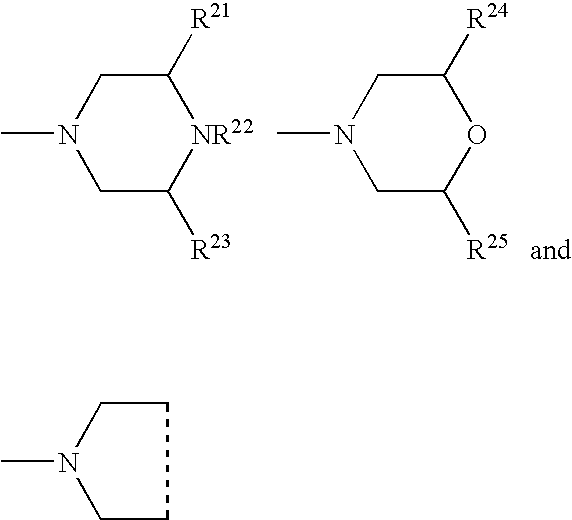
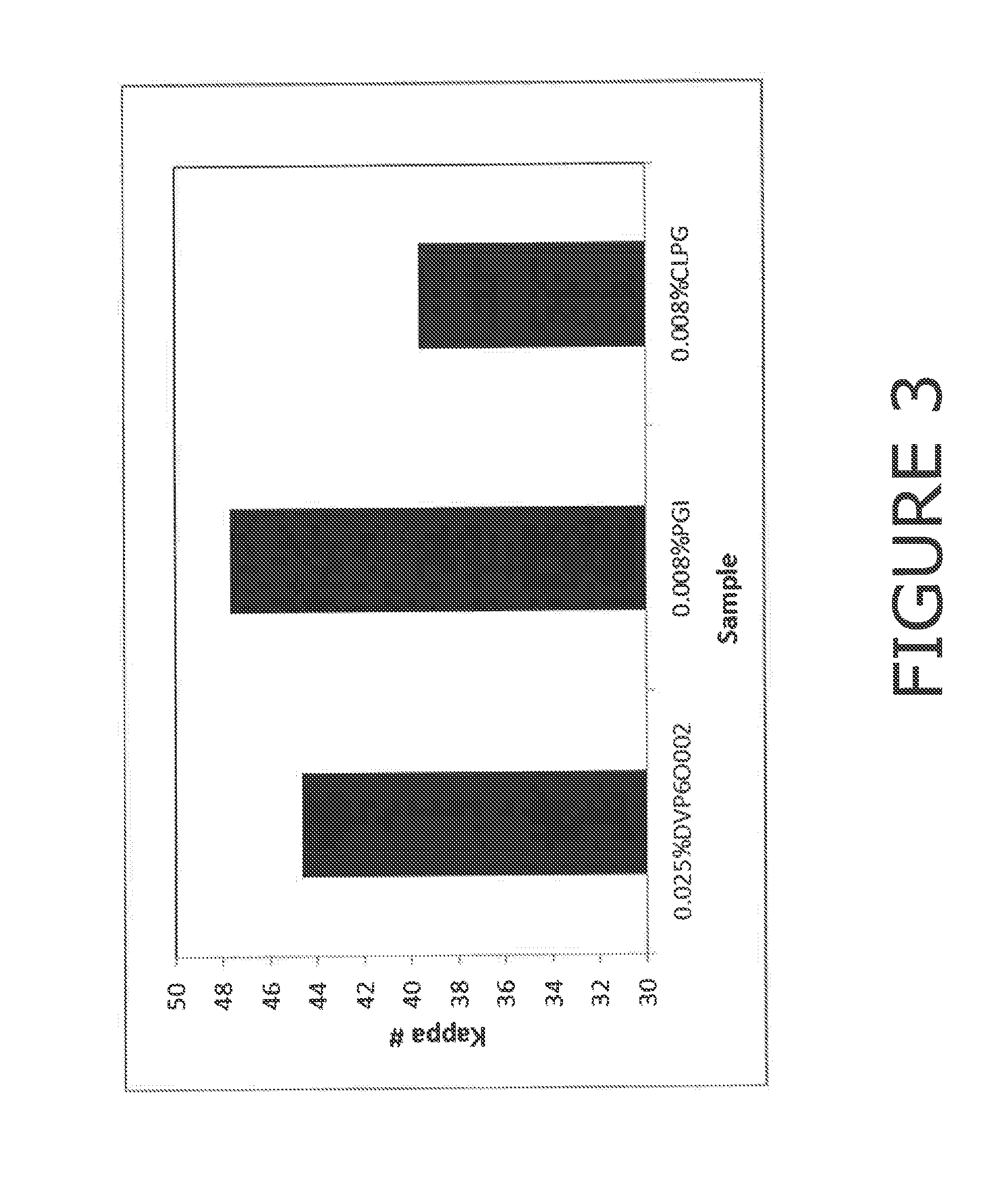
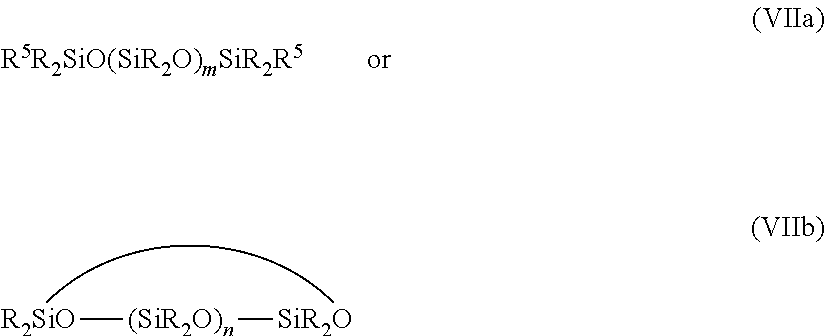
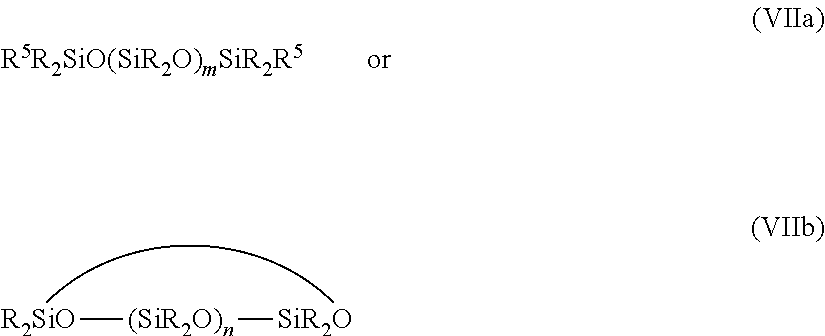
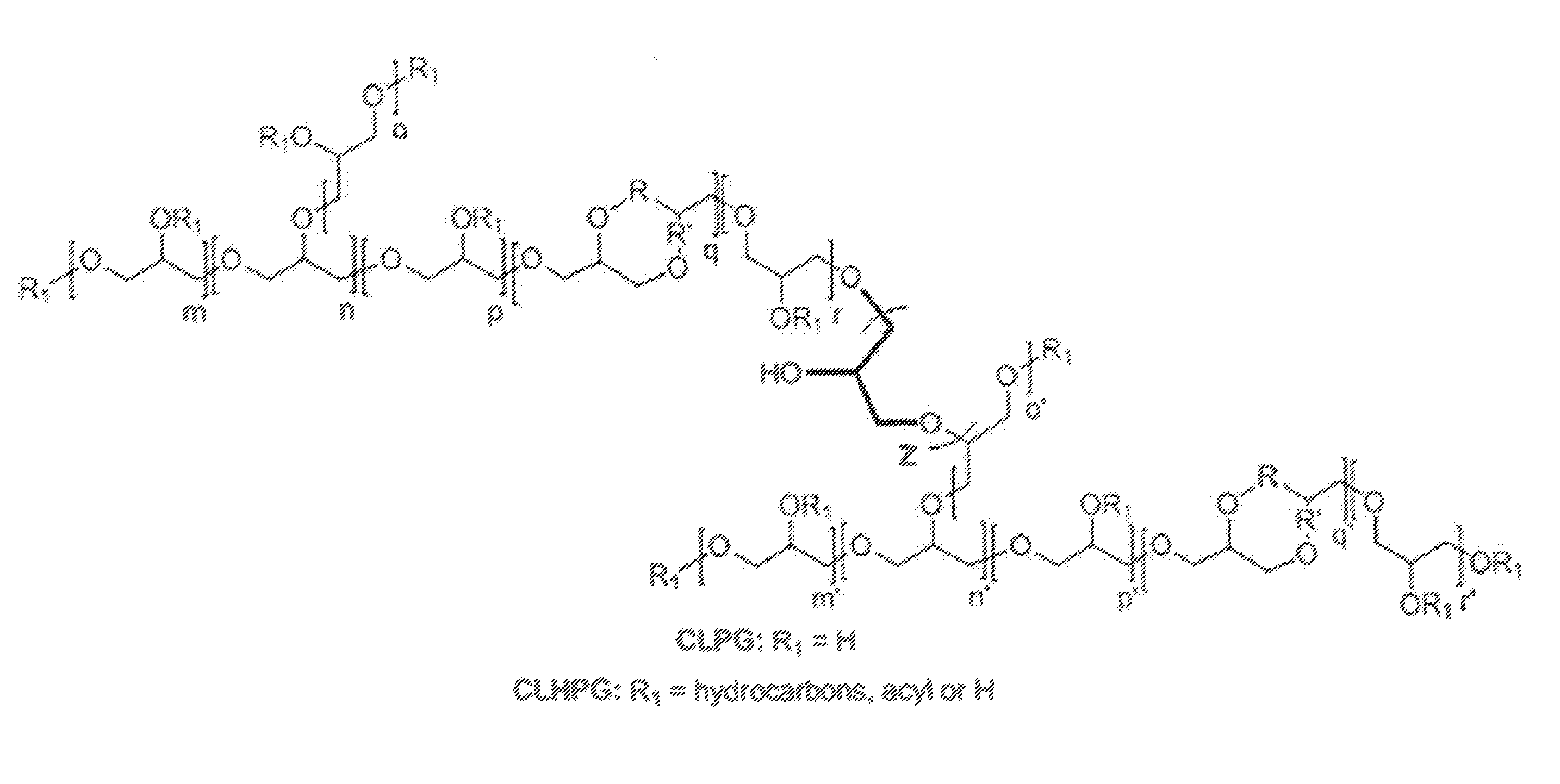
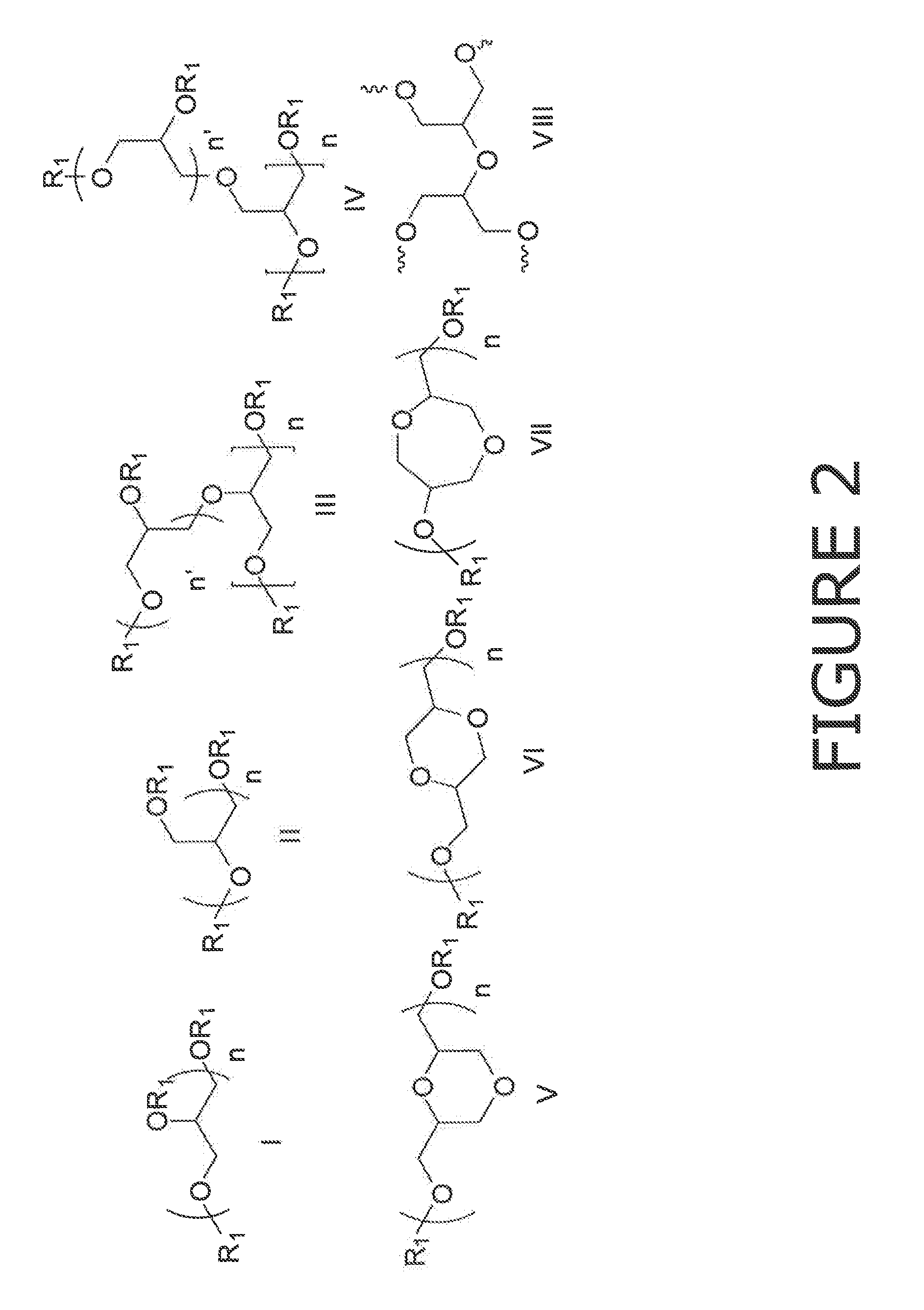
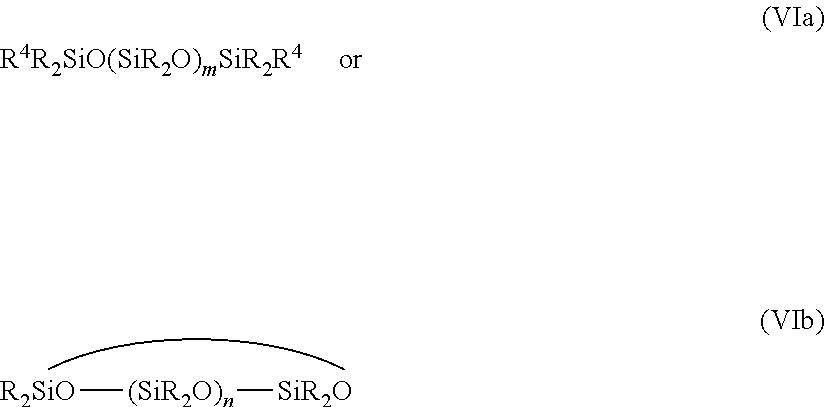
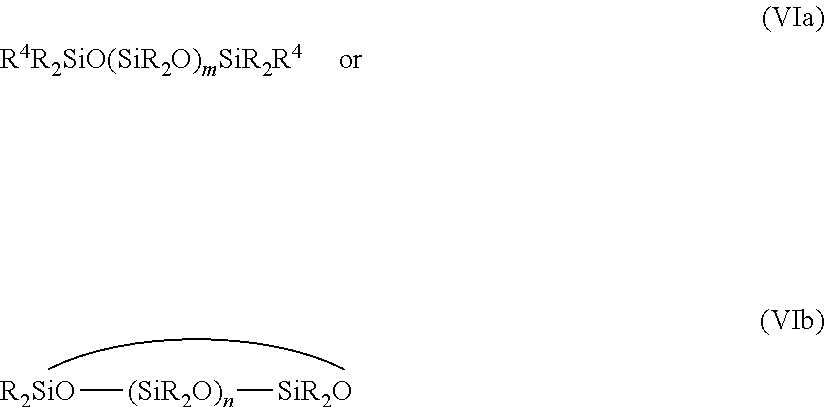
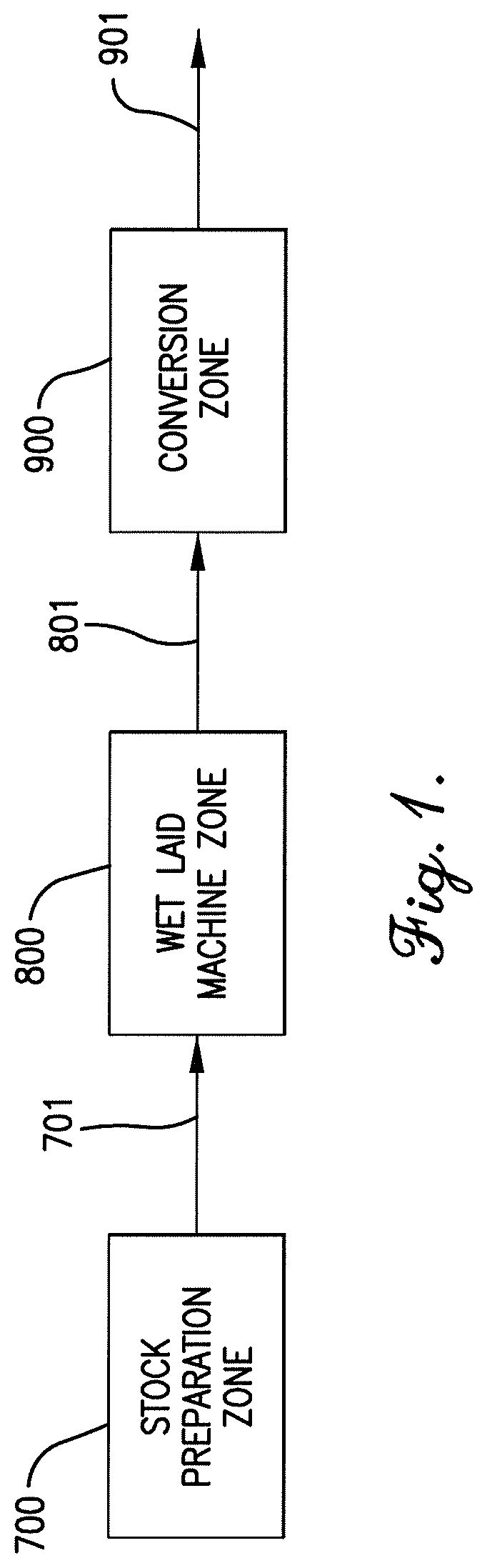
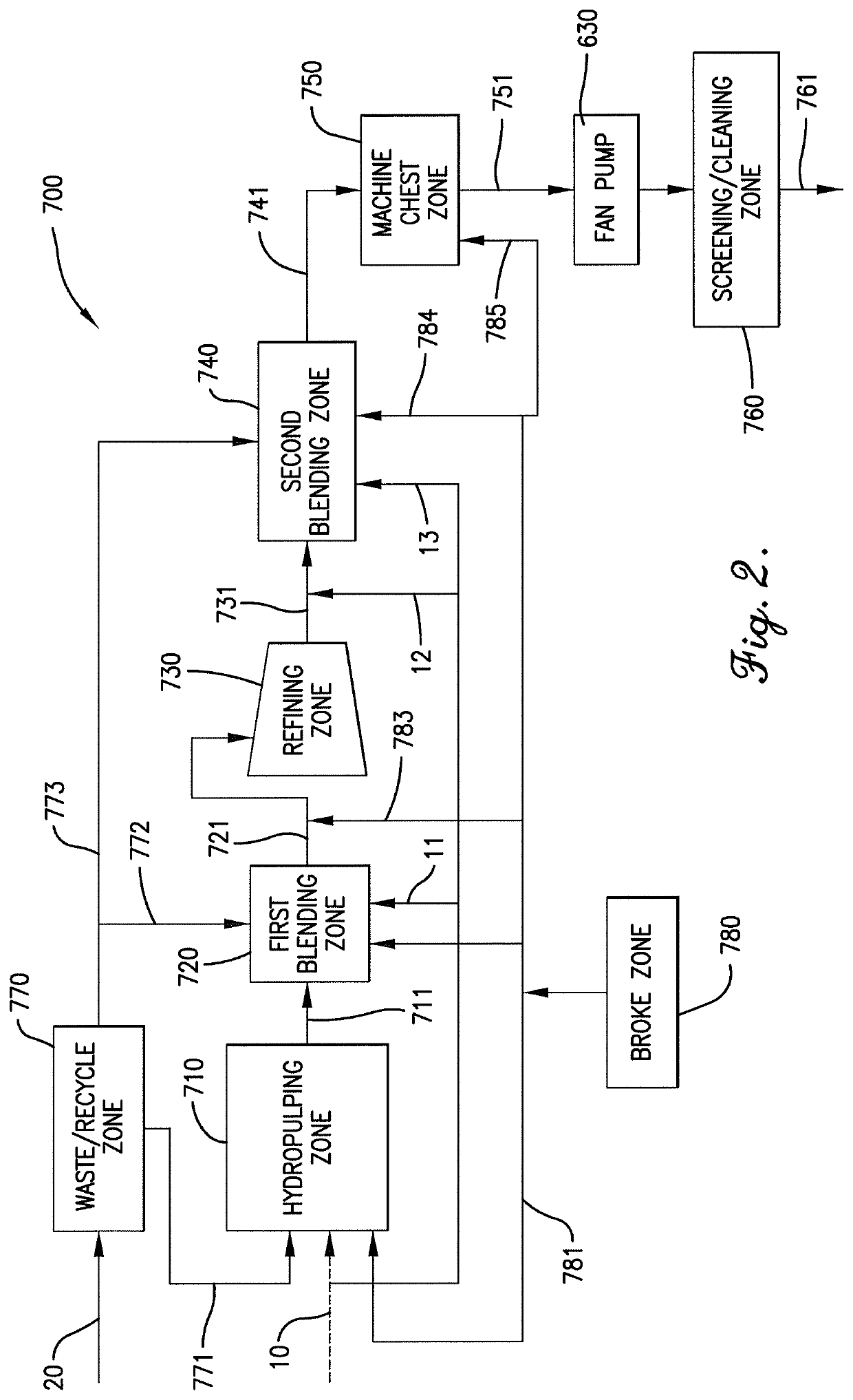
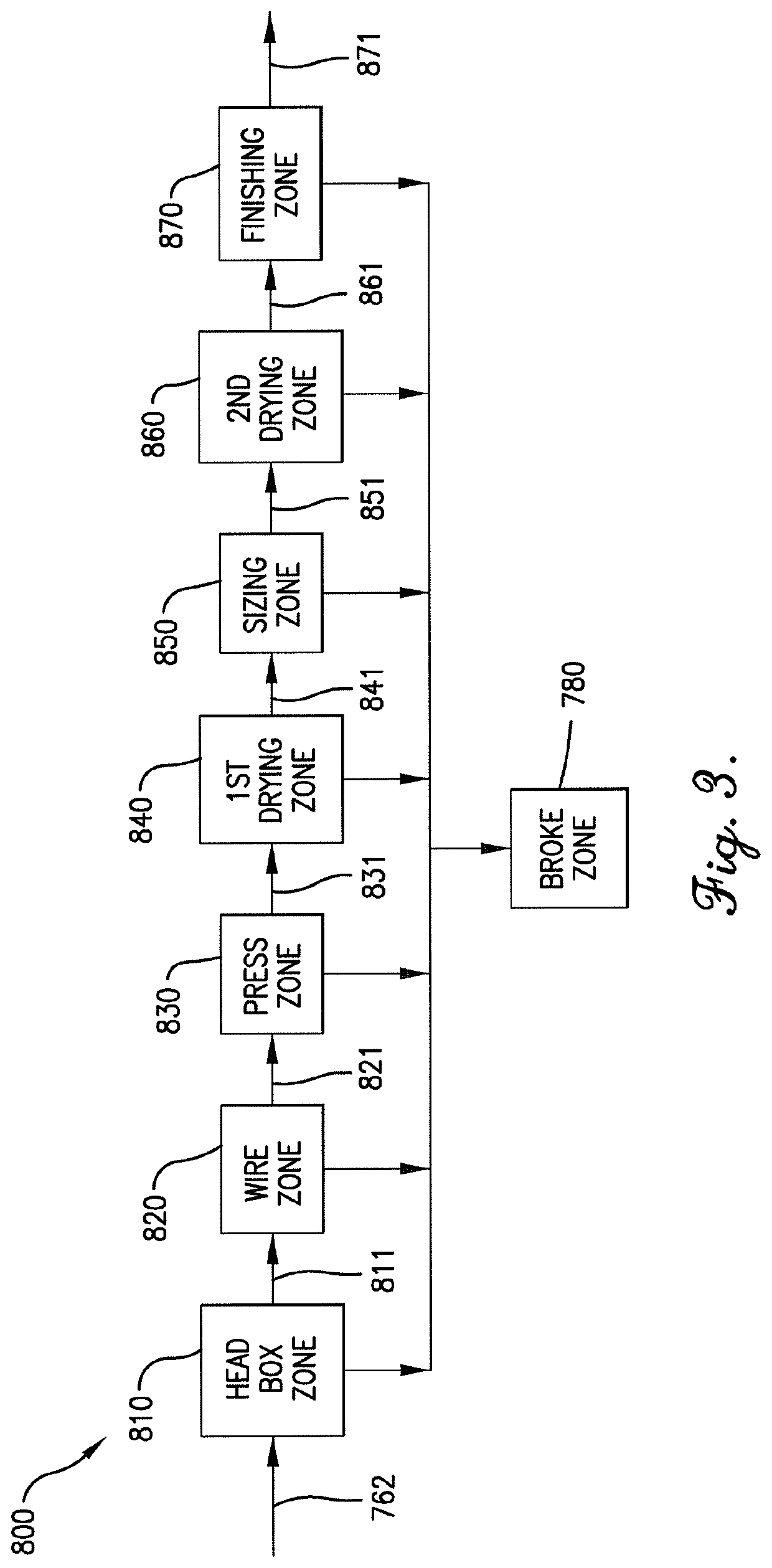
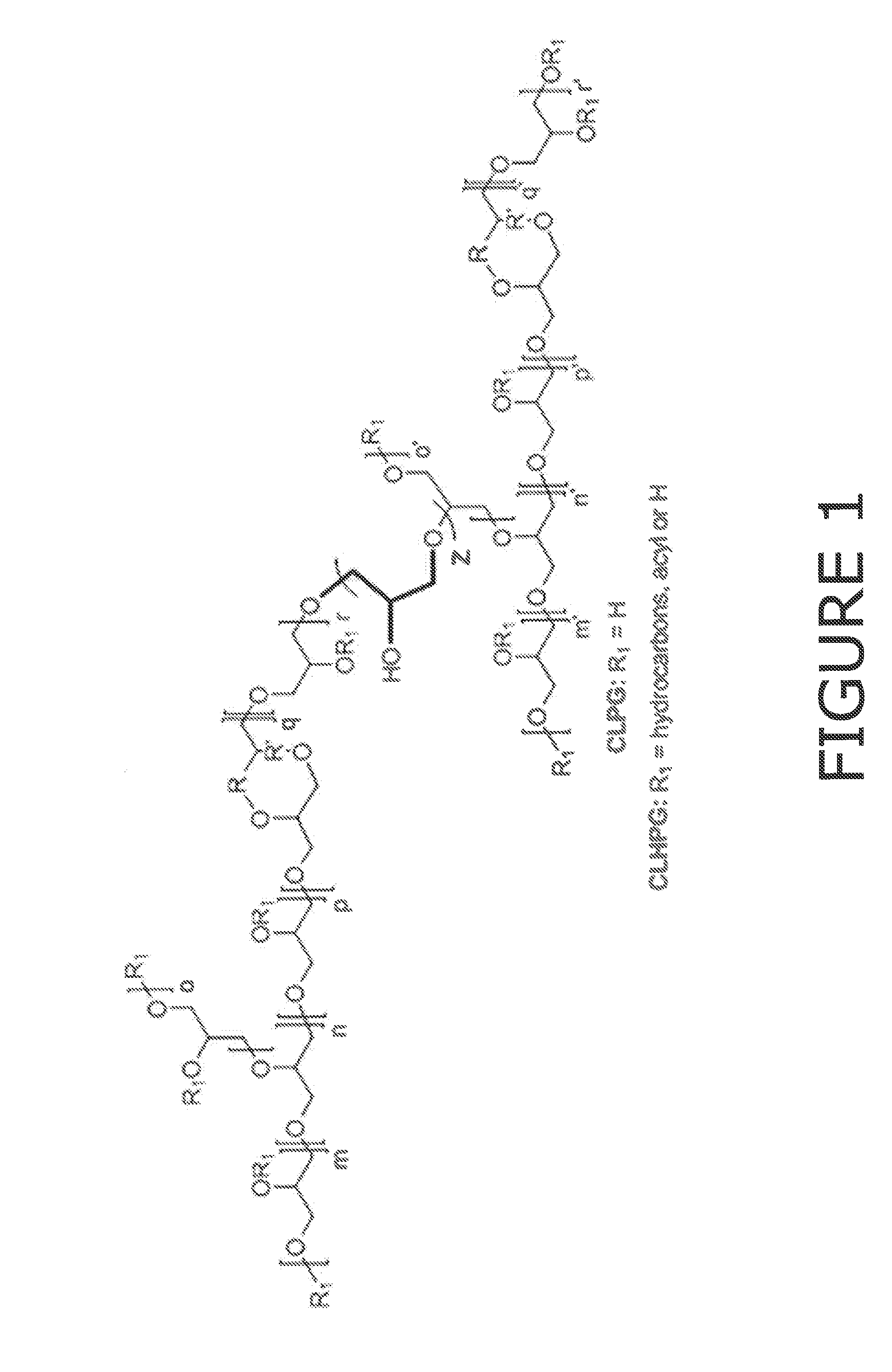
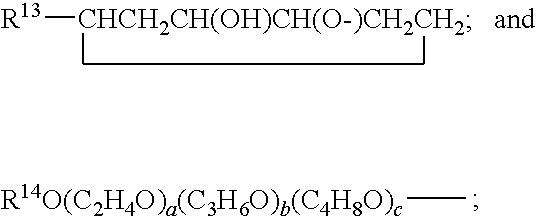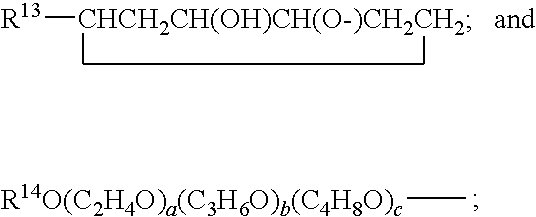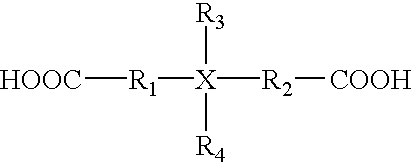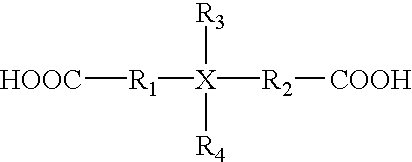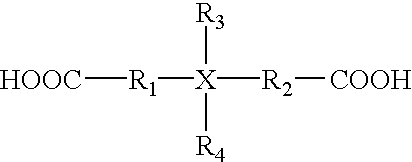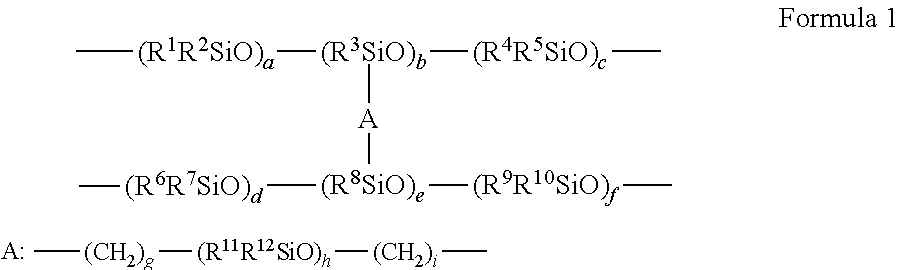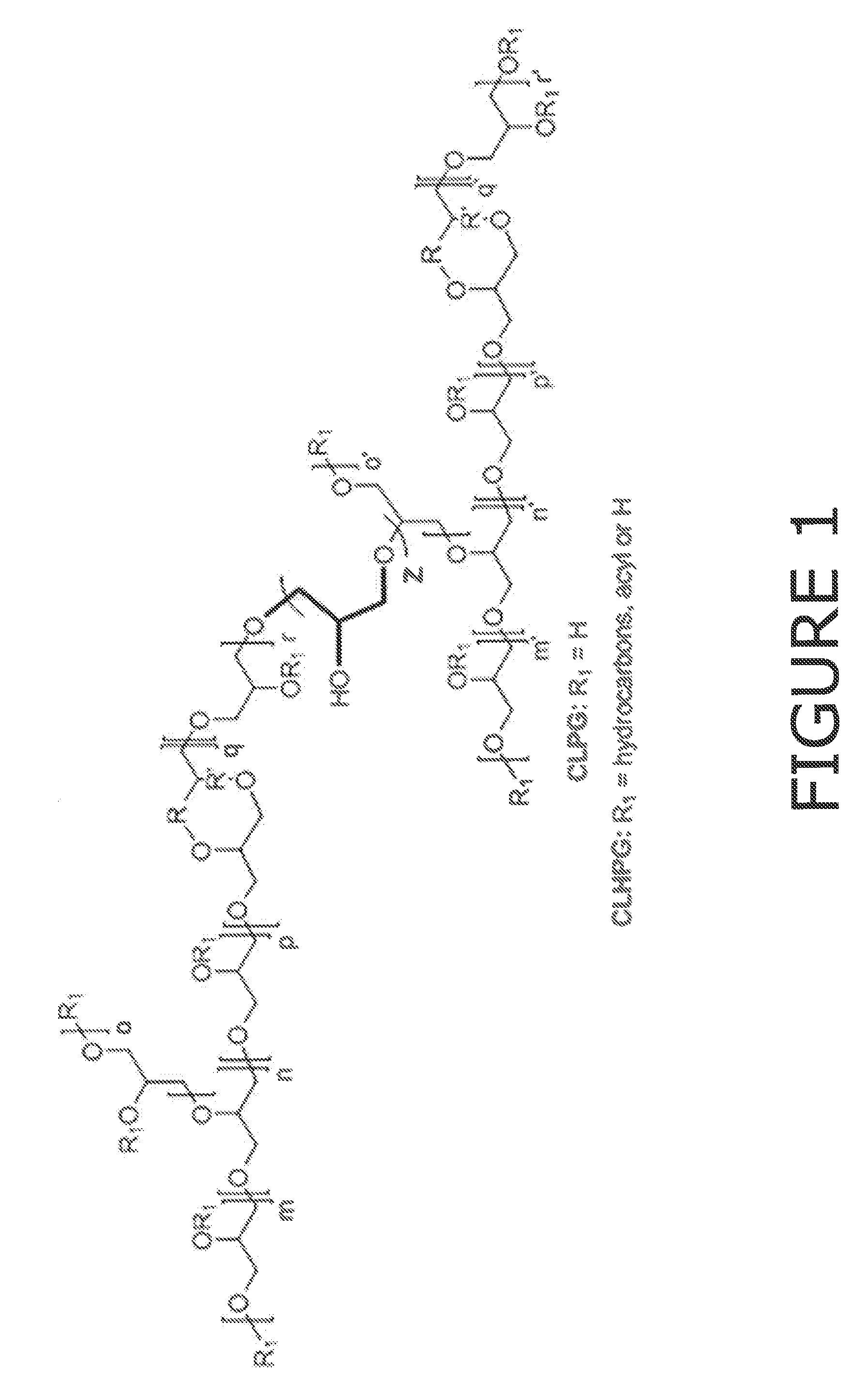Patents
Literature
32results about "Pulping foam prevention" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
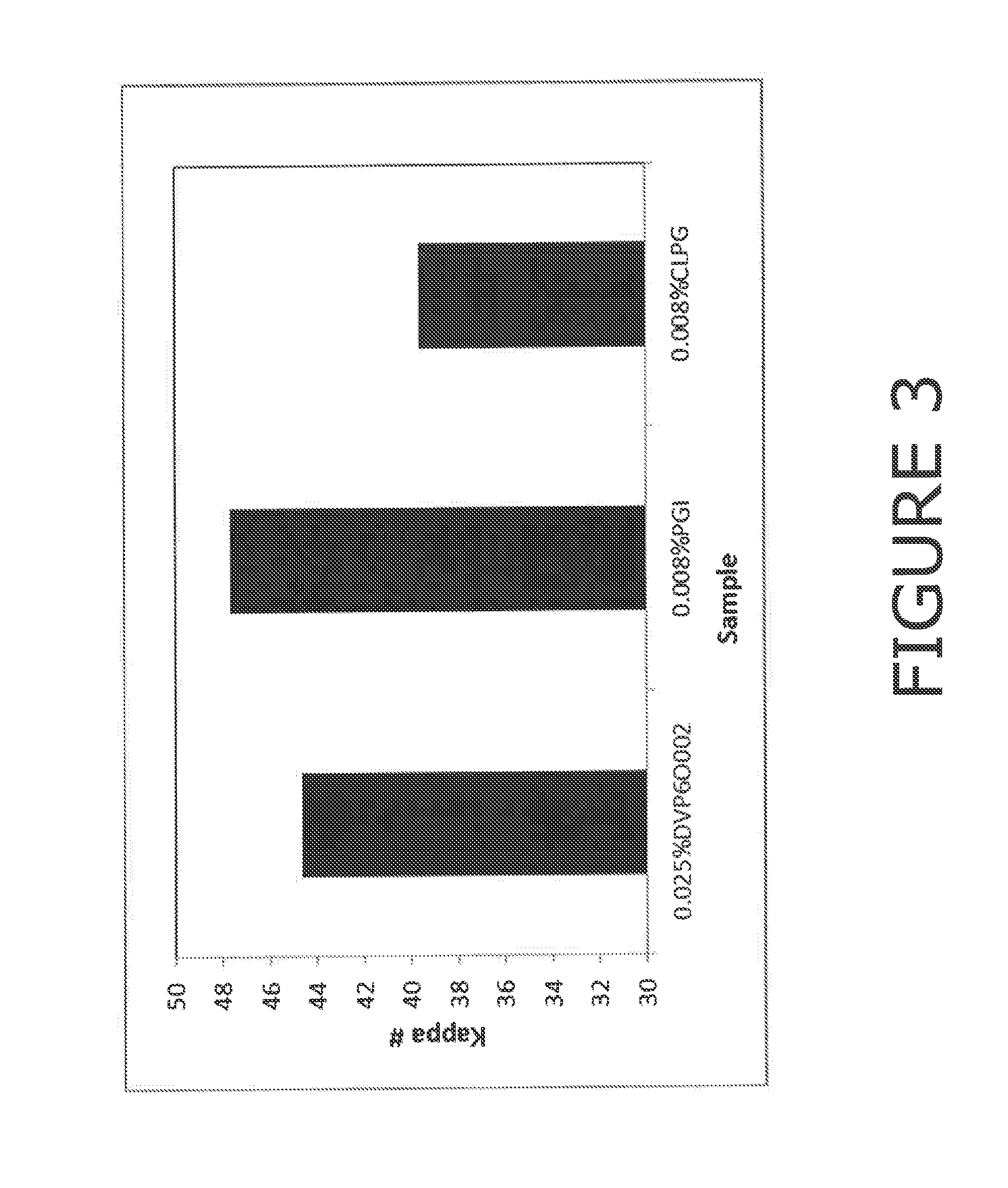
Foam control formulations
ActiveUS20150080273A1Lower Level RequirementsInhibition formationDewatering/demulsification with chemical meansDefoamers additionProcedure AgentsWater insoluble
The invention provides a foam control formulation in the form of a microemulsion, the formulation comprising: (a) from S to 70% w / w of primary surfactant, this surfactant having an HLB of from 1 to 12 and / or a cloud point of from 20 to 70° C.; (b) from 2 to 40% w / w of water-insoluble organic carrier liquid; and (c) water. Also provided is the use of this formulation to prevent and / or reduce foam in a fluid system, or as a processing aid to control foam production in a fluid system. The formulation may be used in an aqueous fluid system, such as an oilfield.
