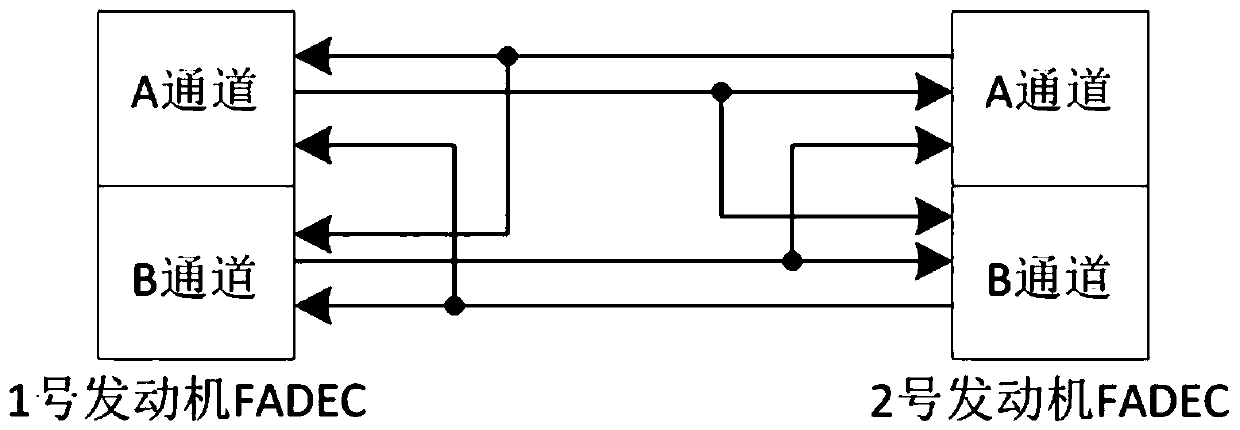
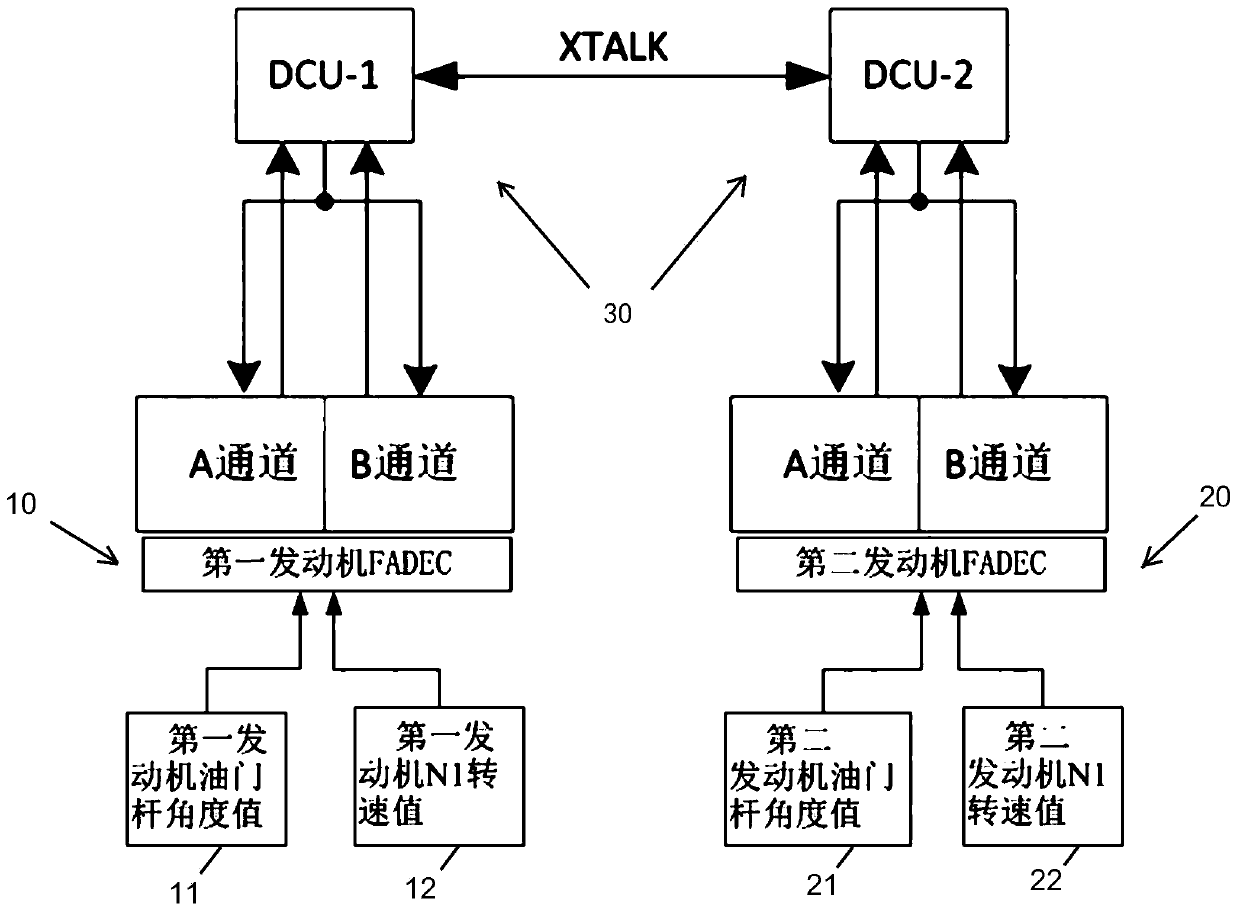
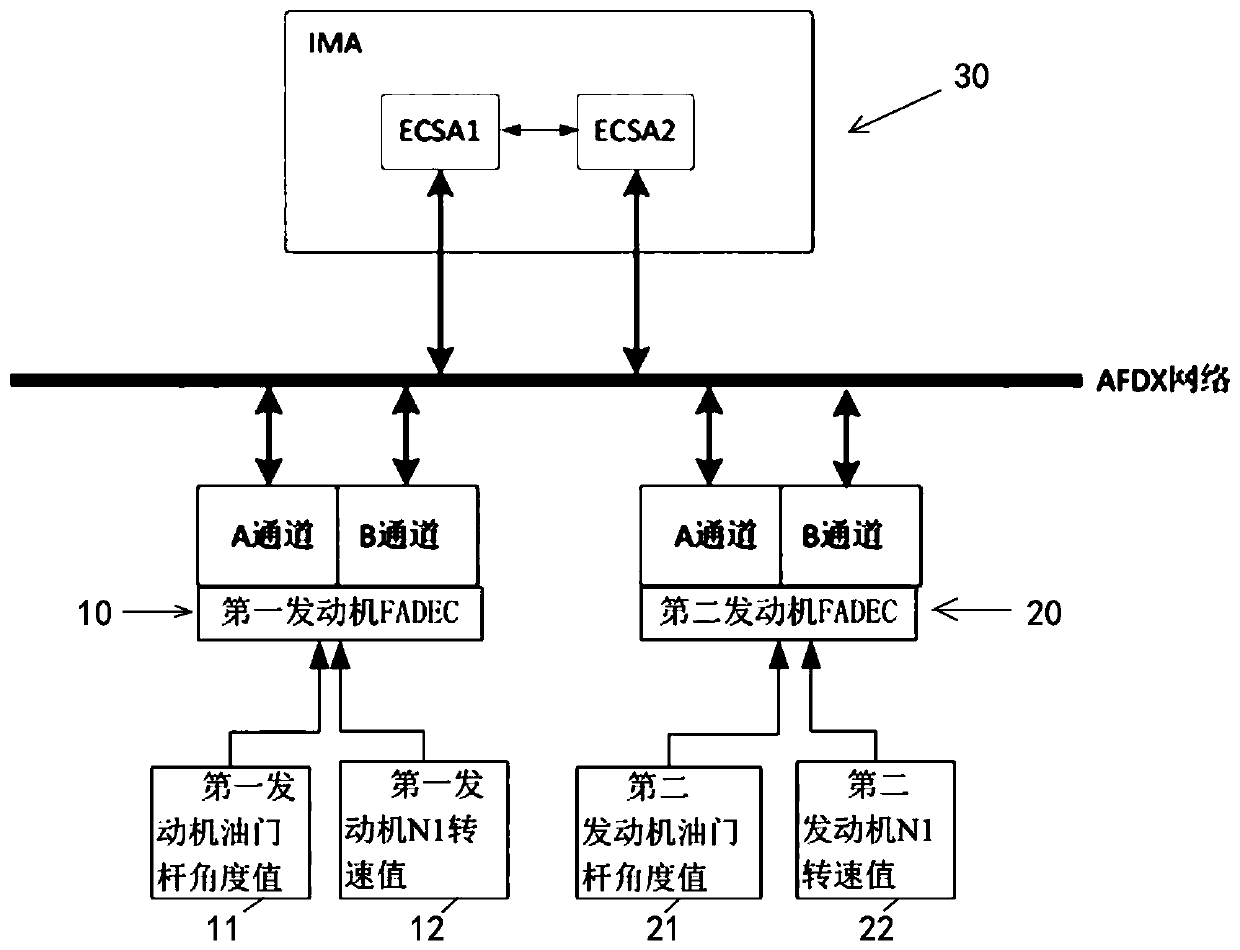
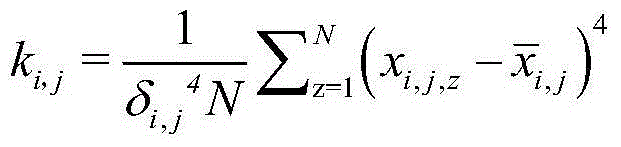Patents
Literature
46 results about "FADEC" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A full authority digital engine (or electronics) control (FADEC) is a system consisting of a digital computer, called an "electronic engine controller" (EEC) or "engine control unit" (ECU), and its related accessories that control all aspects of aircraft engine performance. FADECs have been produced for both piston engines and jet engines.
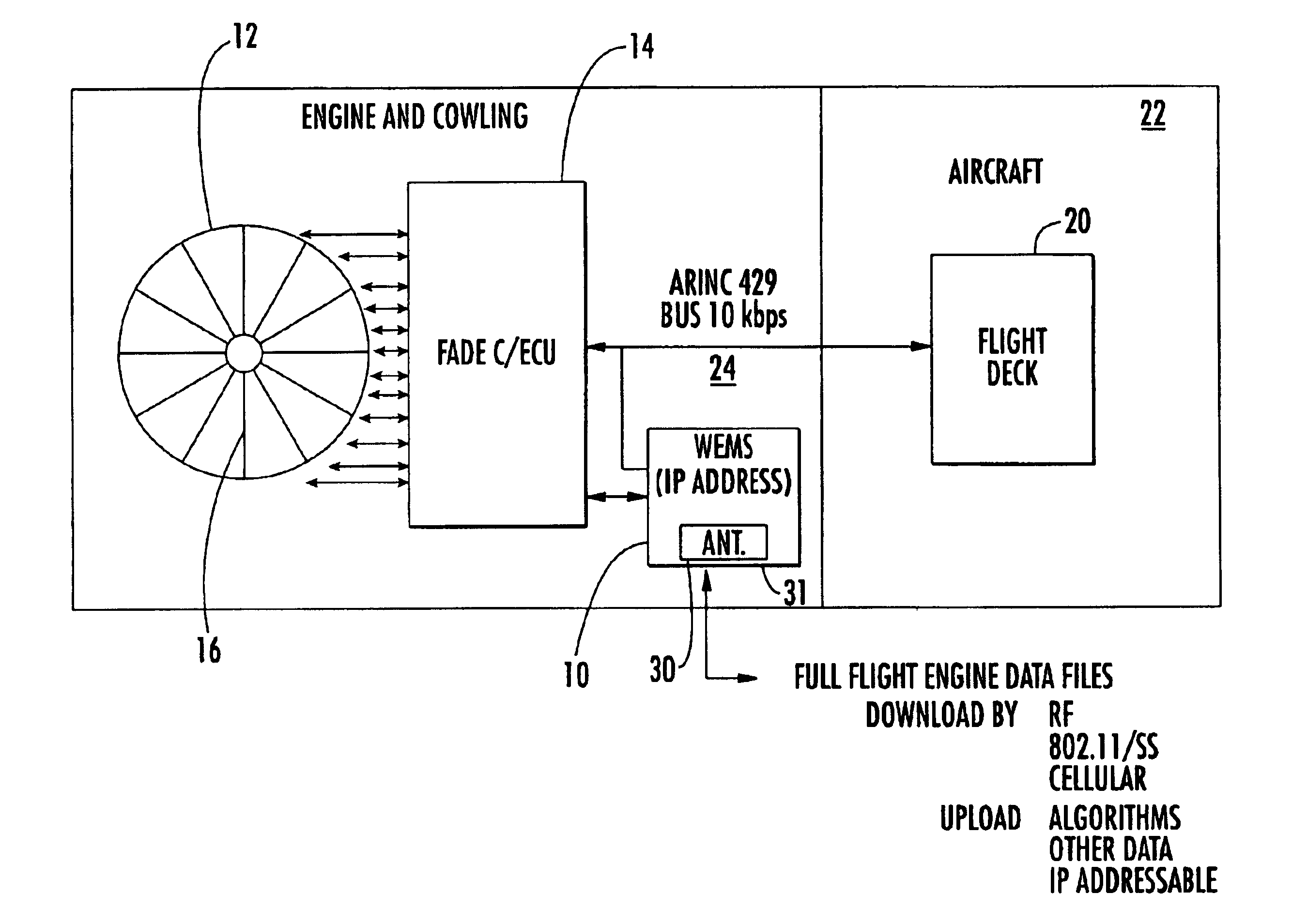
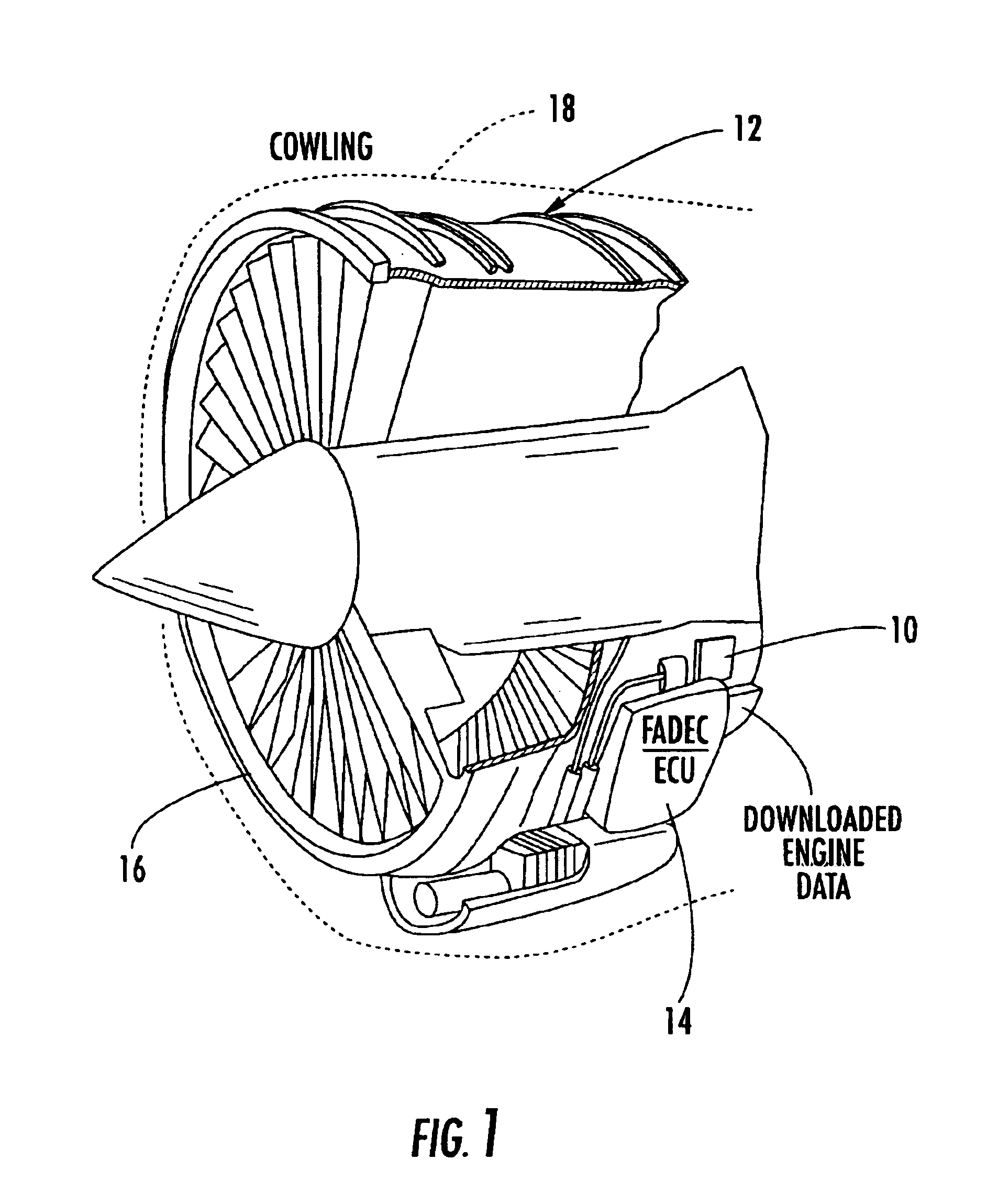
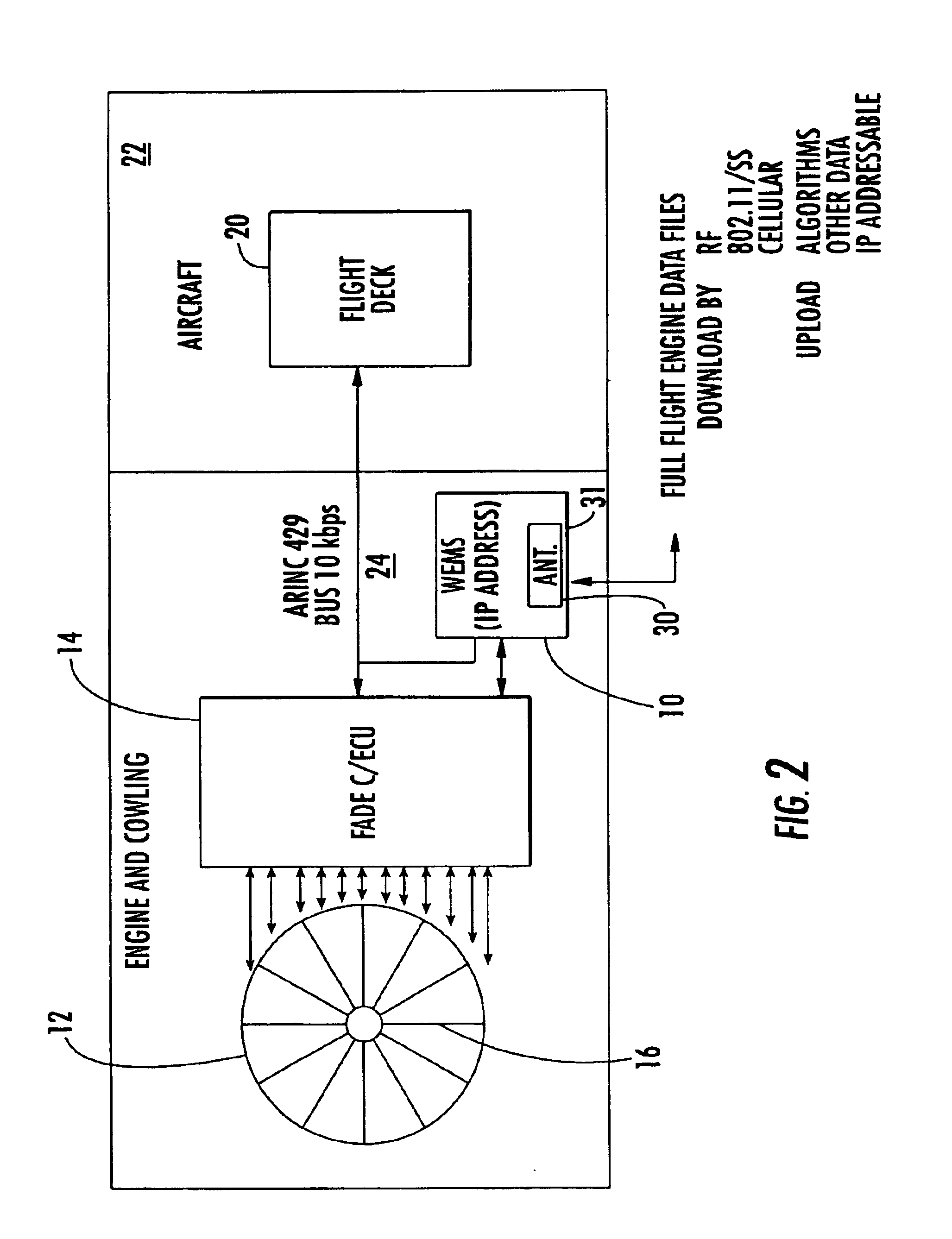
Wireless engine monitoring system
ActiveUS6943699B2Extension of timeReduce maintenance costsVehicle testingInternal combustion piston enginesMonitoring systemConformal antenna
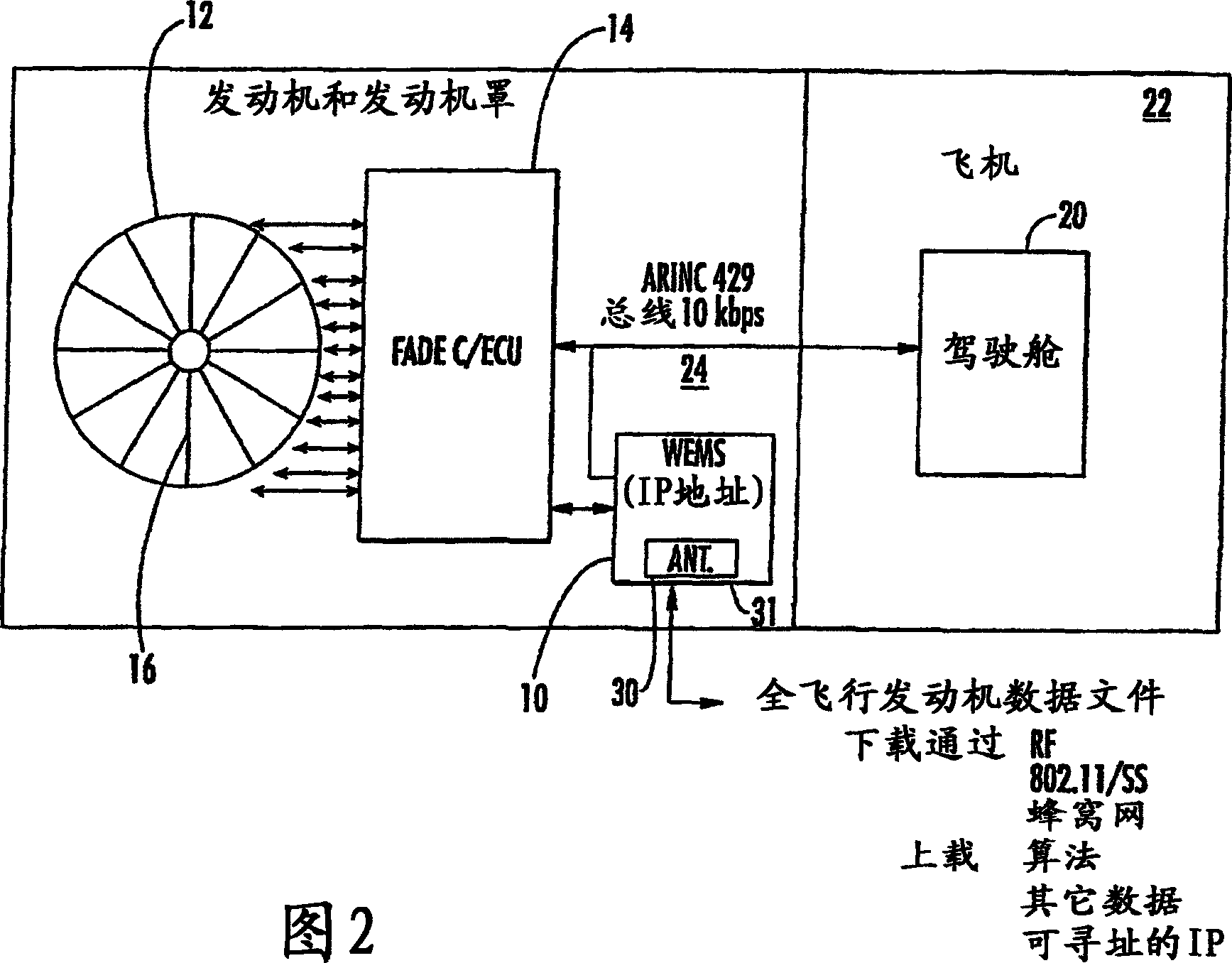
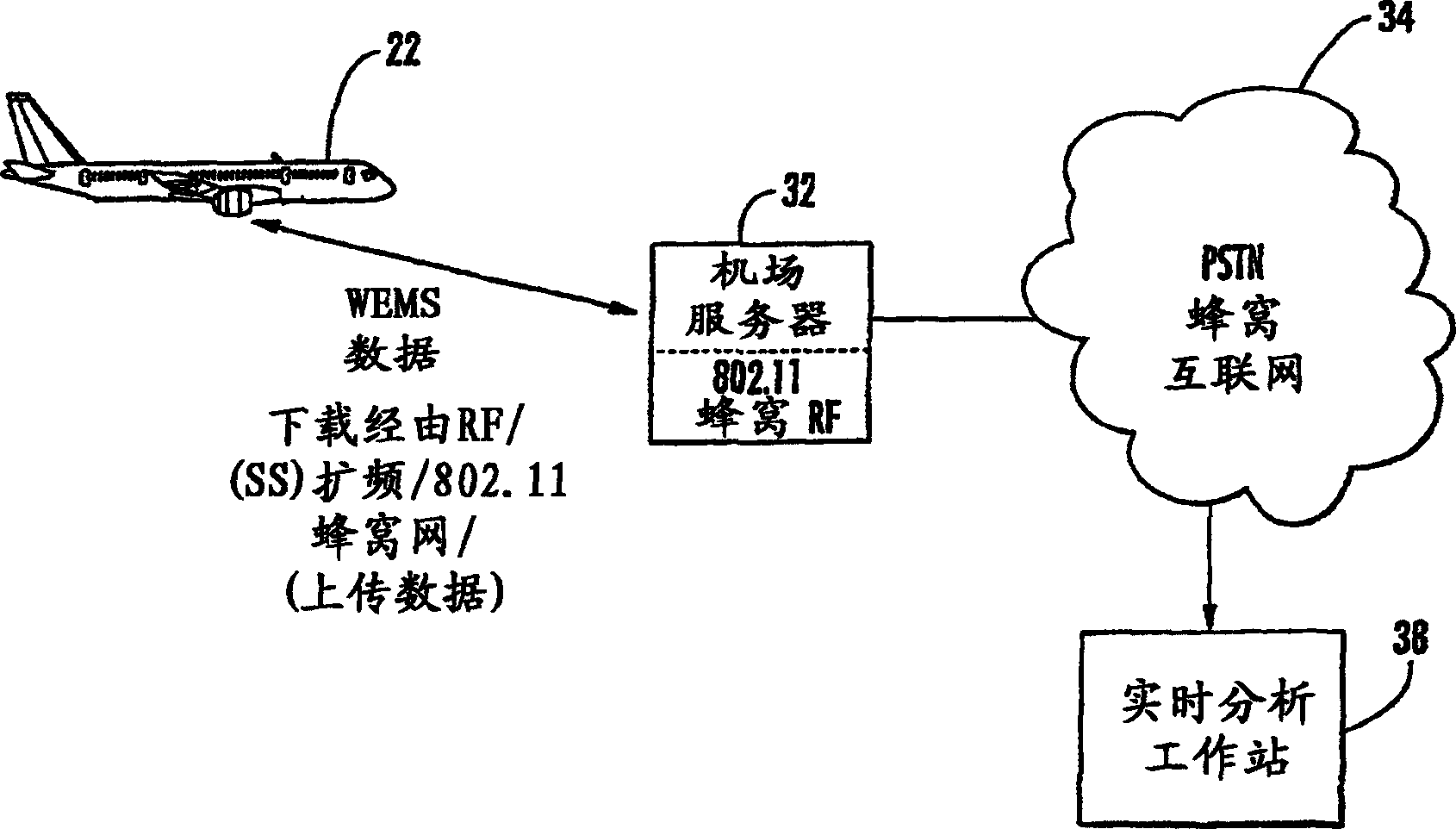
A wireless engine monitoring system (WEMS) includes an engine monitoring module that is mounted directly on an aircraft engine and records, stores, encrypts and transmits full flight engine data. The system preferably interfaces to the Full Authority Digital Engine Controller / Engine Control Unit (FADEC / ECU) and can record hundreds of engine parameters with a preferred sampling frequency of about one second. The engine monitoring module is preferably formed as a miniaturized module directly mounted on the aircraft engine within its cowling and has a conformal antenna. The engine monitoring module can also upload data for onboard processing.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Turbojet electromechanical thrust reverser with servo-controlled door displacement
ActiveUS7370468B2Mitigate such drawbackDifference can be detectedPower plant arrangements/mountingEngine controlActuatorControl theory
A turbojet thrust reverser includes two doors each displaceable between an open position and a closed position of the reverser by at least one respective control actuator. Two electric motors drive the control actuators for the doors; each motor being controlled by an electronic control unit connected to a full authority digital engine control. Two servo-control devices control the displacement of the doors as a function of determined position references. The servo-control devices enable the doors to be displaced synchronously as a function of any variation in the forces exerted on the reverser and as a function of any force difference between the two doors.
