Patents
Literature
97 results about "EMG - Electromyography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
Wearable electromyography-based human-computer interface
ActiveUS20120188158A1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectromyographyHuman–machine interfacePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
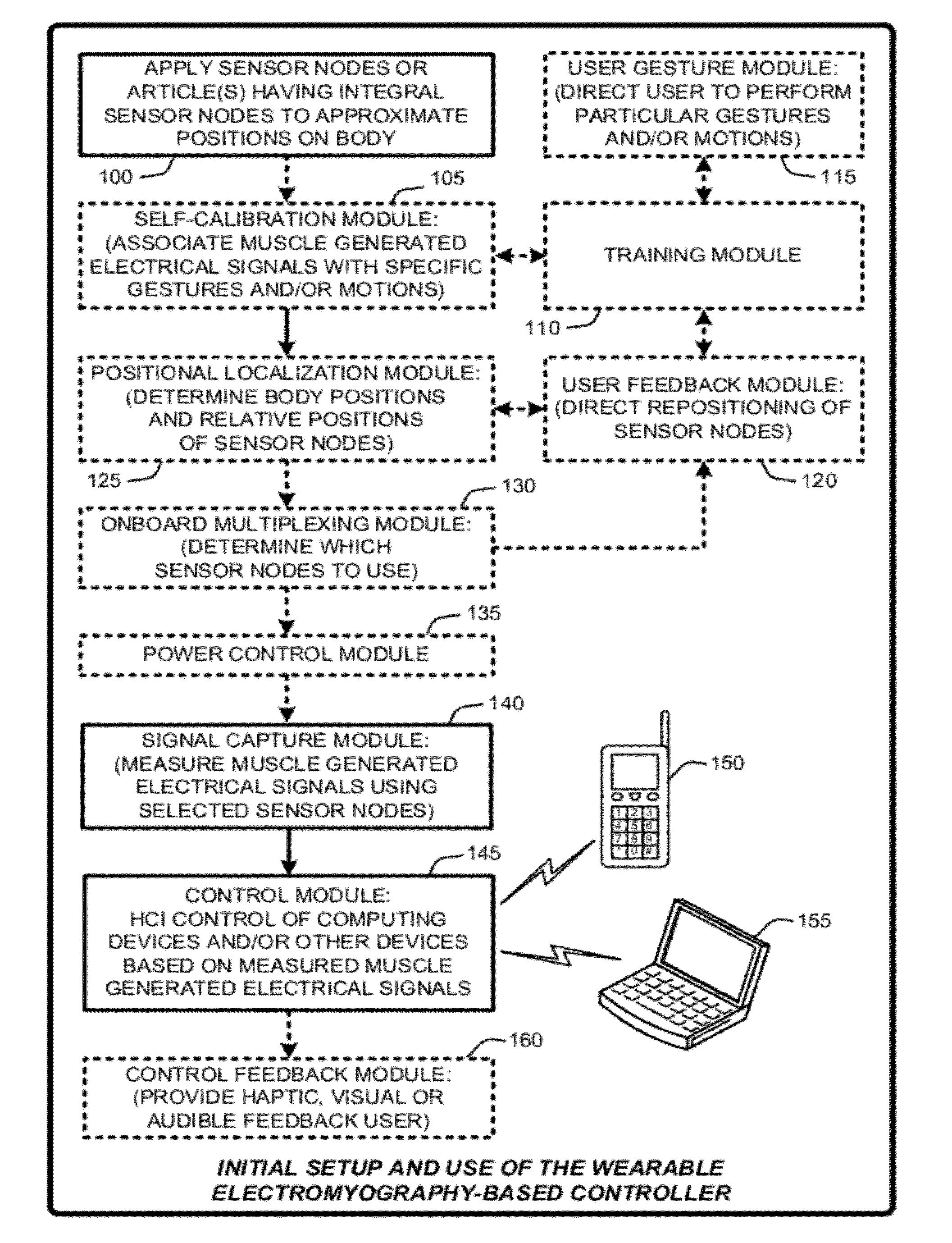
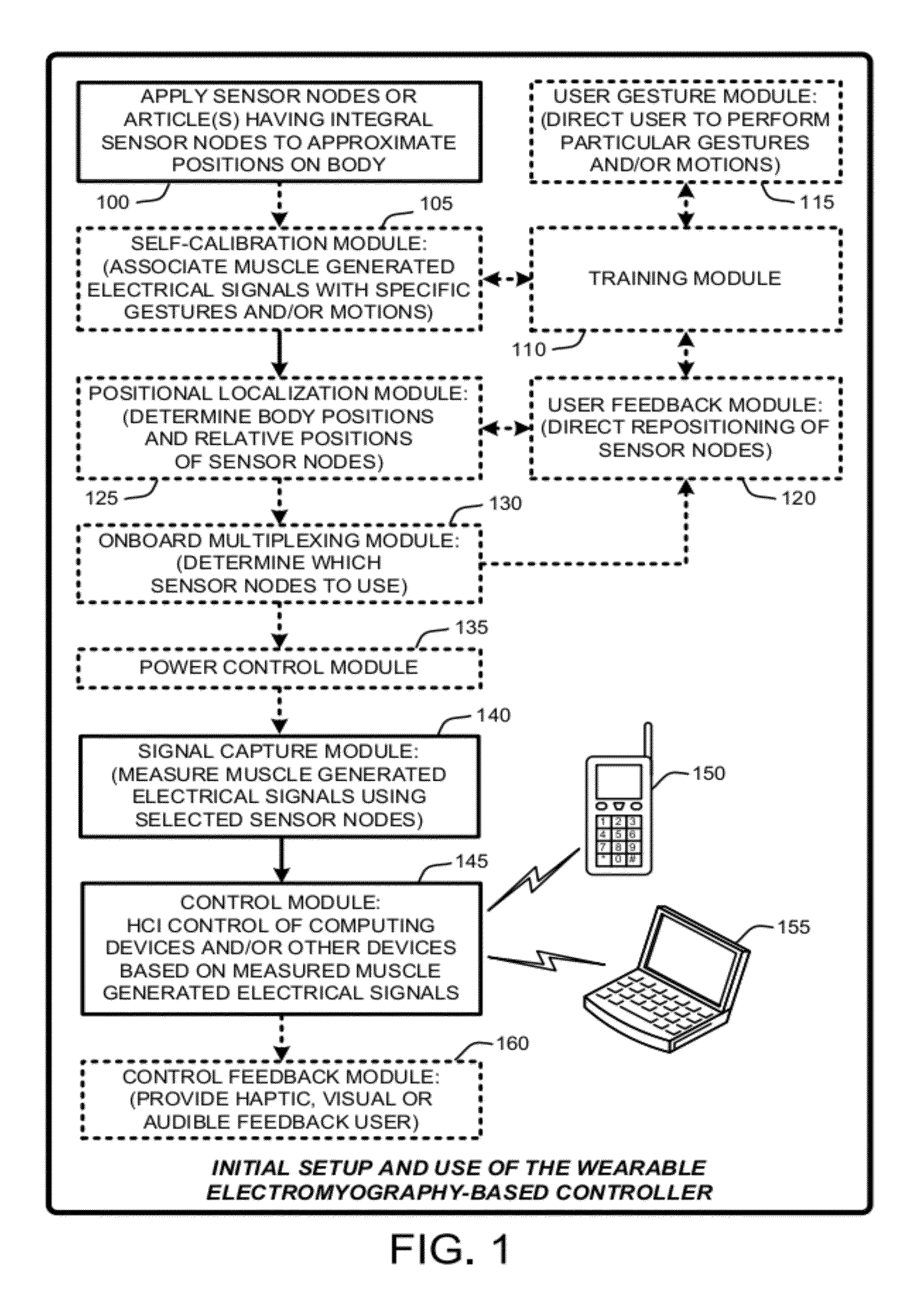
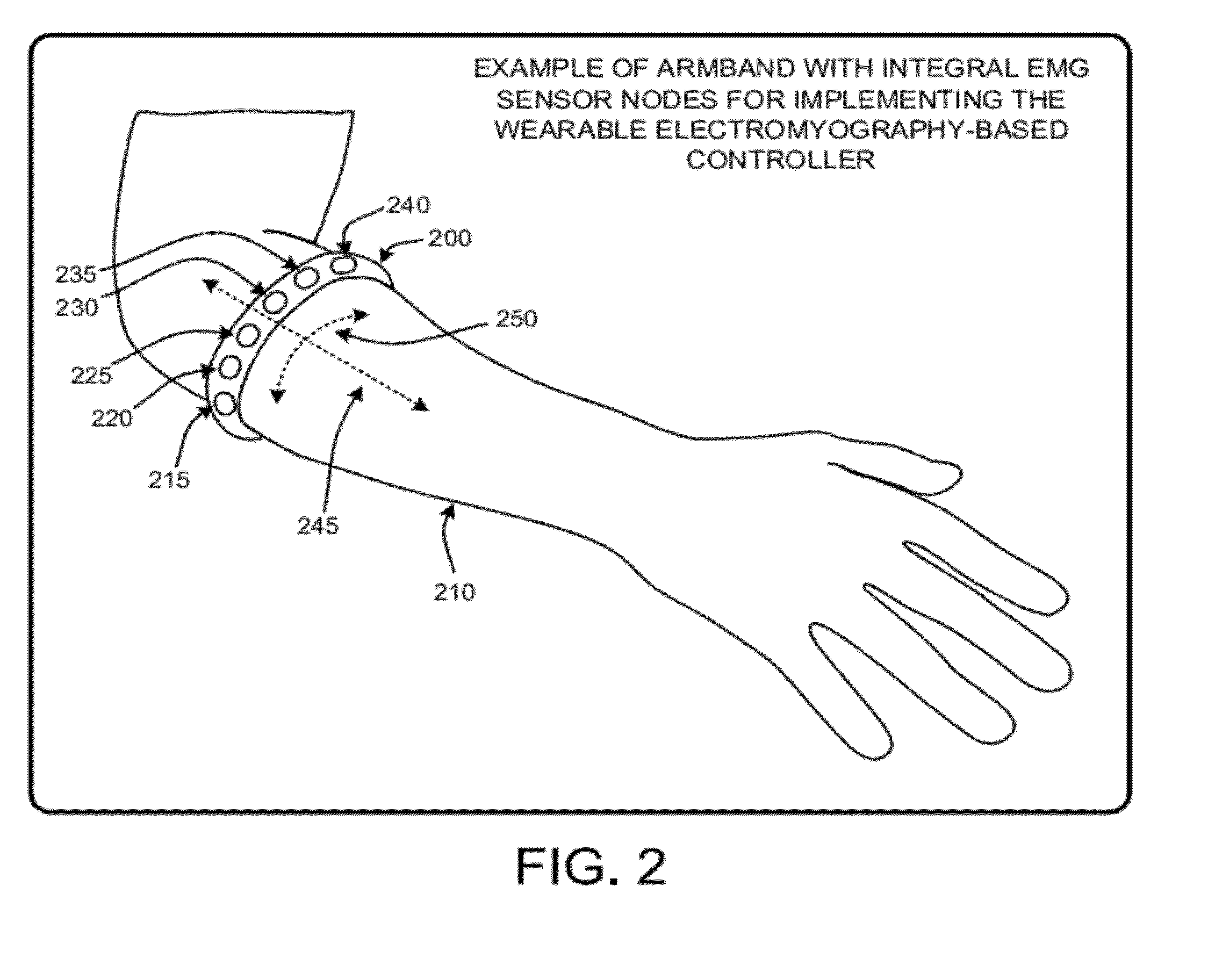
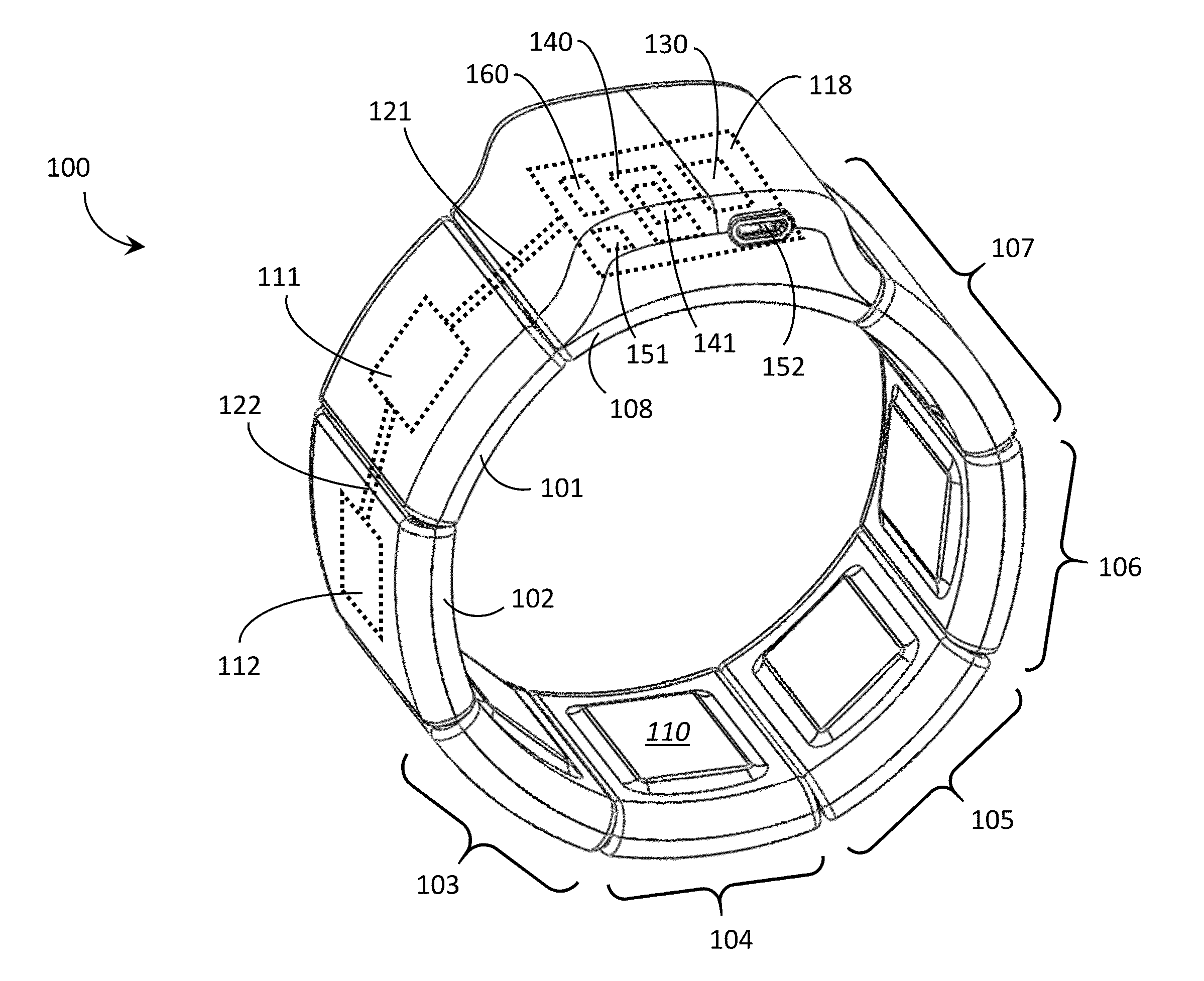
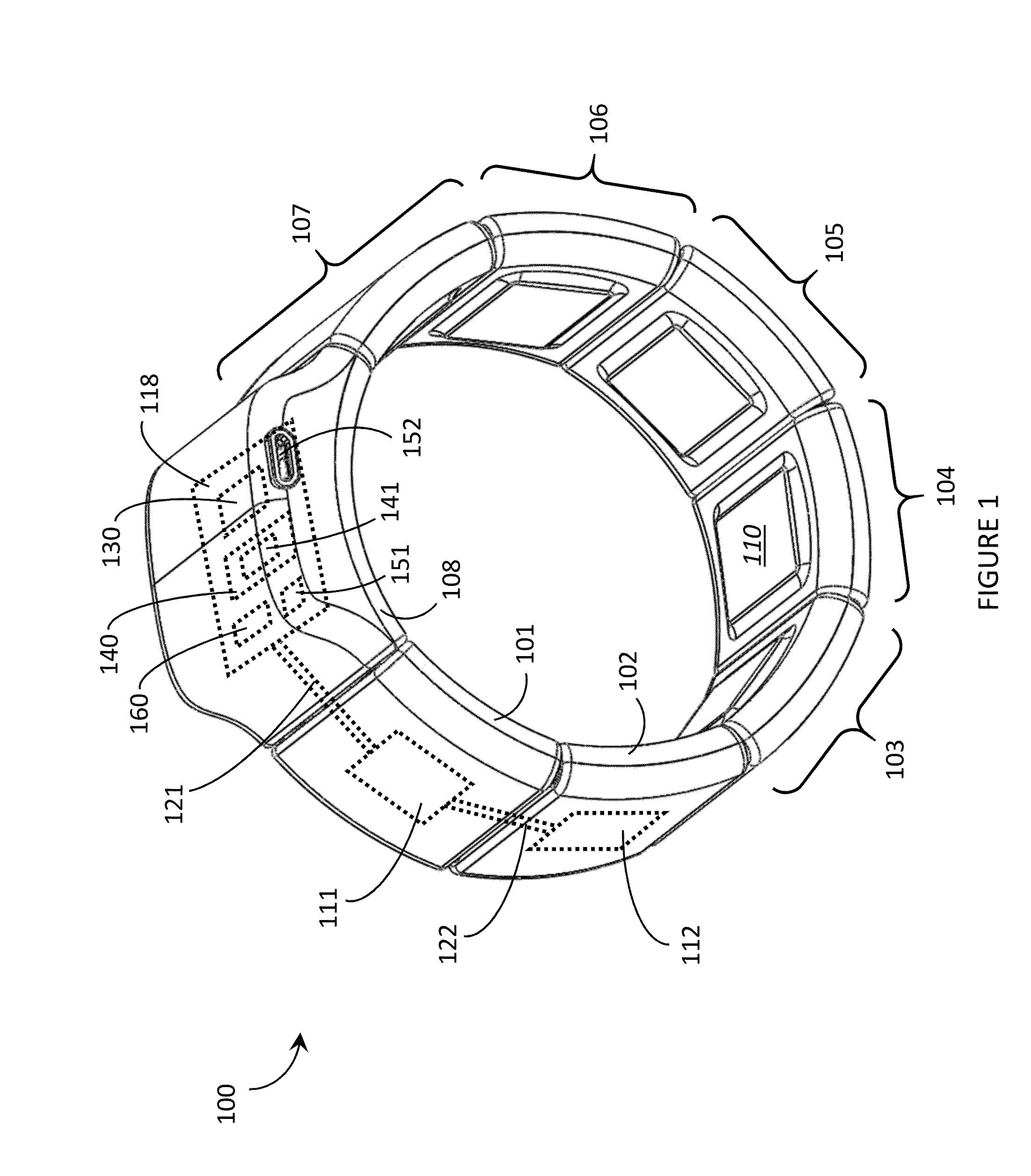
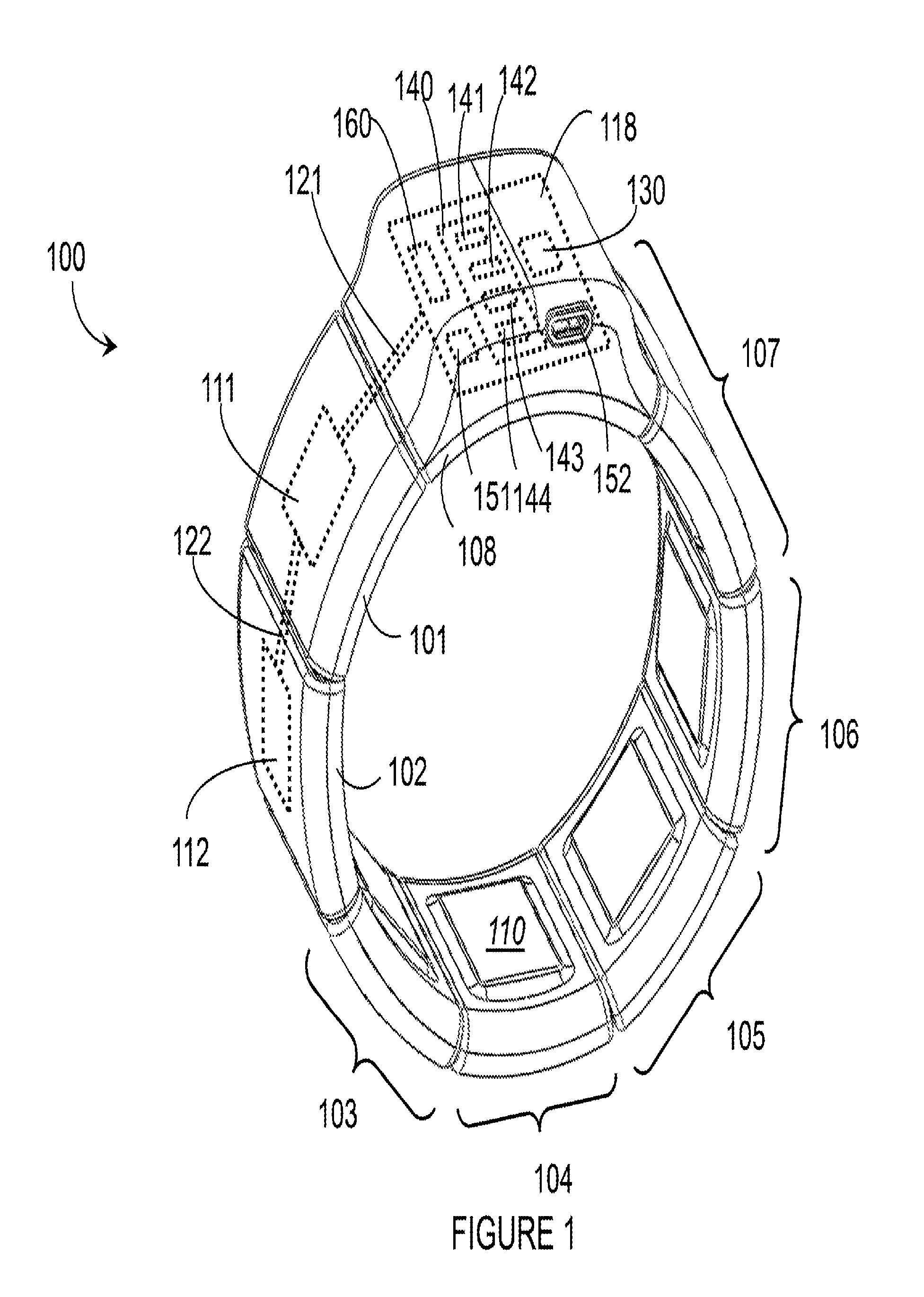
A “Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller” includes a plurality of Electromyography (EMG) sensors and provides a wired or wireless human-computer interface (HCl) for interacting with computing systems and attached devices via electrical signals generated by specific movement of the user's muscles. Following initial automated self-calibration and positional localization processes, measurement and interpretation of muscle generated electrical signals is accomplished by sampling signals from the EMG sensors of the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller. In operation, the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller is donned by the user and placed into a coarsely approximate position on the surface of the user's skin. Automated cues or instructions are then provided to the user for fine-tuning placement of the Wearable Electromyography-Based Controller. Examples of Wearable Electromyography-Based Controllers include articles of manufacture, such as an armband, wristwatch, or article of clothing having a plurality of integrated EMG-based sensor nodes and associated electronics.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
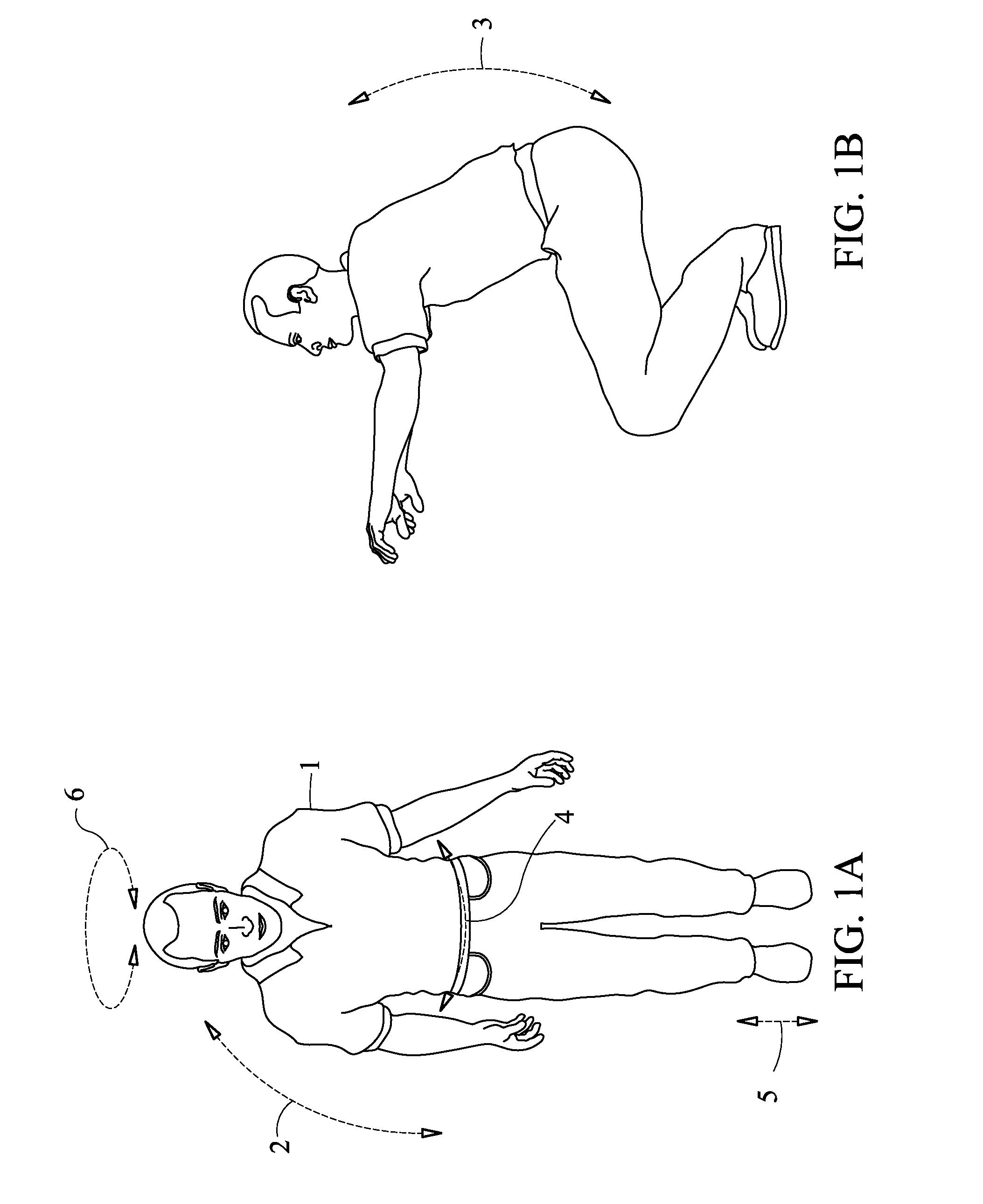
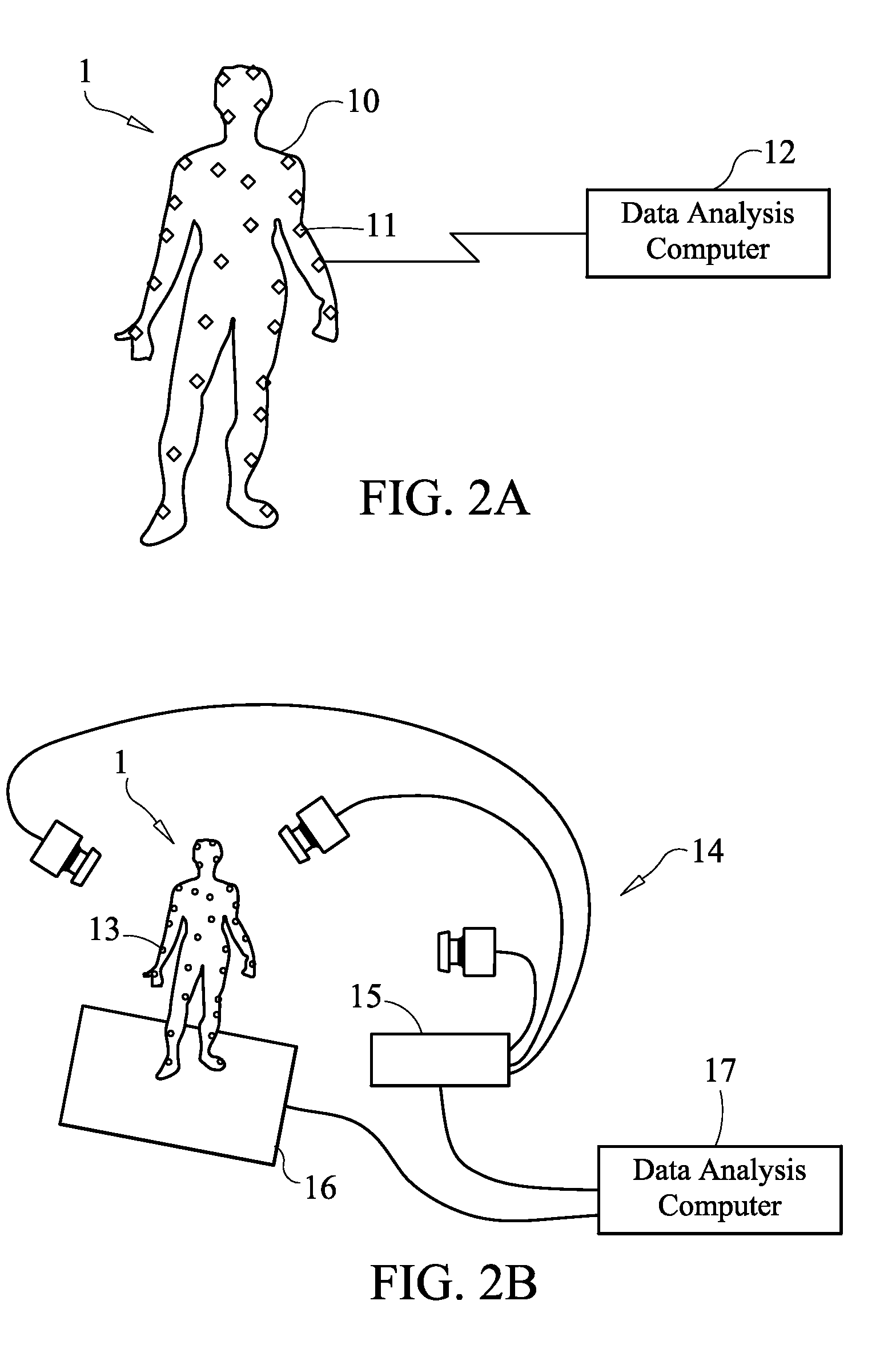
Designation of a Characteristic of a Physical Capability by Motion Analysis, Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20110052005A1Physical therapies and activitiesMedical automated diagnosisData dredgingOriginal data
Motion Analysis is used to classify or rate human capability in a physical domain via a minimized movement and data collection protocol producing a discreet, overall figure of merit of the selected physical capability. The minimal protocol is determined by data mining of a more extensive movement and data collection. Protocols are relevant in medical, sports and occupational applications. Kinematic, kinetic, body type, Electromyography (EMG), Ground Reactive Force (GRF), demographic, and psychological data are encompassed. Resulting protocols are capable of transforming raw data representing specific human motions into an objective rating of a skill or capability related to those motions.