Owner:ENERGY SOLUTIONS (US) LLC
Defoamer Formulations
InactiveUS20110021688A1Efficient defoaming formulationStable to hydrolysisDefoamers additionOther chemical processesHydrosilylationBonds hydrogen
(A) Siloxane-based antifoams and(B) silicone polyethers prepared by reactingorganopolysiloxanes (1) containing 0.05% to 1.6% by weight of Si-bonded hydrogen atomswith unsaturated polyethers (3) of the formulae:CH2═CR1—(CH2)aO(C2H4O)bR1 (Ia)CH2═CR1—(CH2)aO(C2H4O)b(C3H6O)cR1 (Ib)CH2═CR1—(CH2)aO(C3H6O)cR1 (Ic),whereR1 is a hydrogen or a C1-6 hydrocarbon radical,a is 0 to 16,b is 1 to 50, andc is 1 to 50,wherein the sum b+c is ≧10 and at least two different polyethers (Ia), (Ib) and (Ic) are used, andoptionally further reacting the reaction productwith organopolysiloxanes (2) containing from 0.01% to 0.5% by weight of Si-bonded hydrogen atoms,wherein the first and second step reactions take place with a hydrosilylation catalyst, and the weight ratio of Si-bonded hydrogen in organopolysiloxane (1) to Si-bonded hydrogen in organopolysiloxane (2) is at least 1.5.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Waste recycle composition
ActiveUS20200063347A1Reduce consistencyLow variabilityPaper recyclingNon-woven fabricsPolymer scienceCellulose fiber
