Patents
Literature
91 results about "Graphics accelerator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
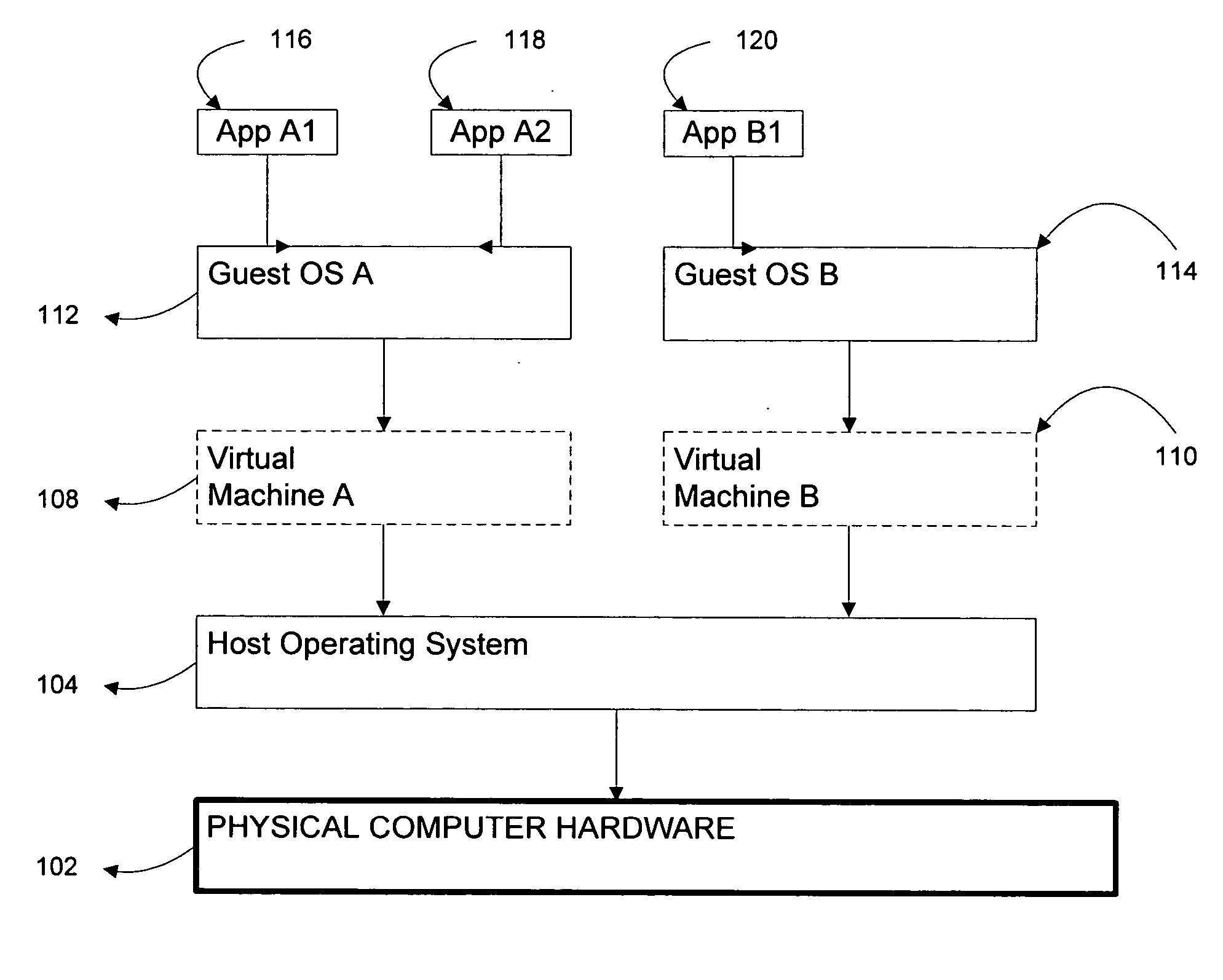
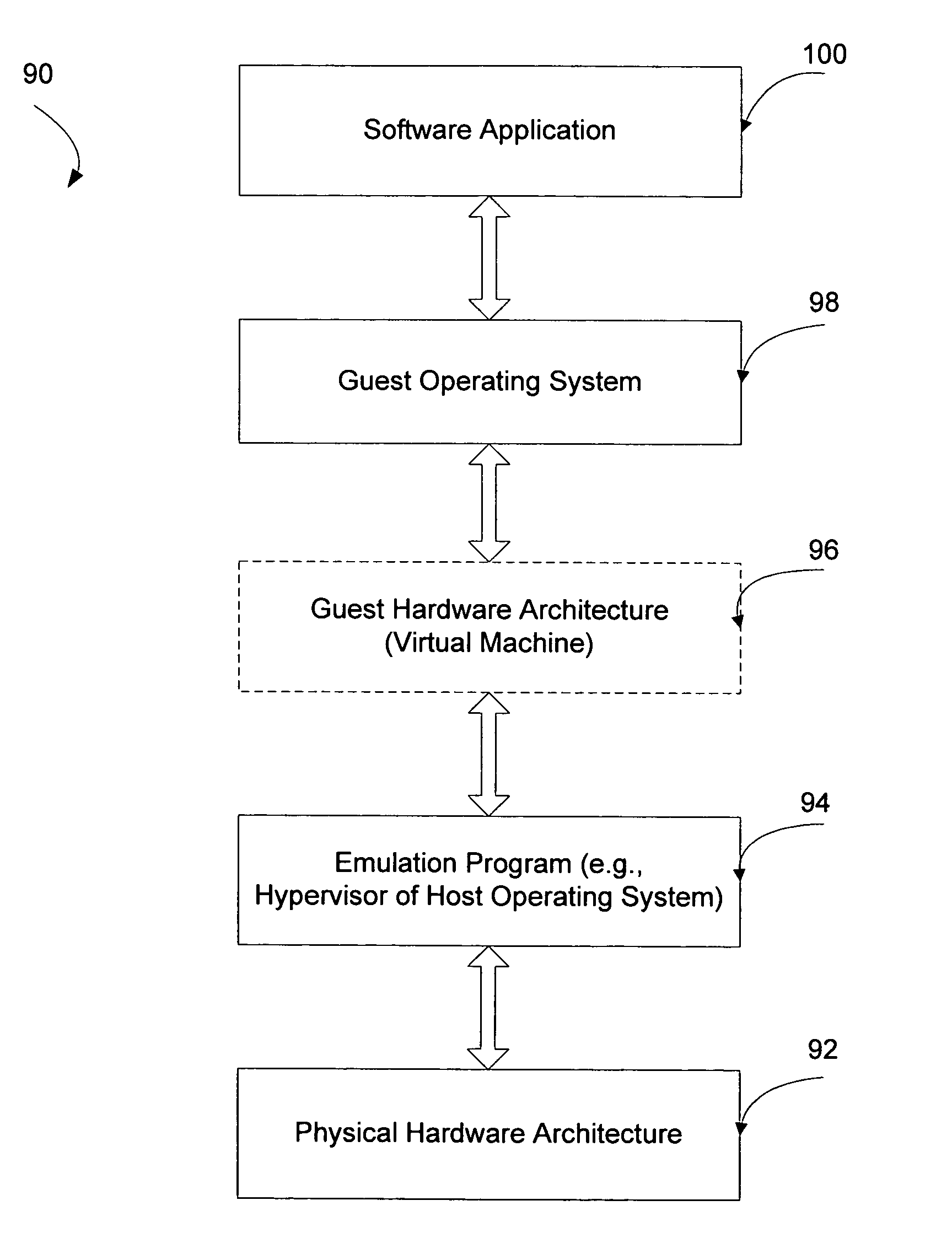
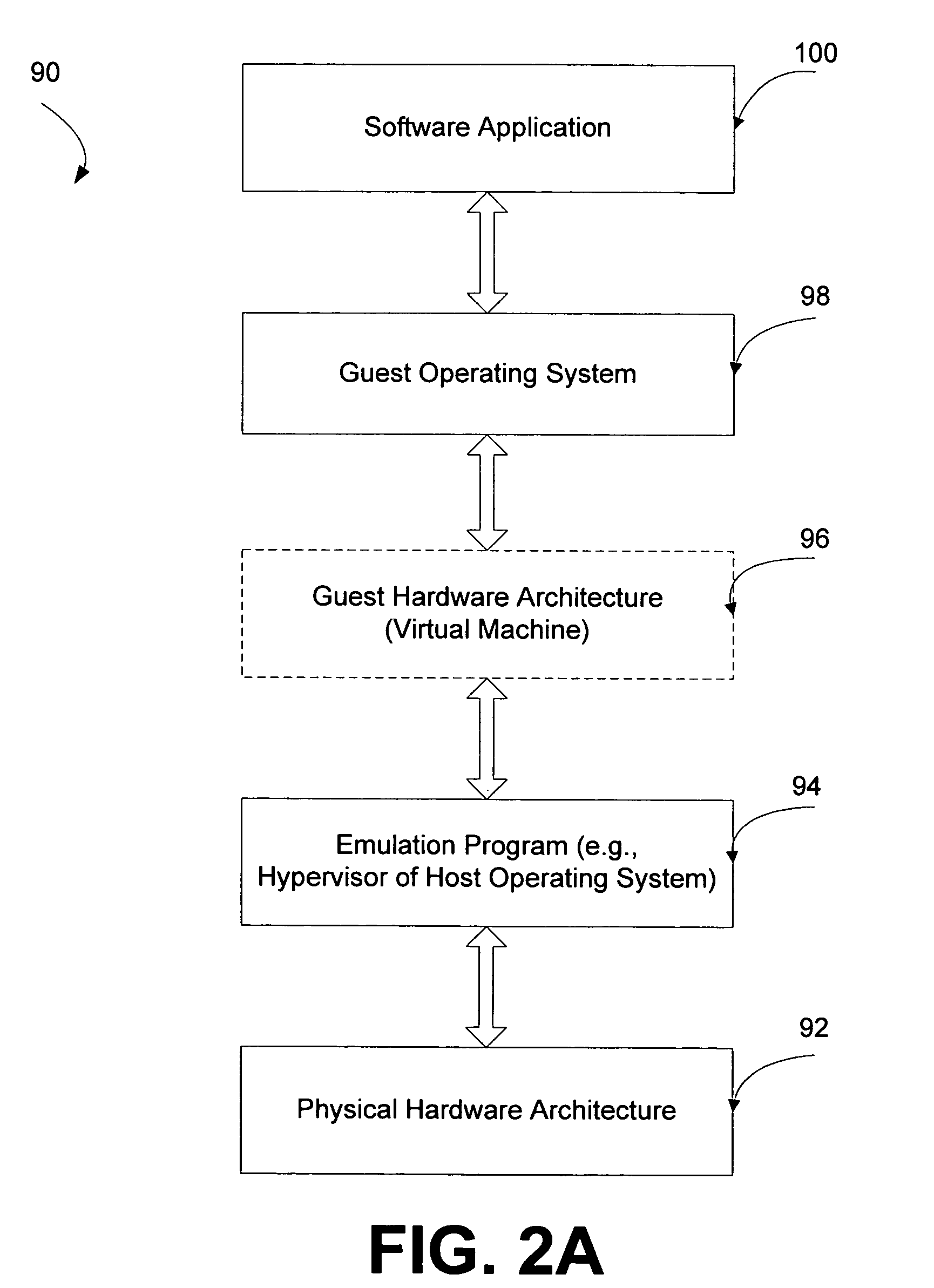
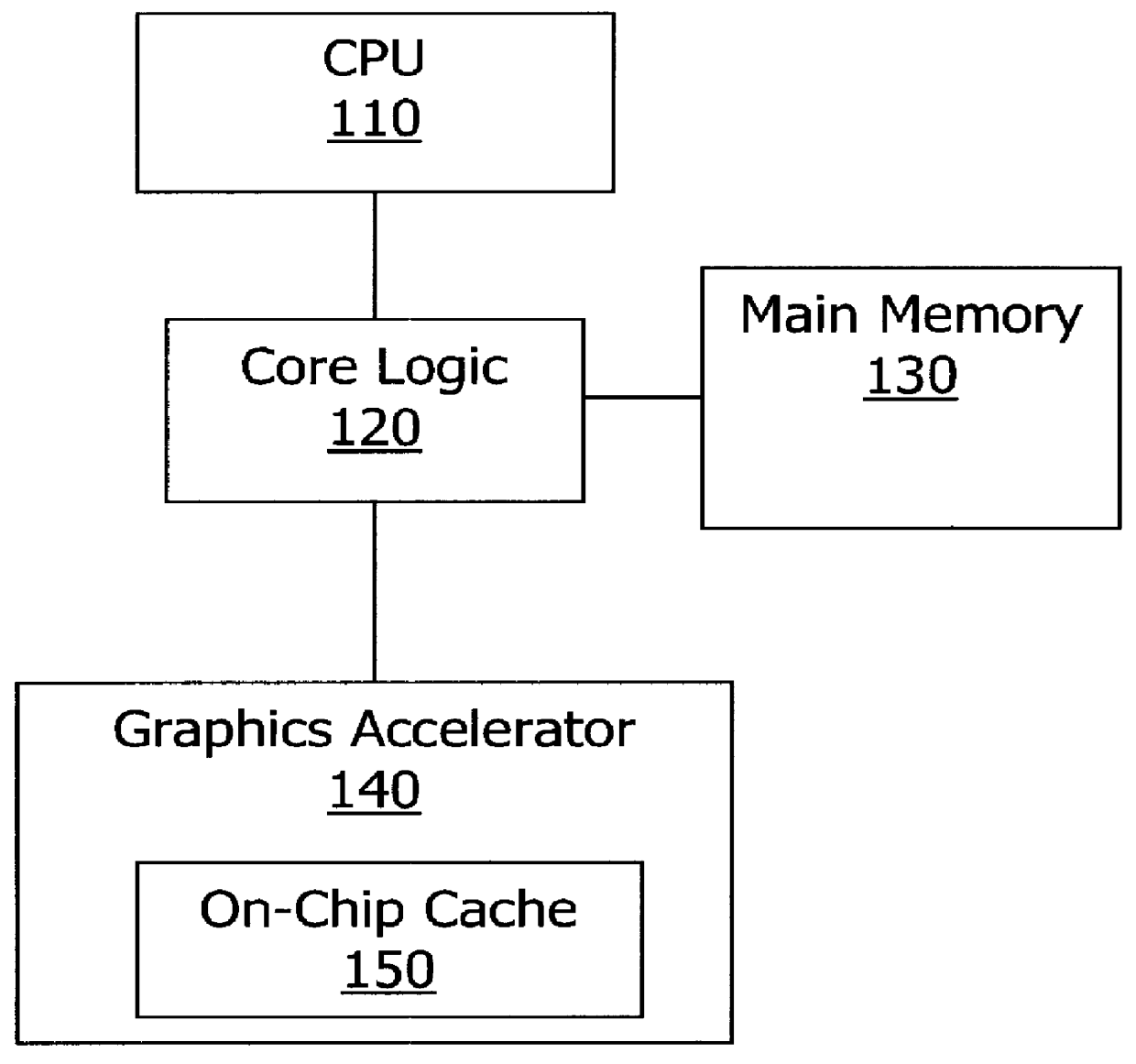
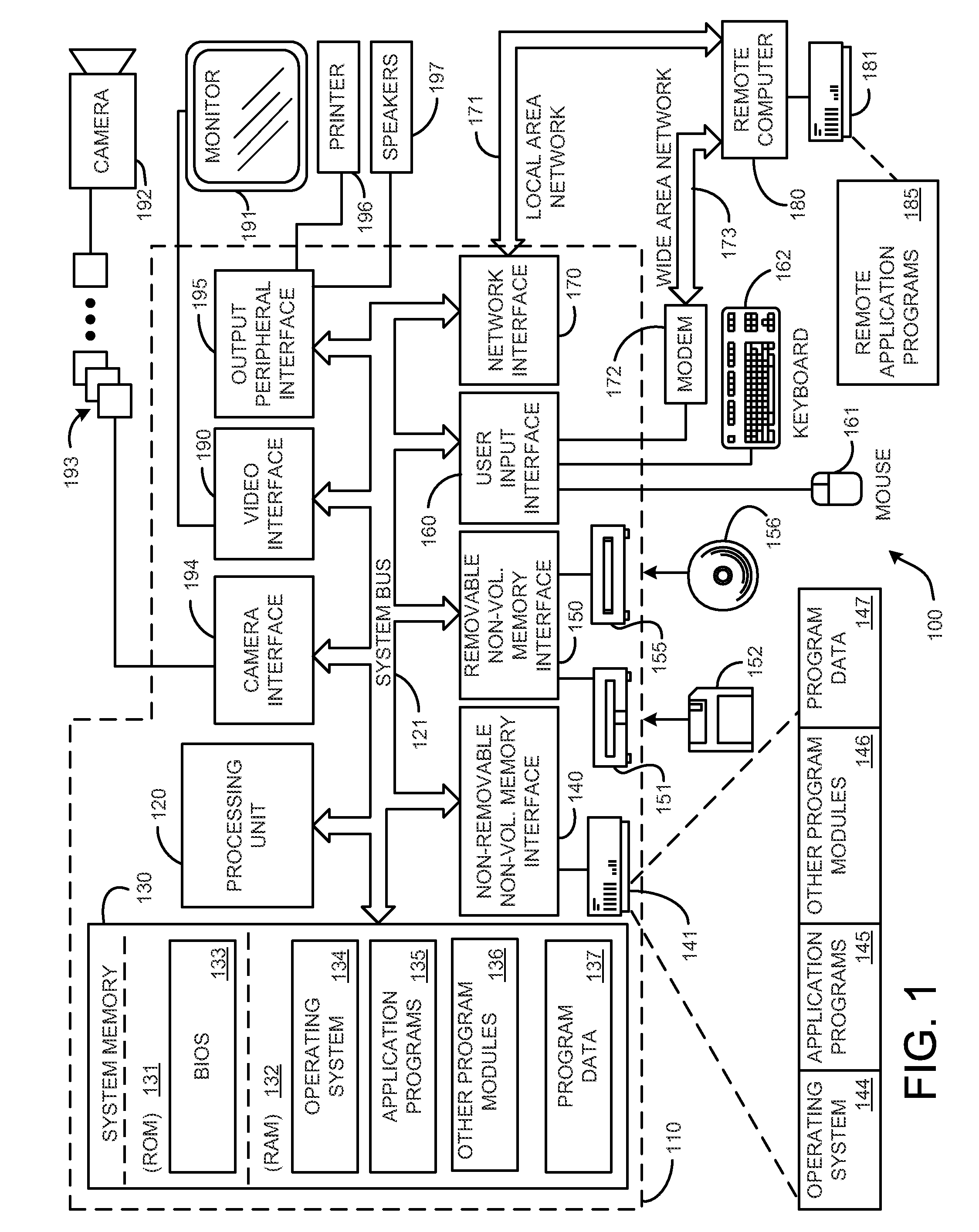
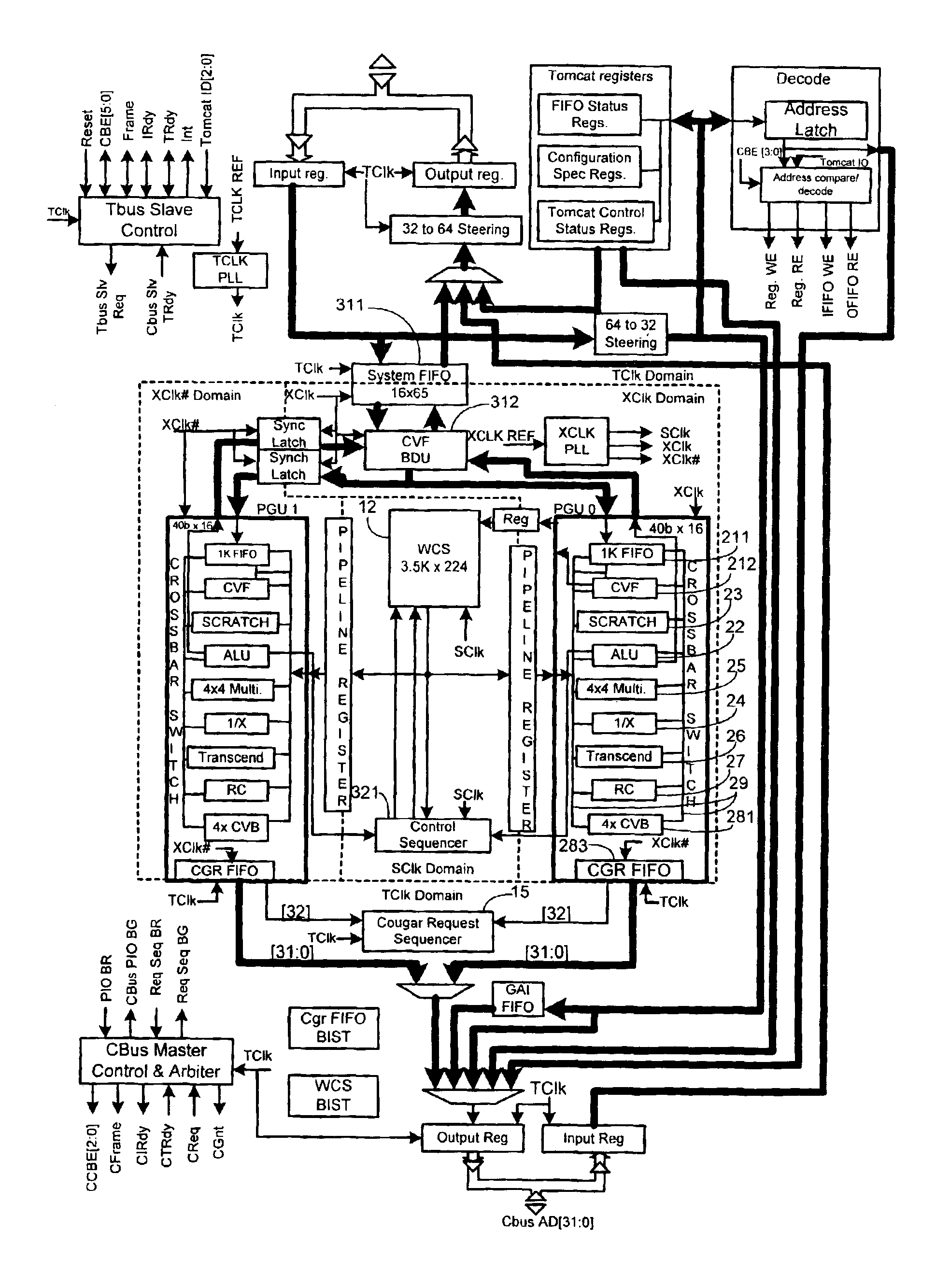
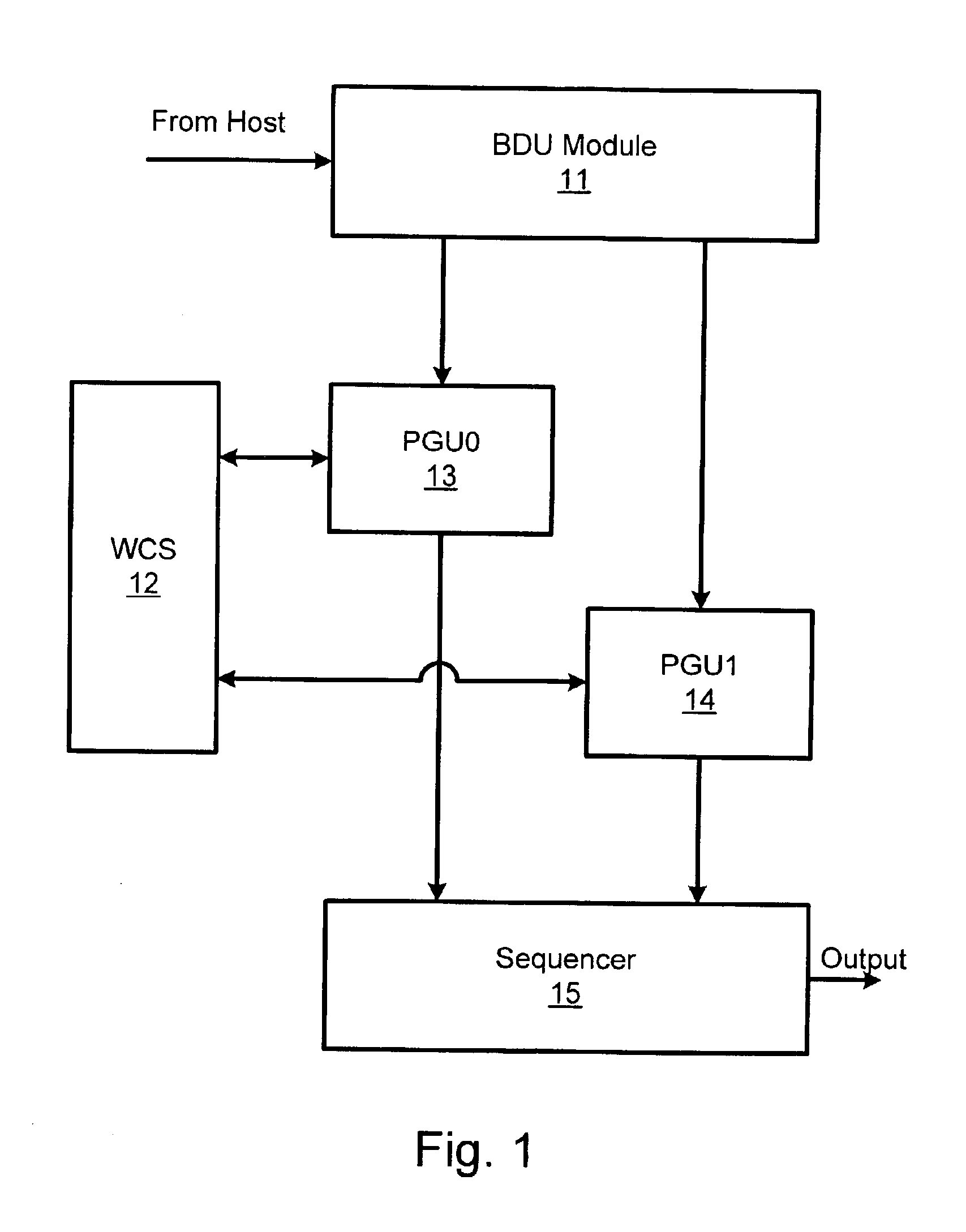
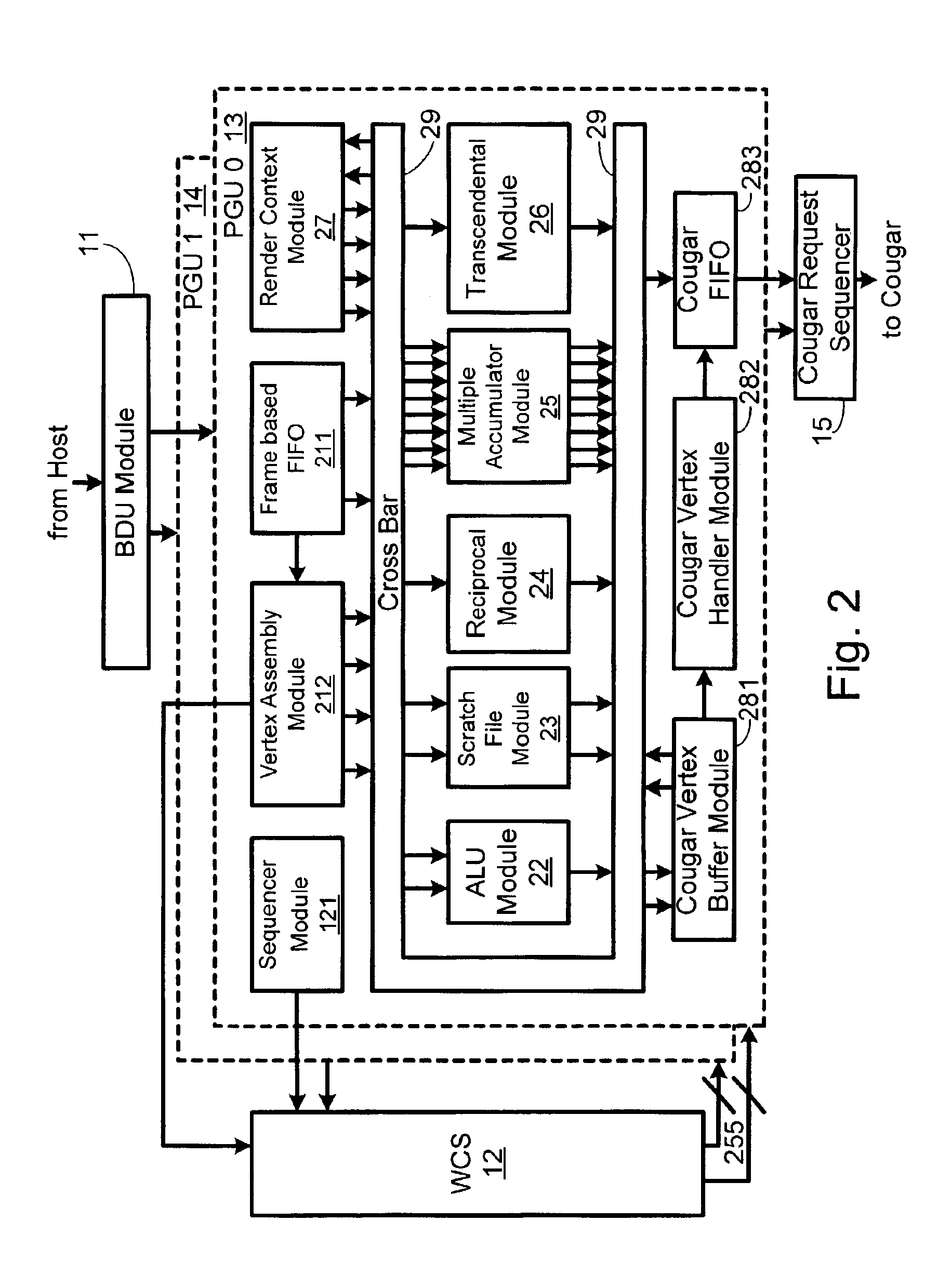
Systems and methods for virtualizing graphics subsystems
ActiveUS20060146057A1Program control using stored programsProcessor architectures/configurationVirtualizationOperational system
Systems and methods for applying virtual machines to graphics hardware are provided. In various embodiments of the invention, while supervisory code runs on the CPU, the actual graphics work items are run directly on the graphics hardware and the supervisory code is structured as a graphics virtual machine monitor. Application compatibility is retained using virtual machine monitor (VMM) technology to run a first operating system (OS), such as an original OS version, simultaneously with a second OS, such as a new version OS, in separate virtual machines (VMs). VMM technology applied to host processors is extended to graphics processing units (GPUs) to allow hardware access to graphics accelerators, ensuring that legacy applications operate at full performance. The invention also provides methods to make the user experience cosmetically seamless while running multiple applications in different VMs. In other aspects of the invention, by employing VMM technology, the virtualized graphics architecture of the invention is extended to provide trusted services and content protection.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
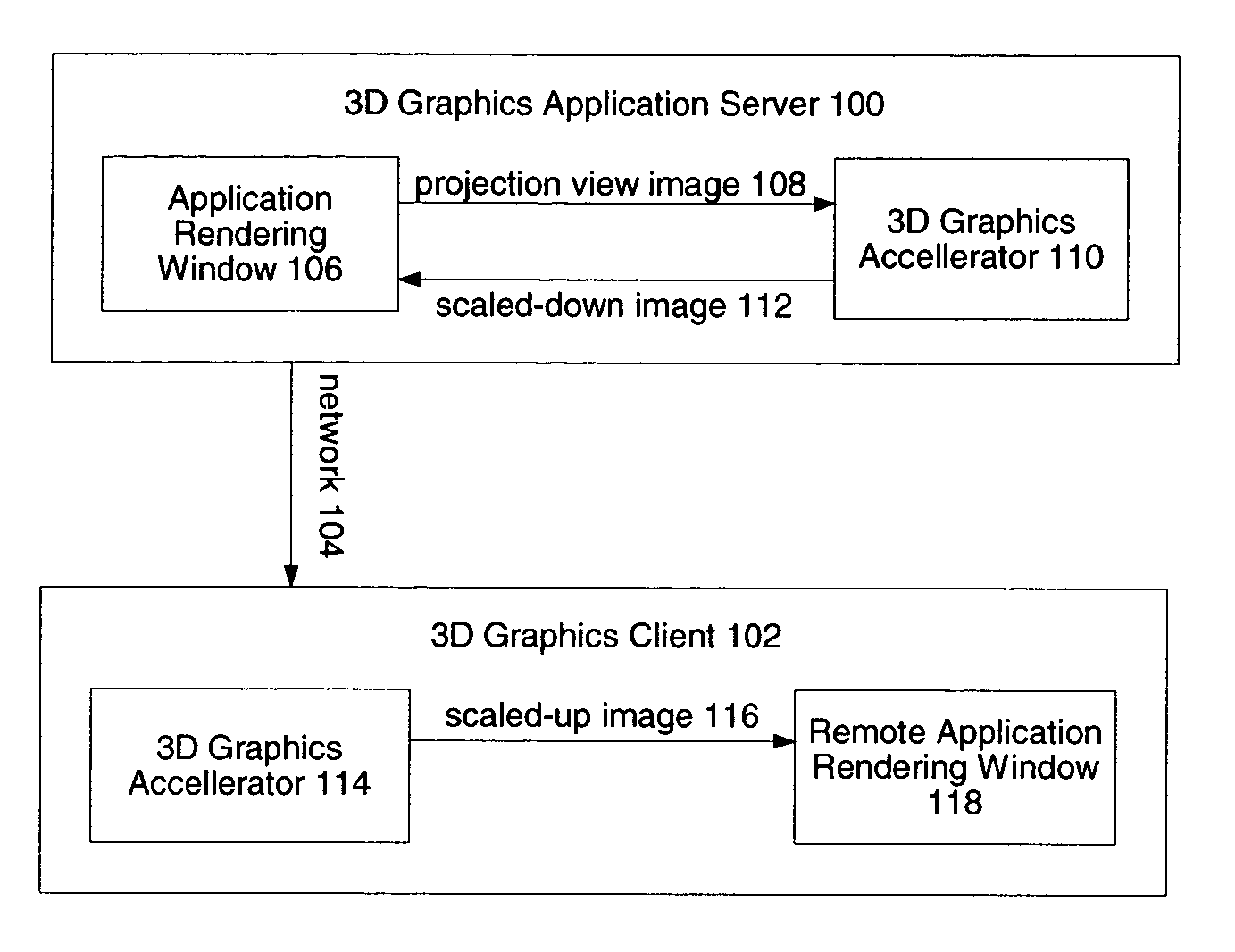
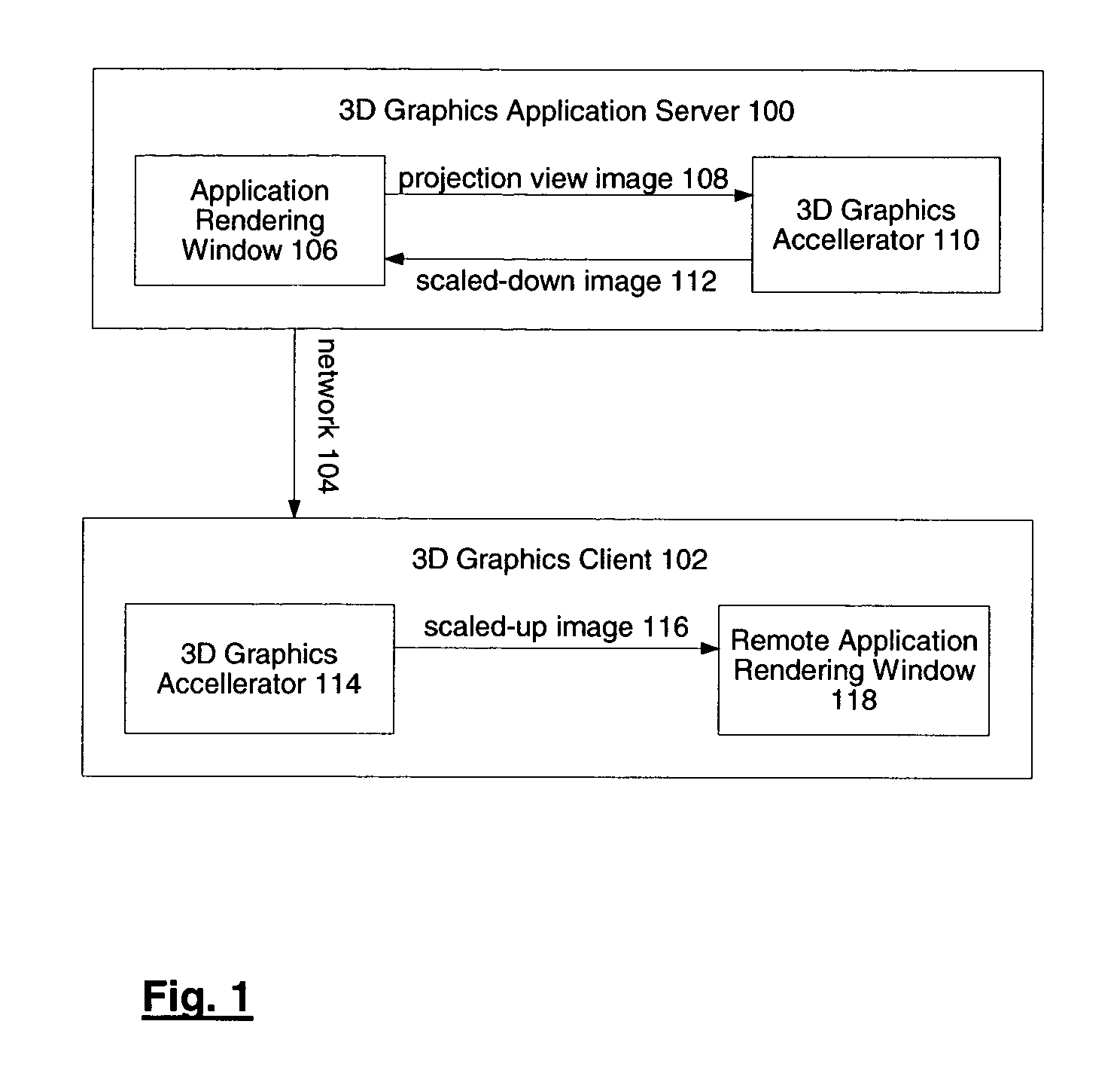
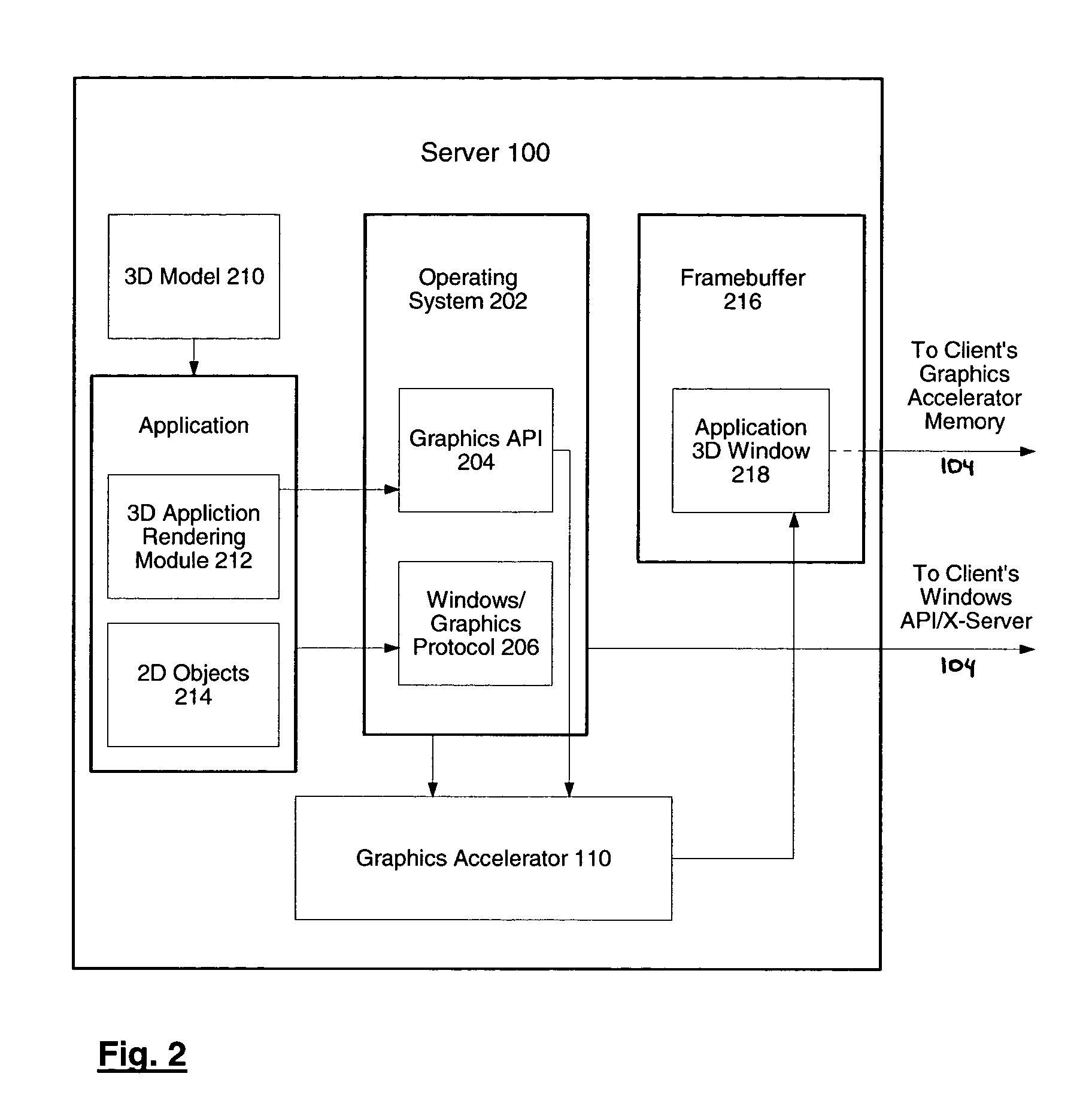
System and method for network transmission of graphical data through a distributed application
InactiveUS7076735B2Reduce network bandwidth requirementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsGraphic cardNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol
Systems and methods for network transmission of three-dimensional graphical data are disclosed. A single graphical application instance can virtually and efficiently exist on multiple local or remote display systems by directly sharing its raw rendered framebuffer memory information among all local or remote graphics accelerators, thus avoiding the need to re-render any application information again on each node. An internal graphics card is used to scale the rendered data prior to transmission. This graphics scaling eliminates the need for data compression or image compression and achieves an adaptive, hardware-accelerated reduction in network bandwidth. Furthermore, since all memory and remote processing support tasks are performed within the graphics card, the CPU, system bus, and memory bandwidth remain available to the system and other applications.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS CORP
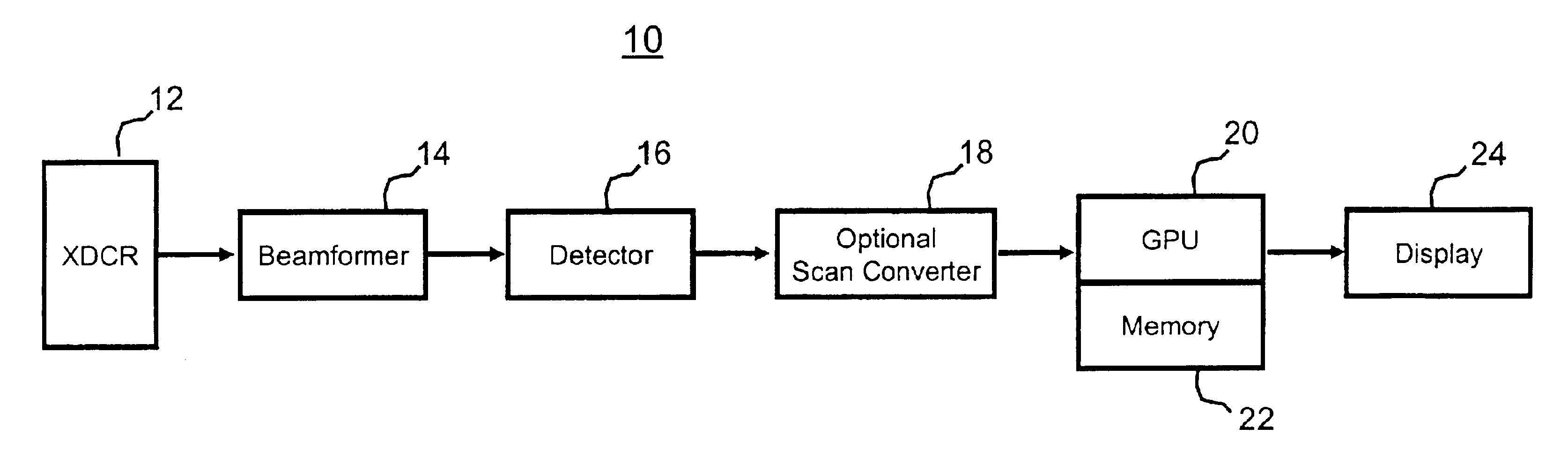
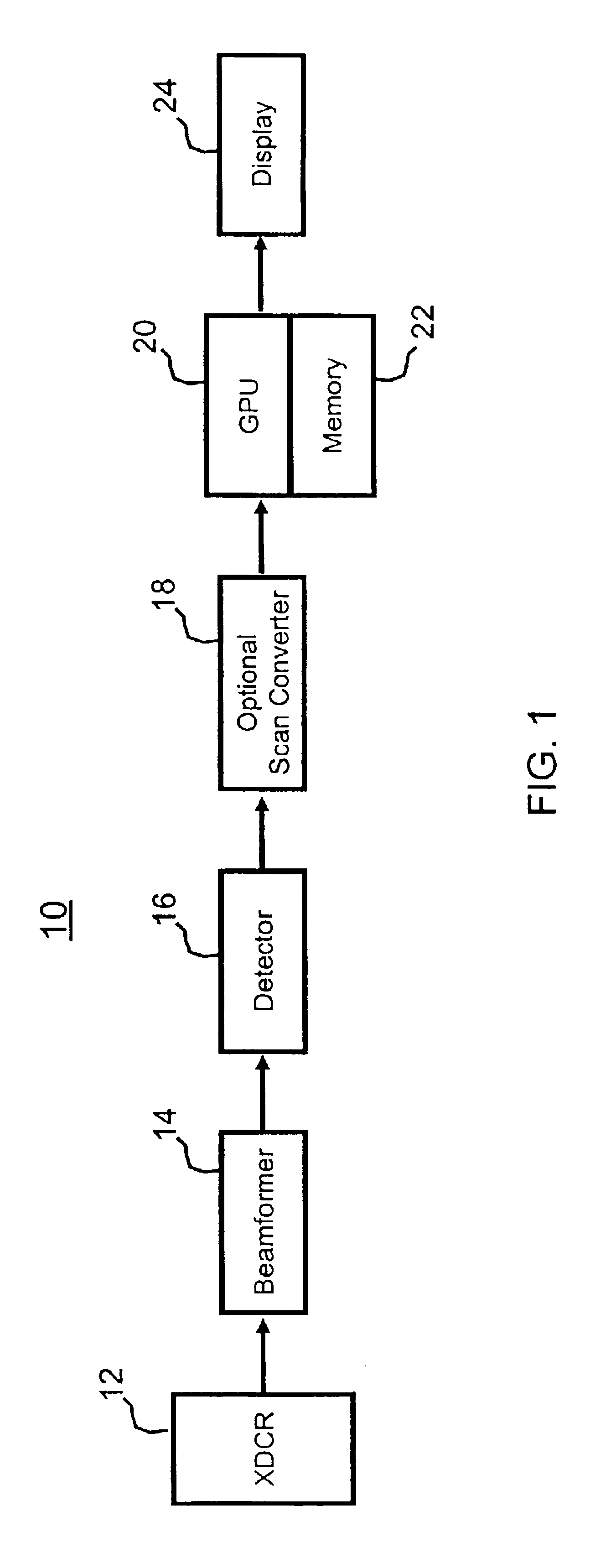
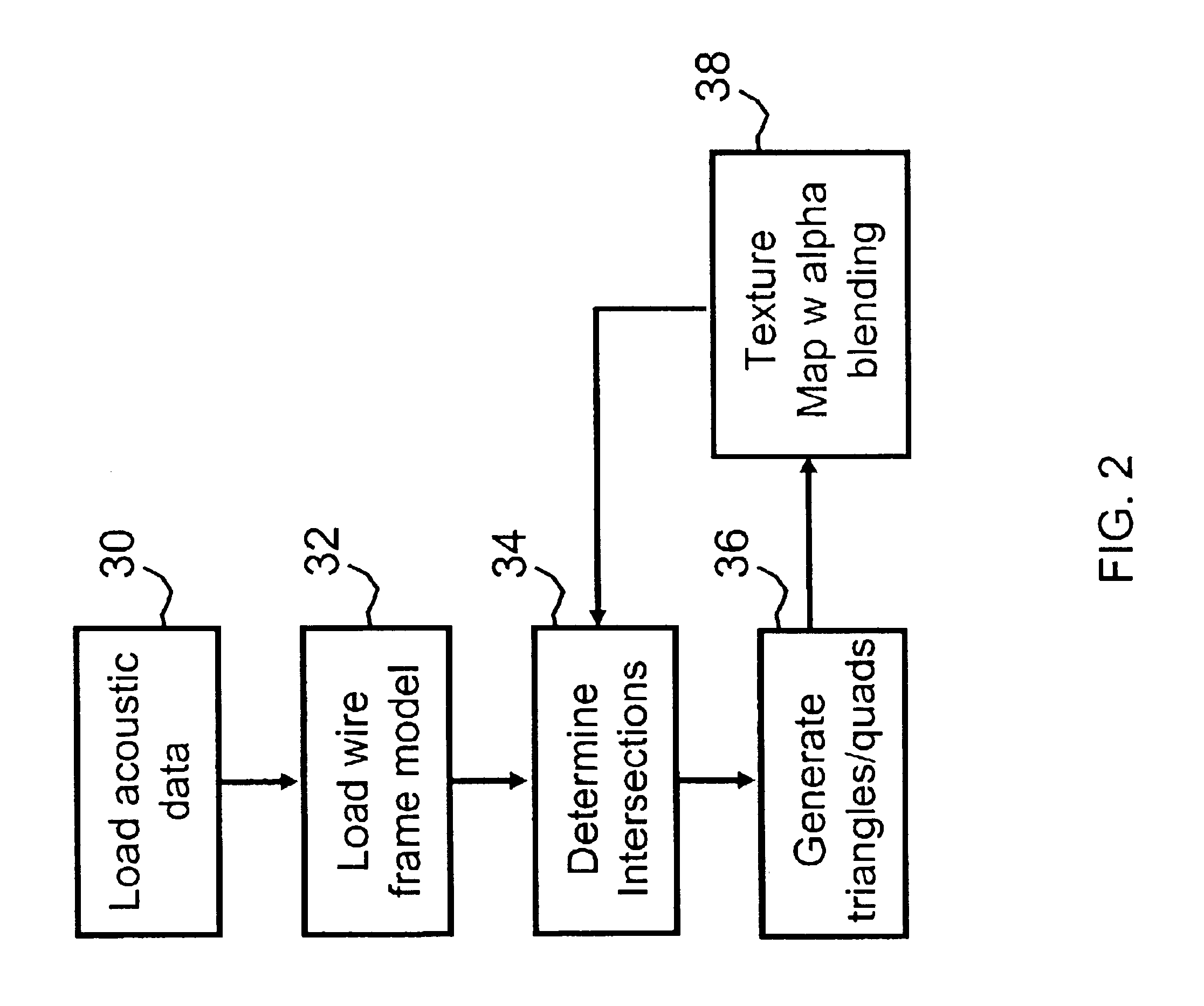
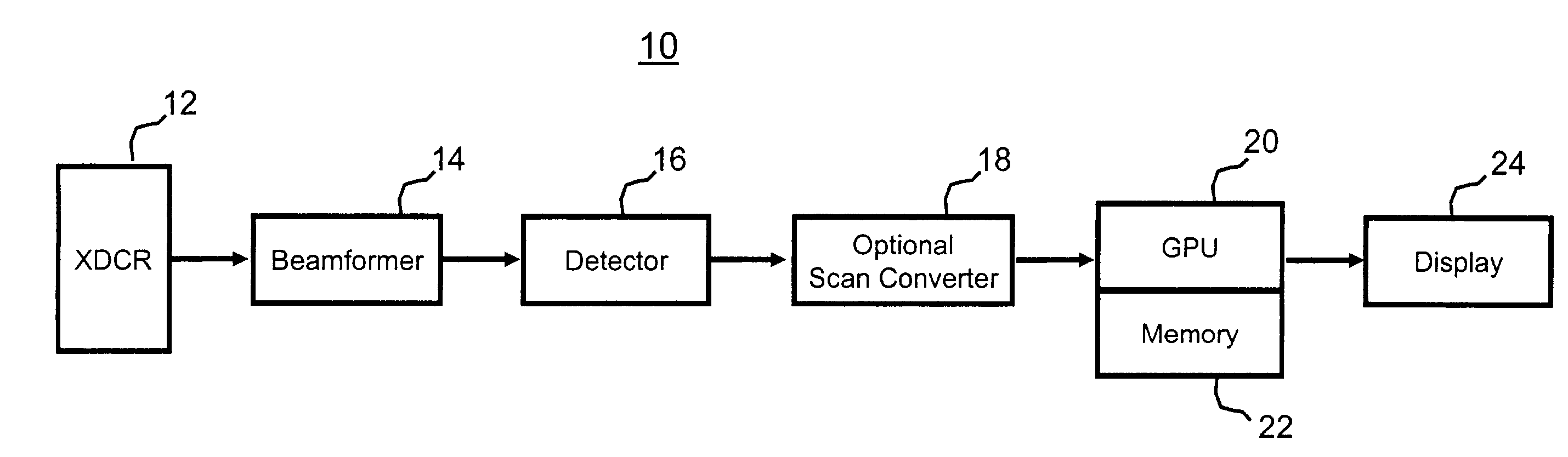
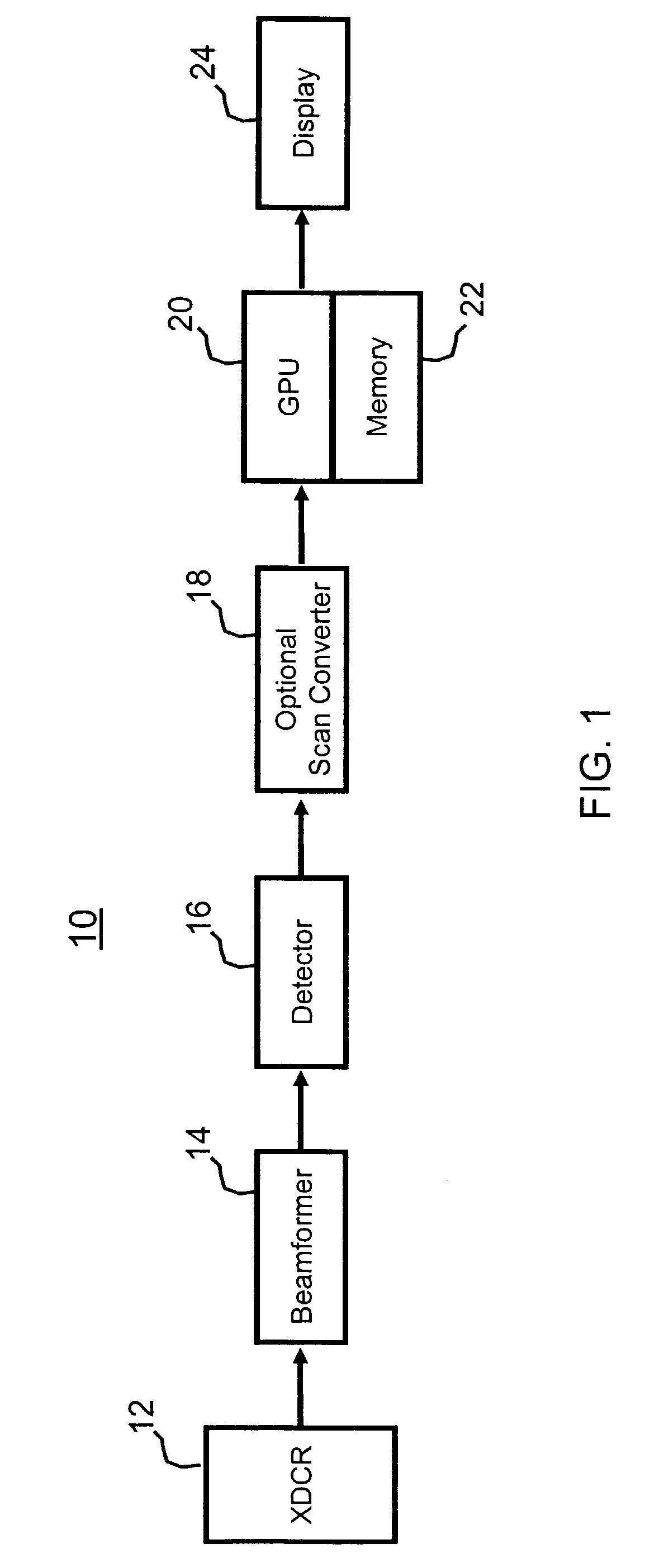
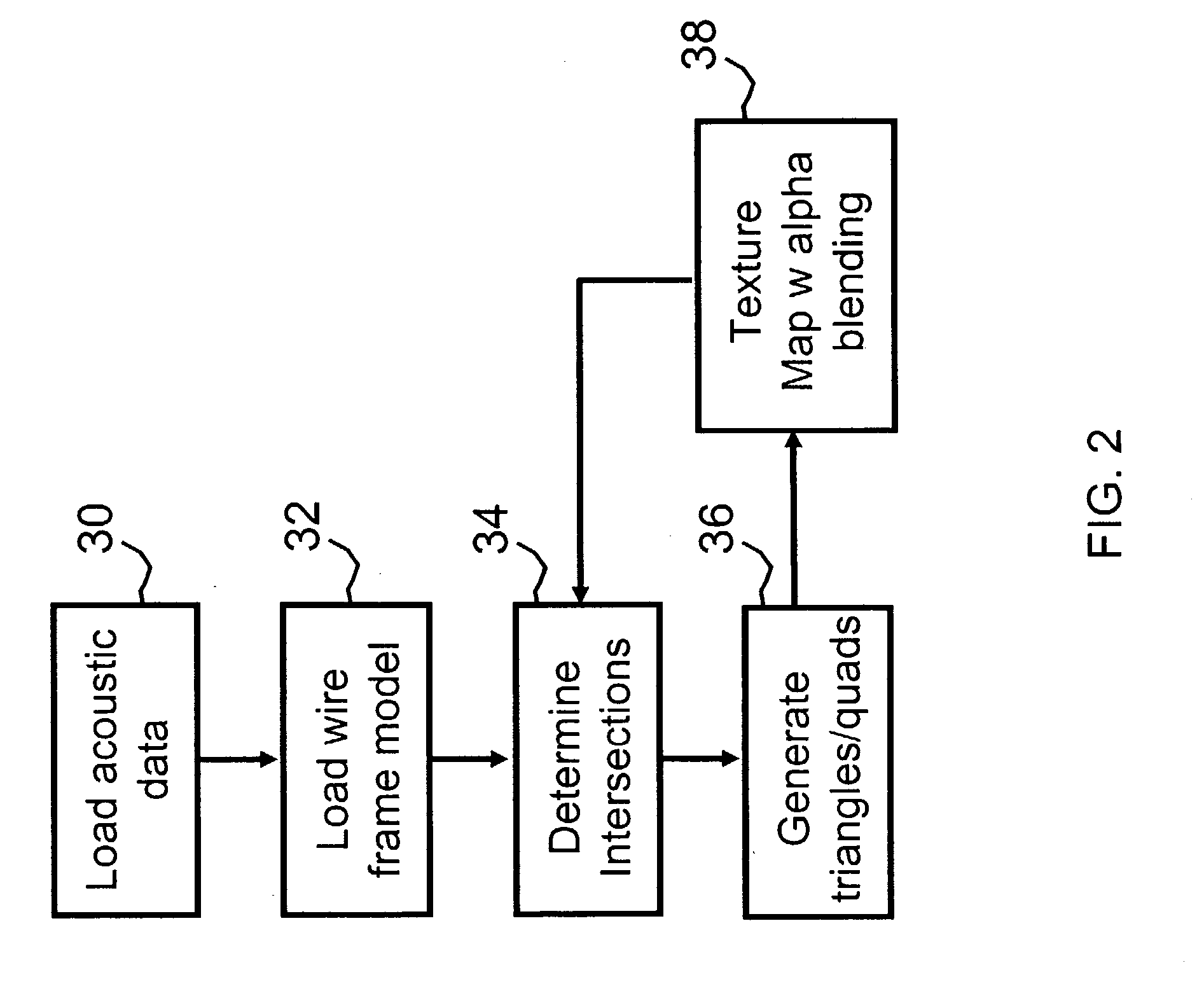
Volume rendering in the acoustic grid methods and systems for ultrasound diagnostic imaging
InactiveUS6852081B2Amount is reduced and eliminatedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryData setSonification
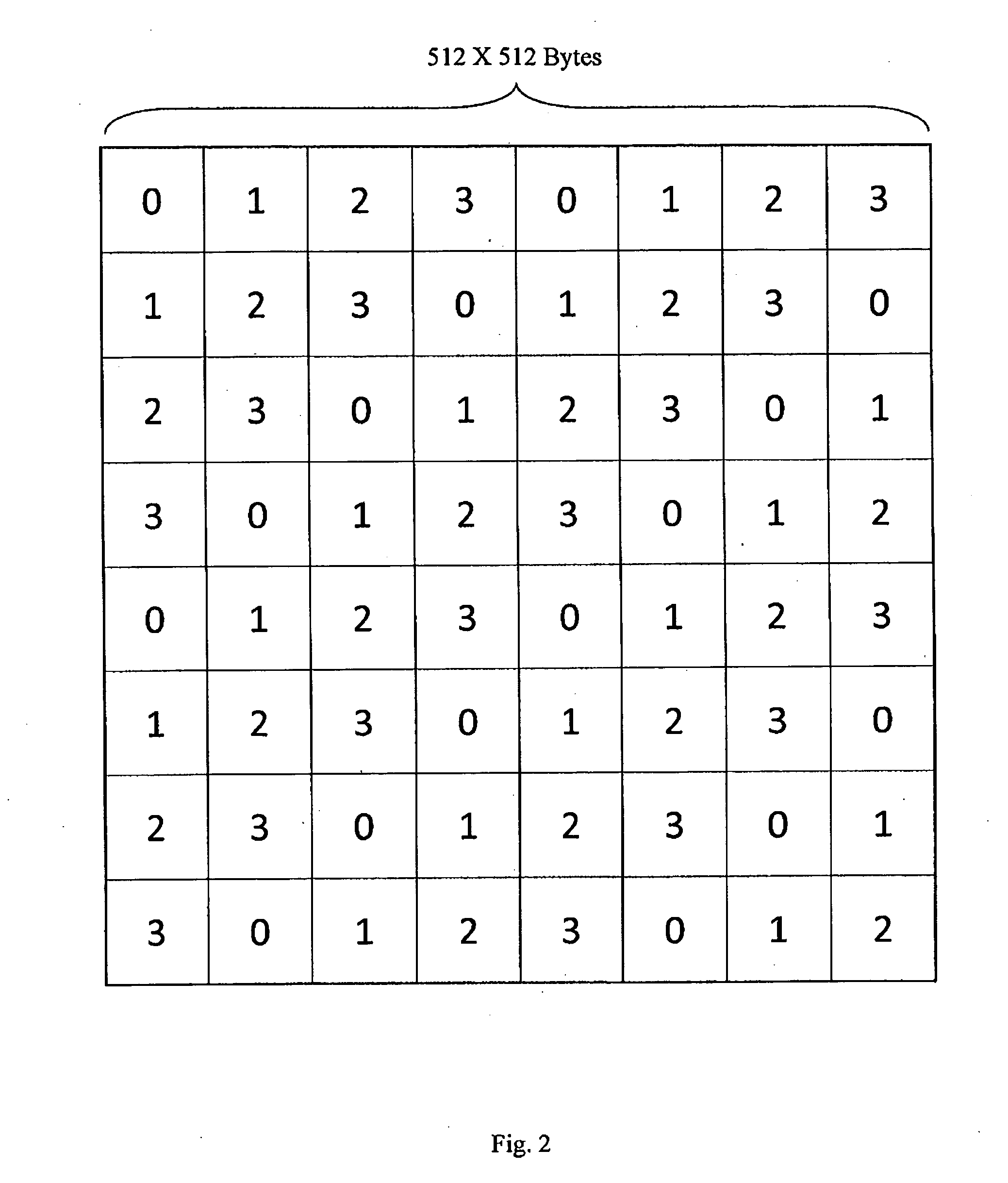
Methods and systems for volume rendering three-dimensional ultrasound data sets in an acoustic grid using a graphics processing unit are provided. For example, commercially available graphic accelerators cards using 3D texturing may provide 256×, 256×128 8 bit volumes at 25 volumes per second or better for generating a display of 512×512 pixels using ultrasound data. By rendering from data at least in part in an acoustic grid, the amount of scan conversion processing is reduced or eliminated prior to the rendering.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
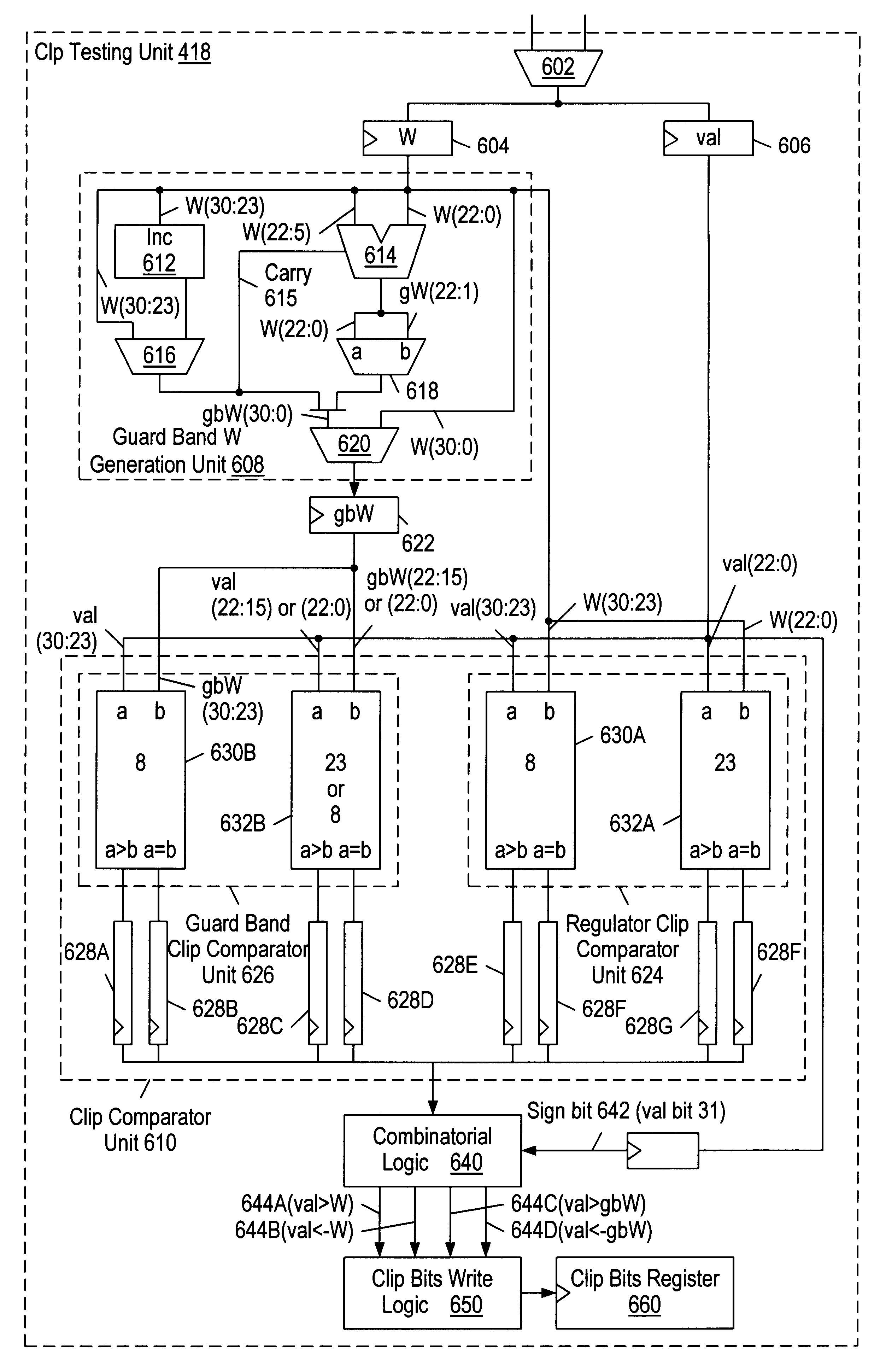
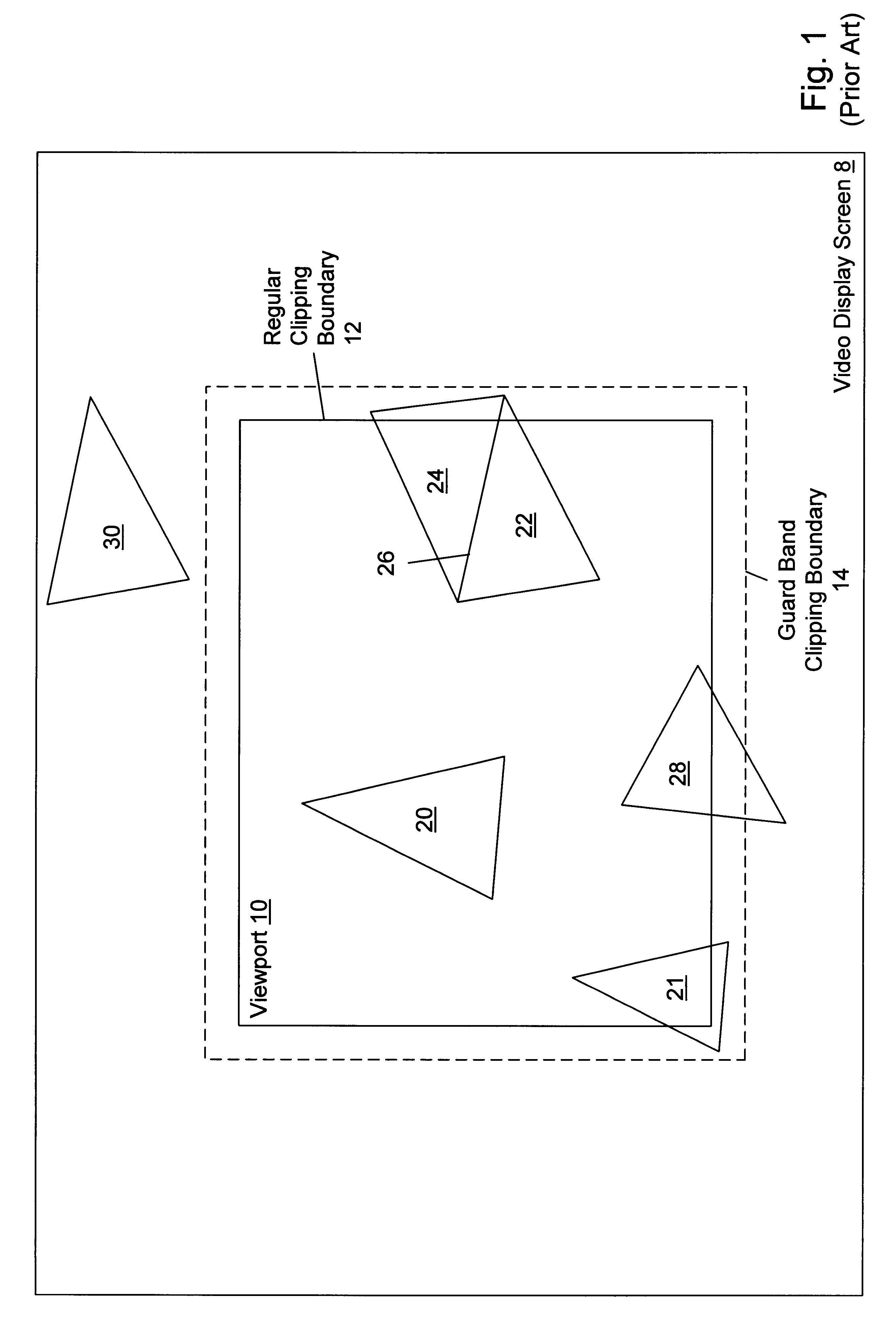
Clip testing unit for a three-dimensional graphics accelerator
InactiveUS6169554B1Input/output processes for data processing3D-image renderingComputational scienceThree dimensional graphics
