Patents
Literature
156results about "Oxygenators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
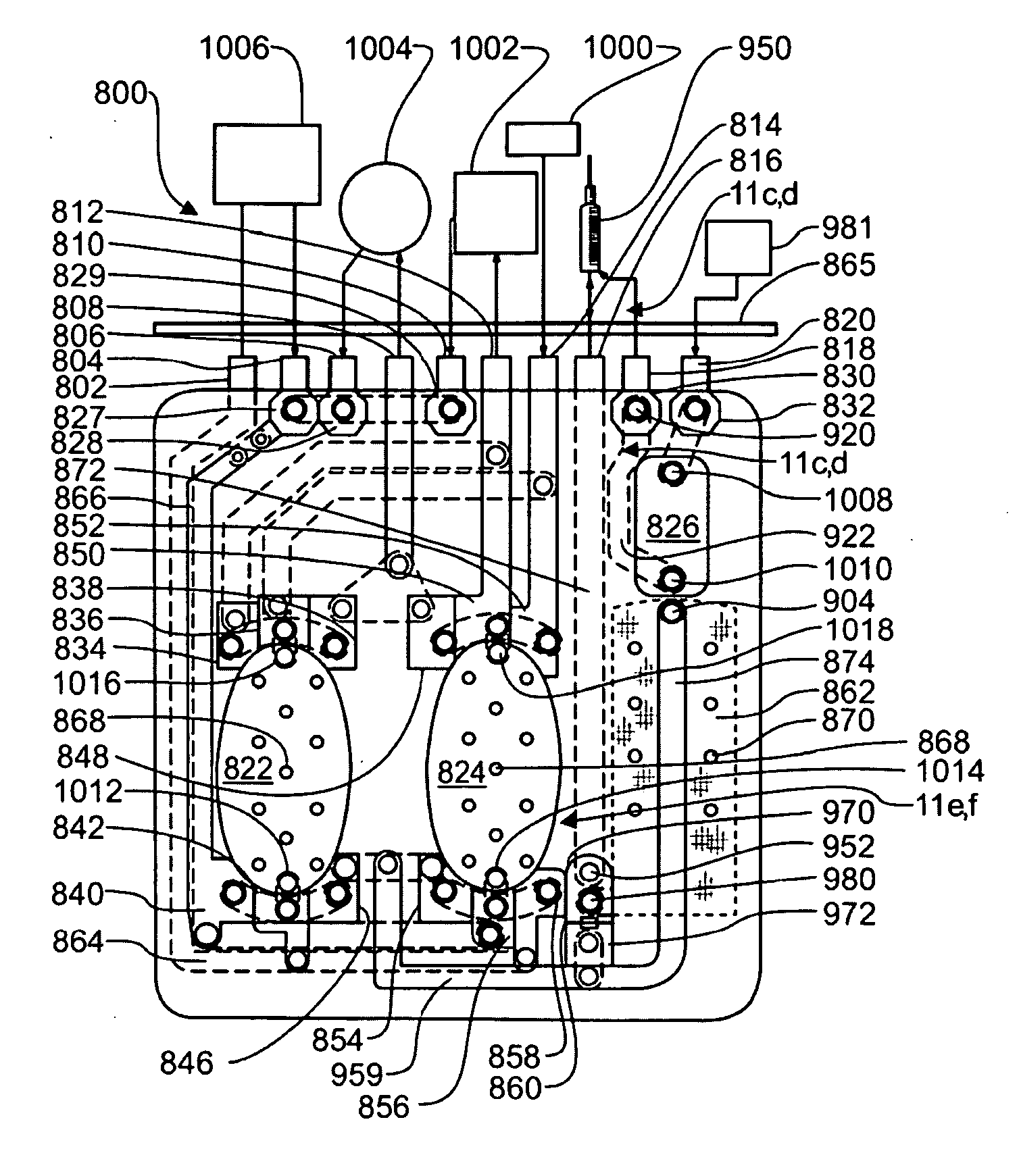
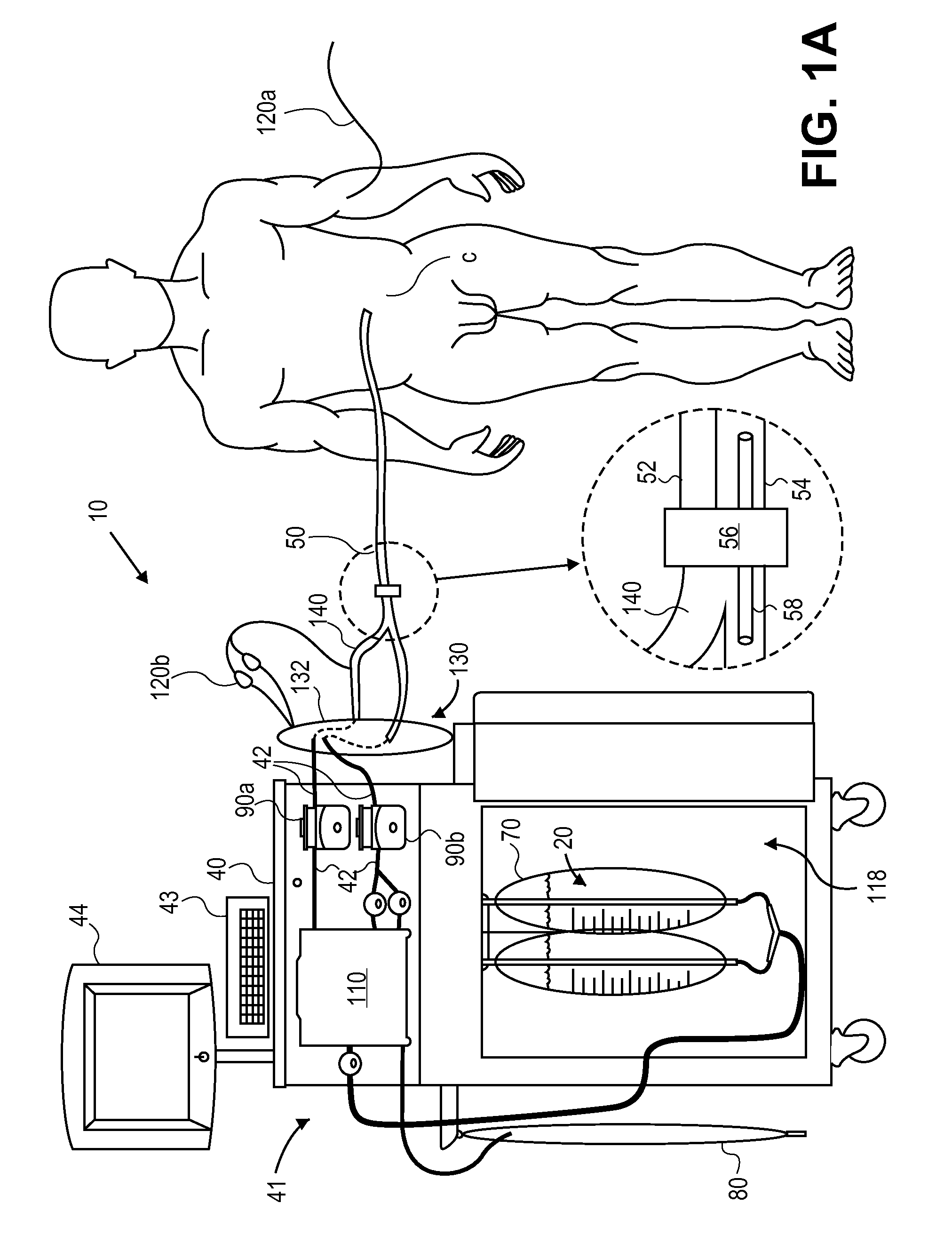
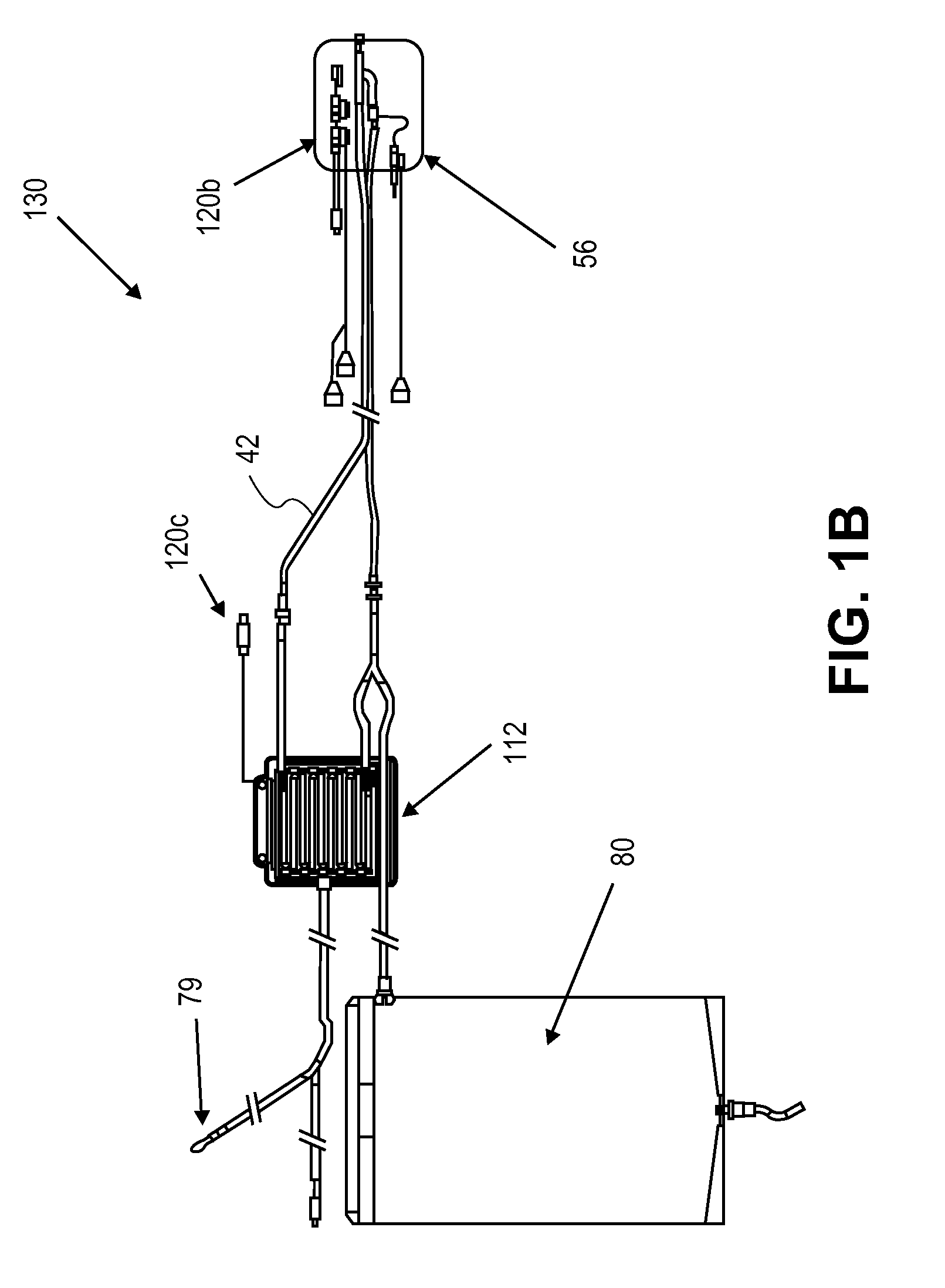
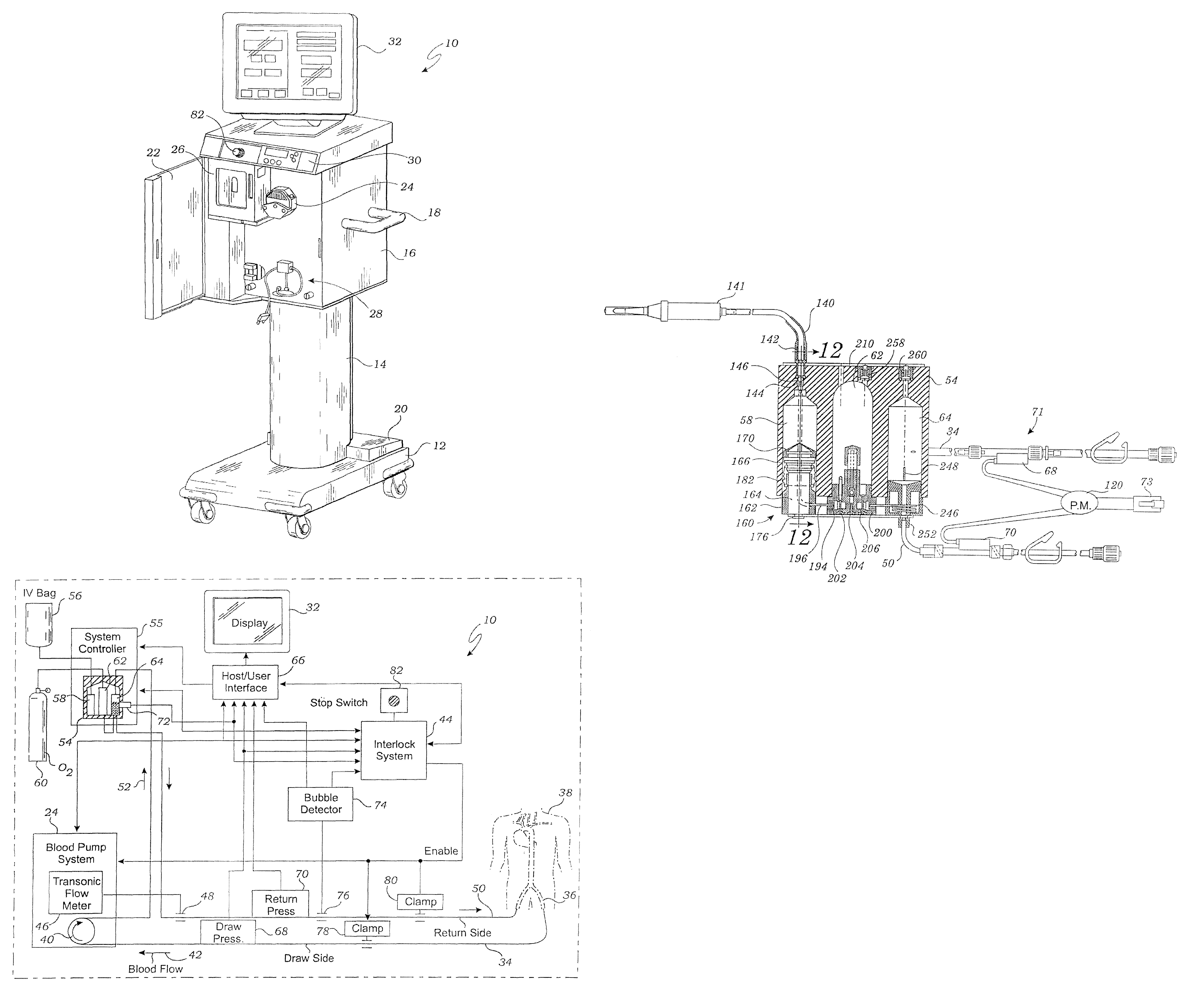
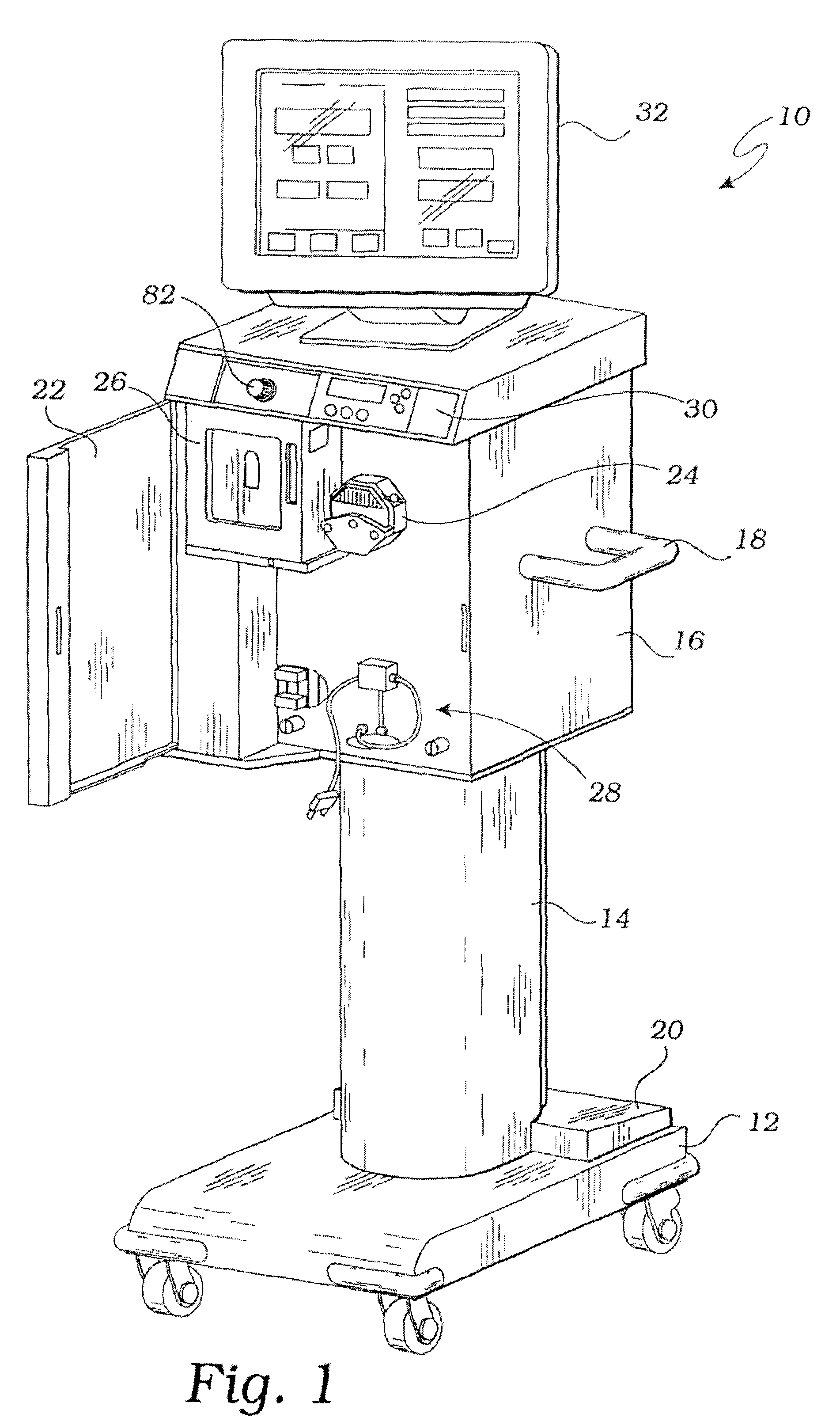
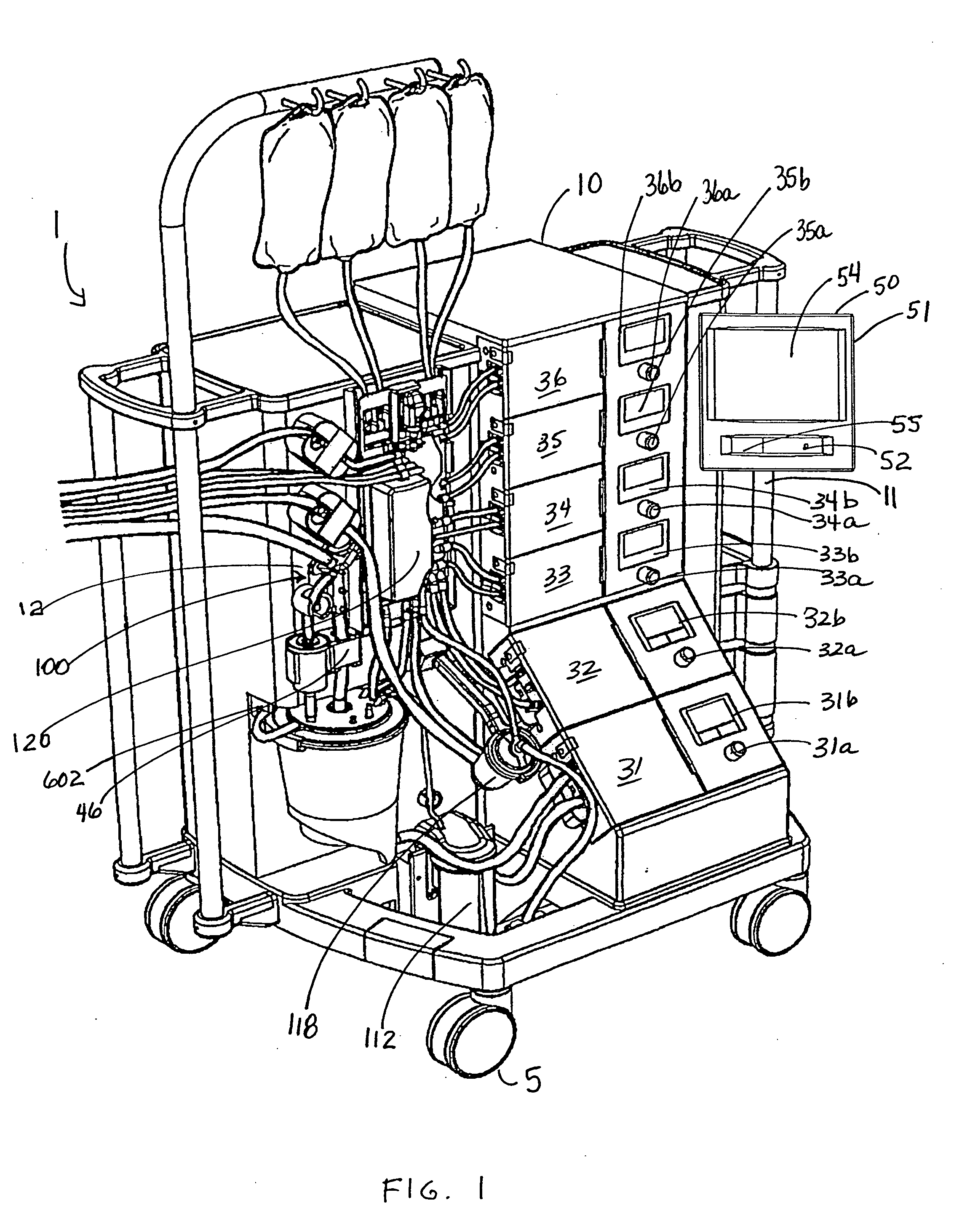
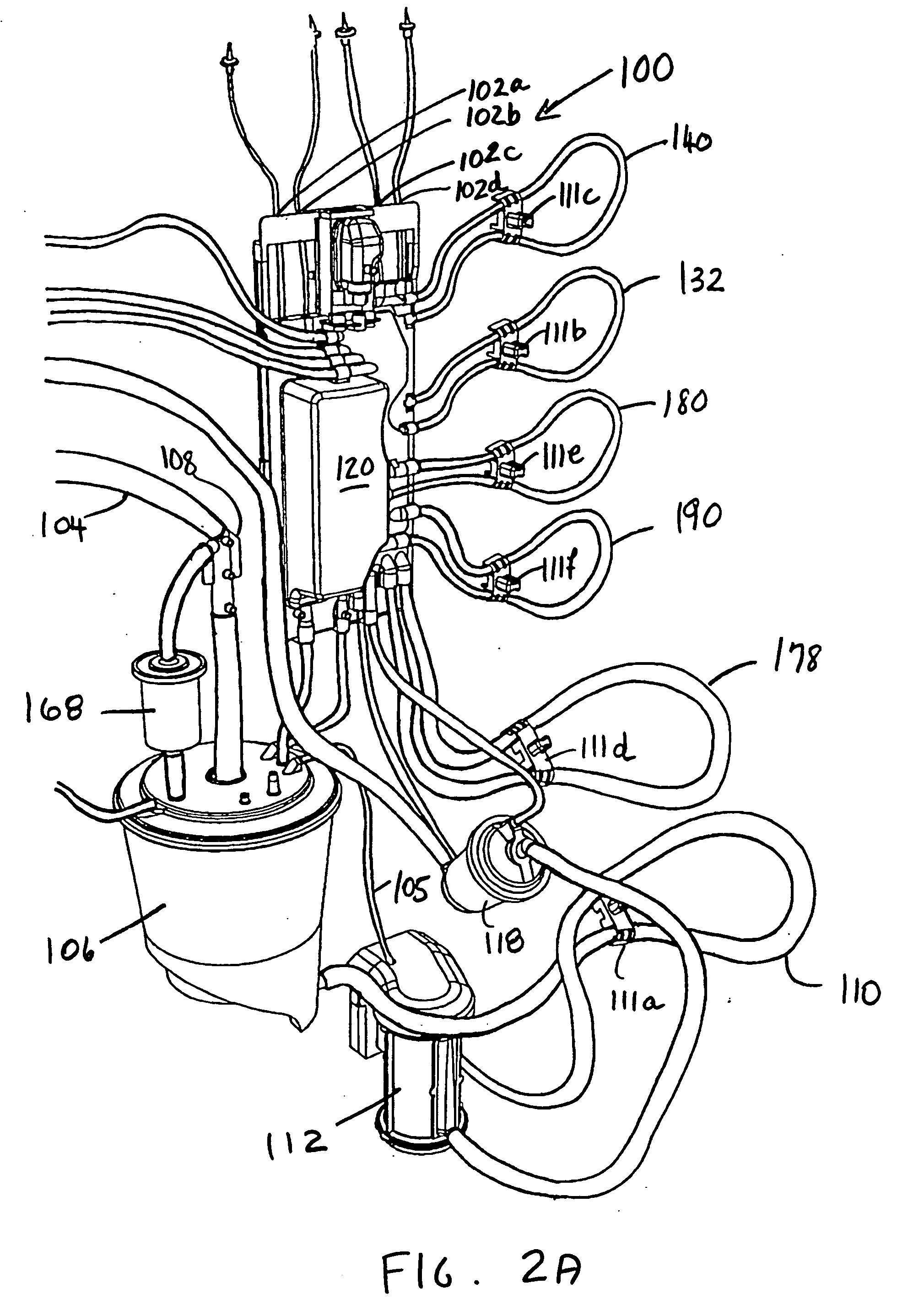
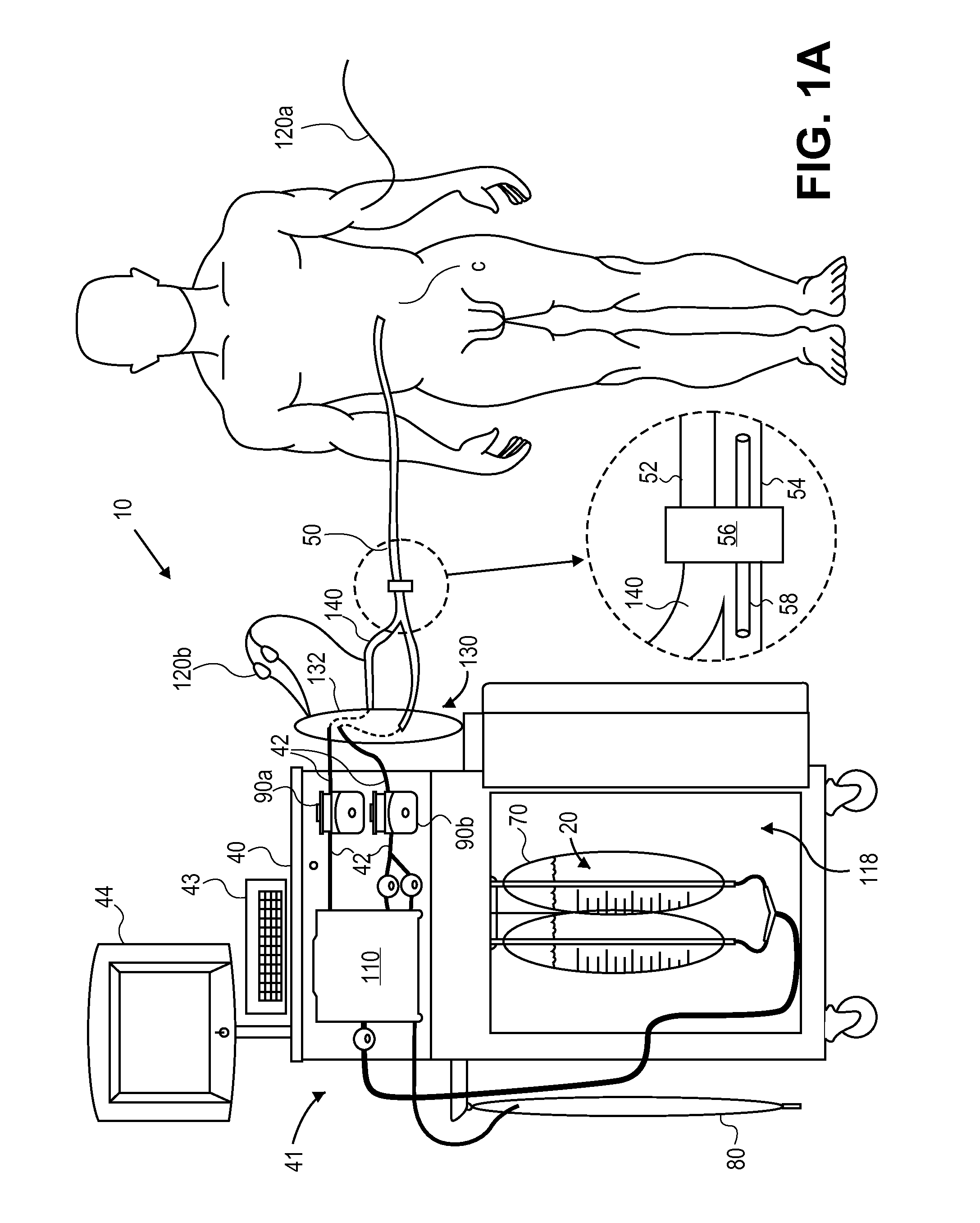
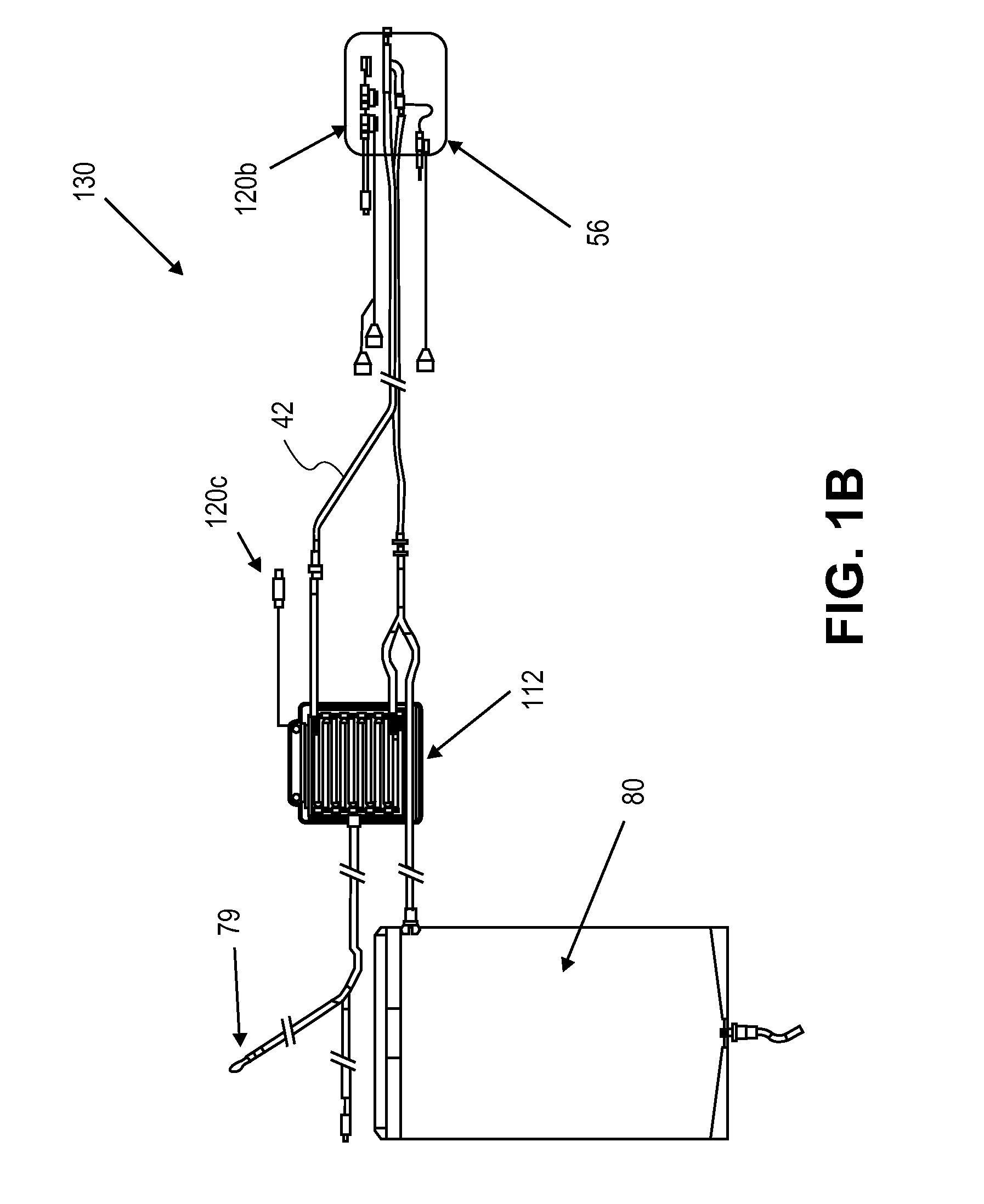
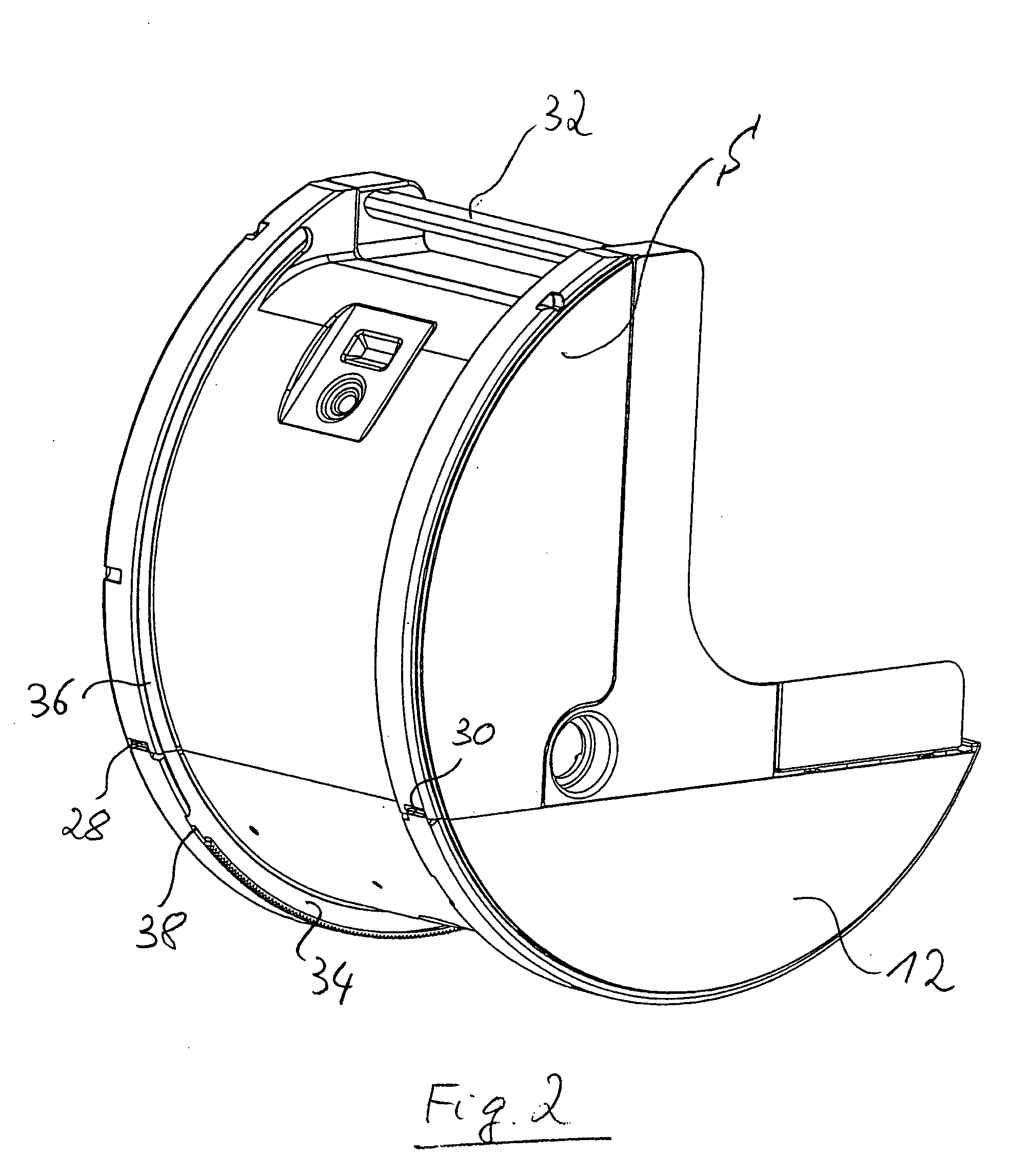
Systems, Devices and Methods for Cardiopulmonary Treatment and Procedures
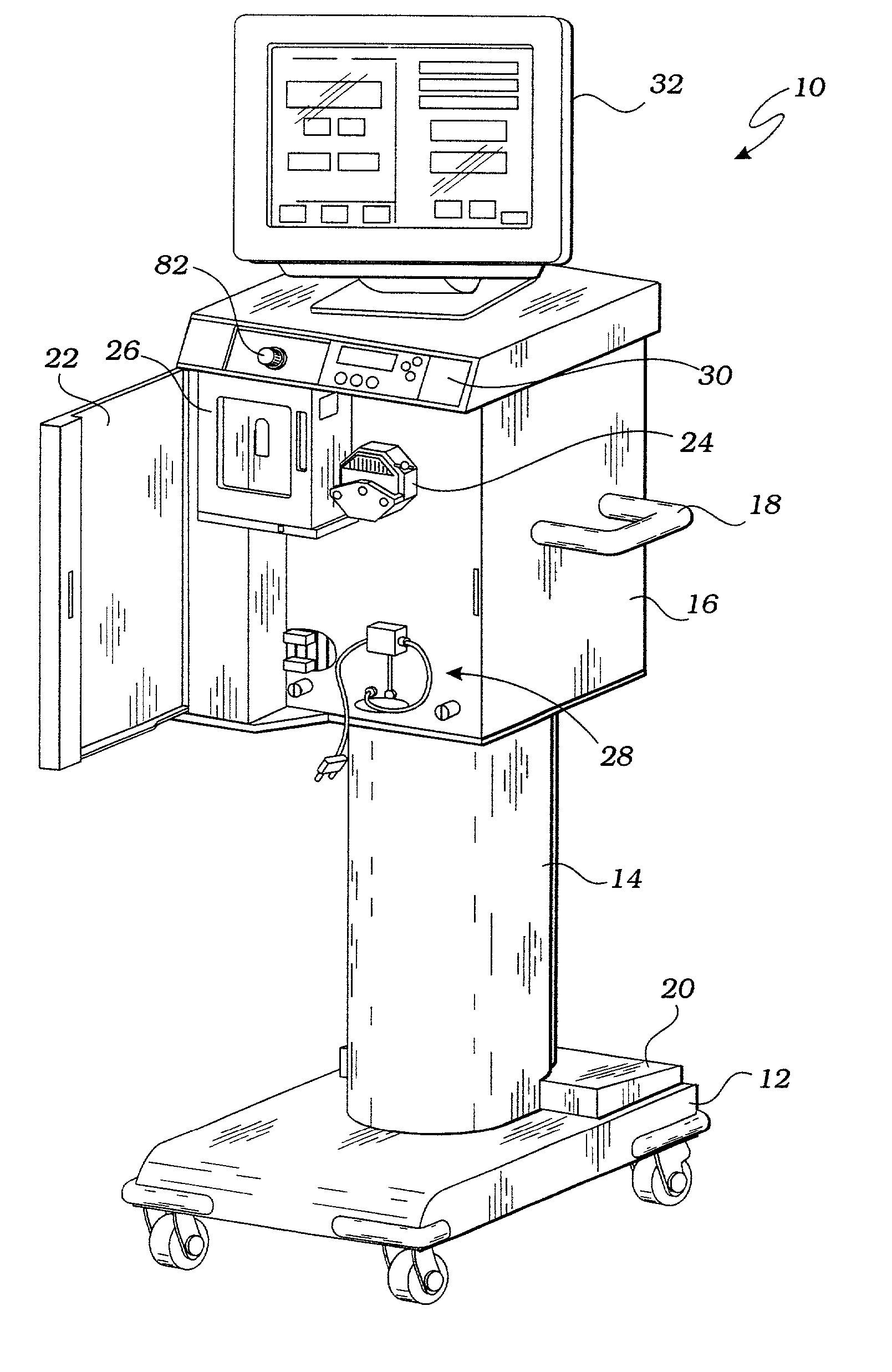
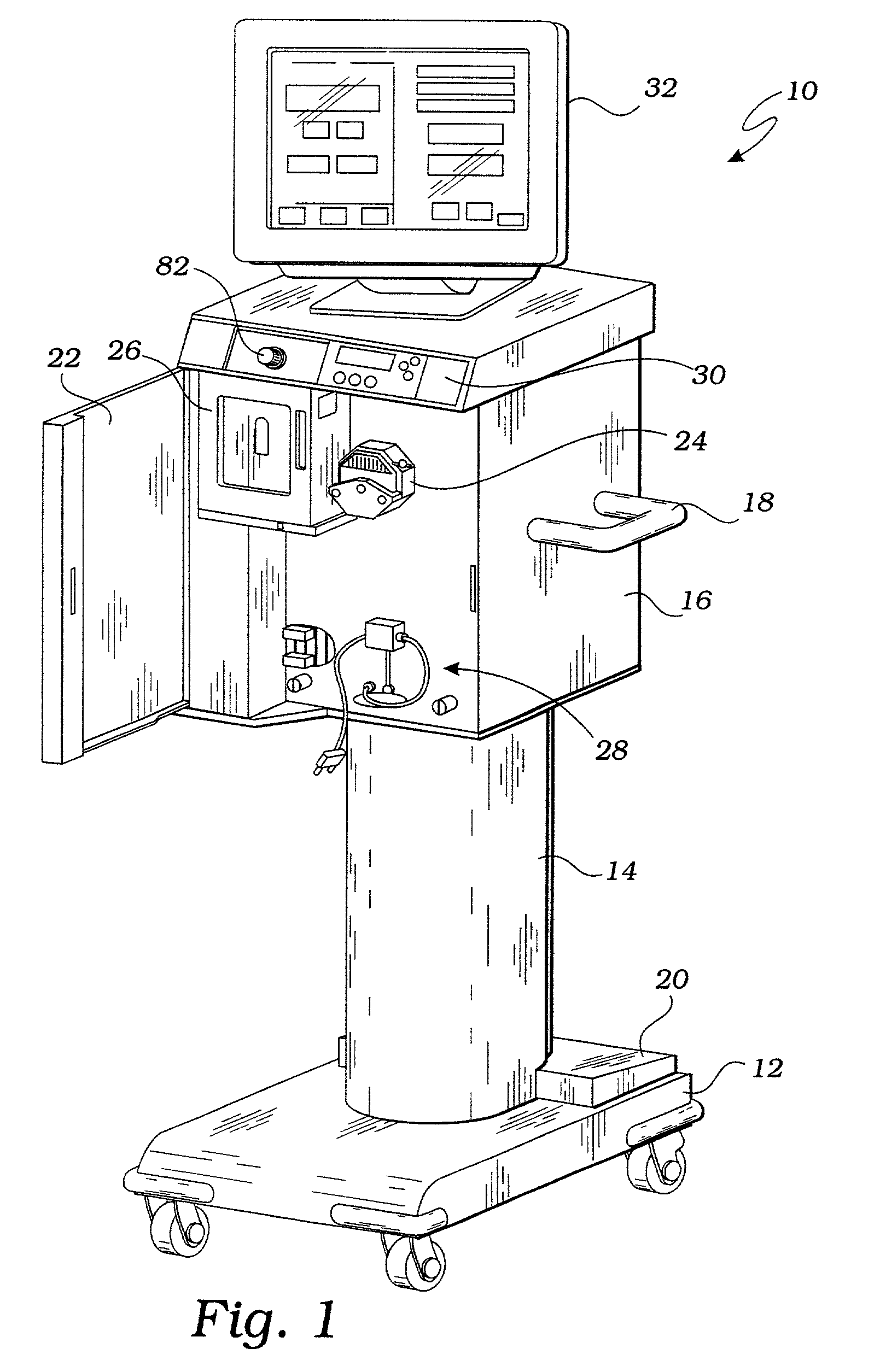
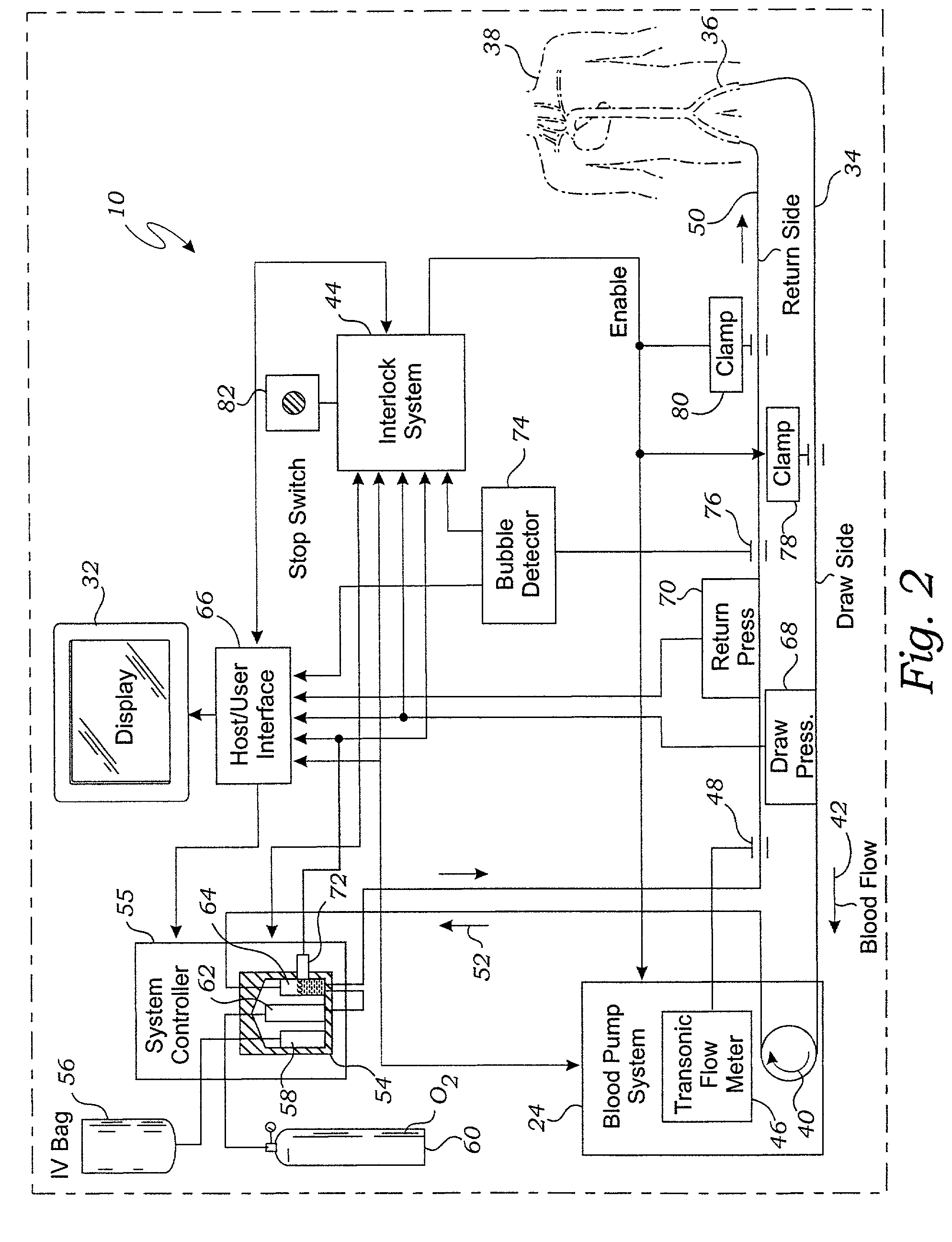
ActiveUS20090099498A1Reduces hard snappingReduce shear forceVolume measurement apparatus/methodsControl devicesBlood pumpControl room
A cardiopulmonary bypass system utilizing membrane-based reciprocating positive displacement blood pumps (“pod pumps”). In one aspect, the pod pumps are constructed to provide reduced shear forces on the blood being pumped. In another aspect blood flow through the pod pumps can be controlled by a controller using