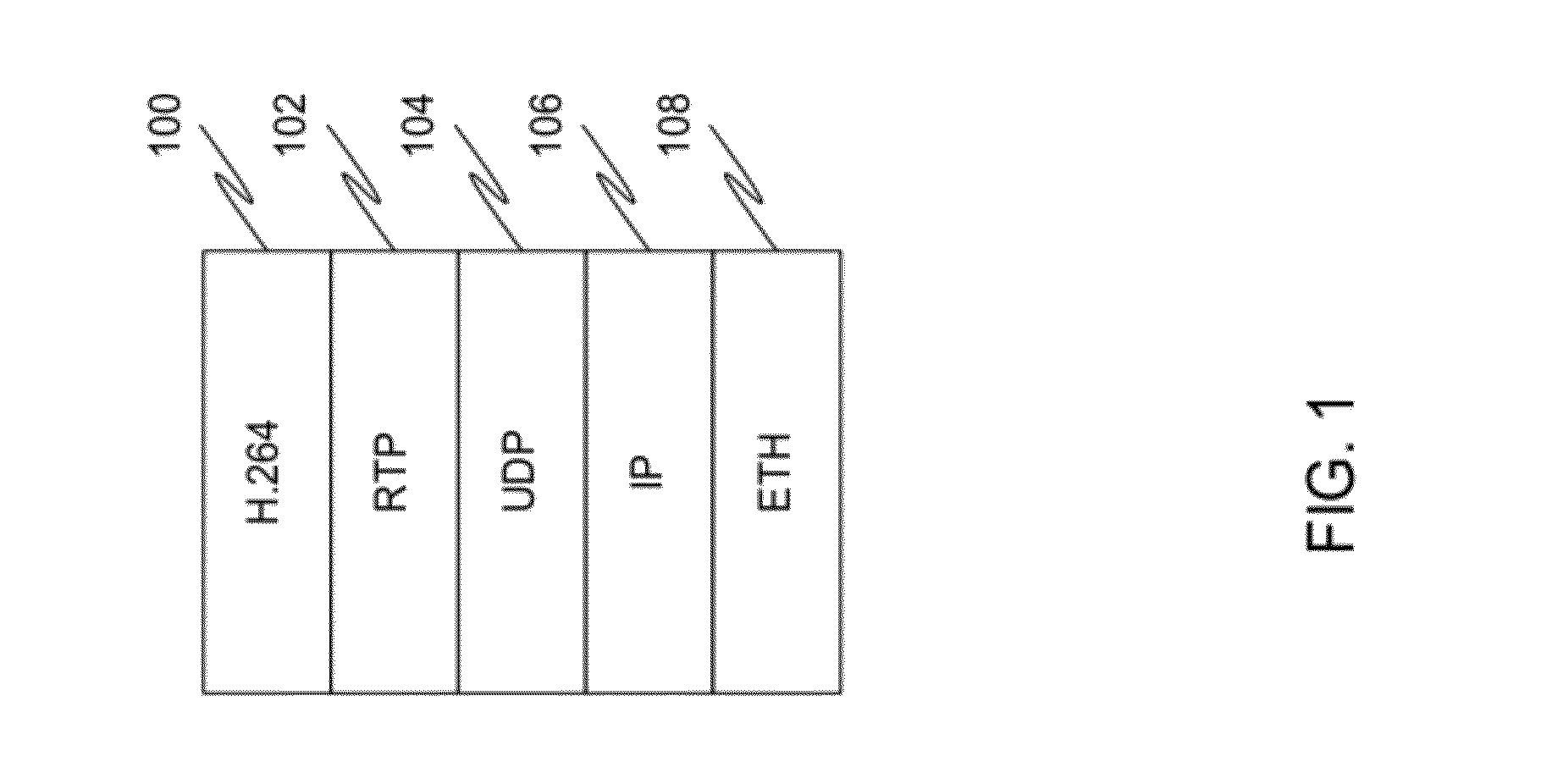
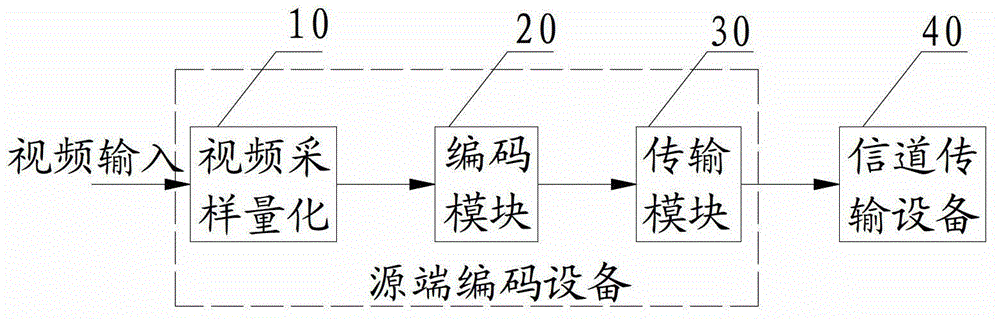
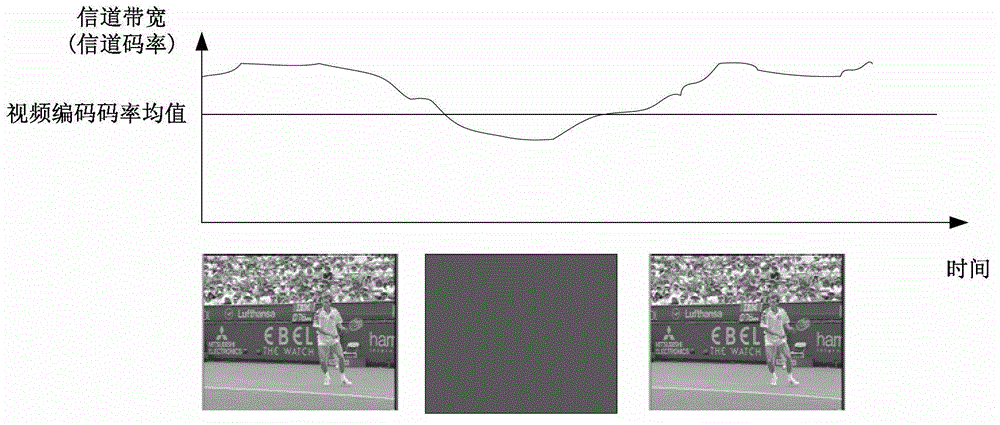
Patents
Literature
79 results about "Constant bitrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Constant bitrate (CBR) is a term used in telecommunications, relating to the quality of service. Compare with variable bitrate. When referring to codecs, constant bit rate encoding means that the rate at which a codec's output data should be consumed is constant. CBR is useful for streaming multimedia content on limited capacity channels since it is the maximum bit rate that matters, not the average, so CBR would be used to take advantage of all of the capacity. CBR would not be the optimal choice for storage as it would not allocate enough data for complex sections (resulting in degraded quality) while wasting data on simple sections.
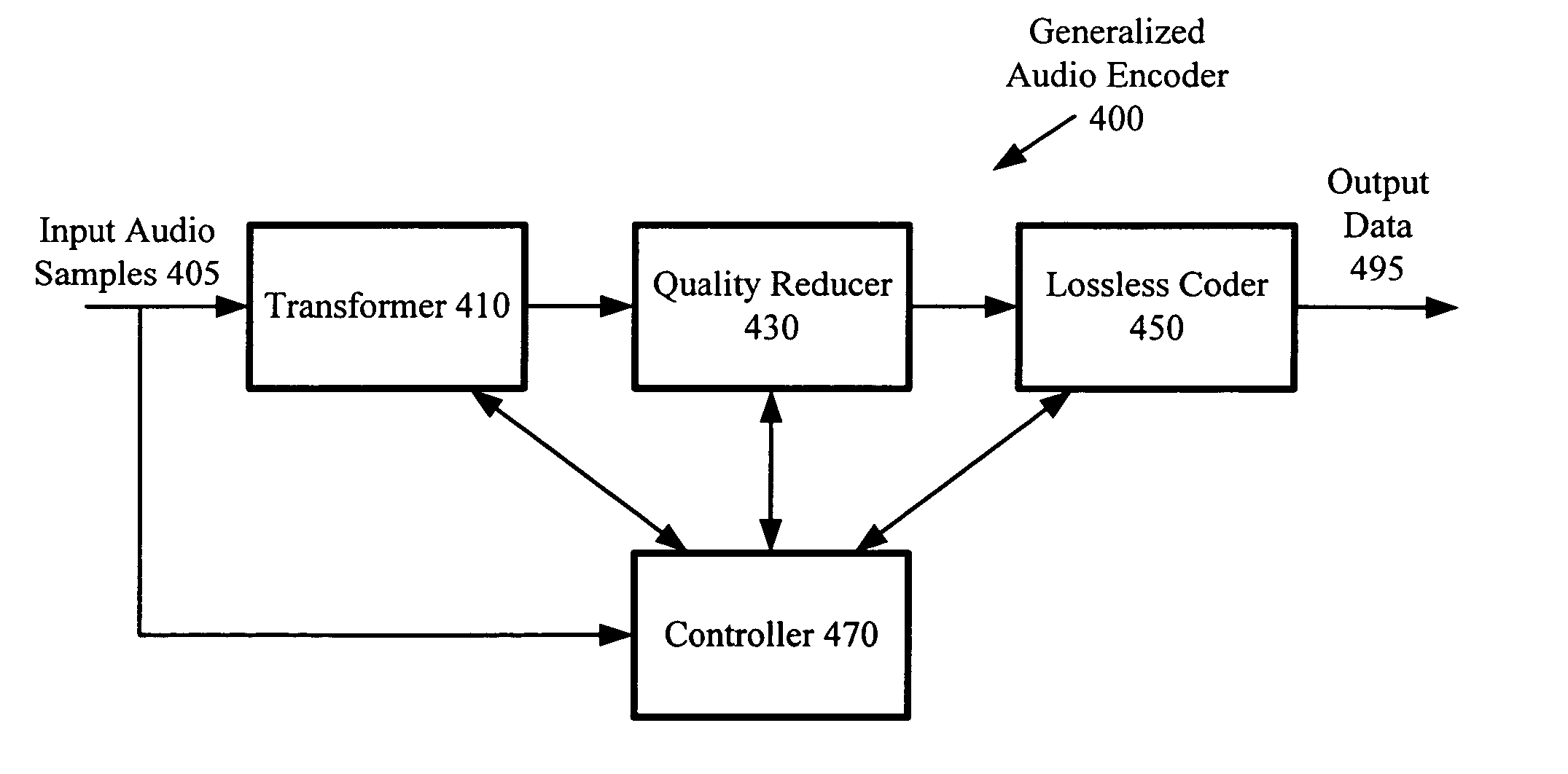
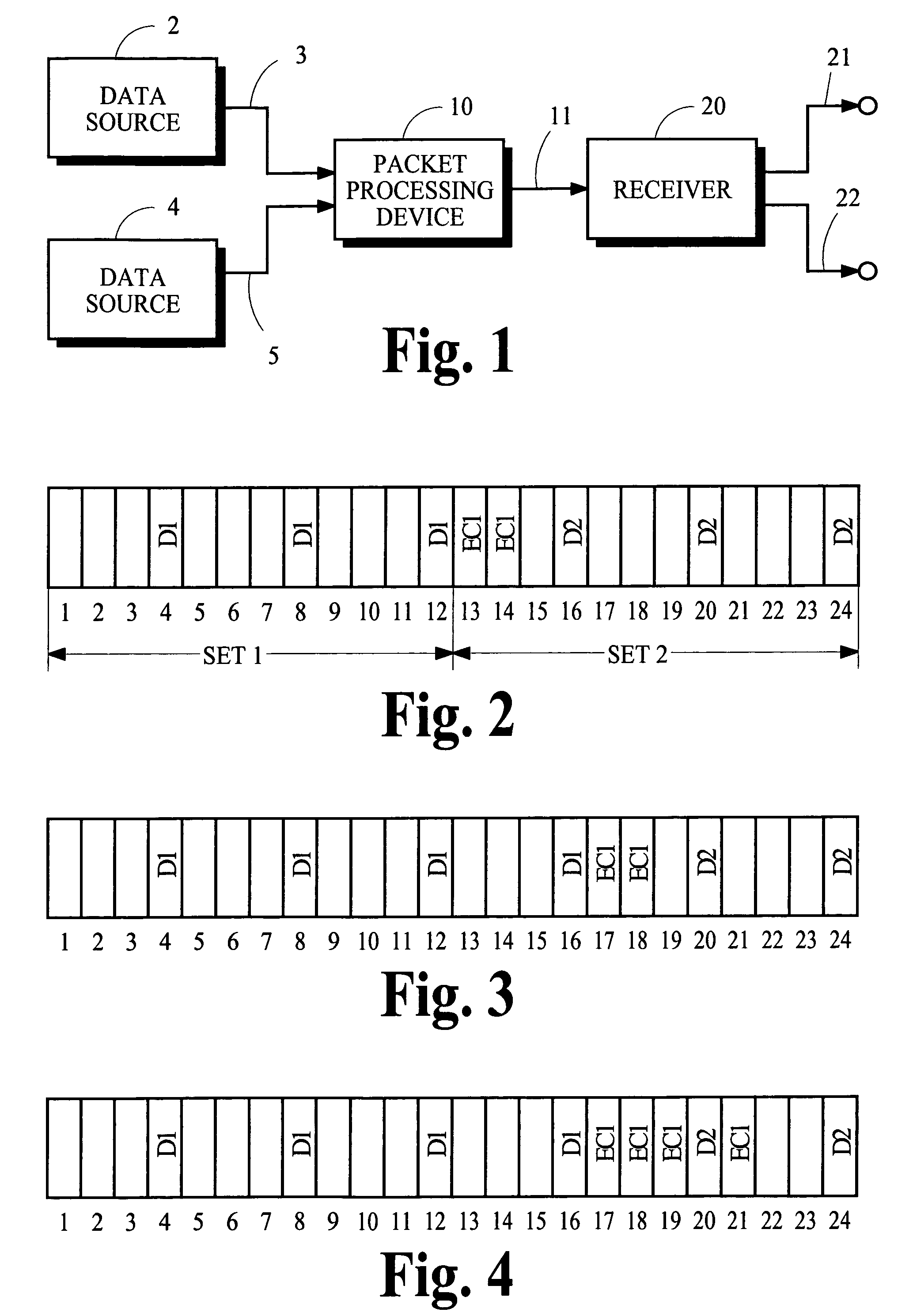
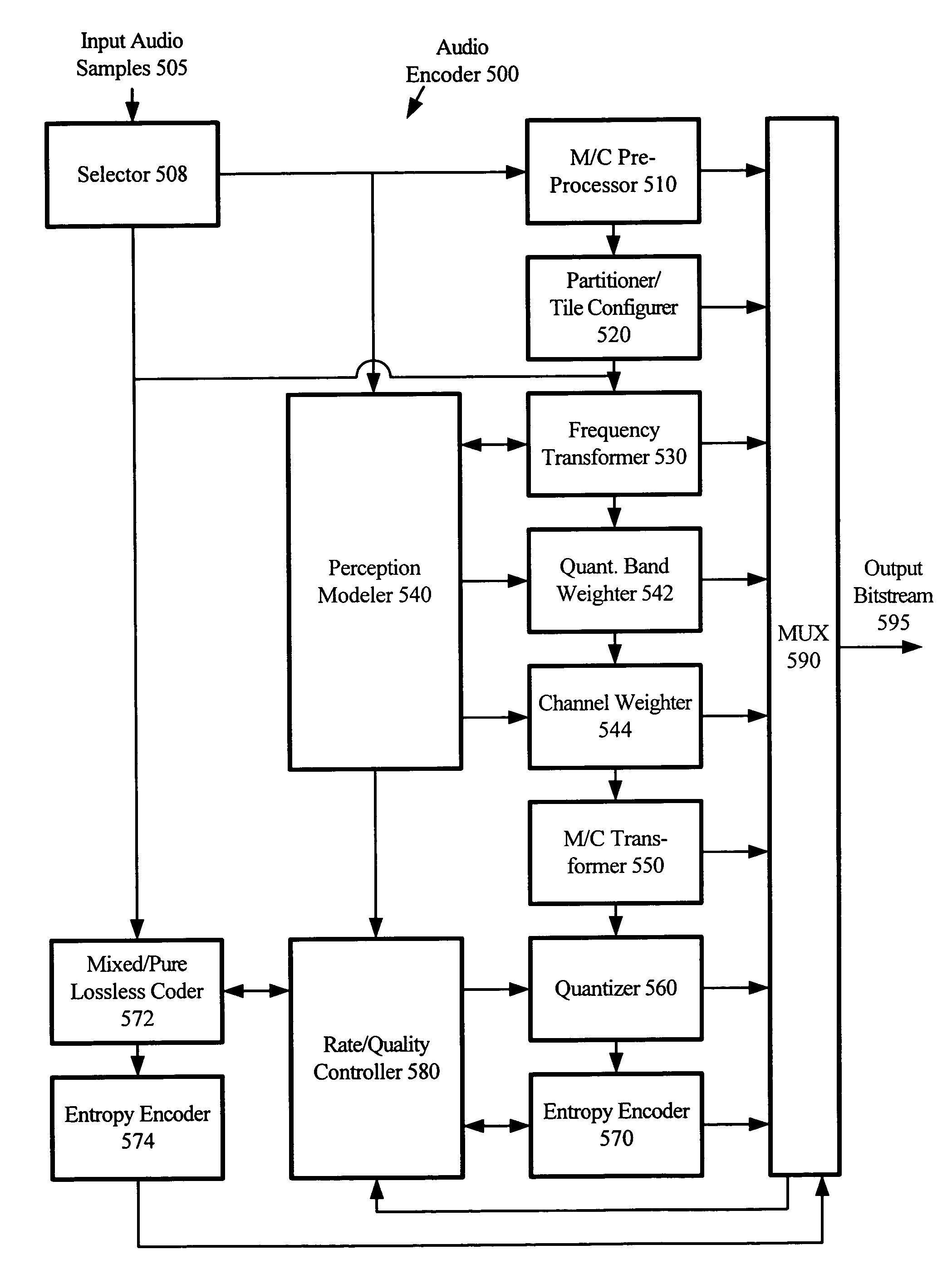
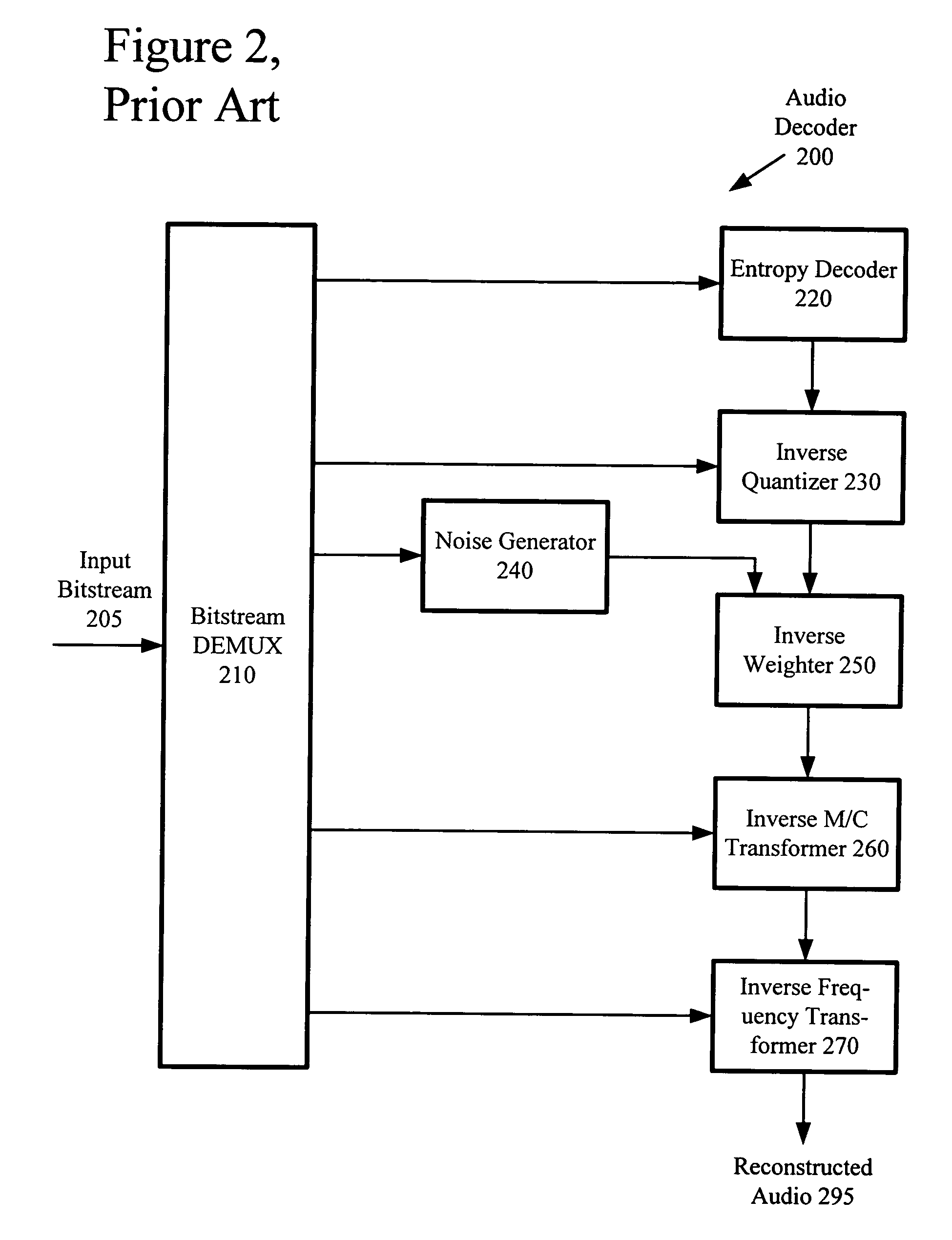
Constant bitrate media encoding techniques
CBR control strategies provide constant or relatively constant bitrate output with variable quality. The control strategies include various techniques and tools, which can be used in combination or independently. For example, an audio encoder uses a trellis in two-pass or delayed-decision CBR encoding. The trellis nodes are states derived by quantizing buffer fullness values. The transitions between nodes of a previous stage and nodes of a current stage depend on encoding a current chunk of audio at different quality levels. When pruning the trellis, the encoder uses a cost function that considers smoothness in quality as well as quality in absolute terms. The encoder may store compressed data at different quality levels, then output the compressed data after simplification of the trellis to a suitable point. If the two-pass or delayed-decision CBR encoding fails, the encoder uses one-pass CBR encoding for the sequence or part of the sequence.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
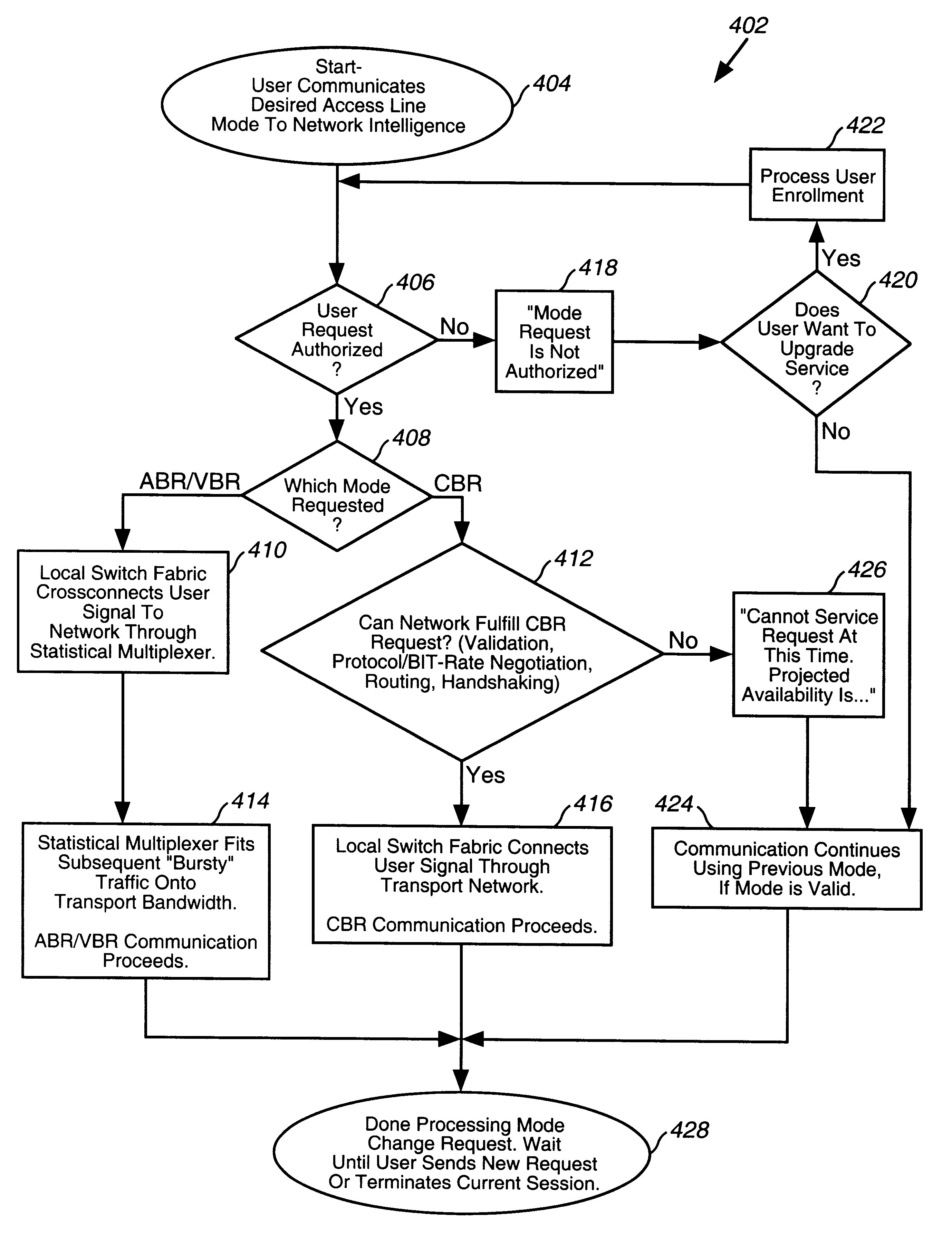
High-speed transparent access to multiple services
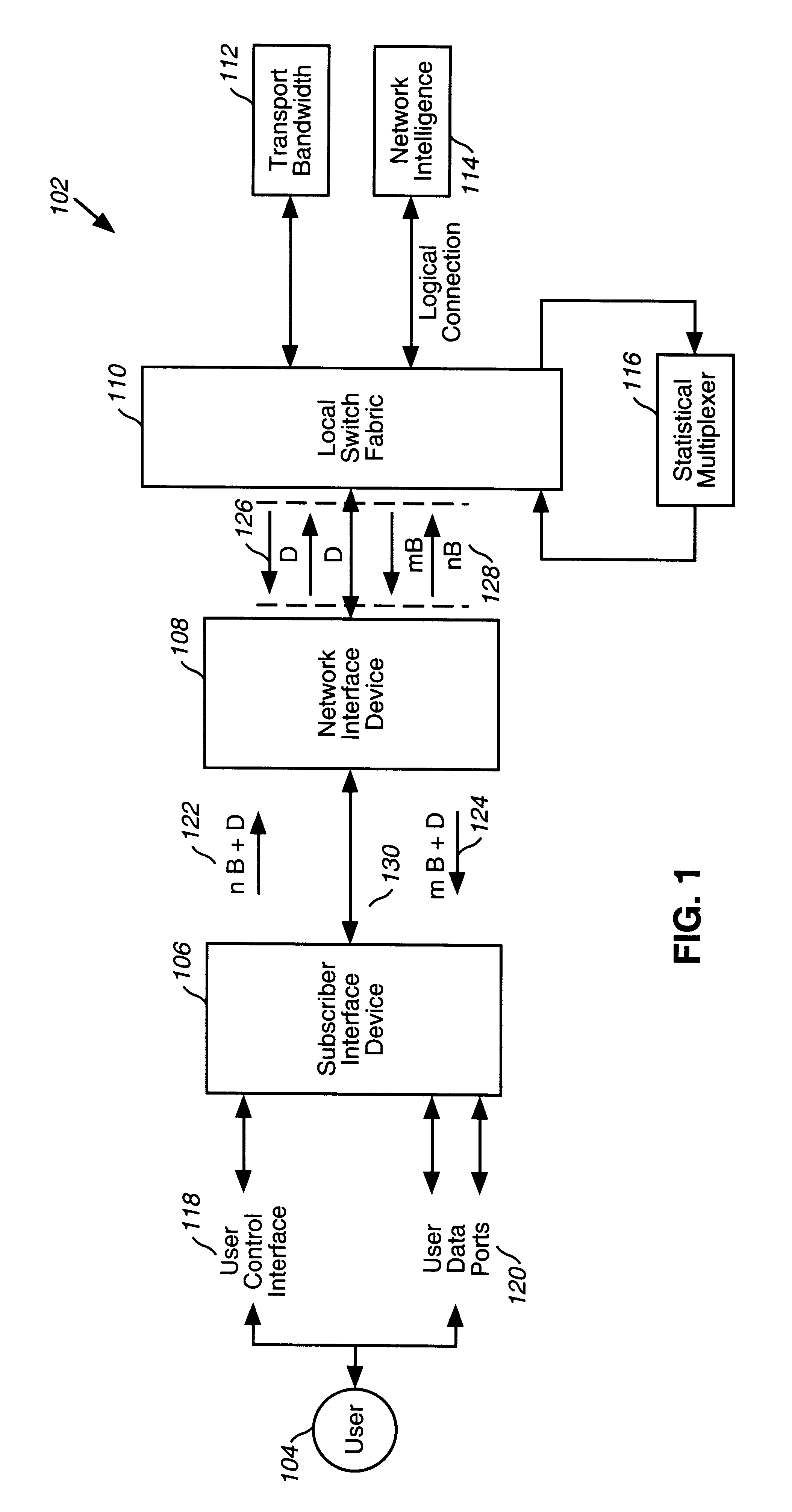
A system, method and computer program product are described, by which a user, through a control interface in a subscriber interface device, requests from network intelligence both transport network bandwidth and type of service line mode as part of call setup. An improved system by which requests to change access line mode and bandwidth are communicated over transmission facilities via D channels through local switch fabric to local or remote network intelligence is detailed. Connections over the transmission facilities, established between user B channels and B channels of transport bandwidth or between user B channels and the Stat Mux function, are described. An improved system is summarized, in which connections directly to transport bandwidth support point-to-point n B+D upstream and m B+D downstream service, and connections via stat mux allow connectionless traffic to share a portion of the transport bandwidth on an as needed basis. The ability to request and change access to available bit rate (ABR), variable bit rate (VBR) and constant bit rate (CBR) services, in a connection-oriented (CONS) or connectionless (CLNS) network, are described.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
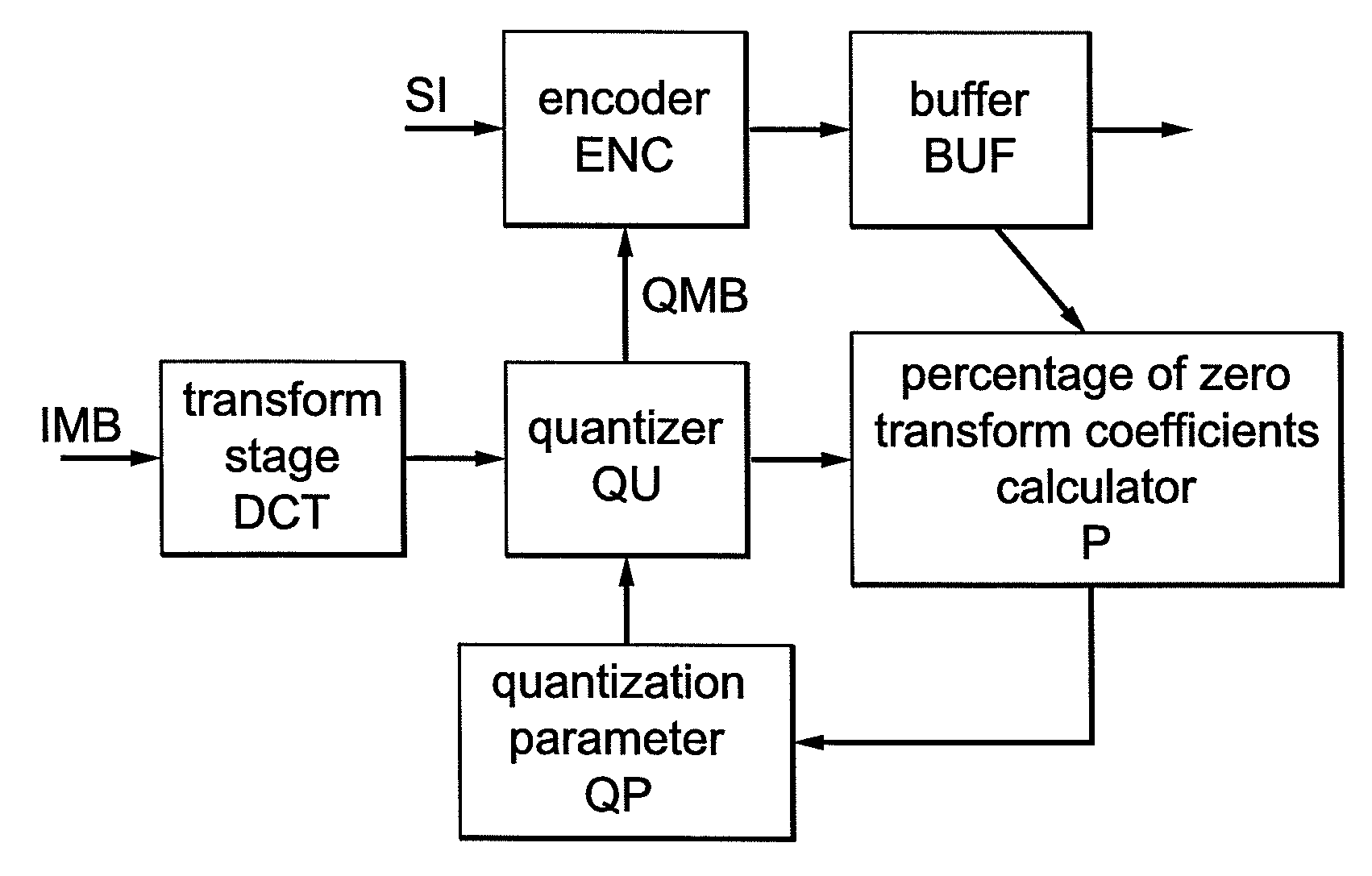
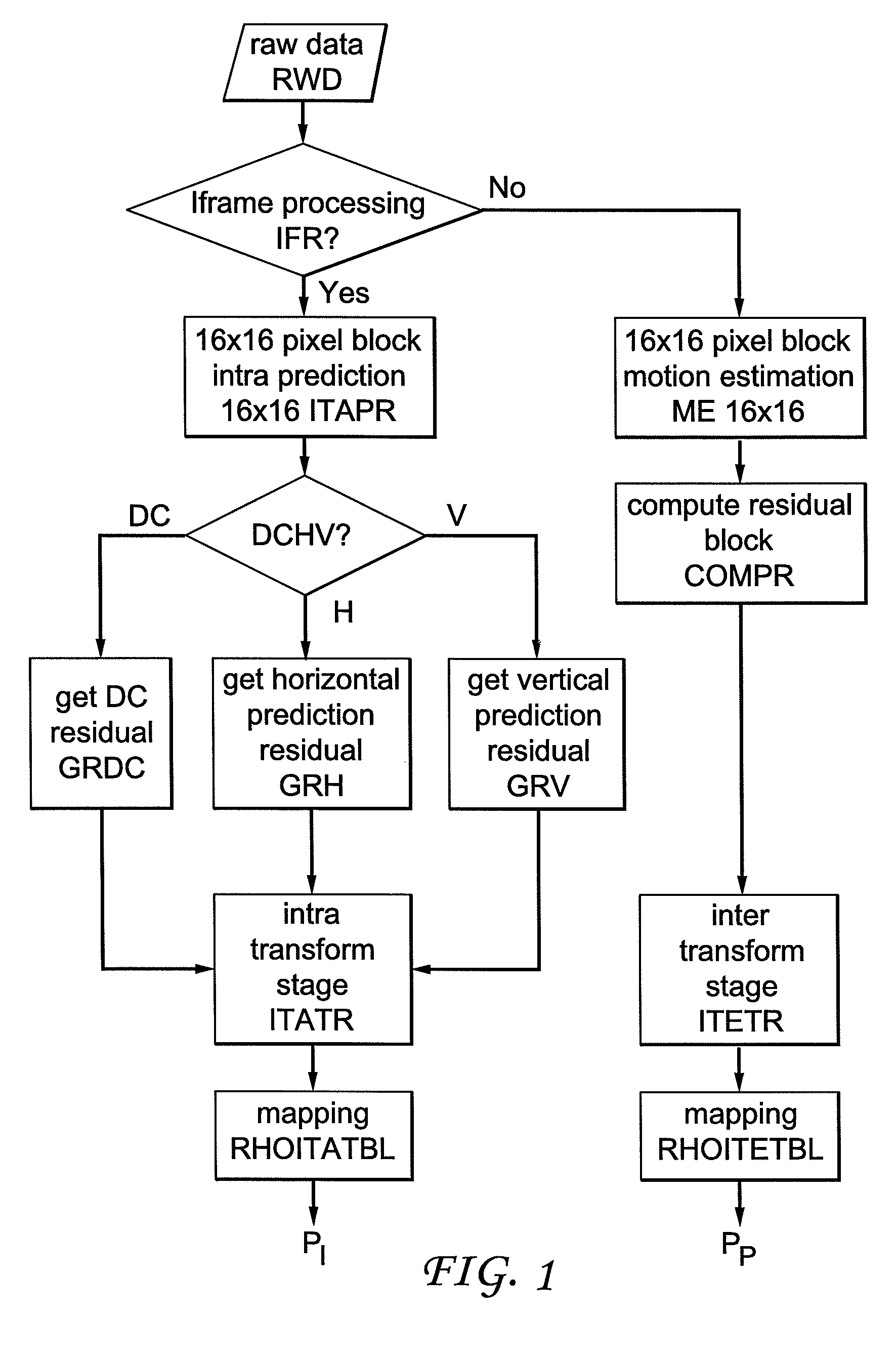
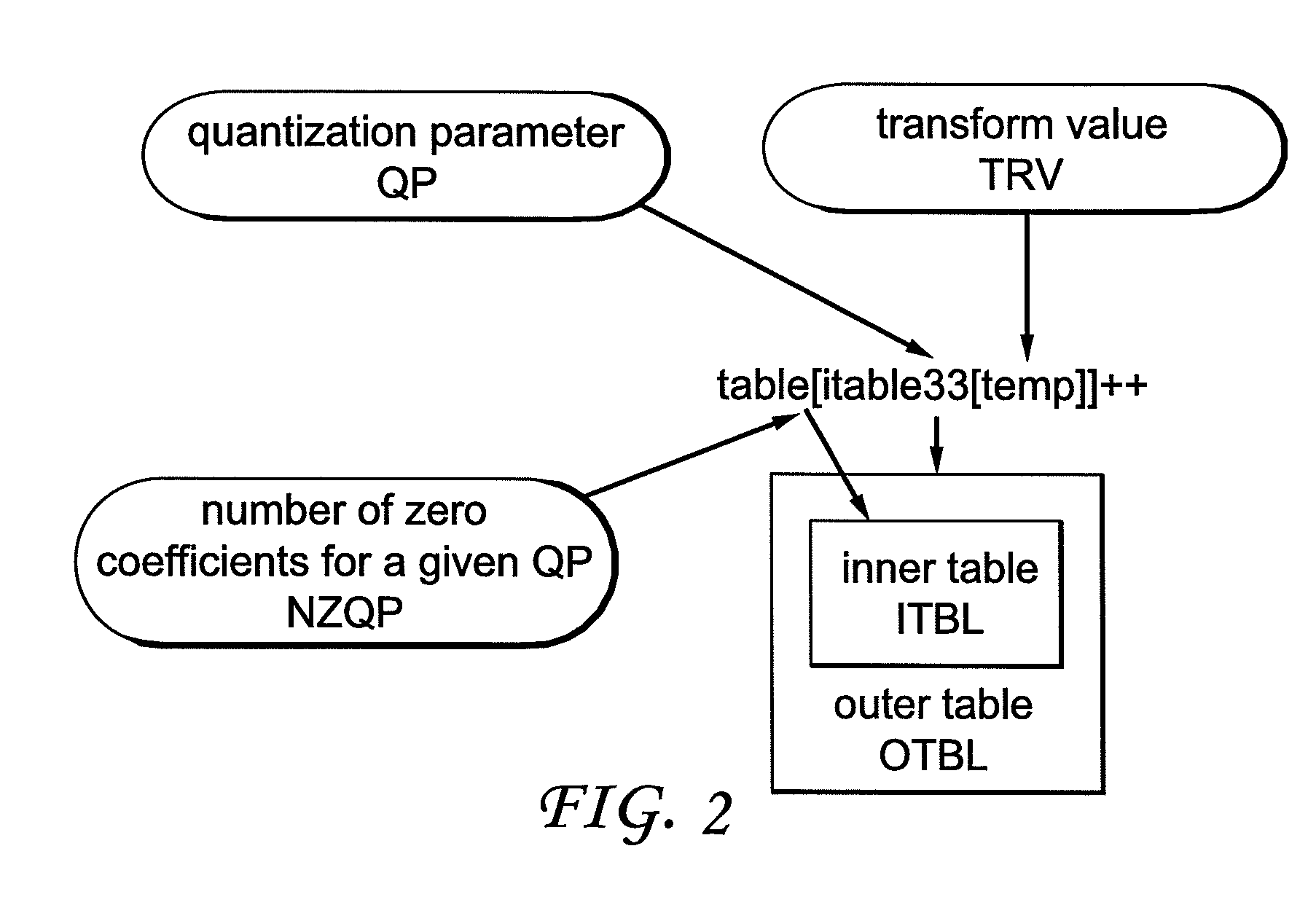
Method for controlling the encoder output bit rate in a block-based video encoder, and corresponding video encoder apparatus
