Patents
Literature
39 results about "Thyroid cartilage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
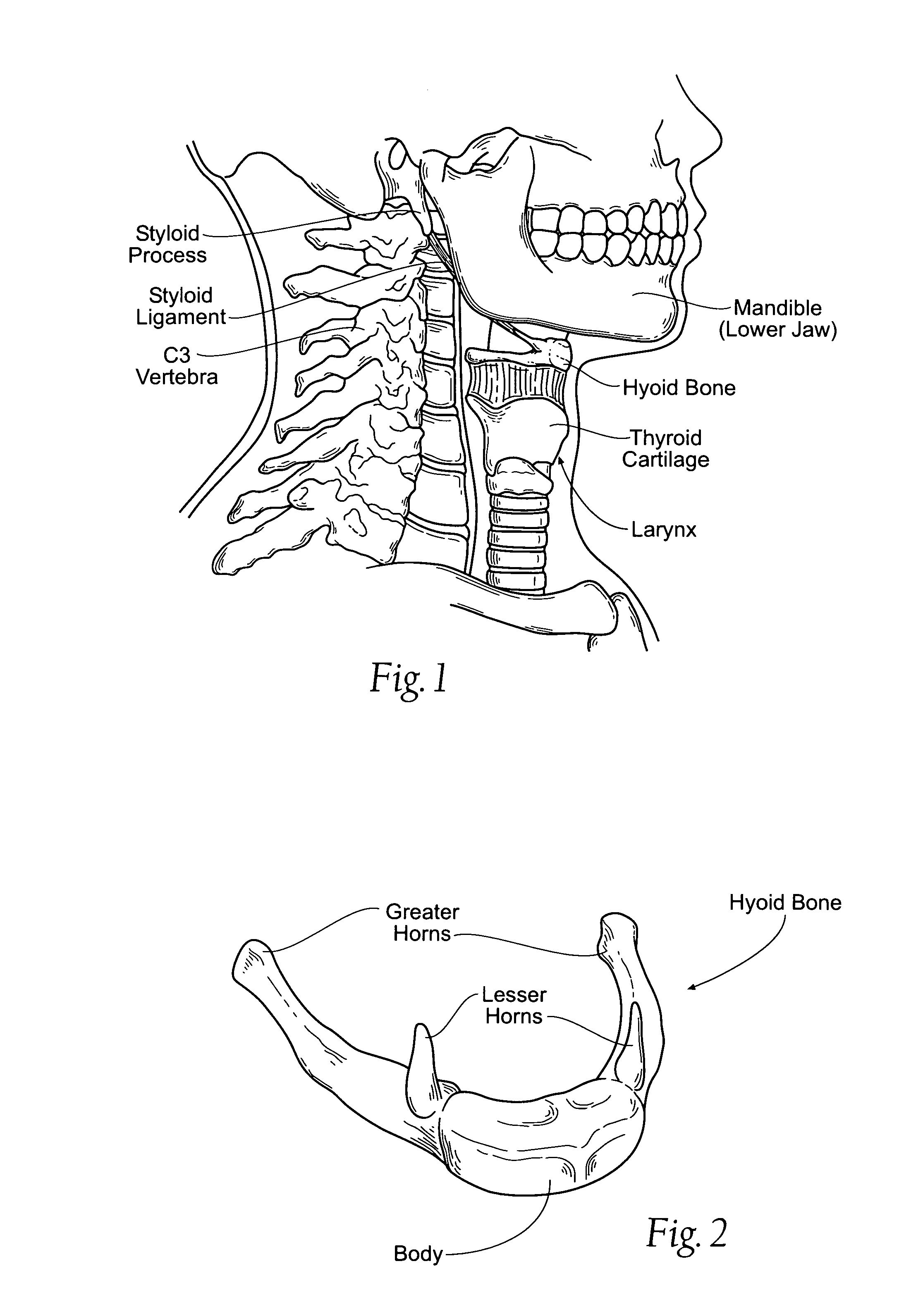
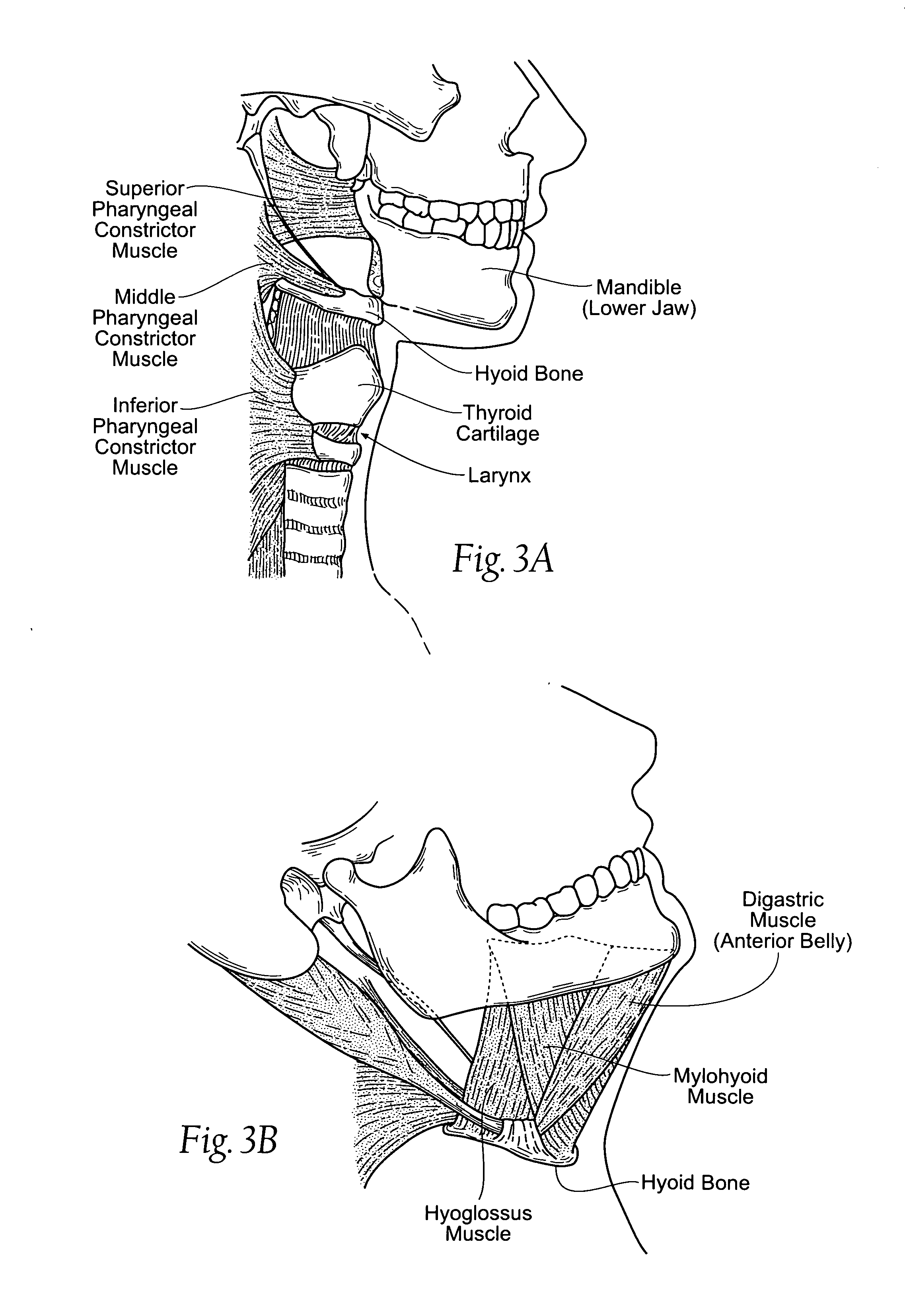
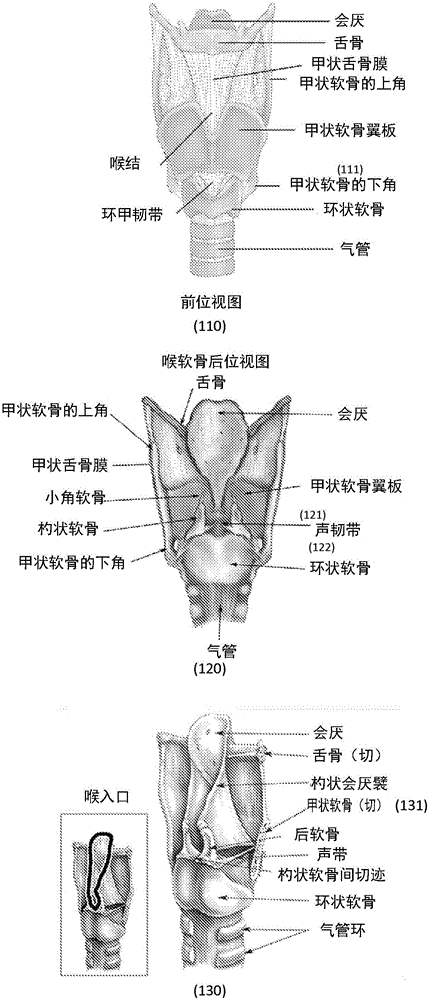
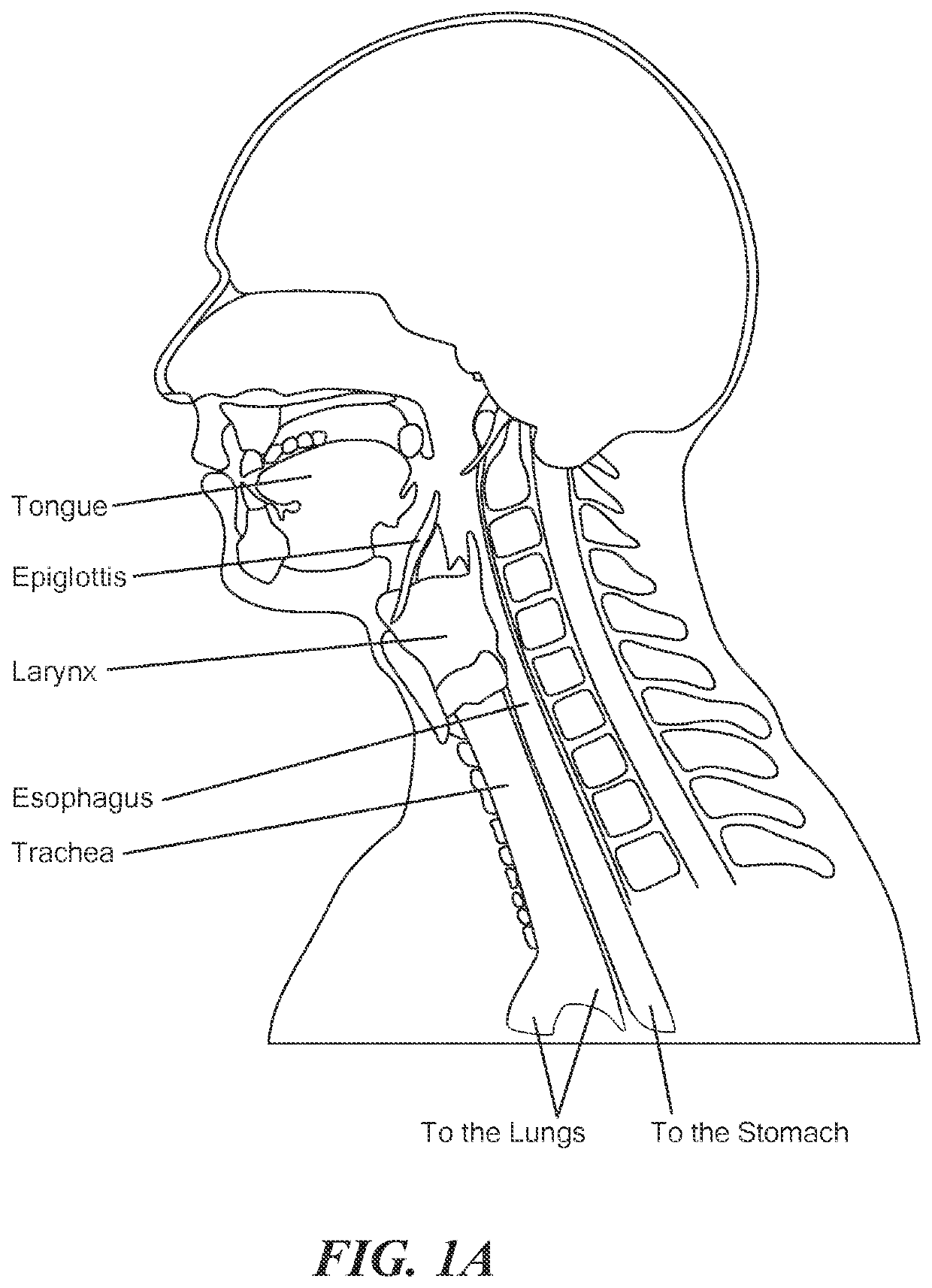
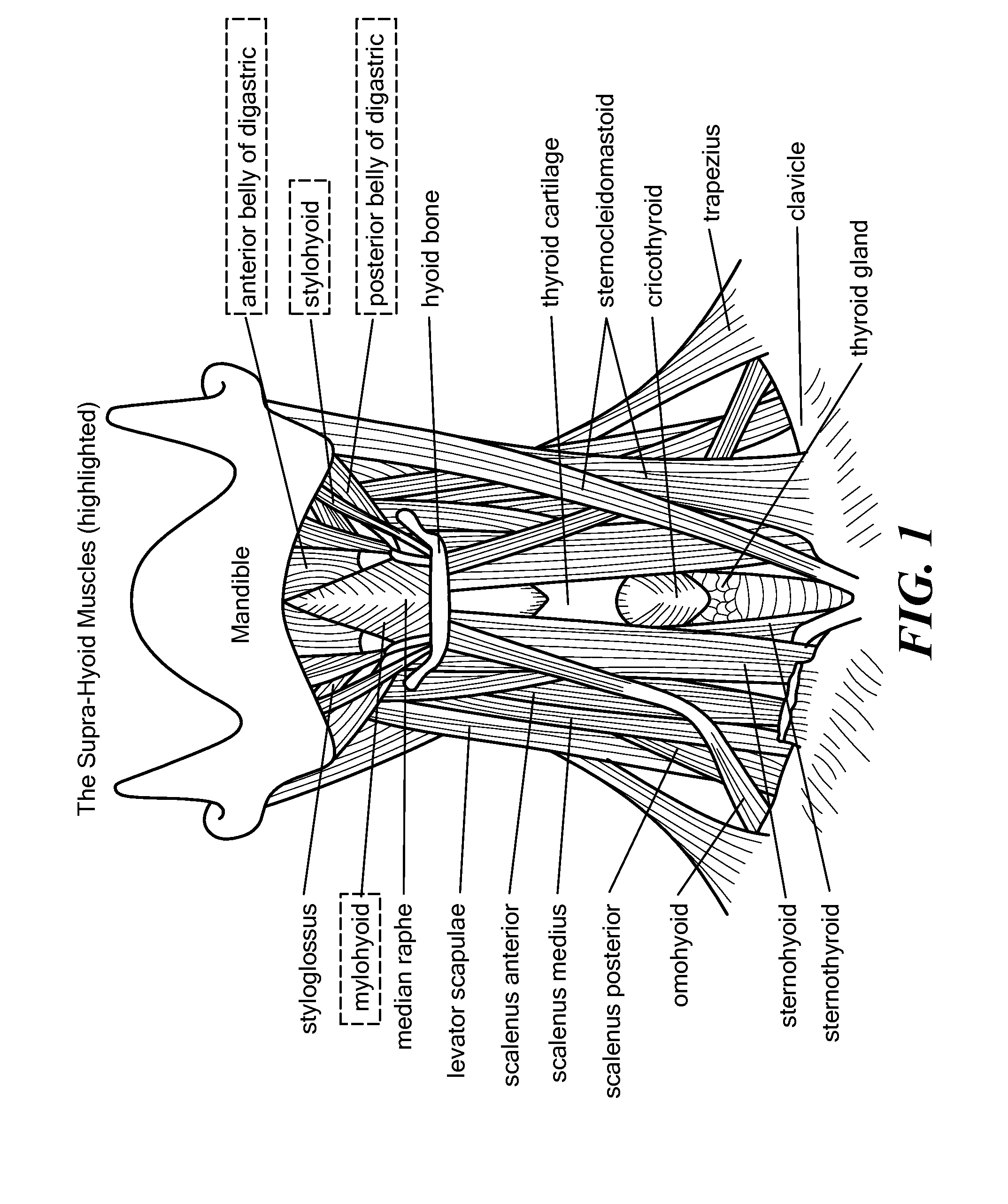
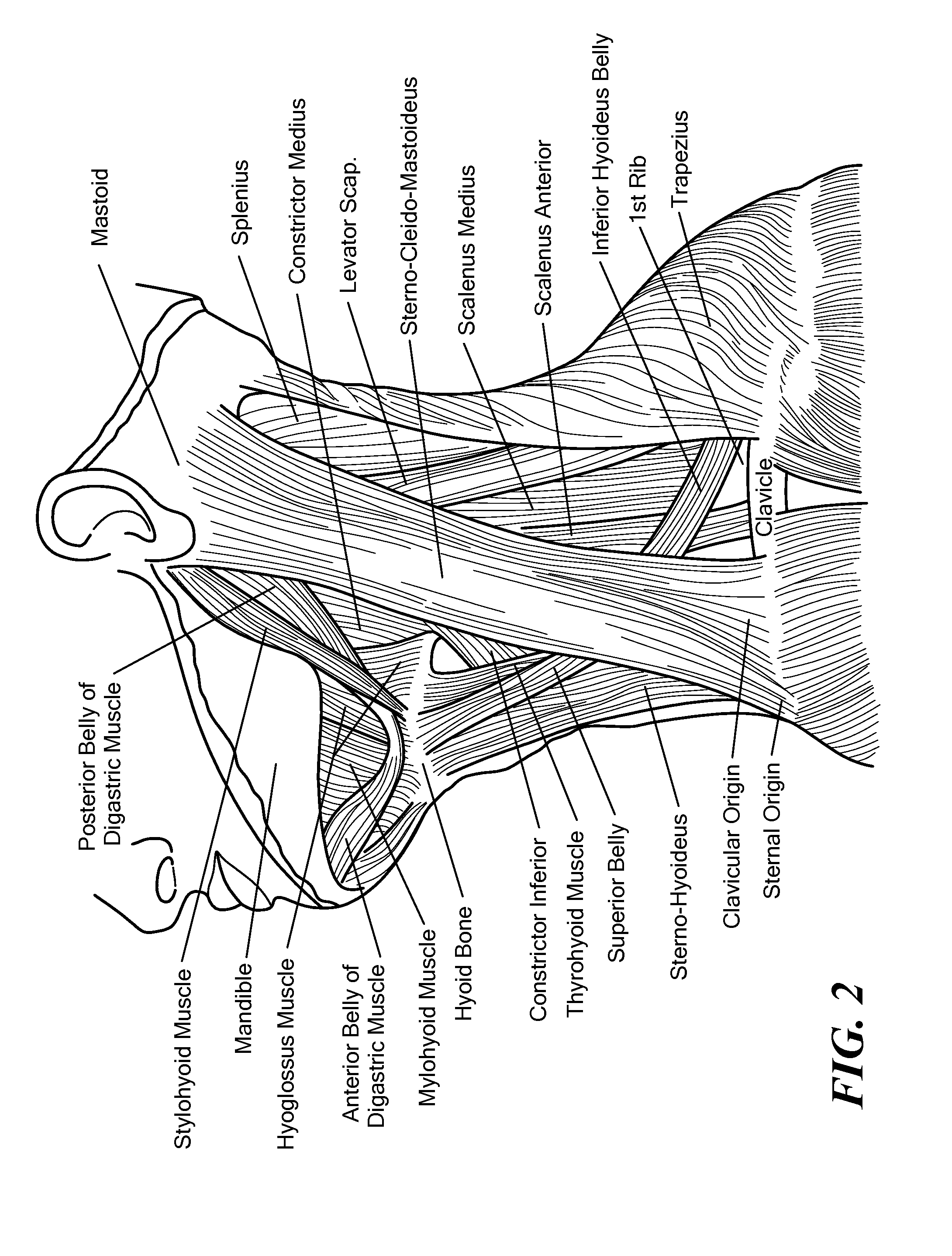
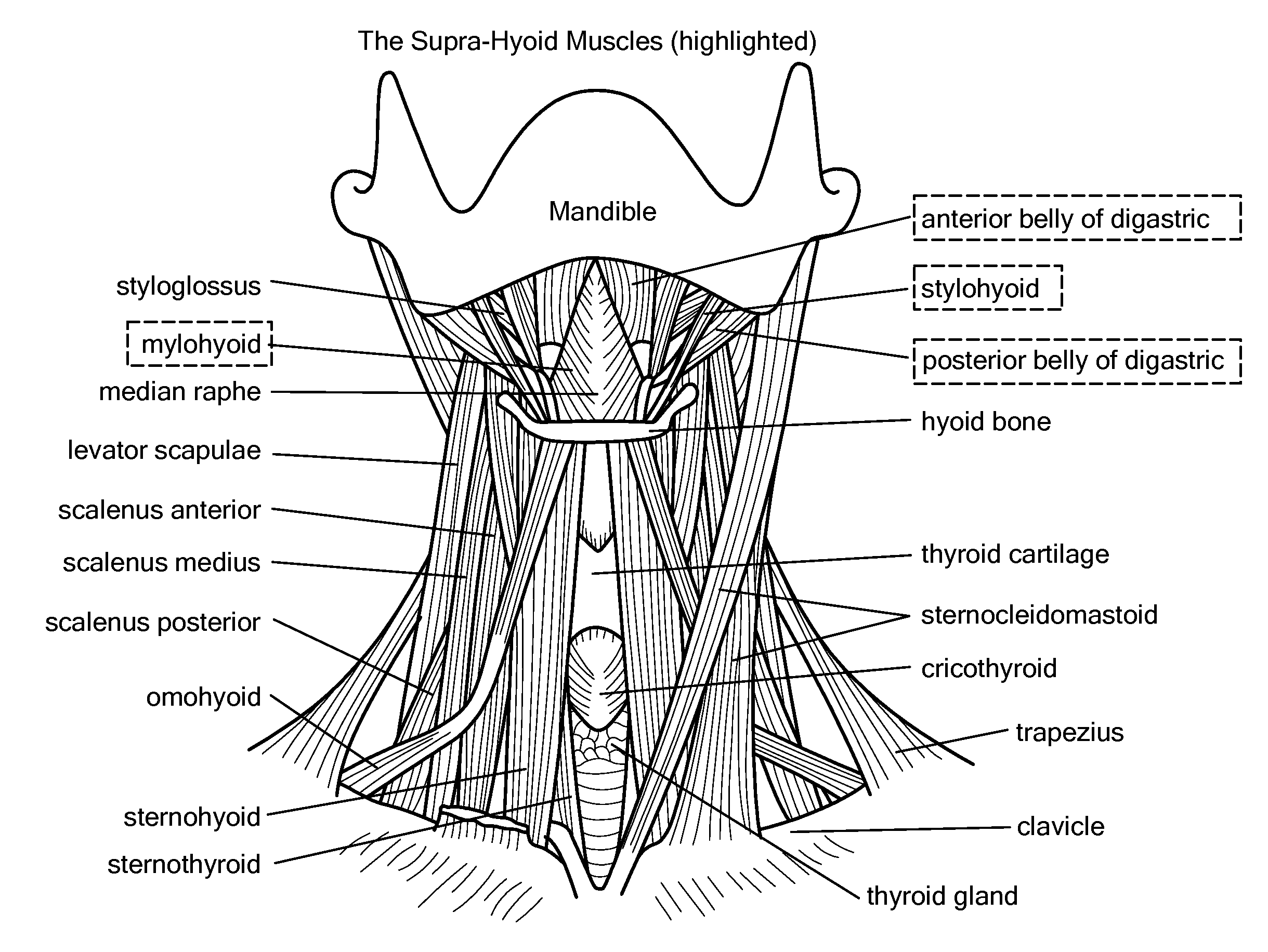
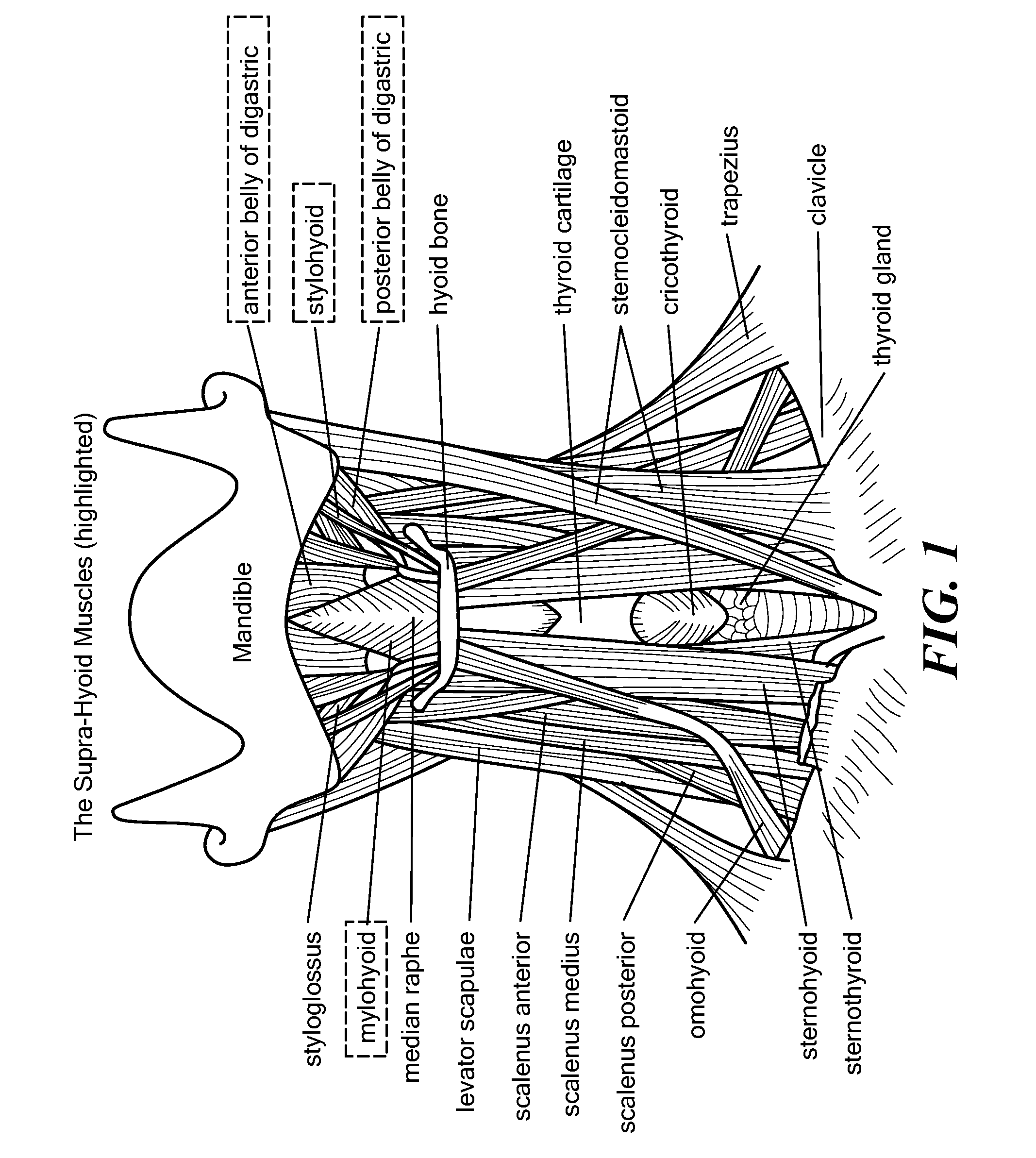
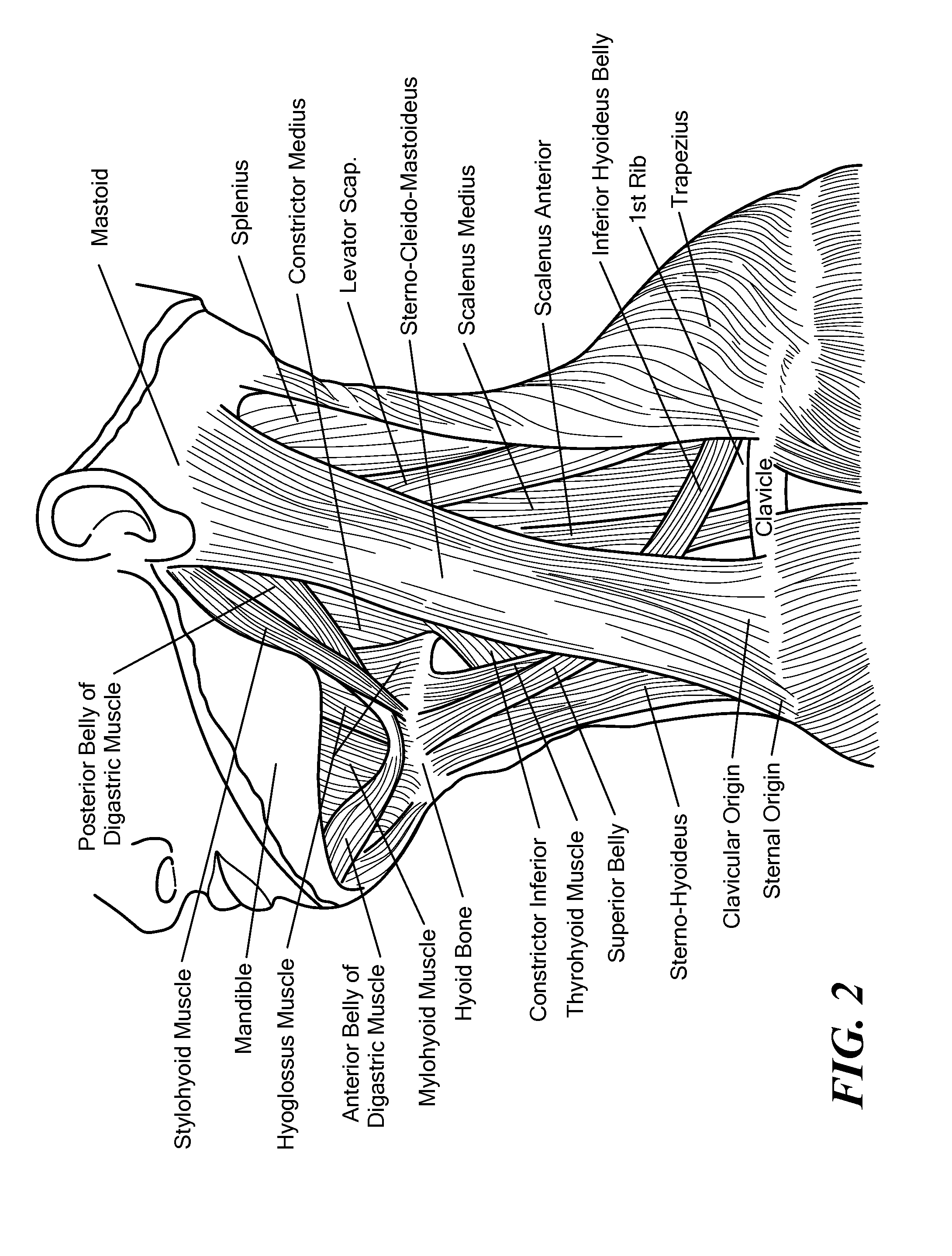
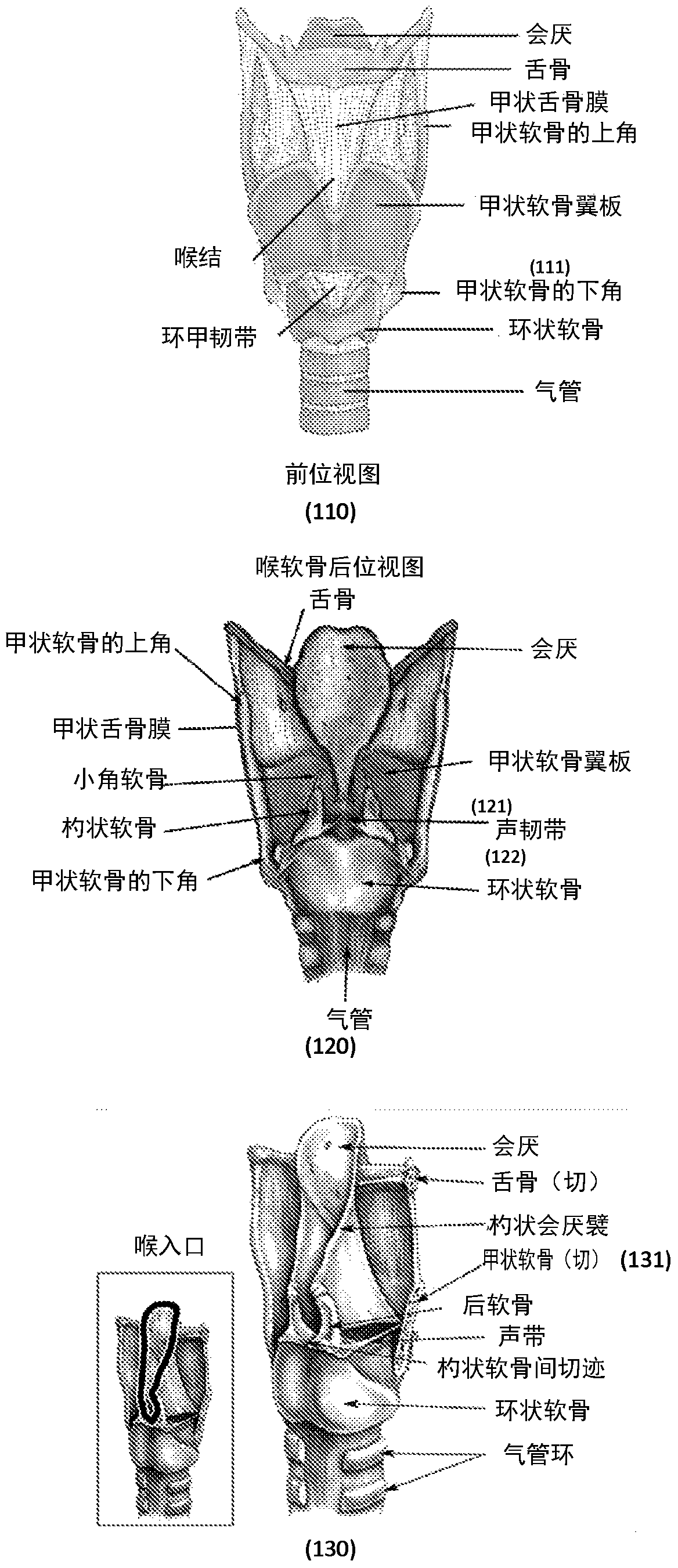
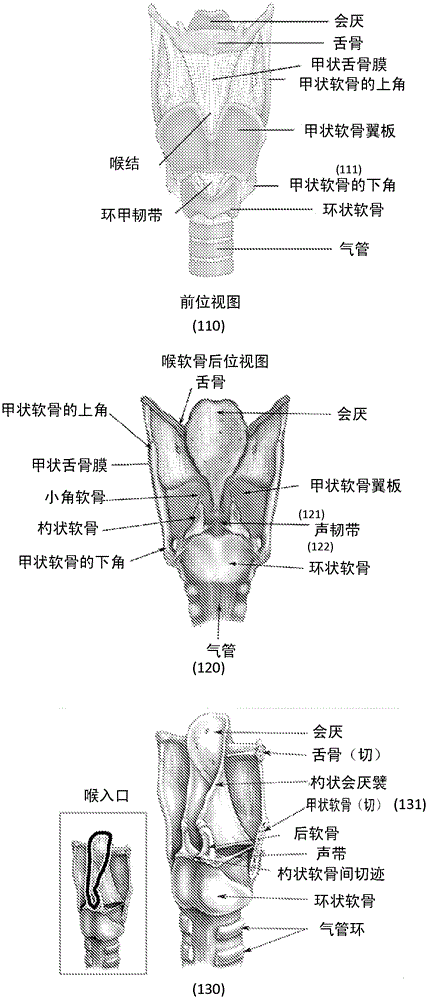
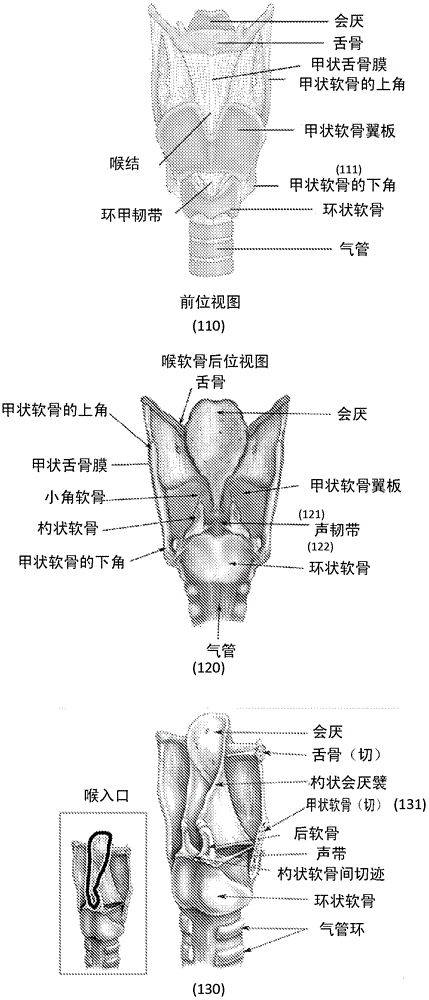
The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the laryngeal skeleton, the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx. It does not completely encircle the larynx; only the cricoid cartilage does.
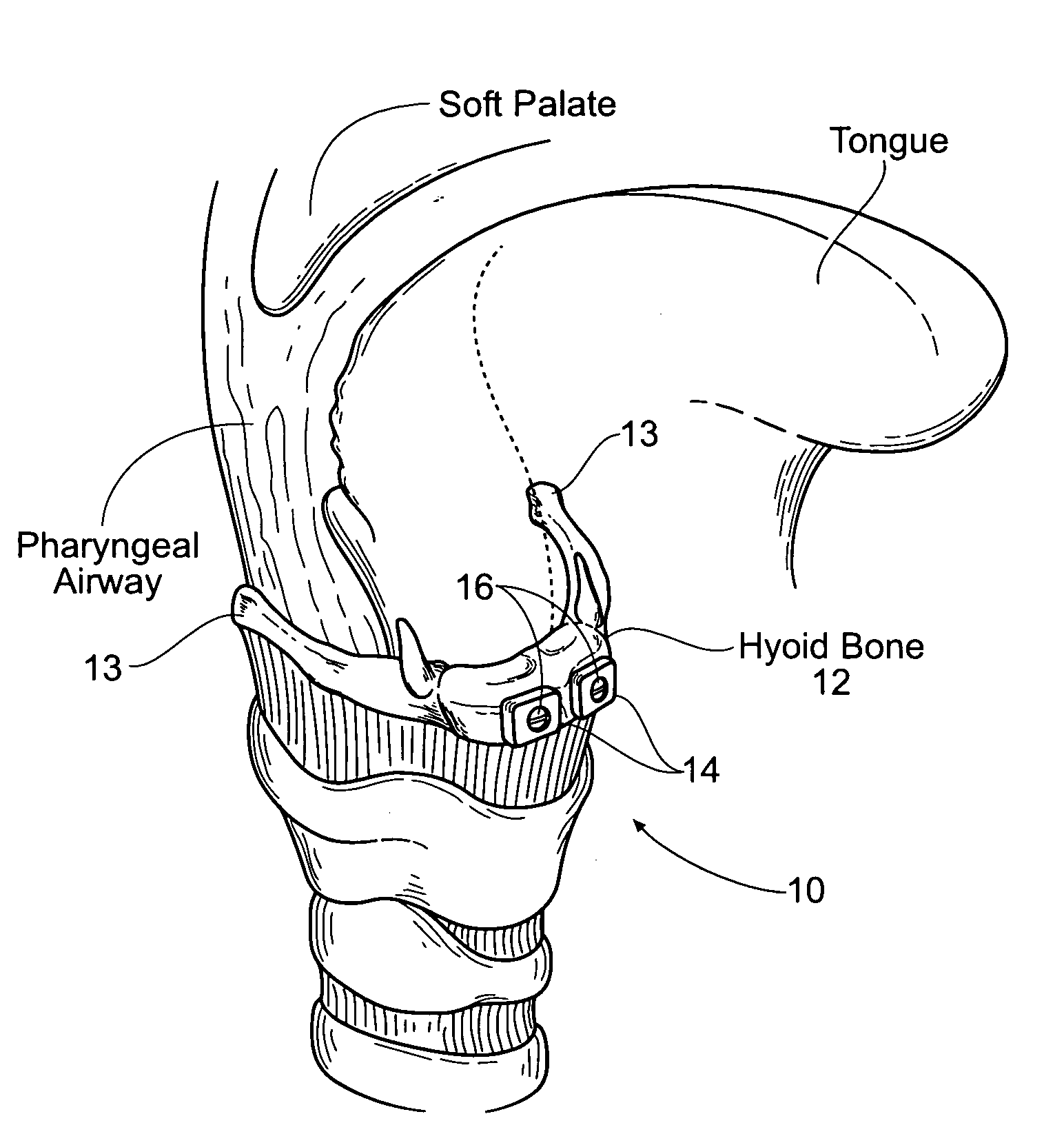
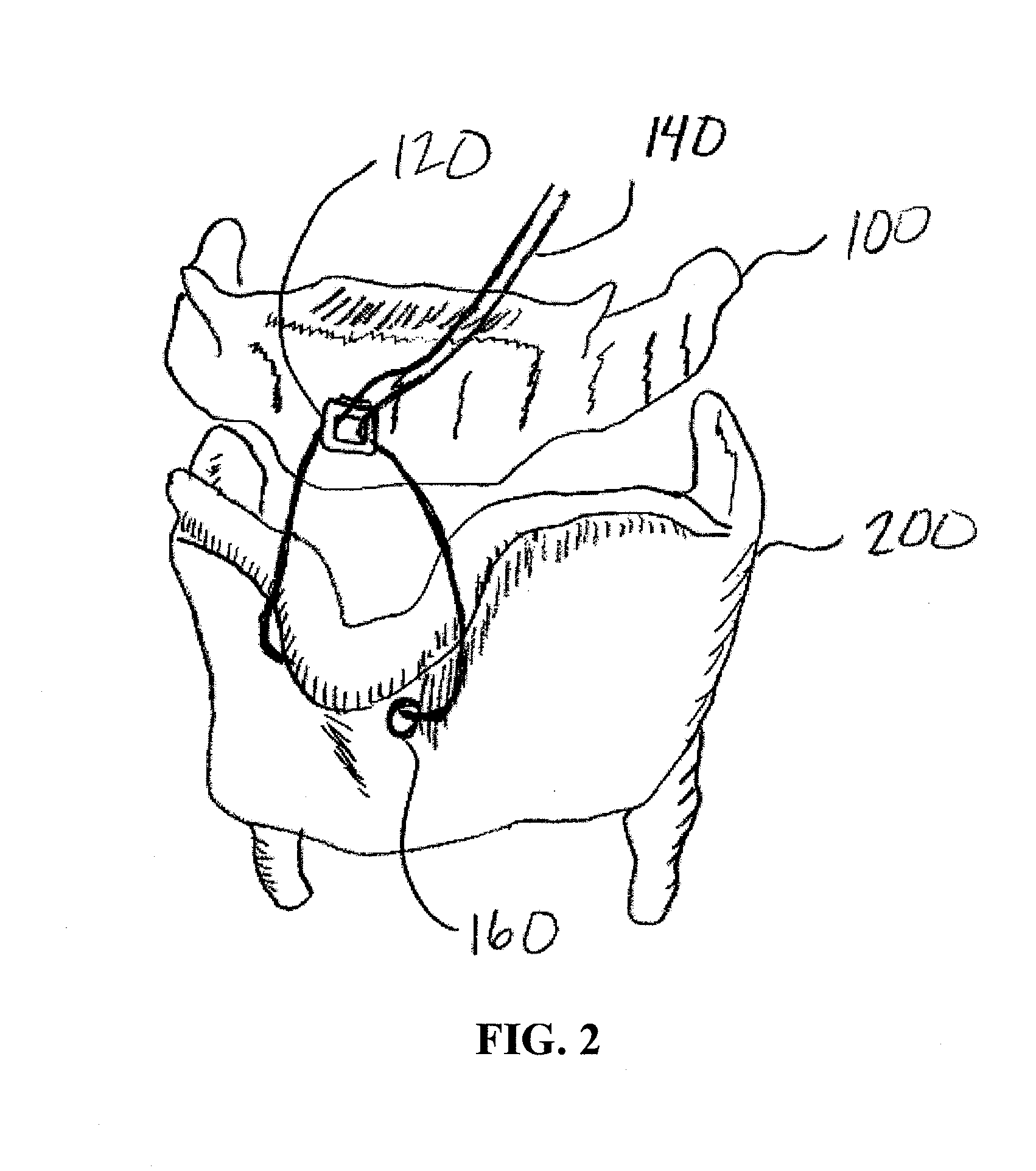
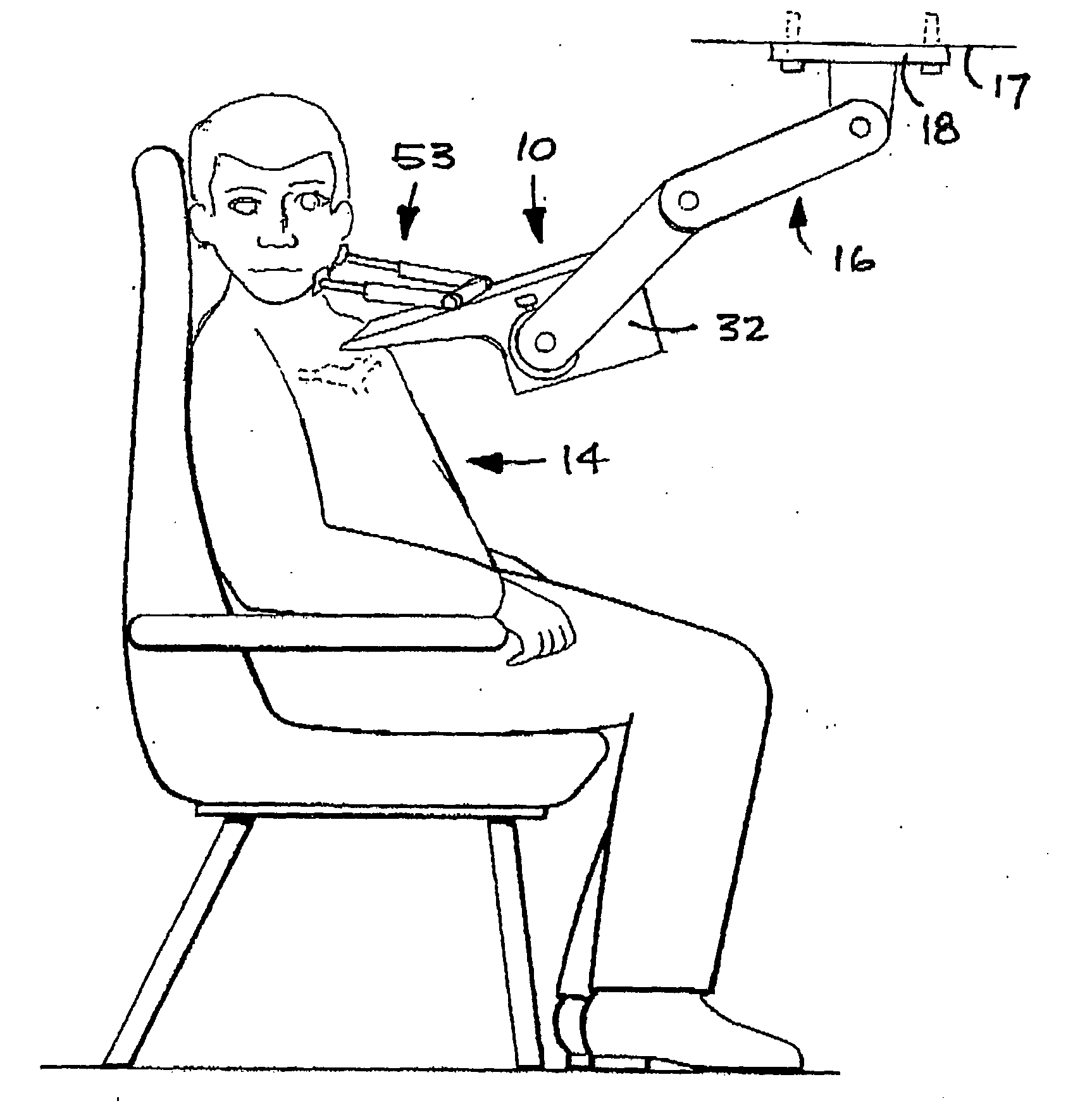
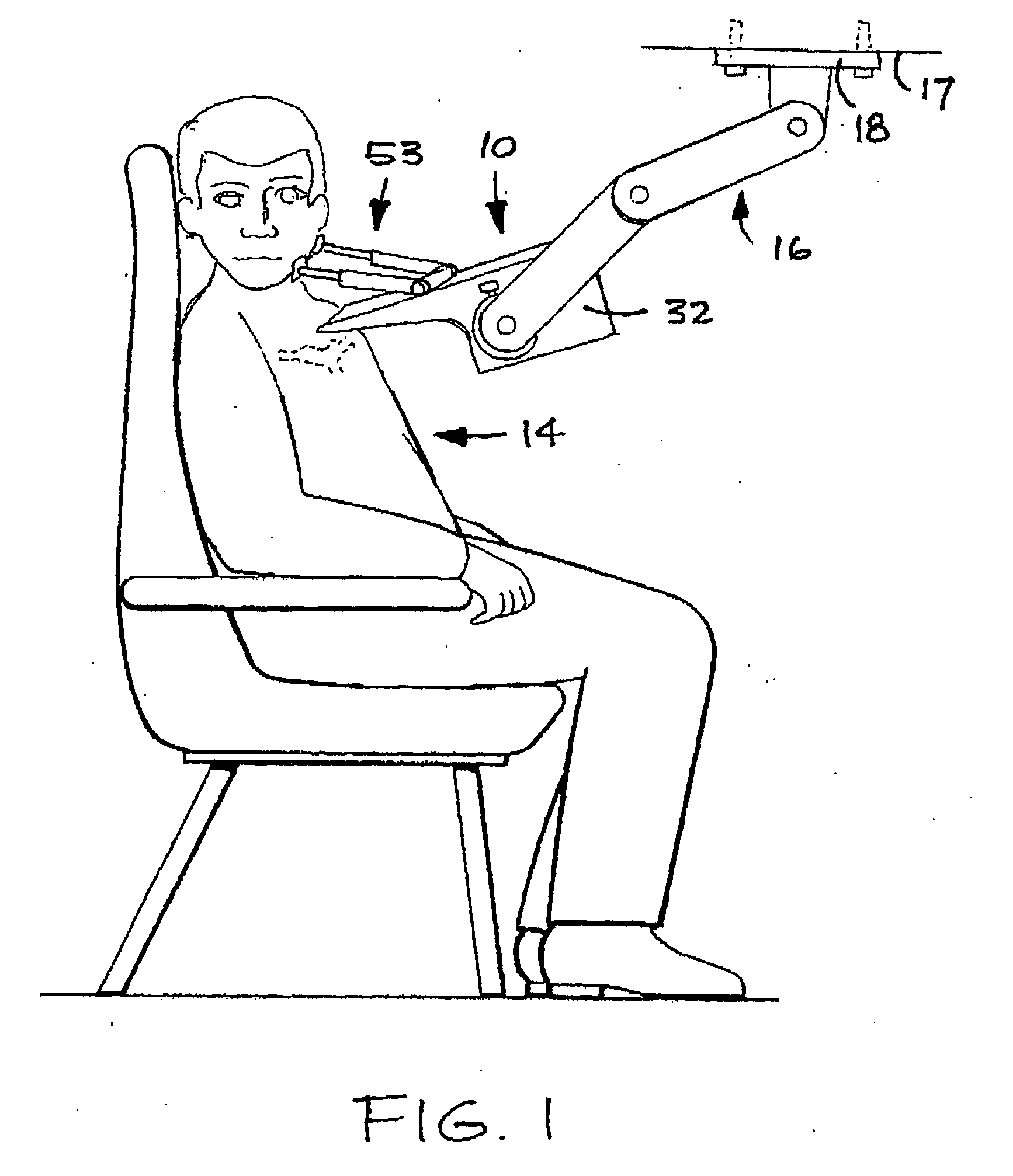
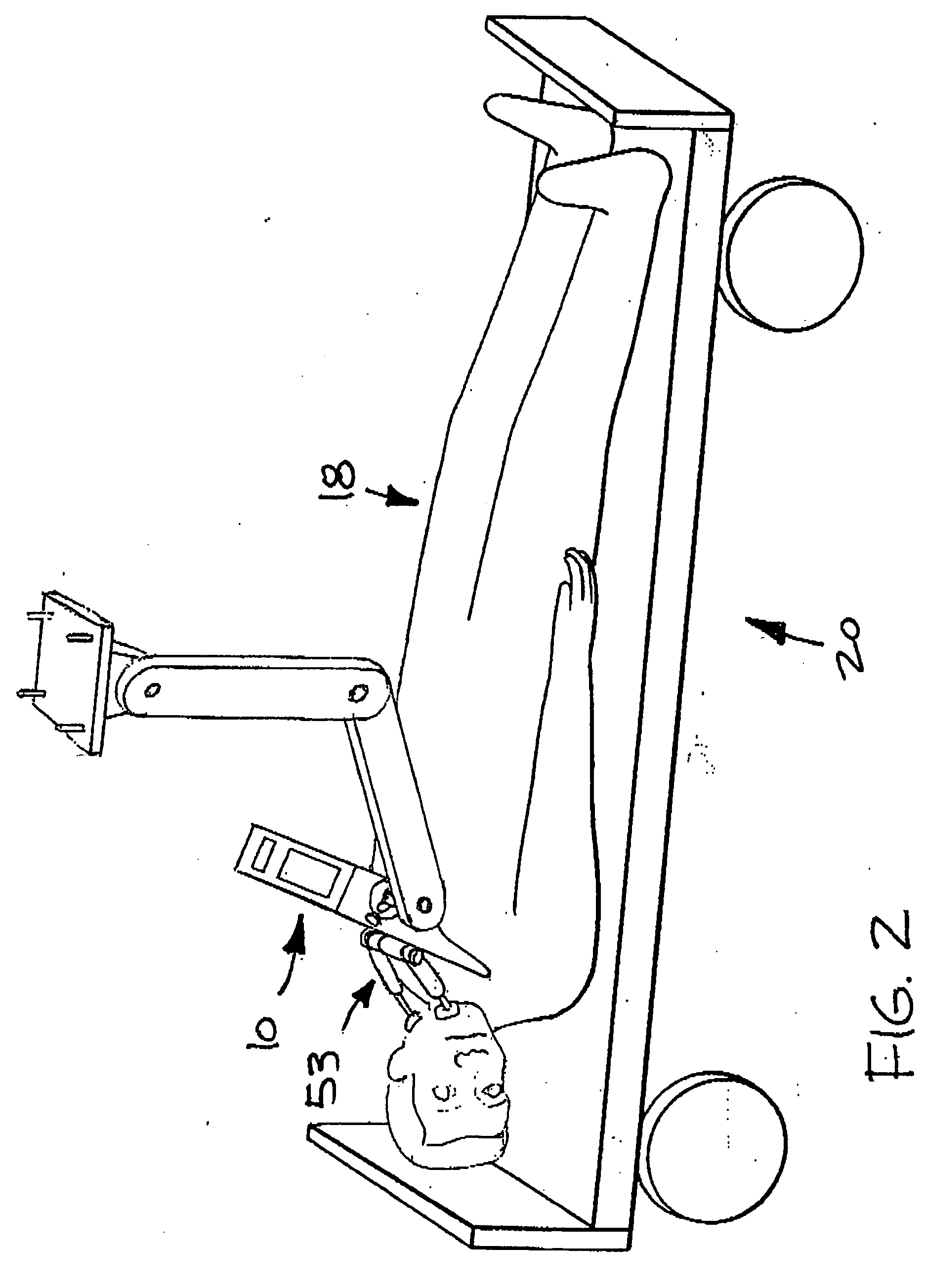
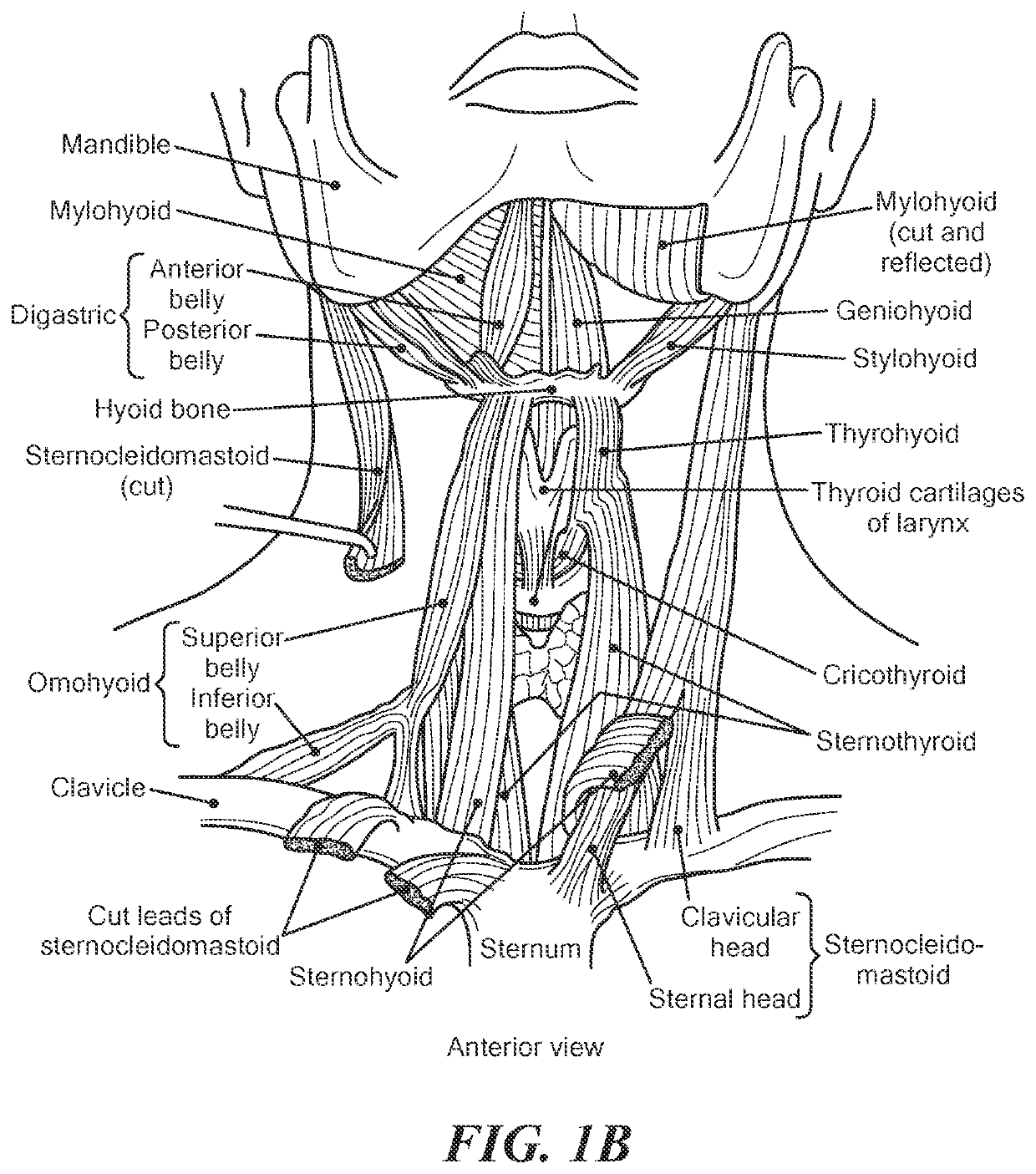
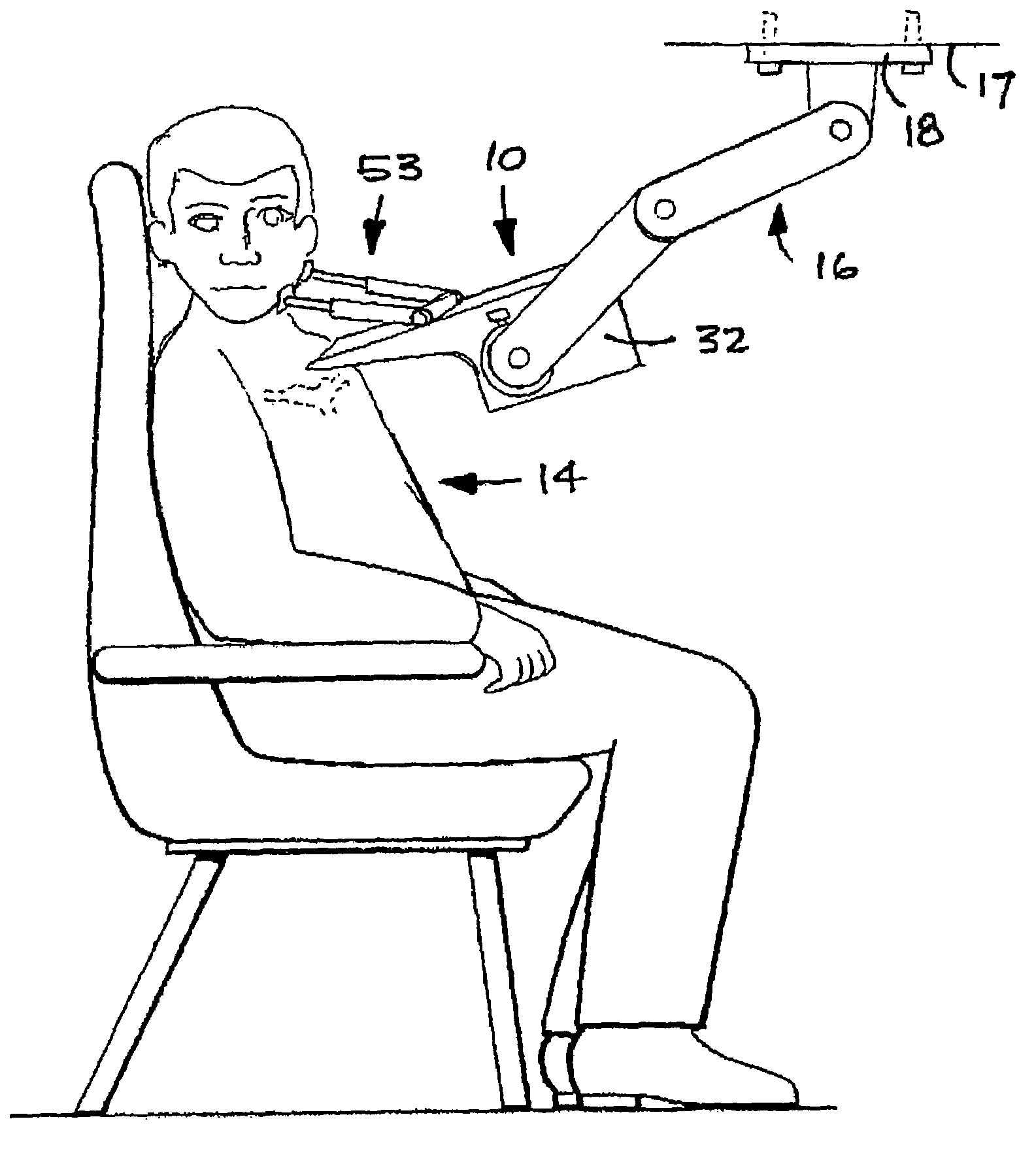
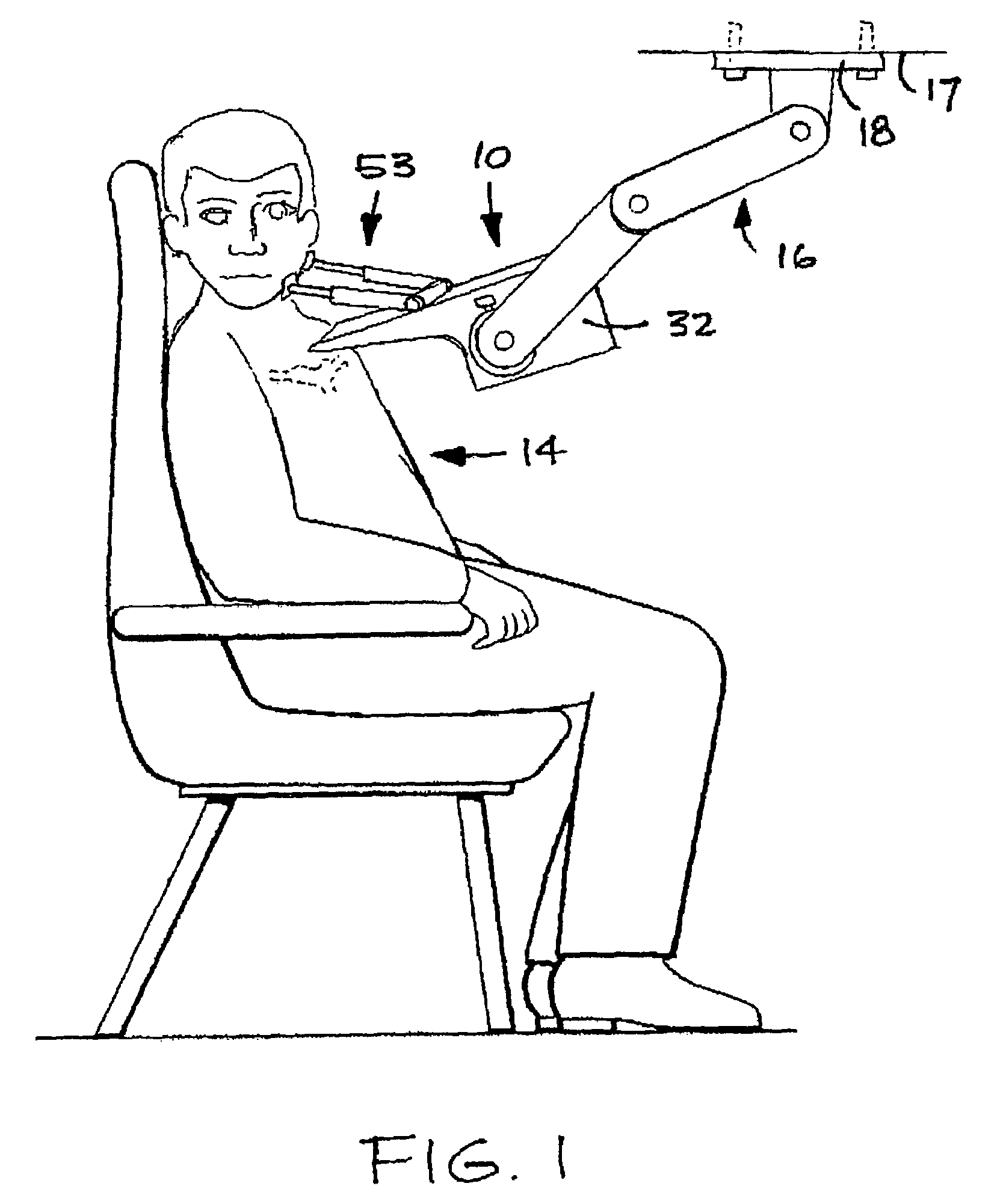
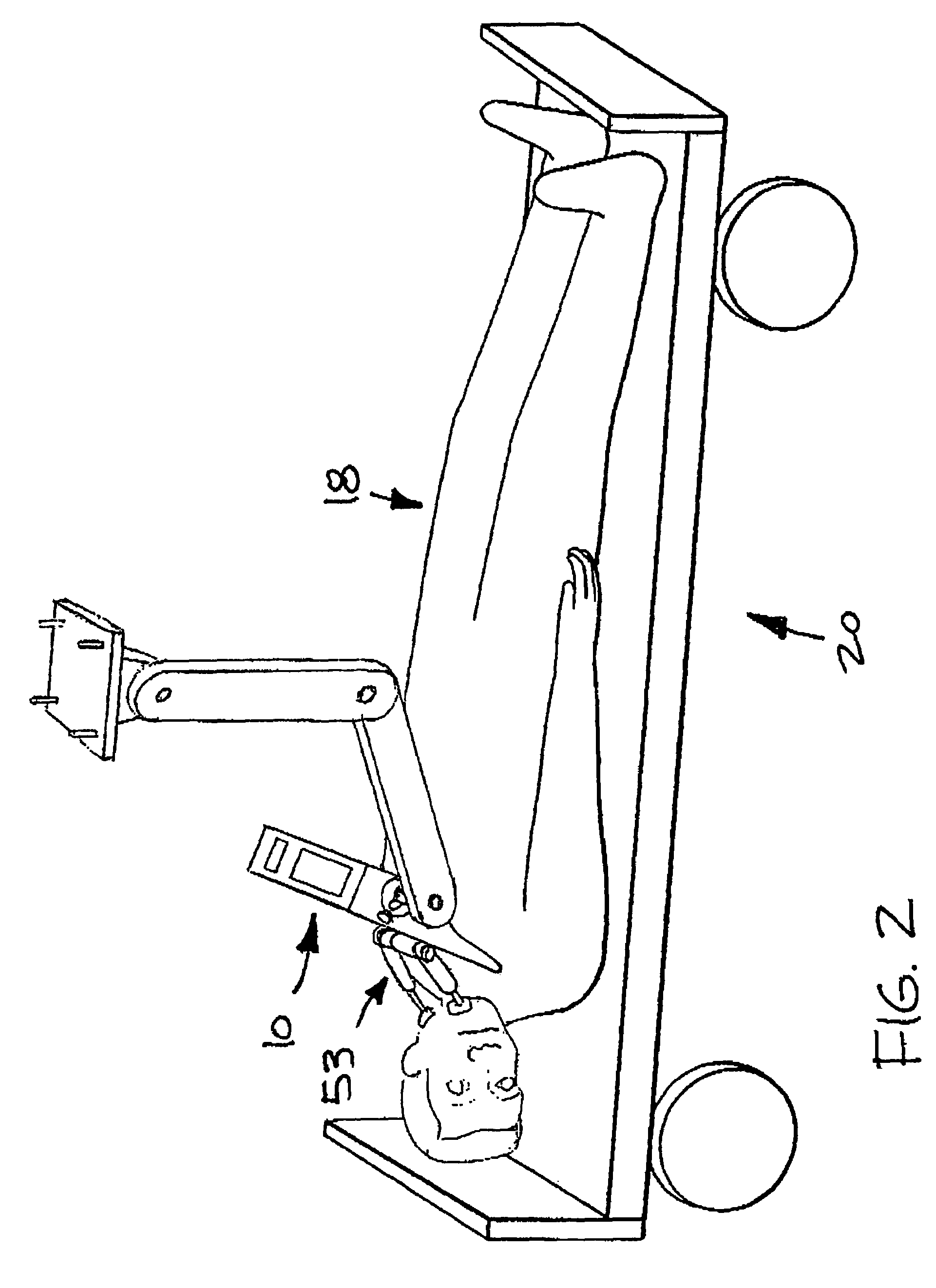
Devices, systems, and methods to move or restrain the hyoid bone
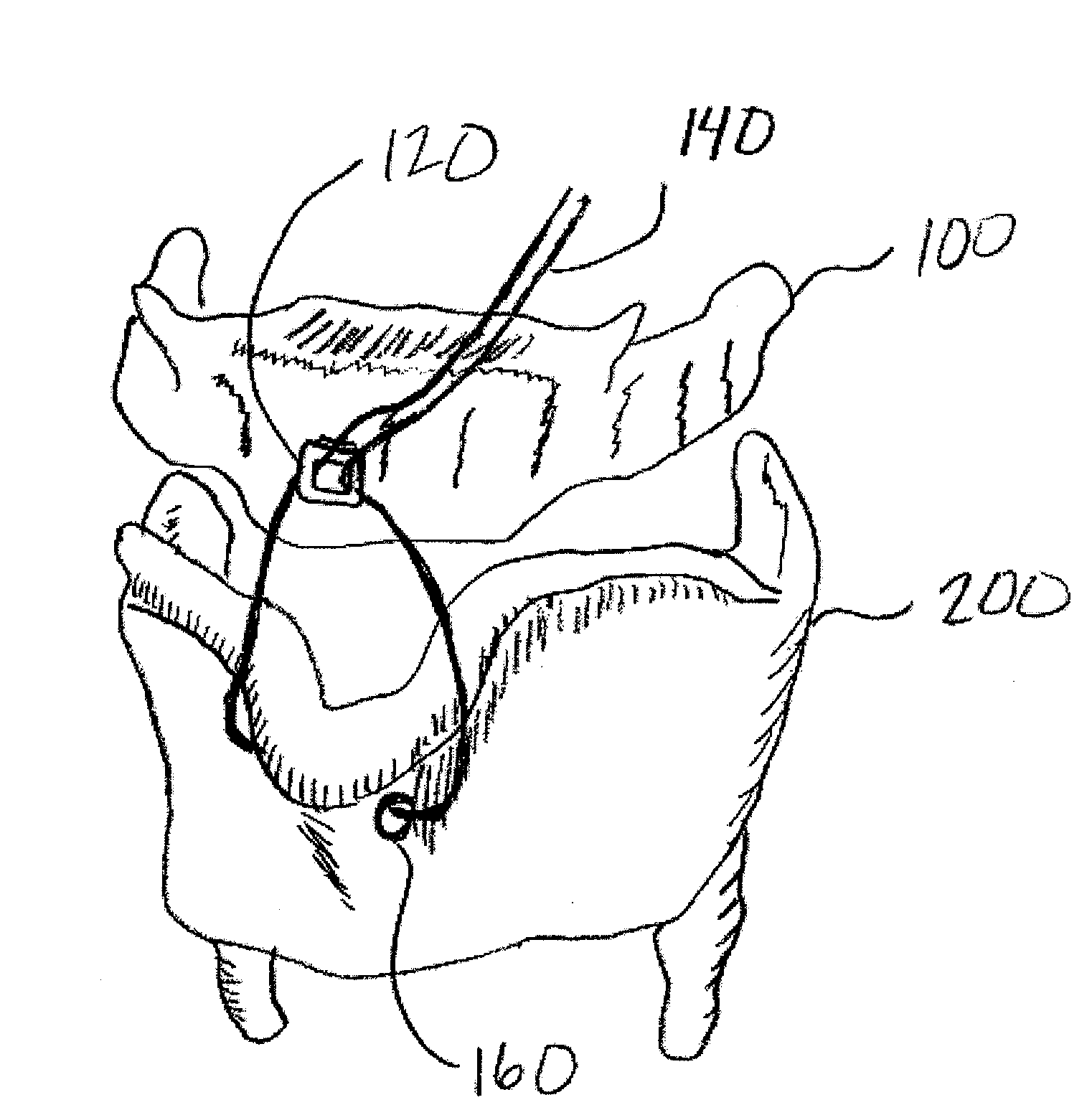
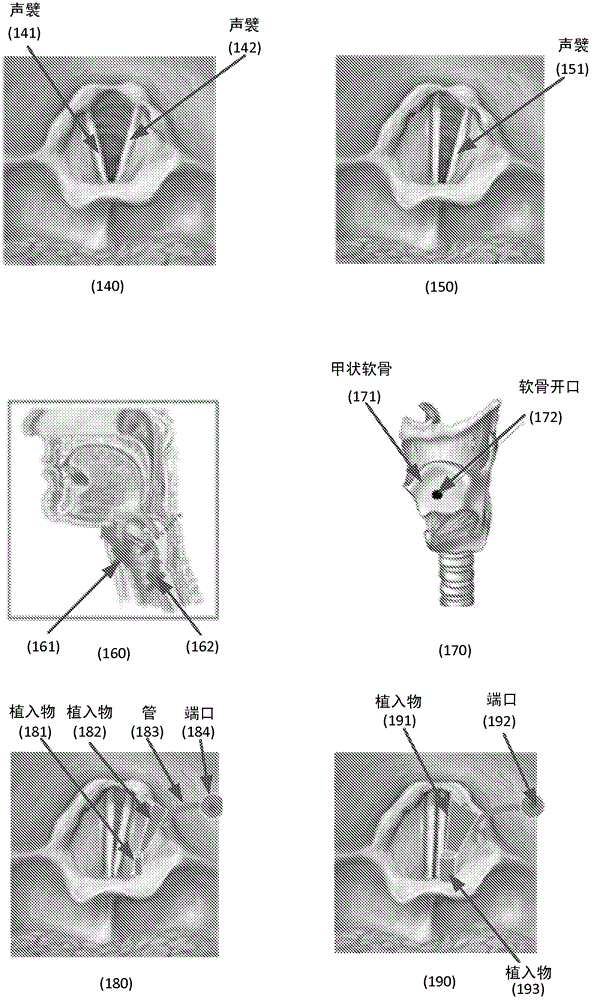
Systems and methods employ implants attached to the hyoid bone, thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, or both the thyroid and cricoid cartilages and a source of magnetic force to move the hyoid bone, thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, or both the thyroid and cricoid cartilages in the treatment of sleep disordered breathing, using attracting, repelling or a combination of attracting and repelling magnetic forces.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
