Patents
Literature
55results about How to "Overcome lack of focus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
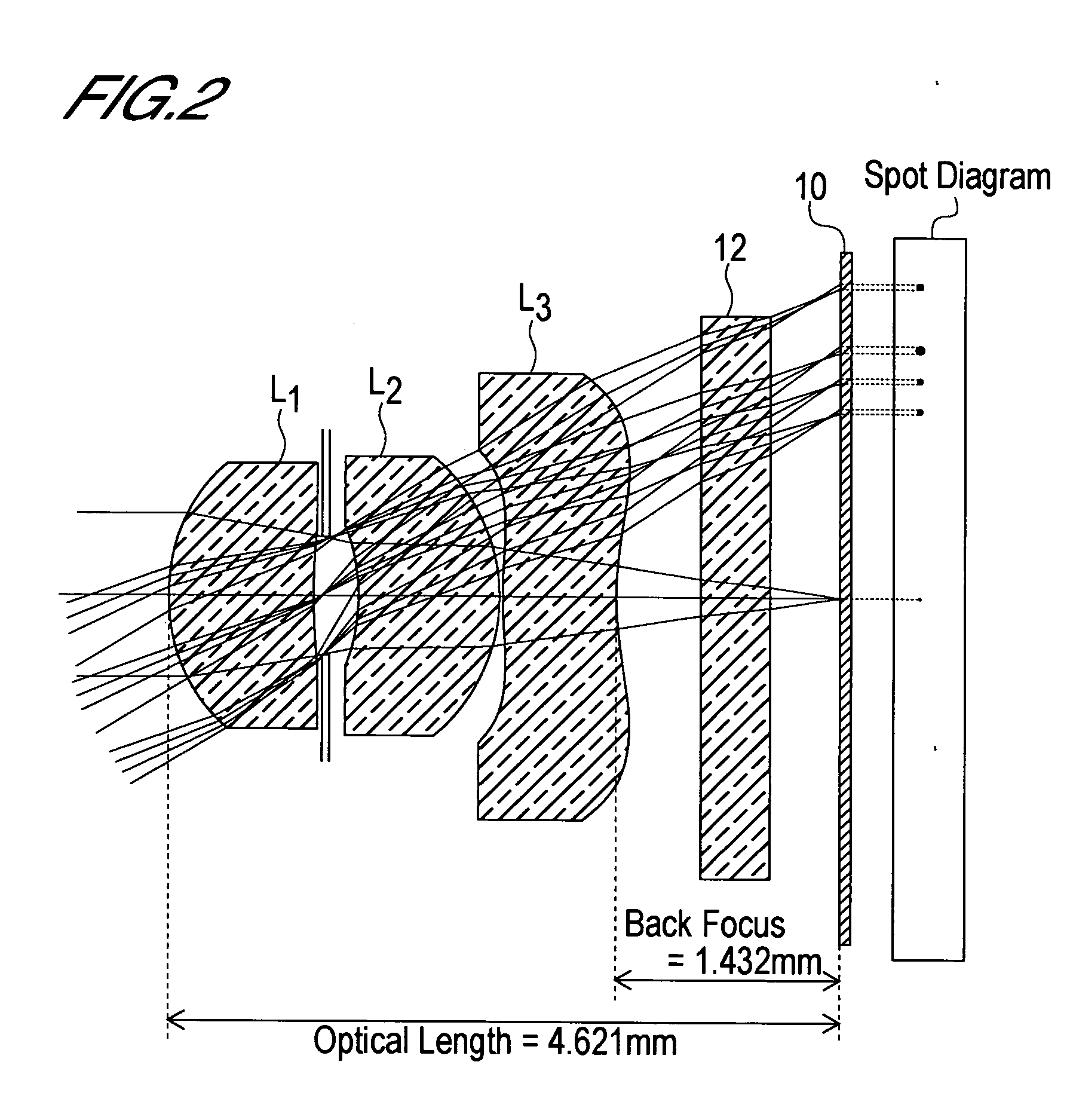
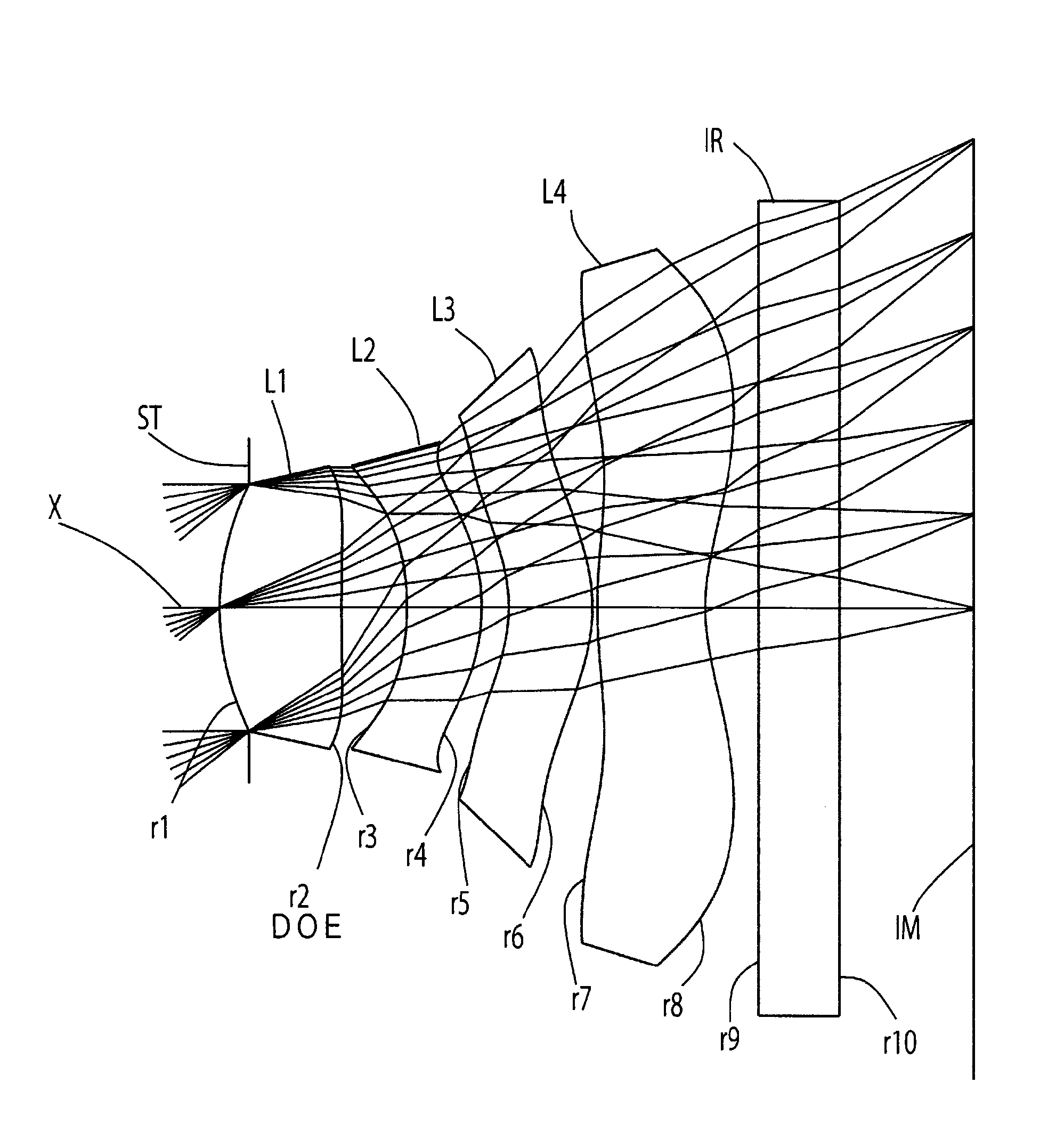
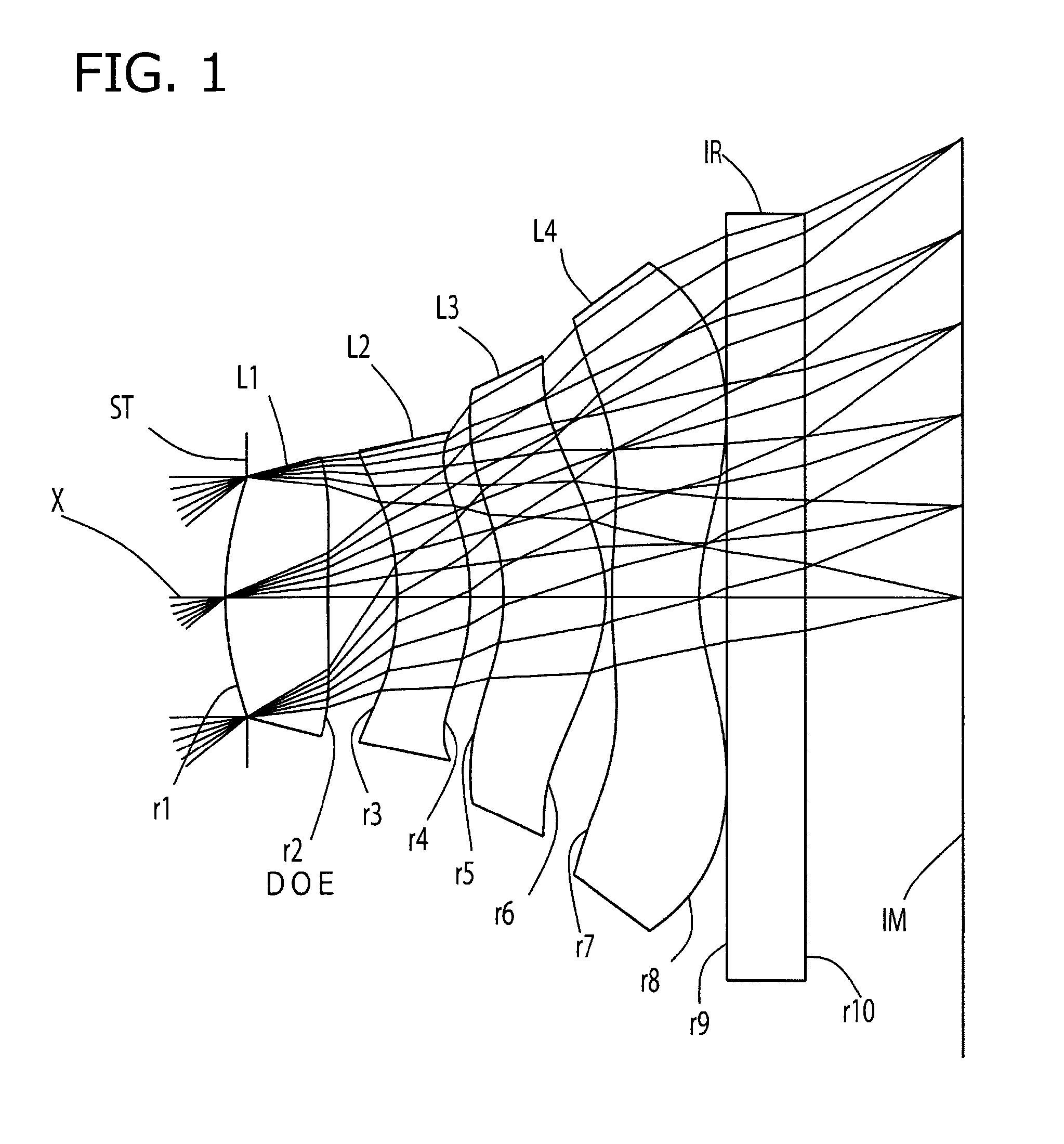
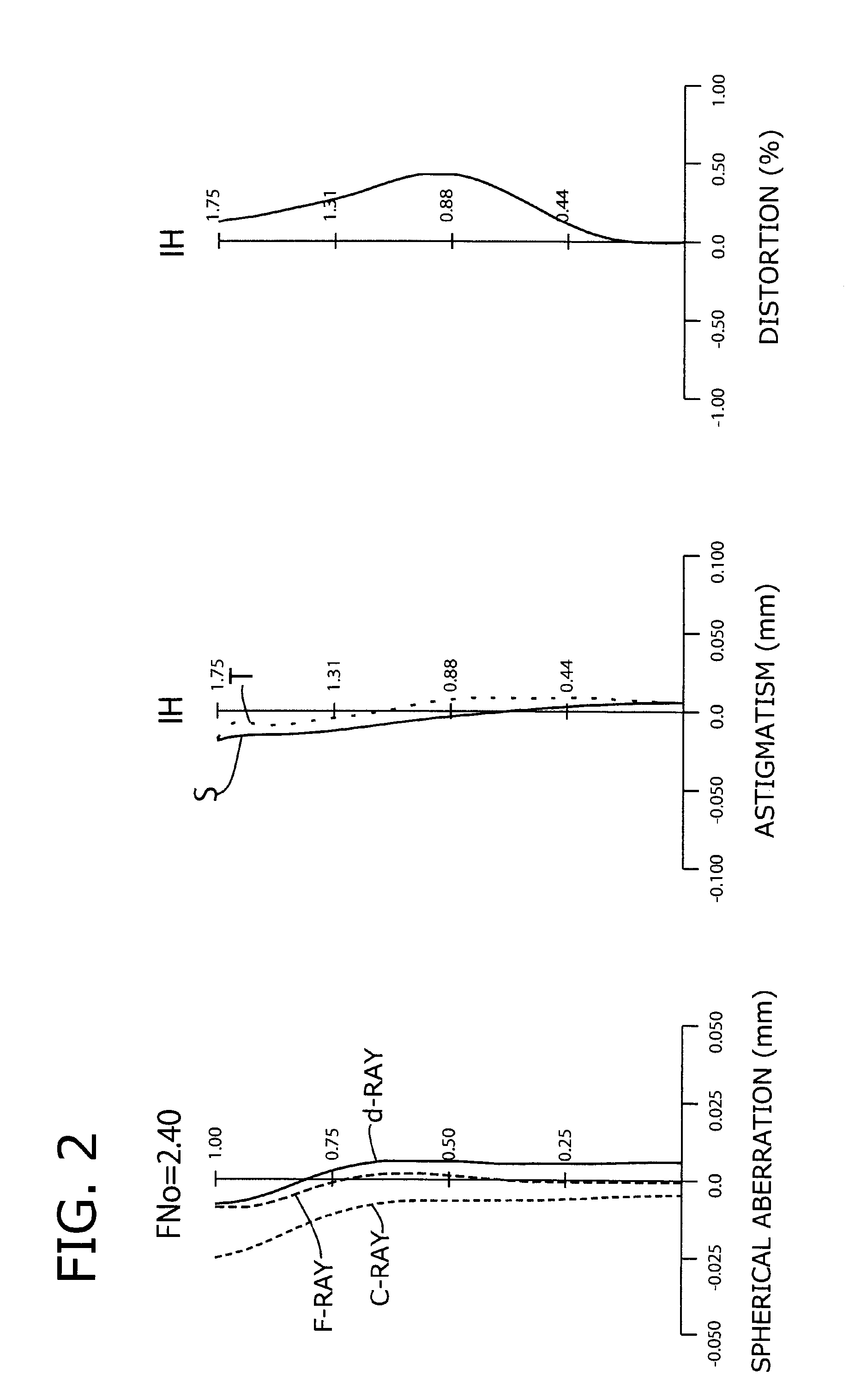
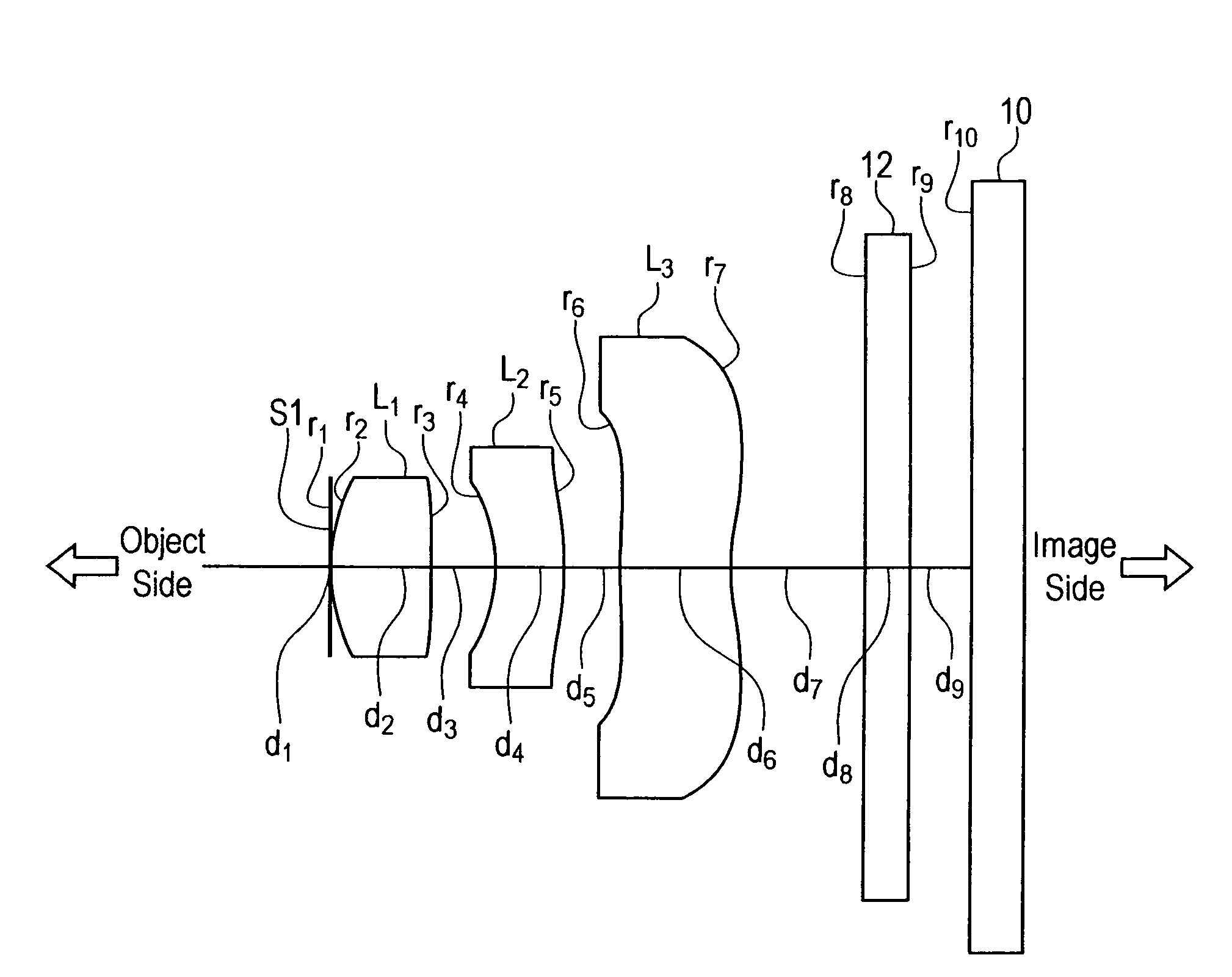
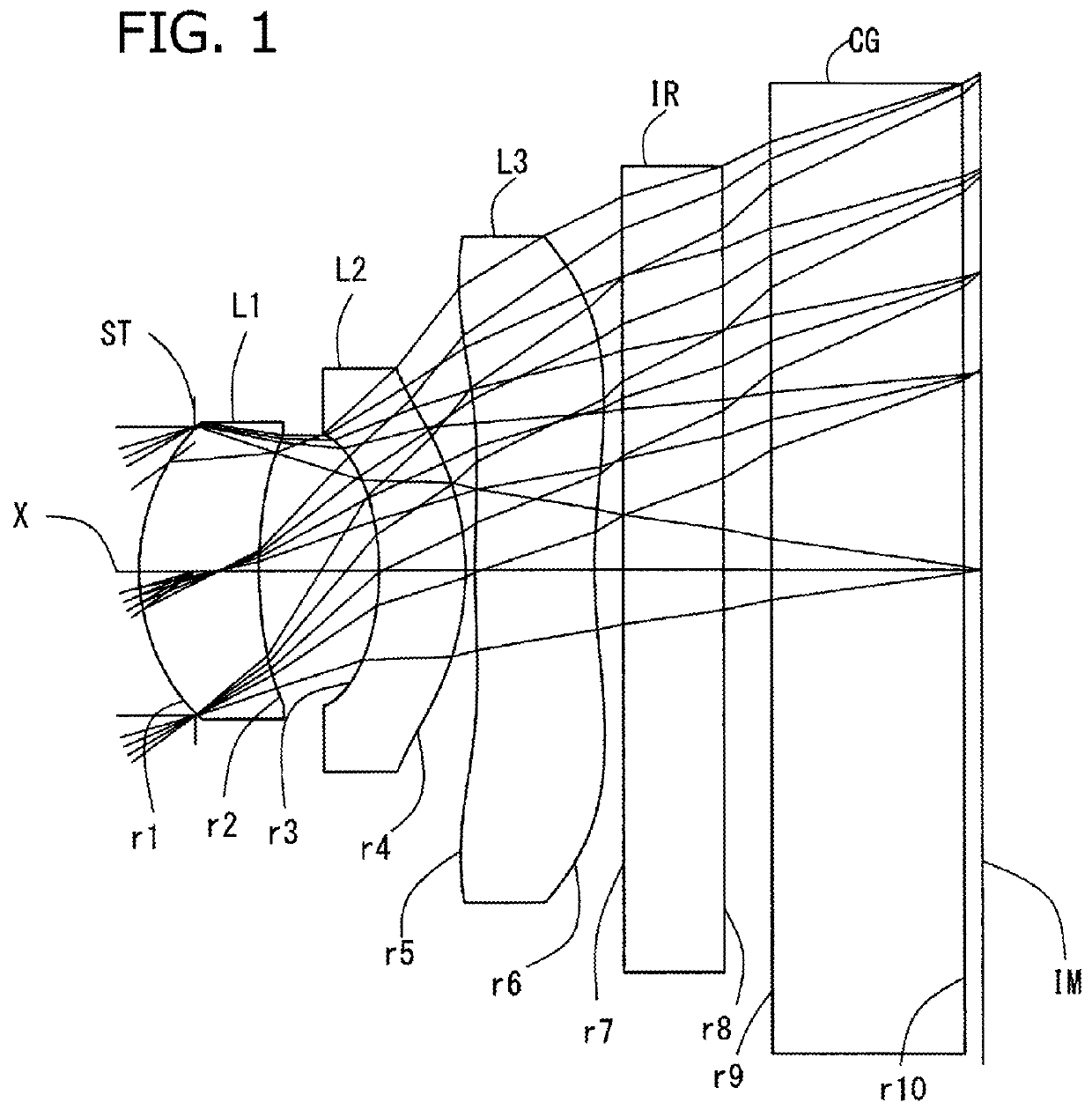
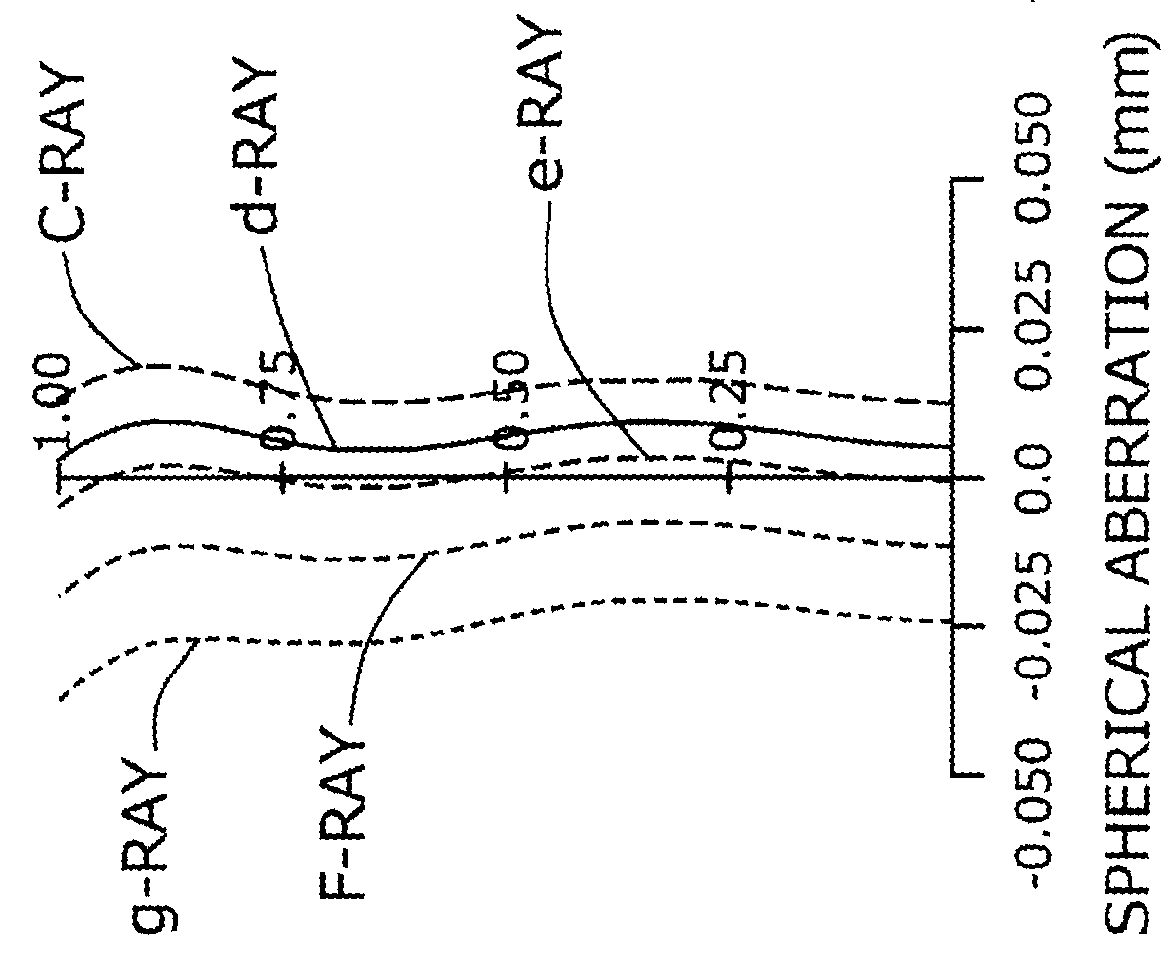
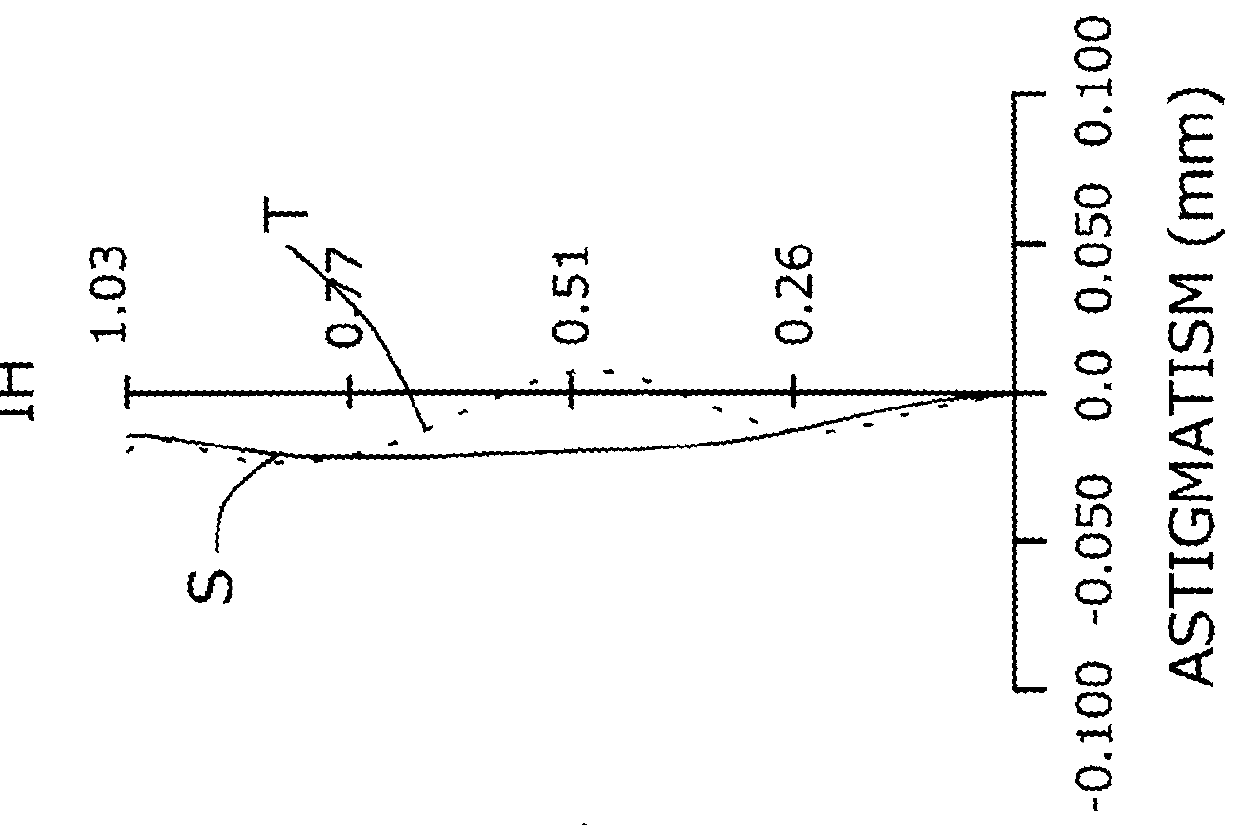
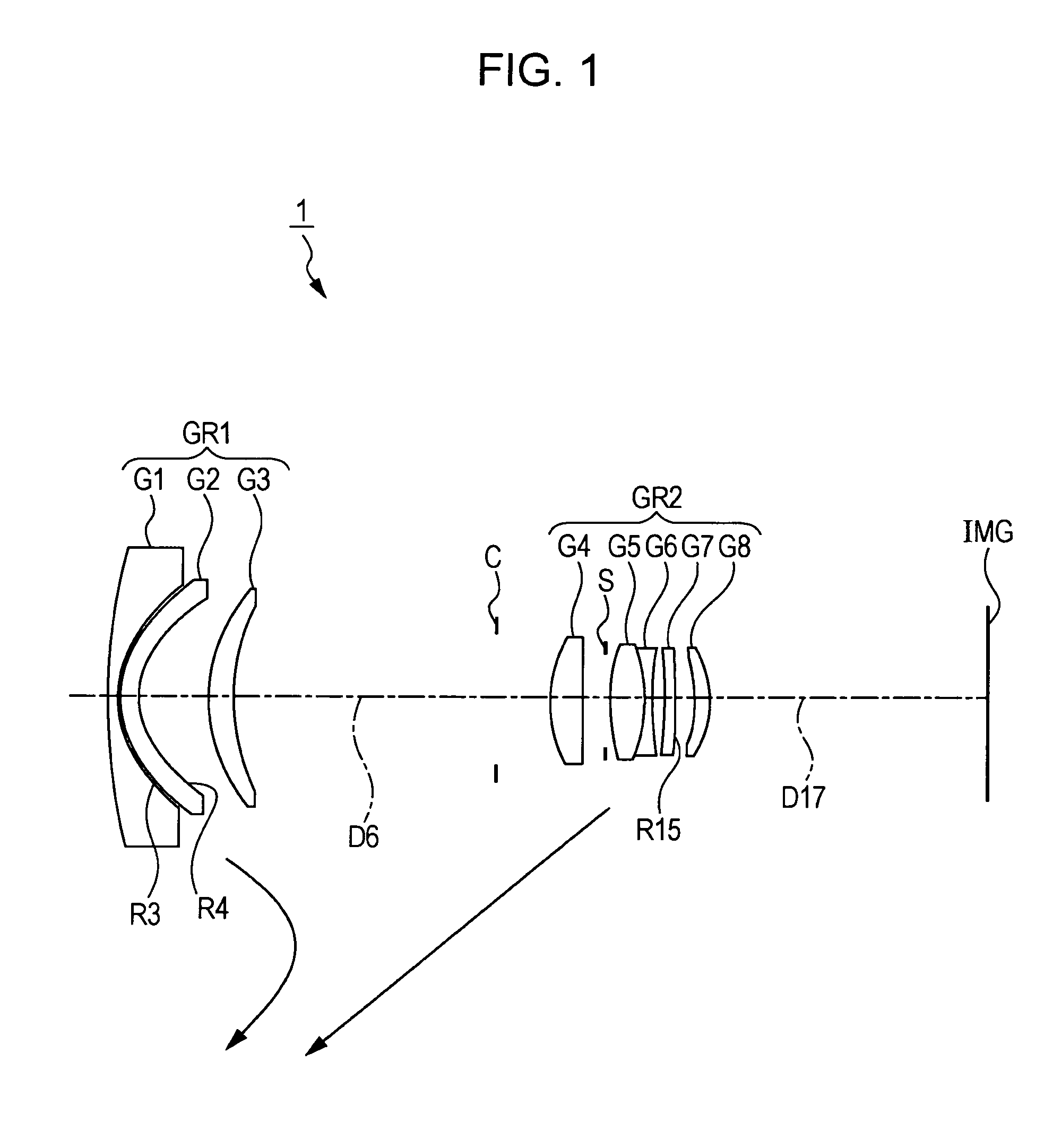
