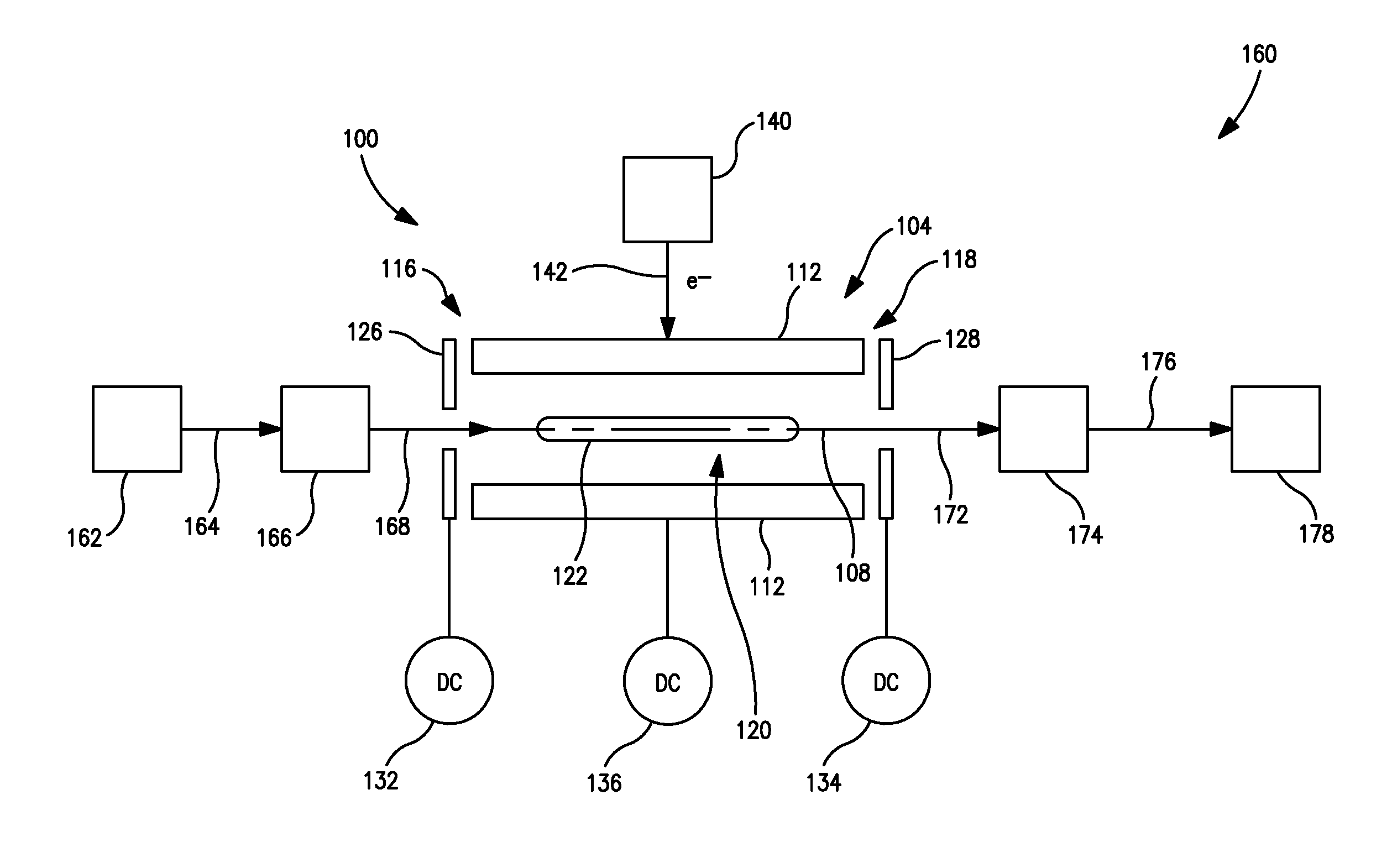
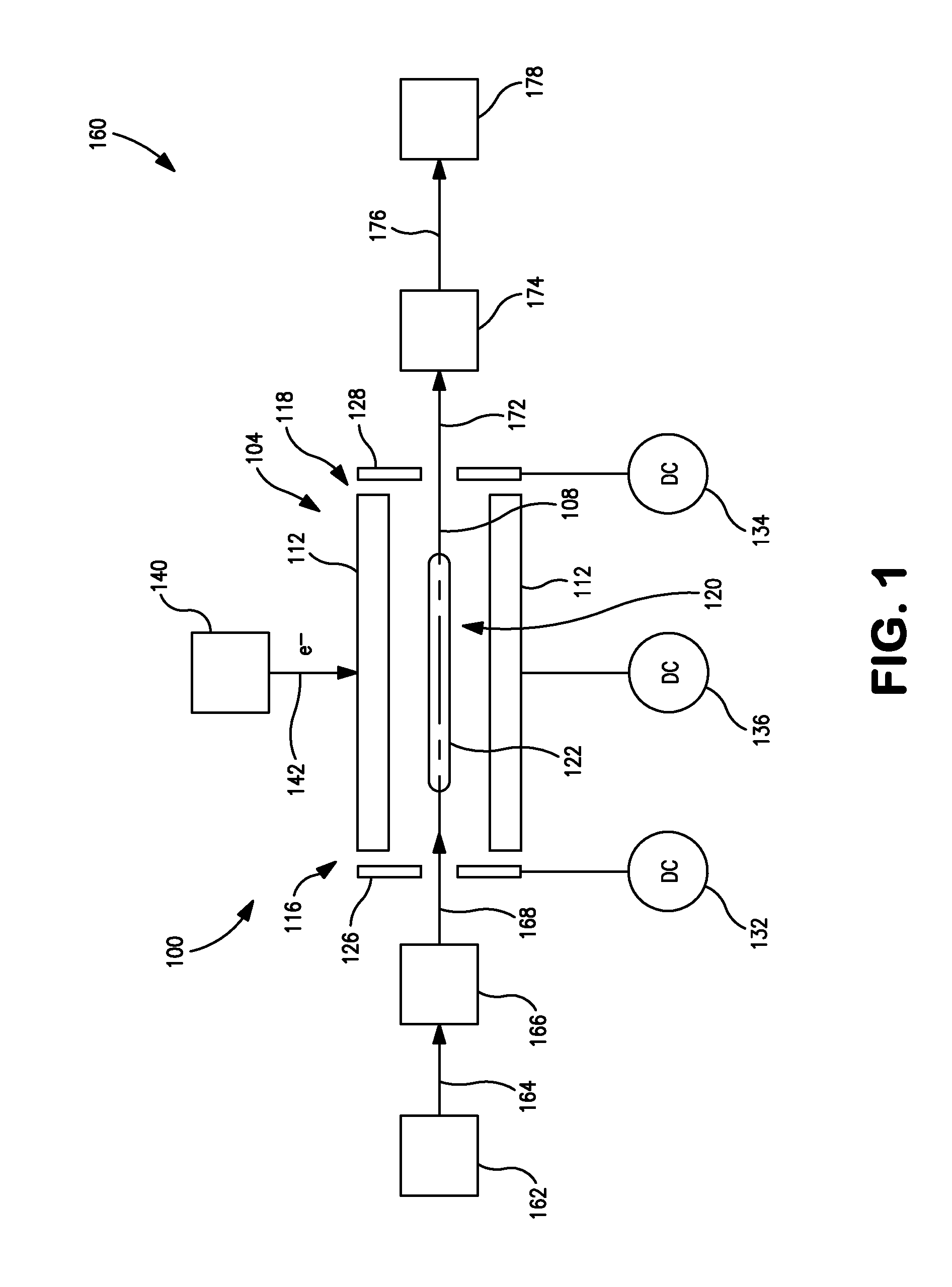
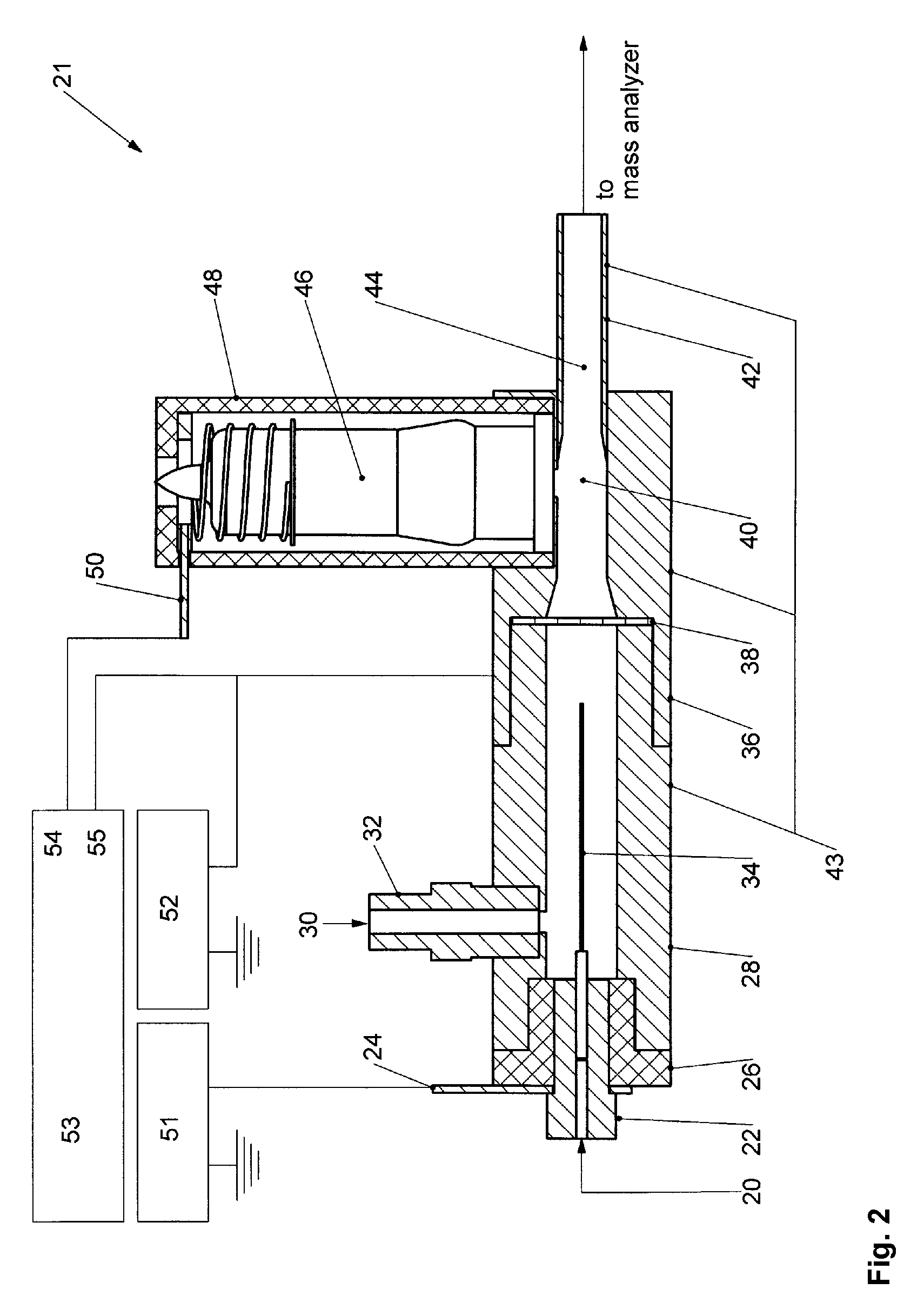
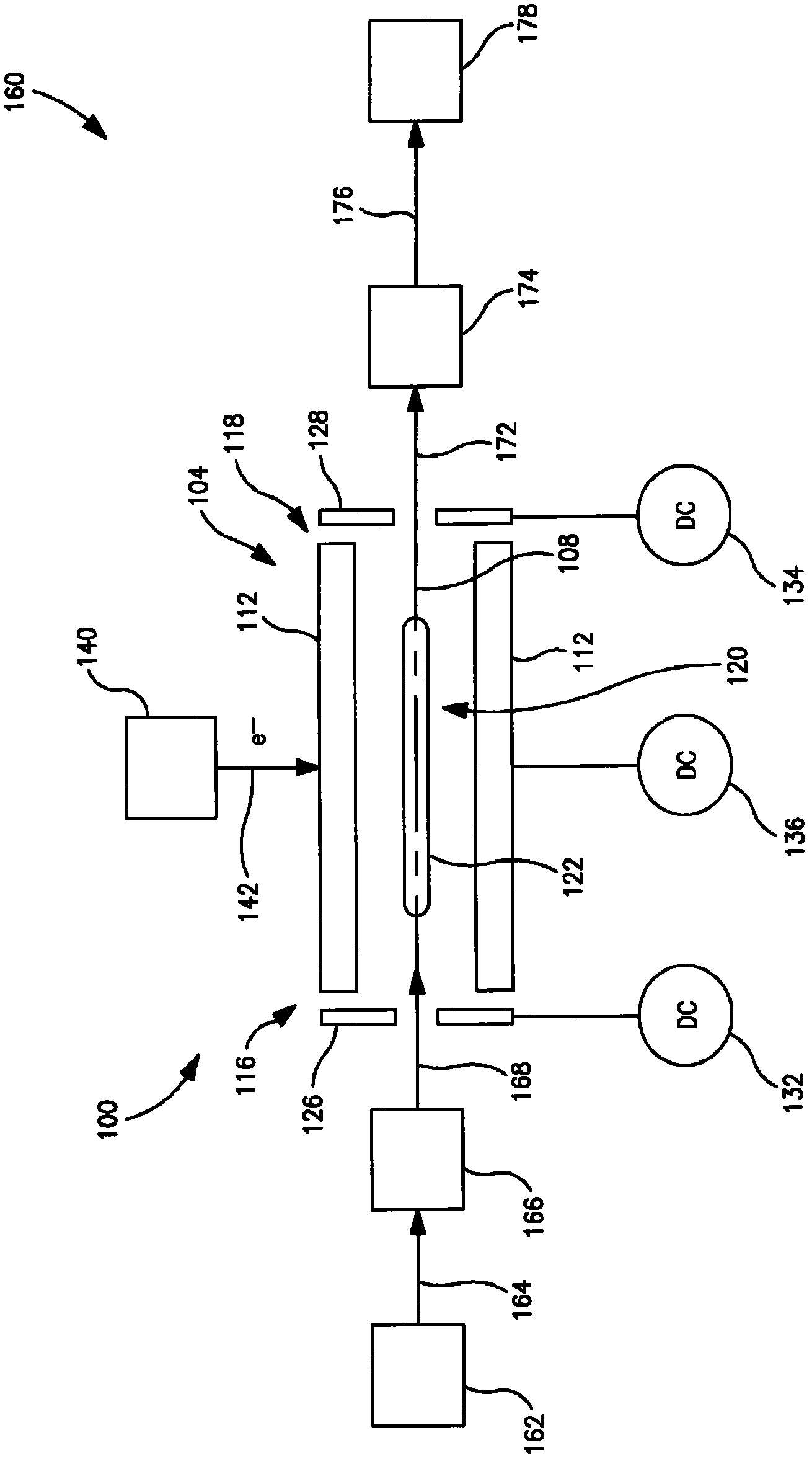
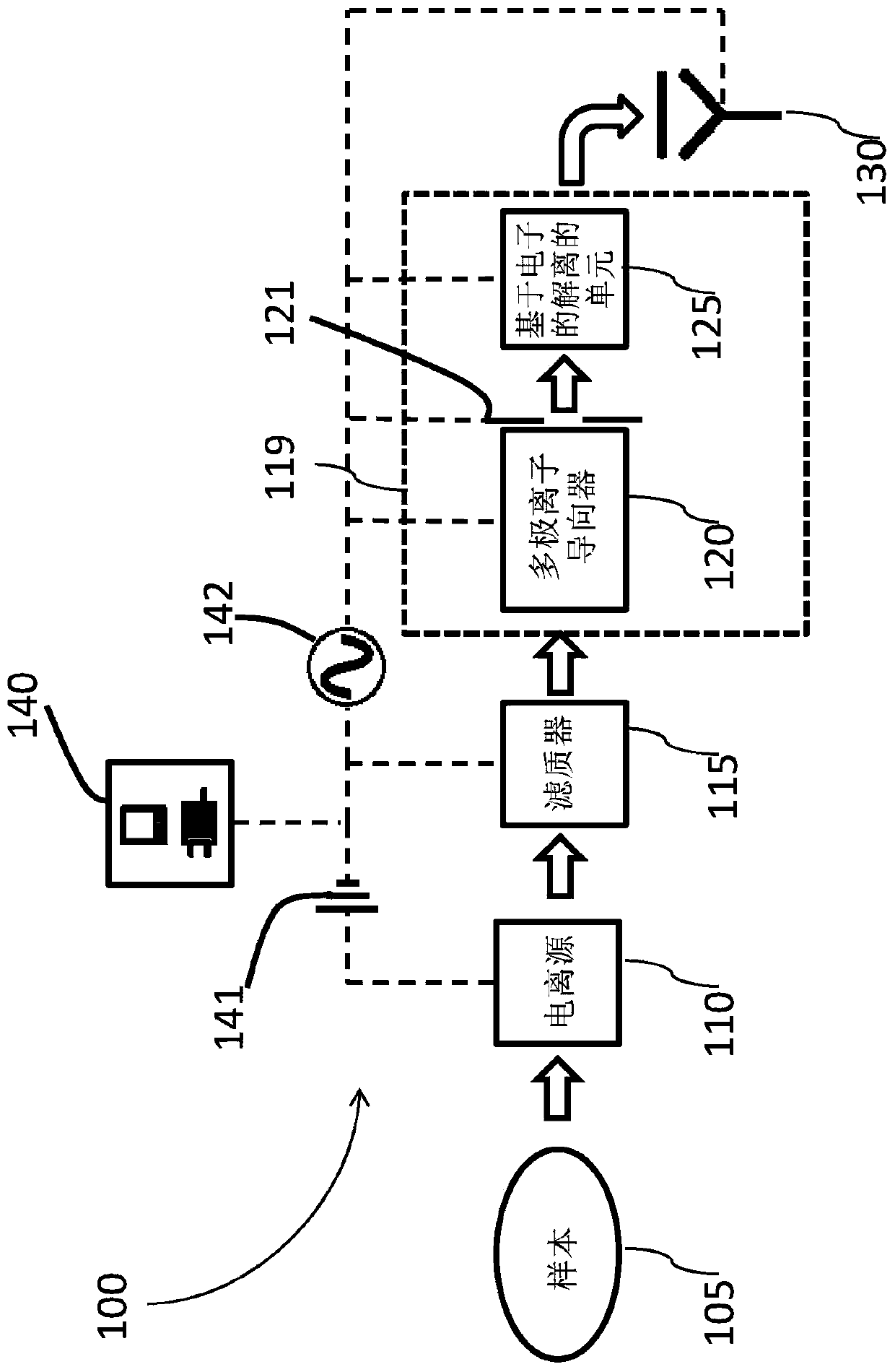
Apparatus and methods are provided that enable the interaction of low-energy electrons and positrons with sample ions to facilitate electron capture dissociation (ECD) and positron capture dissociation (PCD), respectively, within multipole ion guide structures. It has recently been discovered that fragmentation of protonated ions of many biomolecules via ECD often proceeds along fragmentation pathways not accessed by other dissociation methods, leading to molecular structure information not otherwise easily obtainable. However, such analyses have been limited to expensive Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FTICR) mass spectrometers; the implementation of ECD within commonly-used multipole ion guide structures is problematic due to the disturbing effects of RF fields within such devices. The apparatus and methods described herein successfully overcome such difficulties, and allow ECD (and PCD) to be performed within multipole ion guides, either alone, or in combination with conventional ion fragmentation methods. Therefore, improved analytical performance and functionality of mass spectrometers that utilize multipole ion guides are provided.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Fragmentation methods for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7049584B1Control outflowReduce stressIsotope separationMass spectrometersMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryElectron-capture dissociation
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Tandem mass spectrometry method