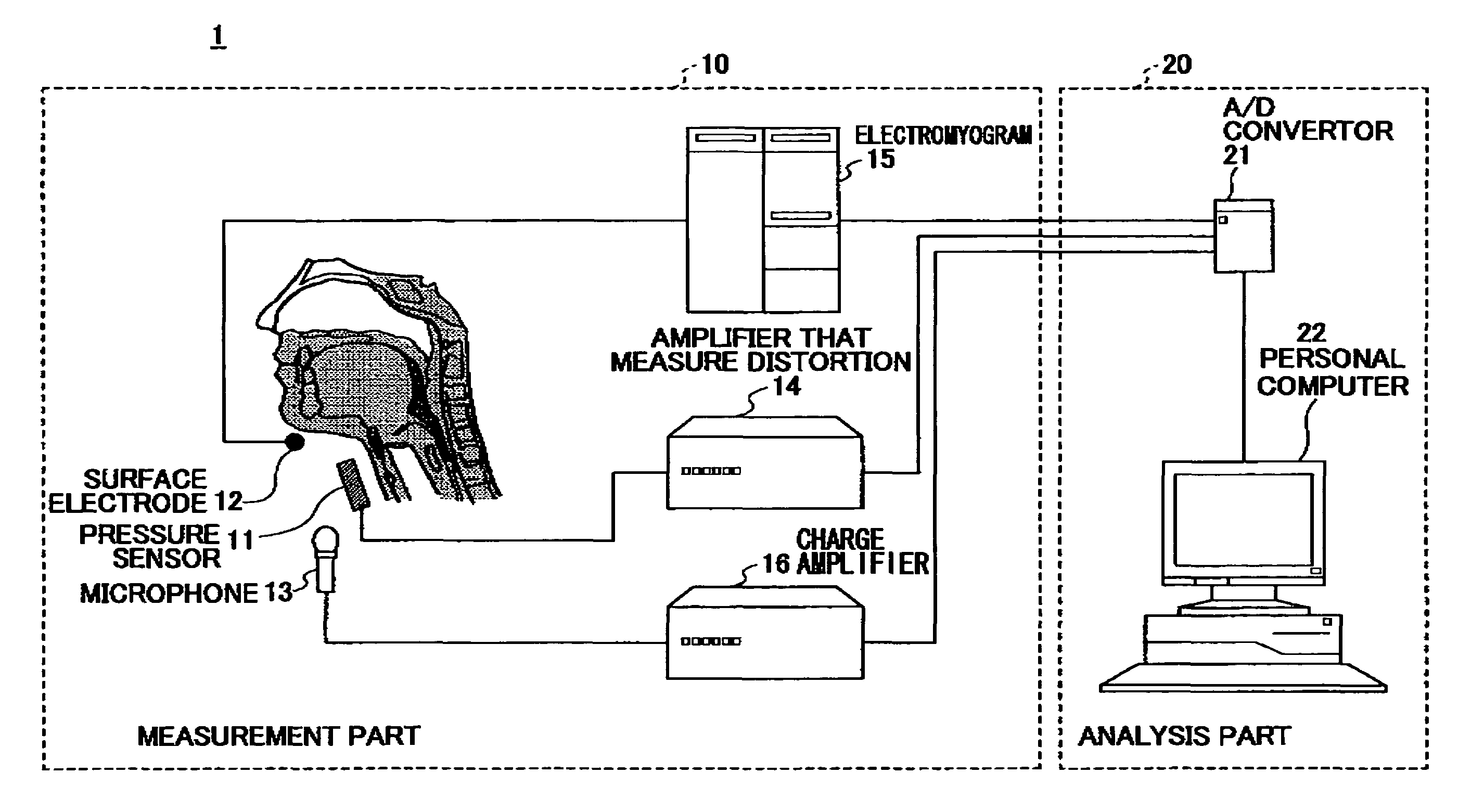
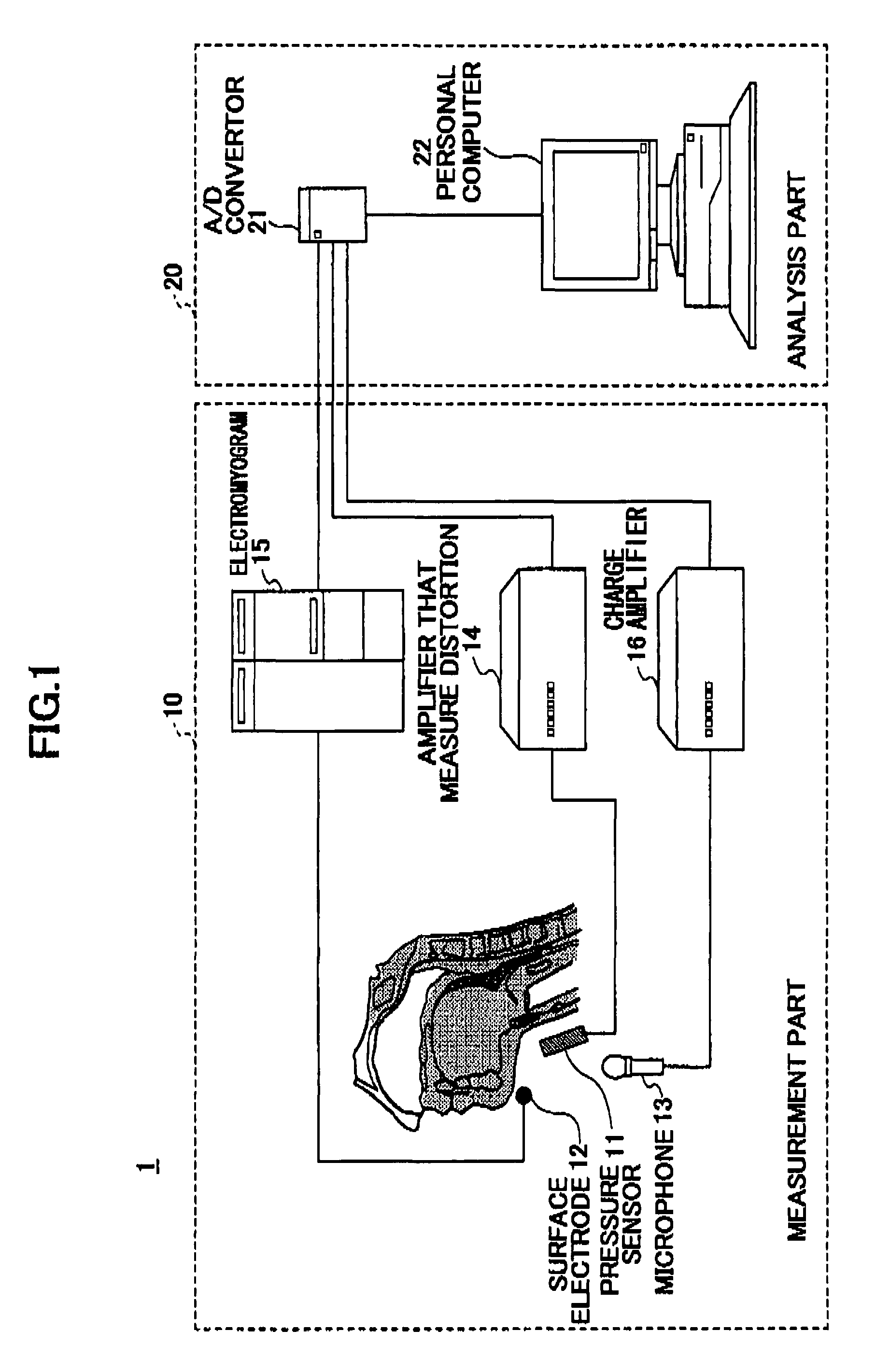
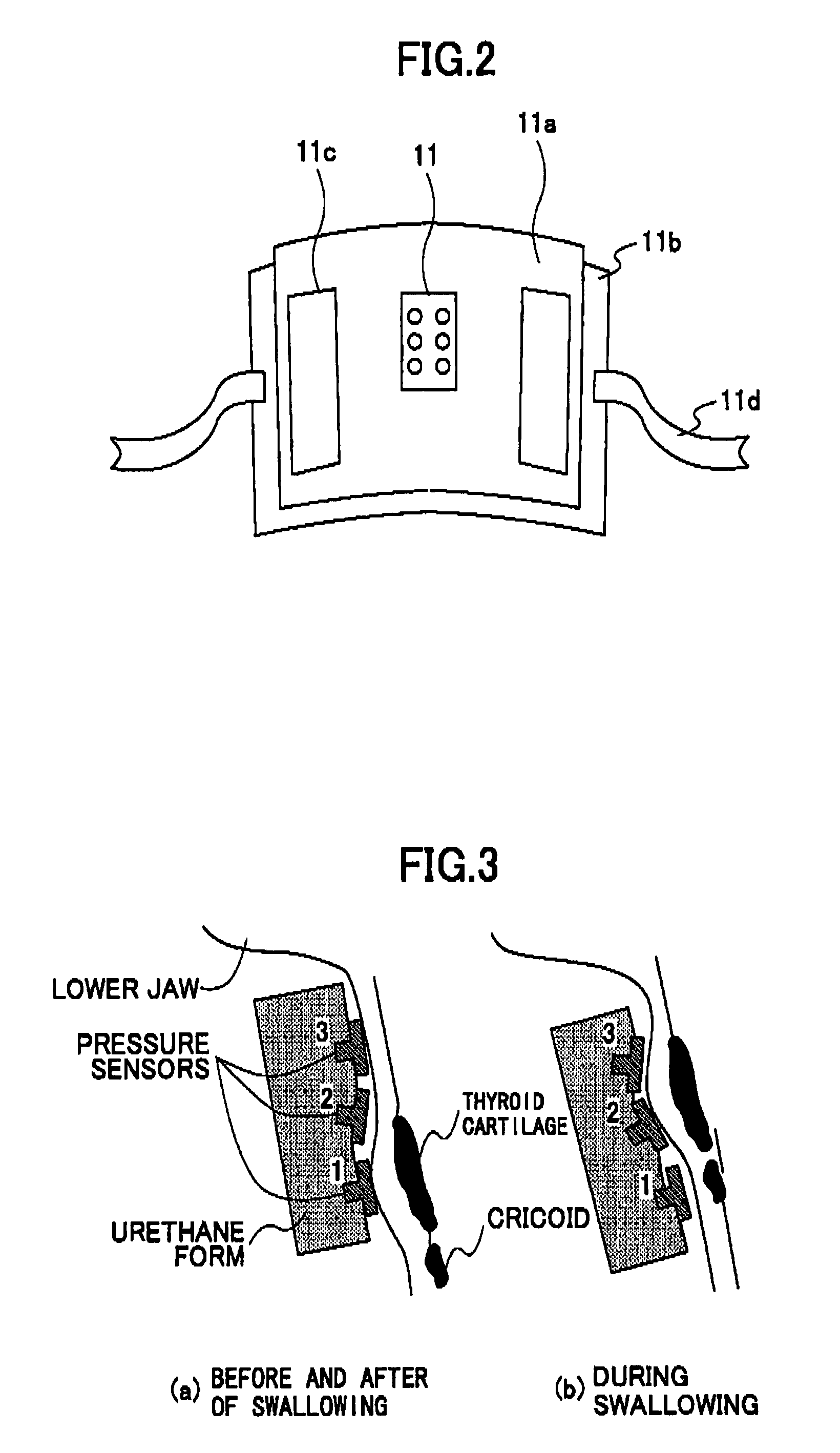
Continuous swallowing movement measuring device and method for measuring a continuous swallowing movement
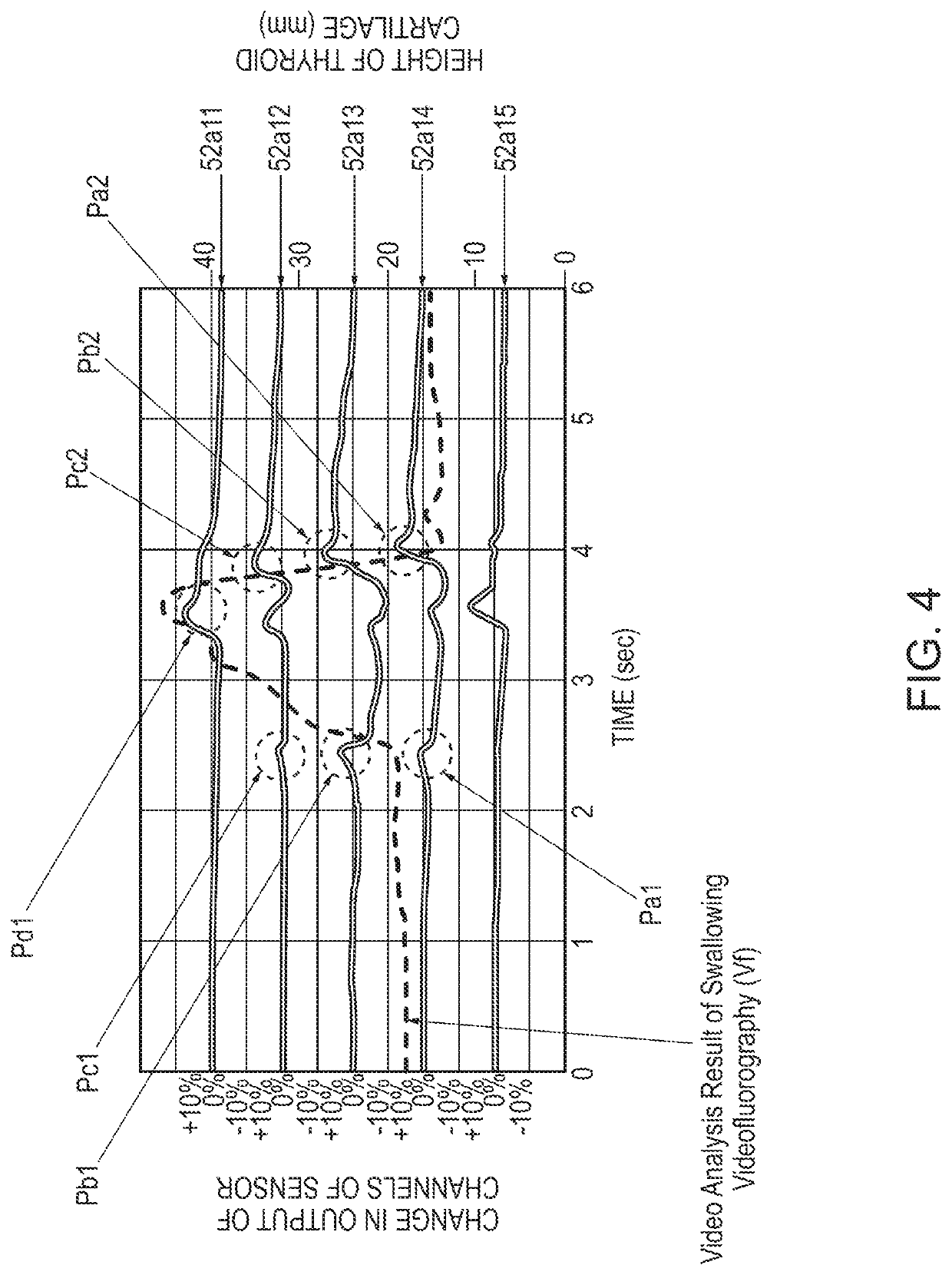
InactiveUS8211040B2Precise swallowing movementPossible to measurePerson identificationAuscultation instrumentsEngineeringForce sensor
A continuous swallowing movement measuring device includes pressure sensors placed in a line along a direction of an up and down movement of a thyroid cartilage when a food is swallowed, a first one of the pressure sensors placed at a top position of the thyroid cartilage, a second one of the pressure sensors placed along the direction to measure swallows included in a continuous swallowing movement. The device also includes a tool for wearing the pressure sensors and for fixing the pressure sensors to touch an anterior region of a neck of a subject. The tool includes a fixing unit fixes the pressure sensors. The tool also includes a supporter of the pressure sensors supports the fixing unit. Further, the tool includes a holding band holds the supporter of the pressure sensors on the anterior region of the neck of the subject.
Owner:SAPPORO BREWERIES
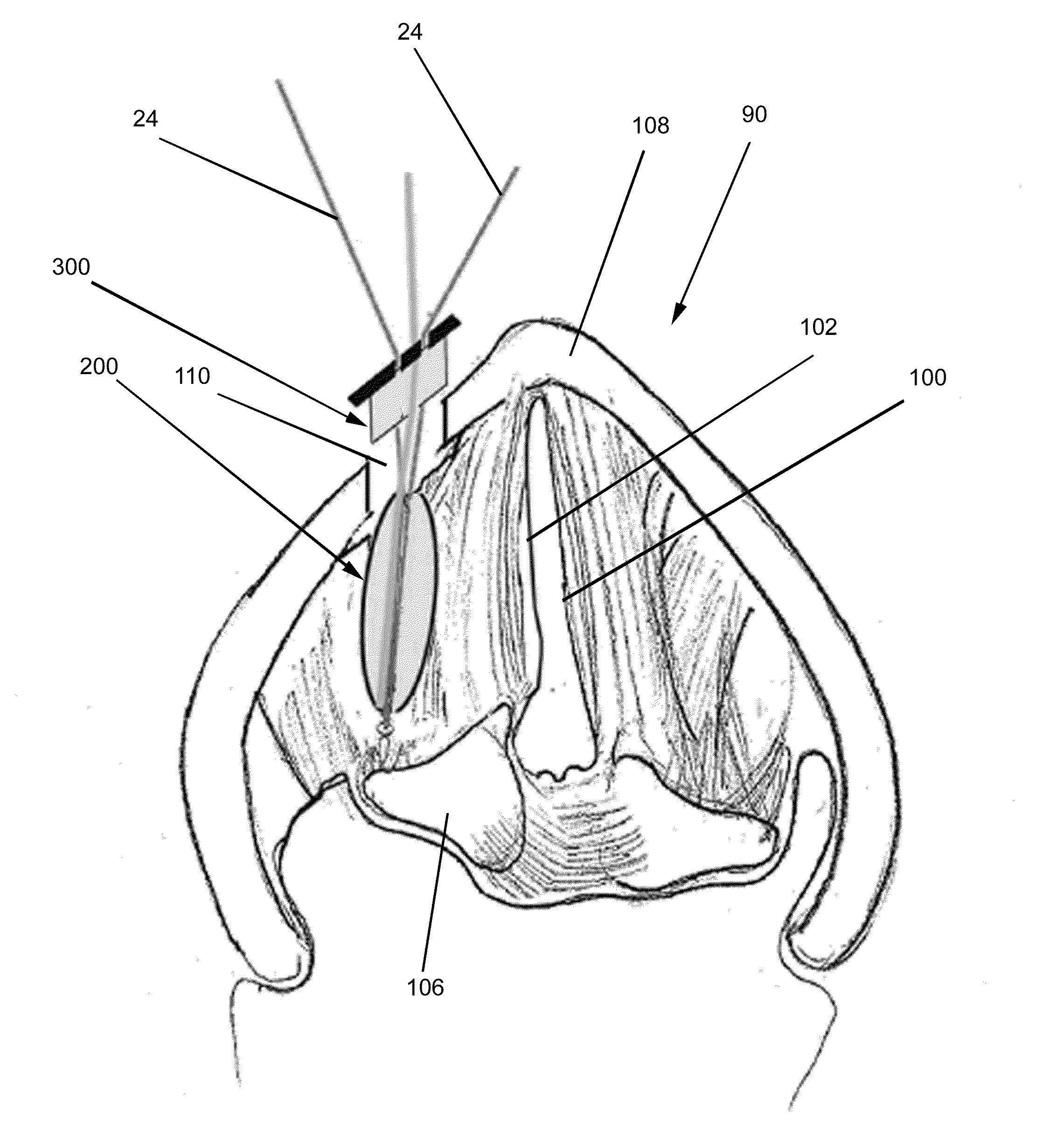
Devices and methods for anterior arytenoid adduction
