Patents
Literature
72results about How to "Long dwell time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
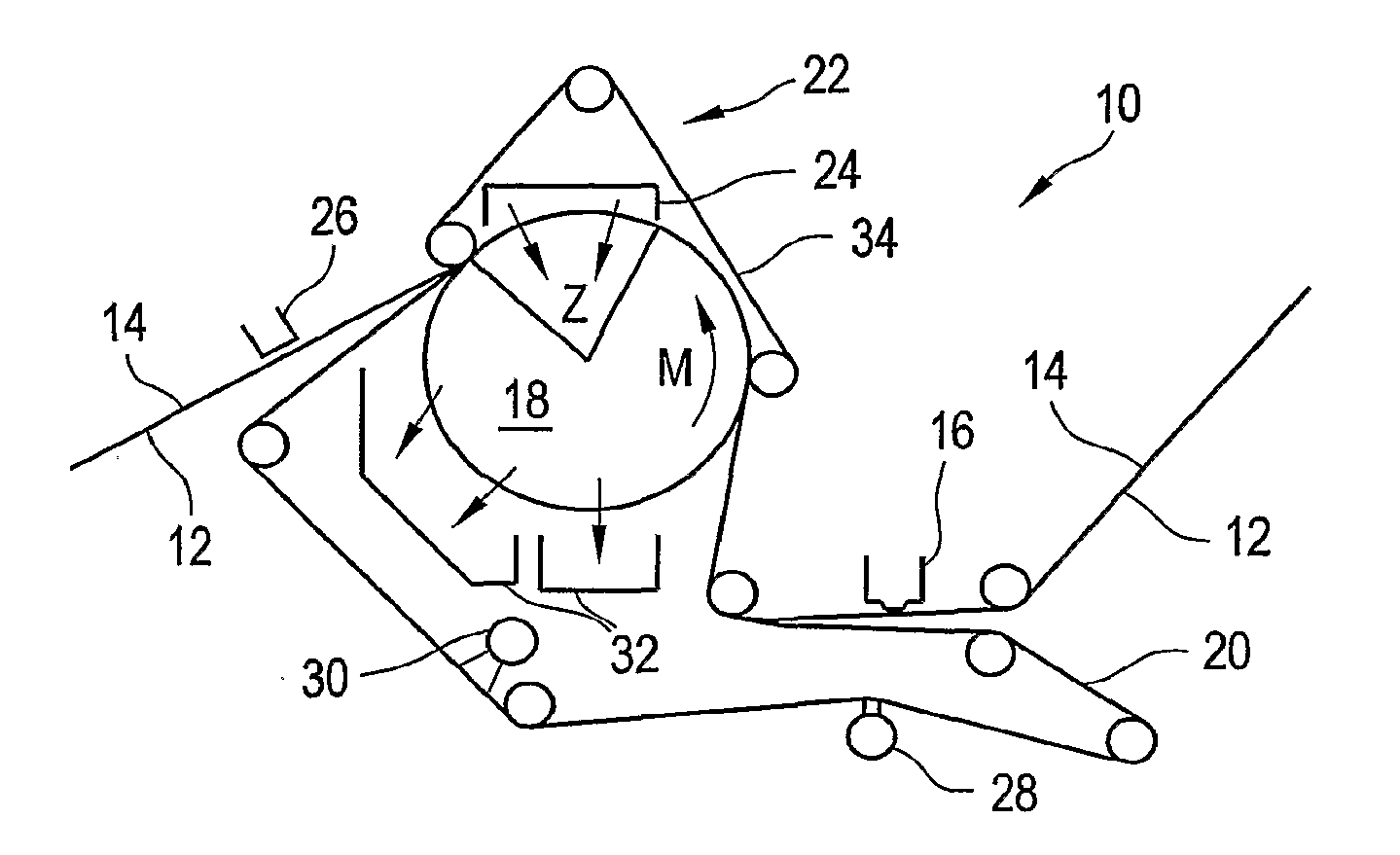
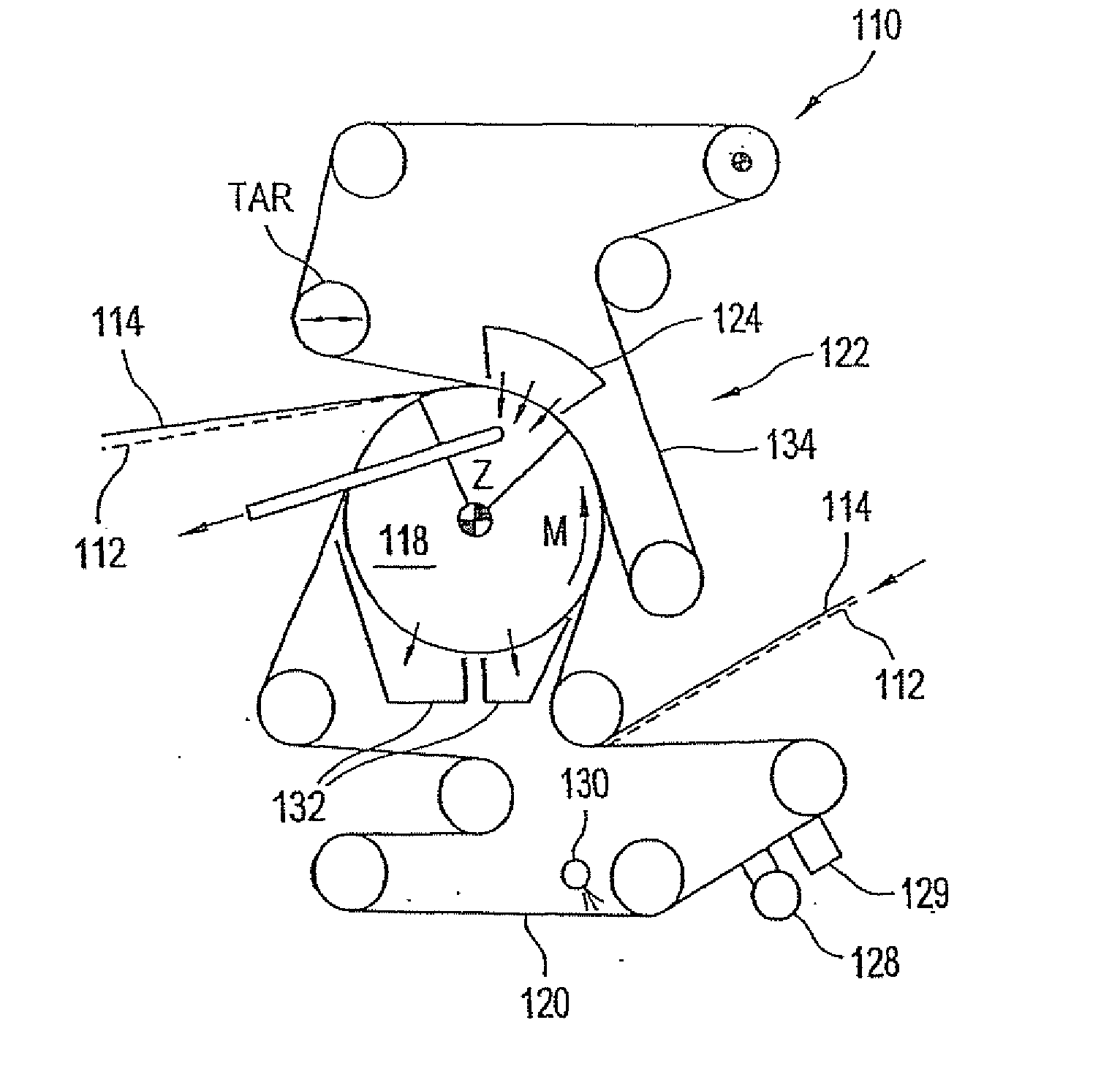
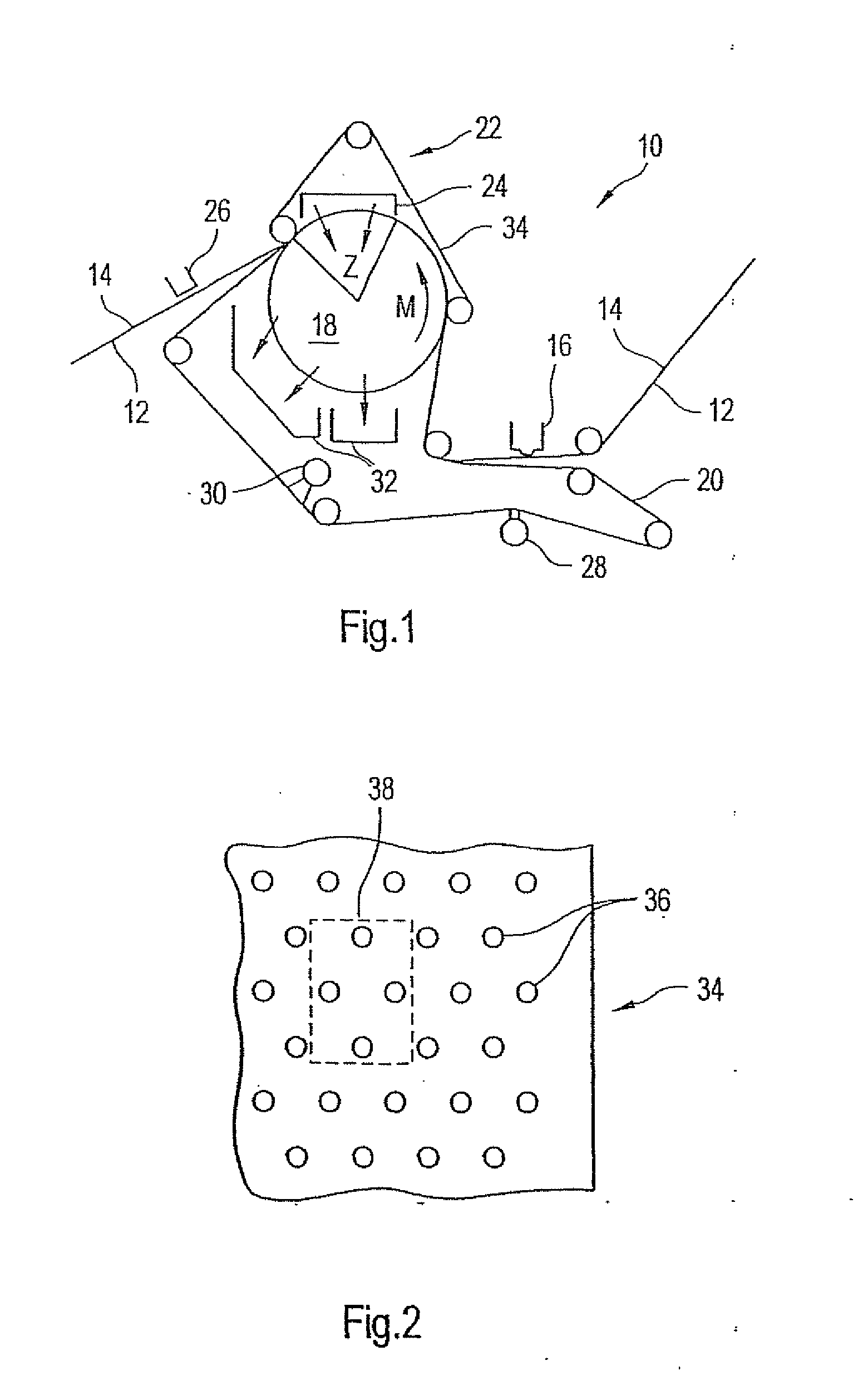