ActiveUS20070009027A1Improve mapping accuracyReduce computing timeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionLinear modelLinearity
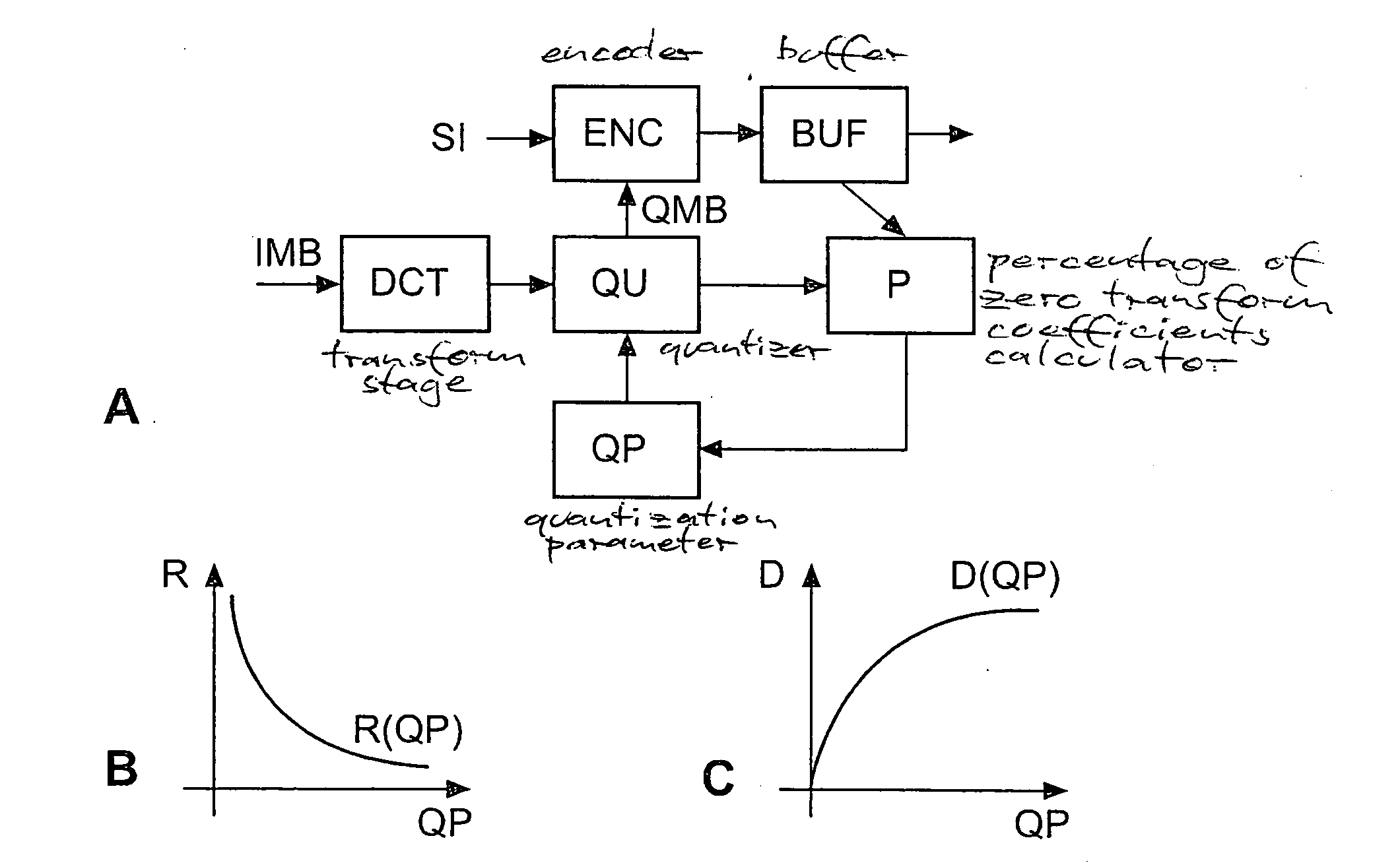
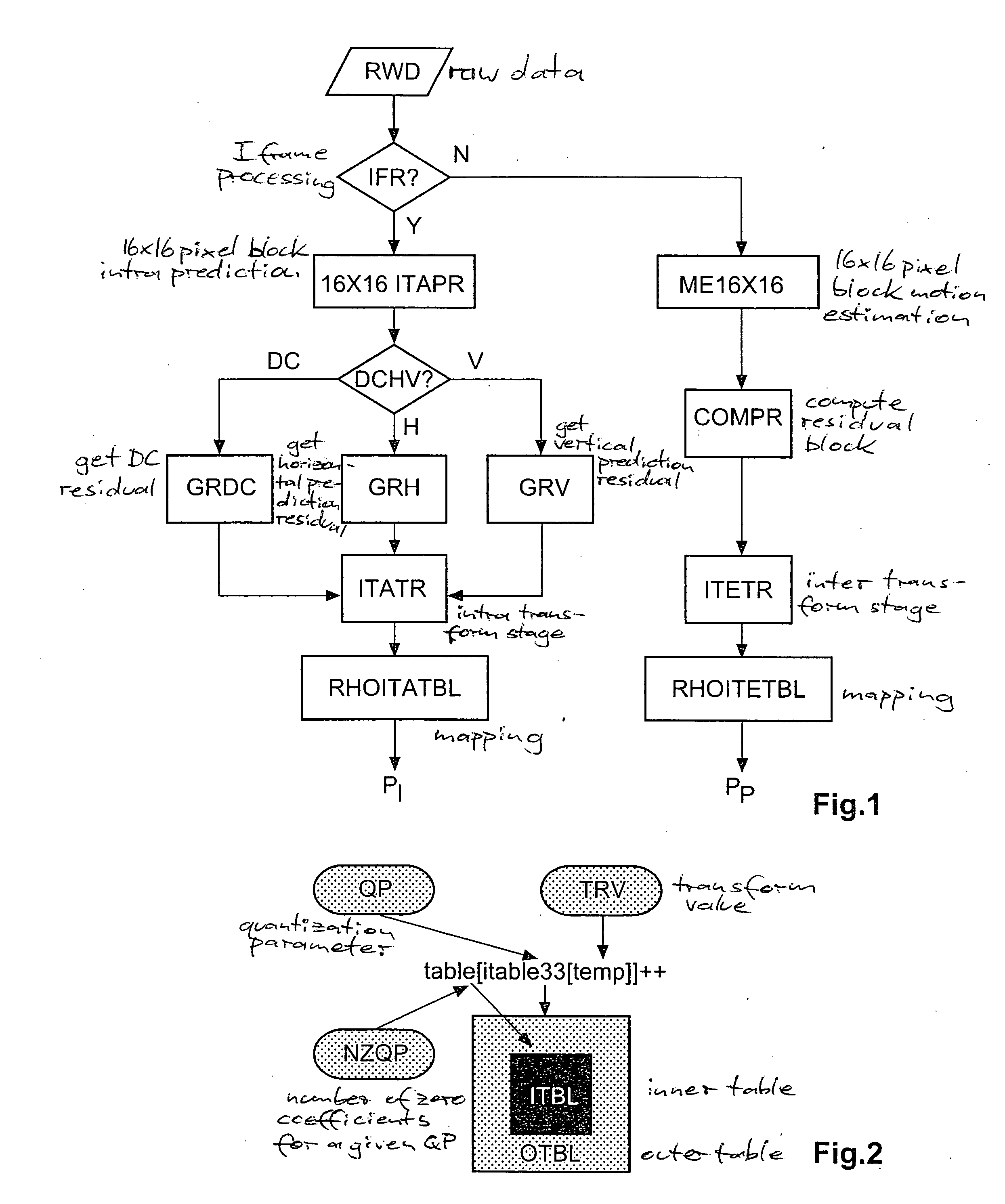
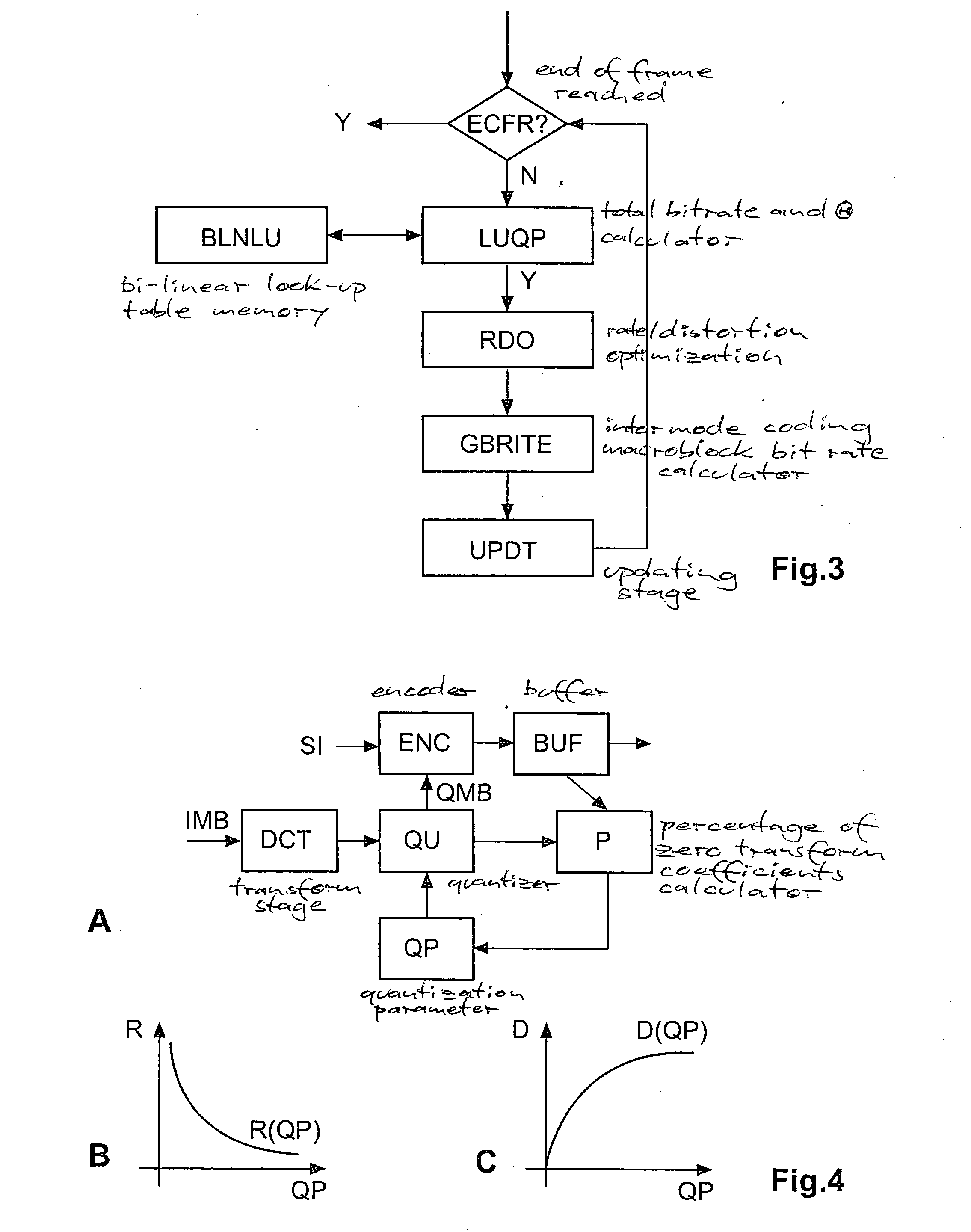
Constant-bitrate rate control is very useful for real-time video transmission. However, it is difficult to realize a good CBR rate control in an MPEG4-AVC video codec. According to the invention, an adapted ρ-domain rate control processing for real-time rate control is applied, whereby ρ is the percentage of zero amplitude transform coefficients following quantisation. A couple of tables are used for mapping between the quantization parameters and ρ. A detailed analysis at transform-level is carried out in order to get the slope of the relationship between the bitrate and ρ. The slope of the linear model is constrained by a look-ahead procedure with respect to the neighbour frames or blocks.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Method for encoding/decoding error correcting code, transmitting apparatus and network
InactiveUS7024616B2Maximizing transmission distanceMaximize distanceError preventionCode conversionCoding blockByte
A client signal having a constant bit rate is segmented every a bytes to create code information blocks. The bit rate of the client signal is increased such that the client signal has the code information block and an empty area comprised of b bytes, and the ratio c / a is equal to or higher than 110% to create a code block 3 comprised of c bytes. The code information block in the code block is encoded such that an error correcting code is included therein to have an encoding gain of 6 dB or higher for a bit error ratio of 10−12. Associated check bits are placed in the empty area to eventually generate a super FEC signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
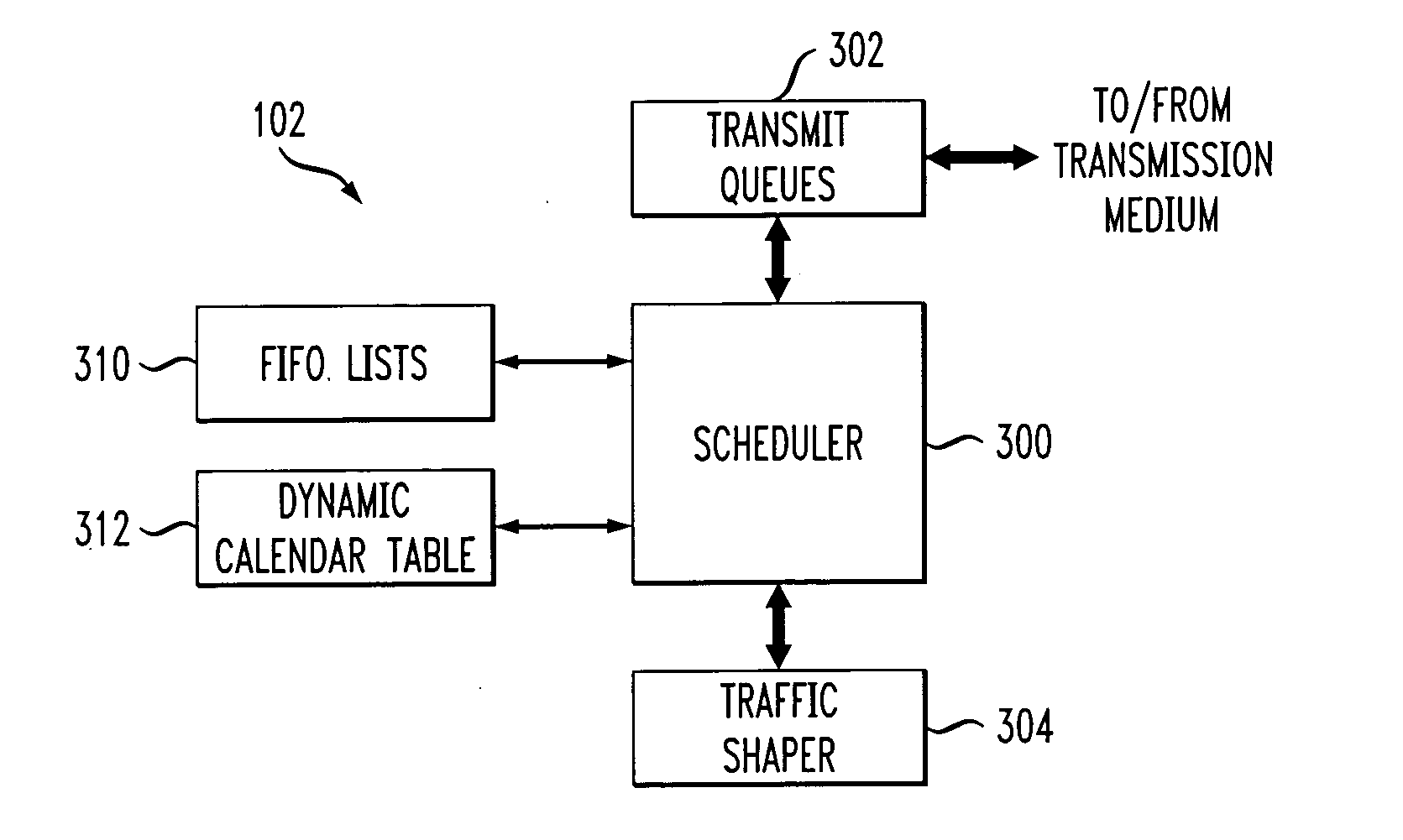
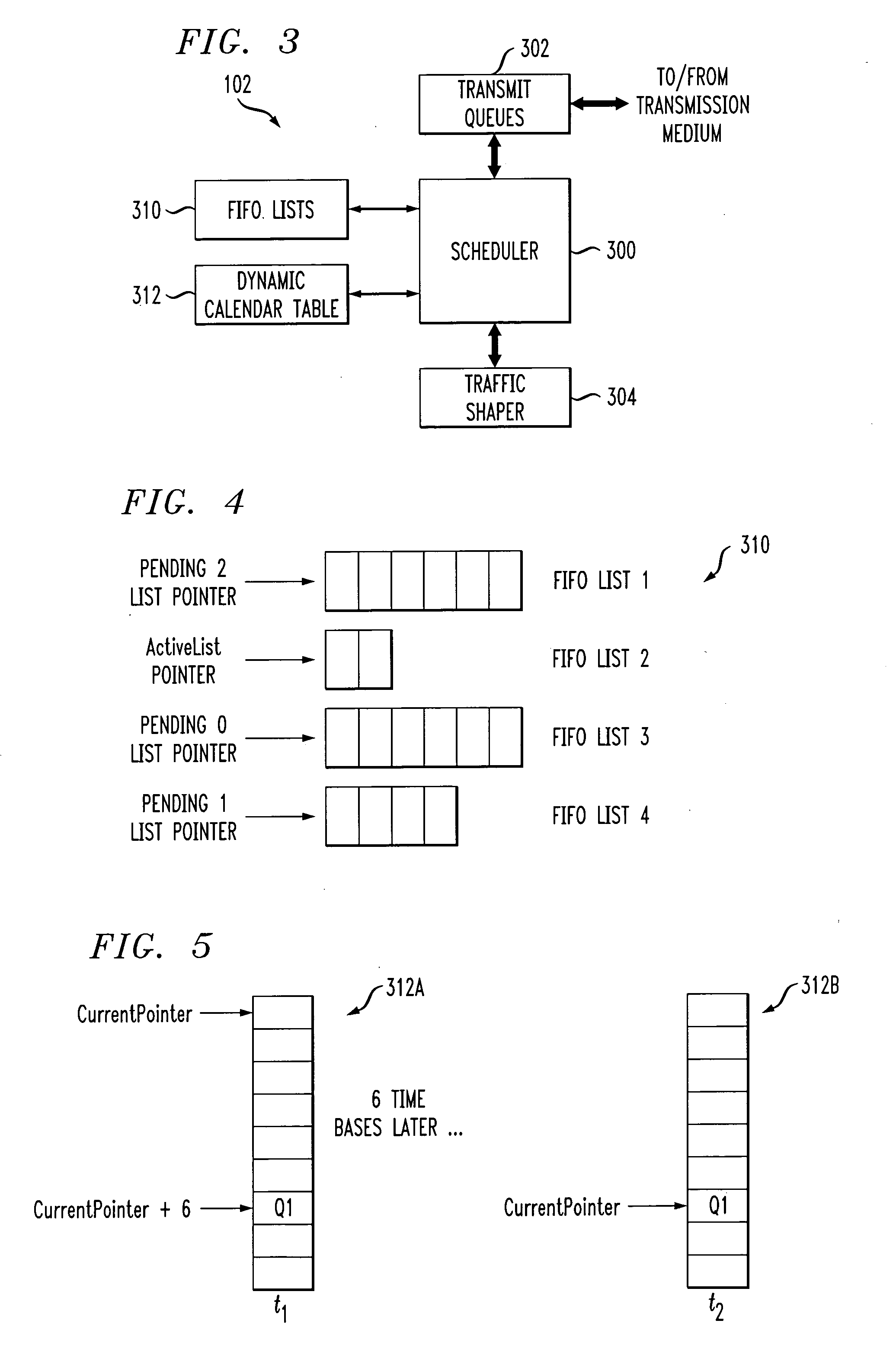
Processor with scheduler architecture supporting multiple distinct scheduling algorithms
InactiveUS20050111461A1Sufficient flexibilityApplication of processData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionFair queuingWeighted fair queueing
A processor includes a scheduler operative to schedule data blocks for transmission from a plurality of queues or other transmission elements, utilizing at least a first table and a second table. The first table may comprise at least first and second first-in first-out (FIFO) lists of entries corresponding to transmission elements for which data blocks are to be scheduled in accordance with a first scheduling algorithm, such as a weighted fair queuing scheduling algorithm. The scheduler maintains a first table pointer identifying at least one of the first and second lists of the first table as having priority over the other of the first and second lists of the first table. The second table includes a plurality of entries corresponding to transmission elements for which data blocks are to be scheduled in accordance with a second scheduling algorithm, such as a constant bit rate or variable bit rate scheduling algorithm. Association of a given one of the transmission elements with a particular one of the second table entries establishes a scheduling rate for that transmission element. The scheduler maintains a second table pointer identifying a current one of the second table entries that is eligible for transmission.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Adaptive audio/video streams proxy
ActiveUS20120192230A1Television system detailsColor television detailsVideo transmissionSelf adaptive
