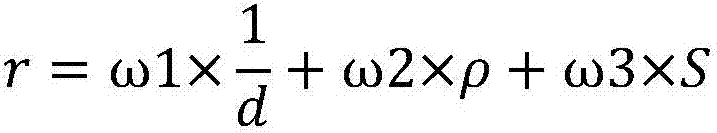Patents
Literature
30 results about "Fibrous cap" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
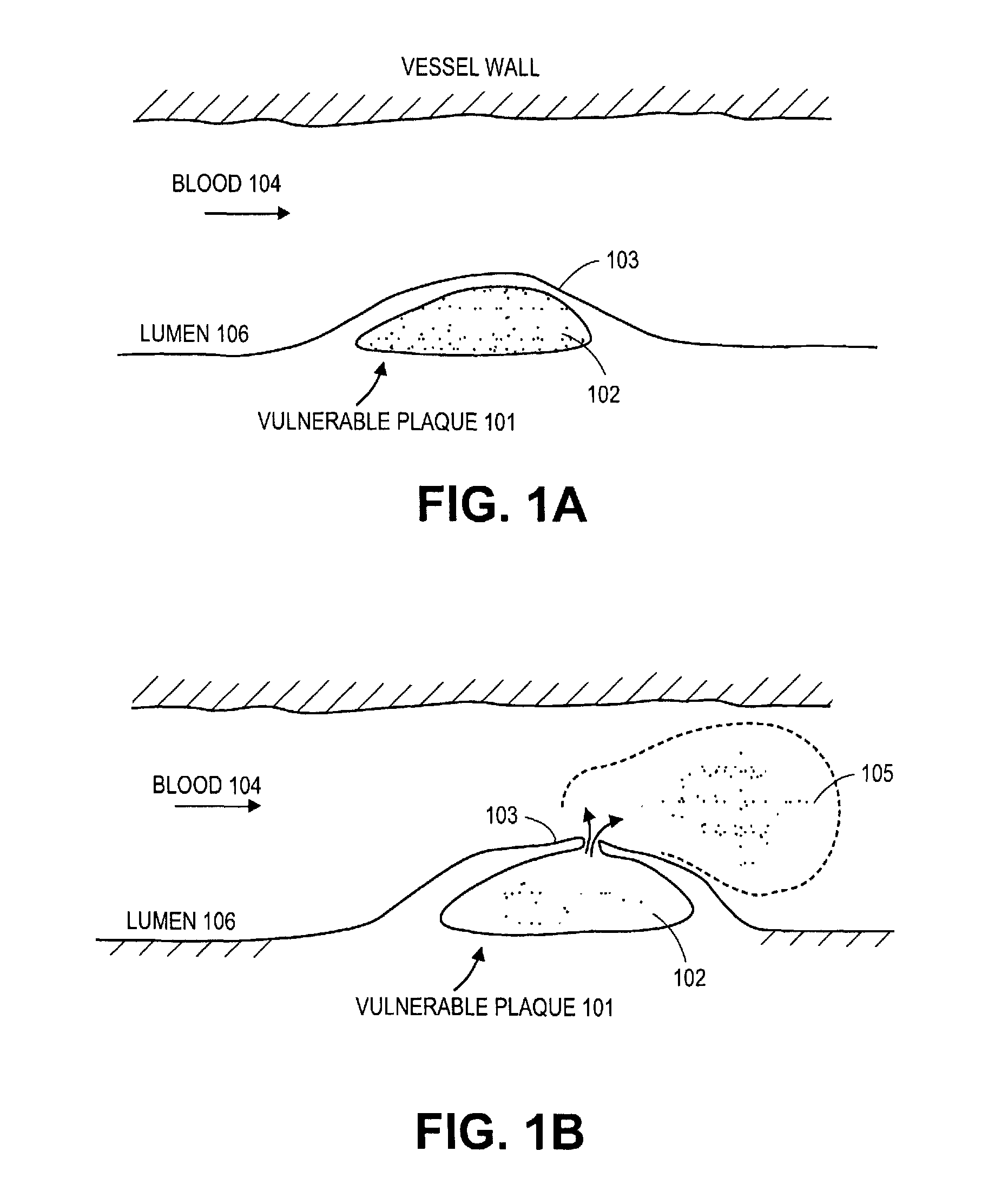
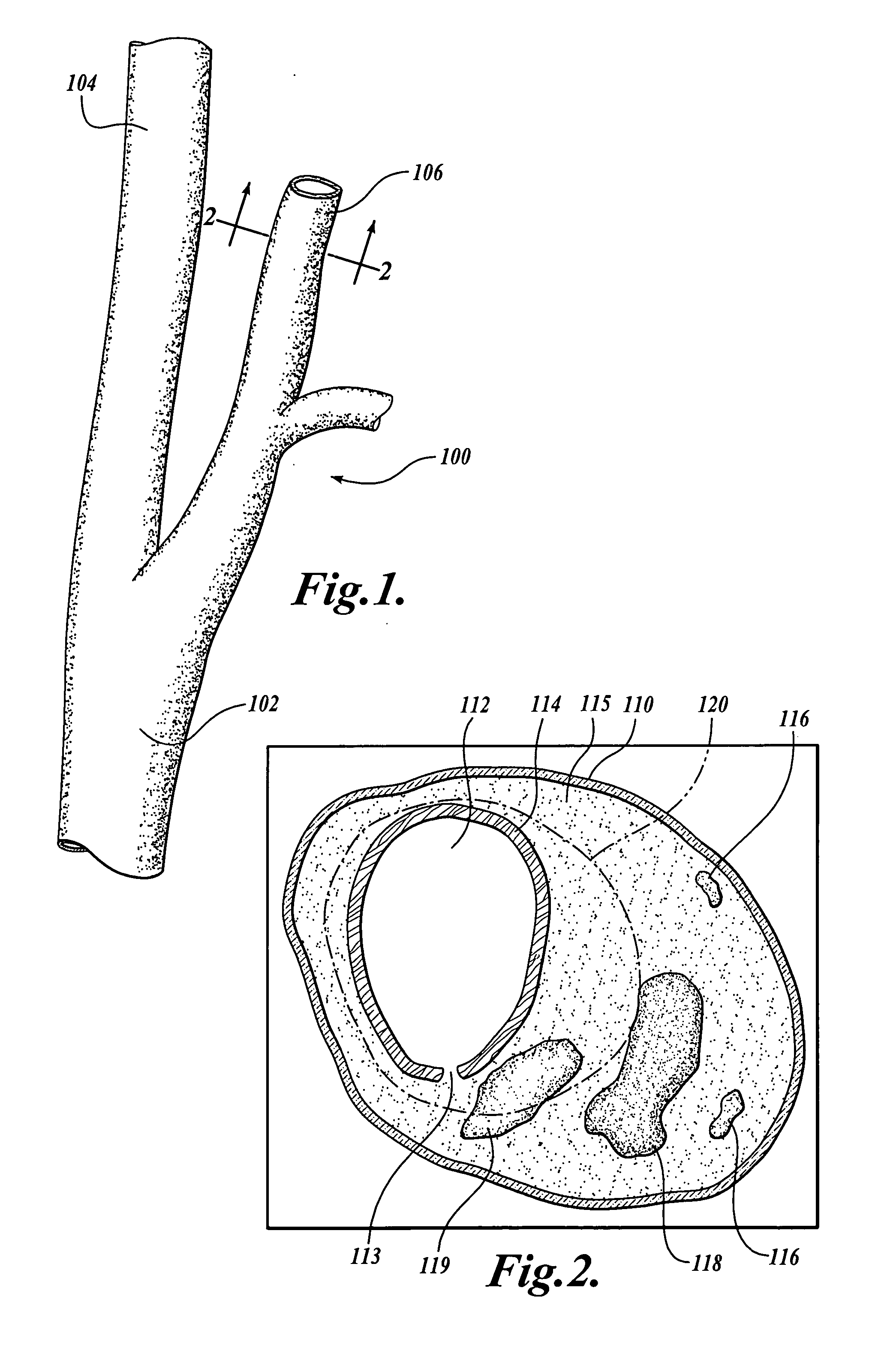
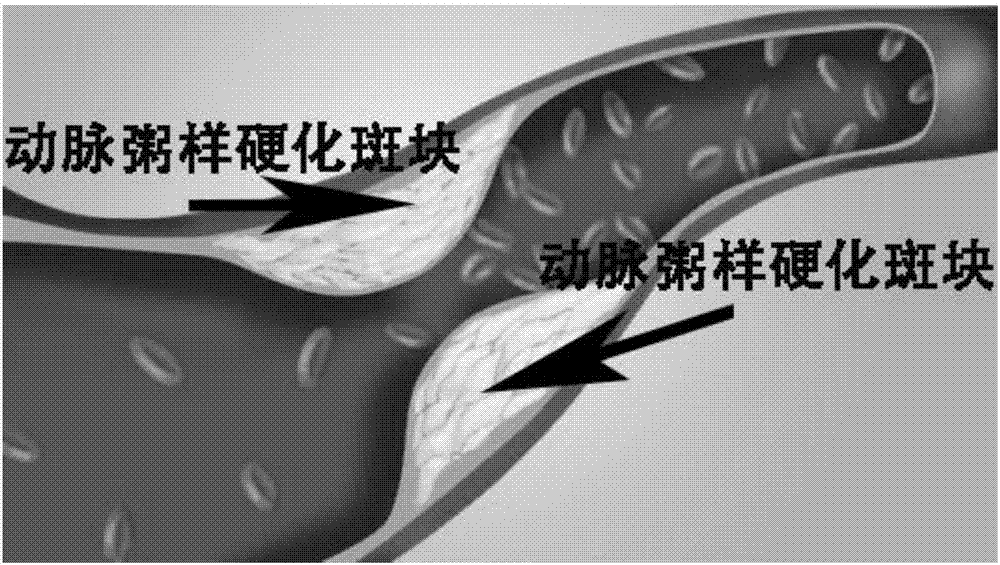
The fibrous cap is a layer of fibrous connective tissue, which is thicker and less cellular than the normal intima, found in atherosclerotic plaques. The fibrous cap contains macrophages and smooth muscle cells. The fibrous cap of an atheroma is composed of bundles of muscle cells, macrophages, foam cells, lymphocytes, collagen and elastin.
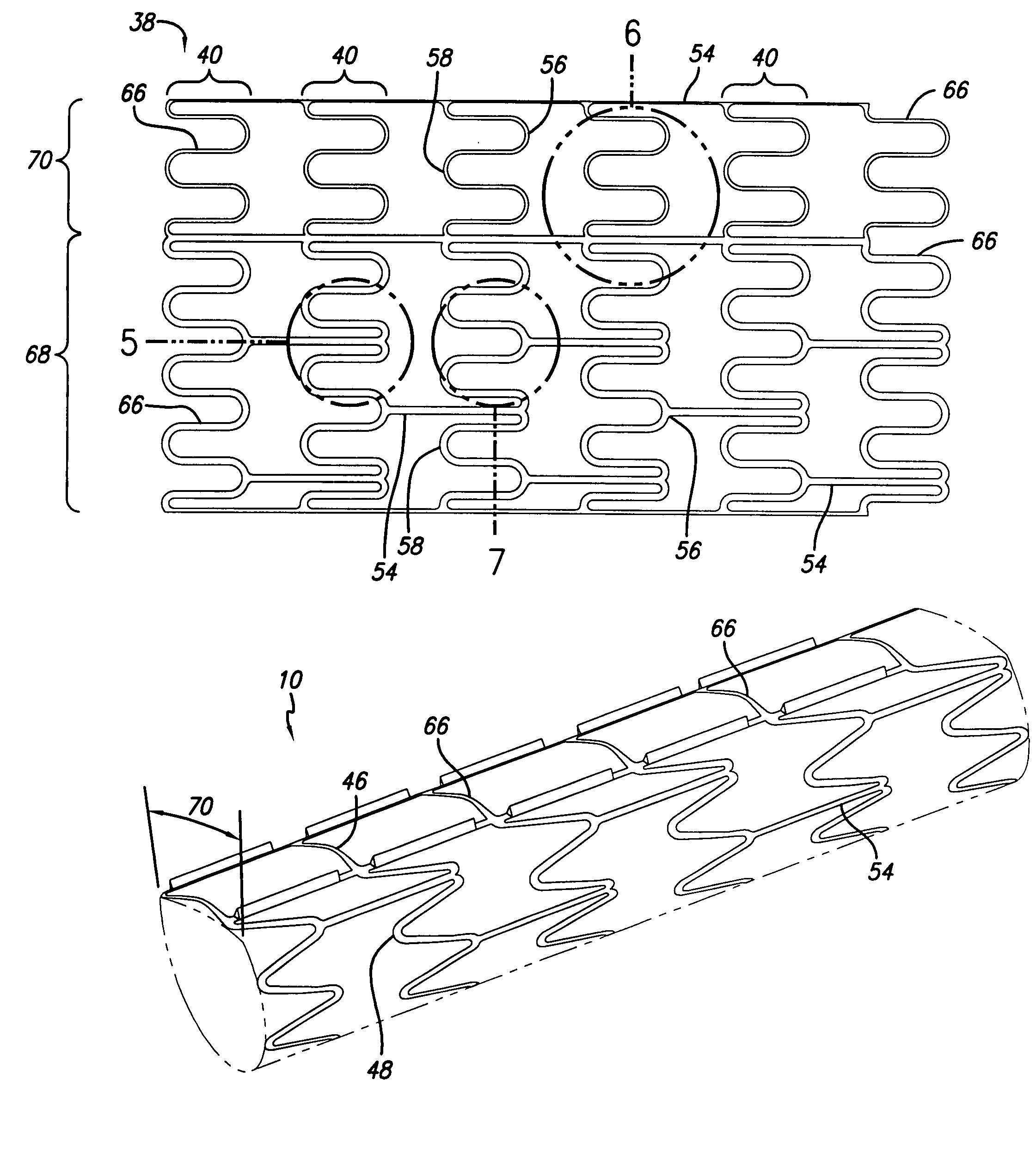
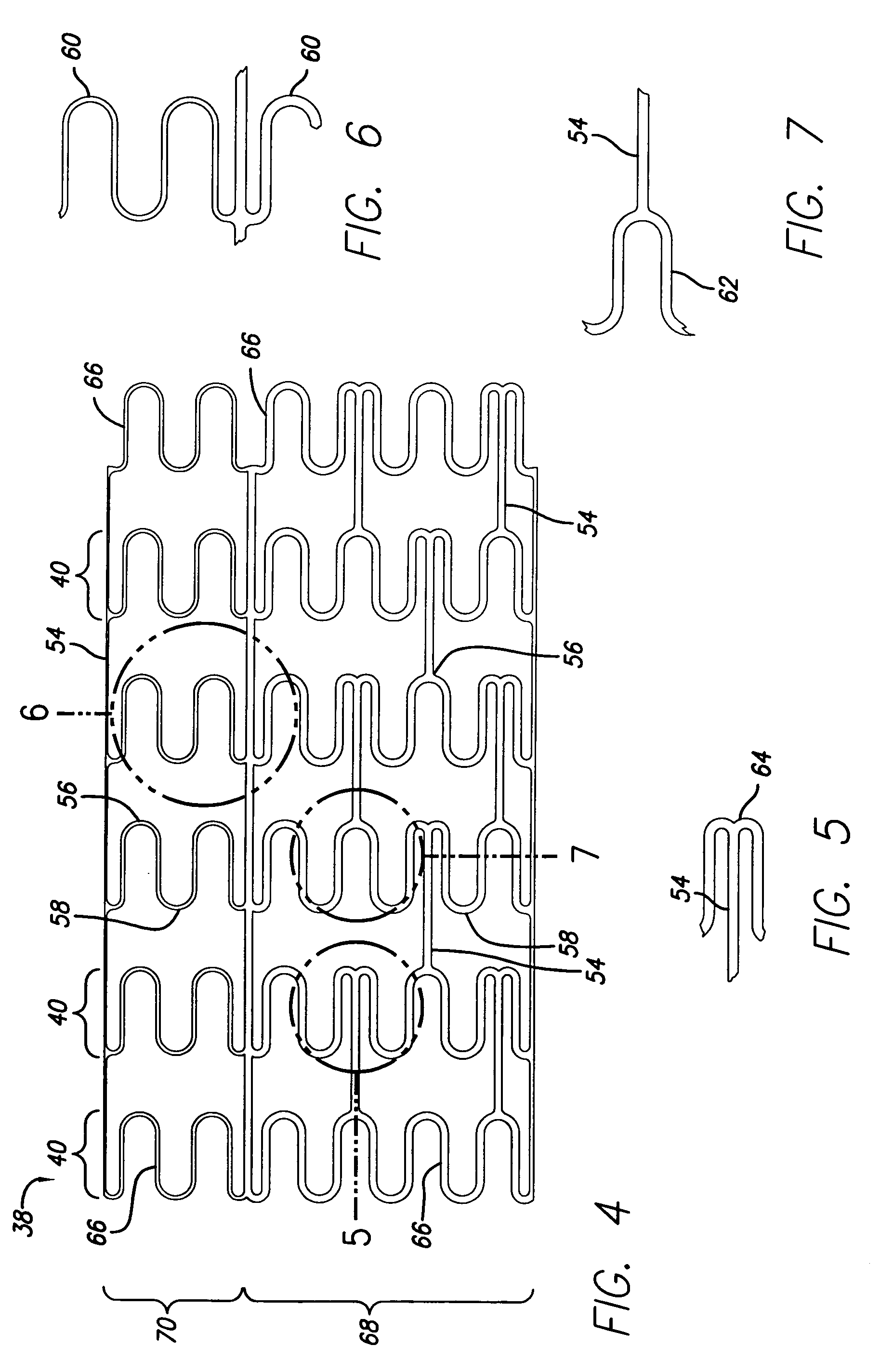
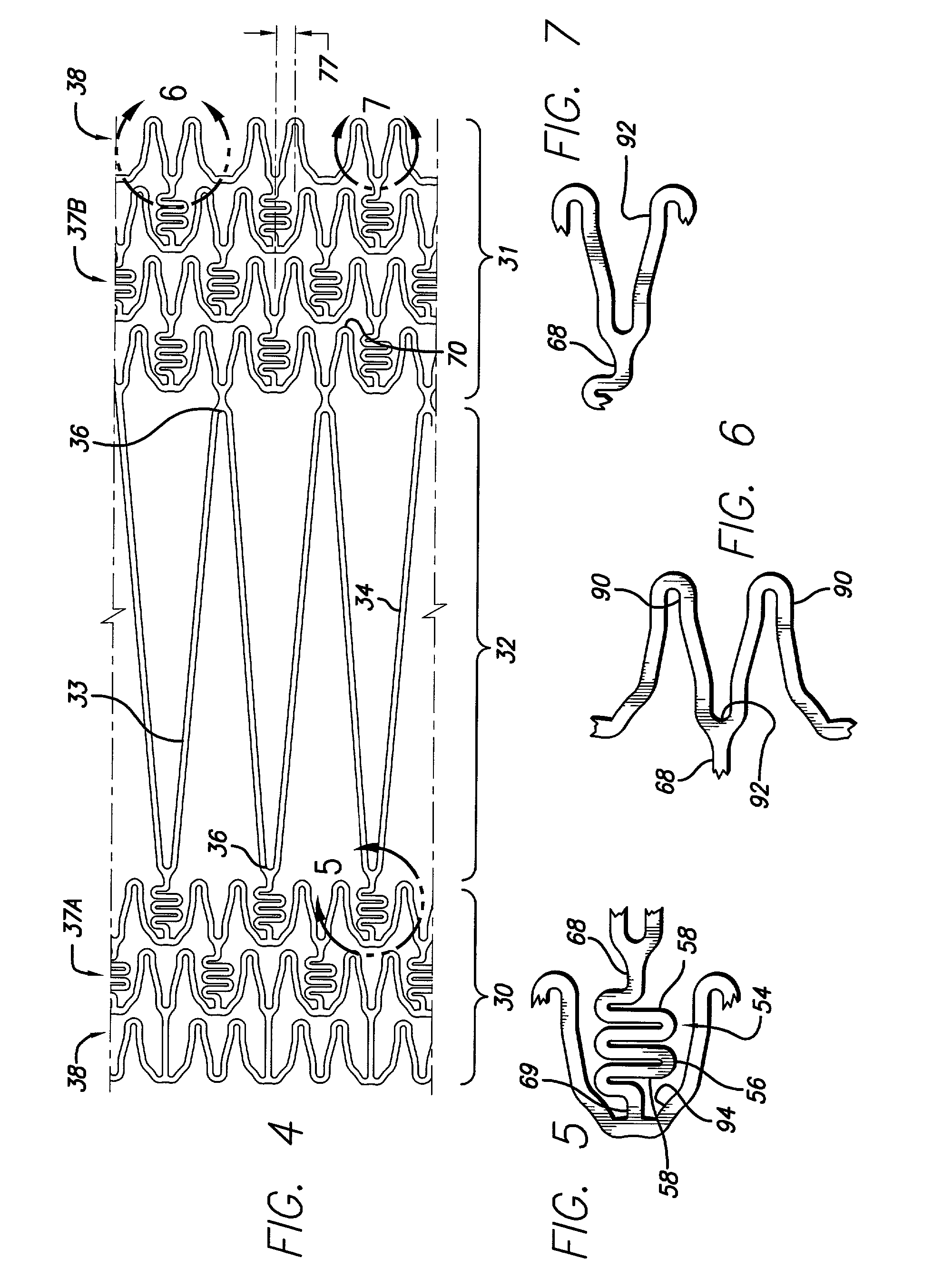
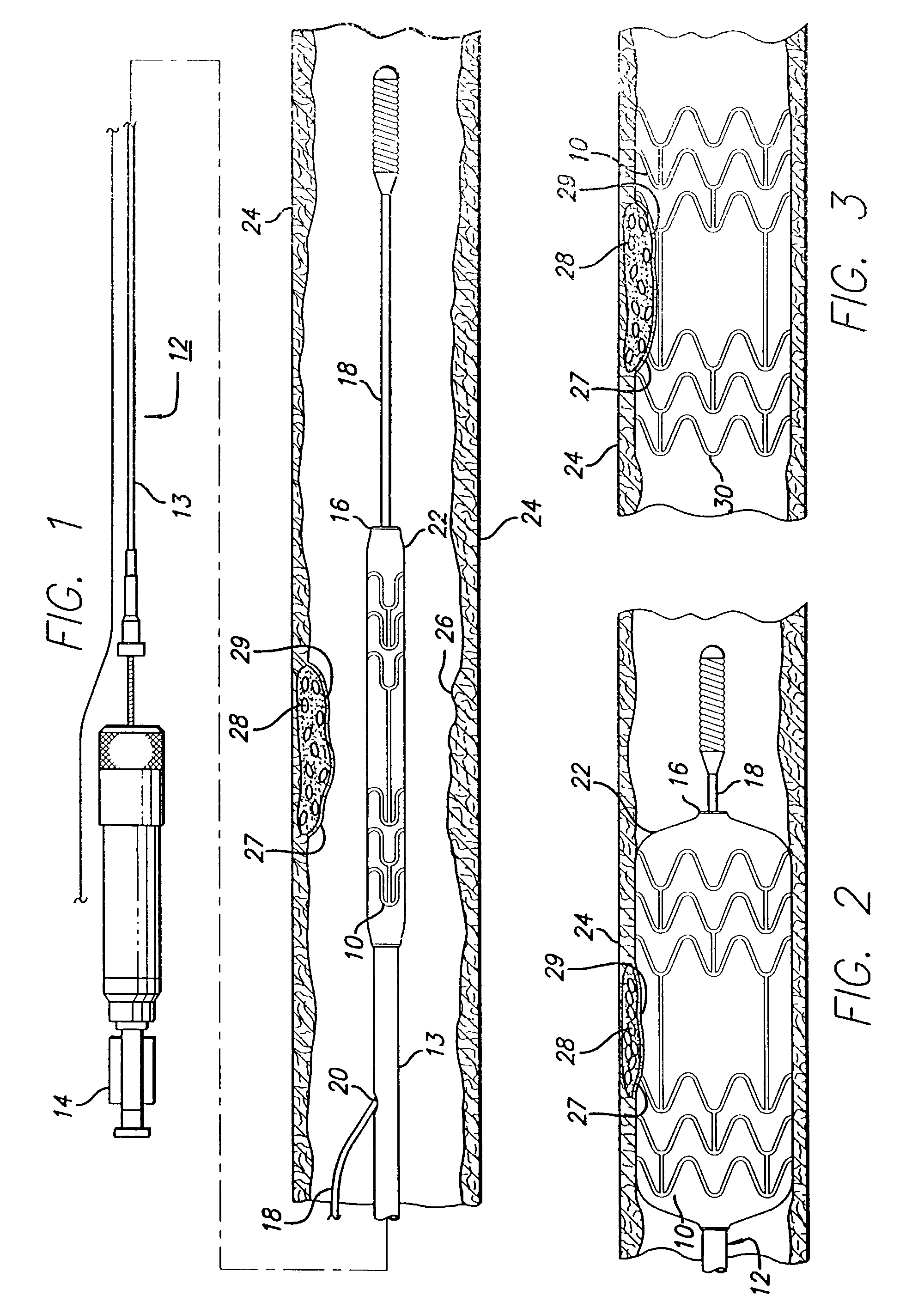
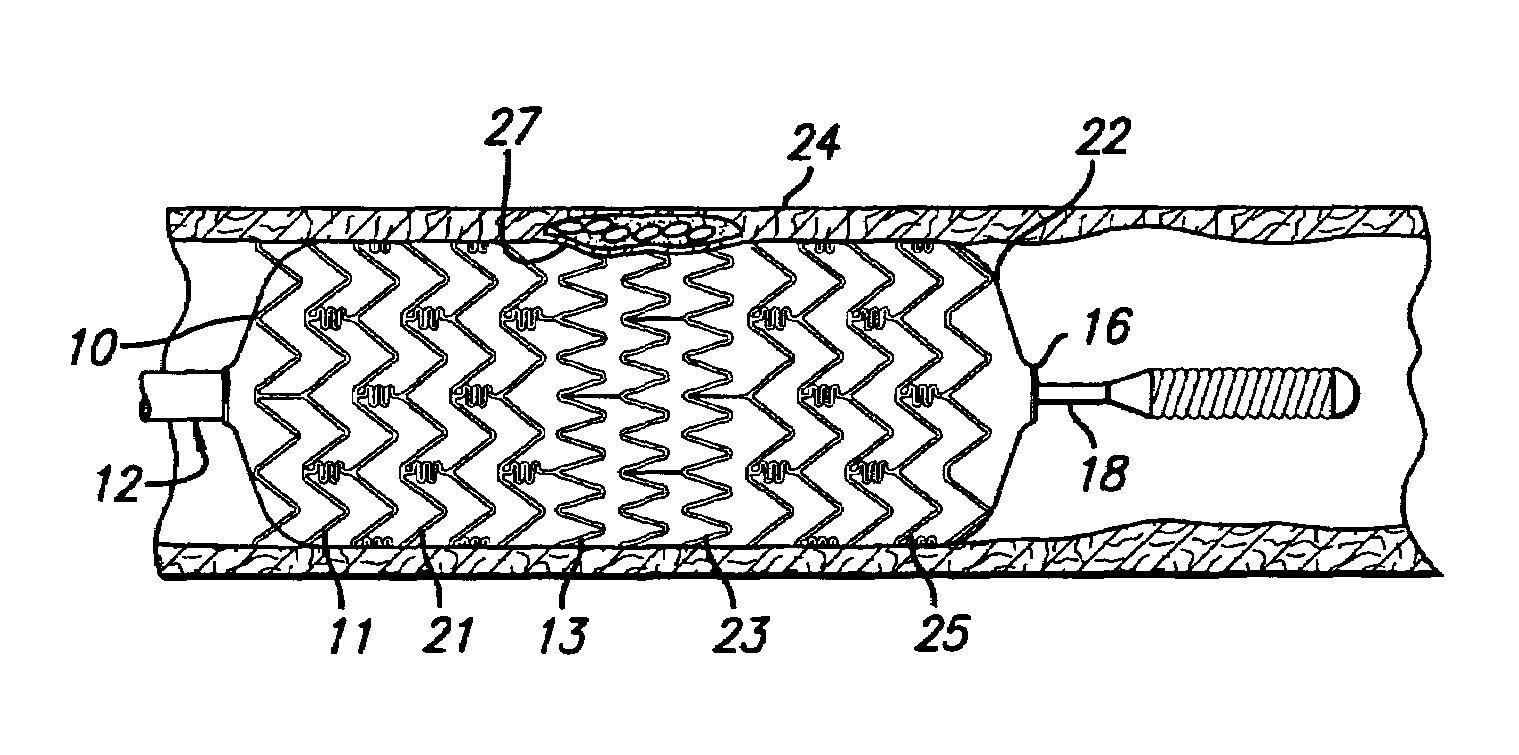
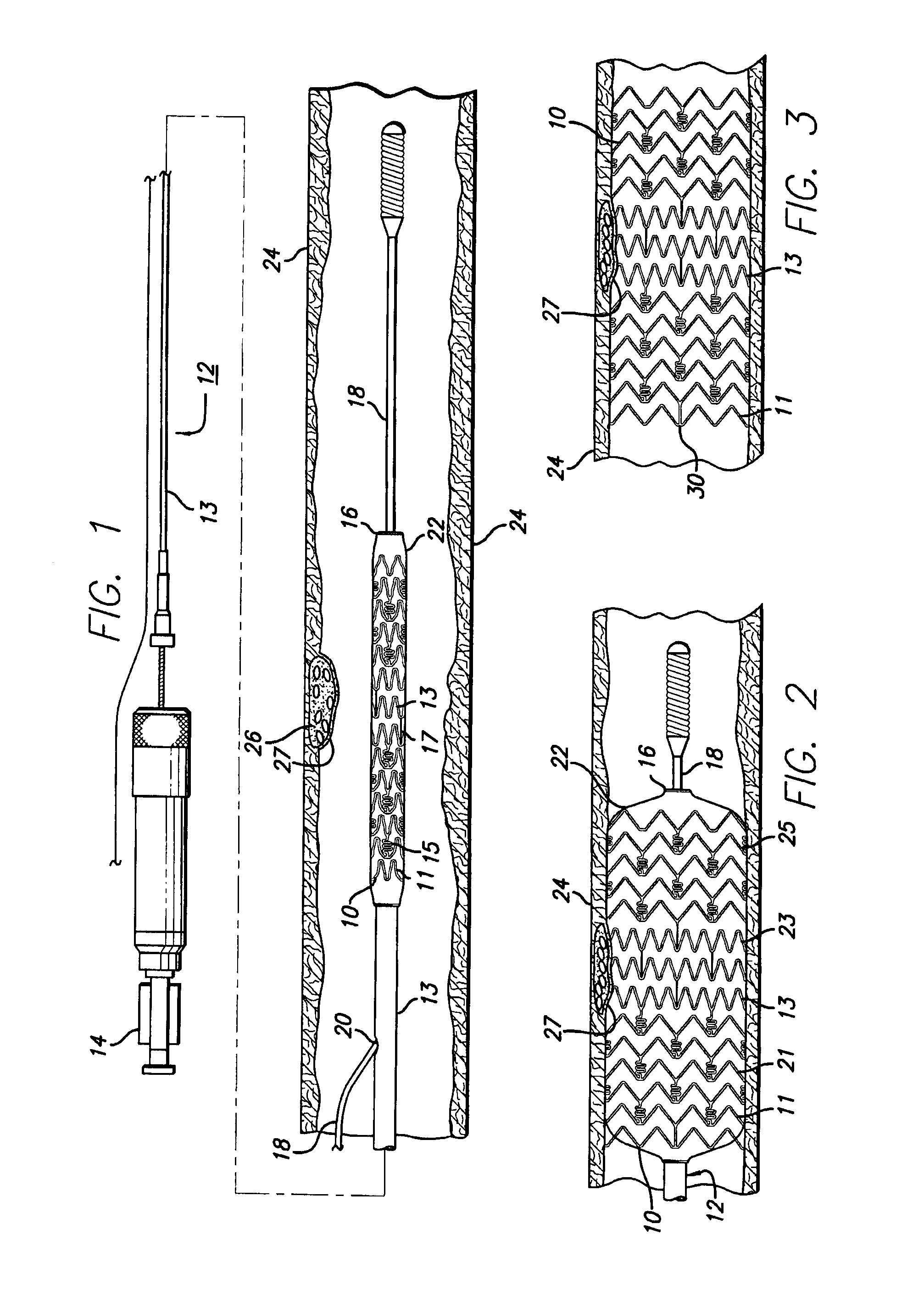
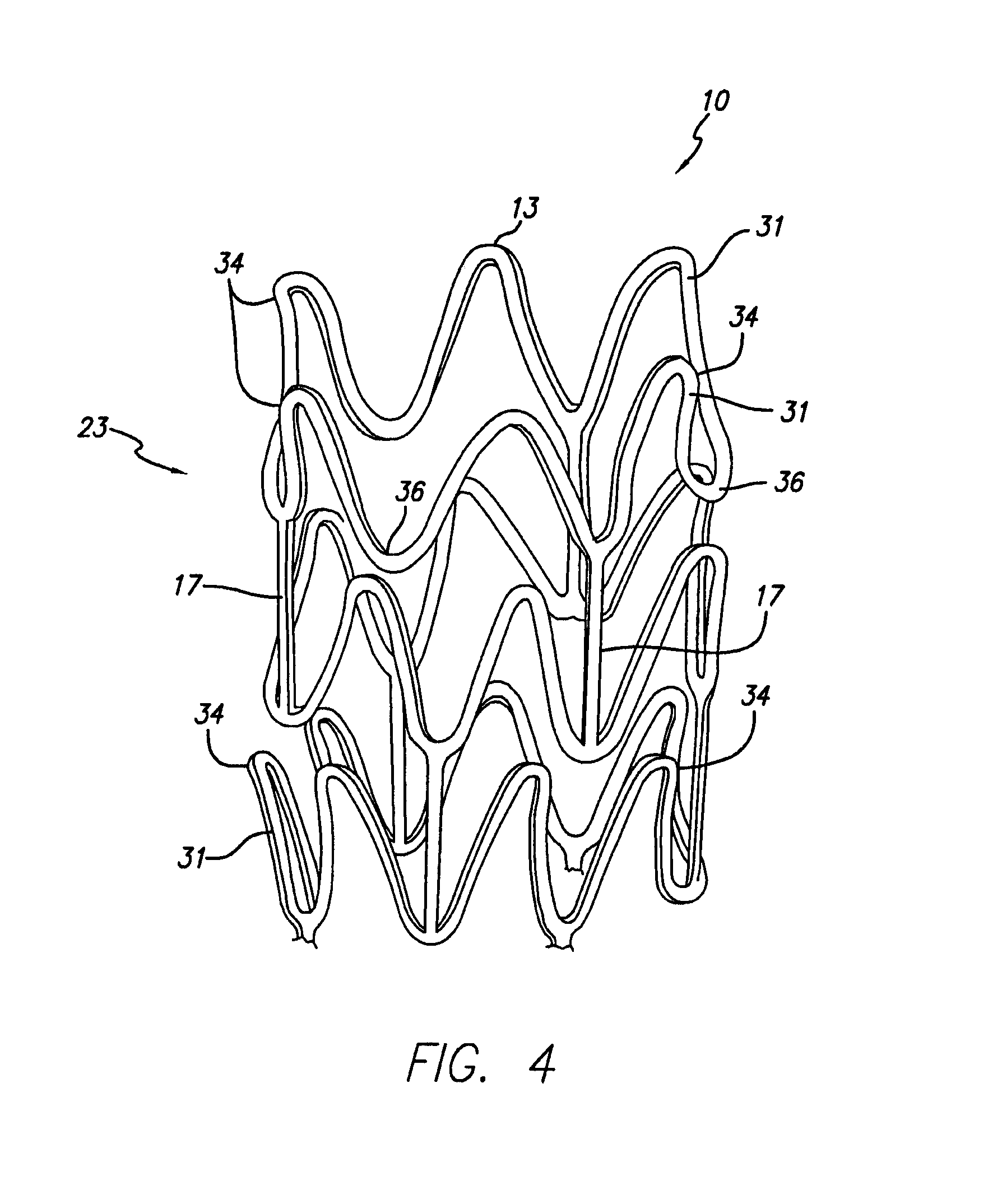
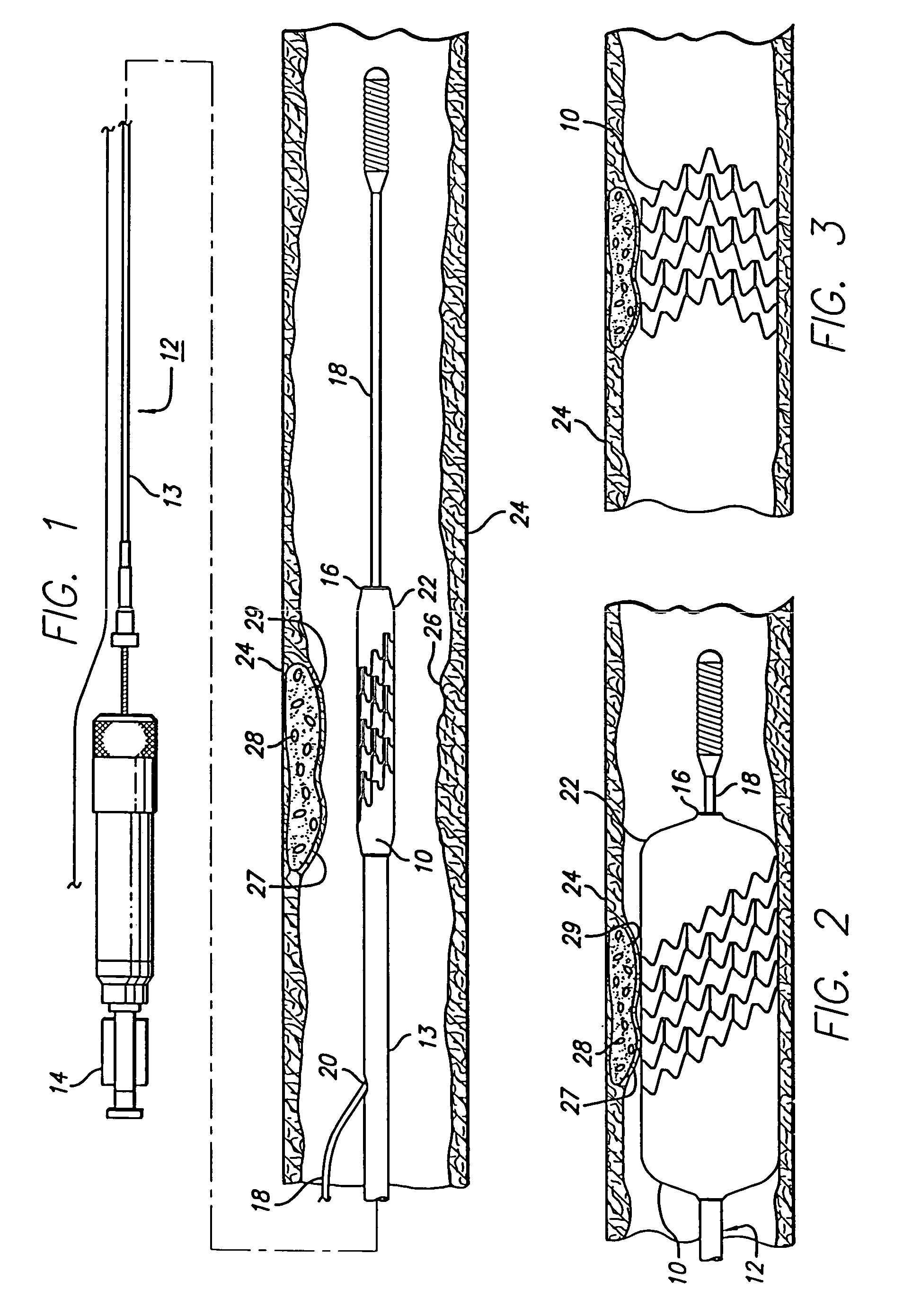
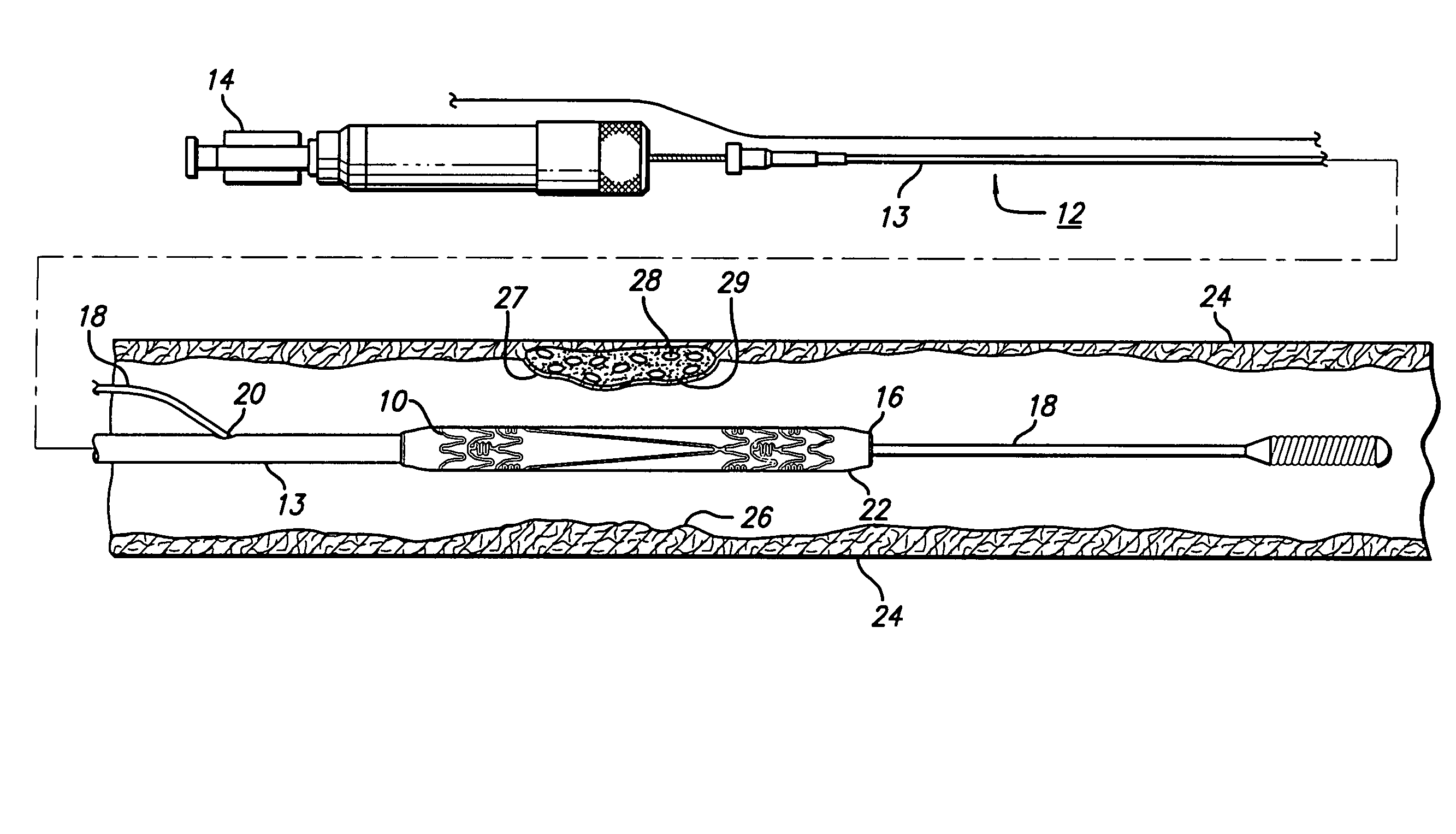
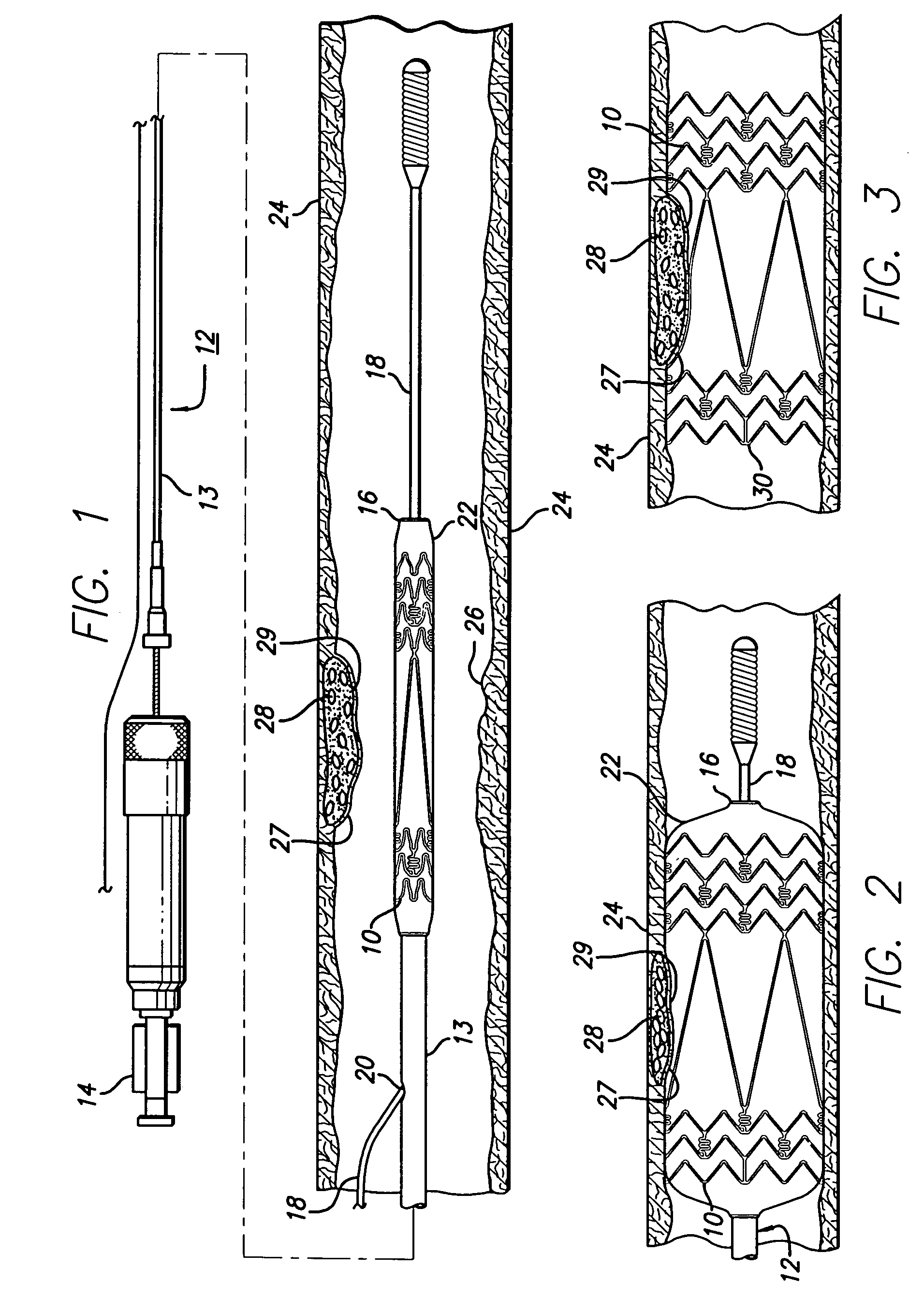
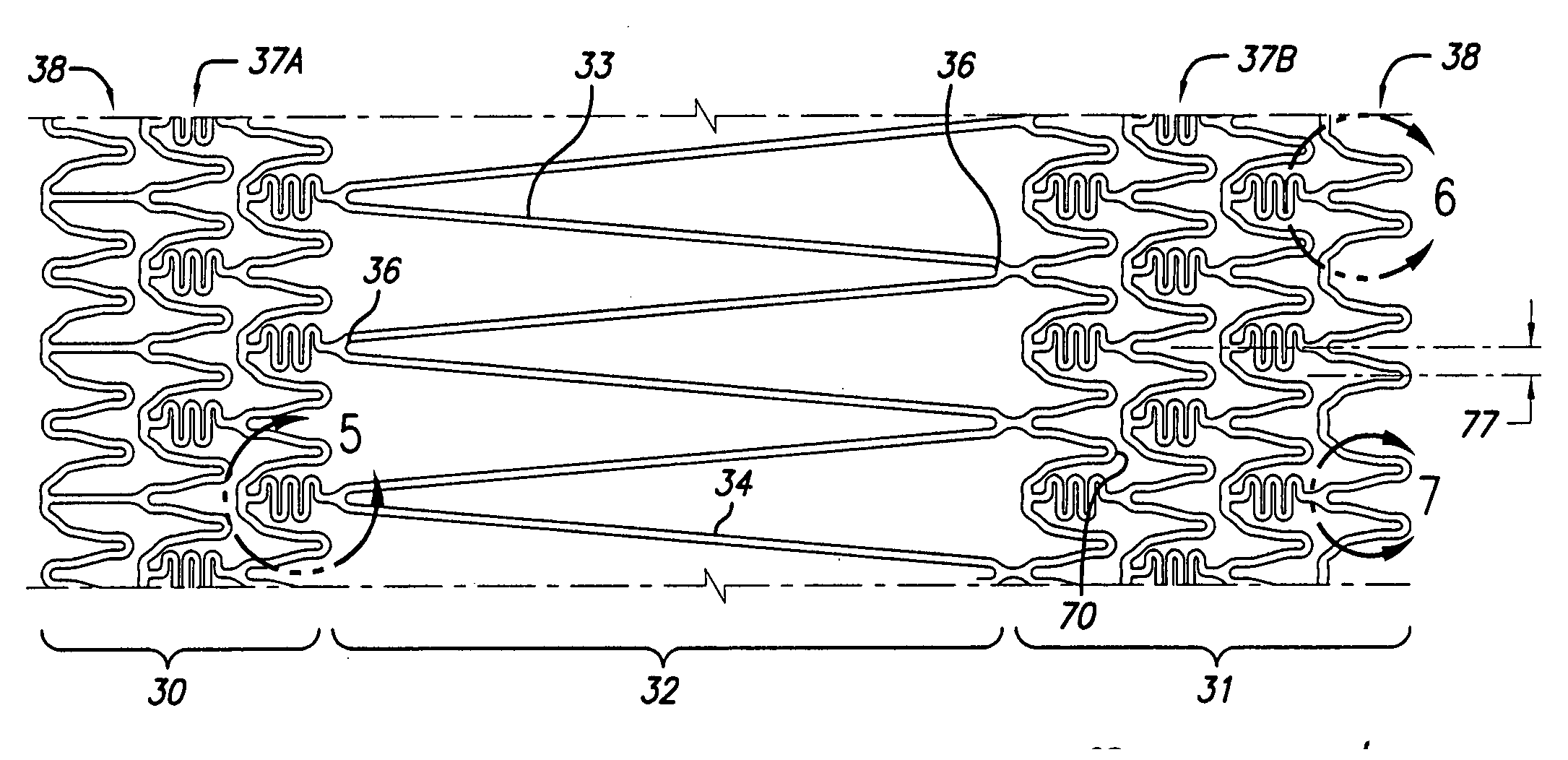
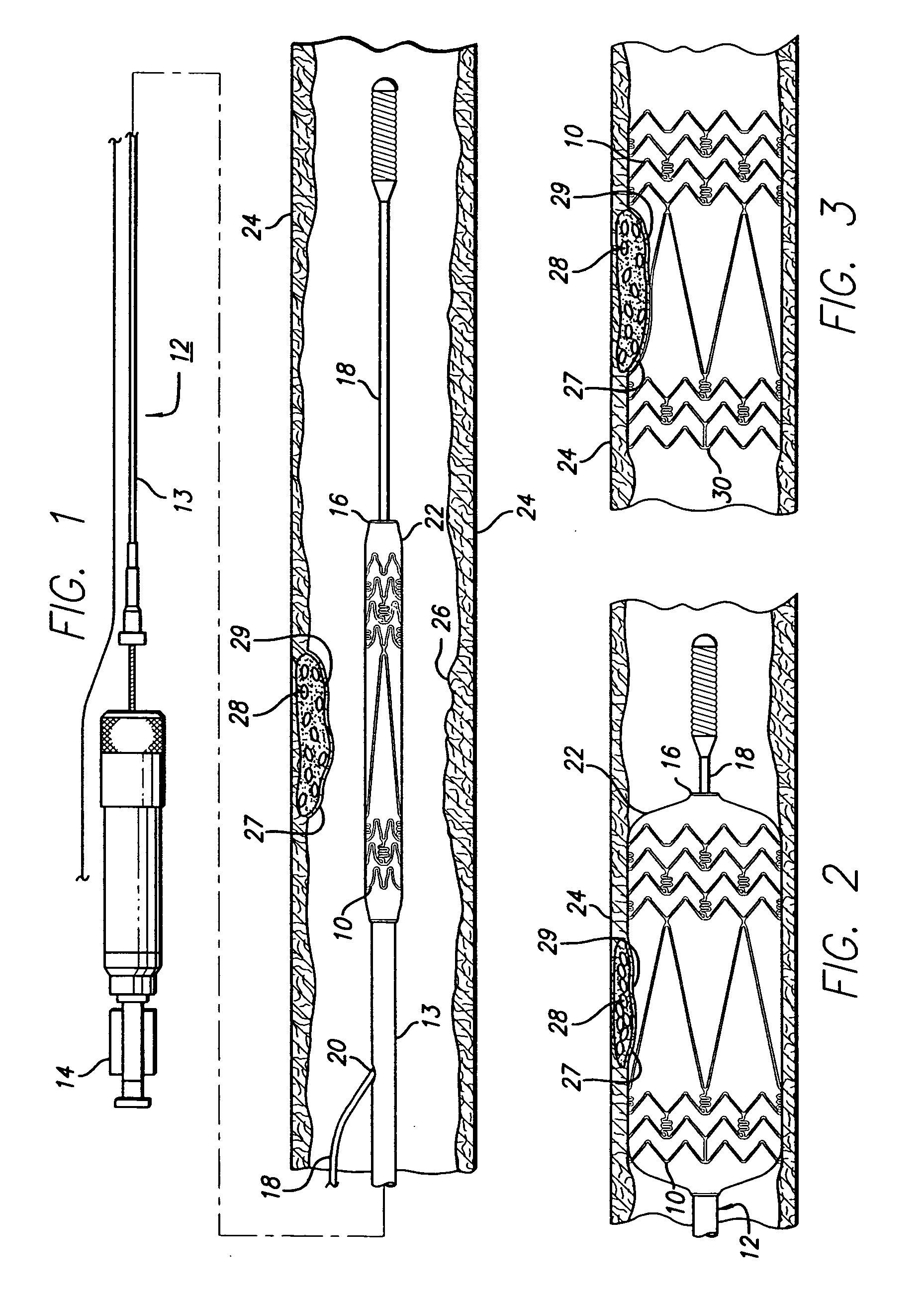
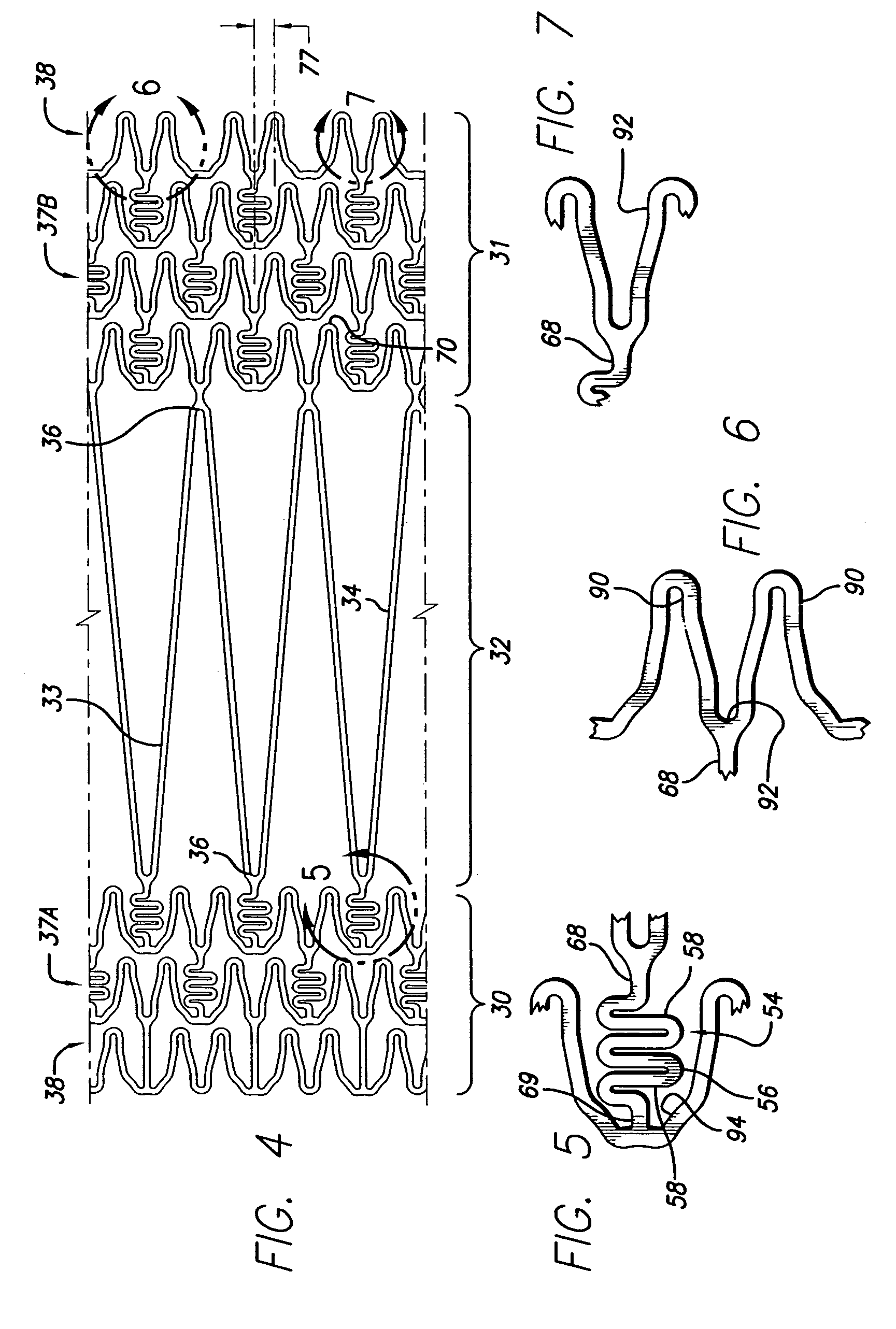
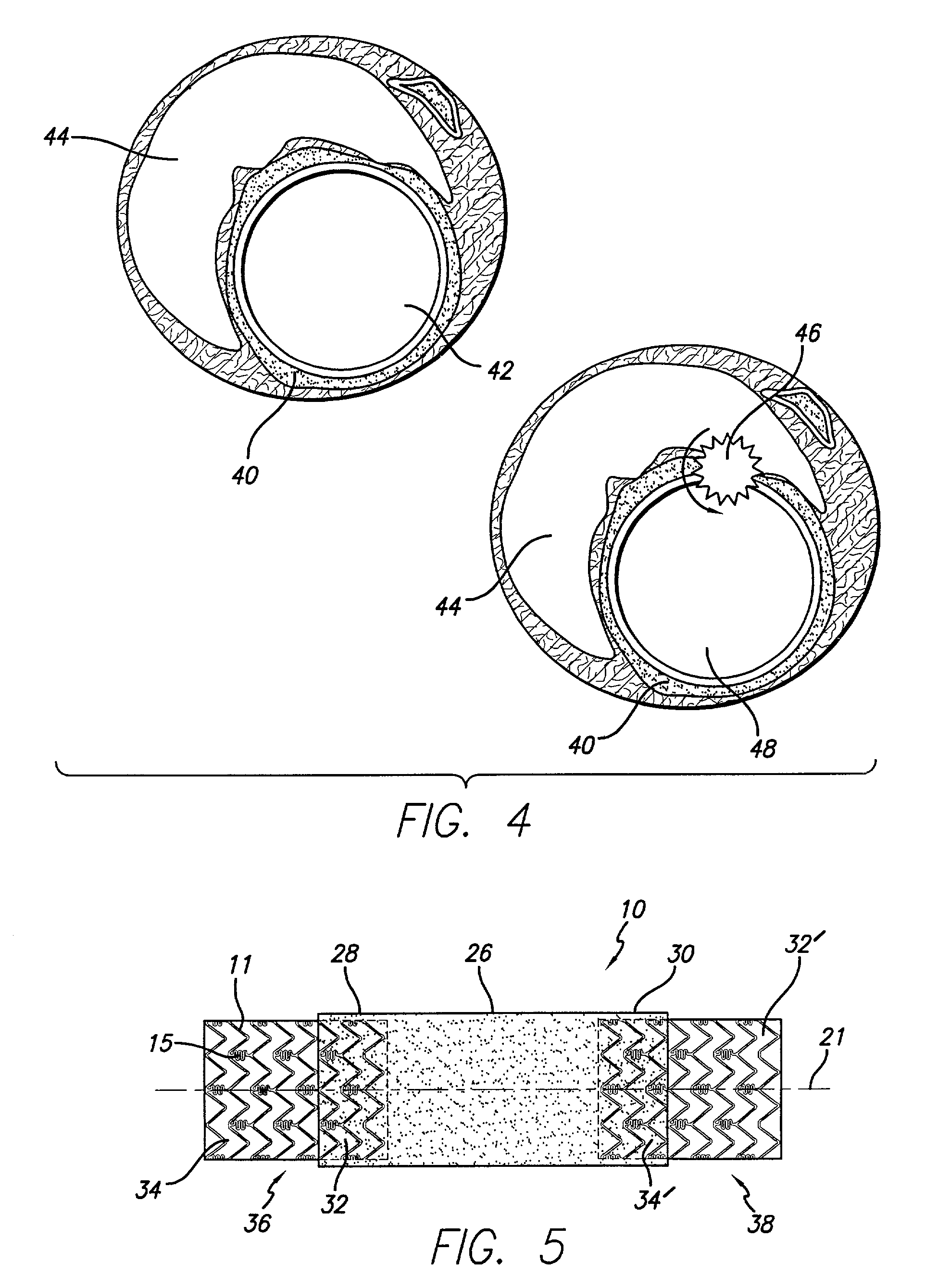
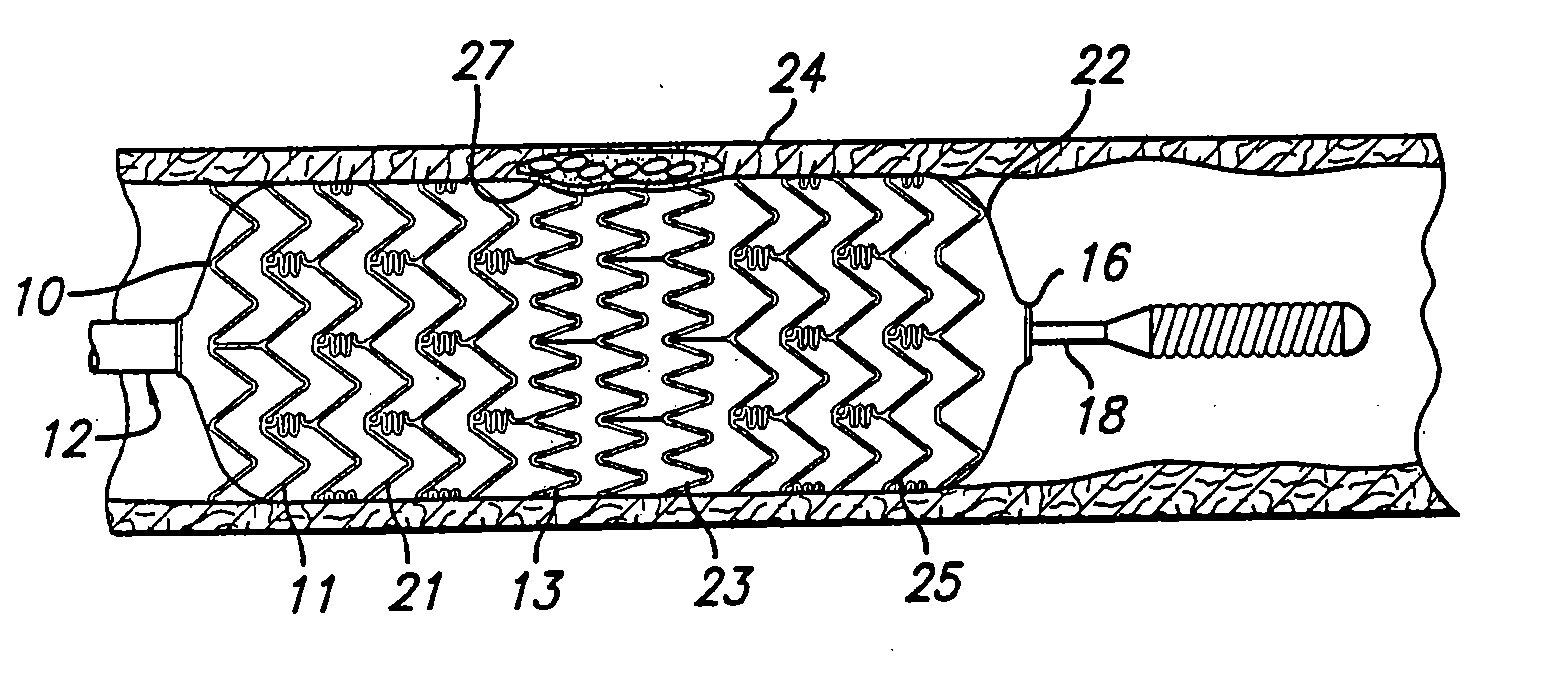
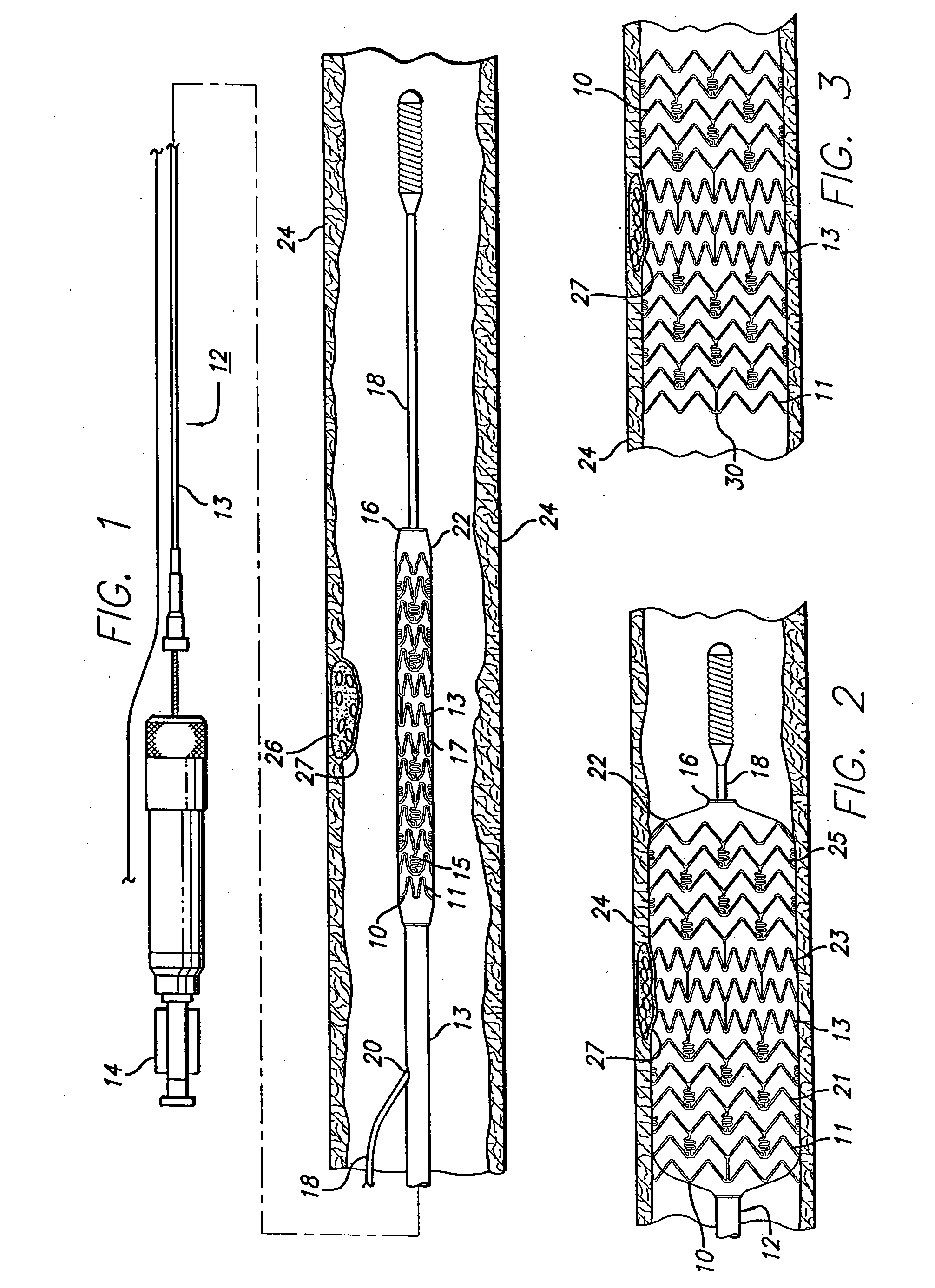
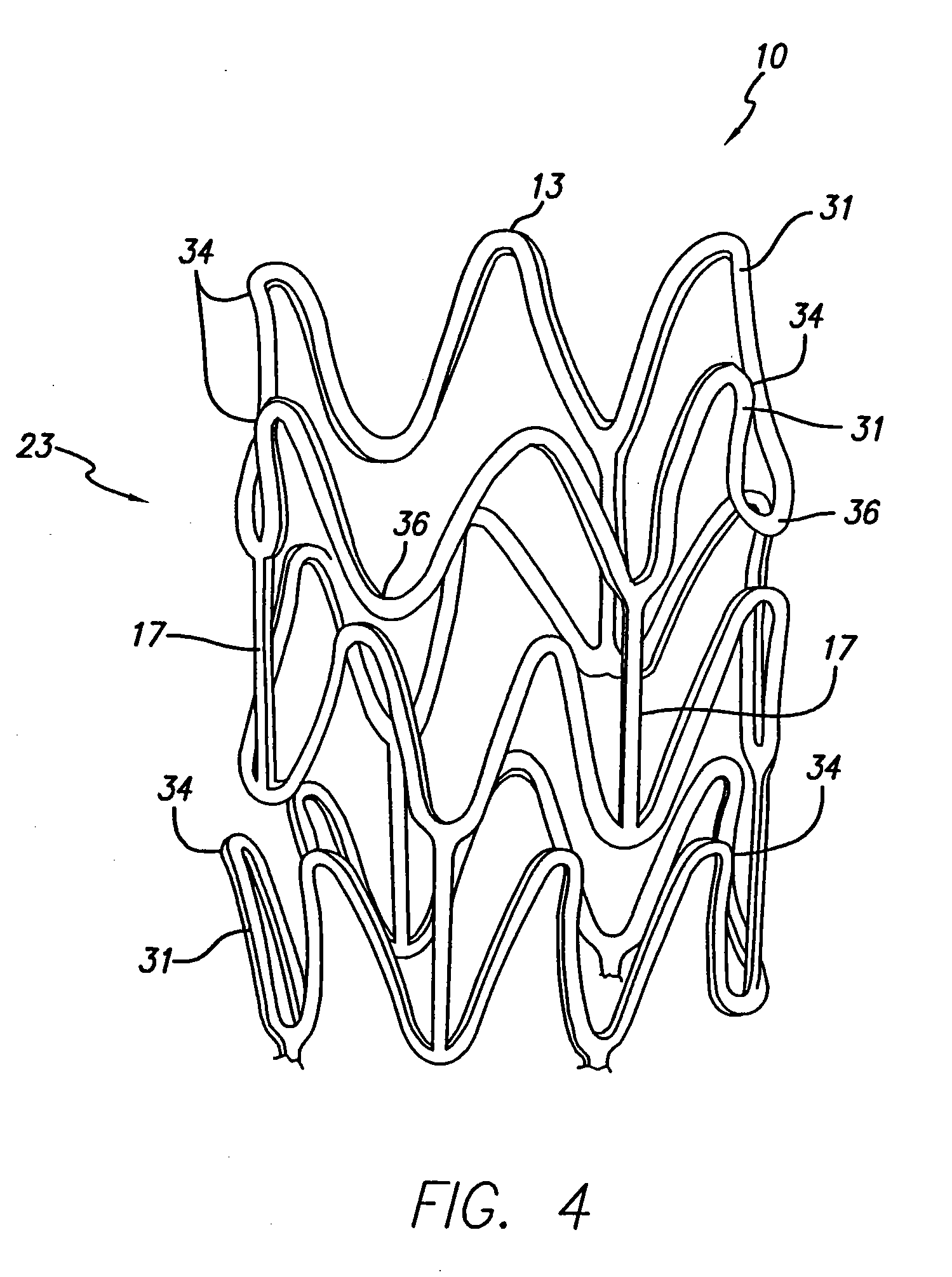
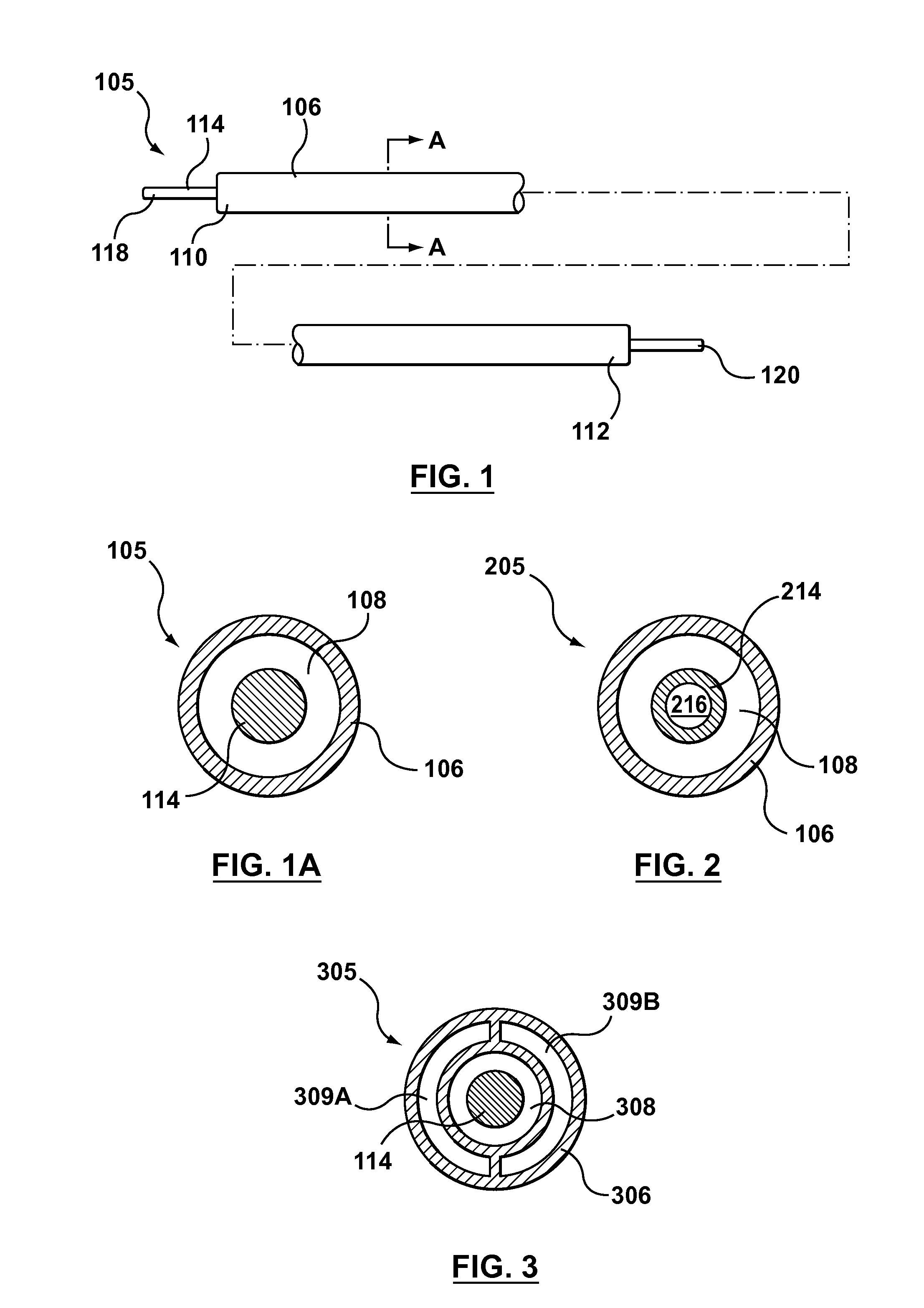
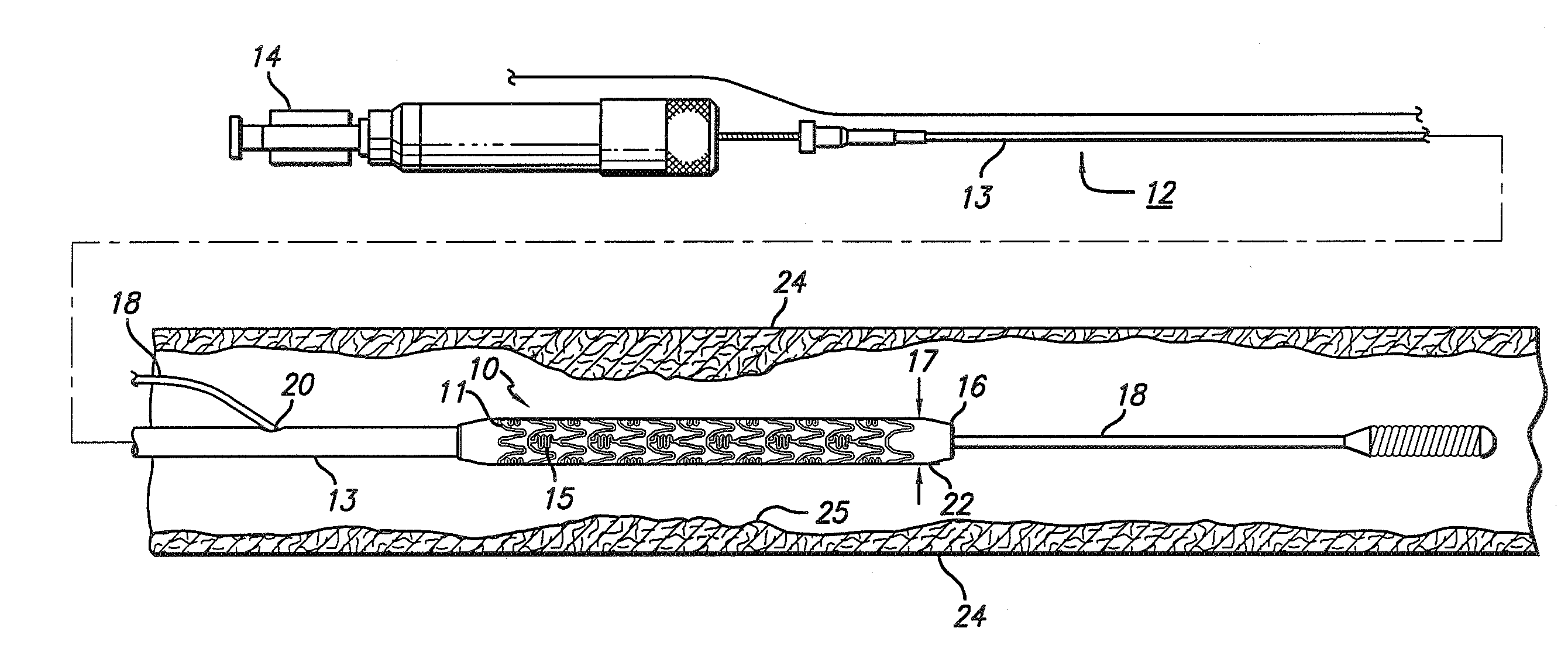
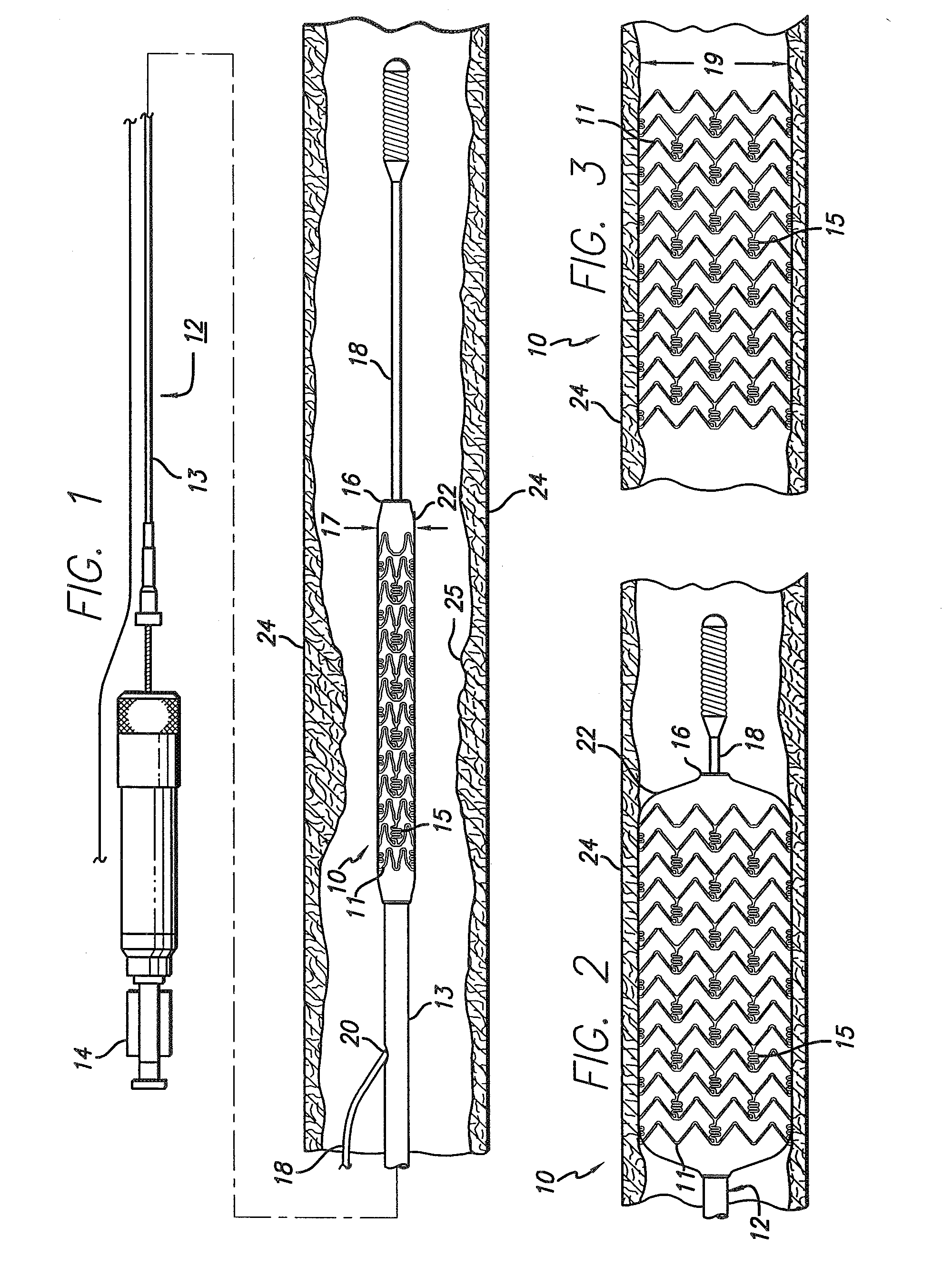
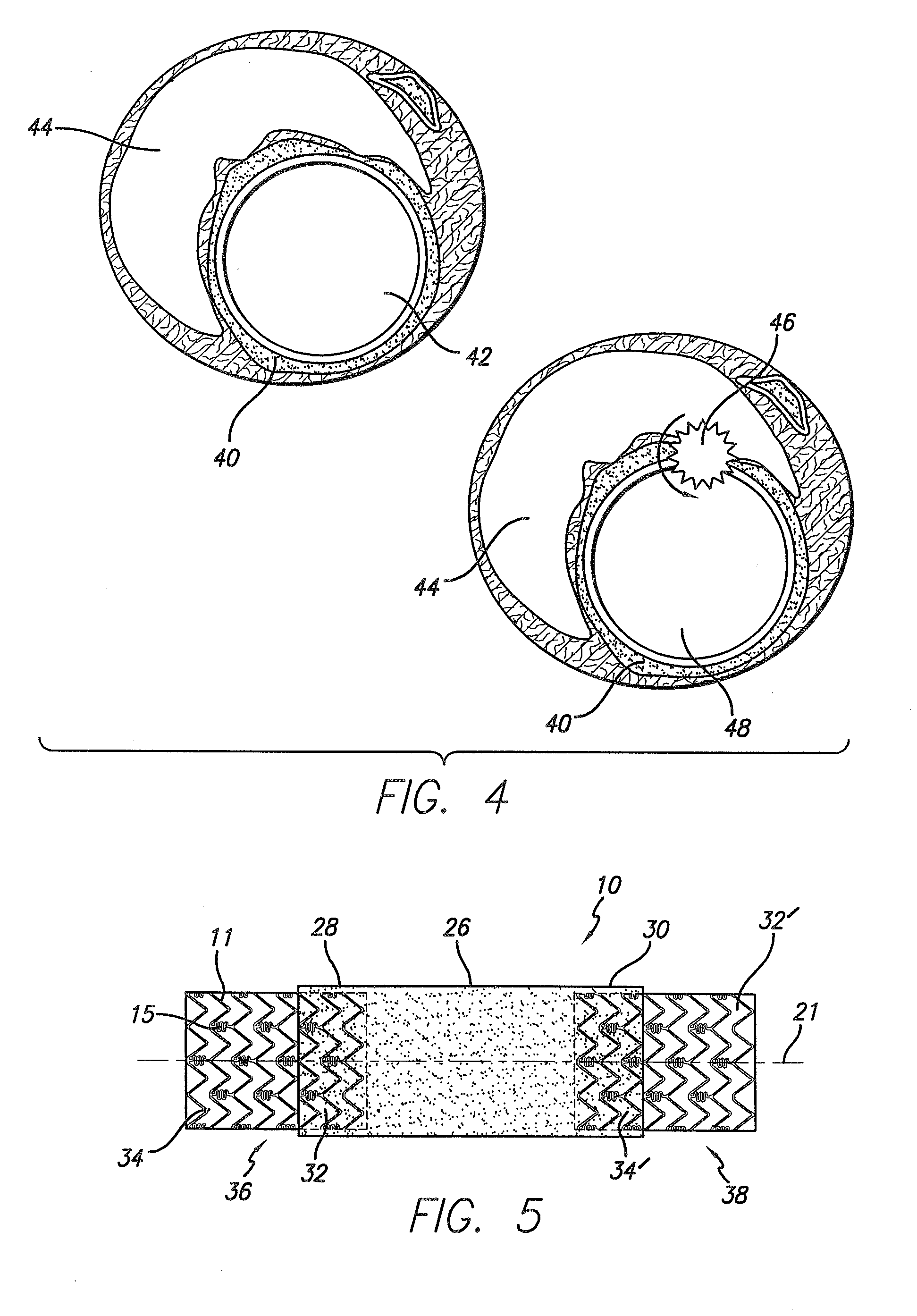
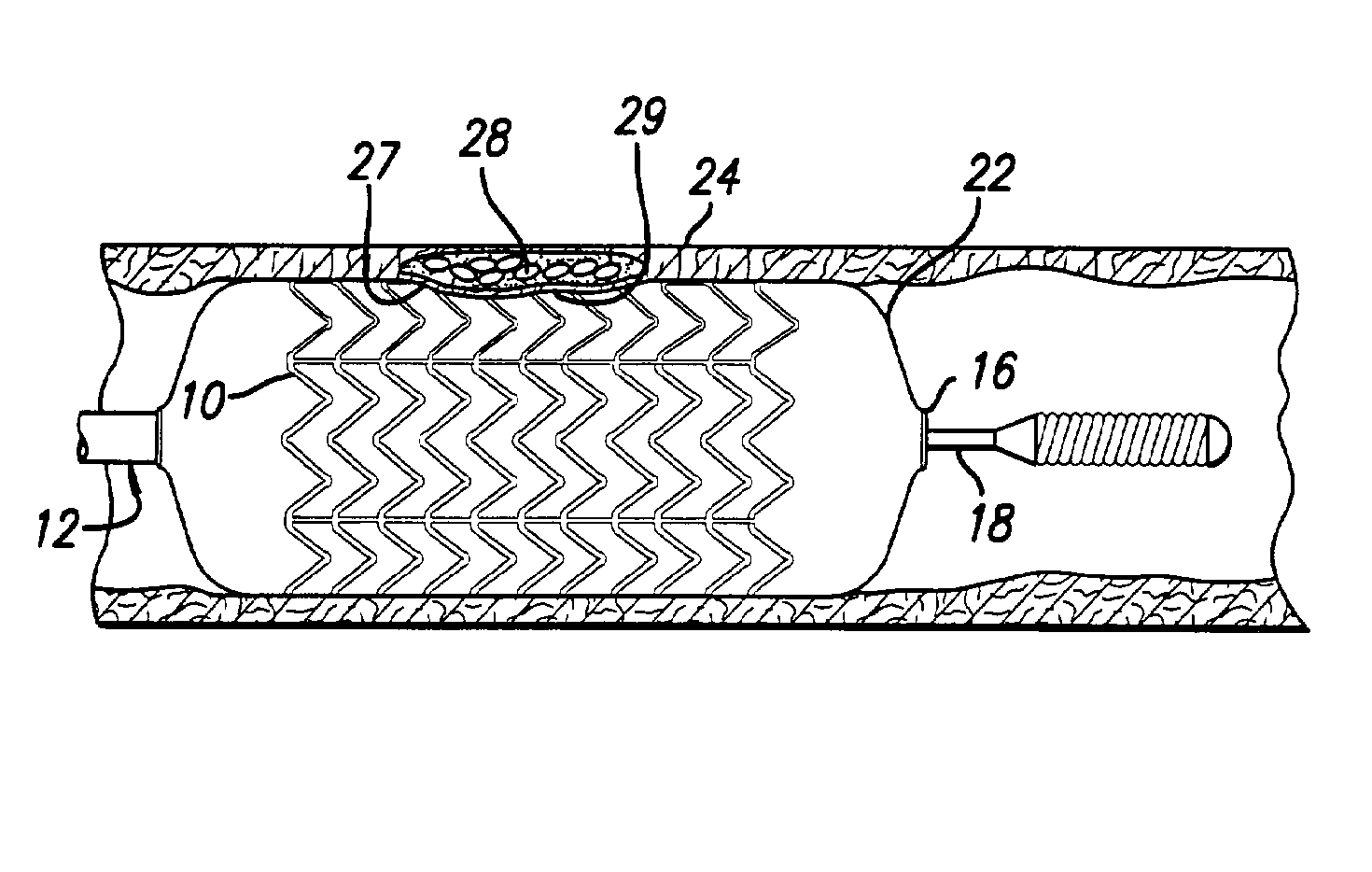
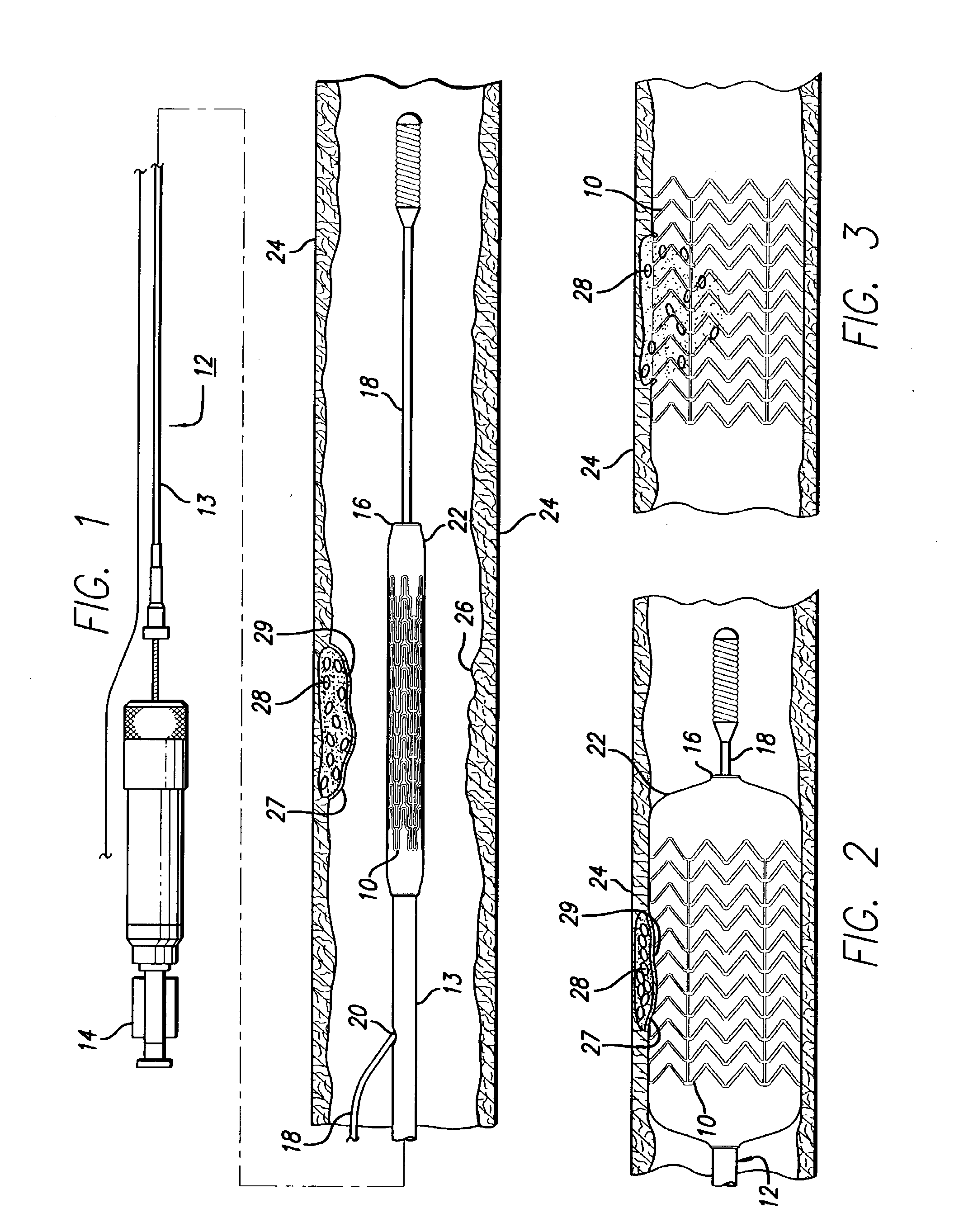
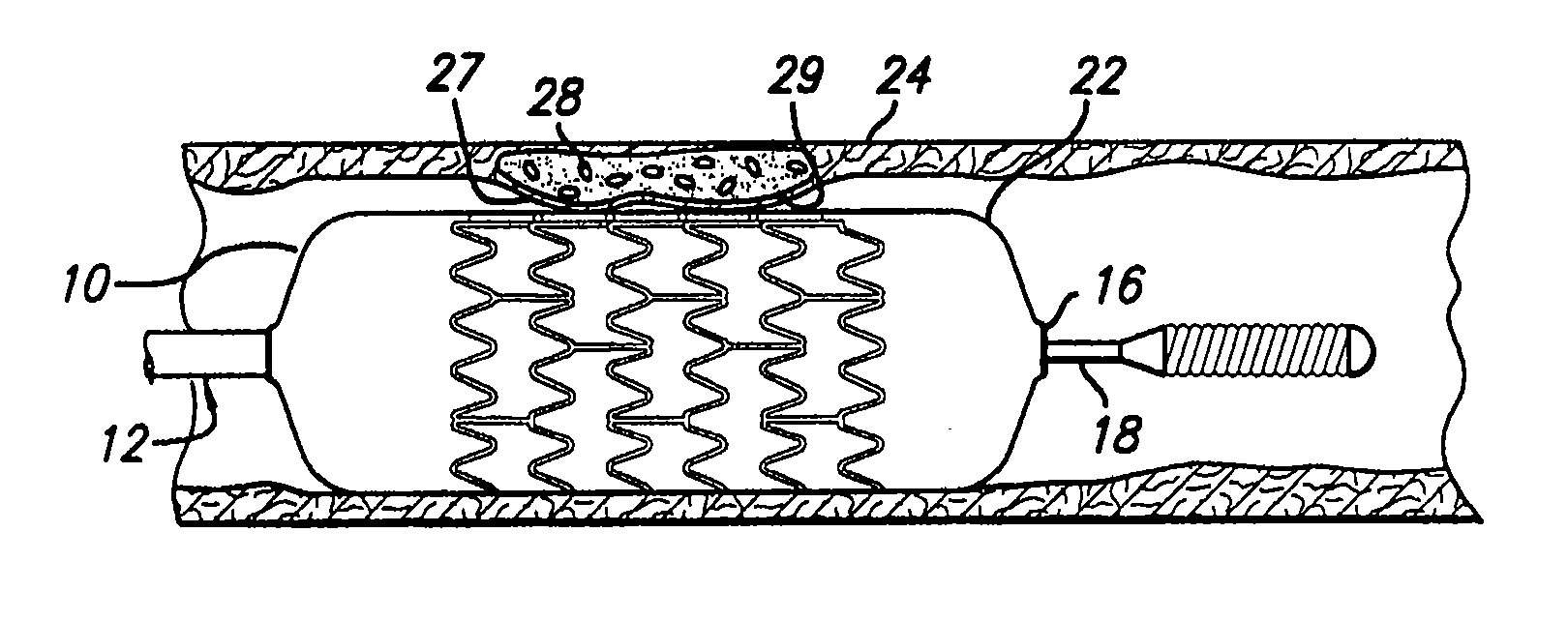
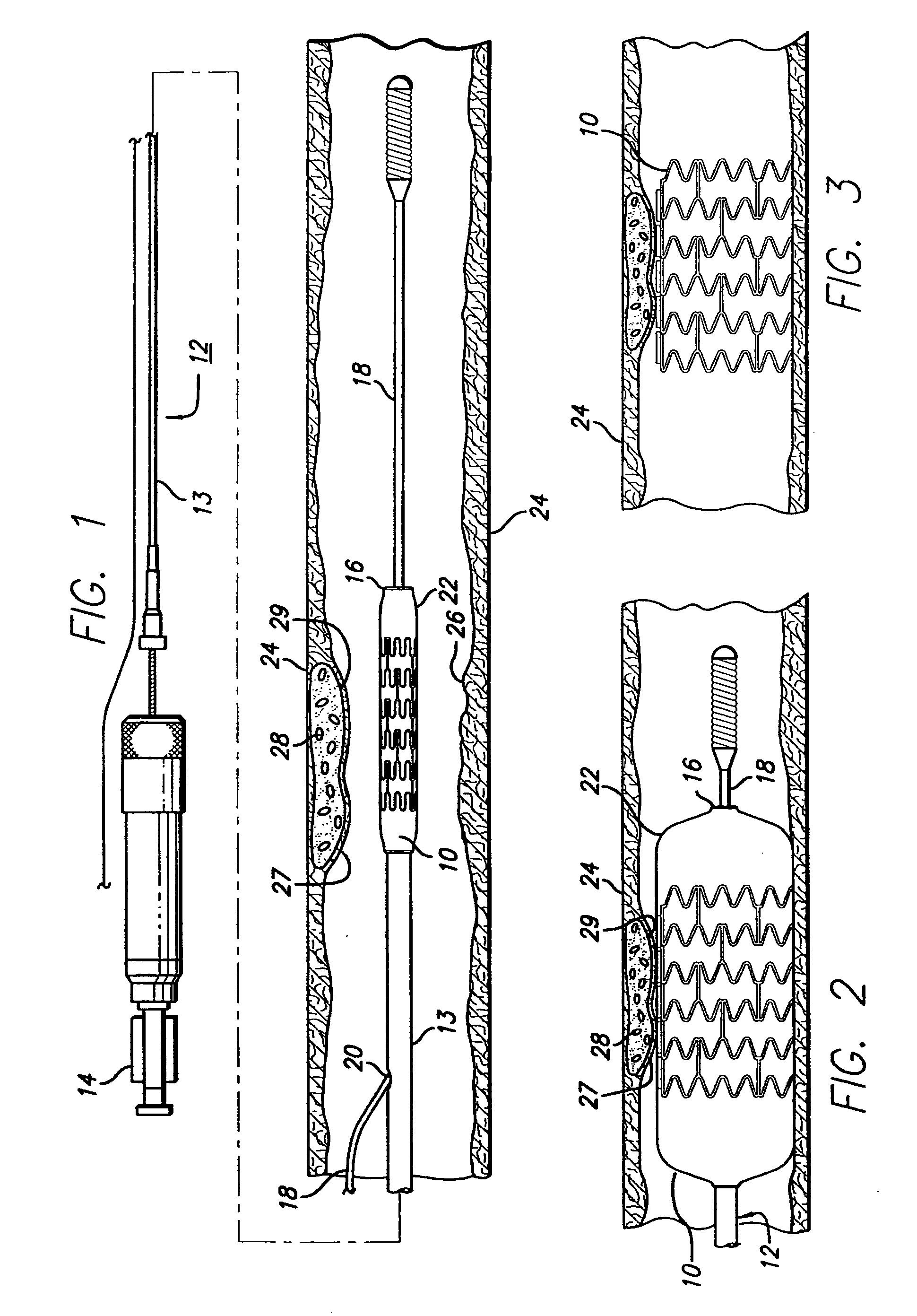
Stent with anchors to prevent vulnerable plaque rupture during deployment
InactiveUS7258697B1Reducing fibrous cap stressPrevent high expansion forceStentsBlood vesselsVulnerable plaqueFibrous cap
A stent for implantation in a body lumen for protecting from rupture a fibrous cap in order to treat vulnerable plaque. One embodiment of the stent achieves staged expansion through stronger and weaker circumferential regions, and includes optional anchors positioned at the circumferential transition between the stronger and weaker regions. During the first stage expansion, the weaker region expands moving the anchors laterally apart. The anchors straddle the fibrous cap and embed into the vessel wall. The second stage expansion of the stent exerts gentler stresses by the weaker region against the fibrous cap while the stronger region exerts greater stresses on the remainder of the vessel wall to open the vessel.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
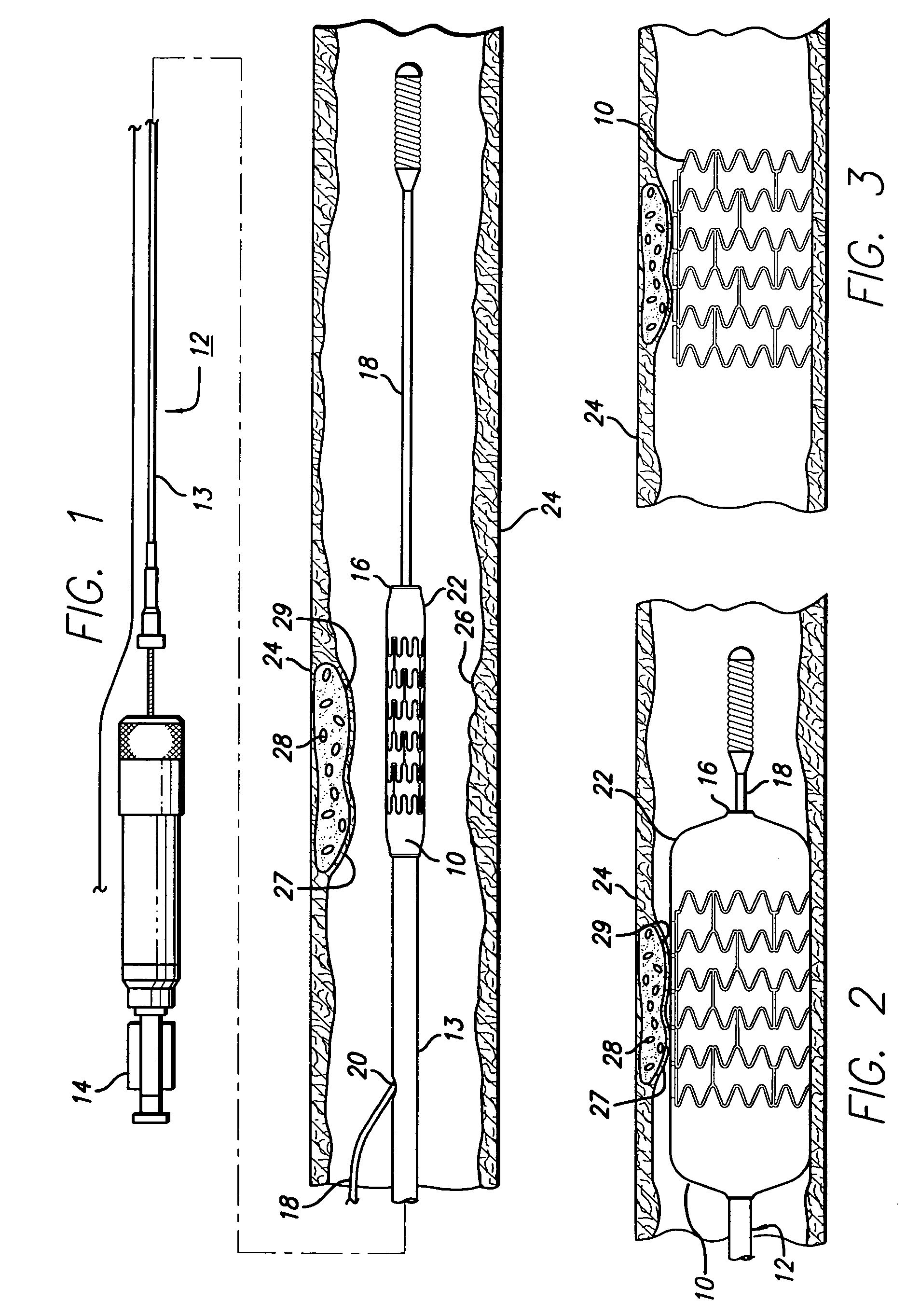
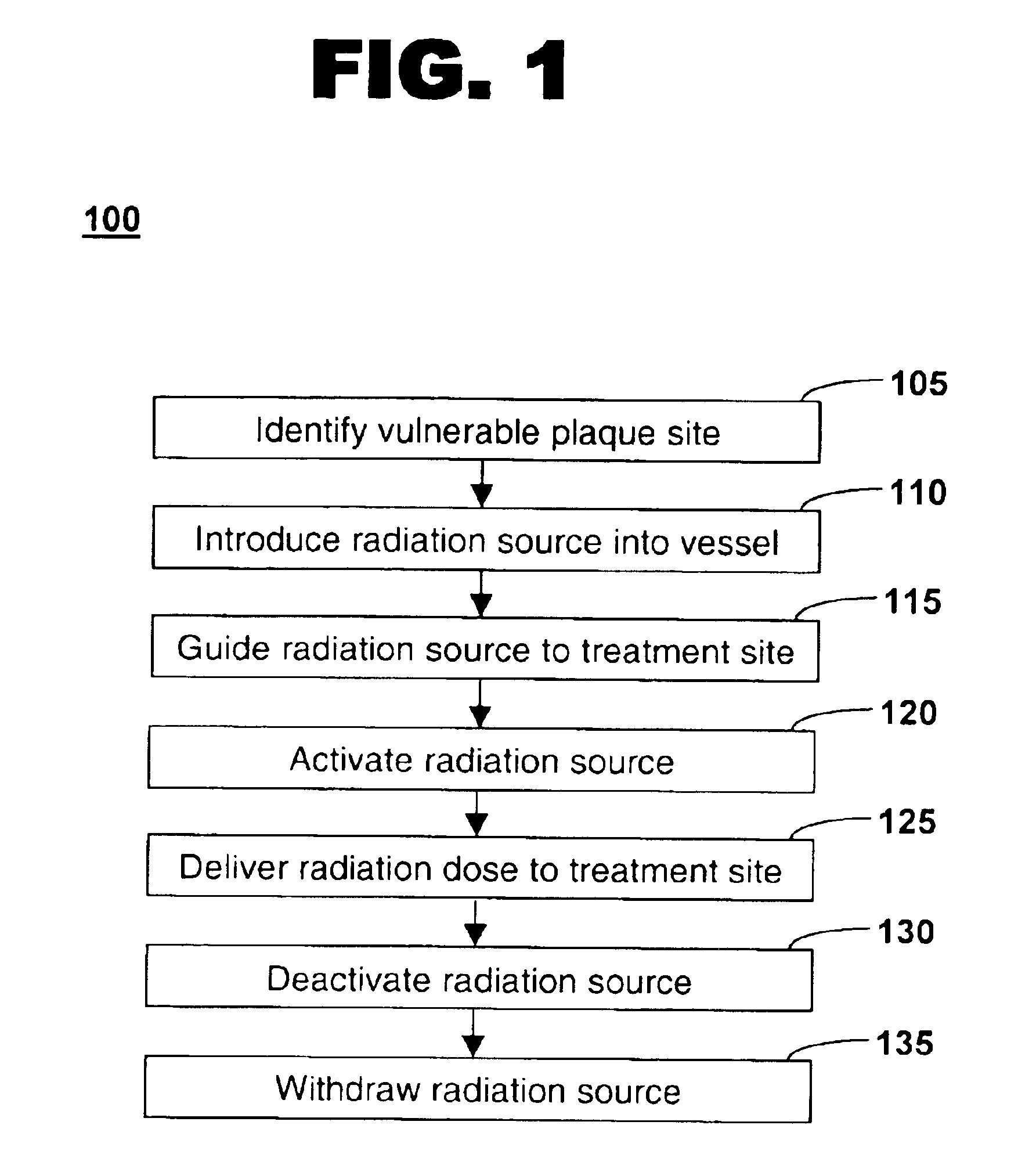
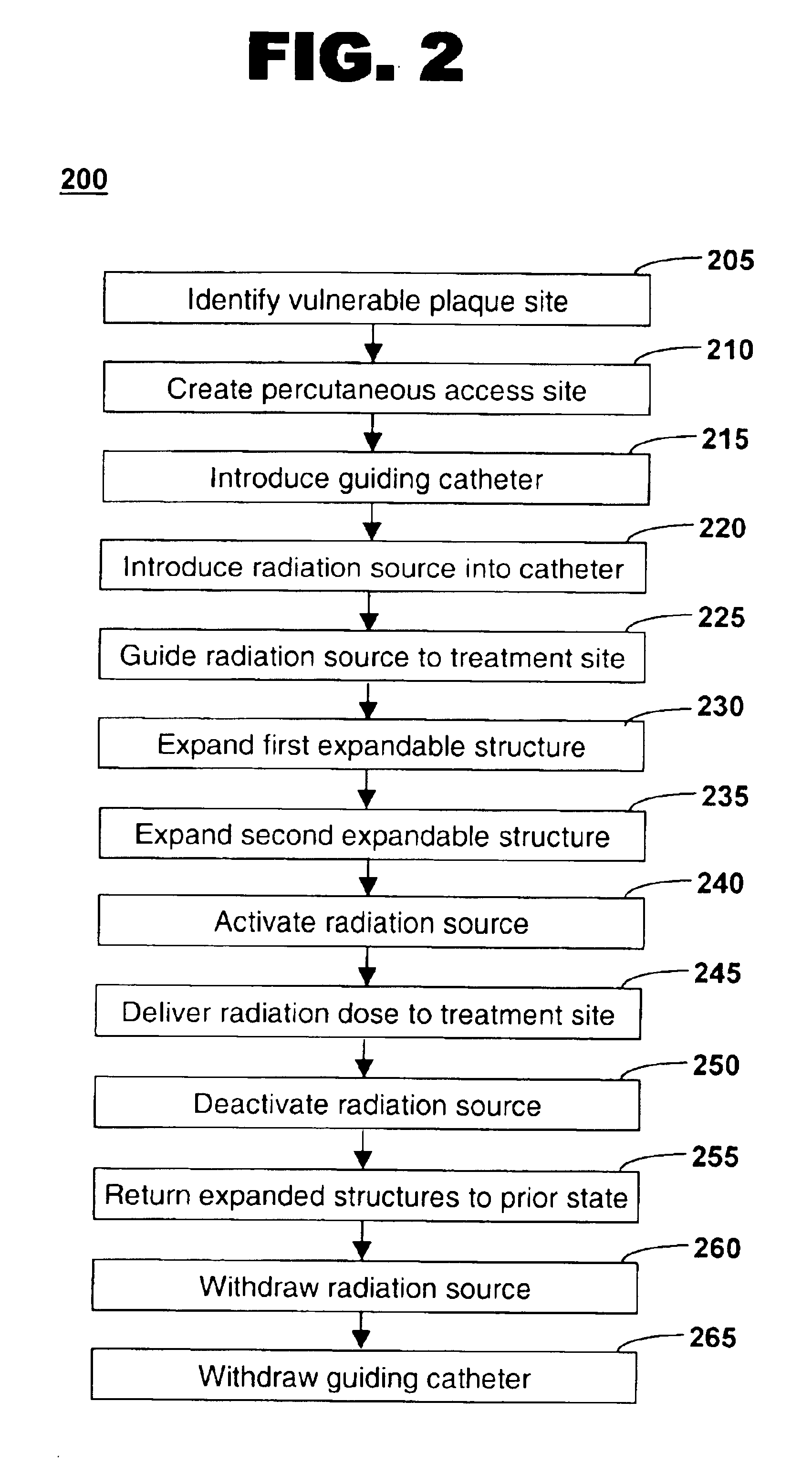