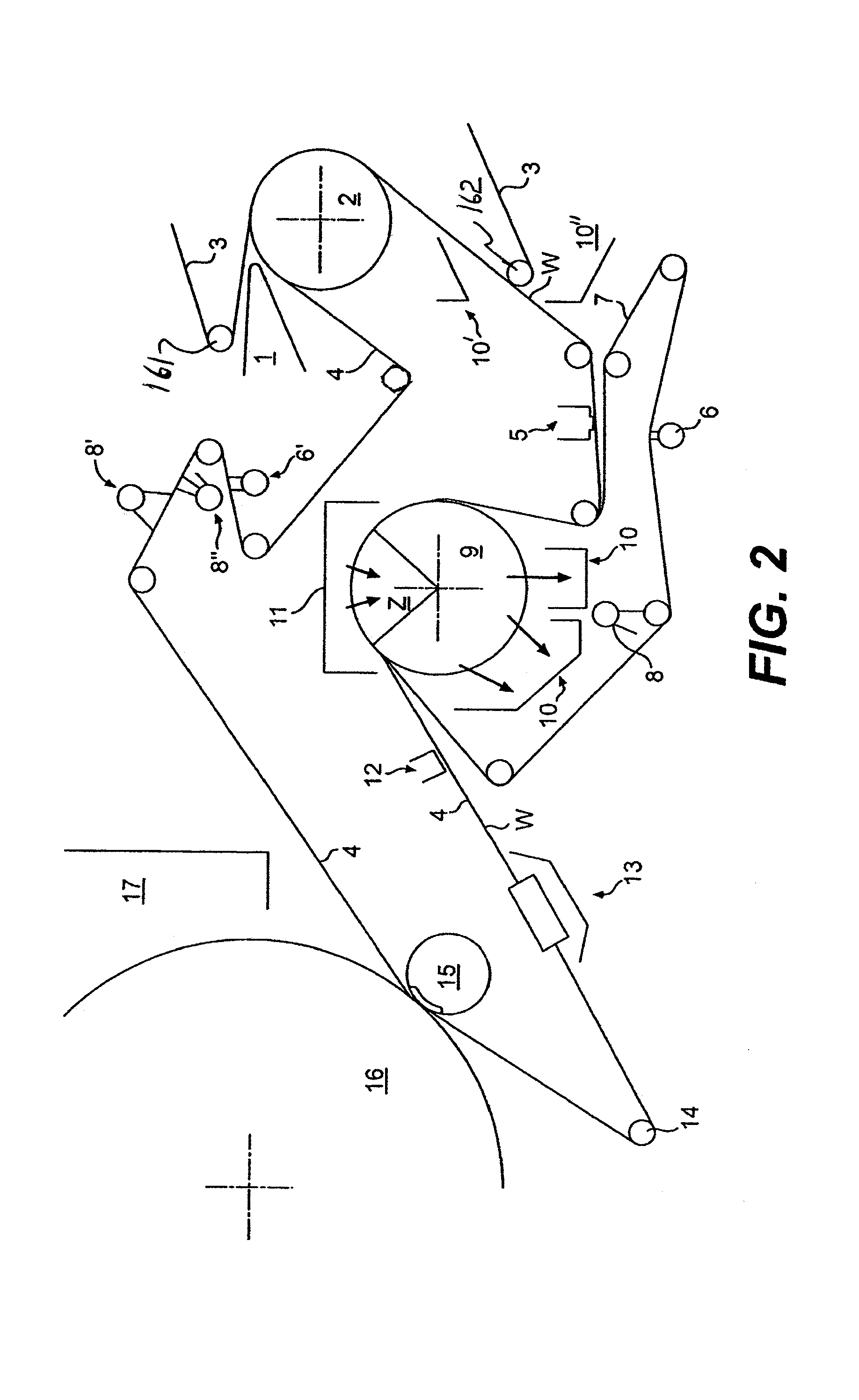
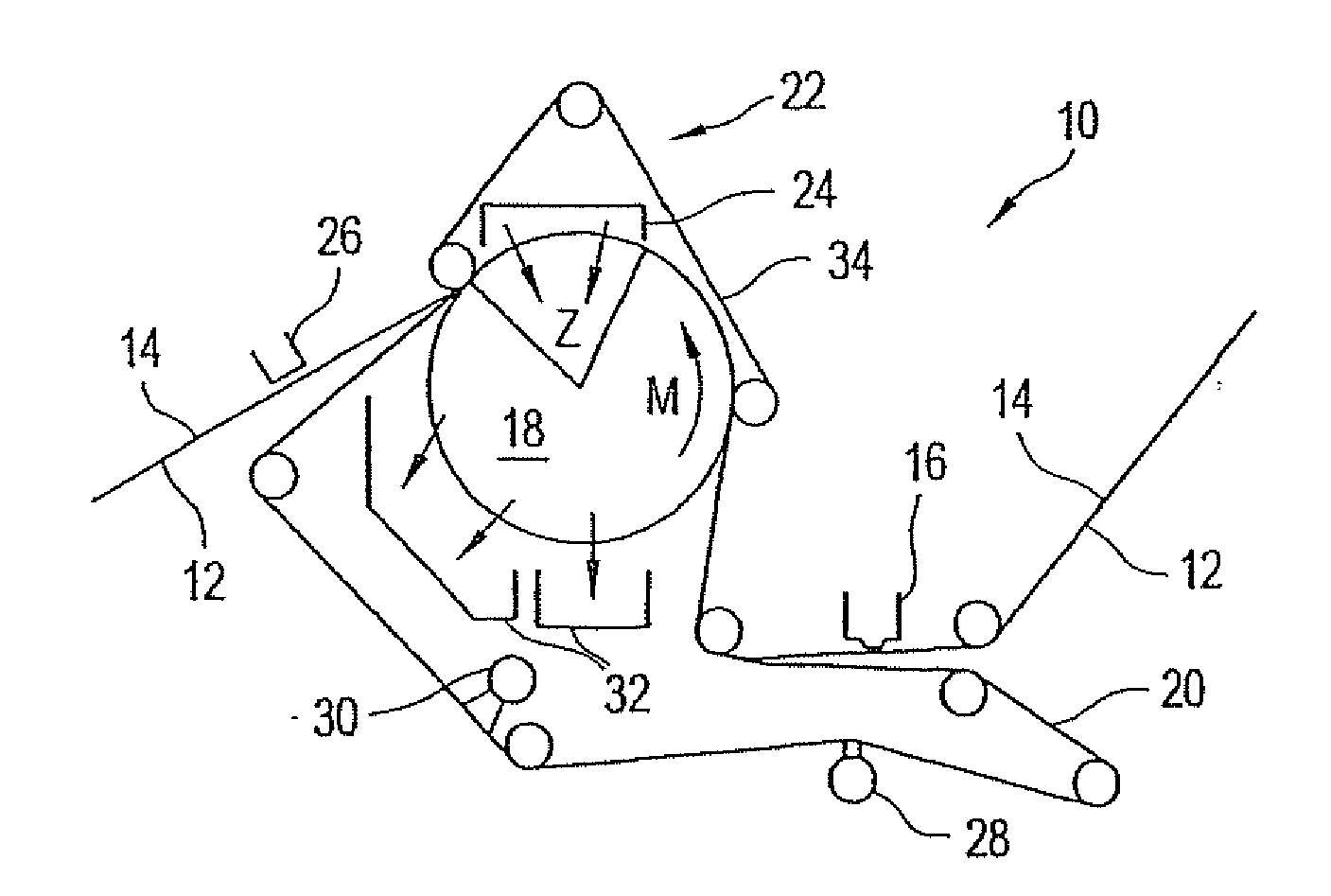
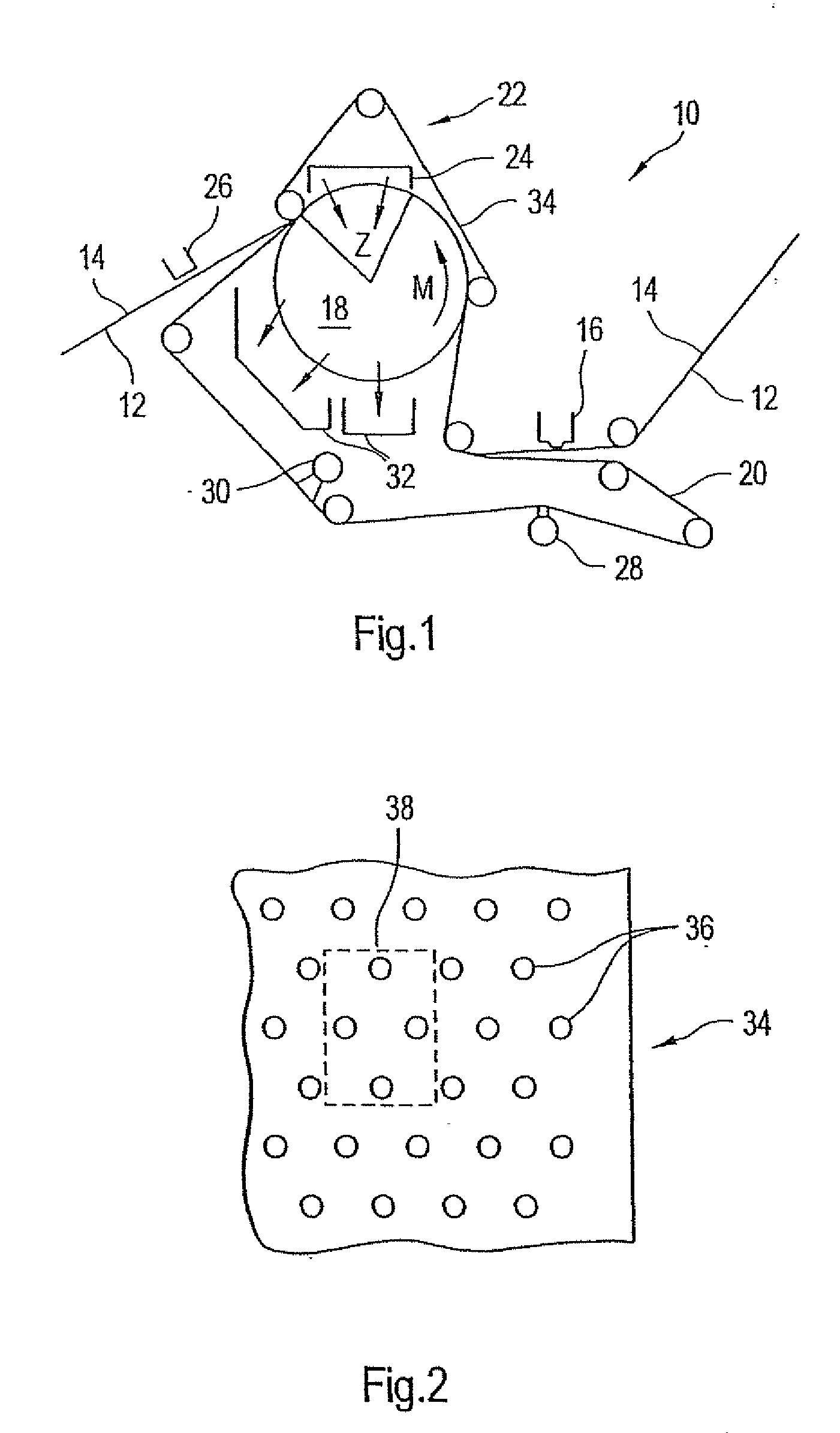