A recycled cellulose pulp composition is provided which comprises recycled cellulosic fibers and cellulose ester staple fibers. The recycled cellulose pulp containing co-refined re-cycled cellulose fibers and cellulose ester staple fibers can be added to a hydropulper and fed back through a refiner to make wet laid products.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Hydrolysis resistant organomodified silylated ionic surfactants
The present invention provides for a composition comprising a silane having the formula:(R1)(R2)(R3)Si—R4—Si(R5)(R6)(R7)whereinR1, R2, R3, R5, and R6 are each independently selected from the group consisting of 1 to 6 monovalent hydrocarbon radicals, aryl, and a hydrocarbon group of 7 to 10 carbons containing an aryl group;R4 is a hydrocarbon group of 1 to 3 carbons;R7 comprises an anionic, cationic or zwitterionic substituent. The silanes of the present invention exhibit resistance to hydrolysis over a wide pH range.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
Antifoam compositions comprising a mixture of organopolysiloxanes
InactiveUS8530401B2Easy to manageHigh and long-lasting effectivenessInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsColloidal silicaSilicon dioxide
Superior defoamer compositions contain a low viscosity linear organopolysiloxane, a higher viscosity, optionally branched organopolysiloxane, a polyethersiloxane with a low cloud point, and both colloidal silica and fumed silica.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Defoamer formulations