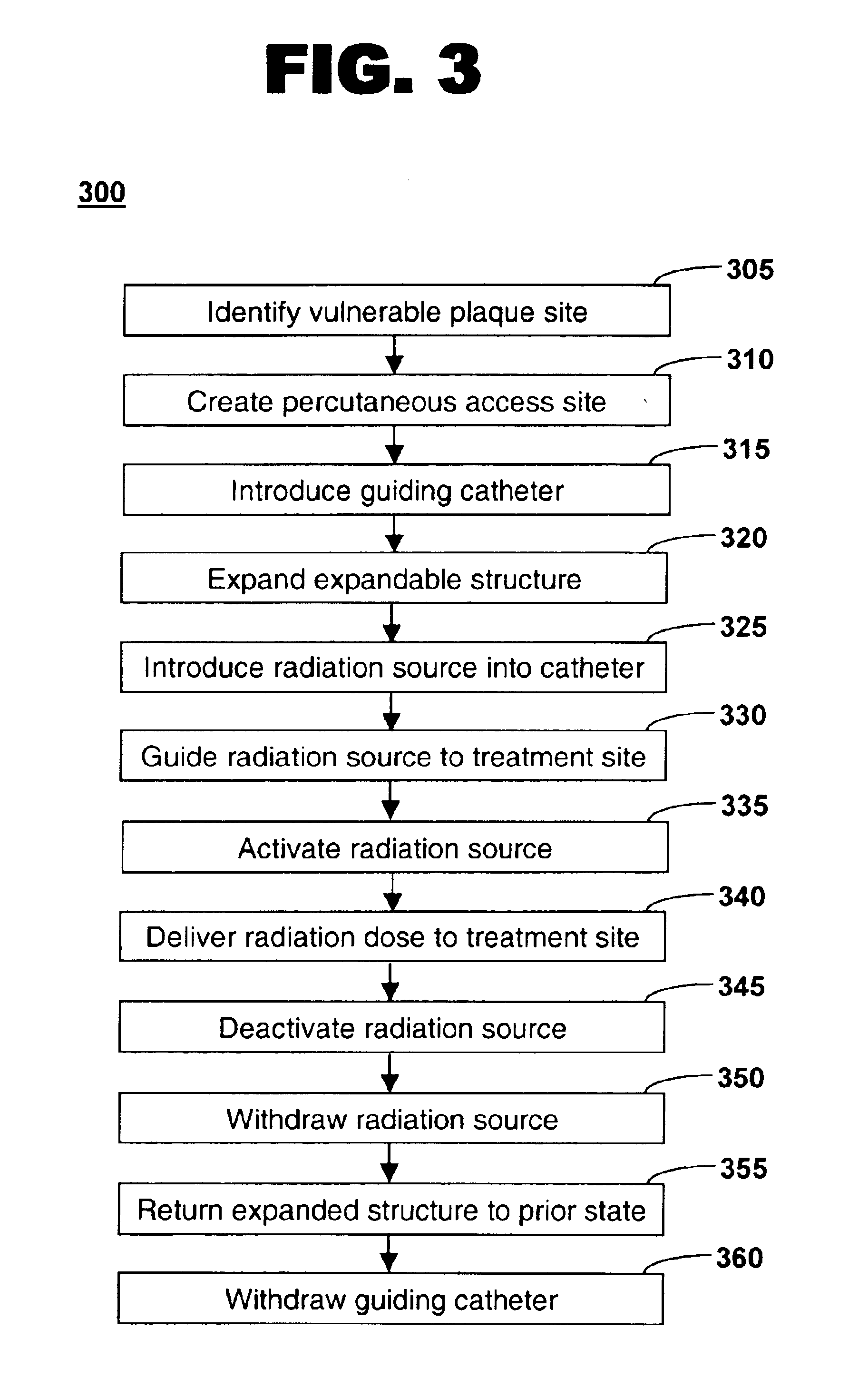
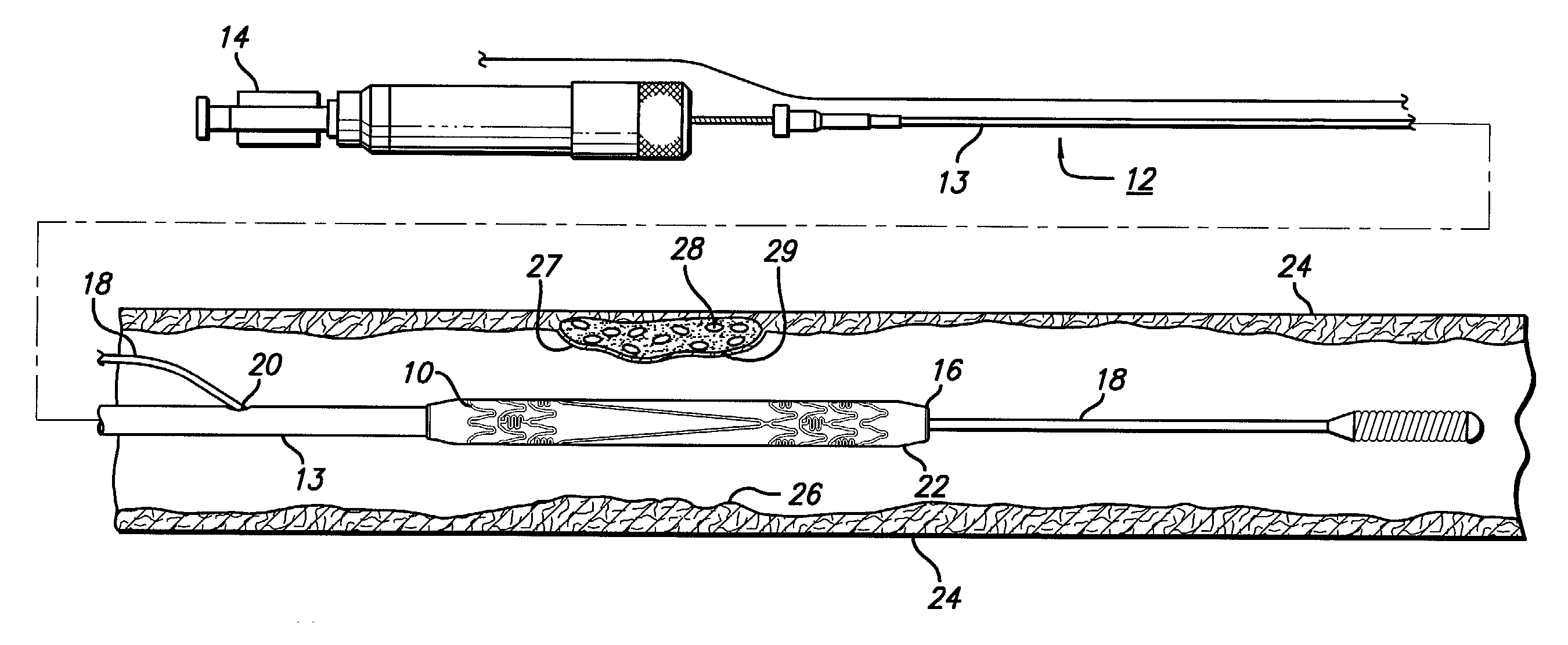
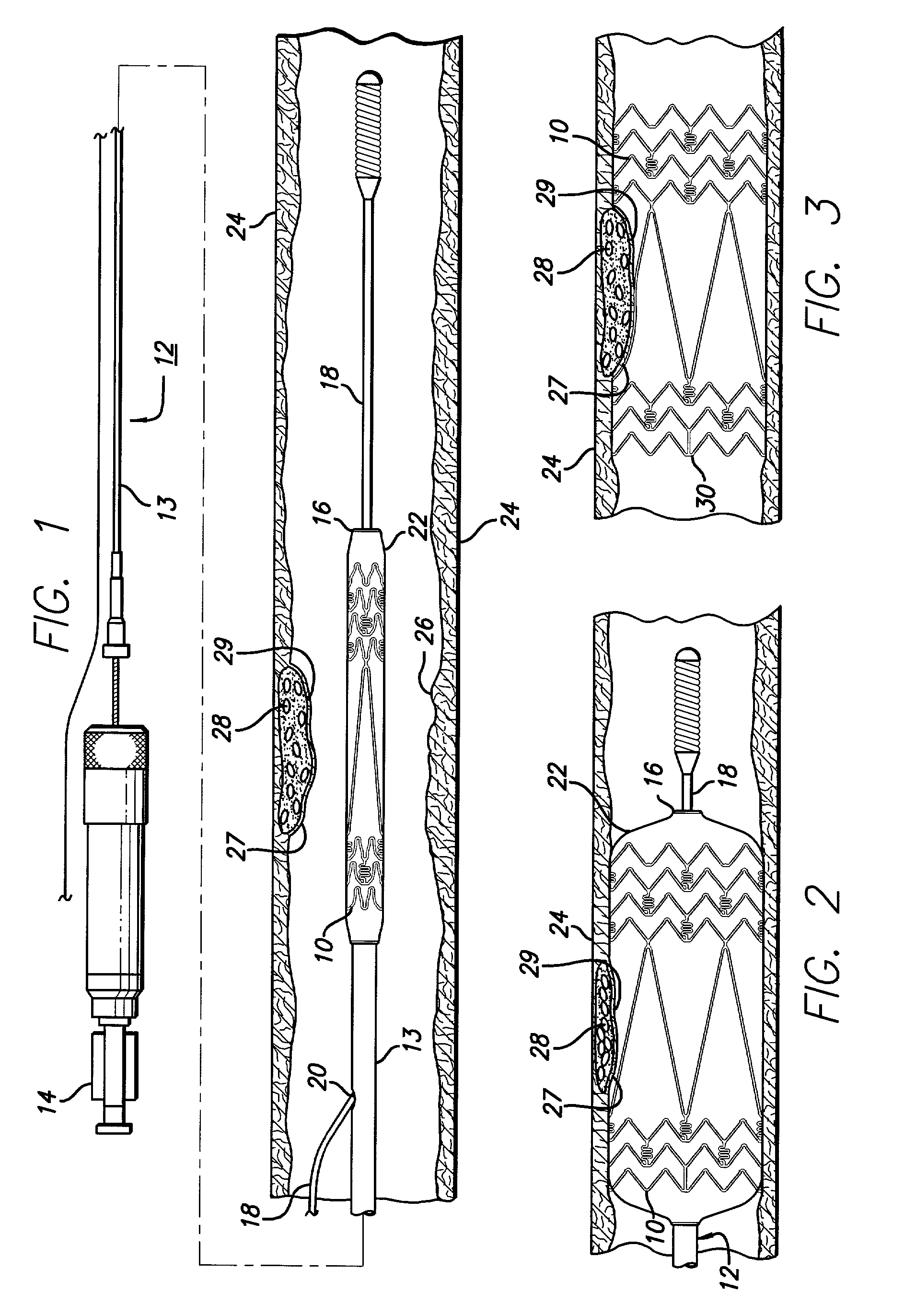
Method of treating vulnerable plaque using a catheter-based radiation system
The invention provides a method of treating vulnerable plaque at a site in a vessel. A vulnerable plaque site is identified for treatment. A radiation source is introduced into a vessel containing a vulnerable plaque site identified for treatment. The radiation source is guided to a position adjacent to the treatment site. A therapeutically effective dose of radiation is delivered to the vulnerable plaque site. As the radiation impinges upon the wall of the lumen, it promotes cell growth. Such growth can serve to strengthen the thin fibrous cap found atop a vulnerable plaque lesion. With the lesion thus stabilized, time is provided for the use of statin drugs or other agents to shrink or remove the lipid pool beneath the cap.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Intravascular stent and method of use
InactiveUS7163553B2Promote cell growthExcellent scaffoldStentsBlood vesselsCoronary arteriesVulnerable plaque
An expandable stent is implanted in a body lumen, such as a coronary artery, peripheral artery, or other body lumen for treating an area of vulnerable plaque. The invention provides for a an intravascular stent having a plurality of cylindrical rings connected by undulating links. The stent has a high degree of flexibility in the longitudinal direction, yet has adequate vessel wall coverage and radial strength sufficient to hold open an artery or other body lumen. A central section is positioned between distal and proximal sections and is aligned with the area of vulnerable plaque to enhance growth of endothelial cells over the fibrous cap of the vulnerable plaque to reinforce the area and reduce the likelihood of rupture.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Intravascular stent and method of use
ActiveUS7331987B1High degreePromote cell growthStentsBlood vesselsCoronary arteriesVulnerable plaque
An expandable stent is implanted in a body lumen, such as a coronary artery, peripheral artery, or other body lumen for treating an area of vulnerable plaque. The invention provides for an intravascular stent having a plurality of cylindrical rings connected by straight links. Alternatively, the cylindrical rings of the distal section and the cylindrical rings of the proximal section are connected directly to adjacent cylindrical rings. The stent has adequate vessel wall coverage and radial strength sufficient to hold open an artery or other body lumen. A central section is positioned between distal and proximal sections and is aligned with the area of vulnerable plaque to enhance growth of cells over the fibrous cap of the vulnerable plaque to reinforce the area and reduce the likelihood of rupture.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