A clip testing unit within a graphics accelerator for comparing a value of a given homogeneous coordinate of a vertex position of a polygon relative to a plurality of clipping planes. The plurality of clipping planes includes both regular and guard band clipping planes. The clip testing unit includes registers for receiving and storing a W value corresponding to the vertex position, as well as a coordinate input register for receiving and storing the given homogeneous coordinate. The W value is conveyed to a guard band W generation unit, which generates a guard band W value in response thereto. The clip testing unit also includes a clip compare unit coupled to receive the W value, the guard band W value and the value of the given coordinate. The clip compare unit receives and compares the W value and the value of the given coordinate, generating one or more first clip signals in response thereto. The one or more first clip signals indicate whether the value of the given coordinate is outside of a regular clipping space defined by the regular clipping planes. Furthermore, the clip compare unit receives and compares the guard band W value and the value of the given coordinate, generating one or more second clip signals in response thereto. The one or more second clip signals indicate whether the value of the given coordinate is outside of a guard band clipping space defined by the guard band clipping planes. Because the first and second clip comparisons are performed substantially concurrently by the clip compare unit, the clip testing performance of the graphics accelerator is advantageously increased.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Systems and methods for virtualizing graphics subsystems
ActiveUS8274518B2Program control using stored programsProcessor architectures/configurationVirtualizationGraphics accelerator
Systems and methods for applying virtual machines to graphics hardware are provided. In various embodiments of the invention, while supervisory code runs on the CPU, the actual graphics work items are run directly on the graphics hardware and the supervisory code is structured as a graphics virtual machine monitor. Application compatibility is retained using virtual machine monitor (VMM) technology to run a first operating system (OS), such as an original OS version, simultaneously with a second OS, such as a new version OS, in separate virtual machines (VMs). VMM technology applied to host processors is extended to graphics processing units (GPUs) to allow hardware access to graphics accelerators, ensuring that legacy applications operate at full performance. The invention also provides methods to make the user experience cosmetically seamless while running multiple applications in different VMs. In other aspects of the invention, by employing VMM technology, the virtualized graphics architecture of the invention is extended to provide trusted services and content protection.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
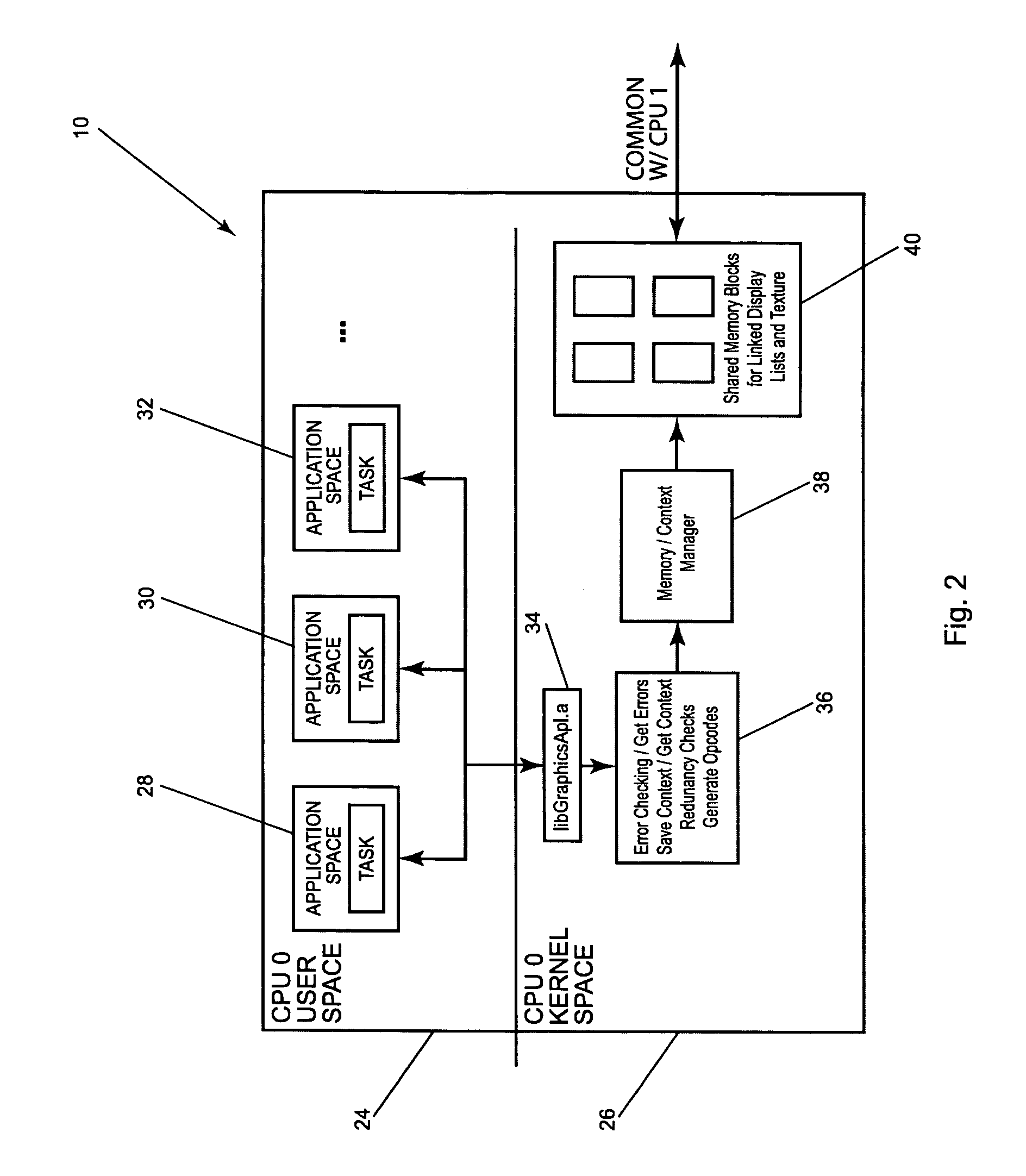
Method and apparatus for multi-level demand caching of textures in a graphics display device
InactiveUS6130680AMemory adressing/allocation/relocationImage memory managementGraphic systemDisplay device
A computer graphics system for caching textures includes an L3 memory, an L2 cache, and an L1 cache for storing such textures and also includes a graphics accelerator (GA) for mapping these stored textures onto primitives for graphics display. The L3 memory, which has the largest capacity also has the slowest retrieval speed, while the L1 cache has the smallest capacity and the quickest retrieval speed. The textures are divided into a plurality of L2 texture blocks and each L2 texture block is subdivided into a plurality of L1 sub-blocks. During its rendering process, the GA searches the L1 cache for a particular L1 sub-block that is to be applied to a primitive. If such L1 sub-block is stored within the L1 cache, the GA will extract the desired texels (i.e., texture pixels) from the L1 sub-block and apply such texels to the primitive. If the L1 sub-block is not located in the L1 cache, the GA will search the L2 cache for the L1 sub-block. If it is found in the L2 cache, the GA will load the L1 sub-block to the L1 cache. However, if the L1 sub-block is not found within the L2 cache, the GA will load the L1 sub-block from the L3 memory to both the L1 and L2 caches. Advantageously, when the GA requires such L1 sub-block again, the GA will have a speedier access to the L1 sub-block via the L1 and L2 caches.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Volume rendering in the acoustic grid methods and systems for ultrasound diagnostic imaging