InactiveUS8222303B2Efficient defoaming formulationStable to hydrolysisDefoamers additionOther chemical processesPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
(A) Siloxane-based antifoams and(B) silicone polyethers prepared by reacting organopolysiloxanes (1) containing 0.05% to 1.6% by weight of Si-bonded hydrogen atomswith unsaturated polyethers (3) of the formulae:CH2═CR1—(CH2)aO(C2H4O)bR1 (Ia)CH2═CR1—(CH2)aO(C2H4O)b(C3H6O)cR1 (Ib)CH2═CR1—(CH2)aO(C3H6O)cR1 (Ic),whereR1 is a hydrogen or a C1-6 hydrocarbon radical,a is 0 to 16,b is 1 to 50, andc is 1 to 50,wherein the sum b+c is ≧10 and at least two different polyethers (Ia), (Ib) and (Ic) are used, andoptionally further reacting the reaction productwith organopolysiloxanes (2) containing from 0.01% to 0.5% by weight of Si-bonded hydrogen atoms,wherein the first and second step reactions take place with a hydrosilylation catalyst, and the weight ratio of Si-bonded hydrogen in organopolysiloxane (1) to Si-bonded hydrogen in organopolysiloxane (2) is at least 1.5.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Polyester water-based defoamer
Polyester water-based defoamers are prepared by reaction of a dimer fatty acid, a fatty acid and two different polyalkylene polyols, e.g. polypropylene glycol and polyethylene glycol. The resulting polyesters are readily dispersible in water to form a water-based macroemulsion in the absence of any oil or short chain alcohols. The macroemulsion is an effective defoamer in ground-wood and thermomechanical pulping operations.