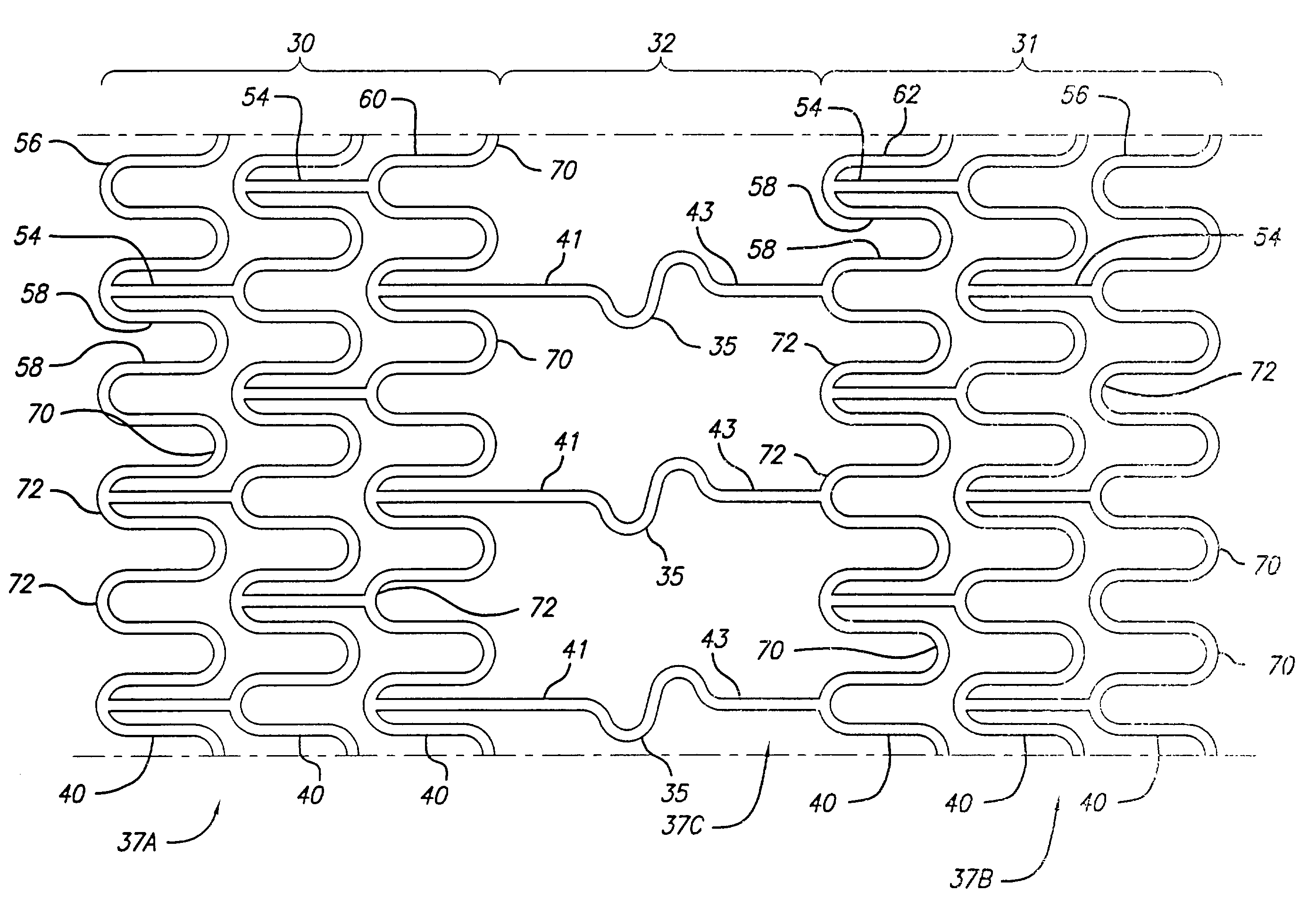
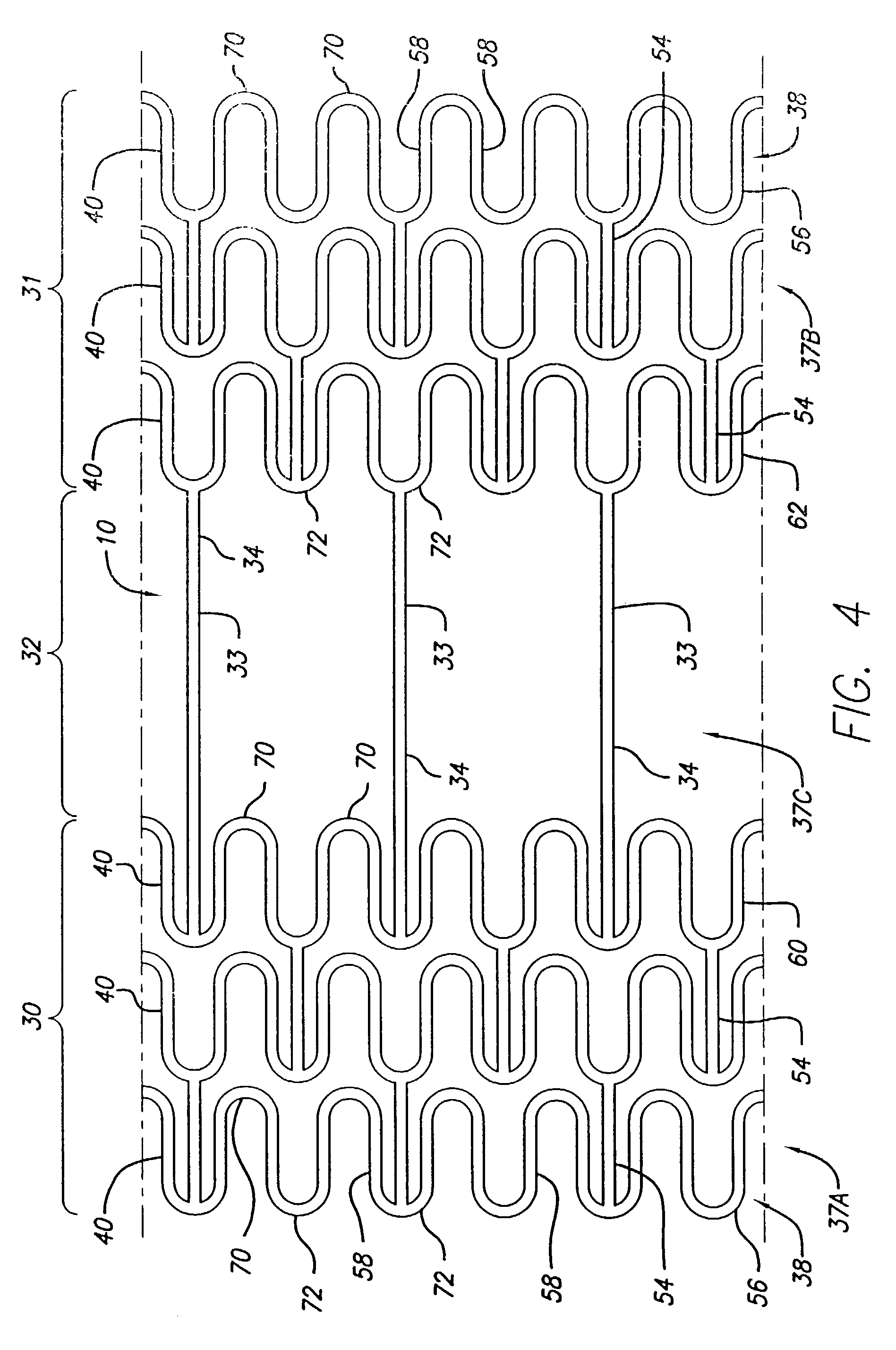
Stent for treating vulnerable plaque
InactiveUS7273492B2Reducing cap stressReduce stressStentsBlood vesselsCoronary arteriesVulnerable plaque
An intravascular stent assembly for implantation in a body lumen, such as a coronary artery, is designed to treat a lesion with vulnerable plaque by reducing the fibrous cap stresses. The stent includes distal, proximal, and center sections where the center section is configured to treat the vulnerable plaque. The stent consists of radially expandable cylindrical rings generally aligned on a common longitudinal stent axis and either directly connected or interconnected by one or more interconnecting links placed so that the stent is flexible in the longitudinal direction while providing high degrees of radial strength and vessel scaffolding.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Inclined stent pattern for vulnerable plaque
InactiveUS7018403B1Reducing outward radial stressMinimize traumaStentsBlood vesselsVulnerable plaqueRadial stress
A stent for implantation in a body lumen for protecting from rupture a fibrous cap in order to treat vulnerable plaque. One embodiment of the stent includes inclined planar rings joined by interconnecting links. The planar rings are inclined relative to a plane perpendicular to a longitudinal axis extending the length of the stent. The inclined planar rings provide vessel support yet require lower balloon pressures to deploy and exert lower radial stresses so that when appositioned with vulnerable plaque are less likely to rupture the fibrous cap.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Intravascular stent and method of use
InactiveUS7273495B2Promote cell growthExcellent scaffoldStentsBlood vesselsCoronary arteriesVulnerable plaque
An expandable stent is implanted in a body lumen, such as a coronary artery, peripheral artery, or other body lumen for treating an area of vulnerable plaque. The invention provides for a an intravascular stent having a plurality of cylindrical rings connected by undulating links. The stent has a high degree of flexibility in the longitudinal direction, yet has adequate vessel wall coverage and radial strength sufficient to hold open an artery or other body lumen. A central section is positioned between distal and proximal sections and is aligned with the area of vulnerable plaque to enhance growth of endothelial cells over the fibrous cap of the vulnerable plaque to reinforce the area and reduce the likelihood of rupture.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
