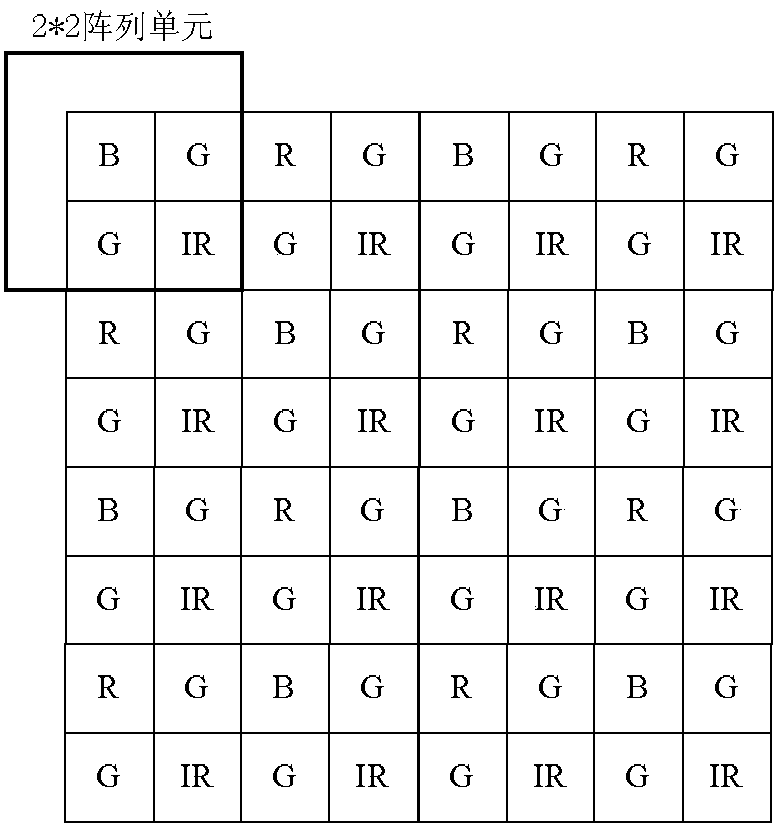
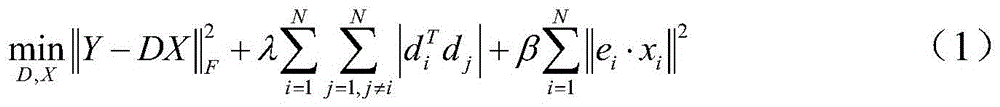Patents
Literature
88 results about "B channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
B channel (bearer) is a telecommunications term which refers to the ISDN channel in which the primary data or voice communication is carried. It has a bit rate of 64 kbit/s in full duplex. The term is applied primarily in relation to the ISDN access interfaces (PRA or PRI and BRA or BRI), since deeper in the PSTN network an ISDN bearer channel is essentially indistinguishable from any other bearer channel.
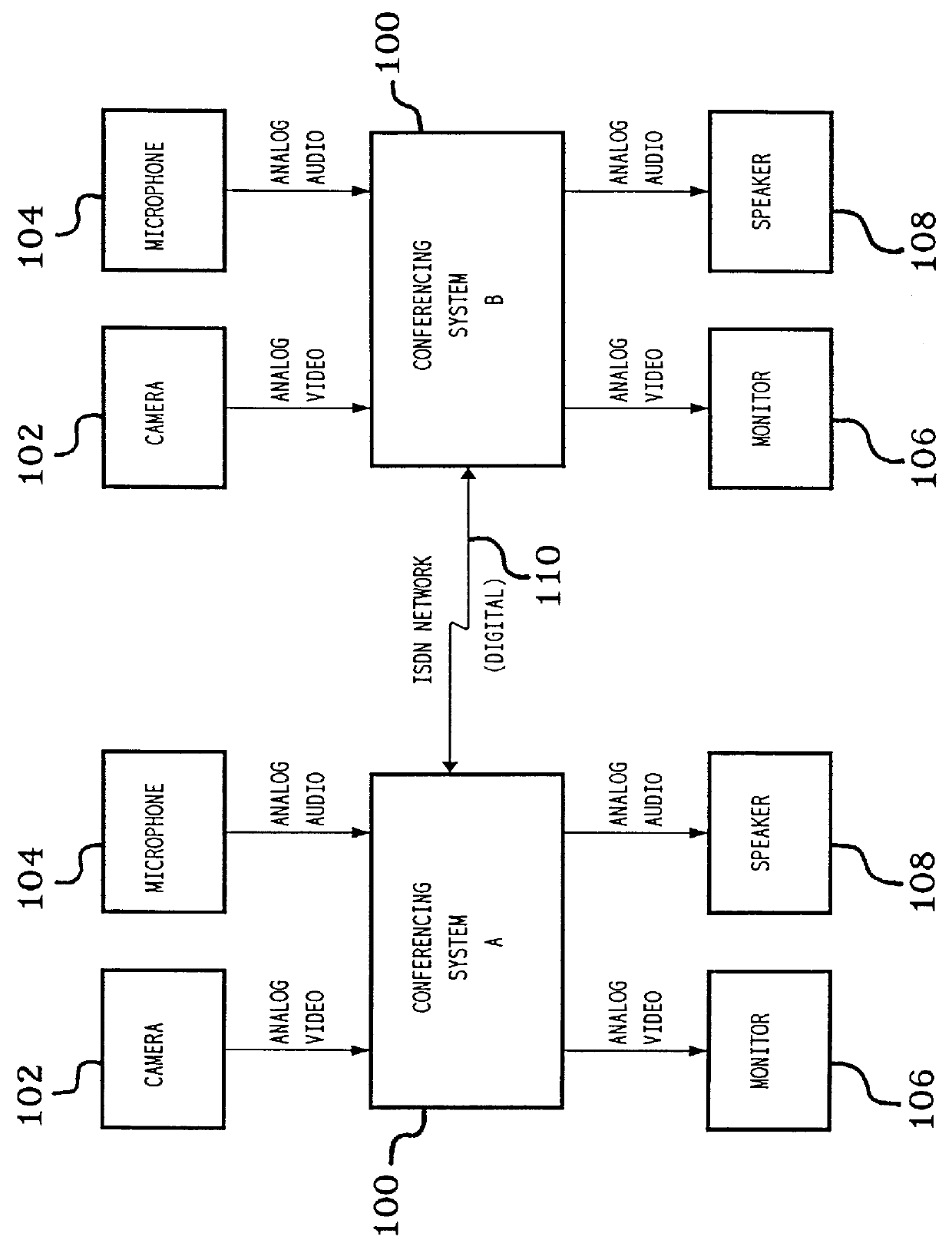
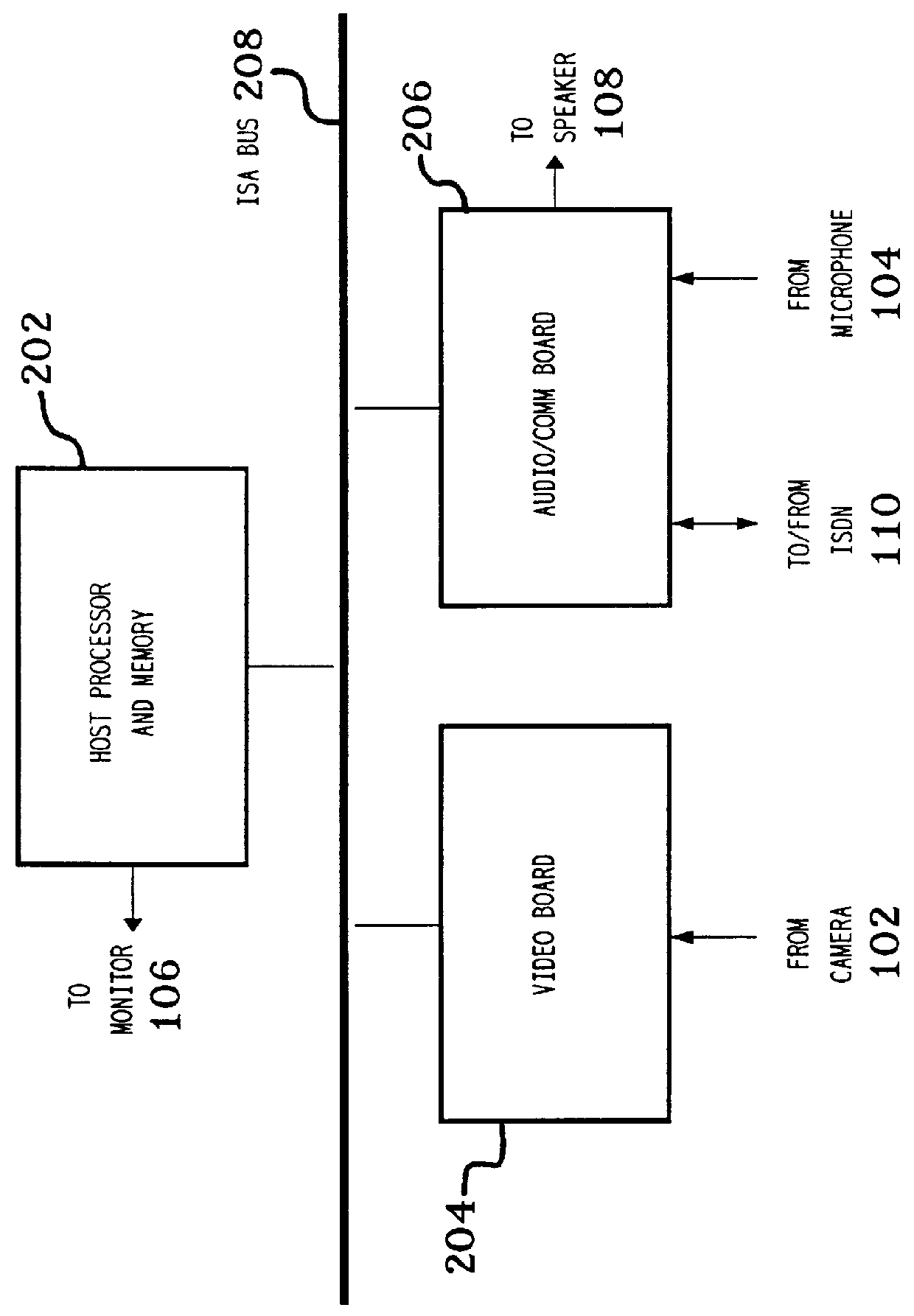
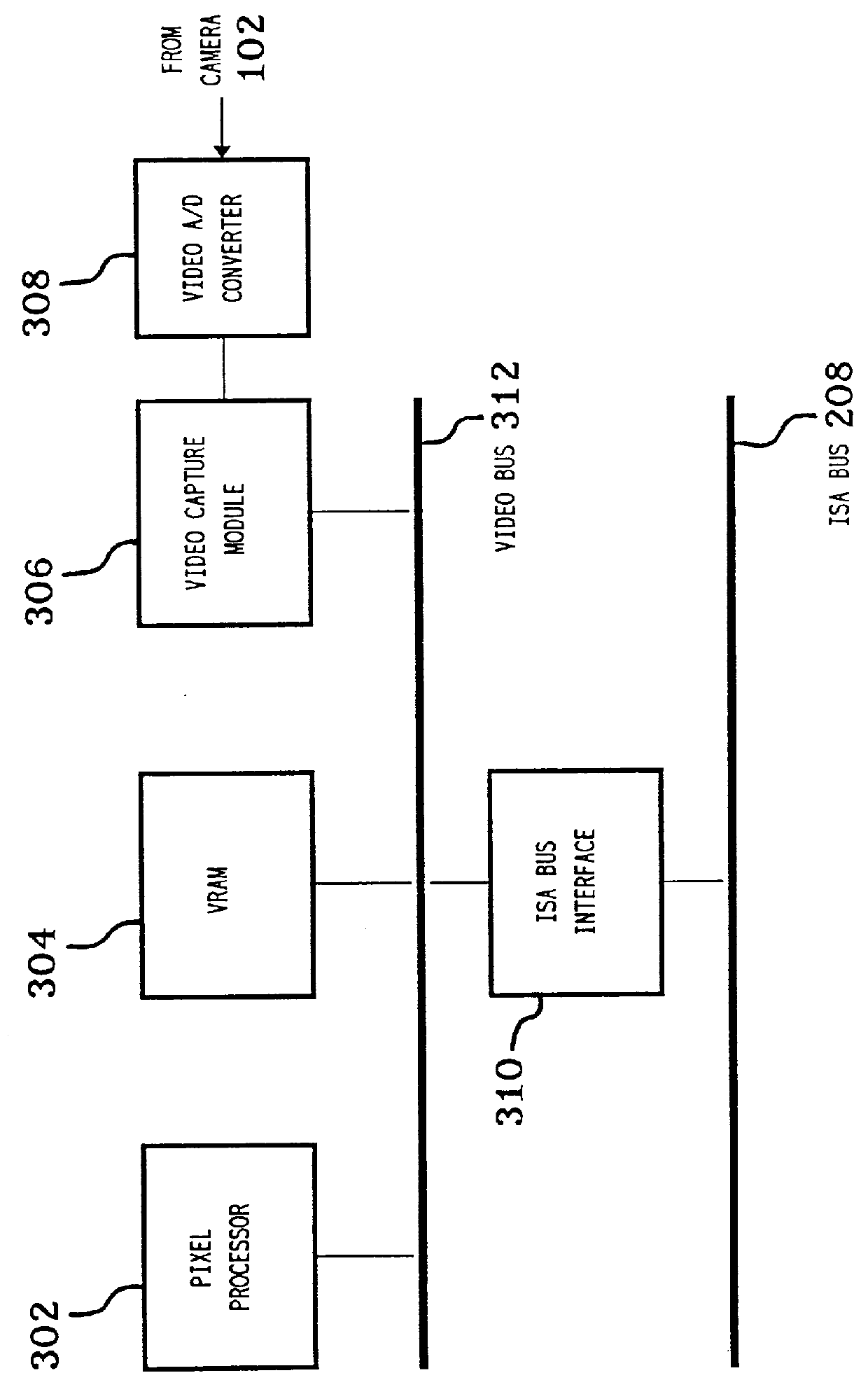
Communications subsystem for computer-based conferencing system using both ISDN B channels for transmission
InactiveUS6125398ASpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A communications task resides on an audio / communications board of the computer conferencing system. A communications manager and a communications application programming interface reside on a general-purpose host-processor of the computer conferencing system. The communications manager receives local compressed video signals from a video subsystem of the computer conferencing system and passes the local compressed video signals to the communications task. The communications task receives local compressed audio signals from an audio task of the computer conferencing system, the audio task residing on the audio / communications board. The communications task transmits the local compressed video signals and the local compressed audio signals over a communications link to a remote computer conferencing system. The communications task receives remote compressed video signals and remote compressed audio signals over the communications link from the remote computer conferencing system. The communications task passes the remote compressed audio signals directly to the audio task for decompression and playback processing. The communications task passes the remote compressed video signals to the video subsystem for decompression and playback processing.
Owner:INTEL CORP
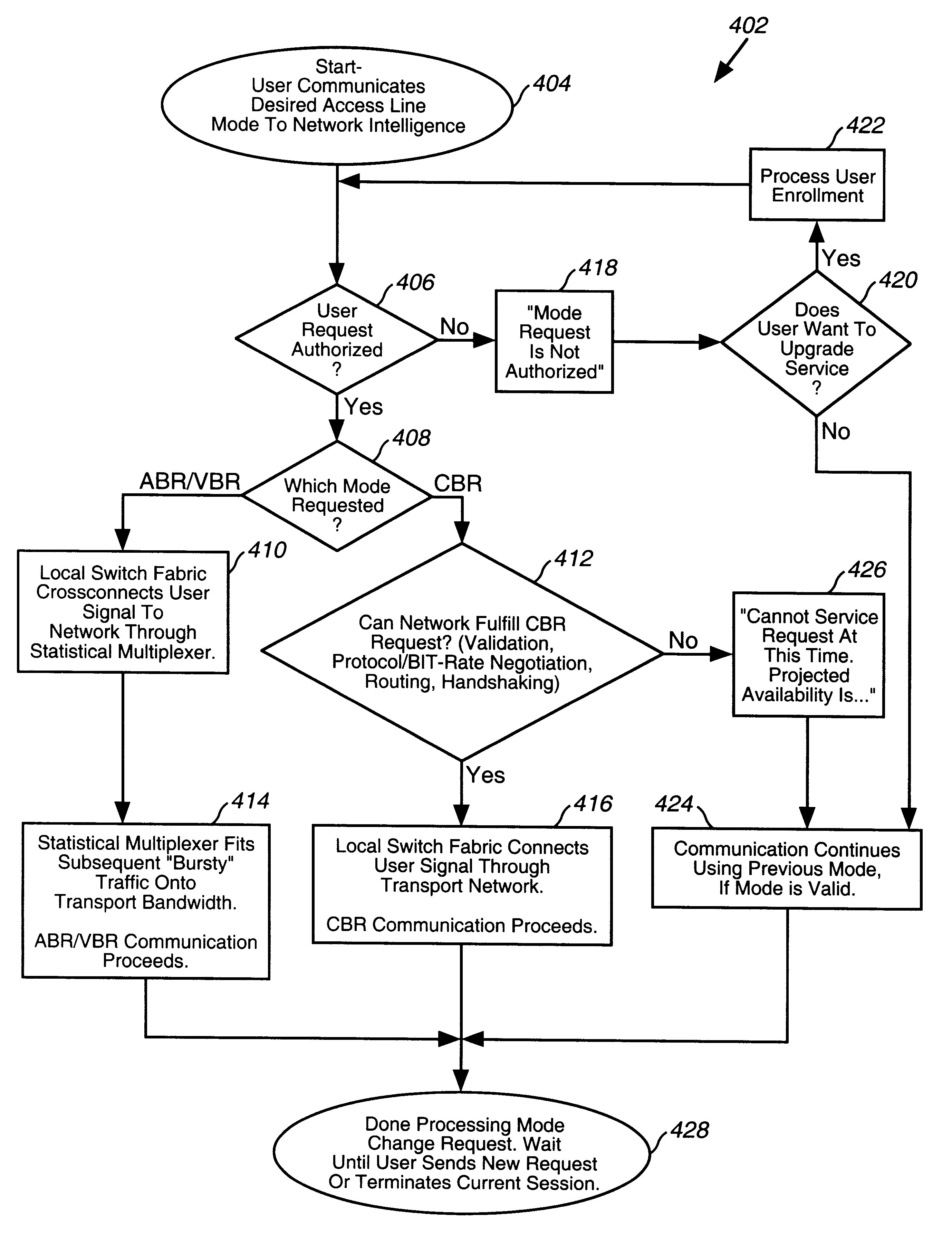
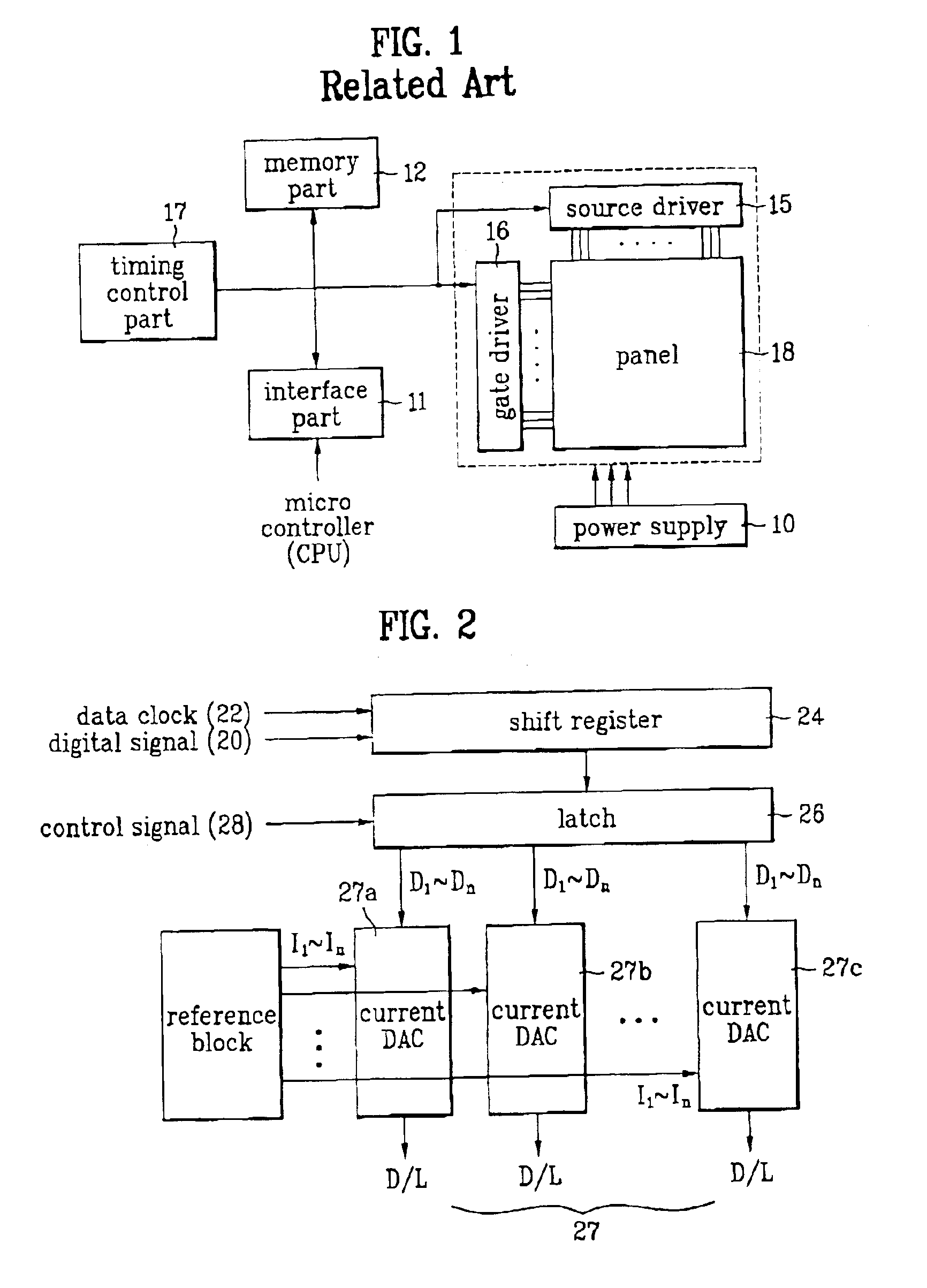
High-speed transparent access to multiple services
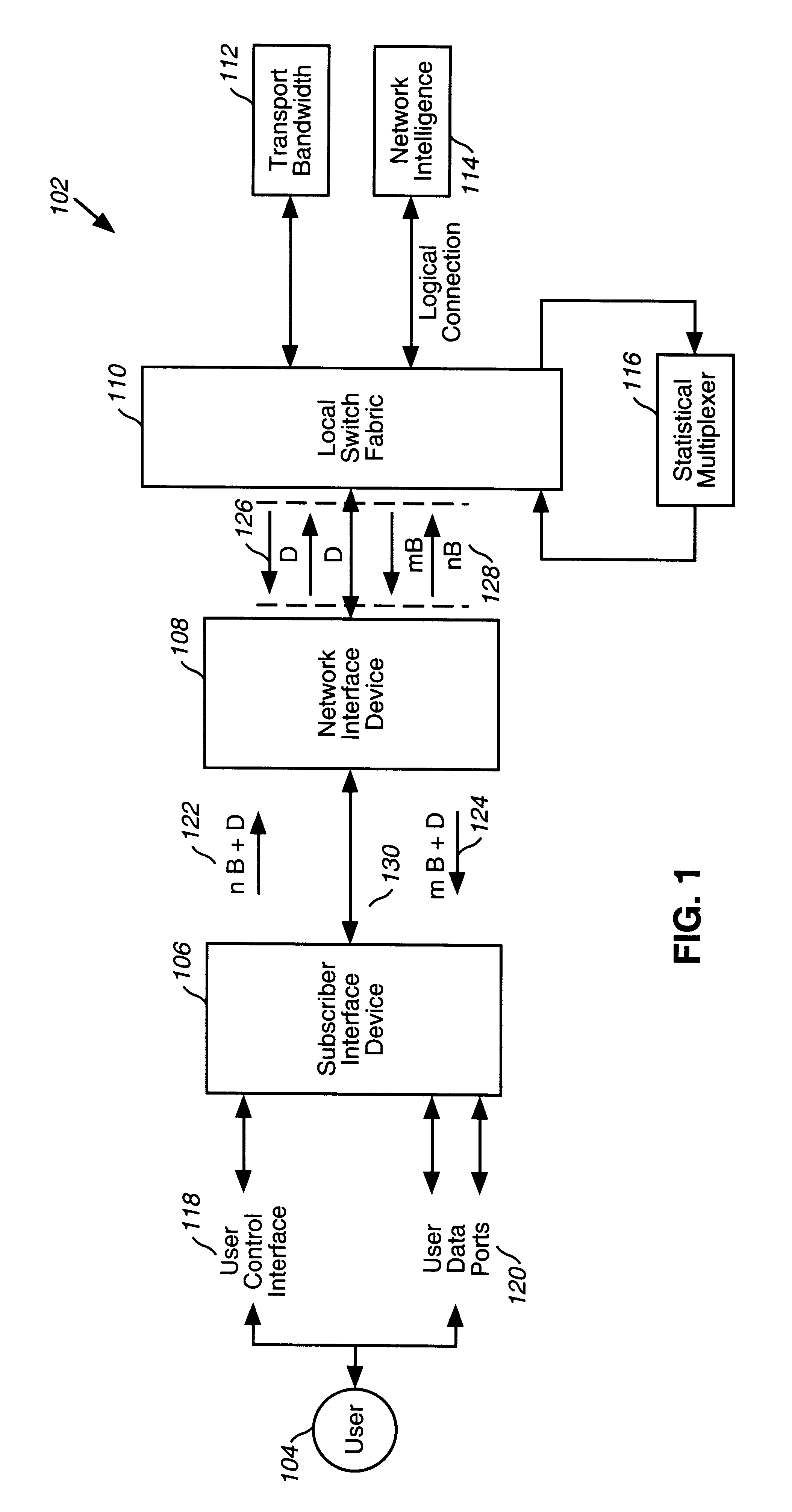
A system, method and computer program product are described, by which a user, through a control interface in a subscriber interface device, requests from network intelligence both transport network bandwidth and type of service line mode as part of call setup. An improved system by which requests to change access line mode and bandwidth are communicated over transmission facilities via D channels through local switch fabric to local or remote network intelligence is detailed. Connections over the transmission facilities, established between user B channels and B channels of transport bandwidth or between user B channels and the Stat Mux function, are described. An improved system is summarized, in which connections directly to transport bandwidth support point-to-point n B+D upstream and m B+D downstream service, and connections via stat mux allow connectionless traffic to share a portion of the transport bandwidth on an as needed basis. The ability to request and change access to available bit rate (ABR), variable bit rate (VBR) and constant bit rate (CBR) services, in a connection-oriented (CONS) or connectionless (CLNS) network, are described.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
