Patents
Literature
76 results about "Cyberphysical systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
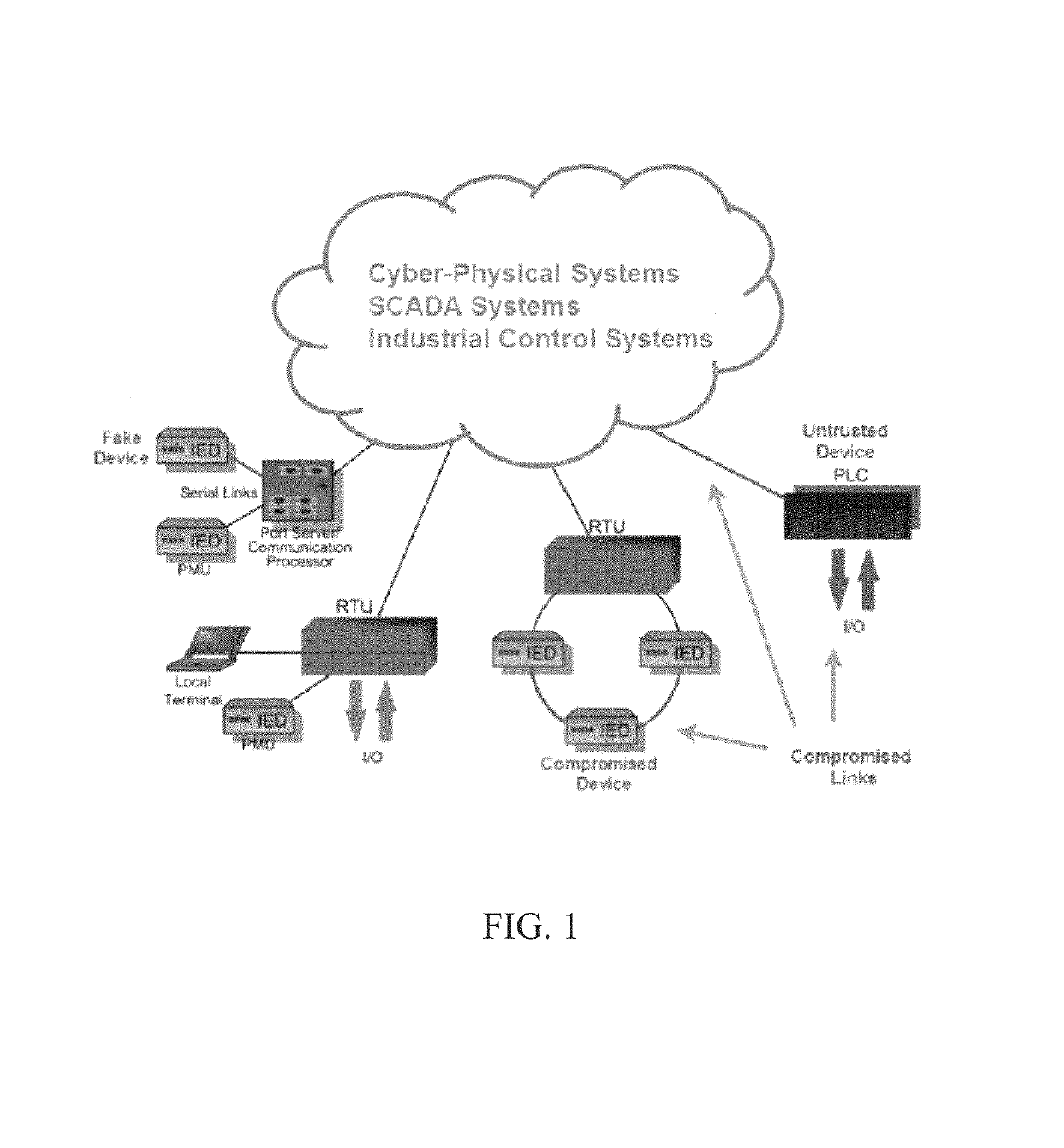
Cyber-Physical Systems. Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) comprise interacting digital, analog, physical, and human components engineered for function through integrated physics and logic. These systems will provide the foundation of our critical infrastructure, form the basis of emerging and future smart services, and improve our quality of life in many areas.
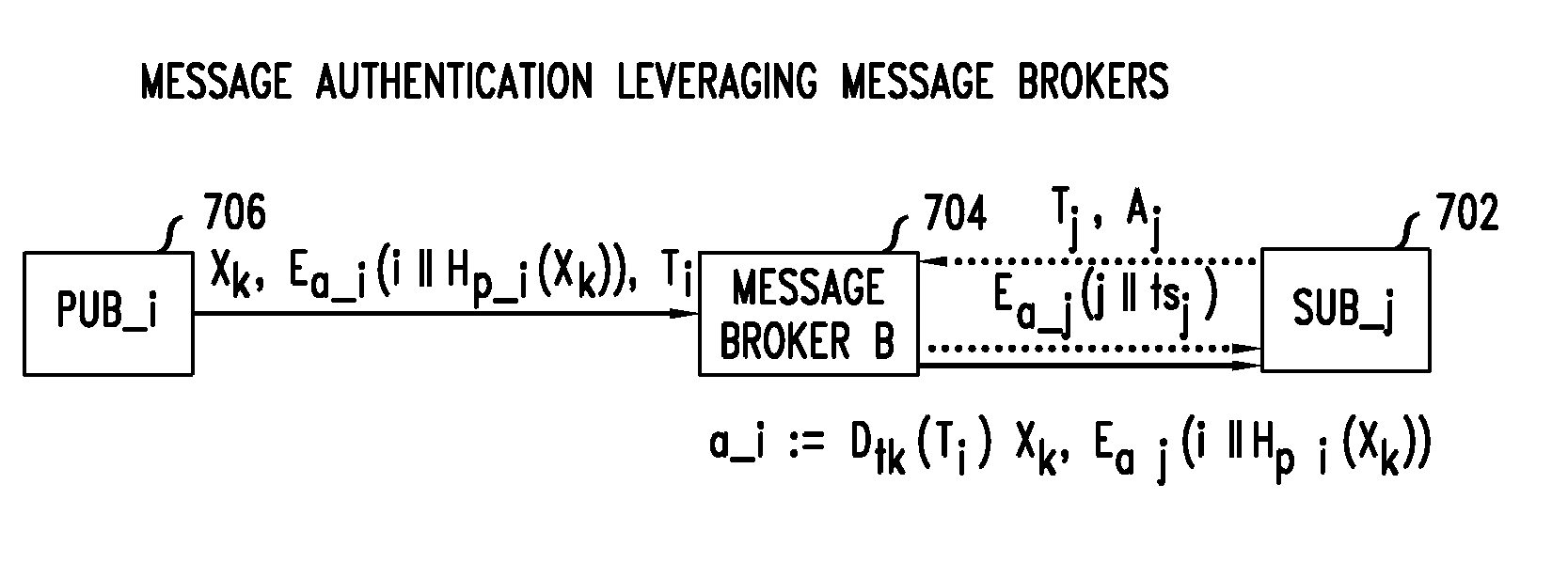
Method and apparatus for resilient end-to-end message protection for large-scale cyber-physical system communications
InactiveUS20140129838A1Reduce overheadCompromising scalabilityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEnd to end securityPhysical system
To address the security requirements for cyber-physical systems, embodiments of the present invention include a resilient end-to-end message protection framework, termed Resilient End-to End Message Protection or REMP, exploiting the notion of the long-term key that is given on per node basis. This long term key is assigned during the node authentication phase and is subsequently used to derive encryption keys from a random number per-message sent. Compared with conventional schemes, REMP improves privacy, message authentication, and key exposure, and without compromising scalability and end-to-end security. The tradeoff is a slight increase in computation time for message decryption and message authentication.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Development platform for robotic systems
InactiveUS20110224828A1Evaluate performanceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsCyberphysical systems
A unified system for development of robotics and other cyber-physical systems is discussed. The unified system includes a platform that integrates the processing of actuators and sensors and other modules. The platform is inter-operable into many existing systems. Various modules are developed to do discrete tasks that are commonly found in robotics such as moving motors or reading and controlling sensors. The modules communicate with each other and with other devices such as computers and user built modules through the use of a commonly supported abstract communication protocol.
Owner:NEURON ROBOTICS
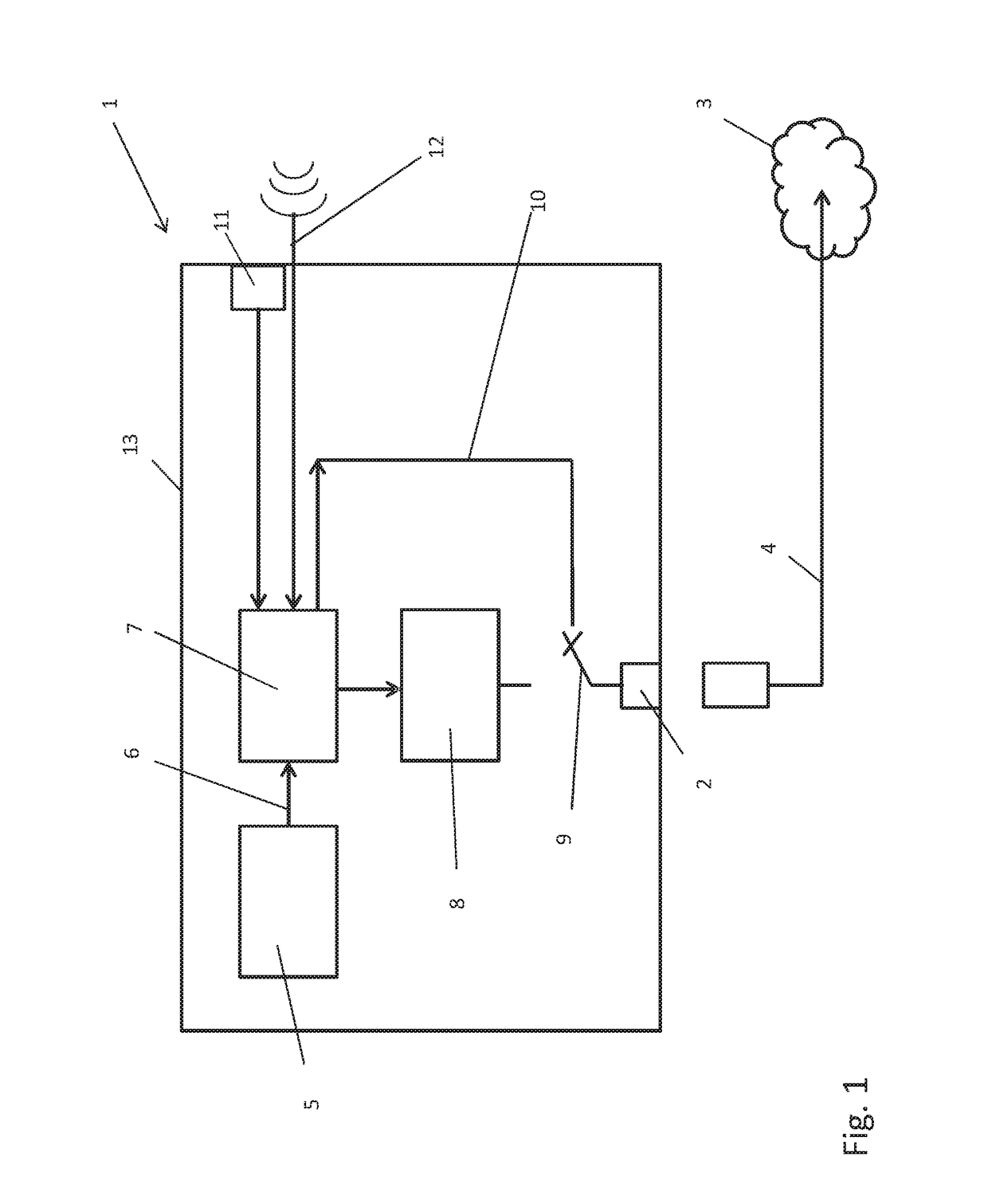
Cyber physical system
InactiveUS10061635B2Improve securityShort timeData switching by path configurationComputer security arrangementsThe InternetPhysical system
A cyber physical system including at least one monitoring and safety device for monitoring various parameters of a machine with regard to the maintenance of setpoint values and for generating an error signal in the event of an error and a hard-wired interface to the Internet and a transmission and / or reception unit for transmitting and / or receiving data over the Internet, wherein the monitoring or safety device is connected to the transmission and / or reception unit for transmitting the error signal over the Internet. The hard-wired interface is connected to a controllable switch for physical disconnection and enabling of the connection between the cyber physical system and the Internet, and the cyber physical system has at least one control unit connected to the monitoring or control device for triggering the controllable switch for brief enabling of the connection between the cyber physical system and the Internet.
Owner:KRIWAN IND ELEKTRONIK
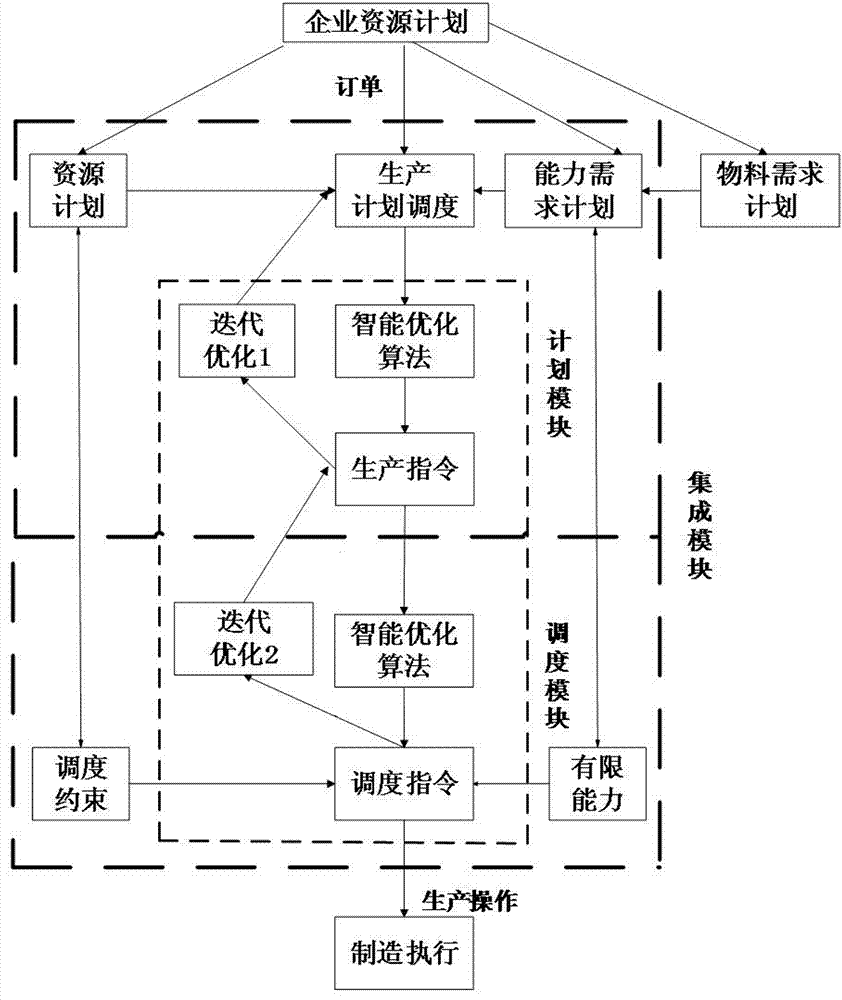
Intelligent machining workshop production planning and scheduling integration method
ActiveCN108009739AClosed loopTimely response to ordersResourcesLogisticsVirtual machiningProgram planning
The invention discloses an intelligent machining workshop production planning and scheduling integration method, which belongs to the field of automated technical application. The method comprises thefollowing steps that: system modeling; data preparation; order form preparation; production planning and scheduling; virtual processing; dynamically monitoring; dynamically scheduling; revising a plan; and carrying out rolling optimization. Through production planning and scheduling integration under the support of an intelligent workshop network physical system, the closed loop of "production planning-production scheduling-production state information" under the dynamic environment of the workshop is realized, and the problem that an existing production planning and scheduling method is difficult in responding to various categories of dynamic events of environment (market) changes and workshop sites in time.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
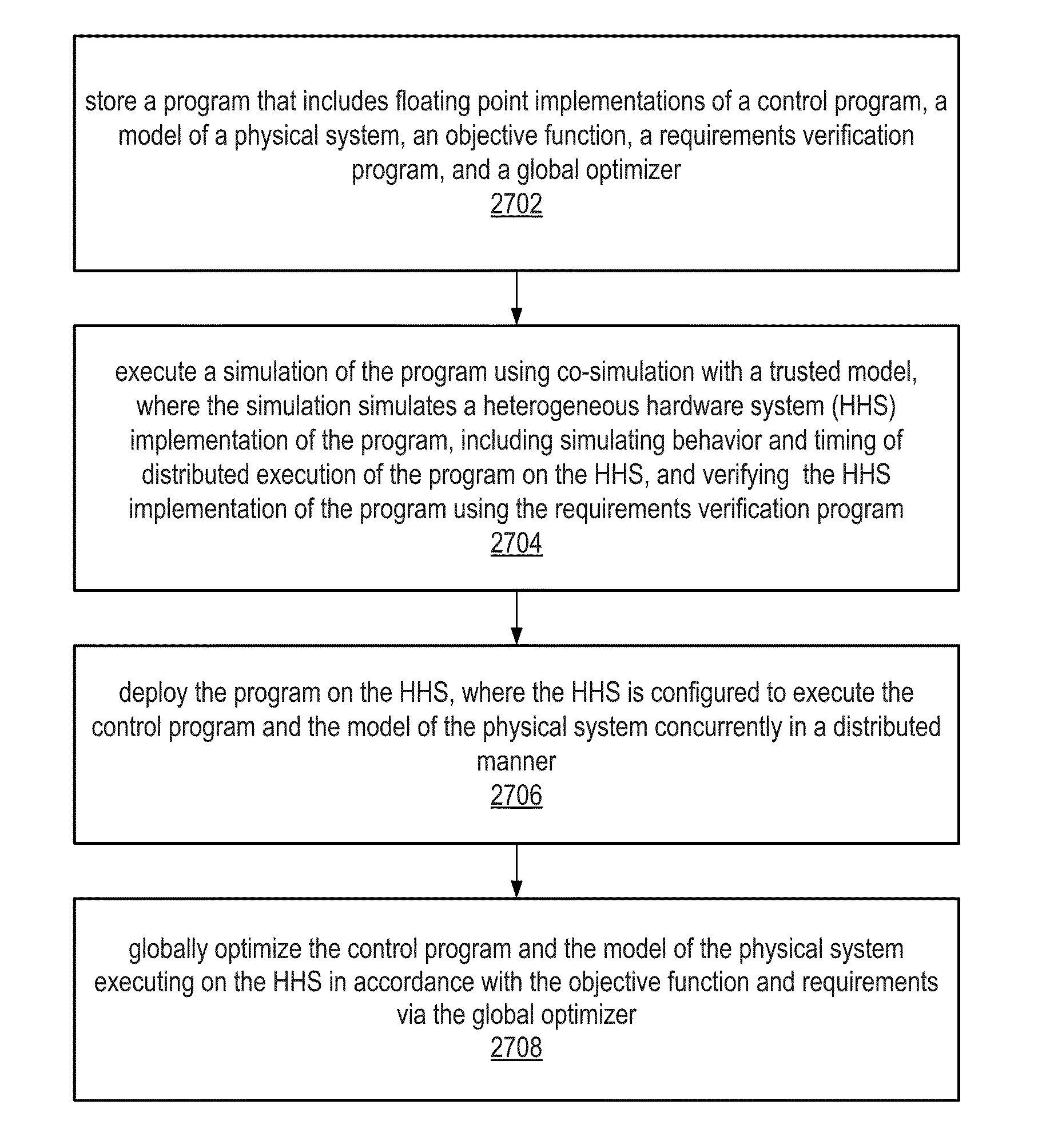
Global Optimization and Verification of Cyber-Physical Systems Using Floating Point Math Functionality on a System with Heterogeneous Hardware Components
Global optimization and verification of cyber-physical systems using graphical floating point math functionality on a heterogeneous hardware system (HHS). A program includes floating point implementations of a control program (CP), model of a physical system (MPS), objective function, requirements verification program (RVP), and / or global optimizer. A simulation simulates HHS implementation of the program using co-simulation with a trusted model, including simulating behavior and timing of distributed execution of the program on the HHS, and may verify the HHS implementation using the RVP. The HHS is configured to execute the CP and MPS concurrently in a distributed manner. After deploying the program to the HHS, the HHS is configured to globally optimize (improve) the CP and MPS executing concurrently on the HHS via the global optimizer. The optimized MPS may be usable to construct the physical system. The optimized CP may be executable on the HHS to control the physical system.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Global optimization and verification of cyber-physical systems using floating point math functionality on a system with heterogeneous hardware components
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
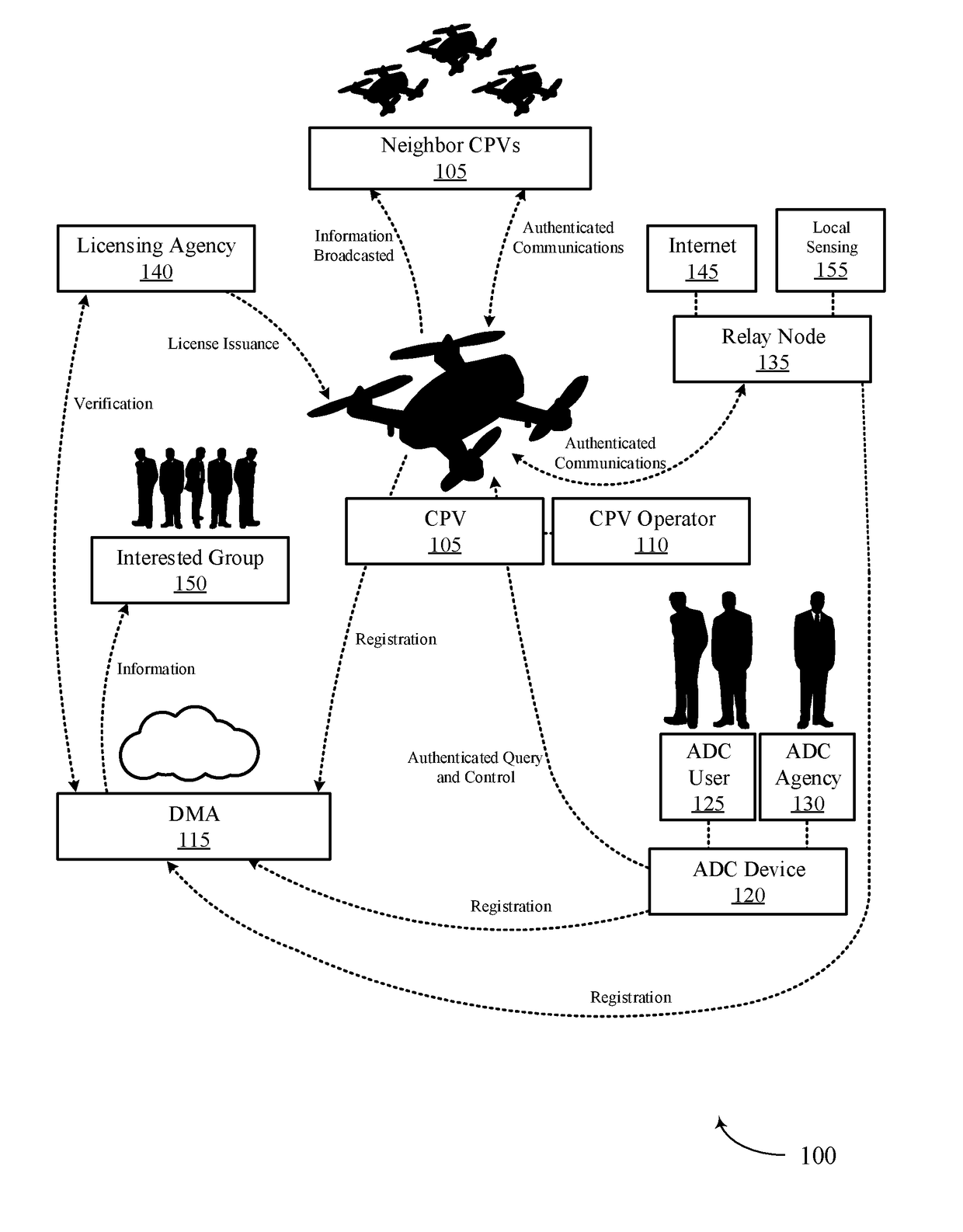
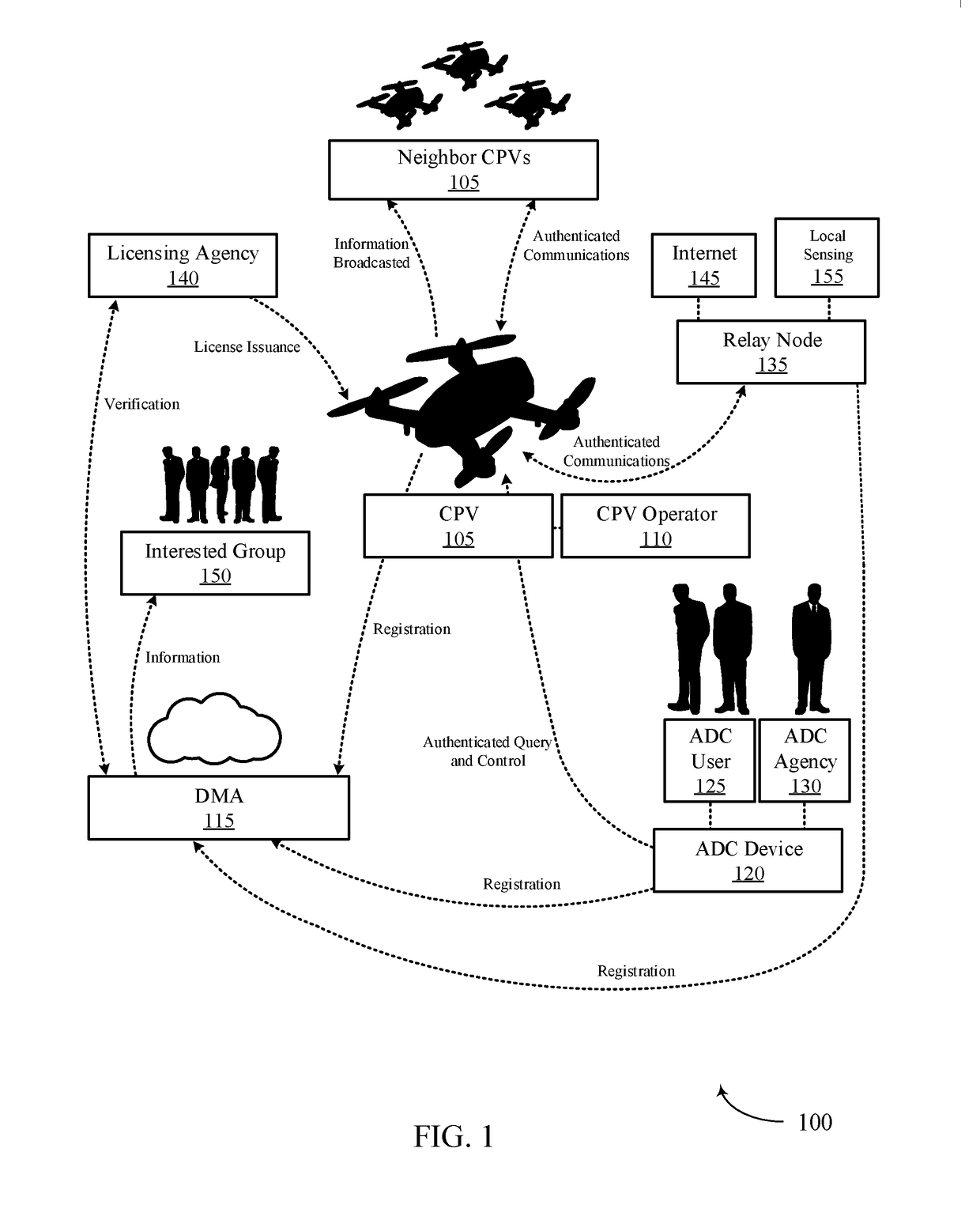
Systems and methods for cyber-physical vehicle management, detection and control
A cyber-physical vehicle management system may allow for highly reliable and authentic identity management of cyber-physical systems, unforgeable legal interception devices, and robust relay nodes. A cyber-physical vehicle management system may also provide for human and object bi-directional authenticity verification. In some cases, a cyber physical management system may enable a cyber physical vehicle (CPV) detection and intervention system which may be capable or detection, identification, capture, seizure, and immobilization of CPVs. In some embodiments the CPV detection and intervention system includes a geocoding laser subsystem for determining a location of a CPV.