InactiveUS20040181151A1Amount is reduced and eliminatedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryData setSonification
Methods and systems for volume rendering three-dimensional ultrasound data sets in an acoustic grid using a graphics processing unit are provided. For example, commercially available graphic accelerators cards using 3D texturing may provide 256x, 256x128 8 bit volumes at 25 volumes per second or better for generating a display of 512x512 pixels using ultrasound data. By rendering from data at least in part in an acoustic grid, the amount of scan conversion processing is reduced or eliminated prior to the rendering.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
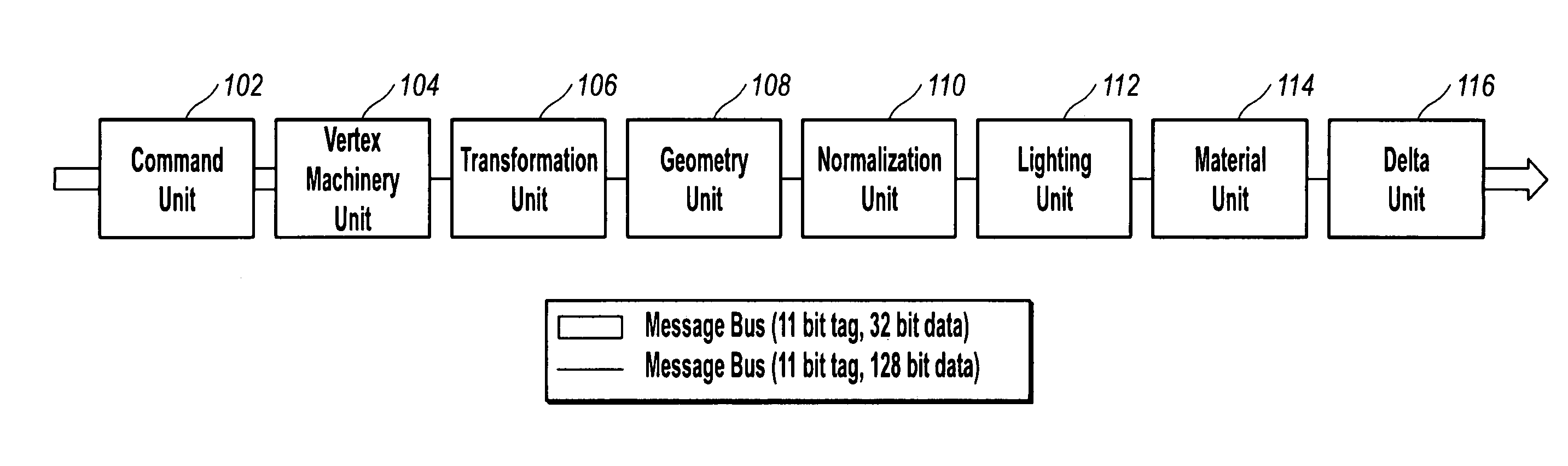
Graphics accelerator with shift count generation for handling potential fixed-point numeric overflows
InactiveUS6037947ACathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
A 3-D graphics accelerator for performing lighting operations using operands within a given fixed point numeric range. The 3-D graphics accelerator includes a first computational unit which is configured to compute a value of an attenuation factor usable for performing said lighting operation for local lights. The attenuation factor is represented in floating point format. The first computational unit is also configured to represent the attenuation factor in an intermediate format including a first intermediate value (a scaled attenuation factor value within the given fixed point numeric range), and a second intermediate value (a shift count usable to convert the scaled attenuation factor value back to the original attenuation factor value). The 3-D graphics accelerator further includes a lighting unit coupled to said first computational unit. The first computational unit is further configured to convey the intermediate representation of the attenuation factor to the lighting unit. The lighting unit performs lighting calculations in fixed point, using operands within the given numeric range (such as the scaled attenuation factors). The lighting unit generates intermediate color values as a result of these lighting calculations. The lighting unit then uses the shift count value to shift the intermediate color values by an appropriate amount, thereby generating a final color value. The lighting unit clamps said final color value to a predetermined maximum color value in response to said final color value exceeding said predetermined maximum color value.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
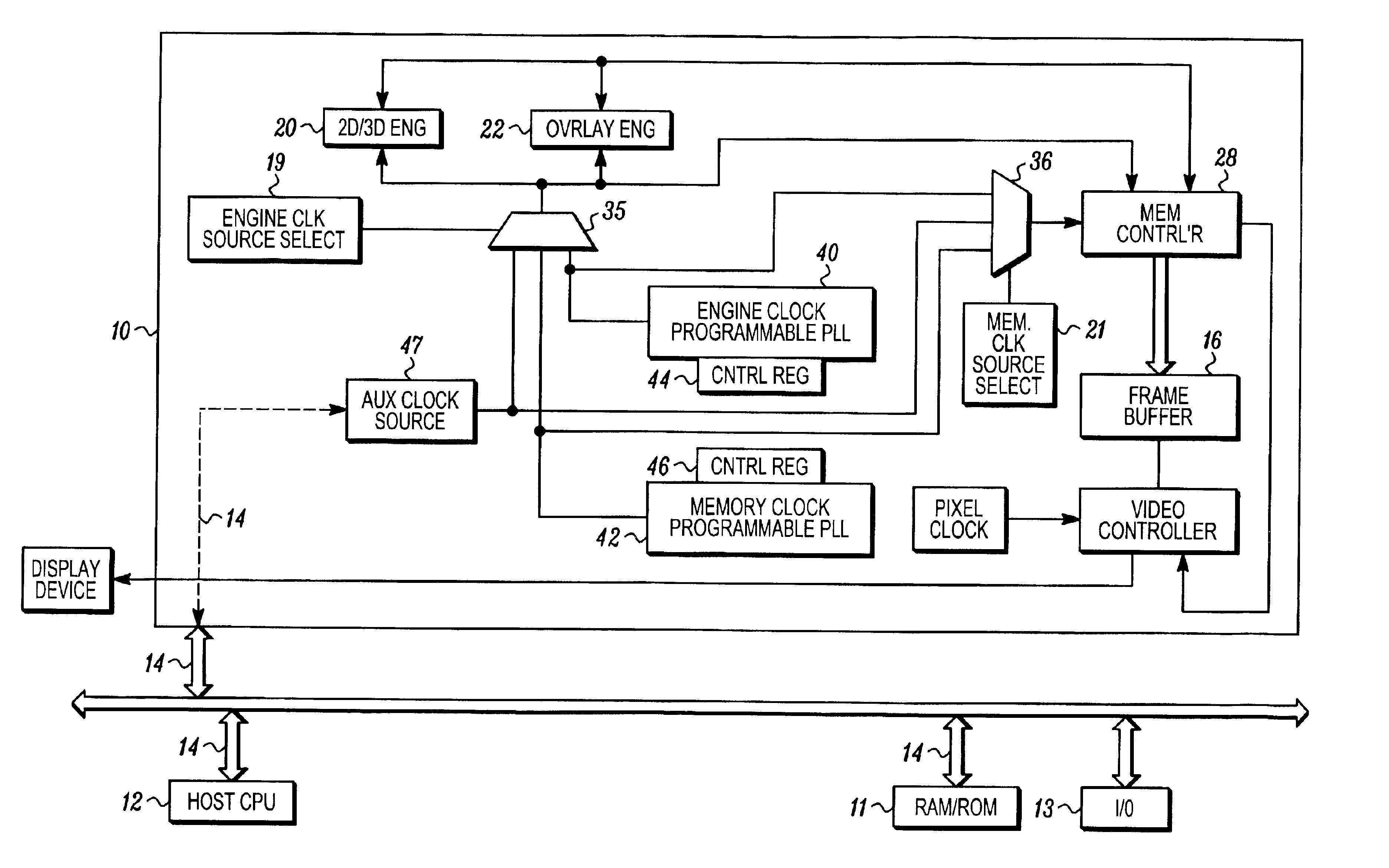
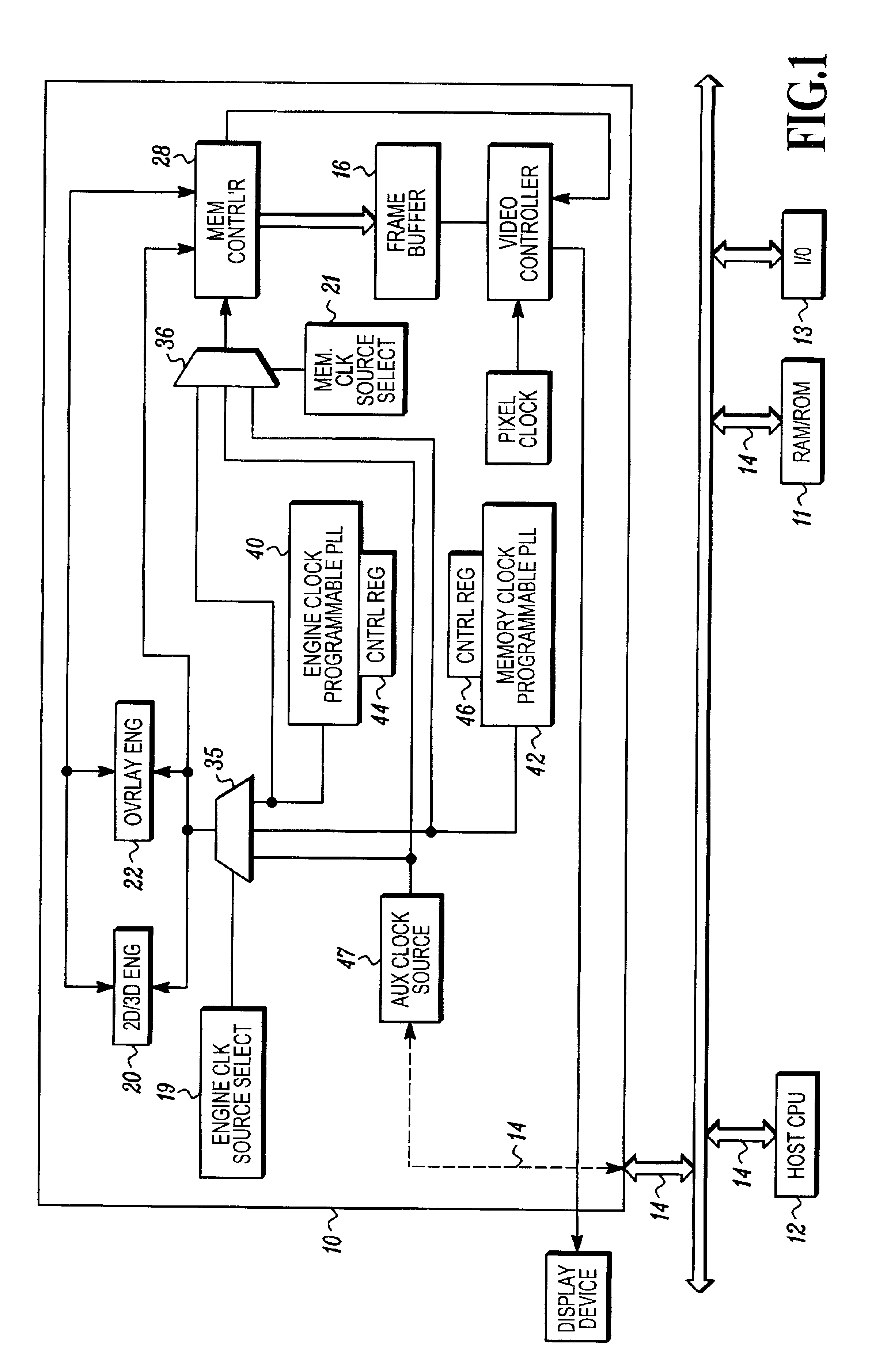
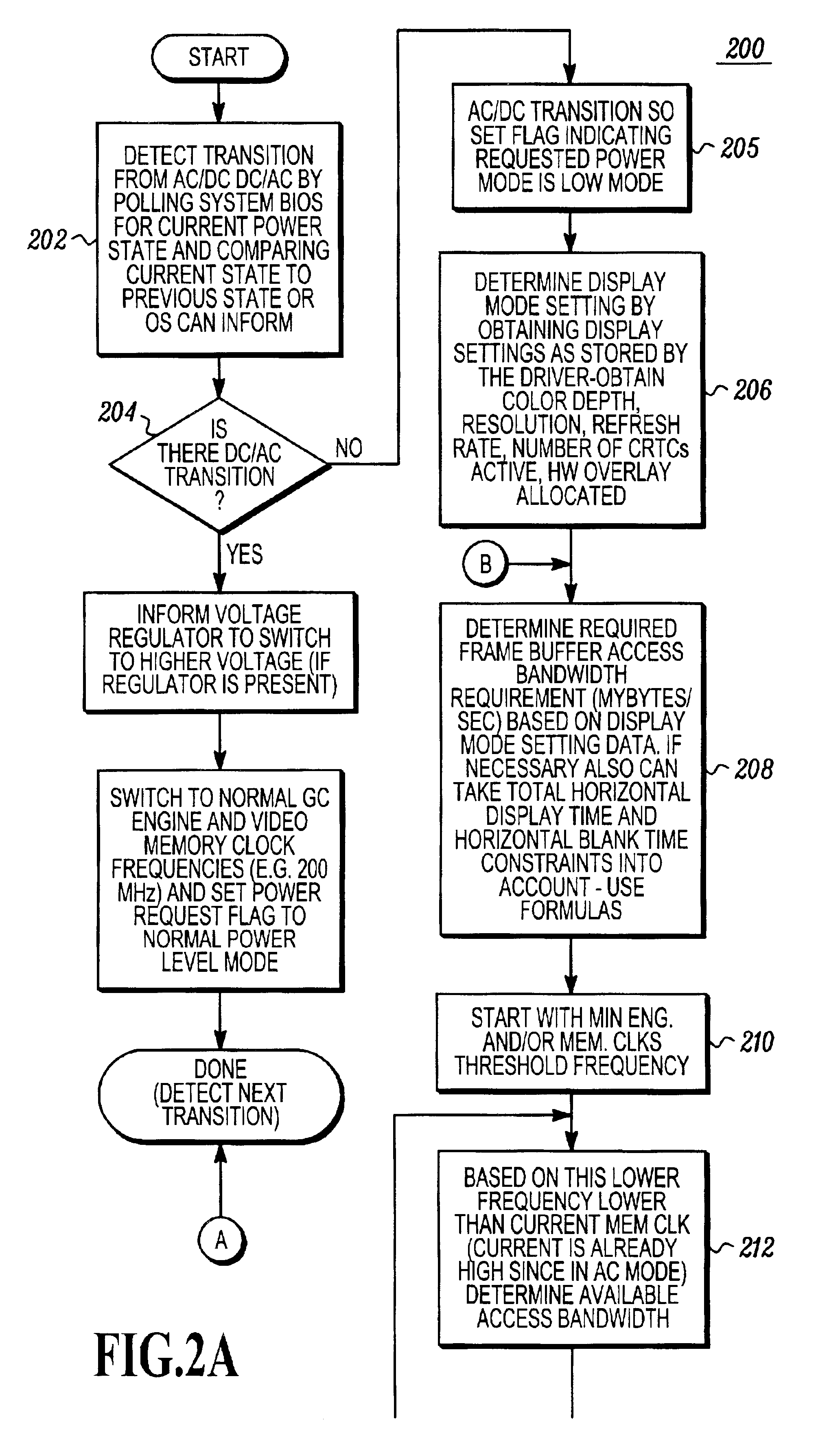
Power consumption management in a video graphics accelerator
InactiveUS6950105B2Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementComputer hardwareComputer architecture
A method and apparatus matches one or more clock speeds used in, or used by, a graphics accelerator so as to match graphics processing requirements to the speed of the clock source or sources. Clock speed is adjusted under software control to match current requirements. Power is conserved by reducing clock speeds from unnecessarily high rates to a rate that can satisfy current display mode settings and other graphics processing demands.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
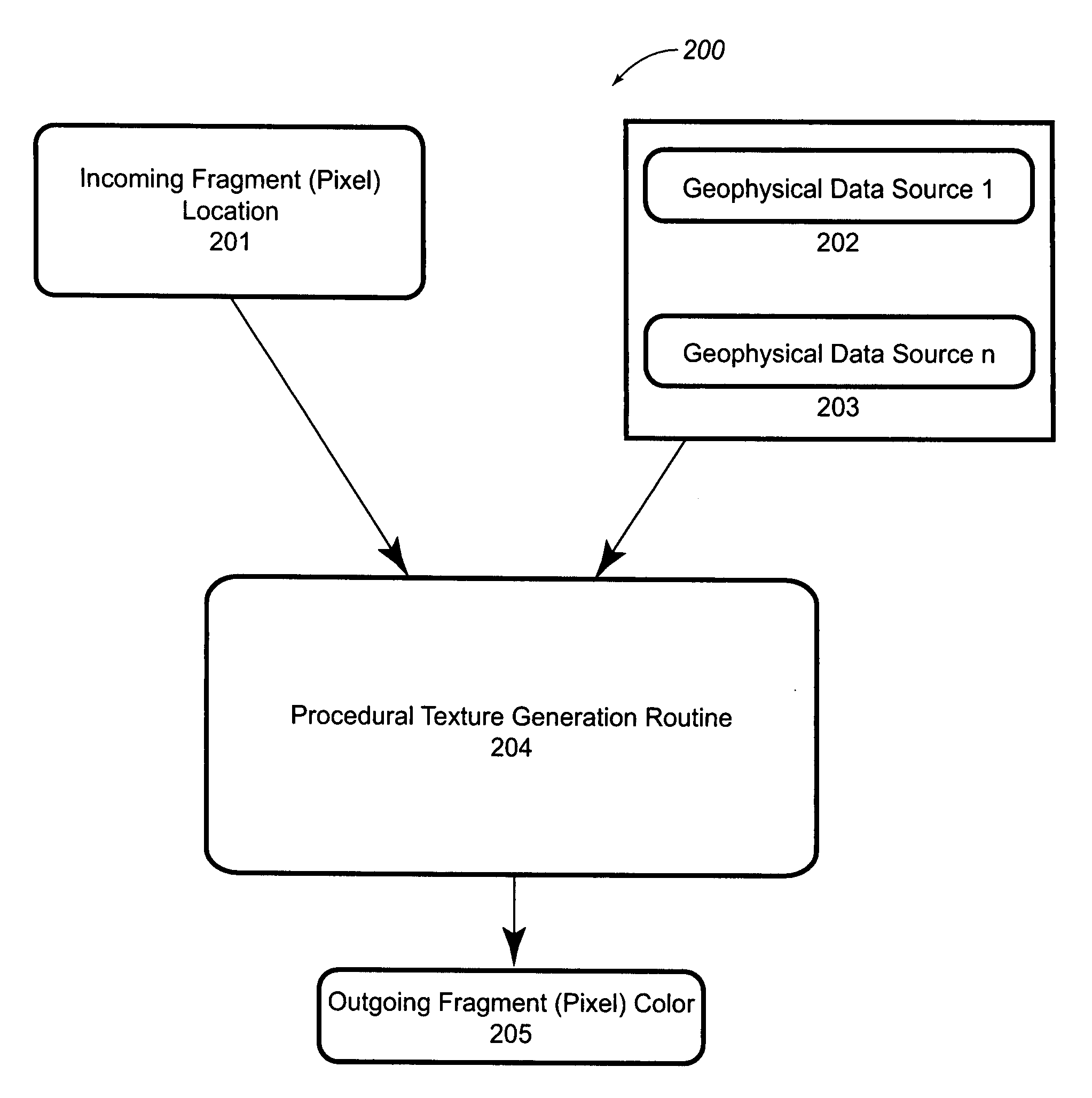
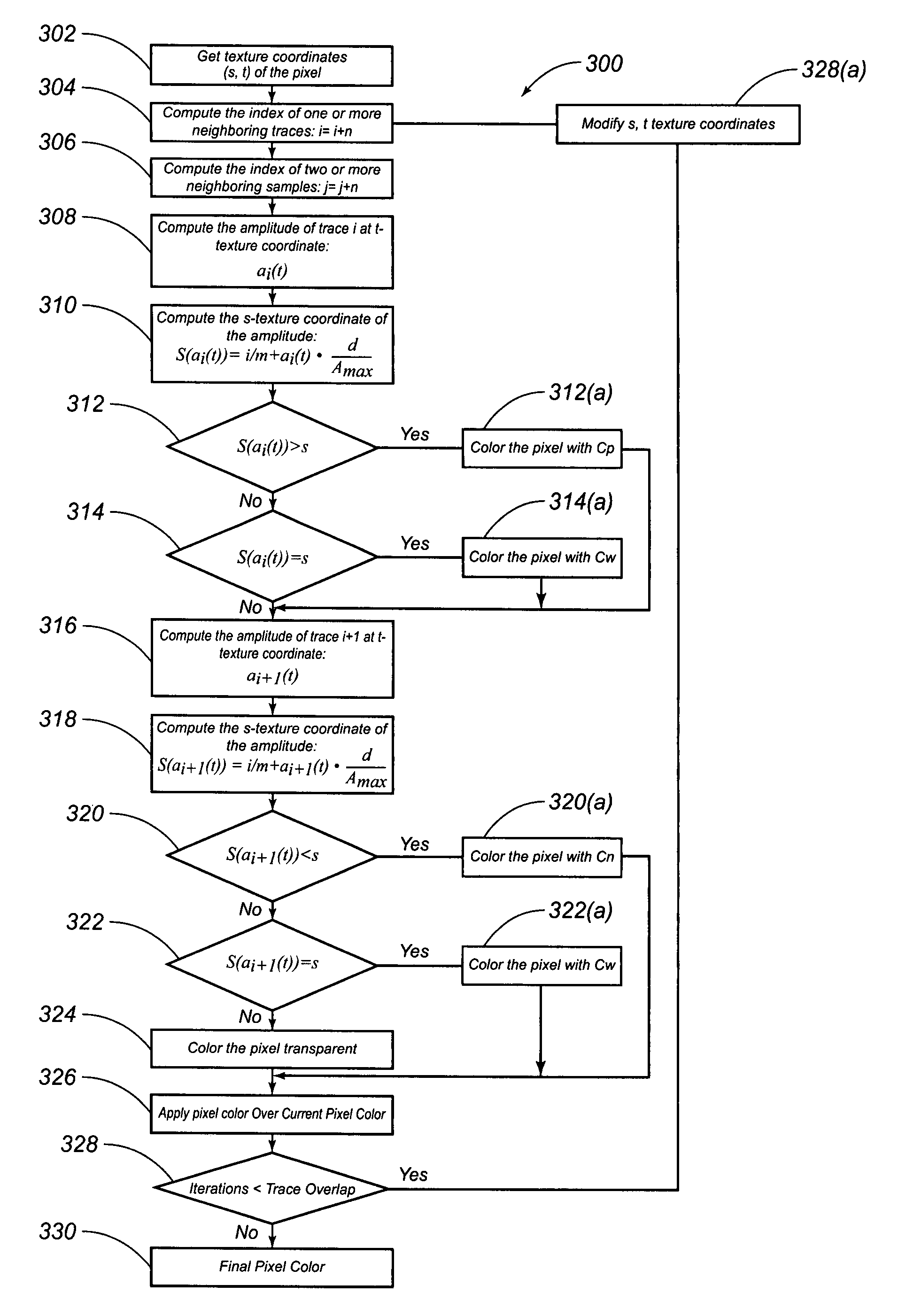
Systems and Methods for Imaging Waveform Volumes
ActiveUS20080059074A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsGraphic cardDisplay device
Systems and methods for imaging waveform volumes. An image of the waveform volume may be drawn on a display device as a two-dimensional image or a three-dimensional image of a sampling probe and redrawn in real-time at interactive rates using a graphics accelerator or a graphics card. The image of the waveform volume may also include seismic-data traces that are color-filled according to texture coordinates for pixels on the display device that intersect the waveform volume.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
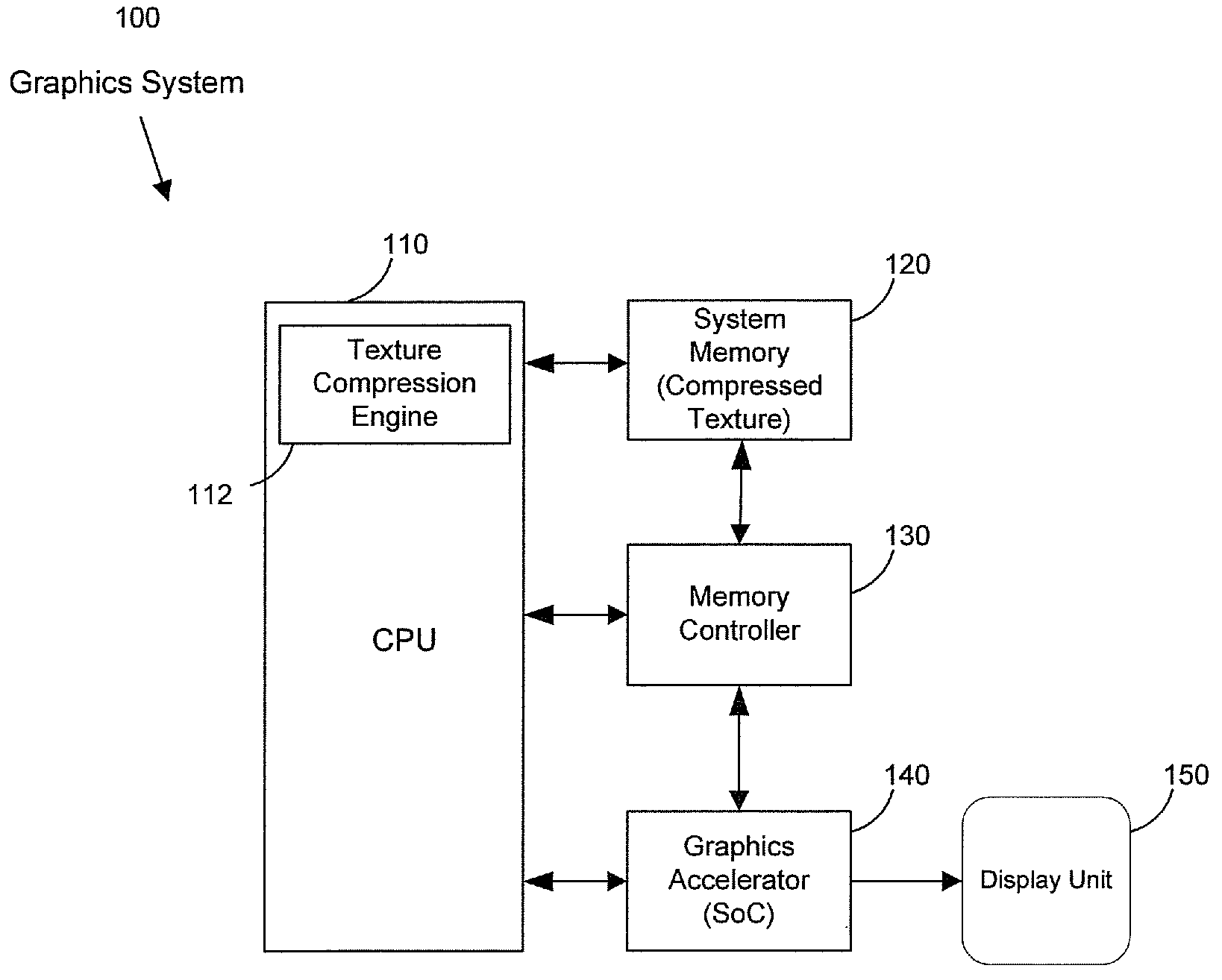
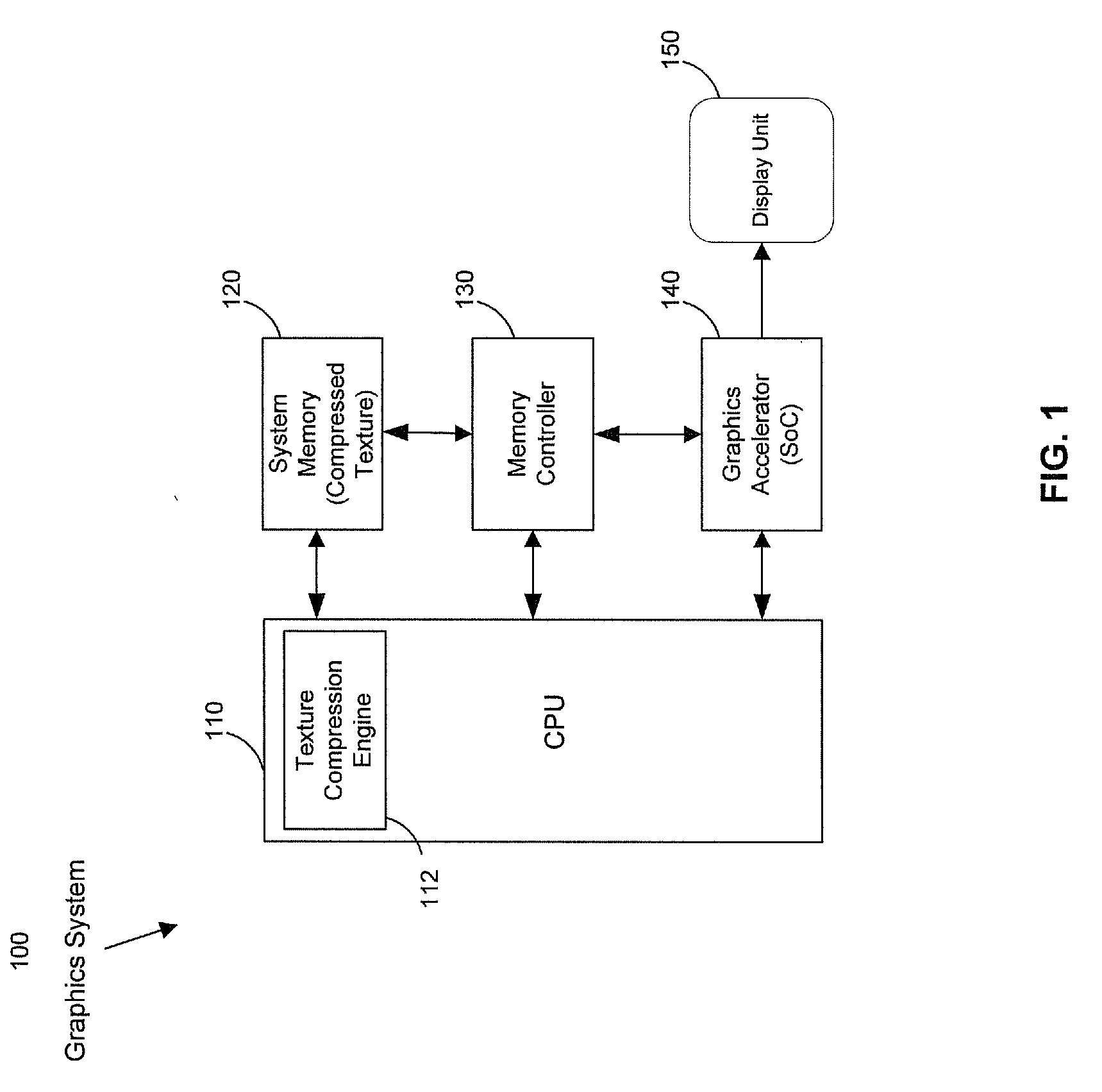
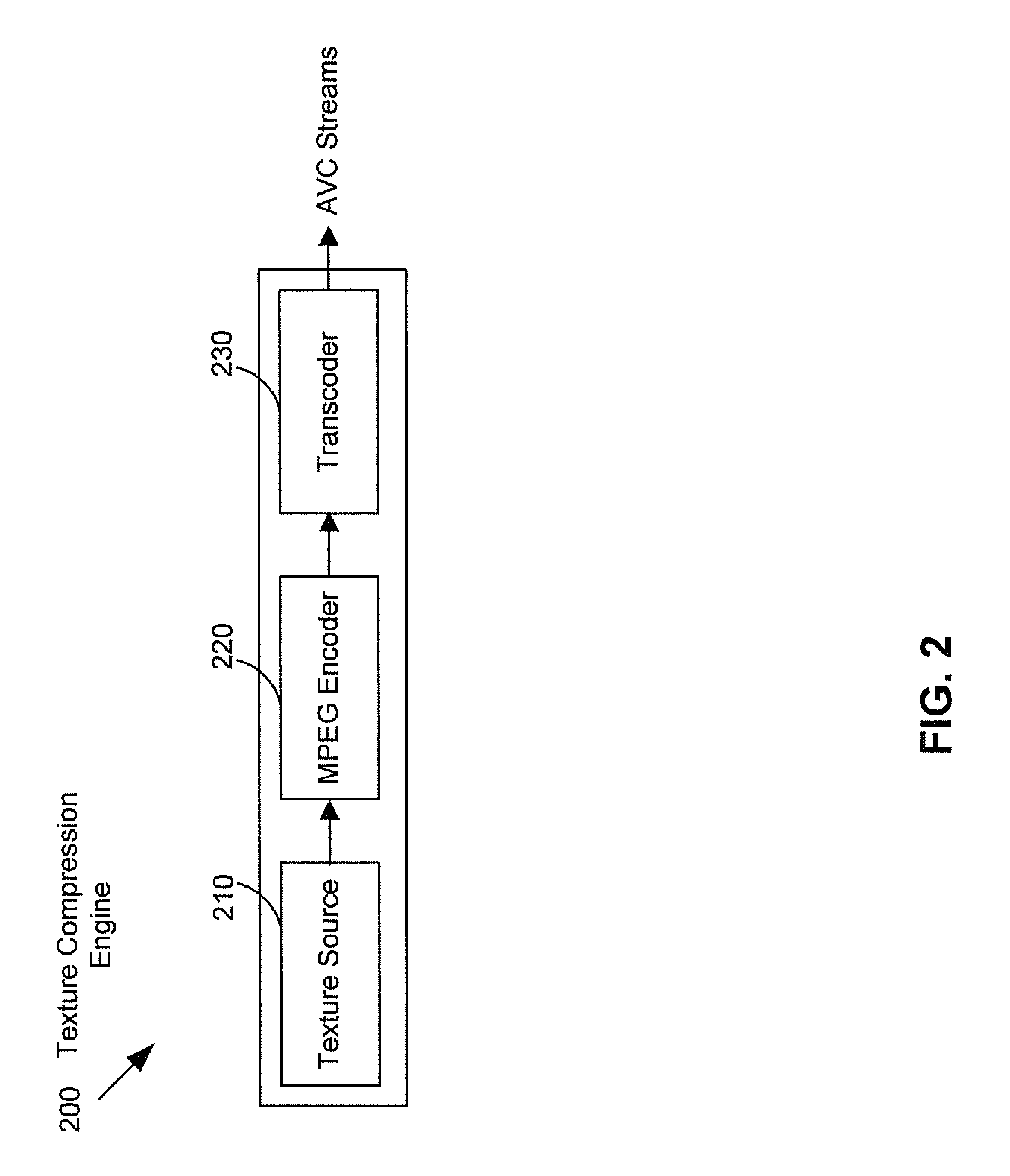
Method and system for texture compression in a system having an avc decoding and a 3D engine