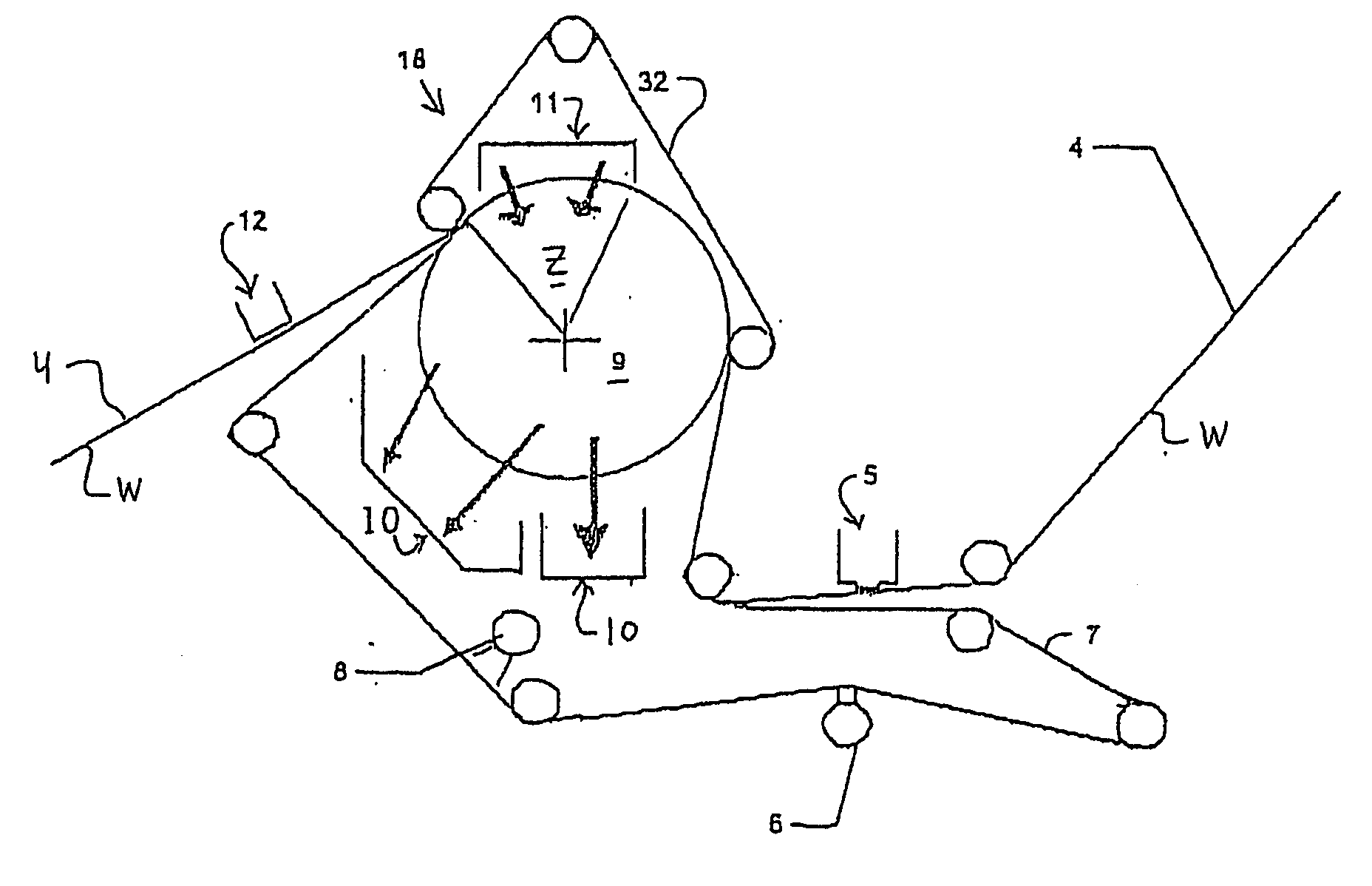
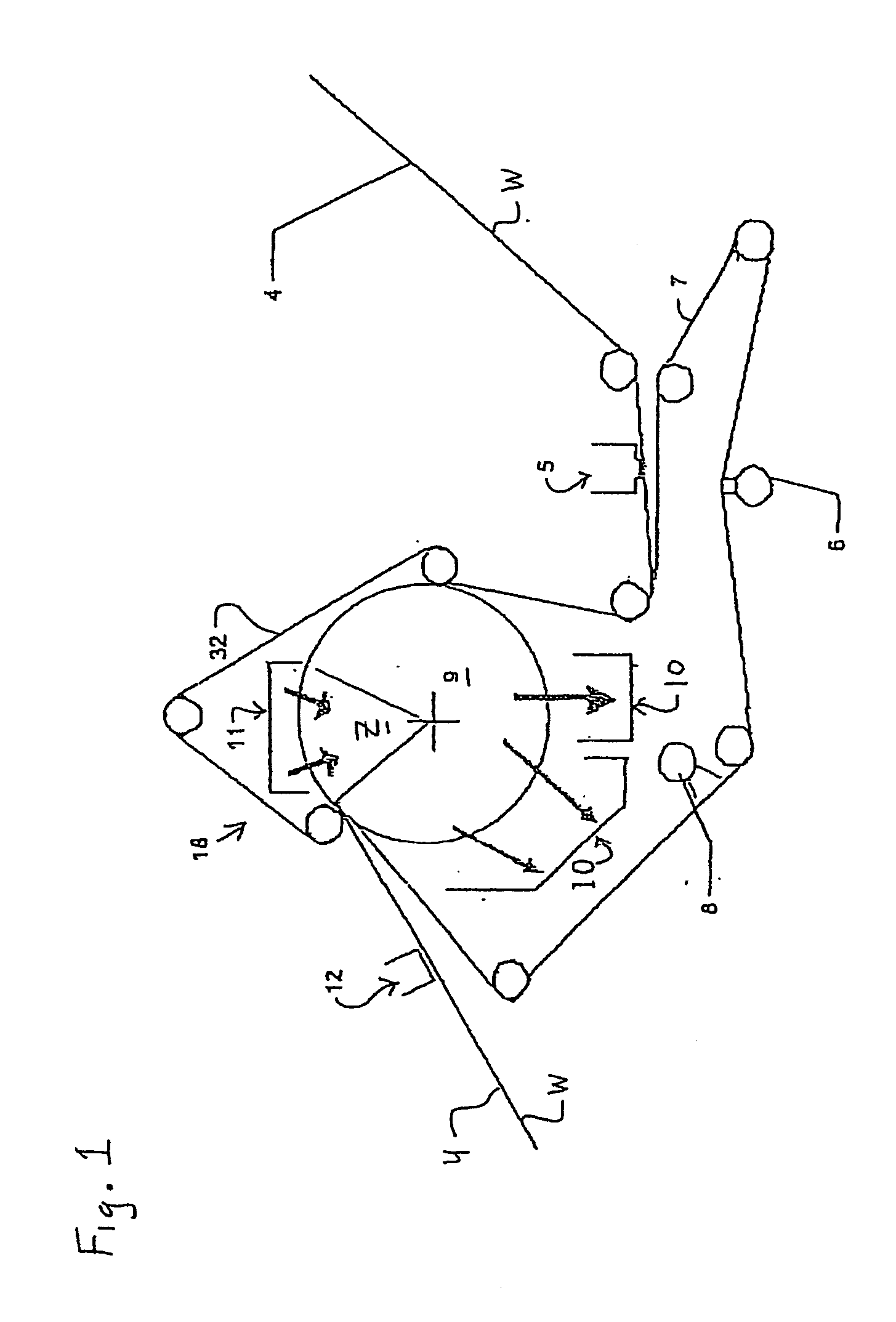
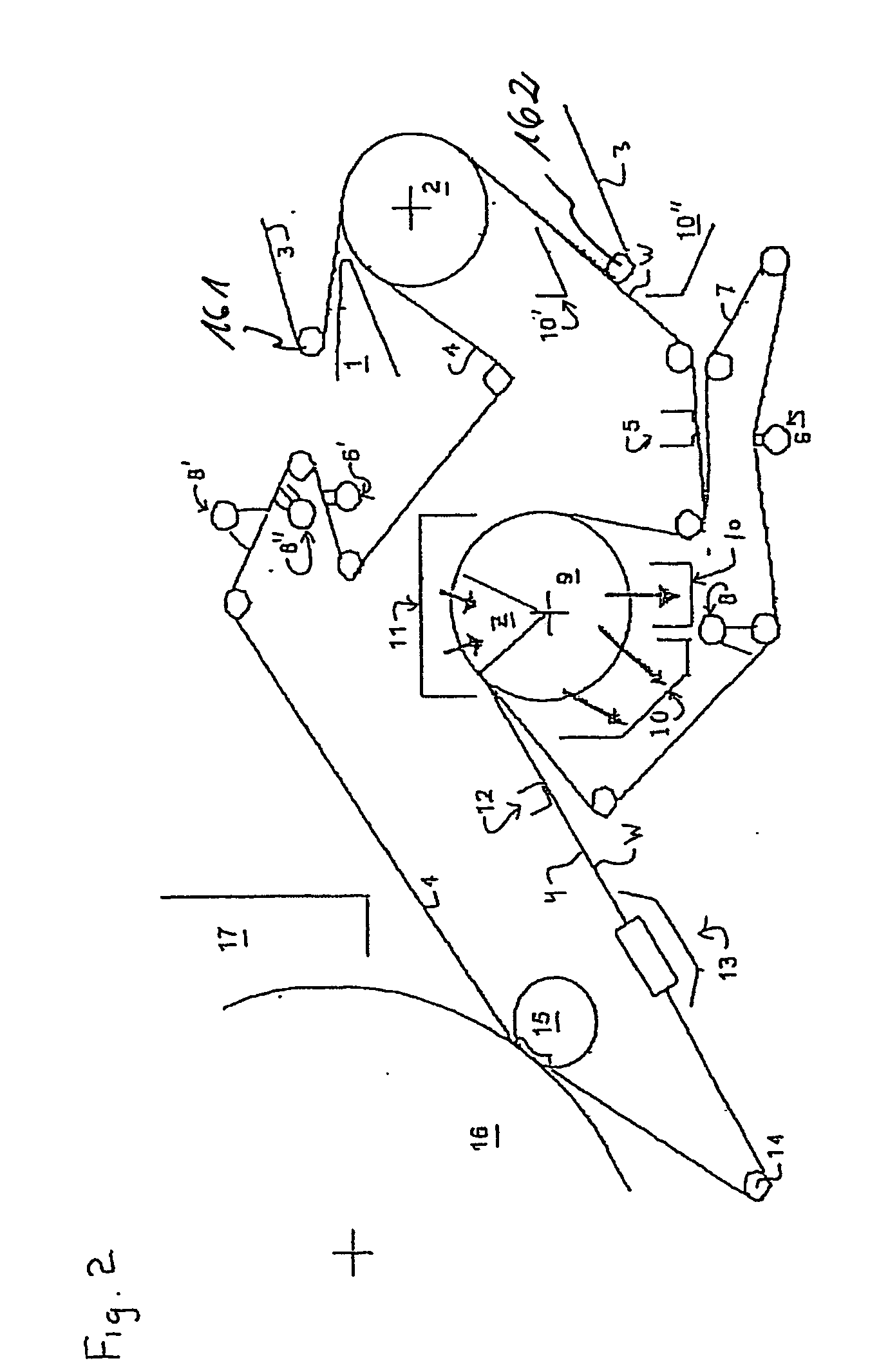