Owner:KEMIRA CHEM
Defoamers for pulp and papermaking applications
InactiveUS20060128884A1Natural cellulose pulp/paperDefoamers additionSilica particleTG - Triglyceride
A defoamer made from a composition that has at least one triglyceride oil or triglyceride oil mixture, at least one silicone, at least one silicone-triglyceride stabilizing agent, hydrophobic silica particles, optionally one or more surfactants and / or dispersants, and optionally one or more thickeners, and optionally one or more biocides. The defoamers described herein have utility in controlling foam in industrial applications. Typically, the defoamer can be used to control foam in pulp and paper applications.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Defoamers for pulp and papermaking applications
InactiveUS7879917B2Defoamers additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperTG - TriglycerideHydrophobic silica
A defoamer made from a composition that has at least one triglyceride oil or triglyceride oil mixture, at least one silicone, at least one silicone-triglyceride stabilizing agent, hydrophobic silica particles, optionally one or more surfactants and / or dispersants, and optionally one or more thickeners, and optionally one or more biocides. The defoamers described herein have utility in controlling foam in industrial applications. Typically, the defoamer can be used to control foam in pulp and paper applications.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Antifoam compositions
InactiveCN102869423AEasy to handleEasy to implementOrganic detergent compounding agentsDefoamers additionPolymer scienceWater insoluble
Novel compositions containing (A) organopolysiloxanes having a viscosity of 10 - 350 mm2 / s at 25 DEG C and 1013 hPa, (B) organopolysiloxanes having a viscosity of 500 - 200 000 mm2 / s at 25 DEG C and 1013 hPa, (C) precipitated silicas having a BET surface area of 20 - 500 m2 / g, (D) pyrogenic silicas having a BET surface area of 100 - 500 m2 / g, (E) polyethersiloxanes having a cloud point below 50 DEG C, (F) optionally organopolysiloxane resins, (G) optionally organopolysiloxanes which are different from (A) and (B), and (H) optionally water-insoluble organic compounds are described.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Defoaming compositions comprising hydroxy terminated siloxanes and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20160184740A1Shorten the timeWeaken energyDefoamers additionOther chemical processesEmulsion dropletDefoamer
Disclosed herein are methods of defoaming industrial process streams, the methods comprising adding to the industrial process stream an emulsion comprising silicone emulsion droplets in a continuous aqueous phase. Also disclosed herein are defoamer compositions comprising these silicone emulsions and methods of making such compositions.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Defoaming formulations containing organopolysiloxanes
ActiveCN109689178AImprove performanceDefoamers additionFoam regulating compositionsPolymer scienceStructural unit
The invention relates to defoaming formulations containing: (1) organopolysiloxanes containing, per molecule, at least one structural unit of general formula O<1 / 2>R2Si-Y-SiRO<2 / 2> (I) and at least 2units of general formula R1R2SiO<1 / 2> (II) and units of general formula R2SiO<2 / 2> (III), wherein R has the designation indicated in claim 1, R1 is the same as R or an alkenyl radical containing between 2 and 30 C atoms, at least one alkenyl radical being contained per molecule, and Y is a bivalent hydrocarbon radical containing between 2 and 30 C atoms, provided that the organopolysiloxane contains a structural element of formula R2Y2SiO-(SiR2o)<x1>-SiRY<1>O-(SiR2o)<x2>-SiR2R1 (IV), in which Y1 is a bivalent hydrocarbon radical containing between 2 and 30 C atoms, which is bound to a group offormula SiR2O<1 / 2>, Y2 is a bivalent hydrocarbon radical containing between 2 and 30 C atoms, which is bound to a group of formula SiRO<2 / 2>, and x1 und x2 are equal to 0 or a whole number, providedthat the sum is x1+x2=x, x on average being larger than 5 and smaller than 100; (2) fillers; and (3) organopolysiloxane resins from units of general formula R<2><e>(R<3>O)fSiO<(4-e-f) / 2> (V), in whichR2 and R3 have the designations indicated in claim 1, e is 0,1, 2 or 3, and f is 0, 1, 2 or 3, provided that the sum e+f is smaller than or equal to 3 and, in less than 50% of all units of formula (V) in the organopolysiloxane resin, the sum e+f is equal to 2.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Additive for physical straw pulping and use method thereof