A texture compression engine of a graphics device receives an uncompressed texture of a 3D graphic application. The received uncompressed texture is transcoded into an AVC reference picture stream. A plurality of mipmaps is constructed from the received uncompressed texture. The texture compression engine determines a texture compression rate based on available memory capacities. The texture compression engine compresses the received texture and its mipmaps at the determined texture compression rate. The compressed texture and mipmaps are further transcoded into the AVC reference picture stream and stored. The transcoded texture and mipmaps comprise either RGB or YCbCr components for a RGB uncompressed texture. The transcoded texture and mipmaps comprise monochrome or luma components for an ARGB uncompressed texture. A graphics accelerator in the graphics device is operable to acquire the stored texture and mipmaps for a 3D graphics scene. The acquired texture and mipmaps are decompressed by AVC decoding.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
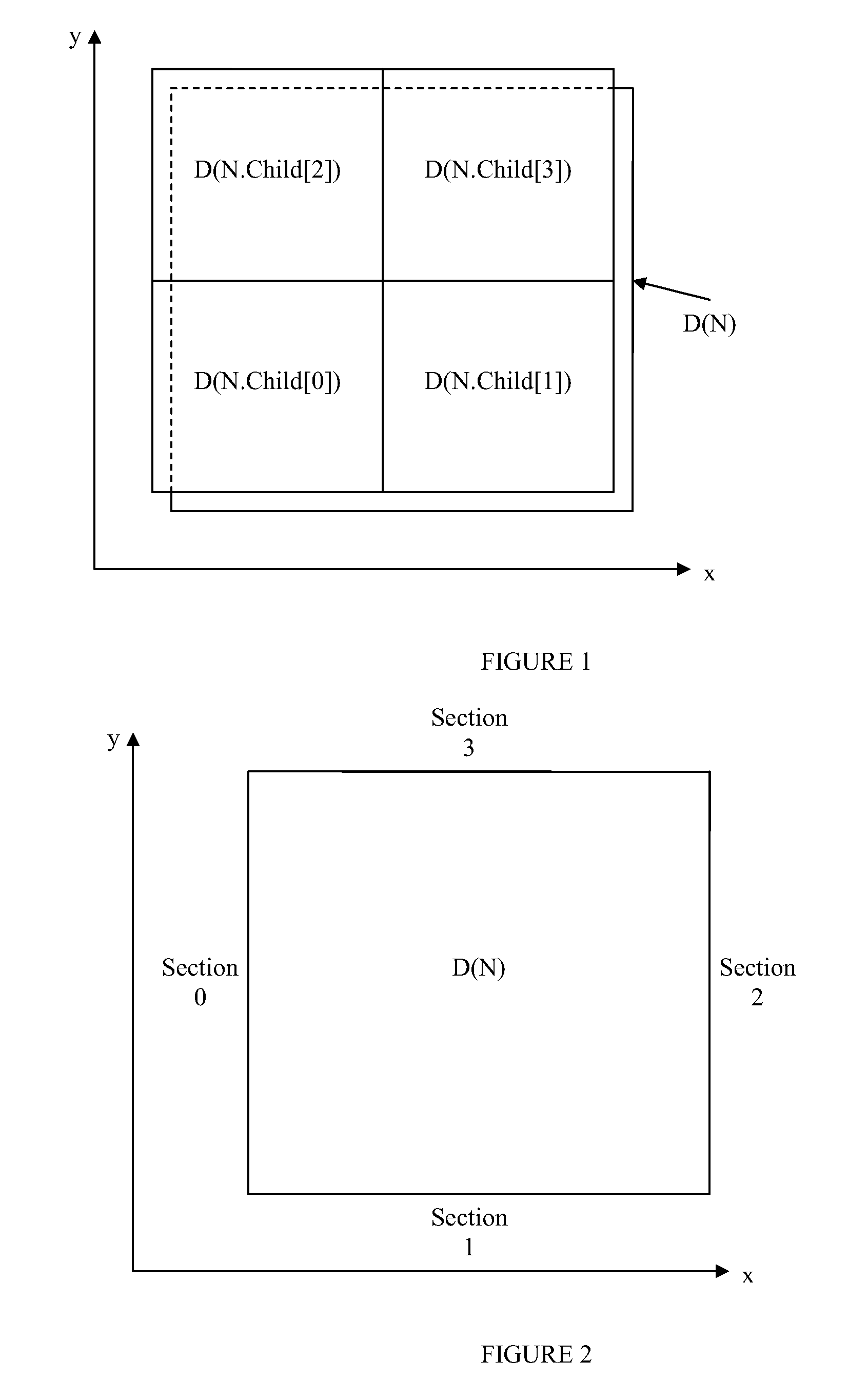
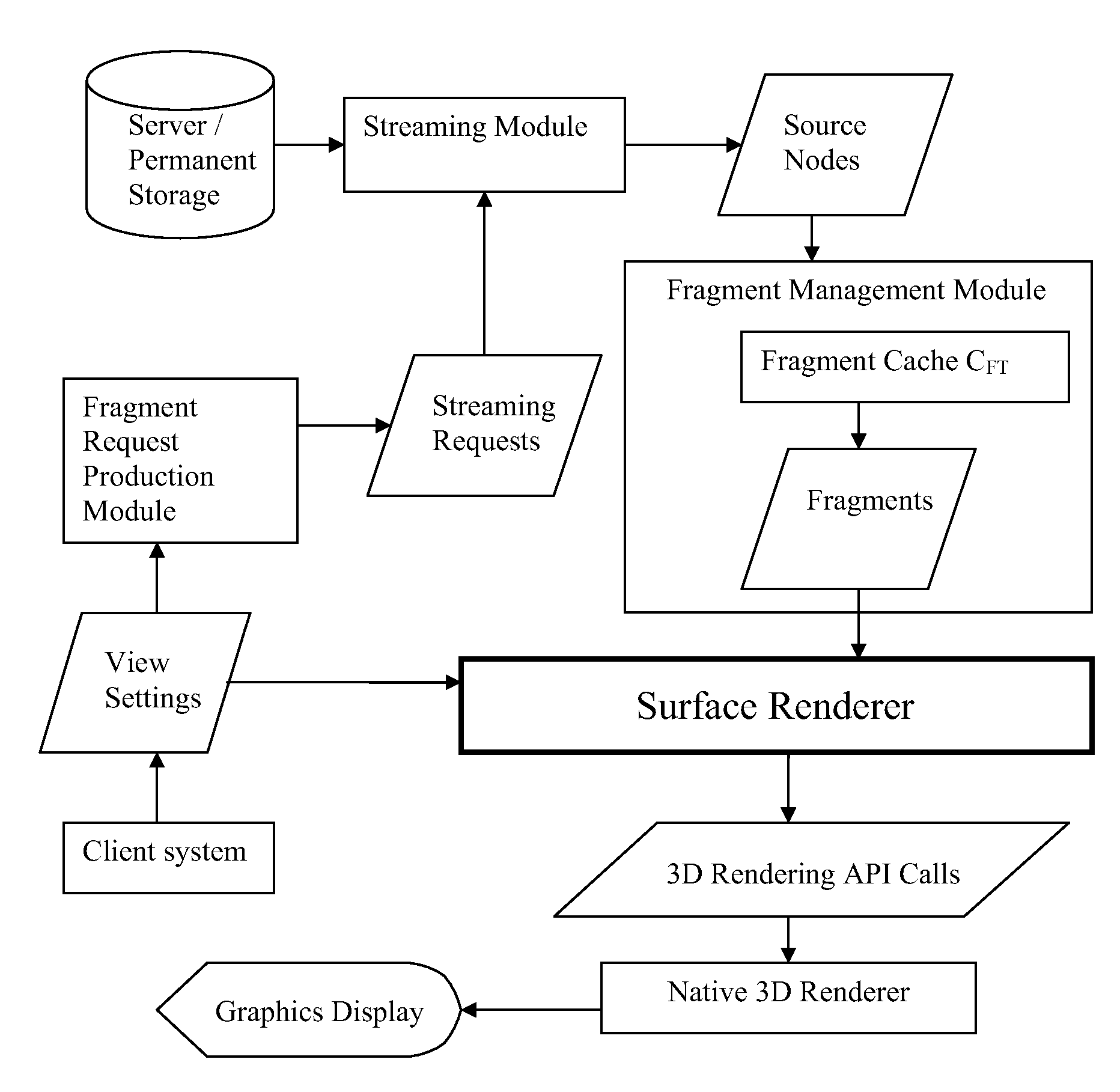
Adaptive Quadtree-based Scalable Surface Rendering
InactiveUS20070182734A1Excellent visible qualityExceptionally effectiveImage generation3D-image renderingLevel of detailGraphics accelerator
The present invention relates to computer graphics. This method allows efficient real-time 3D rendering of high-detail smooth surfaces. It is exceptionally effective with software rendering and low-end weaker graphics accelerators, and provides excellent visible quality per the amount of polygons used, while retaining low CPU processing overhead and high efficiency on graphics hardware. Also, it can be used under very restrictive memory requirements. In particular the invention relates to real time rendering of extremely detailed smooth surfaces with view-dependent tessellation using an improved level of detail approach. The invention utilizes a quad-tree map and geometric boundaries consisting of manifold non-self-intersecting surfaces. All cached fragments keep all of the information loaded from their corresponding source nodes in system memory, and additional information computed by the rendering system.
Owner:3DVU LTD 2000 ISRAEL +2
Web application system, web application server device and web client device
InactiveUS20060284867A1High-speed drawingCAD network environmentSpecial data processing applicationsWeb applicationApplication server
A screen image for operating a modeling application in a web application server device is displayed in a browser window of a web client device. When an operator inputs an operation related to a three-dimensional model whose CG should be displayed in the screen, the web application server device transmits a drawing command to draw CG of the three-dimensional model to the web client device. The web client device draws CG of the three-dimensional model according to the drawing command through the use of its own graphic accelerator. The invention allows the high-speed drawing of CG of a three-dimensional model on the web client device even when the web application server device provides a modeling service to the web client device.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
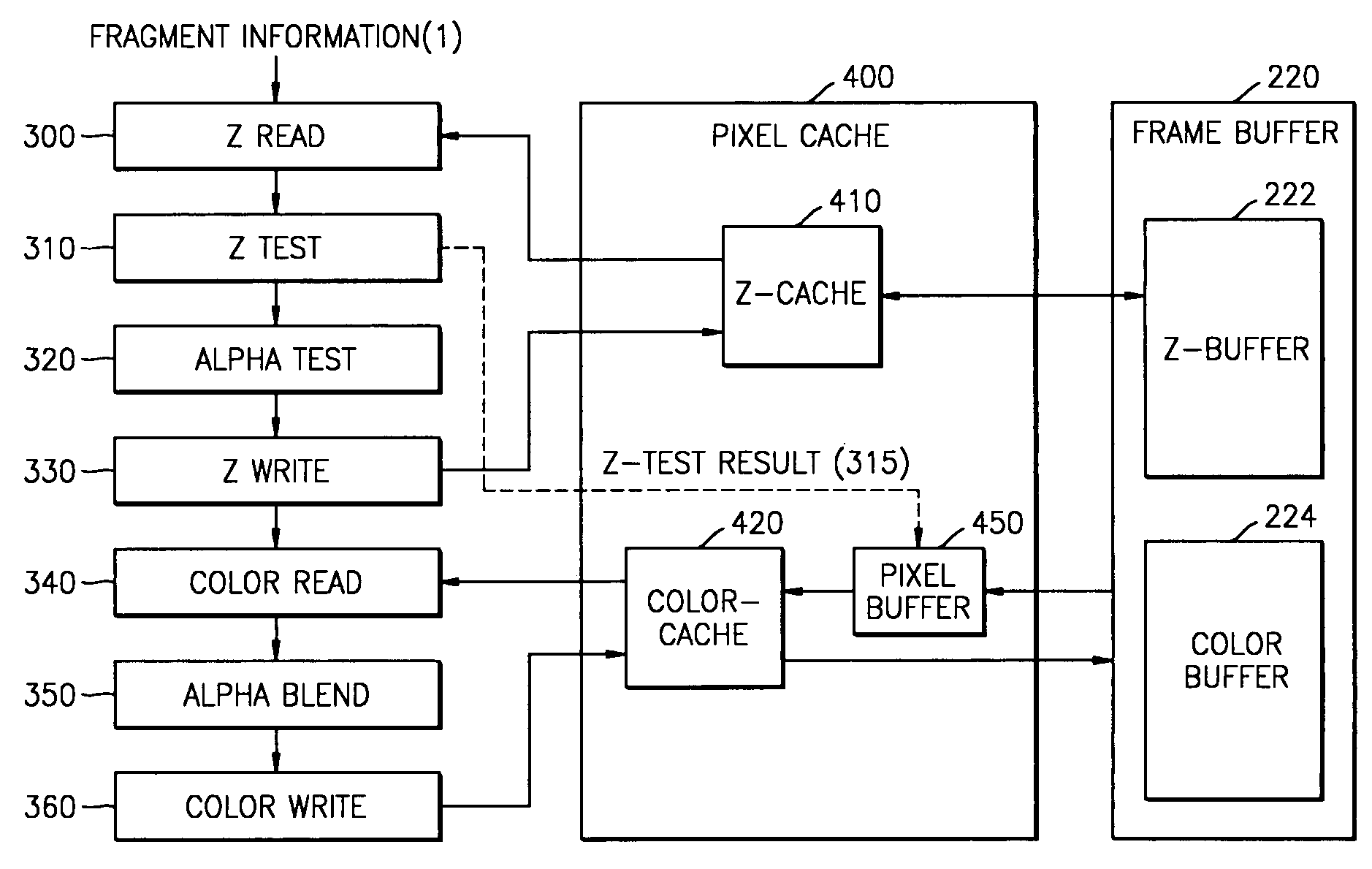
Pixel cache, 3D graphics accelerator using the same, and method therefor
ActiveUS7042462B2High hit-ratio structureEffective structureImage memory managementCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphics acceleratorData store
An effective structure of a pixel cache for use in a three-dimensional (3D) graphics accelerator is provided. The pixel cache includes a z-data storage unit that reads z-data from a frame memory and provides the read z-data to a pixel rasterization pipeline; and a color data storage unit that in advance reads and stores color data from the frame memory at the same time when the z-data storage unit reads the z-data from the frame memory, and provides the color data to the pixel rasterization pipeline only when the result of predetermined z-test is determined to be a success in the pixel rasterization pipeline. Accordingly, the pixel cache structure enables only color data required to be read and stored in advance before processing of the color data, thereby preventing access latency, increasing the efficiency of a color cache, and reducing power consumption.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
