Patents
Literature
78 results about "Self aware" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
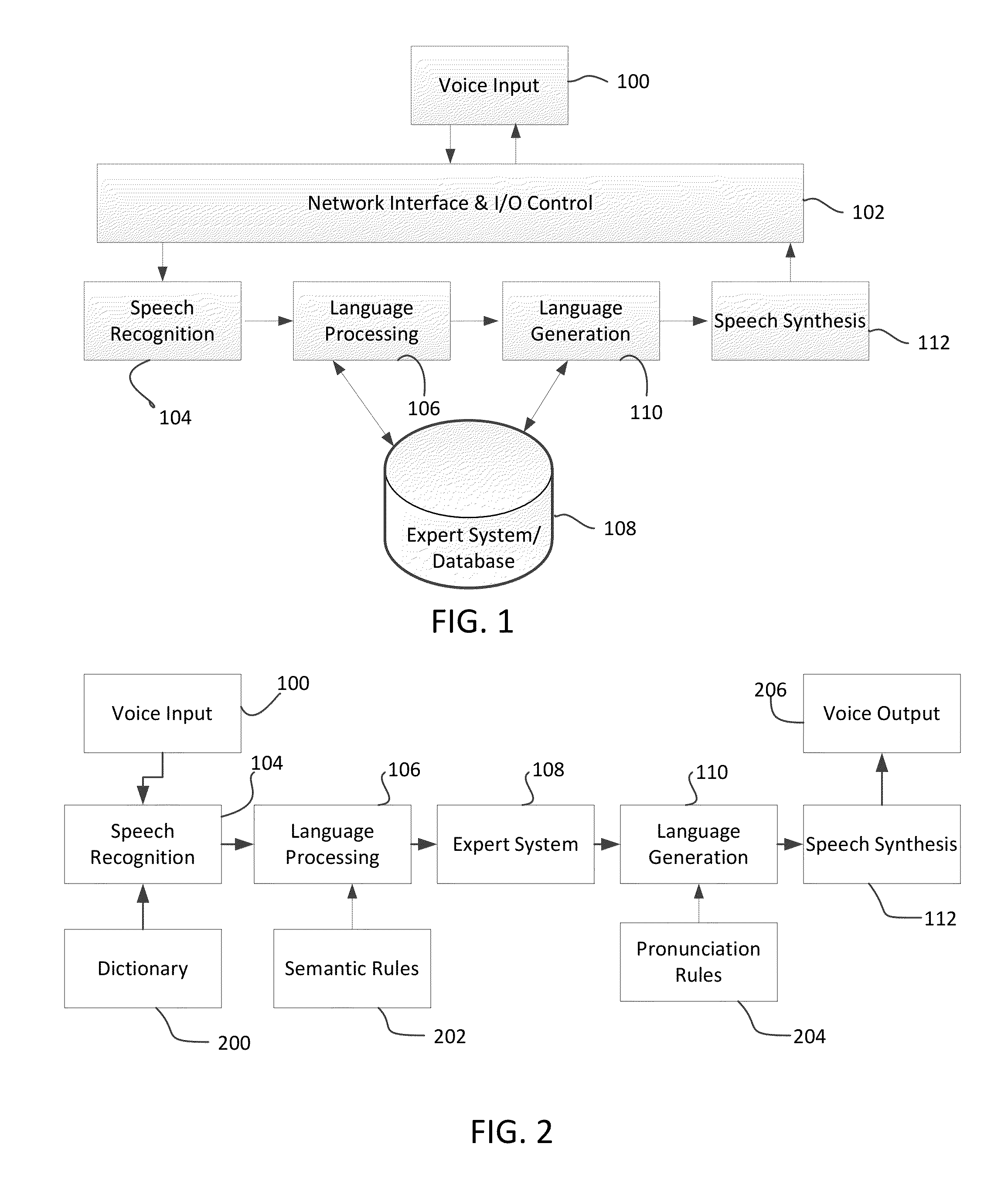
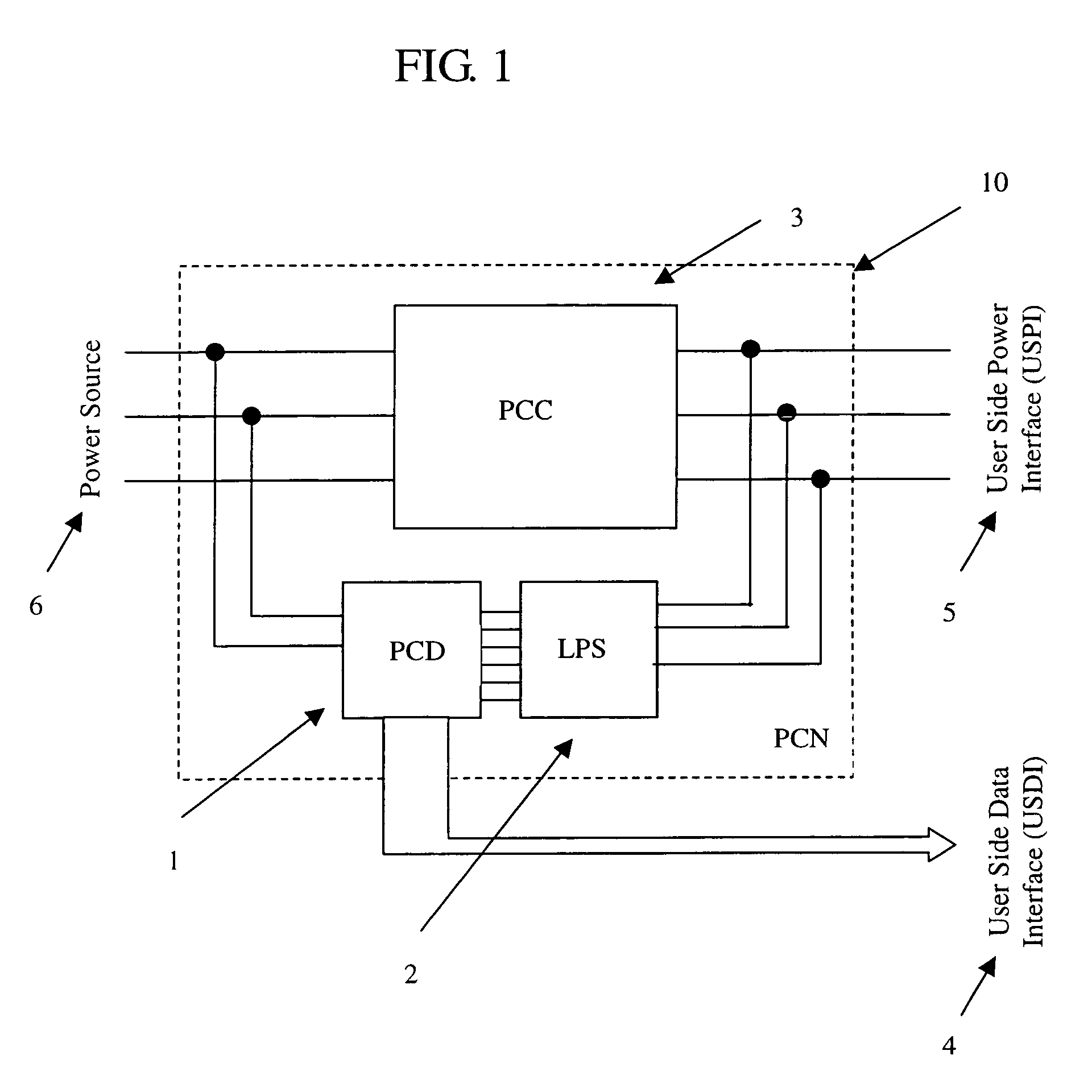
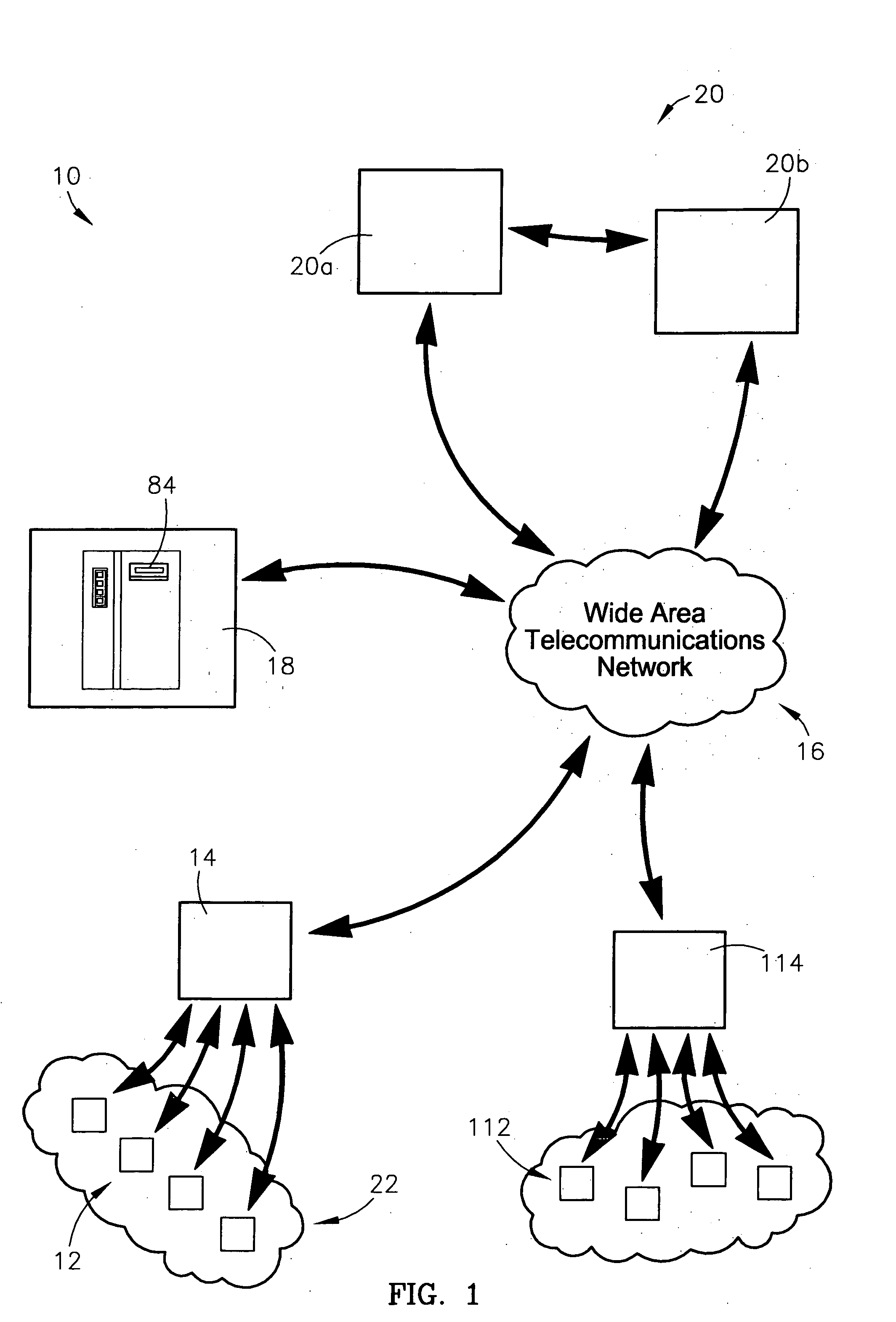
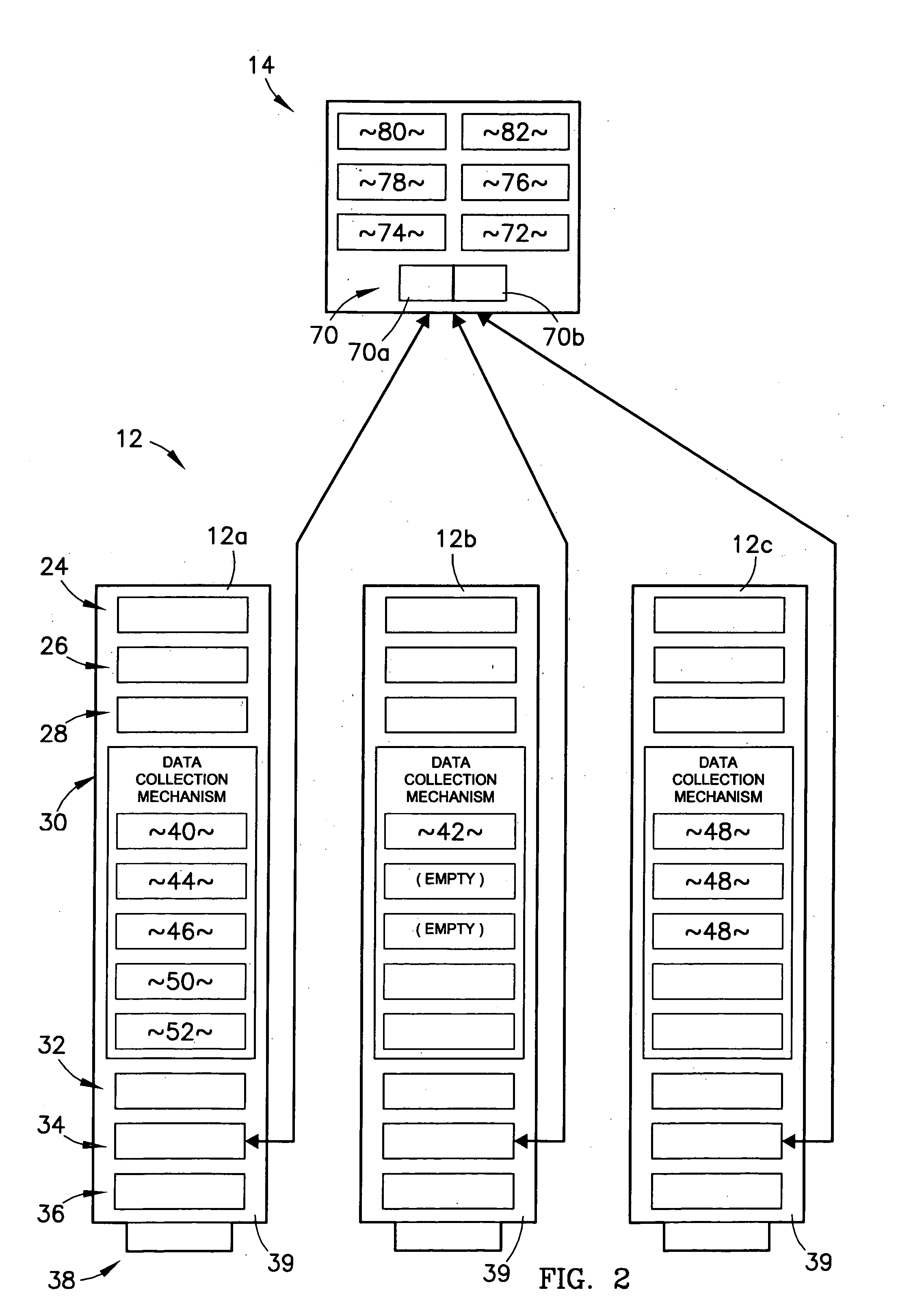
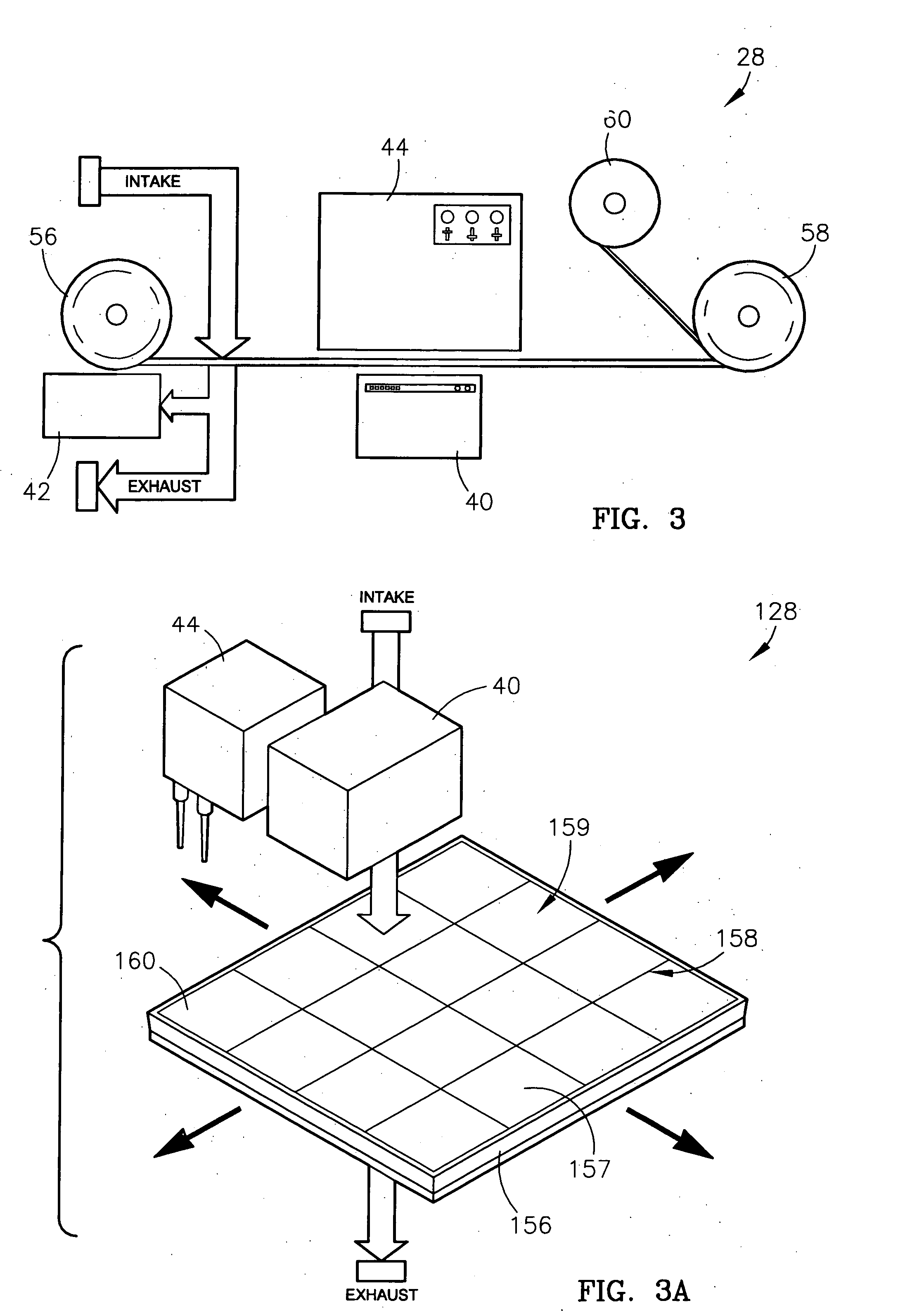
System and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating presence of substance
ActiveUS20120030130A1Rapid deploymentEliminates exposure riskComponent separationDigital data processing detailsRadioactive agentComputer science
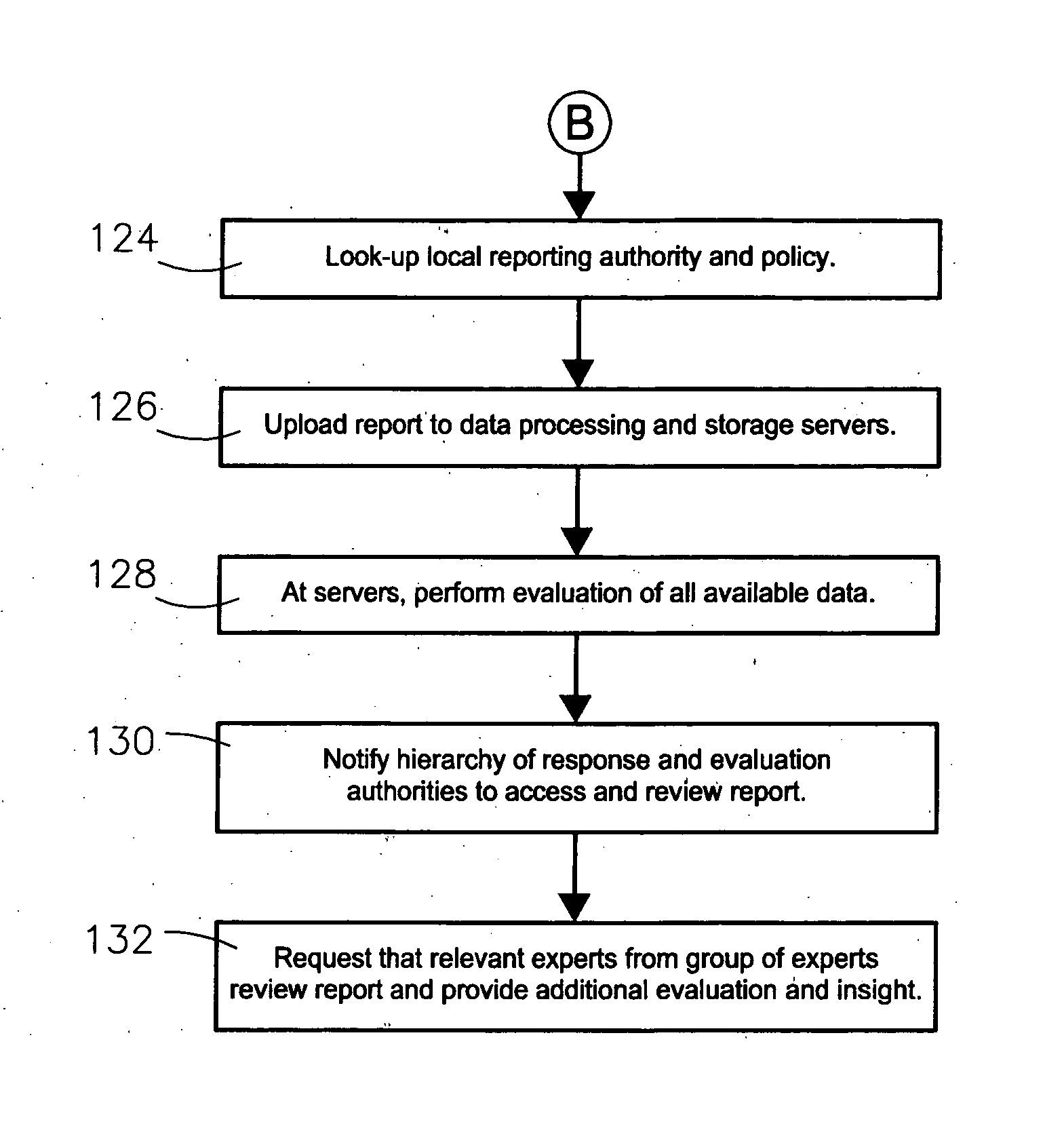
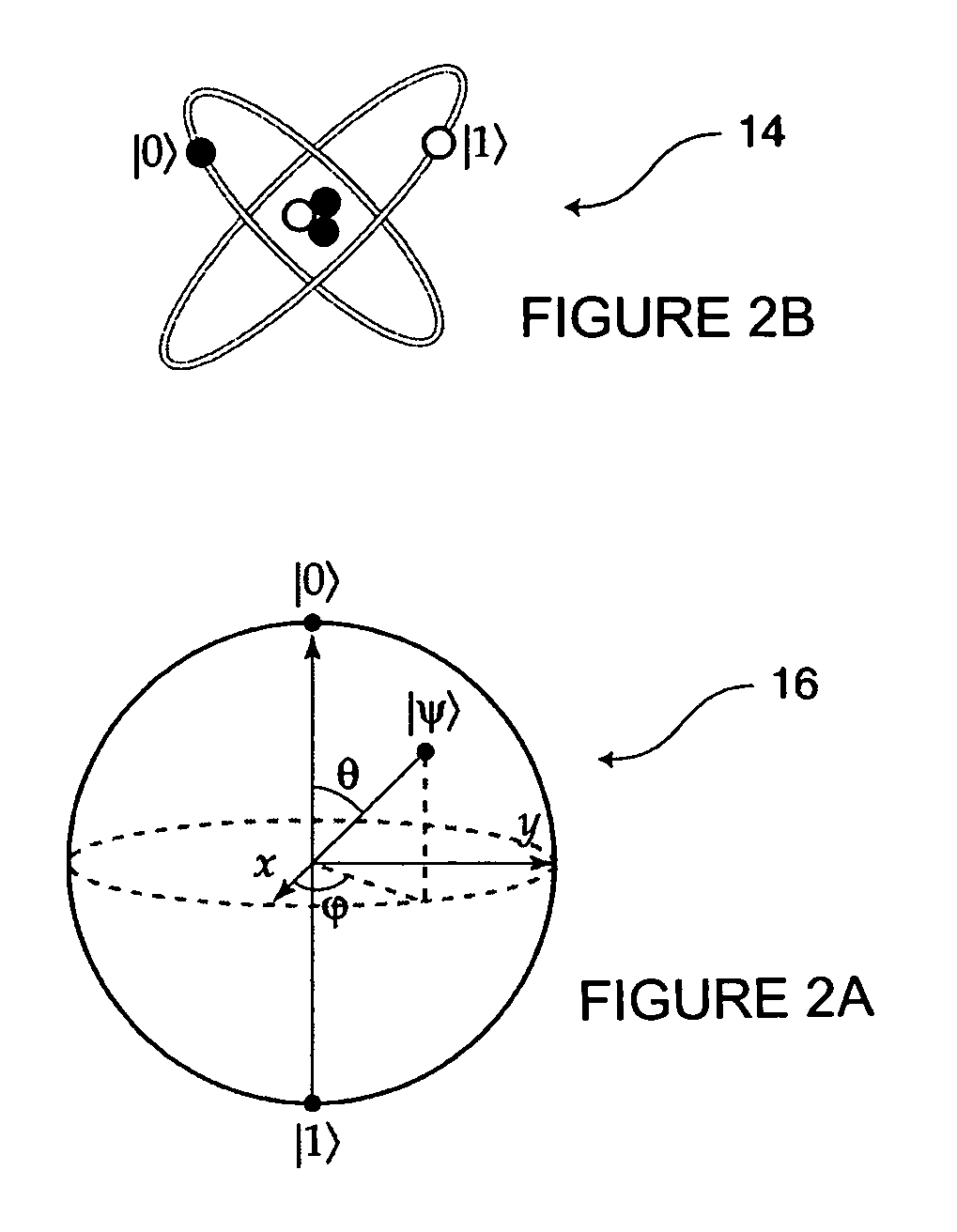
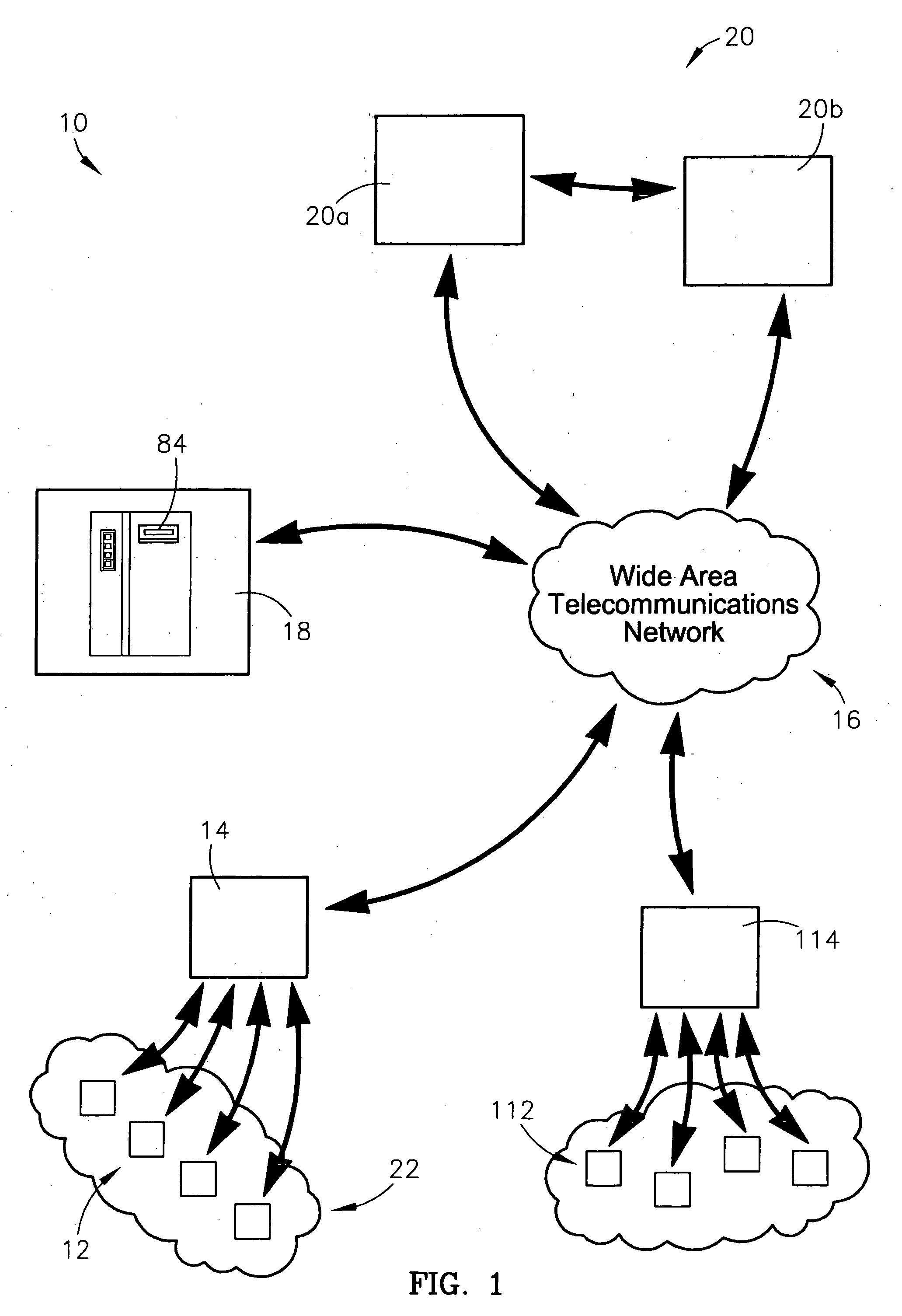
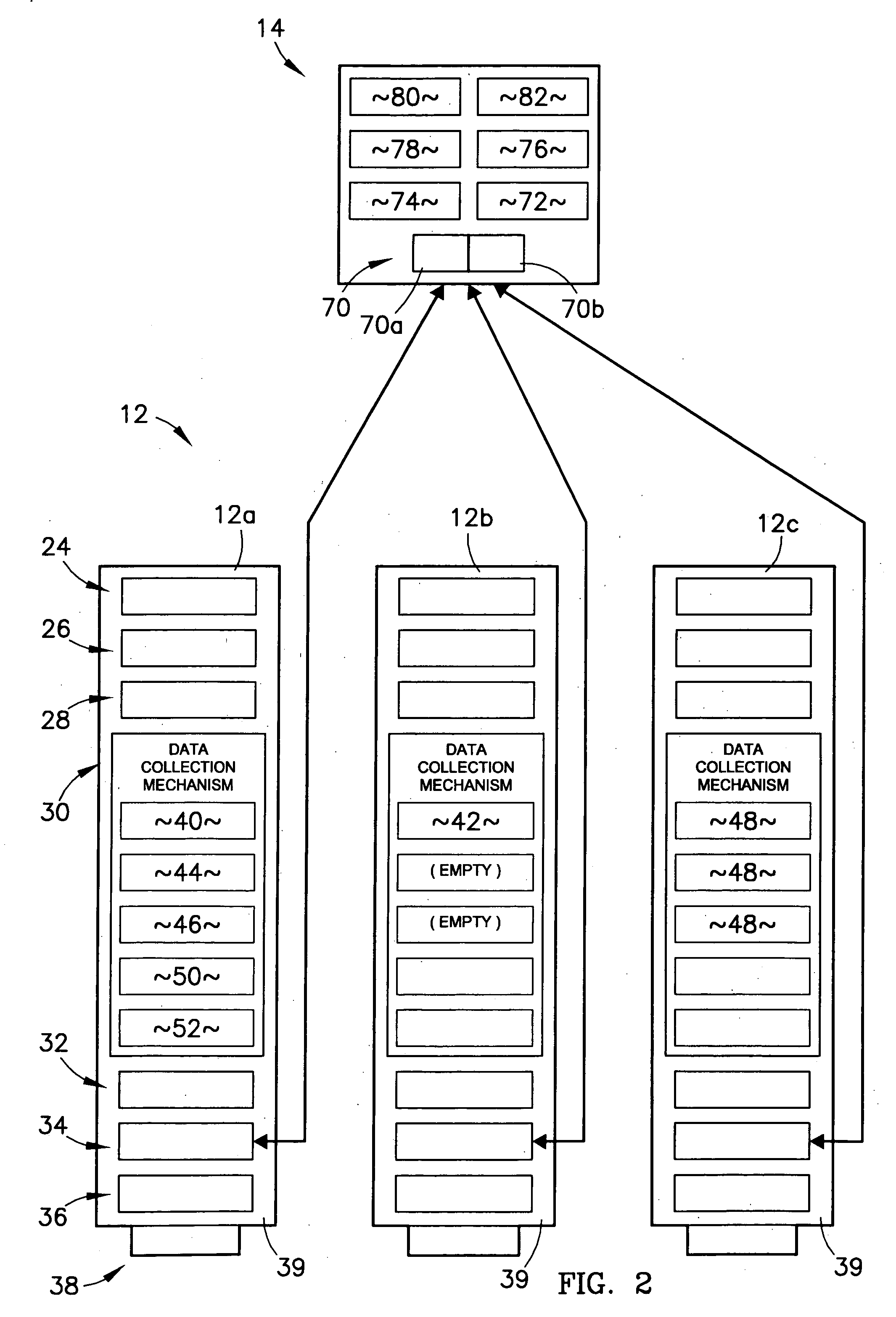
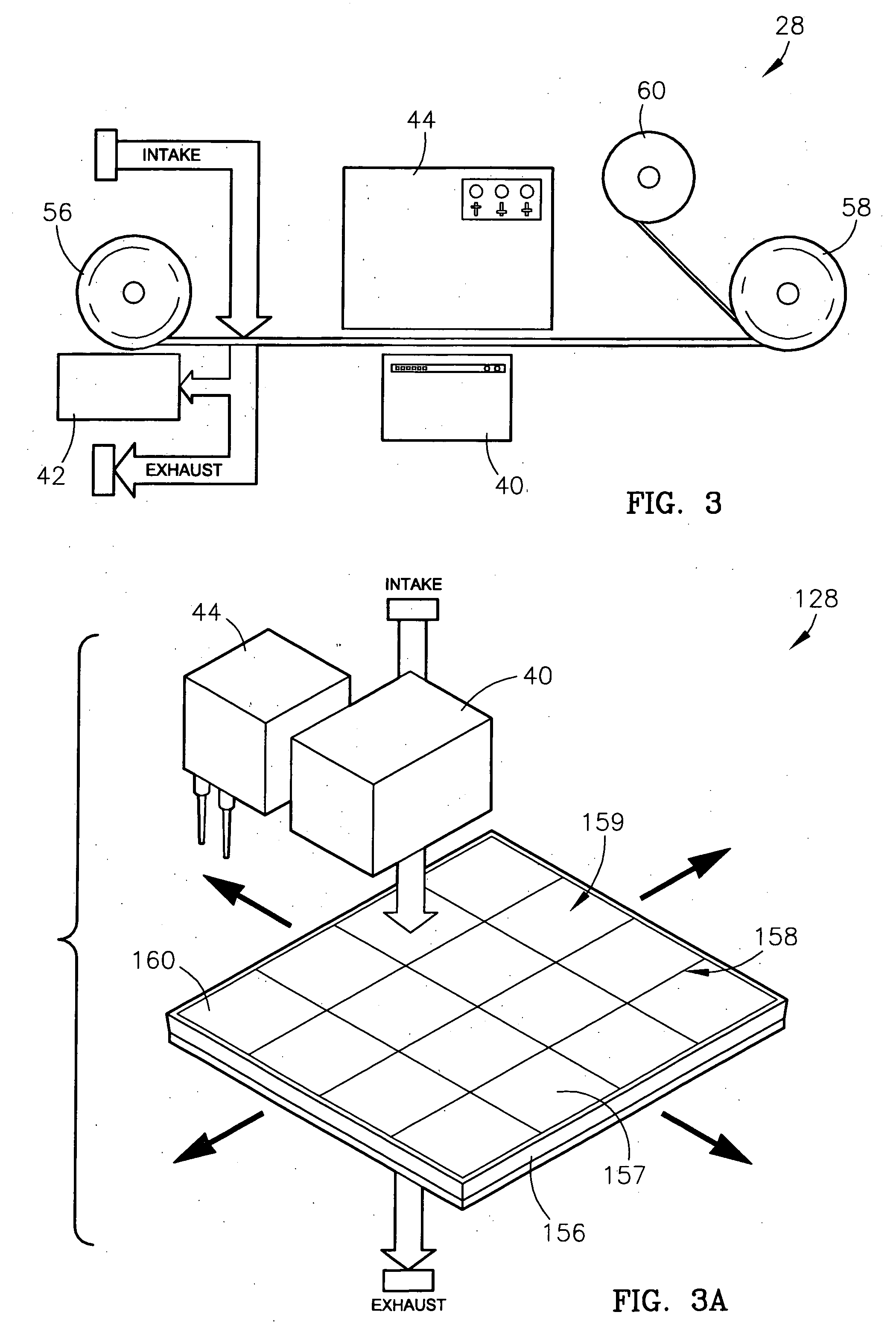
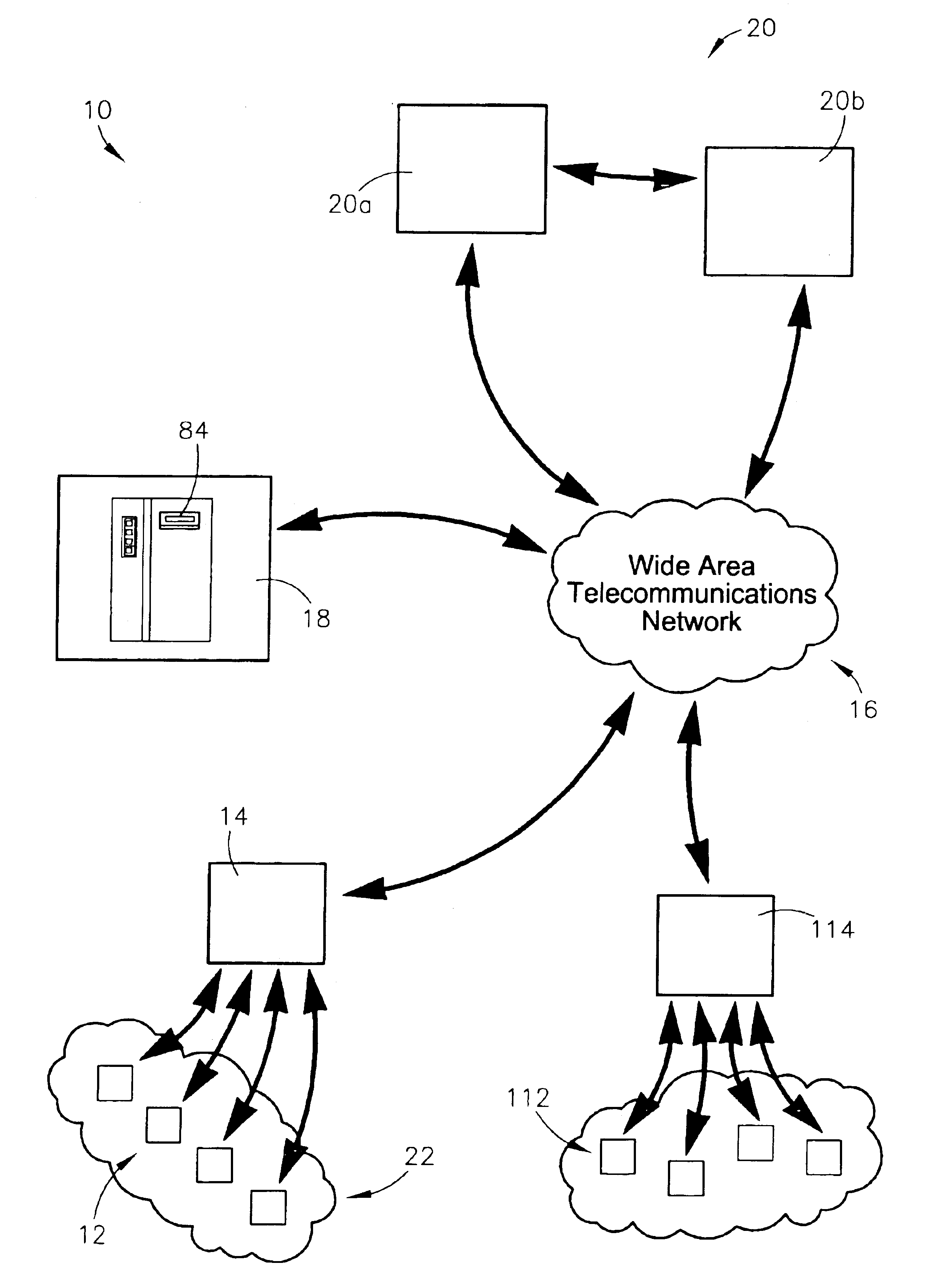
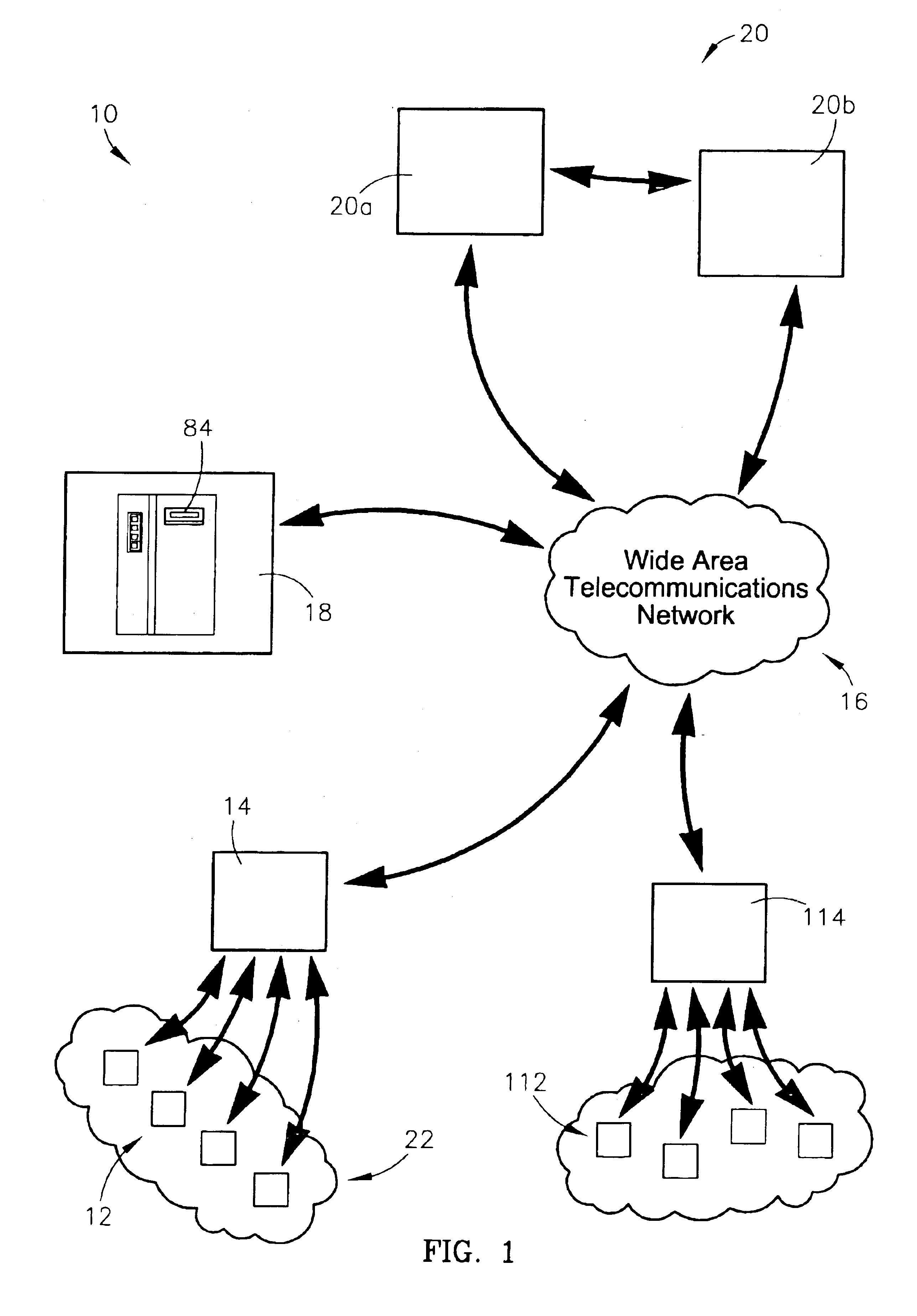
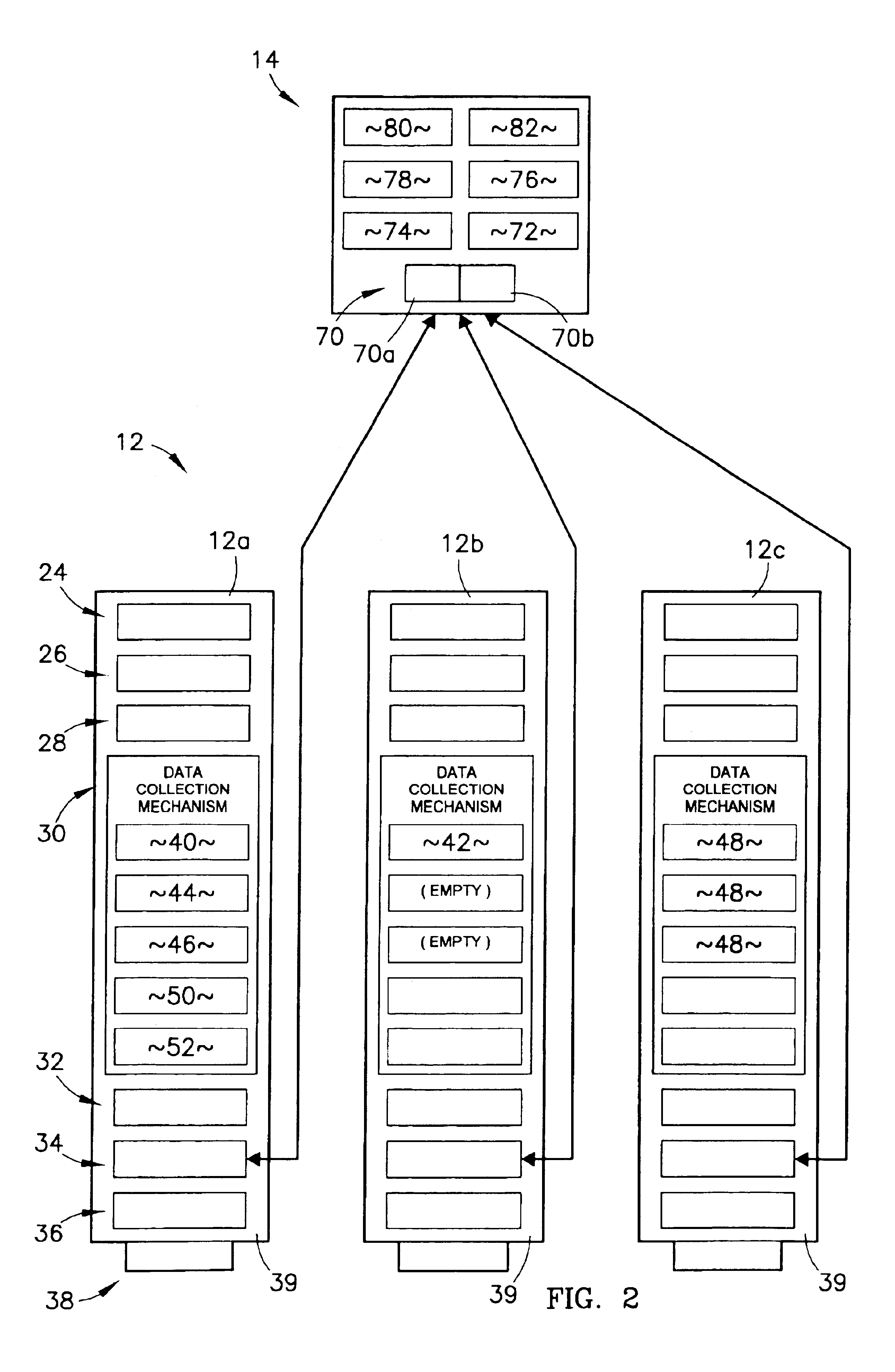
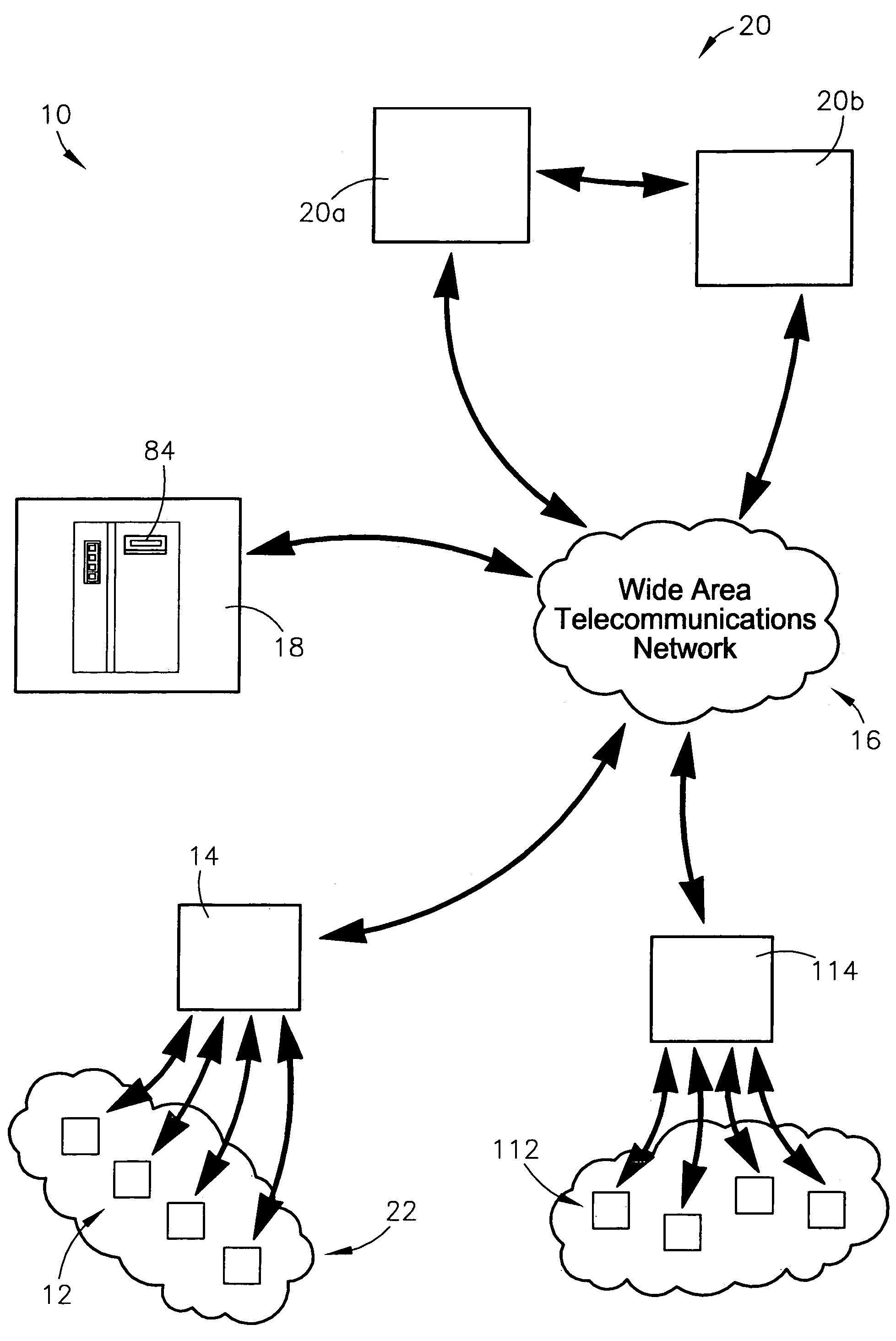
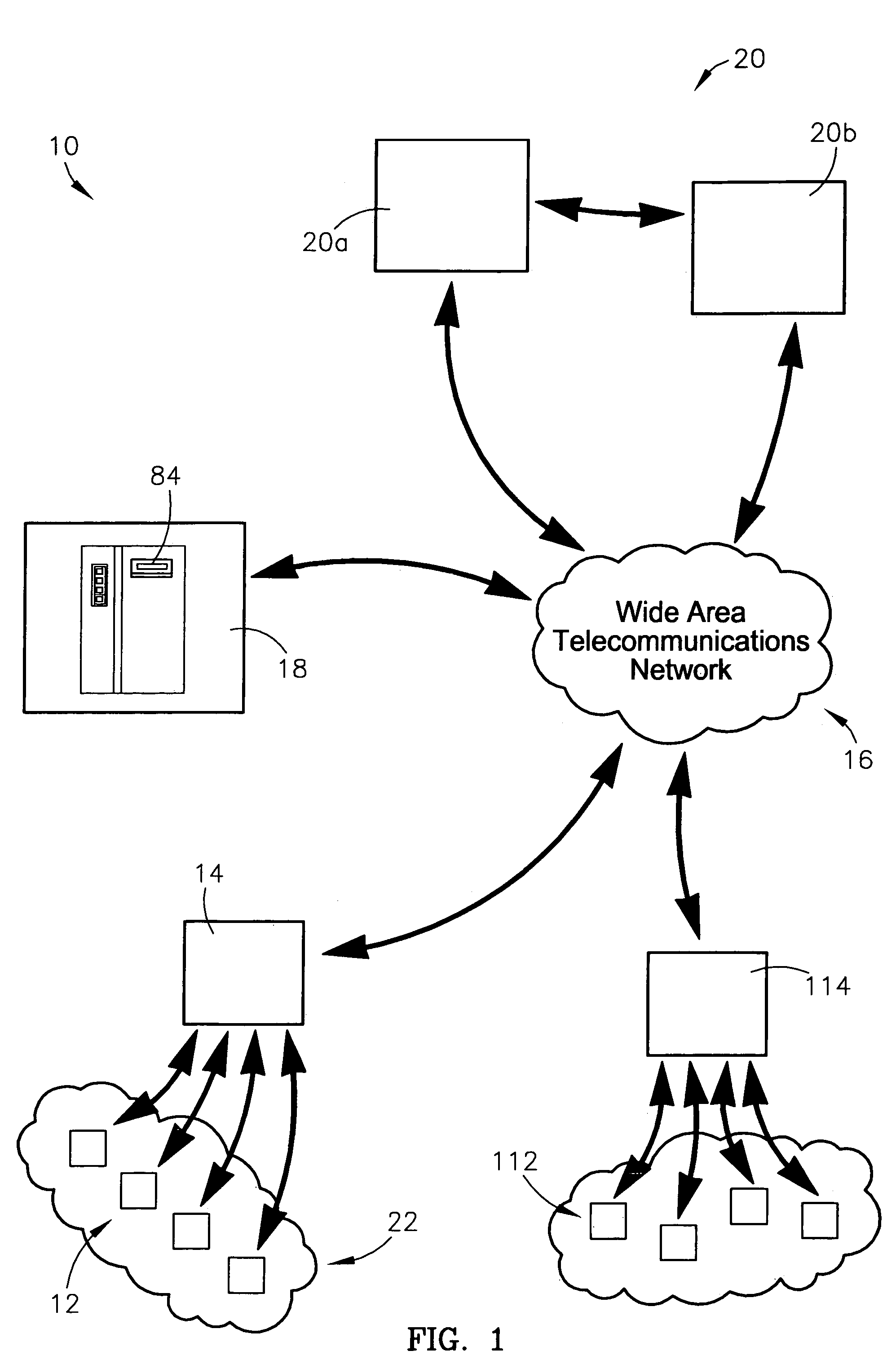