information from pressure sensors in the control chamber of the pod pumps. In another aspect, the pod pumps are included on a disposable unit that can be received and held by a receptacle means on a base unit, the base unit also providing pressurized control fluid to the pod pumps on the disposable unit through the receptacle means.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
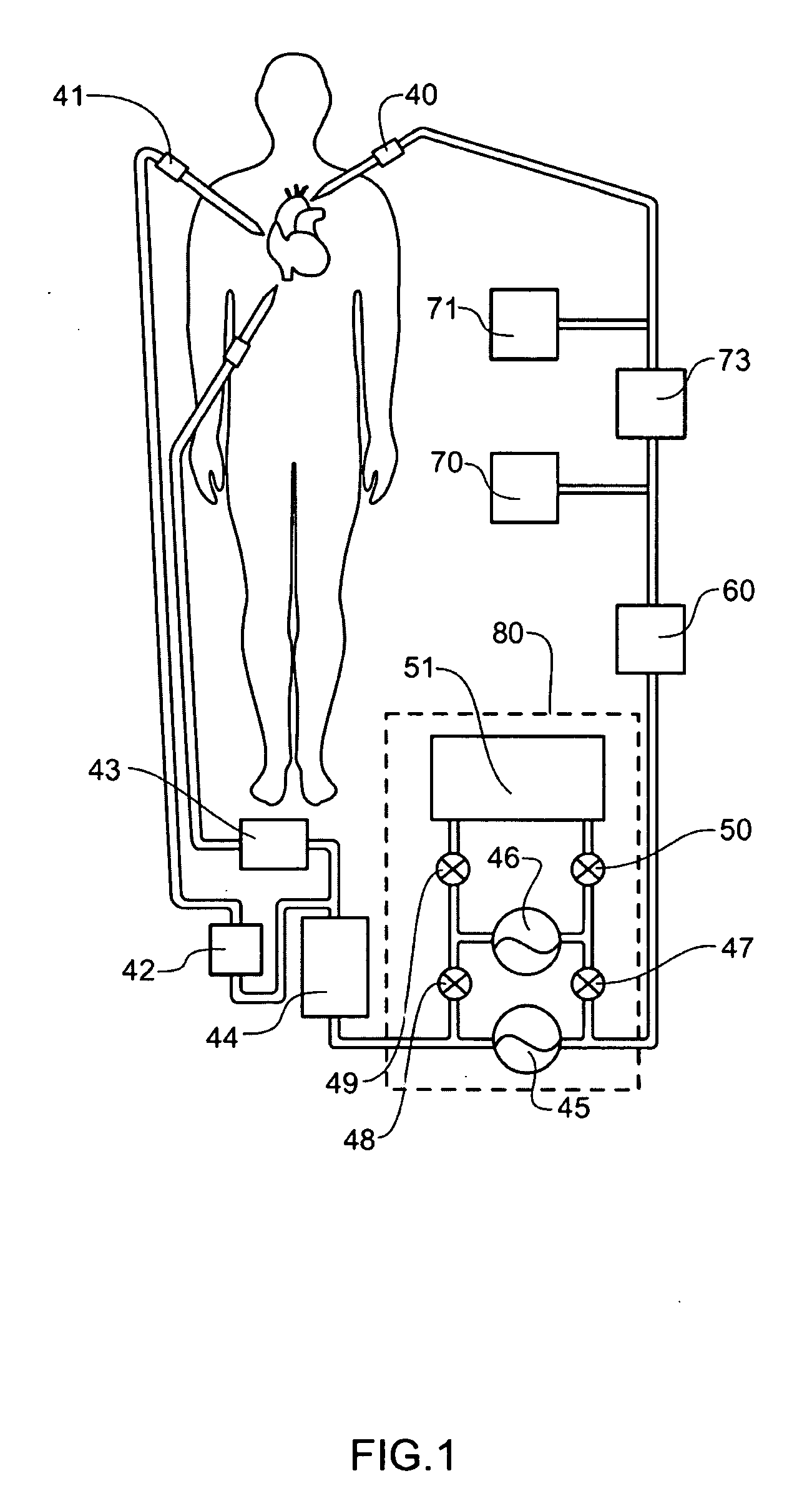
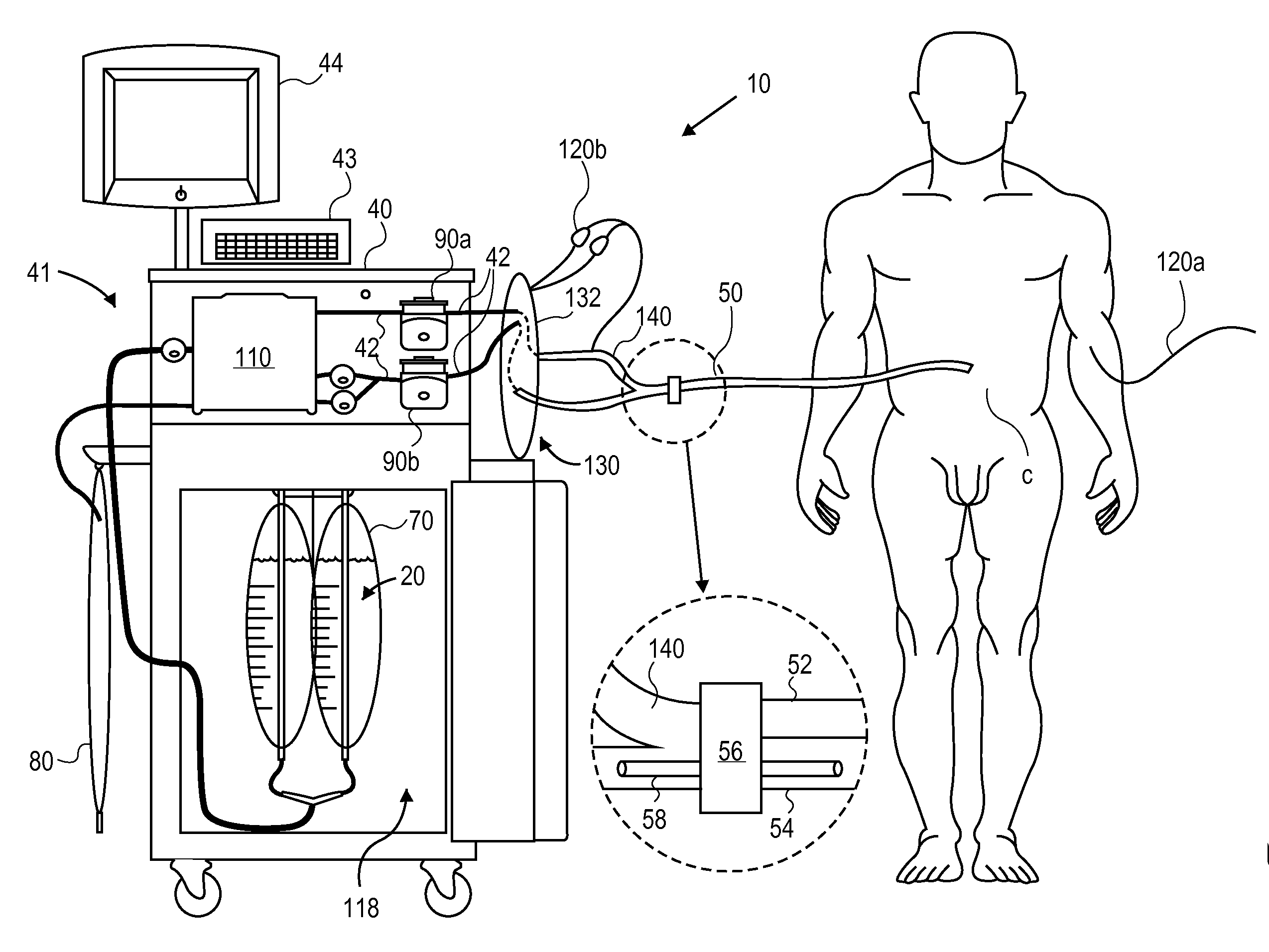
Method and Apparatus for Inducing Therapeutic Hypothermia
Methods and apparatus for delivering therapeutic hypothermia to a patient are provided which may include any number of features. One feature is a hypothermia system comprising a fluid source, a heat exchanger assembly, a catheter in fluid communication with the fluid source, and a pump system configured to infuse hypothermic fluid into a patient cavity and extract hypothermic fluid from the patient cavity. The hypothermia system can infuse and extract fluid automatically from the patient cavity. In one embodiment, the patient cavity is a peritoneal cavity. A safe access device to gain access to the patient cavity is also provided.