Owner:SELNER ALLEN JOSEPH
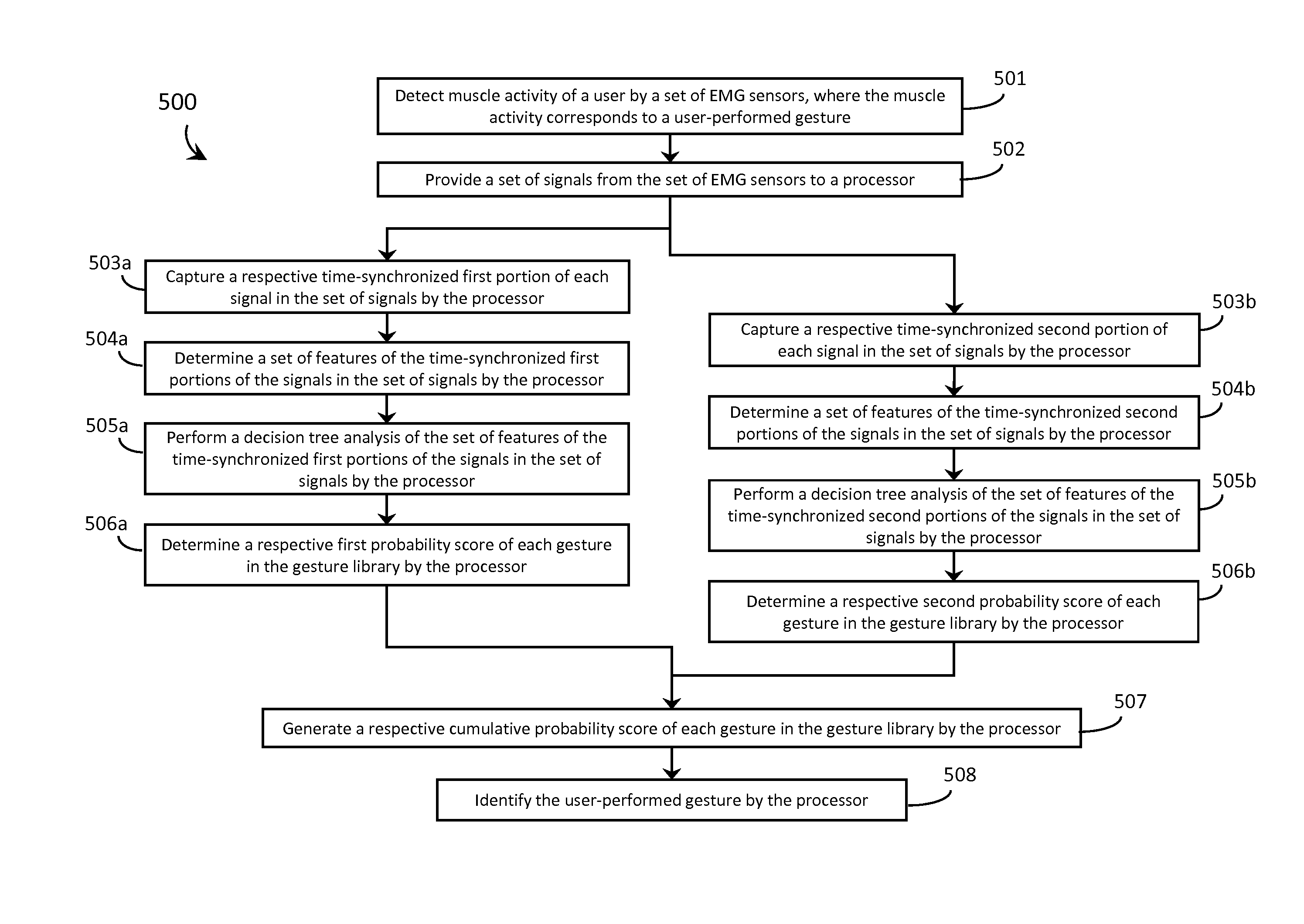
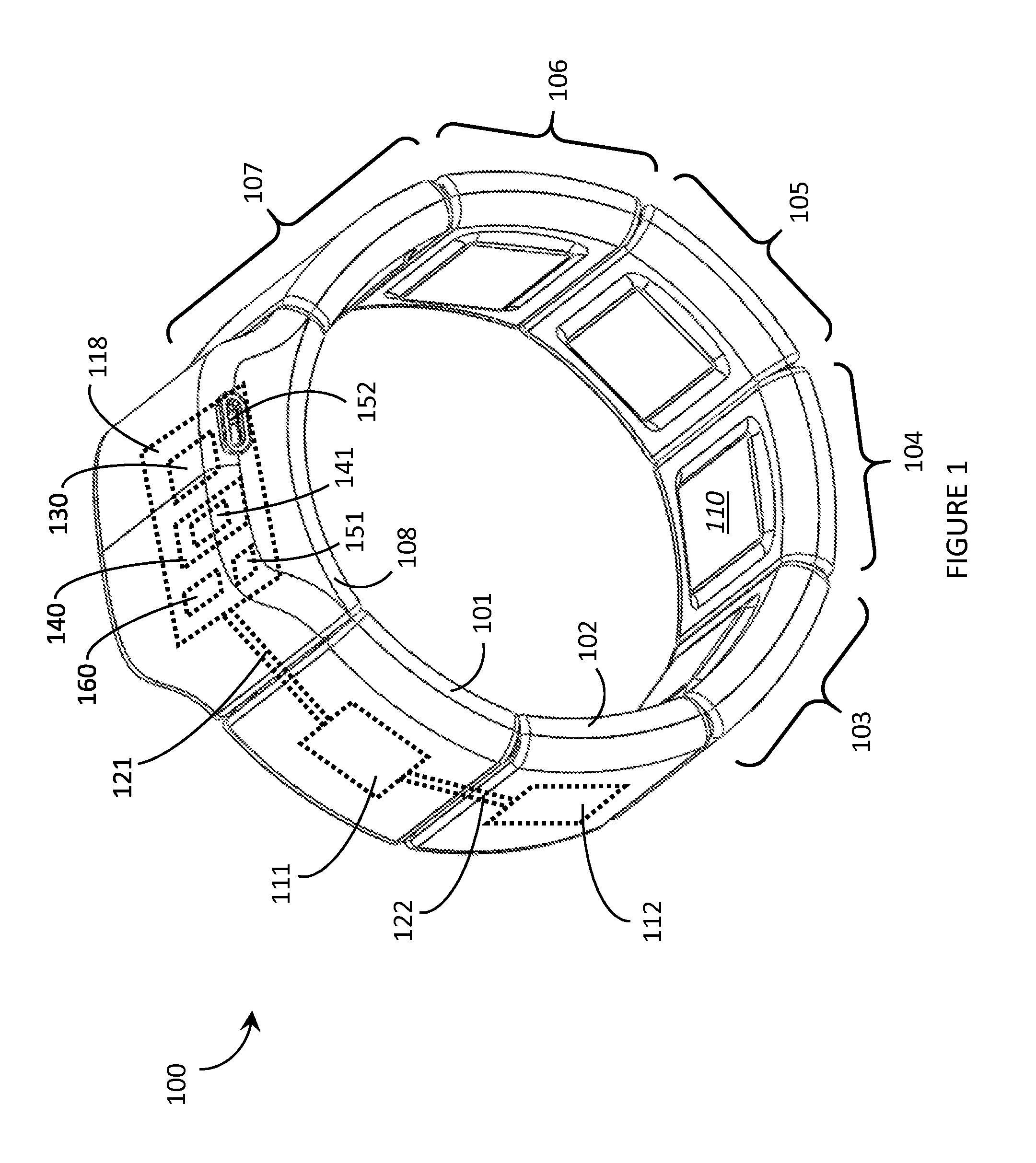
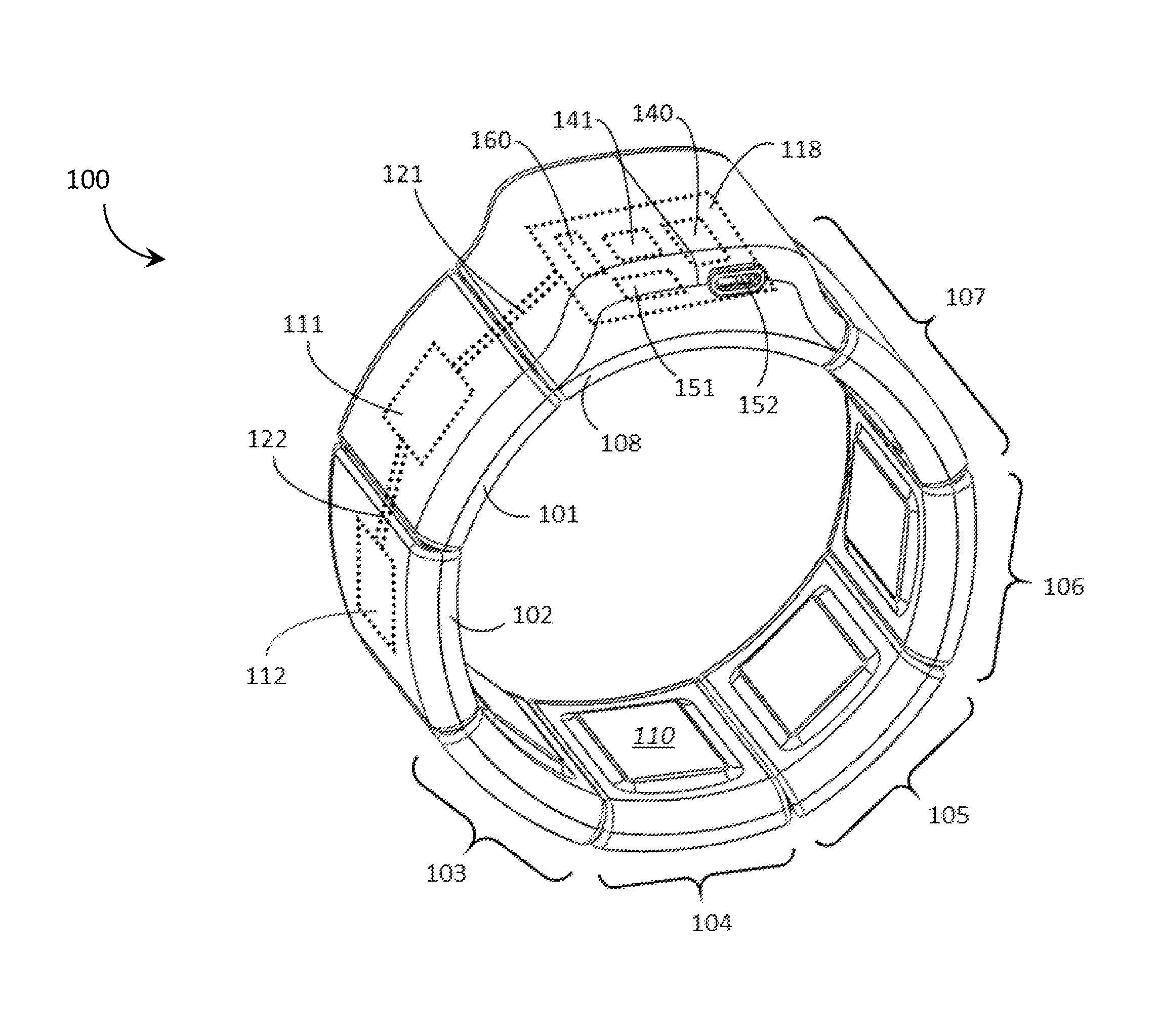
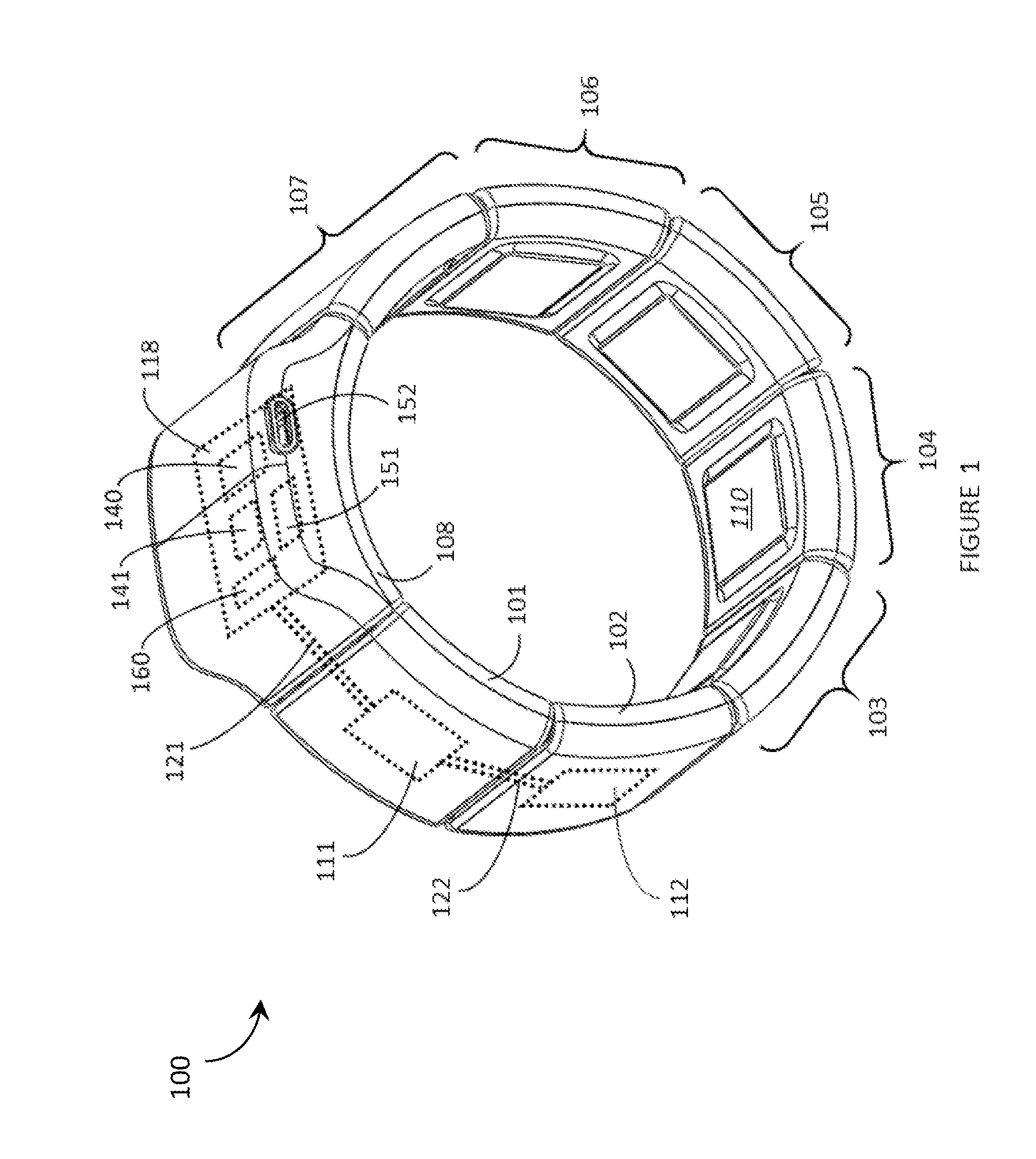
Systems, articles, and methods for gesture identification in wearable electromyography devices
ActiveUS20150109202A1Input/output for user-computer interactionMedical data miningEngineeringBoard processor
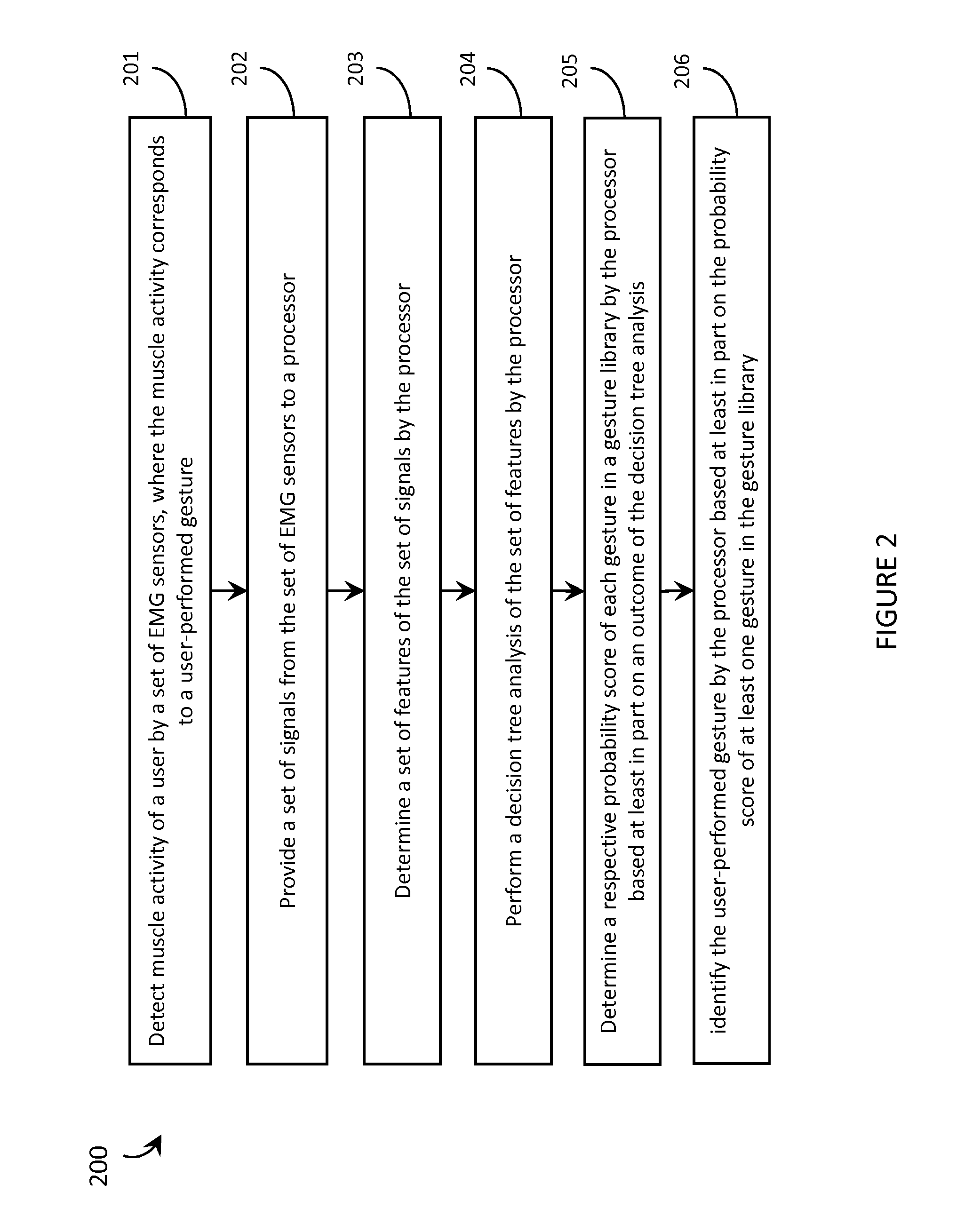
Systems, articles, and methods perform gesture identification with limited computational resources. A wearable electromyography (“EMG”) device includes multiple EMG sensors, an on-board processor, and a non-transitory processor-readable memory that stores data and / or processor-executable instructions for performing gesture identification. The wearable EMG device detects and determines features of signals when a user performs a physical gesture, and processes the features by performing a decision tree analysis. The decision tree analysis invokes a decision tree stored in the memory, where storing and executing the decision tree may be managed by limited computational resources. The outcome of the decision tree analysis is a probability vector that assigns a respective probability score to each gesture in a gesture library. The accuracy of the gesture identification may be enhanced by performing multiple iterations of the decision tree analysis across multiple time windows of the EMG signal data and combining the resulting probability vectors.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
Systems, articles, and methods for gesture identification in wearable electromyography devices
ActiveUS20150084860A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsEMG - ElectromyographyPhysical therapy
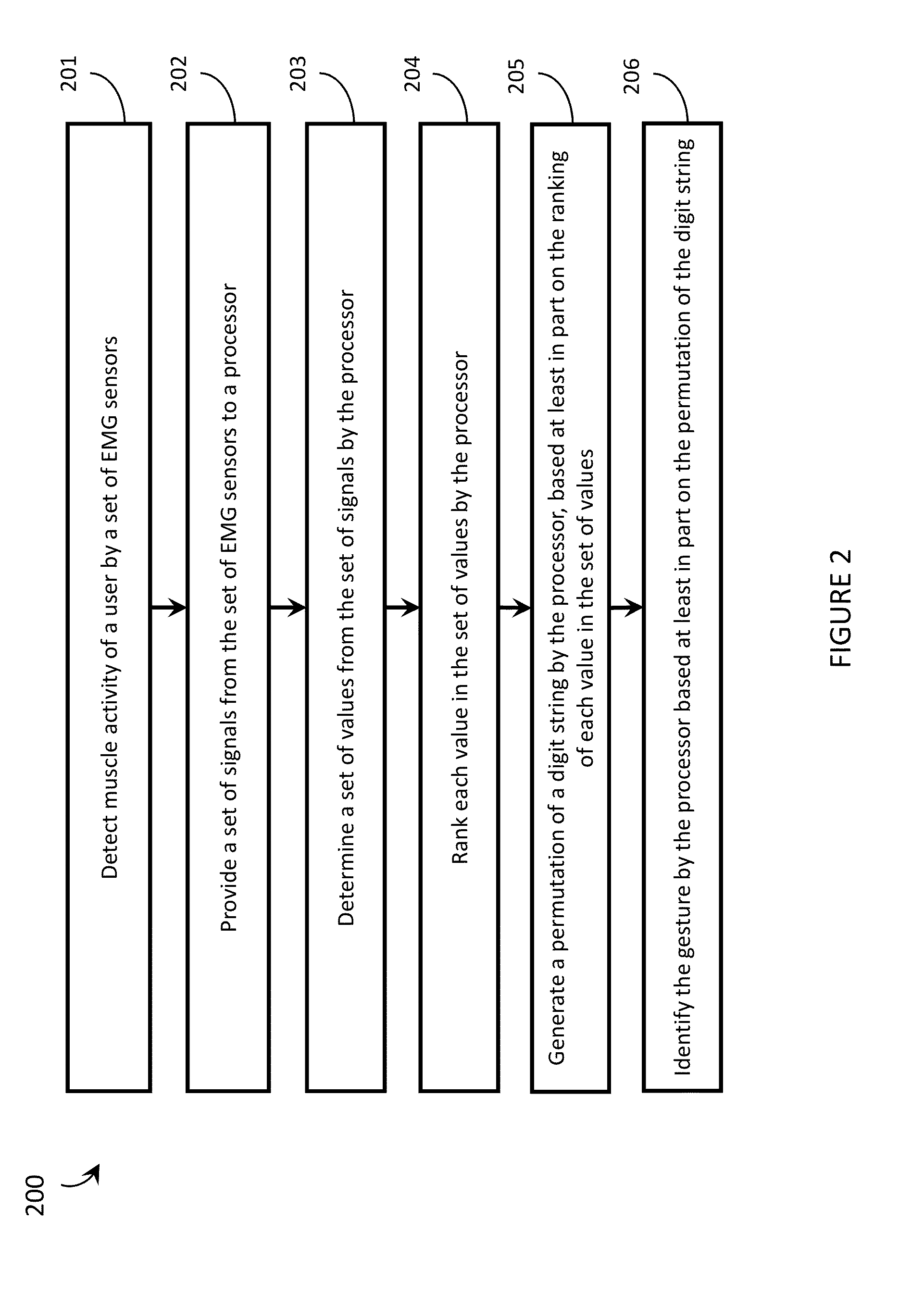
Systems, articles, and methods for performing gesture identification with improved robustness against variations in use parameters and without requiring a user to undergo an extensive training procedure are described. A wearable electromyography (“EMG”) device includes multiple EMG sensors, an on-board processor, and a non-transitory processor-readable storage medium that stores data and / or processor-executable instructions for performing gesture identification. The wearable EMG device detects, determines, and ranks features in the signal data provided by the EMG sensors and generates a digit string based on the ranked features. The permutation of the digit string is indicative of the gesture performed by the user, which is identified by testing the permutation of the digit string against multiple sets of defined permutation conditions. A single reference gesture may be performed by the user to (re-)calibrate the wearable EMG device before and / or during use.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
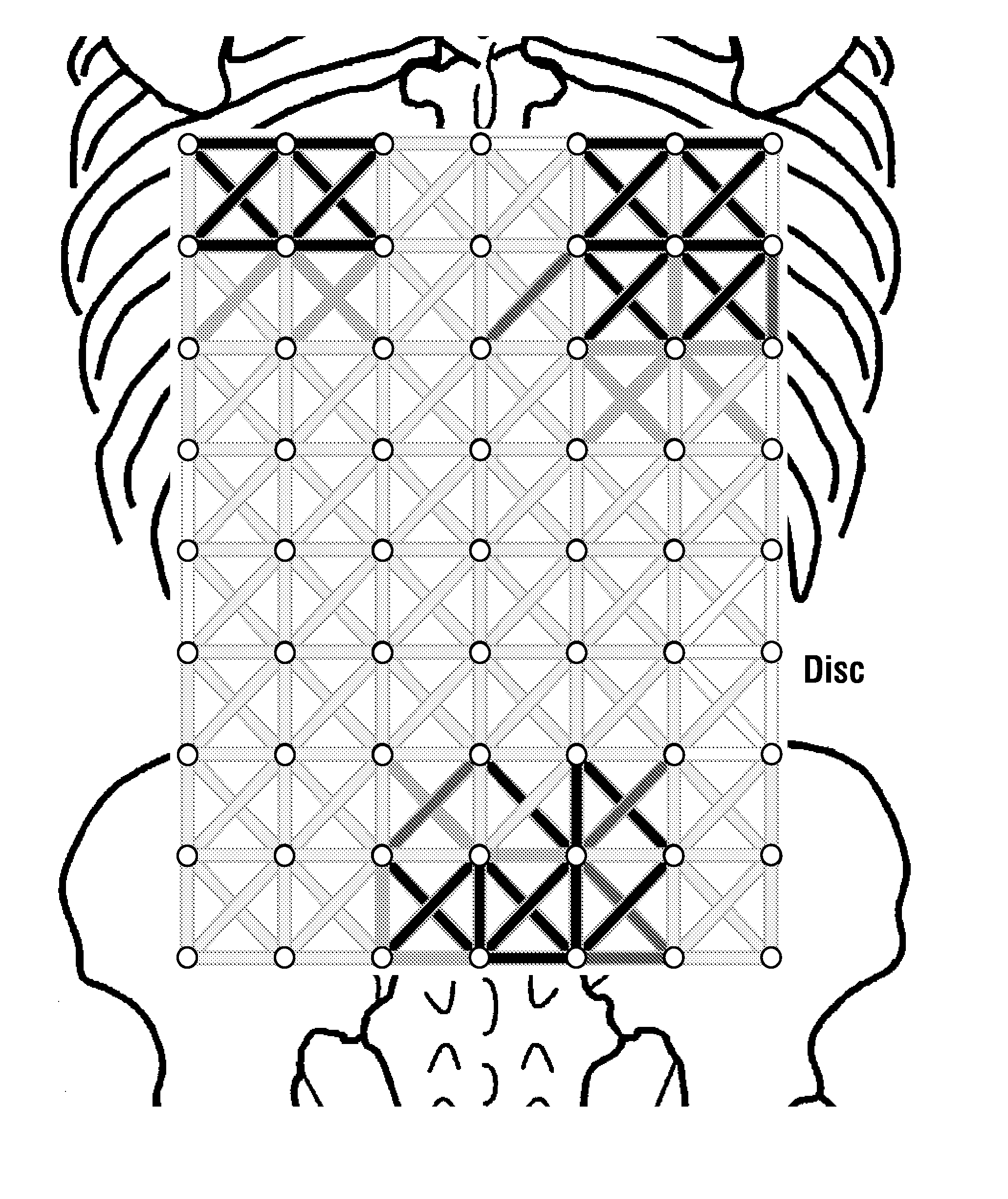
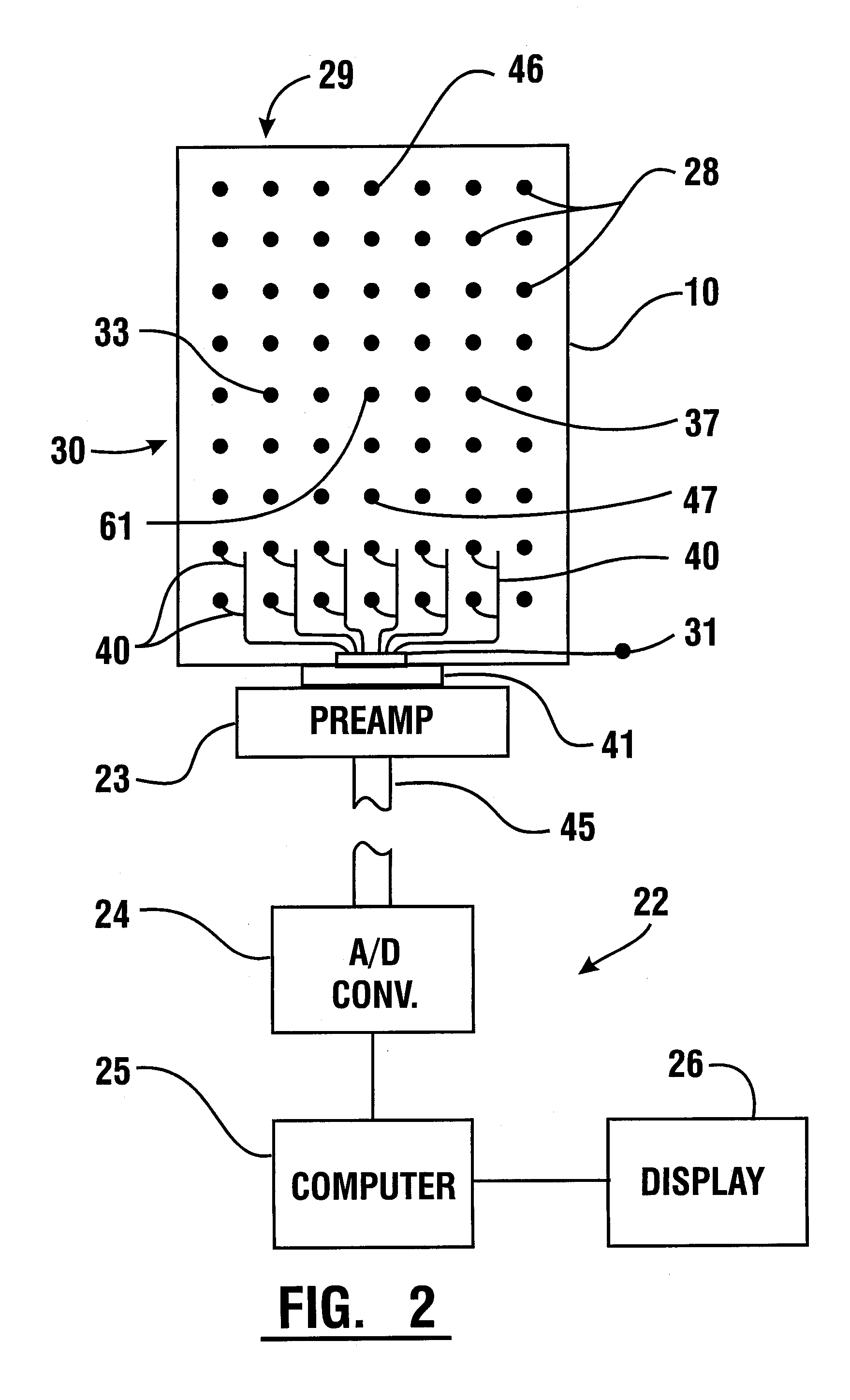
EMG Diagnostic System and Method
A system for detecting and analyzing electrical activity in the anatomy of an organism underlying an electromyographic (EMG) sensor device provides signals corresponding to electrical activity adjacent each electrode of sensor device. A method using the system may comprise determining EMG data for a patient responsive to EMG signals detected from a detection area on a back of the patient using the EMG sensor device. The method may further include determining whether the determined EMG data for the patient corresponds to predetermined EMG data associated with at least one of a facet condition, a disc condition, and a muscle condition.
Owner:SPINEMATRIX
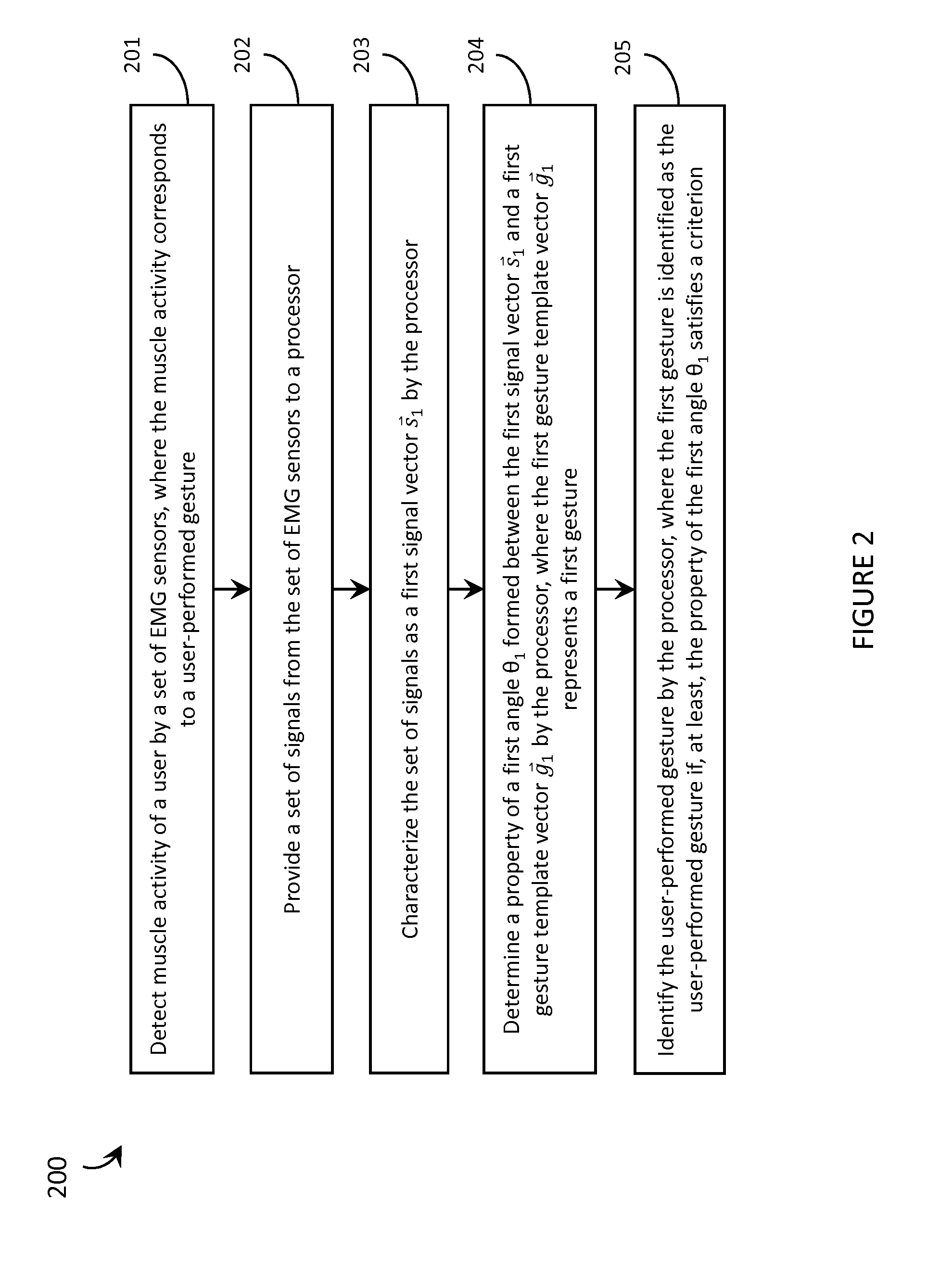
Systems, articles, and methods for gesture identification in wearable electromyography devices
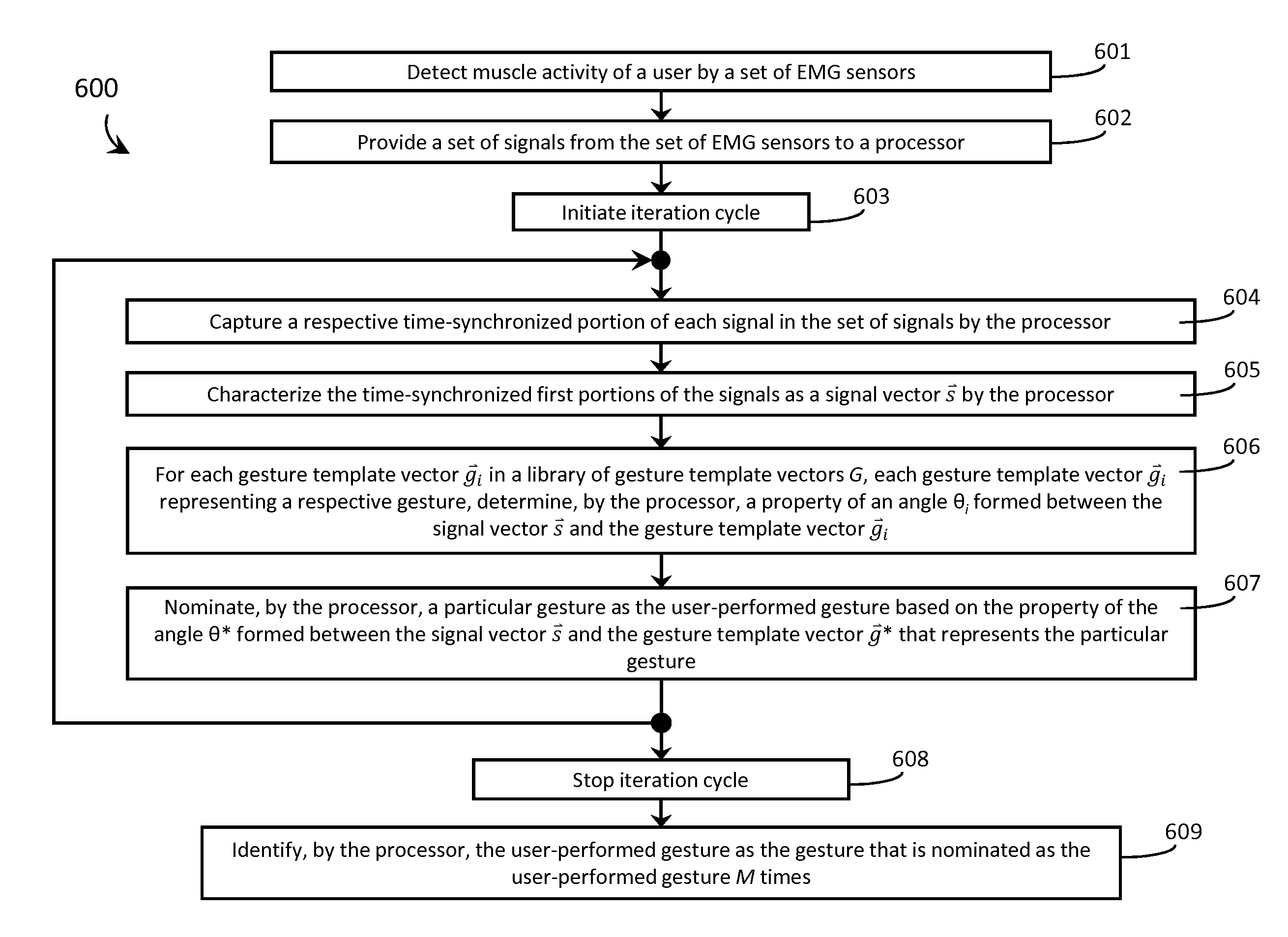
ActiveUS20150169074A1Input/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisElectromyographyComputational resource
Systems, articles, and methods perform gesture identification with limited computational resources. A wearable electromyography (“EMG”) device includes multiple EMG sensors, an on-board processor, and a non-transitory processor-readable memory storing data and / or instructions for performing gesture identification. The wearable EMG device detects signals when a user performs a physical gesture and characterizes a signal vector {right arrow over (s)} based on features of the detected signals. A library of gesture template vectors G is stored in the memory of the wearable EMG device and a respective property of each respective angle θi formed between the signal vector {right arrow over (s)} and respective ones of the gesture template vectors {right arrow over (g)}i is analyzed to match the direction of the signal vector {right arrow over (s)} to the direction of a particular gesture template vector {right arrow over (g)}*. The accuracy of the gesture identification may be enhanced by performing multiple iterations across multiple time-synchronized portions of the EMG signal data.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
Systems, articles, and methods for human-electronics interfaces
InactiveUS20150057770A1Input/output for user-computer interactionComputer controlHuman–machine interfaceElectronics
Human-electronics interfaces in which a wearable electromyography (“EMG”) device is operated to control virtually any electronic device are described. In response to detected muscle activity and / or motions of a user, the wearable EMG device transmits generic gesture identification flags that are not specific to the particular electronic device(s) being controlled. An electronic device being controlled is programmed with user-definable instructions for how to interpret and respond to the gesture identification flags.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
Illuminated endoscopic pedicle probe with dynamic real time monitoring for proximity to nerves
InactiveUS20150342621A1Prevent breachDirectly and accurately determinedSpinal electrodesElectromyographyVisual observationMonitoring system
An endoscopic pedicle probe for use during spinal surgery to form a hole in a pedicle for reception of a pedicle screw has an enlarged proximal end for cooperation with the hand of the surgeon and an elongate shaft terminating in a distal tip that may be pushed through the pedicle to form the hole. An integrated endoscope and light extend through the shaft to enable the surgeon to visually observe the target area, and a conduit extends through the shaft to convey a fluid to irrigate the target area. In a preferred form the probe is connected with an electromyographic or mechanomyographic monitoring system to alert the surgeon when a breach is about to occur. In a further embodiment, two endoscopes are associated with the probe. The complete probe may be disposable, or just the tip may be detachable for disposal or replacement.