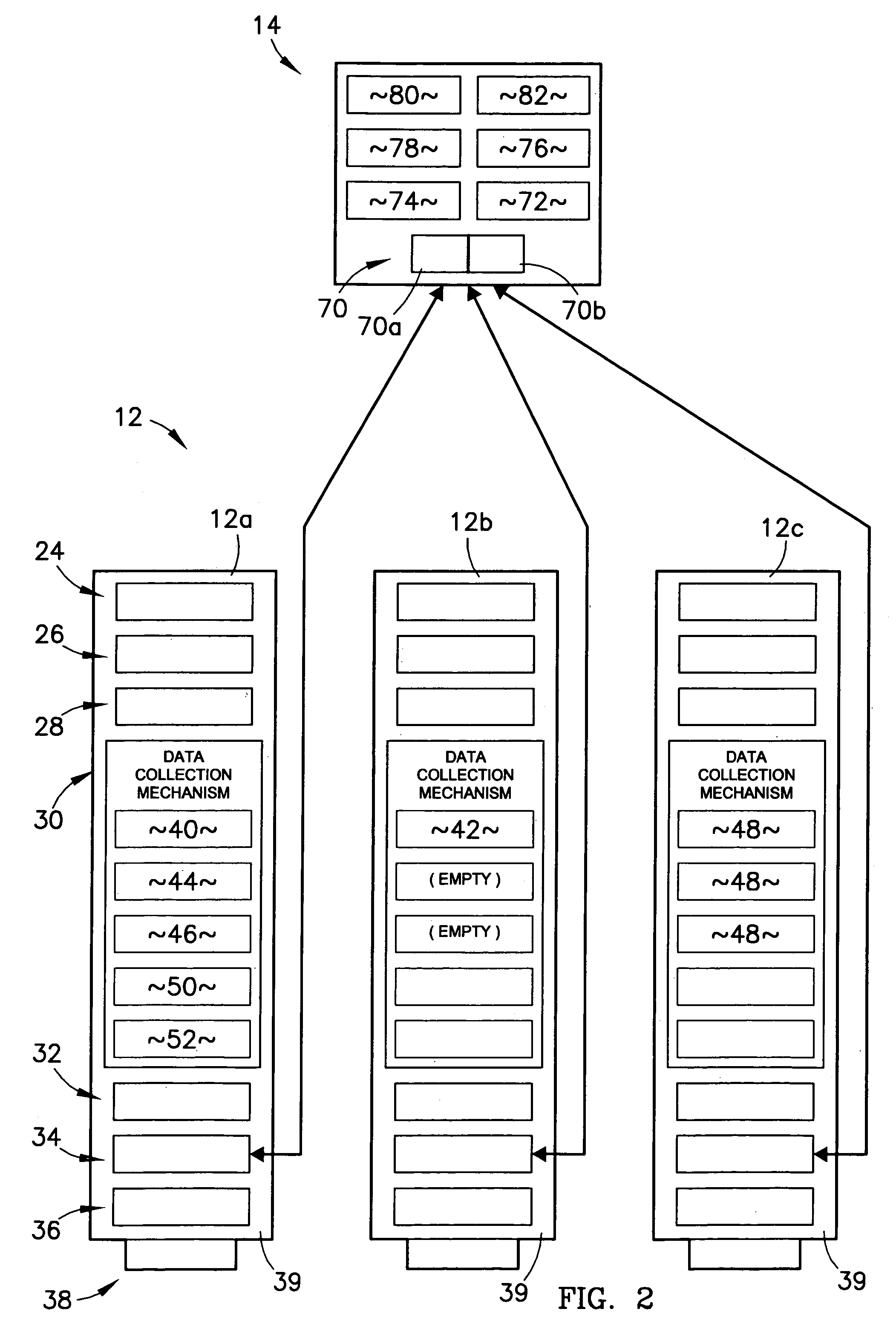
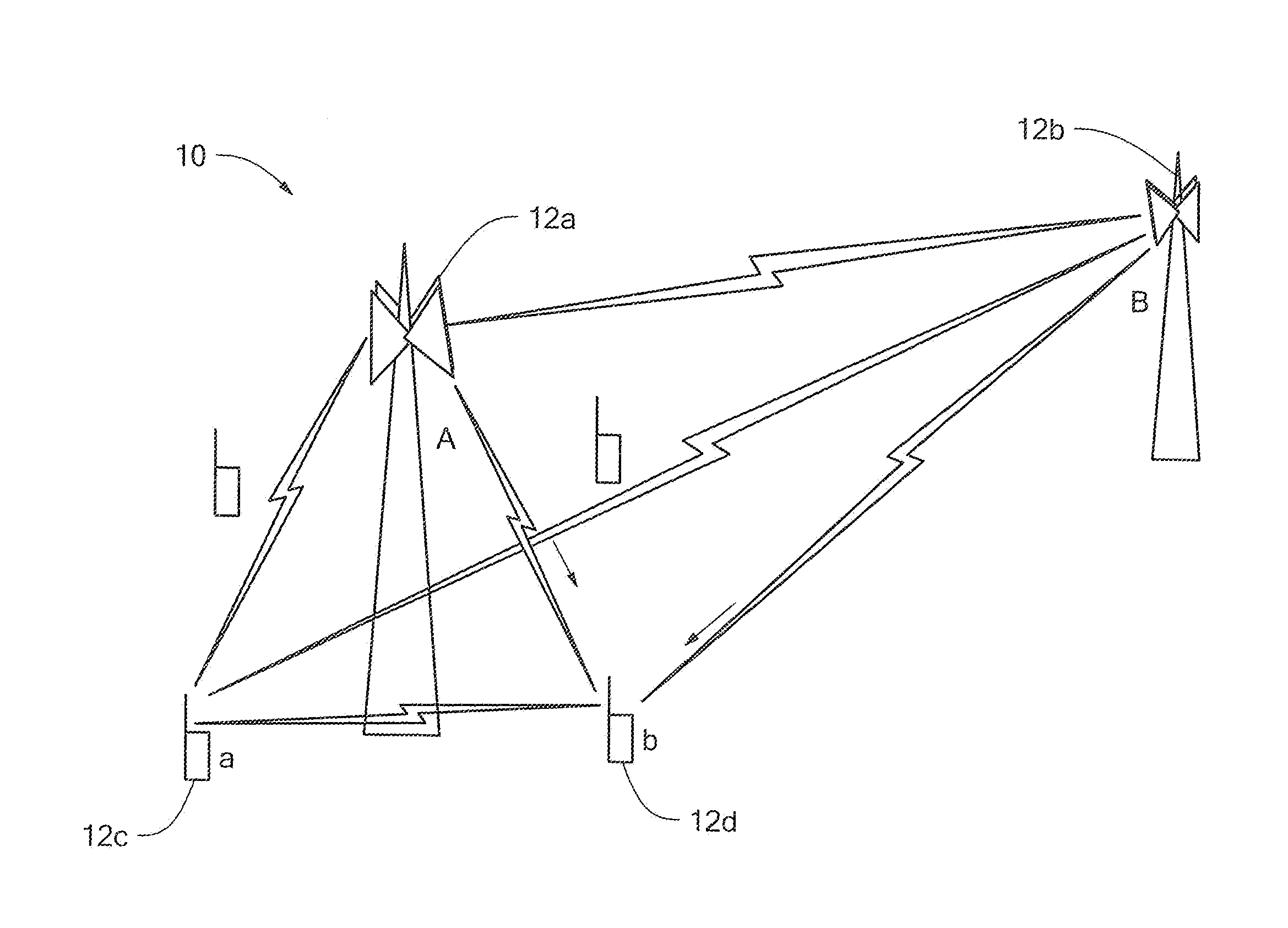
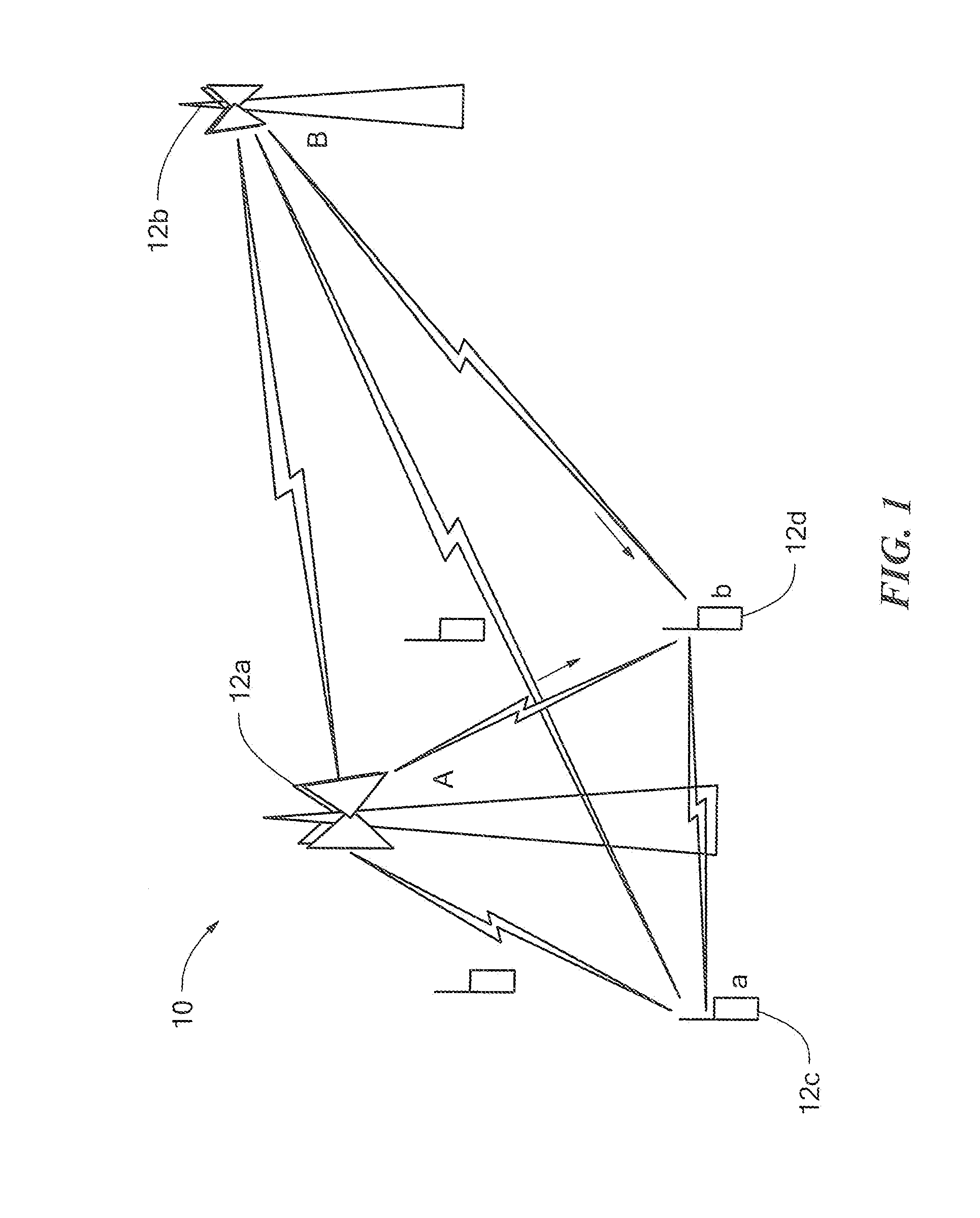
A system and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating a presence of a solid, liquid, gas, or other substance of interest, particularly a dangerous, hazardous, or otherwise threatening chemical, biological, or radioactive substance. The system comprises one or more substantially automated, location self-aware remote sensing units; a control unit; and one or more data processing and storage servers. Data is collected by the remote sensing units and transmitted to the control unit; the control unit generates and uploads a report incorporating the data to the servers; and thereafter the report is available for review by a hierarchy of responsive and evaluative authorities via a wide area network. The evaluative authorities include a group of relevant experts who may be widely or even globally distributed.
