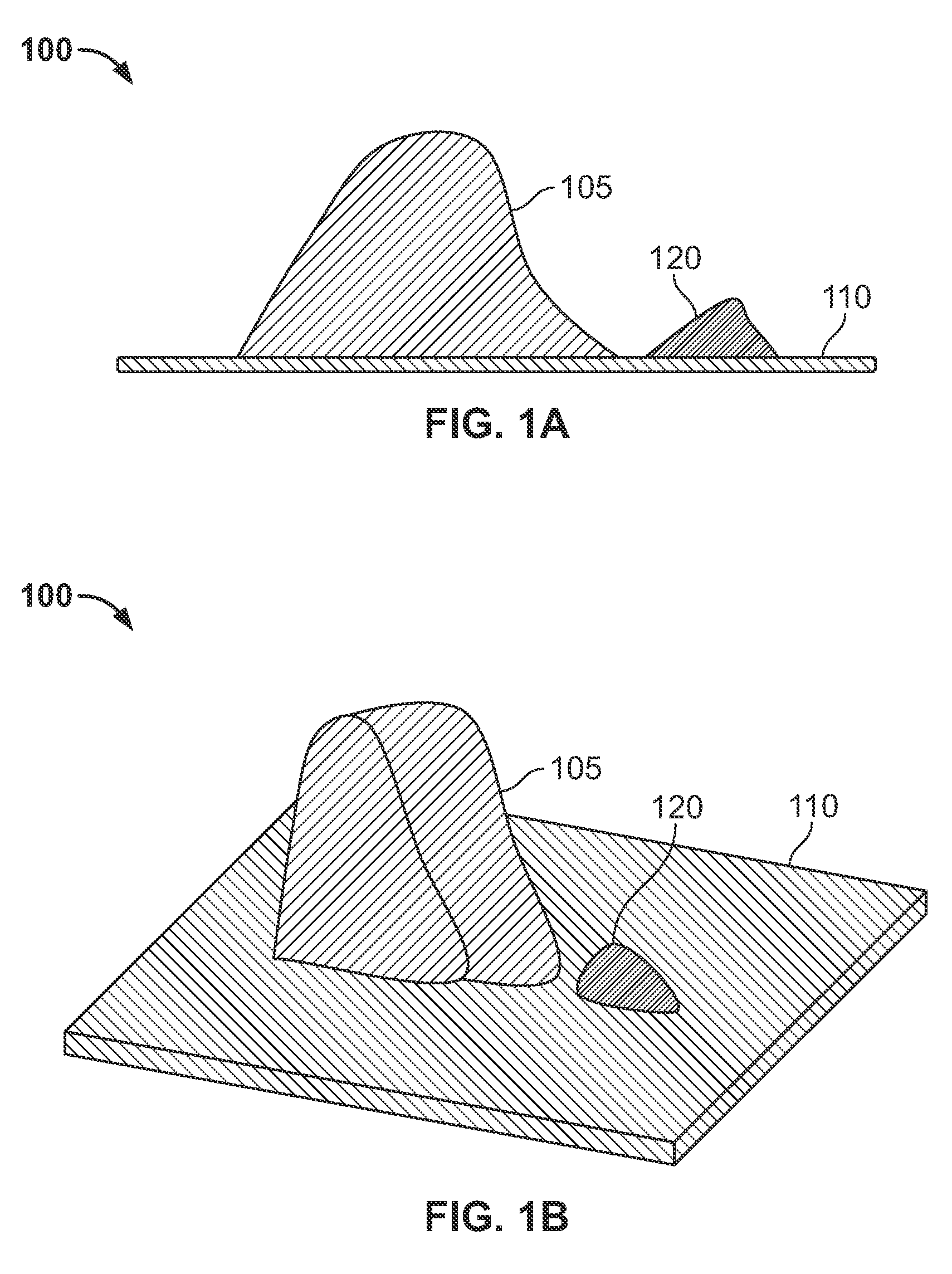
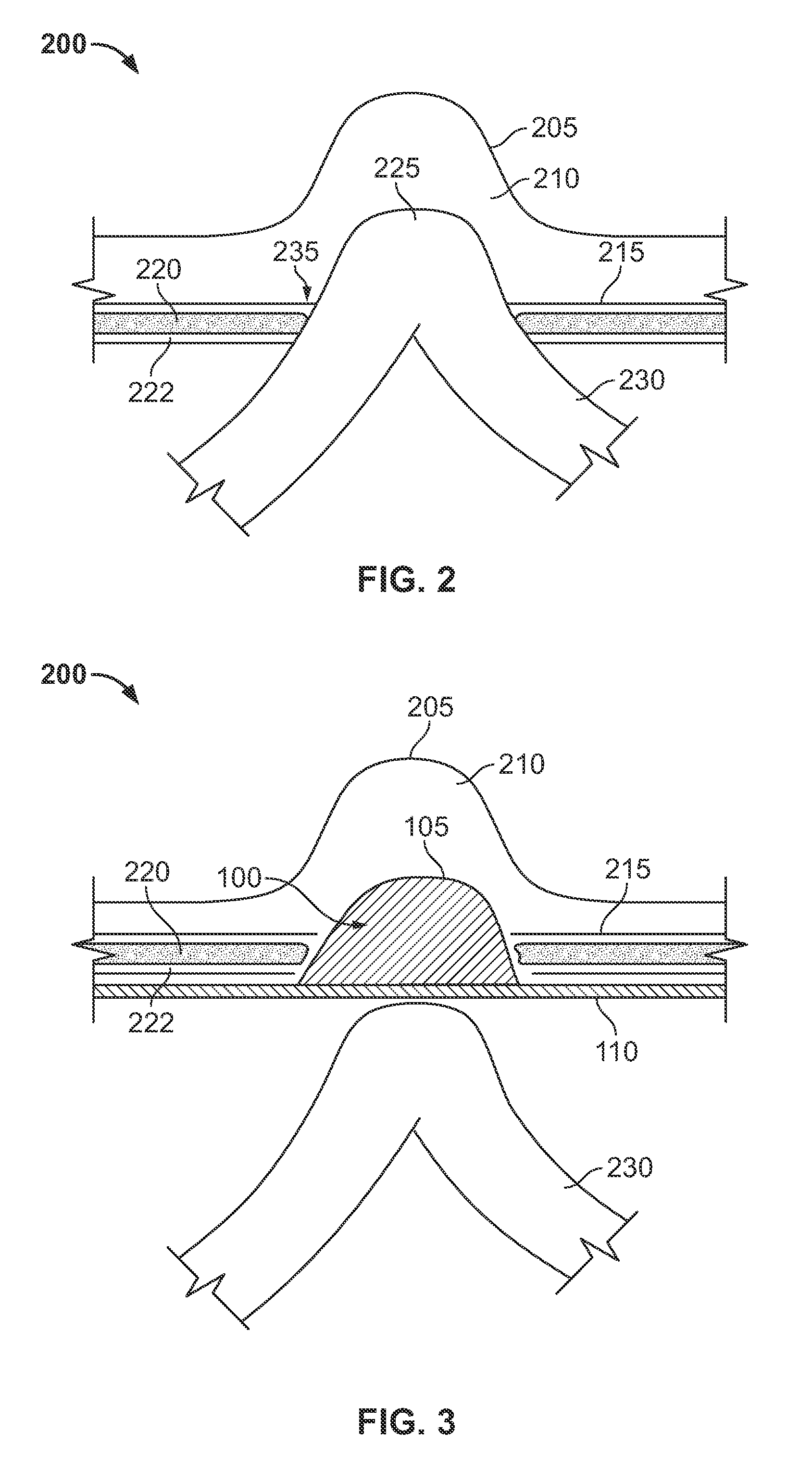
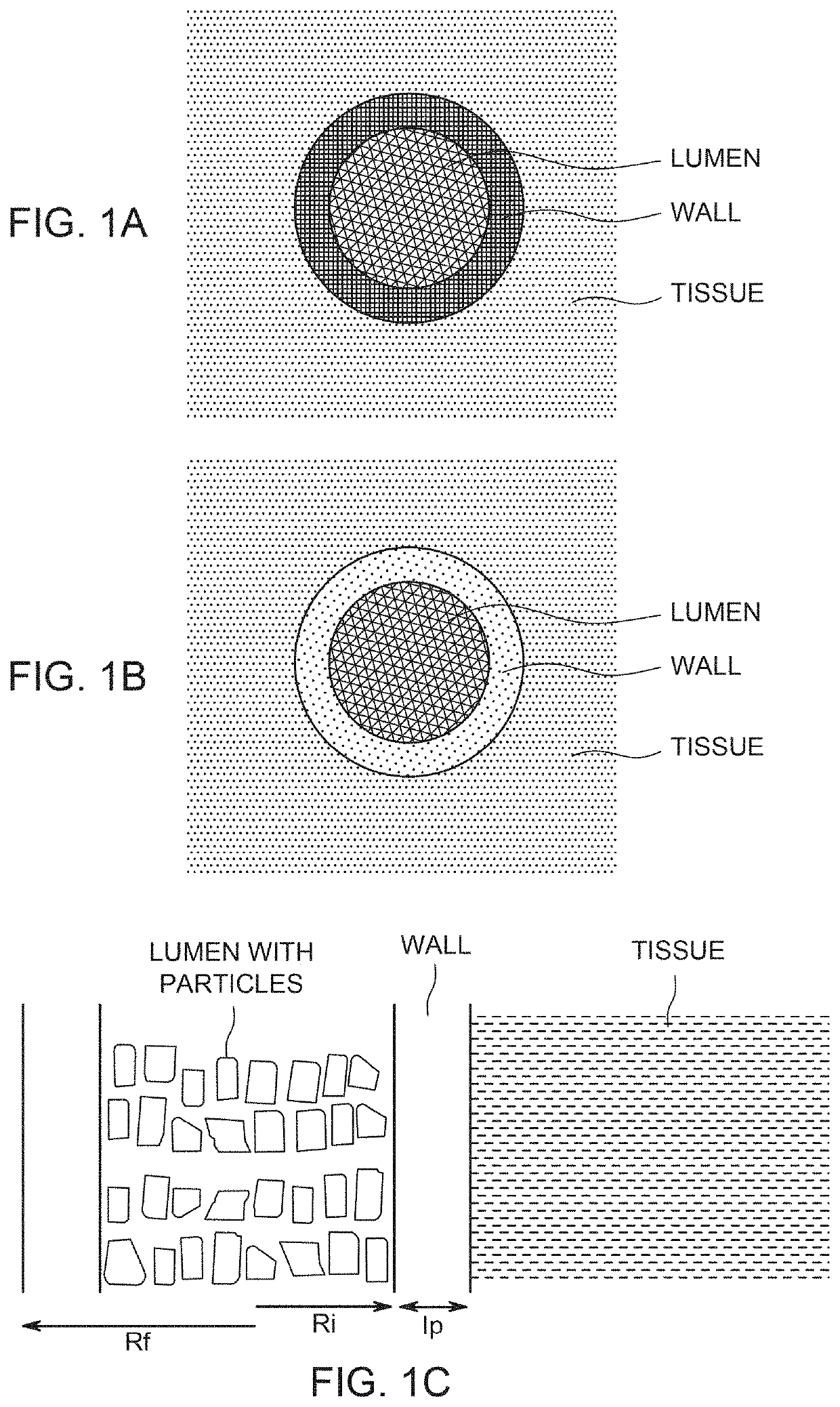
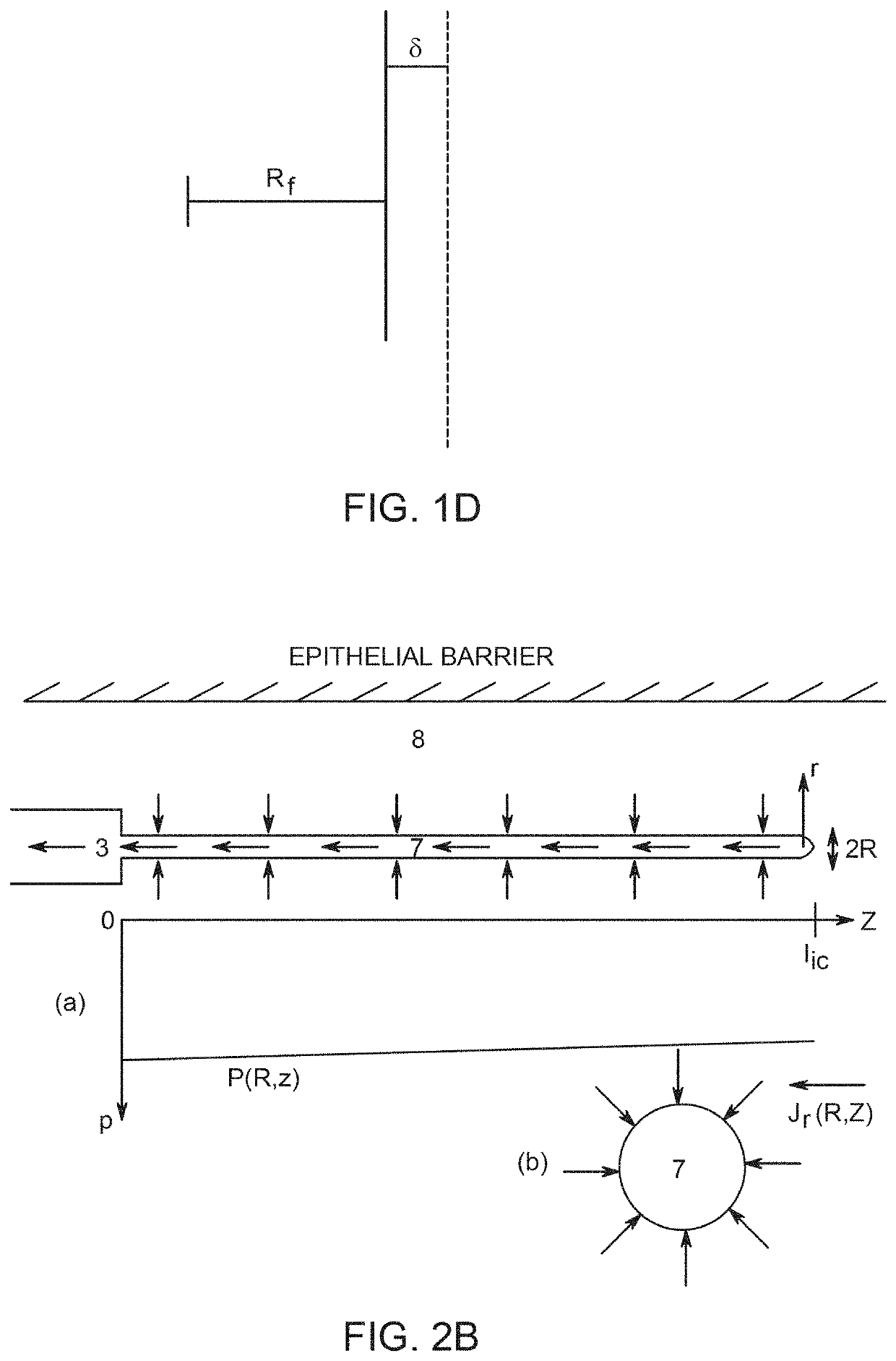
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Hernia mesh" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
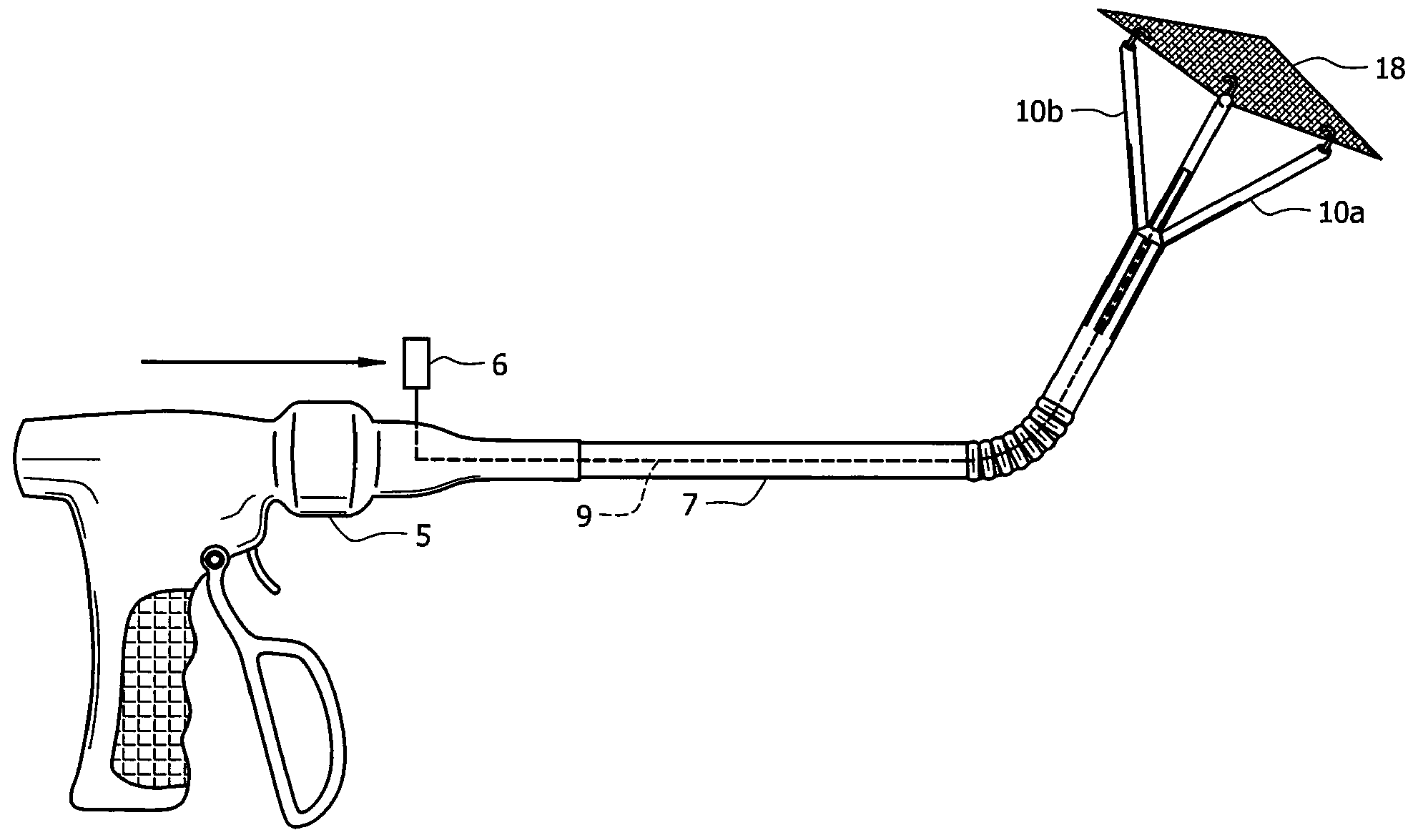
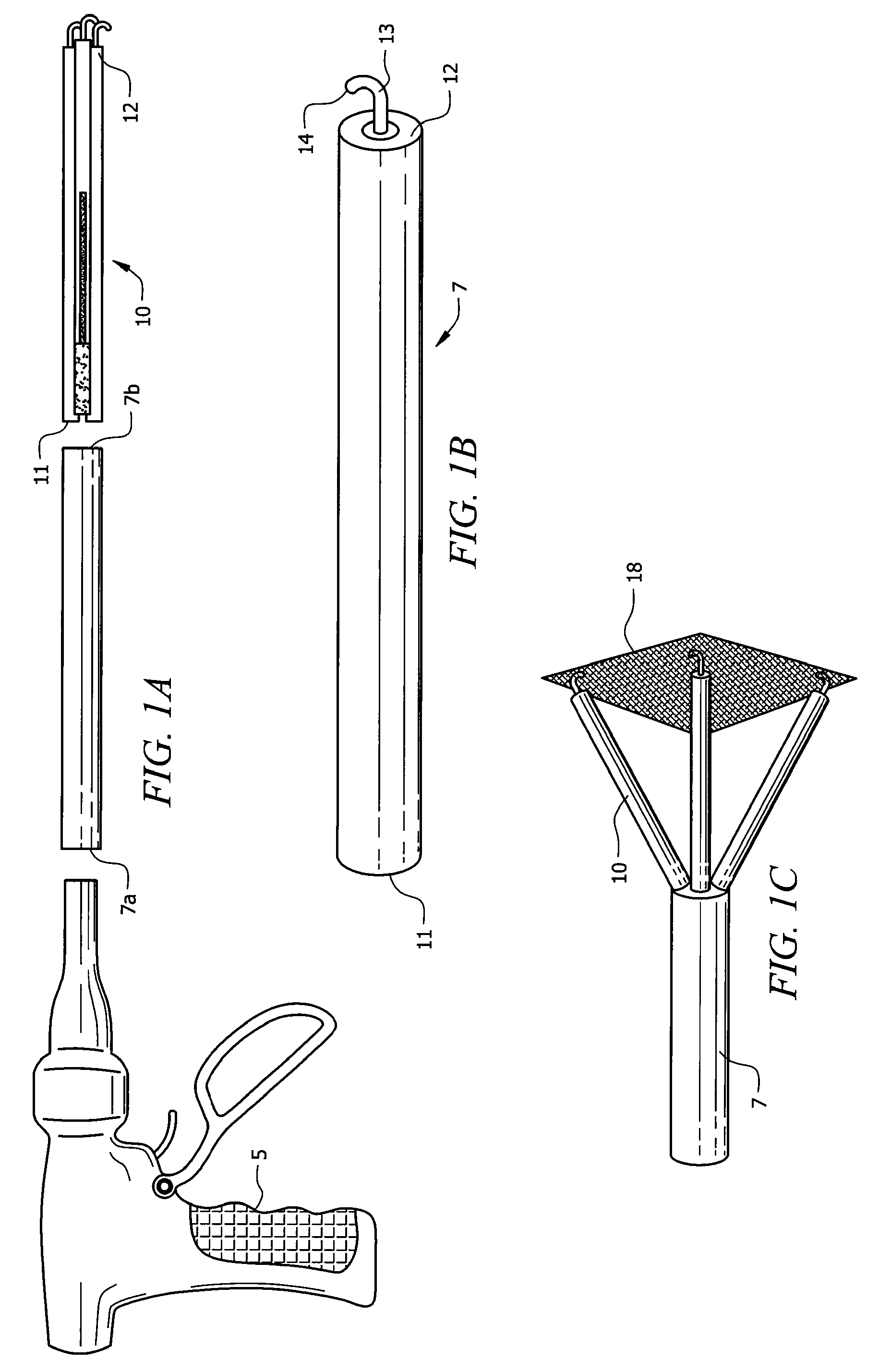
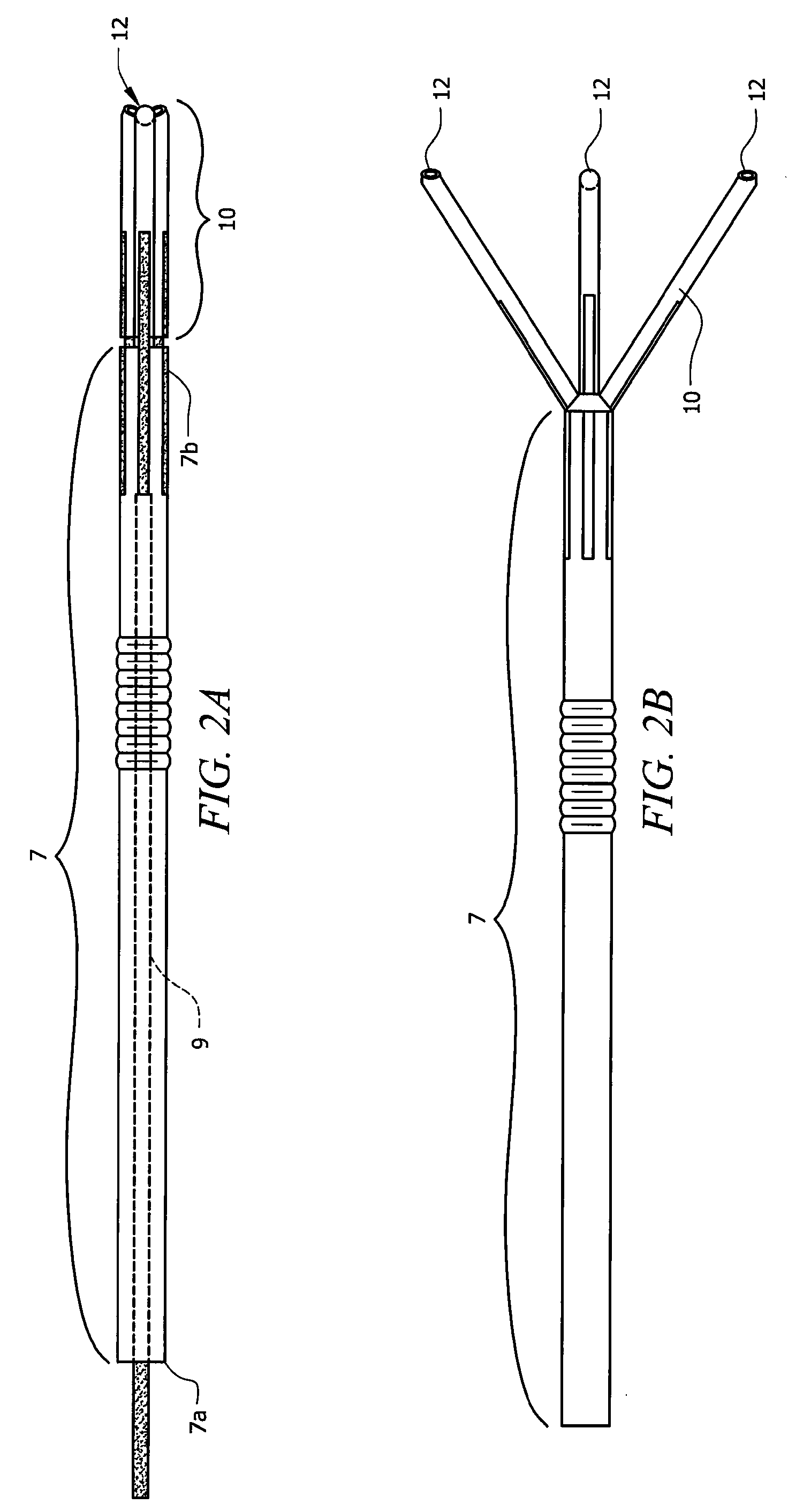
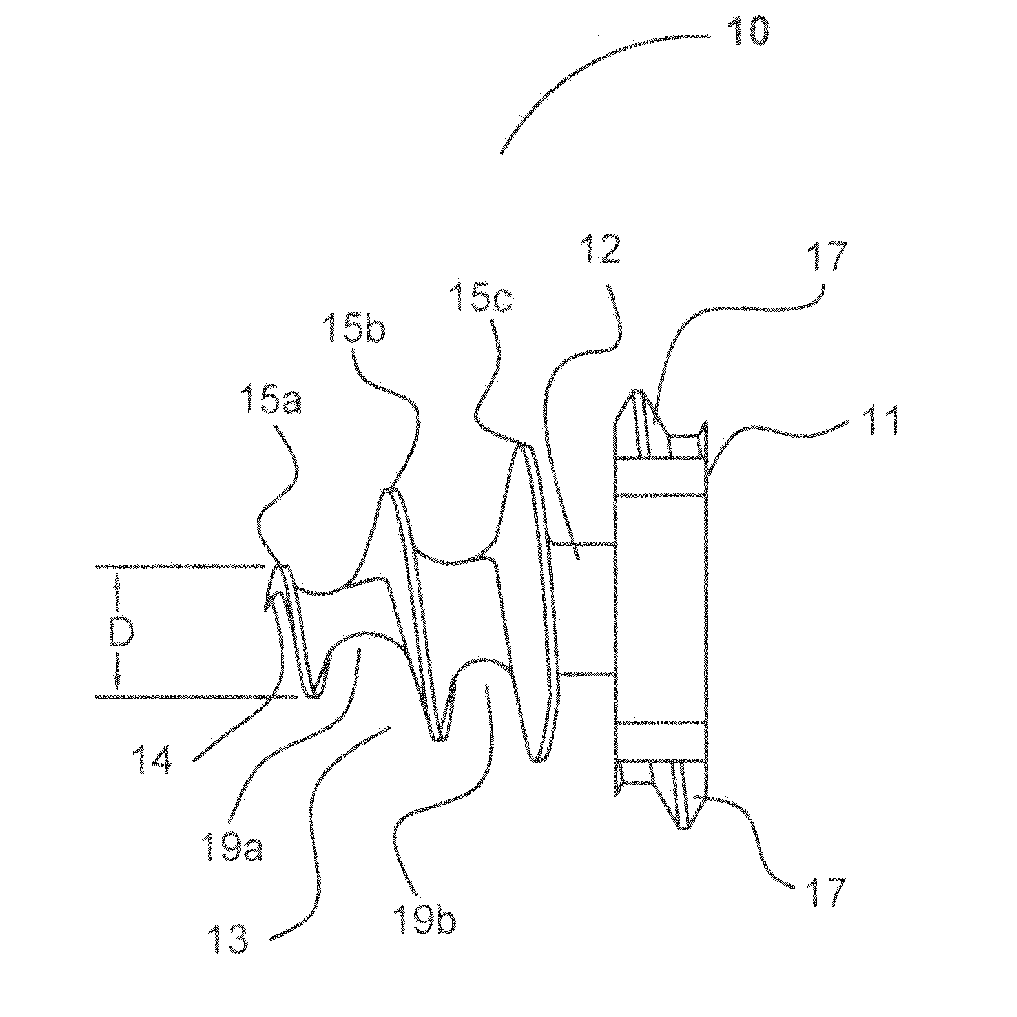
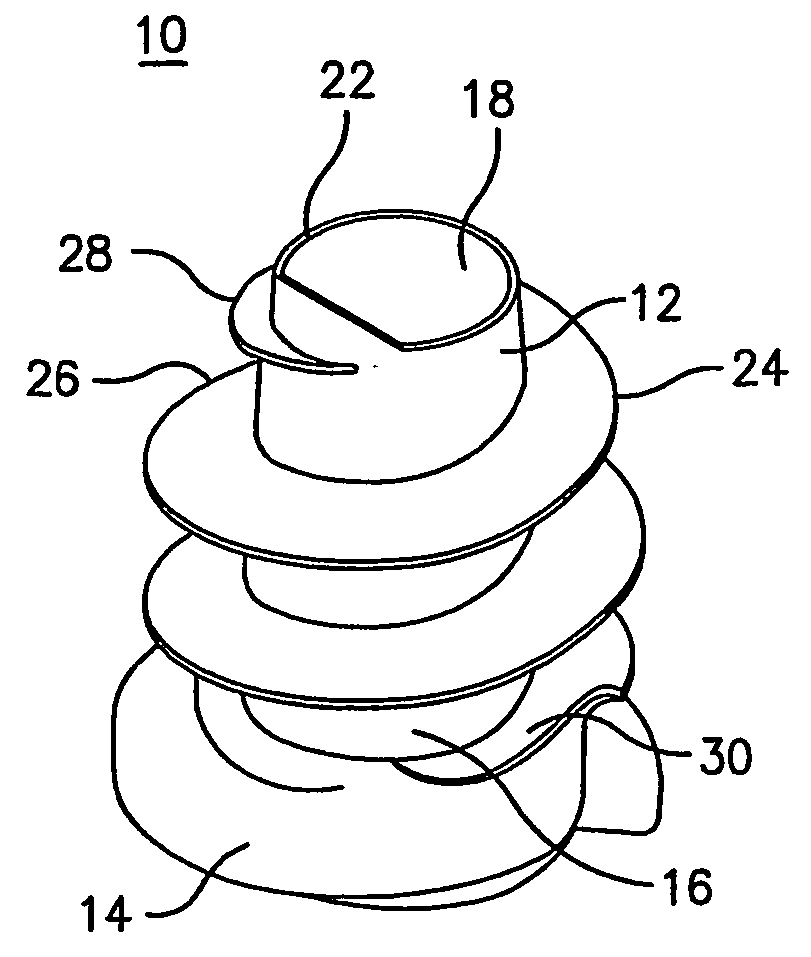
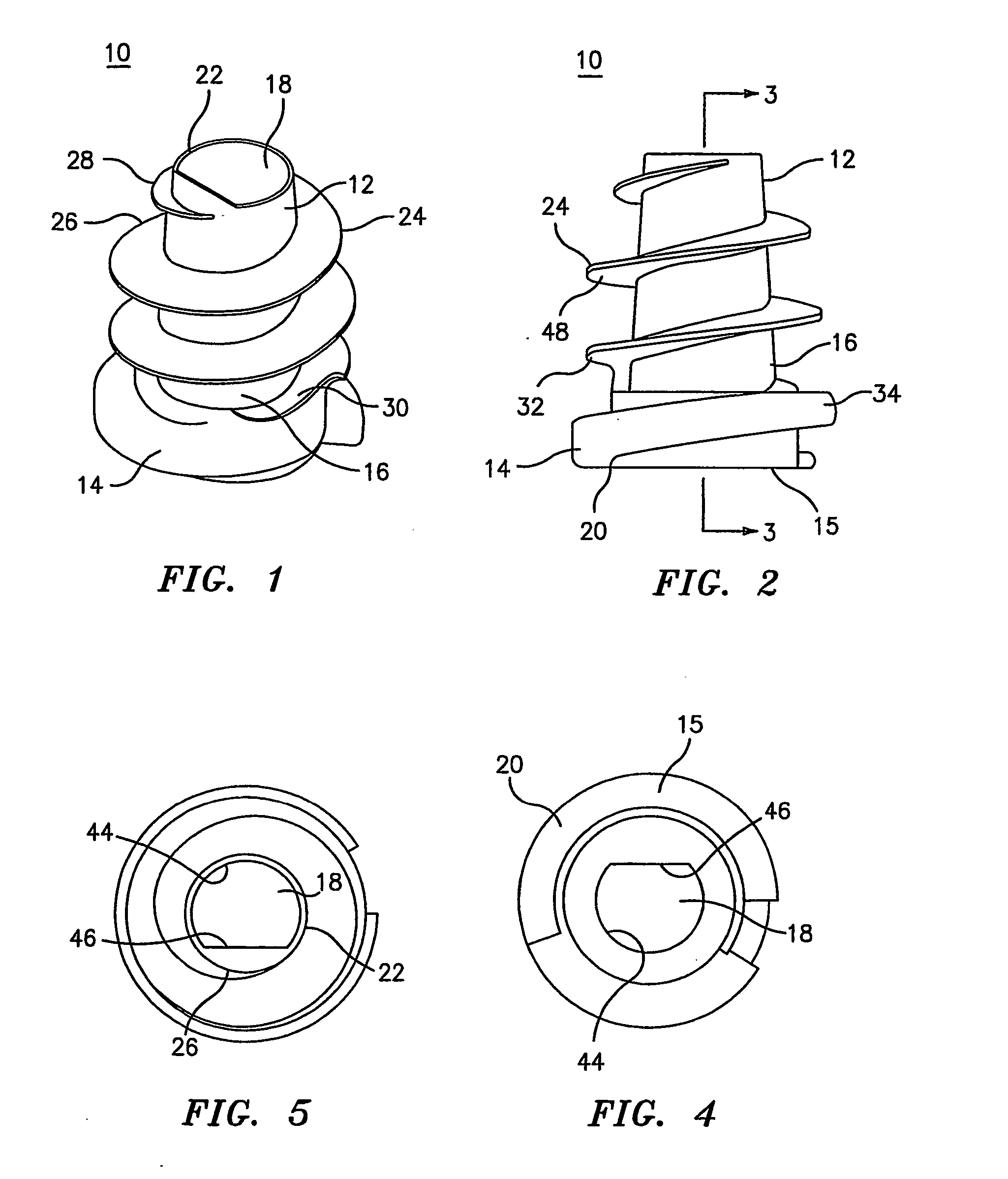
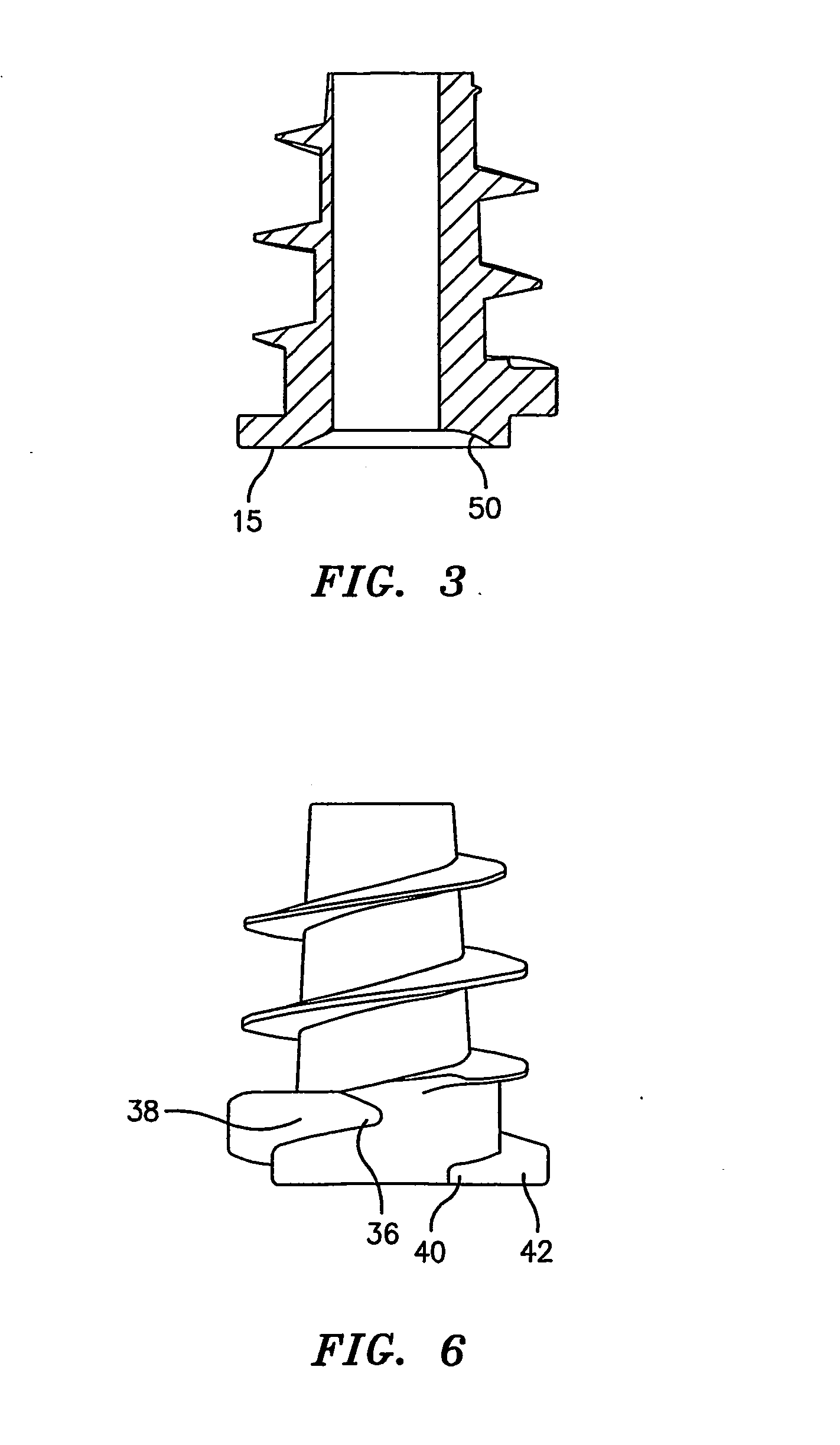
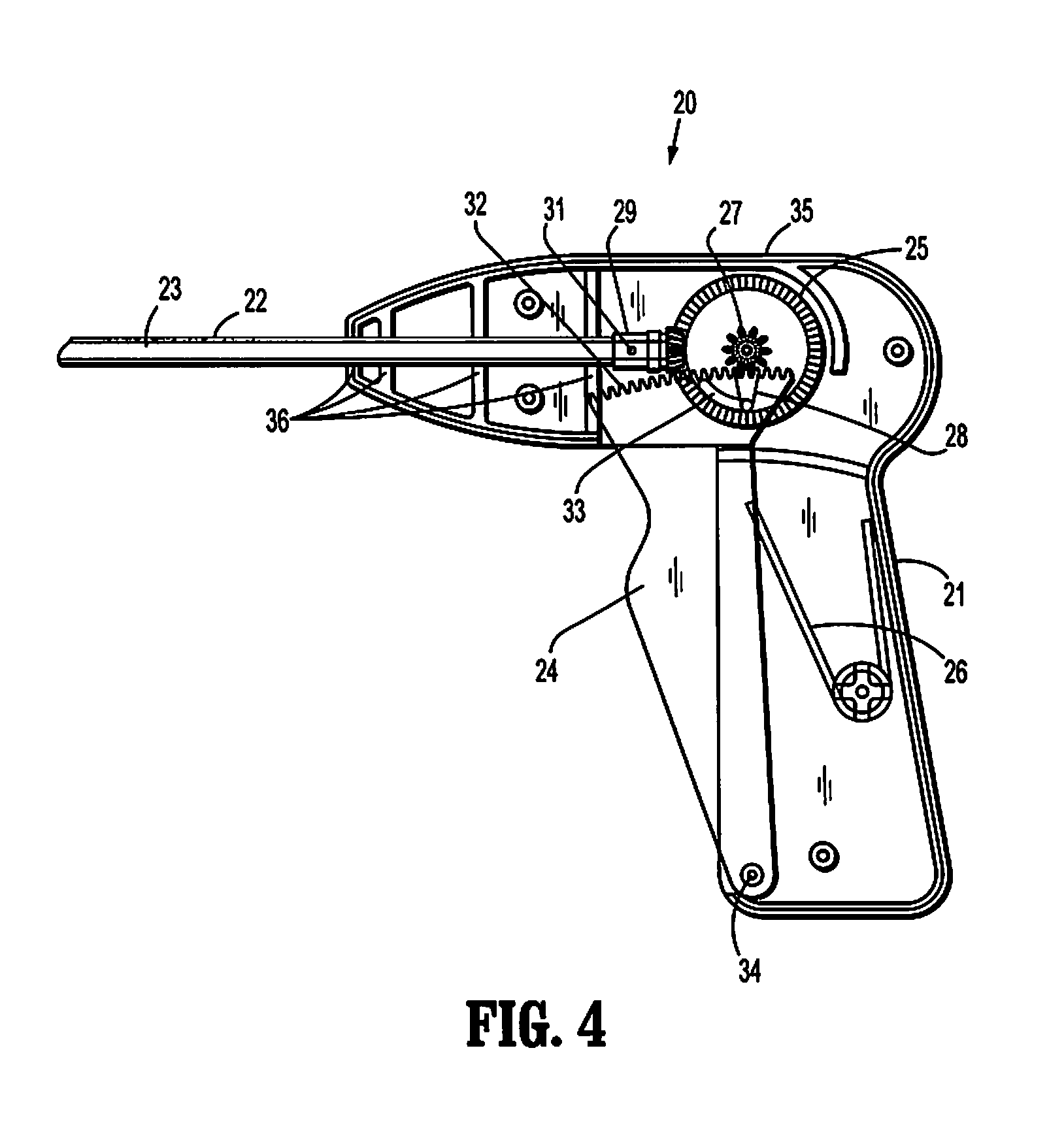
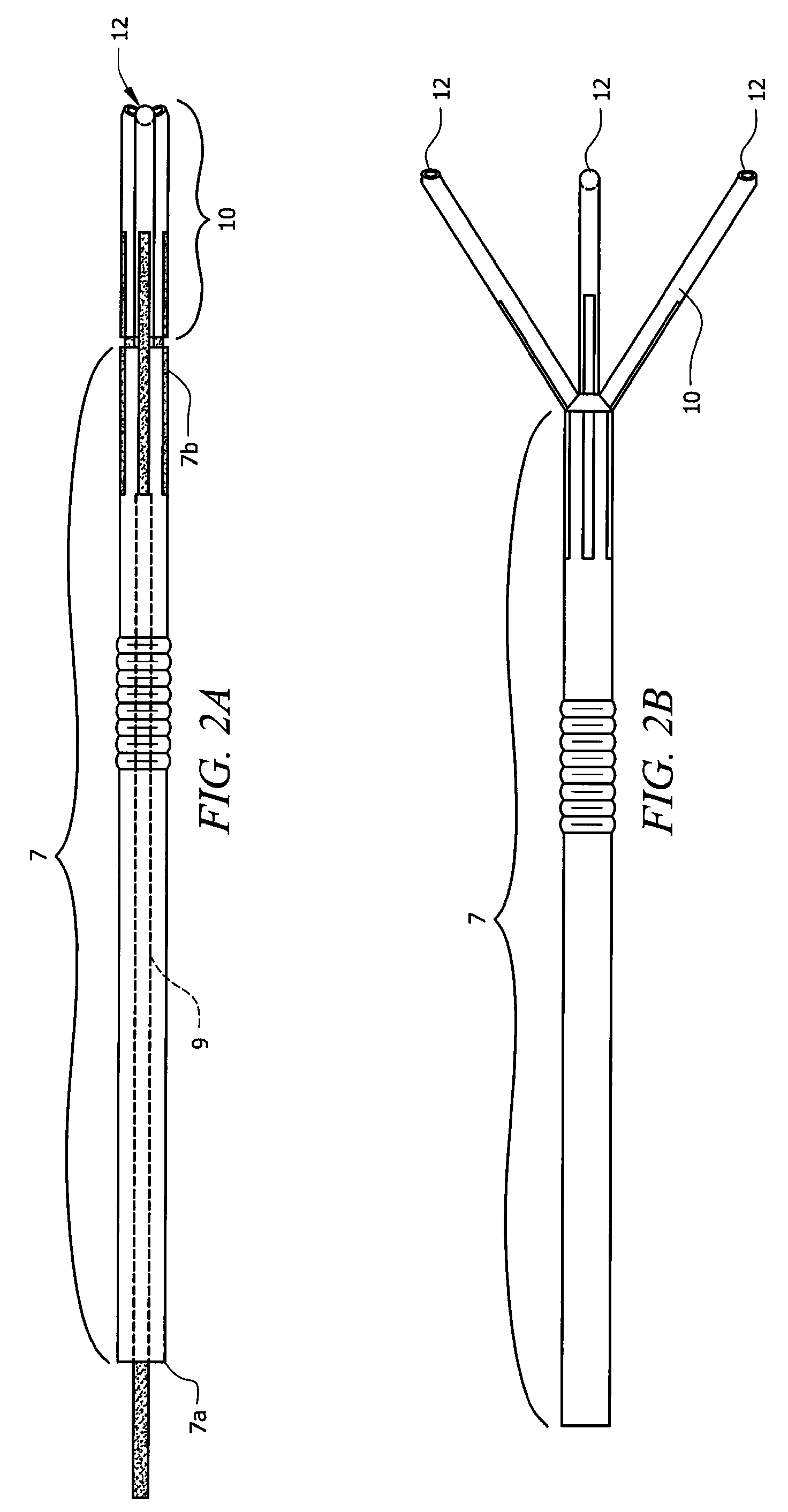
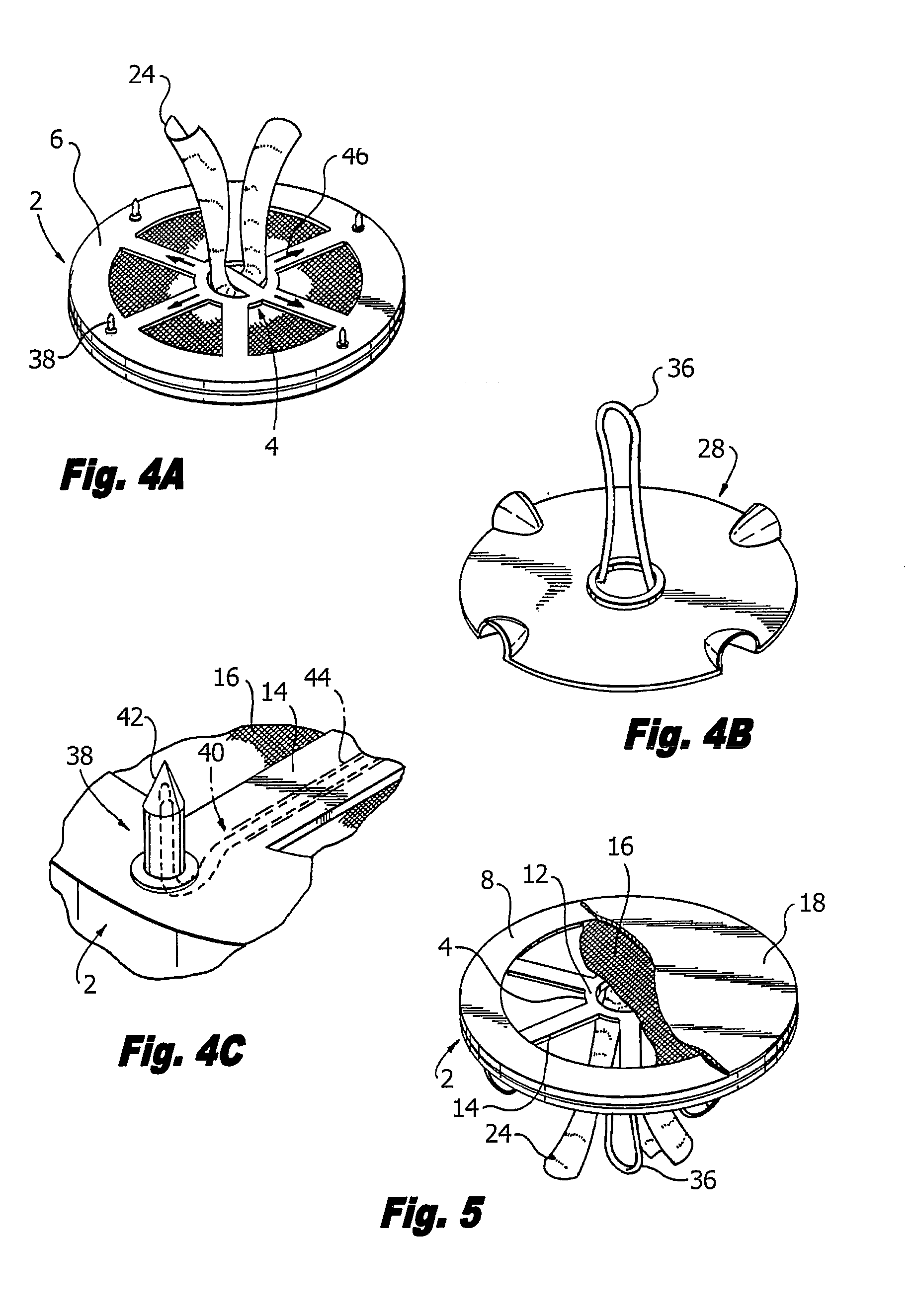
Laparoscopic hernia mesh spreader
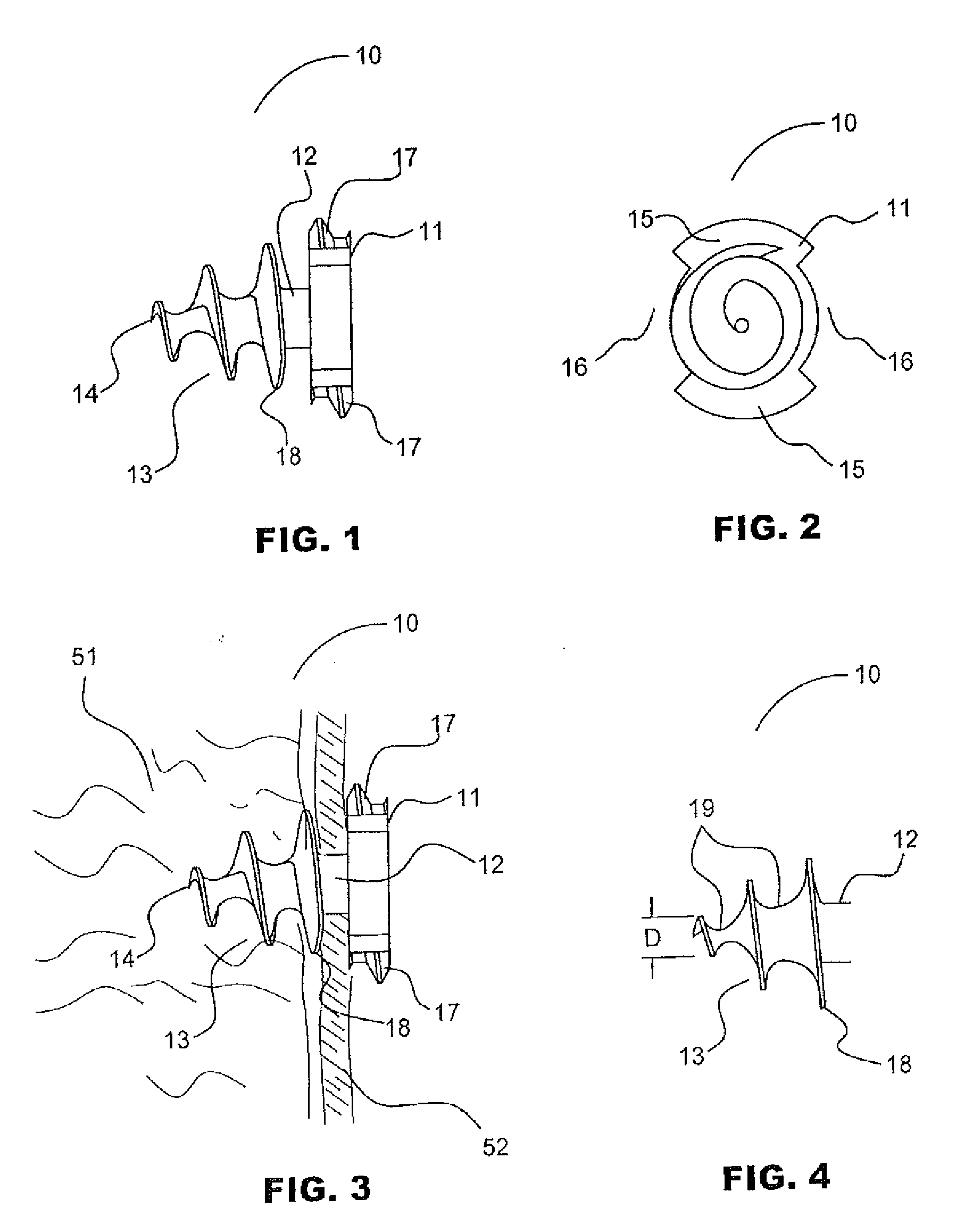
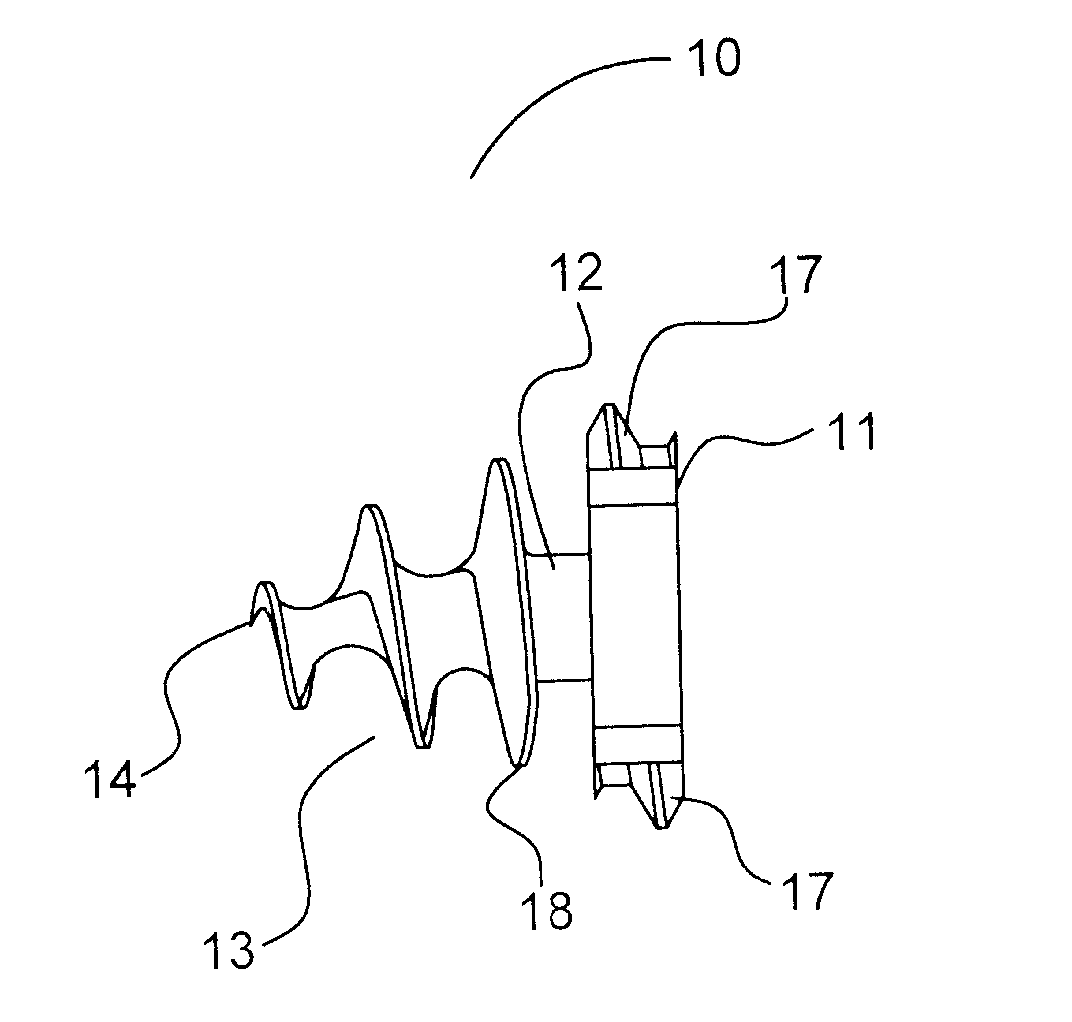
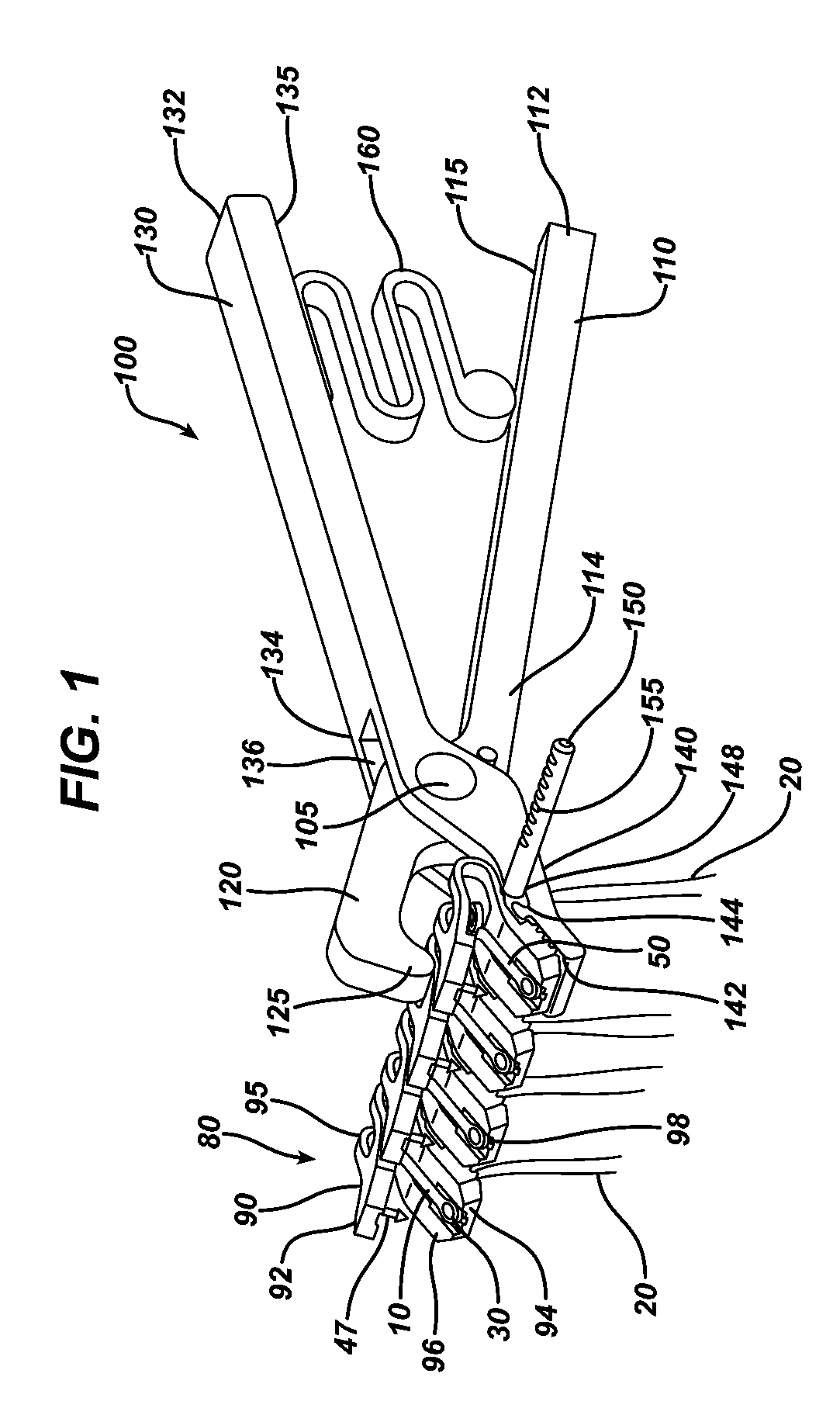
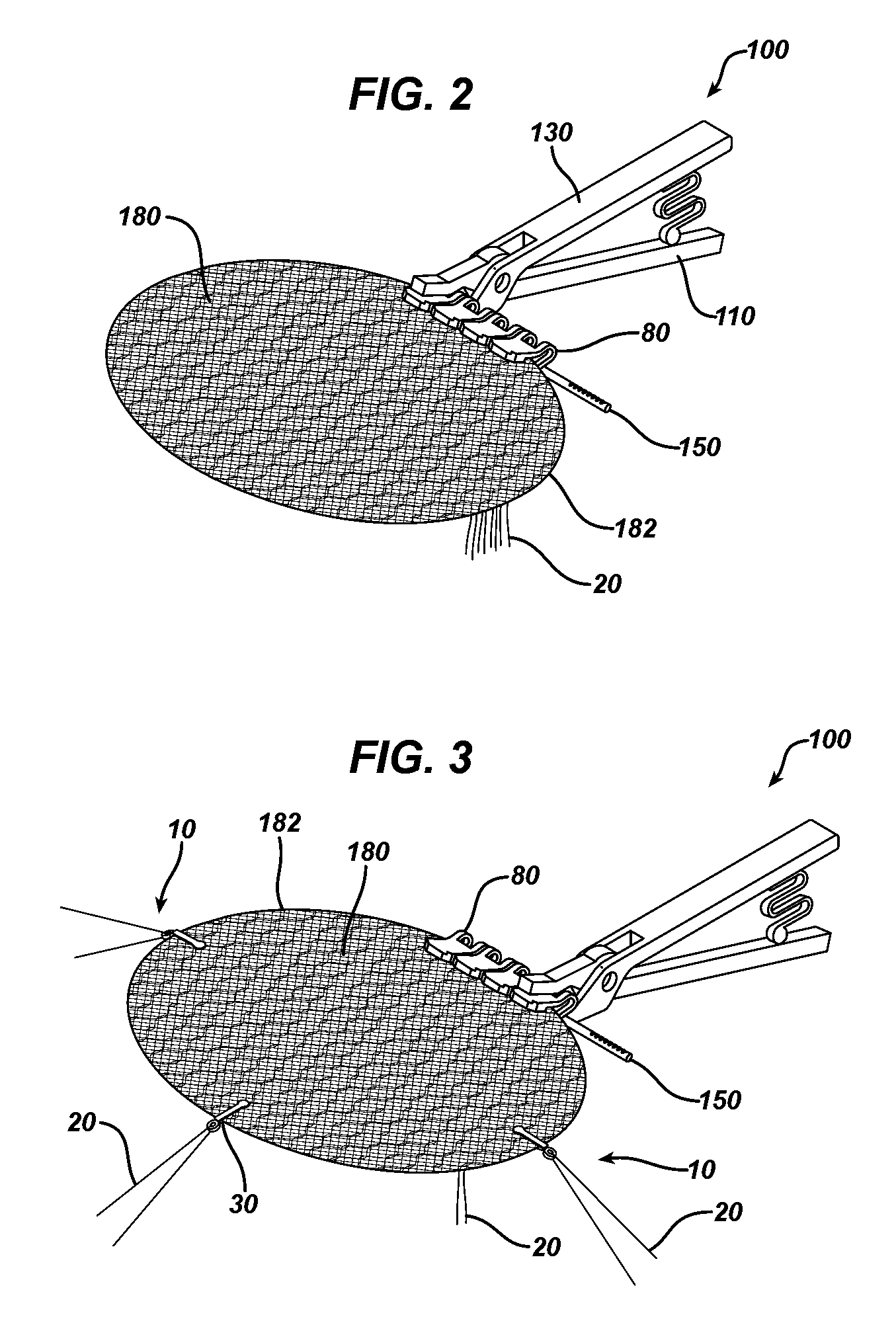
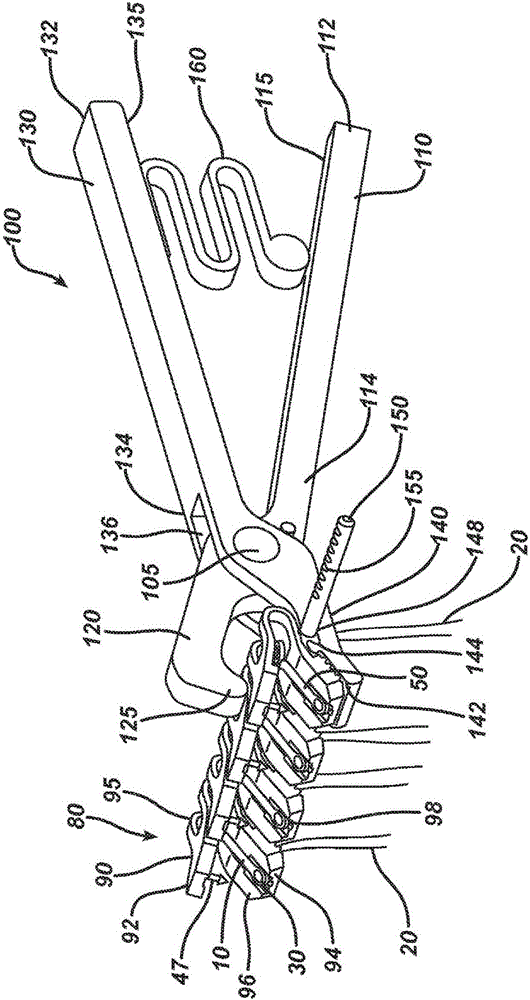
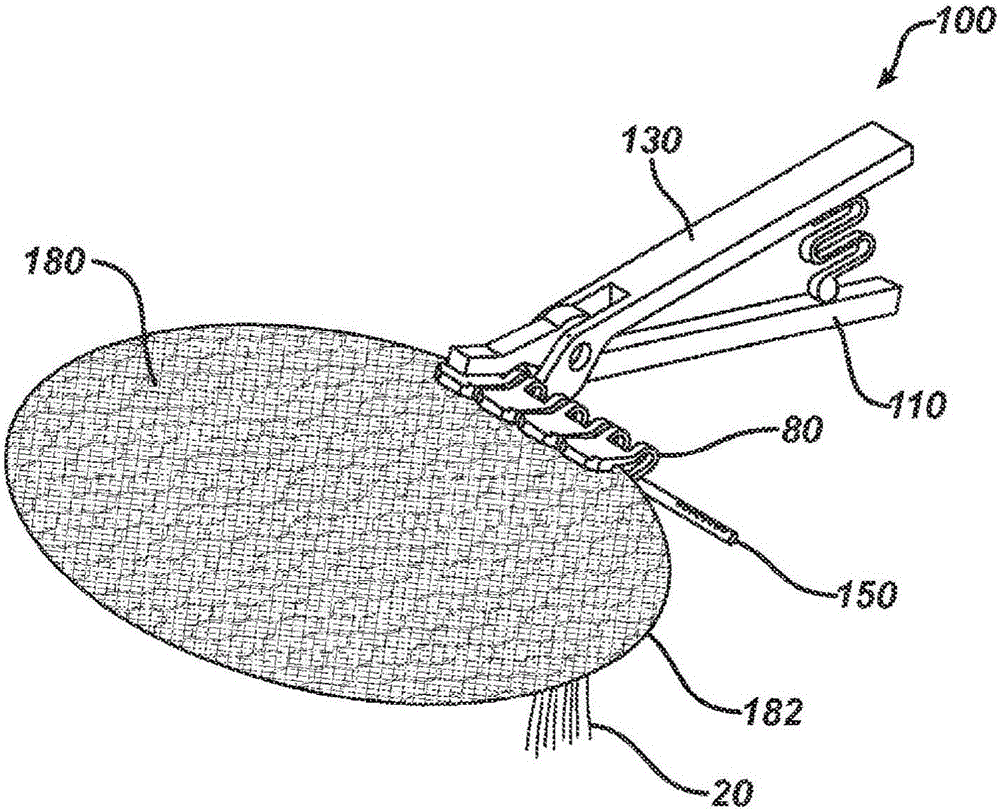
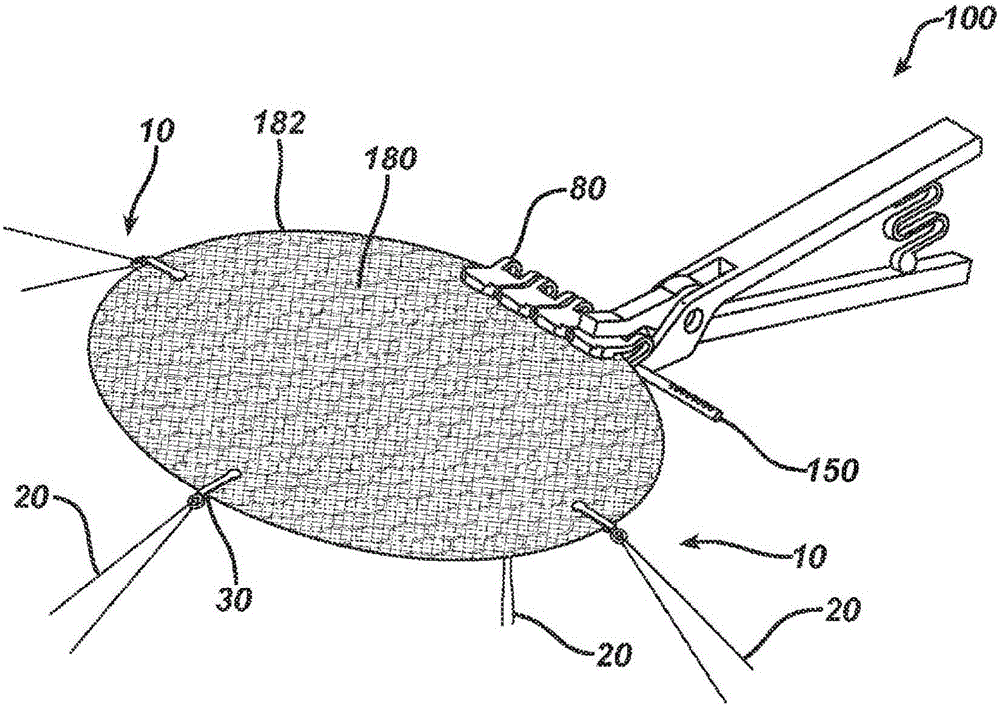
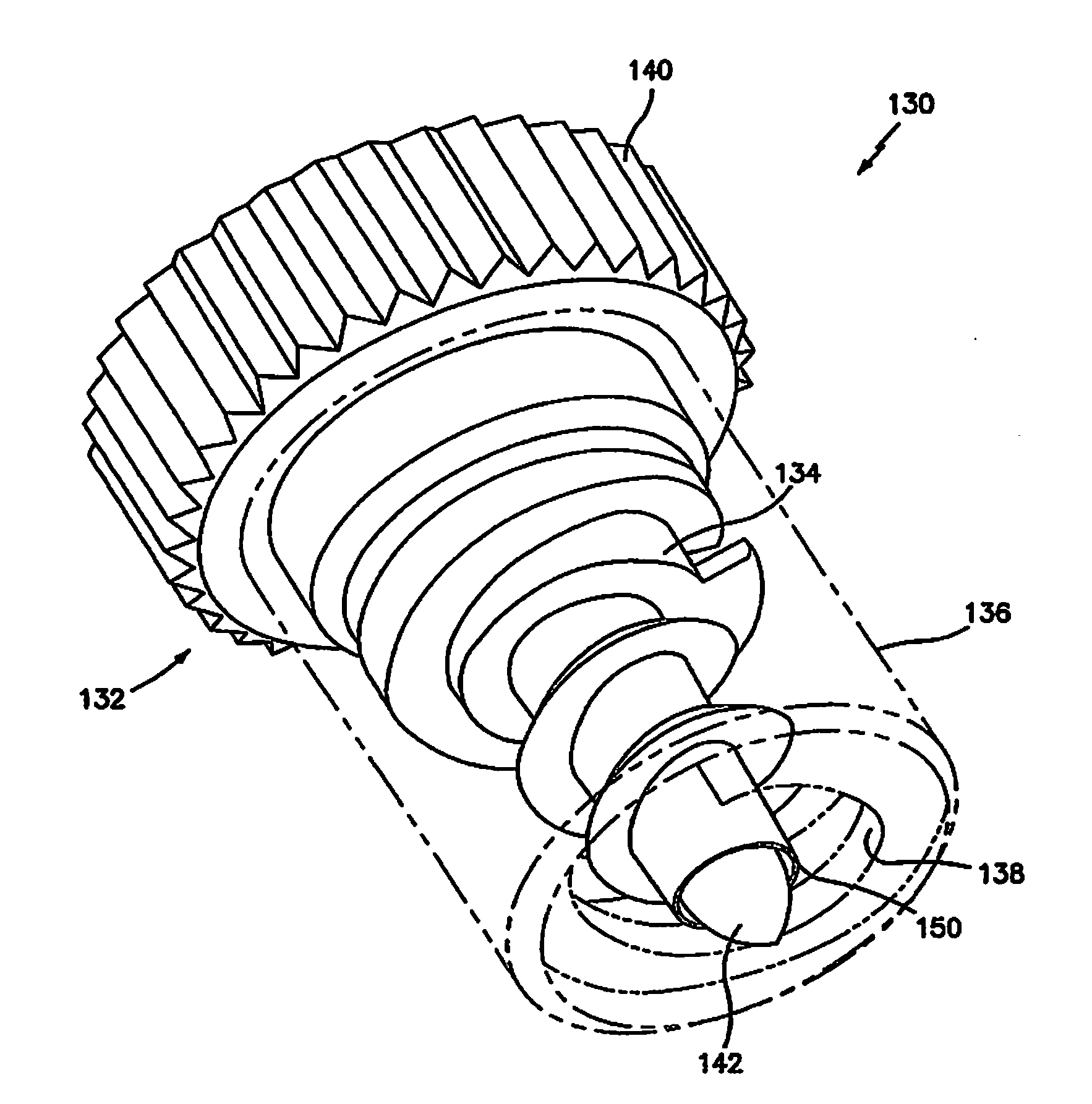
An apparatus is provided for the laparoscopic deployment and positioning of surgical materials, such as mesh. The mesh is applied by at least one extension arm which radiates from a central shaft. Alternate embodiments employ simultaneously and / or individually extended rigid arms, and simultaneously deployed resilient arms. Various methods are also disclosed for attaching the mesh to the abdominal wall once it is deployed by the extension arms. Illustrative attaching methods include staples, low viscosity adhesives, and electro-cauterization.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