ActiveUS6924478B1Shorten analysis timeHigh sensitivityStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Multiply charged ions are trapped and accumulated in a spatially limited region before being injected into an ion trap mass spectrometer such as a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer (FTICR MS). In the ion trap electron capture dissociation (ECD) and vibrational excitation dissociation are sequentially applied on ions of the same ion ensemble. The first dissociation process does not fragment all primary ions. Following the detection of the dissociation products, the primary ions that remain undissociated undergo the vibrational excitation and again, a part of them dissociate, and the fragments are detected. Thus, the same ion ensemble is used for two fragmentation processes. During these processes, further ions generated in the external ion source are accumulated in the spatially limited region for subsequent analyses.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Mass spectrometer
ActiveUS20060169892A1Speedup of acquisitionEasy to combineIsotope separationSpecific reaction combinationsIon trap mass spectrometryElectron source
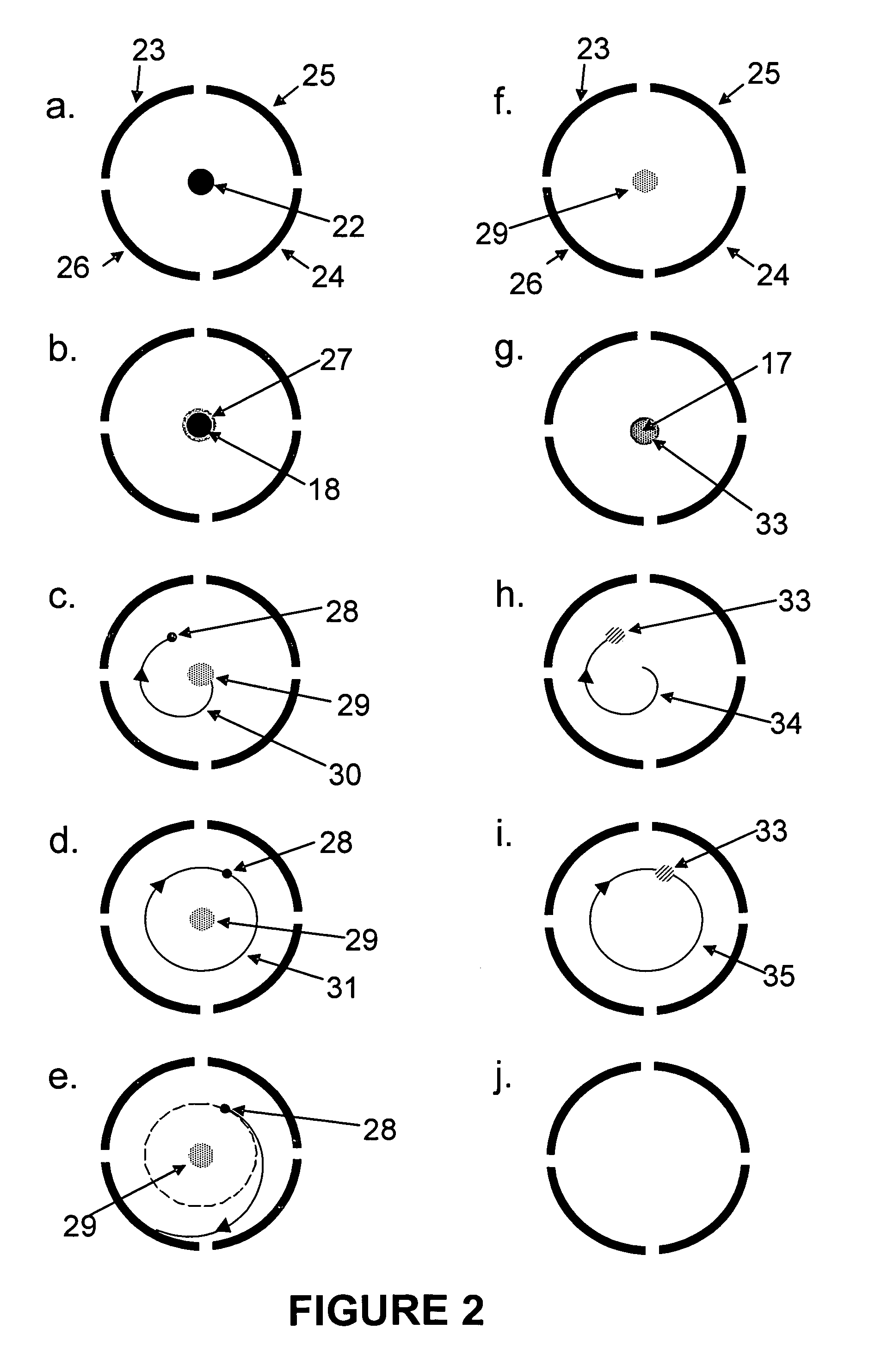
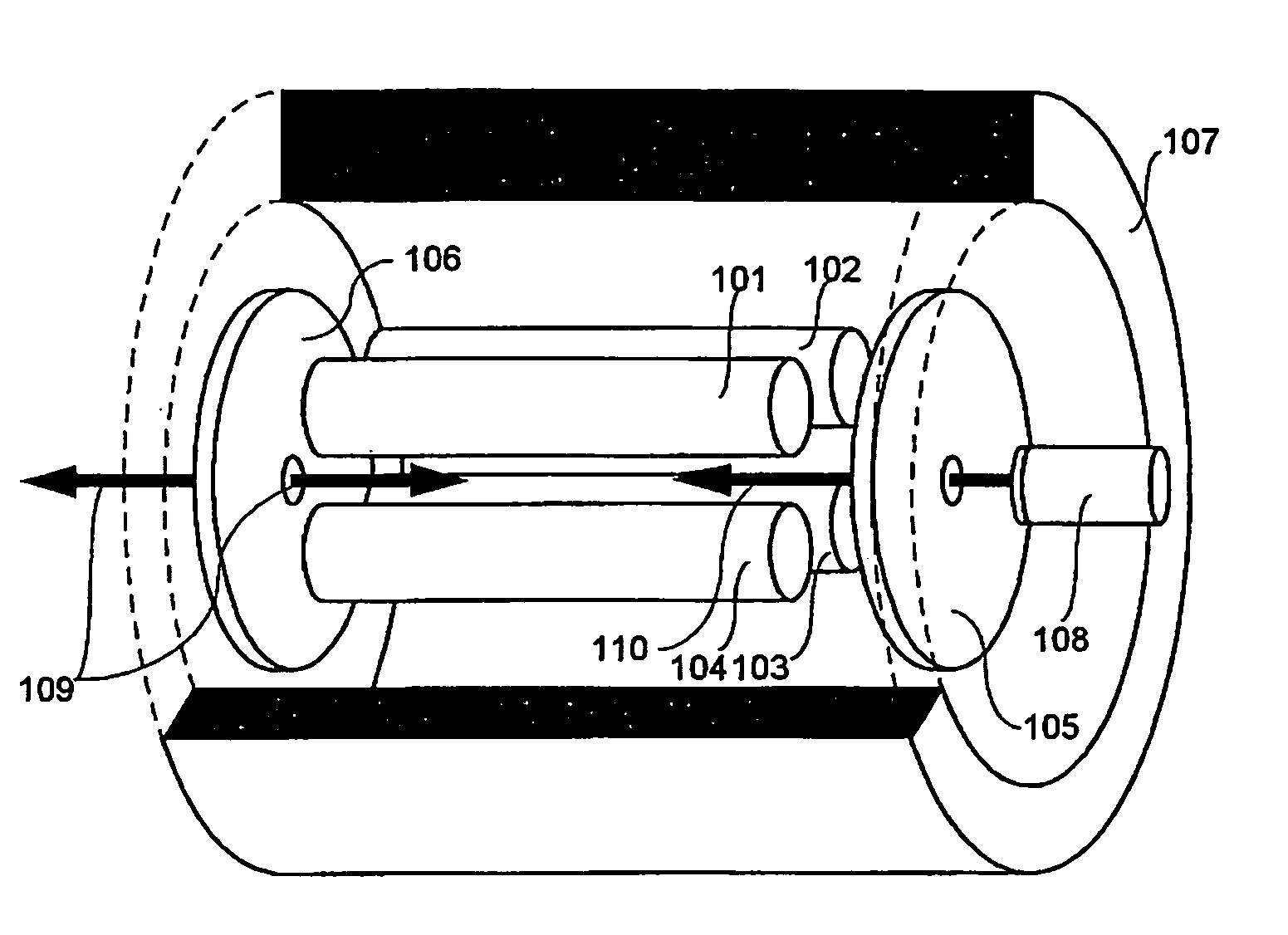
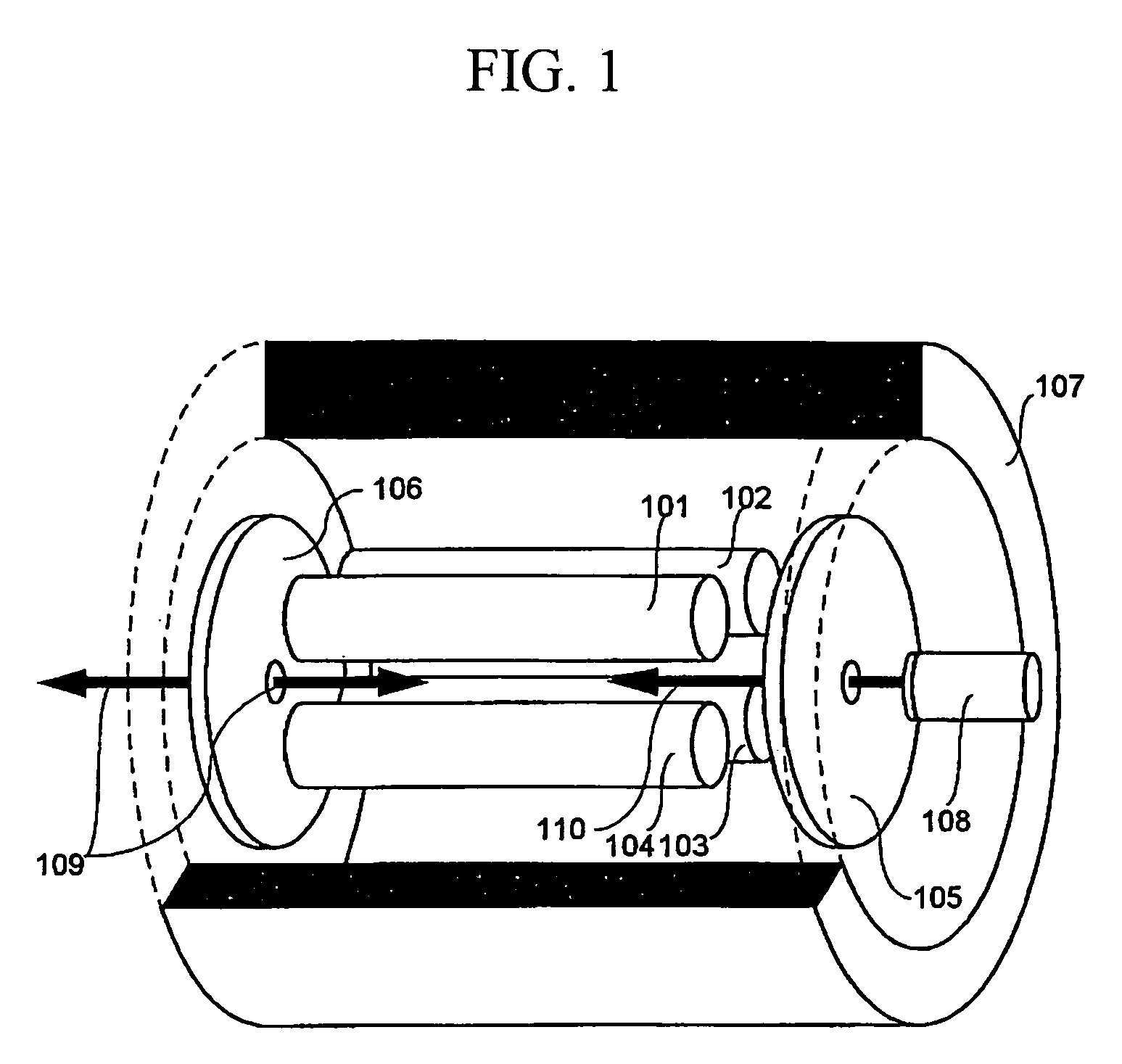
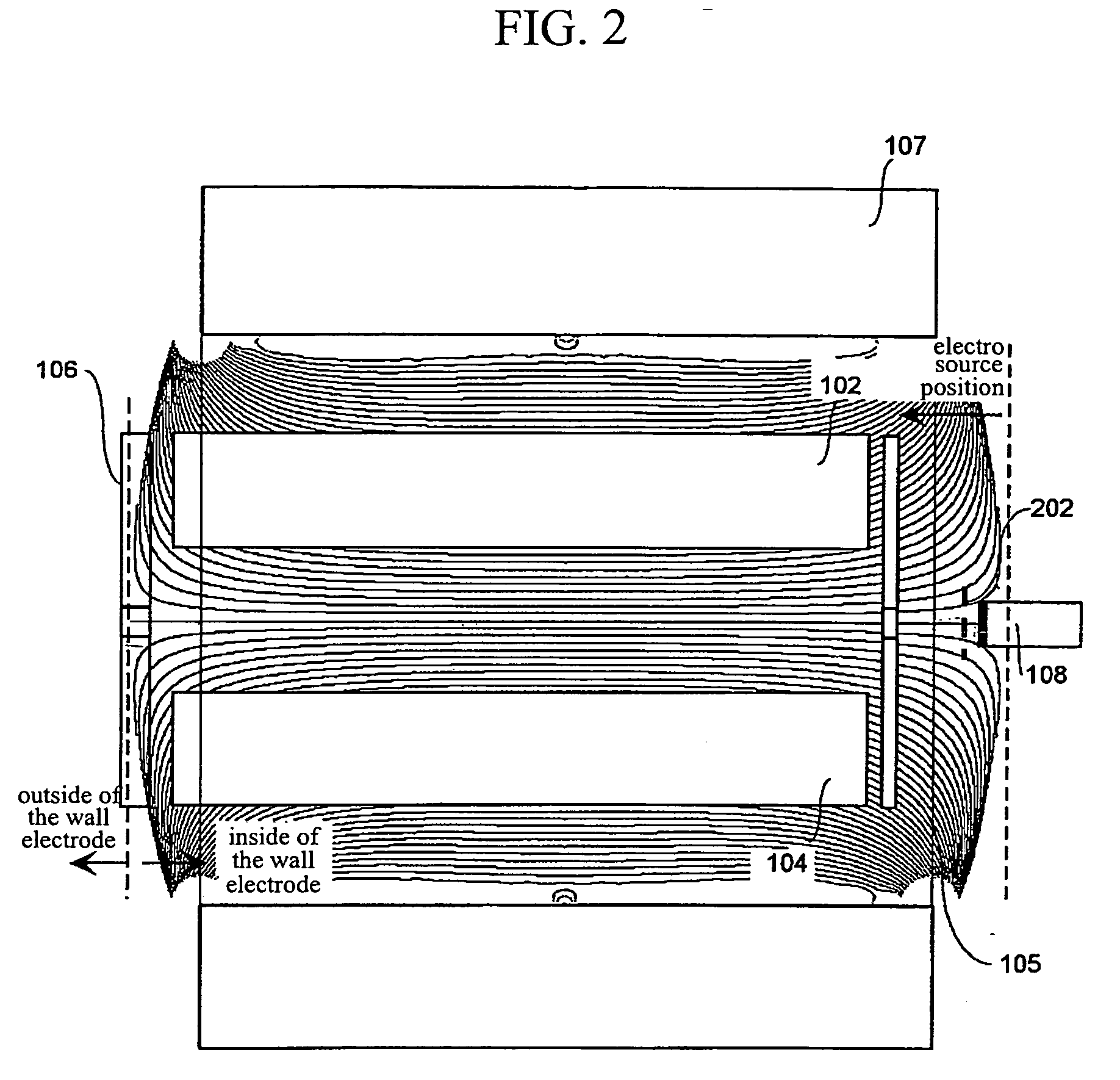
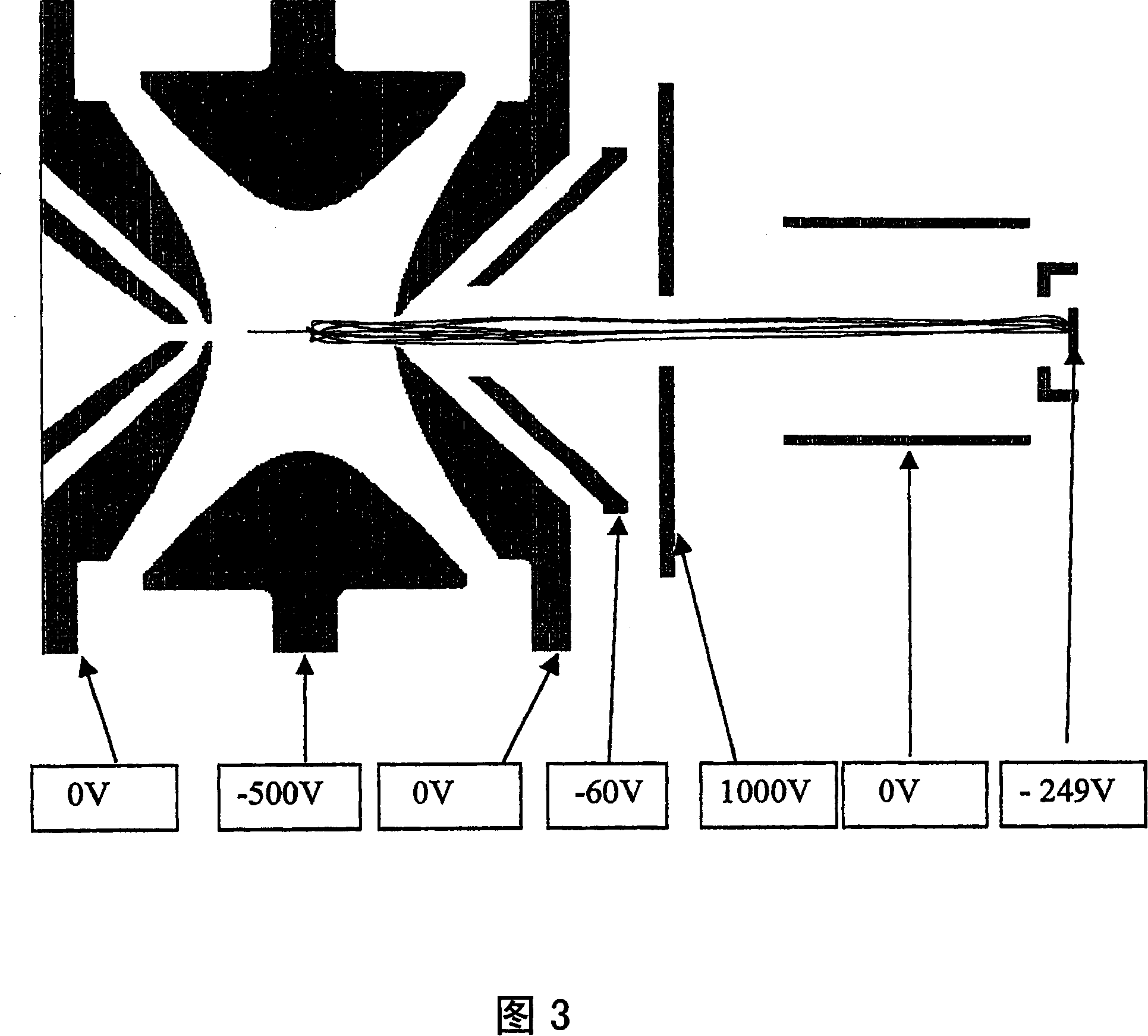
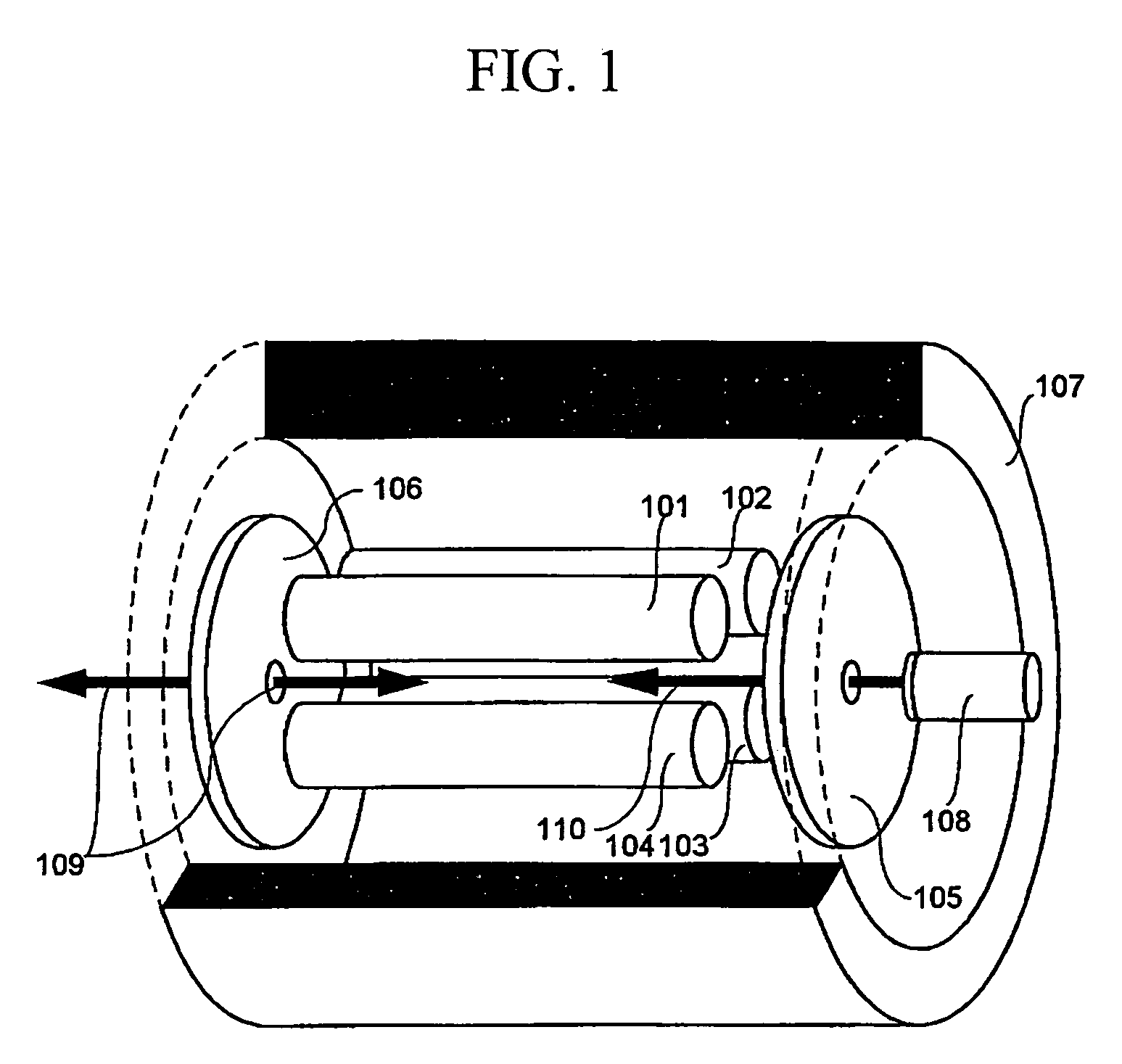
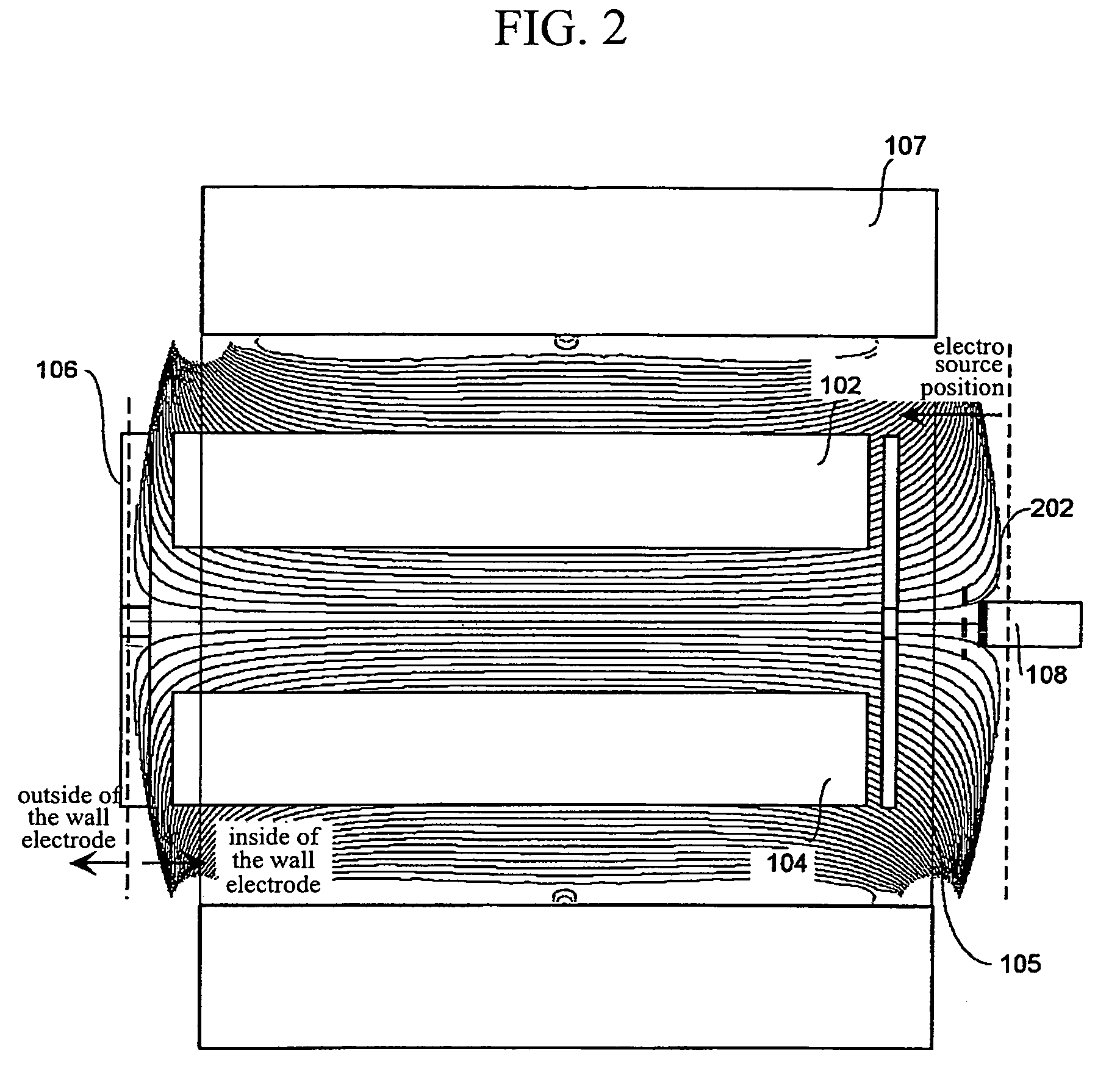
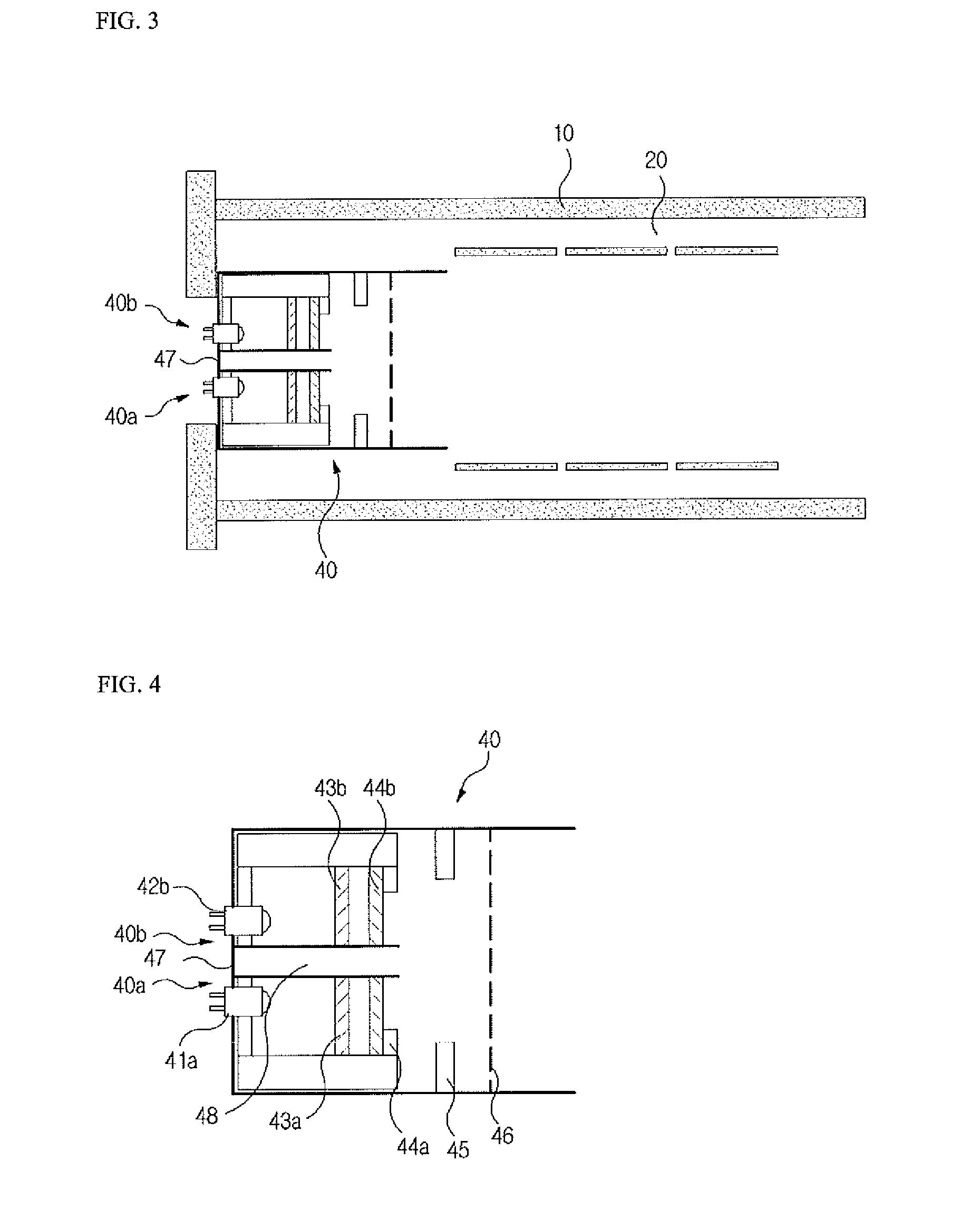
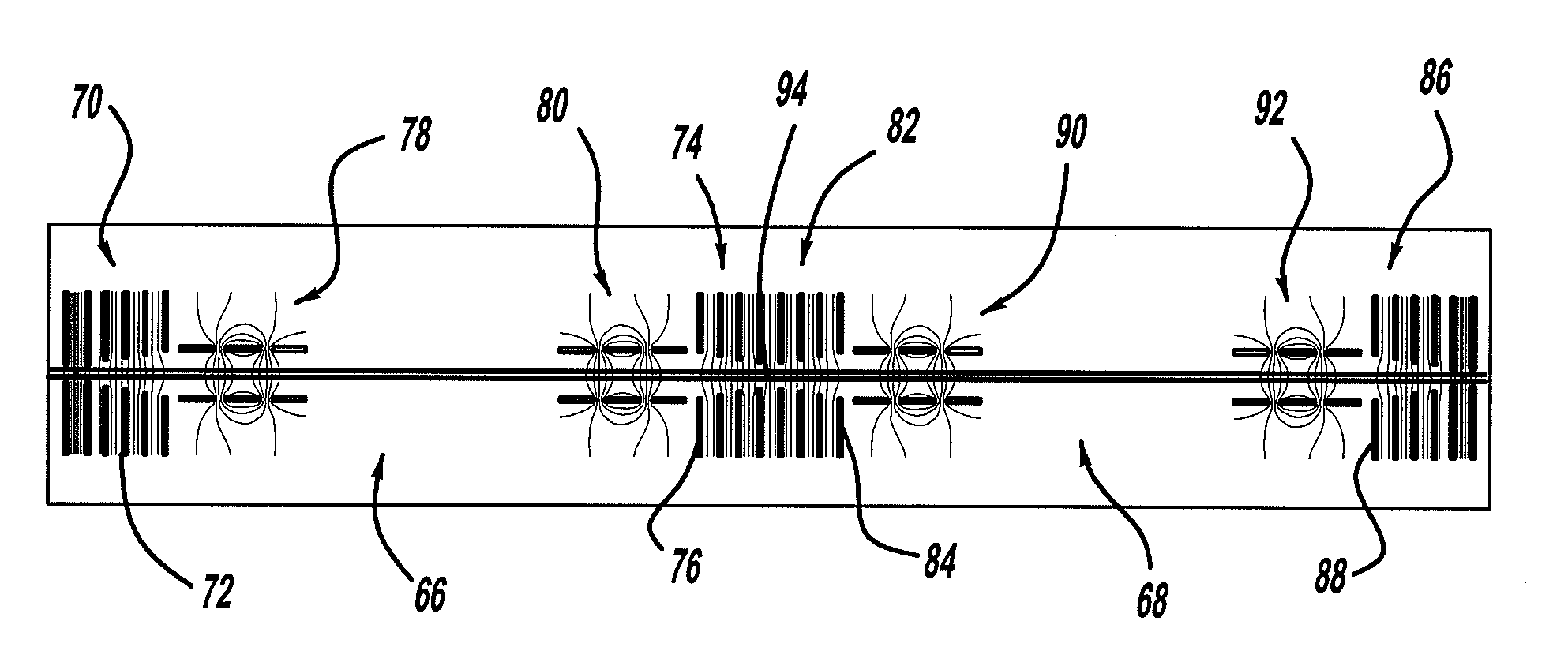
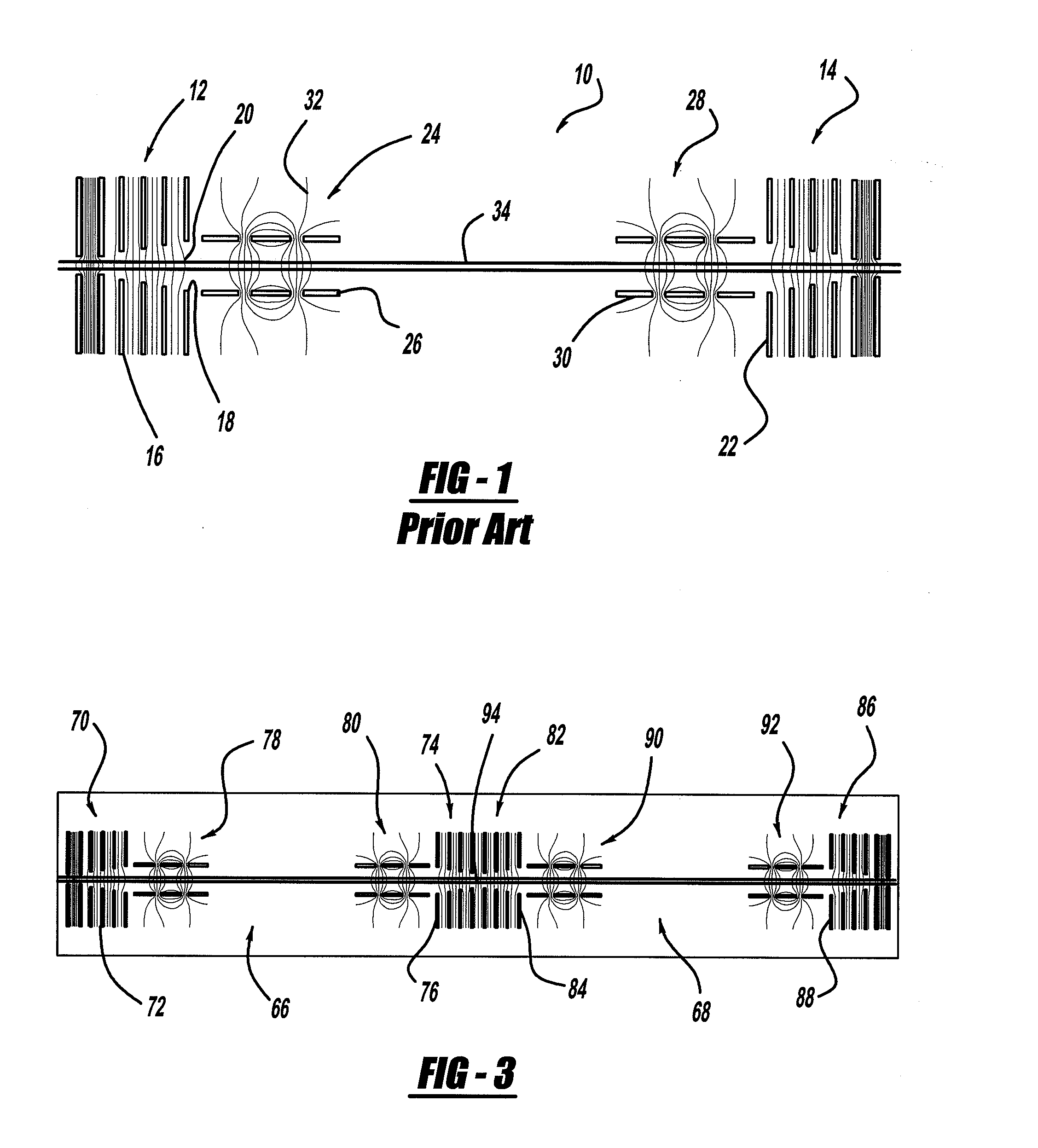
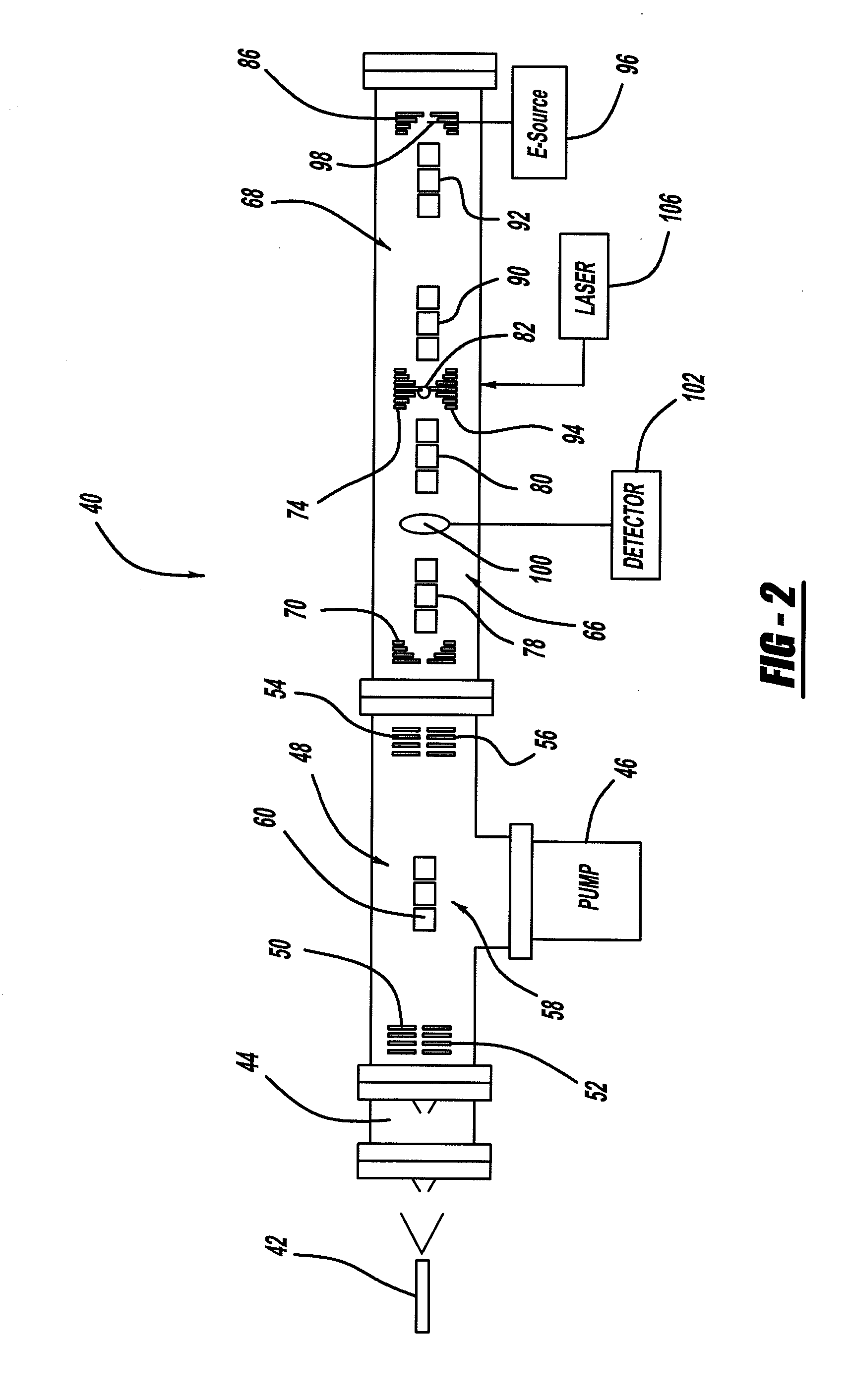
An electron capture dissociation device to implement a combination of electron capture dissociation and collision dissociation and a mass spectrometer with the use thereof are provided. This device includes a linear ion trap provided with linear multipole electrodes applied with a radio frequency electric field and wall electrodes