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
Sapient or Sentient Artificial Intelligence
InactiveUS20140046891A1Knowledge representationMachine learningHuman interactionHuman–robot interaction
A method for creating an artificial intelligence entity, specifically an artificial intelligence that is sentient and sapient is provided. The invention is capable of intelligence, human interaction, adaptive / modifiable code and thought, reasoning, learning; autonomous self-organization based on environment changes, interaction, and / or internal activity only; and other advance features. This permits a non-human, including a computer software entity, to become conscious or self-aware and interact, with the ability for sapience and understanding, as if it were human. It also has the ability to integrate with other electronic, non-electronic, or suitable devices.
Owner:BANAS SARAH
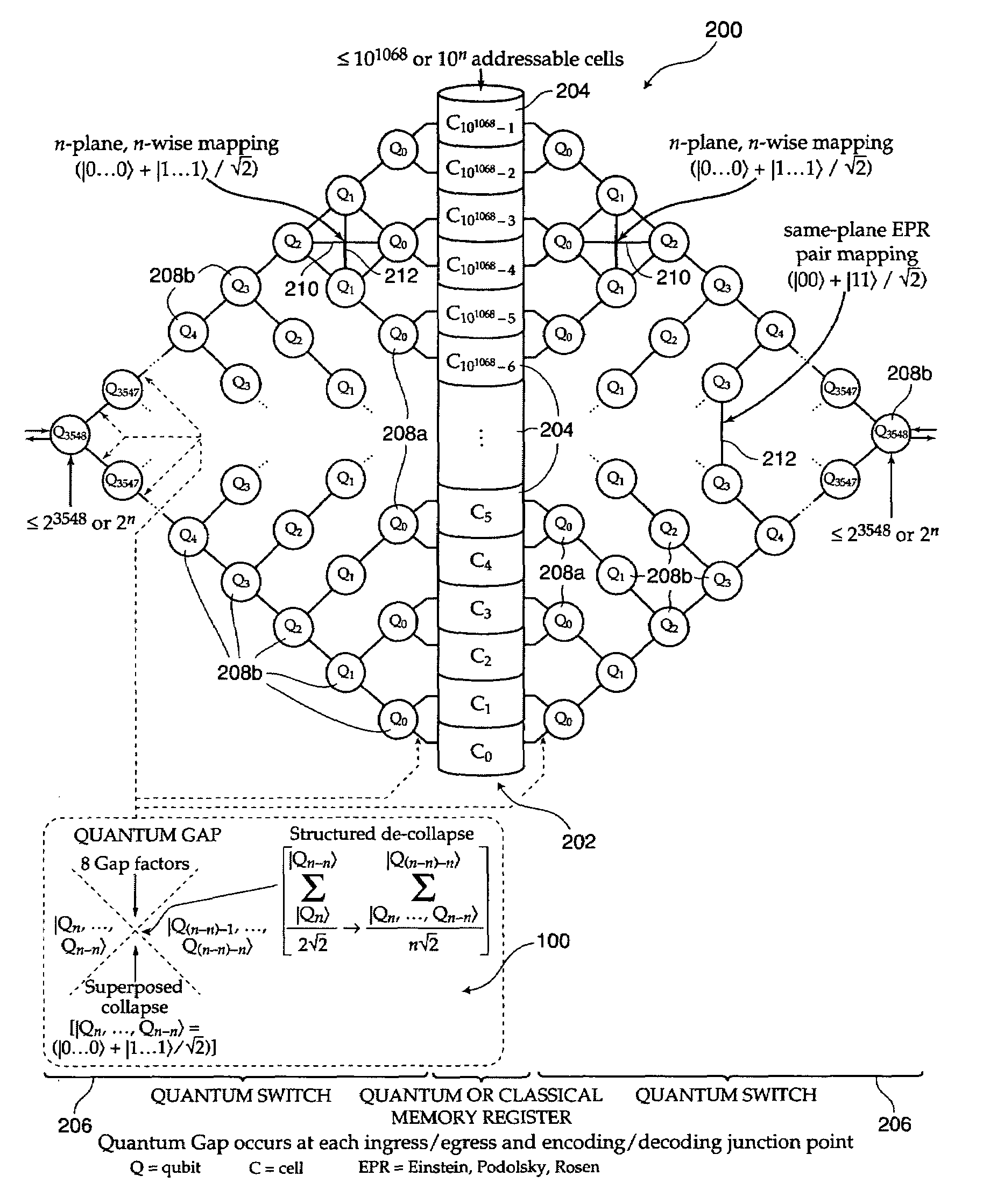
Methods for transmitting data across quantum interfaces and quantum gates using same
ActiveUS7451292B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsTheoretical computer scienceInterface (computing)
Quantum gaps exist between an origin and a destination that heretofore have prevented reliably utilizing the advantages of quantum computing. To predict the outcome of instructions with precision, the input data, preferably a qubit, is collapsed to a point value within the quantum gap based on a software instruction. After collapse the input data is restructured at the destination, wherein dynamics of restructuring are governed by a plurality of gap factors as follows: computational self-awareness; computational decision logic; computational processing logic; computational and network protocol and logic exchange; computational and network components, logic and processes; provides the basis for excitability of the Gap junction and its ability to transmit electronic and optical impulses, integrates them properly, and depends on feedback loop logic; computational and network component and system interoperability; and embodiment substrate and network computational physical topology.
Owner:TELERON TECH
System and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating presence of substance
ActiveUS20040120857A1Easy to removeEasy to replaceSolid-state devicesInvestigating moving sheetsRadioactive agentComputer science
A system and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating a presence of a solid, liquid, gas, or other substance of interest, particularly a dangerous, hazardous, or otherwise threatening chemical, biological, or radioactive substance. The system comprises one or more substantially automated, location self-aware remote sensing units; a control unit; and one or more data processing and storage servers. Data is collected by the remote sensing units and transmitted to the control unit; the control unit generates and uploads a report incorporating the data to the servers; and thereafter the report is available for review by a hierarchy of responsive and evaluative authorities via a wide area network. The evaluative authorities include a group of relevant experts who may be widely or even globally distributed.
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
Relevance based digital building
InactiveUS20180188712A1High activityHigh evolutionProgramme controlData processing applicationsNetwork structureREMS Stakeholder
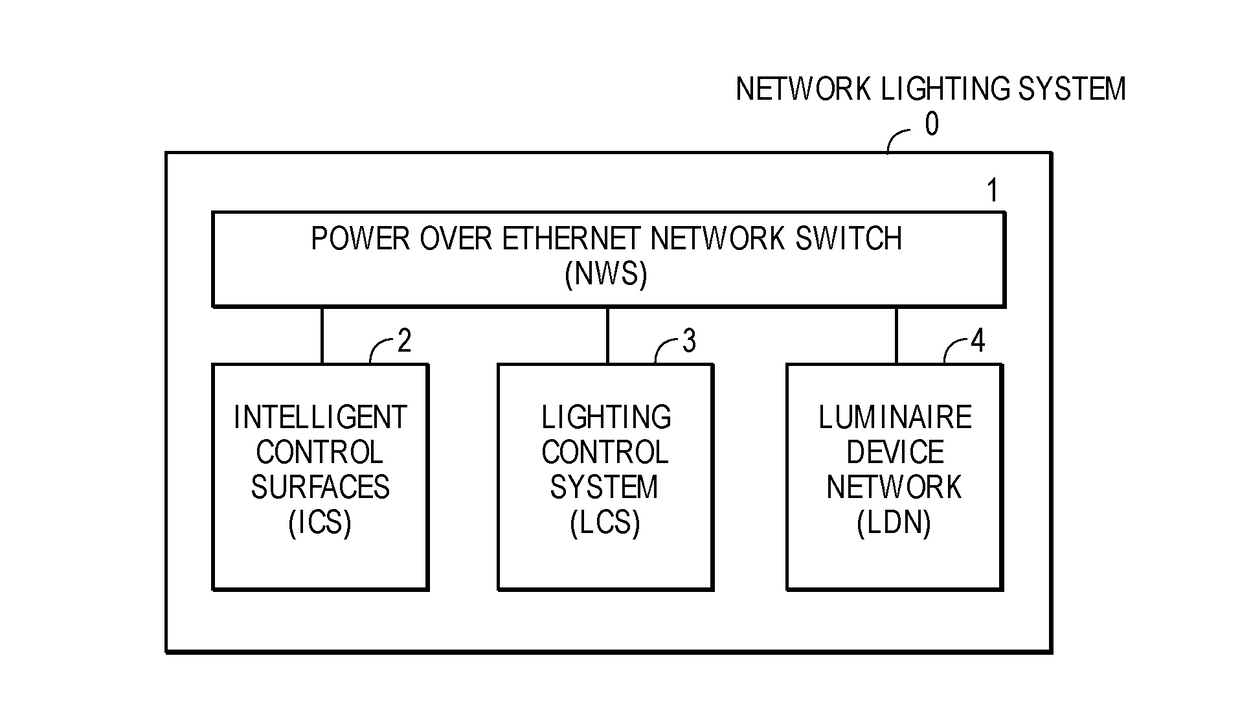
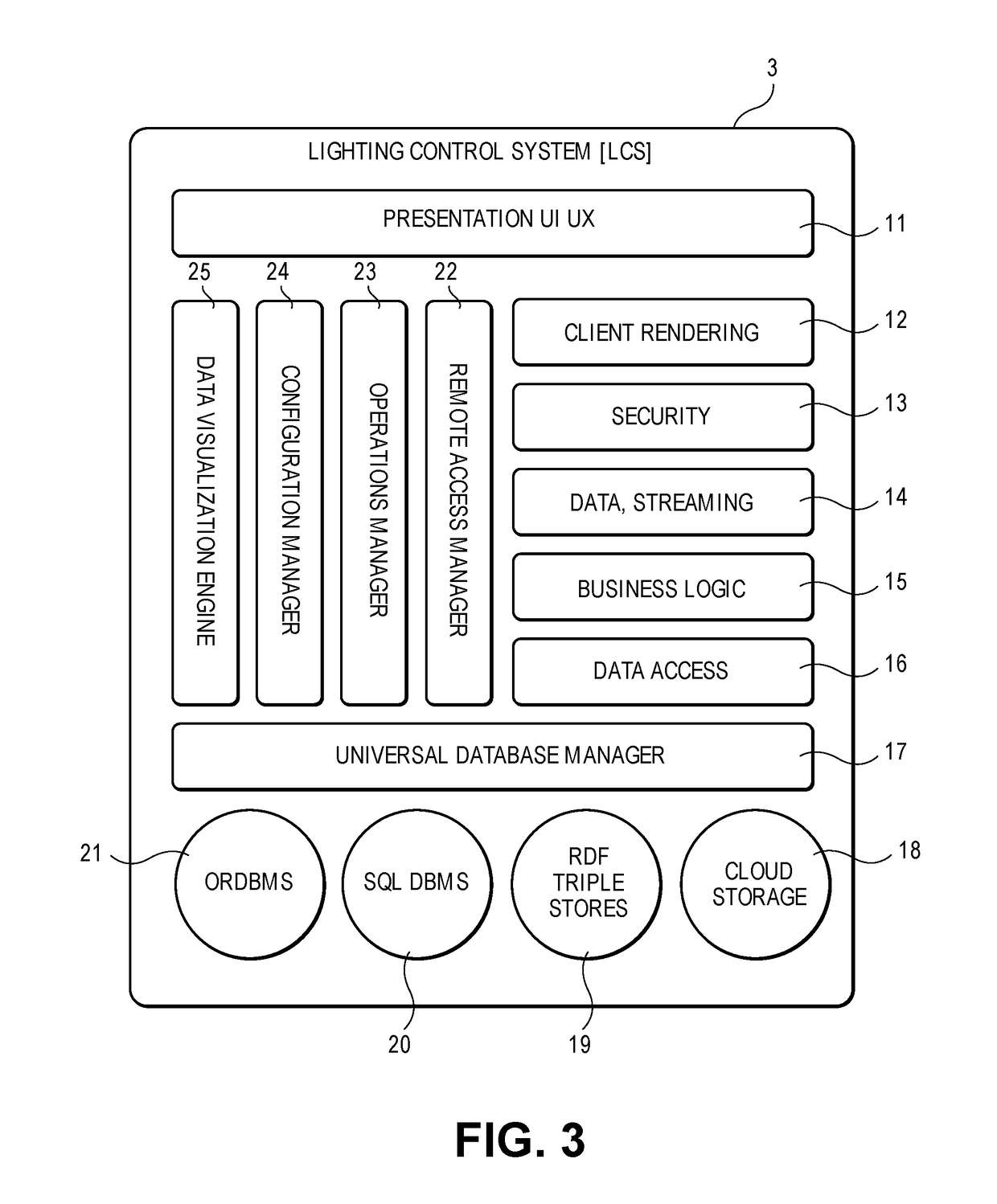
The Relevance Based Digital Building [RBDB] invention describes a method and apparatus consisting of a hardware and software environment that creates a relevance based digital building intelligence system. RBDB defines a Network Lighting System [NLS] that delivers the network fabric for an array of intelligent luminaries configured with Internet of Things [IoT] devices. Layered on the NLS network fabric is a Digital Building Intelligence information architecture that enables the building to become Self-Aware with Digital Personas. The building can manage many of its own needs through operational optimization, Machine to Machine [M2M] and machine to stakeholder interactions. RBDB allows the stakeholders associated with the building to take on a multiplicity of digital personas enabling high relevance interactions with the building and each other through these digital intelligence representations. The digital building adapts to the occupants (stakeholders) preferences and requirements and empowers he interaction between individuals (stakeholders) and their environment (Digital Building Intelligence).