Provided herein are devices and methods for anterior arytenoid adduction. The device may comprise a wire having a first end and a second end at opposite ends of a longitudinal axis, the wire forming a spiral along the longitudinal axis and having a double hook at the first end, a suture threaded through the spiral of the wire from the second end to the first end, the suture forming a turn at the first end and passing exterior to the spiral to the second end. The method may comprise advancing a suture and hook from the subject's anterior thyroid cartilage or cricothyroid membrane to the muscular process of the subject's arytenoid, attaching the hook to the muscular process, and applying tension to the suture to rotate the muscular process and adduct the arytenoid.
Owner:MCCULLOCH TIMOTHY M +1
System, Apparatus, and Method for Facilitating Interface with Laryngeal Structures
ActiveUS20080071245A1Simple structureReduce stepsHead electrodesCannulasEngineeringThyroid cartilage
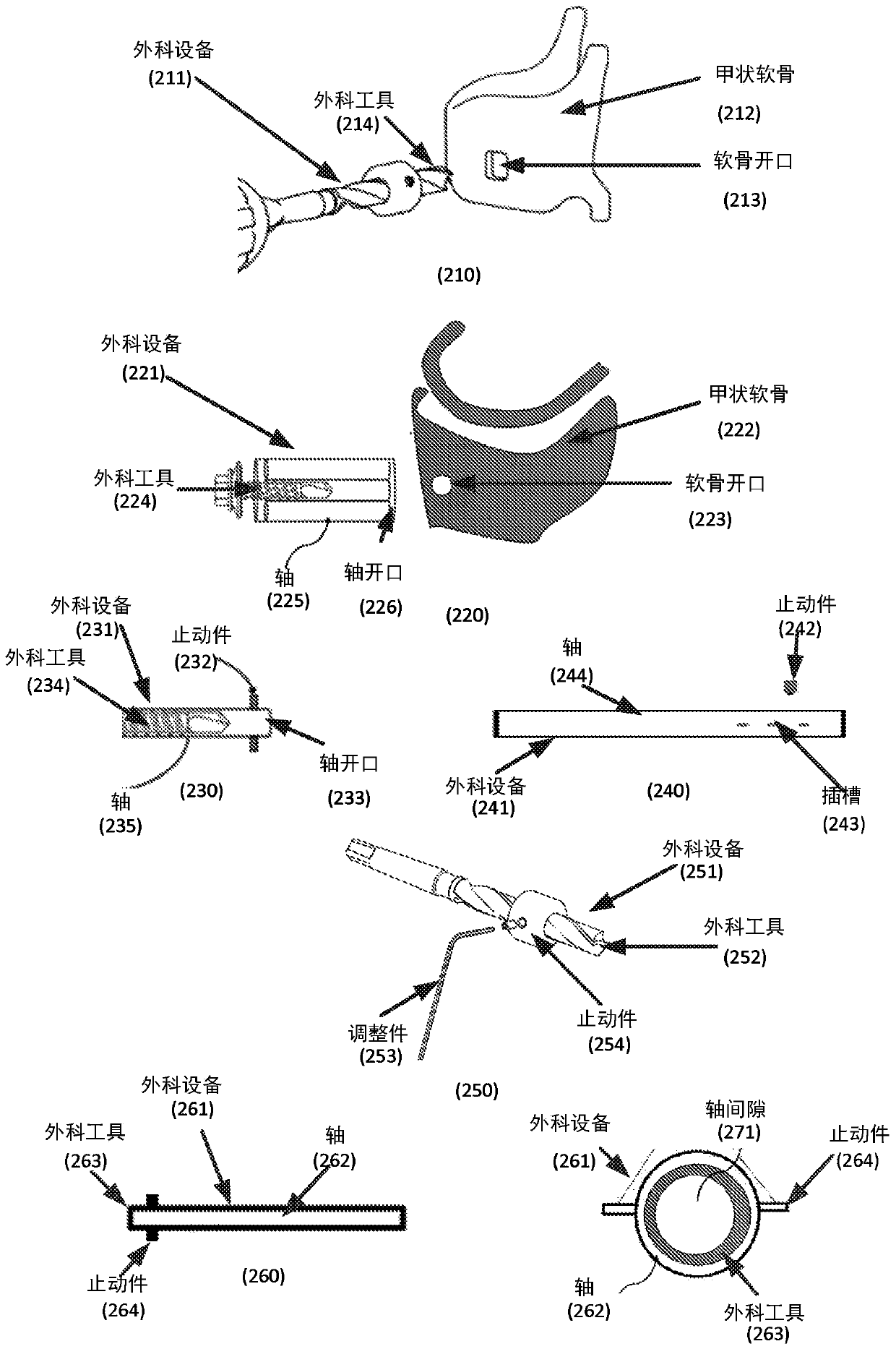
A system and method of introducing interface elements for interfacing with laryngeal structures of a subject is presented. Illustratively, a tunnel is generated in geographical relation to the lateral wing of the thyroid cartilage of the subject and at least one interface element is introduced via the tunnel for interfacing with at least one laryngeal structure of the subject.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Method for preparing individual porous thyroid cartilage support
ActiveCN103656760ASurgical needs to ensure personalized defect repairImprove adsorption capacitySpecial data processing applicationsProsthesisData acquisitionHydroxylapatite
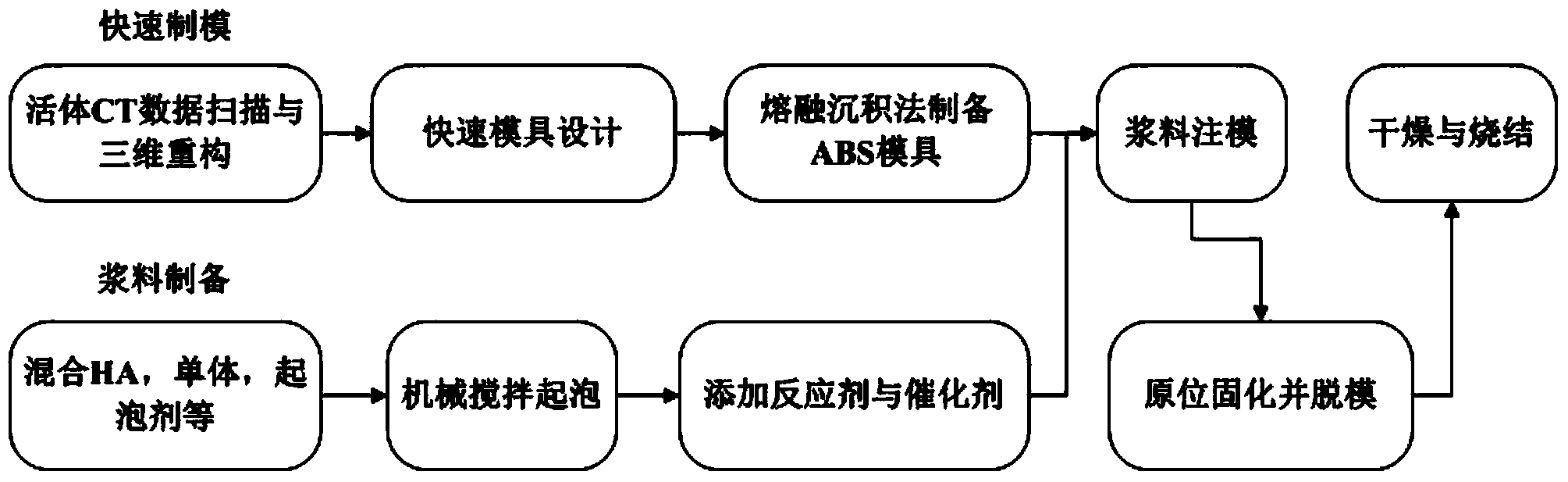
The invention discloses a method for preparing an individual porous thyroid cartilage support. The method comprises the following steps: performing data acquisition on a living body by using high-precision medical CT, partitioning a thyroid cartilage area by using a partitioning algorithm, and exporting the data in a text format; performing in-vitro isolated point removal, noise reduction, surface smoothing and reverse three-dimensional modeling on the acquired data in reverse engineering software; performing rapid mold design by using industrial CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software UG-NX, and preparing a rapid mold through rapid molding; preparing foam slurry which takes hydroxylapatite particles as a filling matrix by using a gel foaming method, injecting the slurry into the rapid mold, and initiating an in-situ curing reaction so as to finish preparation of a cartilage support blank; demolding and drying the support blank, and performing high-temperature sintering, thereby obtaining the individual porous thyroid cartilage support. After the support is implanted into the body of a patient, the surrounding cartilage metrocyte and growth factors can be effectively absorbed, a metabolism channel is provided for growth of the cartilage metrocyte, and the cartilage metrocyte grows into individual bones.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method and system for displacing hyoid bone
A system and method for moving a hyoid bone closer to thyroid cartilage in a patient. Systems and methods may comprise sutures, suture anchors, clips and grommets to move the hyoid bone closer to the thyroid cartilage.