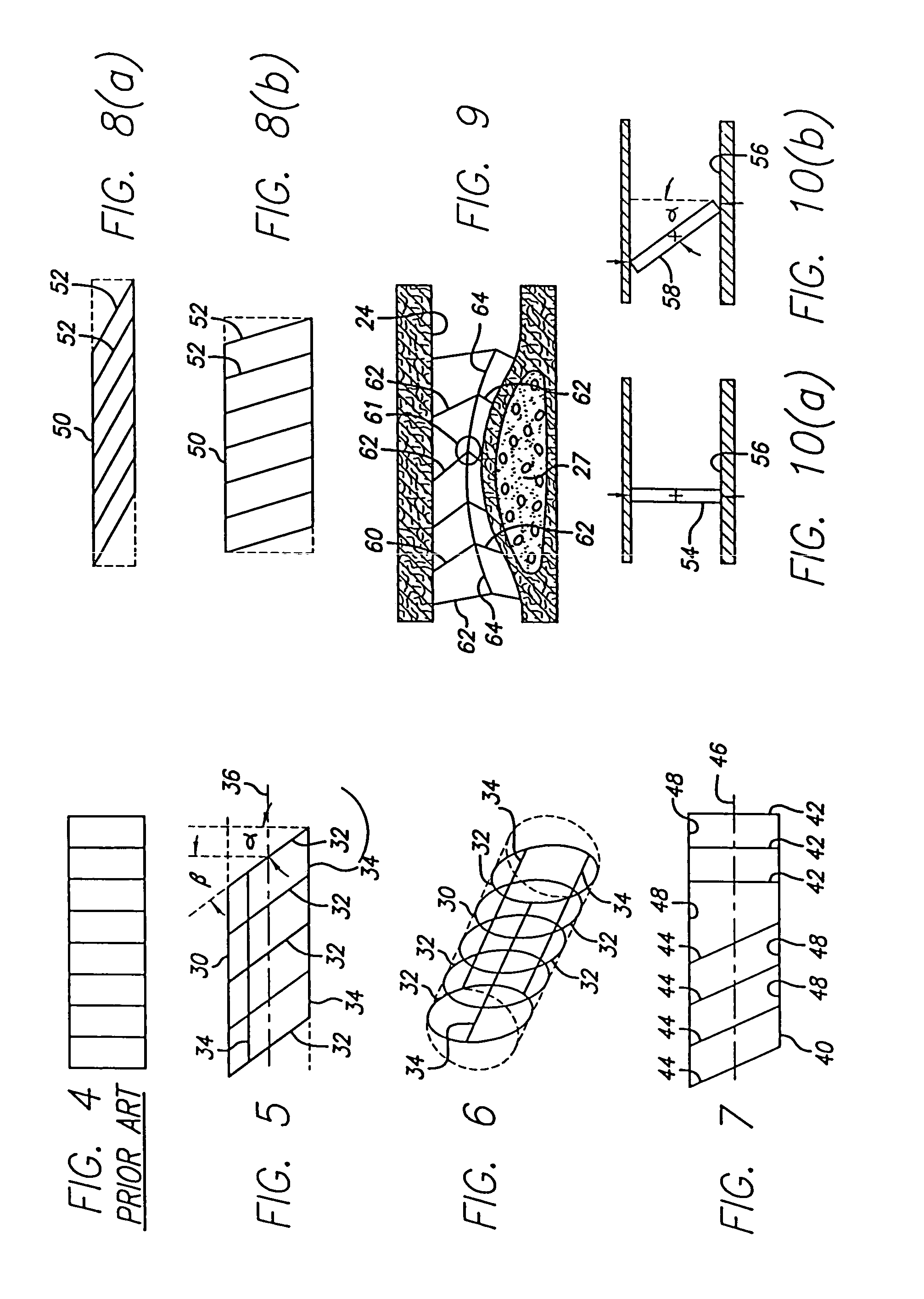
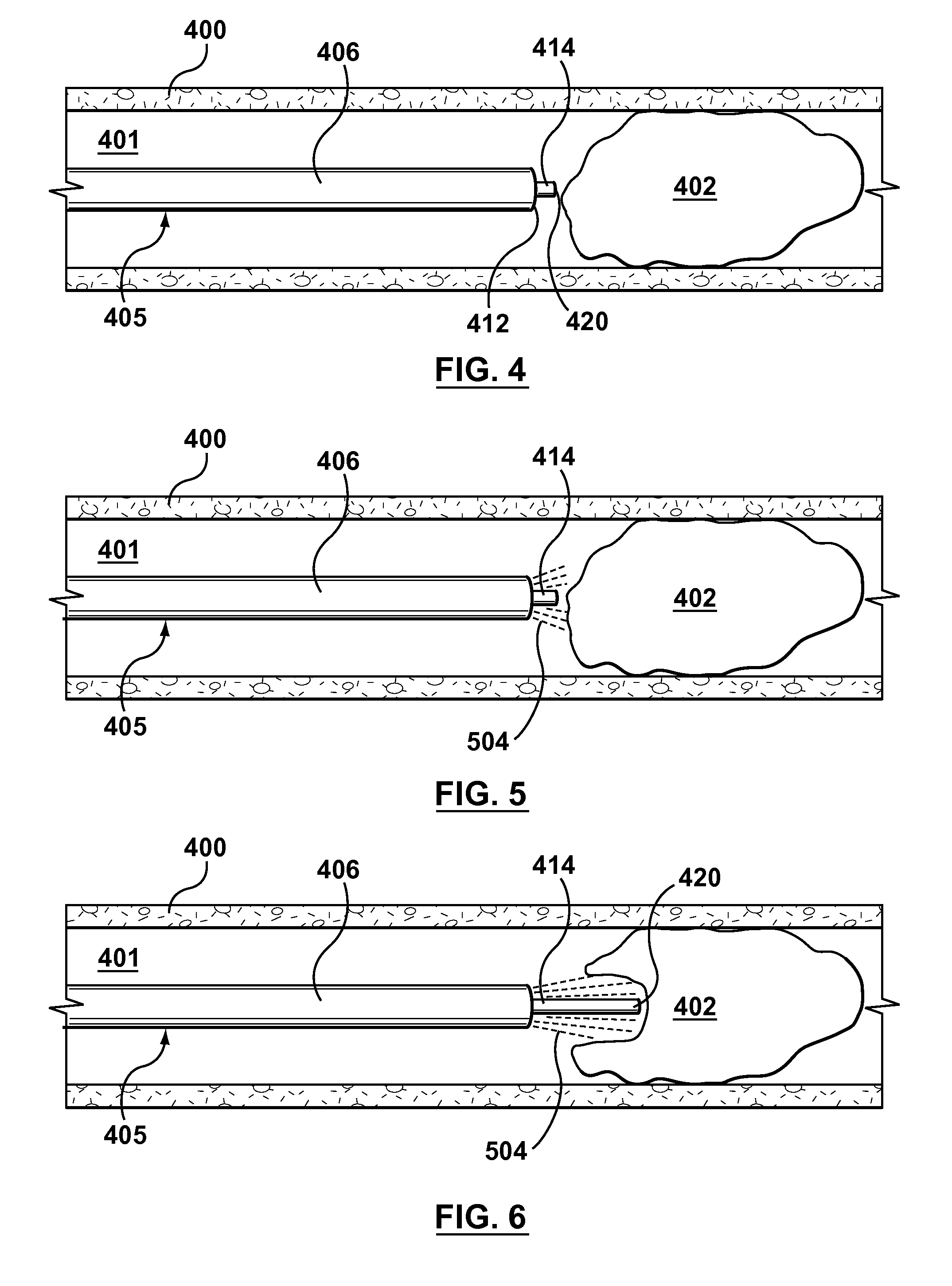
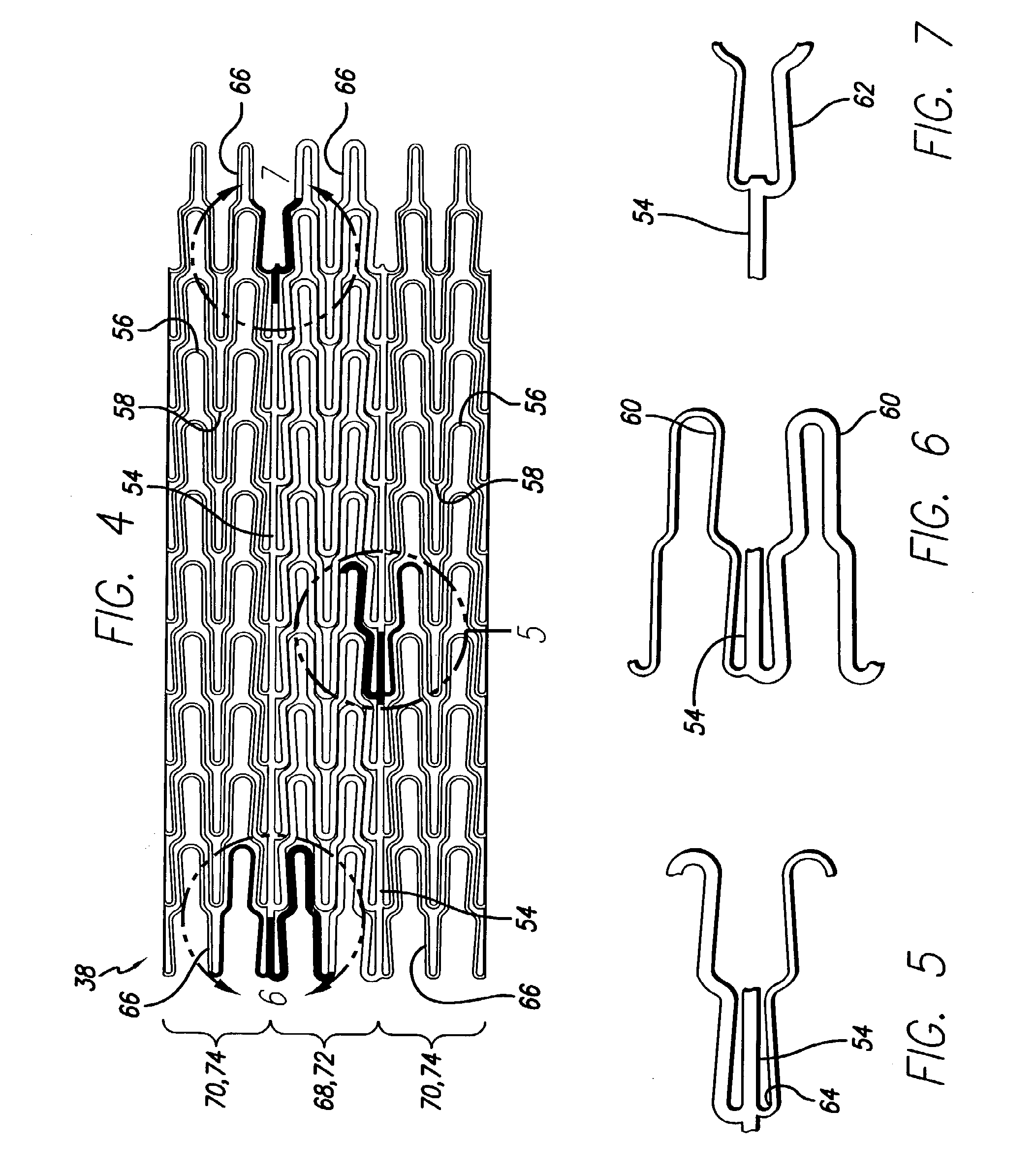
Intravascular stent for treating vulnerable plaque and method of use
InactiveUS7731744B1Increase flexibilityIncrease volumeStentsBlood vesselsStress concentrationCoronary arteries
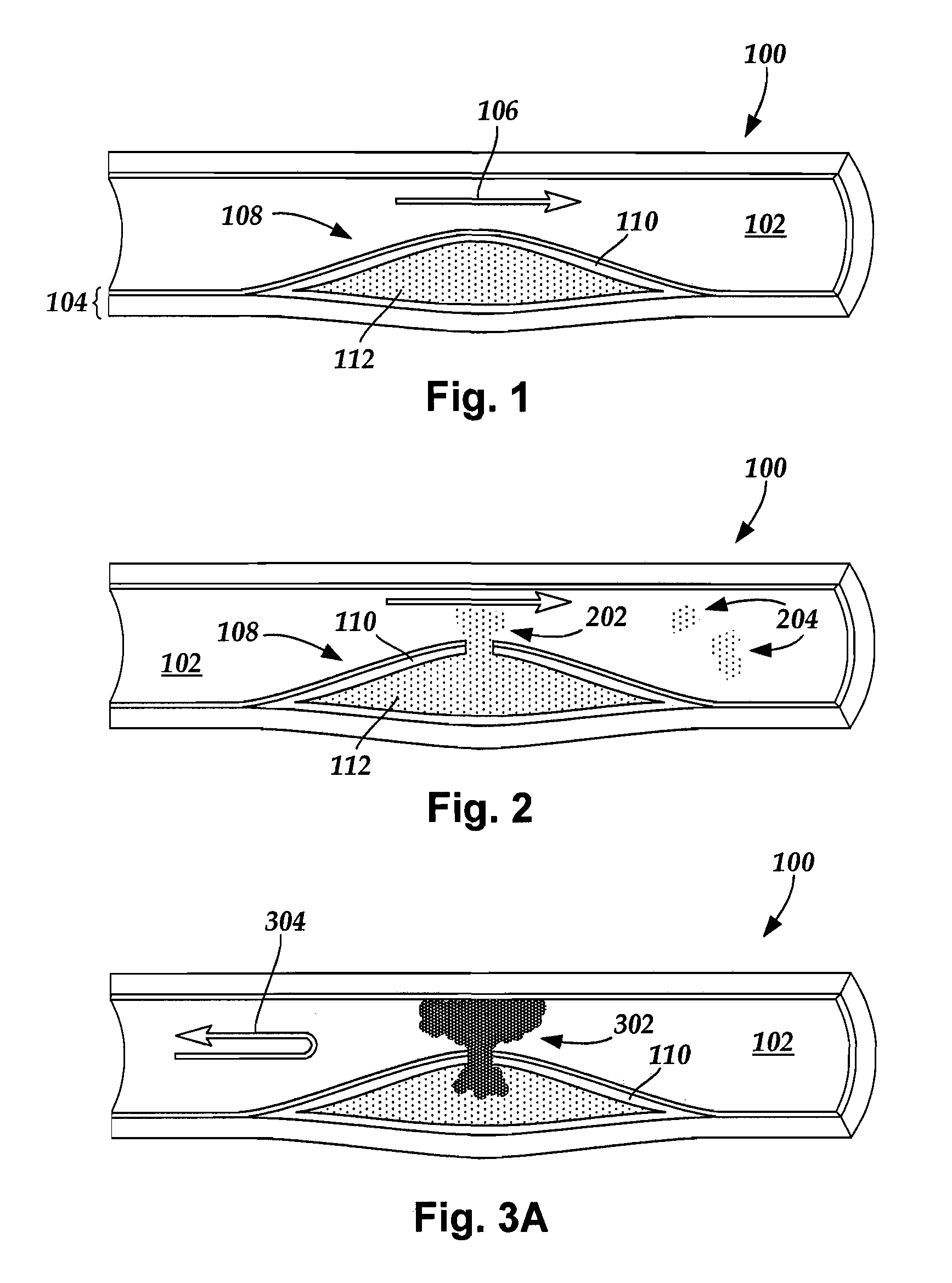
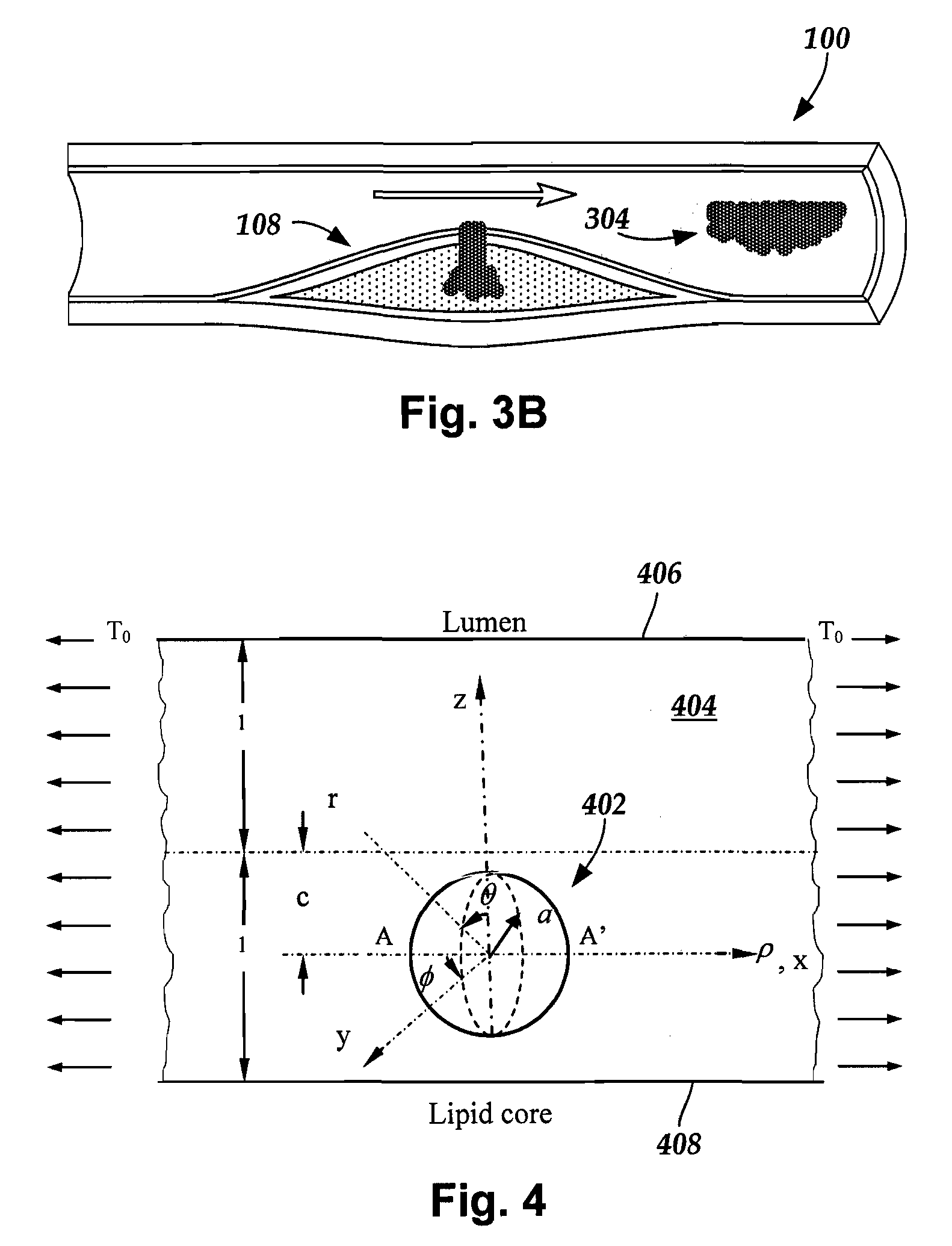
An expandable stent is implanted in a body lumen, such as a coronary artery, peripheral artery, or other body lumen for rupturing a fibrous cap to controllably release vulnerable plaque. The invention provides for a an intravascular stent having a plurality of cylindrical rings connected by links. The stent includes struts and links of varying strengths about the circumference of the stent. The weaker struts and links require less force to open and, hence, may apply more stress to rupture the fibrous cap while the stronger struts and links protect the healthy portions of the body lumen. In another embodiment, the stent may include stress concentrators positioned on outer surfaces of the links. The stress concentrators are aligned with the fibrous cap prior to stent expansion so that upon stent expansion, the stress concentrators induce stress to rupture the fibrous cap, thereby releasing the vulnerable plaque.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Intravascular stent and method of use
InactiveUS20070100433A1Promote cell growthExcellent scaffoldStentsBlood vesselsCoronary arteriesVulnerable plaque
An expandable stent is implanted in a body lumen, such as a coronary artery, peripheral artery, or other body lumen for treating an area of vulnerable plaque. The invention provides for a an intravascular stent having a plurality of cylindrical rings connected by undulating links. The stent has a high degree of flexibility in the longitudinal direction, yet has adequate vessel wall coverage and radial strength sufficient to hold open an artery or other body lumen. A central section is positioned between distal and proximal sections and is aligned with the area of vulnerable plaque to enhance growth of endothelial cells over the fibrous cap of the vulnerable plaque to reinforce the area and reduce the likelihood of rupture.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
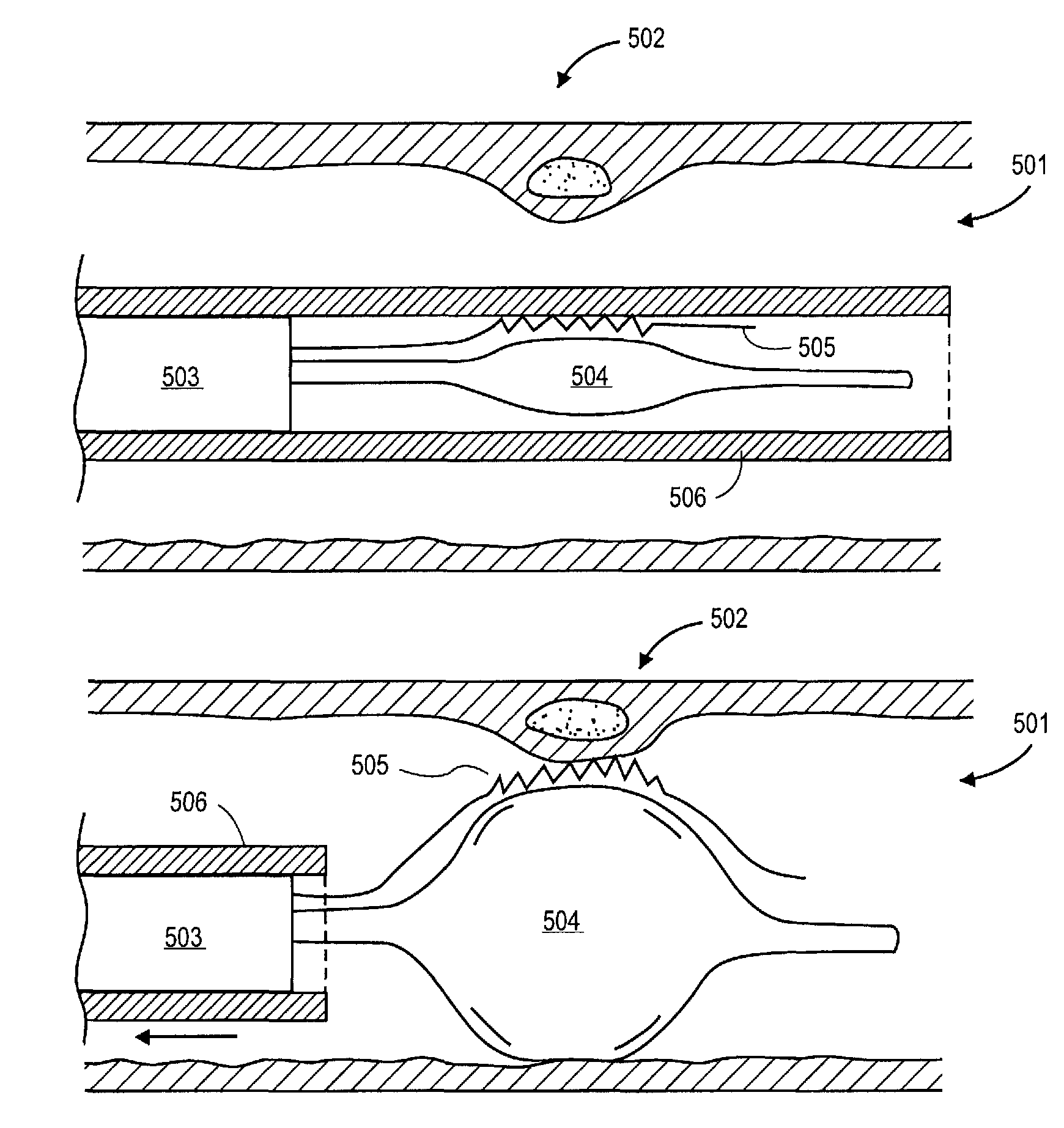
Method and apparatus for rupturing a vulnerable plaque
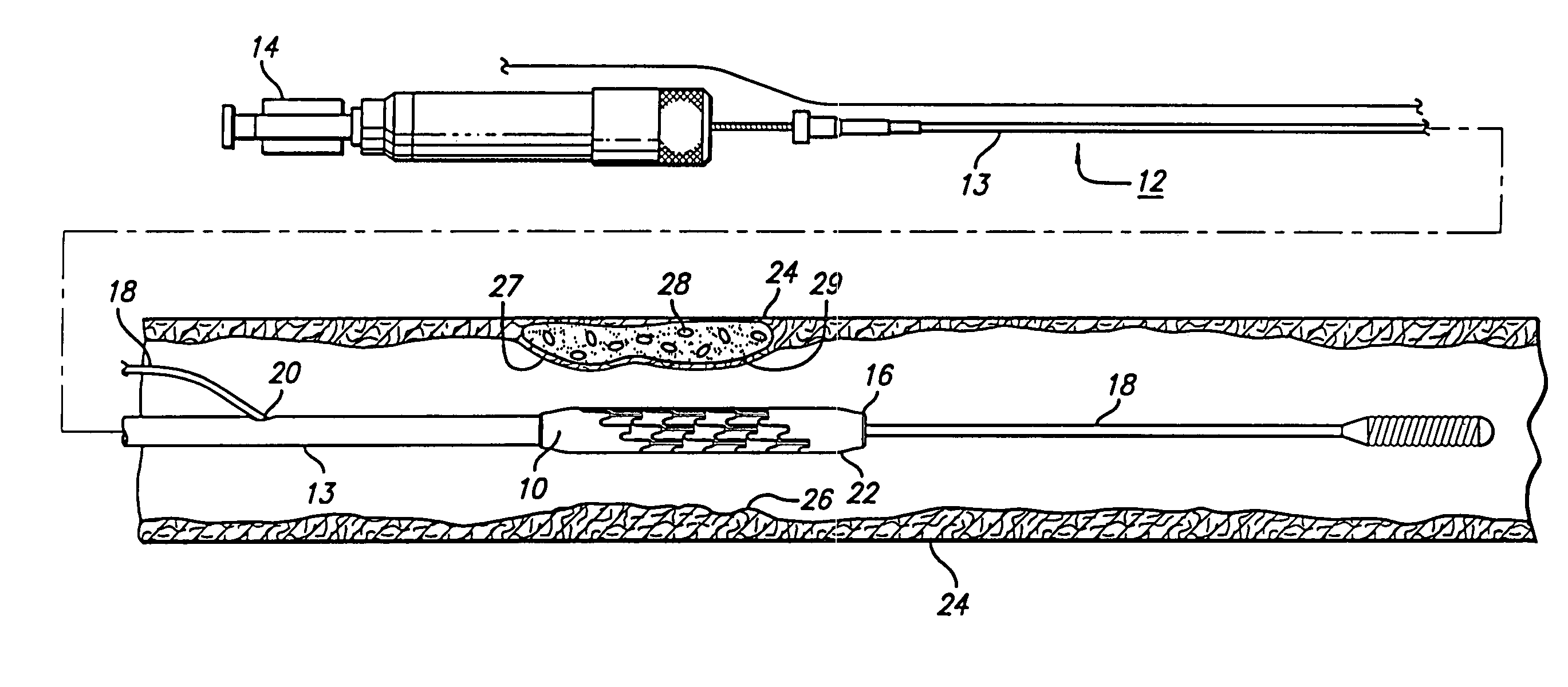