Owner:VELOMEDIX
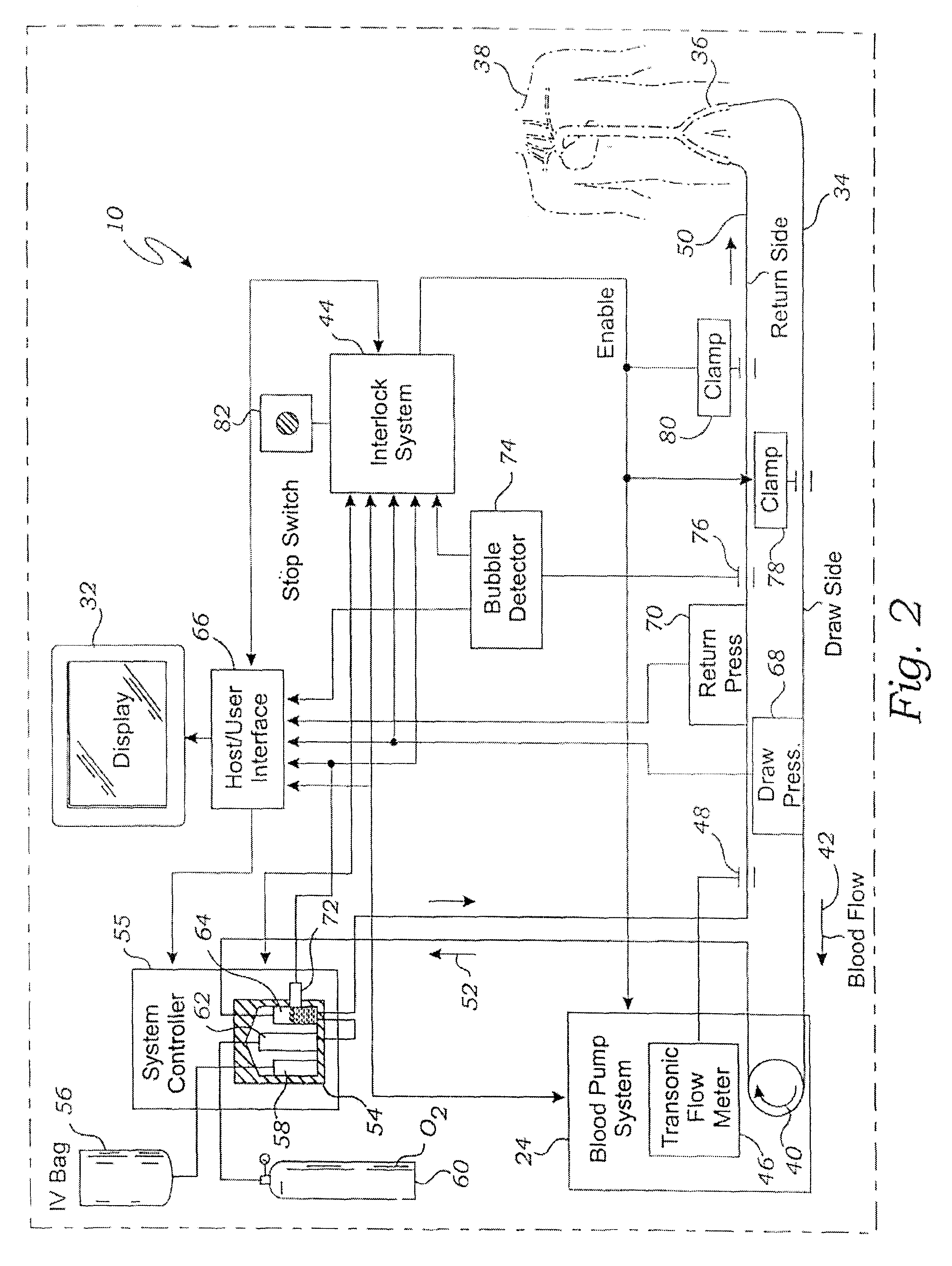
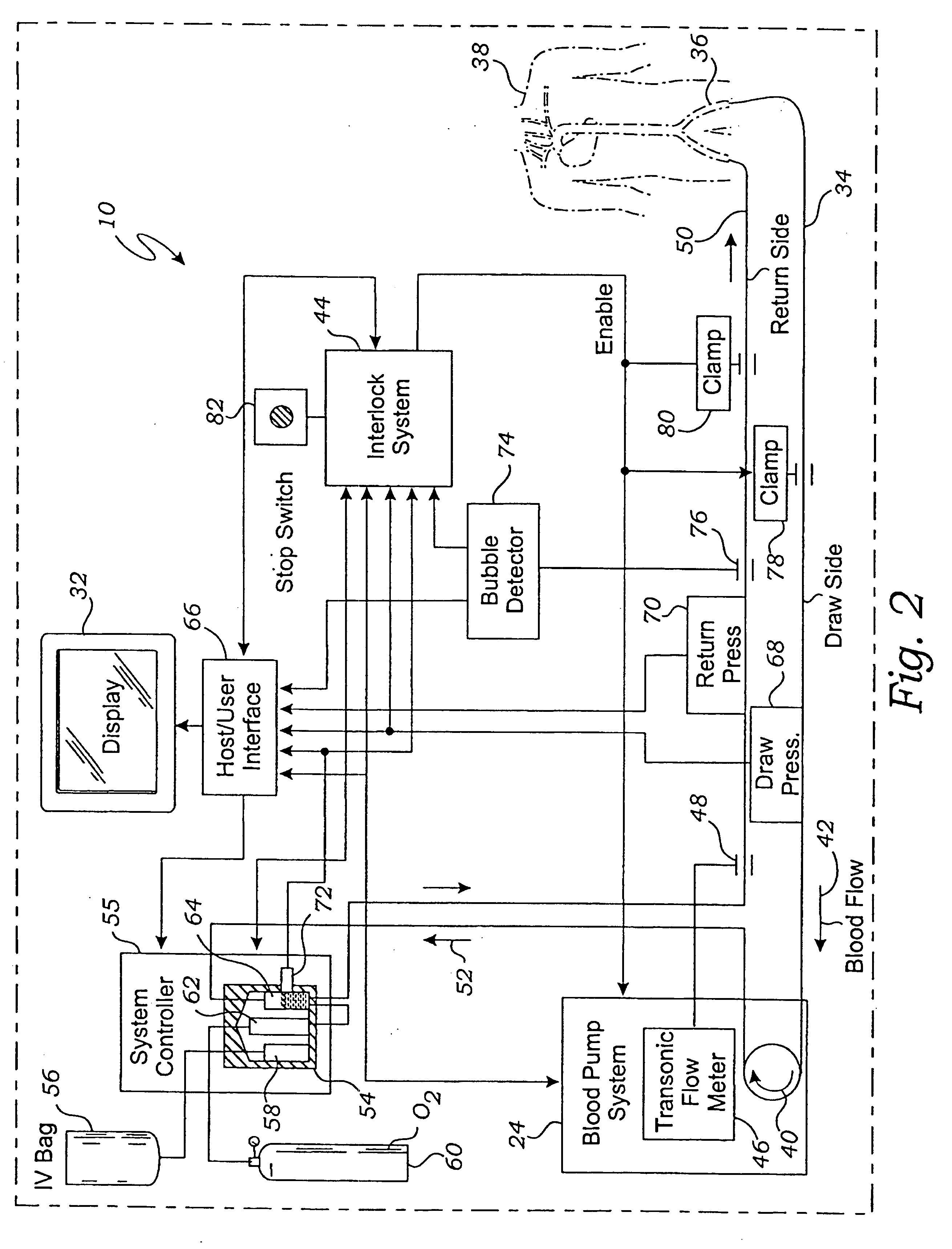
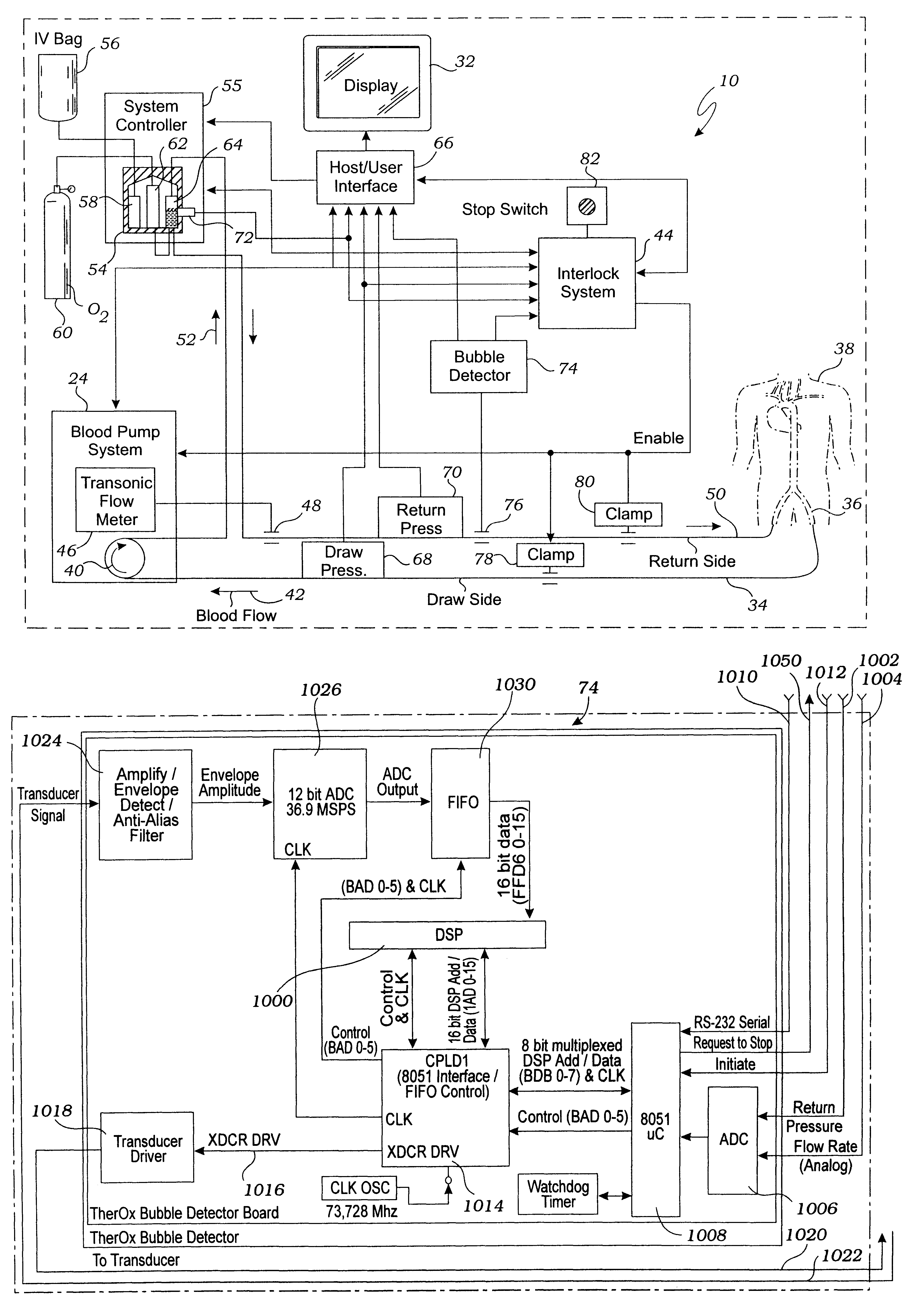
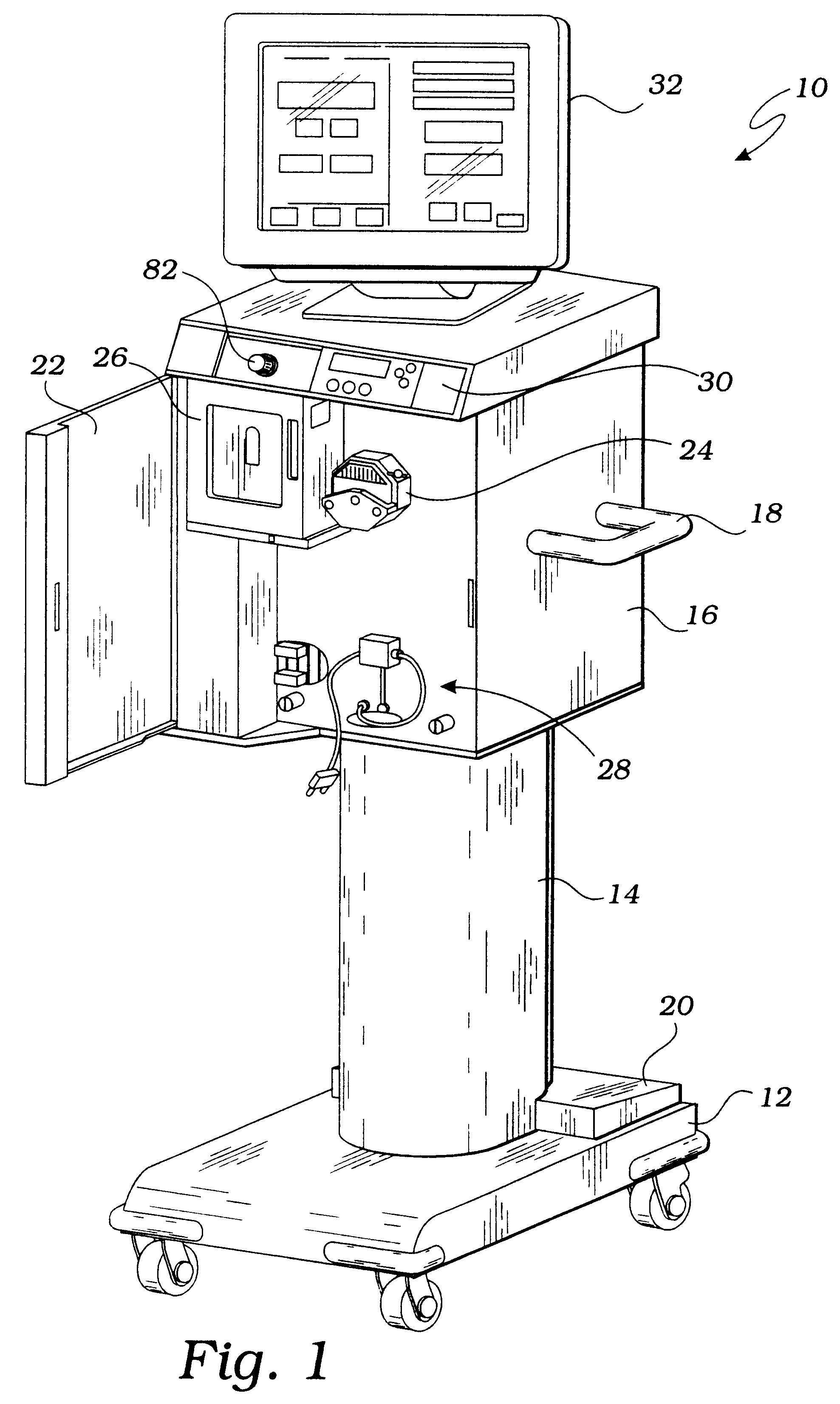
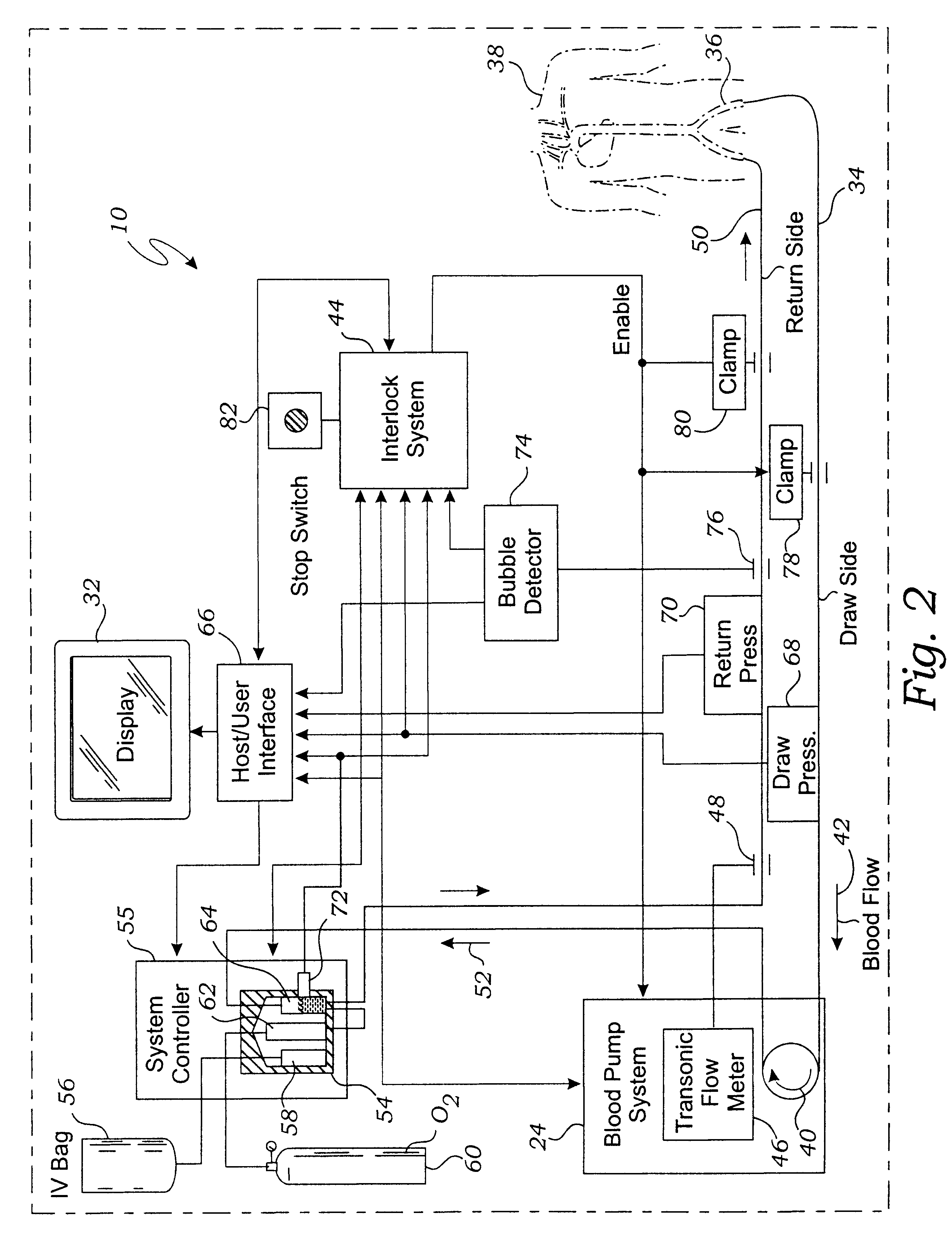
Bubble detector and method of use thereof
InactiveUS6622542B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOther blood circulation devicesUltrasonic sensorImage resolution
Owner:THEROX
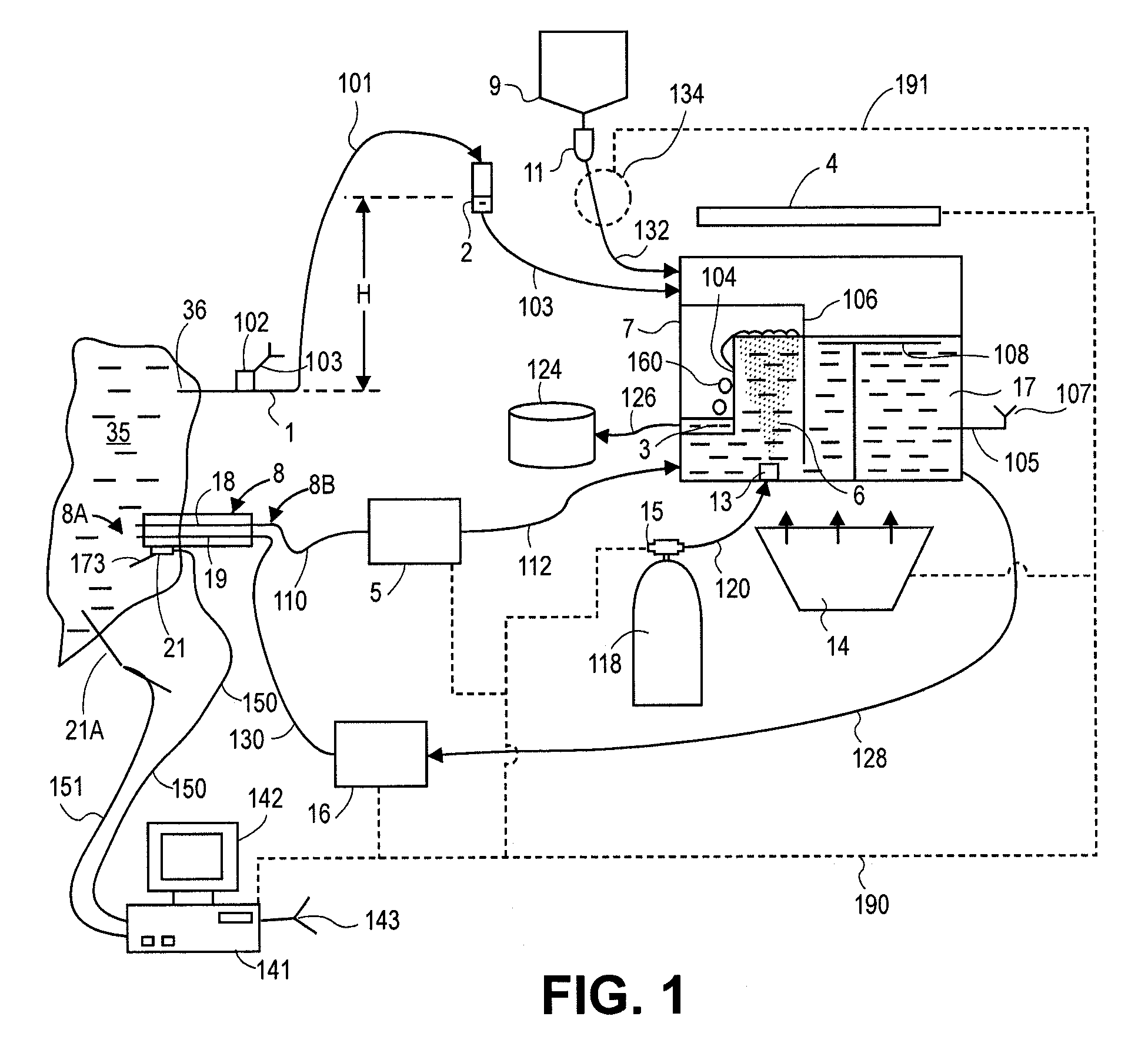
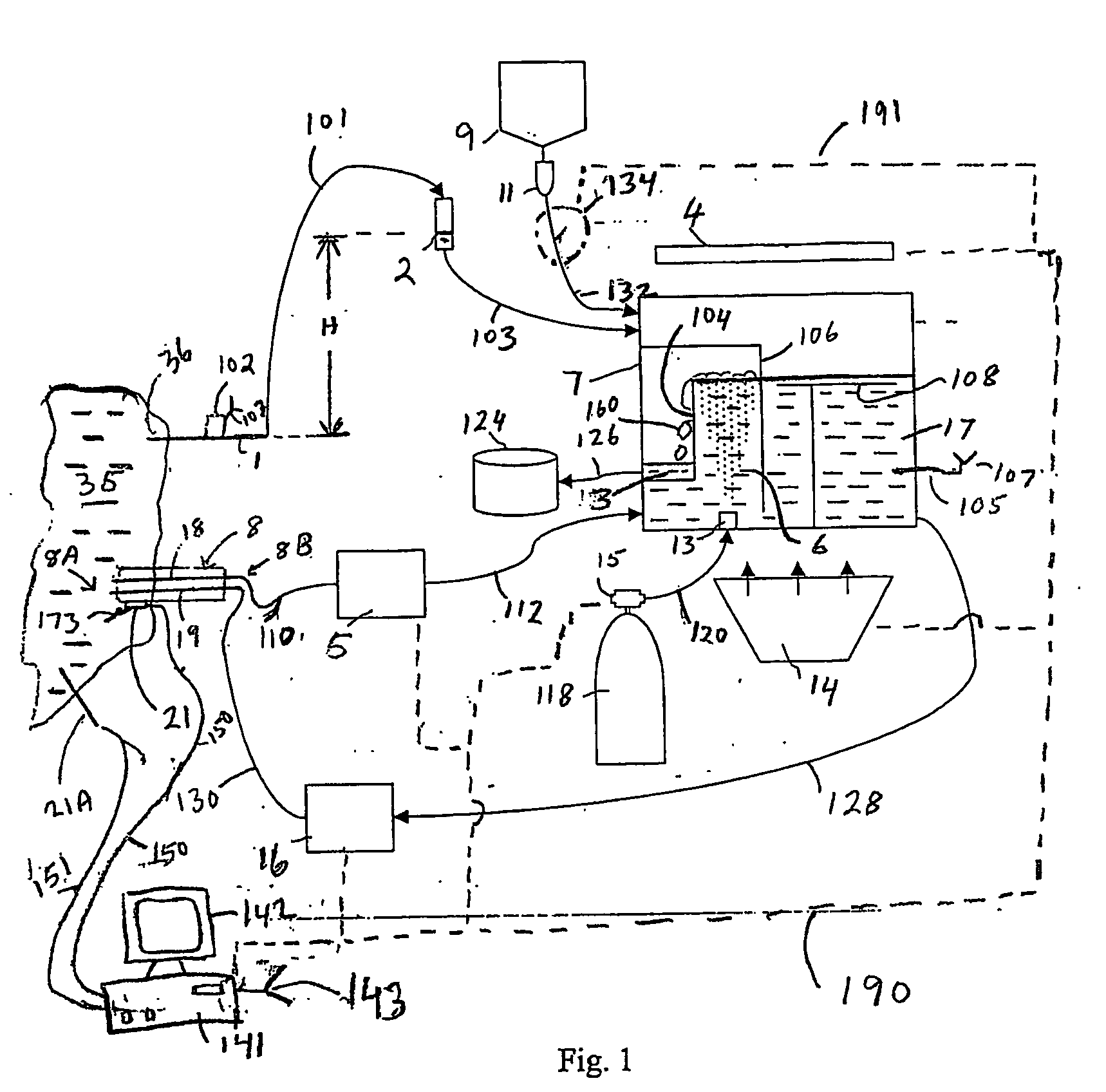
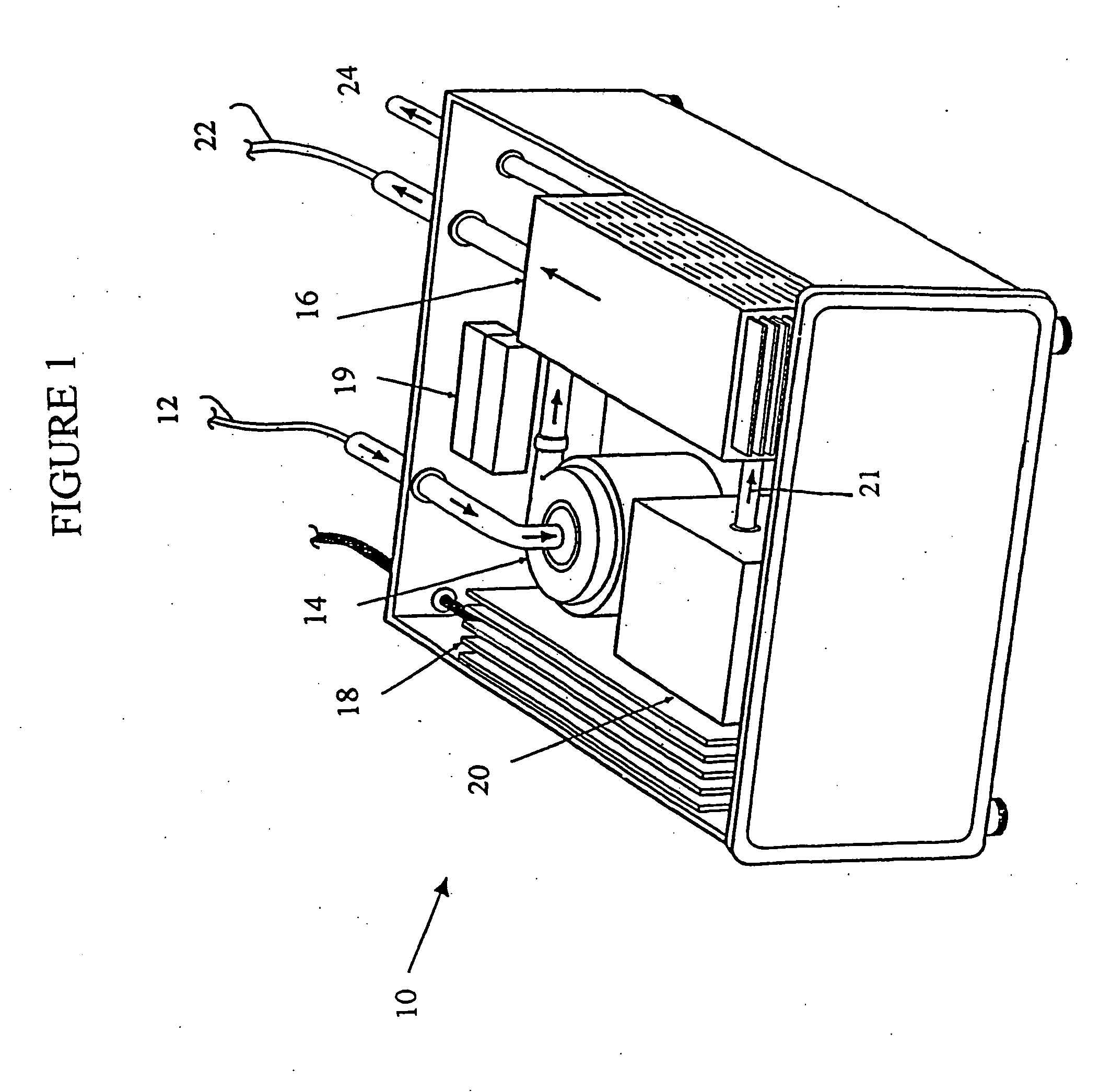
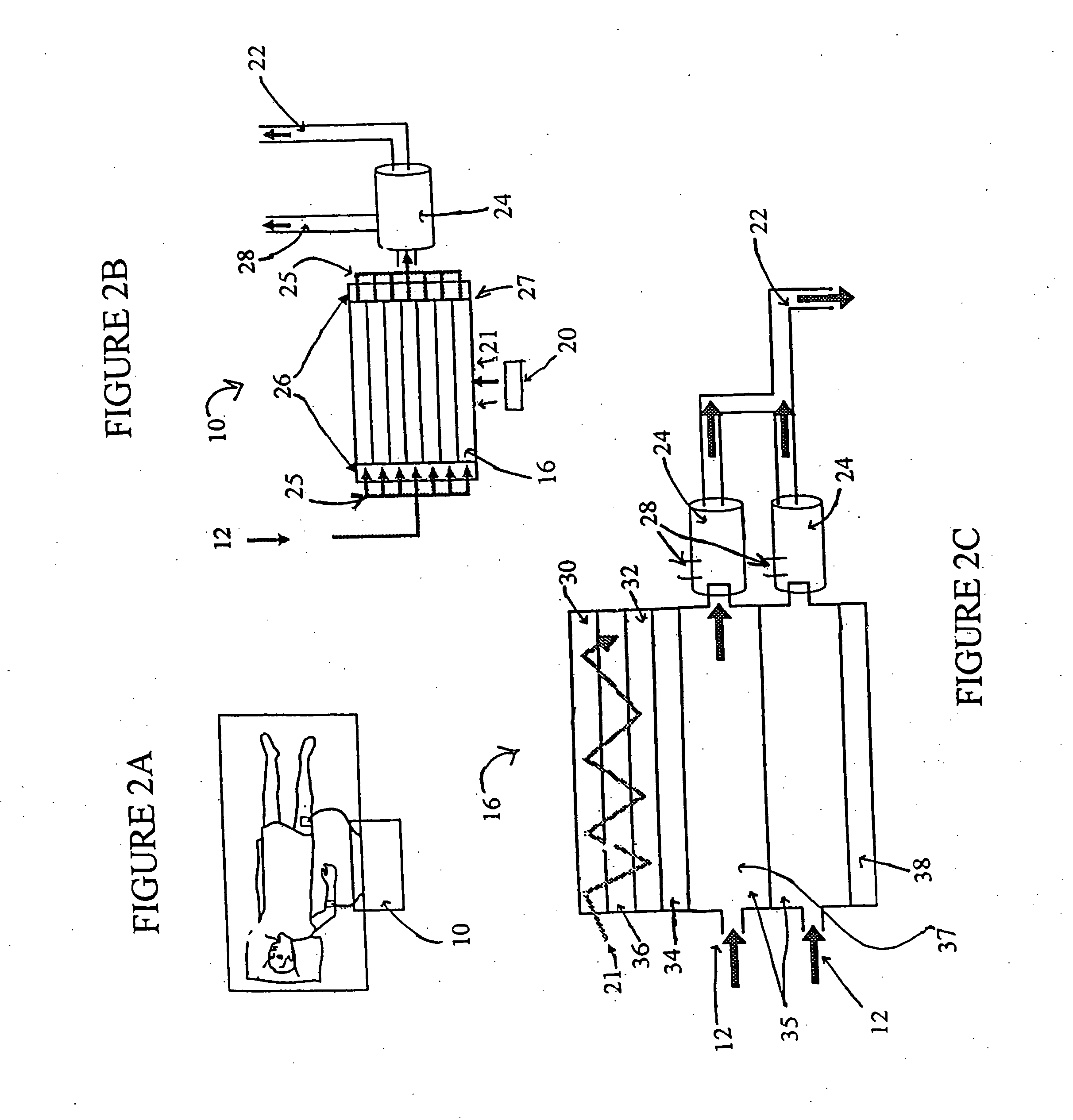
System for enriching a bodily fluid with a gas
A system utilizes an oxygenation device to generate a gas-enriched physiologic fluid and to combine it with a bodily fluid to create a gas-enriched bodily fluid. The oxygenation device may take the form of a disposable cartridge, which is placed within an enclosure. An electronic controller manages various aspects of the system, such as the production of gas-enriched fluids, flow rates, bubble detection, and automatic operation and shut down.