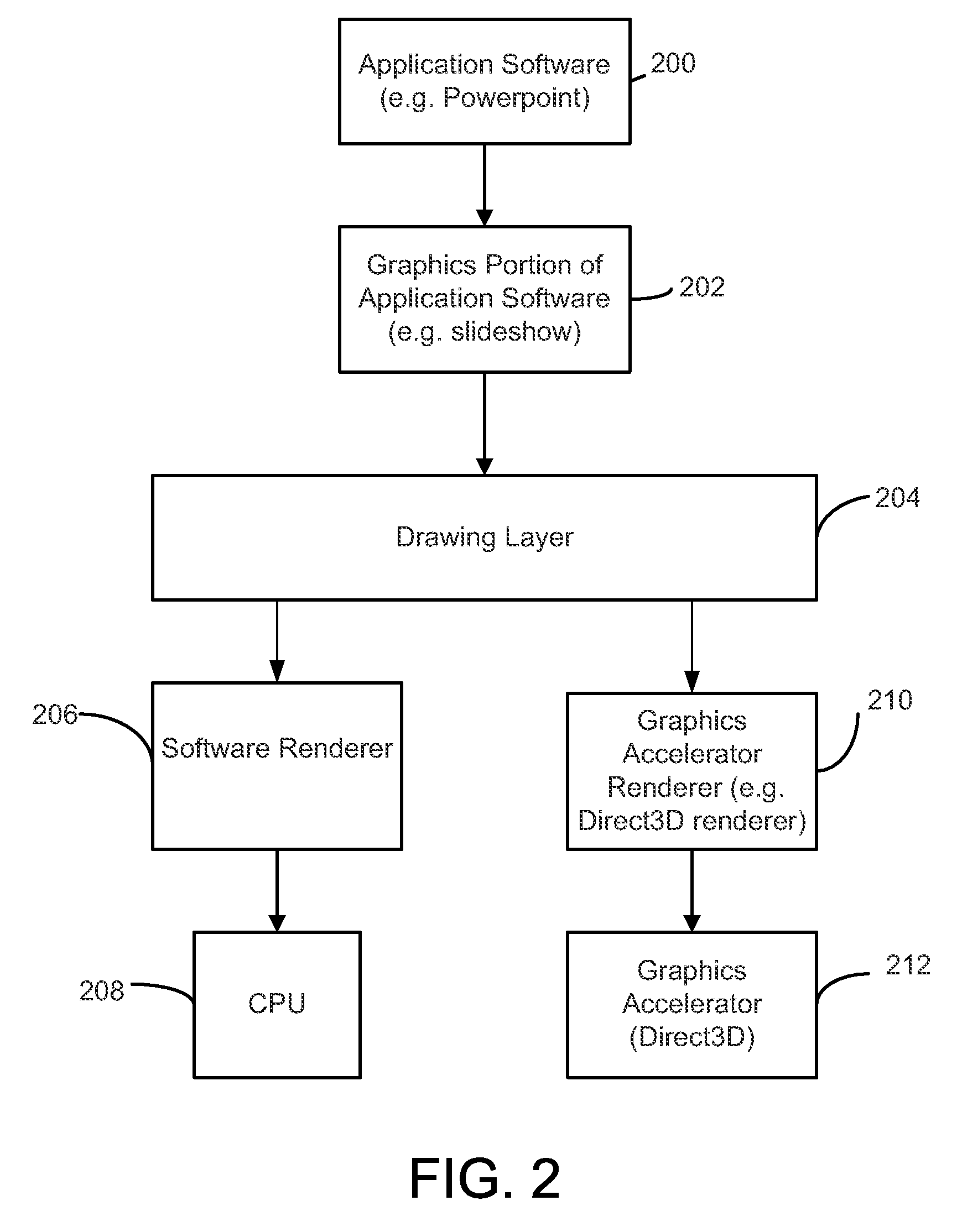
System and Method for Optimizing a Graphics Intensive Software Program for the User's Graphics Hardware
InactiveUS20070002053A1Best software application performanceImprove reliabilityDrawing from basic elementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareComputer compatibility
A system and method for optimizing the performance of a graphics intensive software program for graphics acceleration hardware. This system and method encompasses a procedure that validates the different functions of a 3D acceleration capable video card, decides whether to use the acceleration hardware and optimizes the software application to selectively use the functions that work on the specific video acceleration card. Functions checked include sub-pixel positioning, opacity, color replacement and fog. If these tests are successful, then the graphics acceleration is used by the software application. However, if the tests are not successful the decision is made not to use graphics accelerator. Those with ordinary skill in the art will realize that it is not necessary to perform all of the tests in a specific order. Additionally, other types of tests could be performed to ensure software application and video card compatibility before the software application is uses graphics acceleration to render 3D graphics.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
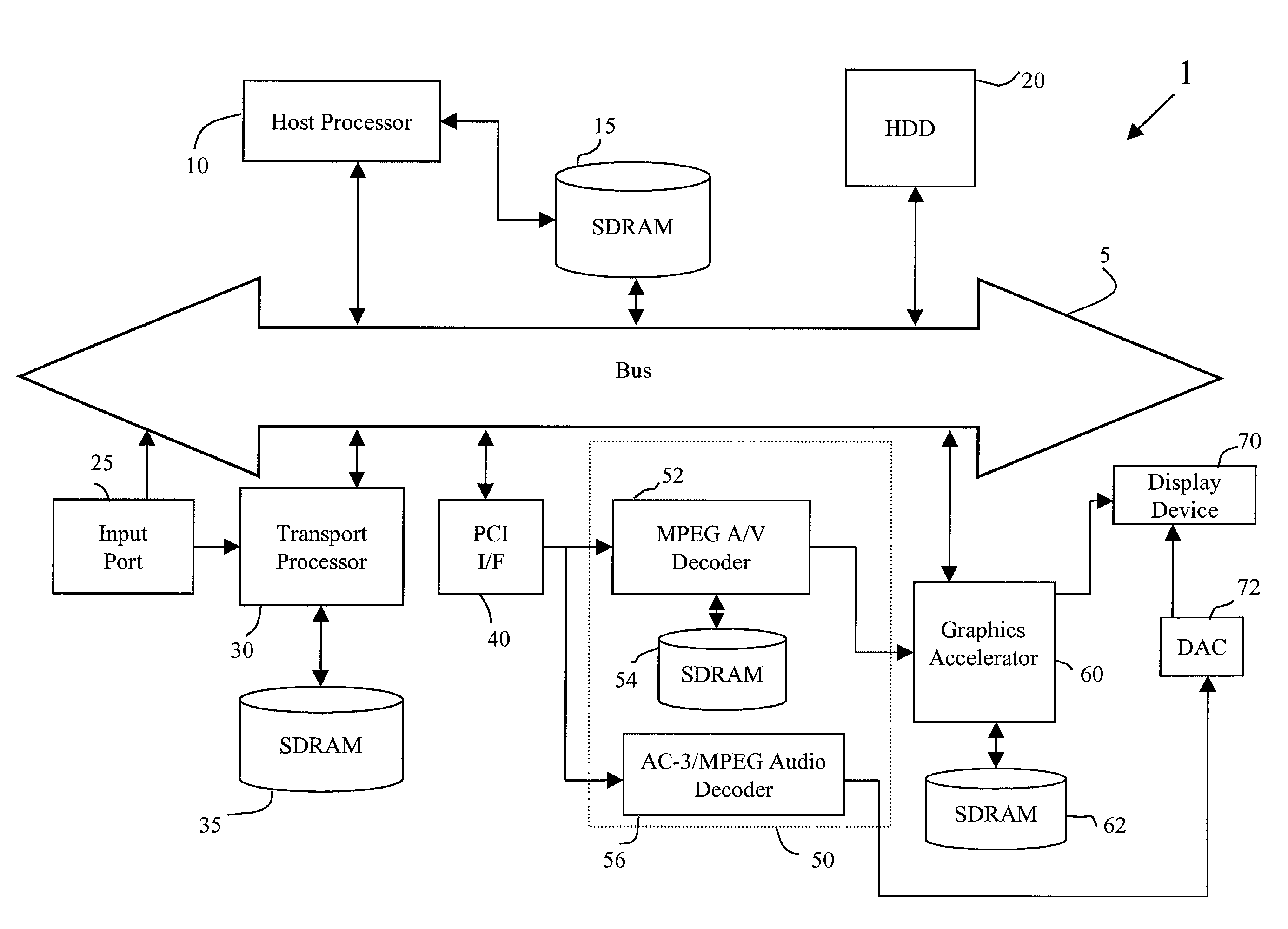
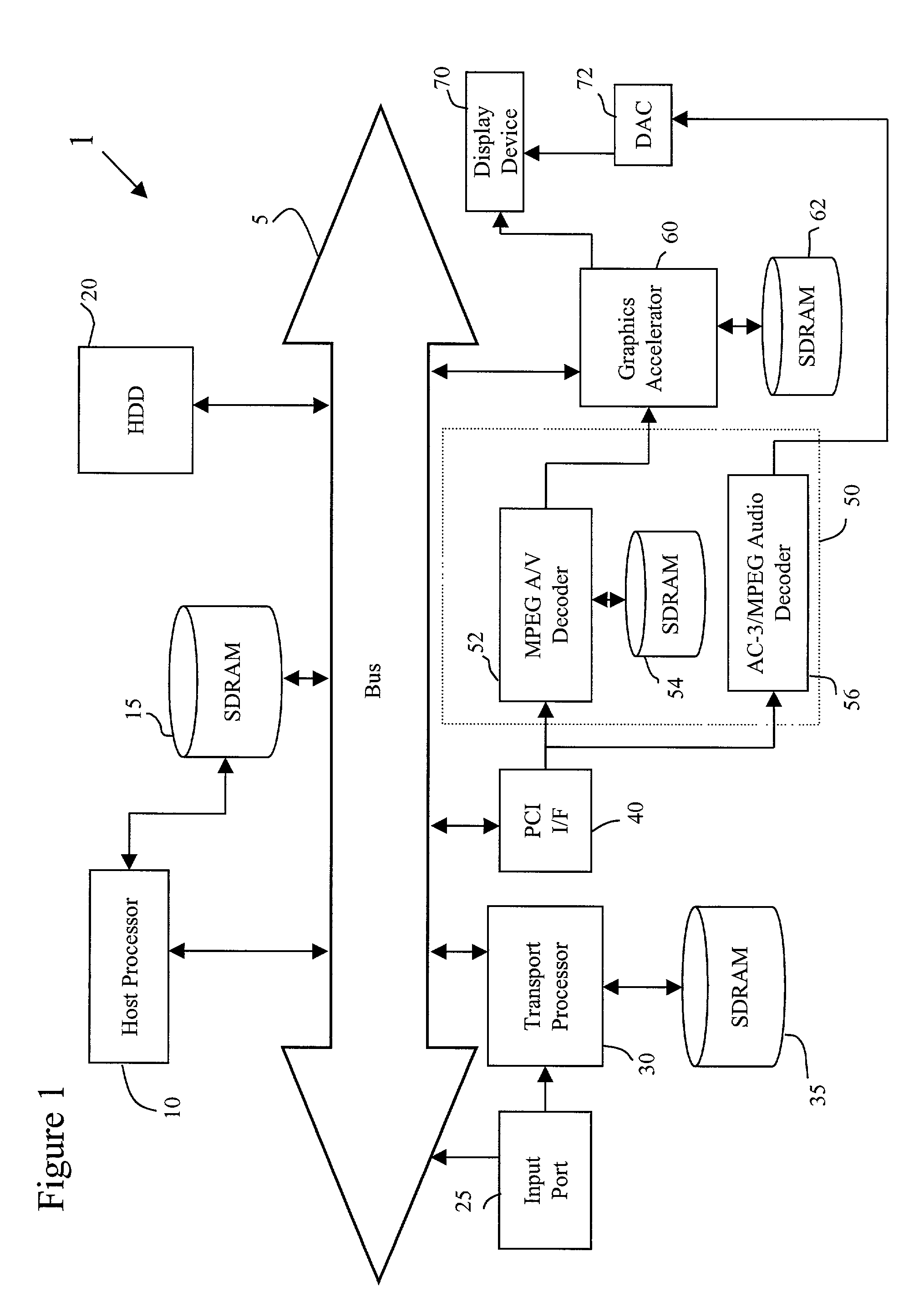
Method and apparatus for facilitating reverse playback
InactiveUS7164844B1Facilitate reverse playbackTelevision system detailsColor television detailsReverse orderGranularity
A method and apparatus for processing recorded coded audiovisual data to facilitate reverse playback permits the user to play back recorded material in a temporally reversed manner at speeds of at least 1X or greater by storing the decoded frames in a graphics accelerator memory of a recording system. By storing decoded MPEG video frames representing the audiovisual data in the graphics accelerator's memory, it is possible to display all the frames of a group of pictures GOP in reverse order. Instead of using the memory of a graphics accelerator, the apparatus may also be configured to have sufficient space available in memory to store the decoded MPEG video frames. In either configuration, reverse playback may be effectuated with a much finer temporal granularity than what is currently achievable by conventional video recording apparatuses.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
System and method for optimizing a graphics intensive software program for the user's graphics hardware
InactiveUS20100201695A1Efficient processingCathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer compatibilityApplication software
A system and method for optimizing the performance of a graphics intensive software program for graphics acceleration hardware. This system and method encompasses a procedure that validates the different functions of a 3D acceleration capable video card, decides whether to use the acceleration hardware and optimizes the software application to selectively use the functions that work on the specific video acceleration card. Functions checked include sub-pixel positioning, opacity, color replacement and fog. If these tests are successful, then the graphics acceleration is used by the software application. However, if the tests are not successful the decision is made not to use graphics accelerator. Those with ordinary skill in the art will realize that it is not necessary to perform all of the tests in a specific order. Additionally, other types of tests could be performed to ensure software application and video card compatibility before the software application is uses graphics acceleration to render 3D graphics.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Wide instruction word graphics processor
InactiveUS6948087B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsConcurrent instruction executionComputational scienceGraphics accelerator
A graphics accelerator includes a vertex input for receiving vertex data, an output for forwarding processed data, and a processor coupled with the vertex input and output. The graphics accelerator also includes an instruction input that receives instructions for processing the vertex data received from the vertex input. The processor is responsive to wide word instructions.