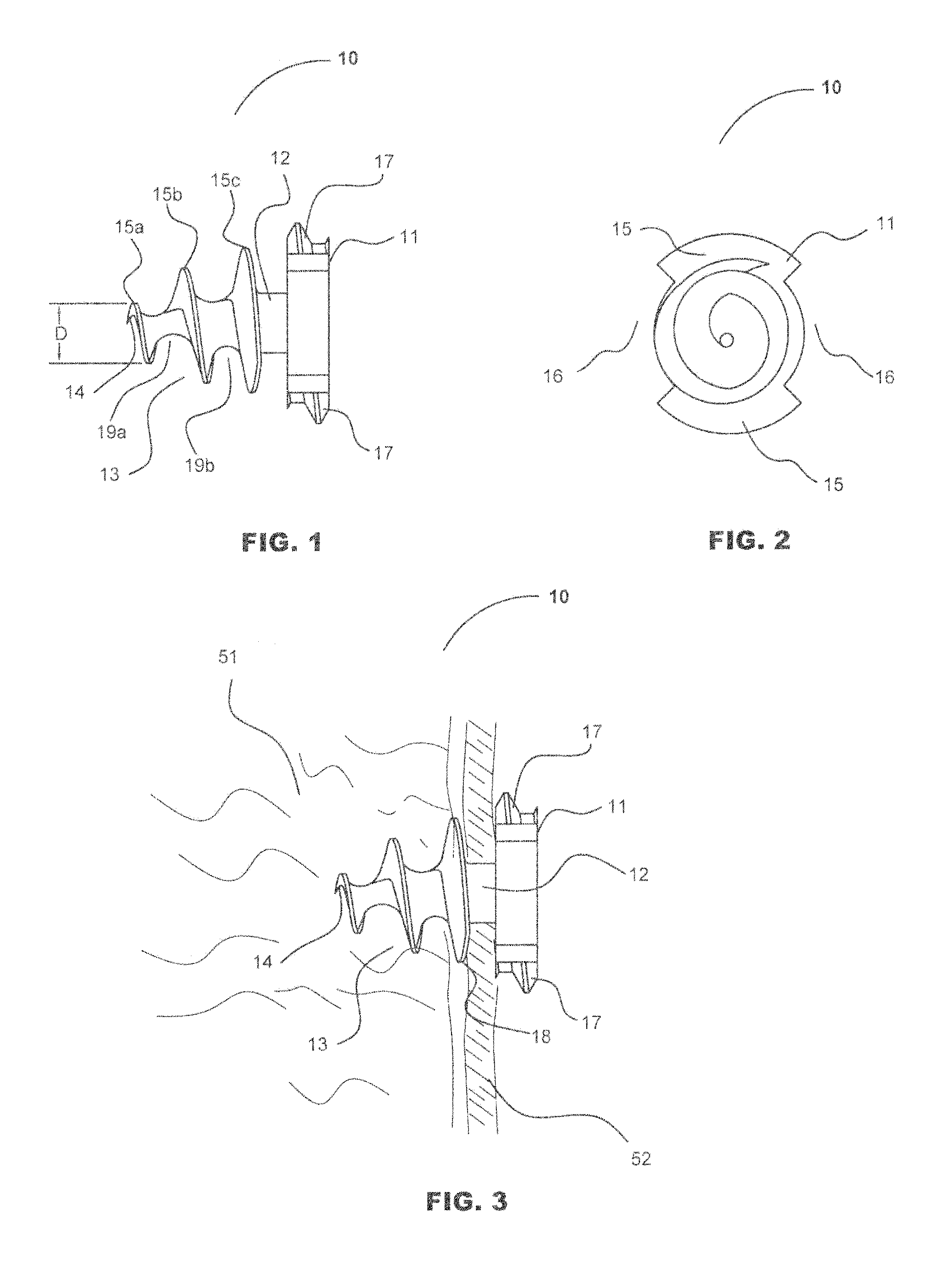
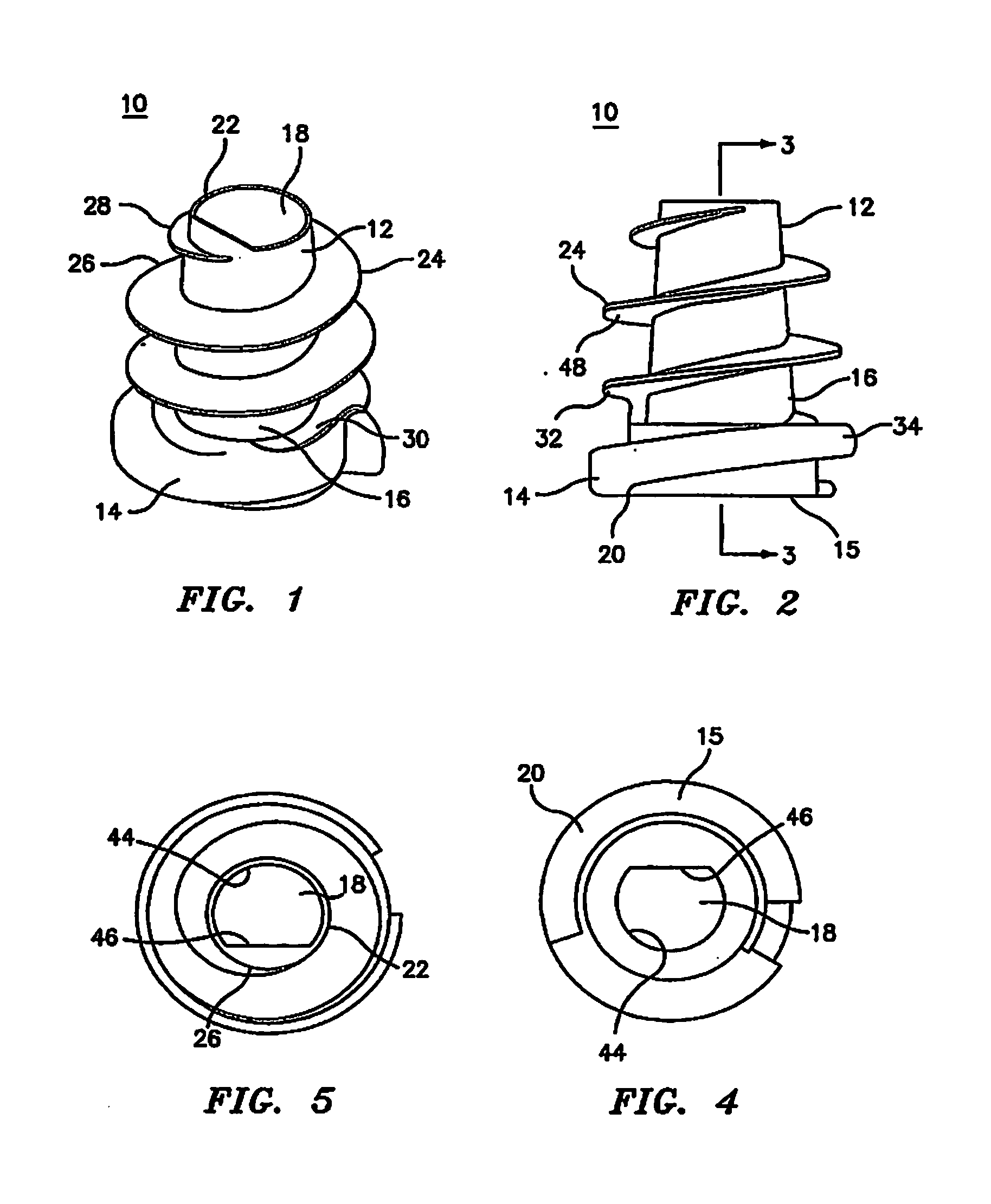
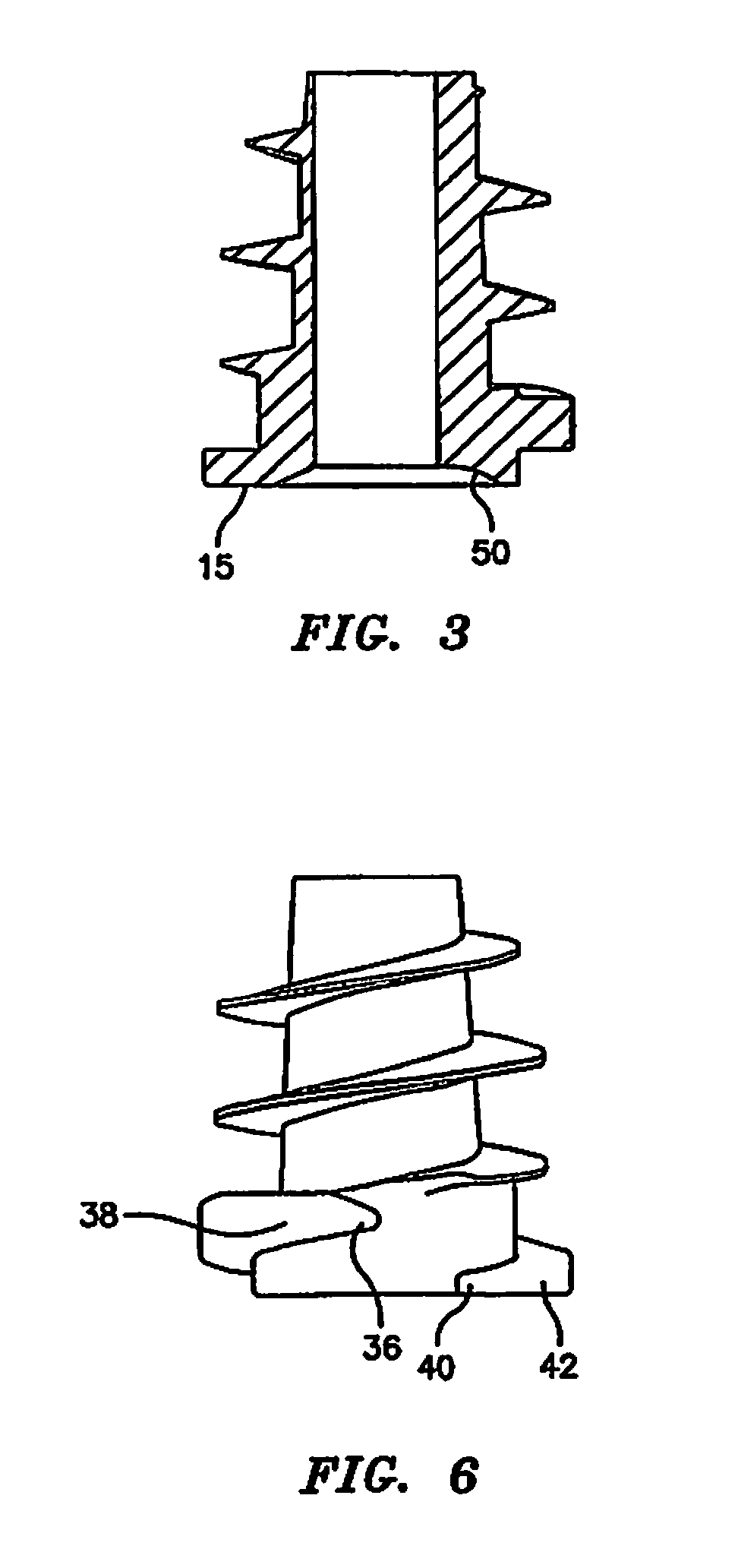
Absorbable Fastener for Hernia Mesh Fixation
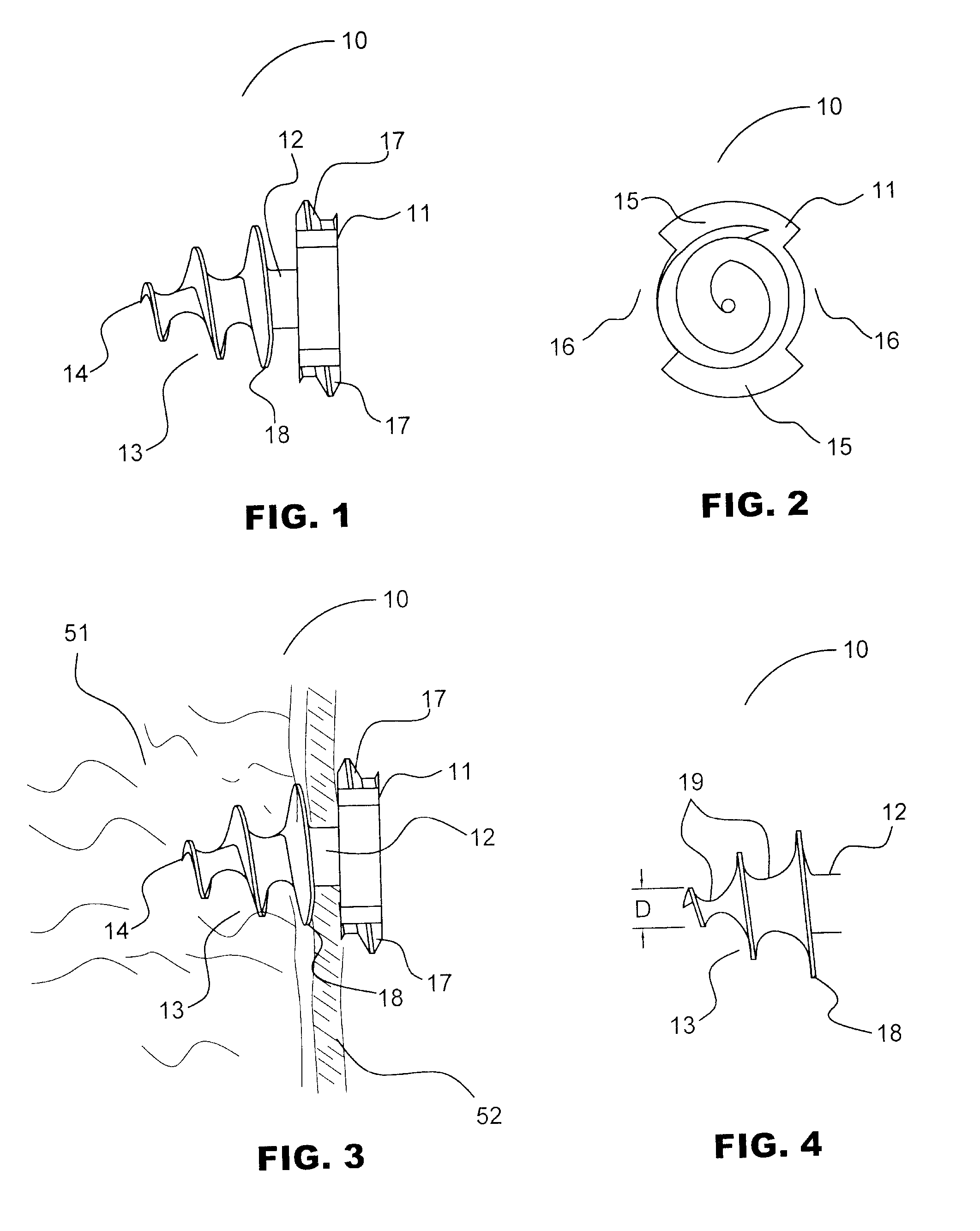
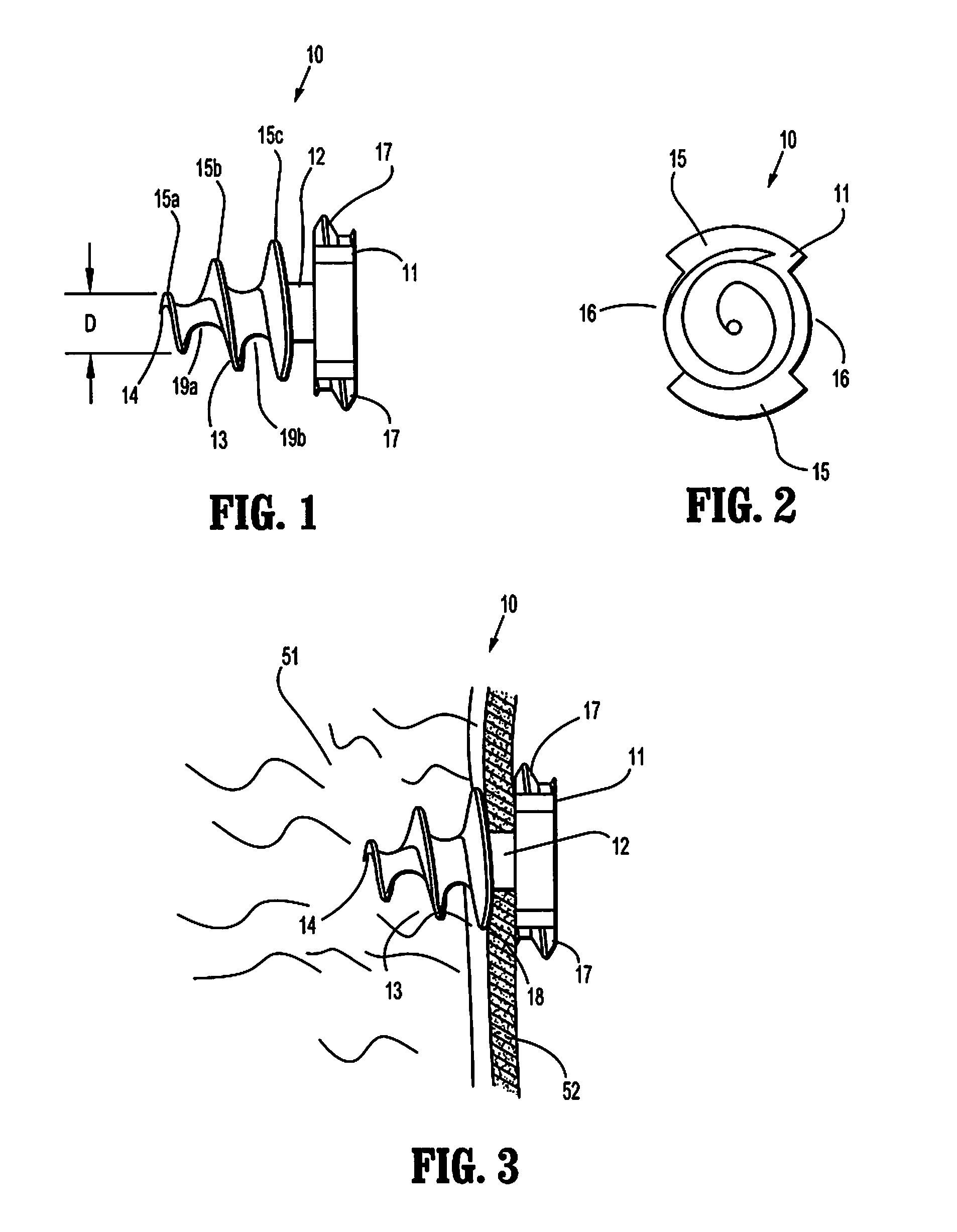
ActiveUS20070038220A1Degraded considerablyReasonable “ kill ” timeSuture equipmentsLigamentsHernia meshSoft tissue
A method of forming and deploying an improved absorbable fastener for hernia mesh fixation is disclosed. The absorbable fastener of the present invention functions to securely fasten tough, non macro-porous, and relative inelastic mesh to soft tissue. The fastener is formed from co-polymers of lactide and glycolide.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
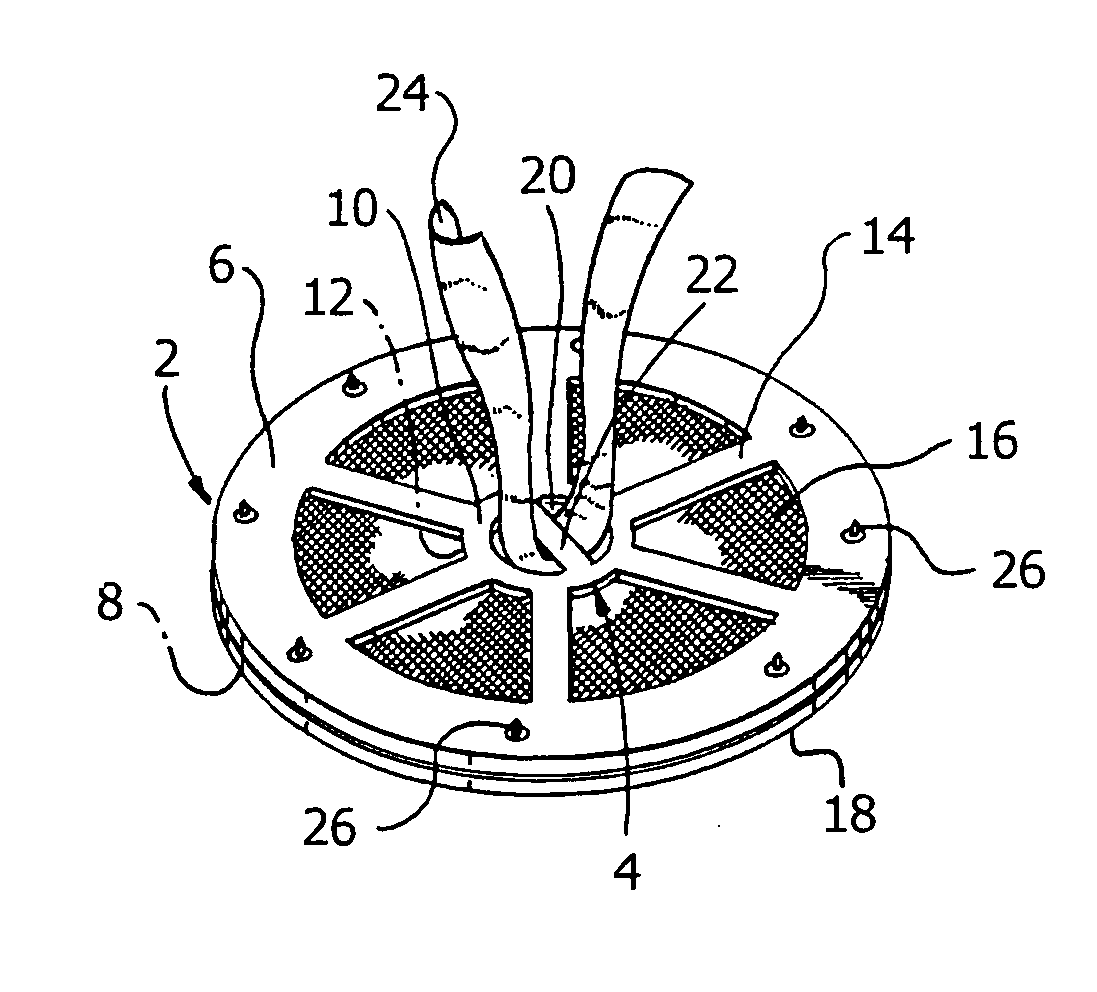
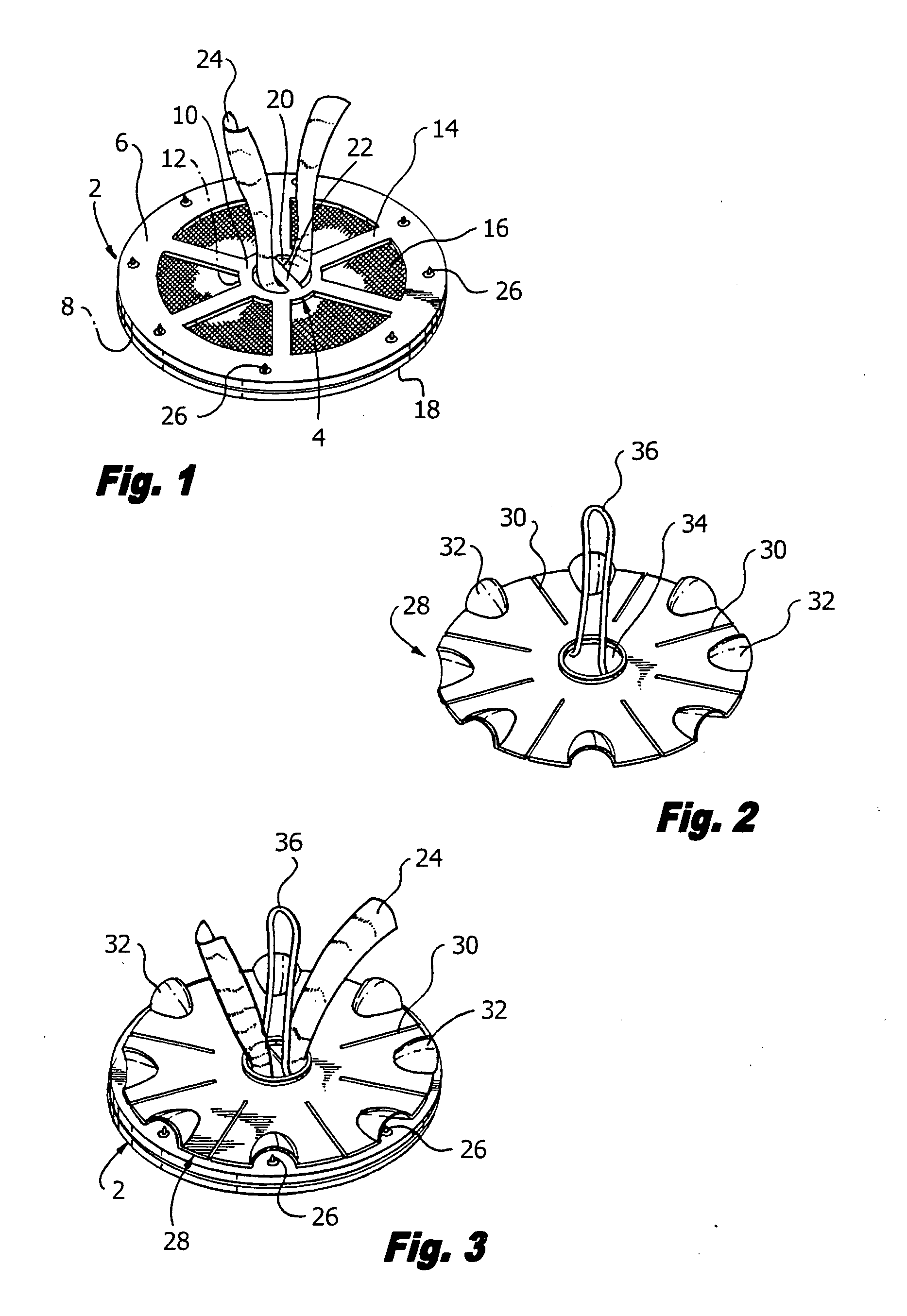
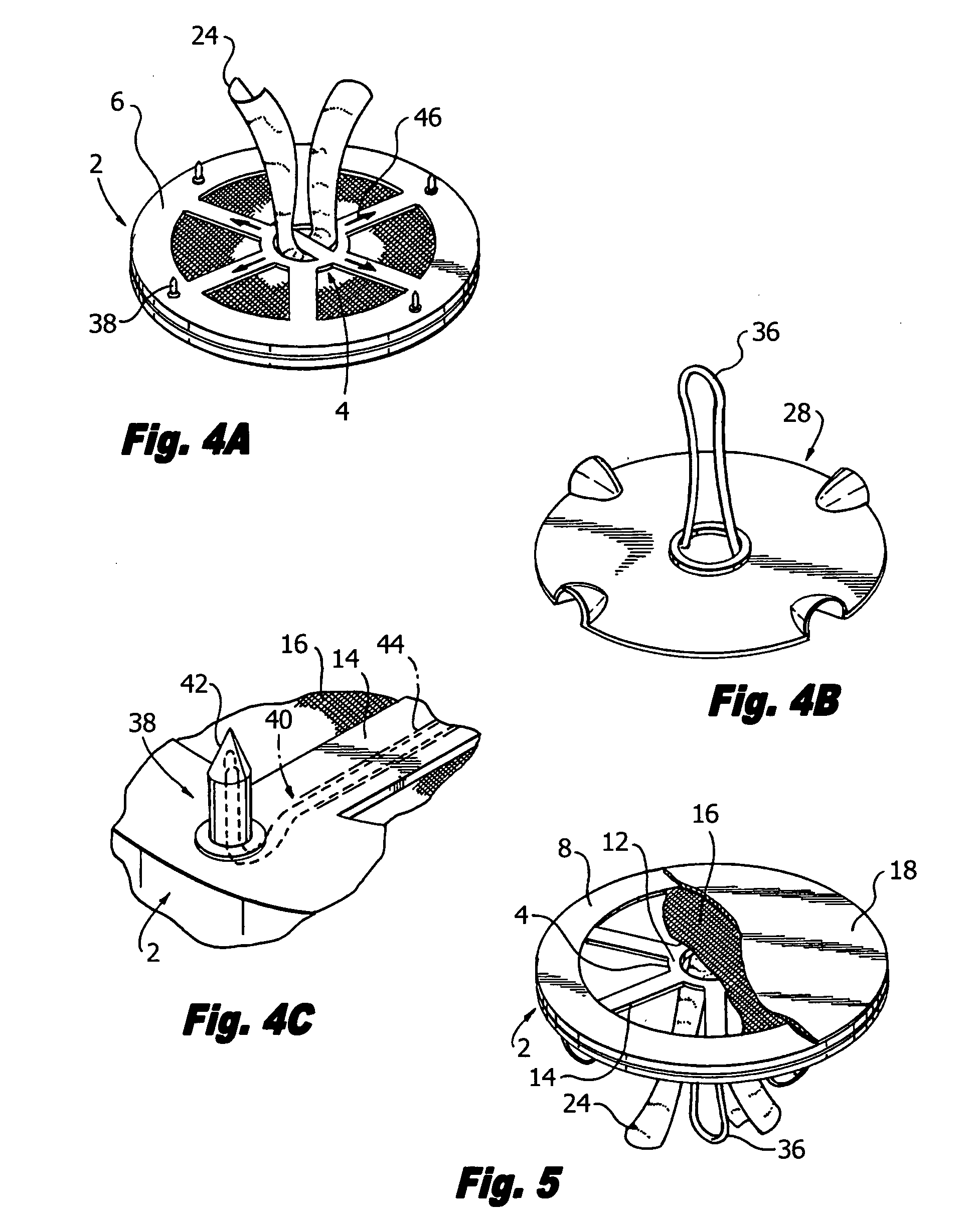
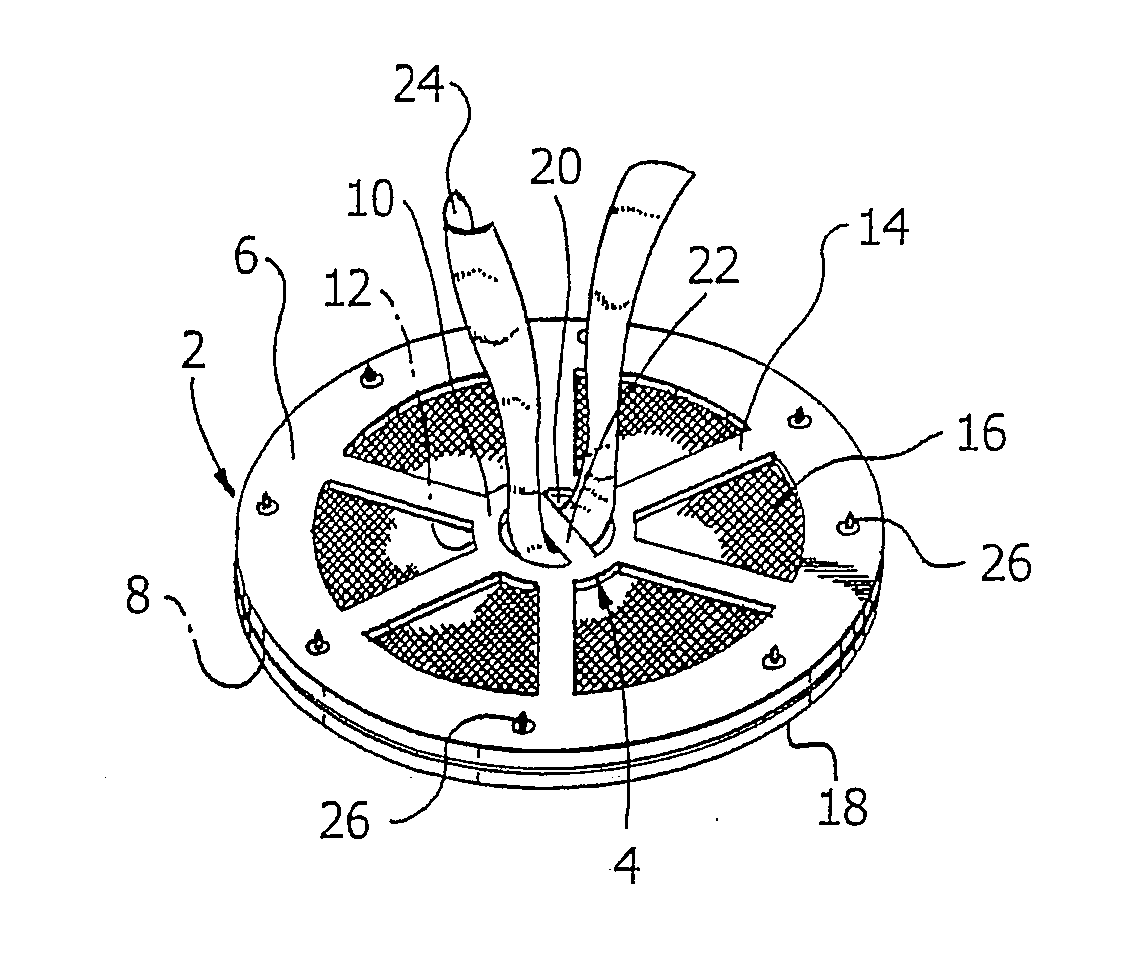
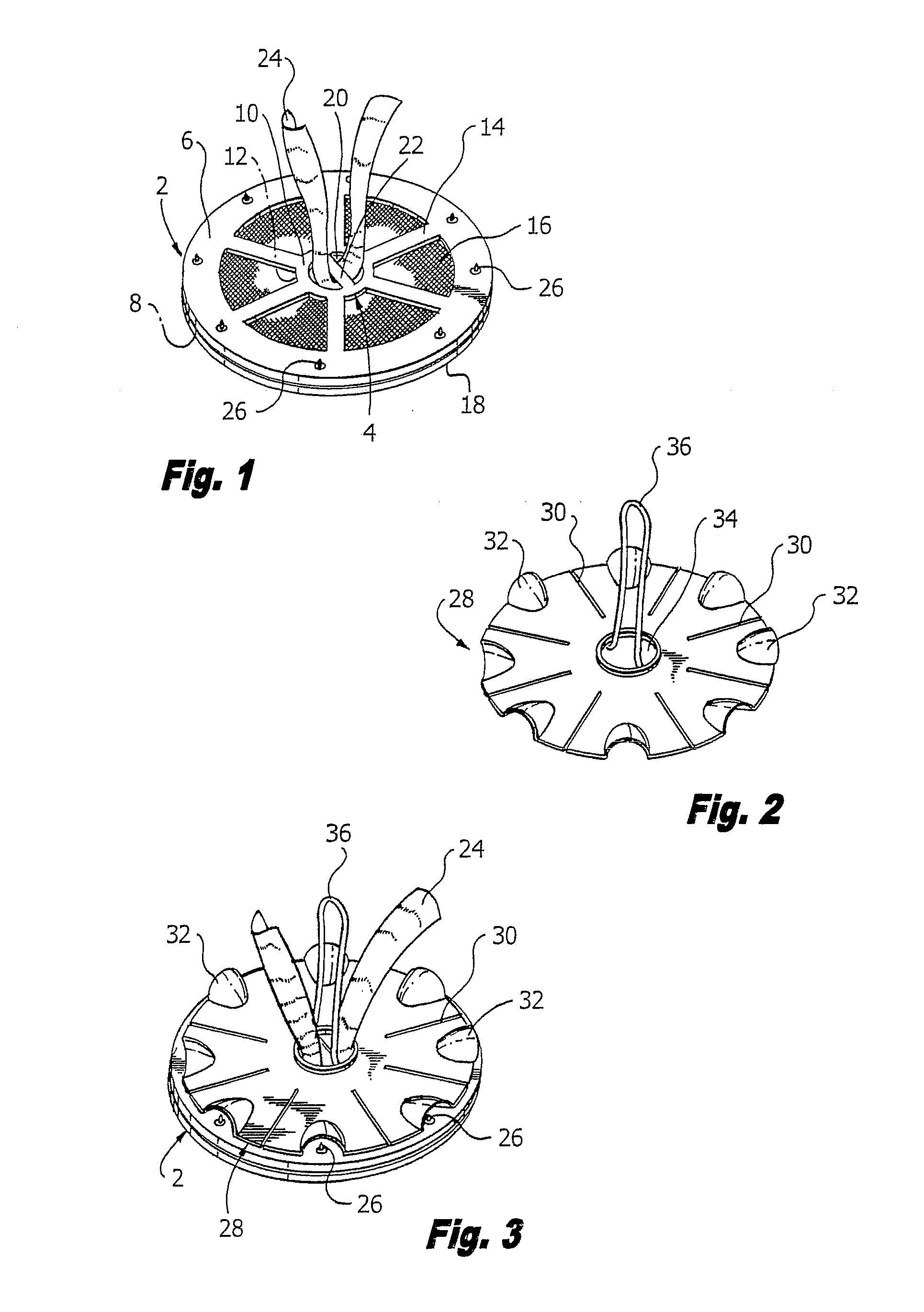
Hernia mesh support device
A hernia mesh support device includes an outer ring, an inner ring and a plurality of ring support members extending between and interconnected to the outer ring and inner ring. On a first axial side of the outer ring and inner ring is situated a layer of mesh material. On a second axial side of the outer ring and inner ring is situated an anti-adhesion barrier. A plurality of barbed pins or hollow needles extend from the first axial side of the outer ring. A removable protective cover covers the plurality of barbed pins or hollow needles.
Owner:ETHICON INC
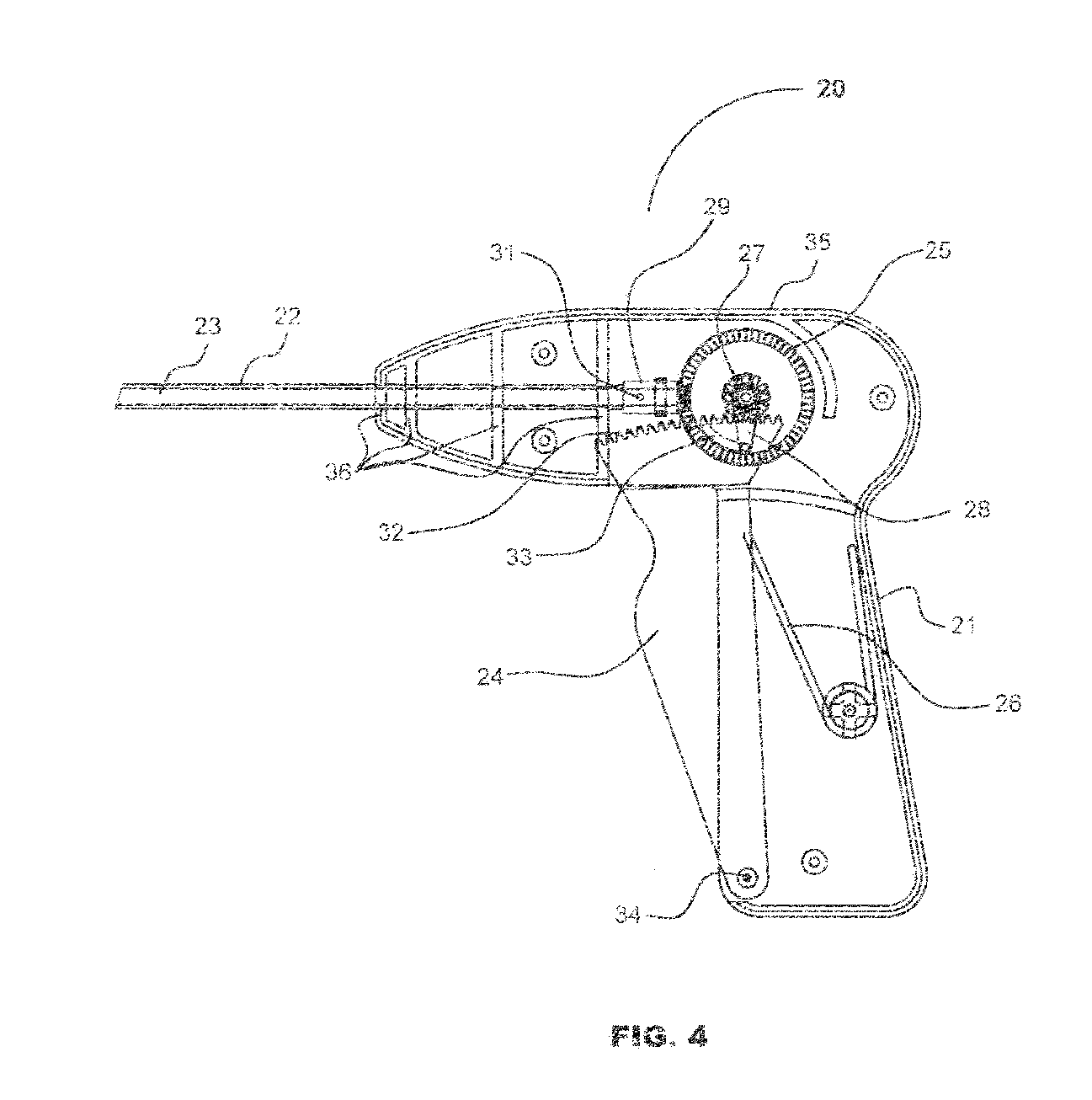
Hernia mesh tacks