Owner:MACKAY MICHAEL T
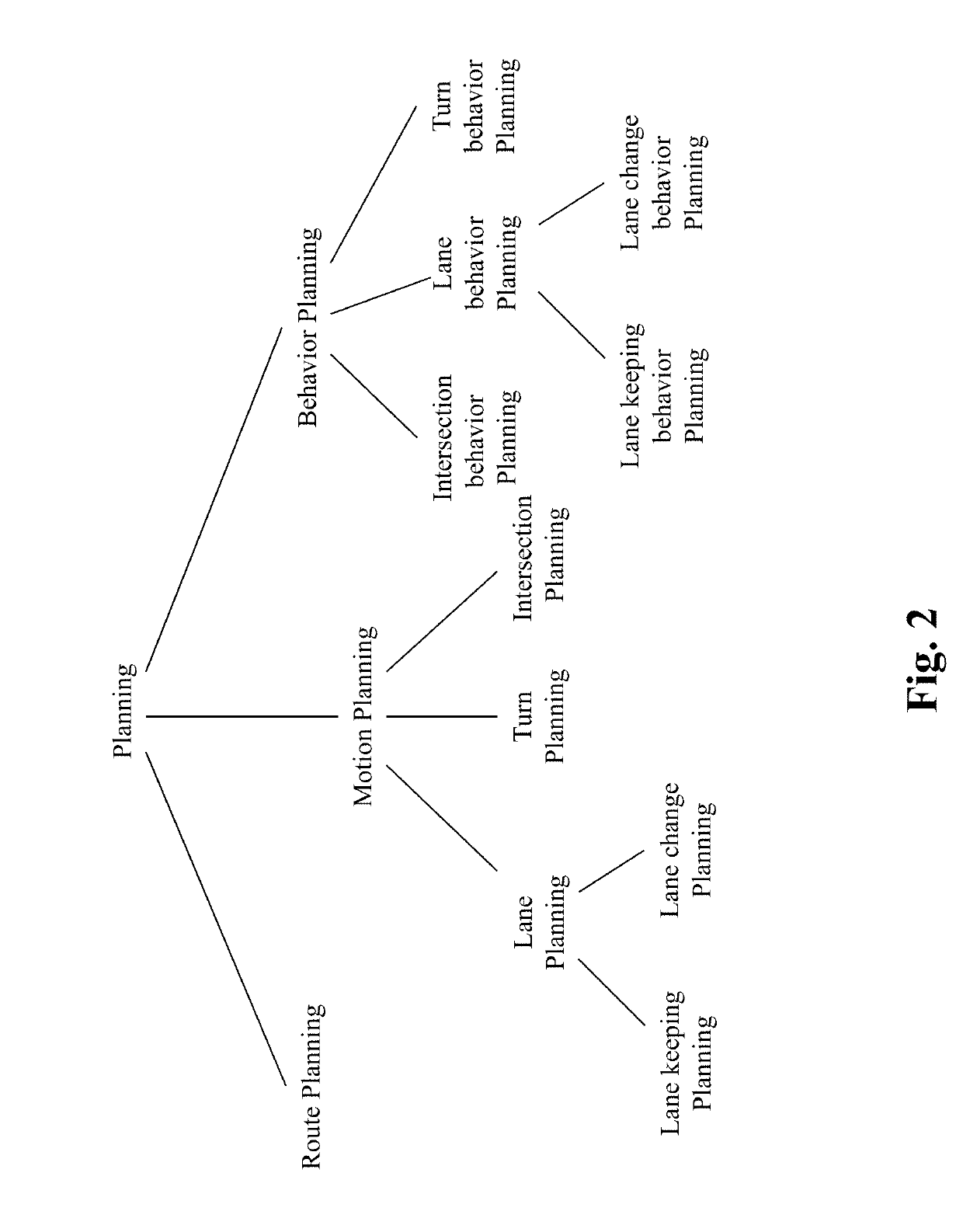
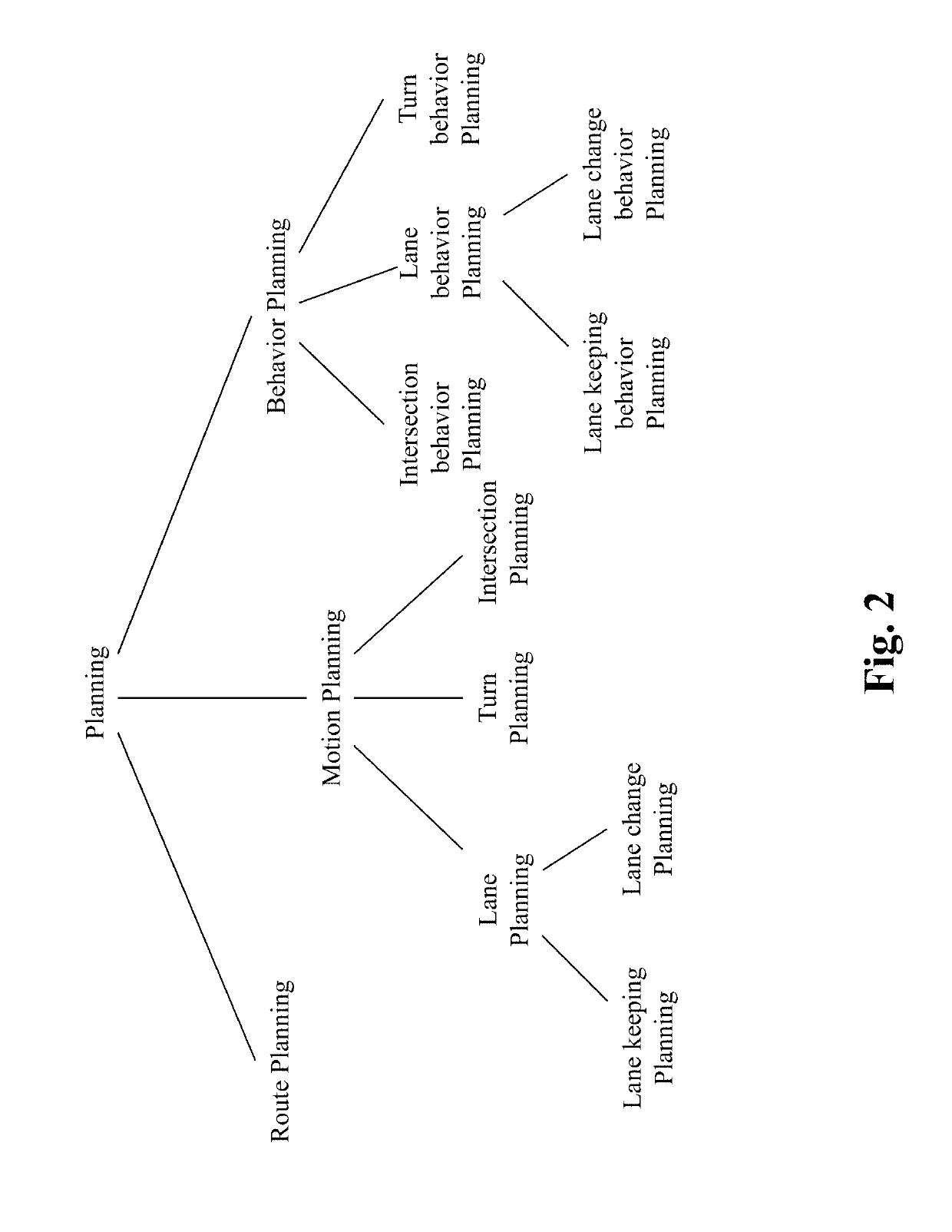
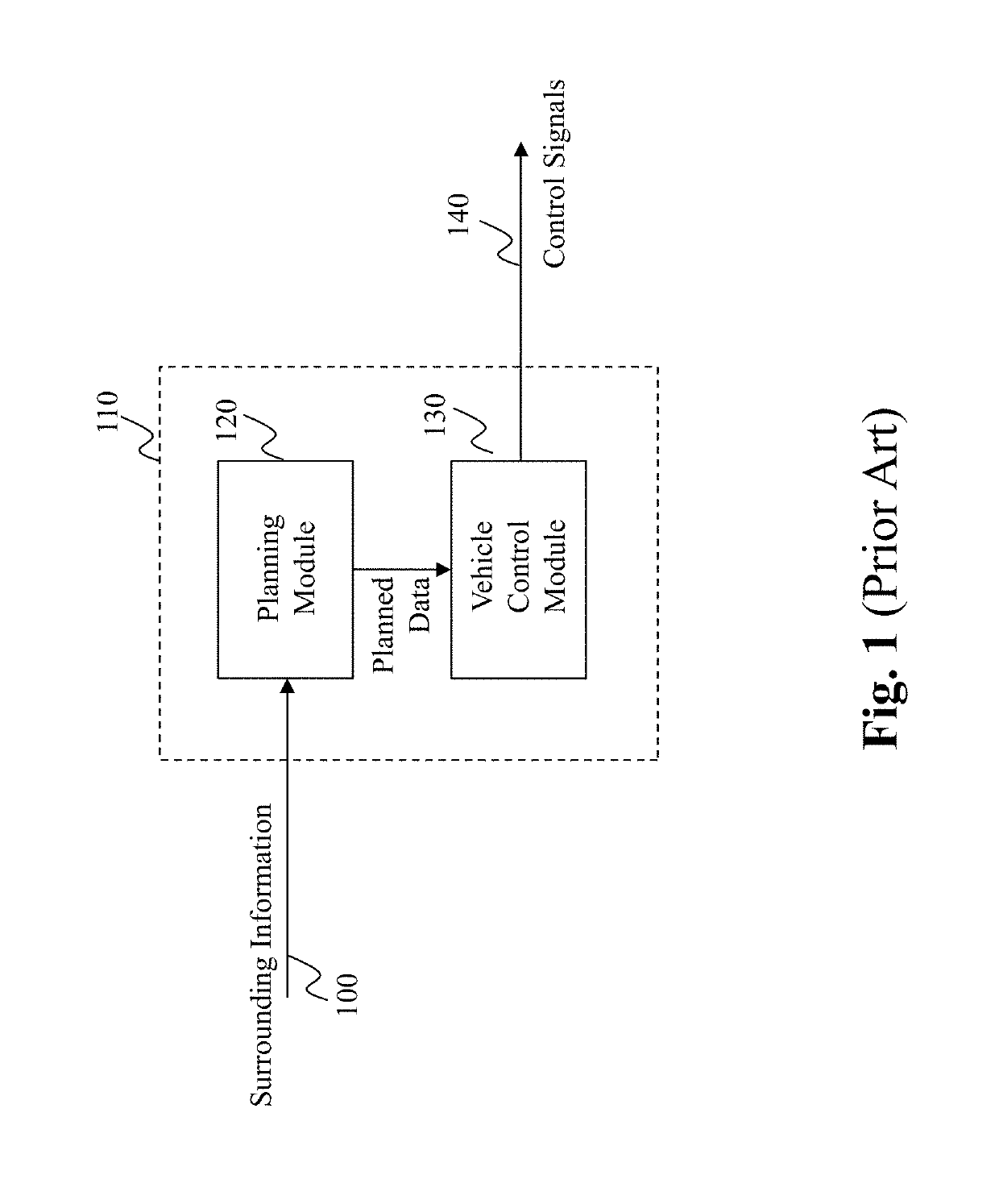
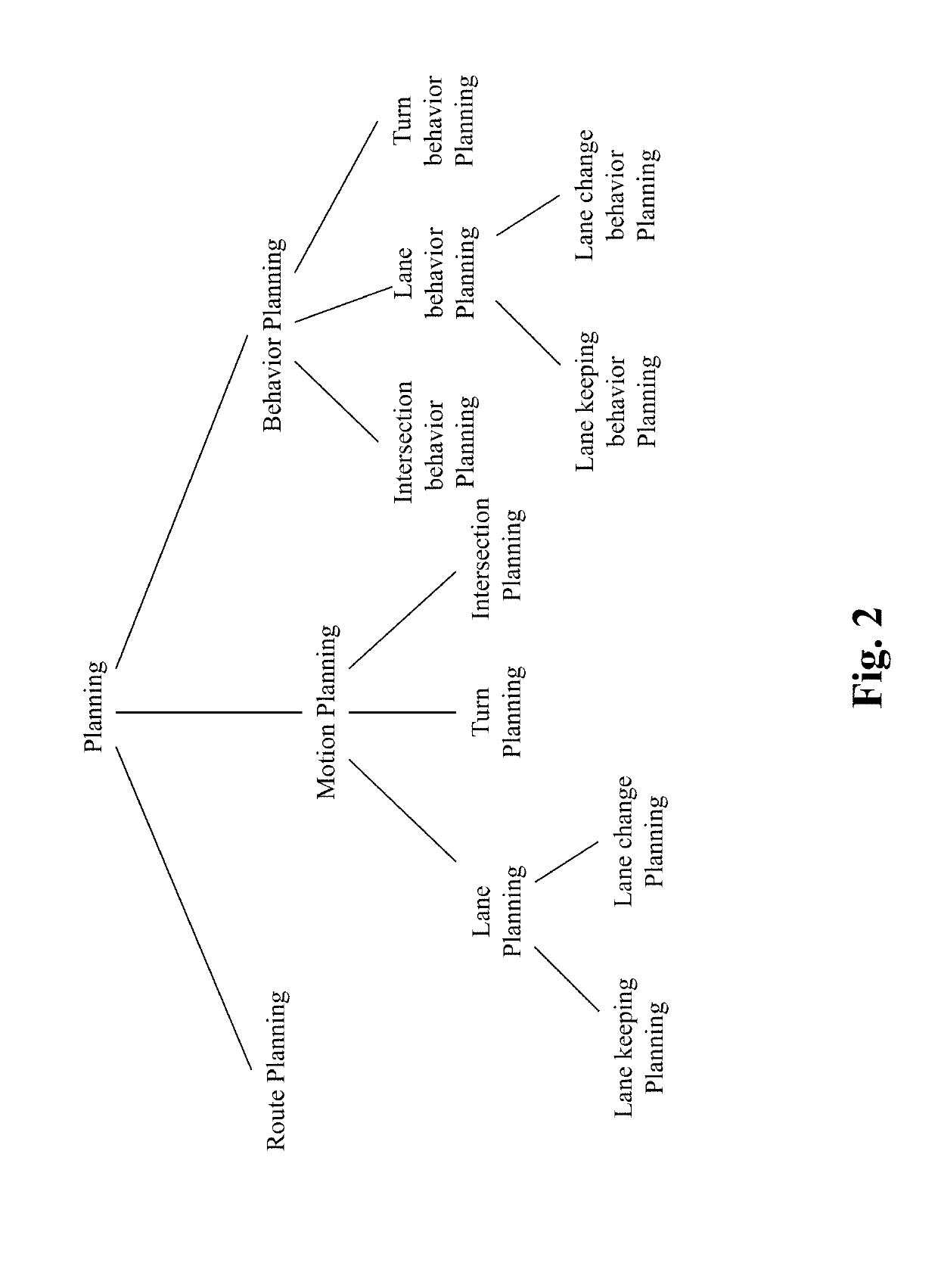
Method and system for personalized driving lane planning in autonomous driving vehicles
ActiveUS20190187707A1Instruments for road network navigationAutonomous decision making processEngineeringOperational capabilities
The present teaching relates to method, system, medium, and implementation of lane planning in an autonomous vehicle. Sensor data are received that capture ground images of a road the autonomous vehicle is on. Based on the sensor data, a current lane of the road that autonomous vehicle is currently occupying is detected. Information indicating presence of a passenger in the vehicle is obtained and used to retrieve a personalized lane control model related to the passenger. Lane control for the autonomous vehicle is planned based on the detected current lane and self-aware capability parameters in accordance with the personalized lane control model. The self-aware capability parameters are used to predict operational capability of the autonomous vehicle with respect to a current location of the autonomous vehicle. The personalized lane control model is generated based on recorded human driving data.
Owner:PLUSAI INC
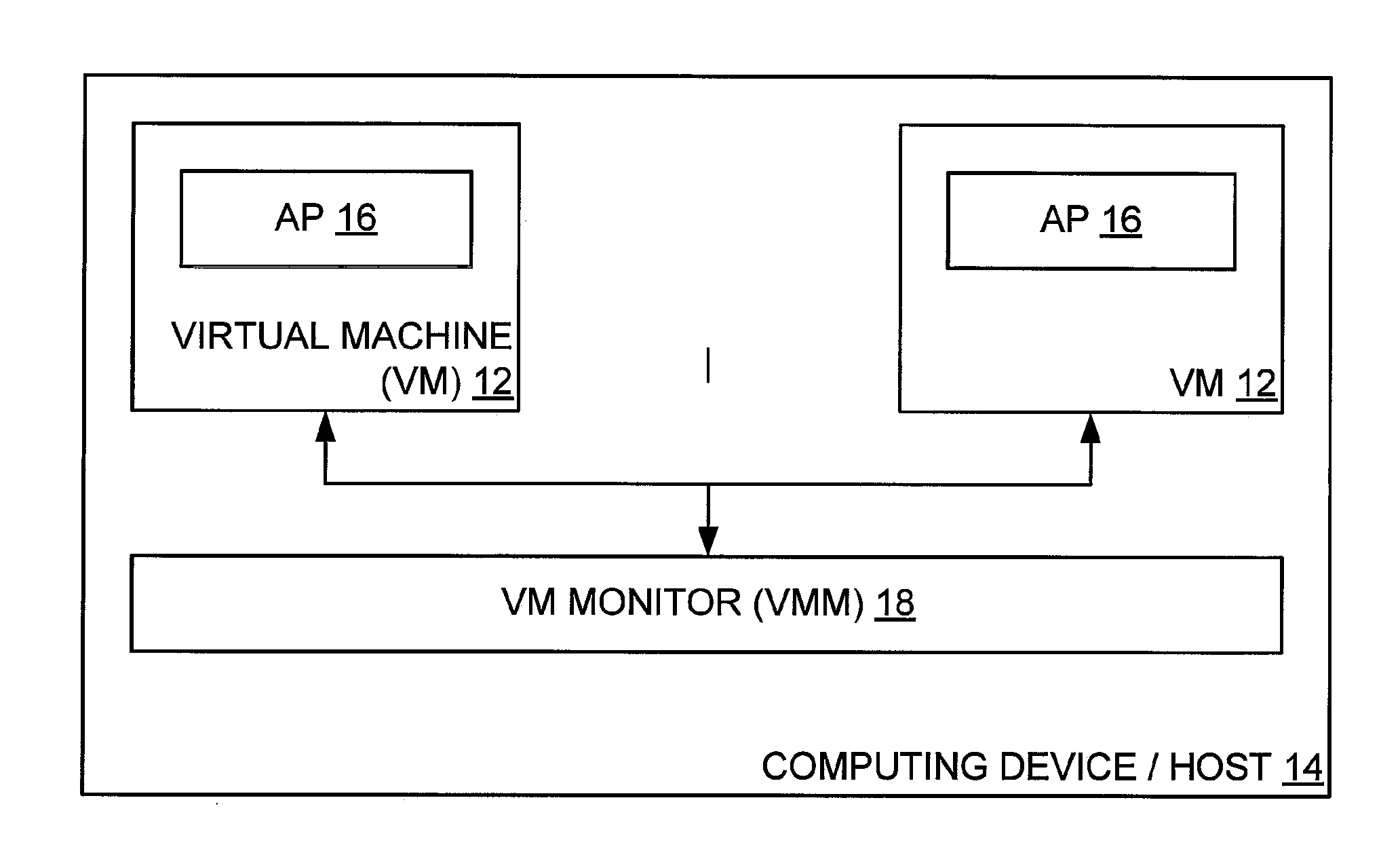
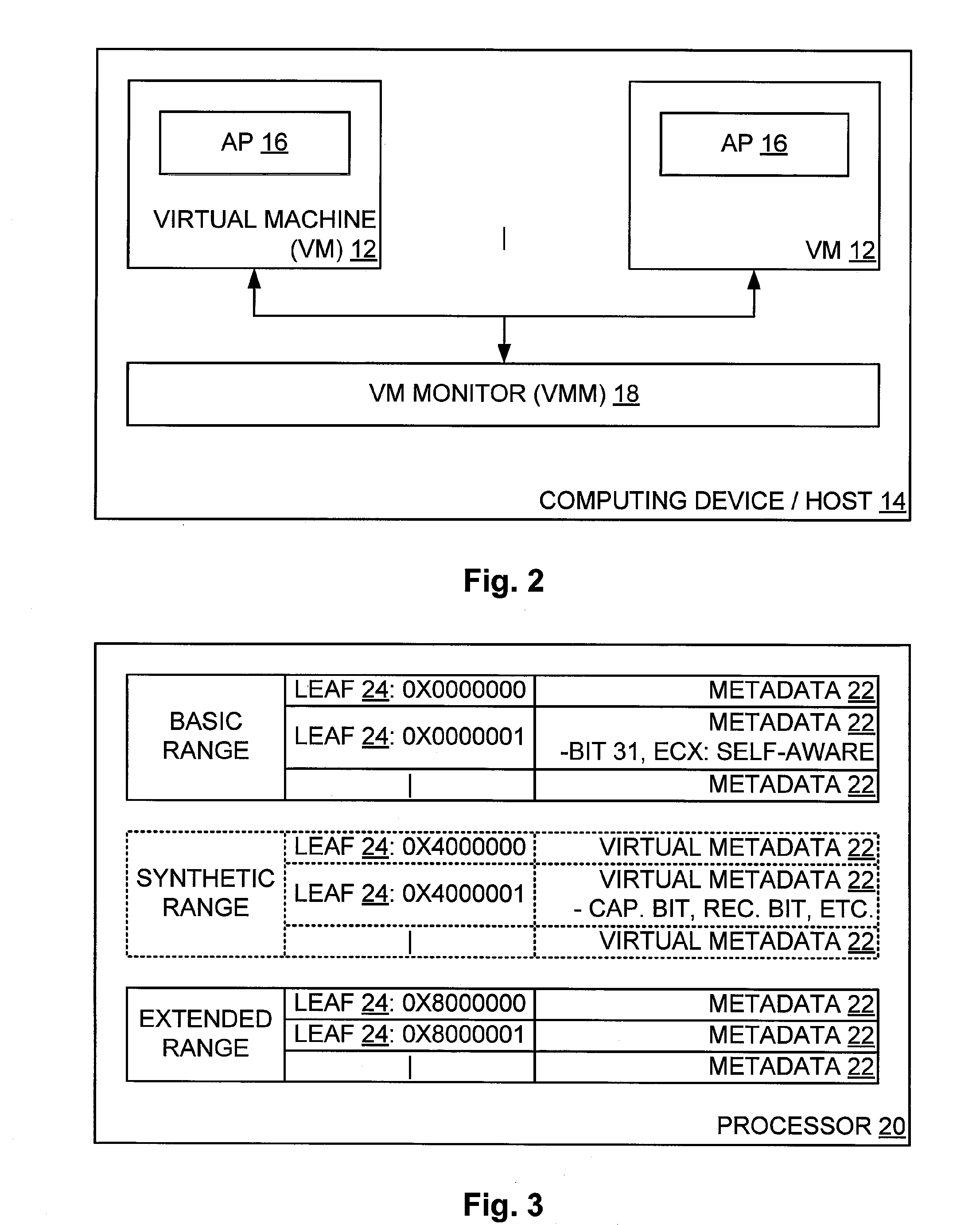
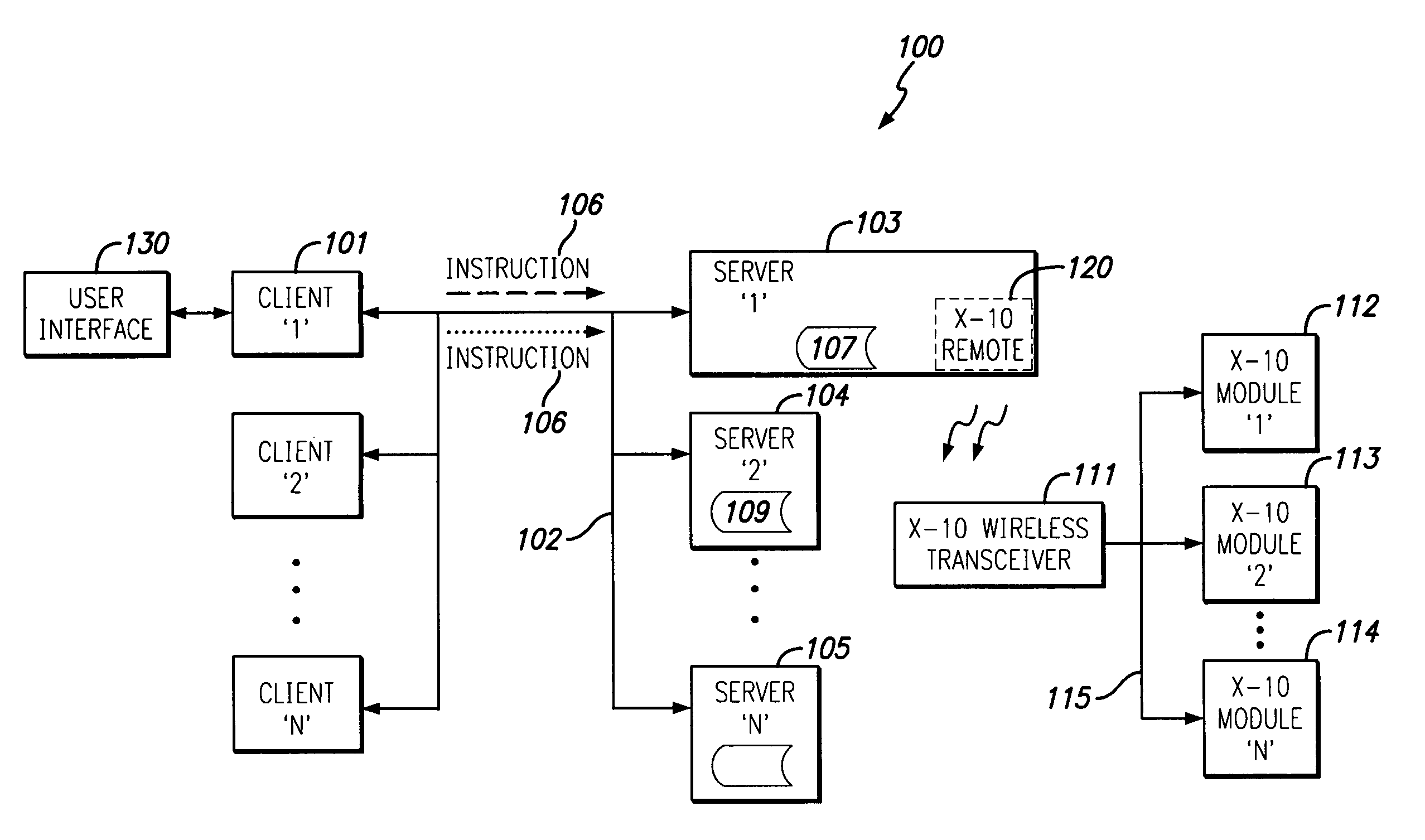
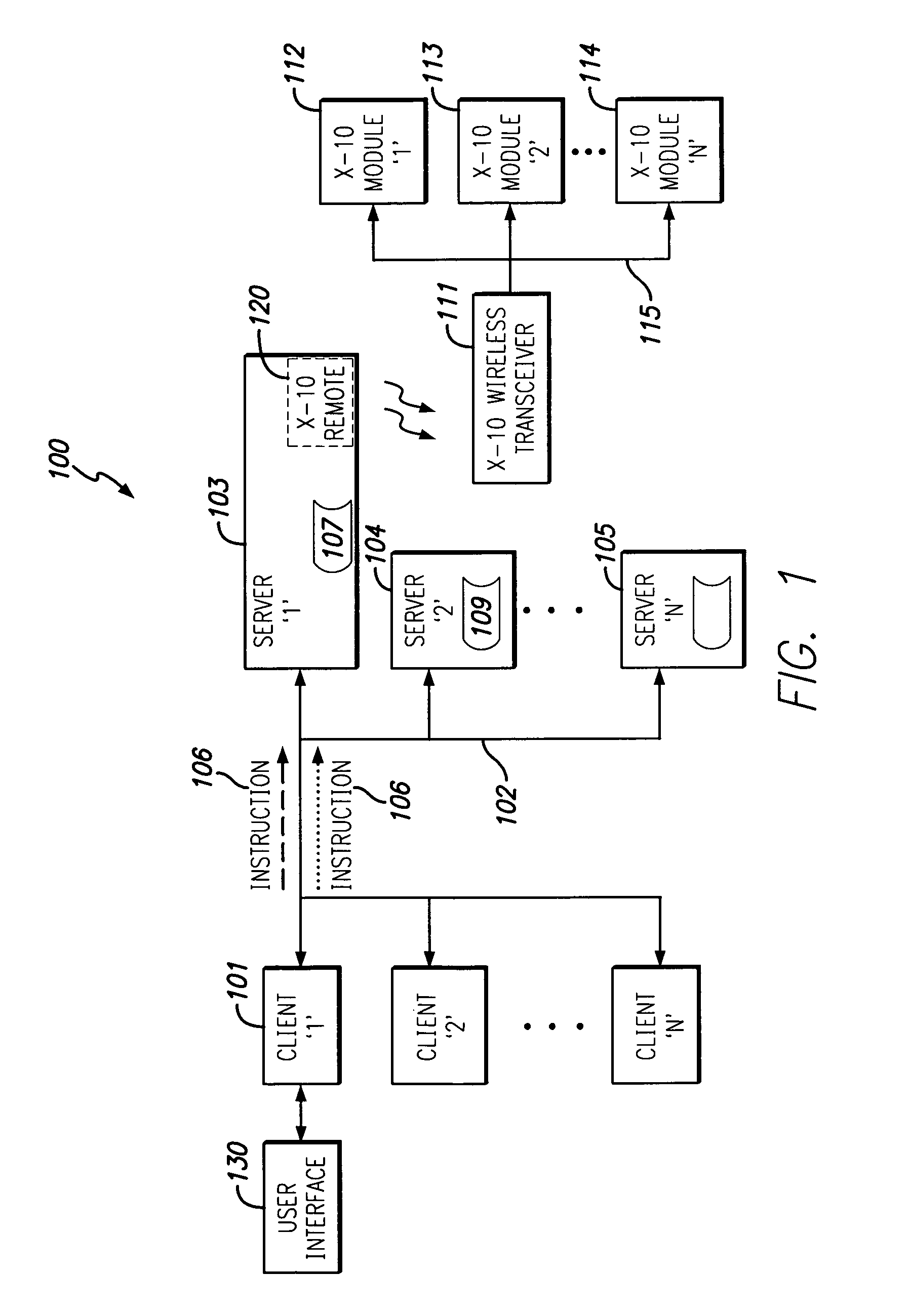
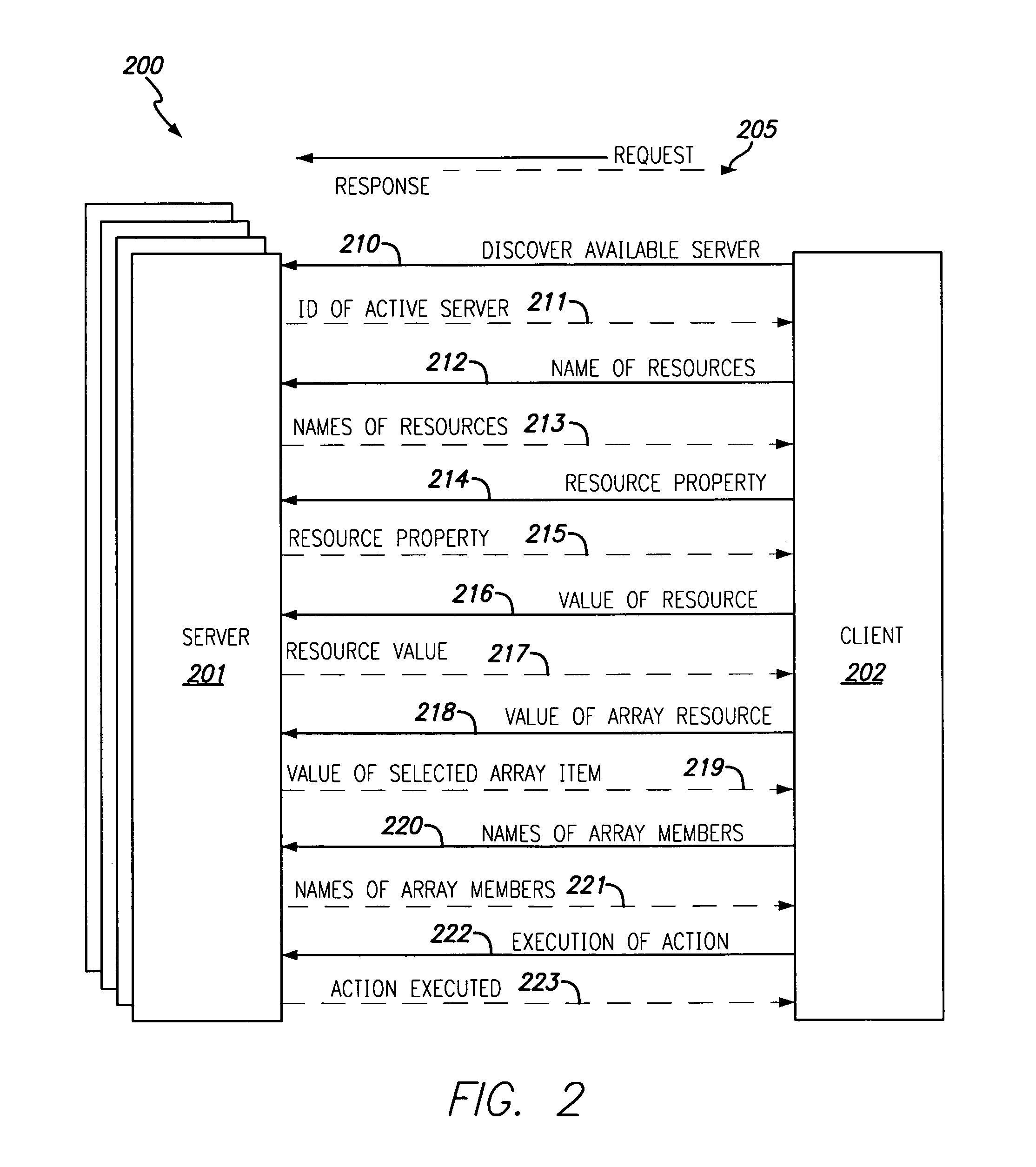
Allowing Virtual Machine to Discover Virtual Status Thereof
InactiveUS20080104586A1Easy to operateSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsPhysics processing unitApplication software
A host computing device has a virtual machine (VM) instantiated thereon. The VM has a virtual application instantiated thereon and a virtual processor. The host also has a virtual machine monitor (VMM) instantiated thereon to oversee the VM and to intercept instructions from a virtual entity comprising one of the virtual application and the VM to the virtual processor of such VM. The virtual entity becomes self-aware of the virtual status thereof based on a self-aware flag as obtained from the VMM, and based thereon obtains particular virtual metadata from a Synthetic range of the virtual processor by way of the VMM to operate efficiently. The Synthetic range of the virtual processor is implemented by the VMM and does not correspond to any defined range of the physical processor corresponding to the virtual processor.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for personalized self capability aware route planning in autonomous driving vehicles
InactiveUS20190187705A1Instruments for road network navigationAutonomous decision making processPersonalizationProgram planning
The present teaching relates to method, system, medium, and implementation of route planning for an autonomous driving vehicle. A source location and a destination location are first obtained, where the destination location is where the autonomous driving vehicle is to drive to. One or more available routes between the source location and the destination location are identified. A self-aware capability model is instantiated with respect to the one or more available routes and is predictive of the operational capability of the autonomous driving vehicle with respect to each of the one or more available routes. The preference of a passenger present in the autonomous driving vehicle is determined in terms of a route to take for the autonomous vehicle to drive to the destination location. Based on the self-aware capability model and the preference of the passenger, a planned route to the destination location is then automatically selected for the autonomous driving vehicle.
Owner:PLUSAI INC
Generating and analyzing business process-aware modules
InactiveUS7313568B2Efficient analysisAccurate predictionDigital computer detailsOffice automationService-level agreementData set
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and system for self capability aware route planning in autonomous driving vehicles
InactiveUS20190185010A1Instruments for road network navigationMathematical modelsProgram planningEngineering
The present teaching relates to method, system, medium, and implementation of route planning for an autonomous driving vehicle. A source location and a destination location are first obtained, where the destination location is where the autonomous driving vehicle is to drive to. One or more available routes between the source location and the destination location are identified. A self-aware capability model is instantiated with respect to the one or more available routes and is predictive of the operational capability of the autonomous driving vehicle with respect to each of the one or more available routes. Based on the self-aware capability model, a planned route to the destination location is then automatically selected for the autonomous driving vehicle.