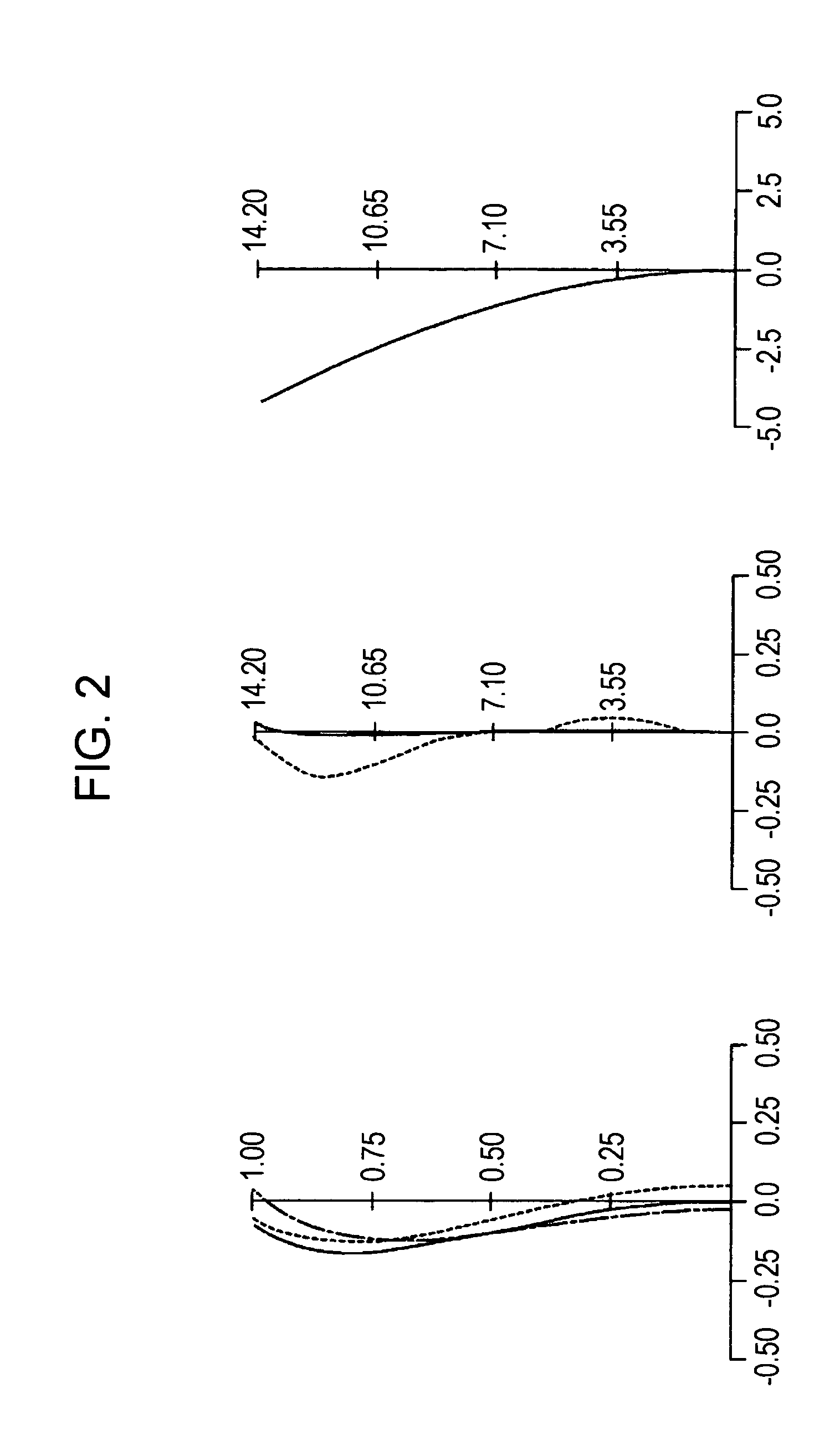
Imaging lens
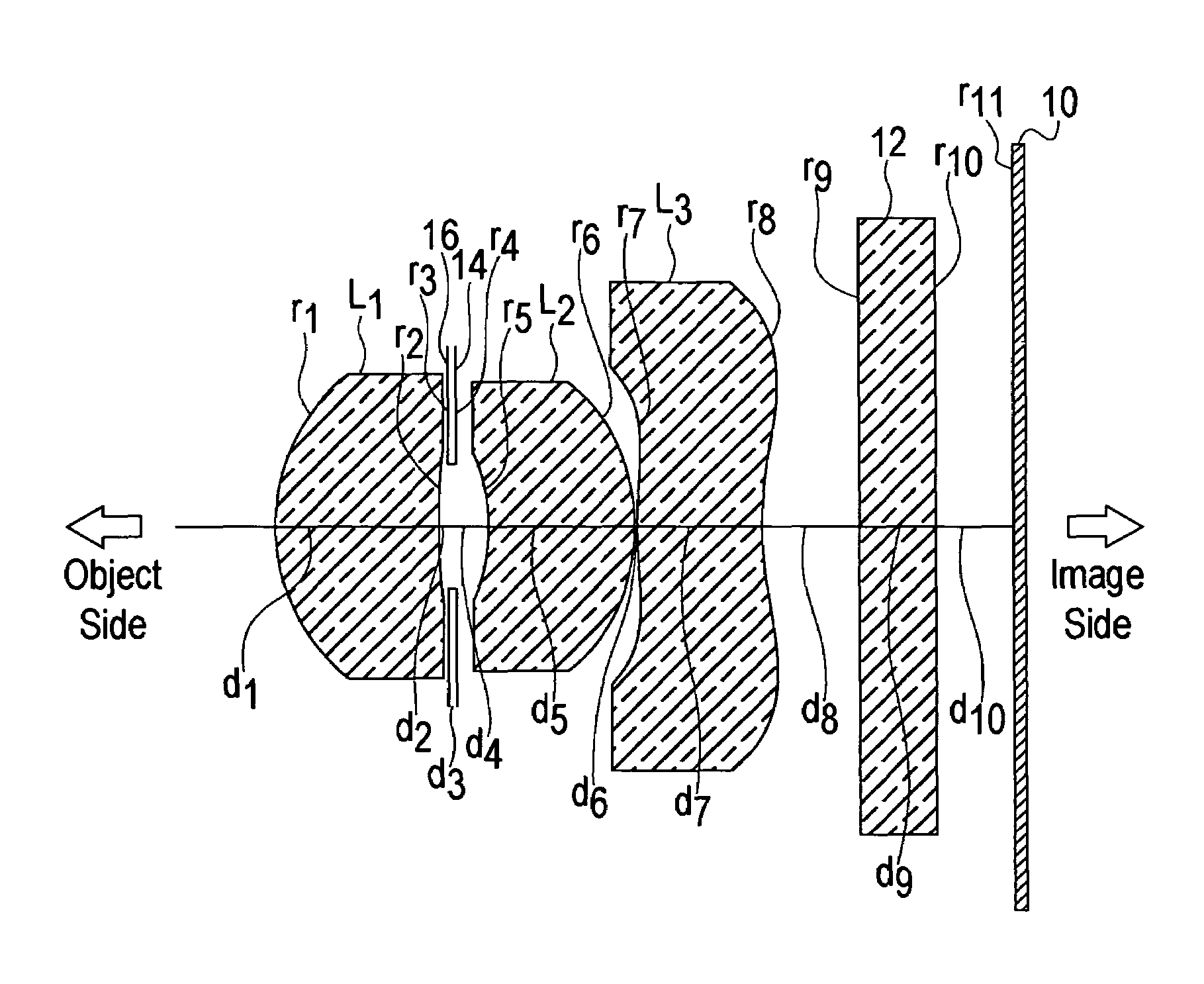
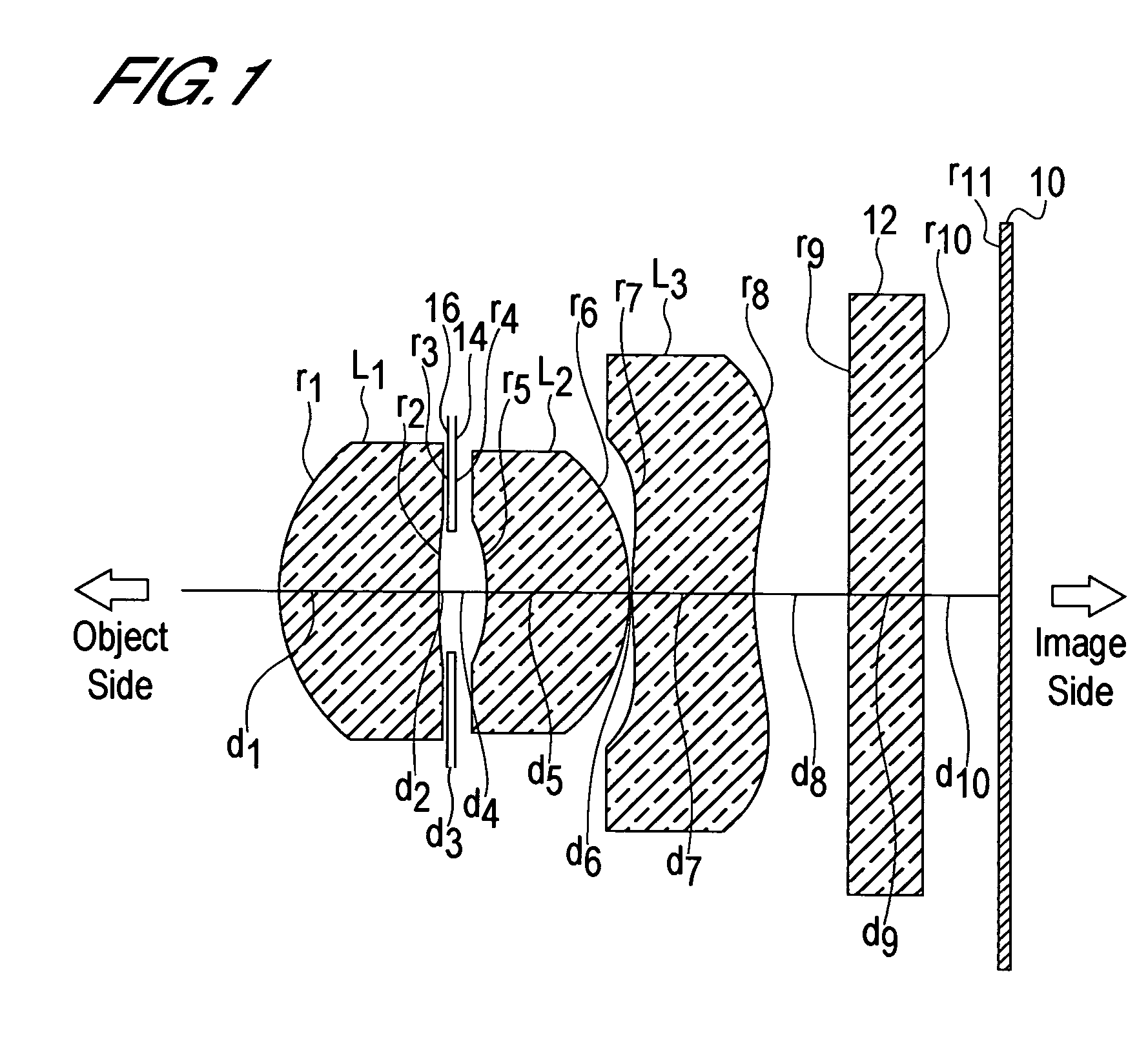
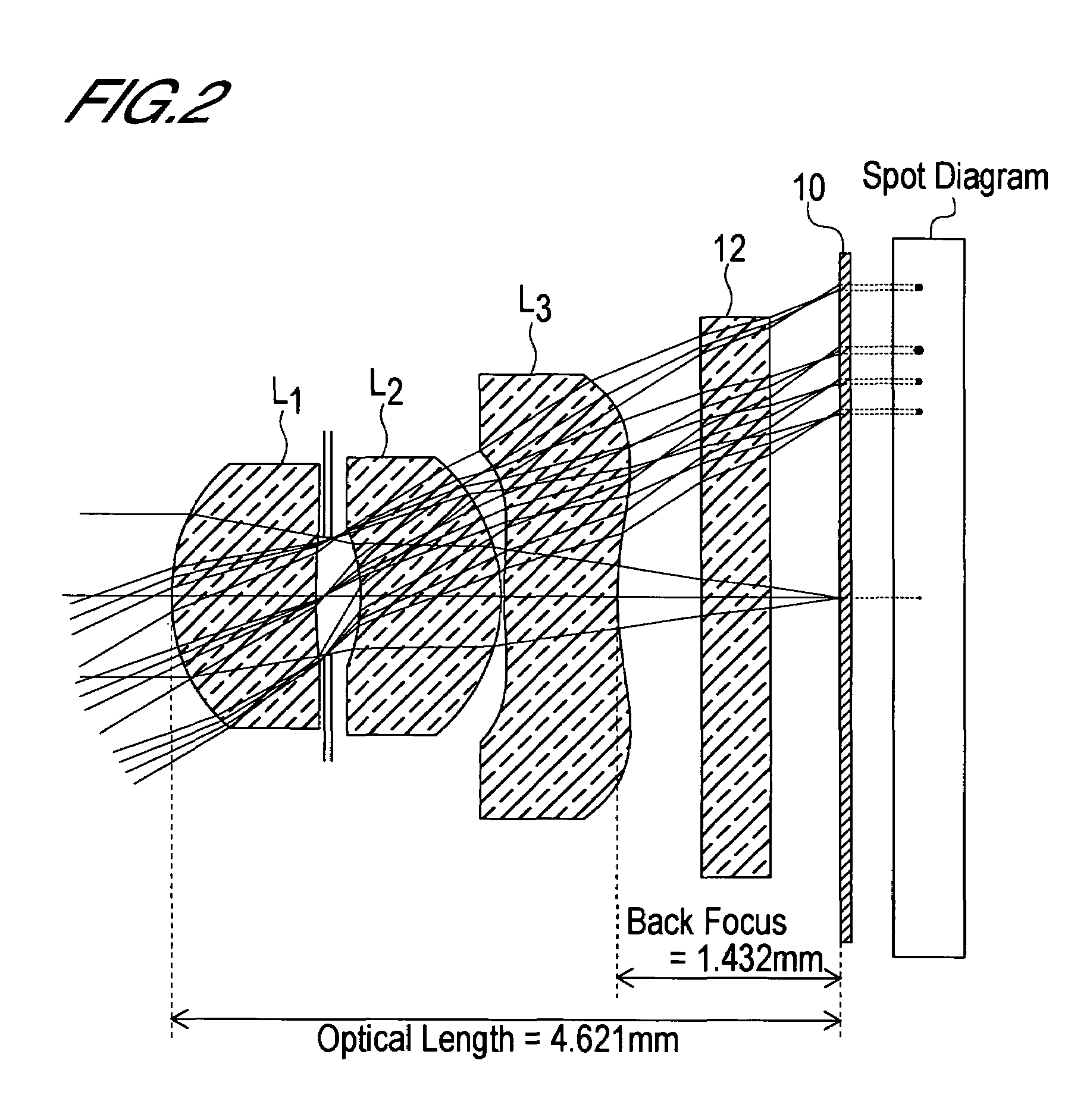
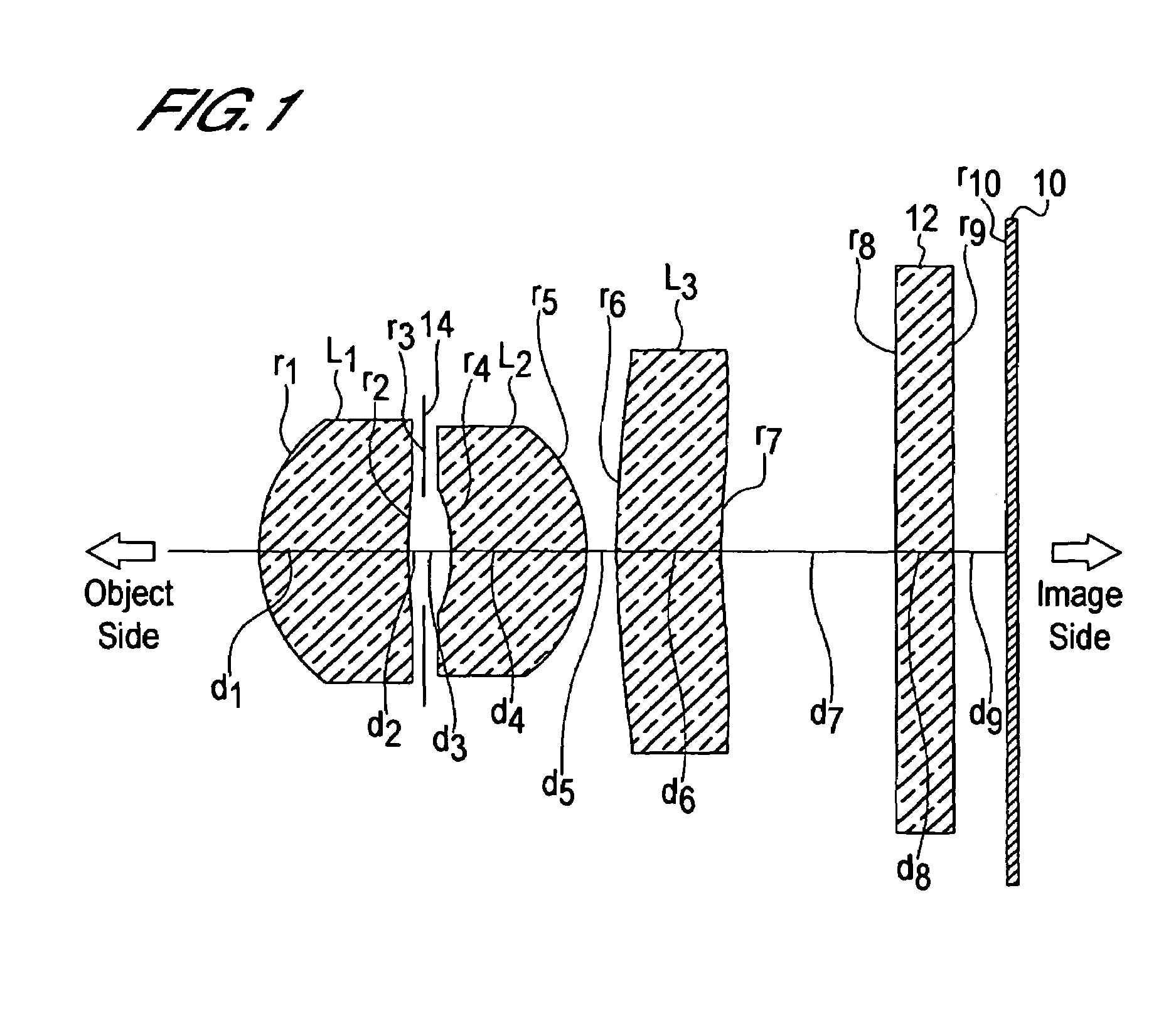
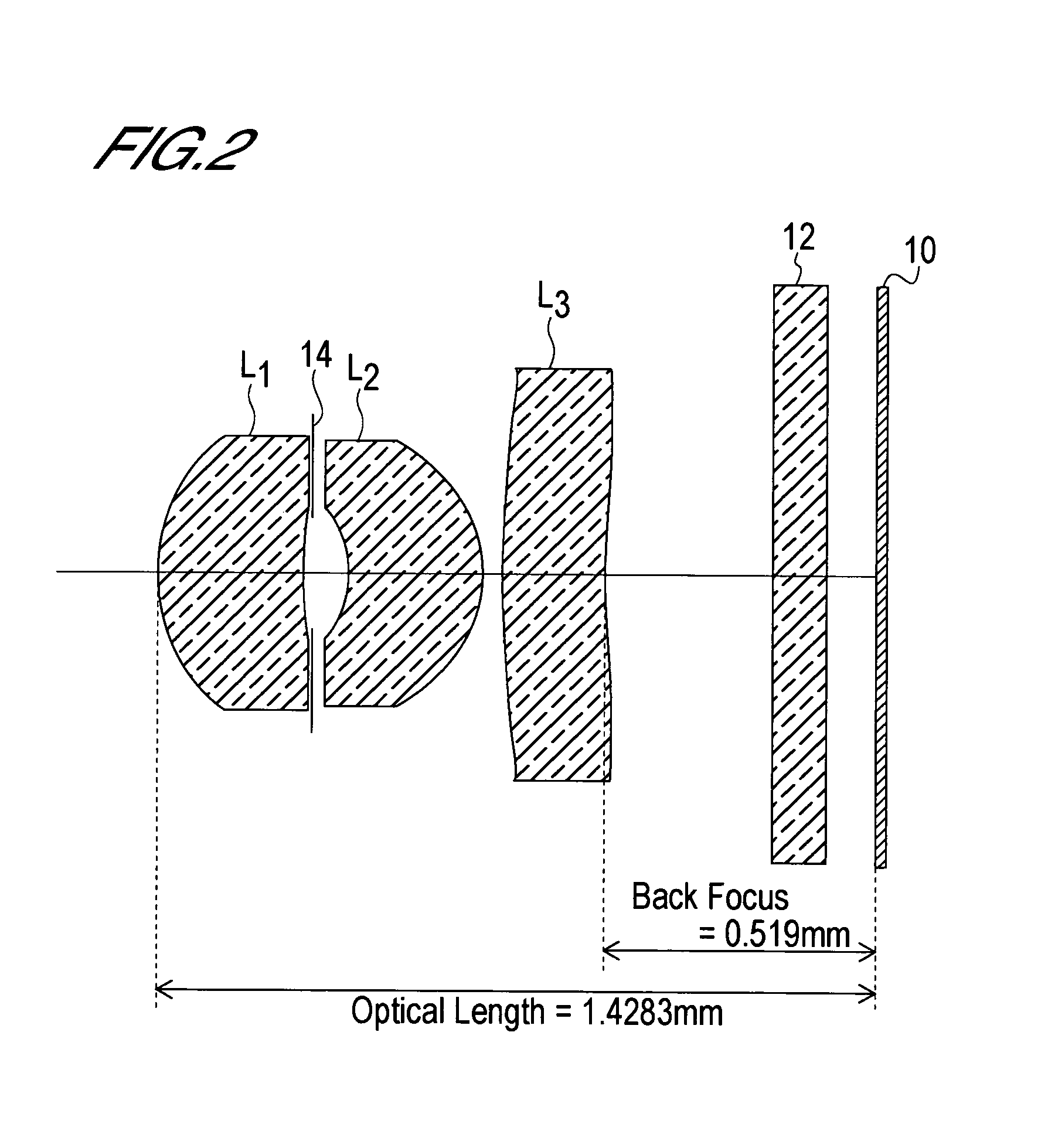
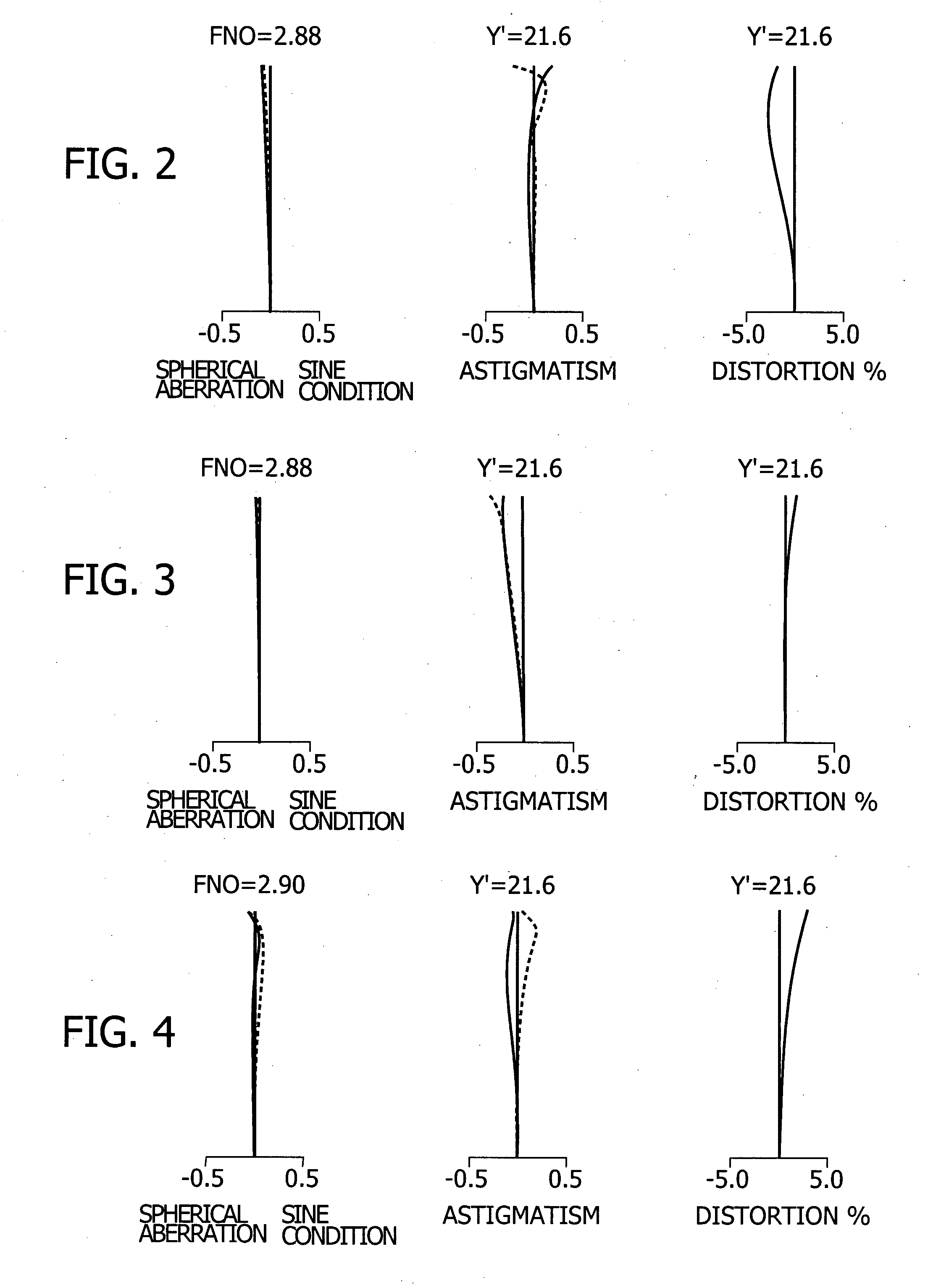
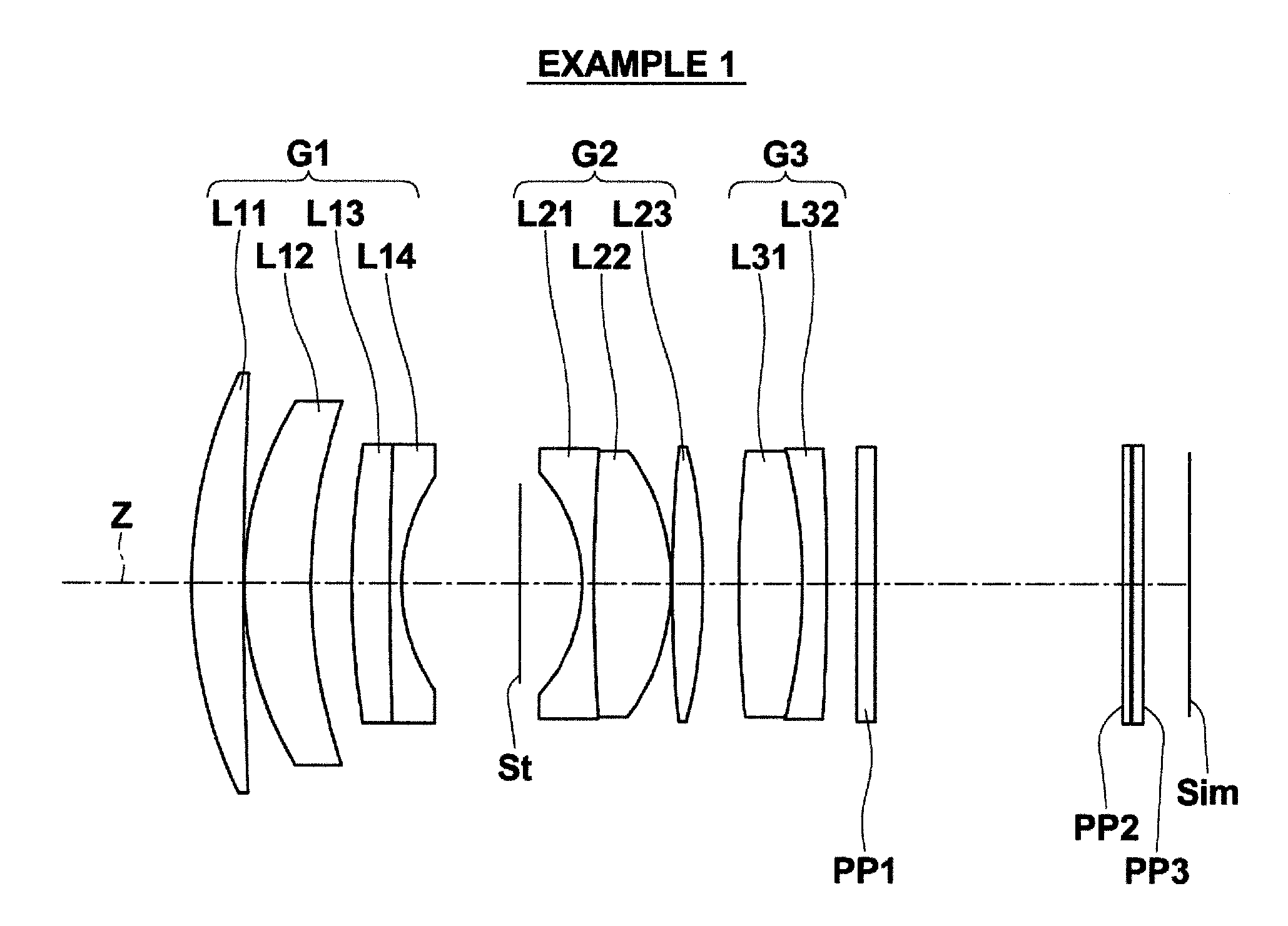
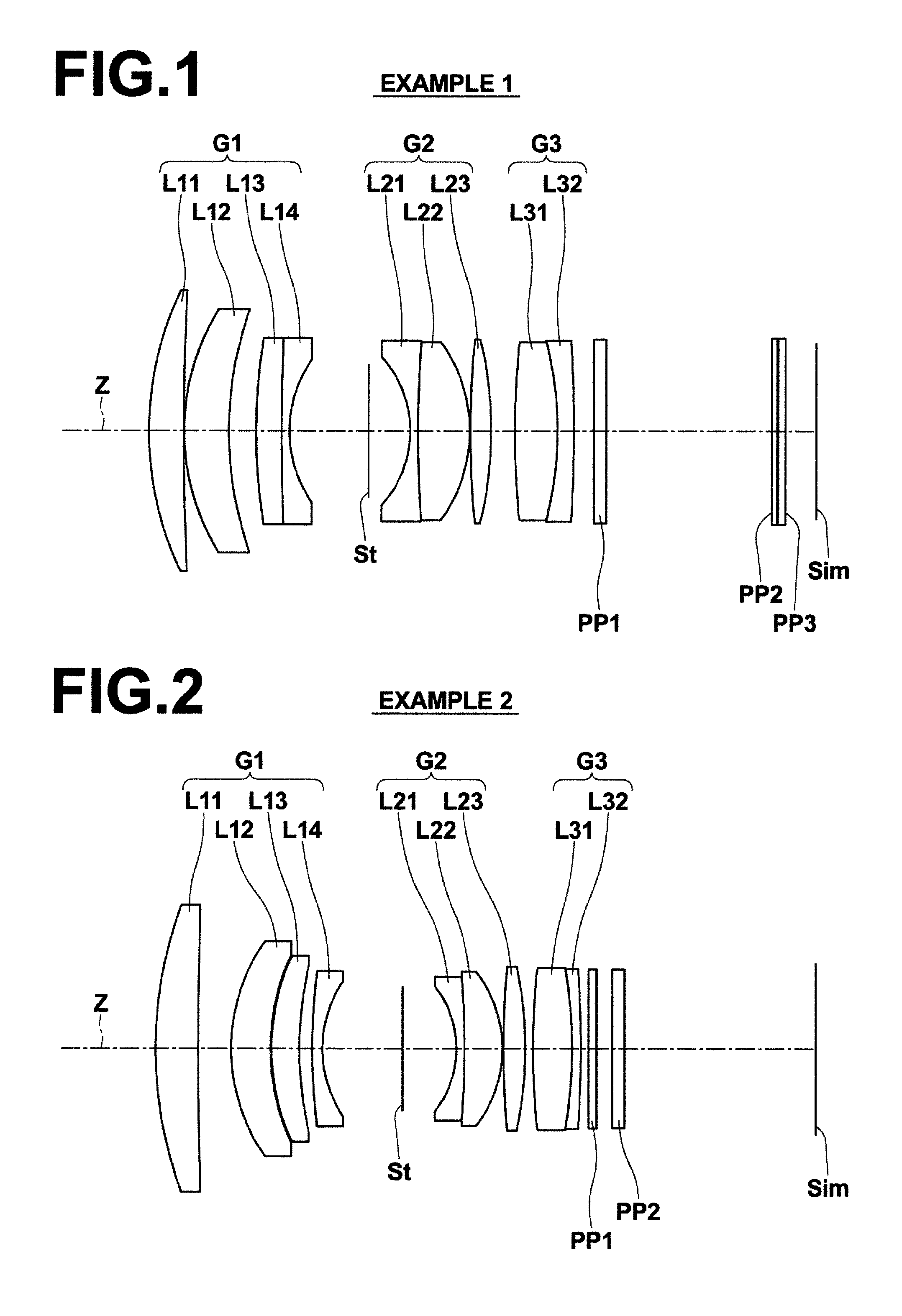
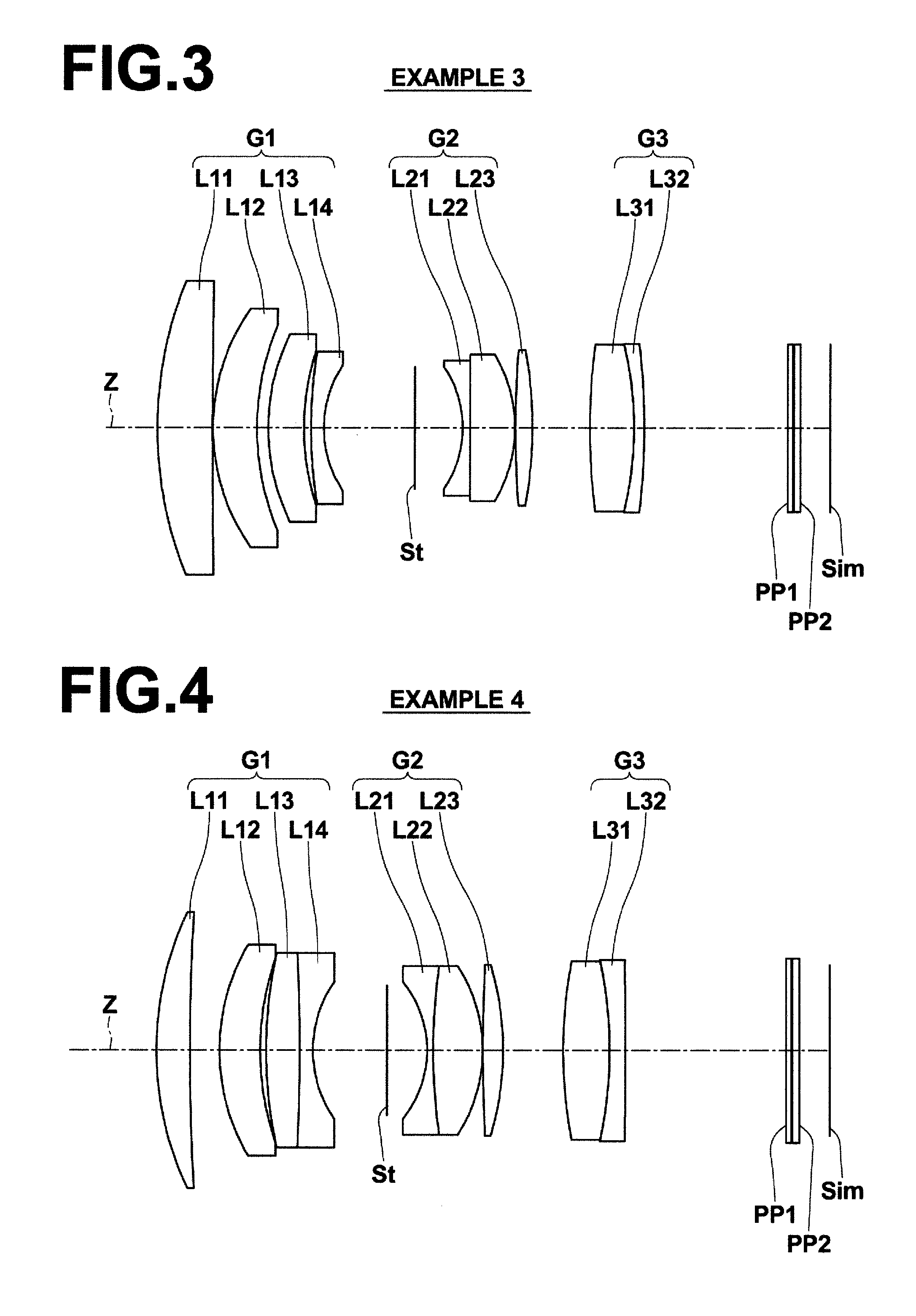
InactiveUS6985307B2Not impair compactnessDistortion can be sufficientlyLensImaging lensOptical path length