Owner:OSA HLDG
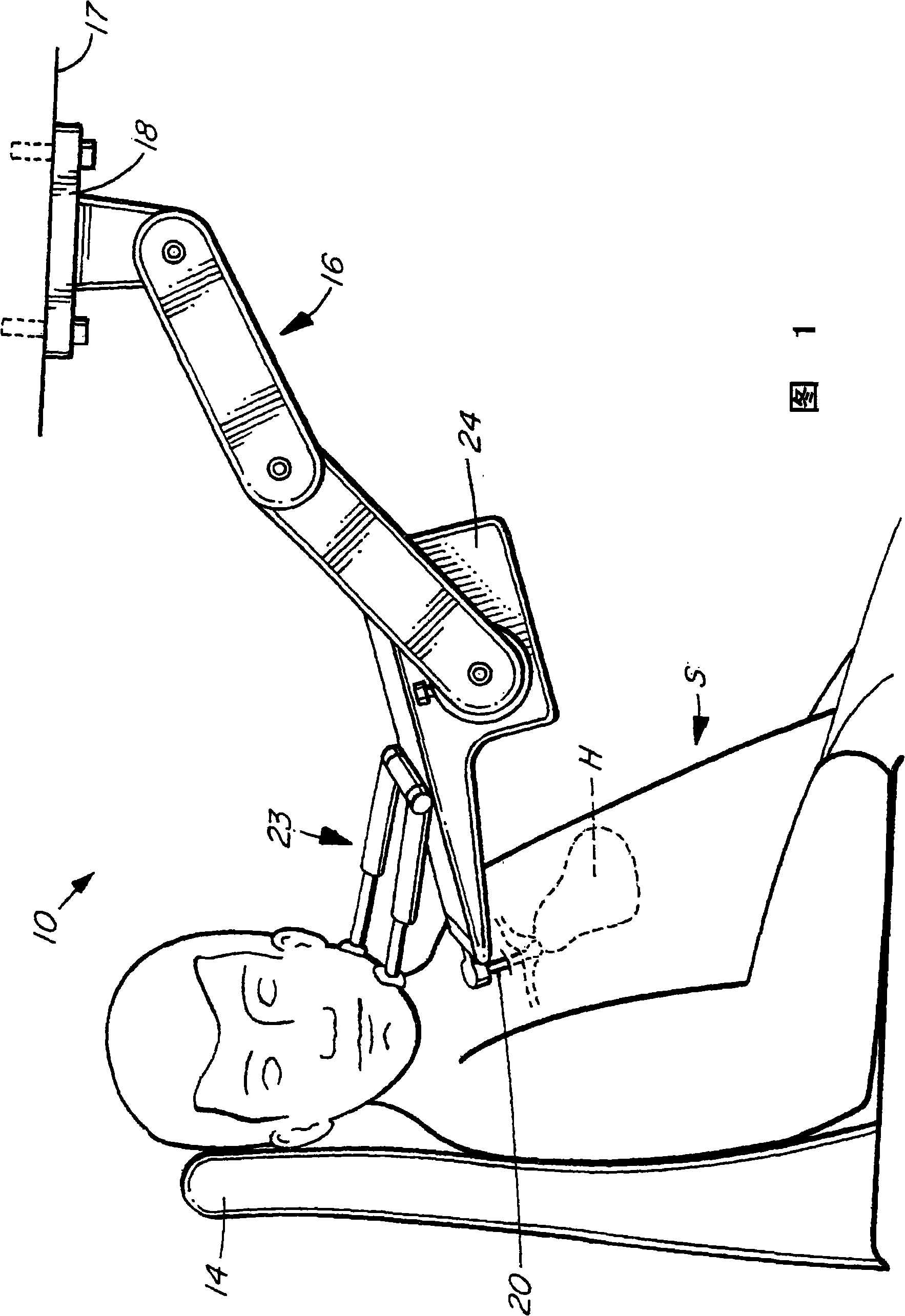
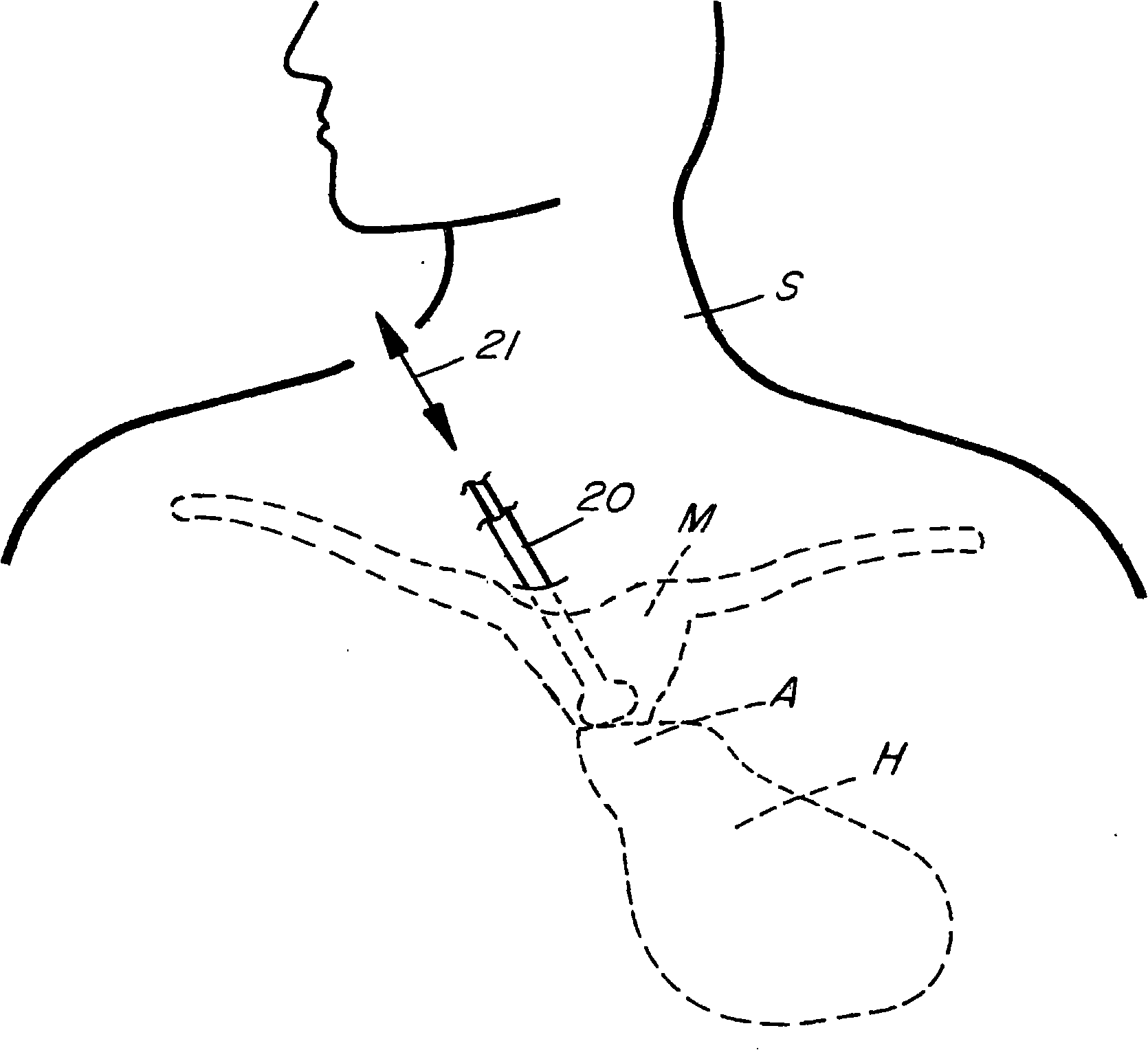
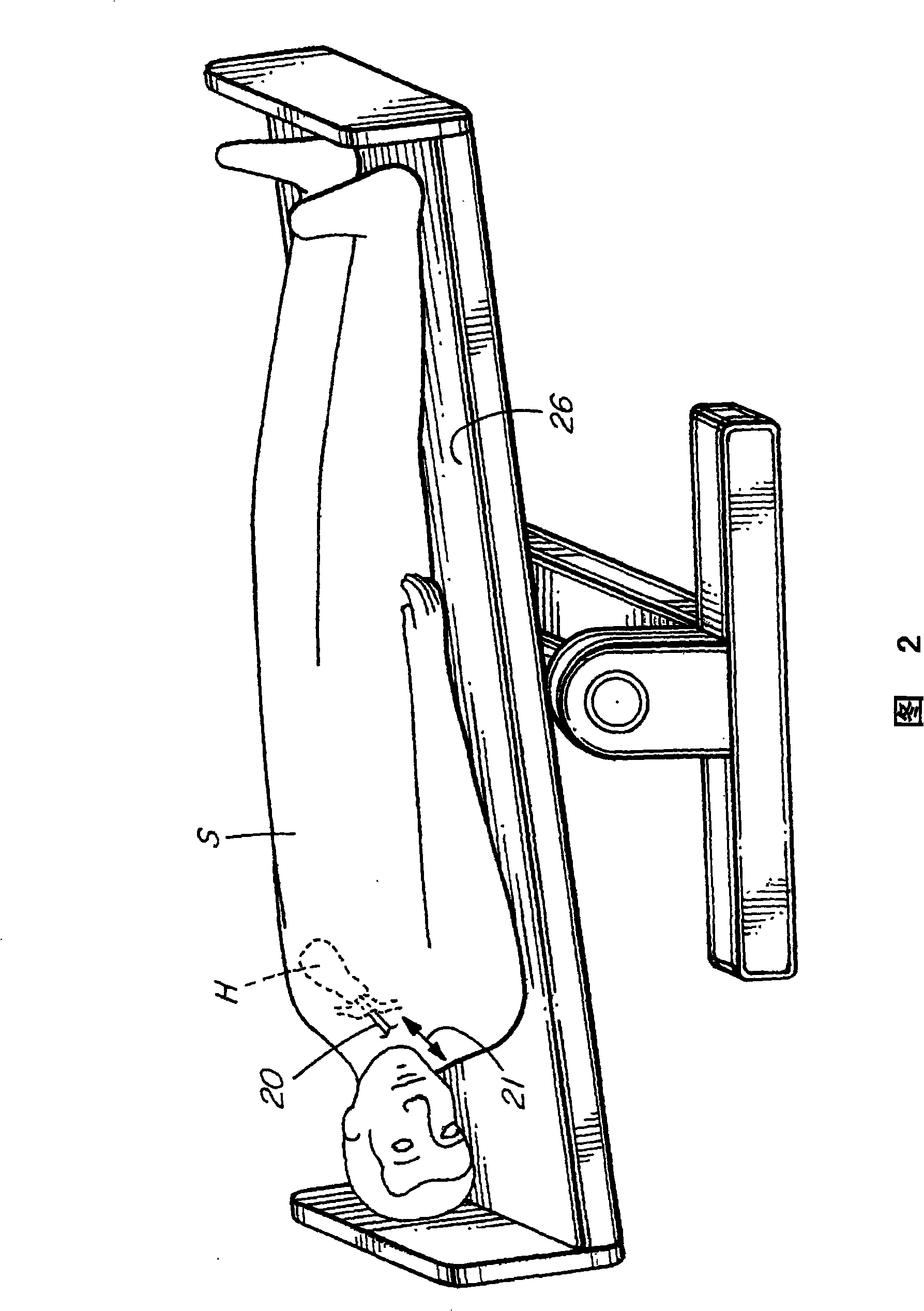
Methods and apparatus for monitoring heart impulses
Methods and apparatus for monitoring the heart motion of a subject employ a probe which can be coupled to a portion of the anatomy of the subject. The probe may couple to the subject's aortic arch or thyroid cartilage, for example. The probe is biased into contact with the subject. The probe detects movements caused by the heart motion. The apparatus may display accelerations and displacements caused by the heart motion. Waveforms from multiple anatomic sites may be acquired, normalized in time and amplitude, and combined to produce resultant waveforms. Combining the waveforms may involve addition or subtraction.
Owner:CANFORM MEDICAL
Methods of and apparatus for monitoring heart motions
InactiveUS20070043300A1Less of noise levelReduce quality control costsElectrocardiographyStethoscopeAudio power amplifierMedicine
A method of and an apparatus for monitoring the heart motion of a subject employ a probe which can be coupled to the aortic arch or to the thyroid cartilage of the subject for detecting movements caused by the heart motion and displaying the accelerations and displacement of the heart motion on an acceleration display and a displacement display. A mechanical motion amplifier amplifies the acceleration and an optical amplifier amplifies the displacement to counteract noise.
Owner:CANFORM MEDICAL
ECG (electroglottograph) measuring method and device for vocal cords
InactiveCN102824164AExclude external interferenceNon-invasiveDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBandpass filteringMeasurement device
The invention relates to ECG (electroglottograph) measuring method and device for vocal cords. The method includes the steps of firstly, coating the surface of an electrode plate to obtain a contact layer; secondly, tightly attaching the electrode plate to a vocal cord position on a neck; thirdly, fixing the electrode plate, allowing a testee to make voice, and outputting vocal cord signals from an audio output end after being processed by the electrode plate and the ECG measuring device. 2MHz signals are applied to thyroid cartilage to apply high frequency excitation to a throat so as to eliminate external interference from myoelectricity, a microphone and the like. The signals of the electrode are measured and are subjected to bandpass filtering, a detecting circuit and bandpass filtering to obtain corresponding impedance changes. Vocal cord vibration is reflected by contacting the electrode with throat and measuring electrical characteristic changes of a volume conductor at the throat. The modes of the vocal cord vibrations can be measured objectively, quantitatively and directly without invasion.
Owner:CHANGZHOU QIANJING REHABILITATION CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for treating glottis insufficiency
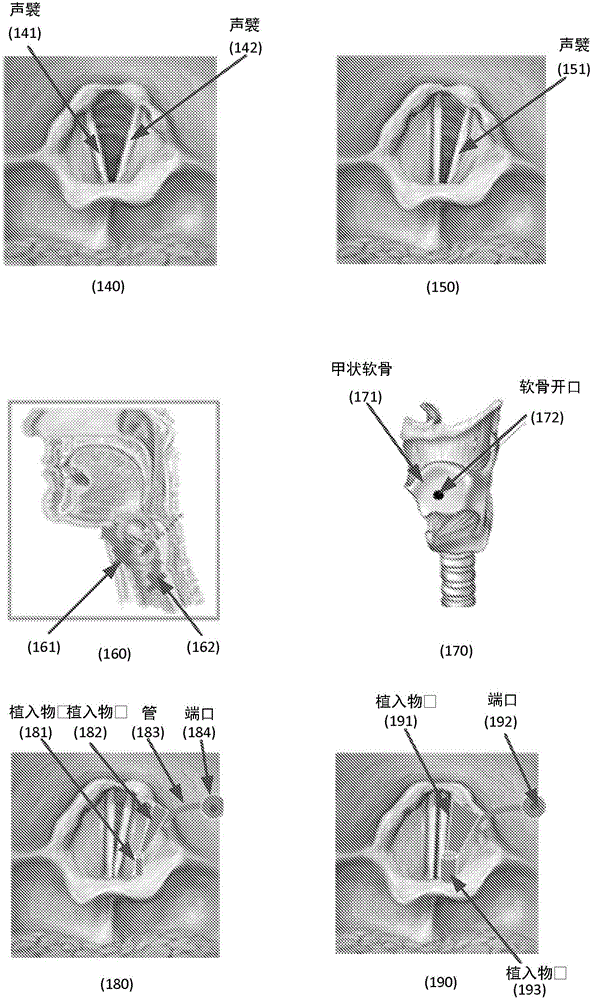
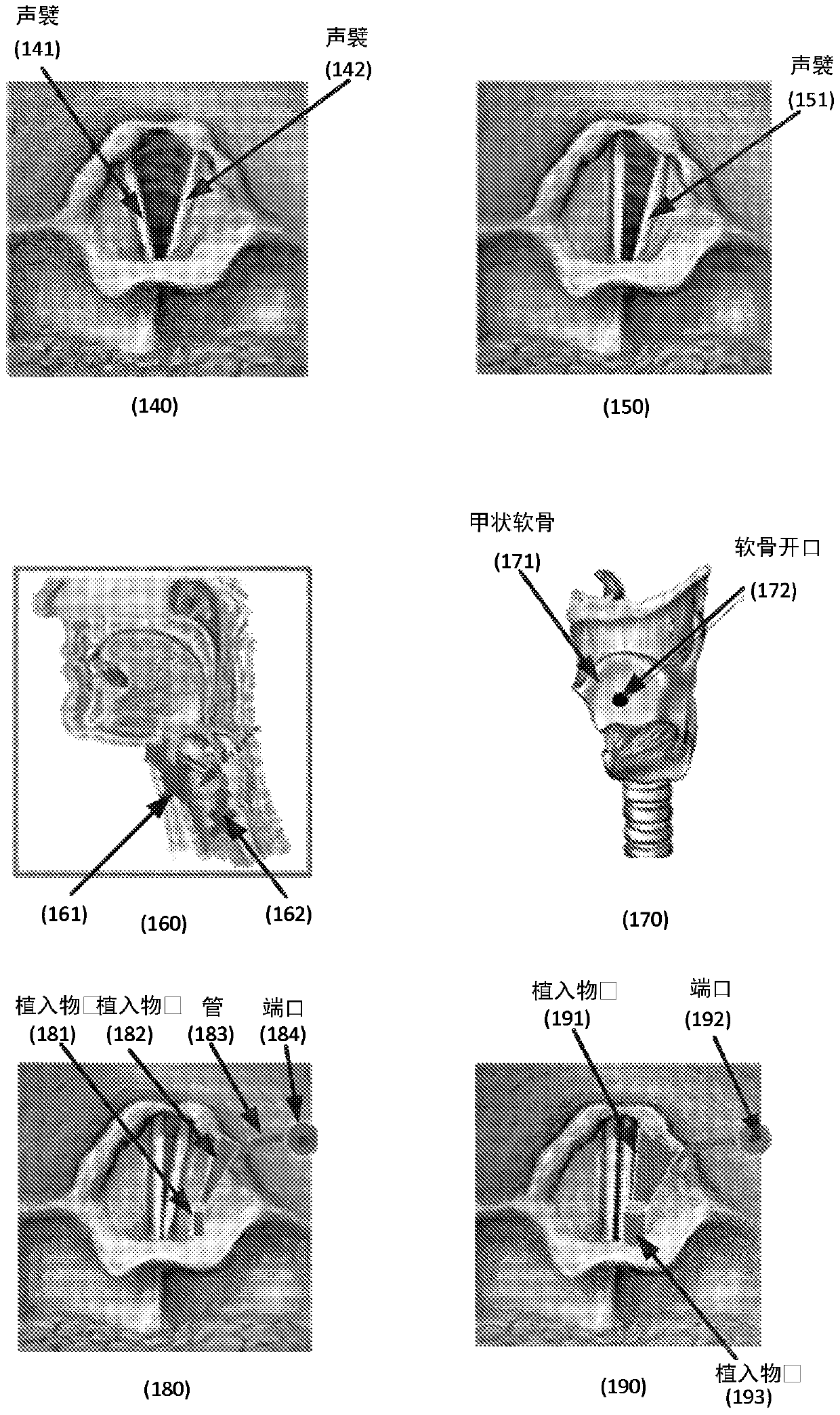
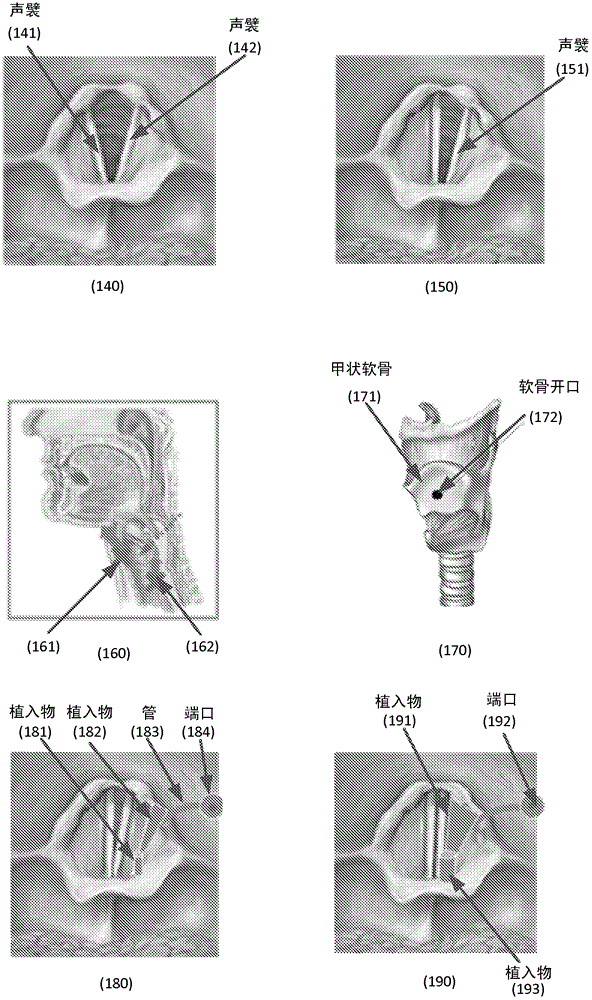
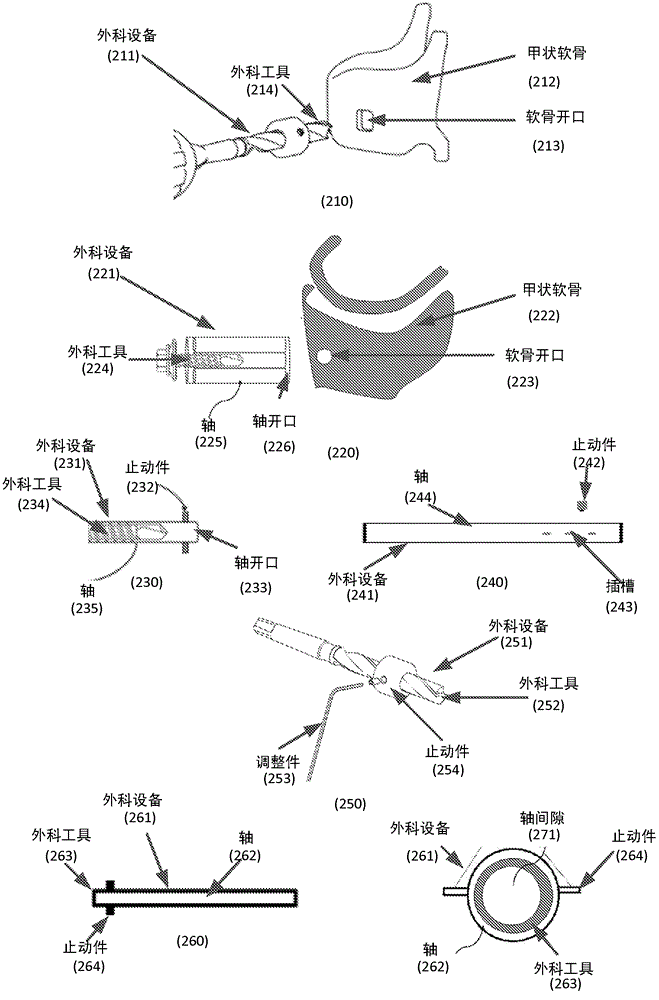
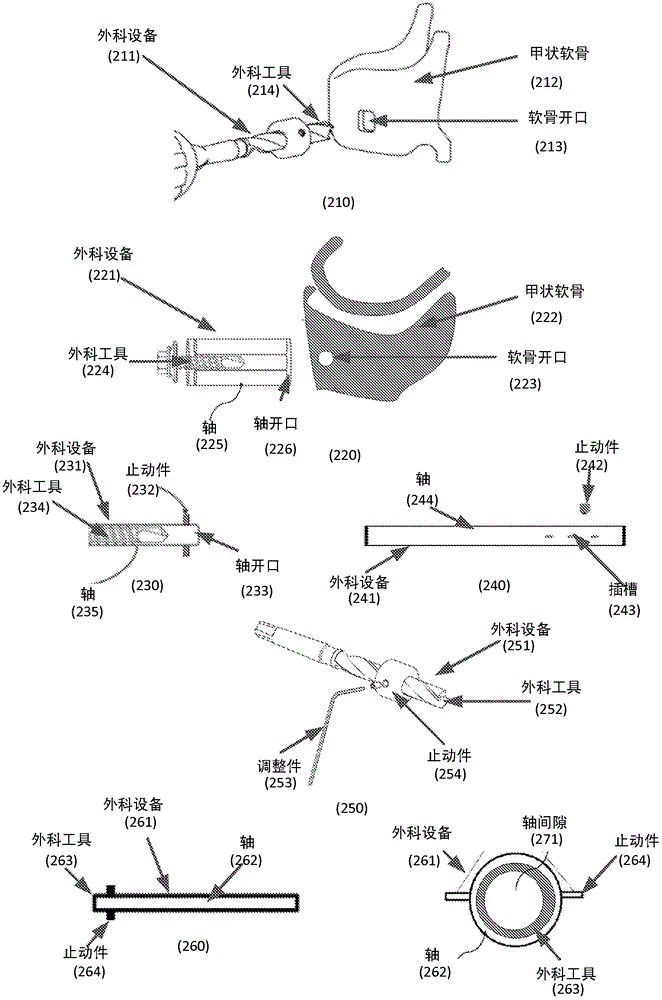
Methods and systems configured to treat a patient's glottic insufficiency are disclosed. An implant system may include a first implant positioned in the patient's paraglottic space. The first implant is adjustable in volume by changing amount of filler in the implant. The implant system may include a fixation device fixated on or through a cartilage opening in the patient's thyroid cartilage. The fixation device may contain a first channel. The implant system may include a first tube having a first end coupled with the first implant. The first tube passes through the first channel of the fixation device to deliver the filler to the implant. The implant system may further contain a port coupled with a second end of the first tube to regulate the amount of filler in the implant.
Owner:APREVENT MEDICAL +1
Simulator for practicing surgery or procedures involving the neck and airway and method of use thereof
The present disclosure provides a medical training simulation apparatus for training medical professionals, emergency medical support personnel, military personnel, parents or families of persons who have or will be undergoing neck or airway surgery, or any other persons requiring a simulator for learning the anatomy or practicing procedures or surgery of the neck and / or airway. The apparatus may include a simulated base that may be free standing or may rest on a mannequin and may have a hole for accessing the simulated airway, simulated skin, simulated fat, simulated lymph nodes, simulated neck musculature, simulated arteries and veins with simulated blood therein, simulated thyroid gland, simulated parathyroid glands, simulated laryngeal and tracheal cartilage including the hyoid bone, thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, tracheal rings, epiglottis and arytenoid cartilages, mucosa, recurrent laryngeal nerves, trachealis muscle, esophagus and prevertebral fascia. The apparatus may include alteration or addition of one or more anatomical parts to simulate congenital or acquired anomalies. One or more parts of the simulation apparatus may be disposable or replaceable.
Owner:AWESIM MEDICAL CORP
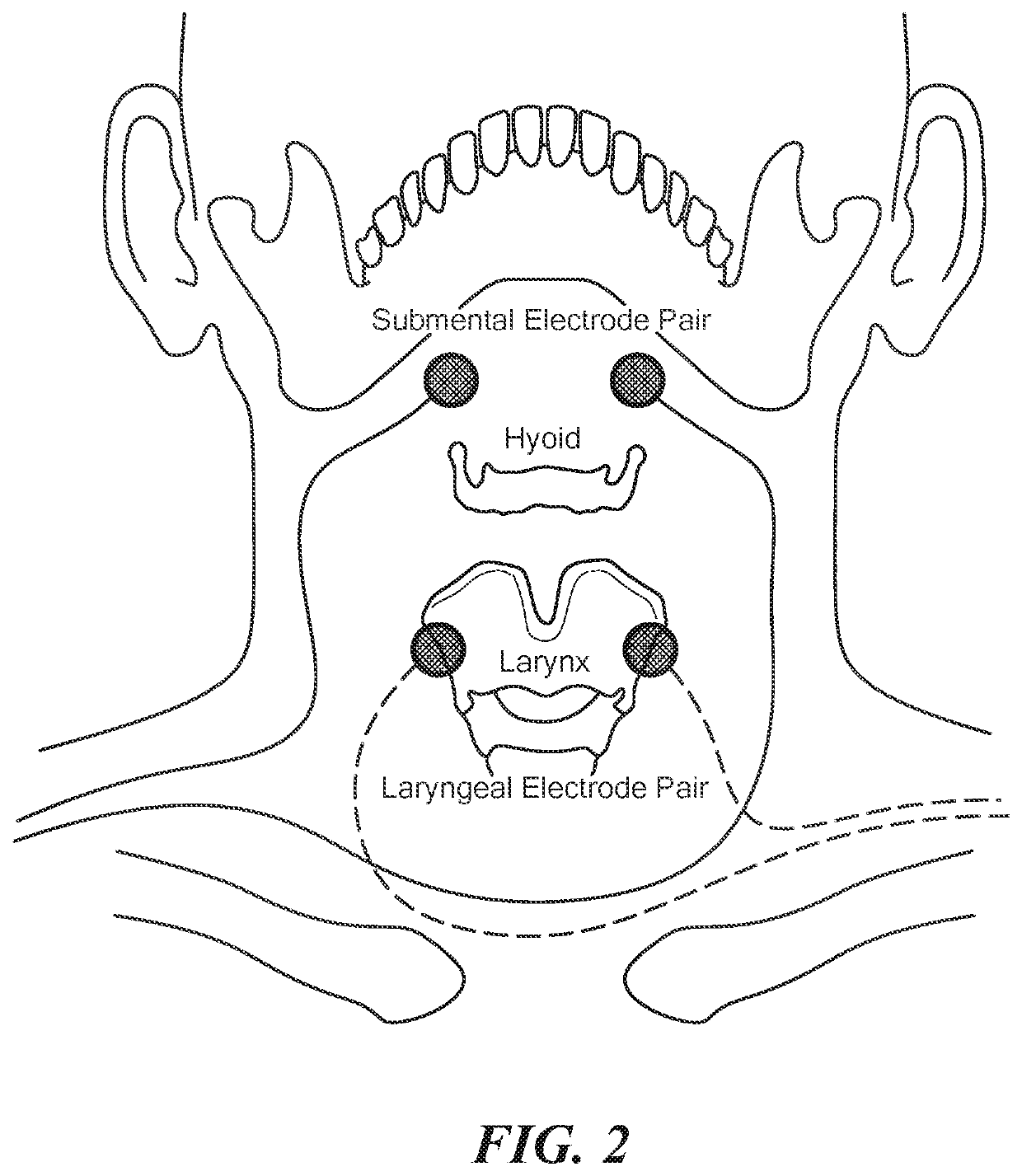
Eliciting Swallowing using Electrical Stimulation Applied via Surface Electrodes
PendingUS20220184379A1External electrodesEsophageal electrodesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationElectro stimulation
A system and method of eliciting a swallowing reflex in a human subject. Stimulation signals are generated for eliciting a full swallowing reflex when applied to skin overlying a region of thyroid cartilage in the neck. The stimulation signals delivered via surface electrodes to the skin overlying at least the region of thyroid cartilage in the neck to elicit the full swallowing reflex in the human subject.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Devices and methods for anterior arytenoid adduction
Provided herein are devices and methods for anterior arytenoid adduction. The device may comprise a wire having a first end and a second end at opposite ends of a longitudinal axis, the wire forming a spiral along the longitudinal axis and having a double hook at the first end, a suture threaded through the spiral of the wire from the second end to the first end, the suture forming a turn at the first end and passing exterior to the spiral to the second end. The method may comprise advancing a suture and hook from the subject's anterior thyroid cartilage or cricothyroid membrane to the muscular process of the subject's arytenoid, attaching the hook to the muscular process, and applying tension to the suture to rotate the muscular process and adduct the arytenoid.