InactiveCN102704299ASoften fastFast refiningPulping foam preventionNon-woody plant/crop pulpPapermakingFormamide
The invention belongs to the fields of biochemical pulping and papermaking, and discloses an additive for physical straw pulping and a use method thereof. The additive for physical straw pulping comprises dimethylsilicone fluid, a fabric softening dispersion agent, sodium lauryl sulfate, formamide, a low-temperature defoaming agent TF-508C and water. After being diluted with water for 4 to 20 times, the additive is added uniformly in a pulping process by a spray device controlled through an electric pump, and the spraying frequency ranges from 2 to 20 L / H, preferably 8 to 20 L / H. The additive for physical straw pulping and the use method thereof realize the technical support of environment-friendly physical straw pulping, a spraying infiltration method is adopted to replace a traditional soaking boiling method, and therefore, the possibility of pollution is low. Environment-friendly production of the physical straw pulping is realized, and the additive used for performing spraying infiltration on straw can be reused. No pollution is caused in the whole pulping process, so that the zero pollution discharge in the papermaking production is realized.
Owner:NANJING BIOFUNCTION CO LTD
Anti-Foaming Agent And Pulp Production Method
ActiveUS20150240424A1Improve performanceSuppress generationNatural cellulose pulp/paperDefoamers additionFoaming agentSURFACTANT BLEND
An anti-foaming agent containing (A) an organopolysiloxane and a finely powdered inorganic filler, (B) a polyoxyalkylene group-containing branched chain organopolysiloxane, and (C) an anionic surfactant. This anti-foaming agent exhibits stable anti-foaming performance even at high temperatures that reach, for example, 80 QC or under strongly alkaline conditions and produces no aggregates.
Owner:DOW TORAY CO LTD +1
Method for deaerating liquids
InactiveUS20120312165A1Improve degassing effectNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPaper productionCopolymer
Efficient deaeration of aqueous suspensions such as those obtained during textile treatment or pulp and paper production is achieved by use of a combination of a polyoxypropylene polyether polymer or copolymer and branched polyether-polysiloxane copolymers.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Method for dispersing higher fatty alcohol mixture
InactiveCN101530759BDefoamers additionTransportation and packagingCarbon numberFatty acid glycerol esters
Owner:JIANGSU SIXIN SCI-TECH APPL RES INST CO LTD
Solid defoaming agent
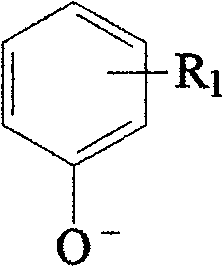
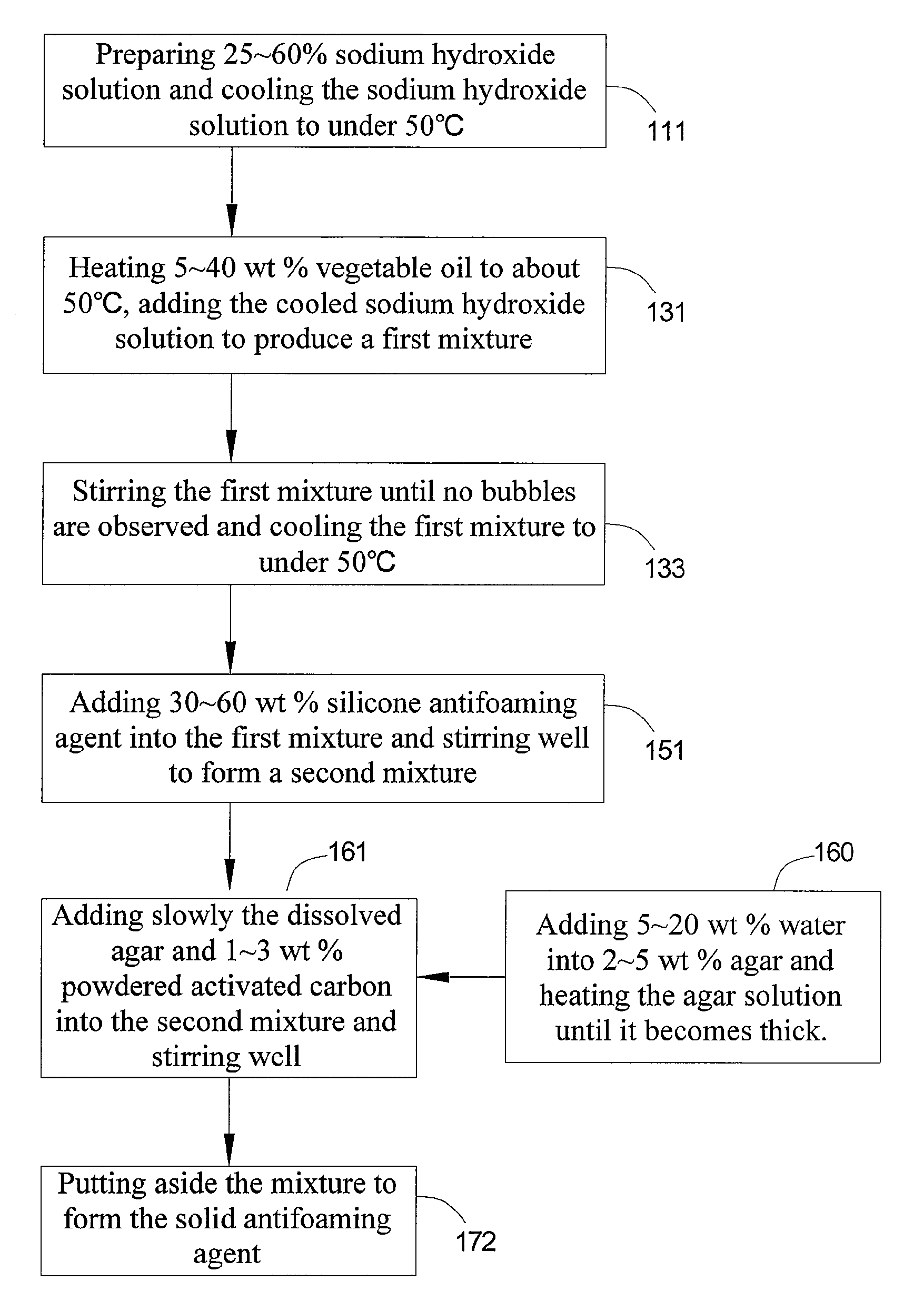
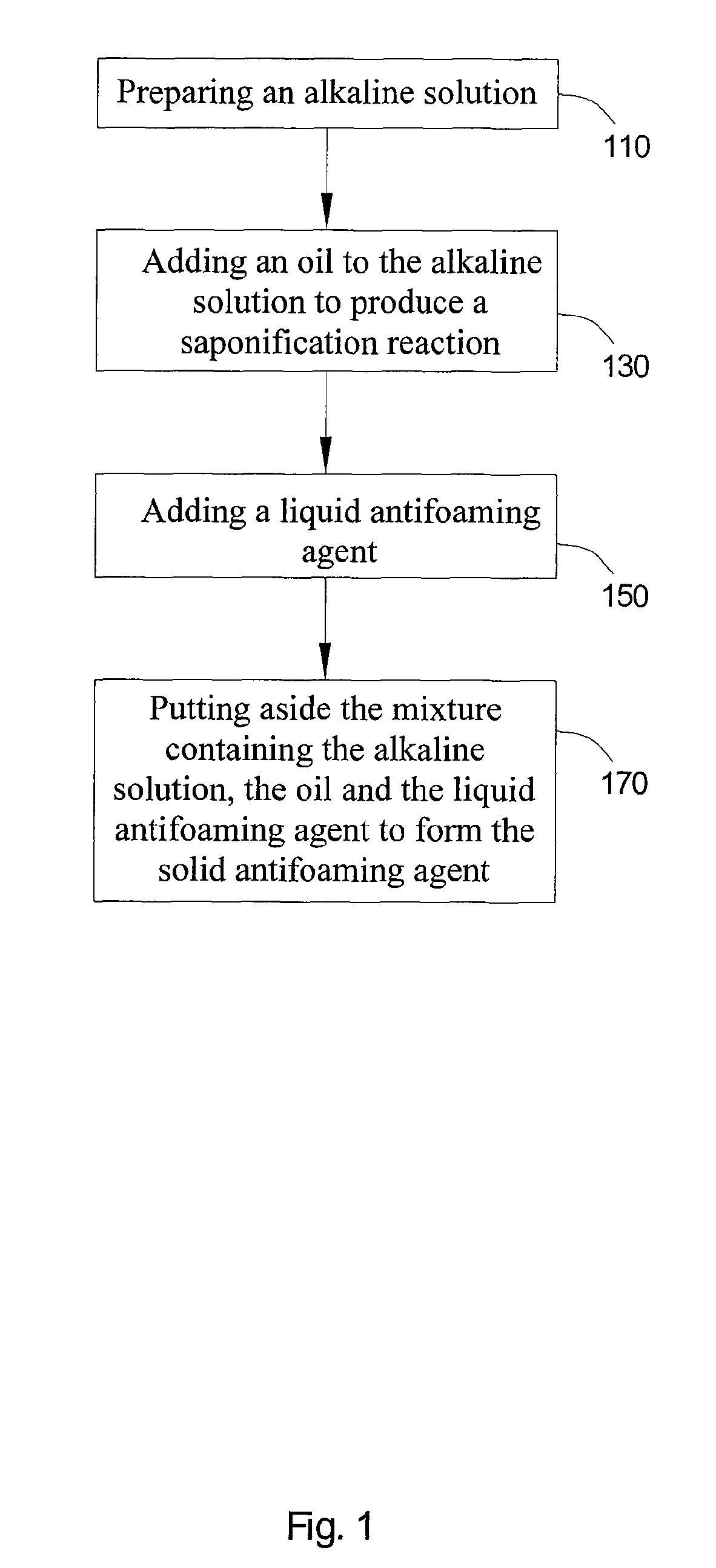
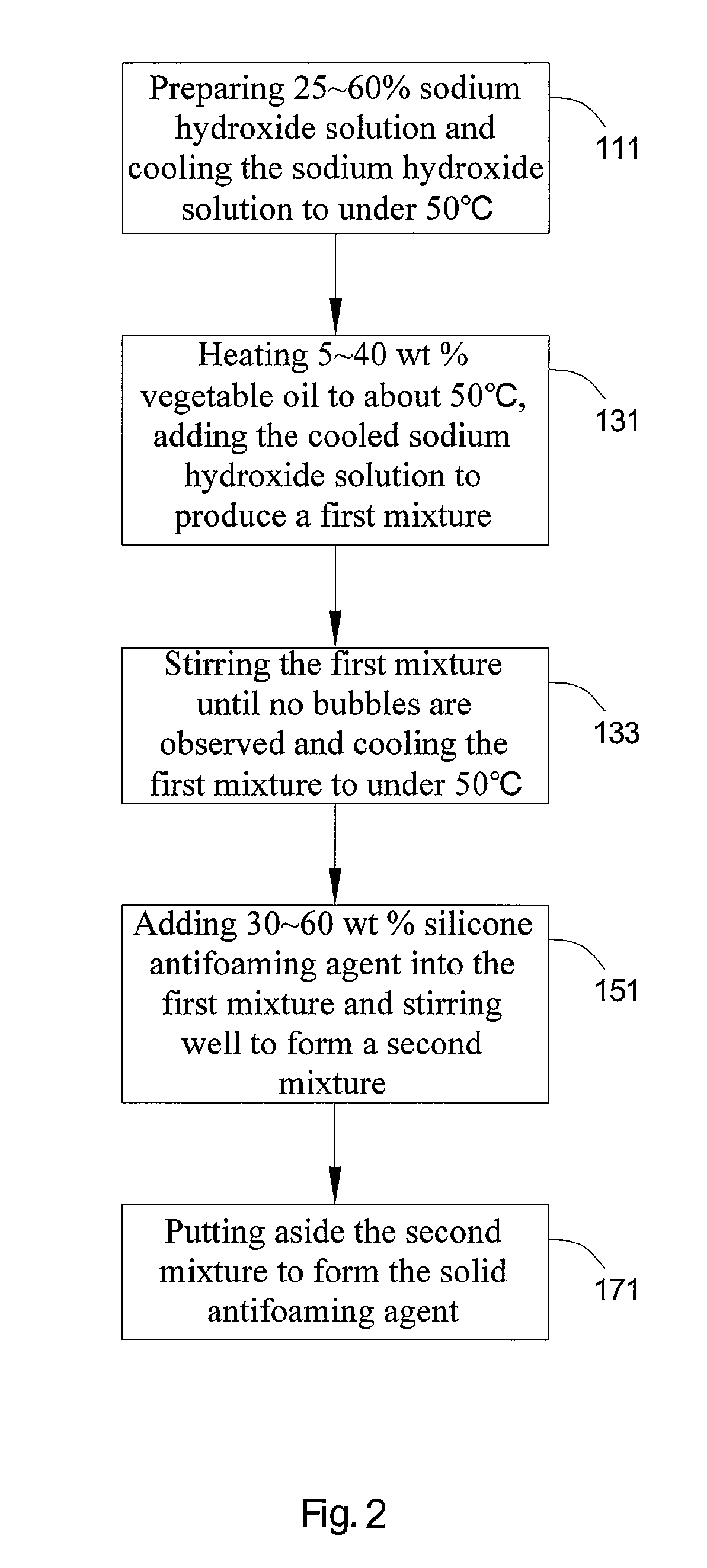
A method for producing a solid antifoaming agent comprising the following steps: providing an alkaline solution; adding an oil to the above alkaline solution to produce a saponification reaction; adding a liquid antifoaming agent; and putting aside the mixture containing the above alkaline solution, the oil and the liquid antifoaming agent to form the solid antifoaming agent. The ingredients of the solid antifoaming agent according to the present invention include 5˜40 weight percent vegetable oil, a 20˜40 weight percent sodium hydroxide solution and a 30˜60 weight percent liquid antifoaming agent.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Anti-foaming agent and pulp production method
ActiveUS9631320B2Improve performanceSuppress generationDefoamers additionPaper/cardboardFoaming agentSURFACTANT BLEND
Owner:DOW TORAY CO LTD +1
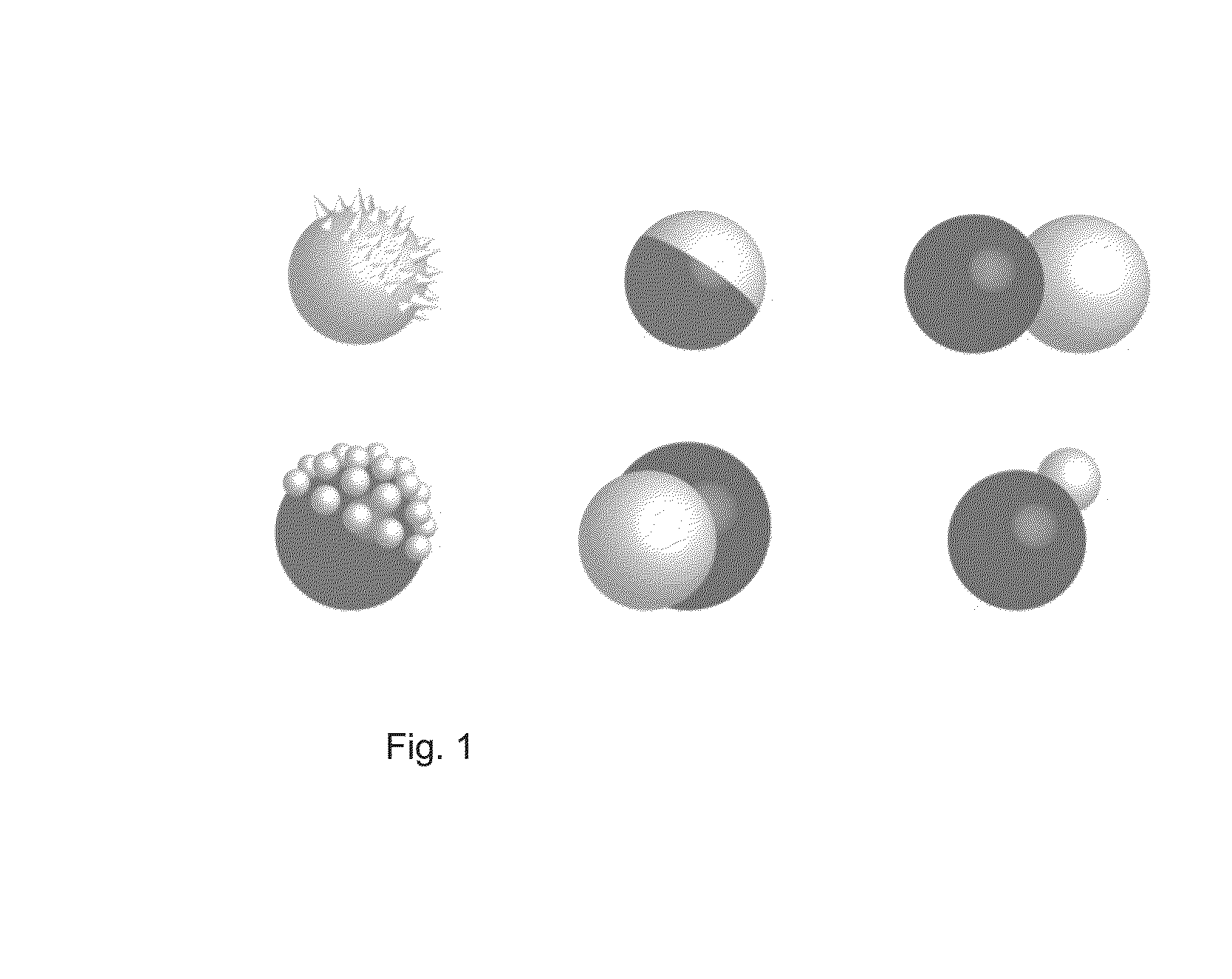
Defoaming compositions comprising amphiphilic particles and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS9999846B2Weaken energyReduce heatDefoamers additionPaper/cardboardJanus particlesEmulsion droplet