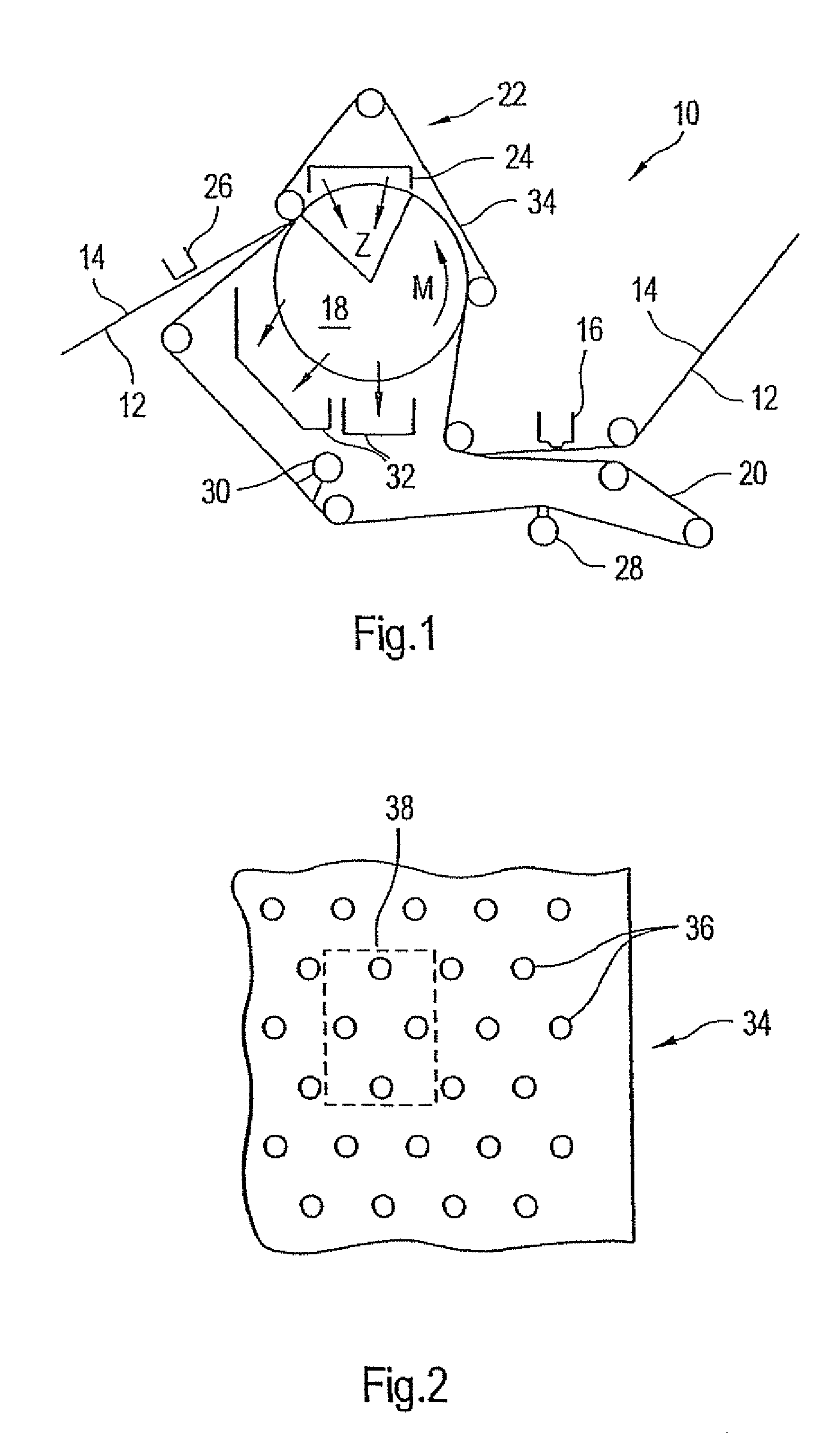
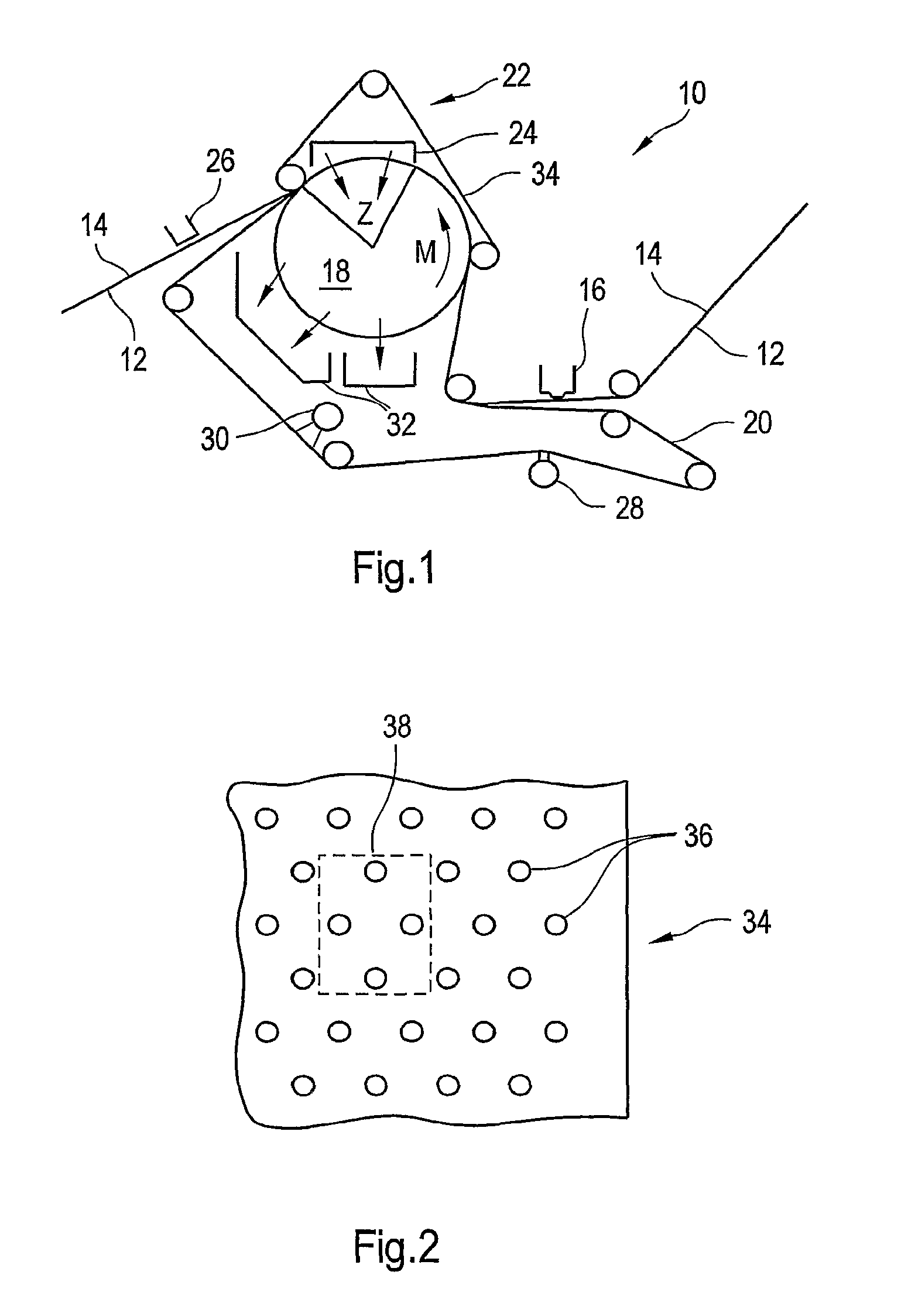
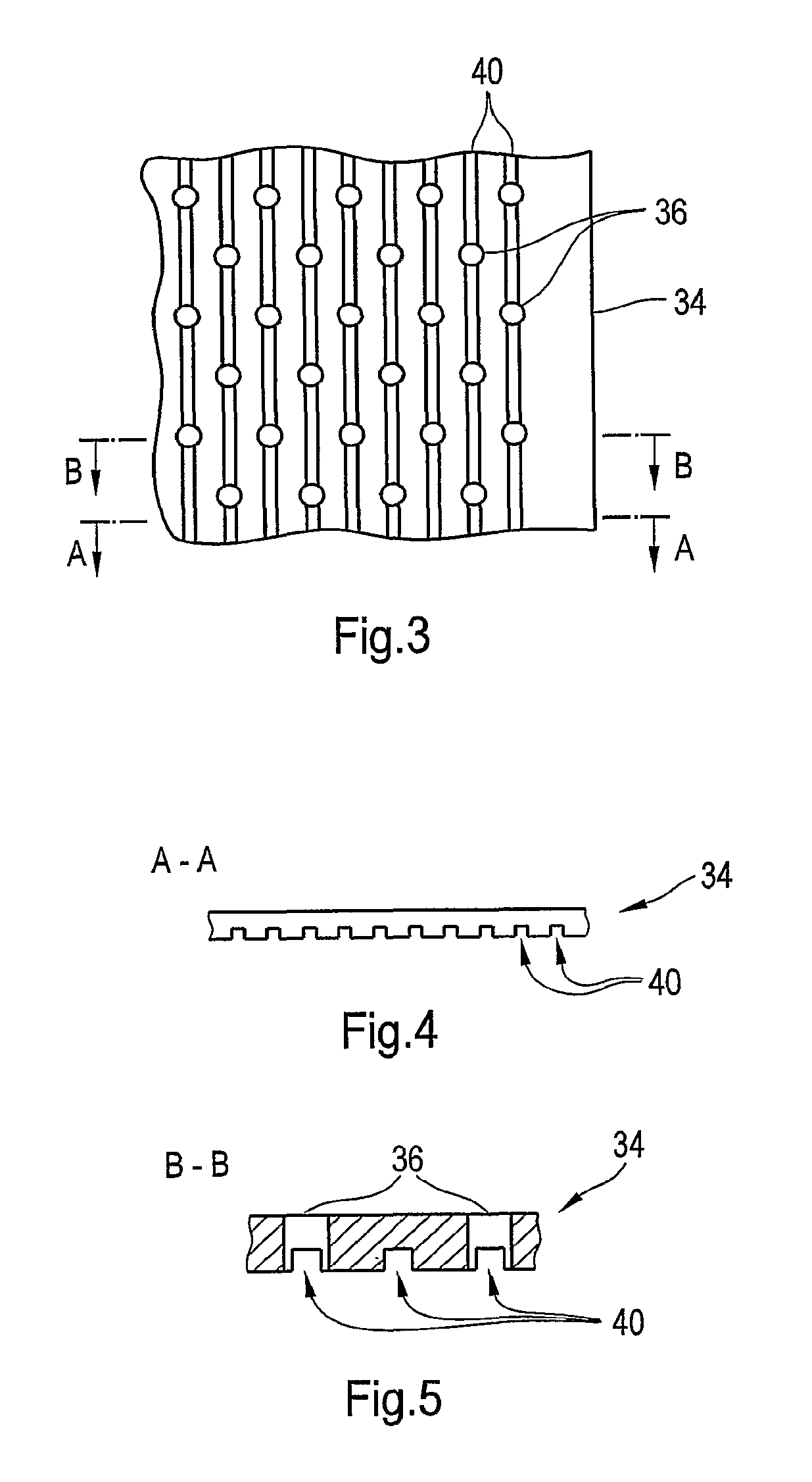