Owner:THEROX
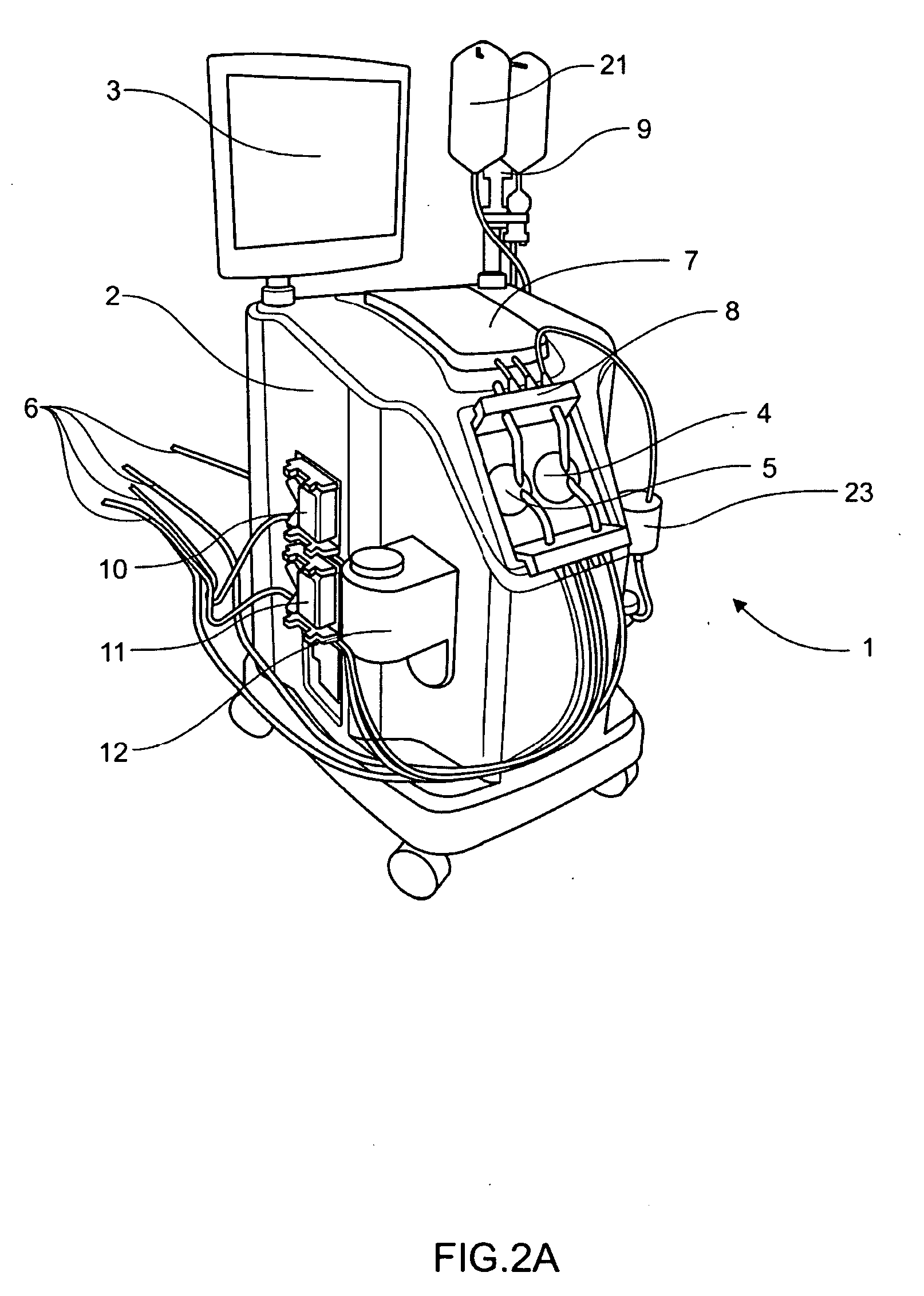
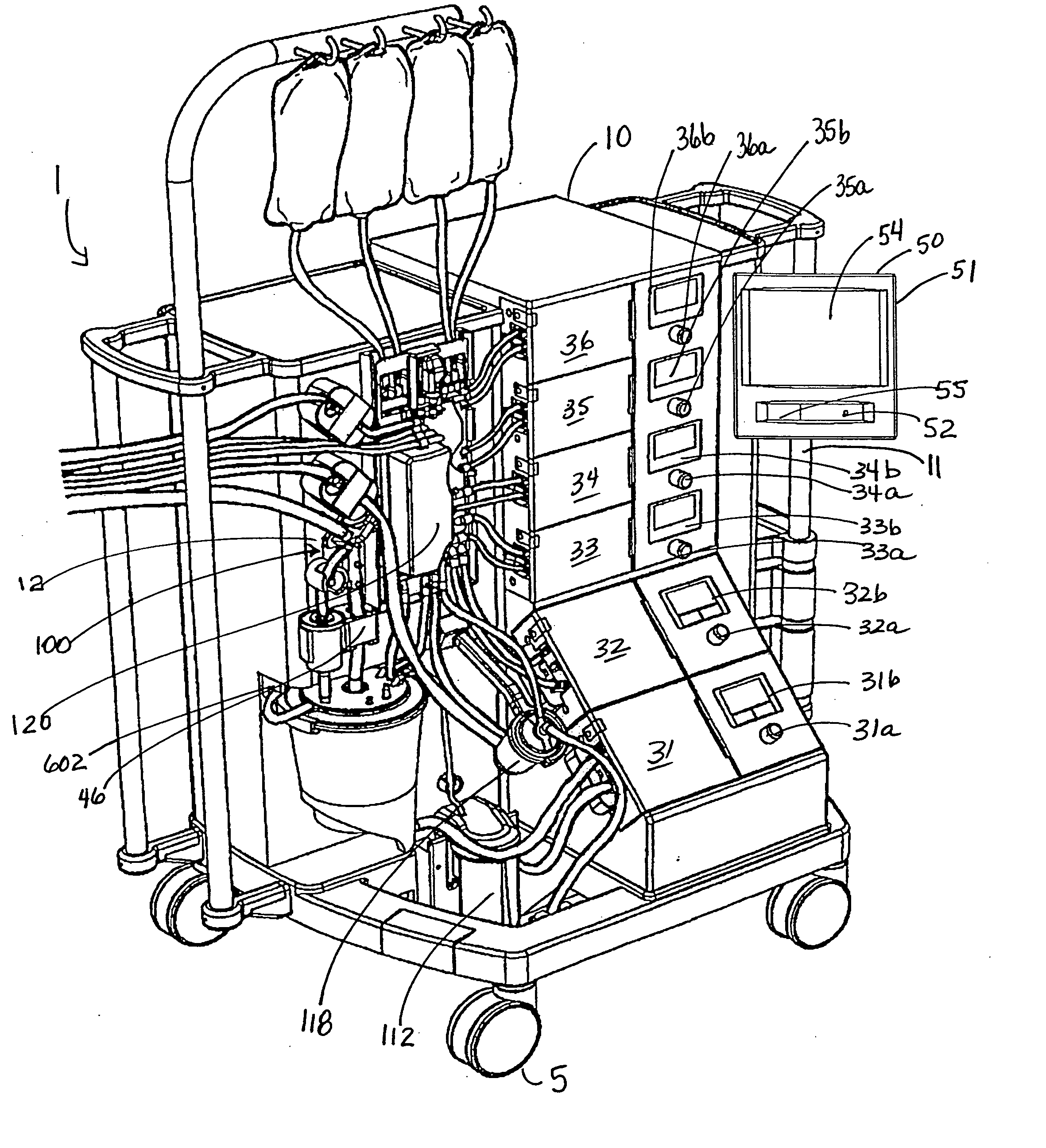
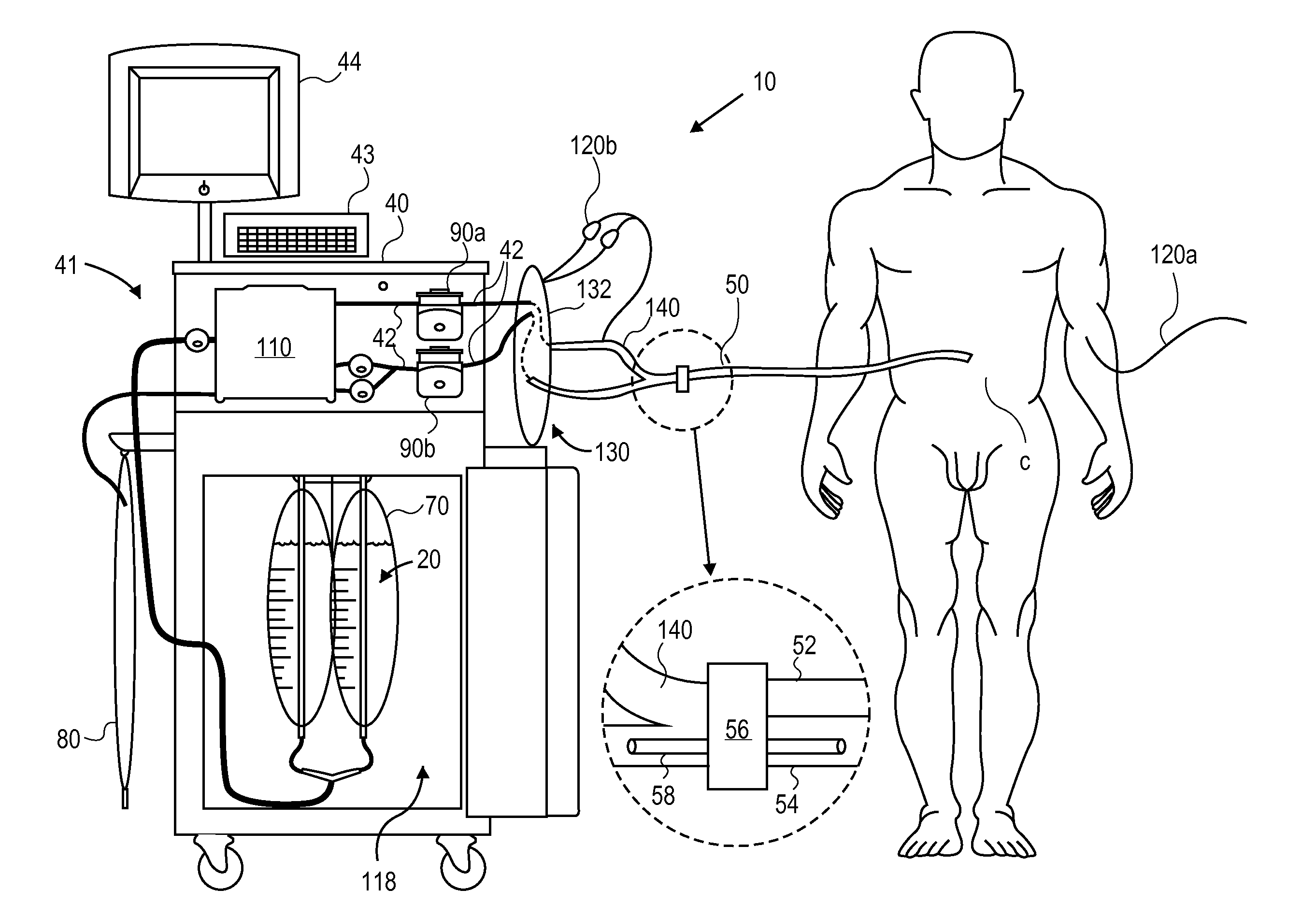
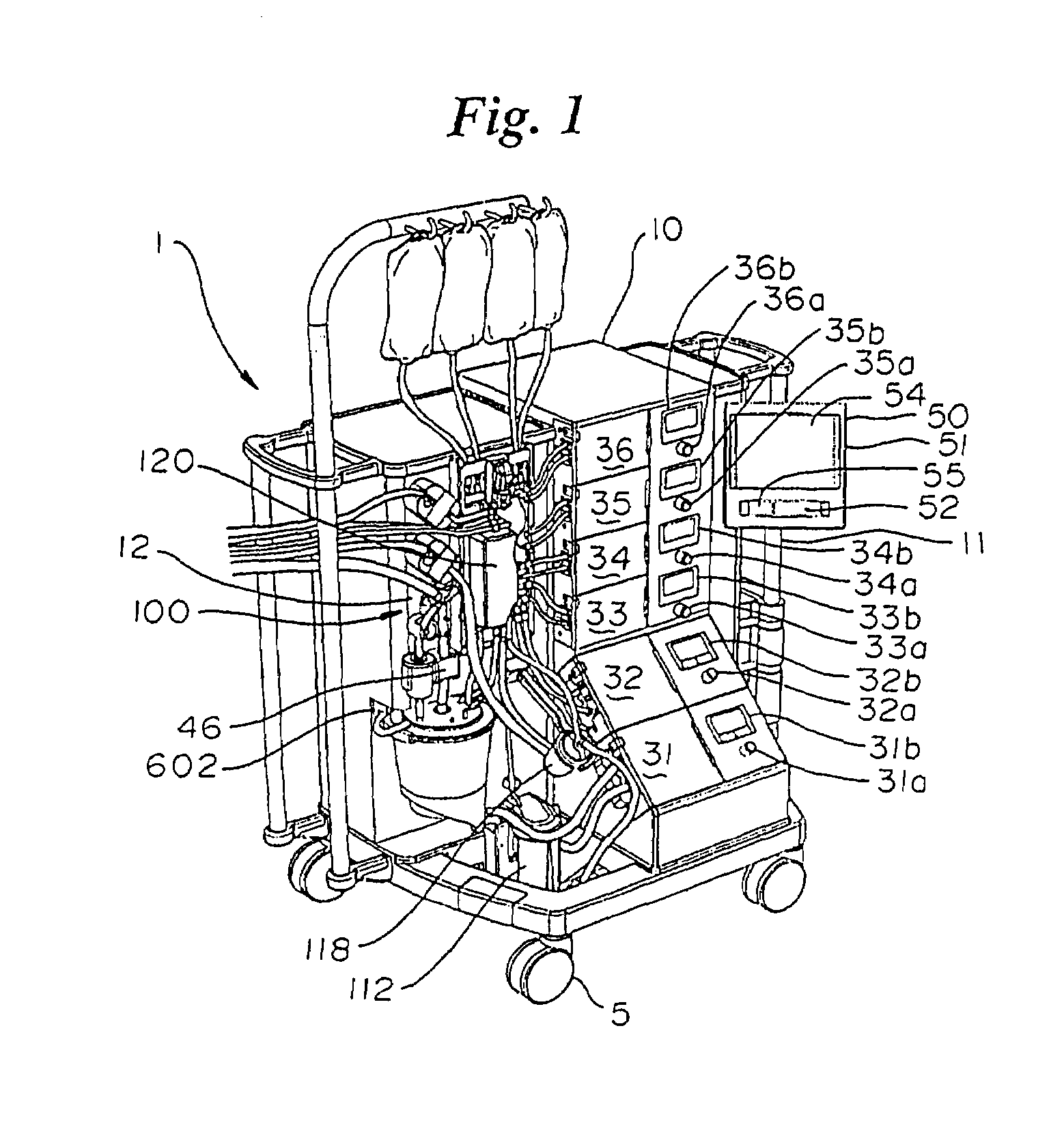
Blood perfusion system
ActiveUS20060167400A1Simplified interconnection/disconnectionSimple setupOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesVenous bloodDisplay device
An extracorporeal blood perfusion system includes a disposable assembly and a control unit having a control interface region. The interface region includes pump assemblies for selective pumping of venous blood, arterial blood, cardioplegia solution, suctioned blood and blood removed from the left ventricle. Valve assemblies control the flow of fluids through the assembly and to / from the patient and sensors monitor various fluid parameters including temperature and pressure within the various fluid circuits. The user interface is a functional screen interface for effecting the operation of the control unit and valve assemblies. The screen interface may be a touch screen having objects that corresponds to the component interface region. The display may be selectively controlled to provide graphic depictions of disposable assembly components with corresponding narrative instructions.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
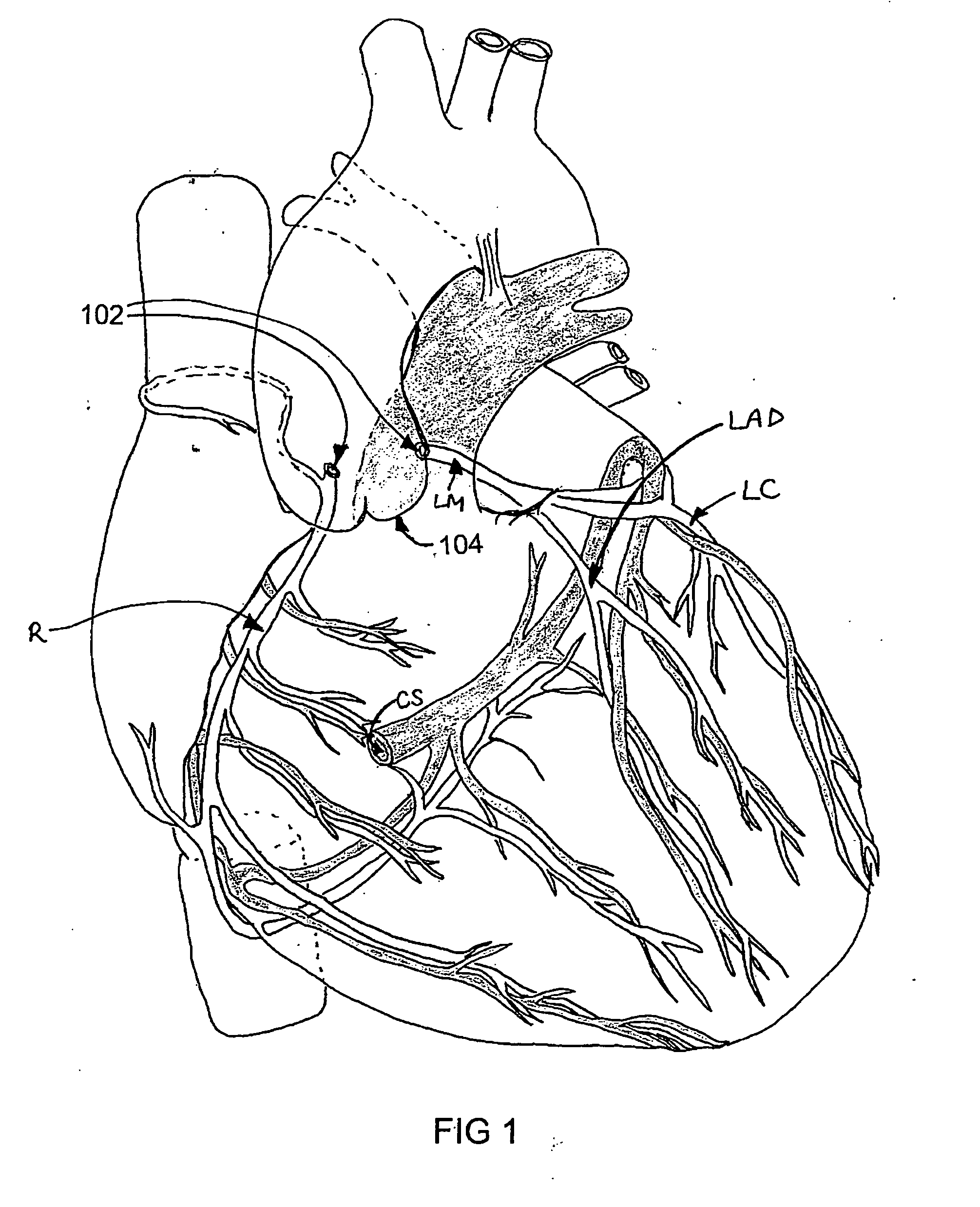
Isolating cardiac circulation
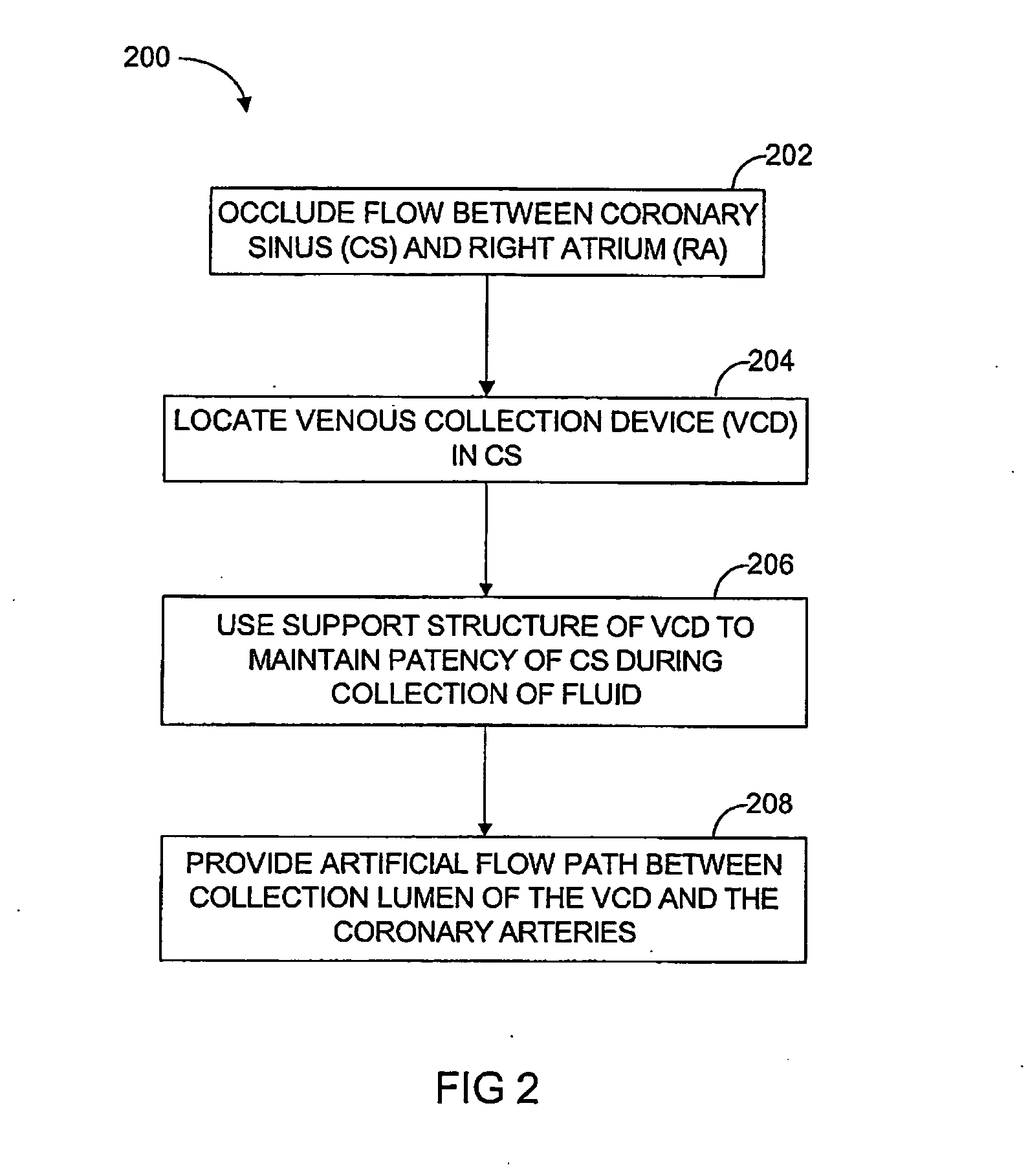
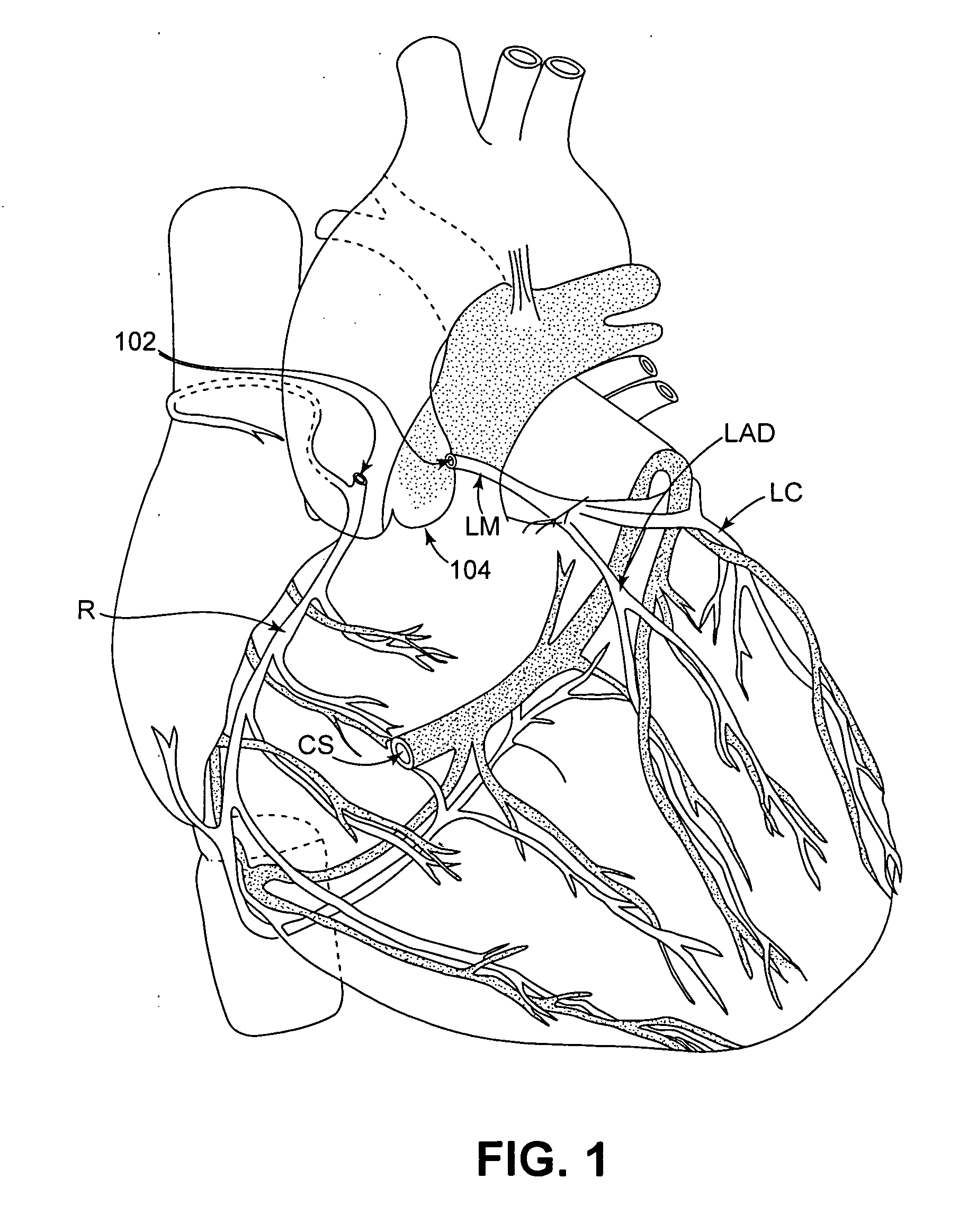
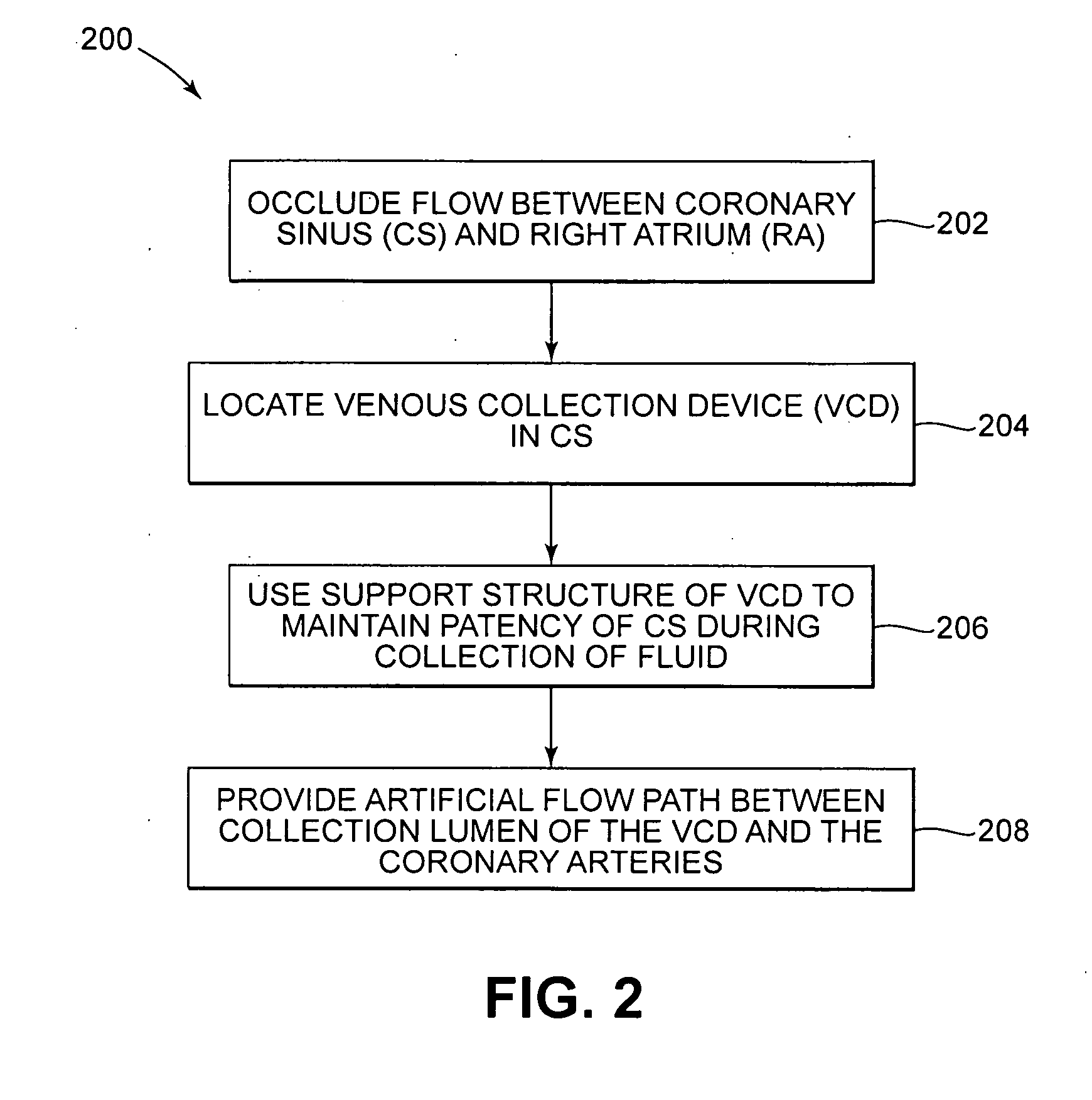
In a method for substantially isolating cardiac circulation from systemic circulation, flow between the coronary sinus and the right atrium is occluded. A venous collection device having a collection lumen and a support structure is located in the coronary sinus. The support structure is used to maintain patency of the coronary sinus during collection of fluid through the collection lumen. An artificial flow path is provided between the collection lumen and the one or more coronary arteries, thus isolating the cardiac circulation. According to the method, cardiac pumping for systemic circulation can be maintained during isolation of the cardiac circulation.