Disclosed herein are methods of defoaming industrial process streams, the methods comprising adding to the industrial process stream an emulsion stabilized by Janus particles, wherein the Janus particles comprise at least one hydrophobic surface and at least one hydrophilic surface, and wherein the emulsion comprises silicone emulsion droplets in a continuous aqueous phase. Also disclosed herein are defoamer compositions comprising Janus particles and methods of making such compositions.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Defoaming compositions comprising amphiphilic particles and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20160175741A1Improve performanceWeaken energyDefoamers additionOther chemical processesJanus particlesEmulsion droplet
Disclosed herein are methods of defoaming industrial process streams, the methods comprising adding to the industrial process stream an emulsion stabilized by Janus particles, wherein the Janus particles comprise at least one hydrophobic surface and at least one hydrophilic surface, and wherein the emulsion comprises silicone emulsion droplets in a continuous aqueous phase. Also disclosed herein are defoamer compositions comprising Janus particles and methods of making such compositions.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
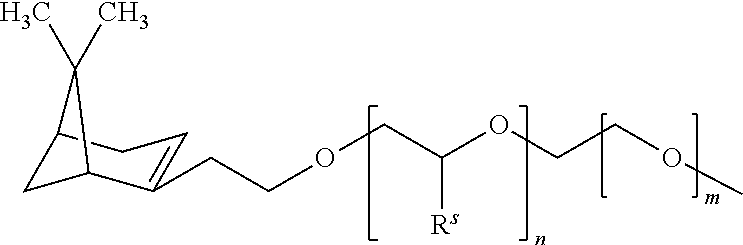
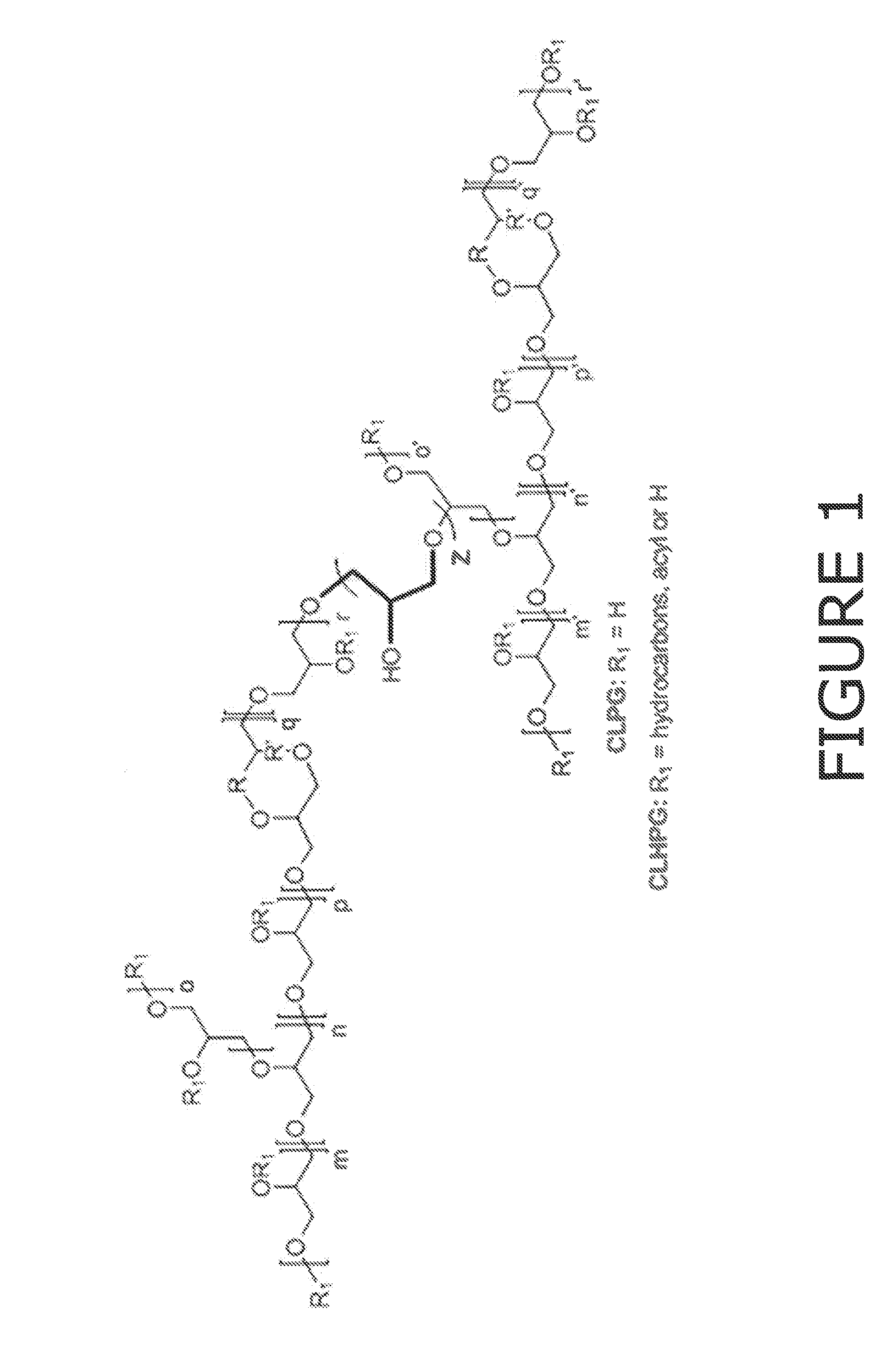
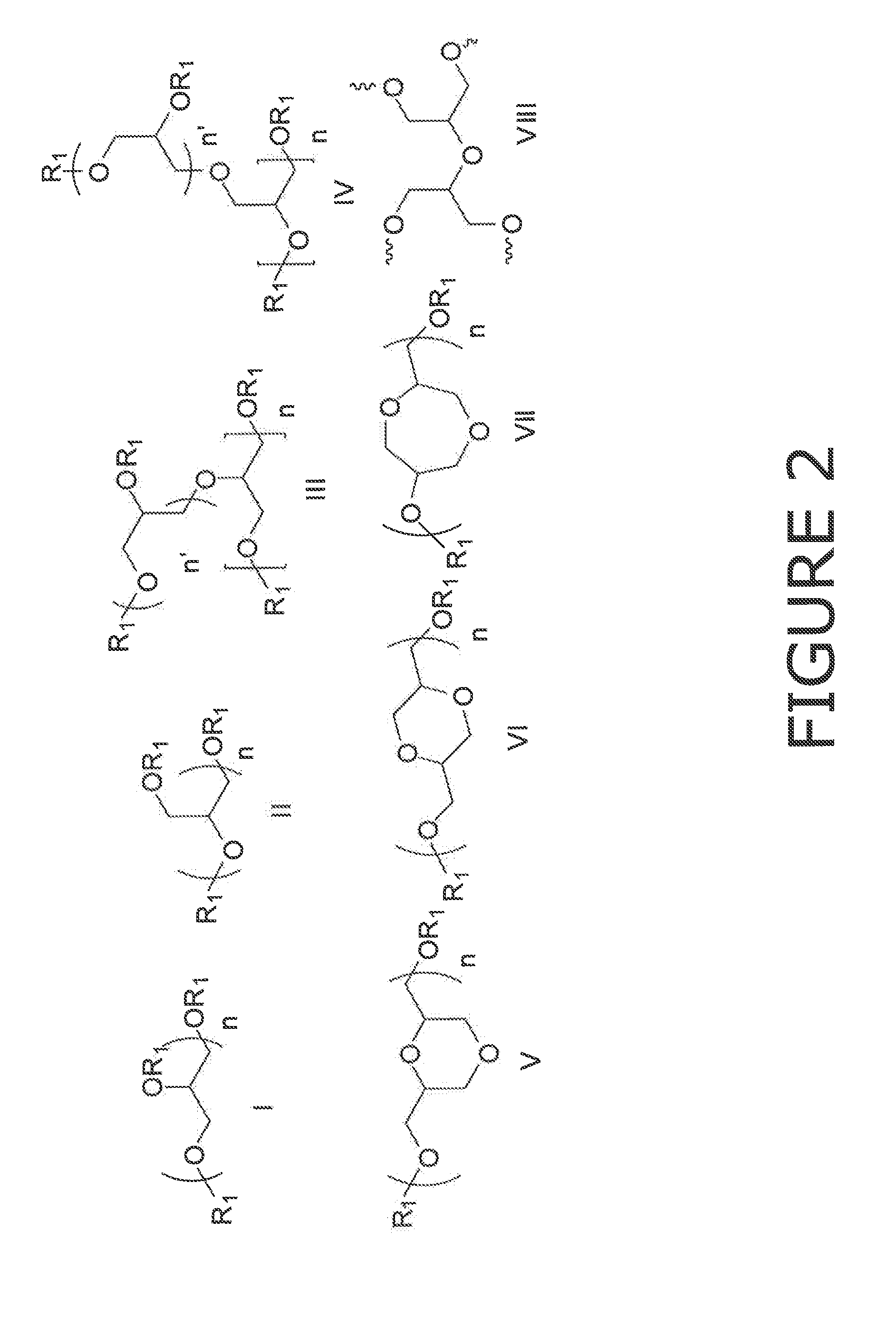
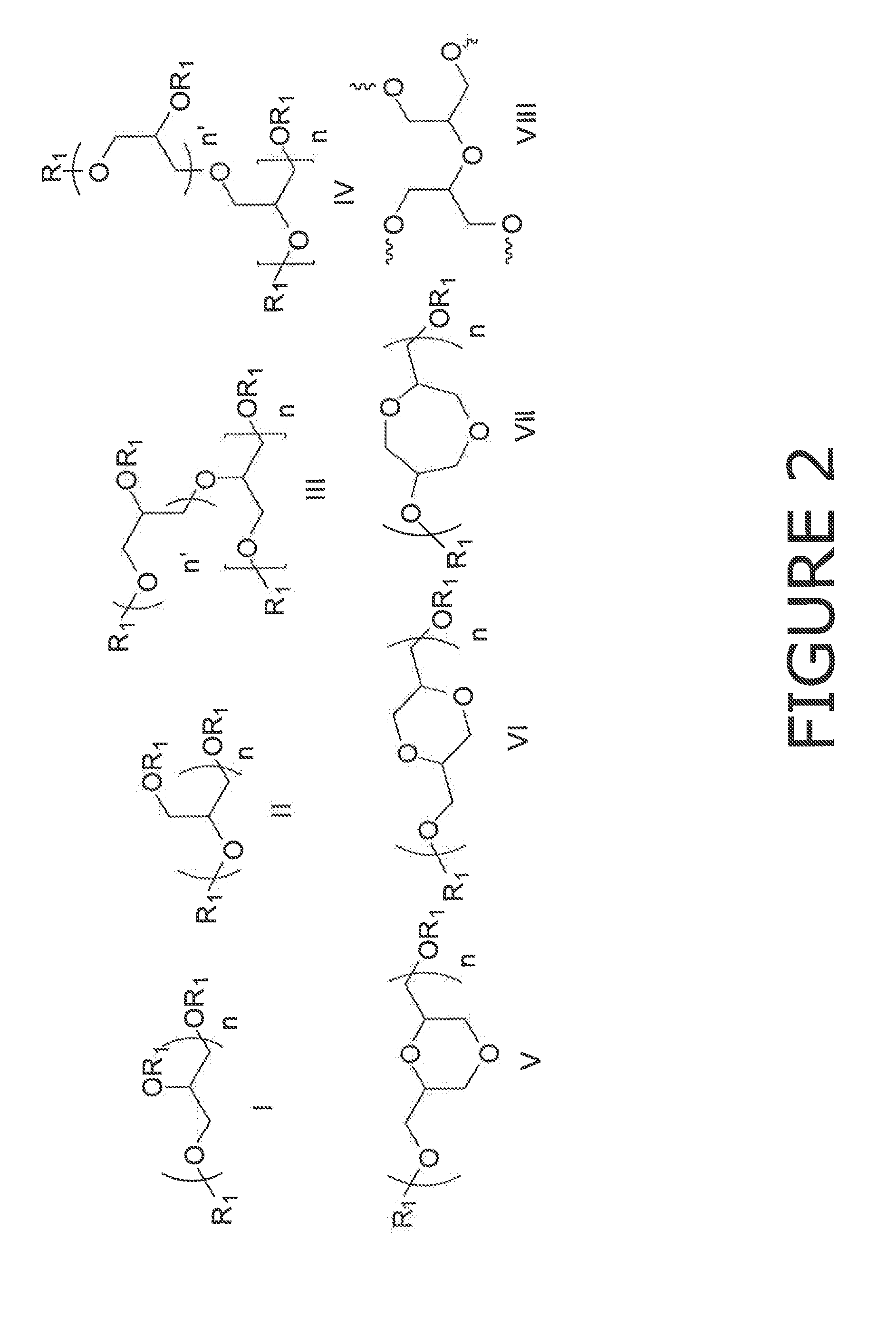
Cross-linked glycerol based polymers as digestion aids for improving wood pulping processes
ActiveUS20130139981A1Increase pulp yieldImprove permeabilityPulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulping with inorganic basesCross-linkGlycerol
The invention provides a method of improving the digestion of wood chips into pulp. The method involves: adding a cross-linked glycerol-based polymer additive to a solution used in the digestion process. This additive is unexpectedly effective at facilitating digestion. The branched and ether structure of the additive allows it to withstand the harsh nature of a high stress environment. In addition, it is more soluble in the harsh condition than other surfactants. The structure, resistance, and particular balance between hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions, causes the additive to increases the interaction between the wood chips and the digestion chemicals. This in turn reduces the costs, the amount of additive needed, and the amount of reject wood chunks that result from the digestion process.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Defoaming formulations containing organopolysiloxanes
PendingUS20220001301A1High viscosityExtended storage timeOrganic detergent compounding agentsDefoamers additionOrganic acidPolymer science
Rapid and long lasting defoaming is accomplished by use of a defoamer formulation employing an organopolysiloxane having siloxy groups linked by an alkylene group, a filler, a silicone resin, a silanol-terminated organopolysiloxane, and an inorganic or organic acid.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Defoaming formulations containing organopolysiloxanes
PendingUS20220001303A1High viscosityExtended storage timeDefoamers additionSurface-active detergent compositionsPolymer scienceActive agent
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Method for deaerating liquids
InactiveUS8563640B2Improve degassing effectNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPaper productionCopolymer
Efficient deaeration of aqueous suspensions such as those obtained during textile treatment or pulp and paper production is achieved by use of a combination of a polyoxypropylene polyether polymer or copolymer and branched polyether-polysiloxane copolymers.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Cross-linked glycerol based polymers as digestion aids for improving wood pulping processes
ActiveUS9416490B2Improve permeabilityReduce the numberPulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulping with inorganic basesCross-linkEther
The invention provides a method of improving the digestion of wood chips into pulp. The method involves: adding a cross-linked glycerol-based polymer additive to a solution used in the digestion process. This additive is unexpectedly effective at facilitating digestion. The branched and ether structure of the additive allows it to withstand the harsh nature of a high stress environment. In addition, it is more soluble in the harsh condition than other surfactants. The structure, resistance, and particular balance between hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions, causes the additive to increases the interaction between the wood chips and the digestion chemicals. This in turn reduces the costs, the amount of additive needed, and the amount of reject wood chunks that result from the digestion process.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Defoaming formulations containing organopolysiloxanes