InactiveUS20050171562A1Increase drive surface areaEasy to insertSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringSurgical department
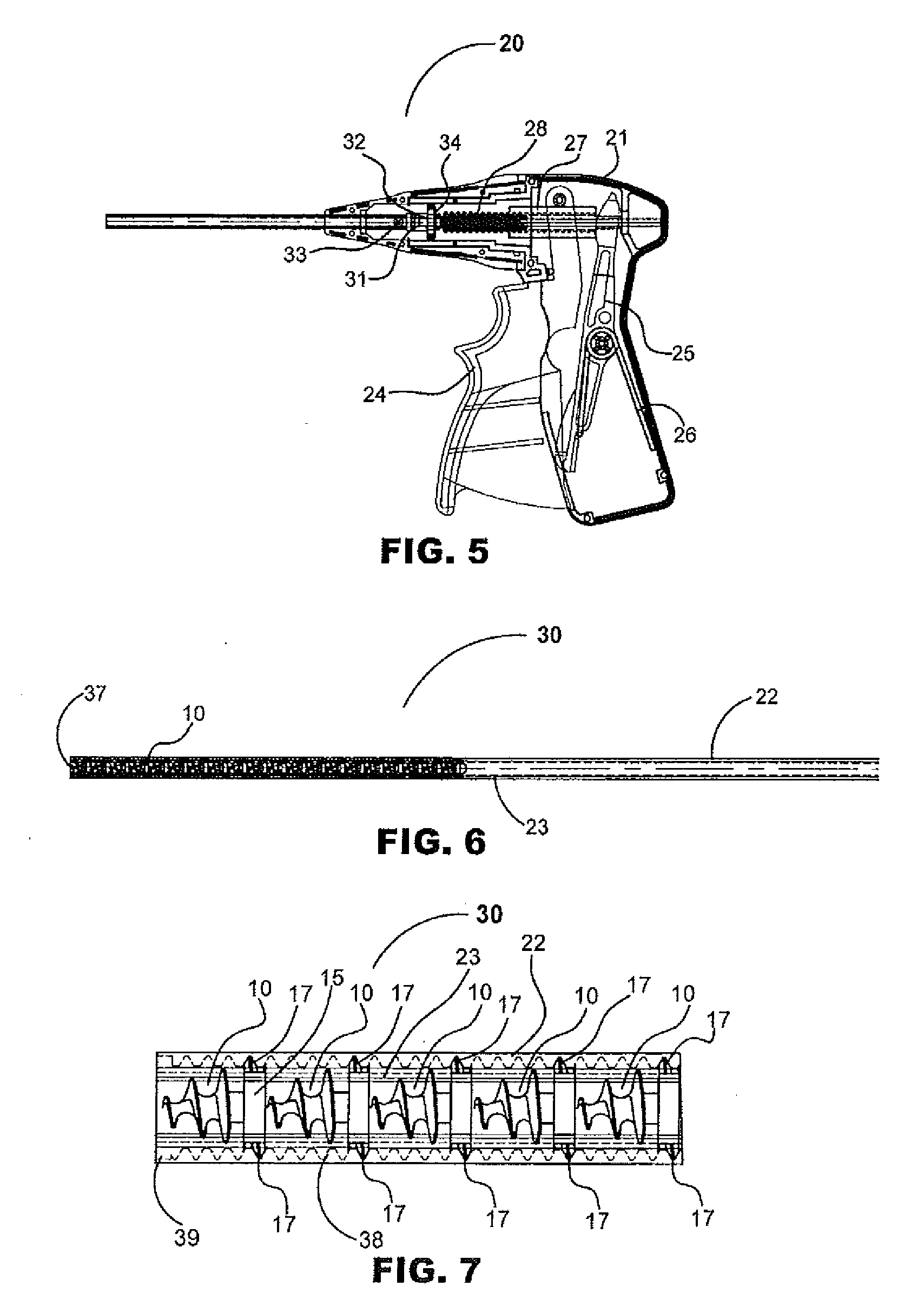
There are disclosed various embodiments of surgical tacks for use in surgical procedures. The tacks generally include a head and a barrel portion extending distally from the head. Preferably the head and the barrel portion define a throughbore for receipt of a drive instrument. A thread on the head is provided to engage threads in the installation tool. A tissue thread is provided on the barrel, portion to engage tissue. Distal and proximal surfaces of the tissue thread may be oriented at various angles relative to the barrel portion. There is also disclosed an insertion instrument to insert one or more tacks as well as a method of use. There is further disclosed a model device for use in explaining the operation of the instrument.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Absorbable anchor for hernia mesh fixation
A method of forming and deploying an improved absorbable anchor for hernia mesh fixation is disclosed. The absorbable anchor of the present invention functions to securely fasten tough, non macro-porous, and relative inelastic mesh to soft tissue. The anchor is formed from co-polymers of lactide and glycolide.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Absorbable Anchor for Hernia Mesh Fixation
A method of forming and deploying an improved absorbable anchor for hernia mesh fixation is disclosed. The absorbable anchor of the present invention functions to securely fasten tough, non macro-porous, and relative inelastic mesh to soft tissue. The anchor is formed from co-polymers of lactide and glycolide.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Absorbable fastener for hernia mesh fixation