Owner:OSPREY MEDICAL
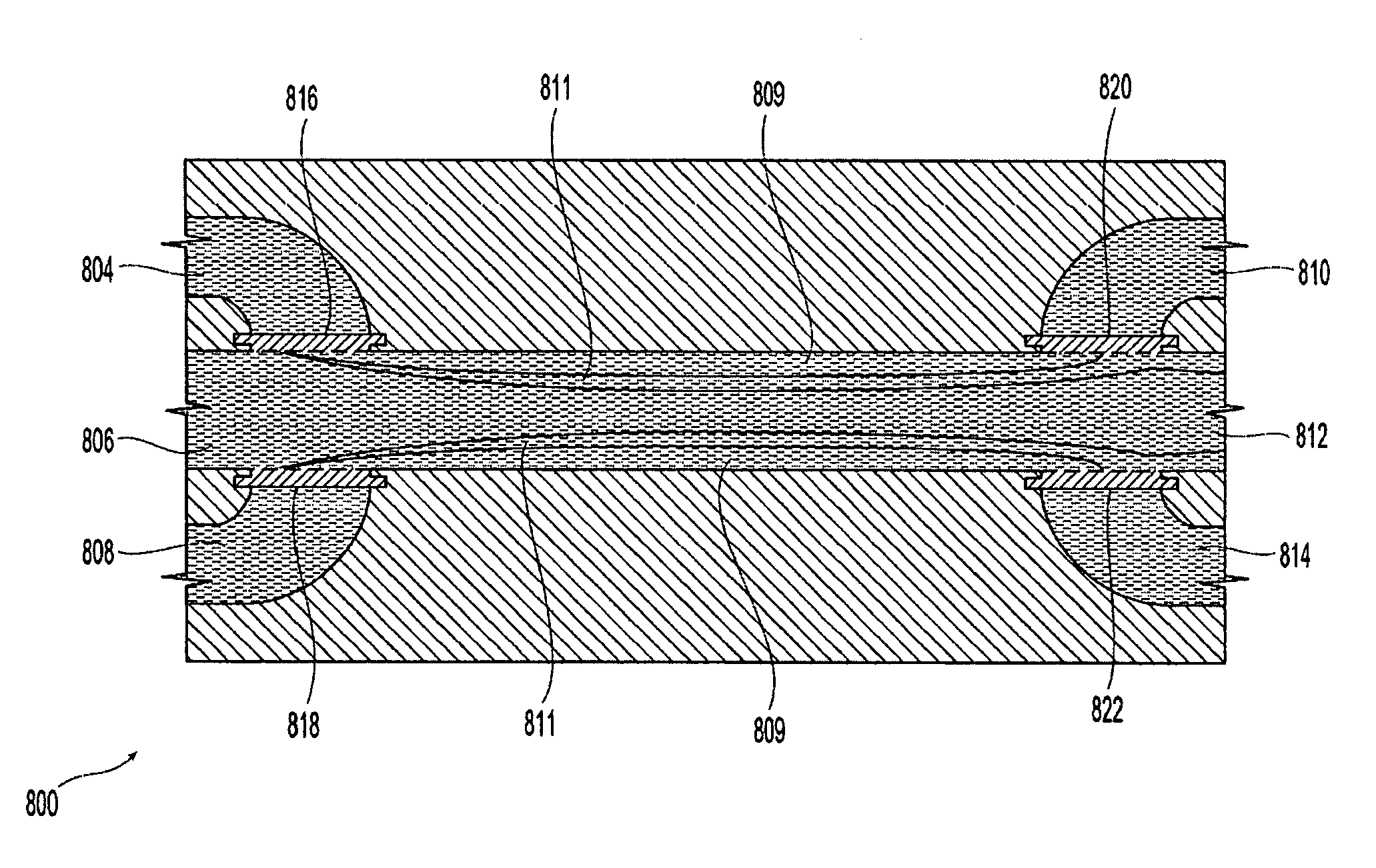
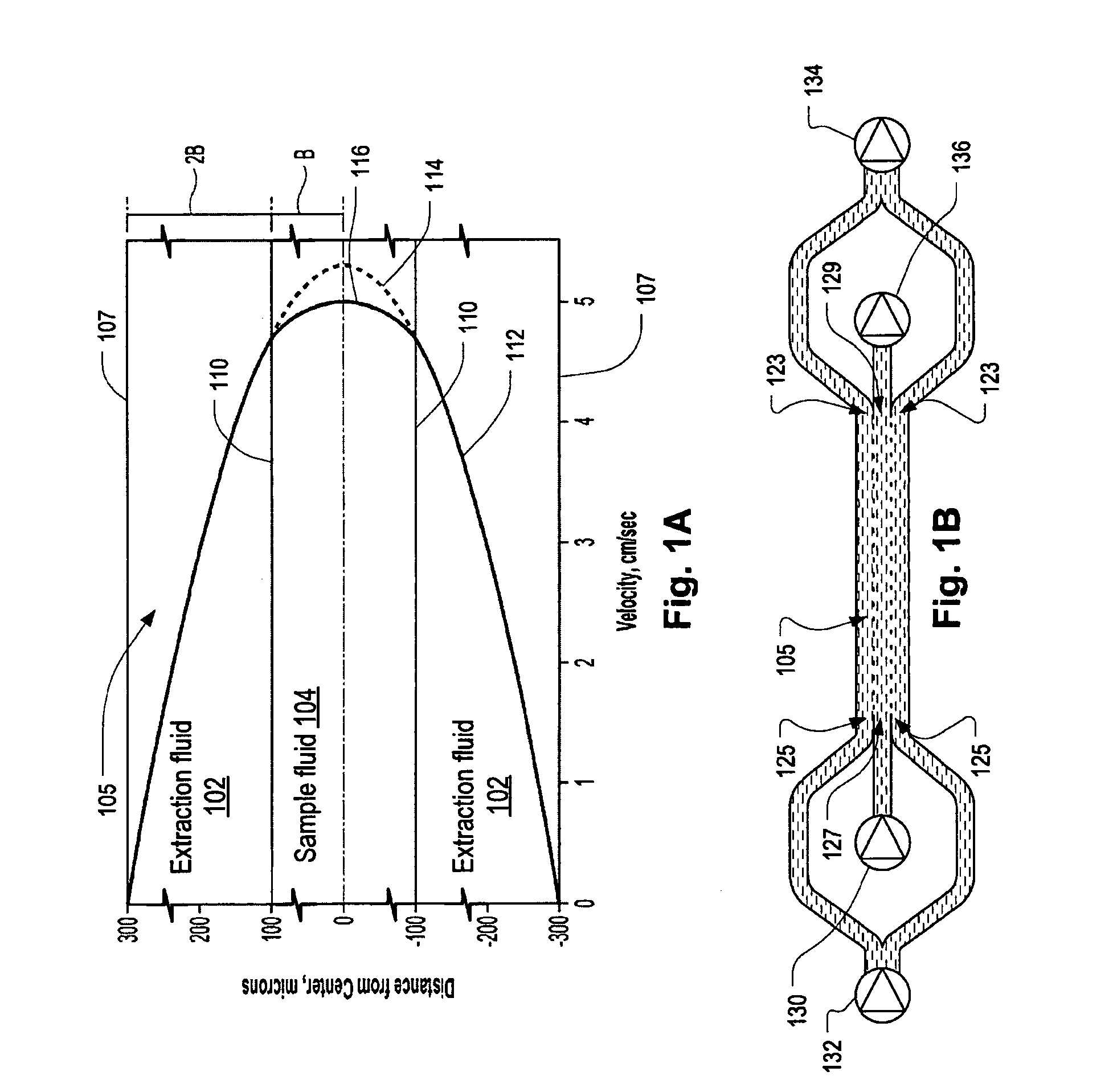
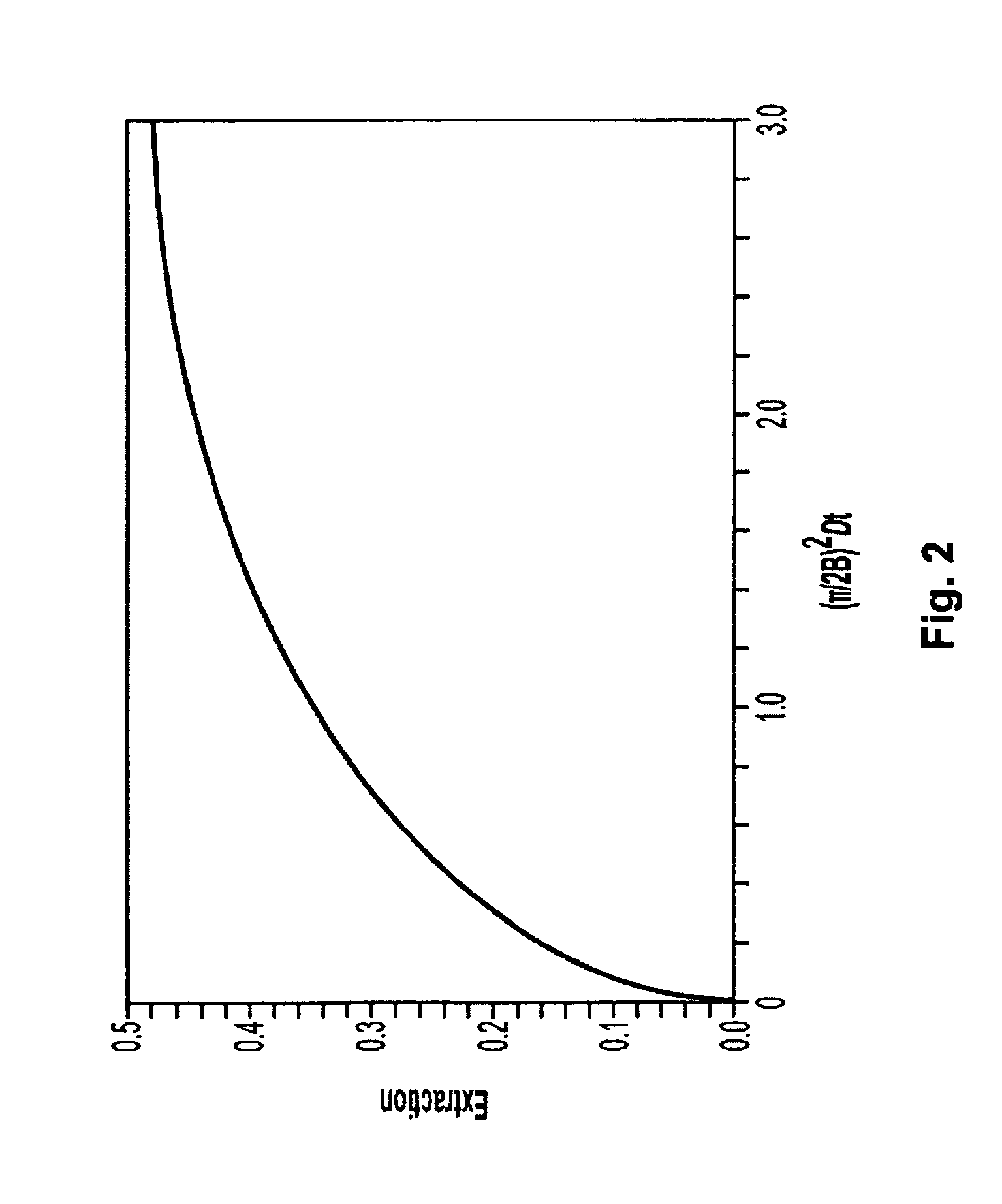
Systems and methods of blood-based therapies having a microfluidic membraneless exchange device
InactiveUS20060076295A1Reduces undesirable activationMinimizing bioincompatibilitiesComponent separationMedical devicesDiffusionThin layer
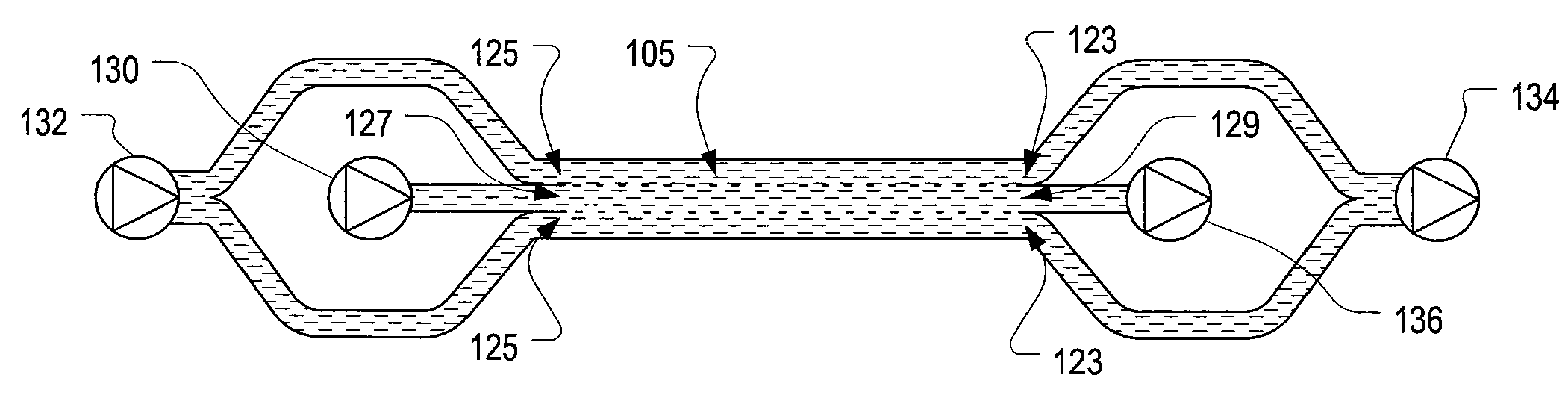
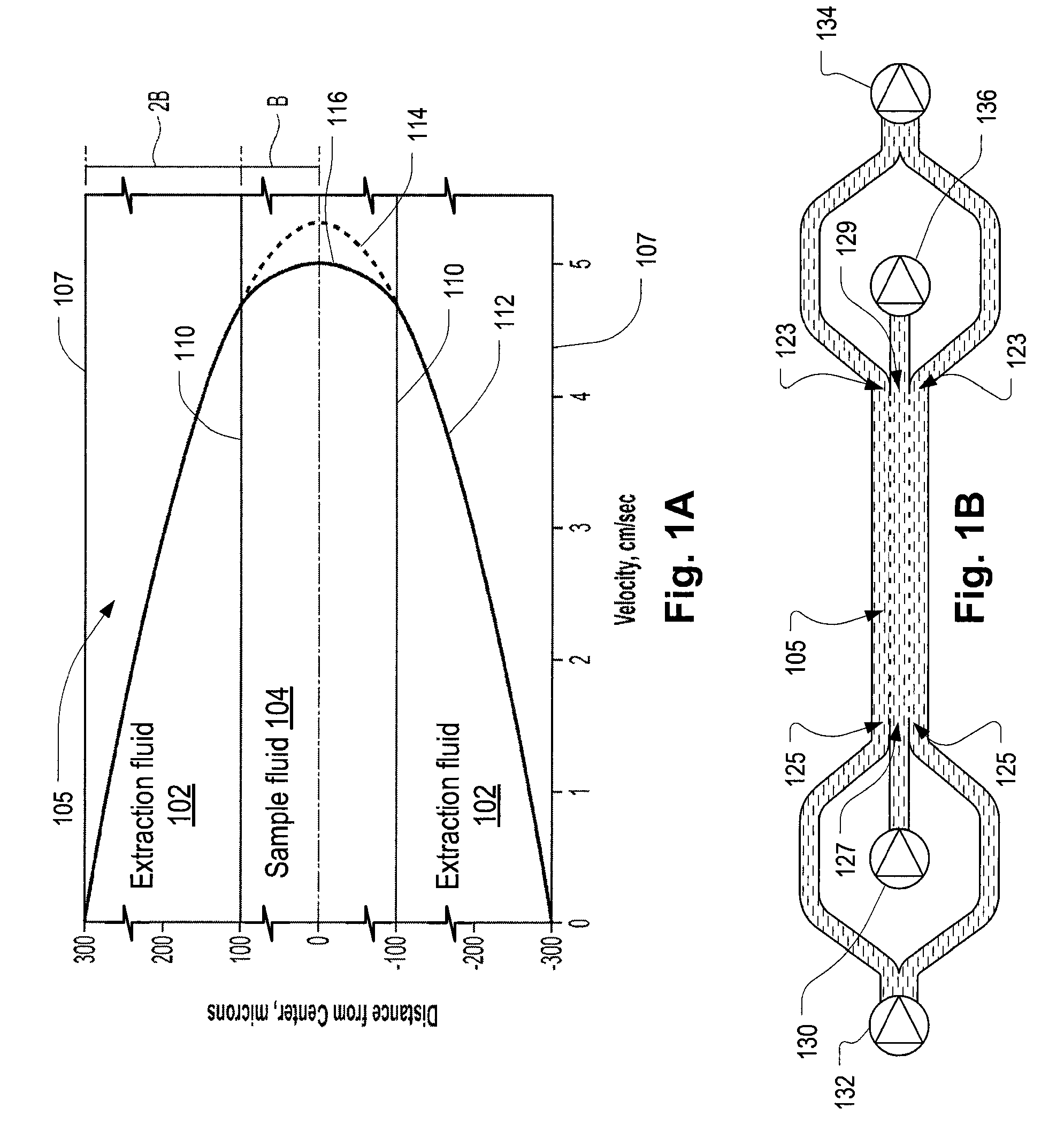
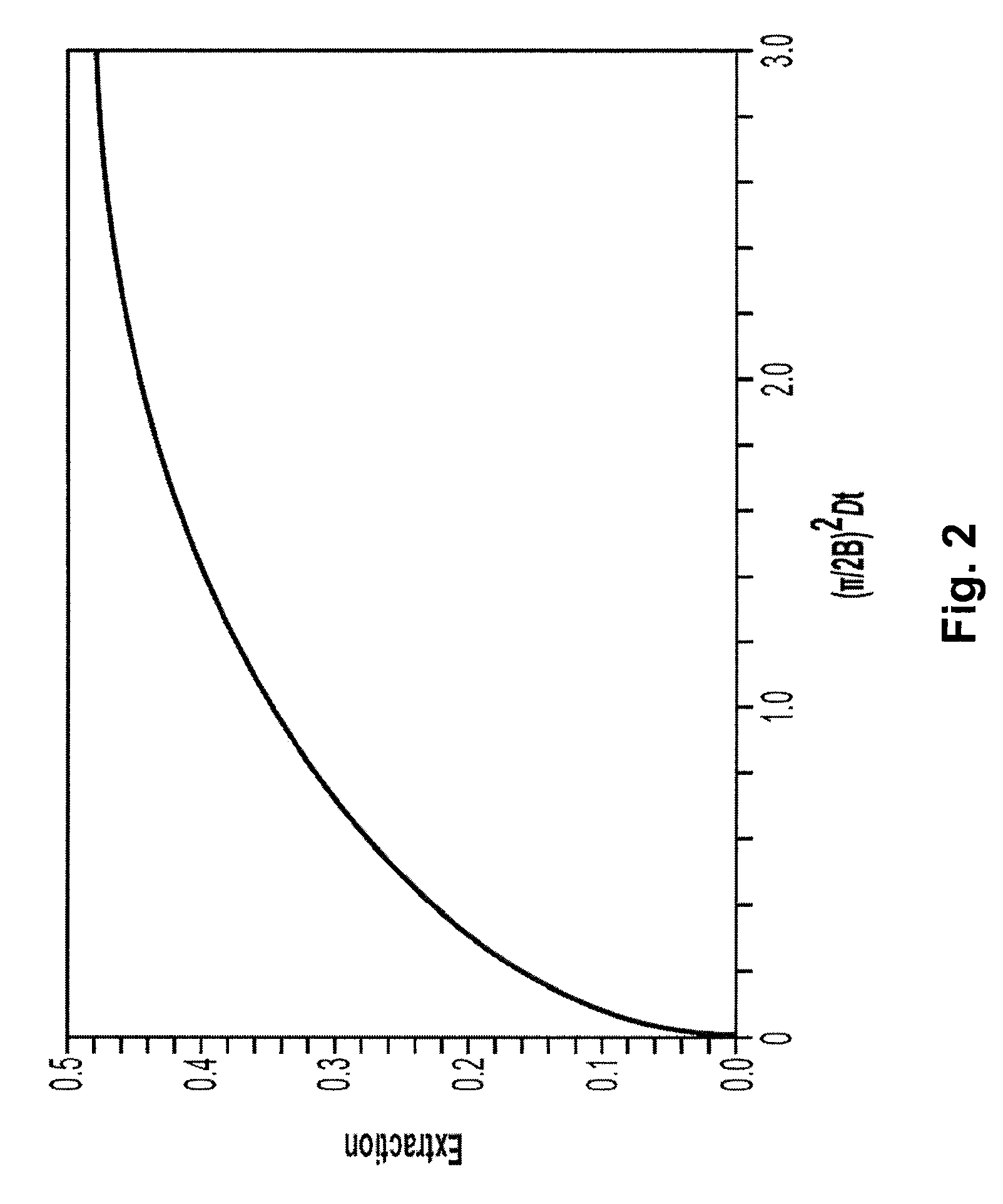
The present invention is directed to devices, systems and methods for removing undesirable materials from a sample fluid by contact with a second fluid. The sample fluid flows as a thin layer adjacent to, or between, concurrently flowing layers of the second fluid, without an intervening membrane. In various embodiments, a secondary separator is used to restrict the removal of desirable substances and effect the removal of undesirable substances from blood. The invention is useful in a variety of situations where a sample fluid is to be purified via a diffusion mechanism against an extractor fluid. Moreover, the invention may be used for the removal of components from a sample fluid that vary in size. When blood is the sample fluid, for example, this may include the removal of ‘small’ molecules, ‘middle’ molecules, macromolecules, macromolecular aggregates, and cells, from the blood sample to the extractor fluid.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
System for enriching a bodily fluid with a gas
InactiveUS20020138034A1Other blood circulation devicesMedical devicesElectronic controllerProduct gas
A system utilizes an oxygenation device to generate a gas-enriched physiologic fluid and to combine it with a bodily fluid to create a gas-enriched bodily fluid. The oxygenation device may take the form of a disposable cartridge, which is placed within an enclosure. An electronic controller manages various aspects of the system, such as the production of gas-enriched fluids, flow rates, bubble detection, and automatic operation and shut down.
Owner:THEROX
Device for the extravascular recirculation of liquid in body cavities
InactiveUS7842002B2Improves liquid distributionOptimize allocationMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesSubarachnoid spaceDouble tube
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Disposable cartridge for producing gas-enriched fluids
InactiveUS20020136662A1Other blood circulation devicesTransportation and packagingPhysiological fluidMedicine
A device generates a gas-enriched physiologic fluid and combines it with a bodily fluid to create a gas-enriched bodily fluid. The device may take the form of a disposable cartridge. The cartridge may include a fluid supply chamber for delivering physiologic fluid under pressure to an atomizer. The atomizer delivers fluid droplets into a gas-pressurized atomization chamber to enrich the physiologic fluid with the gas. The gas-enriched physiologic fluid is delivered to a mixing chamber in the cartridge where the gas-enriched physiologic fluid is mixed with a bodily fluid, such as blood, to create a gas-enriched bodily fluid.
Owner:THEROX
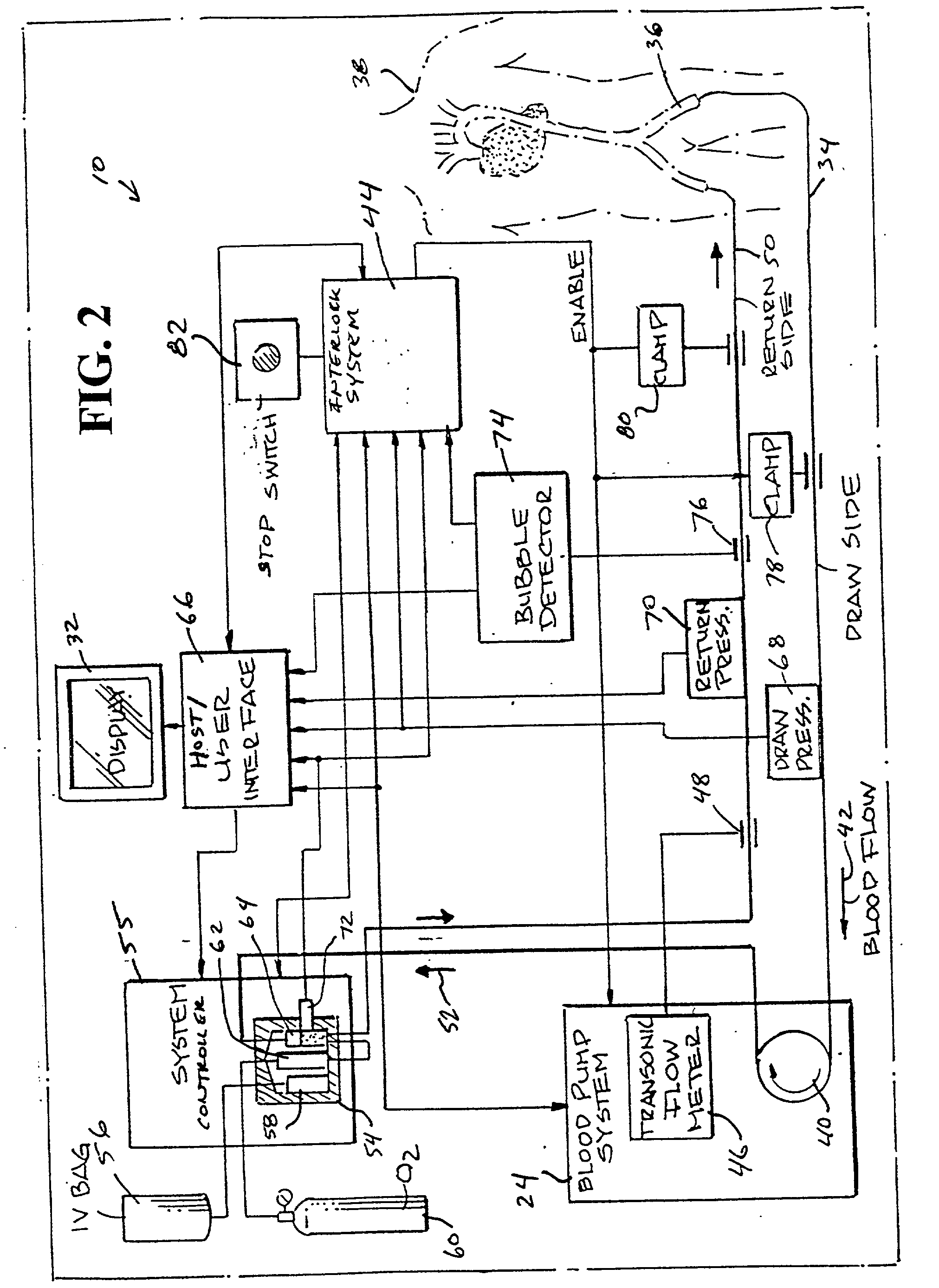
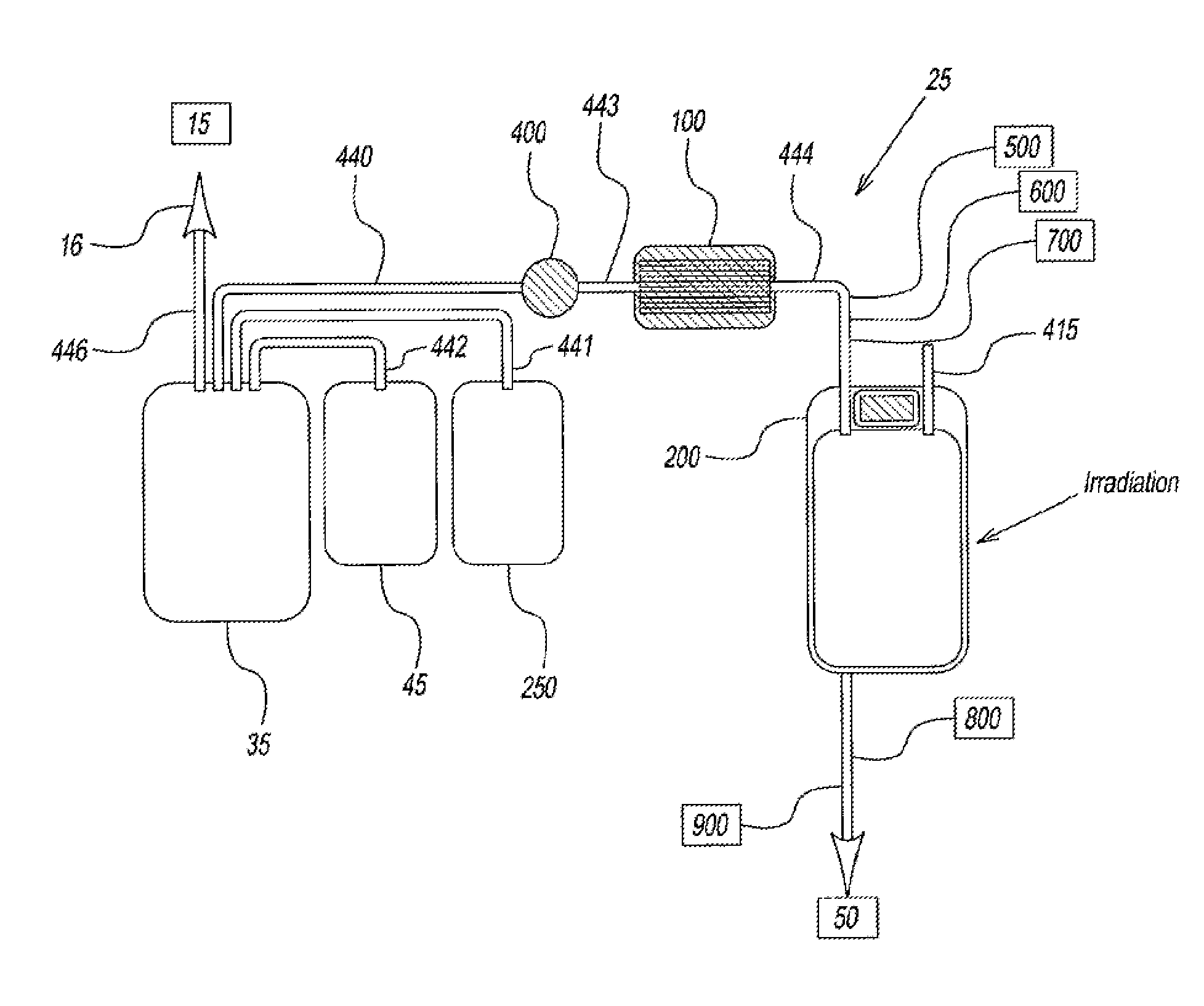
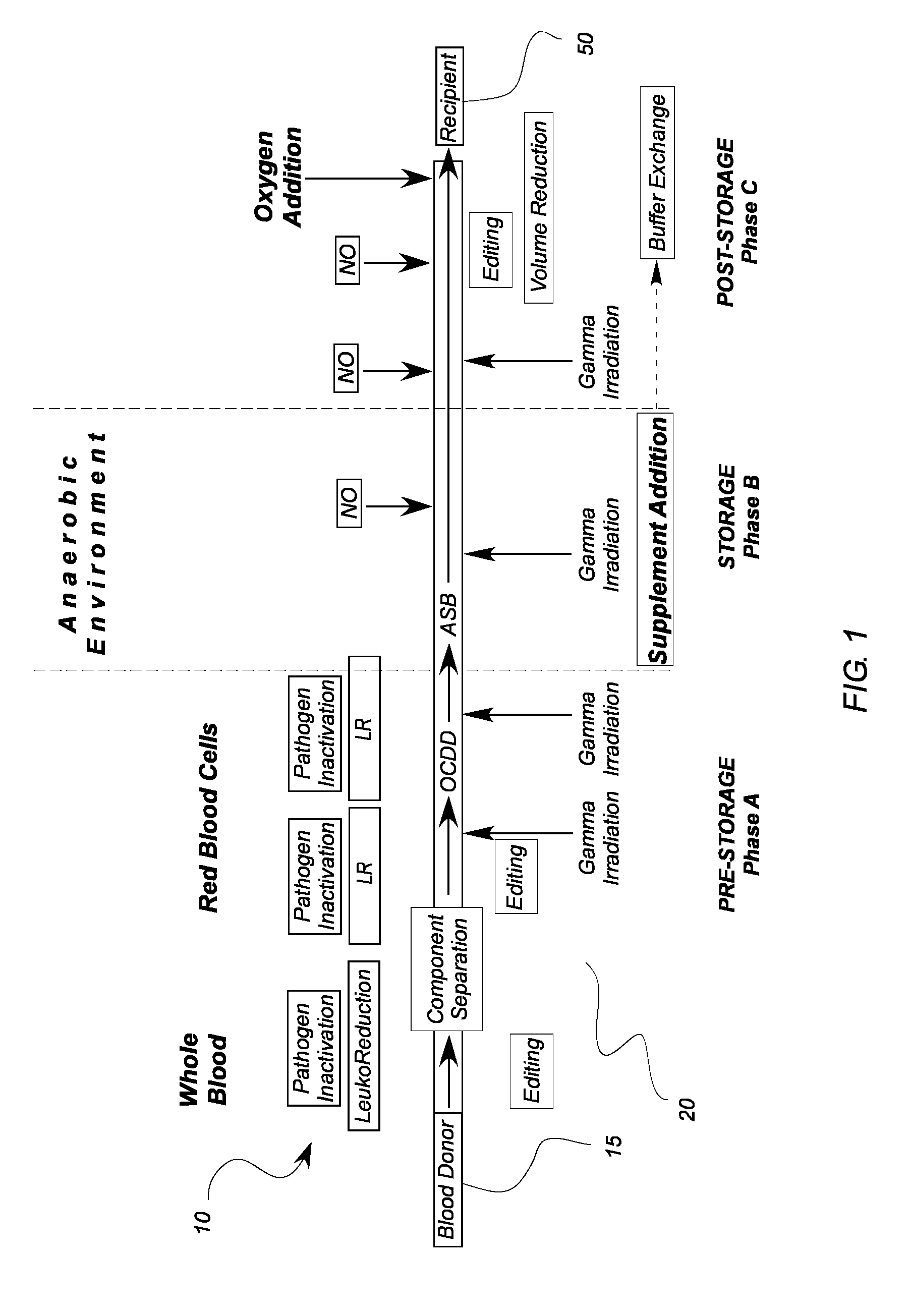
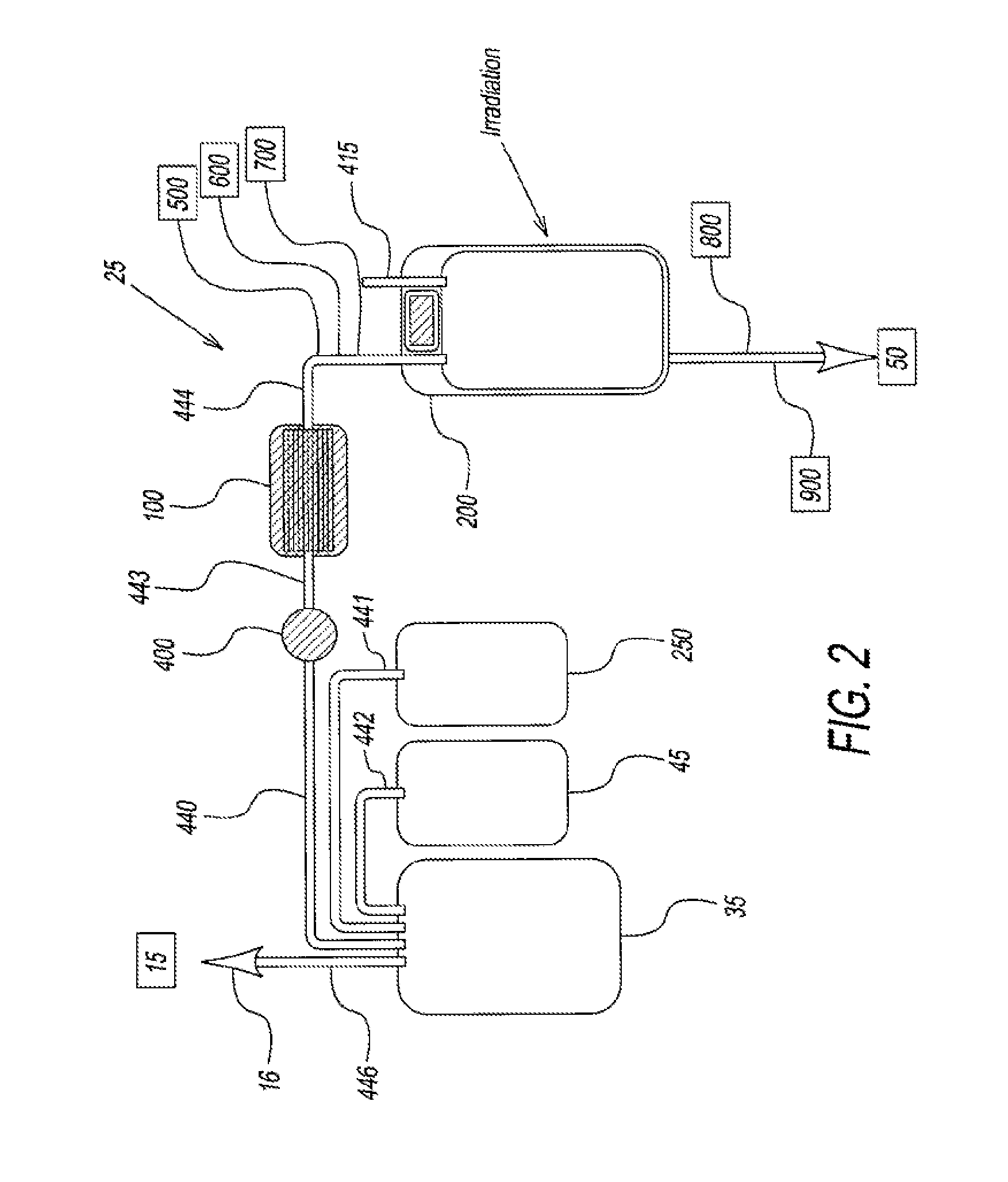
System for extended storage of red blood cells and methods of use
ActiveUS20130004937A1Extension of timeImprove radiation effectMedical devicesDead animal preservationOxygenRed Cell
A system and methodology for the preservation of red blood cells is described in which red blood cells are oxygen or oxygen and carbon dioxide depleted, treated and are stored in an anaerobic environment to optimize preparation for transfusion. More particularly, a system and method for extended storage of red blood cells from collection to transfusion that optimizes red blood cells prior to transfusion is described.