Owner:OPTICAL SPINE LLC
Systems, articles, and methods for electromyography-based human-electronics interfaces
ActiveUS20150070270A1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectromyographyHuman–machine interfaceEngineering
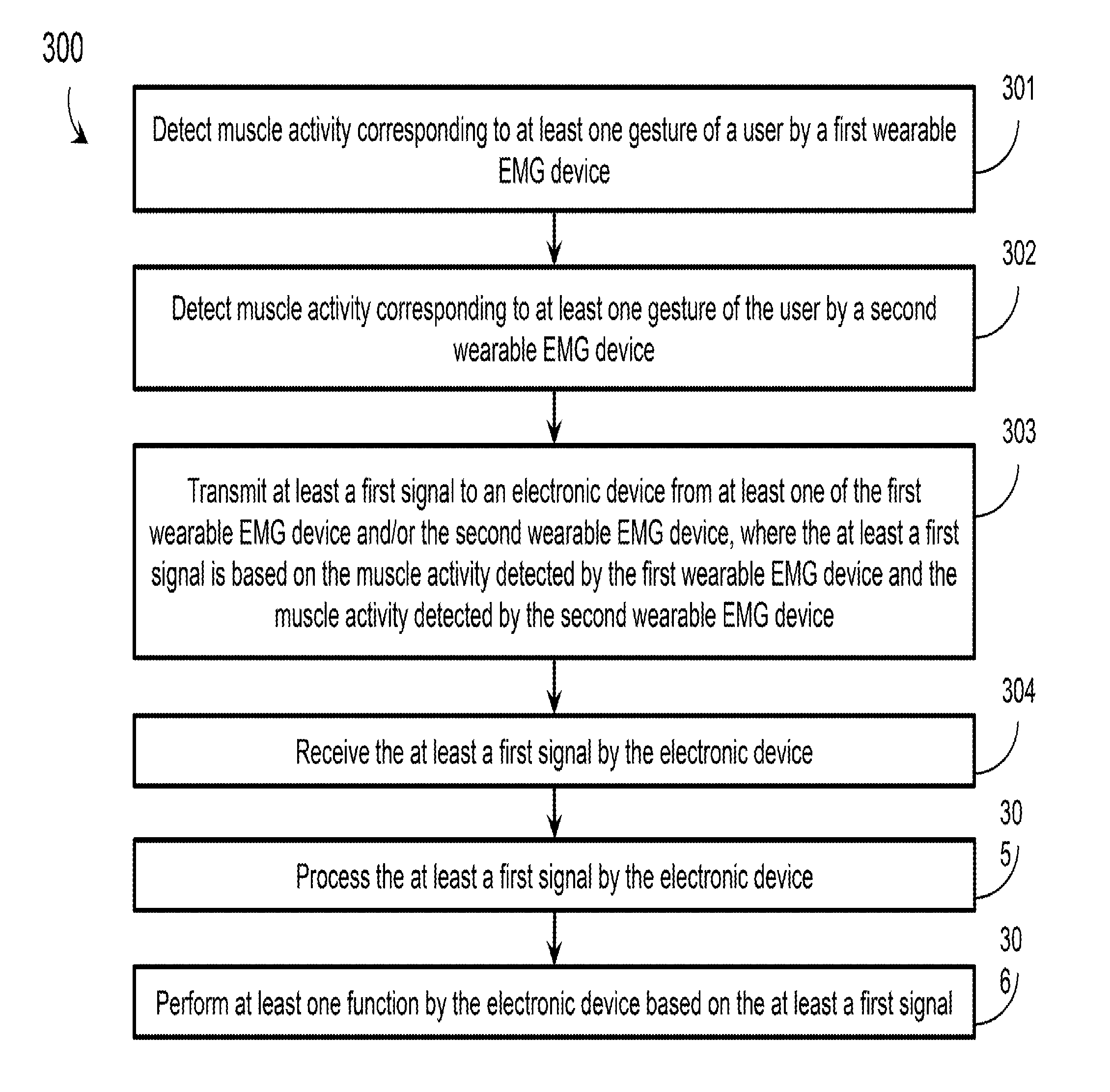
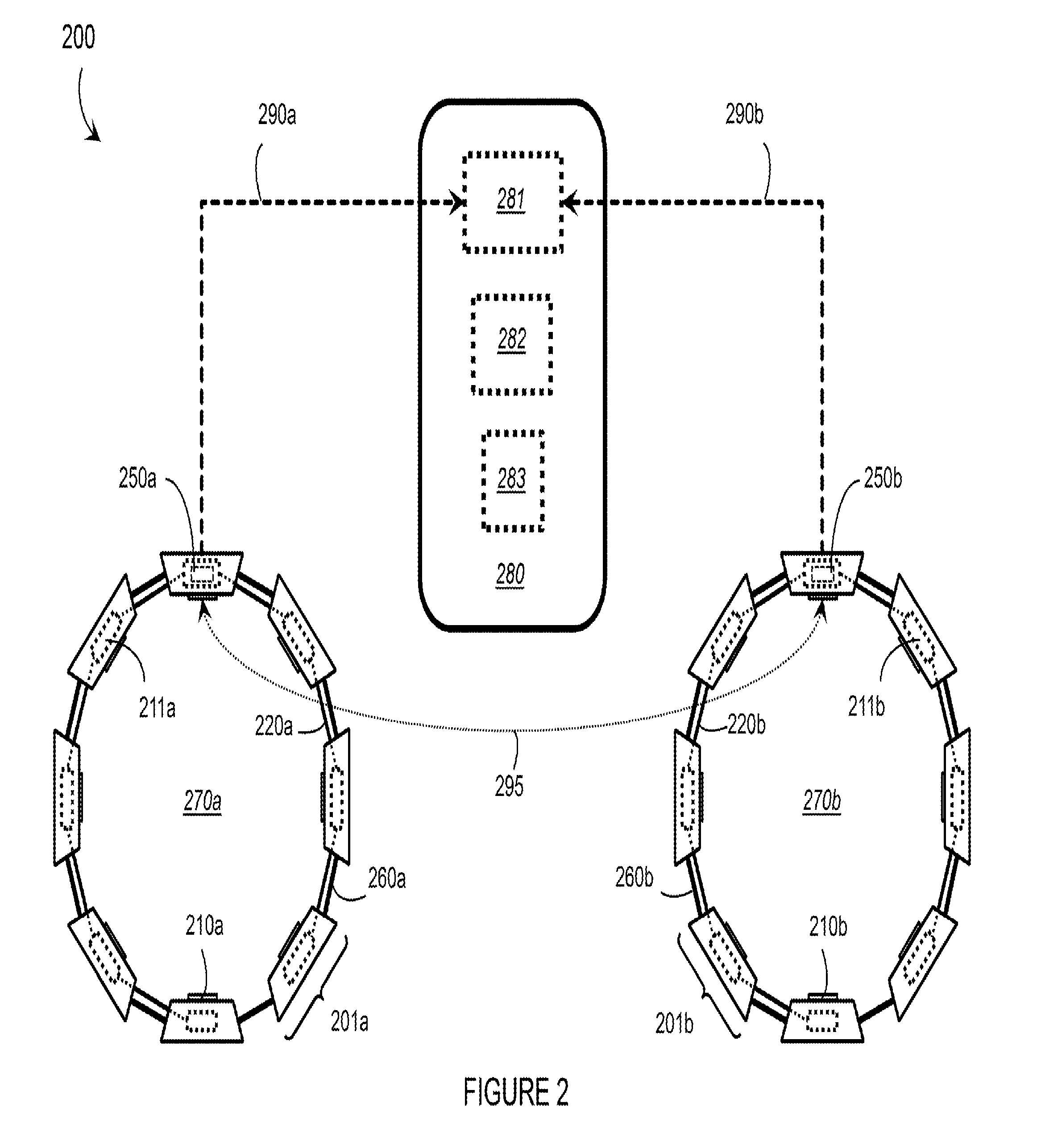
Human-electronics interfaces in which at least two wearable electromyography (“EMG”) devices are operated to control virtually any electronic device are described. A first wearable EMG device is worn on a first part / location of a user's body and a second wearable EMG device is worn on a second part / location of the user's body. Muscle activity is detected by the two wearable EMG devices and corresponding communication signals are transmitted to an electronic device to control functions thereof. The two wearable EMG devices may communicate with one another. This configuration enables a user to perform elaborate gestures having multiple components (e.g., “two-arm” gestures) with each wearable EMG device detecting a different component, as well as separate gestures (e.g., separate “one-arm” gestures) individually detected and processed by each wearable EMG device.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
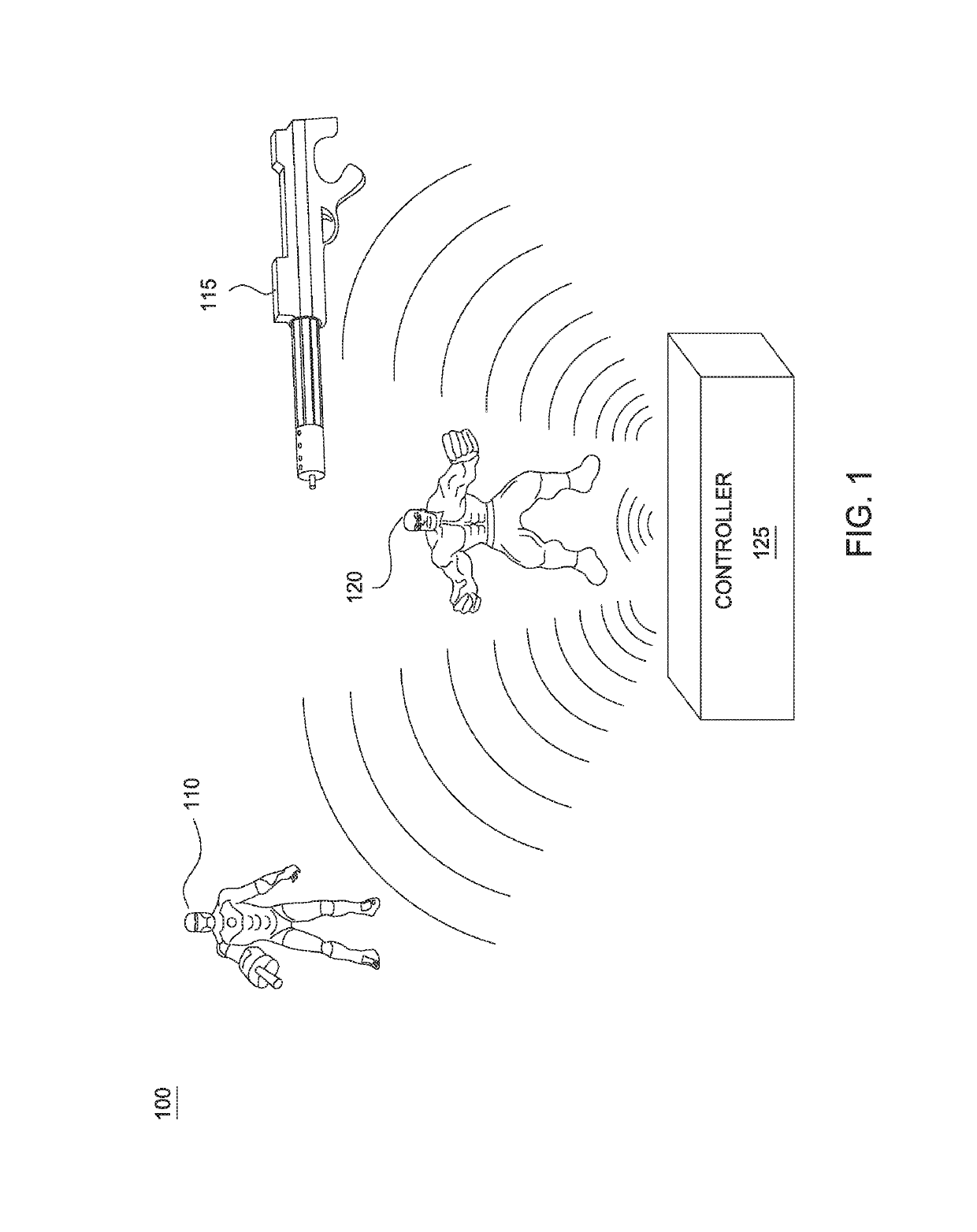
Virtual blaster
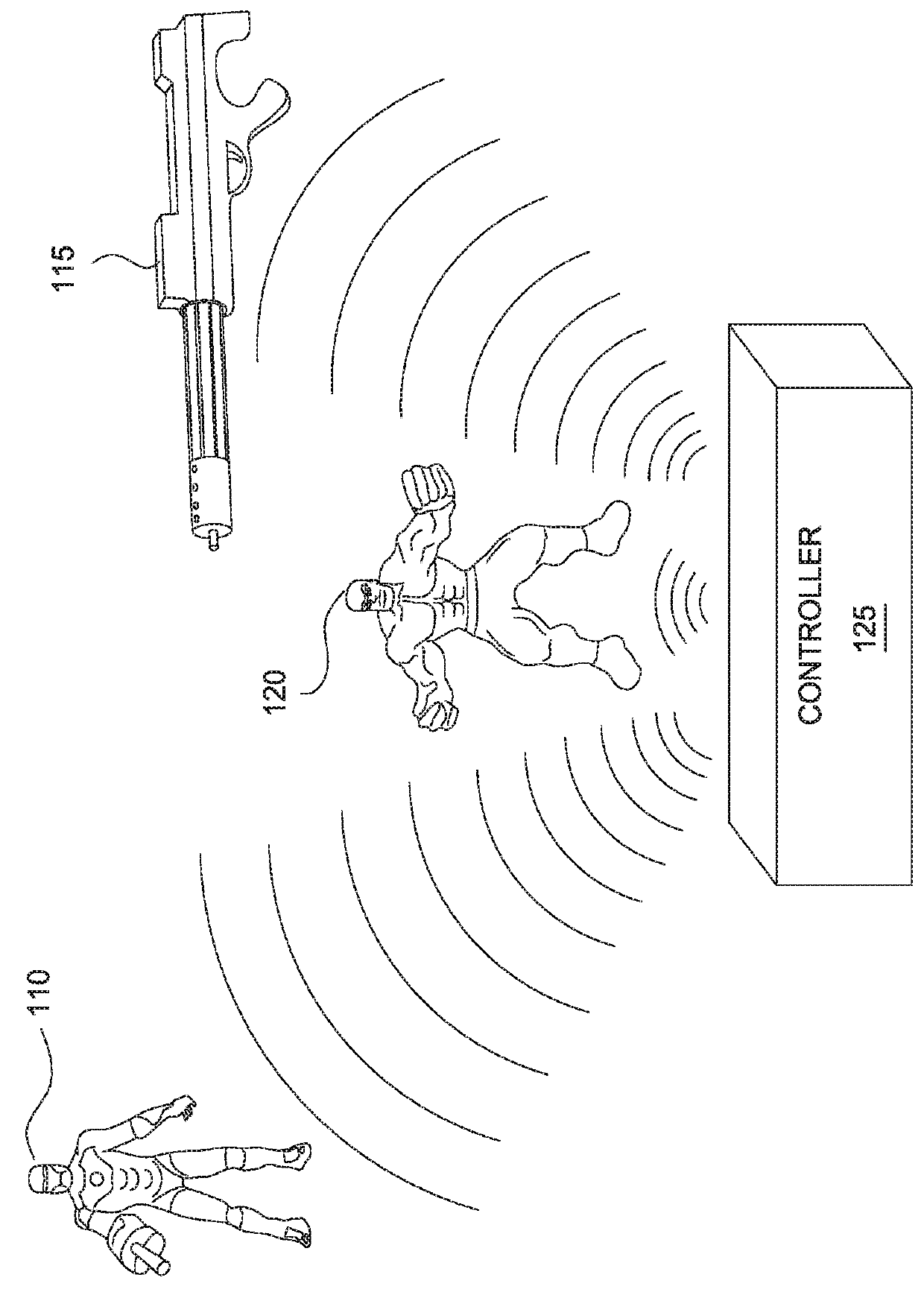
Embodiments provide techniques for automating control of electronic device. A first interactive game playing within the physical environment using one or more electronic devices is detected. Embodiments collect electromyogram data from one or more electromyography sensors within the physical environment and analyze the electromyogram data collected to determine muscle activations made by the user. Upon determining that the determined muscle activations made by the user match a predefined pattern of electromyography data, embodiments determine a gameplay action corresponding to the predefined pattern of electromyography data and transmit an instruction, to at least one of the one or more electronic devices within the physical environment, instructing the electronic device to perform the determined gameplay action.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
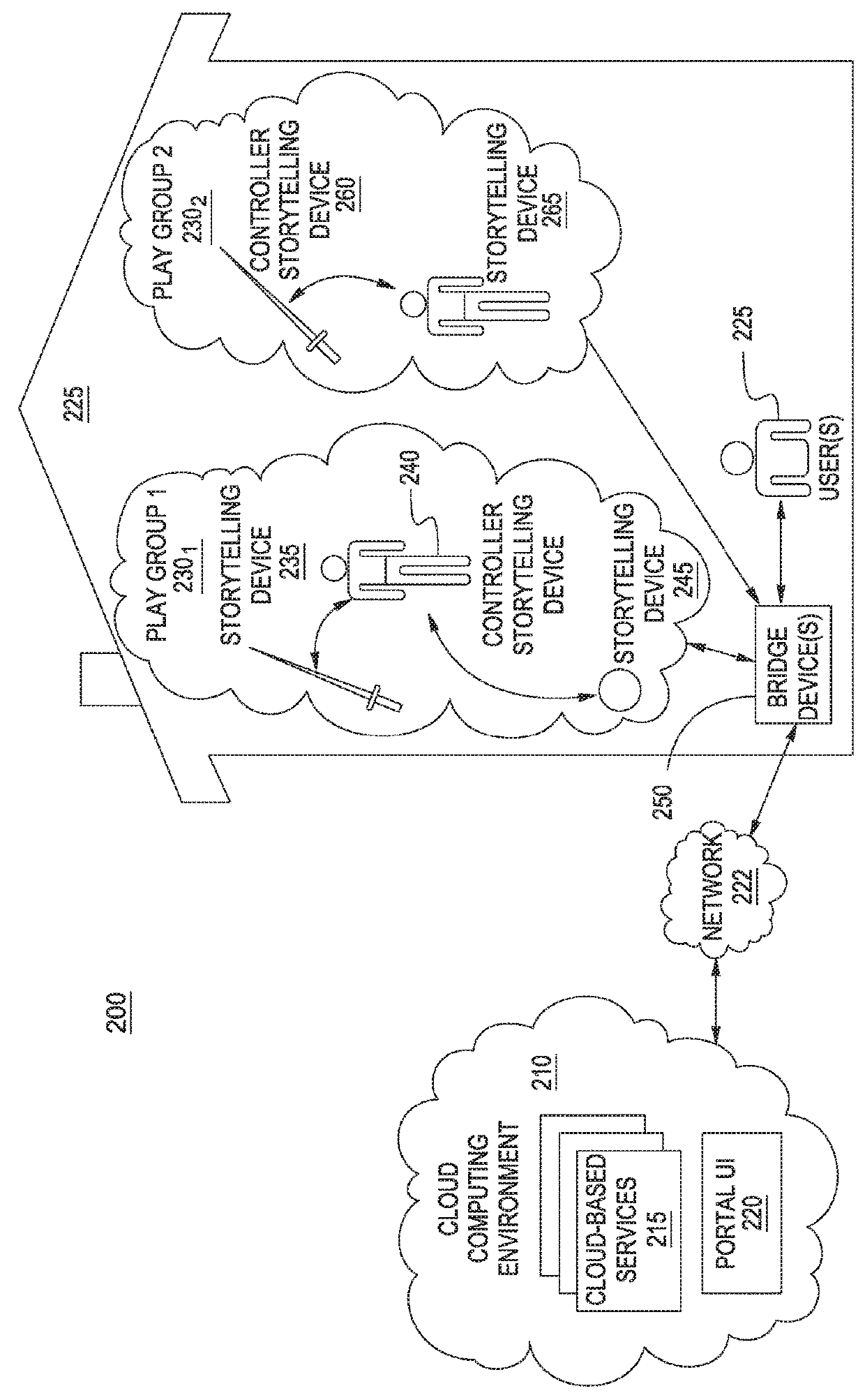
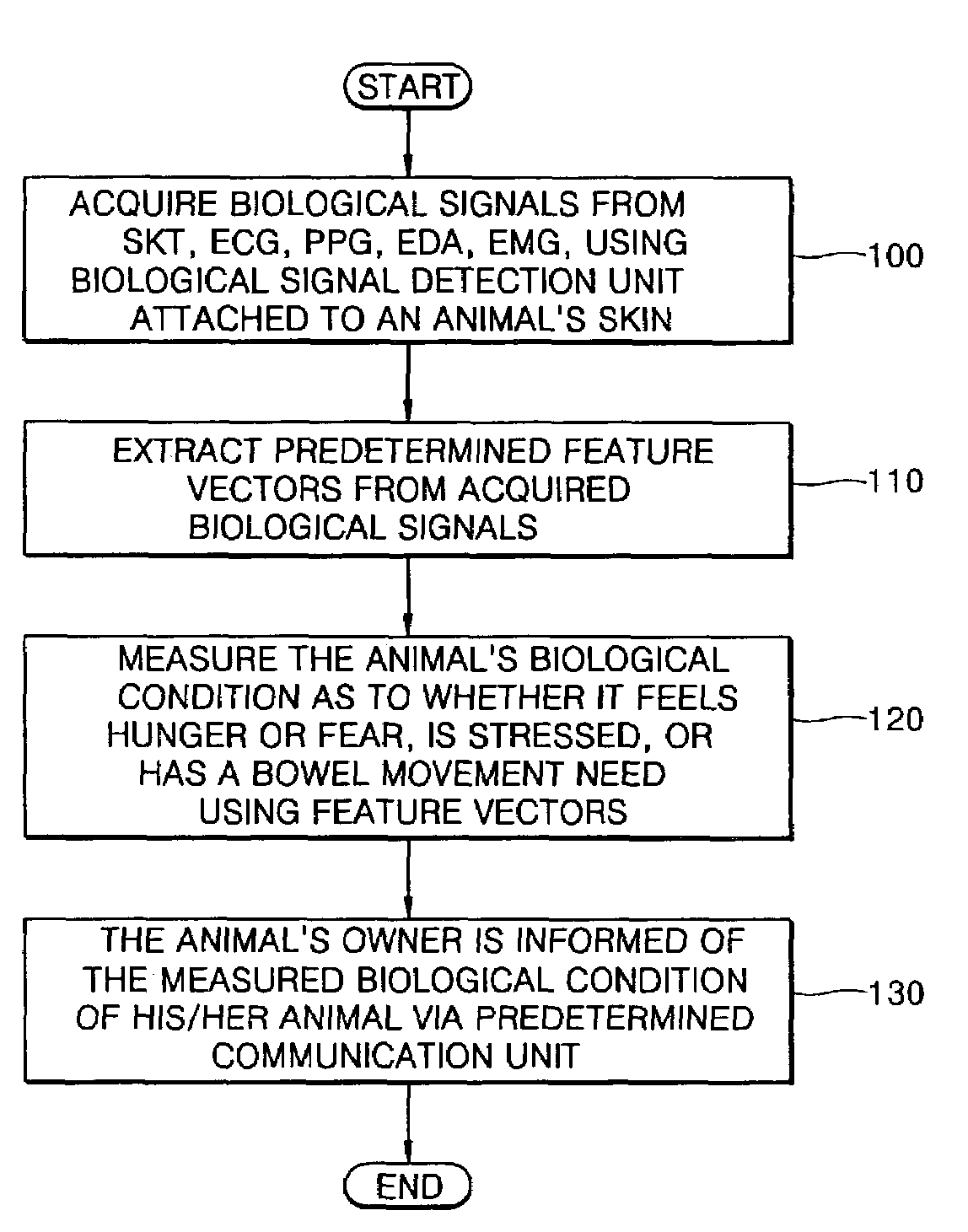
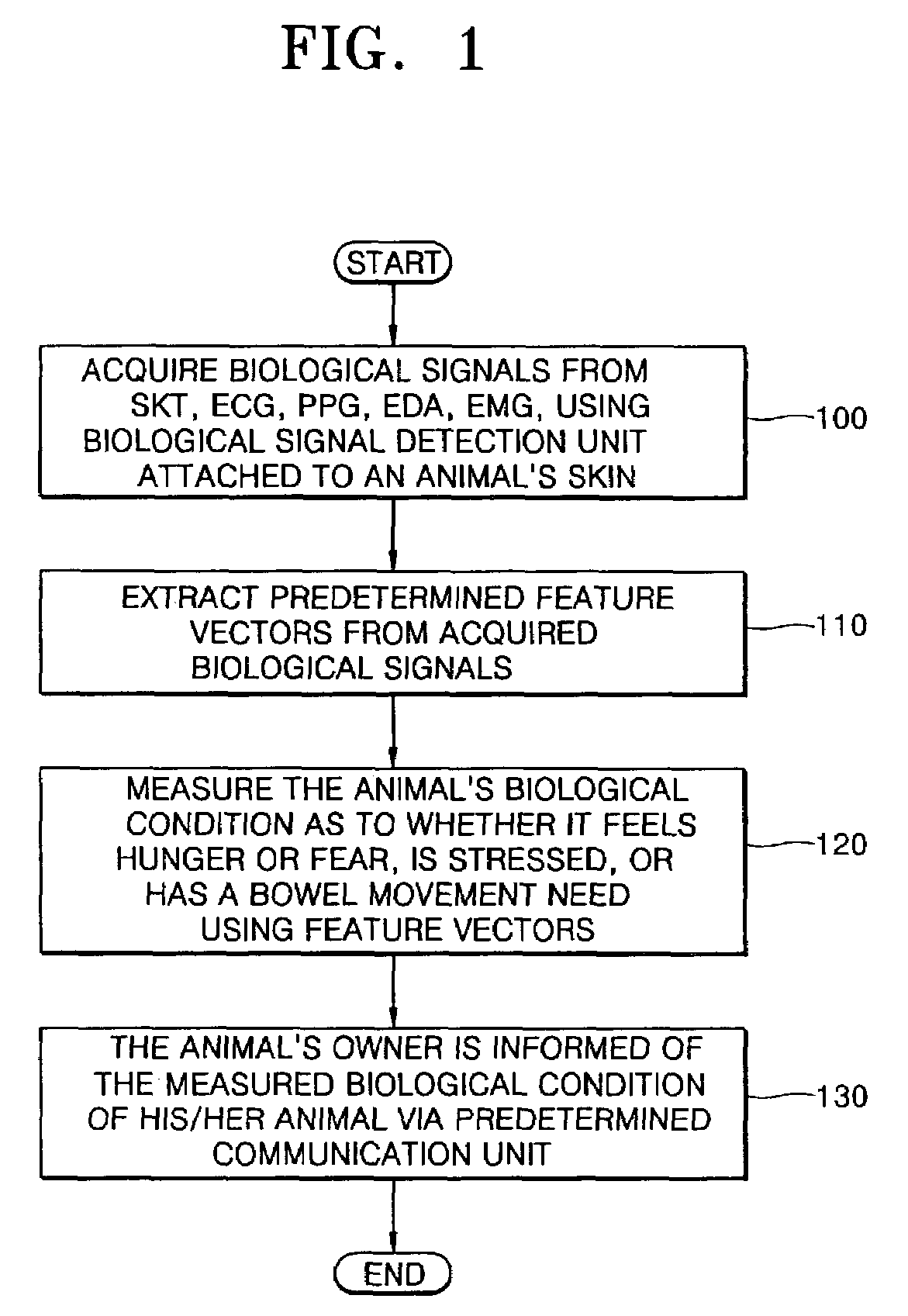
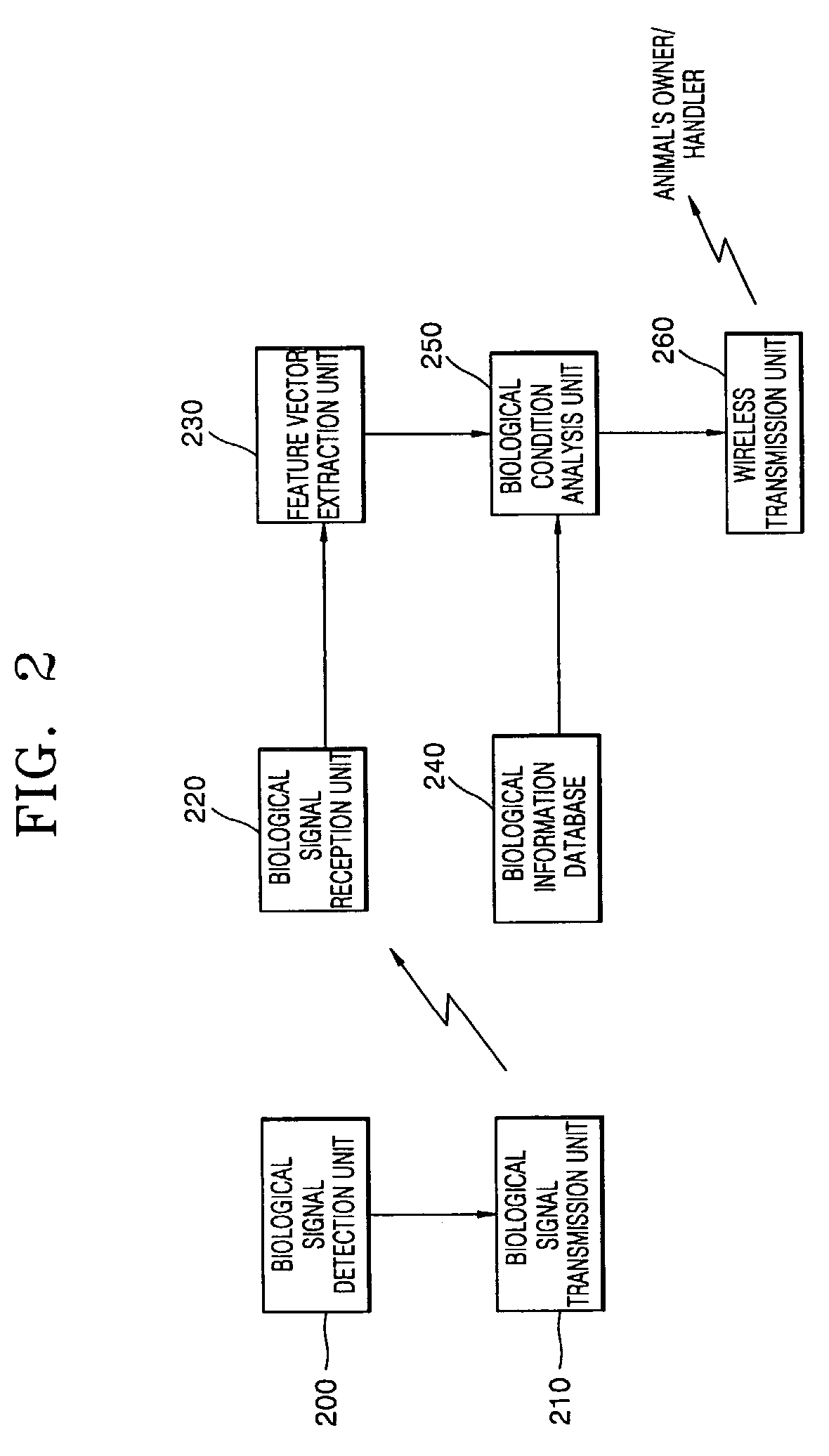
Method and apparatus for measuring animal's condition by acquiring and analyzing its biological signals
A method and apparatus for measuring the biological condition of an animal by acquiring and analyzing its biological signals are provided. The biological signals from skin temperature, a photoplenthysmogram (PPG), an electrocardiogram (ECG), electrodermal activity (EDA), an electromyogram (EMG), and an electrogastrogram (EGG) are detected using a biological signal detection unit which is attached to the animal's skin. Feature vectors, including the mean heart rate of the photoplenthysmogram and its standard deviation, the very low frequency, low frequency, and high frequency components of heart rate variability, the frequency and mean amplitude of skin conductance responses, and the mean and maximum skin temperatures, are extracted from the detected biological signals. The biological condition, including needs and emotions, of the animal as to whether or not the animal feels hunger or fear, how much the animal is stressed, or whether or not the animal needs to have a bowel movement, is determined using a pattern classifier which has learned reference vectors, which reflect the behaviors, needs, and emotions of different kinds of animals for various biological conditions and are stored in a predetermined database. Therefore, the biological condition of the animal can be determined through instrumental communication, not through human languages, and the breeding of pets can be efficiently managed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
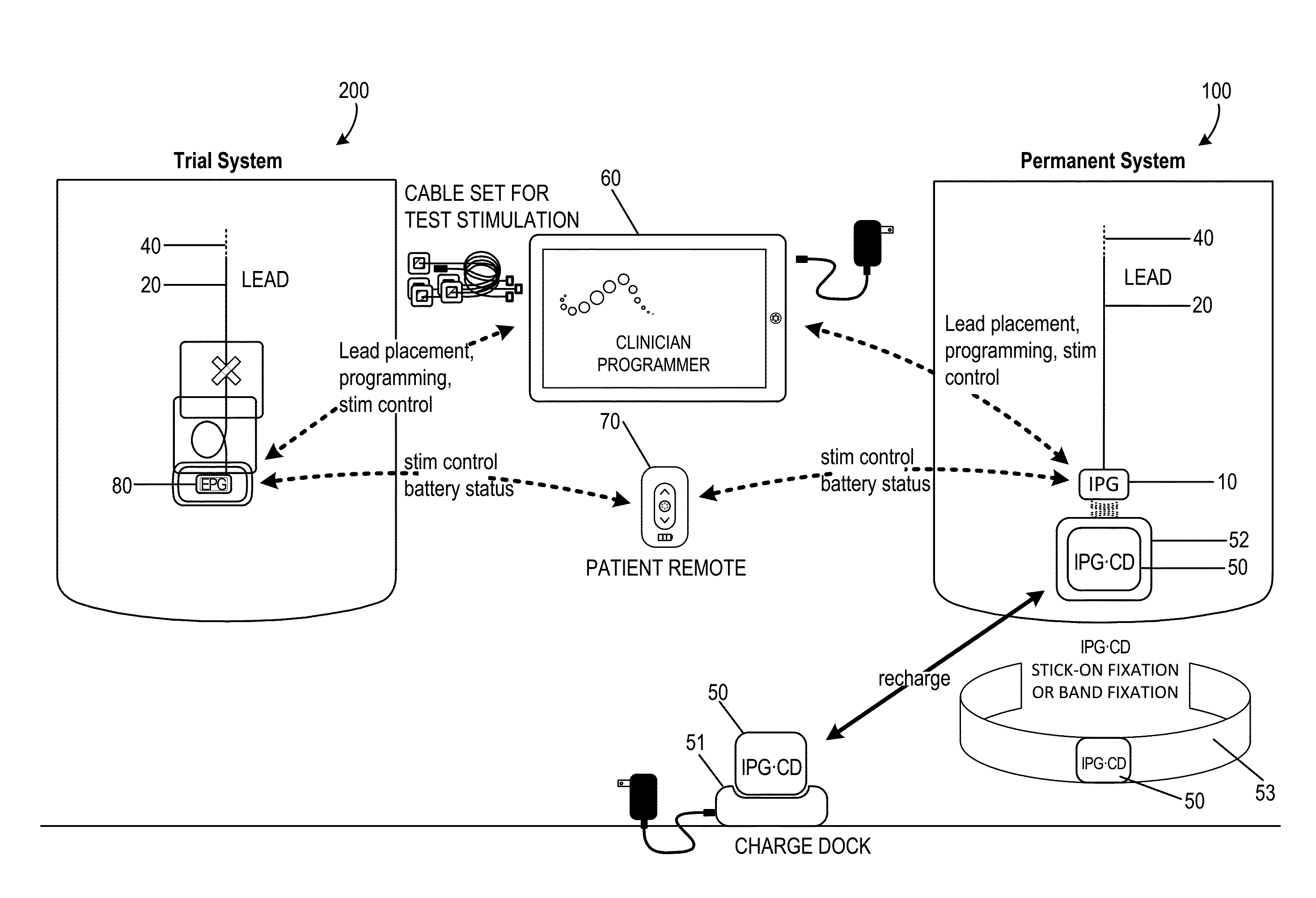
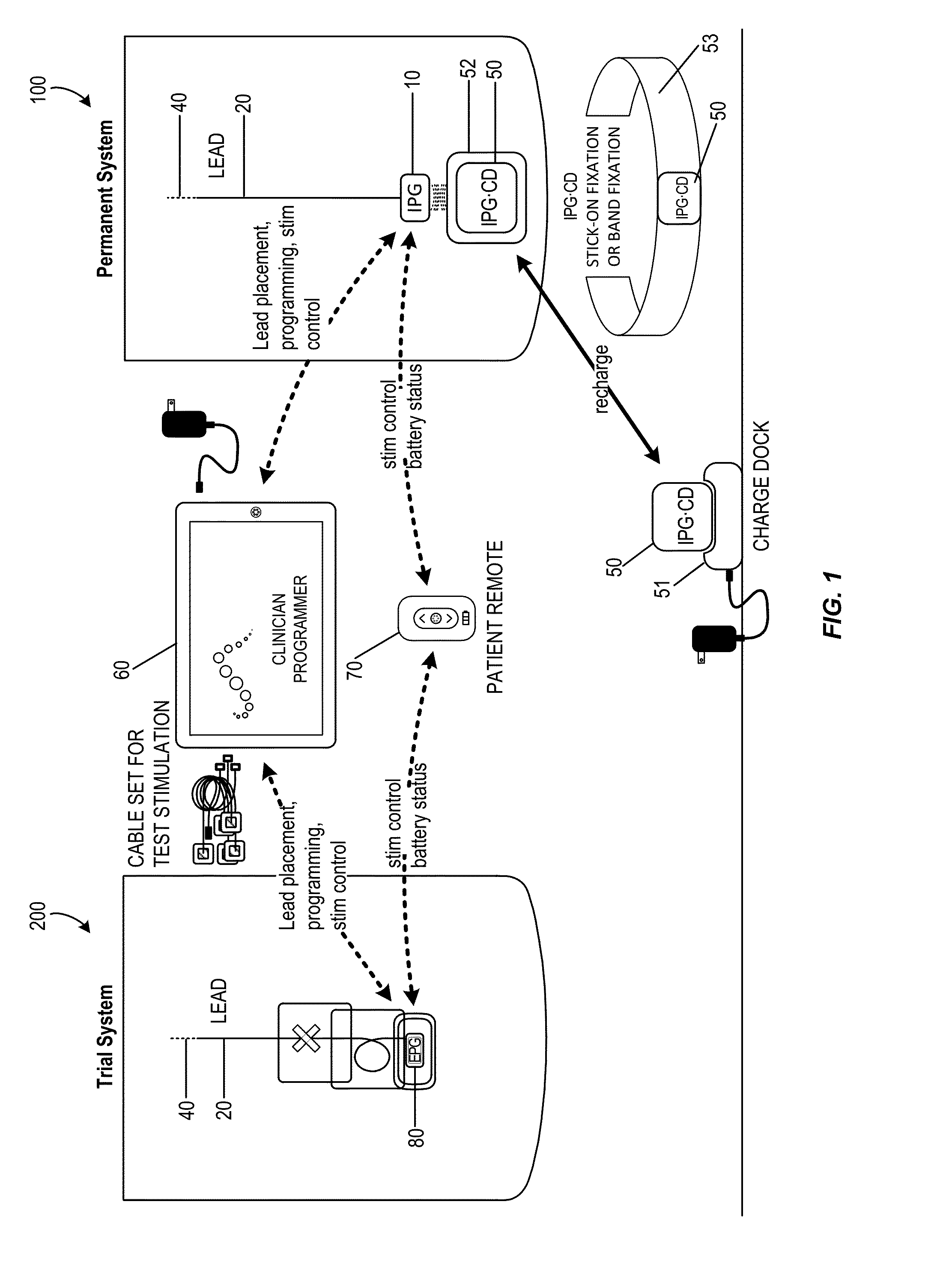
Integrated Electromyographic Clinician Programmer for Use with an Implantable Neurostimulator
ActiveUS20160045746A1Improve positionAccelerated programSpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringGraphical user interfaceMedicine
An integrated electromyography (EMG) and signal / stimulation generation clinician programmer may be coupled with an implantable temporary or permanent lead in a patient and at least one EMG sensing electrode minimally invasively positioned on a skin surface or within the patient. Generally, the integrated clinician programmer may comprise a portable housing, a signal / stimulation generator, and EMG signal processor, and a graphical user interface. The housing has an external surface and encloses circuitry at least partially disposed within the housing. The signal / stimulation generator may be disposed within the housing and configured to deliver test stimulation to a nerve tissue of the patient via the implantable lead. The EMG signal processor may be disposed within the housing and configured to record a stimulation-induced EMG motor response for each test stimulation via the at least one EMG sensing electrode. The graphical user interface at least partially comprises the external surface of the housing and has a touch screen display for direct user interaction or for use with a keyboard, mouse, or the like.
