Patents
Literature
86results about How to "Increase fuel injection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
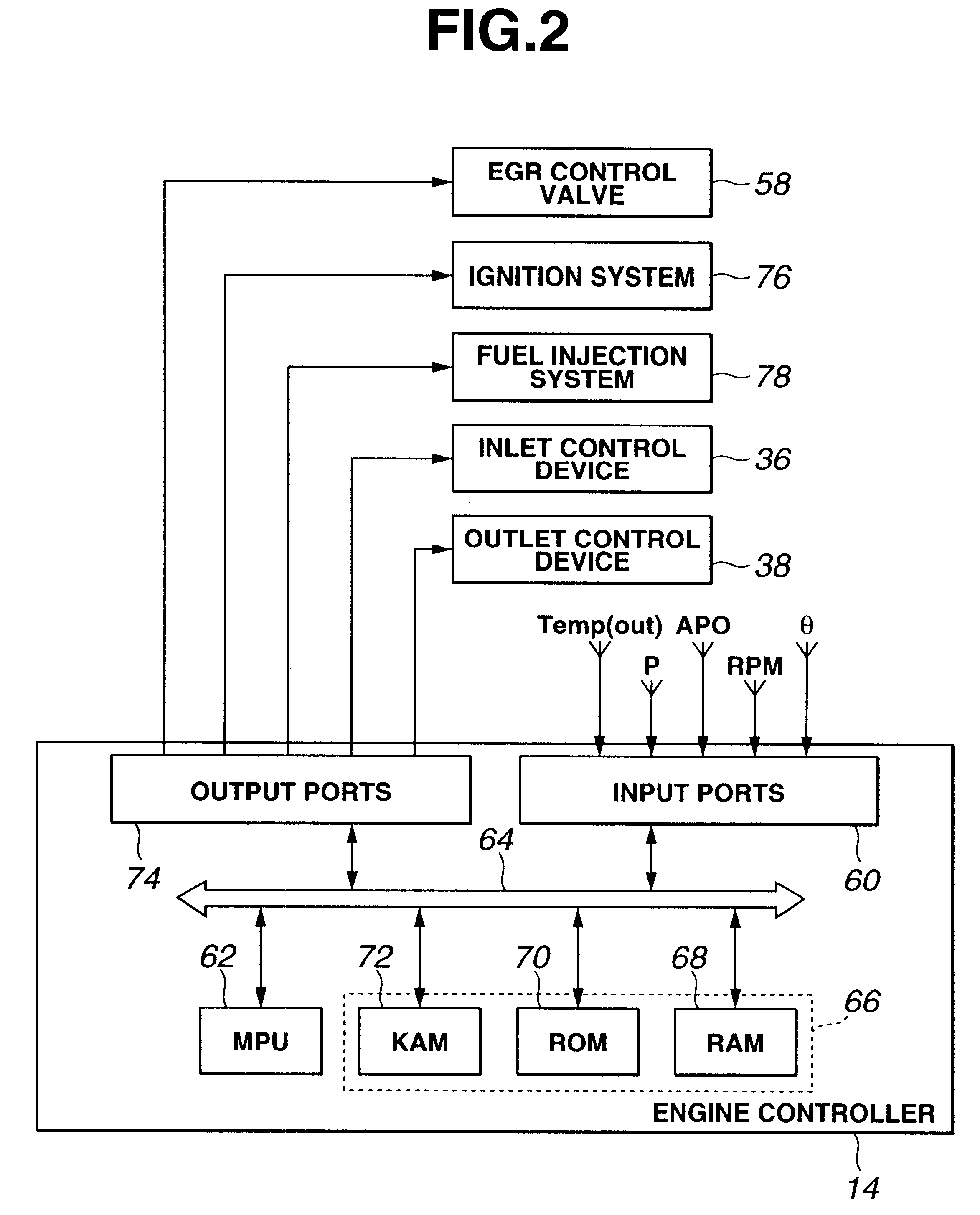
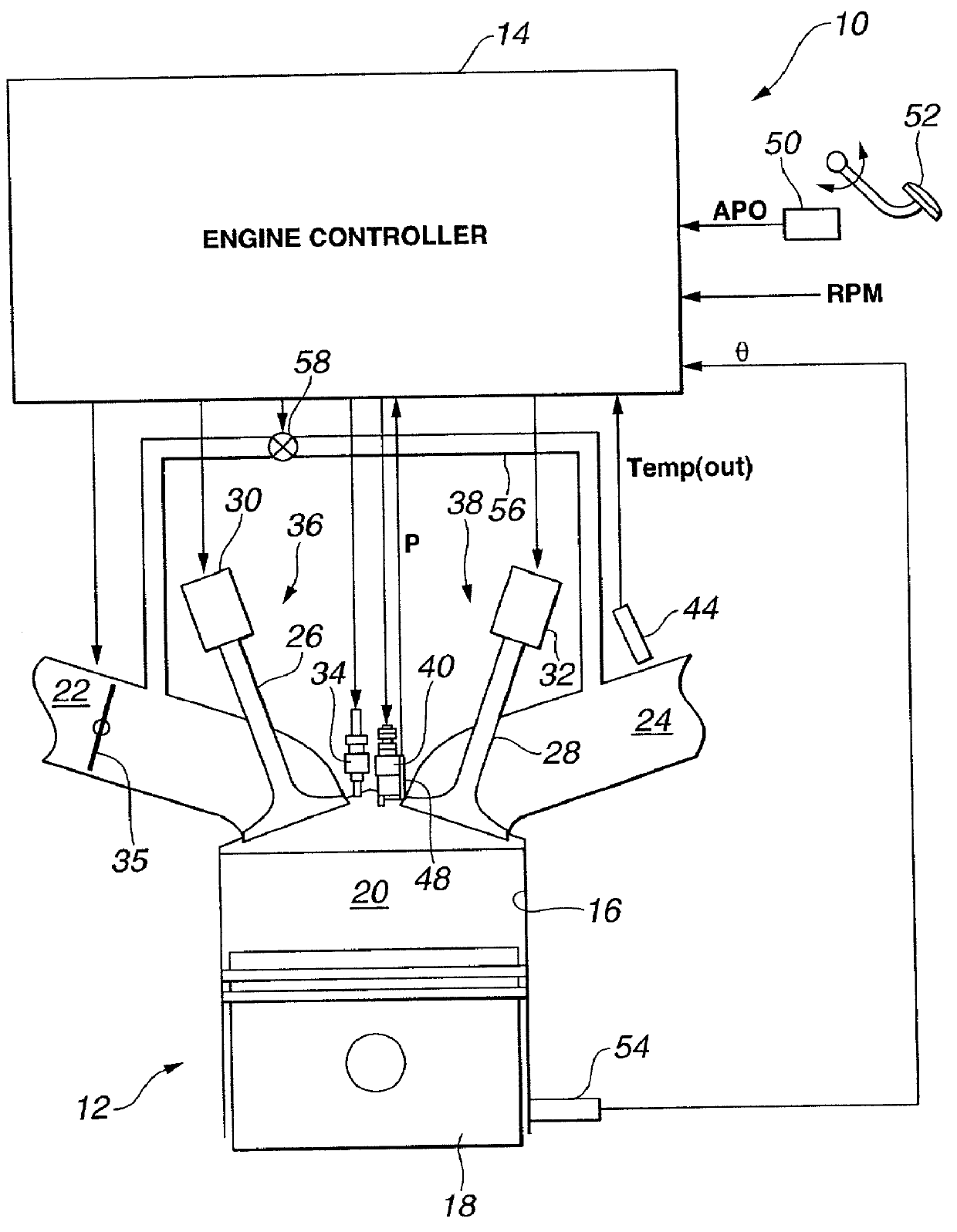
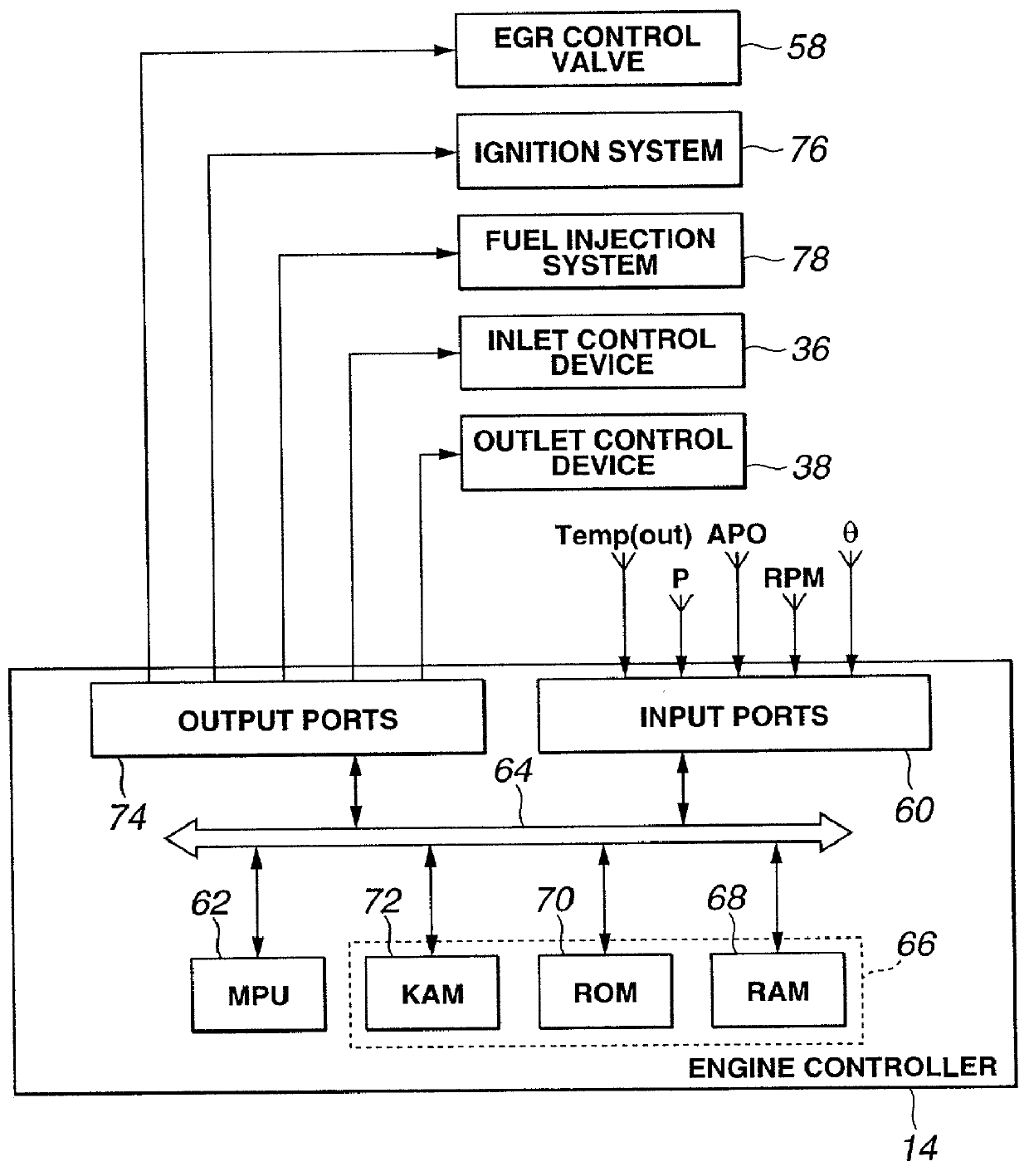
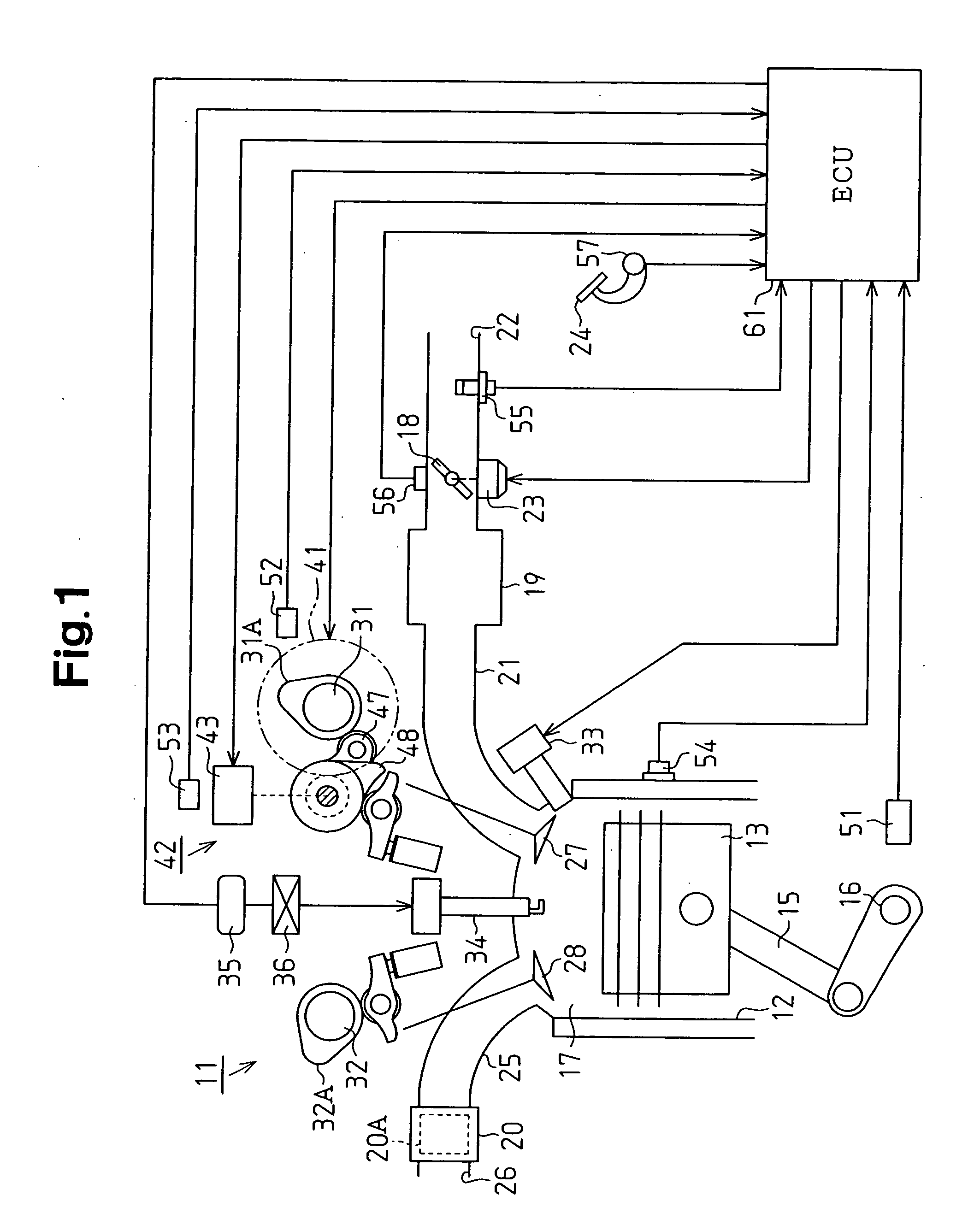
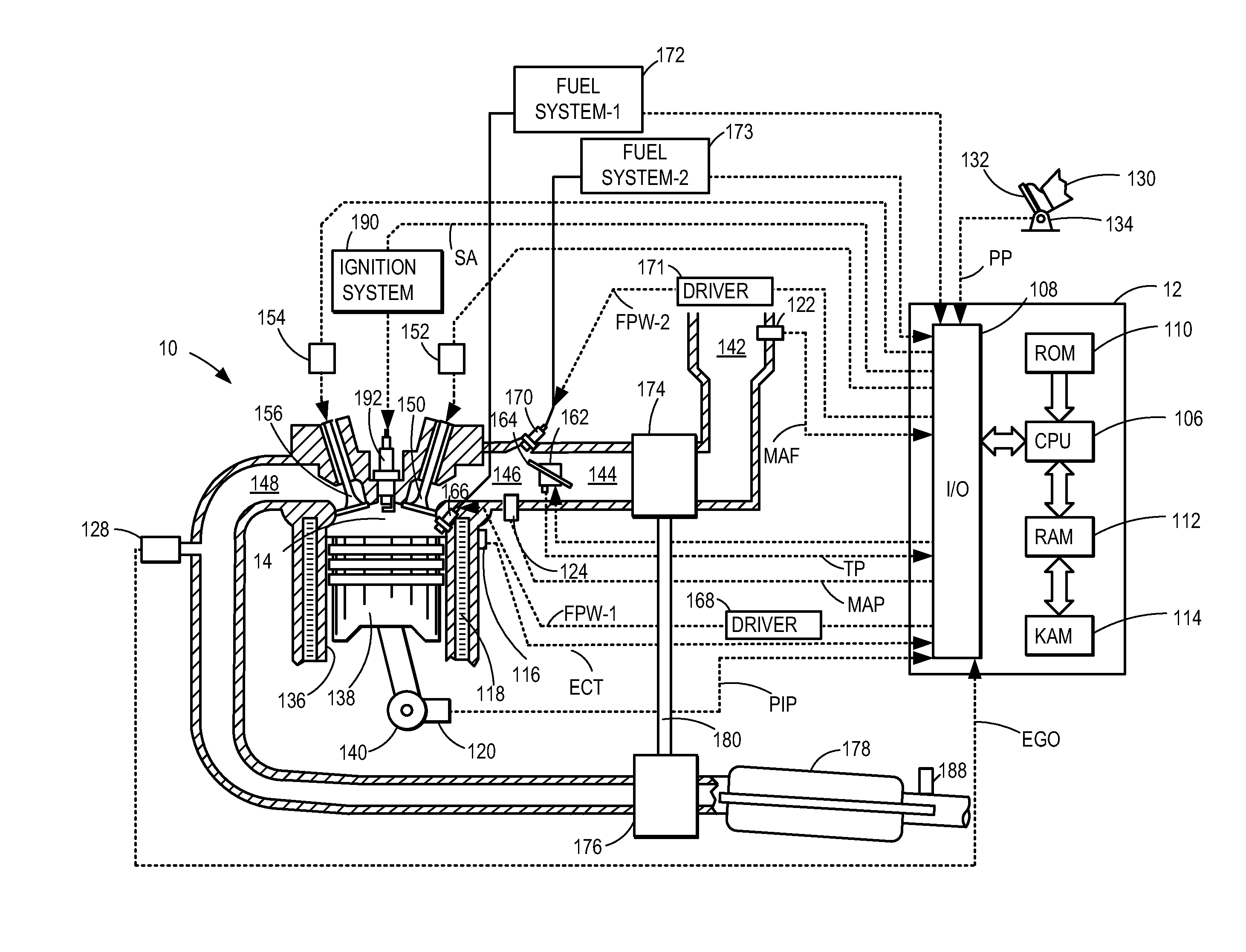
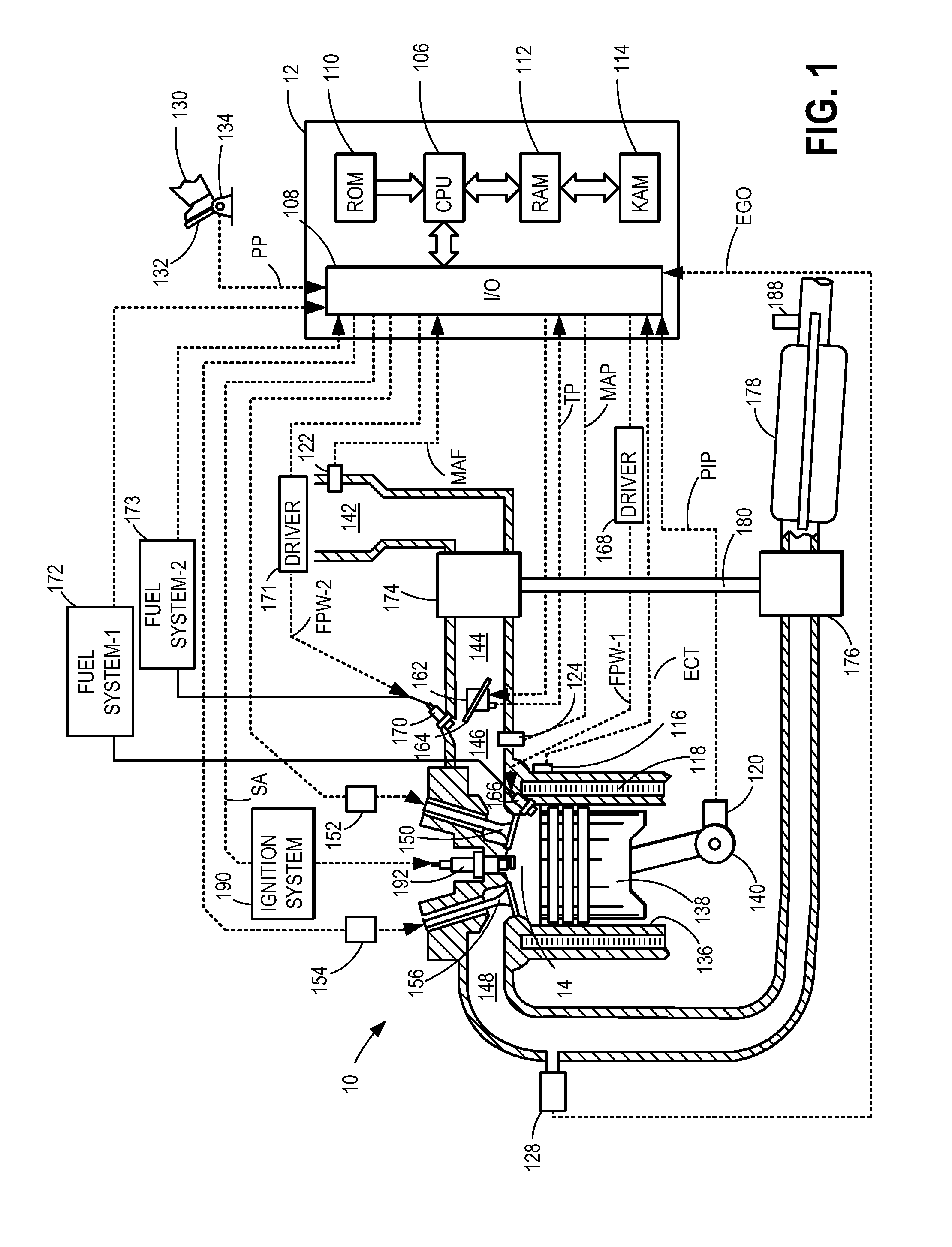
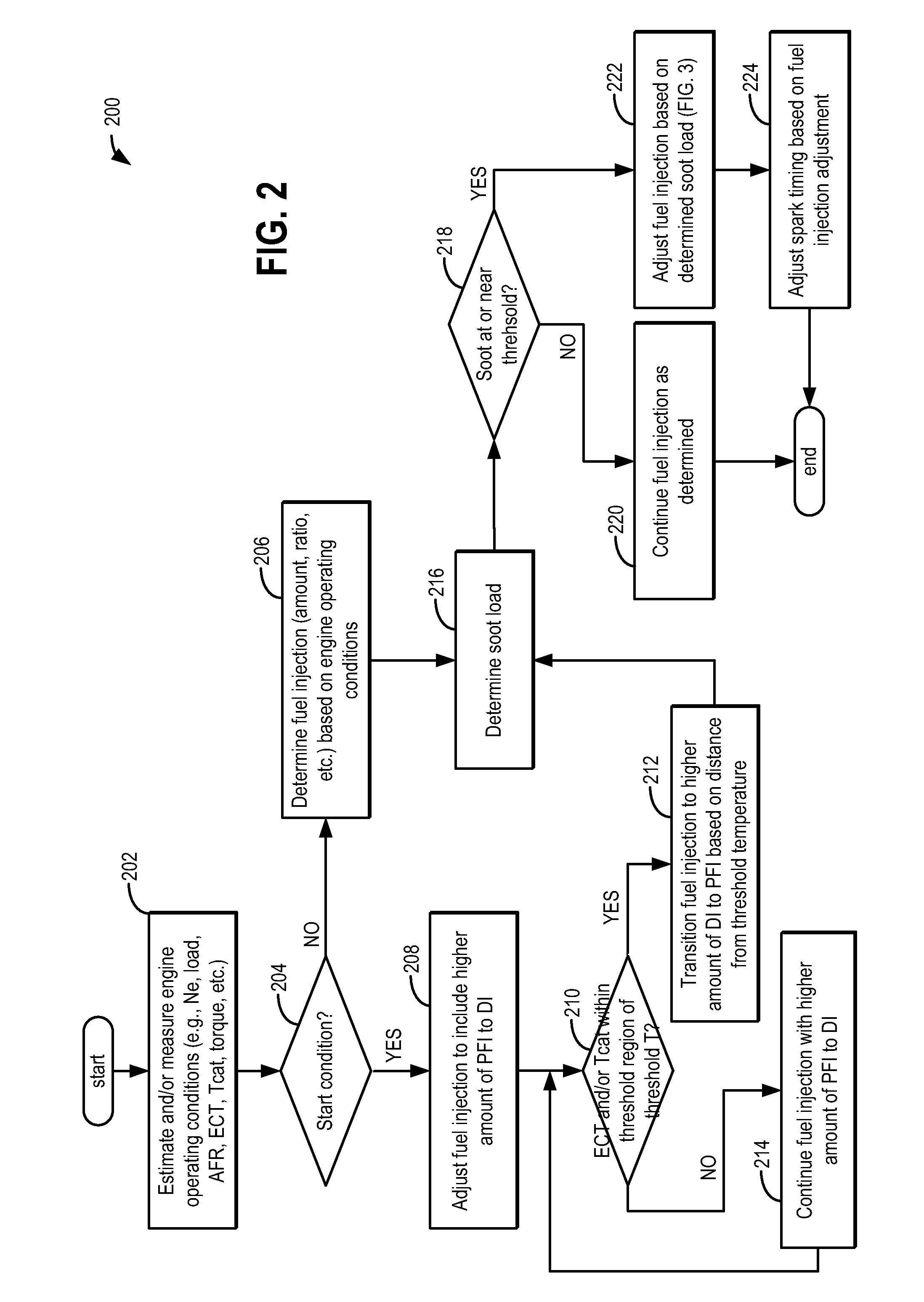
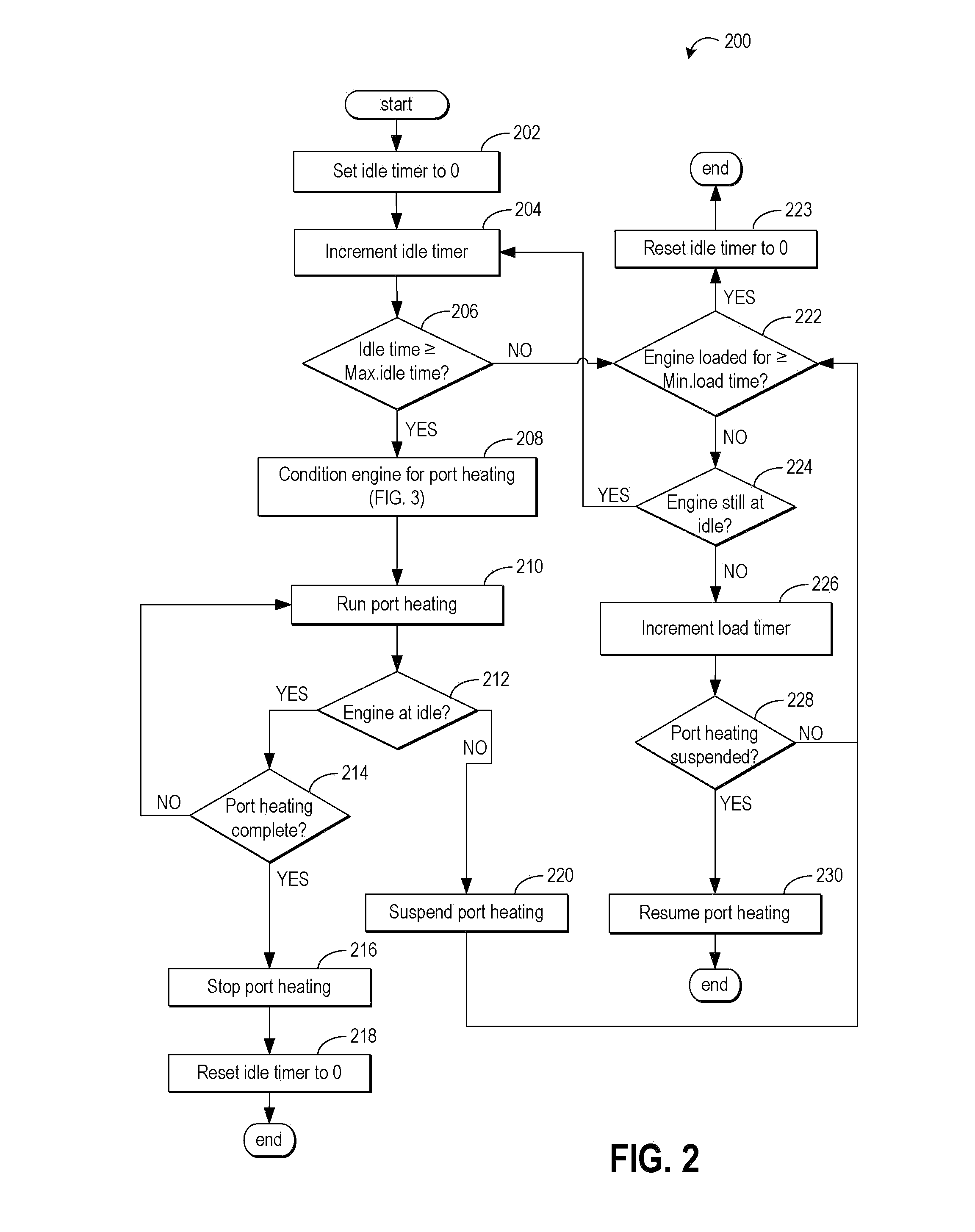
Method and system for engine control
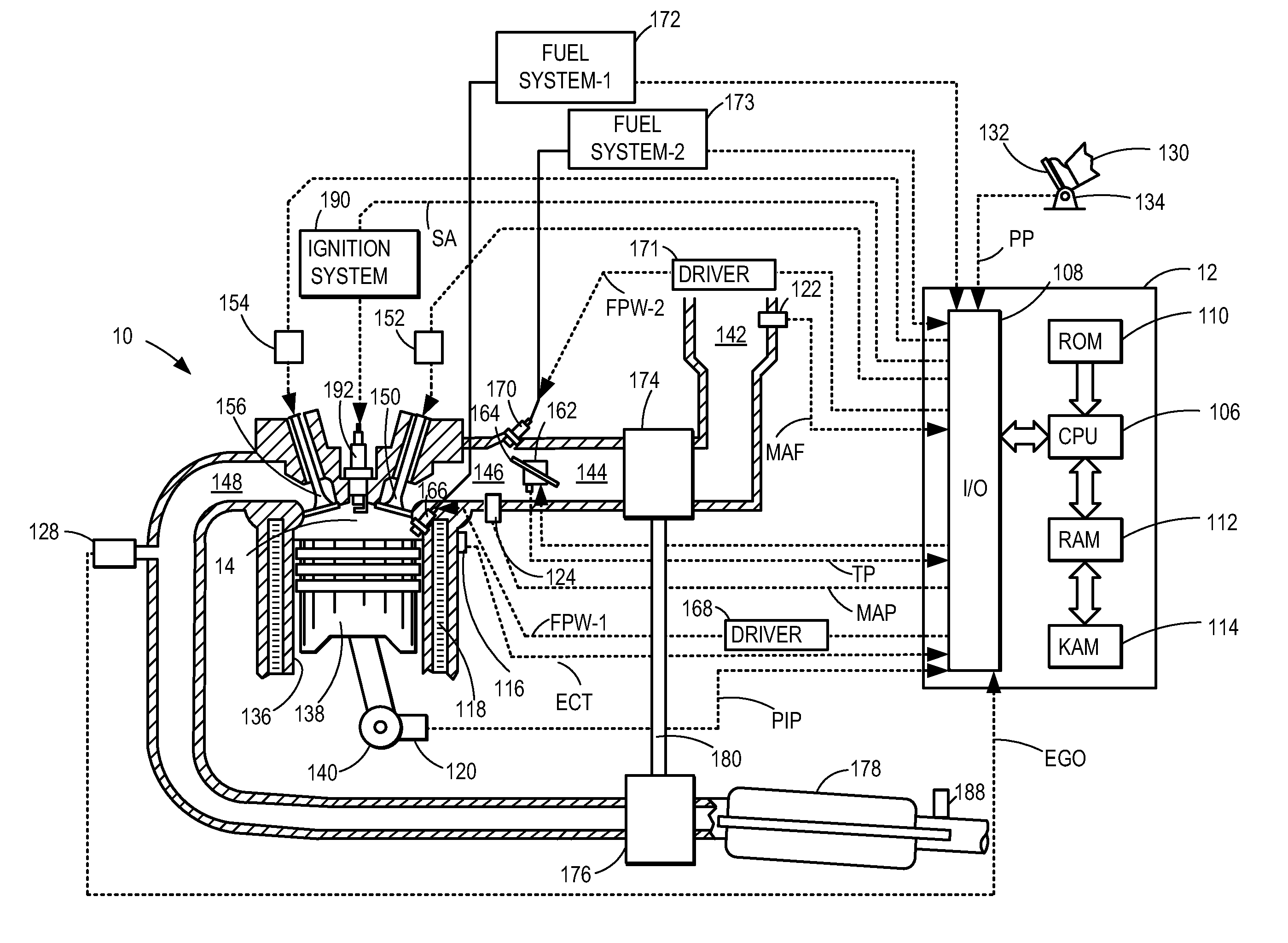
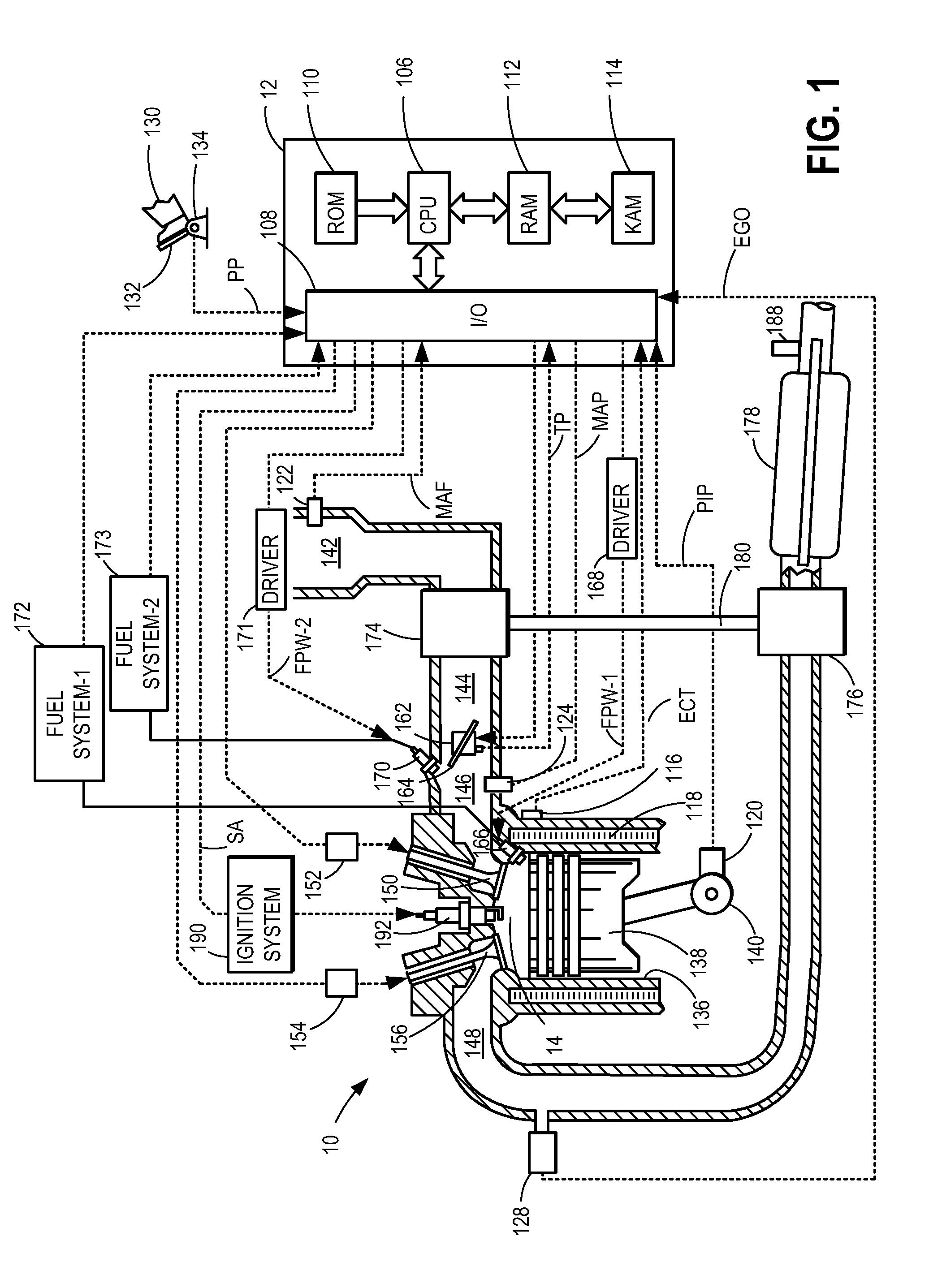
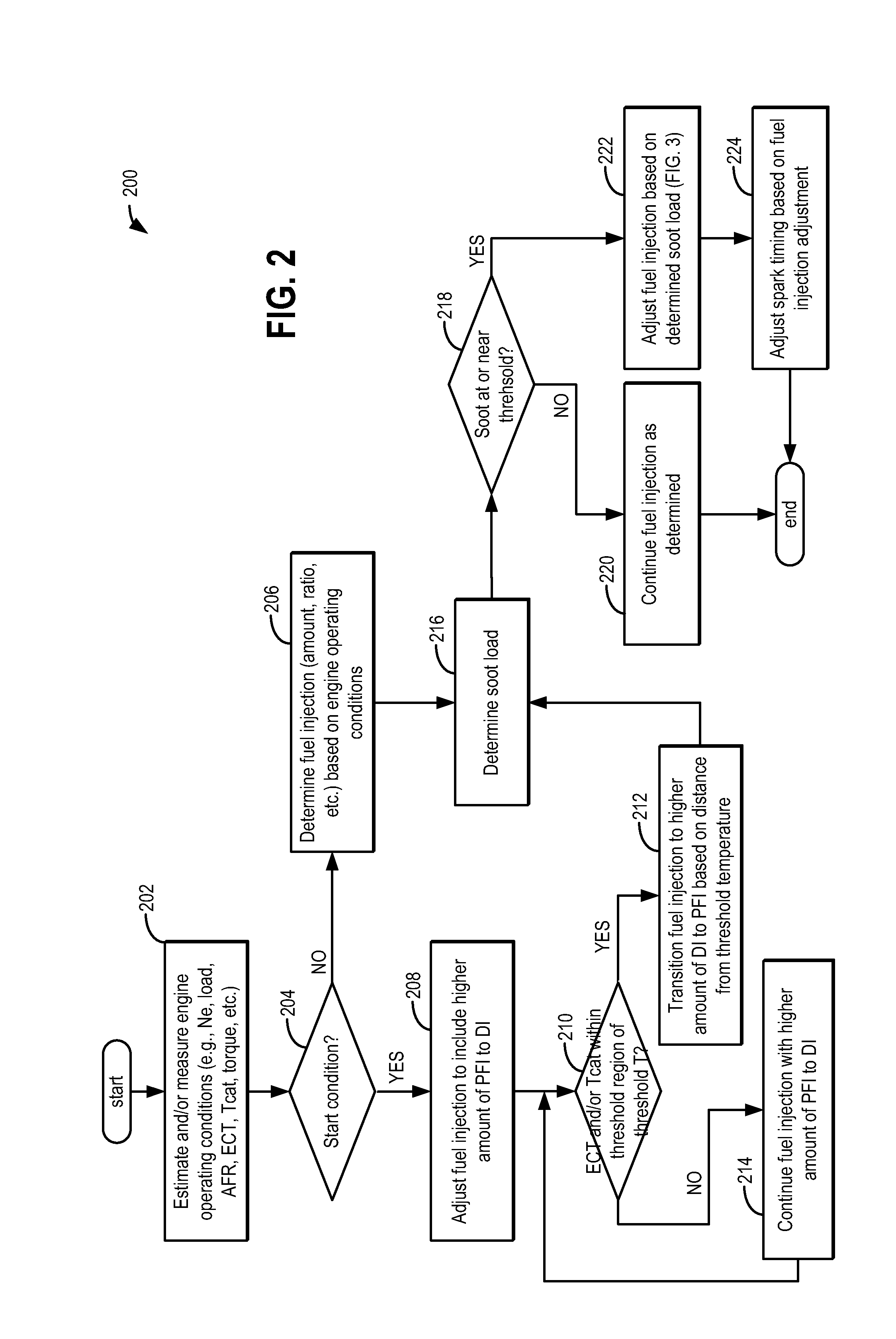
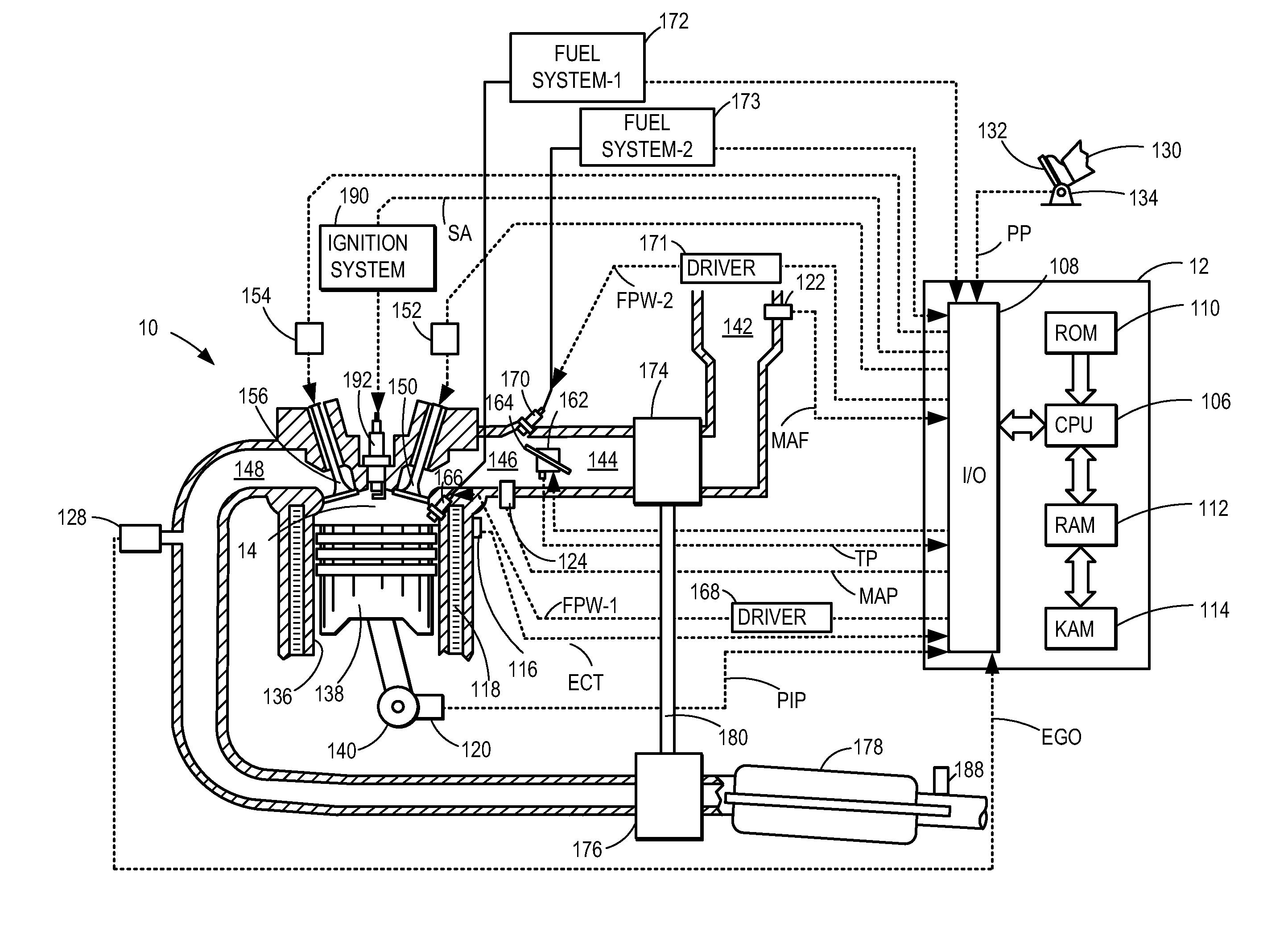
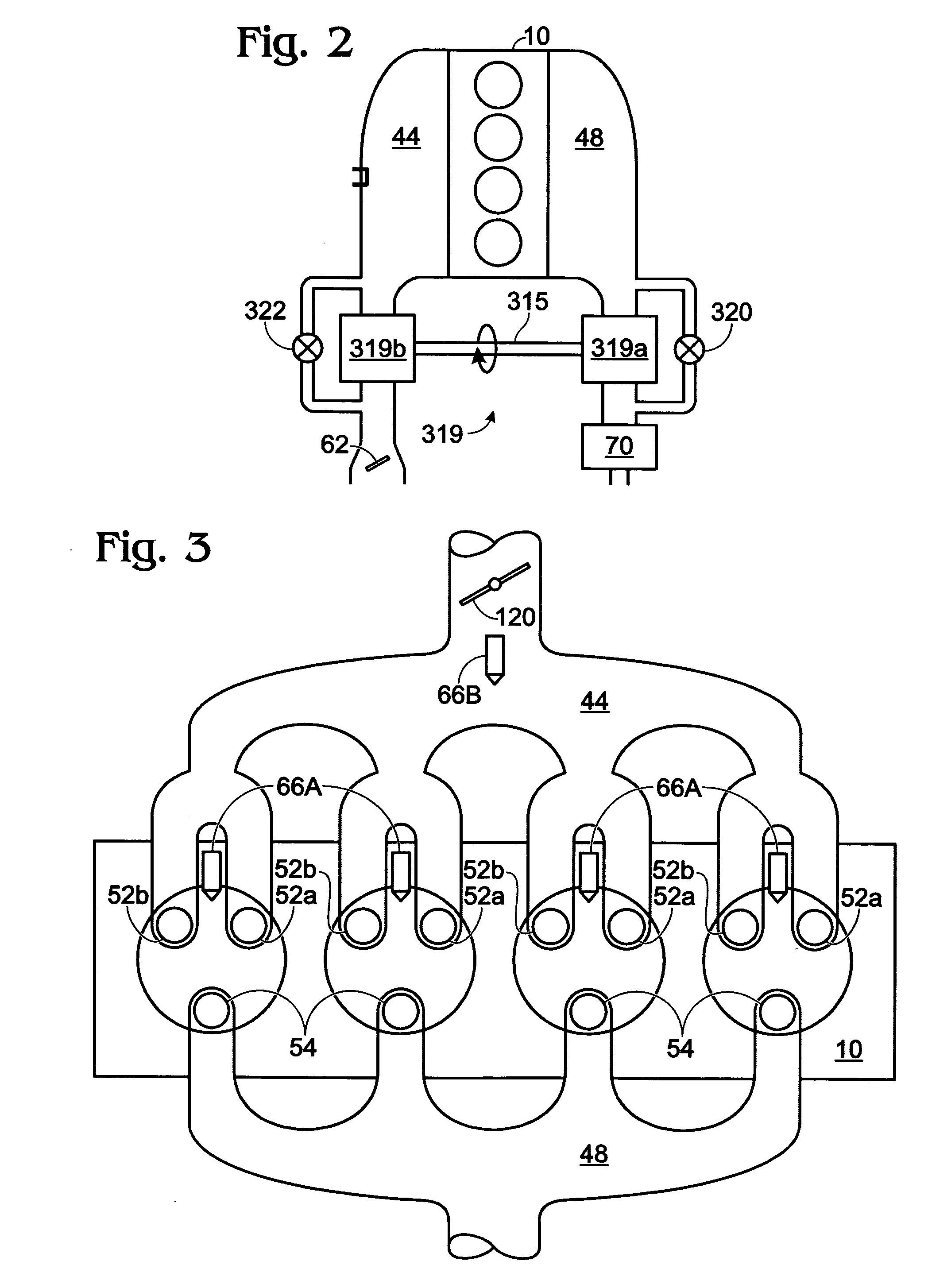
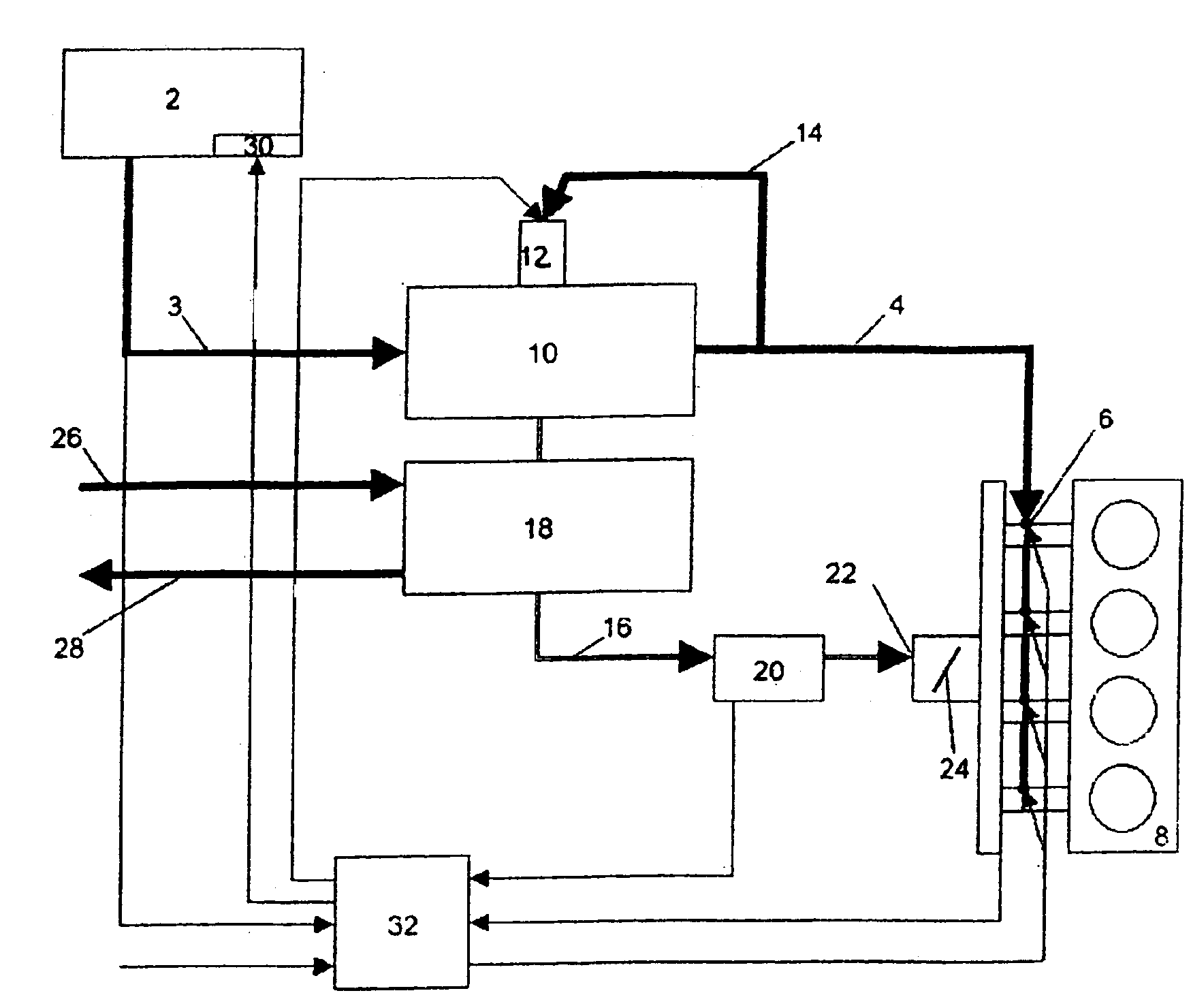
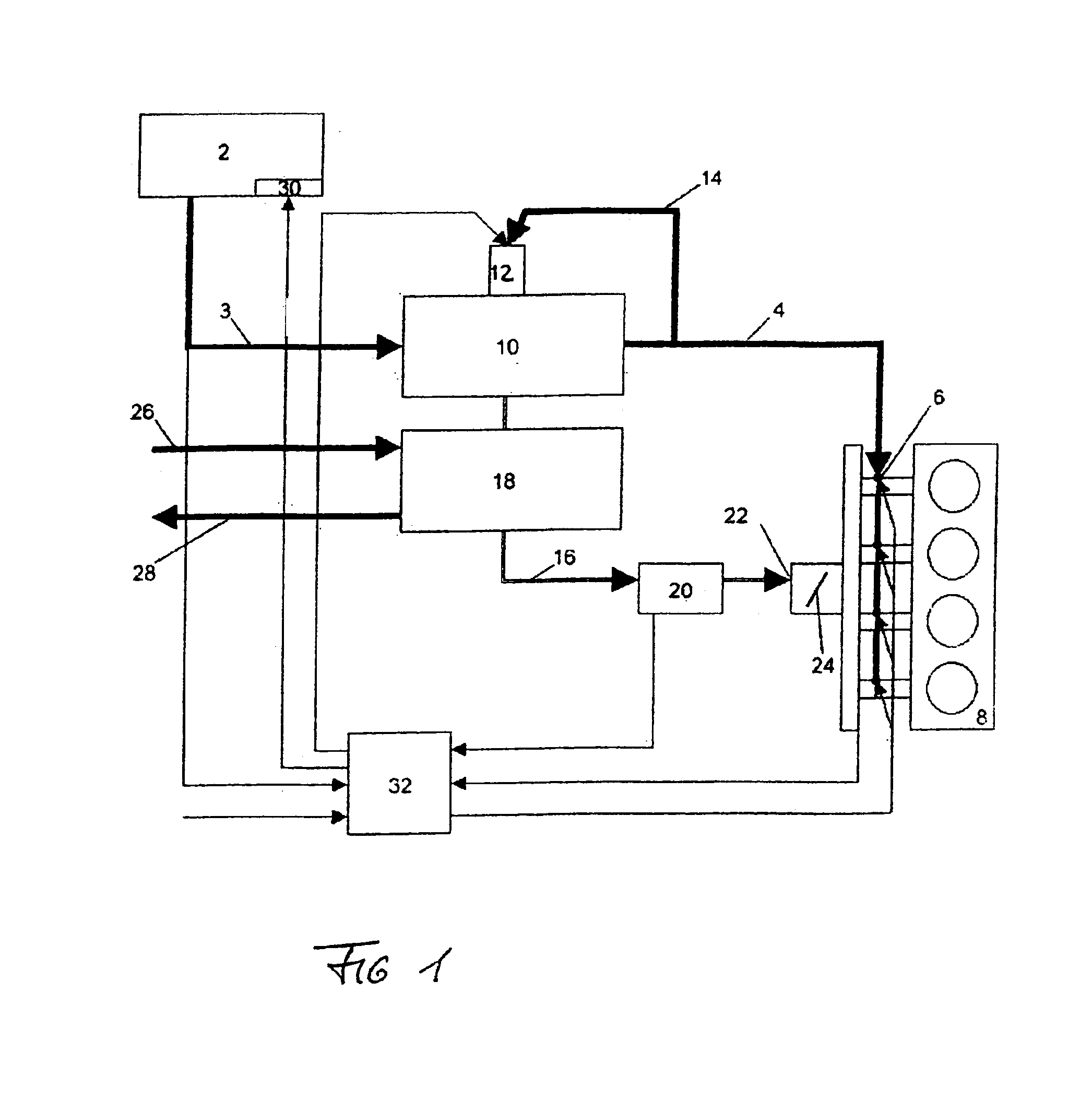
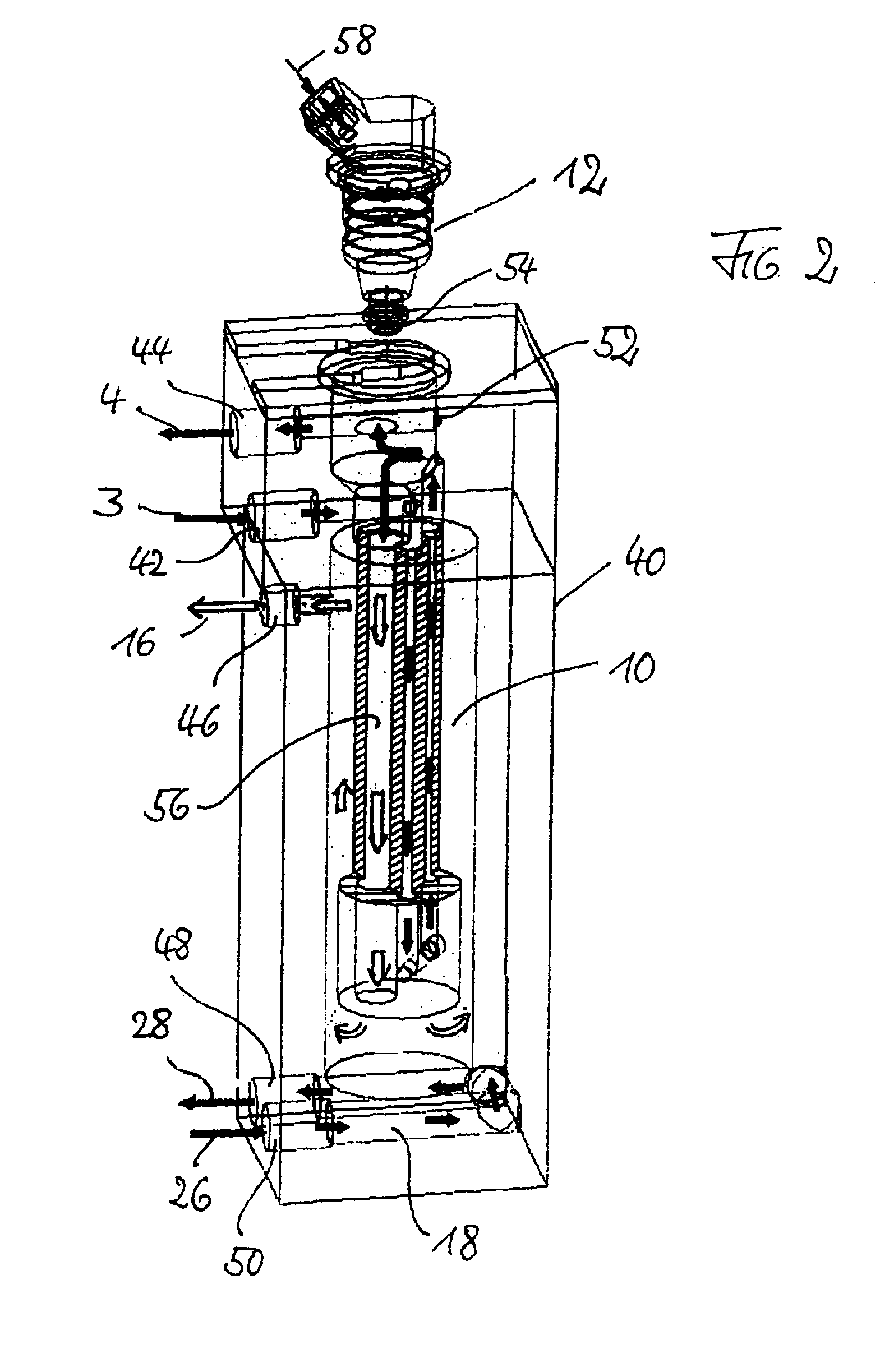
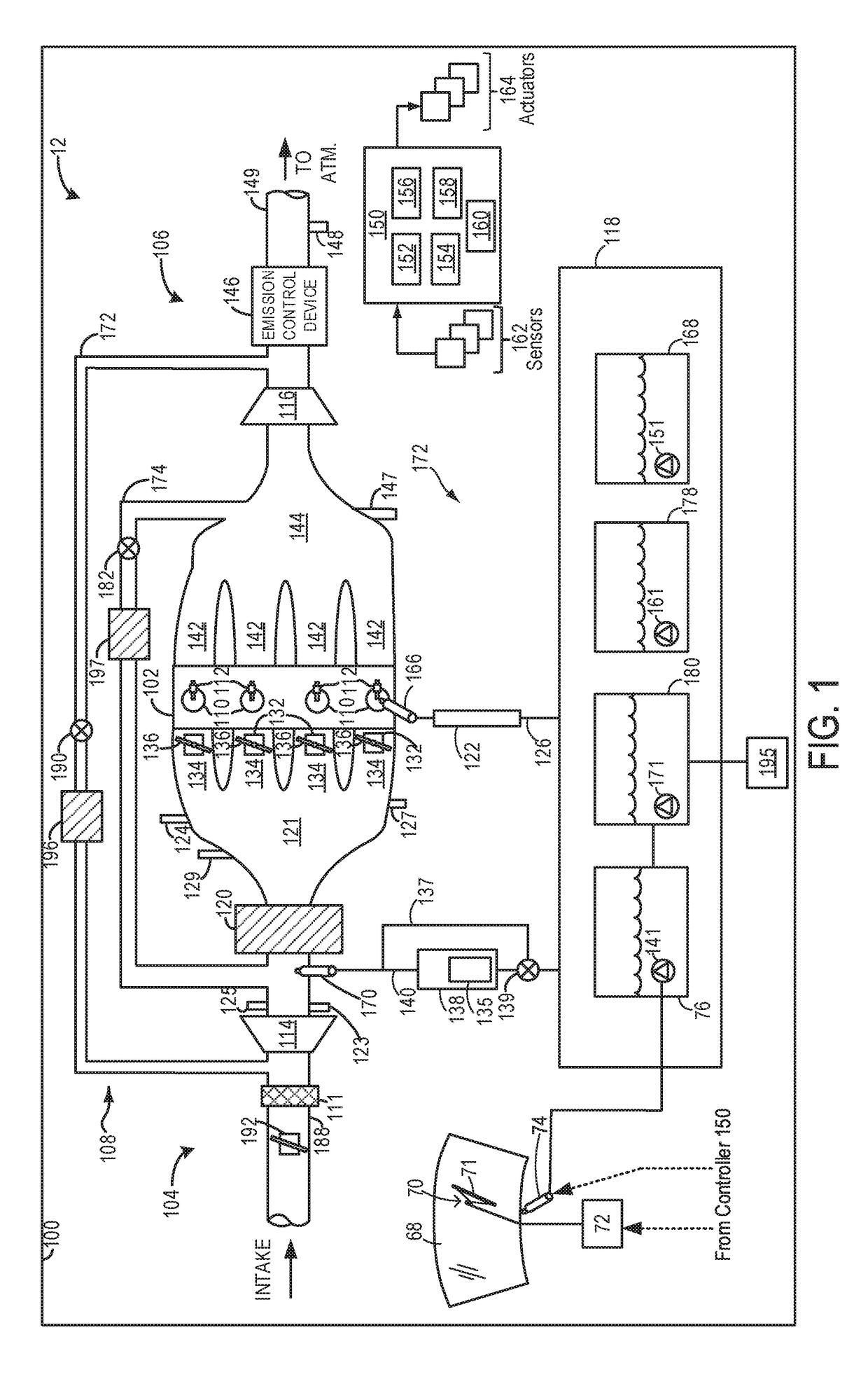
ActiveUS20110162620A1Improve fuel efficiencyImprove cooling effectElectrical controlExhaust apparatusExhaust fumesLoad regulation
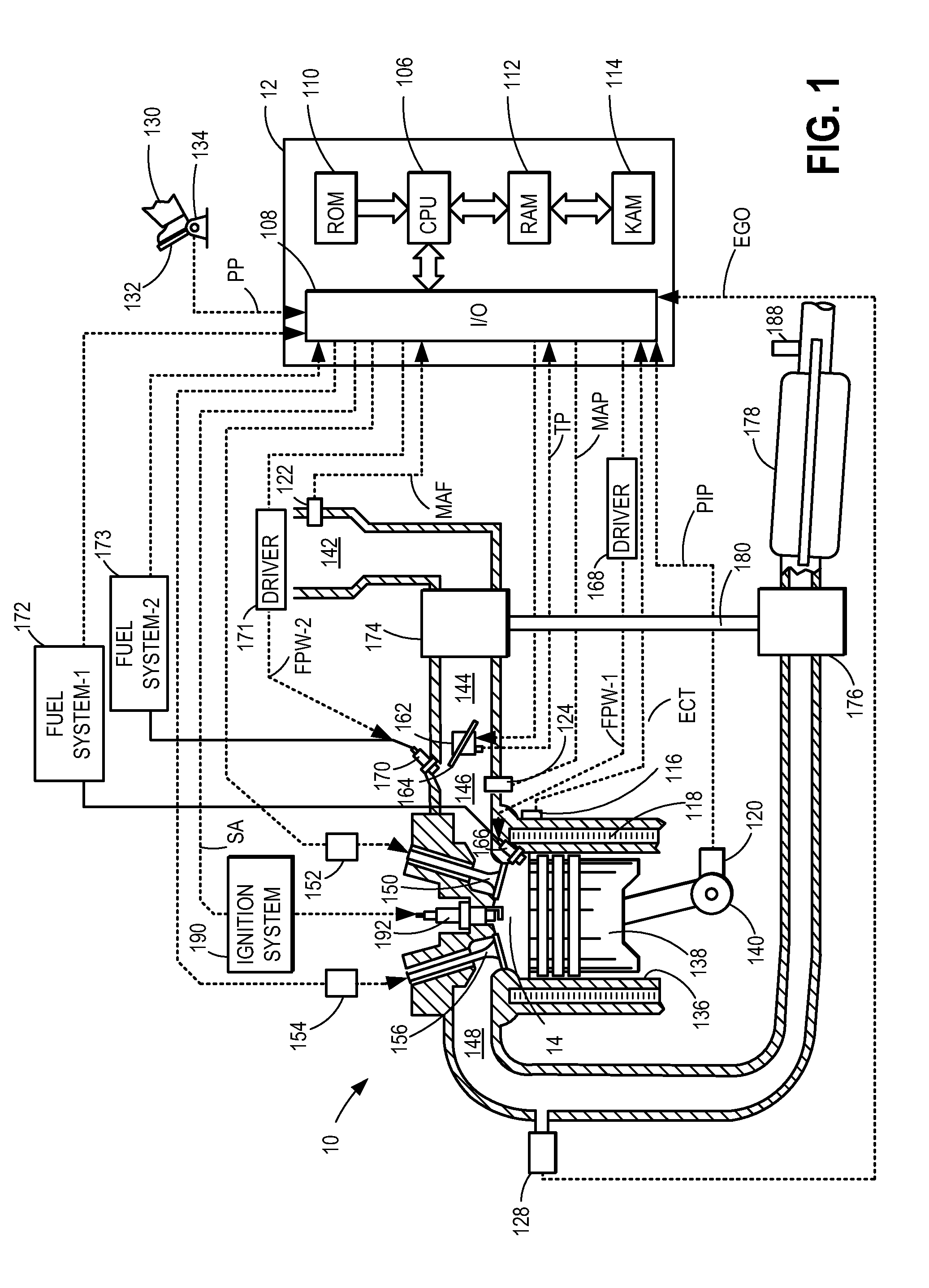
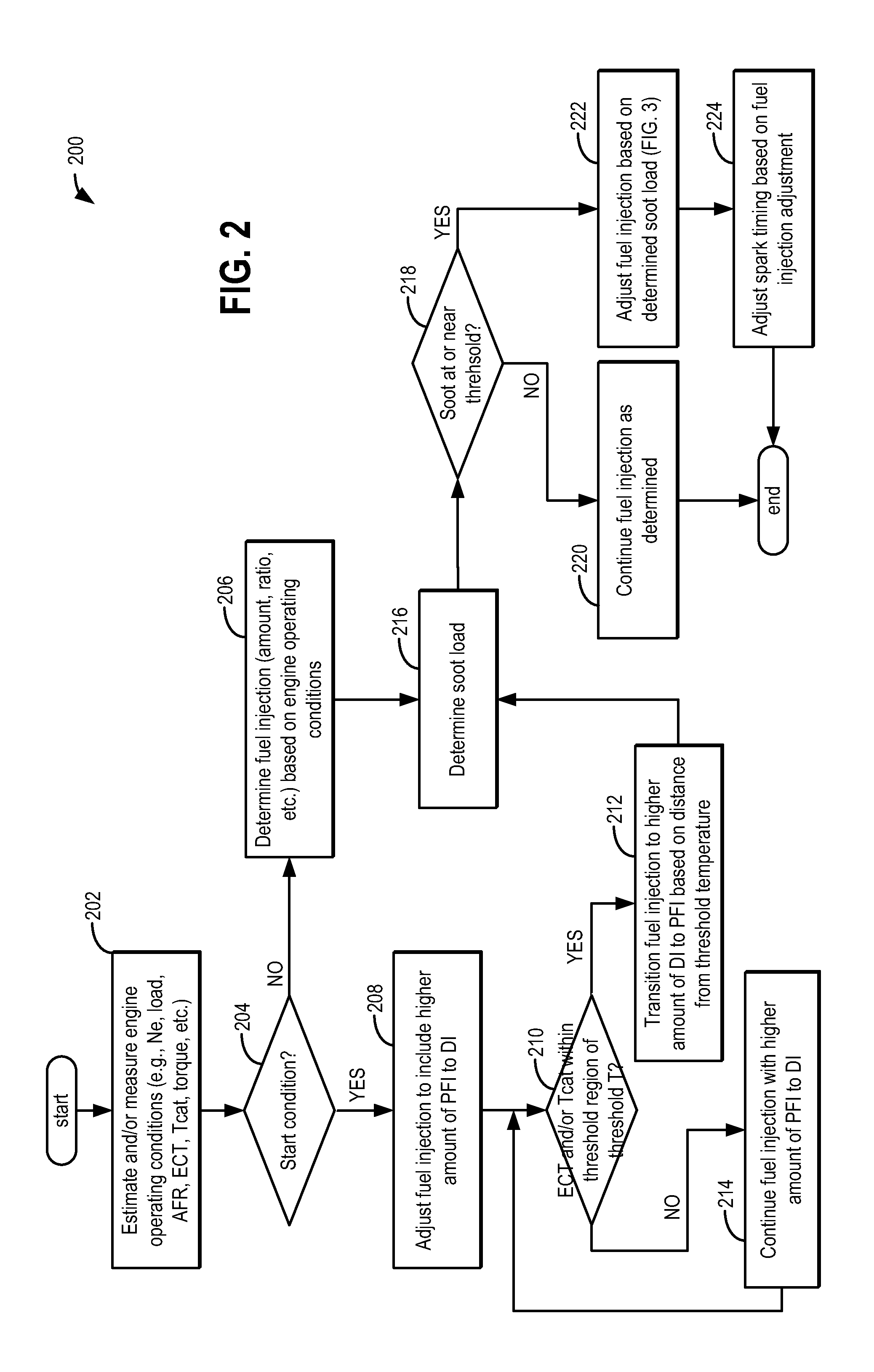
Methods and systems are provided for controlling exhaust emissions by adjusting a fuel injection into an engine cylinder from a plurality of fuel injectors based on the fuel type of the injected fuel and further based on the soot load of the engine. Soot generated from direct fuel injection is reduced by decreasing an amount of direct injection into a cylinder as the engine soot load increases.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and system for engine control
ActiveUS8100107B2Improve cooling effectImprove fuel efficiencyElectrical controlExhaust apparatusExhaust fumesFuel type
Methods and systems are provided for controlling exhaust emissions by adjusting a fuel injection into an engine cylinder from a plurality of fuel injectors based on the fuel type of the injected fuel and further based on the soot load of the engine. Soot generated from direct fuel injection is reduced by decreasing an amount of direct injection into a cylinder as the engine soot load increases.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
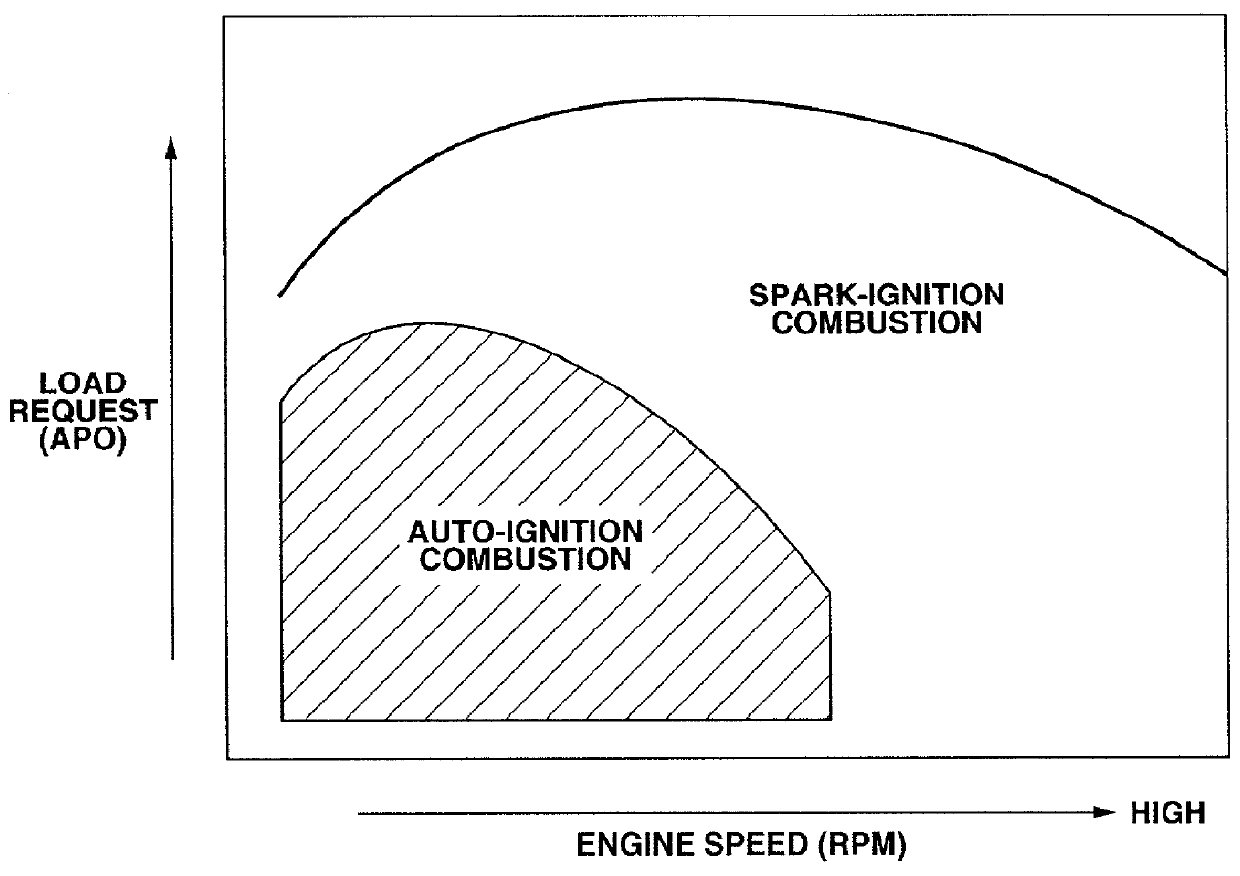
Enhanced multiple injection for auto-ignition in internal combustion engines
InactiveUS6636797B2Increase fuel injectionImprove operationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMultiple injectionCombustion chamber
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Enhanced multiple injection for auto-ignition in internal combustion engines
InactiveUS20010056322A1Increase fuel injectionImprove operationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMultiple injectionExternal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine has a fuel injection system capable of performing a multiple injection wherein a main injection event and a trigger injection event take place in this order in one cycle. With main injection, fuel is widely dispersed within a combustion chamber to create a main mixture for main combustion. With trigger injection, fuel is dispersed locally within the combustion chamber to create an ignitable mixture for auto-ignition. Auto-ignition of the ignitable mixture creates condition under which auto-ignition of the main mixture takes place. Fuel quantity and timing for each of main and trigger injections are varied corresponding to engine speed and load request to cause the main mixture to burn at a target crank angle after TDC of compression stroke.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
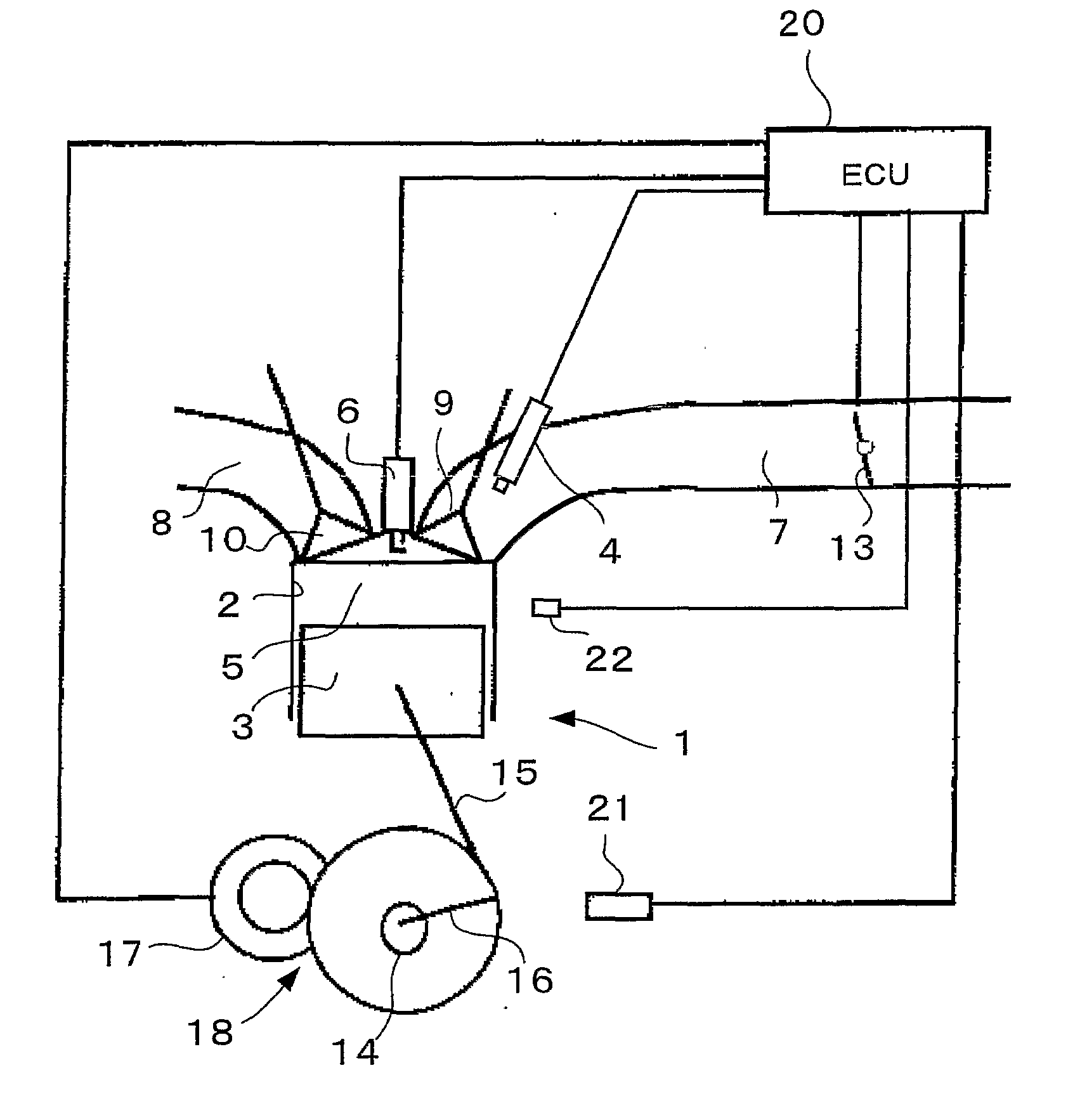
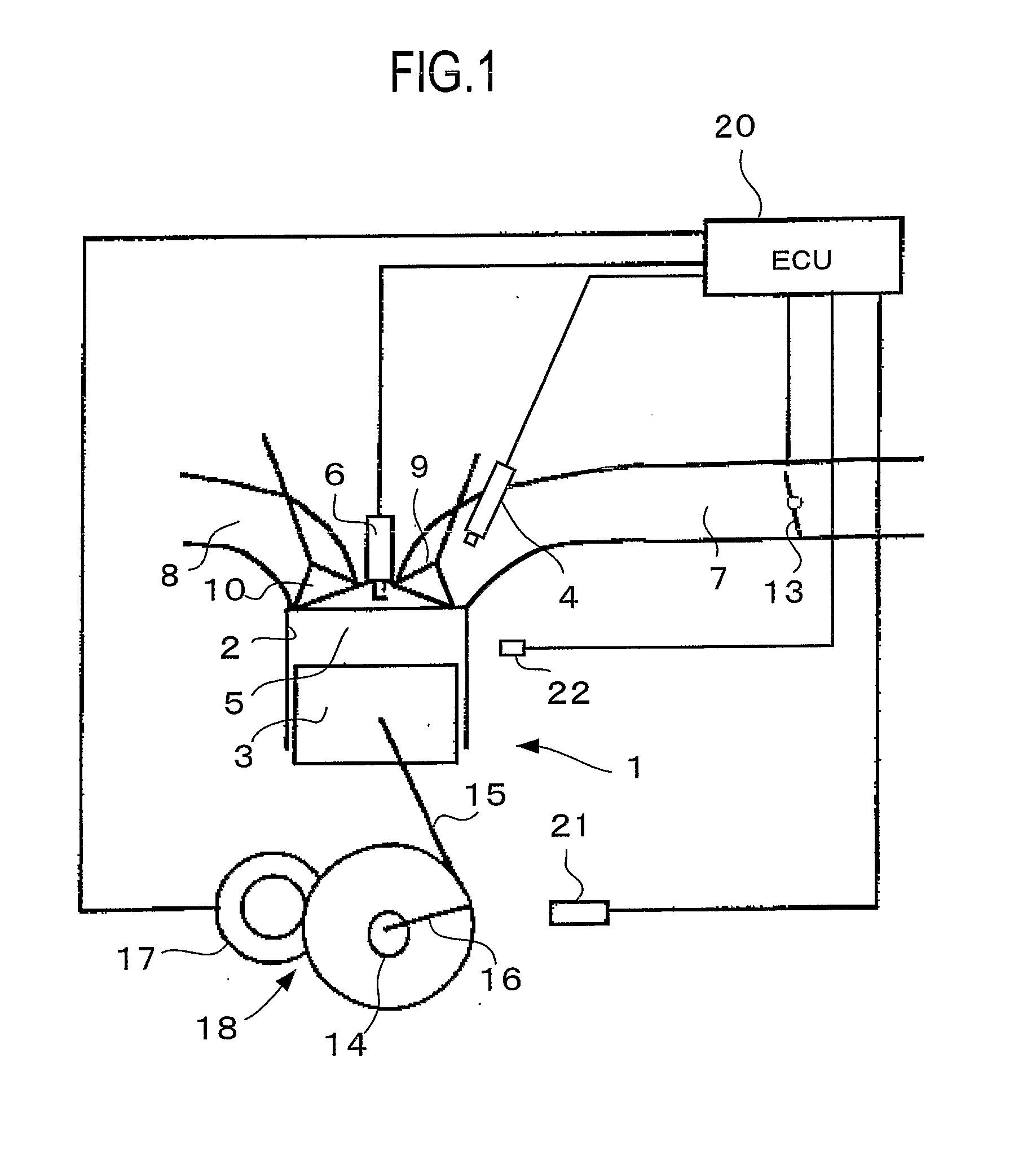
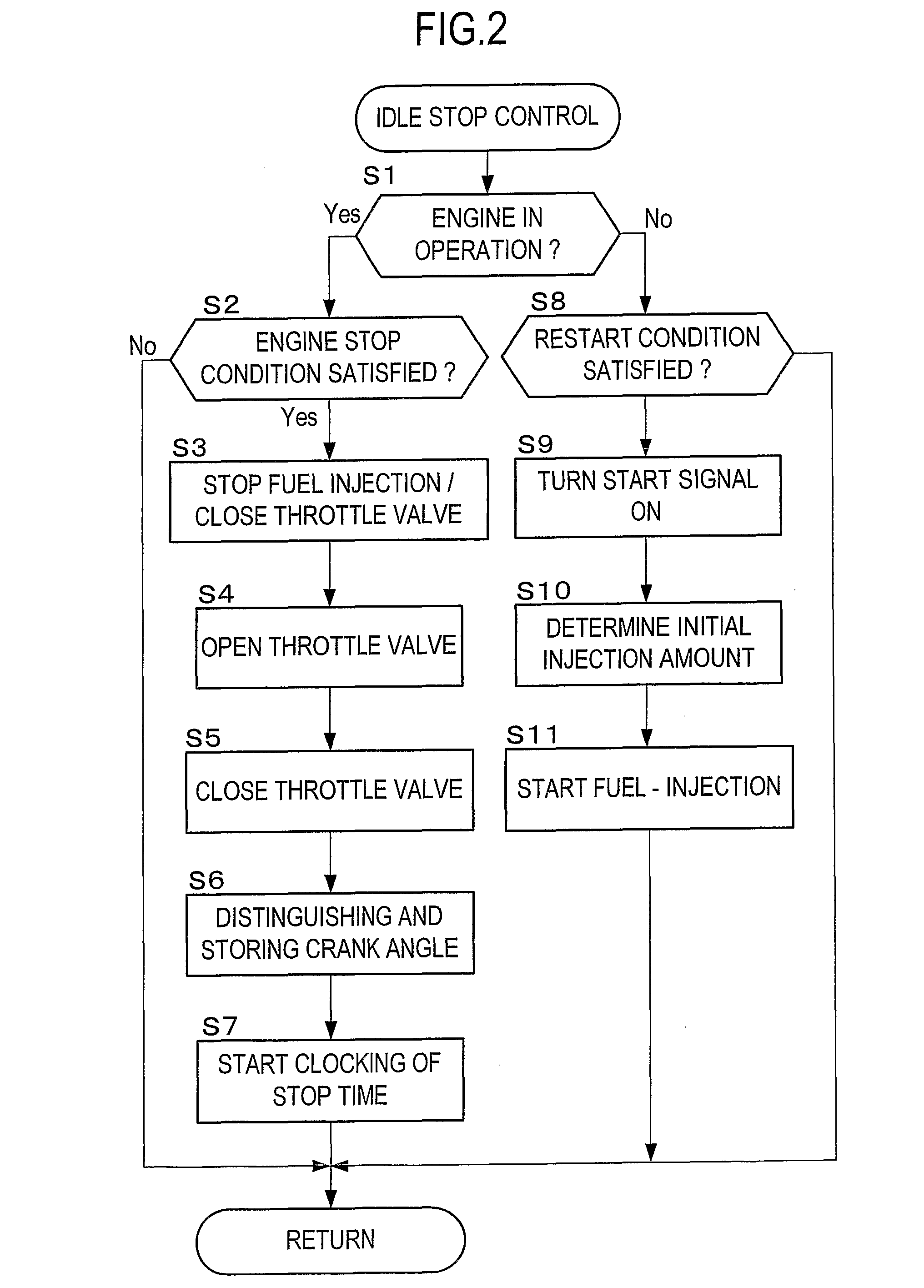
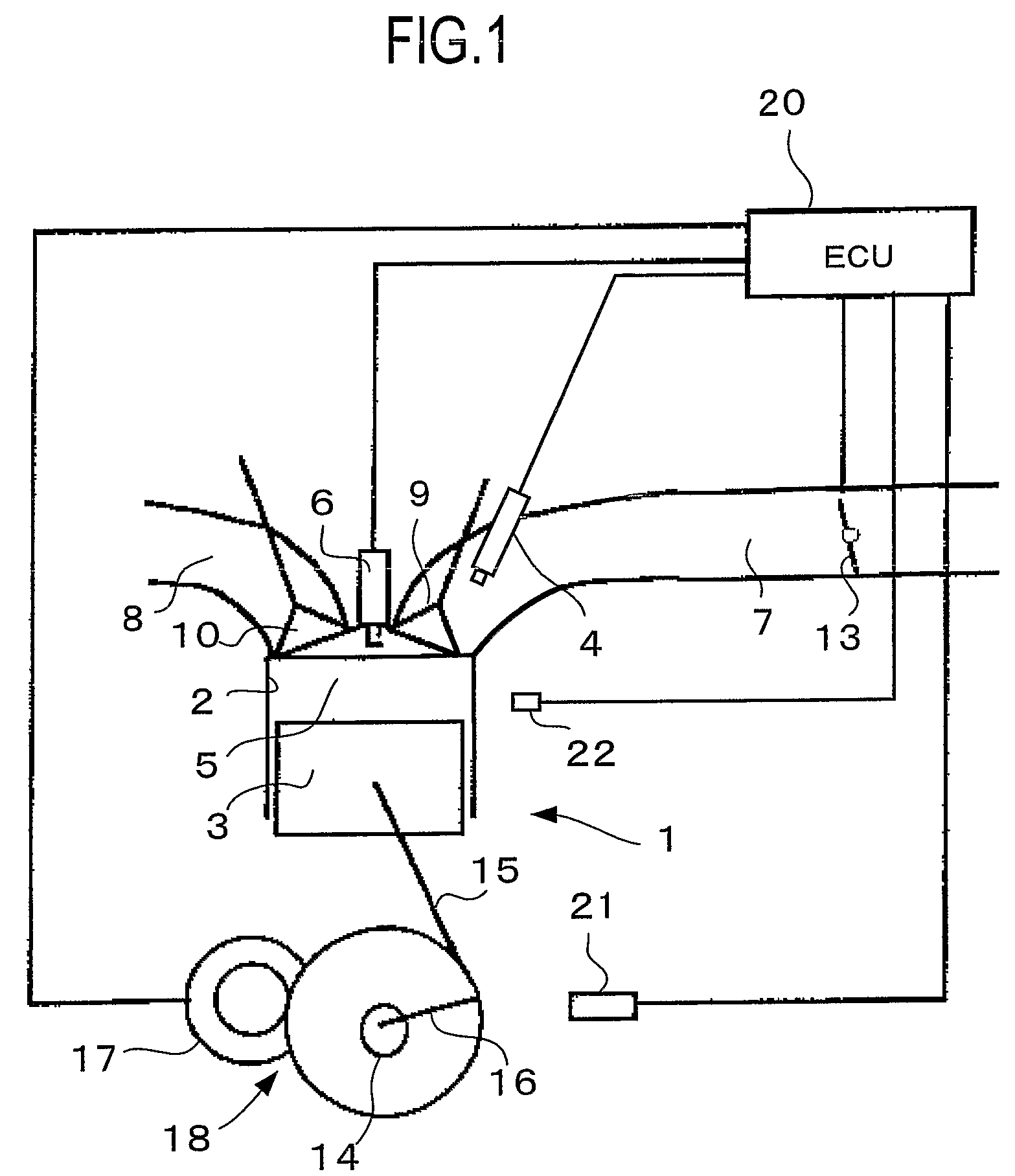
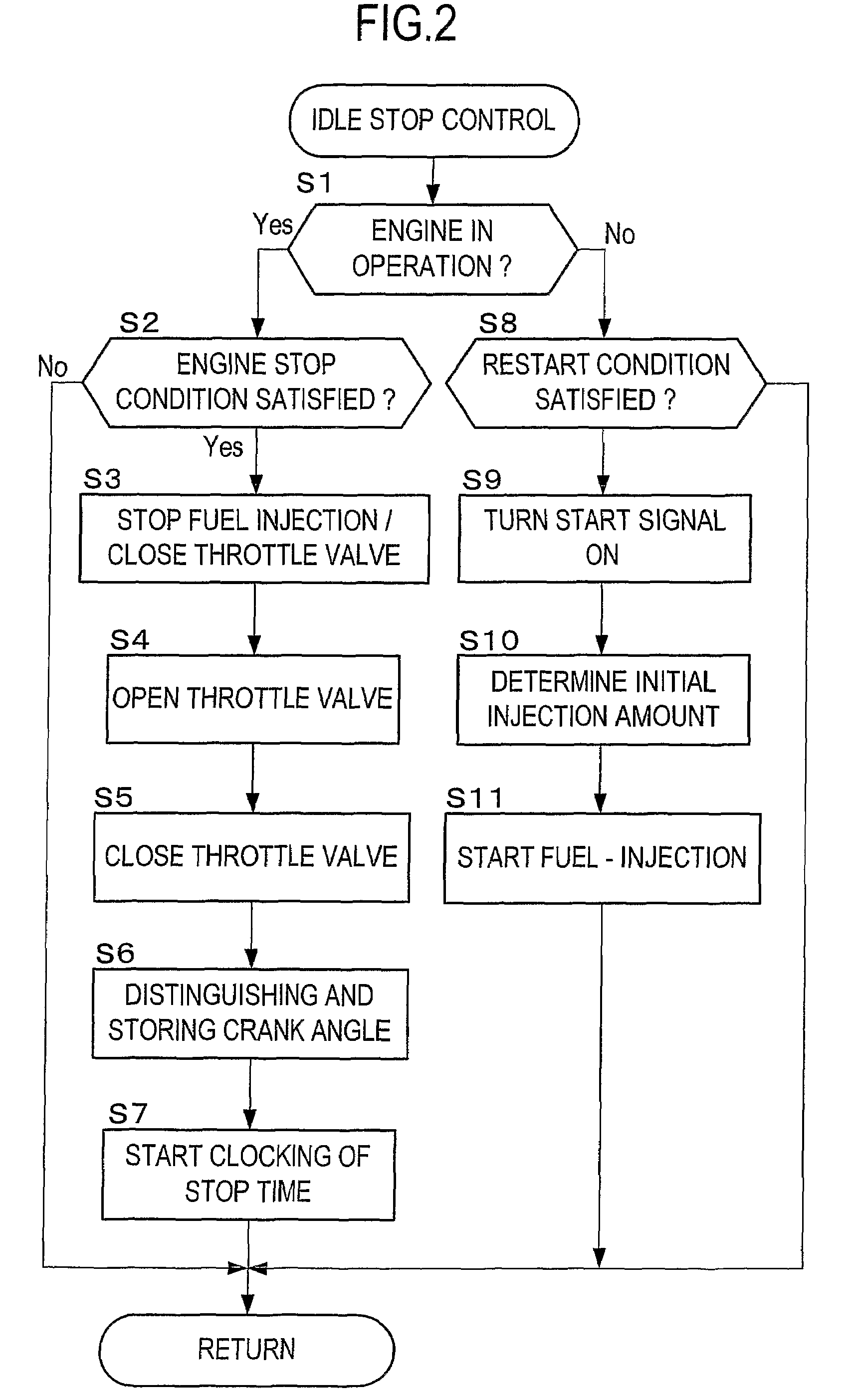
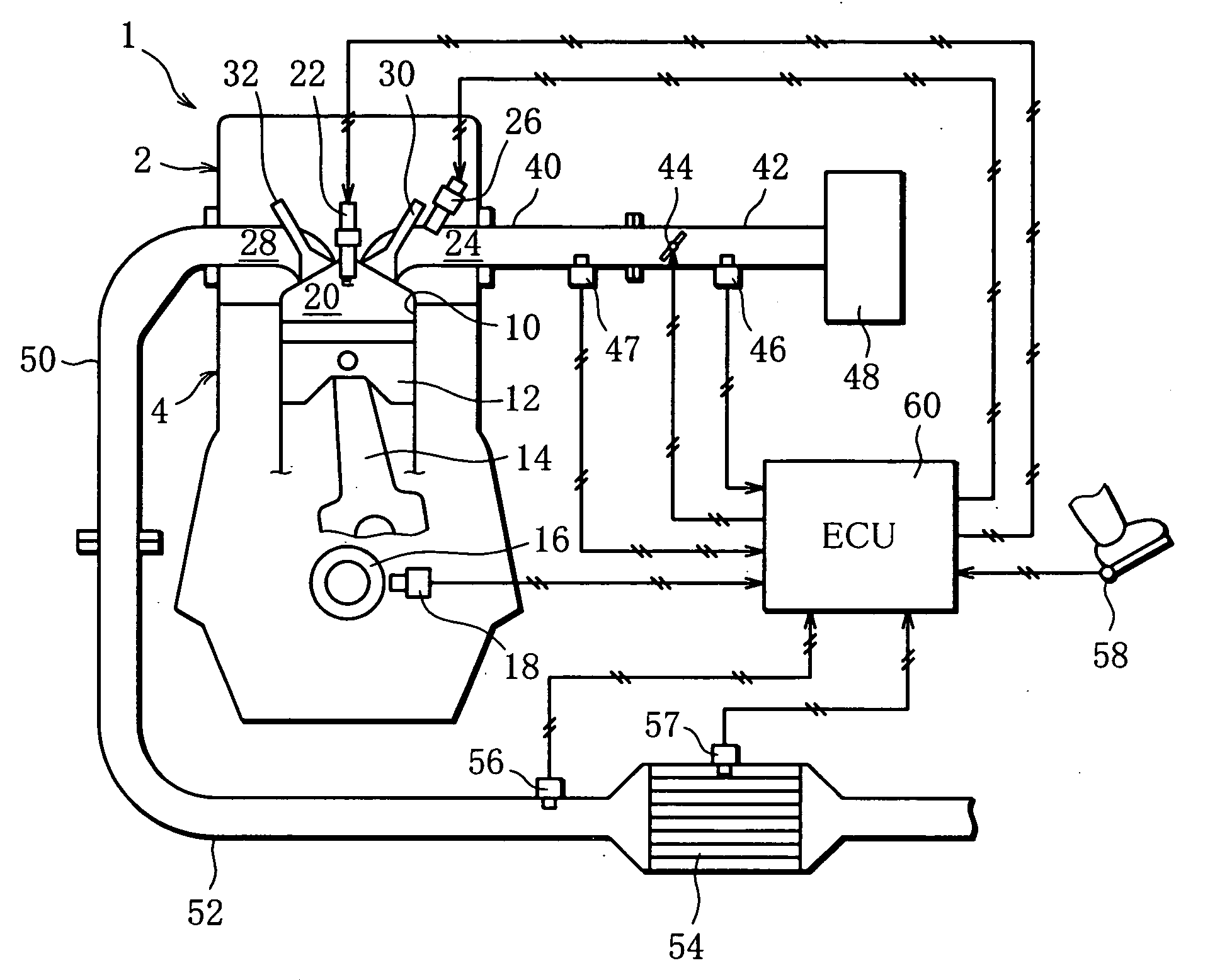