A method of forming and deploying an improved absorbable fastener for hernia mesh fixation is disclosed. The absorbable fastener of the present invention functions to securely fasten tough, non macro-porous, and relative inelastic mesh to soft tissue. The fastener is formed from co-polymers of lactide and glycolide.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Laparoscopic hernia mesh spreader
An apparatus is provided for the laparoscopic deployment and positioning of surgical materials, such as mesh. The mesh is applied by at least one extension arm which radiates from a central shaft. Alternate embodiments employ simultaneously and / or individually extended rigid arms, and simultaneously deployed resilient arms. Various methods are also disclosed for attaching the mesh to the abdominal wall once it is deployed by the extension arms. Illustrative attaching methods include staples, low viscosity adhesives, and electro-cauterization.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
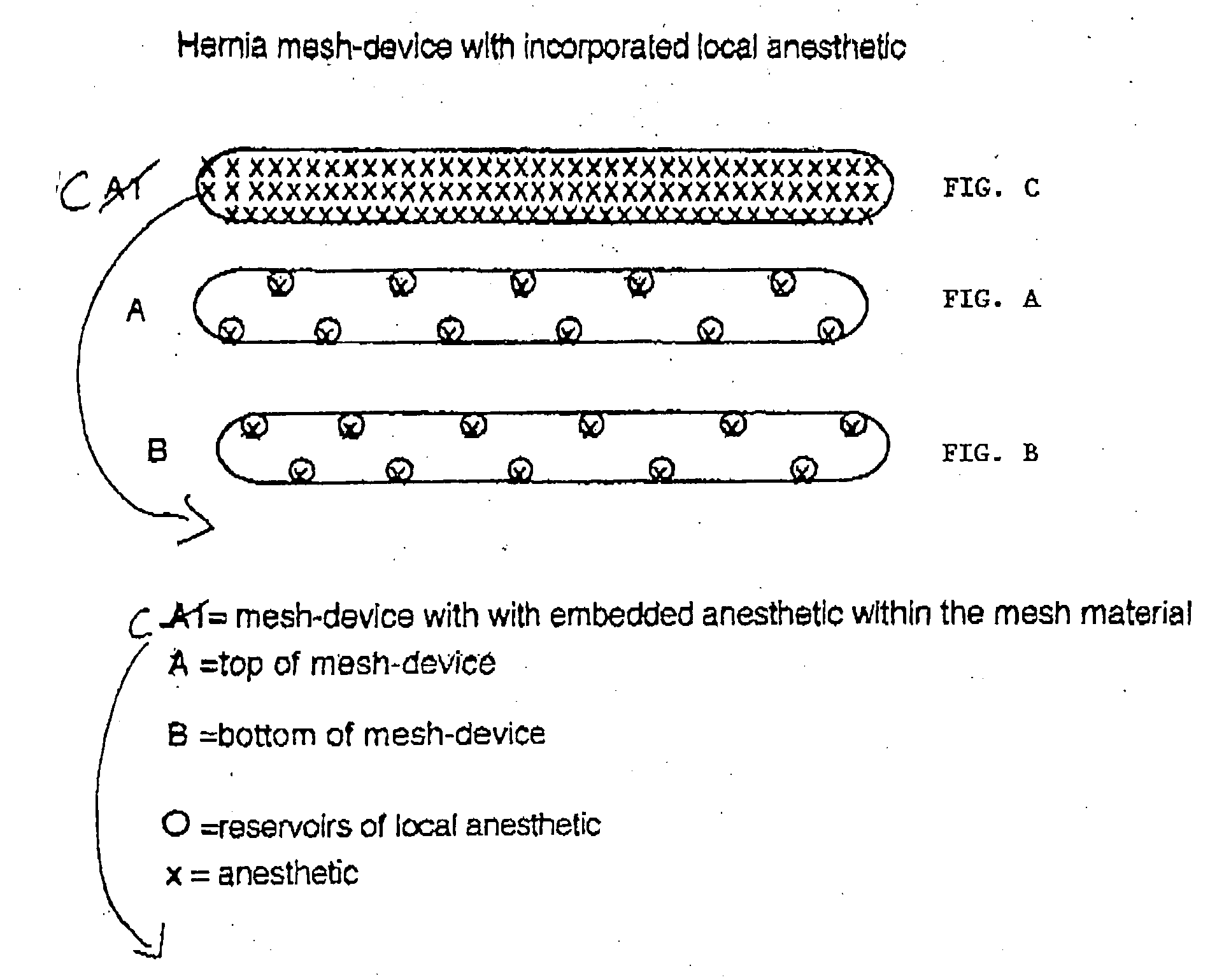
Hernia mesh-device with incorporated local anesthetic
InactiveUS20050015102A1Reduce postoperative painEqually distributedProsthesisWound clampsHerniaSurgical repair
A mesh-device for surgical repair of a hernia which includes a local anesthetic. The local anesthetic may be either embedded within the mesh, or provided in reservoirs, but is generally evenly distributed across the mesh-device. The local anesthetic is released over a predetermined duration at a predetermined rate.