Owner:WHITEFOX DEFENSE TECH INC
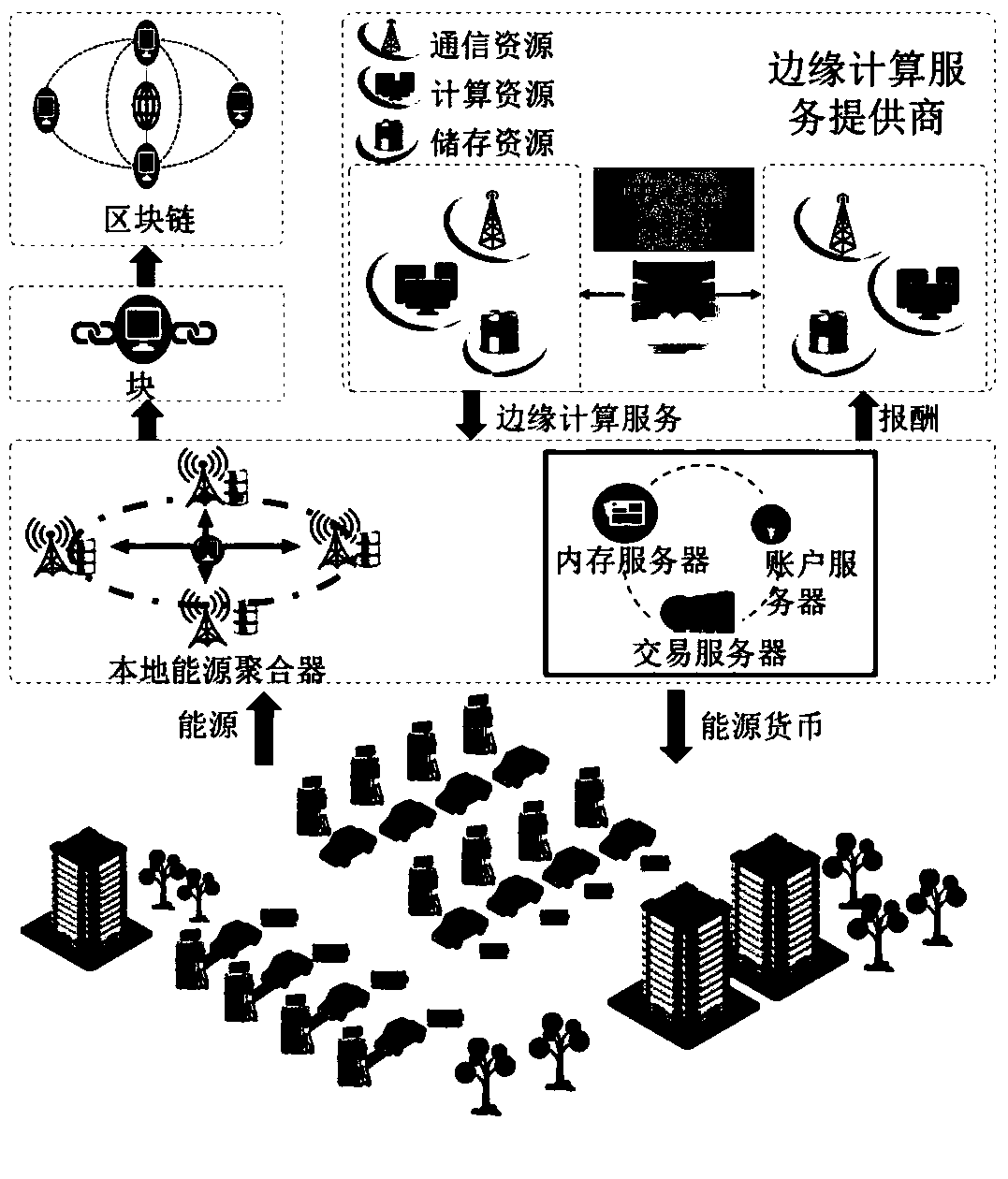
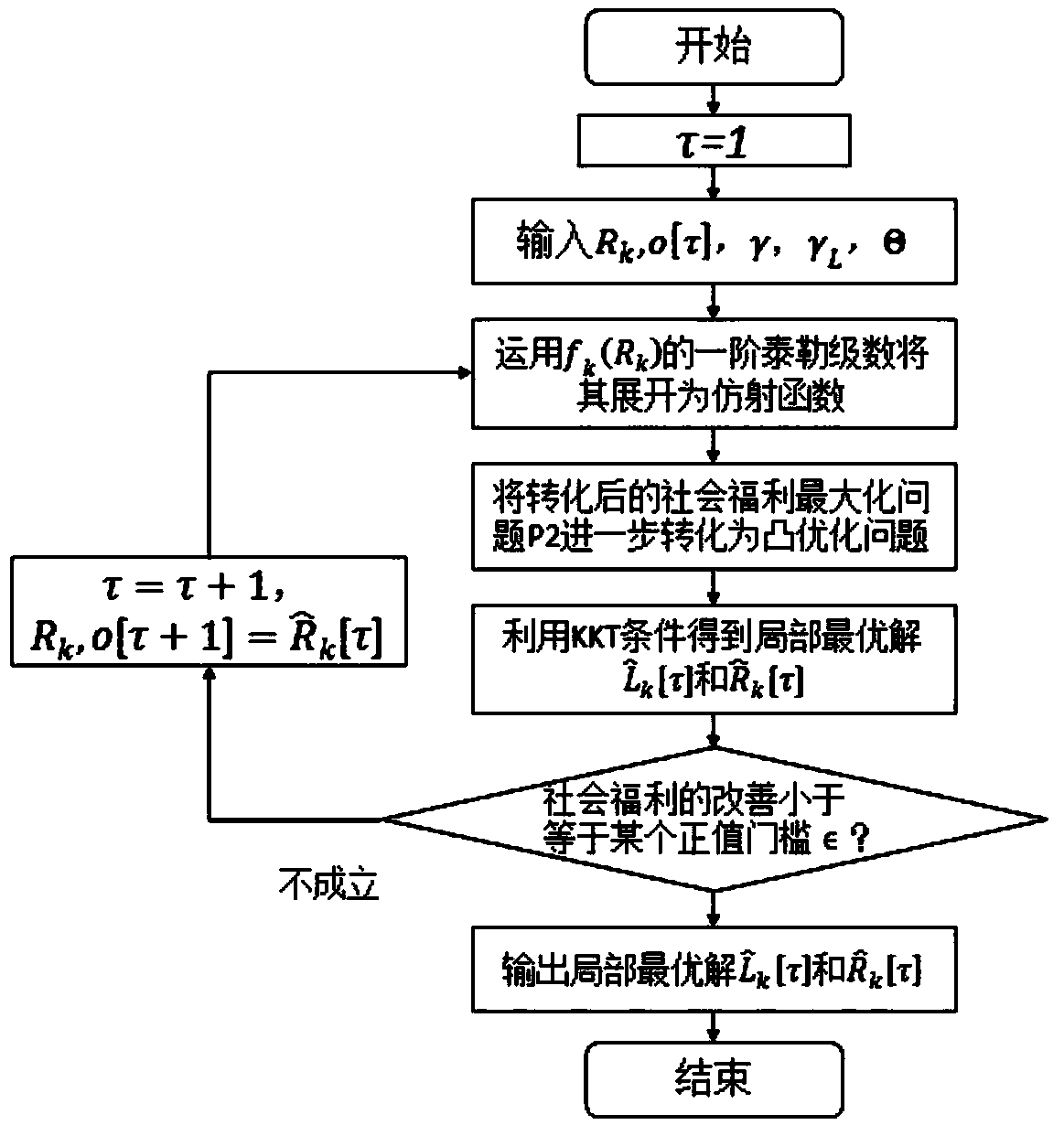
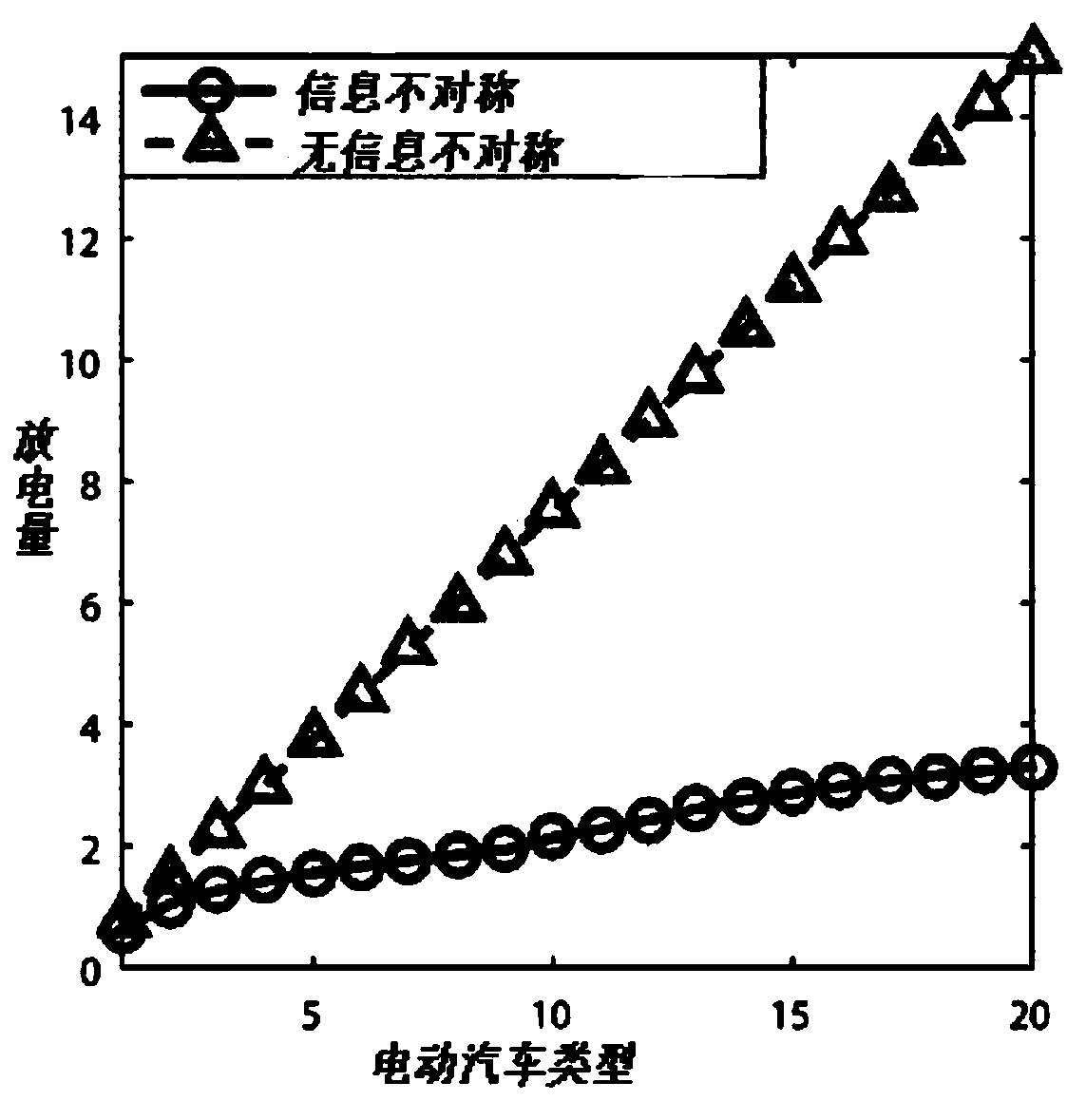
A V2G energy trading mechanism based on a block chain and a contract theory
ActiveCN109166036ASolve the problem of service price optimization in the first stageFinanceProtocol authorisationEdge computingParallel computing
The invention designs a secure and efficient V2G energy trading mechanism in a network physical system using a block chain, edge computing and a contract theory. In this invention, a secure and efficient V2G energy trading framework is provided by exploring the block chain, the contract theory and marginal computing. First of all, a secure energy trading mechanism based on alliance block chain isdeveloped for V2G. Then, considering the asymmetric information scenario, an effective incentive mechanism based on contract theory is proposed. The social welfare optimization problem belongs to thedifference category of convex (DC) programming and is solved by iterative convex-concave process (CCP) algorithm. Next, edge computations have been incorporated to increase the probability of successin block creation. The computational resource allocation problem is modeled as a two-stage Steinberg game, and the optimal strategy is obtained by backward induction.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
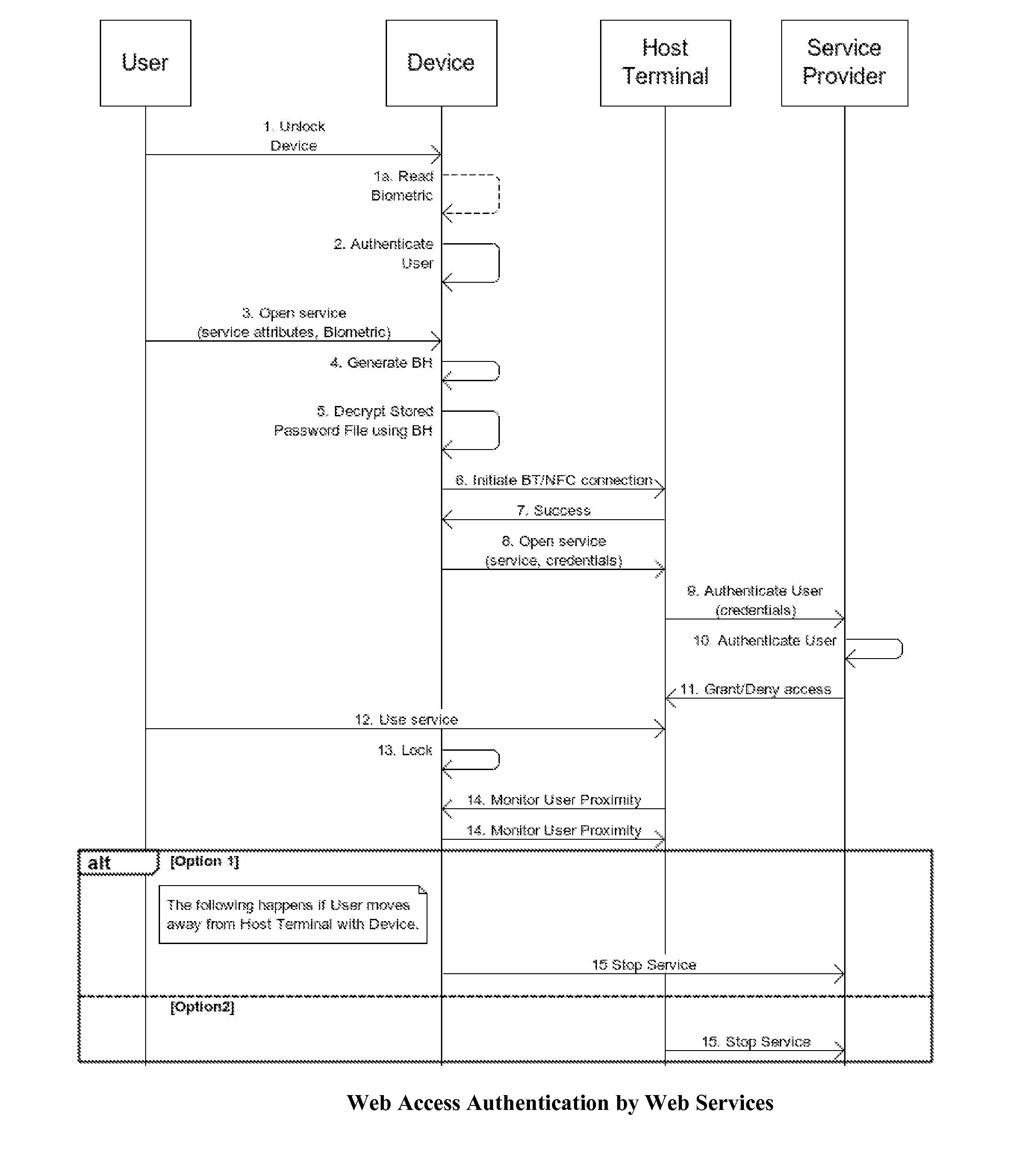
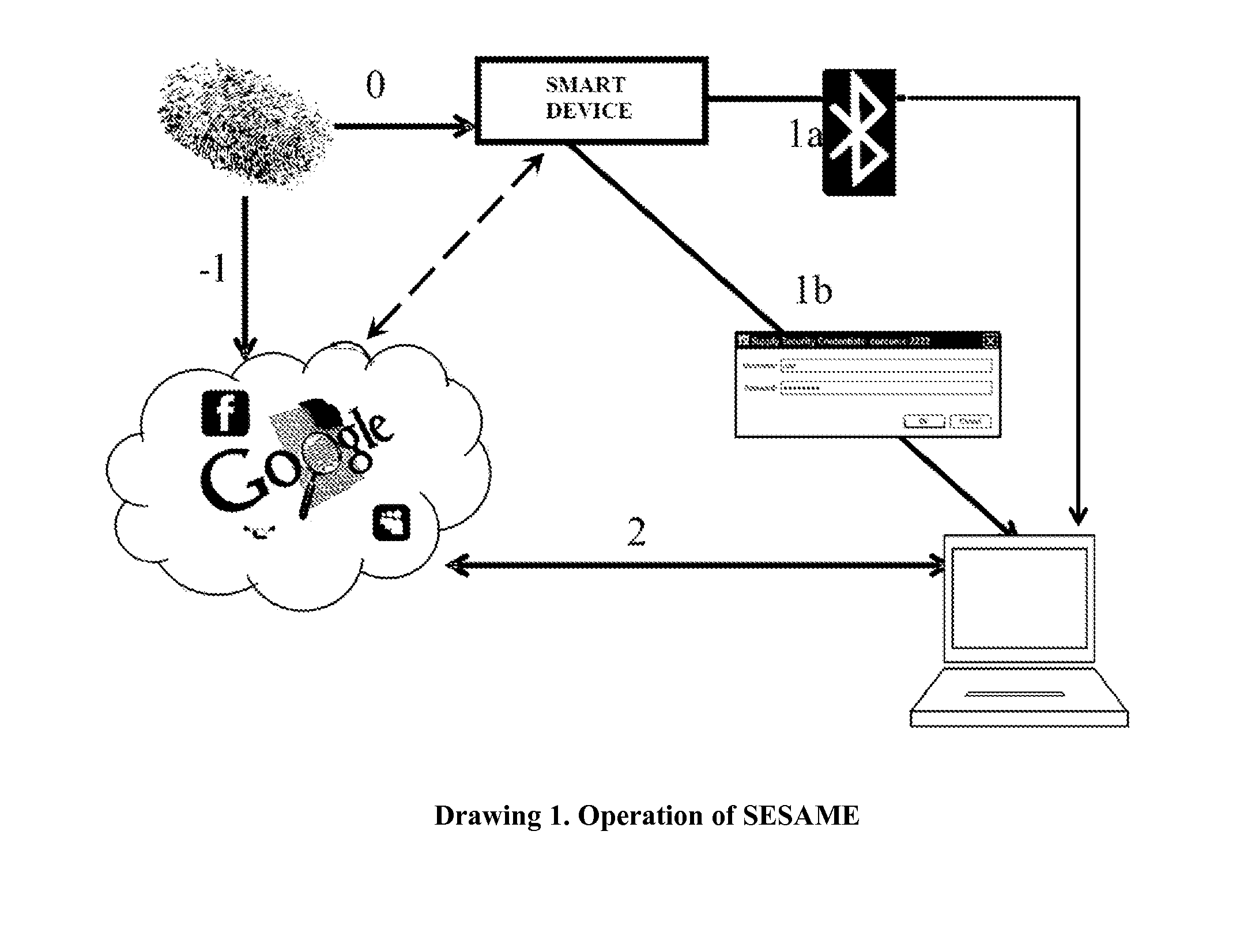
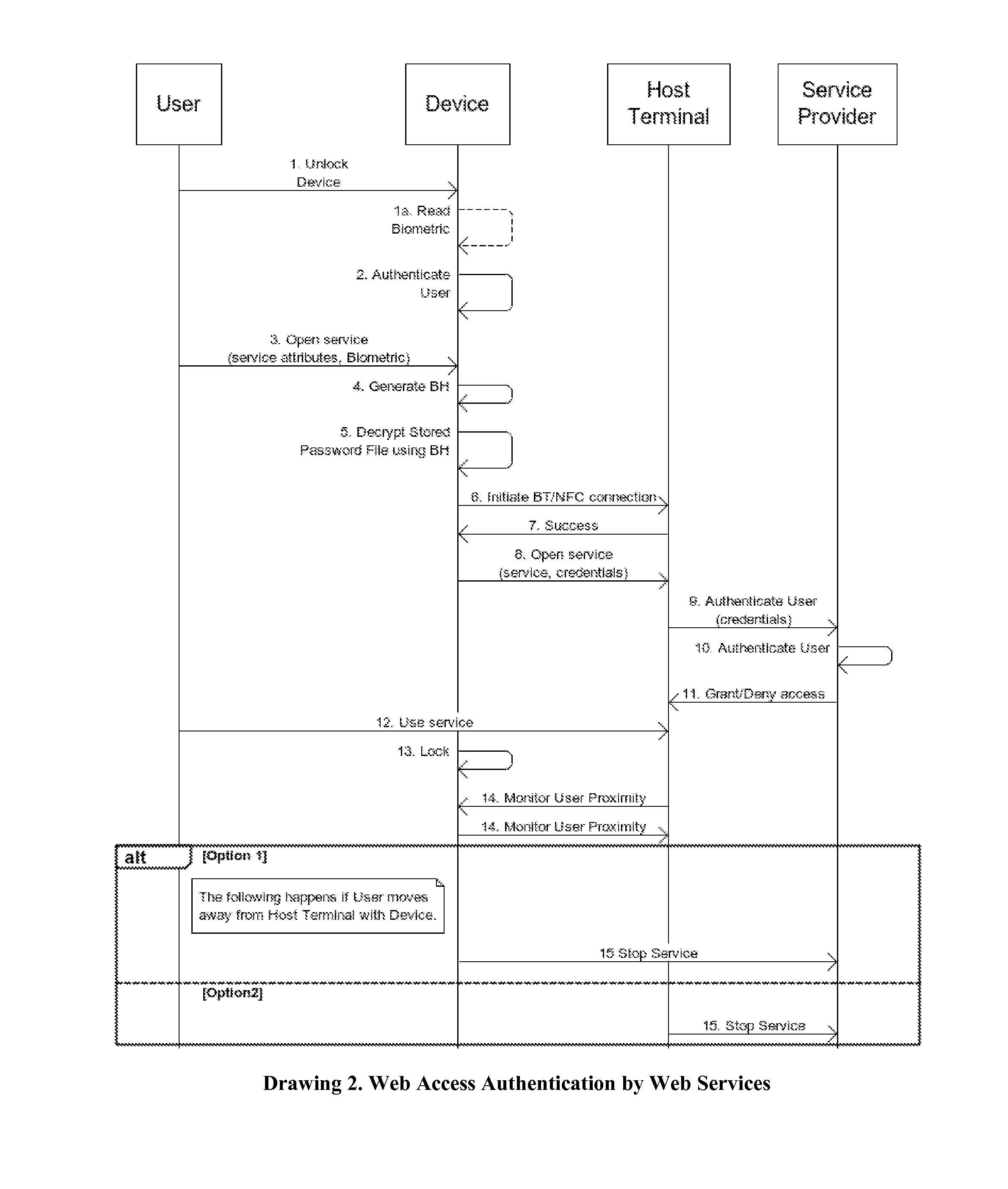
Smartdevices Enabled Secure Access to Multiple Entities (SESAME)
InactiveUS20140329497A1Suppress energyLong standby time is presentUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsCyberphysical systemsSmart meter
This invention proposes novel systems, methods and apparatus that utilize smart devices (e.g., smartphones) capable of reading / processing biometric inputs, and wireless communications over secure, short-range wireless channels (e.g., near field communications (NFC)) to securely access websites and cyber-physical system (CPS) entities such as vehicles, rooms and control knobs as well as sensors and smart meters. A user accesses a website on a display terminal or CPS entity by using her smart device to send her biometric credentials to request access for a service, and communicates with either the said terminal or the said CPS entity which is also capable of short-range wireless communications, using secure and short-range wireless channels to ensure the authenticity of the user when using the service. This system also protects the stored credentials of the user against loss or theft of the smart device since the credentials are encrypted by the user's biometrics, and the stored credentials on the smart device can only be accessed by a legitimate user using her biometrics.
Owner:SANZGIRI AMEYA M +3
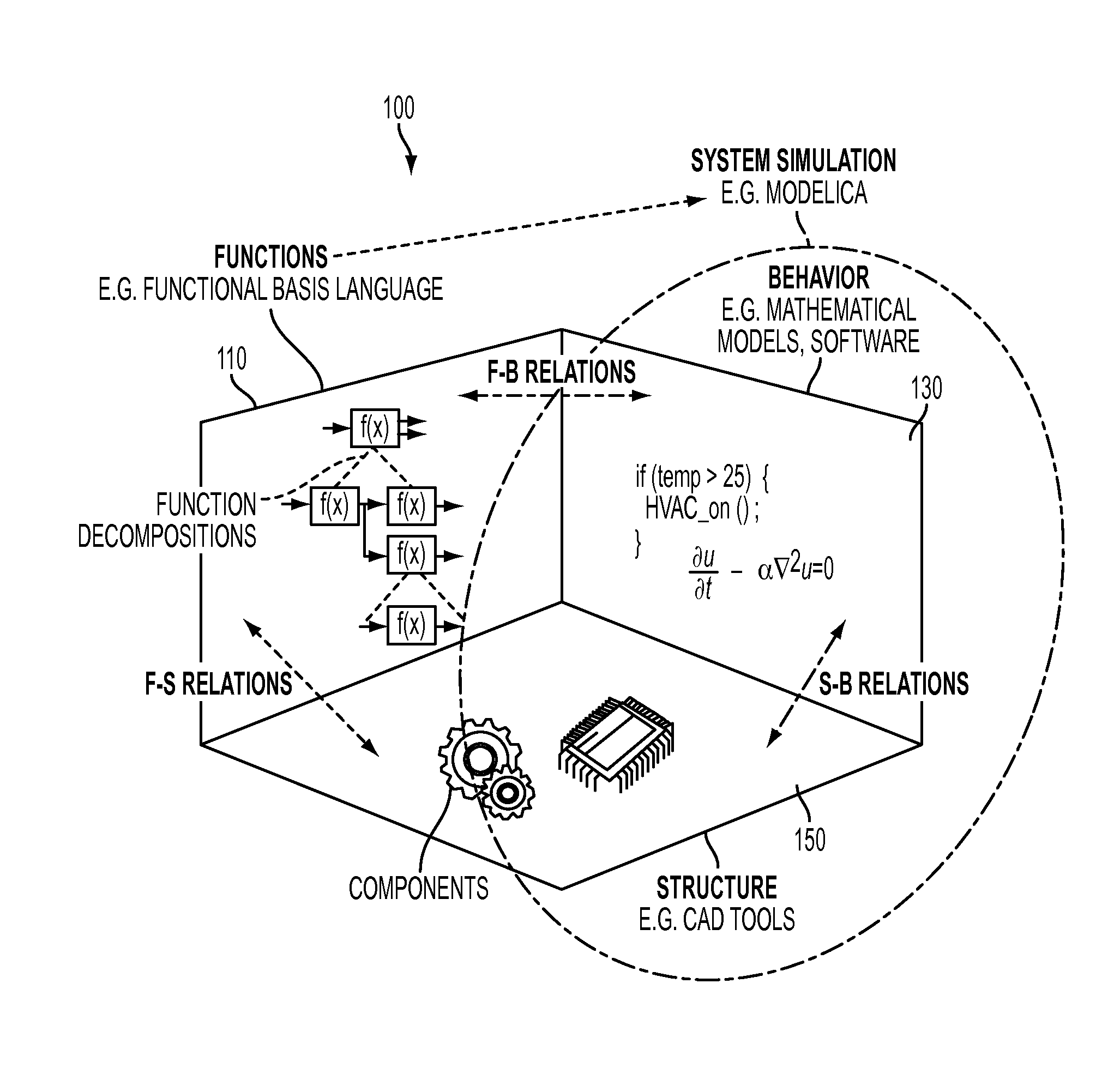
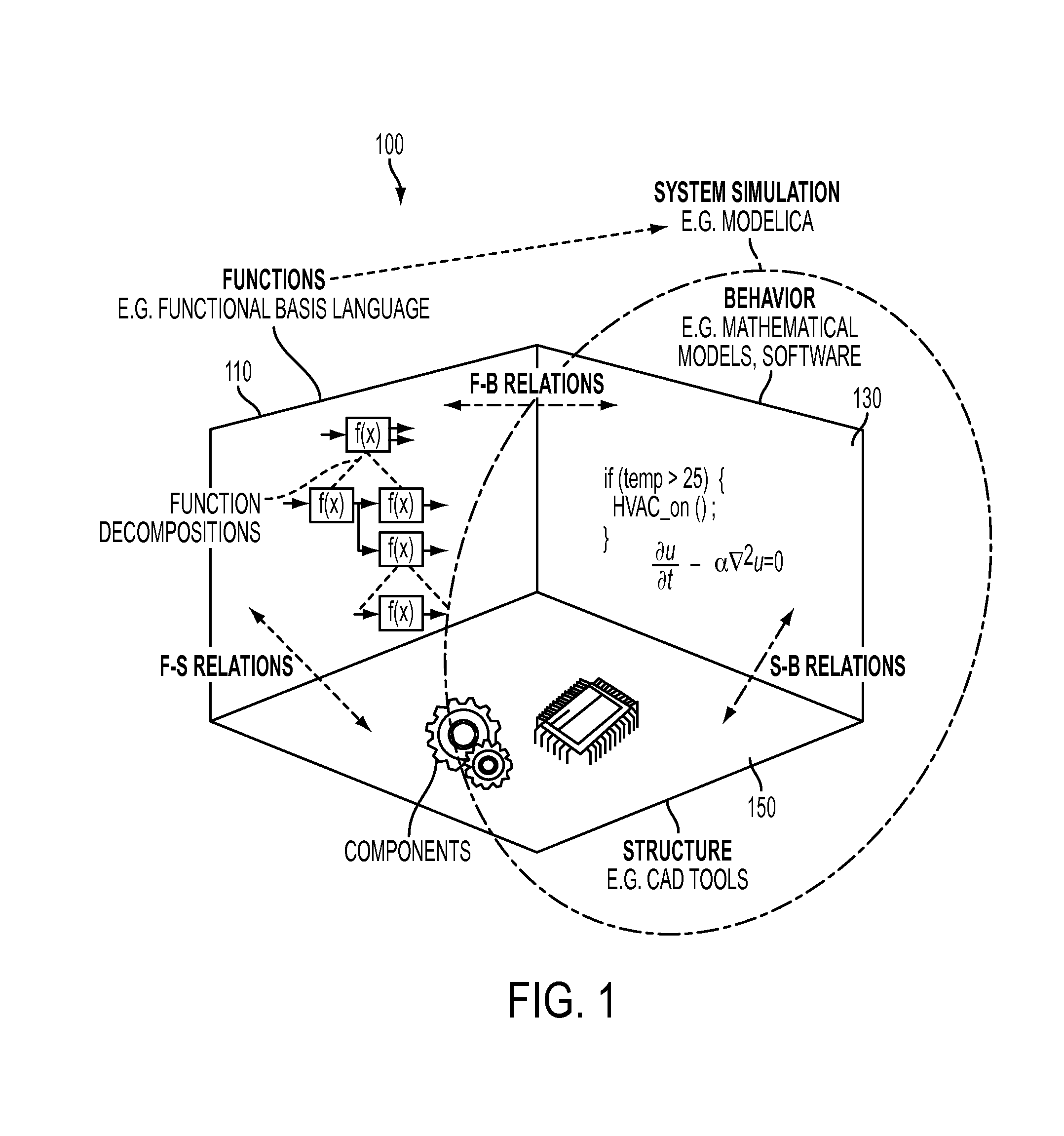
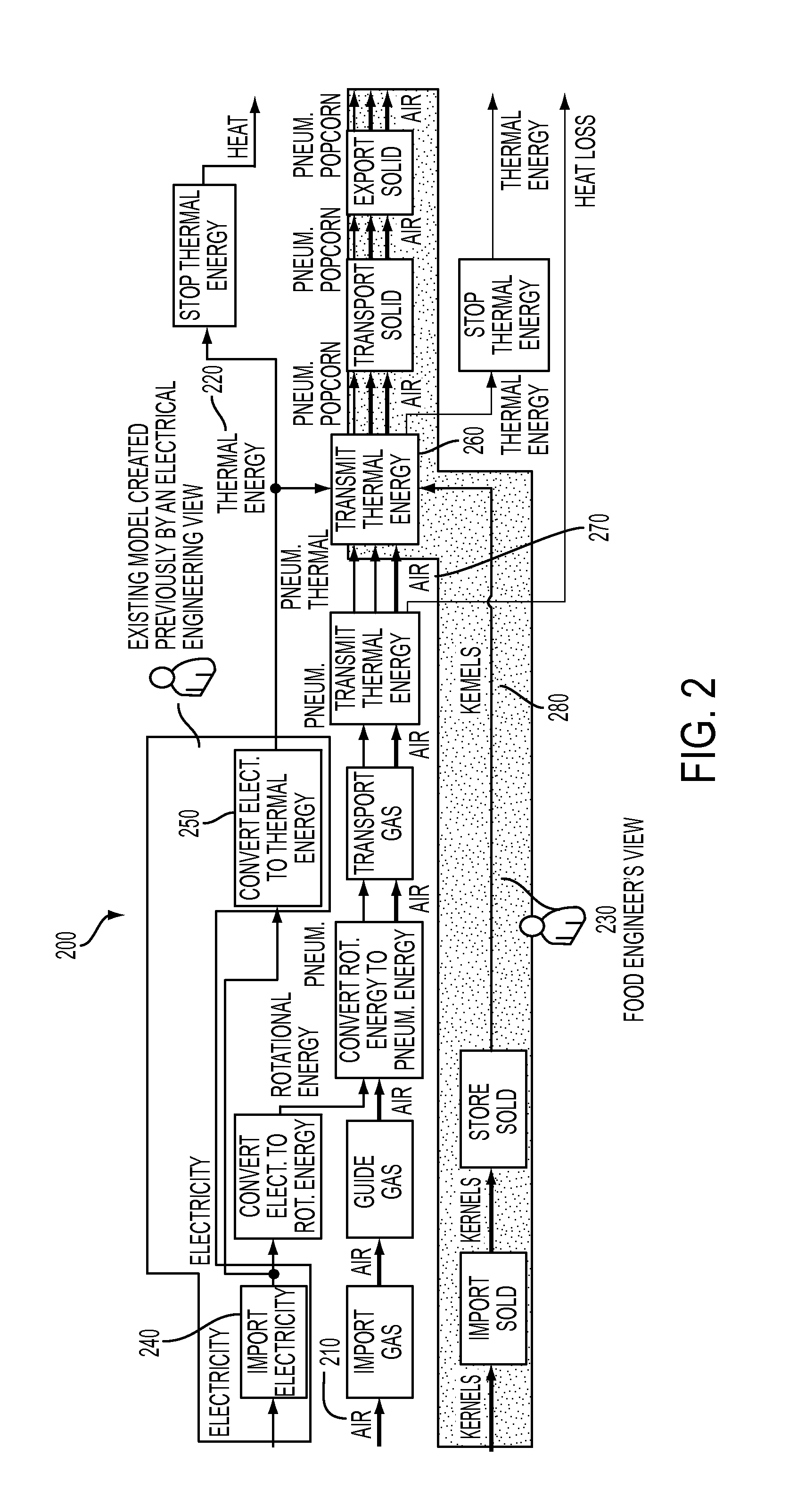
Context-based synthesis of simulation models from functional models of cyber-physical systems
ActiveUS20140019104A1Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSystems designSimulation
An approach and tool integrate cyber-physical systems design based on the function-behavior-state (FBS) methodology where multi-domain simulation models capturing both the behavioral and structural aspects of a system are automatically generated from its functional description. The approach focuses on simulation-enabled FBS models using automatic and context-sensitive mappings of functional basis elementary functions to simulation components described in physical modeling languages. Potentially beneficial process loops are recognized and inserted in the functional model.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
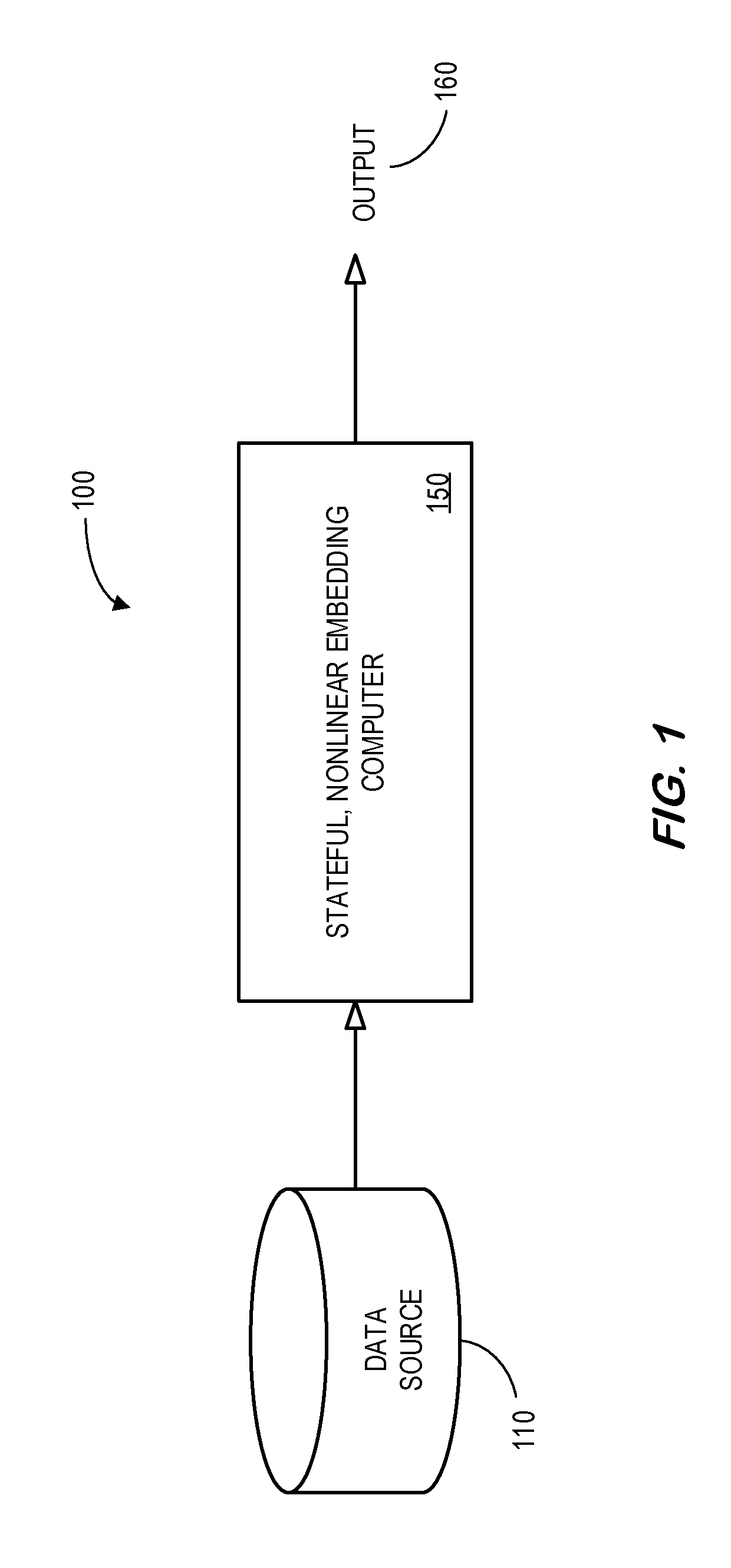
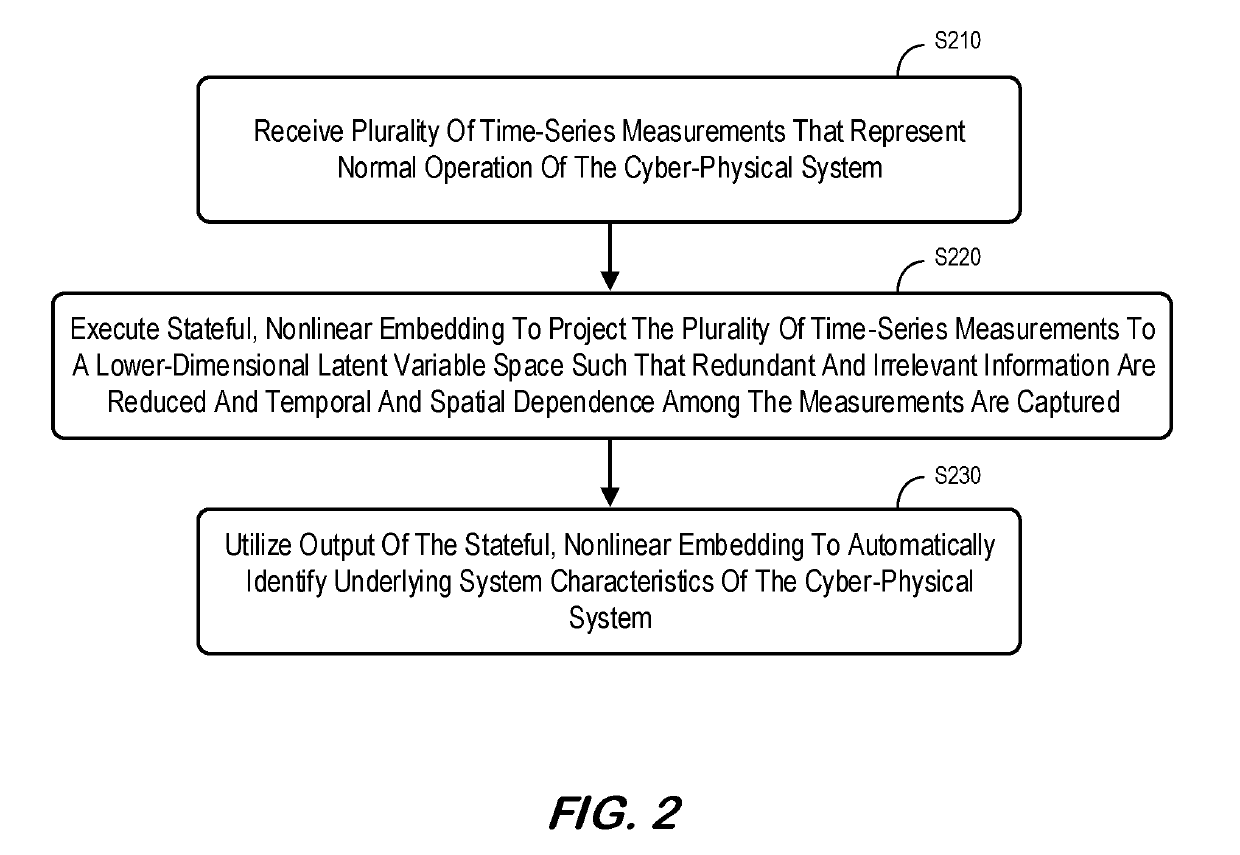
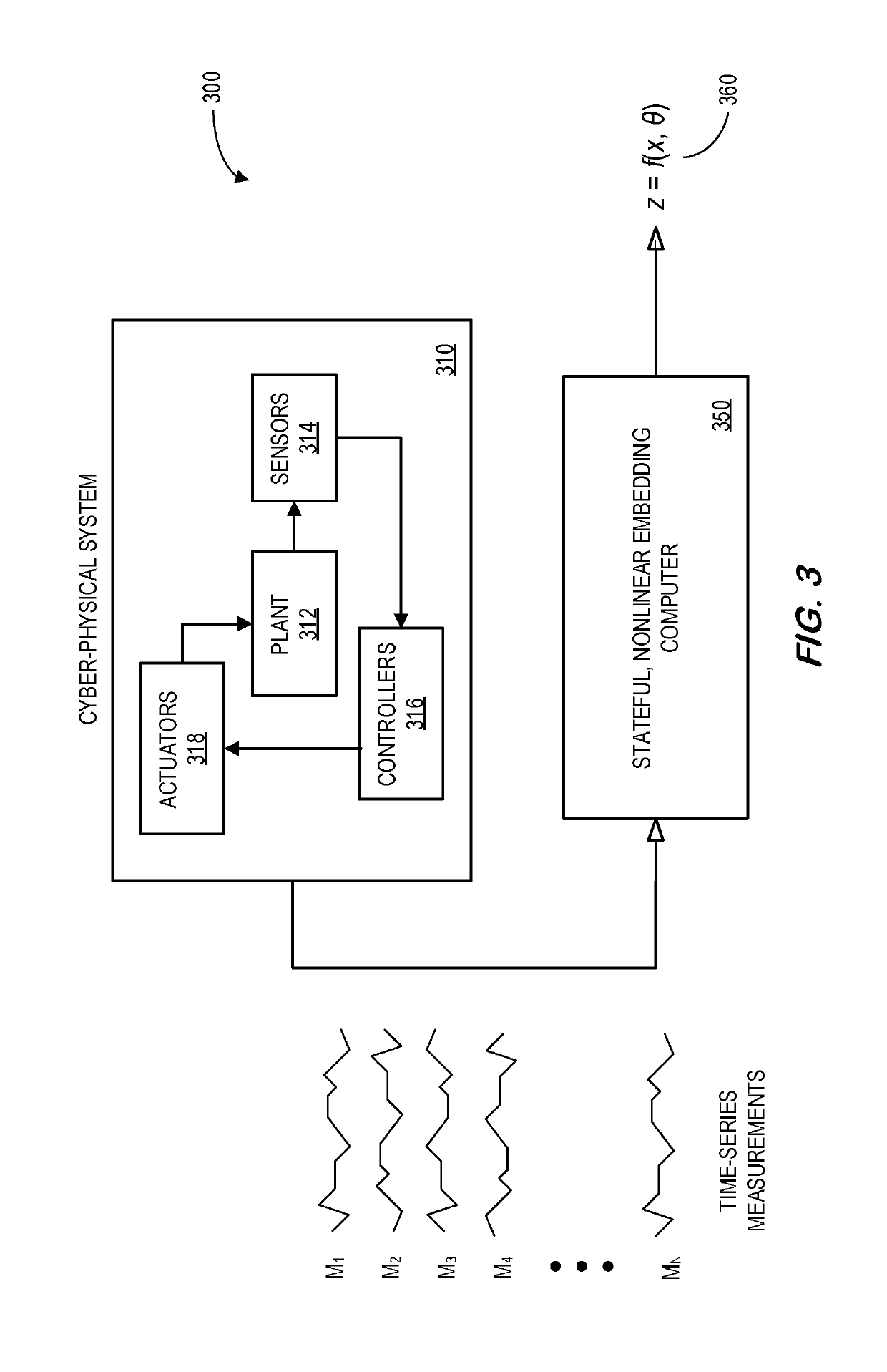
System and method for abstracting characteristics of cyber-physical systems
PendingUS20190228110A1Rapid and accurate mannerRedundant informationNeural architecturesTransmissionNonlinear embeddingData source