Owner:SAFRAN ELECTRICAL & POWER
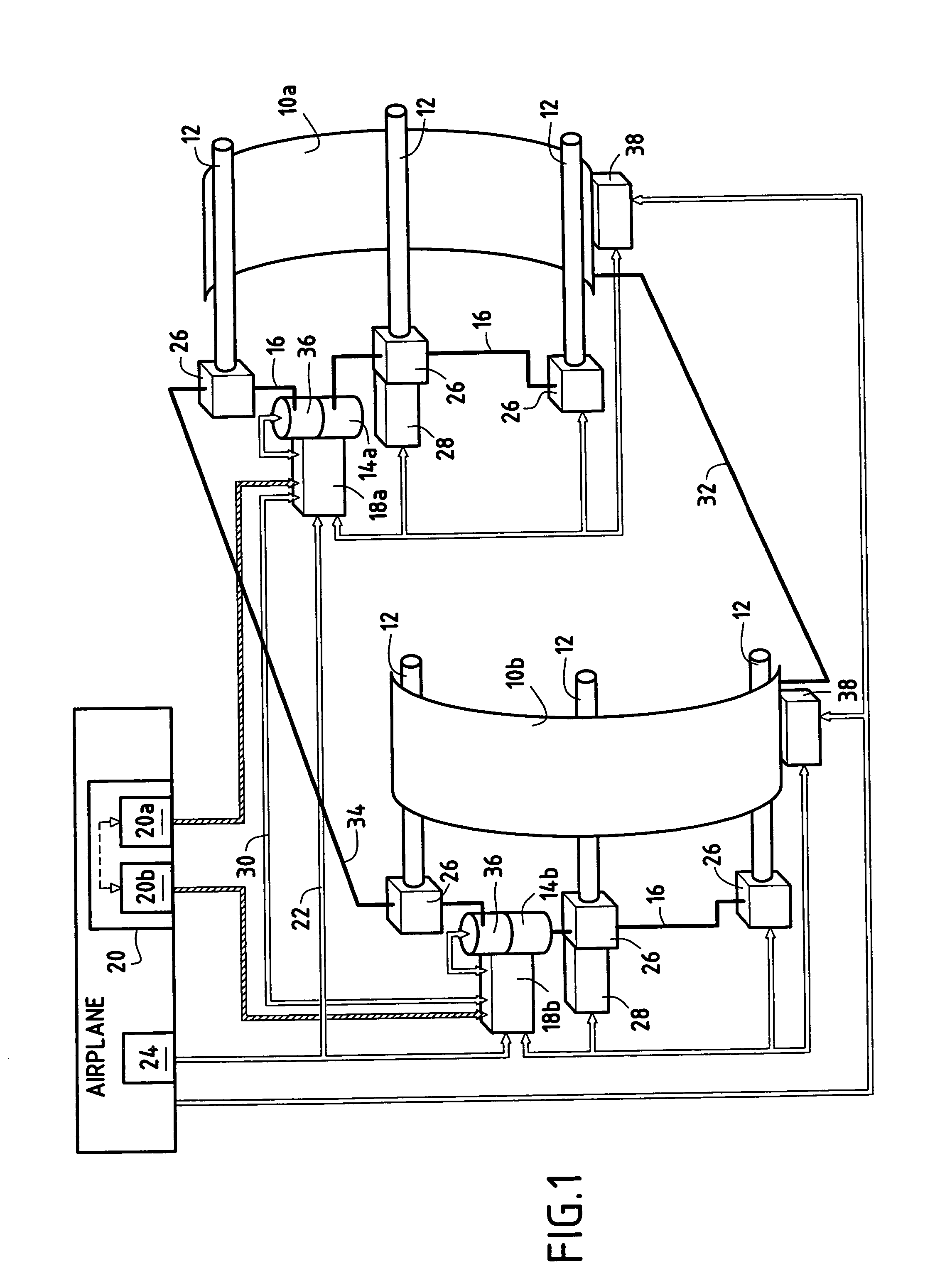
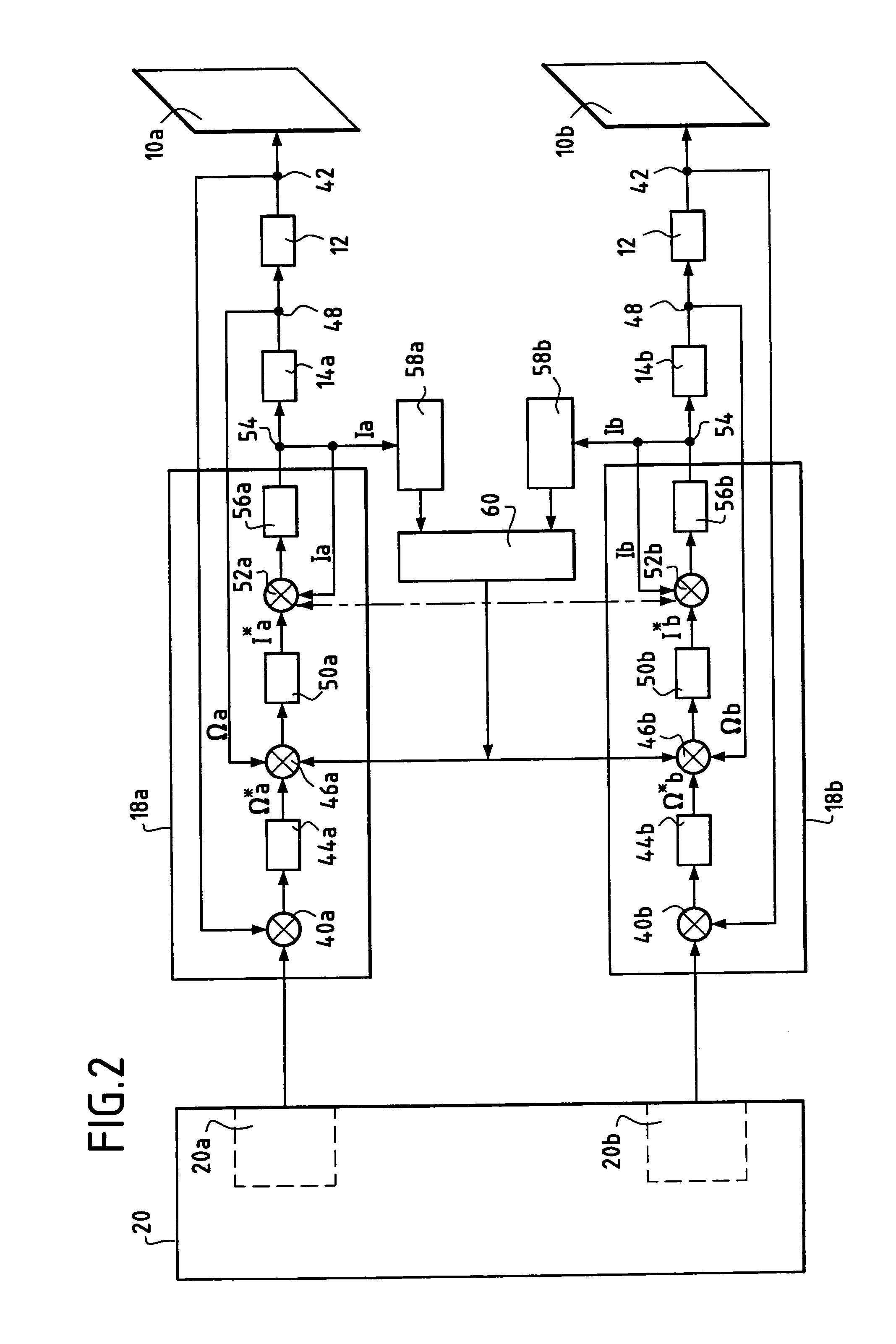
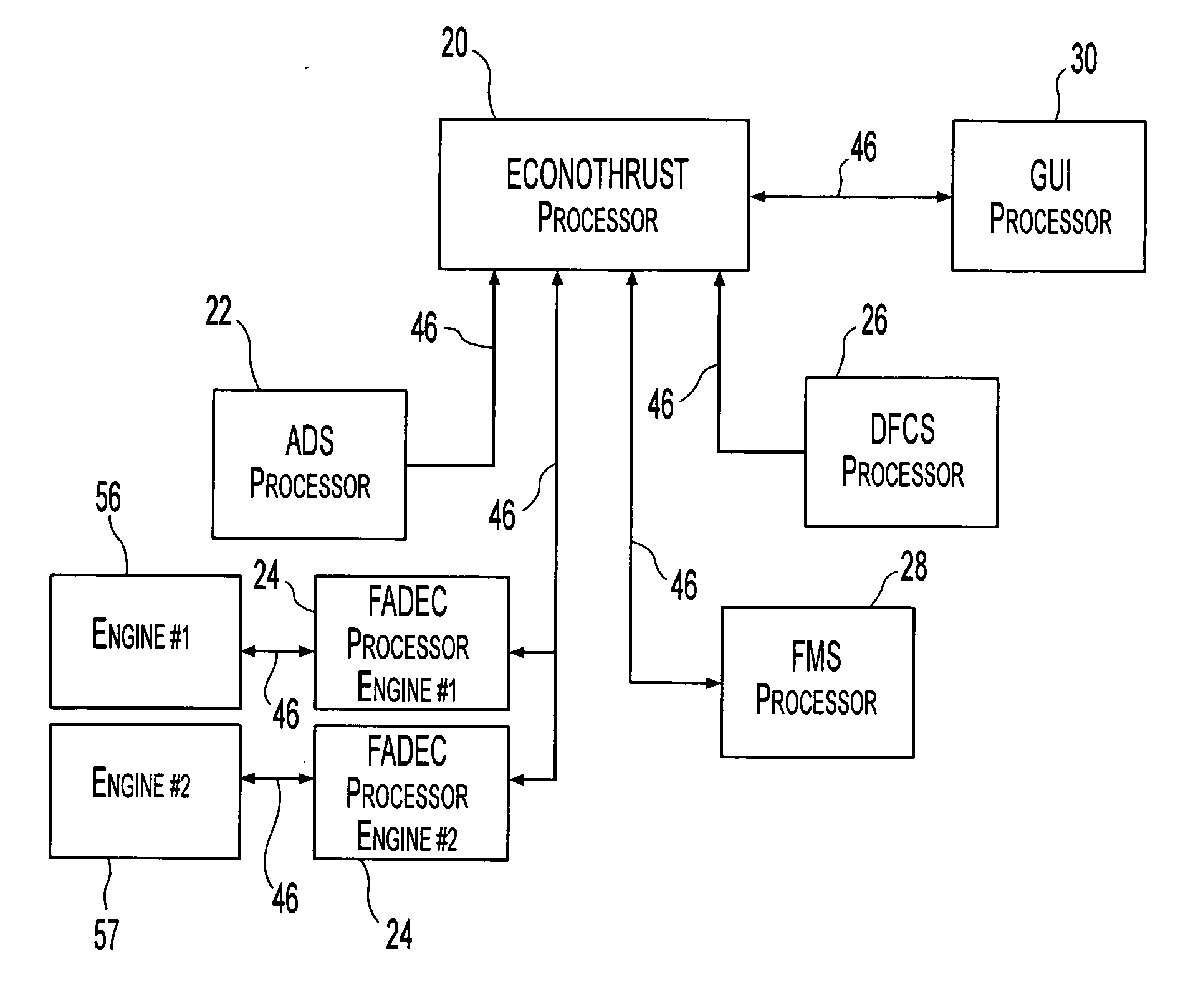
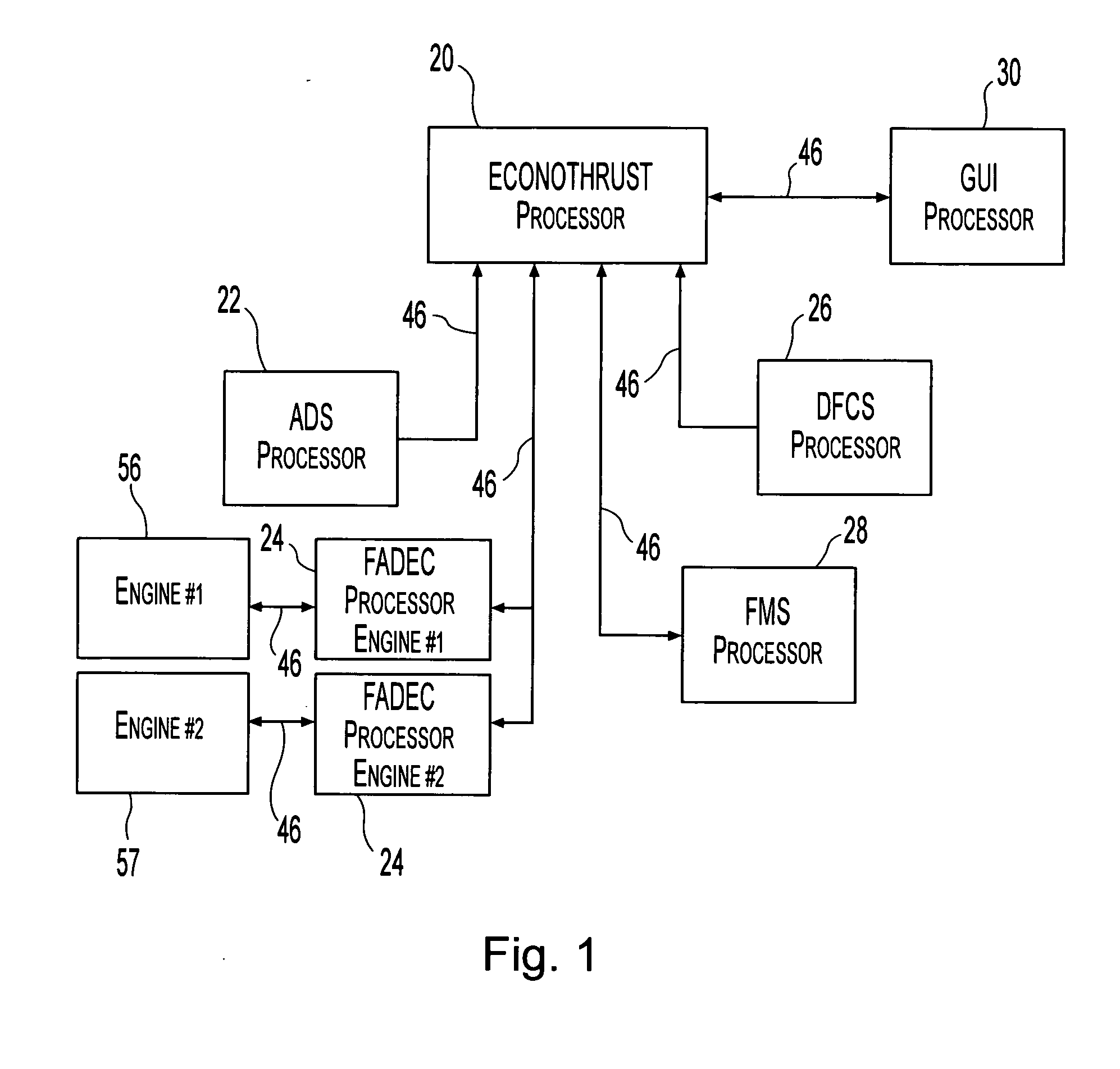
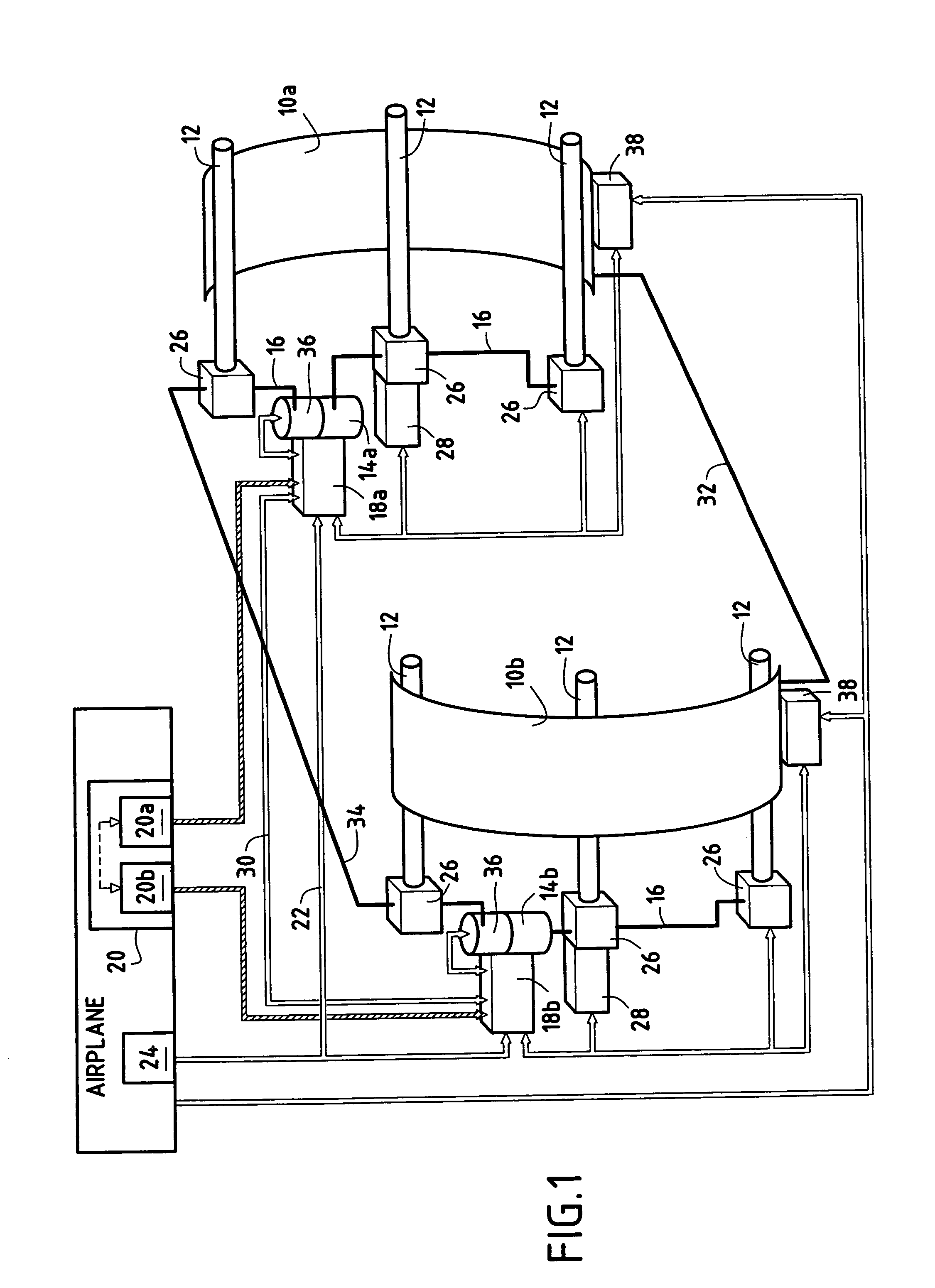
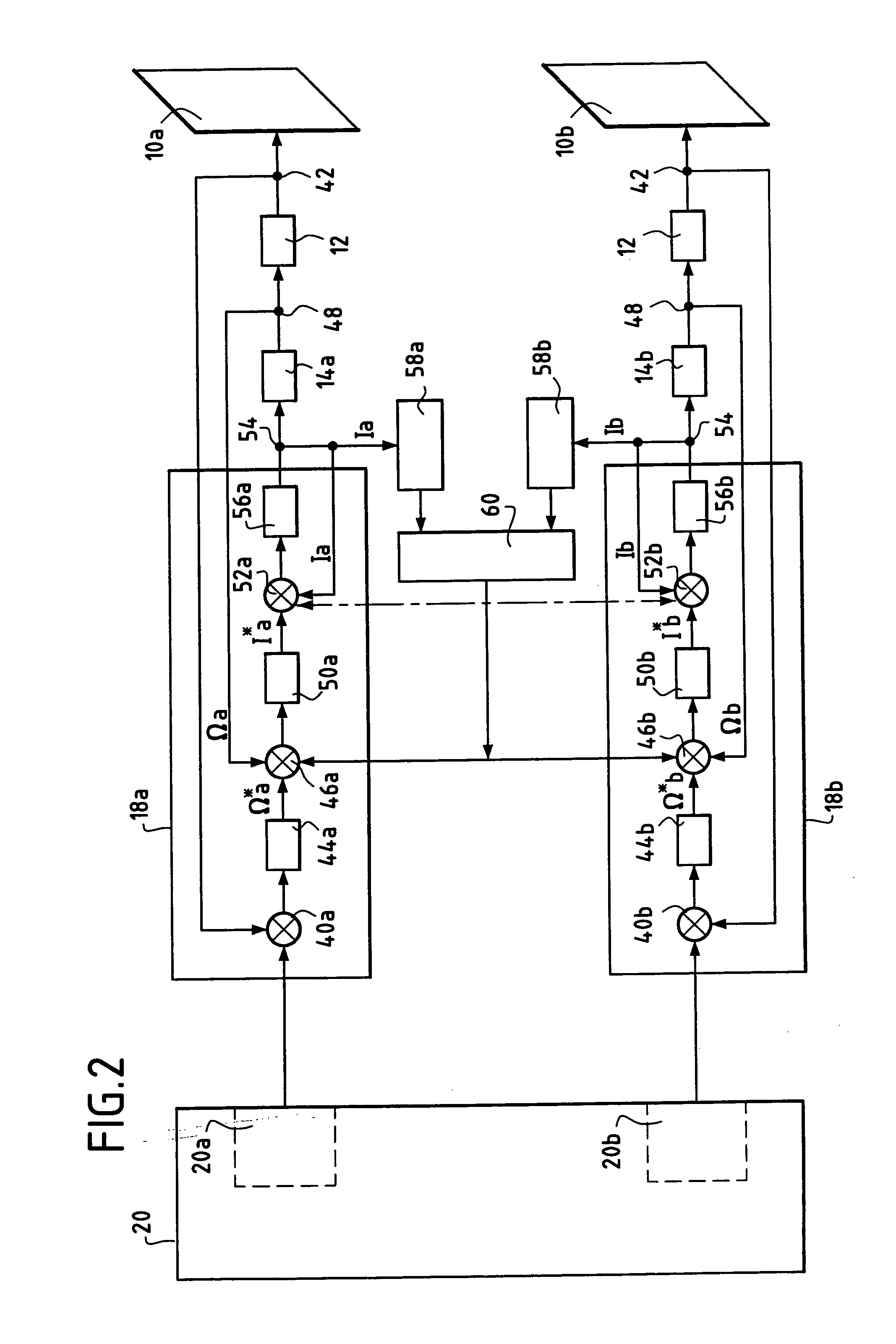
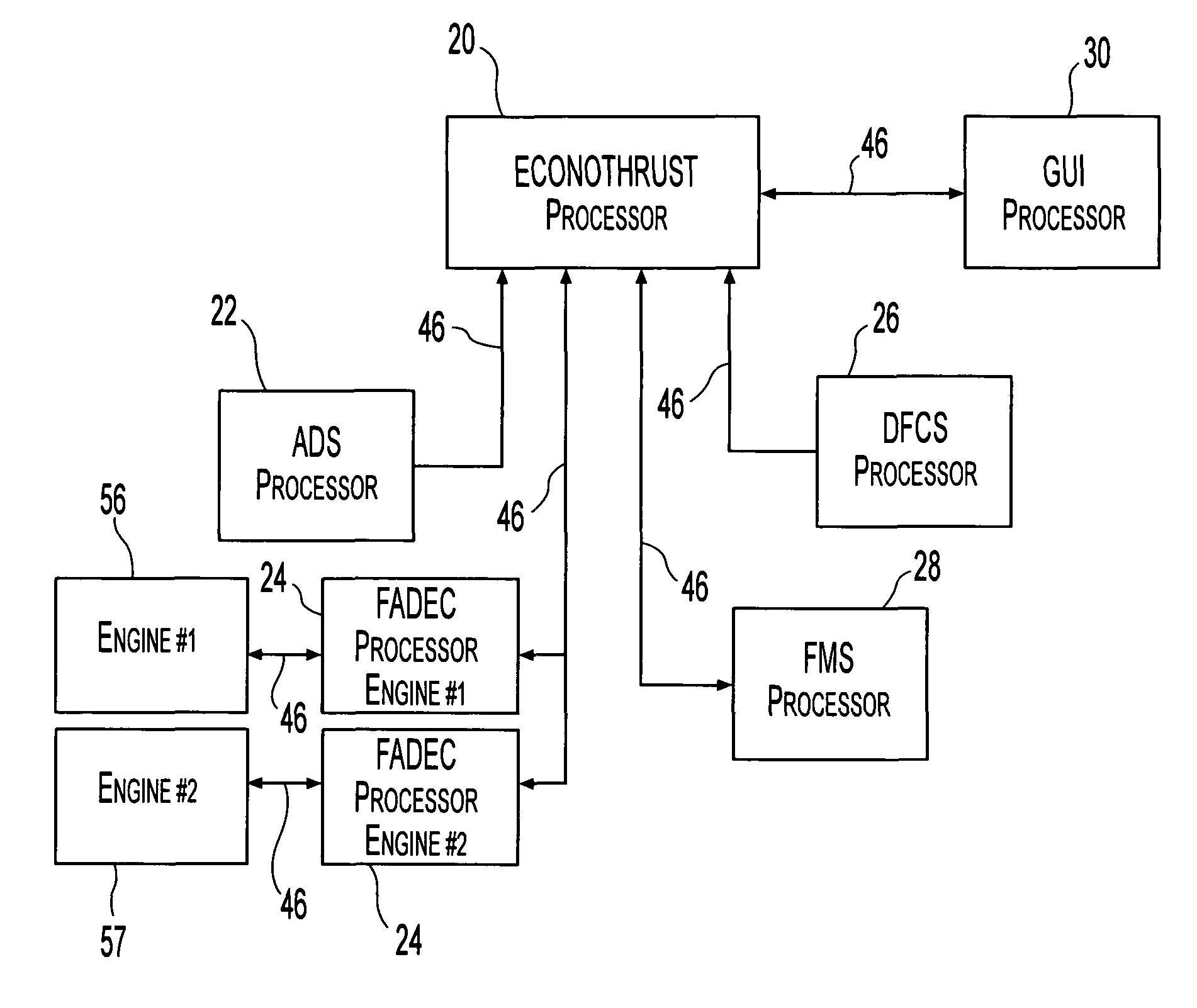
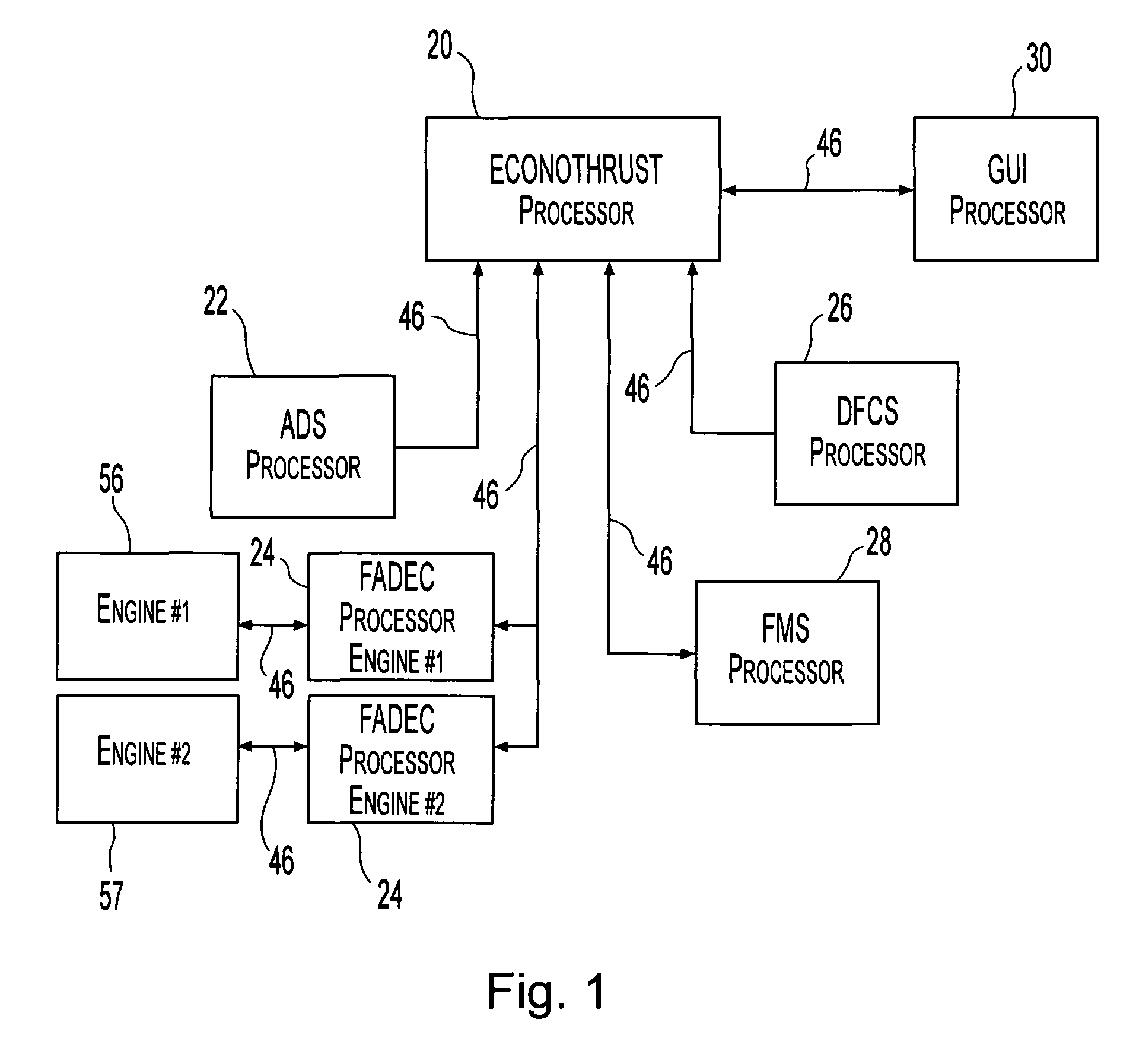
Apparatus and method for reducing aircraft fuel consumption
InactiveUS20110202251A1Improve fuel efficiencyFuel consumptionAnalogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsAviationElectronic systems
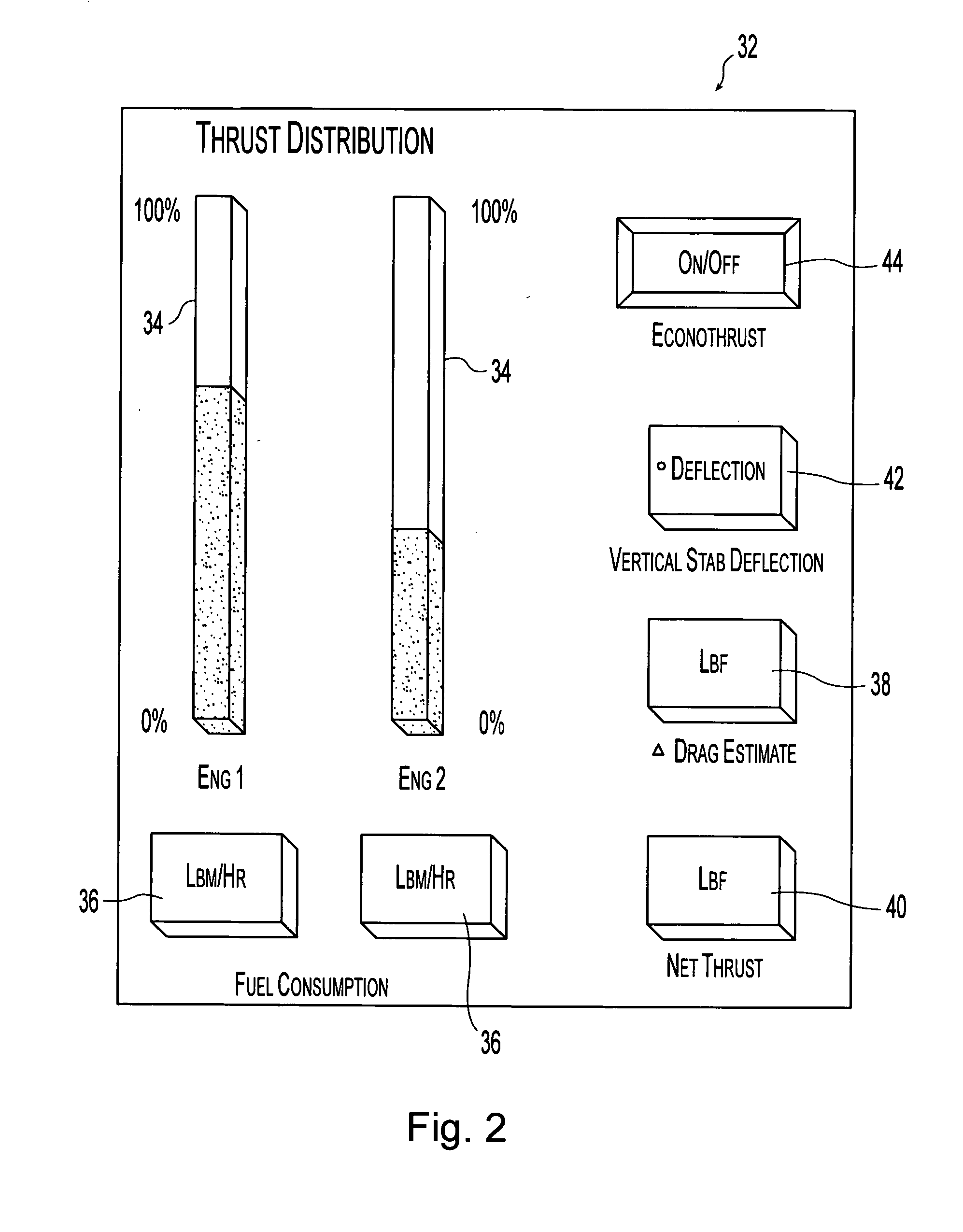
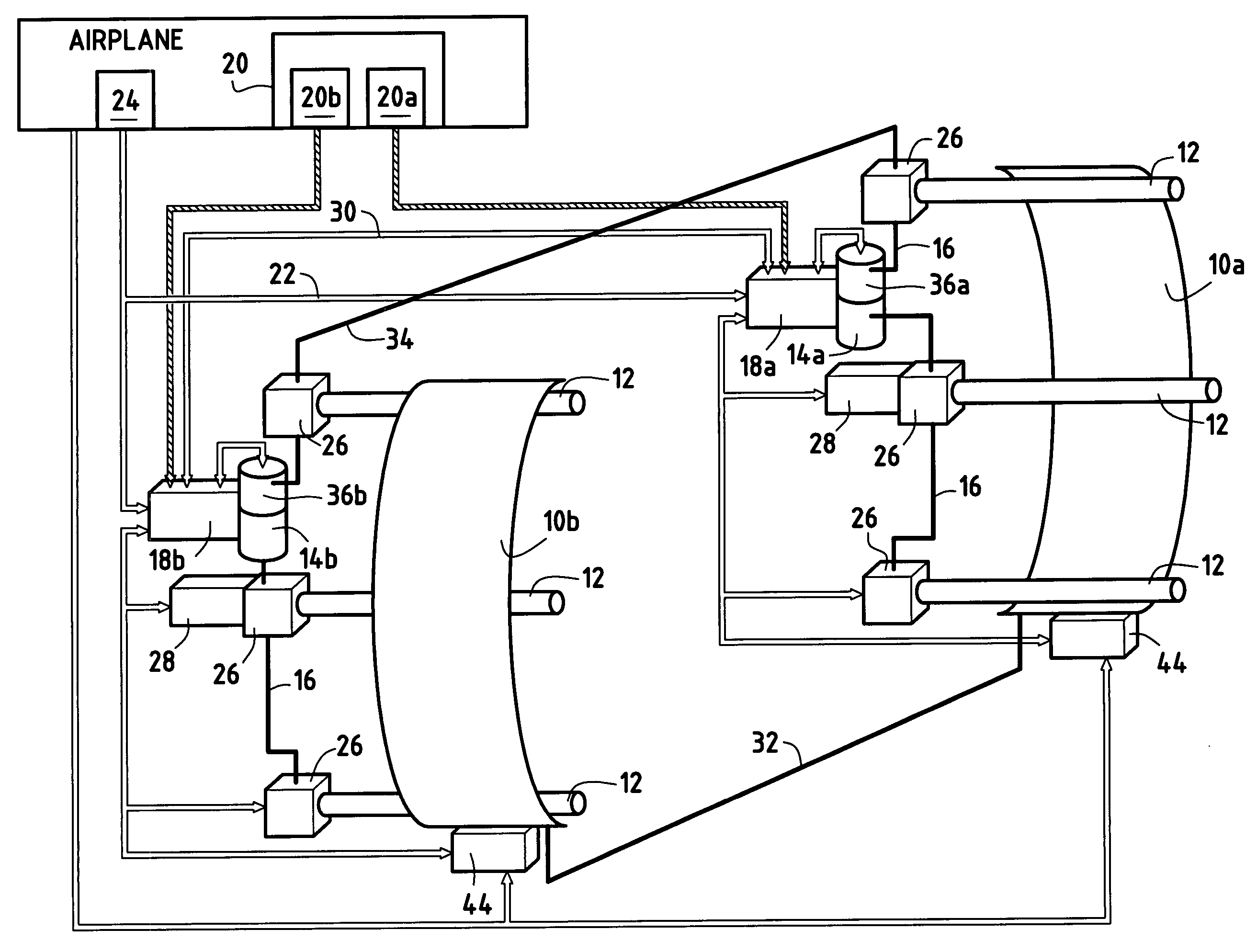
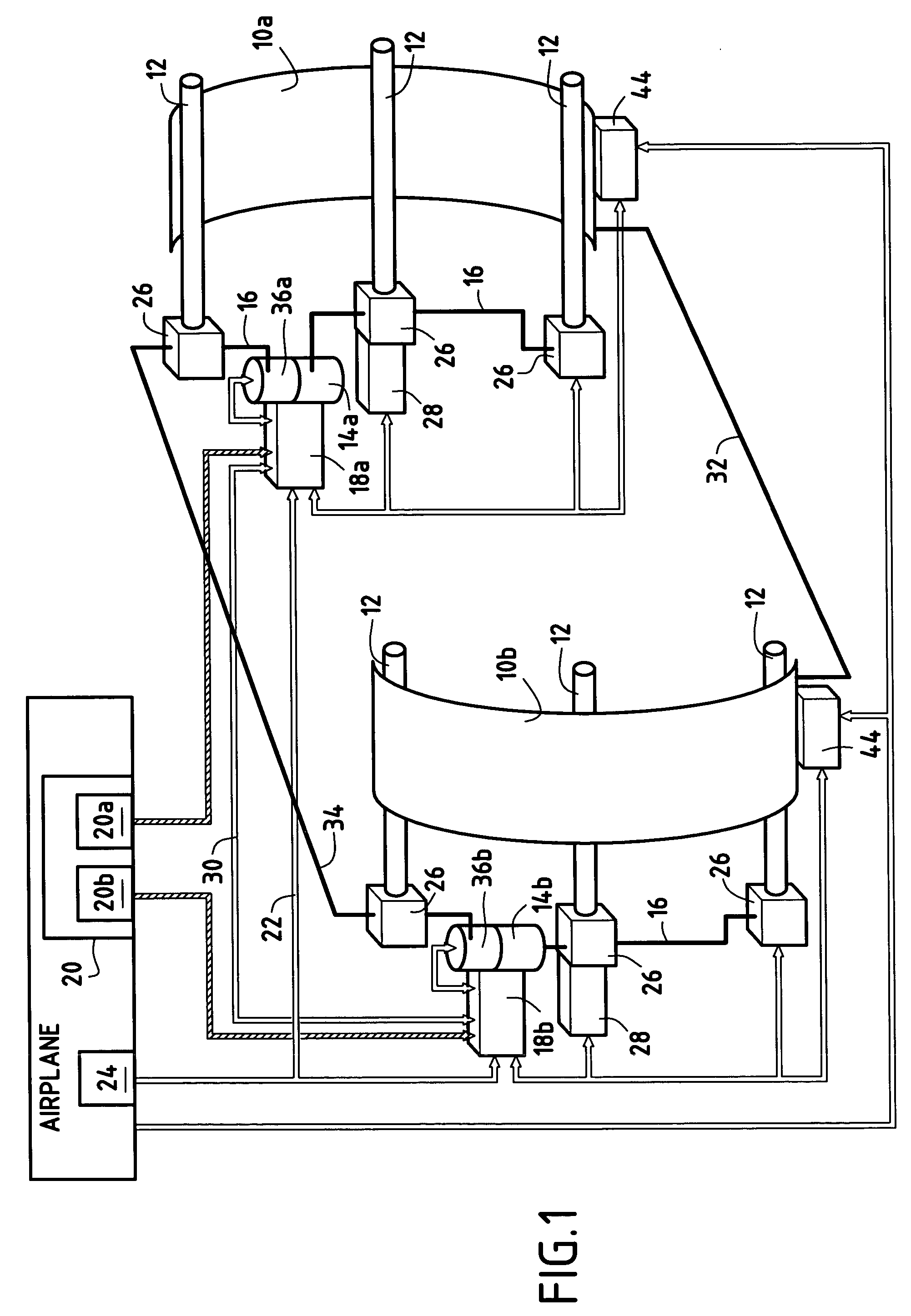
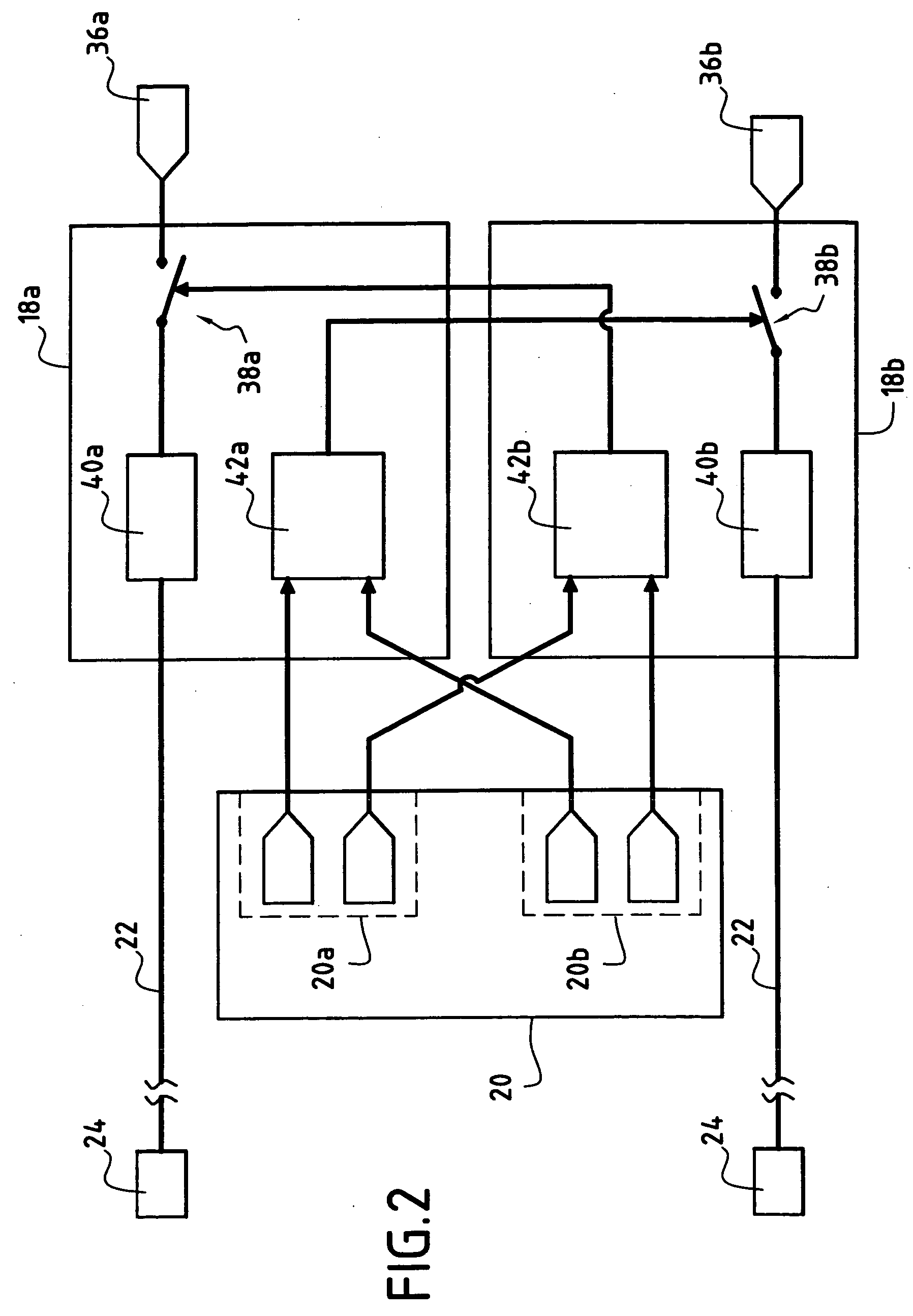
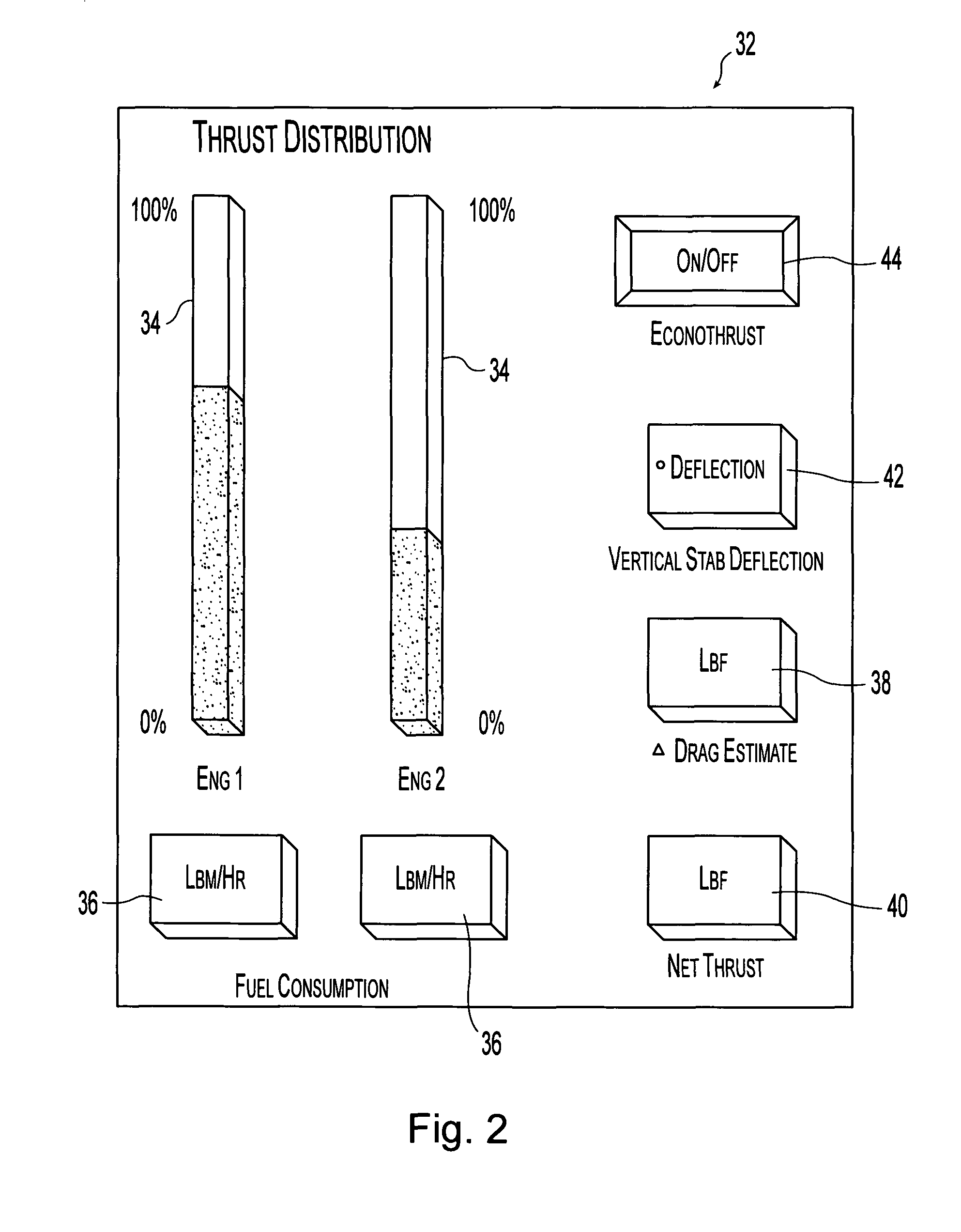
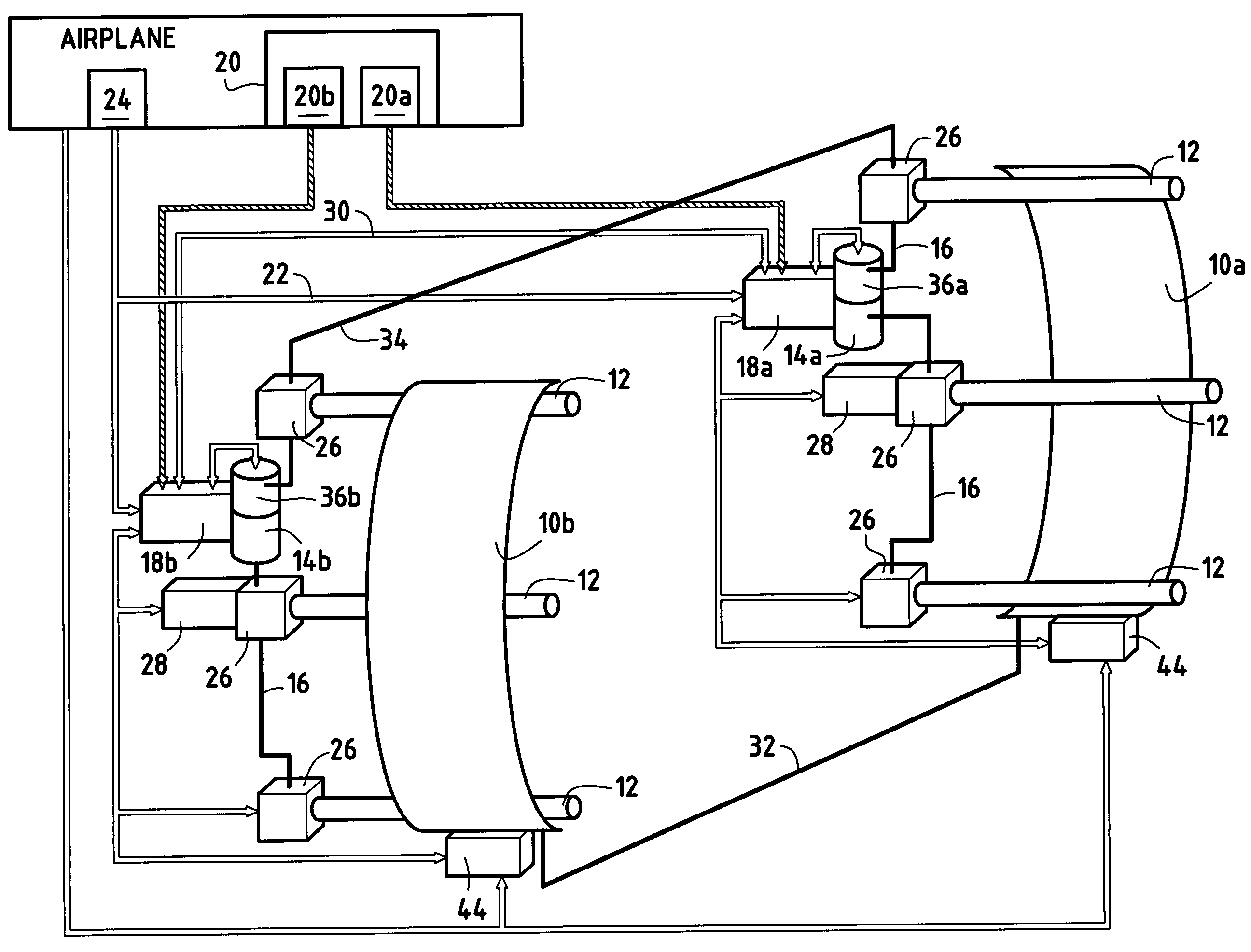
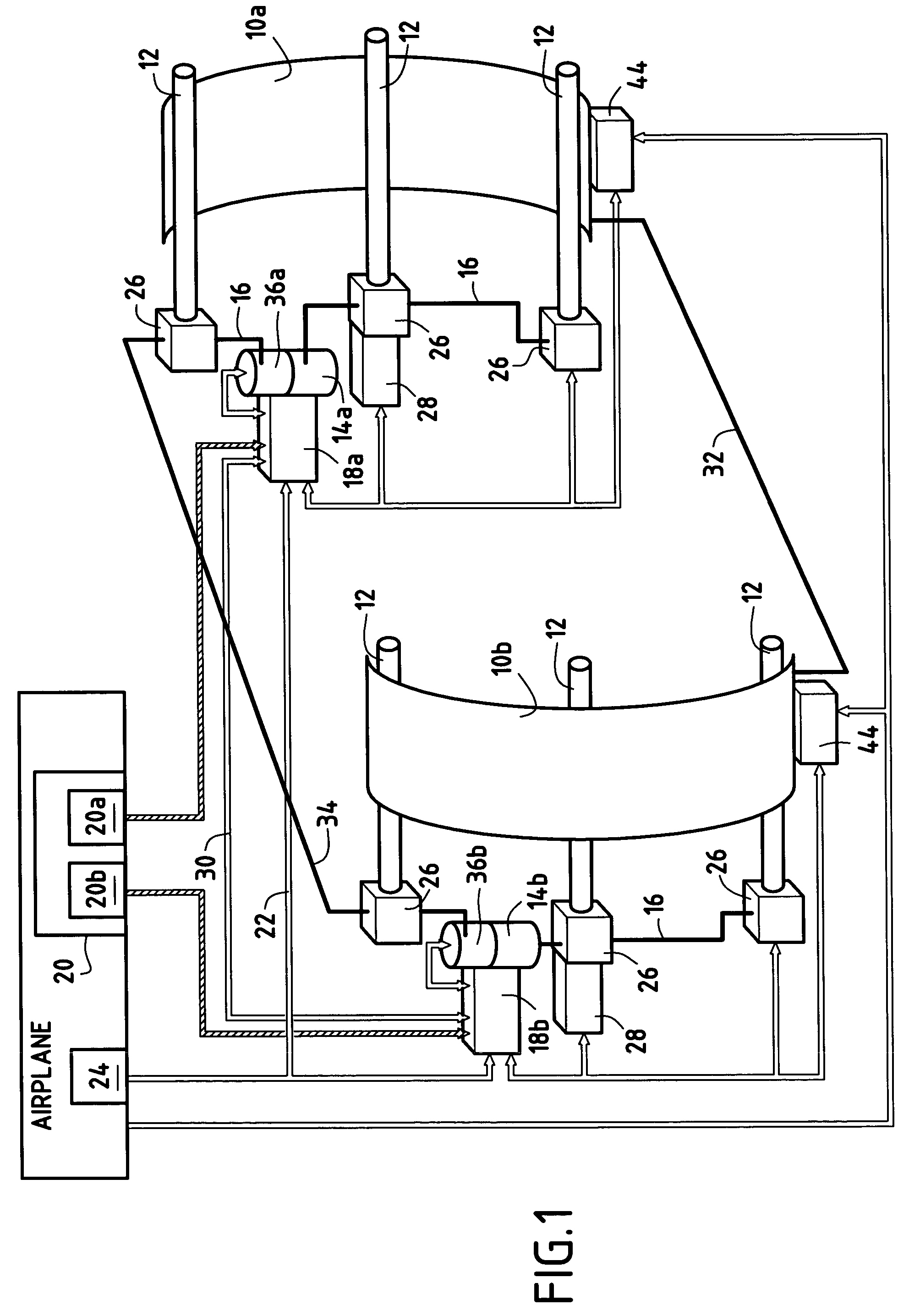
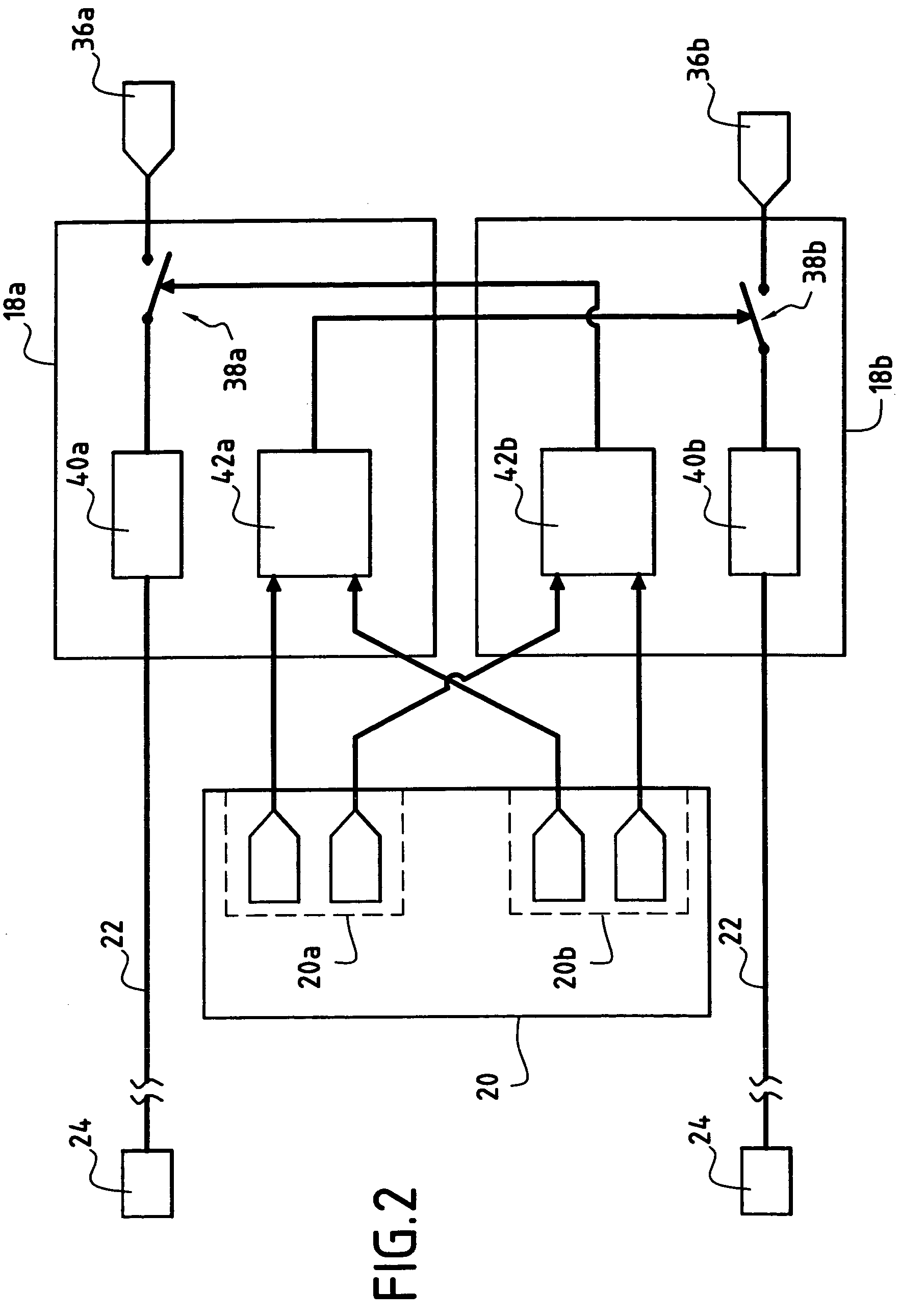
A method and apparatus for improving fuel efficiency in an aircraft having a digital avionics system and at least first and second engines. The avionics system includes first and second full-authority digital engine control (FADEC) systems and corresponding first and second engines. At least one processor is provided that is programmed with a differential specific fuel consumption (DSFC) algorithm and first and second engine optimization algorithms. The DSFC algorithm adjusts the throttle of the first and second engines to substantially equalize the differential specific fuel consumption of the engines and thereby improve the fuel efficiency of the aircraft. The first and second engine optimization algorithms adjust at least one operating parameter of the first and second engines respectively to improve the fuel efficiency of the first and second engines.
Owner:TELECTRO MEK
Turbojet electromechanical thrust reverser with synchronized locking devices
ActiveUS20040139725A1Improve securityEasy to controlPower plant arrangements/mountingSpraying apparatusTurbojetThrust reversal
A turbojet thrust reverser has two doors that are displaceable between a reverser open position and a reverser closed position, each door being controlled by a respective electronic control unit connected to a FADEC, and each door having a respective locking device for locking the position of the door associated therewith. Each locking device can be unlocked solely on receiving orders that come simultaneously from both electronic control units.
Owner:SAFRAN ELECTRICAL & POWER
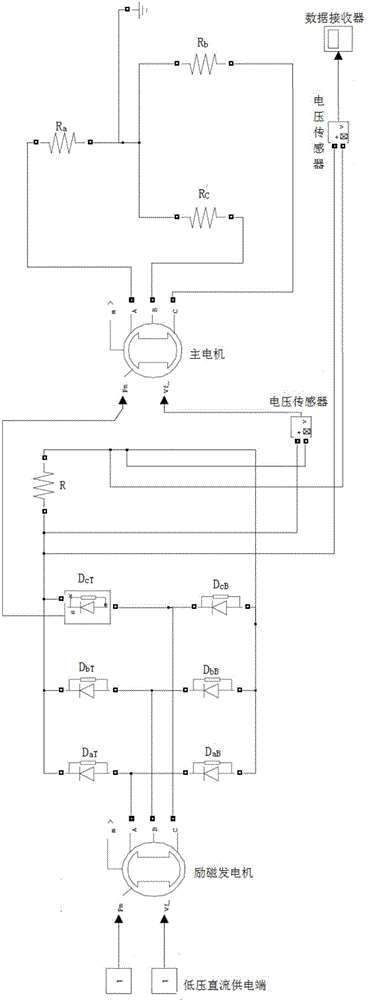
Engine starting system using stored energy
ActiveUS20140260306A1Turbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionStored energyChannel power