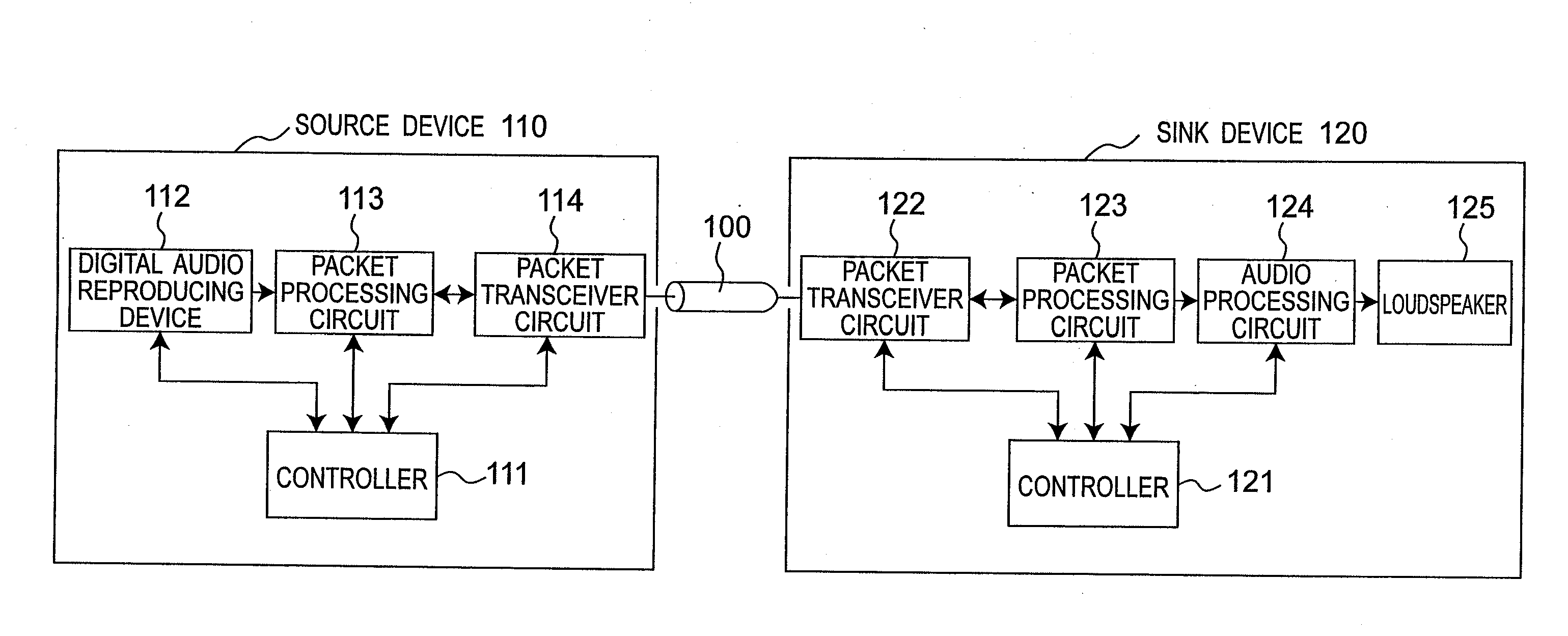
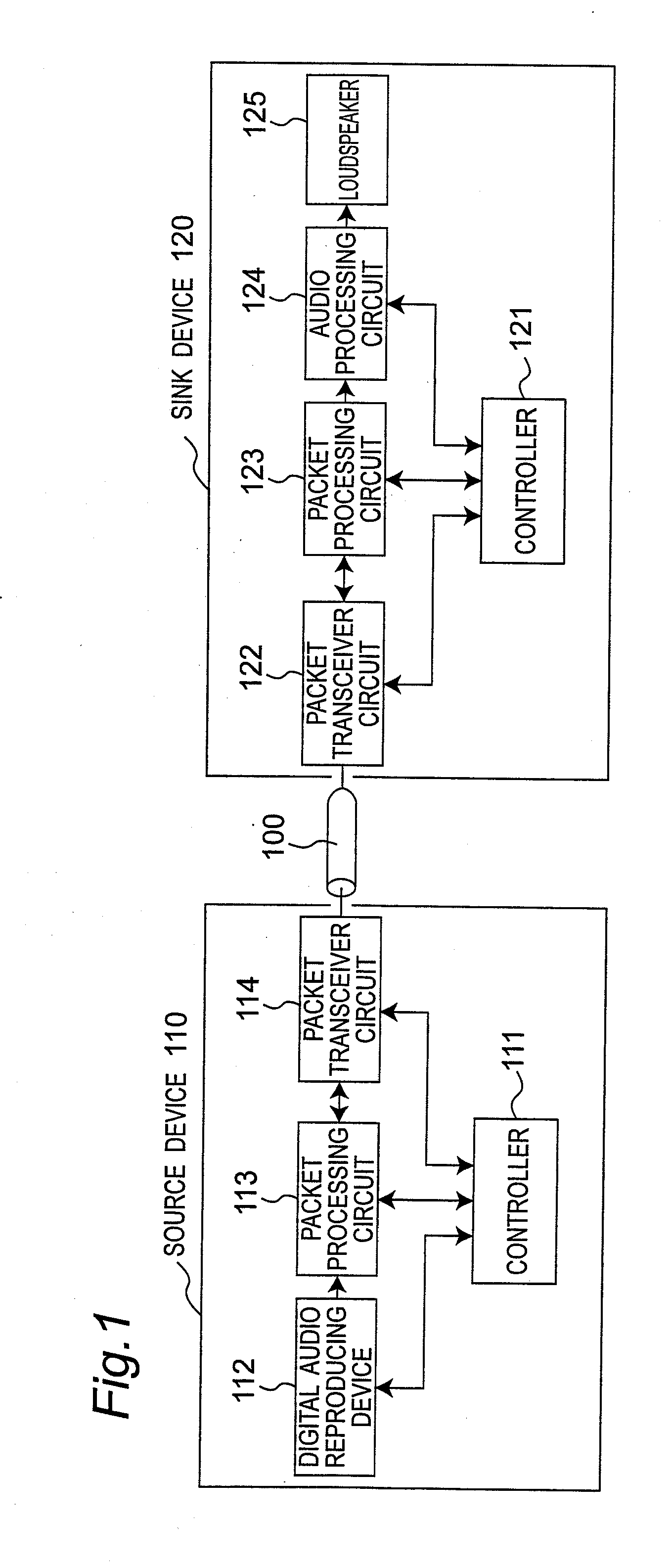
Communication system provided with transmitter for transmitting audio contents using packet frame of audio data
ActiveUS20090290600A1Guaranteed normal transmissionData efficientSpeech analysisTime-division multiplexComputer hardwareCommunications system
An audio frame format includes a channel field indicating a number of audio multi-channels, an ignore bit indicating whether or not an audio sample is present in a predetermined region of a packet format, an A channel audio sample field for transmitting the audio sample, and a B channel audio sample field for transmitting the audio sample, and a payload of the packet includes a repetition of an audio frame.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
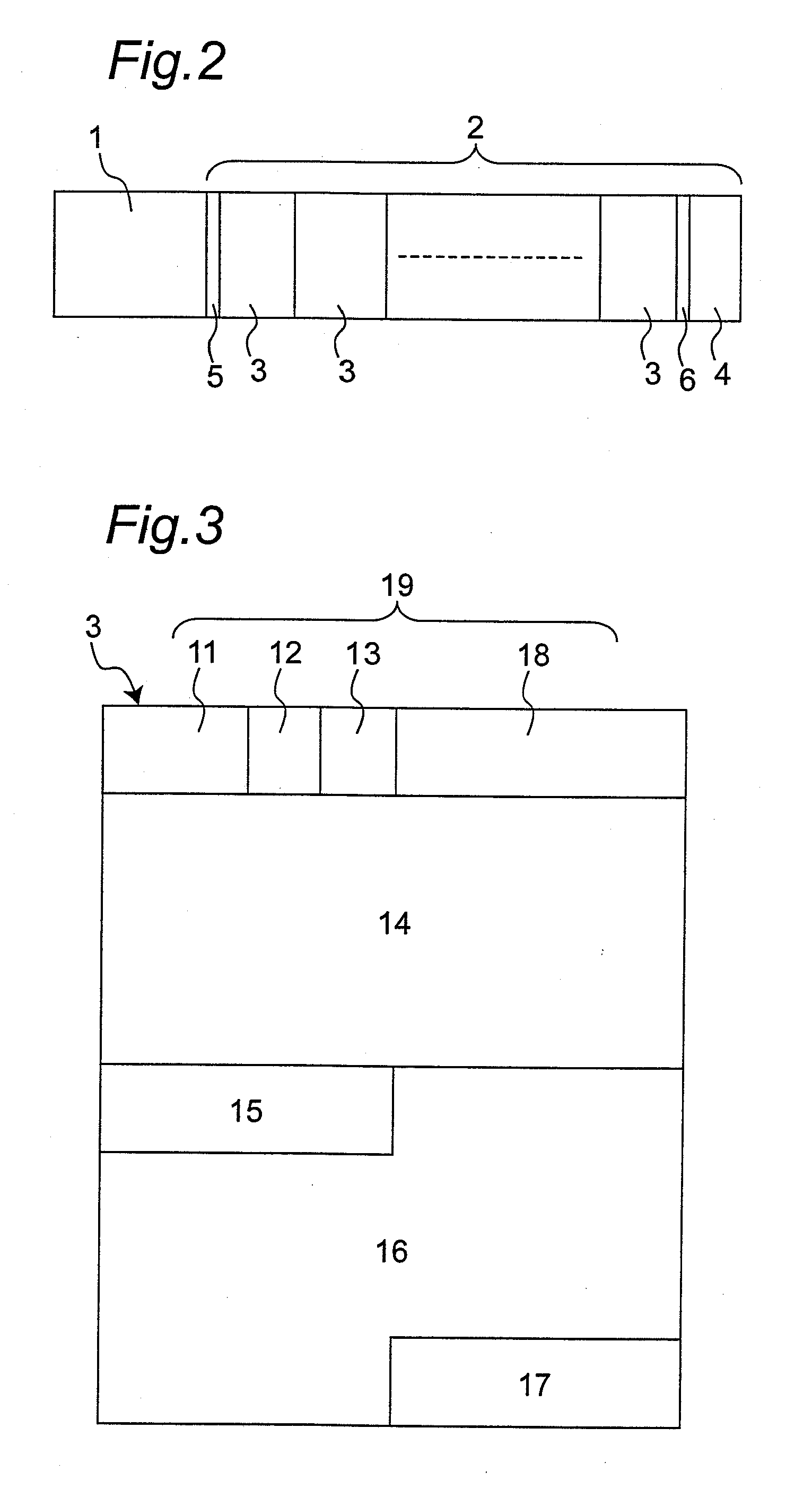
Driving IC of an active matrix electroluminescence device
A driving circuit for an active matrix electroluminescence device (AMELD) can control an output current value according to R / G / B channels by receiving a digital signal of n bits. In the driving circuit of the AMELD having data and gate drivers that respectively transmit a data signal and a scan signal to each pixel region, the data driver includes a latch for latching a control signal temporarily stored, and a plurality of digital to analog converters (DAC) for outputting a reference current of a certain level as a data signal according to R / G / B channels is latched by the control signal.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method and apparatus for communicating maintenance messages and/or test messages of digital subscriber line services
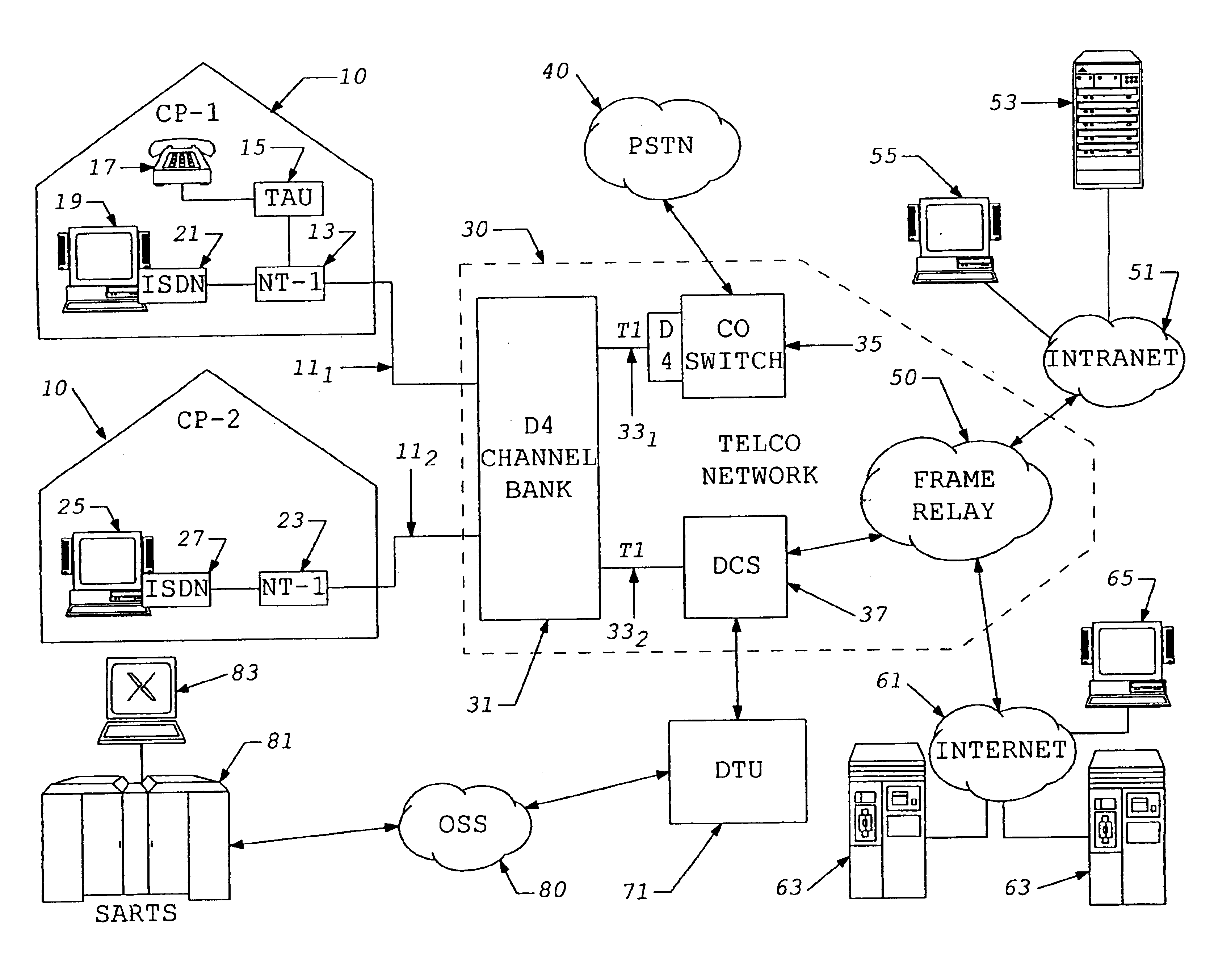
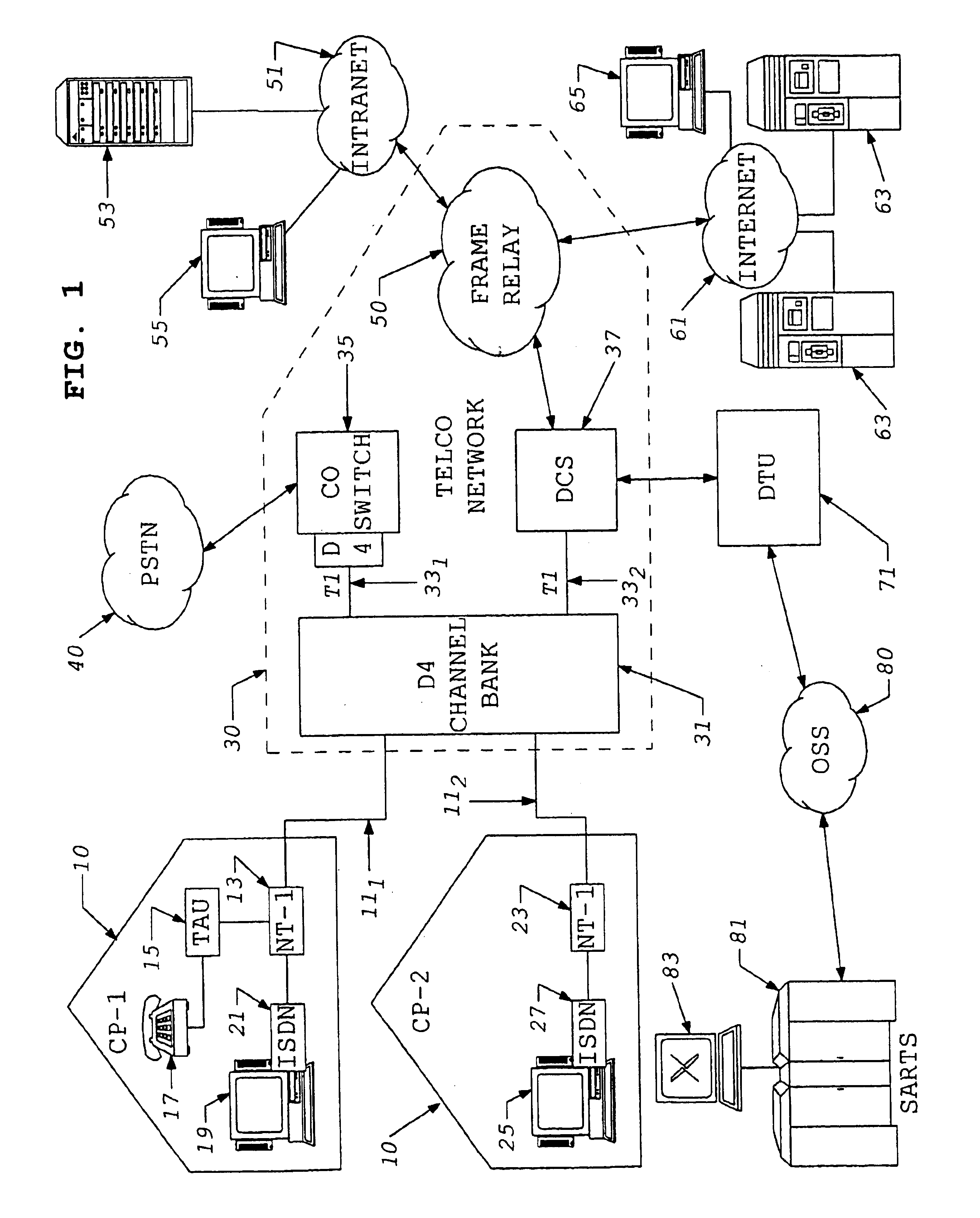
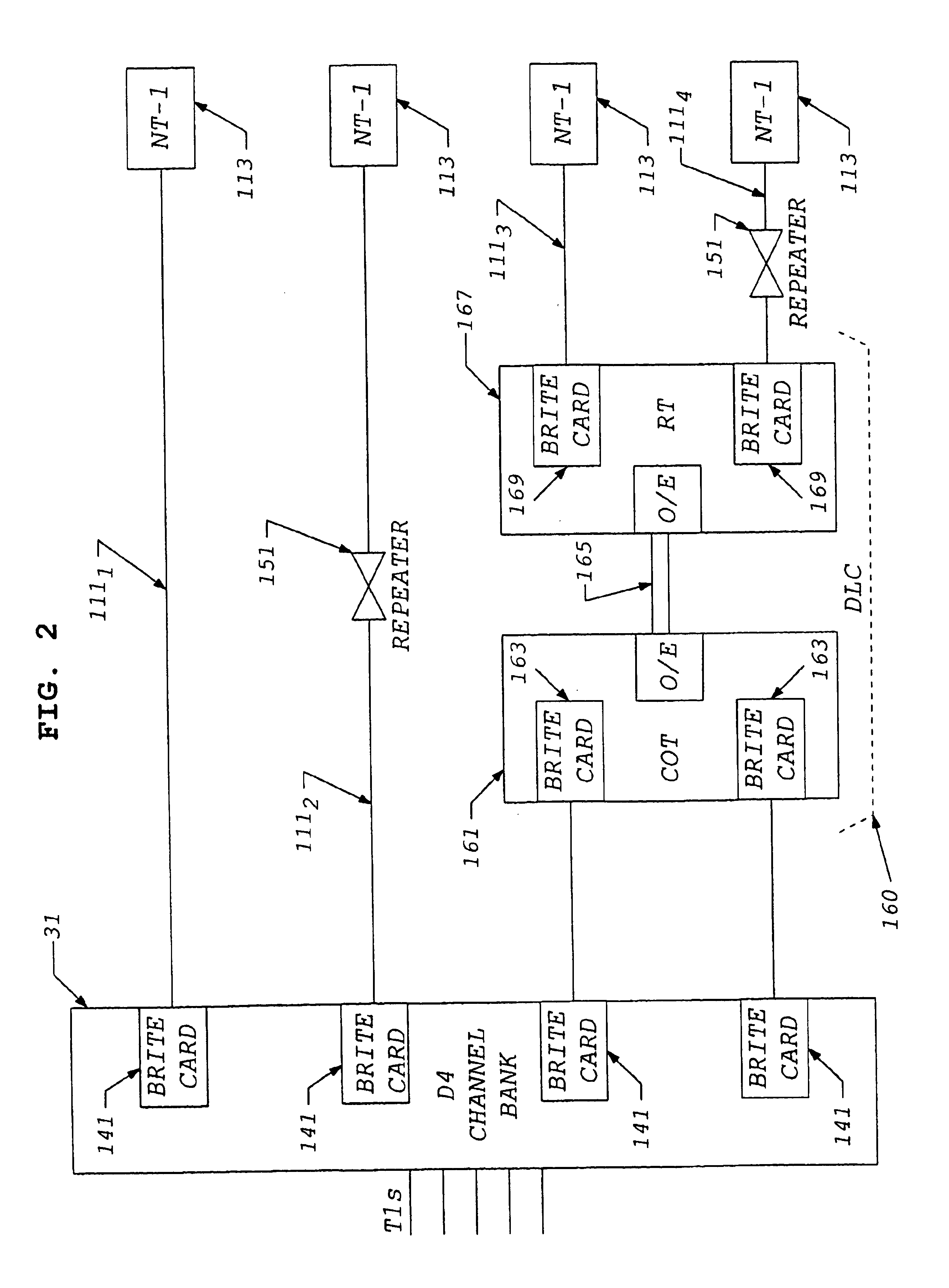
A subscriber's data circuit between channel bank and the customer premises carries fractional T1 bandwidth on a digital subscriber line (DSL) circuit. For example, for an ISDN rate digital subscriber line (IDSL), the circuit between the network termination at the customer premises and a D4 channel bank carries data on two combined B-channels. Such a circuit also carries a D-channel and an embedded operations channel (EOC), in normal ISDN fashion. A data service using such a line circuit, however, only transports the data (combined B-channels) through the network. The D-channel and the EOC are not carried through the network. To facilitate testing of the subscriber's circuit, the carrier operations and testing facilities transmit loop-back commands or the like in band to the channel bank. A command may be addressed to any active node along the subscriber's DSL circuit. The line card serving the subscriber in the channel bank detects the commands, removes the commands from the in-band data and reformats the commands for transmission over the EOC channel. The line card addresses the commands and sends the EOC format commands over the DSL circuit to the appropriate node along the subscriber's line. In response, the node connects the circuit in a loop-back mode, to enable test signal transmission and analysis.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