Owner:PLUSAI INC
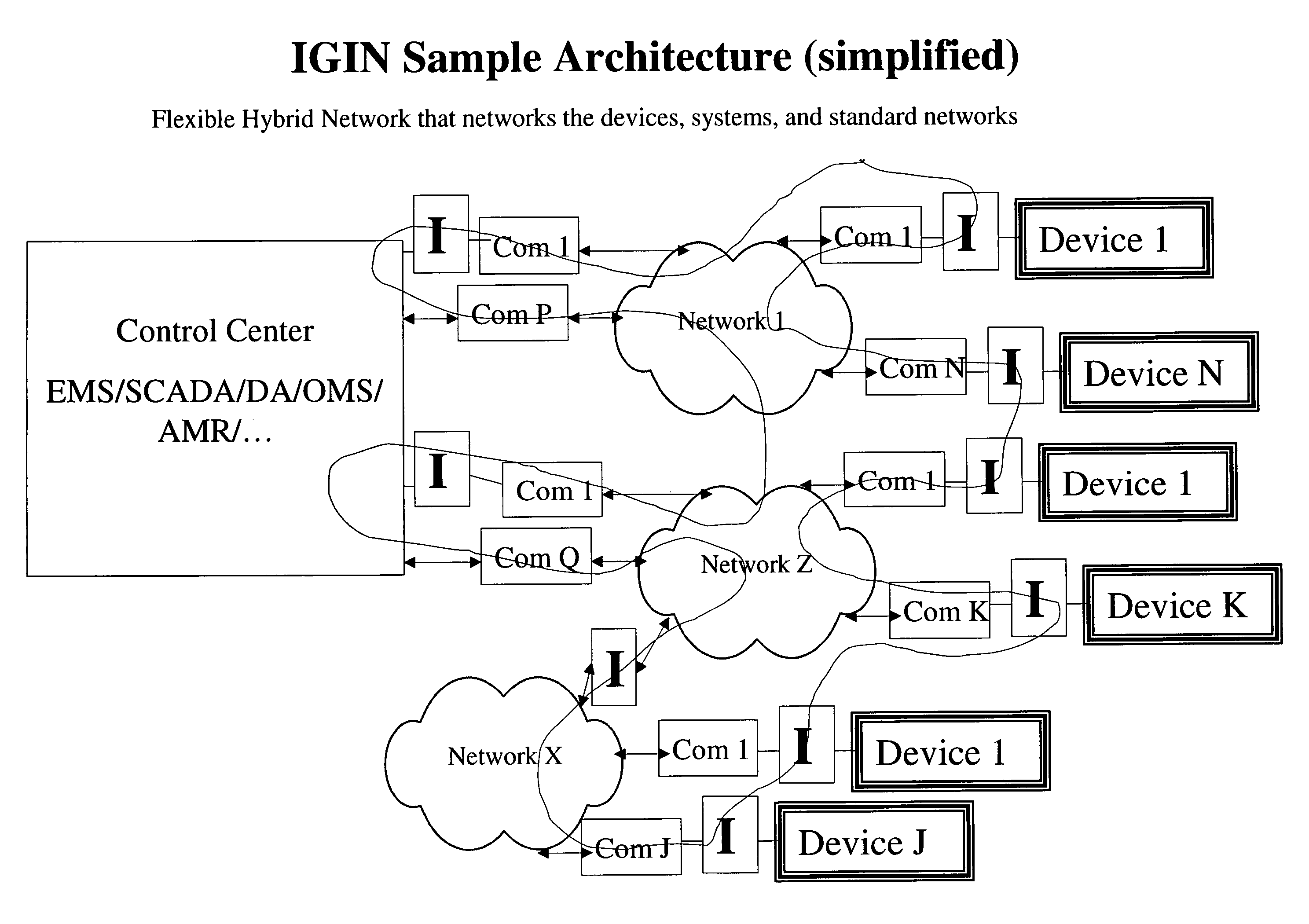
Intelligent grid system
ActiveUS7499762B2Electric signal transmission systemsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsGuidelineThe Internet
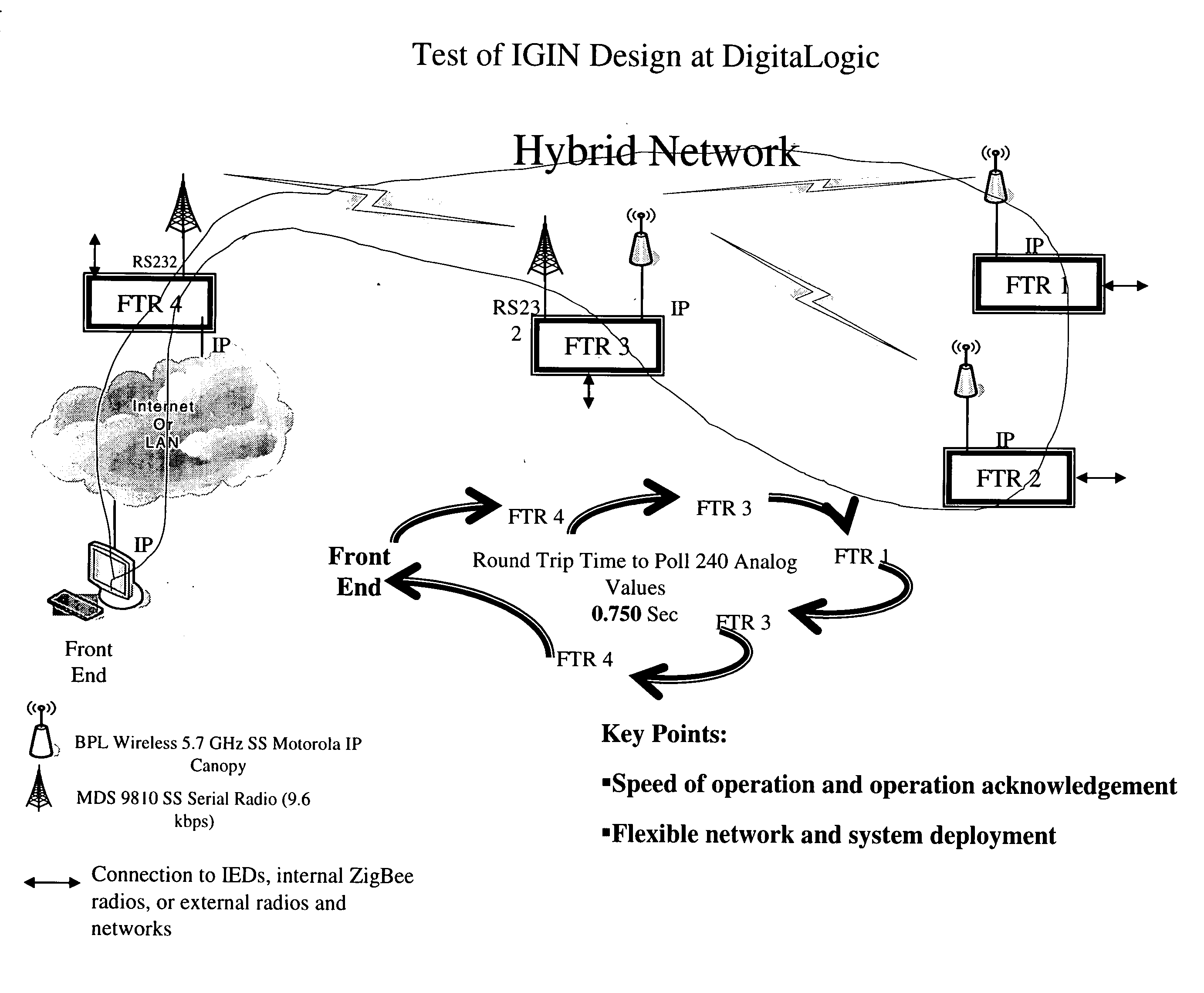
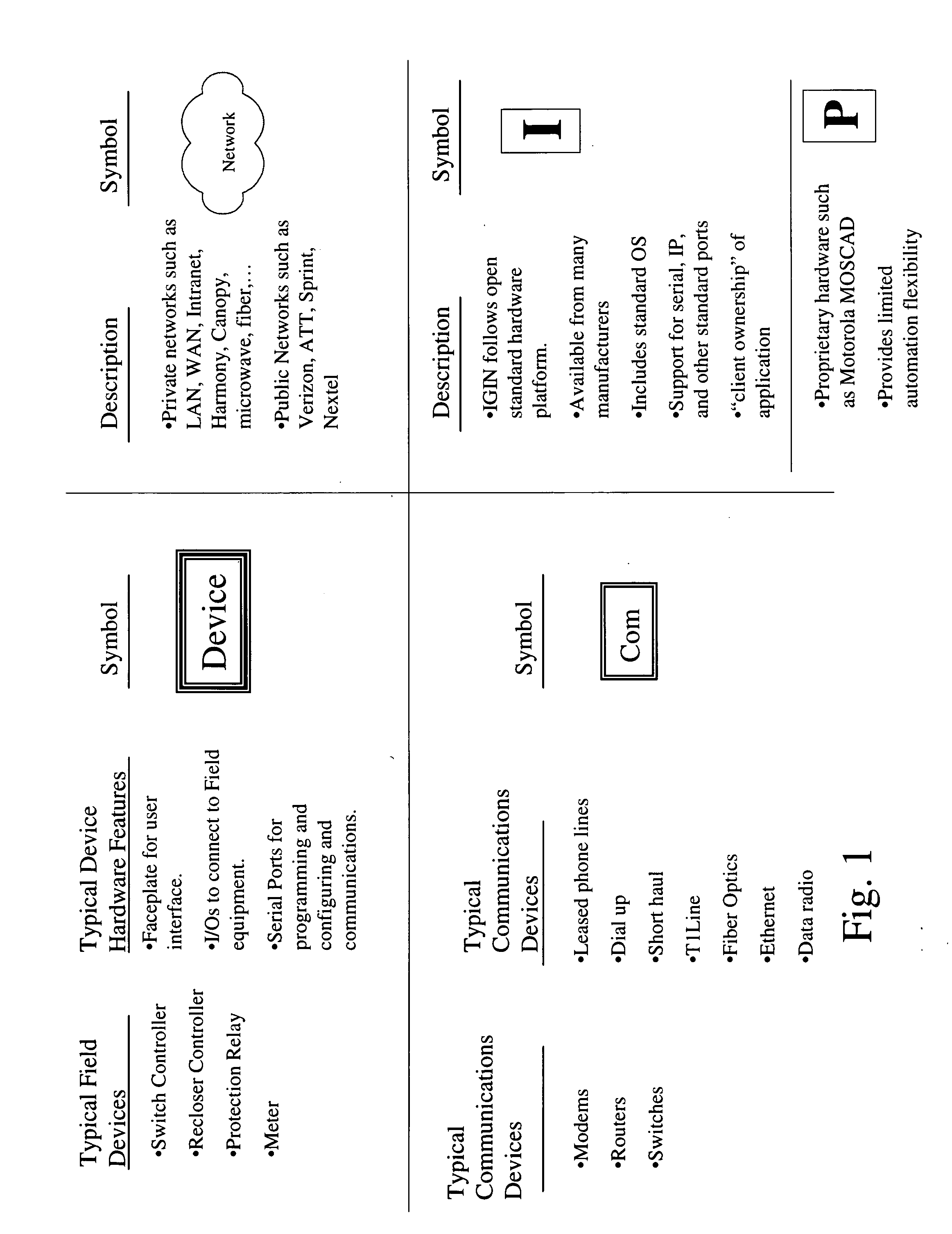
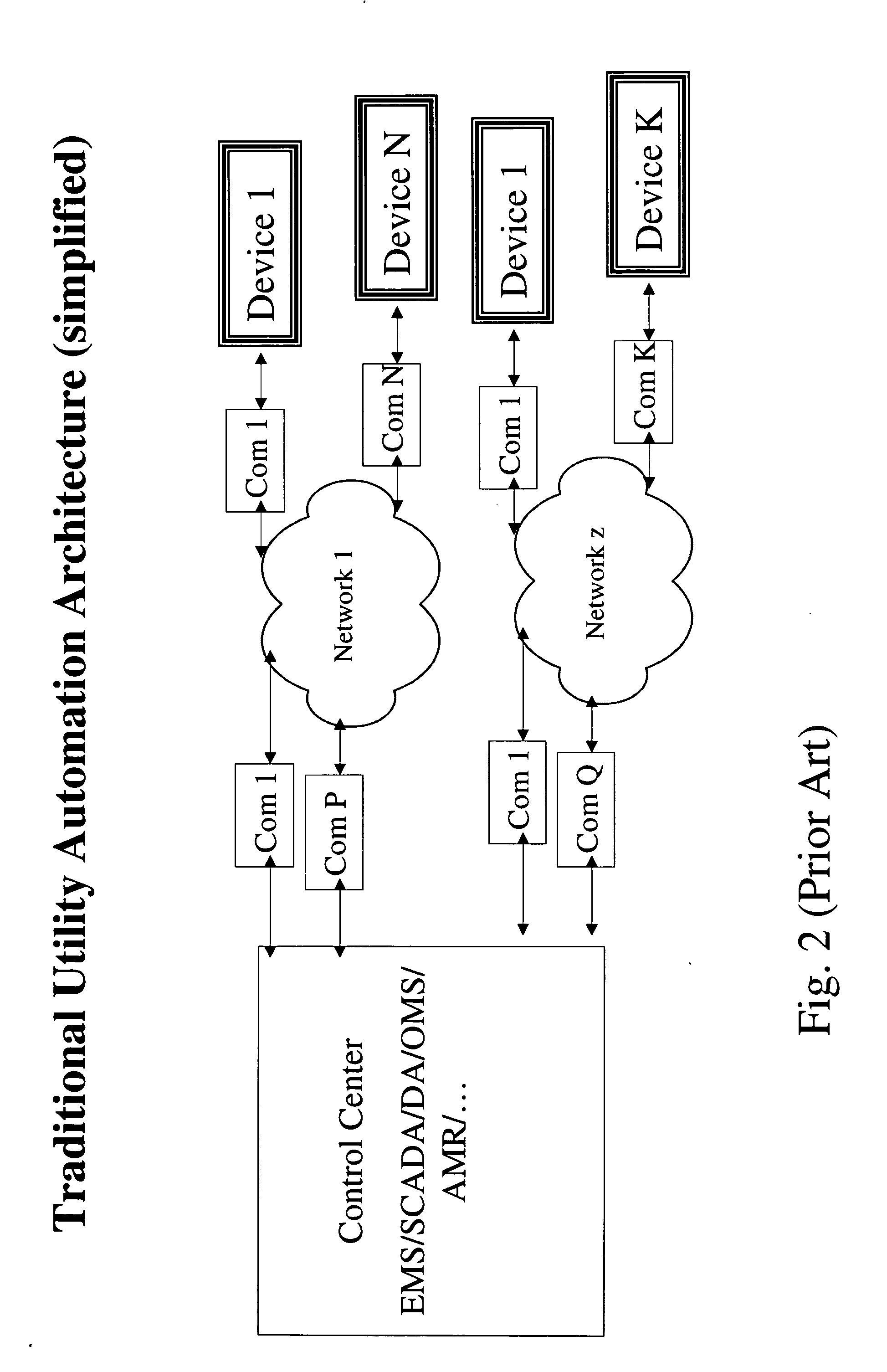
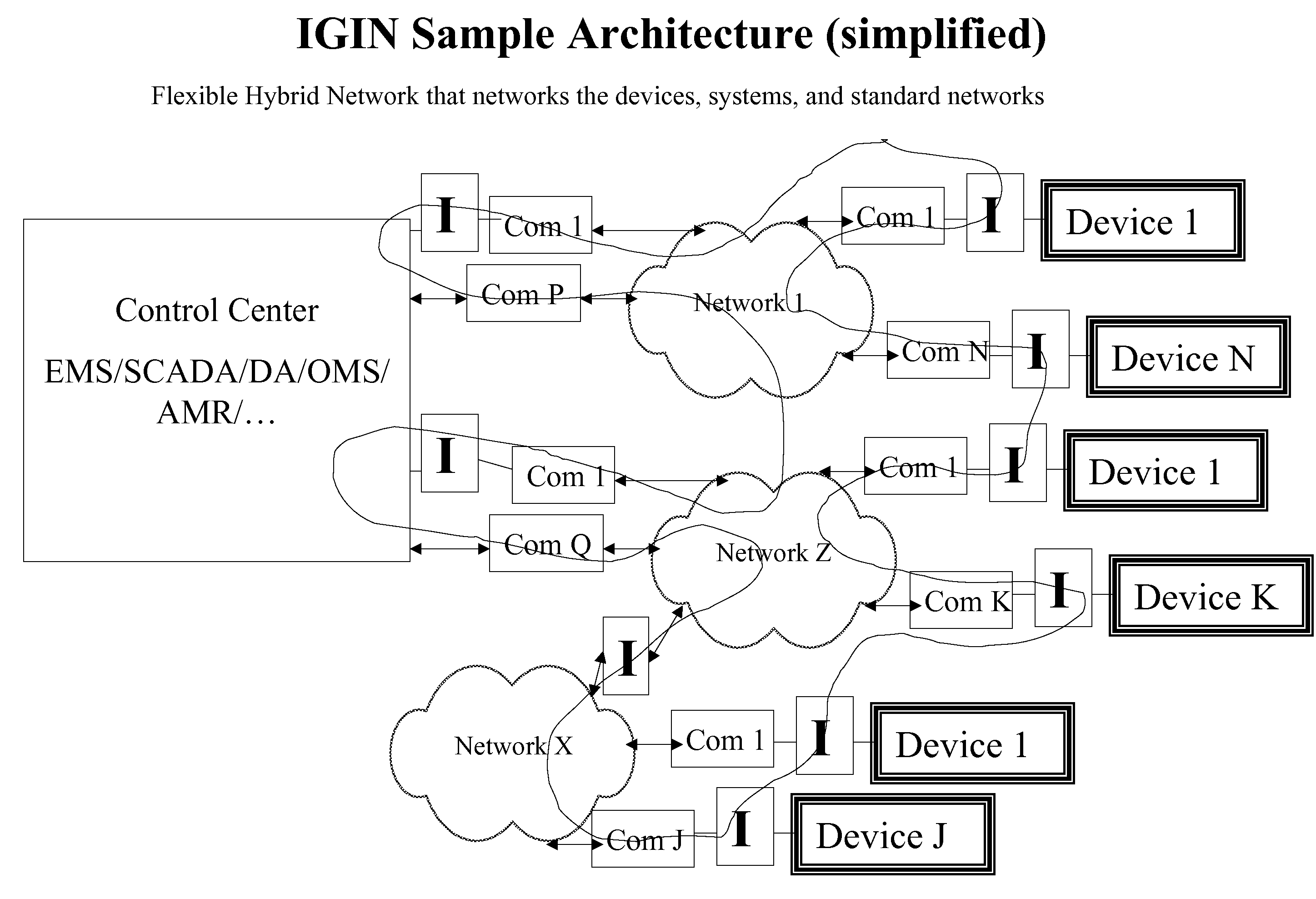
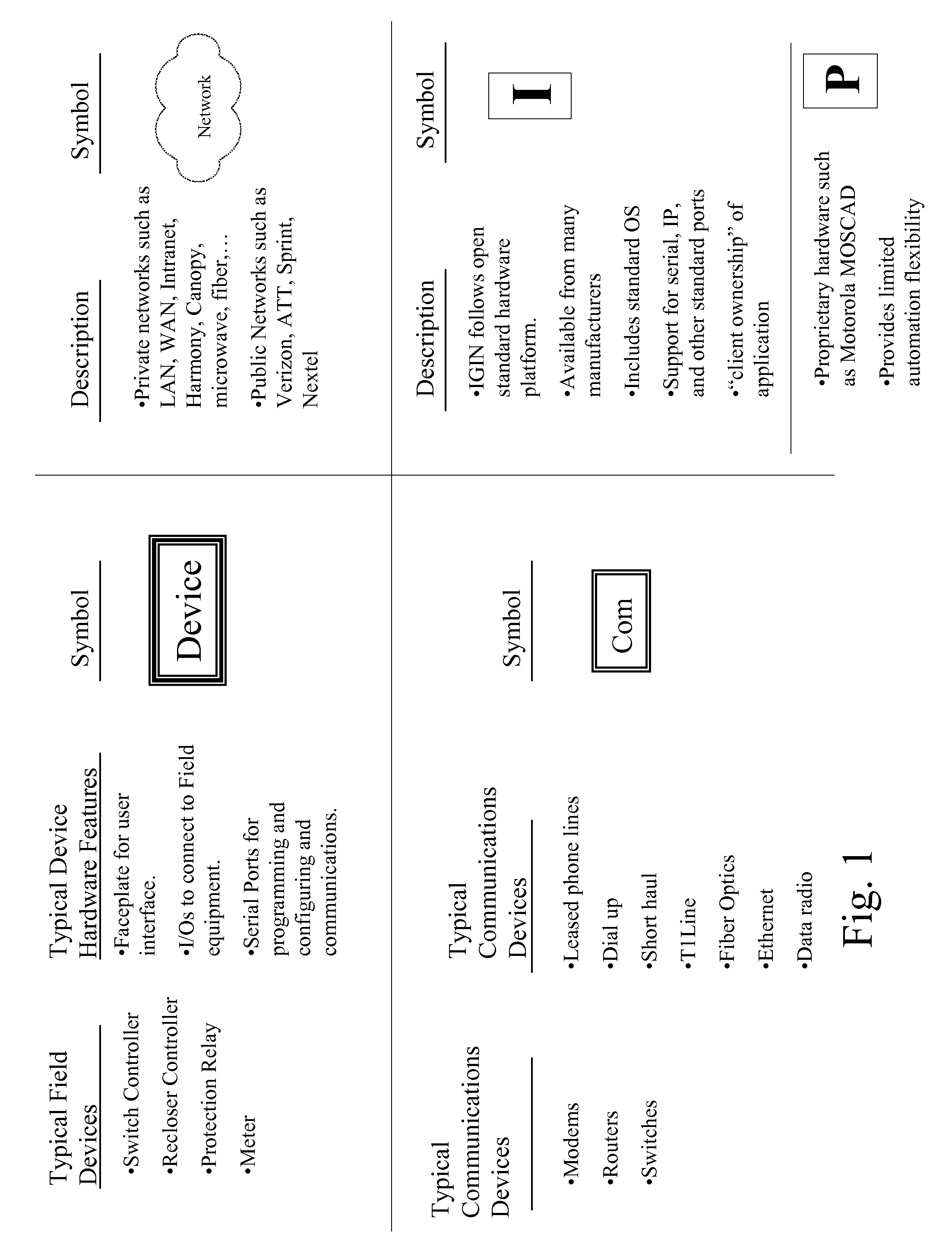
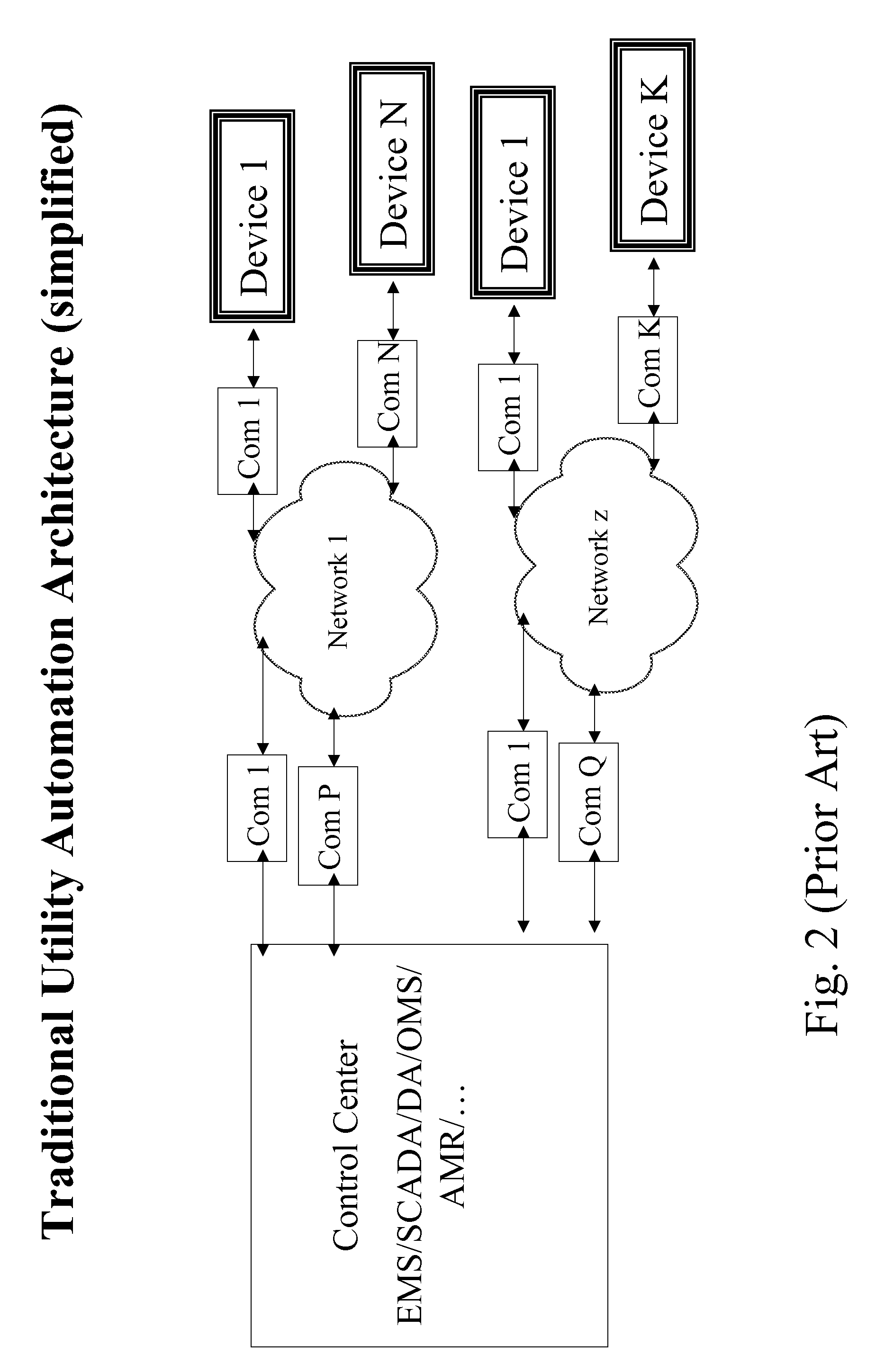
The future of the utility industry will be defined by how its leaders can transform the grid from a “passive” network of cables, wires, poles, and other hardware to a self-aware and fully controllable grid system—an Intelligent Grid System (IGS). We will discuss a novel set of design guidelines for utilities (and other industries) to build their own Open Intelligent Grid System with the lowest possible risk and cost, while achieving the architectural criteria, technical features and functions required. We will discuss how to avoid the dead ends to which limited design and architecture can lead, and we will lay out the design solutions that will overcome the business and technical challenges posed by an array of technology products and business imperatives. Using IGIN (Intelligent Grid Interface Node), one can integrate or connect hybrid networks for different purposes, such as power electric industry, telecommunication, computer network, and Internet.