Methods and apparatuses for treating a vulnerable plaque are described herein. In one aspect of the invention, the exemplary apparatus includes a medical device to treat a vulnerable plaque within a body lumen, where the medical device is adapted to position a rupturing device to rupture a fibrous cap of a vulnerable plaque. In one particular embodiment, the medical device includes a rupturing wire having a predetermined pattern to enable the rupturing device to rupture the fibrous cap of the vulnerable plaque. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Stent assembly for the treatment of vulnerable plaque
InactiveUS7572286B1Reducing cap stressReduce stressStentsBlood vesselsCoronary arteriesVulnerable plaque
An intravascular stent assembly for implantation in a body lumen, such as a coronary artery, is designed to treat a lesion with vulnerable plaque by reducing the fibrous cap stresses. A polymeric sleeve having first and second ends interconnects a first metallic stent and a second metallic stent. The first end is bonded to a distal end region of the first stent and the second end to a proximal end region of the second stent. The polymeric sleeve can be loaded with a therapeutic drug or agent to further control local thrombosis and / or induce healing if the plaque fibrous cap ruptures during or after implantation. Methods of making an intravascular stent assembly for the treatment of vulnerable plaque are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
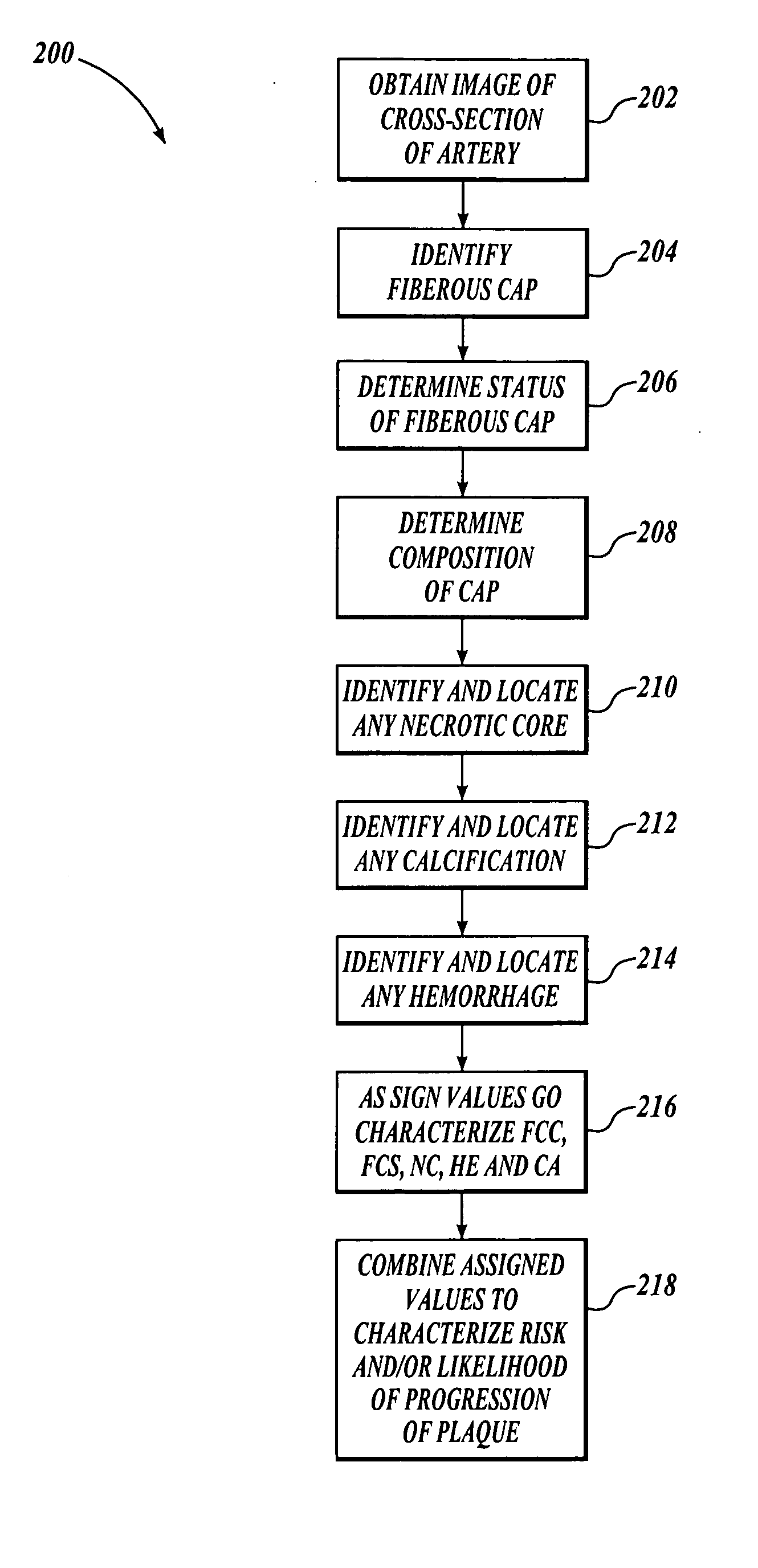
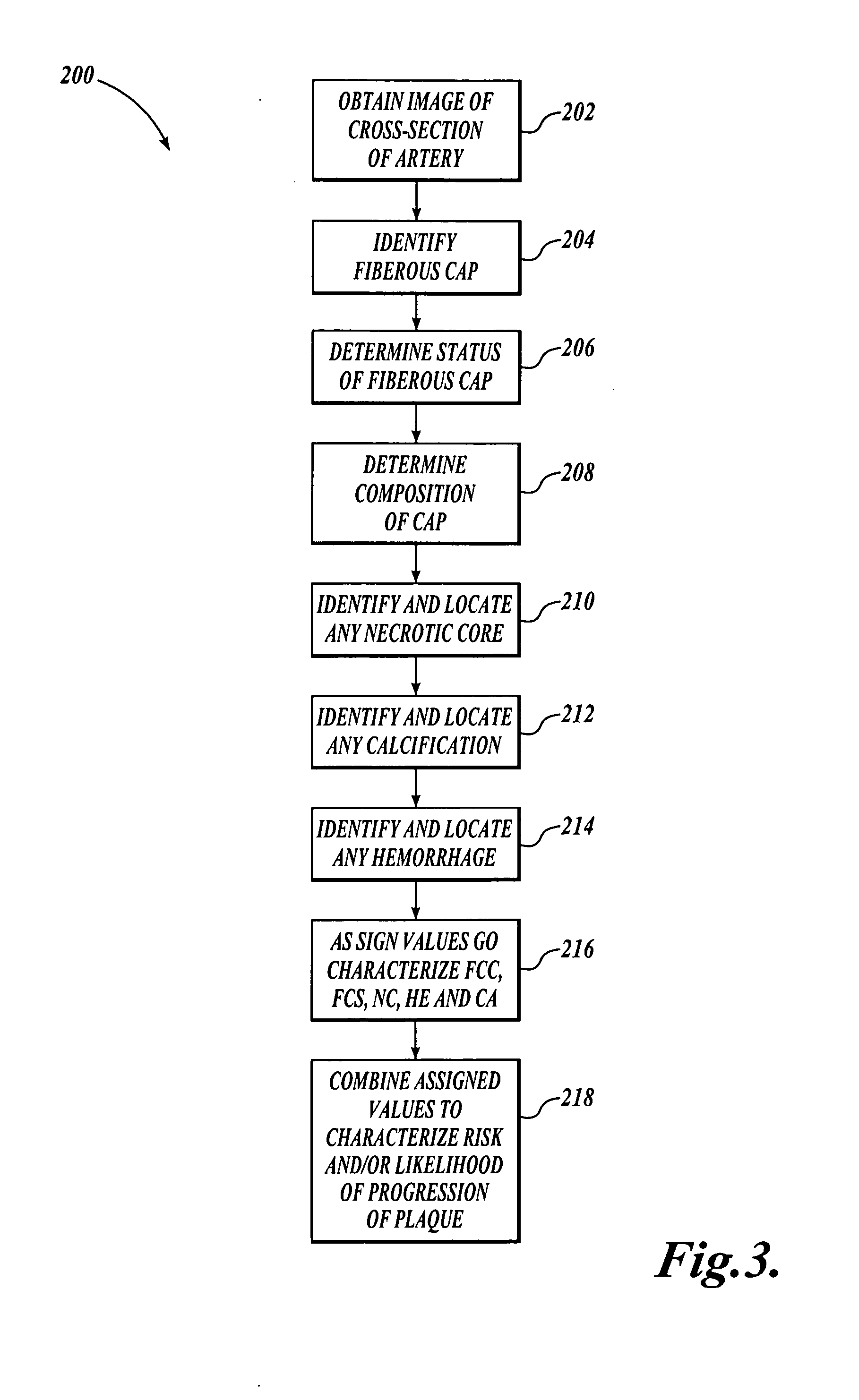
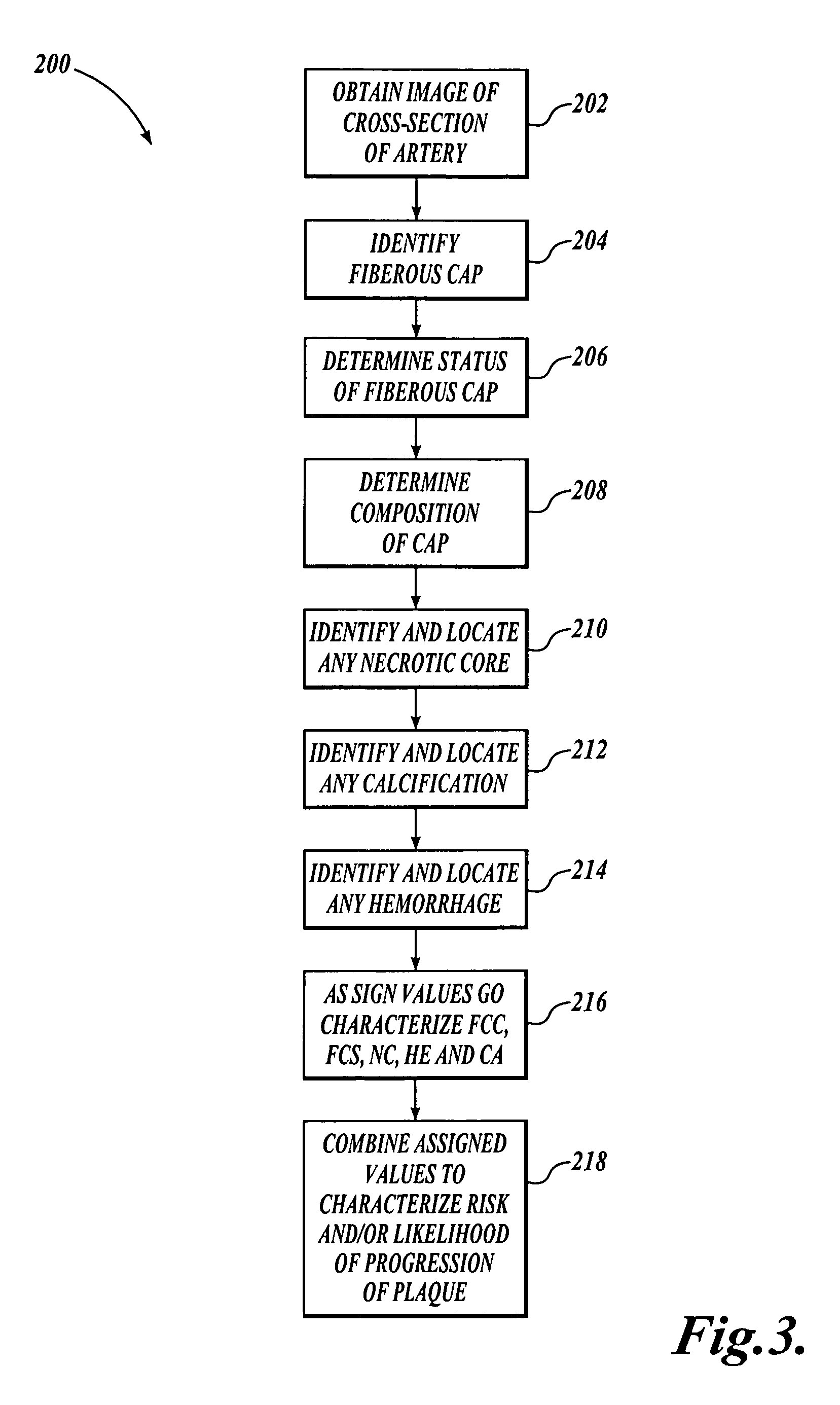
Method and system for atherosclerosis risk scoring
InactiveUS20070003116A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementNecrotic coreImaging modalities
A method for characterizing the risk associated with atherosclerosis is disclosed. The method uses one or more images of cross-sections of the artery or other vessel of interest to identify and locate components of the atherosclerotic deposit, including any hemorrhage, necrotic core, and calcification, and to determine the status and composition of the fibrous cap. In one embodiment, high resolution MRI images are utilized, although other imaging modalities may alternatively be used. A simple scoring system is applied that accounts for the presence of these components and more heavily weights the presence of these components in the juxtaluminal portion of the deposit. The status of the fibrous cap (intact or ruptured) and the composition of the fibrous cap (collagen or mixed tissue) are also incorporated into a final atherosclerosis risk score.
Owner:CVPATH INST +1
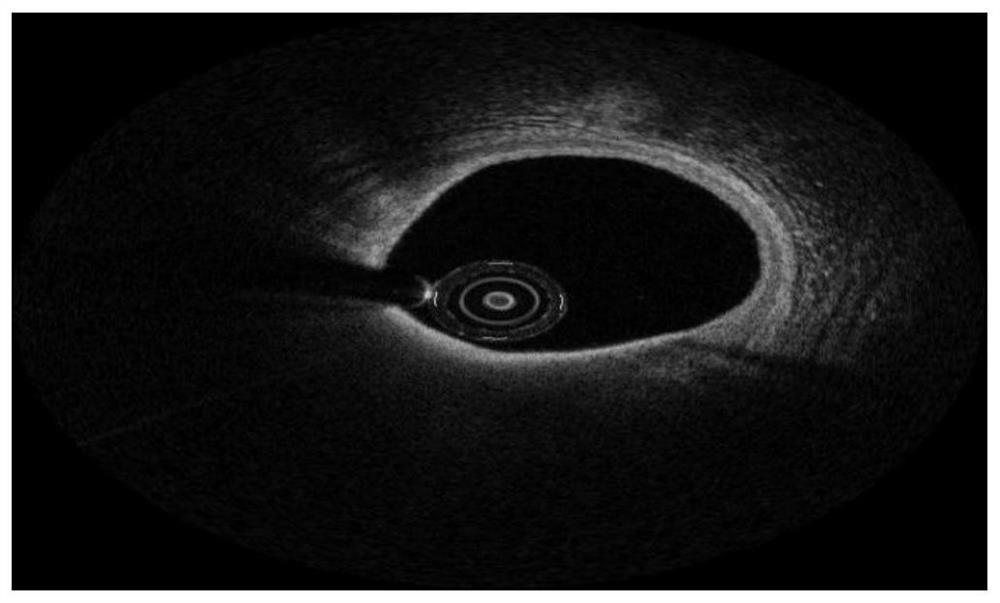
Plaque stability determination method and system based on optical coherence tomography
ActiveCN106974622AComprehensive and efficient measurement and analysisImprove accuracyCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringCoronary arteriesImaging processing