that are arranged on both ends in the axis direction of the linear multipole electrodes, have holes on the central axis thereof, and generate a wall electric field by being applied with a direct-current voltage, a cylindrical magnetic field-generating unit that generates a magnetic field parallel to the central axis of the linear multipole electrodes and surrounds the linear ion trap, and an electron source arranged opposite to the linear multipole electrodes with sandwiching one of the wall electrodes. The electron generation site of the electron source is placed in the inside of the magnetic field generated by the magnetic field-generating unit.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method of ion fragmentation in a multipole ion guide of a tandem mass spectrometer
InactiveUS6858840B2Promote fragmentationImprovement in tandem mass spectrometry capabilityStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron injectionIon beam
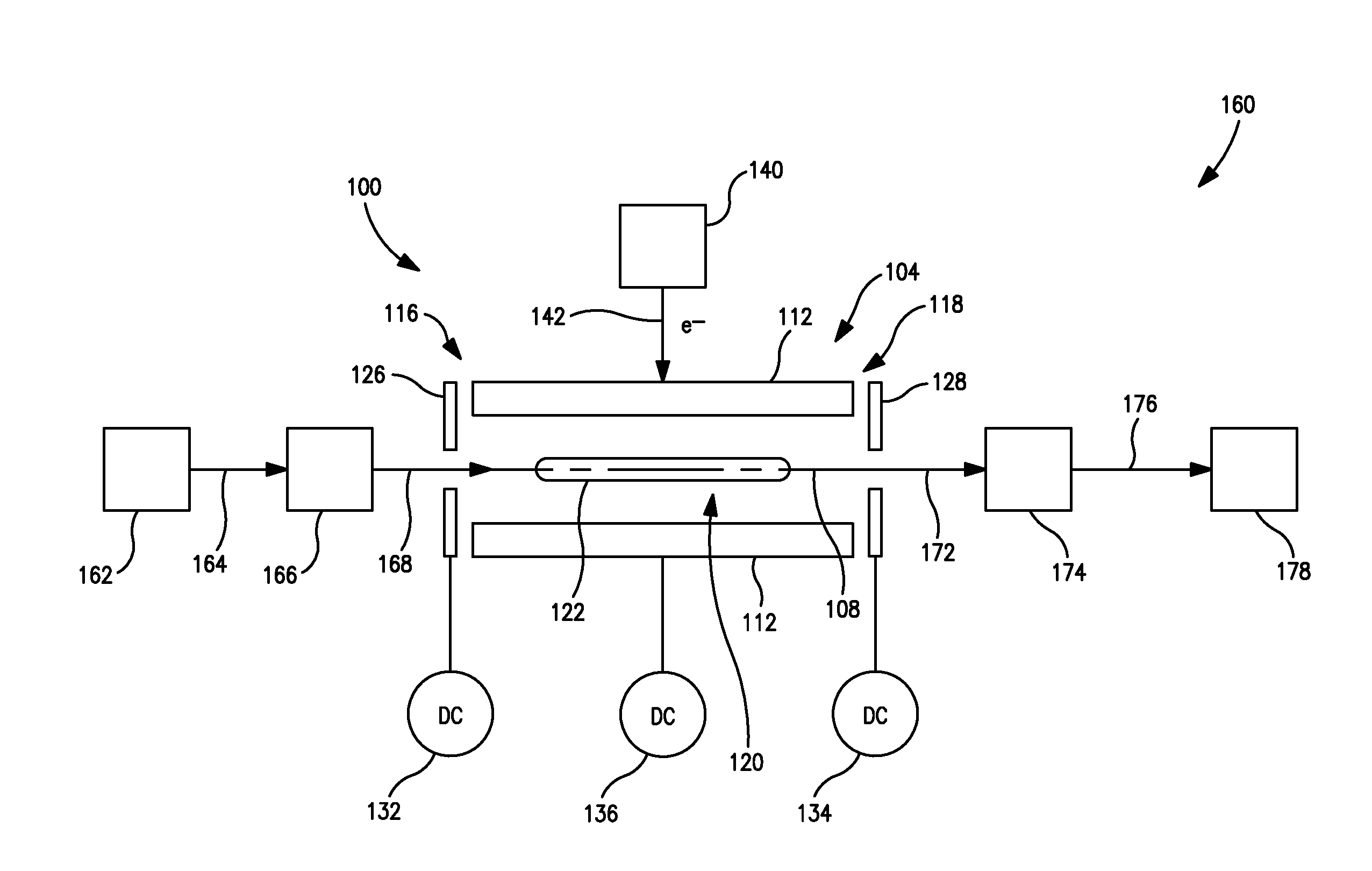
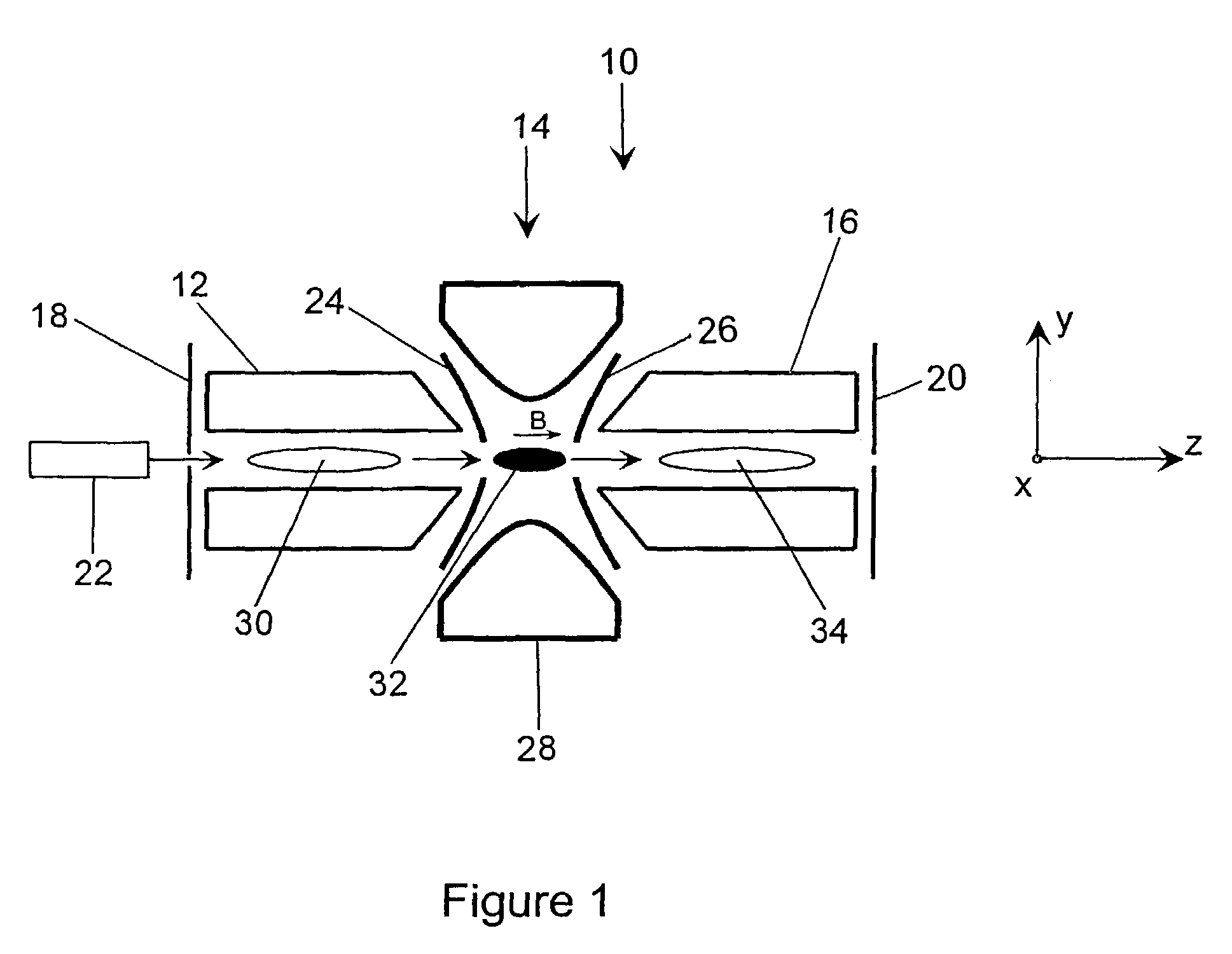
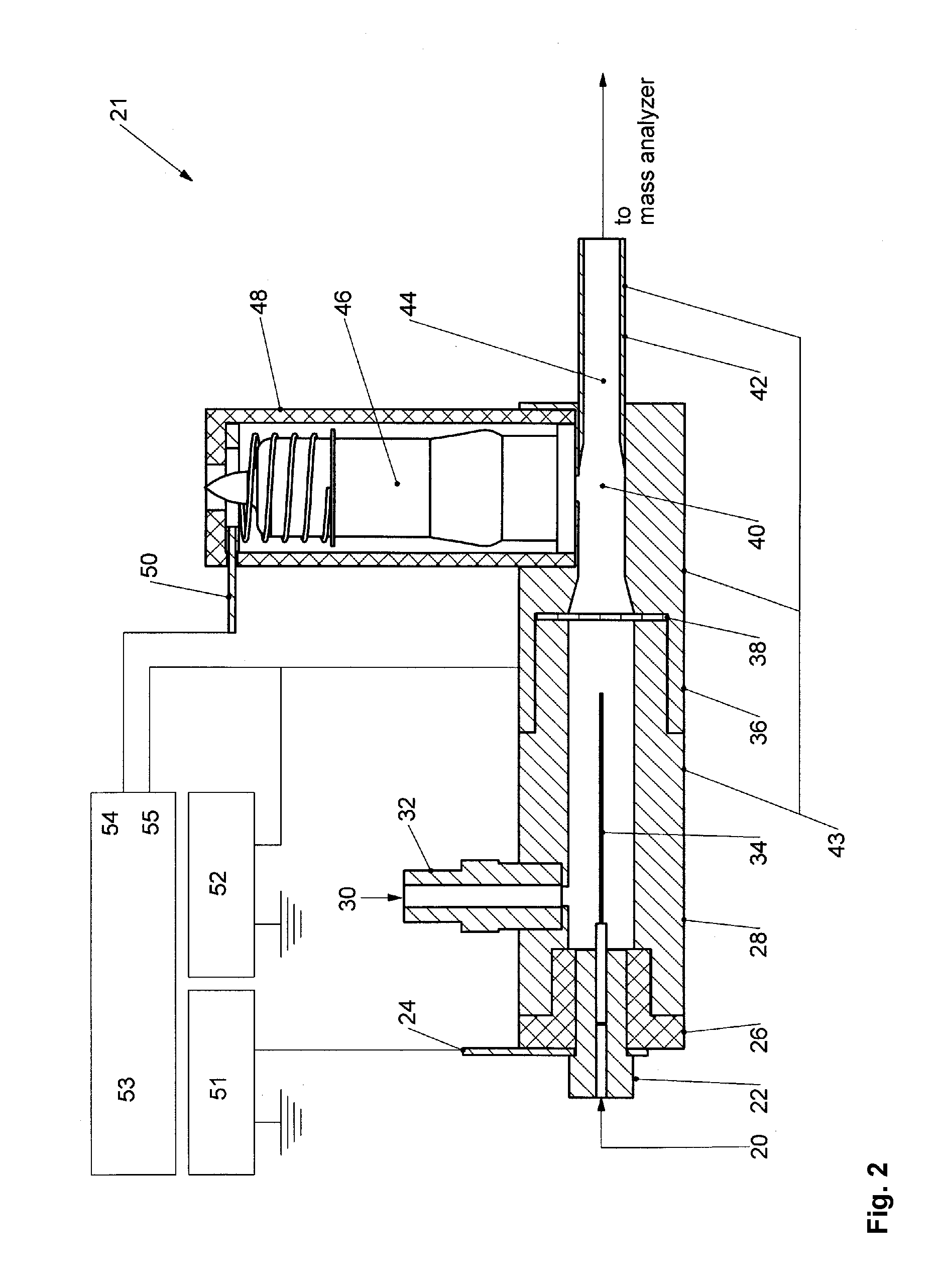
A system and method for mass analysis of an ion beam. The system includes a mass selector, at least one multipole ion guide, and a mass analyzer. In the system and method, precursor ions are selected with a desired mass to charge ratio. Electrons are injected into the multipole ion guide. The precursor ions are fragmented into product ions via electron capture dissociation from the injected electrons. The product ions are passed to a mass analyzer for a mass analysis.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
Electron capture dissociation apparatus and related methods
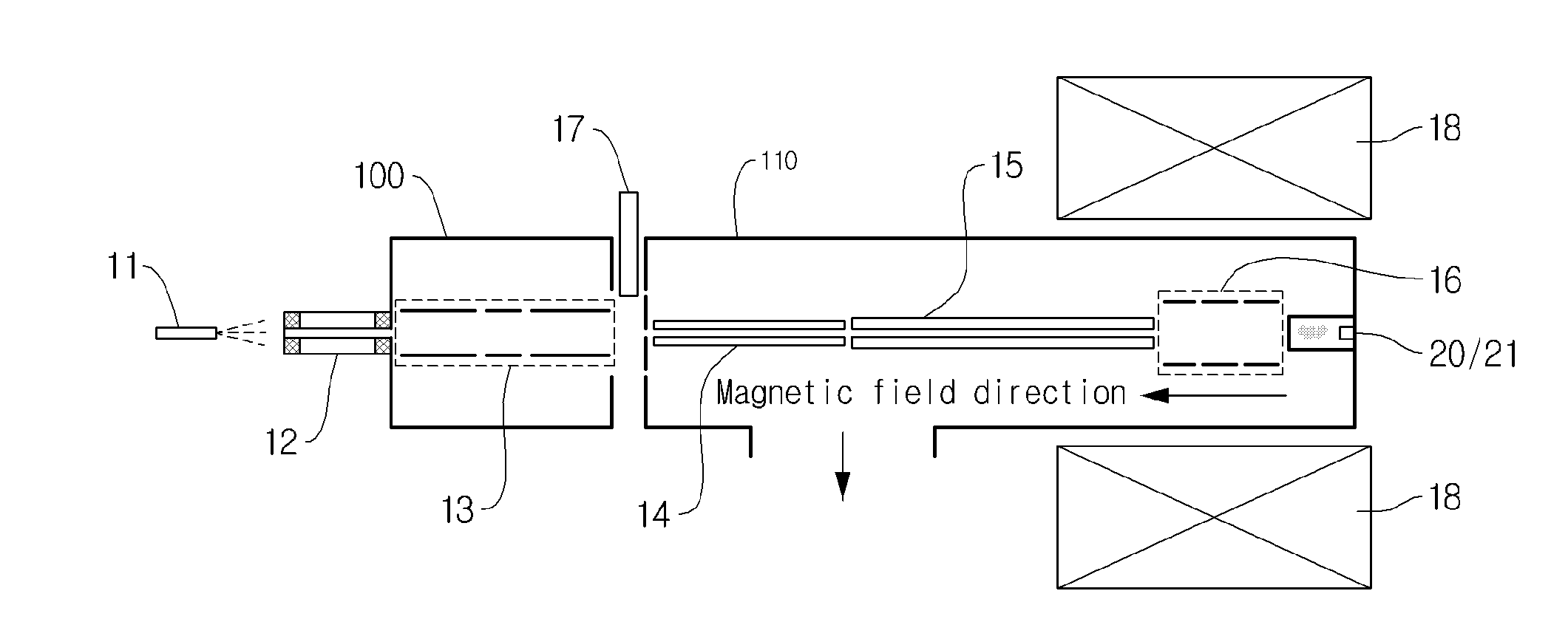
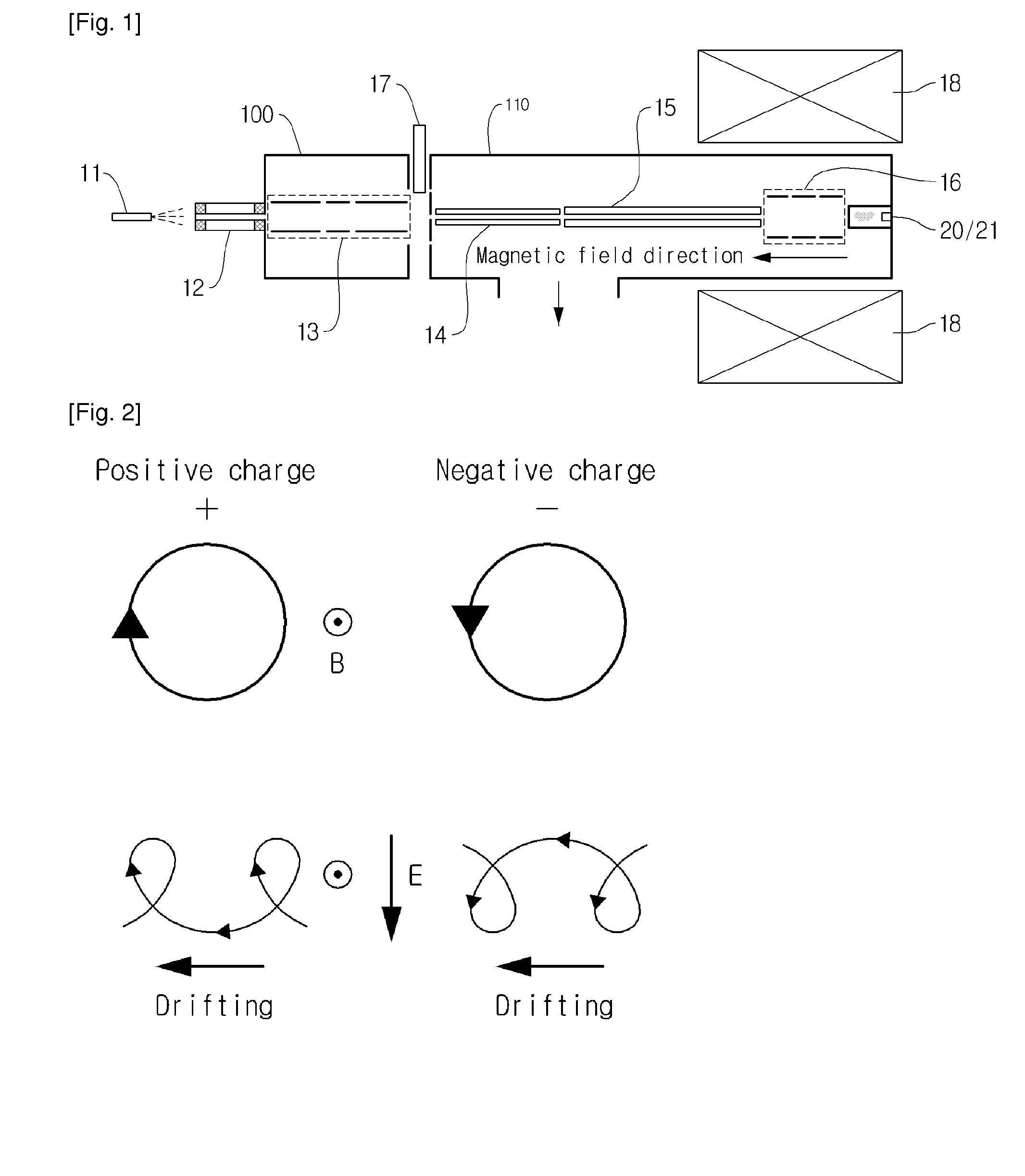
ActiveUS20110049347A1Weaken energyShort time windowIsotope separationMass spectrometersInterior spaceBeam direction