A method is provided comprising: receiving a constant bit rate video stream representing a single video from a video source via a managed broadband connection; converting the constant bit rate video stream into a single non-adaptive bit rate video stream by modifying a video transport stack of the video to be compatible with a home device media player video transport stack; modifying a video control stack of the video to be compatible with a device in a home network; adding a home networking transport stack to the video stream, wherein the home networking transport stack is such that it would appear to the device in the home network as if the video stream came from a server local to the home network; and delivering the video stream to a device in the home network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
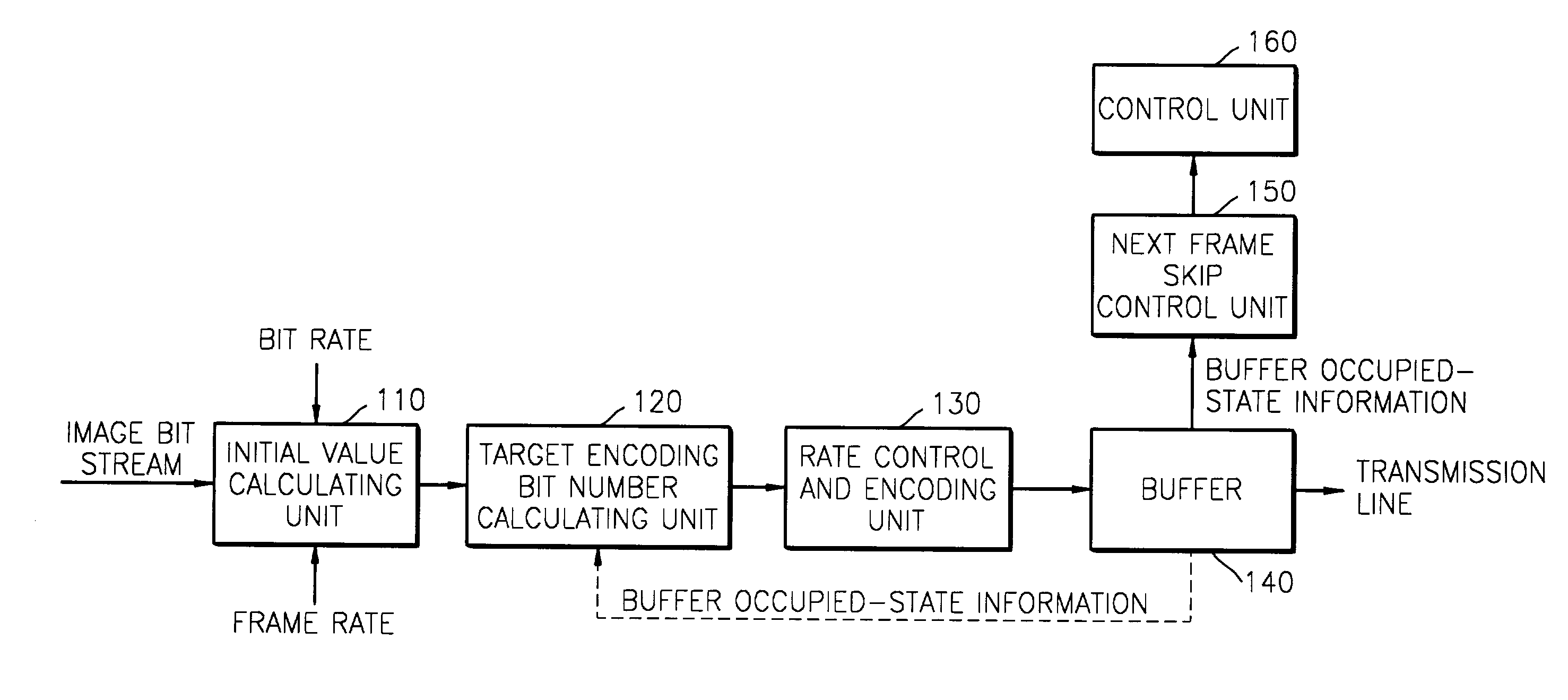
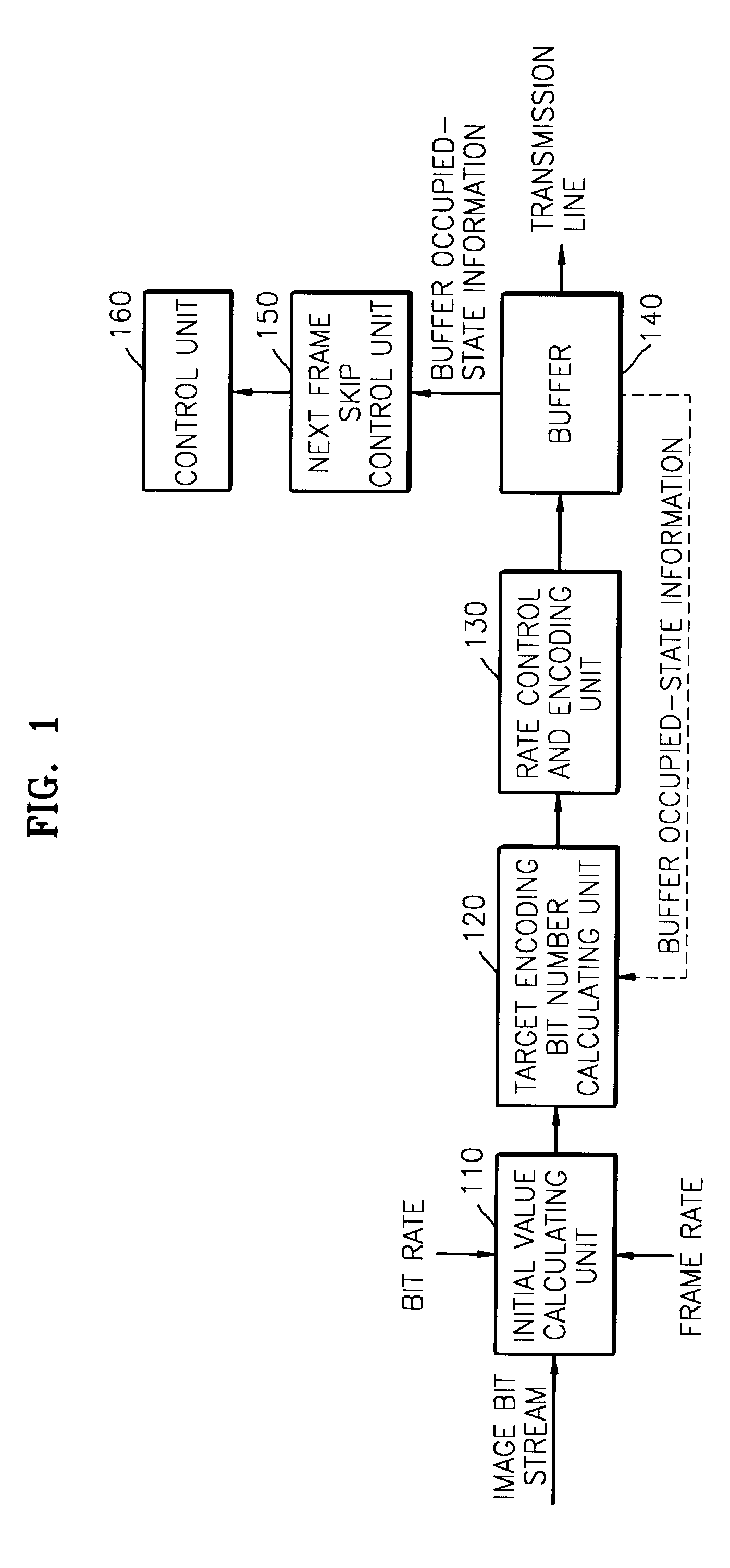
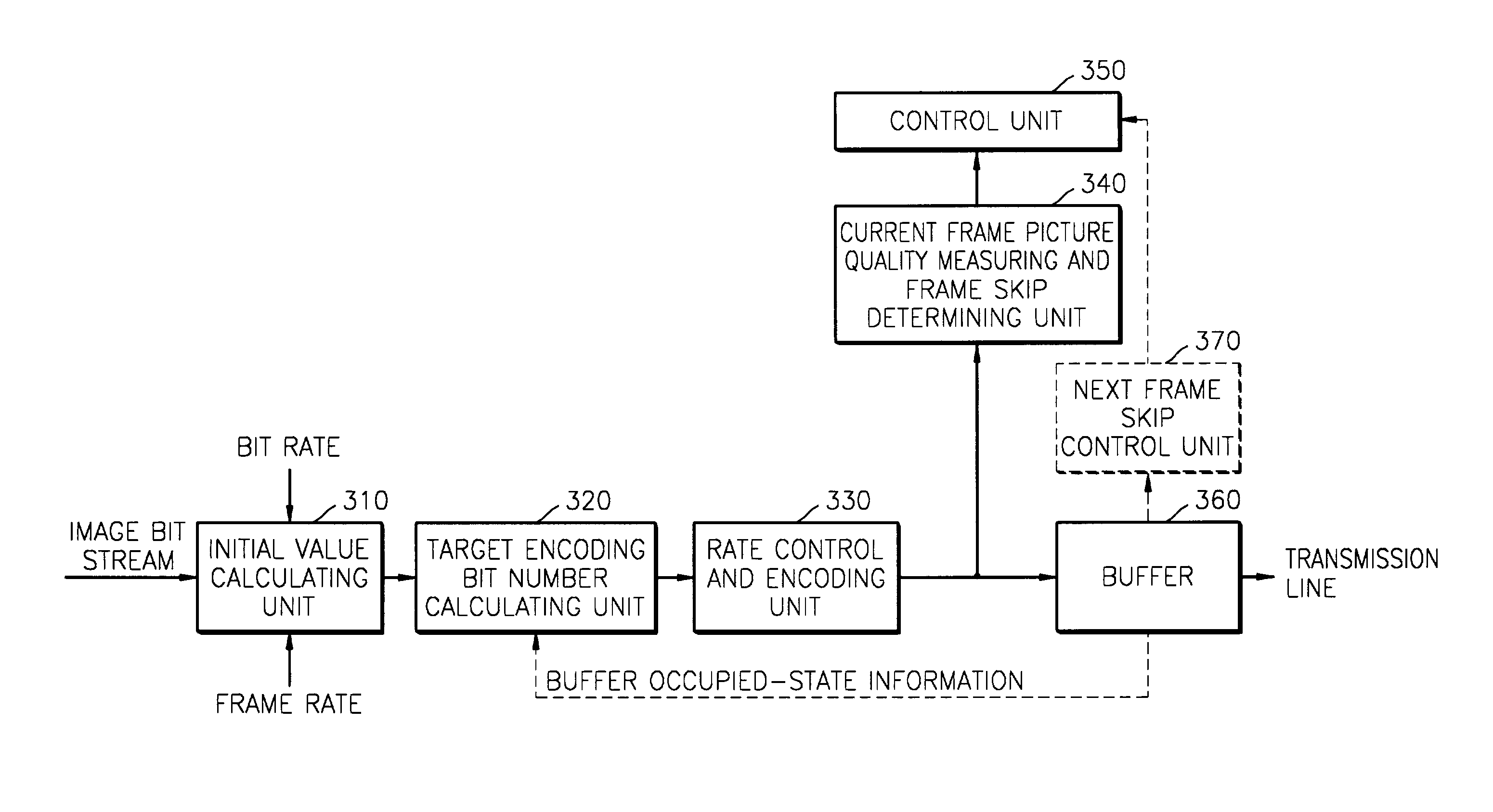
Advanced method for rate control and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20040017850A1Color television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionControl signalComputer science
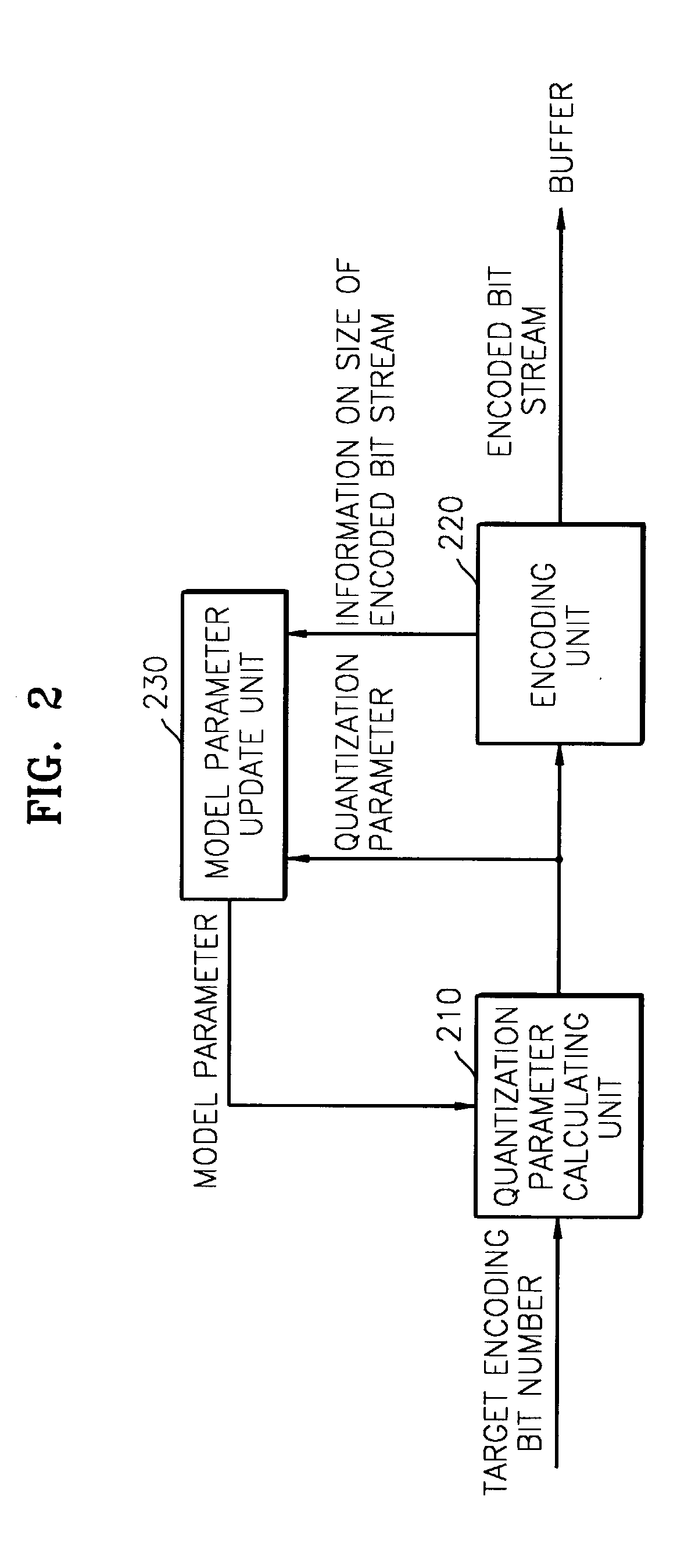
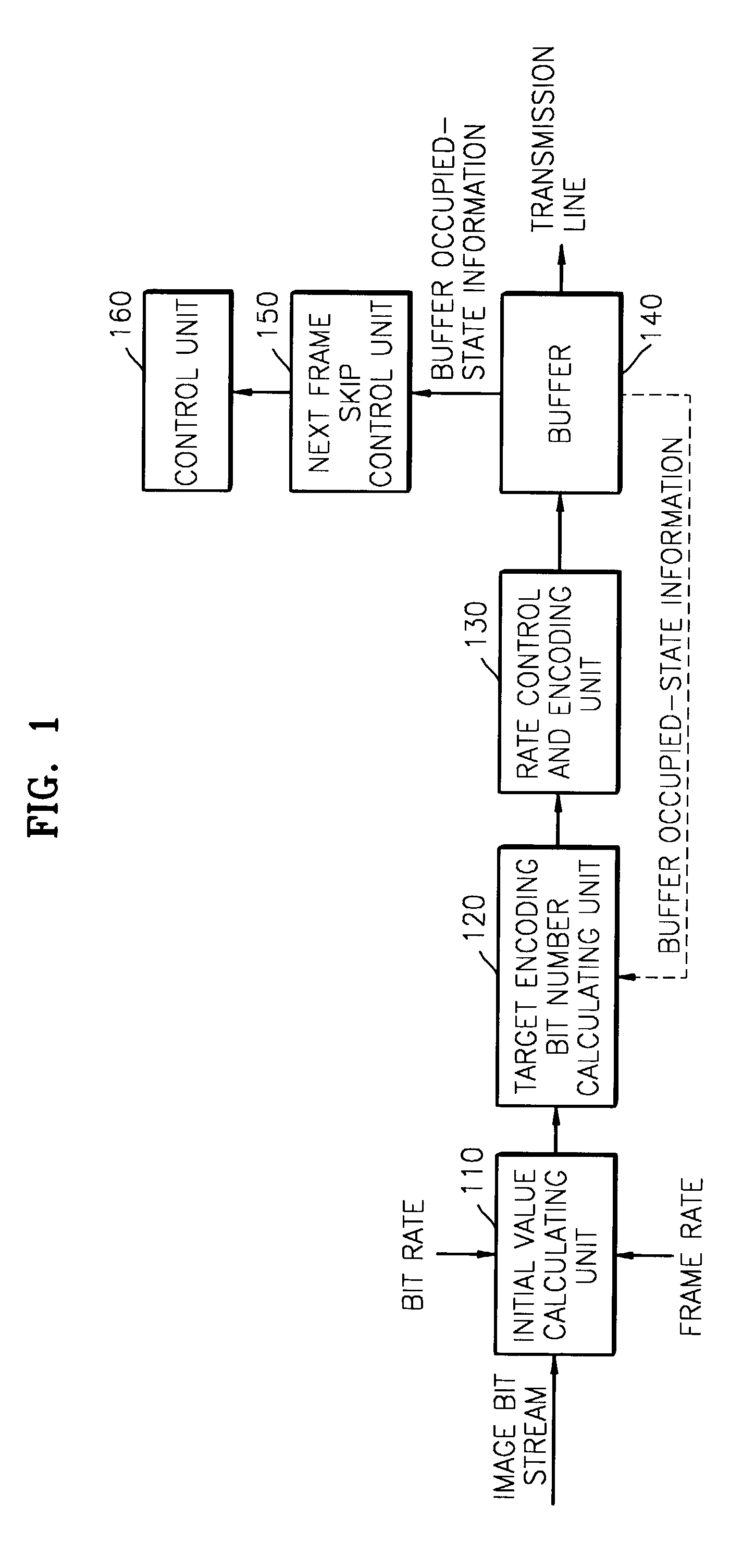
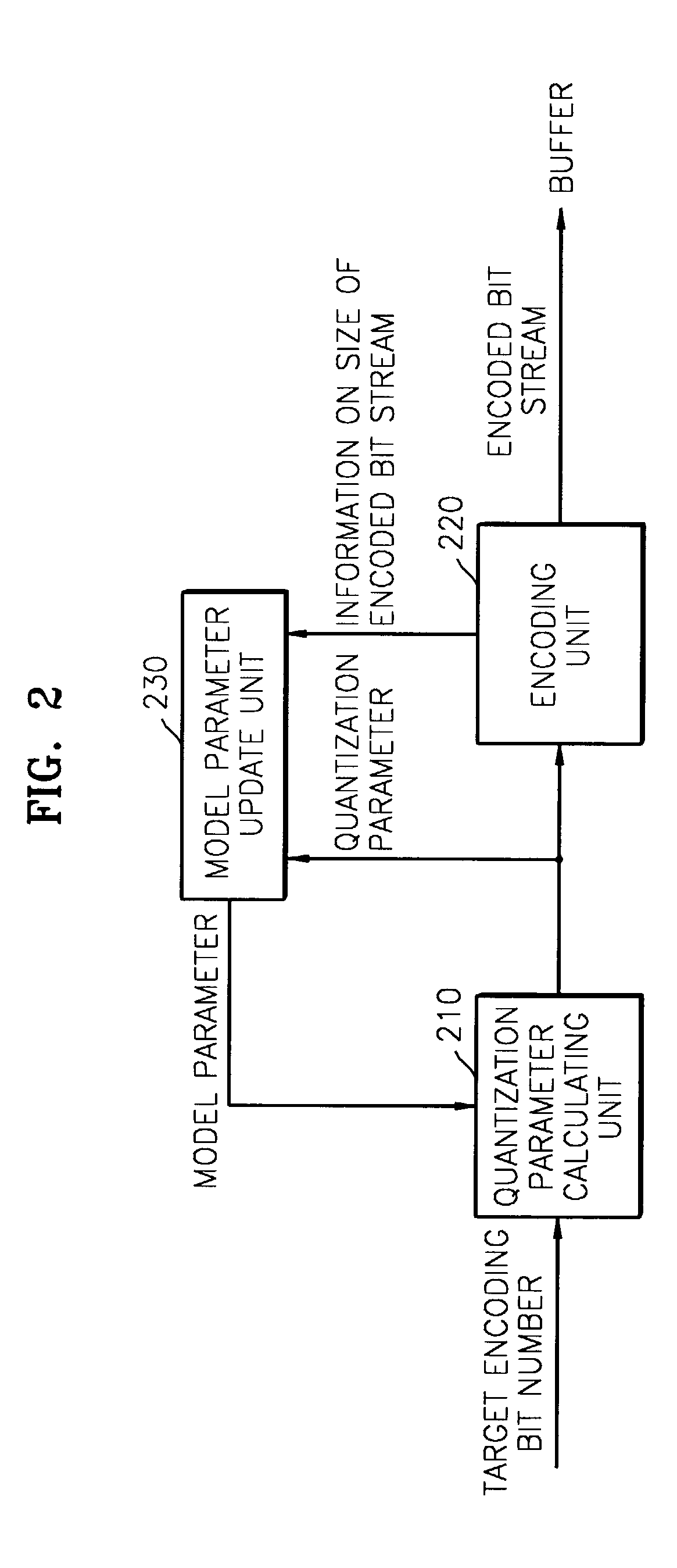
A rate control method used in encoding images is provided, including setting initial values for rate control and encoding; calculating a target encoding bit value based on the set initial values; performing rate control and encoding of a current bit stream based on the calculated target encoding bit value; measuring the picture quality of the current encoded bit stream, determining whether or not to skip the current encoded bit stream based on the measured picture quality, and generating a current encoded bit stream skip control signal; and controlling skipping of the current encoded bit stream, based on the current bit stream skip control signal provided by a picture quality measuring and skip control signal generating unit. In the method, a bit rate is controlled by considering the picture quality of an encoded bit stream such that a constant bit rate and appropriate picture quality can be maintained simultaneously.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for encoding/decoding error correcting code, transmitting apparatus and network
A client signal having a constant bit rate is segmented every a bytes to create code information blocks. The bit rate of the client signal is increased such that the client signal has the code information block and an empty area comprised of b bytes, and the ratio c / a is equal to or higher than 110% to create a code block 3 comprised of c bytes. The code information block in the code block is encoded such that an error correcting code is included therein to have an encoding gain of 6 dB or higher for a bit error ratio of 10−12. Associated check bits are placed in the empty area to eventually generate a super FEC signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
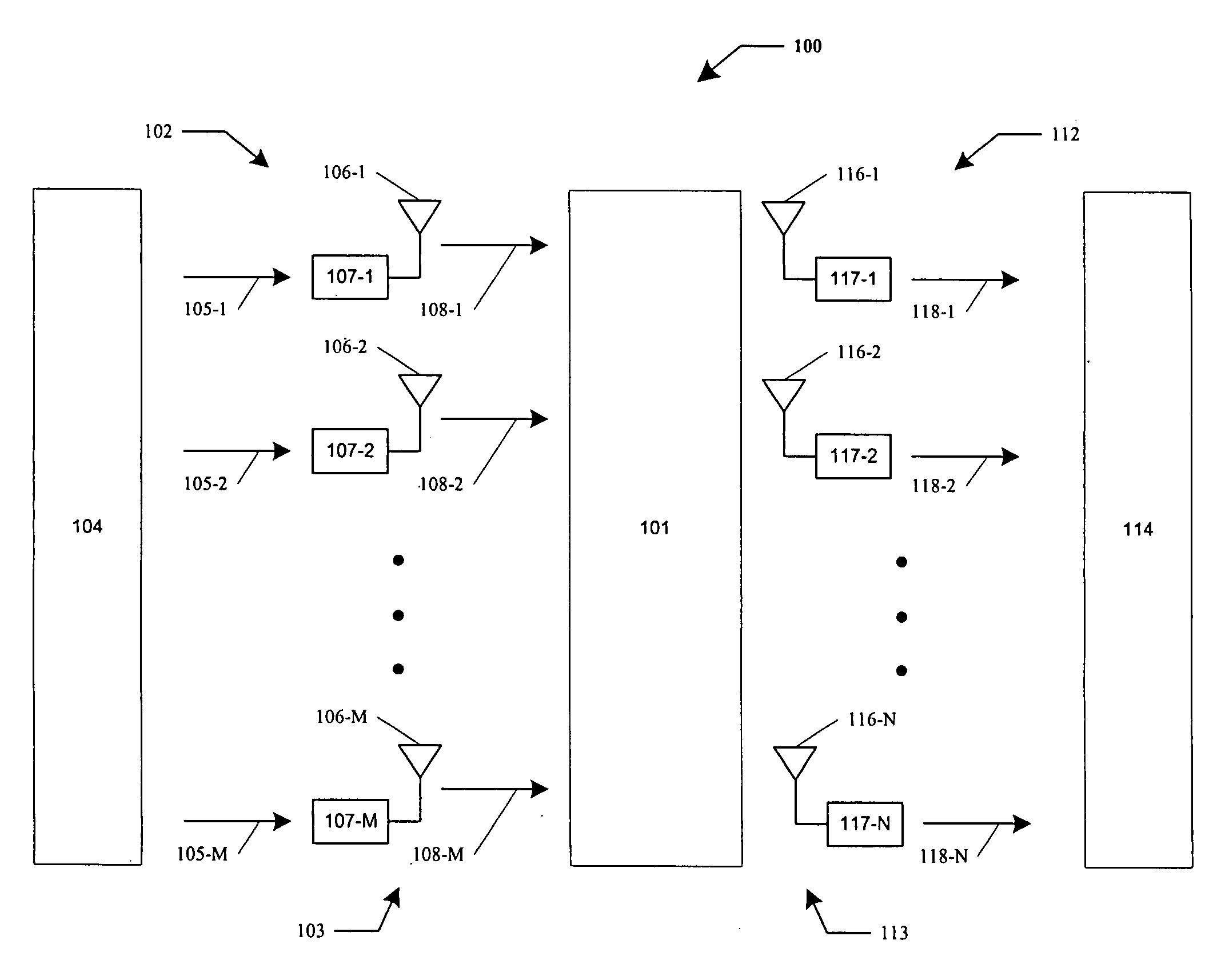
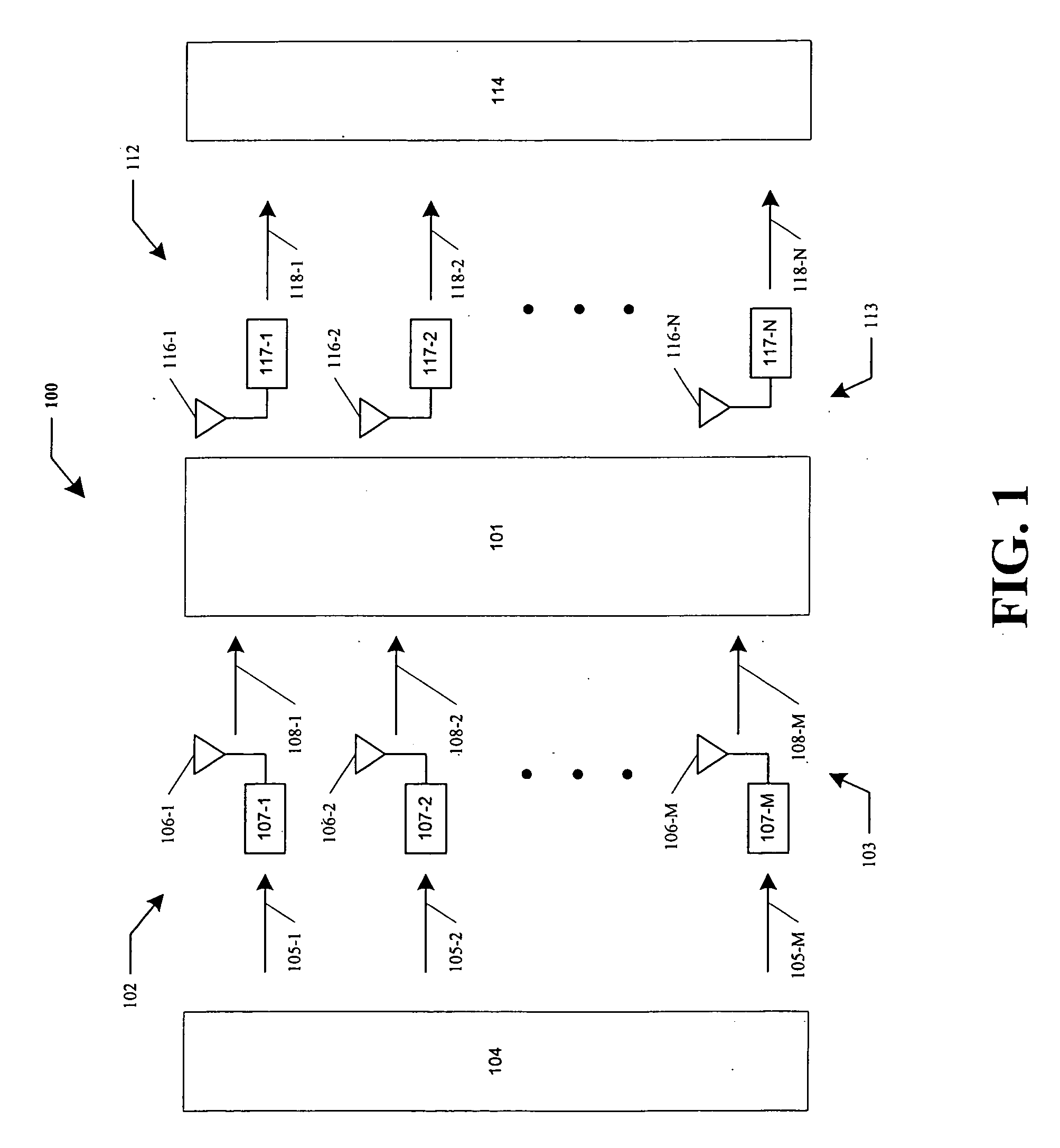
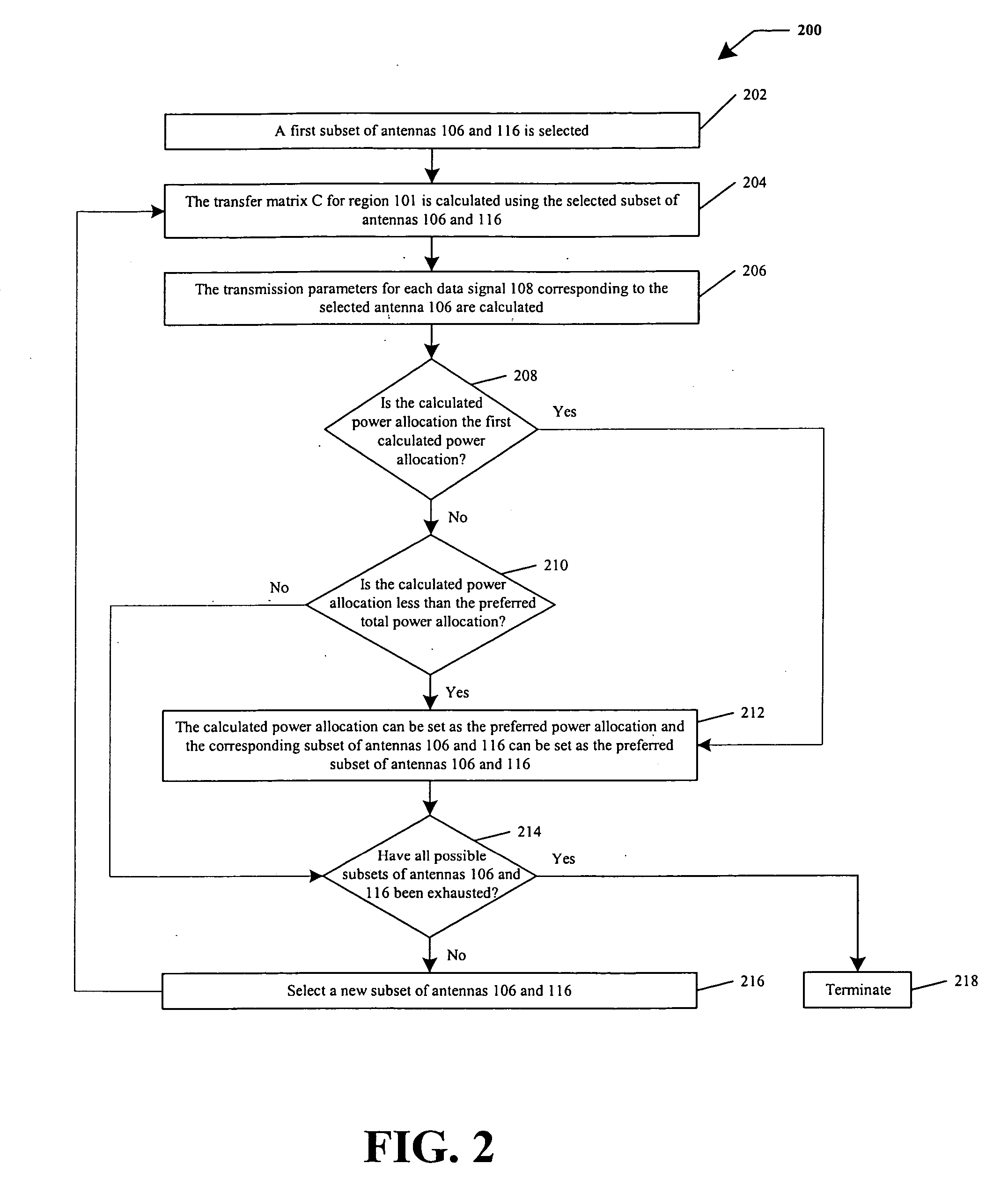
Systems and methods for resource allocation to multiple antenna arrays for maintaining a constant bit rate (CBR) channel
ActiveUS20060018288A1Spatial transmit diversityBroadcast transmission systemsCommunications systemData signal