Owner:AXONICS
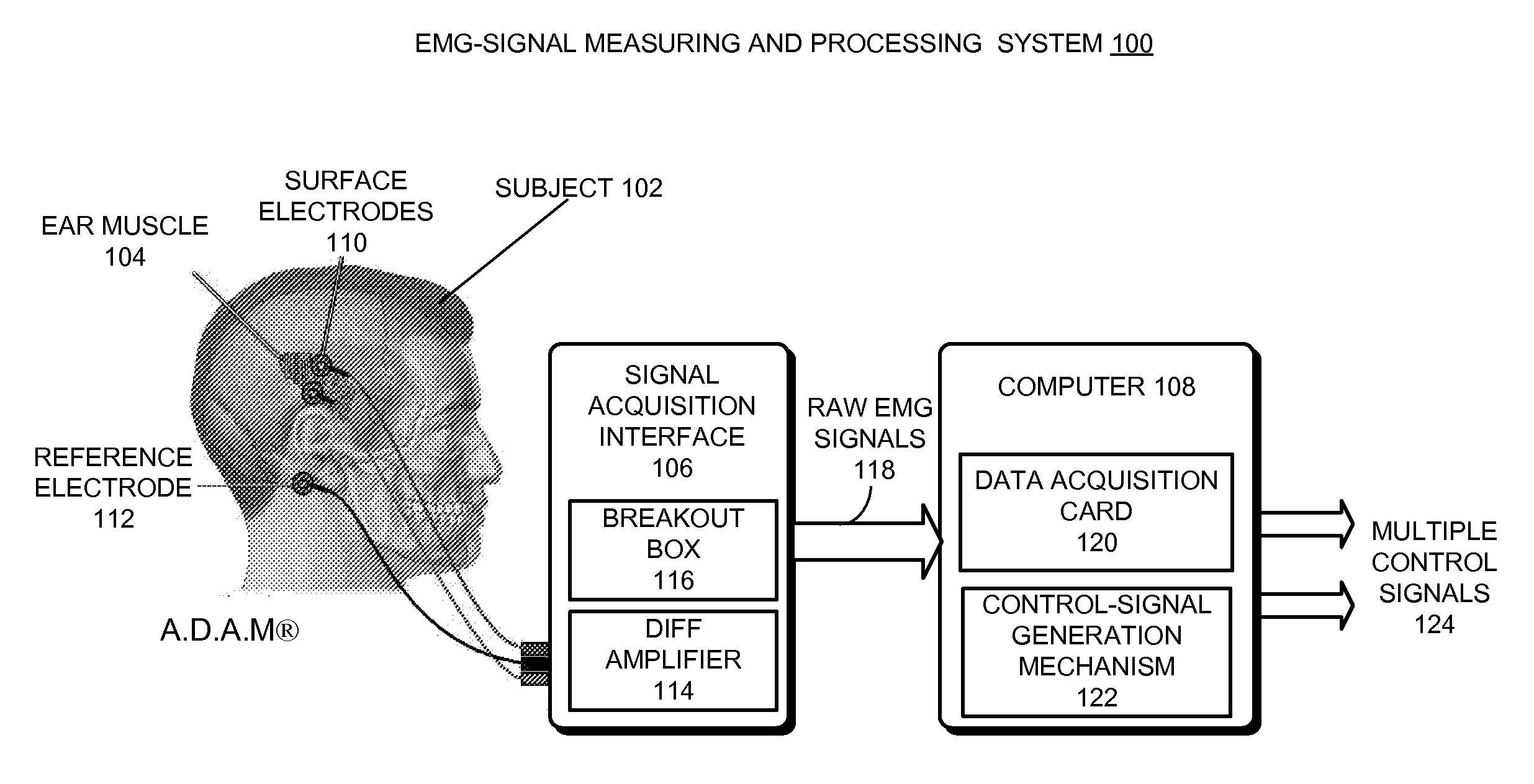
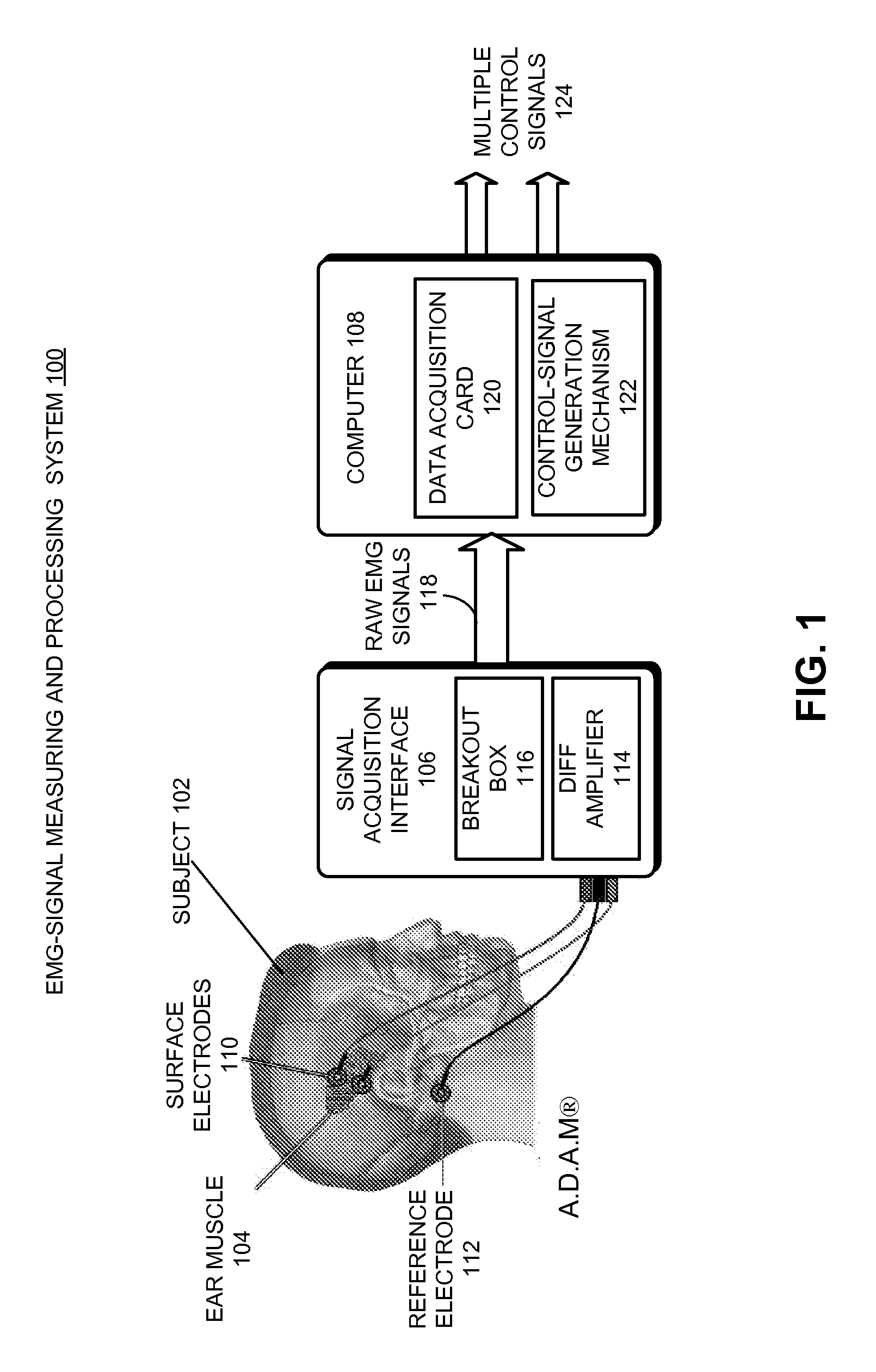
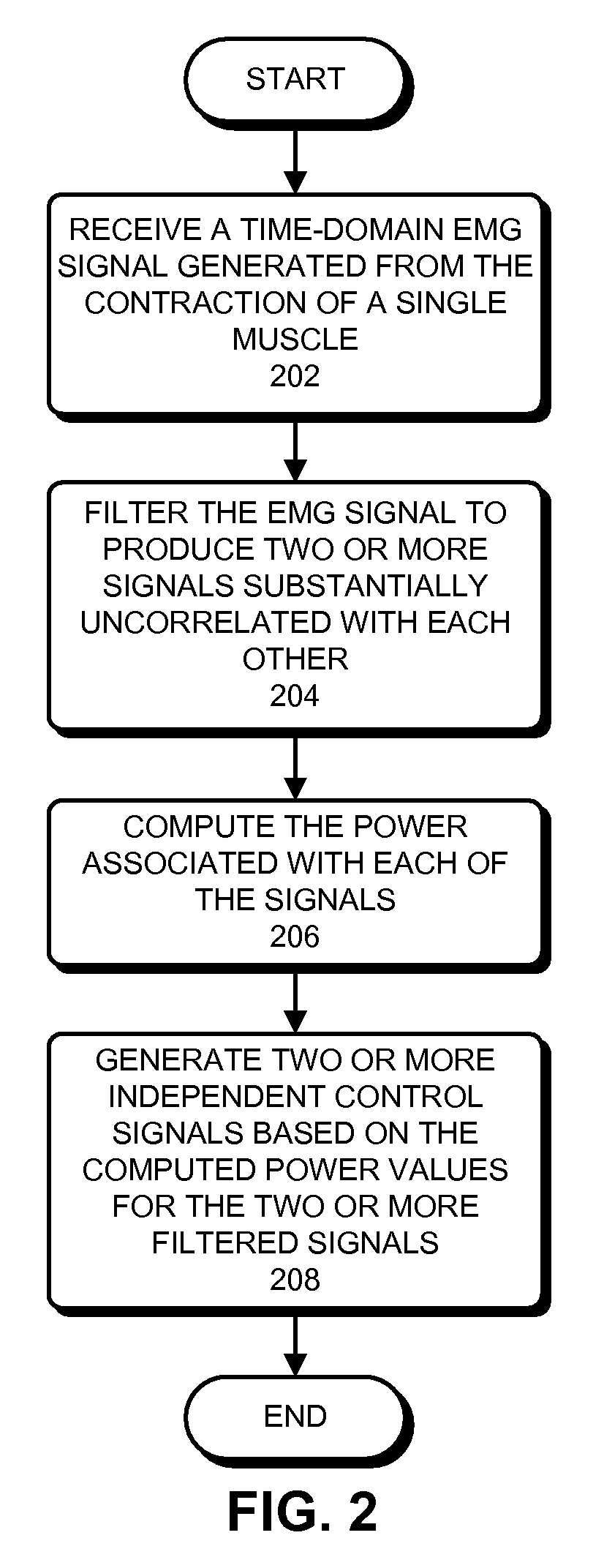
Multi-channel myoelectrical control using single muscle
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that generates multiple control signals from an electromyographic (EMG) signal produced by a single muscle. During operation, the system obtains an EMG signal from a single muscle of a subject. The system then processes the EMG signal to generate two or more independent control signals from the single muscle.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Orthotic device
An orthotic device including a forearm support section configured to be releasably attached to a user's arm, a hand support section configured to be releasably attached to the user's hand, and an adjustable joint coupled to the forearm support section and the hand support section. At least one electromyography sensor is coupled to the forearm support section and positioned to sense activity of muscles in the user's arm, at least one electrode is coupled to the forearm support section and configured to provide electrical stimulation to muscles in the user's arm, and a controller is operatively coupled to the at least one electrode, the controller being configured to deliver electrical stimulation to the at least one electrode.
Owner:SAEBO
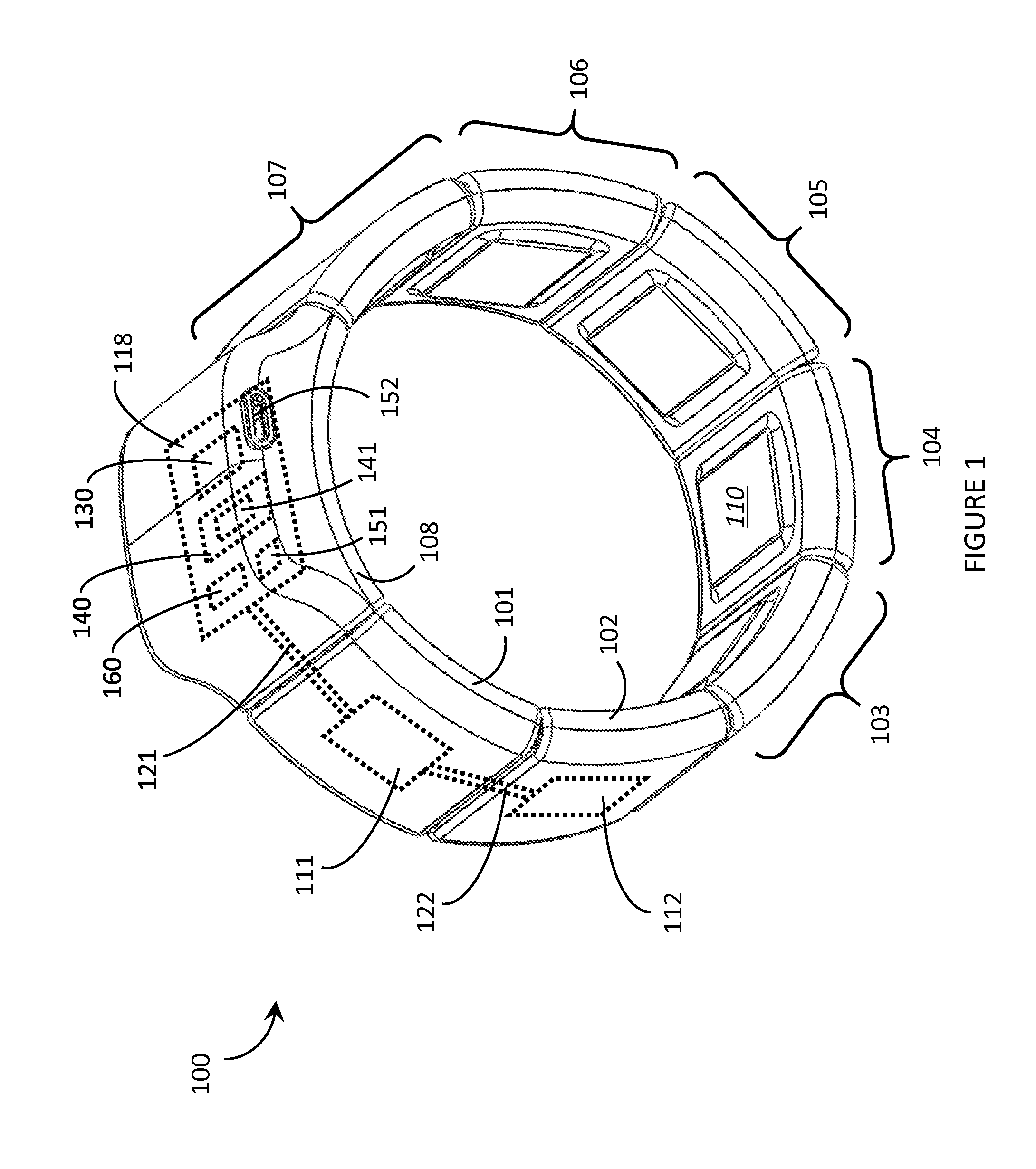
Systems and methods for determining axial orientation and location of a user's wrist
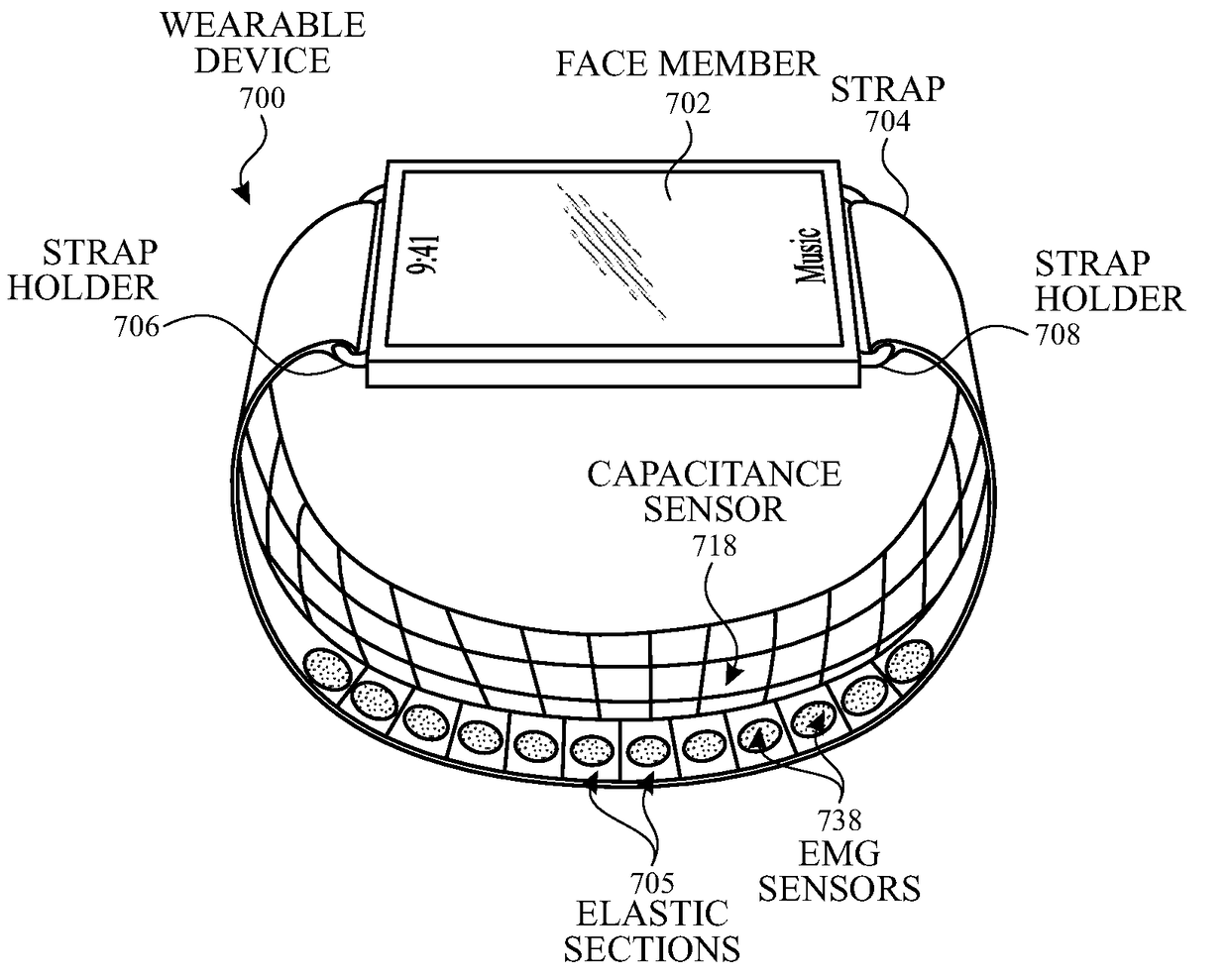
ActiveUS20180078183A1Fine granularityHigh sensitivityElectromyographyGymnastic exercisingGranularityEngineering
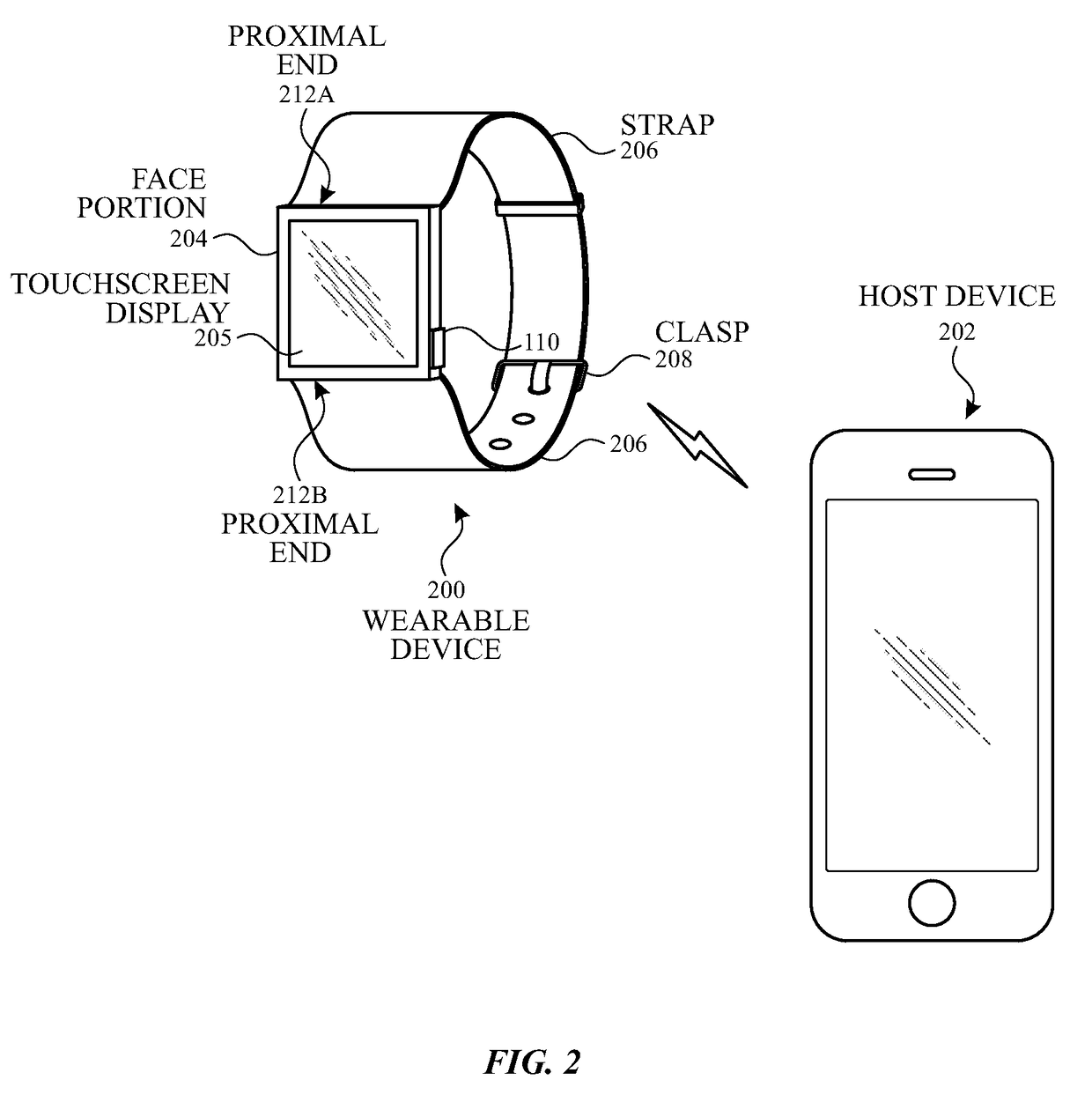
This relates to systems and methods for determining the axial orientation and location of the user's wrist using one or more sensors located on the strap, the device underbody, or both. For example, the strap can include a plurality of elastic sections and a plurality of rigid sections. Each elastic section can include one or more flex sensors. In some examples, on or more electromyography (EMG) sensors can be included to measure the user's electrical signals, and the user's muscle activity can be determined. In some examples, a plurality of strain gauges can be included to generate one or more signals indicative of any changes in shape, size, and / or physical properties of the user's wrist. In some examples, the device can include a plurality of capacitance sensors for increased granularity and / or sensitivity in measuring the amount of tension exerted by the user's wrist.
Owner:APPLE INC
Characterizing a physical capability by motion analysis
ActiveCN102438519AAdvantage managementEfficient and reliable semi-automatic analysisMedical data miningHealth-index calculationData acquisitionHuman motion
Motion analysis is used to classify or rate human capability in a physical domain via a minimized movement and data collection protocol producing a discreet, overall figure of merit of the selected physical capability. The minimal protocol is determined by data mining of a more extensive movement and data collection. Protocols are relevant in medical, sports and occupational applications. Kinematic, kinetic, body type, electromyography (EMG), ground Reactive Force (GRF), demographic, and psychological data are encompassed. Resulting protocols are capable of transforming raw data representing specific human motions into an objective rating of a skill or capability related to those motions.