Owner:CHEFITZ ALLEN B
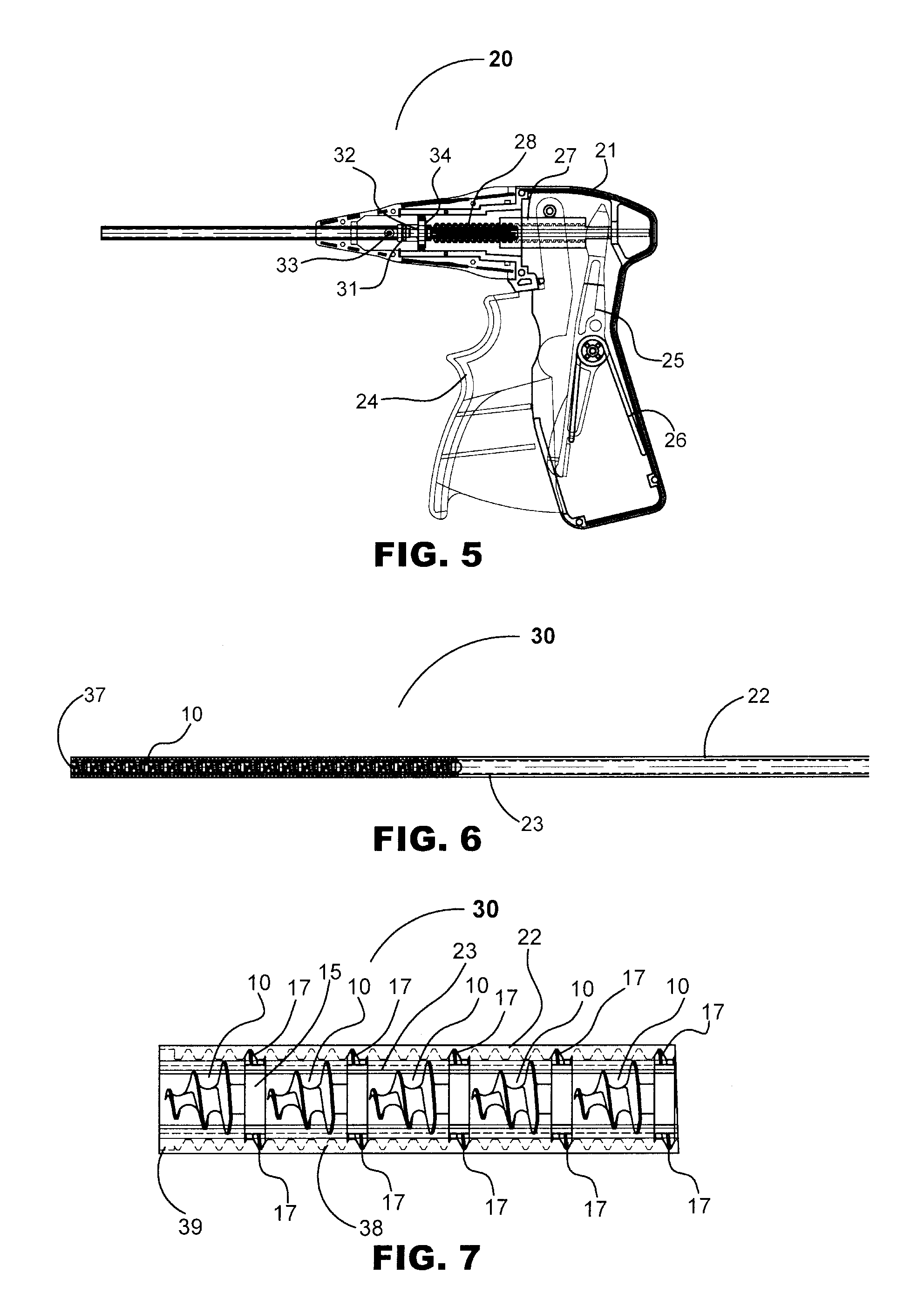
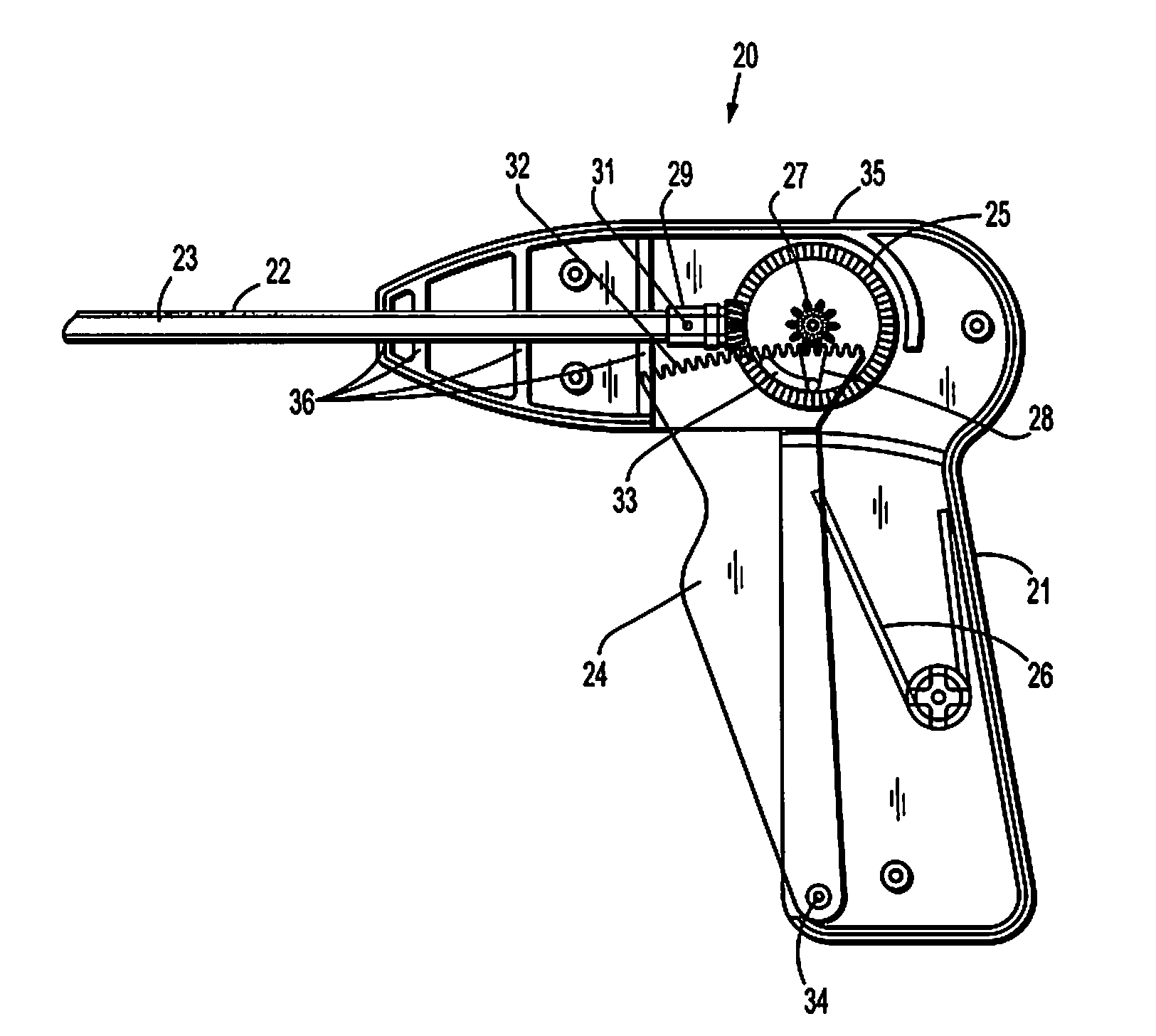
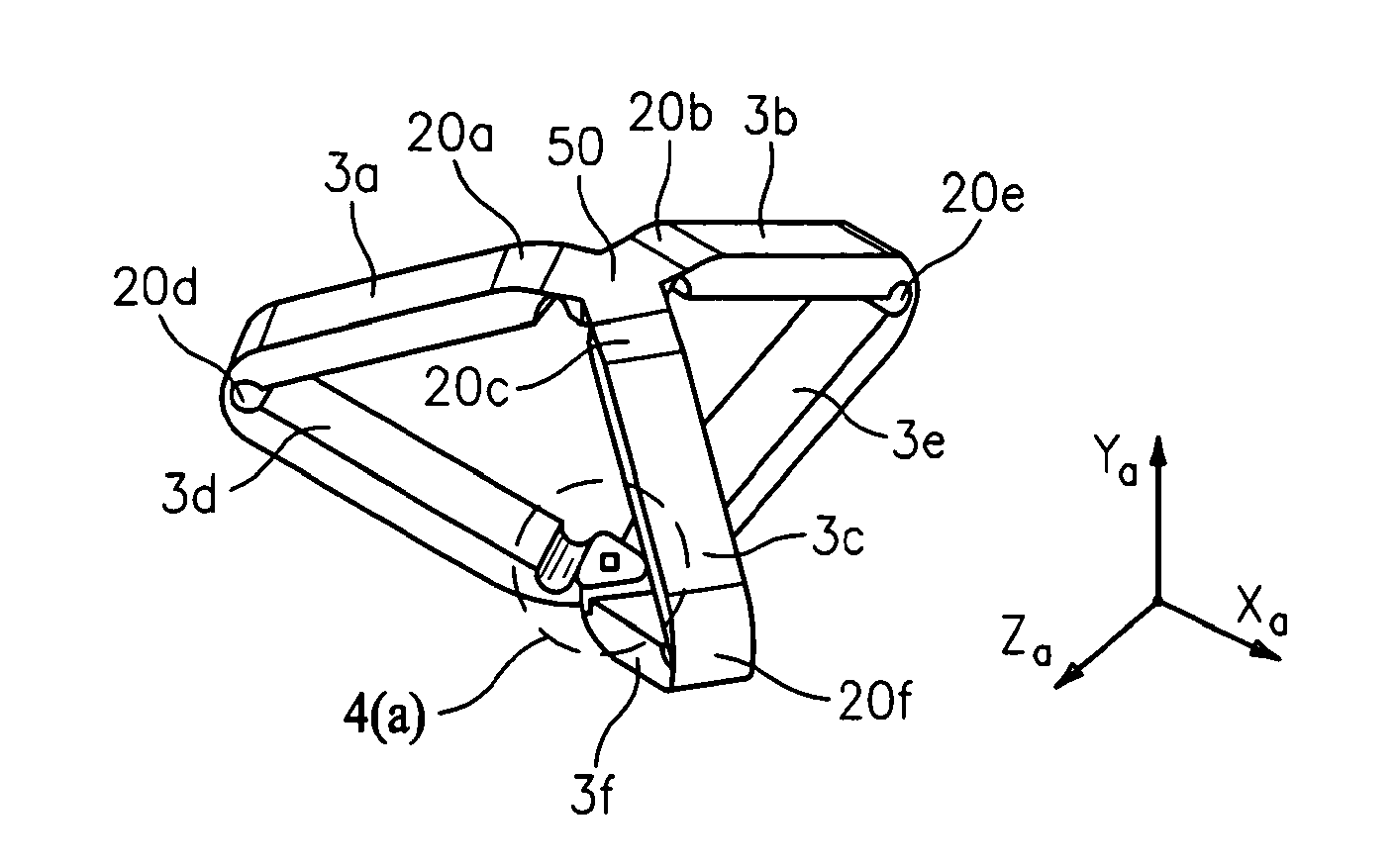
System and method for hernia mesh fixation
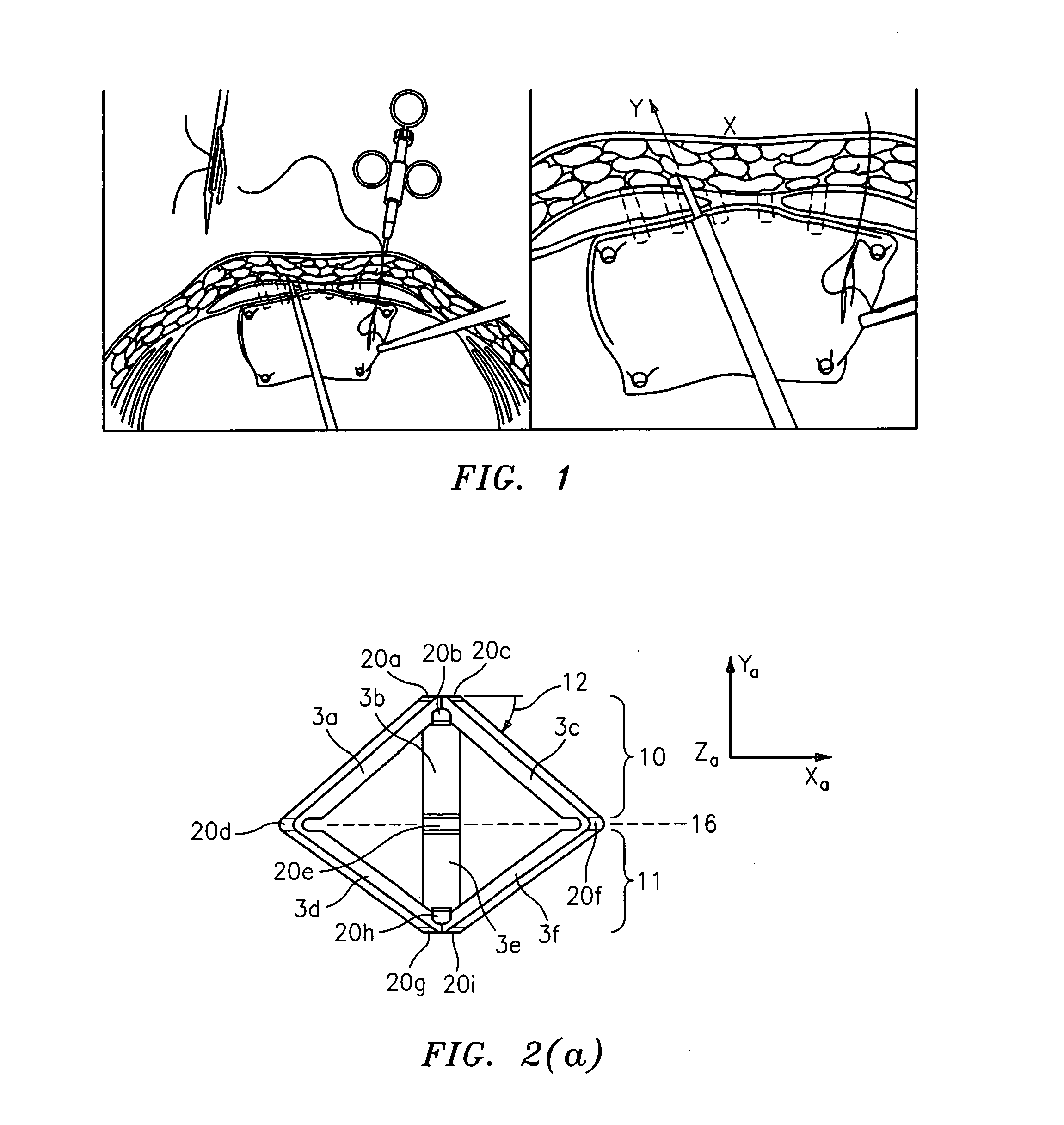
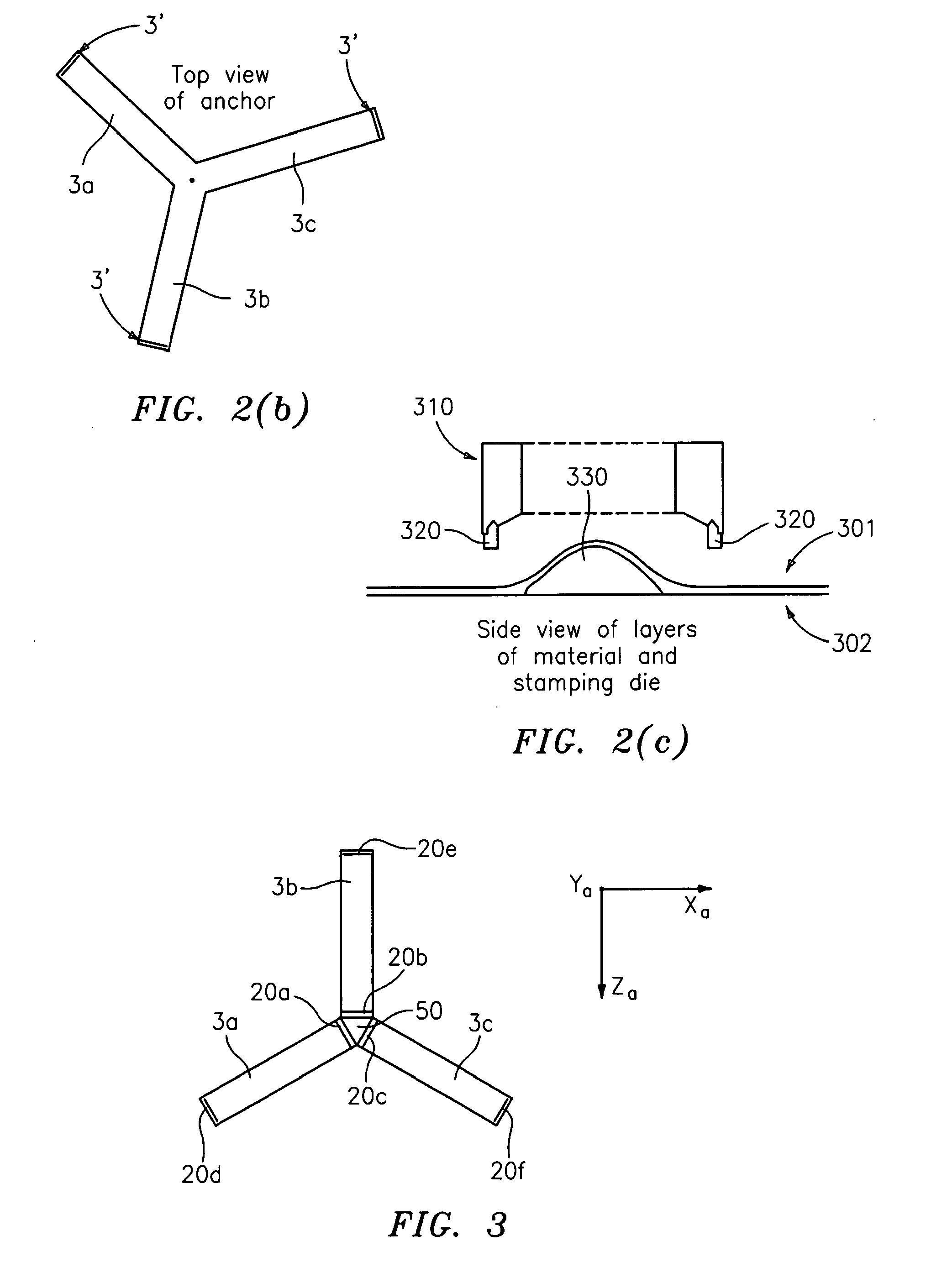
InactiveUS20110106113A1Avoid damagePermit transfascial fixationSurgical staplesWound clampsState of artEngineering
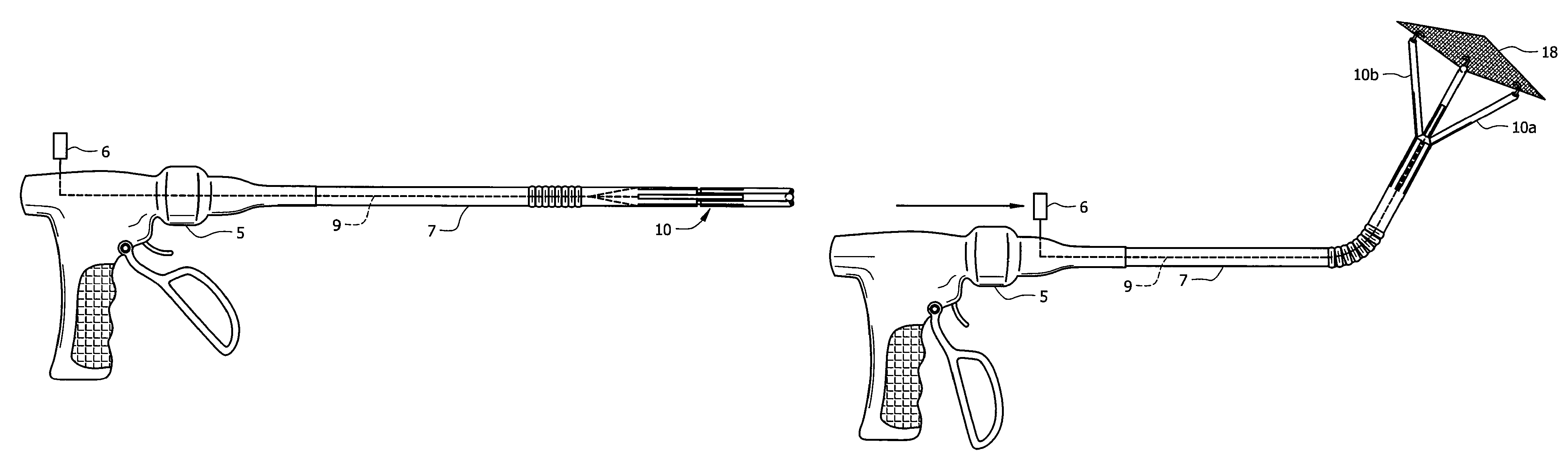
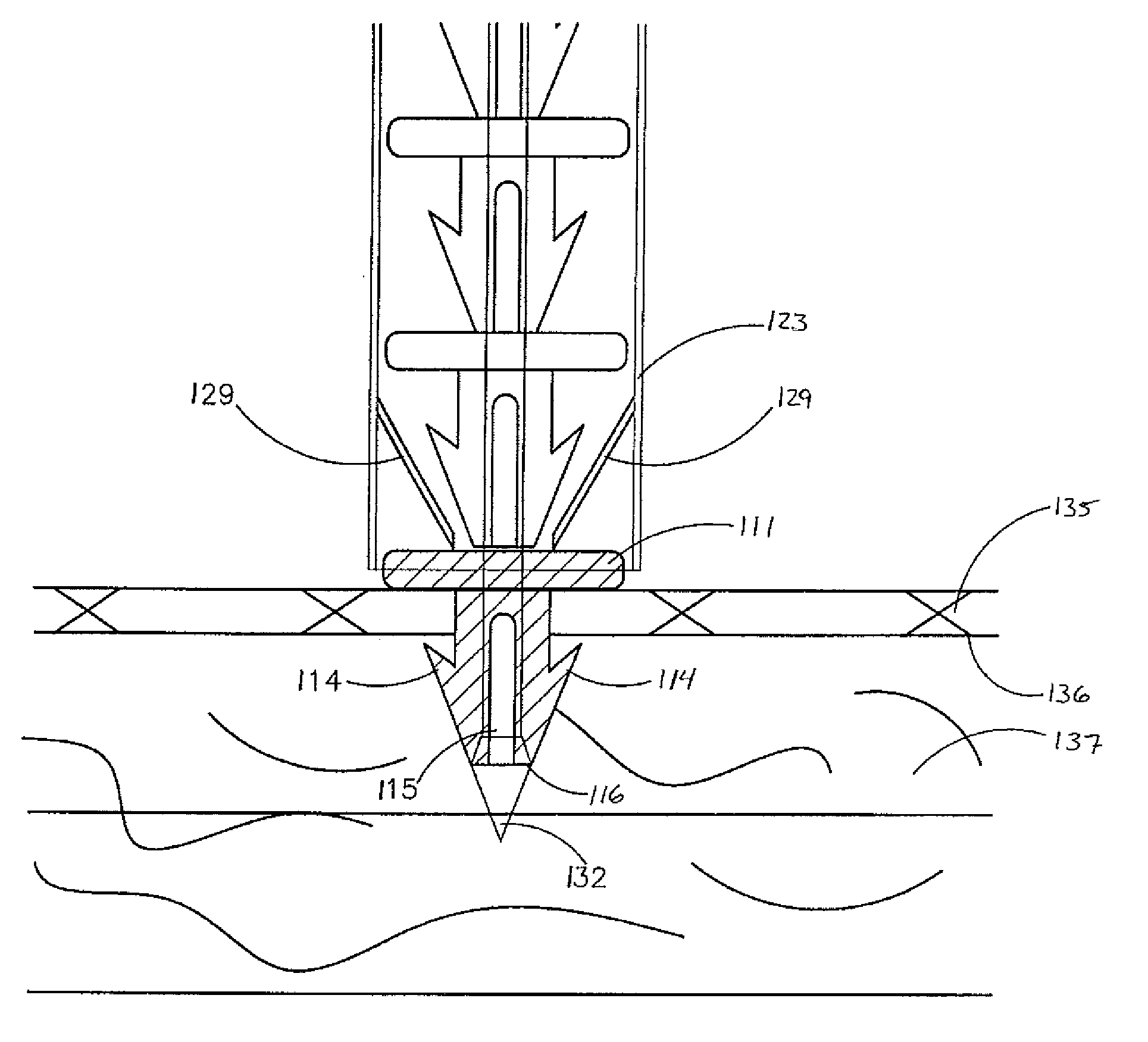
The invention includes a surgical fastener and associated deployment system and method that overcomes the drawbacks of prior art surgical mesh fixation devices. The surgical fastener and deployment system may be used to fixate a surgical mesh material to the abdominal wall for the purpose of hernia repair. In accordance with one embodiment, the fastener may include an anchor head comprising a bi-pyramid framework. The anchor head is preferably made from a highly deformable and biocompatible material that withstands high flexural strain within an oscillatory environment. The anchor head may be provided in an elongate, undeployed configuration, and then expanded during deployment into a second, generally planar configuration. The anchor head may be biased to expand into the generally planar configuration from the undeployed configuration in a variety of manners.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Surface Treated Polymeric Synthetic Hernia Mesh Prosthesis, Surface Treated Sutures and Staples and Methods of Manufacturing the Same
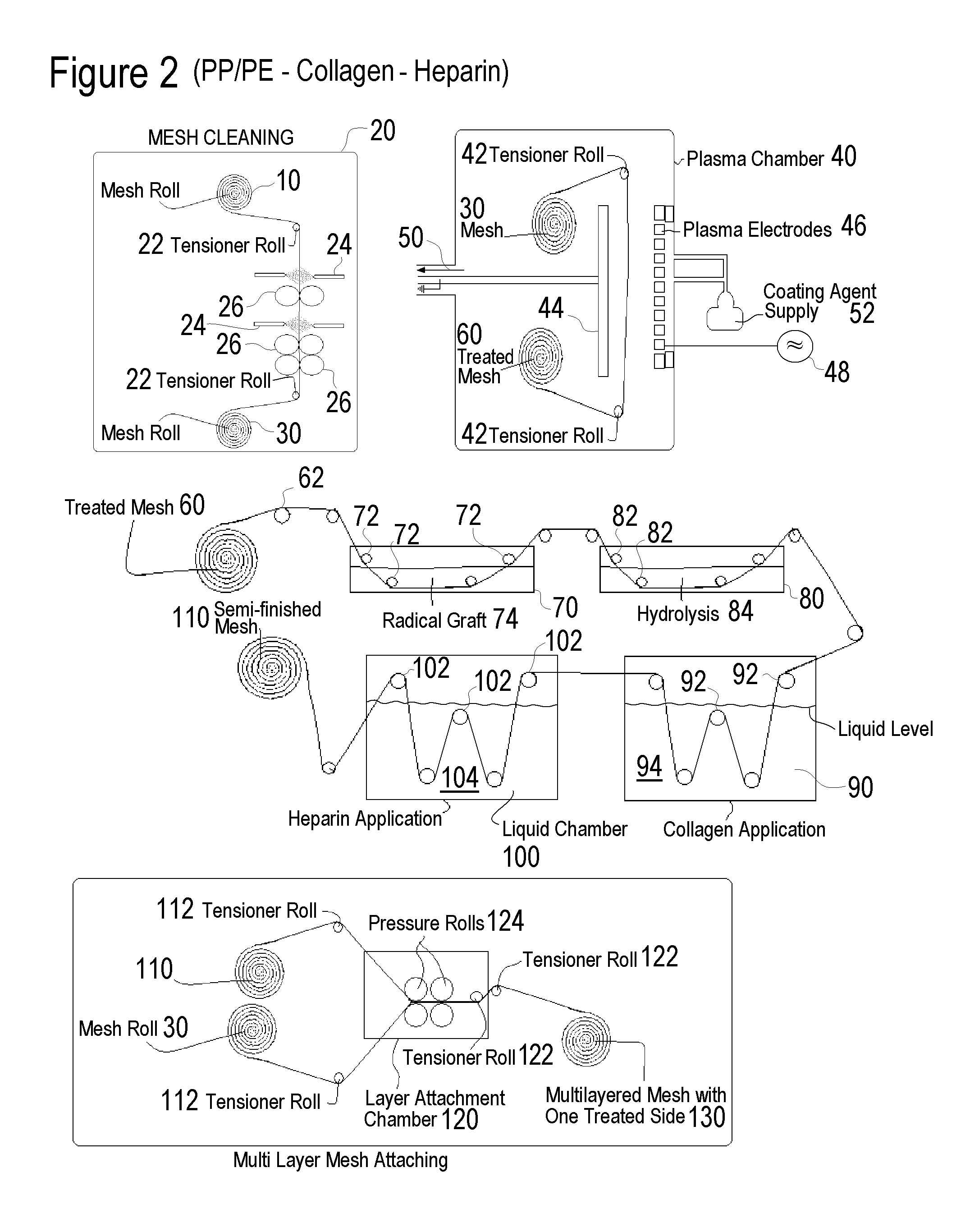
A variety of polymeric synthetic hernia mesh prosthesis with surface treatment on at least one tissue-facing surface to control tissue adhesion are disclosed including heparin surface treatment which provides heparin present in an amount to yield heparin bioactivity of at least one of i) an ATIII binding of at least 2 pmol / cm2, and ii) a thrombin deactivation of at least 0.2 IU / cm2; an acrylic surface treatment for coupling thereto of a heparin surface treatment, a collagen surface treatment or both; and an amino-functional polysiloxane surface treatment for coupling thereto of a heparin surface treatment. The synthetic hernia mesh may be formed of monofilament or multifilament polypropylene or polyester, and may be formed as a multi-layer prosthesis with an outer layer formed of a polymeric synthetic hernia mesh with surface treatment to control tissue adhesion coupled to one or more polymeric synthetic hernia meshes without such surface treatments.
Owner:ENSION
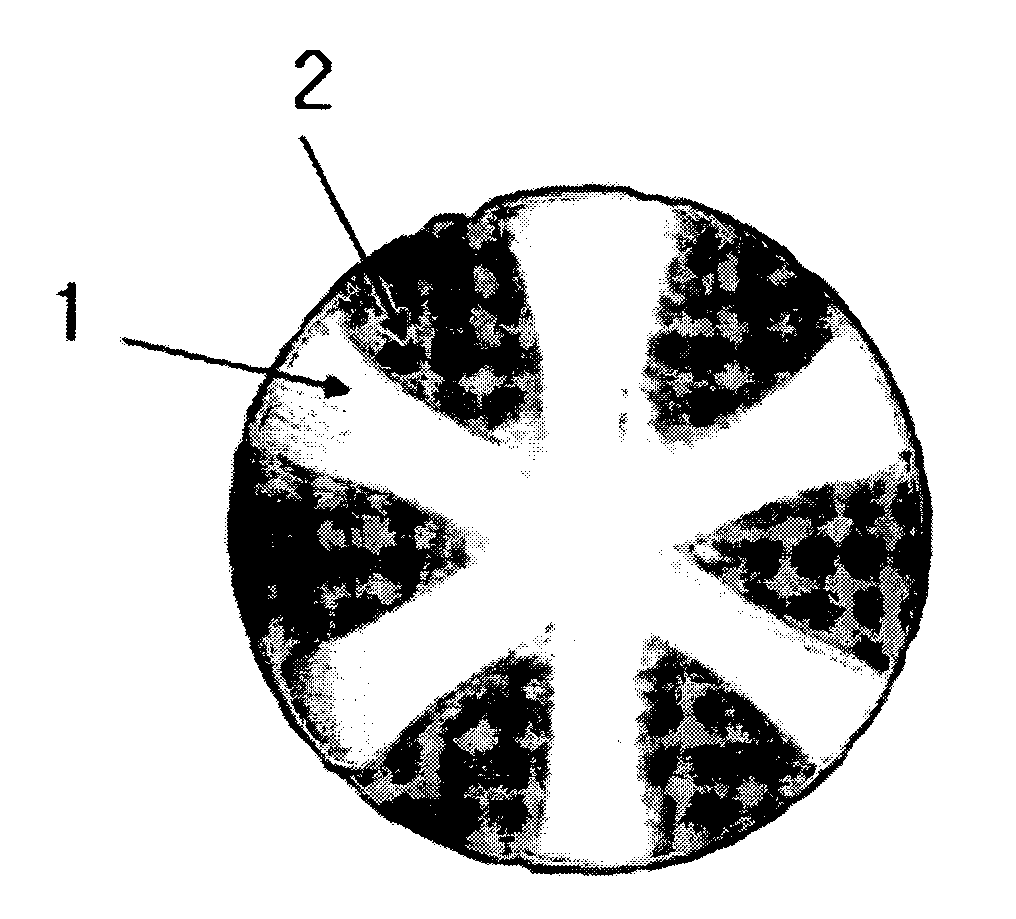
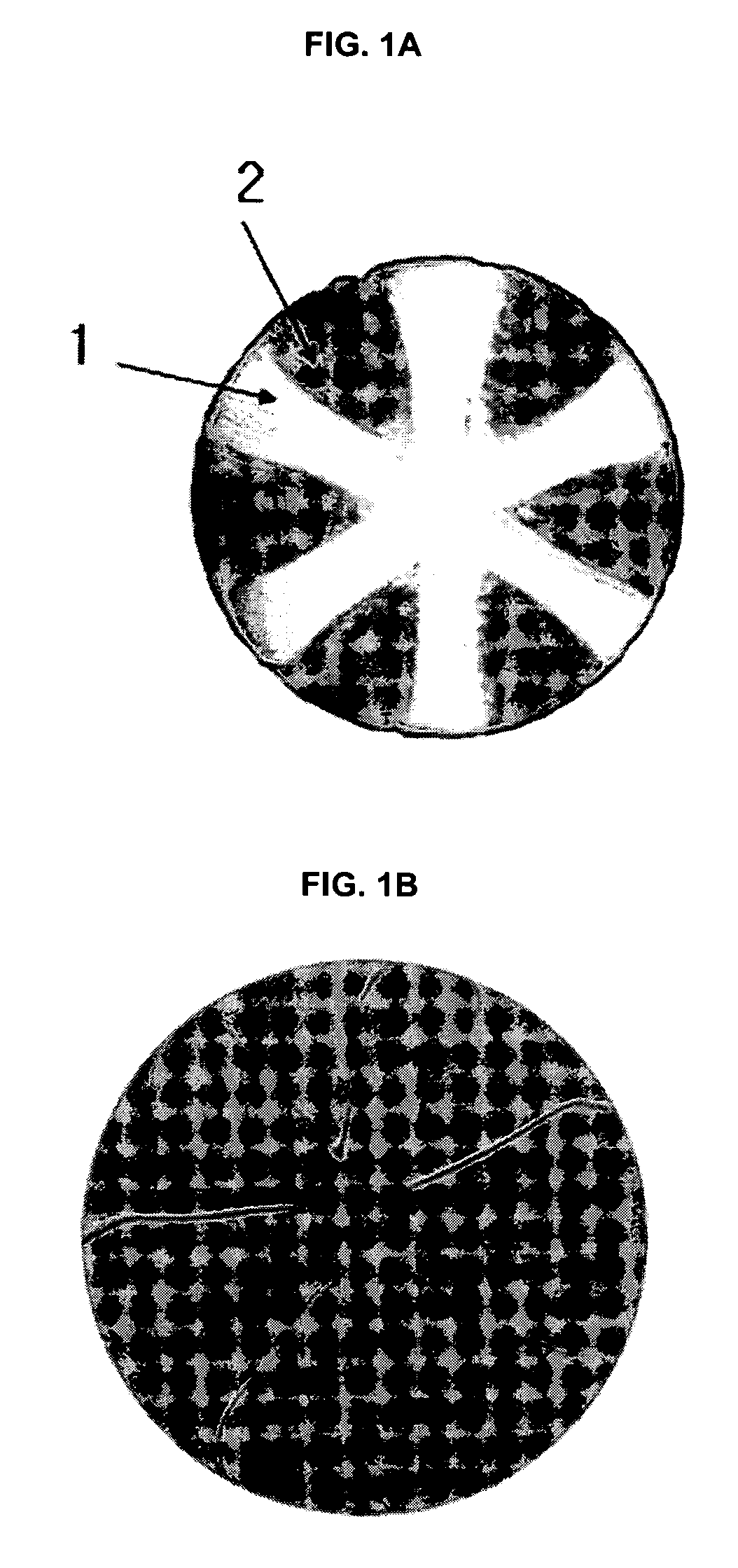
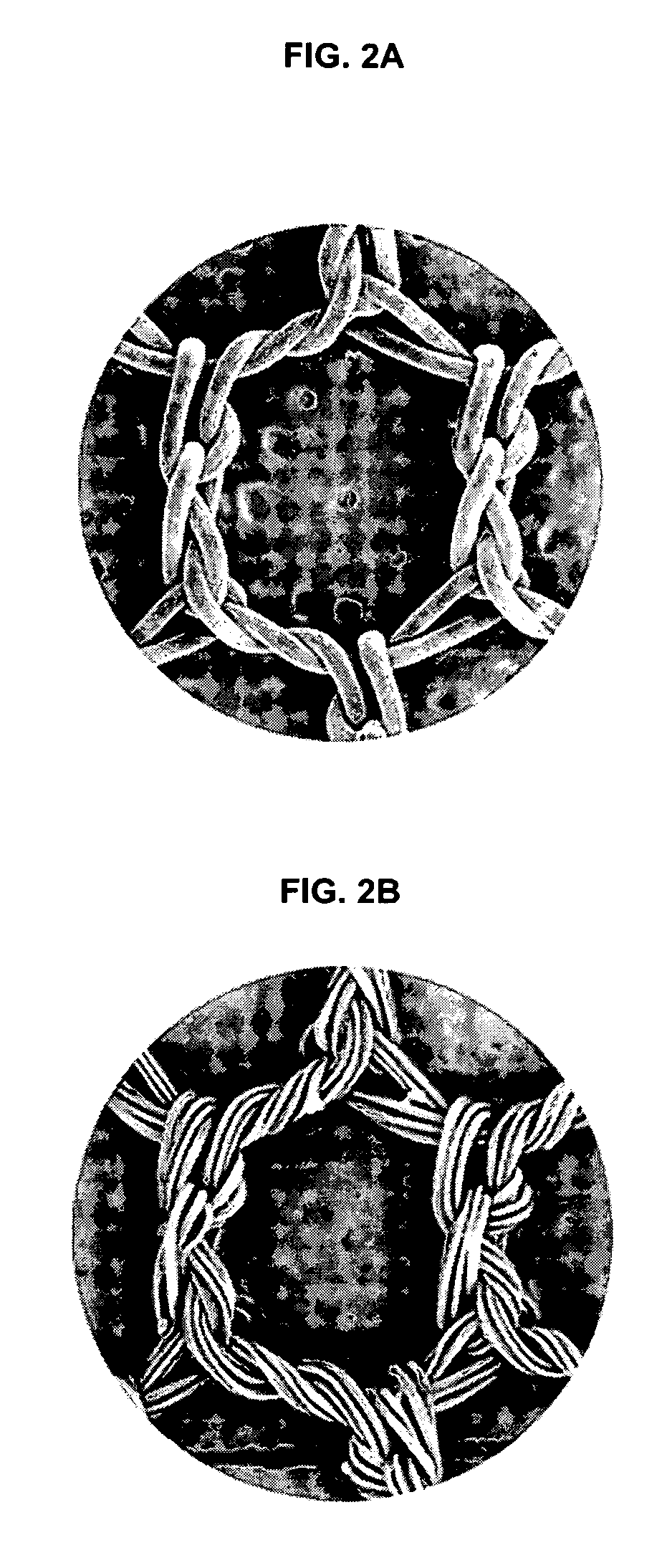
Monofilament, Surgical Mesh Having Improved Flexibility and Biocompatibility, and Process for Preparing the Same
InactiveUS20070219568A1Improved flexibility and biocompatibilityAnti-incontinence devicesWarp knittingMedicinePliability
The present invention relates to a monofilament with a segmented pie structure formed by conjugated spinning of degradable polymers and non-degradable polymers, a hernia mesh having improved flexibility and biocompatibility, and a preparation method thereof. More specifically, the hernia mesh of the present invention having improved flexibility and biocompatibility is prepared using the monofilament obtained by conjugated spinning of degradable polymers and non-degradable polymers into a segmented pie form, to control it to be gradually degraded in the body, whereby the stiffness of the early stage is removed, and thereby the foreign body sensation is also removed.