A wireless communication system configured for the efficient allocation of resources is provided. The wireless communication system can include a transmit system having a first set of one or more antennas each configured to transmit a data signal over a region to a receive system having a second set of two or more antennas each configured to receive the transmitted data signal. The transmit system can be configured to adjust a transmission parameter of a data signal based on a level of signal fading in the region to sustain a target bit rate, adjust a power and a bit rate at which a data signal is transmitted based on the level of signal fading in the region and select a subset of antennas within the first set of antennas to be used to transmit a data signal based on the level of signal fading in the region.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Advanced method for rate control and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS7068718B2Prevent image quality degradationColor television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionControl signalComputer science
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for optimizing forward error correction of multimedia streaming over wireless networks
The loss of packets in a communication system can be minimized in an optimal manner by adapting a set of error correction (EC) parameters in response to a calculated probability of packet loss. The calculated probability is obtained from derived algorithms that are applied to a set of communication parameters. Algorithms are derived from Bernoulli-distributed traffic models and constant bit rate (CBR) traffic models of the communication system. A collapsed-state model is used to derive a very efficient algorithm that calculates an approximate probability of packet loss. Alternate applications for the algorithms are also disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
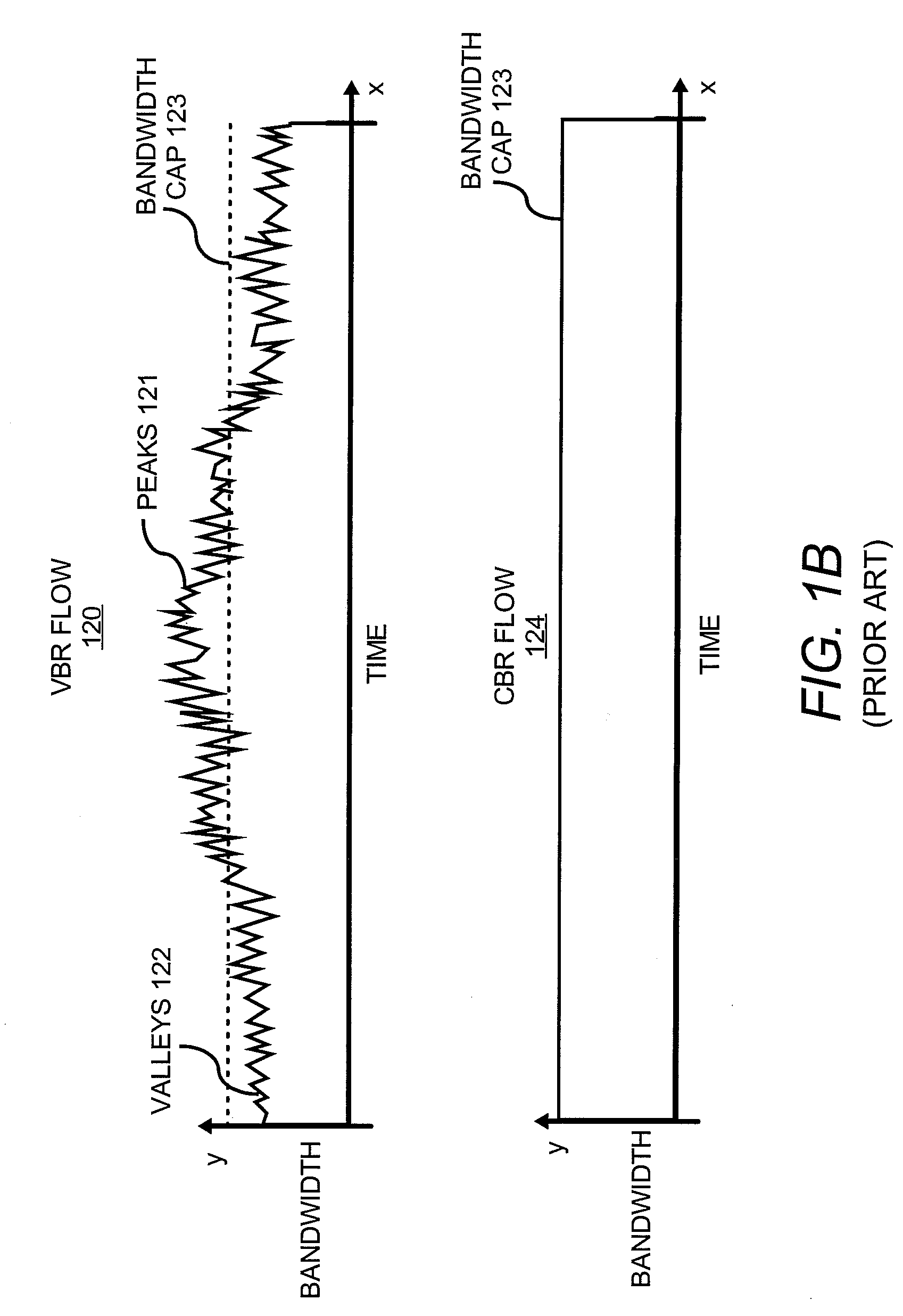
Enabling Trick Plays during VBR Playback of a CBR Transmitted Media File
ActiveUS20090161765A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer scienceBit rate
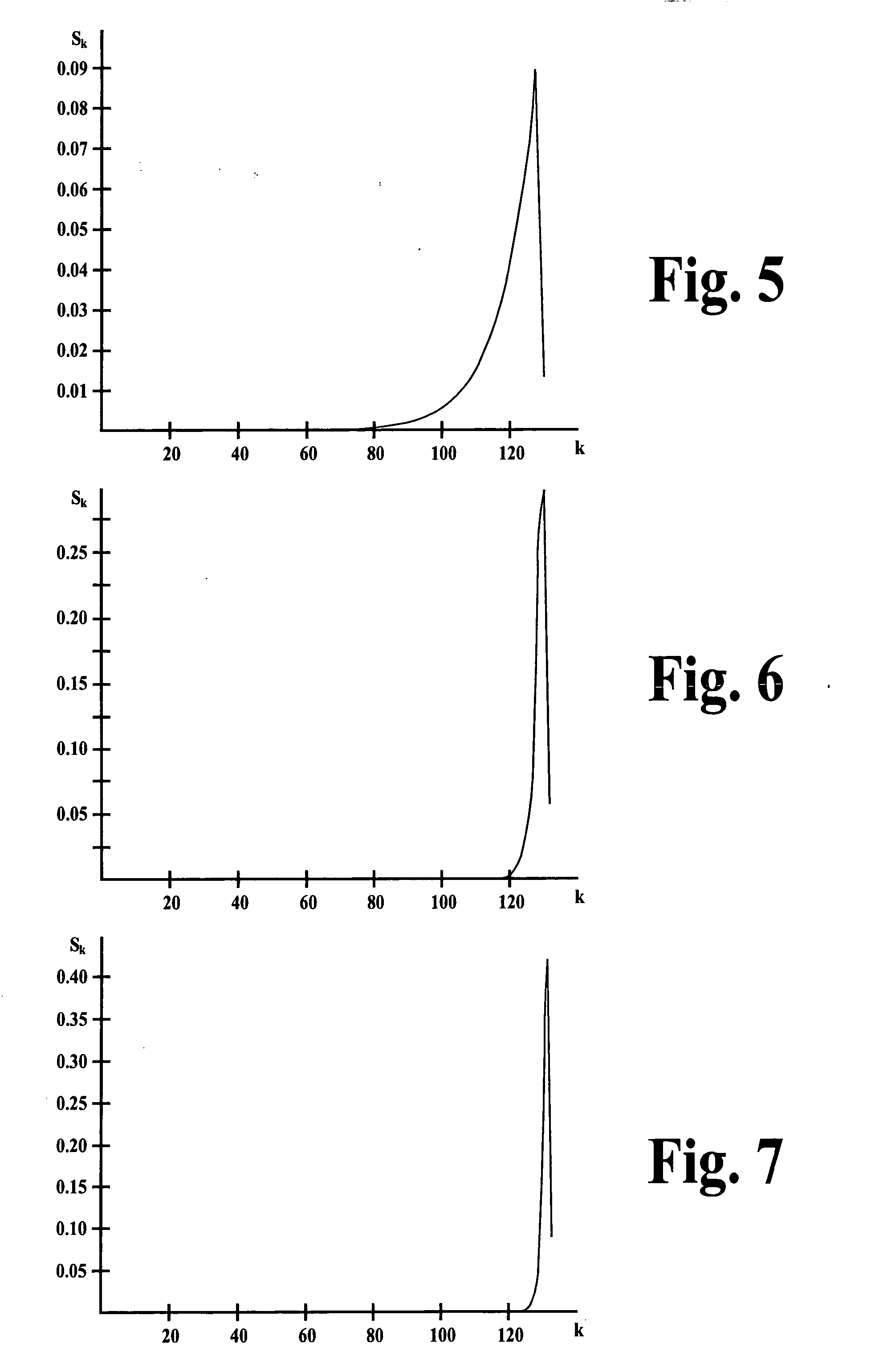
A method and system for enabling trick plays during a variable bit rate (VBR) playback of a media file transmitted to a user media device as a constant bit rate (CBR) flow includes determining a plurality of access points within the media file. The media file is configured to be played back from each of the plurality of access points. A minimum buffer value is calculated for each of the plurality of access points. The minimum buffer value identifies a minimum amount of the media file to transmit to the user media device before beginning playback of the media file from each of the plurality of access points to substantially ensure that the media file is configured to be played back from each of the plurality of access points continuously and uninterruptedly at a variable bit rate.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Method and system for multiple pass video coding
InactiveUS20050058200A1Efficient algorithmColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingInformation processor
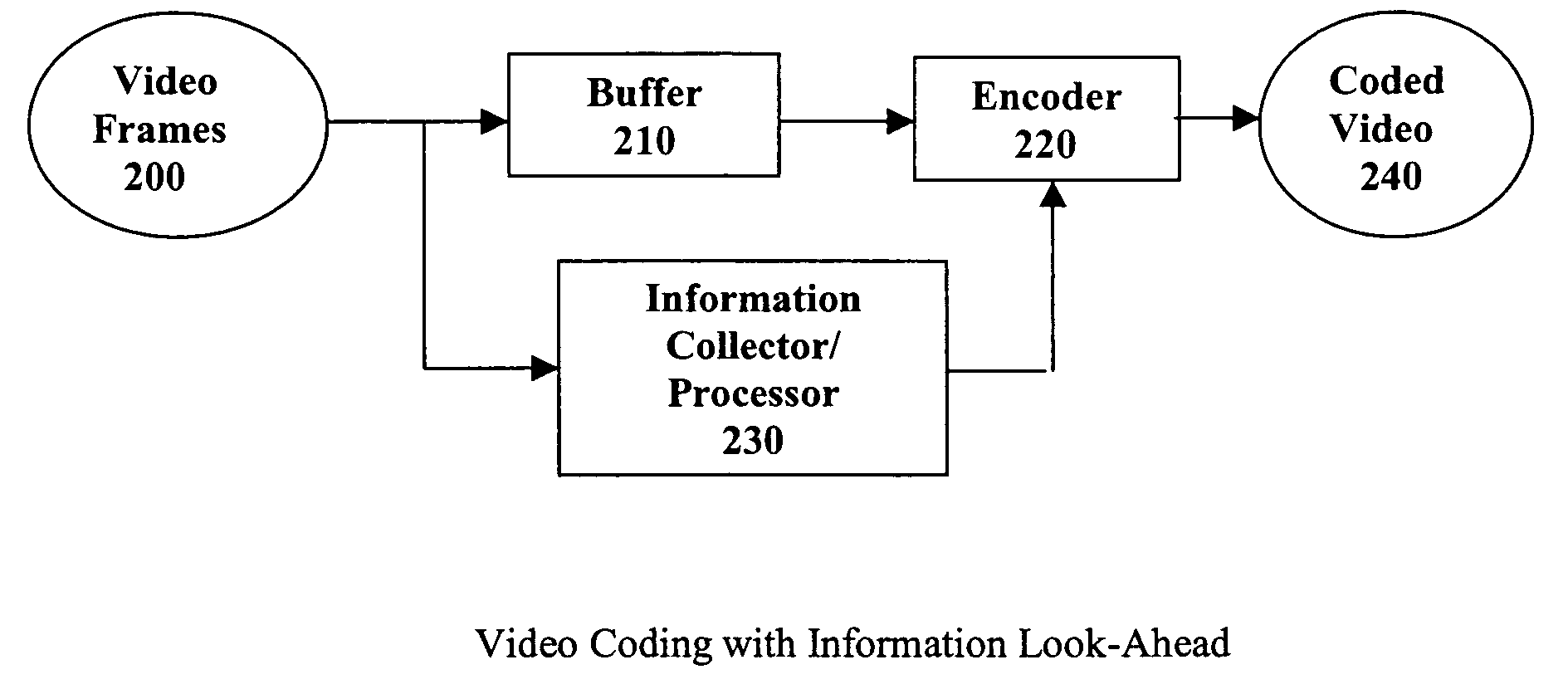
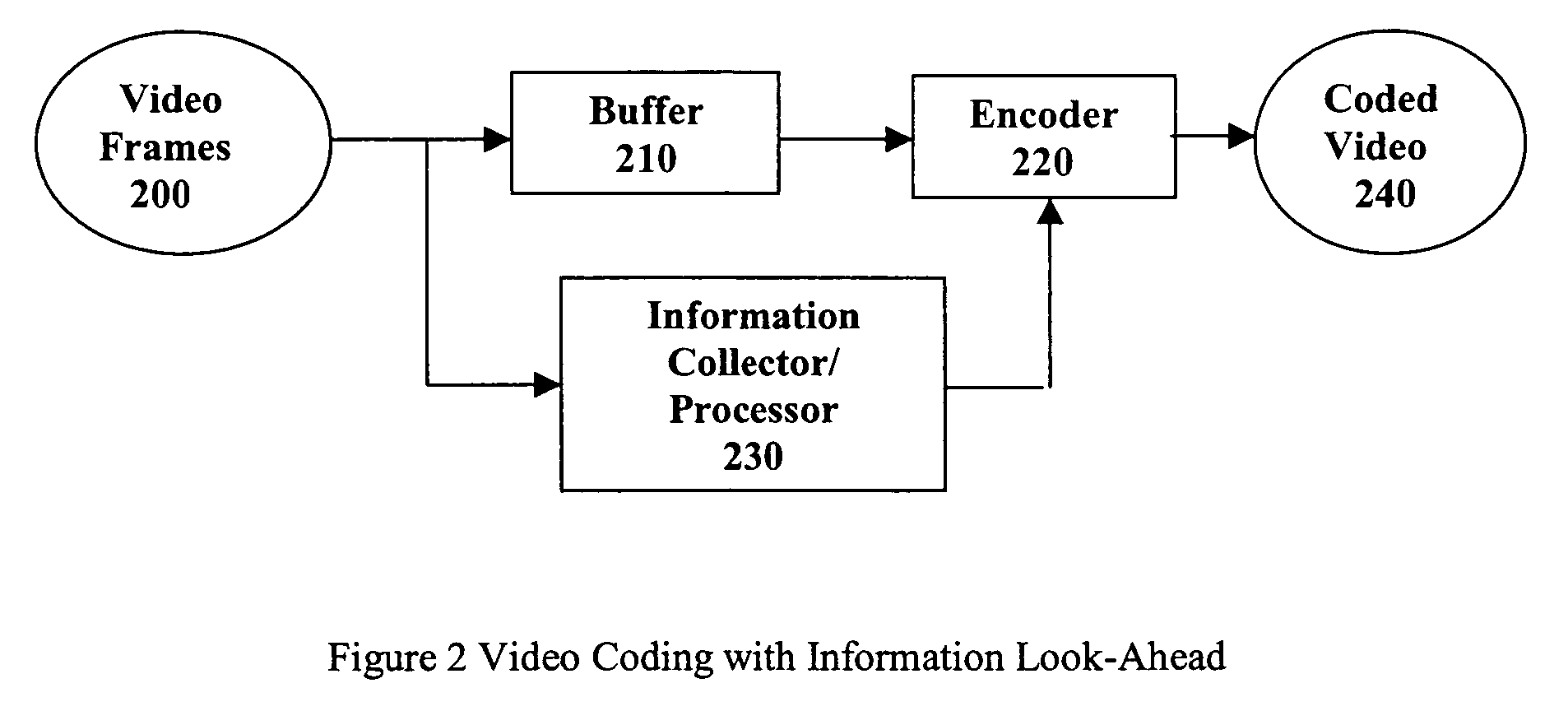
A real-time MPEG video coding system with information look-ahead for constant bit rate (CBR) applications, such as, for example, Video-on-Demand (VoD) over ADSL. This scheme employs two MPEG encoders. The second encoder has a buffer to delay the input by an amount of time relative to the first encoder to create a look-ahead window. In encoding, the first encoder collects the information of statistics and rate-quality characteristics. An on-line information processor then uses the collected information to derive the best coding strategy for the second encoder to encode the incoming frames in the look-ahead window. The second encoder uses the encoding parameters from the processor as the coding guide to execute the coding strategy and generate the final bitstream.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for optimizing forward error correction of multimedia streaming over wireless networks