Owner:RPX CORP
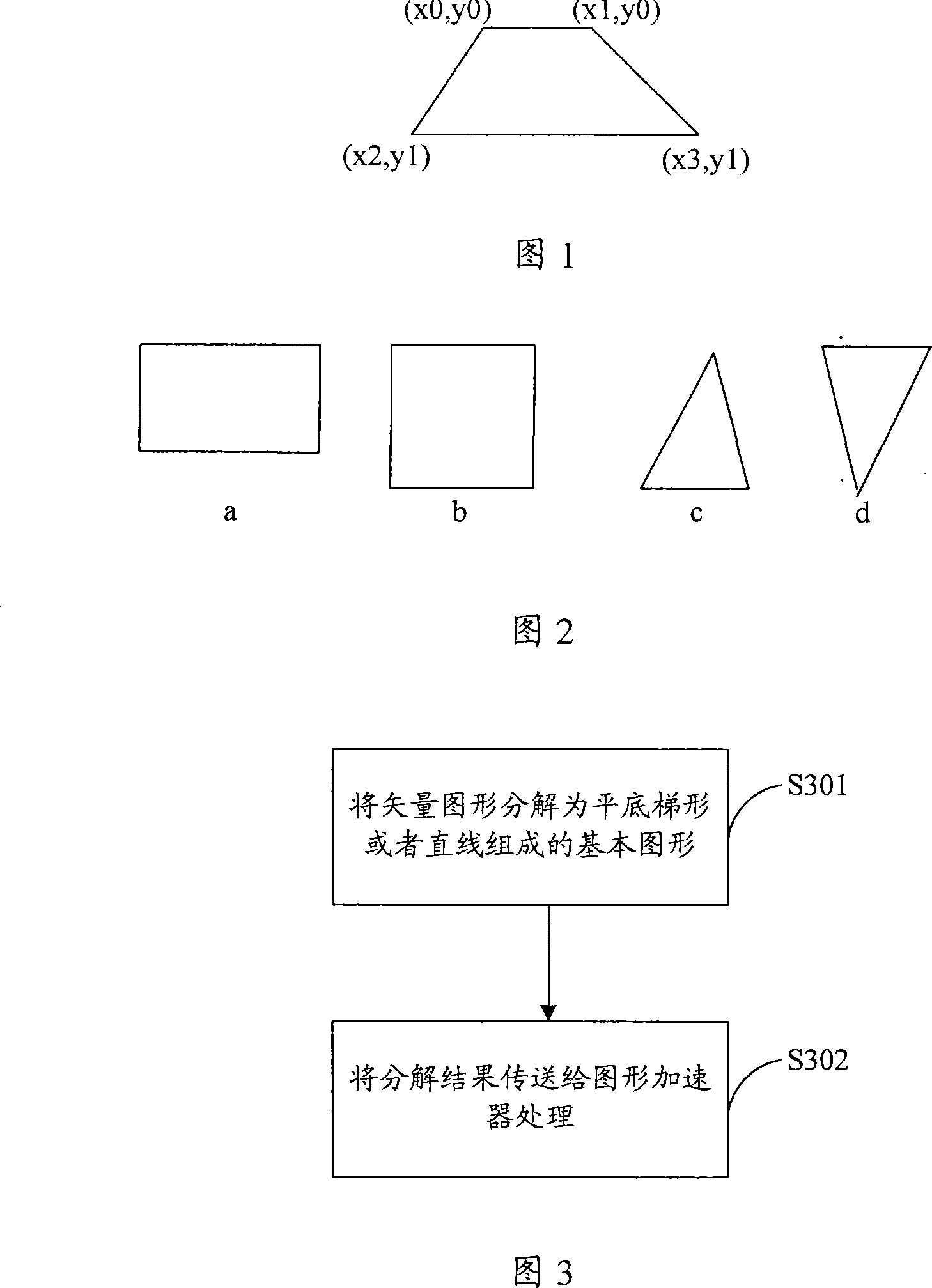
Vector graph acceleration method and multimedia player
InactiveCN101211462ASimple designEasy to implementDrawing from basic elementsAlgorithmGraphics accelerator
The invention is applicable to multimedia data processing field, which provides a vector graph accelerating method and a multimedia player. The method comprises the following steps: decomposing the vector graph into basic graphs formed by flat-bottom trapezoids or straight lines; and transmitting the decomposing result of the vector graph to a hardware accelerating logic for processing. The invention allows the basic graphs processed by a graph accelerator to be standard, simple and convenient for hardware design and implementation through decomposing the vector graph into combinations with the flat-bottom trapezoids or straight lines as the basic graphs, thus promoting acceleration performance, reducing power consumption of products and shortening the development cycle of products.
Owner:ACTIONS SEMICONDUCTOR
High bandwidth, efficient graphics hardware architecture
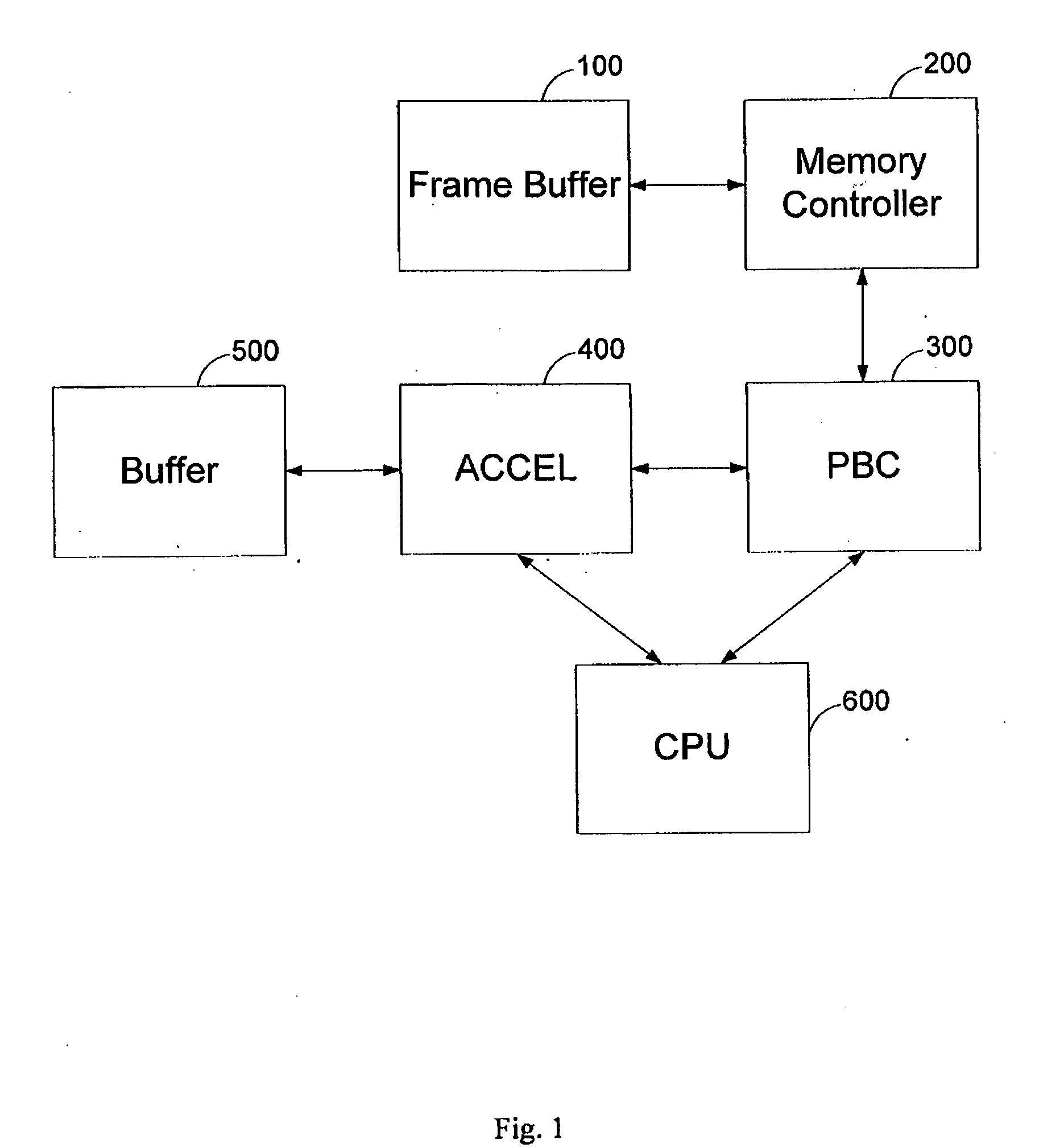
The present invention relates to a system according to claim 1, where the pixel buffer cache comprises at least one row descriptor for tracking and monitoring the activities of read and write requests of a particular tile. A system for providing a high bandwidth memory access to a graphics processor comprising: (a) a frame buffer for storing at least one frame, where said frame is stored in a tiled manner; (b) a memory controller for controlling said frame buffer; (c) a pixel buffer cache for storing multiple sections of at least one memory row of said frame buffer, and for processing requests to access pixels of said frame buffer; (d) a graphics accelerator having an interface to said pixel buffer cache for processing a group of related pixels; and (e) a CPU for processing graphic commands and controlling said graphics accelerator and said pixel buffer cache.
Owner:DIGITALPTICS CORP INT
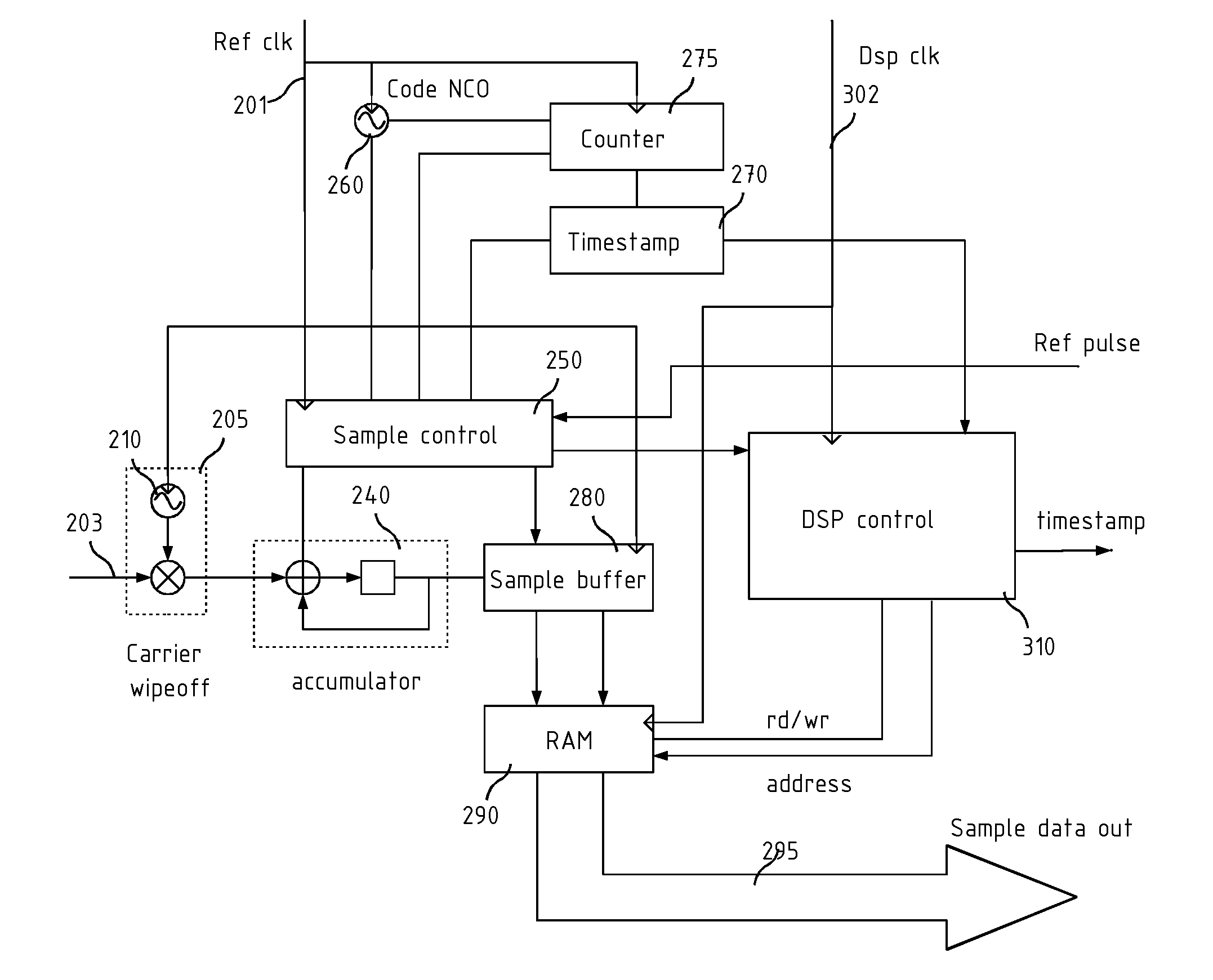
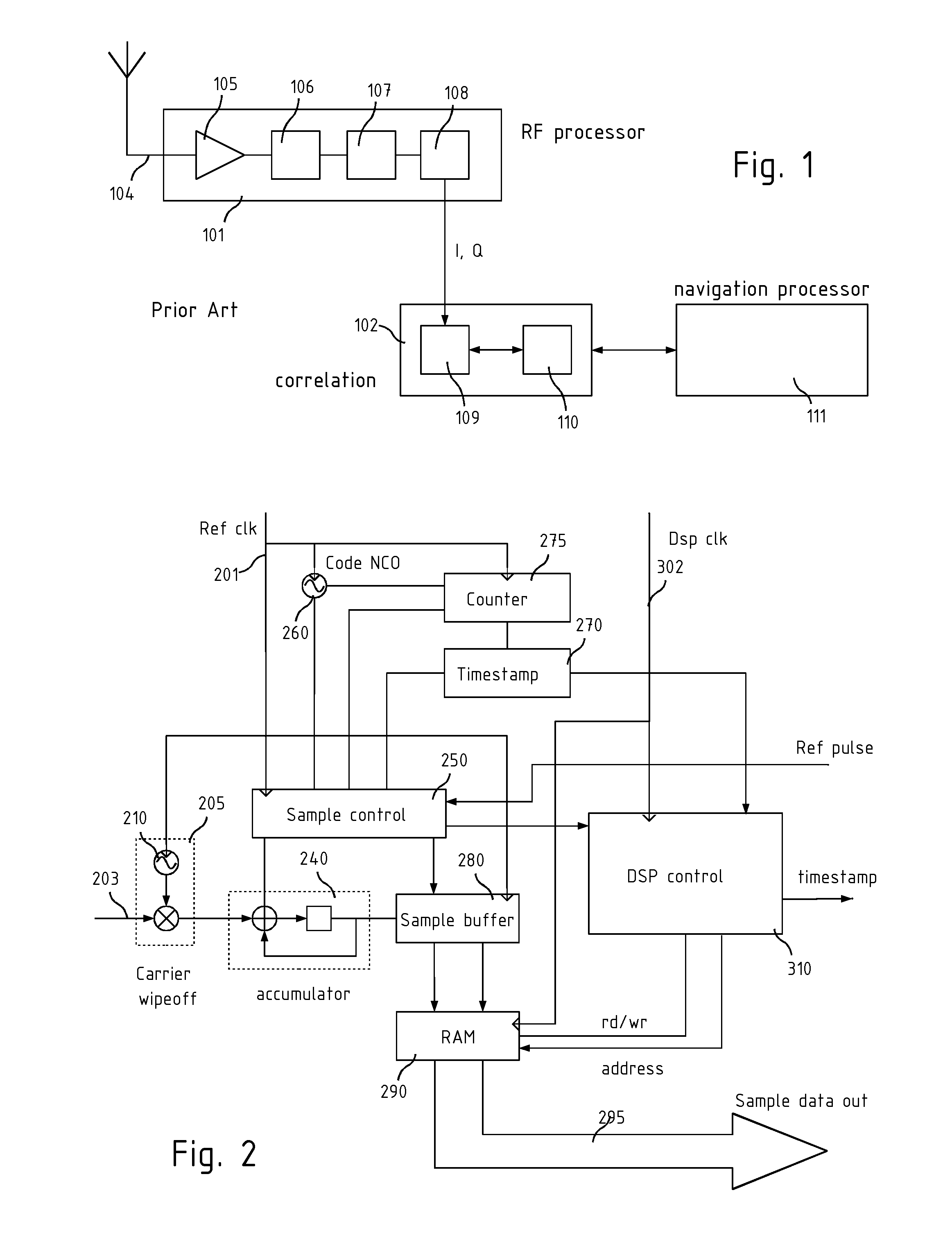
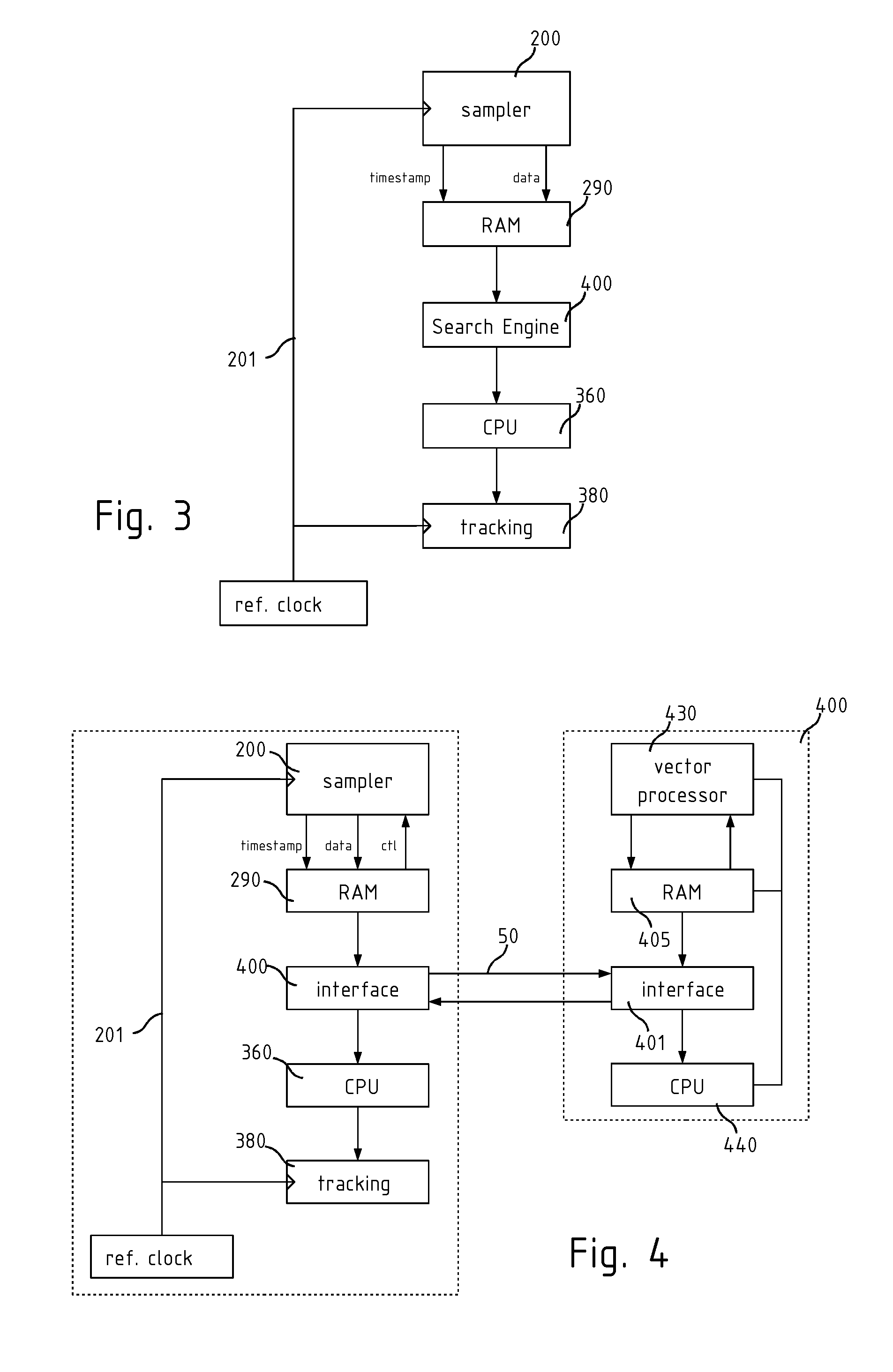
Global navigation receiver
A signal processing system and method for a GNSS digital signal wherein a carrier-stripped GNSS signal, is sampled according to a variable rate, determined by the code NCO, and including a timing circuit arranged to generate a timestamp code determining the sampling time of at least one of the samples in the buffer memory. By taking code samples in this way it is possible to transfer the samples asynchronously to a separate processor for the search task to be performed, for example an asynchronous parallel correlator implemented in the same silicon in hardware, or a media processor such as a graphics accelerator implemented in the same device or a separate physical device.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Triangle clipping for 3D graphics
InactiveUS7215344B2Not consume memory spaceComputationally intensive steps are savedCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingCircular bufferGraphics accelerator
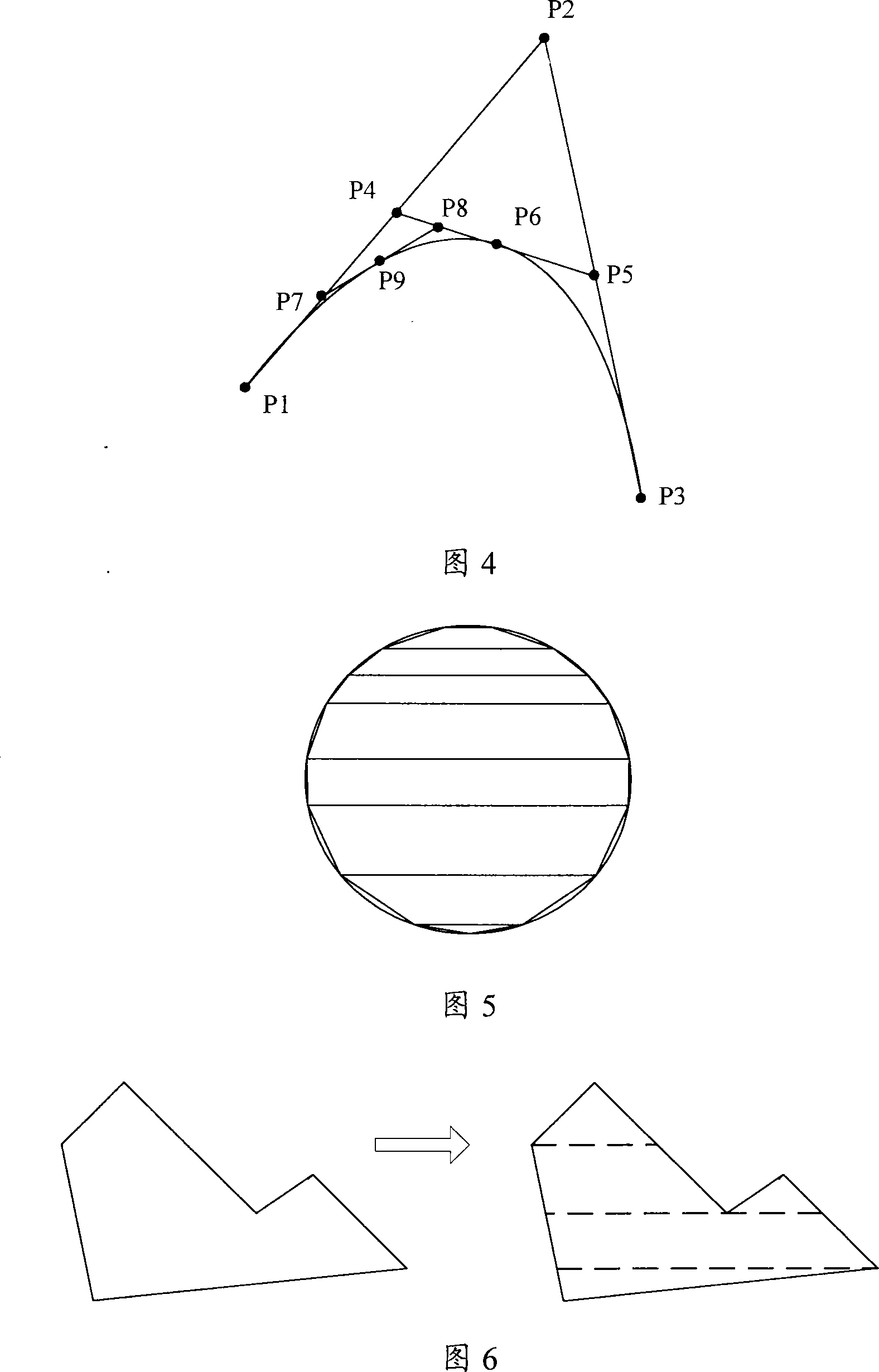
A geometry and lighting graphics accelerator with an improved clipping process. Clipping is performed prior to any calculation or evaluation of primitives for lighting, texture, fog, or color. Barycentric coordinates are used to define all vertices: original, intermediate, and final intersection points. Use of barycentric coordinates results in less storage space. A circular buffer is used during the clipping process to store input and output polygons. Use of the circular buffer also results is reduced storage requirements.