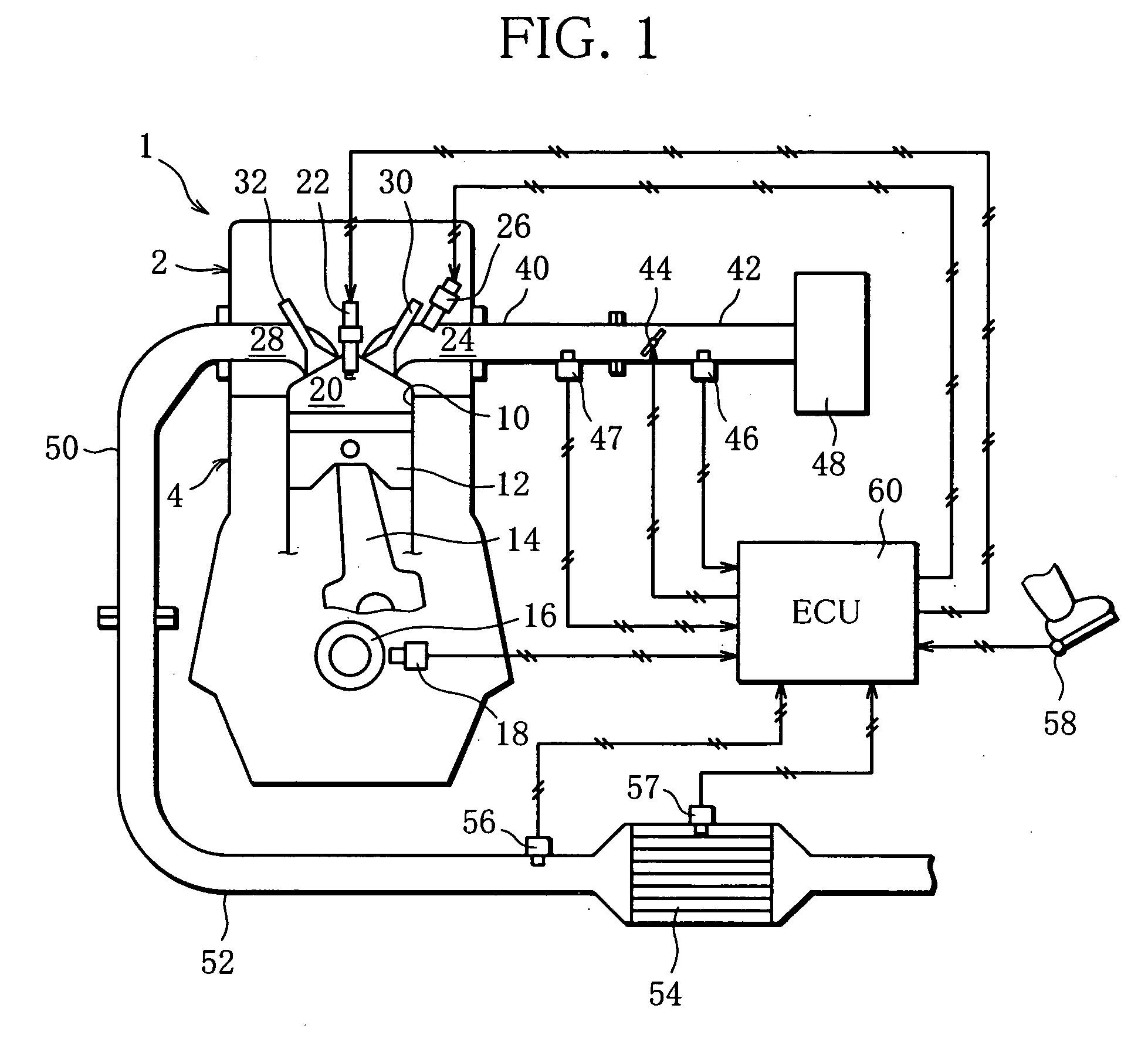
Start Control Apparatus for Internal Combustion Engine
InactiveUS20080154484A1Avoid it happening againIncrease pressureAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
There is provided a start control apparatus for an internal combustion engine (1) which starts the engine with injecting fuel to each cylinder (2) of the internal combustion engine in an intake stroke. The apparatus comprises a stop position distinction device (20) which distinguishes a piston position at a time of a stop of the internal combustion engine, and a fuel injection amount control device (20) which specifies a cylinder in which a piston stops in the intake stroke based on a distinction result of the stop position distinction device and which increases a fuel injection amount at starting for the specified cylinder more than a fuel injection amount for other cylinders.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
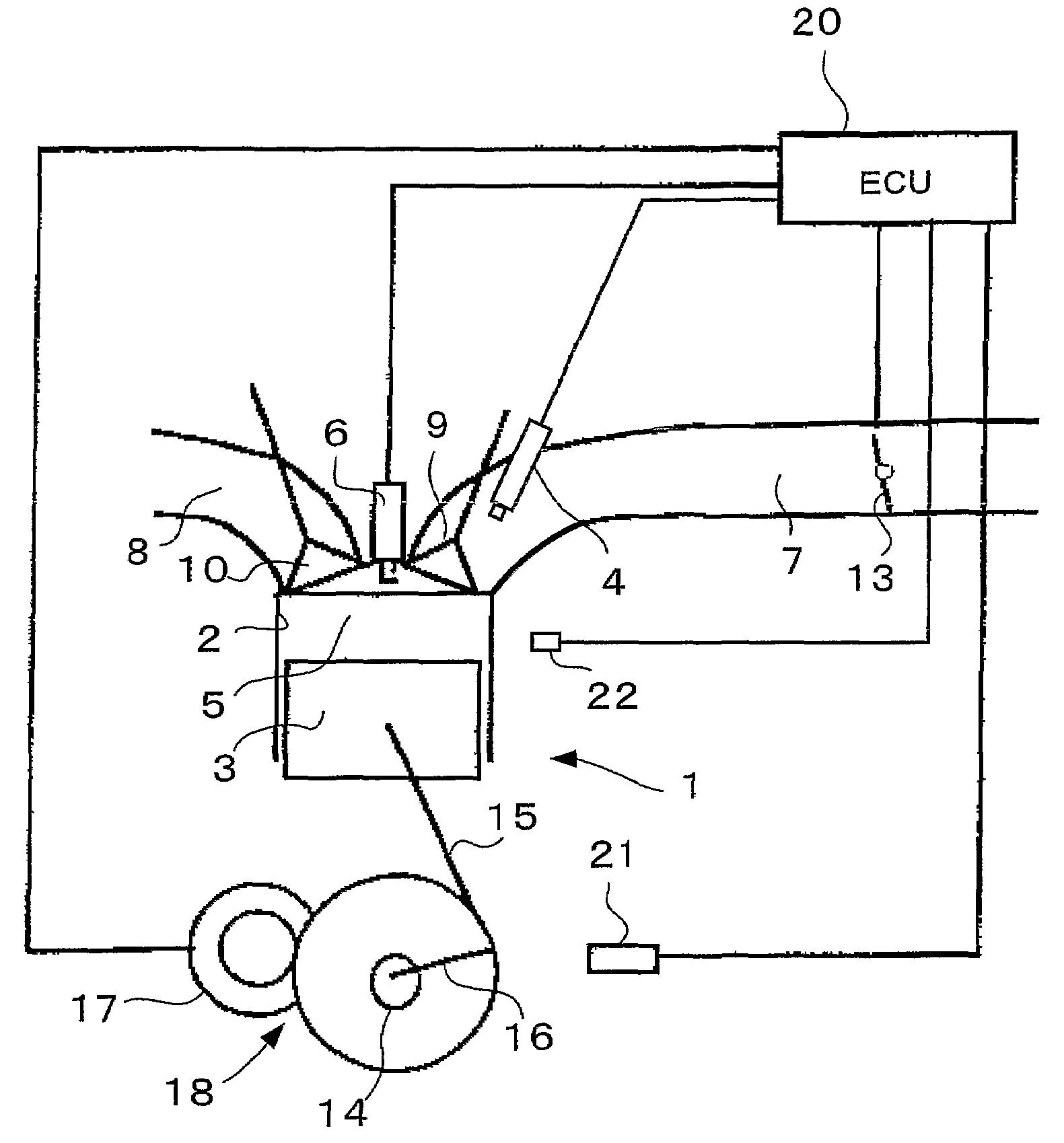
Start control apparatus for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7472016B2Suppress spontaneous combustionAvoid it happening againAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
There is provided a start control apparatus for an internal combustion engine (1) which starts the engine with injecting fuel to each cylinder (2) of the internal combustion engine in an intake stroke. The apparatus comprises a stop position distinction device (20) which distinguishes a piston position at a time of a stop of the internal combustion engine, and a fuel injection amount control device (20) which specifies a cylinder in which a piston stops in the intake stroke based on a distinction result of the stop position distinction device and which increases a fuel injection amount at starting for the specified cylinder more than a fuel injection amount for other cylinders.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Engine having multiple injector locations
InactiveUS20070215112A1Maintain ratio controlReduce fuel injectionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringInjector
A method for controlling a first and second injector of an engine, the first injector located in a first cylinder of the engine and the second injector located upstream of, and configured to inject fuel into, the first and a second cylinder of the engine, the method comprising of decreasing total injection from the first and second injectors when decreasing injection from the second injector, and increasing total injection from the first and second injectors when increasing injection of the second injector.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
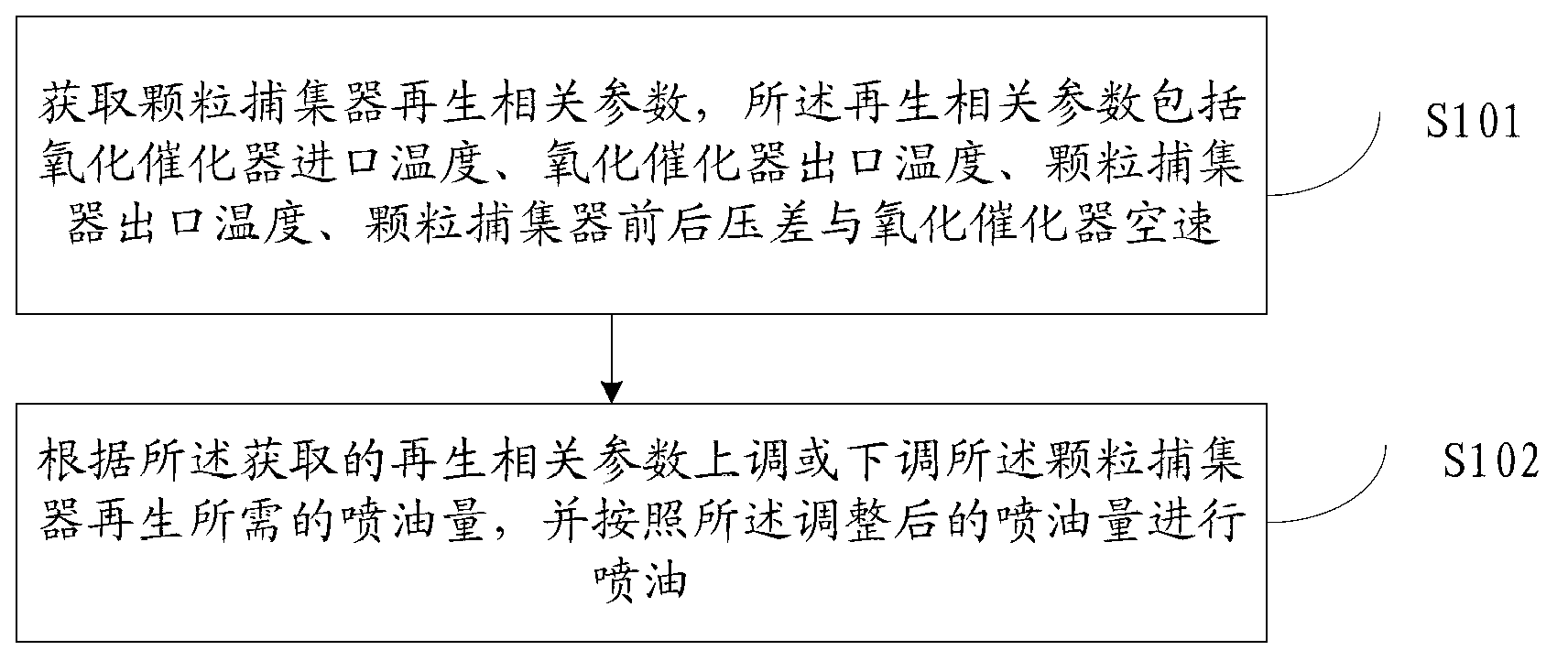
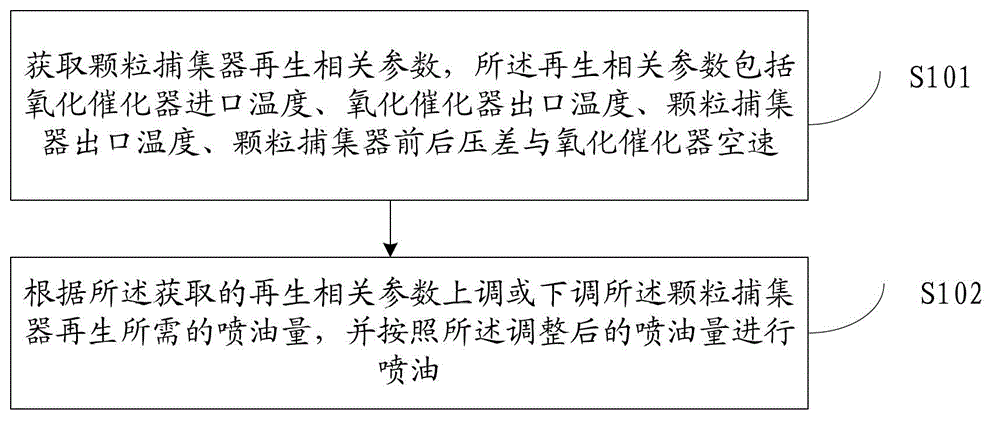
Control method and device for preventing regeneration and sintering of particle catcher
ActiveCN103016118AReduce fuel injectionIncrease fuel injectionInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusEngineeringPressure difference
The invention discloses a control method for preventing regeneration and sintering of a particle catcher. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring regeneration related parameters of the particle catcher, wherein the regeneration related parameters comprise inlet temperature of an oxidation catalyst, outlet temperature of the oxidation catalyst, outlet temperature of the particle catcher, pressure difference of the particle catcher and air speed of the oxidation catalyst; increasing or decreasing the fuel injection quantity required by regeneration of the particle catcher according to the acquired regeneration related parameters; and injecting fuel according to the adjusted fuel injection quantity. The invention further discloses a control device for preventing regeneration and sintering of the particle catcher.