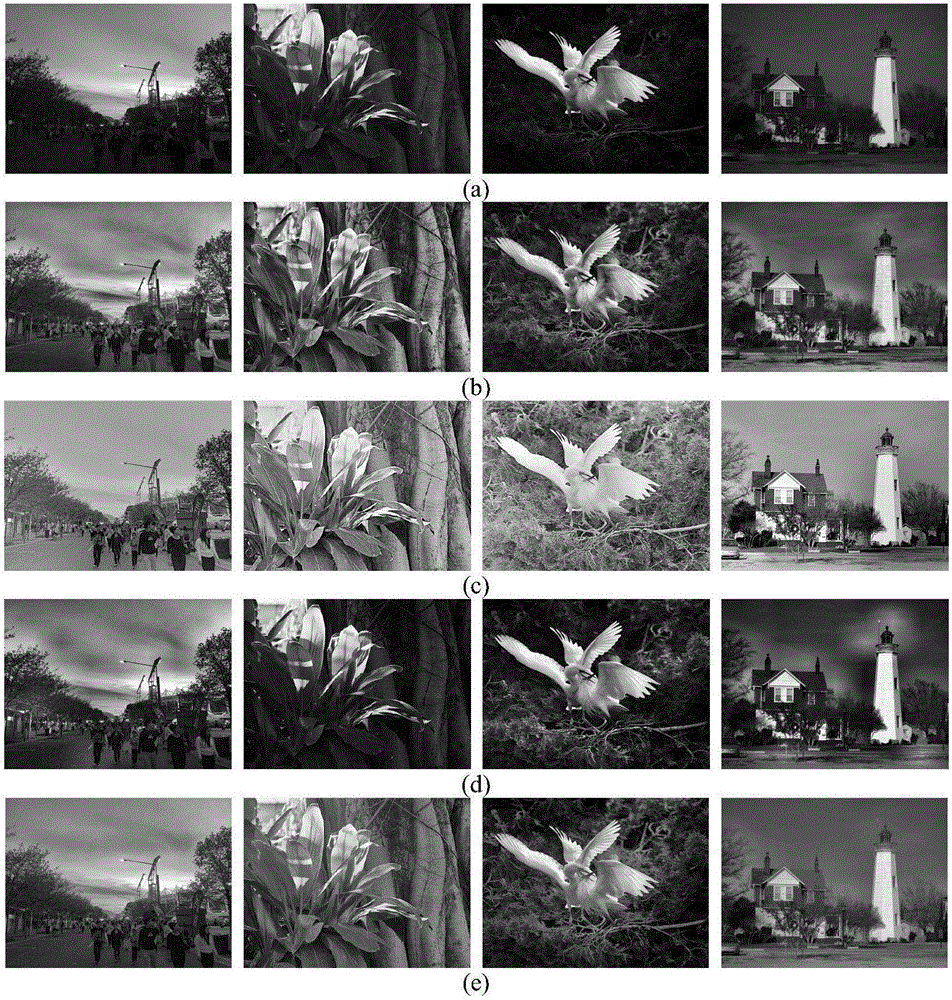
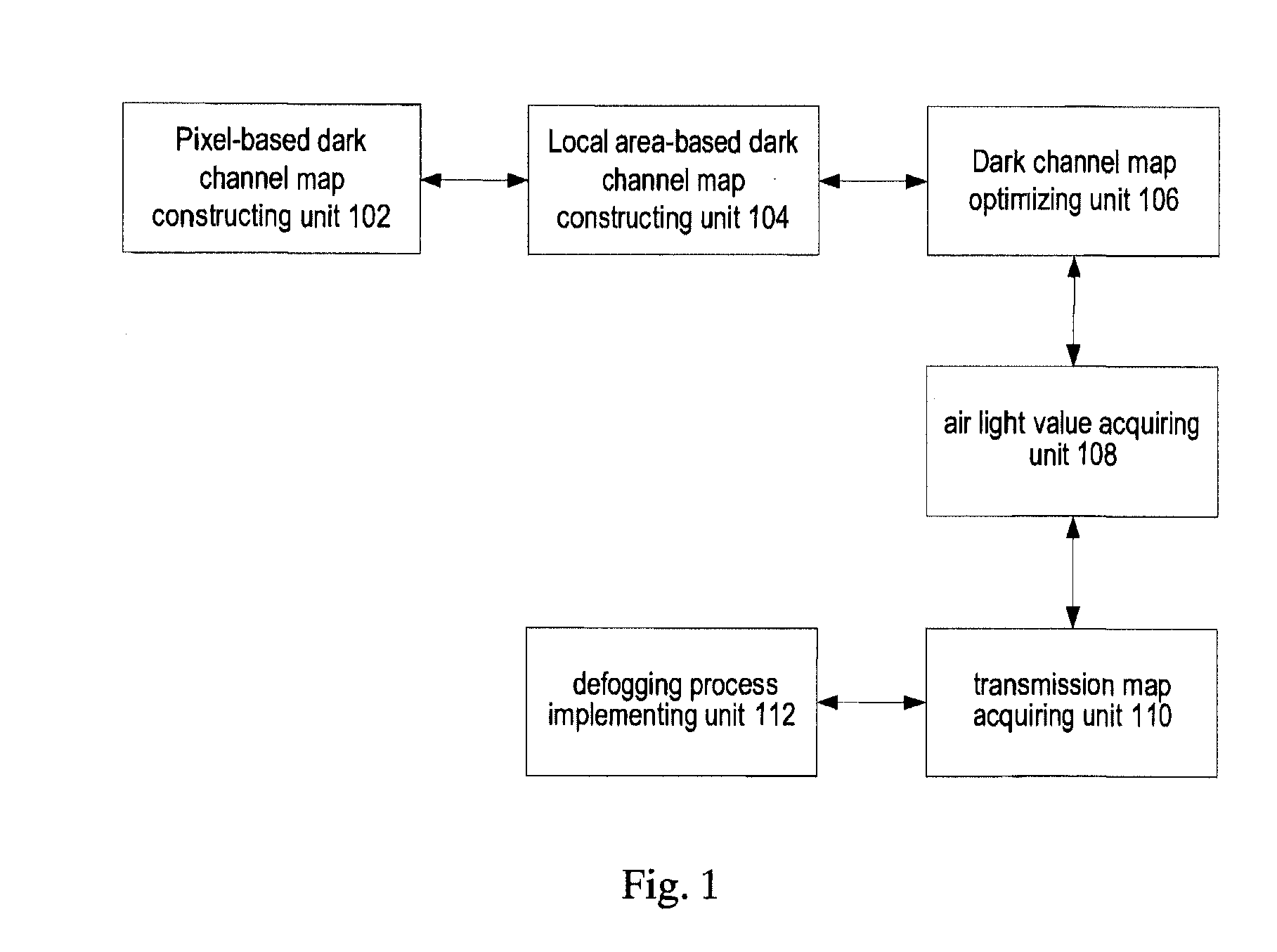
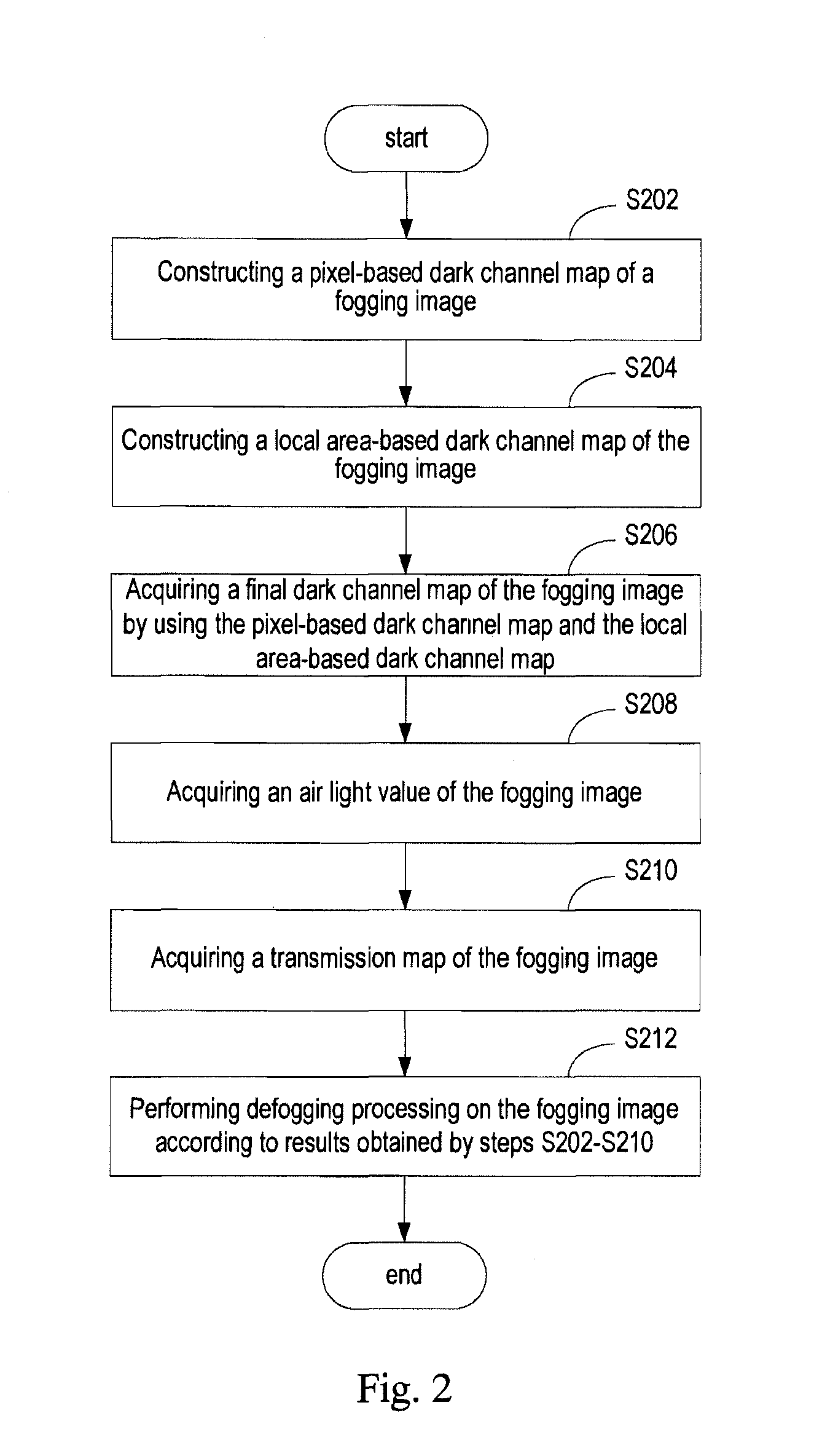
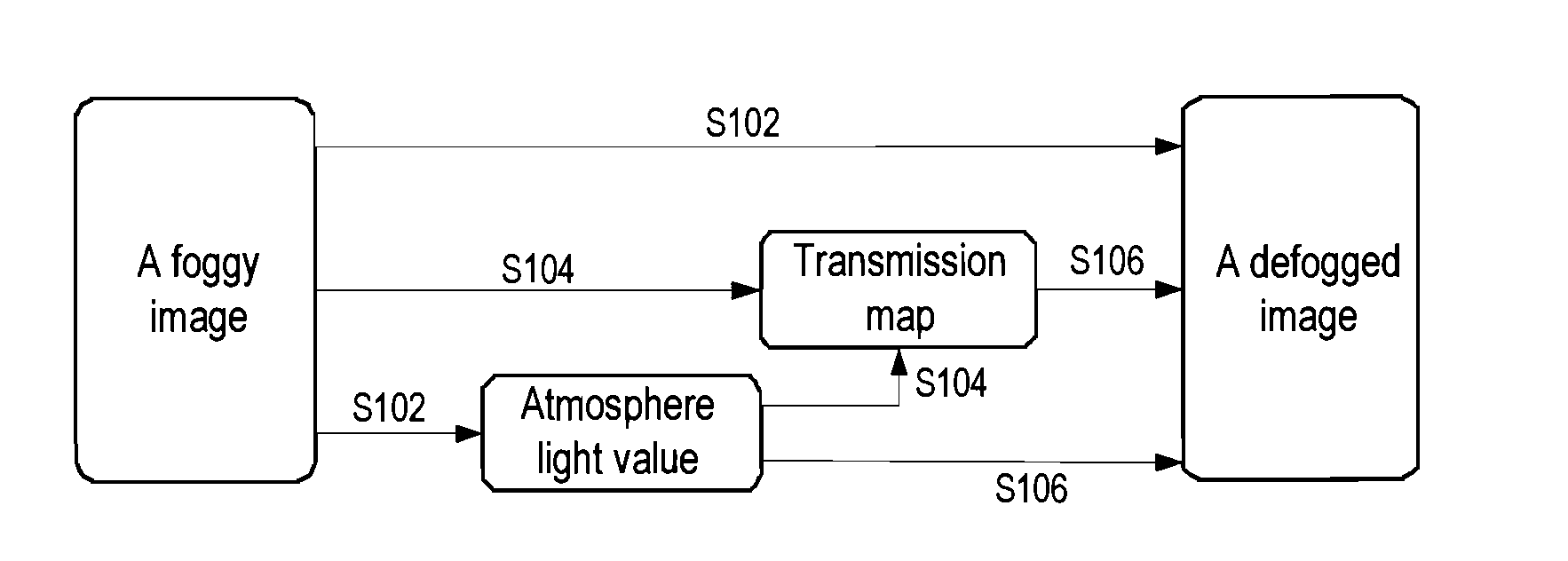
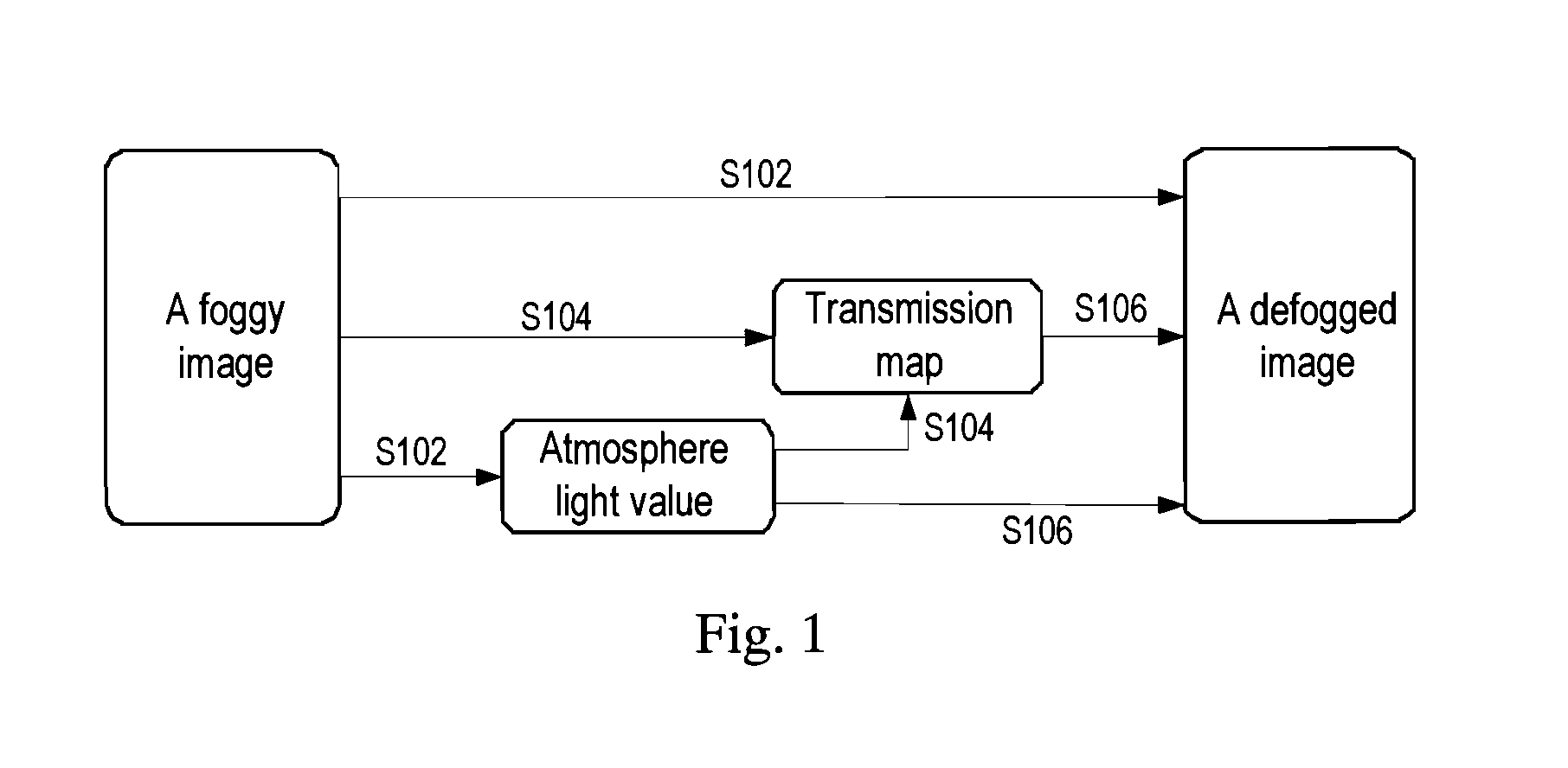
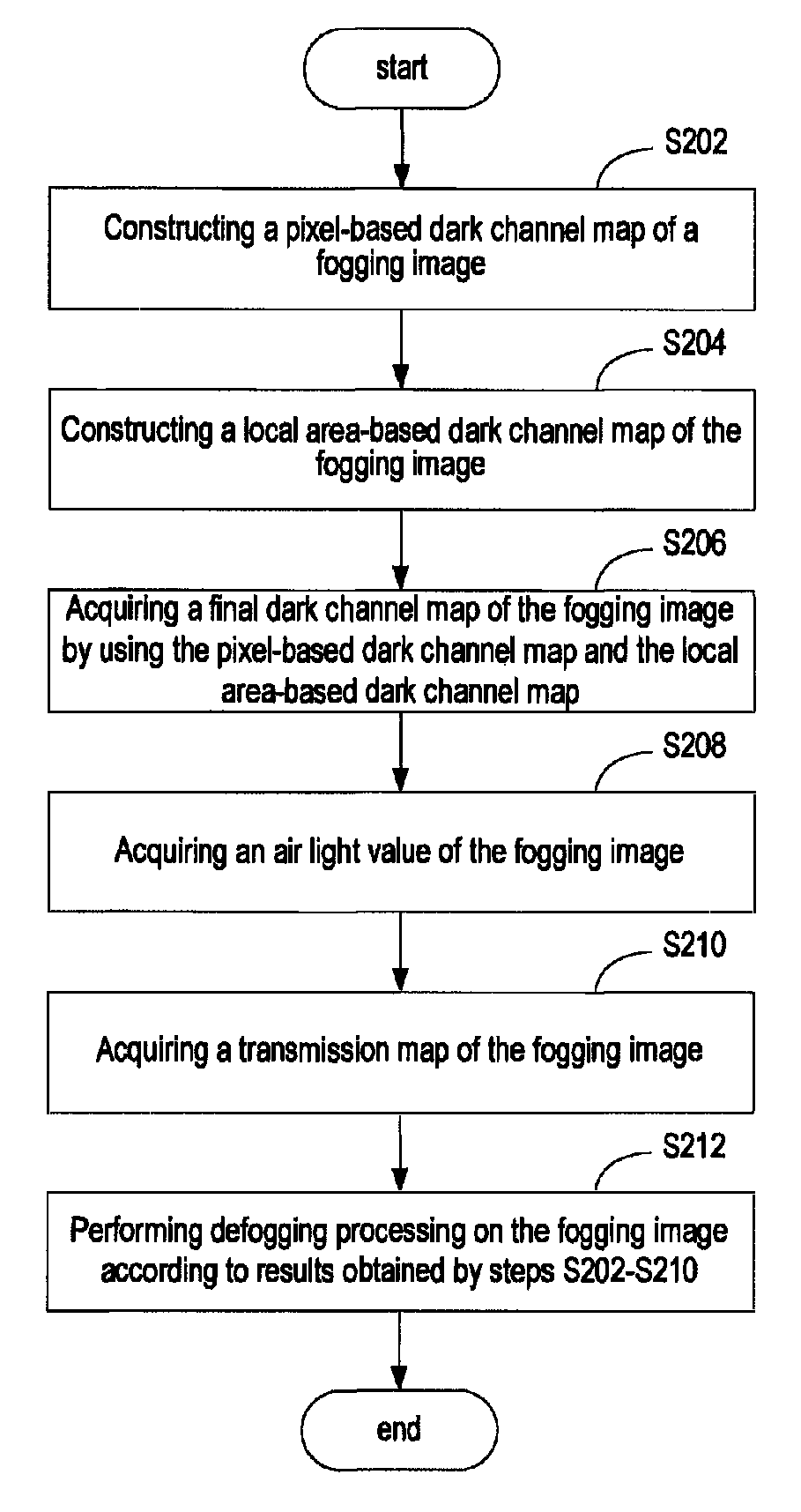
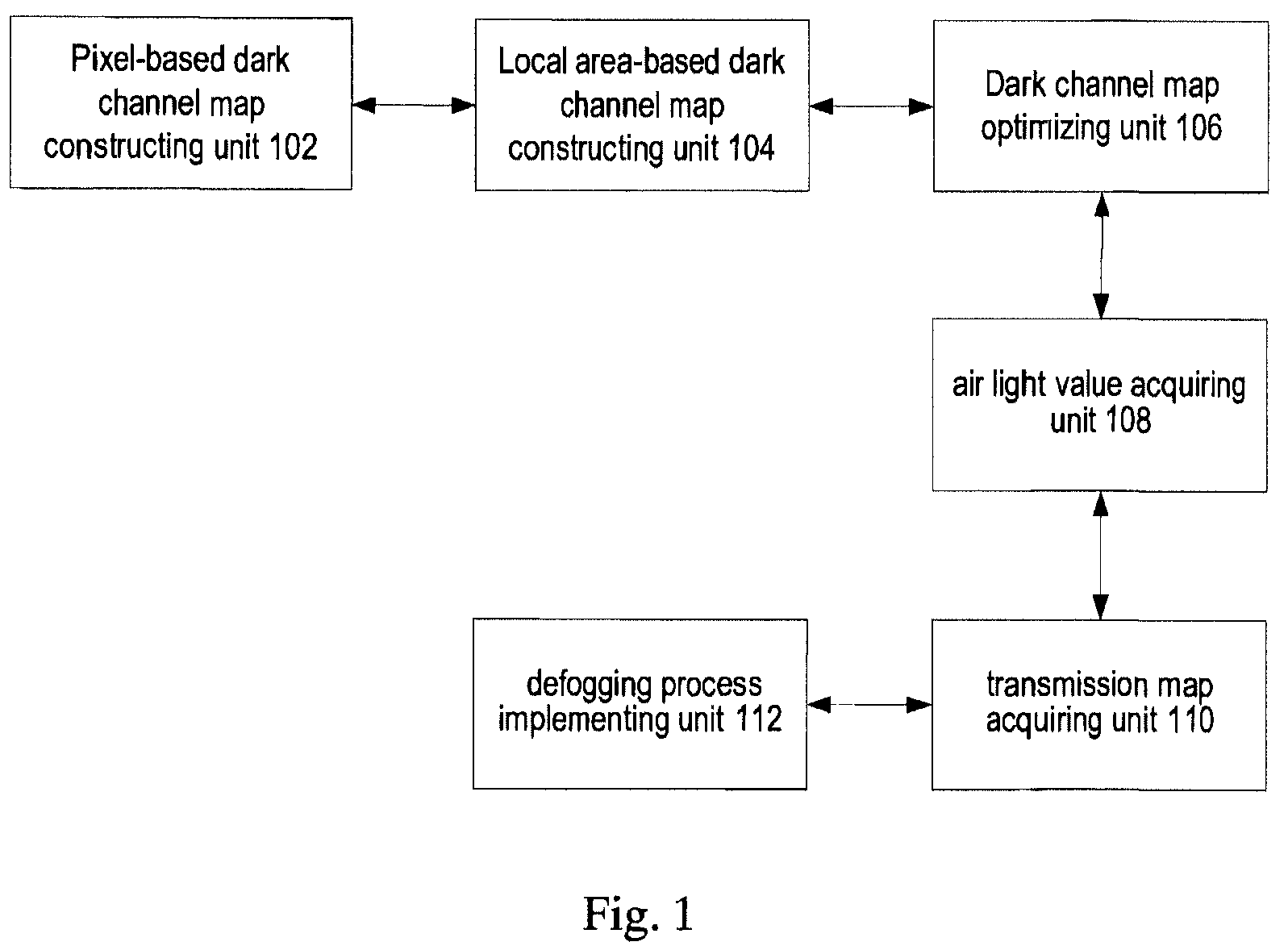
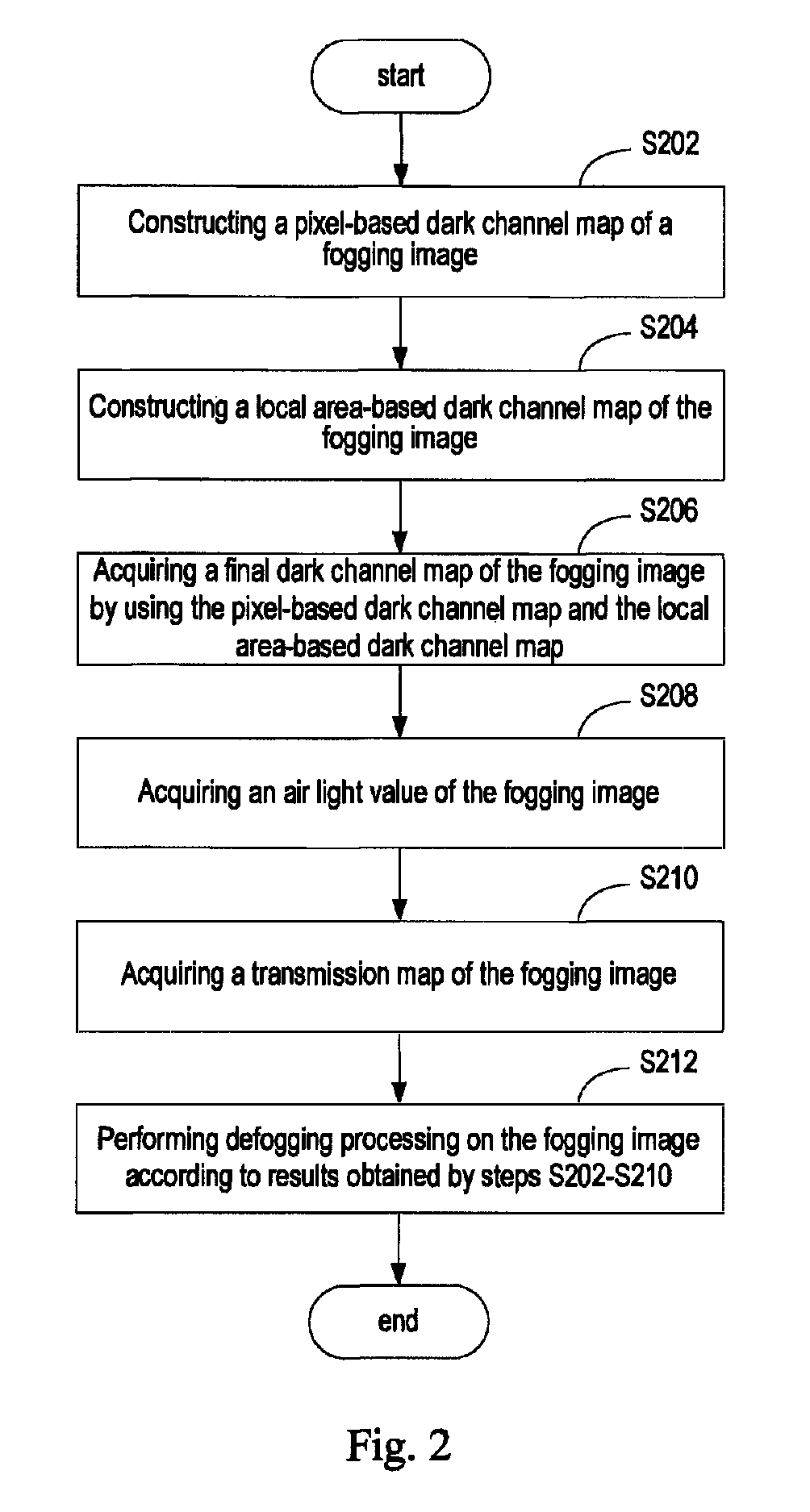
Image defogging method and system
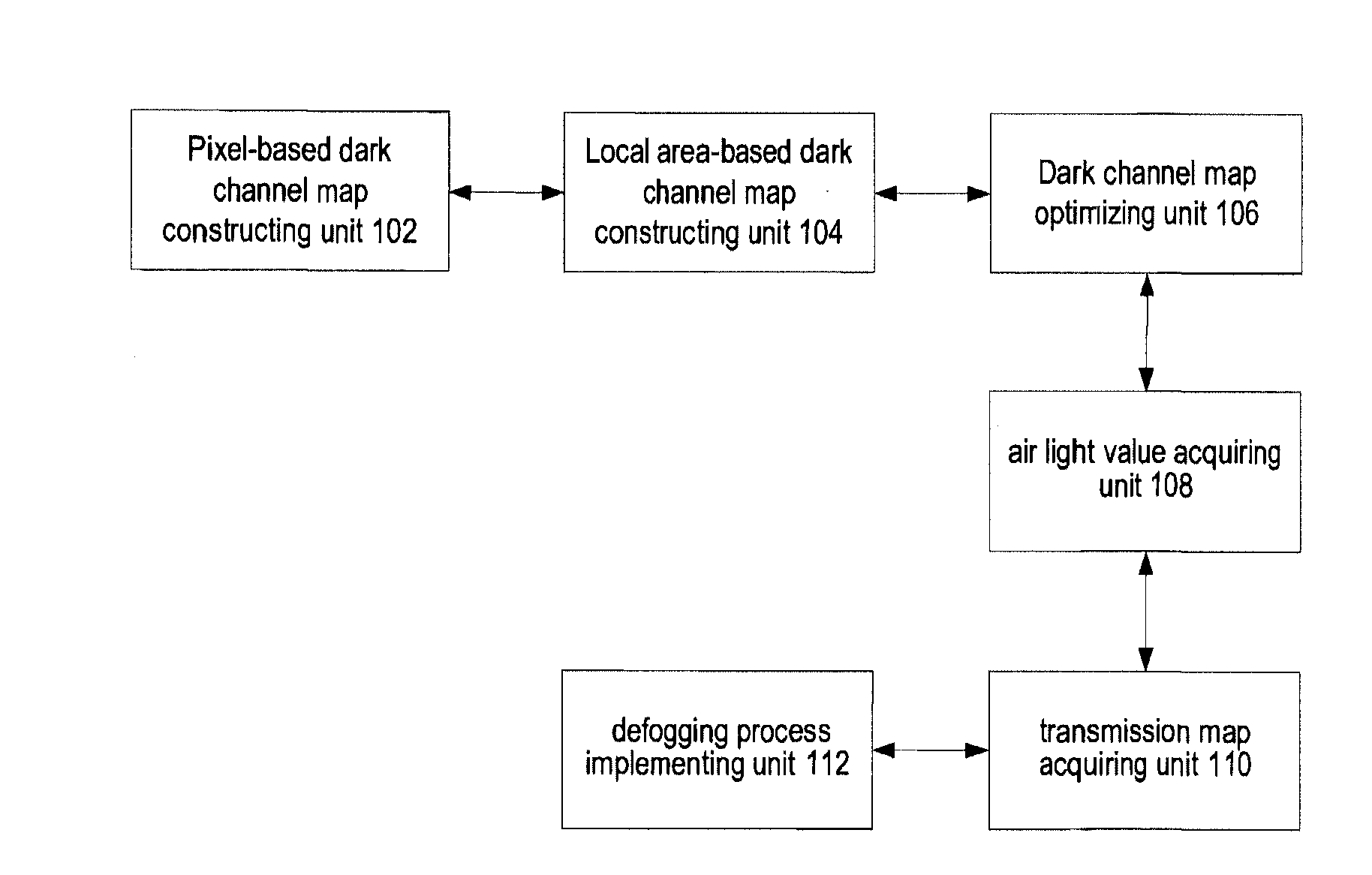
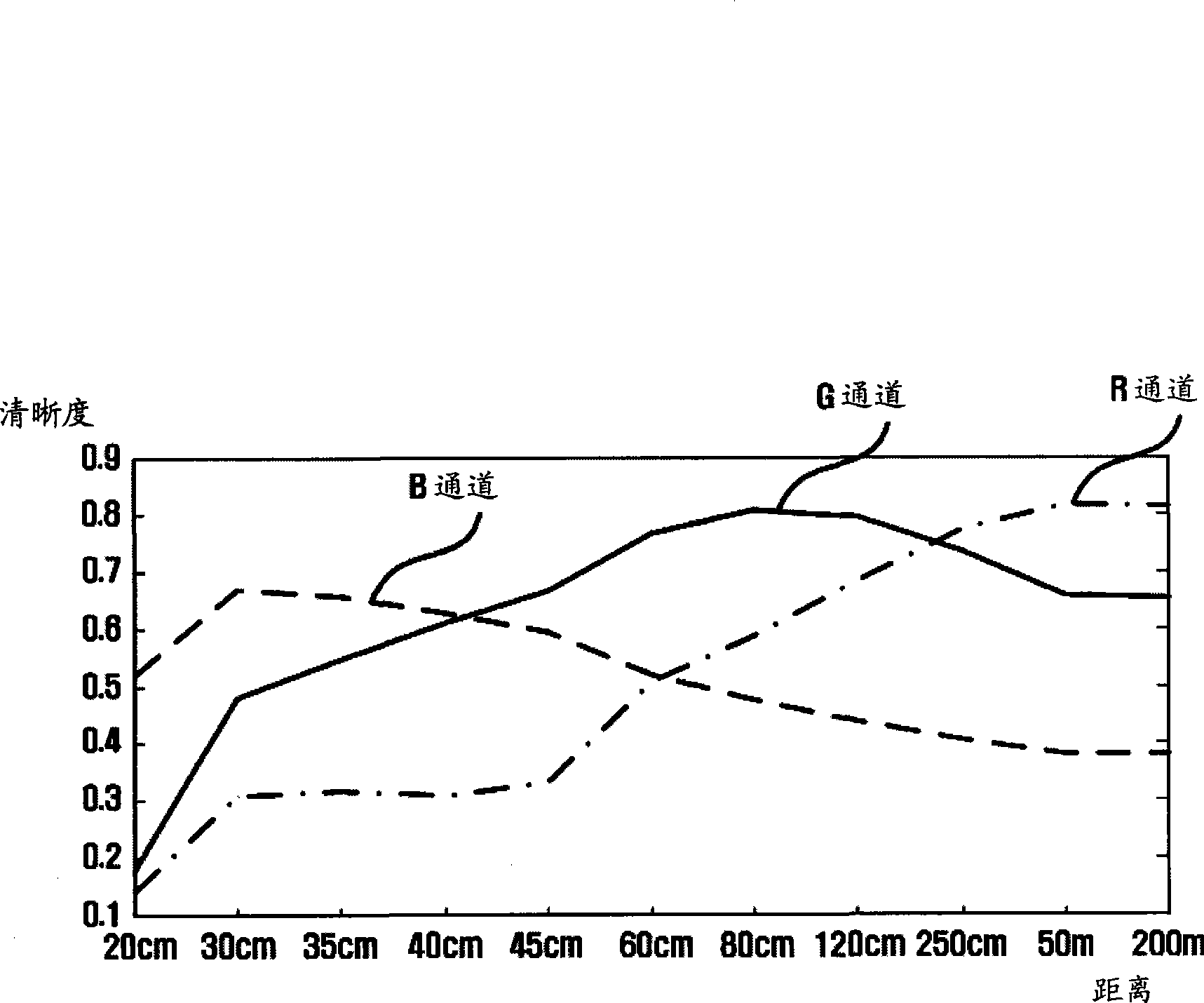
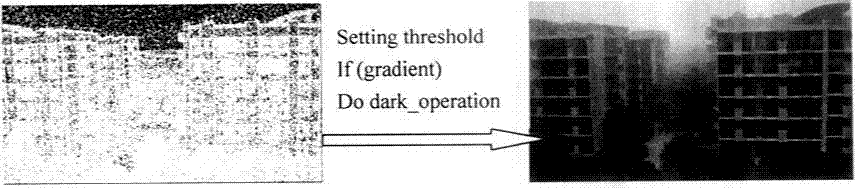
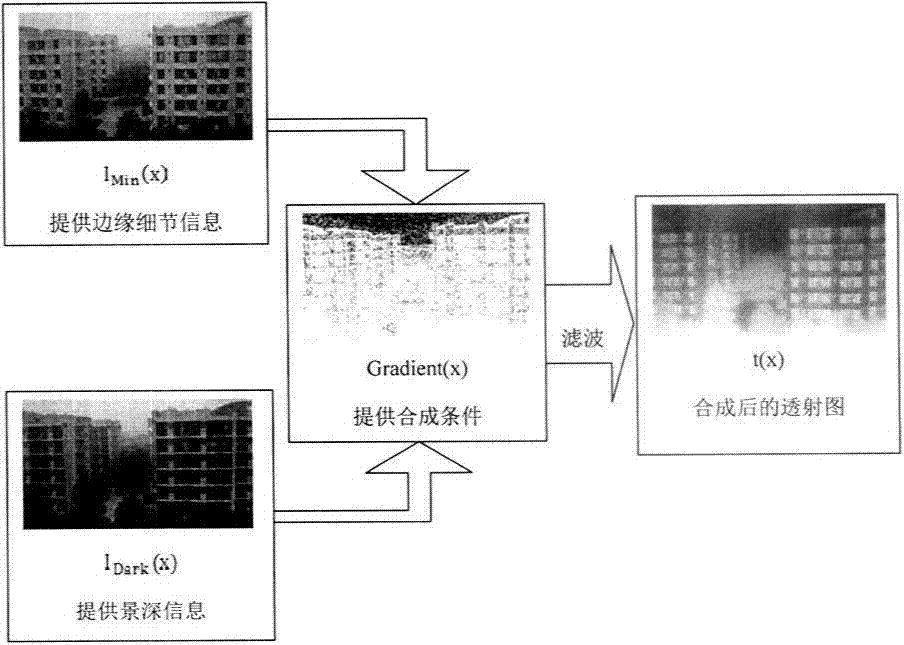
Image defogging method and system, the method including: constructing a pixel-based dark channel map of a fogging image; constructing a local area-based dark channel map of the image; acquiring a final dark channel map of the image; acquiring intensity values of R, G, B channels of a pixel having a maximum grey value of all pixels in an area, covered by a brightest area in the local map, in the fogging map, as R, G, B components of an air light value of the image; acquiring a transmission map of the image by using the final map, a maximum value of the components of the air light value, and a defogging parameter; and acquiring intensity values of the channels of pixels in a defogged image by using the transmission map, the air light value, and the intensity values of the R, G, B channels of the pixels in the image.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
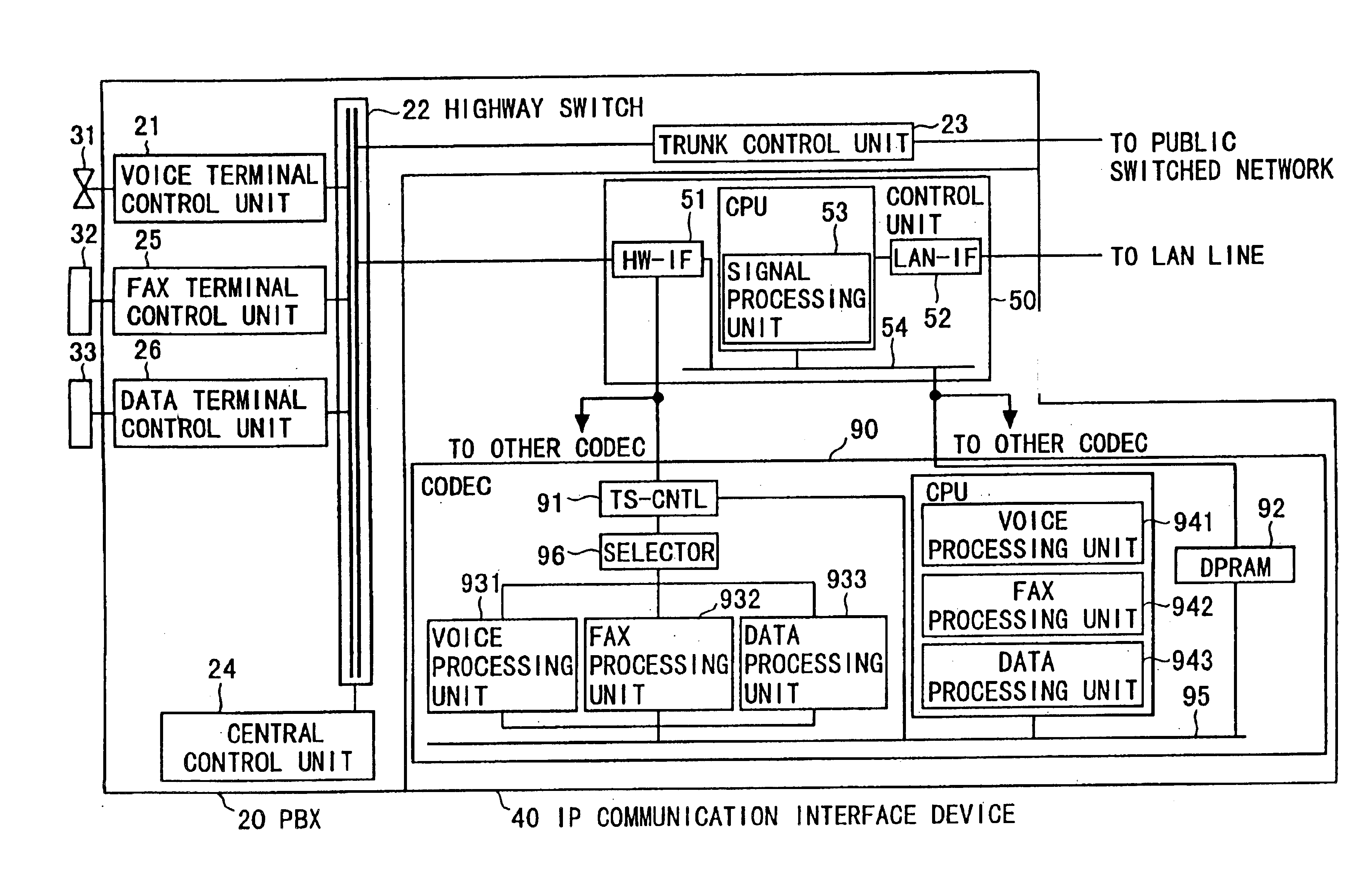
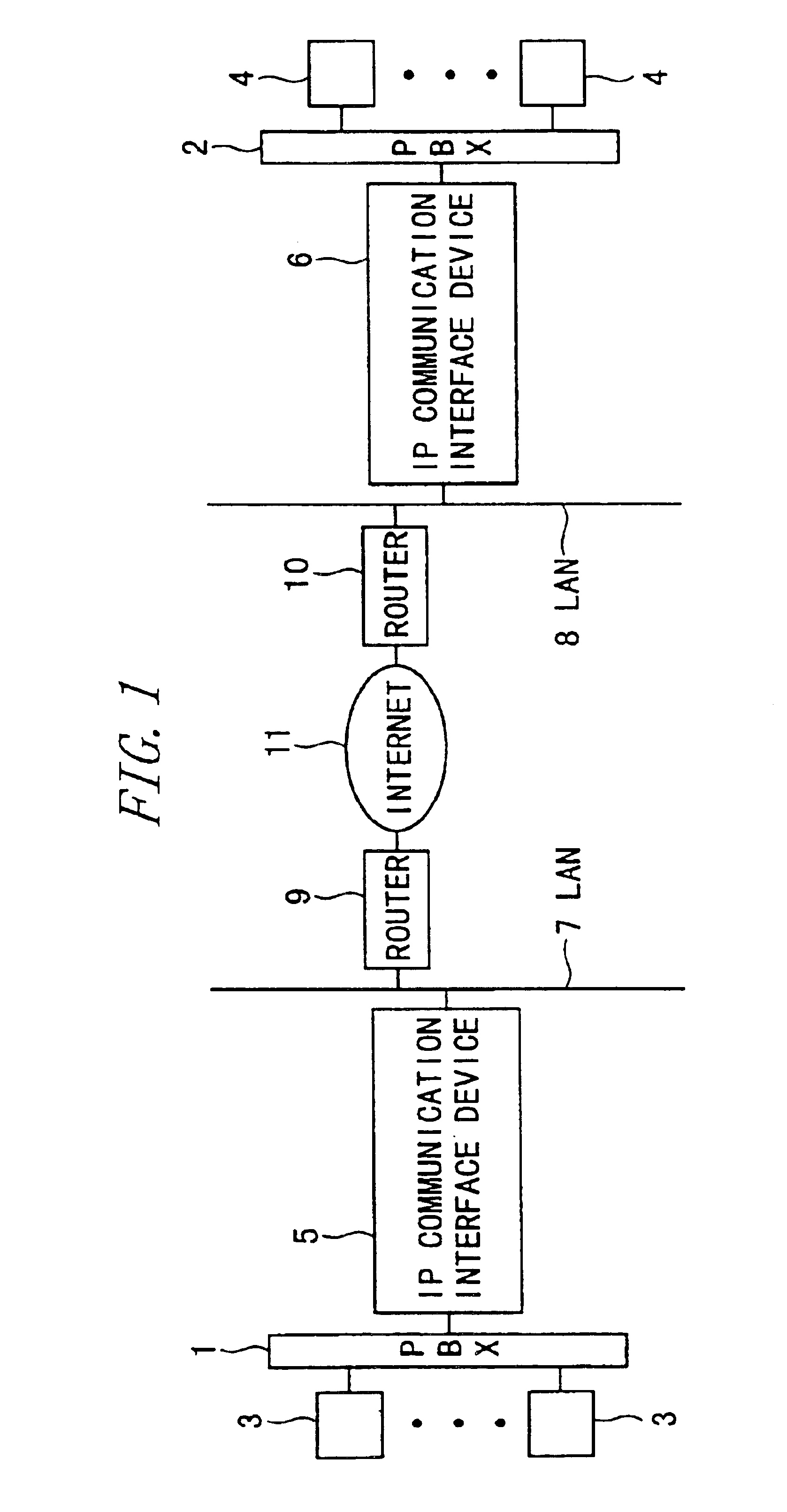
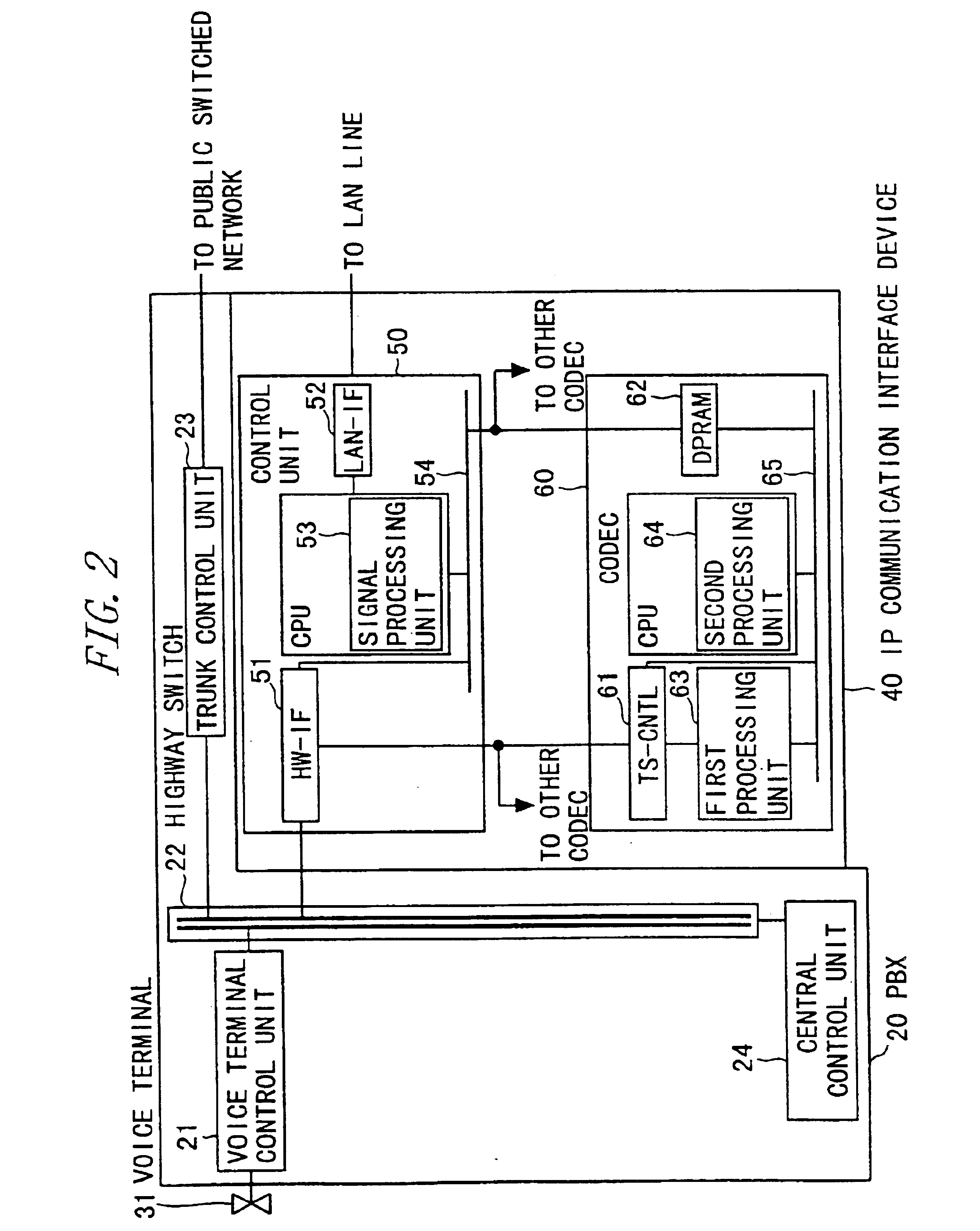
IP communication network system having a gateway function with communication protocol conversion between a switched circuit network and a packet switched network including data over tcp/ip and voice/fax over rtp
InactiveUS6914898B2Easy to introduceEasy constructionMultiplex system selection arrangementsHybrid switching systemsCommunication interfaceNetwork packet
An IP communication interface device includes first and second connecting units, and first, second and third processors. The first processor coding first media data as B-channel data inputted to the first connecting unit from a circuit switched network, decoding packet-disassembled media data into which a packet of second media data inputted to the second connecting unit from a LAN is disassembled, and transmitting the decoded media data to the first connecting unit for forwarding as the first media data to the circuit switched network. The second processor packetizing first coded media data, disassembling the packer of the second media data, and transmitting as packet-disassembled media data to the first processor. The third processor generating second media data by adding header data to the packet-assembled media data of the second processors forwarding the second media data to the LAN via the second connecting unit, removing header data, and transmitting the header-less second media data to the second processor.