There is described a method for and system for starting at least one engine from a twin engine installation. The starting system comprises a first engine arrangement comprising a first electric machine having a single rotor dual stator configuration, a first dual channel power control unit coupled to the first electric machine, and a first dual channel full authority digital engine control (FADEC) coupled to the first dual channel power control unit; a second engine arrangement comprising a second electric machine having a single rotor dual stator configuration, a second dual channel power control unit coupled to the second electric machine, and a second dual channel full authority digital engine control (FADEC) coupled to the second dual channel power control unit; an energy storage unit coupled to the first engine arrangement and the second engine arrangement and having at least a first super-capacitor and a second super-capacitor; and a DC to DC converter configured to receive a first voltage level from a power source, increase the first voltage level to a second voltage level, and charge the first super-capacitor and the second super-capacitor to the second voltage level.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Turbojet electromechanical thrust reverser with servo-controlled door displacement
ActiveUS20040139726A1Mitigate such drawbackAccurate displacementPower plant arrangements/mountingEngine controlActuatorControl theory
A turbojet thrust reverser comprising two doors each displaceable between an open position and a closed position of the reverser by means of at least one respective control actuator; two electric motors each driving said at least one control actuator for each door; each motor being controlled by an electronic control unit connected to a full authority digital engine control; and two servo-control means for controlling the displacement of corresponding ones of said doors as a function of determined position references, said servo-control means enabling said doors to be displaced synchronously as a function of any variation in the forces exerted on the reverser and as a function of any force difference between the two doors.
Owner:SAFRAN ELECTRICAL & POWER
Apparatus and method for reducing aircraft fuel consumption
InactiveUS8290683B2Improve fuel efficiencyFuel consumptionAnalogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsAviationElectronic systems
A method and apparatus for improving fuel efficiency in an aircraft having a digital avionics system and at least first and second engines. The avionics system includes first and second full-authority digital engine control (FADEC) systems and corresponding first and second engines. At least one processor is provided that is programmed with a differential specific fuel consumption (DSFC) algorithm and first and second engine optimization algorithms. The DSFC algorithm adjusts the throttle of the first and second engines to substantially equalize the differential specific fuel consumption of the engines and thereby improve the fuel efficiency of the aircraft. The first and second engine optimization algorithms adjust at least one operating parameter of the first and second engines respectively to improve the fuel efficiency of the first and second engines.
Owner:TELECTRO MEK
Turbojet electromechanical thrust reverser with synchronized locking devices