Owner:WEICHAI POWER CO LTD
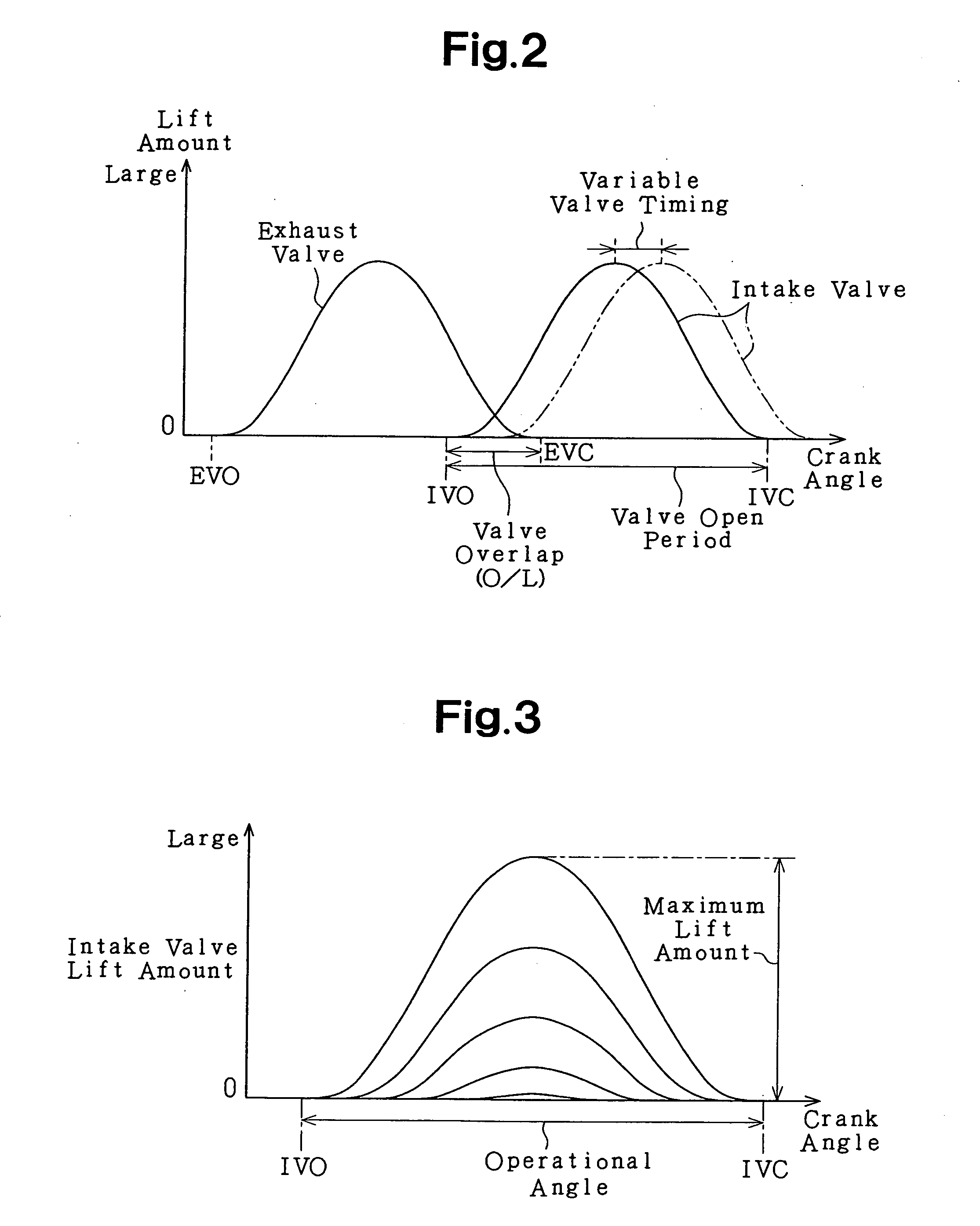
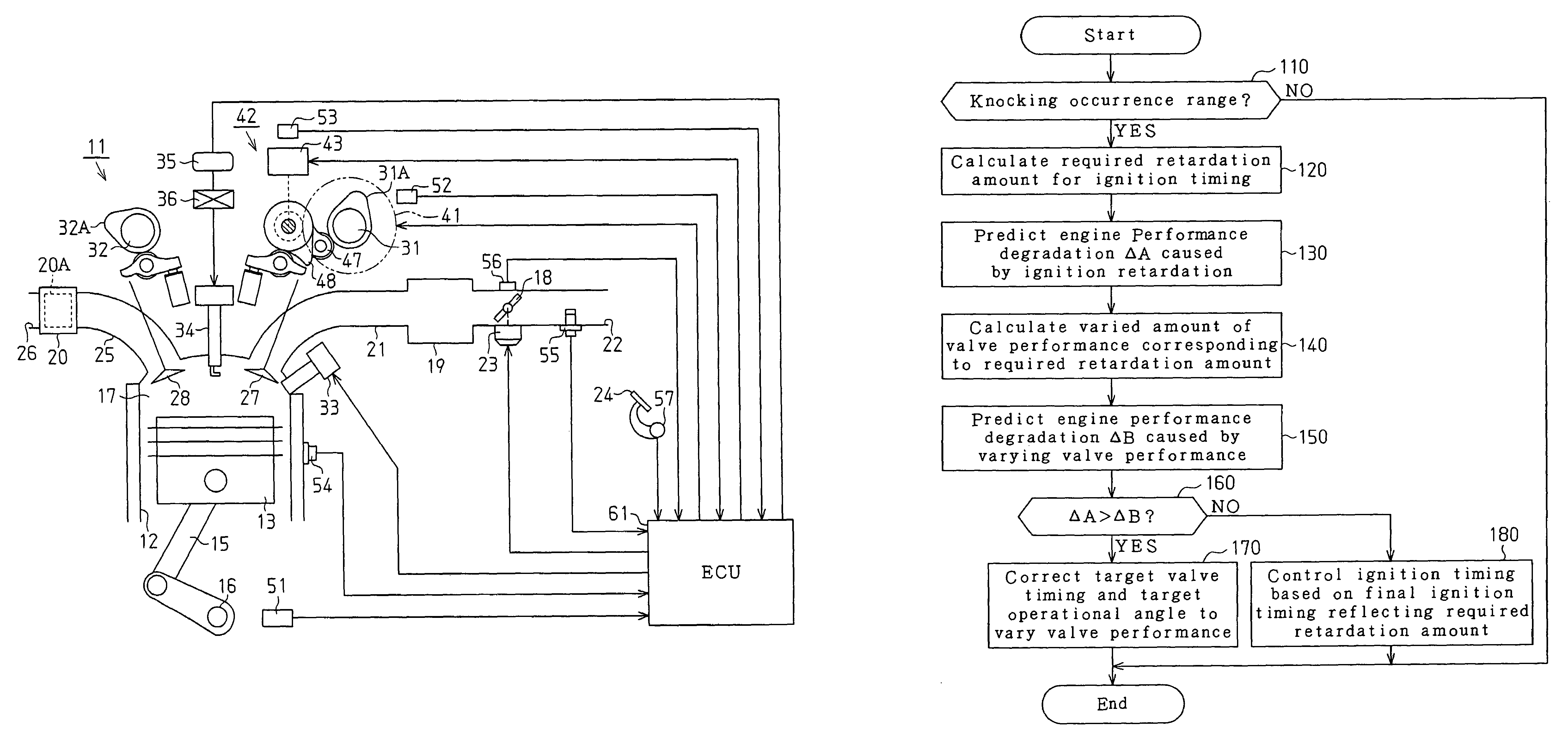
Engine valve performance controller
InactiveUS20060016407A1Avoid knockingReduce the temperatureValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberIgnition timing
A valve performance controller for use in an engine that performs ignition timing retardation control to prevent knocking. The controller variably controls valve performance of an intake valve in accordance with an operation state of the engine. The controller corrects a control target so that the compression end temperature of a combustion chamber decreases when a retardation amount of the ignition timing obtained through the retardation control is greater than a predetermined value. The correction is performed only when the engine performance degradation that would occur when the ignition timing is retarded in a state in which the control target is uncorrected is predicted to be greater than the engine performance degradation that would occur when the control target is corrected.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method and system for reducing unburned fuel and oil from exhaust manifolds
ActiveUS20100030448A1Increase exhaust temperatureReduce needElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsCombustionLow load
Methods and systems are provided for operating an internal combustion engine having an exhaust system and a plurality of cylinders that utilize fuel and / or oil for combustion and engine lubrication purposes. In one example, a method comprises, while the engine is operating in a low-load mode or an idle mode, successively operating distinct subsets of said cylinders at a cylinder load sufficient to increase an exhaust temperature for burning unburned fuel and / or oil deposited in the cylinders or engine exhaust system. Herein, each successively operated subset comprises at least one but fewer than all of the plurality of cylinders, and the cylinders that are not currently being operated in a subset are operated in a low- or no-fuel mode.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
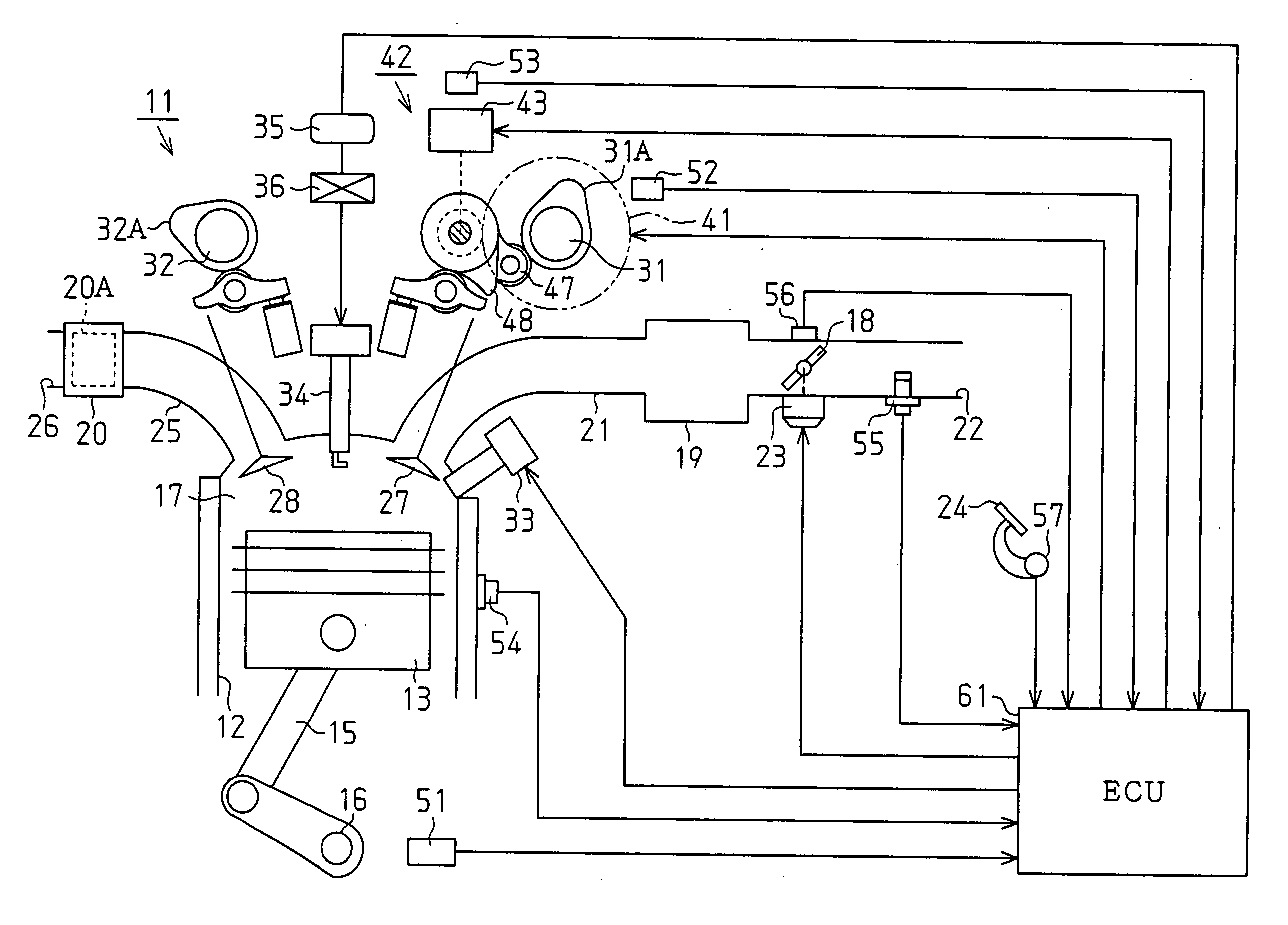
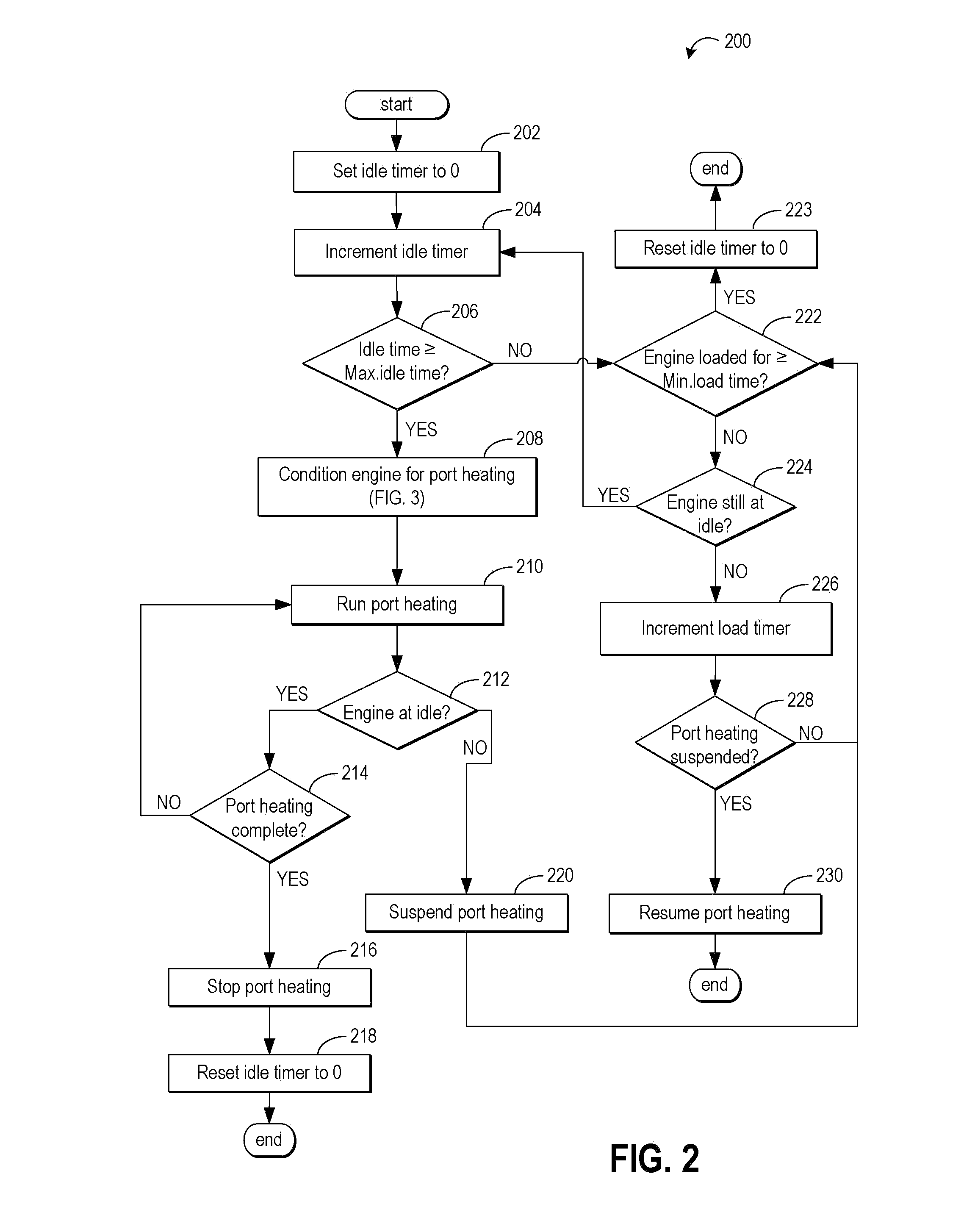
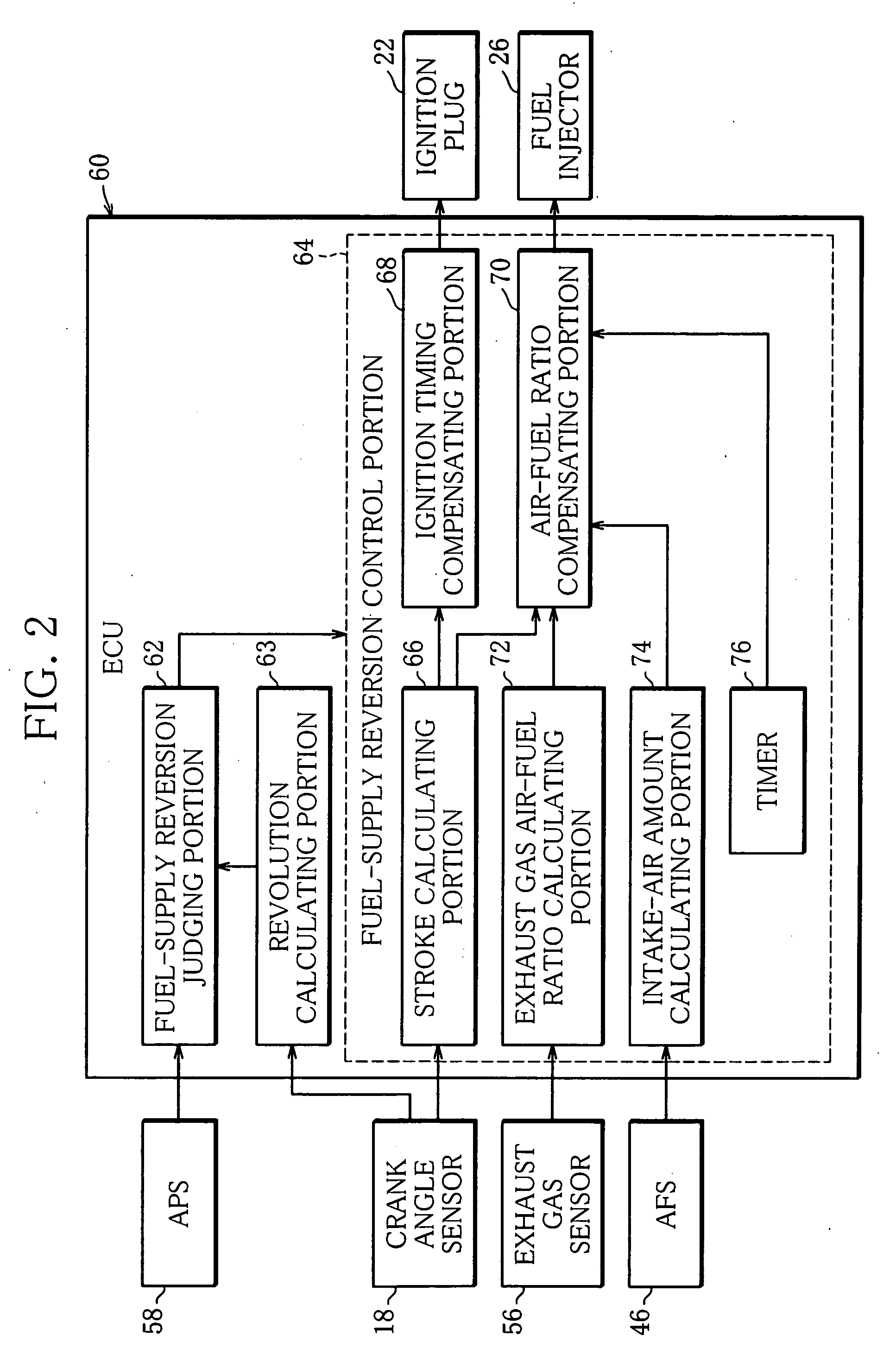
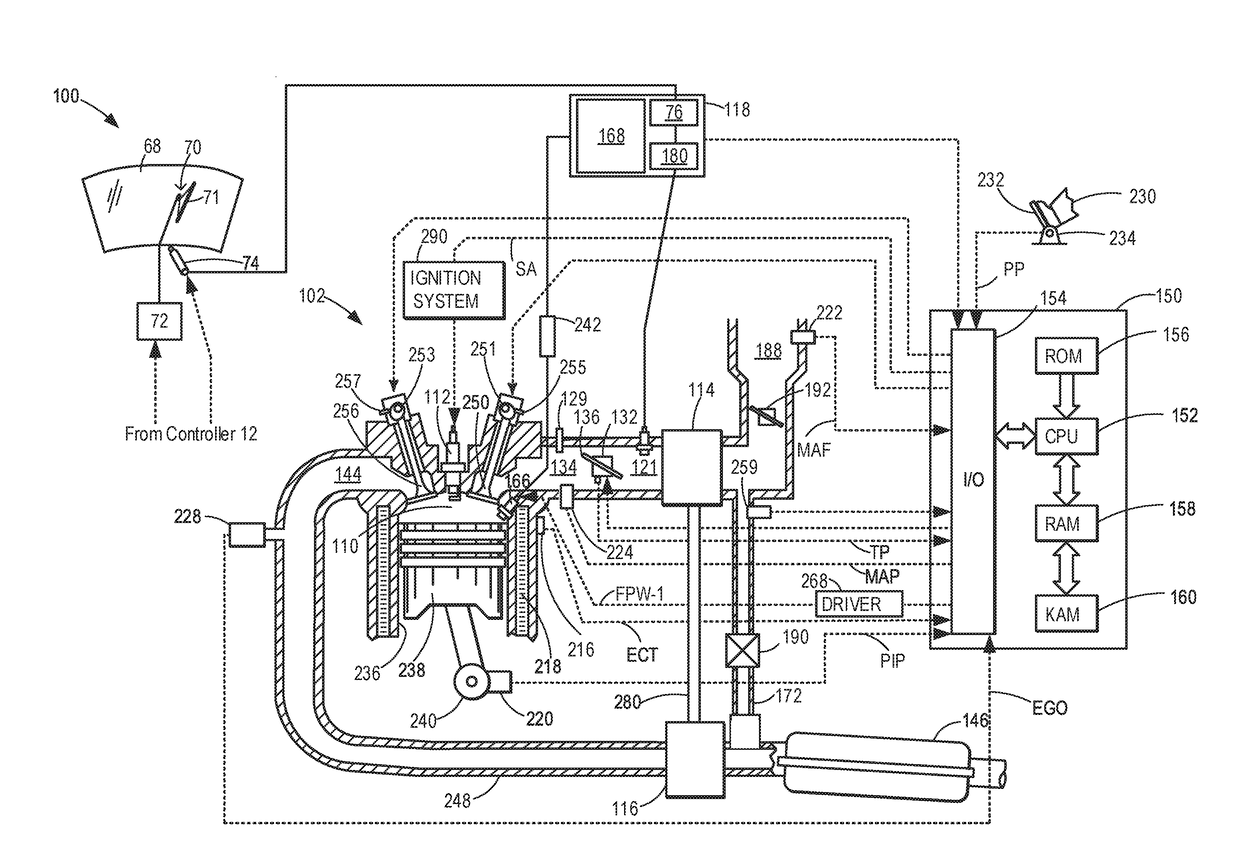
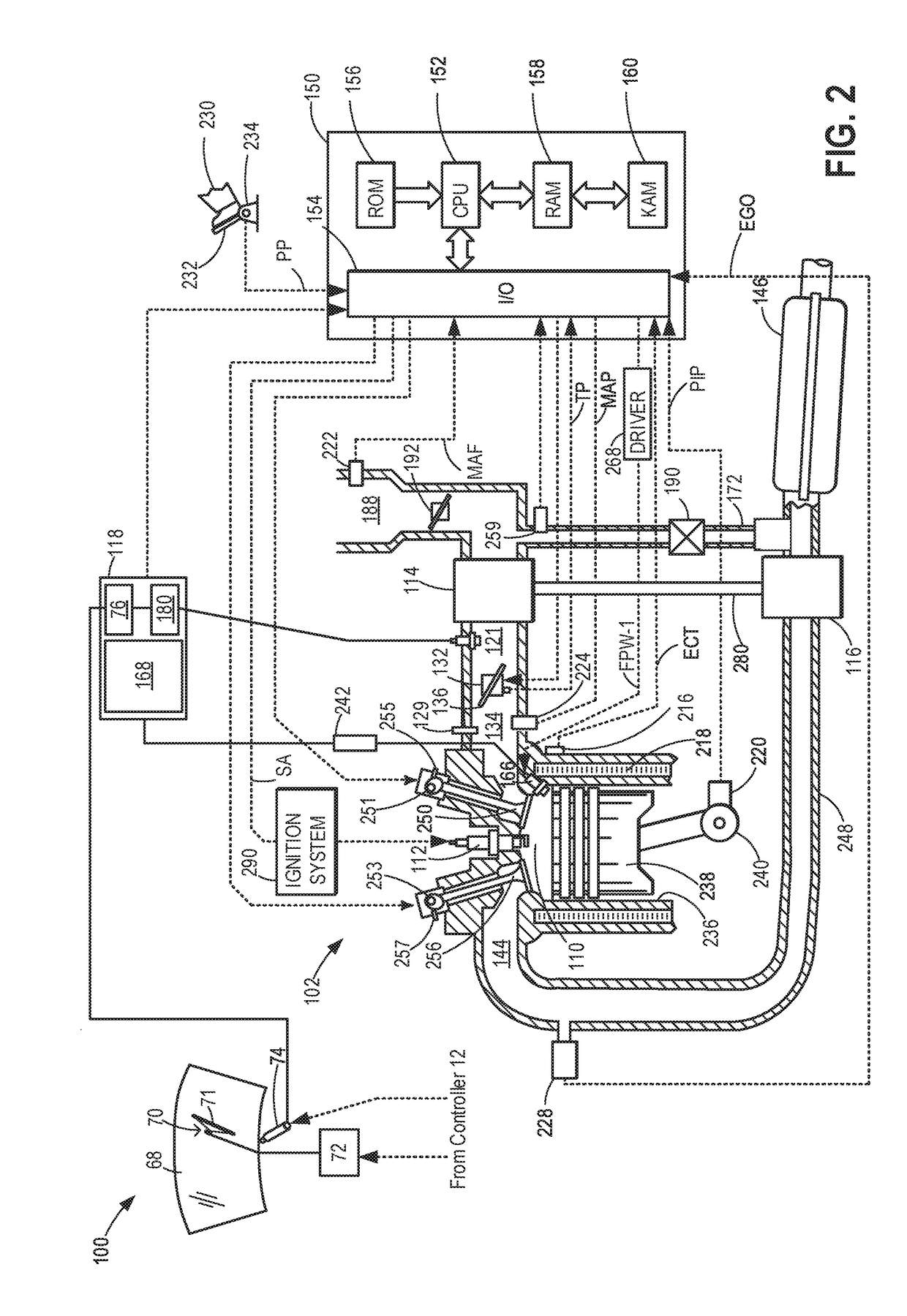
Controller of an internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20070062489A1Increase fuel injectionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringIgnition timing
When the first fuel injection is performed after reversion from the fuel cut, the fuel pulse width Ka·INJ.PW is set so that a fuel supply amount is greatly increased in relation to an intake air amount, and the ignition timing is set to the first retarded ignition timing θa. When the second and subsequent fuel injections are performed, the fuel pulse width Kb·INJ.PW that is smaller in increase width of fuel is set, and the ignition timing is set to the second retarded ignition timing θb that has a retardation amount smaller than that of the first retarded ignition timing θa.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORP
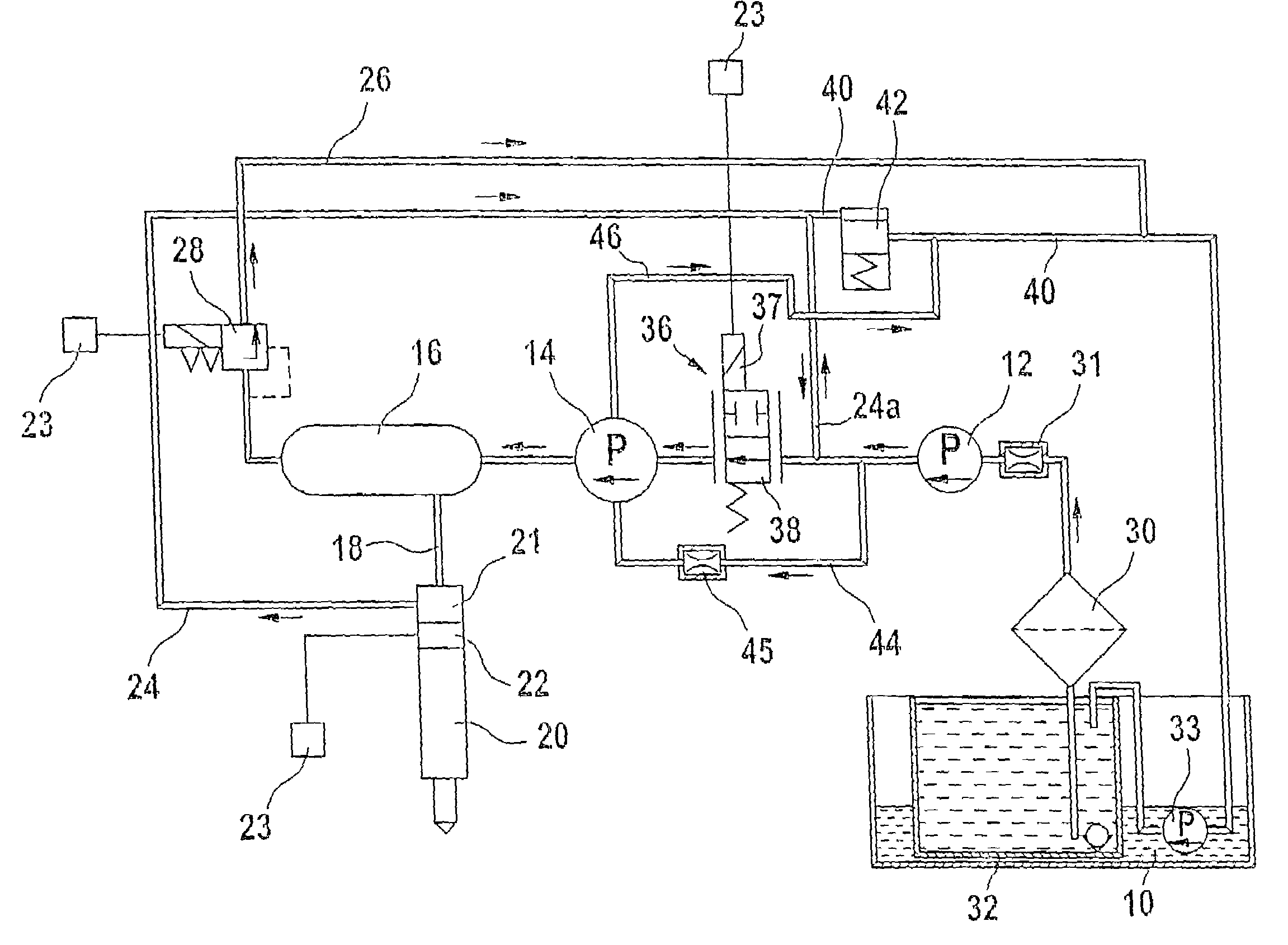
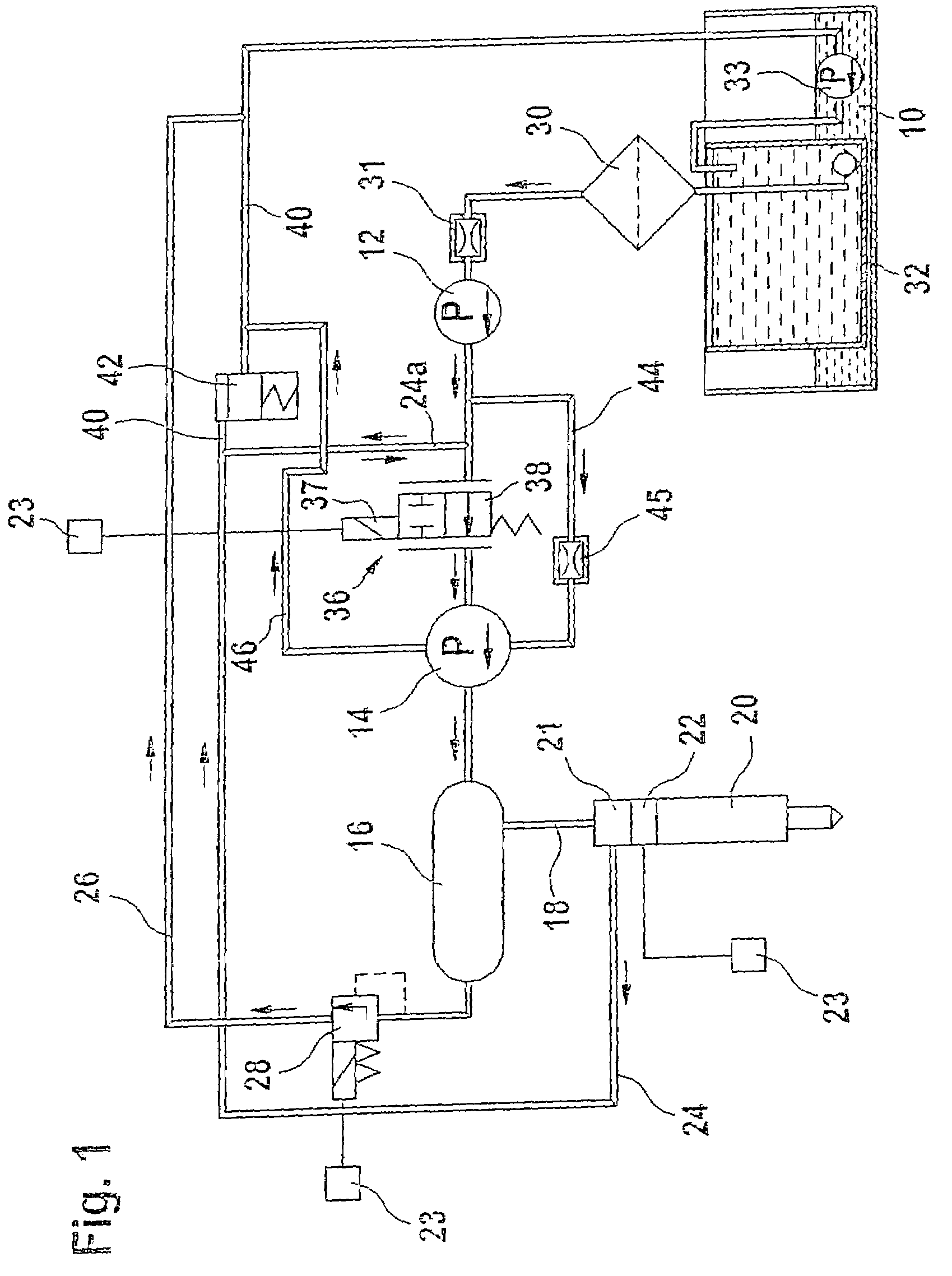
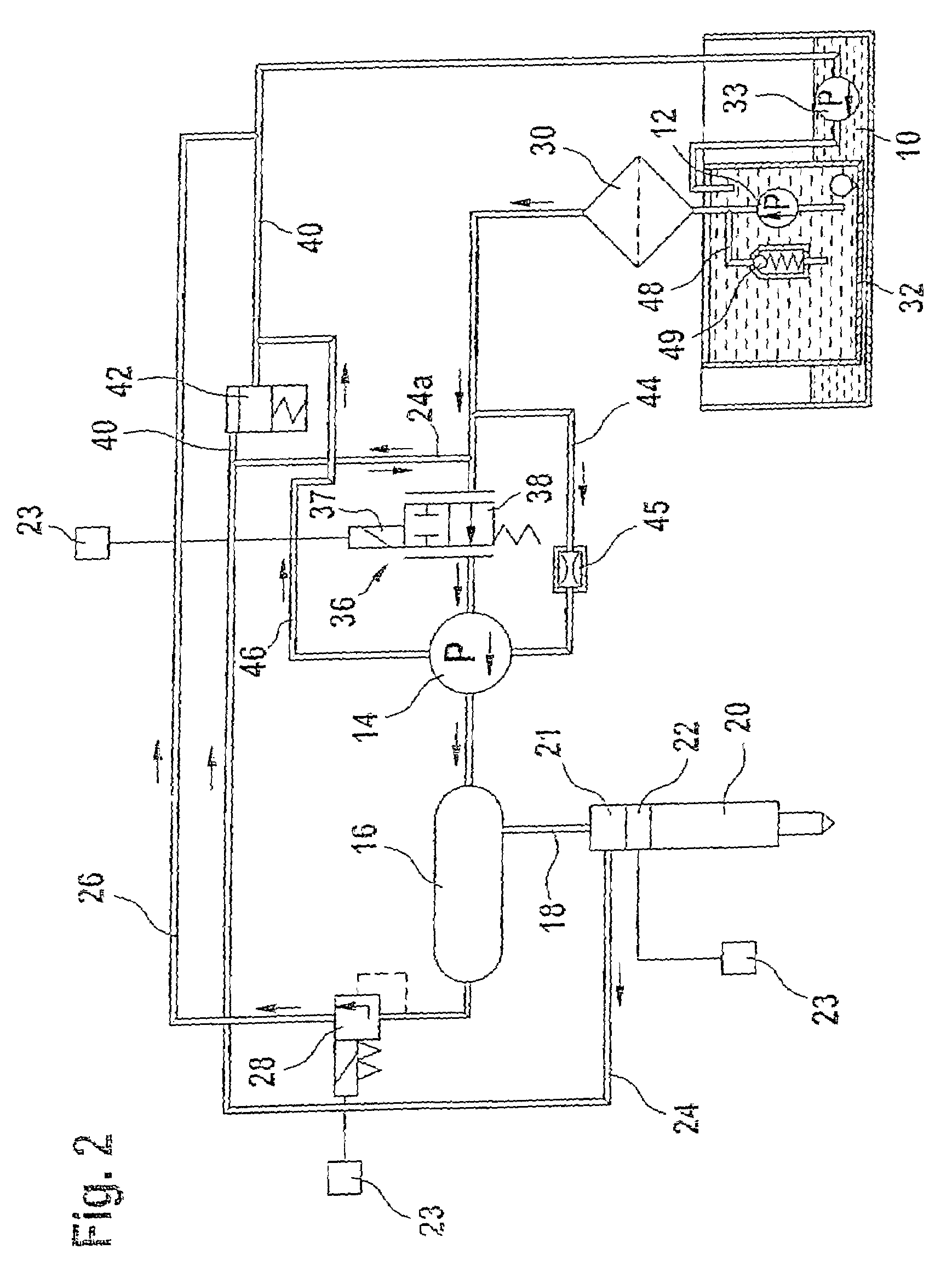
Fuel injection device for an internal combustion engine
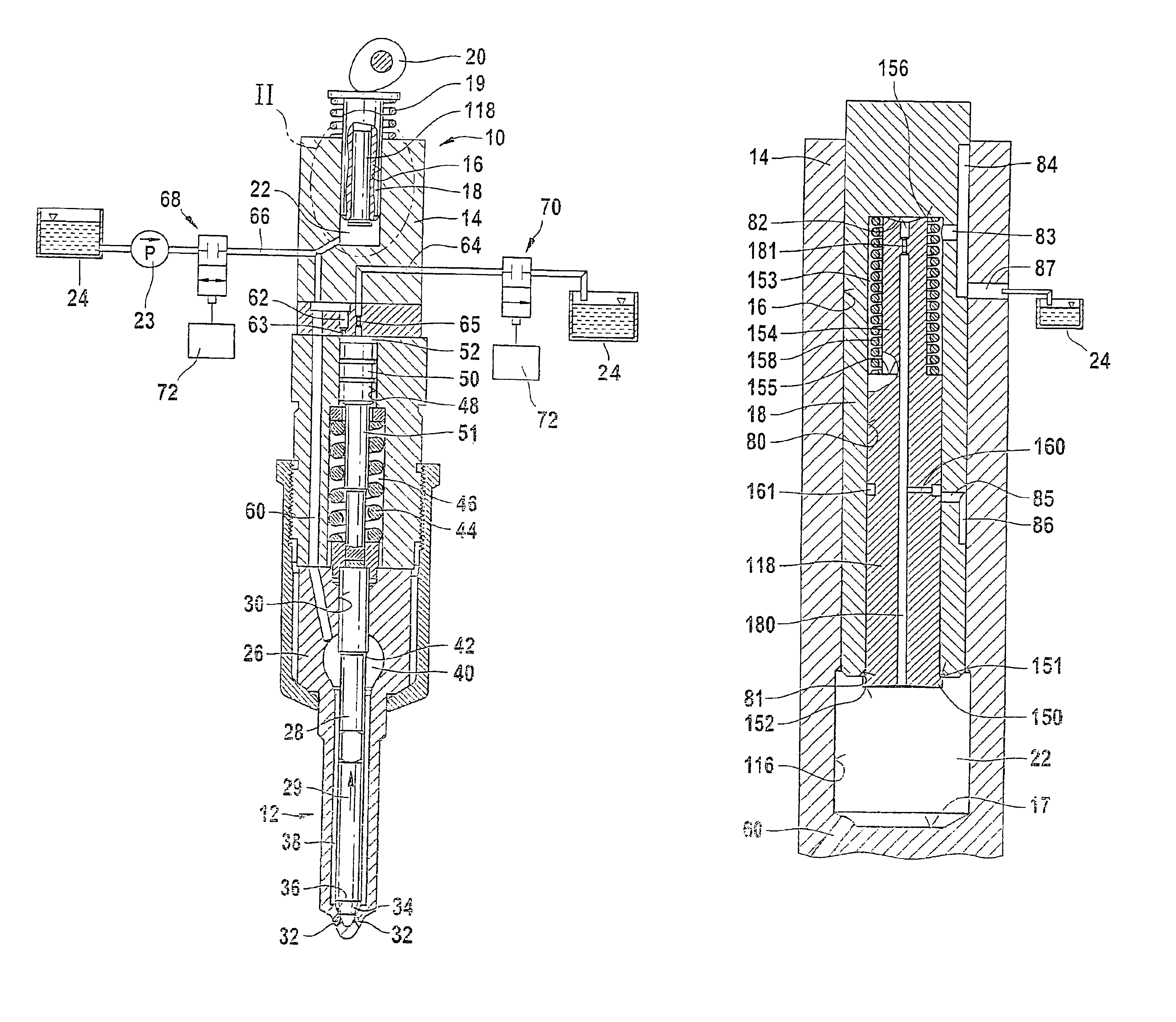
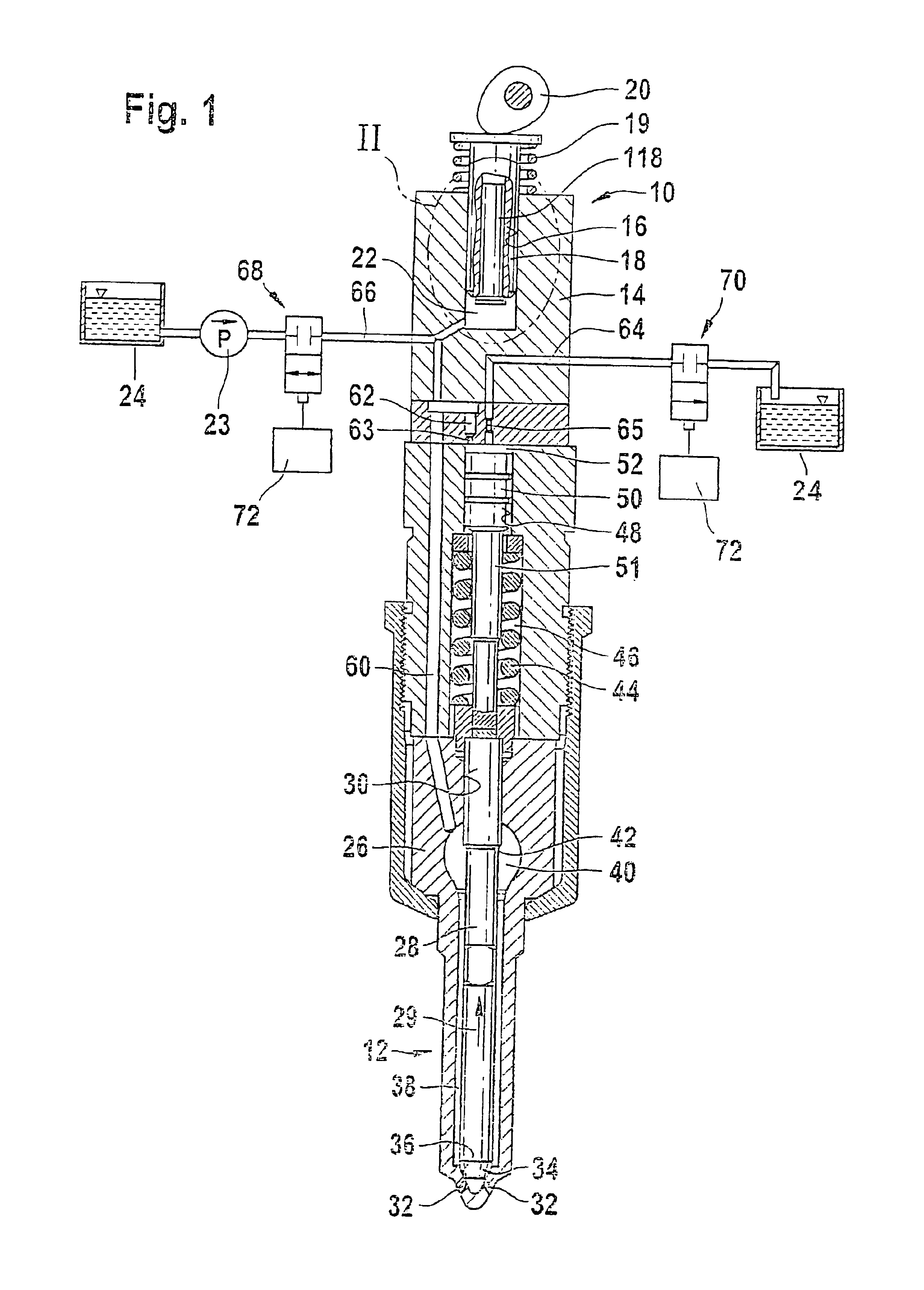
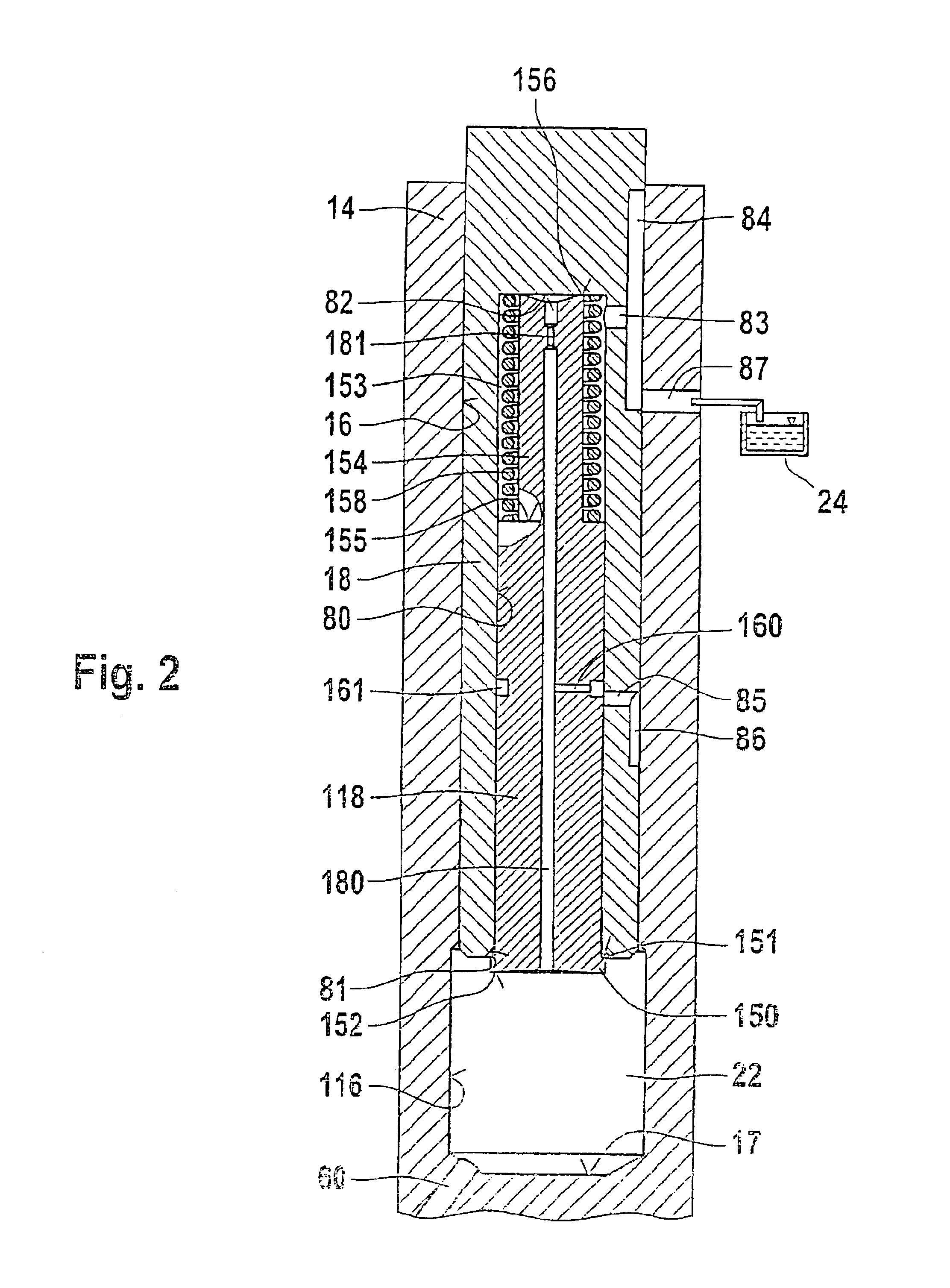
InactiveUS7219654B2Minimize space required and weight and costIncrease fuel injectionMachines/enginesFuel injecting pumpsInternal combustion engineHigh pressure