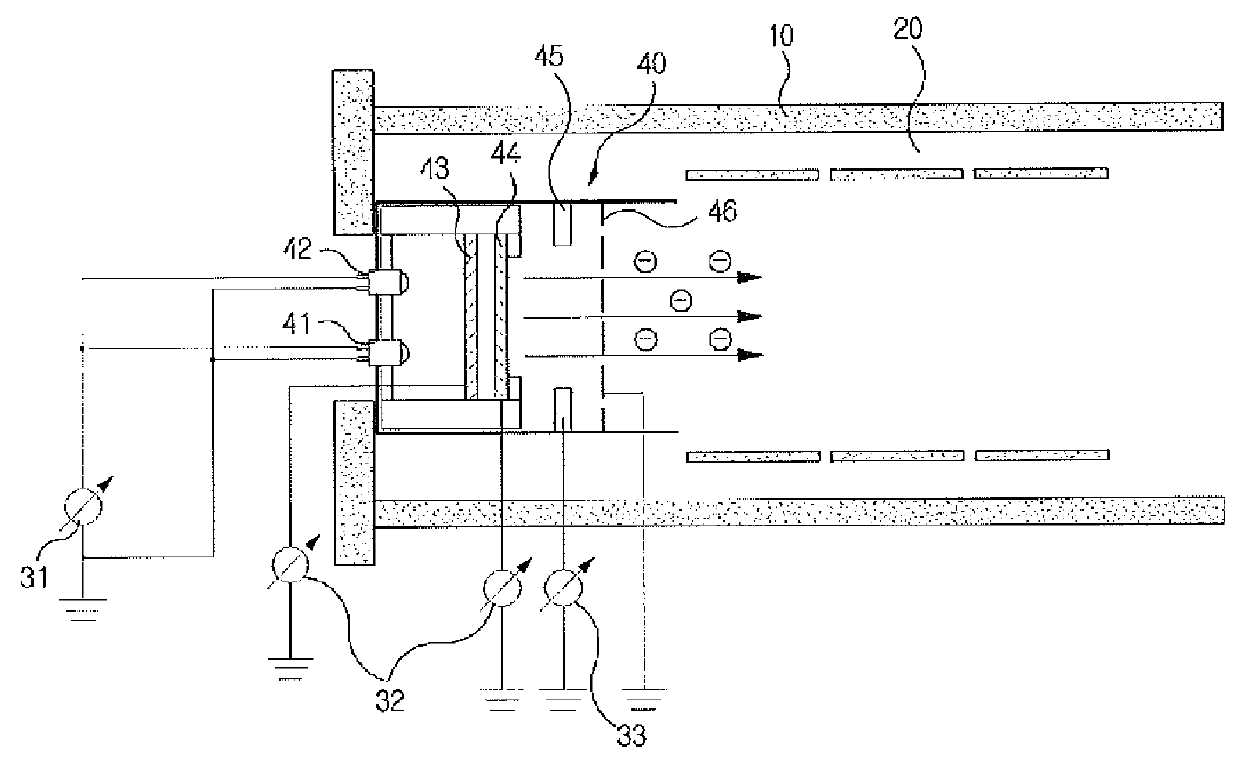
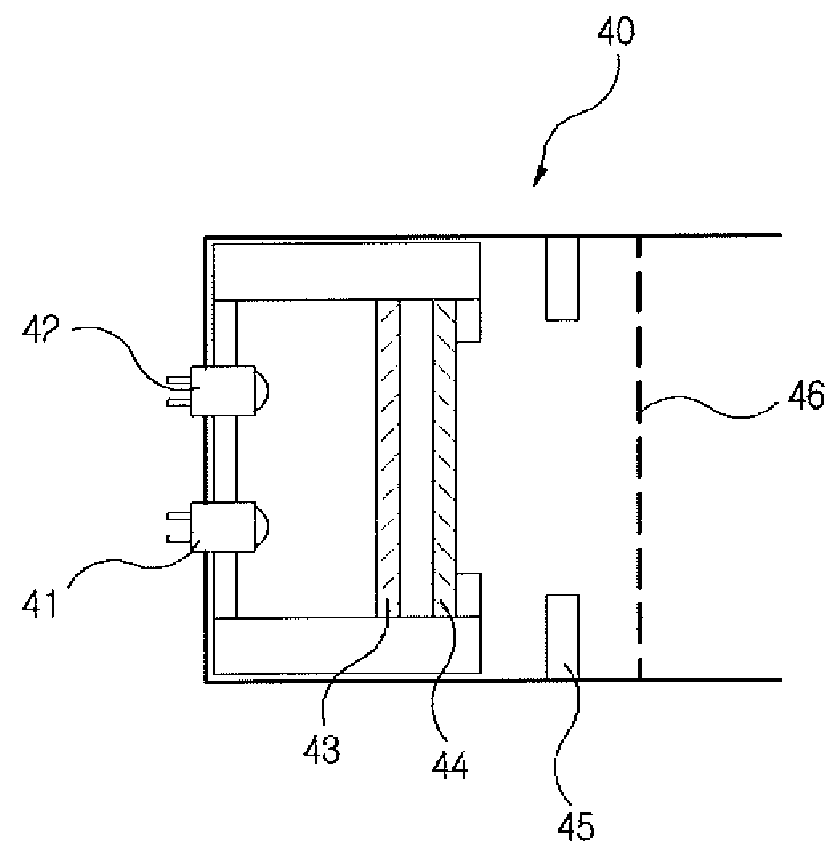
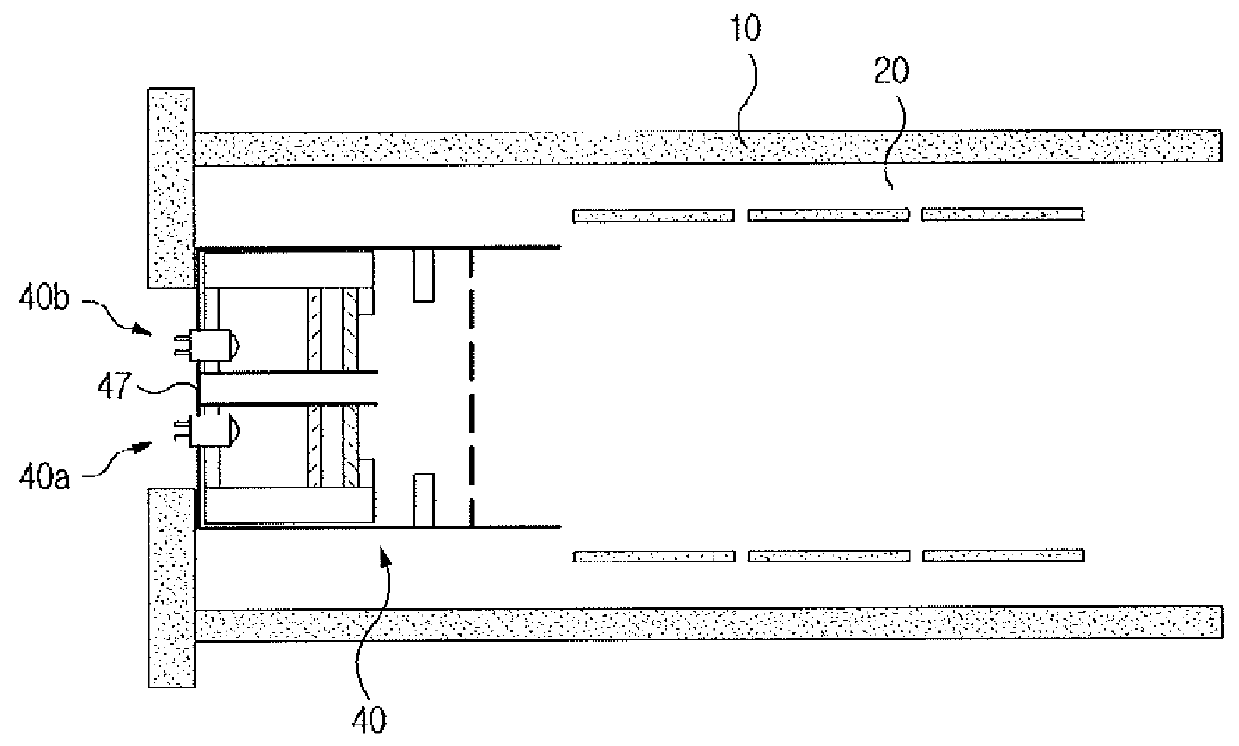
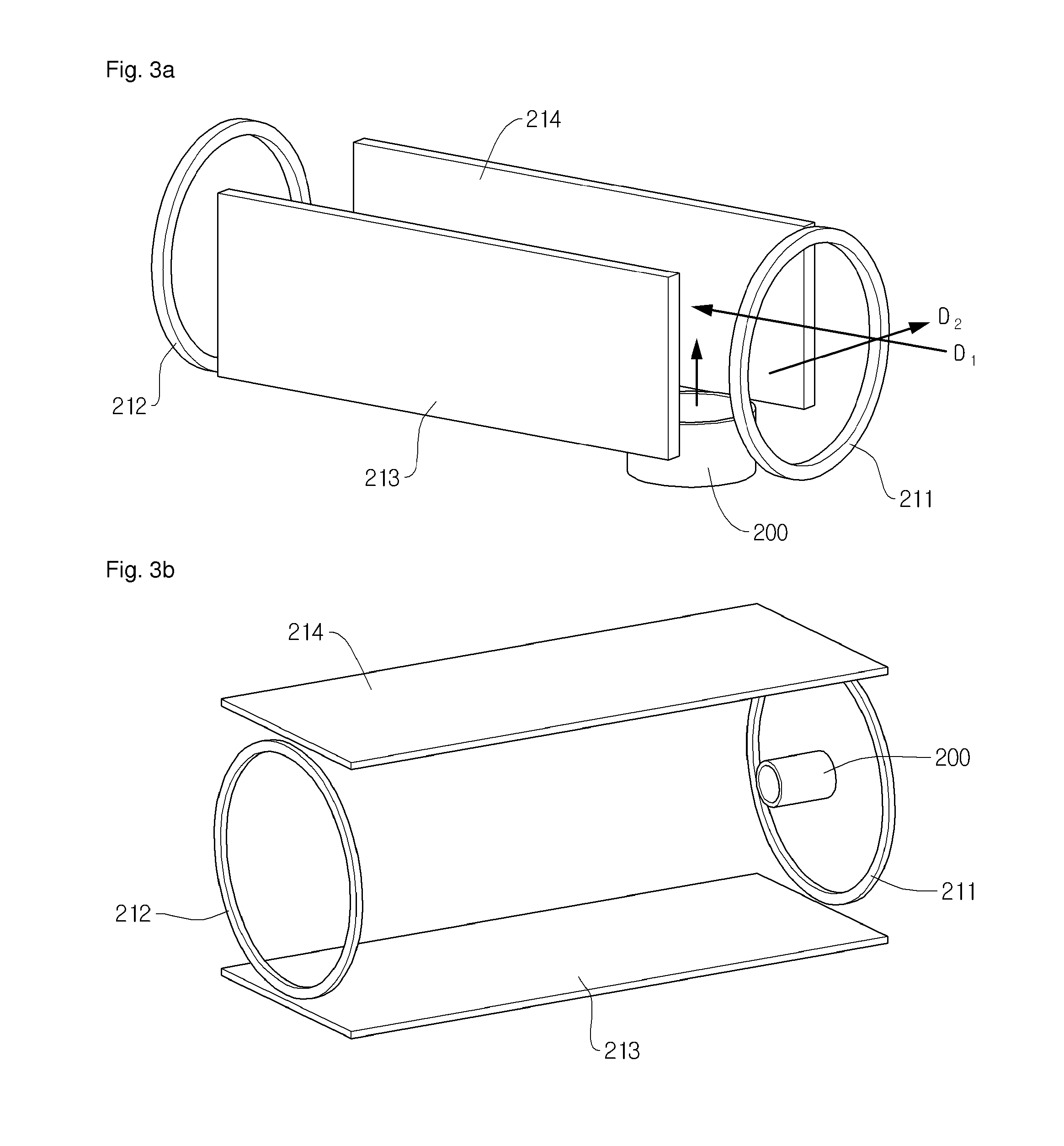
An electron capture dissociation apparatus comprises ion guide electrodes, an electron emitter, and an electron control device. The ion guide electrodes are arranged along a central axis and spaced circumferentially to circumscribe an interior space extending along the central axis. The electron emitter is disposed outside the interior space. The electron control device is configured for focusing an electron beam from the electron emitter toward the central axis, along a radial electron beam direction between two of the ion guide electrodes, and for decelerating the electron beam in a DC decelerating field of adjustable voltage potential directed along the electron beam direction.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
An ion trap and a method for dissociating ions in an ion trap
ActiveCN1922711AReduce electric field strengthRelieve pressureStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryElectron injection
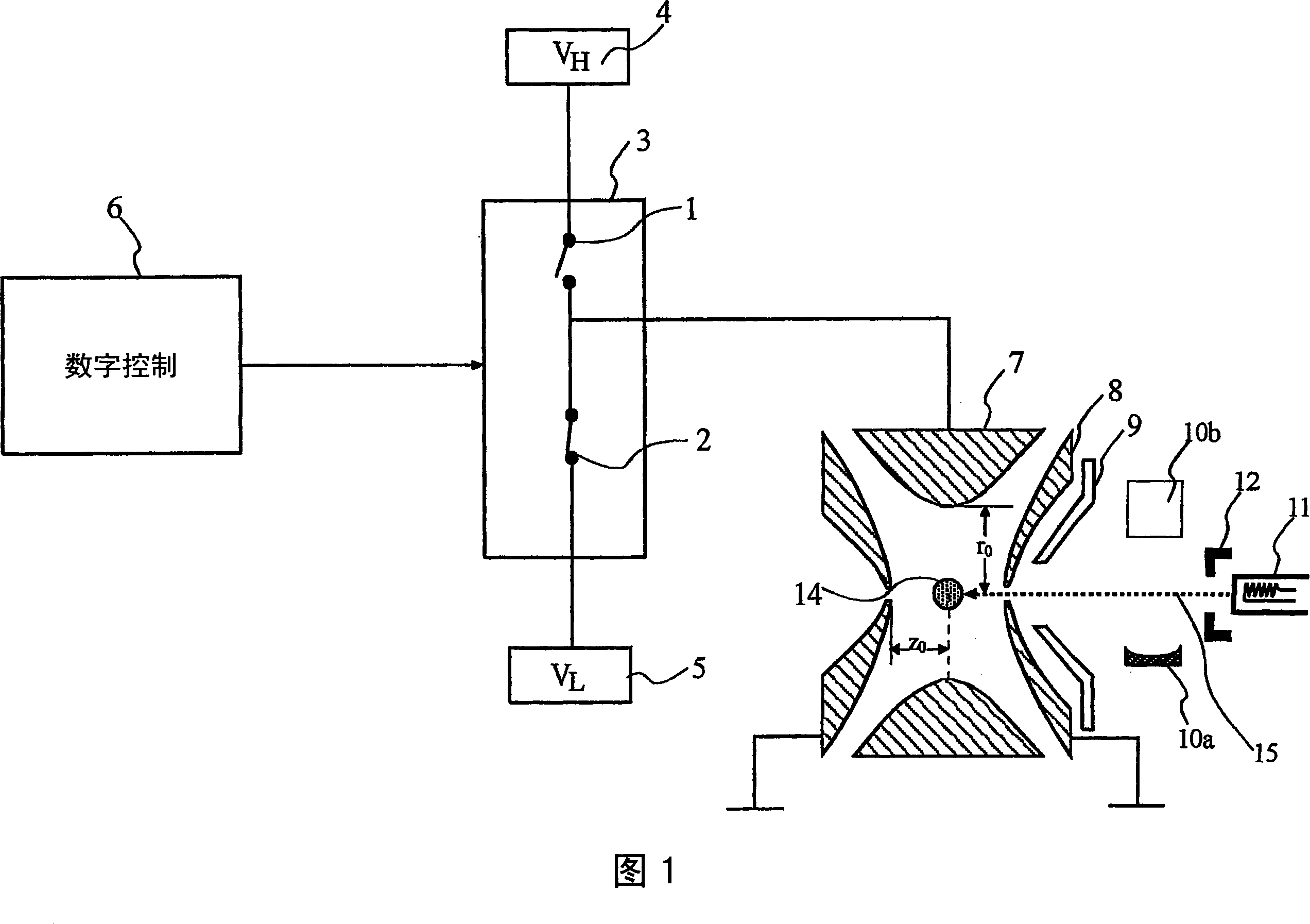
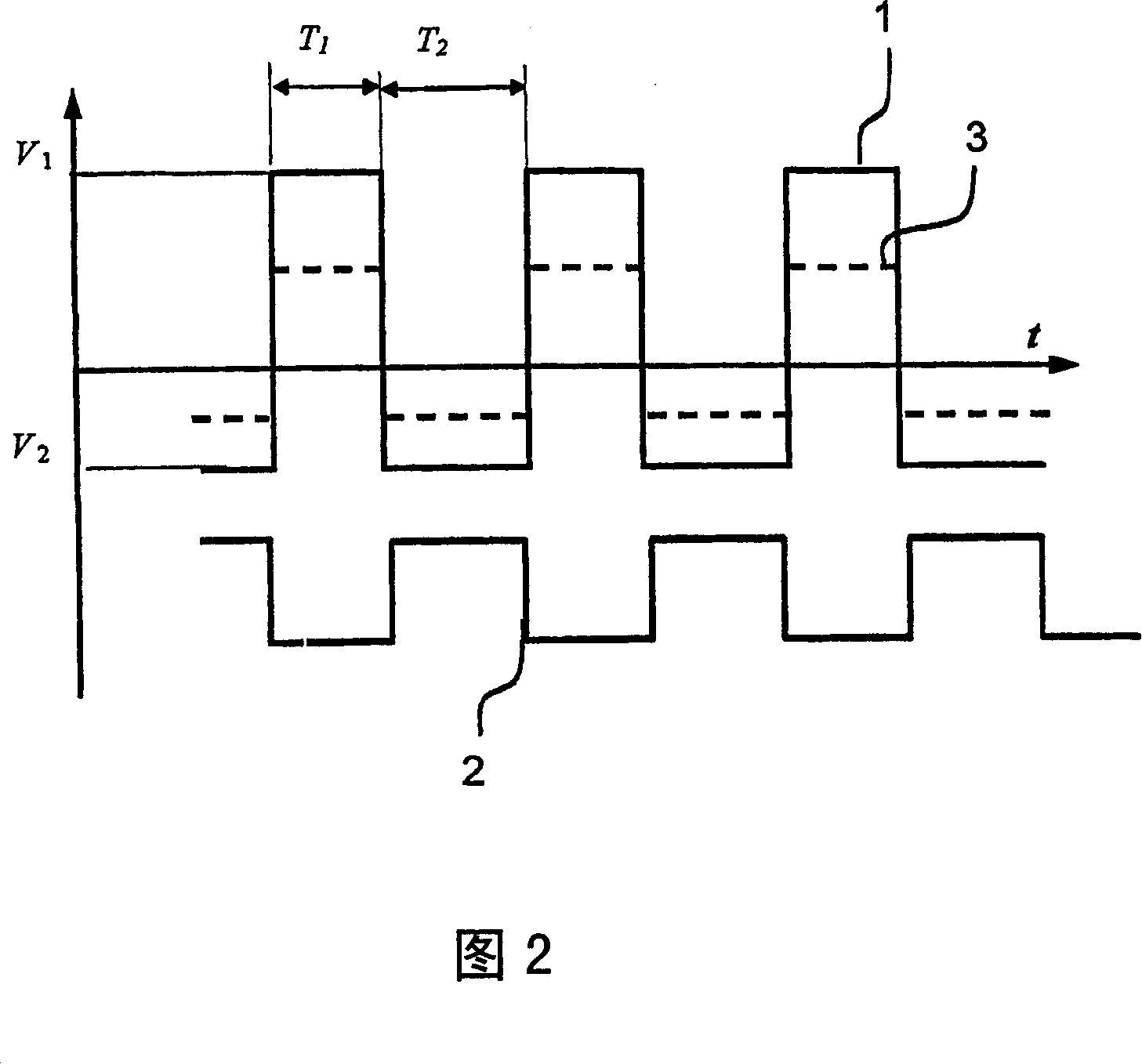
A quadrupole ion trap includes a switch (3) for switching a trapping voltage between discrete voltage levels VH, VL. This creates a digital trapping field for trapping precursor ions and product ions in a trapping region of the ion trap. A gating voltage is applied to a gate electrode (12) to control injection of source electrons into the ion trap. Application of the gating voltage is synchronised with the switching so that electrons are injected into the trapping region while the trapping voltage is at a selected one of the voltage levels and can reach the trapping region with a kinetic energy suitable for electron capture dissociation to take place.