A data source may provide a plurality of time-series measurements that represent normal operation of a cyber-physical system (e.g., in substantially real-time during online operation of the cyber-physical system). A stateful, nonlinear embedding computer may receive the plurality of time-series measurements and execute stateful, nonlinear embedding to project the plurality of time-series measurements to a lower-dimensional latent variable space. In this way, redundant and irrelevant information may be reduced, and temporal and spatial dependence among the measurements may be captured. The output of the stateful, nonlinear embedding may be utilized to automatically identify underlying system characteristics of the cyber-physical system. In some embodiments, a stateful generative adversarial network may be used to achieve stateful embedding.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
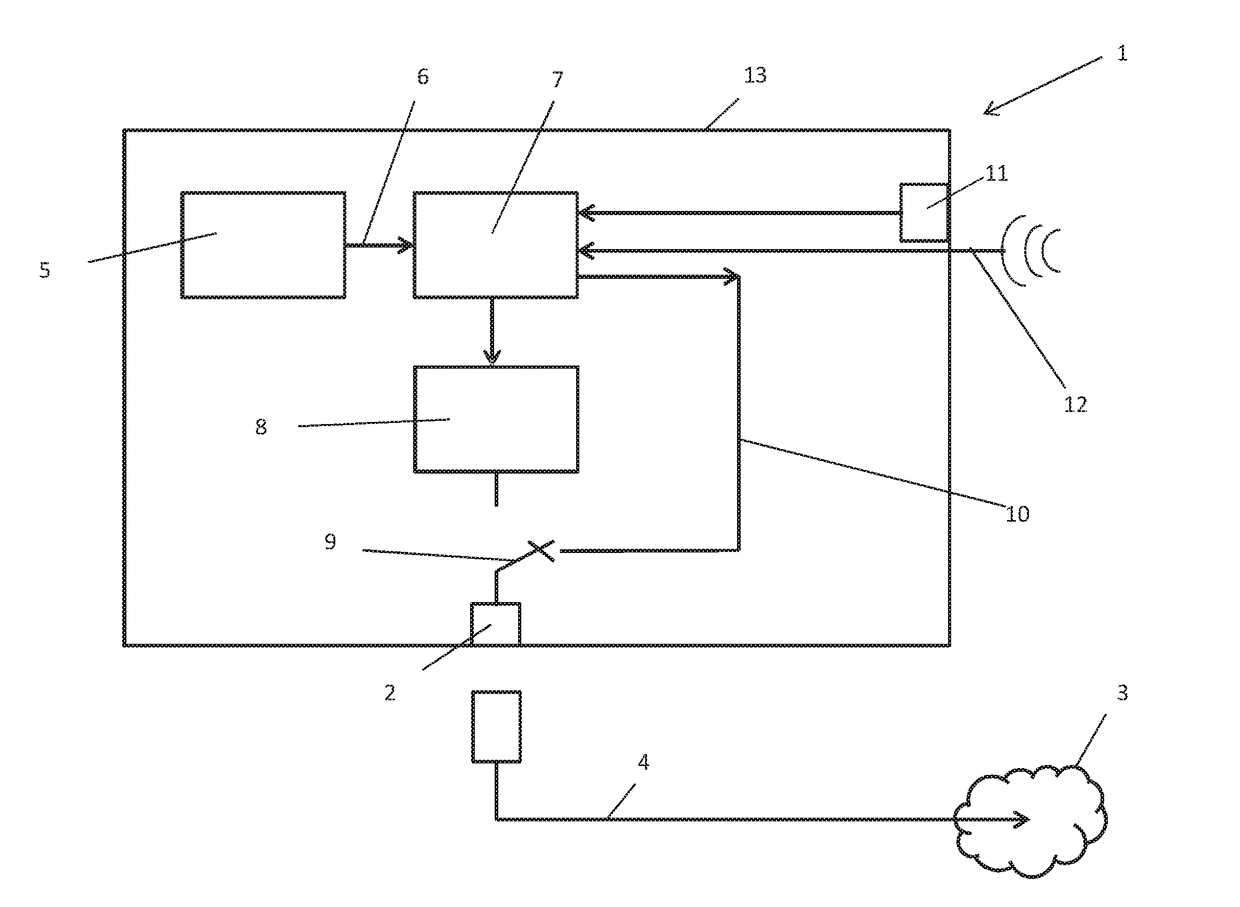
Cyber physical system
InactiveUS20170139763A1Improve cyber securityImprove securityData switching by path configurationComputer security arrangementsThe InternetEngineering
A cyber physical system including at least one monitoring and safety device for monitoring various parameters of a machine with regard to the maintenance of setpoint values and for generating an error signal in the event of an error and a hard-wired interface to the Internet and a transmission and / or reception unit for transmitting and / or receiving data over the Internet, wherein the monitoring or safety device is connected to the transmission and / or reception unit for transmitting the error signal over the Internet. The hard-wired interface is connected to a controllable switch for physical disconnection and enabling of the connection between the cyber physical system and the Internet, and the cyber physical system has at least one control unit connected to the monitoring or control device for triggering the controllable switch for brief enabling of the connection between the cyber physical system and the Internet.
Owner:KRIWAN IND ELEKTRONIK
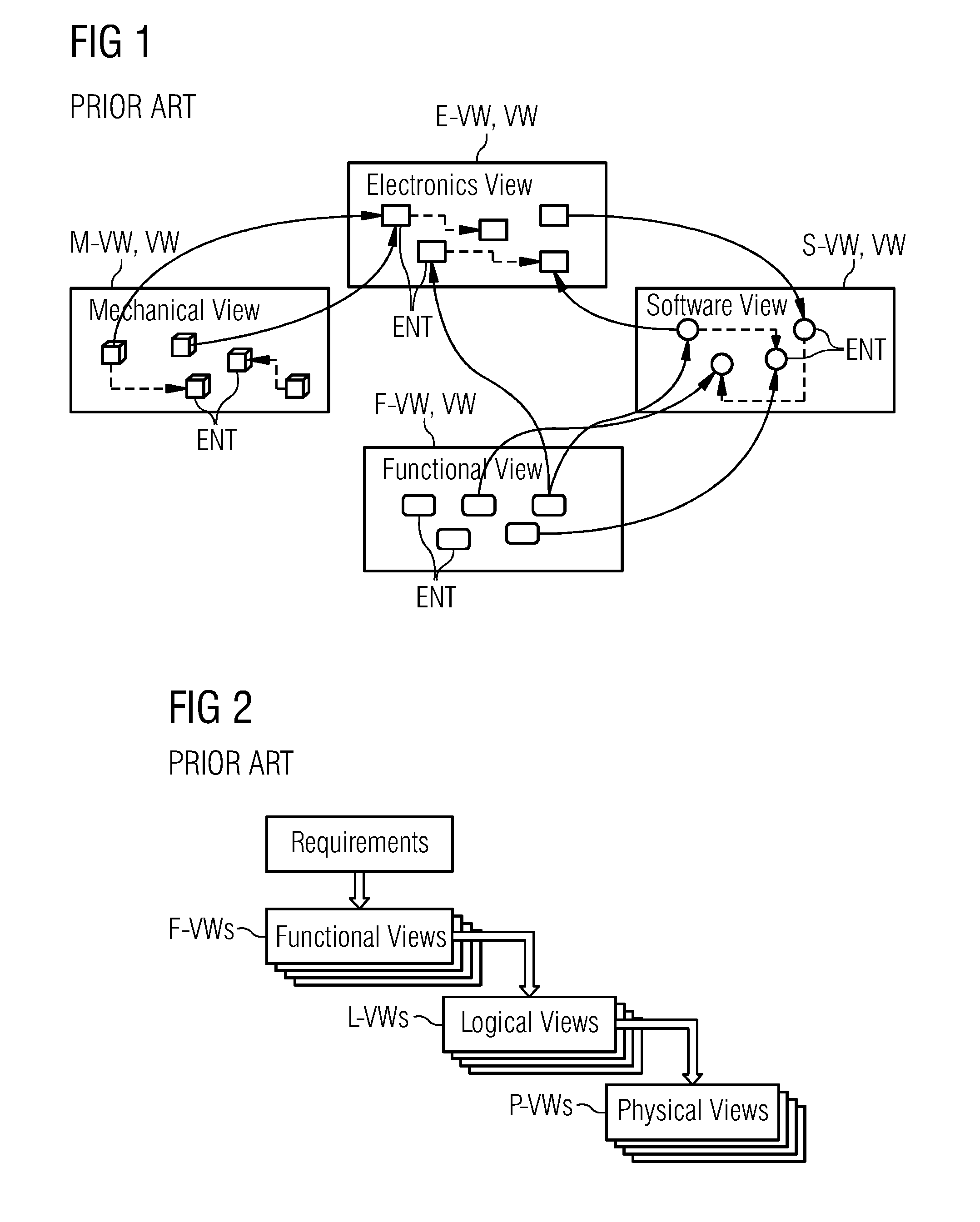
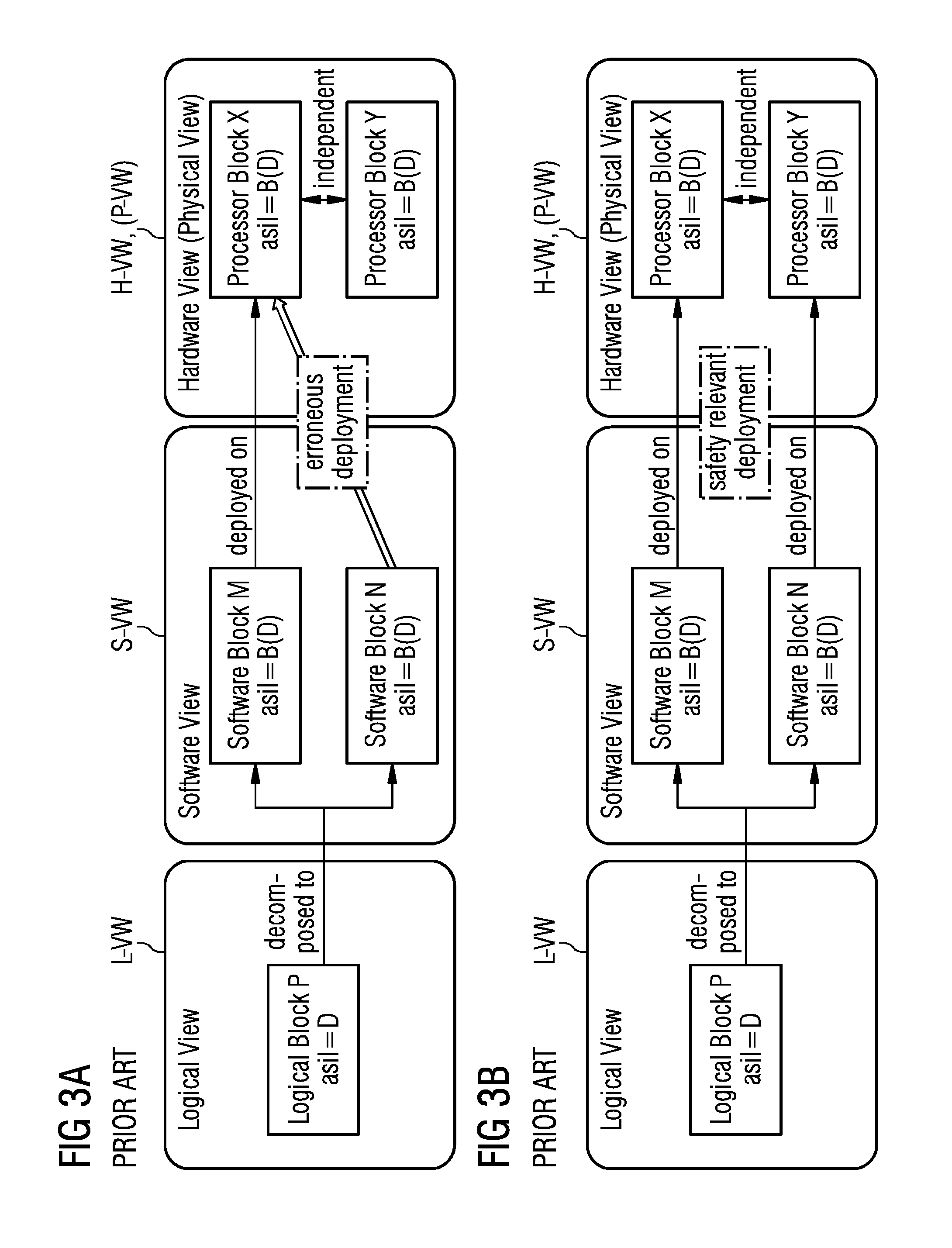
Method and Digital Tool for Engineering Software Architectures of Complex Cyber-Physical Systems of Different Technical Domains
ActiveUS20160261466A1Efficient executionEfficient implementationDigital data information retrievalModel driven codeCOLA (software architecture)Software architecture
In order to engineer software architectures of complex cyber-physical systems of different technical domains such that both time and effort efficient and truly interactive engineering of software architectures of complex cyber-physical systems is enabled, it is proposed to provide an automatic enforcement of multi-level Constraints across architectural Views. This provides, (i) with regard to architectural aspects of such a complex cyber-physical system being captured in Views including various Entities being related to each other and entities being related across various Views and (ii) that these multi-view Constraints particularly implying that the Constraints placed on the Entities in one View may affect the validity of the relations of the Entities in another View, an error-free engineering, (e.g., without violating at least one Constraint), together with a rapid, in particular visual, feedback of Constraints being invalidated and Entities involved in the Constraints.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
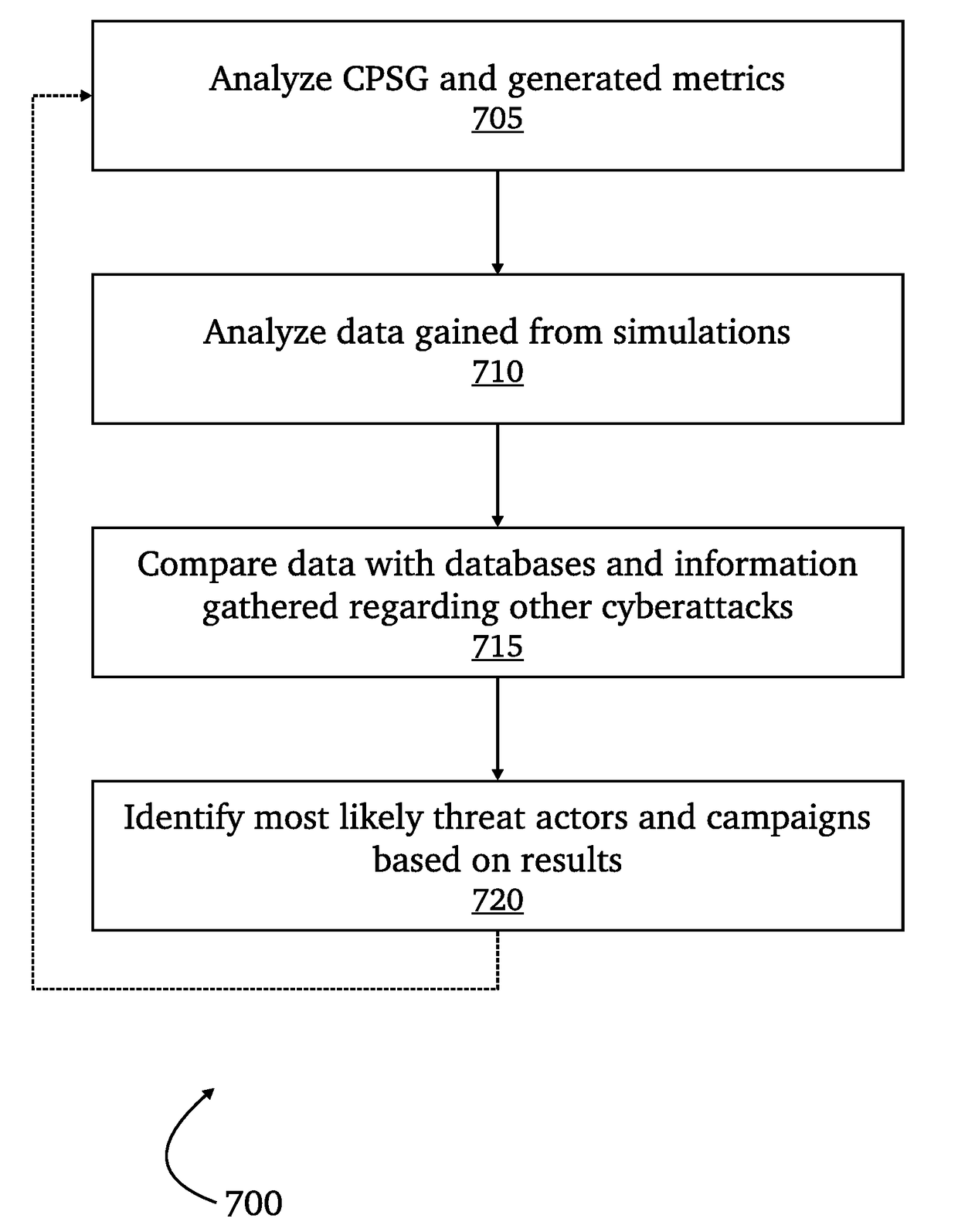
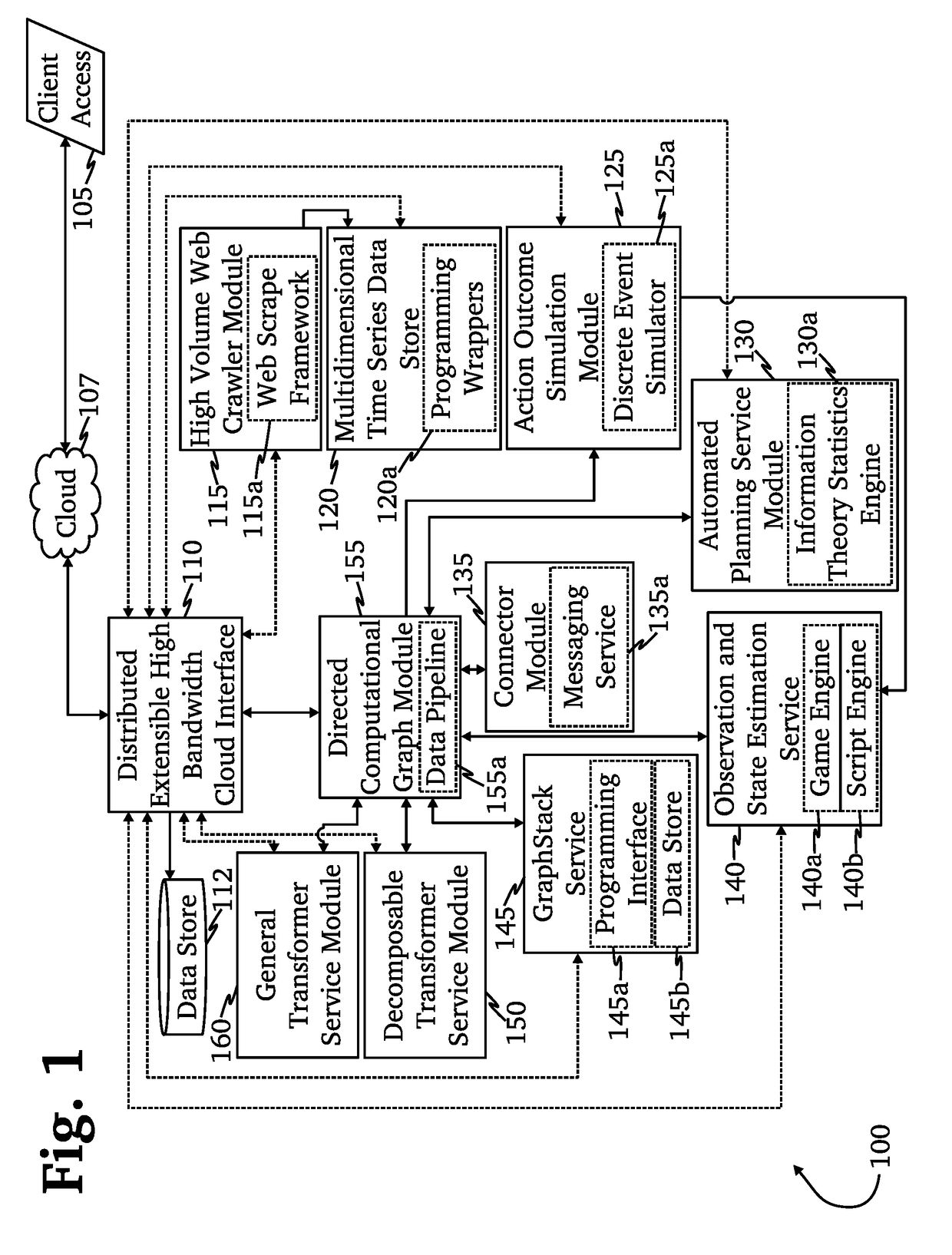
Automated cyber physical threat campaign analysis and attribution
ActiveUS20180159881A1Digital data information retrievalComputer security arrangementsDirect computationData set
A system for automated cyber physical threat campaign analysis and attribution, comprising a multi-dimensional time series and graph hybrid data server, an automated planning service module, and a directed computation graph module. A dataset is gathered from a monitored network and aggregated into a cyber-physical systems graph. Cyberattack simulations on the monitored network are made using exogenously collected data as input. Metrics are generated based on the cyber-physical systems graph and results from the cyberattack simulations, and the generated metrics are used to develop a threat profile.