Owner:PROTUS IP SOLUTIONS
Image defogging method and system
ActiveUS20140205192A1Reduce complexityImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionAtmosphere
Image defogging method and system. The method includes: acquiring minimum intensity values corresponding to pixels in a foggy image, and selecting the largest values of intensity values of R, G, and B channels of pixels in an area, covered by a brightest area of a predetermined size in a local minimum intensity image, in the foggy image as component values of R, G, and B channels of an atmosphere light value; acquiring a transformation image of the foggy image with atmosphere light value of the foggy image; acquiring a transmission map of the foggy image by edge-preserving filtering the transformation image; and acquiring intensity values of R, G, and B channels of pixels in a defogged image using transmission map and atmosphere light value of the foggy image and intensity values of R, G, and B channels of pixels in the foggy image.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Video image processing method, device, and video coding system
InactiveCN108062746AFast operationImprove computing efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisVideo encodingContrast enhancement
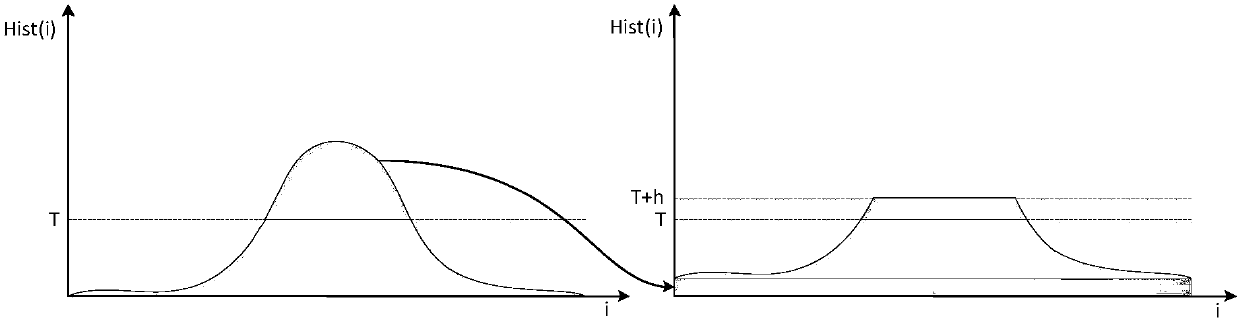
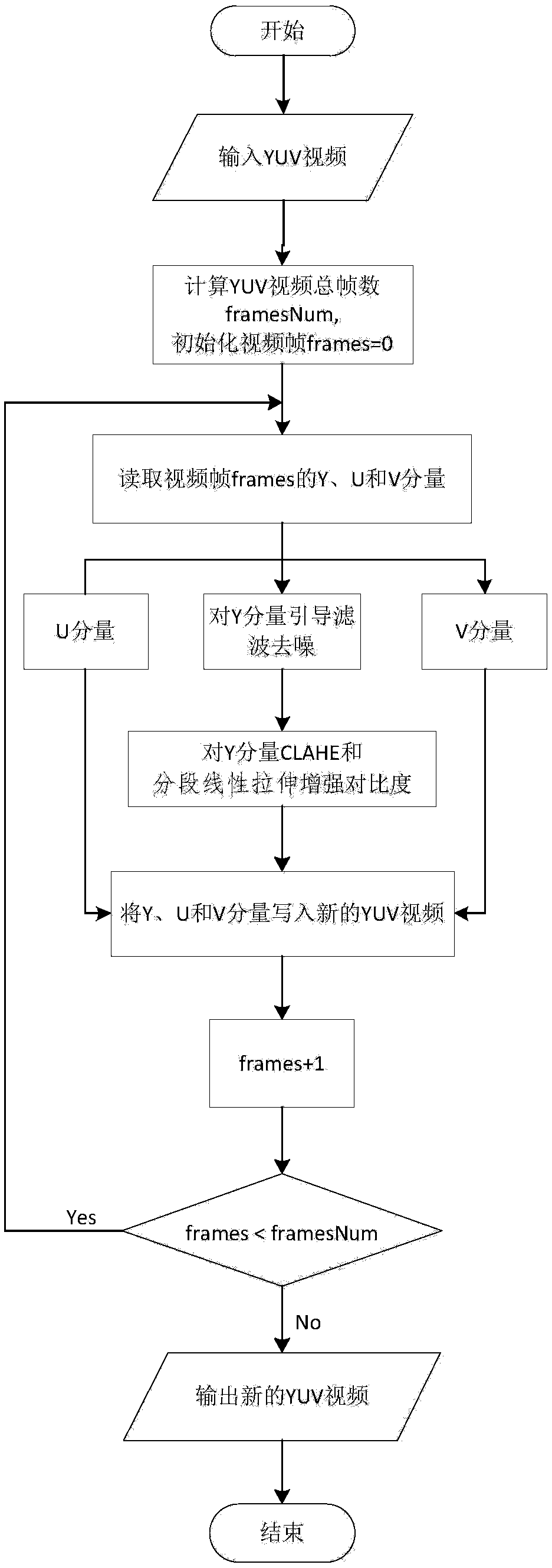
The invention discloses a video image denoising and contrast enhancement method and device. The method includes the following steps that: a video file in a YUV format is obtained and is divided into aplurality of video frames; Y, U, and V components in each frame of image in the plurality of video frames are read; guided filtering denoising, contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization, and piecewise linear stretching are performed on the Y components; and Y components which are obtained after the stretching operation is performed are synthesized with the original U and V components of the frames, so that new YUV video image frames can be obtained. With the method adopted, mutual conversion between an RGB format and a YUV format is not required; only the Y components are processed; the problems of the overall excessive brightness and color undersaturation of images which are caused by a condition that an R channel, a G channel and a B channel are denoised simultaneously in the prior art can be solved; and the problems of the color distortion and unsatisfactory overall contrast of images which are caused by a condition that a Y component, a U component and a V component are simultaneously subjected to contrast enhancement can be solved.
Owner:深圳市优朋普乐传媒发展有限公司
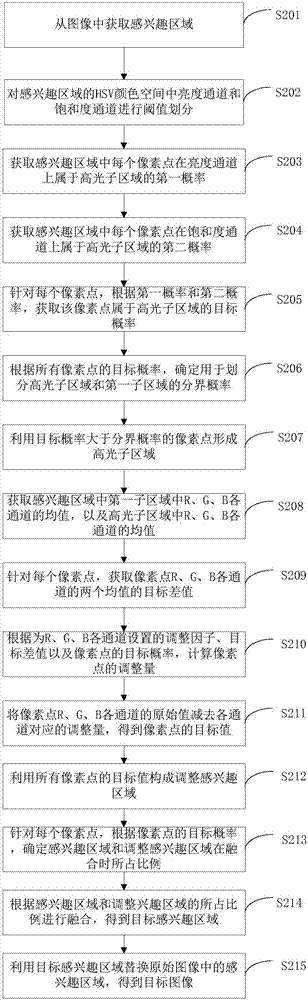
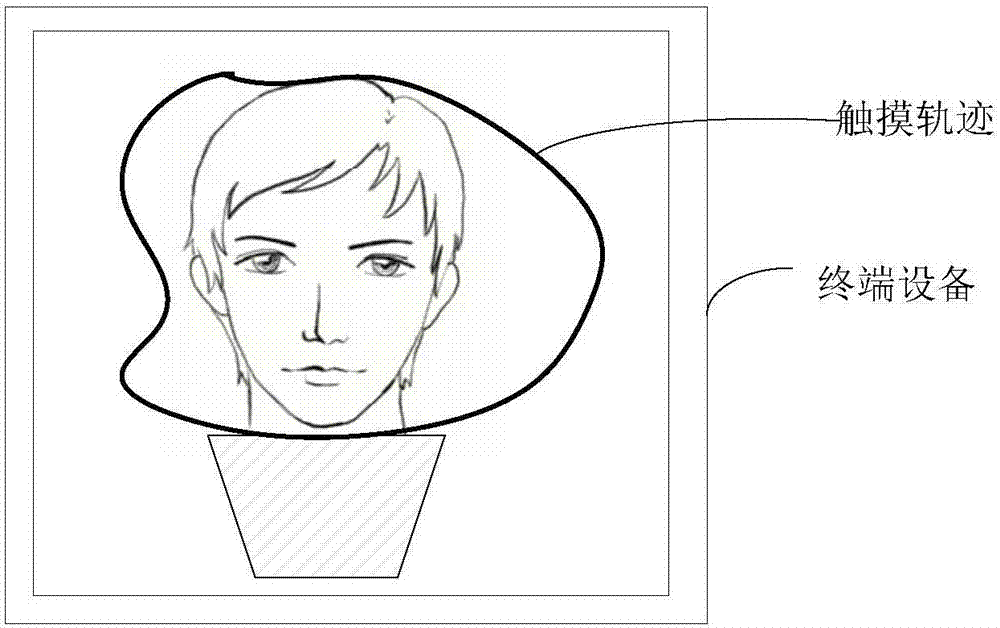
Image processing method and device and terminal equipment
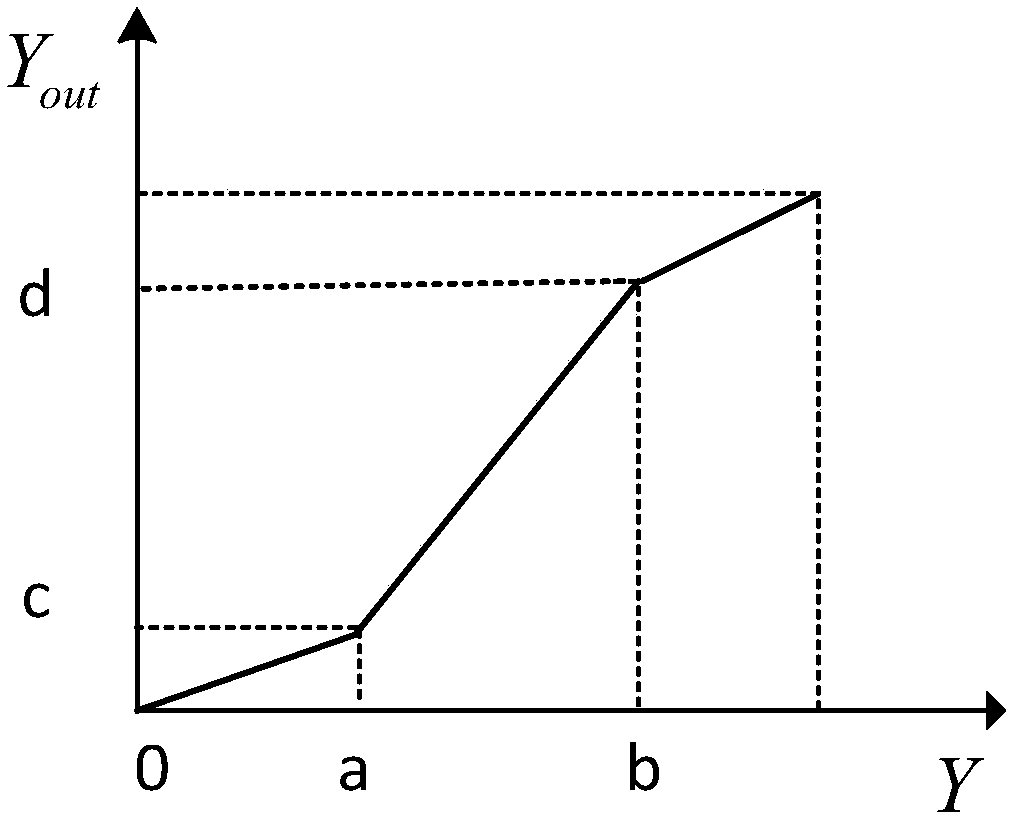
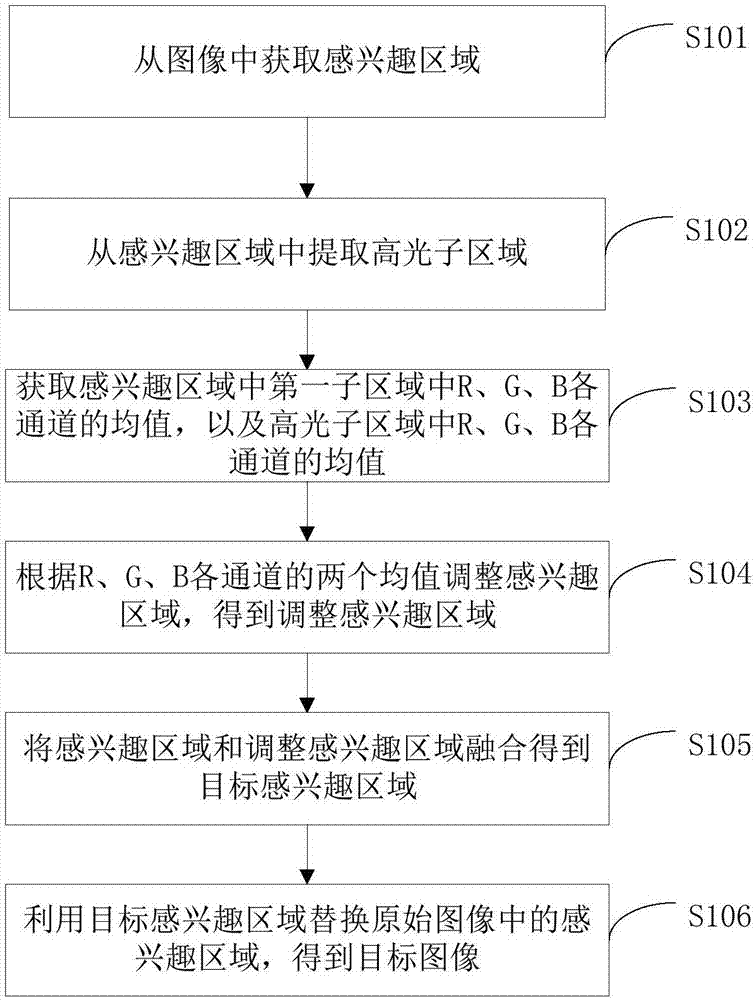
The invention proposes an image processing method and device and terminal equipment. The method includes obtaining an area of interest from an image; extracting a highlight subarea from the area of interest; obtaining the mean value of R, G and B channels in a first subarea in the area of interest and the mean value of R, G and B channels in the highlight subarea; wherein the first subarea is an area in the area of interest except the highlight subarea; adjusting the area of interest according to the two mean values of R, G and B channels to obtain the adjusted area of interest; fusing the area of interest and the adjusted area of interest to obtain a target area of interest; and utilizing the target area of interest to replace the area of interest in the original image to obtain a target image. Thus, on the premise of keeping details in the original image, the highlight area in the image is effectively removed, so that a processed image is more natural.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
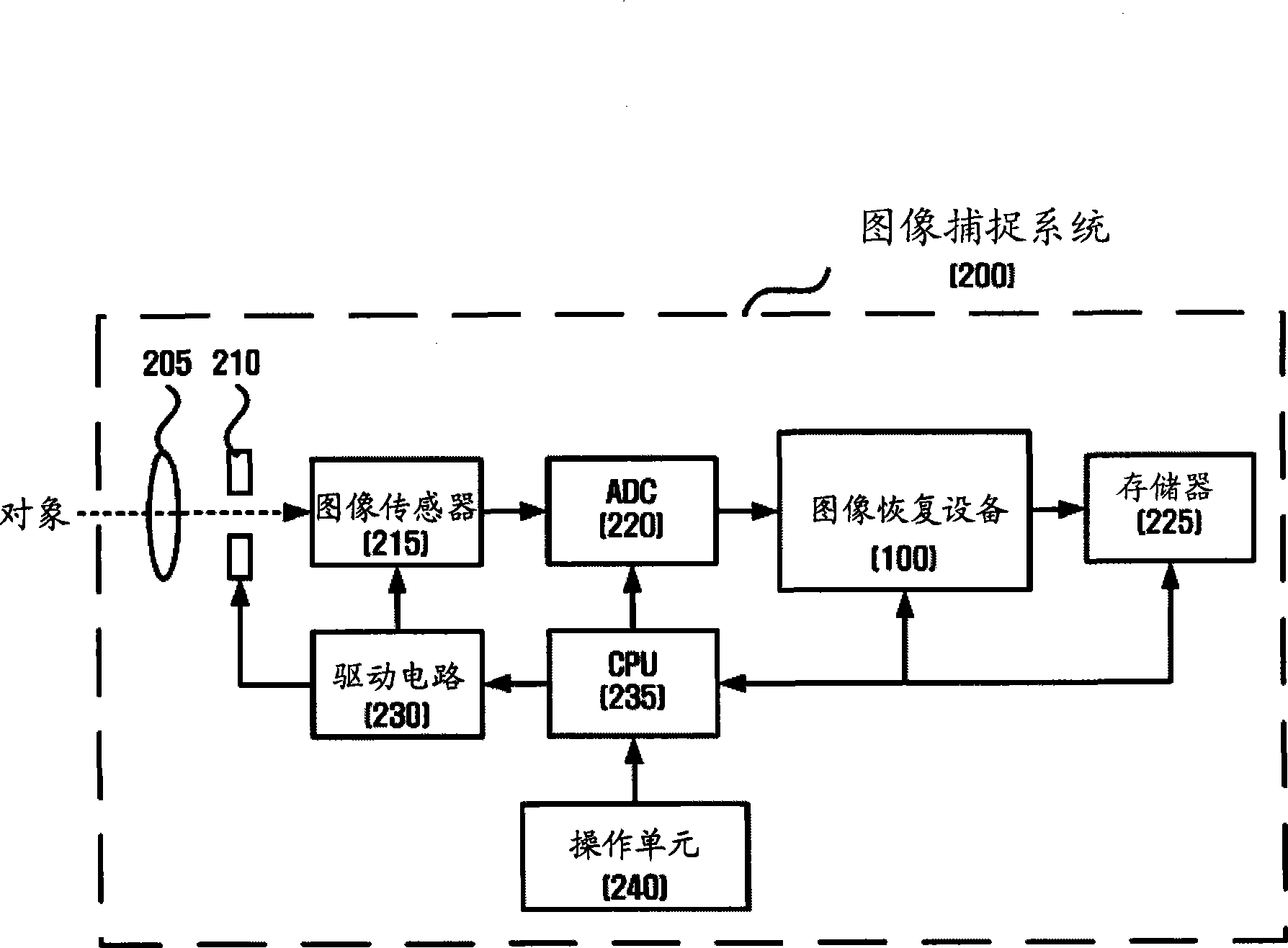
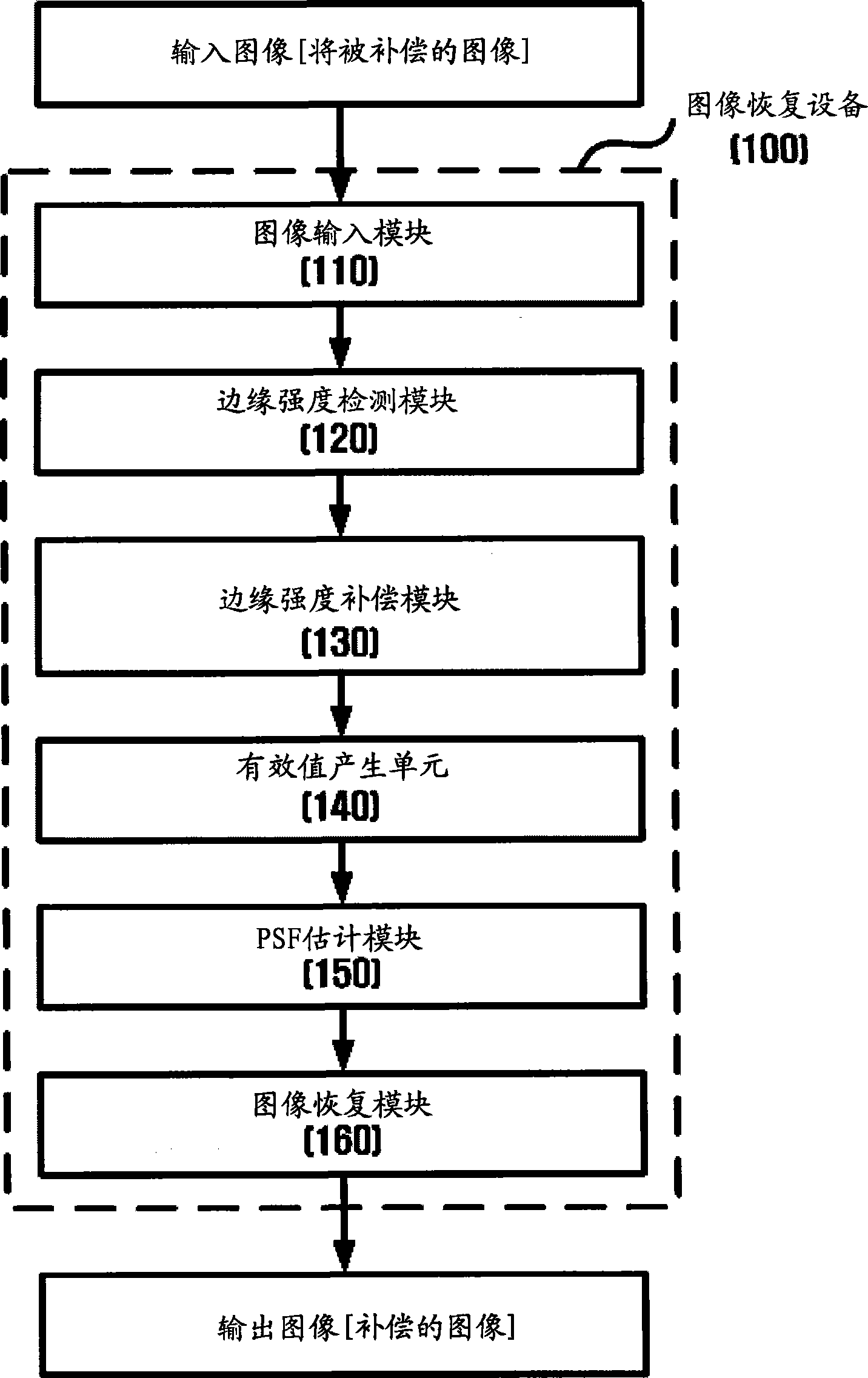
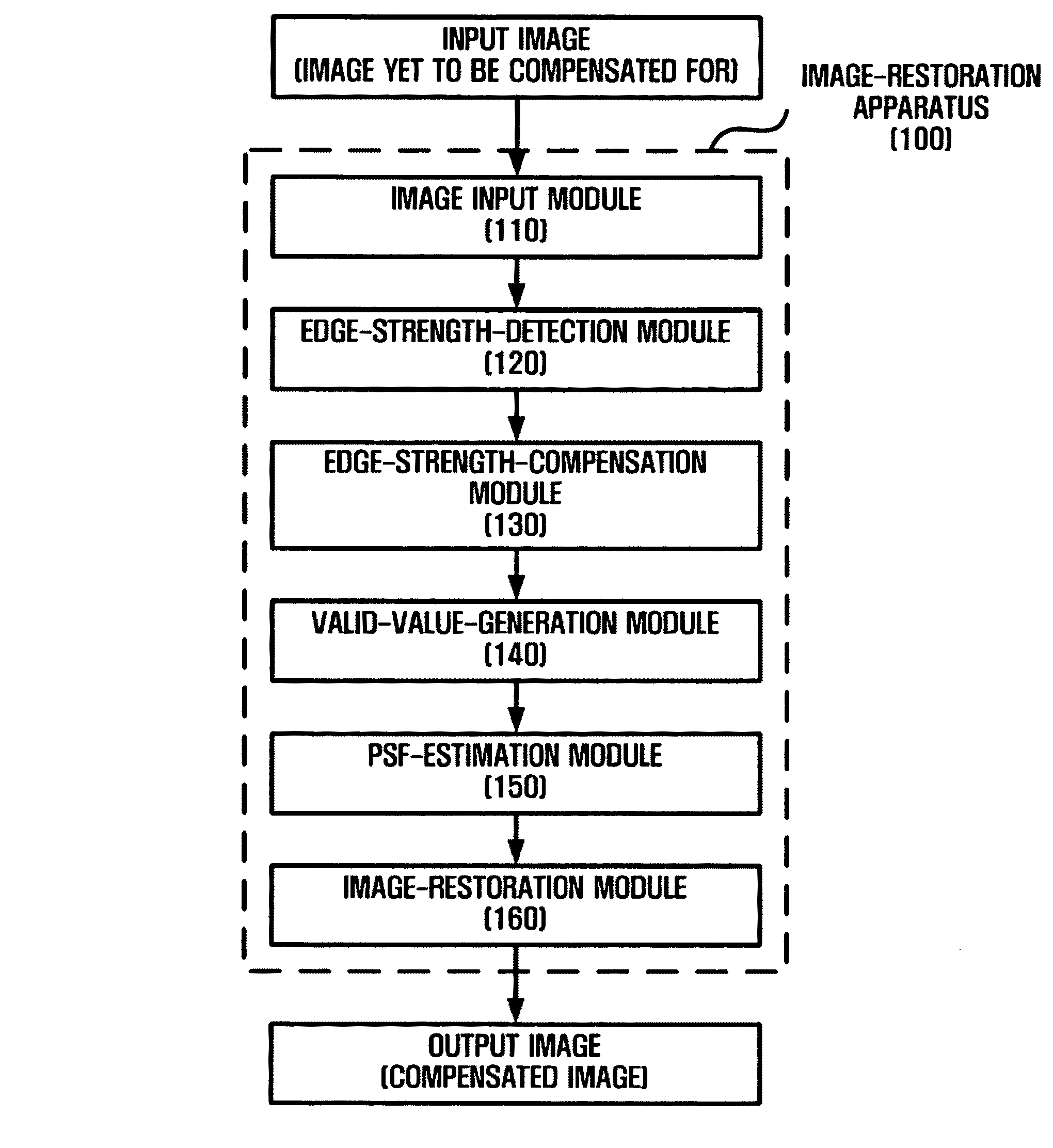
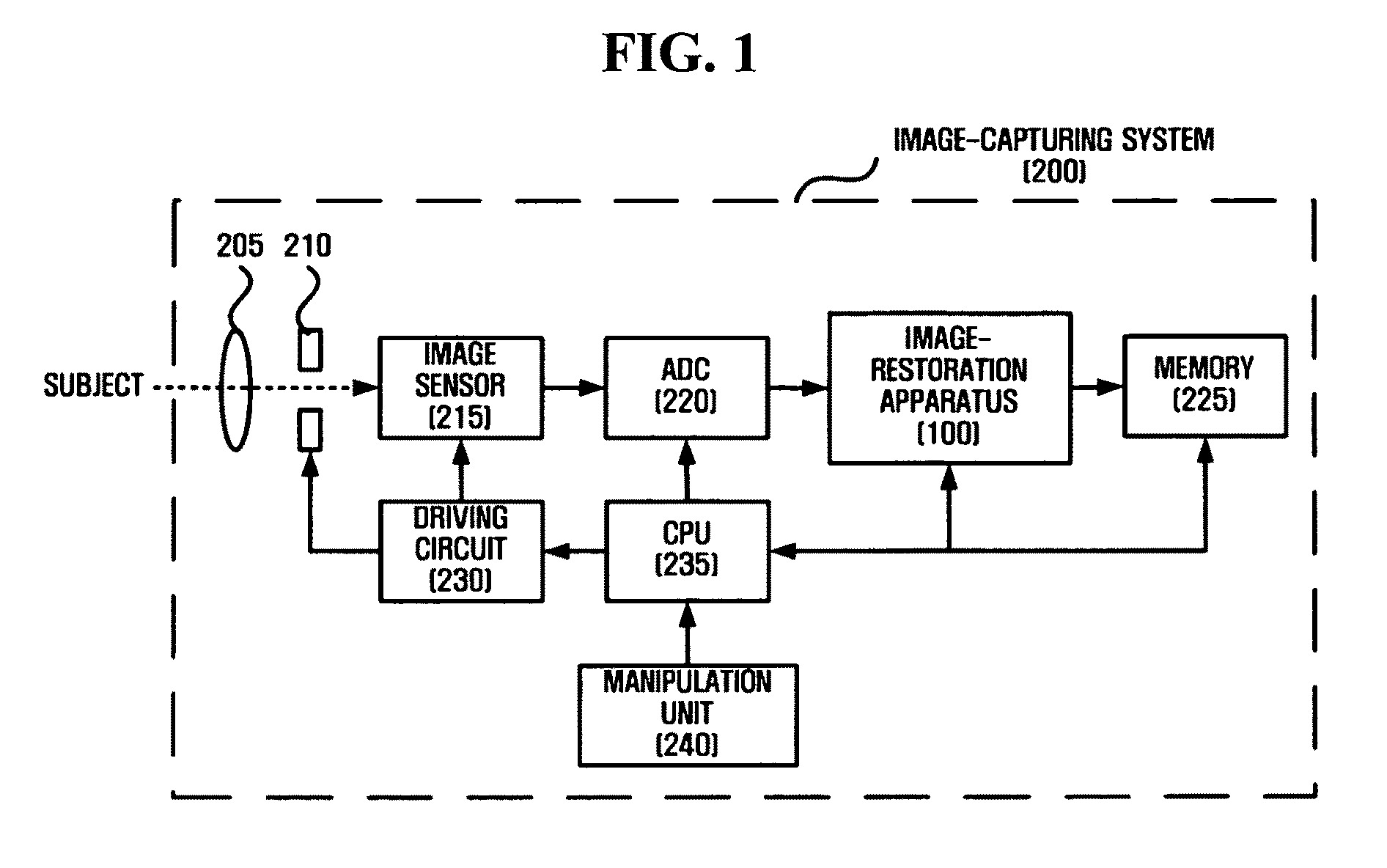
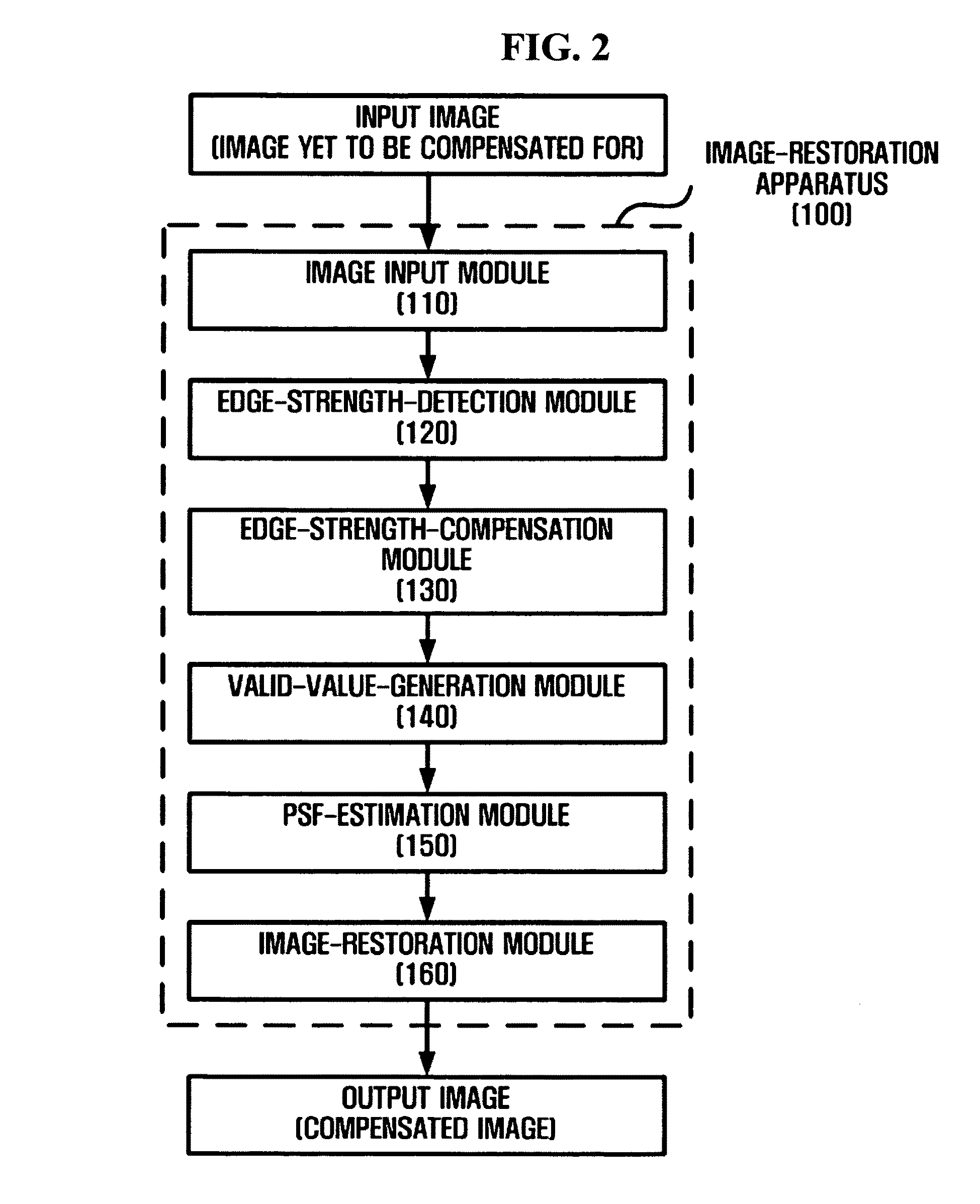
Apparatus and method for restoring image
An apparatus and a method for restoring an image are provided. The apparatus includes an edge-strength-detection module which detects an R-channel edge strength, a G-channel edge strength and a B-channel edge strength from an input image and generates an R-channel edge map, a G-channel edge map and a B-channel edge map based on the R-channel edge strength, the G-channel edge strength and the B-channel edge strength; an edge-strength-compensation module which compensates for the R-channel edge strength and the B-channel edge strength based on the G-channel edge strength; a valid-value-generation module which generates a valid value indicating a blur level based on the compensated R-channel edge strength and the compensated B-channel edge strength; a point spread function (PSF) estimation module which estimates a PSF corresponding to the valid value; and an image-restoration module which restores the input image using the PSF.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