ActiveUS7278257B2Improve securityEasy to controlPower plant arrangements/mountingSpraying apparatusTurbojetThrust reversal
A turbojet thrust reverser has two doors that are displaceable between a reverser open position and a reverser closed position, each door being controlled by a respective electronic control unit connected to a FADEC, and each door having a respective locking device for locking the position of the door associated therewith. Each locking device can be unlocked solely on receiving orders that come simultaneously from both electronic control units.
Owner:SAFRAN ELECTRICAL & POWER
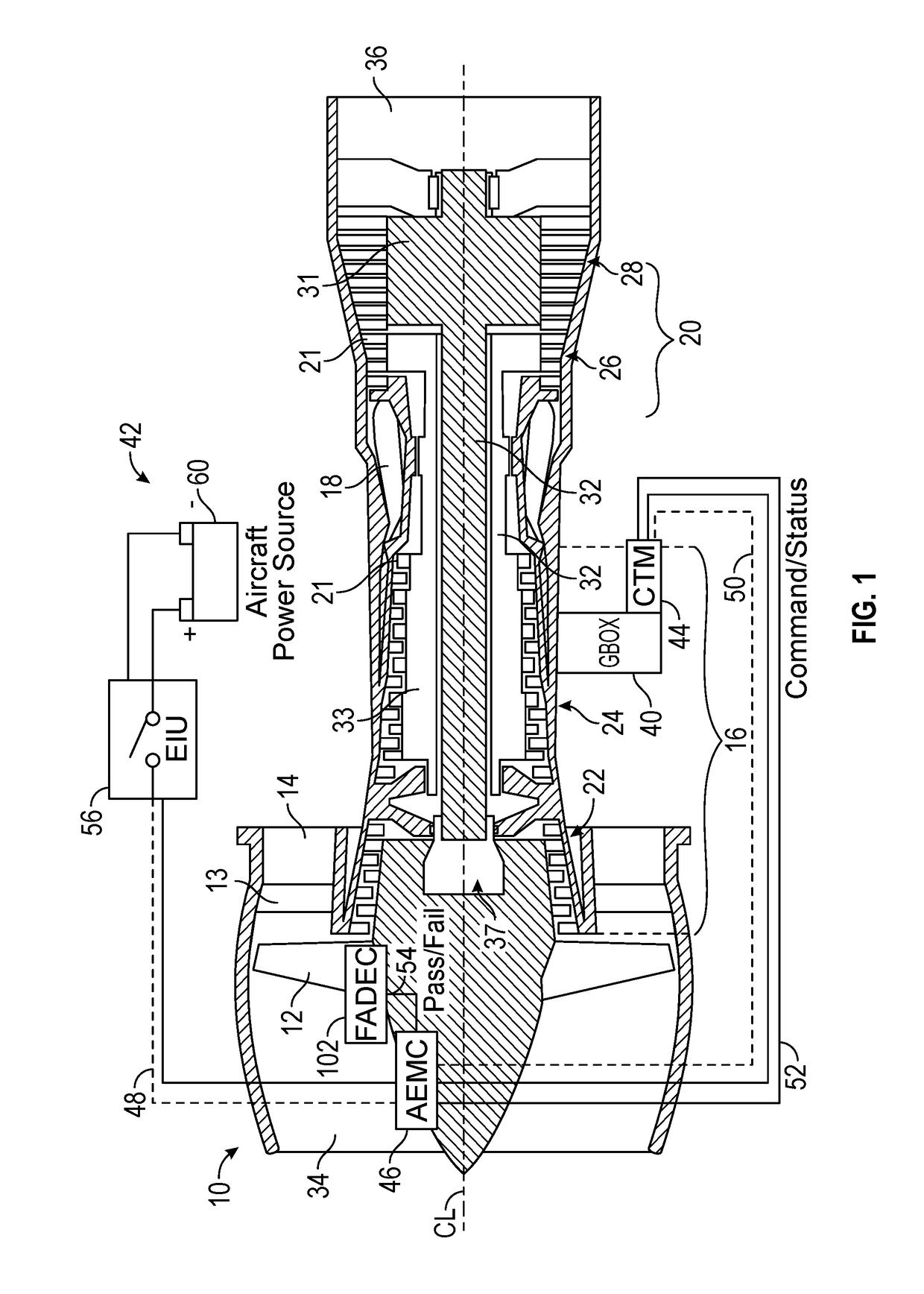
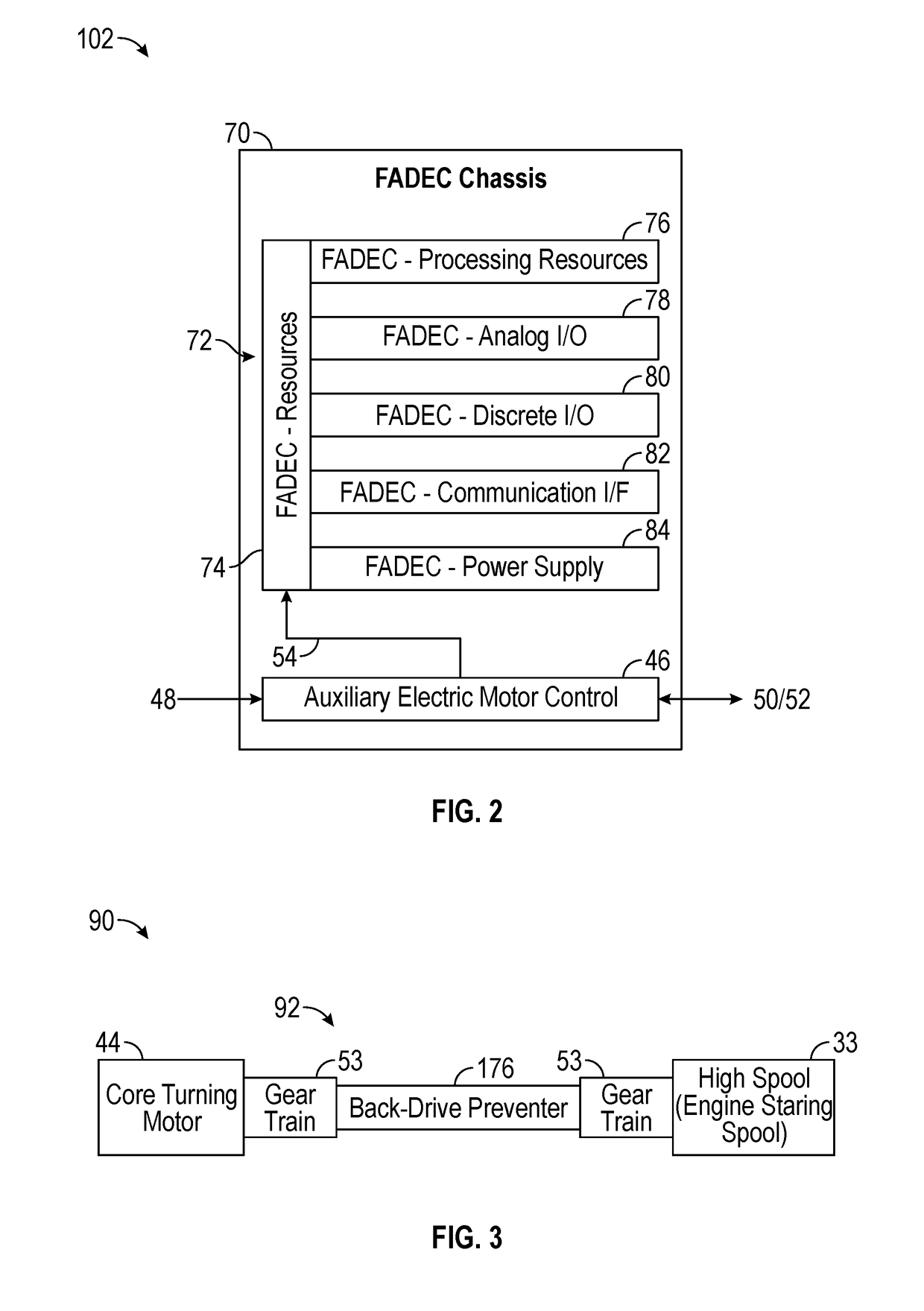
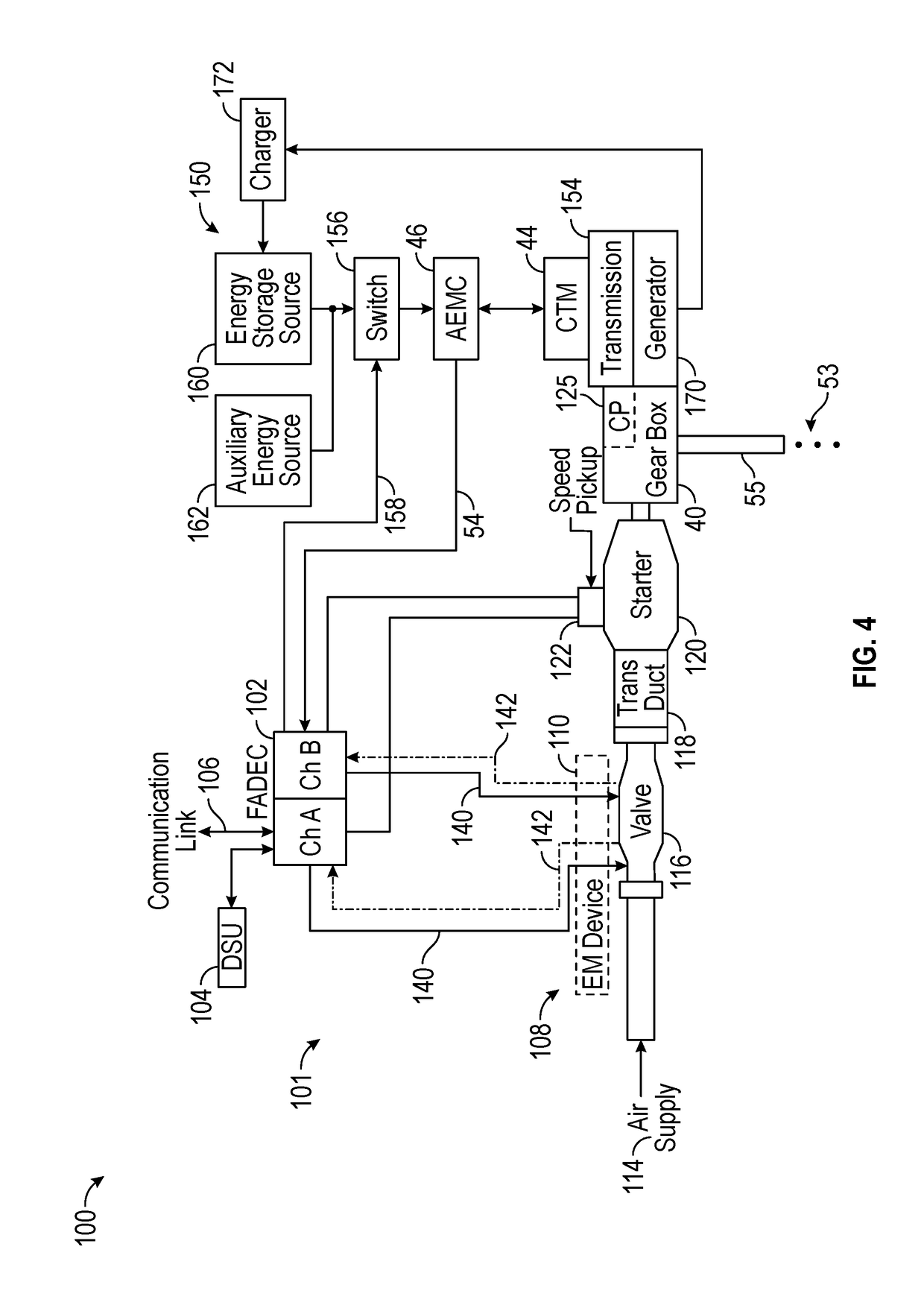
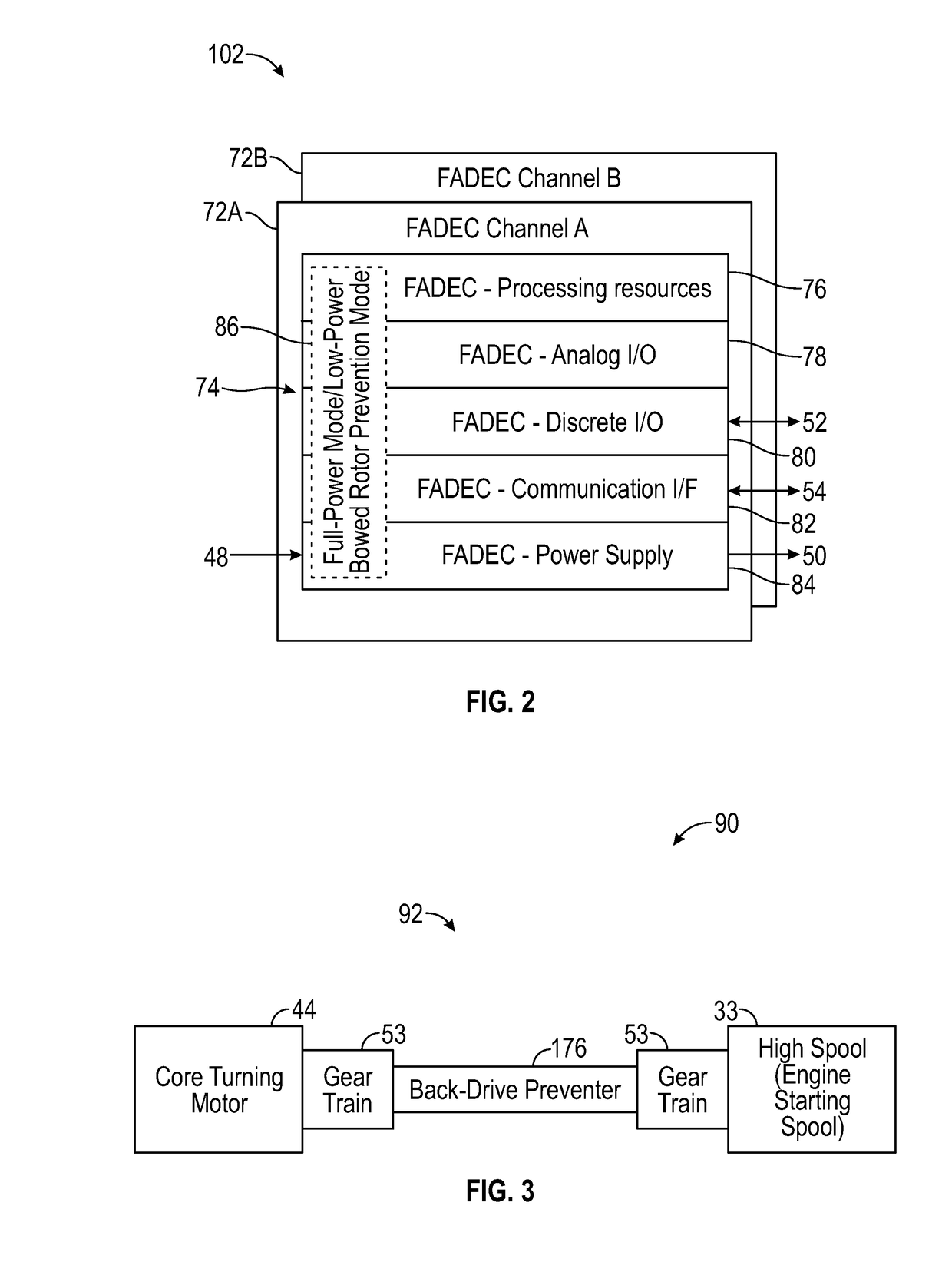
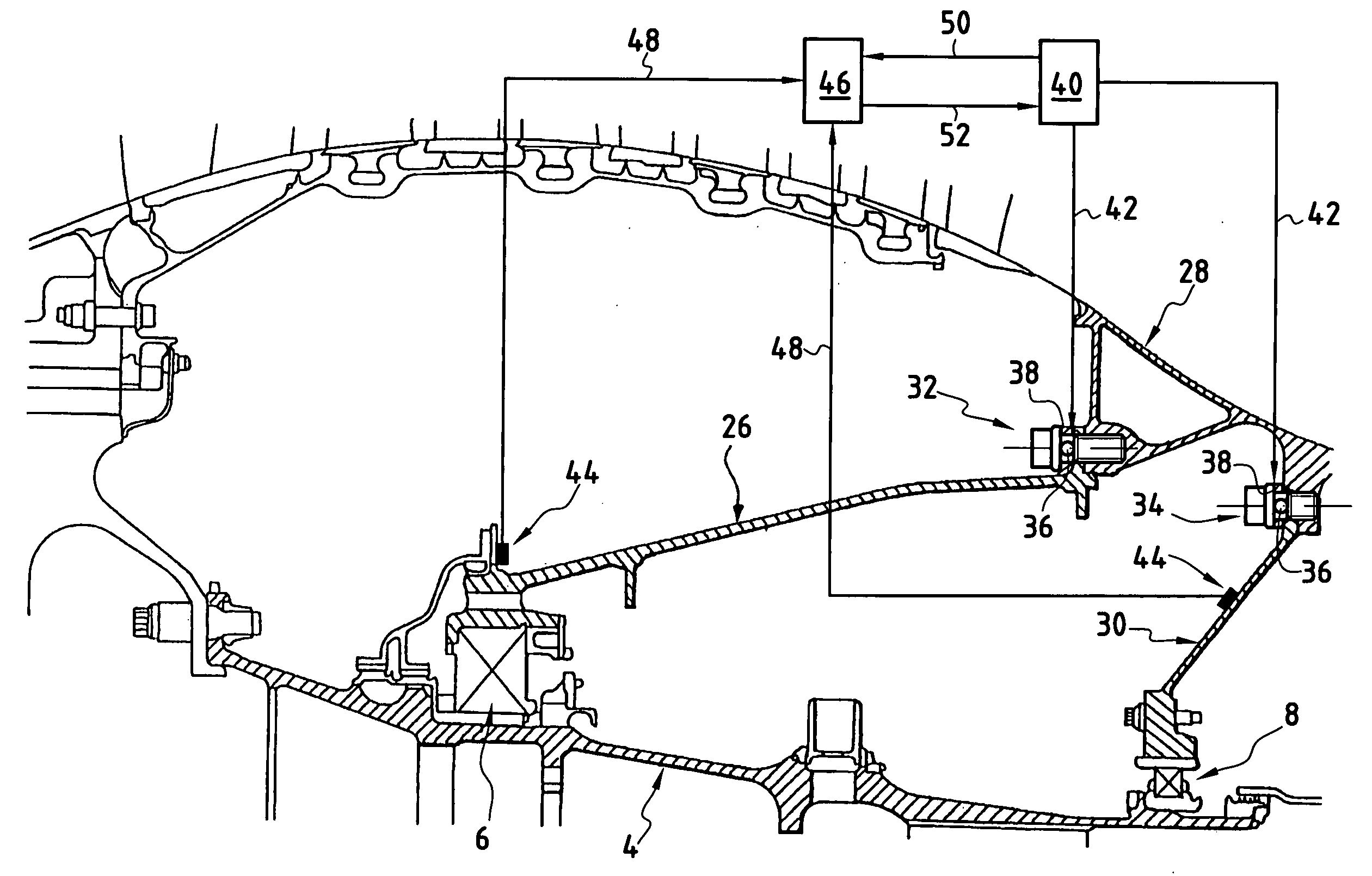
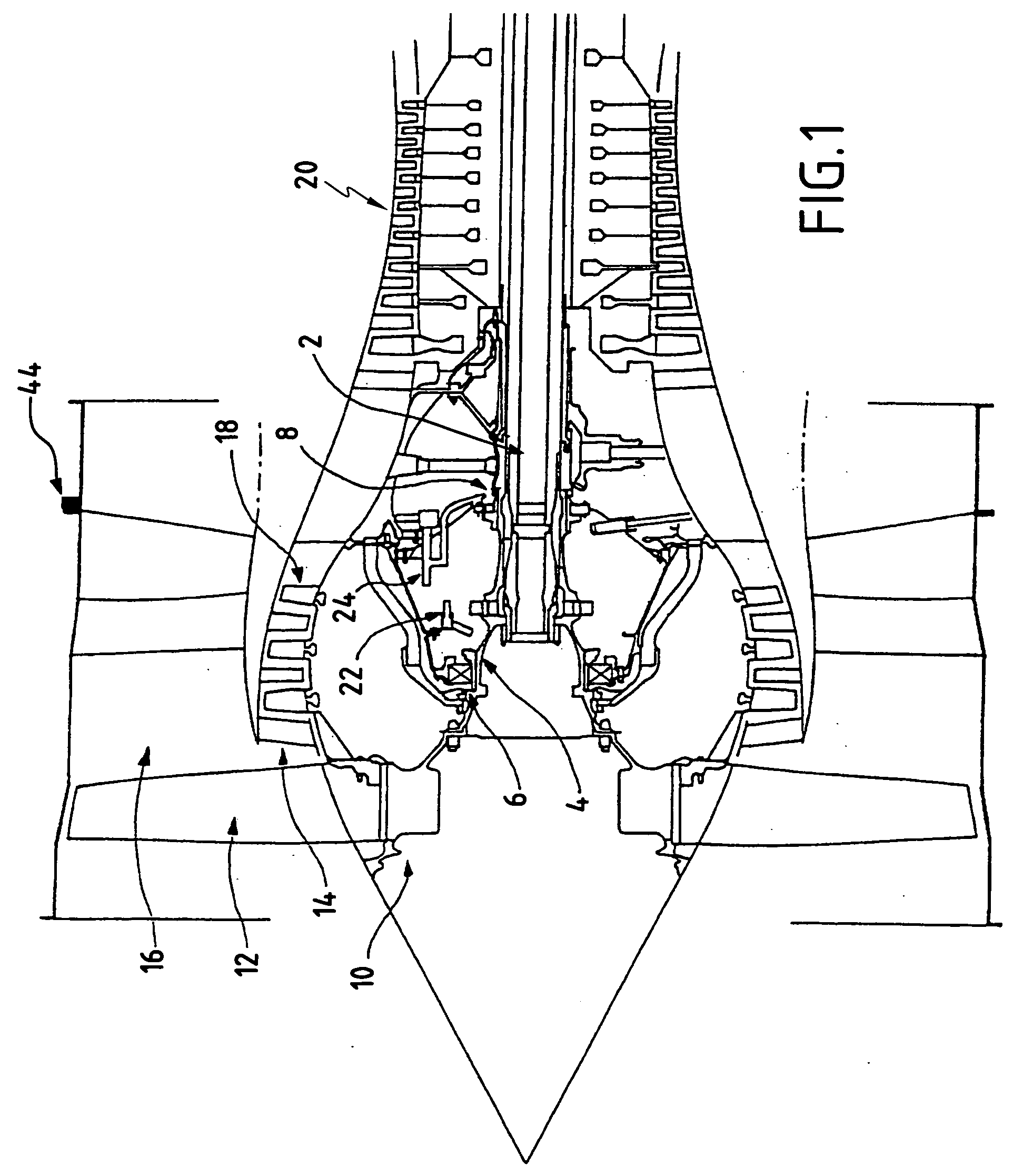
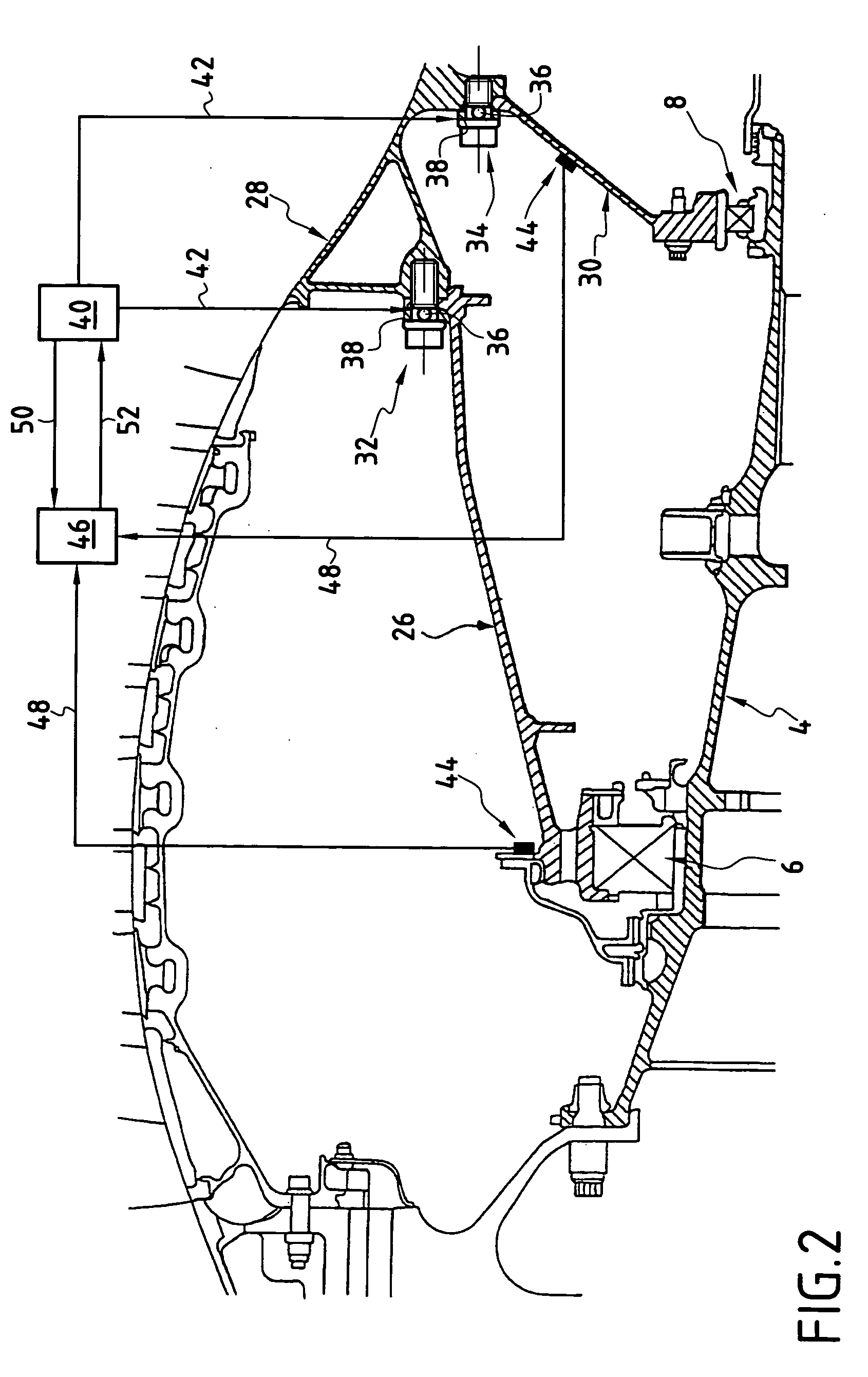
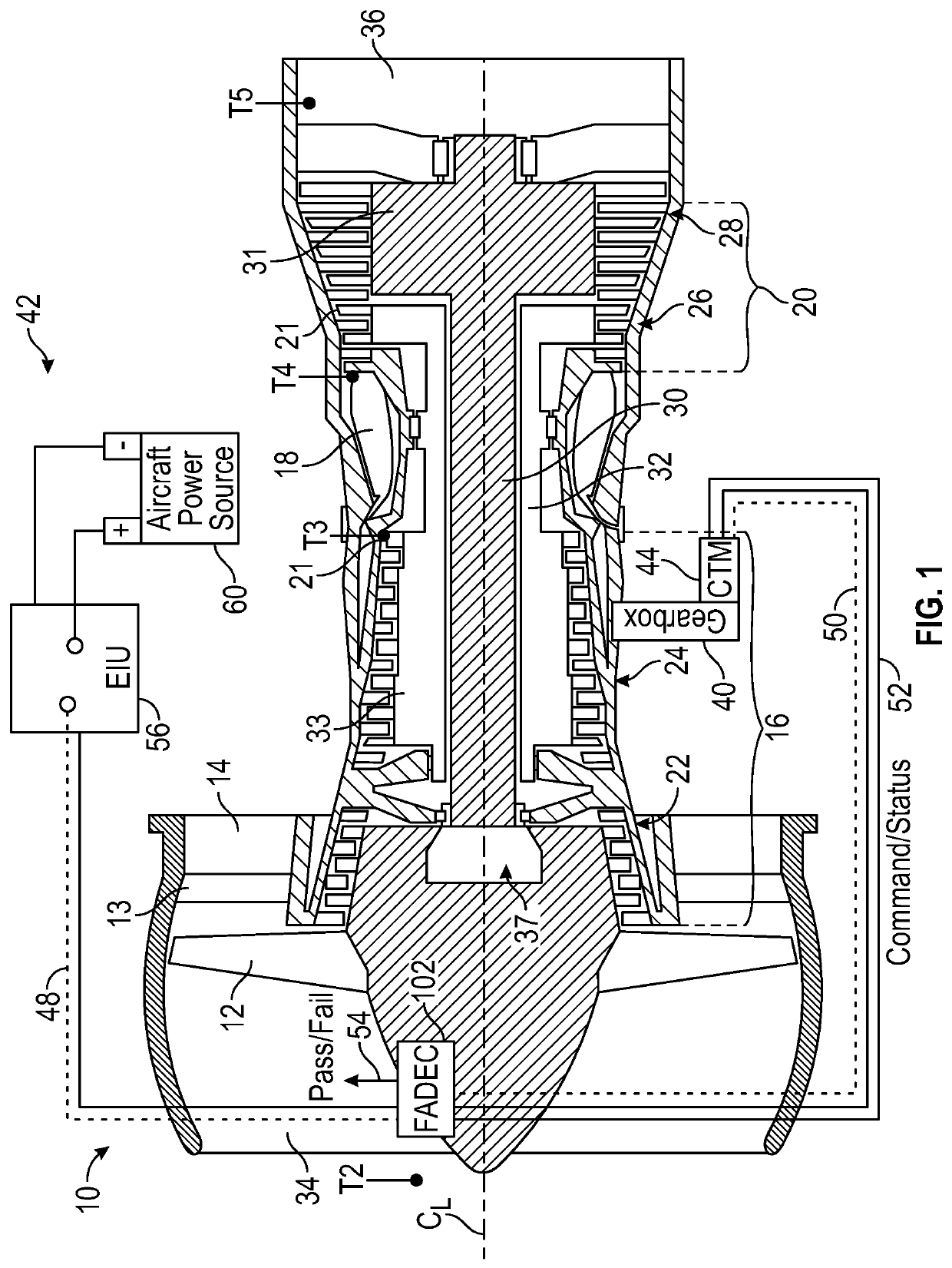
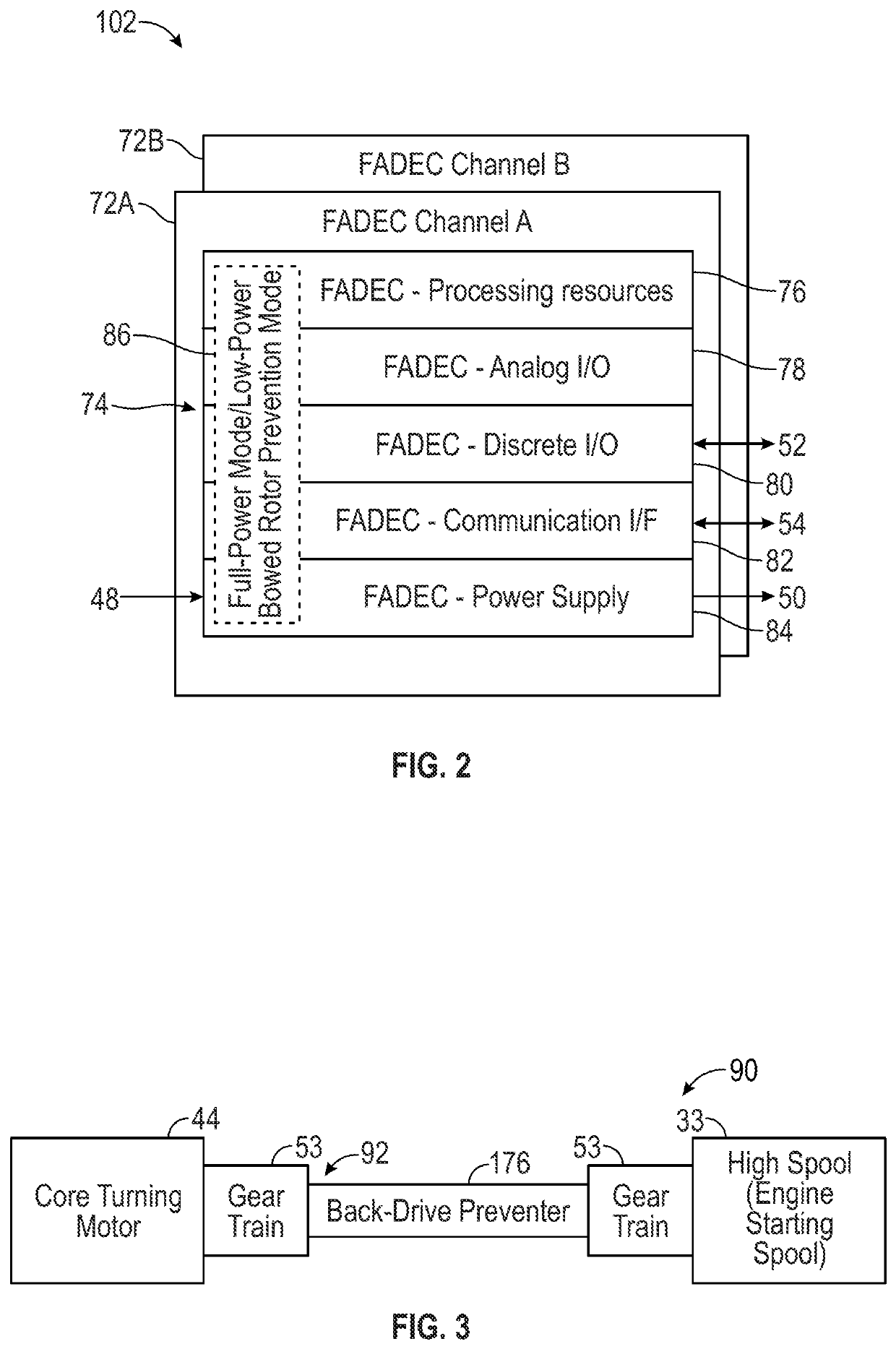
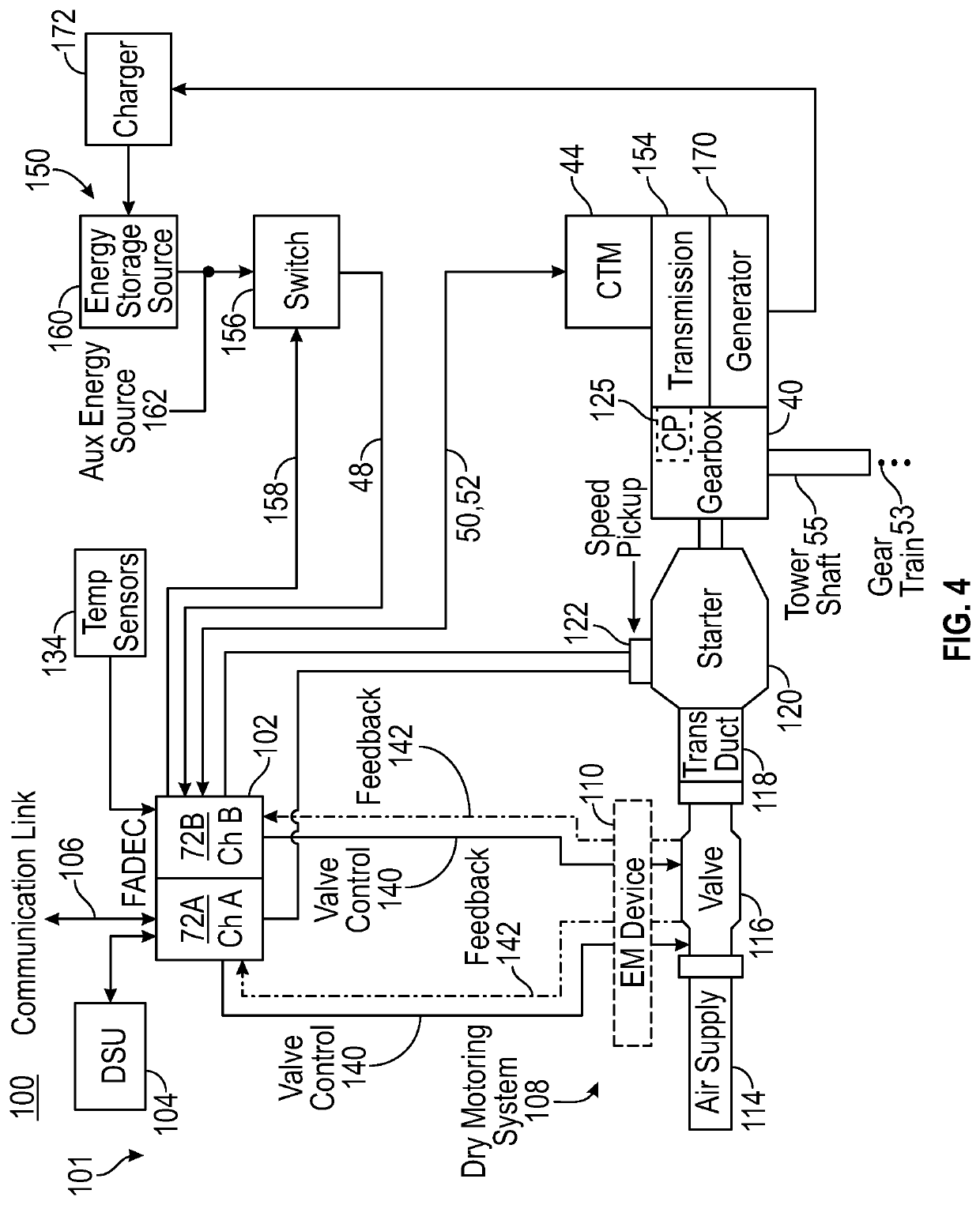
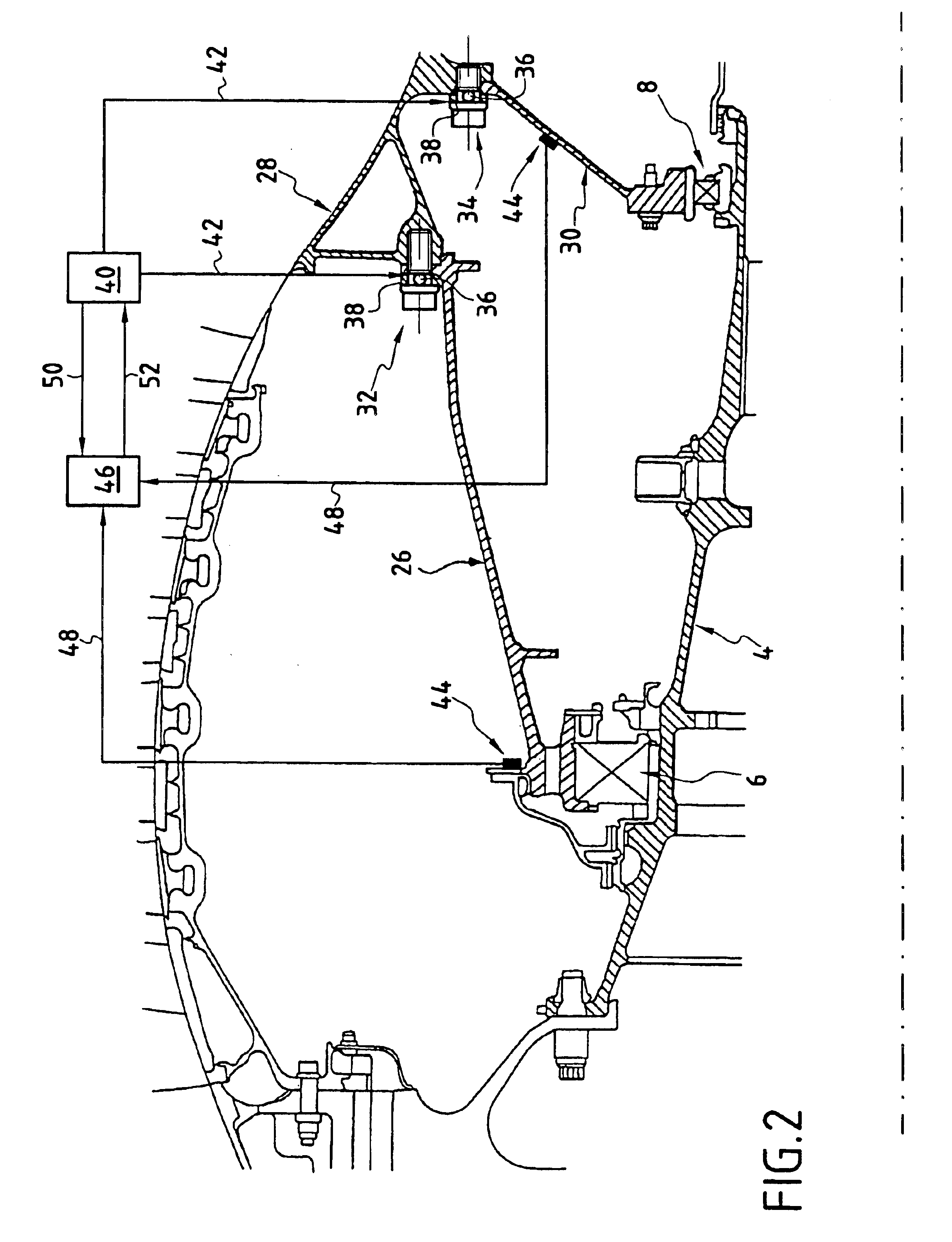
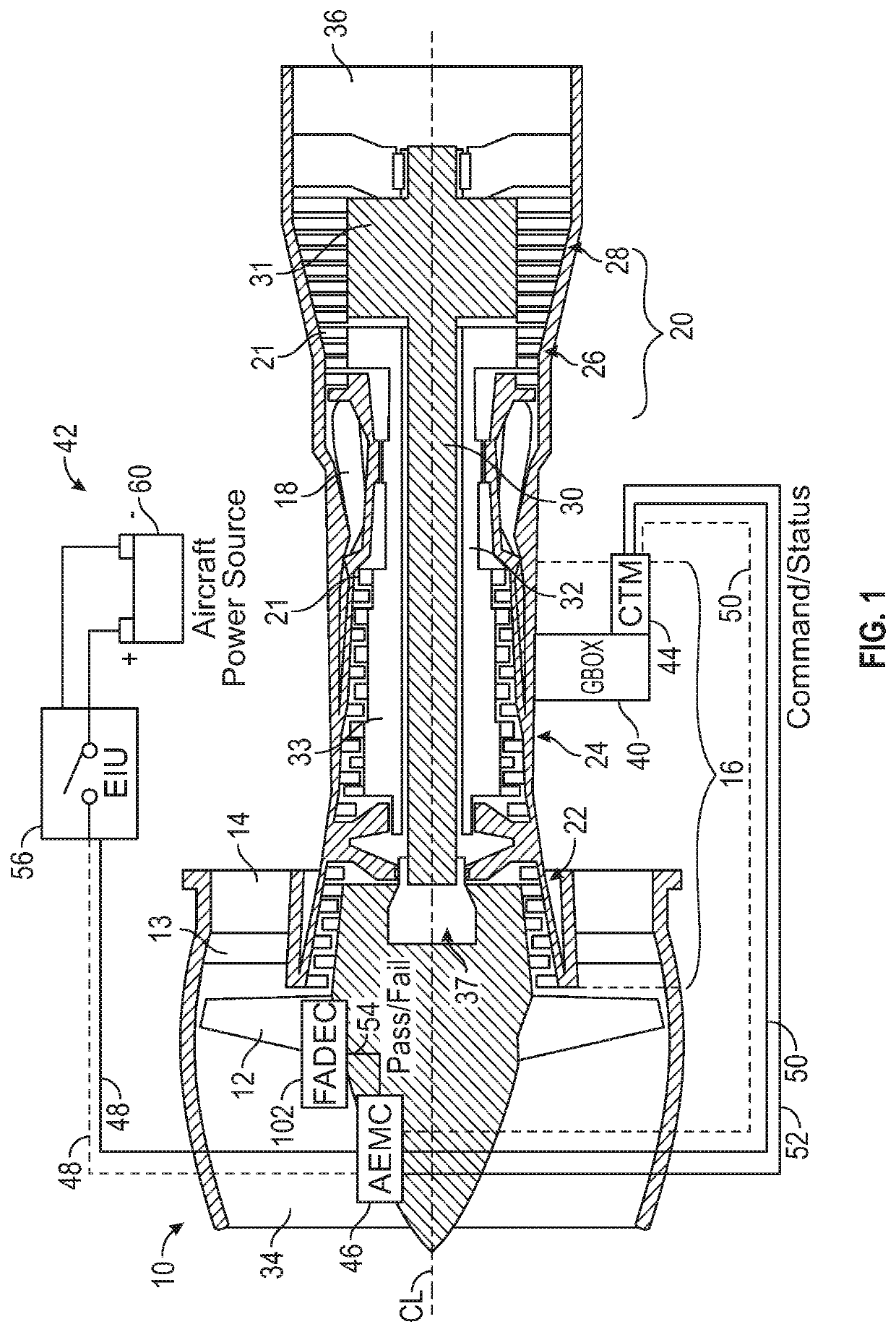
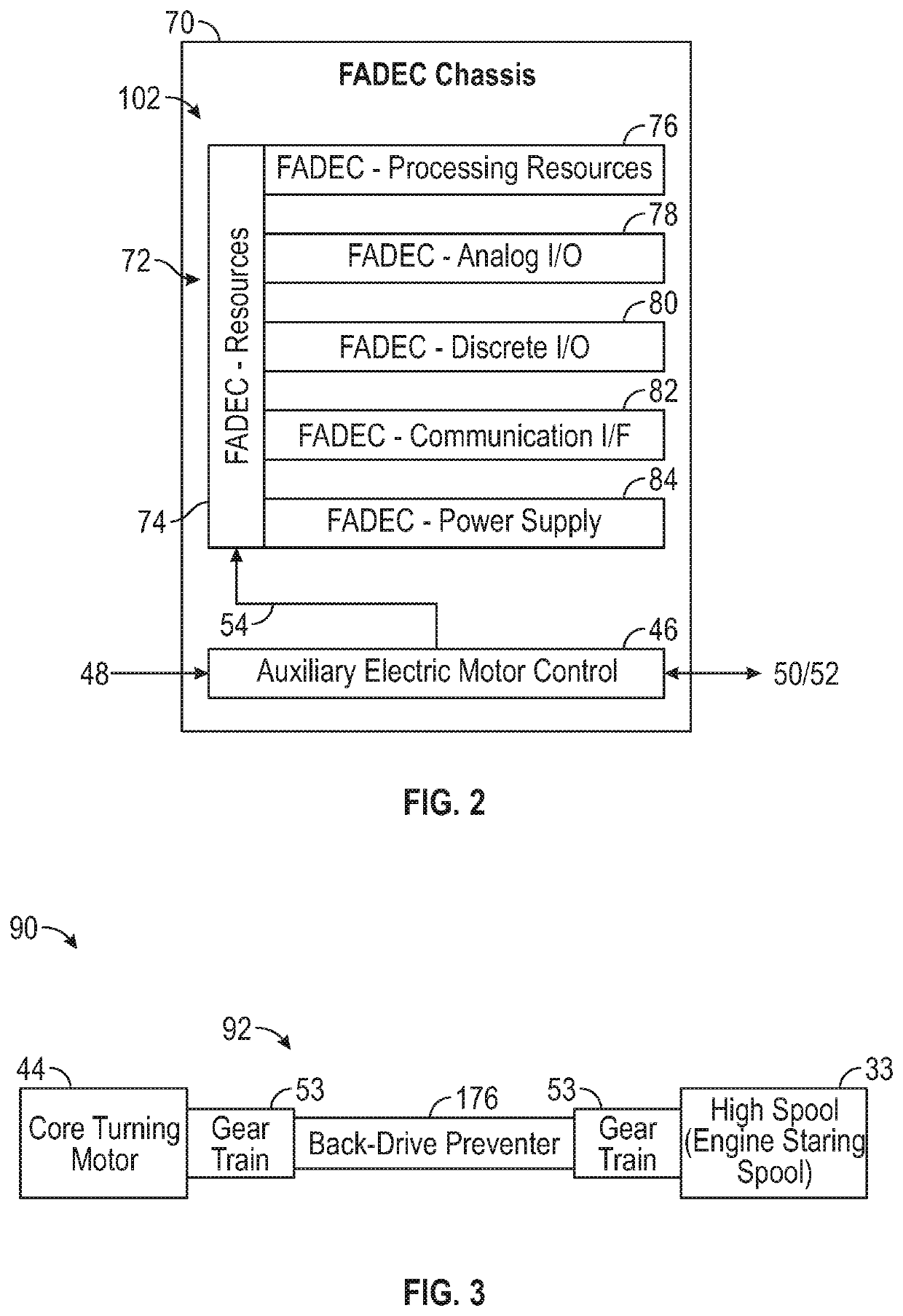
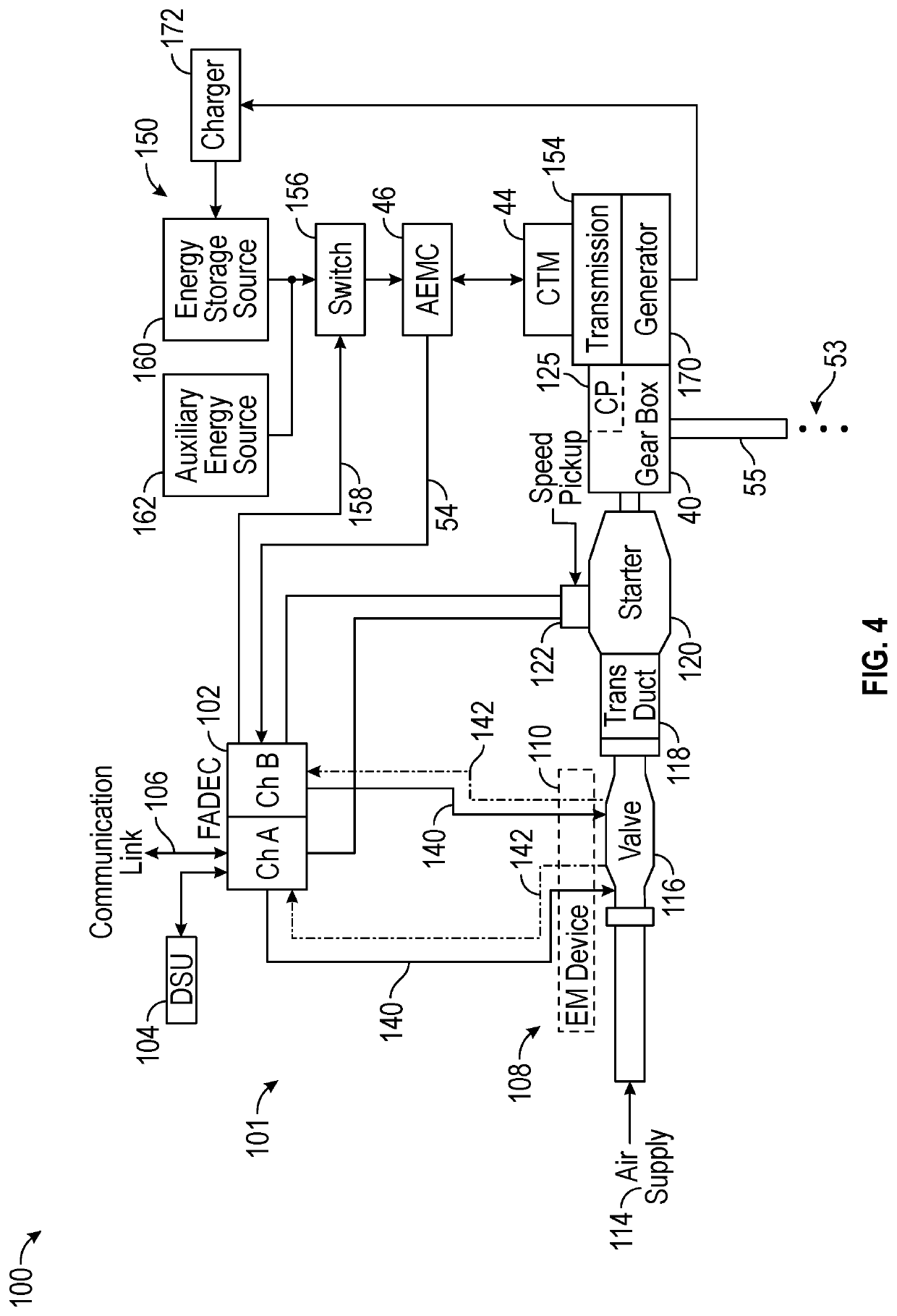
Low-power bowed rotor prevention system
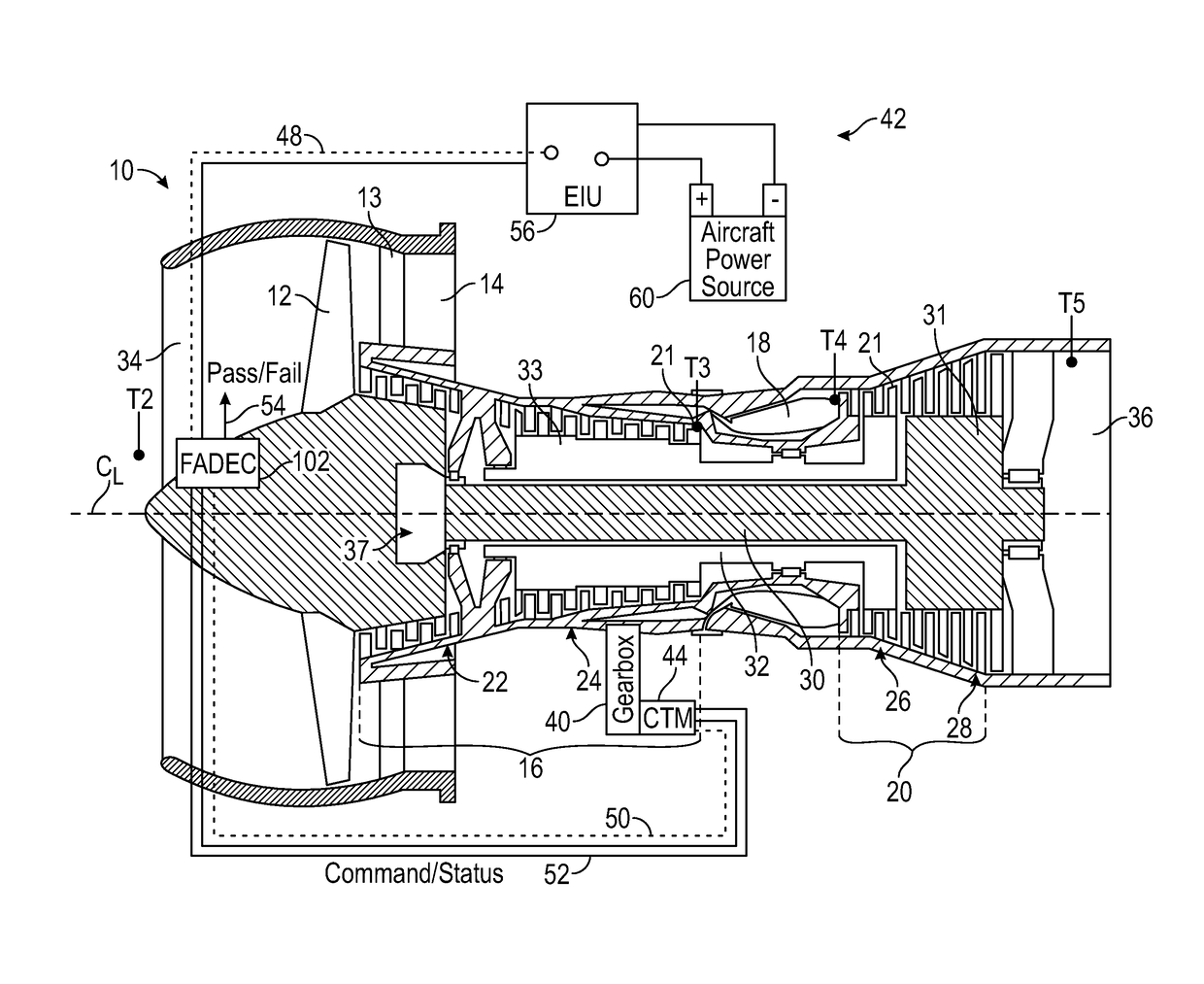
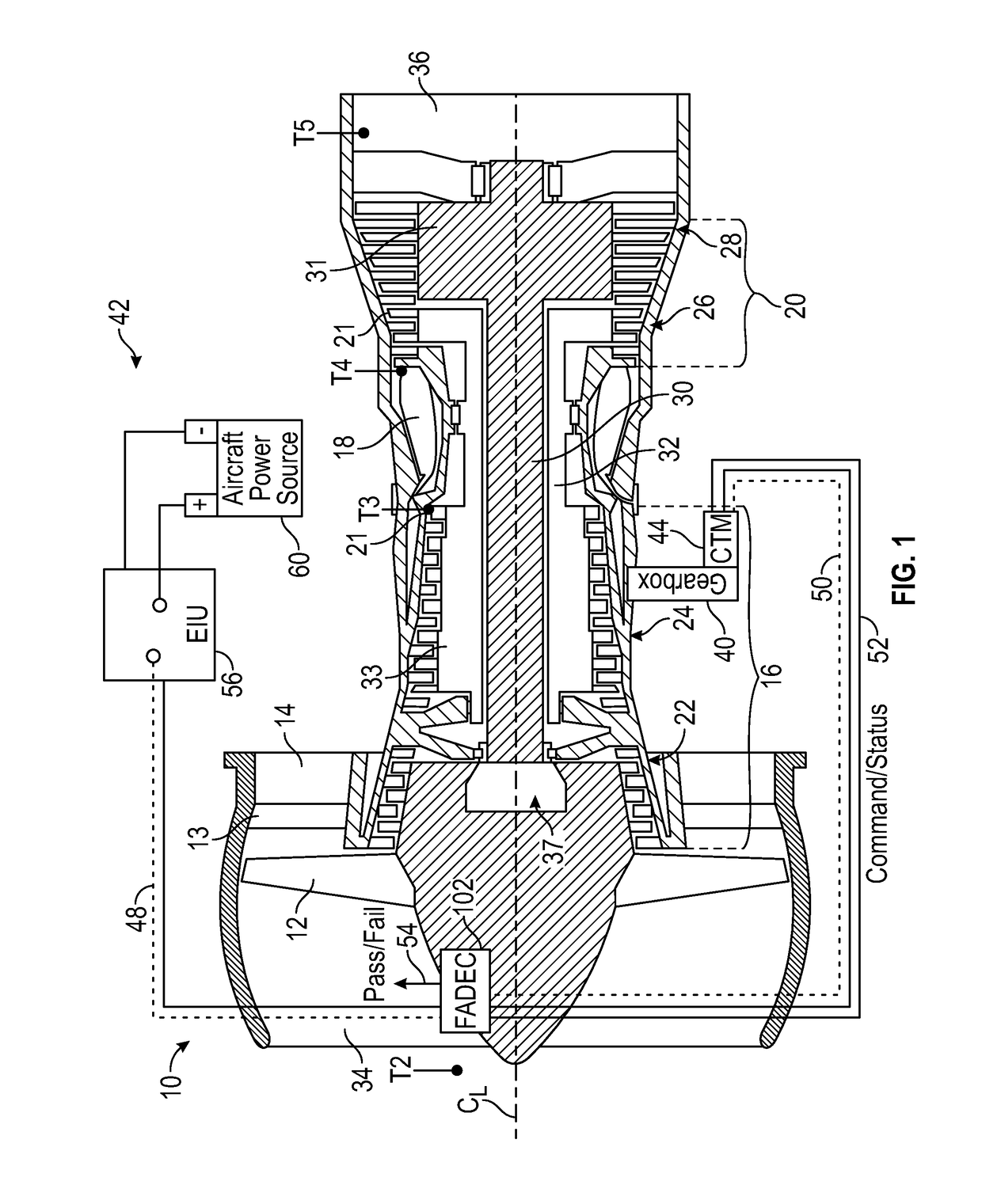
A bowed rotor prevention system for a gas turbine engine includes a core turning motor operable to drive rotation of an engine core of the gas turbine engine. The bowed rotor prevention system also includes an auxiliary electric motor control operable to control the core turning motor to drive rotation of the engine core using electric power while a full authority digital engine control that controls operation of the gas turbine engine is either depowered or in a power state that is less than a power level used by the full authority digital engine control in flight operation.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Wireless engine monitoring system
InactiveCN1846238ALarge megabyte fileEfficient propulsion technologiesAlarmsMonitoring systemConformal antenna
A wireless engine monitoring system (WEMS) includes an engine monitoring module that is mounted directly on an aircraft engine and records, stores, encrypts and transmits full flight engine data. The system preferably interfaces to the Full Authority Digital Engine Controller / Engine Control Unit (FADEC / ECU) and can record hundreds of engine parameters with a preferred sampling frequency of about one second. The engine monitoring module is preferably formed as a miniaturized module directly mounted on the aircraft engine within its cowling and has a conformal antenna. The monitoring module can also upload data for onboard processing.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Low-power bowed rotor prevention and monitoring system