Owner:SAMYANG BIOPHARMLS CORP
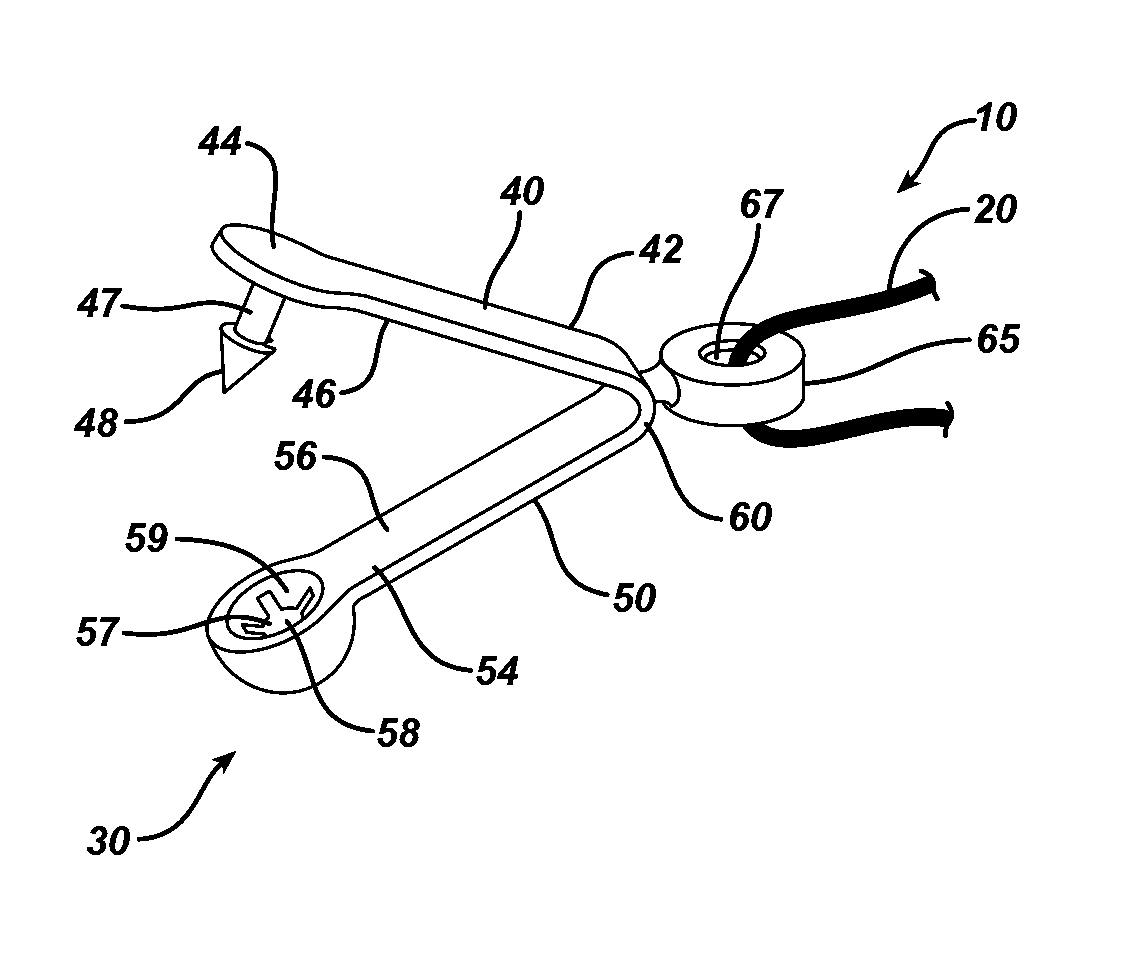
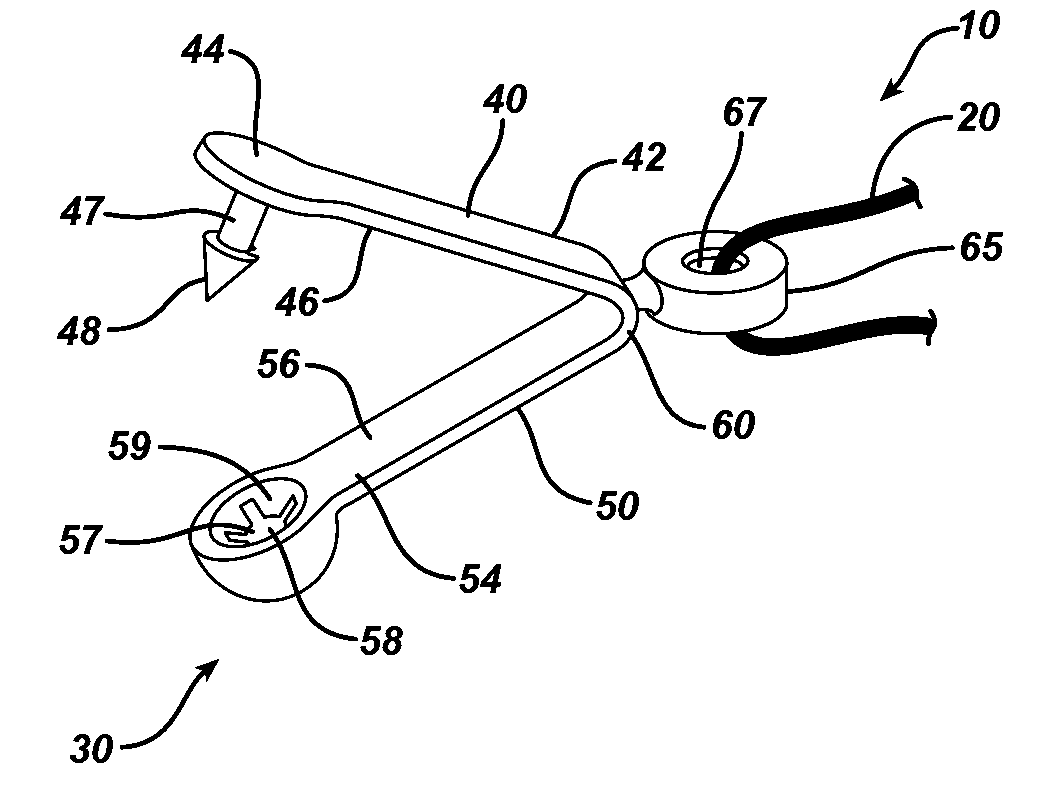
Method and means to attach anchor suture onto mesh implants
Novel stay suture devices and stay suture combinations with meshes are disclosed. The stay suture devices have a clip and a suture. The clip has leg members that are mounted to a hernia mesh implant such that the leg members are locked in a closed configuration. Also disclosed are novel methods of mounting stay sutures to a surgical mesh implant and repairing a body wall defect such as a hernia defect.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Method and Means to Attach Anchor Suture onto Mesh Implants
Novel stay suture devices and stay suture combinations with meshes are disclosed. The stay suture devices have a clip and a suture. The clip has leg members that are mounted to a hernia mesh implant such that the leg members are locked in a closed configuration. Also disclosed are novel methods of mounting stay sutures to a surgical mesh implant and repairing a body wall defect such as a hernia defect.
Owner:ETHICON INC
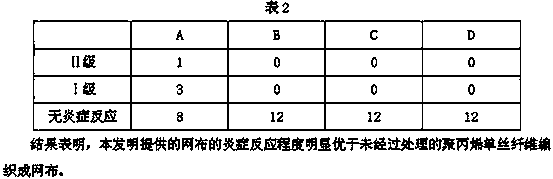
Hernia mesh and its preparation method
ActiveUS20180049858A1Promote recoveryLow costAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgeryMedicineBiocompatibility Testing
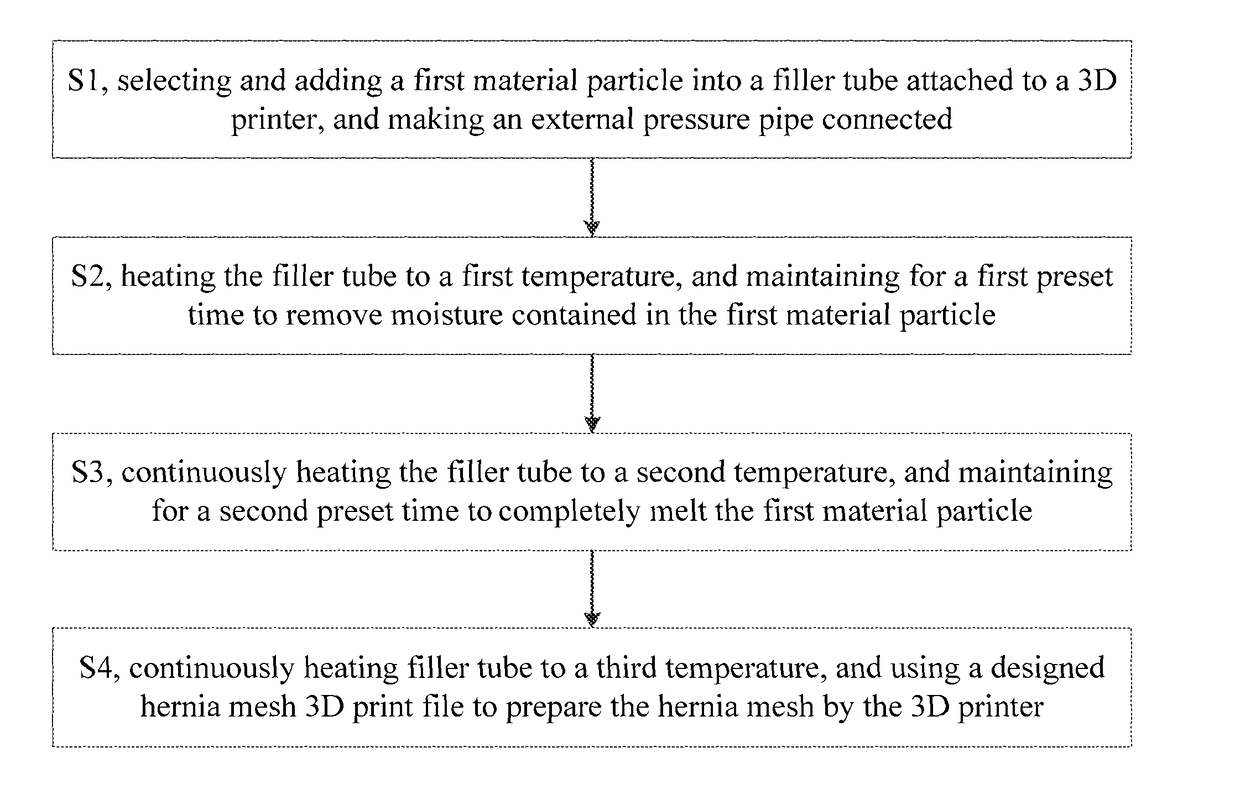
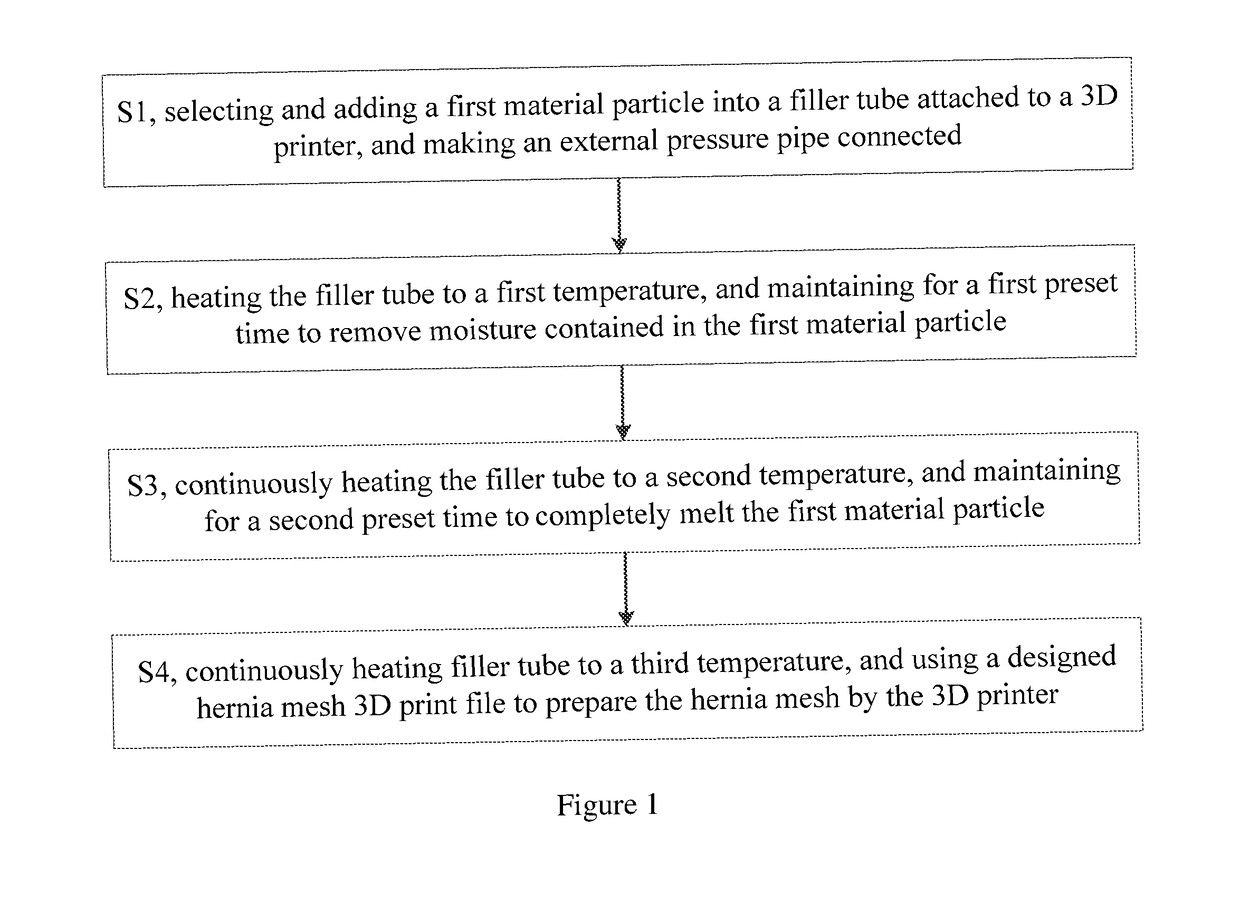
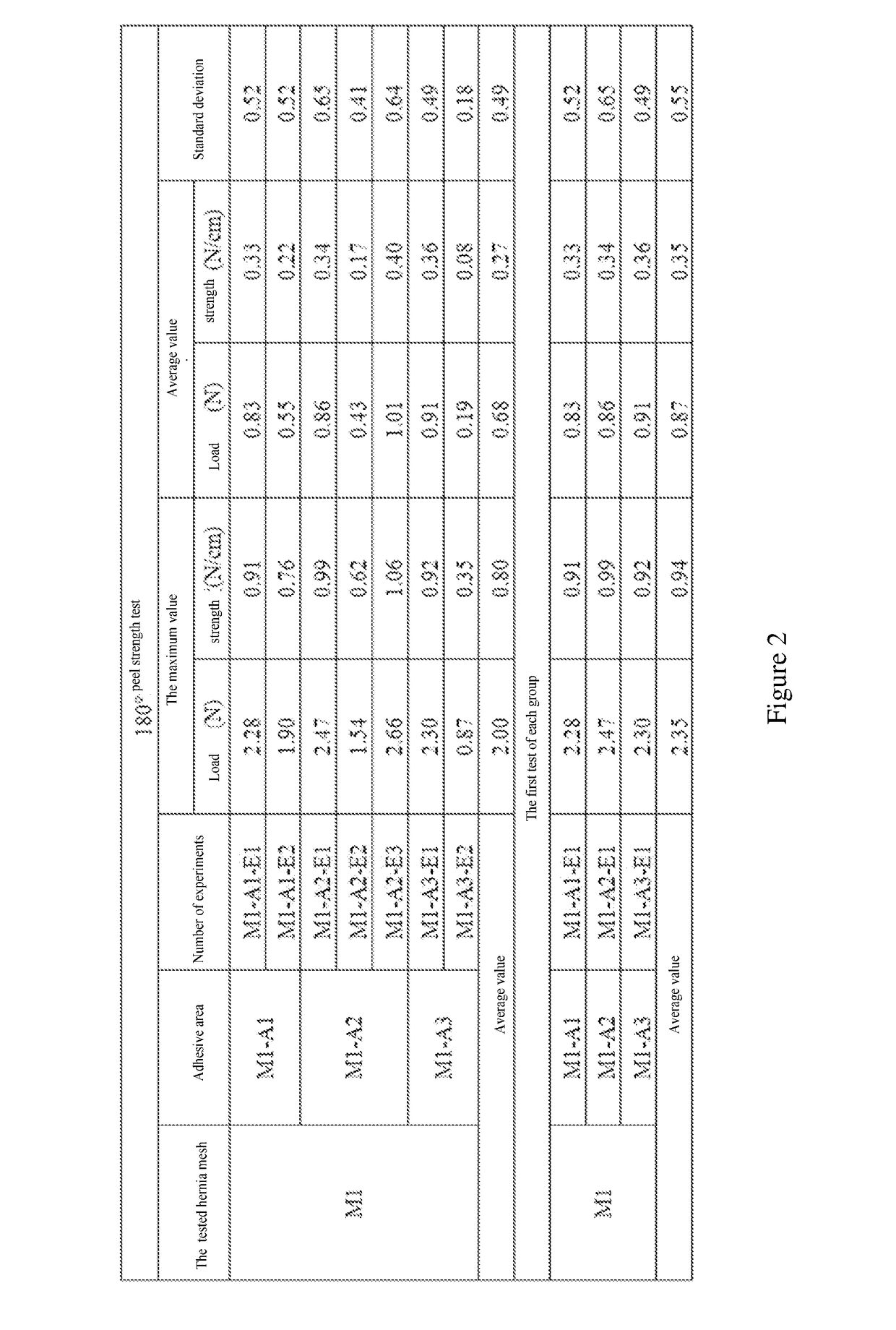
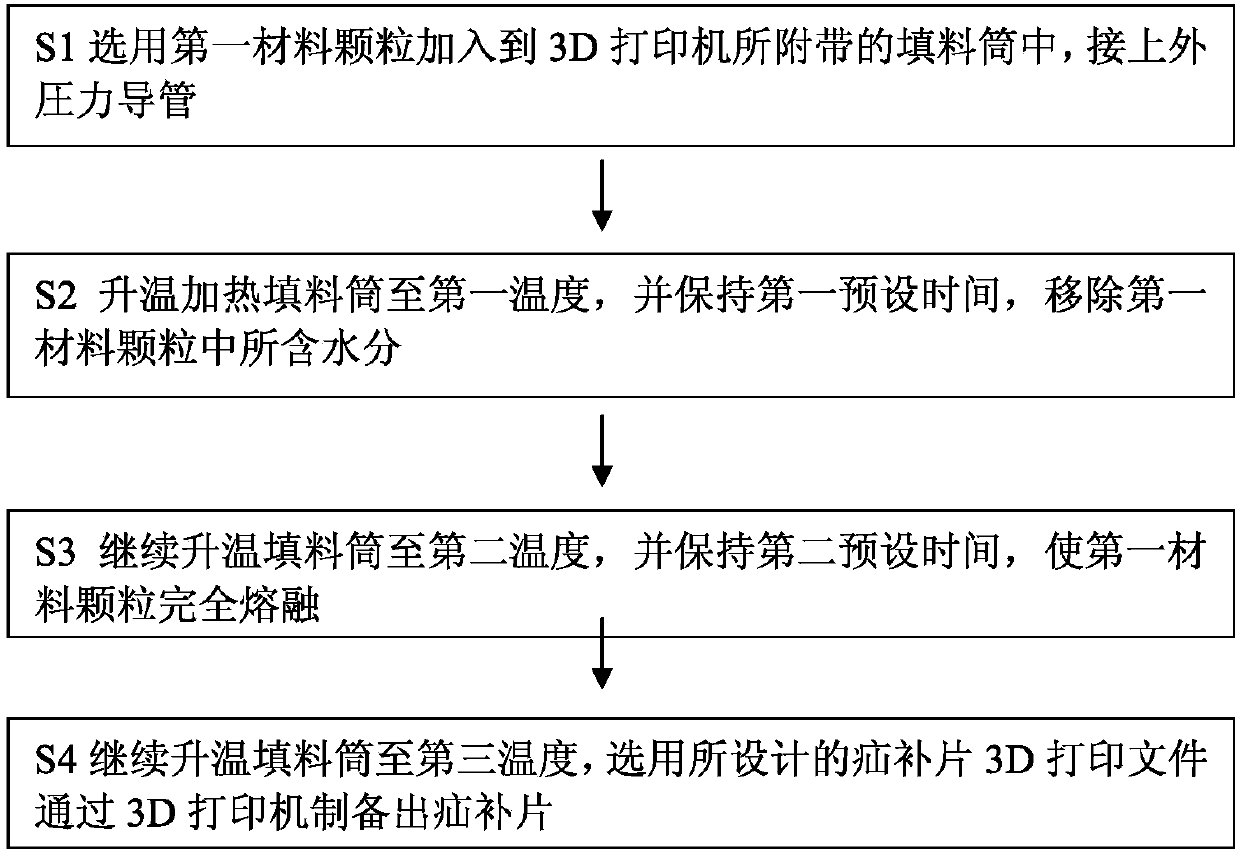
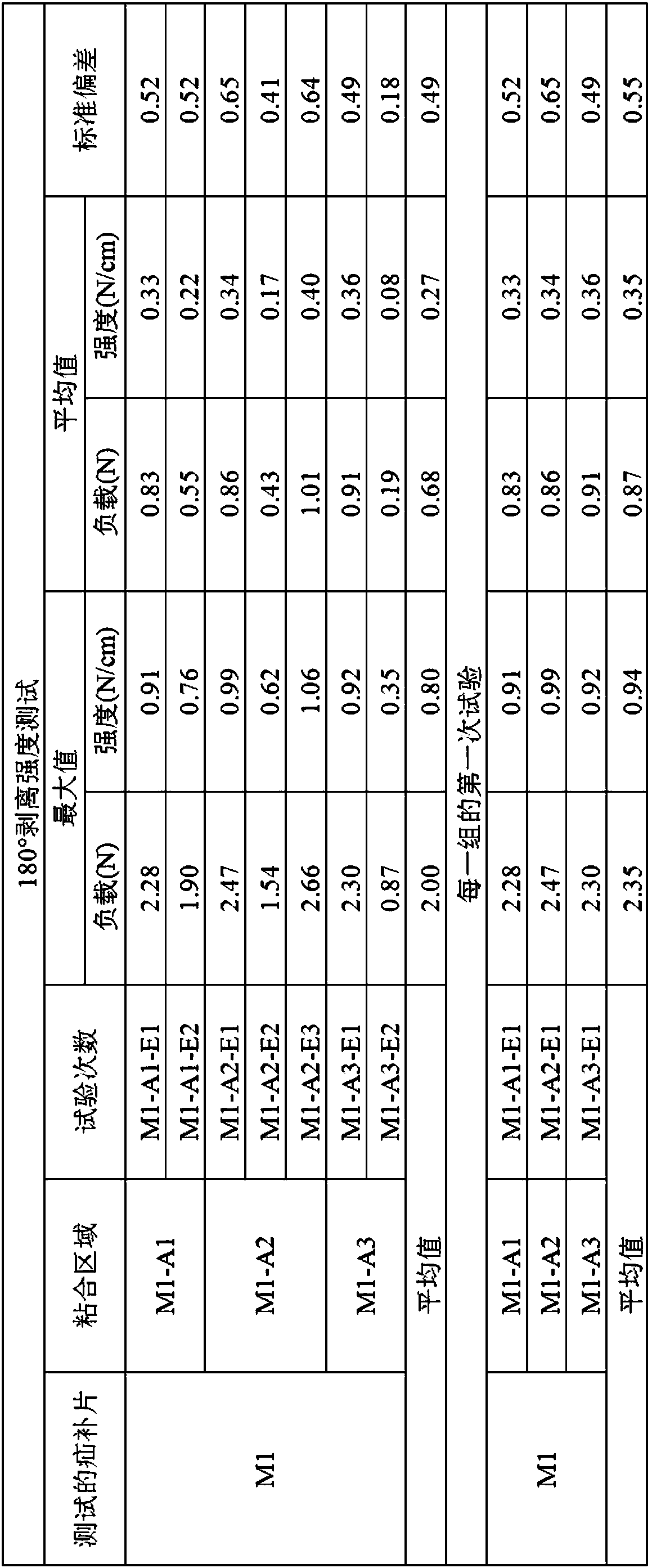
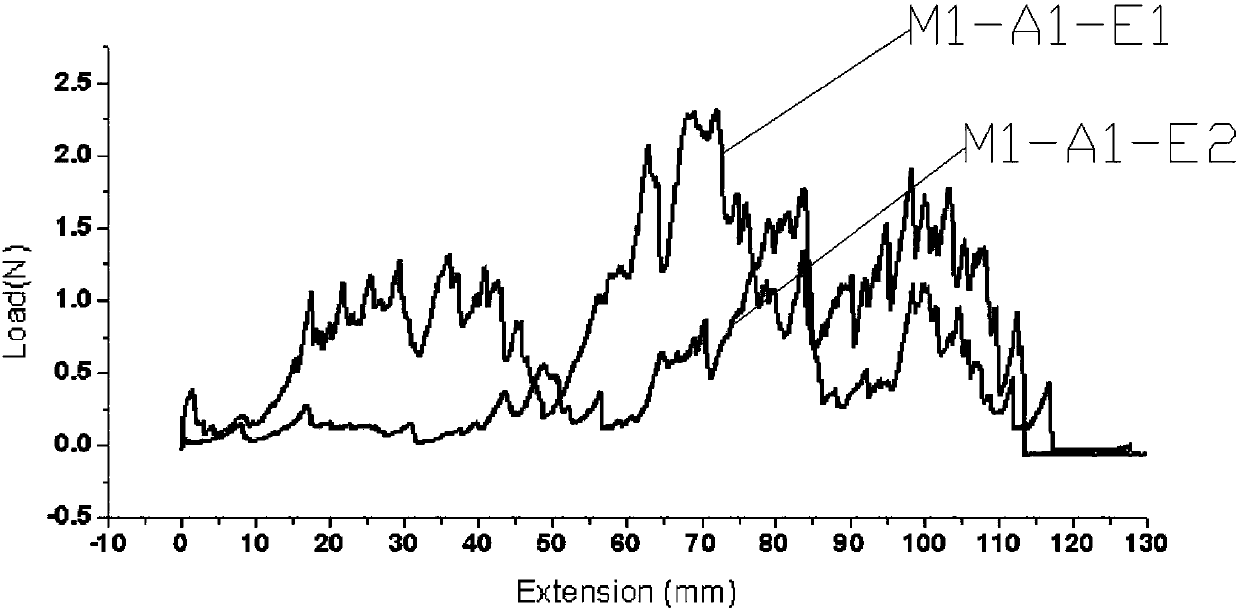
The present application relates to a hernia mesh and its preparation method. A preparation method of hernia mesh comprises selecting and adding a first material particle into a filler tube attached to a 3D printer, and making an external pressure pipe connected; heating the filler tube to a first temperature, and maintaining for a first preset time to remove moisture contained in the first material particle; continuously heating the filler tube to a second temperature, and maintaining for a second preset time to completely melt the first material particle; continuously heating filler tube to a third temperature, and using a designed hernia mesh 3D print file to prepare the hernia mesh by the 3D printer. The hernia mesh prepared has controllable pore size, biocompatibility, tensile strength, and elasticity; the preparation process is convenient and quick, reducing the cost; the patient's foreign body sensation and discomfort can be reduced.