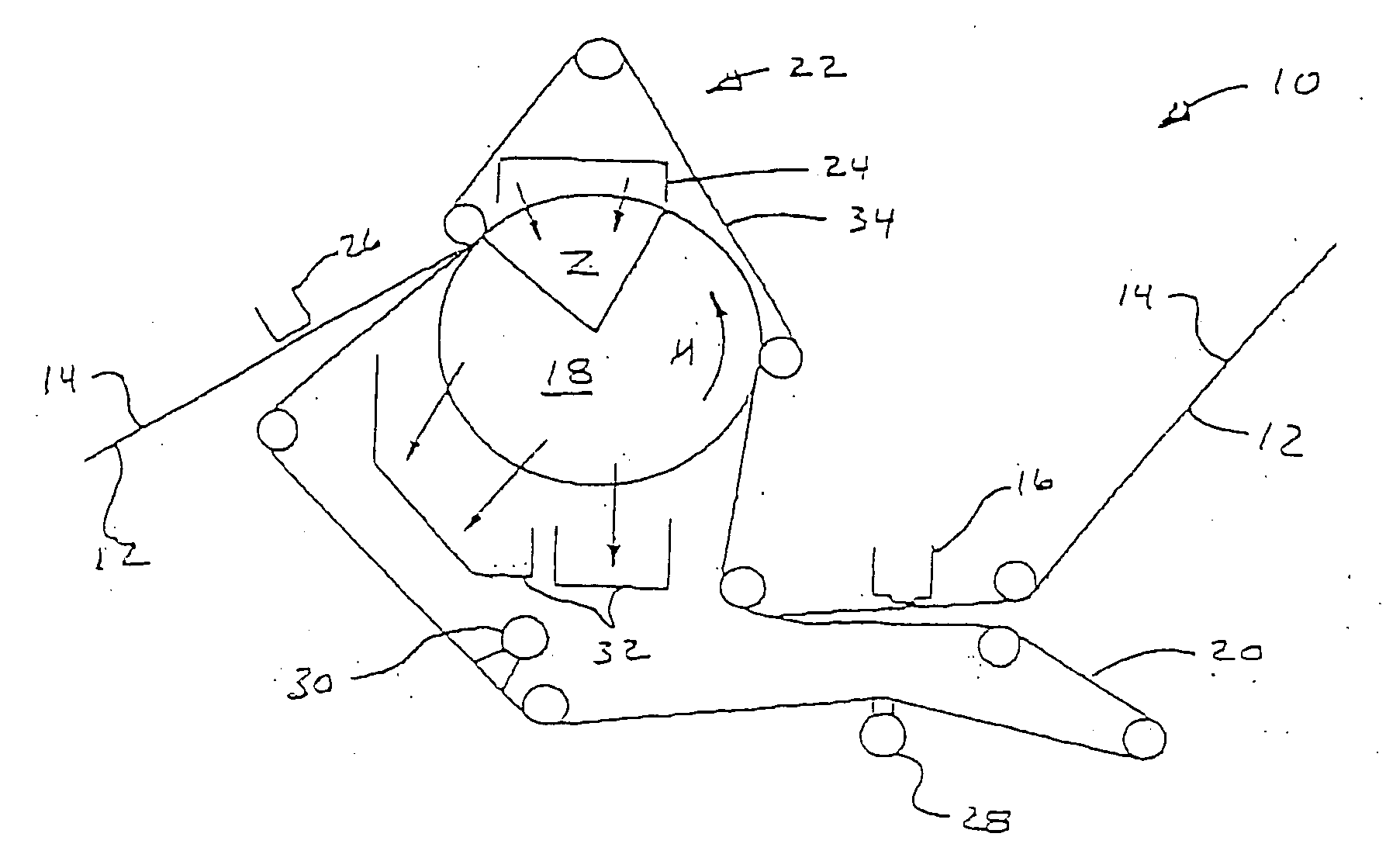
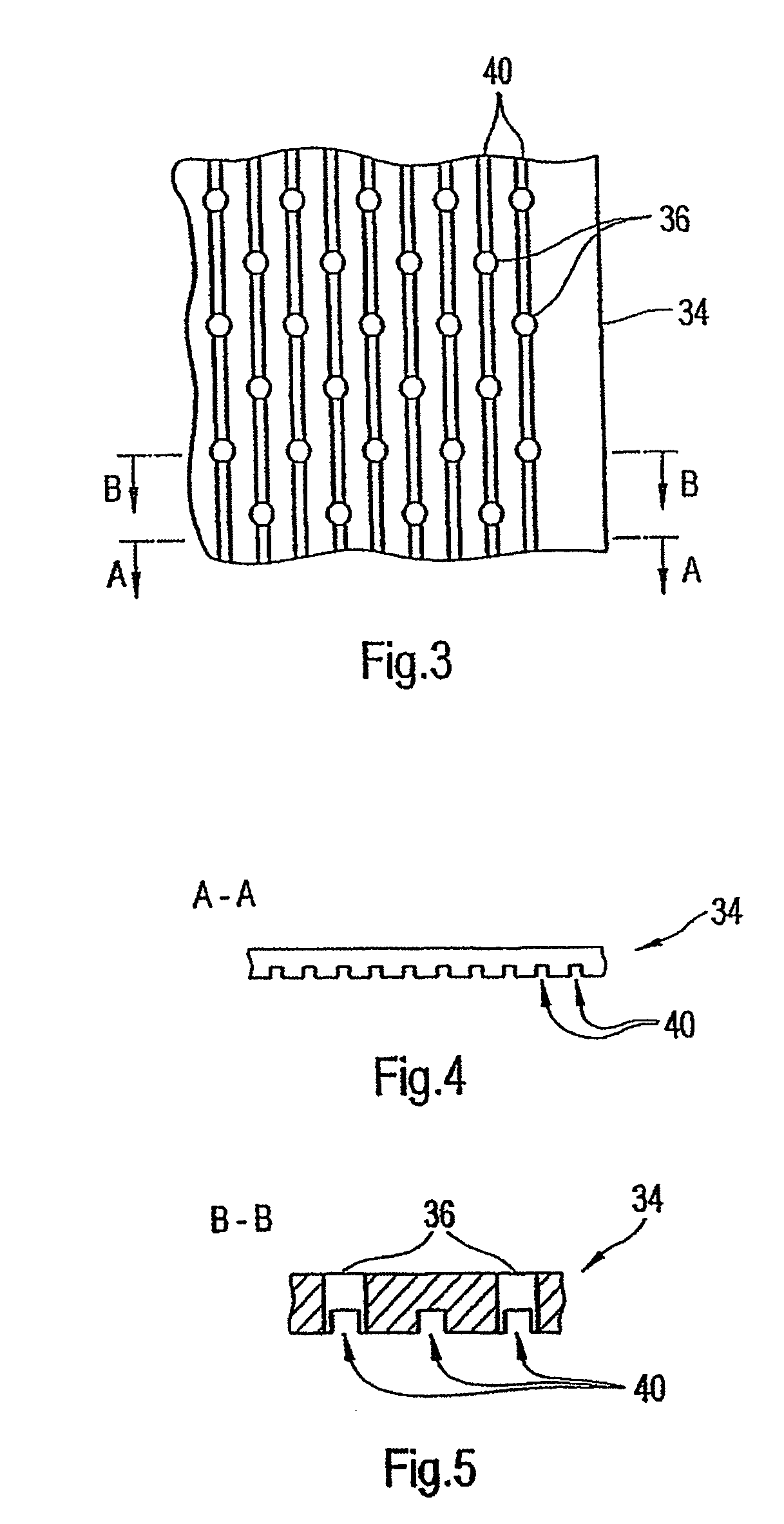
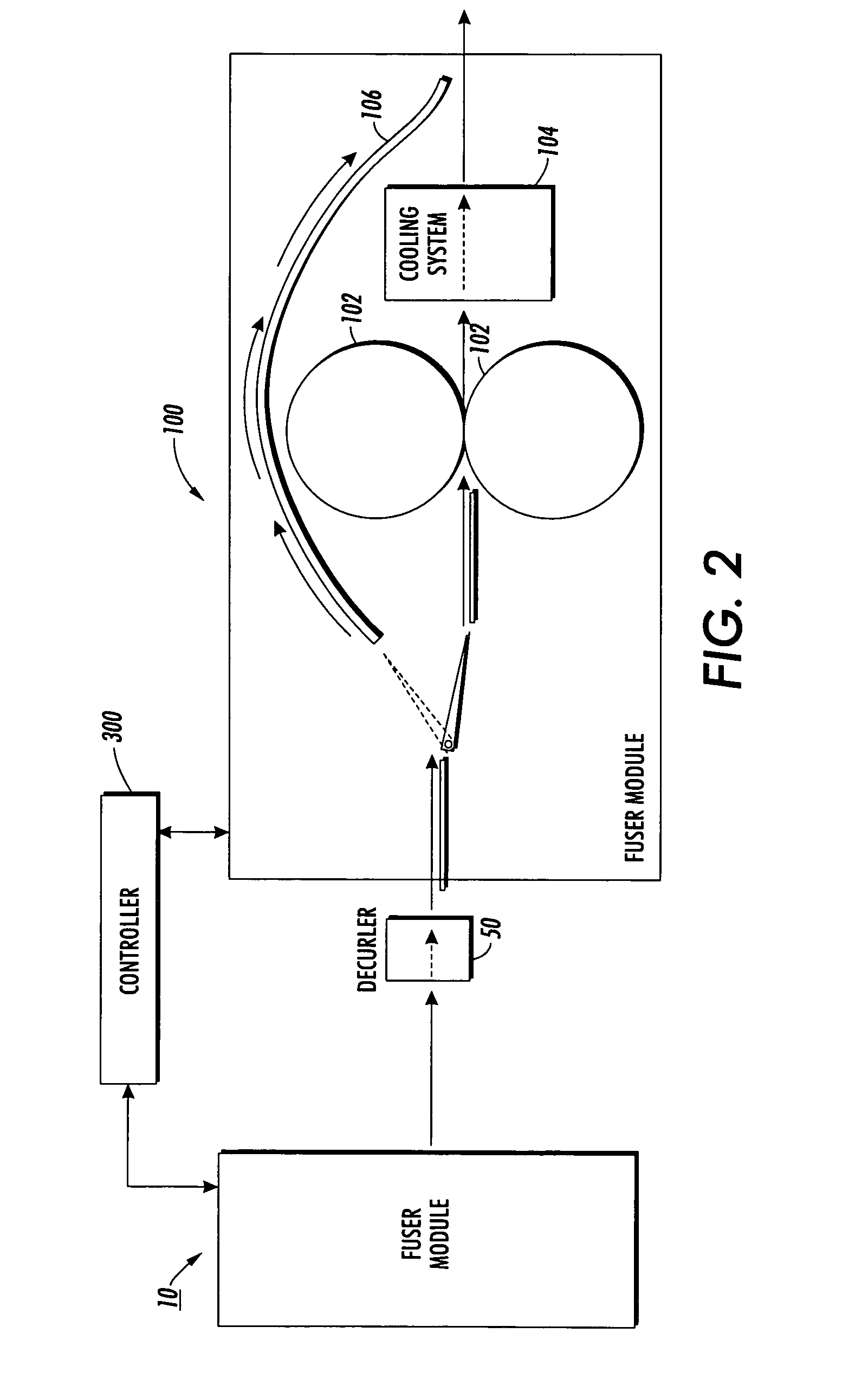