Owner:艾伦·约瑟夫·泽尔纳
Apparatus and method for selecting and outputting character by teeth-clenching
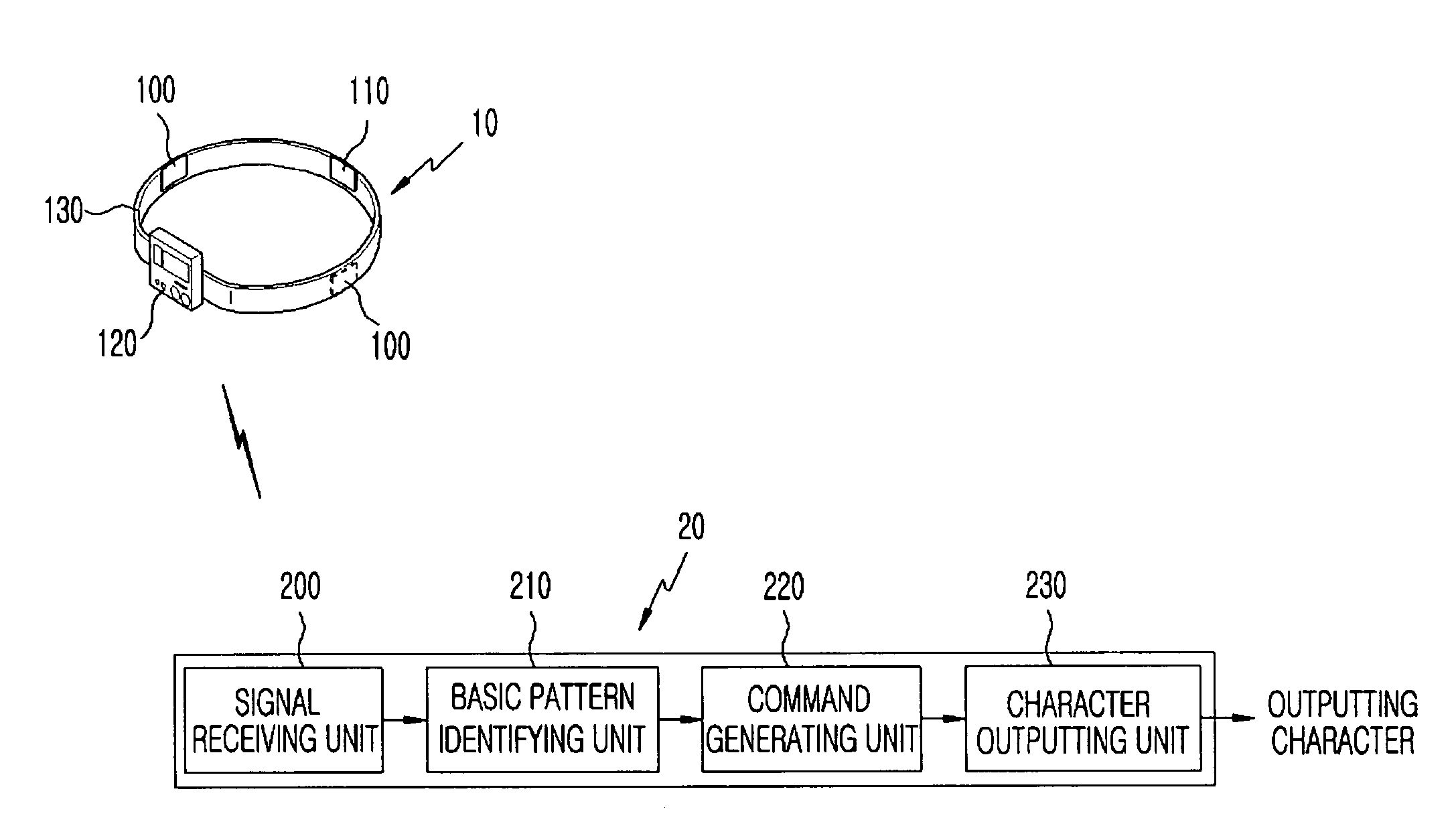
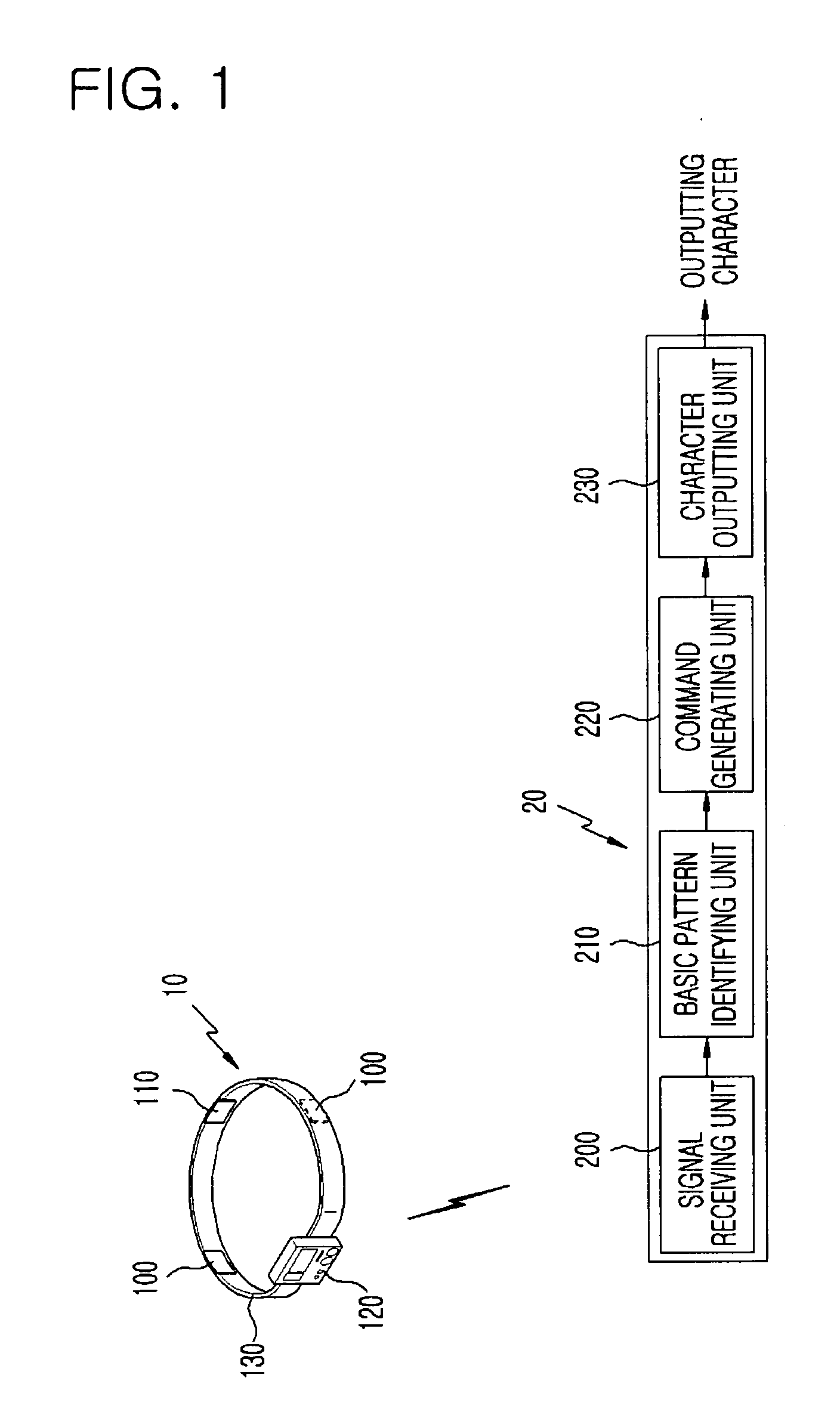
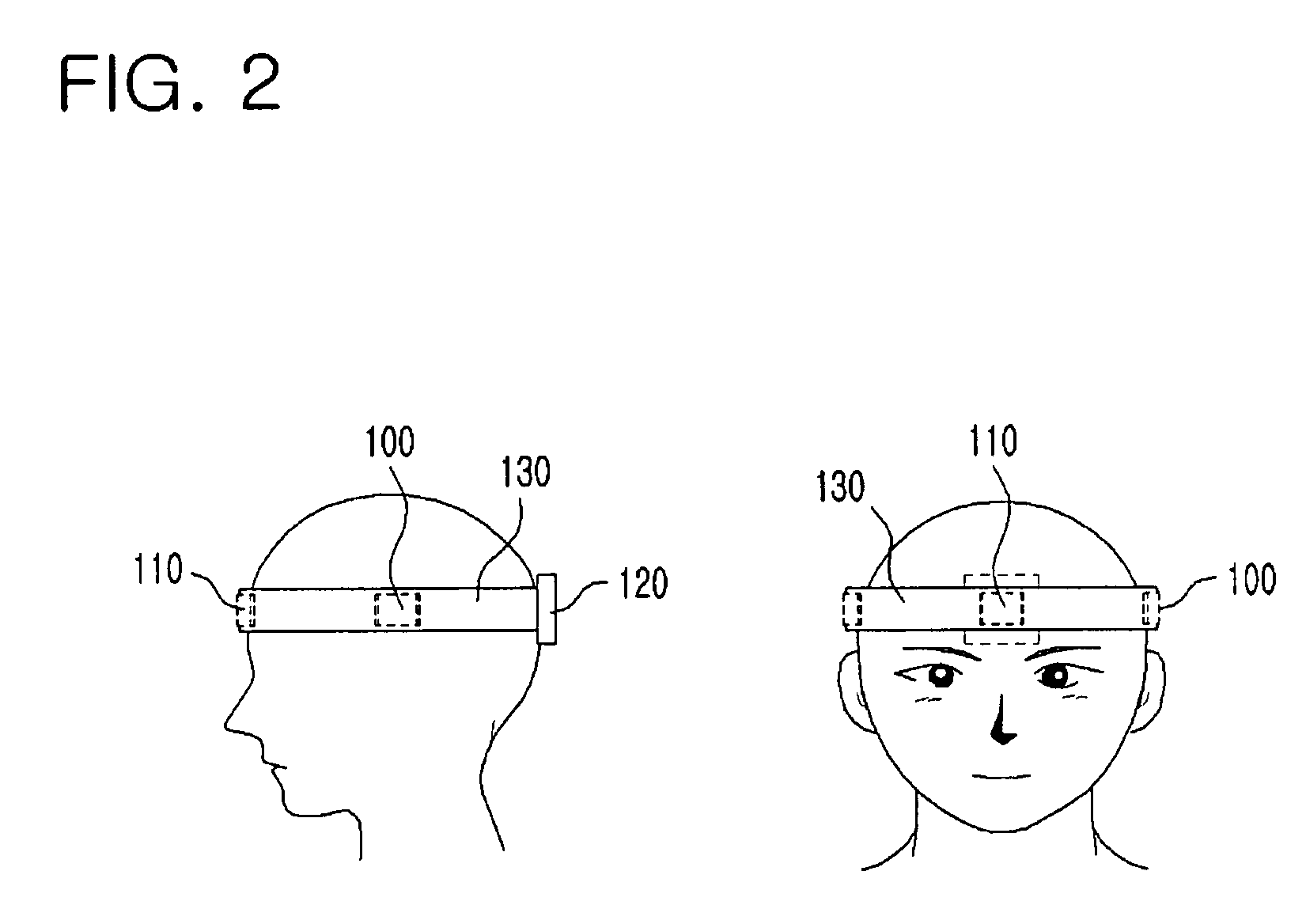
InactiveUS20070164985A1Minimize discomfortData processing applicationsTeeth fillingClenching teethPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
An apparatus and method for selecting and outputting characters by making a teeth clenching motion for disabled person are disclosed. The apparatus includes: an electromyogram signal obtaining unit including electromyogram sensors disposed at both sides for generating an electromyogram signal according to a predetermined muscle activated when a disabled person clenches teeth, and a ground electrode connected to a body of the disabled persons for providing a reference voltage; and an electromyogram signal processing unit for outputting a character by identifying a teeth clenching motion pattern of each block according to a side of teeth clenched, a duration of clenching teeth and consecutive clenching motions through analyzing the obtained electromyogram and selecting characters according to the identified teeth clenching motion pattern.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Virtual blaster
Embodiments provide techniques for automating control of electronic device. A first interactive game playing within the physical environment using one or more electronic devices is detected. Embodiments collect electromyogram data from one or more electromyography sensors within the physical environment and analyze the electromyogram data collected to determine muscle activations made by the user. Upon determining that the determined muscle activations made by the user match a predefined pattern of electromyography data, embodiments determine a gameplay action corresponding to the predefined pattern of electromyography data and transmit an instruction, to at least one of the one or more electronic devices within the physical environment, instructing the electronic device to perform the determined gameplay action.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
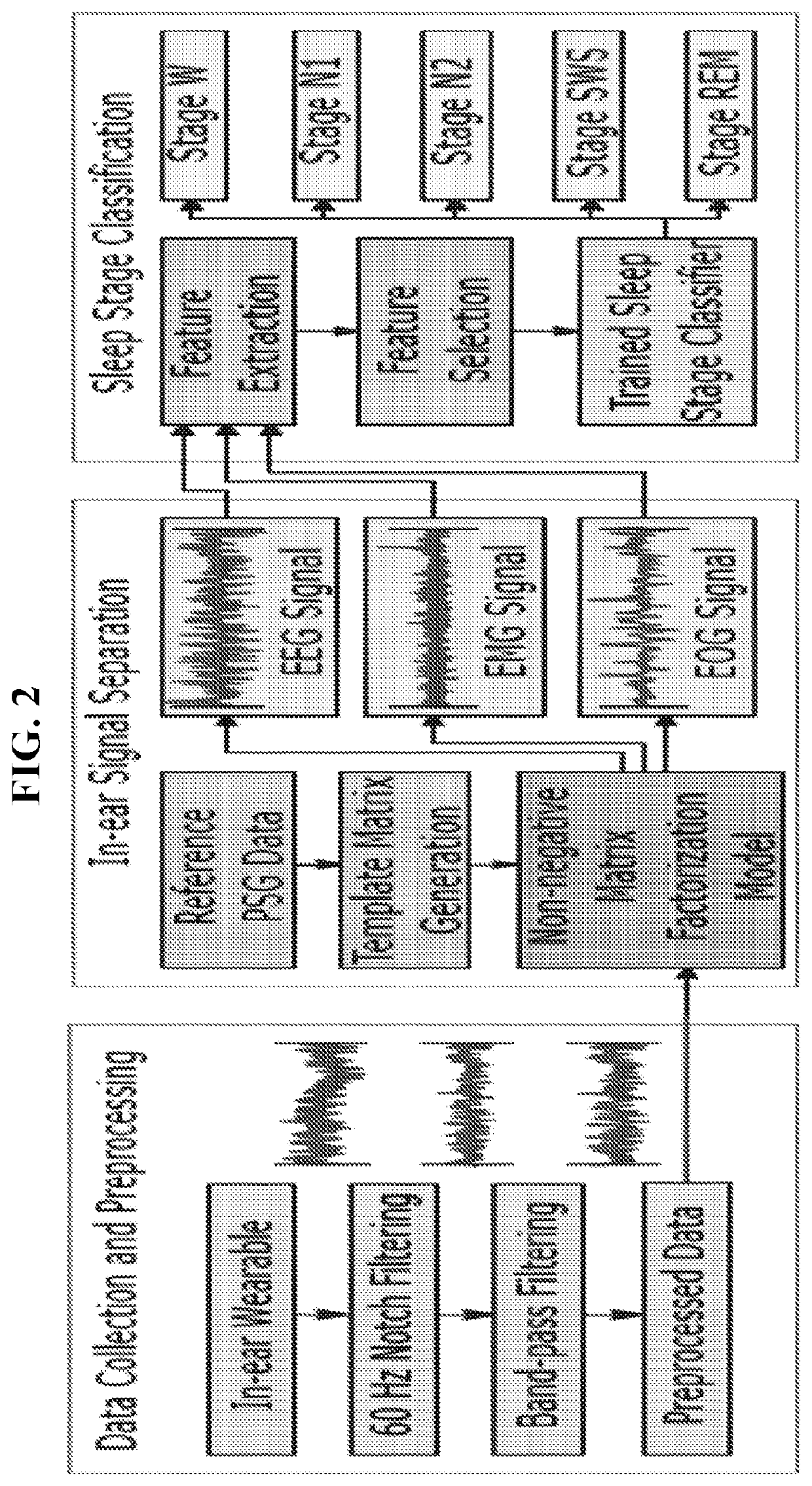
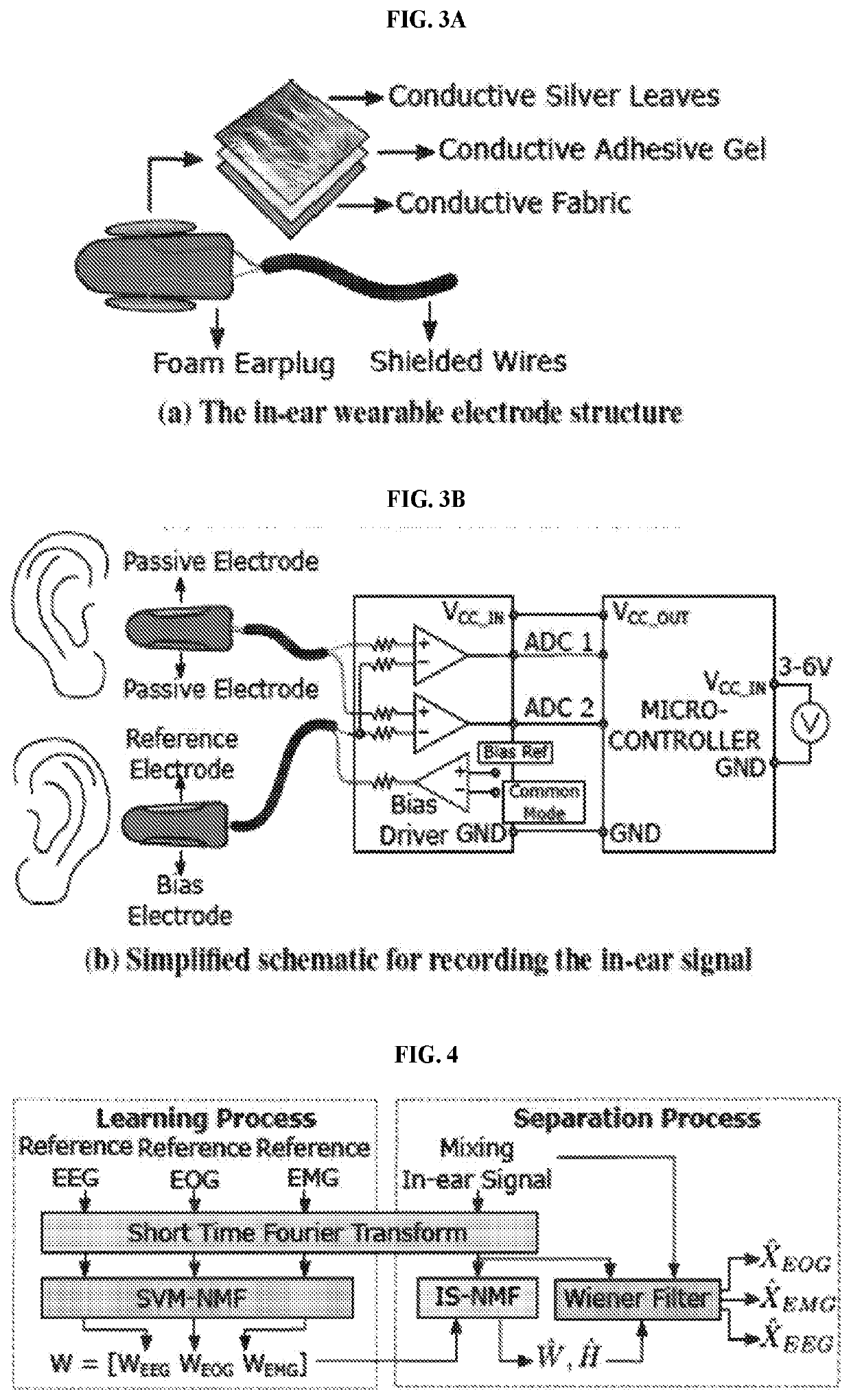
In-ear sensing systems and methods for biological signal monitoring
ActiveUS20200085369A1ElectroencephalographyMedical data miningElectro encephalogramBiological signaling
The present invention provides a light-weight wearable sensor that can capture electroencephalogram (EEG or brain signals), electromyography (EMG or muscle signal), and electrooculography (EOG or eye movement signal) using a pair of modified off-the-shelf earplugs. The present invention further provides a supervised non-negative matrix factorization learning algorithm to analyze and extract these signals from the mixed signal collected by the sensor. The present invention further provides an autonomous and whole-night sleep staging system utilizing the sensor's outputs.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
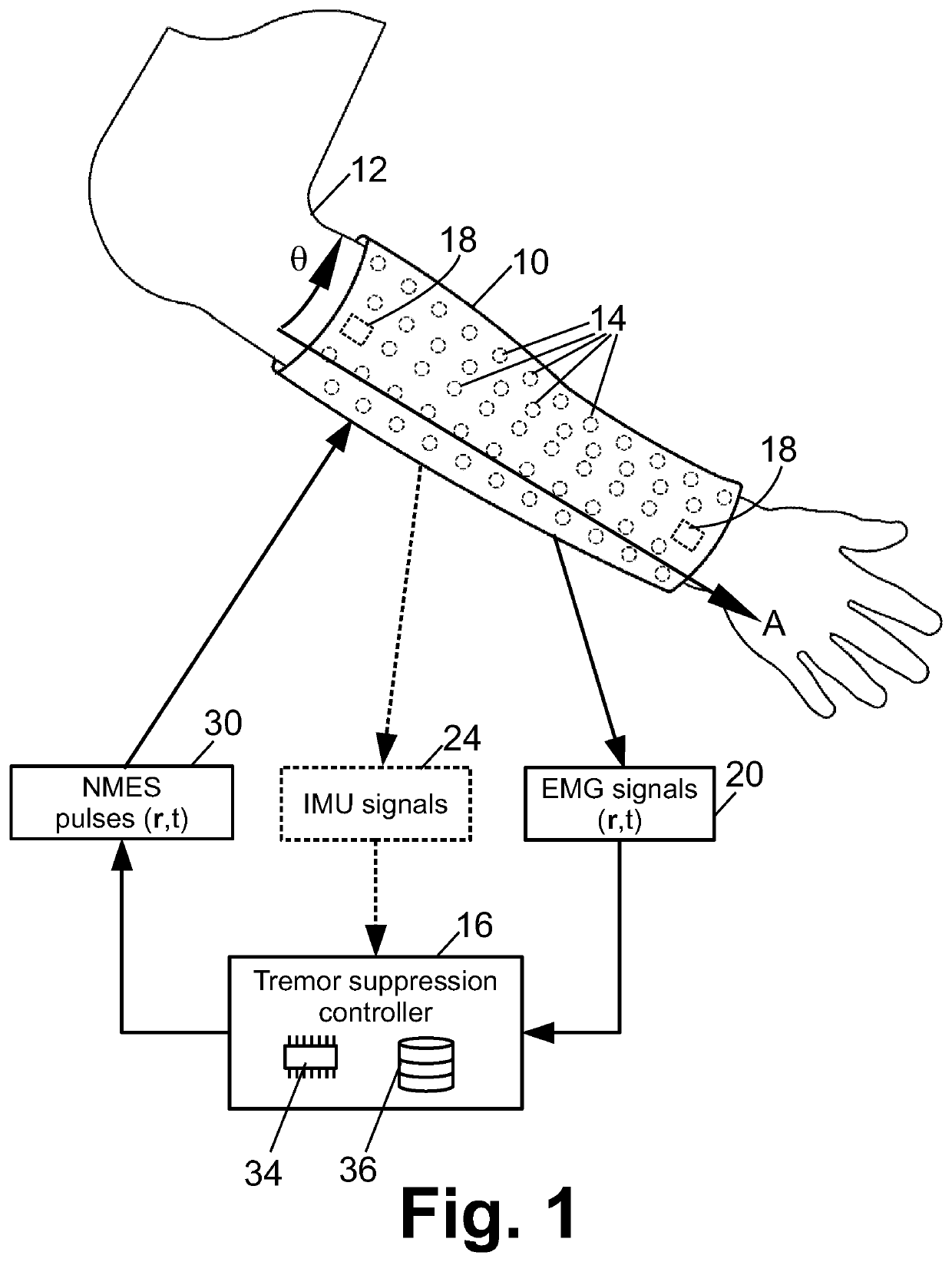
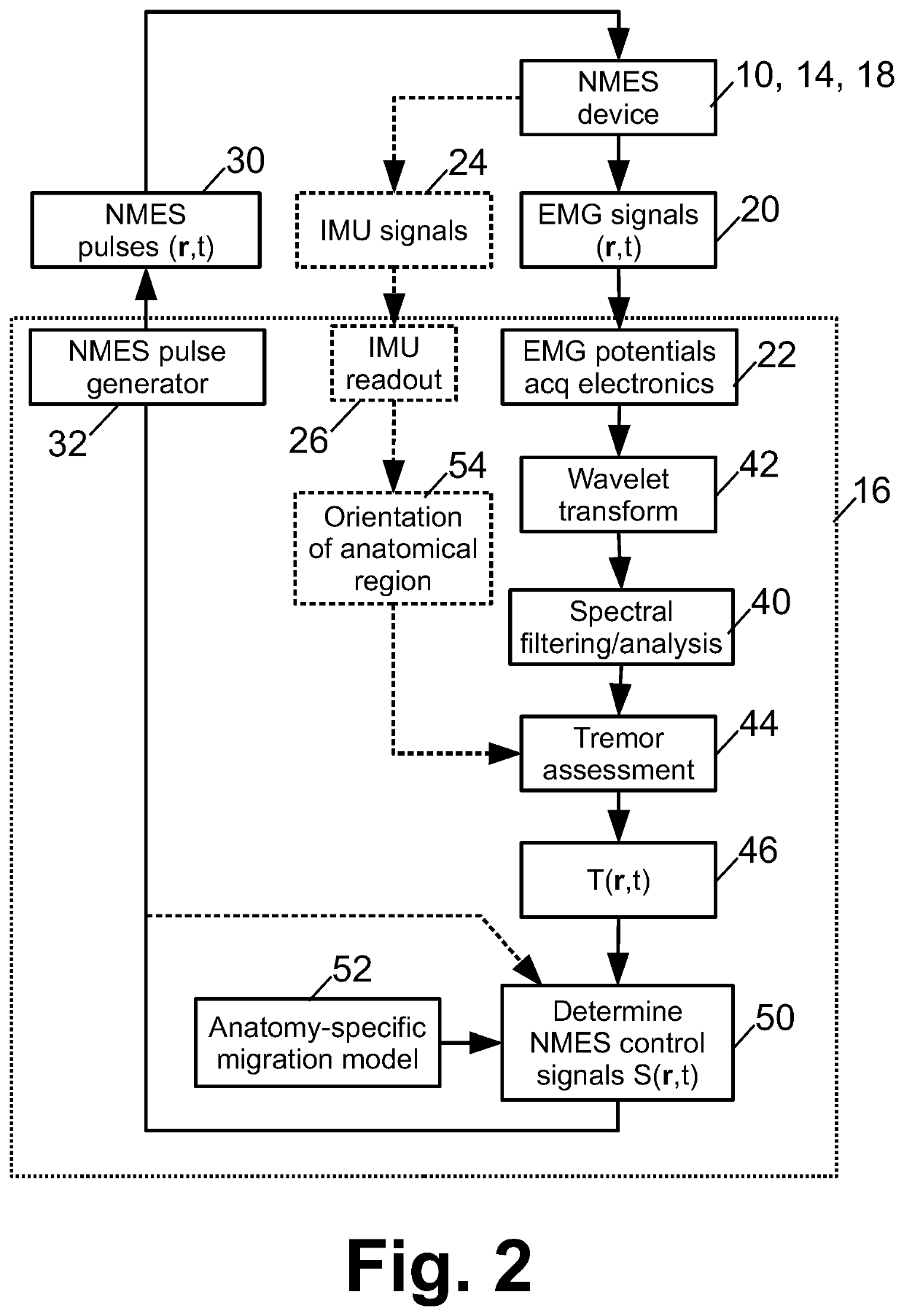
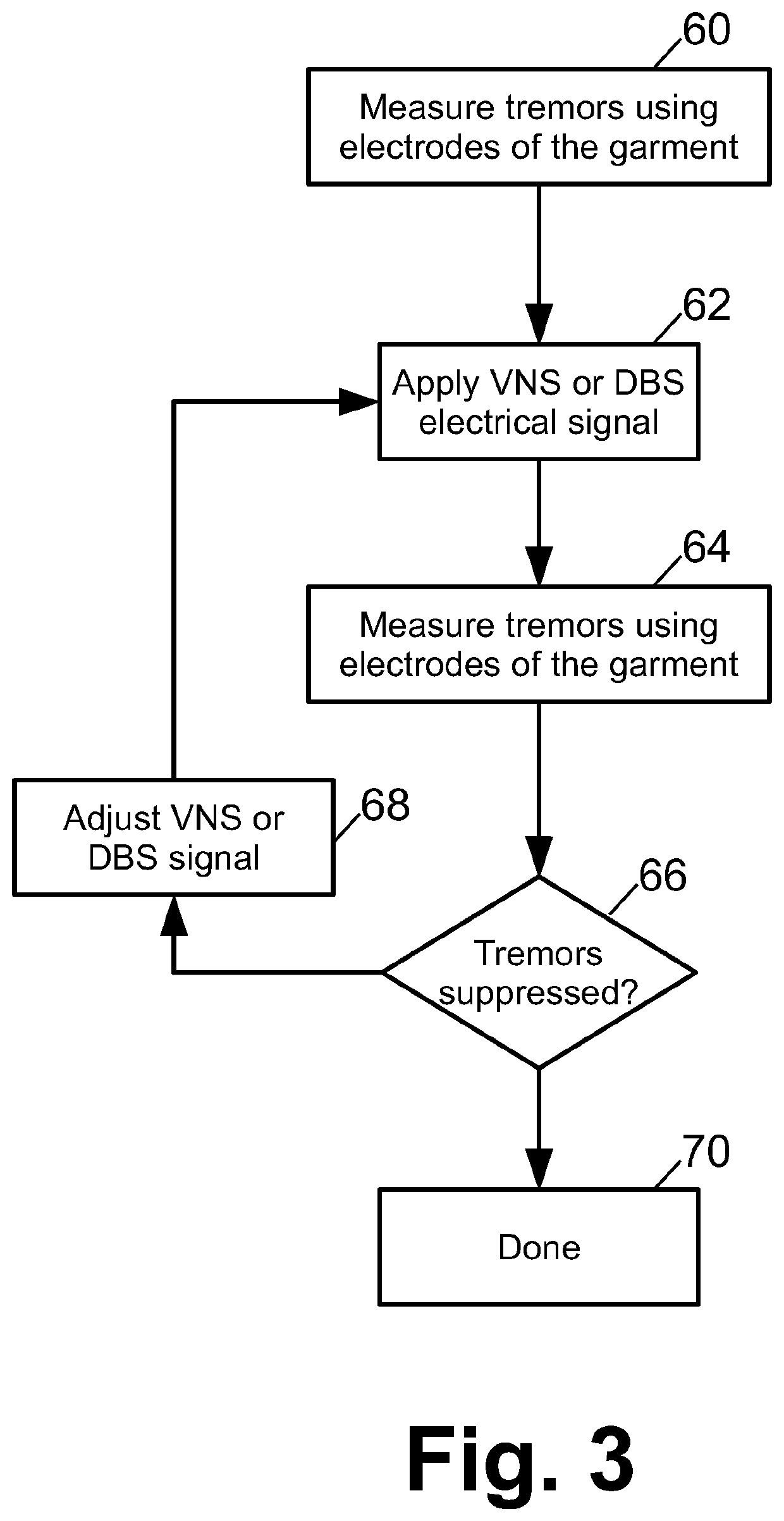
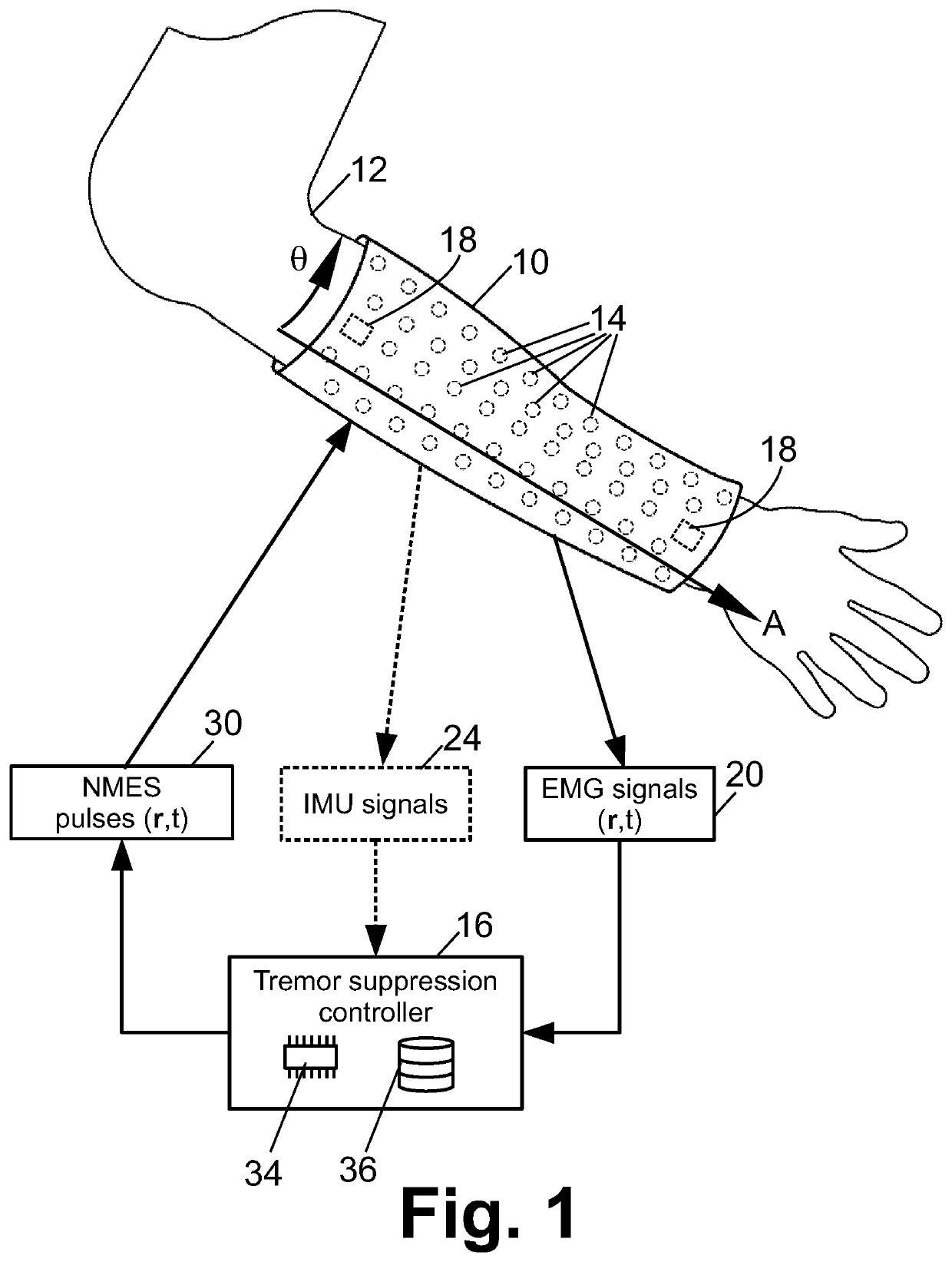
Neurosleeve for closed loop emg-fes based control of pathological tremors