Owner:岛津欧州研究所
Mass spectrometer
ActiveUS7309860B2Efficient trappingImprove responseMaterial analysis by optical meansIsotope separationElectron sourceMass analyzer
An electron capture dissociation device to implement a combination of electron capture dissociation and collision dissociation and a mass spectrometer with the use thereof are provided. This device includes a linear ion trap provided with linear multipole electrodes applied with a radio frequency electric field and wall electrodes that are arranged on both ends in the axis direction of the linear multipole electrodes, have holes on the central axis thereof, and generate a wall electric field by being applied with a direct-current voltage, a cylindrical magnetic field-generating unit that generates a magnetic field parallel to the central axis of the linear multipole electrodes and surrounds the linear ion trap, and an electron source arranged opposite to the linear multipole electrodes with sandwiching one of the wall electrodes. The electron generation site of the electron source is placed in the inside of the magnetic field generated by the magnetic field-generating unit.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Methods and apparatus for electron or positron capture dissociation
InactiveUS7227133B2Stability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationMass analyzerElectron-capture dissociation
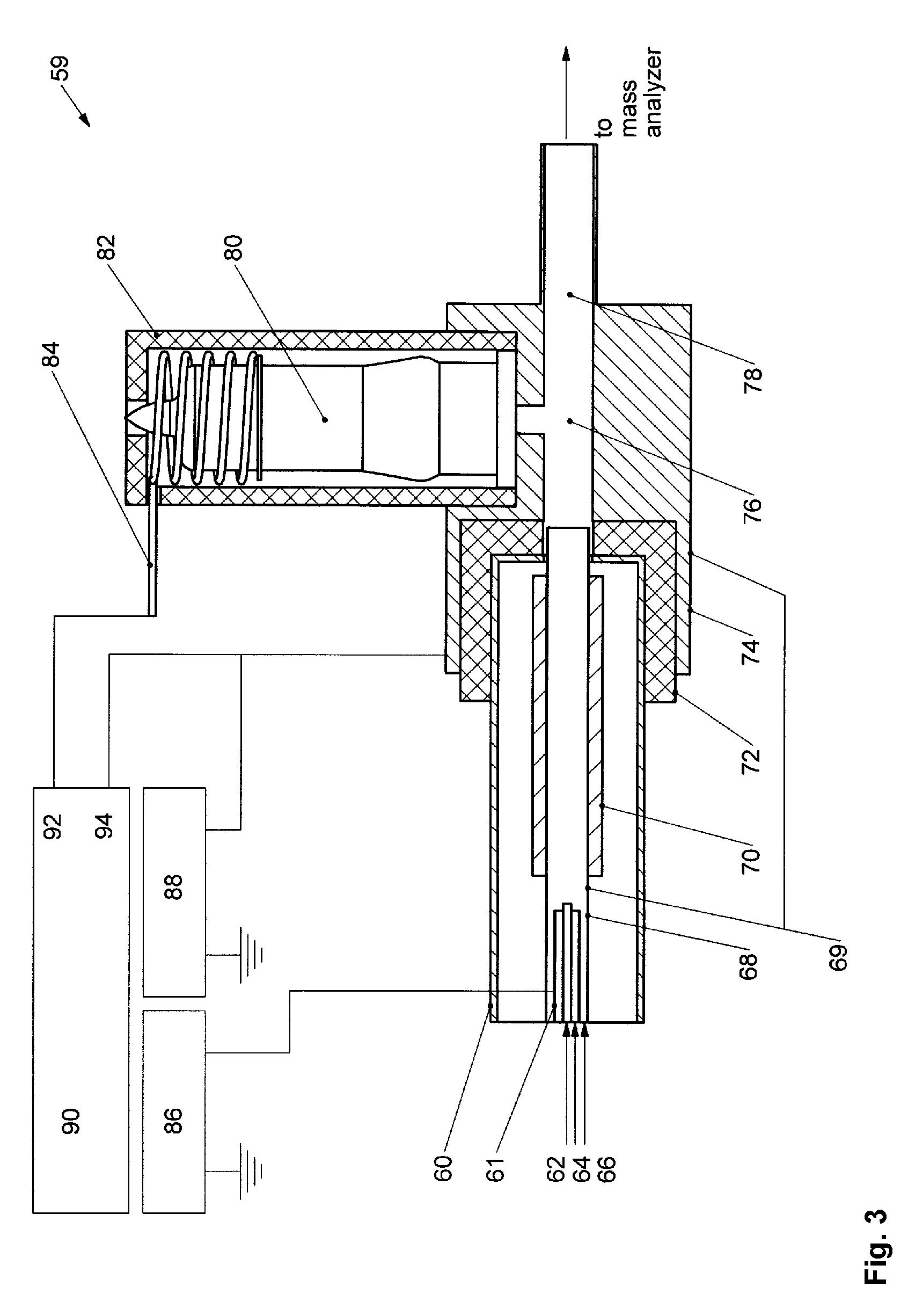
The present invention relates to mass spectrometers capable of performing electron (or positron) capture dissociation, methods of performing tandem mass spectrometry, methods of performing electron capture dissociation, and methods of performing positron capture dissociation. In one embodiment, a mass spectrometer capable of performing electron or positron capture dissociation is provided that comprises a first mass analyzer, a magnetic trap downstream of the first mass analyzer, a second mass analyzer downstream of the magnetic trap, and an electron or positron source positioned such that electrons or positrons may be supplied to the magnetic trap.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
AP-ECD methods and apparatus for mass spectrometric analysis of peptides and proteins
InactiveUS20110303839A1Low costImproved generation and transmissionIsotope separationMass spectrometersSprayerMass analyzer
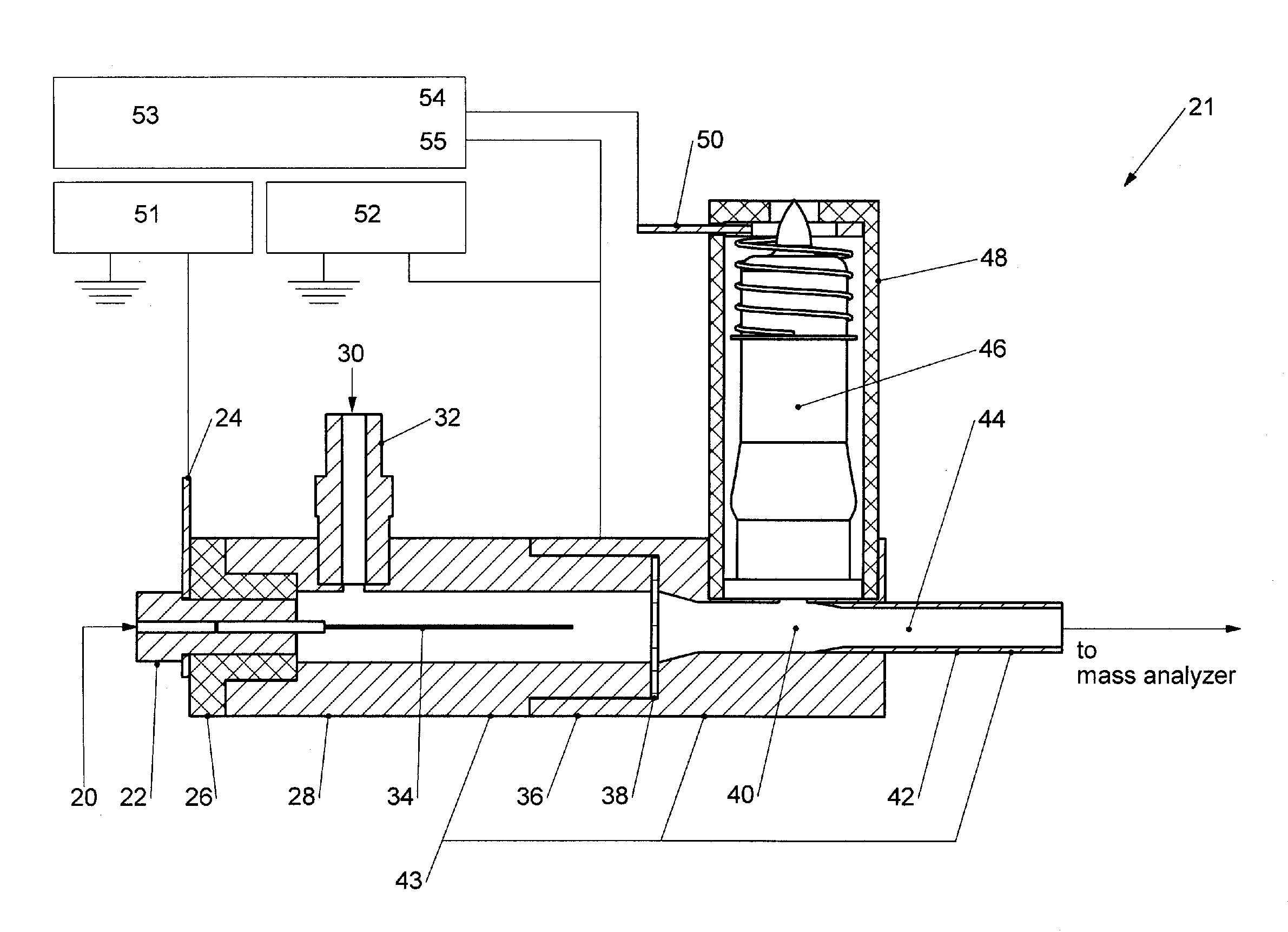
An in-source atmospheric pressure electron capture dissociation (AP-ECD) method and apparatus for mass spectrometric analysis of peptides and proteins. An electrified sprayer generates a multiply-charged peptide / protein ions from a sample solution, a source of electrons for negative reagents, and a flow of gas for guiding positively charged ions from the electrified sprayer to a downstream reaction region within the guide. The reaction region being at or near atmospheric pressure and substantially free of the electric field from the electrified sprayer. In another embodiment, the method uses electron transfer dissociation (ETD), in the event that anions are substituted for electrons as the negative reagents. Fragment ions exiting the reaction region are subsequently passed into a mass analyzer of a mass spectrometer for mass analysis of the ions.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Mass spectrometric ion storage device for different mass ranges
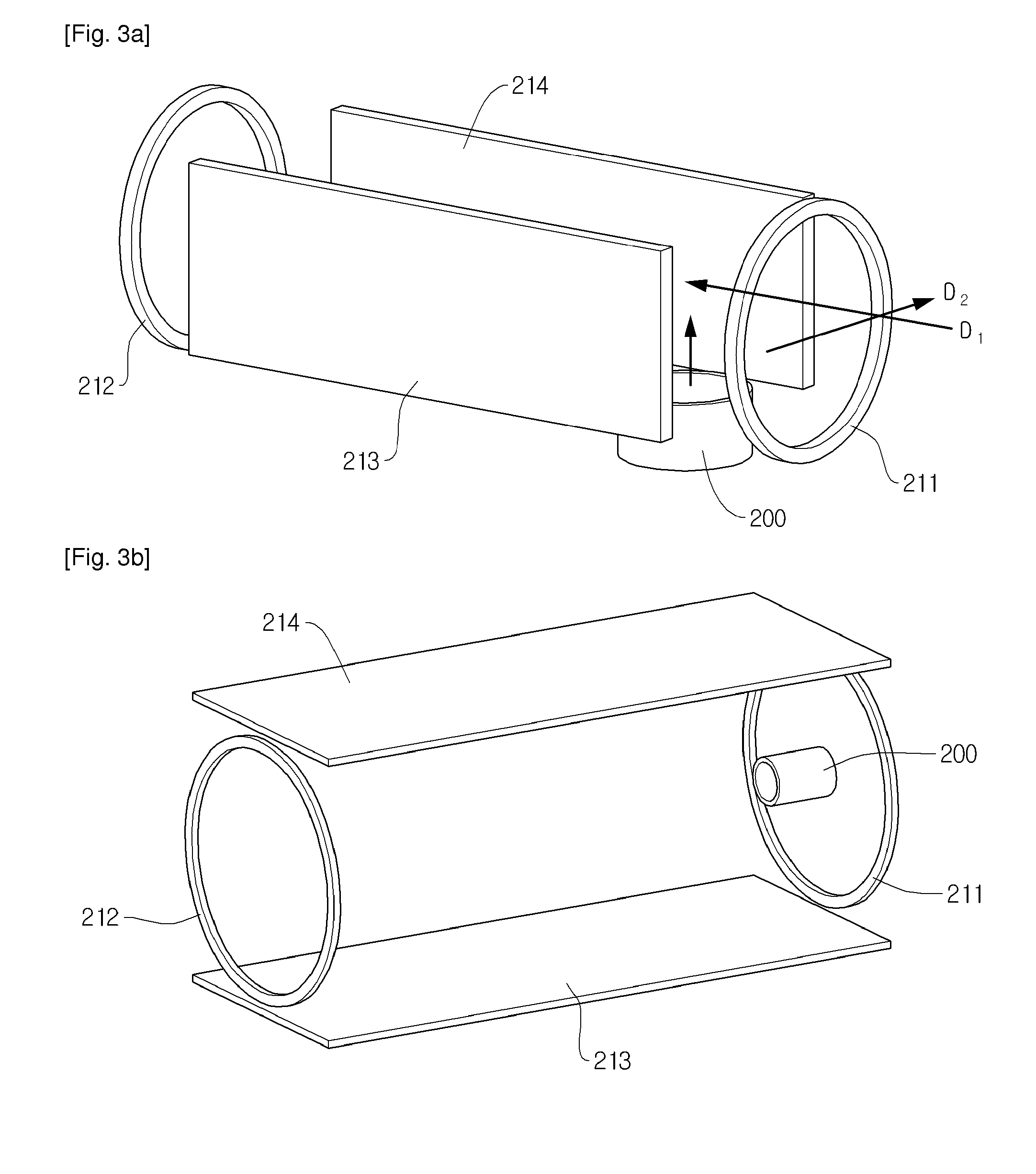
ActiveUS20130075602A1High yieldIsotope separationRadio frequency spectrometersQuadrupole fieldAnalyte
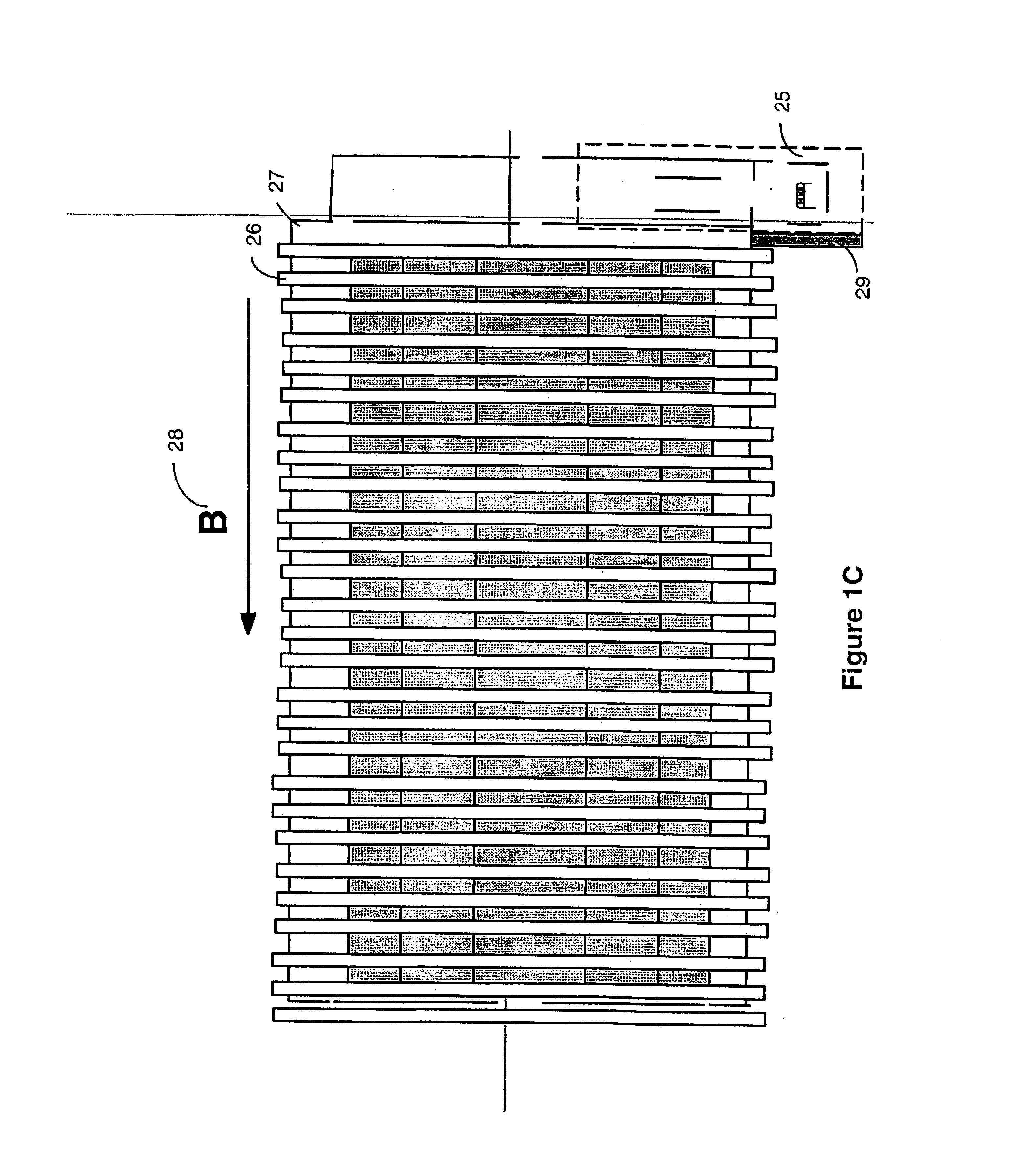
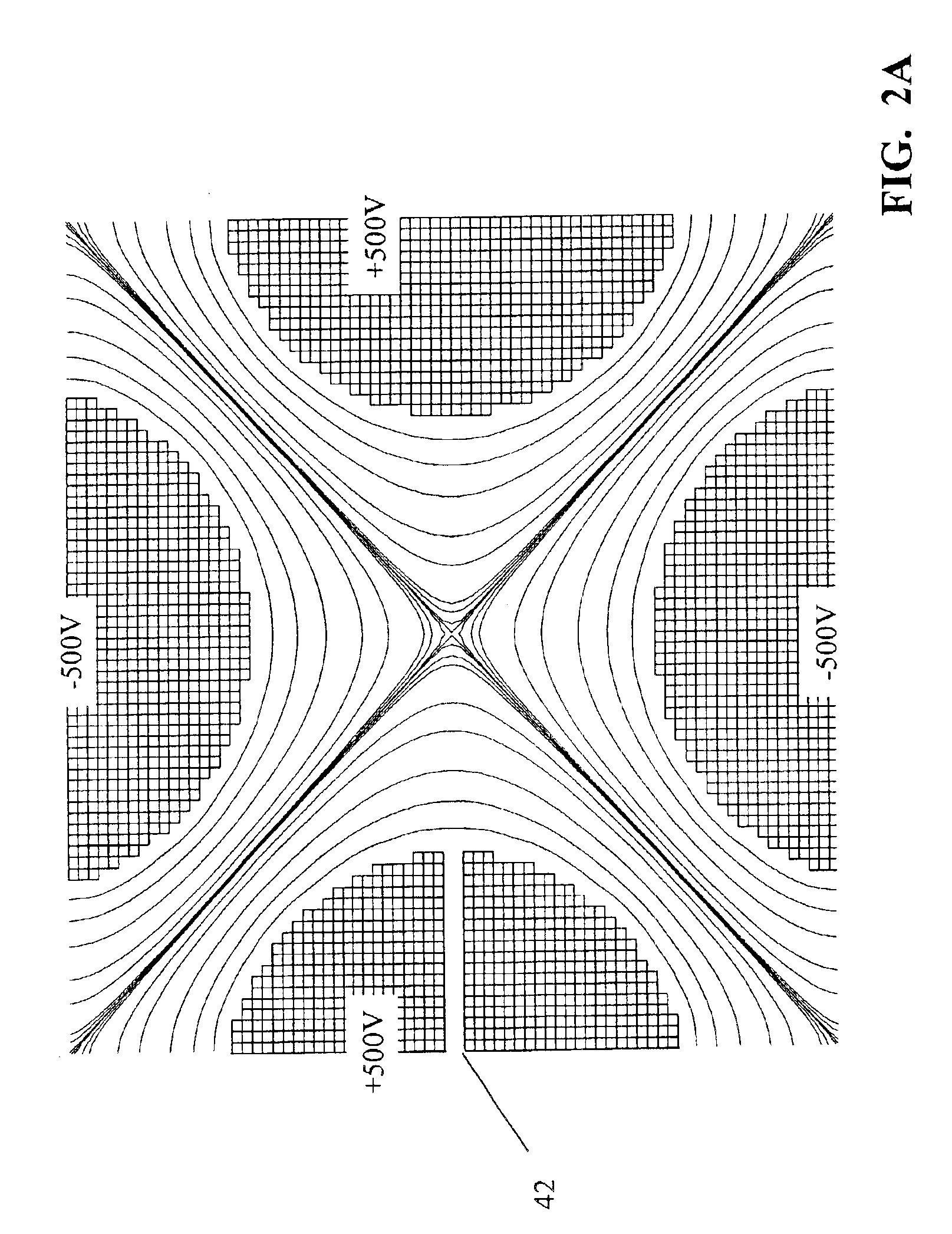
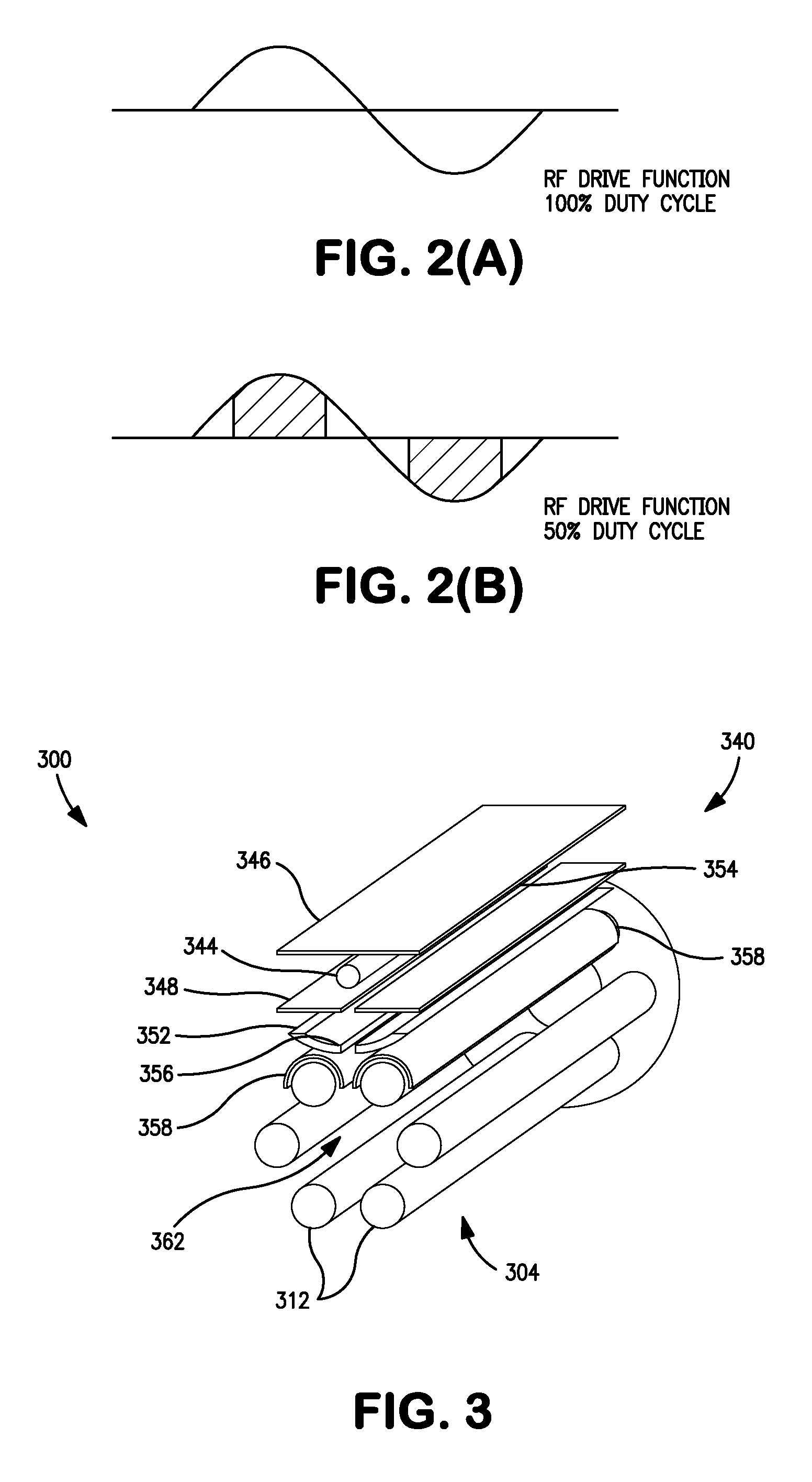
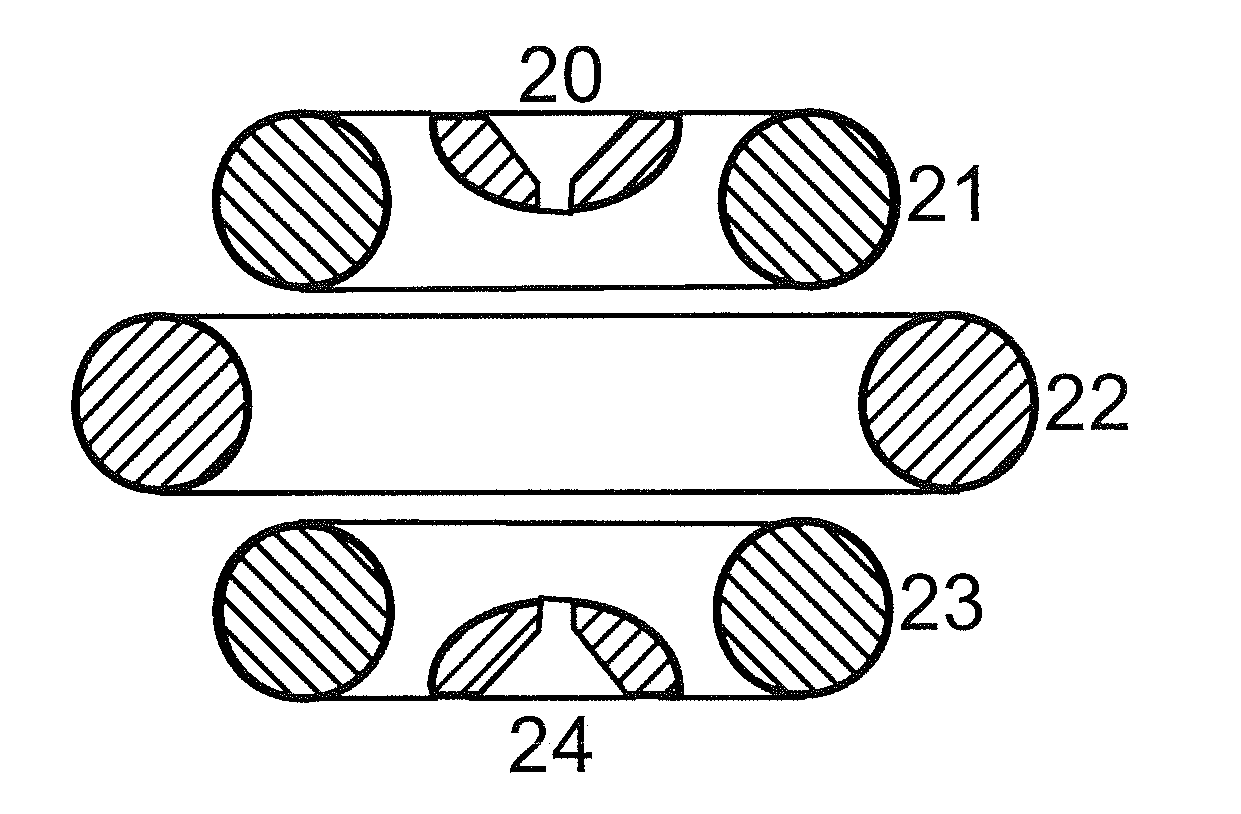
The invention relates to devices and methods for the storage of ions in mass spectrometers. The invention proposes the generation and superposition of two multipole fields of different order, independent of each other, in an RF multipole rod system. In an embodiment with eight pole rods, for example, it is thus possible to jointly store low-energy electrons in a central RF quadrupole field, which effectively acts only on electrons and holds them together radially, on the one hand, and multiply charged heavy positive ions in an RF octopole field, which effectively acts only on the ions, on the other hand, in order to fragment the positive ions by electron capture dissociation (ECD). In a different embodiment, multiply charged positive analyte ions and suitable negative reactant ions can react with each other in an octopole field by electron transfer dissociation (ETD) with a high fragmentation yield, and the fragment ions can subsequently be bundled by a transition to a quadrupole field to form a fine ion beam, which can leave the multipole rod system axially. A mixture of hexapole and dodecapole systems is also possible.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Labeling peptides with tertiary amines and other basic functional groups for improved mass spectrometric analysis
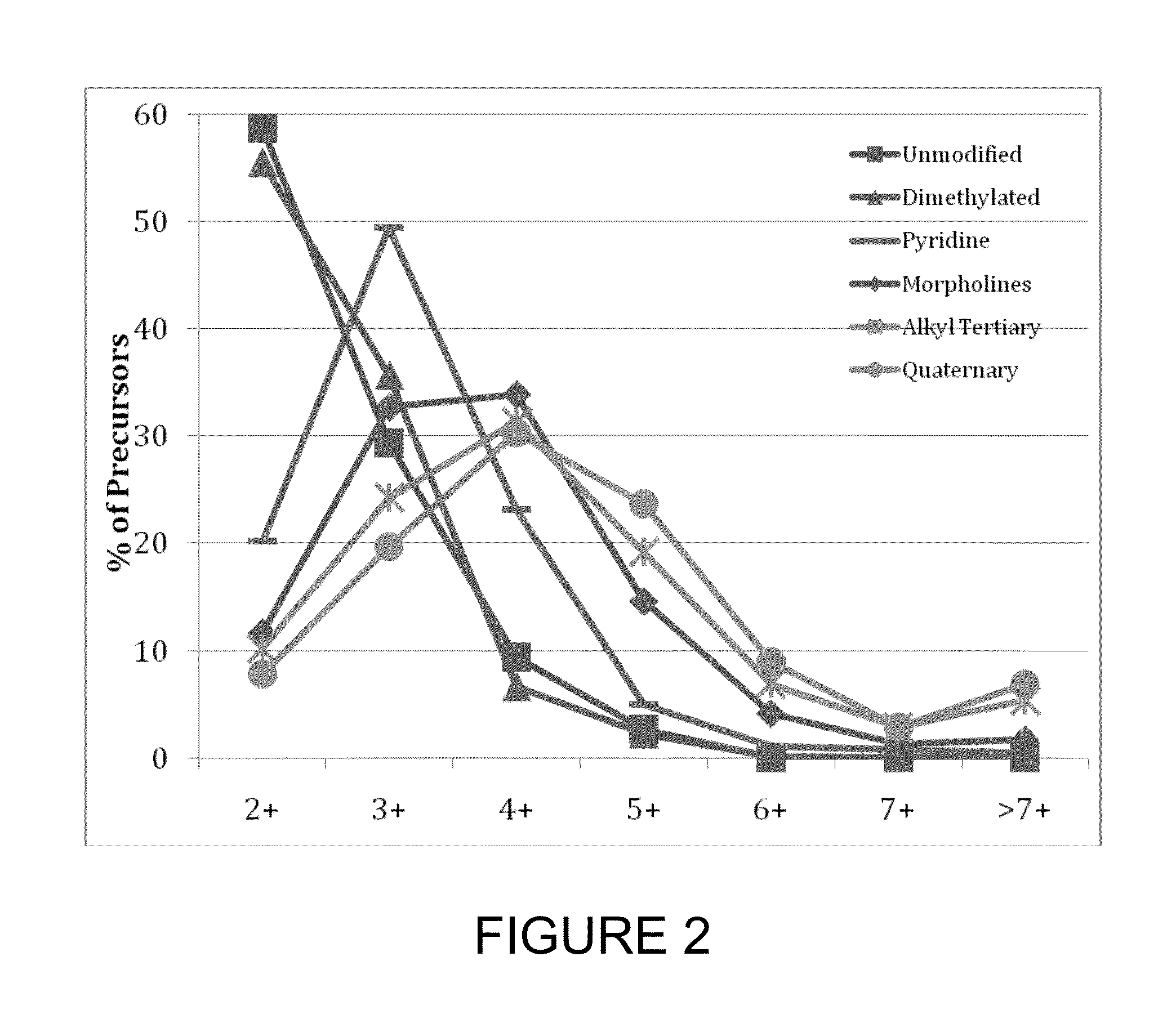
ActiveUS20100330680A1Easy to analyzeImprove fragmenting characteristicPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesHighly charged ionGas phase
The present invention provides methods for enhancing the fragmentation of peptides for mass spectrometry by modifying the peptides with a tagging reagent containing a functional group, such as a tertiary amine, having a greater gas-phase basicity than the amide backbone of the peptide. These high gas-phase basicity functional groups are attached to a peptide by reacting the tagging reagent to one or more available carboxylic acid groups of the peptide. Linking these high gas-phase functional groups to the peptides leads to higher charge state ions from electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), which fragment more extensively during fragmentation techniques, particularly non-ergodic fragmentation techniques such as electron capture dissociation (ECD) and electron transfer dissociation (ETD).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Electron capture dissociation apparatus and related methods
An electron capture dissociation apparatus comprises ion guide electrodes, an electron emitter, and an electron control device. The ion guide electrodes are arranged along a central axis and spaced circumferentially to circumscribe an interior space extending along the central axis. The electron emitter is disposed outside the interior space. The electron control device is configured for focusing an electron beam from the electron emitter toward the central axis, along a radial electron beam direction between two of the ion guide electrodes, and for decelerating the electron beam in a DC decelerating field of adjustable voltage potential directed along the electron beam direction.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Mass spectrometry methods using electron capture by ions