Owner:QPX LLC
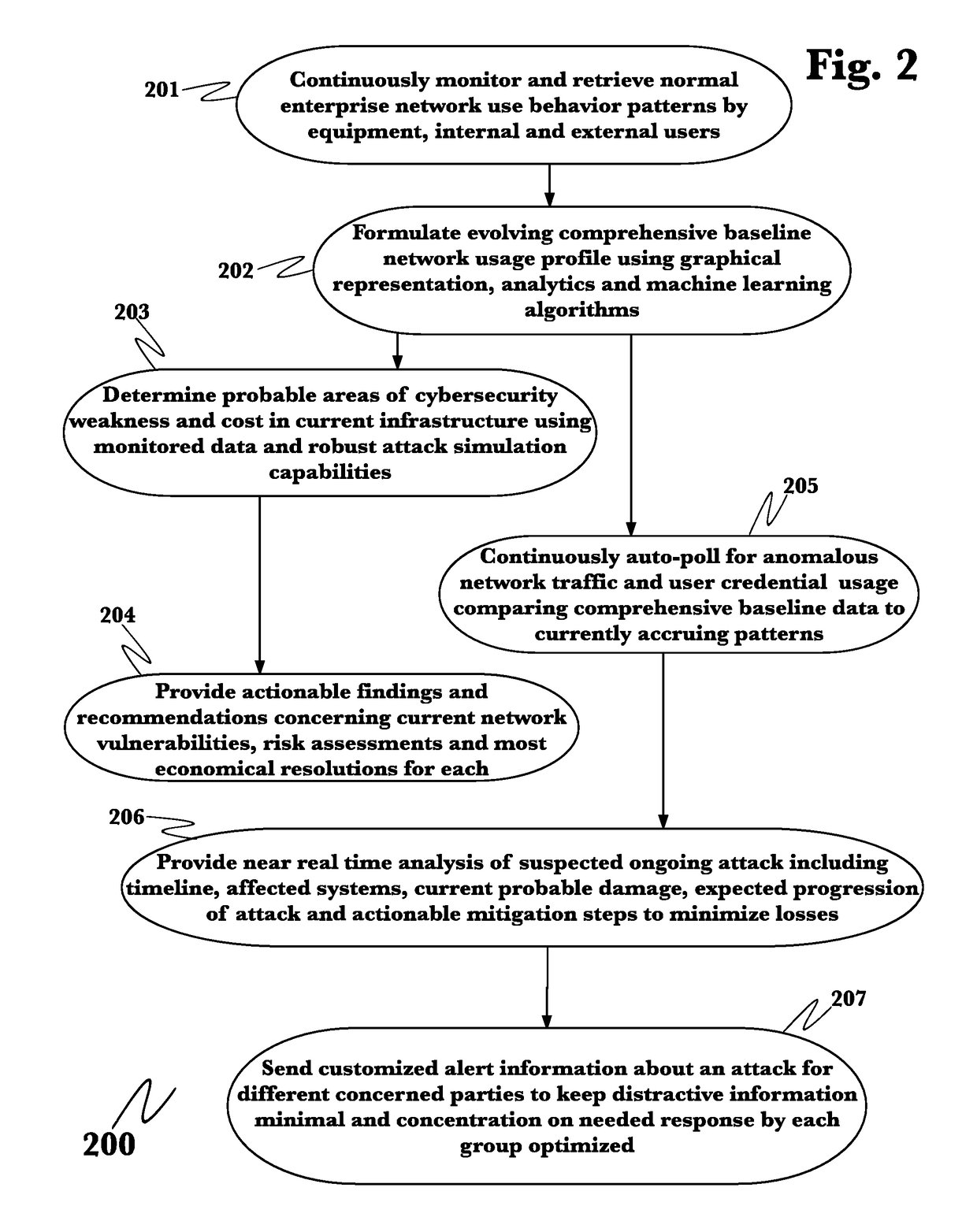
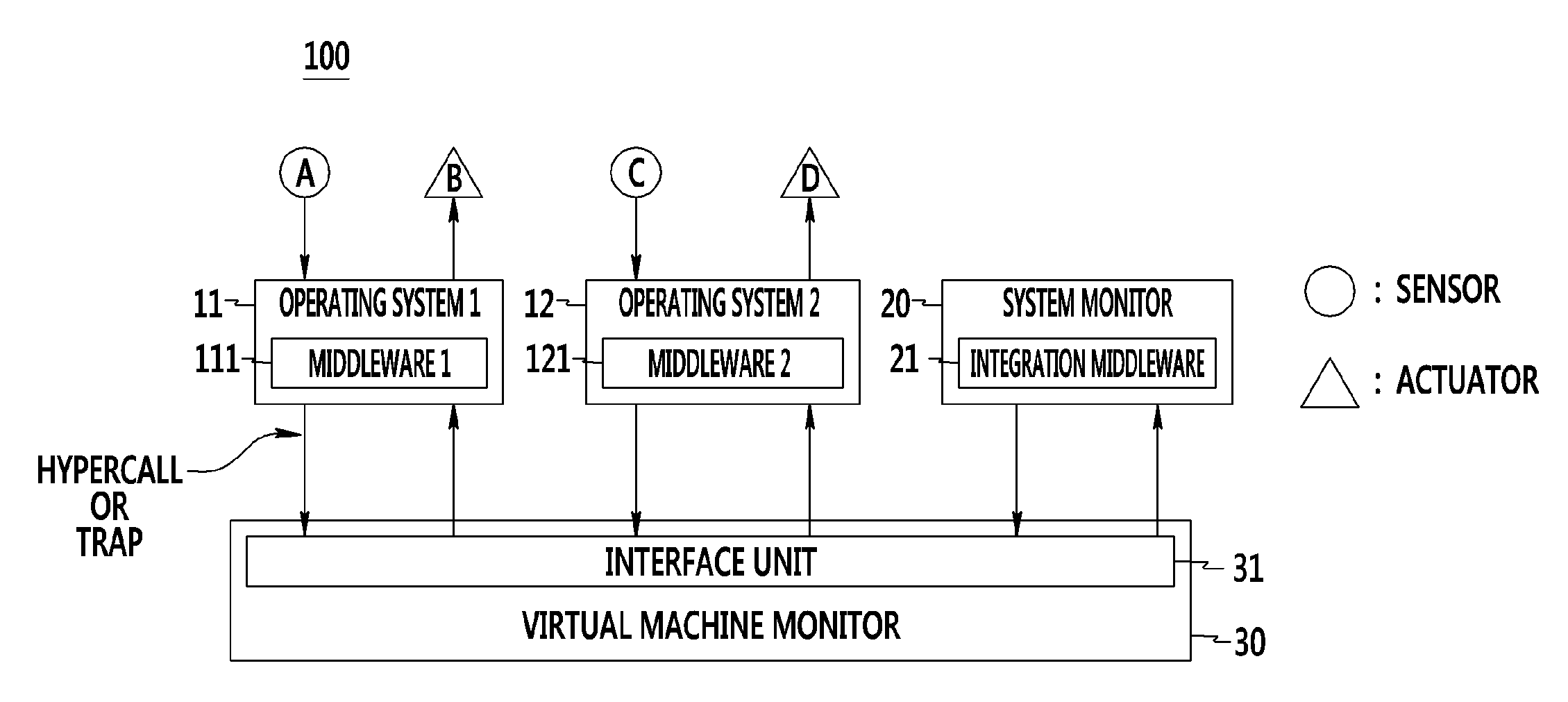
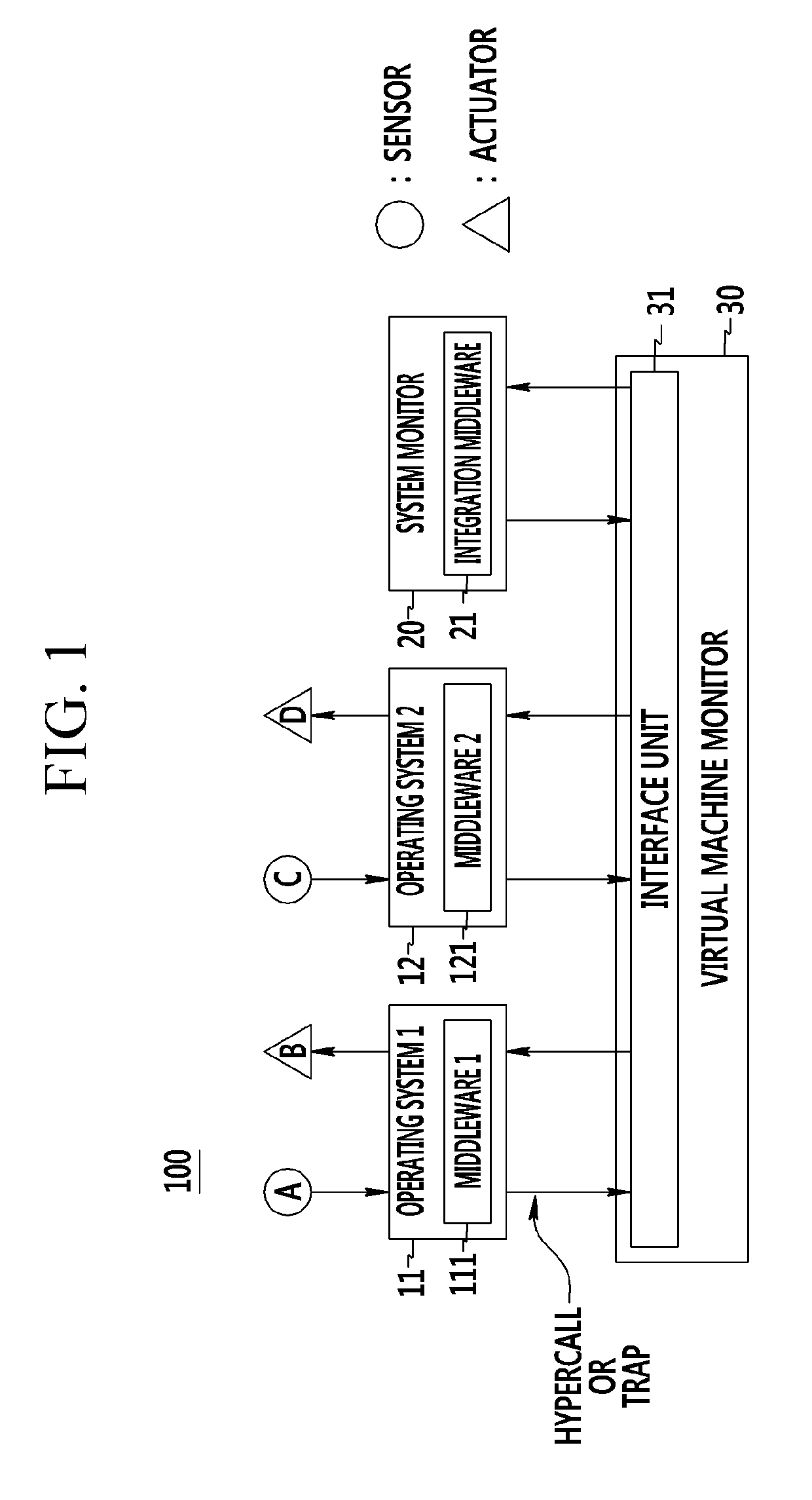
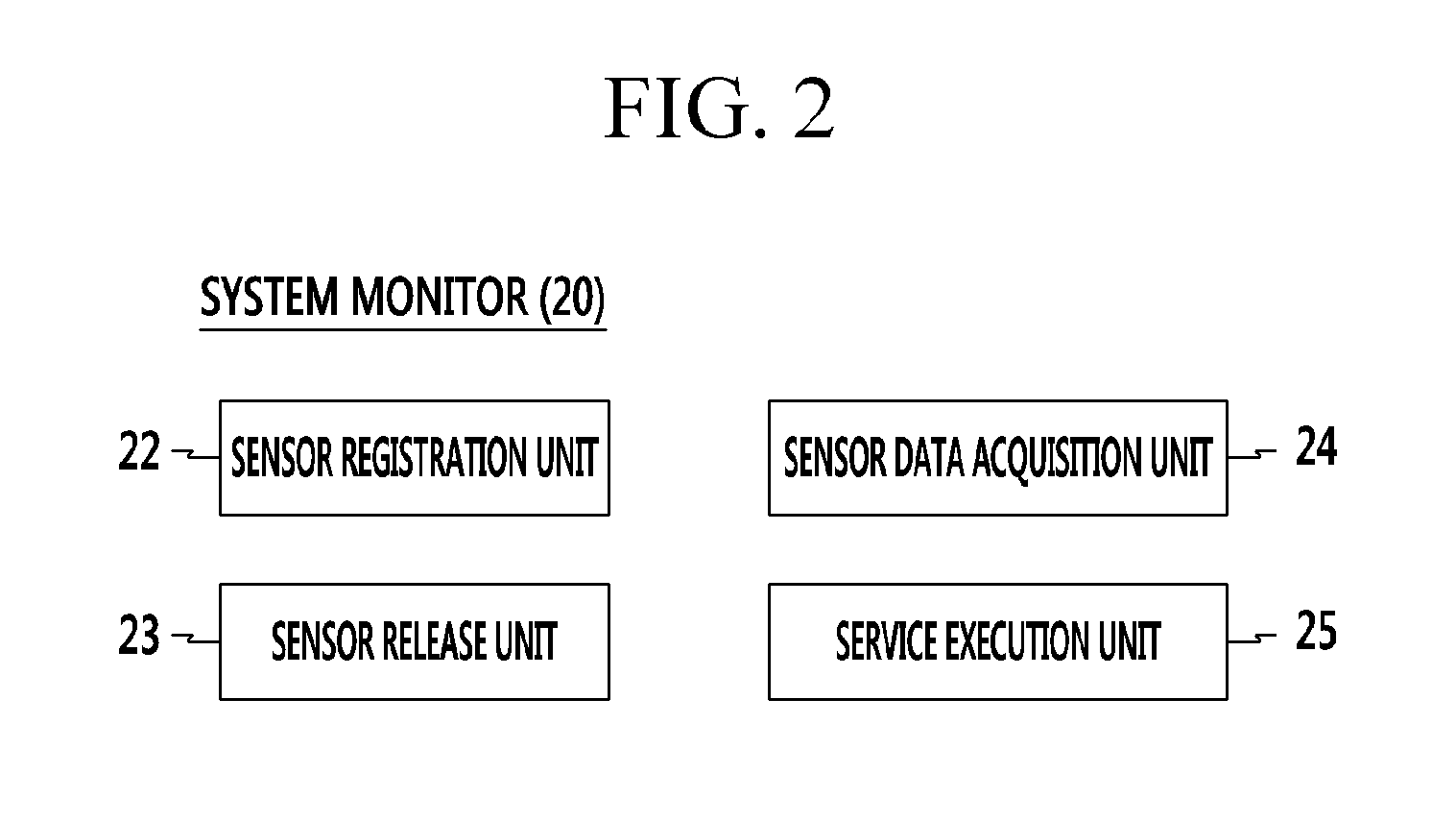
Cyber-physical system and method of monitoring virtual machine thereof
ActiveUS9417904B2Stably performing independent processingHardware monitoringMicrocontrol arrangementsVirtualizationCyberphysical systems
A cyber-physical system and a method of monitoring a virtual machine thereof are provided. The cyber-physical system includes a plurality of target controllers that includes middleware operating based on different operating systems and that control different targets, and a system monitor that includes integrated middleware of analyzing and synthesizing information collected from the middleware. First virtual machines corresponding to virtualization of the target controllers and a second virtual machine corresponding to virtualization of the system monitor are independently formed through a virtual machine monitor.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method of resource-limited device and device class identification using system and function call tracing techniques, performance, and statistical analysis
ActiveUS10242193B1Improve securityImprove cyber securityPlatform integrity maintainanceTransmissionCyberphysical systemsStatistical analysis
Methods for cyber physical systems device classification are provided. A method can include receiving system and function calls and parameters and a device performance index from an unknown CPS device and a device performance index of similar class of CPS devices, calculating an autocorrelation value between different realizations of the system and function calls and parameters of the known CPS device, determining whether the autocorrelation value is greater than a threshold amount, and storing the system and function calls and parameters and the device performance characteristics of the known CPS device in the database. A method can also include calculating a correlation between system and function calls and parameters of an unknown CPS device and known CPS devices classes included in the database, as well as determining whether the maximum correlation is also greater than a threshold amount.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
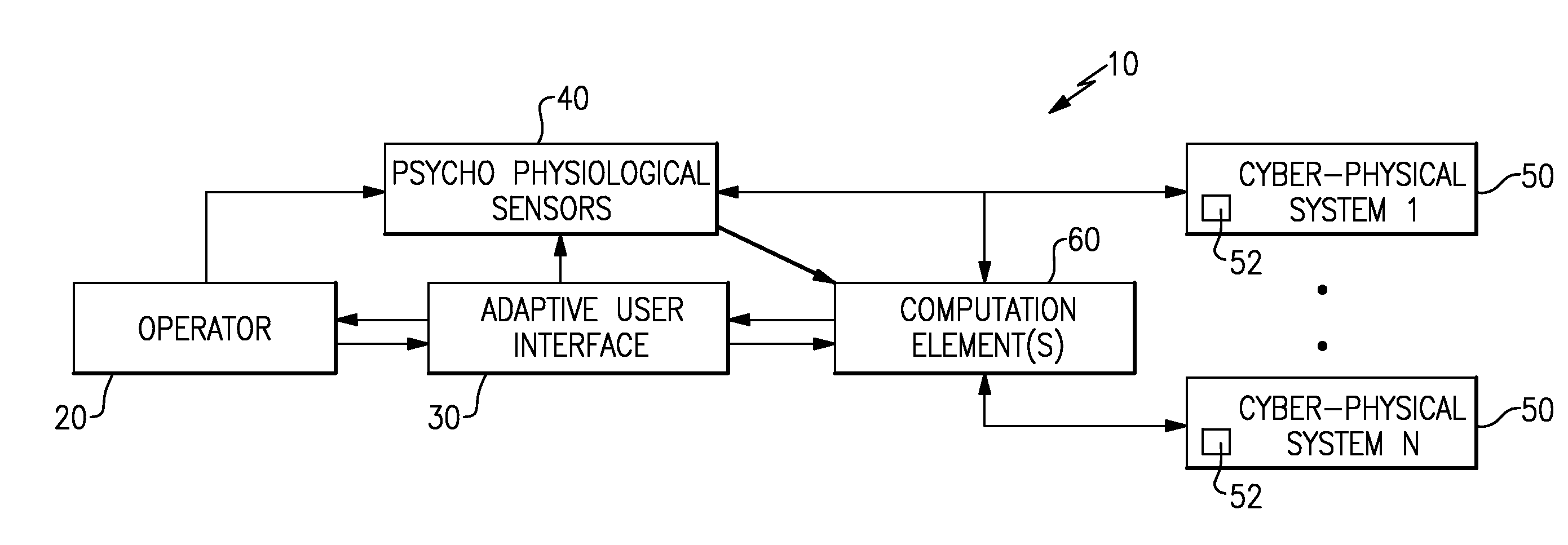
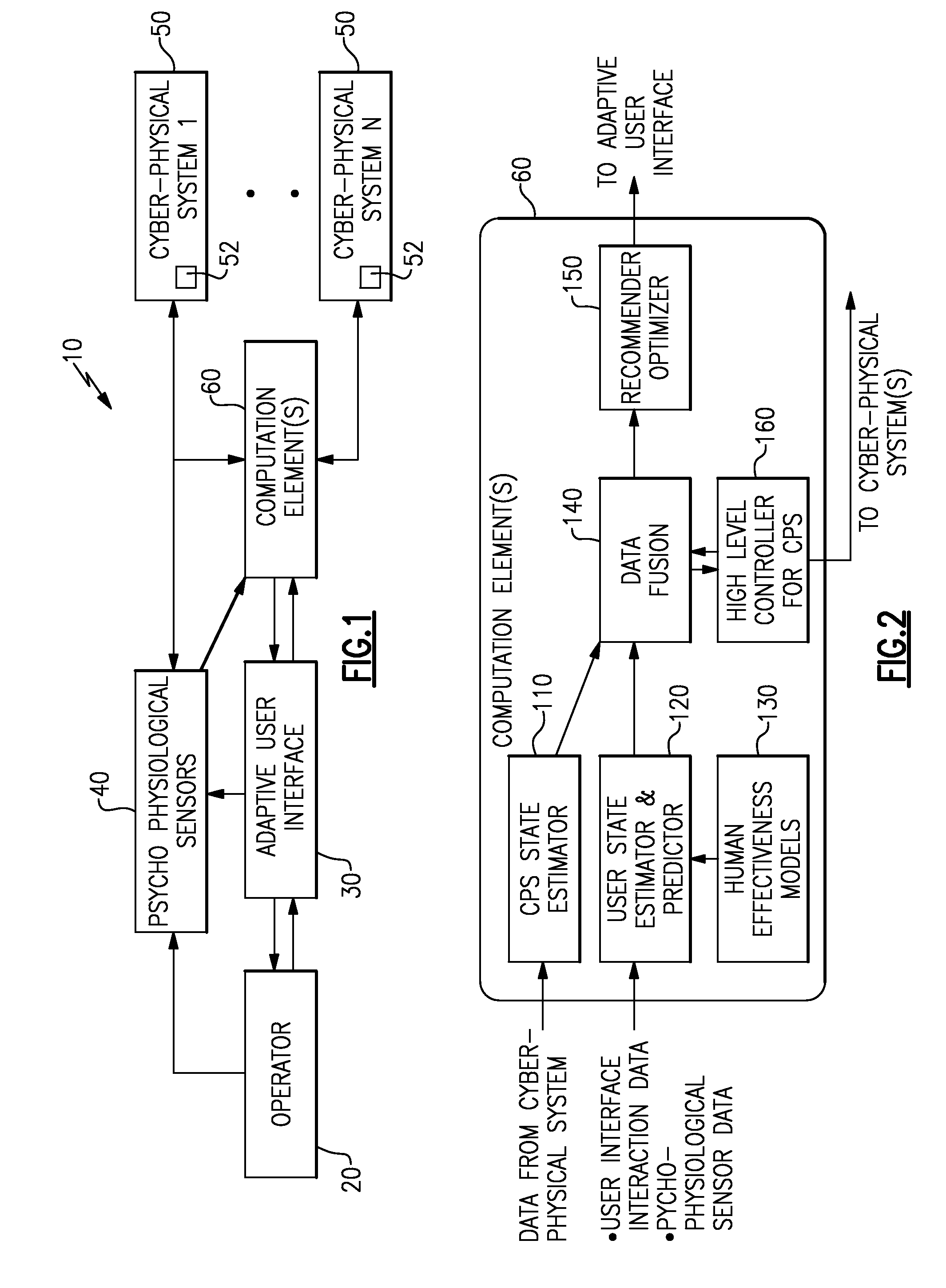
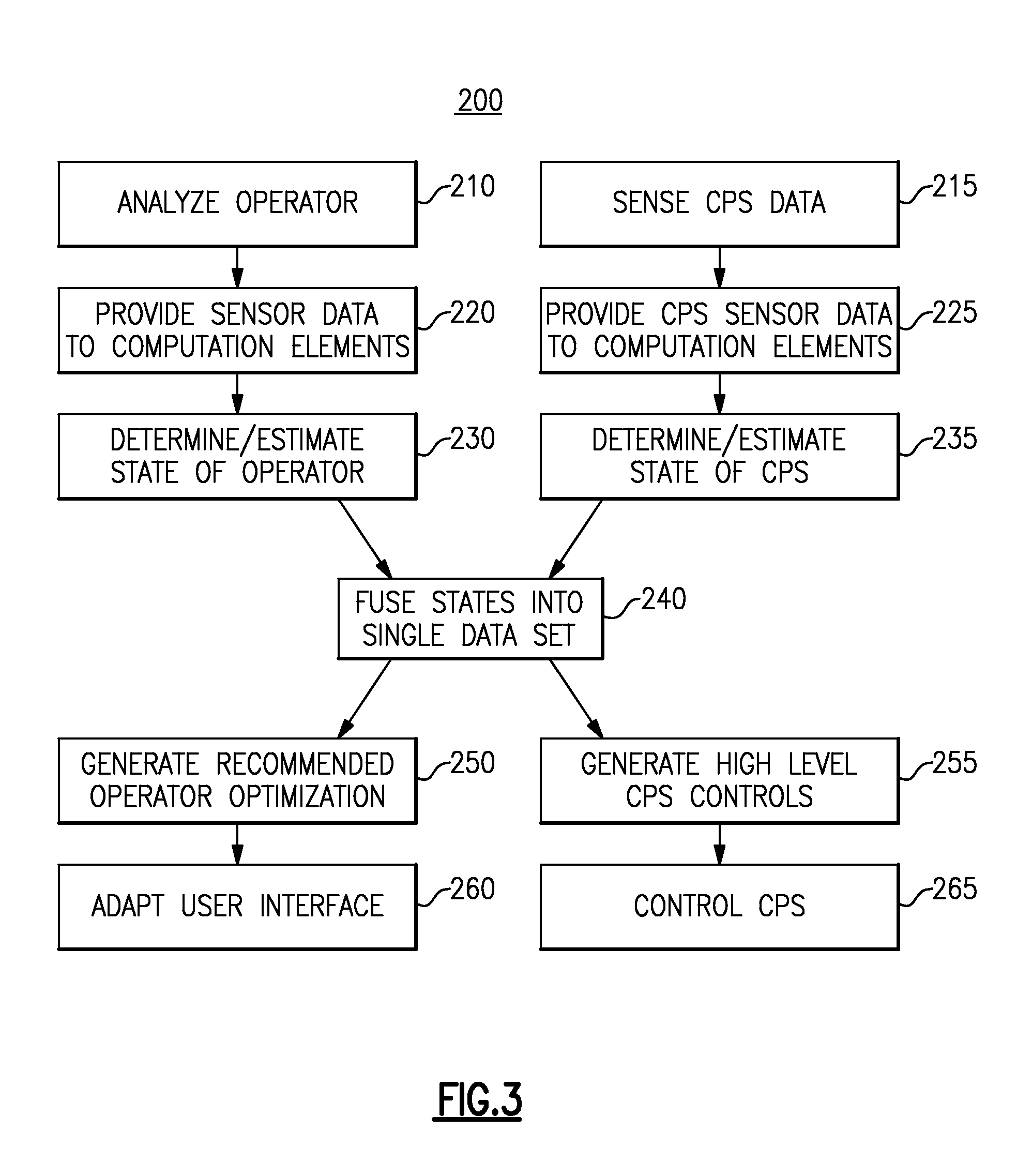
Optimization of human supervisors and cyber-physical systems
ActiveUS20160041535A1Computer controlTesting/monitoring control systemsPhysical systemCyberphysical systems
A method and system for optimizing a human supervised cyber-physical system determines a state of the human operator based on data from multiple psycho physiological sensors, determines a state of each of multiple cyber-physical systems in the human supervised cyber-physical system based on data provided by the cyber-physical systems, and fuses the state of the human operator and the state of each of the plurality of cyber-physical systems into a single state of the human supervised cyber-physical system. The single state is then used to generate recommendations for optimizing a user interface and to generate high level control signals for the cyber-physical systems.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Systems and methods for skyline prediction for cyber-physical photovoltaic array control