The fuel injection system has a high-pressure pump that delivers fuel to an accumulator and fuel supply pump delivers fuel to the suction side of the high-pressure pump, with a fuel metering unit between the fuel supply and high-pressure pumps to variably adjust the fuel quantity taken in by the high-pressure pump. The accumulator is connected to at least one fuel injector and a return leads from the fuel injector(s). The fuel return from the injector(s) feeds into the connection between the fuel supply pump and the fuel metering unit. A connection controlled by a pressure valve leads from the fuel return to a discharge region. The high-pressure pump only draws fuel from the fuel return in operating states in which the fuel quantity delivered by the fuel supply pump is less than the required intake quantity of the high-pressure pump.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Engine valve performance controller
InactiveUS7152560B2Reduce the temperatureAvoid excessive heatValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberInlet valve
A valve performance controller for use in an engine that performs ignition timing retardation control to prevent knocking. The controller variably controls valve performance of an intake valve in accordance with an operation state of the engine. The controller corrects a control target so that the compression end temperature of a combustion chamber decreases when a retardation amount of the ignition timing obtained through the retardation control is greater than a predetermined value. The correction is performed only when the engine performance degradation that would occur when the ignition timing is retarded in a state in which the control target is uncorrected is predicted to be greater than the engine performance degradation that would occur when the control target is corrected.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel injection control device
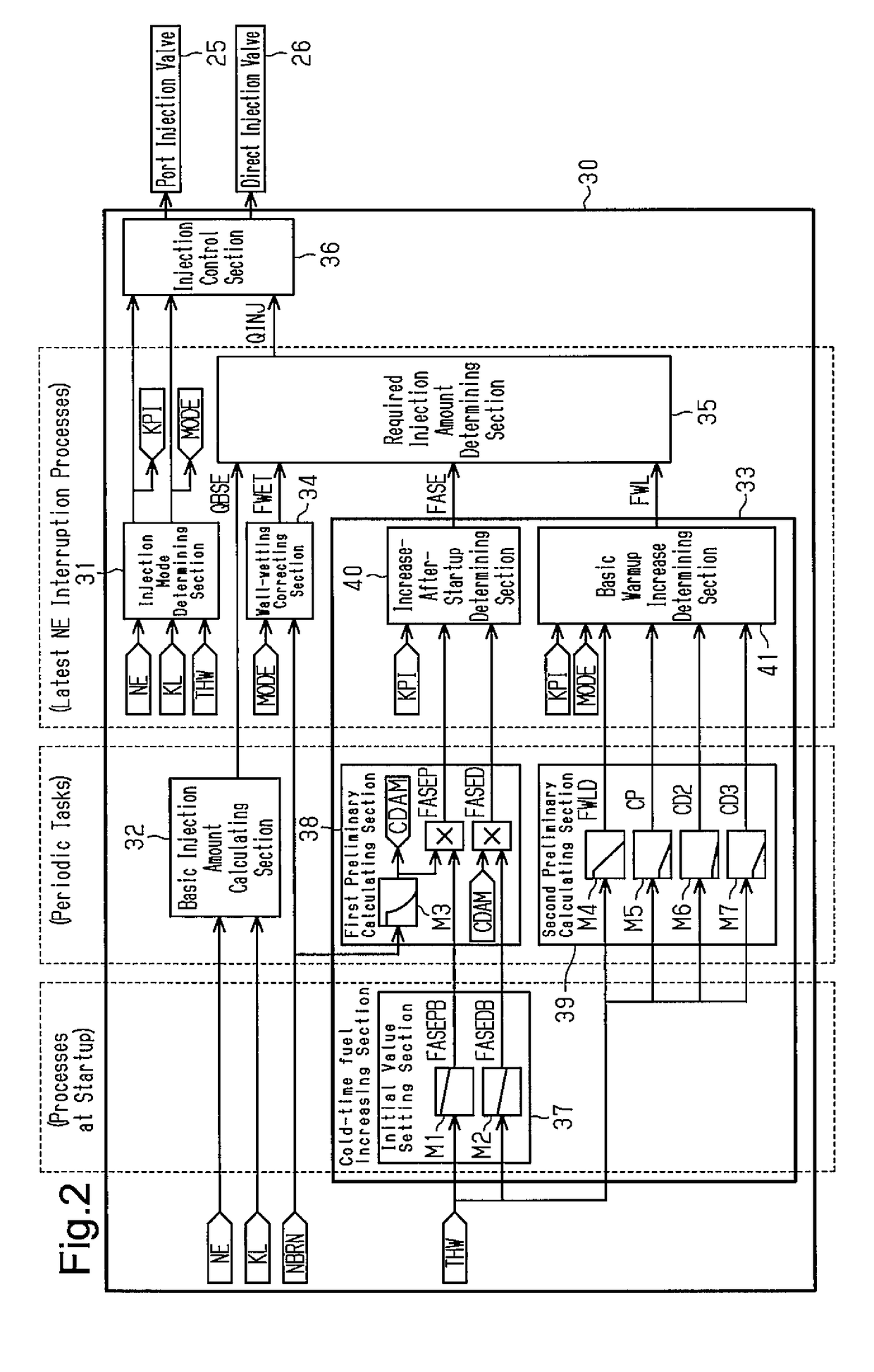
ActiveUS20180230928A1Increase fuel injectionElectrical controlMachines/enginesCombustionExternal combustion engine
A cold-time fuel increasing section calculates, as increase correction values for a required injection amount, an increase-after-startup correction value, which attenuates with an increment of the number of times of combustion carried out after startup of the internal combustion engine, and a basic warmup increase correction value, which attenuates with an increase in a temperature of coolant in the internal combustion engine. The cold-time fuel increasing section calculates the increase correction values such that the increase-after-startup correction value when the port injection mode is selected is greater than the increase-after-startup correction value when the single direct injection mode is selected, and that the basic warmup increase correction value when the port injection mode is selected is less than the basic warmup increase correction value when the single direct injection mode is selected.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
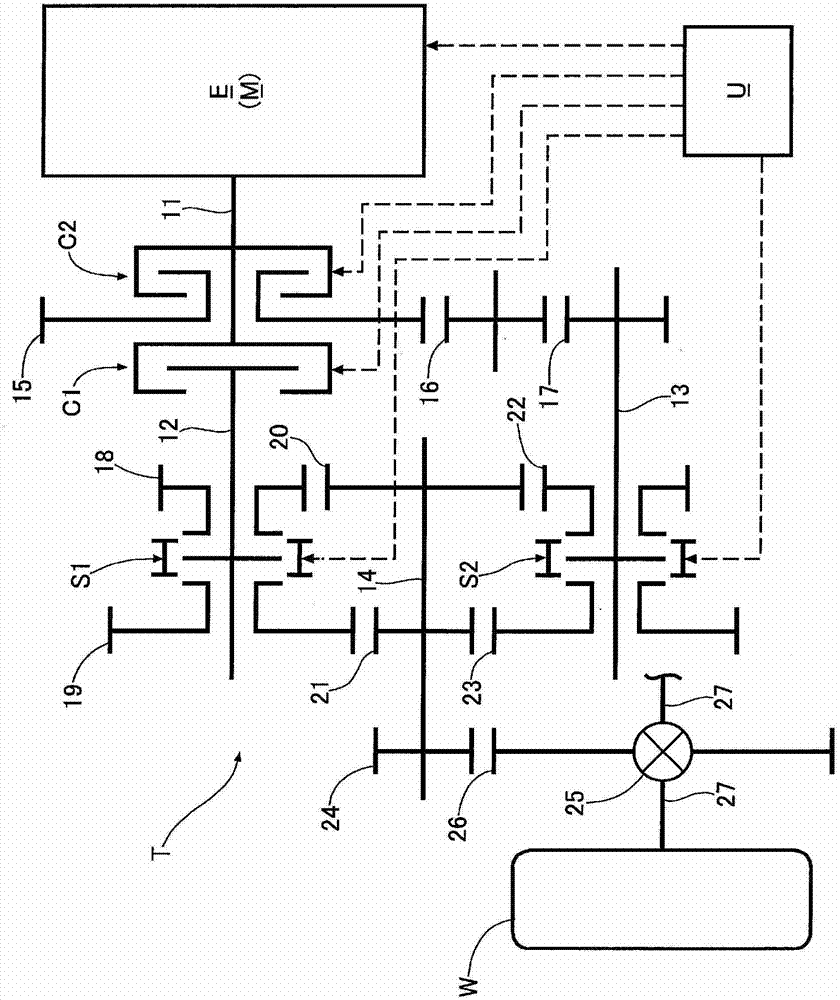
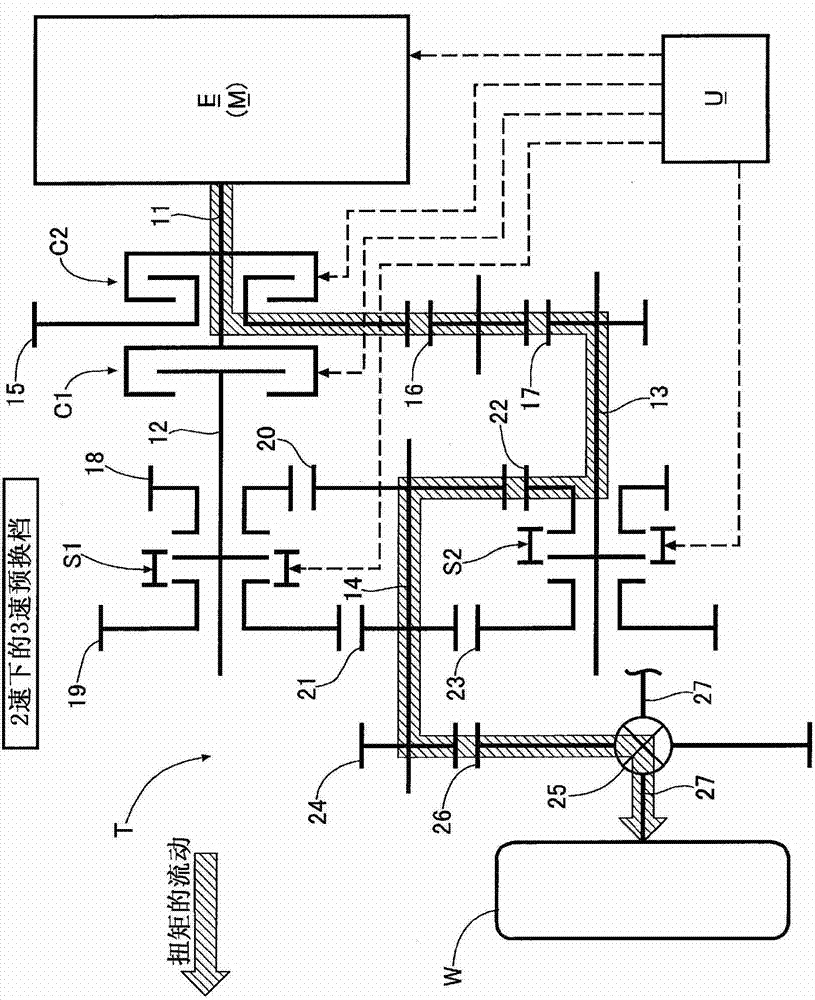
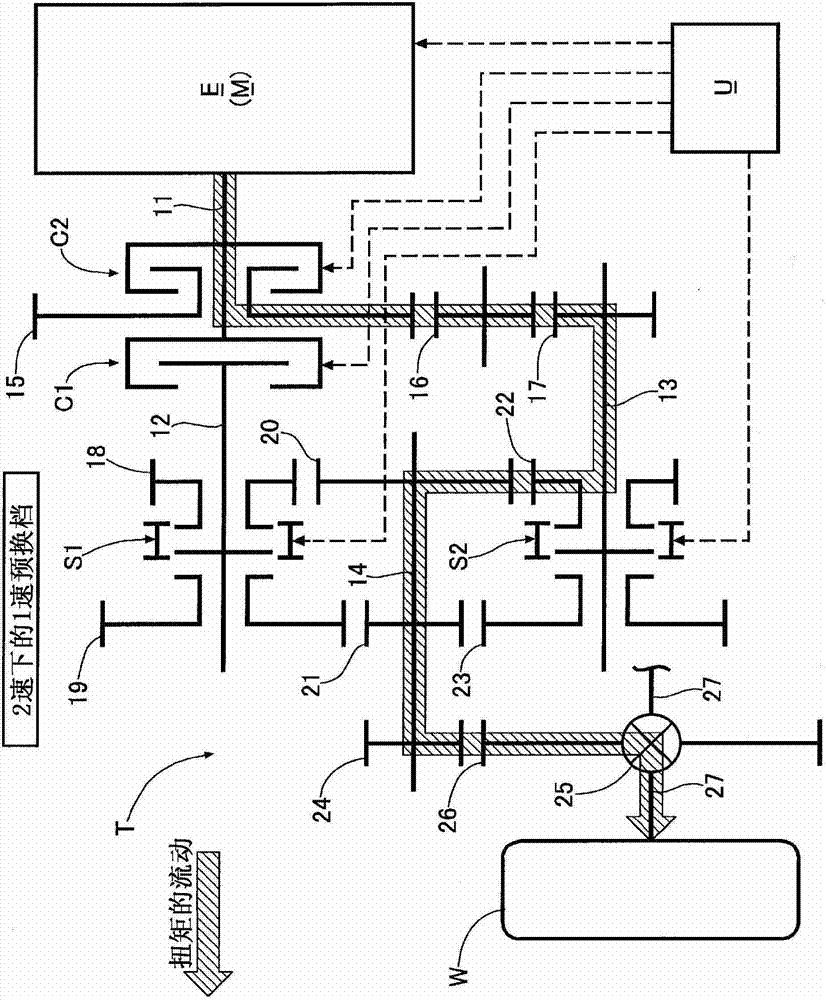
Dual clutch transmission
ActiveCN102959210ASuppress changesReduce shift shockElectrical controlToothed gearingsExternal combustion engineEngineering
Disclosed is a dual clutch transmission wherein, during a pre-shifting operation wherein, when a vehicle is driven using either a first or a second drive force transmission path extending from first and second input shafts (12, 13) to an output shaft (14), a synchronizer (S1, S2) of the other drive force transmission path is operated, the drive force of an internal combustion engine (E) is changed by a command from an electronic control unit (U), and accordingly, even when a drive force or a braking force is generated by inertia, due to a change in the number of