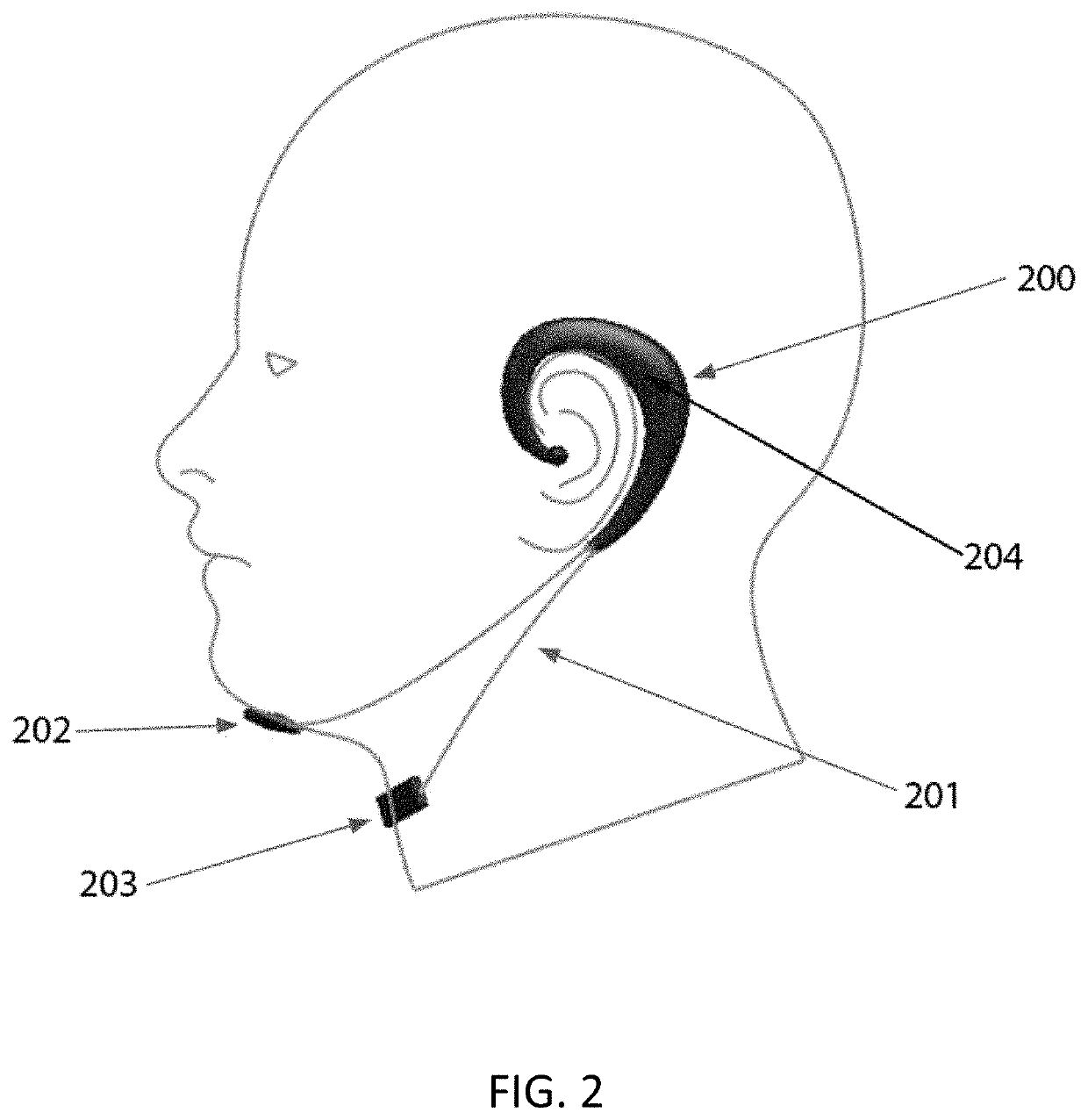
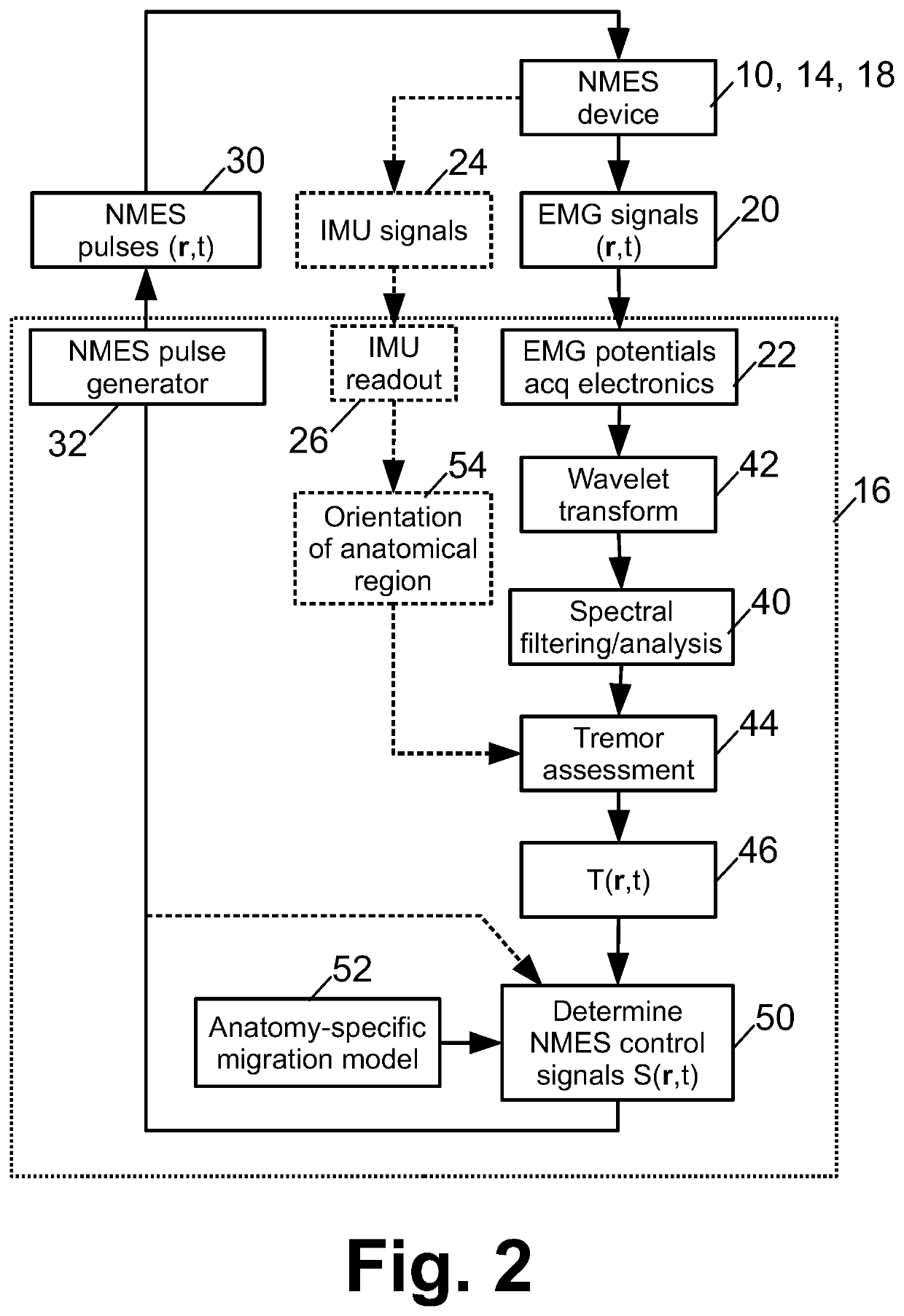
A tremor suppression device includes a garment wearable on an anatomical region and including electrodes contacting the anatomical region when the garment is worn on the anatomical region, and an electronic controller configured to: detect electromyography (EMG) signals as a function of anatomical location and time using the electrodes; identify tremors as a function of anatomical location and time based on the EMG signals; and apply neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) at one or more anatomical locations as a function of time using the electrodes to suppress the identified tremors.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
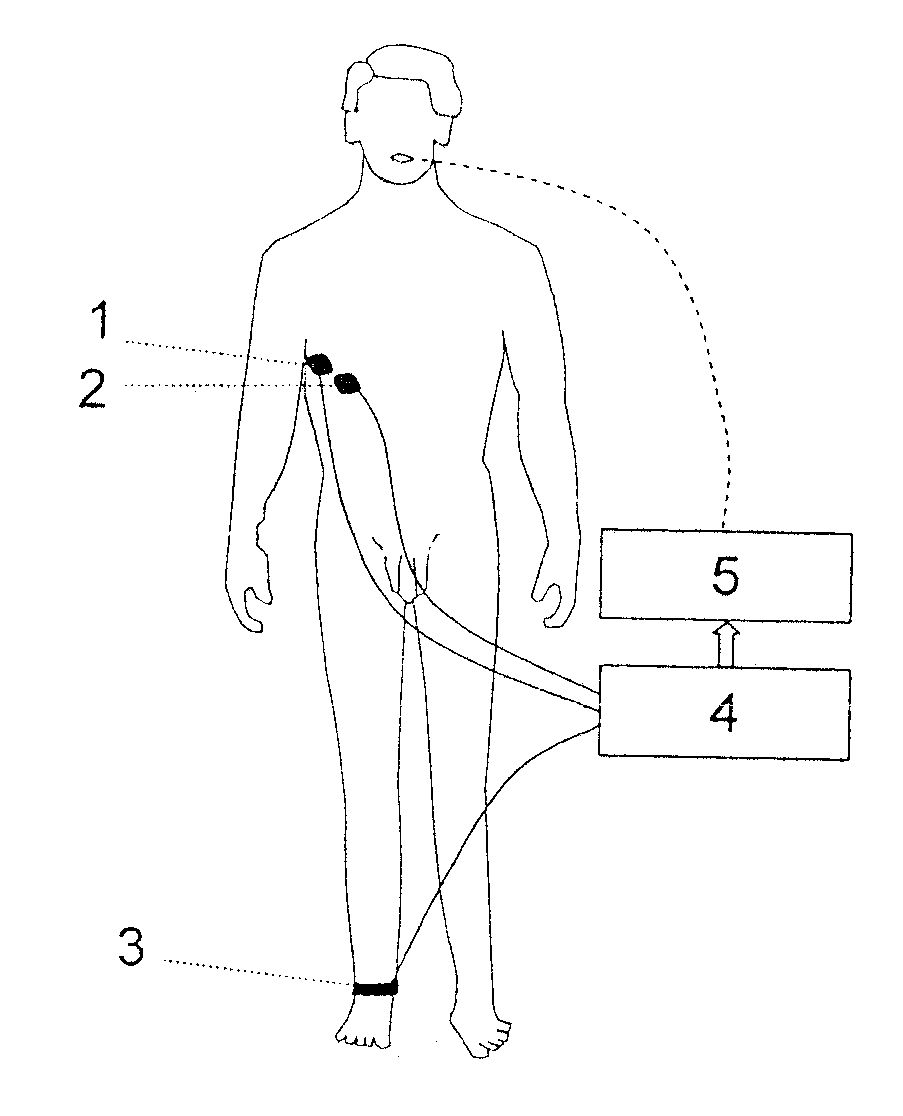
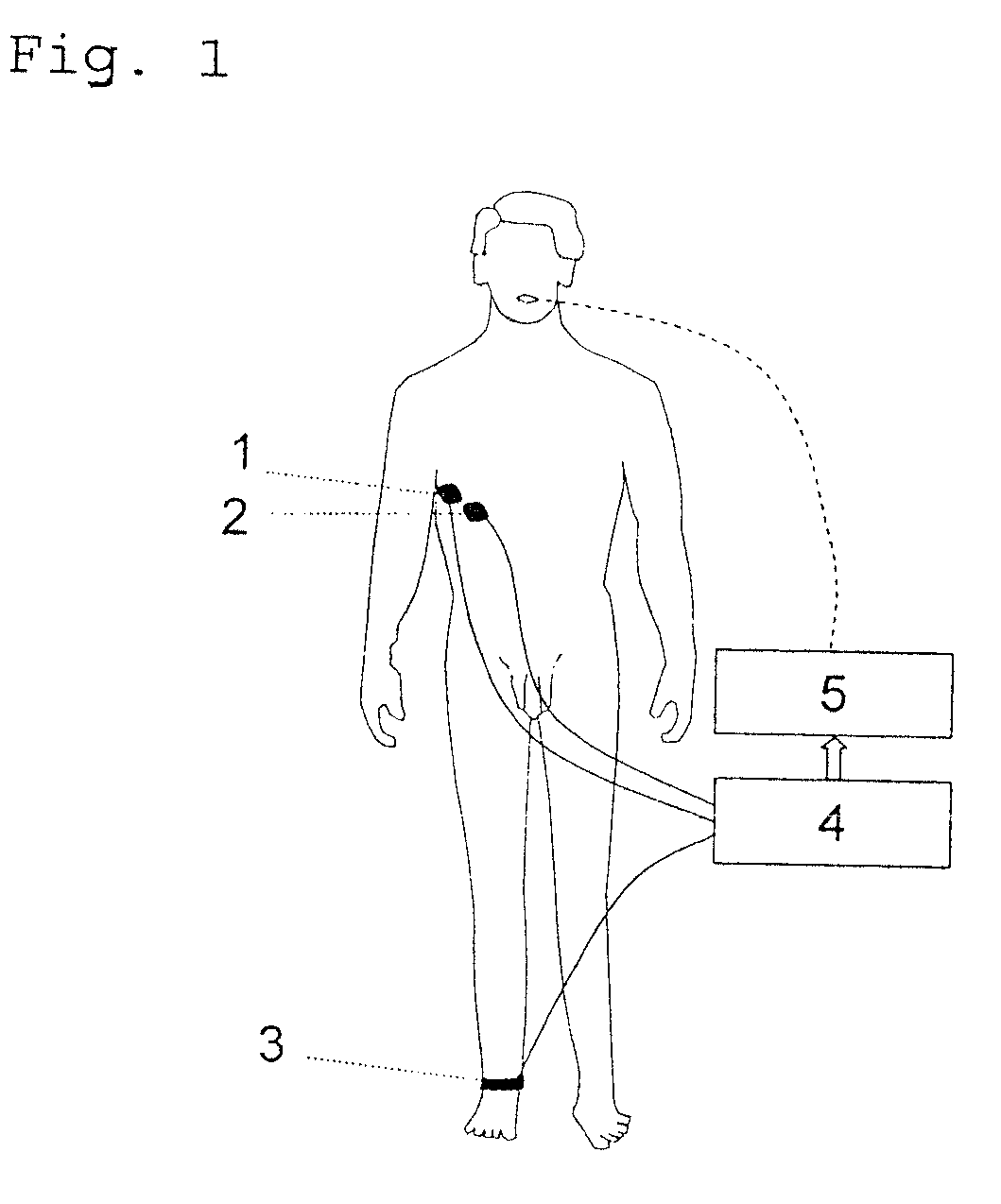
Method of automatically controlling a respiration system and a corresponding respirator
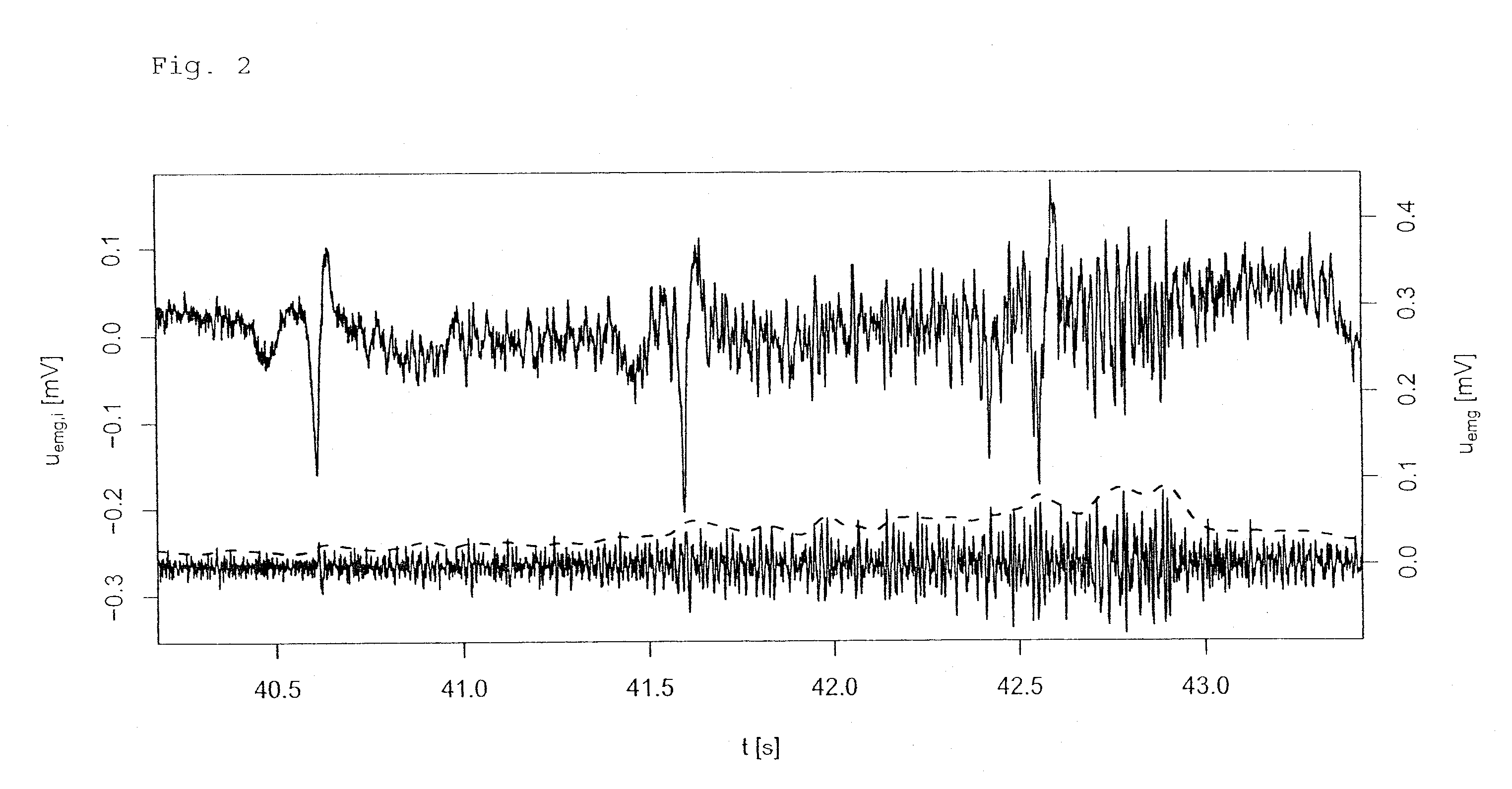
ActiveUS8109269B2Convenient for patientAccurate operationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory muscleAutomatic control
A method of automatically controlling a respiration system for proportional assist ventilation with a control device and with a ventilator. An electrical signal is recorded by electromyography with electrodes on the chest in order to obtain a signal uemg(t) representing the breathing activity. The respiratory muscle pressure pmus(t) is determined by calculating it in the control unit from measured values for the airway pressure and the volume flow Flow(t) as well as the patient's lung mechanical parameters. The breathing activity signal uemg(t) is transformed by means of a preset transformation rule into a pressure signal pemg(uemg)(t)) such that the mean deviation of the resulting transformed pressure signal pemg(t) from the respiratory muscle pressure pmus(t) is minimized. The respiratory effort pressure ppat(t) is determined as a weighted mean according to ppat(t)=a·pmus(t)+(1−a)·pemg(t), where a is a parameter selected under the boundary condition 0≦a≦1.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
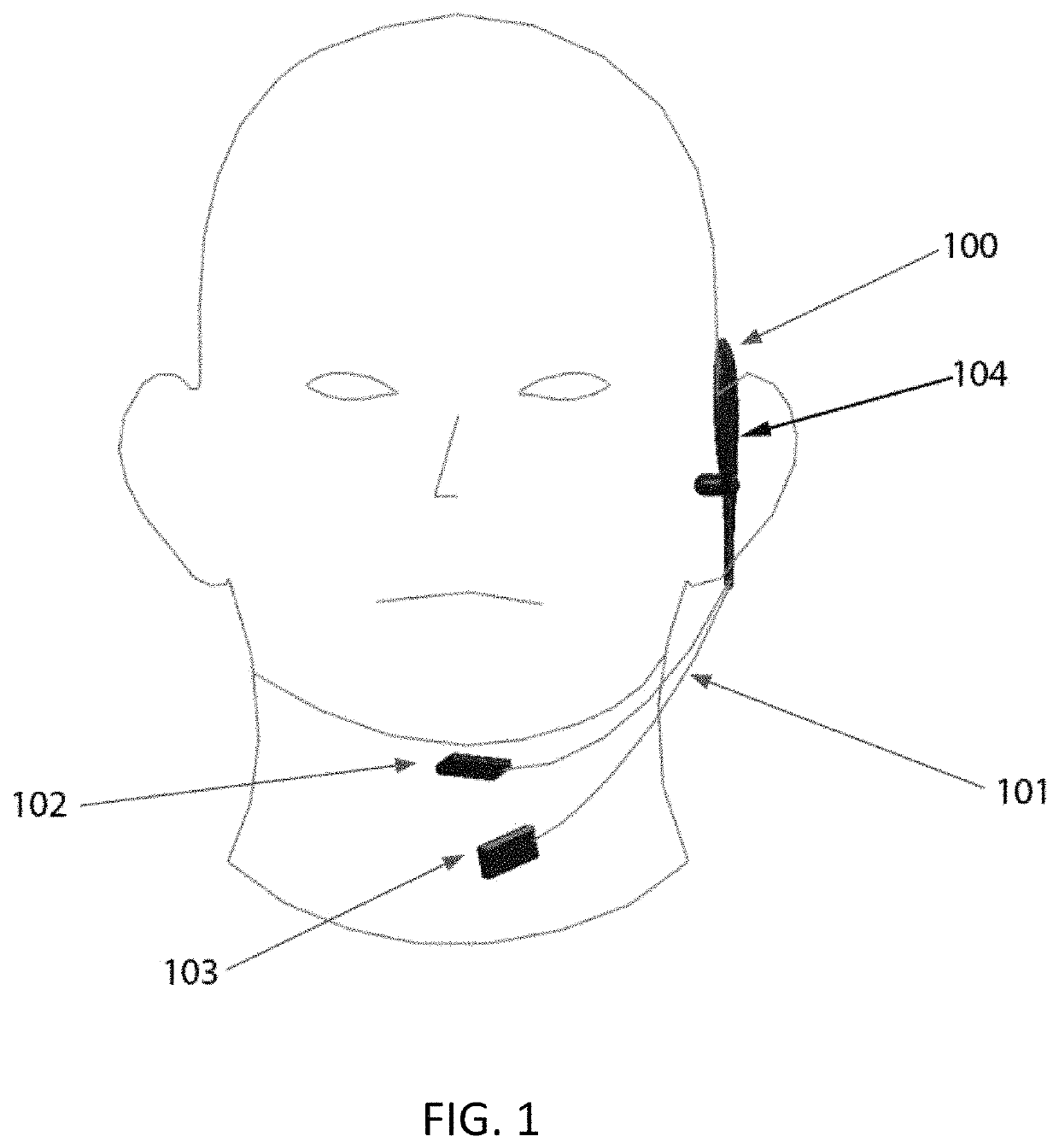
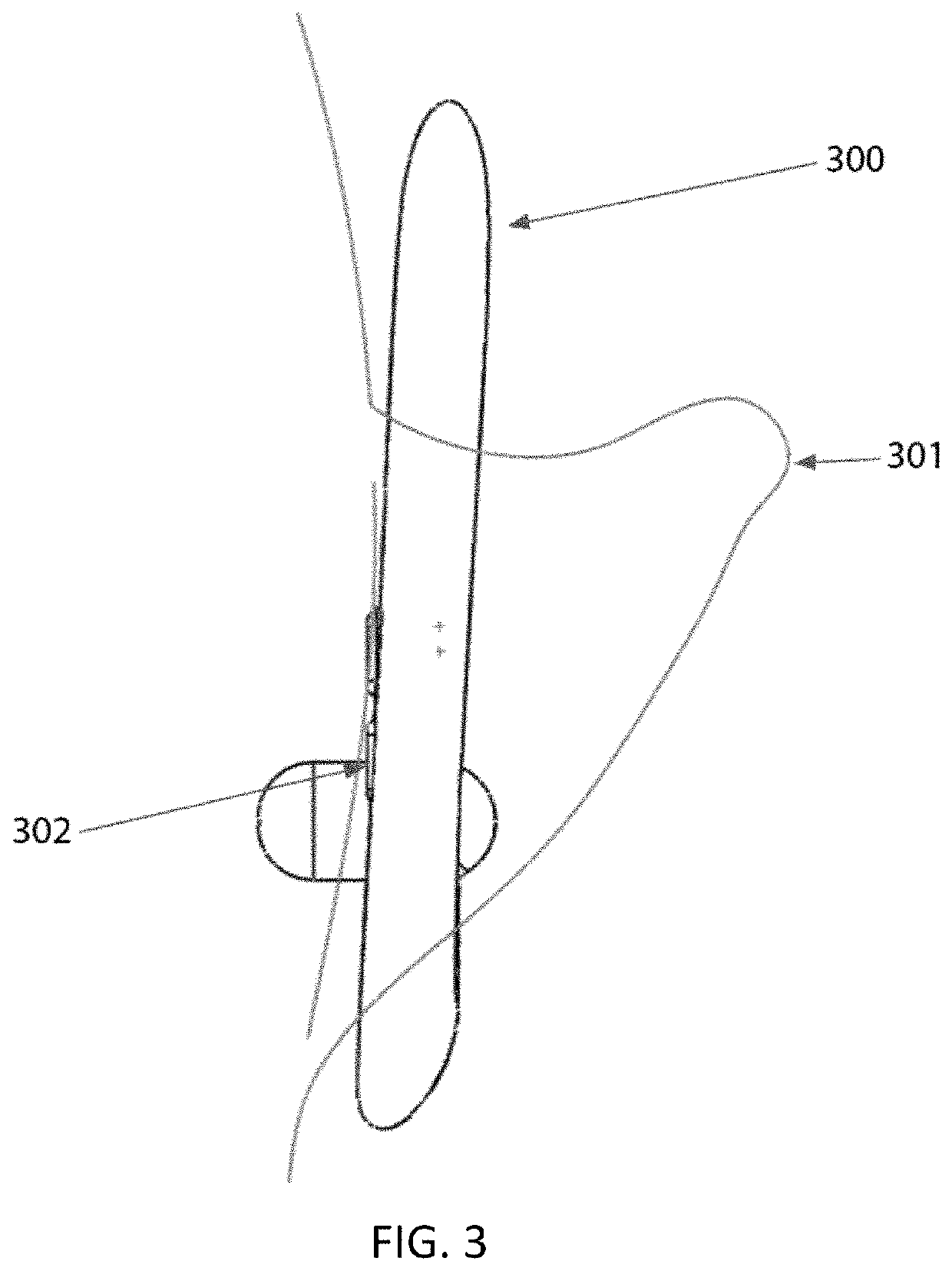
Sub-vocal speech recognition apparatus and method
A sub-vocal speech recognition (SVSR) apparatus includes a headset that is worn over an ear and electromyography (EMG) electrodes and an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in contact with a user's skin in a position over the neck, under the chin and behind the ear. When a user speaks or mouths words, the EMG and IMU signals are recorded by sensors and amplified and filtered, before being divided in multi-millisecond time windows. These time windows are then transmitted to the interface computing device for Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) conversion into aggregated vector representation (AVR). The AVR is the input to the SVSR system, which utilizes a neural network, CTC function, and language model to classify the phoneme. The phonemes are then combined into words and sent back to the interface computing device, where they are played either as audible output, such as from a speaker, or non-audible output, such as text.