ActiveUS20190384983A1Image analysisSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCyberphysical systemsComputer science
Various embodiments of a cyber-physical system for providing cloud prediction for photovoltaic array control are disclosed herein.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
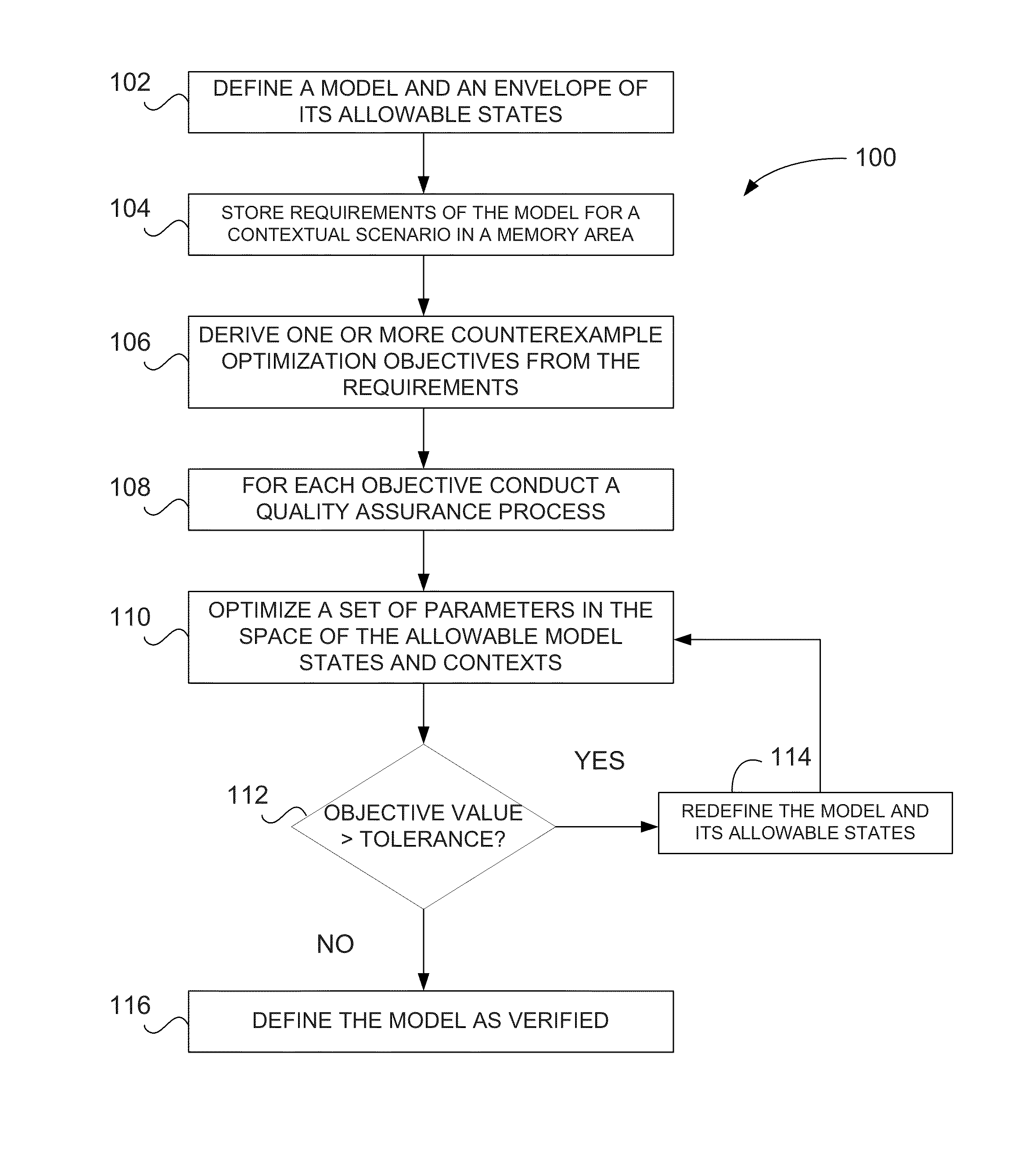
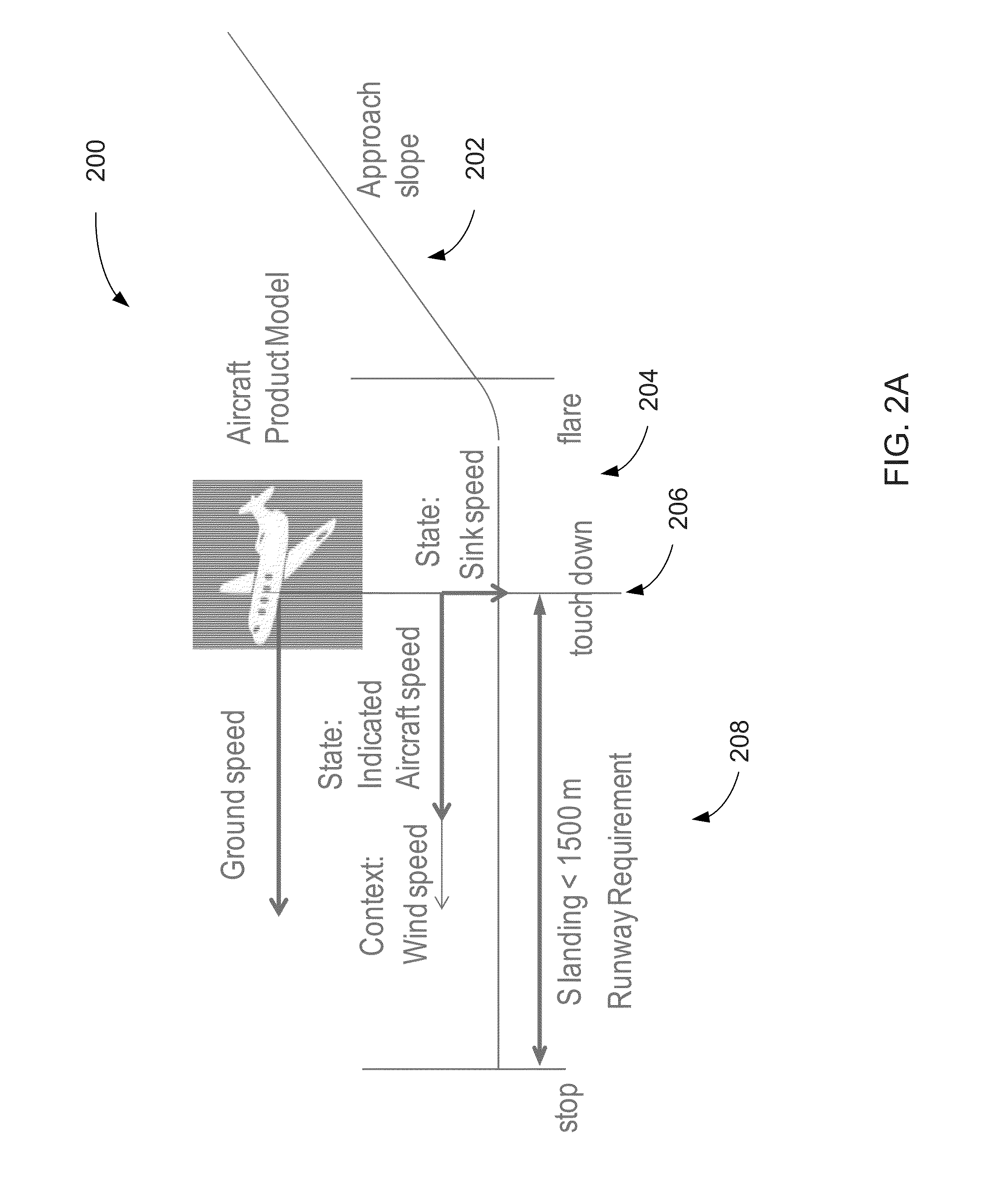
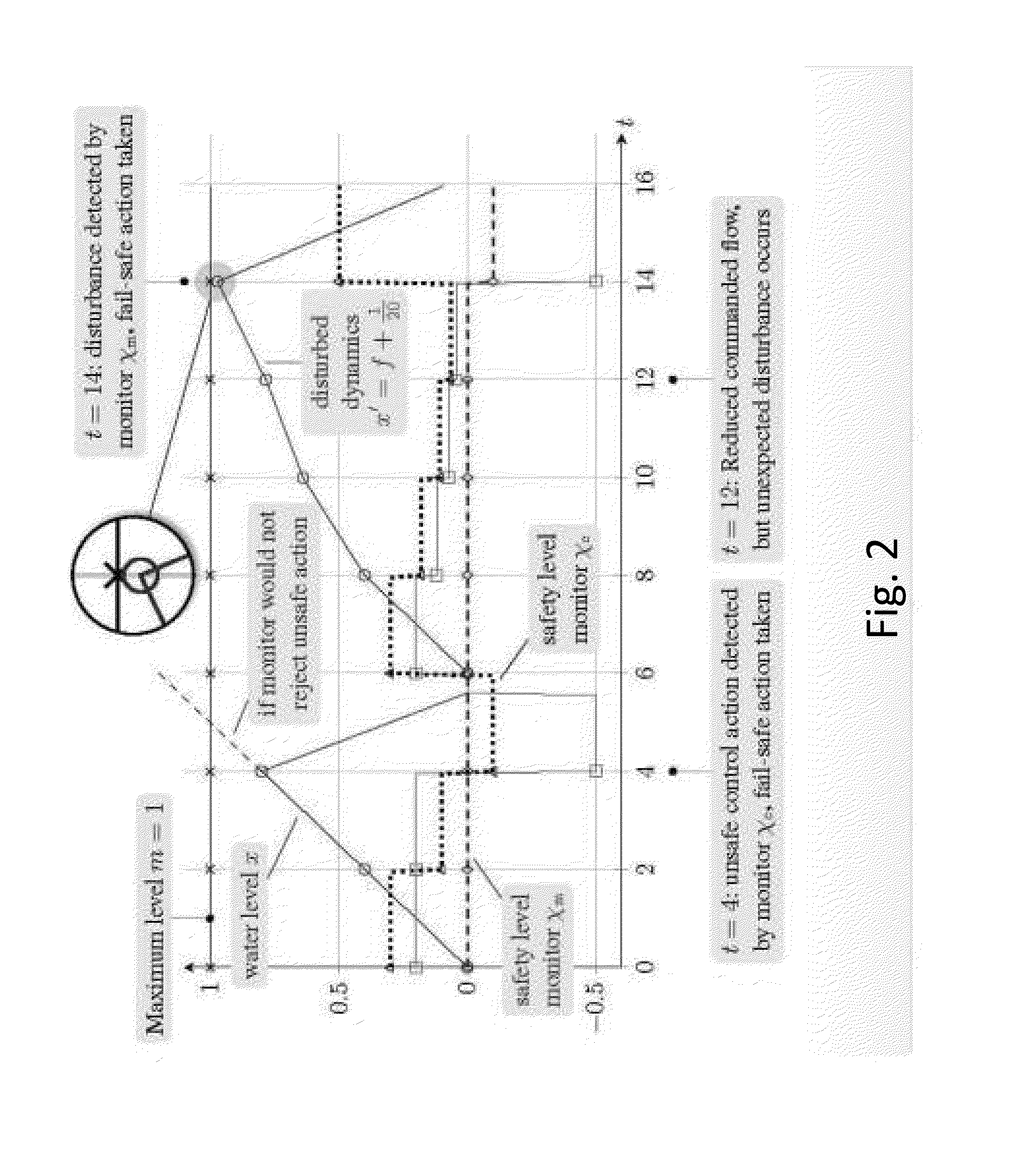
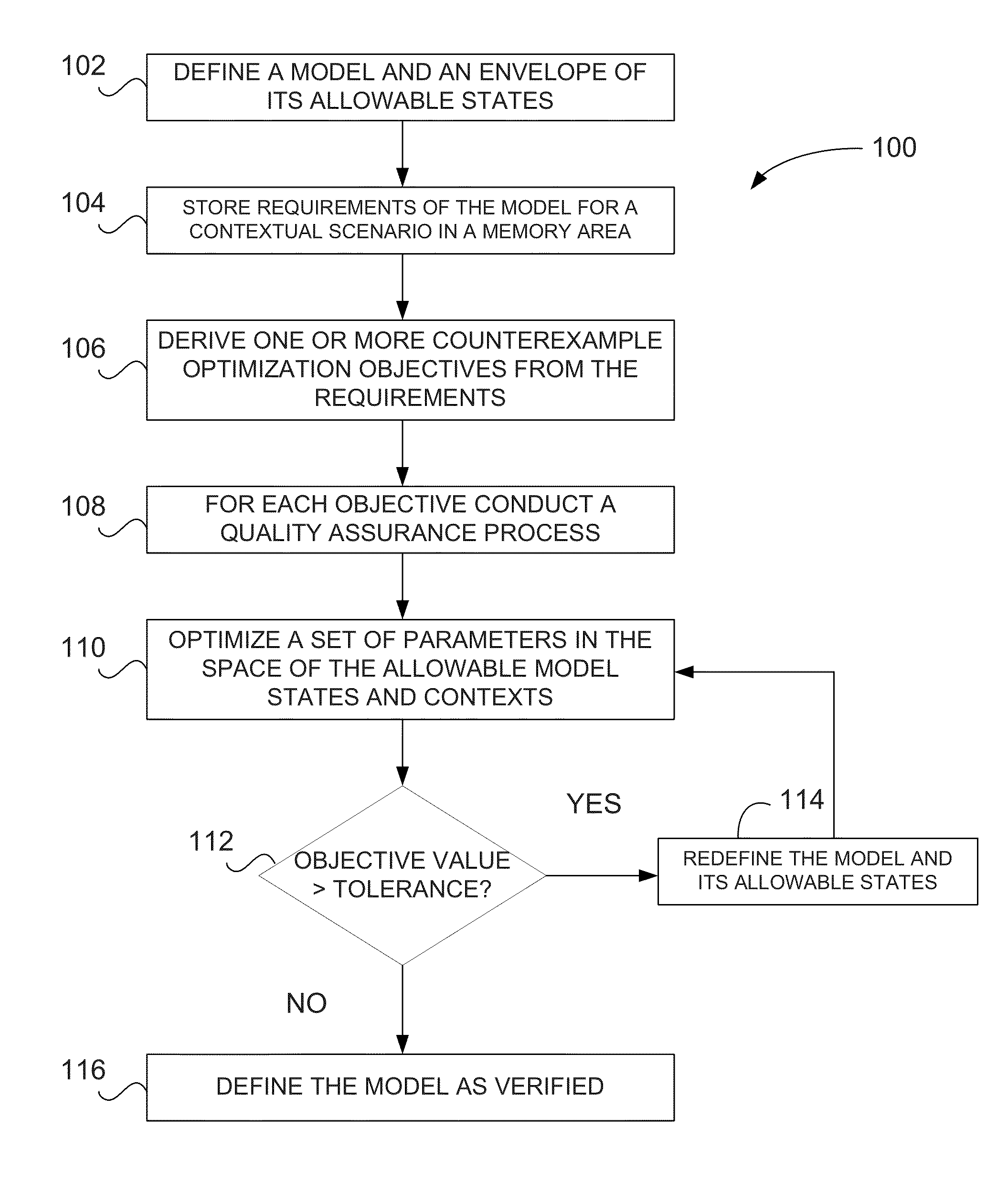
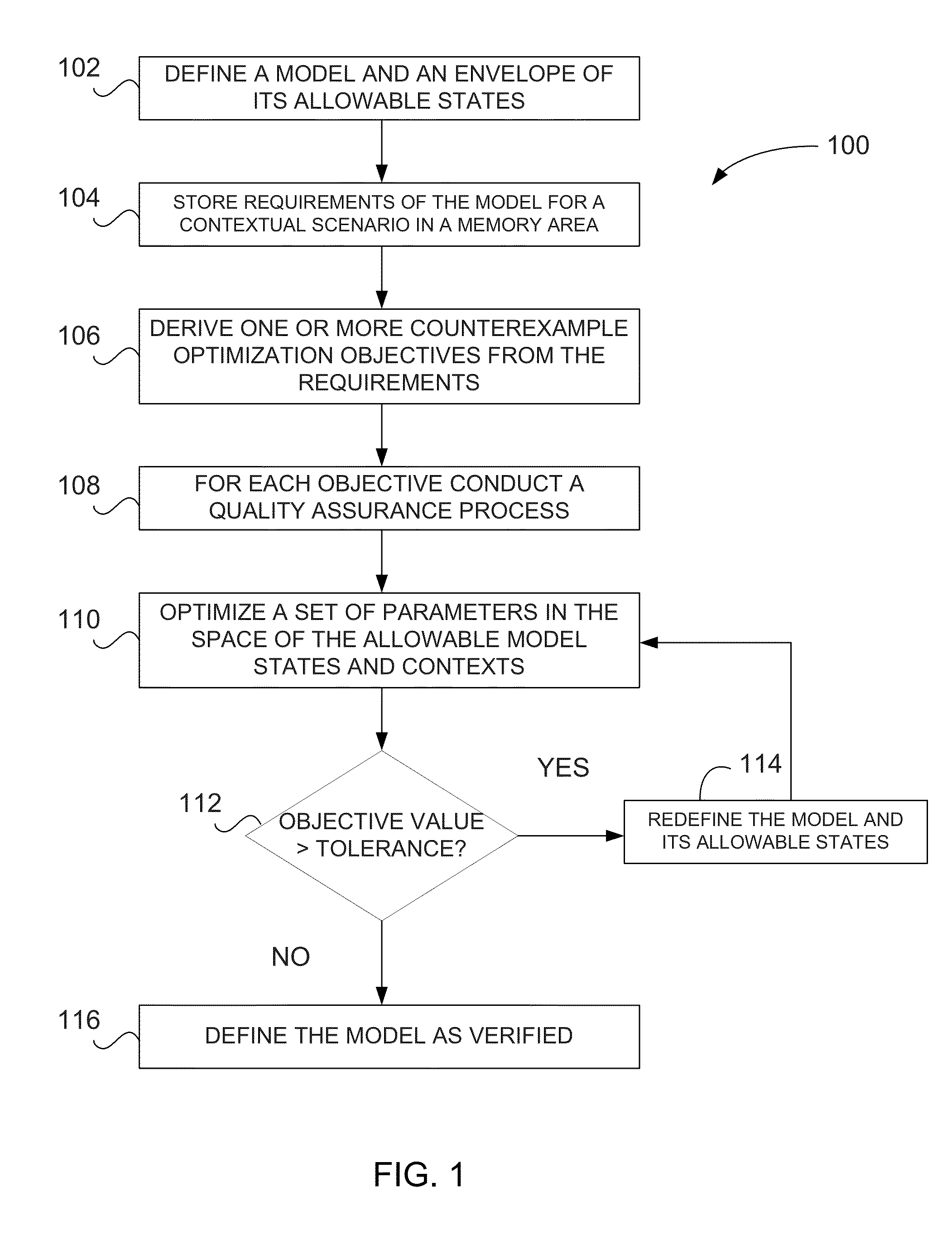
Verification of cyber-physical systems using optimization algorithms
A computer-implemented method for verifying a model in a product lifecycle management (PLM) system includes defining a model and an envelope of allowable model states and, based on one or more requirements, deriving at least one counterexample objective. The method also includes optimizing a set of parameters related to the allowable model states and the allowable model context, redefining at least one of the model and the allowable model states when the at least one counterexample objective is outside of a specified tolerance, and, after a predefined number of iterations, defining the model as verified.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES SIMULIA CORP
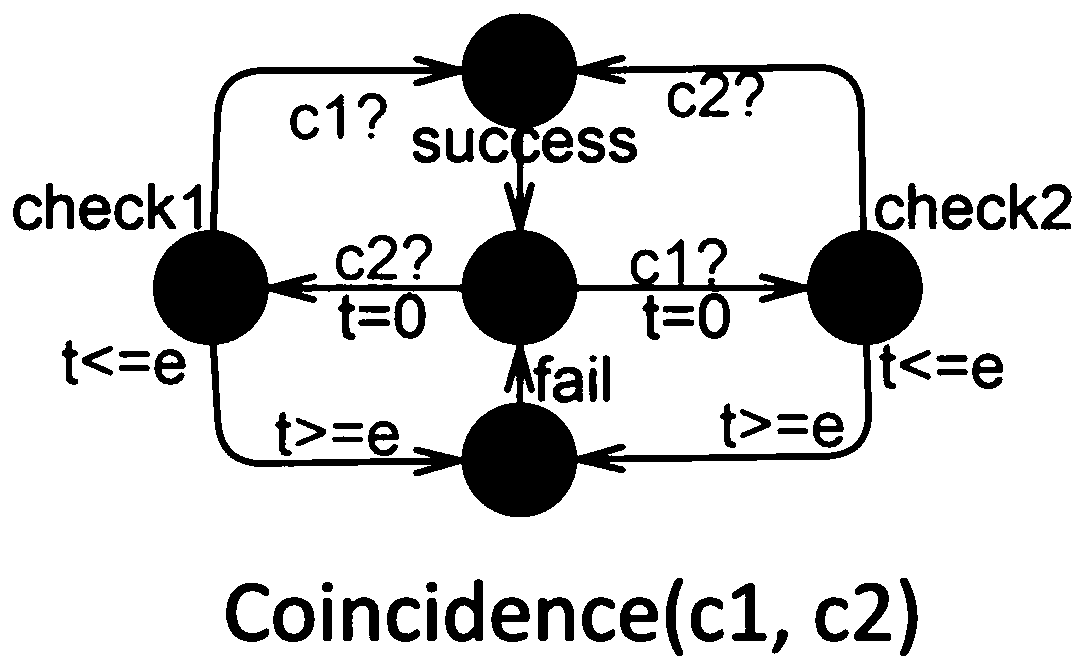
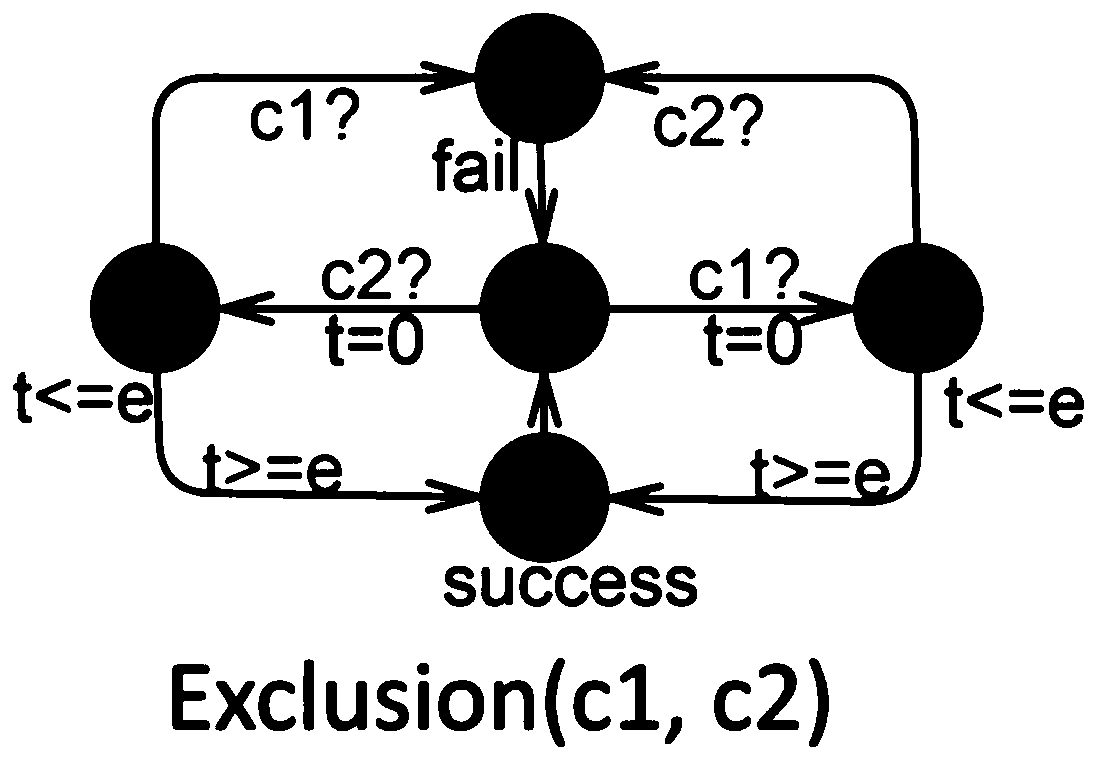
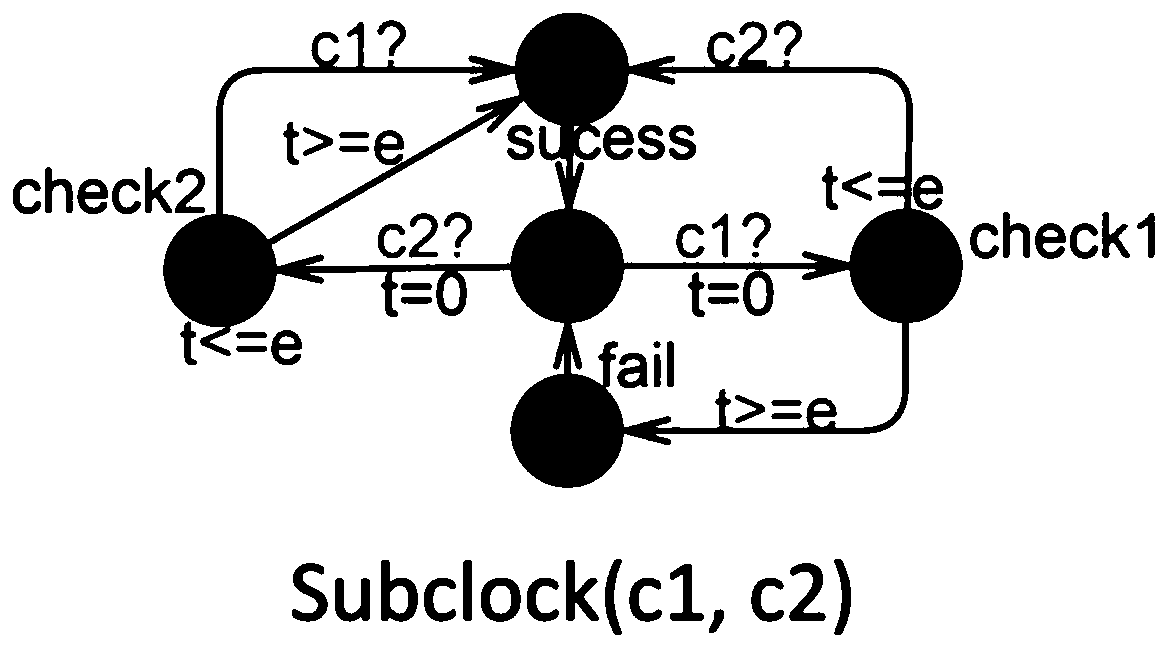
Formalized verification method for network physical system requirements based on UPPAAL-SMC
InactiveCN109976712ARequirement analysisSpecial data processing applicationsProbabilistic descriptionClock constraint
The invention discloses a formalized verification method for network physical system requirements based on UPPAAL-SMC. The method comprises the following steps: expressing a demand model of a networkphysical system CPS in an EAST-ADL architecture model by using a probabilistic clock constraint normative language form; inputting the PrCCSL statement into a grammar parser, and parsing the PrCCSL statement to generate an abstract syntax tree AST; traversing the abstract syntax tree AST to extract key information of each relation or expression statement in the PrCCS L statement; matching a corresponding template for each relation or expression statement according to the content of the key information to generate an STA model and a query statement thereof, generating an STAs model, storing theSTAs model as an STAs file, inputting the STAs file into an integrator, integrating a system behavior model of a network physical system, and outputting a verifiable Net-STA model, the verifiable Net-STA model calling the formalized verification engine Verifyta of the UPPAAL-SMC model; and the Query generator outputs the current query verification statement to the Verify, and starts the Verify toexecute formalized verification. The method is based on PrCCS L and UPPAAL-SMC, and describes the probabilistic description of the network physical system demand, and carries out formalized verification on the demand.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
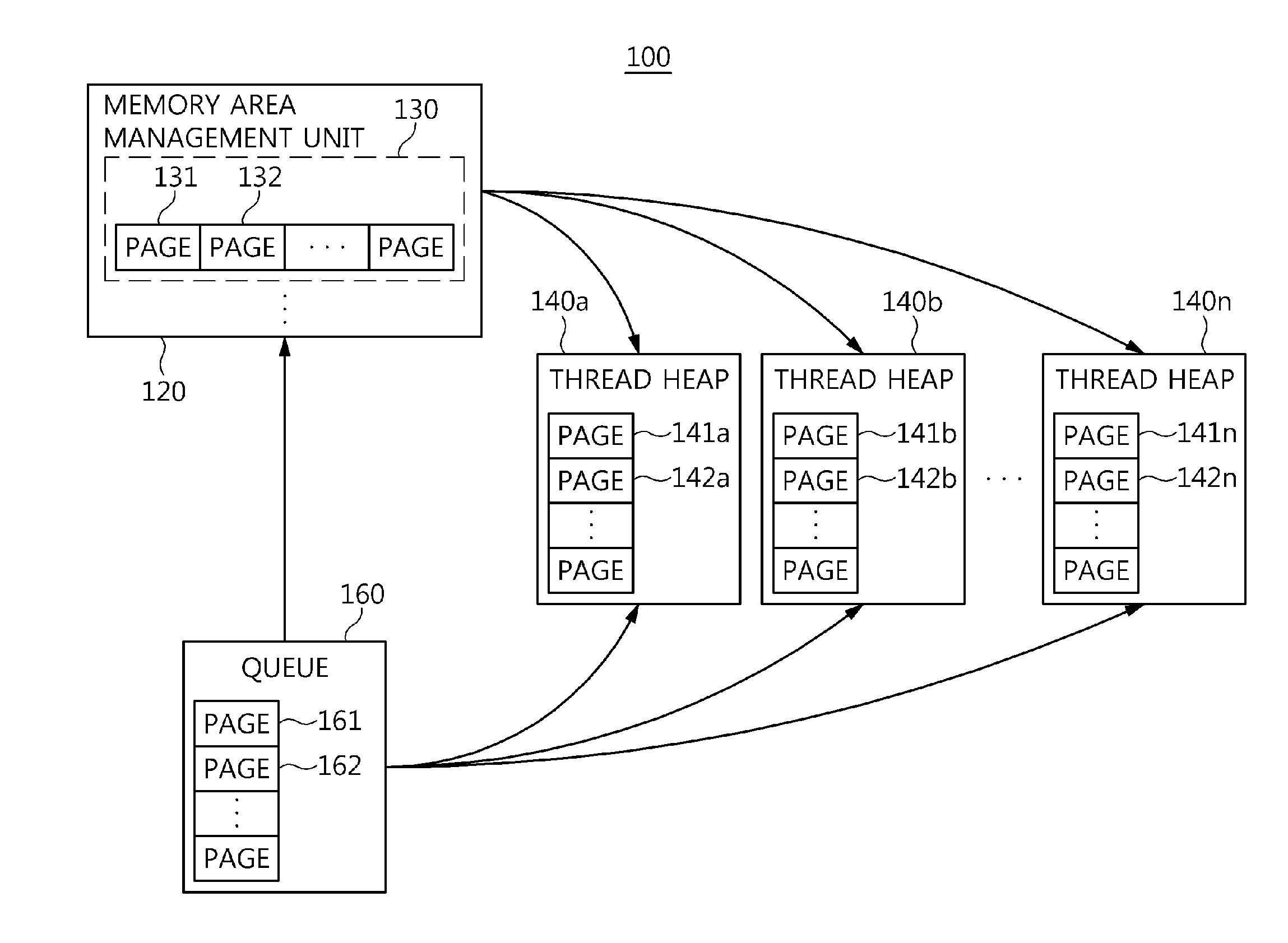
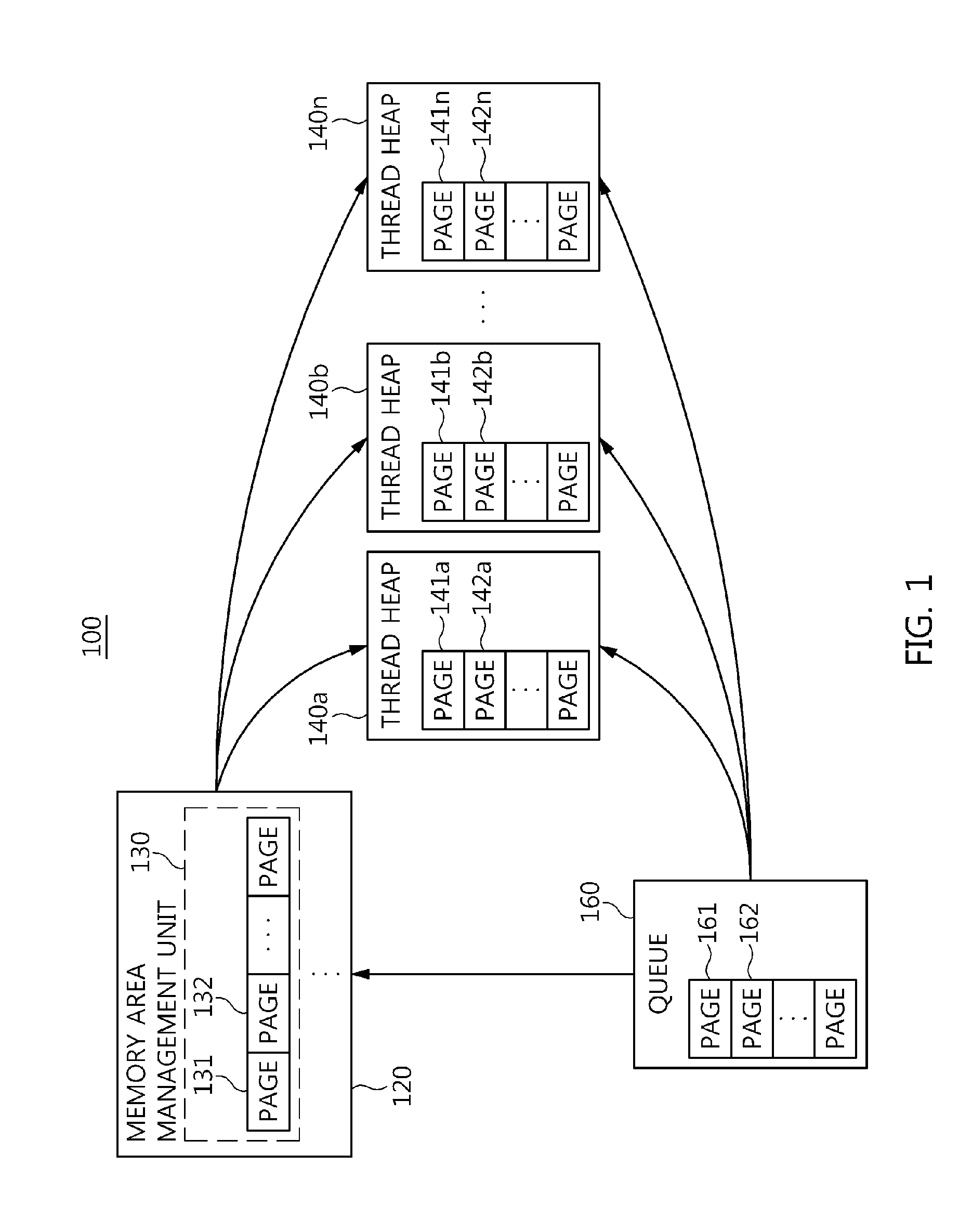
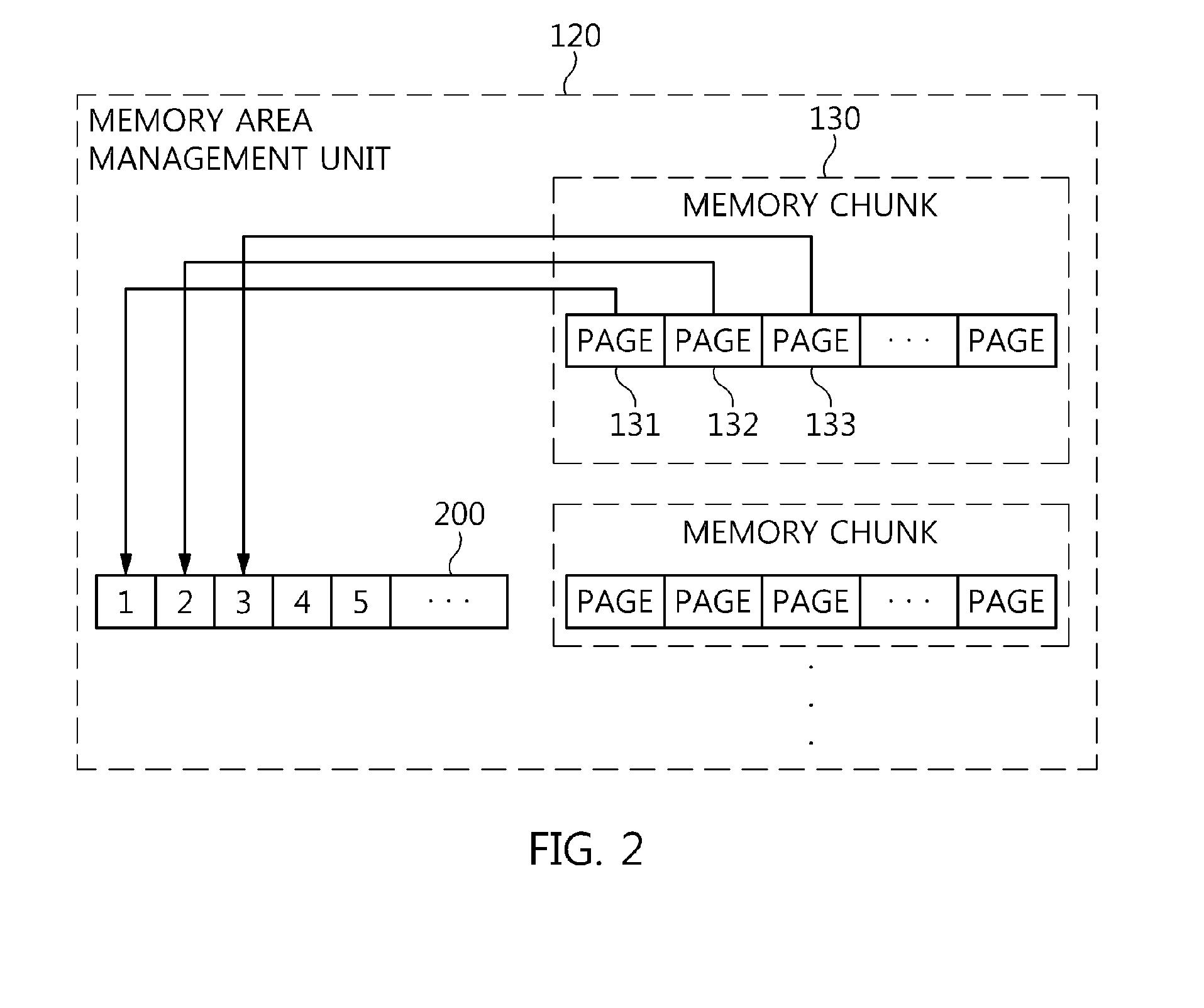
Memory management apparatus and method for threads of data distribution service middleware
InactiveUS20140351550A1Preventing memory contentionEfficient allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationManagement unitCyberphysical systems