Owner:HEMANEXT INC
Method of treating atherosclerosis
InactiveUS6669965B2Reduce the number of cellsReadily phagocytosedBiocideEnergy modified materialsAtheromaStressor
A method of treating or preventing atherosclerosis in a mammalian subject comprises: (a) extracting the aliquot of blood from the subject; (b) treating the aliquot of blood ex vivo with at least one stressor selected from the group consisting of an oxidizing agent, ultraviolet radiation and elevated temperature; and (c) administering the aliquot of blood treated in step (b) to the subject. Preferably, the aliquot has a volume of from about 0.01 ml to about 400 ml and is treated simultaneously by ozone gas and ultraviolet radiation at a temperature of from 37-55° C.
Owner:VASOGEN IRELAND LTD
Device for the extravascular recirculation of liquid in body cavities
InactiveUS20060161107A1Improves liquid distributionOptimize allocationMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesSubarachnoid spaceDouble tube
Biocompatible liquid is pumped into a body cavity (eg. subarachnoid space, peritoneum, mediastinum, pleural space) by means of one pump and removed from it by means a second pump, preferably via a double-barreled catheter is used for insertion and removal of the liquid. An optional secondary catheter removes liquid from a distal area of the body cavity. Temperature and pressure are sensed within the cavity and can be controlled by adjusting liquid flow rates. While outside the body, the liquid can be ultraviolet-sterilized, foam fractionated to remove contaminants, oxygenated and pH balanced, cooled or warmed, and augmented with exogenous liquid that may contain drugs.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Method of pulsatile neurovascular aspiration with telescoping catheter
A method of aspirating a vascular occlusion from a remote site is provided. The method includes the steps of advancing a first elongate tubular body through a vascular access site and into a body vessel, advancing a second tubular body distally to extend beyond the first elongate tubular body to reach the remote site, and aspirating thrombus from the site into the lumen by applying pulsatile vacuum to the first elongate tubular body. The second tubular body has a lumen and a length that is shorter than the first elongate tubular body. The pulsatile application of vacuum may cause the distal tip of the second tubular body to open and close like a jaw, which facilitates reshaping the thrombus or biting or nibbling the thrombus material into strands or pieces to facilitate proximal withdrawal under negative pressure through the lumen of the second tubular body.
Owner:INCEPT LLC +1
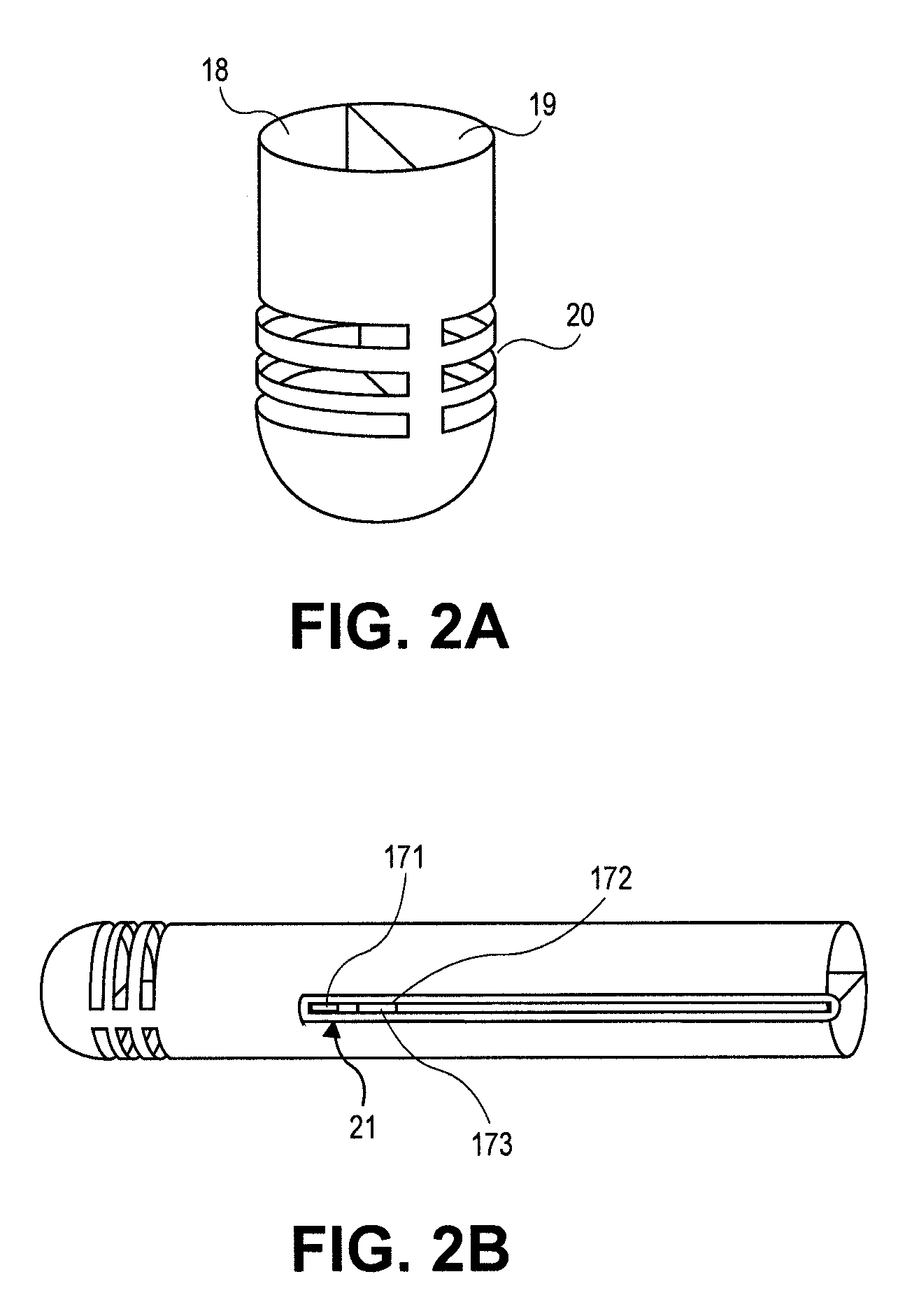
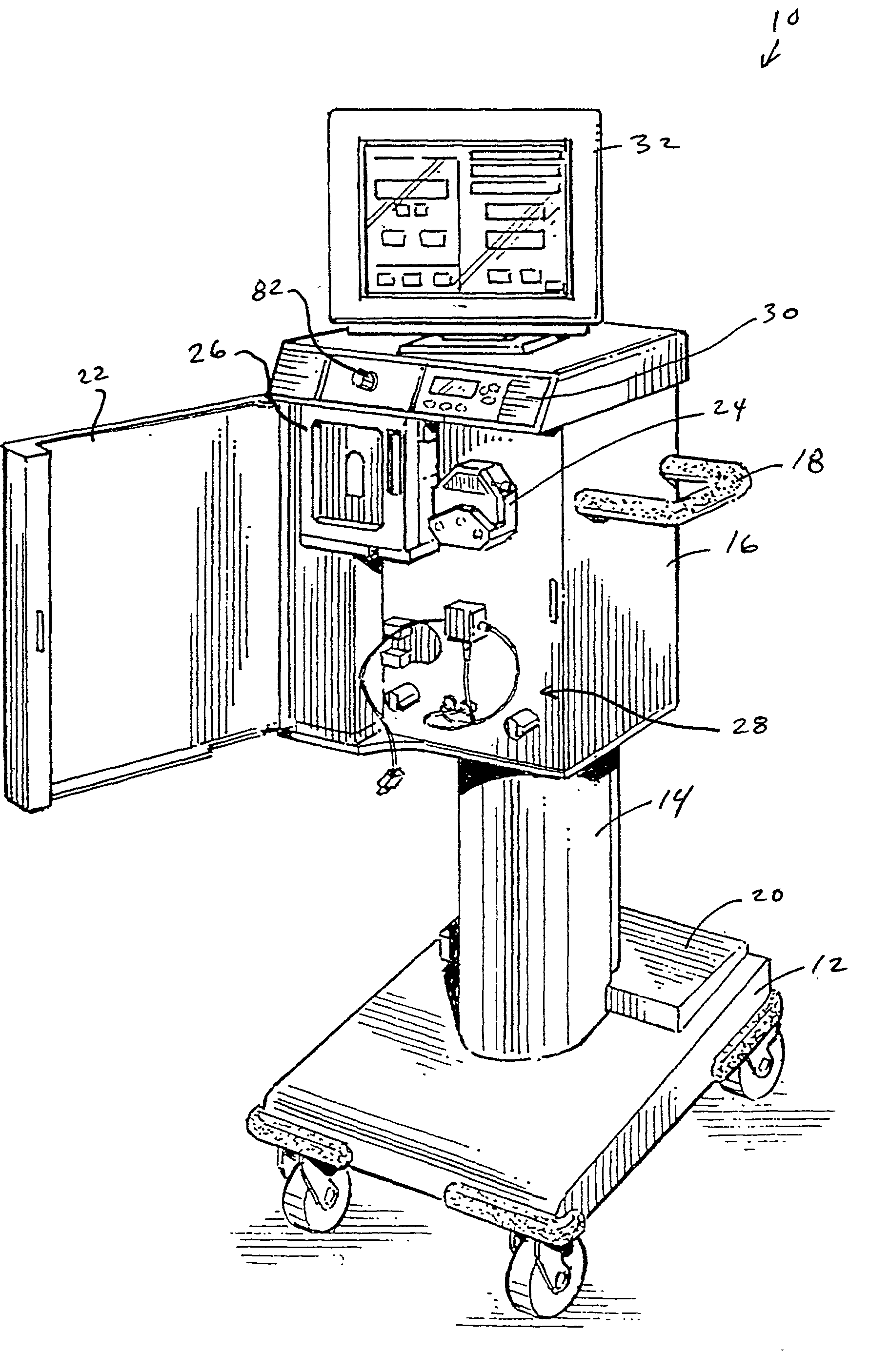
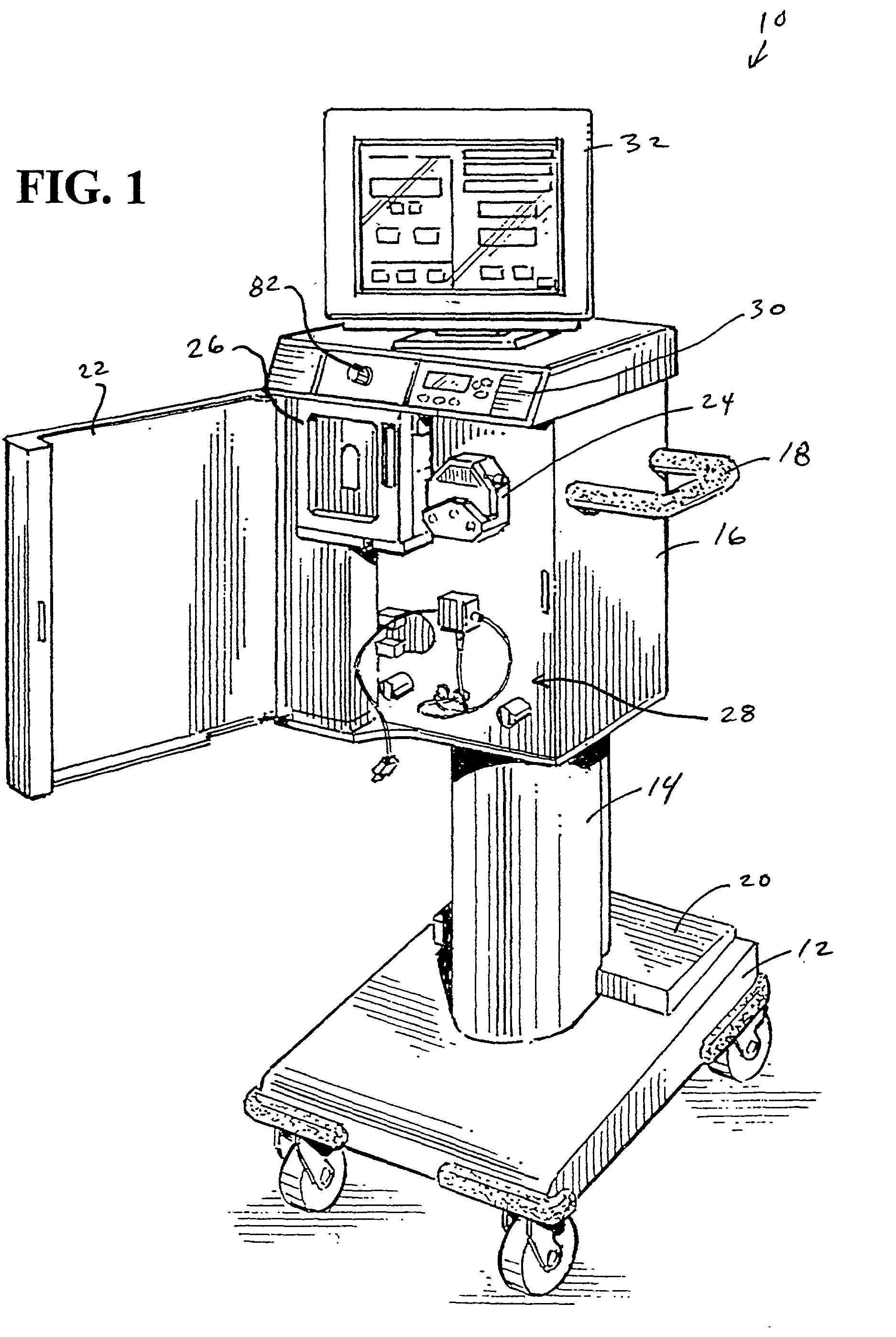
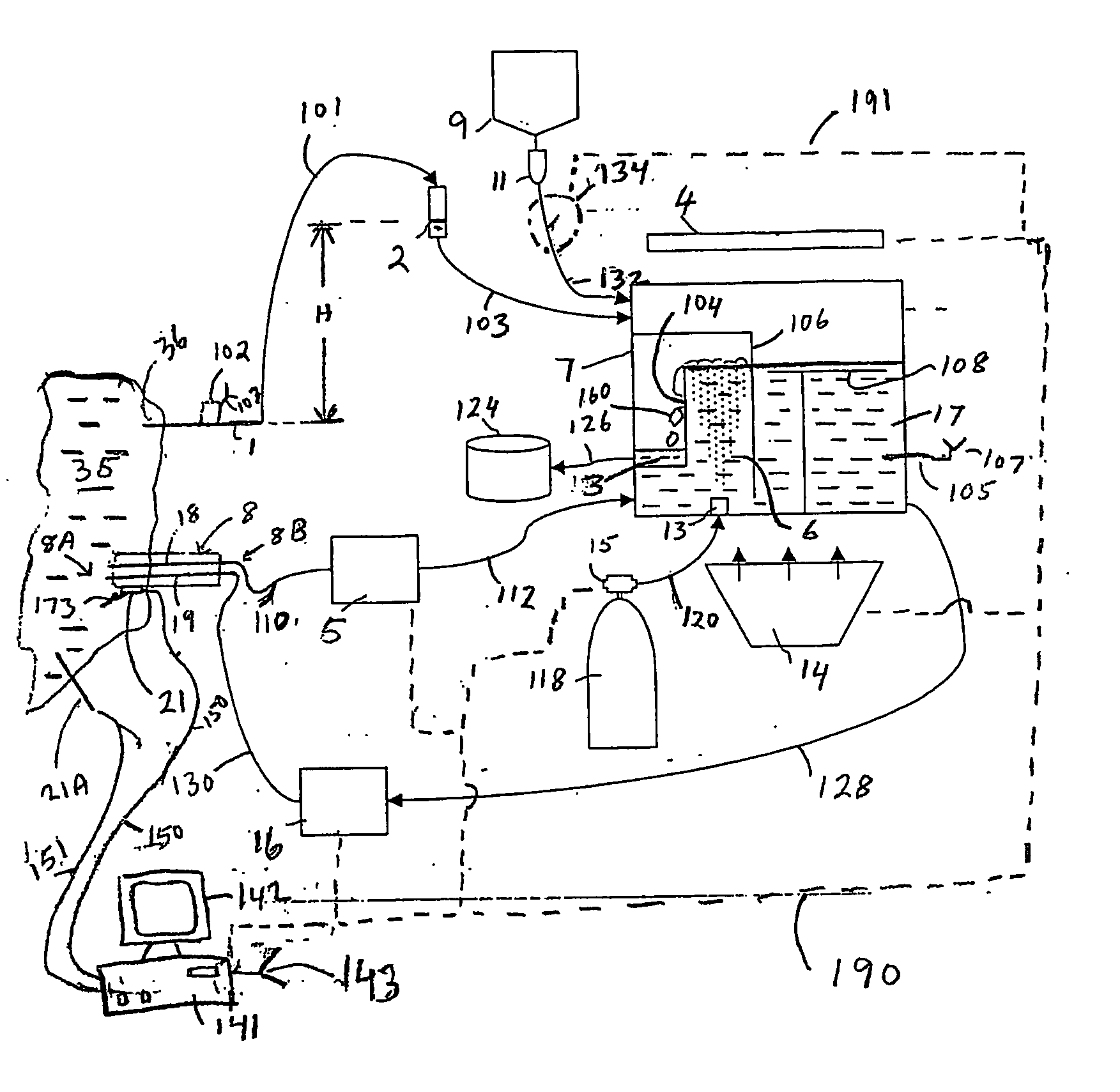
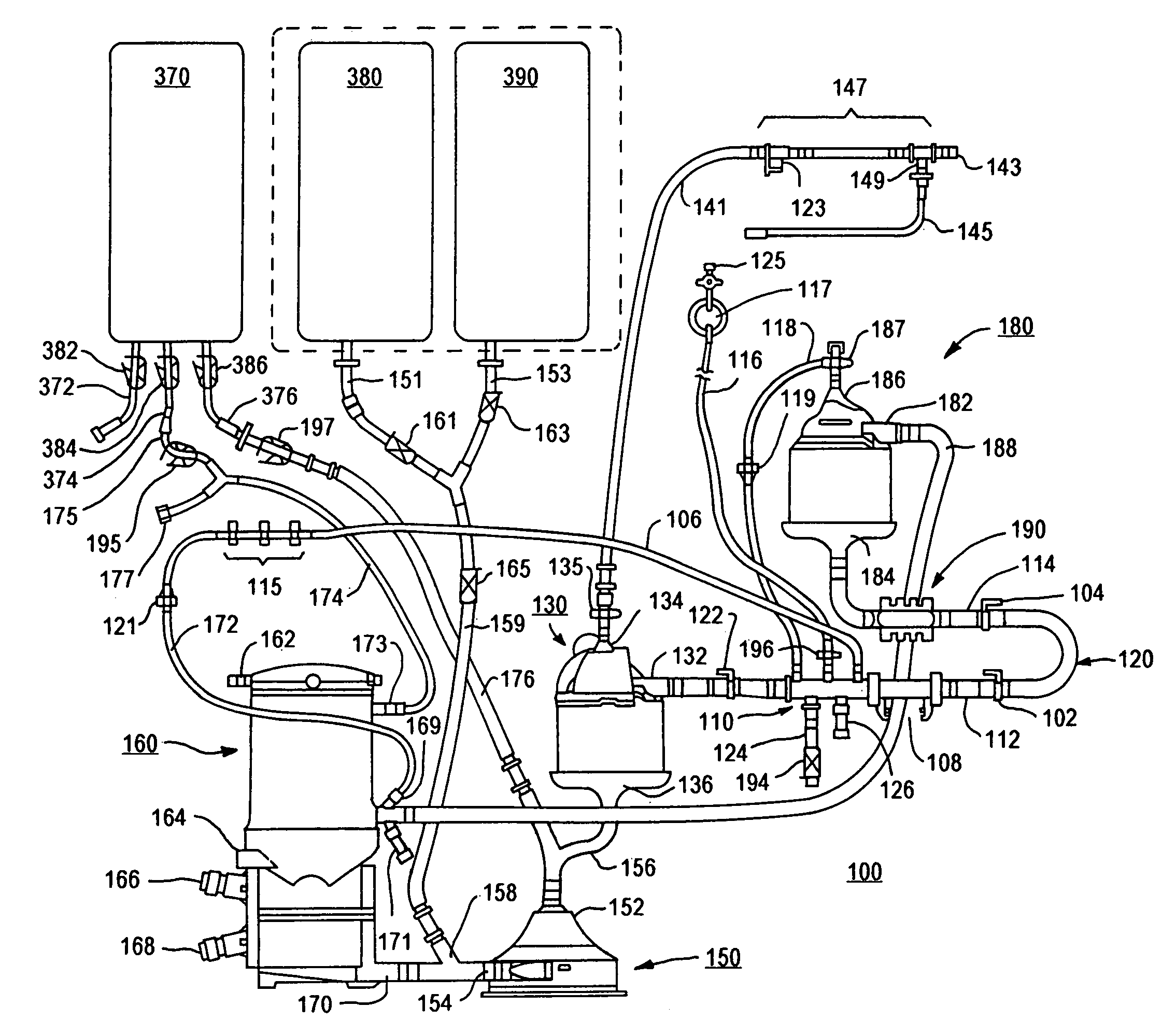
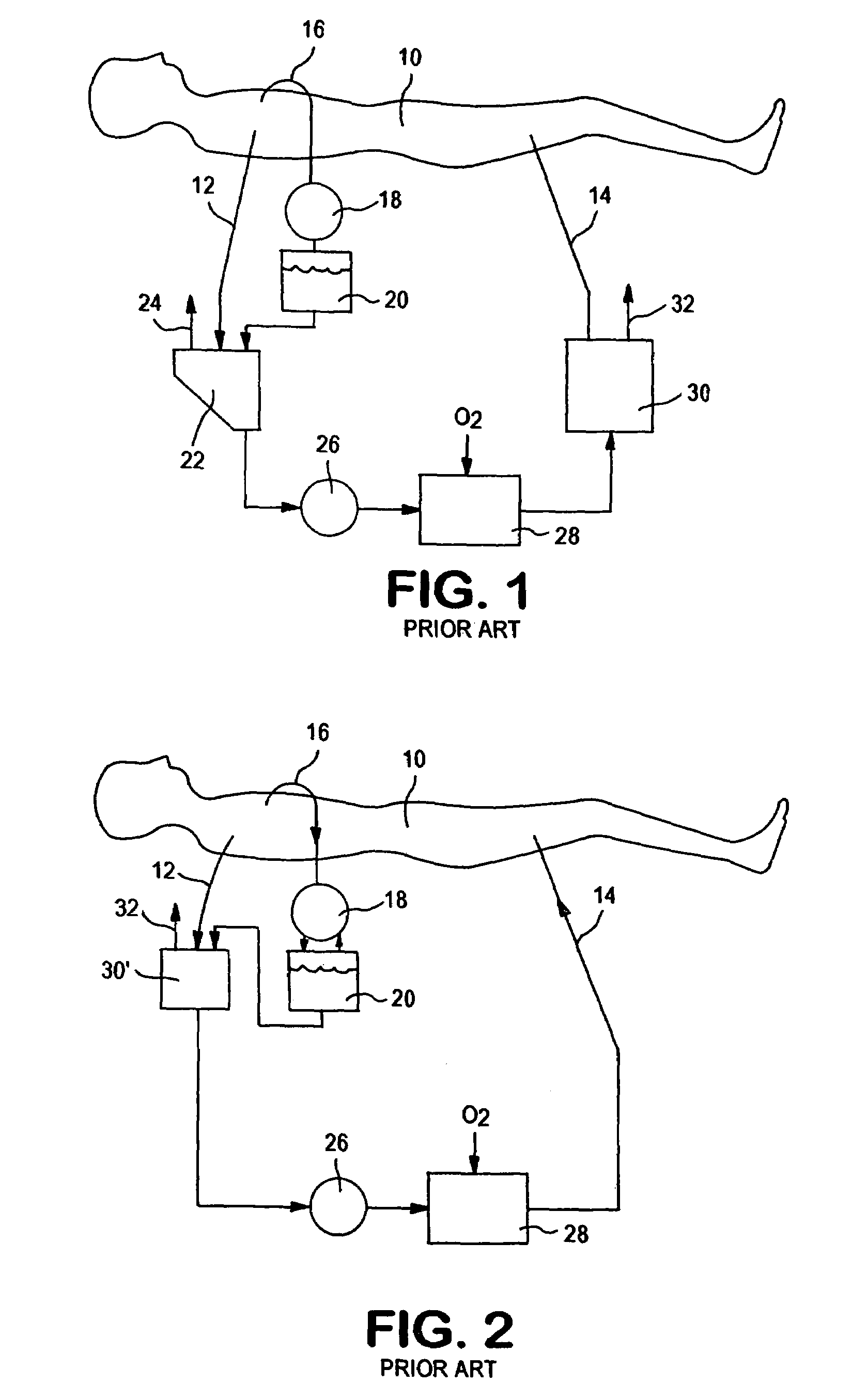
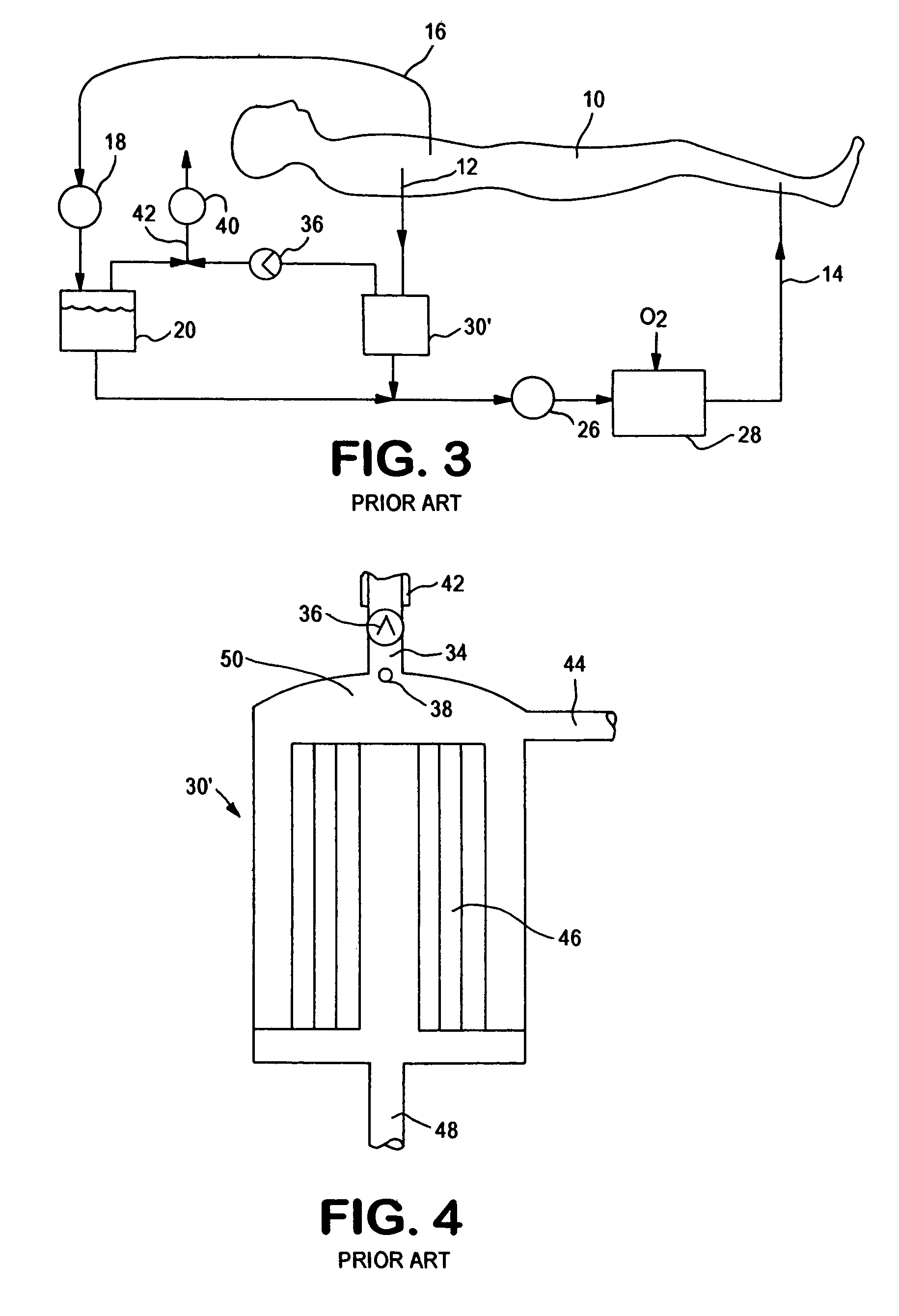
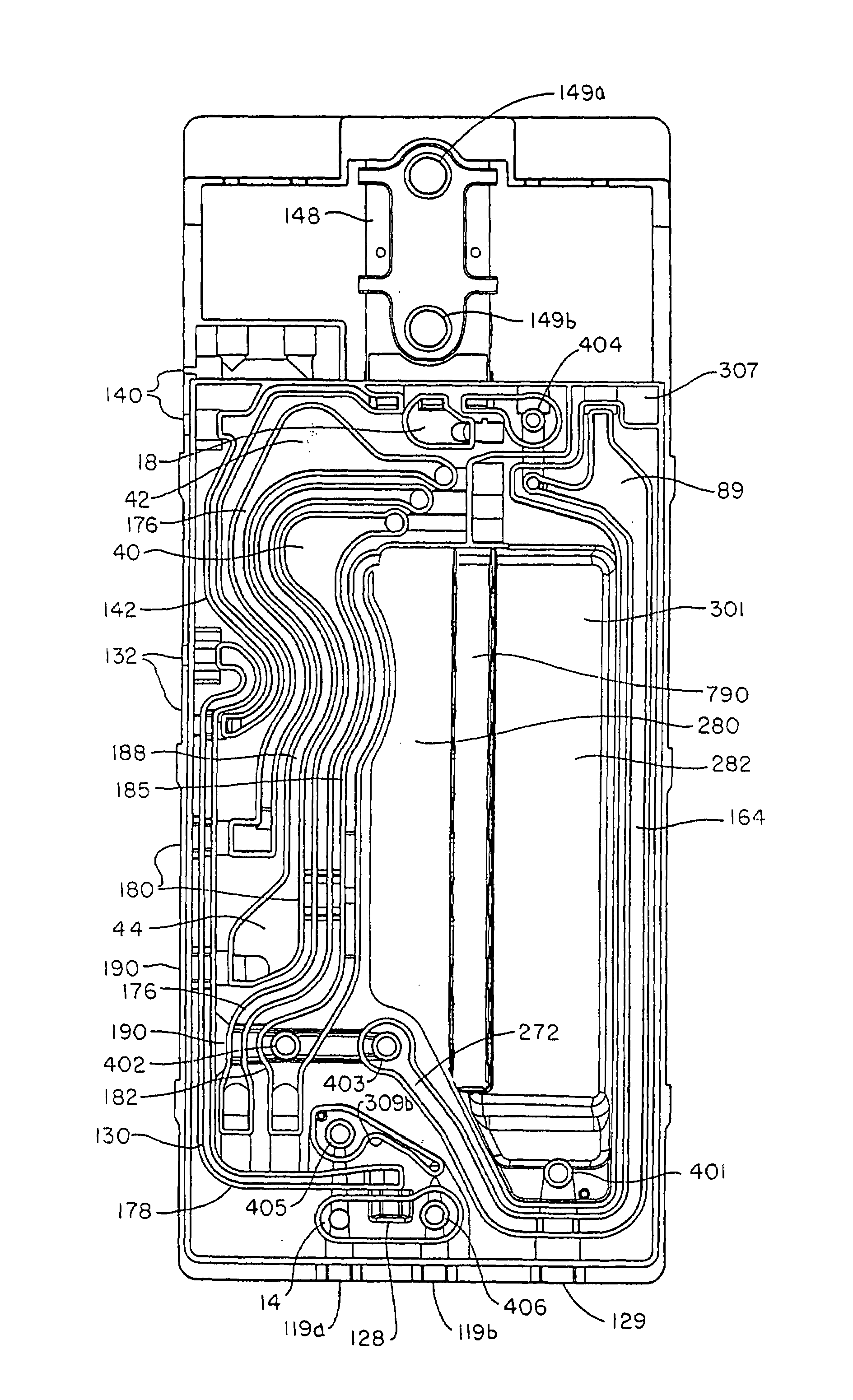
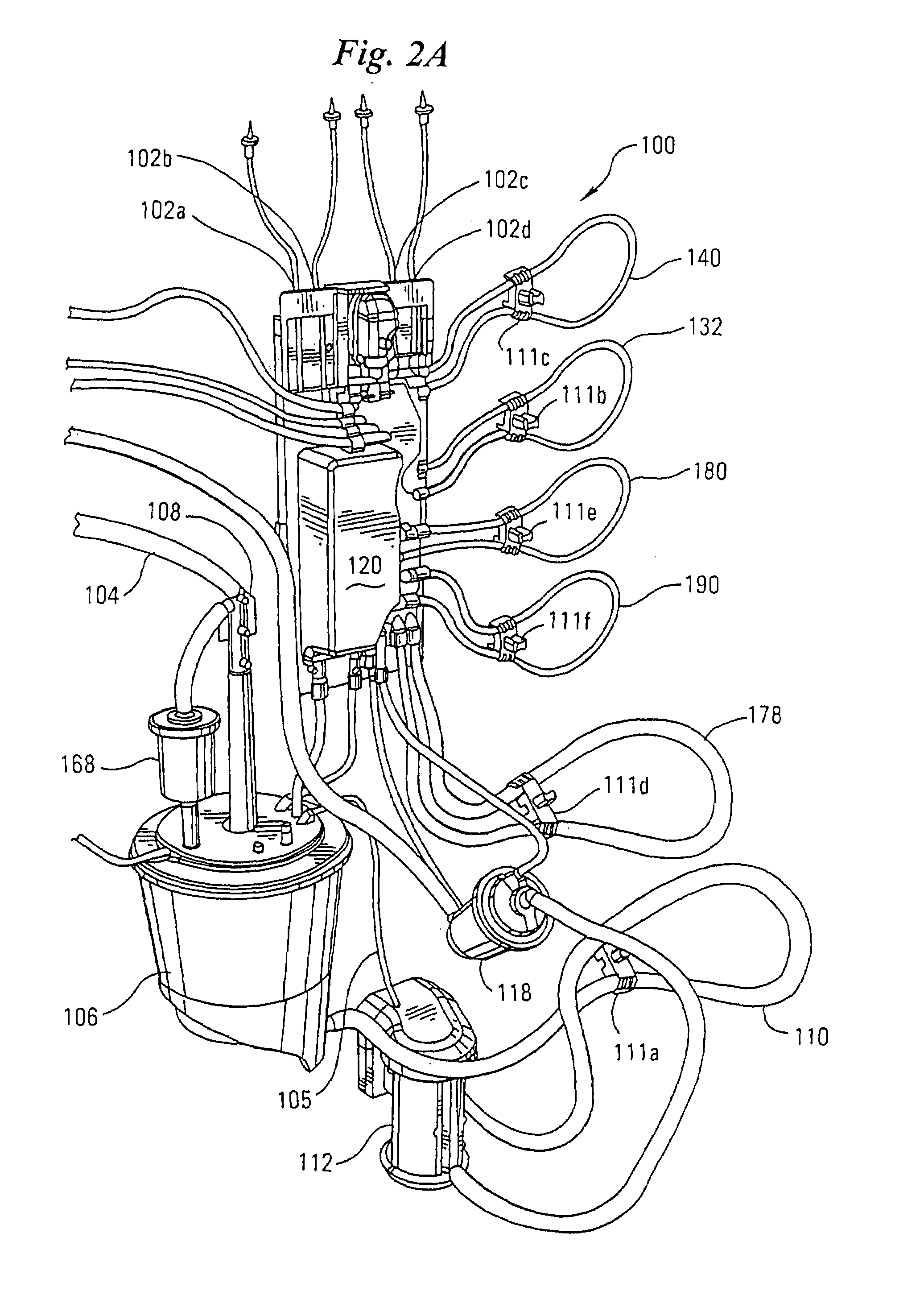
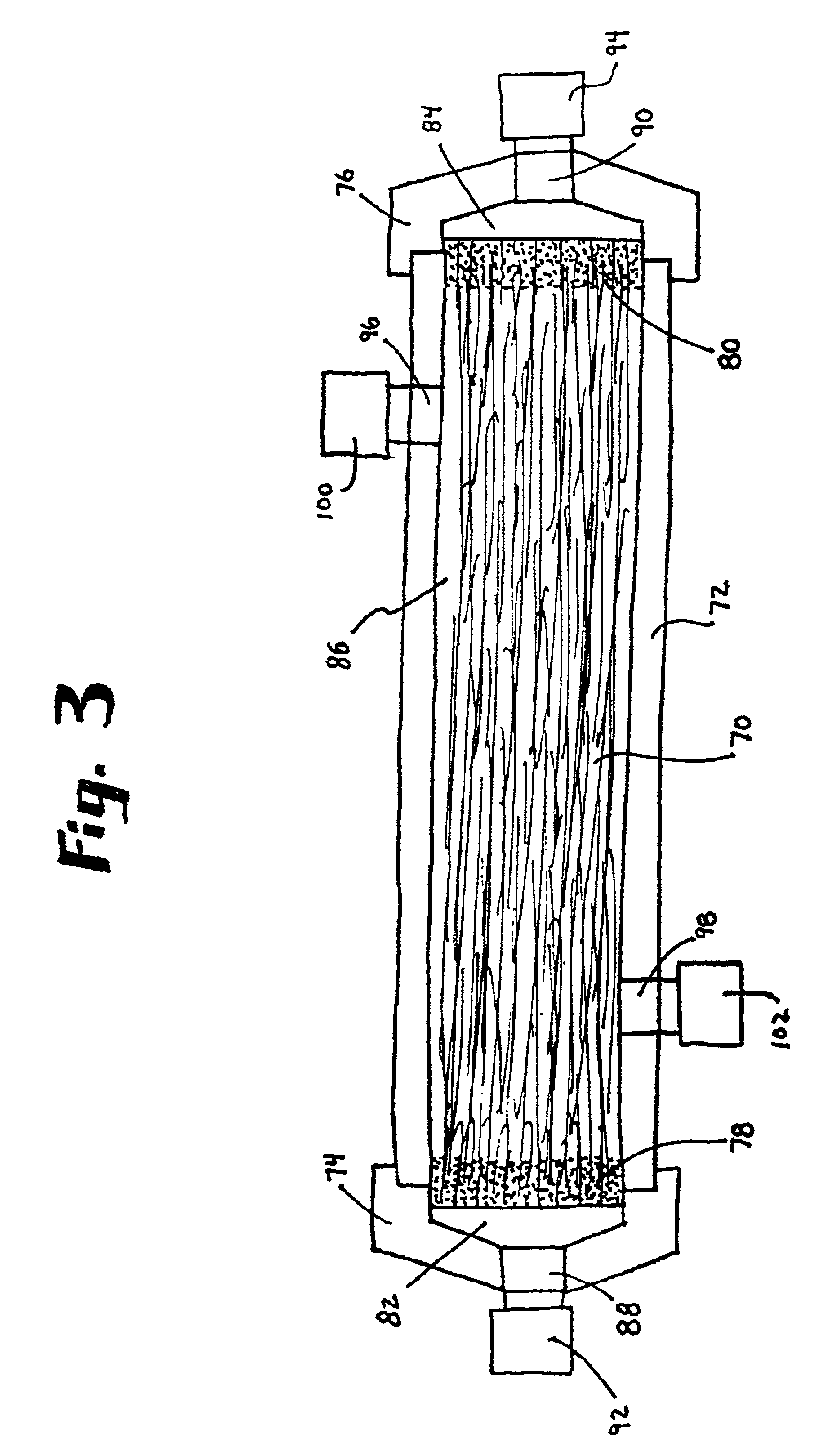
Disposable, integrated, extracorporeal blood circuit
ActiveUS7198751B2Save spaceIncrease contactSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationVenous blood
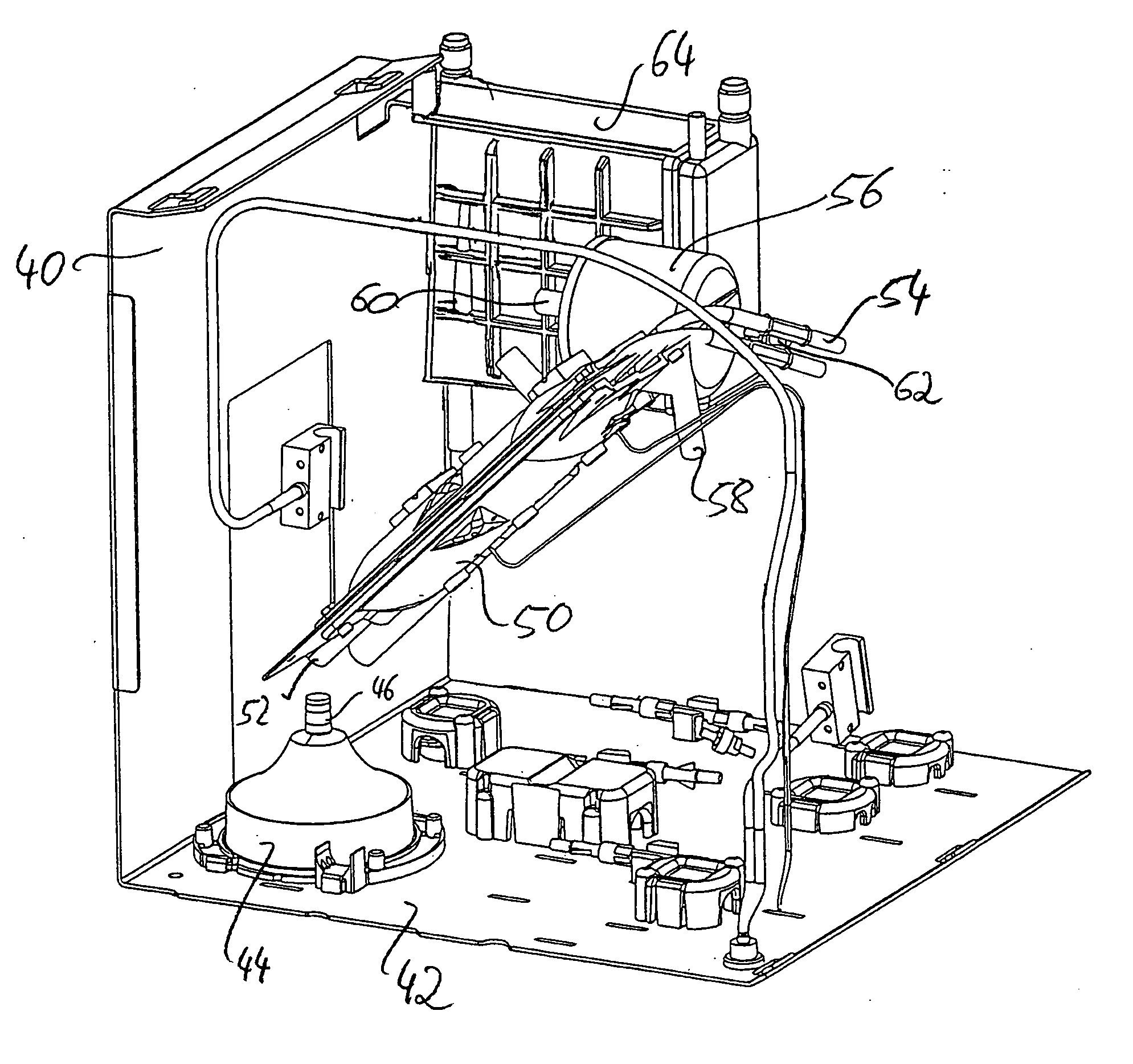
A disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit employed during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery performs gas exchange, heat transfer, and microemboli filtering functions in a way as to conserve volume, to reduce setup and change out times, to eliminate a venous blood reservoir, and to substantially reduce blood-air interface. Blood from the patient or prime solution is routed through an air removal device that is equipped with air sensors for detection of air. An active air removal controller removes detected air from blood in the air removal device. A disposable circuit support module is used to mount the components of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit in close proximity and in a desirable spatial relationship to optimize priming and use of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit. A reusable circuit holder supports the disposable circuit support module in relation to a prime solution source, the active air removal controller and other components.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
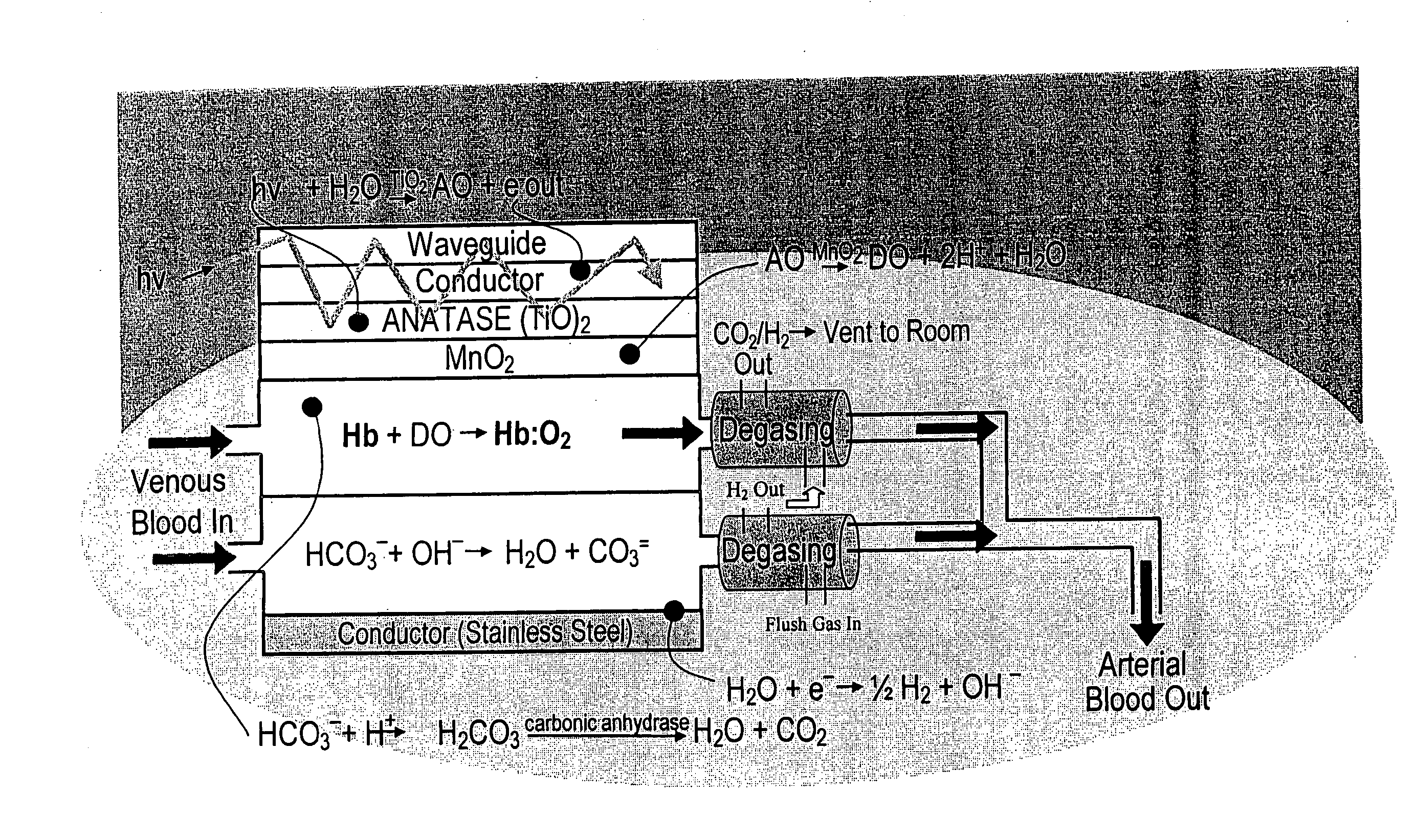
Photolytic cell for providing physiological gas exchange
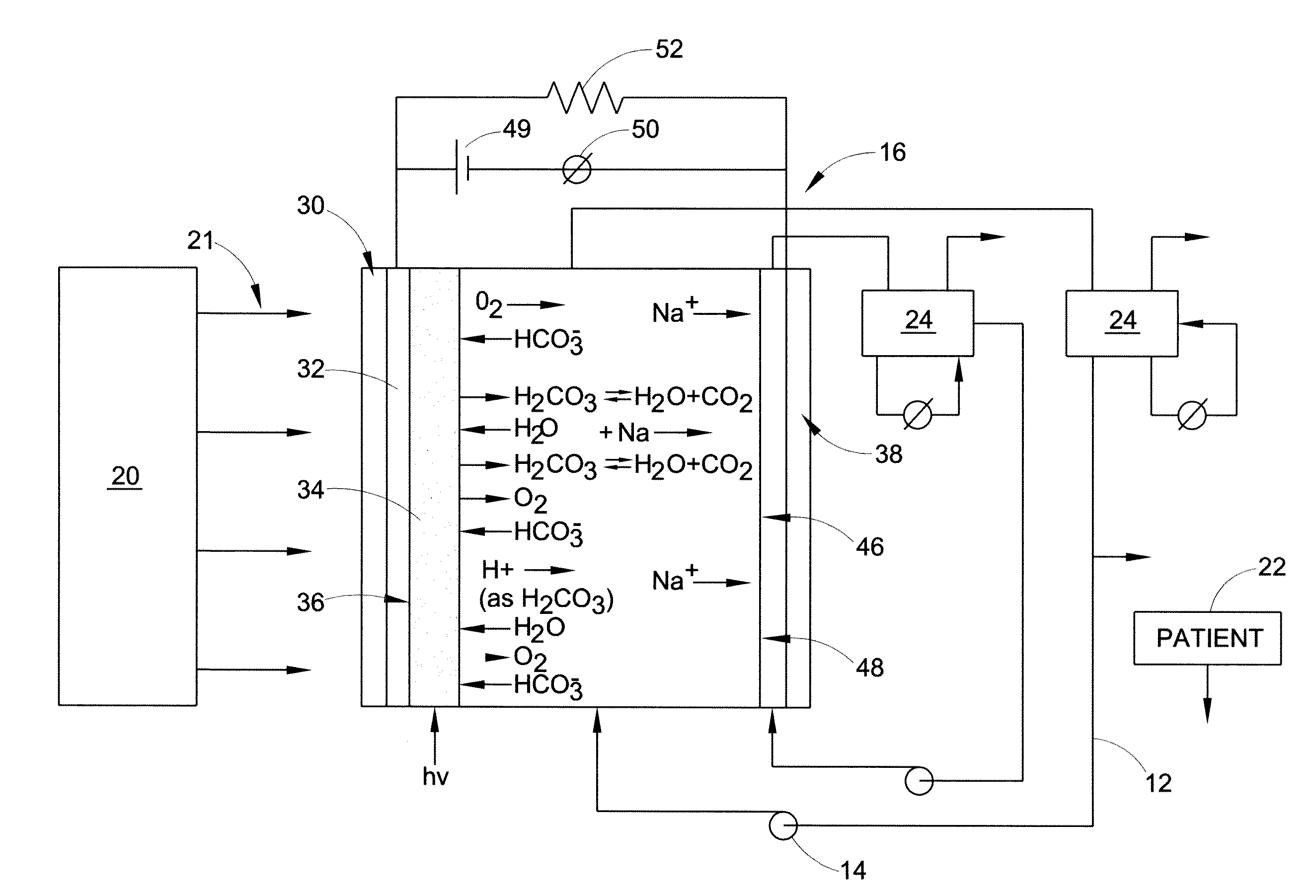
InactiveUS20050025680A1Low costLimited commercial valueOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesChemical reactionCompound (substance)
The present invention is directed to a photolytic cell, and to a photolytic artificial lung incorporating such a cell. The photolytic artificial lung converts water to oxygen for blood absorption, regulates pH, the removes carbon dioxide, and co-produces electrical power. The photolytic artificial lung includes a photolytic cell where all of the chemical reactions occur. Additionally, the present invention relates to photolytically sensitive materials for oxygen generation. These materials are useful for gas-free artificial lung fabrication. The photolytic cell disclosed herein can also be used to direct chemical reactions in organs other than the lung. It can also be used to maintain breathing air in confined systems.
Owner:THORATEC CORPORTION +1
Method and Apparatus for Inducing Therapeutic Hypothermia
Methods and apparatus for delivering therapeutic hypothermia to a patient are provided which may include any number of features. One feature is a hypothermia system comprising a fluid source, a heat exchanger assembly, a catheter in fluid communication with the fluid source, and a pump system configured to infuse hypothermic fluid into a patient cavity and extract hypothermic fluid from the patient cavity. The hypothermia system can infuse and extract fluid automatically from the patient cavity. In one embodiment, the patient cavity is a peritoneal cavity. A safe access device to gain access to the patient cavity is also provided.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Dynamic brake with backlash control for peristaltic pump
InactiveUS20020127115A1Prevent reboundMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOther blood circulation devicesPeristaltic pumpBrief periods
The present invention involves a dynamic brake for use in a peristaltic (i.e., roller) pump. The dynamic brake avoids backlash, due to counter rotation. In addition, it does not preclude the option of hand operating the roller pump. This is achieved by initiating the braking operation after the roller pump set-point has been set to zero and only after the roller pump has decelerated below a predefined speed (e.g., 20 rpm). In addition, the braking operation is activated for only a very brief period of time (i.e., a period of time required for the pressure in the roller pump fluid conduit to subside).