Owner:MCCULLOCH TIMOTHY M +1
Method for Modifying Larynx Position by Trans-Positioning Muscle and Electrode Stimulation
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
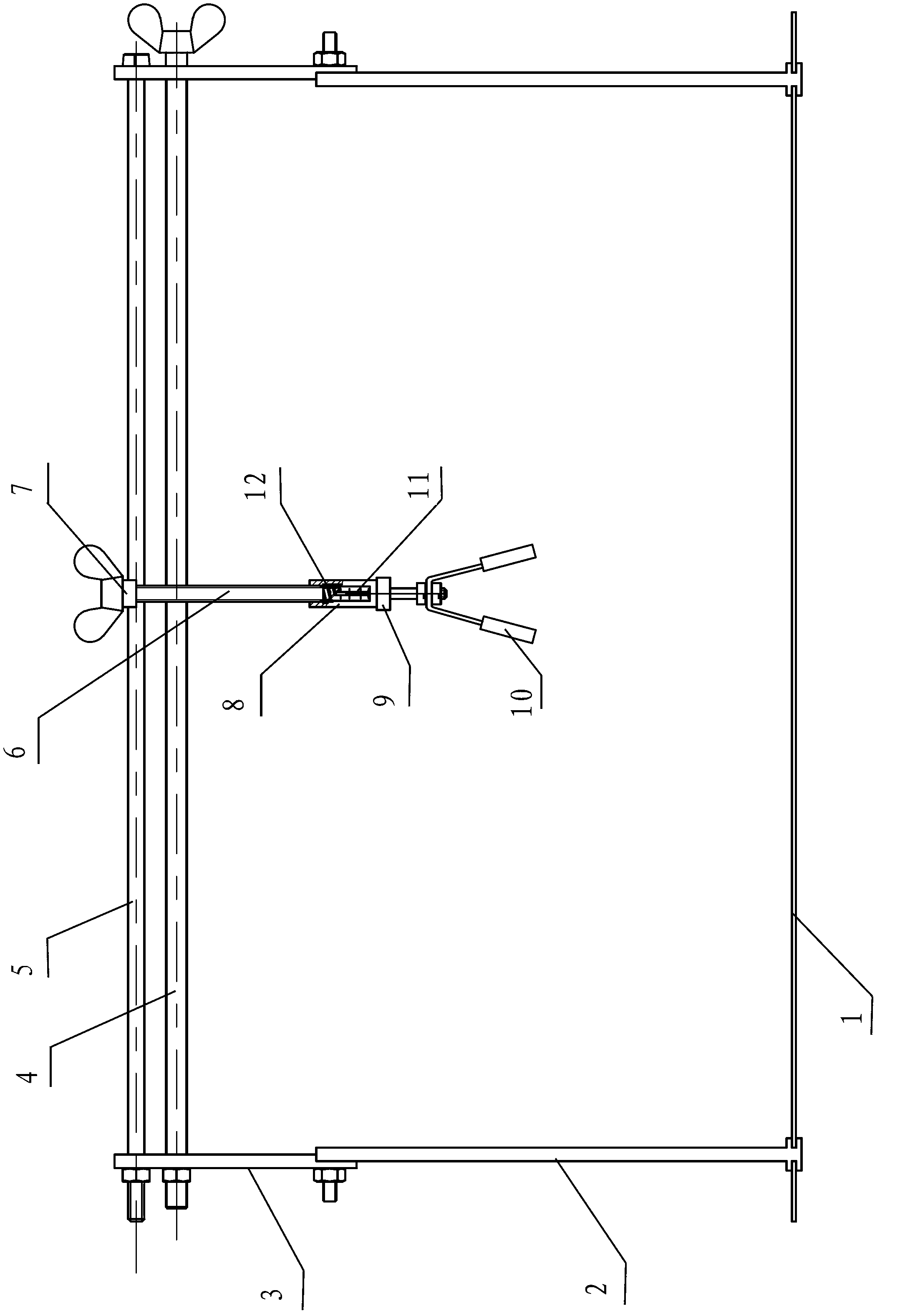
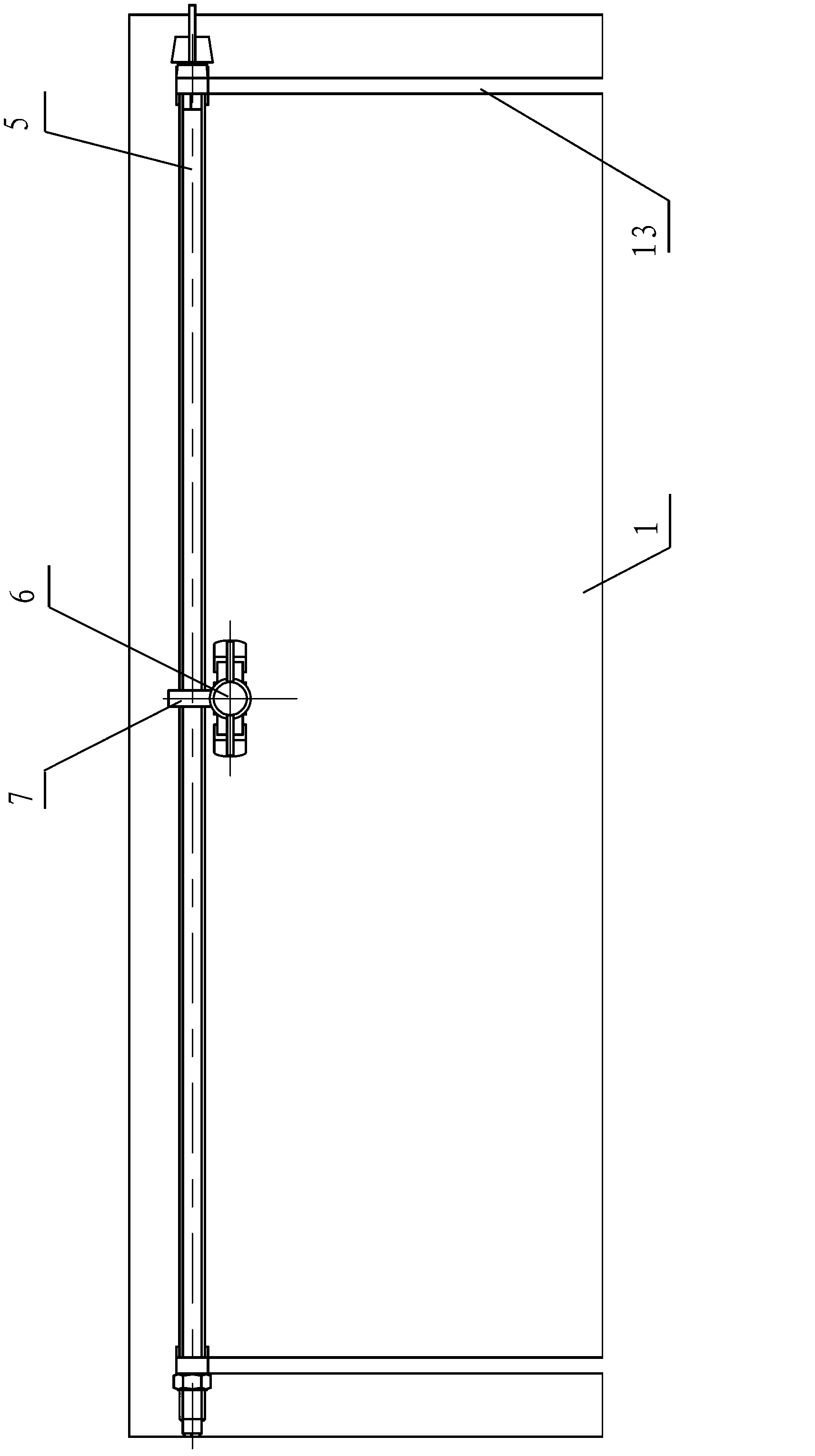
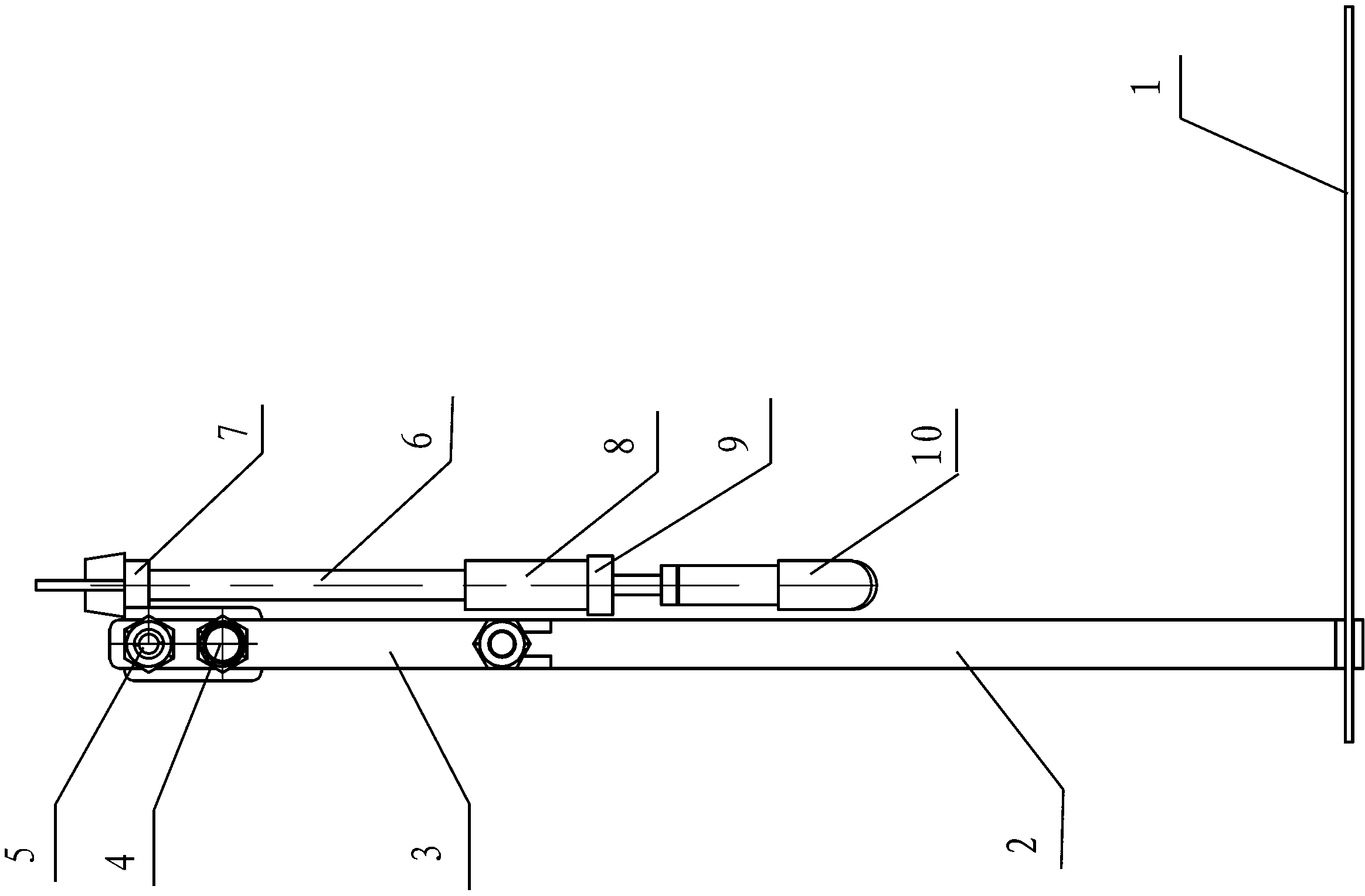
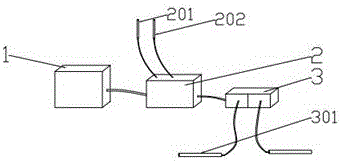
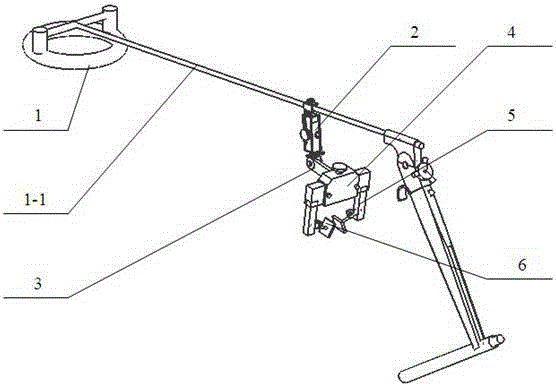
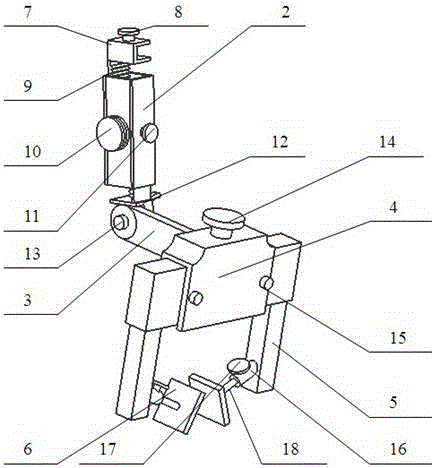
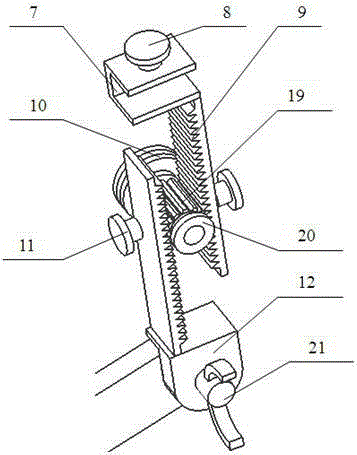
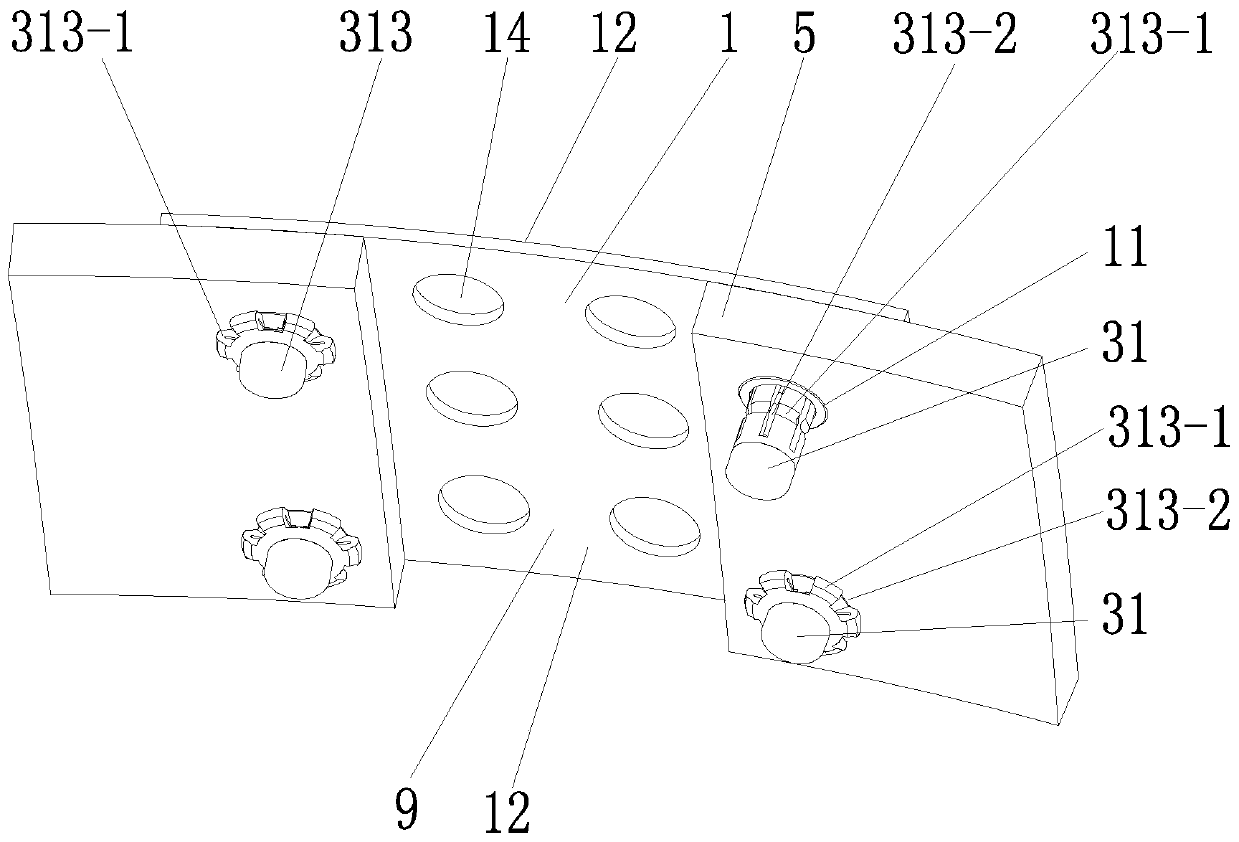
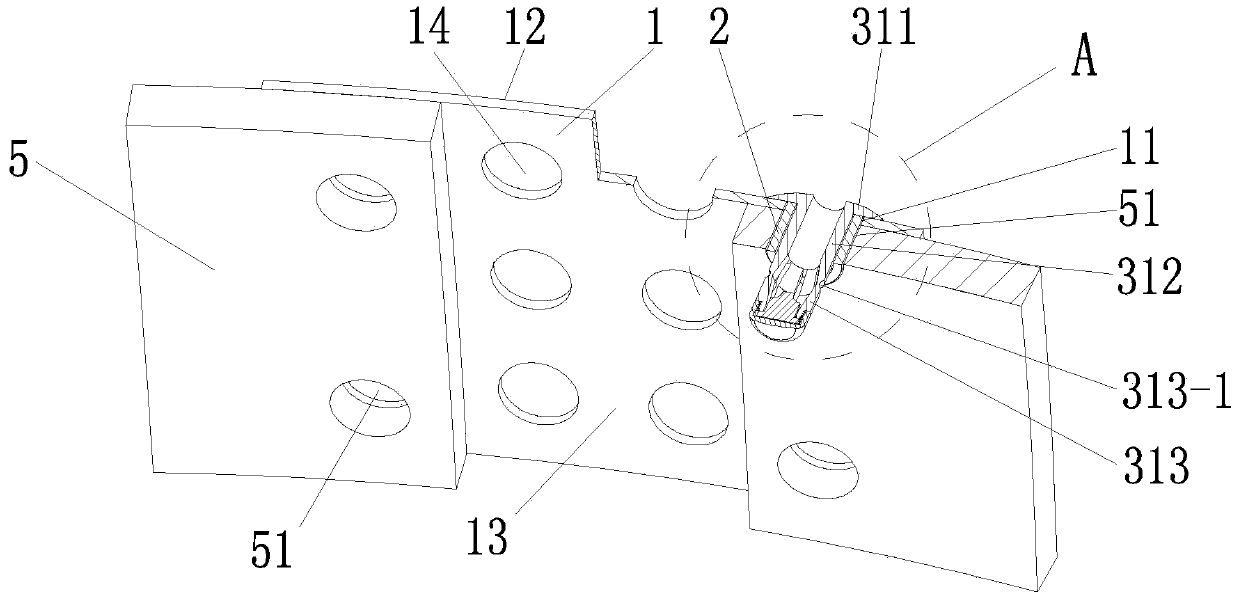
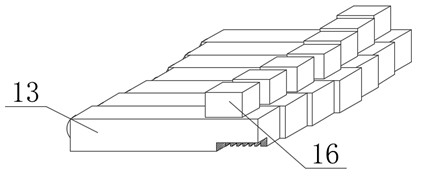
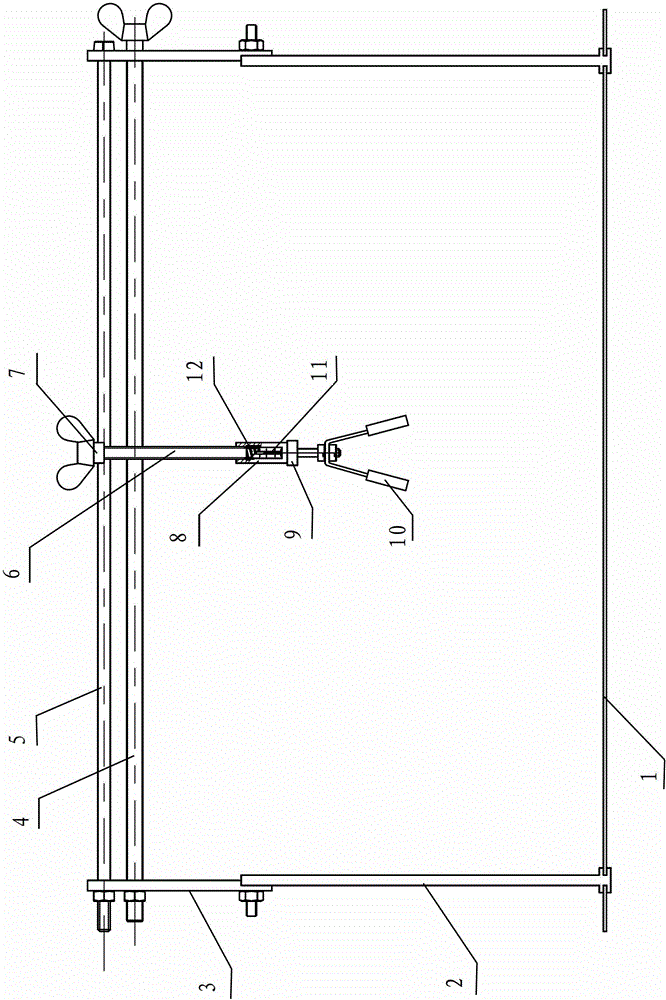
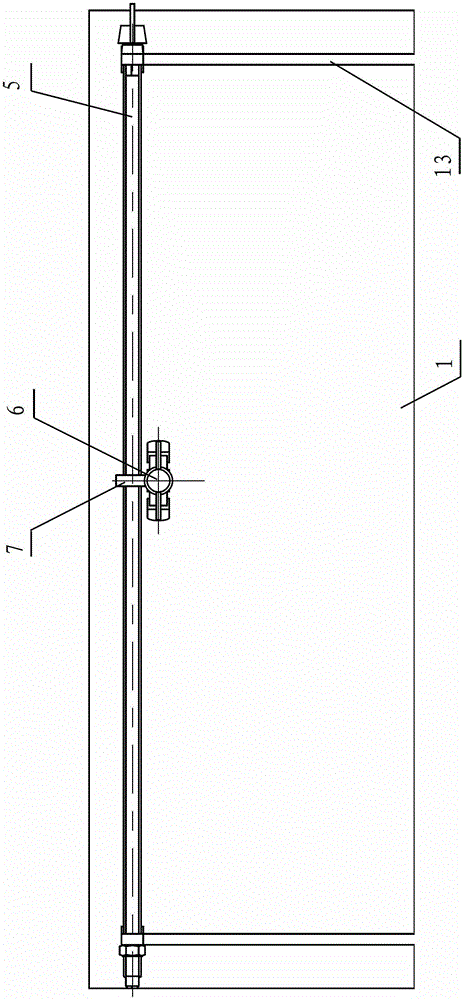
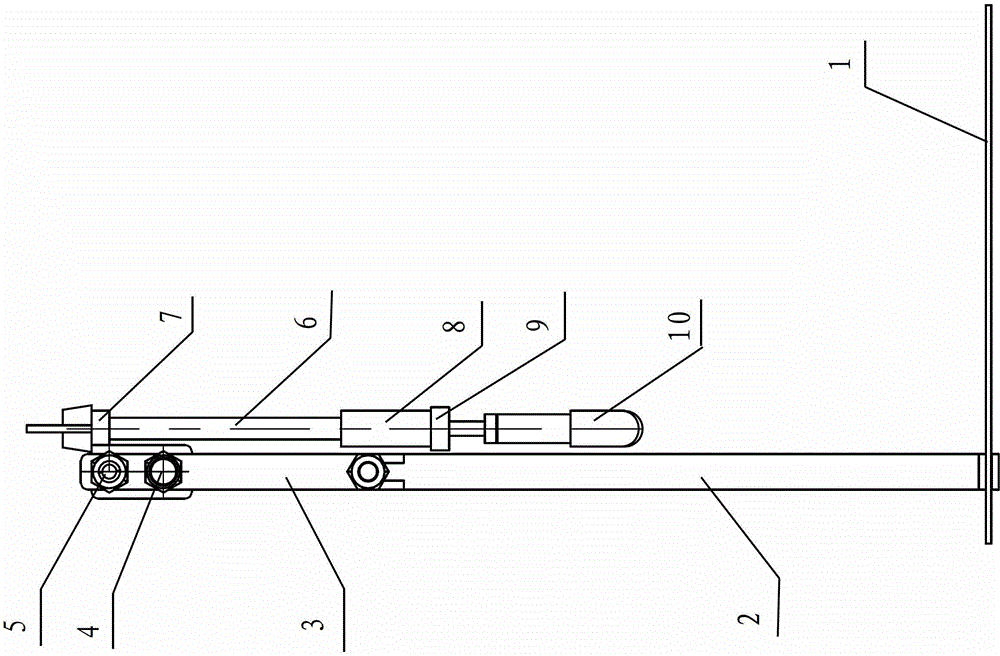
Thyroid cartilage fixing device for laryngeal operation
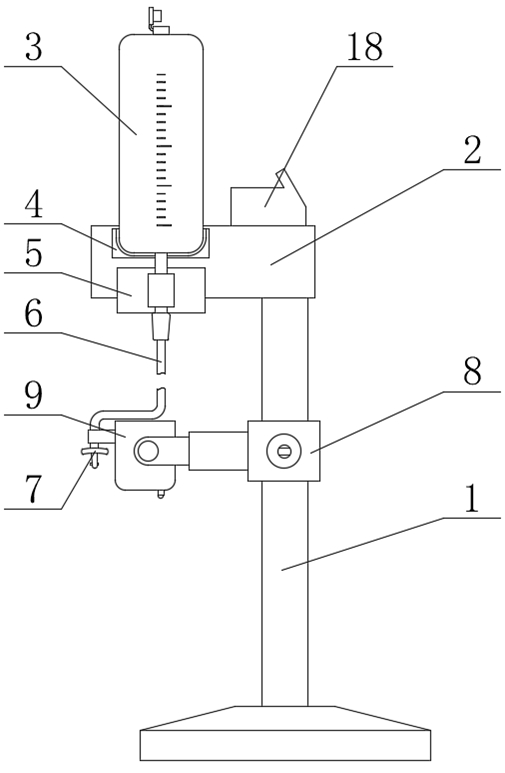
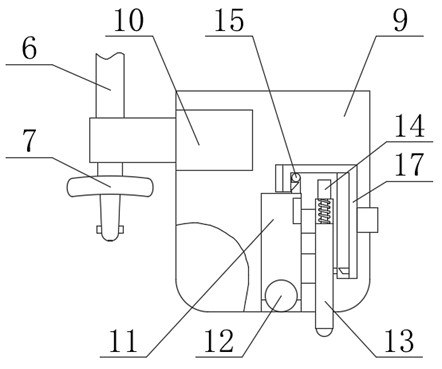
The invention provides a thyroid cartilage fixing device for a laryngeal operation. Lower columns capable of moving vertically are installed on a base plate, the upper ends of the two lower columns are connected with upper columns respectively, and the upper columns can be moved and fixed. A transverse adjusting screw and a guide polish rod which are parallel are arranged between the two upper columns, the transverse adjusting screw can rotate, a connection seat is arranged on the guide polish rod, and the transverse adjusting screw can be in threaded fit with a transverse screw hole of the connection seat. One end of a vertical adjusting screw is installed in a vertical screw hole of the connection seat, a pointer box capable of rotating is installed at the other end, a spring seat is installed in the pointer box, the upper end and the lower end of a pressure spring abut against the vertical adjusting screw and the spring seat respectively, and the spring seat is provided with a pointer and an elastic fixed clamping claw. The thyroid cartilage fixing device for the laryngeal operation is provided according to the actual requirement of the laryngeal operation and achieves the aims of saving operation assistants, ensuring operation effects, avoiding medical accidents, improving operation efficiency and reducing pains of patients.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Recurrent laryngeal nerve real-time monitor and monitoring method
PendingCN106510703ARealize real-time monitoringLower requirementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectricityRecurrent laryngeal nerve
The invention discloses a recurrent laryngeal nerve real-time monitor and a monitoring method. The monitor comprises a host, an interface box and a branch box, and is characterized in that the interface box comprises a positive electrode needle and a negative electrode needle, the branch box is electrically connected with a surgical instrument, the host is electrically connected to the branch box through the interface box, and the positive electrode needle and the negative electrode needle are connected to the interface box. The monitoring method includes the steps: first, inserting the positive electrode needle and the negative electrode needle to two sides of a thyroid cartilage notch respectively, and forming a loop between a vocal muscle and a recurrent laryngeal nerve; second, stimulating the recurrent laryngeal nerve by the surgical instrument with weak current. At the moment, the vocal muscle vibrates to form myoelectric signals, and the myoelectric signals are transmitted into the host through the interface box and analyzed to monitor the recurrent laryngeal nerve in real time. Real-time monitoring can be realized in a twilight anesthesia state, and a vocal cord cannot be injured while the nerve is monitored.