Disclosed herein are a memory management apparatus and method for threads of Data Distribution Service middleware. The apparatus includes a memory area management unit, one or more thread heaps, and a queue. The memory area management unit partitions a memory chunk allocated for the DDS middleware by a Cyber-Physical System on a memory page basis, manages the partitioned memory pages, and allocates the partitioned memory pages to the threads of the DDS middleware that have requested memory. The thread heaps are provided with the memory pages allocated to threads of the DDS middleware by the memory area management unit, and manage the provided memory pages. The queue receives memory used pages returned by the thread heaps. The thread heaps are provided with the memory pages for the threads by the queue if a memory page is not present in the memory area management unit when the threads request memory.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
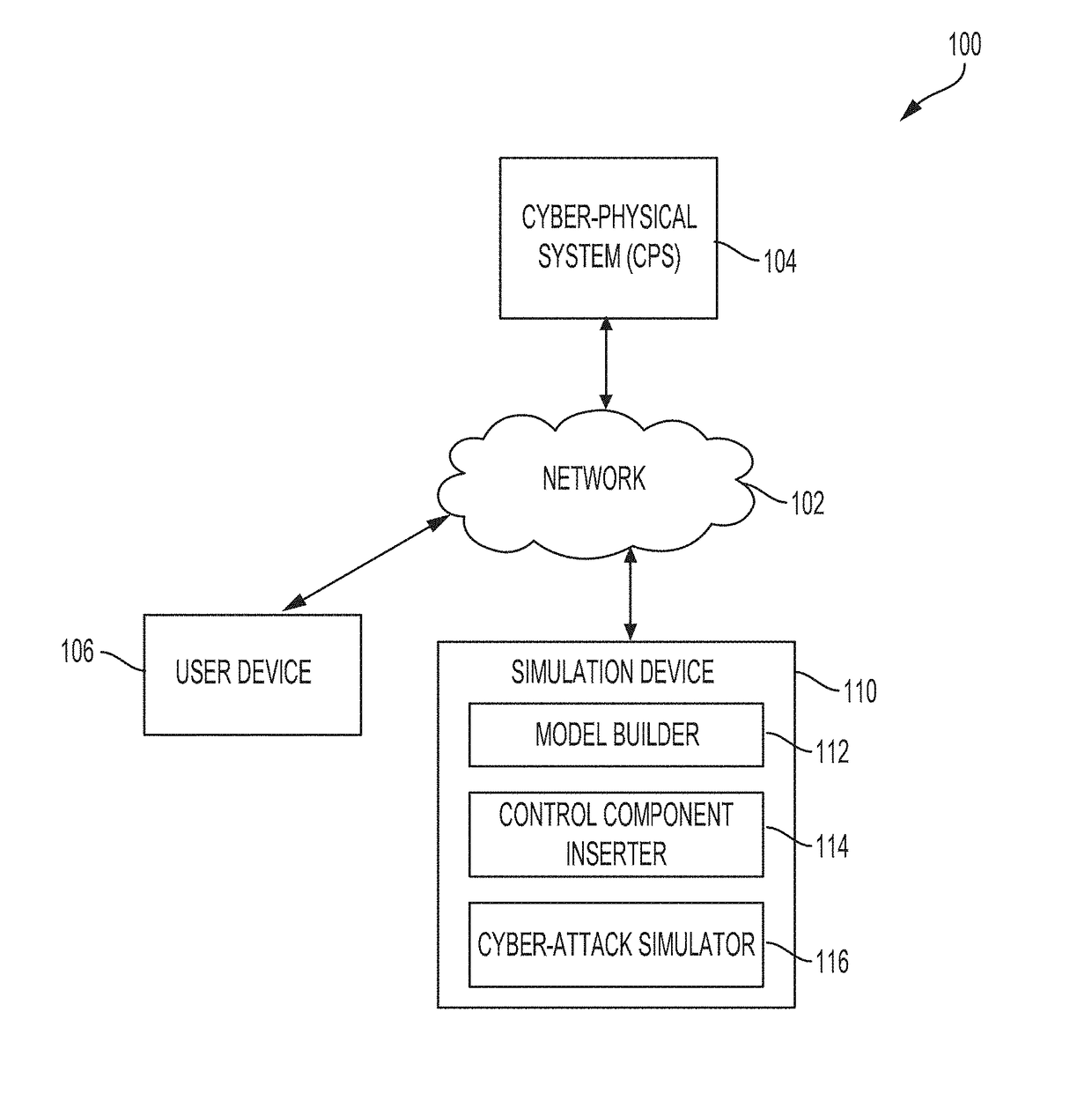
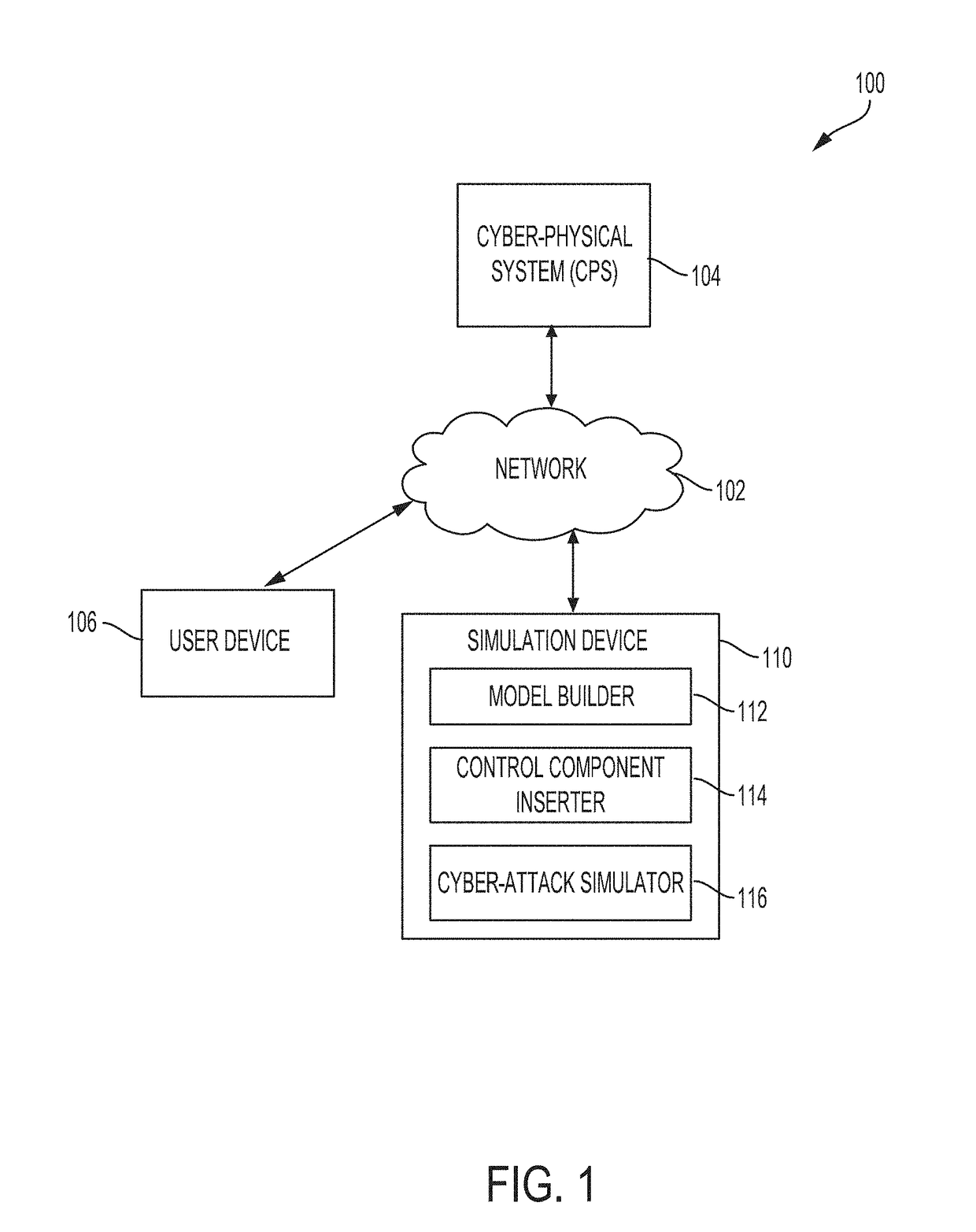
Methods and systems for evaluating effects of cyber-attacks on cyber-physical systems
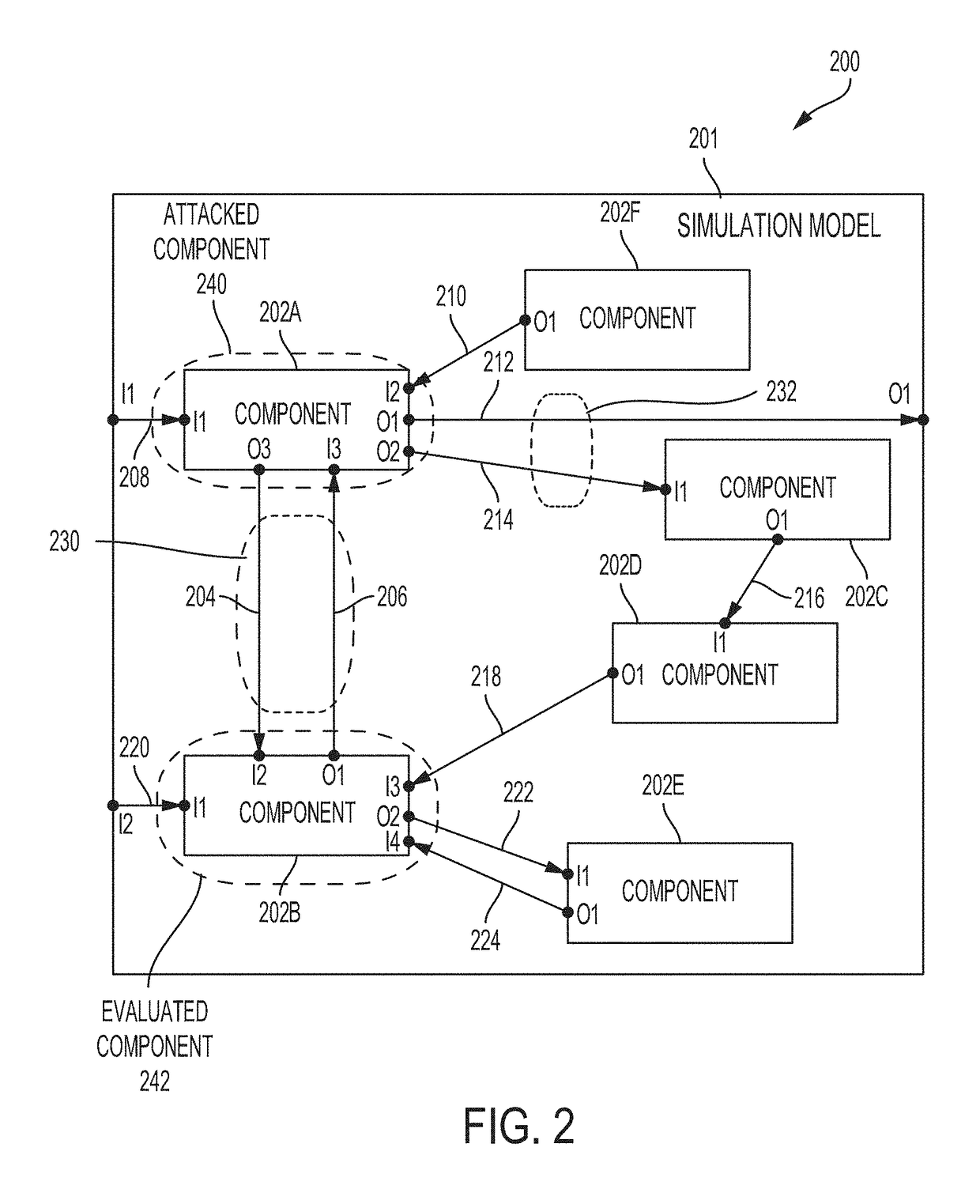
ActiveUS20180309780A1Improve cyber-attackImprove evaluation fidelityPlatform integrity maintainanceData switching networksCyber-attackParallel computing
Described are systems and methods for evaluating cyber effects in a cyber-physical system (CPS). In some embodiments, a simulation model of the CPS is built and includes an attacked component set and an evaluated component set. A control component is inserted into the simulation model. One or more direct connections between the attacked component set and the evaluated component set are disconnected. One or more indirect connections are identified and then disconnected from the simulation model with disconnected direct connections. The one or more direct connections and indirect connections are routed through the control component. A cyber-attack on the attacked component set can be simulated by configuring the control component to control outputs transmitted via a routed connection, the routed connection being one of the routed direct or indirect connections. The simulated components of the simulation model can be progressively and iteratively replaced by corresponding components from the CPS.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
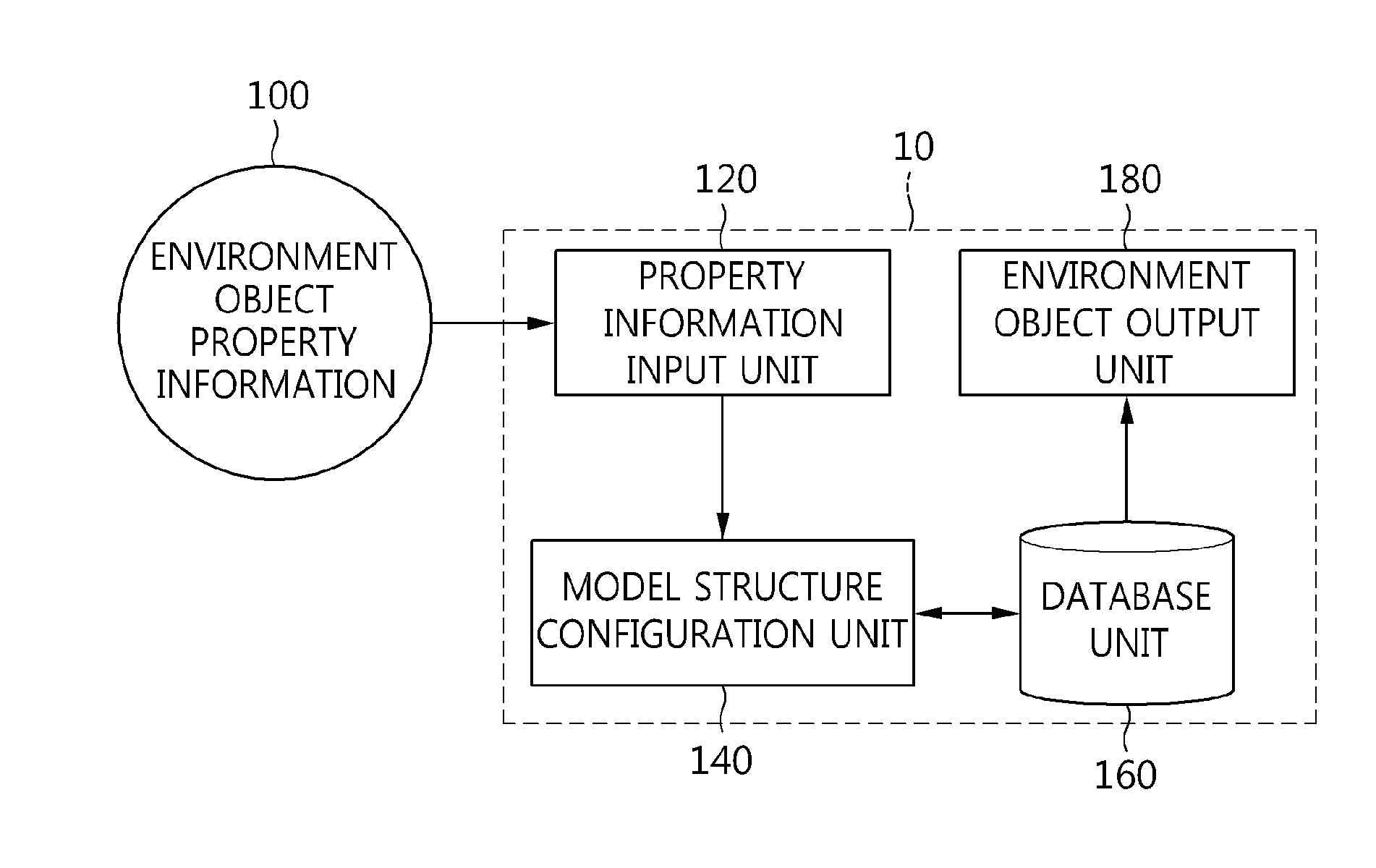
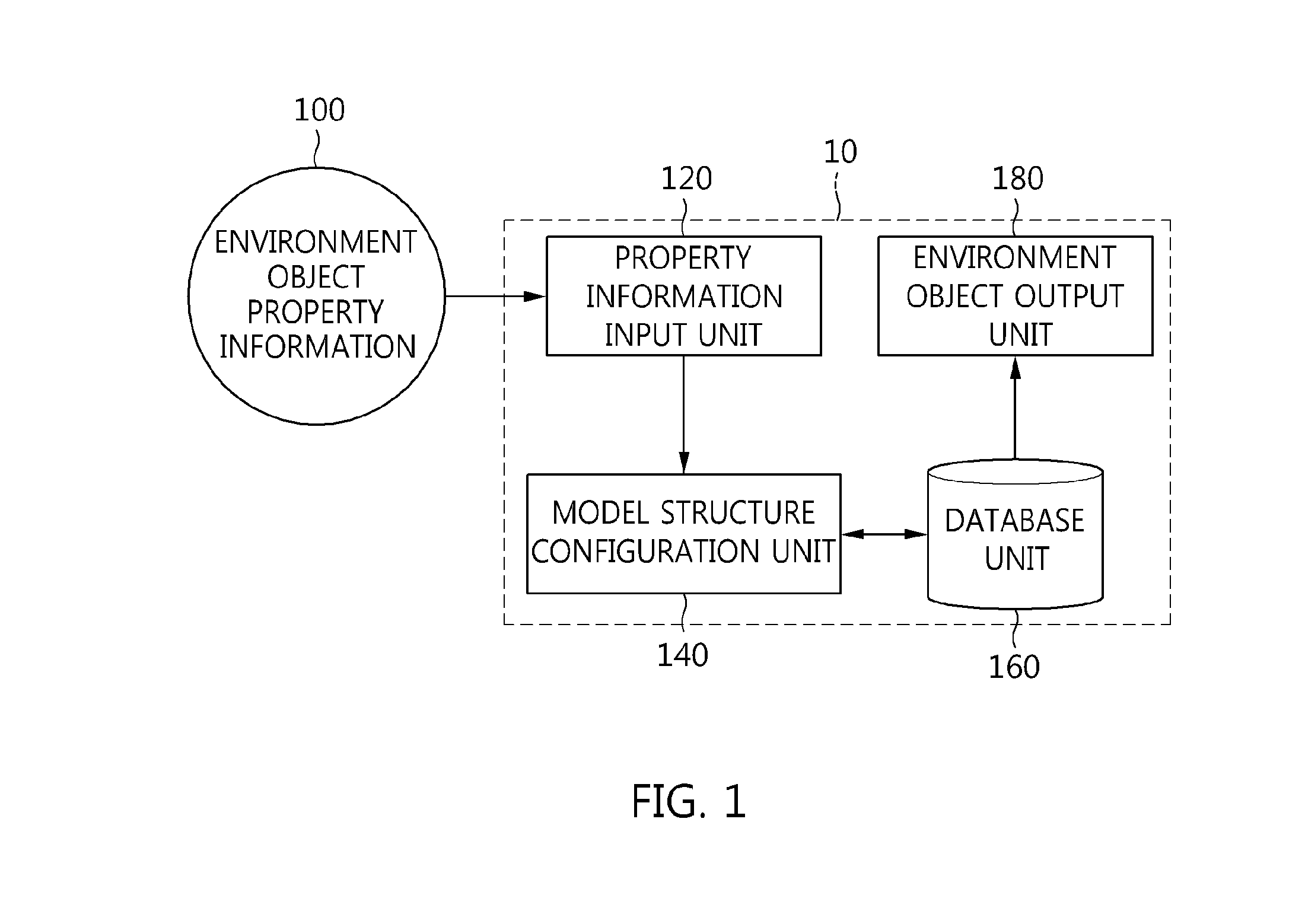
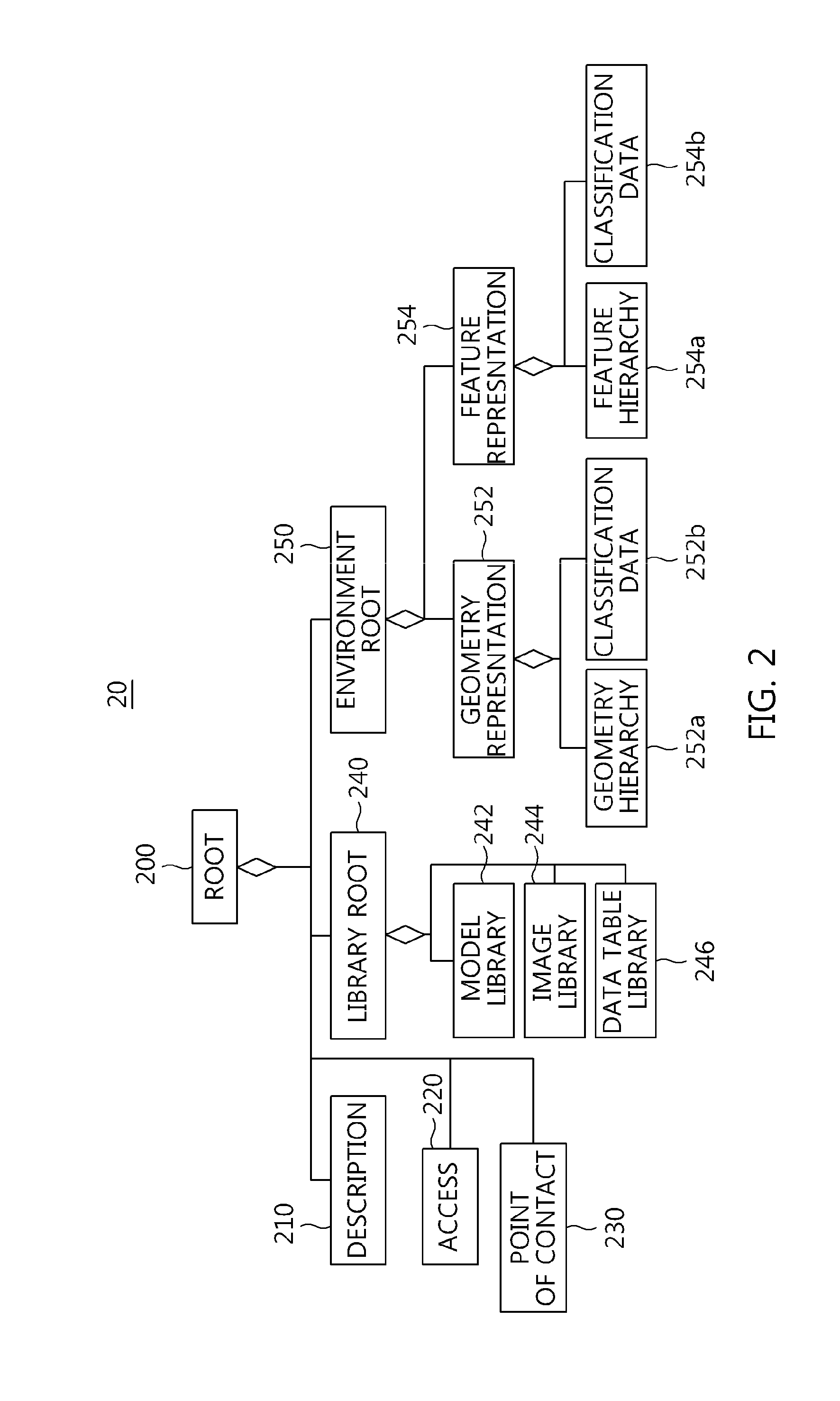
Method of representing environment object in cyber-physical system using environment data model structure and computer-readable storage medium storing program therefor
InactiveUS20140340396A1Efficient managementLow costSpecial data processing applications3D modellingComputer graphics (images)Data file
Disclosed herein are a method of representing an environment object in a cyber-physical system using an environment data model structure and a computer-readable storage medium storing a program therefor. A library model for storing information required to visualize environment data as an environment object in a cyber-physical system is generated. A geometry representation model having geometry structure information of the environment data is generated. A feature representation model having two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) information of the environment data is generated. A model structure of the environment data including the library model, the geometry representation model, and the feature representation model is configured. An environment data file having information about the model structure of the environment data is stored in a database (DB). The environment object in the cyber-physical system is visually represented using the environment data file stored in the DB.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