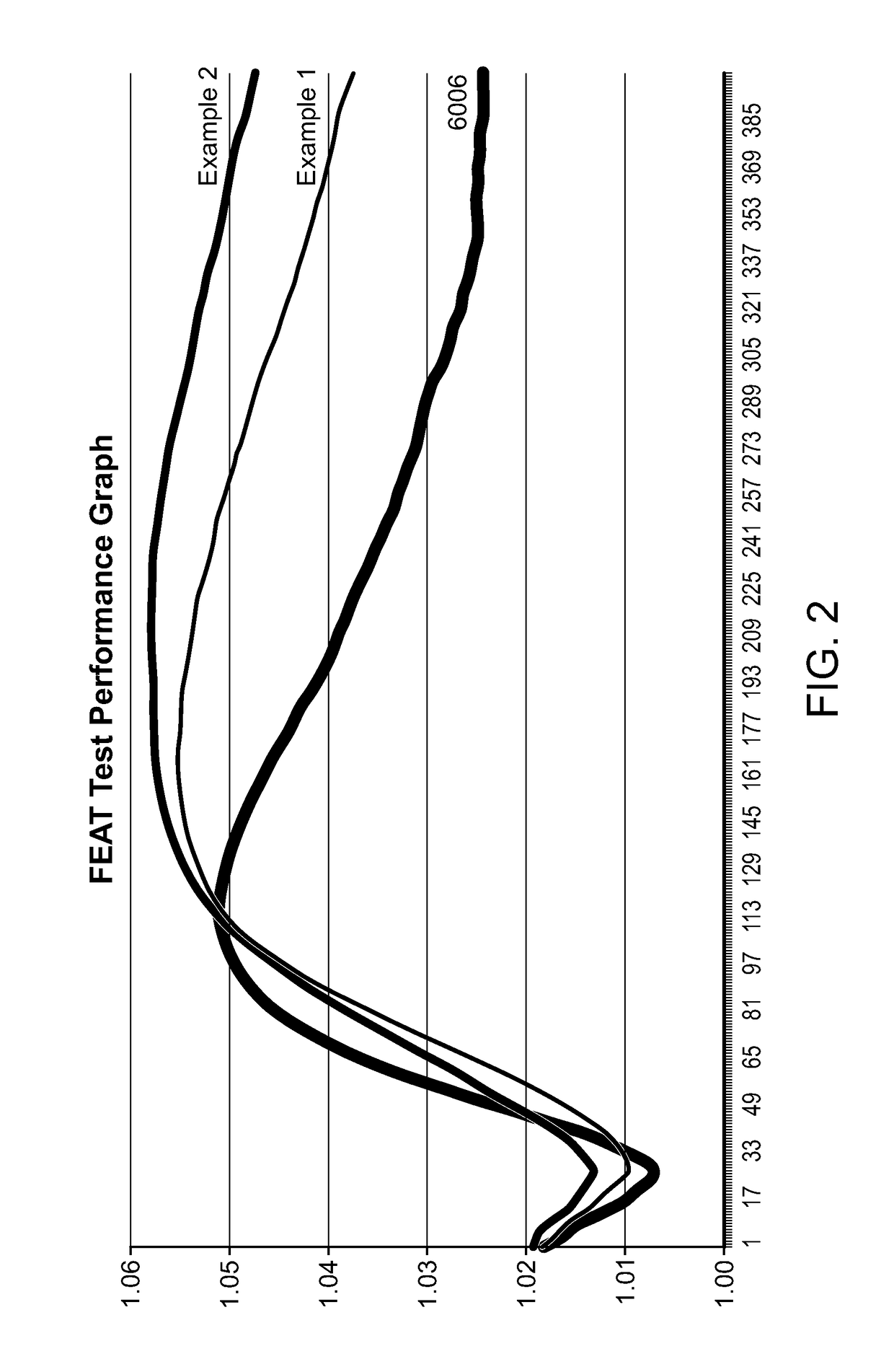
ActiveUS10870071B2High and long-lasting performanceLow addition amountOrganic detergent compounding agentsDefoamers additionPolymer scienceAqueous medium
Defoamer compositions containing a plurality of defined organopolysiloxanes exhibit very short initial foam collapse and yet exhibit long lasting defoaming activity when added to aqueous media prone to foaming.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Waste recycle composition
ActiveUS11492755B2Reduce consistencyLow variabilityPaper recyclingPaper/cardboardPolymer scienceCellulose fiber
A recycled cellulose pulp composition is provided which comprises recycled cellulosic fibers and cellulose ester staple fibers. The recycled cellulose pulp containing co-refined re-cycled cellulose fibers and cellulose ester staple fibers can be added to a hydropulper and fed back through a refiner to make wet laid products.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Cross-linked glycerol based polymers as digestion aids for improving wood pulping processes
ActiveUS20160215449A9Improve permeabilityReduce the numberPulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulping with inorganic basesCross-linkEther
The invention provides a method of improving the digestion of wood chips into pulp. The method involves: adding a cross-linked glycerol-based polymer additive to a solution used in the digestion process. This additive is unexpectedly effective at facilitating digestion. The branched and ether structure of the additive allows it to withstand the harsh nature of a high stress environment. In addition, it is more soluble in the harsh condition than other surfactants. The structure, resistance, and particular balance between hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions, causes the additive to increases the interaction between the wood chips and the digestion chemicals. This in turn reduces the costs, the amount of additive needed, and the amount of reject wood chunks that result from the digestion process.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Hydrolysis resistant organomodified silylated ionic surfactants
The present invention provides for a composition comprising a silane having the formula:(R1)(R2)(R3)Si—R4—Si(R5)(R6)(R7)whereinR1, R2, R3, R5, and R6 are each independently selected from the group consisting of 1 to 6 monovalent hydrocarbon radicals, aryl, and a hydrocarbon group of 7 to 10 carbons containing an aryl group;R4 is a hydrocarbon group of 1 to 3 carbons;R7 comprises an anionic, cationic or zwitterionic substituent. The silanes of the present invention exhibit resistance to hydrolysis over a wide pH range.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
Additive for physical straw pulping and use method thereof
InactiveCN102704299BSoften fastFast refiningPulping foam preventionNon-woody plant/crop pulpPapermakingFormamide
The invention belongs to the fields of biochemical pulping and papermaking, and discloses an additive for physical straw pulping and a use method thereof. The additive for physical straw pulping comprises dimethylsilicone fluid, a fabric softening dispersion agent, sodium lauryl sulfate, formamide, a low-temperature defoaming agent TF-508C and water. After being diluted with water for 4 to 20 times, the additive is added uniformly in a pulping process by a spray device controlled through an electric pump, and the spraying frequency ranges from 2 to 20 L / H, preferably 8 to 20 L / H. The additive for physical straw pulping and the use method thereof realize the technical support of environment-friendly physical straw pulping, a spraying infiltration method is adopted to replace a traditional soaking boiling method, and therefore, the possibility of pollution is low. Environment-friendly production of the physical straw pulping is realized, and the additive used for performing spraying infiltration on straw can be reused. No pollution is caused in the whole pulping process, so that the zero pollution discharge in the papermaking production is realized.
Owner:NANJING BIOFUNCTION CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com