Owner:MCVICKER RYAN
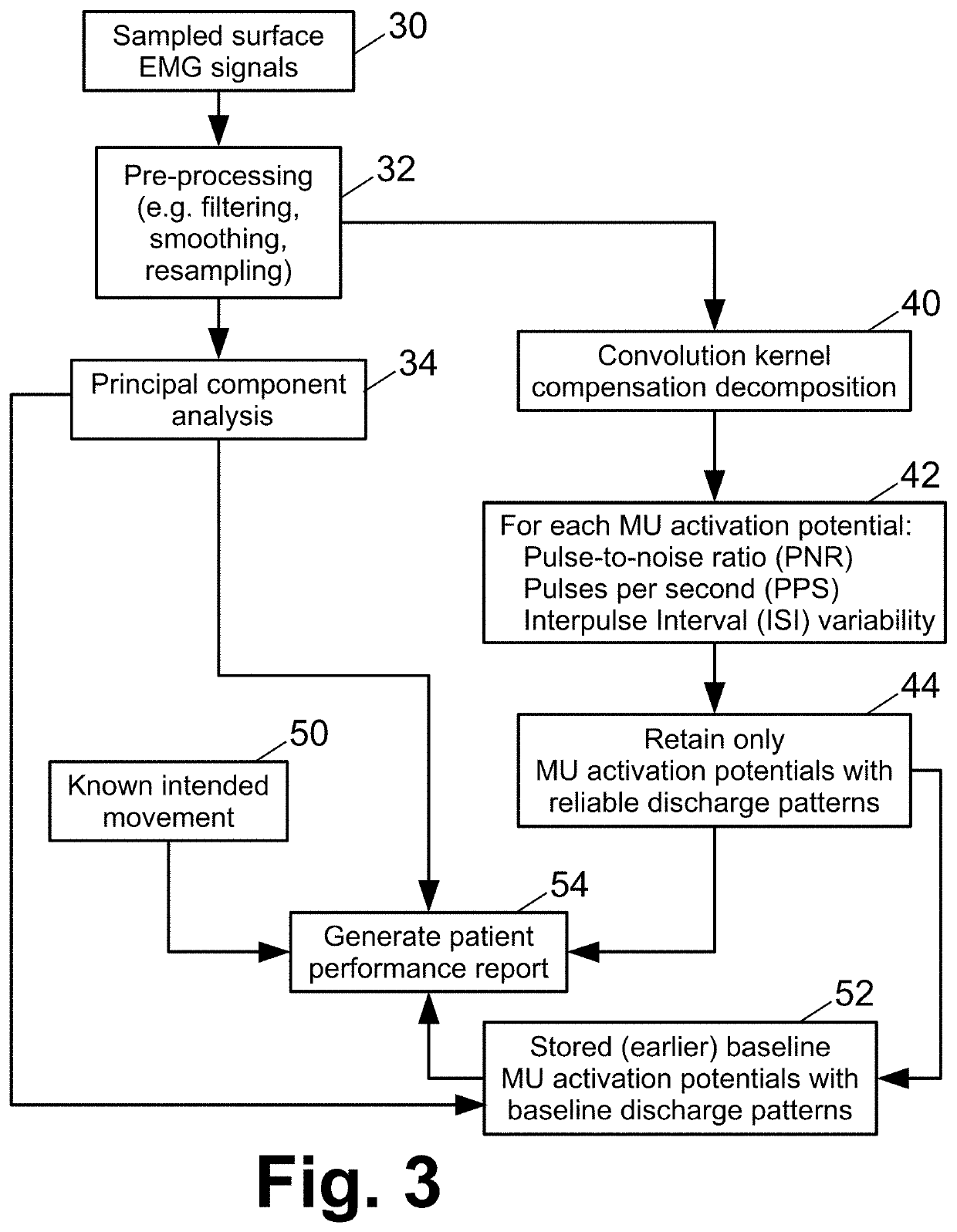
Control of functional electrical stimulation using motor unit action potentials
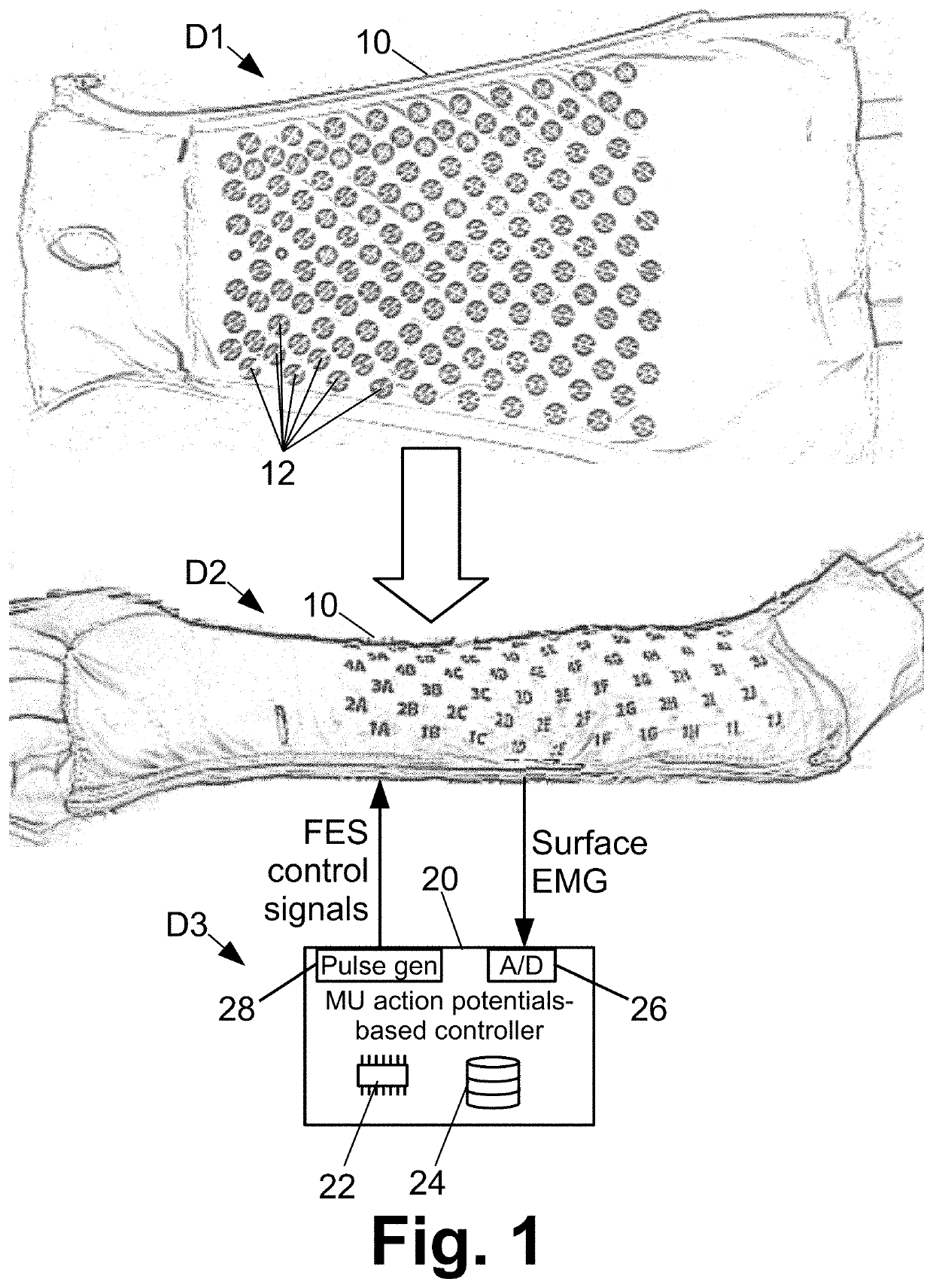
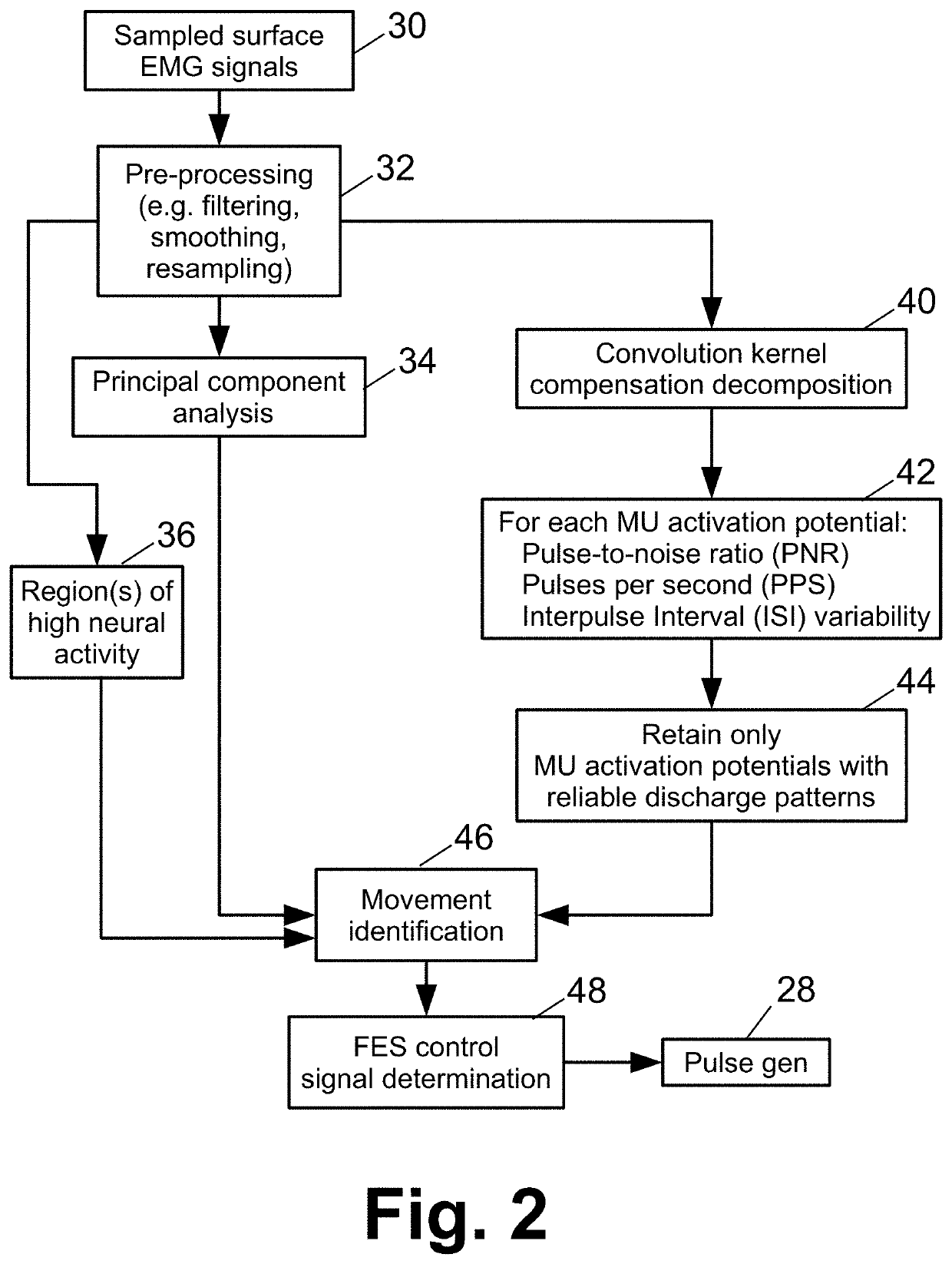
ActiveUS20200406035A1Efficient implementationPhysical therapies and activitiesDiagnostic recording/measuringElectronic controllerElectro stimulation
A therapeutic or diagnostic device comprises a wearable electrodes garment including electrodes disposed to contact skin when the wearable electrodes garment is worn, and an electronic controller operatively connected with the electrodes. The electronic controller is programmed to perform a method including: receiving surface electromyography (EMG) signals via the electrodes and extracting one or more motor unit (MU) action potentials from the surface EMG signals. The method may further include identifying an intended movement based at least on features representing the one or more extracted MU action potentials and delivering functional electrical stimulation (FES) effective to implement the intended movement via the electrodes of the wearable electrodes garment. The method may further include generating a patient performance report based at least on a comparison of features representing the one or more extracted MU action potentials and features representing expected and / or baseline MU action potentials for a known intended movement.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
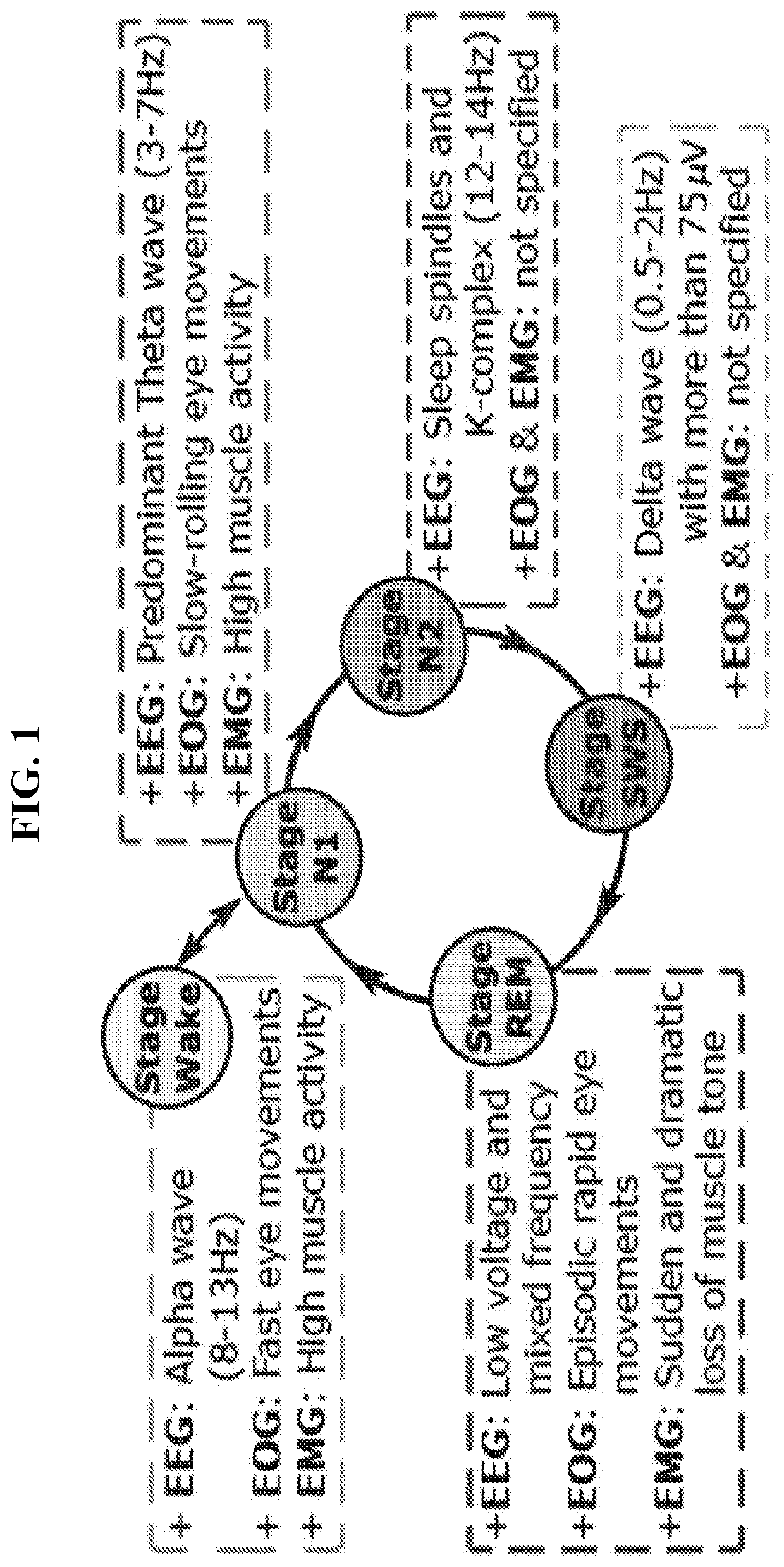
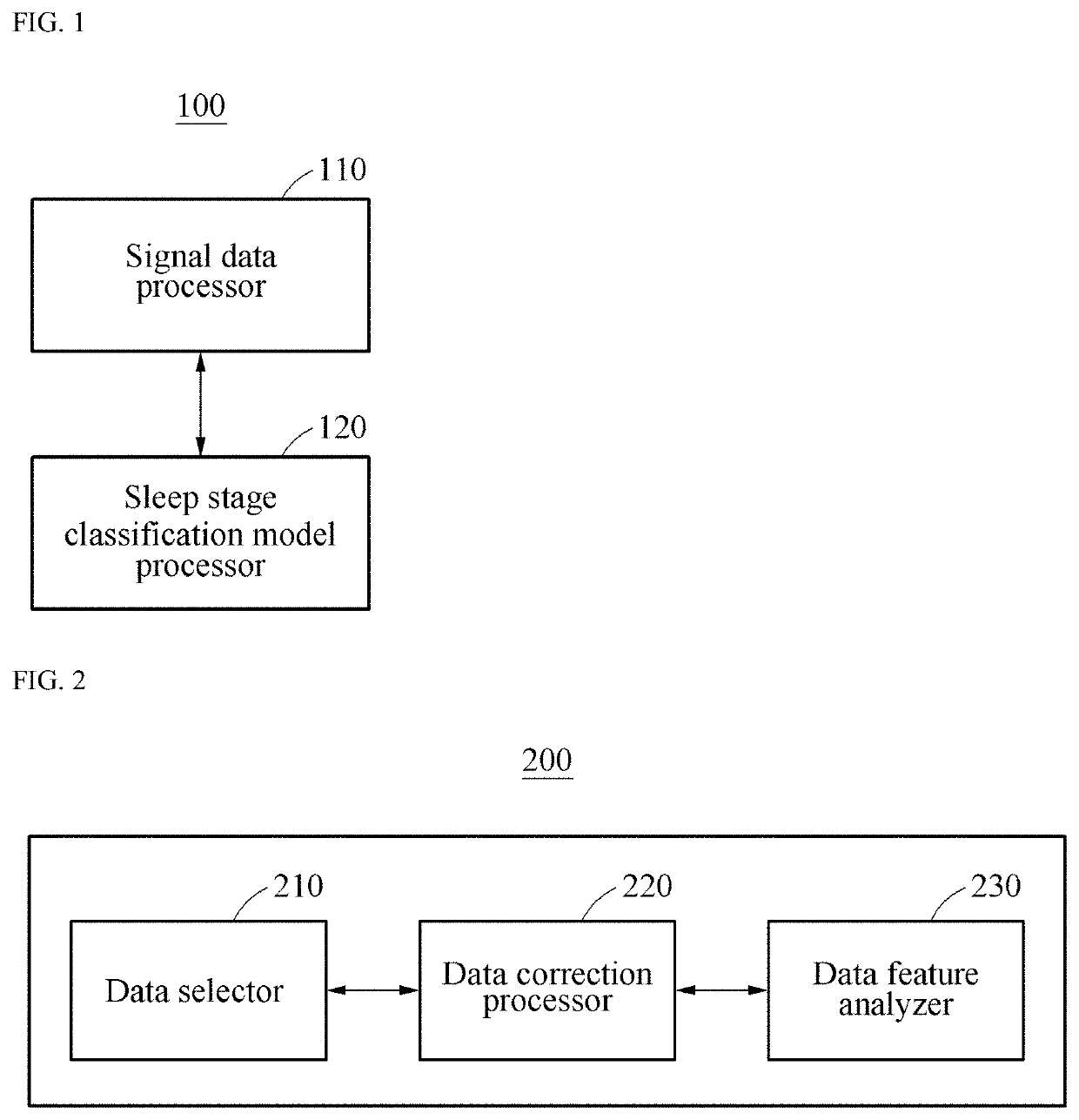
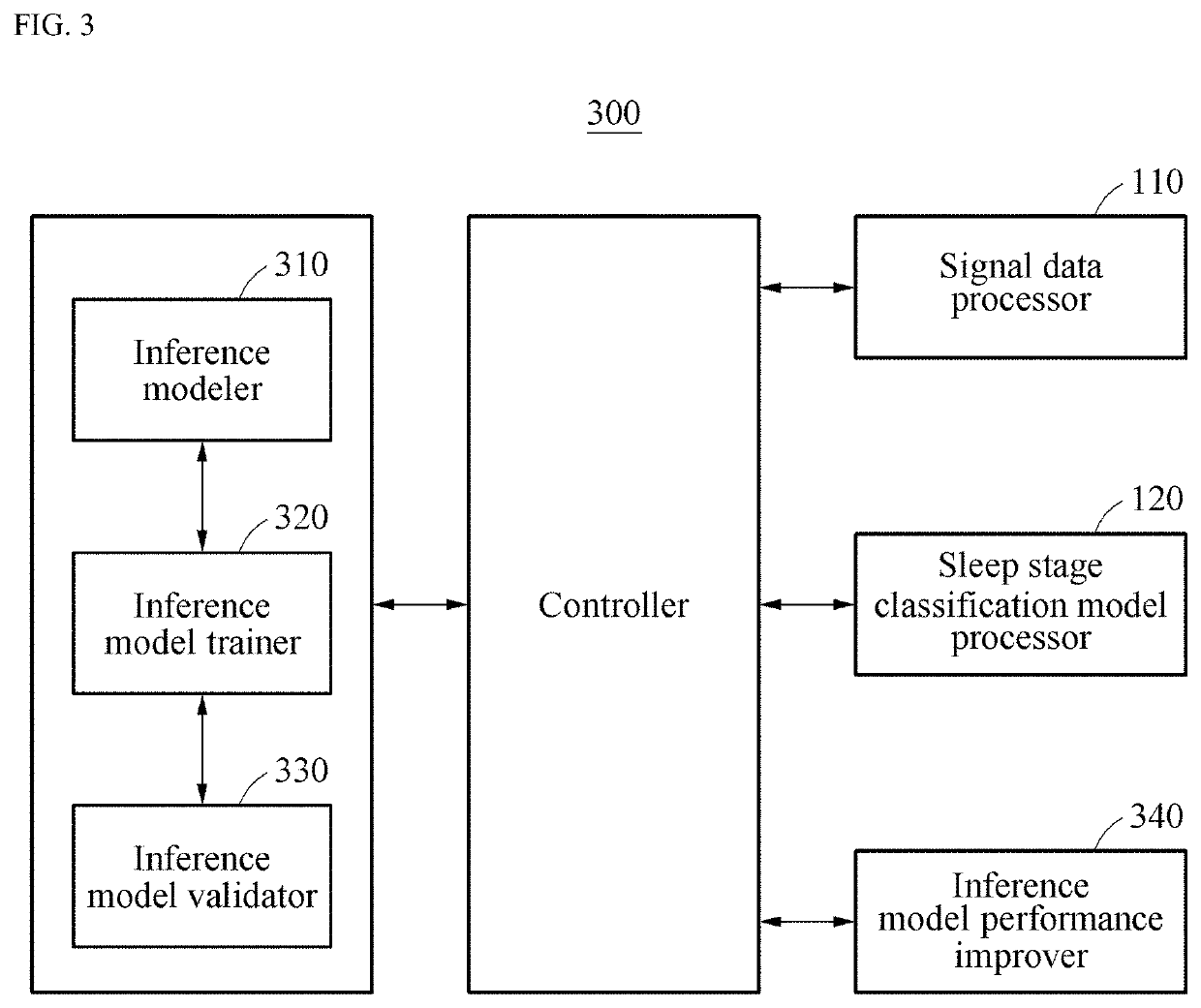
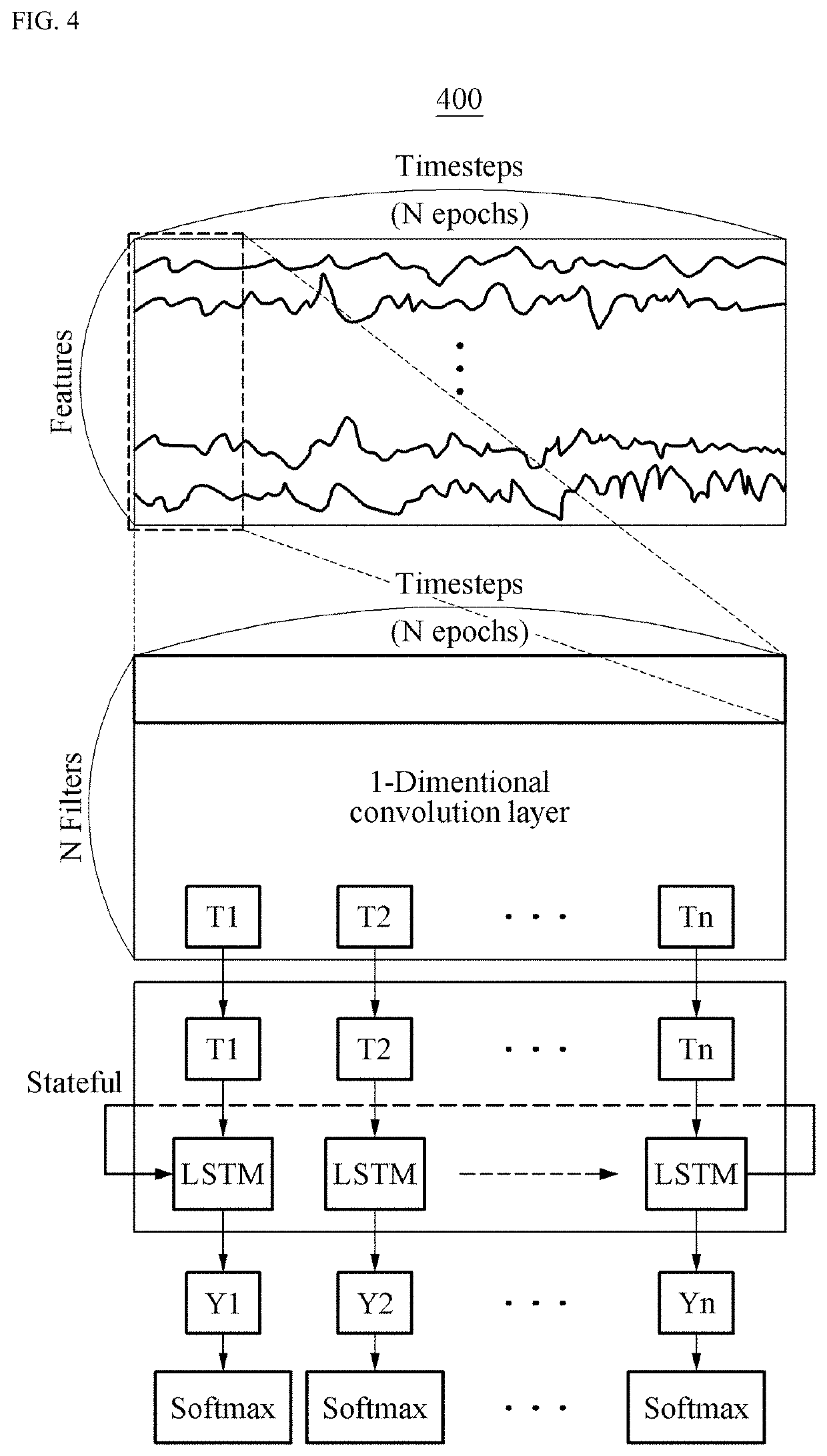
Data processing apparatus for automatically determining sleep disorder using deep running and operation method of the data processing apparatus
Provided is a data processing apparatus including a signal data processor configured to collect signal data detected through polysomnography, to extract feature data by analyzing a feature of the collected signal data, and to transform the extracted feature data to time series data; and a sleep stage classification model processor configured to input the processed signal data to a pre-generated sleep stage classification model, and to classify a sleep stage corresponding to the signal data. The signal data processor is configured to extract feature data by analyzing a feature of each of an electroencephalographic (EEG) signal, an electro-oculographic (EOG) signal, and an electromyographic (EMG) signal with respect to the signal data, and to transform the extracted feature data to an epoch unit of time series data to input the extracted feature data to the pre-generated sleep stage classification model.
Owner:HONEYNAPS CO LTD
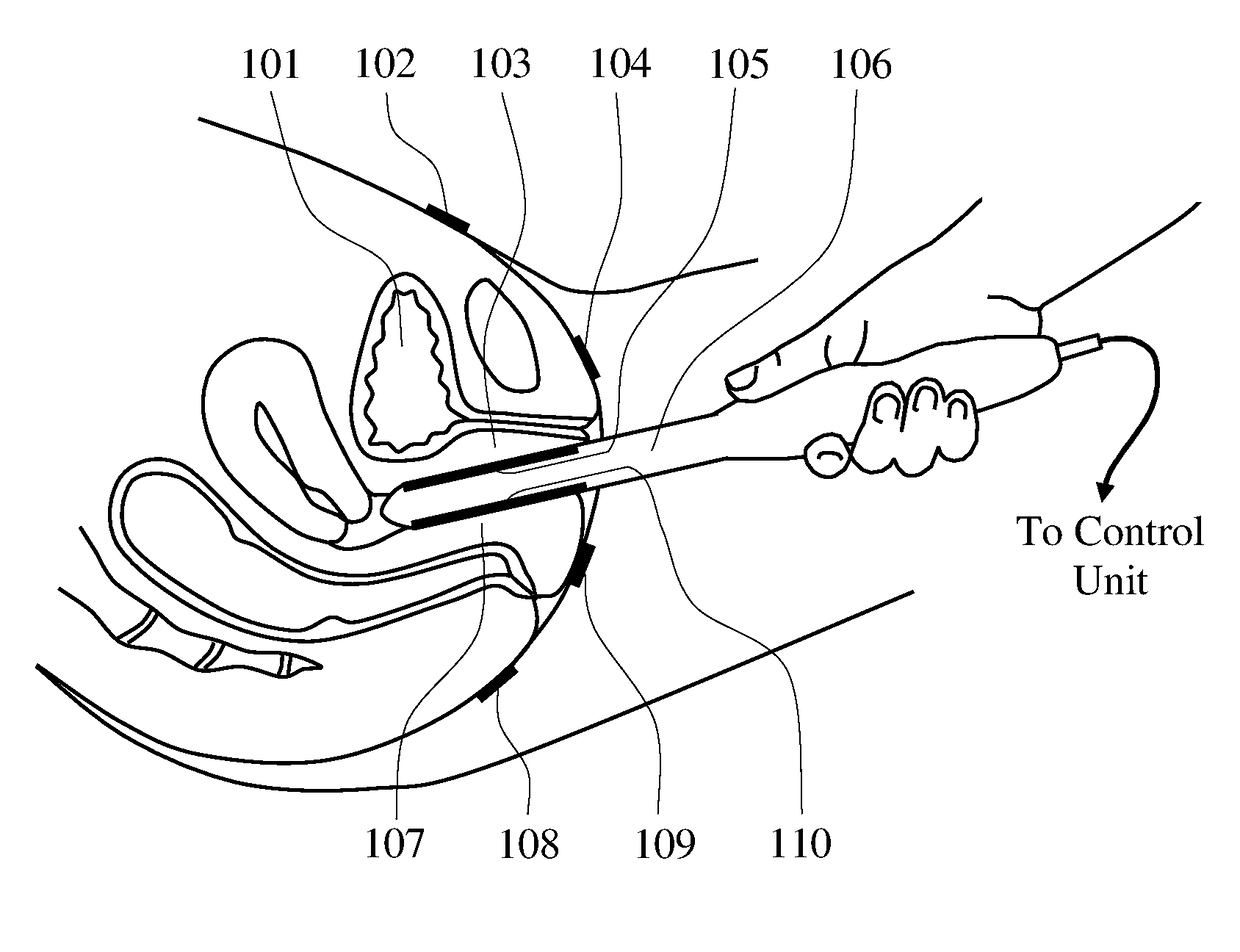
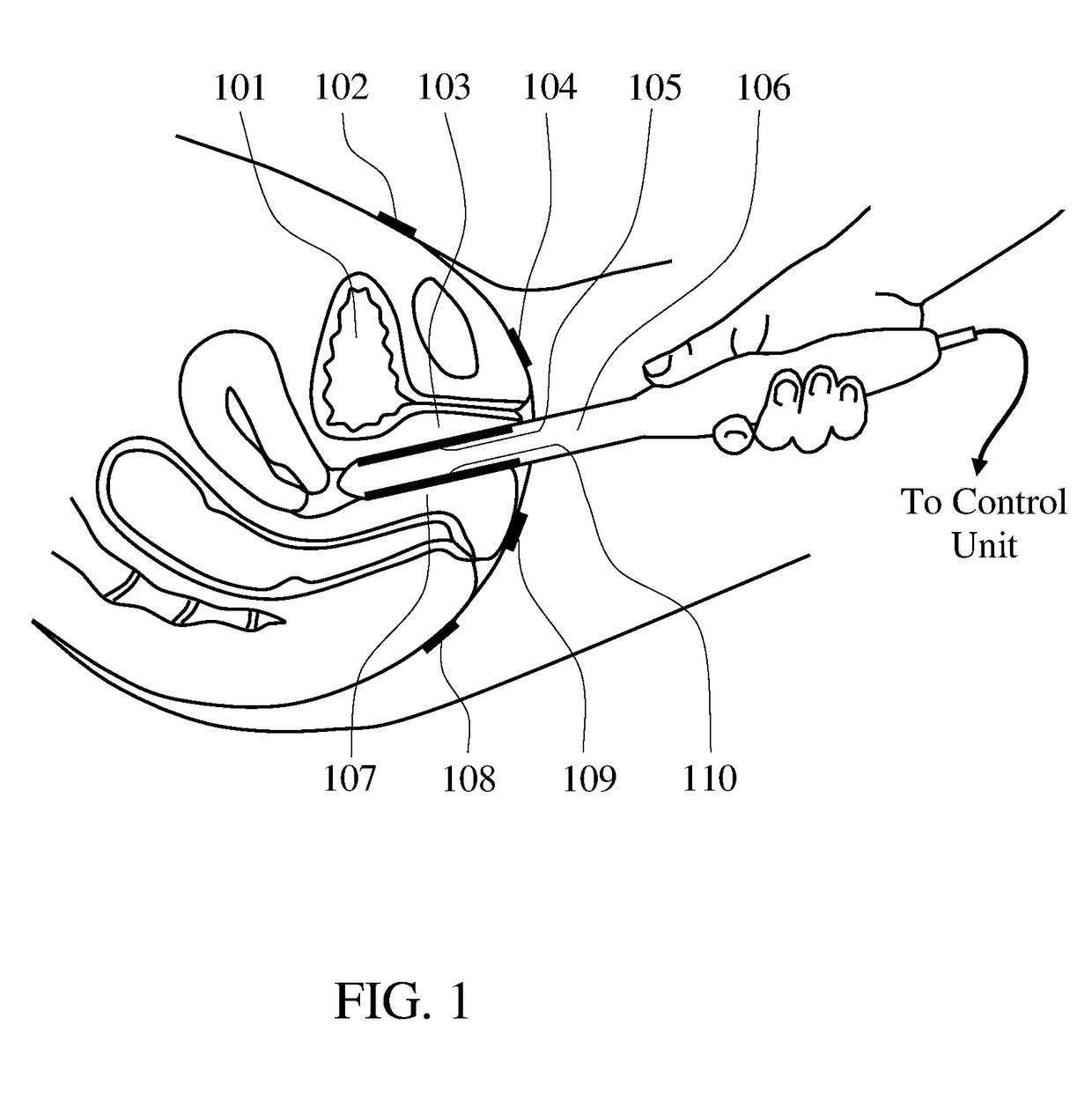
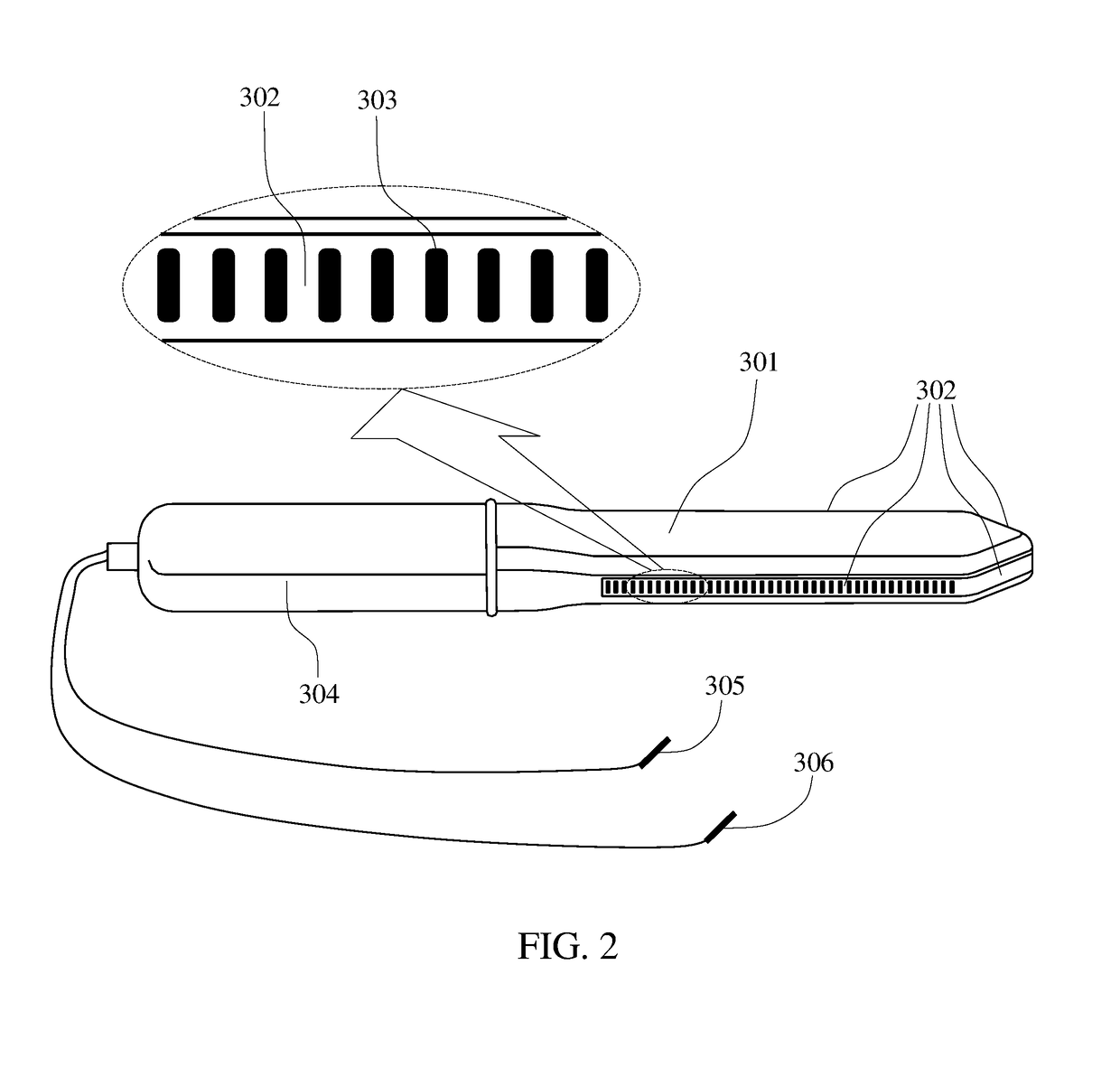
Methods and probes for vaginal tactile and electromyographic imaging and location-guided female pelvic floor therapy
Methods and a probes are disclosed for vaginal tactile and electromyographic imaging, and location-guided female pelvic floor therapy. Methods include the steps of inserting a vaginal probe equipped with tactile sensors and electrodes acting as electromyographic sensors into a vagina along a vaginal canal to separate apart two opposing vaginal walls, recording a tactile response and an electromyographic response from at least one of two opposing vaginal walls during pelvic floor muscle contraction, determining locations along the vaginal canal for delivery of therapy based on presence of tactile response above a predetermined tactile threshold and / or presence of electromyographic response above a predetermined EMG threshold along the vaginal probe, selecting at least one of target locations to be used for location-guided therapy, and applying the therapy such as electrical muscle stimulation to at least one of selected locations using the same electrodes at these locations. The probe comprises a probe housing, a tactile sensors array, a plurality of electrodes which can be used as an electromyography array or as an electric muscle stimulation array, and at least one reference electrode.