A bowed rotor prevention system for a gas turbine engine includes a core turning motor operable to drive rotation of an engine core of the gas turbine engine. The bowed rotor prevention system also includes a full authority digital engine control (FADEC) that controls operation of the gas turbine engine in a full-power mode and controls operation of the core turning motor to drive rotation of the engine core using a reduced power draw when the FADEC is partially depowered in a low-power bowed rotor prevention mode.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
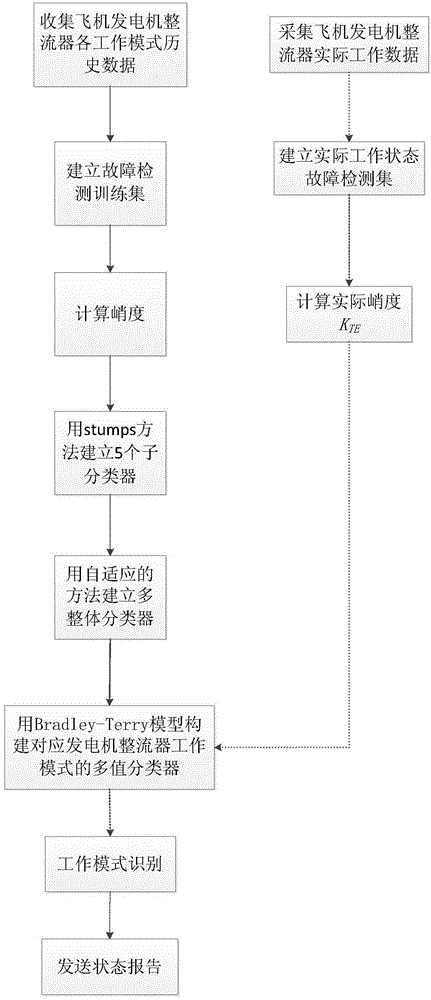
Adaptive fault diagnosis method of aircraft generator rectifier
ActiveCN104635081AIncrease weightReduce the sample weightElectrical testingDiagnosis methodsSelf adaptive
The invention provides an adaptive fault diagnosis method of an aircraft generator rectifier. State monitoring and fault detection of the aircraft generator rectifier are realized. The implementation contents of the method comprise the following steps: determining working modes of a diode of the aircraft generator rectifier; acquiring historical data of the diode of the aircraft generator rectifier under various working modes; training by using the historical data; establishing classifiers for various working modes of the diode of the aircraft generator rectifier on the basis of a stumps method; changing weights of the different classifiers by using an adaptive method to generate an integral binary classifier; finally introducing an active learning mechanism by using a Generalized Bradley-Terry model to form a multi-classifier. The method is integrated in FADEC (Full Authority Digital Engine Control) of an aircraft engine, so fault monitoring of the generator rectifier can be realized, the accuracy and the efficiency for fault diagnosis of the aircraft generator rectifier are improved, and connection can be automatically cut off by the system when a fault of the rectifier occurs to prevent damage from being caused to subordinate equipment.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
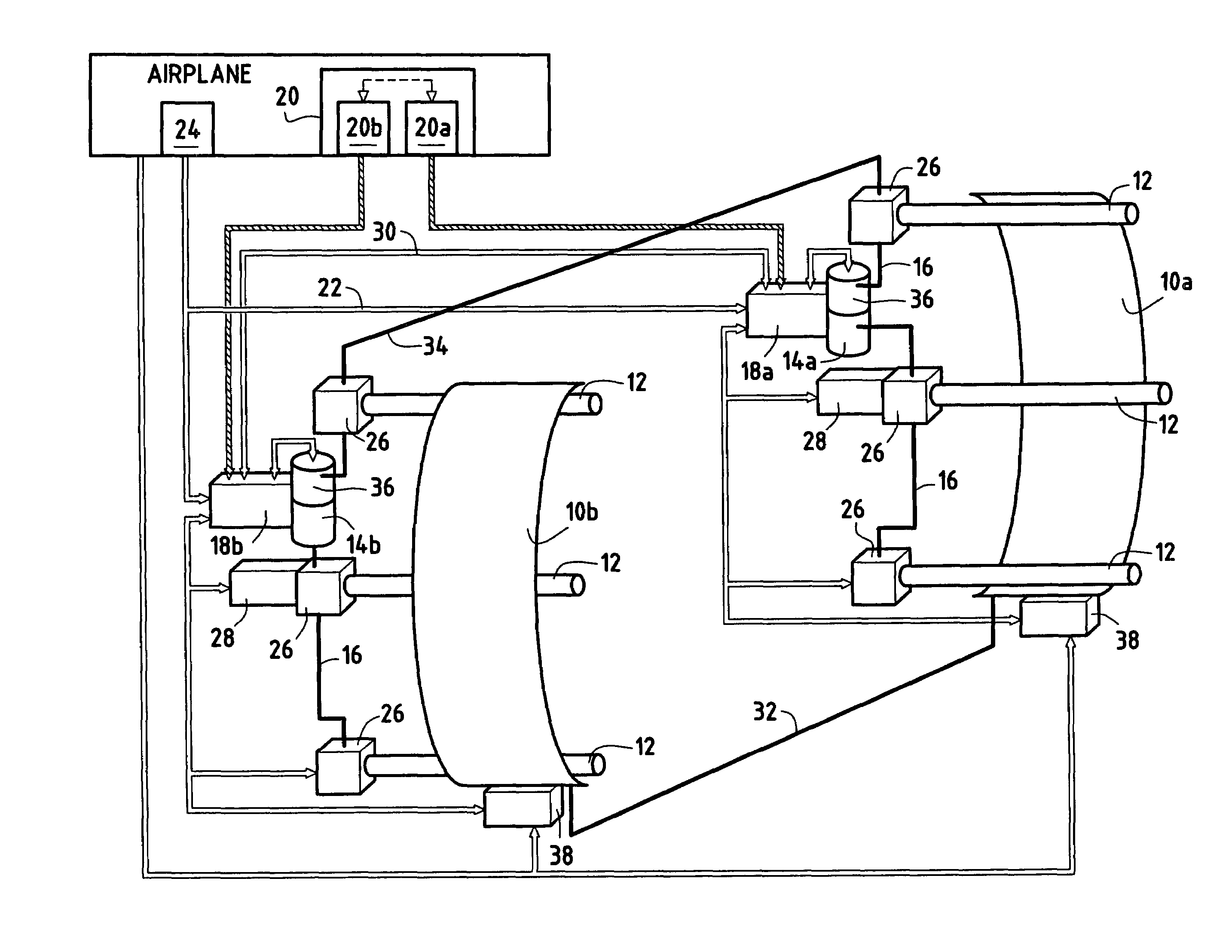
Engine control computer of aircraft, and aircraft
ActiveUS20150148994A1Remove and ease restrictionProcess safety and stabilityAircraft power plantsDigital data processing detailsMode controlMode change
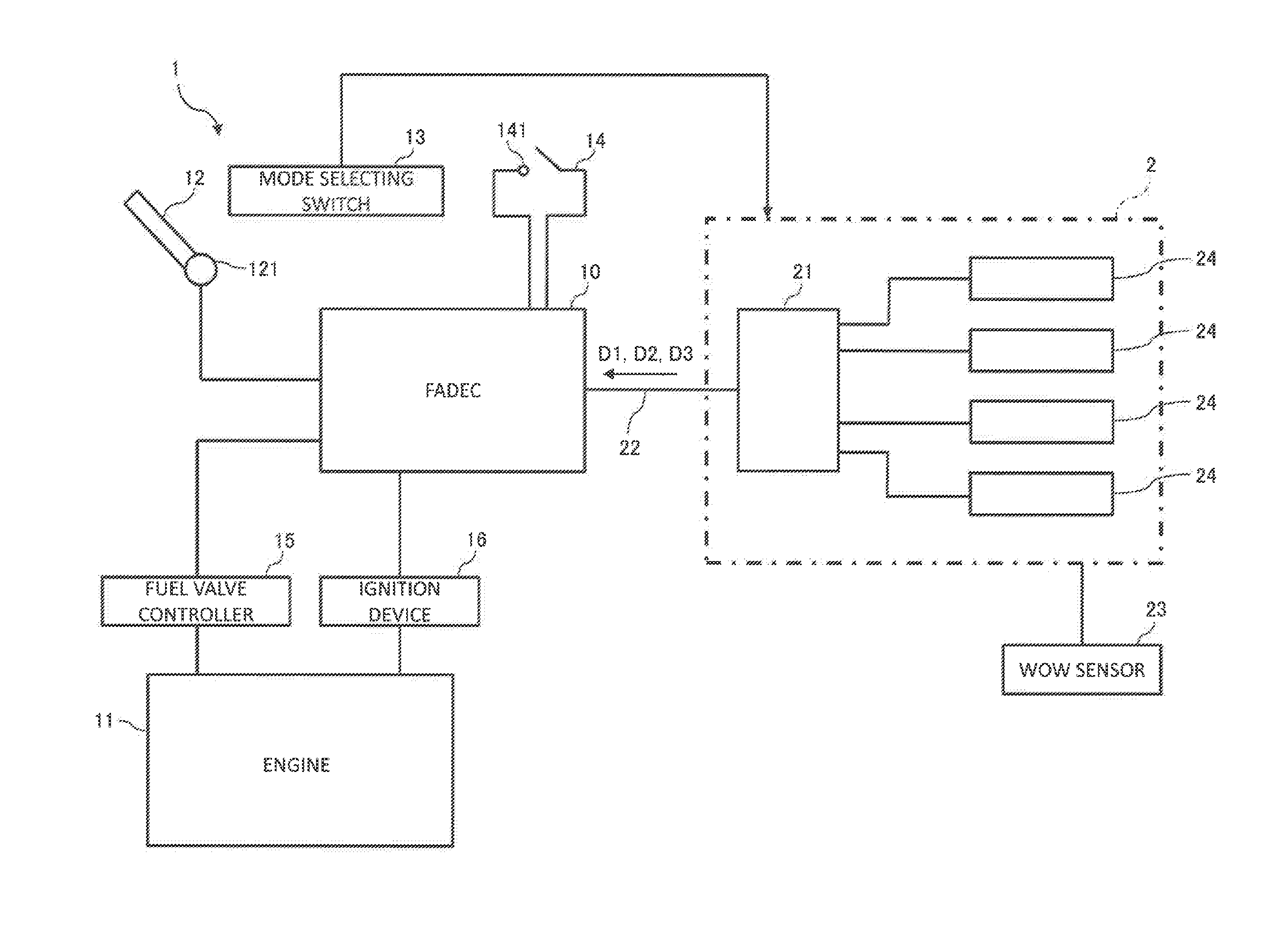
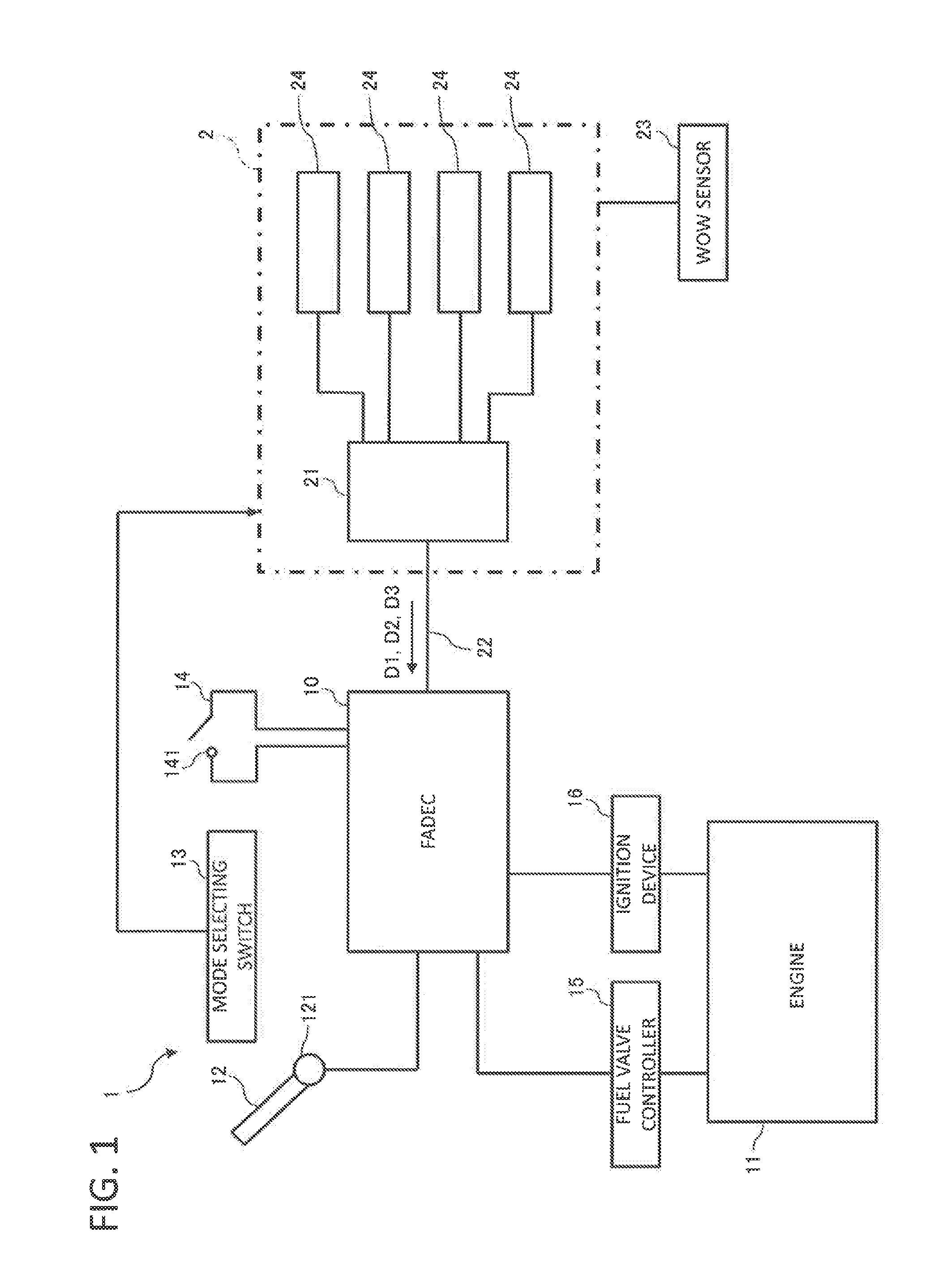
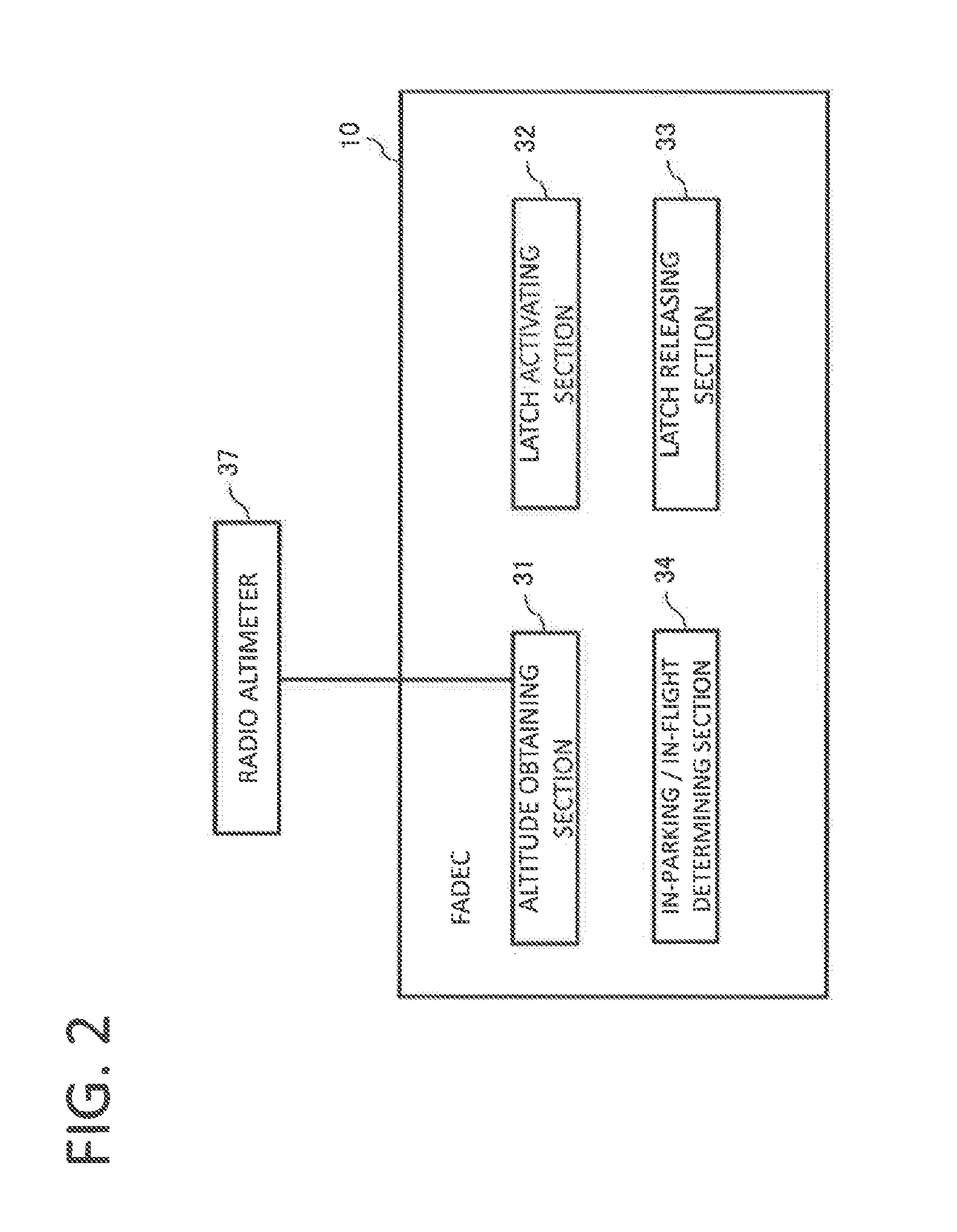
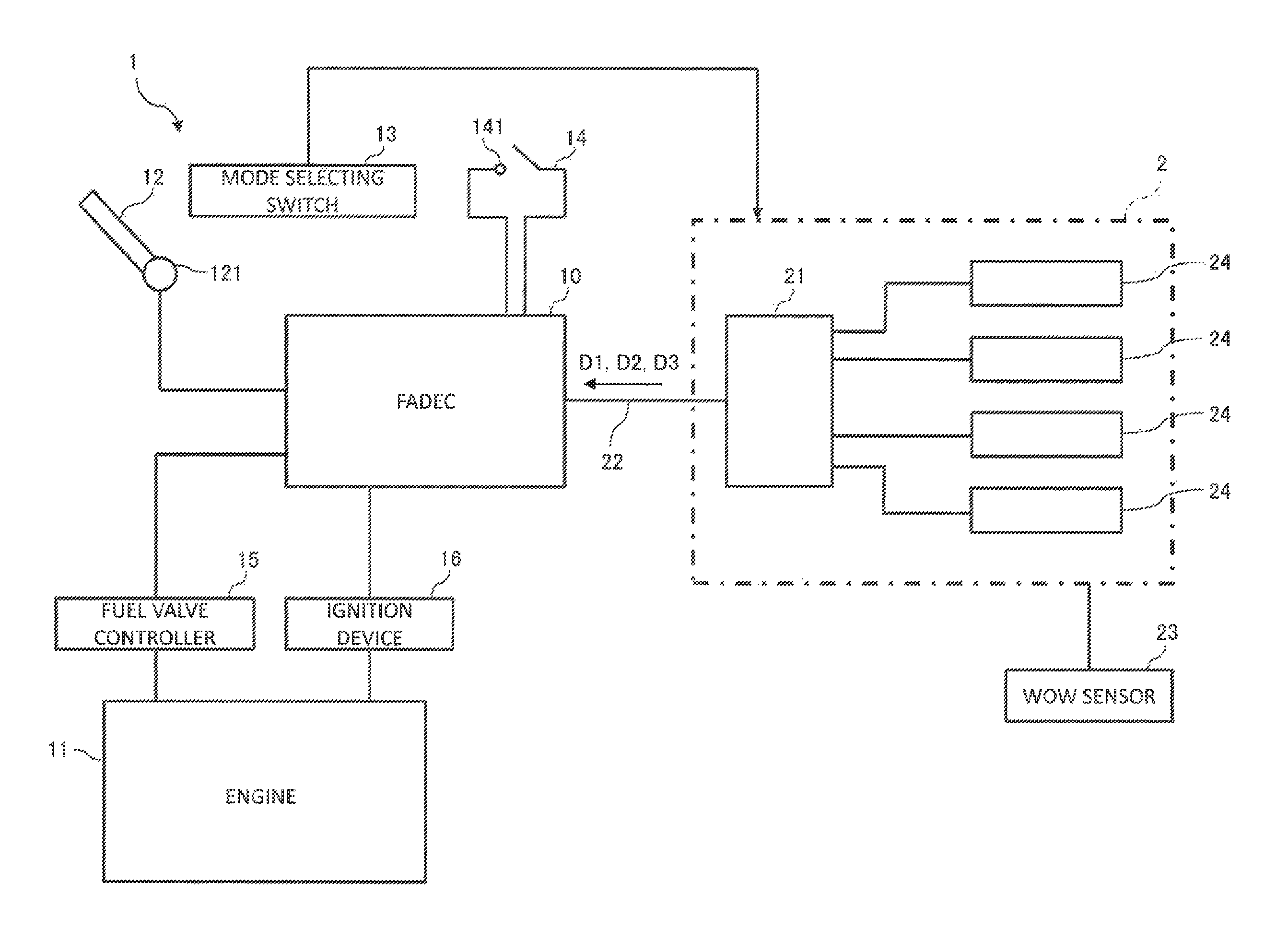
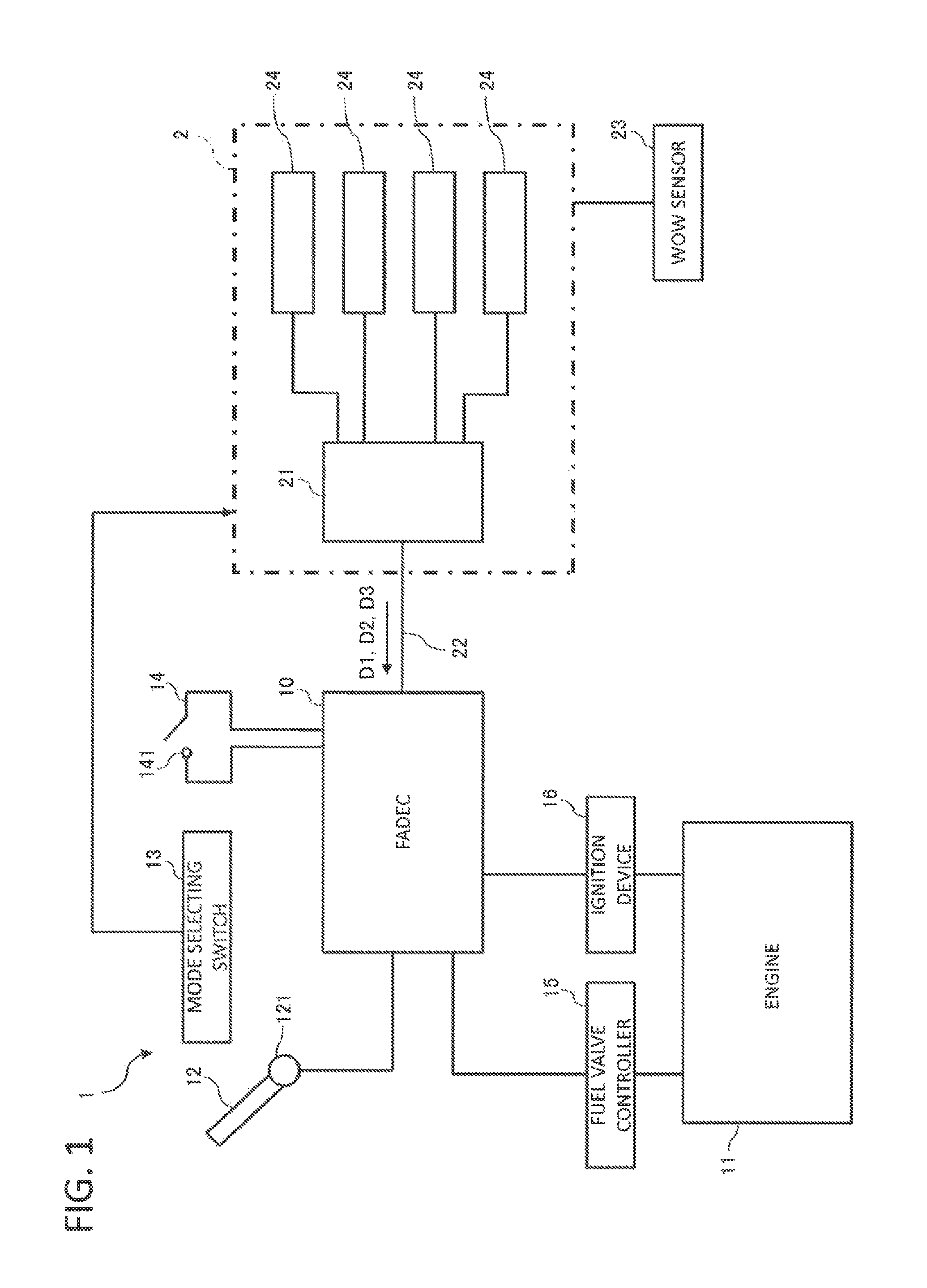
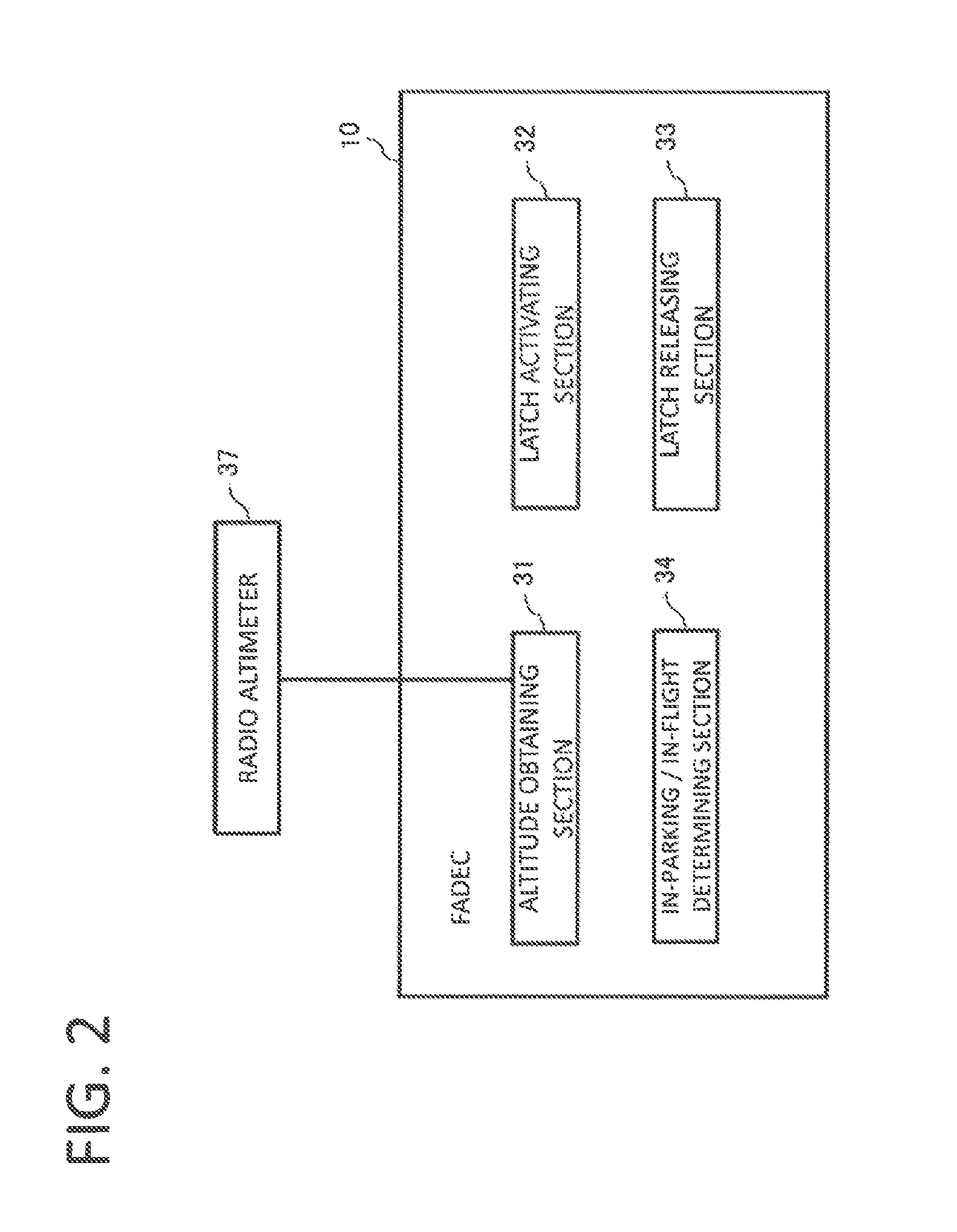
The invention deals with the restriction on the mode change of an engine due to latching in the case of restarting the engine that has stopped in flight. A FADEC that controls an engine of an aircraft in accordance with a mode, includes a latch operating section that latches the mode, and an in-parking / in-flight determining section that determines whether the aircraft is on the ground or flying off the ground. The latch operating section operates when the in-parking / in-flight determining section determines the aircraft is on the ground, and does not operate when the in-parking / in-flight determining section determines that the aircraft is in fight.