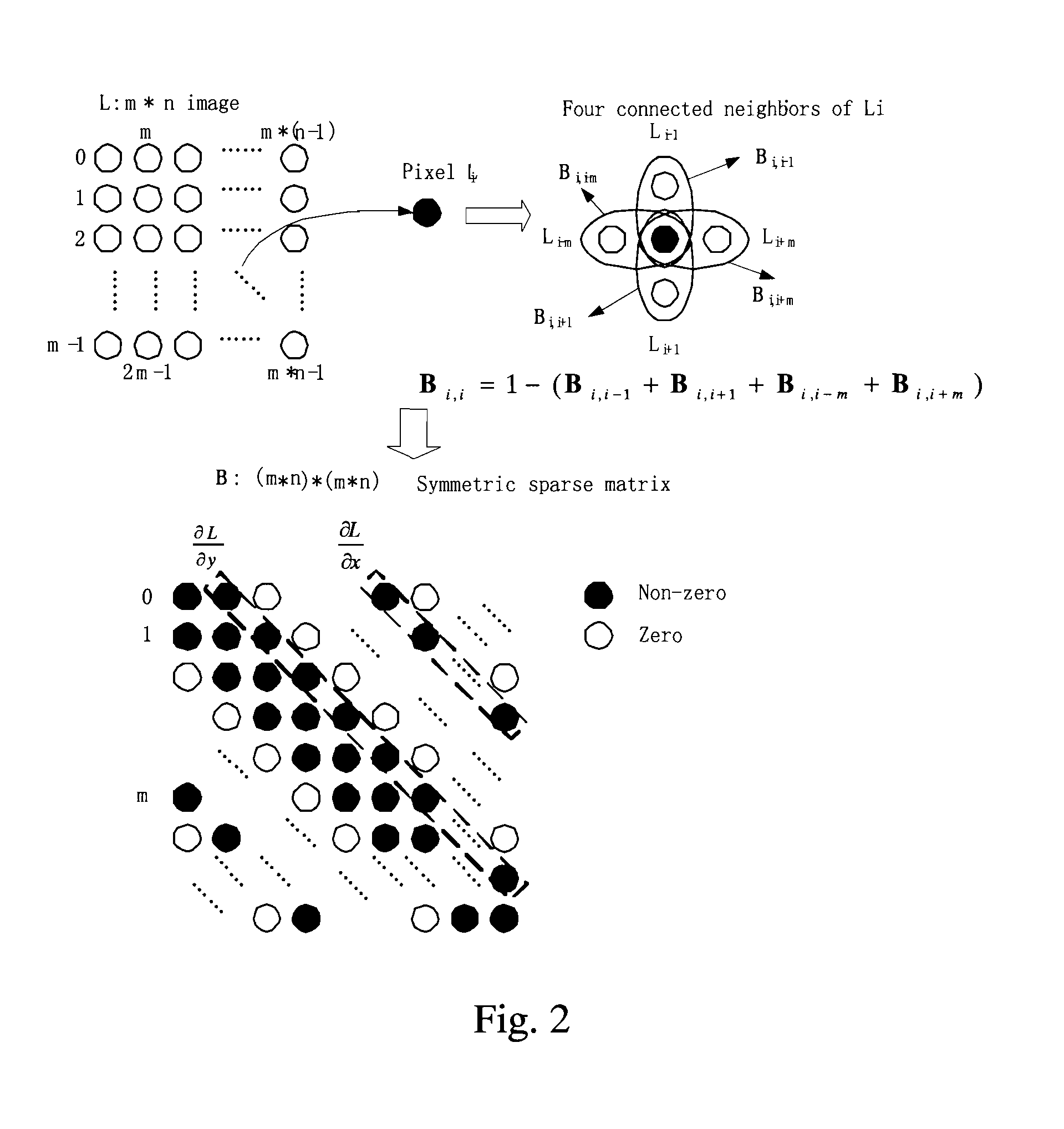
Rapid single-image defogging algorithm
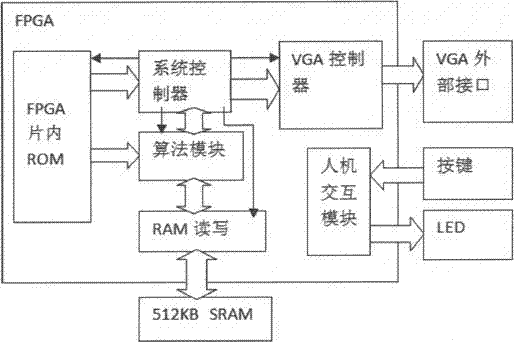
The invention discloses a rapid single-image defogging algorithm based on dark channel prior and information synthesis and implementation of the rapid single-image defogging algorithm based on dark channel prior and information synthesis on hardware platforms. A transmission image required by a defogging model is rapidly synthesized through the minimum value in an R channel, a G channel and a B channel in image color space, image gradients and a dark channel image with specific conditions, the step of solving the transmission image with a soft matting method in an original dark channel prior defogging algorithm is replaced, and dark channel calculation is optimized. By means of the rapid single-image defogging algorithm, original calculation of large-scale sparse matrixes is changed into comparison among corresponding pixels of several different information images, the calculation amount is greatly decreased, and results with the ideal degree the same as that of results of the original algorithm can be obtained under most conditions; meanwhile, as the calculation amount is decreased, and floating point calculation with the quite high accuracy requirement in the original algorithm is replaced by the pixel comparison method, the rapid single-image defogging algorithm can be more easily implemented on the hardware platforms such as FPGA and DSP; in addition, as the consumed time of the rapid single-image defogging algorithm is greatly shortened, and the rapid single-image defogging algorithm can be implemented on the hardware platforms, the real-time processing capacity is theoretically achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Adaptive transmission in multi-access asynchronous channels
ActiveUS20050111477A1Prevent unacceptable latencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDecision networksTime-division multiplexing
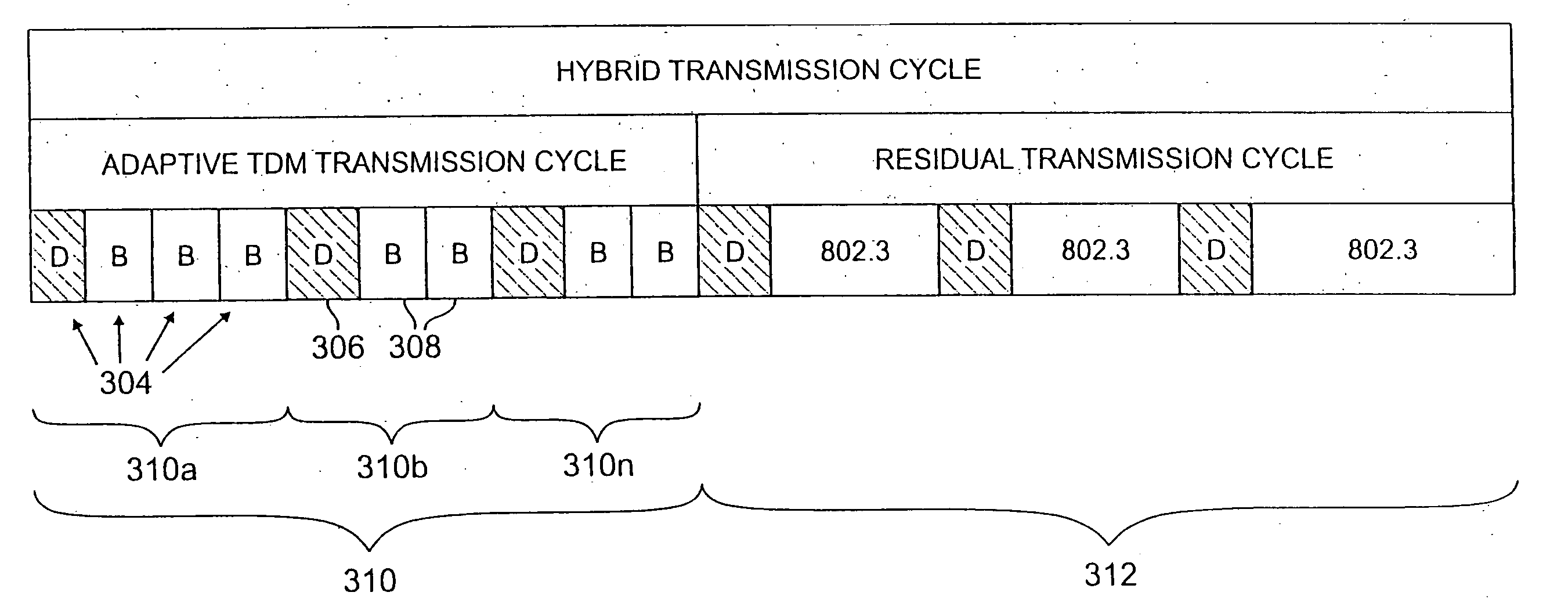
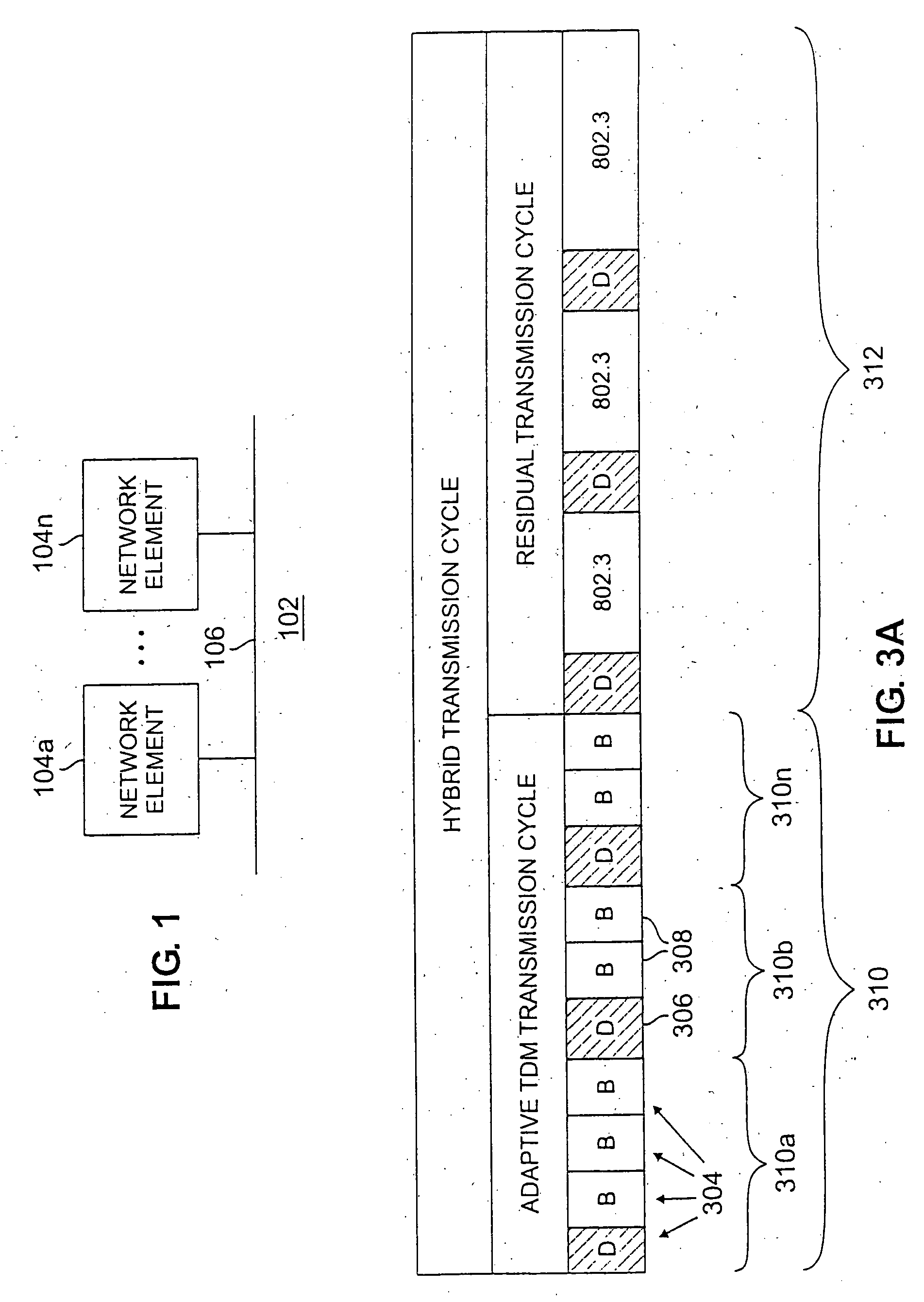
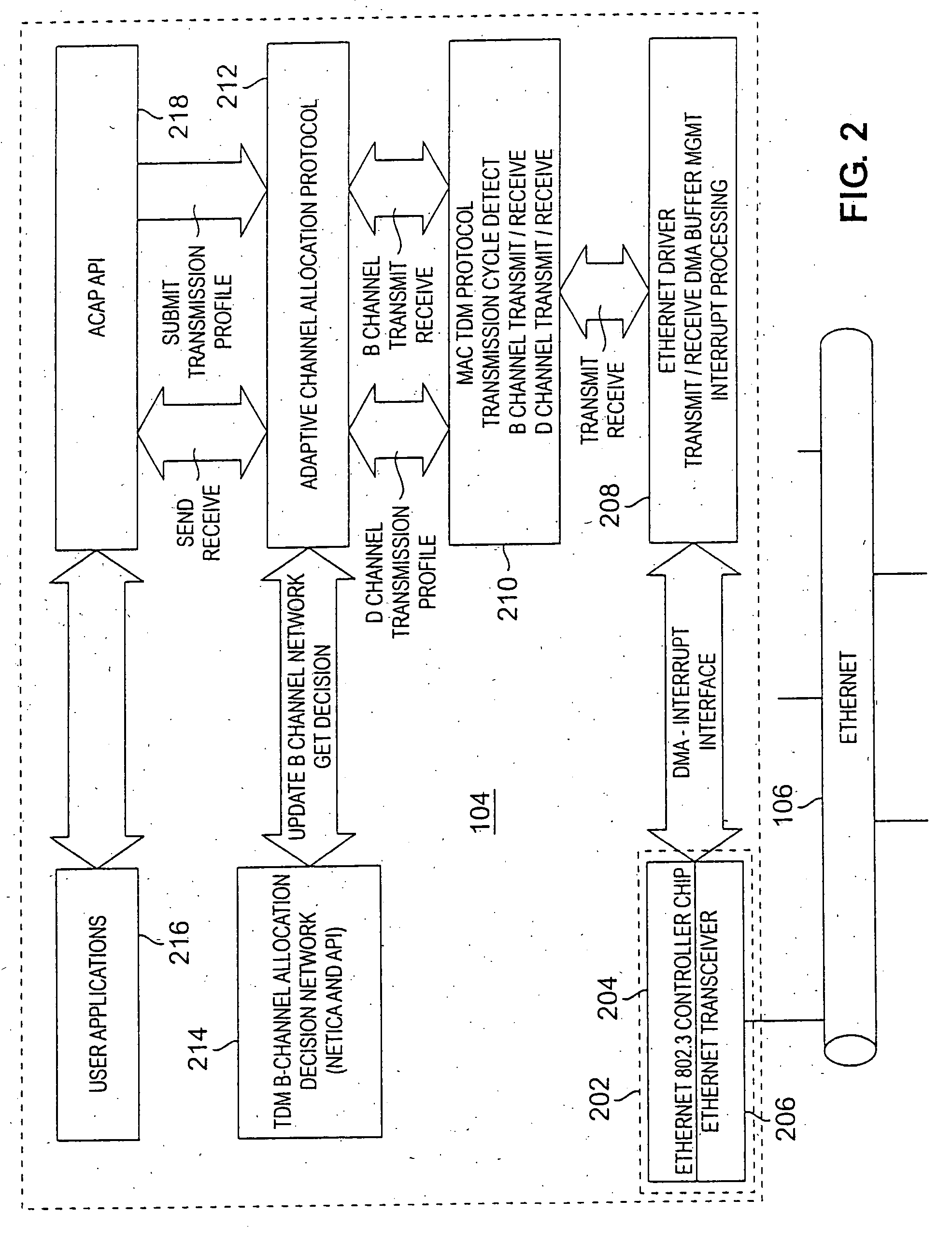
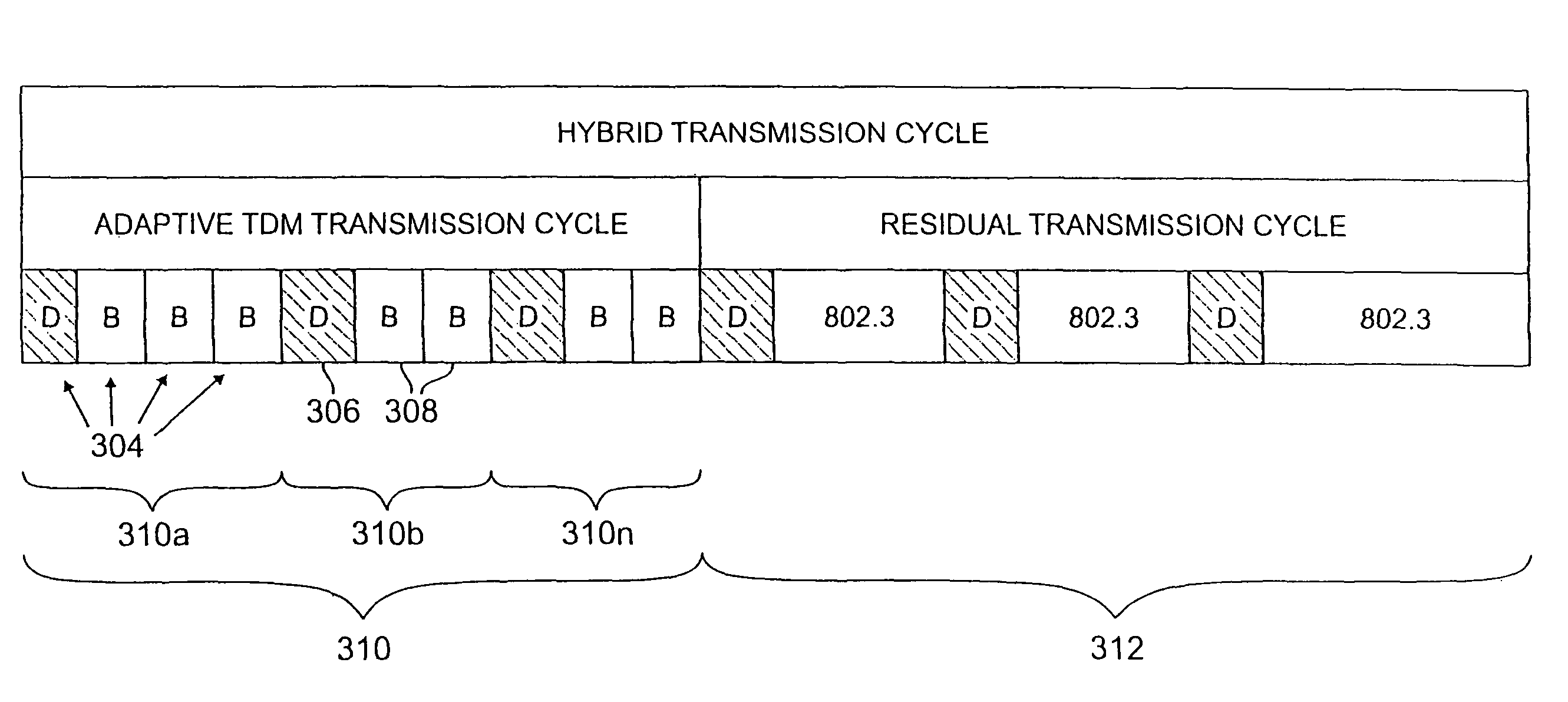
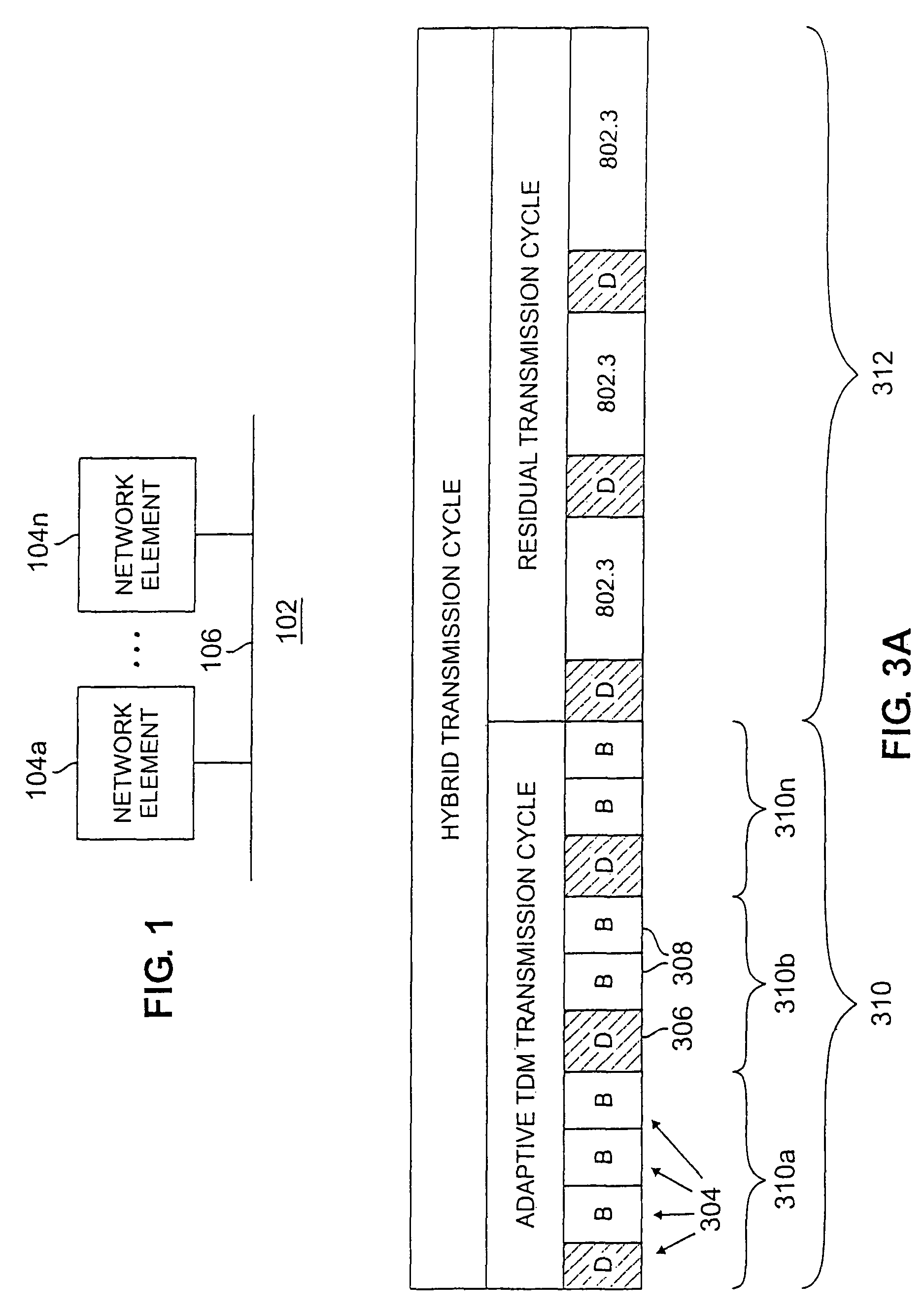
A hybrid transmission cycle (HTC) unit of bandwidth on a shared transmission medium is defined to include an adaptive, time division multiplexing transmission cycle (ATTC), which is allocated in portions sequentially among all participating network entities, and a residual transmission cycle (RTC), which is allocated in portions, as available, to the first network entity requesting access to the shared medium during each particular portion. The ratio of logical link virtual channels, or D-Channels, to data payload virtual channels, or B-Channels, within the ATTC is adaptive depending on loading conditions. Based on transmission profiles transmitted on the D-Channels during the ATTC, each network entity determines how many B-Channels it will utilize within the current HTC. This calculation may be based on any decision network, such as a decision network modelling the transmission medium as a marketplace and employing microeconomic principles to determine utilization. The ratio of the duration of the ATTC segment to the duration of the RTC segment is also adaptive depending on loading conditions, to prevent unacceptable latency for legacy network entities employing the shared transmission medium. During the RTC, utilization of the shared medium preferably reverts to IEEE 802.3 compliant CSMA / CD transmission, including transmissions by HTC-compliant network entities.
Owner:GLOBAL COMM INVESTMENT LLC
Method of transmitting broadband multimedia data on comprehensive business digital network
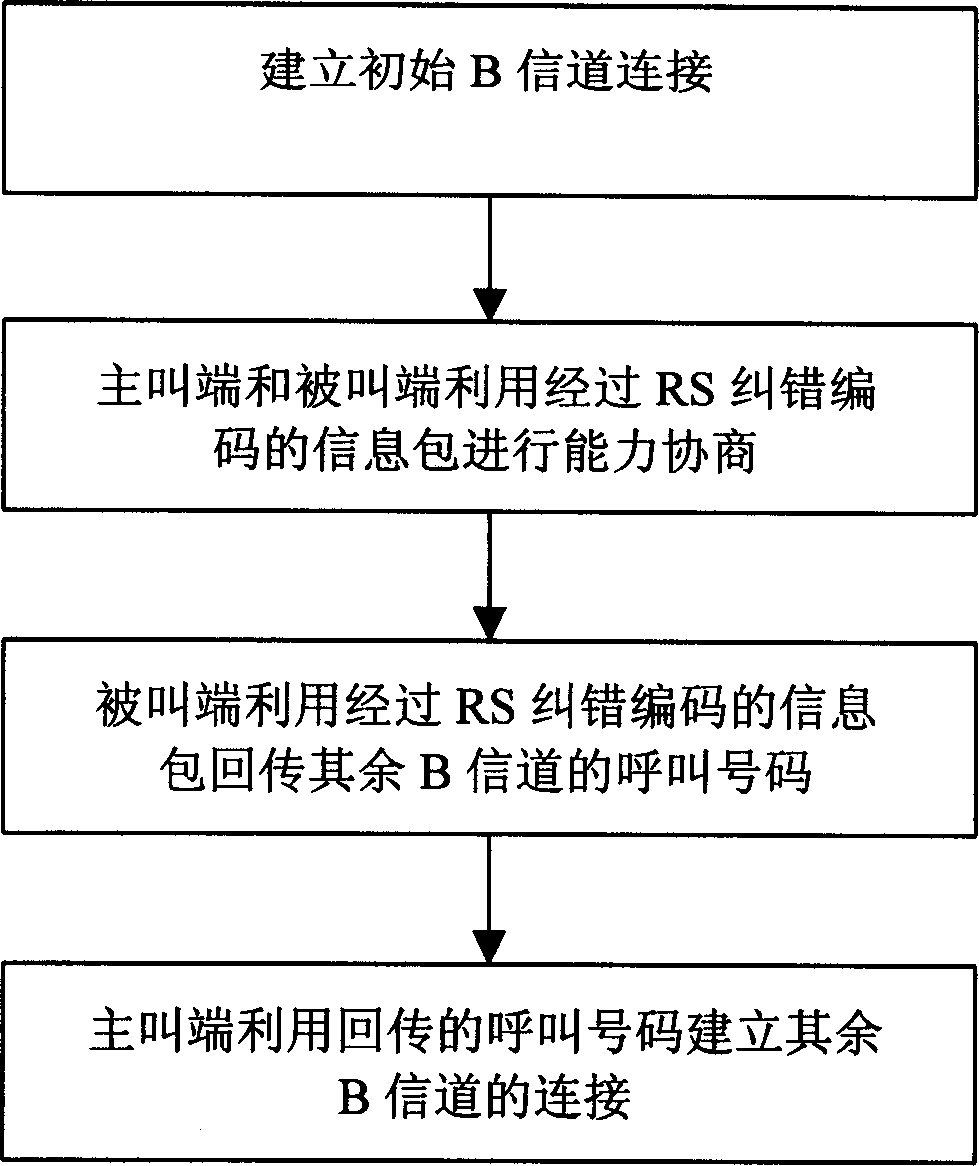
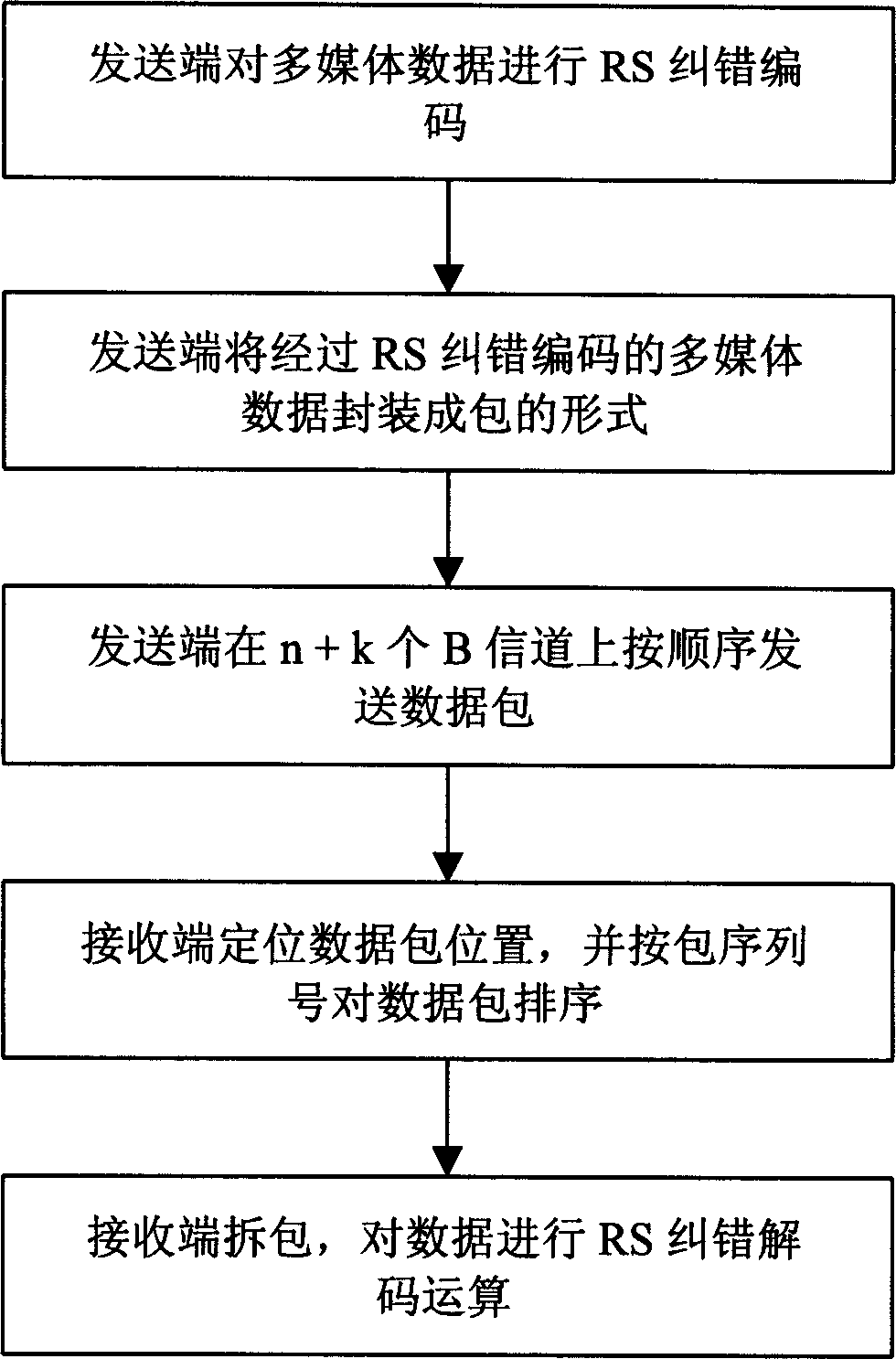
InactiveCN1479489AReduce bit error rateAvoid bad consequencesSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareNetwork packet
The method includes creating B channel and transmitting multimedia data. Creation of B channel includes following steps: building initial B channel connection, negotiating about capacity parameters is carried out in initial B channel between calling and called ends by using information packets through RS error correction coding; Then, the called end feedbacks other calling number in B channel by using the said information packets; the calling end creates connection of other B channels. Transmitting multimedia data includes following steps: multimedia data are carried out RS error correction coding at sending end; multimedia data are packed; data packets are sent in sequence in n+k pieces of B channels; receiving end positions data packets, ordering, unpacking packets and carrying RS error correction decoding data.