InactiveUS6958472B2Effective electron capture dissociationEfficient captureStability-of-path spectrometersIon sources/gunsTrappingElectron-capture dissociation
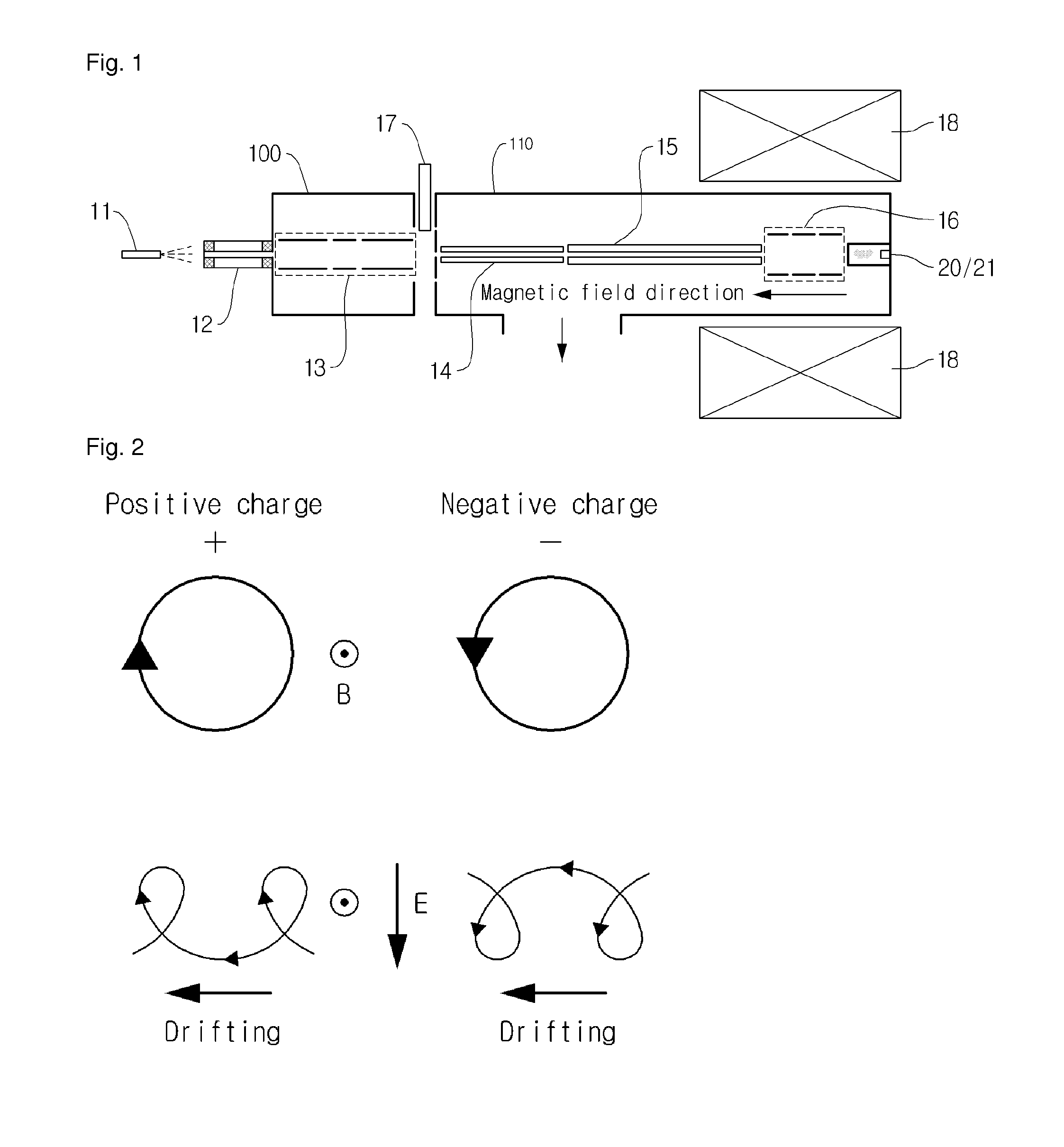
Methods and apparatus are provided to obtain efficient Electron capture dissociation (ECD) of positive ions, particularly useful in the mass spectrometric analysis of complex samples such as of complex mixtures and large biomolecules of peptides and proteins. Due to the low efficiency of ECD as previously used, the technique has so far only been employed with Penning cell ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers, where the ions are confined by a combination of magnetic and electrostatic fields. To substantially increase the efficiency of electron capture, the invention makes use of a high-intensity electron source producing a high-flux low-energy electron beam of a diameter comparable to that of the confinement volume of ions. Such a beam possesses trapping properties for positive ions. The ions confined by electron beam effectively capture electrons, which leads much shorter analysis time. The invention provides the possibility to employs ECD in other trapping and non-trapping instruments beside ICR mass spectrometers.
Owner:ZUBAREV ROMAN A
Anion generating and electron capture dissociation apparatus using cold electrons
InactiveUS20140367568A1Stability-of-path spectrometersElectron multiplier detailsUltravioletField electron emission
The present invention relates to an anion generating and electron capture dissociation apparatus using cold electrons, which uses an MCP electron multiplier plate for generating an electron beam for ionization within an ion trap of a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectroscope, injects ultraviolet photons emitted from an ultraviolet diode across the entire surface of the MCP electron multiplier plate, uses an electron focusing lens to focus and inject an electron beam into the trap, and generates an ECD reaction by coupling electrons to molecules having multiple positive charges using a low energy electron beam emitting apparatus for the negative ionization of neutral molecules in the ion trap. The anion generating and electron capturing and analyzing apparatus of the present invention, which uses cold electrons and is configured of a cold electron generating module which generates a large number of cold electrons from ultraviolet photons emitted into a mass spectroscope in a high vacuum state, comprises a plurality of ultraviolet diodes emitting ultraviolet photons in the mass spectroscope, an MCP electron multiplier plate inducing and amplifying an initial electron emission of ultraviolet photons from the ultraviolet diodes, and generating a high capacity electron beam from a back plate, an electron focusing lens for focusing the electron beam amplified through the MCP electron multiplier plate, and a grid for adjusting the energy and current of electrons.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
AP-ECD methods and apparatus for mass spectrometric analysis of peptides and proteins
InactiveUS8598514B2Low costMore accessStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by optical meansSprayerMass analyzer
An in-source atmospheric pressure electron capture dissociation (AP-ECD) method and apparatus for mass spectrometric analysis of peptides and proteins. An electrified sprayer generates a multiply-charged peptide / protein ions from a sample solution, a source of electrons for negative reagents, and a flow of gas for guiding positively charged ions from the electrified sprayer to a downstream reaction region within the guide. The reaction region being at or near atmospheric pressure and substantially free of the electric field from the electrified sprayer. In another embodiment, the method uses electron transfer dissociation (ETD), in the event that anions are substituted for electrons as the negative reagents. Fragment ions exiting the reaction region are subsequently passed into a mass analyzer of a mass spectrometer for mass analysis of the ions.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Coupled Electrostatic Ion and Electron Traps for Electron Capture Dissociation - Tandem Mass Spectrometry
InactiveUS20070221862A1Particle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansIon trap mass spectrometryMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer employing an electrostatic ion trap and electron trap. An ion source generates a stream of ions that are directed into the mass spectrometer. The mass spectrometer includes an ion-focusing region for focusing the ions along a predetermined axis. The focused ions are injected into the electrostatic ion trap where they oscillate between two electrostatic mirror assemblies. A stream of electrons is directed into the electron trap, where the electrons interact with the ions at an interaction region between adjacent electrode assemblies of the ion trap and the electron trap. The interaction between the ions and electrons creates ions, fragments and particles of various masses that can be detected by a pick-up electrode.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Method of MS/MS Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20150144780A1Increase atmospheric pressureIsotope separationSpecific reaction combinationsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryAtmospheric pressure
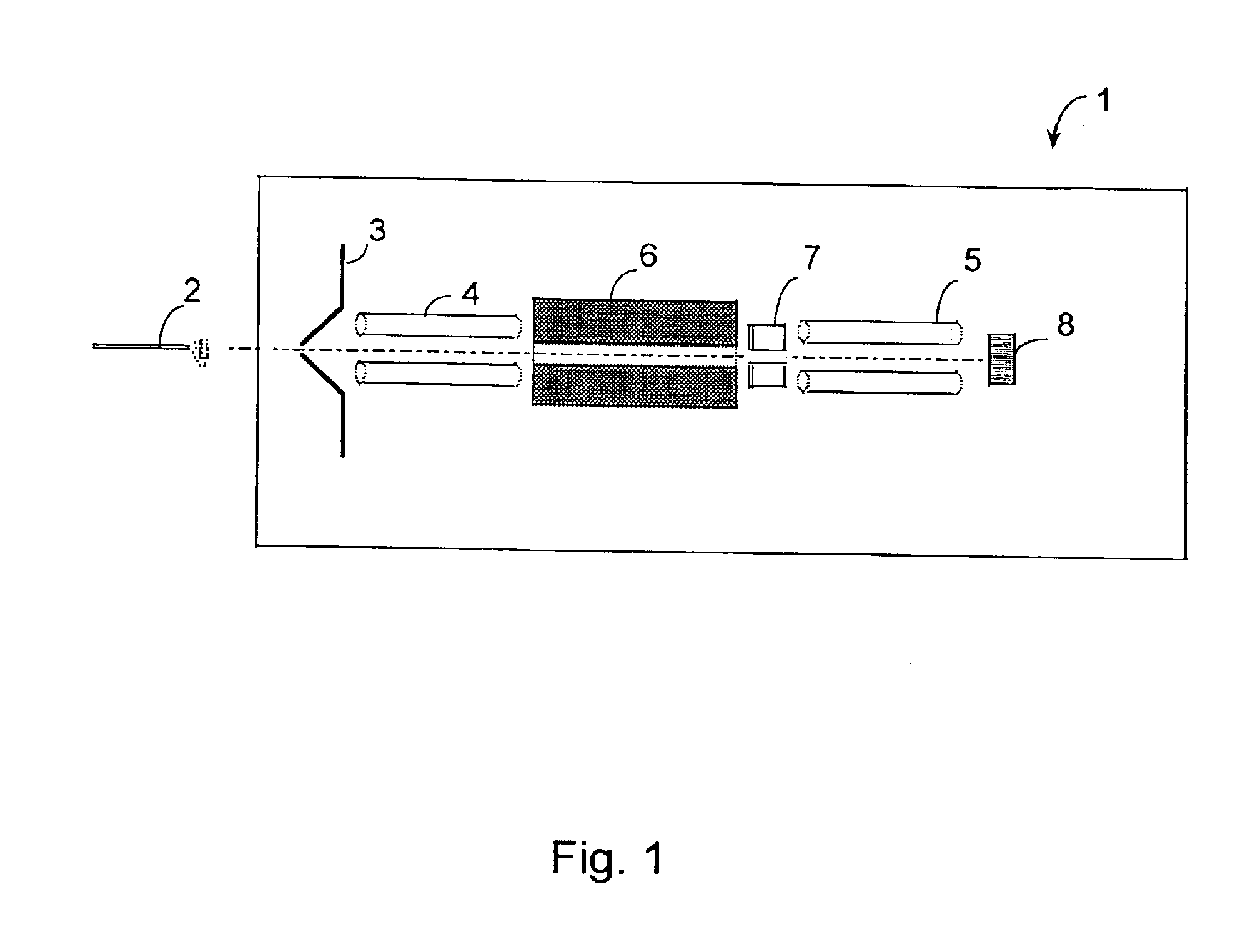
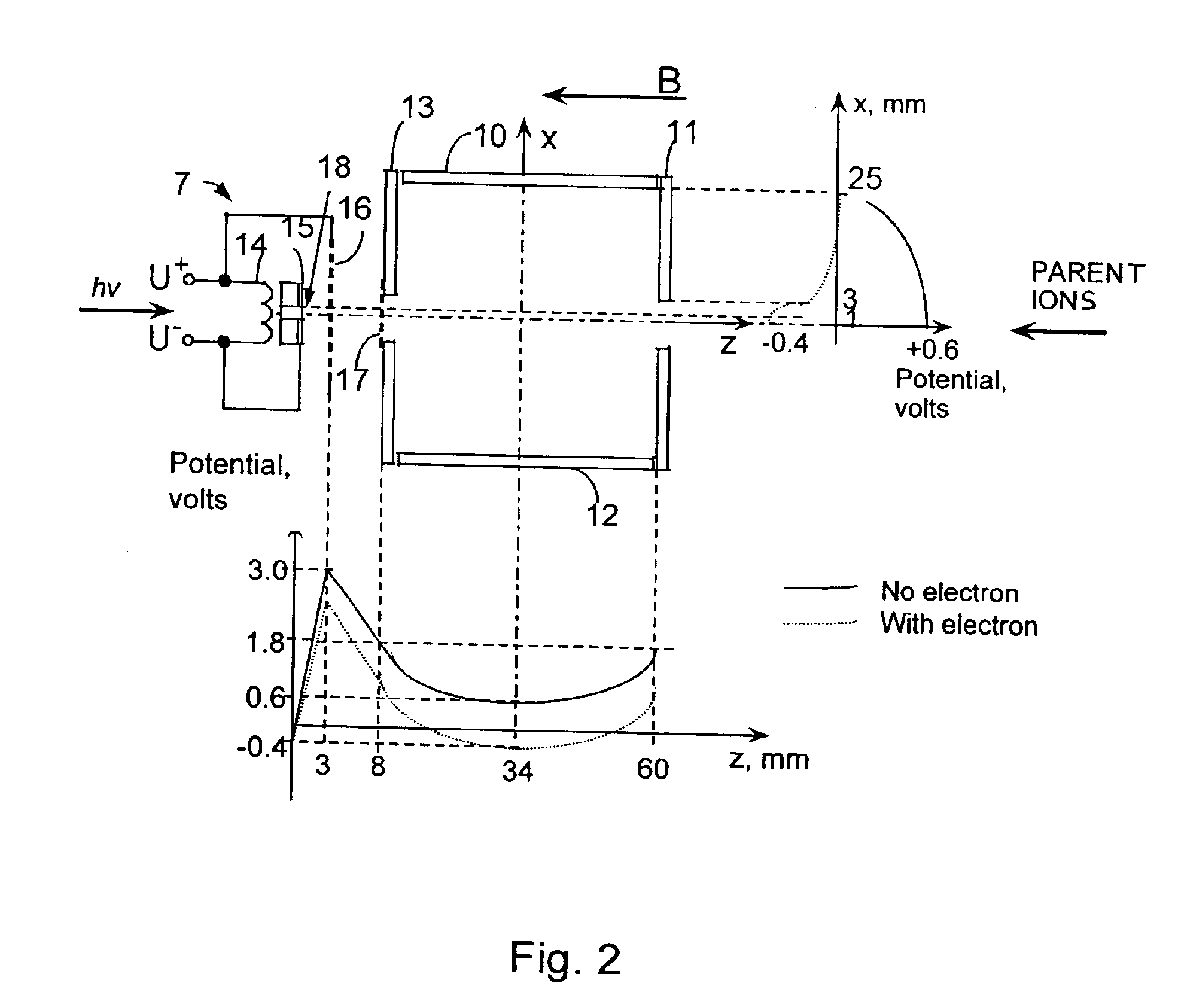
A method of mass spectrometry is disclosed comprising alternating between a first mode in which parent ions are mass analysed and a second mode in which the parent ions are subjected to Electron Capture Dissociation (“ECD”) at atmospheric pressure so as to produce fragment ions which are then mass analysed. The parent ions are associated with their fragment ions based on the times at which they were detected. This method enables parent ions to be associated with their fragment ions, even when the ECD fragmentation is performed at atmospheric pressure.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Electron capture dissociation in radiofrequency ion traps
InactiveUS20090256067A1Particle separator tubesIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryElectron-capture dissociation
A system and method that includes injecting low-energy electrons in a radiofrequency (RF) ion trap in order to dissociate positive ions by electron capture. The system includes an ion trap, a controller to provide RF that can be switched on and off rapidly, and a source of low-energy electrons that can be turned on and off synchronously with the radiofrequency on / off periods.