Owner:RPX CORP
Adaptive quadtree-based scalable surface rendering
InactiveUS7561156B2Exceptionally effectiveQuality improvementImage generation3D-image renderingLevel of detailGraphics accelerator
A 3D scalable surface renderer allows efficient real-time 3D rendering of high-detail smooth surfaces. The renderer is exceptionally effective with software rendering and low-end weaker graphics accelerators, and provides excellent visible quality per the amount of polygons used, while retaining low CPU processing overhead and high efficiency on graphics hardware. The 3D scalable surface renderer provides real time rendering of extremely detailed smooth surfaces with view-dependent tessellation using an improved level of detail approach.
Owner:3DVU LTD 2000 ISRAEL +2
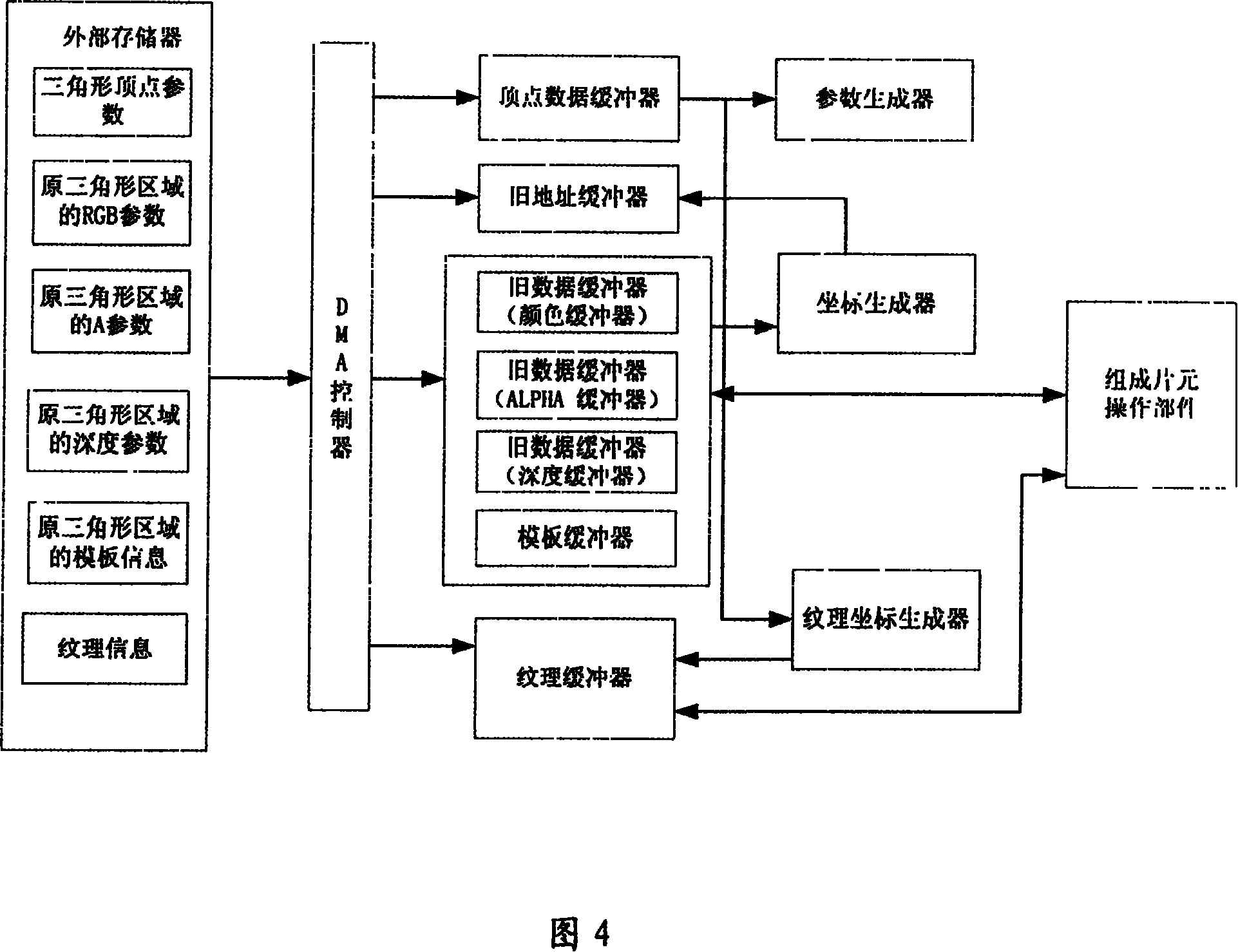
Graphic accelerators and graphic processing method
ActiveCN101118644AProcessing speedReduce areaEnergy efficient ICTProcessor architectures/configurationImaging processingExternal storage
The present invention provides an image accelerator and an image processing method. The image accelerator includes: a DMA controller, a buffer, a creater, and a composing slice element operation component. The DMA controller transfers the corresponding data stored in an external memory to the buffer; the creater takes data out from the buffer, conducts value inserting according to parameters, produces information of every point of a triangle, makes calculation on data of every pixel which is gotten after the value inserting, the composing slice element operation component conducts composing slice element operation on the parameter according to the signal of the creater, and writes results back to the buffer. The present invention does not excessively occupy the resource of the microprocessor and the accessing bandwidth of the memory, can meet the real time performance of the 3D image processing, can meet the requirement of the low power consumption of the equipment, and has low cost.
Owner:ANYKA (GUANGZHOU) MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
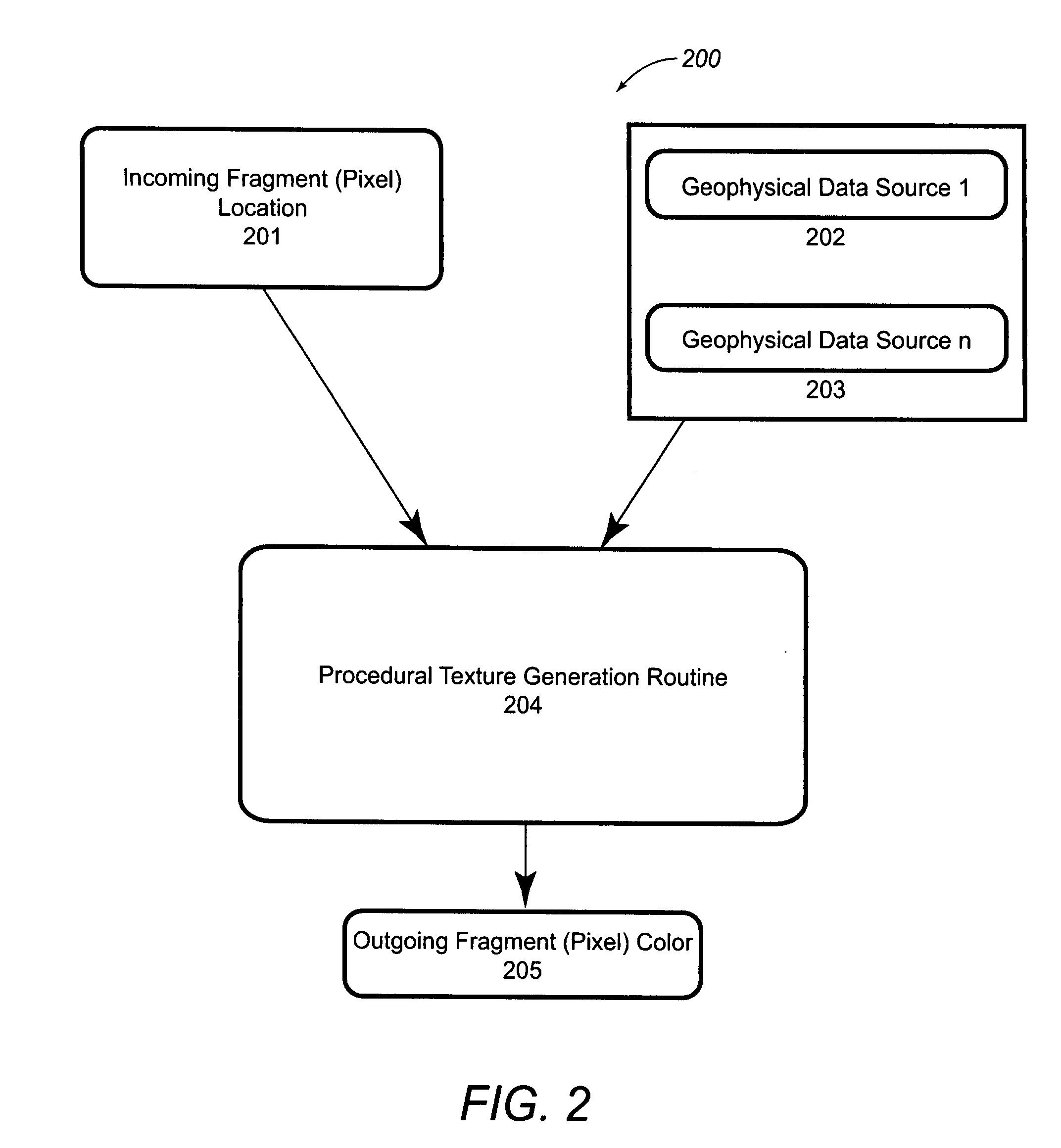
Systems and methods for imaging waveform volumes
InactiveUS8022947B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsGraphic cardDisplay device
Systems and methods for imaging waveform volumes. An image of the waveform volume may be drawn on a display device as a two-dimensional image or a three-dimensional image of a sampling probe and redrawn in real-time at interactive rates using a graphics accelerator or a graphics card. The image of the waveform volume may also include seismic-data traces that are color-filled according to texture coordinates for pixels on the display device that intersect the waveform volume.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS CORP
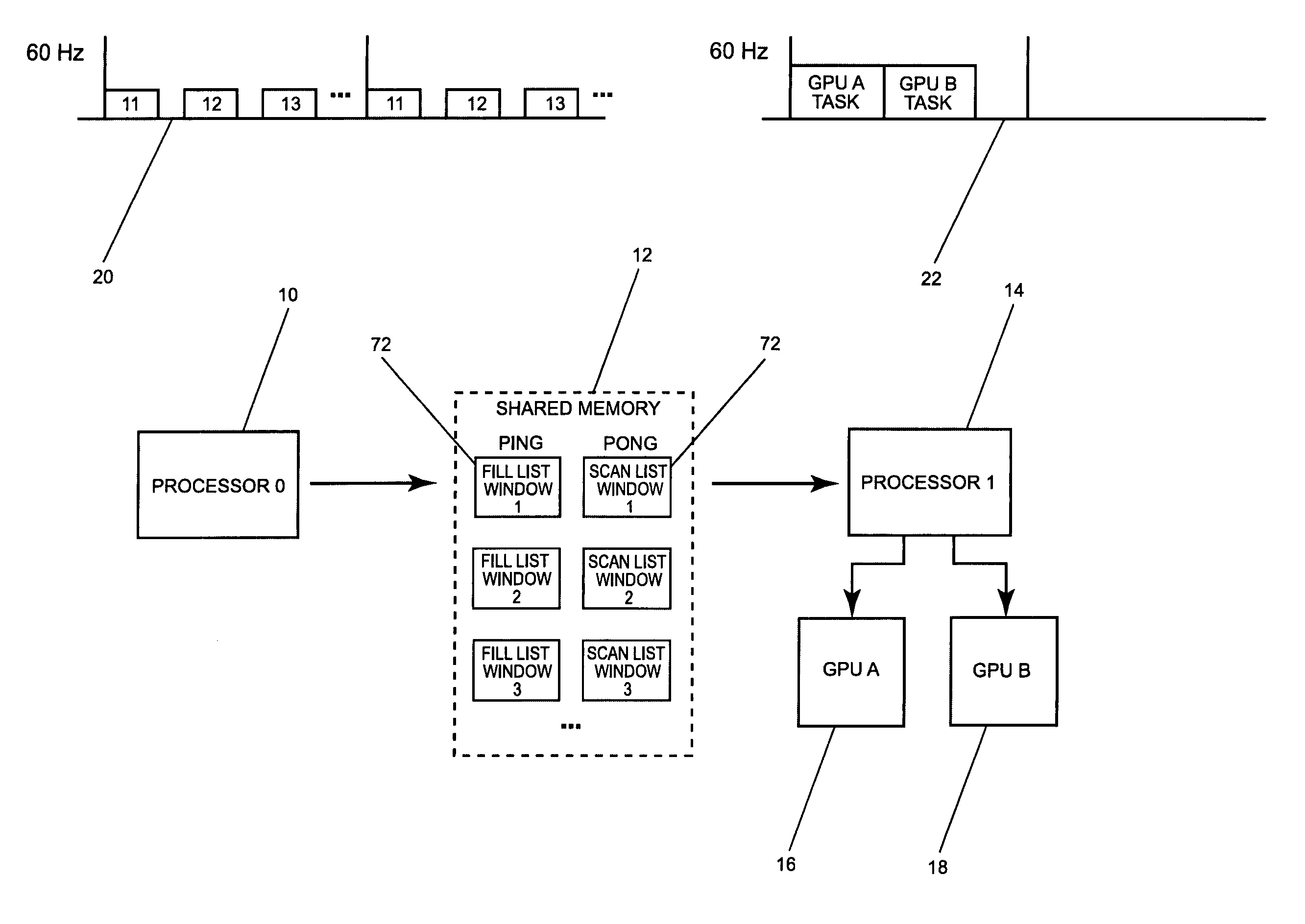
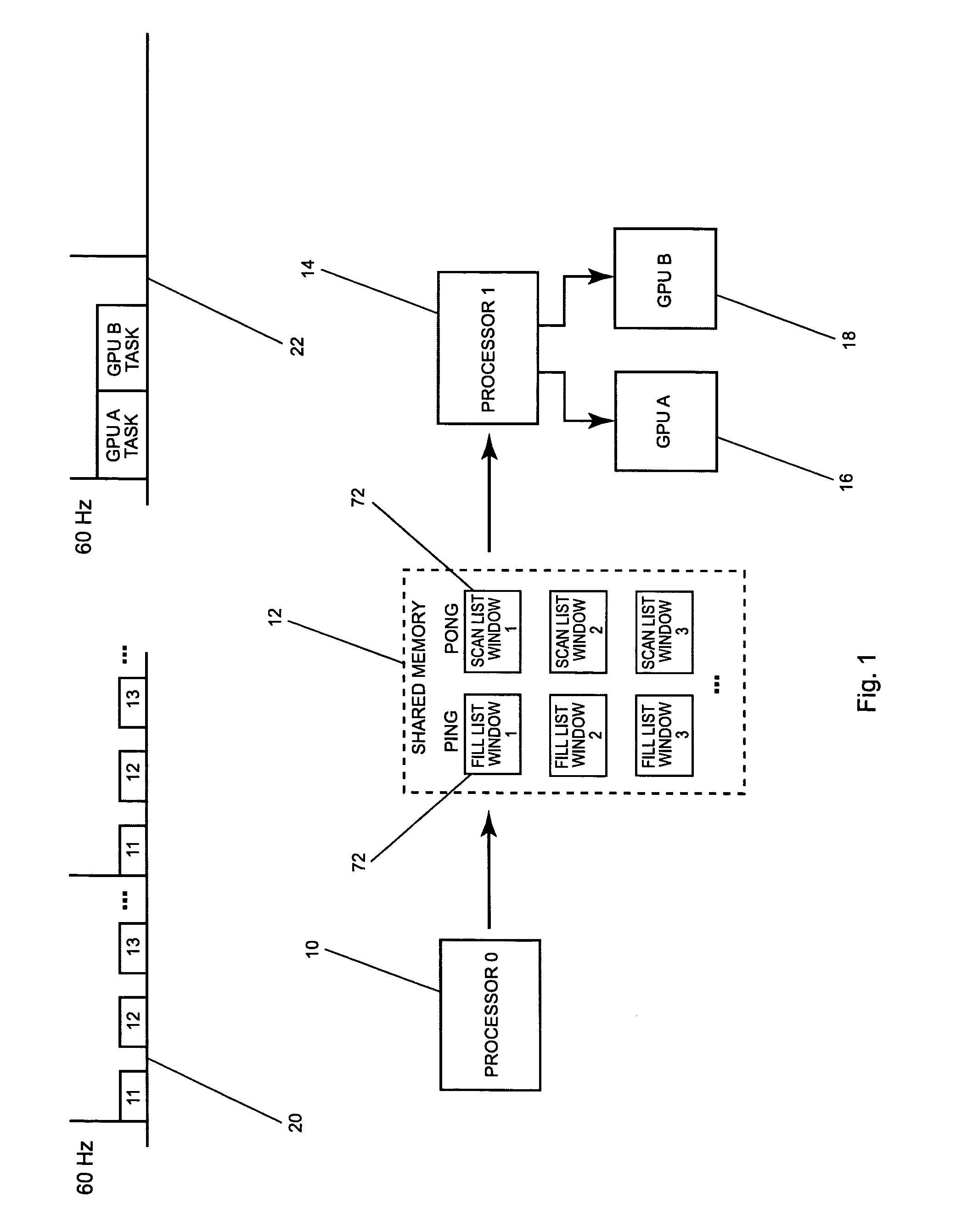
Dual processor accelerated graphics rendering
ActiveUS7830389B2TimelyImprove performanceMultiprogramming arrangementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputational scienceGraphics accelerator
Dual processor accelerated graphics rendering is a method which allows for optimizing graphics performance using two processors and 3D hardware accelerators. This method allows for real time embedded systems to have multiple partitions to render to multiple windows with non-blocking graphics calls. One processor queues up graphics calls within a discrete time because they do not interface with the graphics accelerator hardware. The second processor supports the hardware accelerator with drivers operating in a single partition. This design abstracts the graphics calls from the native interface of the graphics hardware accelerator.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
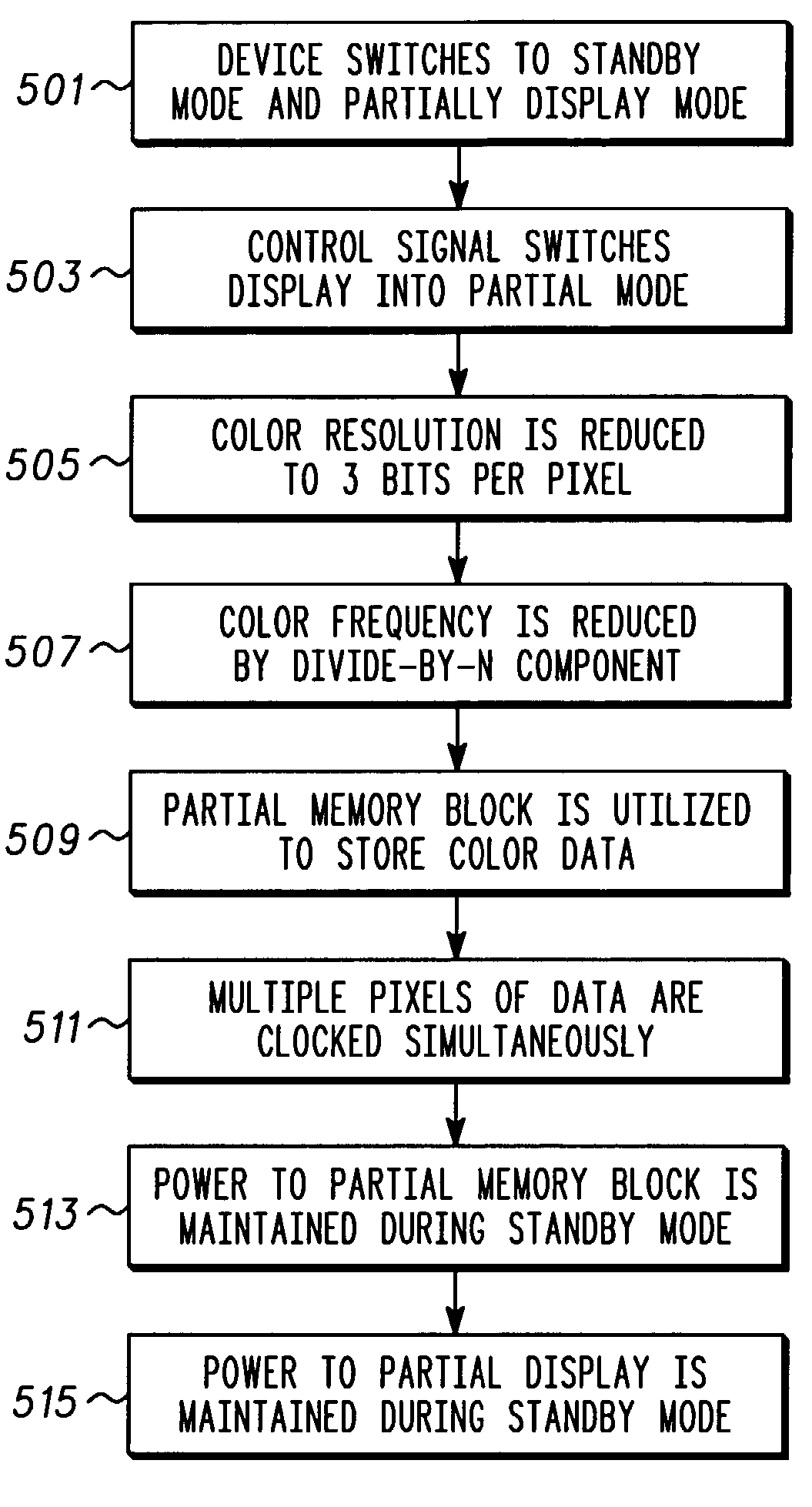