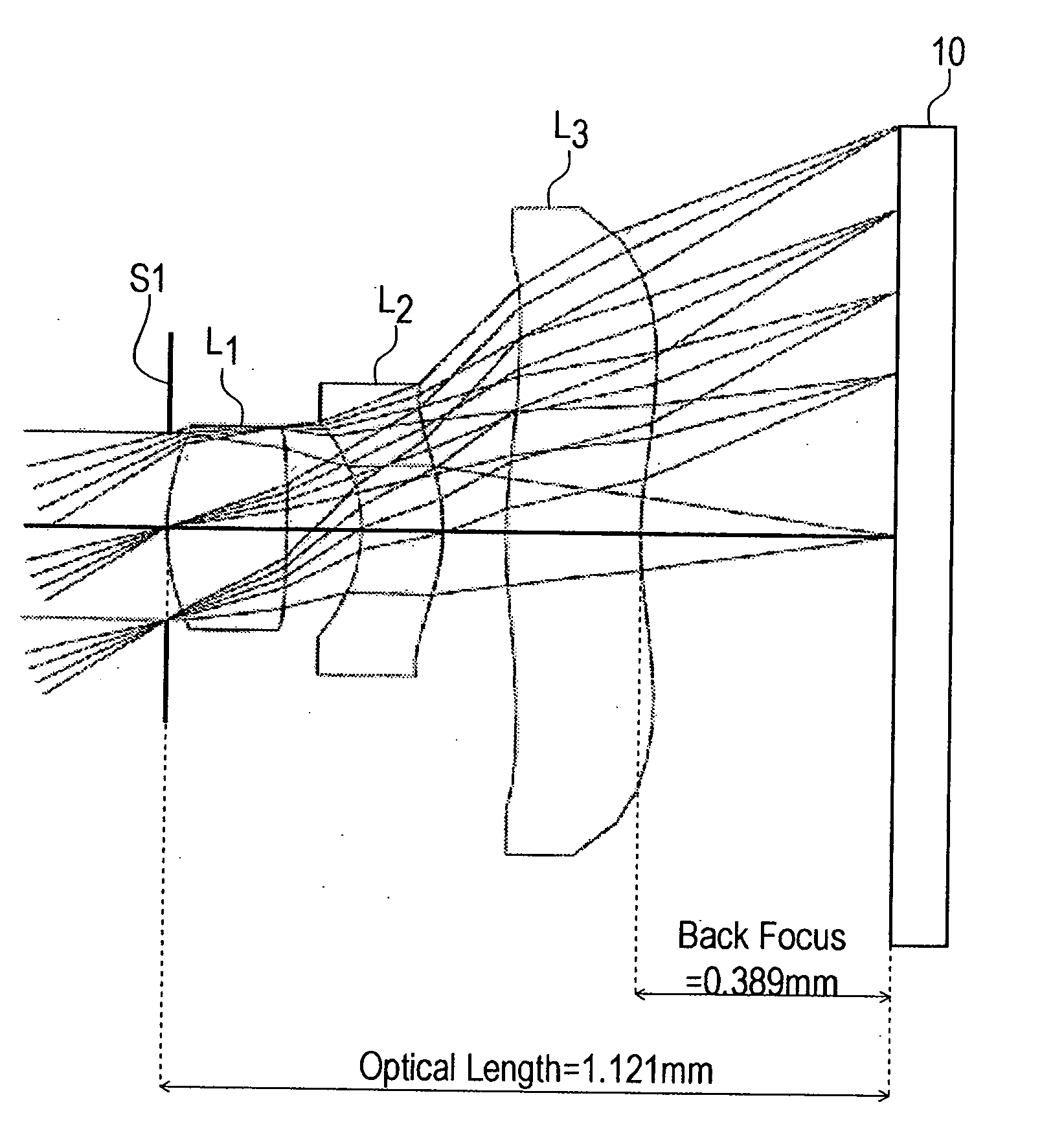
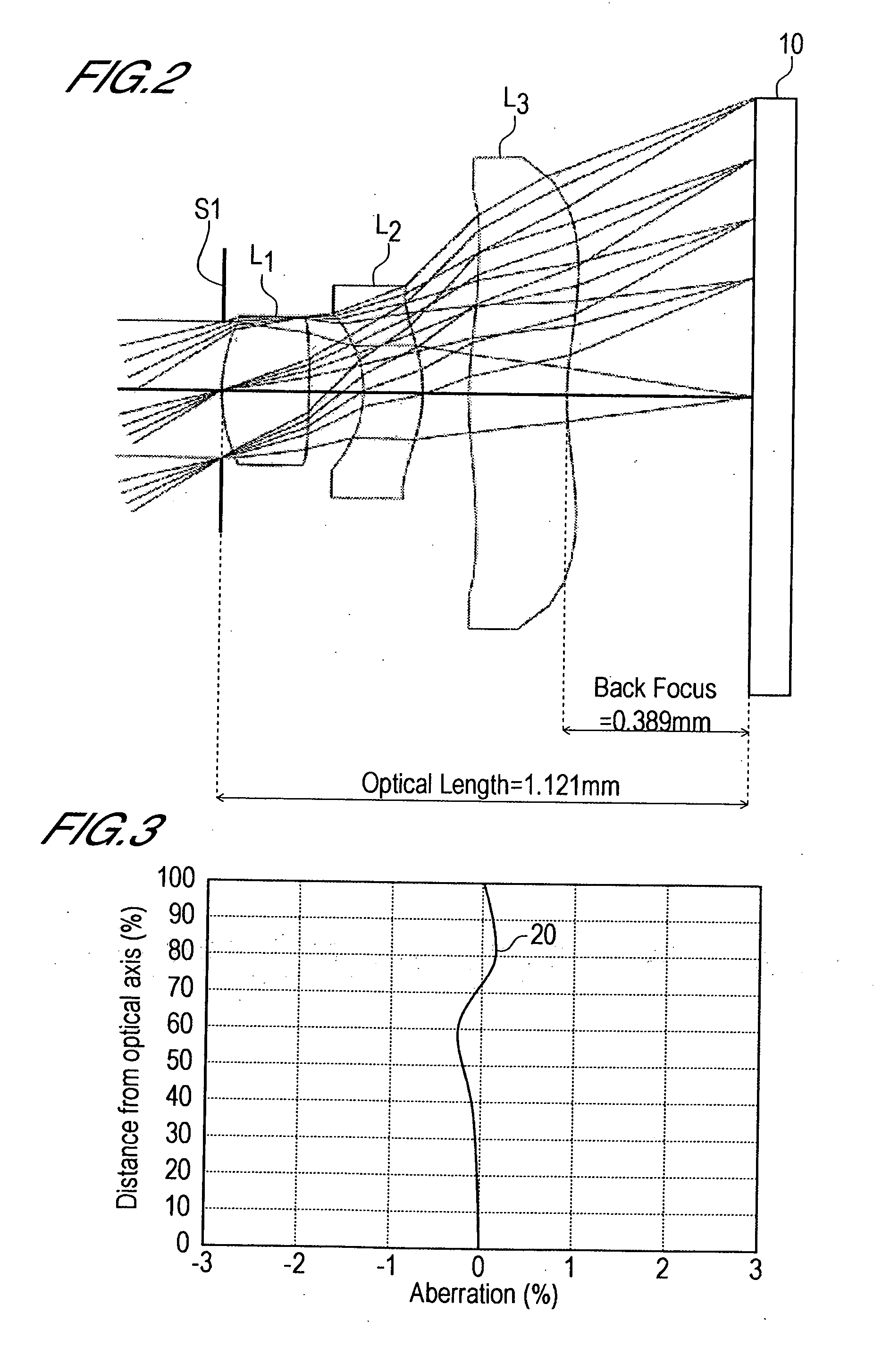
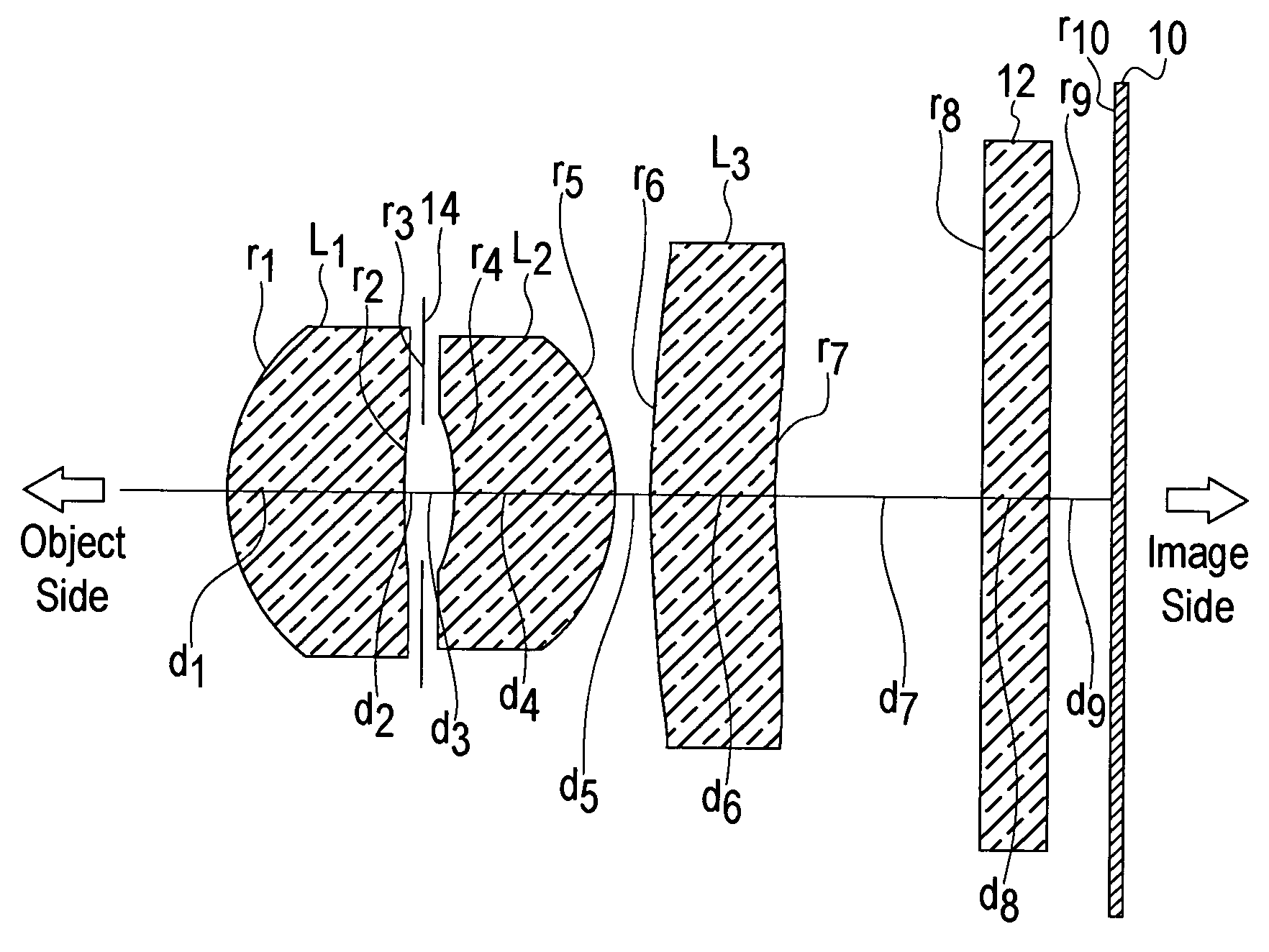
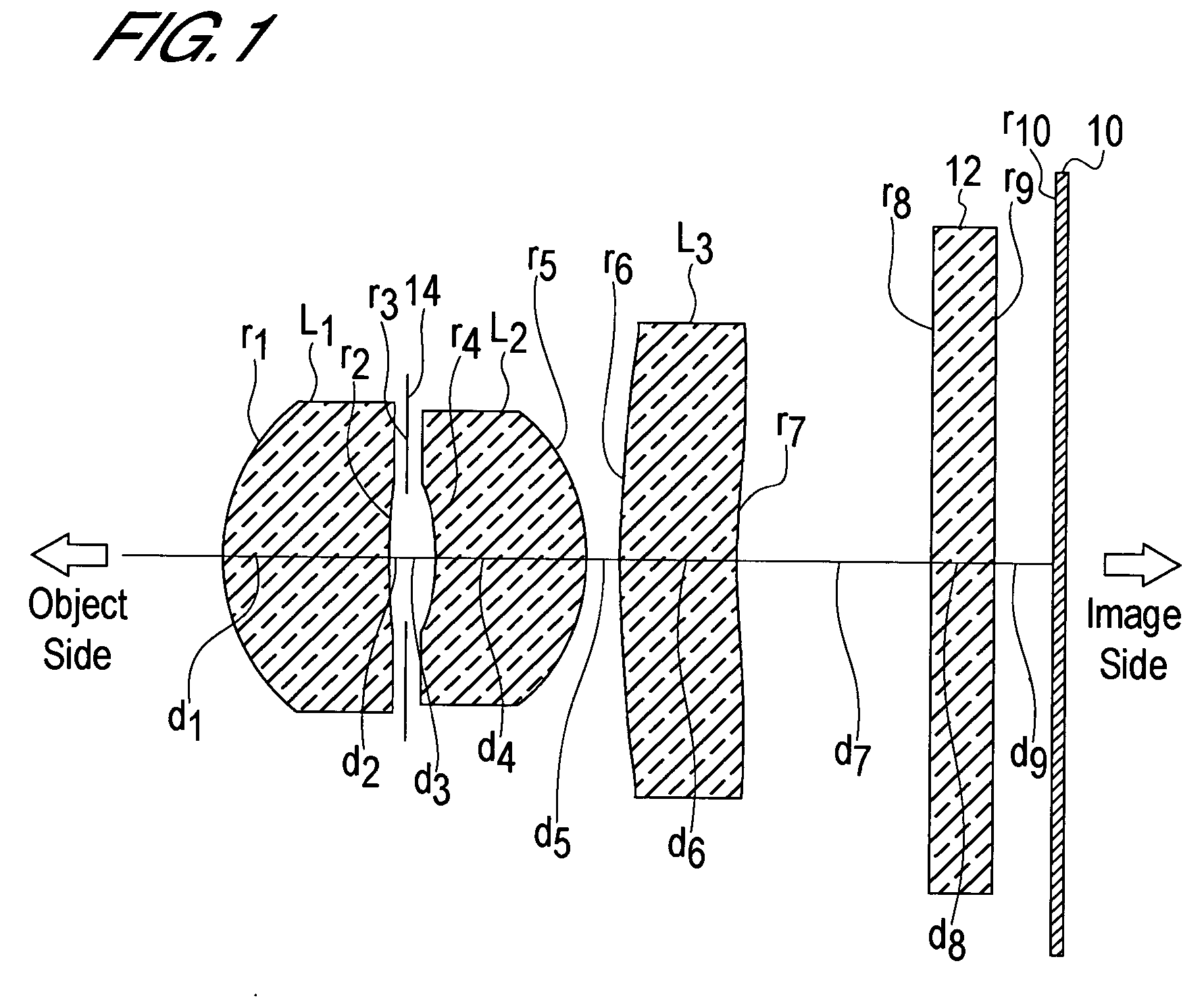
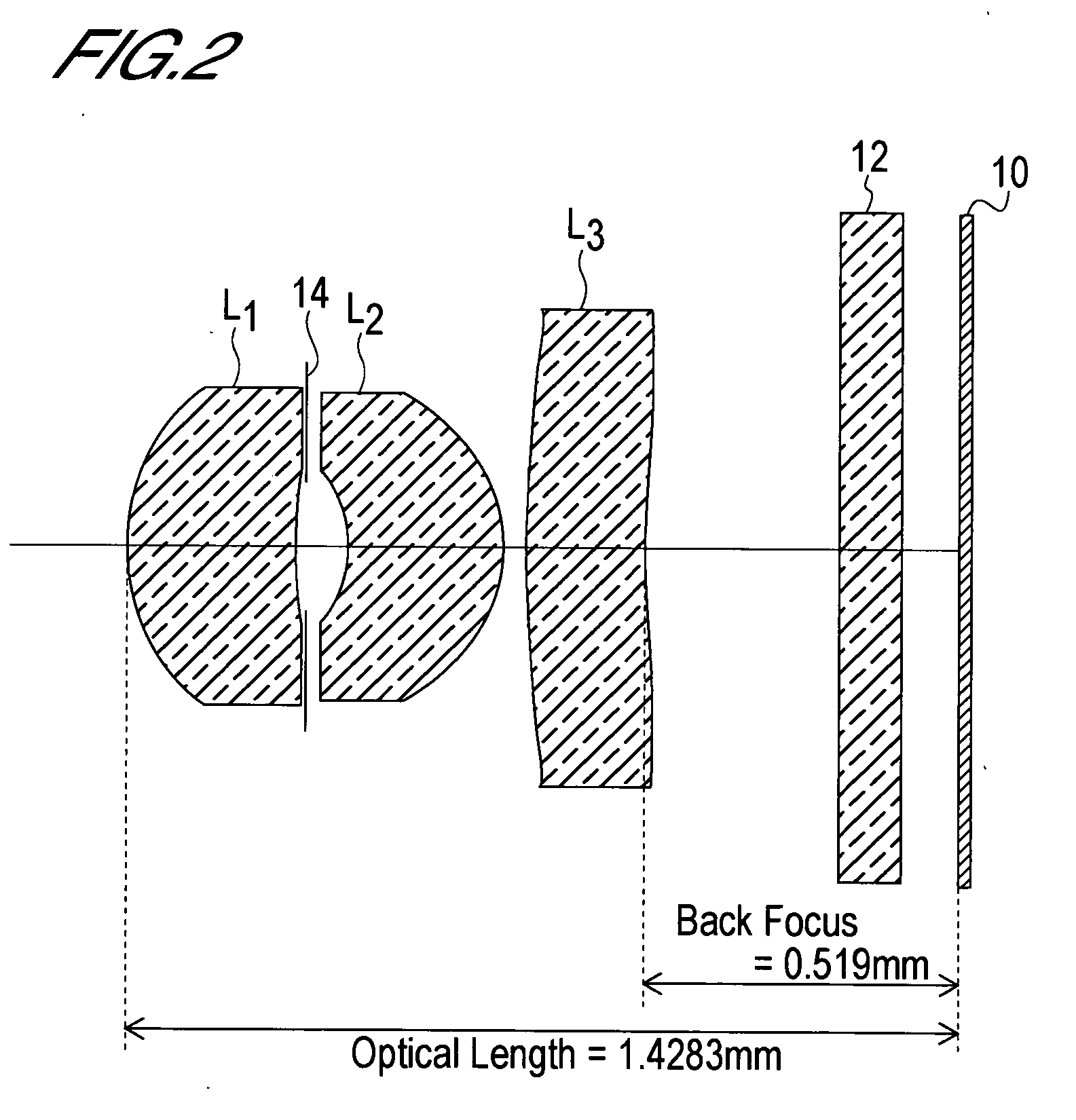
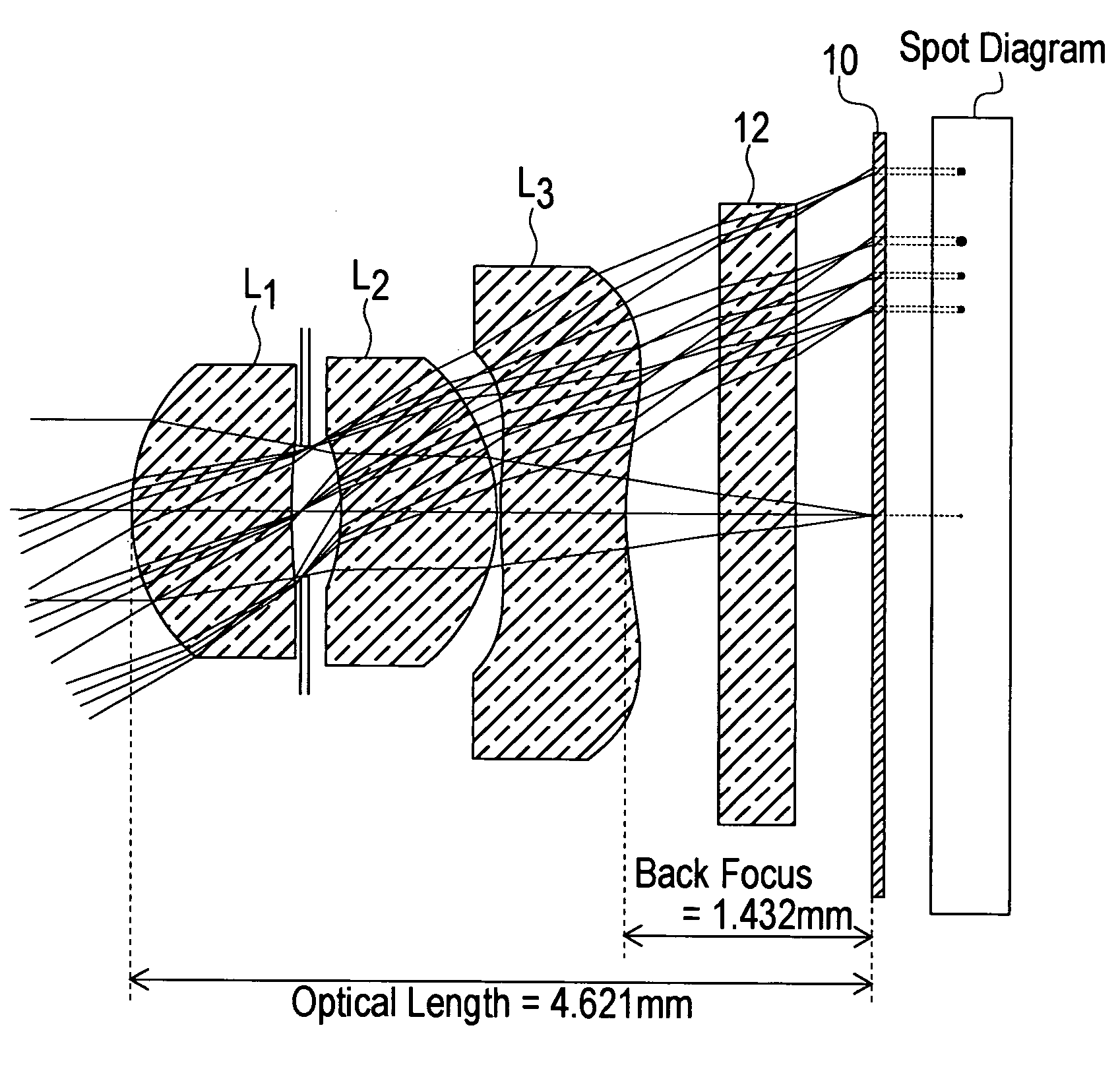
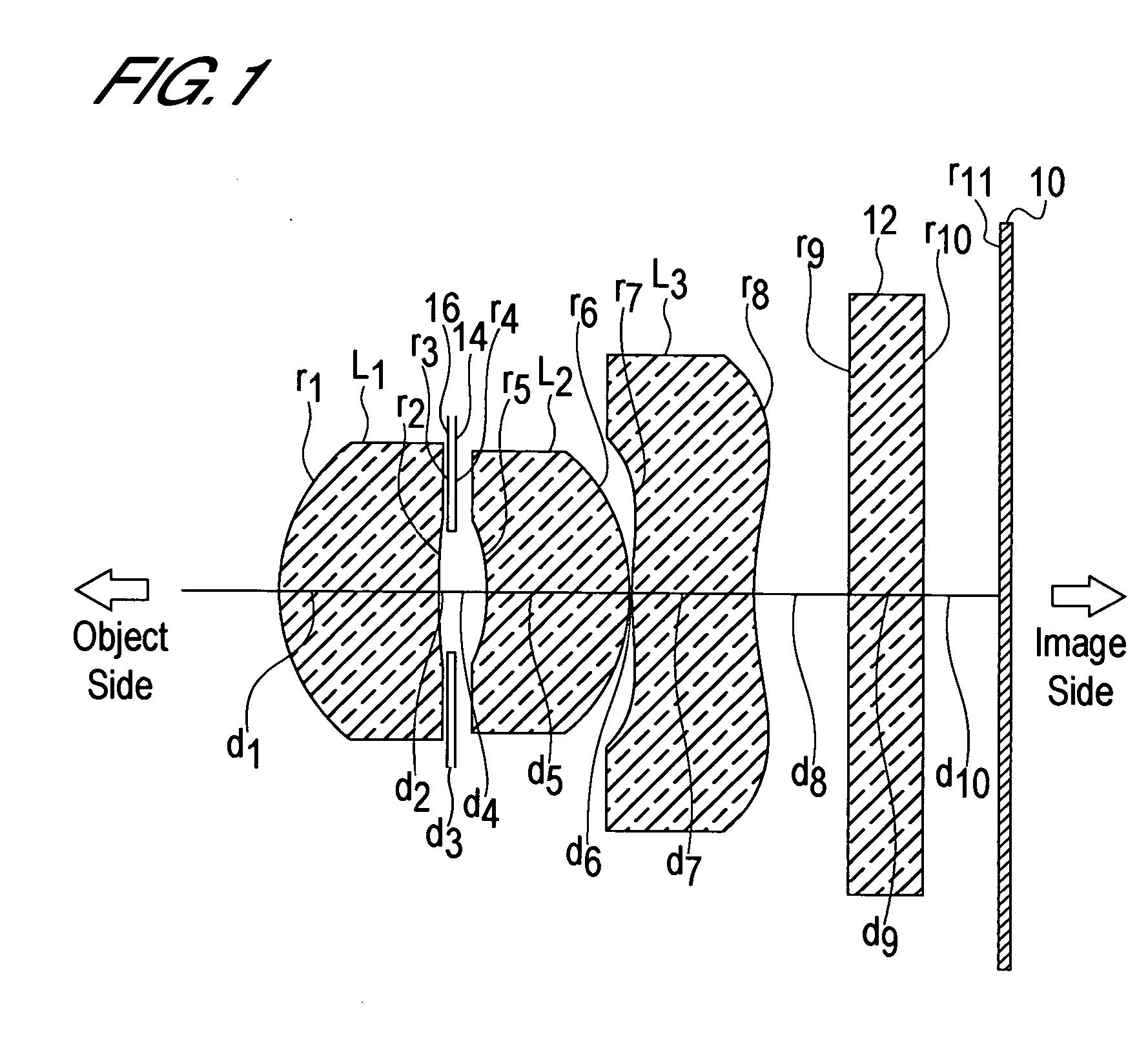
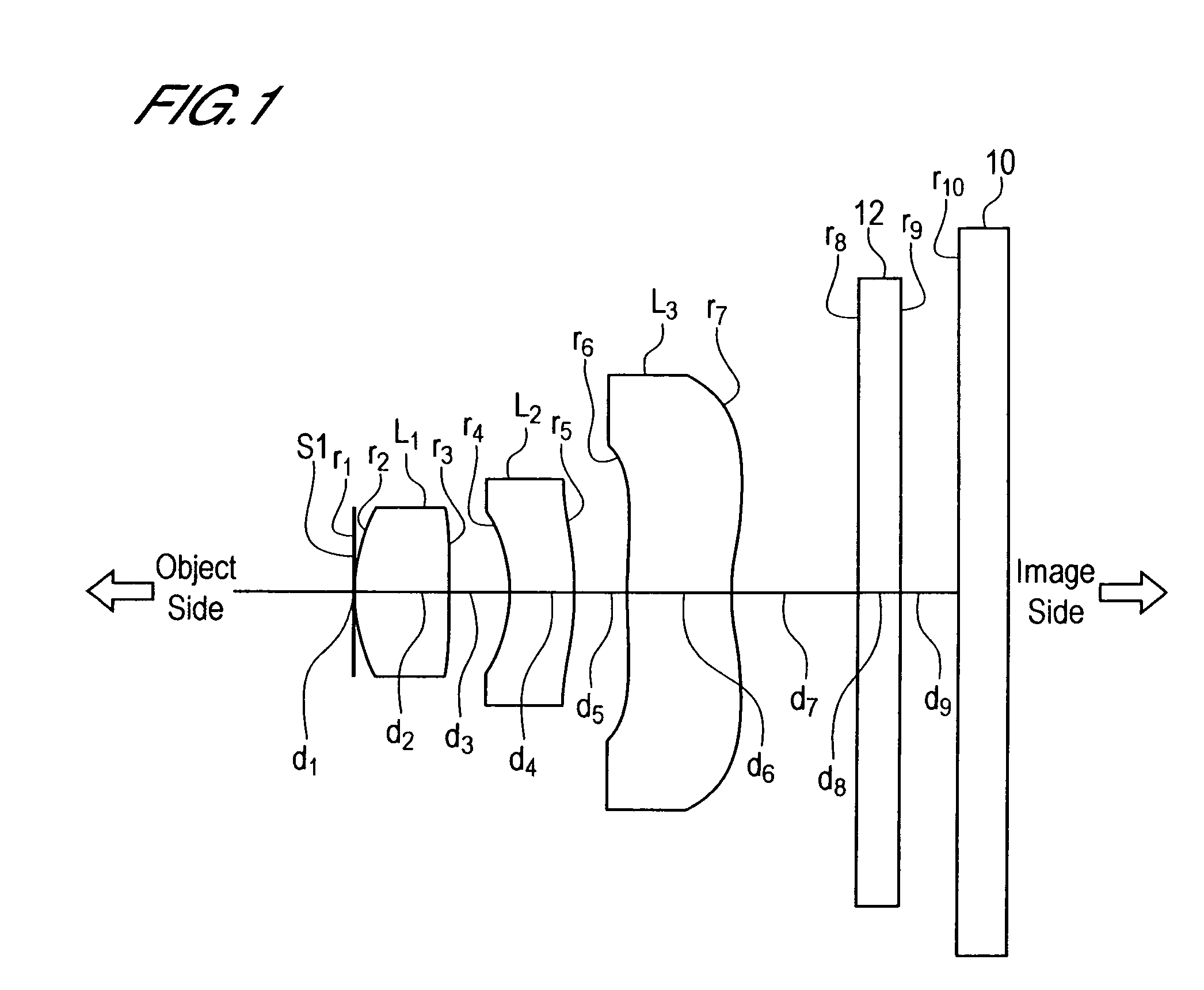
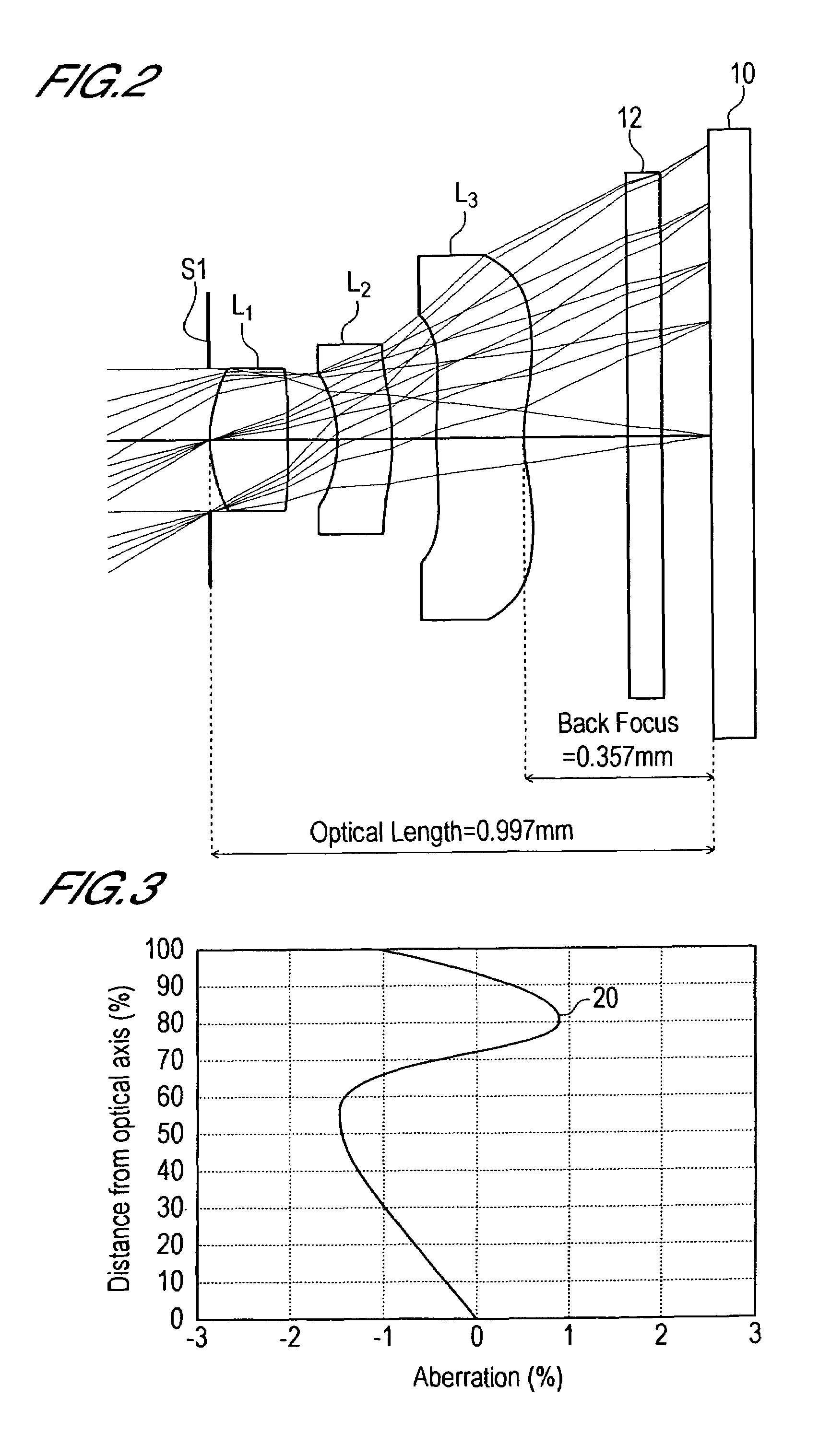
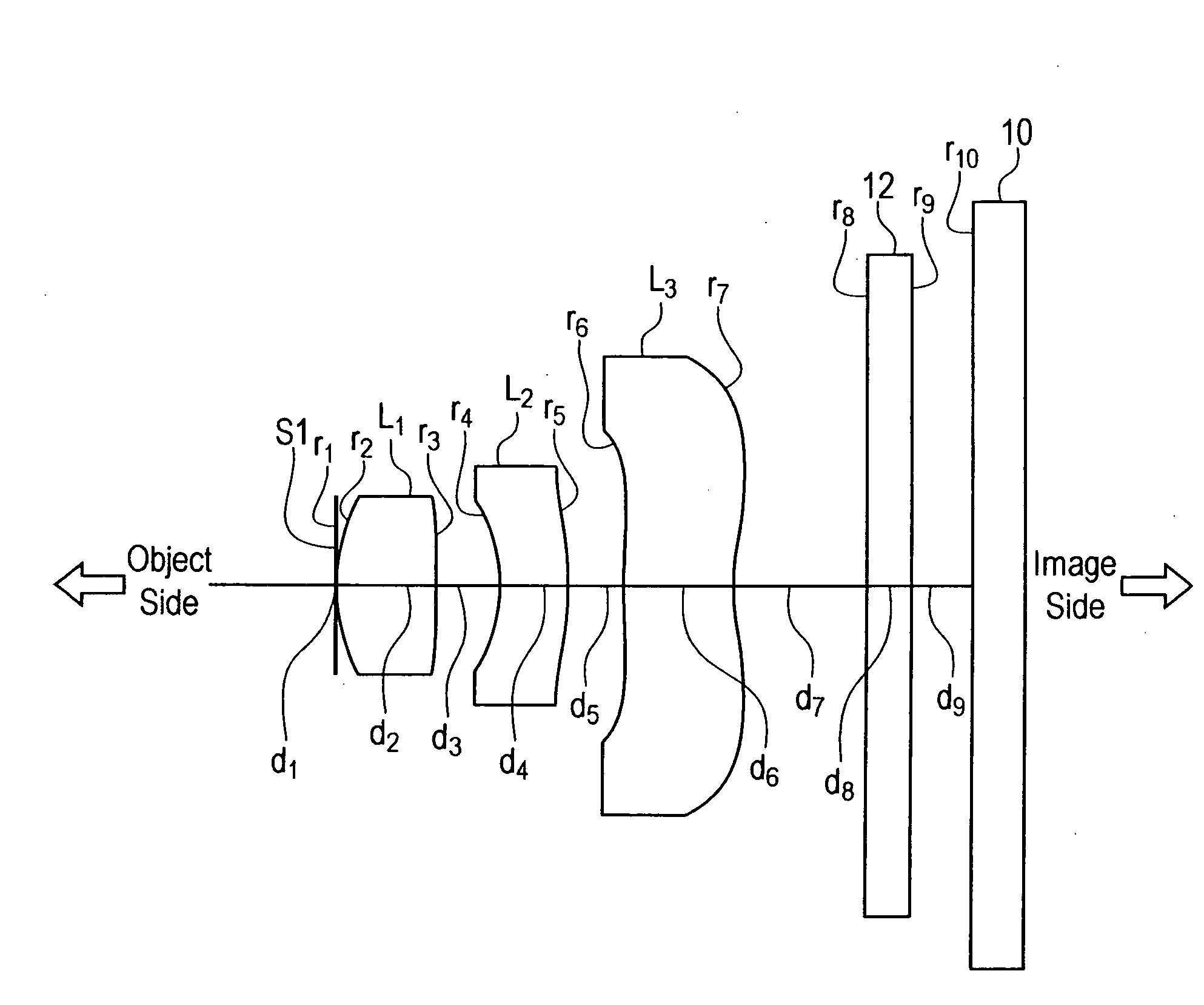
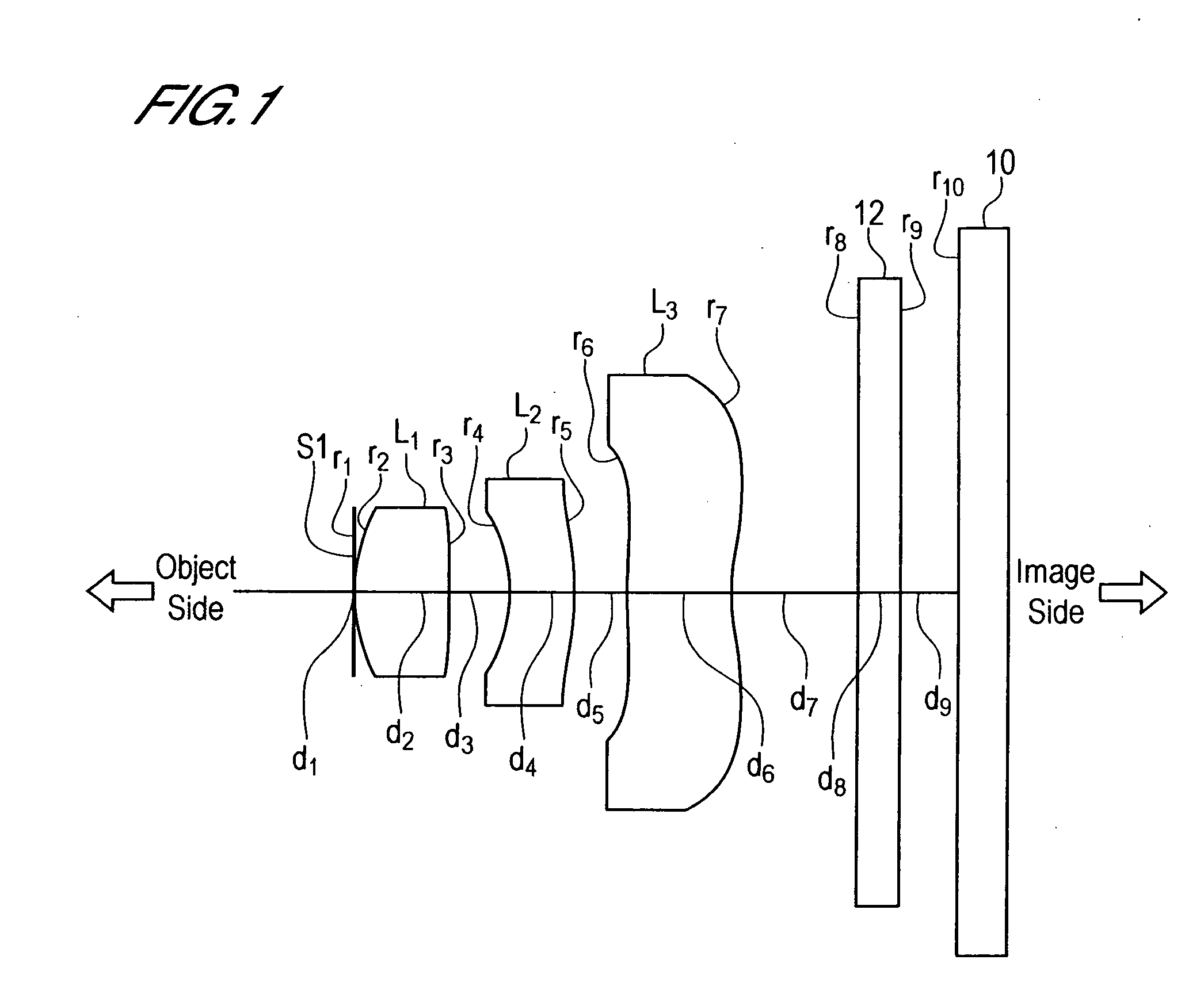
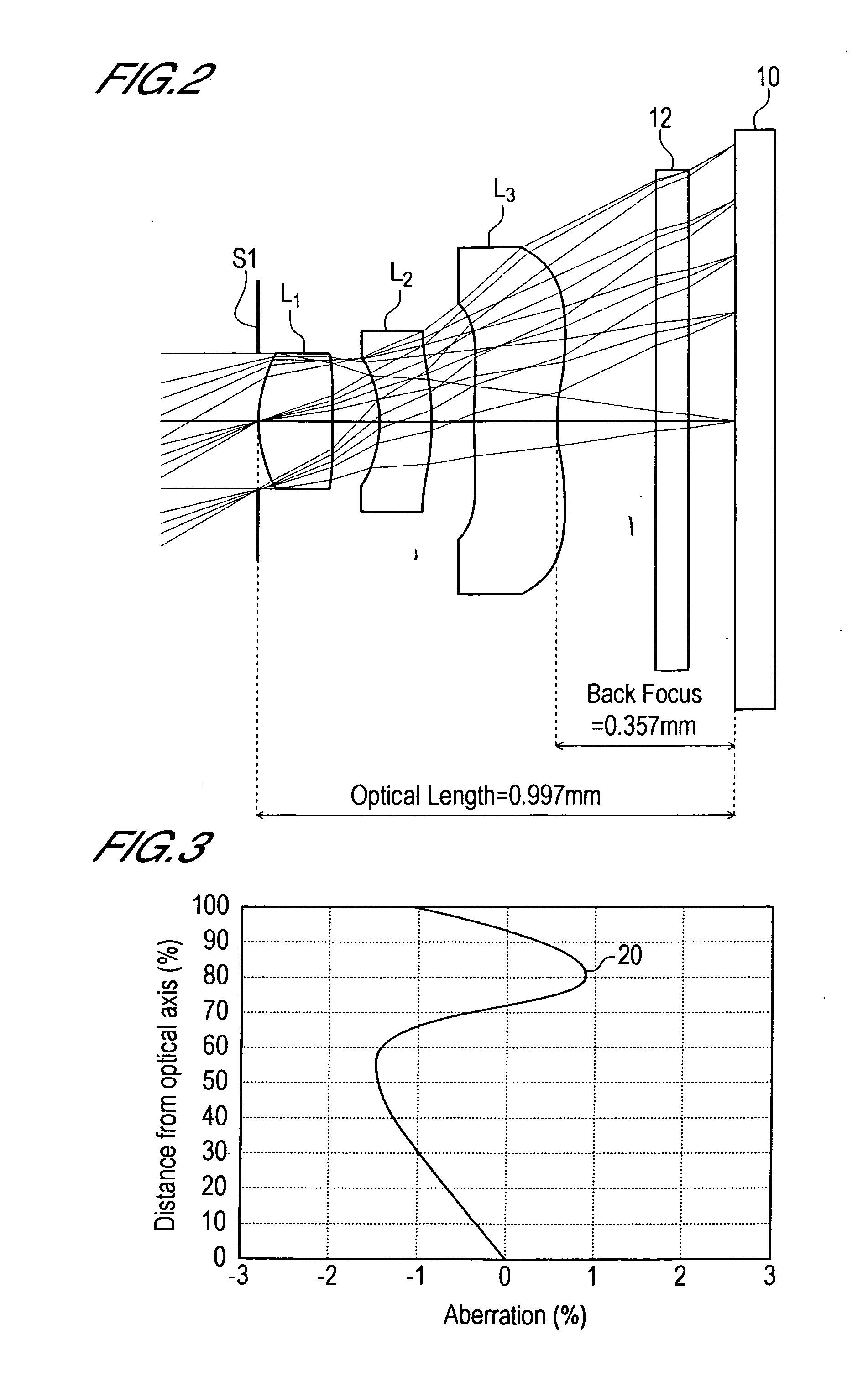