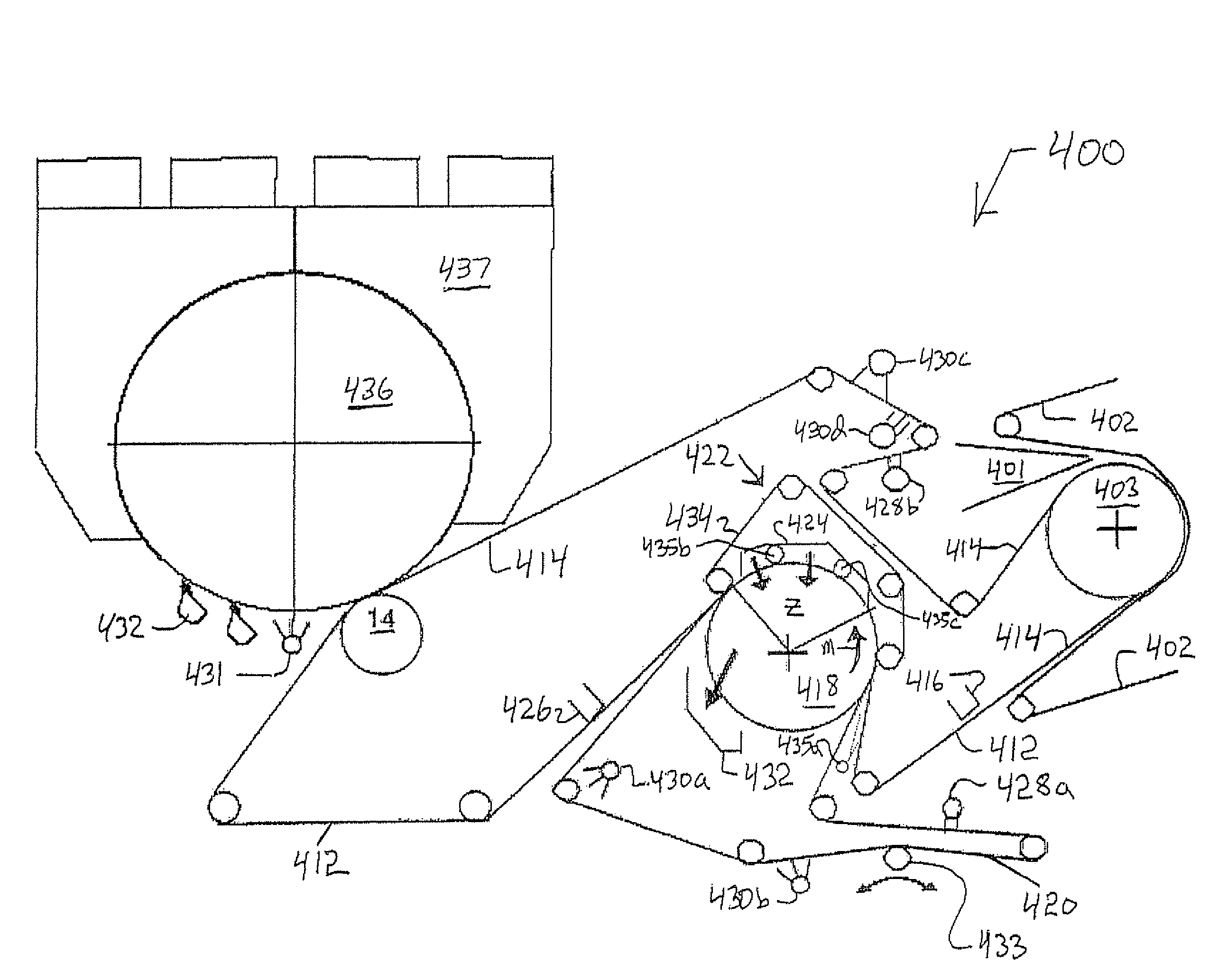
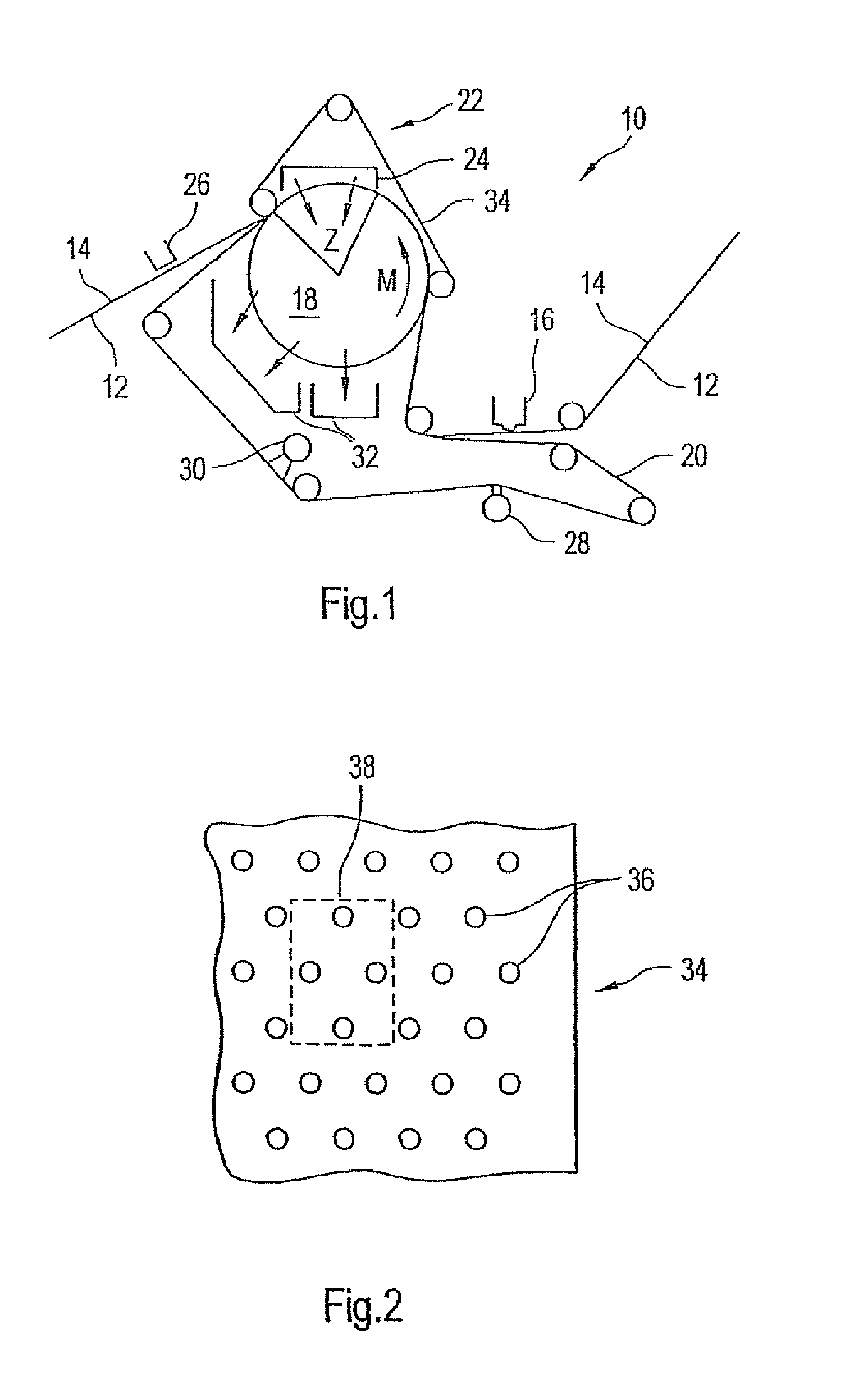
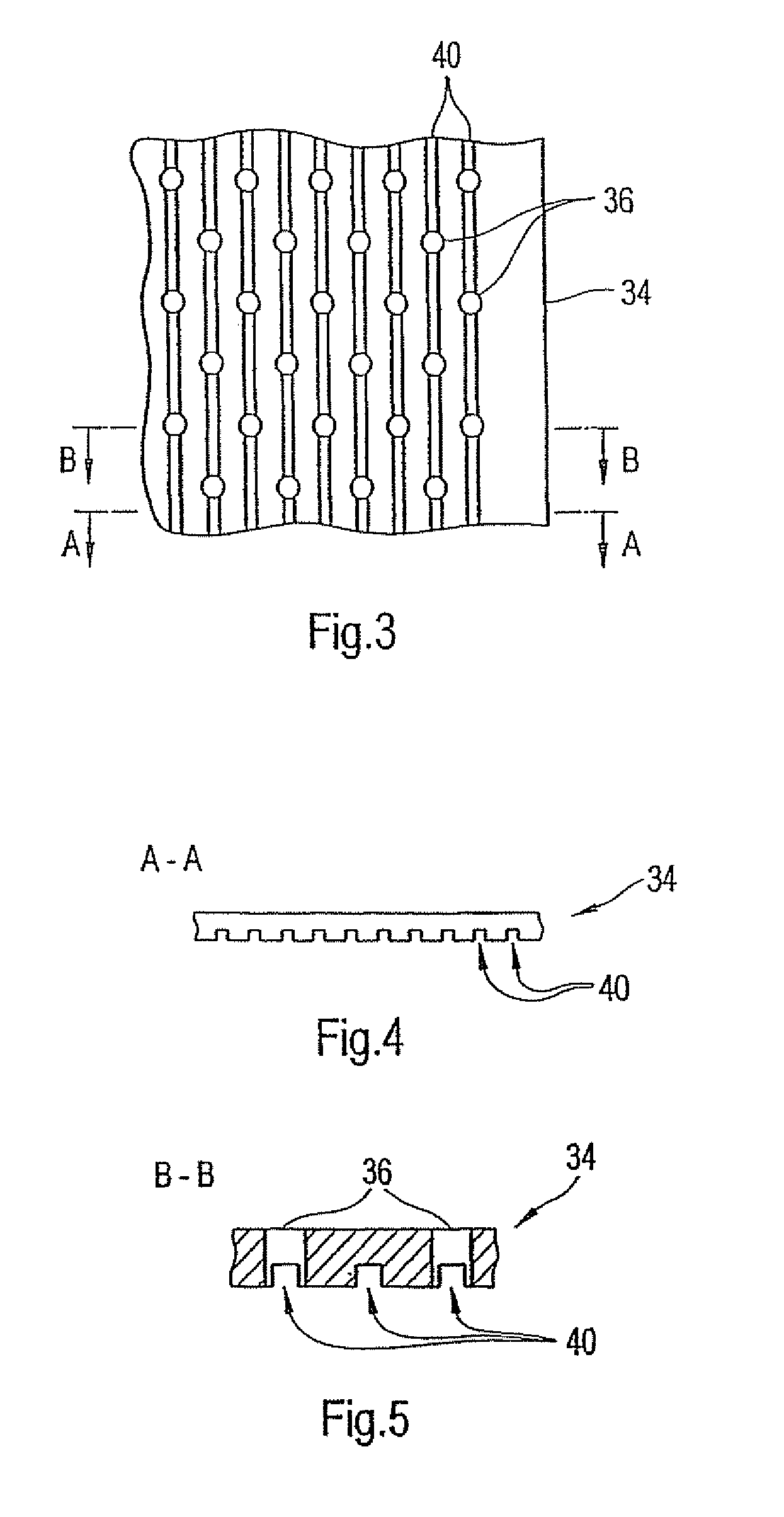