Owner:SYAGEN TECH
Lens for electron capture dissociation, fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer comprising the same and method for improving signal of fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer
InactiveUS20140284470A1Enhanced signalIncrease collisionStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsElectron-capture dissociationSpectrometer
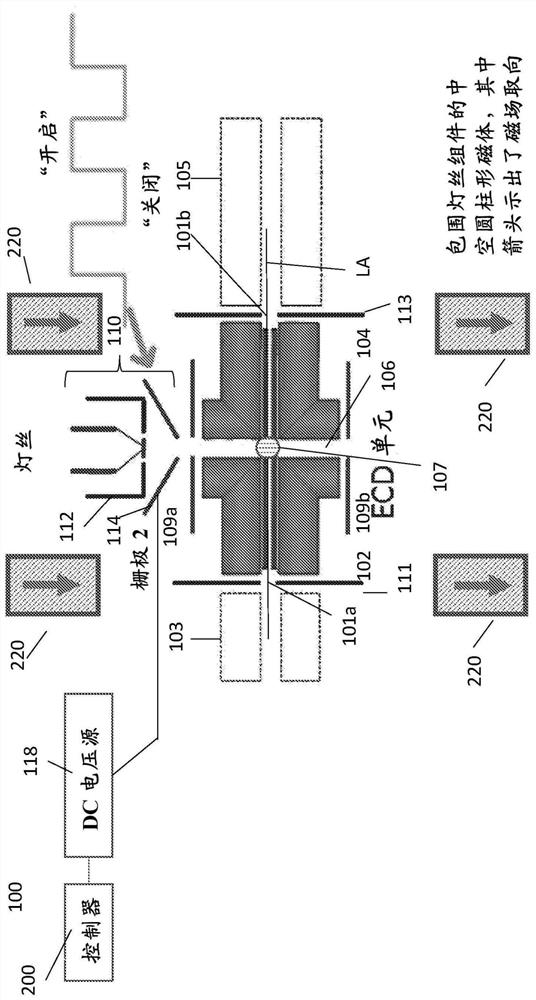
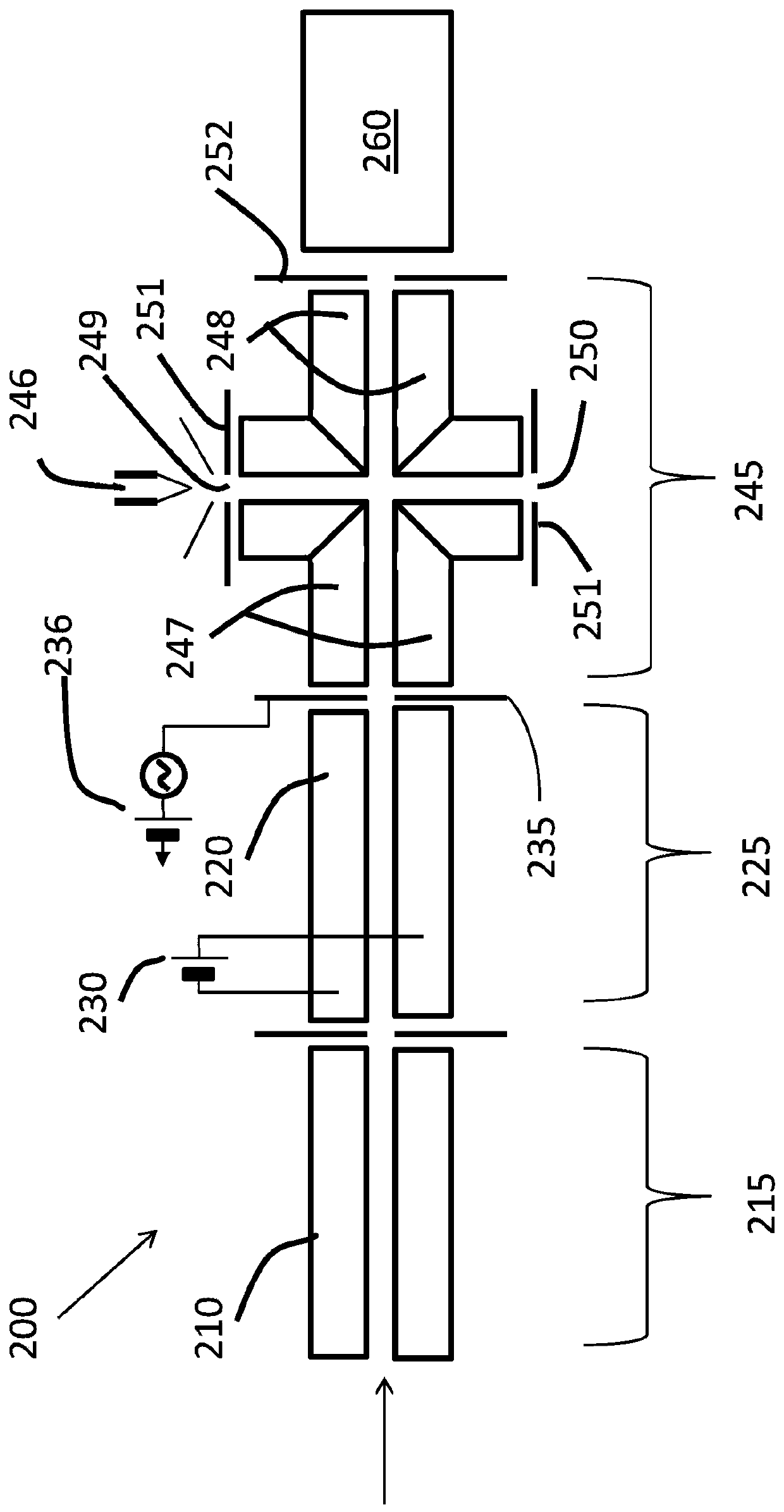
A lens for electron capture dissociation may include: a first electrode and a second electrode spaced apart from each other and arranged along a first direction; and a third electrode and a fourth electrode spaced apart from each other and arranged along a second direction perpendicular to the first direction. The first electrode and the second electrode may be disposed in a space in which a magnetic field is formed in the first direction and trap electrons. The third electrode and the fourth electrode may be in the form of a flat plate and may apply an electric field to the trapped electrons in the second direction.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
Electron capture dissociation apparatus and related methods
An electron capture dissociation apparatus comprises ion guide electrodes, an electron emitter, and an electron control device. The ion guide electrodes are arranged along a central axis and spaced circumferentially to circumscribe an interior space extending along the central axis. The electron emitter is disposed outside the interior space. The electron control device is configured for focusing an electron beam from the electron emitter toward the central axis, along a radial electron beam direction between two of the ion guide electrodes, and for decelerating the electron beam in a DC decelerating field of adjustable voltage potential directed along the electron beam direction.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
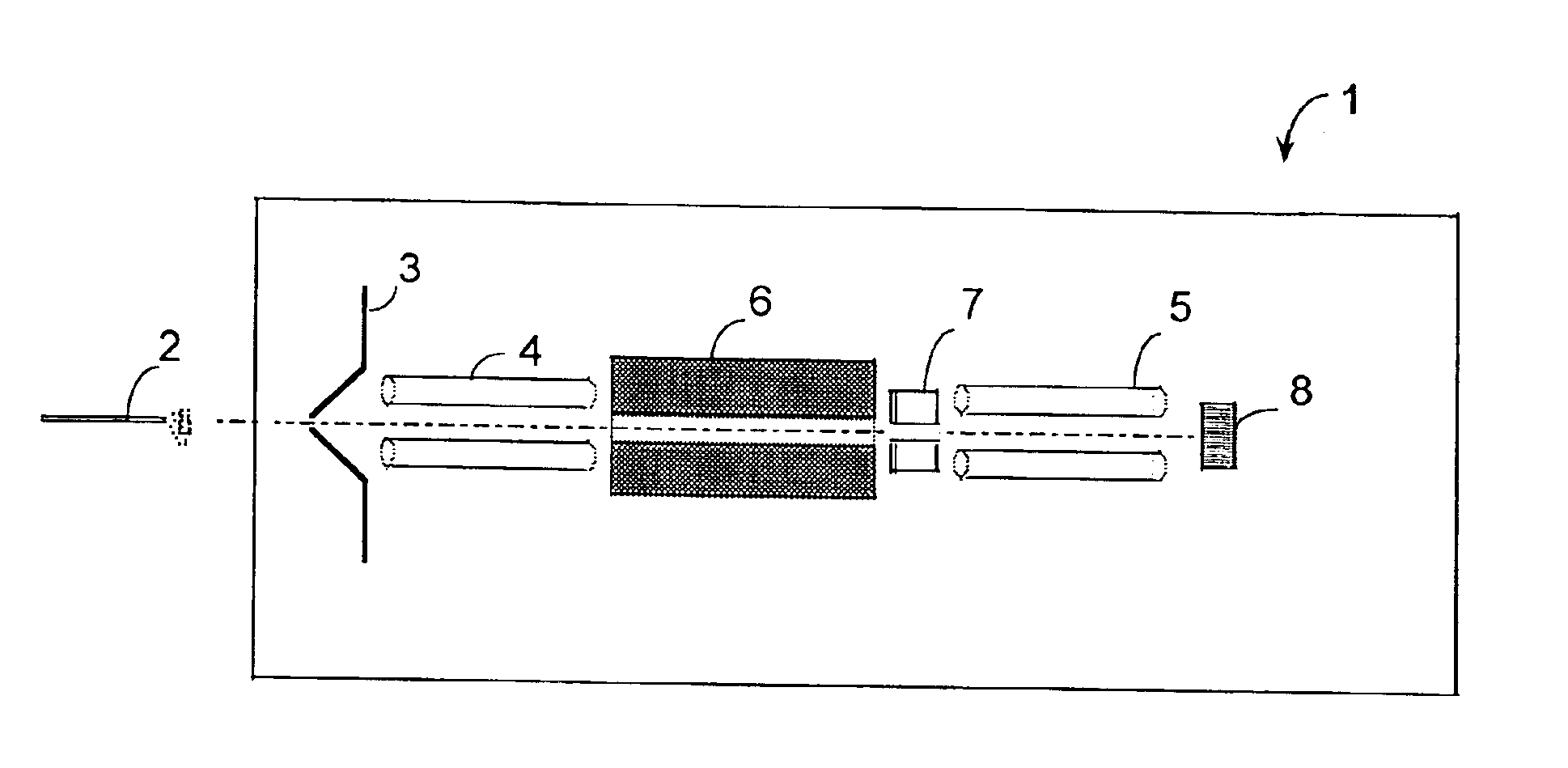
Mass spectroscope and mass spectrometry
ActiveUS8274044B2Easy to detectTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationTime-of-flight mass spectrometryIon dissociation
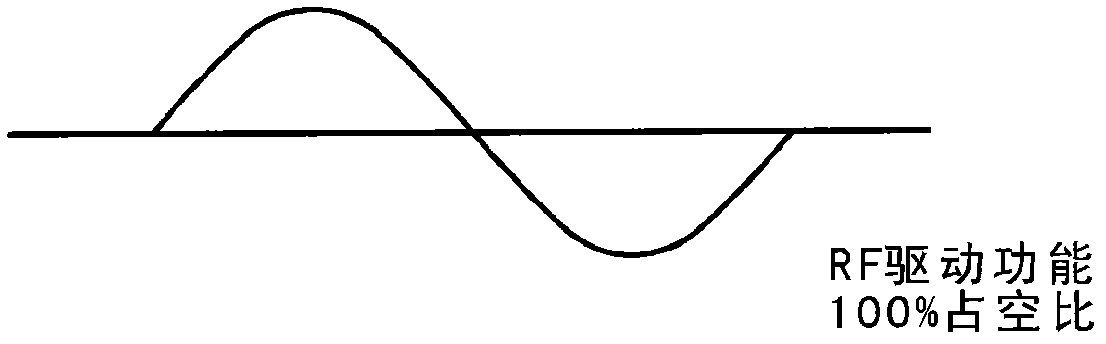
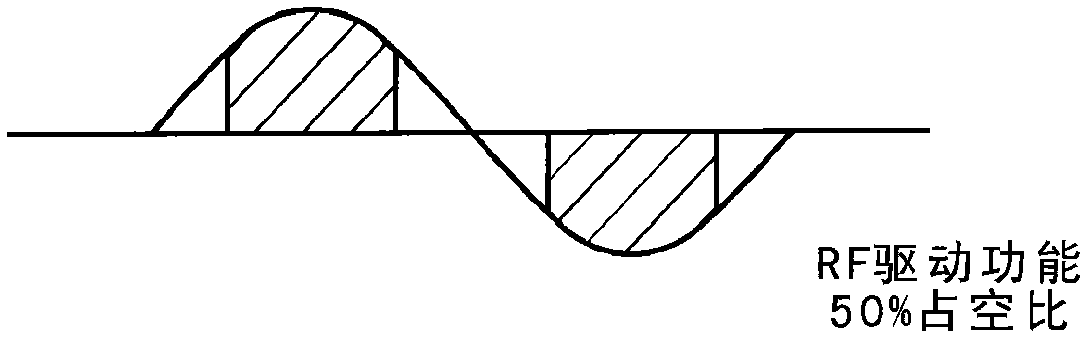
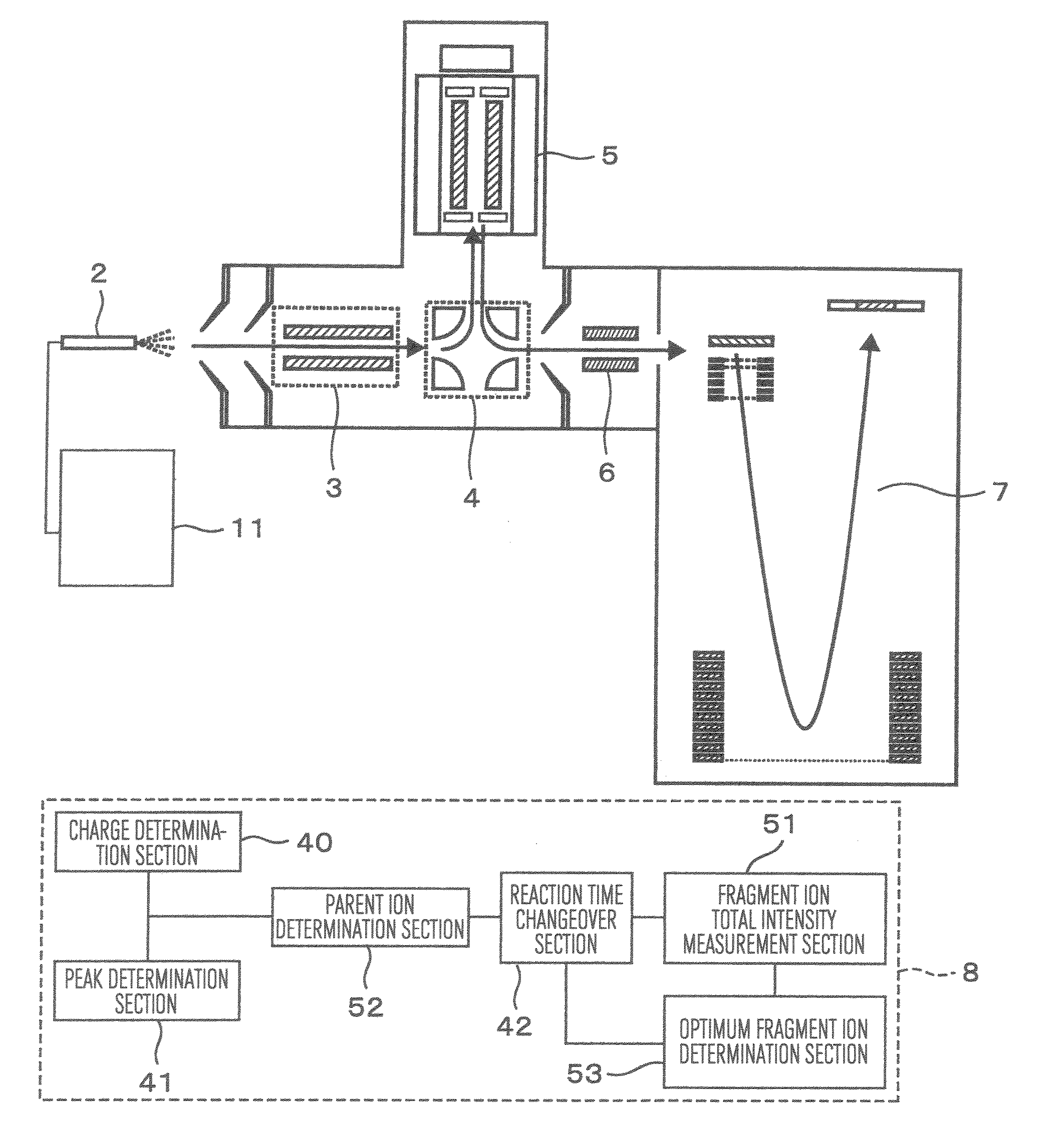
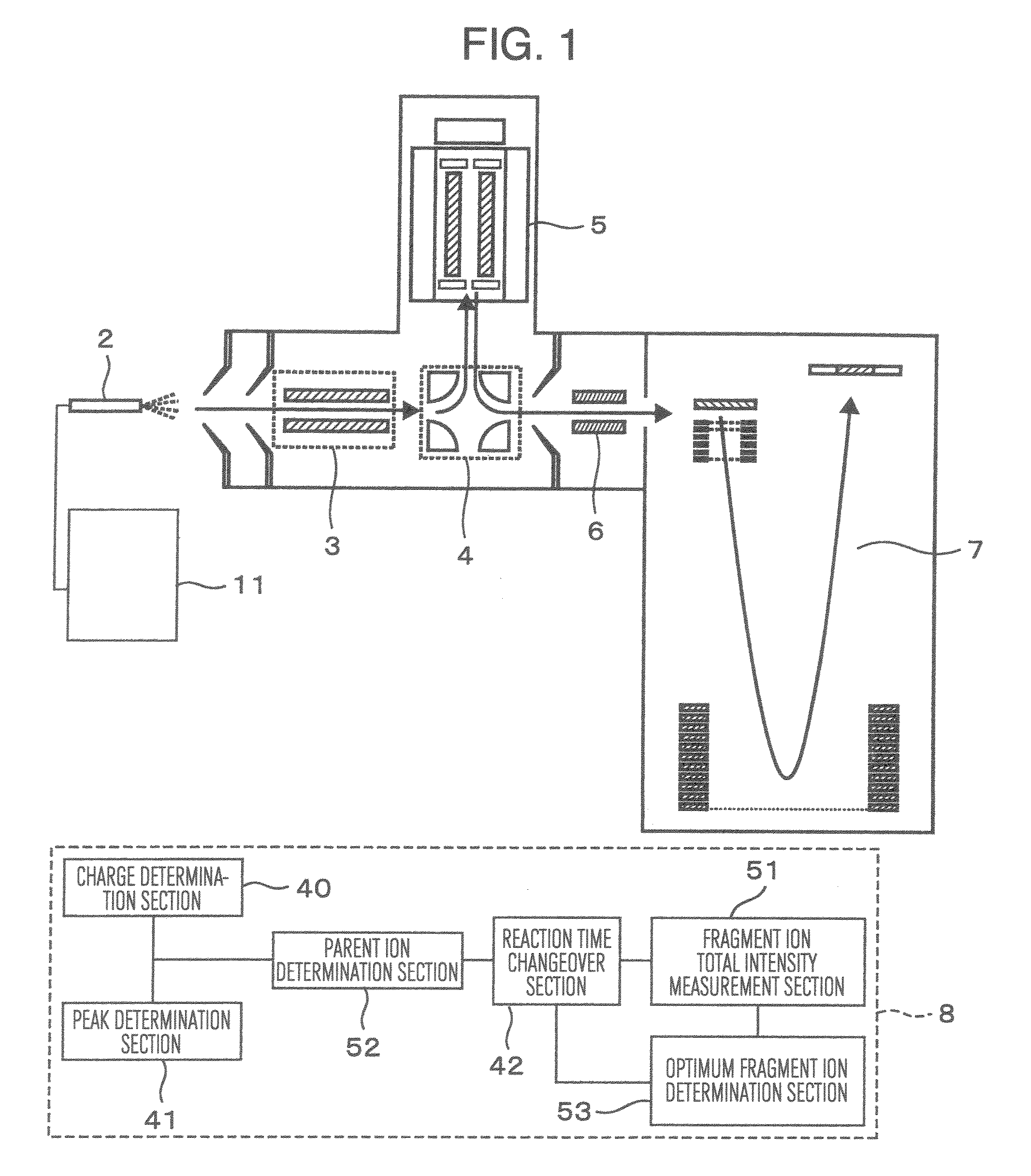
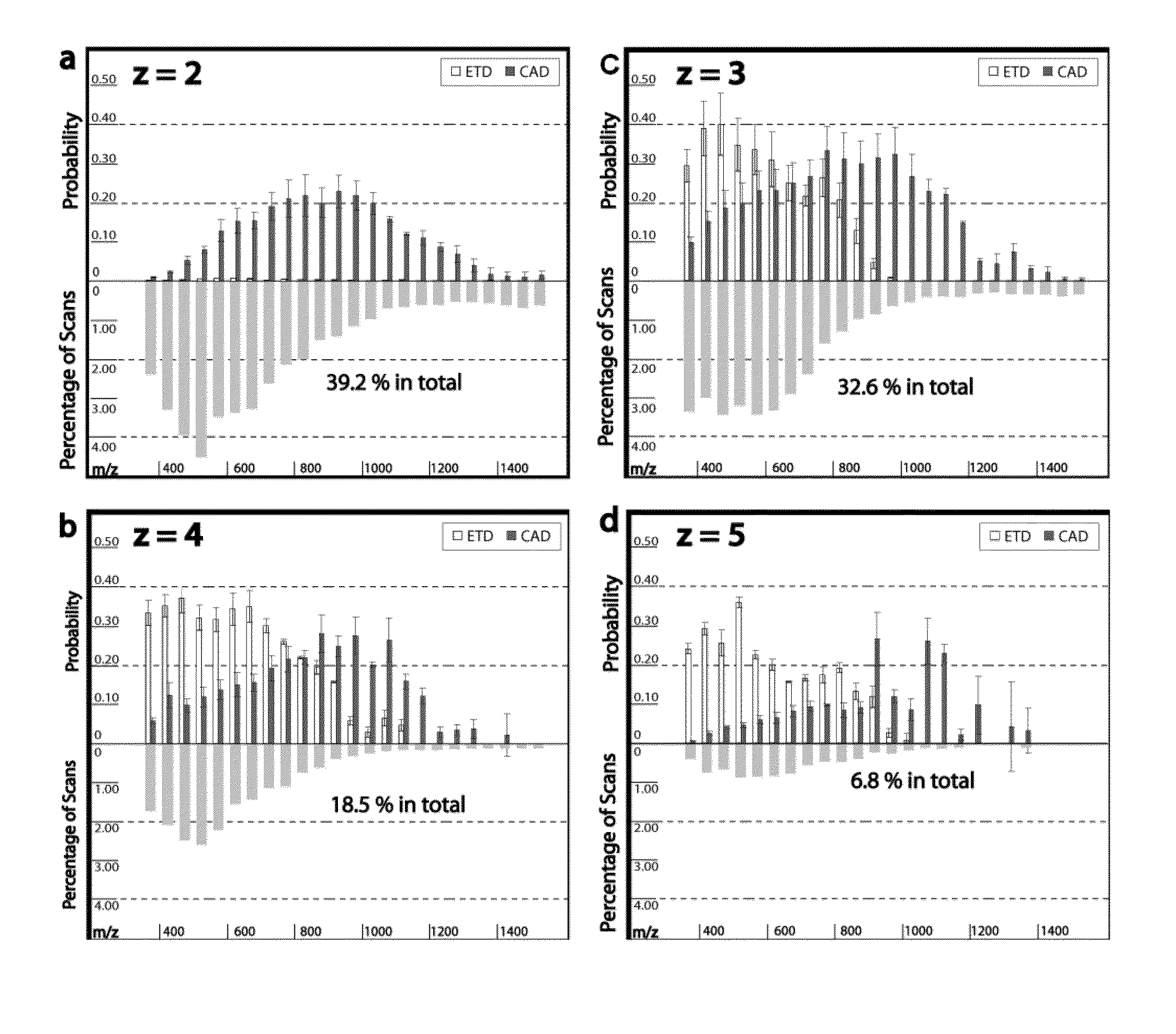
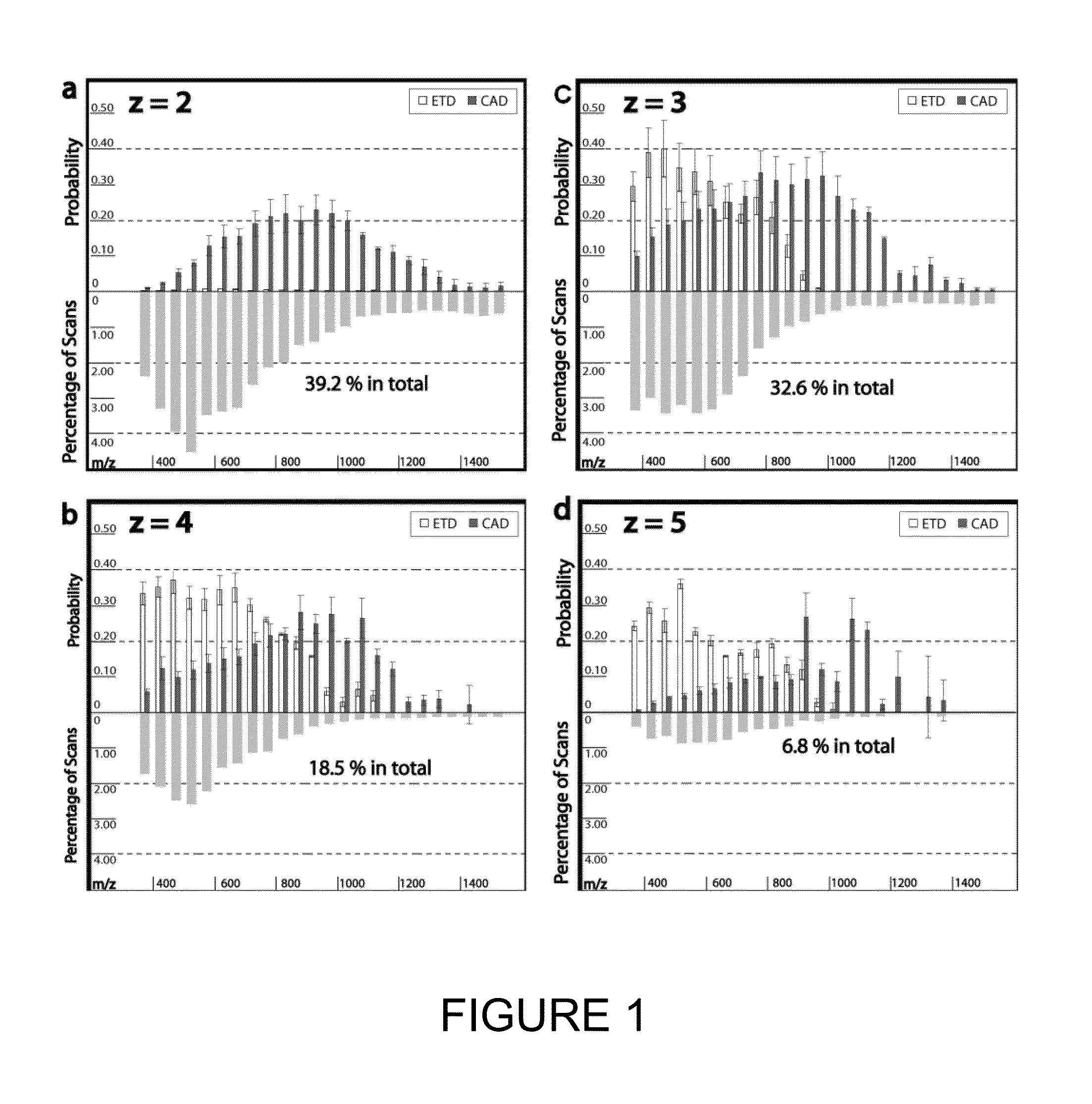
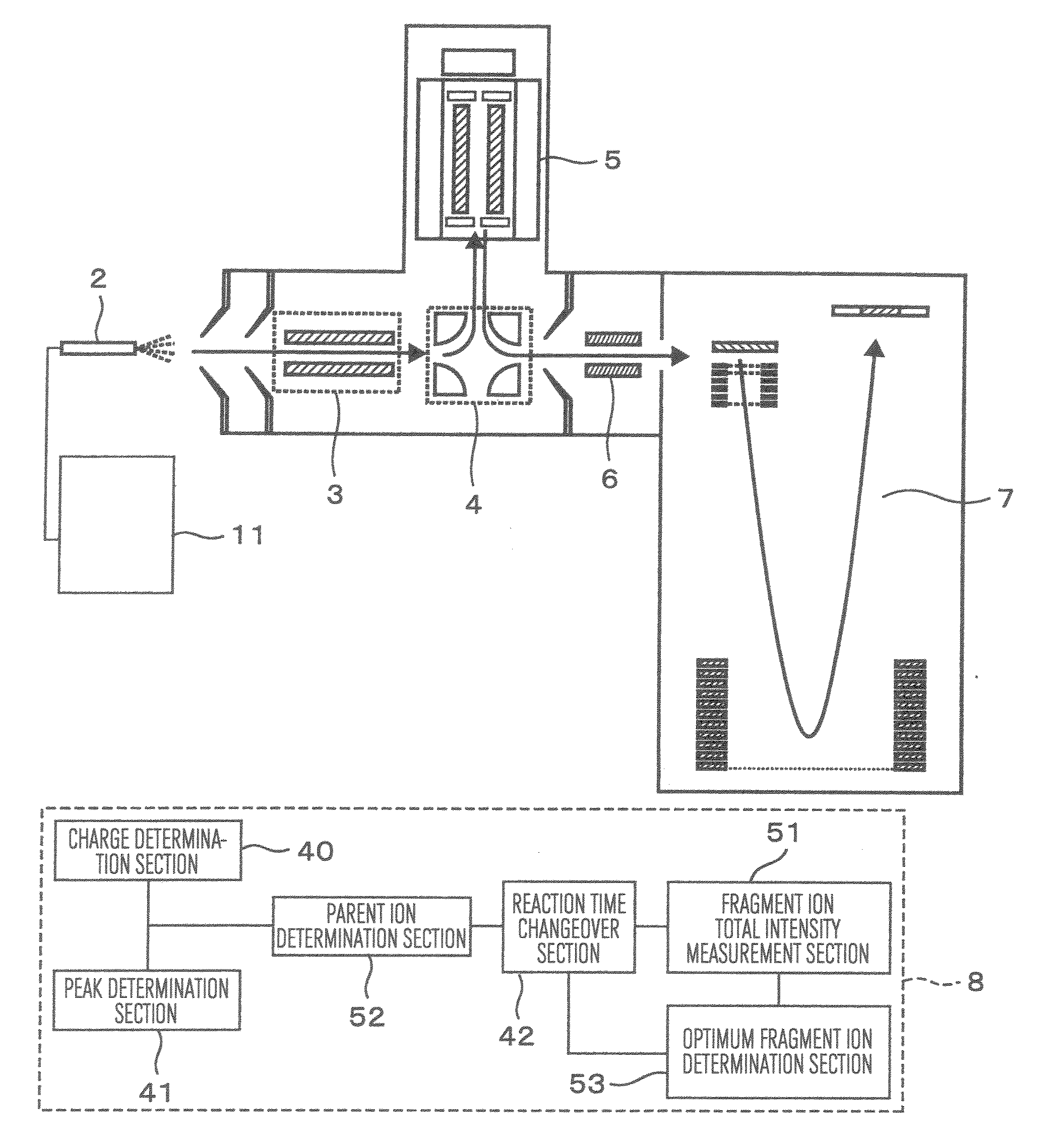
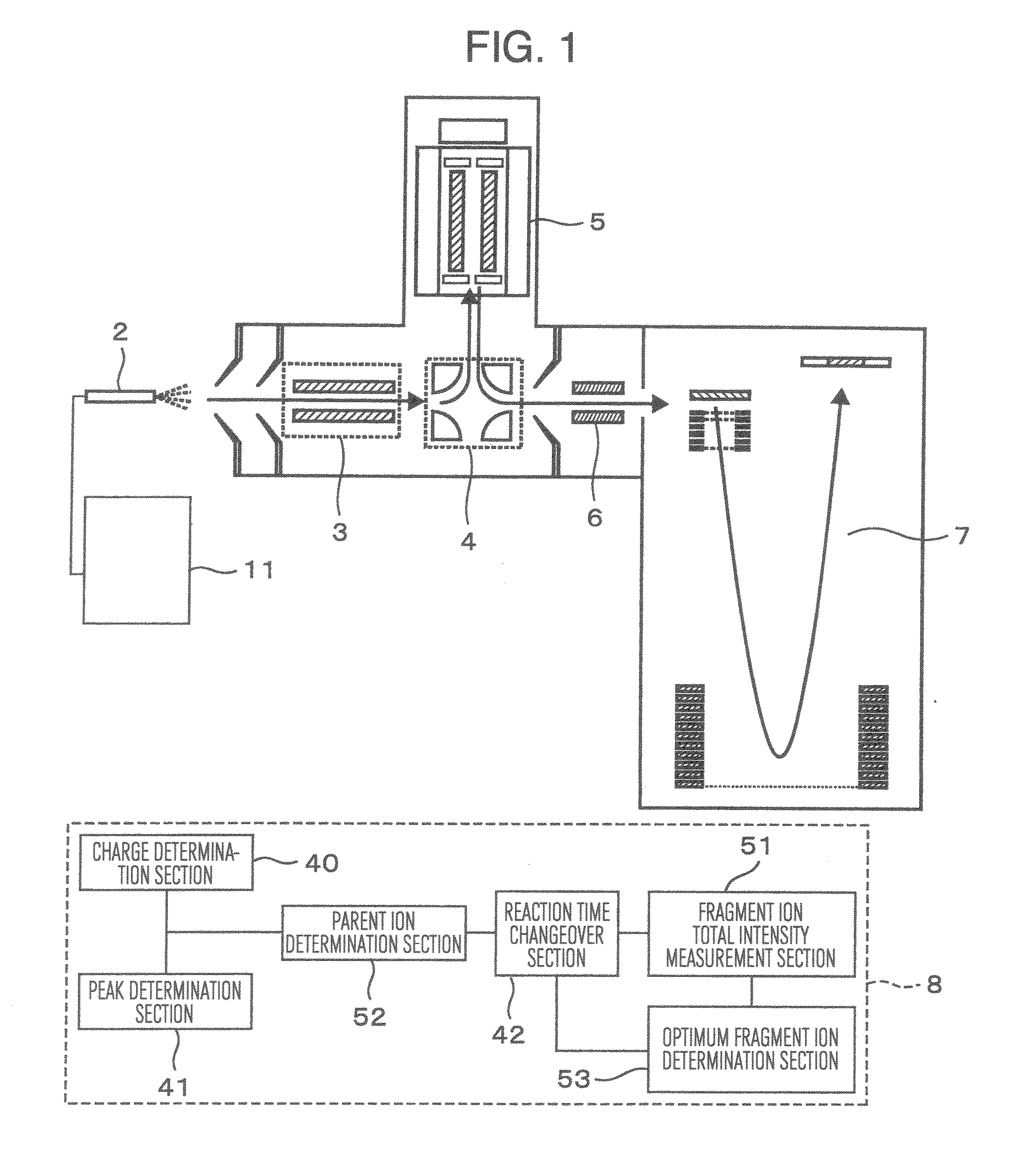
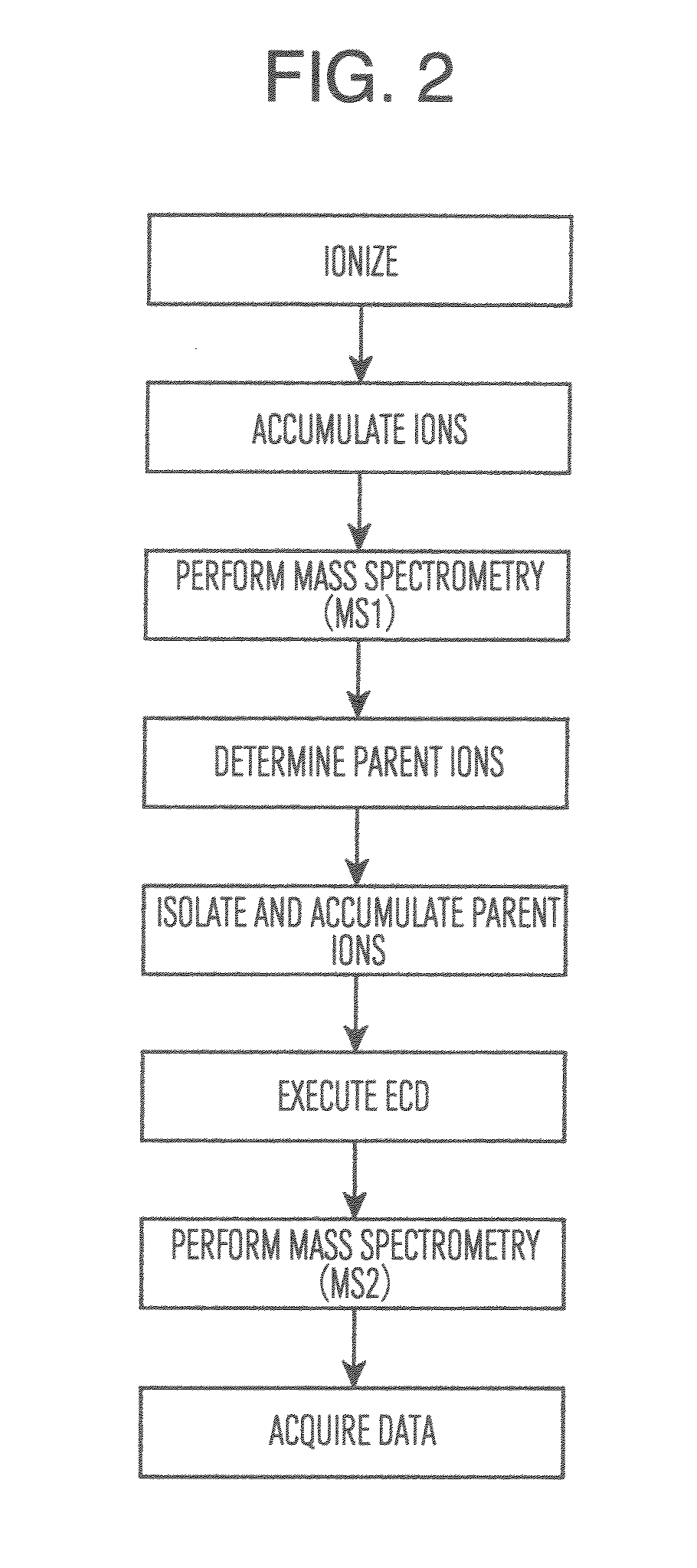
Provided is a mass spectroscope employing electron capture dissociation wherein the peak number of detectable fragment ions is increased. The mass spectroscope comprises an ion source (2) for generating ions from a sample, an ion trap (3) for storing and selecting ions, an ion dissociation section (4) performing electron capture dissociation on ions, and a time-of-flight mass spectrometry section (7) performing mass spectrometry on ions, wherein the reaction time of electron capture dissociation is variable depending on the valence of ions subjected to mass spectrometry.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Anion generating and electron capture dissociation apparatus using cold electrons
InactiveUS9230791B2Stability-of-path spectrometersTube electron sourcesUltravioletField electron emission
An anion generating and electron capture dissociation apparatus using cold electrons, which comprises a cold electron generation module configured to generate a large quantity of cold electrons from ultraviolet photons radiated into a mass spectrometer vacuum chamber which is in a high vacuum state has a plurality of ultraviolet diodes configured to emit the ultraviolet photons in the mass spectrometer vacuum chamber. Micro-channel plate (MCP) electron multiplier plates induce and amplify initial electron emissions of the ultraviolet photons from the ultraviolet diodes, and generate a large quantity of electron beams from a rear plate. An electron focusing lens is configured to focus the electron beams amplified through the MCP electron multiplier plates. A grid is configured to adjust energy and an electric current of the electron beams together with the electron focusing lens.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
Labeling peptides with tertiary amines and other basic functional groups for improved mass spectrometric analysis
ActiveUS8592216B2Improve fragmenting characteristicRaise the basicityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesHighly charged ionGas phase
The present invention provides methods for enhancing the fragmentation of peptides for mass spectrometry by modifying the peptides with a tagging reagent containing a functional group, such as a tertiary amine, having a greater gas-phase basicity than the amide backbone of the peptide. These high gas-phase basicity functional groups are attached to a peptide by reacting the tagging reagent to one or more available carboxylic acid groups of the peptide. Linking these high gas-phase functional groups to the peptides leads to higher charge state ions from electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), which fragment more extensively during fragmentation techniques, particularly non-ergodic fragmentation techniques such as electron capture dissociation (ECD) and electron transfer dissociation (ETD).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Mass spectroscope and mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20110121174A1Increase number of detectable peakEasy to detectIsotope separationMass spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryTime-of-flight mass spectrometry