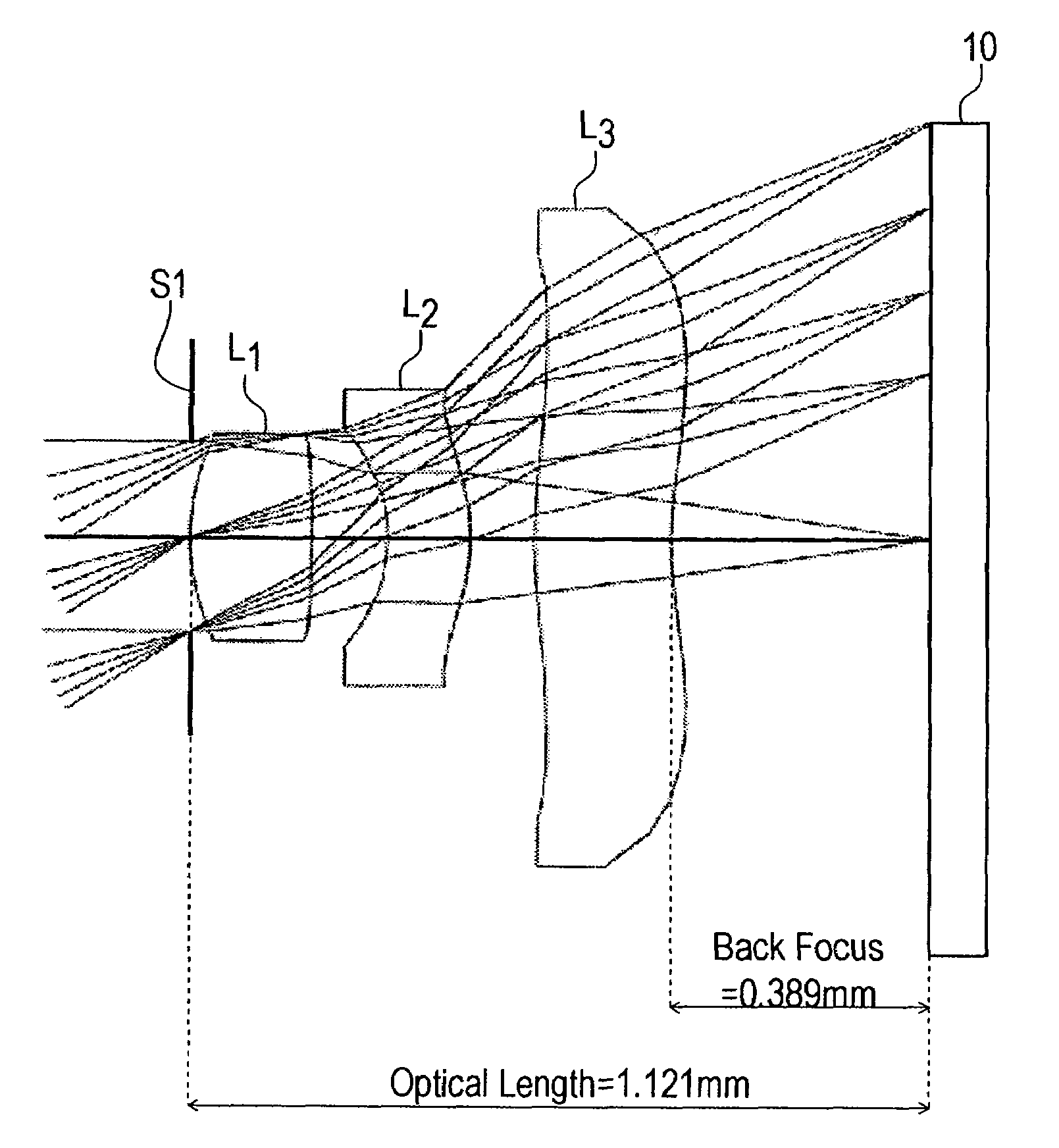
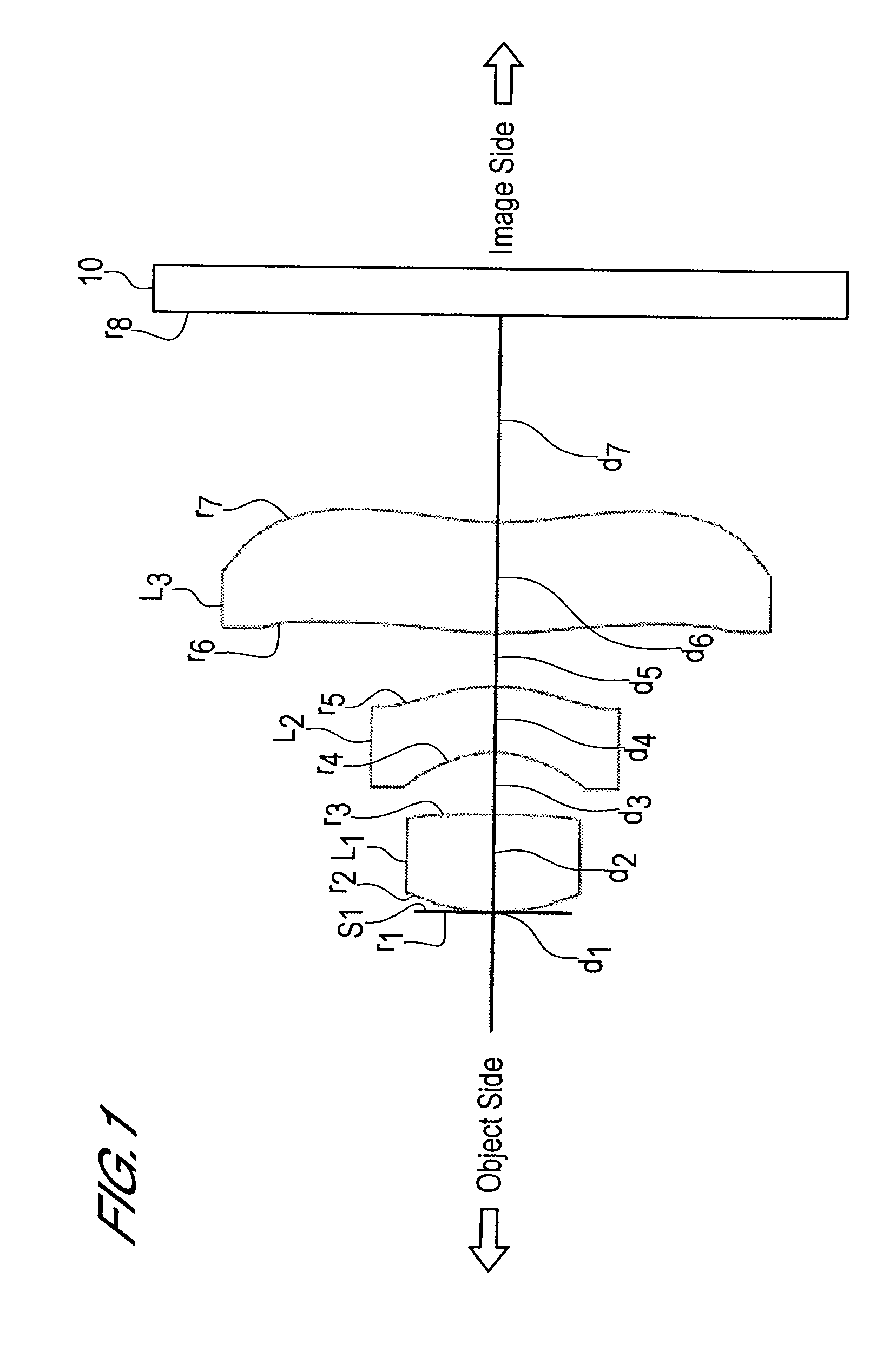
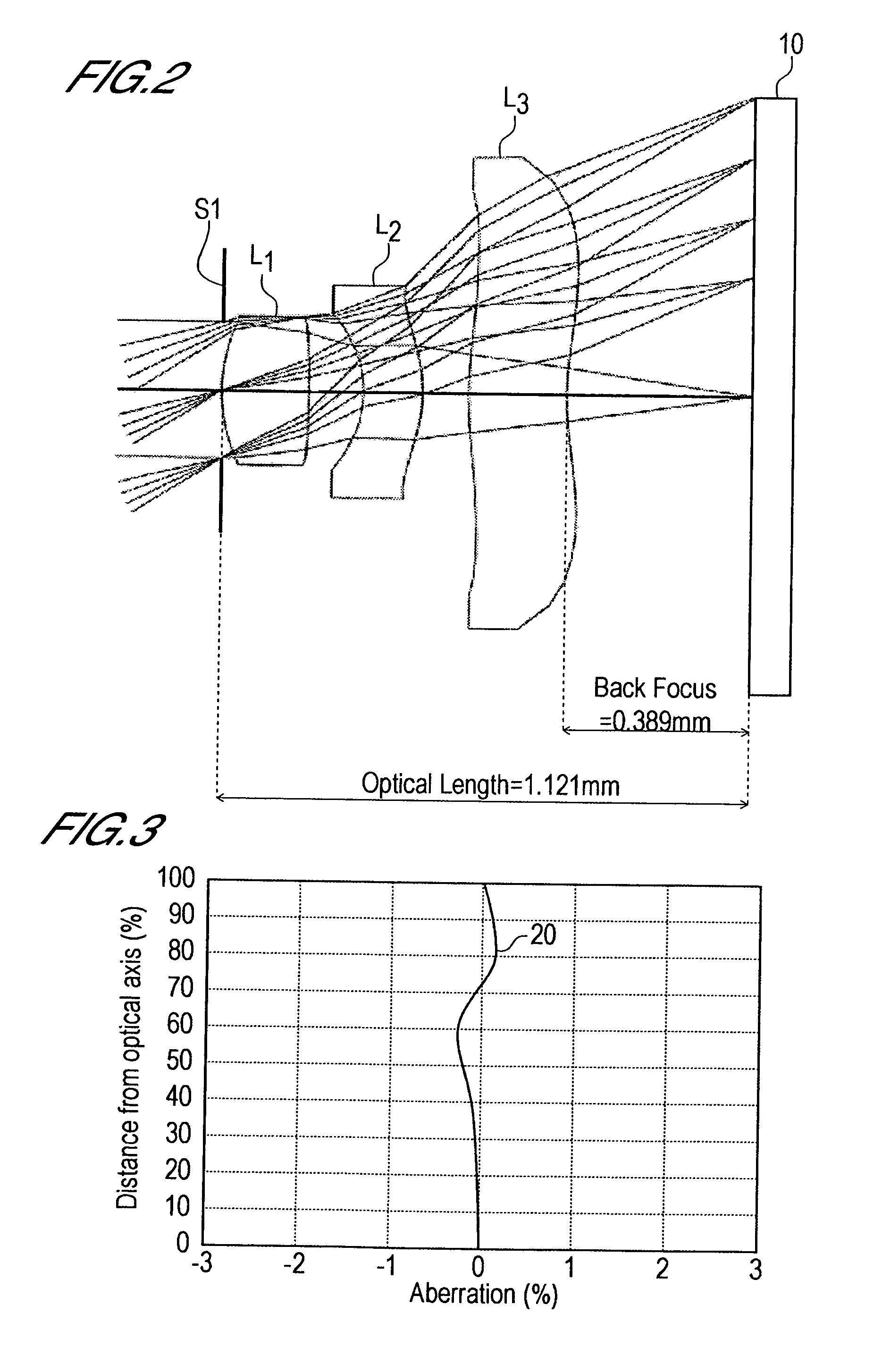
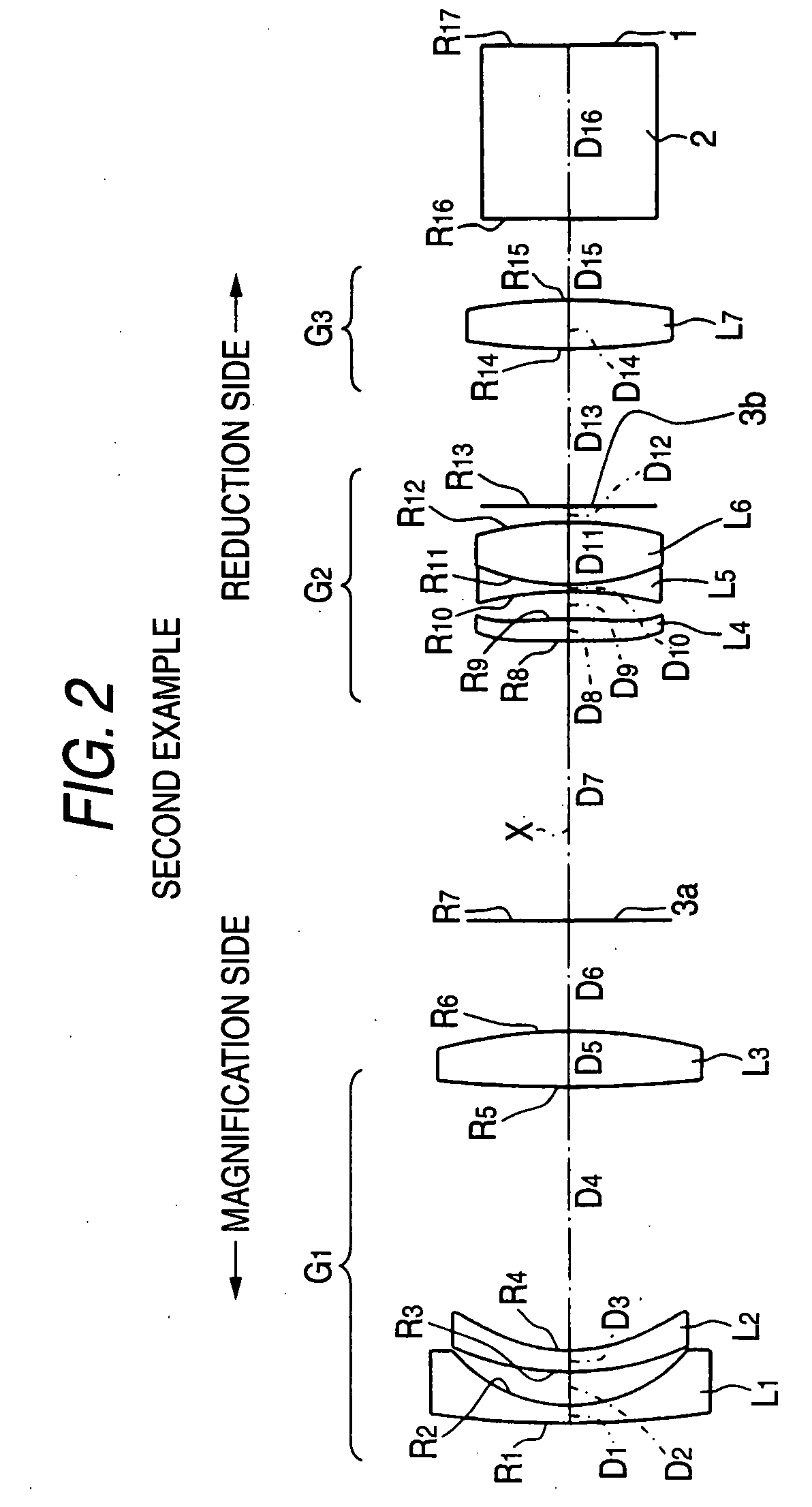
In an imaging lens of the present invention, aberration is satisfactorily corrected, the optical length is short, and sufficient back focus is secured. The imaging lens of the present invention is constituted by arranging a first lens L1, an aperture diaphragm S1, a second lens L2, and a third lens L3 in succession from the object side to the image side.