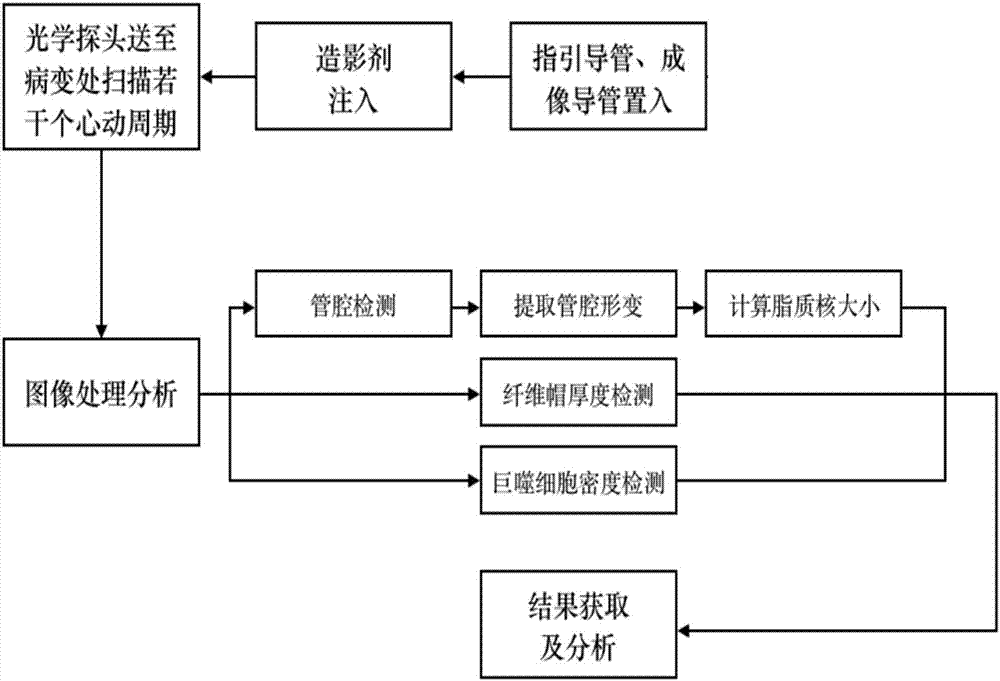
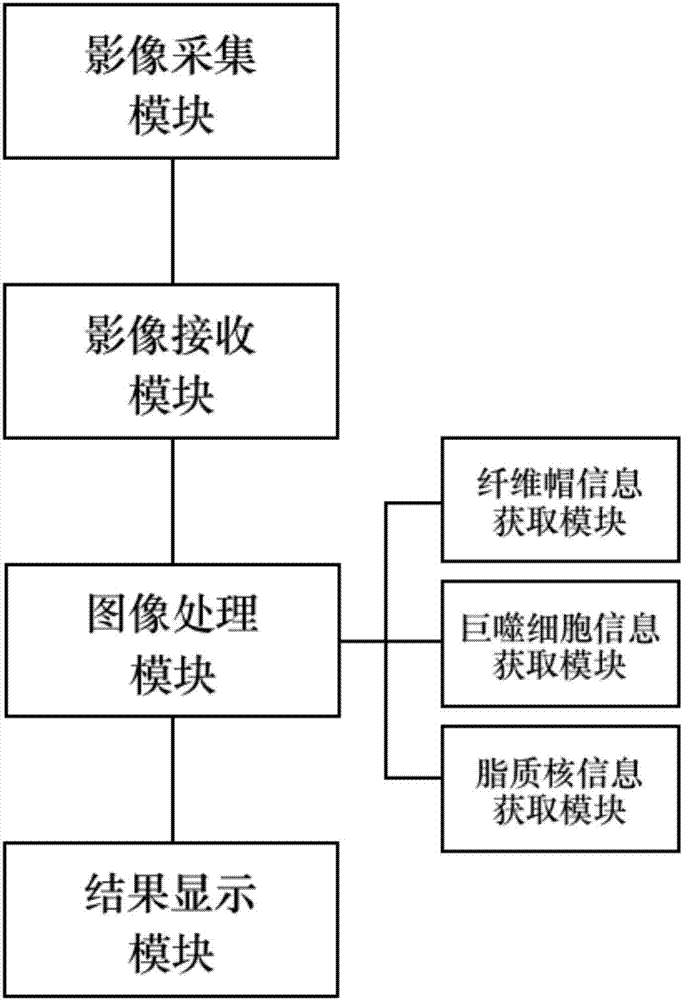
The invention provides a plaque stability determination method and system based on the optical coherence tomography. The system comprises an image collection module, an image reception module, an image-processing module and a result display module, wherein the image collection module is used for acquiring an coronary-artery image and producing an image signal; the image reception module is used for receiving the image signal produced by the image collection module and transmitting the image signal to the image processing module; the image processing module can be used for processing and analyzing the received image signal; the result display module is used for displaying the analyzed result of the image processing module. The image processing module comprises the sub-modules of a fibrous cap information acquisition module, a macrophage information acquisition module and a lipid nucleus information acquisition module. The method solves the problem that the lipid nucleus size parameter cannot be acquired using the traditional optical coherence tomography, and can not only guarantee the optical coherence tomography with a high resolution result, but also add information about the lipid nucleus size and plaque stresses.
Owner:PULSE MEDICAL IMAGING TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
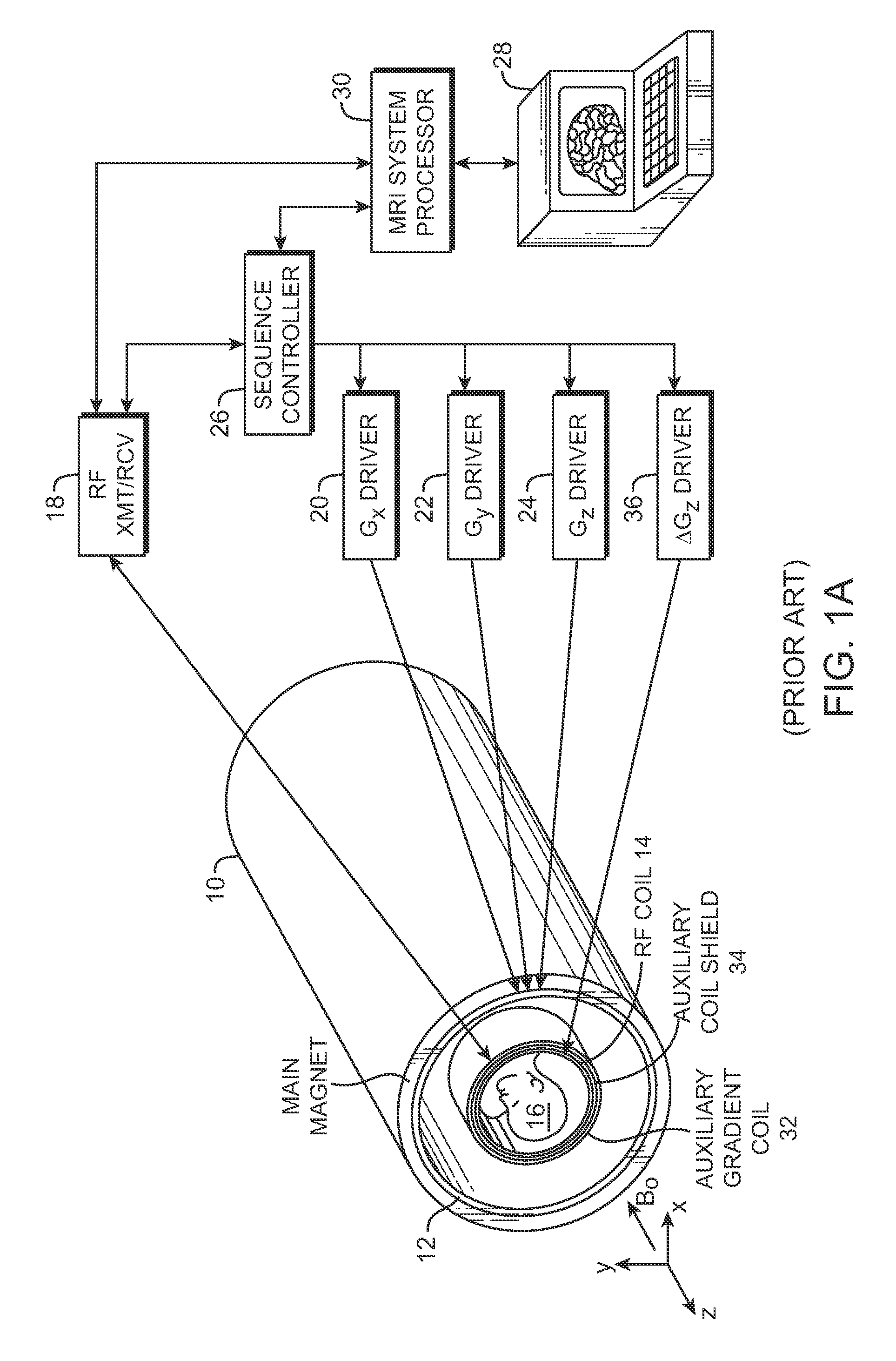
Sensor array for nuclear magnetic resonance imaging systems and method
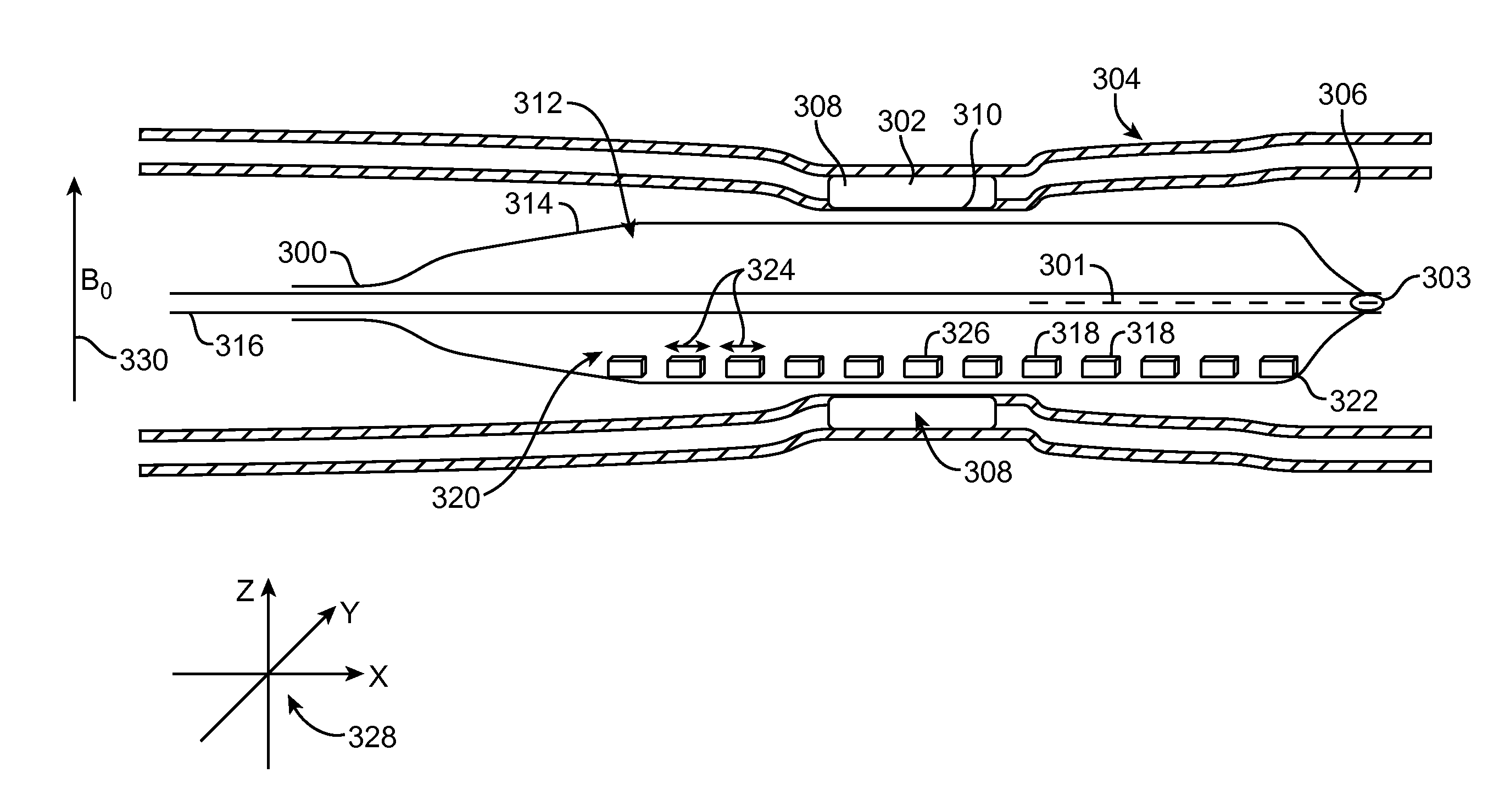
ActiveUS7535228B2Improve spatial resolutionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSensor arrayNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The present invention generally provides improved devices, systems, and methods for measuring materials with NMR and / or MRI. Exemplary embodiments provide a sensor array for NMR mapping of the material. For example tissue can be measured with the sensor array mounted on a probe body having a distal portion which can be inserted through a minimally invasive aperture. While many tissues can be measured and / or diagnosed, one exemplary embodiment includes a probe adapted for insertion into a lumen of a blood vessel. The sensor array can provide improved spatial resolution of tissue and / or tissue structures positioned near the sensor array to diagnose potentially life threatening diseases, for example a fibrous cap covering a vulnerable plaque. In specific embodiments, the sensors are attached to an expandable member, for example a balloon, which can be inflated to urge the probe sensors radially outward to position the sensors near the tissue structures.