Owner:THE HONG KONG RES INST OF TEXTILES & APPAREL
Preparation method for absorbable anti-infective hernia mesh
The invention discloses a preparation method of an absorbable anti-infection hernia repair sheet, which comprises a polypropylene base sheet, and a composite film composed of a degradable polymer material and a chitosan solution is arranged on the outside of the polypropylene base sheet. The patch is distributed by dissolving the degradable polymer material in the polymer material solvent, dissolving chitosan in the organic acid, mixing the two solutions, pouring them on a flat plate, and evaporating to form a thin film; Brush rice bran glue, stick the side coated with rice bran glue to one side of the polypropylene base sheet, and get the fibrous membrane hernia repair sheet. In the present invention, the polypropylene substrate has a single-layer network structure, is easily infiltrated by connective tissue, has little foreign body reaction, and has good tensile strength. Polylactic acid can have good degradation performance, chitosan has good moldability and biocompatibility, and can promote wound healing. Rice bran gum is also a biodegradable binder. The invention can prevent the viscera from sticking to the patch, reduce the probability of complications, and has good practical value.
Owner:武汉蓝普医品有限公司
Hernia mesh and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107756781AAperture controllableControlled BiocompatibilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgeryBiocompatibility TestingUltimate tensile strength
The invention specifically relates to a hernia mesh and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of medical supplies. The preparation method for the hernia mesh comprises the following steps: S1, selecting first material particles, adding the first material particles into an accessory filler drum of a 3D printer, and connecting the filler drum with an external pressure conduit; S2, heating the filler drum to a first temperature, and maintaining the filler drum at the temperature for a first preset time to remove moisture in the first material particles; S3, continuing heating the filler drum to a second temperature and then maintaining the filler drum at the temperature for a second preset time to allow the first material particles to be completely fused; and S4, continuing heating the filler drum to a third temperature, selecting a designed 3D printing file for the hernia mesh and printing the hernia mesh via the 3D printer. The hernia mesh prepared in the invention has controllable pore sizes, biocompatibility, tensile strength and elasticity; the preparation method for the hernia mesh is convenient and fast and can reduce the making cost of the hernia mesh; and the hernia mesh can reduce foreign body sensation and discomfort for patients.
Owner:THE HONG KONG RES INST OF TEXTILES & APPAREL
Method and means to attach anchor sutures onto mesh implants
Novel stay suture devices and stay suture combinations with meshes are disclosed. The stay suture devices have a clip and a suture. The clip has leg members that are mounted to a hernia mesh implant such that the leg members are locked in a closed configuration. Also disclosed are novel methods of mounting stay sutures to a surgical mesh implant and repairing a body wall defect such as a hernia defect.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Hernia mesh tacks
InactiveUS20100256658A1Easy to insertIncrease the areaInternal osteosythesisStaplesEngineeringSurgical department
There are disclosed various embodiments of surgical tacks for use in surgical procedures. The tacks generally include a head and a barrel portion extending distally from the head. Preferably the head and the barrel portion define a throughbore for receipt of a drive instrument. A thread on the head is provided to engage threads in the installation tool. A tissue thread is provided on the barrel portion to engage tissue. Distal and proximal surfaces of the tissue thread may be oriented at various angles relative to the barrel portion. There is also disclosed an insertion instrument to insert one or more tacks as well as a method of use. There is further disclosed a model device for use in explaining the operation of the instrument.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
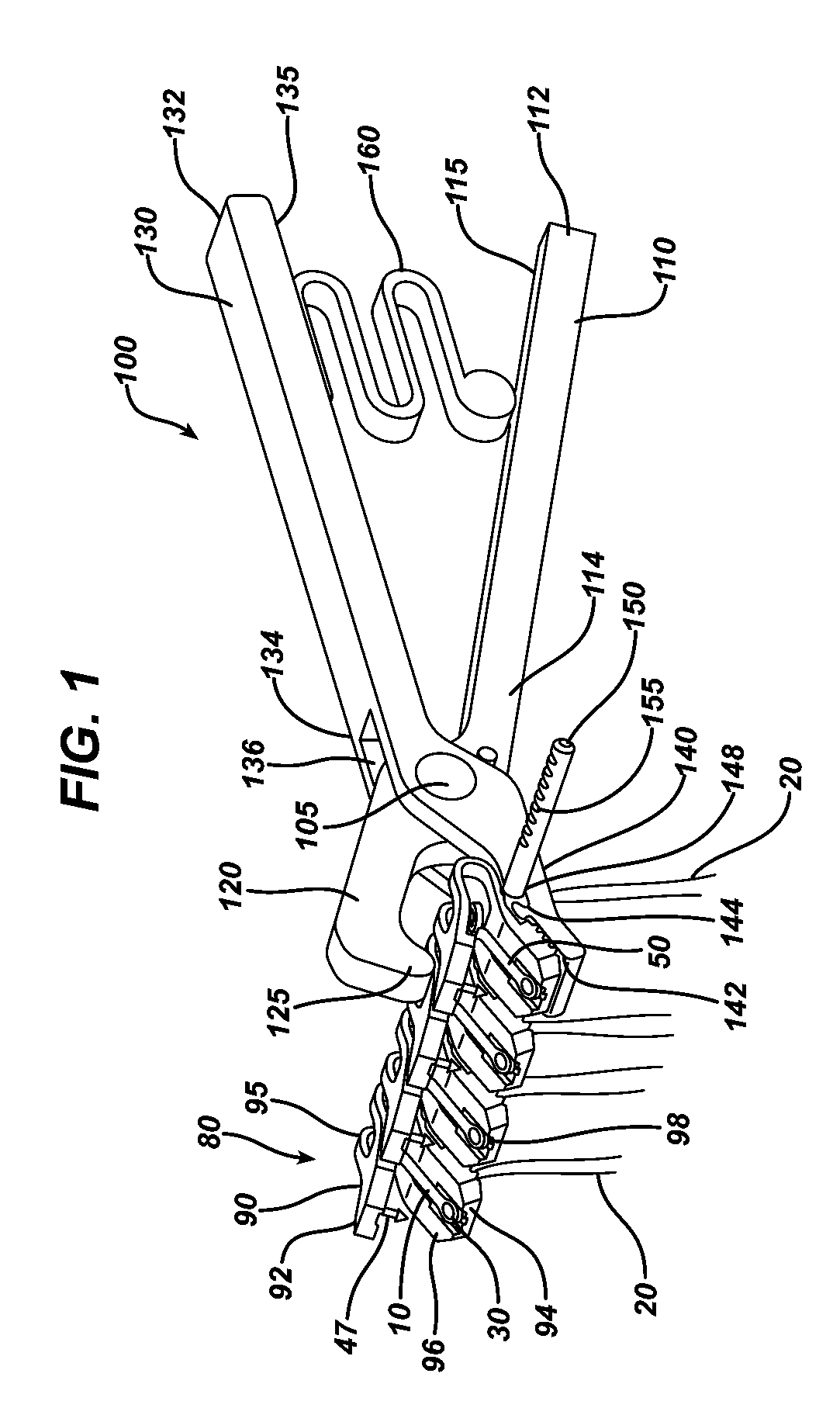
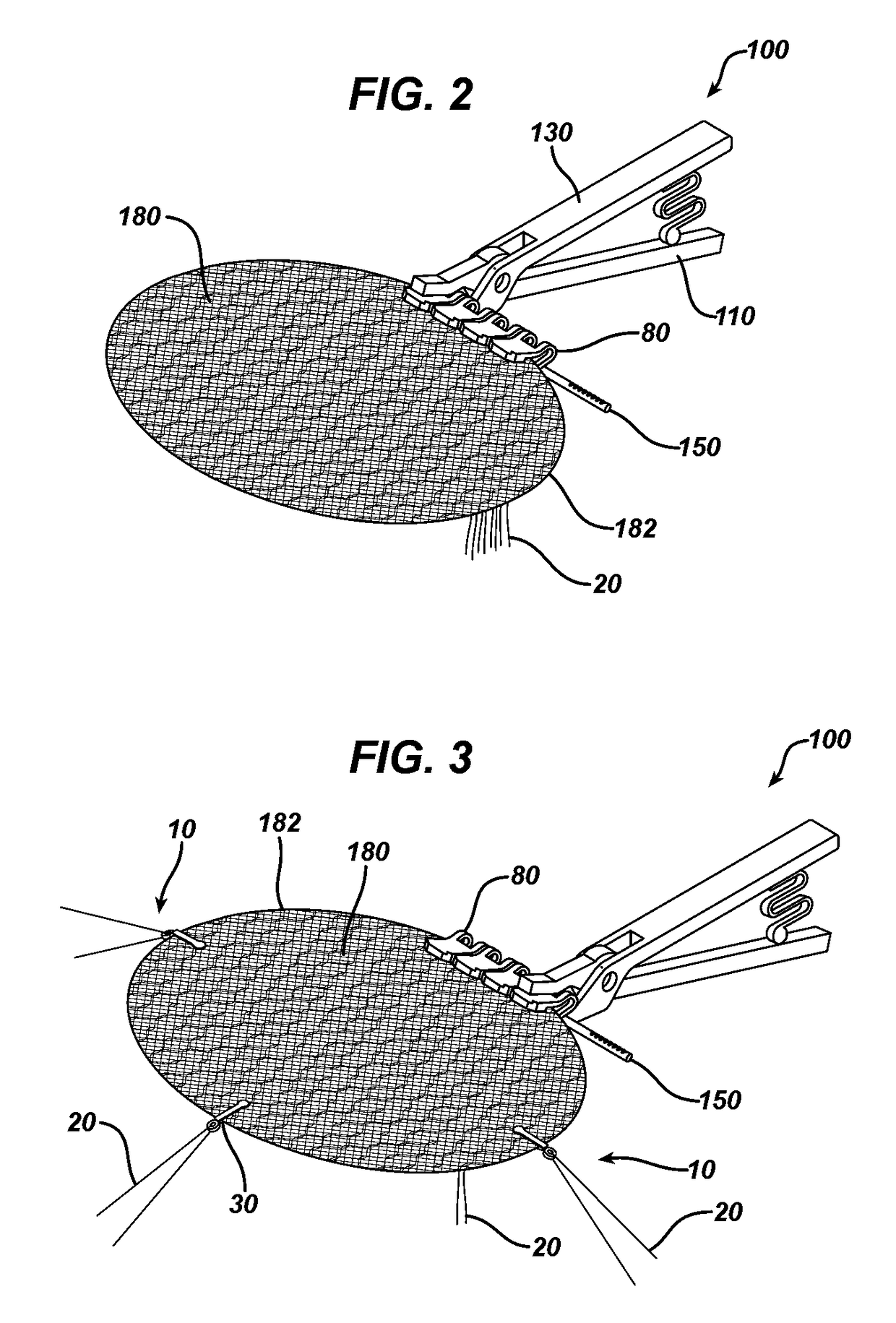
Methods of repairing a hernia using a hernia support device
A method of repairing a hernia using a hernia mesh support device includes providing a hernia mesh support device, reducing a hernia within a patient's abdomen, inserting the hernia mesh support device into the abdomen and positioning the device in alignment with the hernia, ensuring that no abdominal organs are present between the device and the abdominal wall, whereby the step of ensuring that no abdominal organ is between the device and the abdominal wall includes the step of digitally sweeping the space between the abdominal wall and the device, removing a protective cover, and pulling on a pull strap joined to an inner ring to place the device tightly against the abdominal wall and to anchor barbed pins and hollow needles into the abdominal wall.
Owner:ETHICON INC
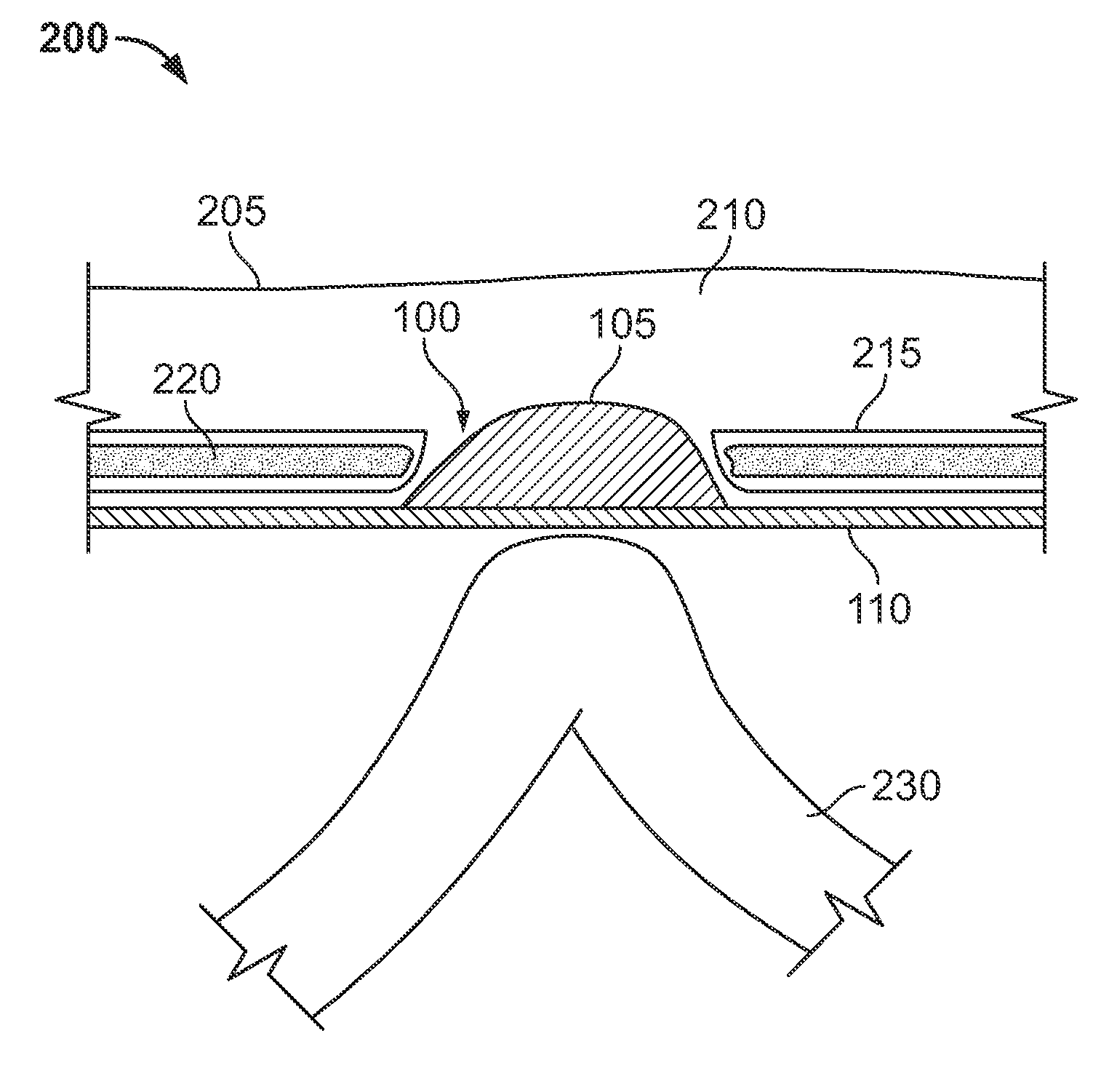
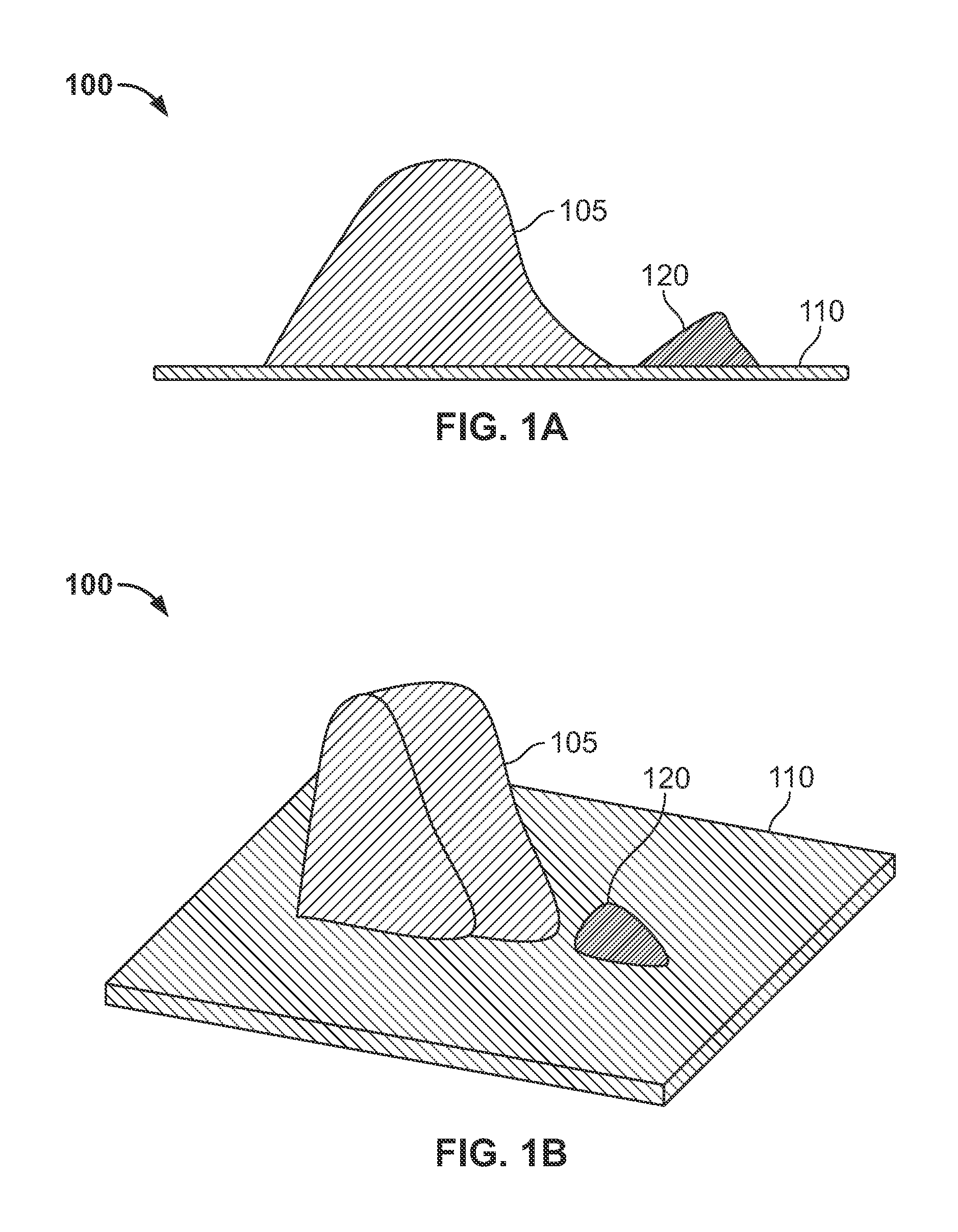
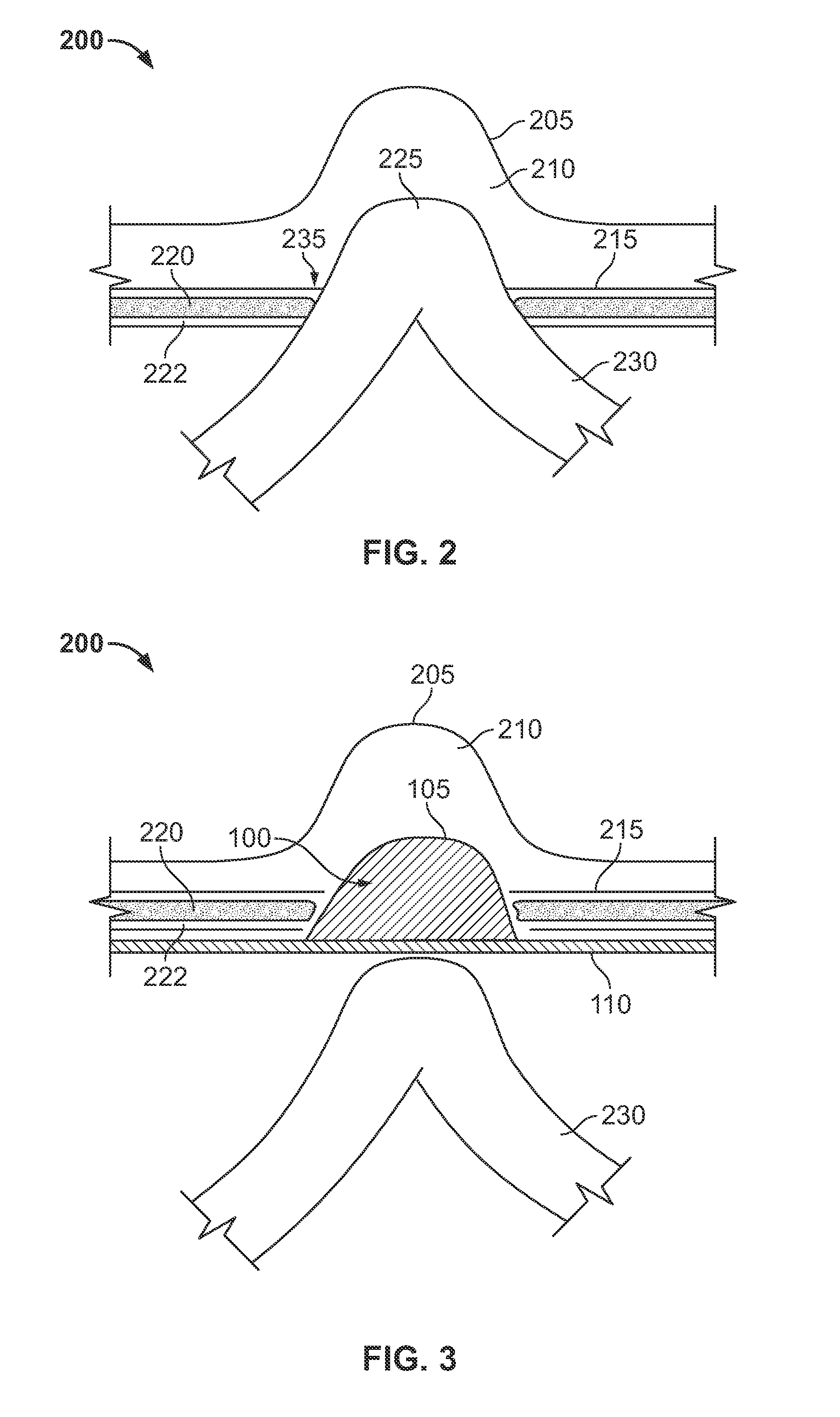
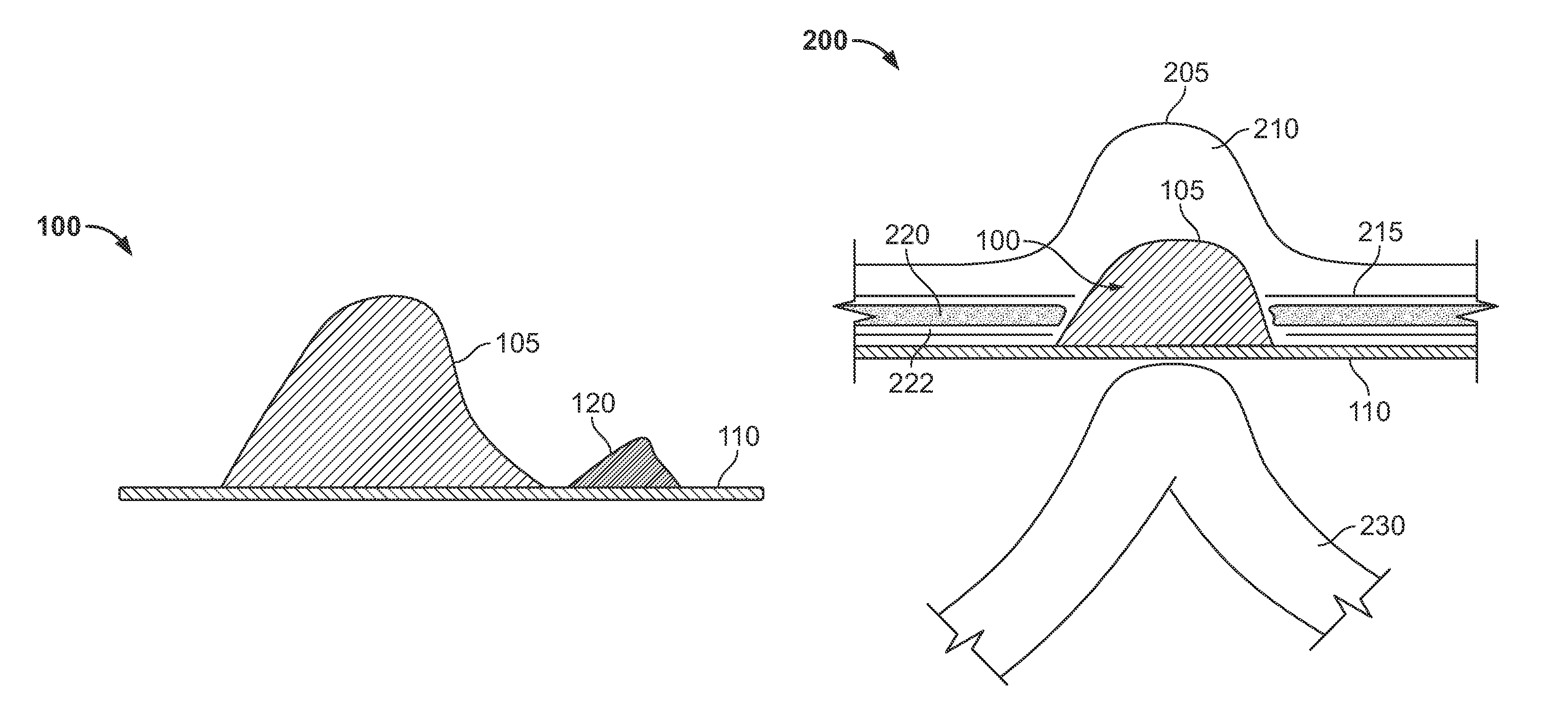
Hernia mesh apparatus and method
ActiveUS20130253545A1Easily placed laparoscopicallyAccurate fitProsthesisWound clampsVariable thicknessHernia
A dual-layer hernia mesh can be configured according to a three-dimensional map of a hernia defect(s) and a hernia volume(s) of a patient. The front portion of the mesh can be configured utilizing, for example, a three dimensional map of hernia sac volumes obtained from a CT scan. The front portion of the mesh exactly fits into the hernia sac. The back portion of the hernia mesh is a sheet of mesh material that overlaps over onto the normal muscles and fascia. A “foam” collapsible mesh and / or a flat mesh with expandable hydrogel deposited in variable thickness according to the hernia defect can be utilized as a dual-layer hernia mesh for repair. The hydrogel mesh when combined with water or saline expands and fits into the hernia defect or defects. Both “foam” and hydrogel meshes adhere to the tissues of the hernia sac and then contracts over time. The hernia sac volume slowly disappears, restoring a more normal contour to the abdominal wall.
Owner:MASSEN RICHARD
Hernia mesh plug prepared from modified polypropylence fiber single silk mesh
ActiveCN103463679ALess wounds and fewer suturesEasy to fill and effectiveProsthesisMesh plugOrganosolv
The invention discloses a hernia mesh plug prepared from a modified polypropylence fiber single silk mesh. The hernia mesh plug is made from the modified polypropylence fiber single silk mesh which is obtained after surface treatment. The surface treatment method for the polypropylence fiber single silk mesh comprises the following steps of: treating the polypropylence fiber single silk mesh by using an oxidizing agent for 40 minutes, and coating the surface of the polypropylence fiber single silk mesh with an organic solvent for 15-24 hours. When used for filling the hernia affected part, the hernia mesh plug provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the wound is small and the suture is less; by virtue of the filling structure of the hernia mesh plug, the hernia affected part can be filled more conveniently and effectively, the hernia mesh plug well complies with the human physiological anatomical structure, and the recurrence rate of a patient is reduced; simultaneously, as the modified polypropylence fiber single silk mesh is used, the contact angle of the material can be reduced by about 30% after the treatment by using the oxidizing agent; the surface properties of the polypropylence fiber single silk can be changed through the surface coating treatment to reduce the rejection reaction of the material; and the experimental data proves that the inflammatory response degree of the mesh provided by the invention is obviously superior to the mesh woven of the untreated polypropylence single silk fiber.
Owner:JIANGSU SEMPOLL PHARMA
Hernia mesh apparatus and method
ActiveUS9308069B2Easily placed laparoscopicallyAccurate fitProsthesisWound clampsVariable thicknessComputed tomography
A dual-layer hernia mesh can be configured according to a three-dimensional map of a hernia defect(s) and a hernia volume(s) of a patient. The front portion of the mesh can be configured utilizing, for example, a three dimensional map of hernia sac volumes obtained from a CT scan. The front portion of the mesh exactly fits into the hernia sac. The back portion of the hernia mesh is a sheet of mesh material that overlaps over onto the normal muscles and fascia. A “foam” collapsible mesh and / or a flat mesh with expandable hydrogel deposited in variable thickness according to the hernia defect can be utilized as a dual-layer hernia mesh for repair. The hydrogel mesh when combined with water or saline expands and fits into the hernia defect or defects. Both “foam” and hydrogel meshes adhere to the tissues of the hernia sac and then contracts over time. The hernia sac volume slowly disappears, restoring a more normal contour to the abdominal wall.
Owner:MASSEN RICHARD
Implants and constructs including hollow fibers
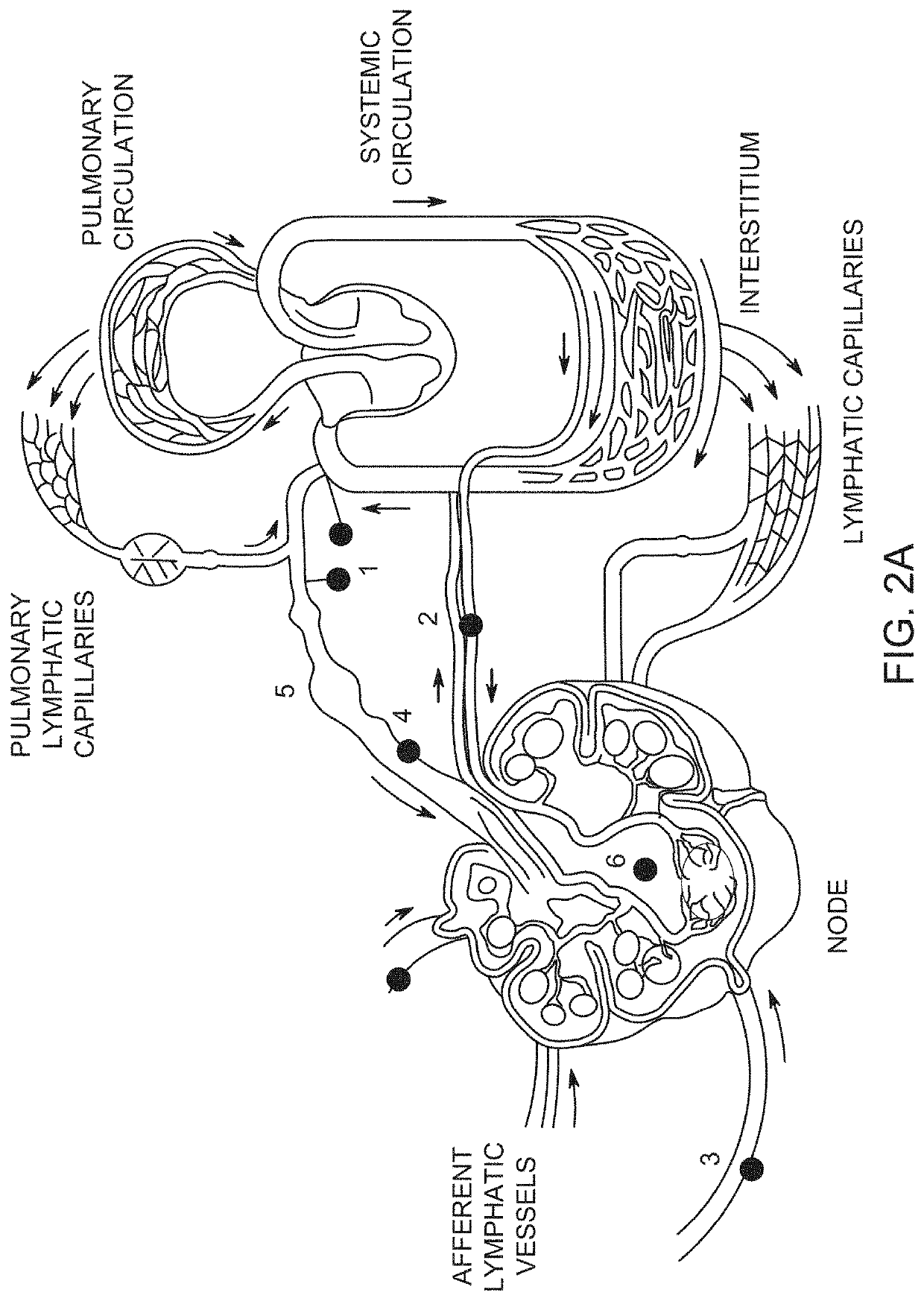
Hollow fiber drug delivery devices are described. Device can contain structural or solid fibers. Fabric can be formed by fibers being interwoven or joined to each other. All or some of the fibers can be resorbable. Fibers can be subdivided, by deformations or closure points, into numerous compartments that separately deliver drug. Deformations can be located at points of fiber intersection or joining. Different drug or drug formulation can be provided in different places. Fibers can be given appropriate surface treatments or coatings to achieve desired properties such as wetting of pores and surfaces. Different release characteristics in different directions can be achieved. The hollow fibers can contain solid particles of drug, and can contain gel. Possible applications include hernia meshes, pouches, sutures, catheters, wound dressings, stents, nerve regrowth guides, refillable / drainable devices, and devices that deliver drug to lymphatic flow.