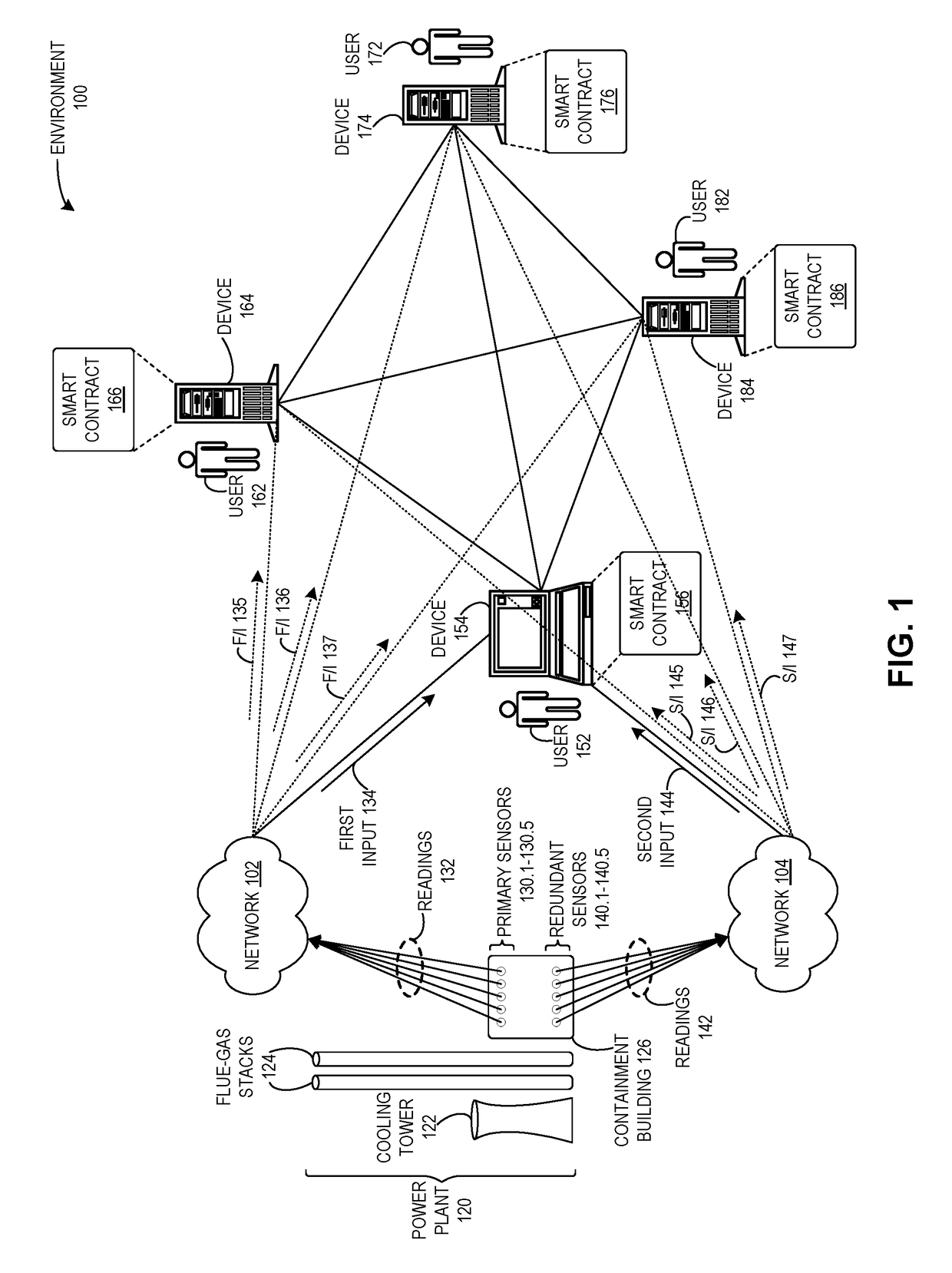
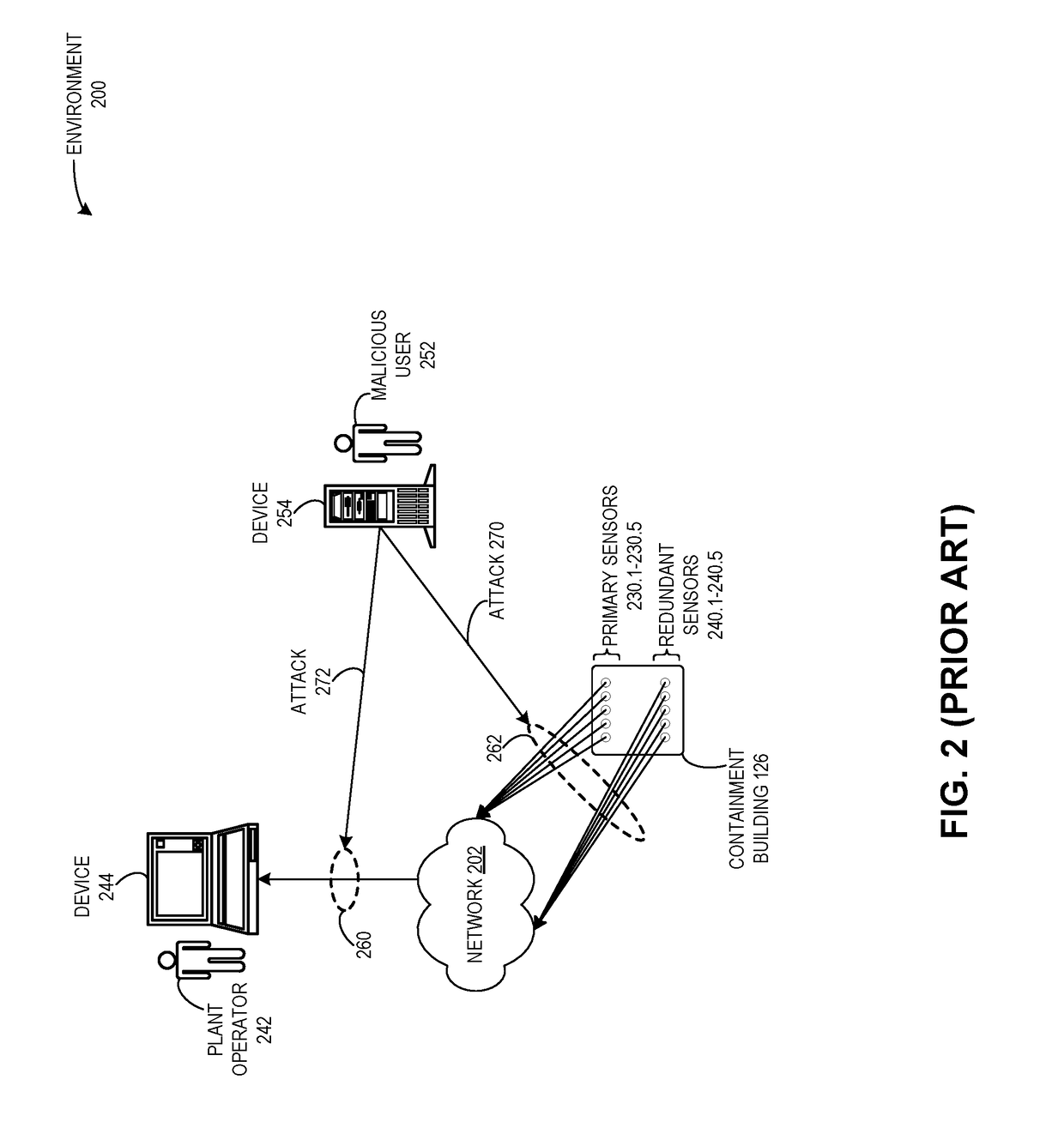
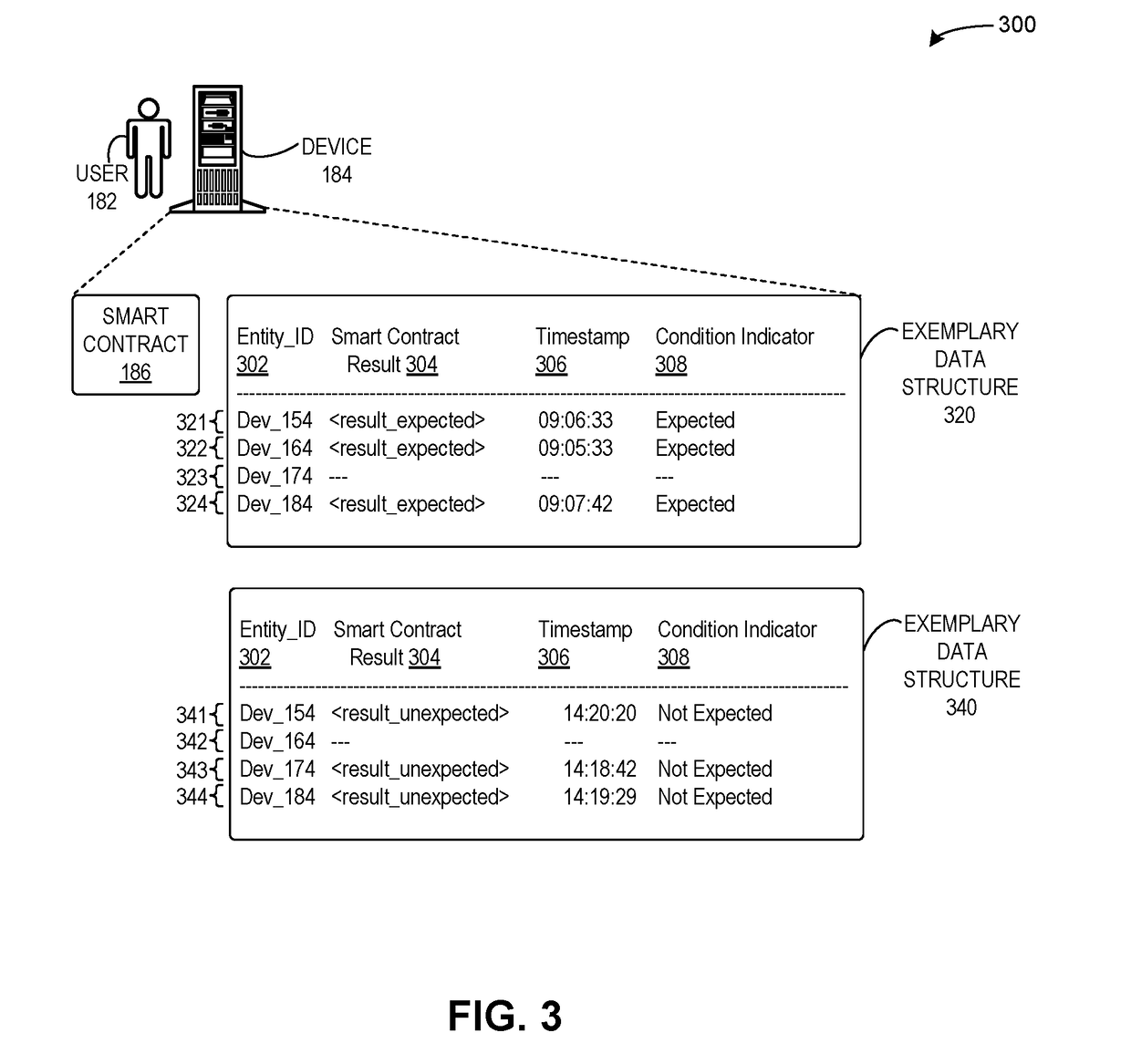
Method and system for detecting attacks on cyber-physical systems using redundant devices and smart contracts
ActiveUS20190087571A1Easy to detectAvoid accessPlatform integrity maintainanceTransmissionRedundant codeSecurity Measure
One embodiment facilitates detection of attacks in a cyber-physical system of interacting elements with physical inputs and outputs. During operation, the system receives, by a first entity of a plurality of entities, a first reading from a first set of sensors of the cyber-physical system via a first network. The system receives, by the first entity, a second reading from a second set of sensors of the cyber-physical system via a second network, wherein the second network includes security measures which prevent access by any external entity or any of the plurality of entities. The system executes a set of instructions based on the first reading and the second reading. The system determines that a result of the executed instructions does not match an expected condition. The system performs a remedial action based on the result.
Owner:XEROX CORP
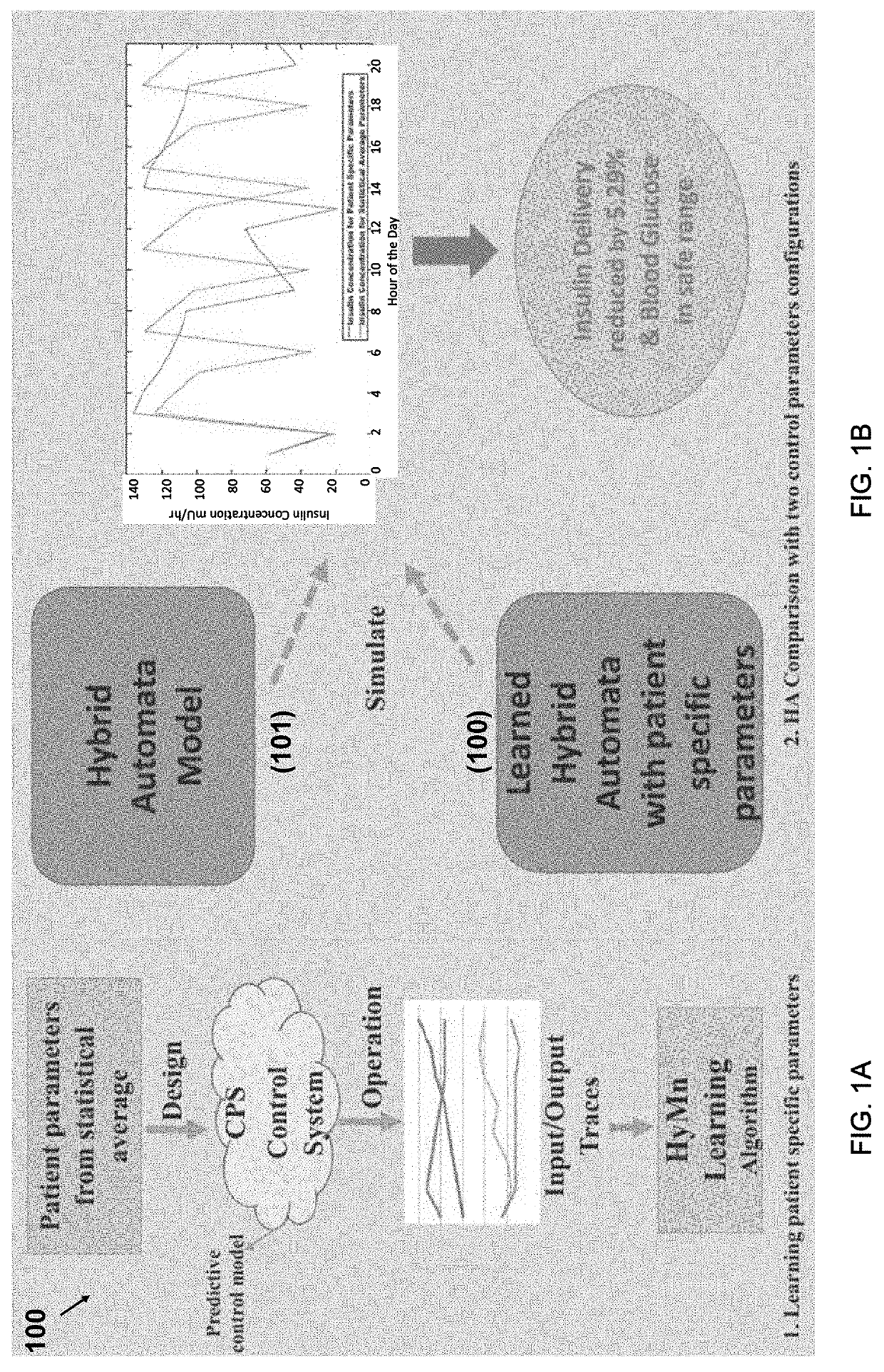
Systems and methods for hybrid automata mining from input-output traces of cyber-physical systems
Systems and methods for mining hybrid automata from input-output traces of cyber-physical systems are disclosed herein.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
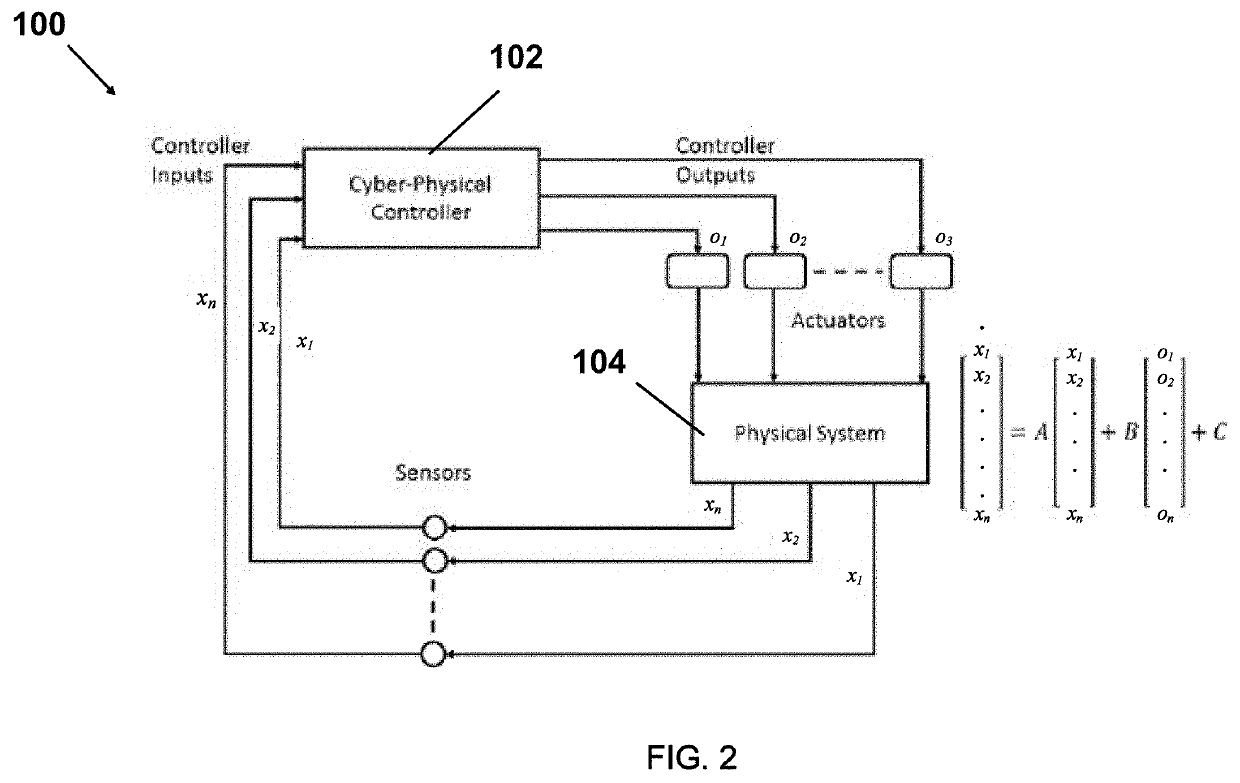
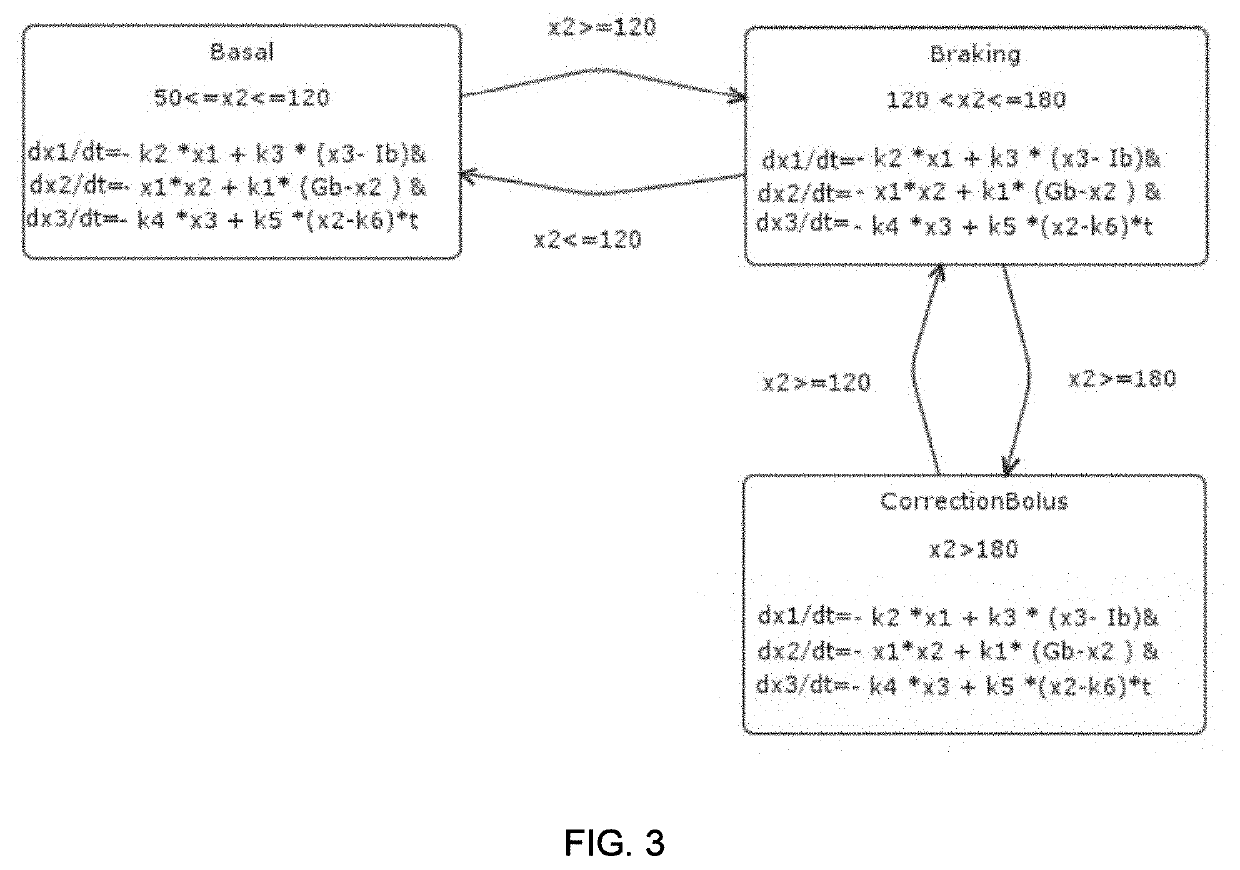
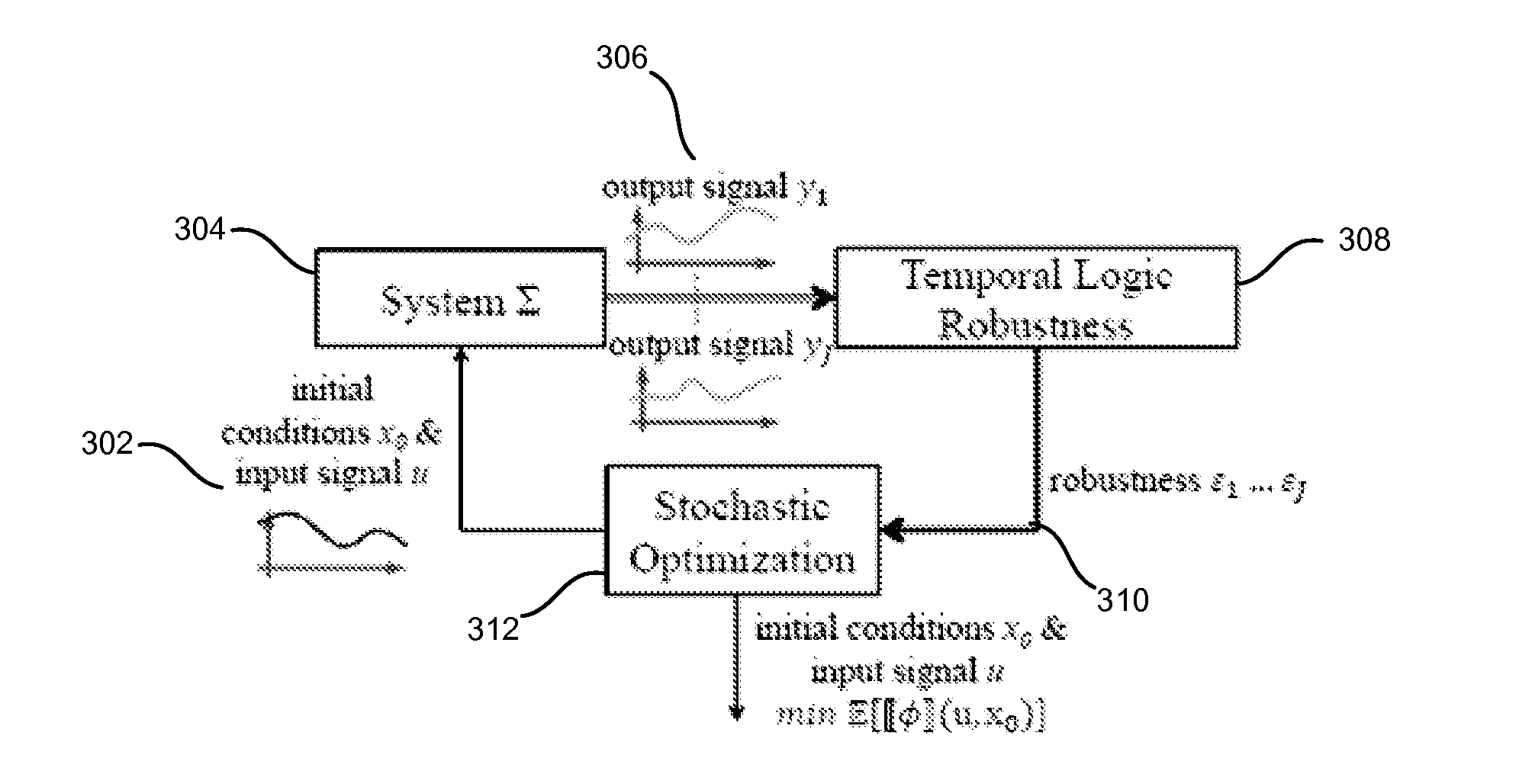
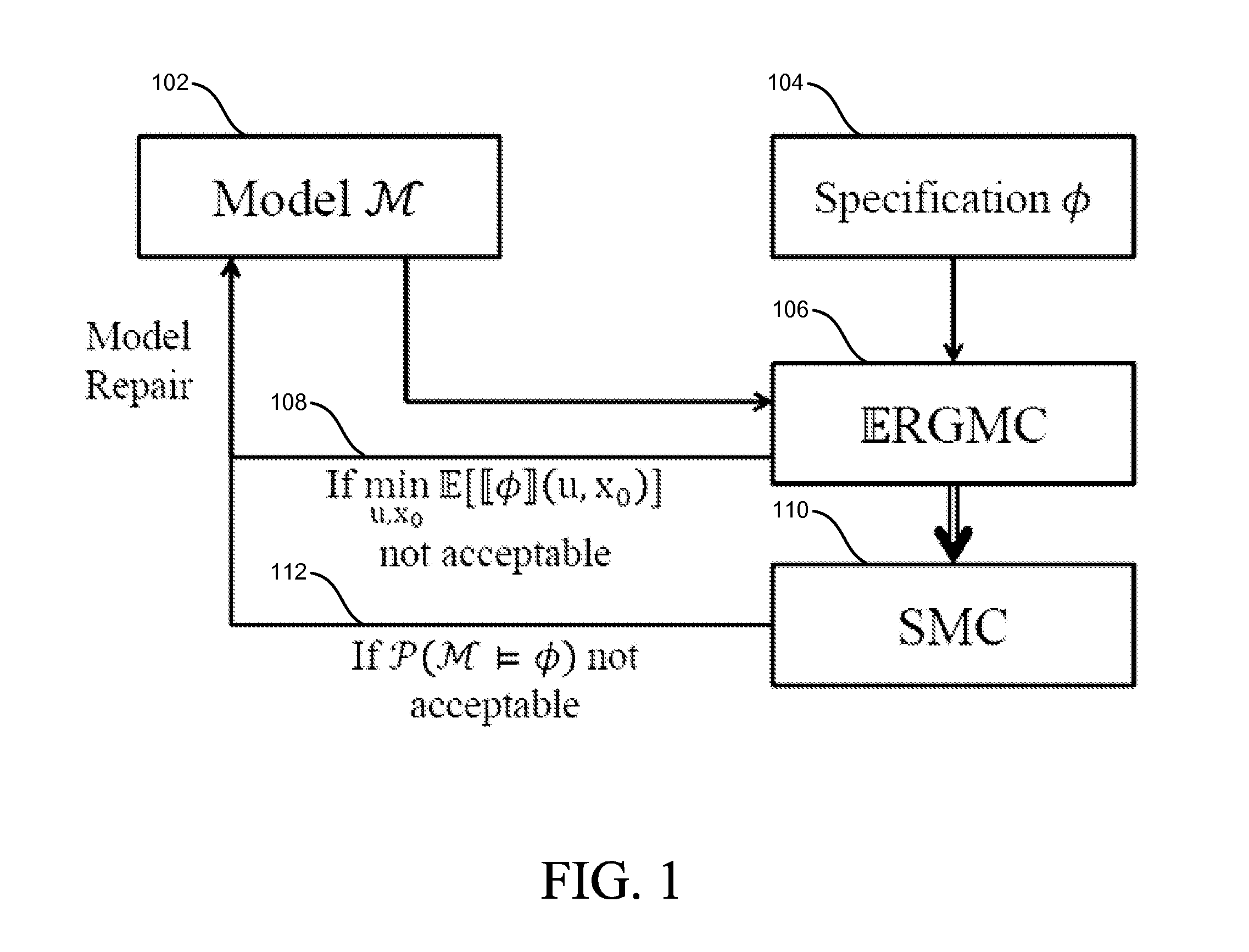
Temporal logic robustness guided testing for cyber-physical systems
Embodiments of model-based system design with model verification are disclosed. An embodiment includes receiving a model for a system and at least one specification for the system. In some embodiments, the system determines at least one of a minimum expected robustness value and a maximum expected robustness value for a region of a search space of the model with respect to the at least one specification. The model may be modified based on the determined minimum or maximum expected robust ness value.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
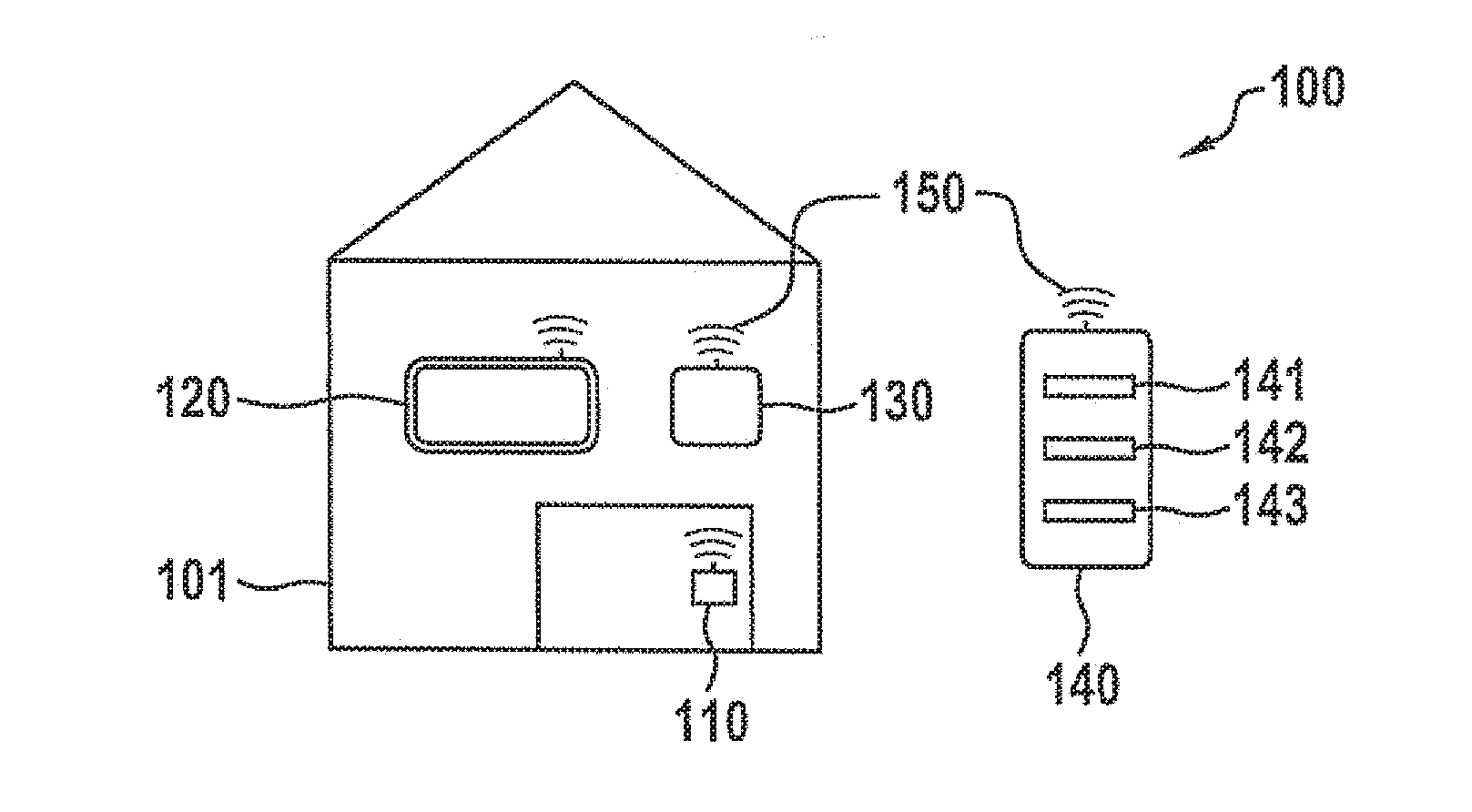
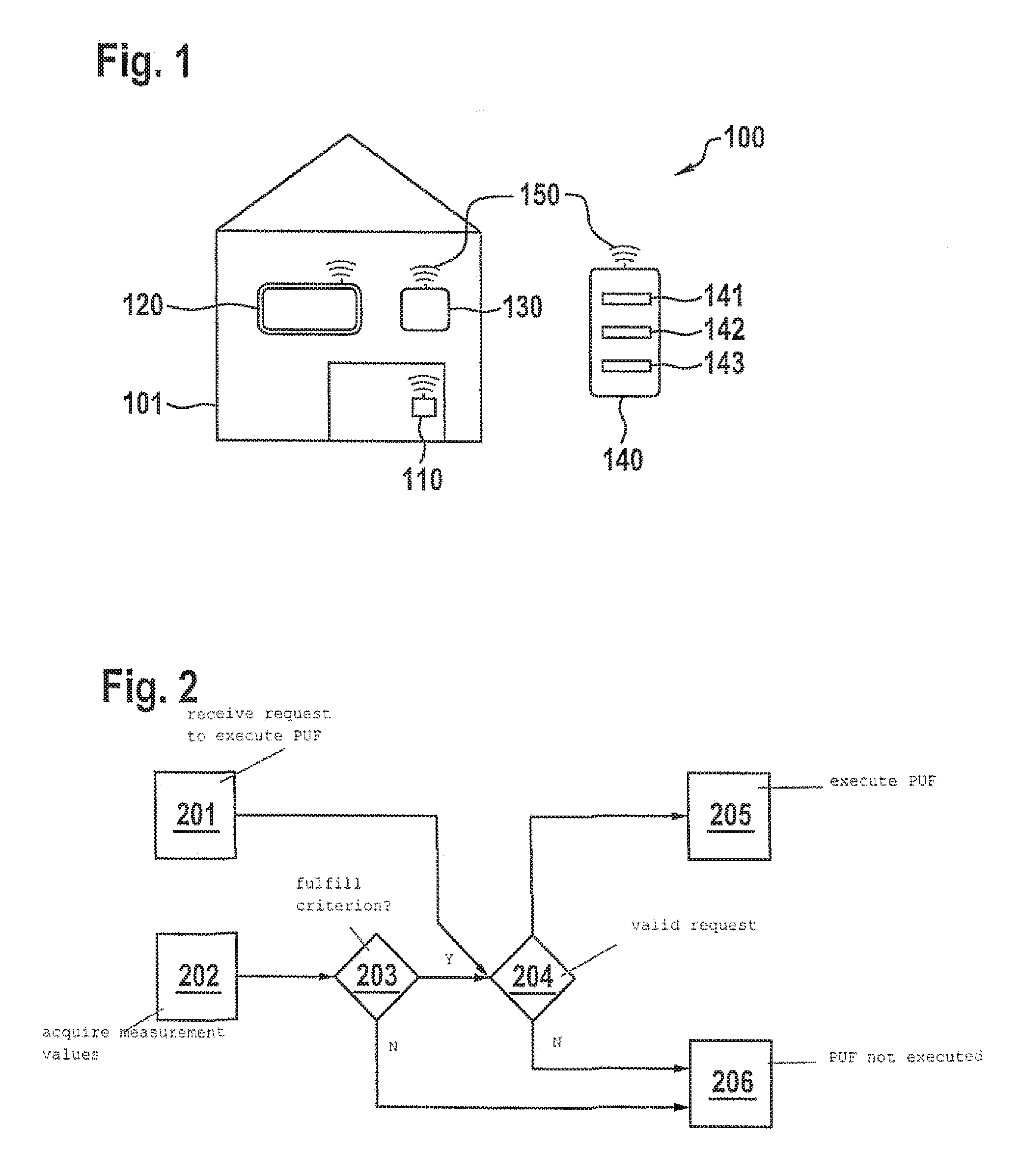
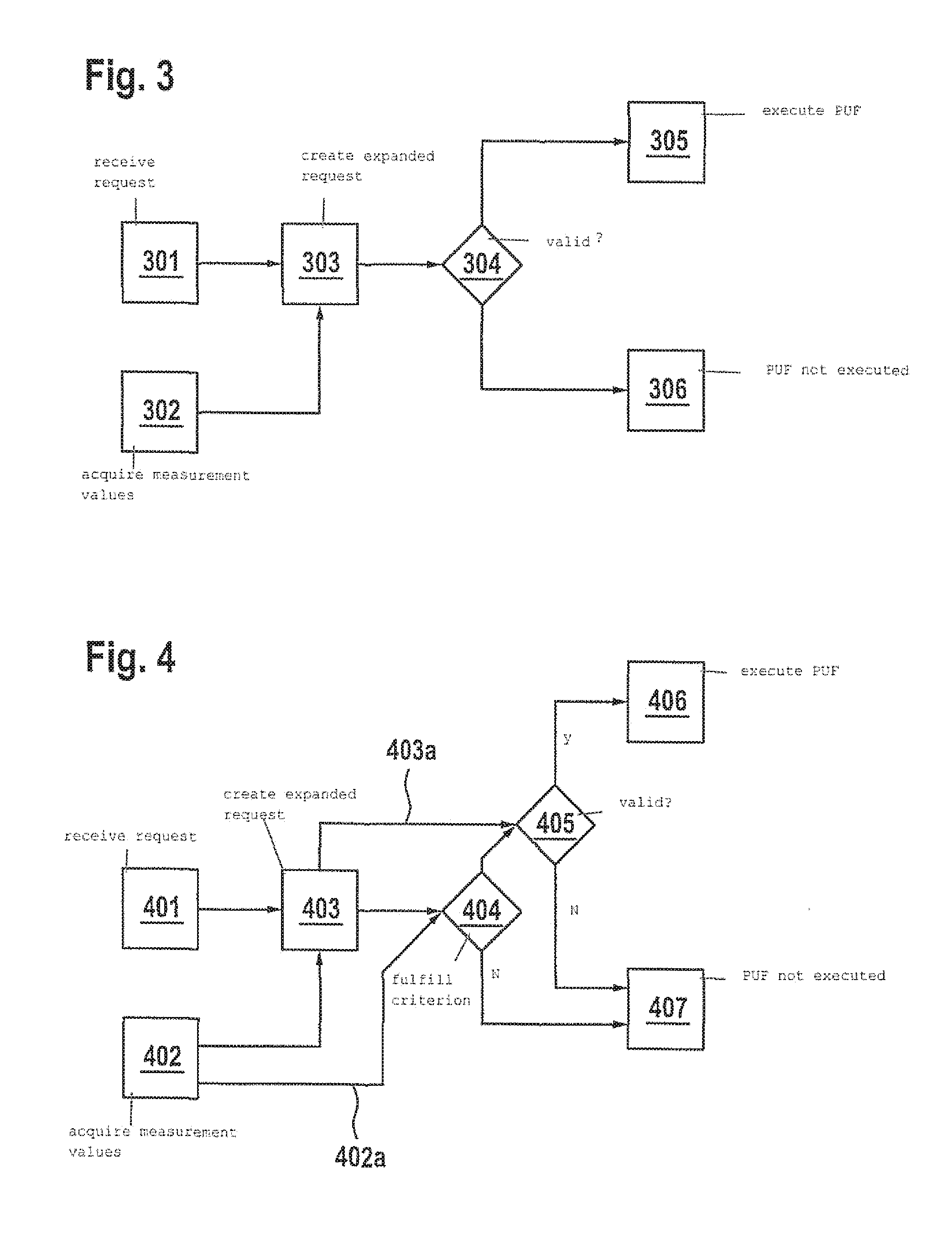
Method for executing a safety-critical function of a computing unit in a cyber-physical system
ActiveUS20160328571A1Process safetyImprove securityDigital data protectionDigital data authenticationCritical sectionPhysical system