Reduced power consumption for a graphics accelerator and display
ActiveUS7388579B2Extended operating timeReduce frequencyFuel re-atomisation/homogenisationCathode-ray tube indicatorsClock rateGraphics accelerator
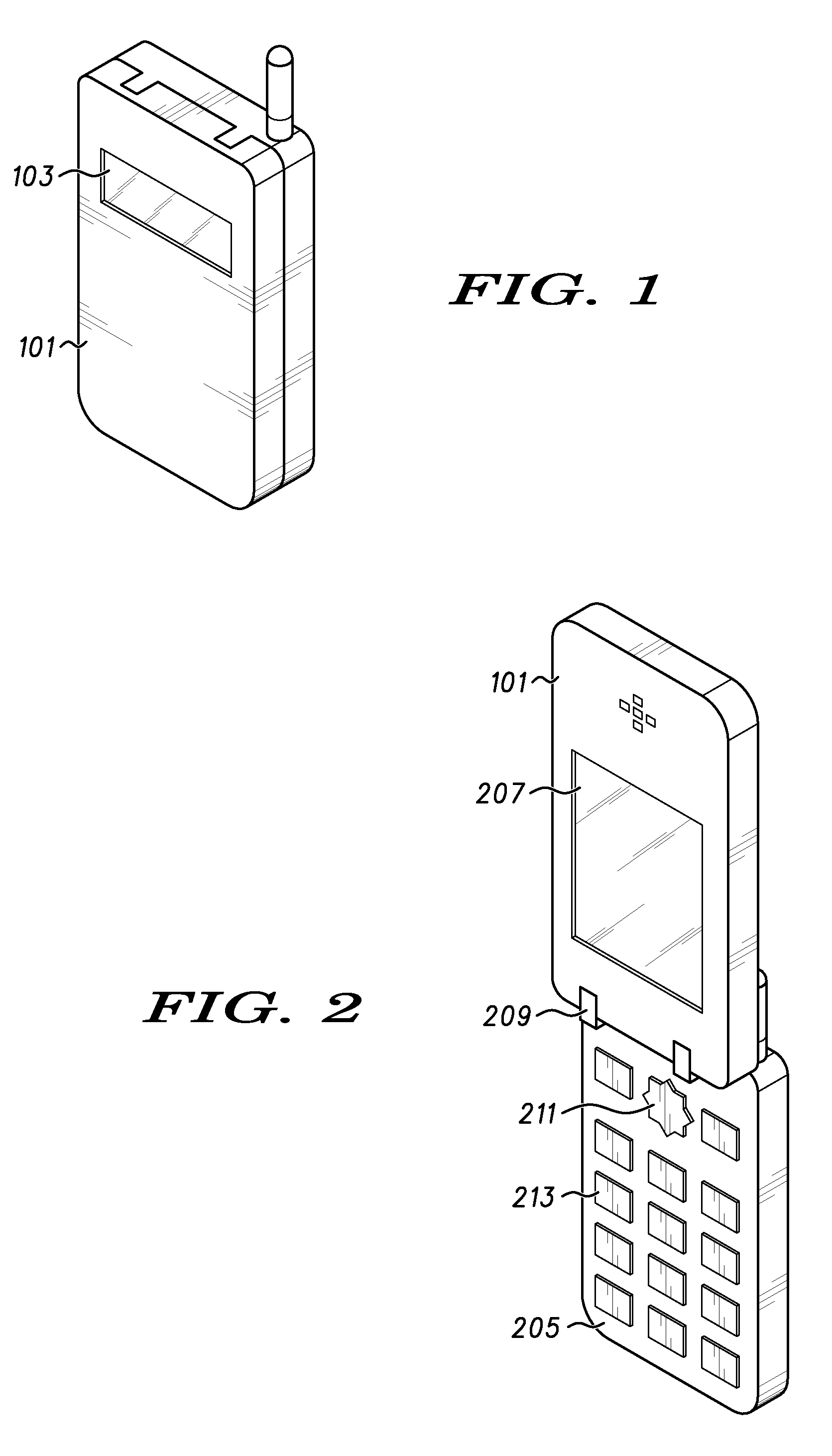
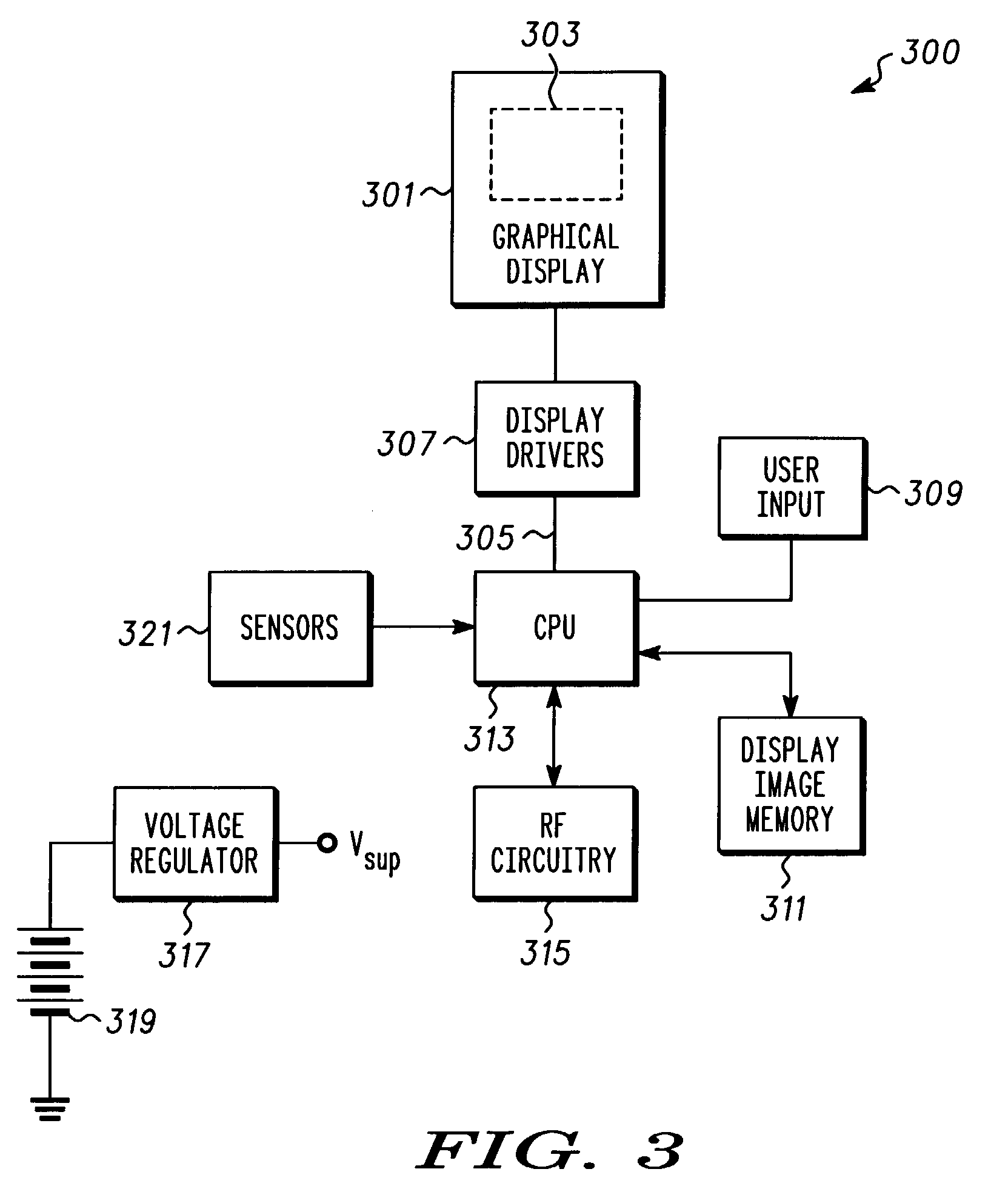
The preferred embodiments of the present invention provide a system and method for reducing the battery power required by a handheld device (300) that incorporates a graphical display (301). Graphical display (301), display drivers (307), LCD controller (403) and a memory (405) are optimized such that several pixels of information may be clocked simultaneously when the device is operating in a partial display mode. The optimized circuitry reduces the required refresh clock frequency (411) and thus the current drain on a device battery (319) thereby improving device operation time.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method, medium, and apparatus controlling graphics accelerator voltage
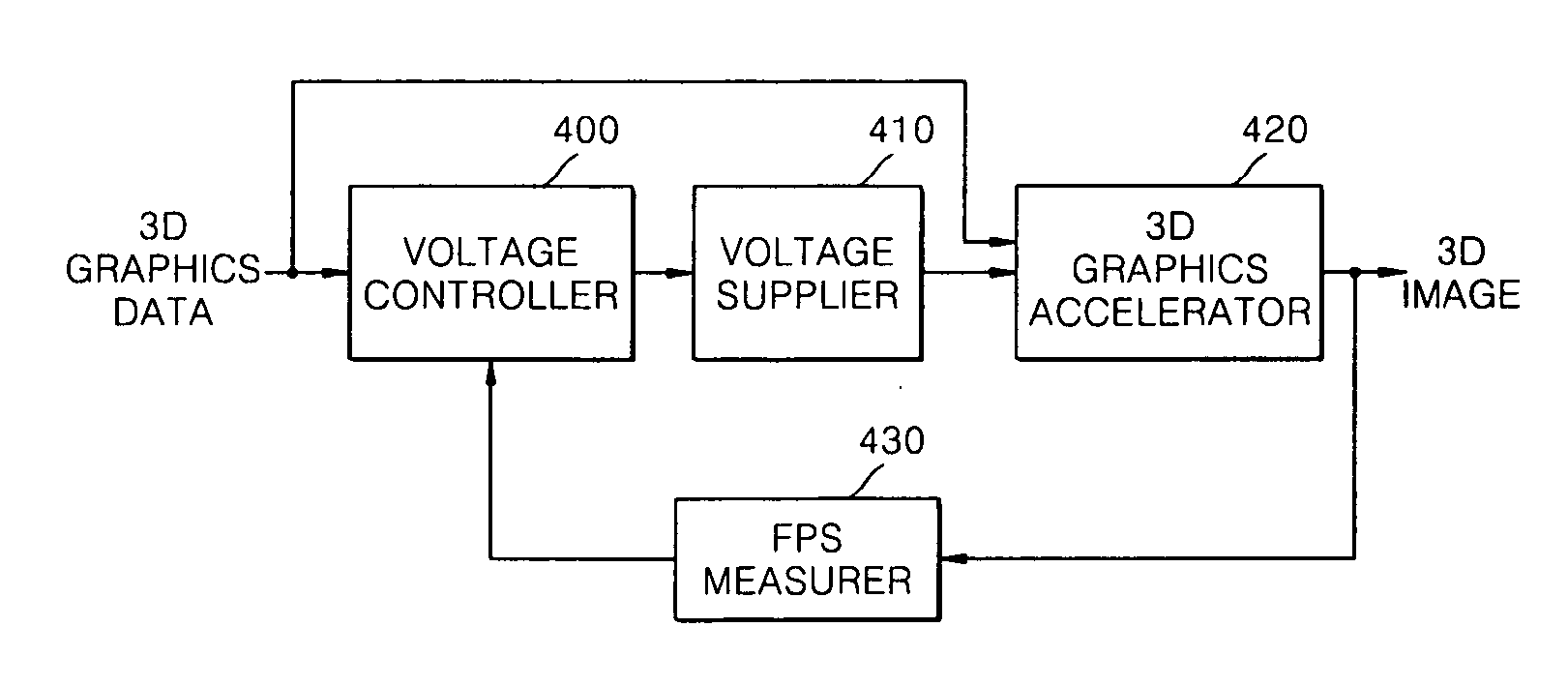
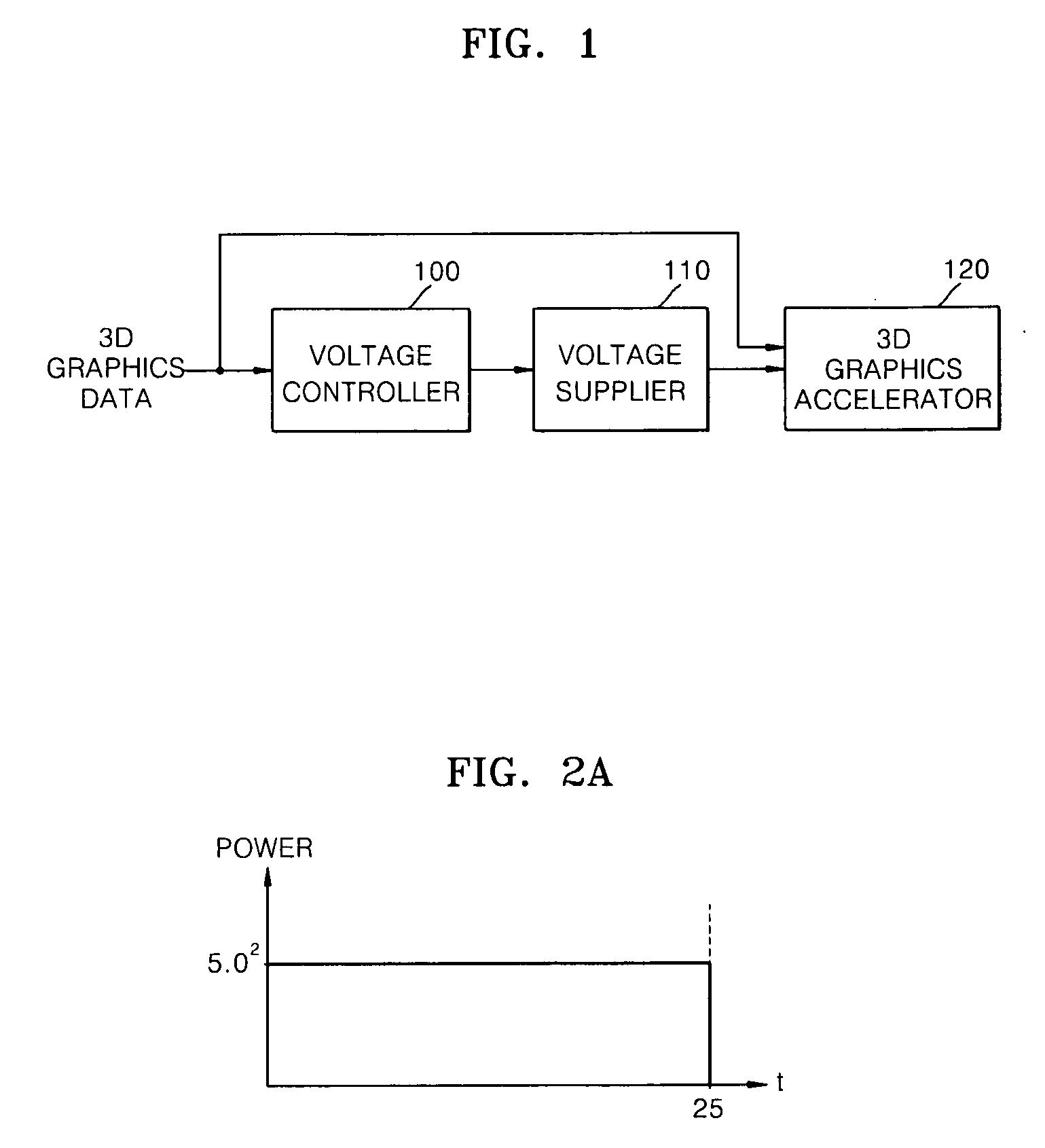
ActiveUS20070030274A1Reduce voltageReduce frequencyDigital computer detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsControl powerGraphics accelerator
A method, medium, and apparatus controlling a 3D graphics accelerator. The apparatus may include a voltage controller to determine a voltage and frequency supplied to the 3D graphics accelerator by using the 3D graphics data, so that a frames per second (FPS) of the image does not exceed a predetermined threshold, and a voltage supplier to supply a voltage and the frequency to the 3D graphics accelerator. The voltage and frequency supplied to the 3D graphics accelerator may be adjusted by a DVS technique so that the FPS of the generated image does not exceed the predetermined threshold. Accordingly, it is possible to control power consumption of the 3D graphics accelerator while maintaining performance at or above a given level. In particular, it is possible to very efficiently process a small amount of 3D graphics data with low power in a portable device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
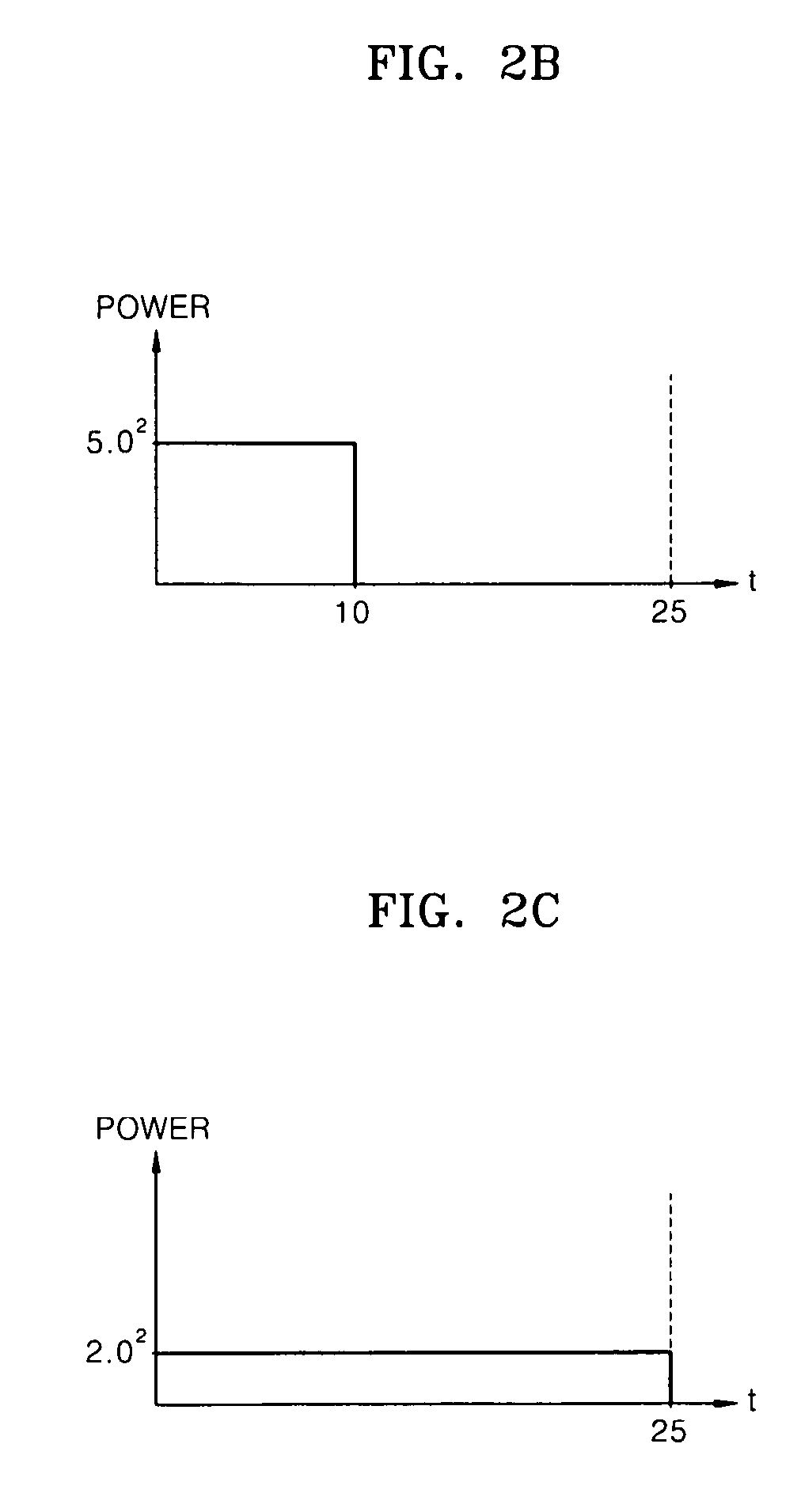
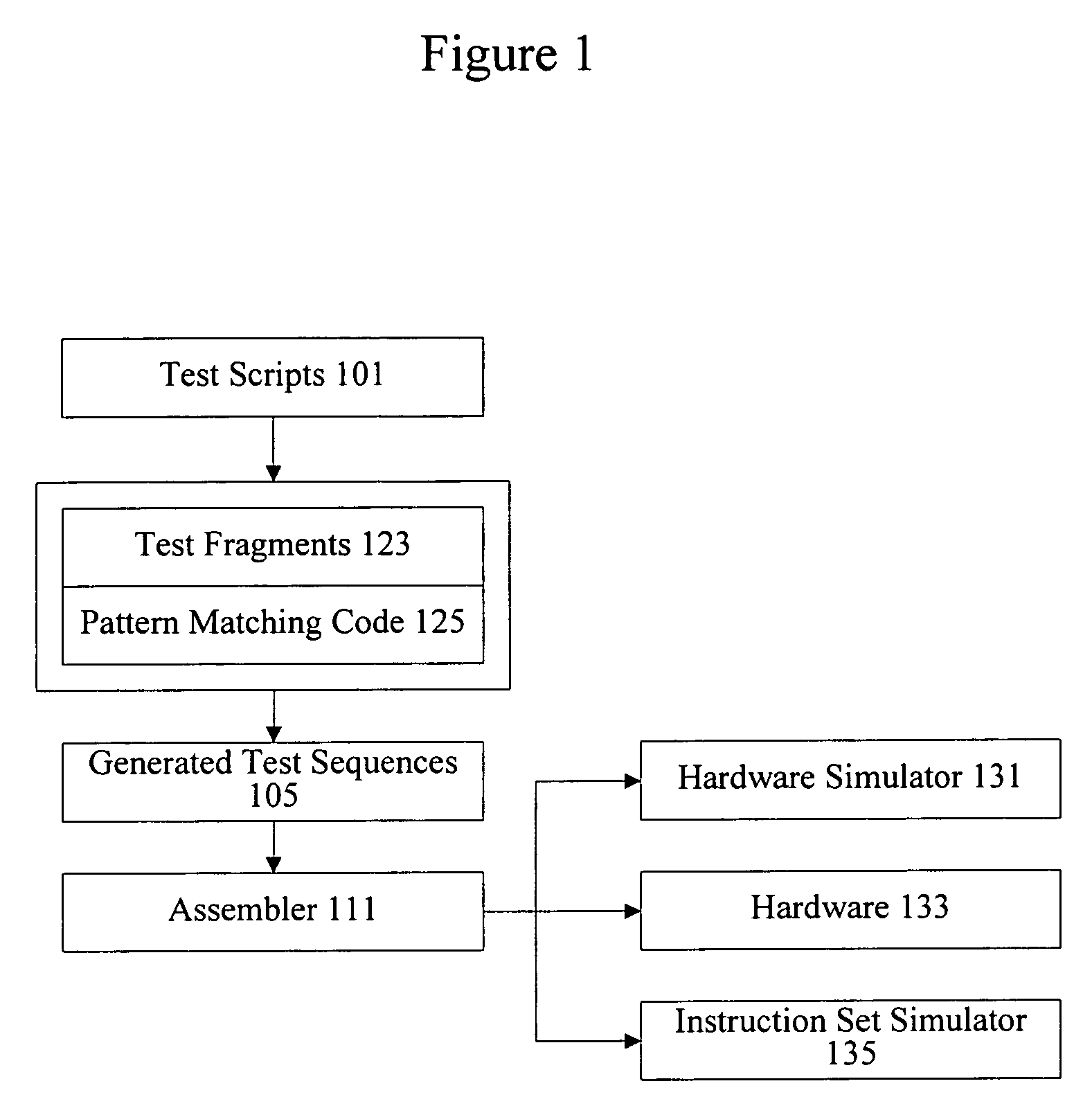
Methods and apparatus for generating test instruction sequences
InactiveUS7290174B1Error detection/correctionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationParallel computingGraphics accelerator
Methods and apparatus are provided for automatically generating instruction sequences for verifying the operation of a processor, such as a central processing unit, a processor core, a graphics accelerator, or a digital signal processor. The instruction sequences can also be used to verify the operation of tools associated with implementing a processor. Test parameters are used to combine test fragments to generate test instructions. Check instructions are also provided to immediately identify faults encountered during operation.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Synchronizing video formats with dissimilar timing
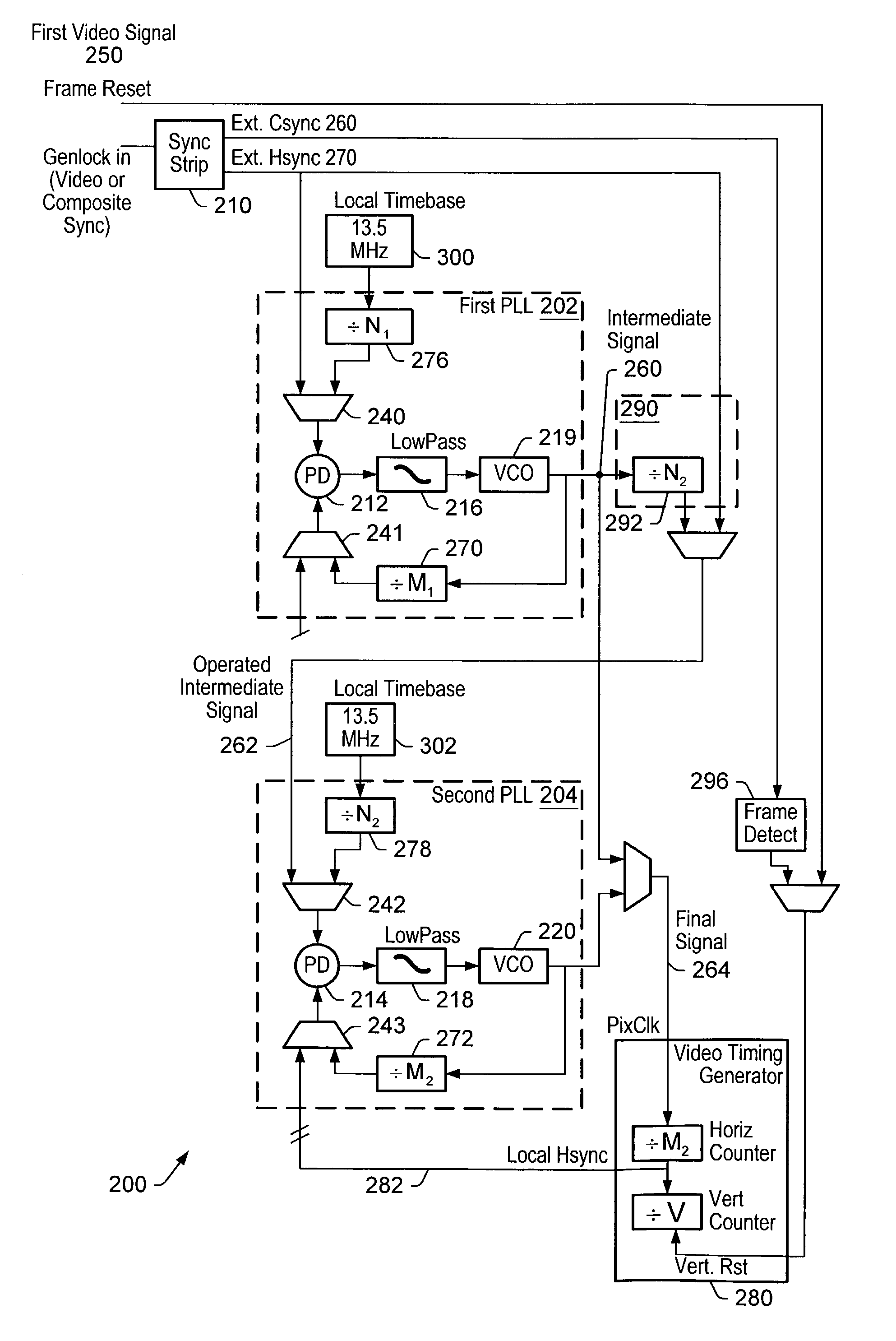
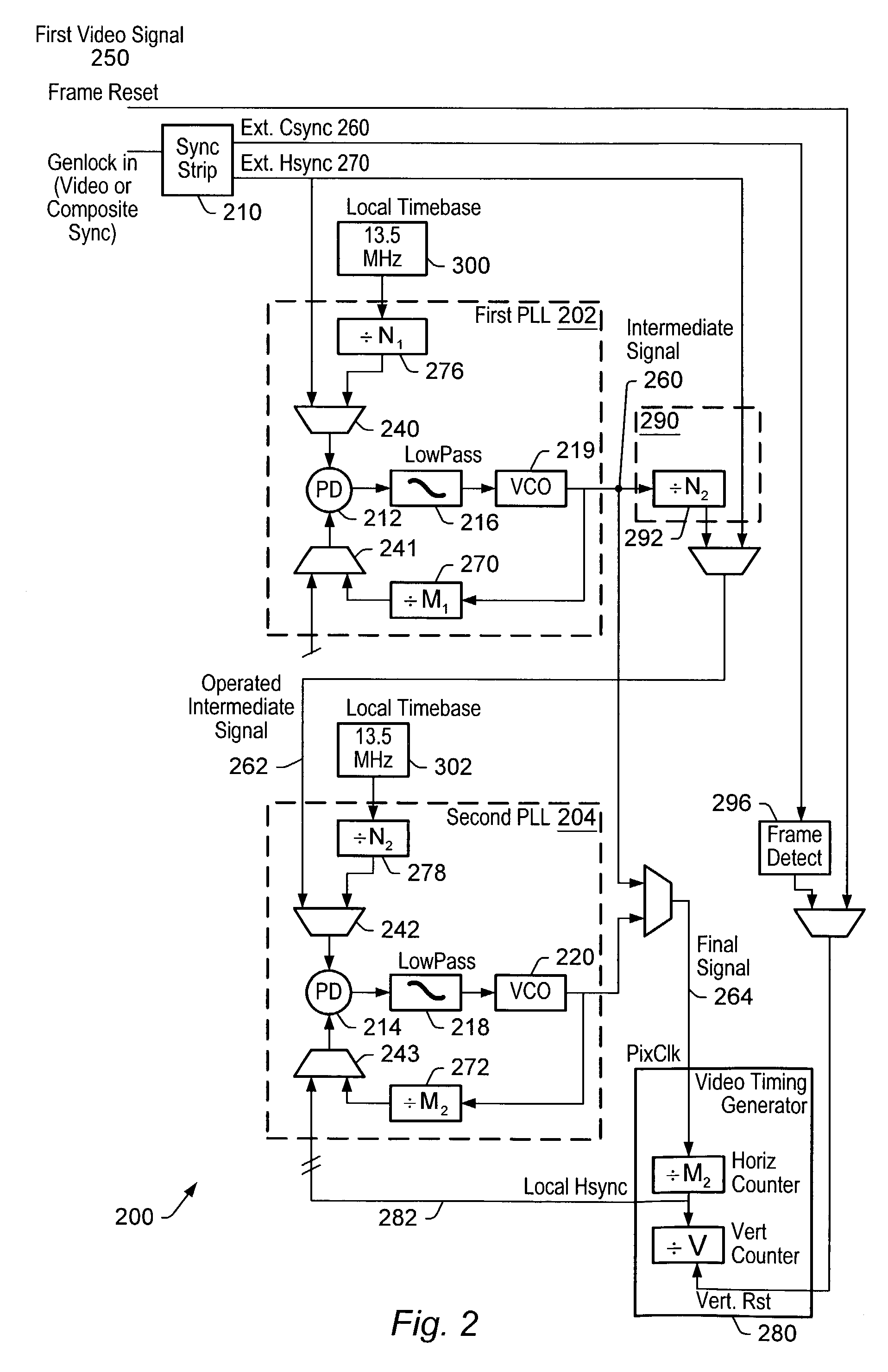
ActiveUS7071996B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhase locked loop circuitIntermediate frequency
In order to synchronize two dissimilar video formats, two or more phase locked loop circuits (PLL's) may be used in tandem. A first PLL circuit may be connected to the first video format (Master) and generate an intermediate frequency. A second PLL circuit may use the intermediate frequency as the timebase for generating the pixel clock for the second video format (Slave). One or more Slaves may be connected to the generated pixel clock. The video synchronizing device may be a part of a graphics system, such as a graphics accelerator.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com