Owner:MILESTONE CO LTD +1
Ultra thin optical joystick and personal portable device having ultra thin optical joystick
InactiveUS20060038776A1Sufficient depth of focusReduce the overall heightCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingJoystickWaveguide
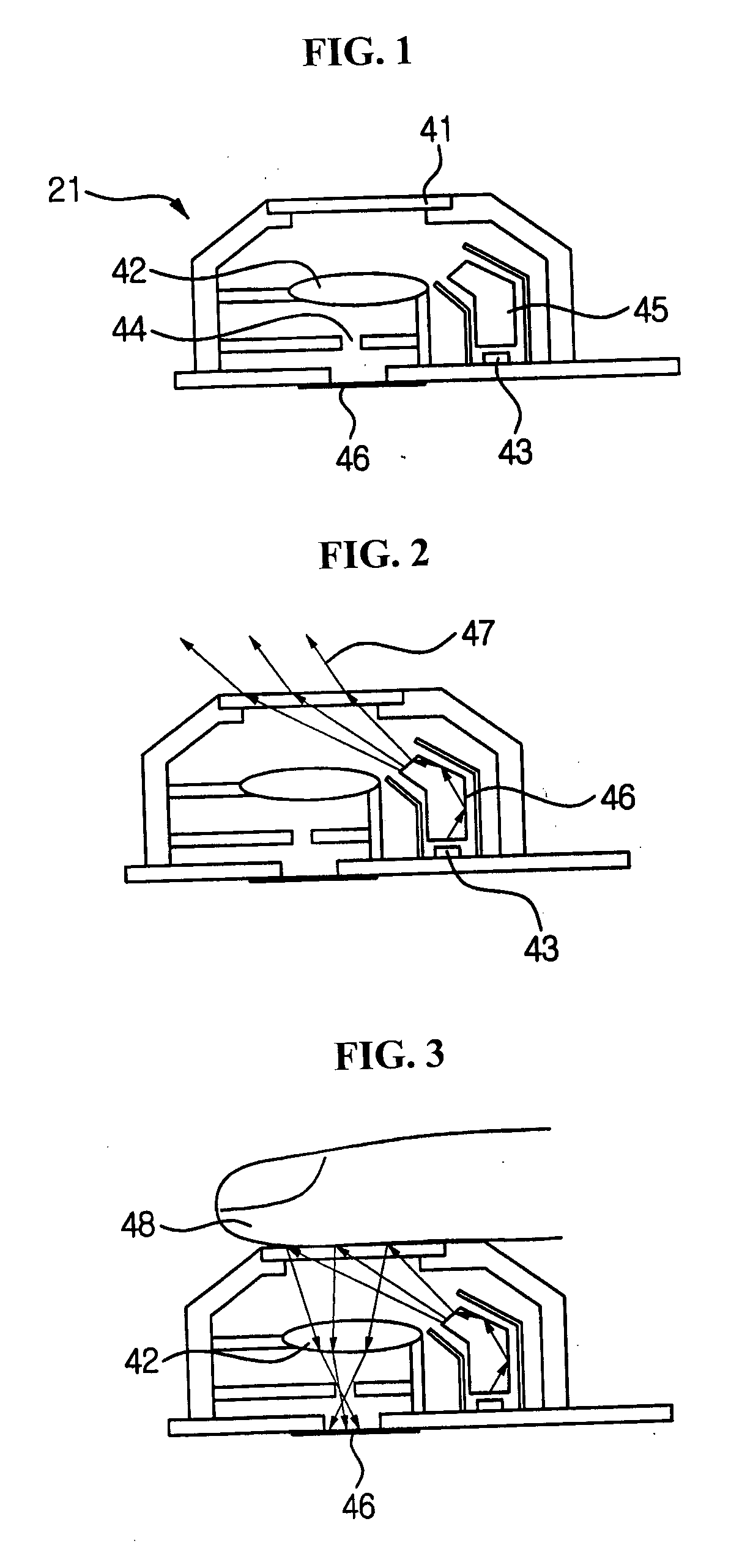
An optical joystick includes a first waveguide including a first reflecting surface located below a reading area for sensing the movement of an object and a first plano-convex lens portion condensing light reflected from the first reflecting surface, a second waveguide including a second plano-convex lens portion facing the first plano-convex lens portion and a second reflecting surface for reflecting light refracted at the second plano-convex lens portion, and an image sensor located below the second reflecting surface. The first reflecting surface and the first plano-convex lens portion form a single body, and the second plano-convex lens portion and the second reflecting surface also form a single body. The reflecting surface and the lens portion are in a single body, thereby notably reducing the thickness of the optical joystick. The first and second waveguides are facing each other, thereby improving refraction and condensing light.
Owner:CRUCIALTEC +1
Pickup lens
A pickup lens is provided with various aberrations corrected satisfactorily, with a short optical length, and with a sufficient back focus secured.The configuration comprises an aperture diaphragm S1, first lens L1, second lens L2, and third lens L3, and is configured by arranging, in order from the object side to the image side, the aperture diaphragm, first lens, second lens, and third lens. The first lens is a lens having positive refractive power, with convex surfaces on the object side and on the image side. The second lens is a lens having negative refractive power, in a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the image side. The third lens is a lens having negative refractive power, in a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the object side. Both of the surfaces of the first lens are aspherical, both of the surfaces of the second lens are aspherical, and both of the surfaces of the third lens are aspherical.
Owner:SEIKOH GIKEN
Imaging apparatus and method
ActiveUS20090115887A1Overcome lack of focusEnough speedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsNarrow rangeAutofocus
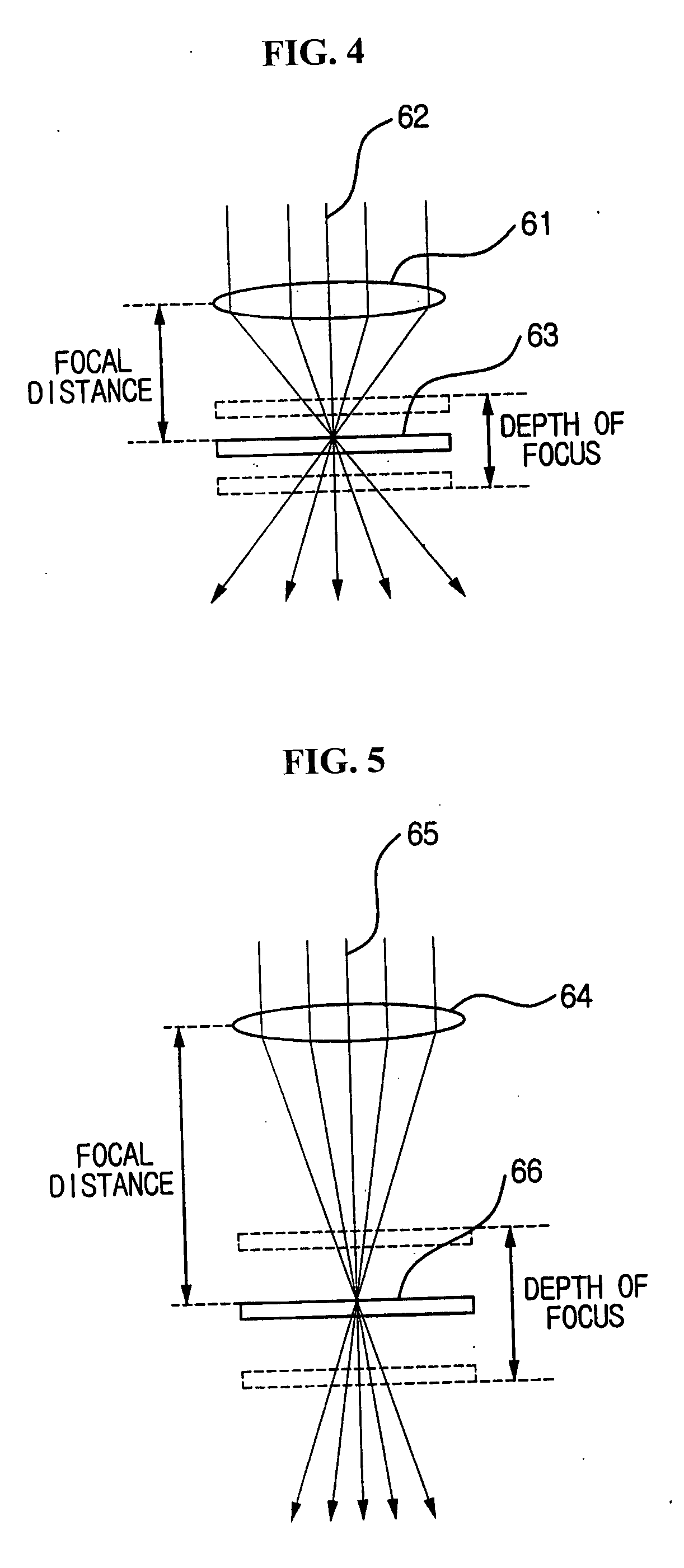
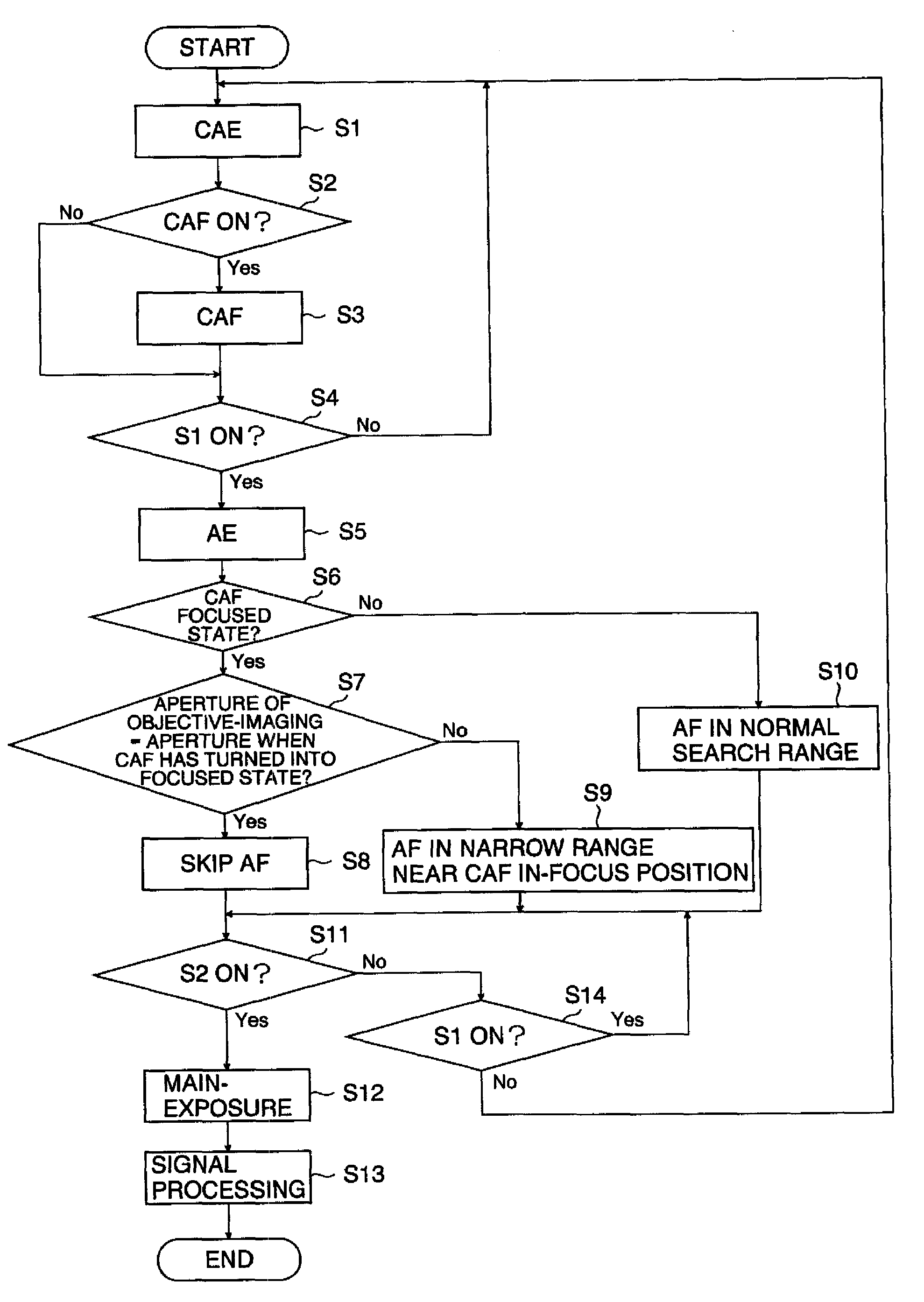
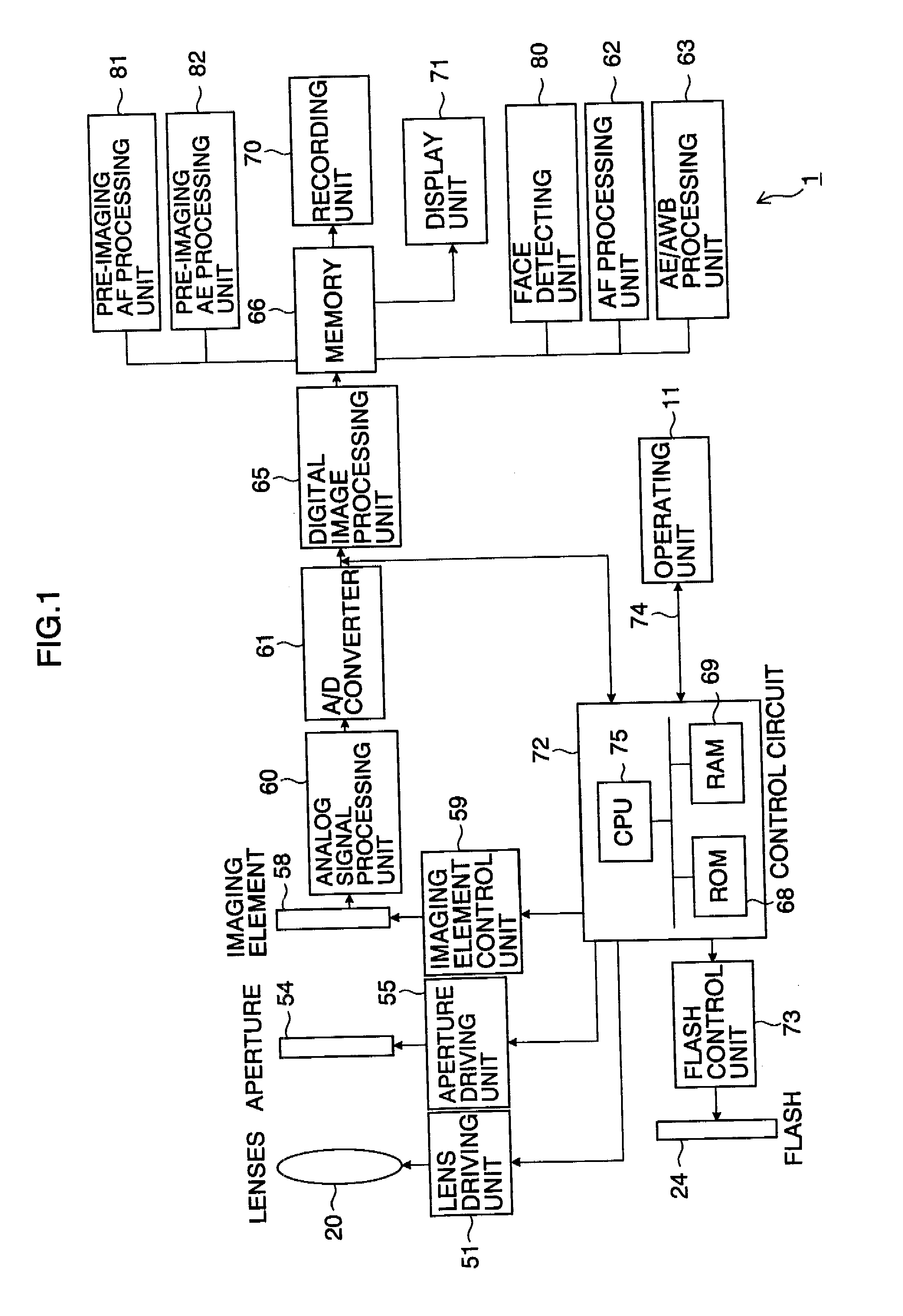
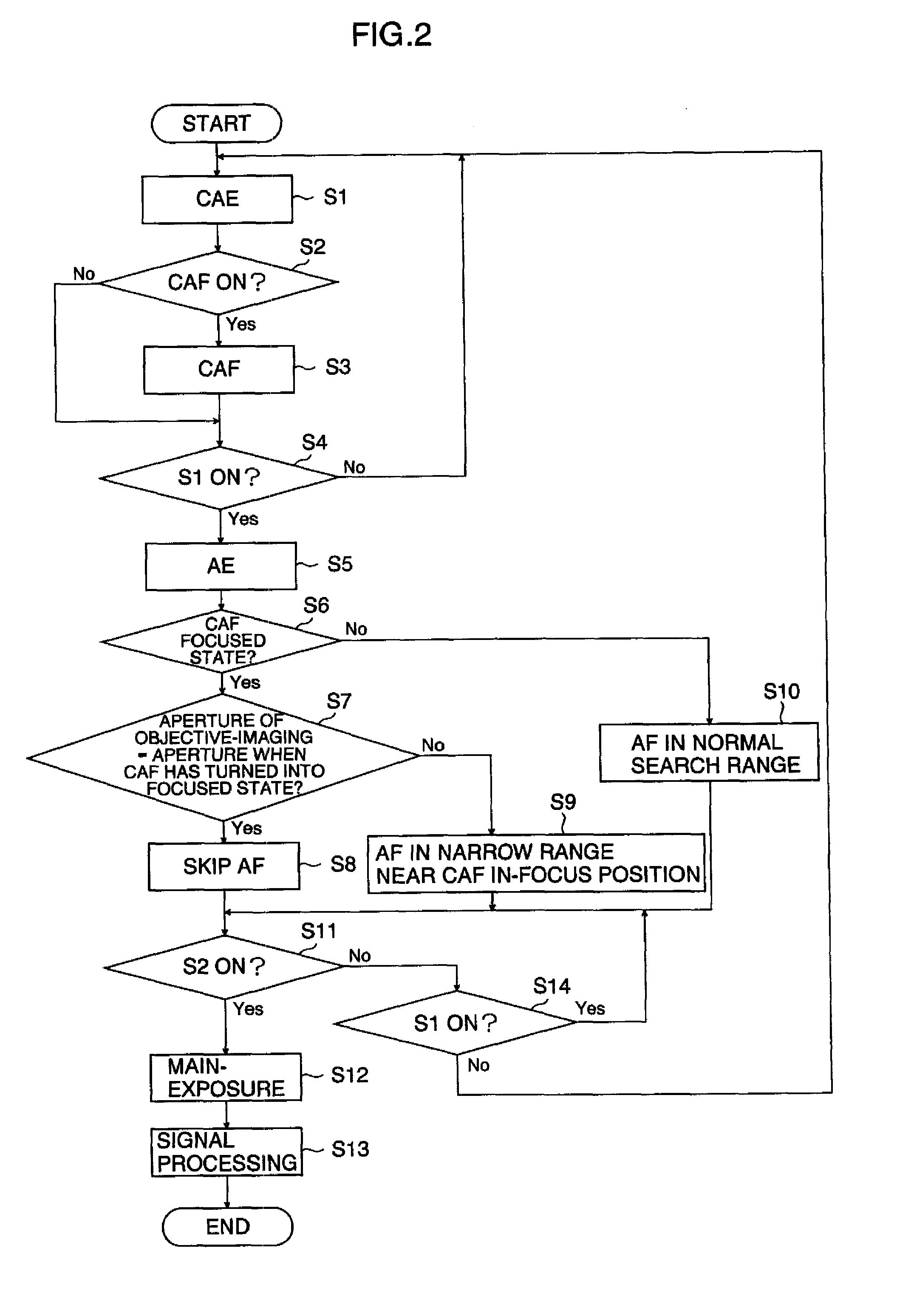
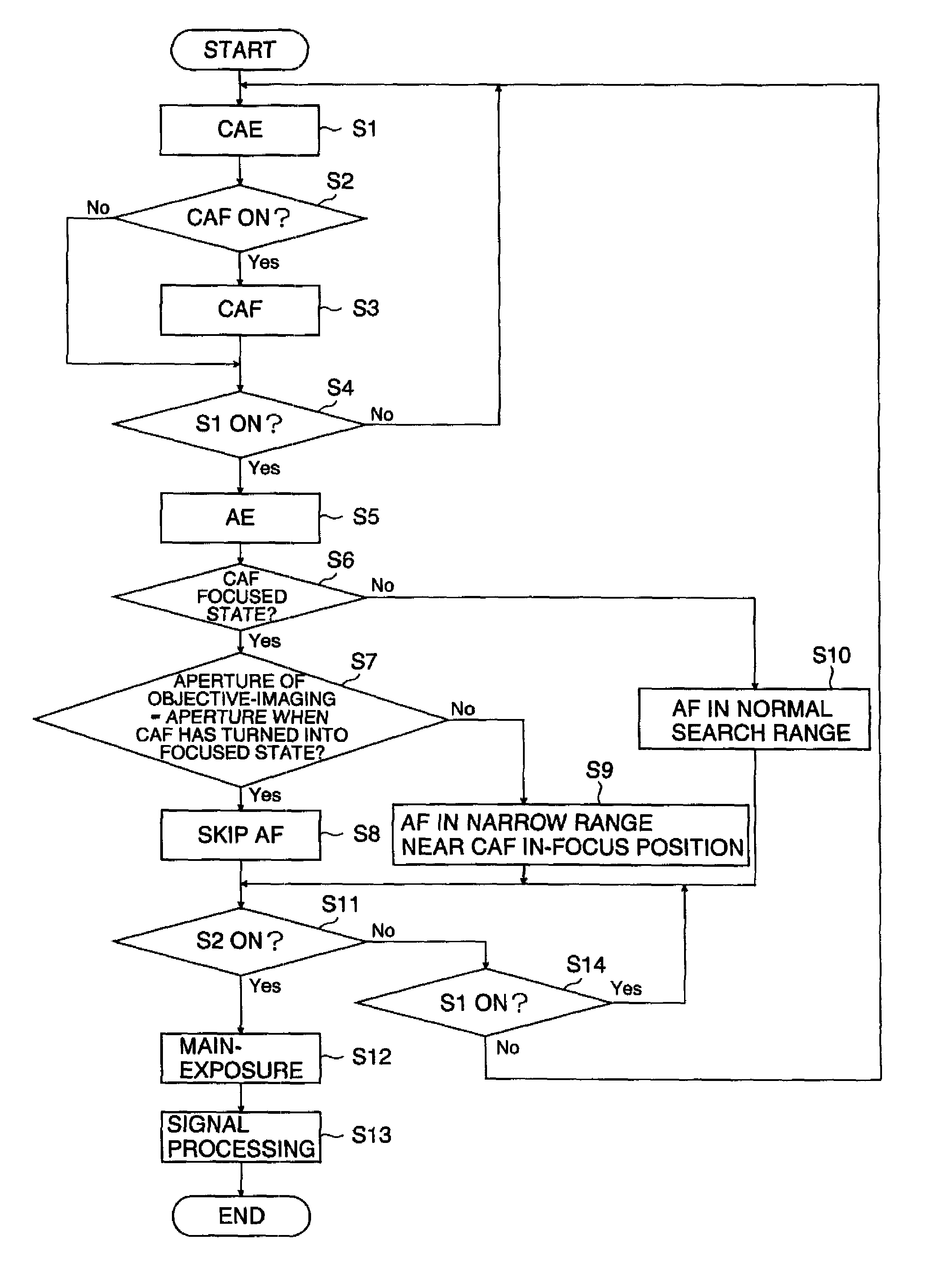
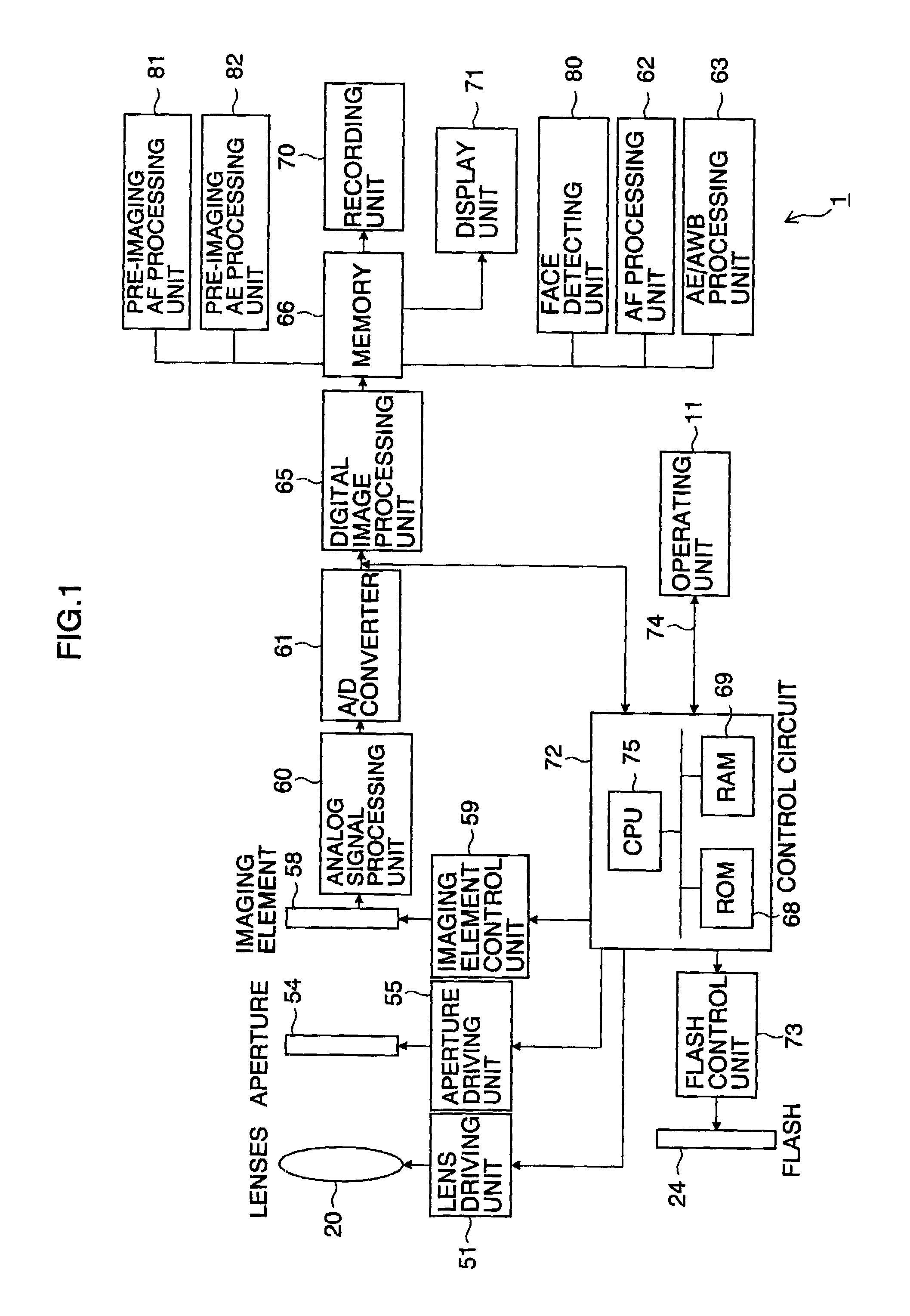
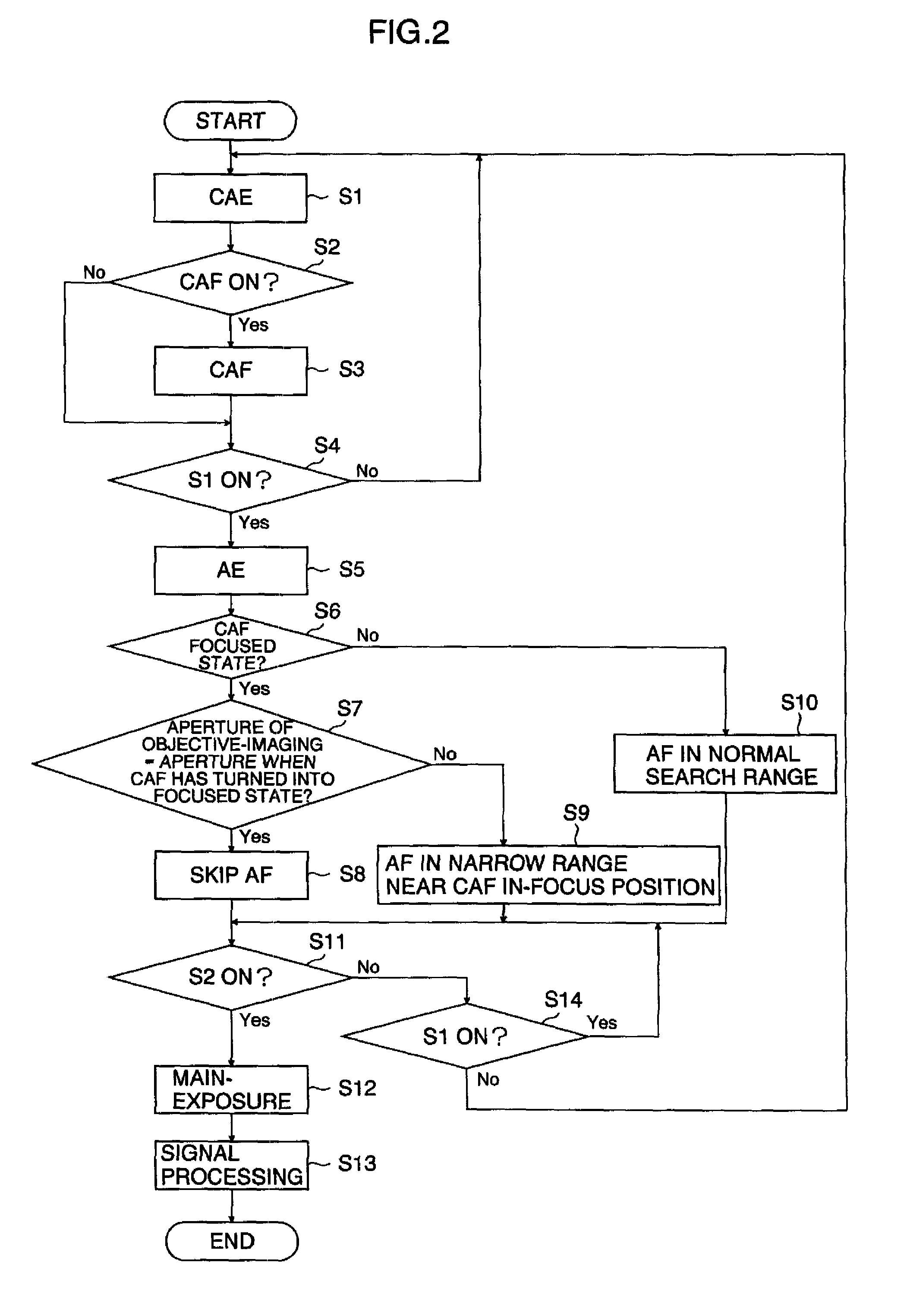
If an aperture of the objective-imaging is the same as an aperture when a state has turned into a focused state with autofocus before the objective-imaging or if an F value of the objective-imaging is equal to or greater than an F value when a state has turned into a focused state with autofocus before the objective-imaging, the focused state is maintained and the focusing of the objective-imaging is skipped. Even in other cases, a in-focus position is detected near the in-focus position before the objective-imaging. Alternatively, if the user selects a speed priority, the in-focus position is detected in a narrow range near the in-focus position before the objective-imaging. This enables to achieve both enough speed and focus accuracy of the main-photographing.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic resonance apparatus and operation method for hyperthermic treatment
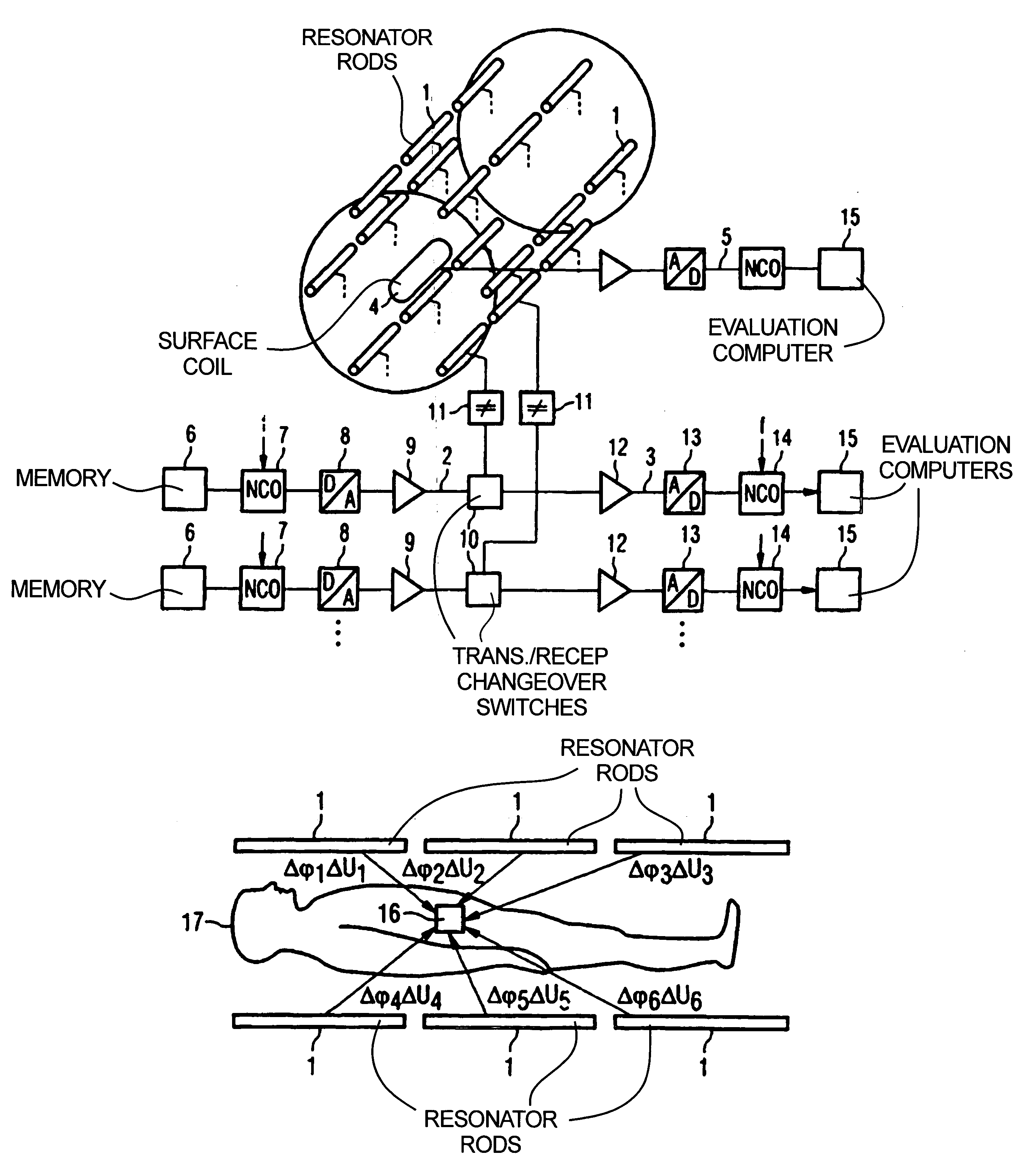
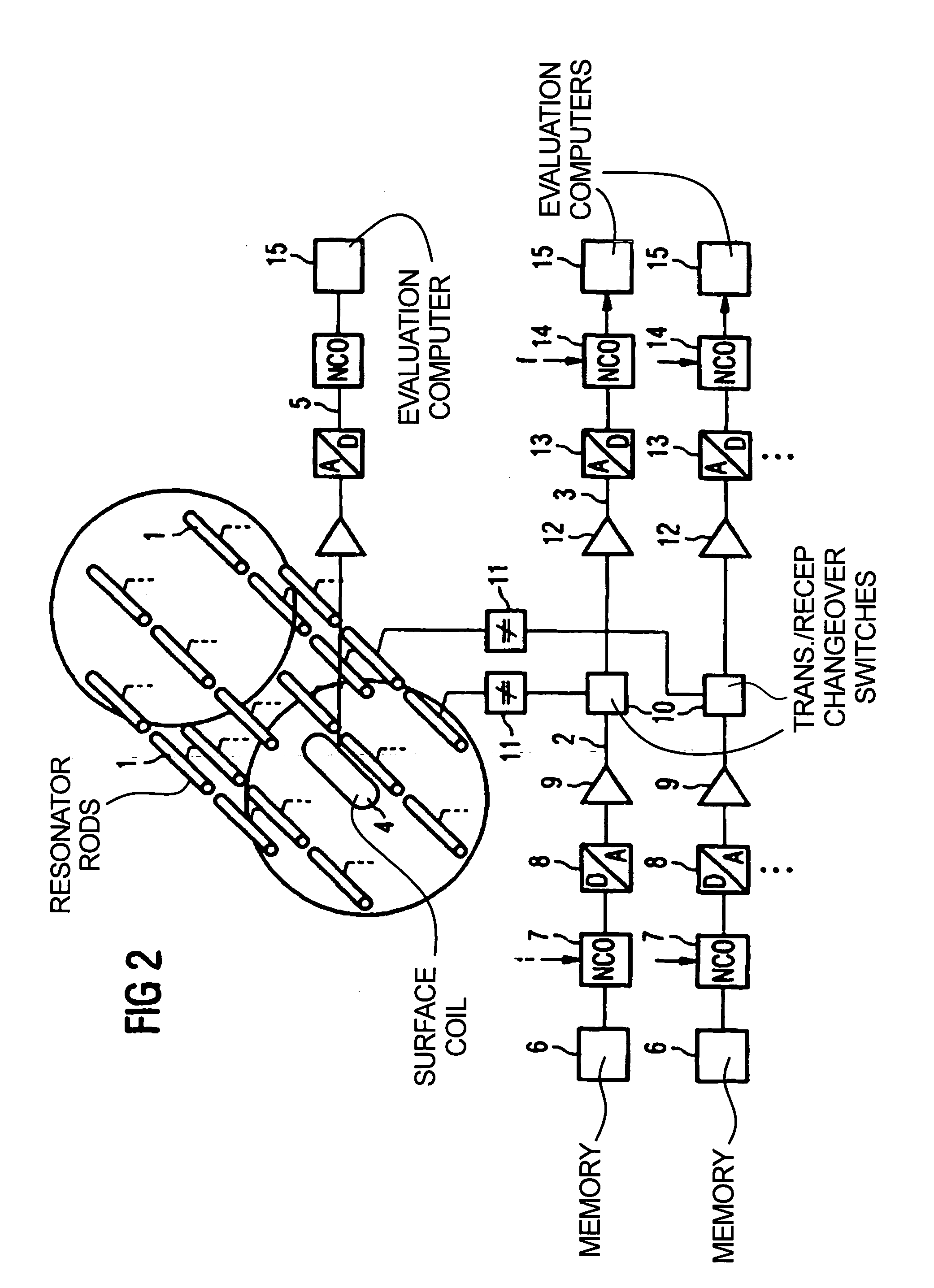
InactiveUS7123010B2Overcome lack of focusHigh precisionElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsTransmission channelAntenna element
In a magnetic resonance system and operating method, antenna elements in an antenna array are disposed around an examination volume, and each antenna element has a separate transmission channel and reception channel associated therewith. The magnetic resonance apparatus is operated to obtain magnetic resonance signals, from which amplitude and phase information are derived for the individual antenna elements, and this information is used to subsequently operate the antenna elements in the array to emit RF energy with a predetermined phase and amplitude so as to generate focused RF energy for hyperthermic treatment. The magnetic resonance apparatus can also be used to obtain magnetic resonance signals in intervals which during which the hyperthermic treatment is interrupted, from which the temperature of the region being treated can be ascertained.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