Owner:DIGITALGIC
Distributed inventory management system
InactiveUS20080099557A1Reliable trackingCommerceBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalTransceiverTriangulation
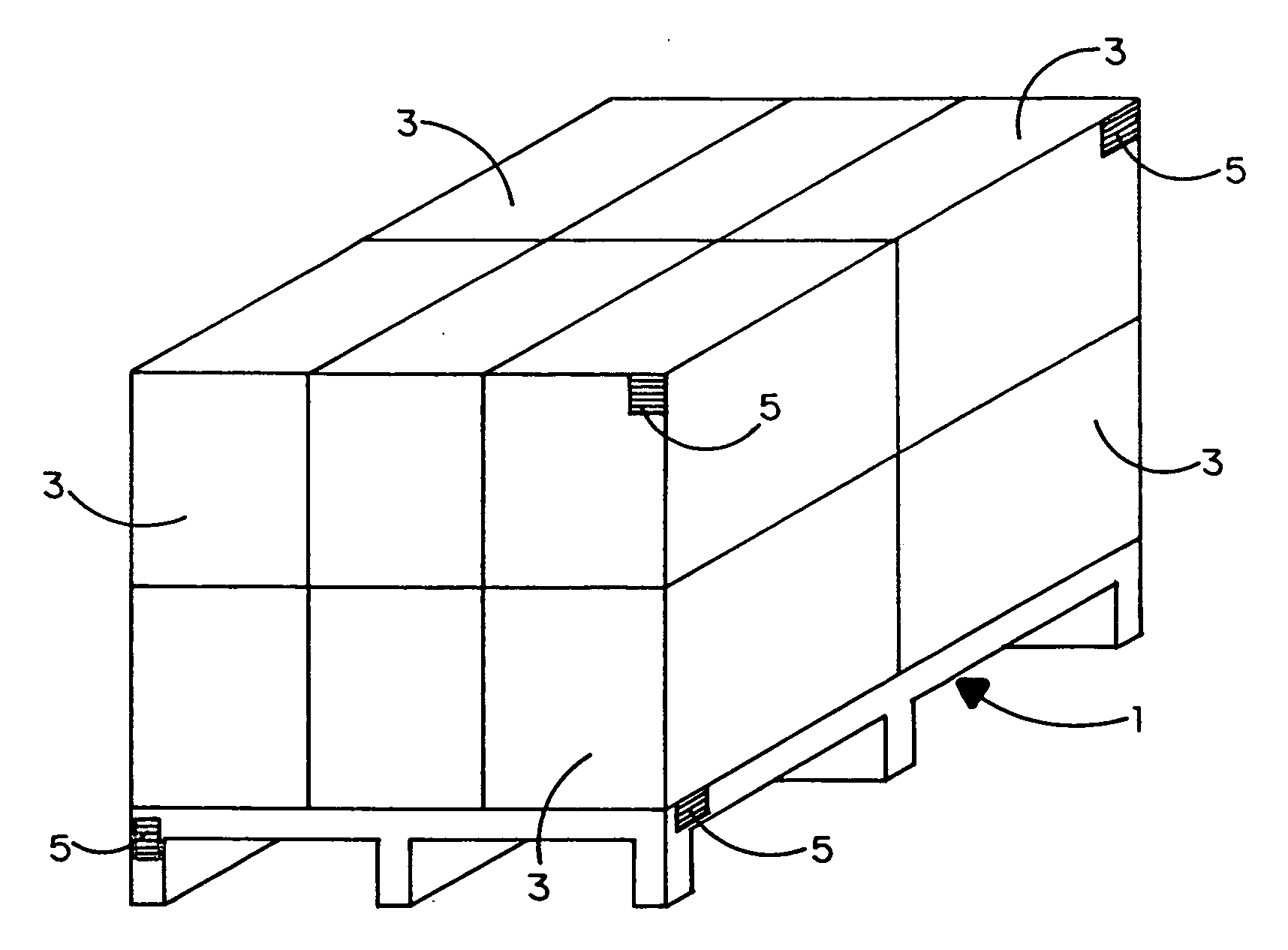
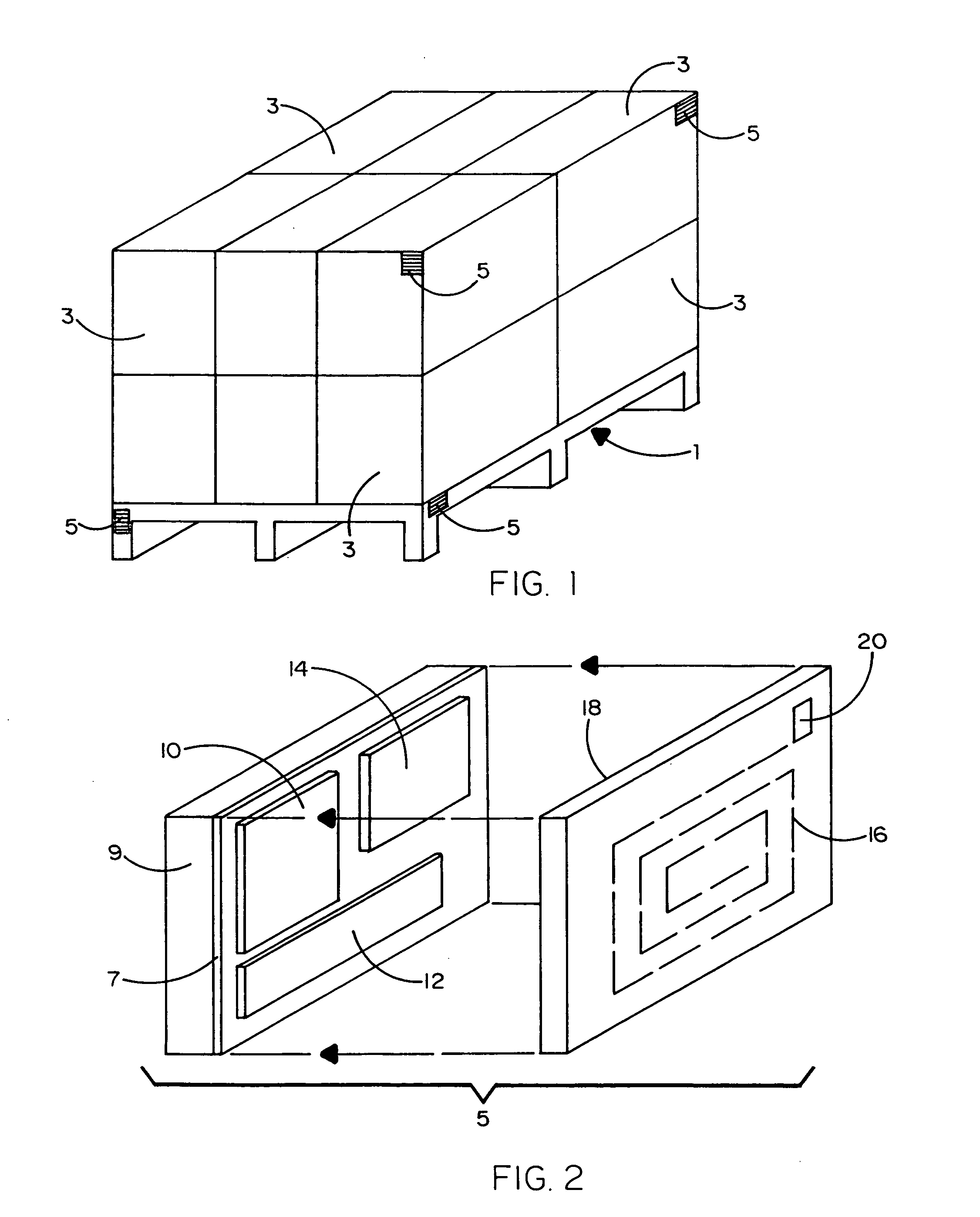
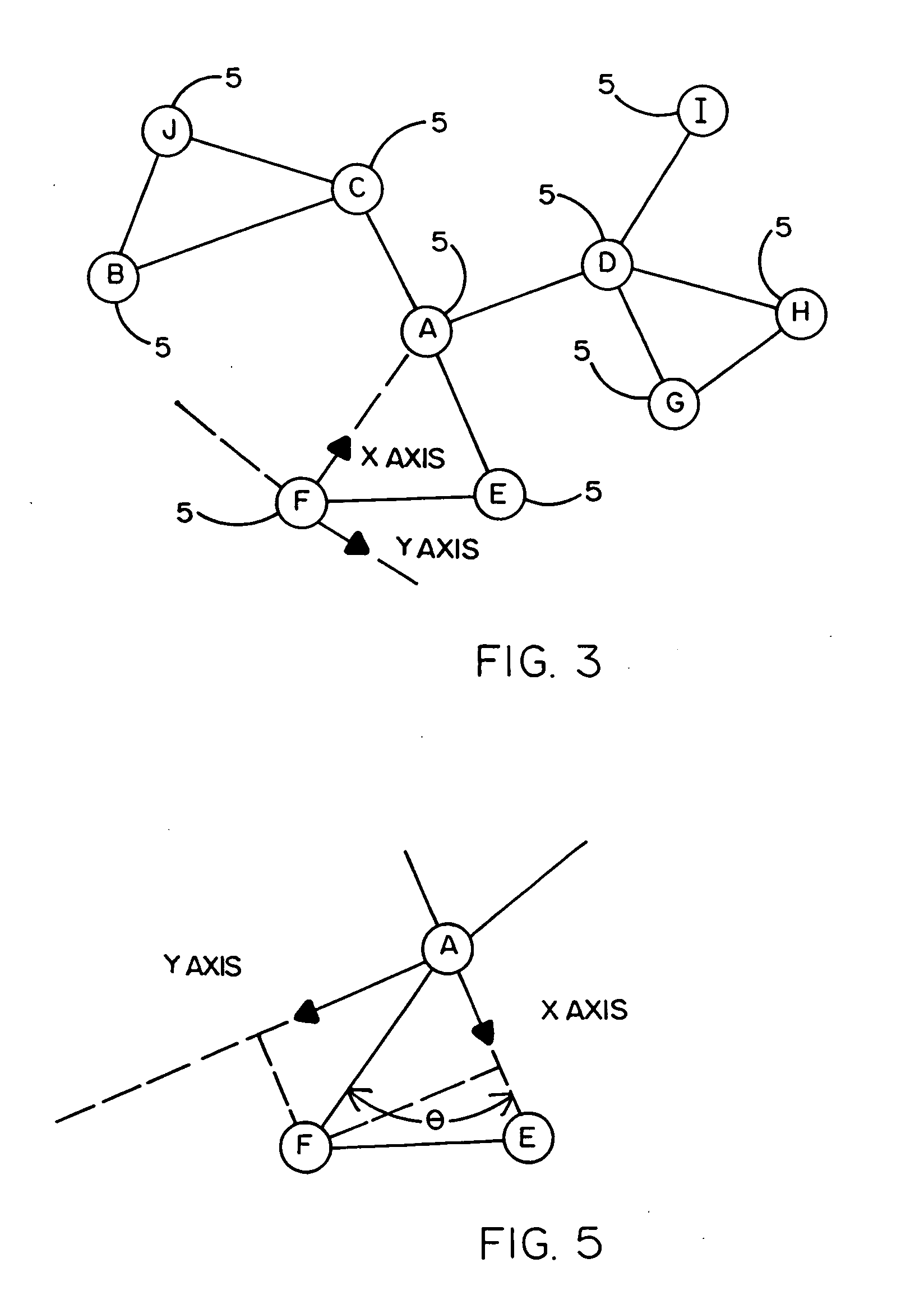
Disclosed is a distributed inventory management system in which a self-awareness, self-regulating and self-organizing method is used to compile on a real-time basis ad hoc databases from which the locations of a number of geographically distributed inventory units (e.g., pallets, shipping containers, trailers, railroad cards, trucks, and even people) can be reliably tracked. Each inventory unit in a neighborhood of inventory units carries an electronic tag that includes an alterable memory, a transceiver and a microprocessor. The distance from one inventory unit in the neighborhood to another is dependent upon the received signal strength intensity transmitted between and calculated by the respective transceivers of the electronic tags of different inventory units. The alterable memory of each electronic tag stores first and second databases in which are listed and updated over time the nearest and next nearest neighbors to a particular inventory unit. A dominant inventory unit in the neighborhood establishes a local coordinate system with itself located at the origin thereof, and the other inventory units apply a triangulation algorithm to orient themselves with respect to the local coordinate system. By virtue of the foregoing, the location of the other inventory units relative to the location of the dominant inventory unit can be calculated.
Owner:JAMES KENNETH A
Multi-platform collaboration appliance
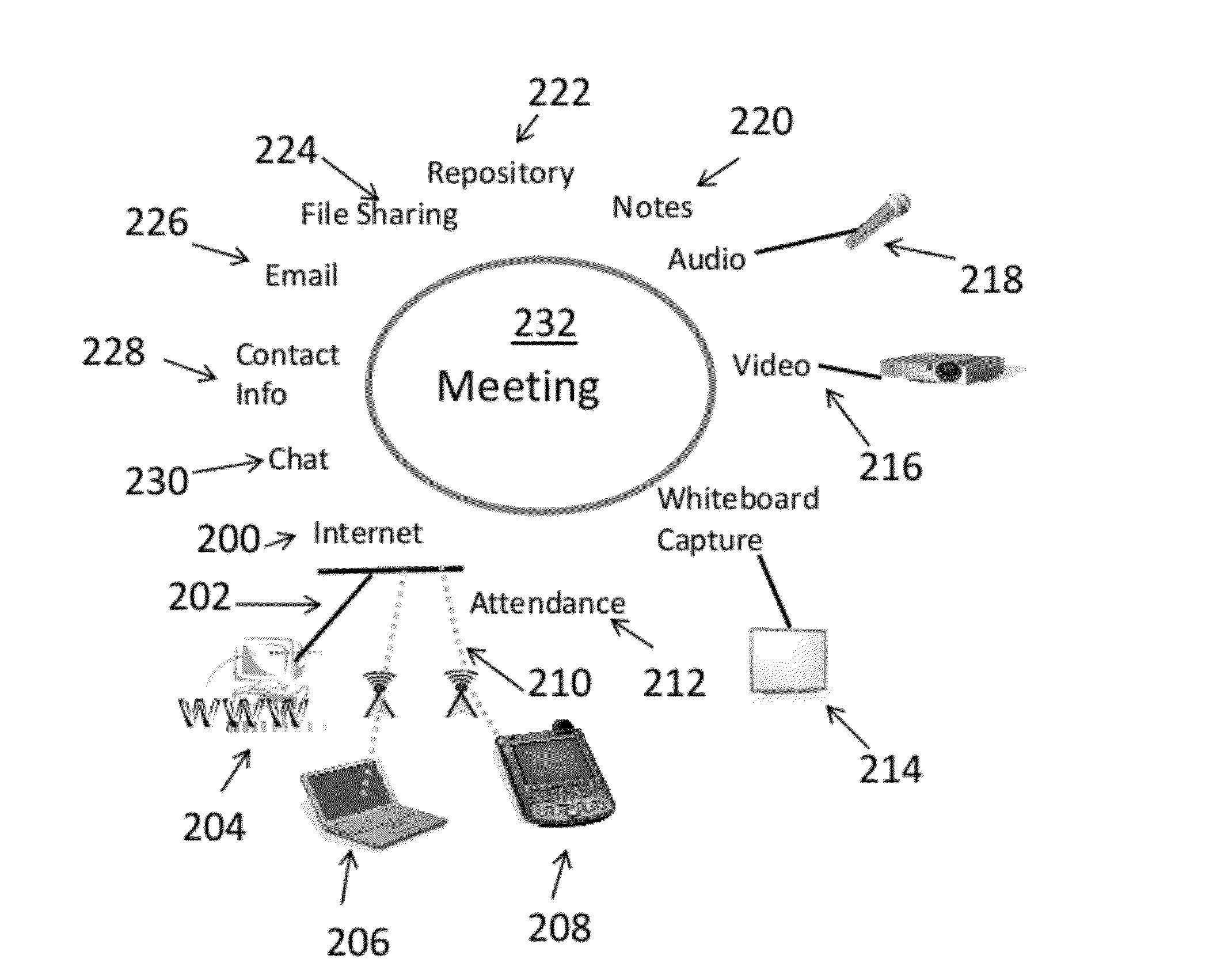
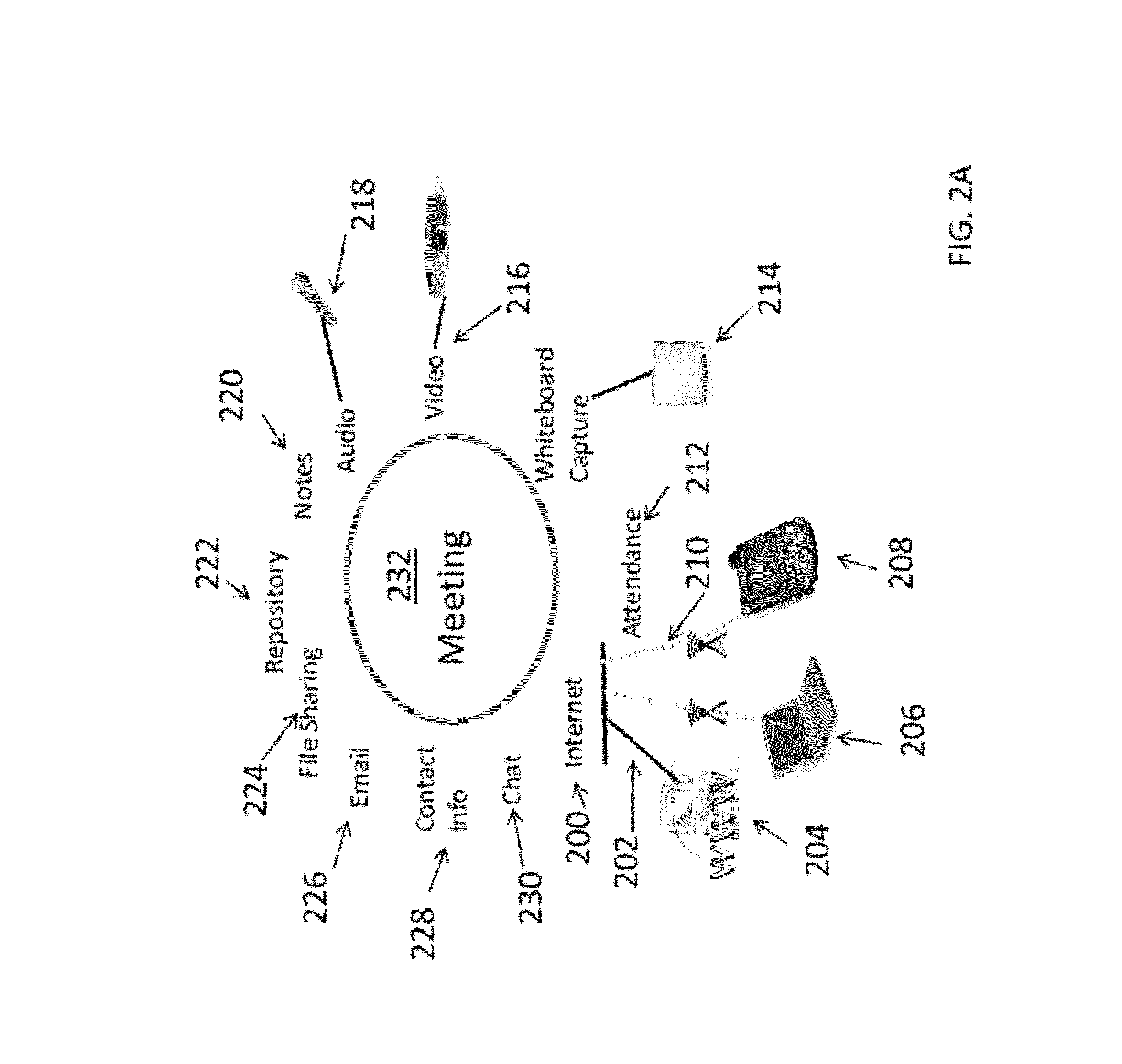
The invention contains a private self-aware network. The network will use multi-point Bluetooth technology or Wi-Fi or a direct connection (though not limited to any of these technologies) to provide this capability. By enabling the invention to detect other invention connections, accessories, and users, it can perform many of the network functions common in today's marketplace. A few examples include instant send or sharing of files to or with anybody linked through the invention or to a specific device. A chat window can be created to talk to specific people or to groups of people on the invention network. Registration information for conference discussion sessions can provide files to update customer databases or CRM type systems. Classroom attendance and assignments can be passed between the teacher and student. These are just a few examples of what can be done using this new network feature but the invention is not limited to just these. Due to a limited number of electrical wall sockets, a daisy chain option can be incorporated into the invention as well. The user has the option for directly connecting the power input of all the inventions in the room together rather than plugging in each one individually. There are four basic settings: Business (coffee shop), Active Conference, Active Classroom, and Professional Client. These offer standard settings usually expected in that kind of environment.
Owner:AUSFELD JEFFREY J
Intelligent grid system
ActiveUS20070226290A1Low possible riskLow possible costComputer controlSimulator controlGuidelineUtility industry
The future of the utility industry will be defined by how its leaders can transform the grid from a “passive” network of cables, wires, poles, and other hardware to a self-aware and fully controllable grid system—an Intelligent Grid System (IGS). We will discuss a novel set of design guidelines for utilities (and other industries) to build their own Open Intelligent Grid System with the lowest possible risk and cost, while achieving the architectural criteria, technical features and functions required. We will discuss how to avoid the dead ends to which limited design and architecture can lead, and we will lay out the design solutions that will overcome the business and technical challenges posed by an array of technology products and business imperatives. Using IGIN (Intelligent Grid Interface Node), one can integrate or connect hybrid networks for different purposes, such as power electric industry, telecommunication, computer network, and Internet.
Owner:DIGITALGIC
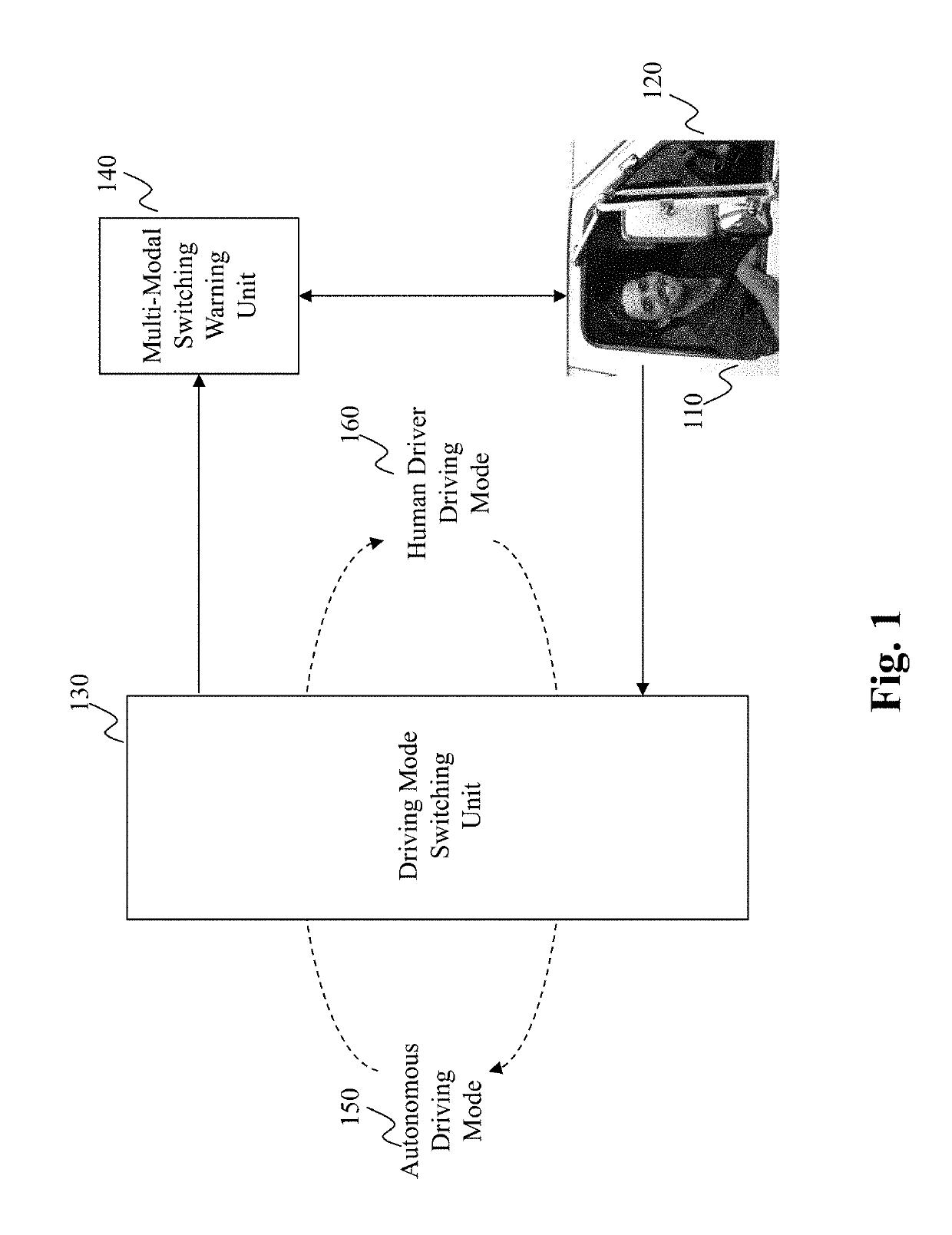
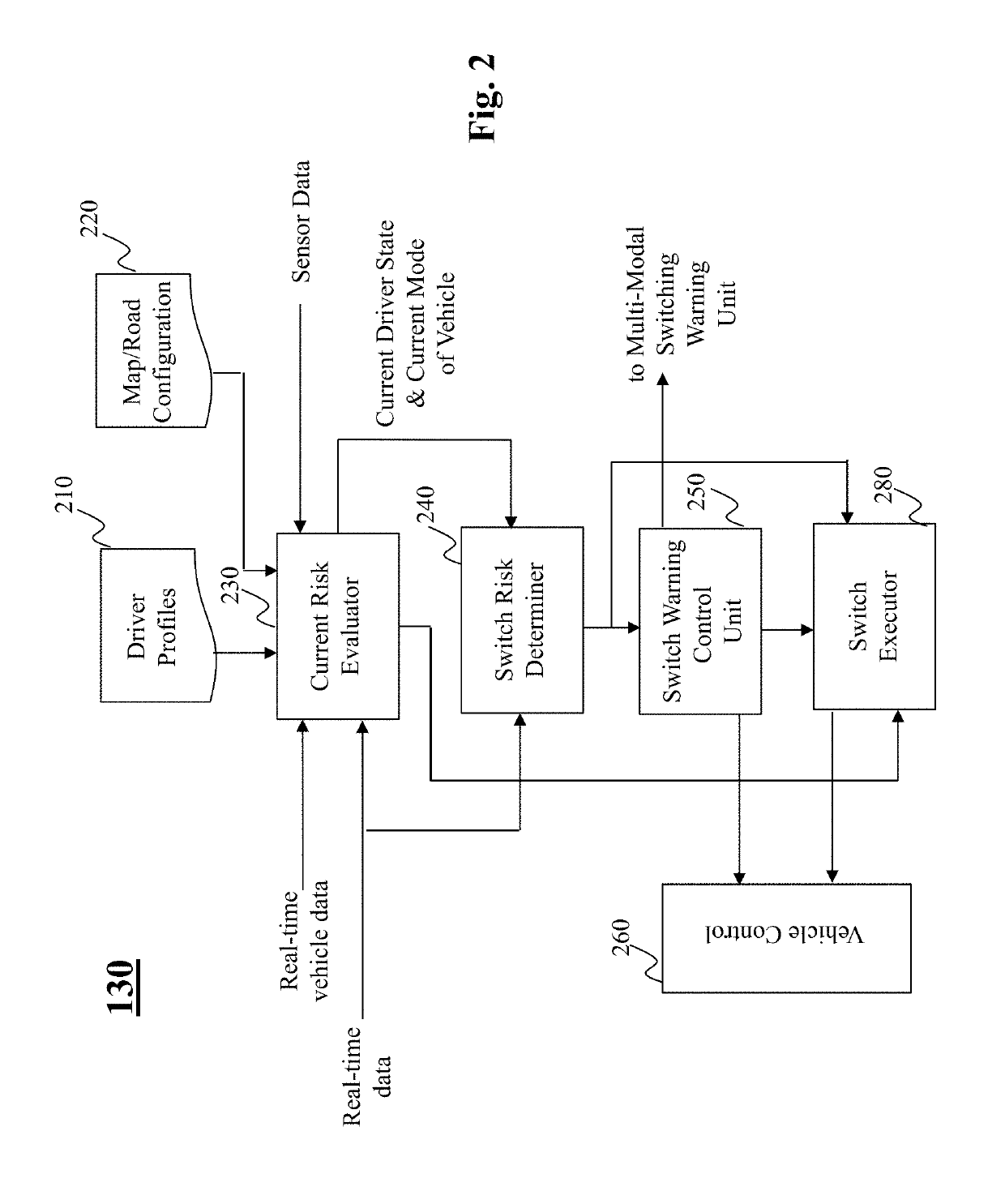
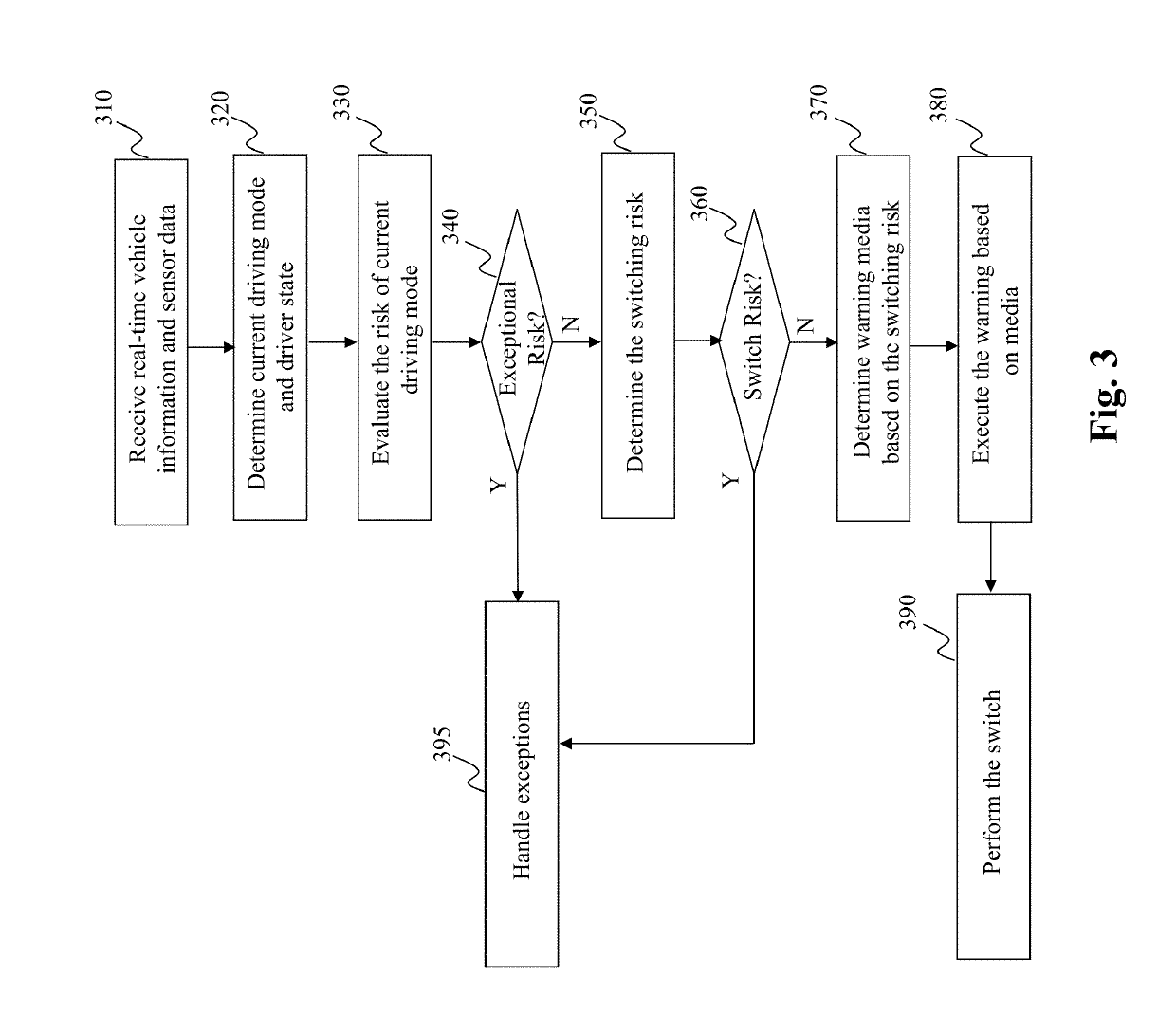
Method and system for driving mode switching based on self-aware capability parameters in hybrid driving
ActiveUS20190187701A1Program initiation/switchingExternal condition input parametersDriver/operatorReal-time data
The present teaching relates to method, system, and medium, for switching a mode of a vehicle. Real-time data related to the vehicle are received, which include intrinsic / extrinsic capability parameters, based on which a set of tasks to switch from a current mode to a different mode is determined. A first duration of time required for the switch is determined based on a first risk evaluated with respect to the current mode and the real-time data. A task duration time needed by a driver to complete the task is estimated for each of the set of tasks. A second risk for the switching is estimated based on the required first duration of time and a total task duration times needed to complete the set of tasks. The switch is carried out when the second risk satisfying a criterion.