Owner:MITSUBISHI AIRCRAFT
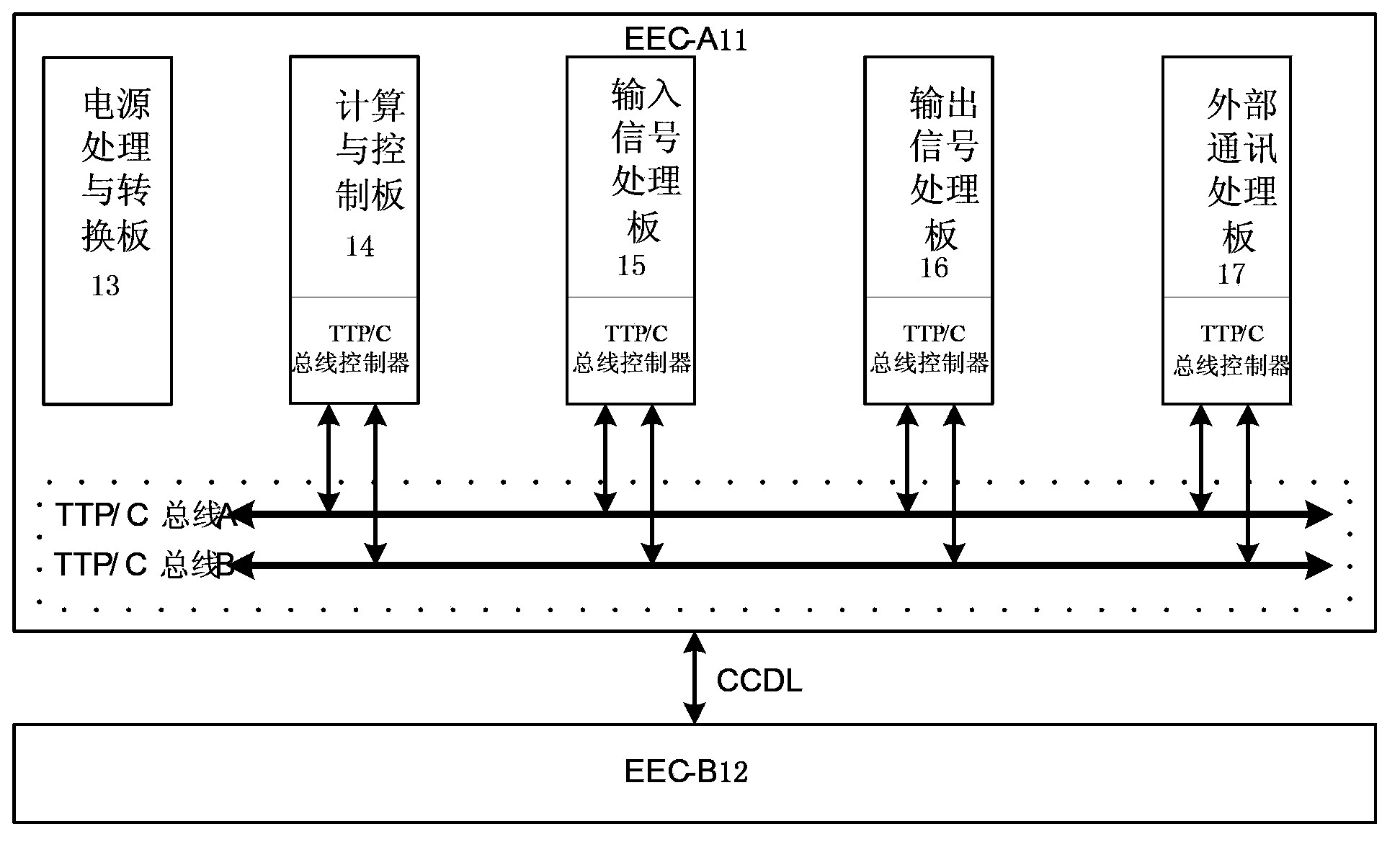
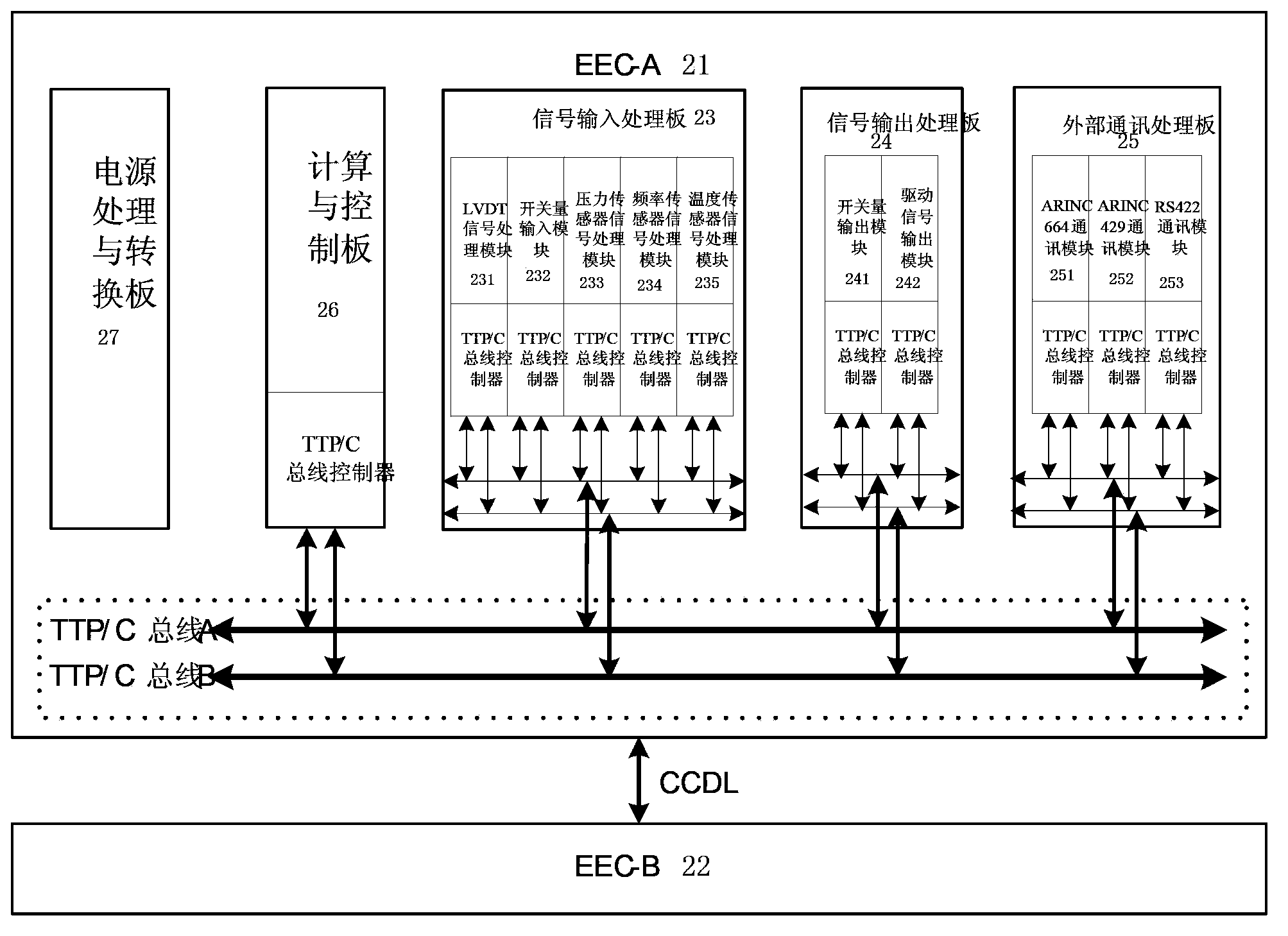
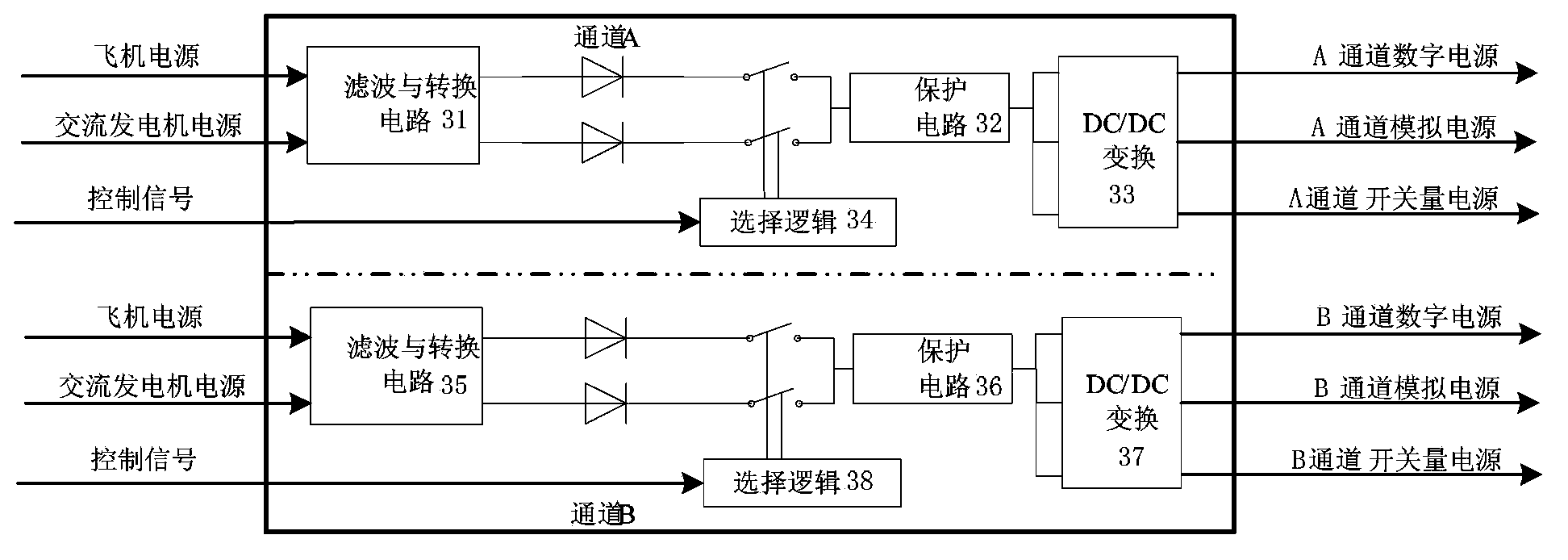
TTP/C (time-triggered protocol communication) bus-based electronic controller and FADEC (full authority digital engine control) system
ActiveCN103850802AReduce distractionsReduce processing burdenGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsBroadbandData exchange
The invention discloses a TTP / C bus-based electronic controller and an FADEC system. Each of the two groups of functional units which are redundant to each other comprises multiple functional daughter boards and inter-board TTP / C buses, each functional daughterboard is integrated with a TTP / C bus controller and the TTP / C bus controllers are connected with the inter-board TTP / C buses, thus the data interaction among functional daughter boards is realized. According to the TTP / C bus-based electronic controller and the FADEC system, buses are adopted for data exchange among the boards, the wiring becomes easy, the interference among the boards is small and the processing burdens of computing and a control board are reduced; by adopting time-triggered protocol, broadband for various tasks can be assigned in real time, the reliability of the whole machine is increased and the design can be more flexible.
Owner:AECC COMML AIRCRAFT ENGINE CO LTD
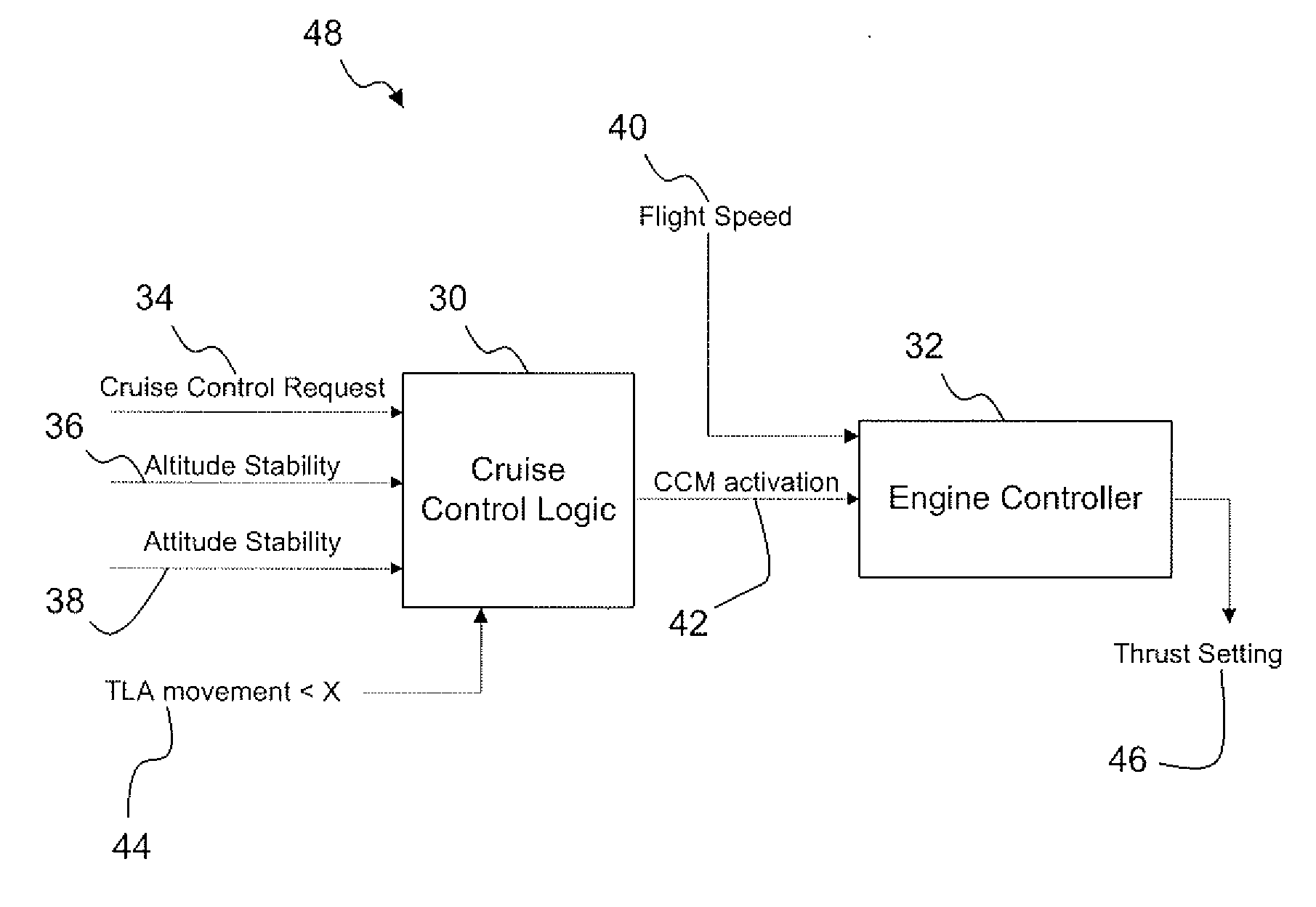
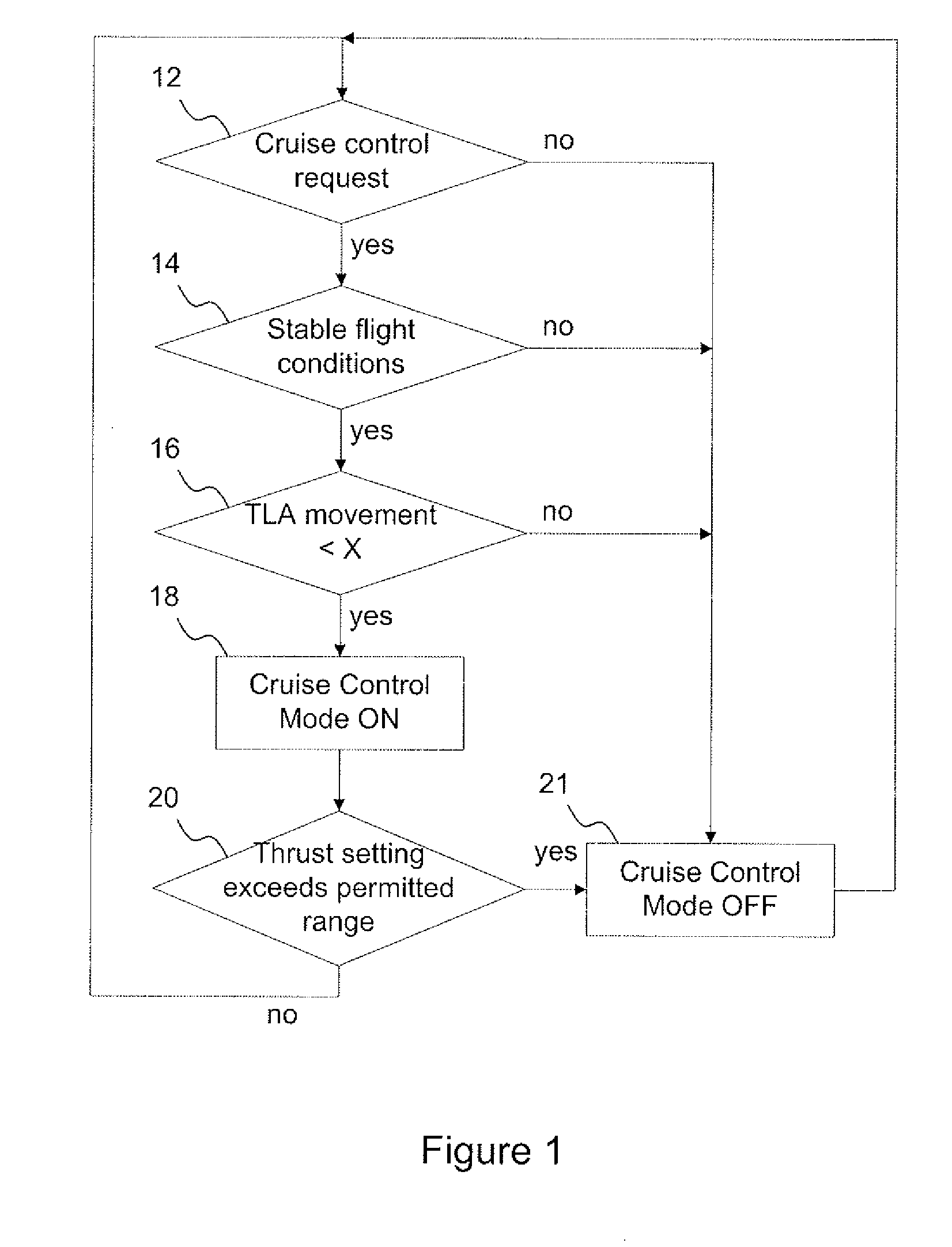
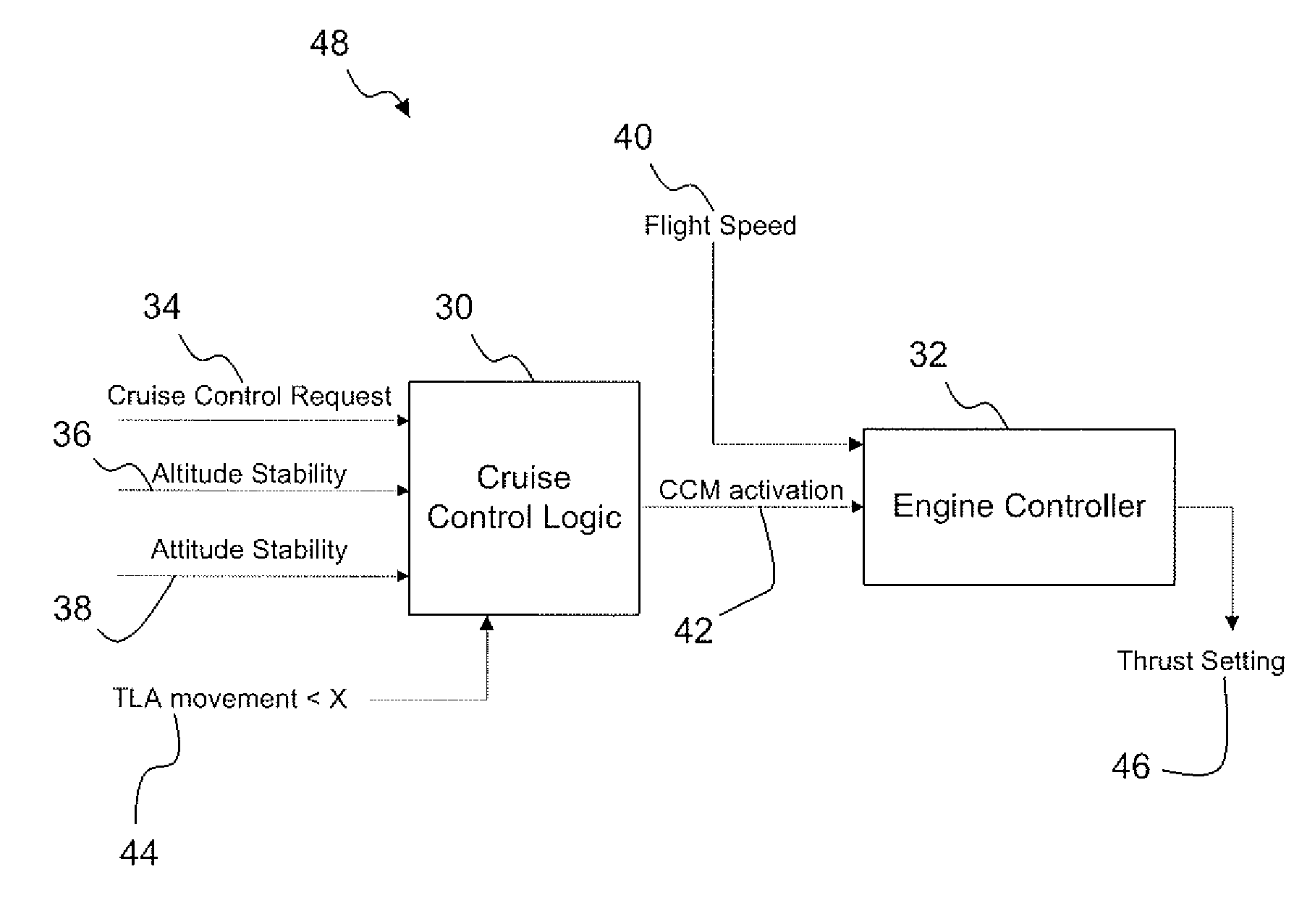
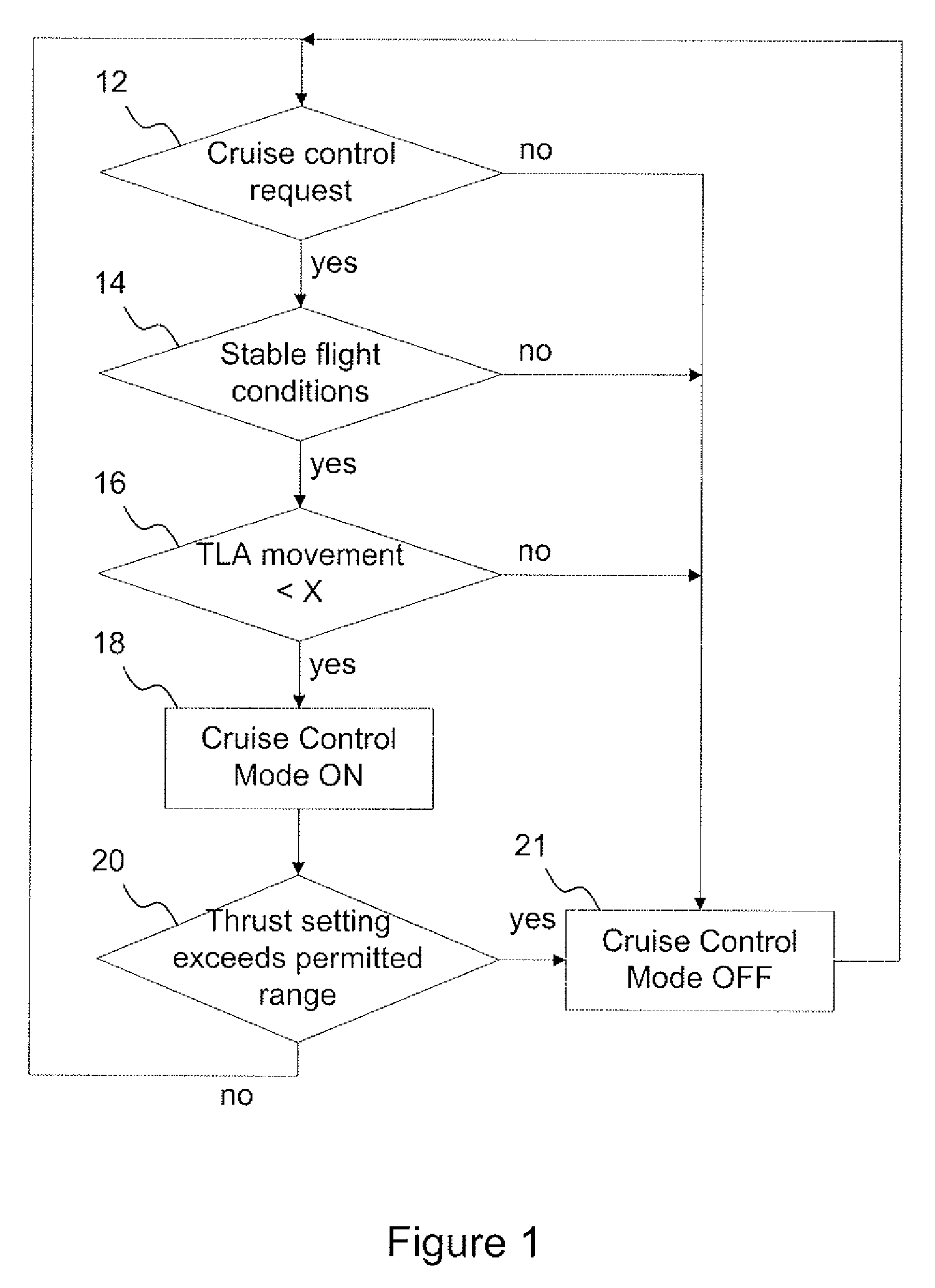
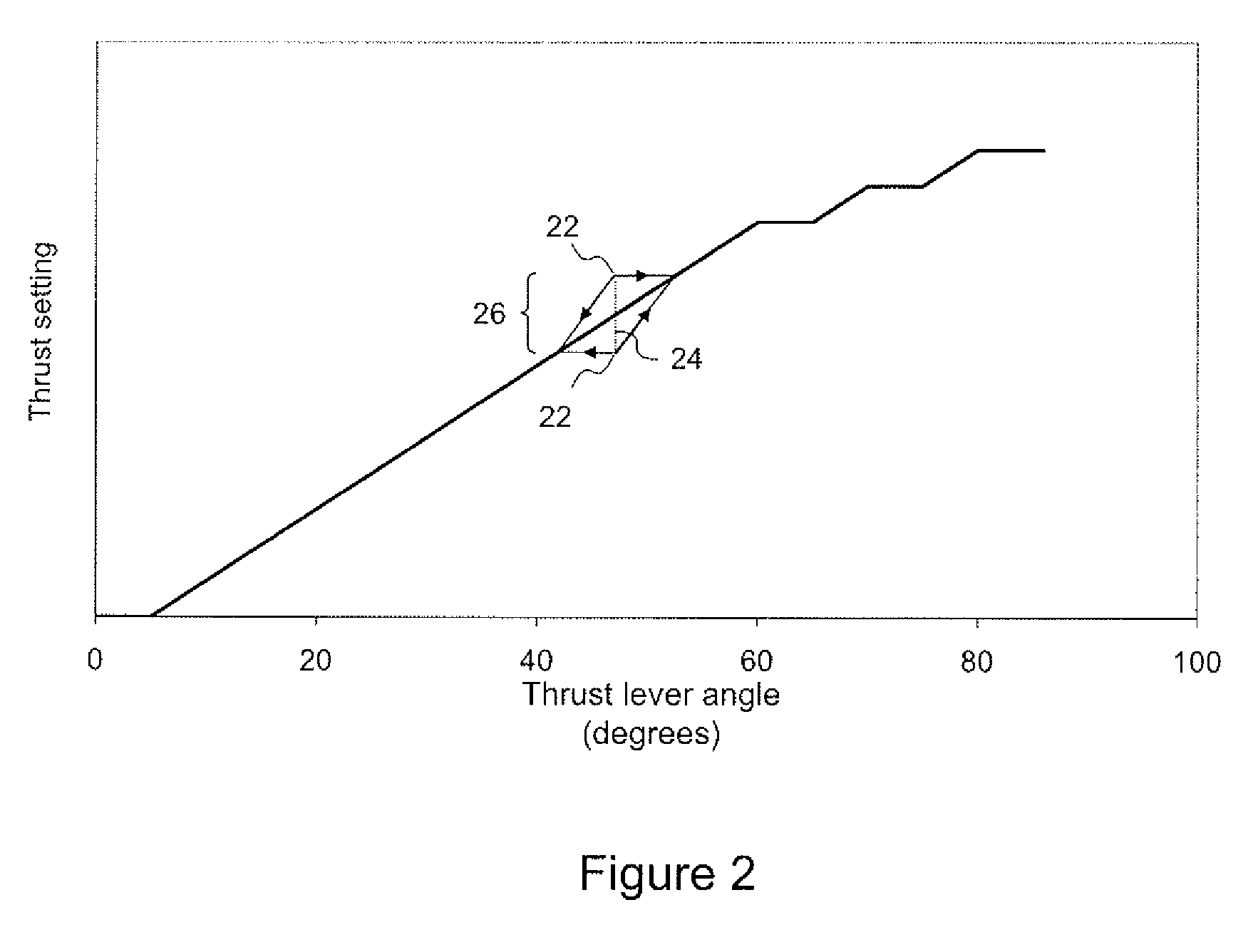
Cruise control fadec logic
ActiveUS20080149778A1Flight speed substantially constantAircraft power plantsAnalogue computers for trafficCruise controlThrottle
The present invention provides an alternative to the auto-throttle integrated in an aircraft autopilot by restricting the conditions in which the system operates. The proposed system removes the auto-throttle function from the autopilot system and gives it directly to the Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC). A Cruise Control mode is available to the pilot only under stable flight conditions.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Distributed type aero-engine full authority digital engine control (FADEC) system
InactiveCN103116320ASmall sizeReduce weight requirementsTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlAviationControl data
The invention provides a distributed type aero-engine full authority digital engine control (FADEC) system which comprises a control unit and a monitoring unit, wherein the control unit and the monitoring unit are independent on hardware but are in data communication with each other through an interconnecting link. The monitoring unit is connected with a plurality of sensors for monitoring to obtain monitoring data. The control unit is connected with a plurality of sensors for controlling to obtain control data. The control data is combined with the monitoring data obtained by the control unit through the interconnecting link to carry out running state control and health monitoring control on an aero-engine. According to the distributed type aero-engine FADEC system, the monitoring function needing to be achieved in the system can be achieved on the monitoring unit independent from the control unit, and the purpose of distributed-type management of control and monitoring functions is achieved. System flexible arrangement is benefited, size, weight and function requirements of the control unit are reduced, and reliability of the system is improved.