Owner:NOVAFLUX INC
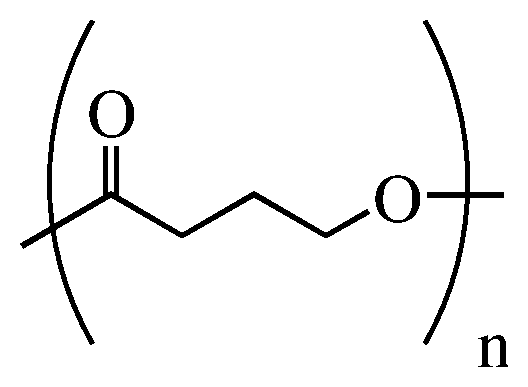
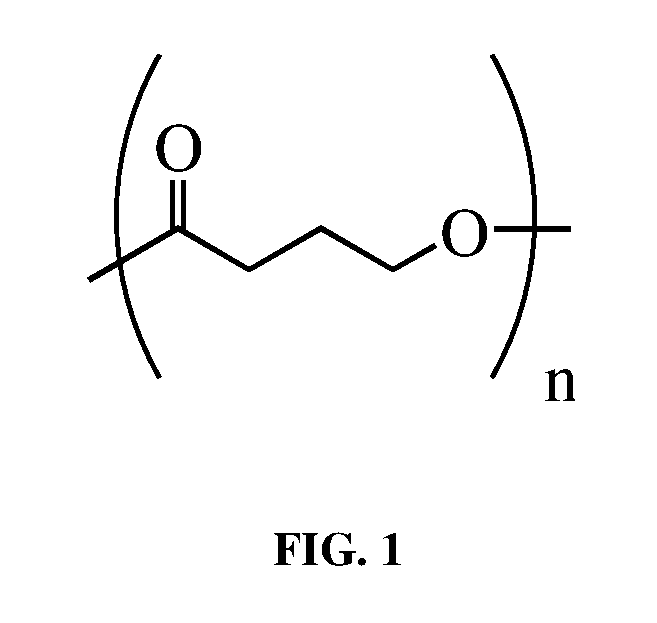
Vacuum membrane thermoformed poly-4-hydroxybutyrate medical implants
Methods to produce thermoformed implants comprising poly-4-hydroxybutyrate homopolymer, copolymer, or blend thereof, including surgical meshes, have been developed. These thermoforms are preferably produced from porous substrates of poly-4-hydroxybutyrate homopolymer or copolymer thereof, such as surgical meshes, by vacuum membrane thermoforming. The porous thermoformed implant is formed by placing a porous substrate of poly-4-hydroxybutyrate homopolymer or copolymer thereof over a mold, covering the substrate and mold with a membrane, applying a vacuum to the membrane so that the membrane and substrate are drawn down on the mold and tension is applied to the substrate, and heating the substrate while it is under tension to form the thermoform. The method is particularly useful in forming medical implants of poly-4-hydroxybutyrate and copolymers thereof, including hernia meshes, mastopexy devices, breast reconstruction devices, and implants for plastic surgery, without exposing the resorbable implants to water and without shrinking the porous substrate during molding.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Vacuum membrane thermoformed poly-4-hydroxybutyrate medical implants
Methods to produce thermoformed implants comprising poly-4-hydroxybutyrate homopolymer, copolymer, or blend thereof, including surgical meshes, have been developed. These thermoforms are preferably produced from porous substrates of poly-4-hydroxybutyrate homopolymer or copolymer thereof, such as surgical meshes, by vacuum membrane thermoforming. The porous thermoformed implant is formed by placing a porous substrate of poly-4-hydroxybutyrate homopolymer or copolymer thereof over a mold, covering the substrate and mold with a membrane, applying a vacuum to the membrane so that the membrane and substrate are drawn down on the mold and tension is applied to the substrate, and heating the substrate while it is under tension to form the thermoform. The method is particularly useful in forming medical implants of poly-4-hydroxybutyrate and copolymers thereof, including hernia meshes, mastopexy devices, breast reconstruction devices, and implants for plastic surgery, without exposing the resorbable implants to water and without shrinking the porous substrate during molding.
Owner:TEPHA INC
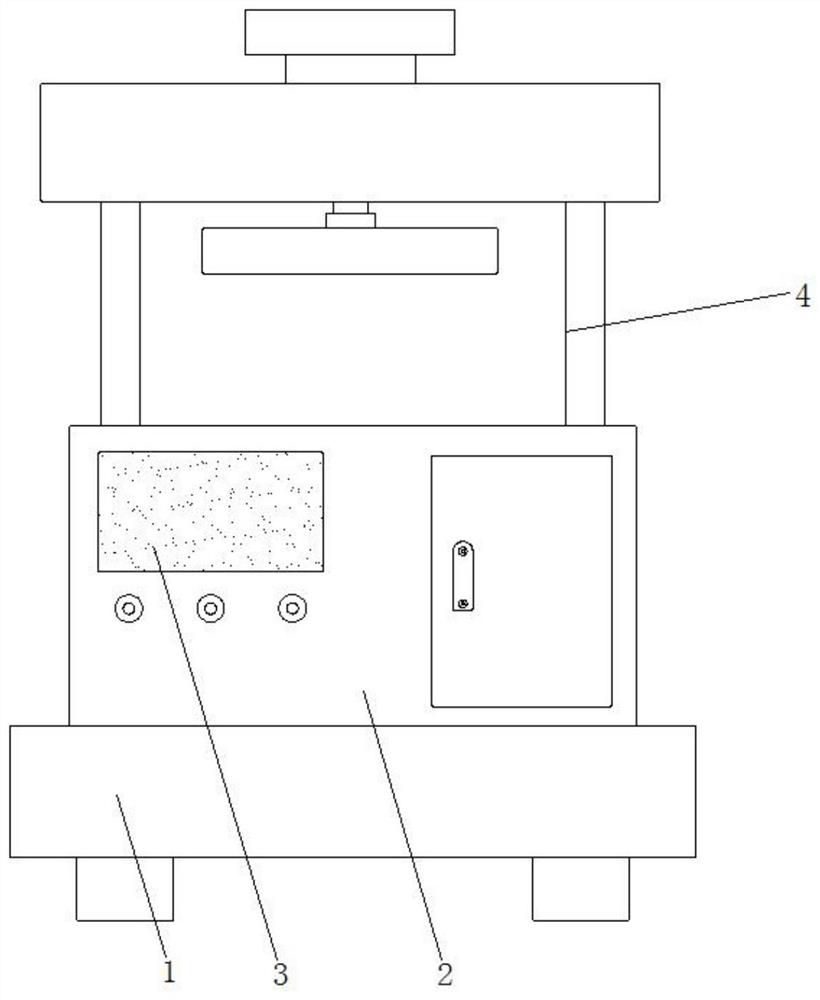
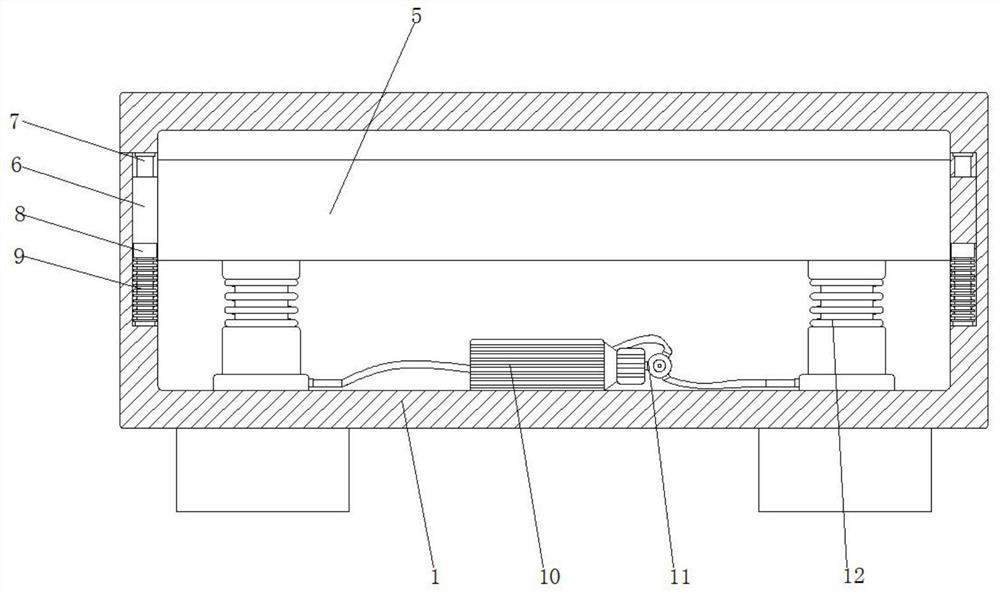
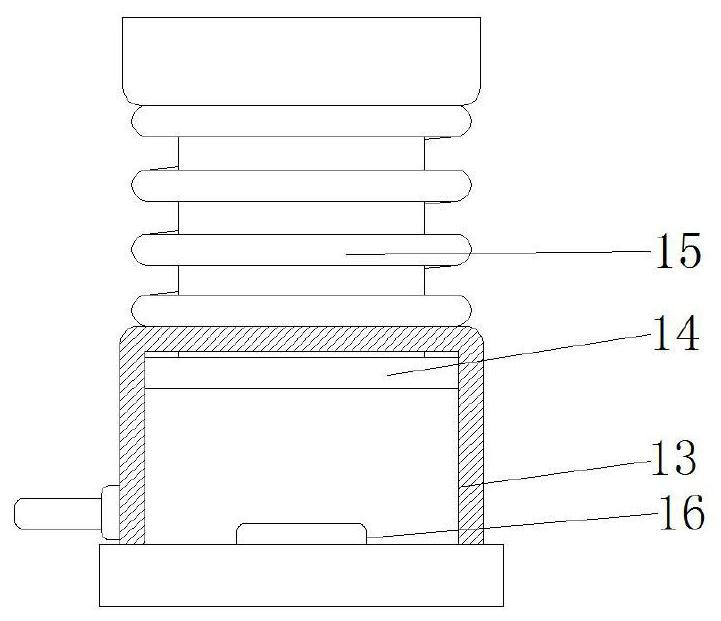
Hernia mesh plug forming machine
PendingCN111631839ASolve the problem that there is no shock absorbing mechanismVibration dampersNon-rotating vibration suppressionMesh plugMolding machine
The invention discloses a hernia mesh plug forming machine. The machine includes a base, a machine table is arranged on the outer wall of the top of the base, grooves are formed in the inner walls ofthe two sides of the base, sliding columns are fixed to the inner walls of the two grooves through bolts, sliding sleeves are uniformly connected to the outer walls of the two sliding columns in a sliding manner, pressure sensors are fixed to the outer walls of the bottoms of the two sliding sleeves through bolts, first springs are connected to the outer walls of the two sliding columns in a sleeving mode, the same bottom plate is fixed to the outer walls of one sides of the two sliding sleeves through bolts, the outer wall of the bottom of the machine table is fixed to the bottom plate through bolts, and damping mechanisms are fixed to the two sides of the inner wall of the bottom of the base through bolts. The forming machine is damped through the damping mechanism in the base, a micro air pump is arranged in the base, the air pressure in the damping mechanism is controlled and adjusted through the air pump, then the acting force generated by vibration is counteracted, and the problem that existing forming machines are not provided with a damping mechanism is solved.
Owner:上海久罗机电设备有限公司
MONOFILAMENT, SURGICAL MESH HAVING IMPROVED FLEXIBILITY AND BlOCOMPATlBILlTY, AND PROCESS FOR PREPARING THE SAME
ActiveUS20150374476A1Improved flexibility and biocompatibilityCrochetingLiquid/gas/vapor article treatmentMedicineBiocompatibility Testing
The present invention relates to a monofilament with a segmented pie structure formed by conjugated spinning of degradable polymers and non-degradable polymers, a hernia mesh having improved flexibility and biocompatibility, and a preparation method of the monofilament. More specifically, the hernia mesh of the present invention having improved flexibility and biocompatibility is prepared using the monofilament obtained by conjugated spinning of degradable polymers and non-degradable polymers into a segmented pie form, to control it to be gradually degraded in the body, whereby the stiffness of the early stage is removed, and thereby the foreign body sensation is also removed.
Owner:SAMYANG HLDG CORP
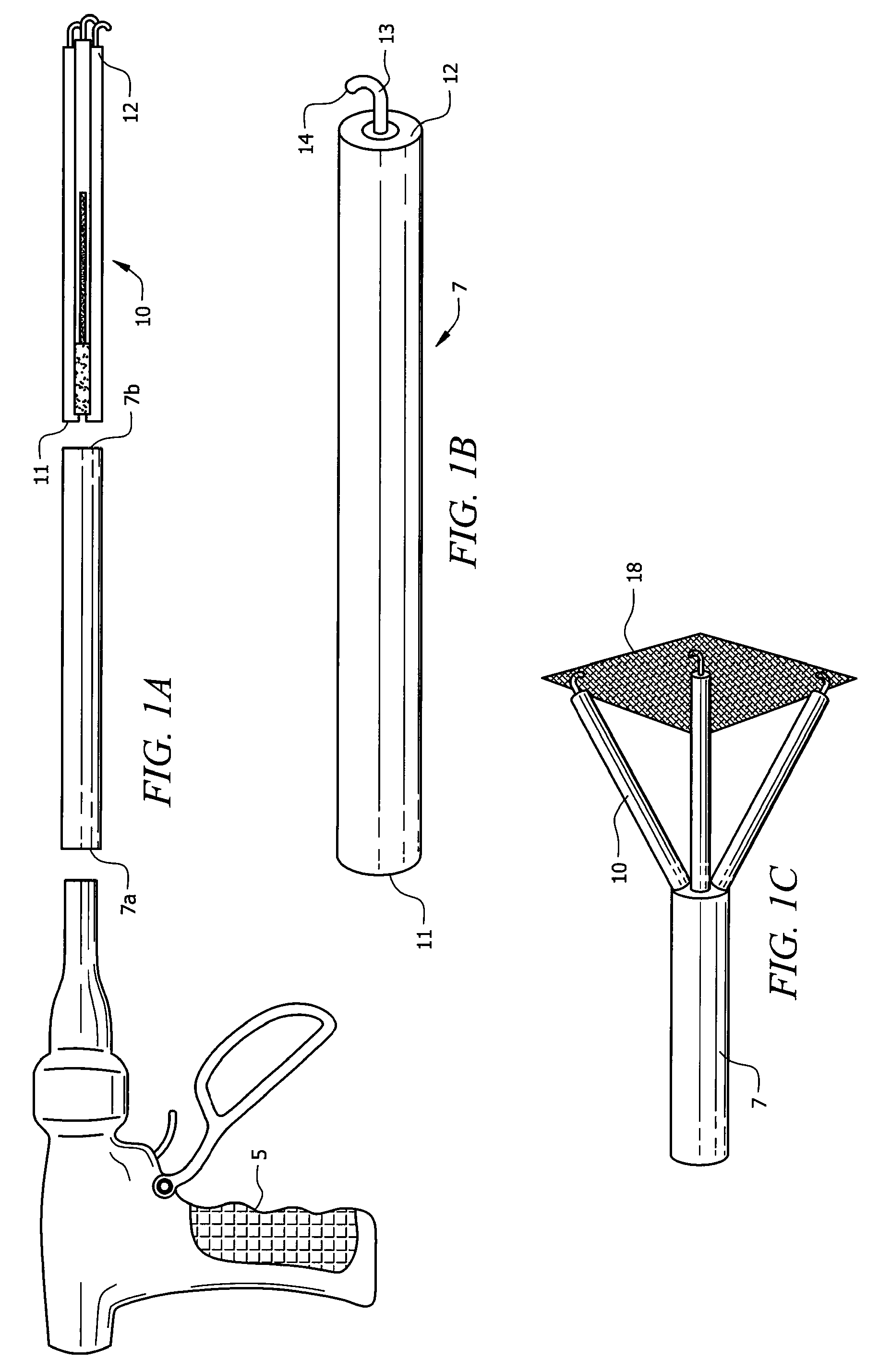
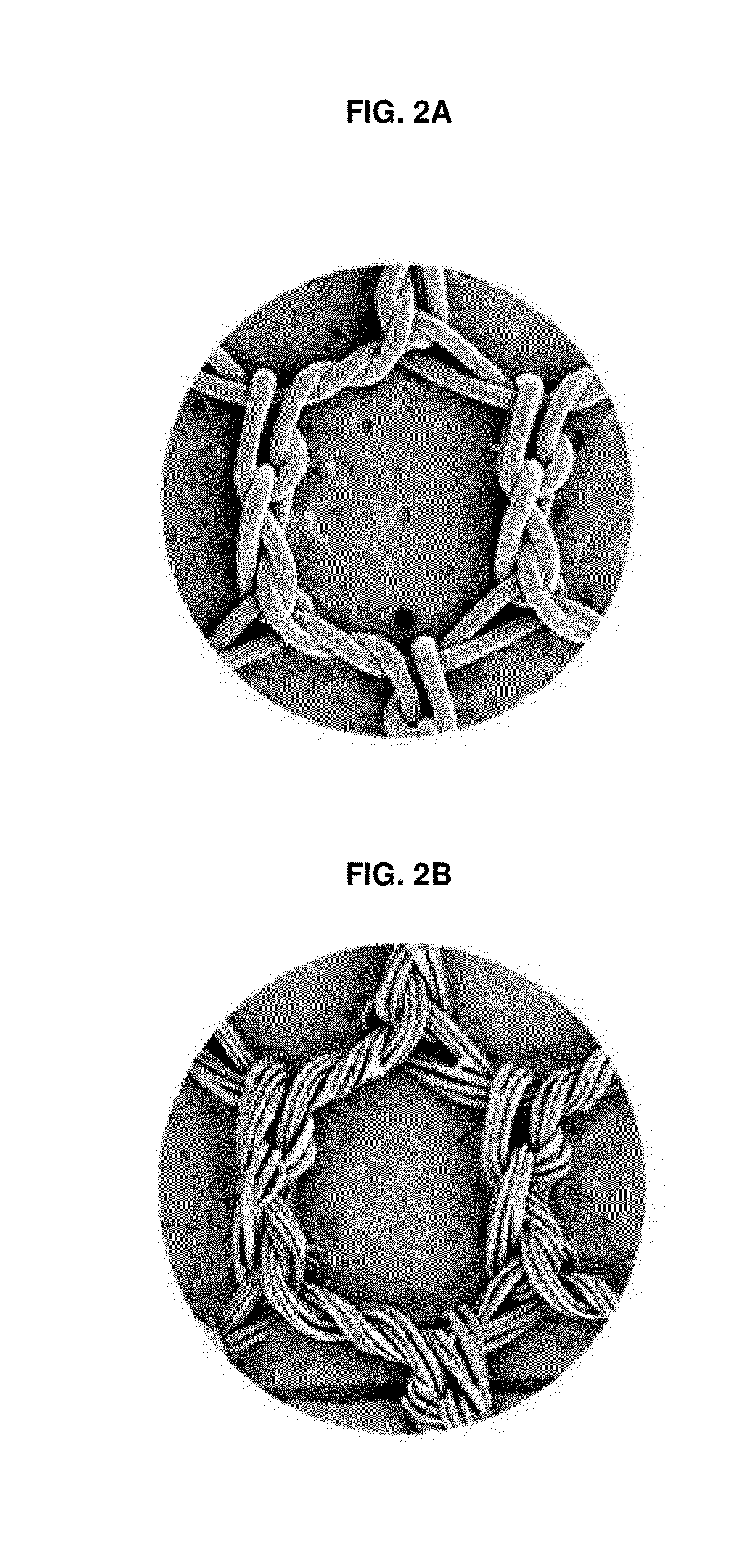
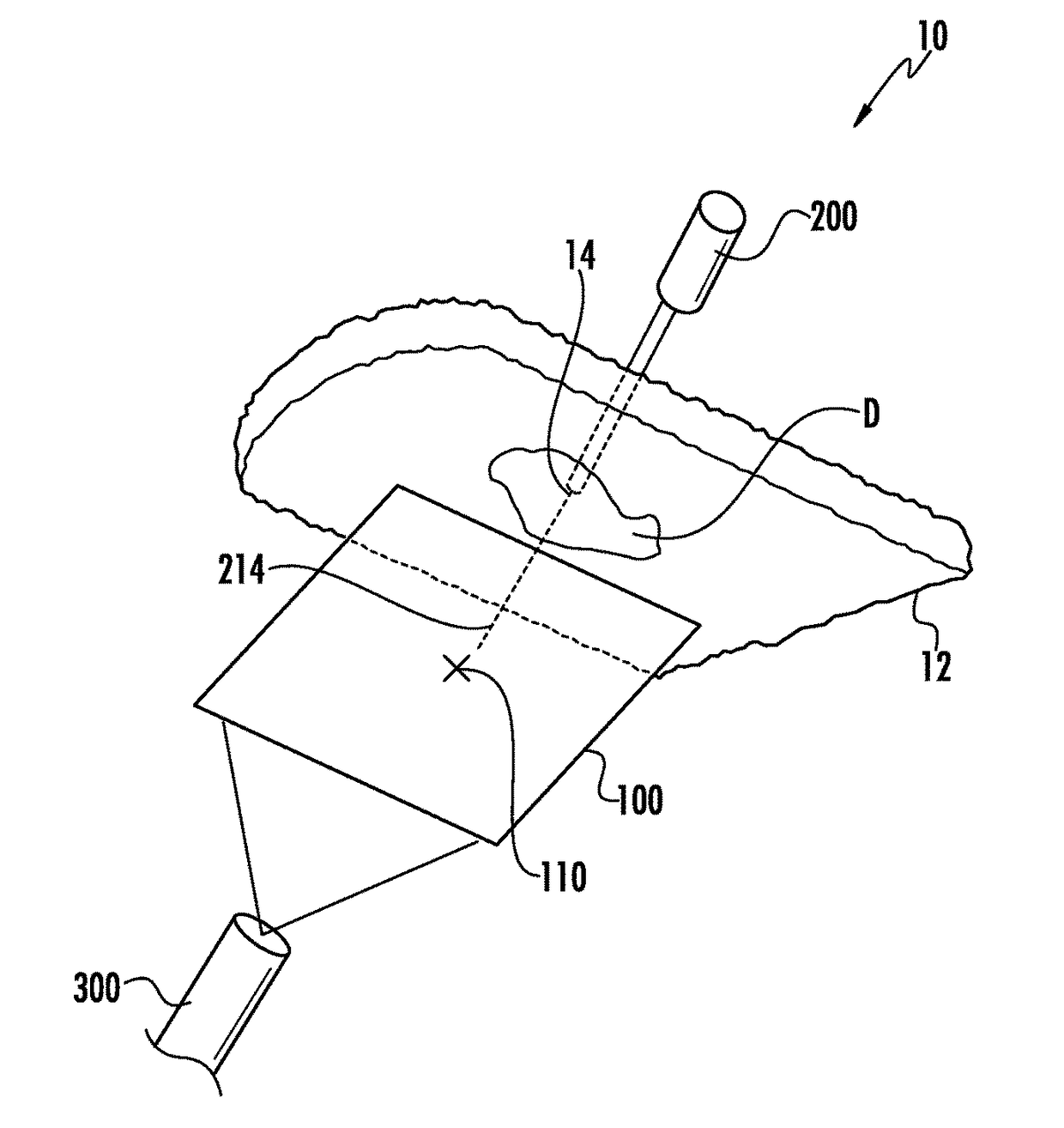
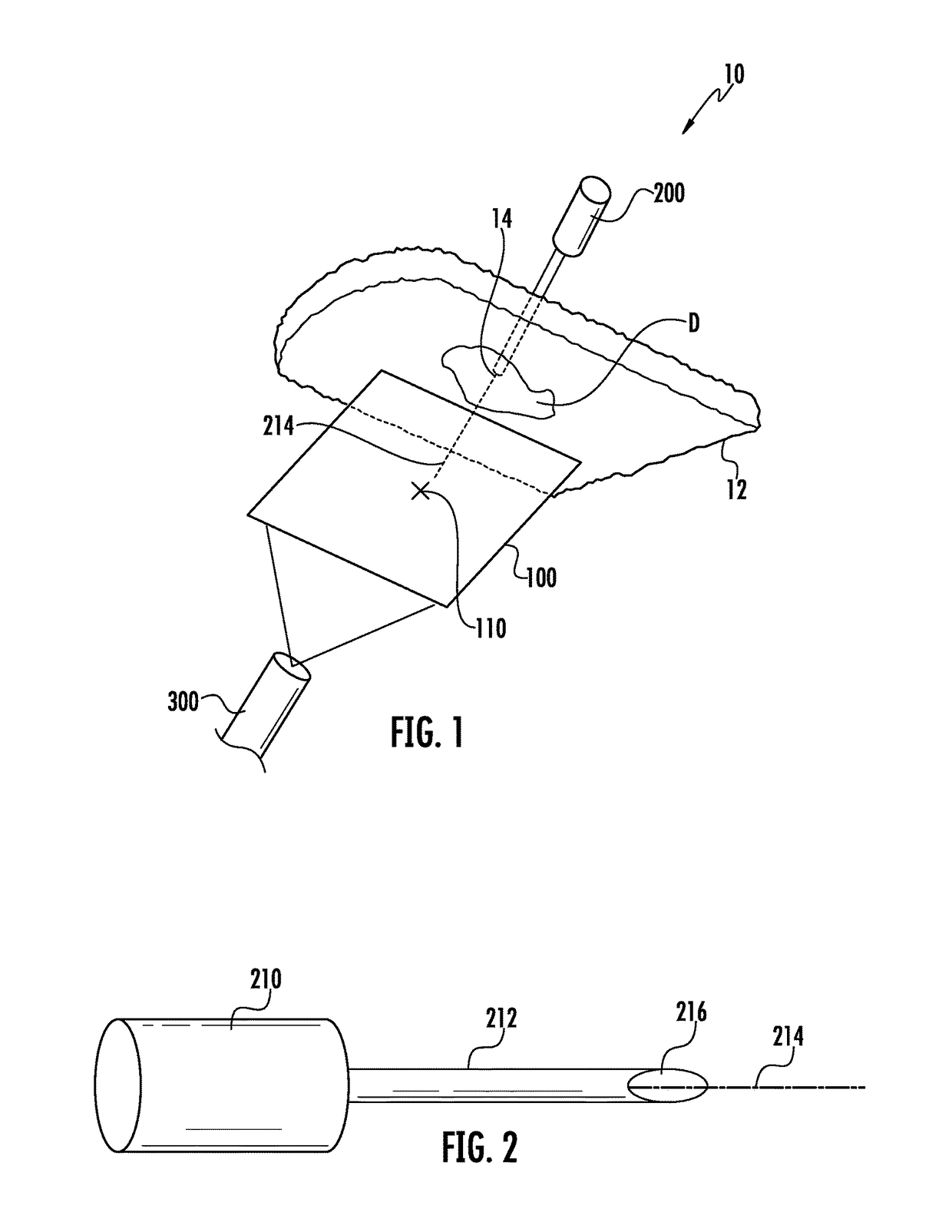
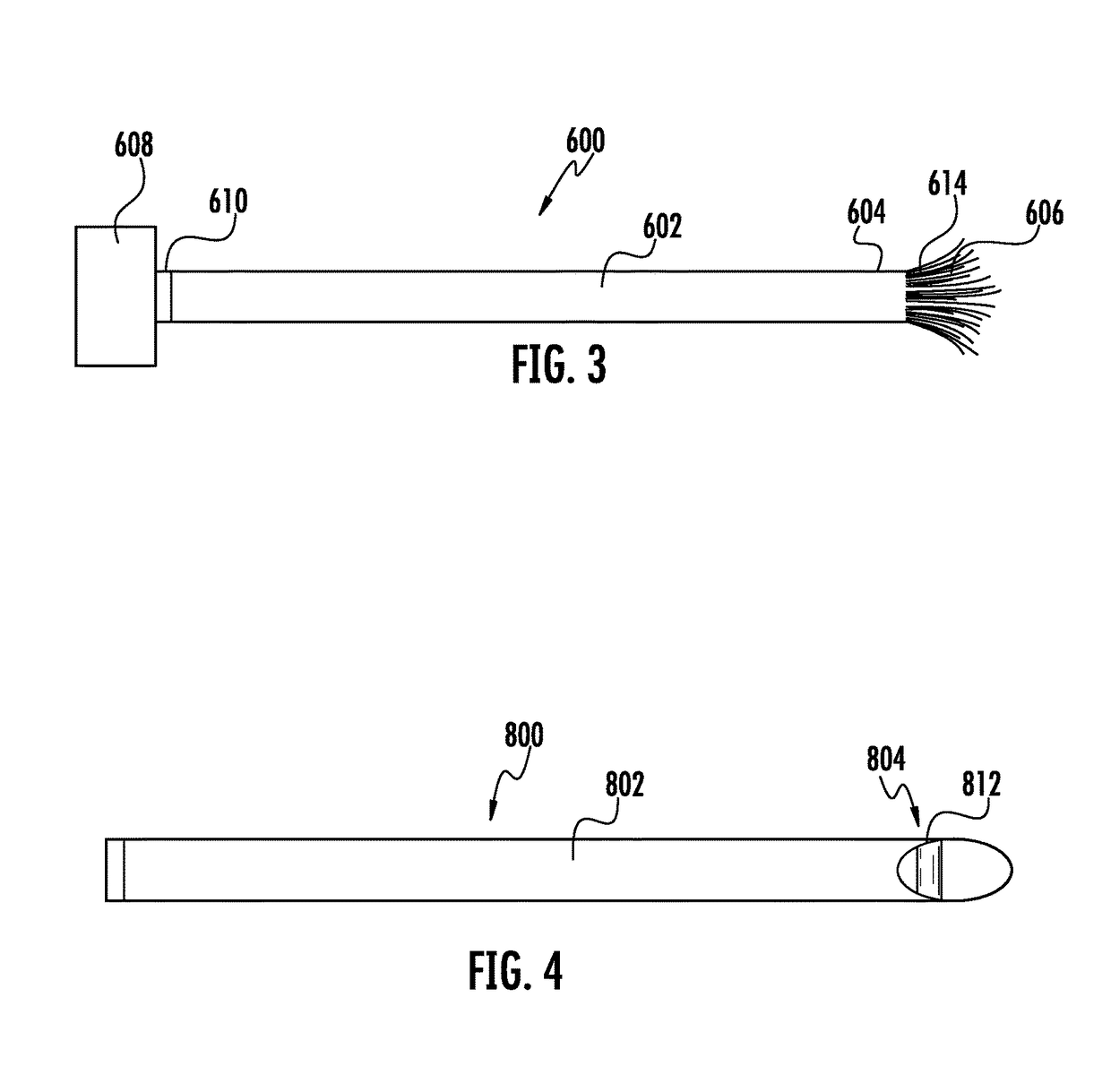
Hernia mesh placement system and method for in-situ surgical applications
ActiveUS9592109B2Improve permeabilityProsthesisInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryAbdominal cavityLight beam
A method for hernia mesh placement during in-situ surgical applications. The method includes the step of positioning a mesh having a center mark within an abdominal cavity near a site of repair. A light assembly projecting a light beam through a free end is provided. Next, the free end of the light assembly is inserted through a central location of the site of repair. Finally, the center mark of the mesh is aligned with the light beam of the light assembly to position the mesh at the central location of the site of repair.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com