Owner:PLUSAI INC
Dynamic object management protocol
ActiveUS8234363B1Time-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsEscape characterMessage type
An extensible communications protocol configured to enable dynamic discovery and management of self-aware devices in a multiple element computing architecture is provided. The protocol enables a message consisting essentially of a destination ID, a source ID, a message type, optional payloads, and a delimiter arrangement. The protocol is based on a scheme which represents structured data. Within the scheme, stacked delimiting characters are used to separate higher level data. Escape sequencers are selected to represent at least the escape character, the delimiting character, and the NULL (nothing at all). The lowest data partition may embed encoded data of any level, and can form nested encapsulation. New optional data types and message types can be added. Basic message types are supported to achieve the dynamic discovery and management of self-aware devices, and such protocol is used as the base of a dynamic device discovery and management system for self-aware devices.
Owner:KUO KUO HUA
Generating and analyzing business process-aware modules
InactiveUS20050223020A1Efficient analysisAccurate predictionDigital computer detailsOffice automationService-level agreementIncome loss
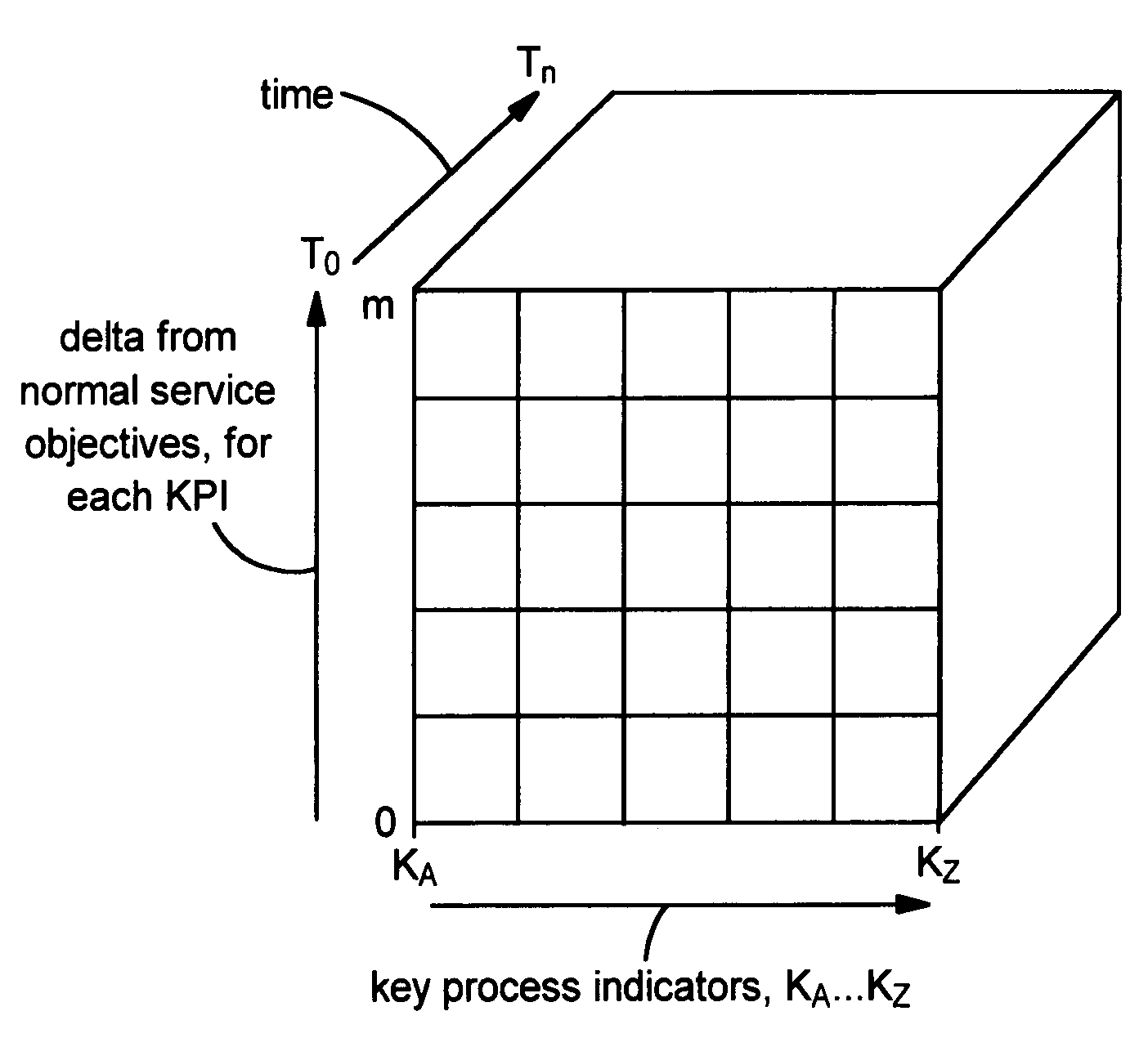
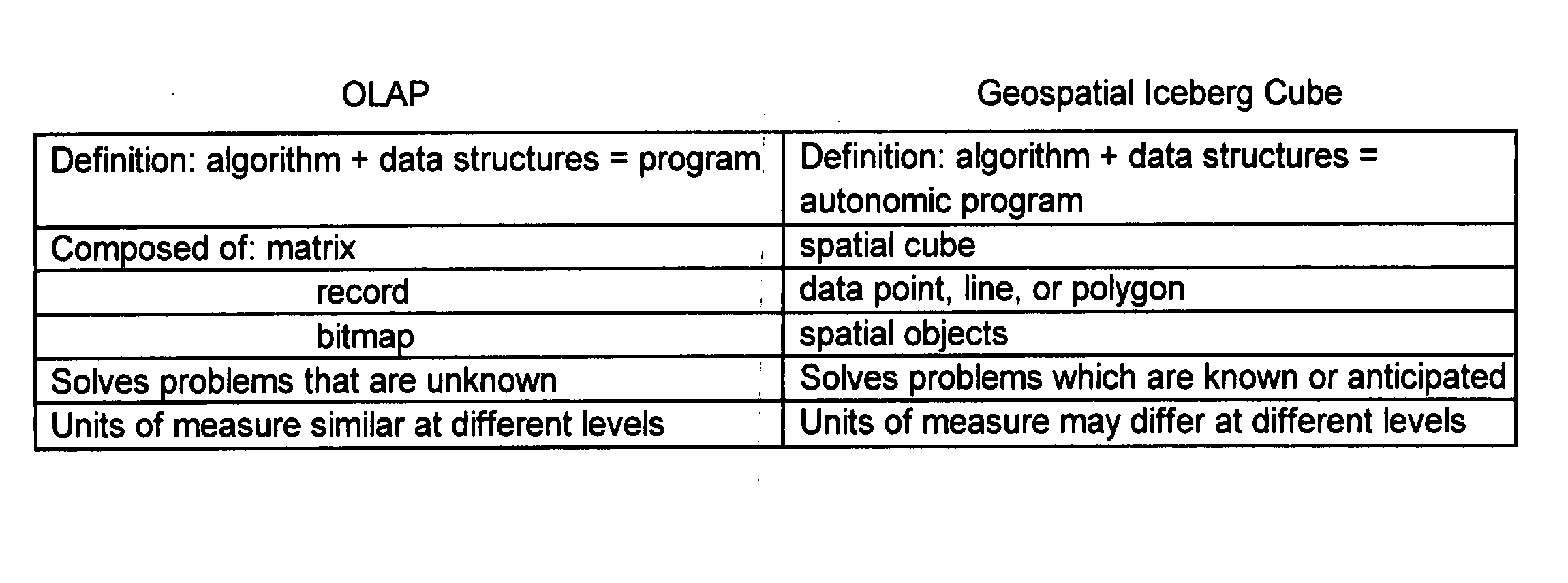
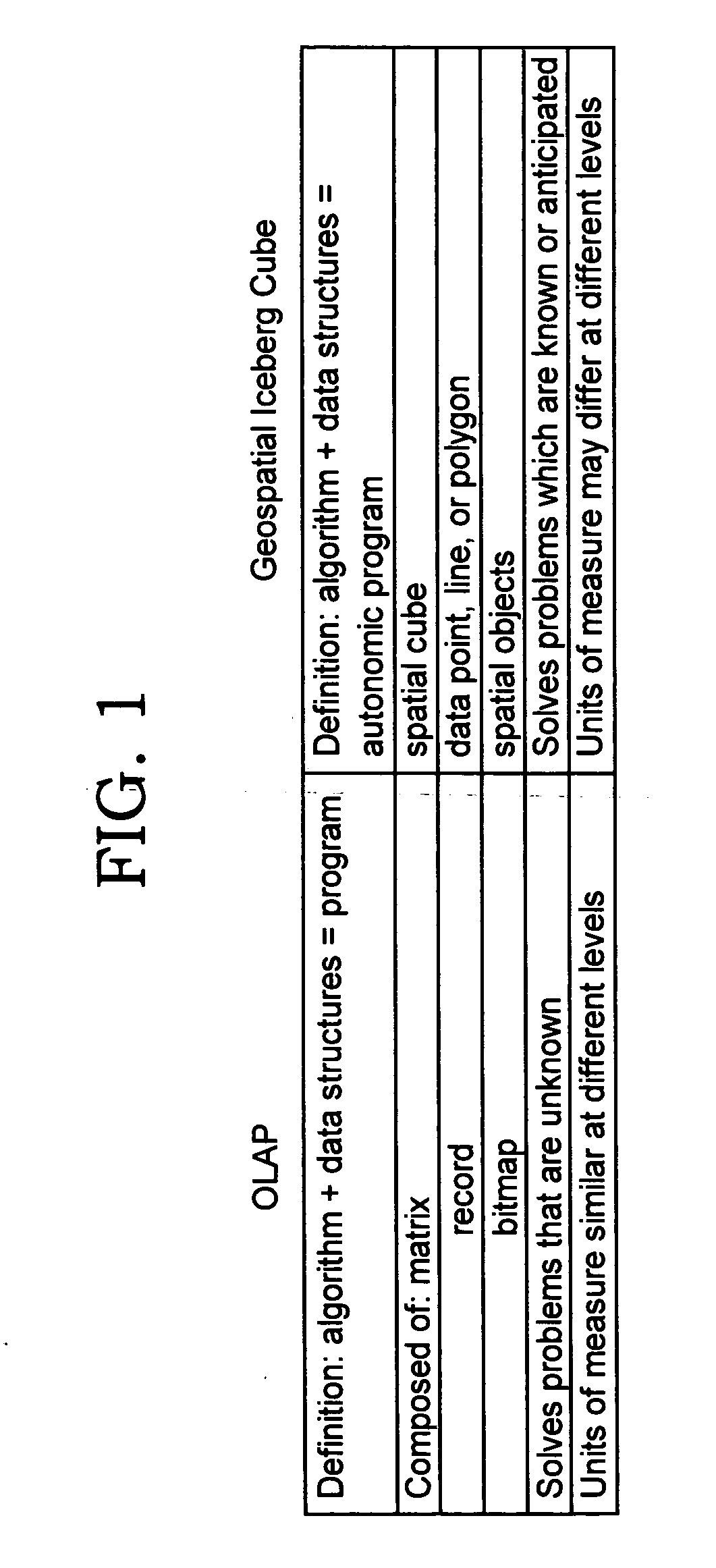
Techniques are disclosed for efficiently analyzing measurement data for business processes (for example, in a service provider environment). Business process-aware modules or “cubes” are created from the measurement data, using features of a spatially-enabled database system. A “drill-down” approach is provided for investigating underlying information for a cube (including lower-level linked cubes). Data types other than cubes, such as planes from which a cube is constructed, may also be analyzed. The disclosed techniques may be used to provide autonomic systems, which are self-aware, at a business process level. That is, based on results of analyzing data represented by a cube, autonomic adjustments may be made. In a service provider environment, the analysis and / or the autonomic adjustments may be directed toward enabling the service provider to avoid jeopardizing commitments in service level agreements (and the revenue loss that may result when the commitments are not met).
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Intelligent Grid System
ActiveUS20090138100A1Electric signal transmission systemsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsGuidelineThe Internet
The future of the utility industry will be defined by how its leaders can transform the grid from a “passive” network of cables, wires, poles, and other hardware to a self-aware and fully controllable grid system—an Intelligent Grid System (IGS). We will discuss a novel set of design guidelines for utilities (and other industries) to build their own Open Intelligent Grid System with the lowest possible risk and cost, while achieving the architectural criteria, technical features and functions required. We will discuss how to avoid the dead ends to which limited design and architecture can lead, and we will lay out the design solutions that will overcome the business and technical challenges posed by an array of technology products and business imperatives. Using IGIN (Intelligent Grid Interface Node), one can integrate or connect hybrid networks for different purposes, such as power electric industry, telecommunication, computer network, and Internet.
Owner:DIGITALGIC
System and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating presence of substance
ActiveUS6946671B2Easily and conveniently removing and replacingEasy to disassembleSolid-state devicesInvestigating moving sheetsRadioactive agentComputer science
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
System and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating presence of substance
ActiveUS7126104B2Easily and conveniently removing and replacingEasy to disassembleInvestigating moving sheetsCounting objects on conveyorsRadioactive agentComputer science
A system and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating a presence of a solid, liquid, gas, or other substance of interest, particularly a dangerous, hazardous, or otherwise threatening chemical, biological, or radioactive substance. The system comprises one or more substantially automated, location self-aware remote sensing units; a control unit; and one or more data processing and storage servers. Data is collected by the remote sensing units and transmitted to the control unit; the control unit generates and uploads a report incorporating the data to the servers; and thereafter the report is available for review by a hierarchy of responsive and evaluative authorities via a wide area network. The evaluative authorities include a group of relevant experts who may be widely or even globally distributed.
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
Method and system for personalized motion planning in autonomous driving vehicles
InactiveUS20190185012A1Autonomous decision making processNavigation instrumentsProgram planningEngineering
The present teaching relates to method, system, medium, and implementation of automatic motion planning for an autonomous driving vehicle. Self-aware capability parameters are obtained that are instantiated with respect to a current location of the autonomous driving vehicle and are to be used to estimate the operational capability of the autonomous driving vehicle with respect to the current location. A preference of a passenger present in the autonomous driving vehicle is estimated with respect to vehicle motion. The motion of the autonomous driving vehicle is planned automatically based on the self-aware capability parameters and the preference of the passenger.
Owner:PLUSAI INC
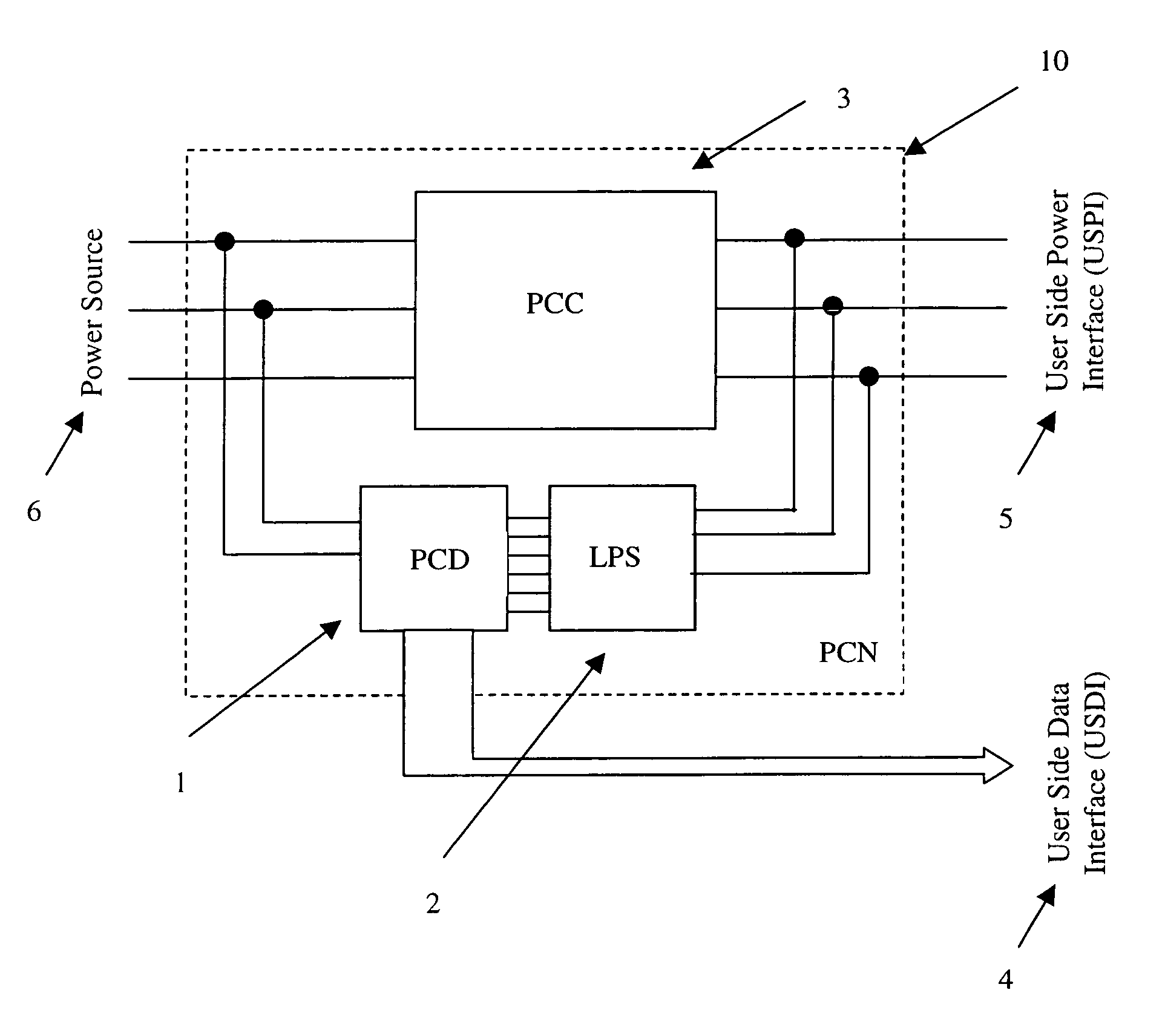
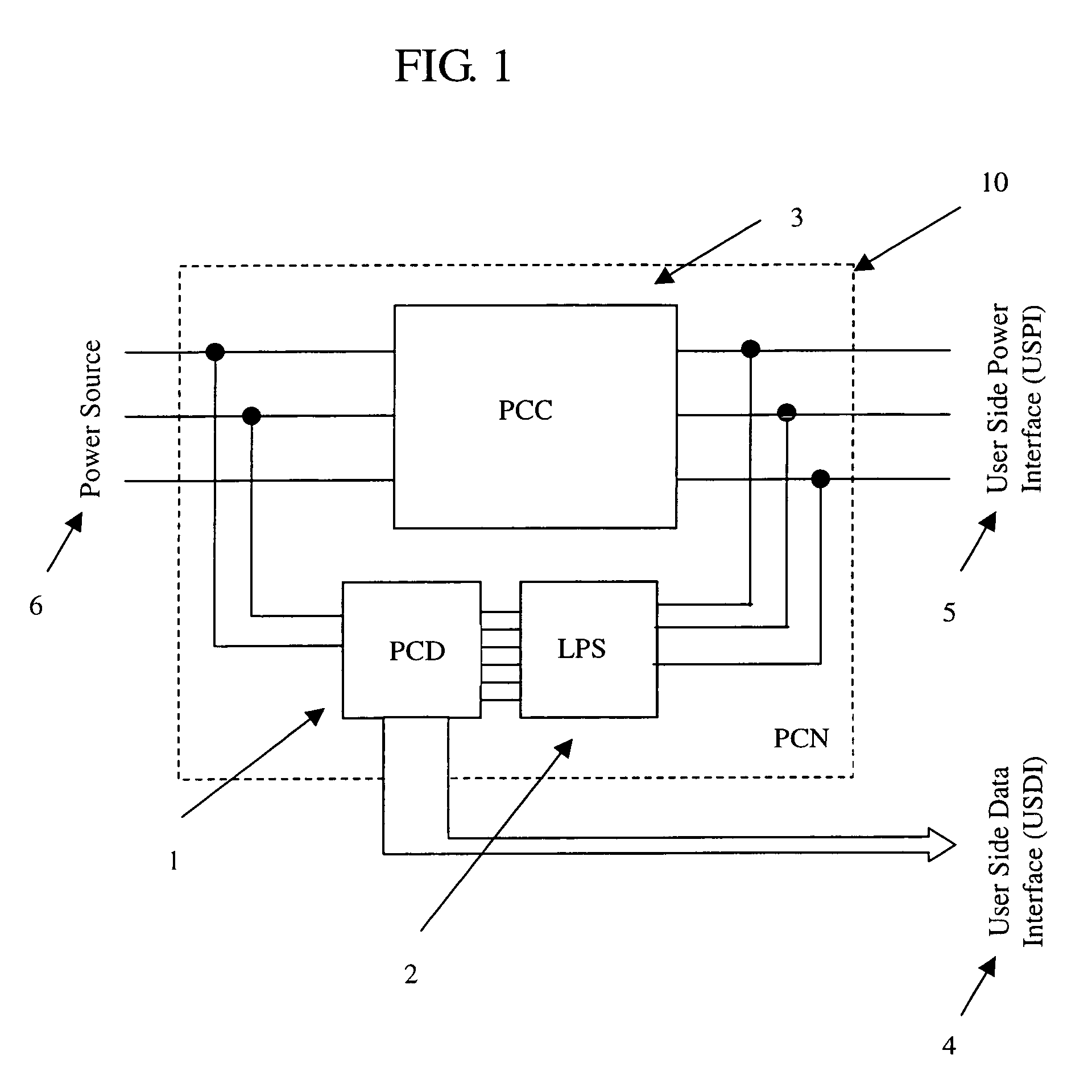
Intelligent, self-aware powerline conditioning and communication node
ActiveUS7804673B2Improve interferenceImprove noiseSystems using filtering and bypassingPower distribution line transmissionEngineeringNoise reduction
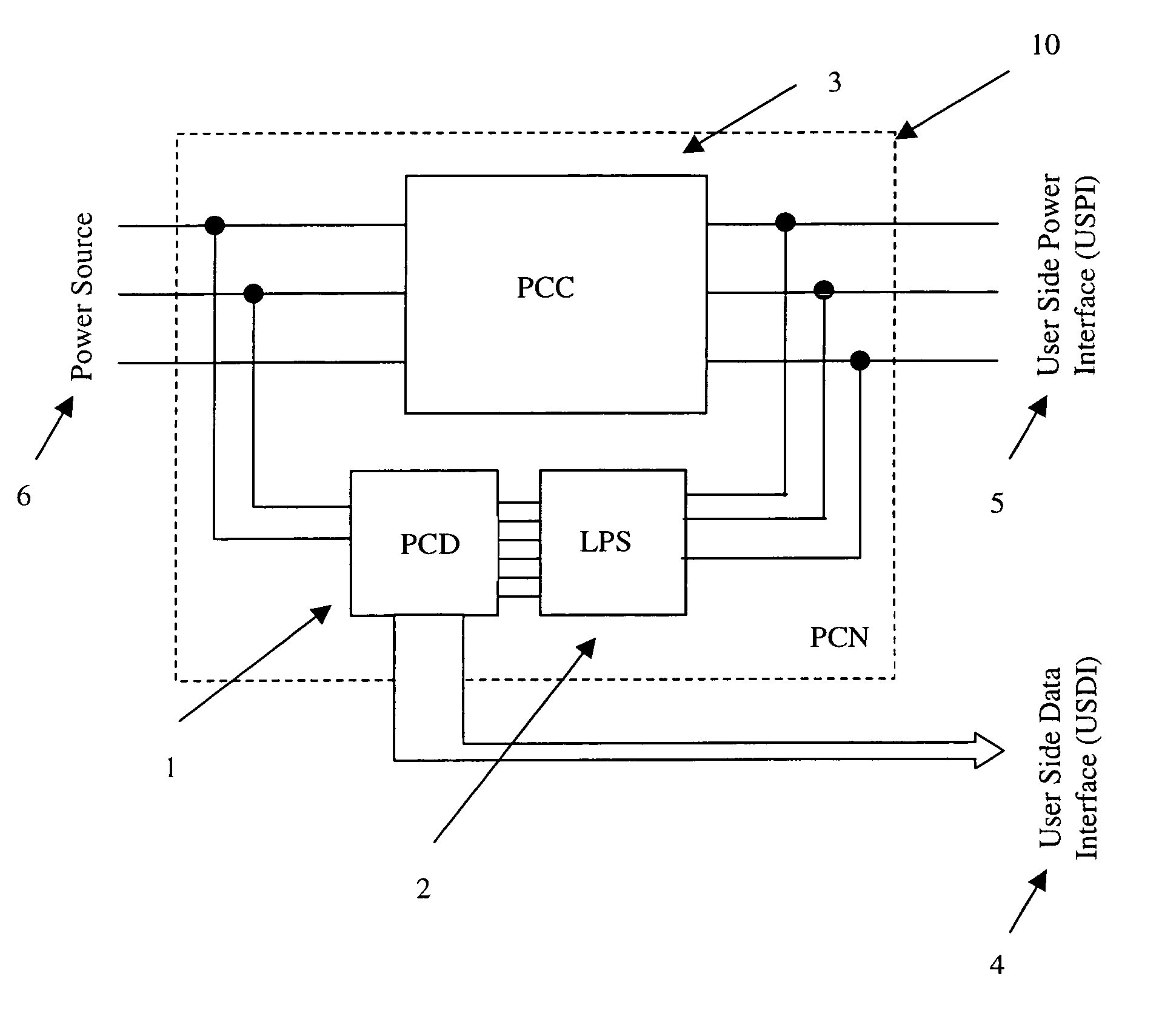
Powerline networks are inherently noisy and subject to power surges, spikes, and other events. Devices exist to combat these issues and protect electrical appliances that are connected downstream from the power sources for theses devices, but these devices usually also severely limit data communication that may also be desired on this network. This invention provides an intelligent, self-aware powerline conditioning and communication node that allows for, or even improves, data communication on the network, and still provides for noise reduction, line filtering, and surge protection for downstream electrical appliances.
Owner:MACALUSO MICHAEL +2
Method and system for human-like driving lane planning in autonomous driving vehicles
ActiveUS20190185011A1Autonomous decision making processNavigation instrumentsEngineeringOperational capabilities
The present teaching relates to method, system, medium, and implementation of lane planning in an autonomous vehicle. Sensor data are received that capture ground images of a road the autonomous vehicle is on. Based on the sensor data, a current lane of the road that autonomous vehicle is currently occupying is detected. Lane control for the autonomous vehicle is planned based on the detected current lane and self-aware capability parameters in accordance with a driving lane control model. The self-aware capability parameters are used to predict operational capability of the autonomous vehicle with respect to a current location of the autonomous vehicle. The driving lane control model is generated based on recorded human driving data to achieve human-like lane control behavior in different scenarios.