Owner:RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES
Method and system for atherosclerosis risk scoring
InactiveUS7340083B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCalcification
A method for characterizing the risk associated with atherosclerosis is disclosed. The method uses one or more images of cross-sections of the artery or other vessel of interest to identify and locate components of the atherosclerotic deposit, including any hemorrhage, necrotic core, and calcification, and to determine the status and composition of the fibrous cap. In one embodiment, high resolution MRI images are utilized, although other imaging modalities may alternatively be used. A simple scoring system is applied that accounts for the presence of these components and more heavily weights the presence of these components in the juxtaluminal portion of the deposit. The status of the fibrous cap (intact or ruptured) and the composition of the fibrous cap (collagen or mixed tissue) are also incorporated into a final atherosclerosis risk score.
Owner:CVPATH INST +1
Stent for treating vulnerable plaque
InactiveUS20080051878A1Reduce stressReduce deliveryStentsBlood vesselsCoronary arteriesVulnerable plaque
An intravascular stent assembly for implantation in a body lumen, such as a coronary artery, is designed to treat a lesion with vulnerable plaque by reducing the fibrous cap stresses. The stent includes distal, proximal, and center sections where the center section is configured to treat the vulnerable plaque. The stent consists of radially expandable cylindrical rings generally aligned on a common longitudinal stent axis and either directly connected or interconnected by one or more interconnecting links placed so that the stent is flexible in the longitudinal direction while providing high degrees of radial strength and vessel scaffolding.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
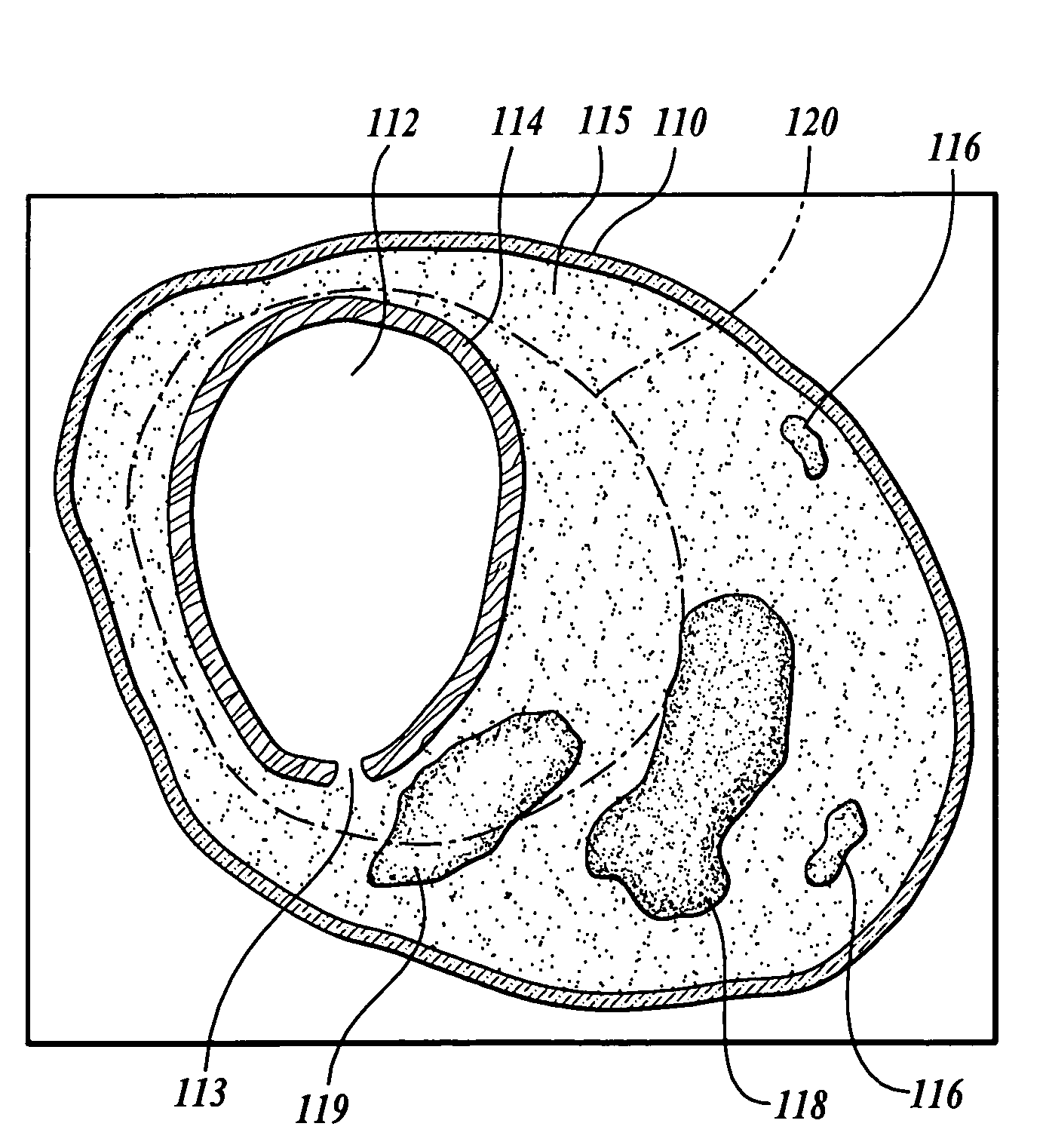
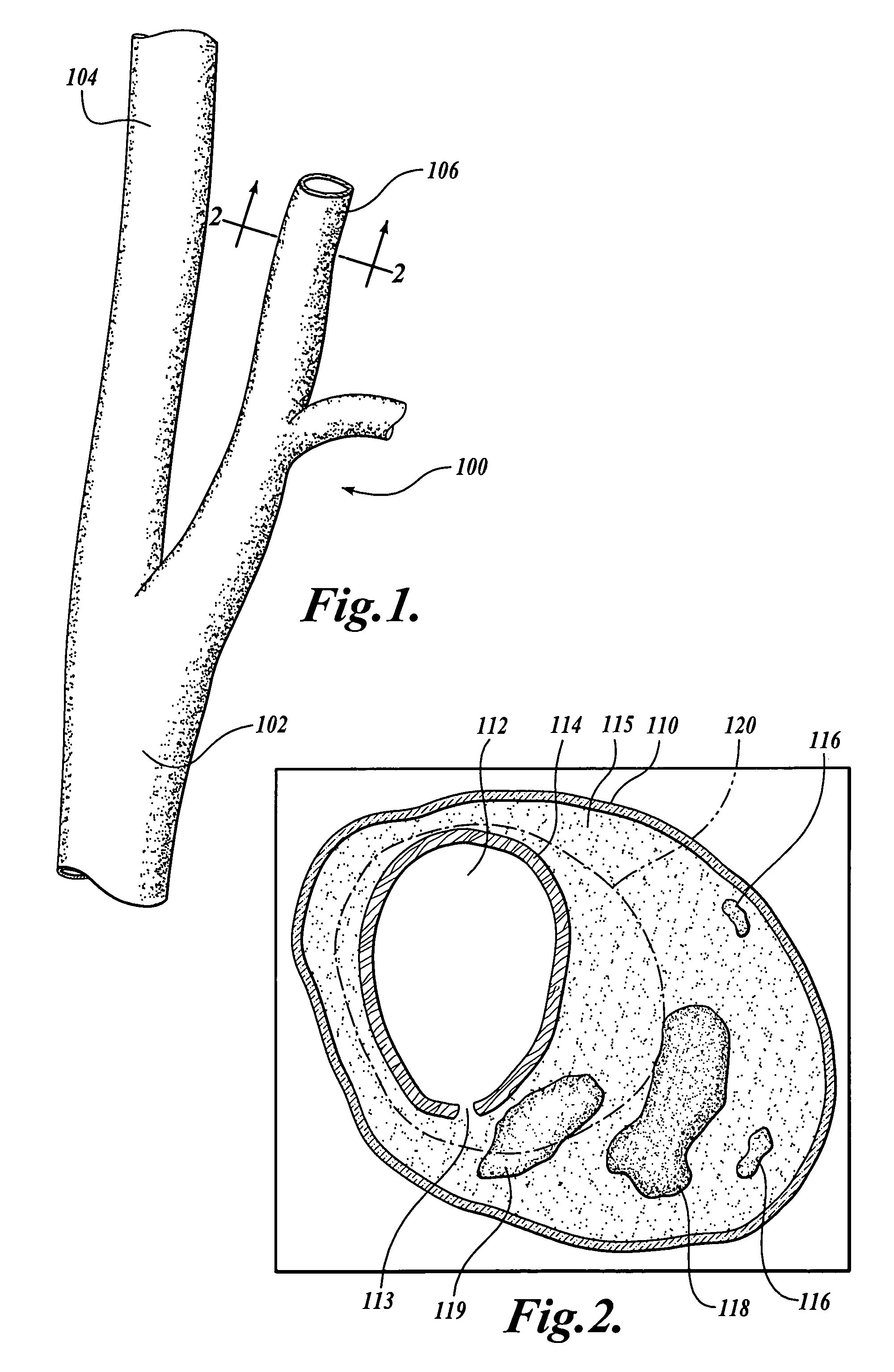
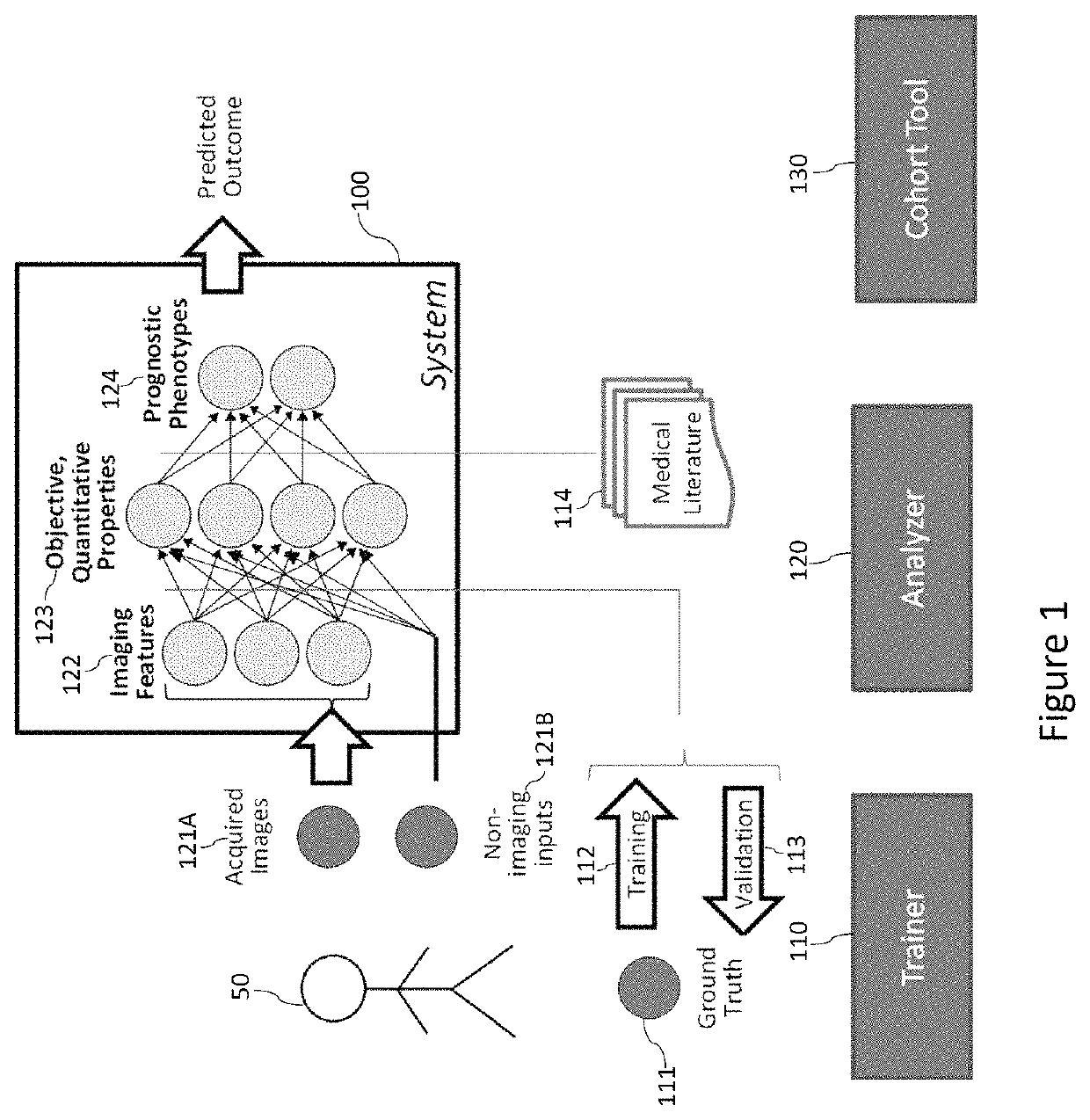
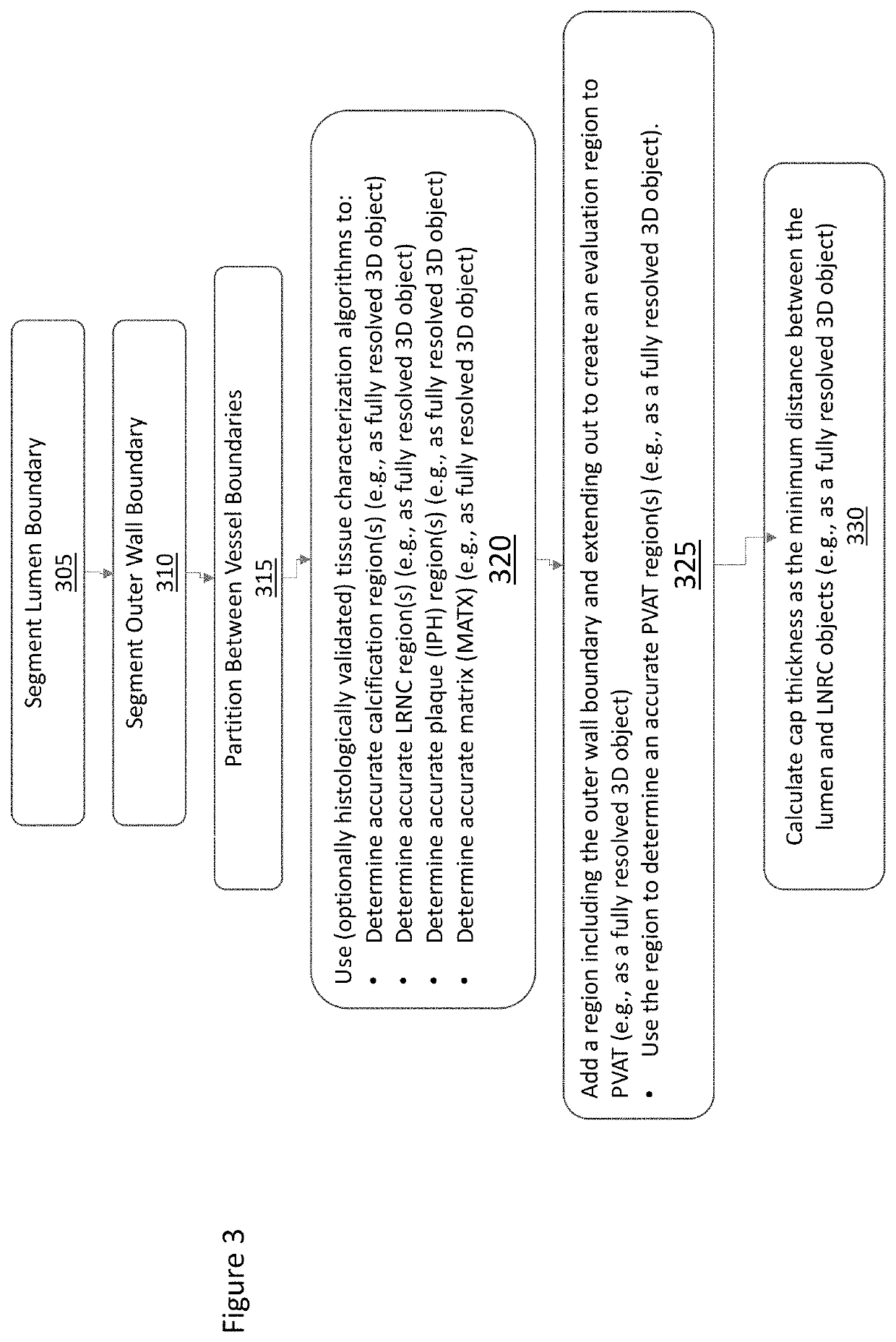
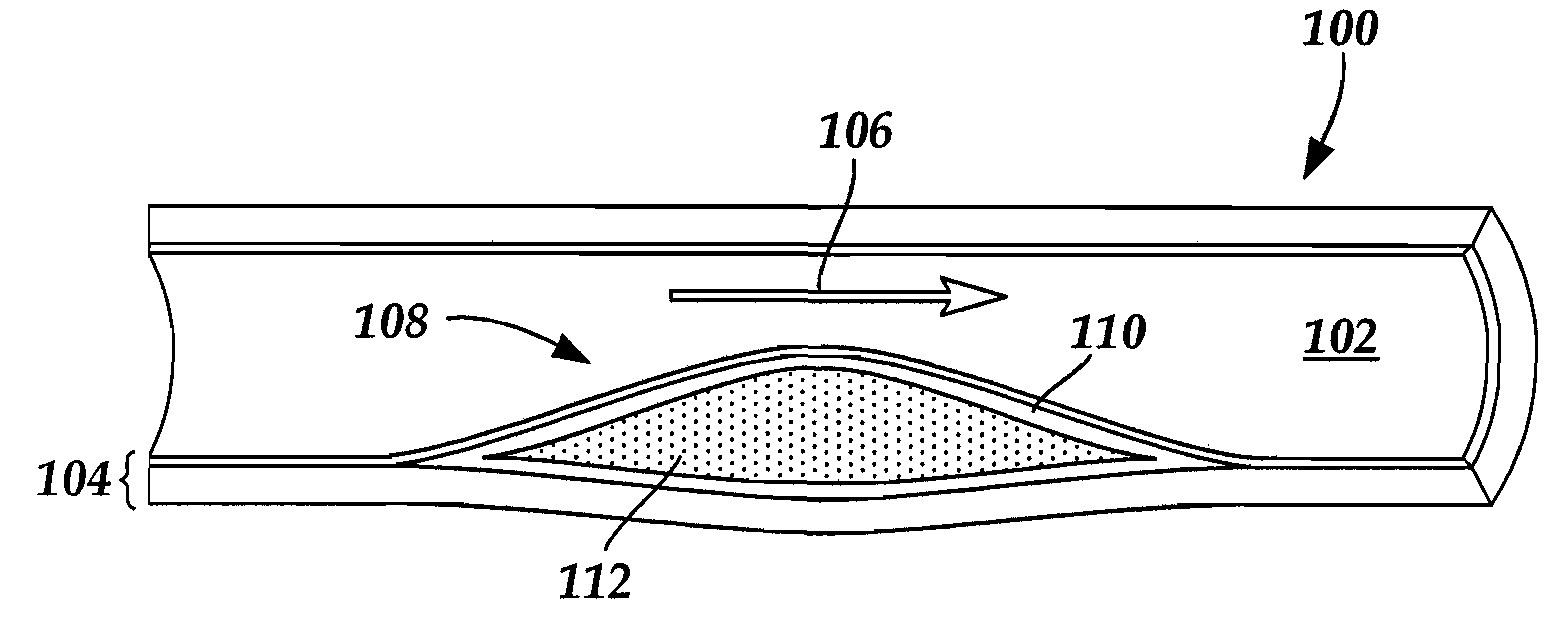
Non-invasive measurement of fibrous cap thickness
A system including a hierarchical analytics framework that can utilize a first set of machine learned algorithms to identify and quantify a set of biological properties utilizing medical imaging data is provided. System can segment the medical imaging data based on the quantified biological properties to delineate existence of perivascular adipose tissue. The system can also segment the medical imaging data based on the quantified biological properties to determine a lumen boundary and / or determine a cap thickness based on a minimum distance between the lumen boundary and LRNC regions.
Owner:ELUCID BIOIMAGING INC
Apparatus and Methods for Recanalization of a Chronic Total Occlusion
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Stent assembly for the treatment of vulnerable plaque
InactiveUS20090270973A1Reduce stressReduce deliveryStentsBlood vesselsCoronary arteriesVulnerable plaque
An intravascular stent assembly for implantation in a body lumen, such as a coronary artery, is designed to treat a lesion with vulnerable plaque by reducing the fibrous cap stresses. A polymeric sleeve having first and second ends interconnects a first metallic stent and a second metallic stent. The first end is bonded to a distal end region of the first stent and the second end to a proximal end region of the second stent. The polymeric sleeve can be loaded with a therapeutic drug or agent to further control local thrombosis and / or induce healing if the plaque fibrous cap ruptures during or after implantation. Methods of making an intravascular stent assembly for the treatment of vulnerable plaque are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
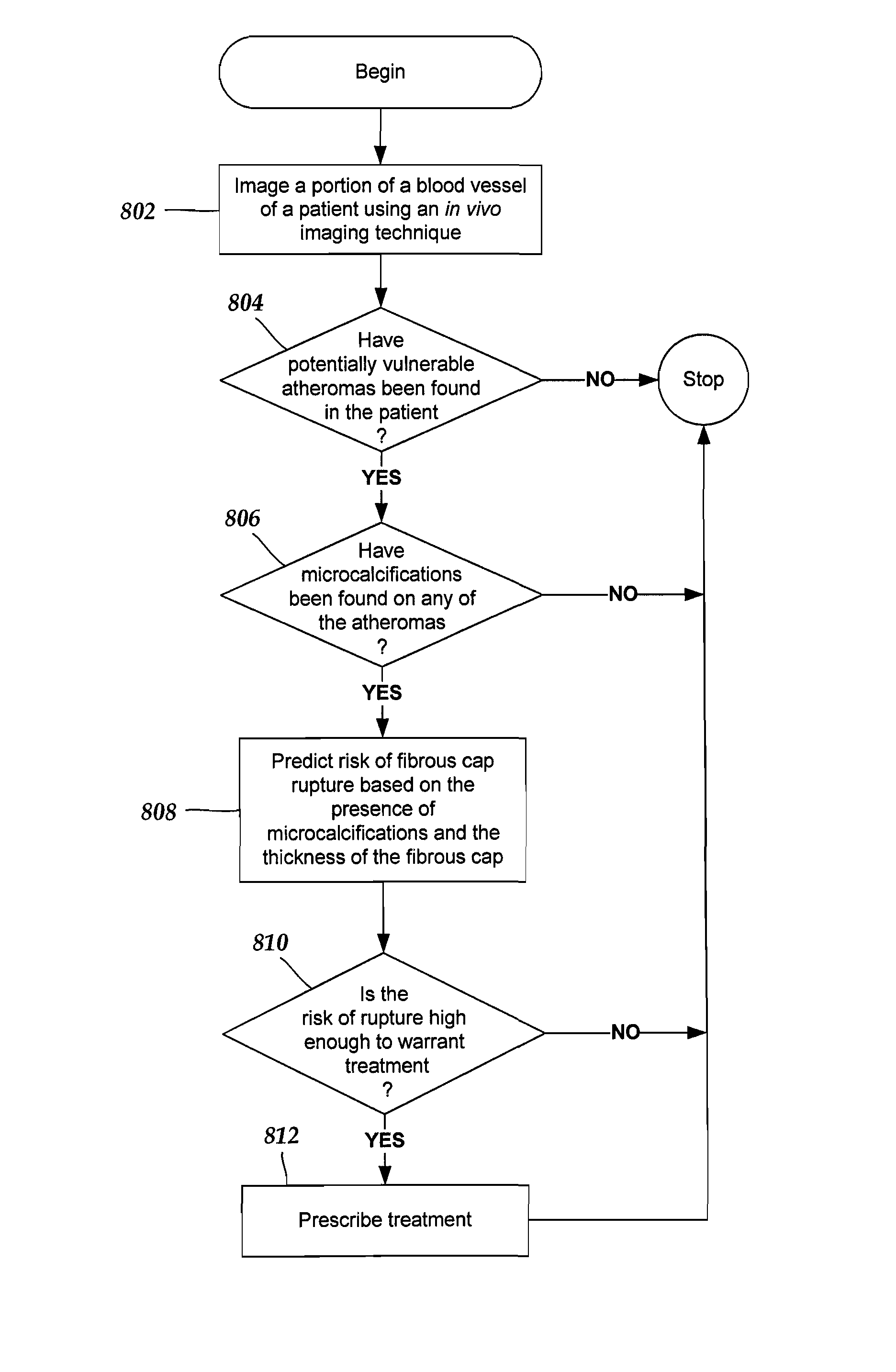
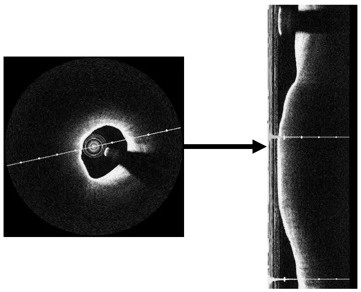
System and method for in vivo imaging of blood vessel walls to detect microcalcifications
InactiveUS20080091105A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using spectroscopyImage resolutionMicrometer
A system includes an in vivo imaging device for imaging a blood vessel with a resolution level of at least fifty micrometers. The in vivo imaging device is capable of detecting a microcalcification in a fibrous cap of an atheroma. The system also includes a processor for receiving an image of the blood vessel from the in vivo imaging device. The processor uses the image to determine whether the blood vessel contains at least one microcalcification within the fibrous cap. In some embodiments, the processor is configured and arranged to predict a risk of rupture of the fibrous cap based, at least in part, on the presence of the at least one microcalcification. In some embodiments, treatment of a patient is based on the determination from the imaging whether the blood vessel includes at least one microcalcification within the fibrous cap of the atheroma.
Owner:COLUMBIA UNIV (US) +1
Intravascular stent for treating vulnerable plaque and method of use
InactiveUS20100174303A1Excellent scaffoldMore cylindrical lumenStentsCannulasCoronary arteriesStress concentration
An expandable stent is implanted in a body lumen, such as a coronary artery, peripheral artery, or other body lumen for rupturing a fibrous cap to controllably release vulnerable plaque. The invention provides for a an intravascular stent having a plurality of cylindrical rings connected by links. The stent includes struts and links of varying strengths about the circumference of the stent. The weaker struts and links require less force to open and, hence, may apply more stress to rupture the fibrous cap while the stronger struts and links protect the healthy portions of the body lumen. In another embodiment, the stent may include stress concentrators positioned on outer surfaces of the links. The stress concentrators are aligned with the fibrous cap prior to stent expansion so that upon stent expansion, the stress concentrators induce stress to rupture the fibrous cap, thereby releasing the vulnerable plaque.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
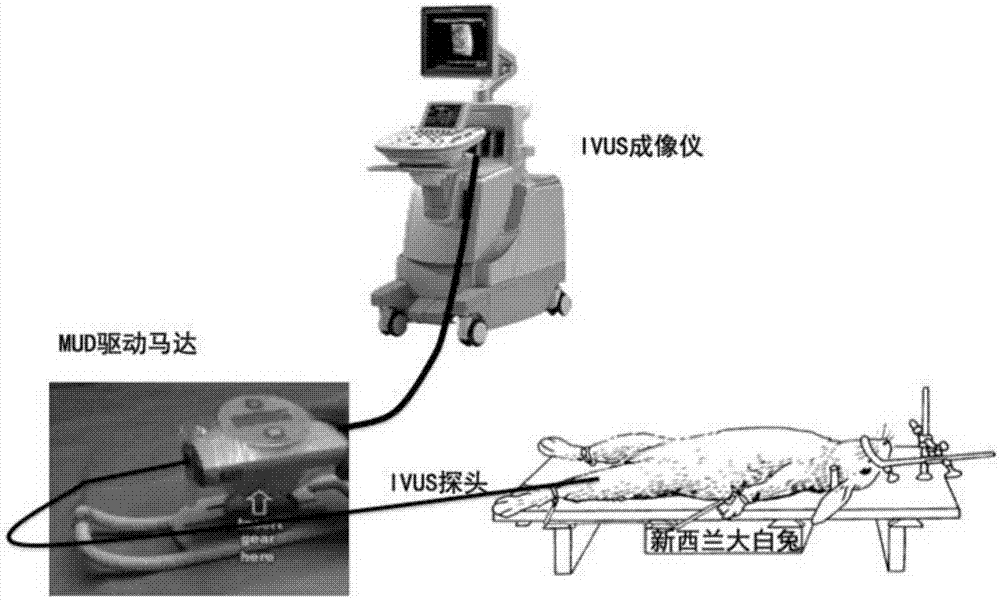
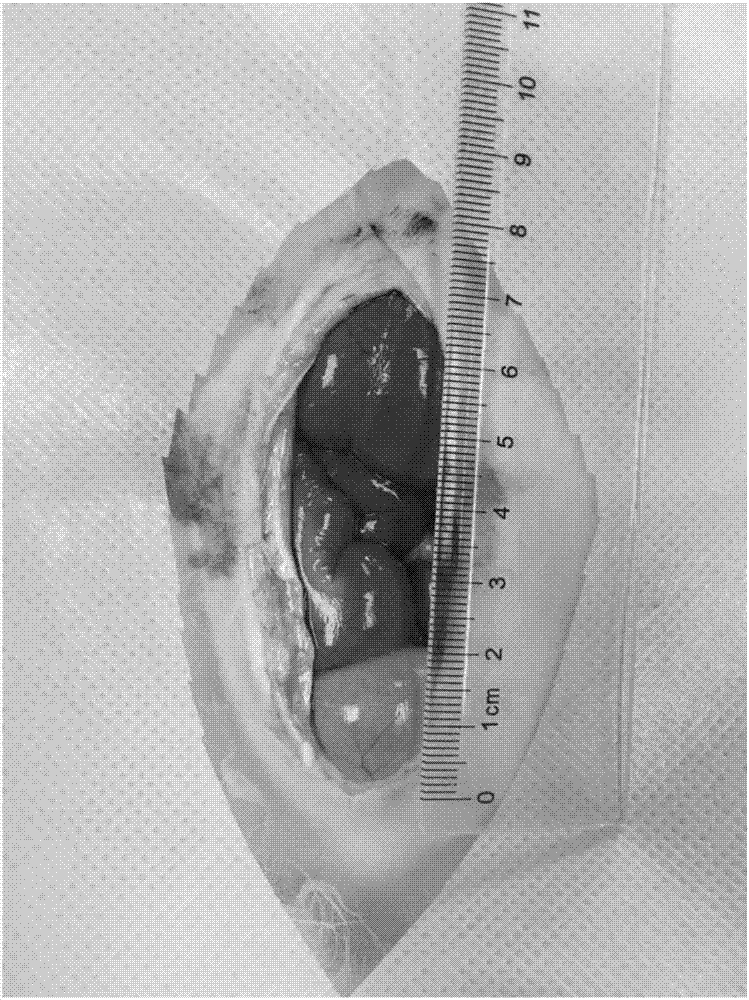
Modeling method for new blood vessels in abdominal aorta atherosclerotic plaques of New Zealand white rabbit
InactiveCN107970436AEfficient constructionPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgical veterinaryBalloon injuryStaining
The invention provides a modeling method for new blood vessels in abdominal aorta atherosclerotic plaques of a New Zealand white rabbit, which comprises the following steps: at nearby positions whereplaques need injection in an abdominal aorta of the New Zealand white rabbit fed by balloon injury plus high cholesterol for 12 weeks, under ultrasonic guidance in the blood vessel, a pair of fine forceps are used for accurate positioning by pressing a vascular lumen at a vascular adventitia to cause local deformation and removing pressure to restore the shape of the lumen; FGF-2, VEGF-A or mixedlentiviruses of both are injected into the plaques; plaque-injected sites are located by both an iliopsoas suture and the distance of iliac arterial bifurcation; and the New Zealand white rabbit continues to be fed by high fat for 8 weeks. The modeling method can effectively construct plaques which are rich in new blood vessels, and a modeling success rate reaches 100 percent. A pathological section and H&E chemical staining prove that the rich new blood vessels can be seen in the plaques no matter which of VEGF-A, FGF-2 or a VEGF-A+FGF-2 mixture is injected, even the new blood vessels alreadygrowing into fibrous caps of the plaques (figure 6) can be seen, and in comparison with a normal saline-injected control group, the difference reaches statistical significance (P<0.05).