rotations of the first and second input shafts (12, 13) in conjunction with the pre-shifting operation, the drive force or the braking force generated by inertia can be compensated by a change in the drive force of the internal combustion engine (E), to reduce shift-shock. Furthermore, the shift-shock can be reduced by only changing the drive force of the internal combustion engine (E) without adding any special structures to the dual clutch transmission (T), and accordingly, the cost and size of the dual clutch transmission (T) can be prevented from increasing.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method of supplying liquid gas to an internal combustion engine, a fuel supply system and a fuel supply aggregate
InactiveUS6953029B2Reduces throttle lossIncrease fuel injectionConveyorsInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineLiquid state
A method and apparatus are provided for supplying liquid gas as fuel to an internal combustion engine. From the liquid gas stream that is supplied to at least one liquid gas injection valve of the internal combustion engine, a portion is branched off and expanded. The liquid gas stream supplied to the internal combustion engine is cooled with coldness that results during the expansion, thus ensuring that the liquid gas stream supplied to the liquid gas injection valve is at least substantially liquid. The expanded liquid gas is supplied in a vaporous state to the internal combustion engine.
Owner:PAUL UITENBROEK HLDG BV
Systems and methods for removing coking deposits in a fuel injection system
InactiveUS20170306892A1Increased particle emissionReduce the amount requiredNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesFuel injectionInjector
Methods and systems are provided for reducing coking deposits in a fuel injection system. In one example, a method may comprise humidifying intake air of an intake system of an engine in response to a determination that fuel injector coking is occurring, or after a duration has passed since a most recent humidification event. A humidifying fluid, such as water, may be injected into the intake system to humidify the intake air, and the resulting humidified intake air may reduce and / or remove coking deposits on one or more direct fuel injectors of the fuel injection system.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
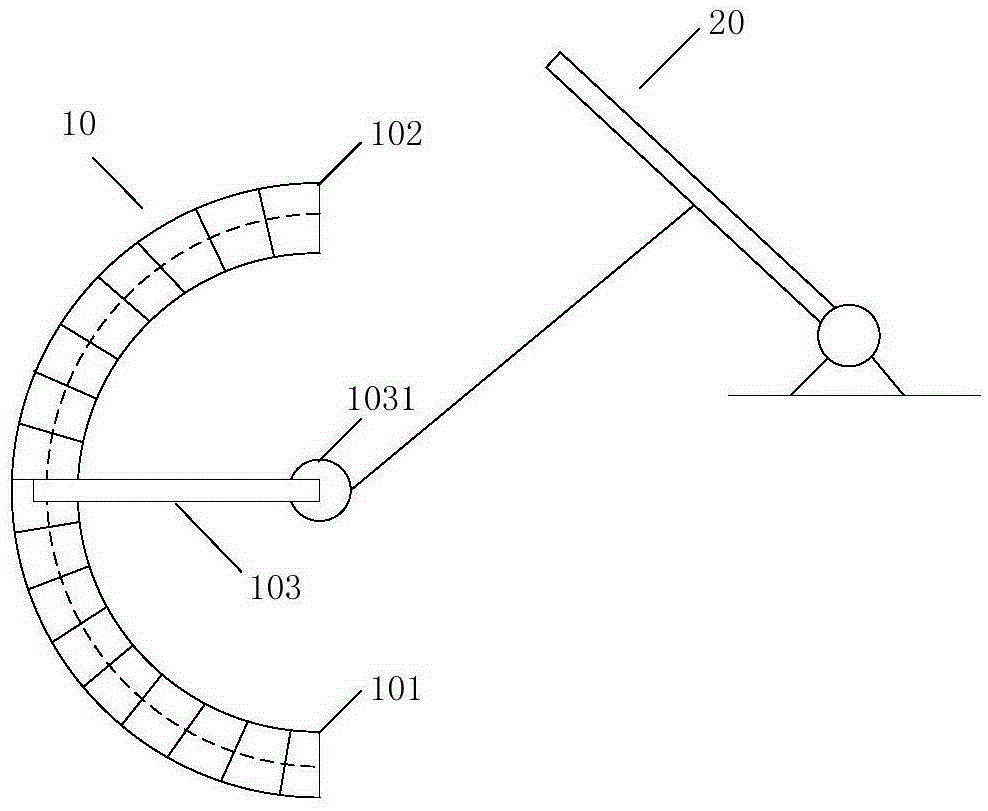
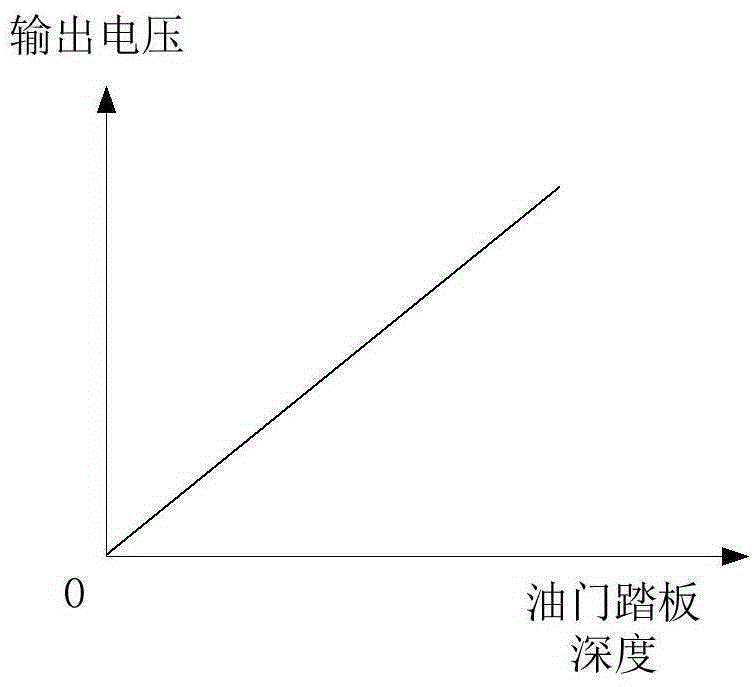
Contact-type throttle pedal position sensor, throttle control system and vehicle
ActiveCN105318832ALarge openingIncrease fuel injectionEngine controllersMachines/enginesThrottle controlElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a contact-type throttle pedal position sensor, a throttle control system and a vehicle. The contact-type throttle pedal position sensor comprises a slide rheostat which comprises a coil and a brush, wherein the coil comprises a first end and a second end; under the condition of loading an input voltage between the first end and the second end, the output voltage between the first end and the brush is used for expressing the depth of a throttle pedal, wherein the coil is configured such that the unit length resistance of the coil gradually decreases from the first end to the second end. Accordingly, when starting or driving at a low speed, the vehicle can rapidly speed up by lightly stepping on the throttle pedal, thereby meeting power demands more rapidly.
Owner:BEIQI FOTON MOTOR CO LTD
Fuel injection system comprising a fuel-guiding component, a fuel injection valve and a mounting
ActiveUS20160003205A1Reduce noiseIncrease fuel injectionNoise reducing fuel injectionMachines/enginesShaft collarFuel injection