Owner:肖玉根
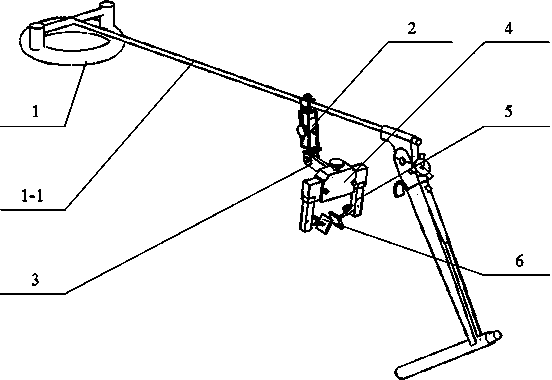
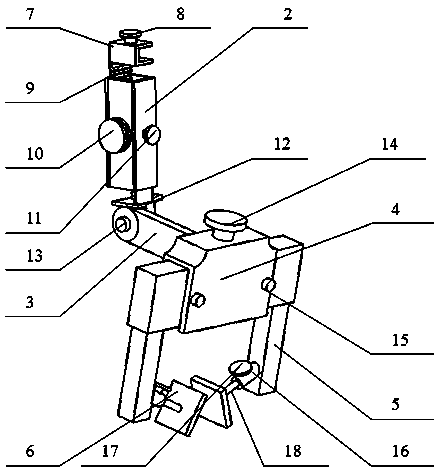
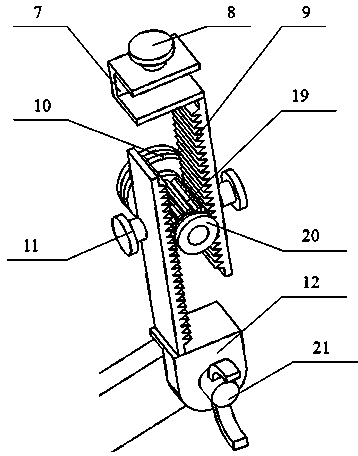
Adjustable type thyroid cartilage positioning device used for prop-up laryngoscope
ActiveCN104055580AEasy to operateAccurate operationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisHuman bodyDisease
The invention relates to an adjustable type thyroid cartilage positioning device used in a laryngeal operation and used for treating the laryngeal diseases of the human body. The adjustable type thyroid cartilage positioning device comprises a support adjusting device shell, a connecting rod, a thyroid cartilage positioning device body, a thyroid cartilage fixing support and a thyroid cartilage attachment plate. According to the adjustable type thyroid cartilage positioning device, the thyroid cartilage positioning device body is added to a traditional prop-up laryngoscope, and therefore the prop-up laryngoscope can be assisted in slightly adjusting the thyroid cartilage downwards or leftwards or rightwards within a certain range so that the thyroid cartilage can be well exposed, the assisting hand, for pressing the larynx, of the surgeon is liberated, and meanwhile operation view field shaking caused when the surgeon exerts uneven force by hand is avoided. By means of the adjustable type thyroid cartilage positioning device for the prop-up laryngoscope, the view field of the surgeon is made clear, the operation is fine, the curative effect is good, operation risks are less, injuries caused by the operation to a patient are less, and post-operation complications are less.
Owner:曹清
An adjustable thyroid cartilage positioning device for supporting laryngoscope
ActiveCN104055580BImprove corrosion resistanceHigh disinfection requirementsSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisInjury causeCurative effect
The invention relates to an adjustable type thyroid cartilage positioning device used in a laryngeal operation and used for treating the laryngeal diseases of the human body. The adjustable type thyroid cartilage positioning device comprises a support adjusting device shell, a connecting rod, a thyroid cartilage positioning device body, a thyroid cartilage fixing support and a thyroid cartilage attachment plate. According to the adjustable type thyroid cartilage positioning device, the thyroid cartilage positioning device body is added to a traditional prop-up laryngoscope, and therefore the prop-up laryngoscope can be assisted in slightly adjusting the thyroid cartilage downwards or leftwards or rightwards within a certain range so that the thyroid cartilage can be well exposed, the assisting hand, for pressing the larynx, of the surgeon is liberated, and meanwhile operation view field shaking caused when the surgeon exerts uneven force by hand is avoided. By means of the adjustable type thyroid cartilage positioning device for the prop-up laryngoscope, the view field of the surgeon is made clear, the operation is fine, the curative effect is good, operation risks are less, injuries caused by the operation to a patient are less, and post-operation complications are less.
Owner:曹清
Novel laryngeal cavity puncture and intracavity suture guide
PendingCN108888306AReduced puncture injuriesReduce re-adhesion rateSuture equipmentsThroatSuturing guide
The invention relates to a novel laryngeal cavity puncture and intracavity suture guide, comprising an outer sleeve and a core. After the core and the outer sleeve are assembled, the distal end of thecore is extended out of the distal end of the outer sleeve, and the distal end of the core is provided with a barb structure. The novel laryngeal puncture and intracavity suture guide has the advantages that after a puncture needle is passed into the laryngeal cavity, the core is removed, and the special core with barb structure is inserted in; the barb structure hooks and fastens a suture in thelaryngeal cavity; a trocar is removed to guide the suture out of the throat (neck) from the laryngeal cavity; compared with the Lichtenberger laryngendoscopic suturing device, the novel puncture needle herein can accurately puncture positioned parts at upper and lower edges of the thyroid cartilage in the midline part of the neck; puncture damage to the throat tissue is effectively reduced; operating is convenient, postoperative re-adhesion rate of the vocal cord is lower, and living quality is improved for a patient.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
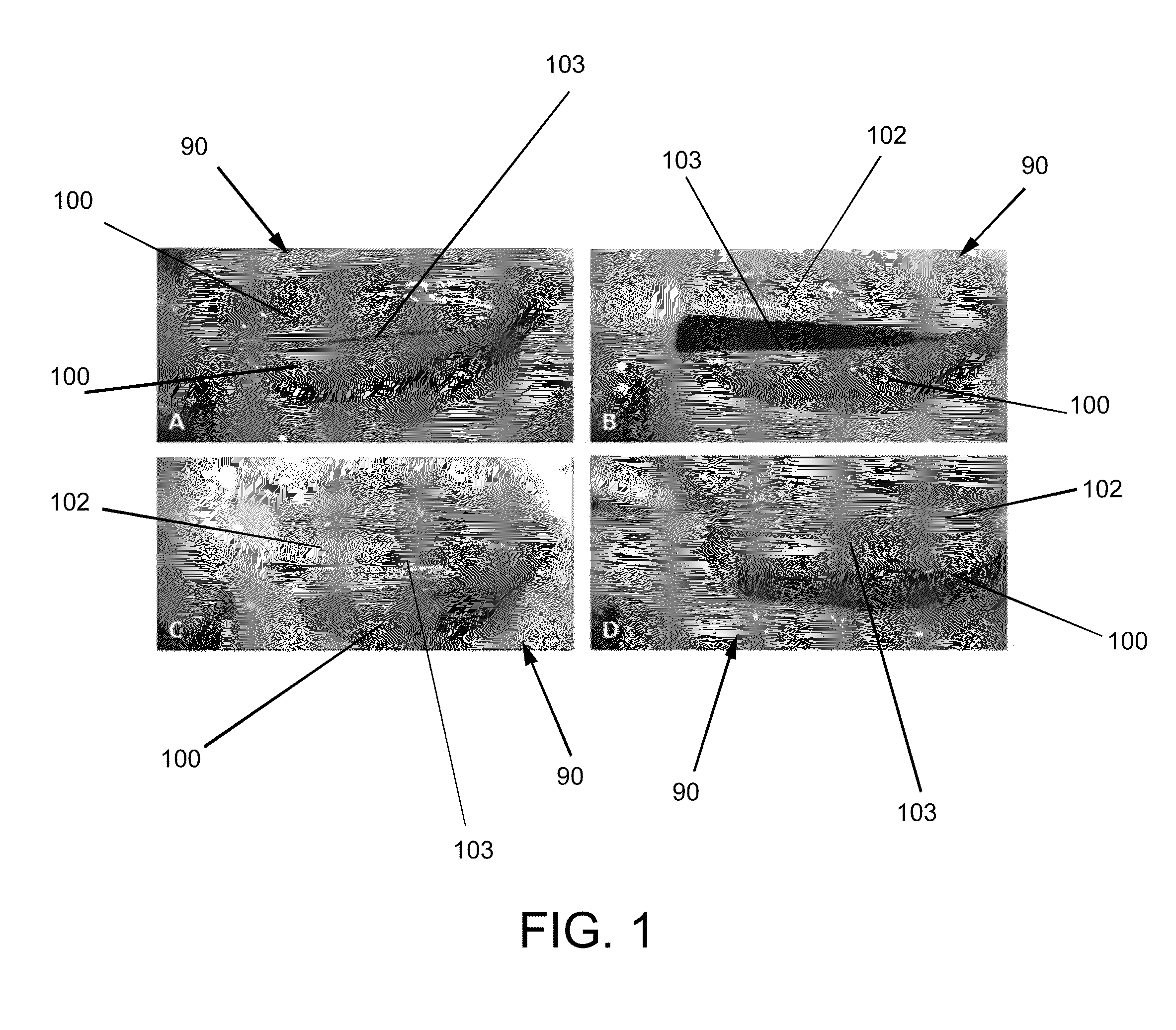
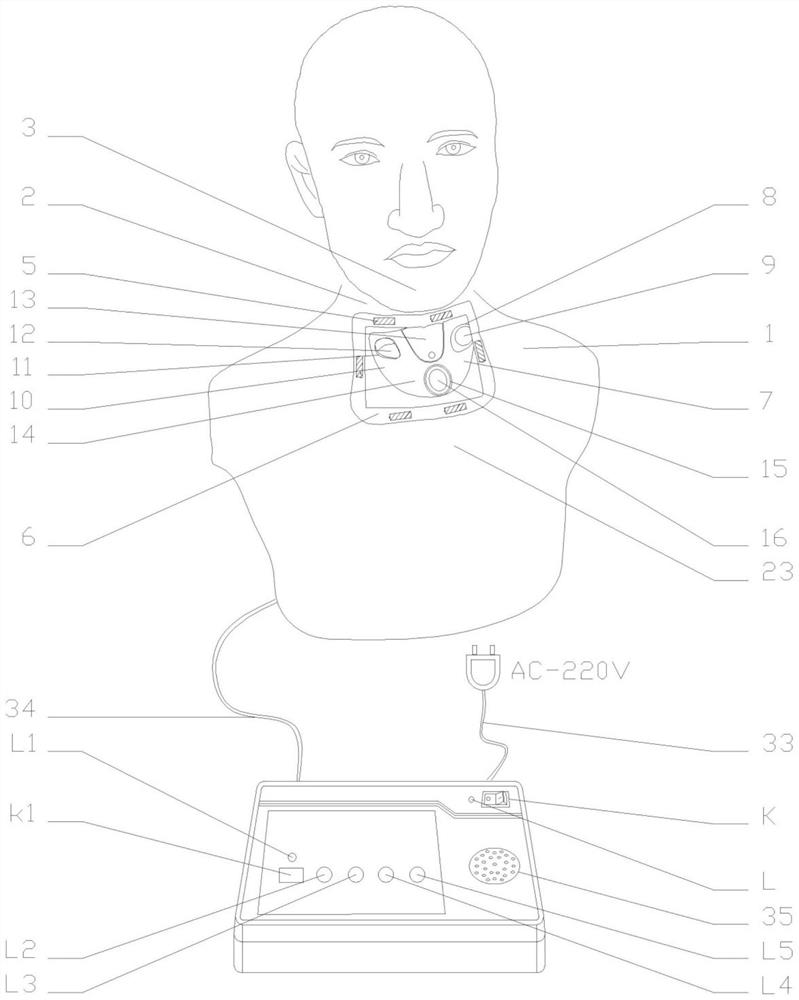
Swallowing analyzing system
PendingUS20200037947A1Reduce power consumptionReduce consumptionStrain gaugeStethoscopeEngineeringAnalog signal
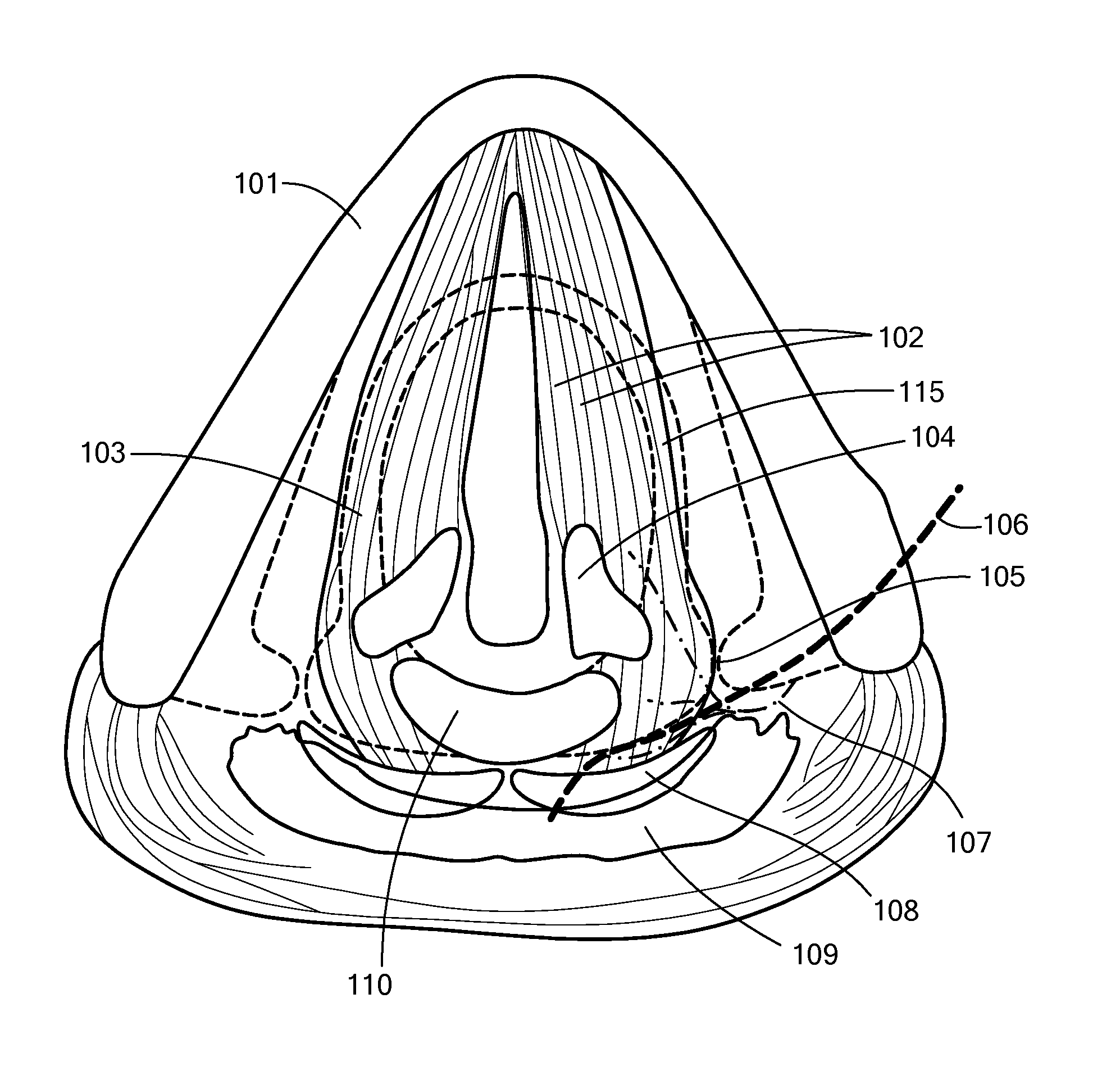
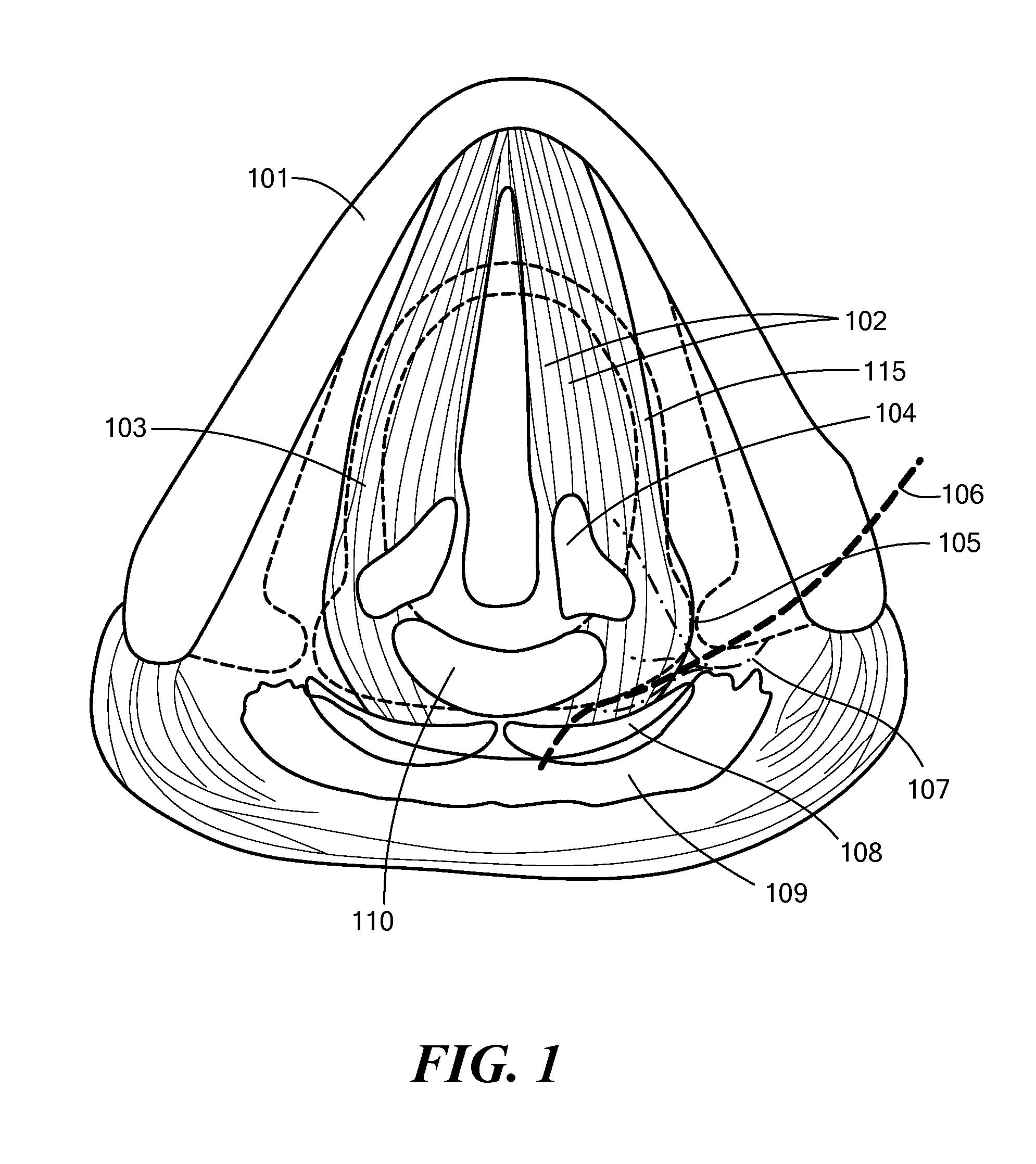
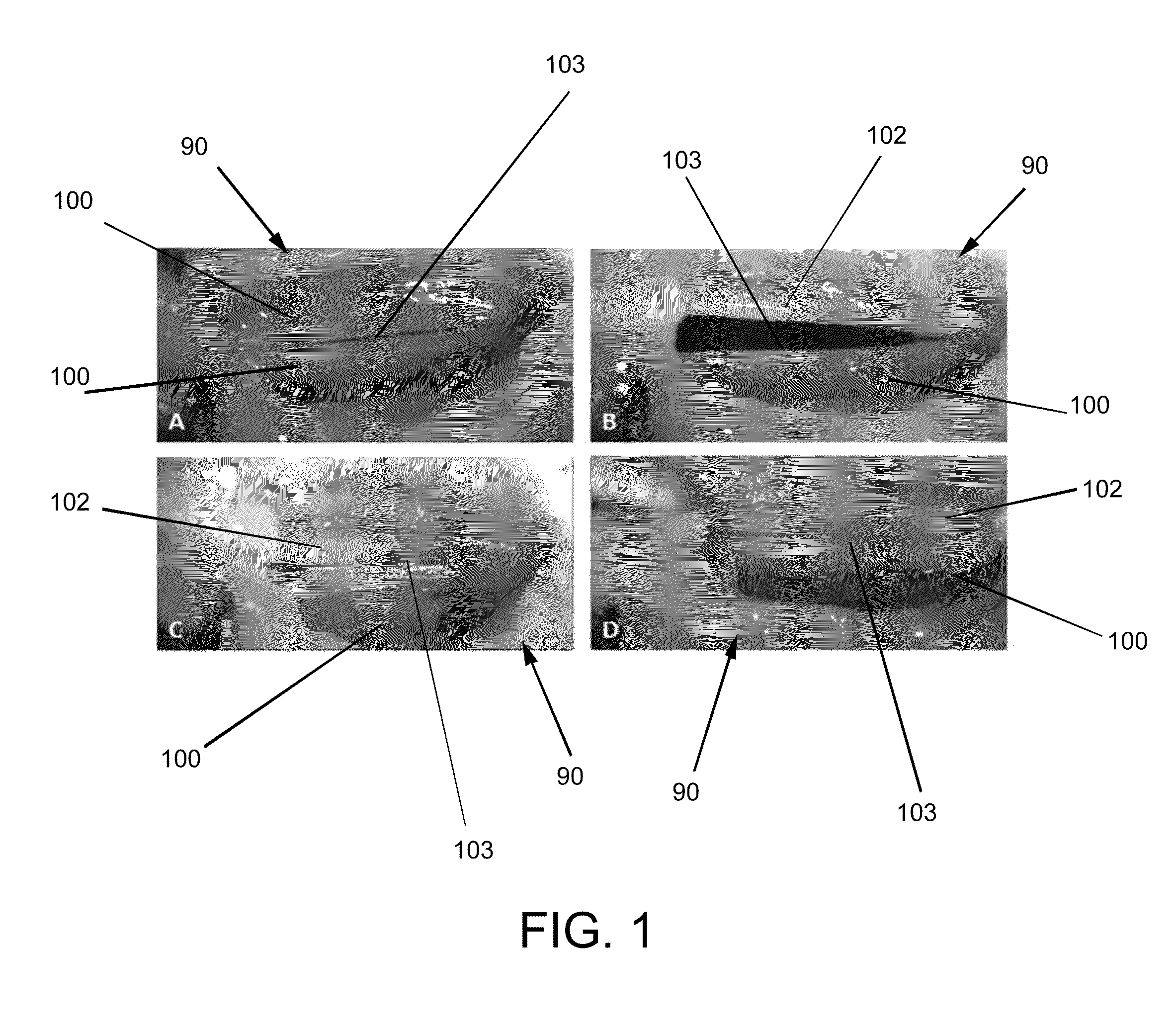
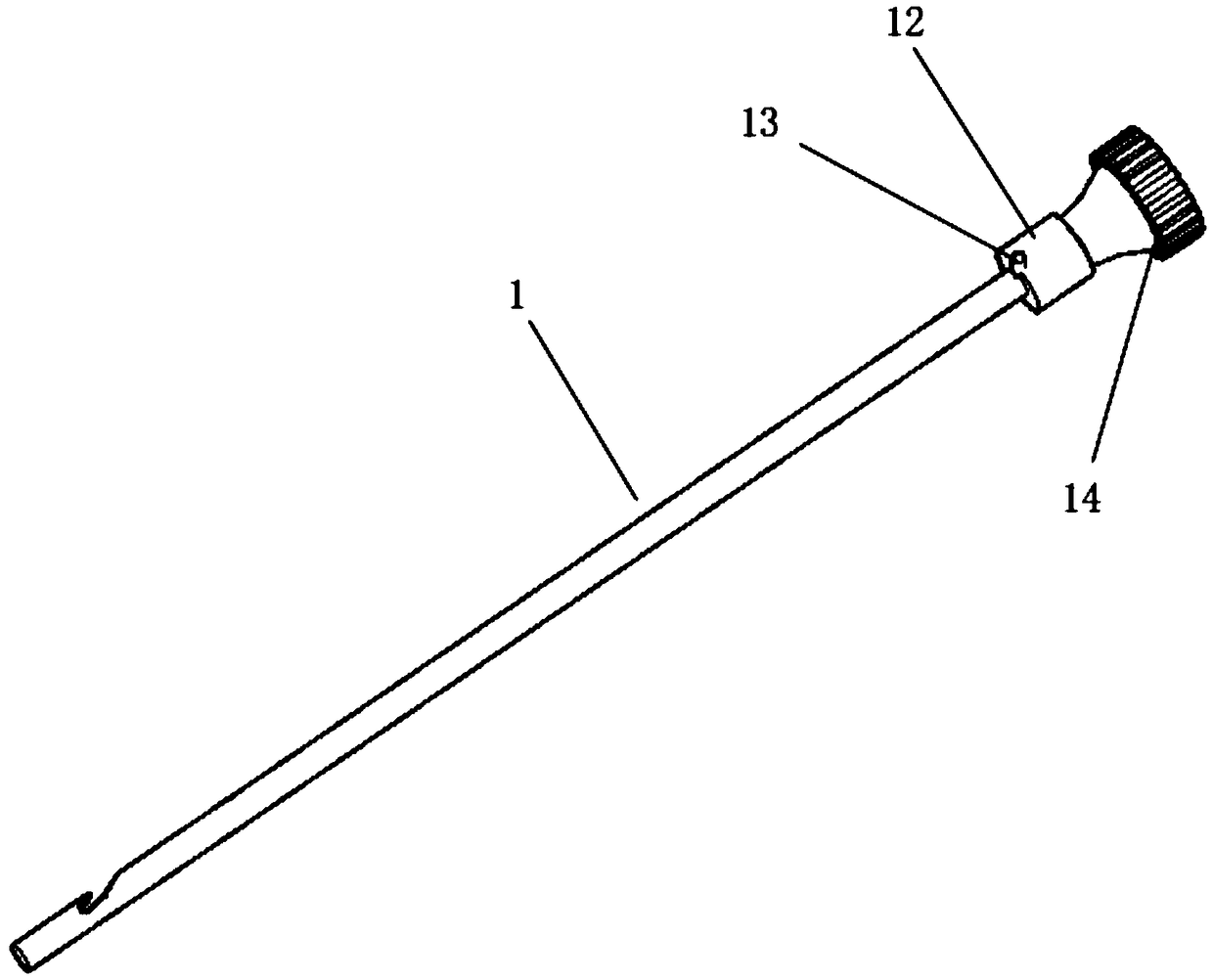
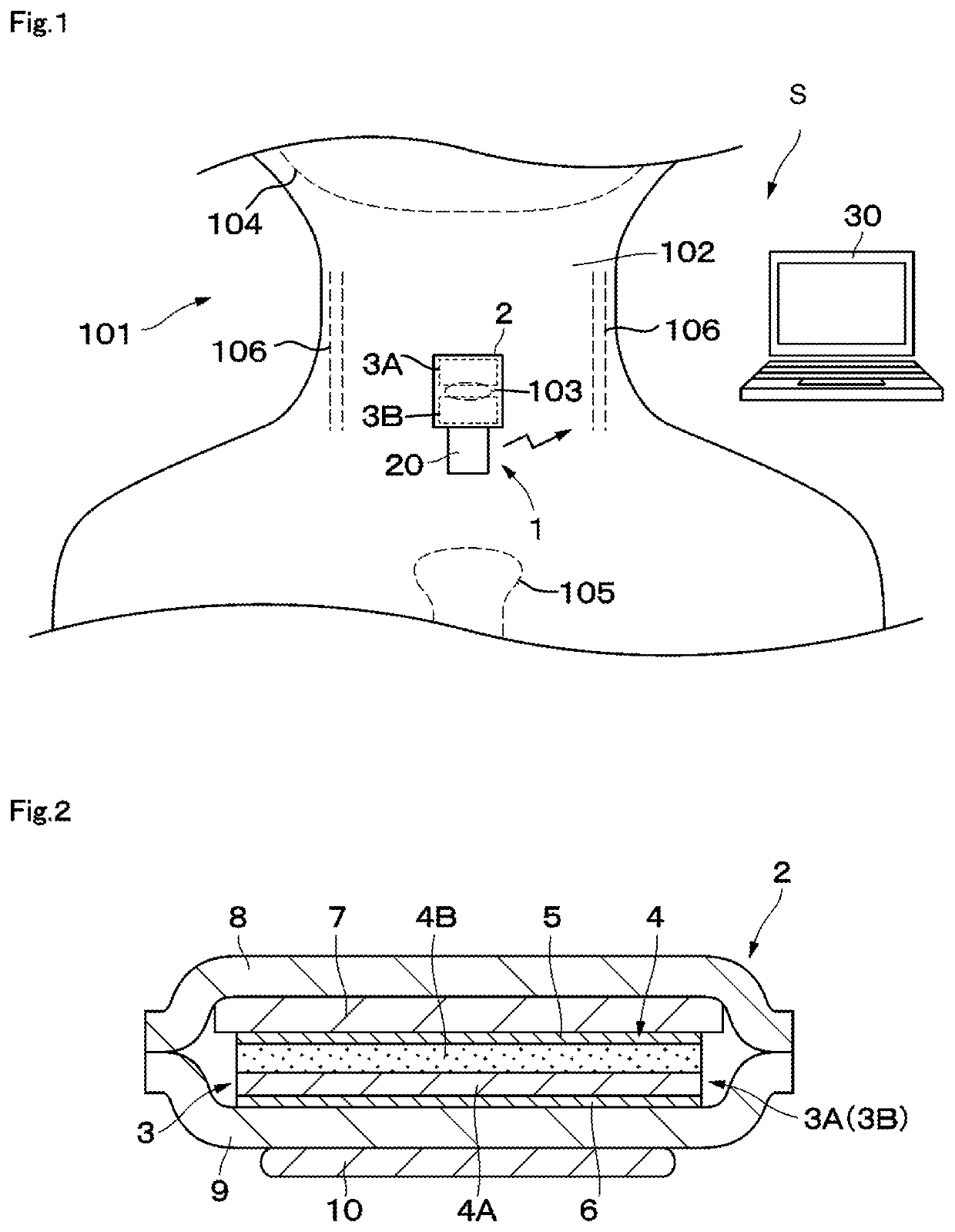
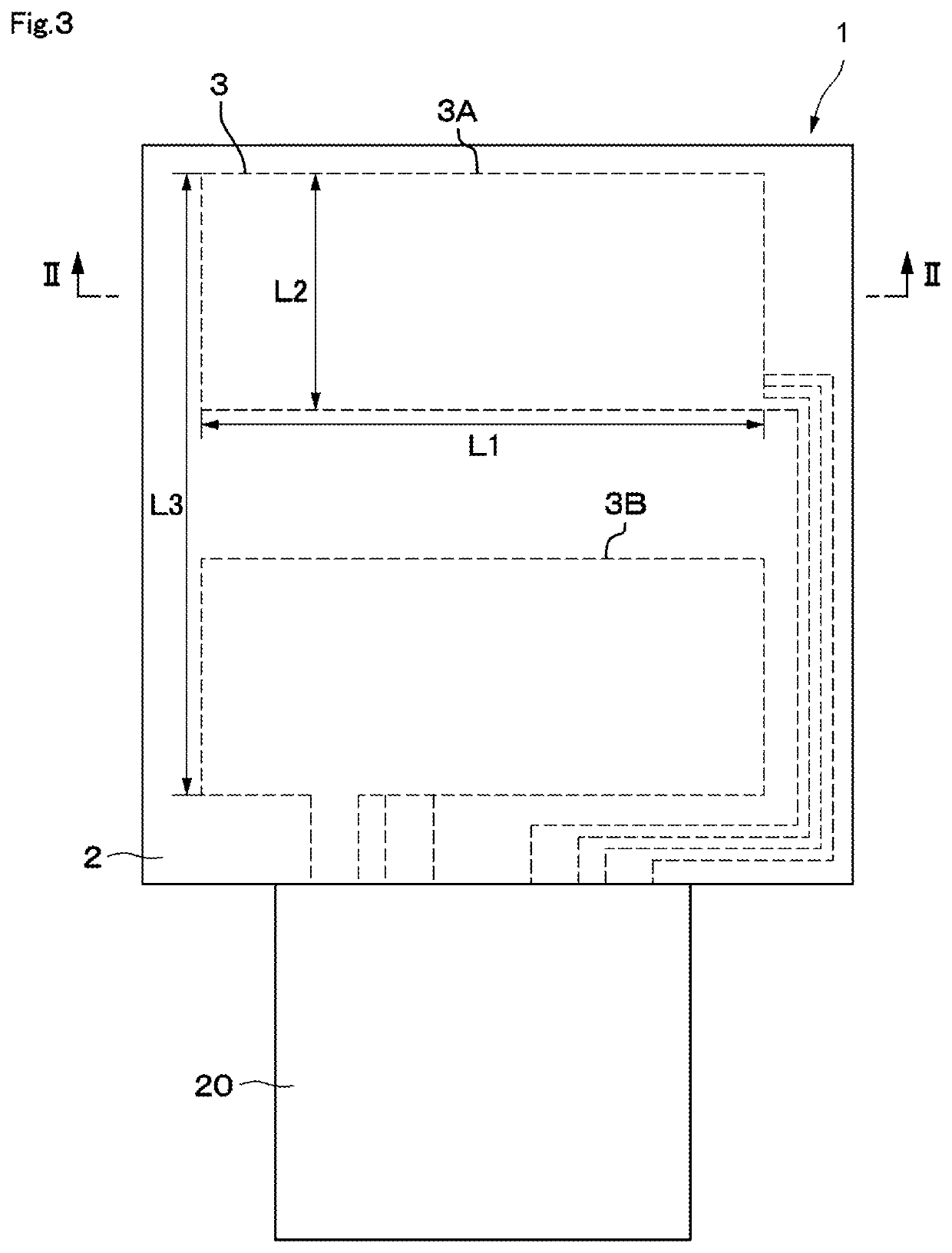
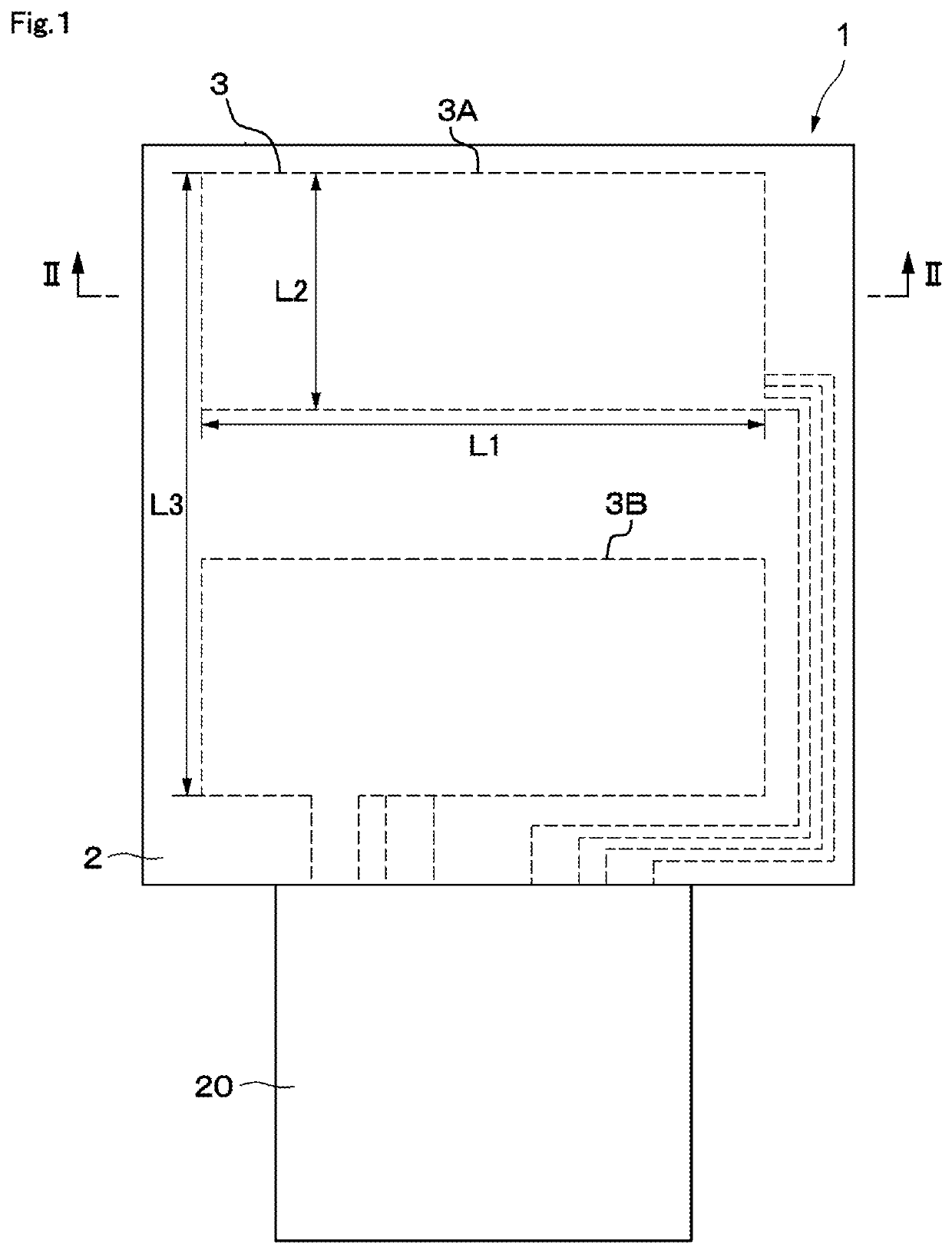
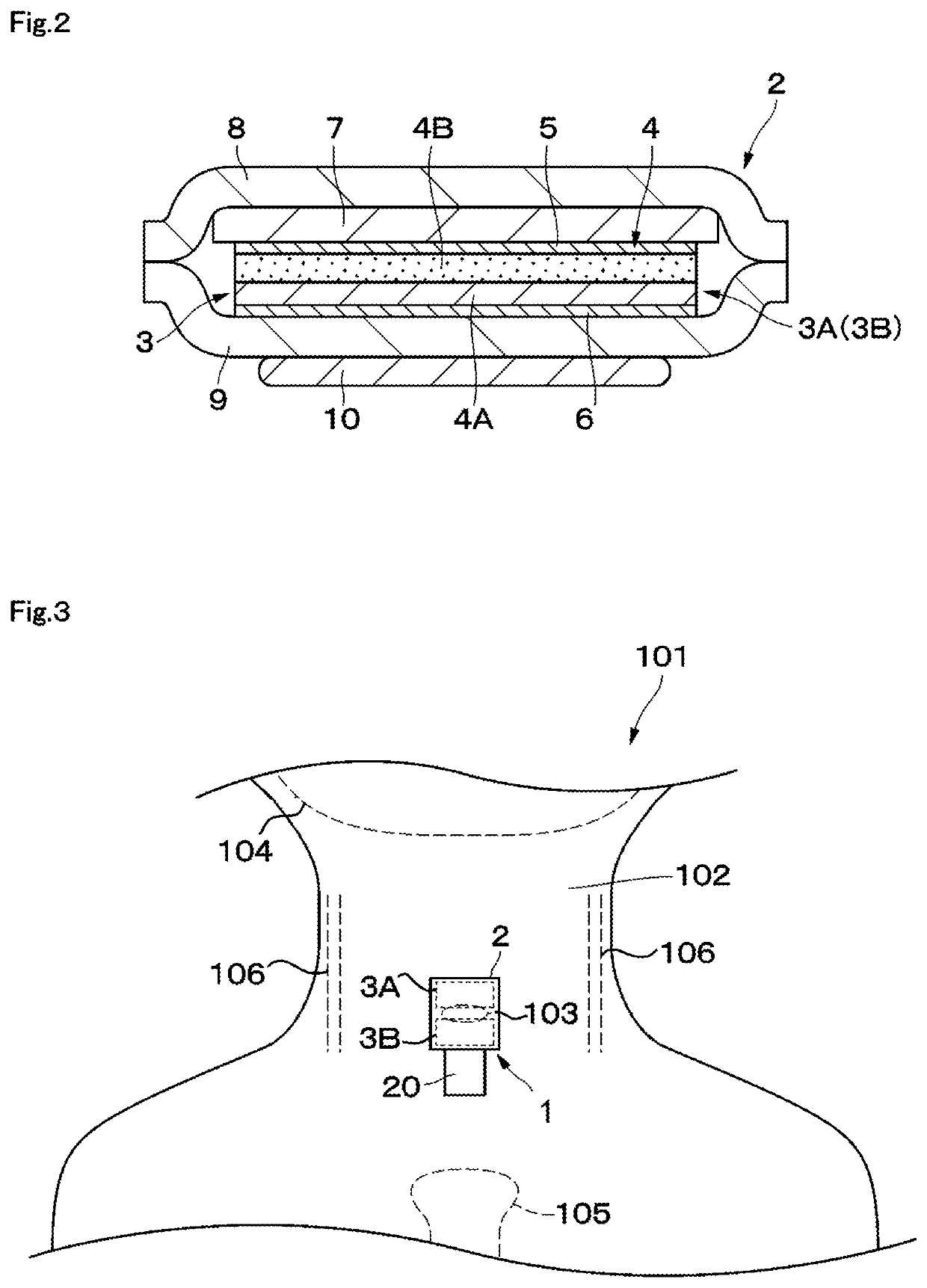
A swallowing analyzing system (S) includes a swallowing sensor (1) and a swallowing analyzer (30). A piezoelectric film sensor (3) of the swallowing sensor (1) includes a plurality of sensing portions (3A) and (3B) in a longitudinal direction of the neck region. The piezoelectric film sensor (3) is located within a range of movement of thyroid cartilage (103), which occurs along with swallowing, and is attached to skin of an anterior neck region (102). The piezoelectric film sensor (3) individually outputs analog signals (S1a) and (S2a) along with deformation of the plurality of sensing portions (3A) and (3B). A body (20) of the swallowing sensor (1) determines whether the swallowing occurs based on displacement signals that are low frequency components of the analog signals (S1a) and (S2a). The body (20) extracts data on the signals during the swallowing and wirelessly outputs the data to the swallowing analyzer (30).
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method for modifying larynx position by trans-positioning muscle and electrode stimulation
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
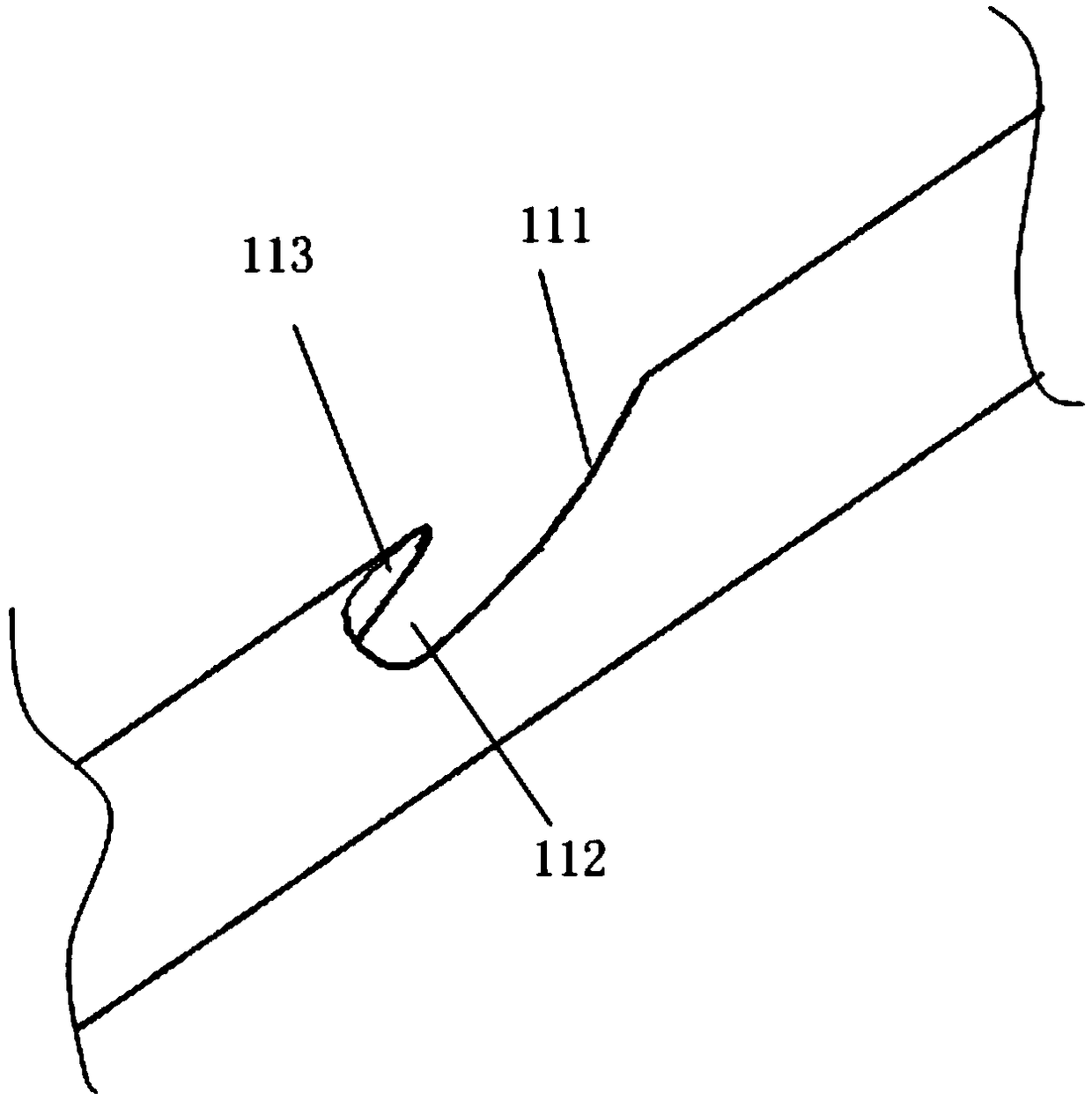
Swallowing sensor
PendingUS20200022639A1Reduce the impactReduce impactStrain gaugeTelemetric patient monitoringFront neckEngineering
A piezoelectric film sensor (3) of a swallowing sensor (1) includes a plurality of sensing portions (3A) and (3B) in a longitudinal direction of the neck region. The piezoelectric film sensor (3) is located within a range of movement of thyroid cartilage (103), which occurs along with swallowing, and is attached to skin of an anterior neck region (102). The piezoelectric film sensor (3) individually outputs analog signals (S1a) and (S2a) along with deformation of the plurality of sensing portions (3A) and (3B). The swallowing sensor (1) includes pre-processing units (21) and (22) and a signal processing unit (23). Each of the pre-processing units (21) and (22) separates the analog signal (S1a) or (S2a) into a displacement signal that is a low frequency component and a sound signal that is a high frequency component. The signal processing unit (23) determines whether the swallowing occurs based on the displacement signal.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Laryngeal function restoration implant system, fixation nails and nail guns