InactiveUS7447977B2Minimize impactUnequal/adaptive error protectionCode conversionPacket lossCommunications system
The loss of packets in a communication system can be minimized in an optimal manner by adapting a set of error correction (EC) parameters in response to a calculated probability of packet loss. The calculated probability is obtained from derived algorithms that are applied to a set of communication parameters. Algorithms are derived from Bernoulli-distributed traffic models and constant bit rate (CBR) traffic models of the communication system. A collapsed-state model is used to derive a very efficient algorithm that calculates an approximate probability of packet loss. Alternate applications for the algorithms are also disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Constant bitrate media encoding techniques
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
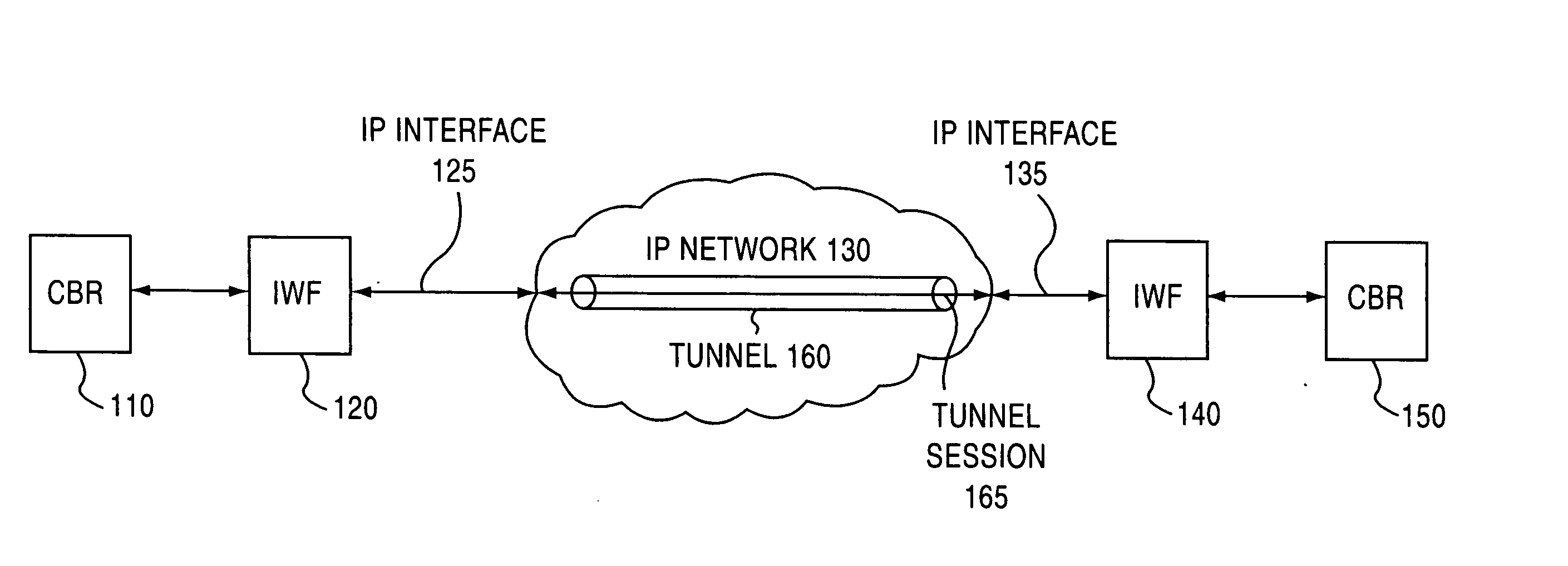
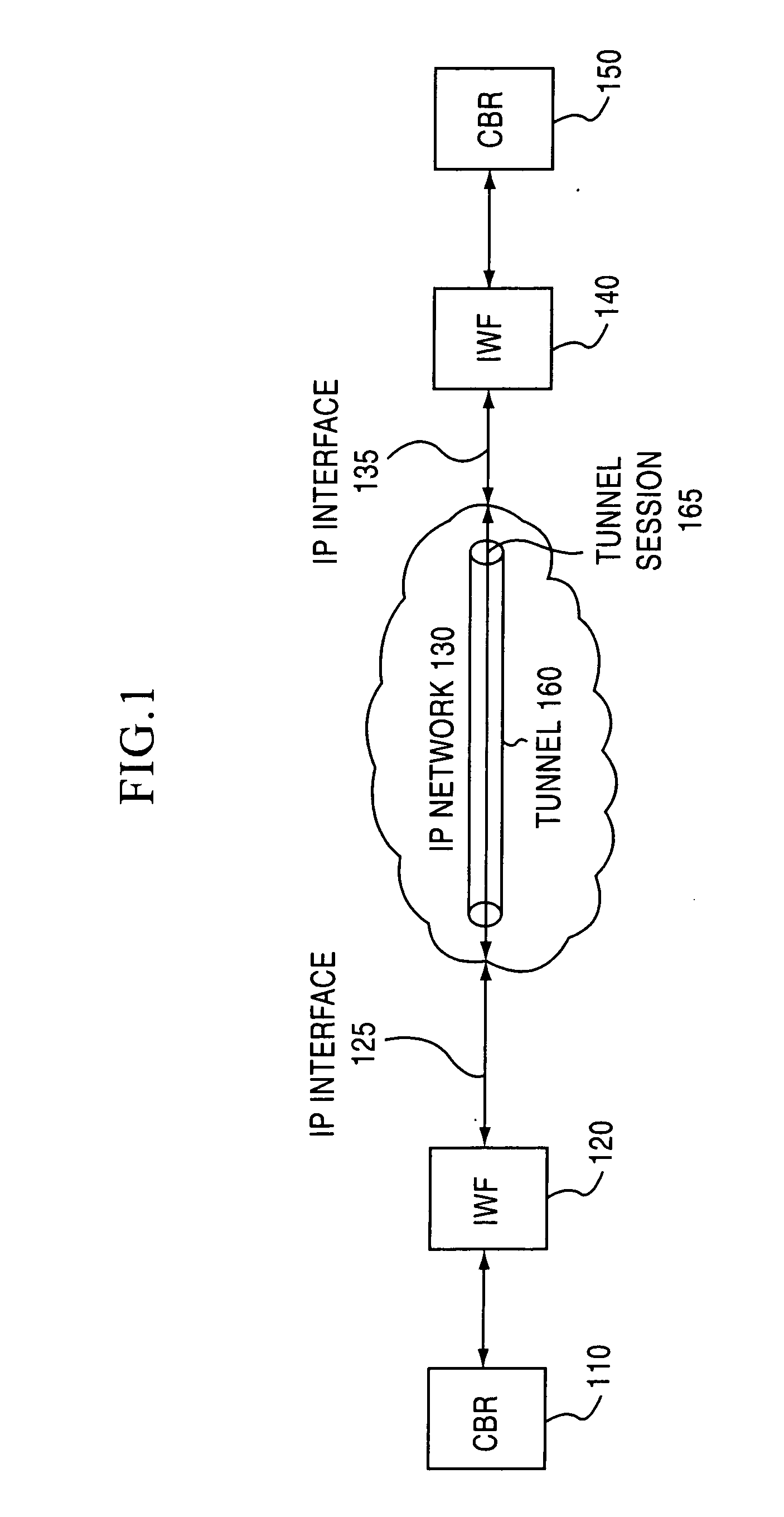
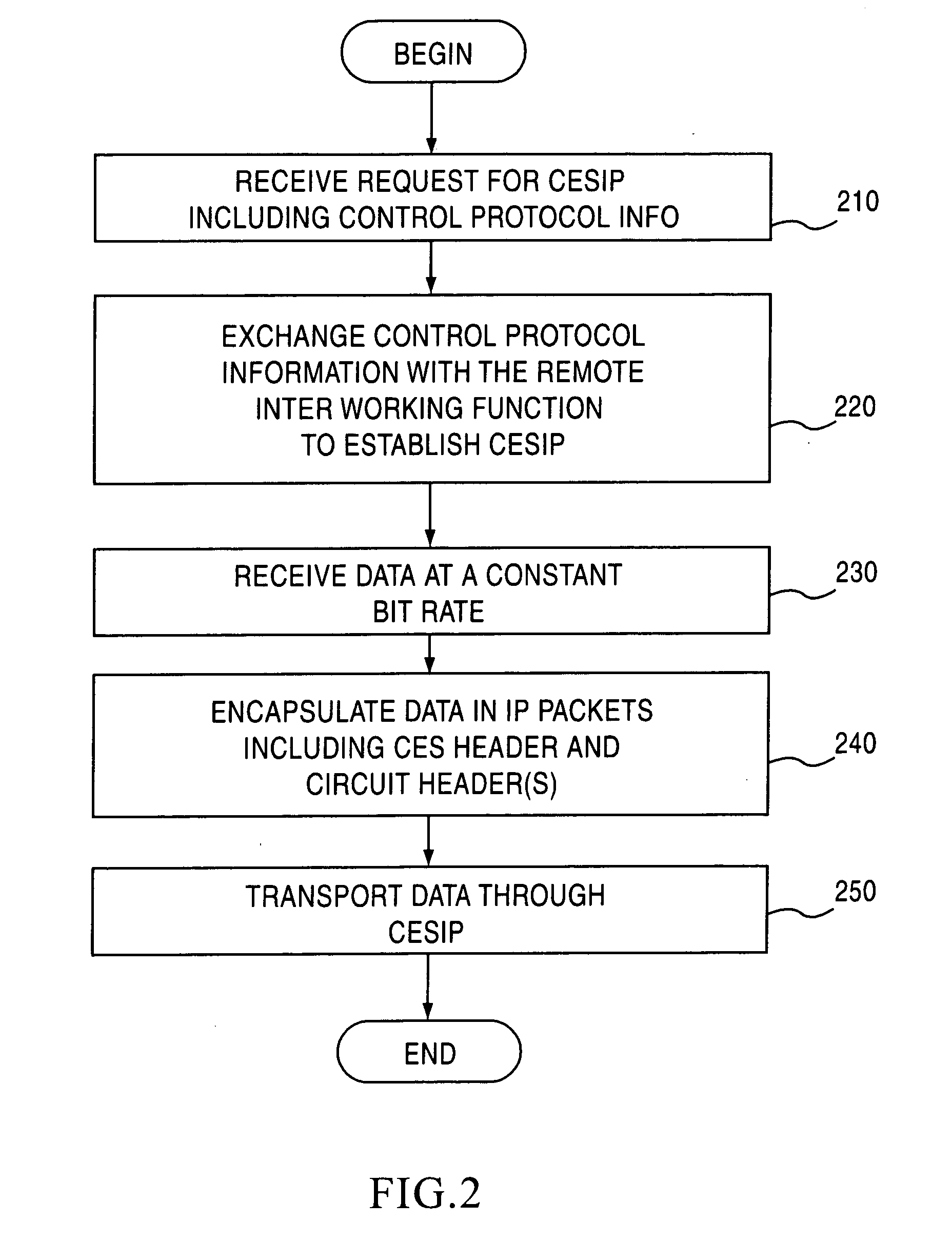
Jitter buffer for a circuit emulation service over an internal protocol network
A jitter buffer receives a plurality of data packets comprising a circuit emulation service over internet protocol (CESIP), buffers the plurality of data packets, and plays data from the plurality of data packets at a constant bit rate corresponding to the CESIP.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Bandwidth allocation method and system for data transmission in EPON
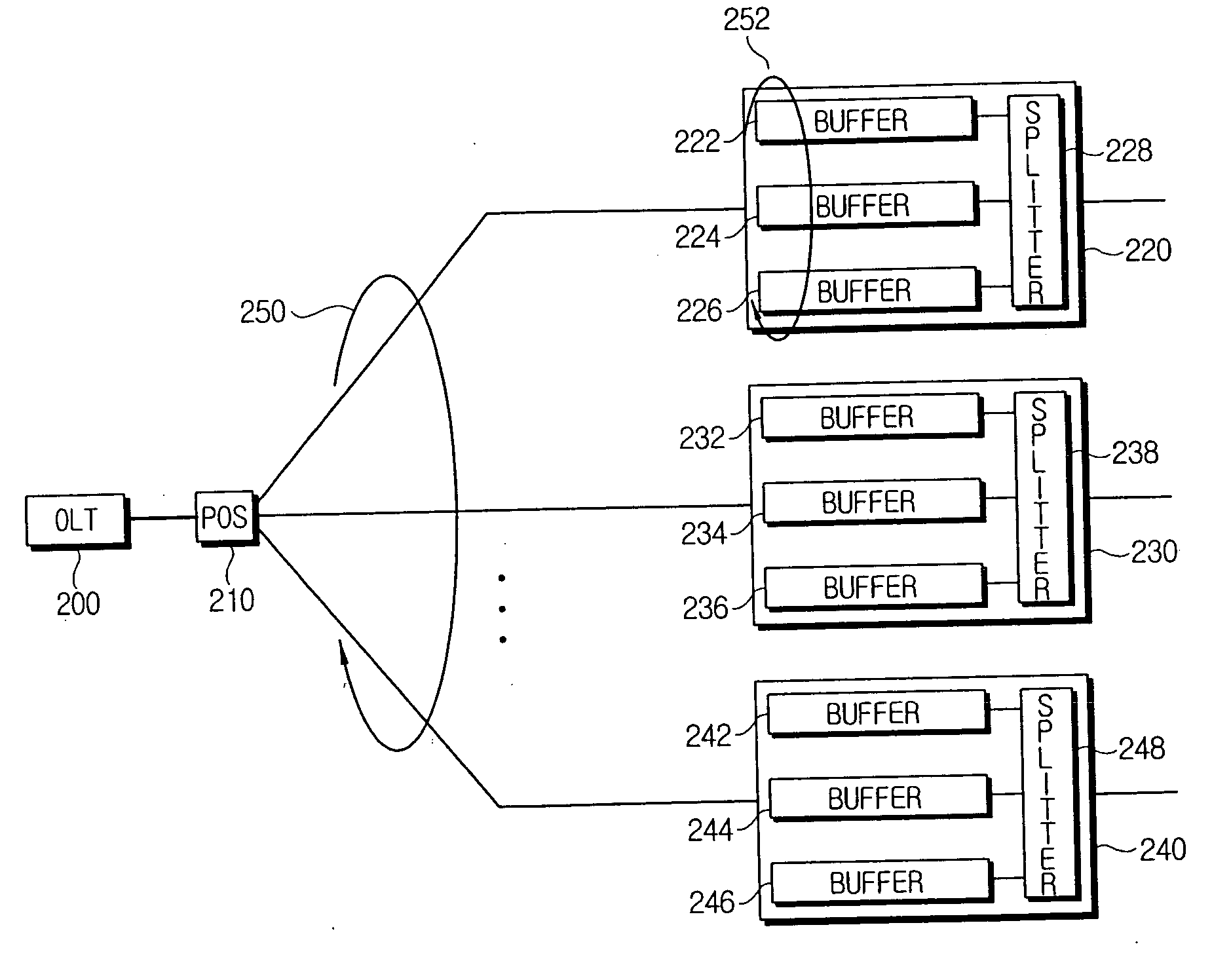
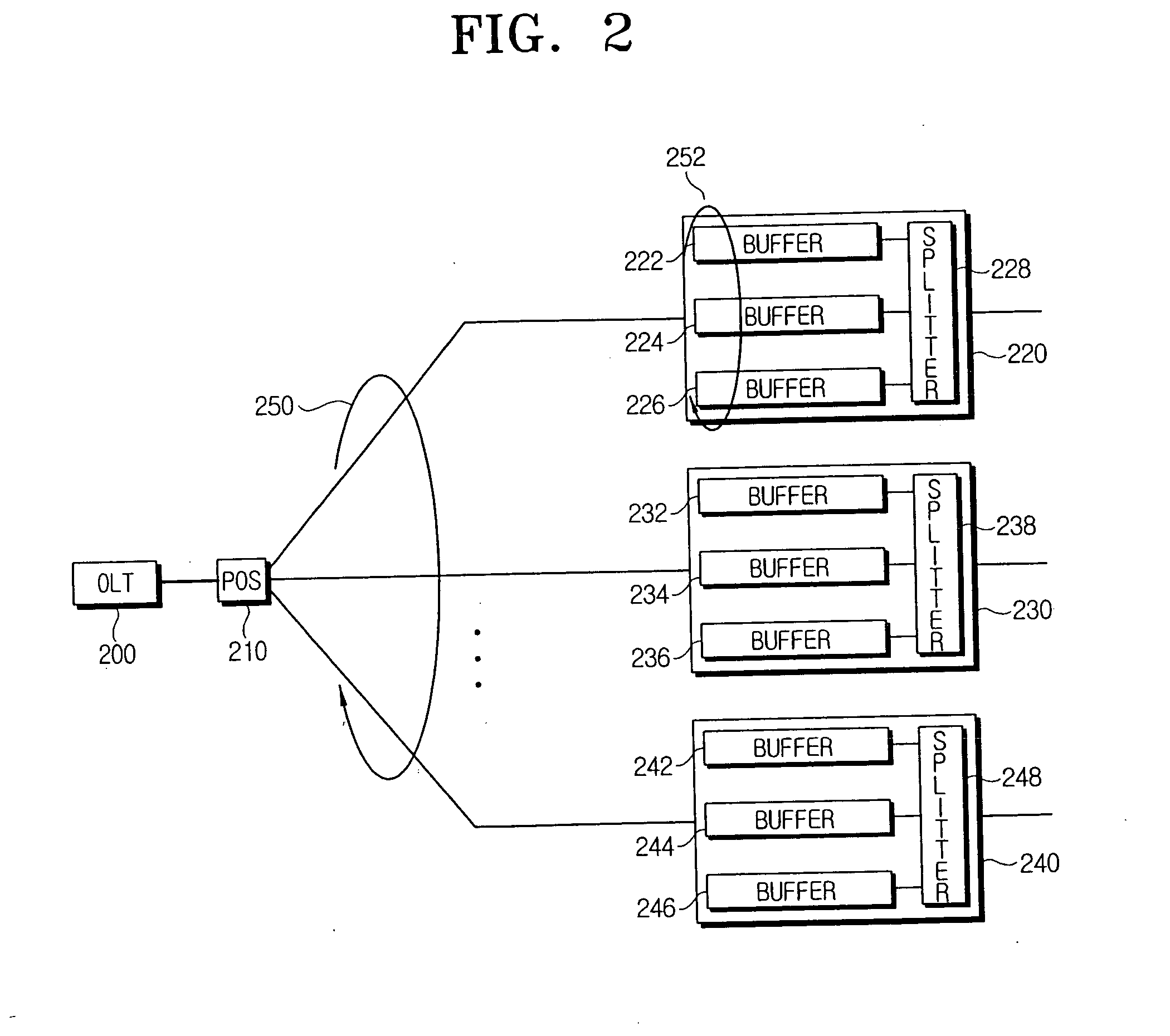
InactiveUS20060153564A1Effective distributionMultiplex system selection arrangementsPositive displacement pump componentsOptical line terminationOptical network unit
A method for efficiently allocating a bandwidth at an optical line terminal (OLT) for upstream transmission in an Ethernet passive optical network (EPON) system. An optical network unit (ONU) divides data to be transmitted into at least two groups that include a group with a constant bit rate (CBR) and a group with a variable bit rate (VBR), and requests a required bandwidth for each of the divided groups. The OLT allocates the requested bandwidth to the group with the CBR within a first bandwidth among an allocated bandwidth including the first bandwidth and a second bandwidth. The ONU transmits data using bandwidth allocated to the divided groups by the OLT.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
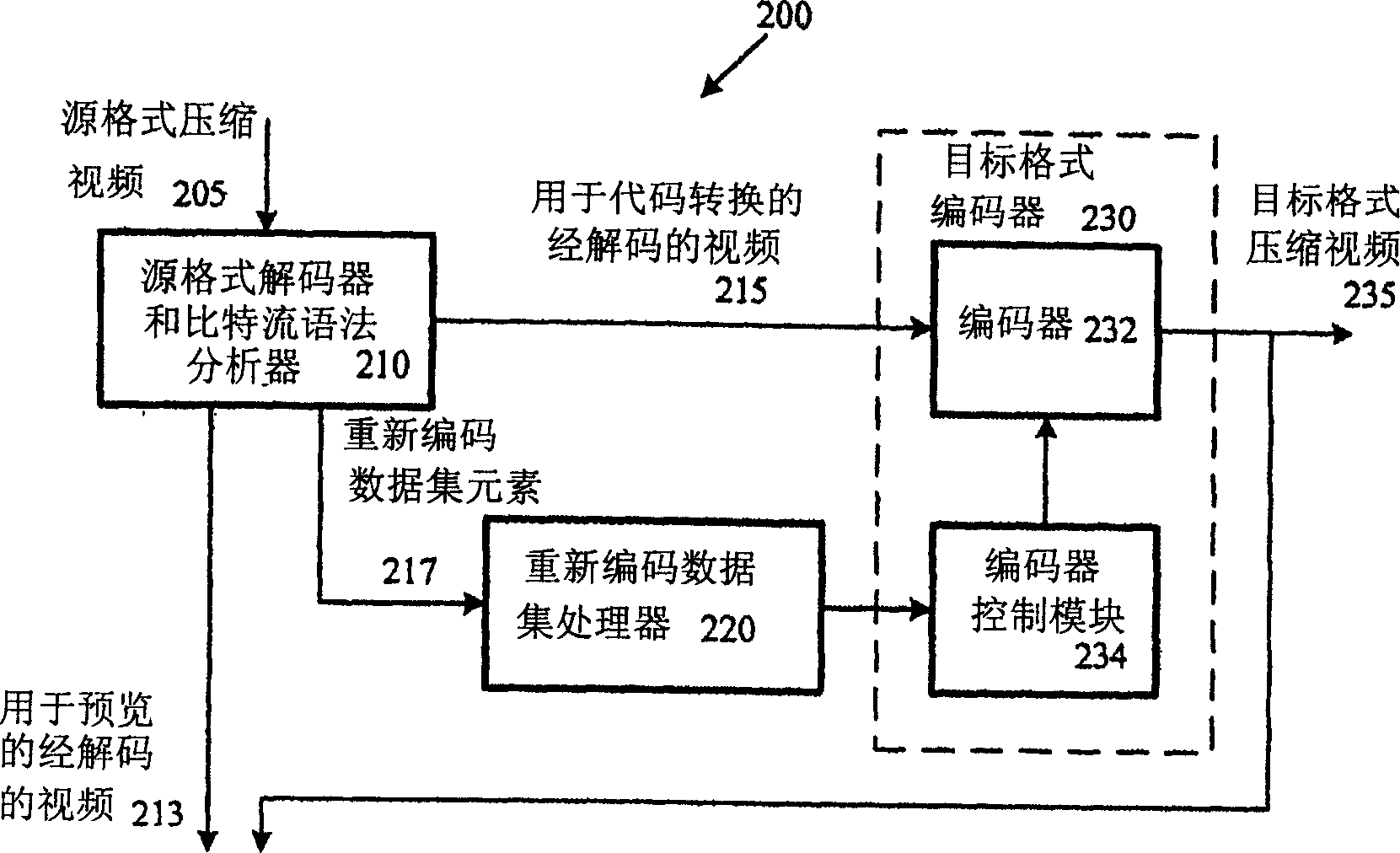
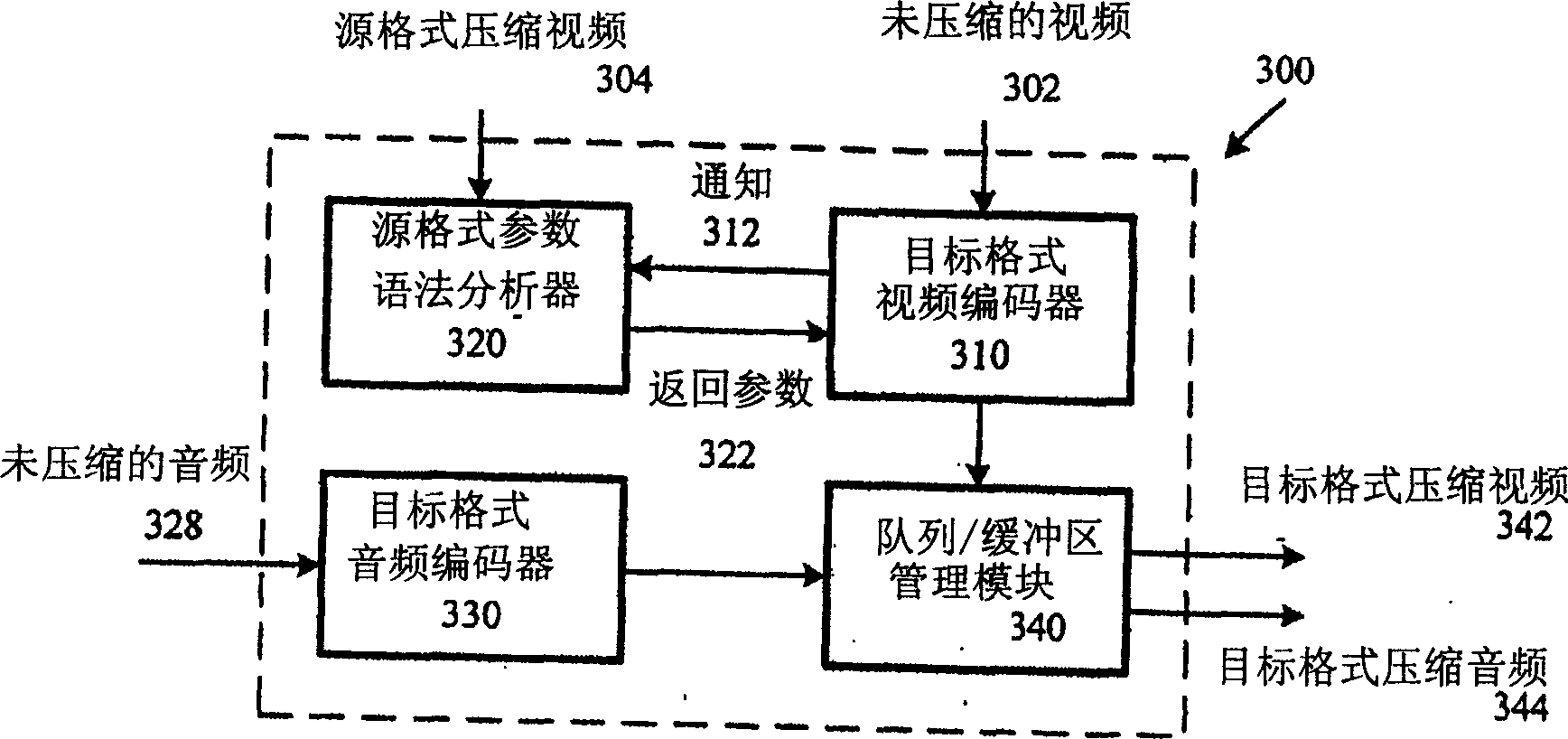
High-fidelity transcoding
High-fidelity transcoding techniques are described. For example, a video transcoder obtains re-coding data set elements for source format compressed video and uses the elements for coding decisions and / or equivalent parameters when compressing the video in a target format. This allows syntax elements and coding decisions to be maintained across the two formats, including picture types, intra / inter macroblock coding types, field / frame coding decisions, and / or quantization levels. This helps the transcoder match quality in the compressed video between the source and target formats, reducing transcoding losses. At the same time, the transcoder gives the target format encoder the freedom to exploit additional compression opportunities to reduce overall bitrate. The transcoder may apply proportional rate control so as to produce output at a constant or relatively constant bitrate.