A mounting is provided for fuel injection systems, the mounting connecting a fuel injection valve to a fuel-conducting component, and having a connecting body and a connecting piece that are connected to one another. Inside the connecting body and the connecting piece there is configured a receptacle space in which a fuel connector of the fuel injection valve is at least partly situated. An inner collar is configured on the connecting piece. In addition, an elastically deformable element is provided. The elastically deformable element is supported at least indirectly on the inner collar of the connecting piece. In addition, the fuel connector is supported at least indirectly on the elastically deformable element. In addition, a fuel injection system having such a mounting is described.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
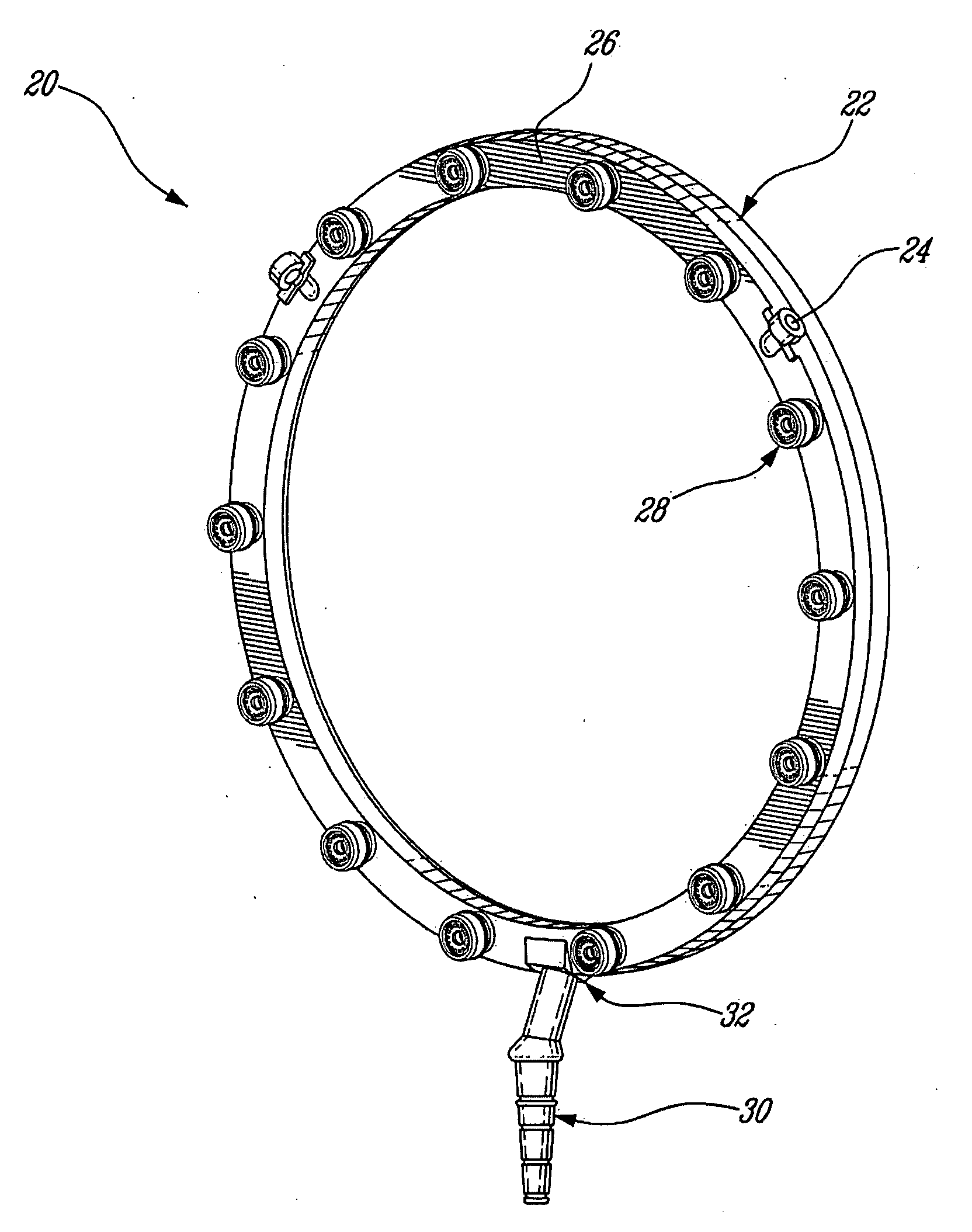
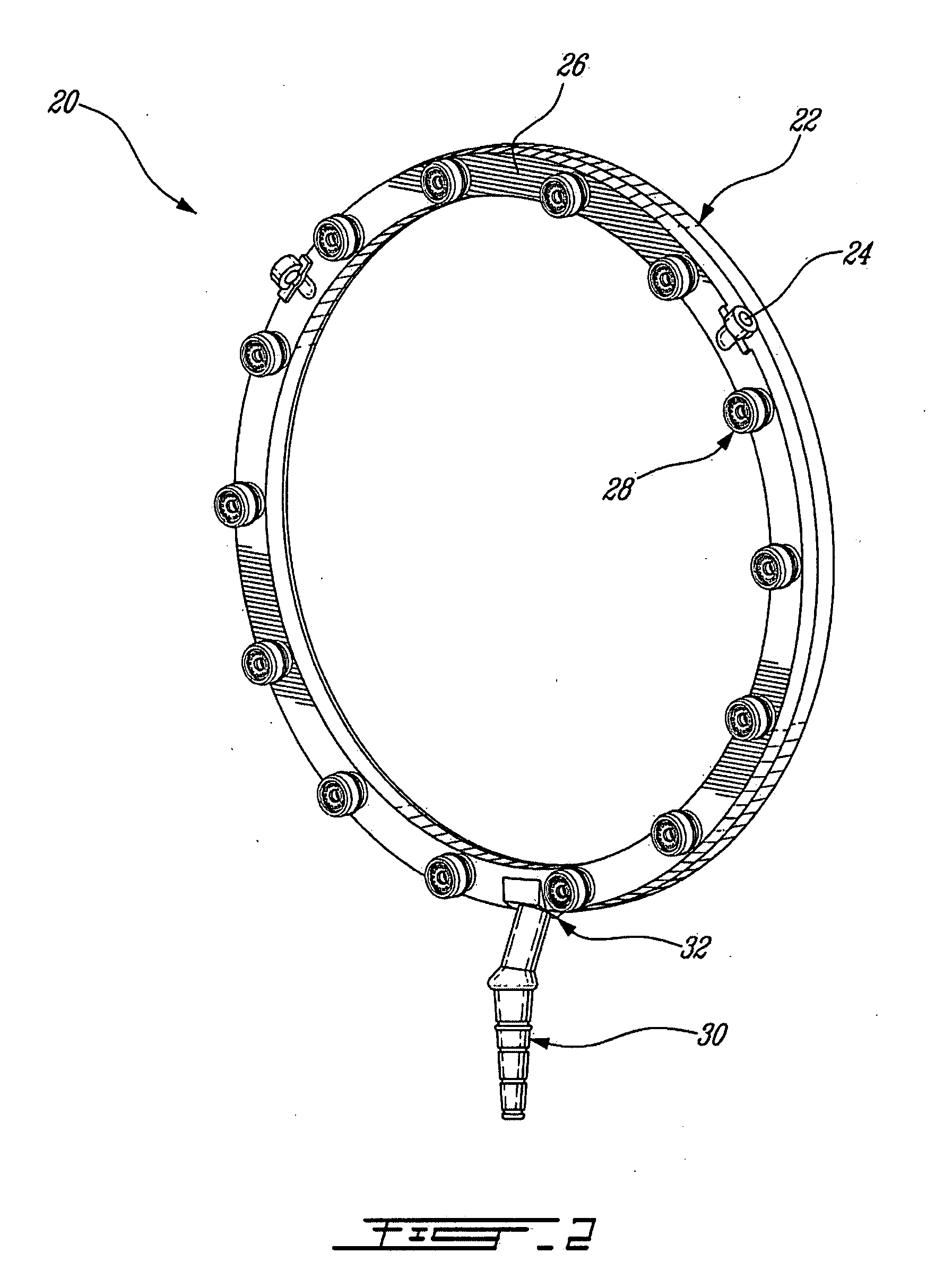
Fuel injection system for a gas turbine engine
ActiveUS20090126368A1Increase fuel injectionBurnersTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsEngineeringGas turbines
A fuel injection system comprises a fuel conveying member and a nozzle tip assembly threadably engaged thereto. A pair of sealing elements is engaged in a fuel passage between the fuel conveying member and the nozzle tip for sealing the junction therebetween. The pair of sealing elements includes a first and a second sealing element located proximate each other and having different cross-sectional shape.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
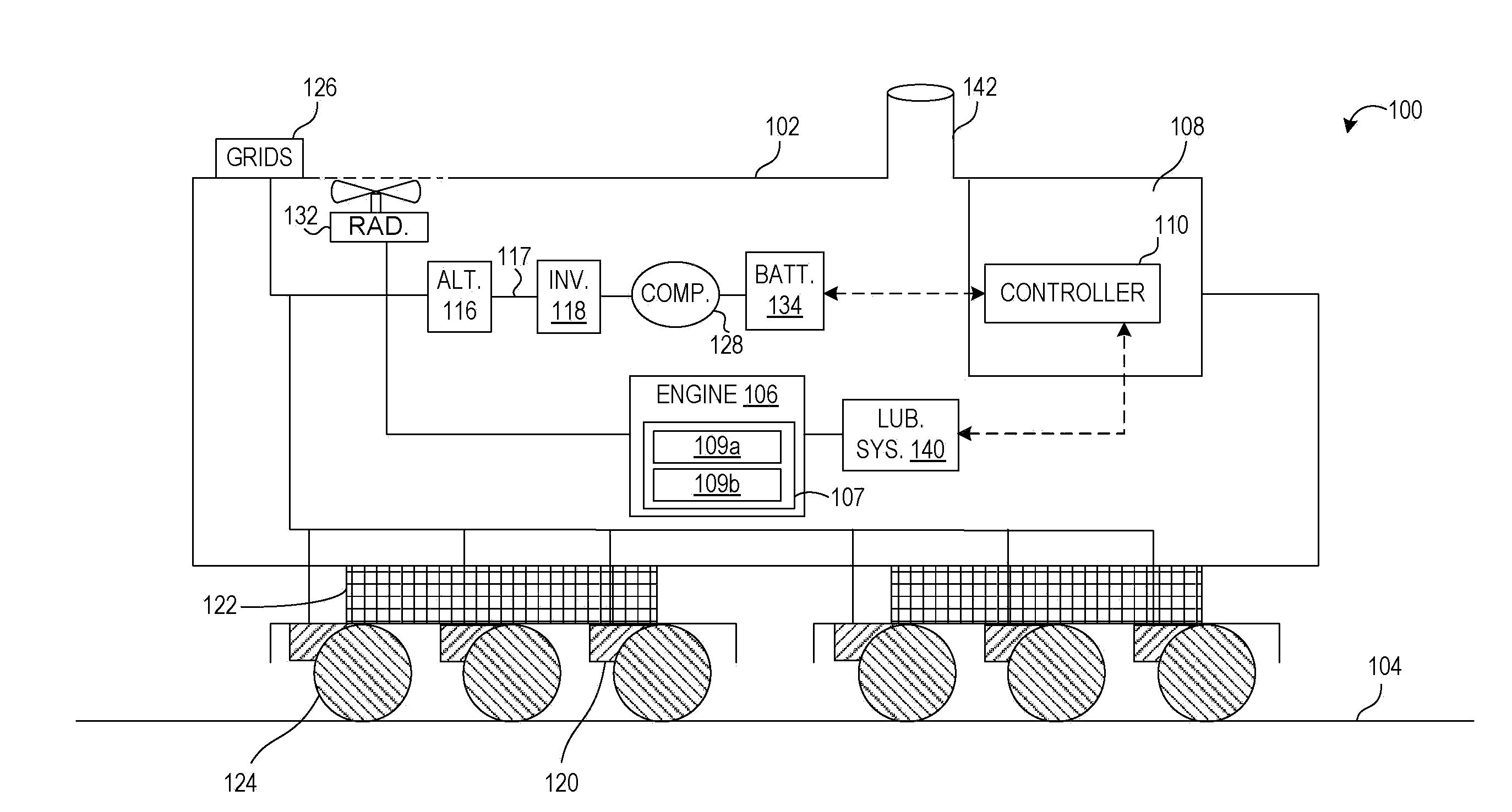
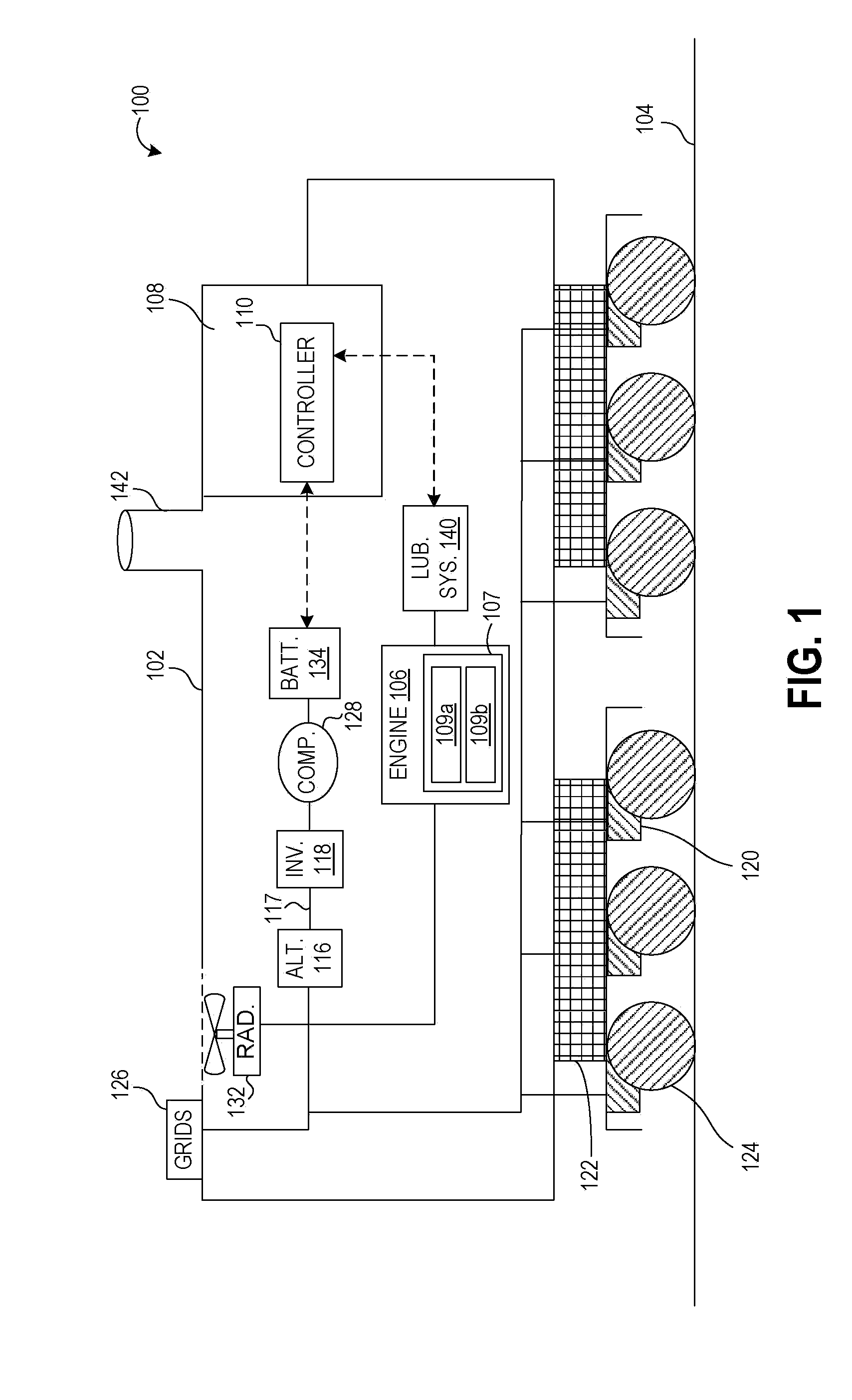
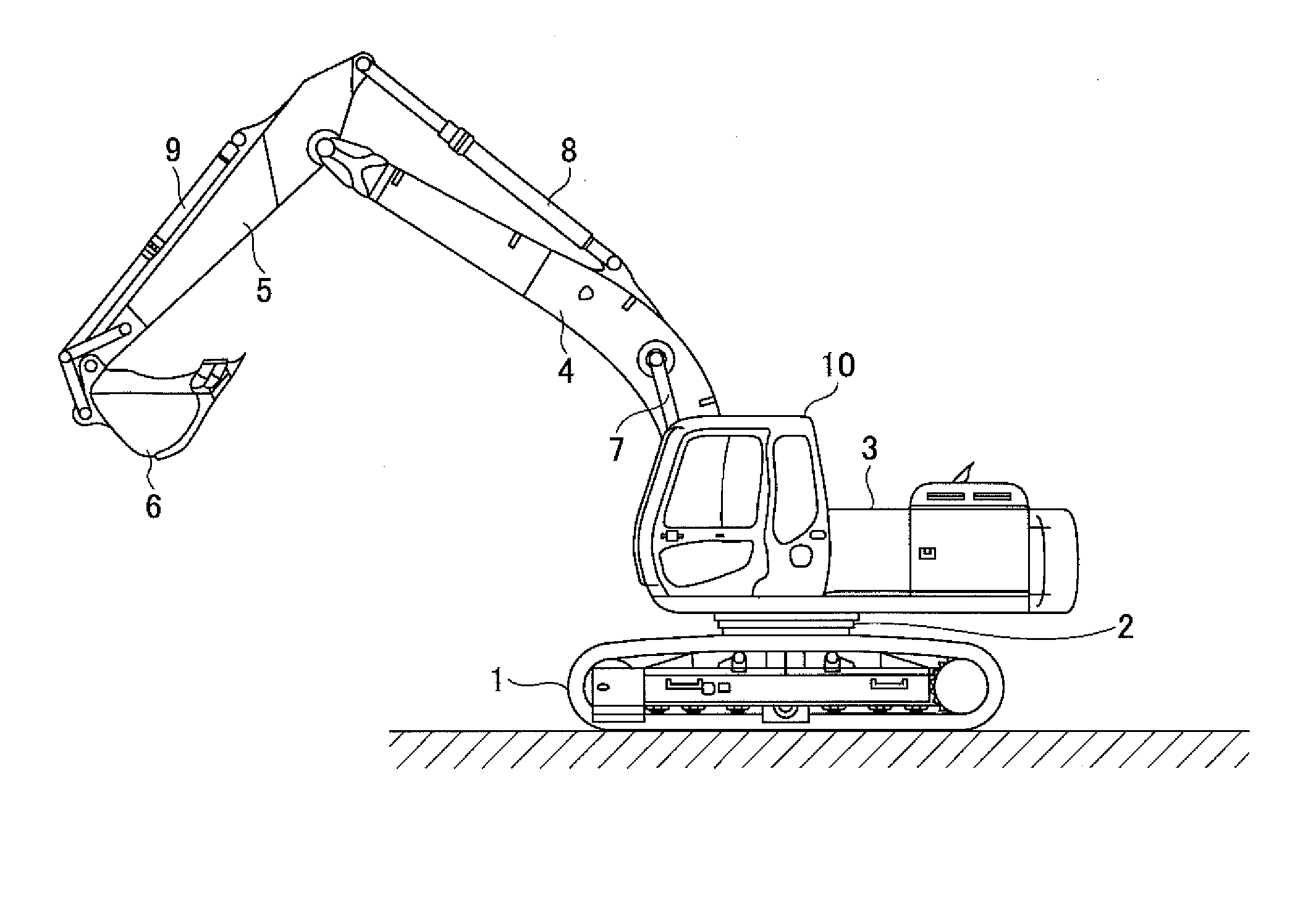
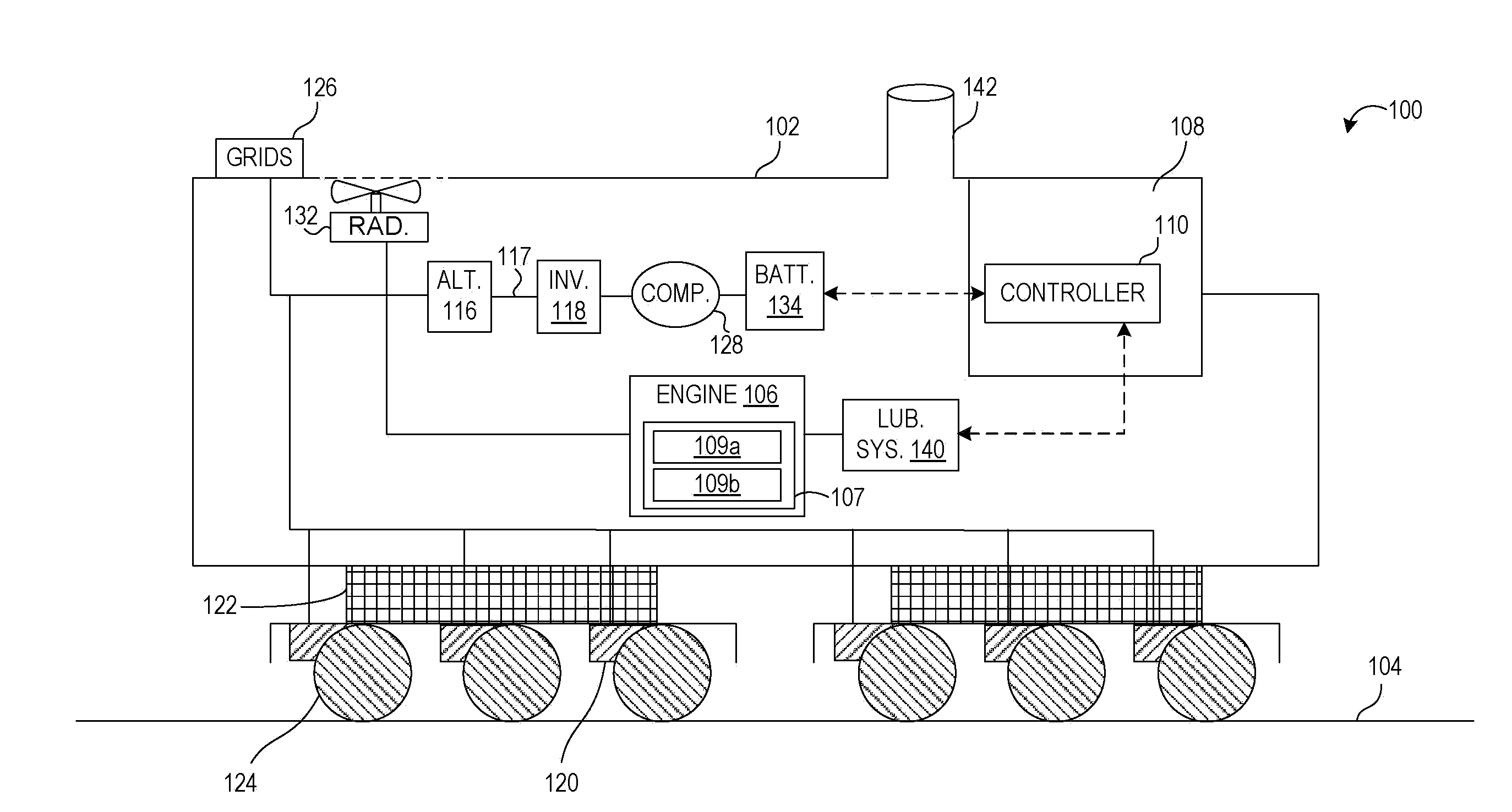
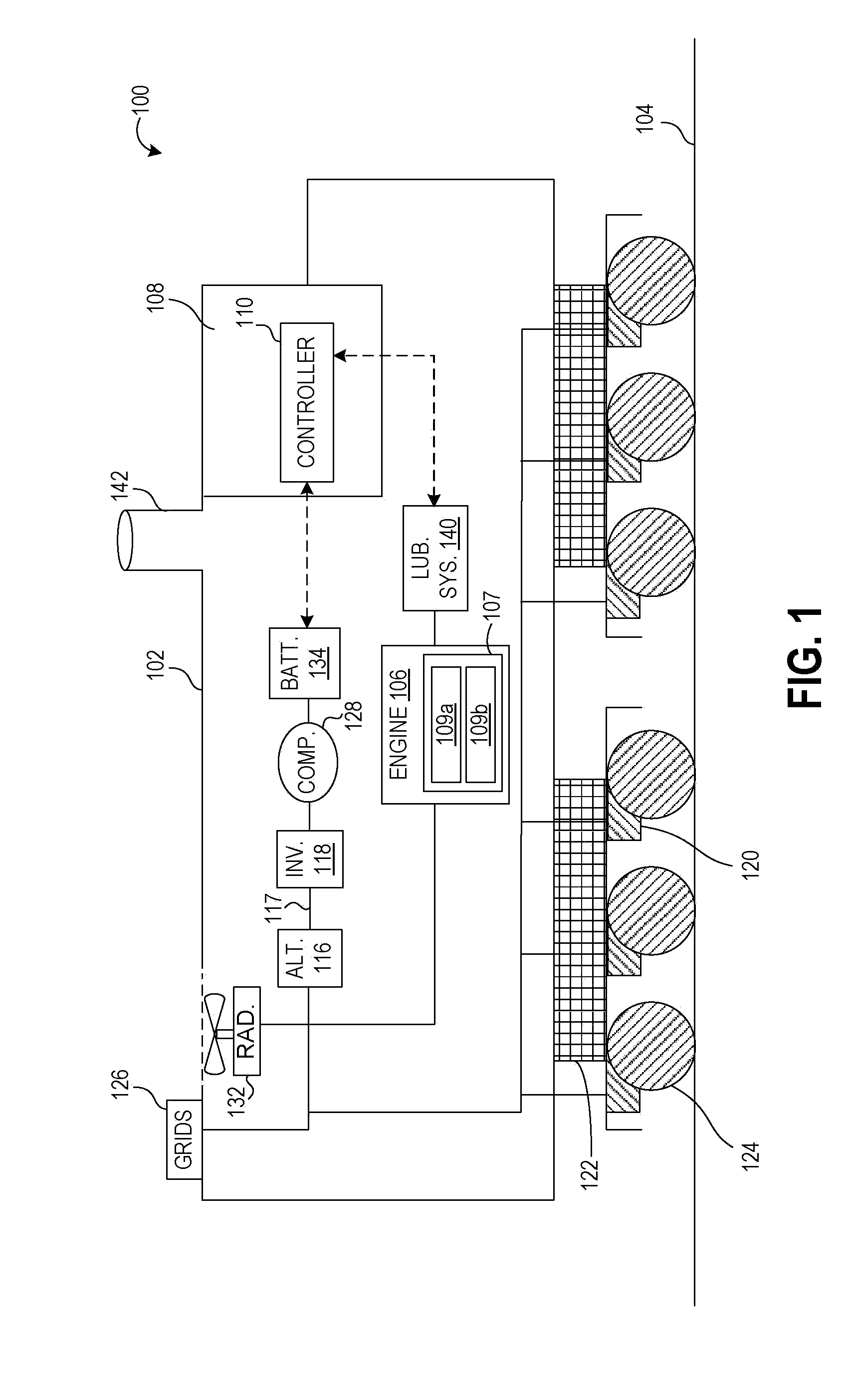
Shovel and method of controlling shovel
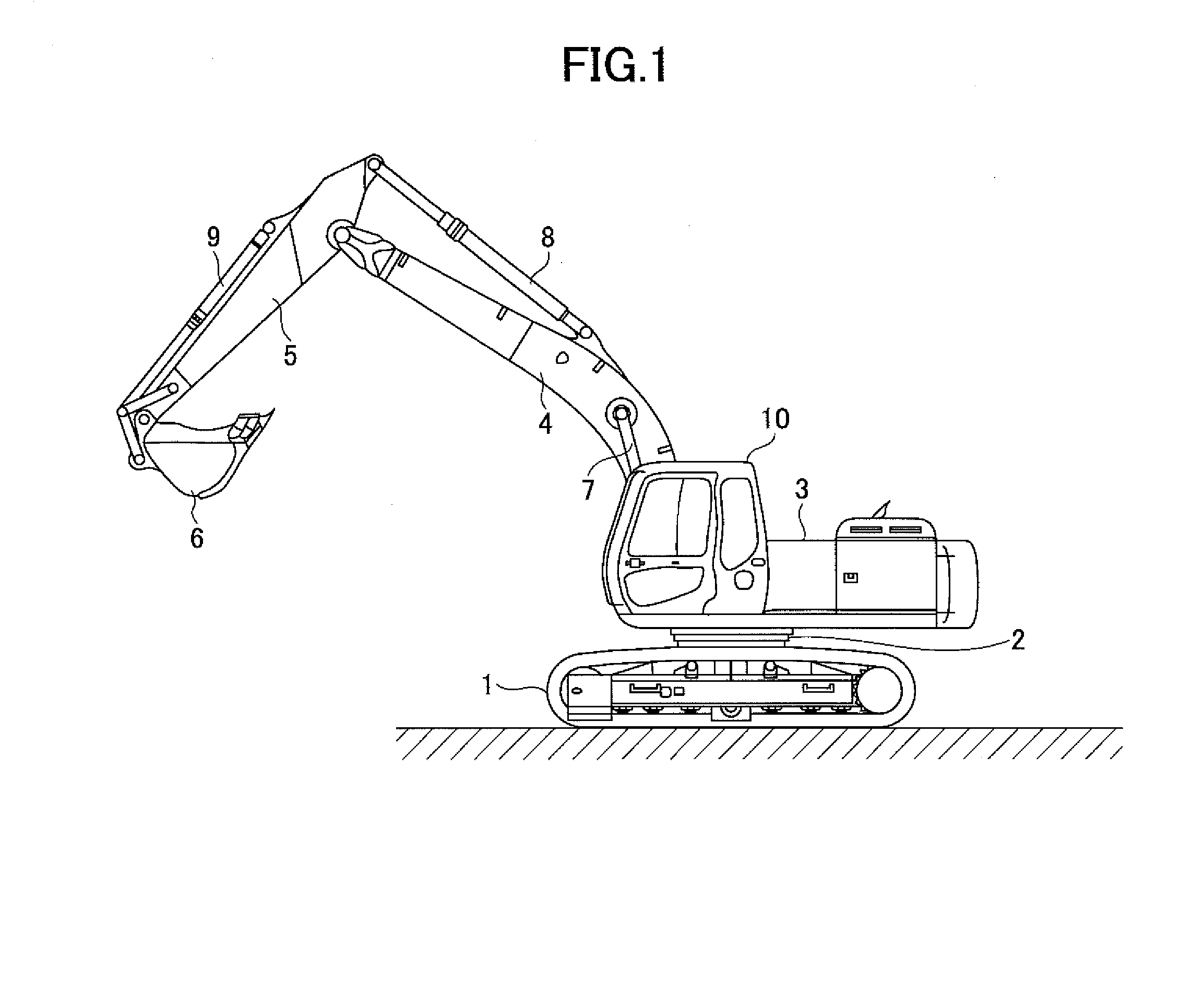
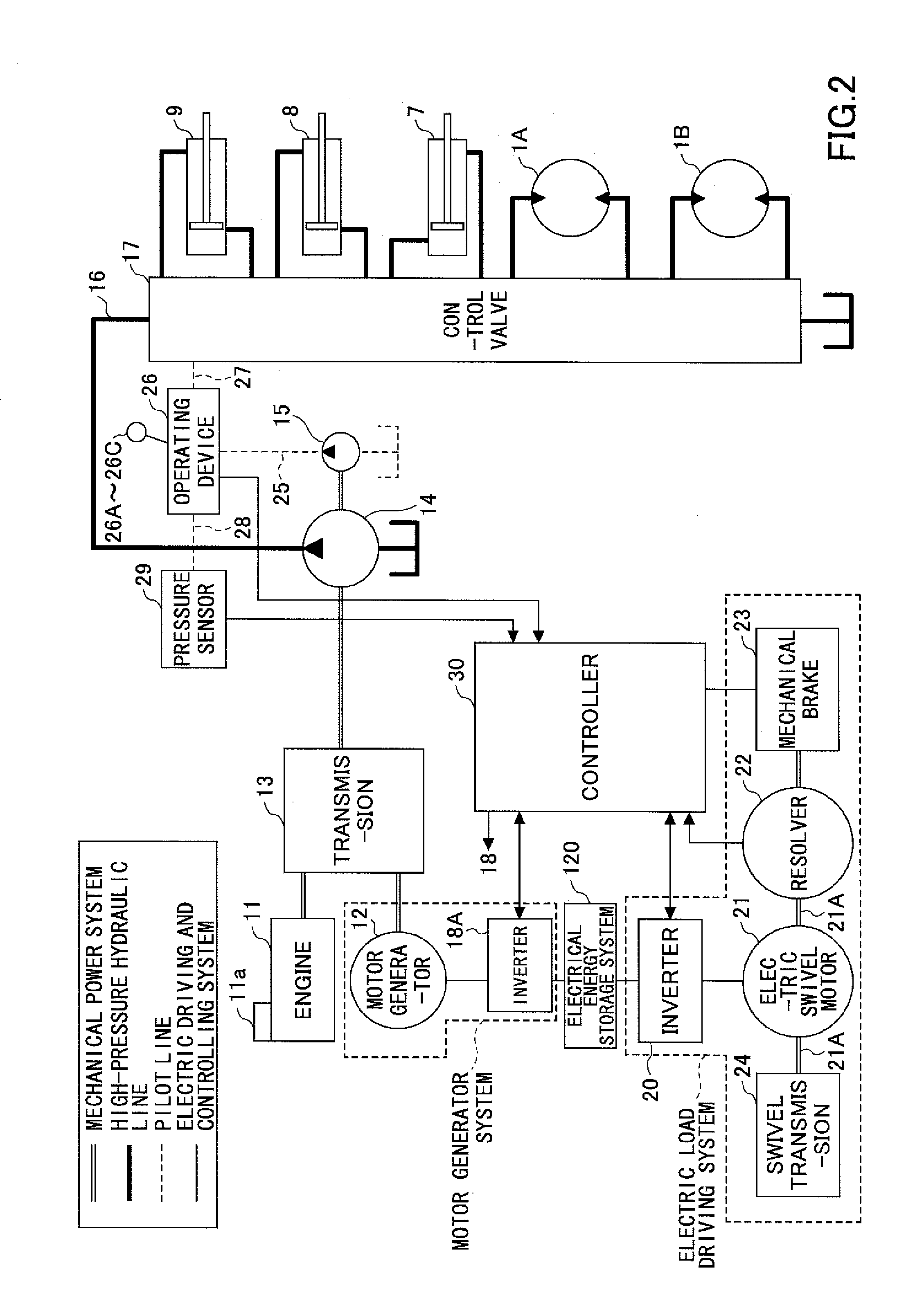
InactiveUS20140058607A1Increase boost pressureEasy loadingHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlHydraulic pumpControl engineering
A shovel includes an internal combustion engine, a hydraulic pump connected to the internal-combustion engine, a generator connected to the internal-combustion engine, and a control part that controls the generator. The control part increases an electric generation load of the generator before a hydraulic load of the hydraulic pump increases.
Owner:SUMITOMO CONSTRUCTION MACHINERY
Fuel injection control device of engine
ActiveUS8596245B2Reduce combustion noiseIncrease fuel injectionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesCombustion noise
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
Fuel supply device and fuel supply method for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20160298587A1Increase in fuel injection quantity variationHigh precisionElectrical controlNoise reducing fuel injectionNuclear engineeringExternal combustion engine
A fuel supply device includes an injector, a fuel pressurization device and an ECU. The fuel pressurization device includes an electromagnetic valve. The fuel pressurization device is configured to pressurize a fuel in accordance with opening / closing of the electromagnetic valve and discharge the fuel toward the injector. The ECU is configured: to control the opening / closing of the electromagnetic valve to adjust the fuel amount discharged toward the injector; to execute an operation sound suppression control during a low-load operation of an engine by reducing an opening / closing frequency of the electromagnetic valve and increasing the fuel amount discharged for each opening / closing of the electromagnetic valve; not to execute the operation sound suppression control when a partial lift injection is in progress; and to execute the operation sound suppression control when the partial lift injection is not in progress.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel-injection device for an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6886535B2Produce some attenuationIncrease pressureMachines/enginesFuel injecting pumpsFuel tankEngineering