Owner:ADVANCED TACTILE IMAGING
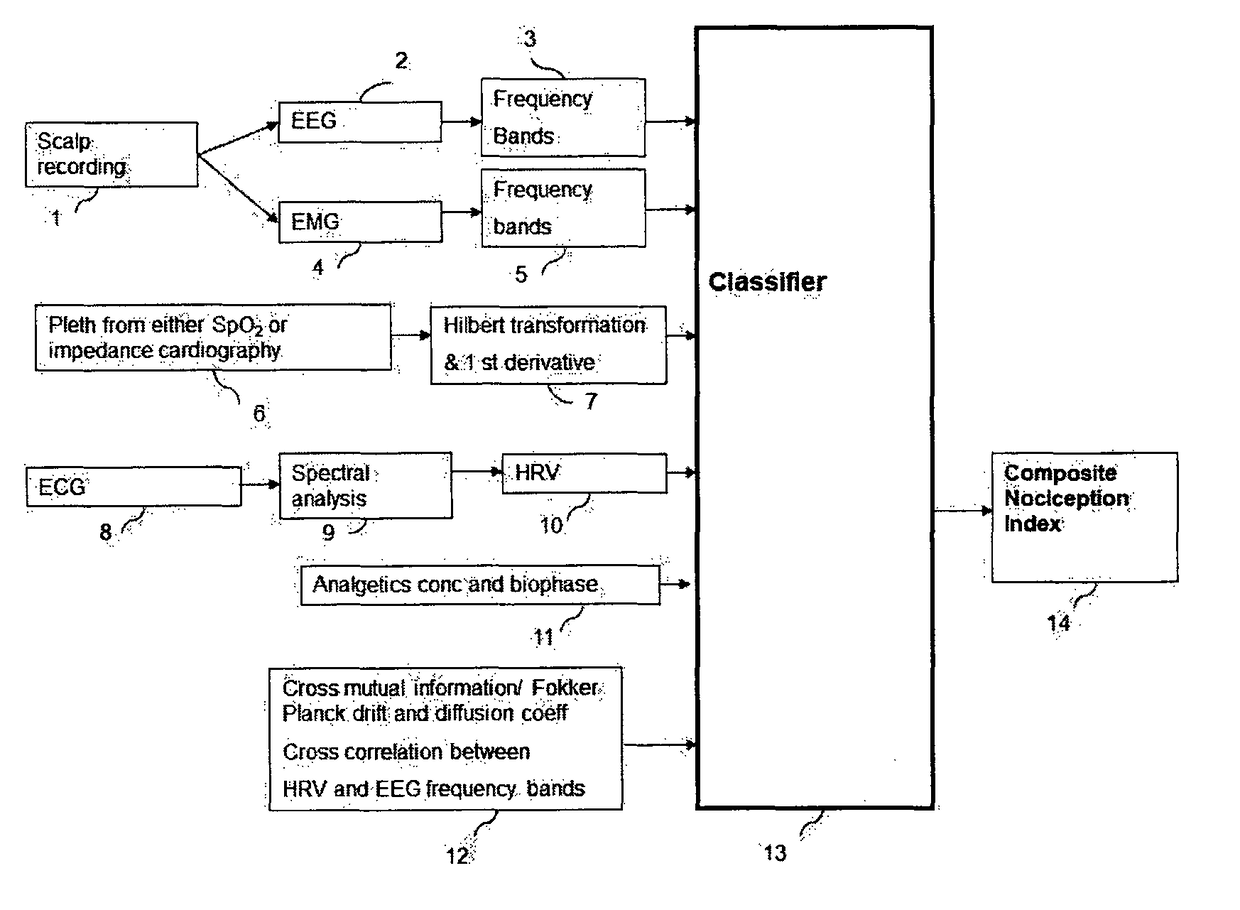
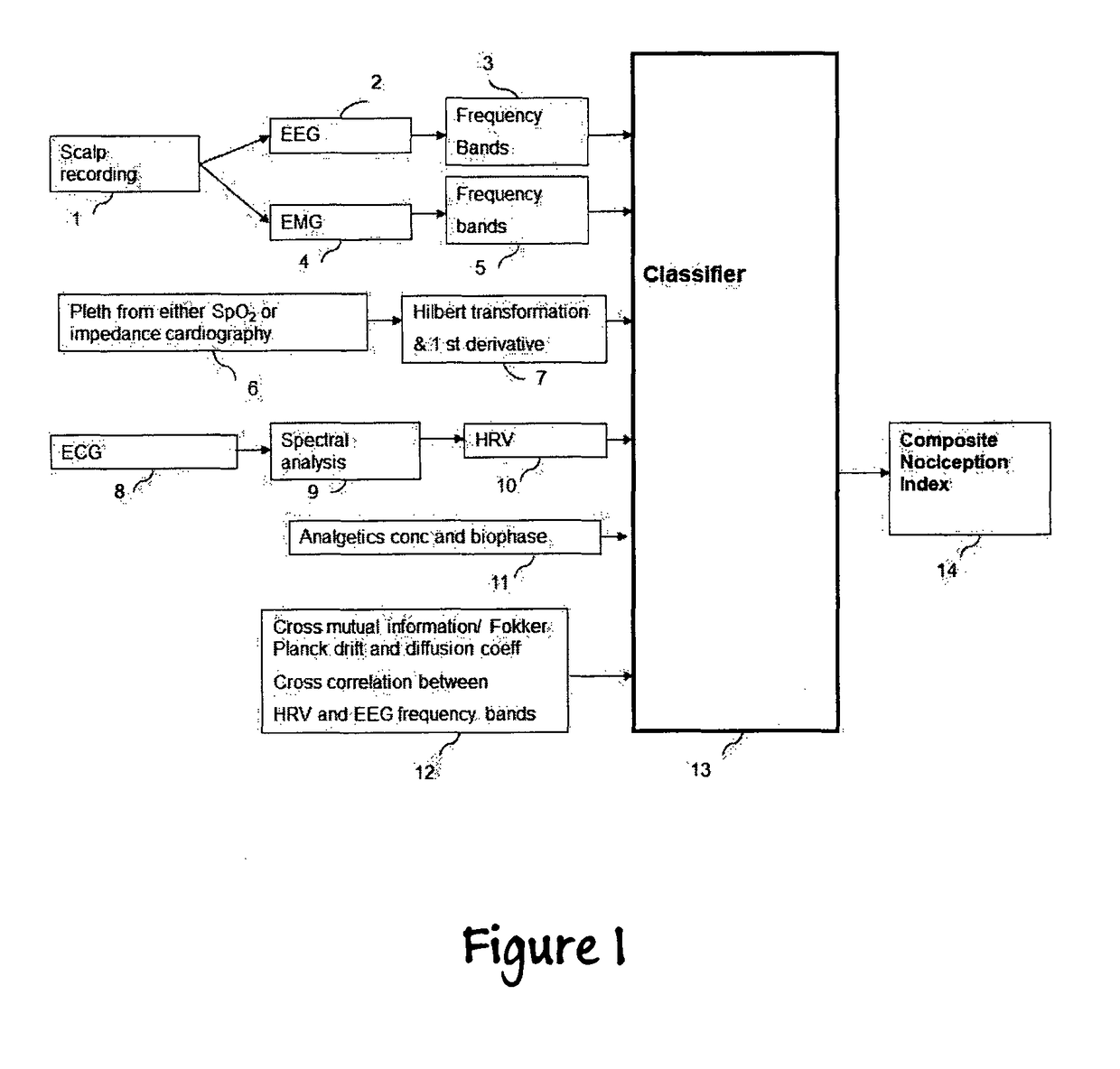
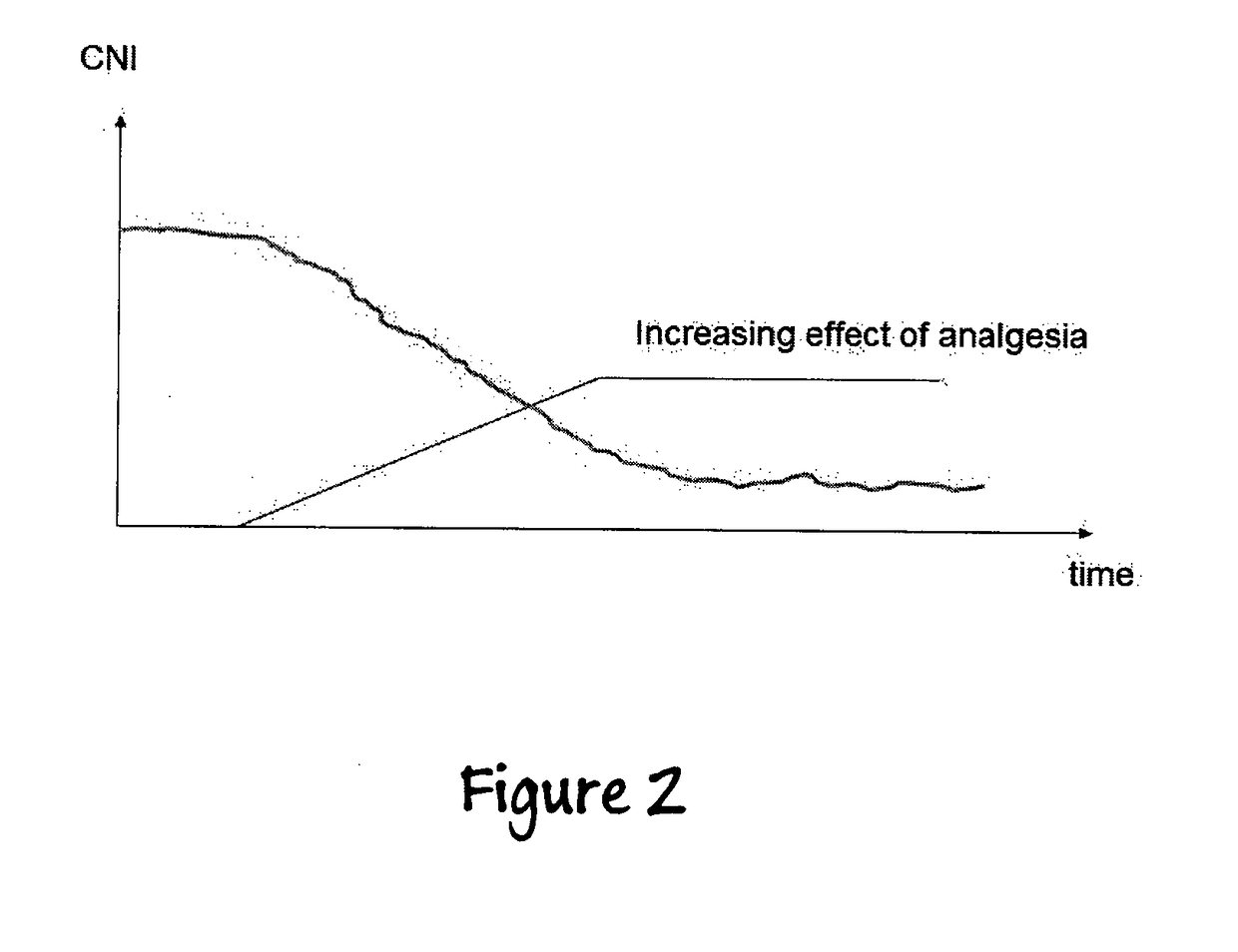
Apparatus for the Assessment of the Level of Pain and Nociception During General Anesthesia Using Electroencephalogram, Plethysmographic Impedance Cardiography, Heart Rate Variability and the Concentration or Biophase of the Analgesics
Means and methods for measuring pain and adapted for calculating the level of nociception during general anesthesia or sedation from data including electroencephalogram (EEG), facial electromyogram (EMG), heart rate variability (HRV) by electrocardiogram (ECG) and plethysmography by impedance cardiography (ICG). In a preferred embodiment of this invention the parameters derived from the EEG, the HRV, the plethysmographic curve and the analgetics concentrations are either combined into one index on a scale from 0 to 100, where a high number is associated with high probability of response to noxious stimuli, while a decreasing index is associated with decreasing probability of response to noxious stimuli. Zero (0) indicates extremely low probability of response to noxious stimuli. In an alternative embodiment, only features from the EEG and ECG will be used or only features from EEG, ECG and ICG, to define the fmal index.
Owner:HOSPITAL CLINIC DE BARCELONA +1
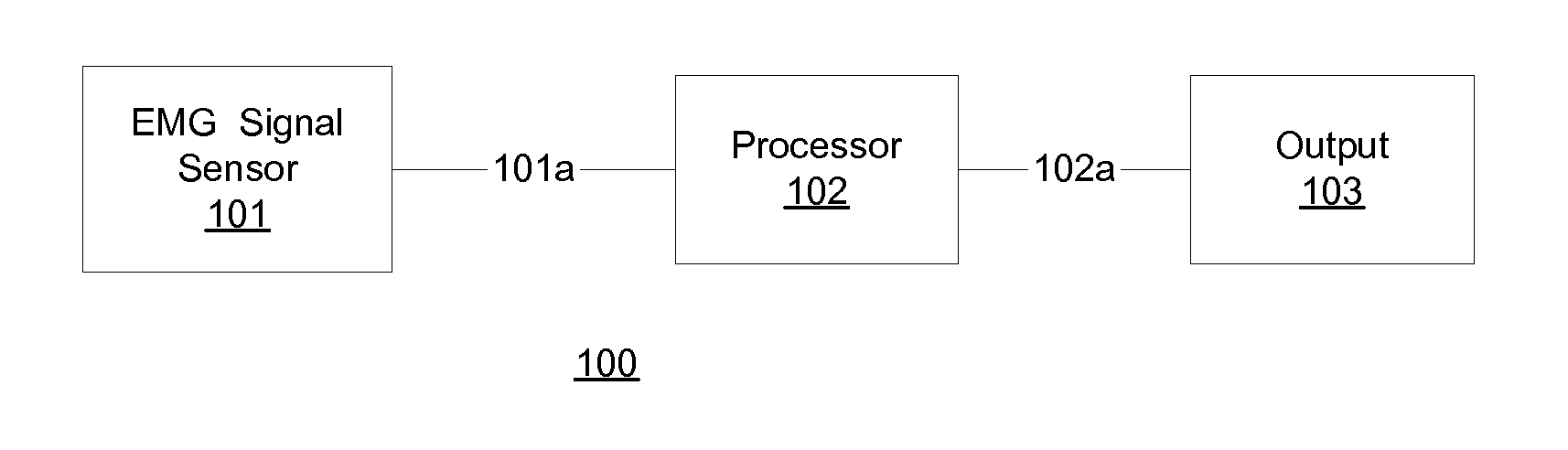
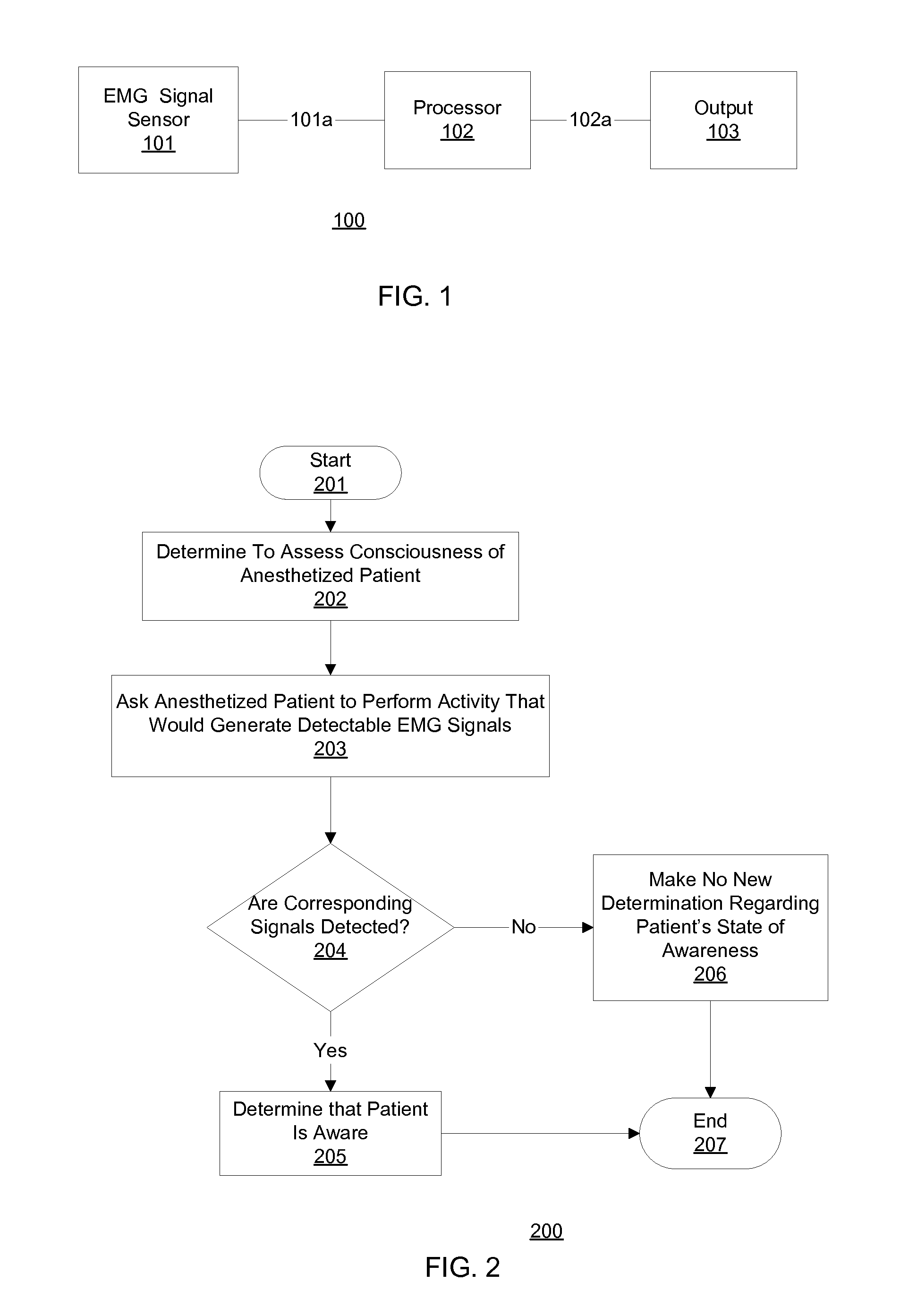
Communication with and consciousness-assessment of anesthetized surgery patients
In one embodiment, prior to undergoing surgery, a patient is trained in the use of an anesthesia-awareness detection (AAD) system to produce an observable output by attempting to move a muscle. The AAD system includes an electromyographic (EMG) signal monitor. While undergoing surgery, the patient is anesthetized with a sedative and a paralytic. During surgery, if the surgical team wishes to asses the consciousness state or communicative ability of the patient, then the surgical team asks the patient to move the muscle. If the patient is unable to speak due to the paralytic but is aware and attempts to comply, then the attempt is detected by the AAD system, which provides a corresponding output to inform the surgical team, which may take appropriate action to ask additional questions of the patient and / or address the patient's anesthesia awareness.
Owner:EGETH MARC J
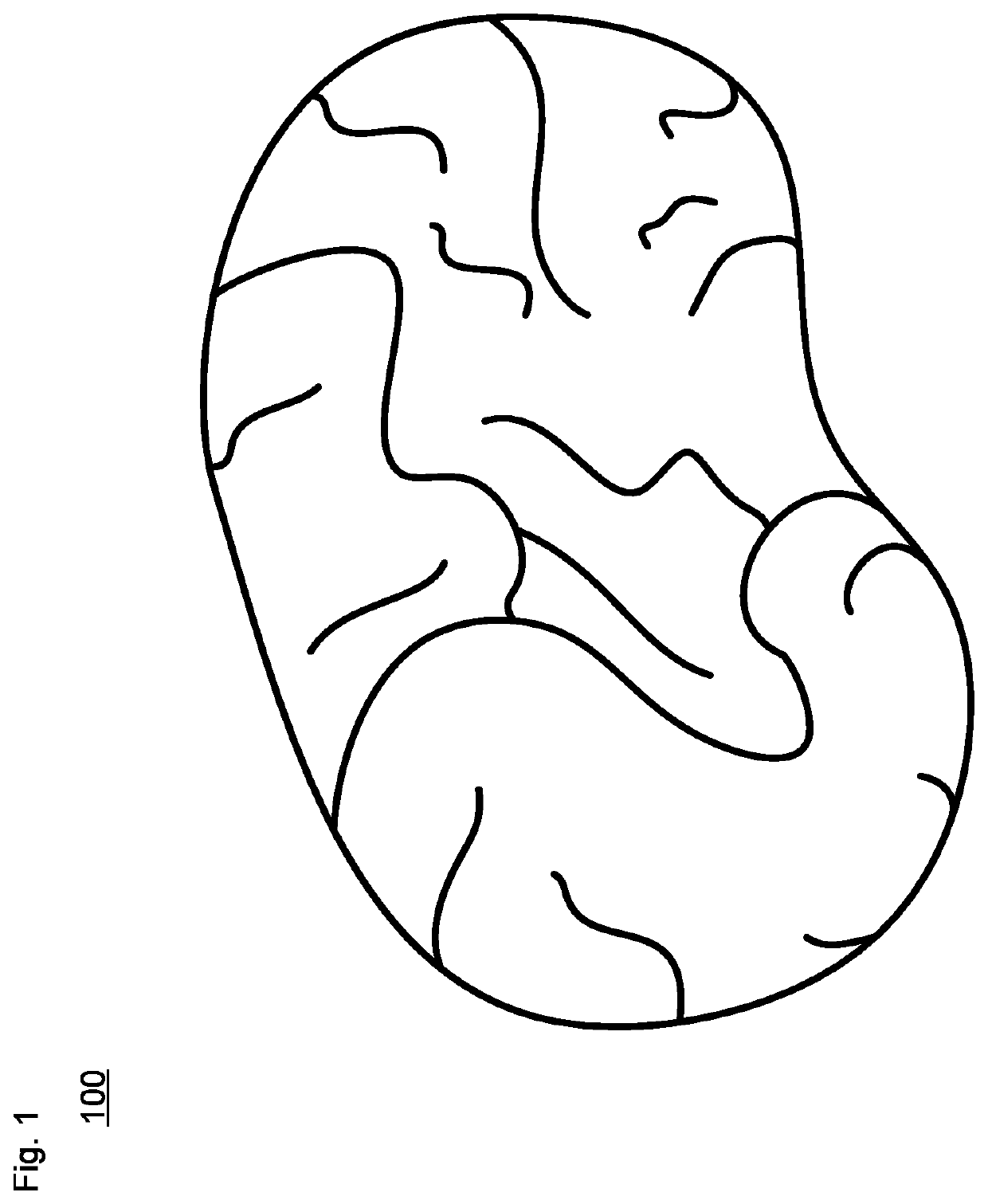
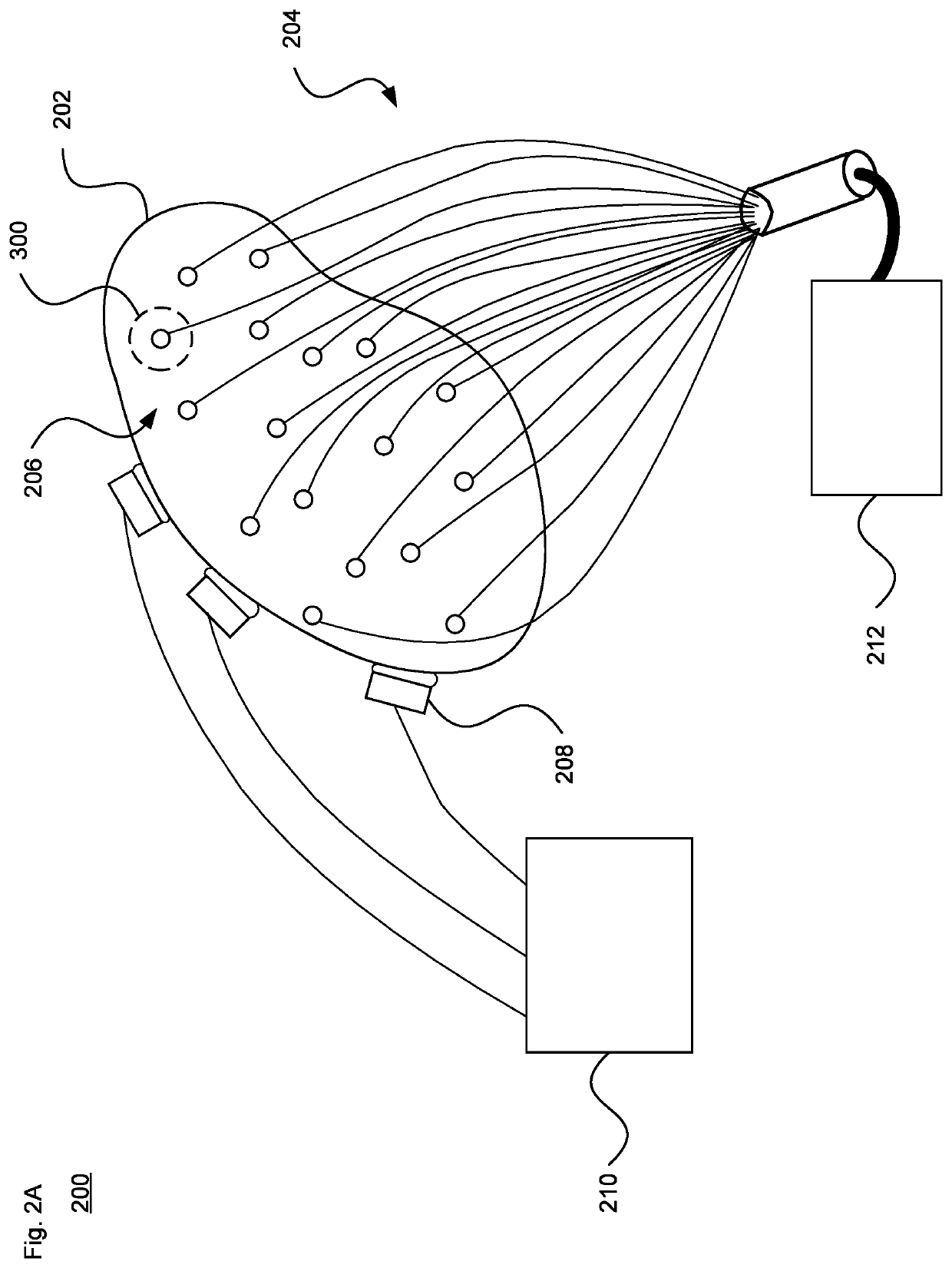
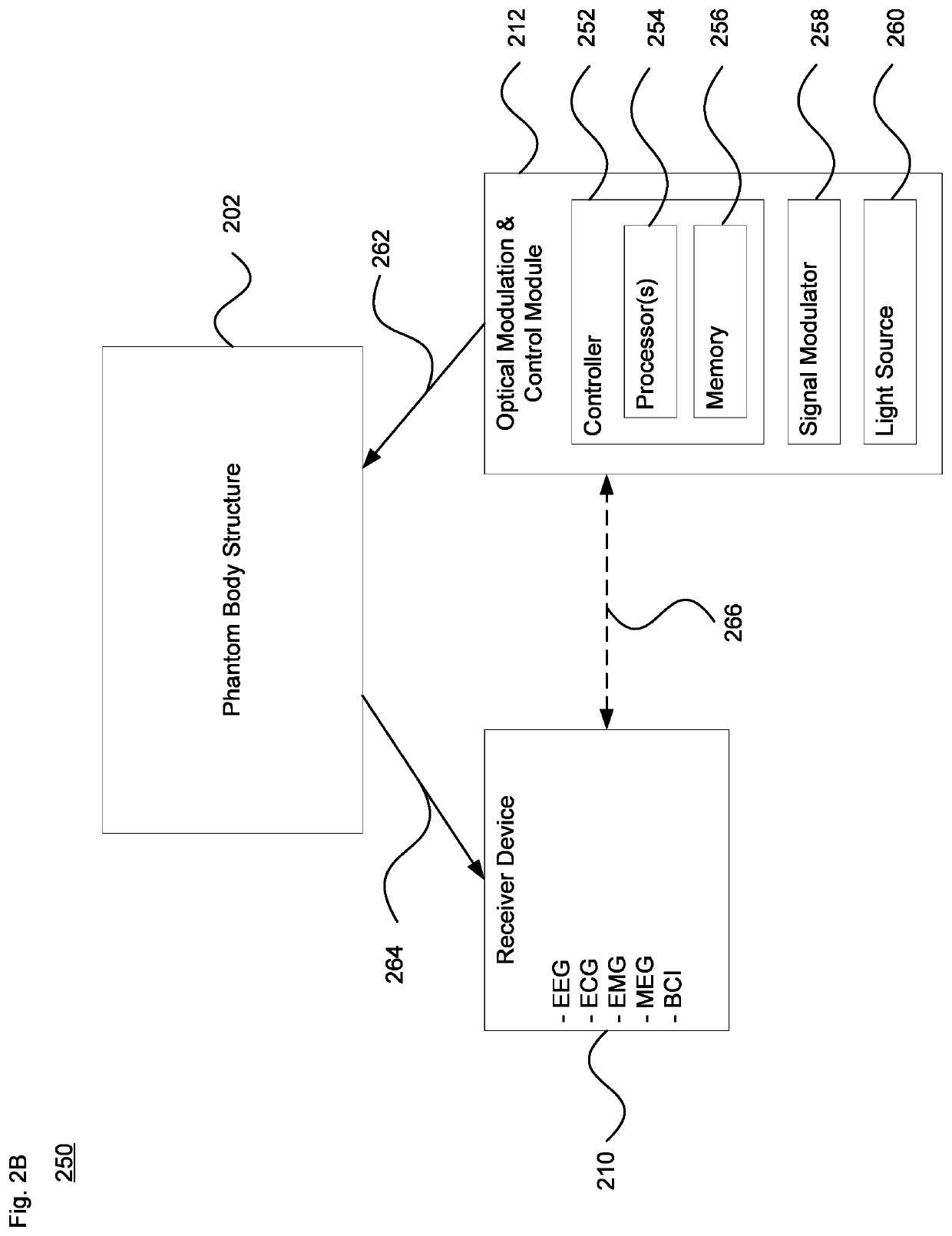
Optically Excited Biopotential Phantom
The technology provides a system and method for simulating and detecting bio signals such as brain bio-signals. The technology can be used for medical or non-medical purposes, for instance to simulate or evaluate certain medical conditions using a physical brain-type phantom body. A set of optical fibers provides modulated signals received from an optical signal modulator, which is managed by a controller to generate repeatable signals with high fidelity. The modulated signals are received by a set of emission elements such as photoreceivers or other optical electrodes disposed within or otherwise about the phantom body. The emission elements output electrical signals corresponding to the input modulated optical signals. The electrical signals are detected by a set of sensors. The sensors are coupled to a receiver device that is able to evaluate the electrical signals, such as for an electroencephalograph (EEG), electrocardiogram (ECG), electromyogram (EMG) or magnetoencephalography (MEG) diagnostic system.
Owner:NEXTSENSE INC
Neurosleeve for closed loop EMG-FES based control of pathological tremors
A tremor suppression device includes a garment wearable on an anatomical region and including electrodes contacting the anatomical region when the garment is worn on the anatomical region, and an electronic controller configured to: detect electromyography (EMG) signals as a function of anatomical location and time using the electrodes; identify tremors as a function of anatomical location and time based on the EMG signals; and apply neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) at one or more anatomical locations as a function of time using the electrodes to suppress the identified tremors.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
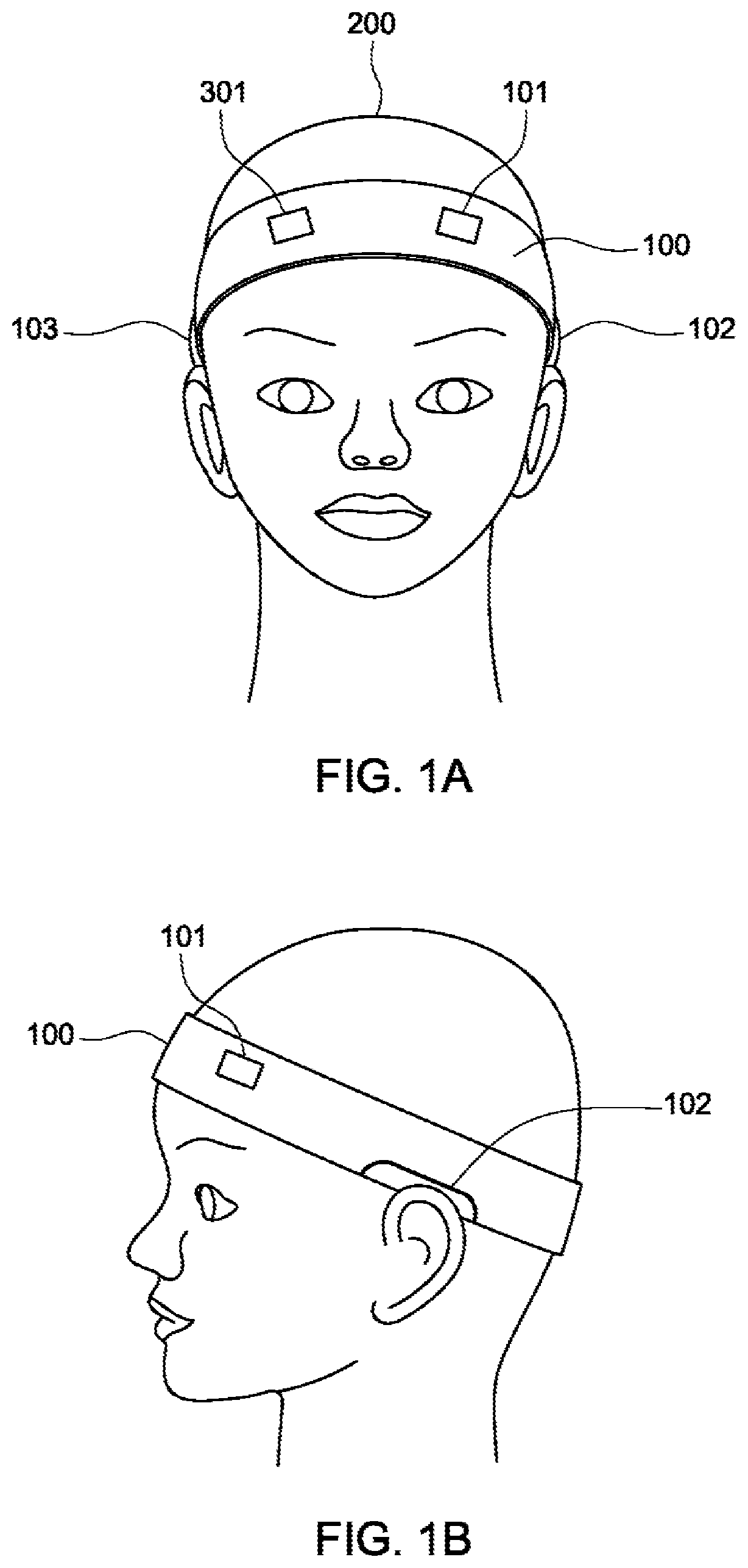
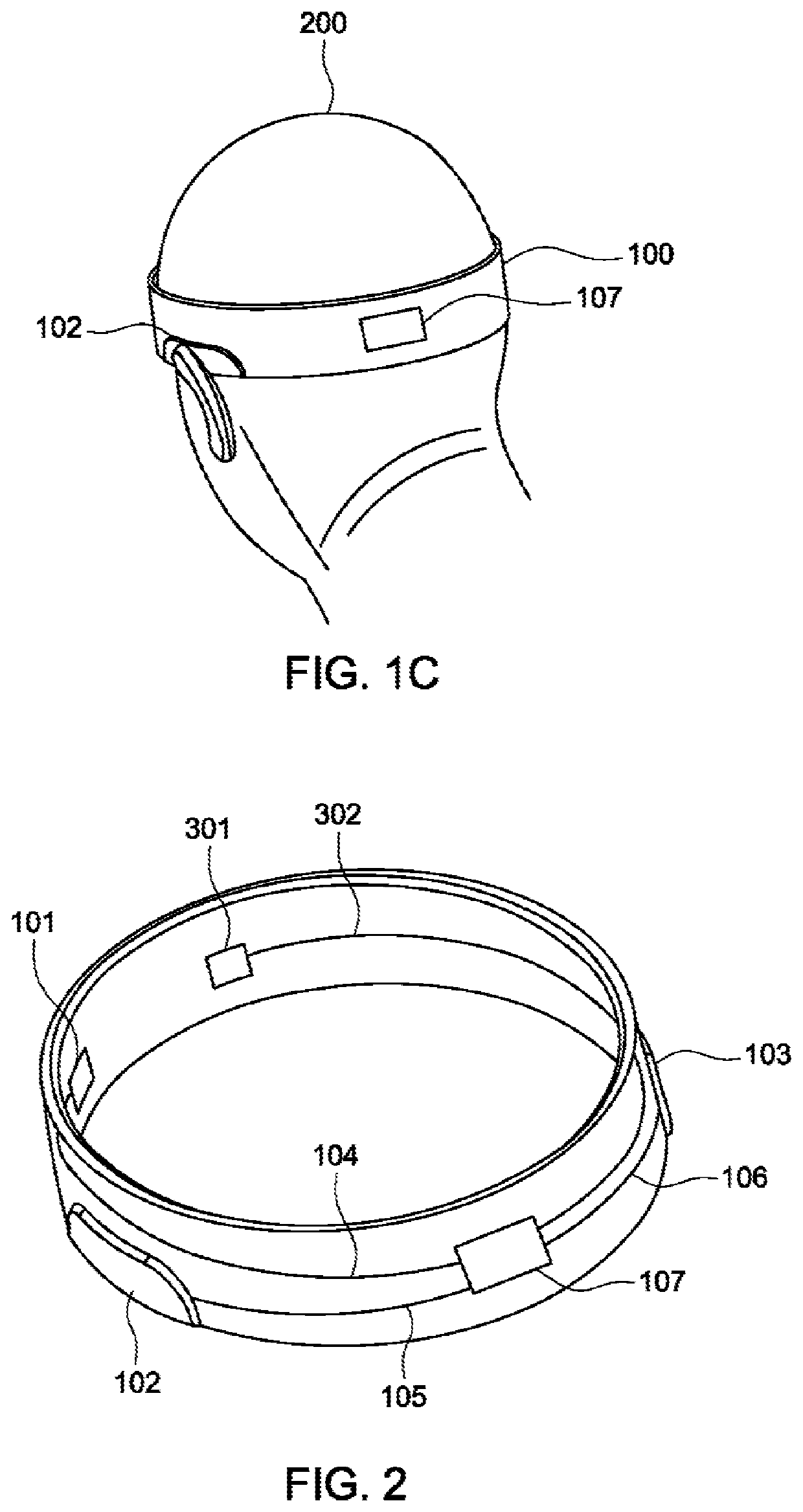
Bio-signal detecting headband
InactiveUS20210022636A1ElectroencephalographyElectromyographyNeural oscillationElectro encephalogram
A sensor device measures bio-signals including one or more of electroencephalogram (EEG), heartbeat, electromyography (EMG), body temperature, body location, time, movement and velocity. The sensor device can include a circular fabric based headband with electrodes (conductive fabric sensing material) embedded therein, along with electronical circuitry and electrical wires. Electrodes can be positioned to make electrical contact with the scalp of a subject. For example, electroencephalography (EEG) measures the voltage changes resulting from ionic current with the neurons of the brain over a time period. By using multiple electrodes in contact with the scalp of the subject, neural oscillations can be detected in EEG measurements.
Owner:MINDSALL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com