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
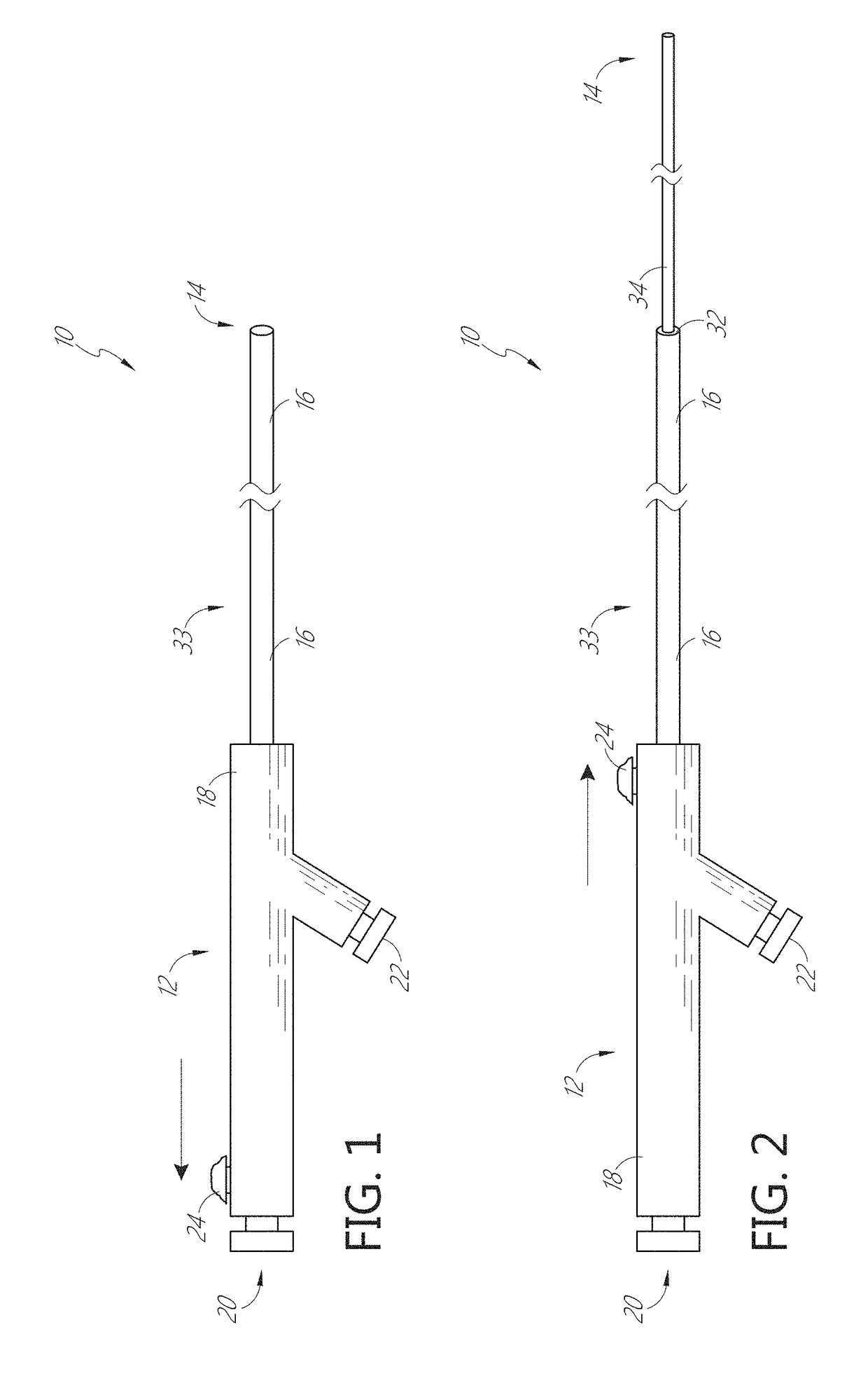
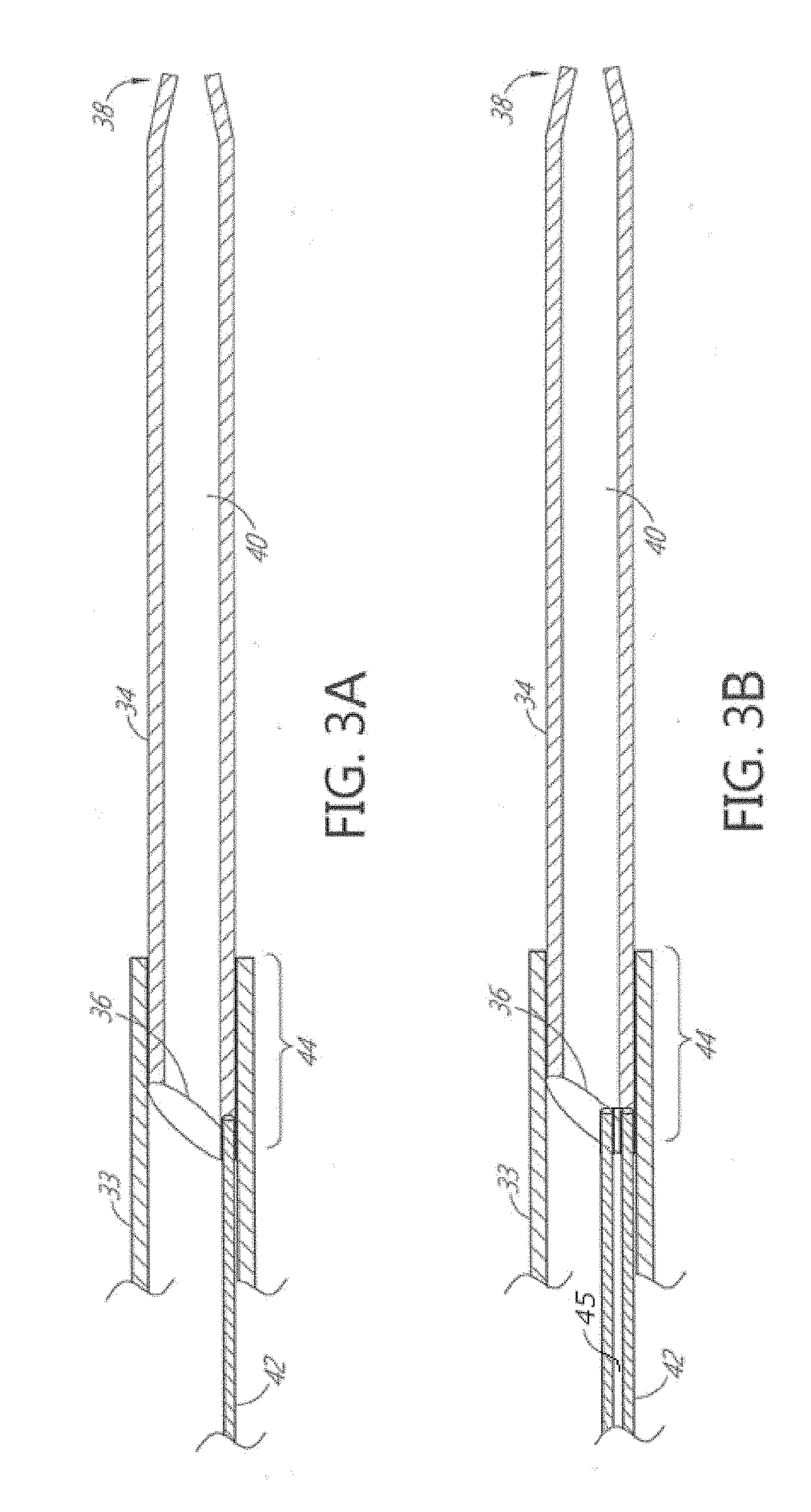
Telescoping neurovascular catheter with active distal tip
ActiveUS20170238953A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedical devicesVascular obstructionDistal portion
A telescoping catheter is provided such as for distal neurovascular aspiration or access. The catheter includes an elongate, flexible tubular body, having a proximal section with at least one lumen and a distal section which is axially movably positioned within the lumen. A control is provided for advancing the distal section from a first, proximally retracted position within the proximal section to a second extended position, extending distally beyond the proximal section. The distal end of at least one of the proximal and distal sections may be provided with at least one active feature, such as at least one movable jaw or rotatable agitator, to assist in the capture of vascular obstruction. The jaw may be operable in response to application of pulsatile negative pressure through the catheter.
Owner:INCEPT LLC +1
Extracorporeal blood circuit air removal system and method
A disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit employed during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery performs gas exchange, heat transfer, and microemboli filtering functions in a way as to conserve volume, to reduce setup and change out times, to eliminate a blood reservoir, and to substantially reduce blood-air interface. Blood from the patient or prime solution is routed through an air removal device that is equipped with air sensors for detection of air. An active air removal controller removes detected air from blood in the air removal device. A disposable circuit support module is used to mount the components of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit in close proximity and in a desirable spatial relationship to optimize priming and use of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit. A reusable circuit holder supports the disposable circuit support module in relation to a prime solution source, the active air removal controller and other components.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Isolating cardiac circulation
In a method for substantially isolating cardiac circulation from systemic circulation, flow between the coronary sinus and the right atrium is occluded. A venous collection device having a collection lumen and a support structure is located in the coronary sinus. The support structure is used to maintain patency of the coronary sinus during collection of fluid through the collection lumen. An artificial flow path is provided between the collection lumen and the one or more coronary arteries, thus isolating the cardiac circulation. According to the method, cardiac pumping for systemic circulation can be maintained during isolation of the cardiac circulation.
Owner:OSPREY MEDICAL
Apparatus for making extracorporeal blood circulation available
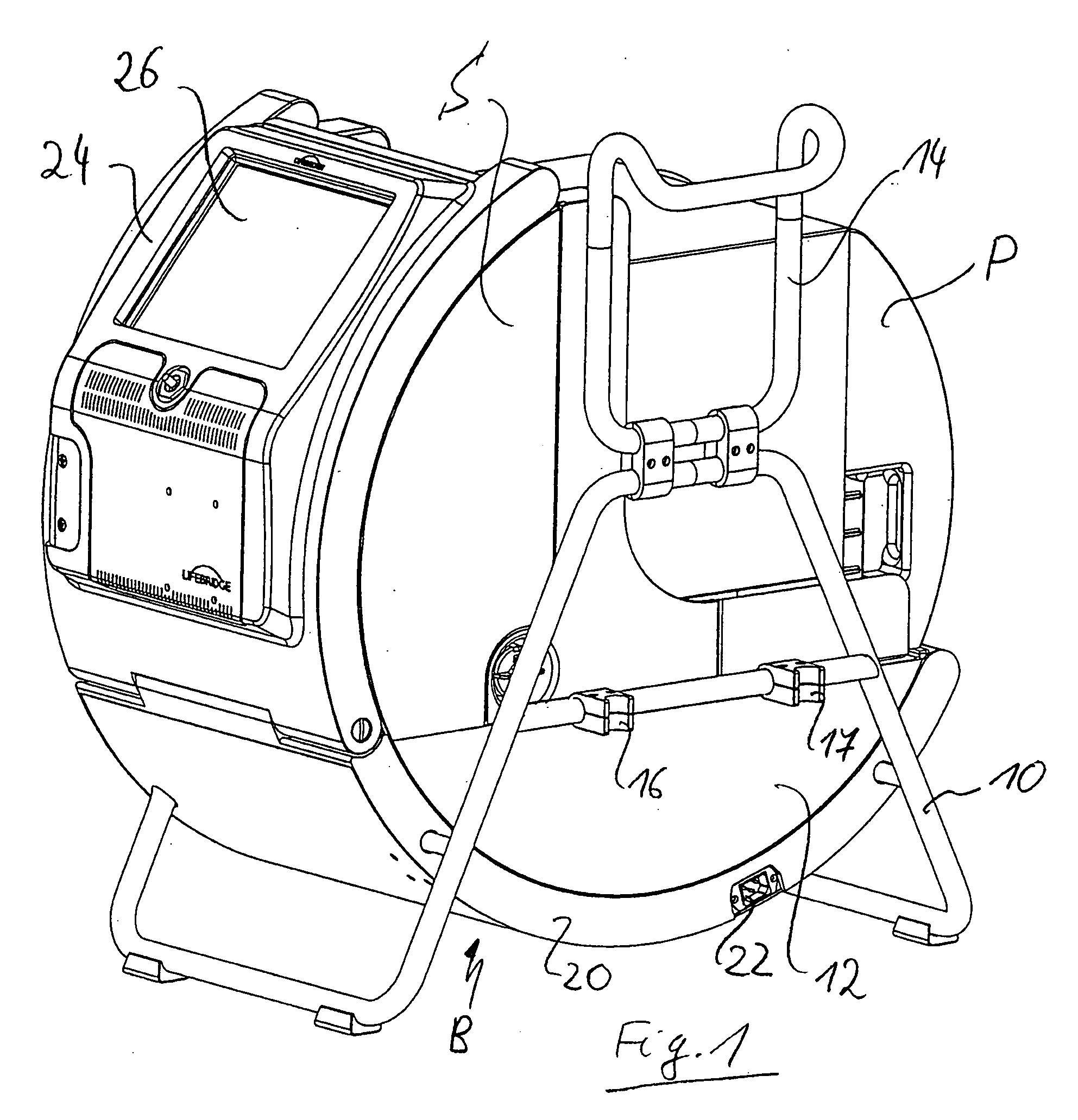
InactiveUS20060122551A1Short timeReliably escapeRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLoop controlMedicine
An apparatus for providing an extracorporeal blood circuit control includes a base module having a control device and a patient module releasably connected to the base module and having blood-conducting components of the extracorporeal blood circuit. A pivot system is also provided at the base module and at the patient module to pivot the patient module relative to the base module about a horizontal axis.
Owner:ZOLL LIFEBRIDGE
Disposable cartridge for a blood perfusion system
InactiveUS7278981B2Simplified interconnection/disconnectionSimple setupOther blood circulation devicesFlexible member pumpsCardioplegiasEngineering
A disposable cartridge for use in extracorporeal blood perfusions systems that have a control unit for controlling the flow of fluids. The cartridge has a housing defining a plurality of internal passageways that connect to a cardiopulmonary circuit, a cardioplegia circuit and a suction circuit. The cartridge may be fitted with one or more of a bubble trap, a filter, and a valve.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
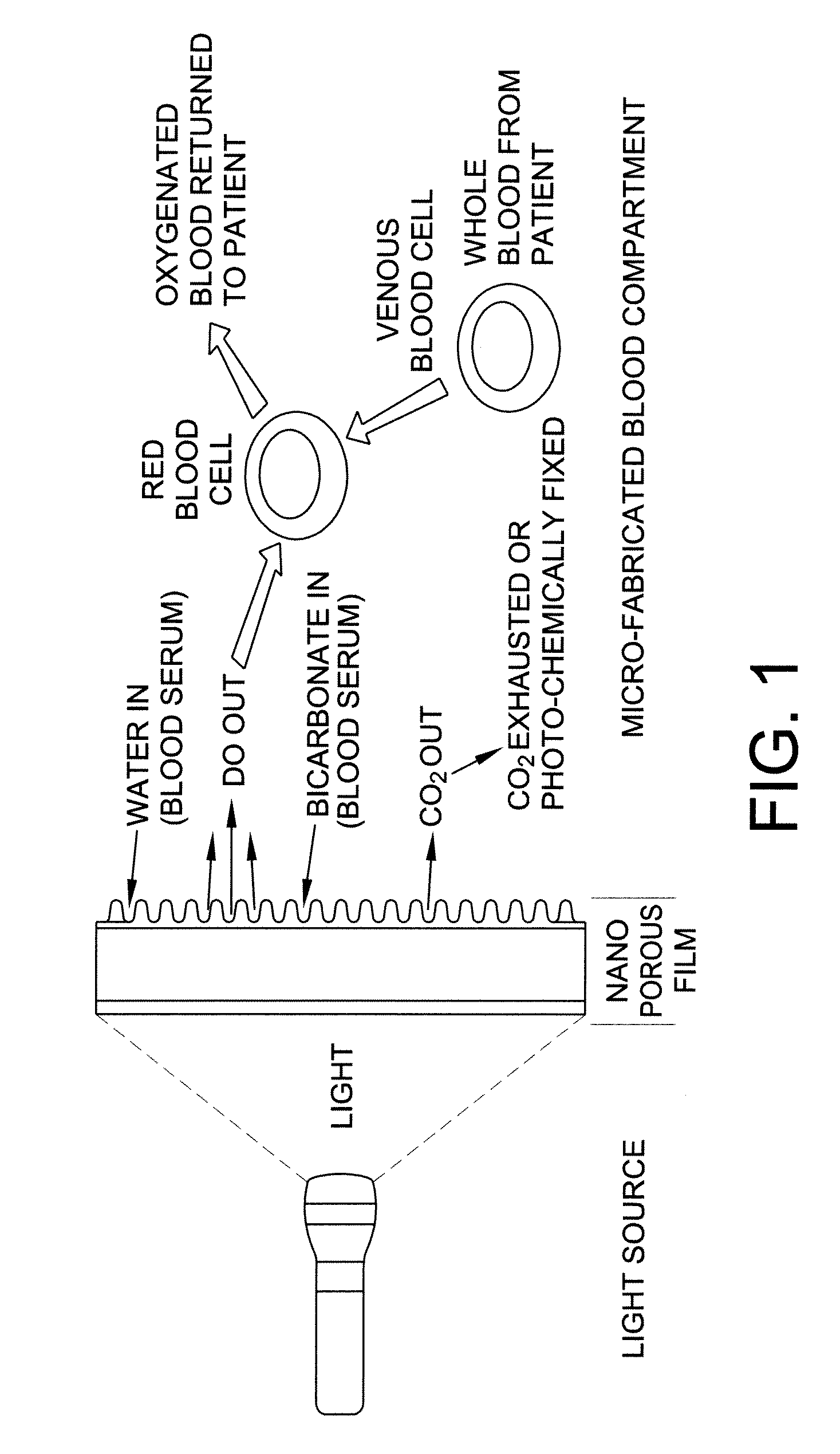
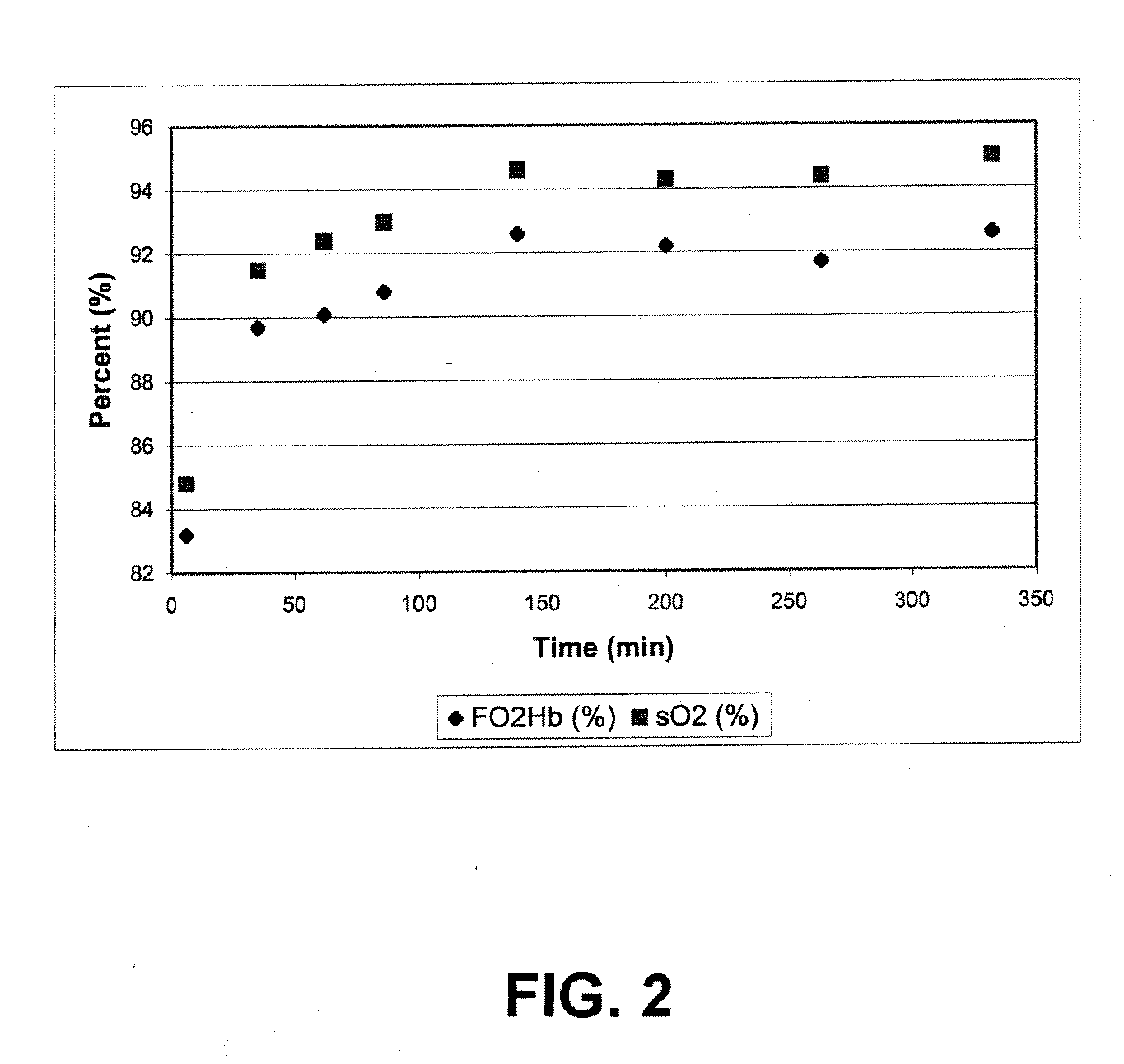
Carbon dioxide removal from whole blood by photolytic activation
Apparatus and methods for removing carbon dioxide from whole blood. Hydrogen ions are generated from water in the blood, resulting in the formation and release of carbon dioxide from the blood.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
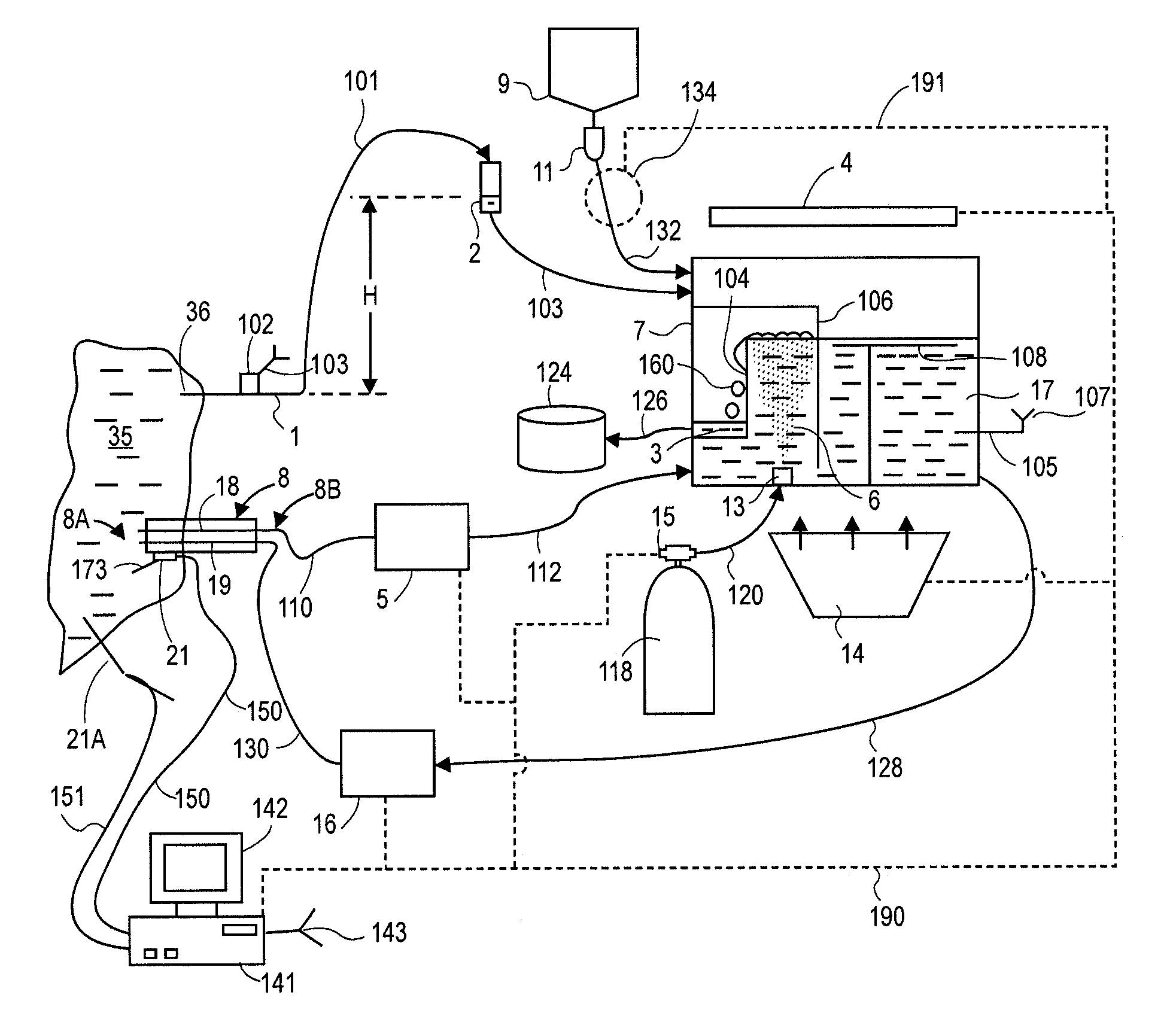
Kit and devices for organ perfusion
InactiveUS20150018597A1Reducing operative traumaReduce operating proceduresBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesMedicineOrgan blood flow
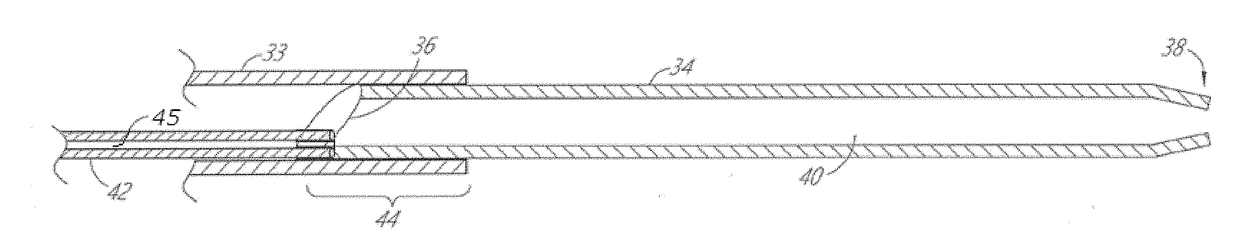
The present invention provides a kit for the delivery a therapeutic agent to an organ blood flow and the removal of the excess of said therapeutic agent from said organ blood flow, said kit comprises: (a) the therapeutic agent, (b) a first retrievable medical device (26), for delivering said therapeutic agent into the organ inflow, (c) a second retrievable medical device for isolating the organ outflow vessel and (d) a separation device (25) comprising at least one filter able to separate the therapeutic agent excess from the organ outflow, having an inlet (38) for the organ outflow having a therapeutic agent excess and an outlet (39) for filtered organ outflow.
Owner:MEDICAL DEVICE WORKS NV
Method of forming gas-enriched fluid
InactiveUS6936221B1Avoid interruptionGood choiceMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesFluid phaseForming gas
A method for forming a gas-enriched fluid is provided. The method includes a step of providing a mixing chamber having a first inlet, a second inlet, and an outlet. A first fluid is delivered into the mixing chamber via the first inlet and flows vertically. A second fluid having a liquid phase supersaturated with a gas is delivered to the mixing chamber via the second inlet to mix with the first fluid and from the gas-enriched fluid.
Owner:THEROX
Systems and methods of microfluidic membraneless exchange using filtration of extraction outlet streams
InactiveUS7727399B2Reduce activationReducing bio-incompatibilitiesComponent separationHaemofiltrationFiltrationThin layer
A device, system and method for exchanging components between first and second fluids by direct contact in a microfluidic channel. The fluids flow as thin layers in the channel. One of the fluids is passed through a filter upon exiting the channel and is recycled through a secondary processor which changes the fluid's properties. The recycled fluid is reused for further exchange. The filter excludes blood cells from the recycled fluid and prevents or limits clogging of the filter. The secondary processor removes metabolic waste and water by diafiltration.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Systems and methods of microfluidic membraneless exchange using filtration of extraction outlet streams
InactiveUS20090139931A1Reduce activationReducing bio-incompatibilitiesComponent separationSolvent extractionMetabolic wasteFiltration
A device, system and method for exchanging components between first and second fluids by direct contact in a microfluidic channel. The fluids flow as thin layers in the channel. One of the fluids is passed through a filter upon exiting the channel and is recycled through a secondary processor which changes the fluid's properties. The recycled fluid is reused for further exchange. The filter excludes blood cells from the recycled fluid and prevents or limits clogging of the filter. The secondary processor removes metabolic waste and water by diafiltration.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
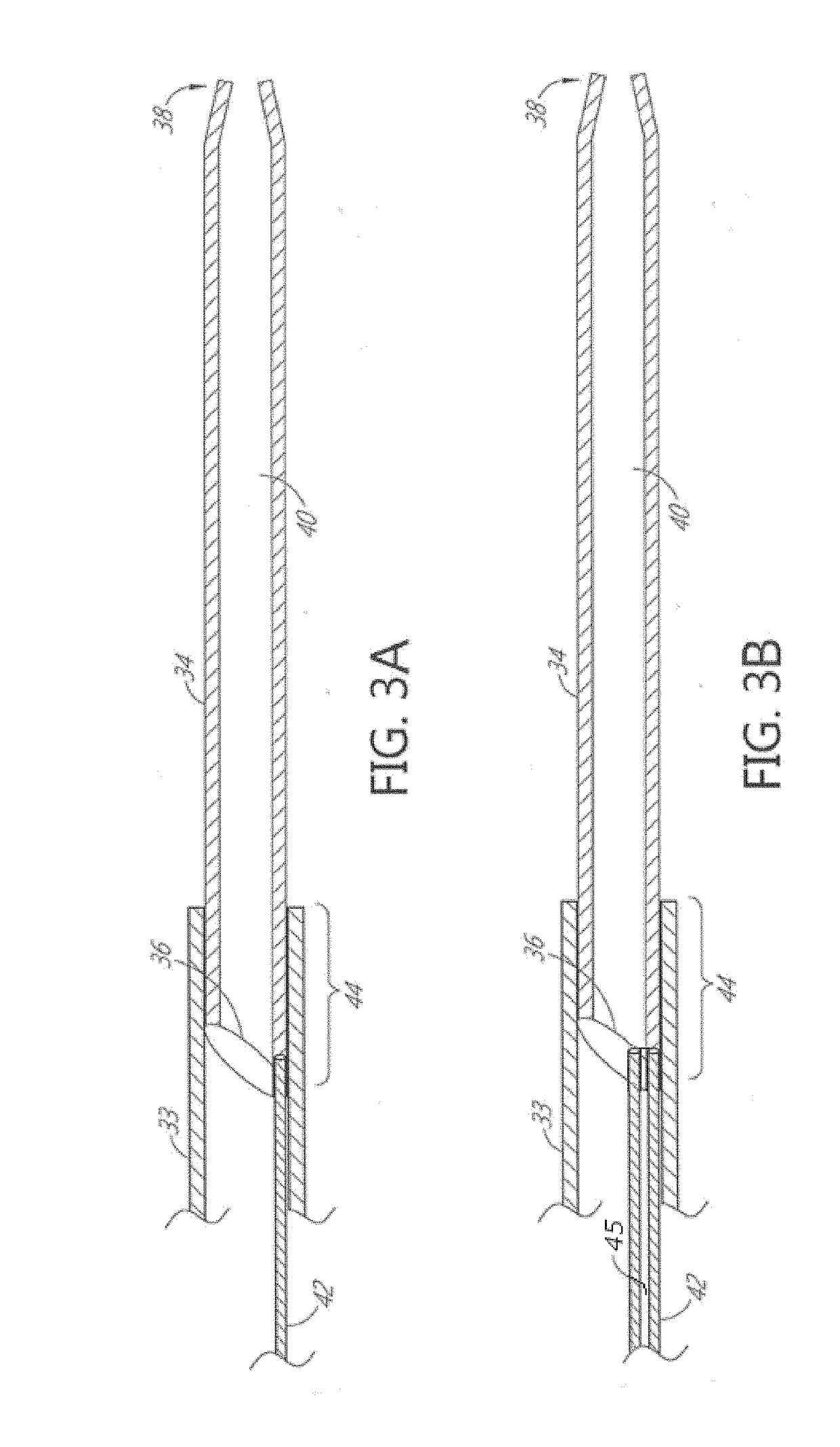
Enhanced flexibility neurovascular catheter
ActiveUS20170252536A1Improve tensile propertiesIncrease flexibilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedical devicesHelical coilCatheter
A catheter is provided, such as for distal neurovascular access or aspiration. The catheter includes an elongate flexible body, having a proximal end, a distal end and a side wall defining a central lumen. A distal zone of the side wall includes a tubular inner liner, a tie layer separated from the lumen by the inner liner, a helical coil surrounding the tie layer, adjacent windings of the coil spaced progressively further apart in the distal direction. An outer jacket surrounds the helical coil. The outer jacket is formed from a plurality of tubular segments positioned end to end, coaxially about the coil. The flexural load profile of the catheter as a function of catheter length is configured to provide enhanced distal flexibility while maintaining high backup support.
Owner:IMPERATIVE CARE INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com