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method and system for engine control
ActiveUS20120116655A1Improve cooling effectImprove fuel efficiencyElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsSootFuel injection
Methods and systems are provided for controlling exhaust emissions by adjusting a fuel injection into an engine cylinder from a plurality of fuel injectors based on the fuel type of the injected fuel and further based on the soot load of the engine. Soot generated from direct fuel injection is reduced by decreasing an amount of direct injection into a cylinder as the engine soot load increases.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and system for reducing unburned fuel and oil from exhaust manifolds
ActiveUS7953541B2Increase exhaust temperatureReduce needElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsCombustionEngineering
Methods and systems are provided for operating an internal combustion engine having an exhaust system and a plurality of cylinders that utilize fuel and / or oil for combustion and engine lubrication purposes. In one example, a method comprises, while the engine is operating in a low-load mode or an idle mode, successively operating distinct subsets of said cylinders at a cylinder load sufficient to increase an exhaust temperature for burning unburned fuel and / or oil deposited in the cylinders or engine exhaust system. Herein, each successively operated subset comprises at least one but fewer than all of the plurality of cylinders, and the cylinders that are not currently being operated in a subset are operated in a low- or no-fuel mode.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
Fuel injection control device of engine
ActiveUS20110040474A1Reduce combustion noiseIncrease fuel injectionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesCombustion noise
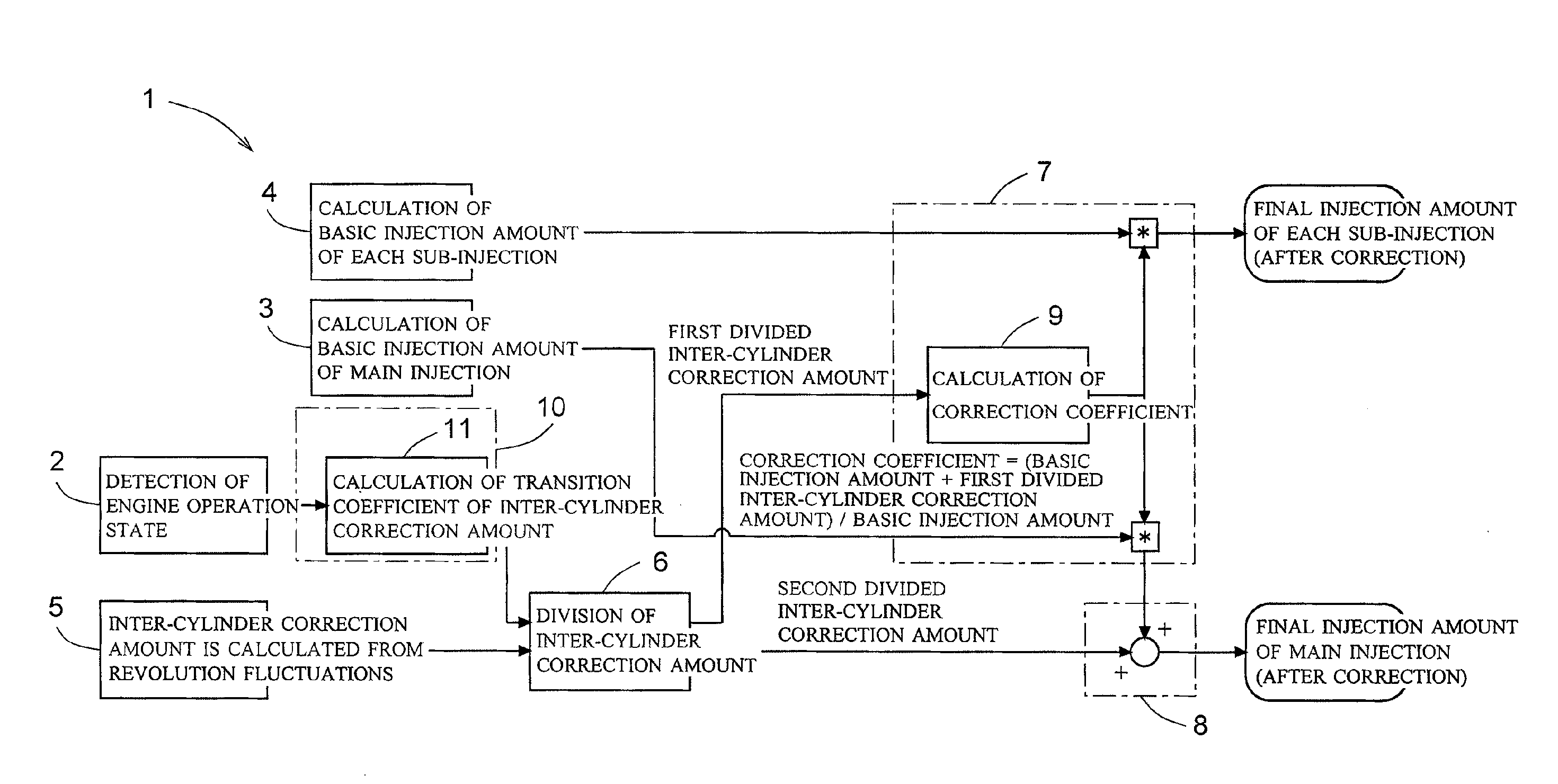
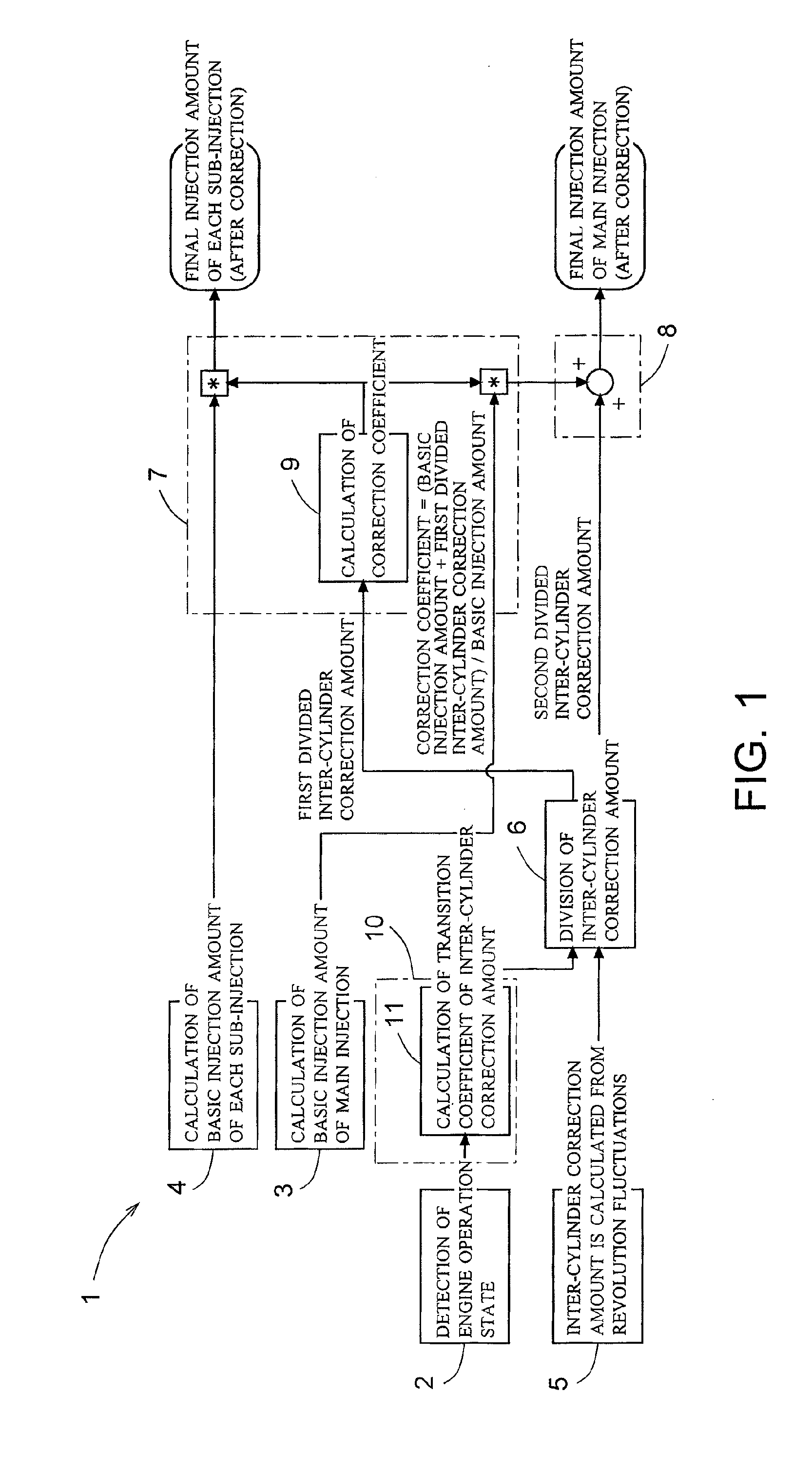
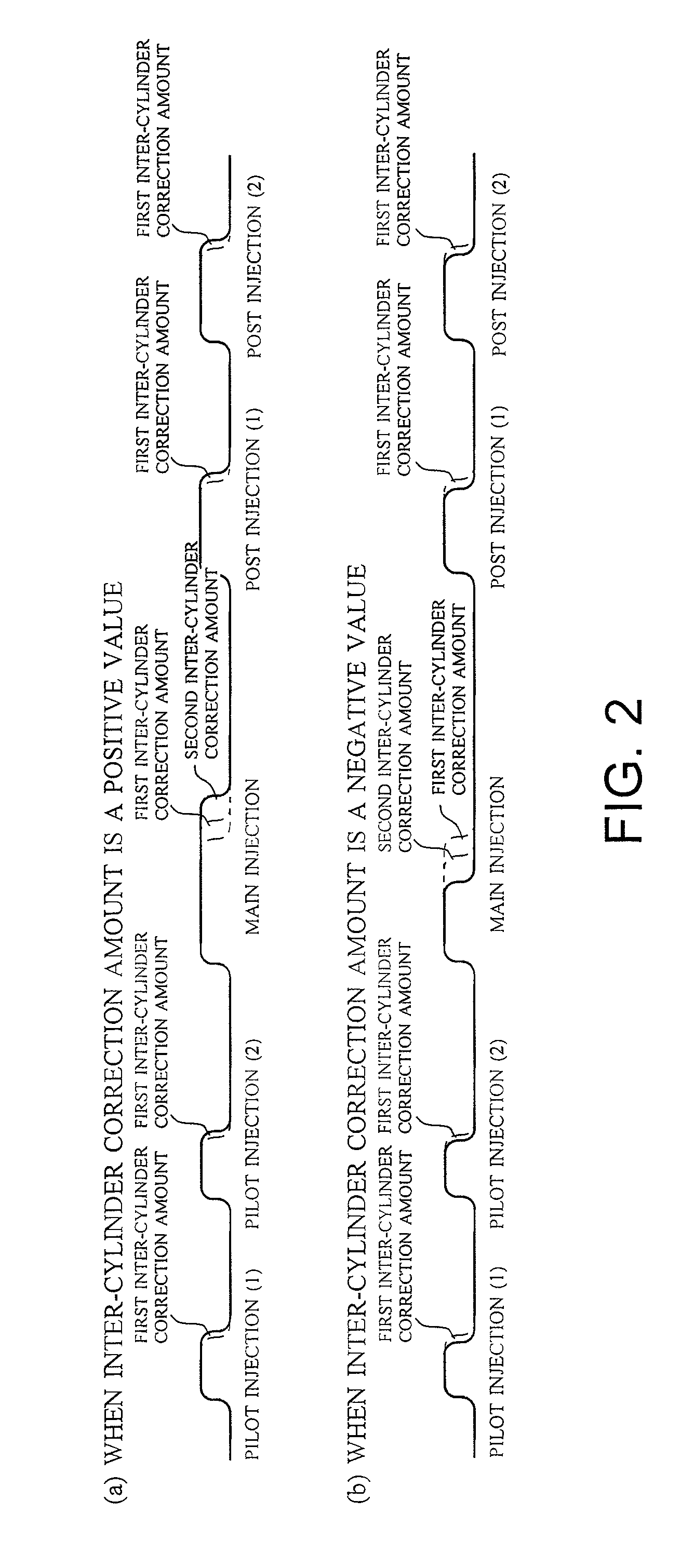
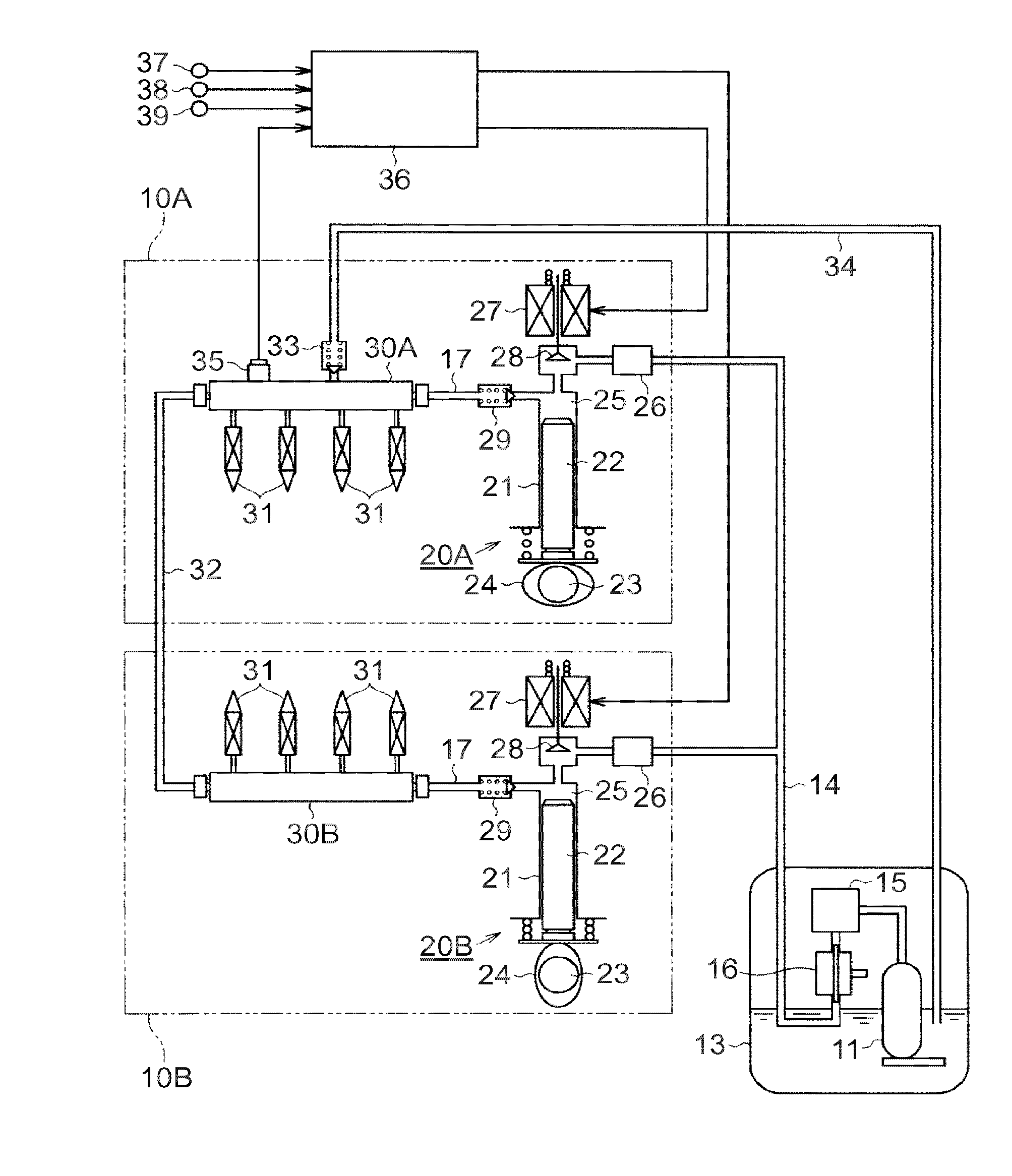
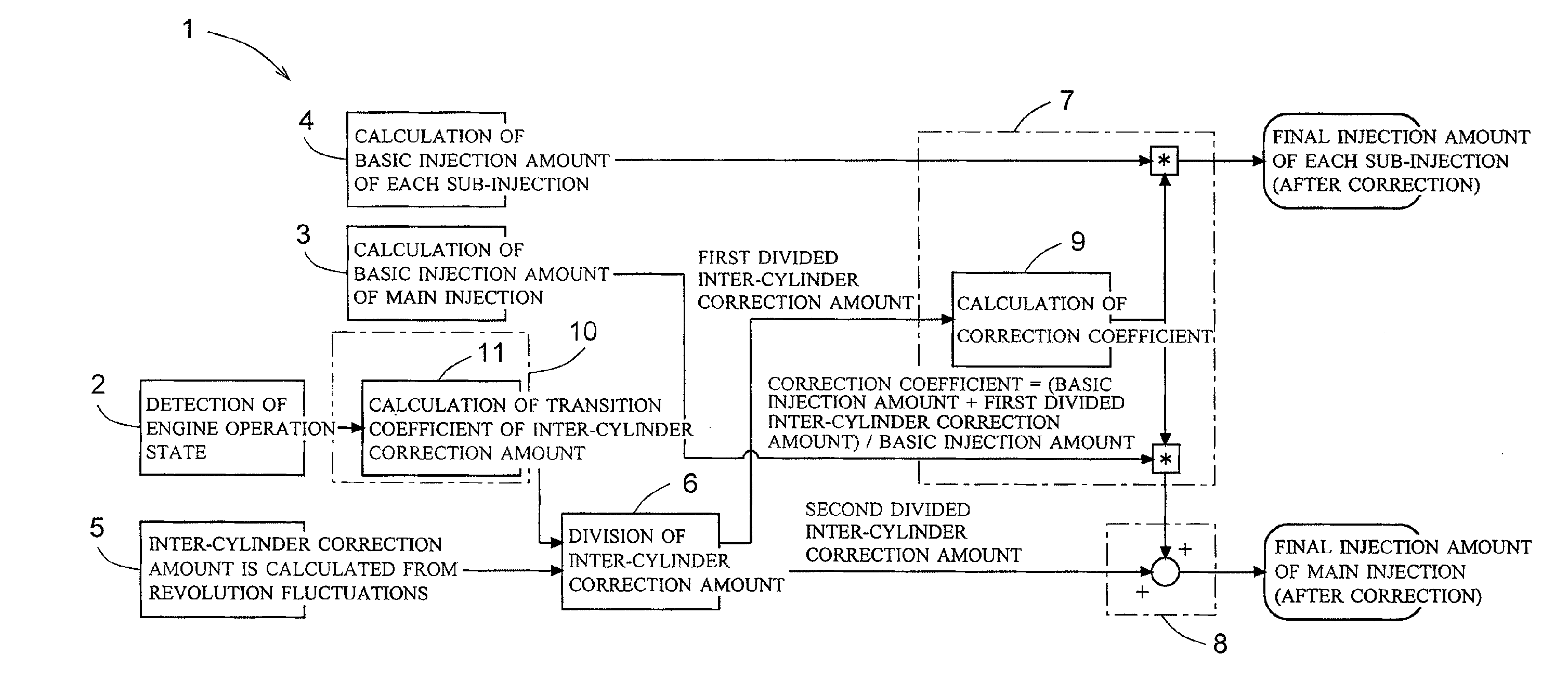
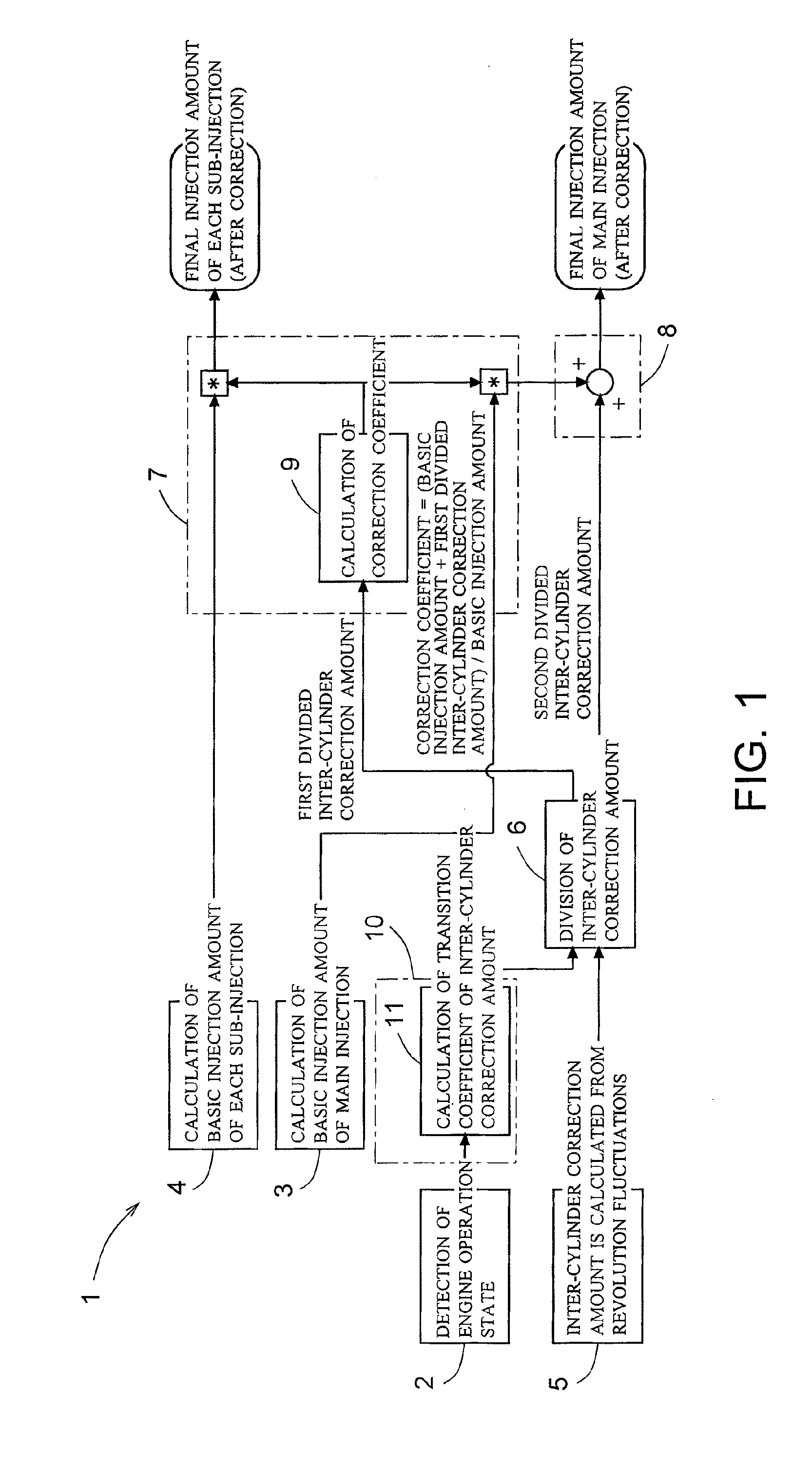
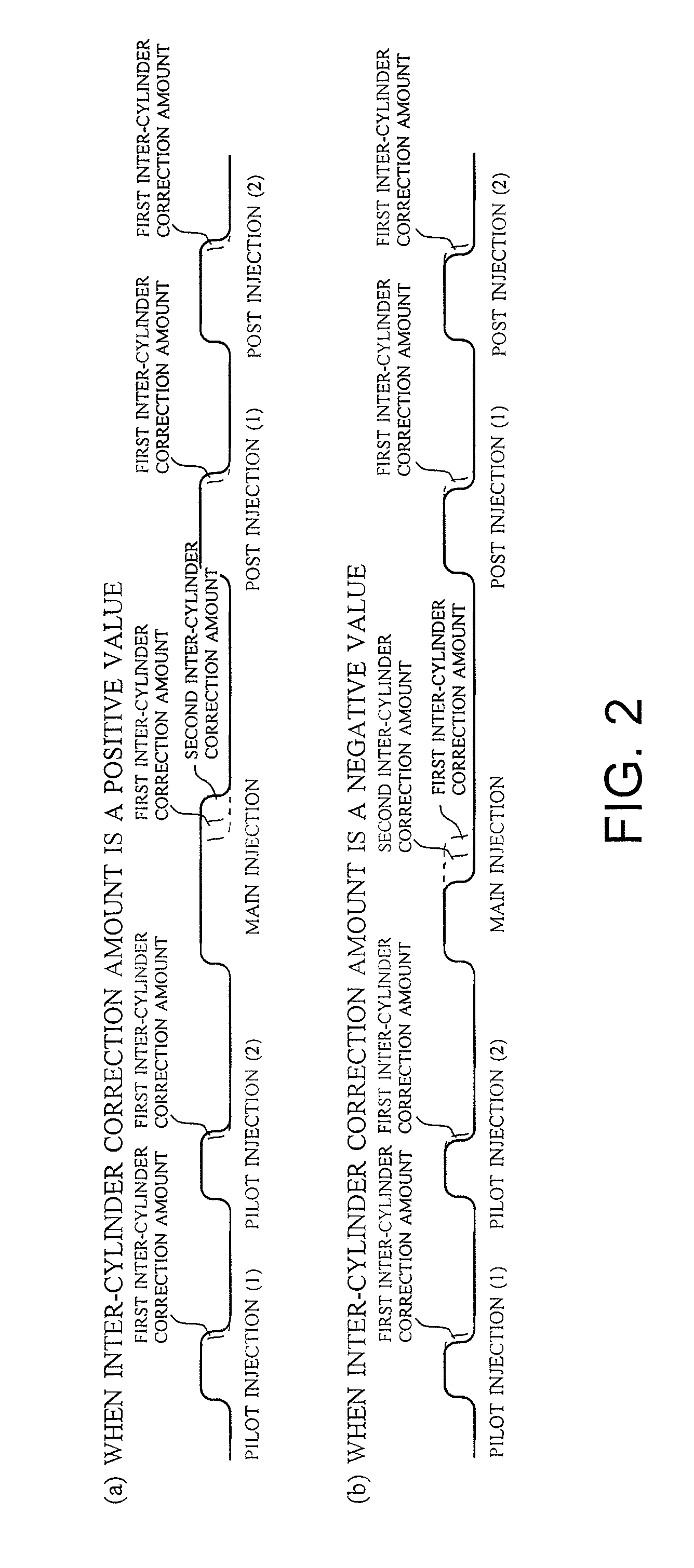
Increase in combustion noise and deterioration of exhaust gas performance caused by inter-cylinder correction are prevented, and decrease in temperature rise performance of a diesel particulate removal device caused by inter-cylinder correction is prevented. A fuel injection control device of an engine comprises inter-cylinder correction amount calculation means 5 for calculating, for each cylinder, an inter-cylinder correction amount for correcting by increasing / decreasing a fuel injection amount in each cylinder according to a difference in engine revolution speed between the cylinders, inter-cylinder correction amount division means 6 for dividing the inter-cylinder correction amount into a first divided inter-cylinder correction amount for correcting by increasing / decreasing the basic injection amounts of main injection and sub-injection and a second divided inter-cylinder correction amount for correcting by increasing / decreasing only the basic injection amount of main injection, first correction means 7 for distributing the first divided inter-cylinder correction amount to main injection and sub-injection according to the basic injection amount of main injection and sub-injection, and second correction means 8 for adding the second divided inter-cylinder correction amount to the basic injection amount of main injection.
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