Owner:MICROSOFT CORP
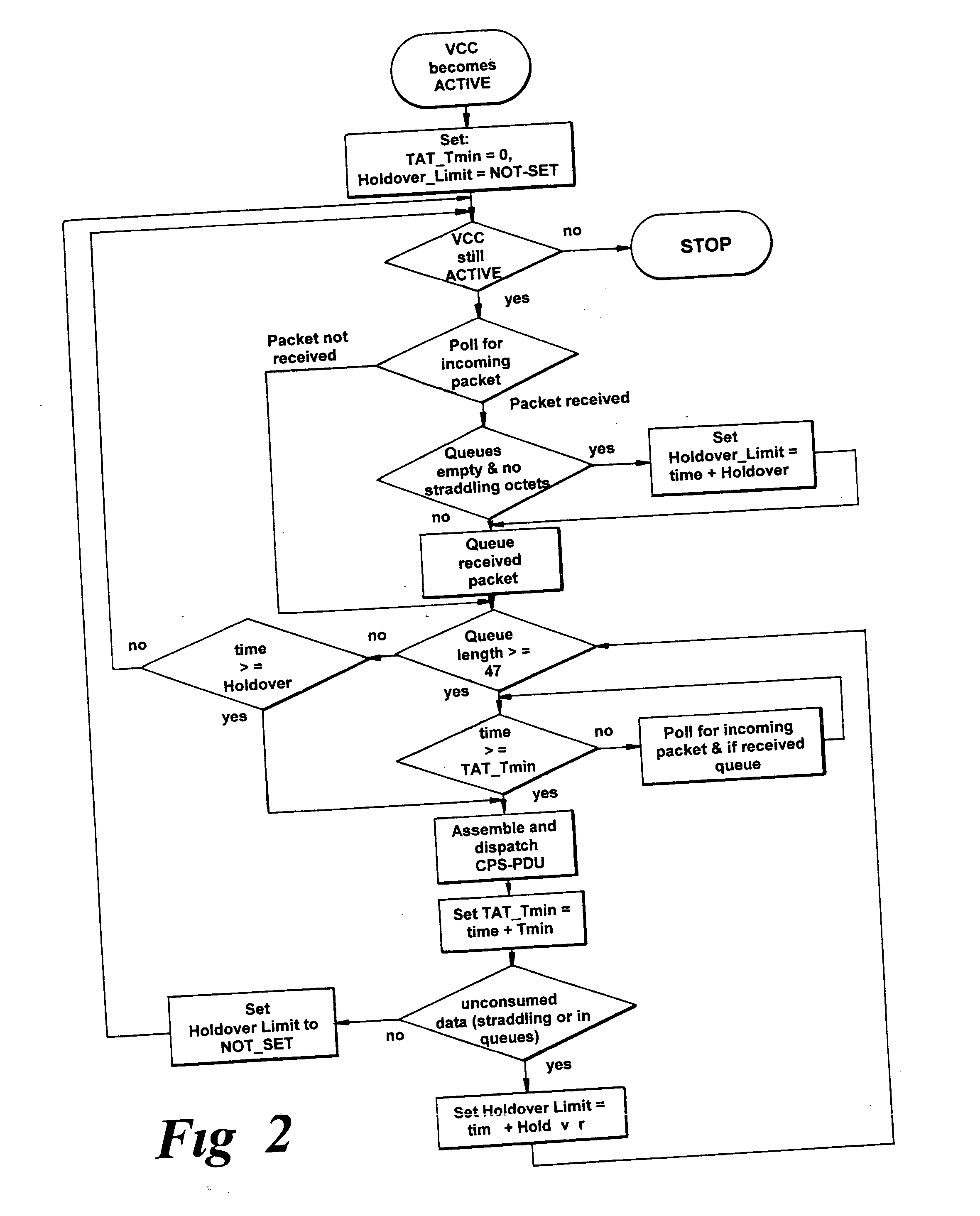
ATM packet scheduler
InactiveUS20050063388A1Stable supportWell-behavedData switching by path configurationMultiplexingTraffic characteristic
A packet scheduler controls dispatch of packets containing constant bit rate (CBR) or real time variable bit rate (rt-VBR) at an ingress operation of multiplexing the packets into payloads of an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) bearer virtual circuit connection. Packets can be queued in one of a number of queues according to priority. The scheduler controls assembly of common part sublayer payload data units (CPS-PDU) comprising any unused octets from a previous packet partially dispatched, and whole packets in order of priority. If a holdover timer period expires before a common part sublayer payload data unit is completed, the payload of that data unit is packed with null data; and dispatched. The packet dispatch is controlled so as to match the traffic characteristics of an underlying bearer channel
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
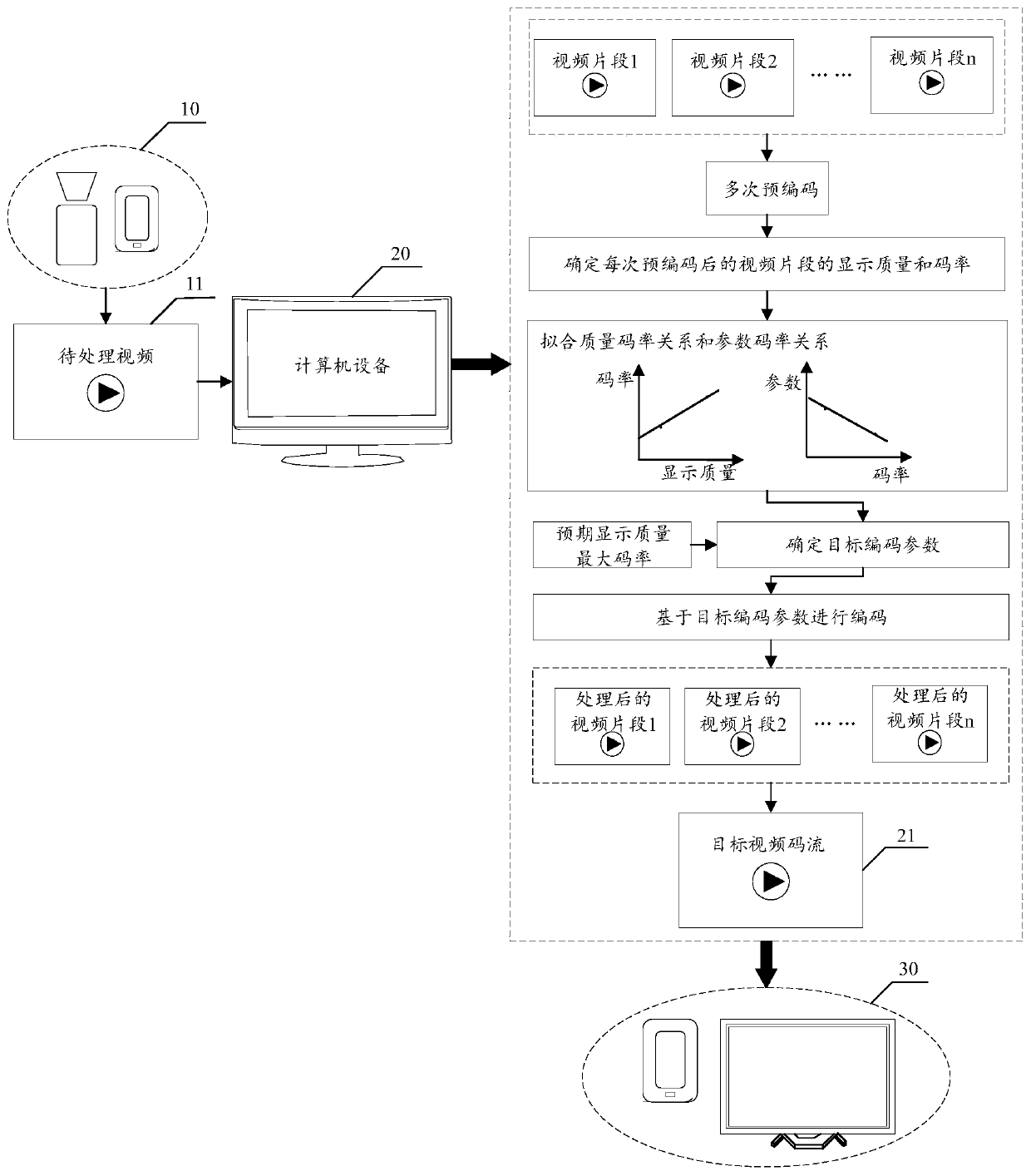
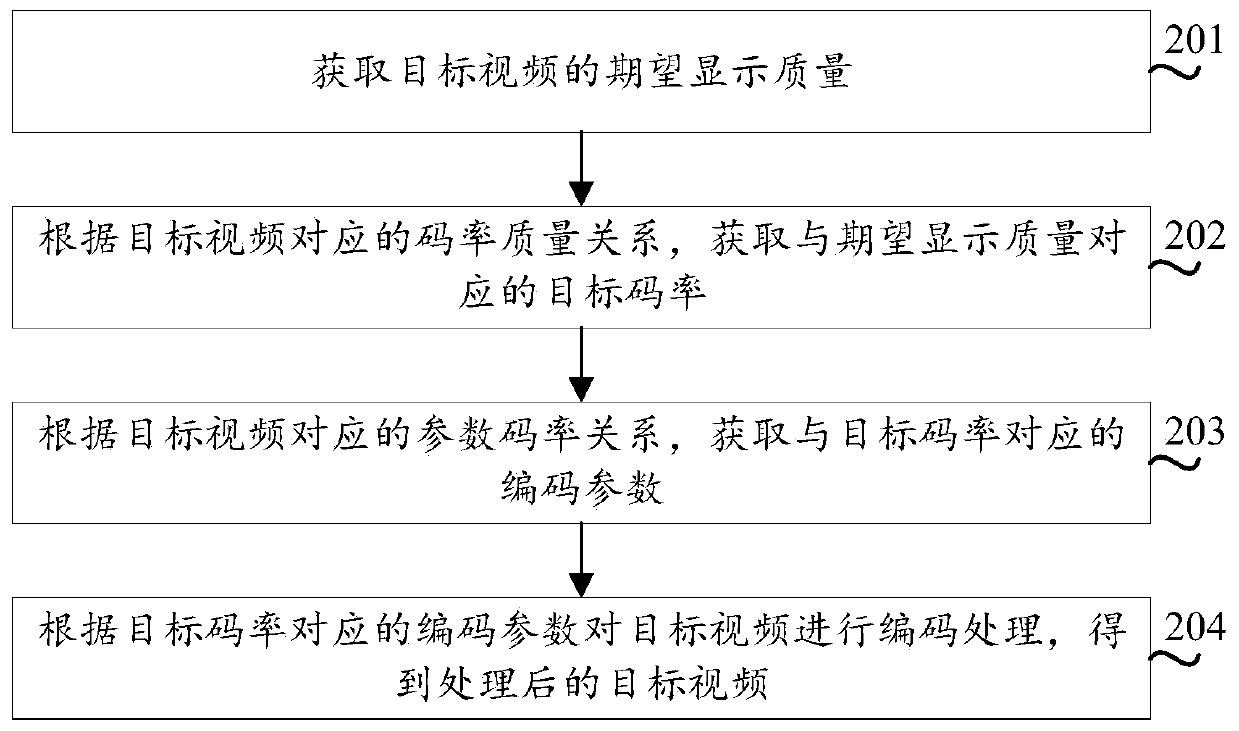
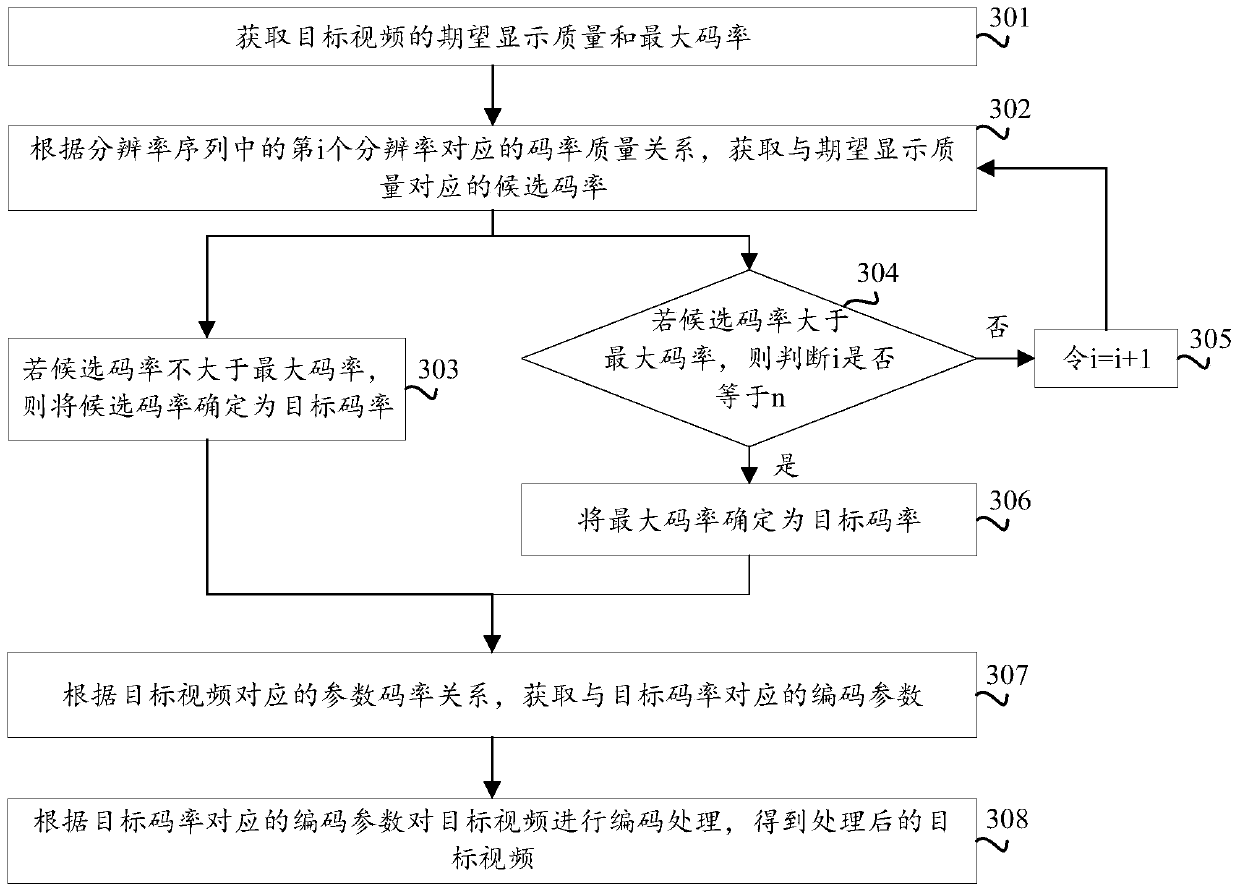
Video encoding method, device and equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN110418177AGuaranteed display qualityDigital video signal modificationSelective content distributionVideo encodingCode rate
The invention provides a video coding method and device, equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining expected display quality of a target video; obtaining a target coderate corresponding to the expected display quality according to the code rate quality relationship corresponding to the target video; obtaining a coding parameter corresponding to the target code rate according to the parameter code rate relationship corresponding to the target video; and performing encoding processing on the target video according to the encoding parameter corresponding to the target code rate to obtain a processed target video. Compared with the prior art in which coding is carried out by adopting a fixed code rate, the technical scheme provided by the invention can effectively ensure the display quality of the video code stream.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
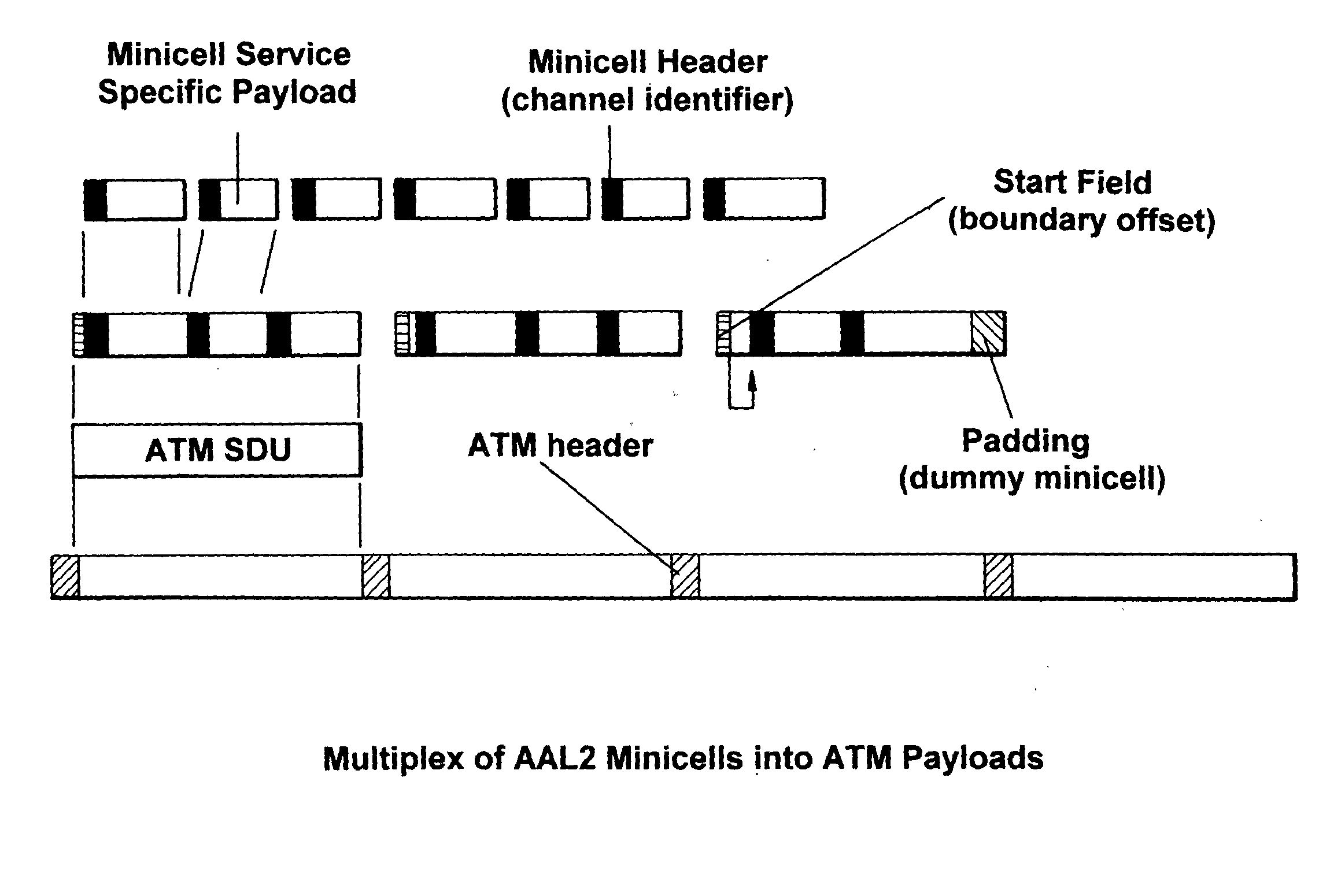
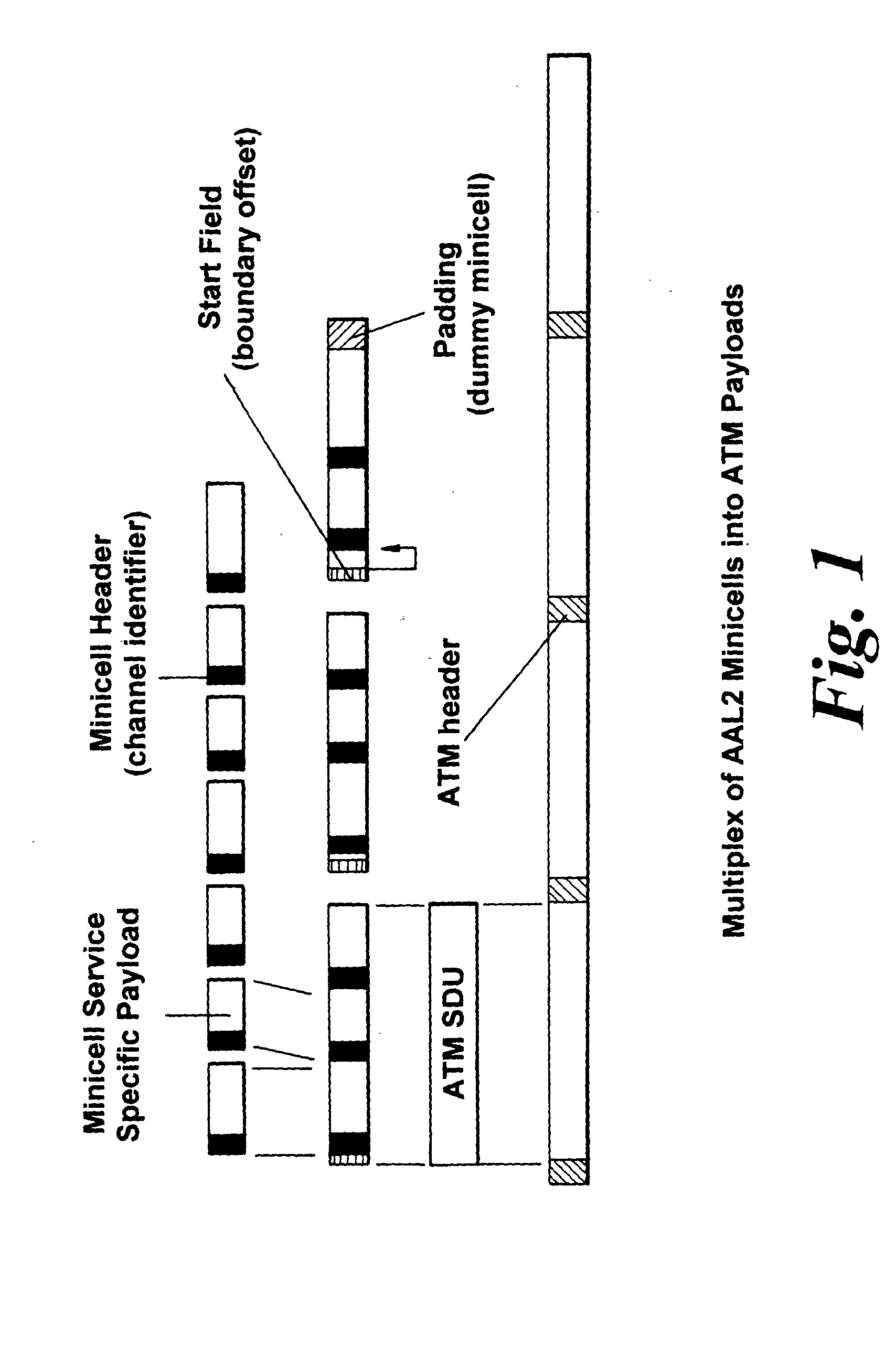
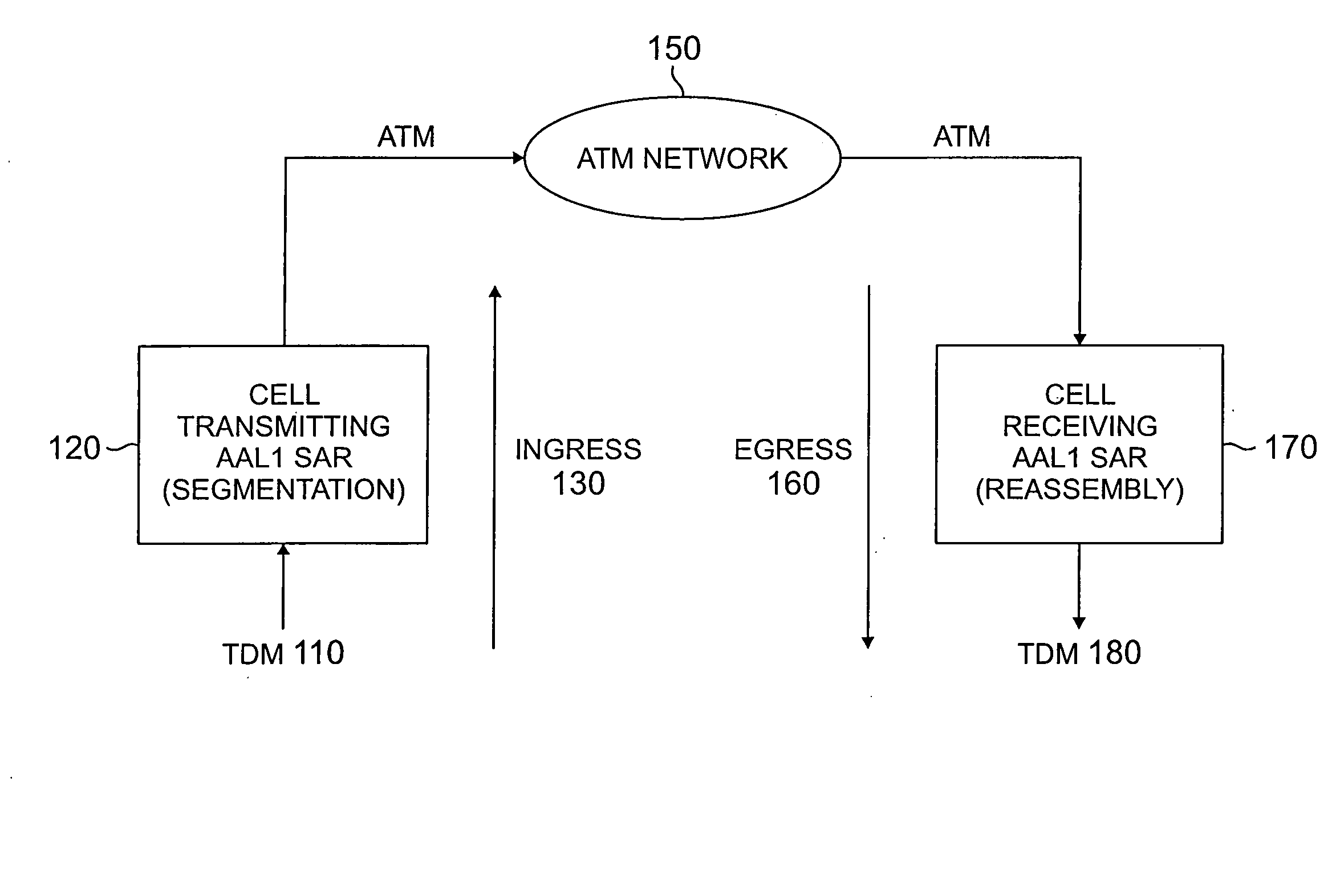
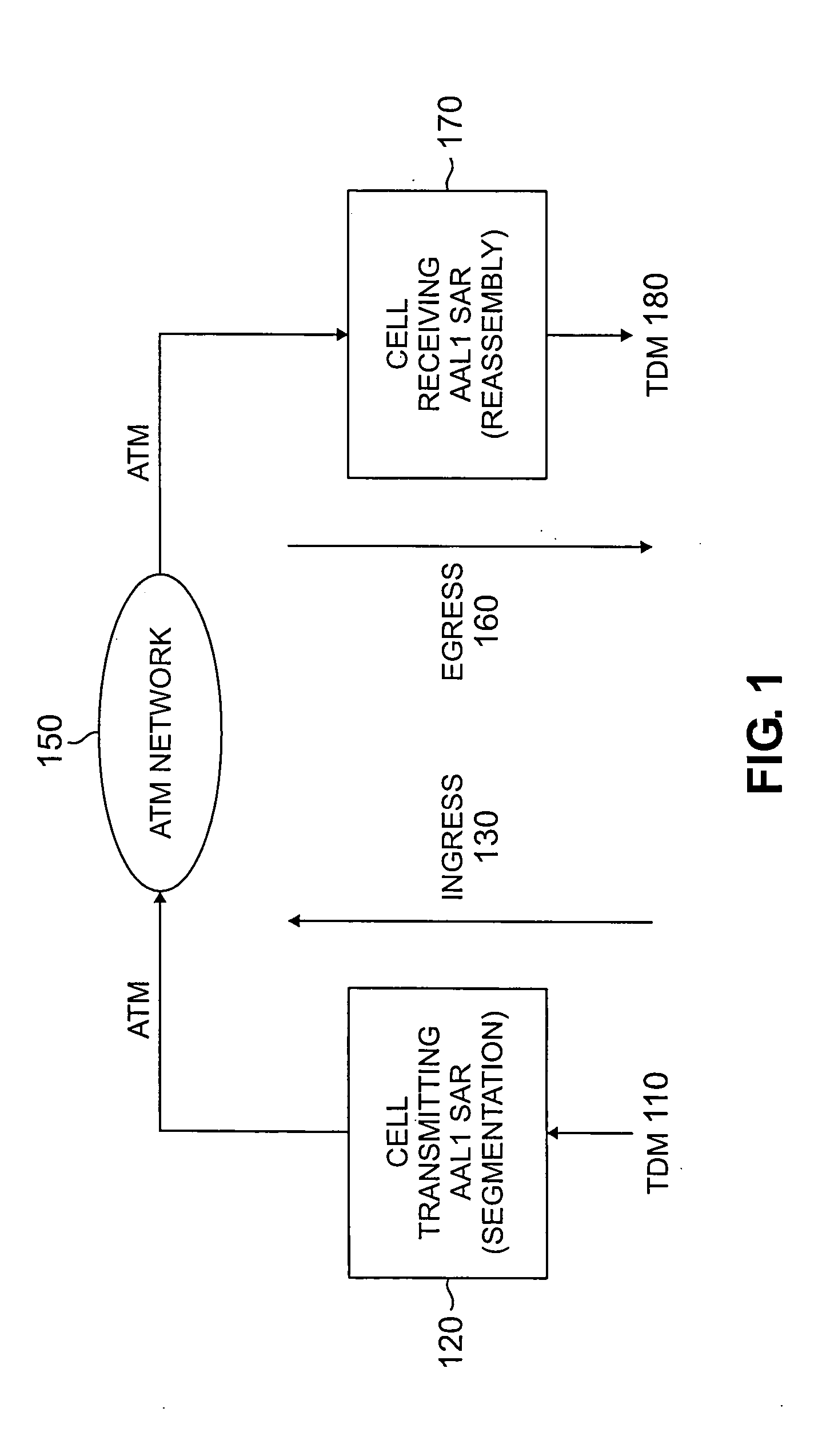
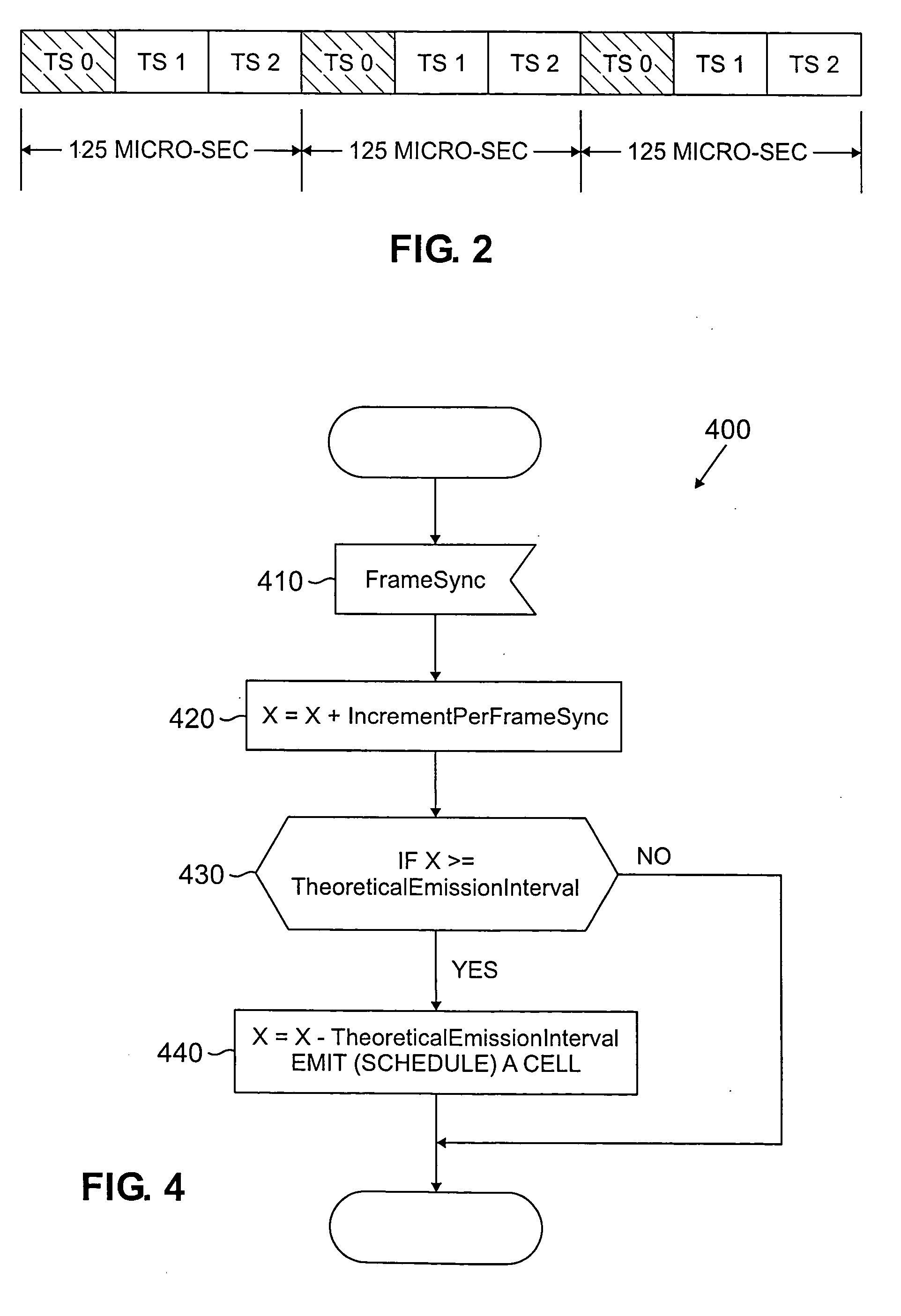
Method and apparatus for ATM adaptation layer staggered constant bit rate cell scheduling
A method and apparatus are disclosed for ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL) staggered constant bit rate cell scheduling. Cells from a plurality of virtual circuits are scheduled. Each of the virtual circuits have a transmission characteristic and each of the plurality of virtual circuits are classified into one of a plurality of stagger groups based on similar transmission characteristics. For each frame synchronization, a cell is transmitted from a given virtual circuit until a predefined cell threshold is exceeded for the stagger group containing the given virtual circuit. A Cell Delay Variation of each of the virtual circuits will not exceed a given time interval. A scheduler can be allocated for each connection or for each period.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
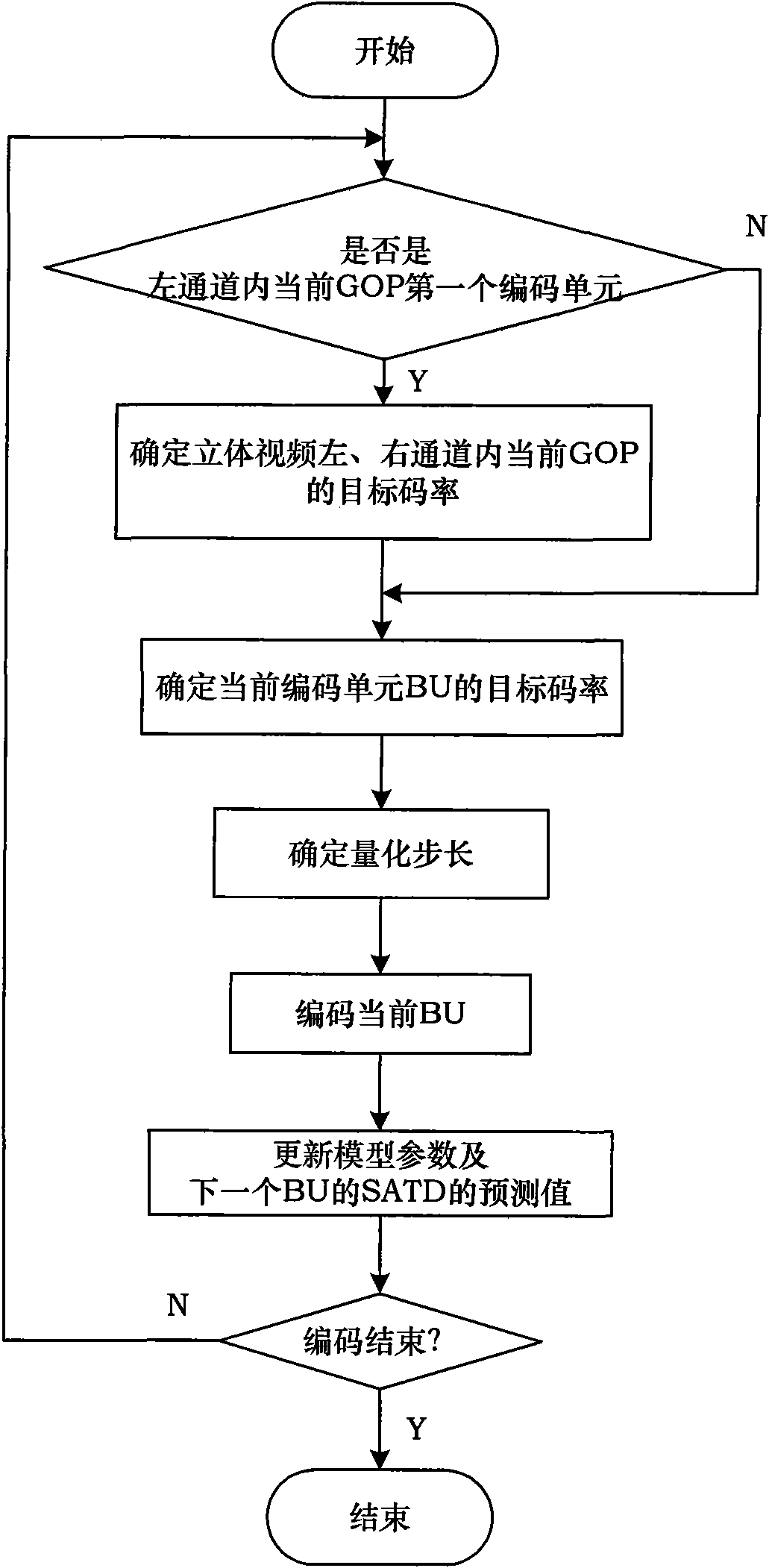
Control method for code rate of three-dimensional video based on SAQD domain
InactiveCN101883283AAccurate descriptionSolve the optimal code rate allocation problemTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationSimulationPeak value
The invention provides a control method for the code rate of a three-dimensional video based on an absolutely quantified residual error and an SAQD domain. In the method, a coding frame of a three-dimensional video with a gradable space coding structure based on an SVC solves the problem of optimal code rate distribution between the channels of the three-dimensional video by introducing the SAQD domain. The invention provides a rate model and a distortion model based on the SAQD domain and obtains the optimal code rates of a left channel and a right channel of the three-dimensional video by the resolution of an Lagrange's equation; and then, the quantified step length of each coding unit is obtained according to the calculated optimal code rate of each coding unit by the calculation of a linear code rate control model, thereby further coding each coding unit. Compared with the modes that the two channels of the three-dimensional video adopt fixed code rate distribution and a code rate control algorithm in an H.264 / SVC standard is adopted in each channel, the peak signal-to-noise ratio of a decoding image obtained by carrying out code rate control by adopting the method is higher, the bias of the output code rate of a coding end and a target code rate is smaller, and the method can adapt to the change of the bandwidth of a network fully.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Dynamic code rate allocation method based on video data importance in wideband clustered system
InactiveCN103338375AGuaranteed codingGuaranteed normal transmissionError preventionTelevision systemsKey frameCode rate
The invention provides a dynamic code rate allocation method based on video data importance in a wideband clustered system. The dynamic code rate allocation method comprises the steps as follows: a channel feedback module detects the channel condition and estimates a channel transmission code rate and a video coding rate; a transmission module divides to-be-transmitted video data output through source coding into a key frame and a non-key frame, preferentially ensures transmission of key frame data via the estimated channel transmission code rate, and stops transmission of non-key frame data when the channel transmission capability is insufficient. The dynamic code rate allocation method provided by the invention has the superior effects that when the channel transmission condition is worse, the coding rate is controlled by a fixed code rate to perform code rate allocation for an area of interest preferentially, and different quantification parameters are adopted for the area of interest and a common area, so that preferential coding of an important video frame is ensured; meanwhile, the transmission module divides the video frame into a key frame and a non-key frame, and performs preferential transmission on the important video key frame preferentially, so that transmission of important video data is ensured.