Owner:PLUSAI INC
Method And Apparatus For Making Optimal Use Of An Asymmetric Interference Channel In Wireless Communication Systems
ActiveUS20140126488A1Improve throughputMeet complex requirementsNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless commuication servicesMultiuser detectionHigh rate
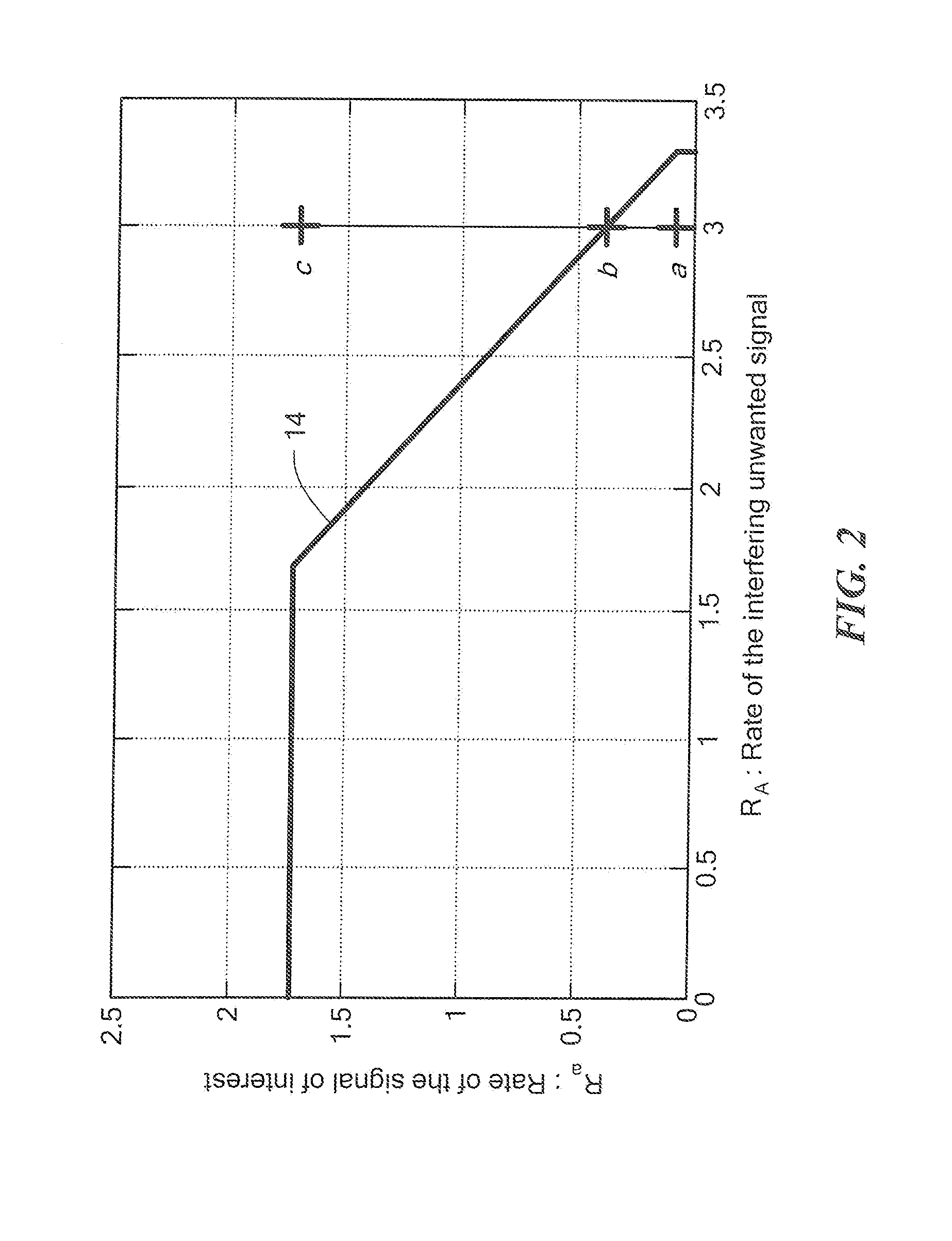
A method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving in black space is described. The asymmetric interference channel is an appropriate model for many realistic scenarios, especially those arising more frequently as dynamic spectrum access (DSA) becomes more prevalent. As DSA nodes evolve to become more cognitive (e.g. self aware, environment aware, and adaptive), the prevailing white space seeking and gray space adapting policies leave a significant portion of the spectrum, namely, the black space, untapped. Described herein is a throughput versus SINR result and a corresponding technique for jointly choosing a transmission rate and multiuser detection algorithm that allows computationally constrained cognitive DSA nodes high rate operation in spectrum black space. Also described is an information theoretic motivated policy for seemingly insignificant waveform design choices that greatly enhance the throughput of a secondary sender-receiver pair while fulfilling a given complexity requirement within the secondary node's receiver.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Intelligent, self-aware powerline conditioning and communication node
ActiveUS20060072621A1Improve interferenceImprove noiseSystems using filtering and bypassingPower distribution line transmissionEngineeringNoise reduction
Powerline networks are inherently noisy and subject to power surges, spikes, and other events. Devices exist to combat these issues and protect electrical appliances that are connected downstream from the power sources for theses devices, but these devices usually also severely limit data communication that may also be desired on this network. This invention provides an intelligent, self-aware powerline conditioning and communication node that allows for, or even improves, data communication on the network, and still provides for noise reduction, line filtering, and surge protection for downstream electrical appliances.
Owner:MACALUSO MICHAEL +2
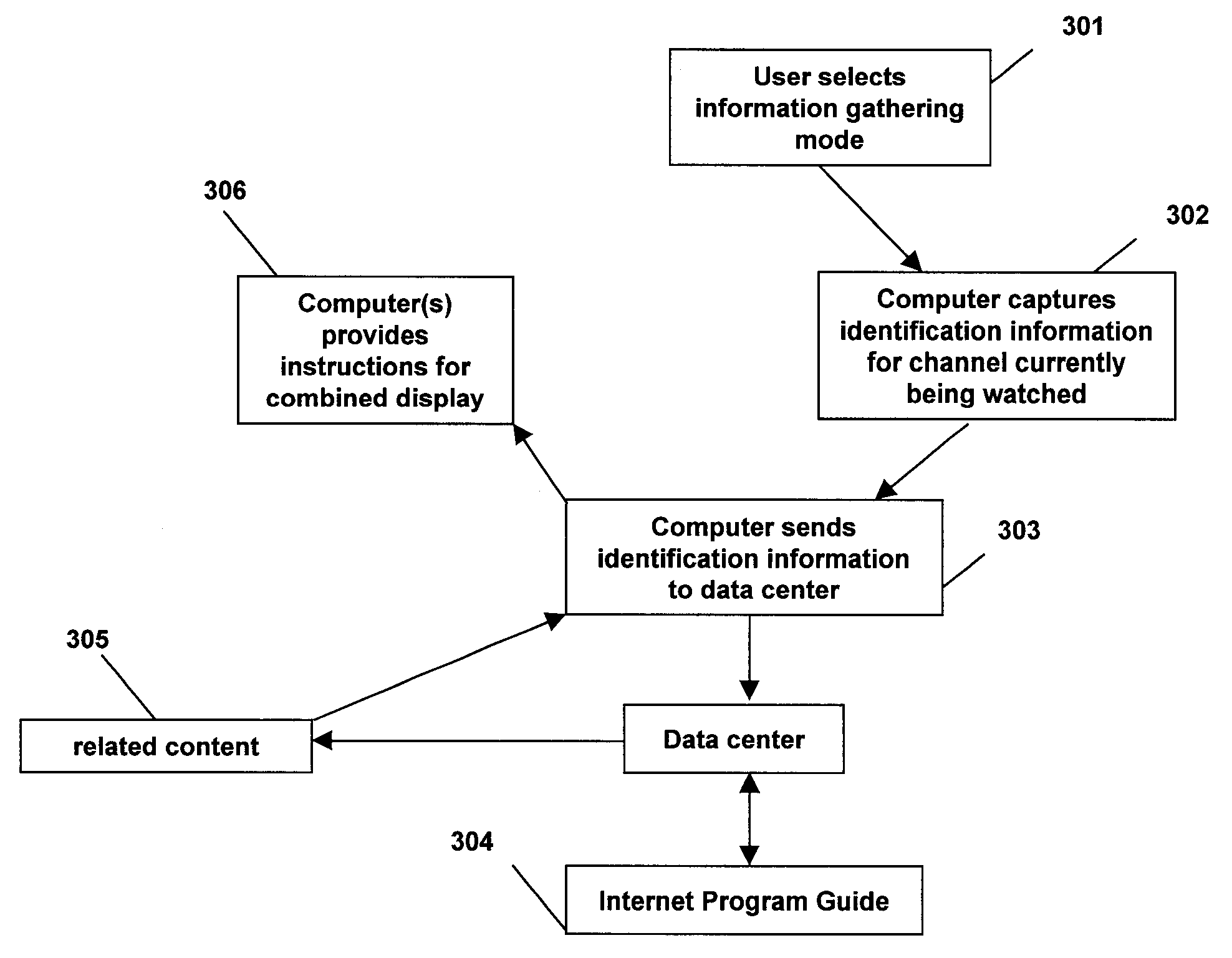
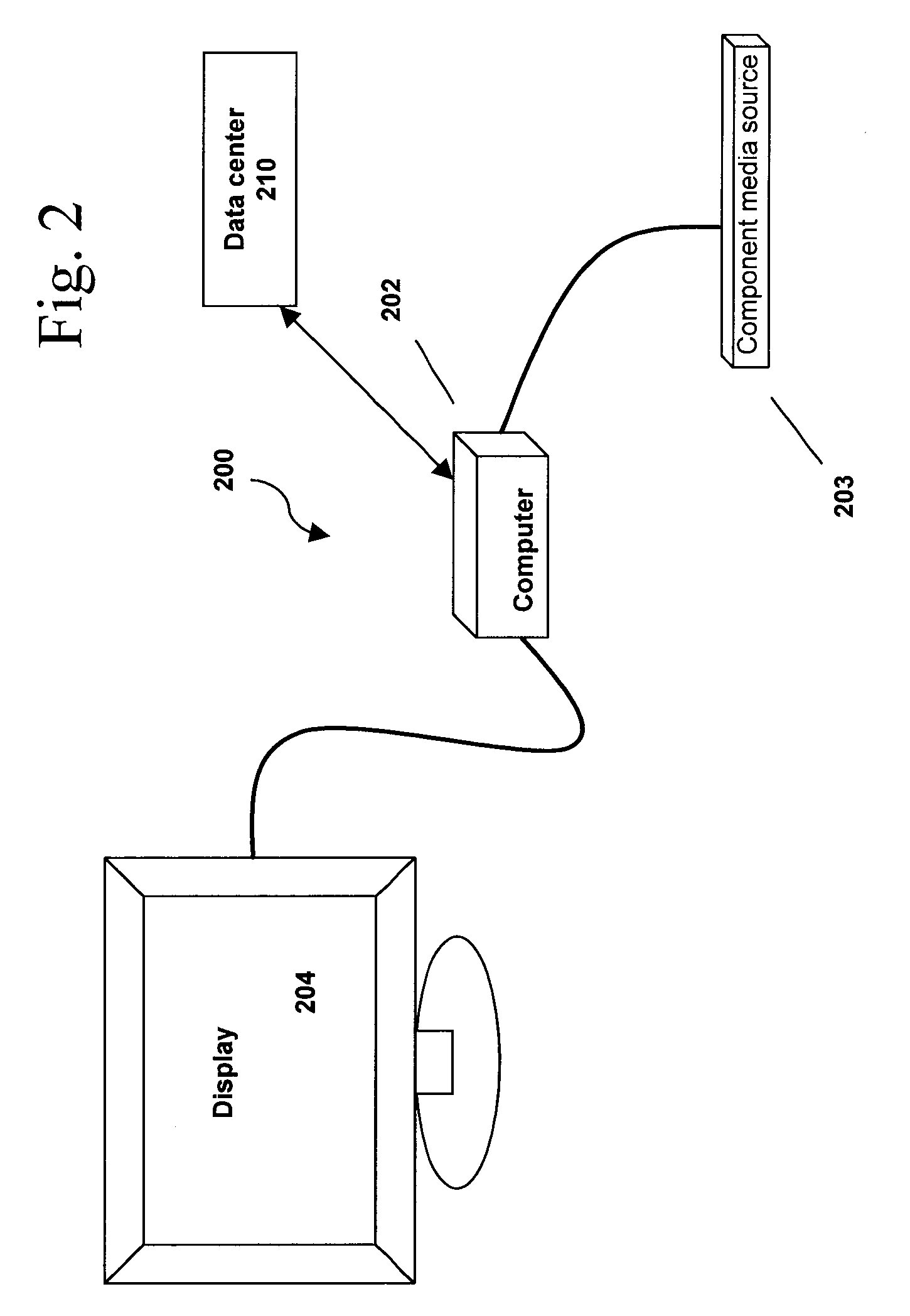
System and method for distributed local content identification
ActiveUS20100131986A1Increase contentTelevision system detailsTransmission systemsMarket placeSystem identification
The invention provides systems and methods to identify local market media content utilizing a disturbed system and to determine what additional content is relevant in a self-aware, automatic way. A central location stores identification information and related content so in the future it is available if and when another user watches the same content. Therefore, the next time local market media content is played, it can be identified and additional related content can be quickly (e.g. in real time) made available.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
System and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating presence of substance
ActiveUS20050171701A1Rapid deploymentEliminates exposure riskInvestigating moving sheetsCounting objects on conveyorsRadioactive agentComputer science
A system and method for identifying, reporting, and evaluating a presence of a solid, liquid, gas, or other substance of interest, particularly a dangerous, hazardous, or otherwise threatening chemical, biological, or radioactive substance. The system comprises one or more substantially automated, location self-aware remote sensing units; a control unit; and one or more data processing and storage servers. Data is collected by the remote sensing units and transmitted to the control unit; the control unit generates and uploads a report incorporating the data to the servers; and thereafter the report is available for review by a hierarchy of responsive and evaluative authorities via a wide area network. The evaluative authorities include a group of relevant experts who may be widely or even globally distributed.
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
Method and apparatus for improved secure computing and communications
InactiveUS20120131316A1Improve securityLow costDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionTheoretical computer scienceSelf aware
A method and apparatus are disclosed that may comprise applying compact markup notation to a general recursive computing system including hardware and software components, the compact markup notation defining things, places, paths, actions and causes within at least one of the hardware and the software of the general recursive computing system, to establish a set of data comprising a definitive description of the general recursive computing system in the compact notation; and synthesizing a self-aware and self-monitoring primitive recursive computing system utilizing the definitive description in the compact markup notation.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Computerized Systems and Methods for Self-Awareness and Interpersonal Relationship Skill Training and Development for Improving Organizational Efficiency
ActiveUS20100055655A1Improve efficiencyFacilitate self-awarenessElectrical appliancesTeaching apparatusViewpointsPerceptual Orientation
A computerized training system and methods are provided for training an individual in self-evaluation and to interact with a partner. The training system and methods comprise an intelligence assessor to identify an intelligence makeup of the individual by scoring a completed intelligence questionnaire. Intelligences include Logic, Emotion and Intuition. An asset assessor assesses the strength of Three Assets of the individual by scoring a completed asset questionnaire. Assets include a Technical, a Psychological, and a Relational asset. A perception assayer identifies a dominant Perceptual Orientation of the individual by cross referencing the intelligence makeup with the viewpoint of the individual. An aggregator collects the profile information of the individual to generate an innate profile report and a self-insight report of the individual. A facilitator aids in exploring the insight report. A synchronizer may synchronize the individual with a partner by forming a dyad between the individual and the partner. A trainer may also train the individual to resolve conflicts with the partner.
Owner:ASHMAN JR WARD
Self-aware adaptive power control system and a method for determining the circuit state
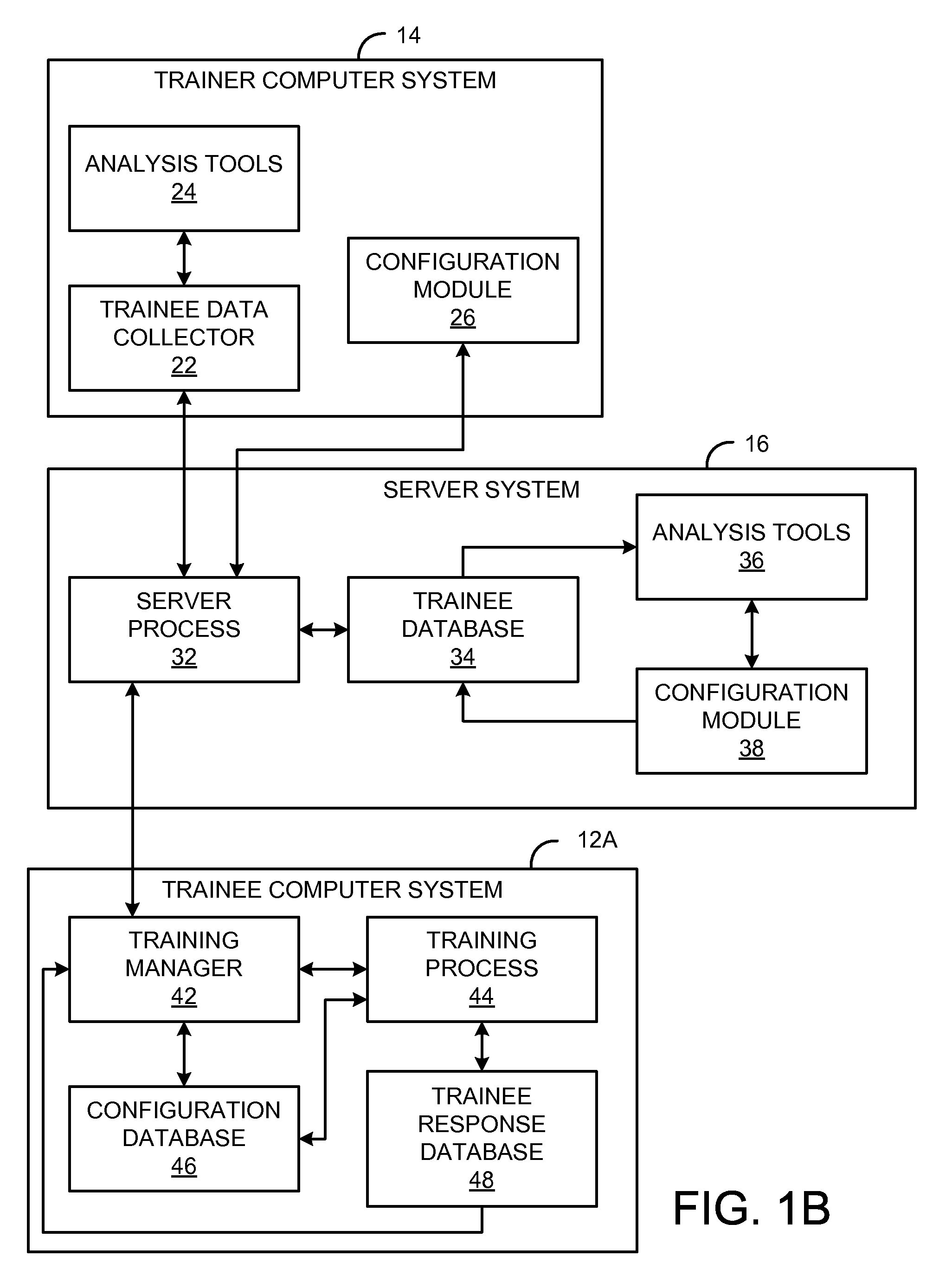
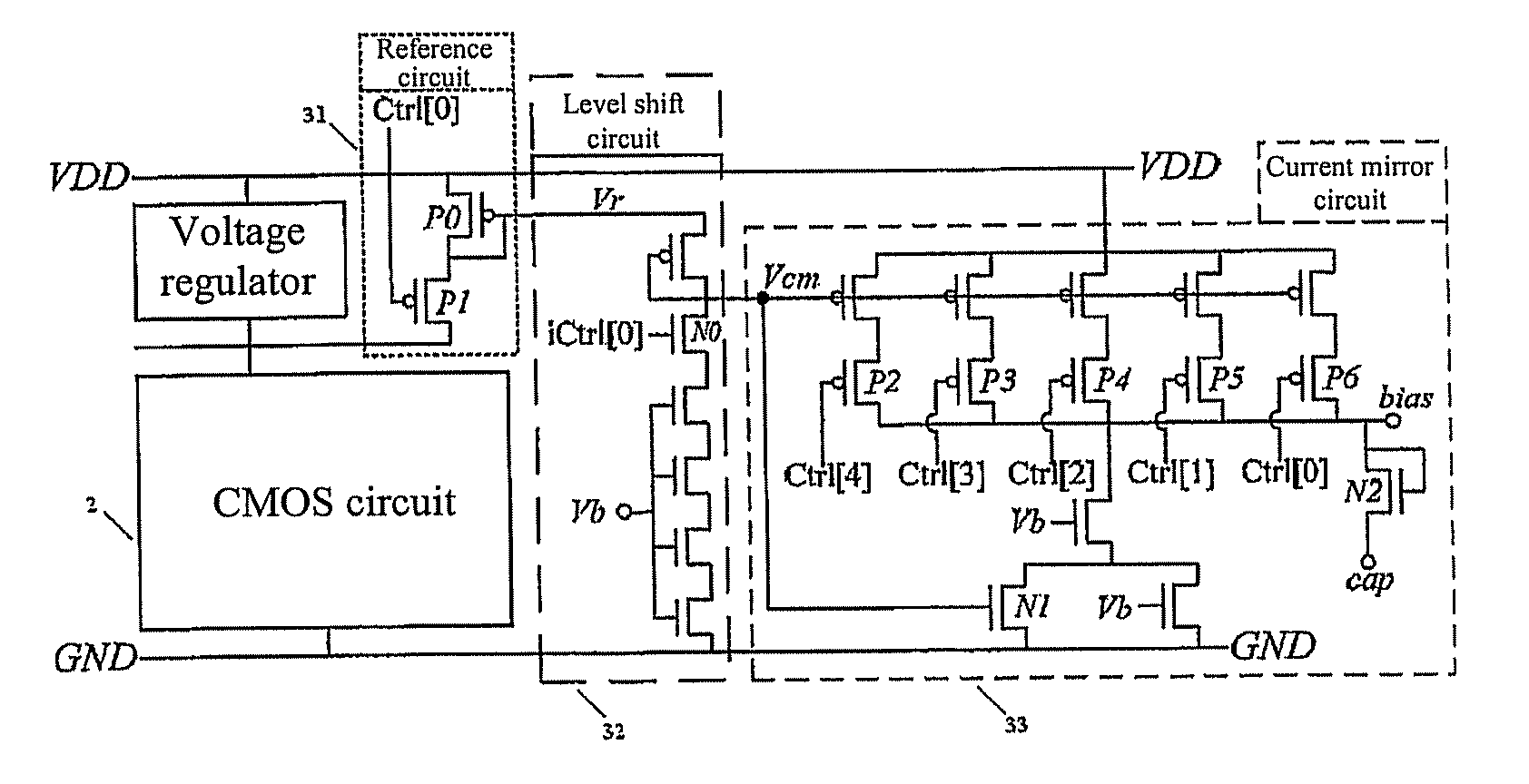
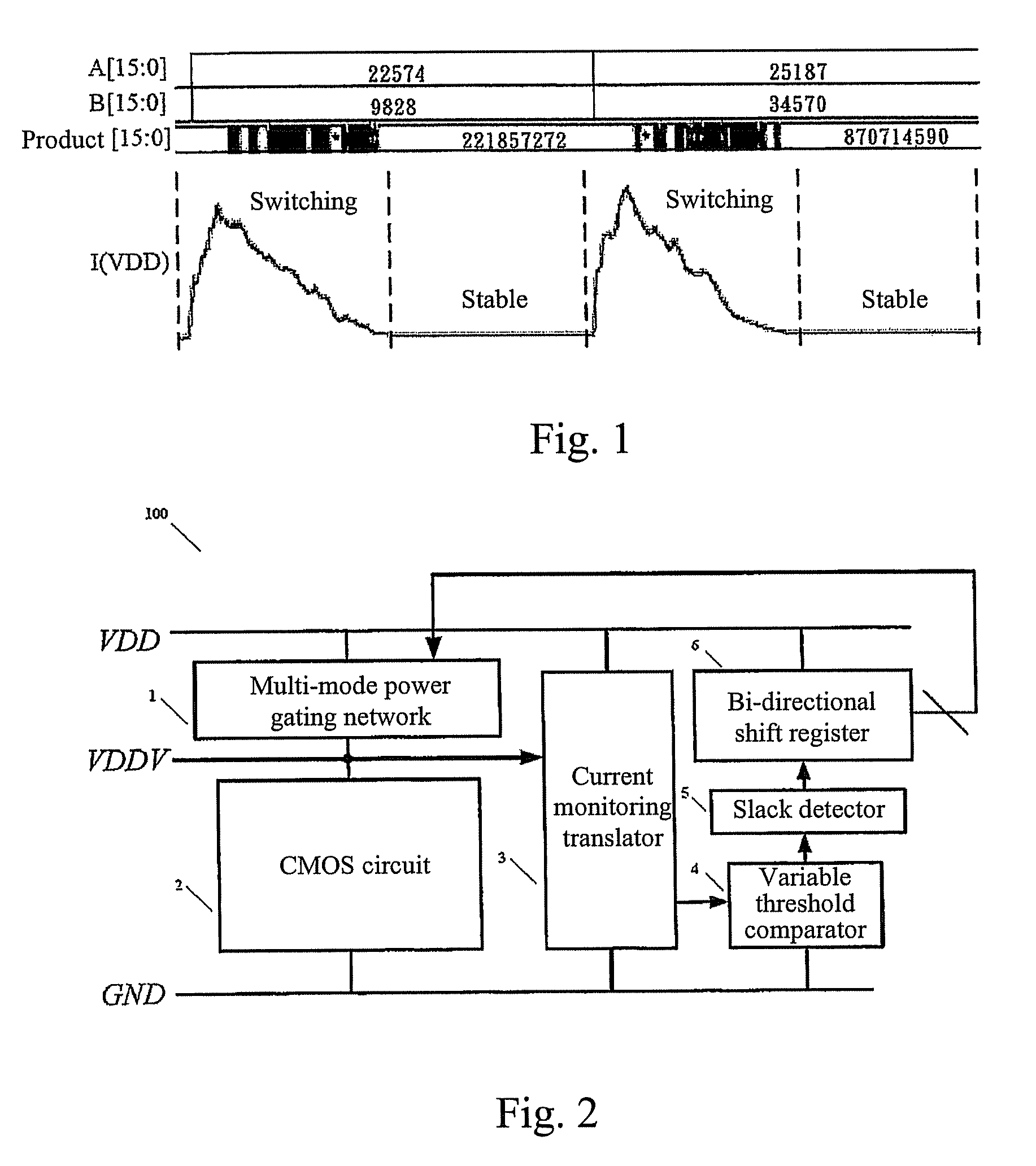
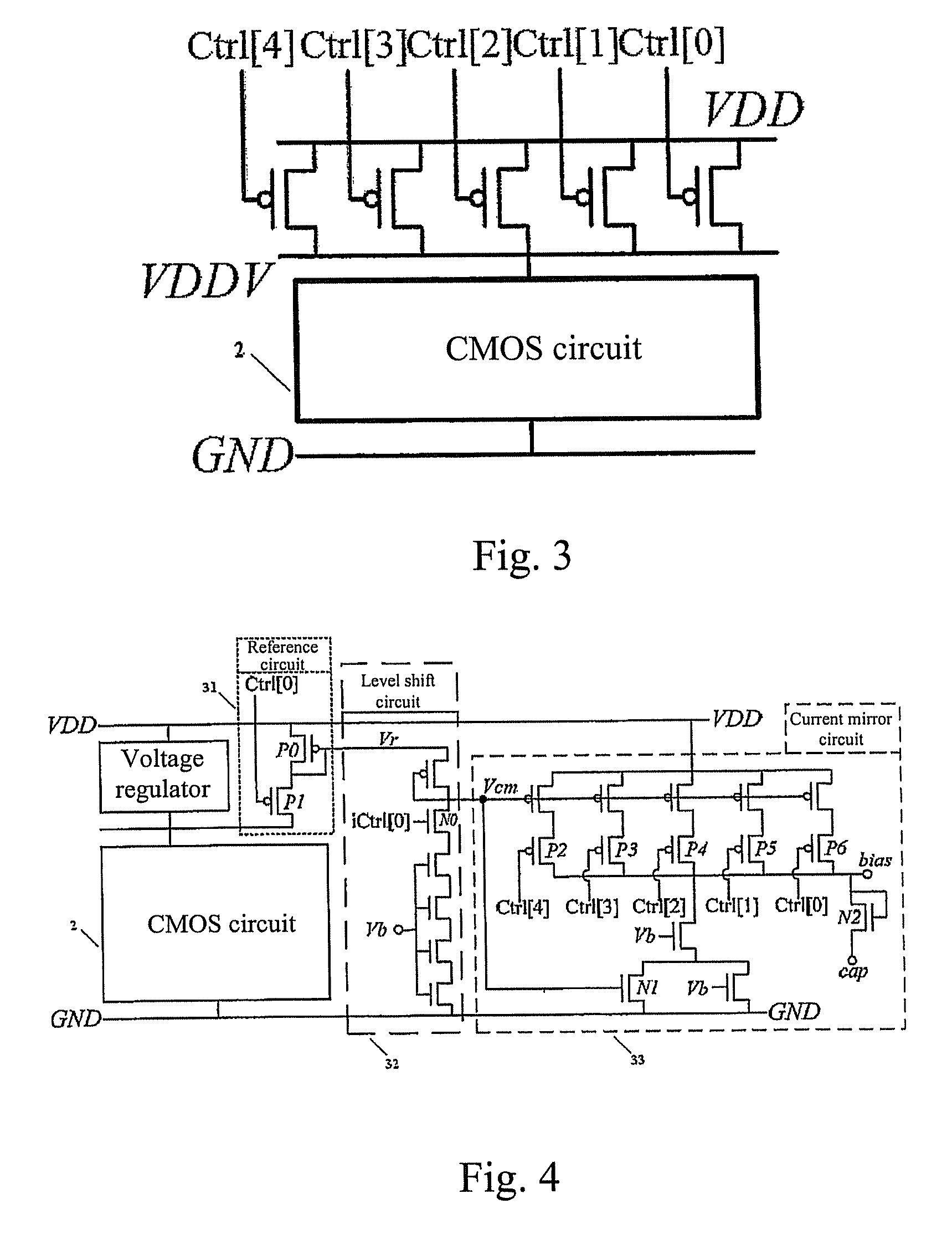
ActiveUS8138795B2Improve energy efficiencyGuaranteed uptimePower reduction by control/clock signalDigital data processing detailsShift registerMOSFET
The present invention provides a self-aware power control system and a method for determining the circuit state. The self-aware adaptive power control architecture comprises of a multi-mode power gating network, a current monitoring translator, a variable threshold comparator, a slack detector, and a bi-directional shift register. The multi-mode power gating network controls the amount of supply current and hence the circuit speed. The power gating network can be composed of either N-type MOSFETs for virtual ground insertion or P-type MOSFETs for virtual supply insertion. The number of MOSFETs in the multi-mode power gating network can be configured according to the supply range and step difference of the supply current. Then, by monitoring the current characteristics drained by target circuit, the circuit state can be determined. No delay matching circuit is required. Together with other peripherals, the supply current can be down controlled to a minimum acceptable level. The circuit will use up all available slack. The smaller current implies lower power consumption as well. Furthermore, the present invention is capable of self adaptation to frequency change. To summarize, the present invention can make the circuit consume least power under various frequency achieving best power efficiency.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com