Particle capturing device regeneration system and control method thereof
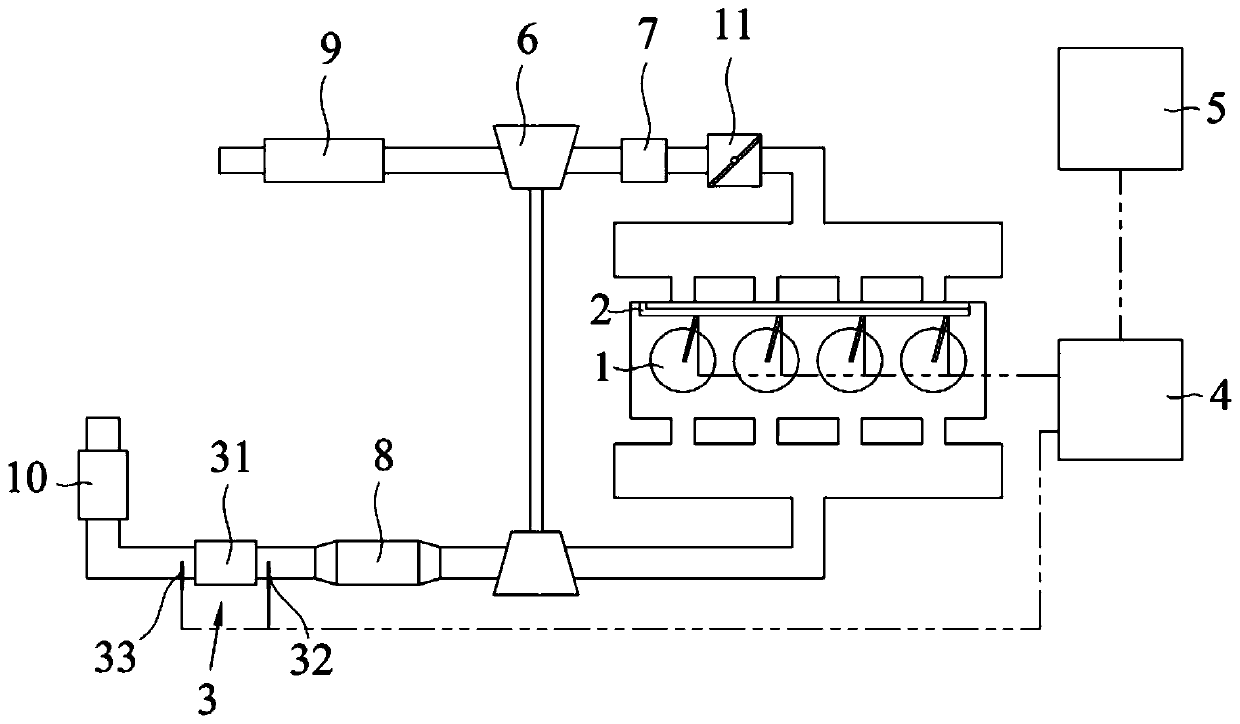
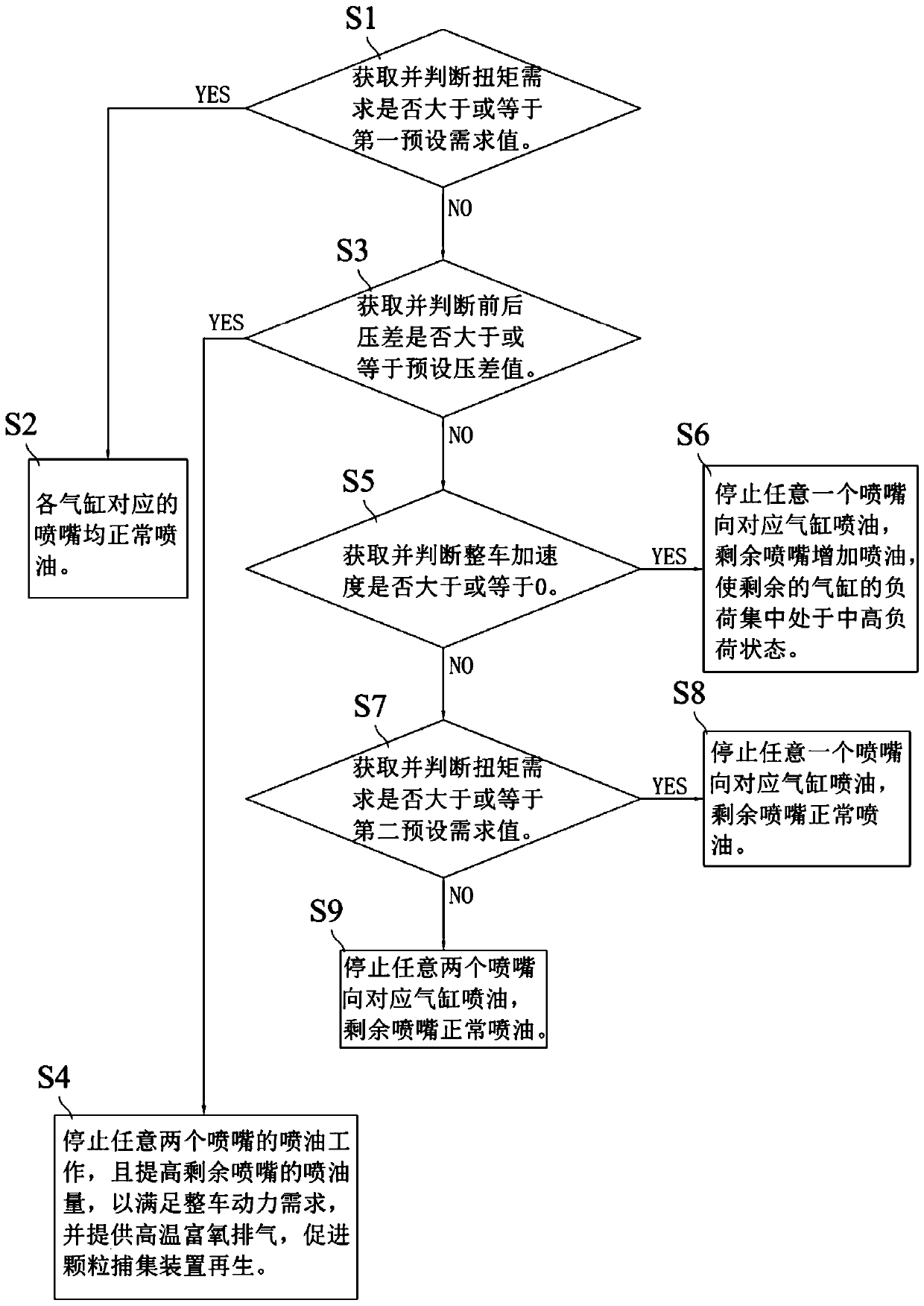
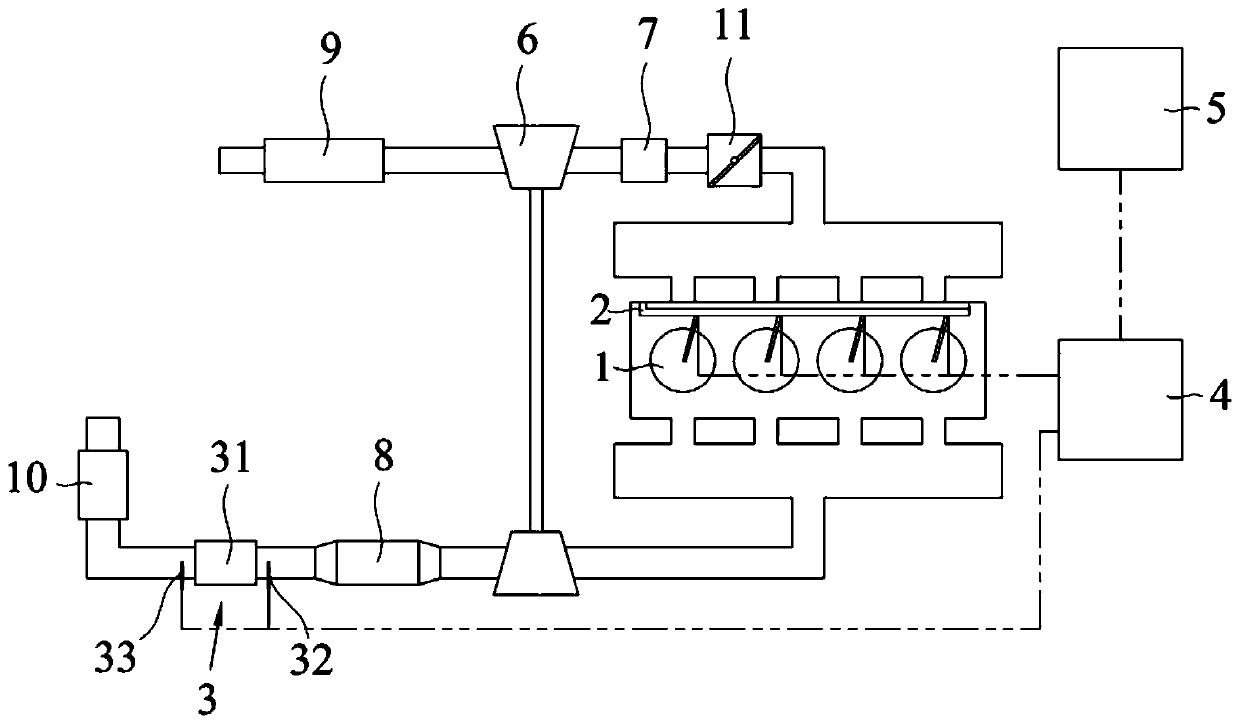
ActiveCN111173595APromote regenerationMeet power needsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesParticle trappingThermodynamics
The invention relates to the technical field of automobiles, and discloses a particle capturing device regeneration system and a control method thereof. The particle capturing device regeneration system comprises an engine, a particle capturing device, an ECU and a vehicle controller; the engine comprises an oil injection mechanism and a plurality of air cylinders, air inlets of the air cylinderscommunicate with an air inlet pipeline, and air outlets of the air cylinders communicate with an air outlet pipeline; the oil injection mechanism comprises a plurality of spray nozzles corresponding to all the air cylinders one to one, and all the spray nozzles inject oil towards the corresponding air cylinders; and the ECU is in signal connection with the particle capturing device and the vehiclecontroller and is controllably connected with the oil injection mechanism. The particle capturing device regeneration system and the control method thereof have the advantages that the ECU can selectively control parts of the spray nozzles to stop oil injection according to the front-back differential pressure delta P and a vehicle signal sent by the vehicle controller, the oil injection amount of the remaining spray nozzles can be increased, thus regeneration of the particle capturing device is promoted by increasing the oxygen content of exhausted gas while the vehicle power demand is met,and compared with the situation that regeneration of the particle capturing device is promoted by increasing the temperature of the exhausted gas through electric heating, more oil is saved.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
System for injecting fuel into a turbomachine
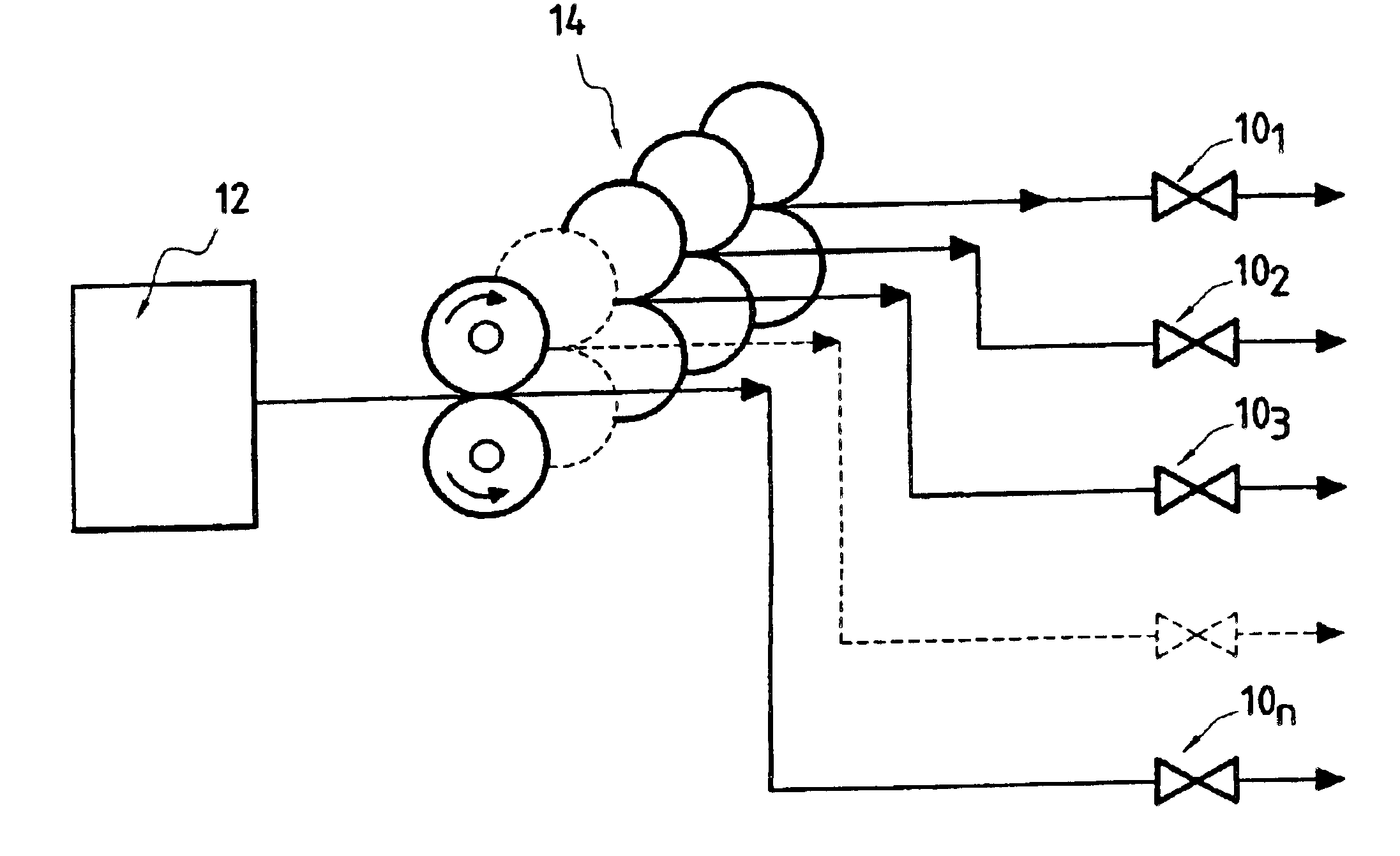
InactiveUS6854257B2Mitigate such drawbackSimplify the hydraulic circuitGas turbine plantsRotary piston pumpsCombustion chamberFuel tank
A system for injecting fuel into a turbomachine comprising N fuel injectors placed in a combustion chamber of the turbomachine and fed from a fuel tank, the injection system further comprising, interposed between the N injectors and the tank, a single pumping means for taking fuel from the tank and delivering N metered flow rates of fuel to the injectors.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
A control method and device for preventing regeneration and sintering of particle filter
ActiveCN103016118BReduce fuel injectionIncrease fuel injectionInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusParticulatesEngineering
The invention discloses a control method for preventing regeneration and sintering of a particle catcher. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring regeneration related parameters of the particle catcher, wherein the regeneration related parameters comprise inlet temperature of an oxidation catalyst, outlet temperature of the oxidation catalyst, outlet temperature of the particle catcher, pressure difference of the particle catcher and air speed of the oxidation catalyst; increasing or decreasing the fuel injection quantity required by regeneration of the particle catcher according to the acquired regeneration related parameters; and injecting fuel according to the adjusted fuel injection quantity. The invention further discloses a control device for preventing regeneration and sintering of the particle catcher.
Owner:WEICHAI POWER CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com