Owner:THE FIRST RES INST OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY +1
Constant bitrate real-time lossless audio encoding and decoding by moving excess data amounts
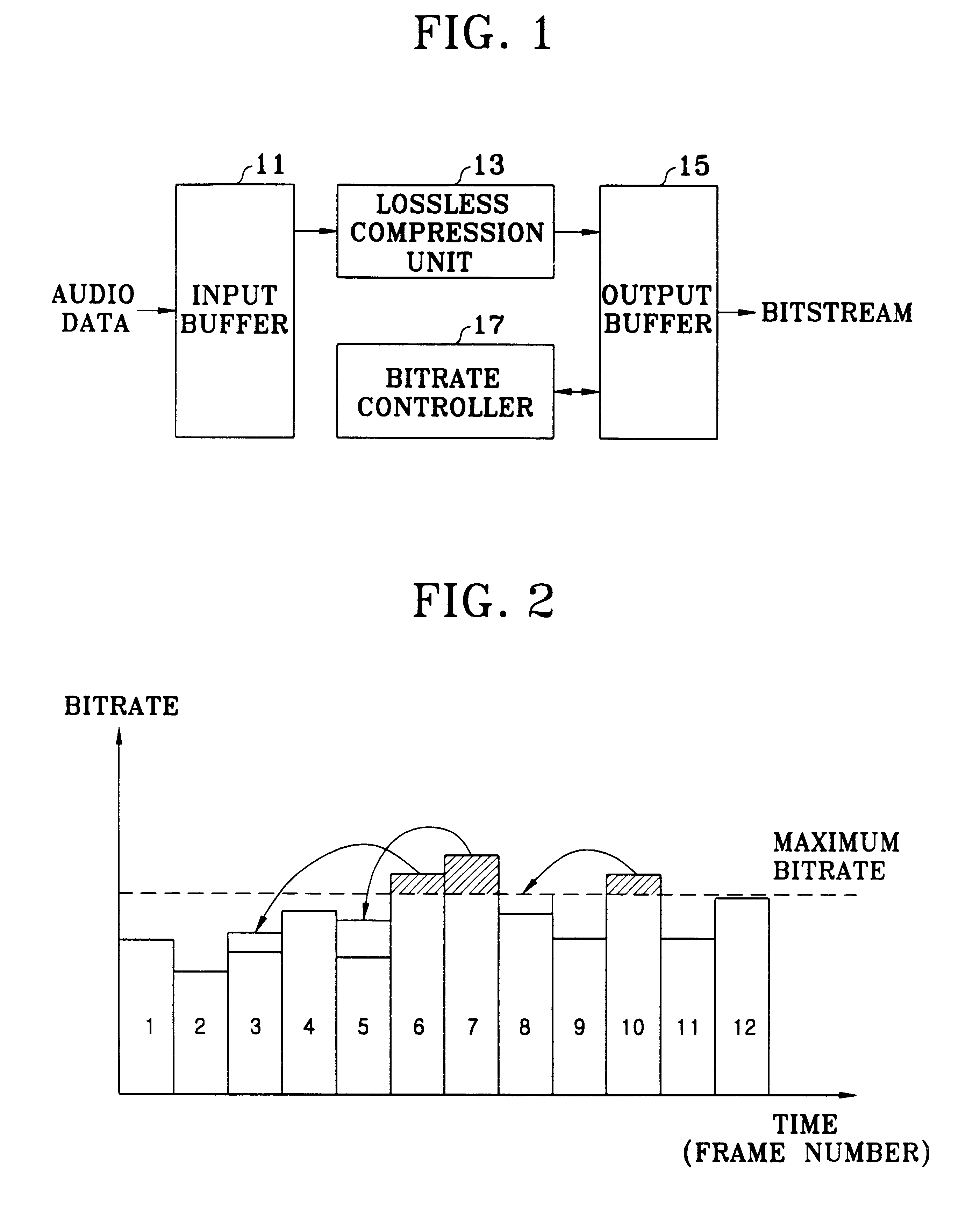
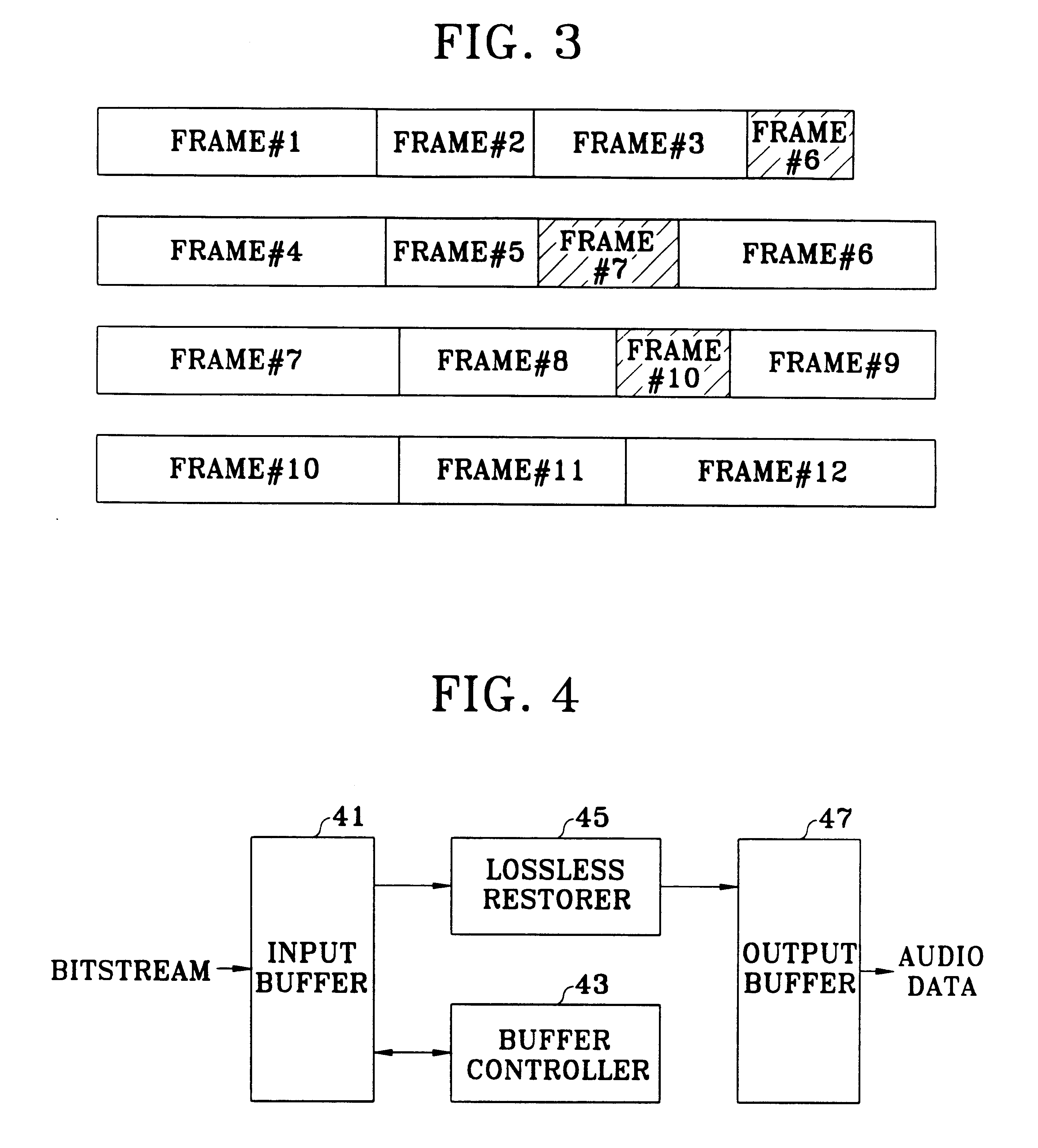
InactiveUS6385587B1Analogue recording/reproducingCode conversionLossless codingArtificial intelligence
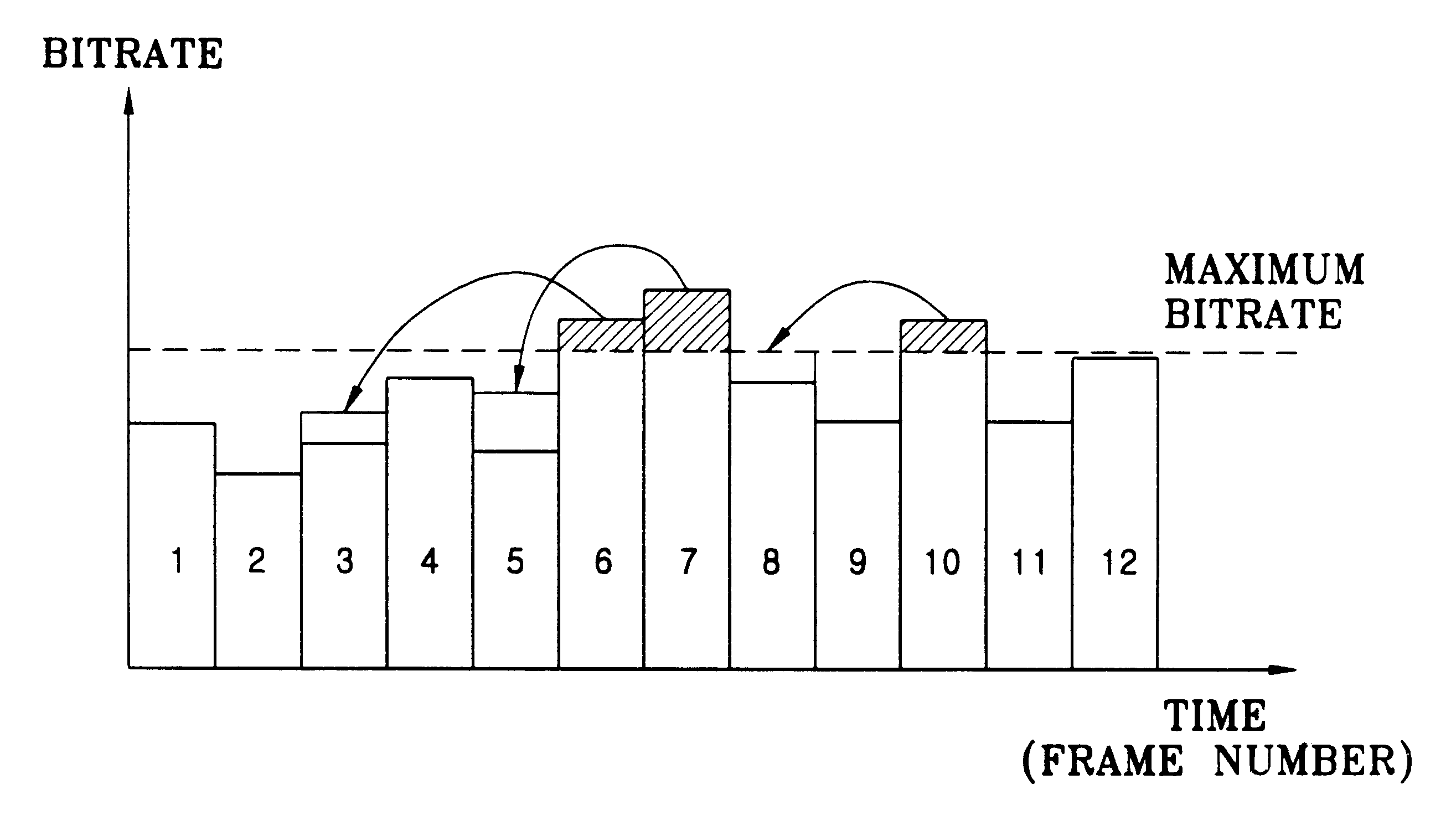
A lossless encoding apparatus encodes audio data and a lossless decoding apparatus restores the losslessly compression encoded audio data on a real-time basis, and a method therefor. The lossless encoding apparatus includes a lossless compression unit which losslessly compression encodes the audio data stored in an input buffer in units of predetermined data and outputs the encoded data in sequence, and an output buffer which stores the encoded audio data output from the lossless compression unit. A bitrate controller divides a plurality of the encoded audio data stored in the output buffer into first data having a data amount exceeding the maximum bitrate and second data having a data amount less than the maximum bitrate, divides the first data into third data being the encoded audio data having a data amount of the maximum bitrate and fourth data being the encoded data of the portion exceeding the maximum bitrate, and controls the output buffer so that the fourth data is output together with the second data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for controlling the encoder output bit rate in a block-based video encoder and corresponding video encoder apparatus
ActiveUS8009730B2Improve mapping accuracyReduce computing timeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionLinear modelSelf adaptive
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
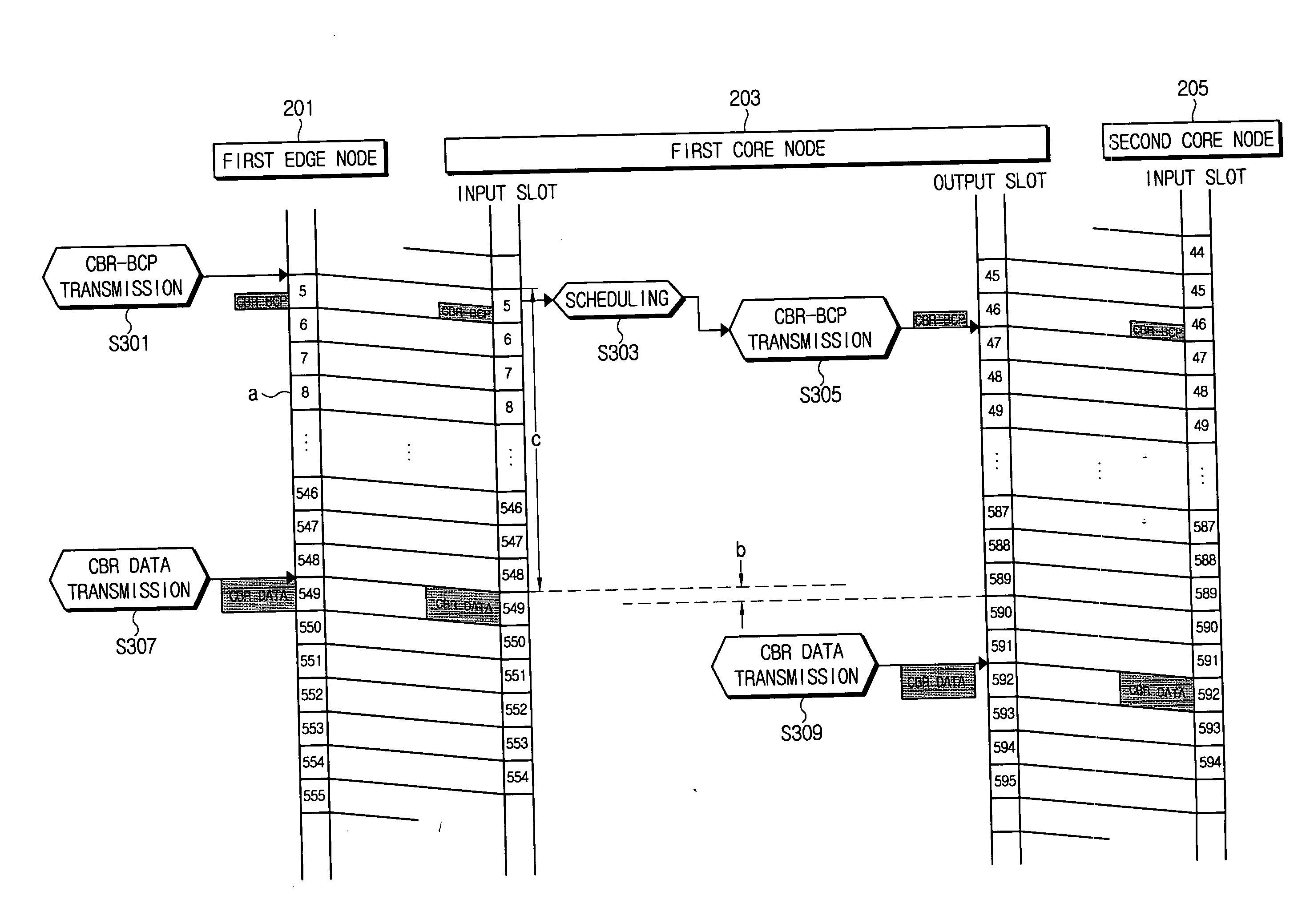
System and method of time-slotted optical burst switching
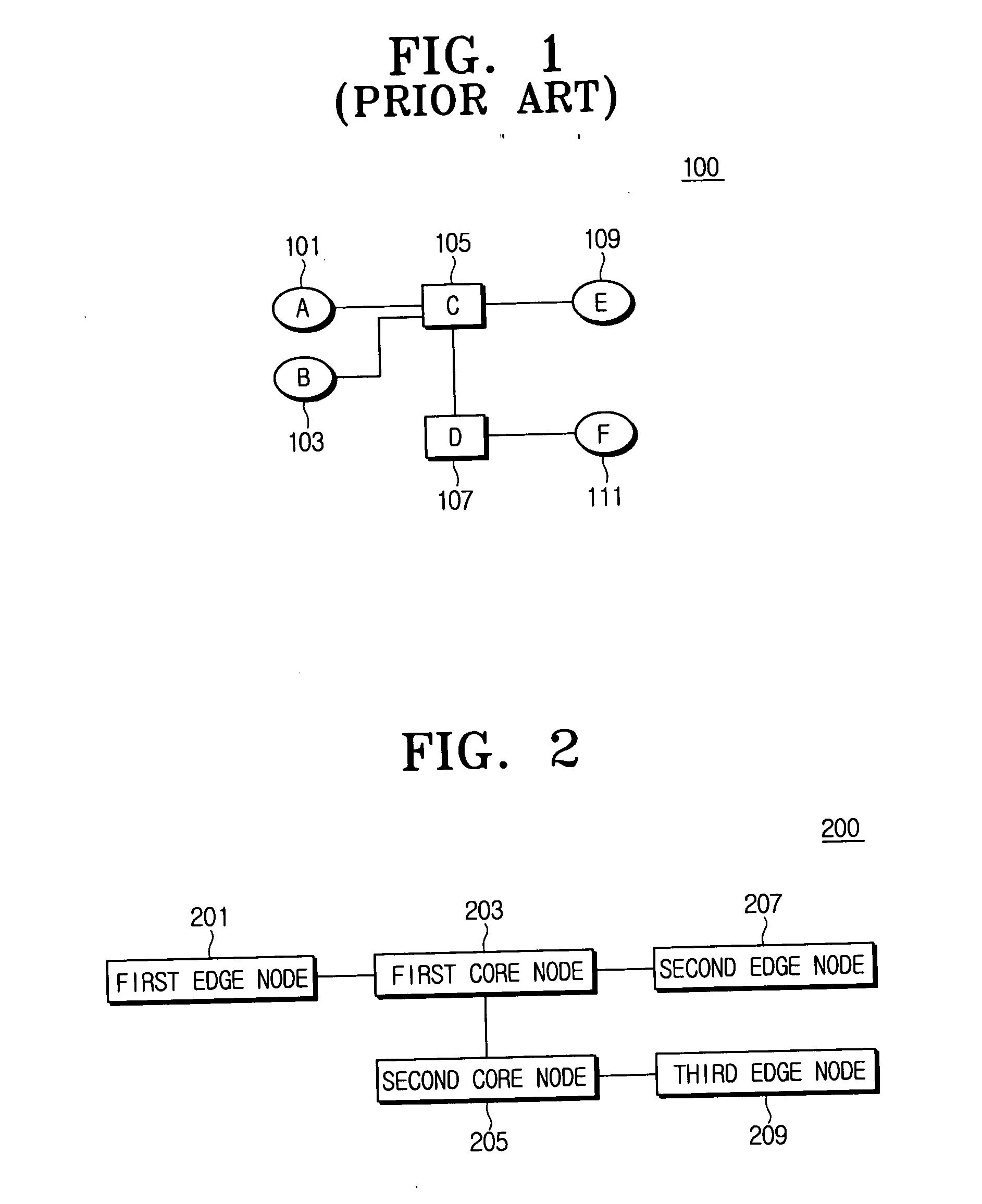
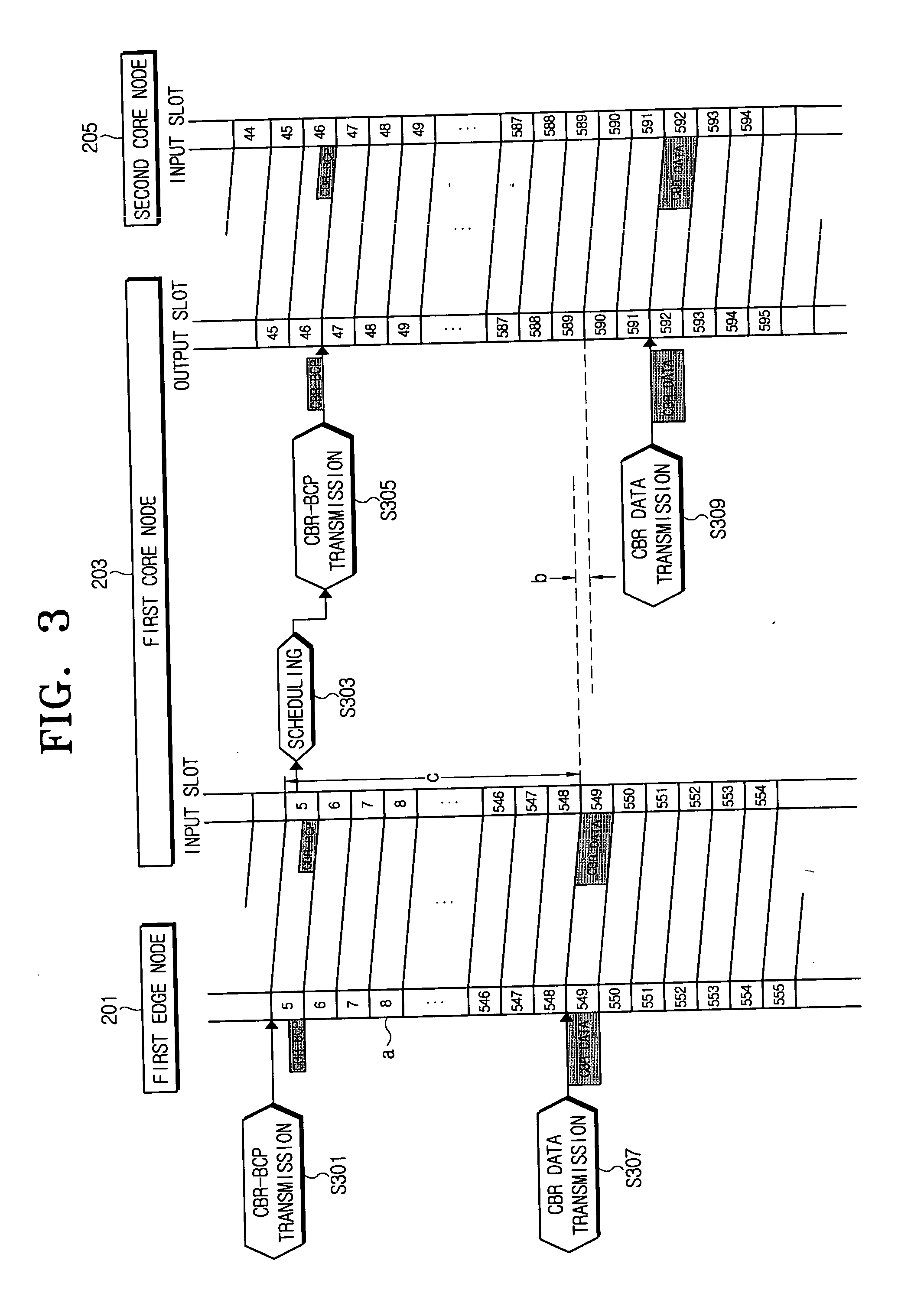
InactiveUS20060147207A1Minimizes data delayMinimize delayMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical burst switchingEdge node
A time-slotted optical burst switching system and method therefor can support data transmissions for a constant bit rate (CBR) and at a variable bit rate (VBR) and improves a data transmission method at an edge node and a core node. Accordingly, it is possible to perform a data service for the constant bit rate and for a variable bit rate and to substantially prevent a delay due to a scheduling for a slot assignment at the core node by transmitting a burst control packet before the data burst to be transmitted at the edge node is generated in case of transmitting the data burst at the constant bit rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
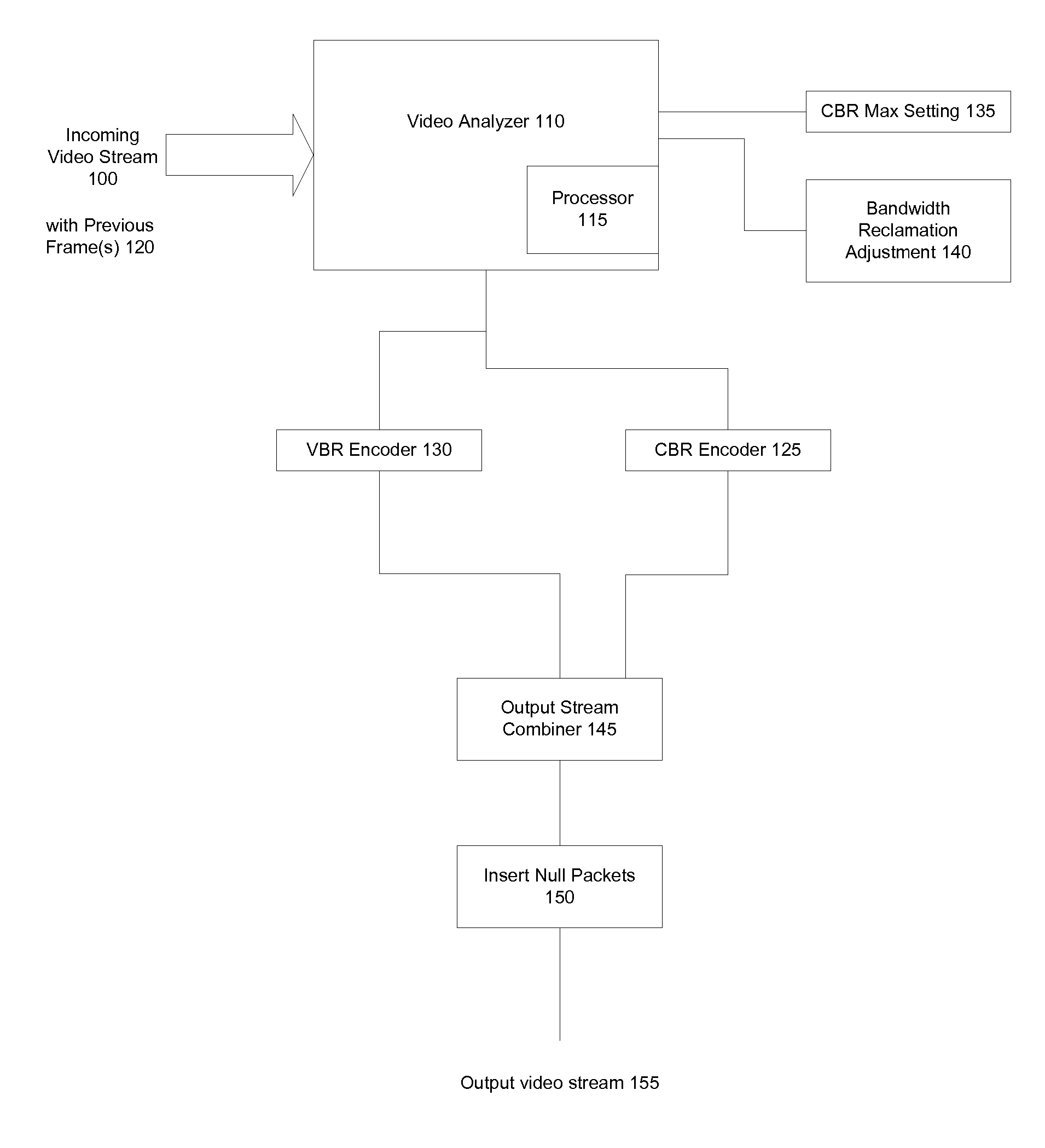
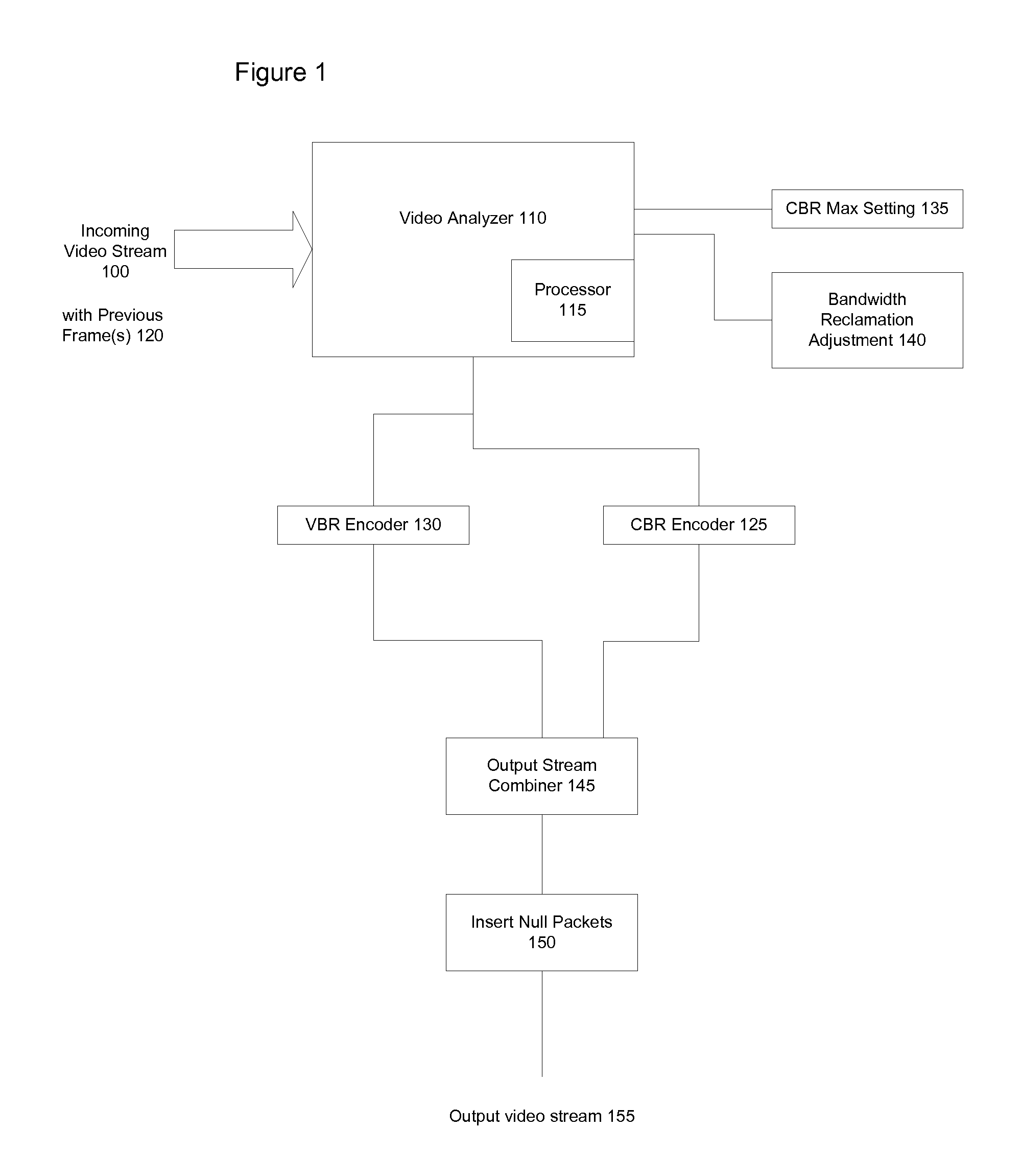
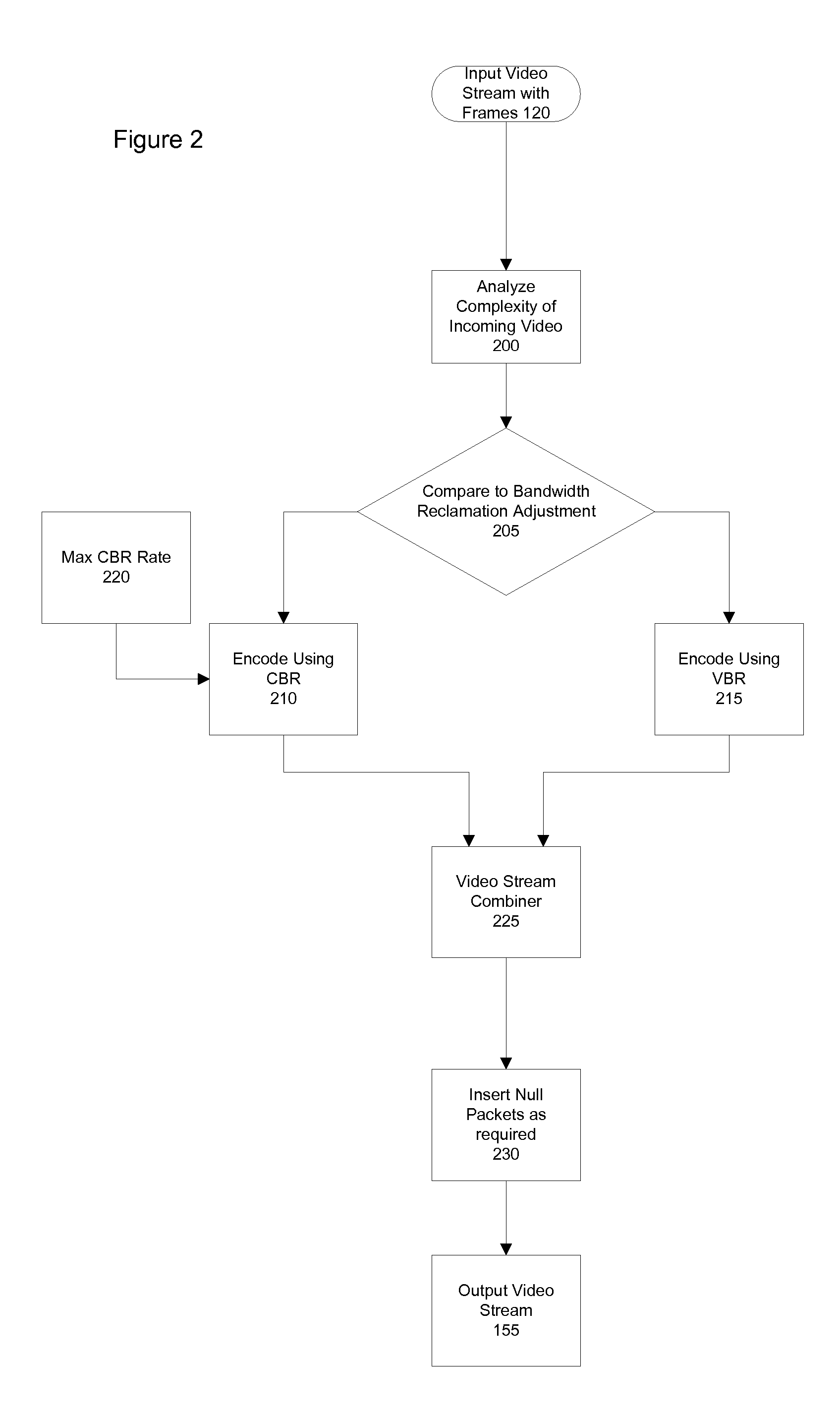
Constrained Fidelity Constant Bit Rate Video Encoding Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20070280294A1Reduces below maximum bandwidthLess bandwidthFrequency-division multiplexDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionRound complexity
A CBR / VBR hybrid implementation encoding video streams for conserving bandwidth usage in a channel comprises, in an exemplary arrangement, CBR encoding for frames whose complexity exceeds a threshold, and uses VBR encoding for frames whose complexity is below the threshold. In some embodiments, the threshold can be dynamically adjusted to permit varying amounts of bandwidth reclamation. The complexity can be determined based on a motion estimation analysis or on other indicia such as the level of detail in a frame.
Owner:MODULUS VIDEO
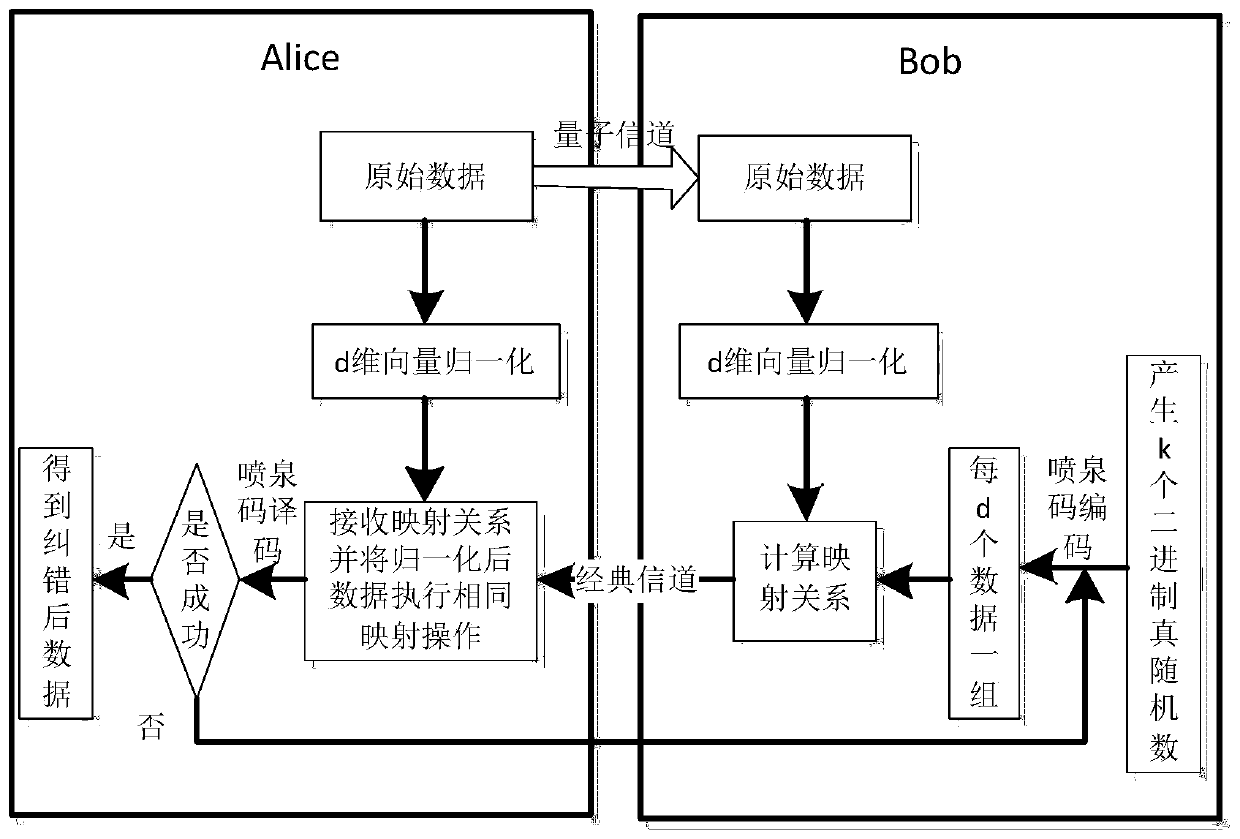
Continuous variable quantum key distribution data error correction method based on fountain codes