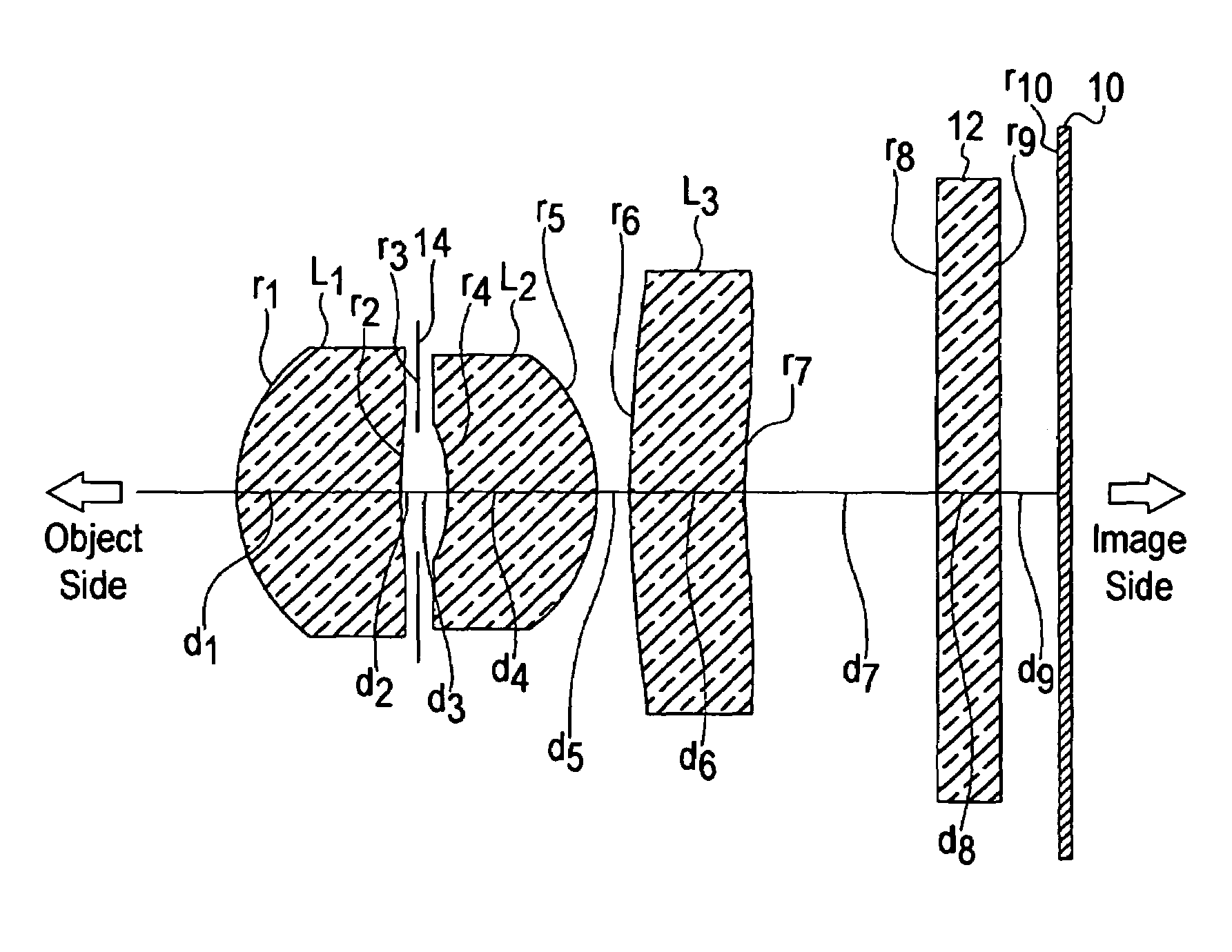
Imaging lens
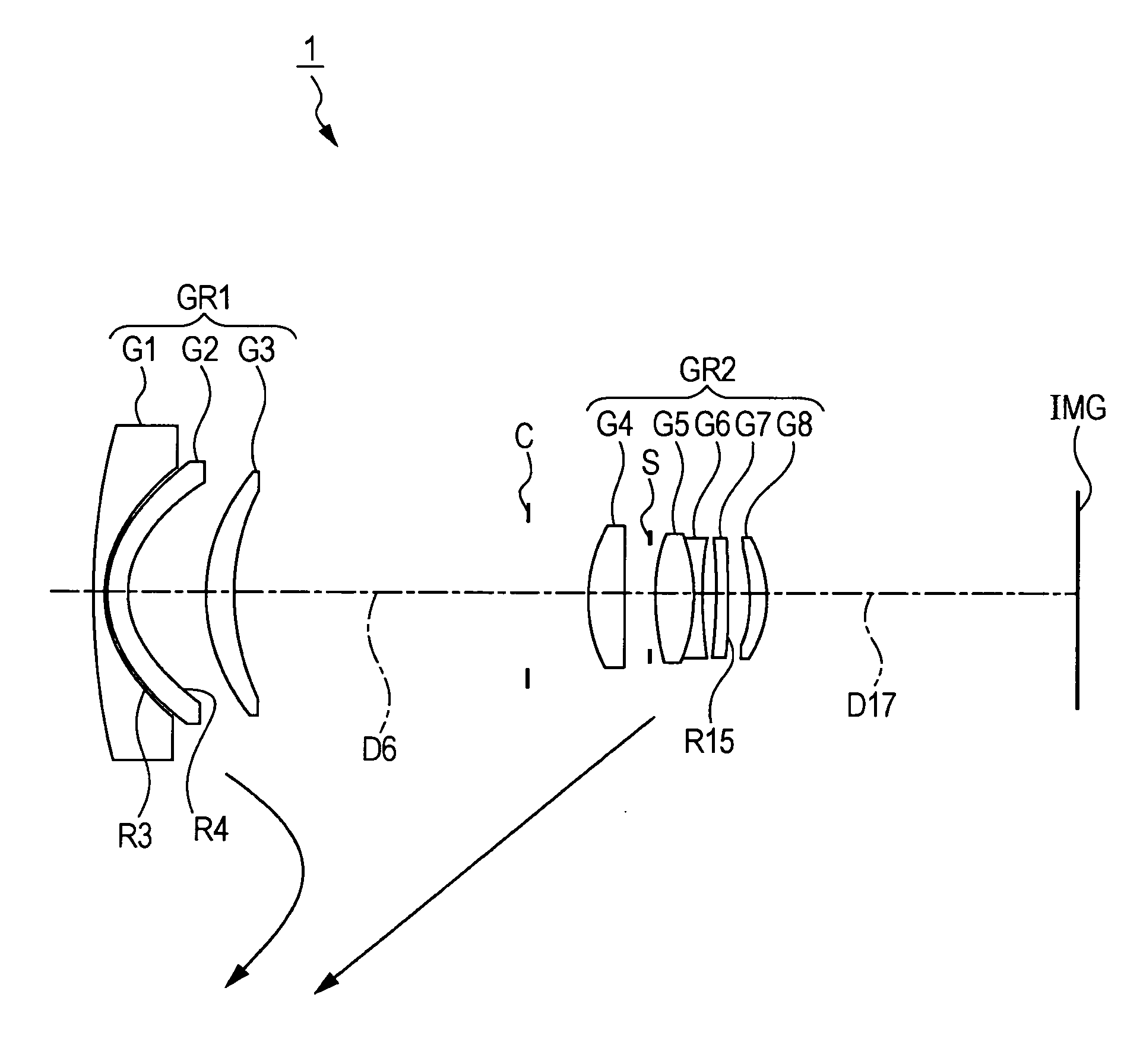
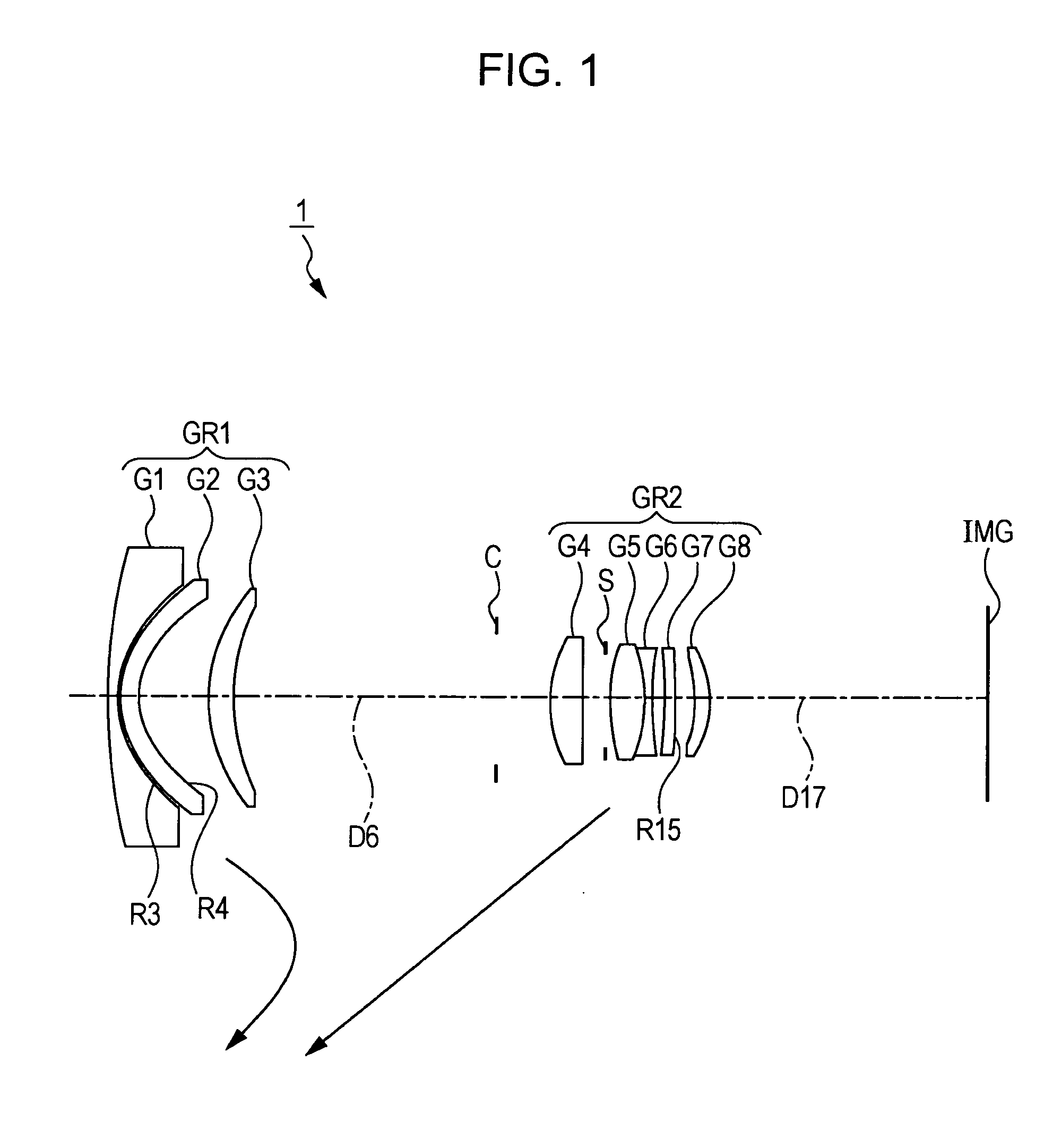
InactiveUS20050128334A1Conveniently implementedImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisImaging lens
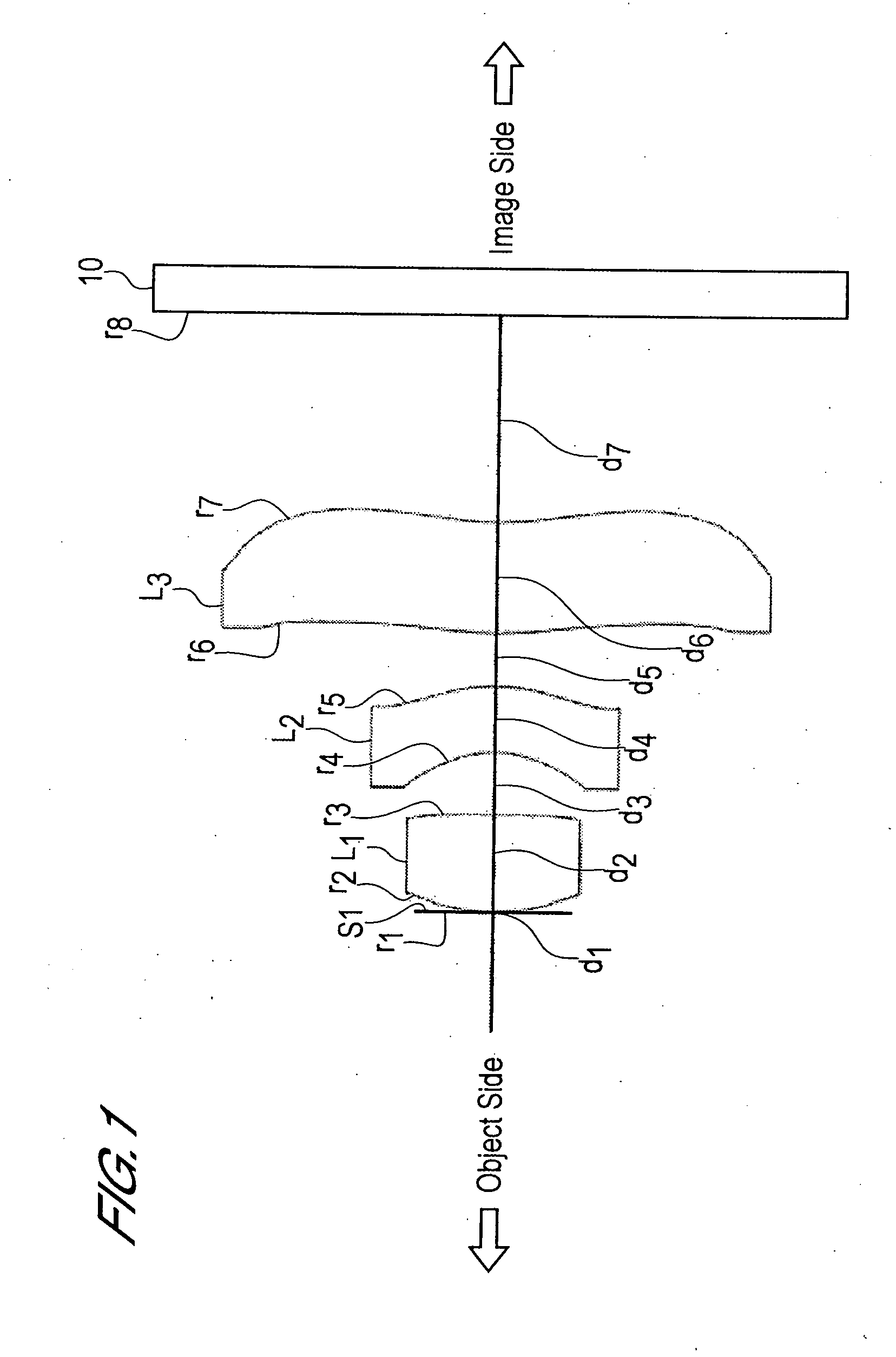
The present invention is an imaging lens in which various aberrations are satisfactorily corrected, the optical length is short, and a sufficient back focus is secured. The imaging lens is constituted by arranging a first lens L1, an aperture diaphragm S1, a second lens L2, and a third lens L3 in succession from the object side to the image side, and thus satisfies the following conditions. 0.40<r1 / r2<0.65 (1) 0.08<D2 / f<0.1 (2) 0.2<D3 / f<0.3 (3) 1.0<d / f<1.5 (4) 0.4<bf / f<0.6 (5) where f is the focal length of the entire lens system, [0001]r1 is the radius of curvature (axial curvature radius) of the object-side surface of the first lens L1 in the vicinity of the optical axis, [0002]r2 is the radius of curvature (axial curvature radius) of the image-side surface of the first lens L1 in the vicinity of the optical axis, [0003]D2 is the interval between the first lens L1 and second lens L2, [0004]D3 is the thickness at the center of the second lens L2, [0005]d is the distance(in air) from the object-side surface of the first lens L1 to the imaging surface, and [0006]bf is the back focus (in air).
Owner:DO CORP LTD +1
Imaging lens
InactiveUS20050030645A1Not impair compactnessDistortion can be sufficientlyLensOptical elementsOptical axisOptoelectronics
In an imaging lens of the present invention, aberration is satisfactorily corrected, the optical length is short, and a sufficient back focus is secured. The imaging lens of the present invention is constituted by arranging a first lens L1, an aperture diaphragm S1, a second lens L2, and a third lens L3 in succession from the object side to the image side, and thus satisfies the following conditions.0.24<r1 / r2<0.34 (1)0.08<D2 / f<0.1 (2)0.24<D3 / f<0.29 (3)1.0<d / f<1.5 (4)where f is the focal length of the entire lens system, r1 is the radius of curvature (axial curvature radius) of the object side surface of the first lens L1 in the vicinity of the optical axis, r2 is the radius of curvature (axial curvature radius) of the image side surface of the first lens L1 in the vicinity of the optical axis, D2 is the distance between the first lens L1 and second lens L2, D3 is the thickness at the center of the second lens L2, and d is the distance(in air) from the object side surface of the first lens L1 to the image surface.
Owner:MILESTONE CO LTD +1
Real-time pushing system and method for delivering advertisement
InactiveCN103985048AOvercome lack of focusAvoid the disadvantage of being easily overwhelmed by many promotional merchantsMarketingRelevant informationClient-side
The invention discloses a real-time pushing system and method for delivering an advertisement. The real-time pushing system comprises a client side, a merchant server side and a data maintenance server, wherein the merchant server carries out corresponding modification on areas, industries and time of advertisement delivering and advertisement content through relevant information statistics of advertisement browsing client sides by the data maintenance server. The real-time pushing method comprises the steps that firstly, the advertisement is delivered by a merchant through the merchant server, information of the client side is sent to the data maintenance server after the client side browses the advertisement, and the merchant carries out modification on the areas, industries and time of advertisement delivering and the advertisement content through the data maintenance server. According to the real-time pushing system and method for delivering the advertisement, the shortcoming of a traditional advertisement delivering mode that data modification is difficult to conduct after data research, collection and type setting at an earlier stage is avoided, and the shortcomings that when the advertisement is delivered in a public communication mode, pertinency of clients who the advertisement is delivered to is lacked, and the advertisement is prone to submergence by many other advertising merchants are also avoided.