Owner:ZTE CORP
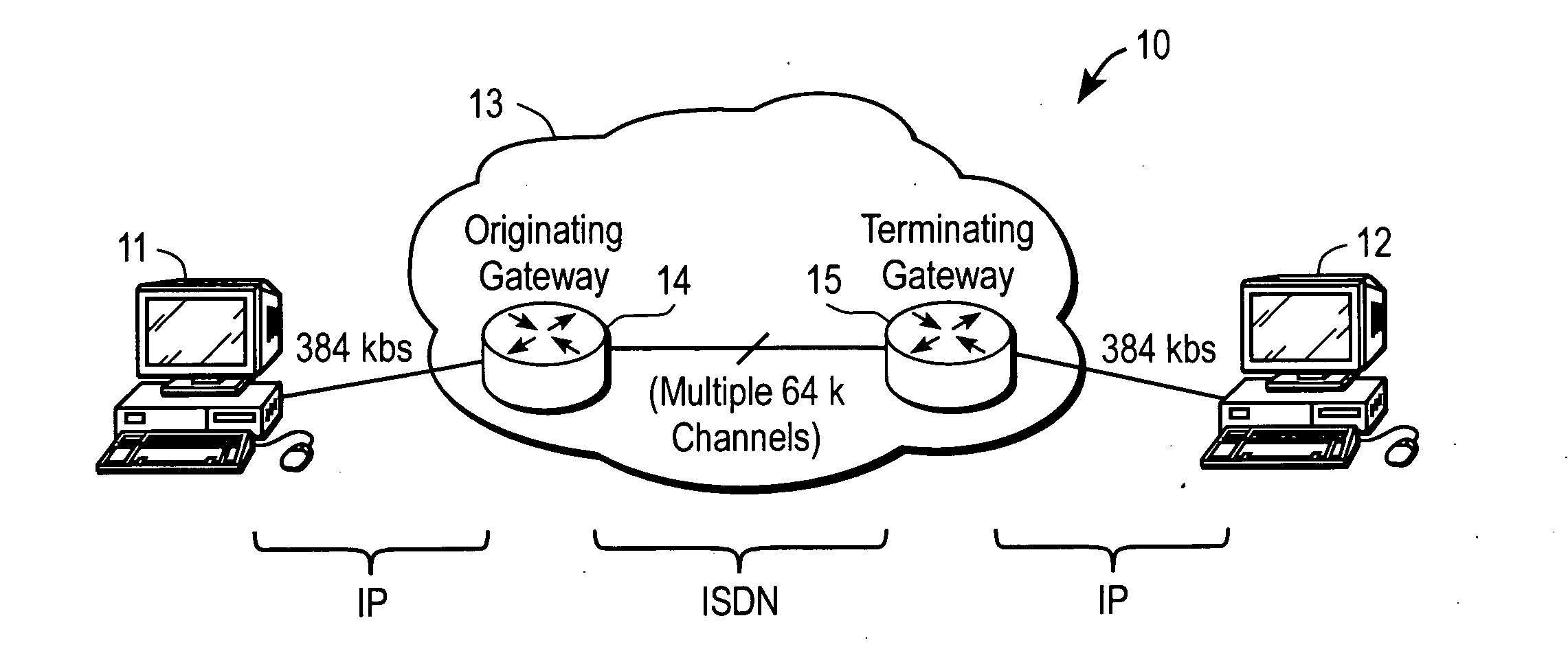
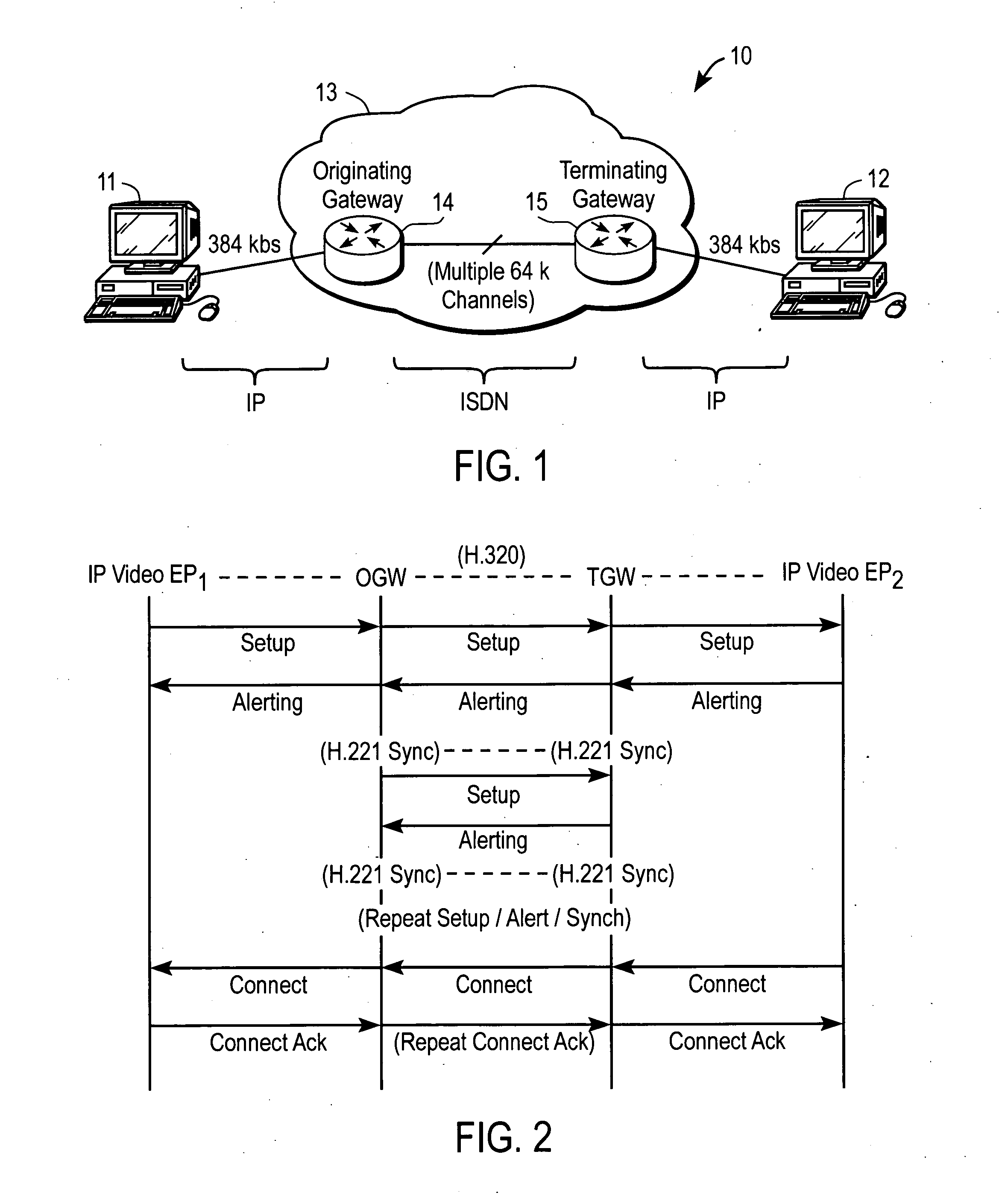
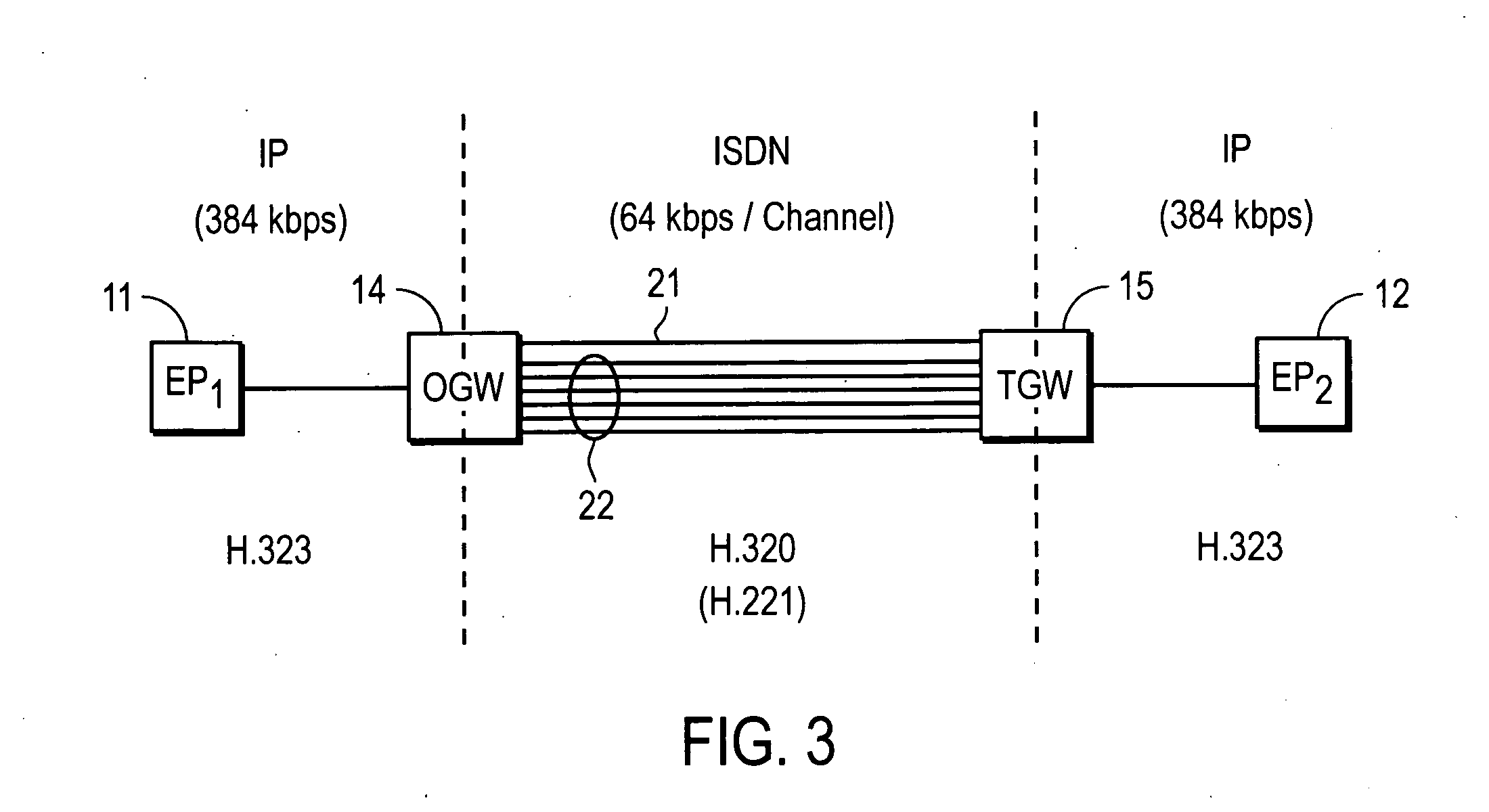
Interconnecting IP video endpoints with reduced H.320 call setup time
ActiveUS20080143816A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTTEthernetSubject matter
In one embodiment, a method includes sending, from an originating gateway device (OGW) to a terminating gateway device (TGW), a setup message for setting up a call on a primary bearer channel (B-channel) of an Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN). The OGW interconnects with a first Internet Protocol (IP) video endpoint, and the TGW interconnects with a second IP video endpoint. In response to an alerting message sent from the TGW, the OGW initiates procedures for synchronizing a plurality of secondary B-channels between the OGW and the TGW prior to the call entering into a connect state. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
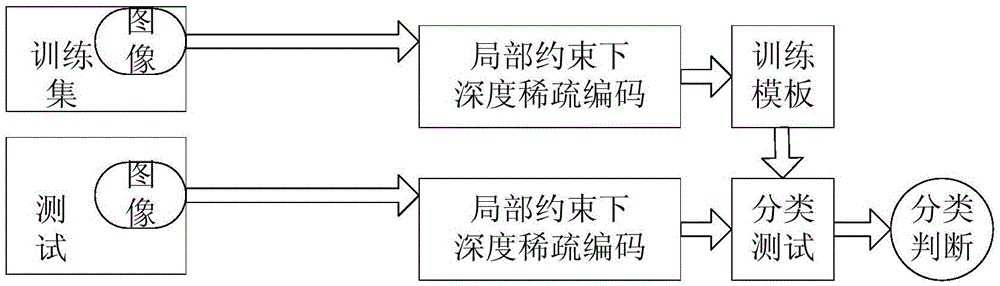
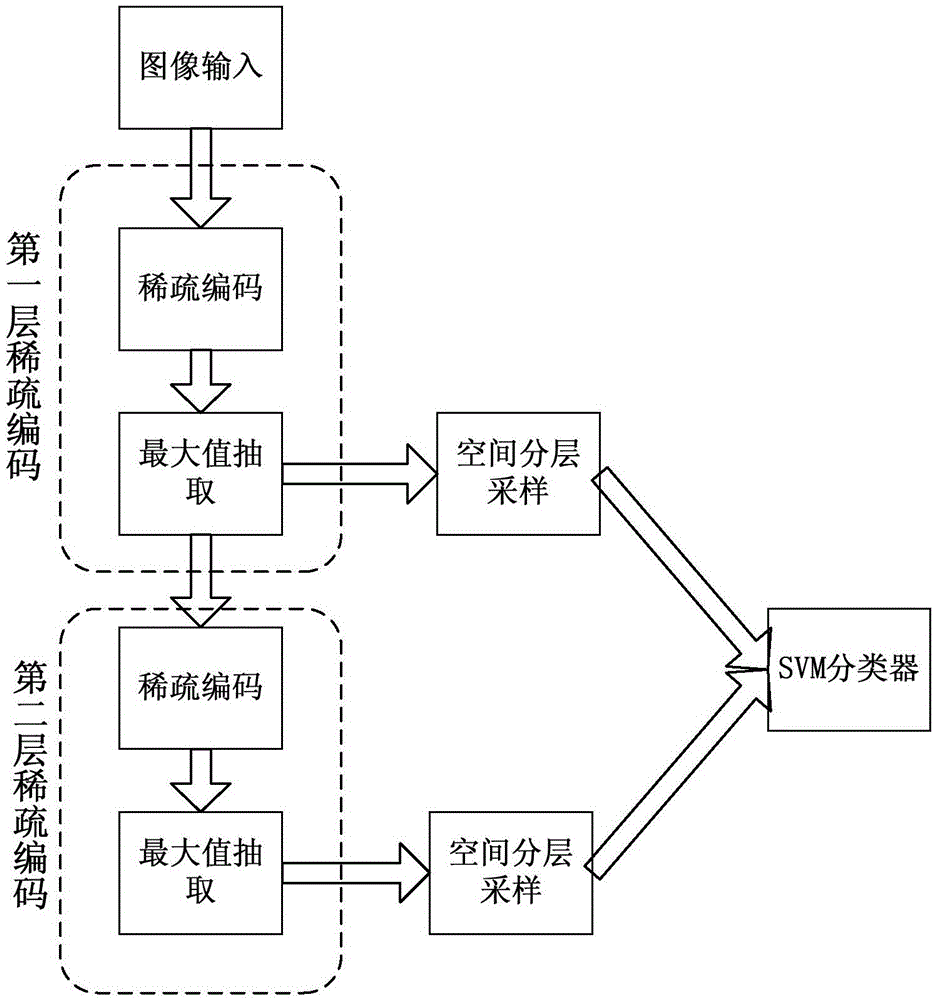
Bird image recognition method by multilayer sparse coding features
InactiveCN105631469AImprove recognition accuracyEmphasis on local smoothnessCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature codingObject function
The invention discloses a bird image recognition method by multilayer sparse coding features. Firstly, a cascaded multilayer sparse coding structure is used on R, G and B channels of a local image block for extracting sparse coding features, wherein each layer of sparse coding structure comprises a feature coding part and a feature maximum value extraction part; and then, in the aspect of output features, the multilayer sparse coding features use a linear kernel for fusion, and an SVM is used as a classifier for classified judgment. In the multilayer sparse coding structure, a local constraint term is added to an optimization objective function, a solved approximate solution for the objective function is iteratively used for sparse coding in the feature coding part, the coding values are then used for minimally reconstructing errors, and a dictionary is updated. According to the bird image recognition method by multilayer sparse coding features, the bird image recognition precision by the system can be greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Adaptive transmission in multi-access asynchronous channels
InactiveUS7719981B2Prevent unacceptable latencyError preventionTransmission systemsDecision networksTime-division multiplexing
A hybrid transmission cycle (HTC) unit of bandwidth on a shared transmission medium is defined to include an adaptive, time division multiplexing transmission cycle (ATTC), which is allocated in portions sequentially among all participating network entities, and a residual transmission cycle (RTC), which is allocated in portions, as available, to the first network entity requesting access to the shared medium during each particular portion. The ratio of logical link virtual channels, or D-Channels, to data payload virtual channels, or B-Channels, within the ATTC is adaptive depending on loading conditions. Based on transmission profiles transmitted on the D-Channels during the ATTC, each network entity determines how many B-Channels it will utilize within the current HTC. This calculation may be based on any decision network, such as a decision network modelling the transmission medium as a marketplace and employing microeconomic principles to determine utilization. The ratio of the duration of the ATTC segment to the duration of the RTC segment is also adaptive depending on loading conditions, to prevent unacceptable latency for legacy network entities employing the shared transmission medium. During the RTC, utilization of the shared medium preferably reverts to IEEE 802.3 compliant CSMA / CD transmission, including transmissions by HTC-compliant network entities.
Owner:GLOBAL COMM INVESTMENT LLC
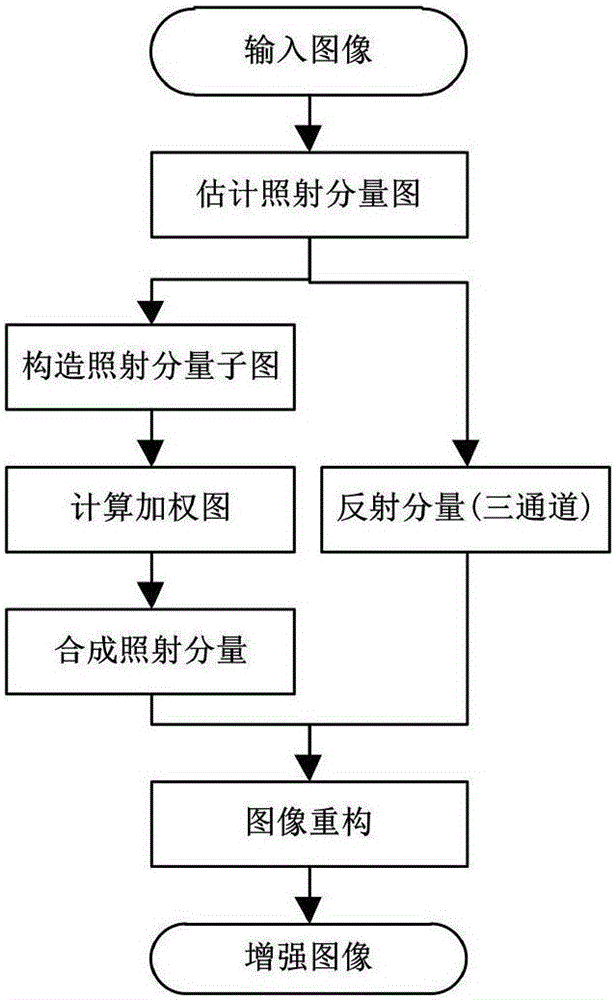
Low-light-level image enhancement method based on fusion technology
InactiveCN106485674AIncrease contrastImprove visual qualityImage enhancementImage contrastContrast enhancement
The invention relates to a low-light-level image enhancement method based on a fusion technology. The method comprises that F<c> is used to represent an input colored low-light-level image, C represents R, G and B channels, and a radiation component L1 and a reflection component RC are calculated; a contrast limited histogram equalization method(CLAHE) is used to process the L1 to obtain a contrast enhanced result image L2; a low-grayscale part in the L1 image is extended, a high-grayscale part is compressed, and a processing result is represented by L3; a radiation component weighted subimage and a chroma component weighted subimage are calculated; a synthesis weight image is calculated; a new radiation component image is synthesized; and an enhanced colored image is reconstructed. According to the method of the invention, the low-light-level image is enhanced effectively, the image contrast is enhanced, color information of the original image is reserved effectively, and the visual image of the image is improved substantially.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
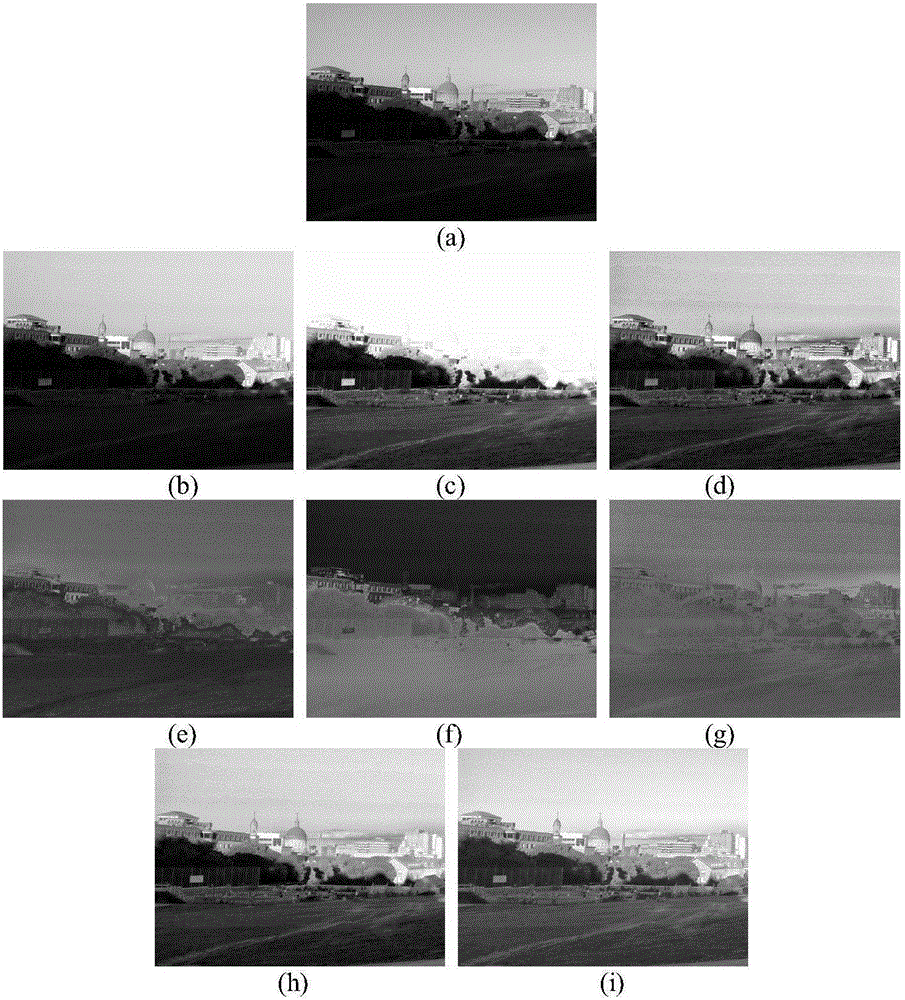
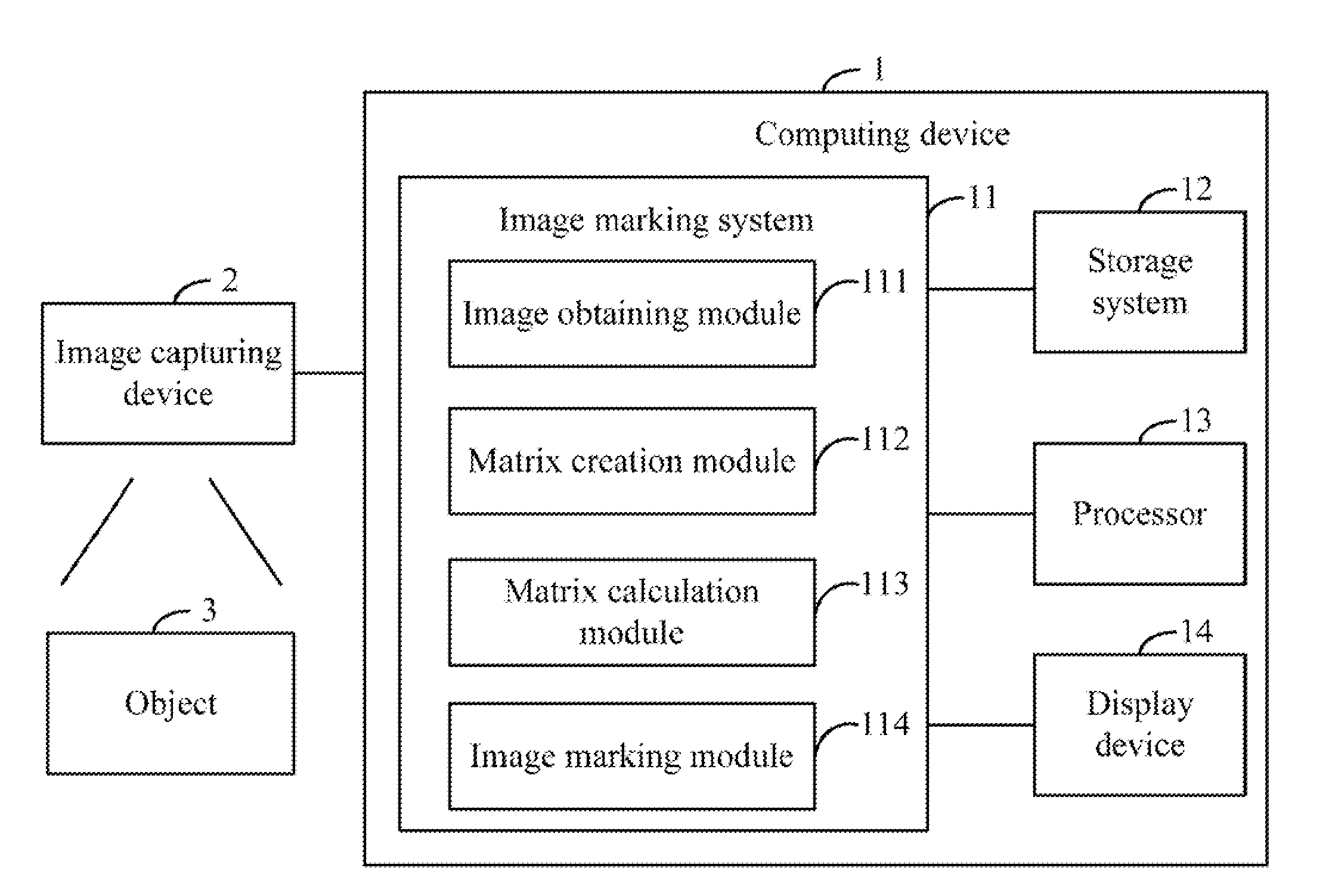
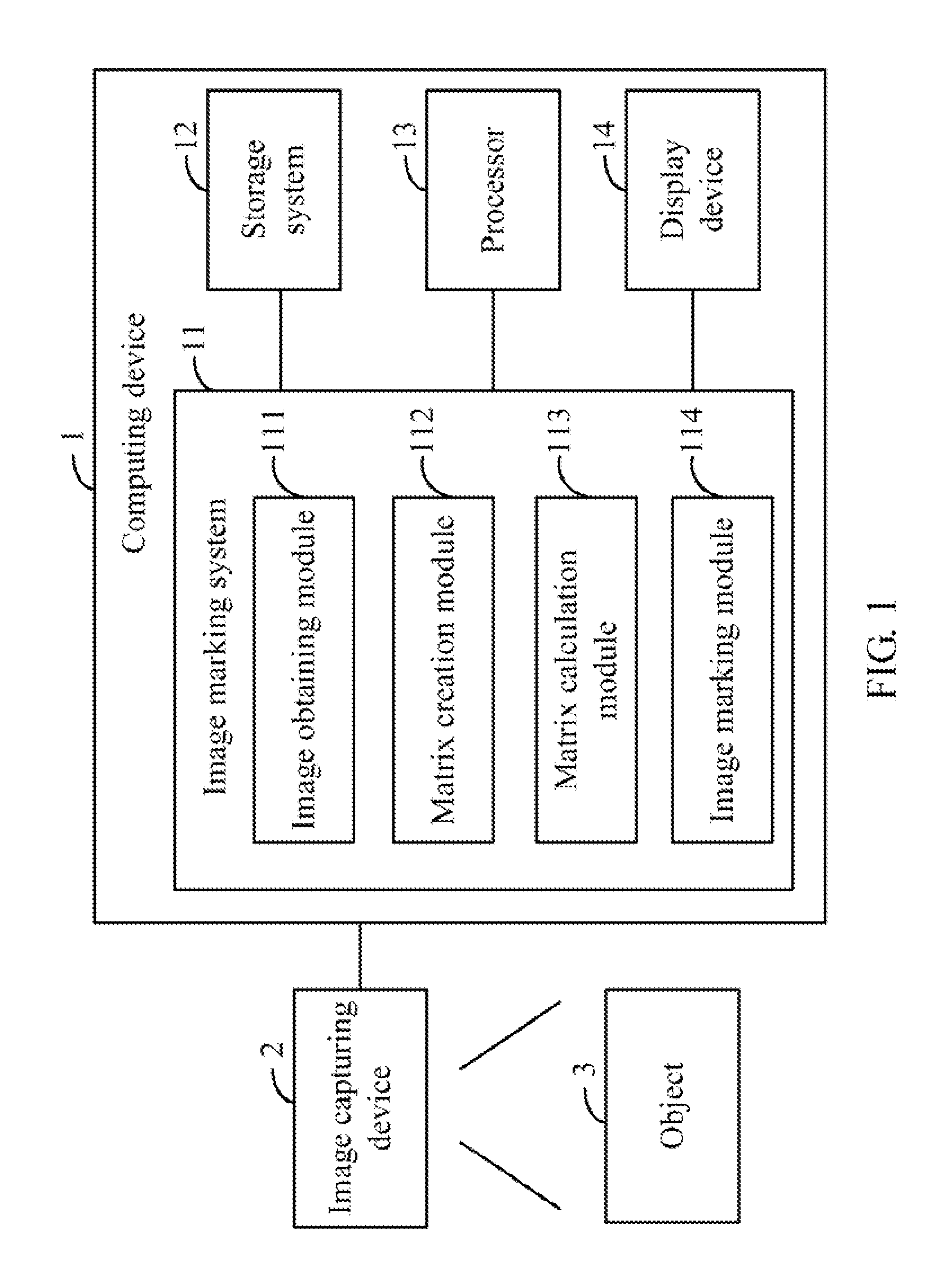
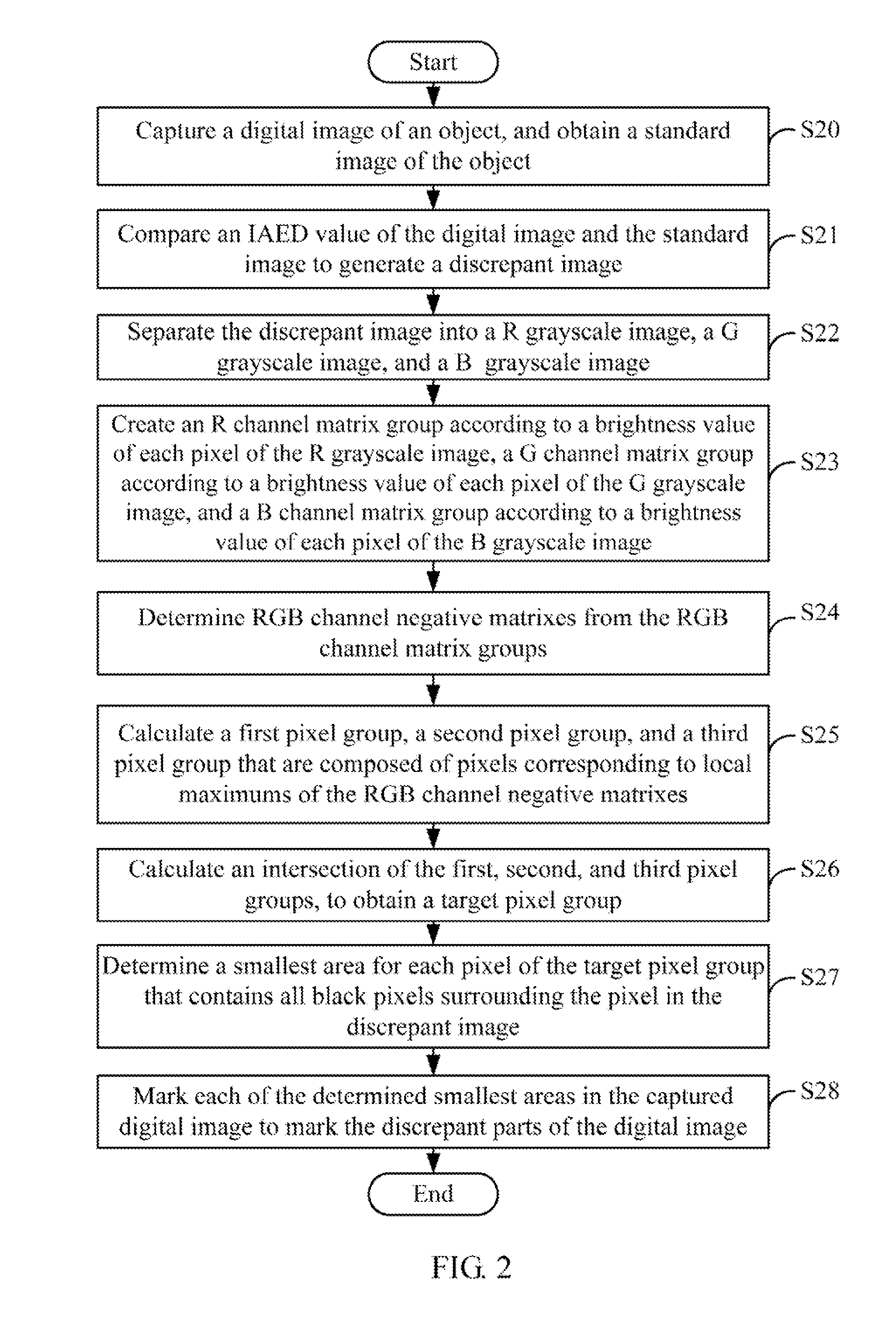
System and method for marking discrepancies in image of object
In a method for marking discrepancies of a captured image of an object, an image is captured and compared to a standard image. A discrepant image showing any discrepancies of the captured image is generated, and is separated into an R grayscale image, a G grayscale image, and a B grayscale image. An R channel matrix group, a G channel matrix group, and a B channel matrix group are created. R channel negative matrixes, G channel negative matrixes, and B channel negative matrixes are determined from the RGB channel matrix groups. RGB pixel groups are calculated based on the R channel negative matrixes, the G channel negative matrixes, and the B channel negative matrixes. A target pixel group to be marked is determined by calculating an intersection of the RGB pixel groups. The discrepancies of the digital image are marked out according to the target pixel group.