A method for executing a safety-critical function of a computing unit in a cyber-physical system, a request being received for the execution of the safety-critical function, an environment-specific and / or user-specific measurement value being acquired by at least one sensor of the computing unit, the environment-specific measurement value describing an environment of the computing unit, the user-specific measurement value describing an interaction of a user with the computing unit, the safety-critical function being executed if the environment-specific and / or the user-specific measurement value fulfills a specified criterion.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
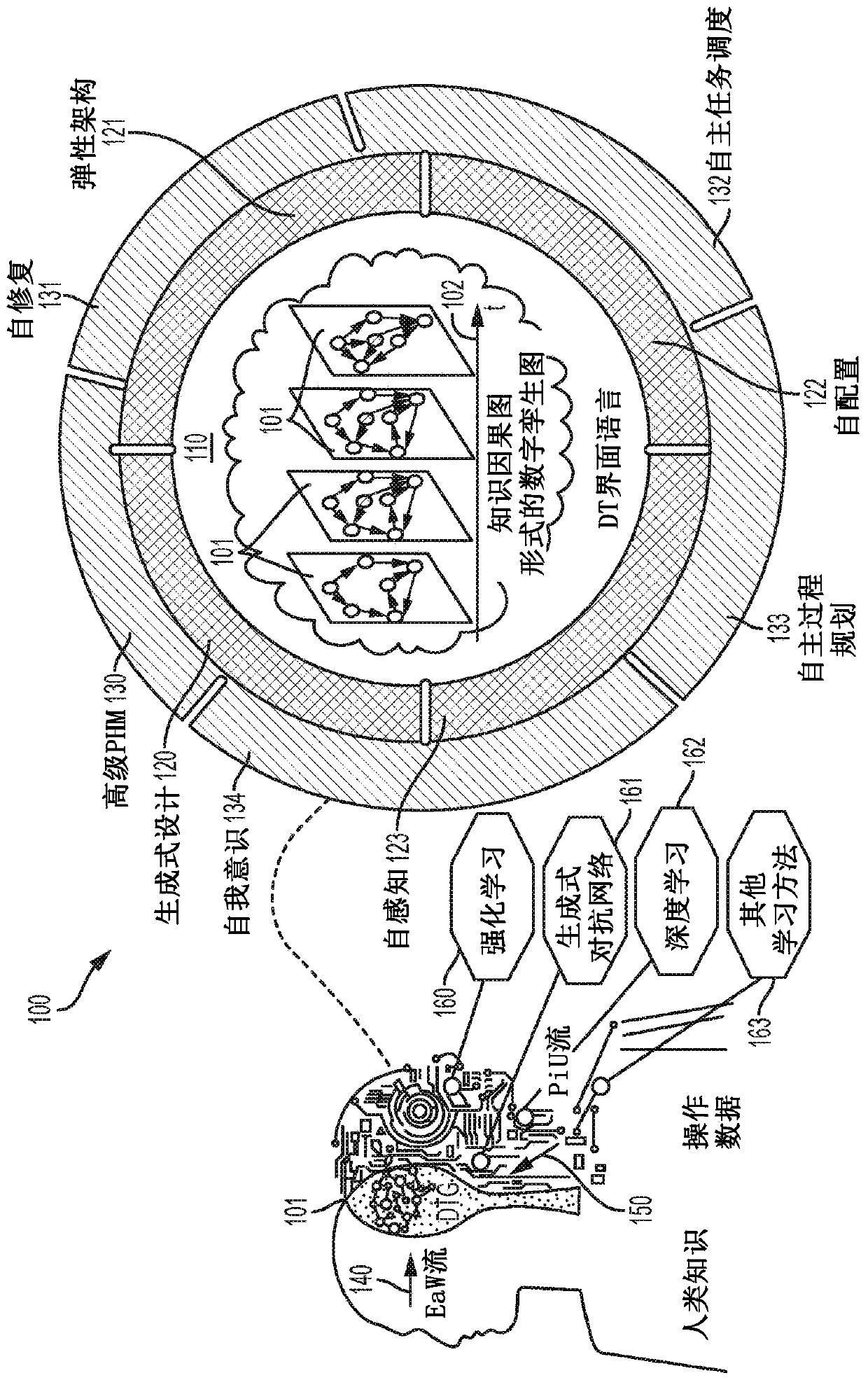
System and method for cognitive engineering technology for automation and control of systems
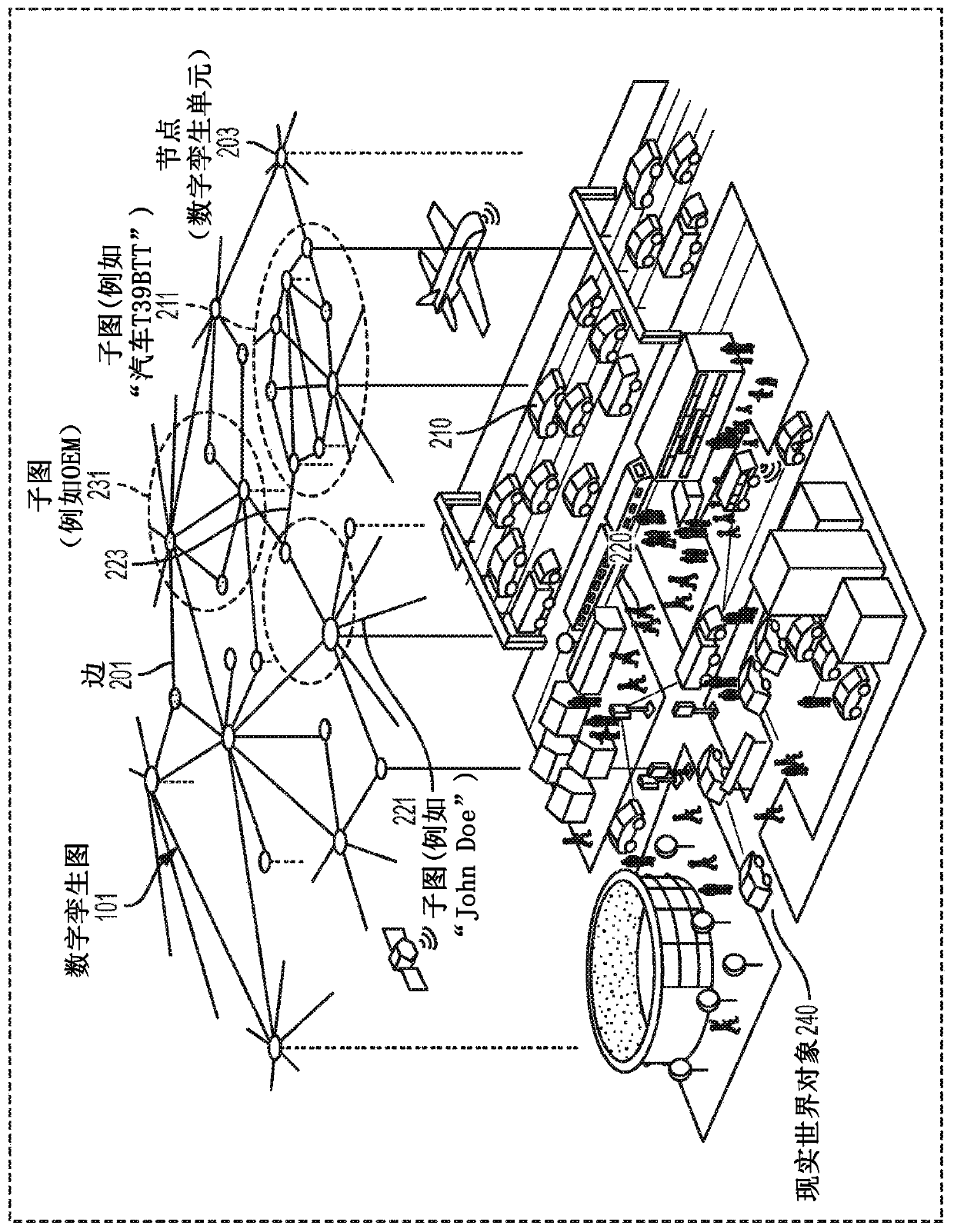
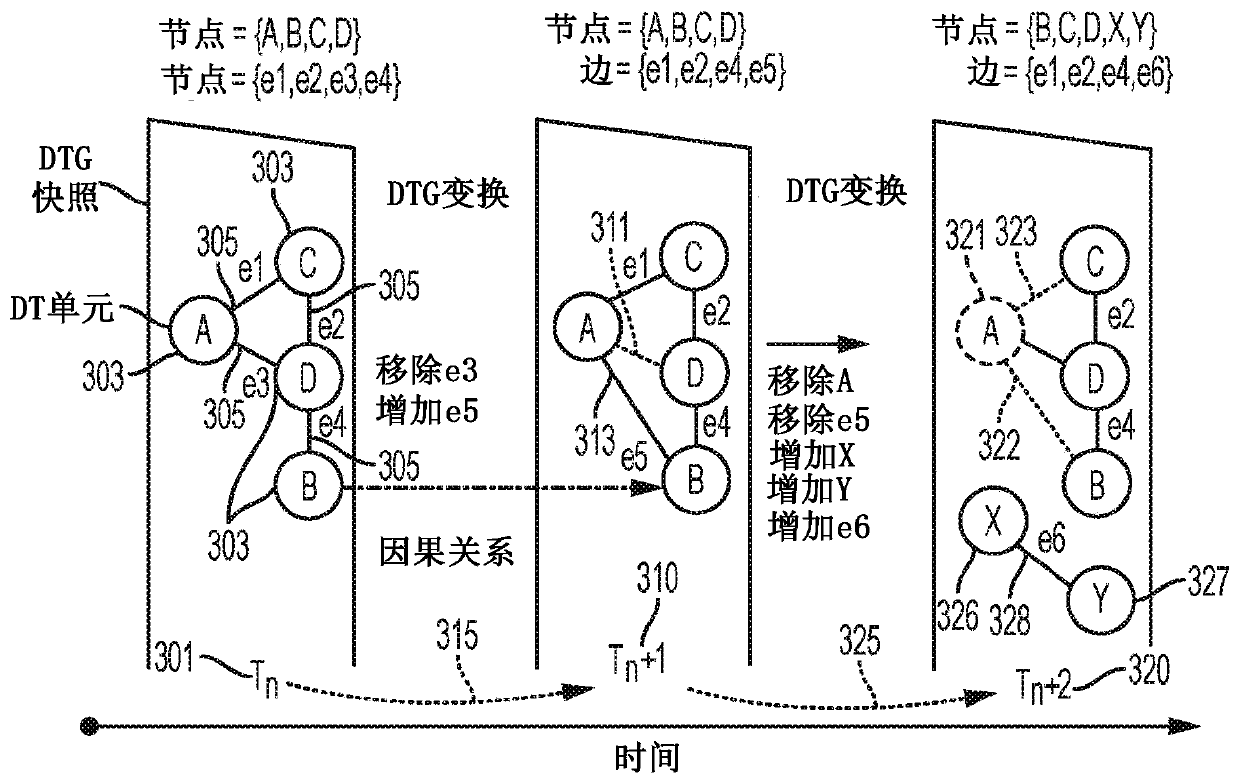
A method of performing cognitive engineering comprises extracting human knowledge from at least one user tool, receiving system information from a cyber-physical system (CPS), organizing the human knowledge and the received system information into a digital twin graph (DTG), performing one or more machine learning techniques on the DTG to generate an engineering option relating to the CPS, and providing the generated engineering option to a user in the at least one user tool. The method may include recording a plurality of user actions in the at least one user tool, storing the plurality of user actions in chronological order to create a series of user actions, and storing historical data relating a plurality of stored series of user actions.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
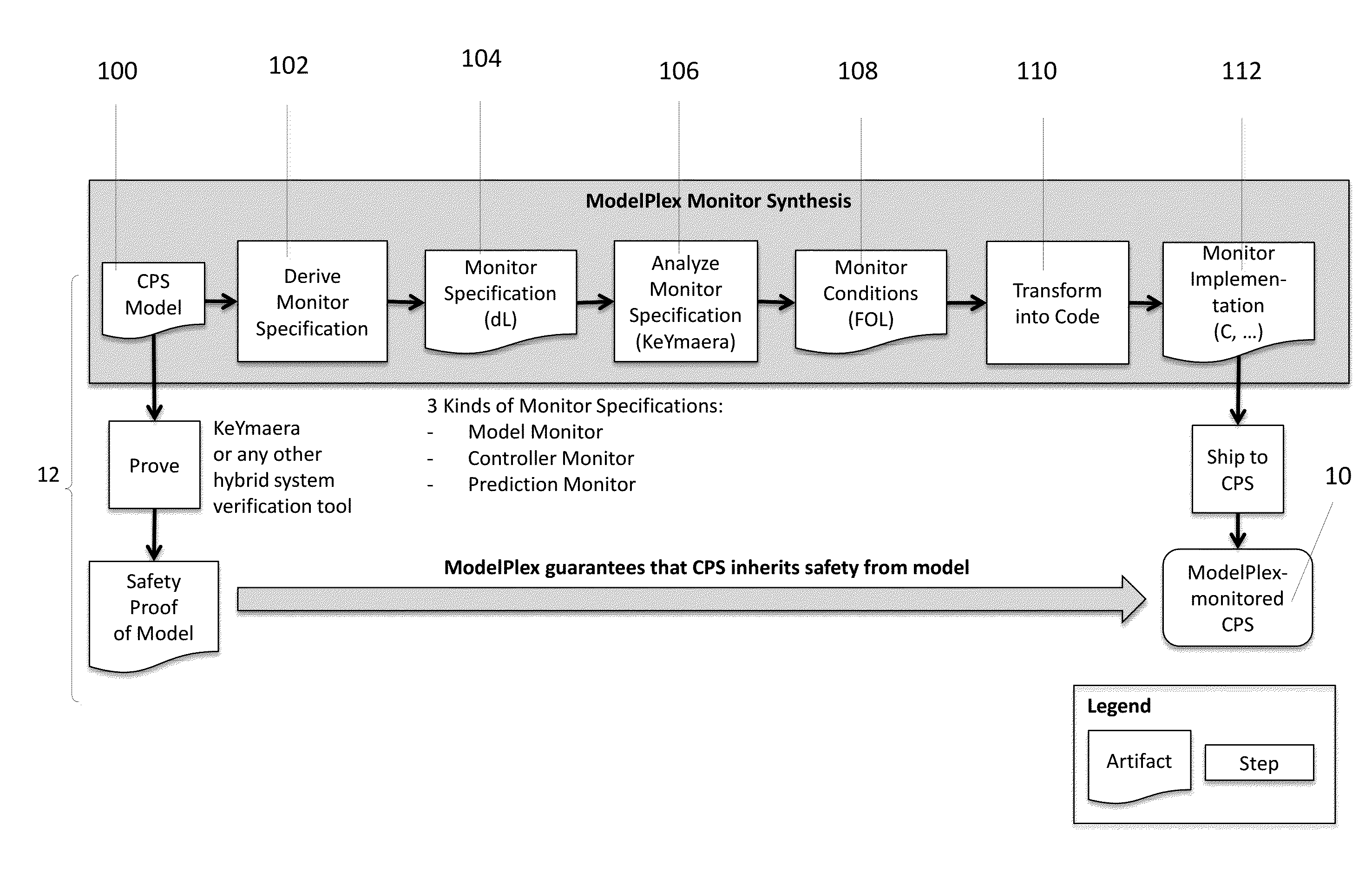
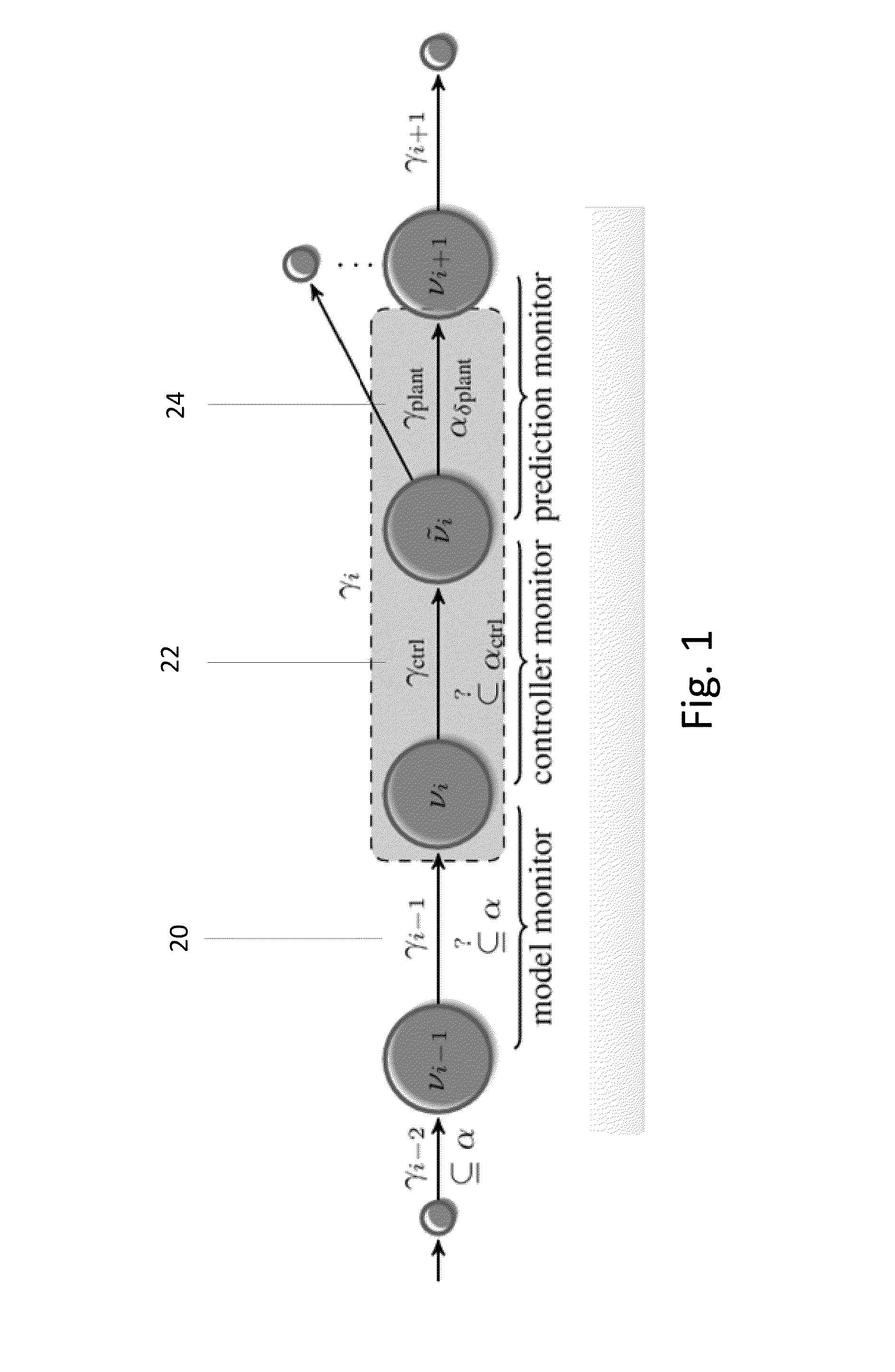
Verified Runtime Validation of Verified Cyber-Physical System Models
ActiveUS20160253437A1Guaranteed normal transferComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsRuntime verificationPhysical system
A method for ensuring that verification results about models apply to cyber-physical systems (CPS) implementations is presented. The invention provides correctness guarantees for CPS executions at runtime. Offline verification of CPS models are combined with runtime validation of system executions for compliance with the model. The invention ensures that the verification results obtained for the model apply to the actual system runs by monitoring the behavior of the world for compliance with the model, assuming the system dynamics deviation is bounded. If, at some point, the observed behavior no longer complies with the model, such that offline verification results no longer apply, provably safe fallback actions are initiated. The invention includes a systematic technique to synthesize provably correct monitors automatically from CPS proofs in differential dynamic logic.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Verification of cyber-physical systems using optimization algorithms
A computer-implemented method for verifying a model in a product lifecycle management (PLM) system includes defining a model and an envelope of allowable model states and, based on one or more requirements, deriving at least one counterexample objective. The method also includes optimizing a set of parameters related to the allowable model states and the allowable model context, redefining at least one of the model and the allowable model states when the at least one counterexample objective is outside of a specified tolerance, and, after a predefined number of iterations, defining the model as verified.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES SIMULIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com