Owner:AECC COMML AIRCRAFT ENGINE CO LTD
Cruise control FADEC logic
ActiveUS7774106B2Flight speed substantially constantAircraft power plantsAnalogue computers for trafficCruise controlAutopilot
The present invention provides an alternative to the auto-throttle integrated in an aircraft autopilot by restricting the conditions in which the system operates. The proposed system removes the auto-throttle function from the autopilot system and gives it directly to the Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC). A Cruise Control mode is available to the pilot only under stable flight conditions.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
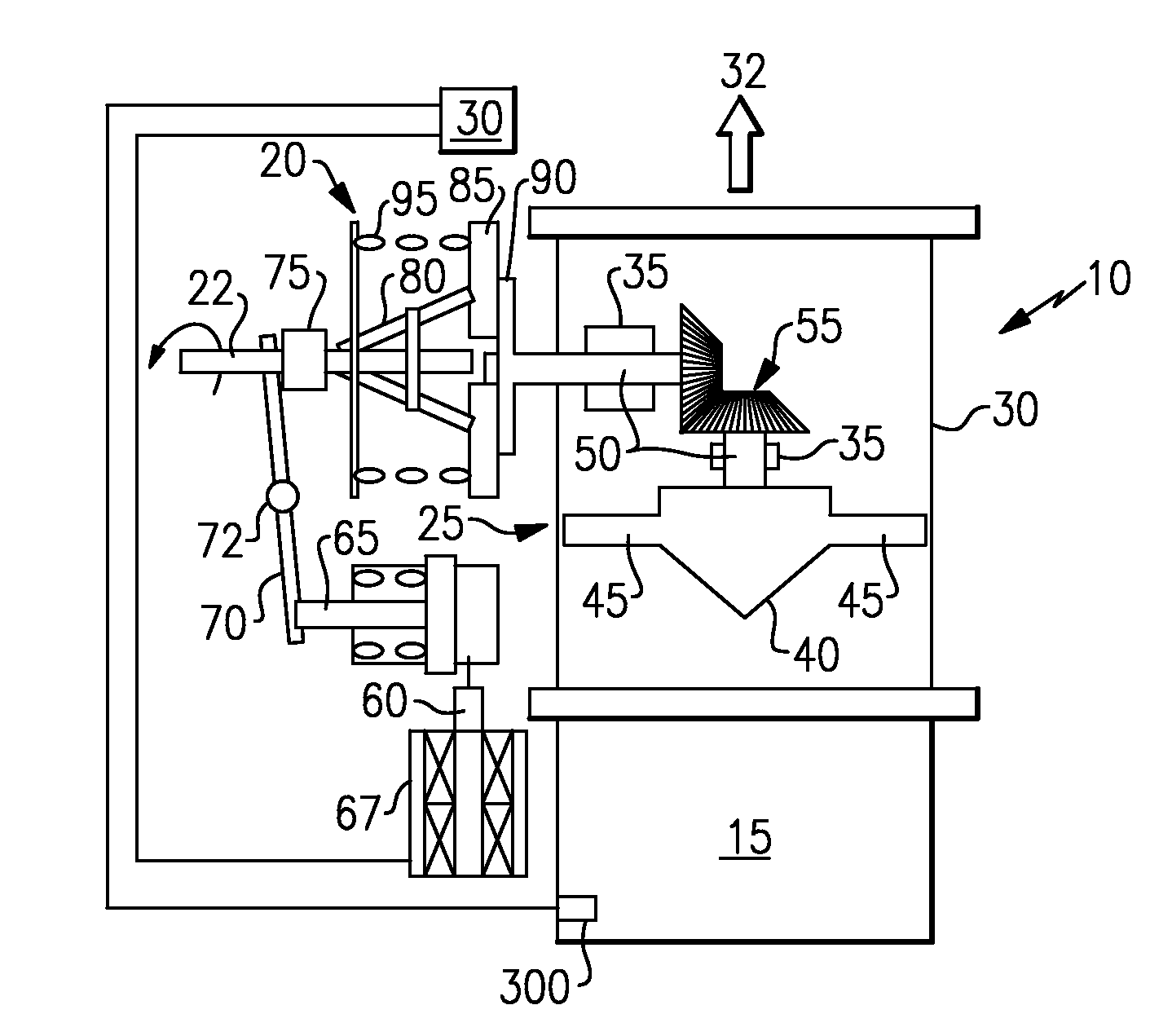
Energy efficient ips blower assembly
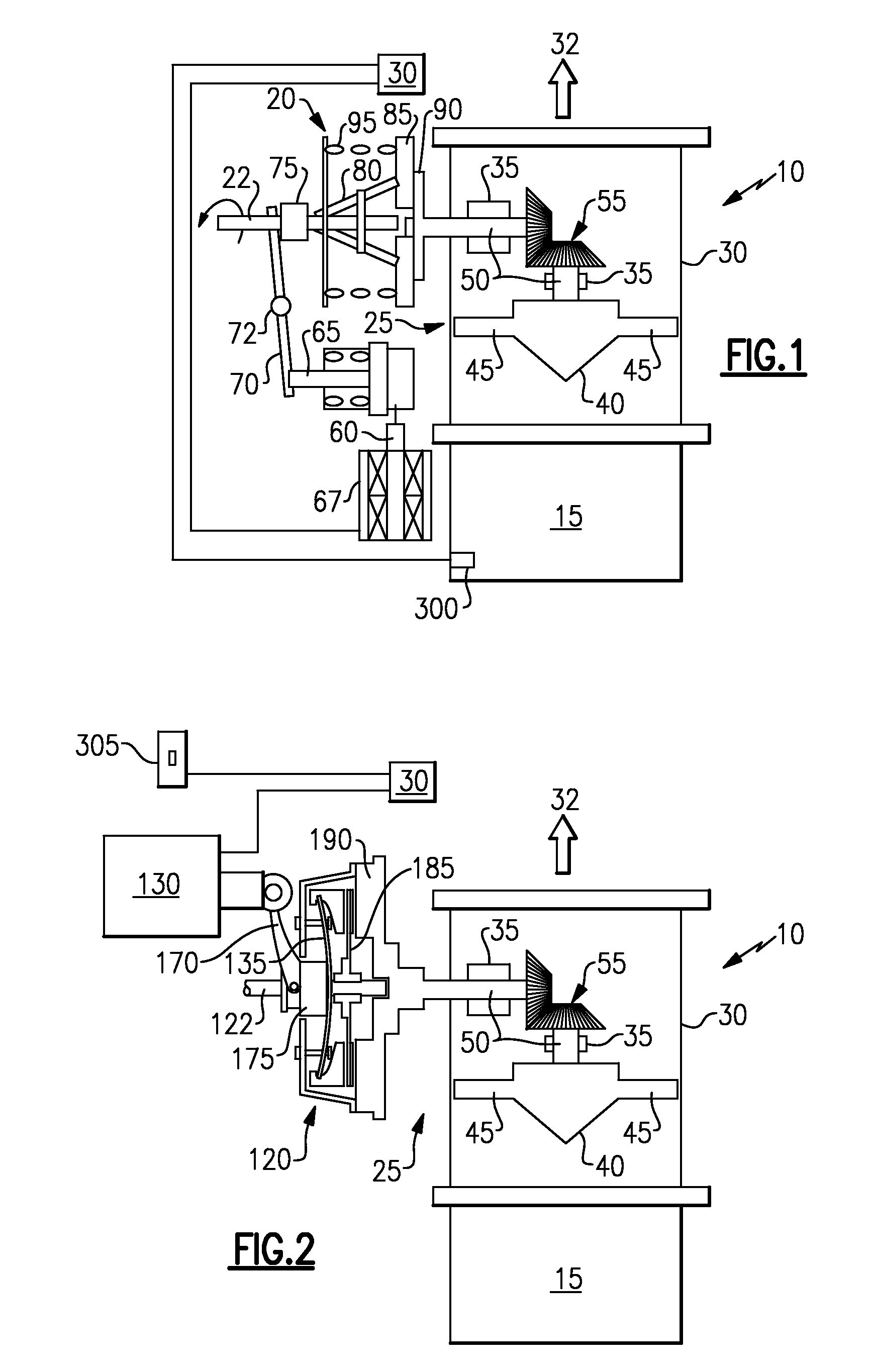
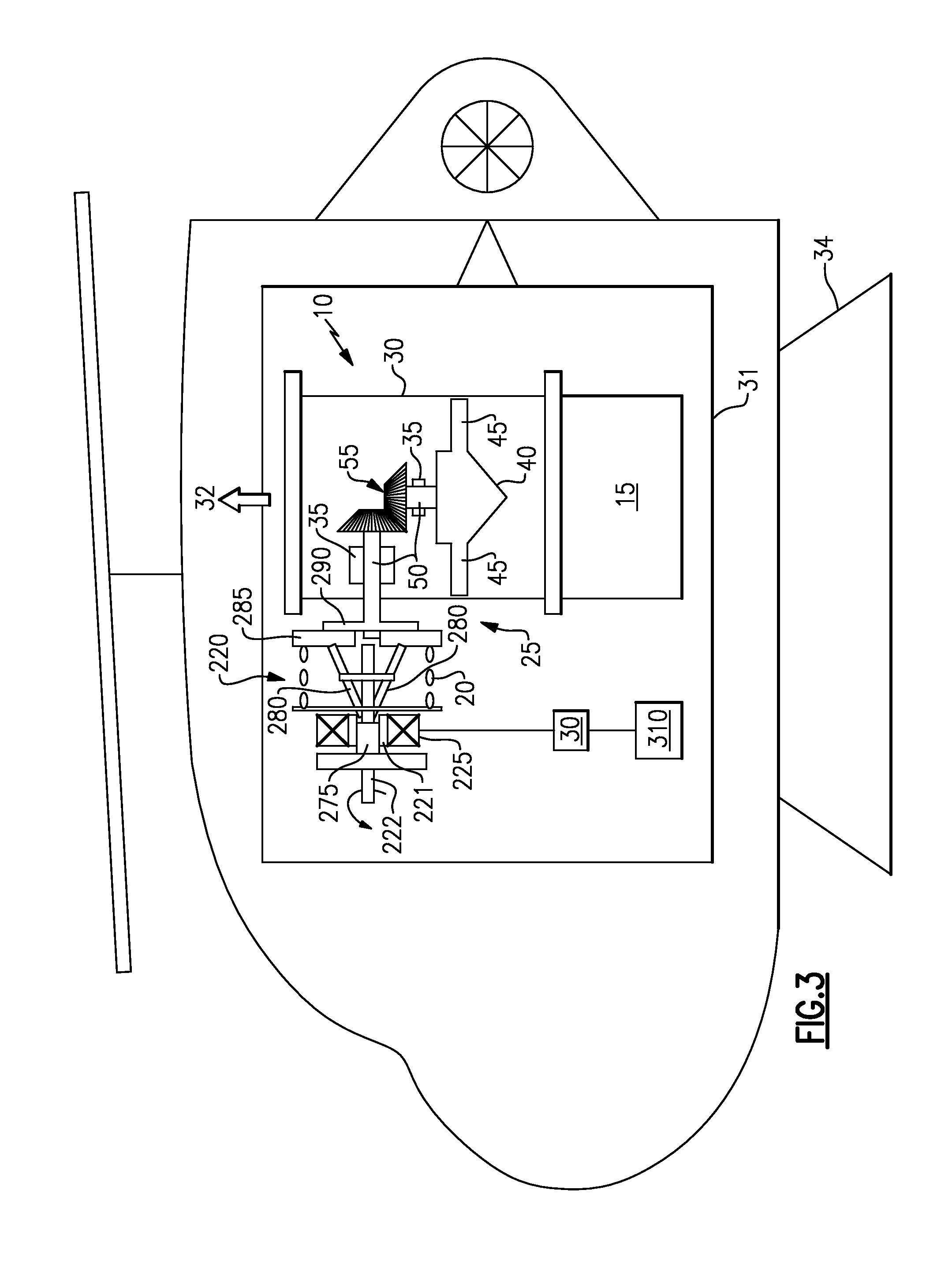
According to the invention a method and apparatus relating to a blower that is used in an environment of particle contaminated air, as with a helicopter engine, is disclosed. The blower has a power input, a fan, a power output attaching to the fan, and a clutch disposed between the power input and the power output whereby the power input may be selectively coupled to the power output to move the fan to vent the particle contaminated air. The clutch, which may be electrically, mechanically or hydraulically engaged, is activated by a user, a particle or altitude sensor, or by a full authority digital electronic controller (“FADEC”).
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Composite material FADEC box support
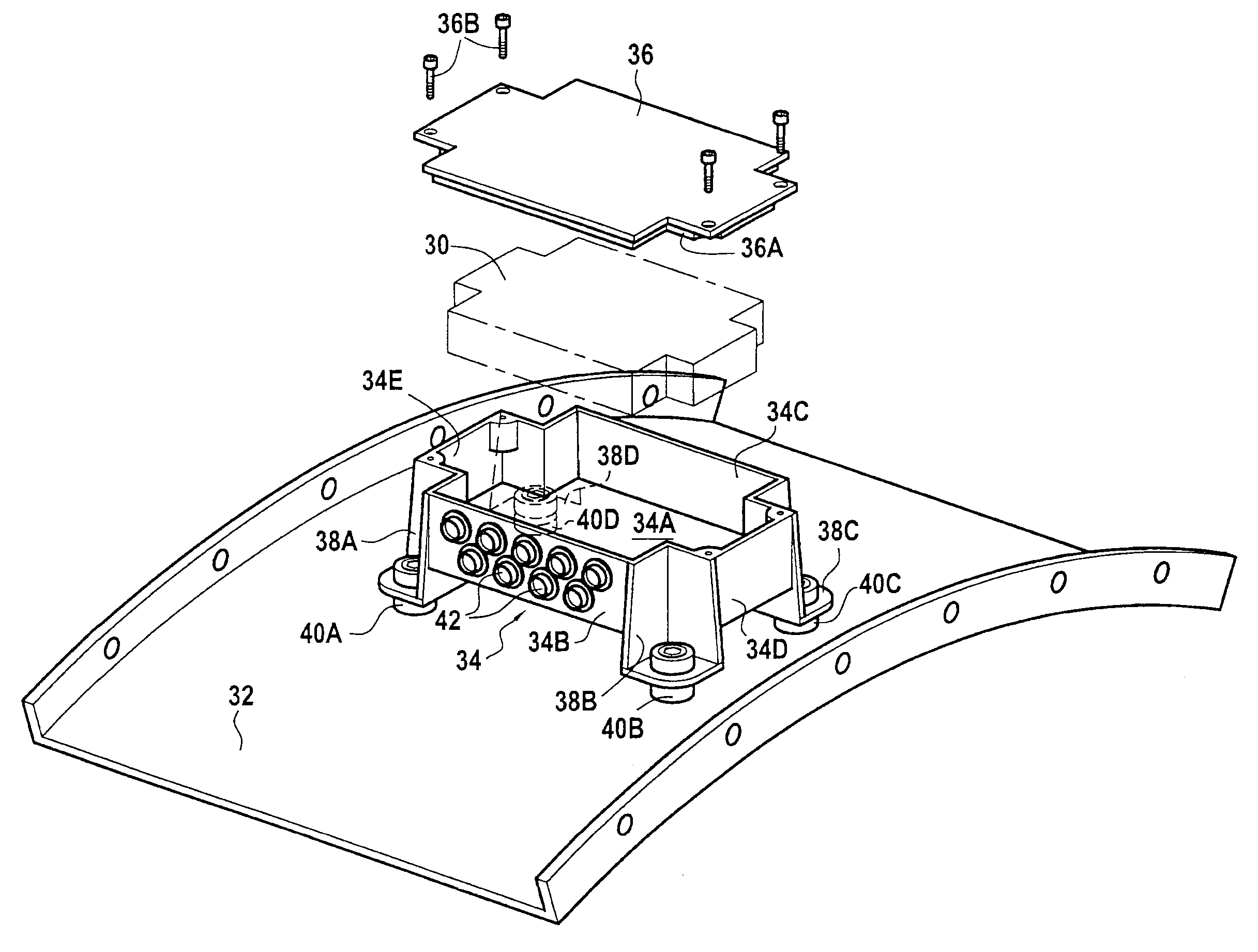
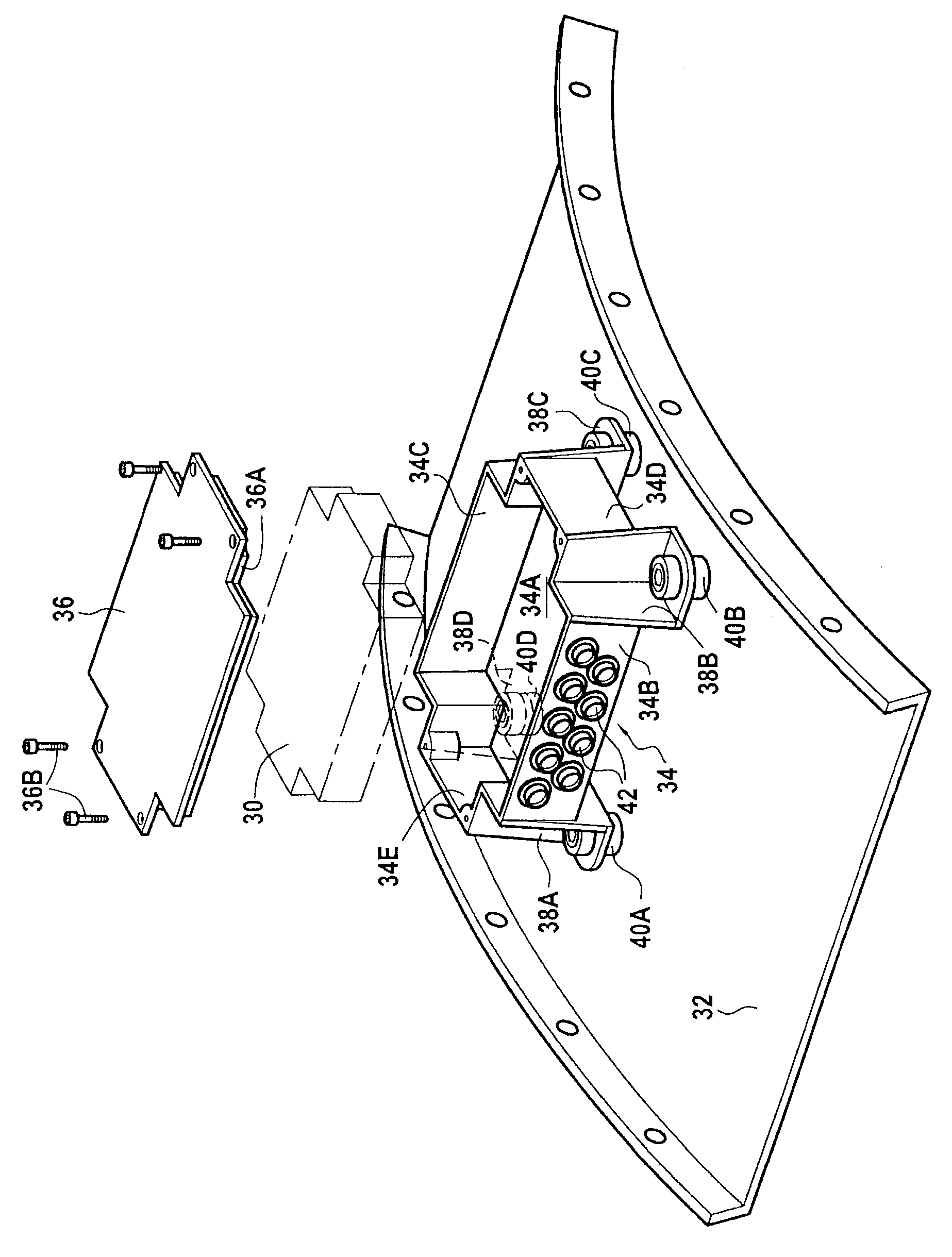
ActiveUS9204566B2Reduce component countReduce weightDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringTurbine
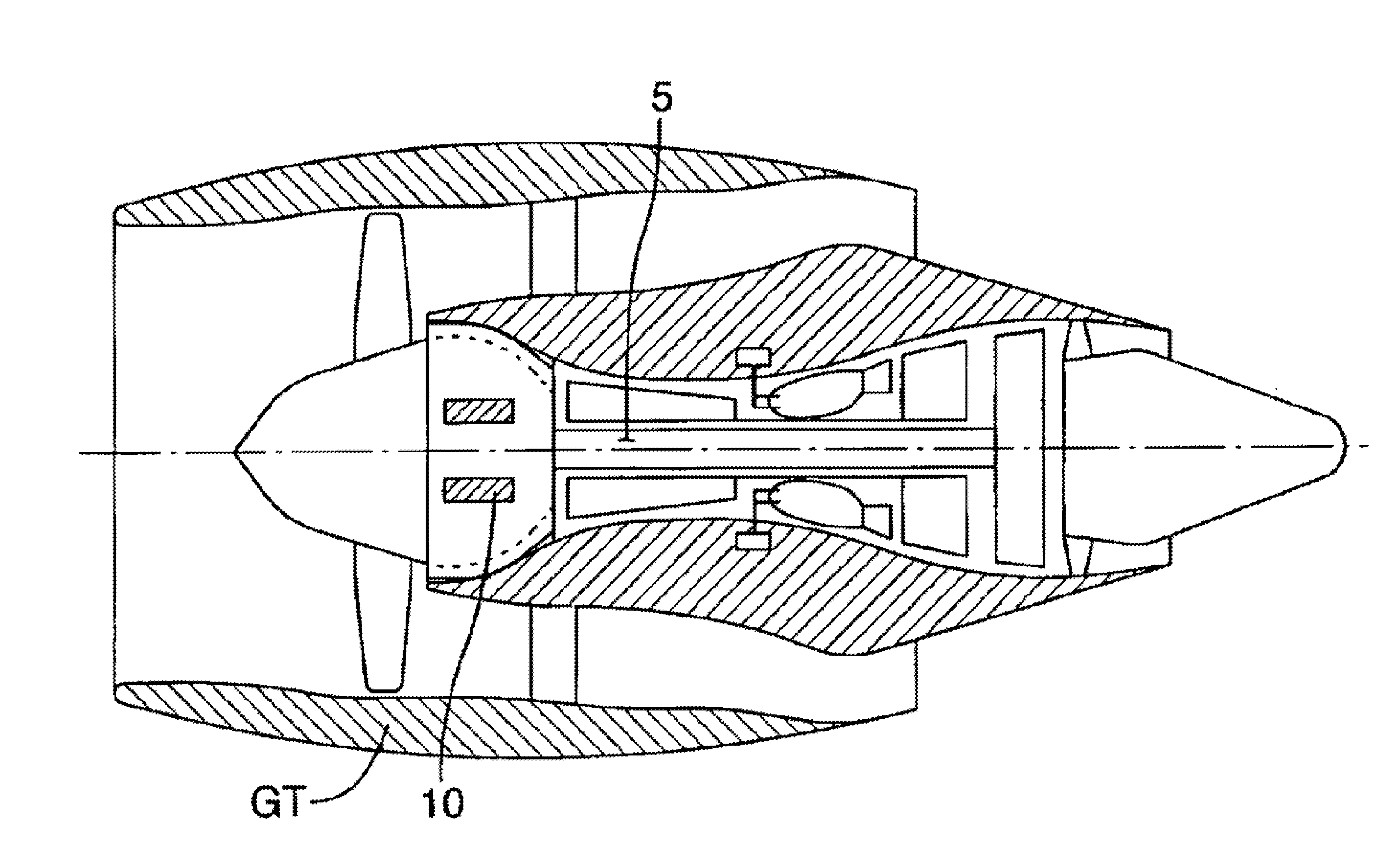
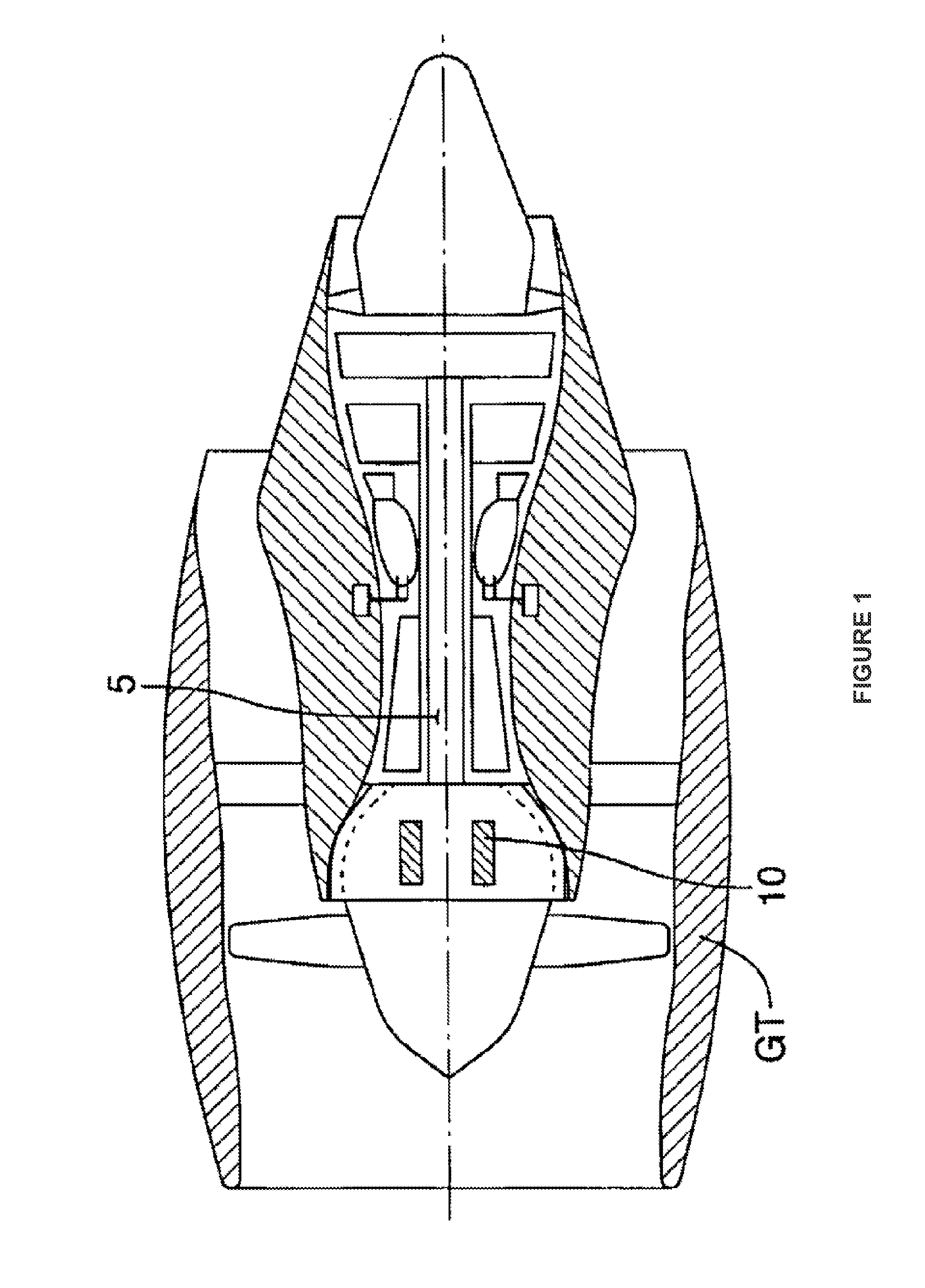
A device for protecting a computer of an aircraft turbine engine, the device comprising a box containing the computer and a cover covering the box, the box being supported by tabs forming integral portions of the box and maintaining a flow of air between the bottom of the box and a portion of the casing of the engine on which they are to come into secure contact via resilient studs, the box being made of a composite material.
Owner:SAFRAN
System for decoupling a fan from a turbojet by means of an explosive charge
ActiveUS20040161331A1Remove uncertaintyMitigate such drawbackPump componentsGas turbine plantsJet engineEngineering
A system for decoupling a fan of a turbojet, the turbojet including a moving fan shaft mounted on bearings each connected to a stationary structure of the turbojet by bearing supports, the bearing supports being fixed to the stationary structure of the turbojet via mechanical links serving, during normal operation of the turbojet, to transmit the forces generated by rotation of the fan, the mechanical links include explosive charges enabling the links to be broken, the explosive charges being controlled by a full authority digital engine control computer on the basis of means for measuring the mechanical stresses in the turbojet and of a computer model simulating the static, dynamic, and thermodynamic behavior of the turbojet.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Low-power bowed rotor prevention and monitoring system
Owner:RTX CORP
System for decoupling a fan from a turbojet by means of an explosive charge
InactiveUS6881024B2Mitigate such drawbackEliminate all uncertaintyPump componentsGas turbine plantsJet engineEngineering
A system for decoupling a fan of a turbojet, the turbojet including a moving fan shaft mounted on bearings each connected to a stationary structure of the turbojet by bearing supports, the bearing supports being fixed to the stationary structure of the turbojet via mechanical links serving, during normal operation of the turbojet, to transmit the forces generated by rotation of the fan, the mechanical links include explosive charges enabling the links to be broken, the explosive charges being controlled by a full authority digital engine control computer on the basis of means for measuring the mechanical stresses in the turbojet and of a computer model simulating the static, dynamic, and thermodynamic behavior of the turbojet.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Low-power bowed rotor prevention system
A bowed rotor prevention system for a gas turbine engine includes a core turning motor operable to drive rotation of an engine core of the gas turbine engine. The bowed rotor prevention system also includes an auxiliary electric motor control operable to control the core turning motor to drive rotation of the engine core using electric power while a full authority digital engine control that controls operation of the gas turbine engine is either depowered or in a power state that is less than a power level used by the full authority digital engine control in flight operation.