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
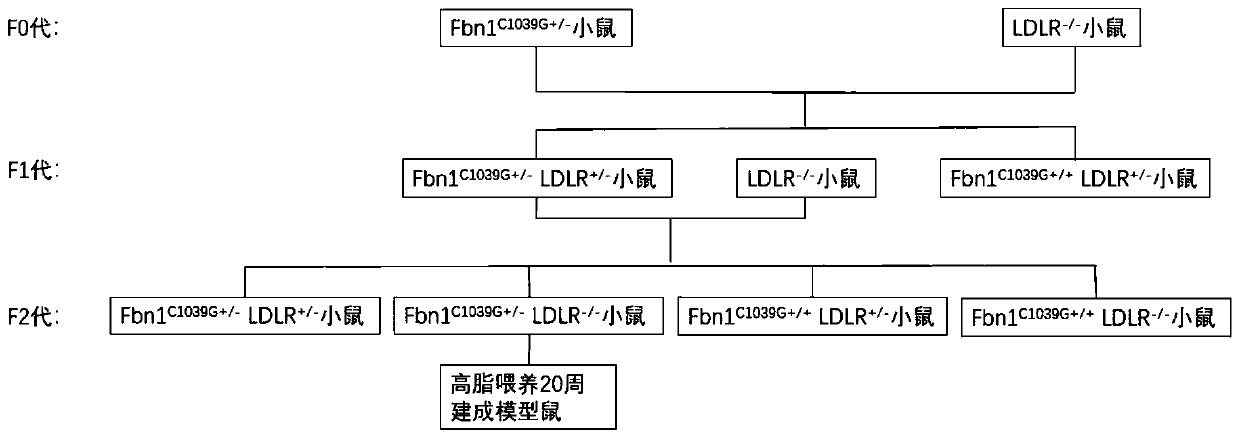
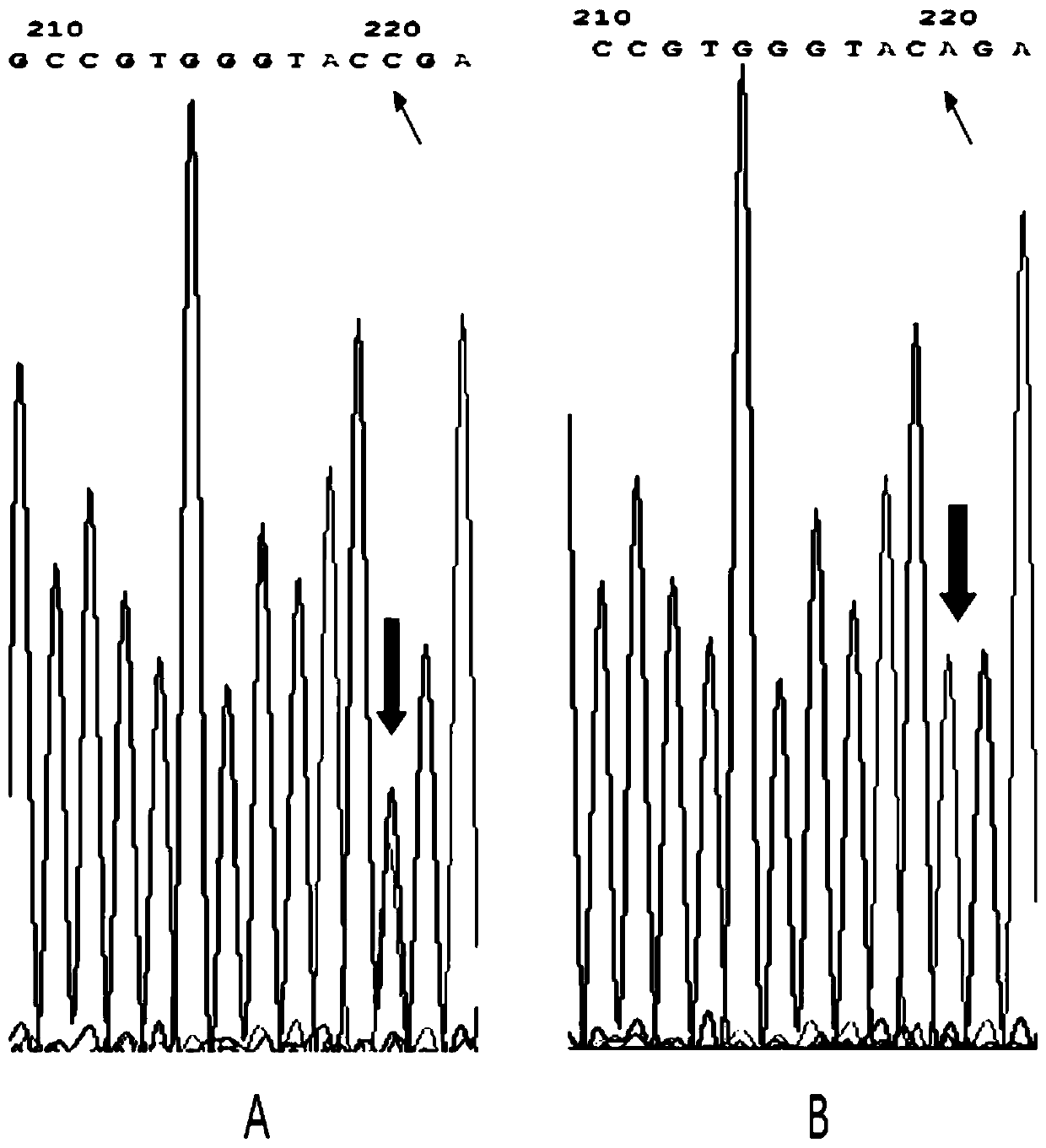
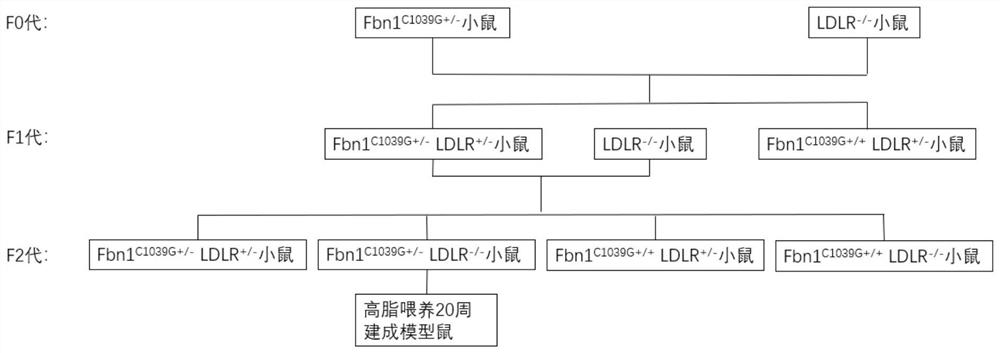
Construction method of atherosclerosis vulnerable plaque mouse model
The invention discloses a construction method of an atherosclerosis vulnerable plaque mouse model. According to the method, a low-density lipoprotein receptor gene (LDLR) with heterozygous point mutation in a fibrillin-1 (Fbn1) gene is obtained through a hybridization method to knock out a mouse. According to the method, Fbn1C1039G+ / - point mutation is introduced into an LDLR- / - mouse genome for the first time, characteristics of two genotypes are combined, the method is simple and easy to implement, and vulnerable plaques with large lipid cores, a large number of inflammatory cells, typical thin fibrous caps, rich new blood vessels and the characteristics of plaque internal hemorrhage, vascular outward reconstruction and the like can be formed; the occurrence of acute cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events such as plaque rupture similar to that of the human body can be observed on the model. The method is high in model forming rate and good in repeatability, a good animal foundation is provided for medicine research and instrument consumable improvement, and a good platform is provided for exploring an atherosclerosis mechanism.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
System and method for in vivo imaging of blood vessel walls to detect microcalcifications
A system includes an in vivo imaging device for imaging a blood vessel with a resolution level of at least fifty micrometers. The in vivo imaging device is capable of detecting a microcalcification in a fibrous cap of an atheroma. The system also includes a processor for receiving an image of the blood vessel from the in vivo imaging device. The processor uses the image to determine whether the blood vessel contains at least one microcalcification within the fibrous cap. In some embodiments, the processor is configured and arranged to predict a risk of rupture of the fibrous cap based, at least in part, on the presence of the at least one microcalcification. In some embodiments, treatment of a patient is based on the determination from the imaging whether the blood vessel includes at least one microcalcification within the fibrous cap of the atheroma.
Owner:COLUMBIA UNIV (US) +1
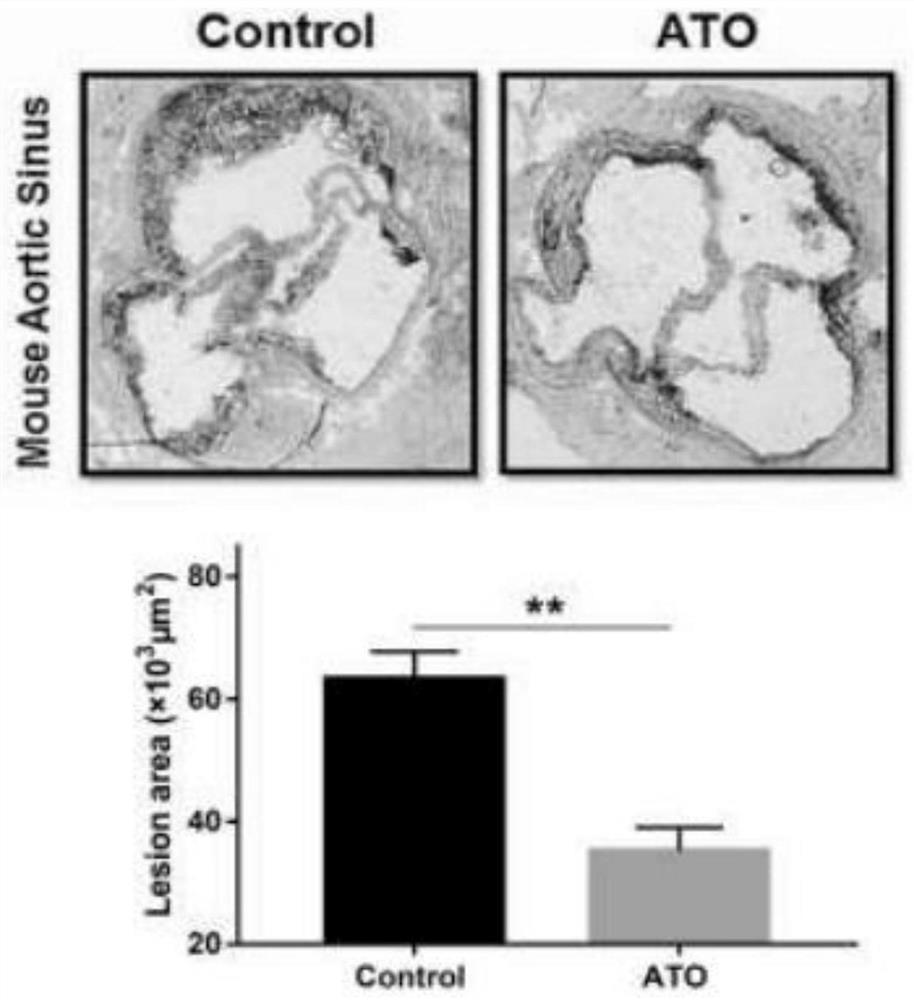
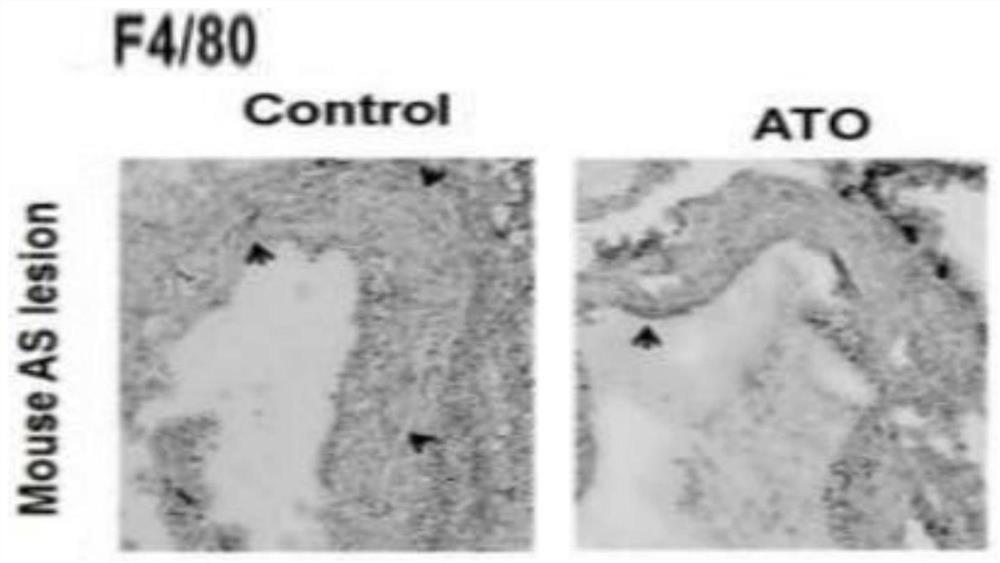
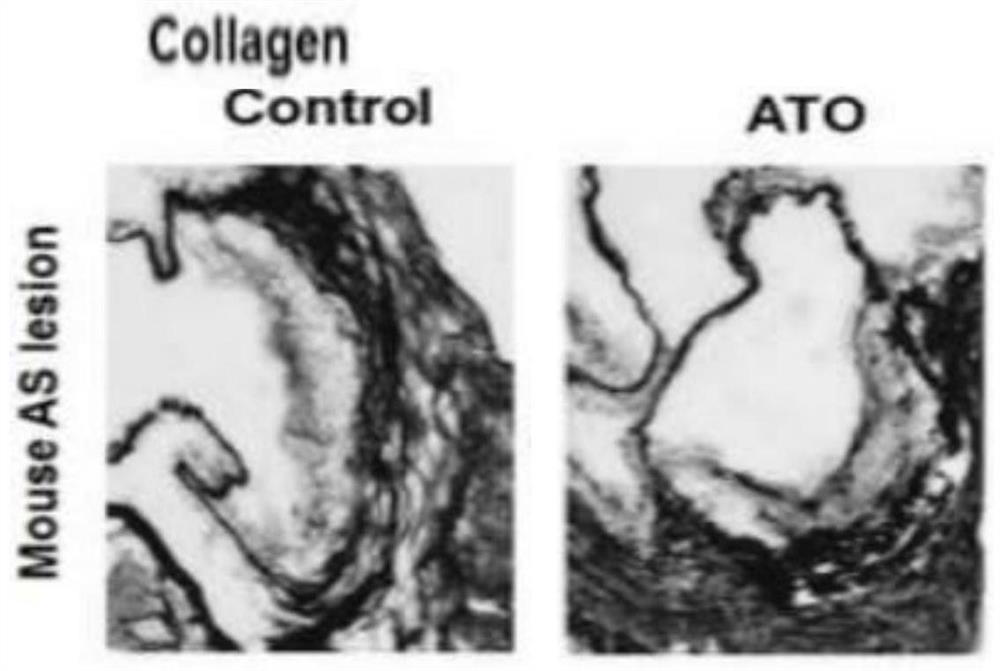
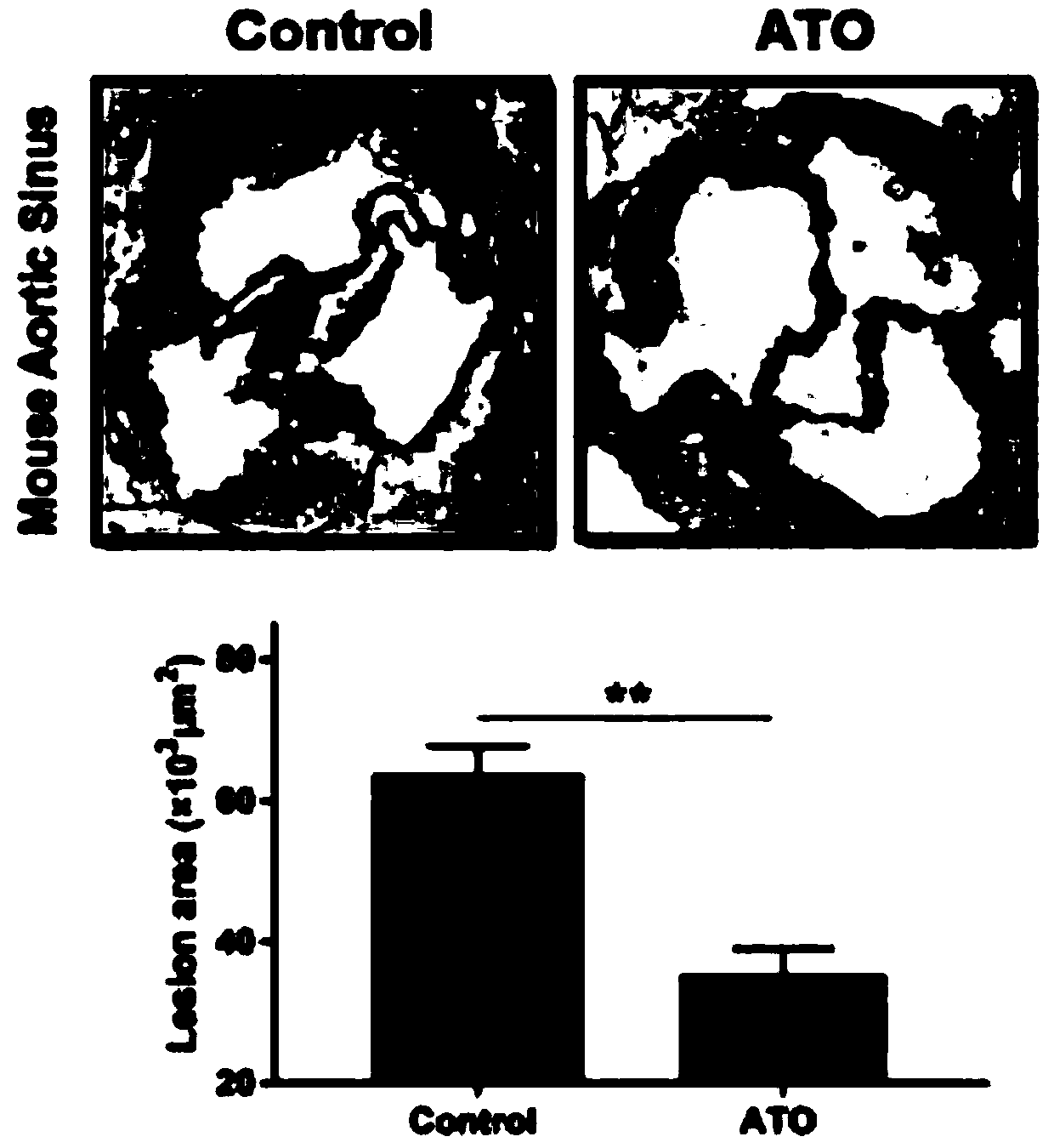
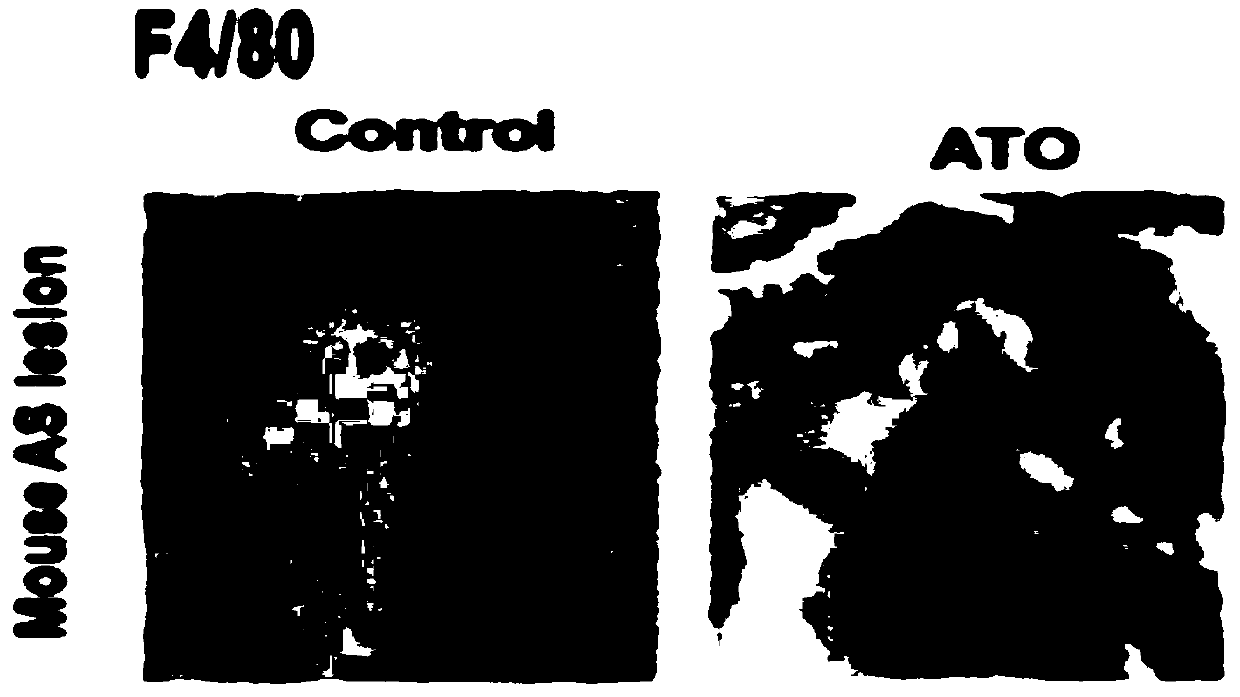
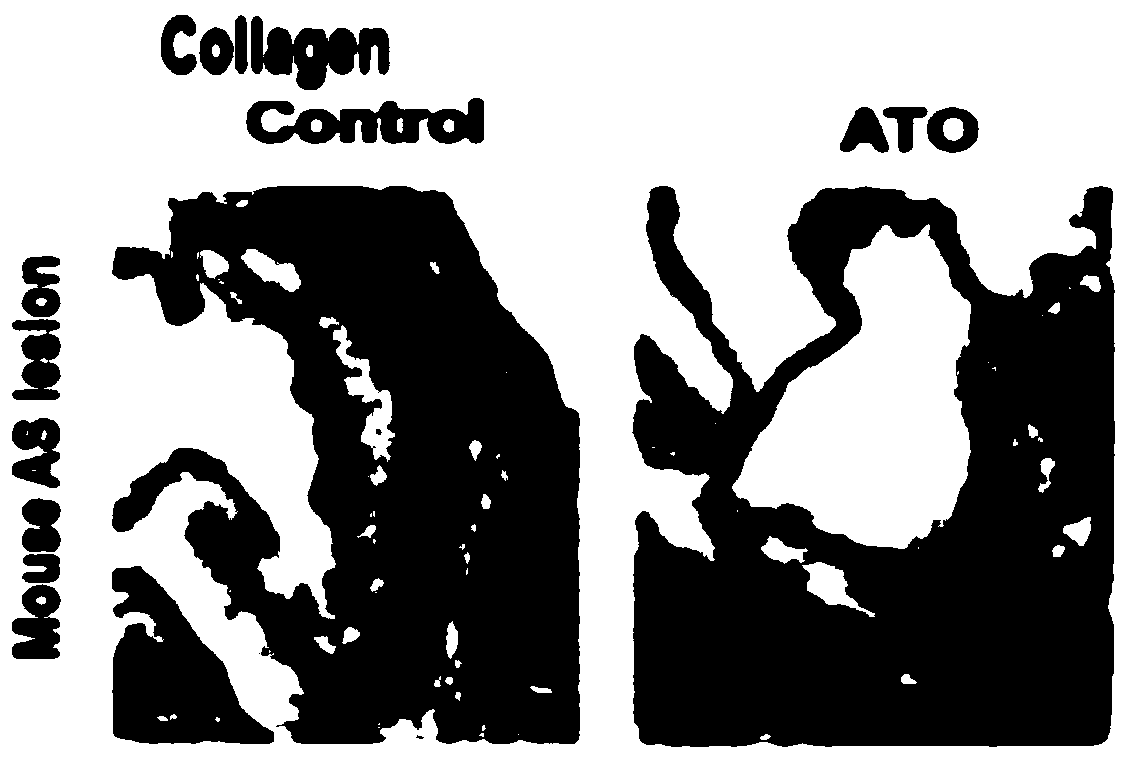
Use of arsenic trioxide in the preparation of drugs for treating advanced atherosclerosis
ActiveCN109674817BImprove stabilityReduce areaInorganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismInflammatory cellPharmacology
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method and device for detecting thin cap fibroplaque based on intracranial artery image
ActiveCN114882017AImprove segmentationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologyIntracranial Artery
The invention discloses a thin fibrous cap plaque detection method and device based on an intracranial artery image. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an intracranial artery OCT image; segmenting a fiber region from the intracranial artery OCT image through the trained fiber segmentation model; determining the inner wall of the lumen according to the fiber area; intercepting the intracranial artery OCT image according to the inner wall of the lumen and a preset distance to obtain an intercepted intracranial artery OCT image; segmenting a lipid region from the intercepted intracranial artery OCT image through a trained lipid segmentation model; and determining a thin cap fibroplaque detection result according to the segmented image. According to the method, the characteristic difference between fibers and lipids is fully considered, two-section segmentation is adopted, namely, the fiber region is segmented through the trained fiber segmentation model, and then the lipid region is segmented through the trained lipid segmentation model, so that the model segmentation performance is improved, the segmentation process is more accurate and controllable, and the segmentation efficiency is improved. And the accuracy of the detection result of the thin fiber cap plaque is improved.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES +2
Stent with anchors to prevent vulnerable plaque rupture during deployment
A stent for implantation in a body lumen for protecting from rupture a fibrous cap in order to treat vulnerable plaque. One embodiment of the stent achieves staged expansion through stronger and weaker circumferential regions, and includes optional anchors positioned at the circumferential transition between the stronger and weaker regions. During the first stage expansion, the weaker region expands moving the anchors laterally apart. The anchors straddle the fibrous cap and embed into the vessel wall. The second stage expansion of the stent exerts gentler stresses by the weaker region against the fibrous cap while the stronger region exerts greater stresses on the remainder of the vessel wall to open the vessel.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Use of arsenic trioxide in preparation of medicines for treating advanced atherosclerosis
ActiveCN109674817AImprove stabilityReduce areaInorganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismNon invasiveFibrous cap
The invention discloses use of arsenic trioxide in preparation of medicines for treating advanced atherosclerosis. The invention introduces the arsenic trioxide into the treatment of the advanced atherosclerosis for the first time, applies the mechanism of the arsenic trioxide promoting autophagy of macrophages in plaques, and treats the atherosclerosis by reducing the area of a lipid core and theinfiltration of inflammatory cells, increasing the thicknesses of fibrous caps and improving the stability of the plaques. The invention provides a novel non-invasive and safe treatment method for treating clinical patients with the advanced atherosclerosis in addition to invasive treatment such as surgery; after the arsenic trioxide is adopted, the occurrence rate of acute cardiovascular eventsis also reduced while the survival rate and the living quality of patients are improved, the manpower, material resources and financial resources which are consumed by the surgery are reduced, and themedical financial burden of the family and society is reduced. In summary, the invention provides novel medicines for the clinical treatment of the advanced atherosclerosis, and the occurrence of theacute cardiovascular events can be reduced, so that the use of the arsenic trioxide has certain clinical significance.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
A method for constructing an atherosclerotic vulnerable plaque mouse model
The invention discloses a method for constructing an atherosclerotic vulnerable plaque mouse model. The method is to obtain a low-density lipoprotein receptor gene (LDLR) knockout mouse with a heterozygous point mutation of the fibrillin 1 (Fibrillin-1, Fbn1) gene by crossing. The present invention for the first time Fbn1 C1039G+ / ‑ Point mutations introduced into LDLR ‑ / ‑ Mouse genome, combining the characteristics of the two genotypes, the method is simple and easy, and can form a large lipid core, a large number of inflammatory cells, a typical thin fibrous cap, abundant new blood vessels and intraplaque hemorrhage, outward remodeling of blood vessels, etc. The characteristic vulnerable plaque, and it can be observed in the model that it is similar to human plaque rupture, which leads to the occurrence of acute cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. It has a high molding rate and good repeatability, providing a good animal basis for drug research and improvement of device consumables, and a good platform for exploring the mechanism of atherosclerosis.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
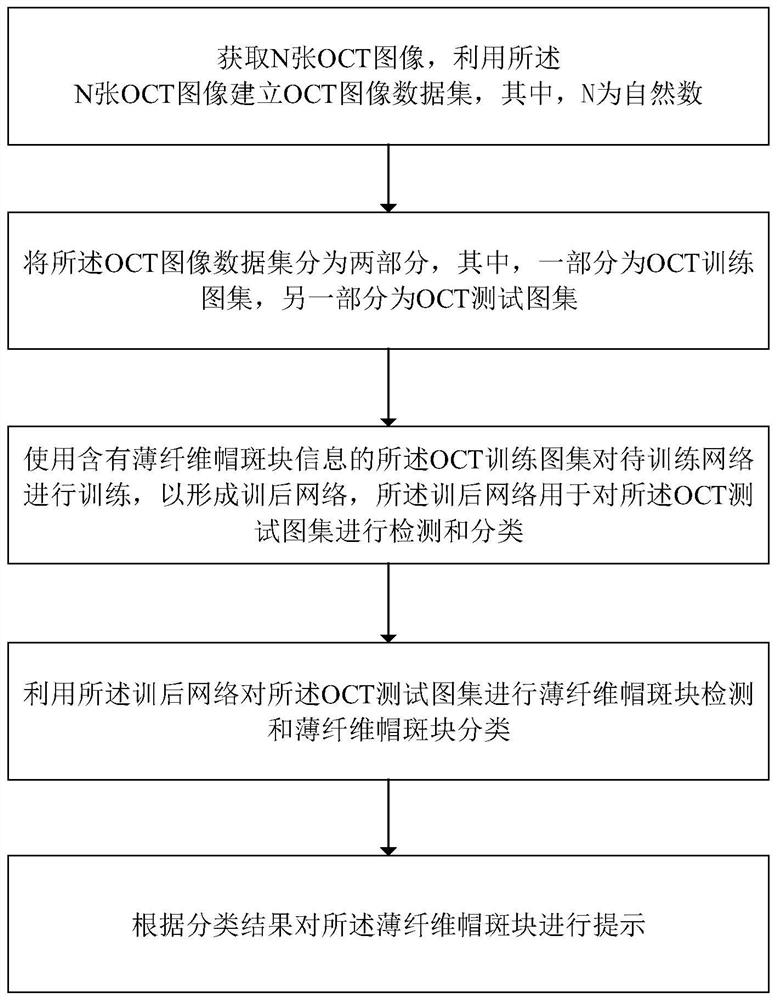
A method and device for automatic detection of thin fibrous cap plaques based on cardiovascular OCT images
ActiveCN108052909BAccurate analysisImprove robustnessRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsFeature extractionRadiology
The present invention relates to a method and device for automatic detection of thin fibrous cap plaques based on cardiovascular OCT images. The method includes: using N OCT images to establish an OCT image data set; Test atlas; use the OCT training atlas containing thin fiber cap plaque information to train the network to be trained to form a post-training network, which is used to detect and classify the OCT test atlas; use the post-training network to detect and classify the OCT test atlas Thin fibrous cap plaque detection and thin fibrous cap plaque classification are performed on the test atlas; thin fibrous cap plaques are prompted according to the classification results. The present invention uses the trained network to extract features from the image, realizes automatic detection and identification of whether there is a thin fibrous cap plaque on the OCT image, does not require manual participation, and is convenient for doctors to accurately analyze the OCT image, and the detection accuracy is relatively high. High, with better robustness and detection speed.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com