Owner:深圳前海维盟网络科技有限公司
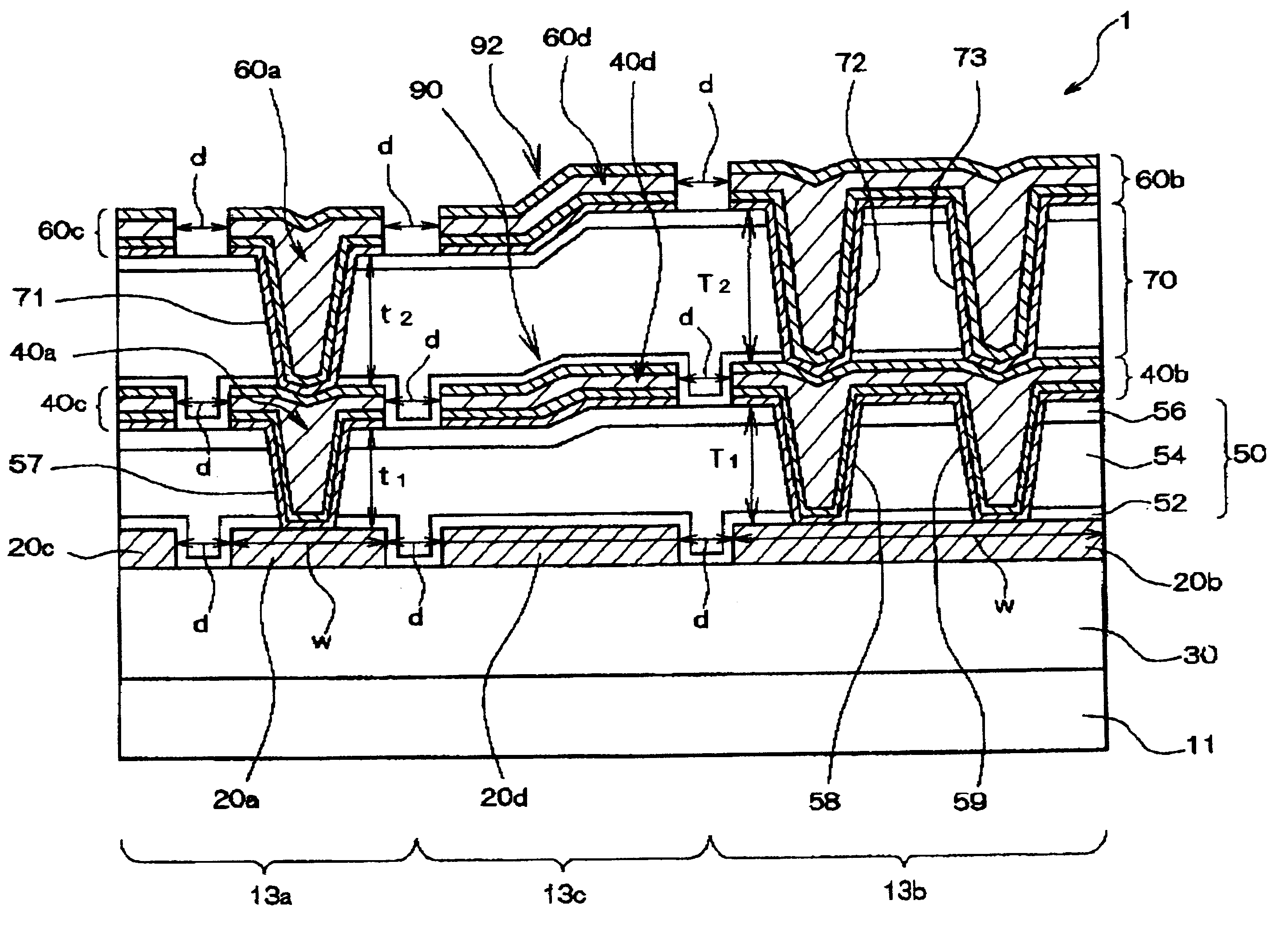
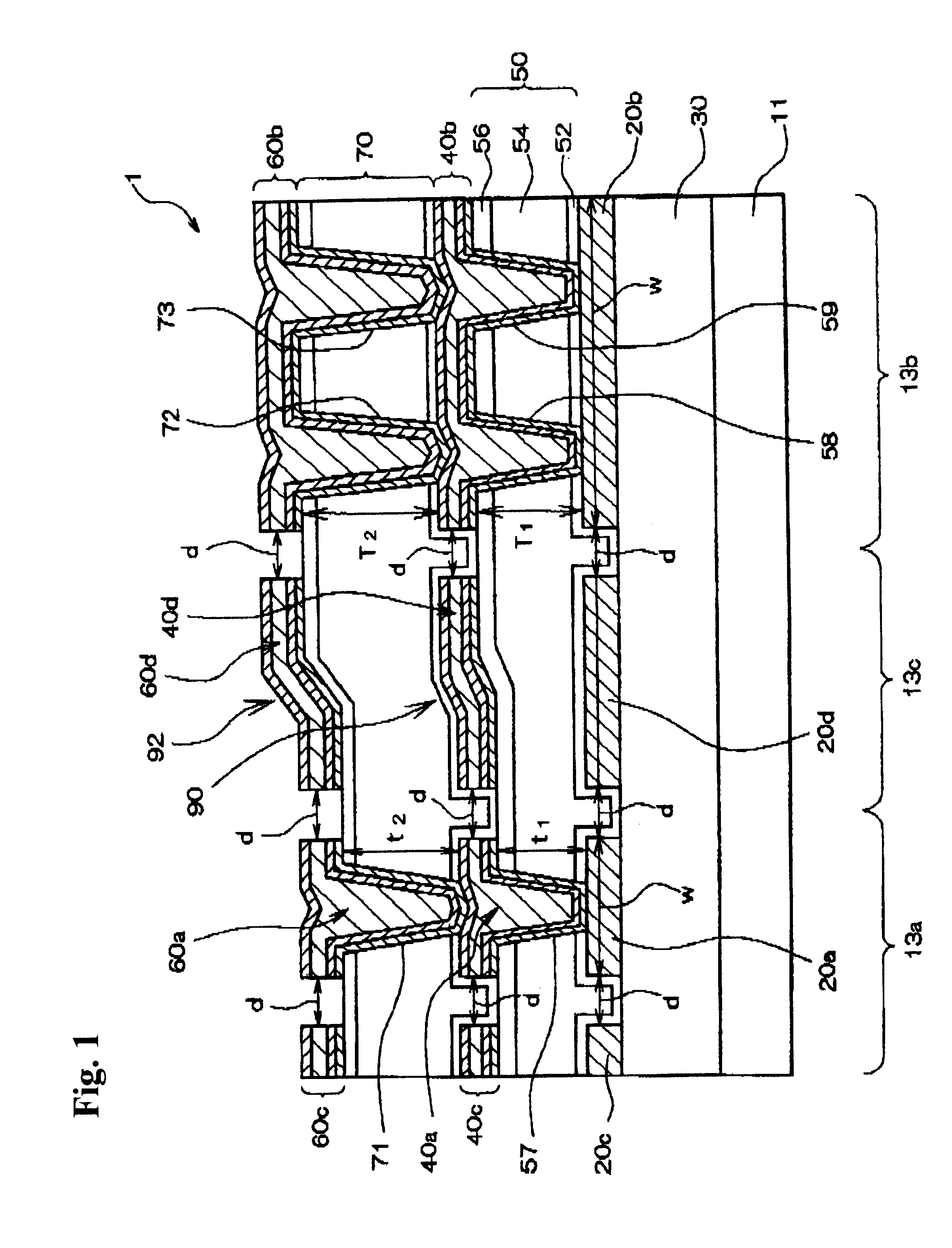
Semiconductor device and method for making pattern data
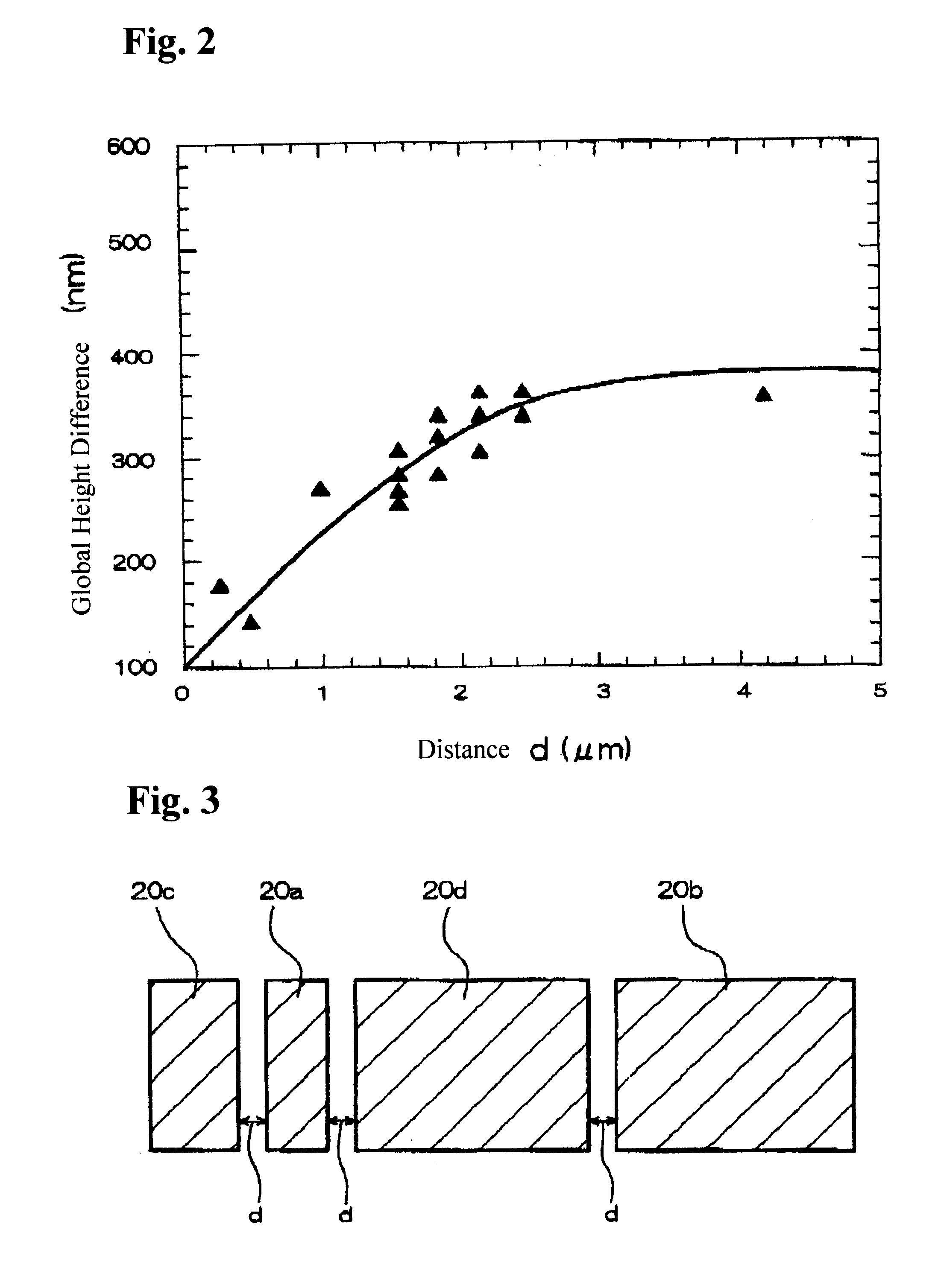
InactiveUS6287948B1Small height differenceOvercome lack of focusTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSilanesEngineering
A semiconductor device has a first region, a second region and a border region between the first region and the second region. The semiconductor device has an interlayer dielectric layer, covering at least the first region and the second region. A first wiring layer is located in the first region and defines a relatively small pattern. A second wiring layer is located in the second region and defines a relatively large pattern that is wider than the small pattern. A first dummy pattern is formed in the first region and a second dummy pattern is formed in the border region. The interlayer dielectric layer includes a planarization silicon oxide film. The planarization silicon oxide film is one of a silicon oxide film formed by a polycondensation reaction between a silicon compound and hydrogen peroxide, an organic SOG (Spin On Glass) film an inorganic SOG film and a silicon oxide film formed by reacting an organic silane with ozone or water. The interlayer dielectric layer located over the first wiring layer is thinner than the interlayer dielectric layer located over the second wiring layer such that a global height difference occurs in the border region between the first region and the second region.
Owner:ADVANCED INTERCONNECT SYST LTD
Zoom lens and image pickup device
InactiveUS20090290227A1Improve performanceSmall sizeOptical elementsEffective radiusConditional expression
A zoom lens includes a first lens group having negative refractive power and a second lens group having positive refractive power, each including at least one plastic aspherical lens. The zoom lens satisfies the following Conditional Expressions (1) and (2),0.40<fw / bkw<0.60 (1)0.01<|(X1−X0) / h0|<0.022 (2)where,fw: focal length of the entire zoom lens in focus at infinity in a wide-angle end state;bkw: back focus when the entire zoom lens is in focus at infinity in the wide-angle end state;X1: thickness at an image-side effective diameter position of the plastic aspherical lens of the first lens group;X0: thickness at the center of the plastic aspherical lens of the first lens group; andh0: image-side effective radius of the plastic aspherical lens of the first lens group.
Owner:SONY CORP
Imaging lens
ActiveUS20130321920A1Reduce distanceImprove batch productivityDiffraction gratingsOptical axisPlastic materials
An imaging lens includes, from the object side to the image side, an aperture stop, a first lens with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface near an optical axis, a second lens with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface near the axis, a third lens with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface near the axis, and a fourth lens with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface near the axis, wherein all lens surfaces are aspheric, all lenses are made of plastic material, a diffractive optical surface is formed on at least one of the lens surfaces from the first lens image-side surface to the second lens image-side surface, and at least one of the three positive lenses satisfies expression (1):1.58<Ndi (1)whereNdi: refractive index of the i-th positive lens at d-ray.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Imaging lens
InactiveUS6989947B2Not impair compactnessDistortion can be sufficientlyCamera diaphragmsOptical elementsImaging lensPhysics
Owner:DO SATOSHI +1
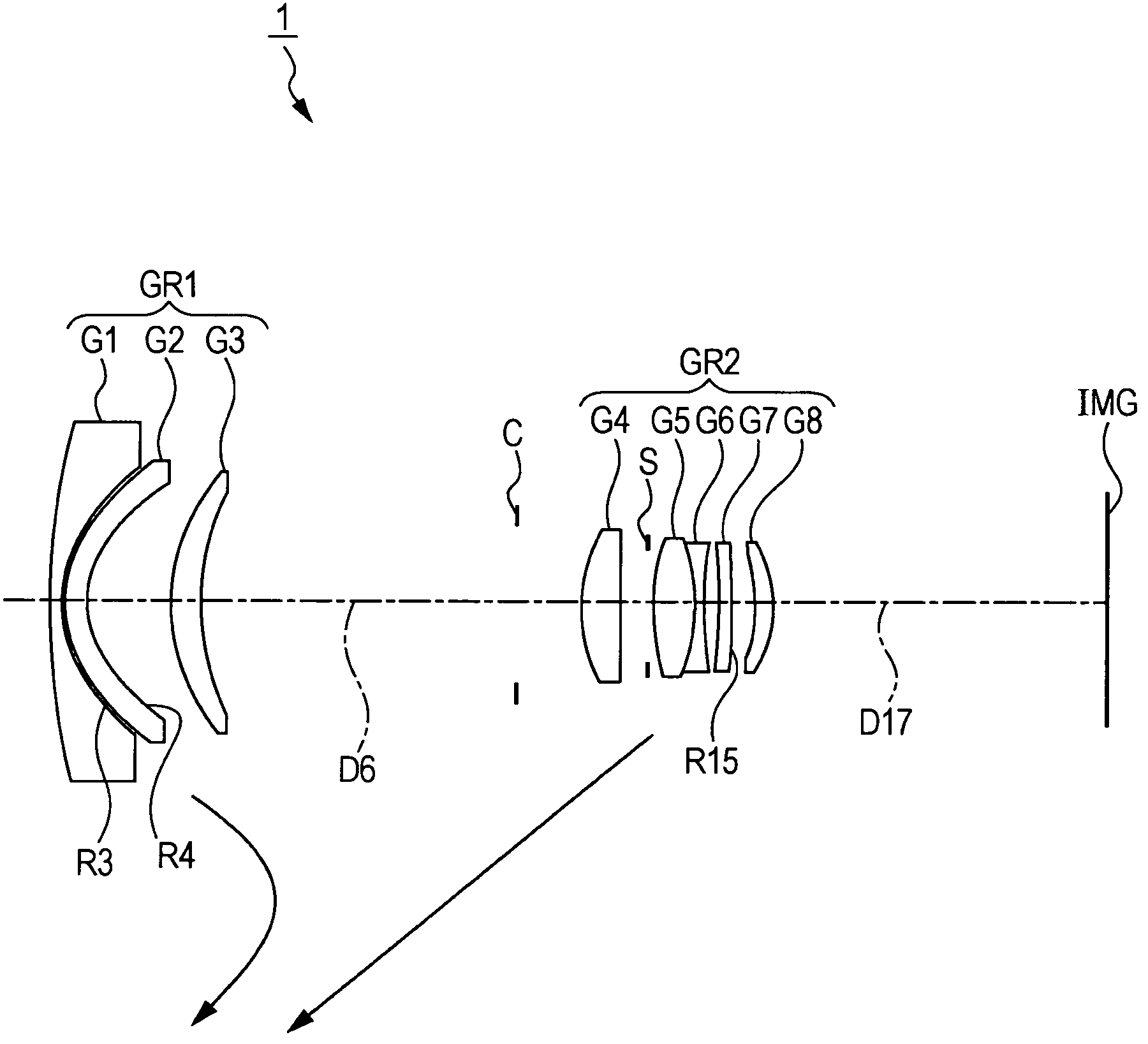
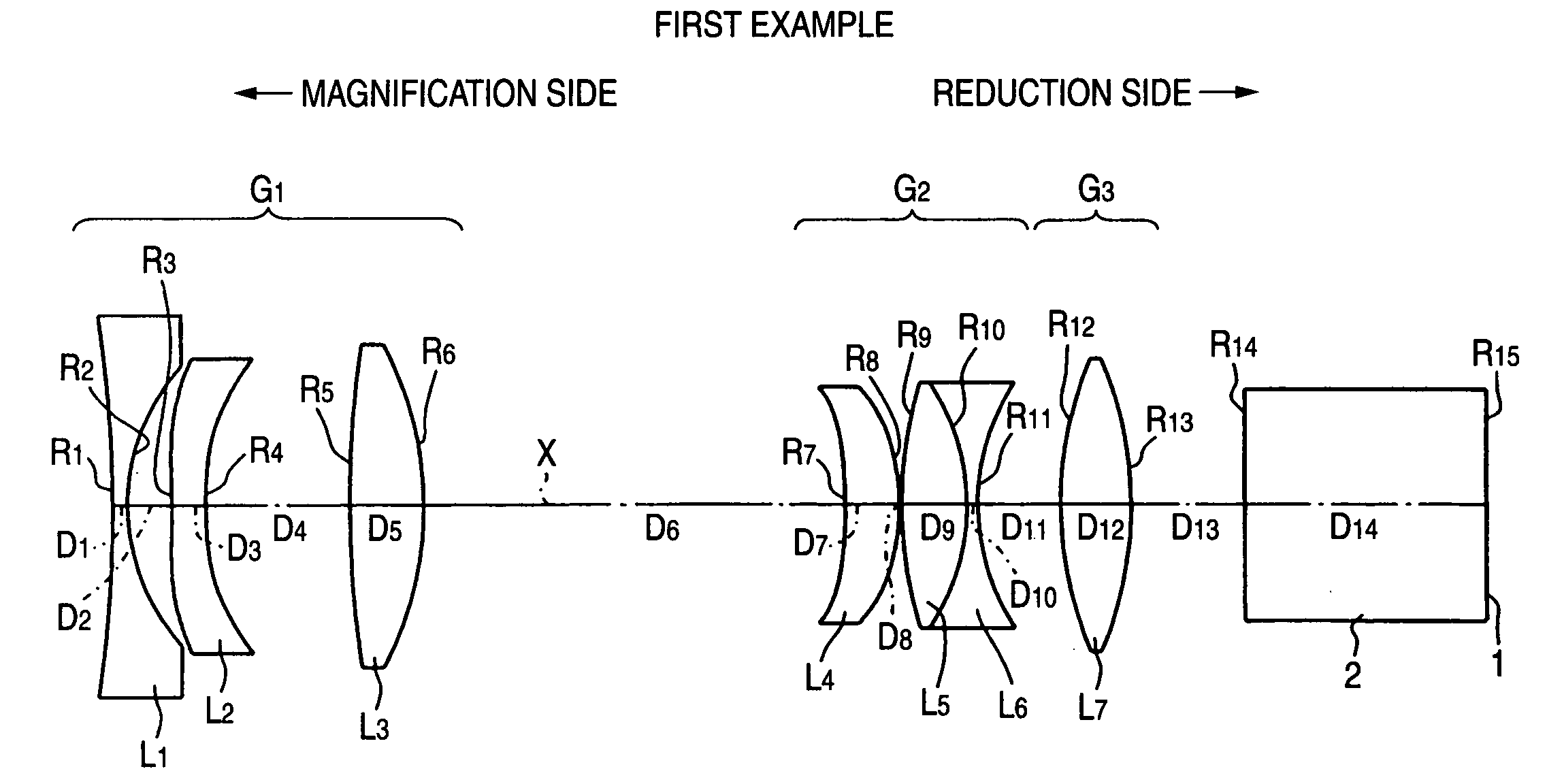
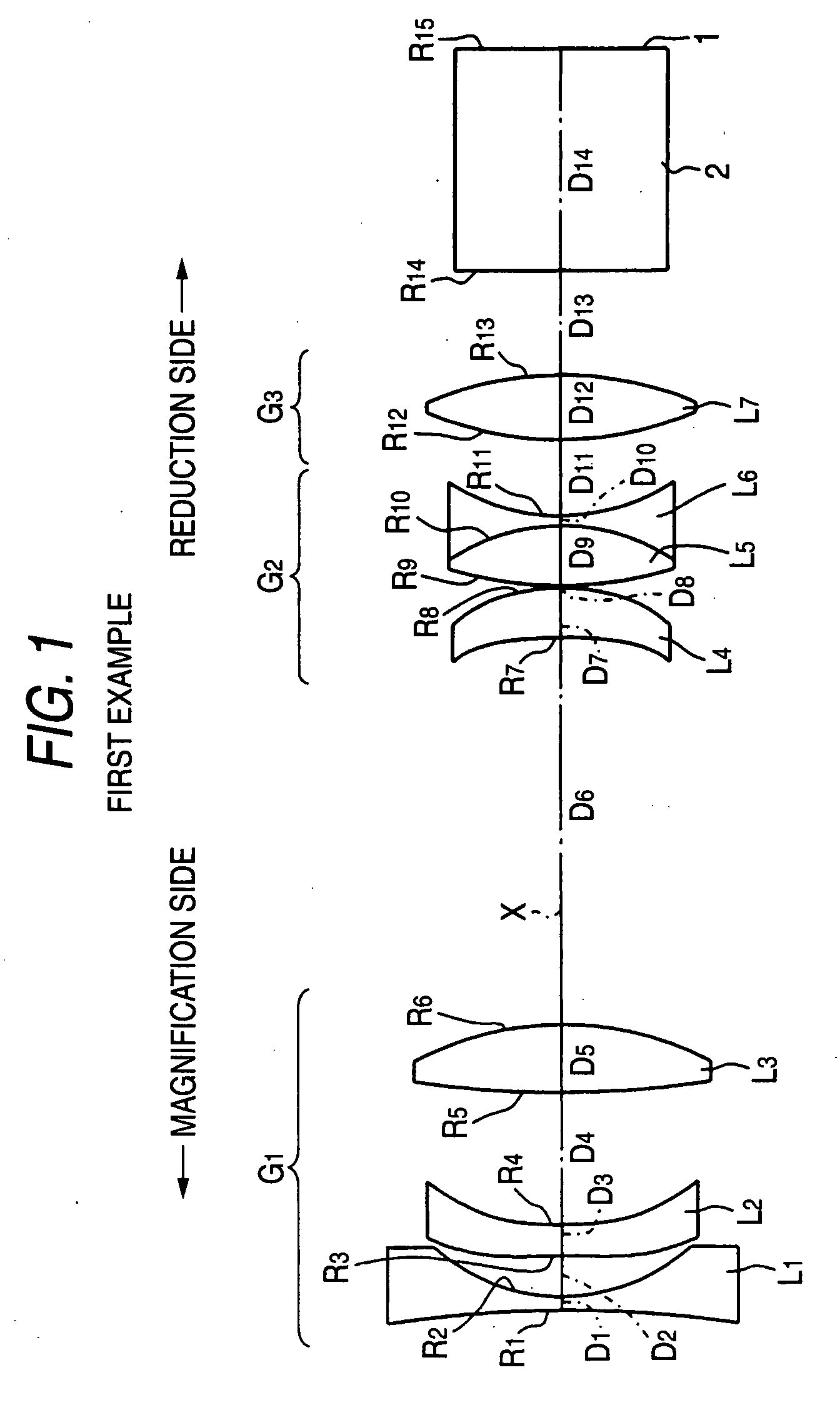
Zoom lens and image capture apparatus
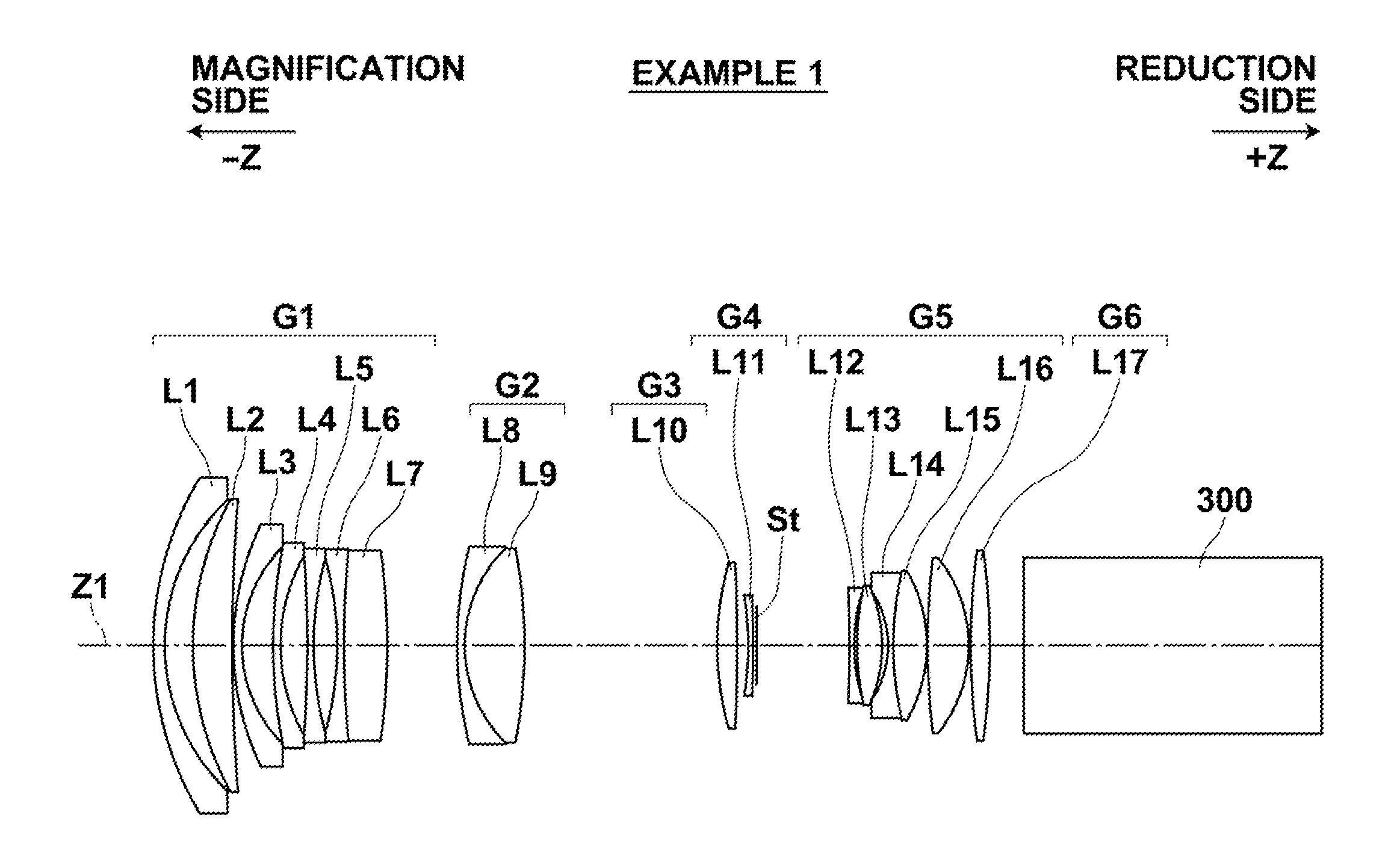
There is provided a zoom lens which includes, in an order from an object side, a first lens group having positive refractive power; a second lens group having negative refractive power; a third lens group having positive refractive power; and a fourth lens group having positive refractive power, and in which, during power variation from a wide-angle end to a telephoto end, a distance between the first lens group and the second lens group increases, a distance between the second lens group and the third lens group decreases, and a distance between the third lens group and the fourth lens group decreases, and the zoom lens includes at least one cemented-triplet lens block having negative refractive power, in the fourth lens group.
Owner:SONY CORP
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus
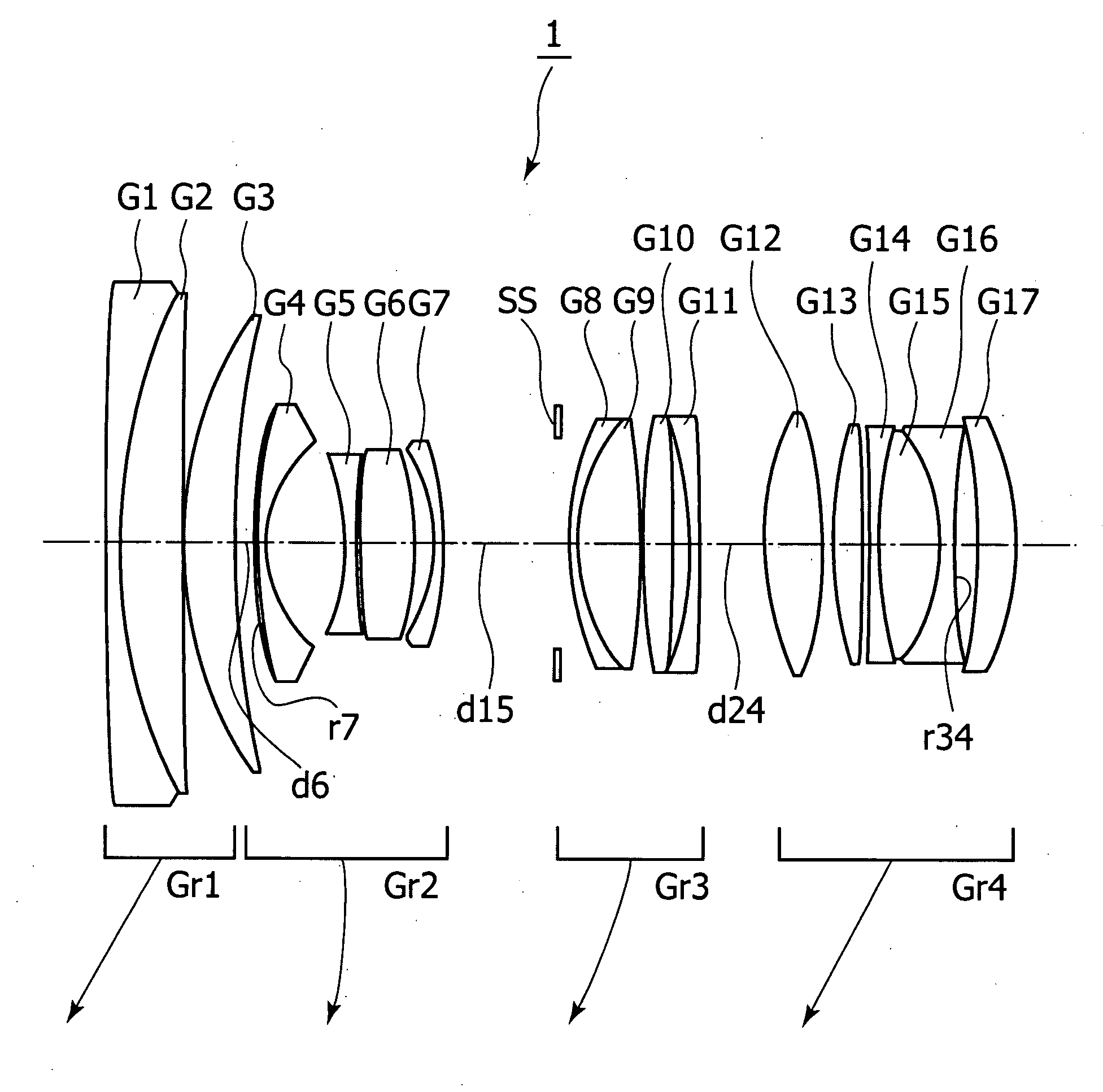
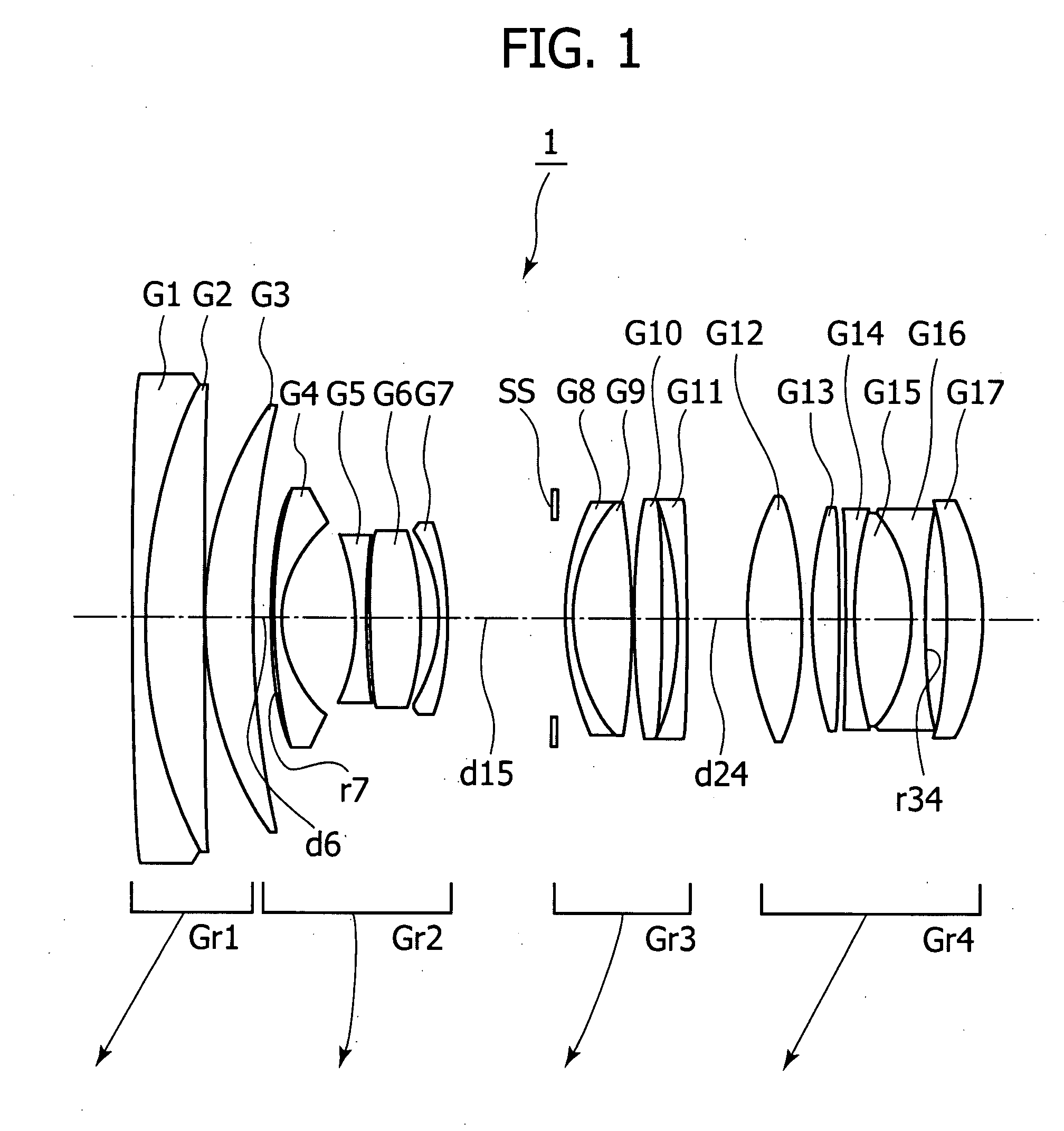
ActiveUS20150168678A1Sufficient back focusExcellently correctedProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensConditional expression
An imaging lens consists of a first lens-group consisting of a positive lens with its surface that has the smaller absolute value of a curvature-radius facing an object-side, a positive lens in meniscus-shape with its convex-surface facing the object-side, a positive lens with its surface that has the smaller absolute value of a curvature-radius facing the object-side, and a negative lens with its surface that has the smaller absolute value of a curvature-radius facing an image-side, an aperture stop, a second lens-group consisting of a negative lens with its surface that has the smaller absolute value of a curvature-radius facing the object-side, a positive lens with its surface that has the smaller absolute value of a curvature-radius facing the image-side, and a positive lens, and a third lens-group consisting of a positive lens and a negative lens in this order from the object-side. A predetermined conditional expression is satisfied.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
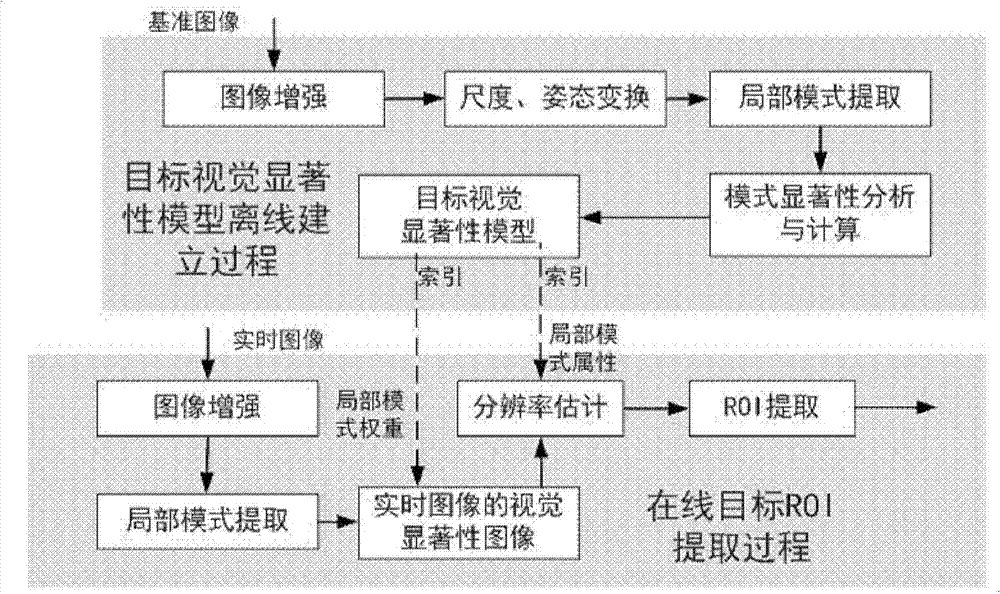
ROI (Region of Interest) extraction method of ground target of unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN103679740AImprove environmental adaptabilityOvercome lack of focusImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionRegion of interest
The invention discloses an ROI extraction method of a ground target of an unmanned aerial vehicle. The ROI extraction method of the ground target of the unmanned aerial vehicle comprises preprocessing a reference satellite image and extracting a mode which can reflect local features of a target; performing statistical analysis on mode distribution condition of a target region and an associated environment region, calculating a saliency value of every mode, and establishing a target visual saliency model; for a real-time image, obtaining the mode of every pixel point and a corresponding saliency value of the mode of every pixel point, wherein the saliency value corresponding to the mode of every pixel point corresponds to the visual saliency image of the real-time image; estimating a target rough position of the visual saliency image; estimating rough resolution of the real-time image with the target rough position as the center and by utilizing size distribution information of modes in a region with a size identical with that of the target region; obtaining an ROI basically identical with the resolution of the reference satellite image according to the target rough position and an estimated resolution value.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vehicle paint sagging experiment board and test method
The invention provides an automobile paint anti-sagging testing plate which is identical to an automobile steel plate, has a smooth surface, and is processed by electrophoresis; the testing plate is characterized in that a group of holes with the same spacing and the same aperture are arranged on the testing plate from top to bottom; and the dimension design of the aperture and the spacing of the holes is determined according to the length allowable value of the sagging. The invention also provides an automobile paint anti-sagging testing method, comprising the steps as follows: the testing plate is vertically arranged on an injection plate bracket and coated with paint uniformly from top to bottom according to the automobile coating process parameters; the coating is in gradient so as to form different coating thickness from top to bottom; the coating is not stopped till sagging appears in a certain hole and the lower hole edge; drying is carried out according to the paint drying specification; and the dry coating thickness correspondingly from the upper hole edge to the lower hole edge when the sagging appears initially is used for expressing the sagging limit of the paint material. The method approaches the practical construction process, has strong practicability and good operability and can carry out the anti-sagging performance test of different paints.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Imaging lens comprising a diffractive optical surface
An imaging lens includes, from the object side to the image side, an aperture stop, a first lens with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface near an optical axis, a second lens with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface near the axis, a third lens with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface near the axis, and a fourth lens with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface near the axis, wherein all lens surfaces are aspheric, all lenses are made of plastic material, a diffractive optical surface is formed on at least one of the lens surfaces from the first lens image-side surface to the second lens image-side surface, and at least one of the three positive lenses satisfies 1.58<Ndi where Ndi is the refractive index of the i-th positive lens at the d-ray.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Pickup lens
A pickup lens is provided with various aberrations corrected satisfactorily, with a short optical length, and with a sufficient back focus secured. The configuration comprises an aperture diaphragm S1, first lens L1, second lens L2, and third lens L3, and is configured by arranging, in order from the object side to the image side, the aperture diaphragm, first lens, second lens, and third lens. The first lens is a lens having positive refractive power, in a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the object side. The second lens is a lens having negative refractive power, in a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the image side. The third lens is a lens having negative refractive power, in a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the object side. Both of the surfaces of the first lens are aspherical, both of the surfaces of the second lens are aspherical, and both of the surfaces of the third lens are aspherical.