Owner:WARECONN TECH SERVICE (TIANJIN) CO LTD
Encoder
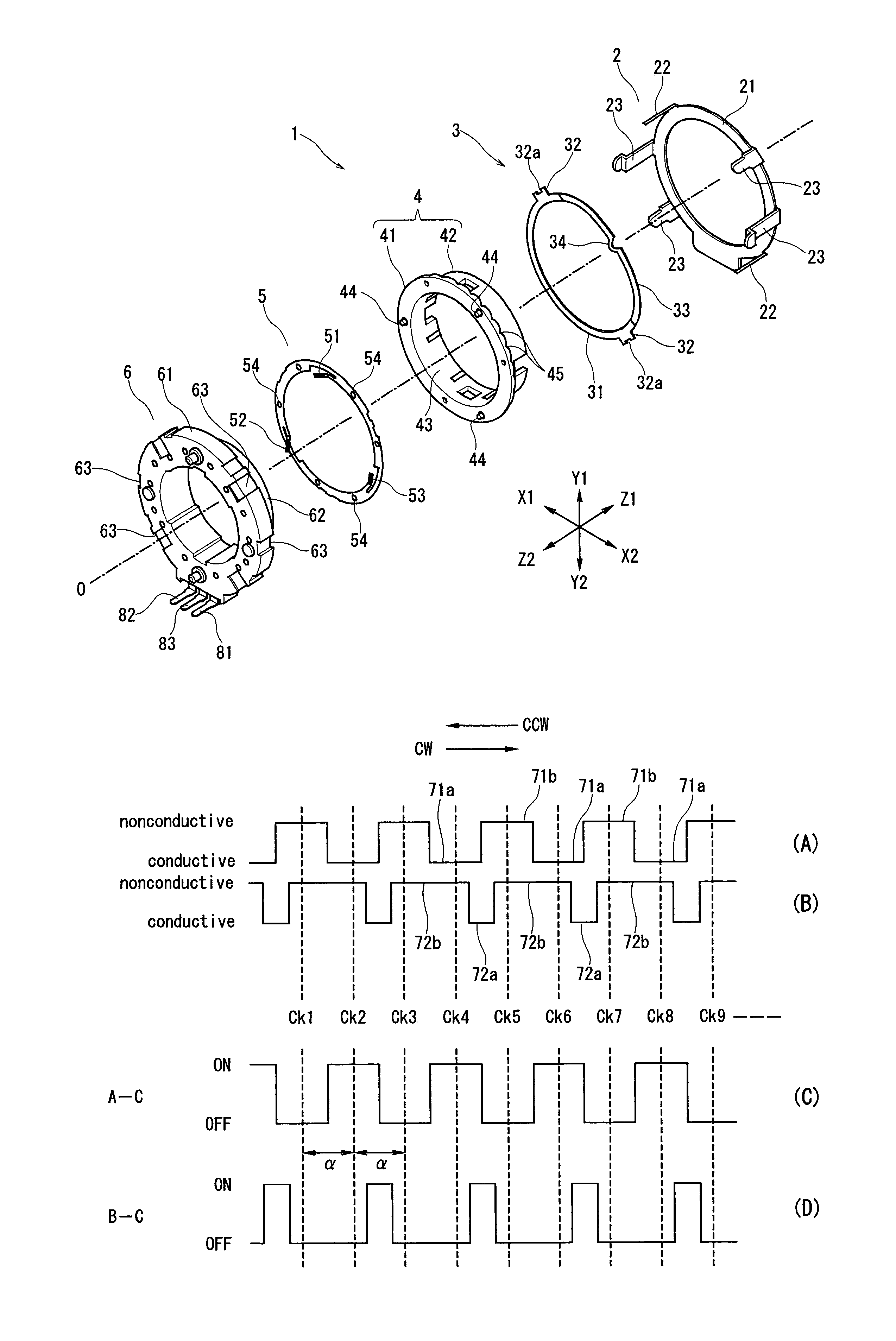
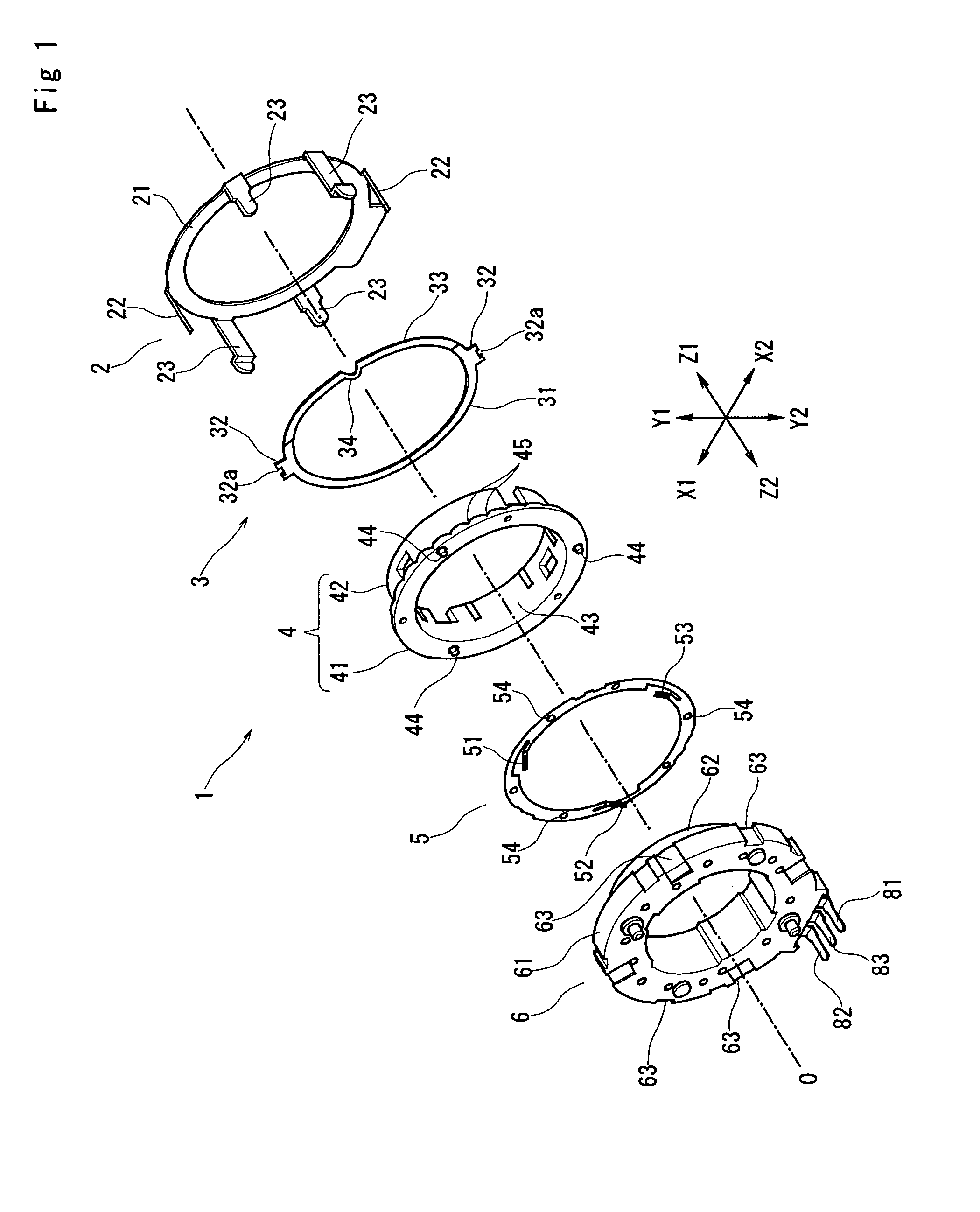
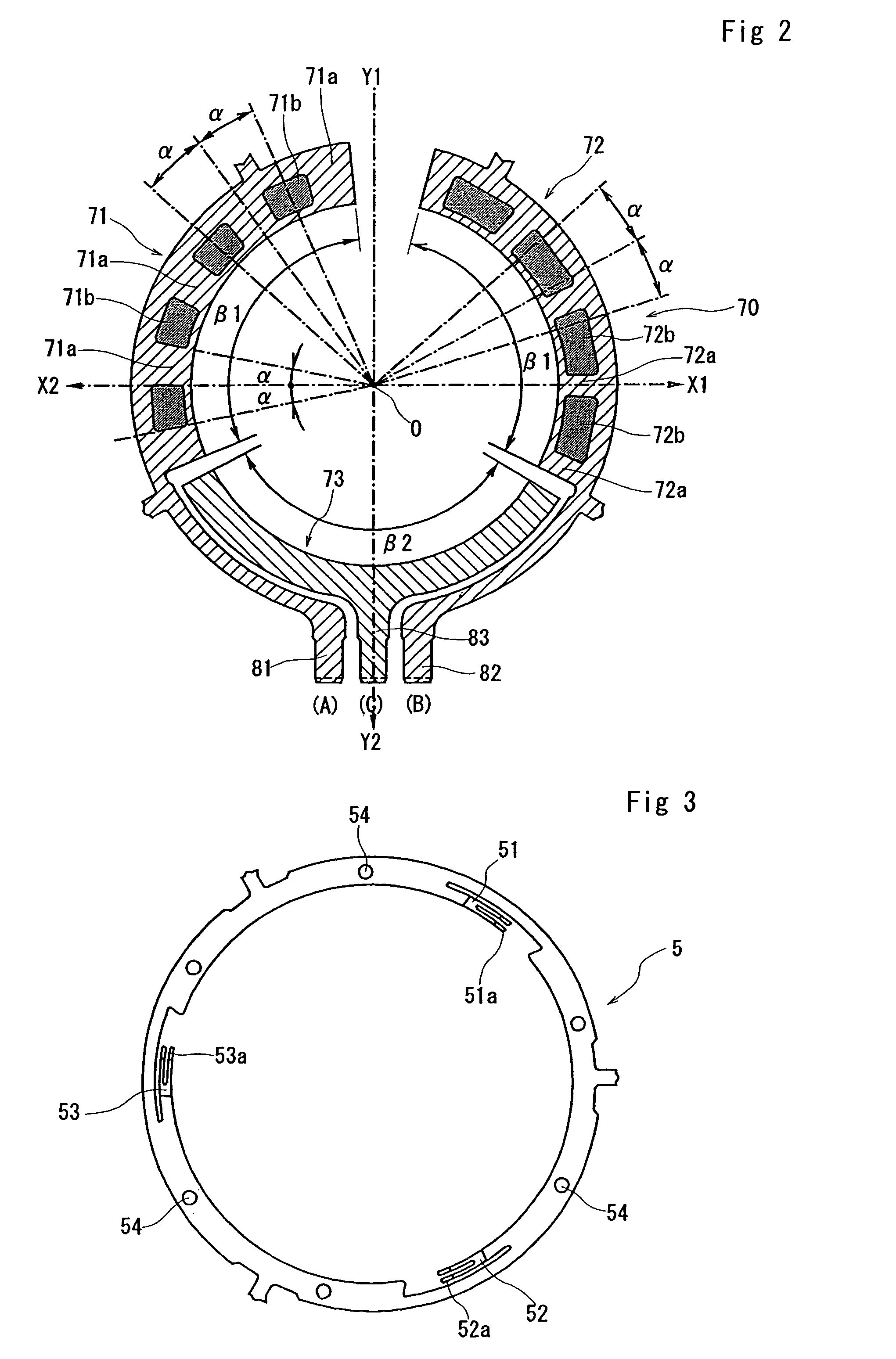
InactiveUS6973731B2Avoid failureEasy to detectAngles/taper measurementsUsing electrical meansEngineeringChannel pattern
Disclosed is an encoder including a rotary member and a fixed member. The fixed member is provided with an electrode having A-channel, B-channel and C-channel patterns, the rotary member is provided with contacts which are to be opposed to the electrode. A-C state switches from OFF to ON at each rotation of the rotary member for one click angle from a stable click position in both CW and CCW direction. During CW rotation for one click angle, B-C state remains unchanged from OFF; during CCW rotation for one click angle, B-C state switches twice between ON and OFF.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
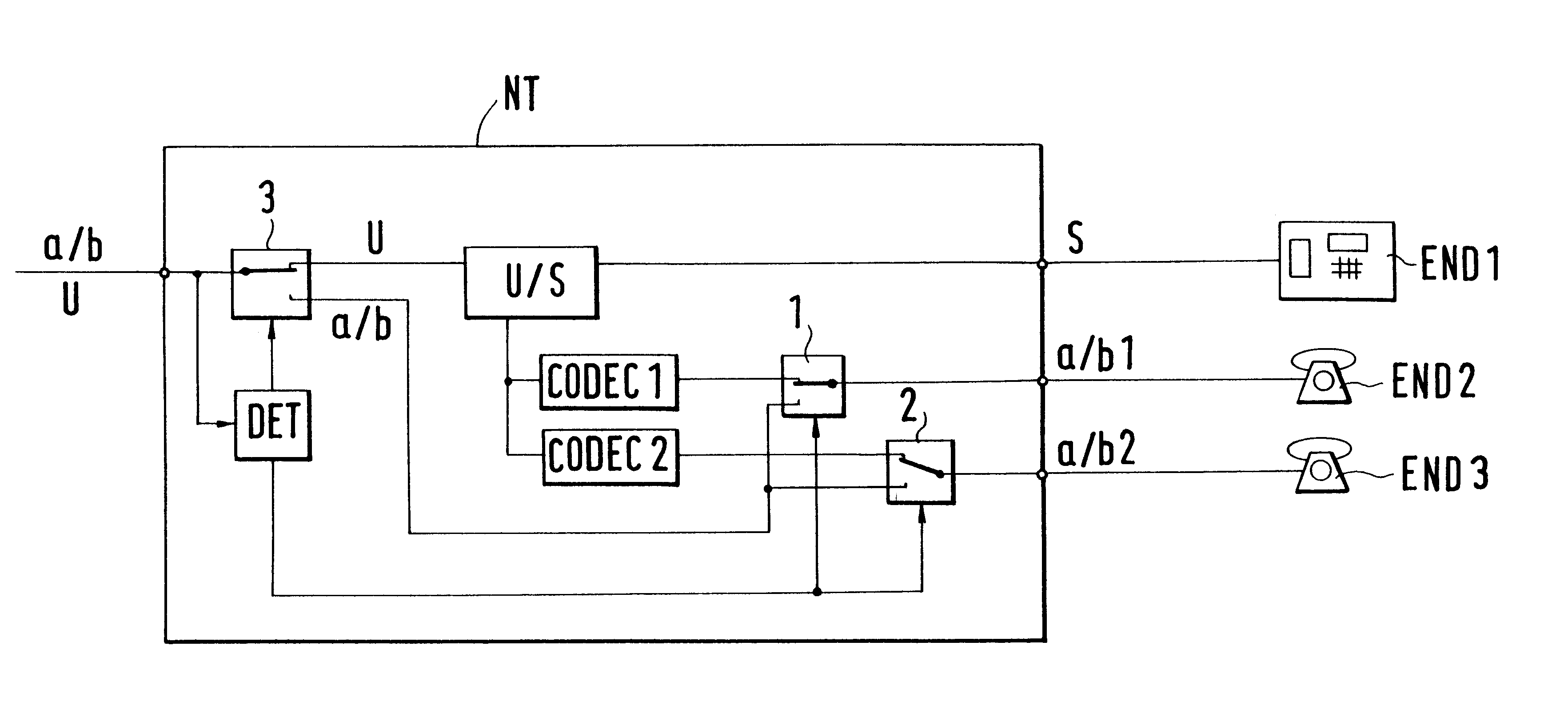
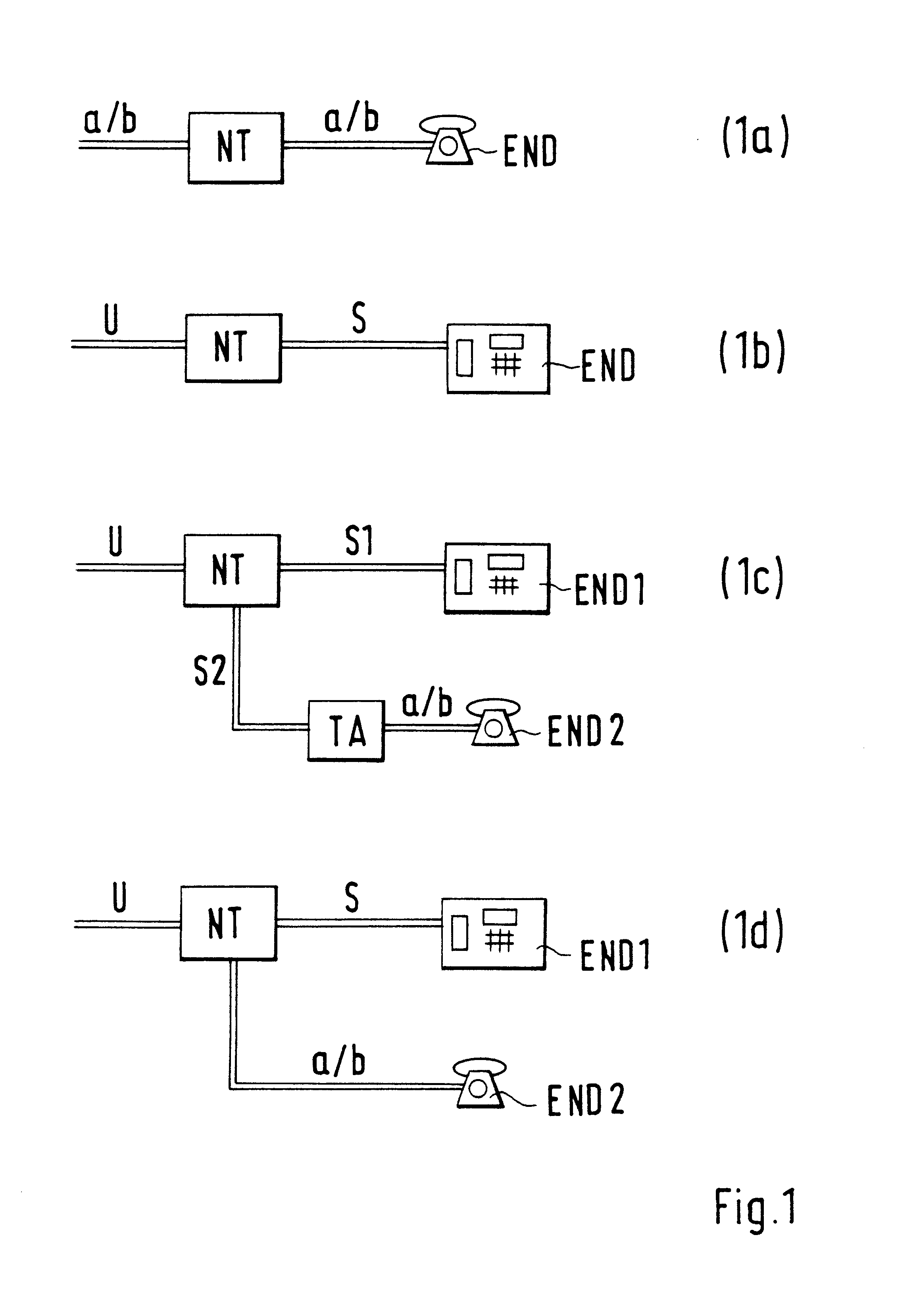
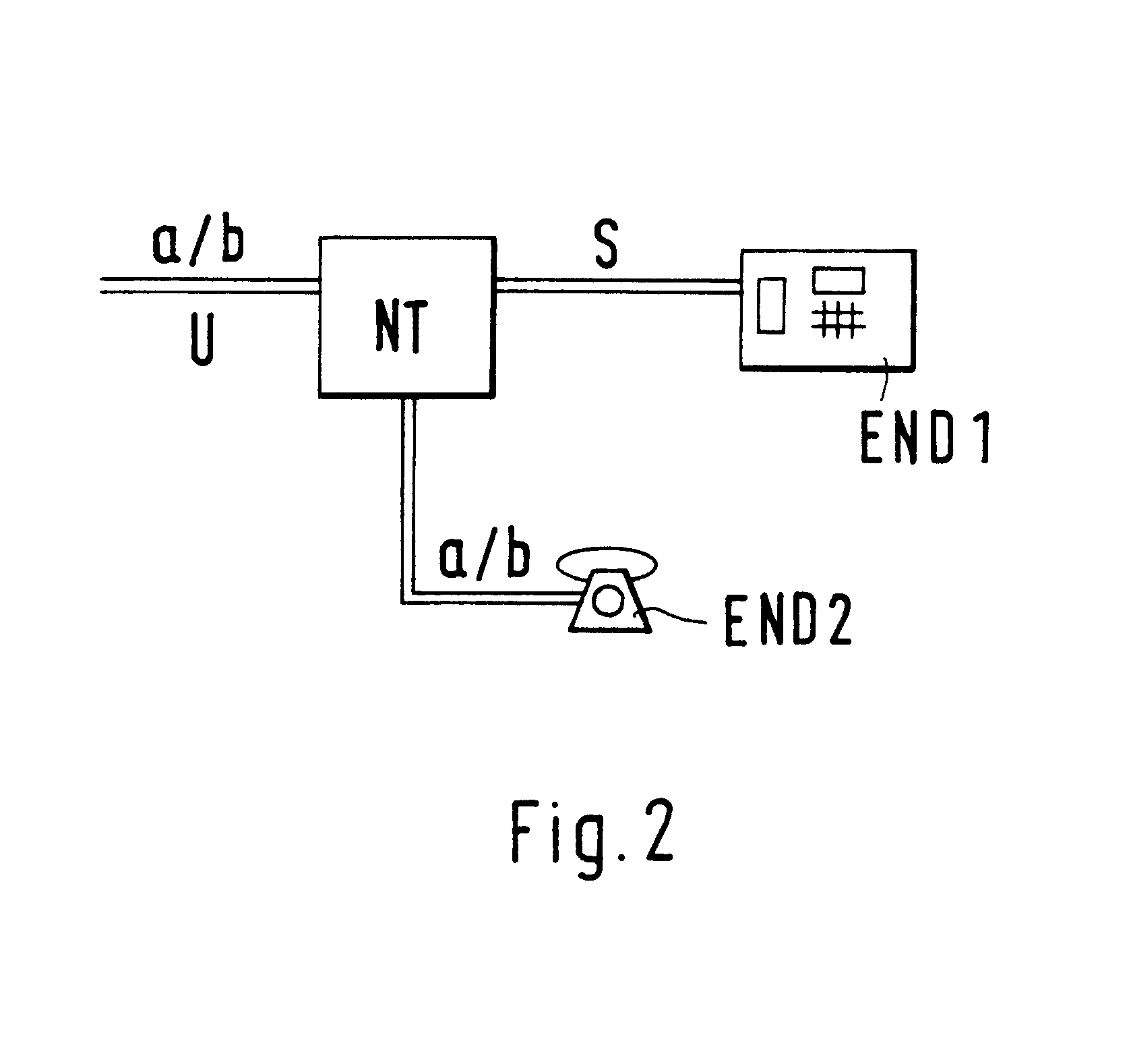
Network termination of a telecommunications network
InactiveUS6901142B1Universally applicableSave connection chargeInterconnection arrangementsSubstation equipmentNetwork terminationSerial digital interface
A network termination (NT) which is universally applicable and permits fair billing. The network termination (NT) according to the invention is characterized in that it comprises a switching facility (DET, 1, 2, 3) whereby the interface (a / b, U) on the network side is switchable from an analog one (a / b) to a digital one (U). A subscriber who needs a digital interface, for example because he wants to have two B channels of the ISDN at his free disposal, can release a digital interface (U) or have it released. A subscriber who wants only an analog access can release an analog access or have it released. To accomplish this, the network termination (NT) contains a switch (3) and a detector (DET). The switching between analog access and digital access on the network side can be effected without replacement of the network termination (NT).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Color image searching method based on multiple features
InactiveCN104484425AGuaranteed accuracyNo manual processingImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageCoupling
The invention discloses a color image searching method based on multiple features. The method comprises the following steps: during a process of searching the color image, extracting R,G, B channels of a to-be-searched color image, respectively calculating an exponential moment value of each channel and taking the exponential moment value as a color feature; converting the color image from an RGB color space into an HIS color space, utilizing an I component to calculate a local corner phase feature and taking the local corner phase feature as a textural feature; comprehensively performing color image searching through the color feature and the textural feature. The color information and the textural information of the image are combined with each other, so that the method provided by the invention can be effectively applied to the color image searching, the precision of the searching result is ensured, the method has the characteristics of simple calculation, no need of manual treatment on to-be-searched image, strong universality, low coupling, and the like, and the practicability for digital image searching is enhanced.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
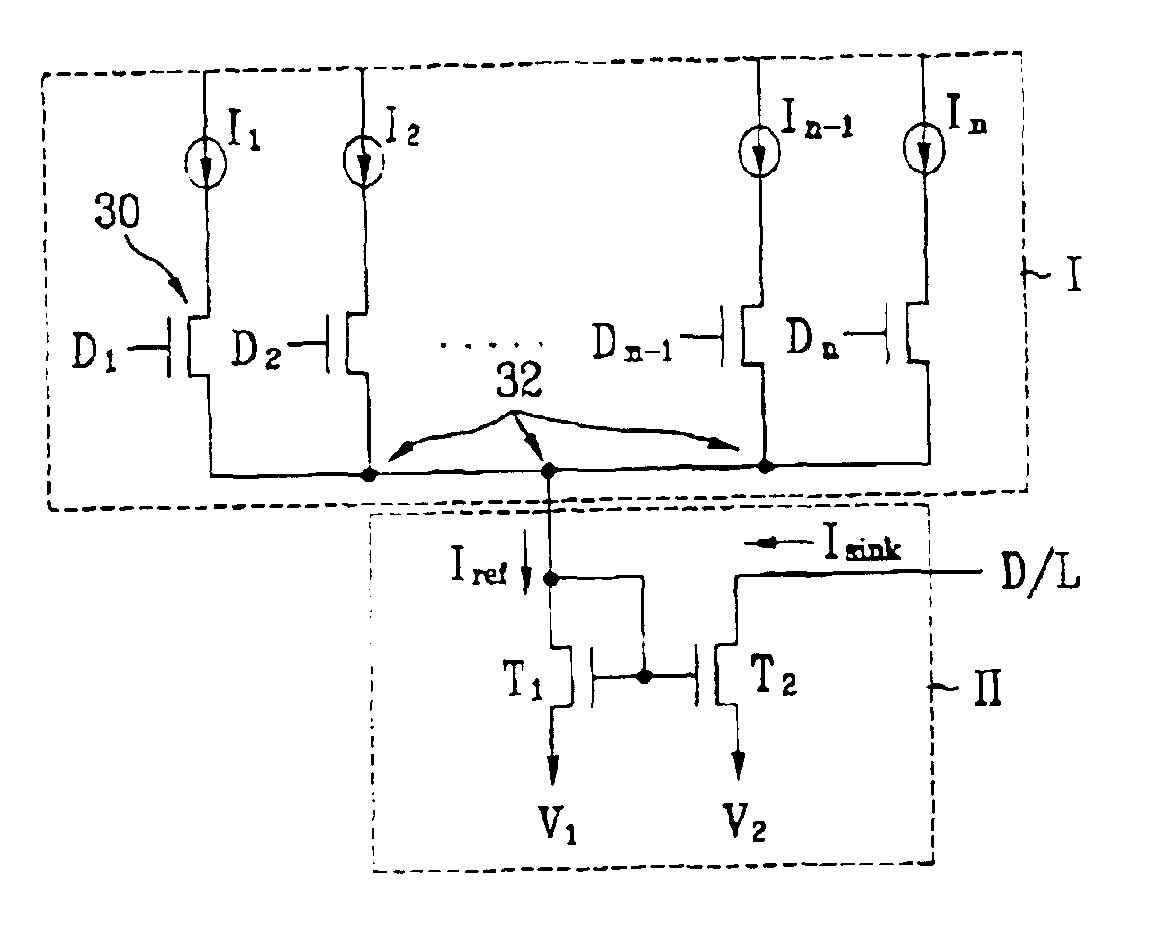
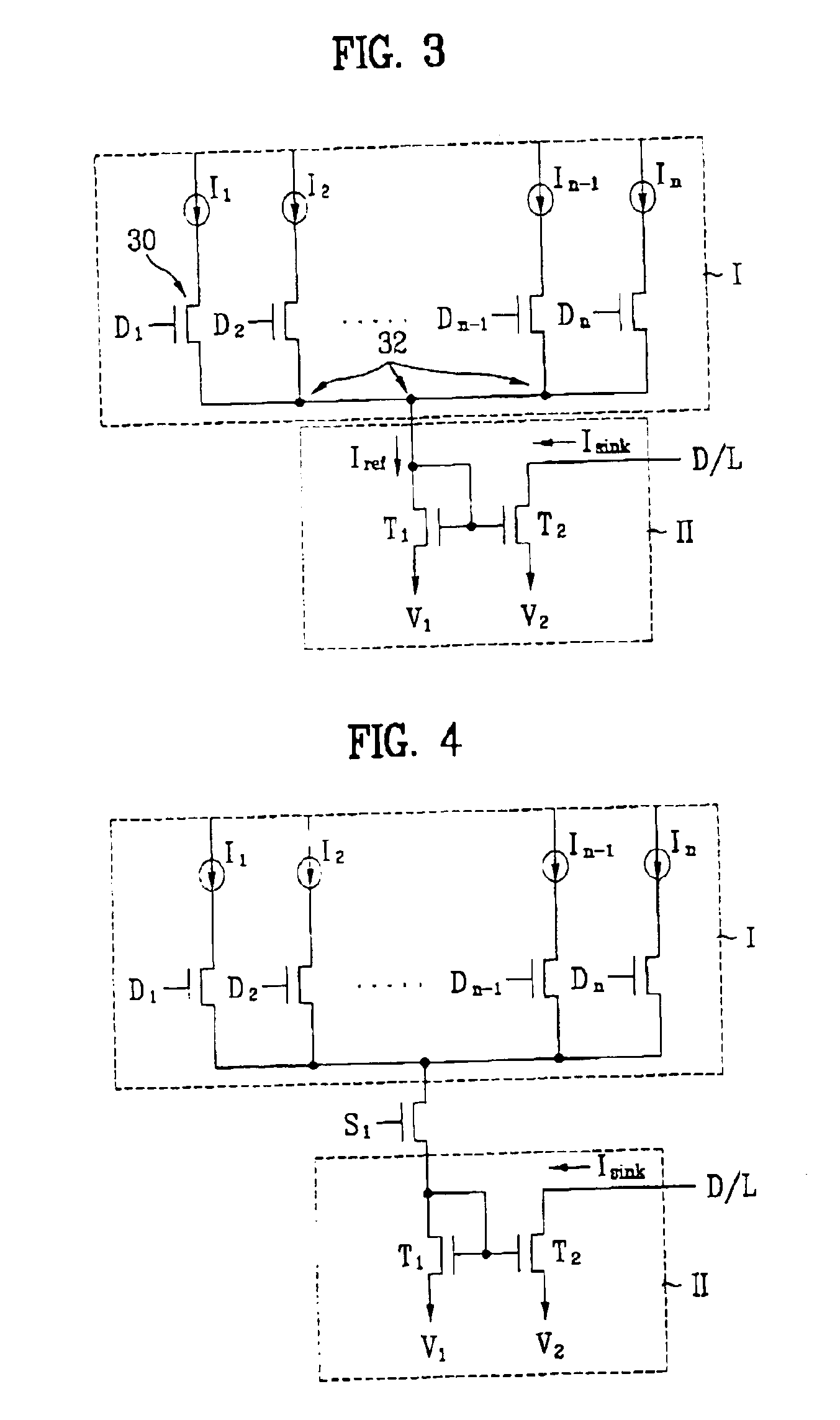
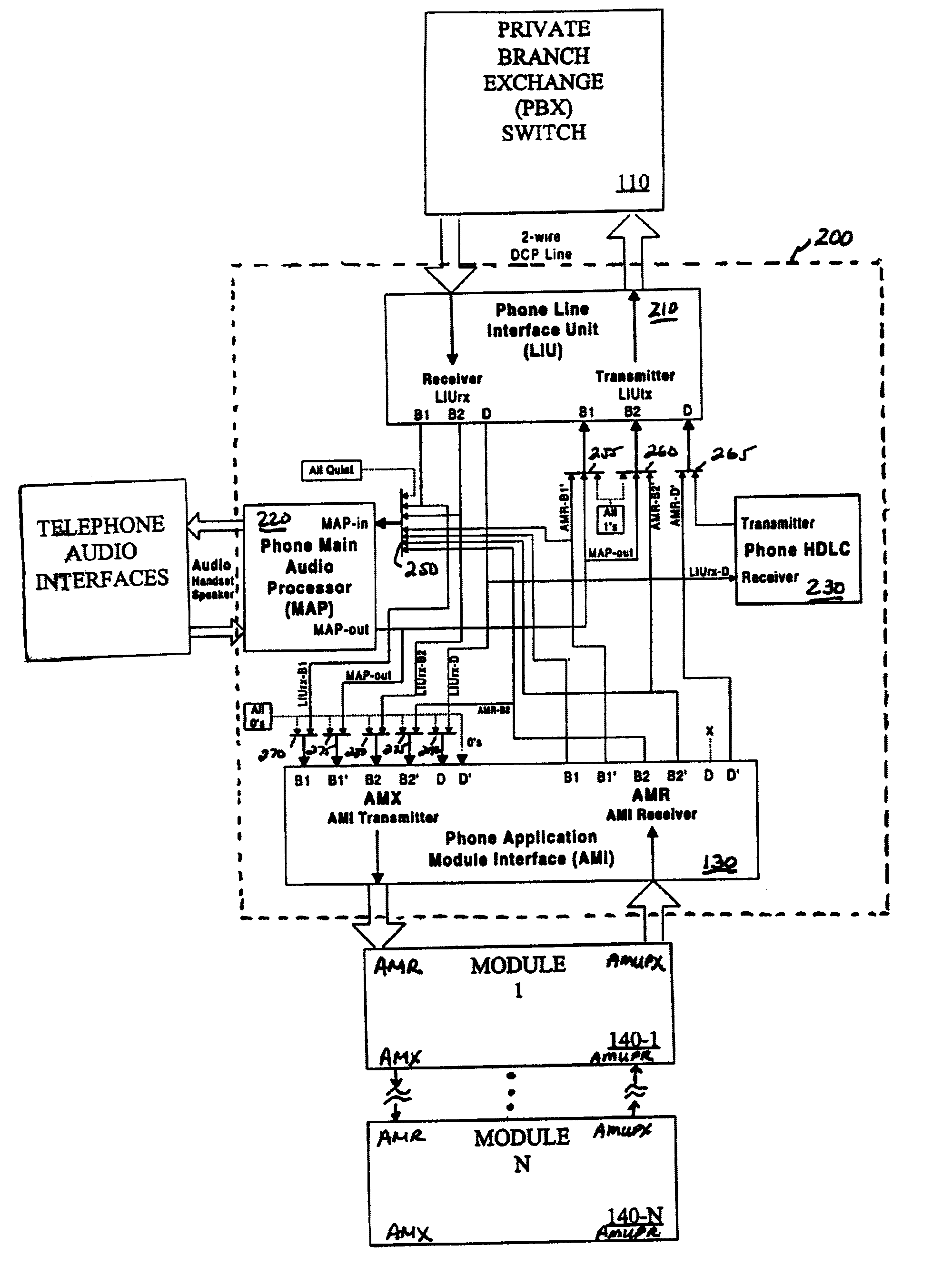
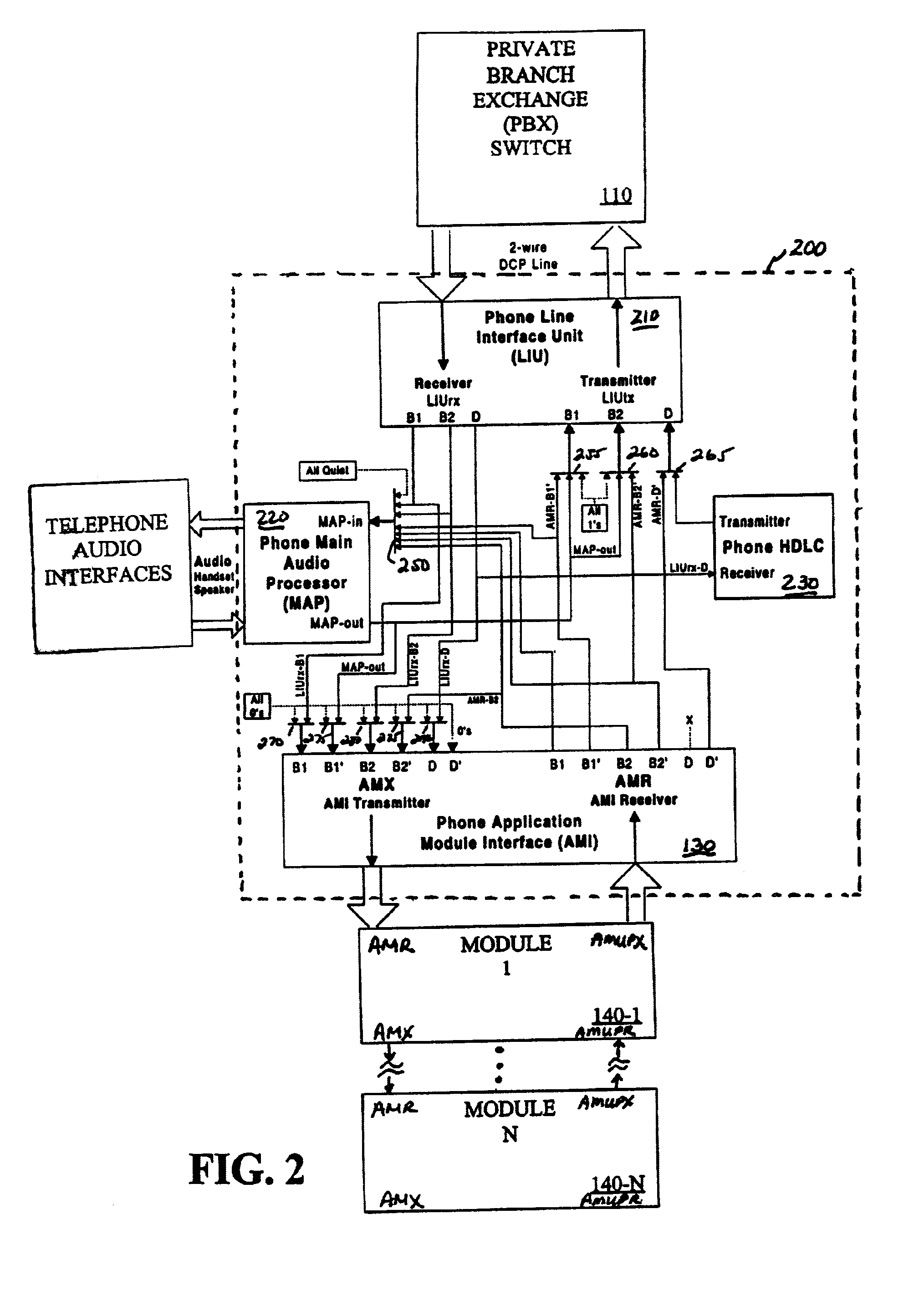
Application module interface for bidirectional signaling and bearer channels in a private branch exchange (PBX) environment
InactiveUS7154865B1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsModem deviceTelephone terminal
An application module interface is disclosed that allows one or more modules to access voice or data channels in a private branch exchange environment that contains one or mole B channels (bearer channels) for transmitting voice or data signals, and one or more D channels (signaling channel) for transmitting data. The application module interface provides a control channel that allows a module to obtain and vary the status and configuration of a telephone terminal. The application module interface provides access to both directions of two B channels (B1 and B2) and one D channel. The application module interface is the only interface required to connect the two B channels (B1 and B2) and one D channel to or from the telephone terminal and the add-on module. A frame format includes a start bit (logic “1”), a number of data bits allocated to the D channels (D, D′) and B channels (B1, B1′, B2, B2′), and eight stop bits (logic “0”). A tip / ring, module allows an analog device, such as a facsimile machine or modem, to access the digital voice and data channels associated with the private branch exchange switch. An RS-232 or a Universal Serial Bus module allows a personal computer or other enabled device to interact with and control the operation of a telephone terminal for computer telephony integration applications.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Apparatus and method for restoring image based on distance-specific point spread function
ActiveUS8159552B2Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionEdge mapsPoint spread function
An apparatus and method for restoring an image are provided. The apparatus includes an edge-strength-detection module which detects an R-channel edge strength, a G-channel edge strength and a B-channel edge strength from an input image and generates an R-channel edge map, a G-channel edge map and a B-channel edge map based on the R-channel edge strength, the G-channel edge strength and the B-channel edge strength; an edge-strength-compensation module which compensates for the R-channel edge strength and the B-channel edge strength based on the G-channel edge strength; a valid-value-generation module which generates a valid value indicating a blur level based on the compensated R-channel edge strength and the compensated B-channel edge strength; a point spread function (PSF) estimation module which estimates a PSF corresponding to the valid value; and an image-restoration module which restores the input image using the PSF.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
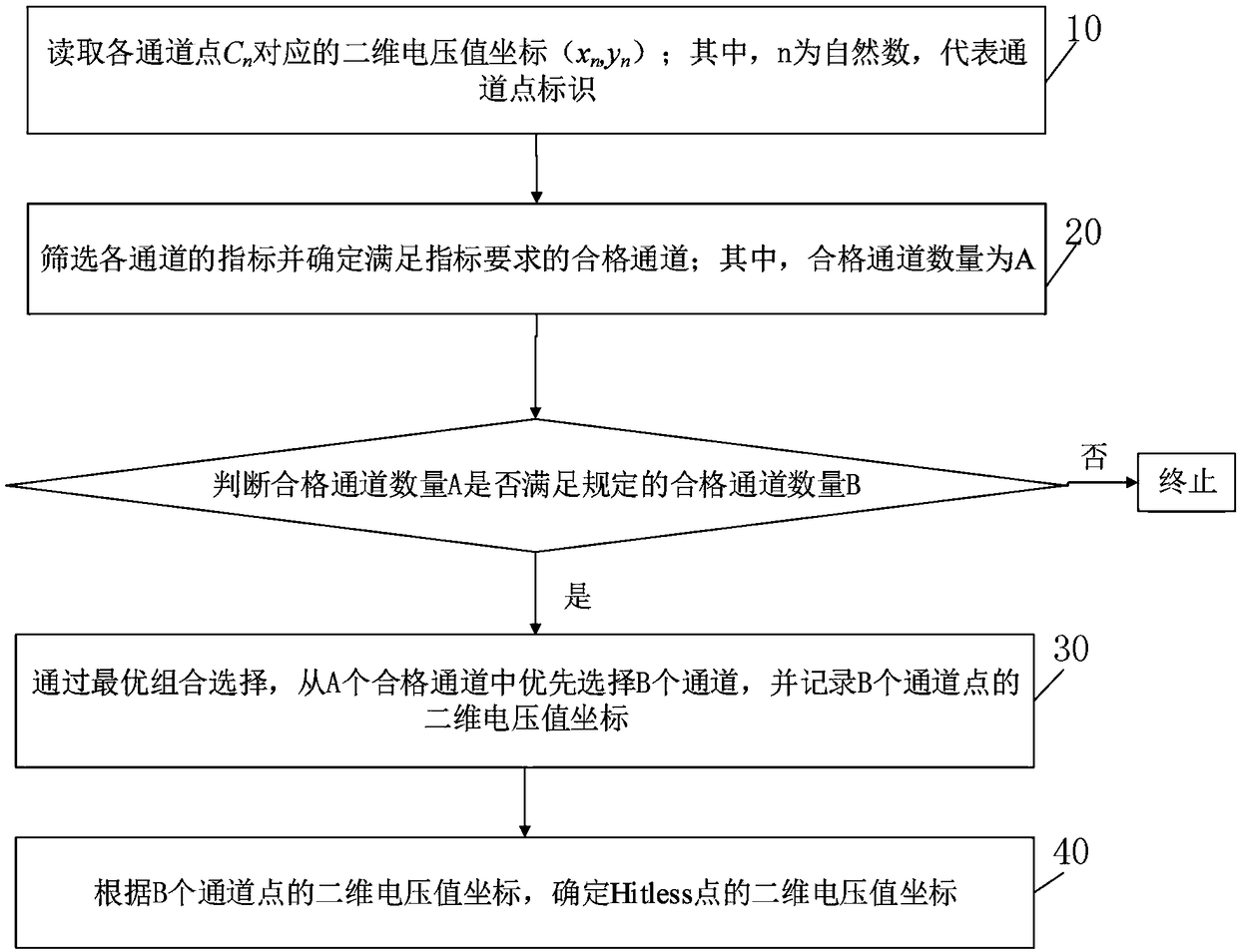
Intelligent selection method and device for two-dimensional MEMS OSW optical switch Hitless point
ActiveCN108768511AImprove screening yieldImprove screening efficiencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionOptical communicationUltimate tensile strength
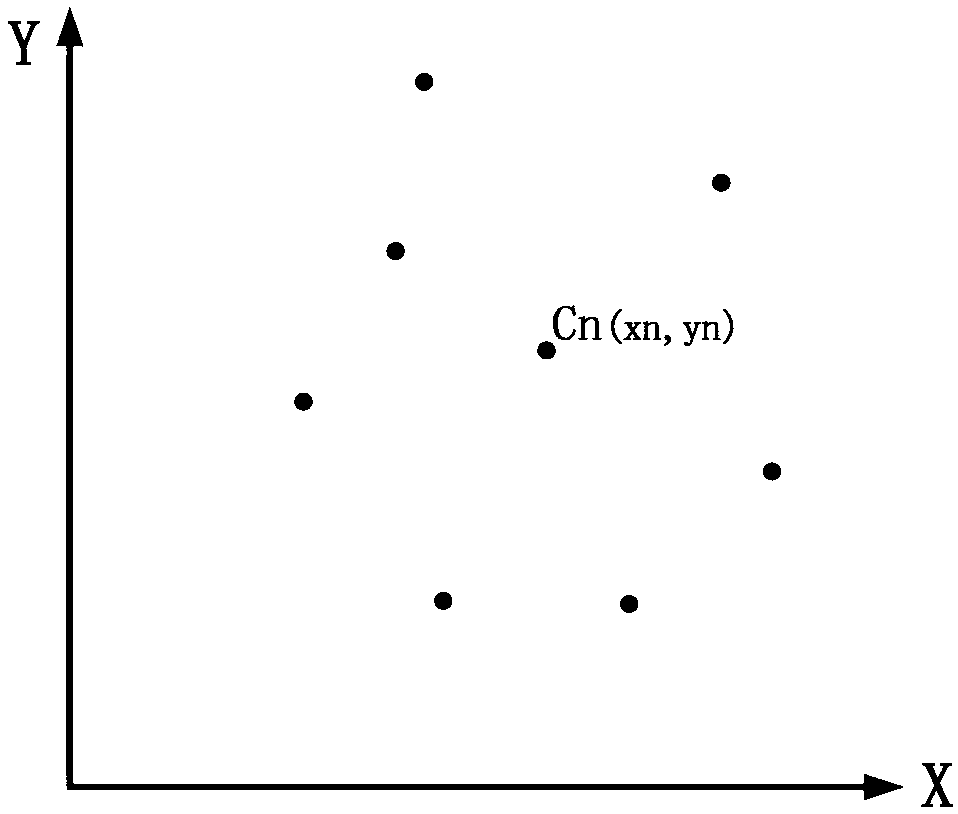