Provided is a mass spectroscope employing electron capture dissociation wherein the peak number of detectable fragment ions is increased. The mass spectroscope comprises an ion source (2) for generating ions from a sample, an ion trap (3) for storing and selecting ions, an ion dissociation section (4) performing electron capture dissociation on ions, and a time-of-flight mass spectrometry section (7) performing mass spectrometry on ions, wherein the reaction time of electron capture dissociation is variable depending on the valence of ions subjected to mass spectrometry.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method of MS/MS mass spectrometry
ActiveUS9337005B2Increase atmospheric pressureSamples introduction/extractionSpecific reaction combinationsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass
A method of mass spectrometry is disclosed comprising alternating between a first mode in which parent ions are mass analyzed and a second mode in which the parent ions are subjected to Electron Capture Dissociation (“ECD”) at atmospheric pressure so as to produce fragment ions which are then mass analyzed. The parent ions are associated with their fragment ions based on the times at which they were detected. This method enables parent ions to be associated with their fragment ions, even when the ECD fragmentation is performed at atmospheric pressure.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Mass spectrometric ion storage device for different mass ranges
ActiveUS20140367566A1High yieldElectron/ion optical arrangementsIon sources/gunsQuadrupole fieldAnalyte
The invention relates to devices and methods for the storage of ions in mass spectrometers. The invention proposes the generation and superposition of two multipole fields of different order, independent of each other, in an RF multipole rod system. In an embodiment with eight pole rods, for example, it is thus possible to jointly store low-energy electrons in a central RF quadrupole field, which effectively acts only on electrons and holds them together radially, on the one hand, and multiply charged heavy positive ions in an RF octopole field, which effectively acts only on the ions, on the other hand, in order to fragment the positive ions by electron capture dissociation (ECD). In a different embodiment, multiply charged positive analyte ions and suitable negative reactant ions can react with each other in an octopole field by electron transfer dissociation (ETD) with a high fragmentation yield, and the fragment ions can subsequently be bundled by a transition to a quadrupole field to form a fine ion beam, which can leave the multipole rod system axially. A mixture of hexapole and dodecapole systems is also possible.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
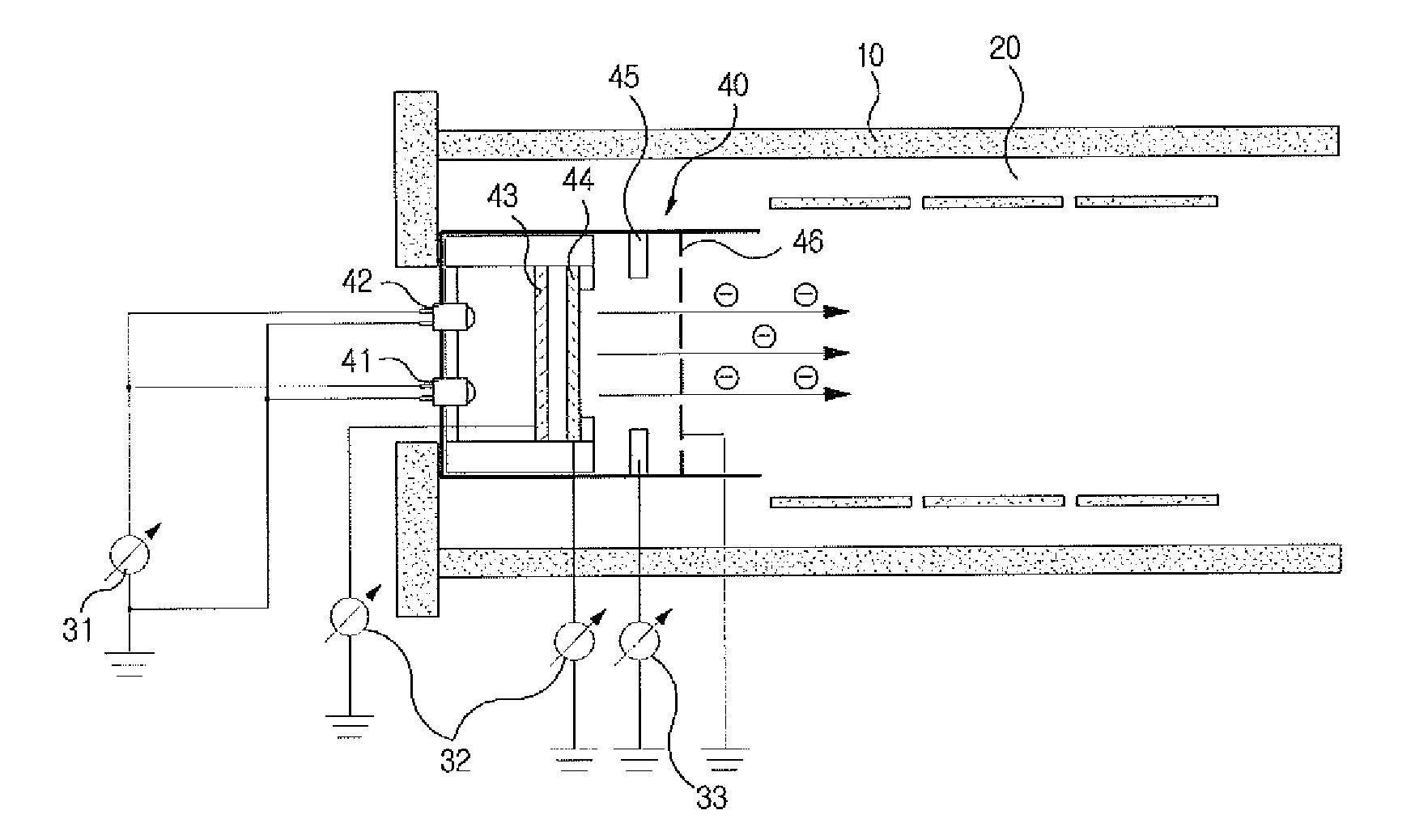
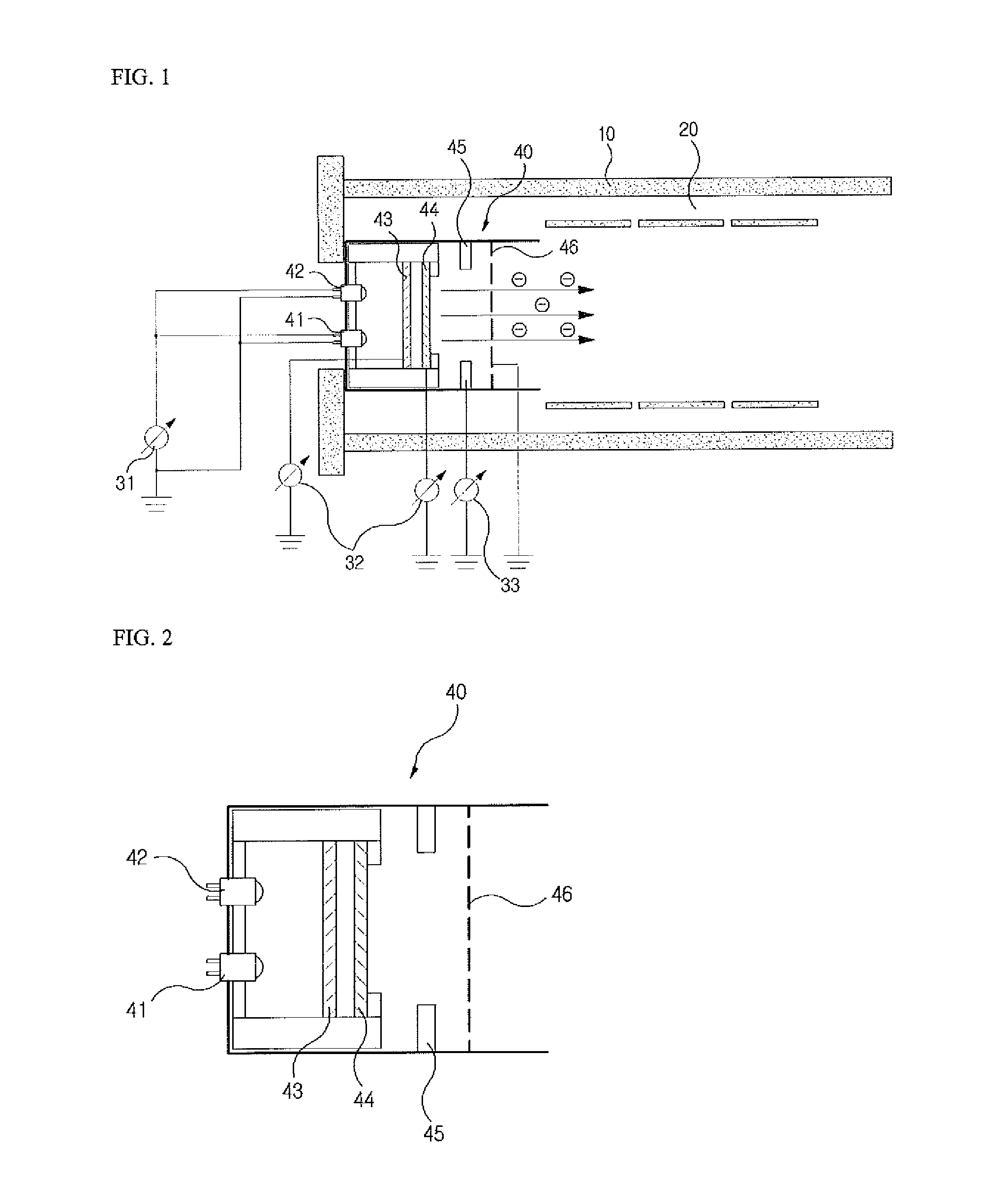
Electron beam throttling for electron capture dissociation
PendingCN112823407ASpectrometer circuit arrangementsElectron/ion optical arrangementsElectron sourceElectron flow
In one aspect, an electron-ion reaction module, e.g., an electron capture dissociation module, for use in a mass spectrometer is disclosed, which comprises a chamber, an electron source for generating electrons and introducing the electrons into the chamber, a gate electrode positioned relative to the electron source and the chamber, and a DC voltage source operatively coupled to the gate electrode for applying control voltages to the gate electrode. The electron-ion interaction module can further include a controller operably coupled to the DC voltage source and configured for adjusting the DC voltage applied to the gate electrode to adjust flow of electrons into the chamber.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Lens for electron capture dissociation, Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer comprising the same and method for improving signal of Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer
InactiveUS9129788B2Enhanced signalIncrease collisionElectron/ion optical arrangementsParticle spectrometer methodsElectron-capture dissociationSpectrometer
A lens for electron capture dissociation may include: a first electrode and a second electrode spaced apart from each other and arranged along a first direction; and a third electrode and a fourth electrode spaced apart from each other and arranged along a second direction perpendicular to the first direction. The first electrode and the second electrode may be disposed in a space in which a magnetic field is formed in the first direction and trap electrons. The third electrode and the fourth electrode may be in the form of a flat plate and may apply an electric field to the trapped electrons in the second direction.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
Apparatus and method for glycopeptide analysis
ActiveCN110870043AStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer circuit arrangementsMass analyzerGlycopeptide
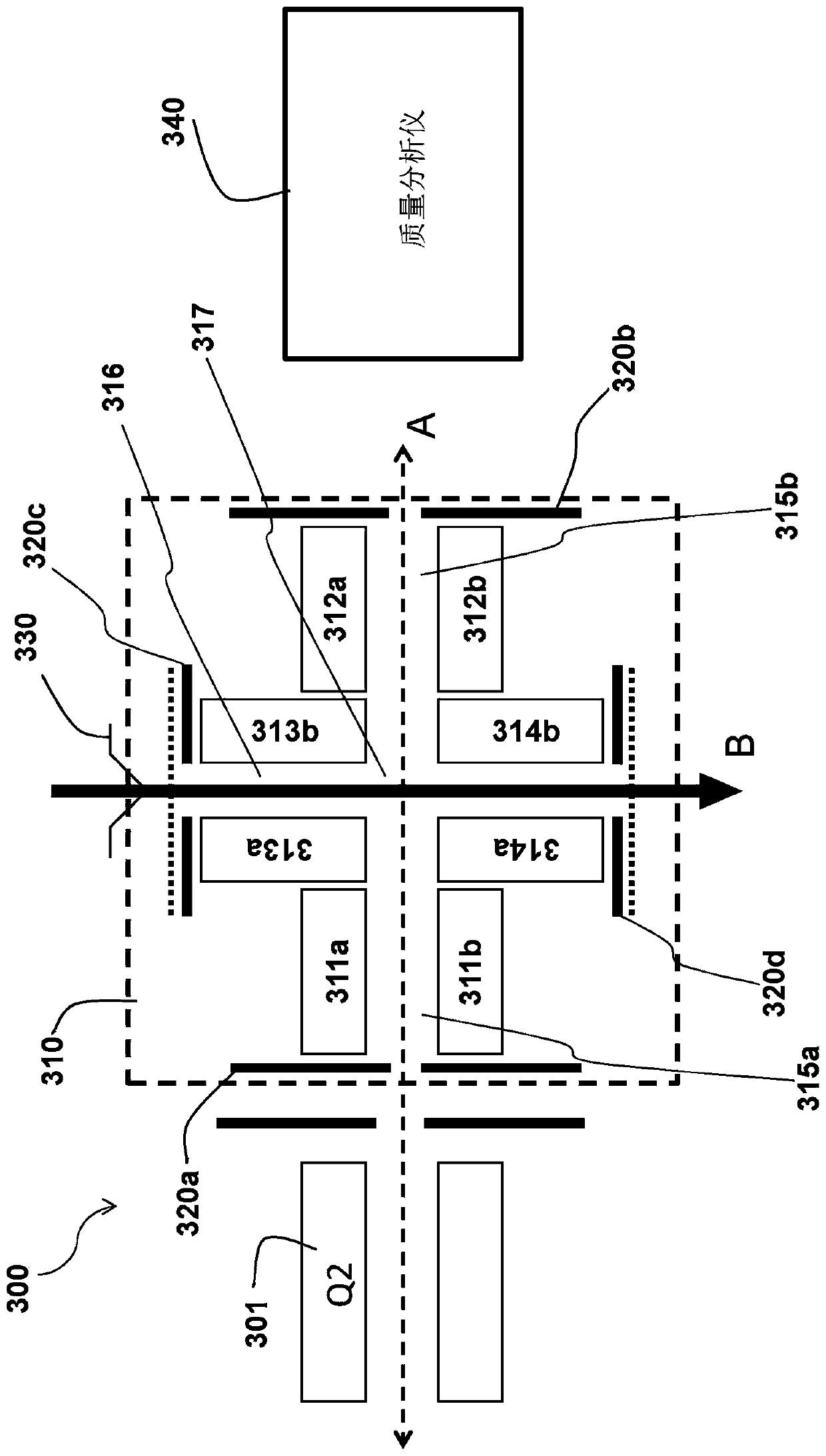
A system and method is described for characterizing glycopeptides which includes a first quadrupole mass filter, a multipole rod set of an ion guide, a lens electrode, an ExD device and a mass analyzer. The multipole rod set is adapted to receive a radial radio frequency (RF) trapping voltage and a radial dipole direct current (DC) voltage. The lens electrode is adapted to receive an axial trapping alternating current (AC) voltage and a DC voltage. The ExD device performs electron capture dissociation or electron transfer dissociation, the ExD device being positioned so that an entrance of theExD device is disposed on the other side of the lens electrode opposite the multipole rod set. The mass analyzer is positioned at an exit of the ExD device for receiving ions from the ExD device.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com