Owner:SEIKOH GIKEN
Projection zoom lens and projection display apparatus
InactiveUS20130314800A1Easy to operateLarge back focusOptical elementsConditional expressionMagnification
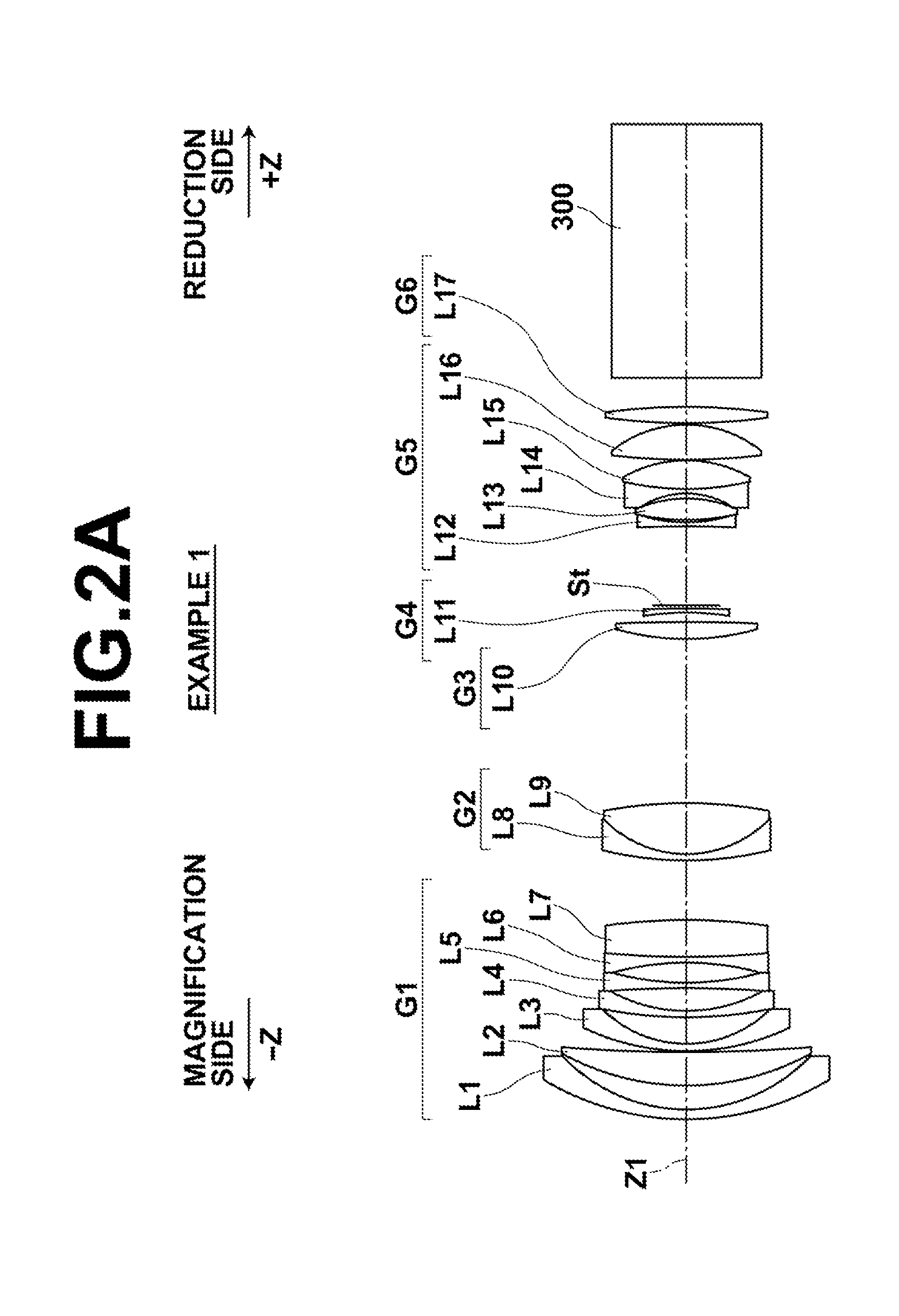
A projection zoom lens having broad angle of view, high zoom ratio, and large back focus while aberrations are corrected satisfactorily, including a negative first lens group, a positive second lens group, a positive third lens group, a negative fourth lens group, a positive fifth lens group, and a positive sixth lens group from the magnification side and is telecentric on the reduction side. When zooming, the first and sixth lens groups are fixed while the second to fifth lens groups are moved and the fourth lens group is composed of one negative lens whose magnification side surface has a greater curvature in absolute value than that of the reduction side surface, and the zoom lens satisfies conditional expression (1): −12.0<f4 / fw<−5.0, where f4 is focal length of the fourth lens group, and fw is focal length of the entire lens system at the wide angle end.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Quasi-Self-Focusing High Intensity And Large Power Ultrasonic Transducer
ActiveUS20080112582A1Increase sound resistanceImprove sound field performanceUltrasound therapyTransducer detailsUltrasonic sensorHigh intensity
A quasi-self focusing high intensity and large power ultrasonic transducer. It includes a backing and piezo-electric crystal sheets. The backing has double layer structure and there is an air cavity between the layers. At least four piezoelectric crystal sheets are adhered tightly on the inside focusing face of the backing. A protective layer is covered on the surface of the sheets.
Owner:CHENGDU HEUK MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Projecting zoom lens and projection display device
InactiveUS20080074756A1Back focal lengthLarge zoom ratioOptical elementsConditional expressionAspheric lens
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Projection zoom lens and projection display apparatus
InactiveUS8699152B2High zoom ratioOvercome lack of focusProjectorsOptical elementsConditional expressionEntire lens
A projection zoom lens having broad angle of view, high zoom ratio, and large back focus while aberrations are corrected satisfactorily, including a negative first lens group, a positive second lens group, a positive third lens group, a negative fourth lens group, a positive fifth lens group, and a positive sixth lens group from the magnification side and is telecentric on the reduction side. When zooming, the first and sixth lens groups are fixed while the second to fifth lens groups are moved and the fourth lens group is composed of one negative lens whose magnification side surface has a greater curvature in absolute value than that of the reduction side surface, and the zoom lens satisfies conditional expression (1): −12.0<f4 / fw<−5.0, where f4 is focal length of the fourth lens group, and fw is focal length of the entire lens system at the wide angle end.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Pickup lens
A pickup lens is provided with various aberrations corrected satisfactorily, with a short optical length, and with a sufficient back focus secured. The configuration comprises an aperture diaphragm S1, first lens L1, second lens L2, and third lens L3, and is configured by arranging, in order from the object side to the image side, the aperture diaphragm, first lens, second lens, and third lens. The first lens is a lens having positive refractive power, in a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the object side. The second lens is a lens having negative refractive power, in a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the image side. The third lens is a lens having negative refractive power, in a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the object side. Both of the surfaces of the first lens are aspherical, both of the surfaces of the second lens are aspherical, and both of the surfaces of the third lens are aspherical.
Owner:SEIKOH GIKEN
Zoom lens and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20150198792A1High zoom ratioOvercome lack of focusOptical elementsOphthalmologyOptical axis
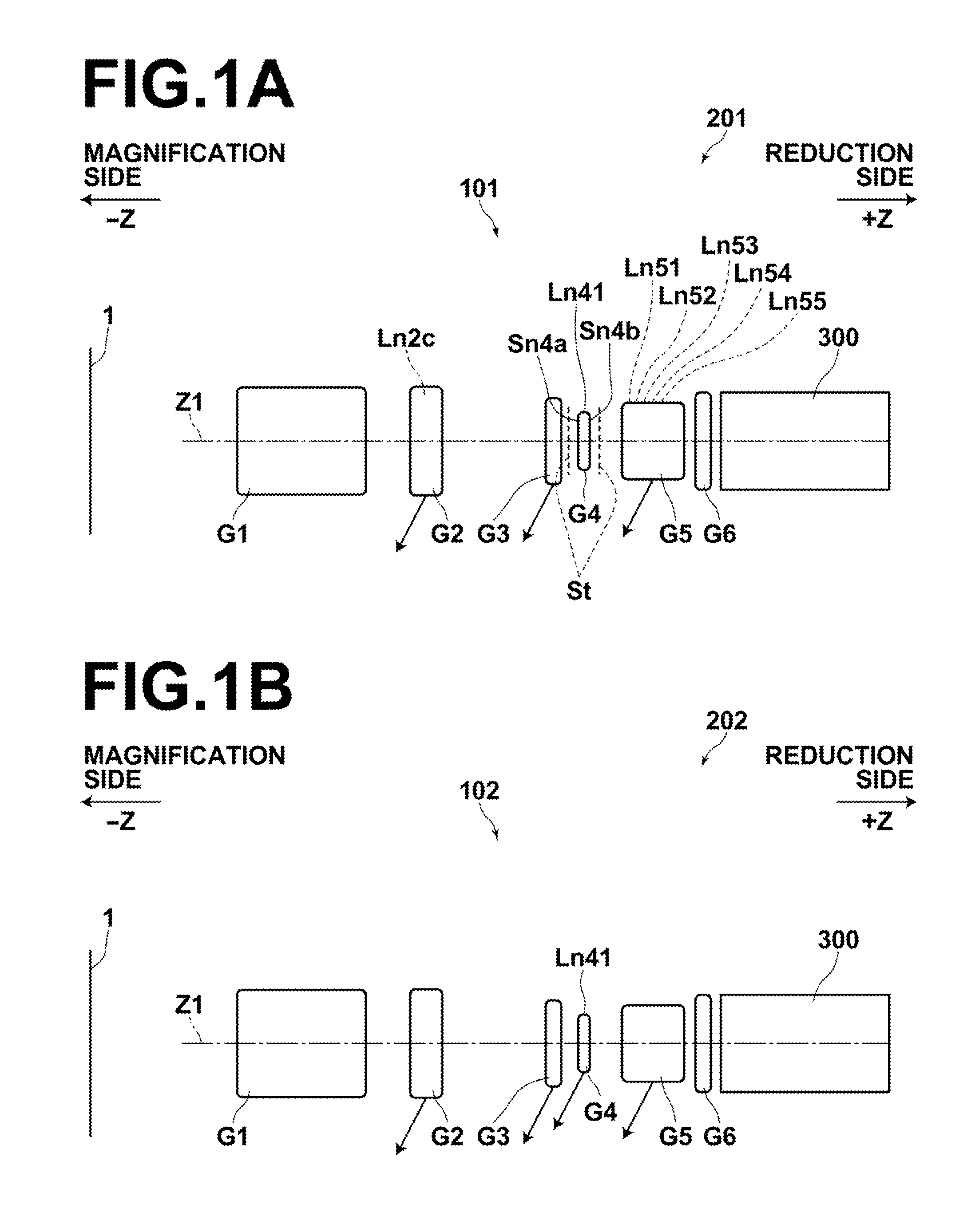
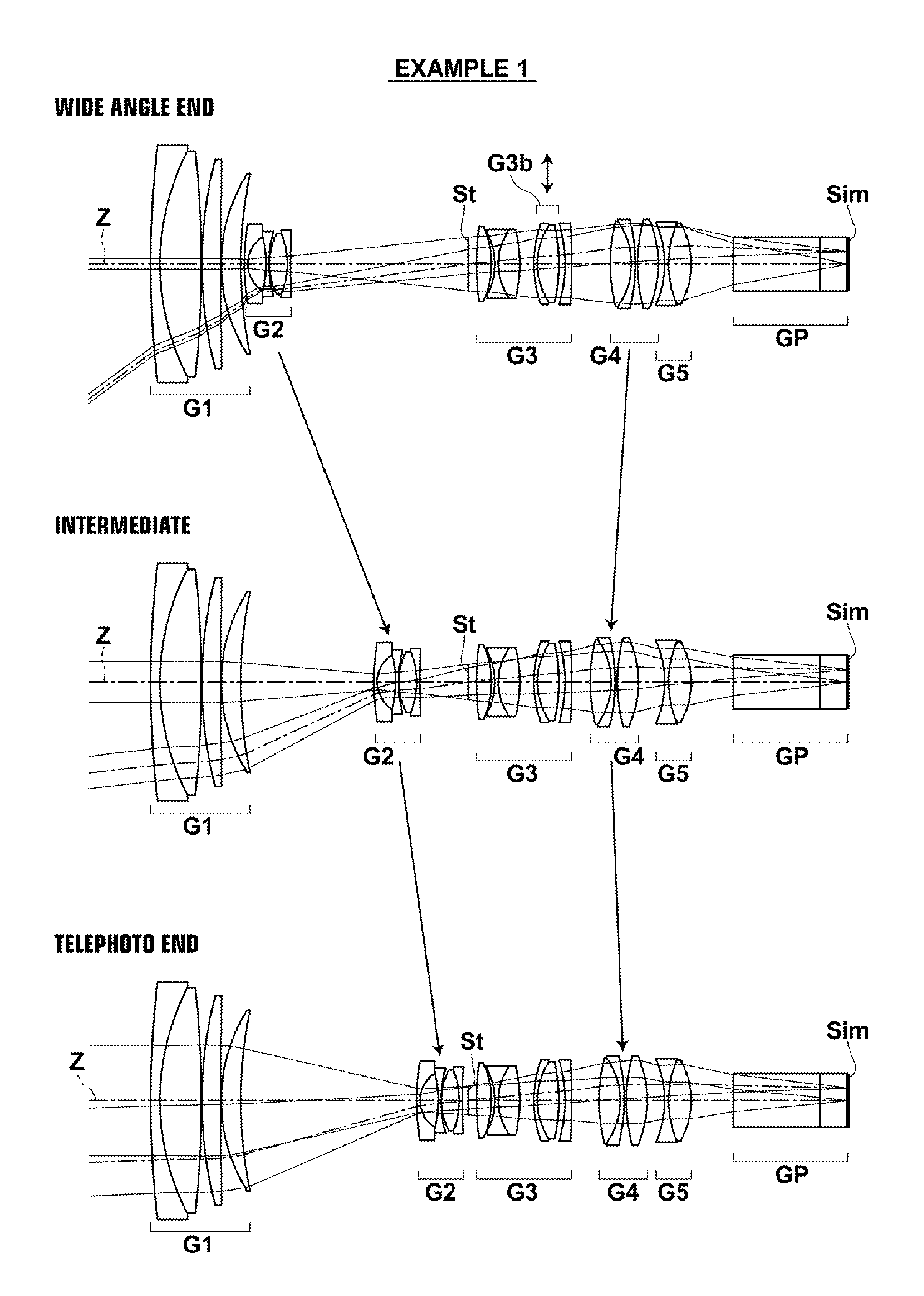
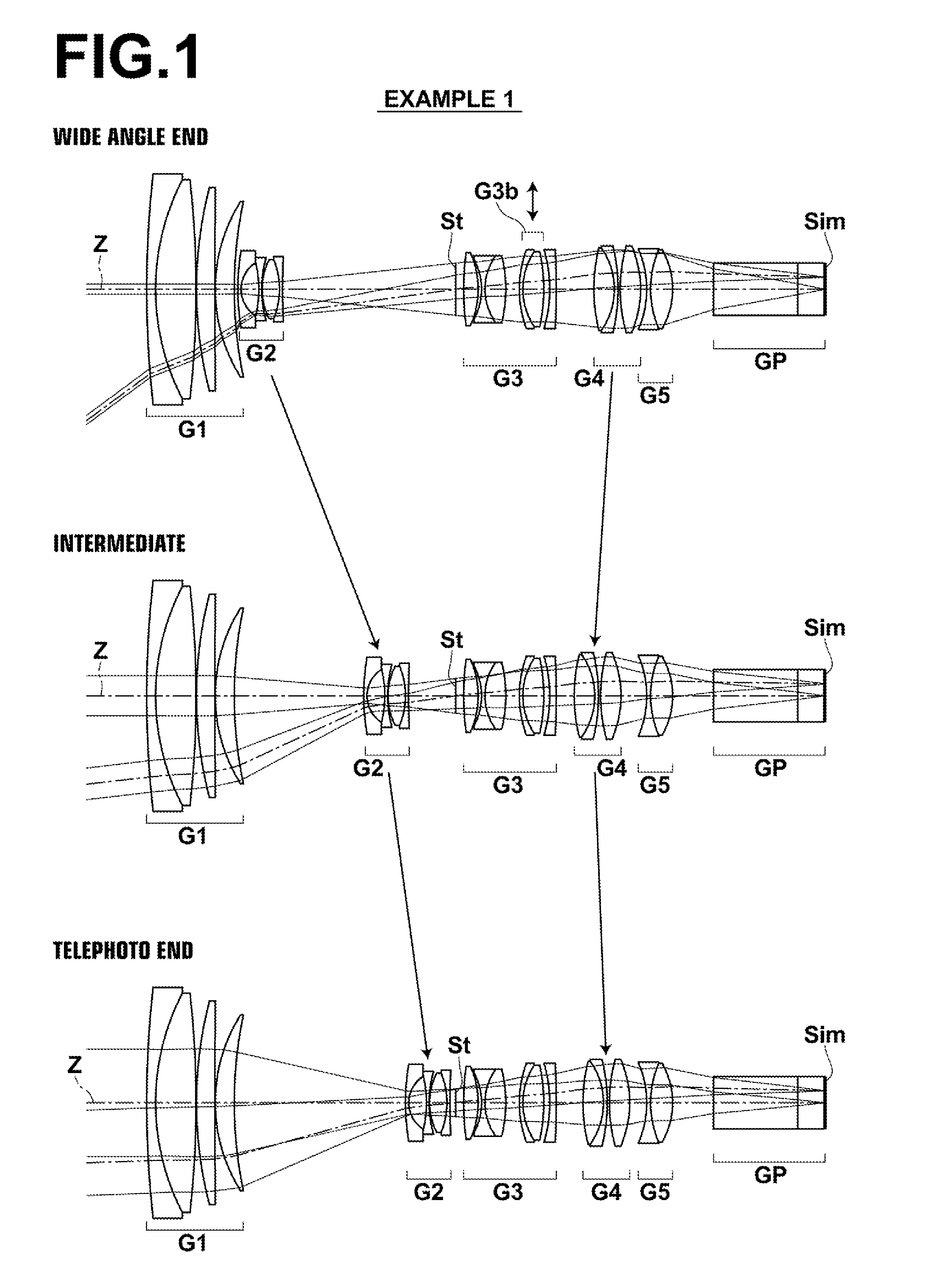
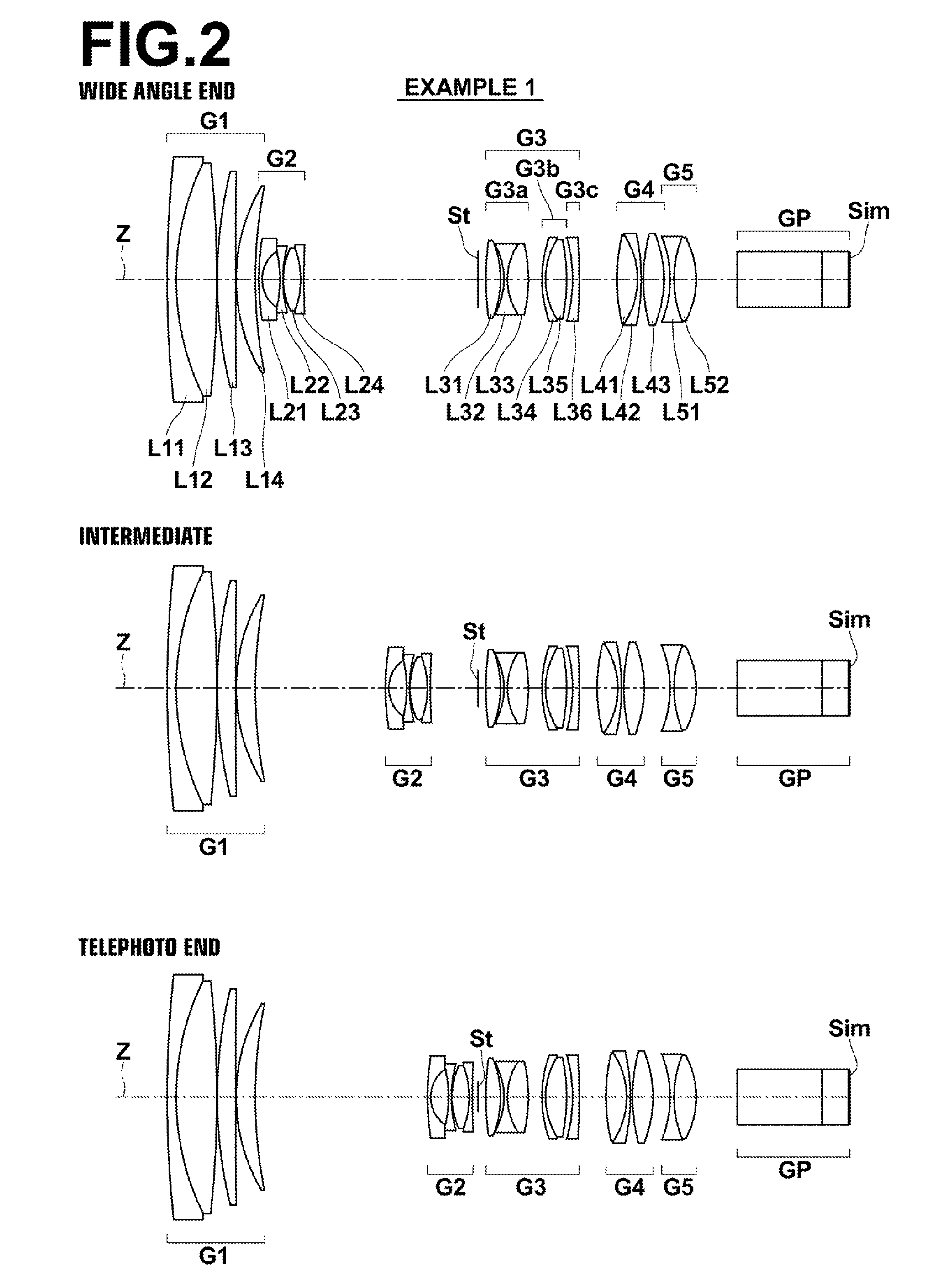
The zoom lens consists essentially of a positive first lens group, a negative second lens group, an aperture stop, a third lens group, a positive fourth lens group and a fifth lens group in this order from the object side. The first, third, and fifth lens groups are fixed while the second and the fourth lens groups move when changing magnification from the wide angle end to the telephoto end, and the fourth lens group moves when focusing is performed. The fifth lens group consists essentially only of a single cemented lens having a meniscus shape with a convex surface toward the image side, and conditional formulas (1), (2) are satisfied when the maximum image height is Y, the air equivalent back focus is Bf and the distance along the optical axis from the aperture stop to the peak of the most-image-side lens surface is Lsr:0.05<Y / Bf<0.20 (1)1.8<Lsr / Bf<3.5 (2).
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Pickup lens
A pickup lens is provided with various aberrations corrected satisfactorily, with a short optical length, and with a sufficient back focus secured.The configuration comprises an aperture diaphragm S1, first lens L1, second lens L2, and third lens L3, and is configured by arranging, in order from the object side to the image side, the aperture diaphragm, first lens, second lens, and third lens. The first lens is a lens having positive refractive power, with convex surfaces on the object side and on the image side. The second lens is a lens having negative refractive power, in a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the image side. The third lens is a lens having negative refractive power, in a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the object side. Both of the surfaces of the first lens are aspherical, both of the surfaces of the second lens are aspherical, and both of the surfaces of the third lens are aspherical.
Owner:SEIKOH GIKEN
Method for testing anti-sagging performance of polyurethane wood paint under construction viscosity
InactiveCN104807723AOvercome lack of focusJudging the sag resistanceFlow propertiesEngineeringViscosity
The invention relates to a device for testing anti-sagging performance of a polyurethane wood paint under construction viscosity. Specifically, the device includes a triangle spraying bracket; the triangle spraying bracket is provided with a base, a first side surface on the base, and a second side surface located on the base and intersecting with the first side surface; a ''Z'' shaped base plate is arranged on the triangle spraying bracket; a recess is arranged near the lower end of the ''Z'' shaped base plate; and a test panel is fixed on a second base plate. The invention also provides a method for testing anti-sagging performance of a polyurethane wood paint under construction viscosity by using the device. The method solves the problem of poor pertinency of the existing test method, can effectively judge the anti-sagging performance of the polyurethane wood paint under construction condition, and is fast, simple and in line with the current furniture painting technology.
Owner:NIPPON PAINT CHINA
Ultracompact image pickup lens
ActiveUS8902513B2Overcome lack of focusExtreme downsizingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensConditional expression
An image pickup lens includes, an aperture stop, a first meniscus lens having positive refractive power with a convex surface facing the object, a second lens having positive refractive power with a concave surface facing the object, a third lens having negative refractive power with a convex surface facing the object, the both surfaces of the third lens are aspheric and having at least one pole-change point, and following conditional expressions are satisfied:TTL<3.0 (1)0.80<f1 / f<0.93 (2)0.35<bf / TTL<0.42 (3)0.70<TTL / (2IH)<0.85 (4)where TTL: a length from the surface closest to the object to an image plane, f: a focal length of an overall optical system, f1: a focal length of the first lens, bf: a length from the image-side surface of the third lens to the image plane, and IH: a maximum image height.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Zoom lens and image pickup device
Owner:SONY CORP
Projection lens and projection type display device using the same
A projection lens includes, in order from a magnification side, a first lens group, a second lens group and a third lens group. The first lens group includes, in order from the magnification side, a negative lens whose lens made of a non-resin, a plastic lens at least one surface of which is aspheric and a positive lens. The second lens group includes a plastic lens at least one surface of which is aspheric, a positive lens and a negative lens. The third lens group includes a positive lens. The following conditional expressions are satisfied.1.0<Bf / f≦1.82.0<f1 / f 2.0<f2 / f where Bf denotes a air-conversion back focus of the entire system, f denotes a focal length of the entire system, f1 denotes a focal length of the first lens group and f2 denotes a focal length of the second lens group.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Imaging apparatus and method
ActiveUS8049810B2Overcome lack of focusEnough speedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsNarrow rangeAutofocus
If an aperture of the objective-imaging is the same as an aperture when a state has turned into a focused state with autofocus before the objective-imaging or if an F value of the objective-imaging is equal to or greater than an F value when a state has turned into a focused state with autofocus before the objective-imaging, the focused state is maintained and the focusing of the objective-imaging is skipped. Even in other cases, a in-focus position is detected near the in-focus position before the objective-imaging. Alternatively, if the user selects a speed priority, the in-focus position is detected in a narrow range near the in-focus position before the objective-imaging. This enables to achieve both enough speed and focus accuracy of the main-photographing.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com