ActiveCN106606371BEasy to fixEasy to operateFastenersBone platesSurgical operationSurgical Manipulation
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Thyroid examination and puncture skill training model
The invention relates to a thyroid examination and puncture skill training model and relates to the technical field of medical education equipment. The model comprises a high-simulation human body upper body model, a thyroid and thyroid nodule, an electric swallowing action simulation device and a microcomputer monitoring controller. The model is characterized in that a left side thyroid gland and a right side thyroid gland of the high-simulation human body upper body model are respectively provided with circular pits, thyroid benign nodules and thyroid malignant nodules are respectively arranged in the circular pits, inflammatory nodules are arranged at the isthmus of the thyroid gland, microswitches are arranged below the inflammatory nodules, palpation examination can be carried out on the three thyroid nodules, corresponding indicator lamps are turned on, the thyroid inflammatory nodules can be pressed to make a cry; A switch of the microcomputer controller swallowing simulation device is pressed down, swallowing actions can be electrically simulated, thyroid cartilage, thyroid gland and thyroid gland nodules can be driven to move up and down along with the thyroid cartilage, the thyroid gland and the thyroid gland nodules, puncture training and examination can be conducted on the three thyroid gland nodules, and due to the fact that the simulation effect is highly simulated, the teaching quality can be remarkably improved.
Owner:营口市贵东医疗器械制造有限公司
Methods and devices for treating glottic insufficiency
Methods and systems configured to treat a patient's glottic insufficiency are disclosed. An implant system may include a first implant positioned in the patient's paraglottic space. The first implant is adjustable in volume by changing amount of filler in the implant. The implant system may include a fixation device fixated on or through a cartilage opening in the patient's thyroid cartilage. The fixation device may contain a first channel. The implant system may include a first tube having a first end coupled with the first implant. The first tube passes through the first channel of the fixation device to deliver the filler to the implant. The implant system may further contain a port coupled with a second end of the first tube to regulate the amount of filler in the implant.
Owner:APREVENT MEDICAL +1
Methods and apparatus for treating glottic insufficiency
Methods and systems configured to treat a patient's glottic insufficiency are disclosed. An implant system may include a first implant positioned in the patient's paraglottic space. The first implant is adjustable in volume by changing amount of filler in the implant. The implant system may include a fixation device fixated on or through a cartilage opening in the patient's thyroid cartilage. The fixation device may contain a first channel. The implant system may include a first tube having a first end coupled with the first implant. The first tube passes through the first channel of the fixation device to deliver the filler to the implant. The implant system may further contain a port coupled with a second end of the first tube to regulate the amount of filler in the implant.
Owner:APREVENT MEDICAL +1
Methods and devices for treating glottic insufficiency
Owner:APREVENT MEDICAL +1
Quantity-controllable water drinking device special for sick children with dysphagia
InactiveCN114522106ADecreased water intakePrevent stray entryFeeding-tubesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDyspharynx
The invention discloses a quantity-controllable water drinking device special for swallowing difficulty children, which comprises a water drinking main frame, a water source placing module, a quantity-controllable adjusting module and a swallowing state detection module, a height adjusting mechanism is arranged on the outer side of the water drinking main frame, and the swallowing state detection module is arranged at one end of the height adjusting mechanism. A tongue bone movement detection assembly and a thyroid cartilage shaping assembly are arranged on the inner side of the swallowing state detection module, a pressure detection sensor is arranged at one end of the tongue bone movement detection assembly, and a magnetic attraction mechanism is arranged between the tongue bone movement detection assembly and the thyroid cartilage shaping assembly; periodic pressure is generated on the pressure detection sensor through movement of the tongue bone of a child patient, the current swallowing state of the child patient is determined, the water intake of the child patient is controlled, and the position of the tongue bone movement detection assembly is changed by sampling the thyroid cartilage of the child patient. And the influence on the swallowing process of the sick child caused by the attachment of the motion detection assembly and the chin of the sick child is reduced.
Owner:郑州大学第三附属医院
Thyroid cartilage fixing device for laryngeal operation
The invention provides a thyroid cartilage fixing device for a laryngeal operation. Lower columns capable of moving vertically are installed on a base plate, the upper ends of the two lower columns are connected with upper columns respectively, and the upper columns can be moved and fixed. A transverse adjusting screw and a guide polish rod which are parallel are arranged between the two upper columns, the transverse adjusting screw can rotate, a connection seat is arranged on the guide polish rod, and the transverse adjusting screw can be in threaded fit with a transverse screw hole of the connection seat. One end of a vertical adjusting screw is installed in a vertical screw hole of the connection seat, a pointer box capable of rotating is installed at the other end, a spring seat is installed in the pointer box, the upper end and the lower end of a pressure spring abut against the vertical adjusting screw and the spring seat respectively, and the spring seat is provided with a pointer and an elastic fixed clamping claw. The thyroid cartilage fixing device for the laryngeal operation is provided according to the actual requirement of the laryngeal operation and achieves the aims of saving operation assistants, ensuring operation effects, avoiding medical accidents, improving operation efficiency and reducing pains of patients.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Methods of and apparatus for monitoring heart motions
InactiveUS7503898B2Provide the displays with noise levels substantially lessLess of noise levelElectrocardiographyStethoscopeAudio power amplifierHeart motion
Owner:CANFORM MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com