The invention relates to the technical field of optical communications, and in particular, to an intelligent selection method and an intelligent selection device for a two-dimensional MEMS OSW opticalswitch Hitless point, wherein the method comprises: reading a two-dimensional voltage value coordinate (xn, yn) corresponding to each channel point Cn; screening the indicators of each channel and determining the qualified channels satisfying the requirements of the indicators; preferentially selecting B channels from the A qualified channels; and determining the two-dimensional voltage value coordinate of the Hitless point according to the two-dimensional voltage value coordinates of the B channel points. In the intelligent selection method of the two-dimensional MEMS OSW optical switch Hitless point provided by the invention, the computer may quickly and intelligently select the optimal B channels and determine the Hitless point according to the optimal B channels and the selection ruleof the Hitless point, which replaces the traditional manual screening process, greatly improves the screening efficiency and accuracy, reduces the labor intensity of manual screening, and may realizemass production. When an interference channel point exists, a transit point is also set to avoid the emergence of the optical signal interference during channel switching.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
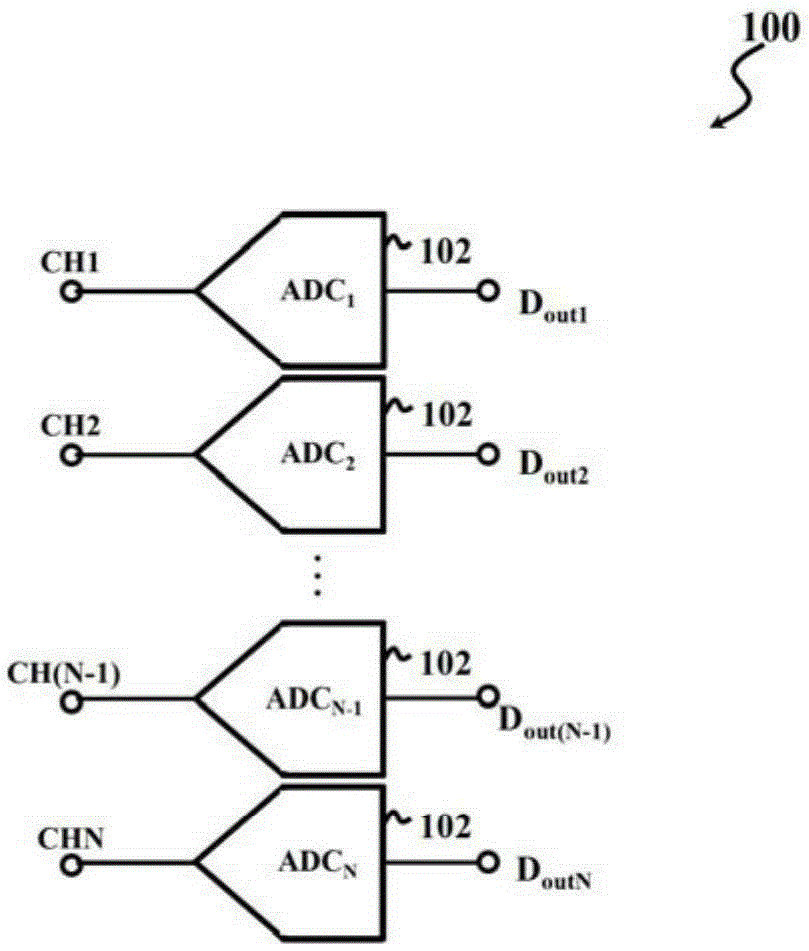
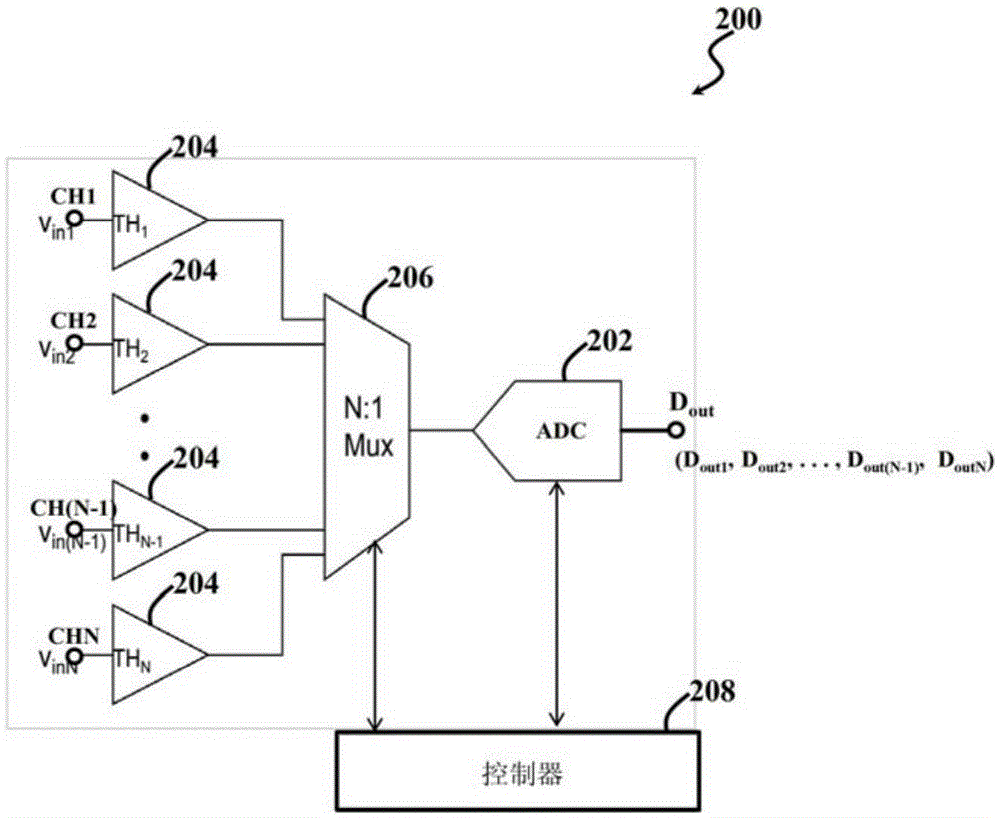
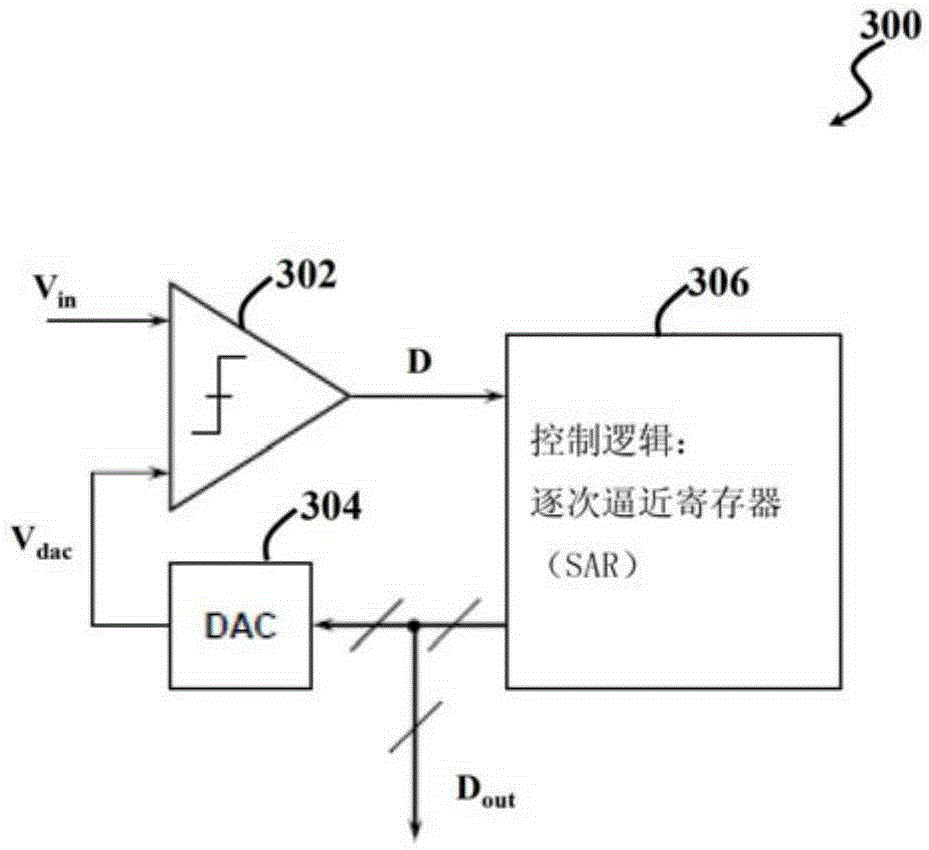
Multichannel analog-to-digital converter
InactiveCN105790766APower saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierMultiplexer
Multichannel successive approximation register (SAR) analog-to-digital converters (ADC), along with methods and systems for multichannel SAR analog-to-digital conversion, are disclosed herein. An exemplary multichannel SAR ADC can include a first SAR ADC for each of a plurality of input channels, and a second SAR ADC, a multiplexer, and a residue amplifier shared among the plurality of input channels. The multiplexer can select an analog residue signal from one of the first SAR ADCs for conversion by the second SAR ADC. The residue amplifier can amplify the selected analog residue signal. The second SAR ADC, multiplexer, and / or residue amplifier may be shared among all of the plurality of input channels. Where the multichannel SAR ADC includes N input channels, the second SAR ADC, multiplexer, and / or residue amplifier may be shared among b channels of the N input channels.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES GLOBAL
Image restoration method and device
The embodiment of the application provides an image restoration method and device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a first pixel set of an image to be restored, wherein the pixel values of pixels in the first pixel set are pixel values obtained through red light R channels, green light G channels, blue light B channels or infrared light IR channels; determining IR components corresponding to the pixel values of the R channels, the G channels and the B channels in the first pixel set according to the pixel values of the IR channels and a preset first interpolation rule; removing the IR components corresponding to the pixel values of the R channels, the G channels and the B channels, and updating the first pixel set into a second pixel set; determining R components or B components corresponding to the pixel values of the IR channels in the second pixel set, and updating the second pixel set into a third pixel set; and restoring the image to be restored according to the third pixel set. Through adoption of the image restoration method and device in the embodiment, the hardware cost can be lowered.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION DIGITAL TECH
Image defogging method and system
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
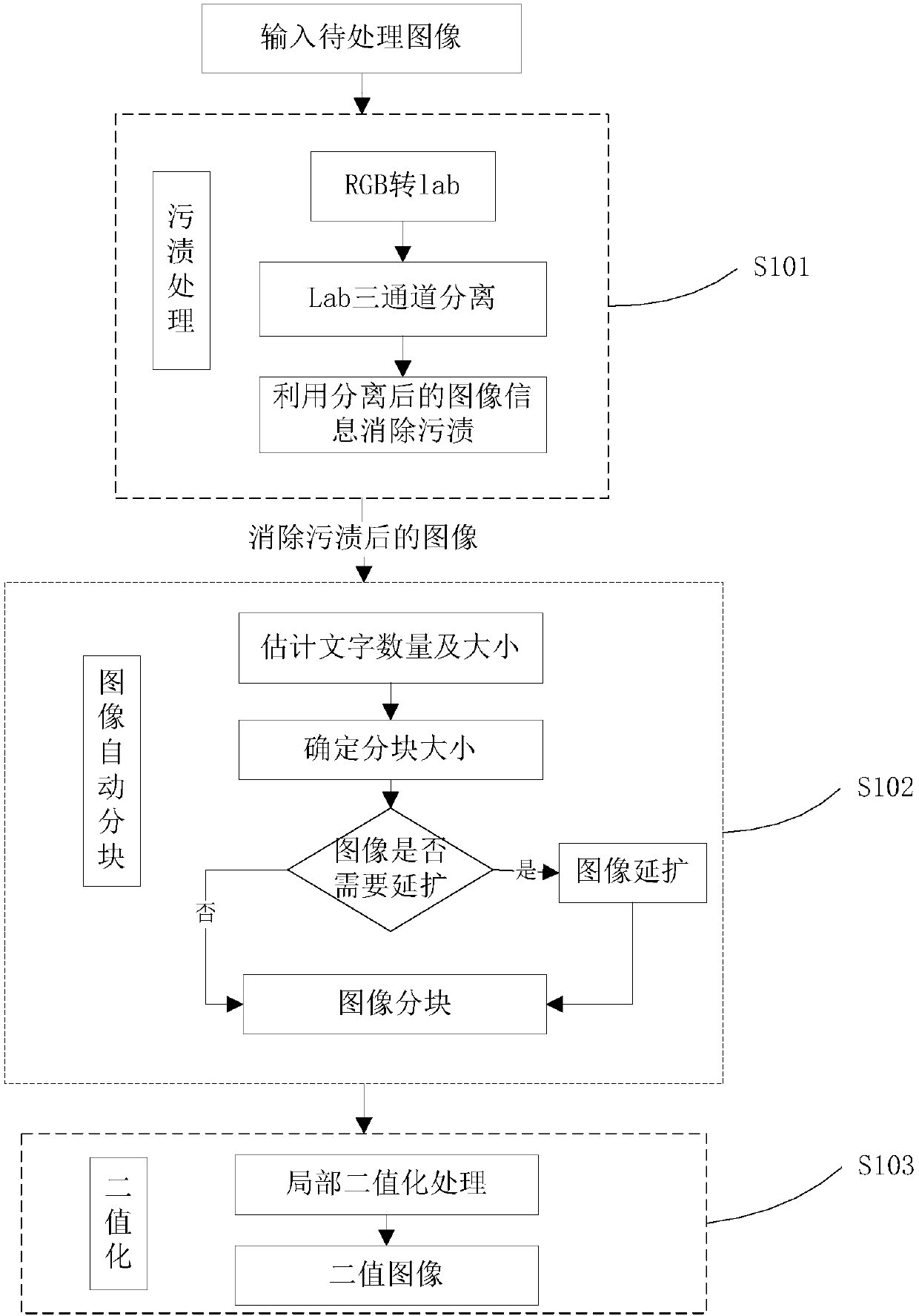
Ancient document image stain removal method
ActiveCN107610132AImprove binarization effectImage enhancementImage analysisLab color spaceDocumentation
The invention discloses an ancient document image stain removal method. The method comprises the following steps of: converting a to-be-processed image from an RGB color space to a Lab color space, separating the to-be-processed image by utilizing three channel images of the Lab color space, and selecting an L channel and a b channel by utilizing own information of separated different channel images so as to weaken or eliminate the influences of stains; automatically determining image text blocks according to the quantity and sizes of characters in the stain eliminated image, and judging whether the blocked image needs expansion or not; and carrying out global and local combined binarization processing on the image blocks to obtain a binary image. According to the method, the three channelimages of the Lab color space are separated and fusion is carried out on two channels, so that the problem of removing stains in ancient document images is solved; and during the binarization processing, the global and local are combined by adoption of an automatic image blocking method, so that the stains in the ancient document images can be effectively removed and the binarization effect is good.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
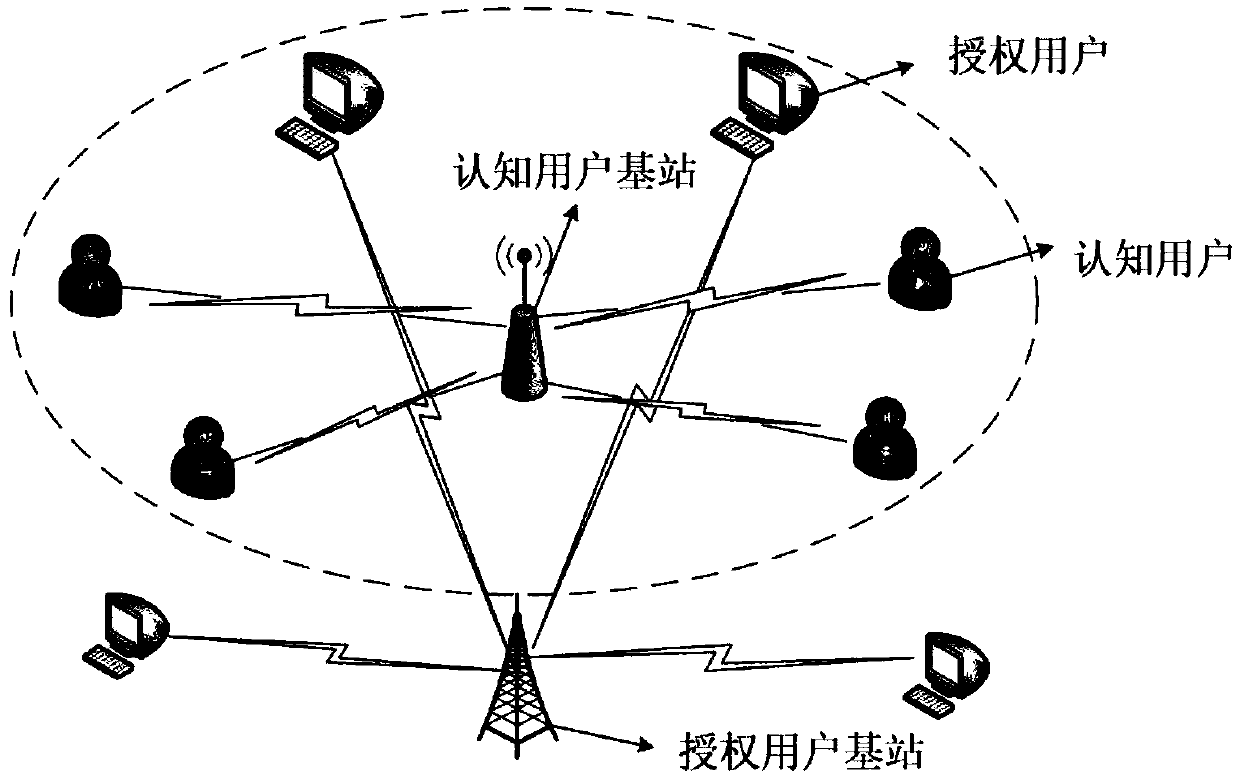
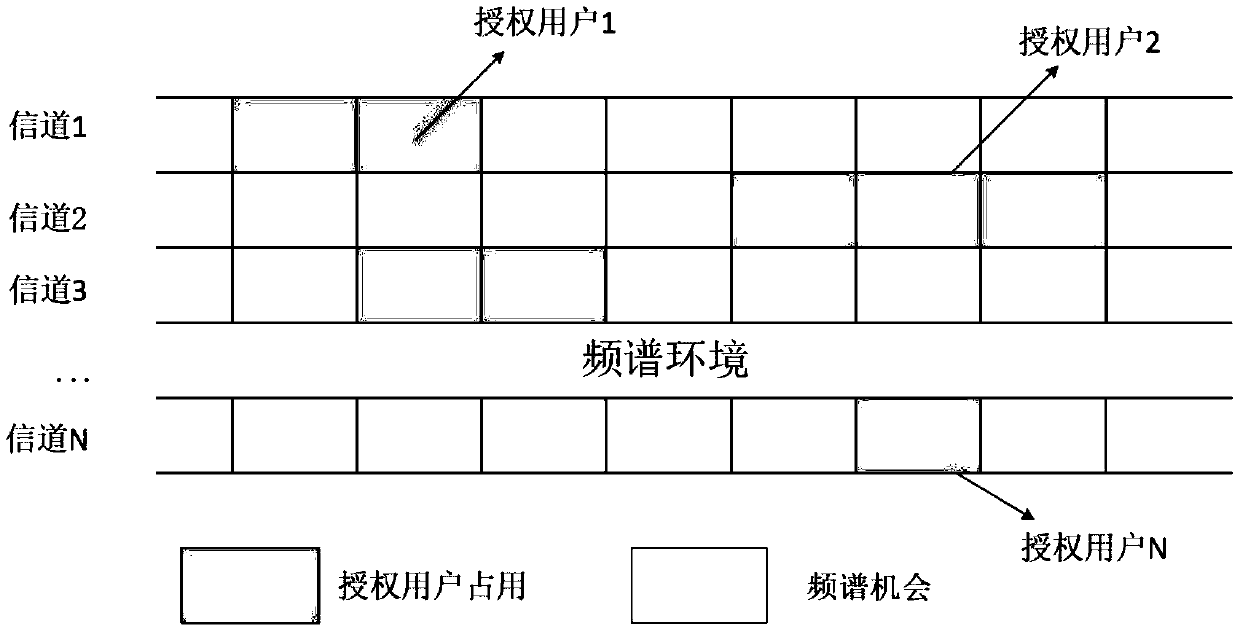
Distributed multi-user dynamic spectrum access method in cognitive wireless network
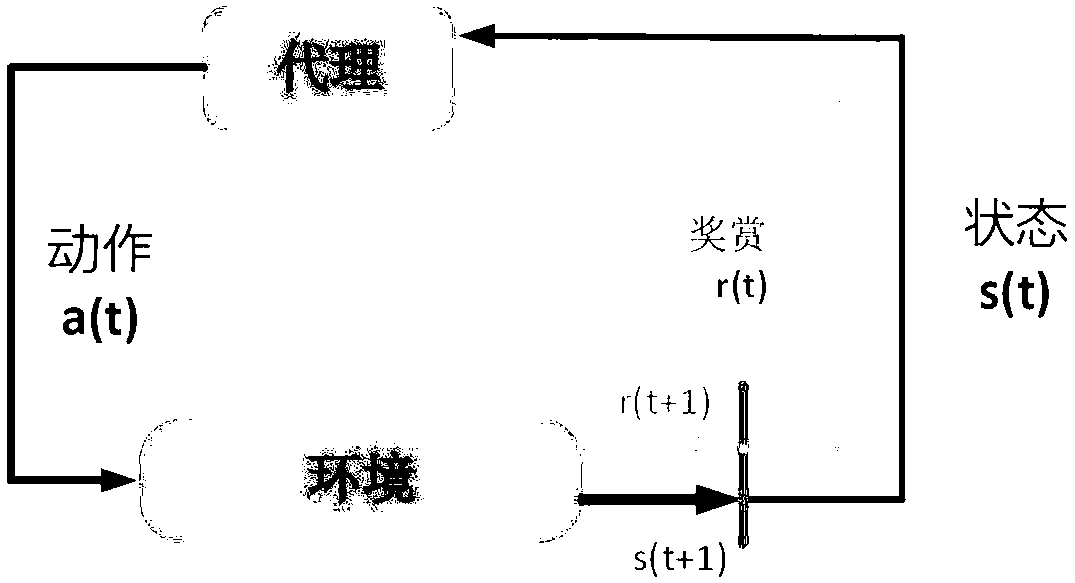
ActiveCN108880709AReduce the probability of collisionLarge capacityTransmission monitoringData switching networksCognitive userFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a distributed multi-user dynamic spectrum access method in a cognitive wireless network. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, constructing a system model, whereinthe system model is as follows: n authorized users and k cognitive users in a cell share b channels, wherein n, k and b are natural numbers that are not zero, values of n and b are equal, and k is larger than n; step 2, performing spectrum selection and access on the cognitive users by adopting a DQN algorithm, specifically, setting an initial Q function, setting each cognitive user as an executor, and performing action selection by each executor according to the DQN algorithm, namely, selecting one of the b channels for transmission, calculating an average utility value of a system, and setting a reward value by adopting an evolutionary game theory; and then training a neural network, and using the neural network as a function approximator to obtain an updated Q function; and step 3, continuing to execute step 2 until the obtained system capacity tends to be a constant value. Under the condition of high frequency spectrum requirements, the bandwidth efficiency is high.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com