Owner:RTX CORP
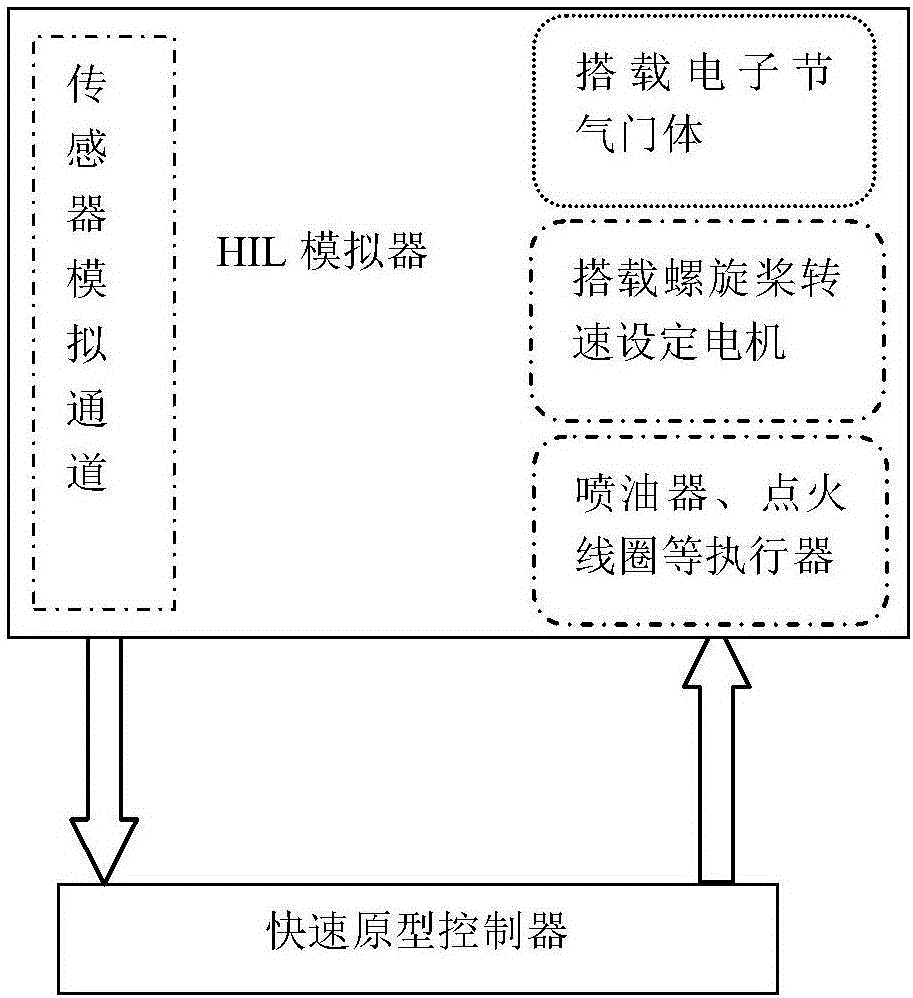
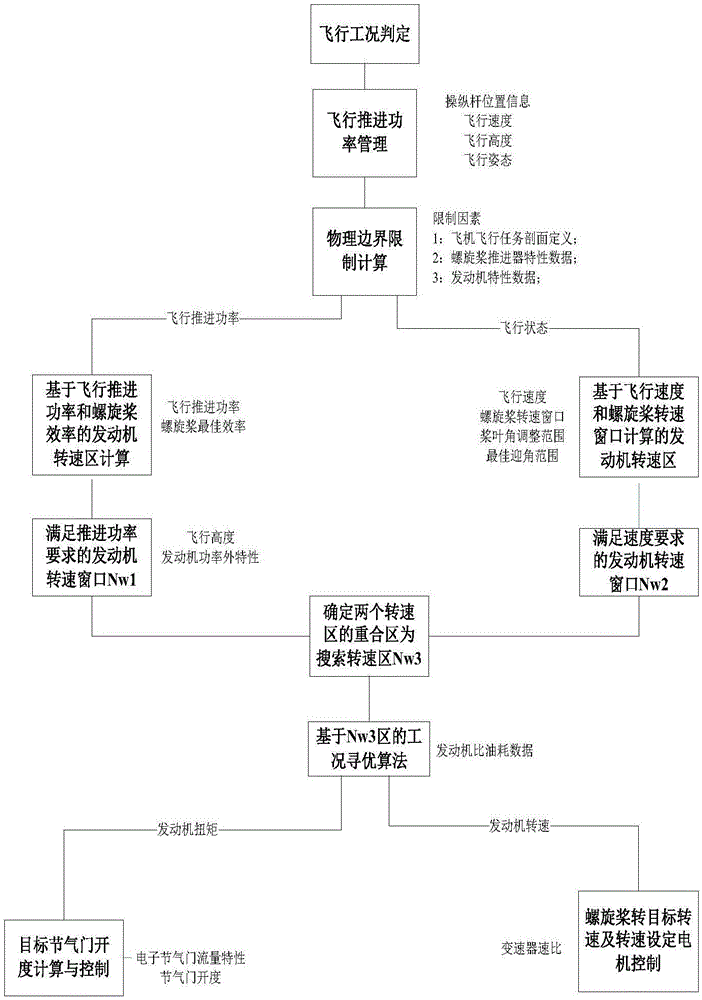
Aircraft piston engine load coordinating and controlling method
ActiveCN106704009AReduce speedReduce working fuel consumptionElectrical controlMachines/enginesAviationOperating point
The invention discloses an aircraft piston engine load coordinating and controlling method. The method is based on an engine load coordinating and controlling system. The engine load coordinating and controlling system comprises an FADEC control system, an electronic throttle body and an electric propeller pitch changing system, wherein the electronic throttle body and the electric propeller pitch changing system are separately connected with the FADEC control system; and the FADEC control system comprises a measurement sensor, a controller and an actuator. The sensor is used for measuring the rotating speed of an engine, the position of an operating lever, and parameters of the percentage of an electronic throttle. The electric propeller pitch changing system is used for mechanical decoupling of the operating lever and the rotating speed of a propeller; and the electronic throttle body is used for the mechanical decoupling of the operating lever and the percentage the throttle valve. The actuator is used for realizing oil injection and ignition of the engine. According to the method, an optimal algorithm is figured out through the operating condition of the engine based on a request for flight thrust power, so that an operating point is obtained through calculation; the expected throttle percentageand the rotating speed of the propeller at present are determined; and the throttle percentage and blade angles are adjusted through a closed-loop control system.
Owner:安徽航瑞航空动力装备有限公司
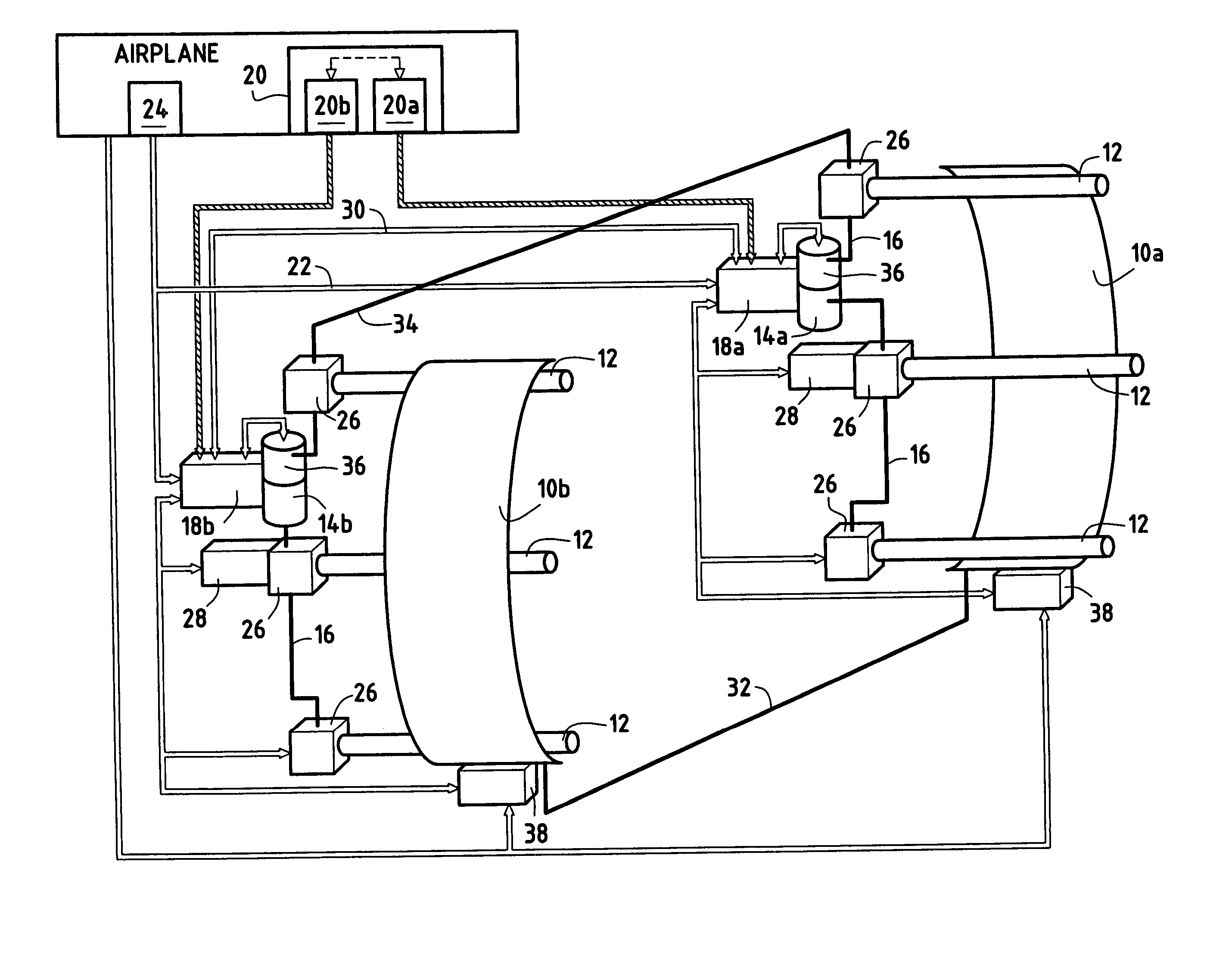
FADEC and avionic component distributed architecture
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Engine control computer of aircraft, and aircraft
ActiveUS9487302B2Process safety and stabilityRemove and ease restrictionAircraft power plantsGas turbine plantsMode controlFlight vehicle
The invention deals with the restriction on the mode change of an engine due to latching in the case of restarting the engine that has stopped in flight. A FADEC that controls an engine of an aircraft in accordance with a mode, includes a latch operating section that latches the mode, and an in-parking / in-flight determining section that determines whether the aircraft is on the ground or flying off the ground. The latch operating section operates when the in-parking / in-flight determining section determines the aircraft is on the ground, and does not operate when the in-parking / in-flight determining section determines that the aircraft is in fight.
Owner:MITSUBISHI AIRCRAFT
System and method for realizing engine automatic takeoff thrust control function
ActiveCN111237062AMeet the requirements of mutual isolationMultiple design autonomyGas turbine plantsEngine controlFlight vehicleControl engineering
The invention relates to a system for realizing an engine automatic takeoff thrust control function. The system comprises a first engine full authority digital engine control (FADEC), a second engineFADEC and an avionics system electrically connected with the first engine FADEC and the second engine FADEC, wherein the first engine FADEC and the second engine FADEC separately send ATTCS trigger input values to the avionics system, the avionics system performs ATTCS trigger logical judgment based on the ATTCS trigger input values to trigger the ATTCS, and sends an instruction of adjusting engine thrust to the first engine FADEC or the second engine FADEC. The invention further relates to a method for realizing the engine automatic takeoff thrust control function. The method comprises the steps that FADEC sends the ATTCS trigger input values of an aircraft to the avionics system of the aircraft; the ATTCS trigger input values sent by the ATTCS are exchanged in the avionics system; the avionics system judges whether the ATTCS function is triggered or not; the avionics system sends a judgment result to the FADEC; and the FADEC controls whether the thrust is increased or not.
Owner:COMAC +1
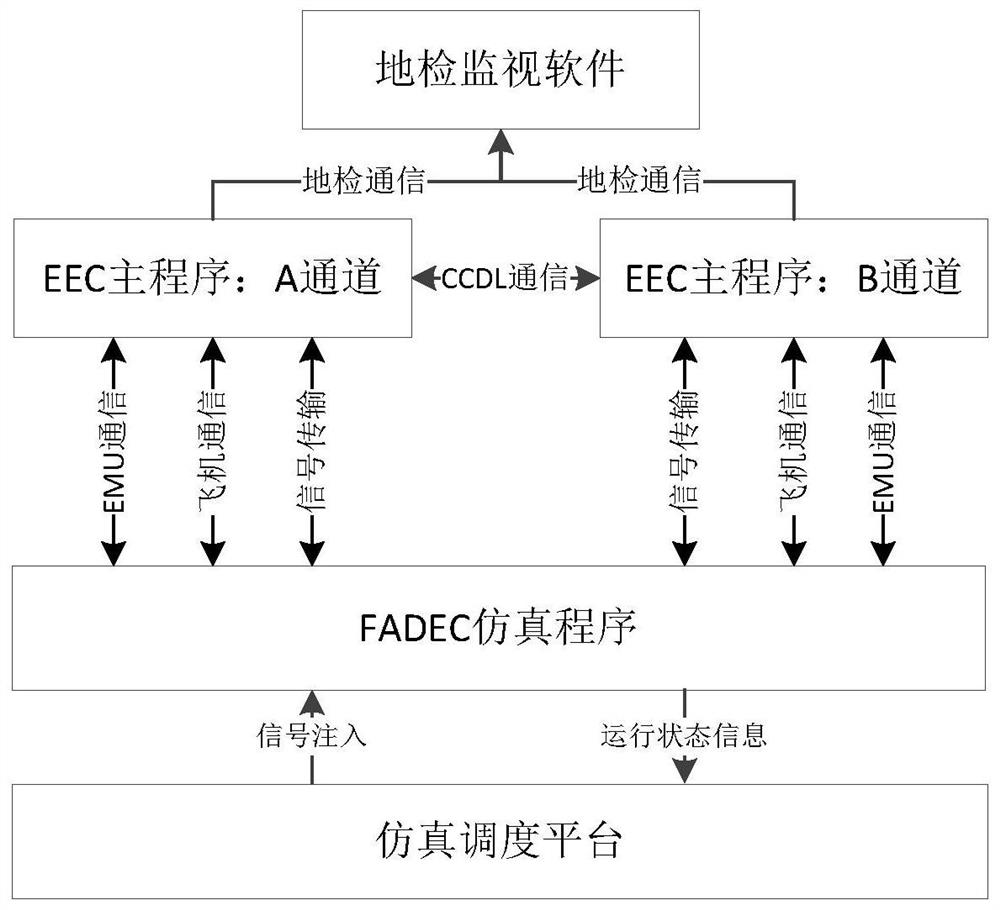
Multi-channel simulation method and system of aero-engine control system
PendingCN113934153AImprove realismImprove design and development efficiencySimulator controlEmbedded systemAero engine
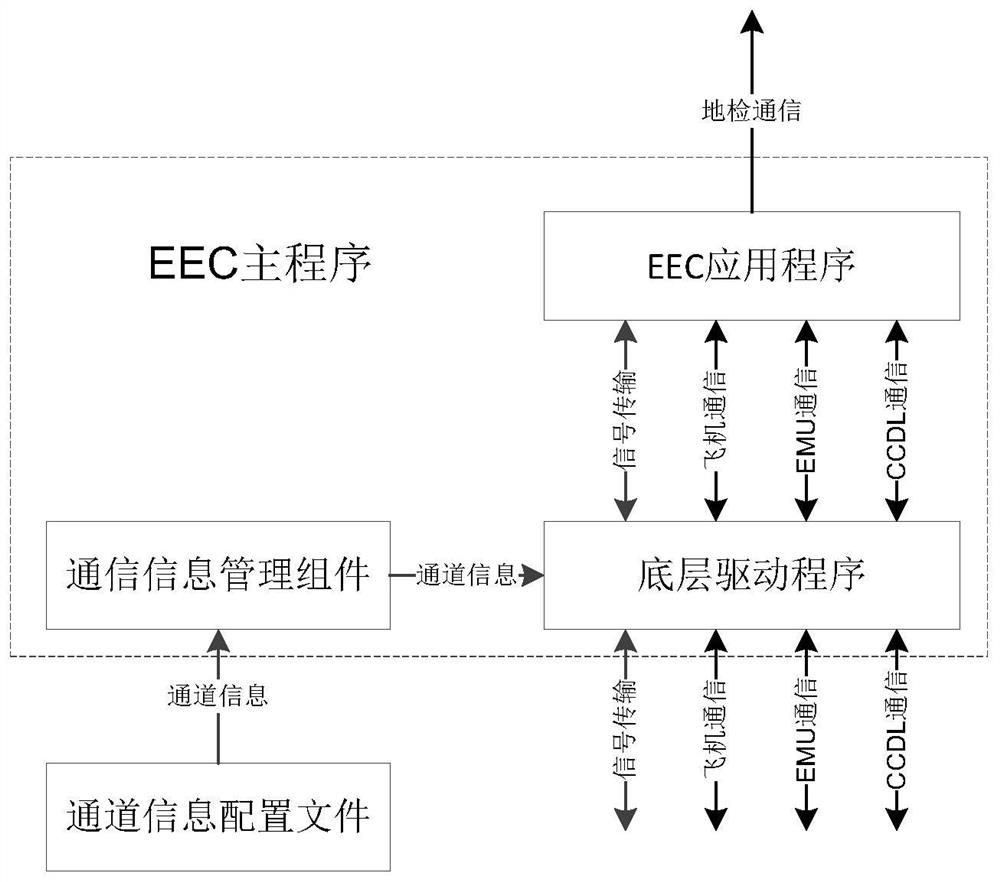
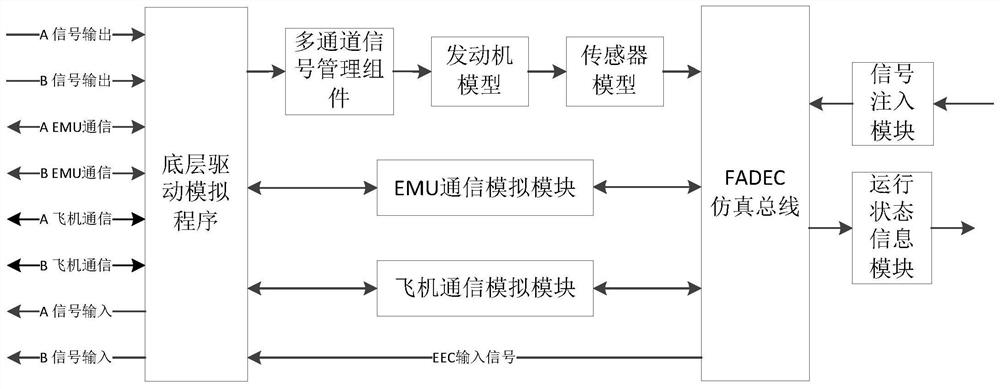
The invention provides a multi-channel simulation method of an aero-engine control system, and the method comprises the following steps of: providing a plurality of EEC main programs, each of which serves as a channel and comprises a communication information management component; providing an FADEC simulation program, which comprises a multi-channel signal management component configured to select a master control channel among a plurality of channels; providing a simulation scheduling platform which comprises a channel information management component; running the simulation scheduling platform, loading the plurality of EEC main programs and the FADEC simulation program to a simulation path, and configuring a channel information configuration file to formulate inter-process communication protocol configuration; and respectively starting the EEC main programs and the FADEC simulation programs of the plurality of channels by using the simulation scheduling platform, opening ground inspection monitoring software, and starting simulation. The invention further provides a multi-channel simulation system of the aero-engine control system, and the multi-channel simulation system is used for achieving the simulation method.
Owner:AECC COMML AIRCRAFT ENGINE CO LTD
Turbine engine and method of cooling thereof
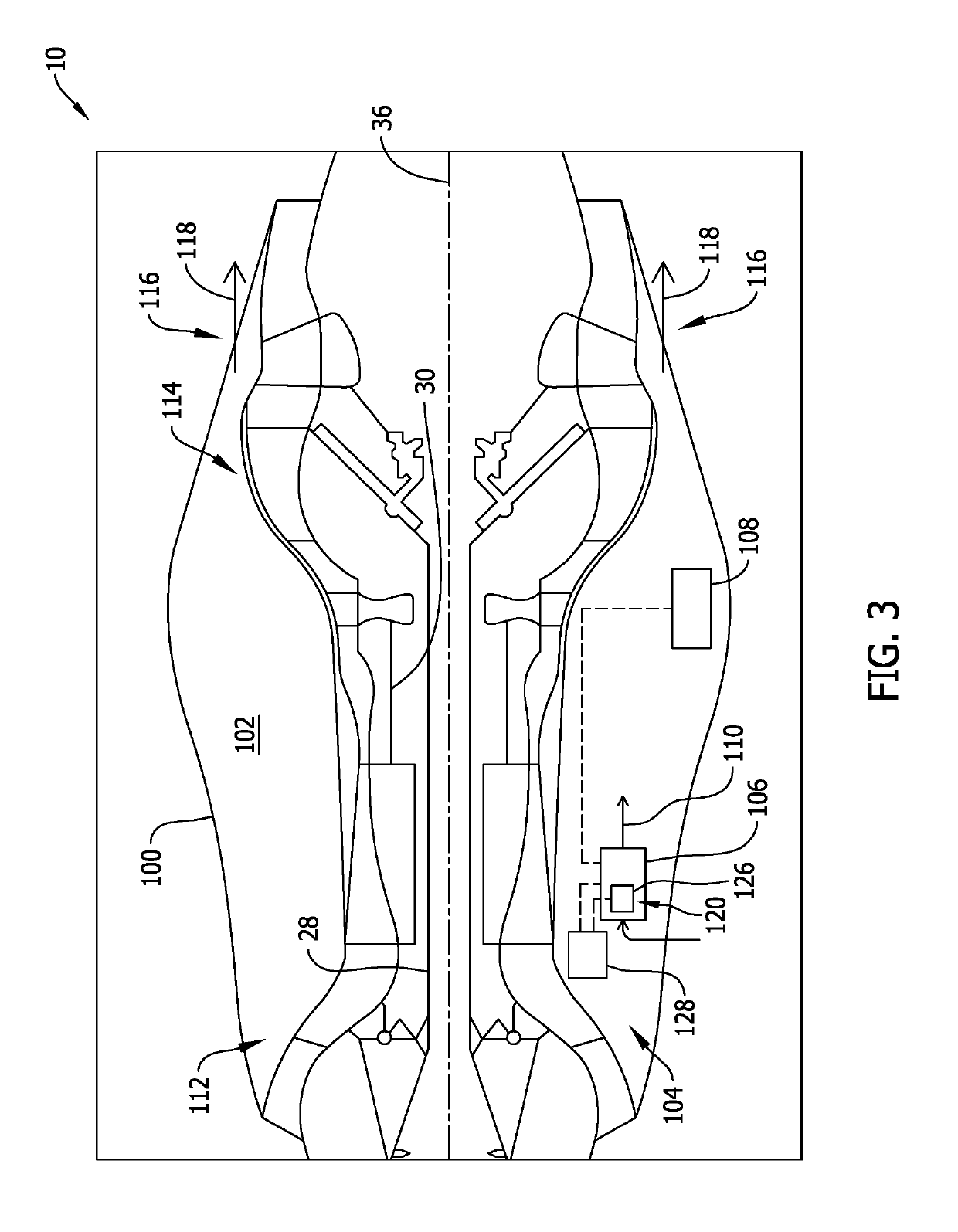
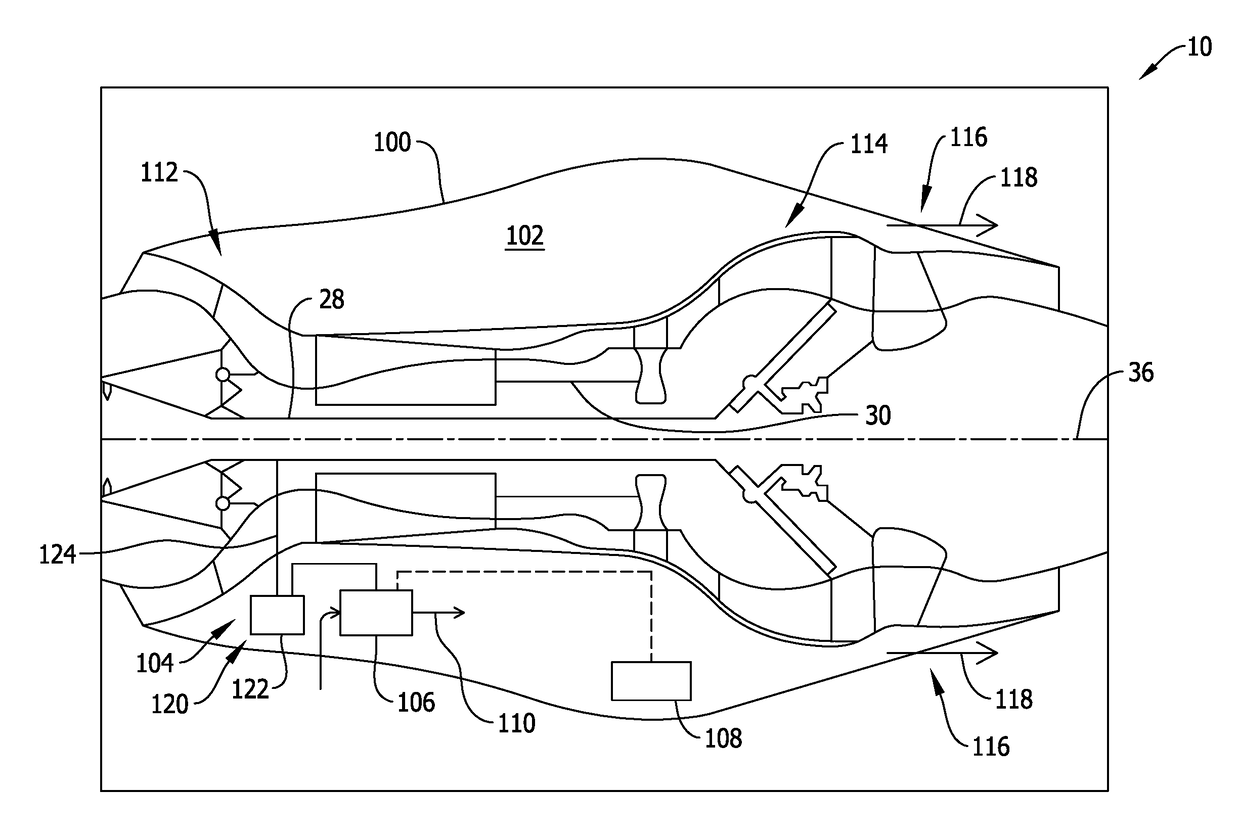
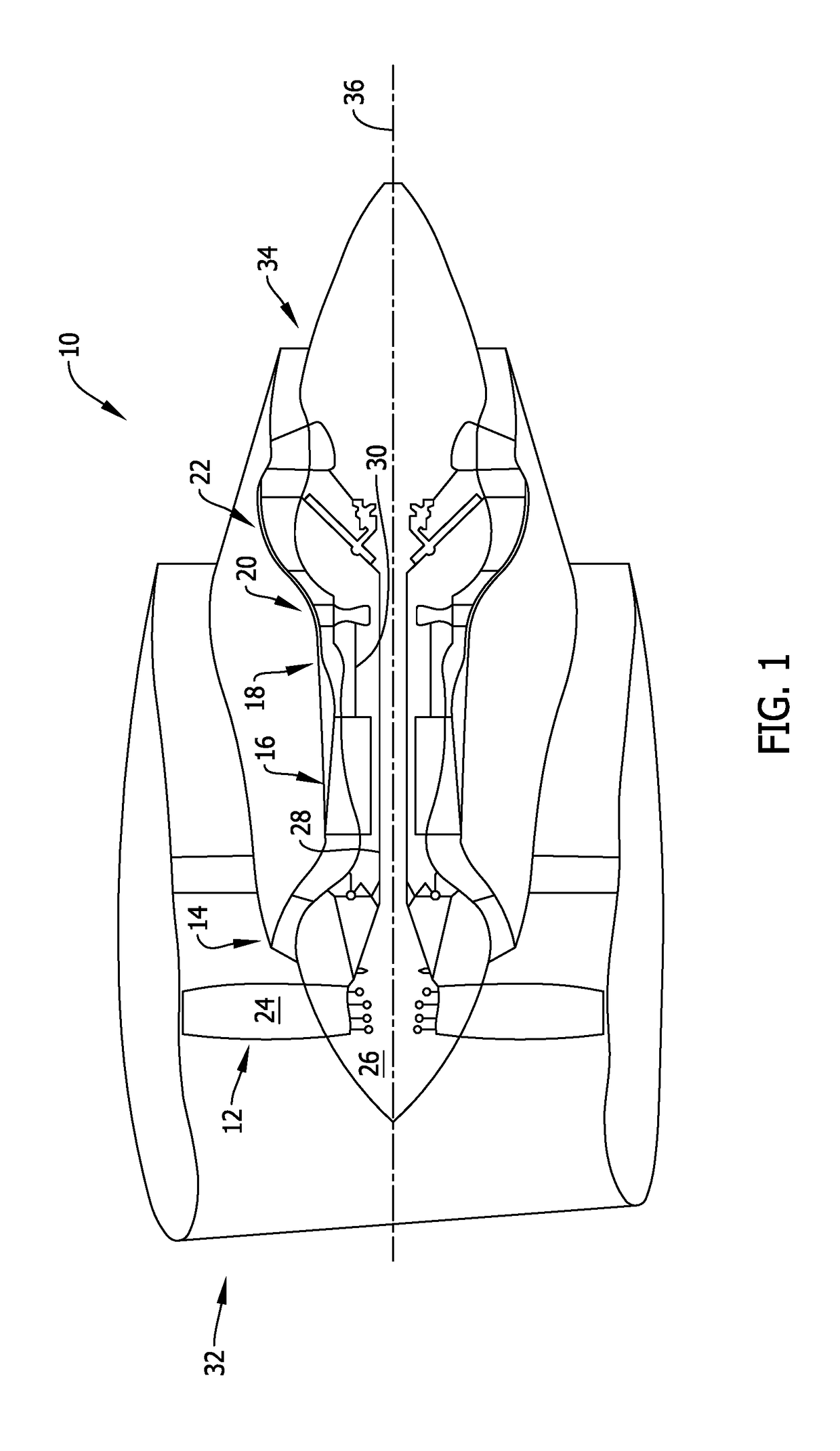
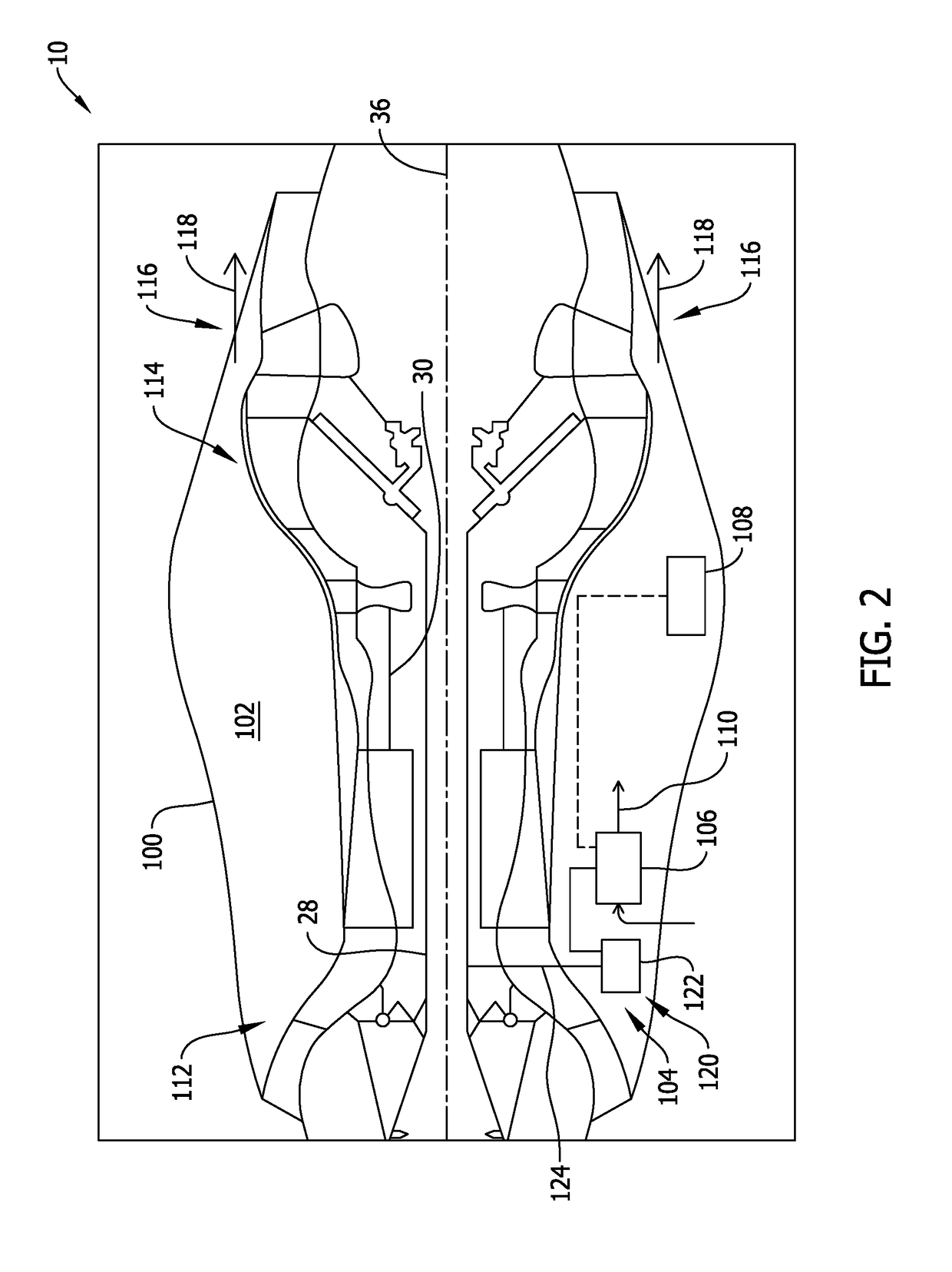
A turbine engine including a core engine cowl including a compartment, a cooling airflow source positioned within the compartment, and a full authority digital engine control (FADEC) system coupled in communication with the cooling airflow source. The FADEC system is configured to determine a flight status of the turbine engine, and actuate the cooling airflow source when the turbine engine is not in flight, and before the turbine engine has been shut down, such that heat is exhausted from the compartment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Turbine engine and method of cooling thereof
A turbine engine including a core engine cowl including a compartment, a cooling airflow source positioned within the compartment, and a full authority digital engine control (FADEC) system coupled in communication with the cooling airflow source. The FADEC system is configured to determine a flight status of the turbine engine, and actuate the cooling airflow source when the turbine engine is not in flight, and before the turbine engine has been shut down, such that heat is exhausted from the compartment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com