ActiveCN110233728AImprove coordination efficiencyWithout compromising securityKey distribution for secure communicationError preventionFountain codeSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to a continuous variable quantum key distribution data error correction method based on fountain codes. The method comprises the following specific implementation steps: step 1,generating a certain number of binary true random numbers as original code words by a data coordination initiating end, and continuously carrying out fountain code coding on the group of random numbers; step 2, calculating a mapping relation between the coded code word and the original data, and sending the mapping relation to the other end; step 3, after the other end receives the mapping relation, executing the same mapping operation on the original data of the other end, and then obtaining error-corrected data through fountain code decoding; and step 4, if the decoding fails, repeating thestep 2 and the step 3 until the decoding is successful, otherwise, performing the next group of key error correction. Based on the characteristic that fountain codes have no fixed code rate, the difficulty of check matrix construction is reduced, error correction under various signal to noise ratio conditions can be realized, and higher coordination efficiency can be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
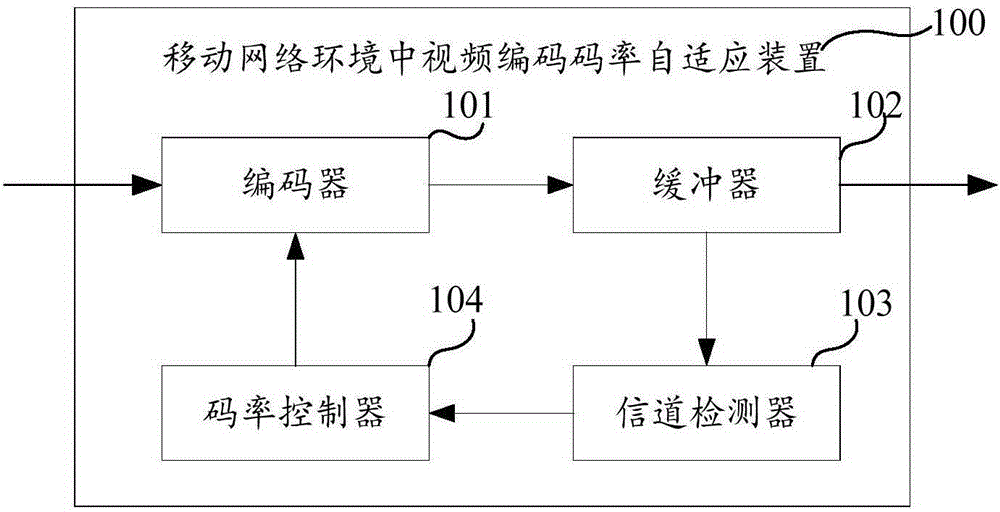
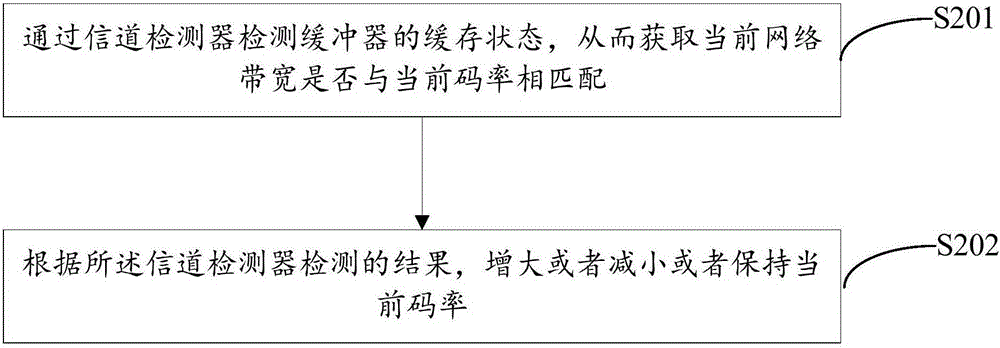
Video encoding rate self-adaptive device and method in mobile network environment
InactiveCN105227956AImprove overall utilizationApply wireless transmission effectivelyDigital video signal modificationCurrent channelVideo encoding
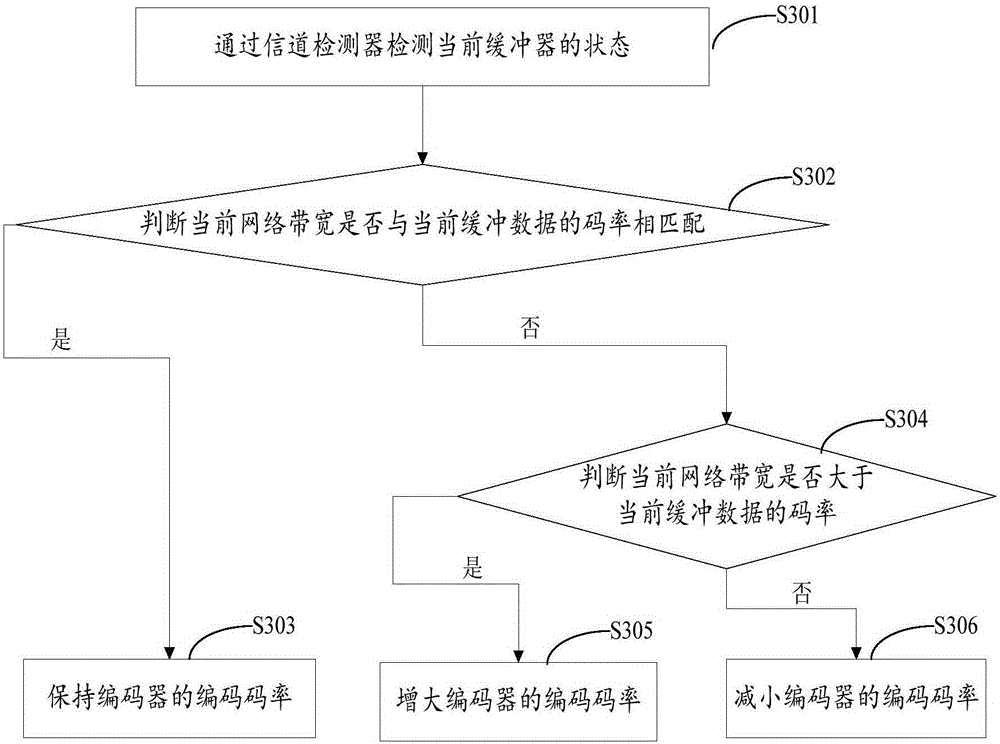
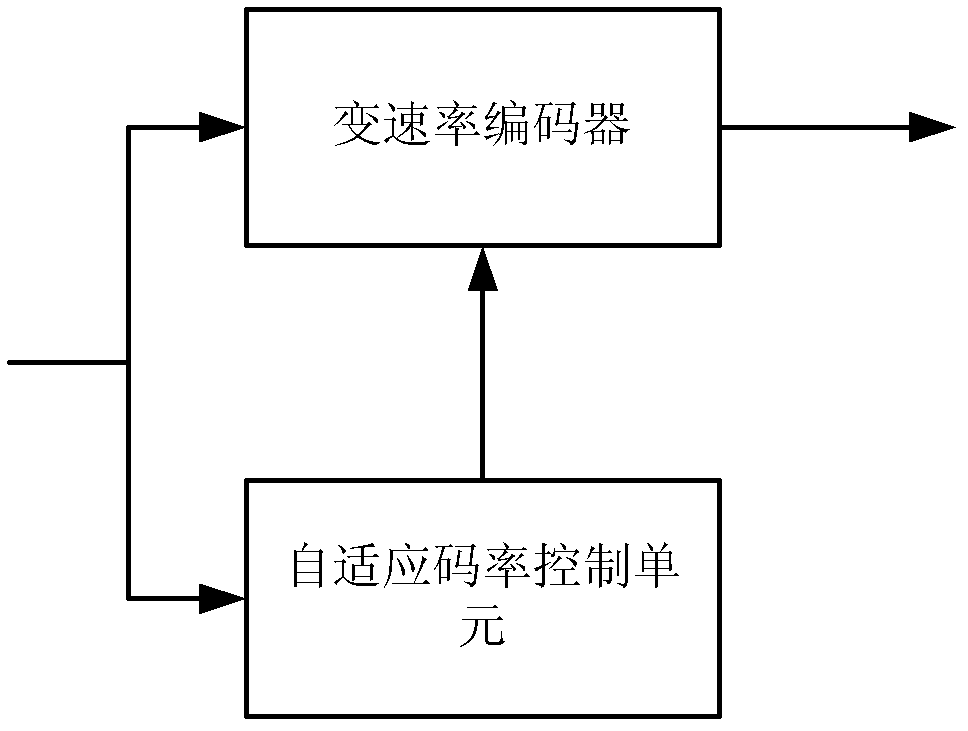
In order to solve the technical problem of network resource waste or insufficiency of a constant code rate in the prior art, the invention provides a video encoding rate self-adaptive device and method in a mobile network environment. The device comprises an encoder, a buffer and a channel detector used for detecting the state of the buffer to determine whether a current network bandwidth is matched with a current code rate; a code rate controller of the encoder used for increasing or decreasing or maintaining the current code rate according to a detection result of the channel detector and making full use of the current channel capability on the premise of guaranteeing the implementation of upload or download; and thus the network utilization rate is expanded on the condition that effective data transmission can be guaranteed.
Owner:北京易视云科技有限公司
Code rate automatic control system applicable to variable bit rate voice and audio coding
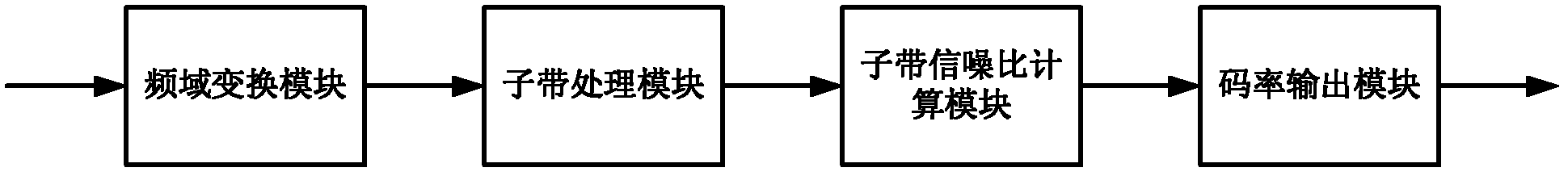
InactiveCN102543090AImprove signal-to-noise ratioSpeech analysisAutomatic controlVoice communication
The invention discloses a code rate automatic control system applicable to variable bit rate voice and audio coding. Coding code rate is automatically regulated by calculating signal to noise ratio of a signal sub-band, when compressed code stream is compared with the compressed code stream with equivalent fixed code rate in the prior art, signal-to-noise ratio decompressed by adopting the code rate automatic control system disclosed by the invention is obviously improved. The automatic code rate regulating manner disclosed by the invention has better robustness compared with the traditional energy judging method; rate control to voice coding is supported, and variable bit rate coding to an audio signal is also supported, and the code rate automatic control system disclosed by the invention can be applied to packet domain mobile voice communication under the condition that bandwidth is limited, so as to improve quality of the transmitted voice and audio signals.
Owner:SHENZHEN MAOBI INFORMATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com