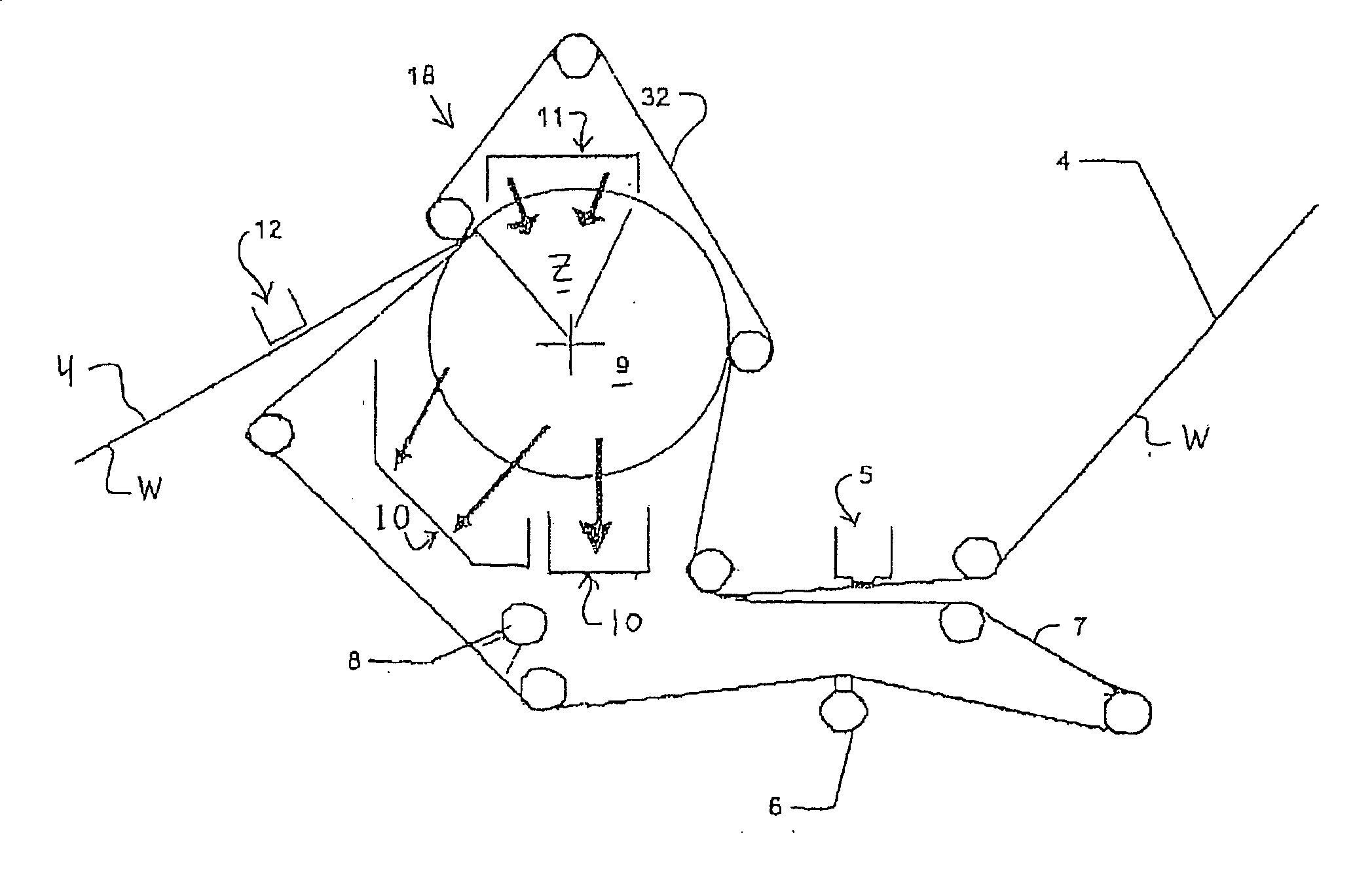
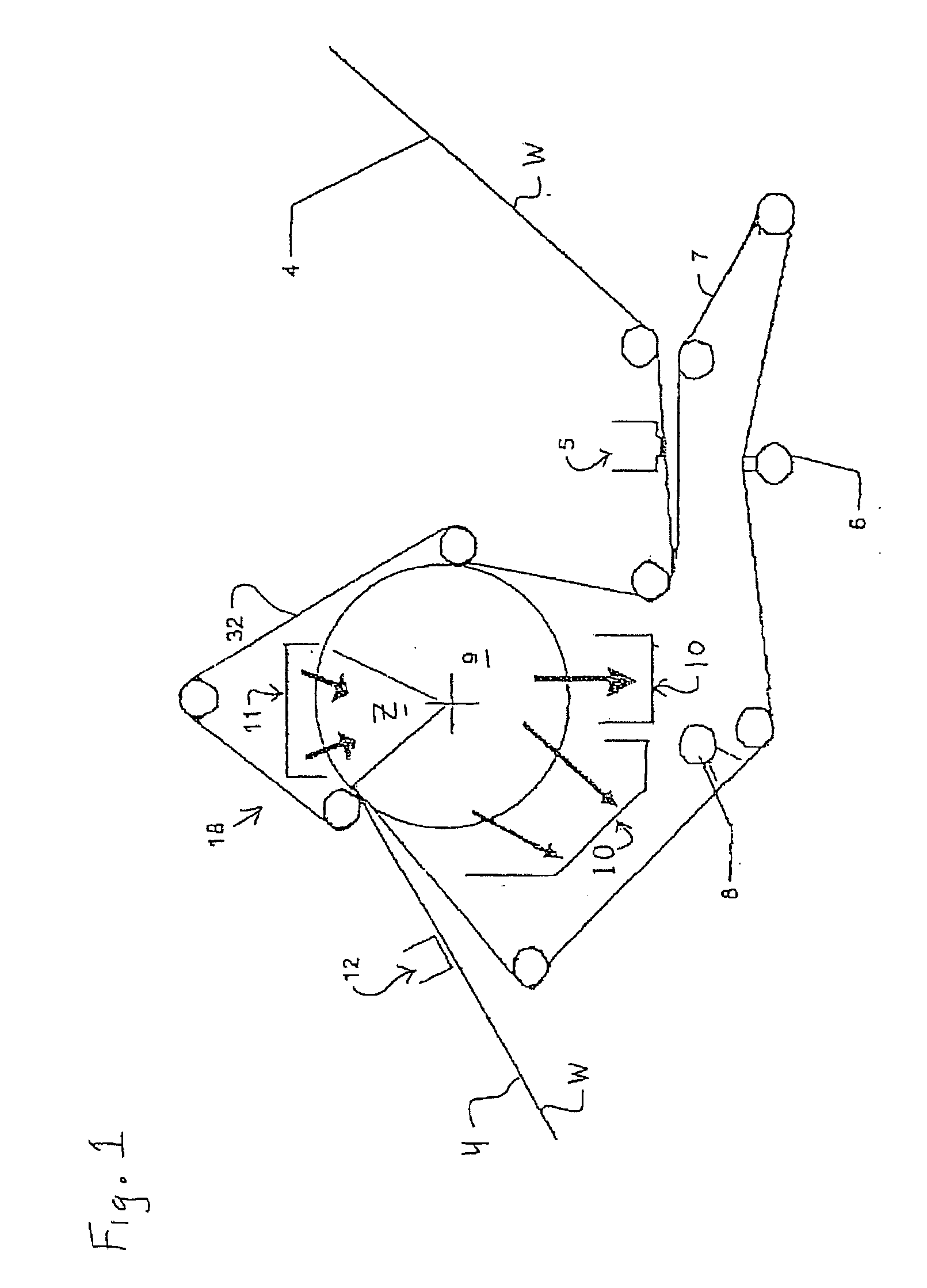
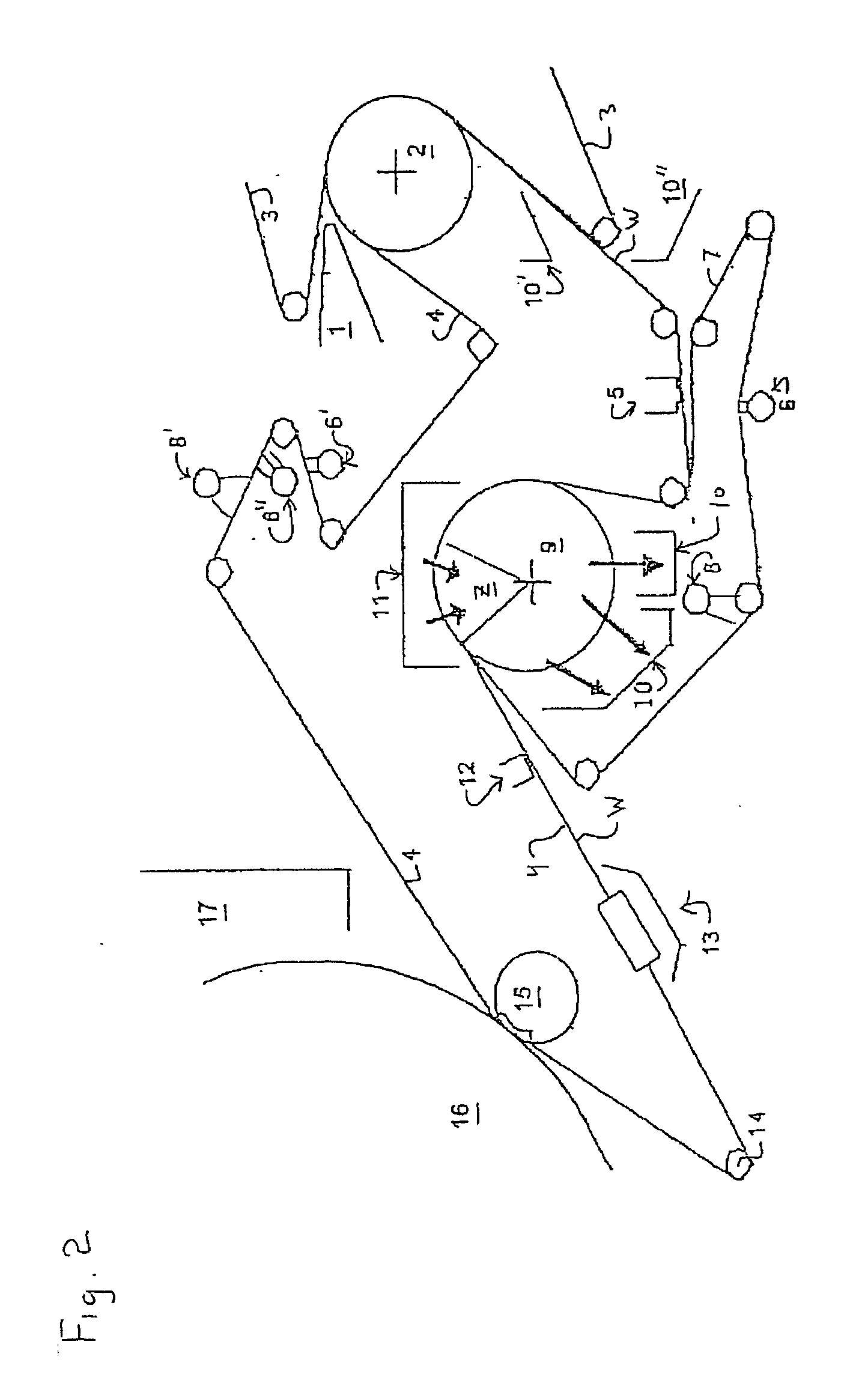
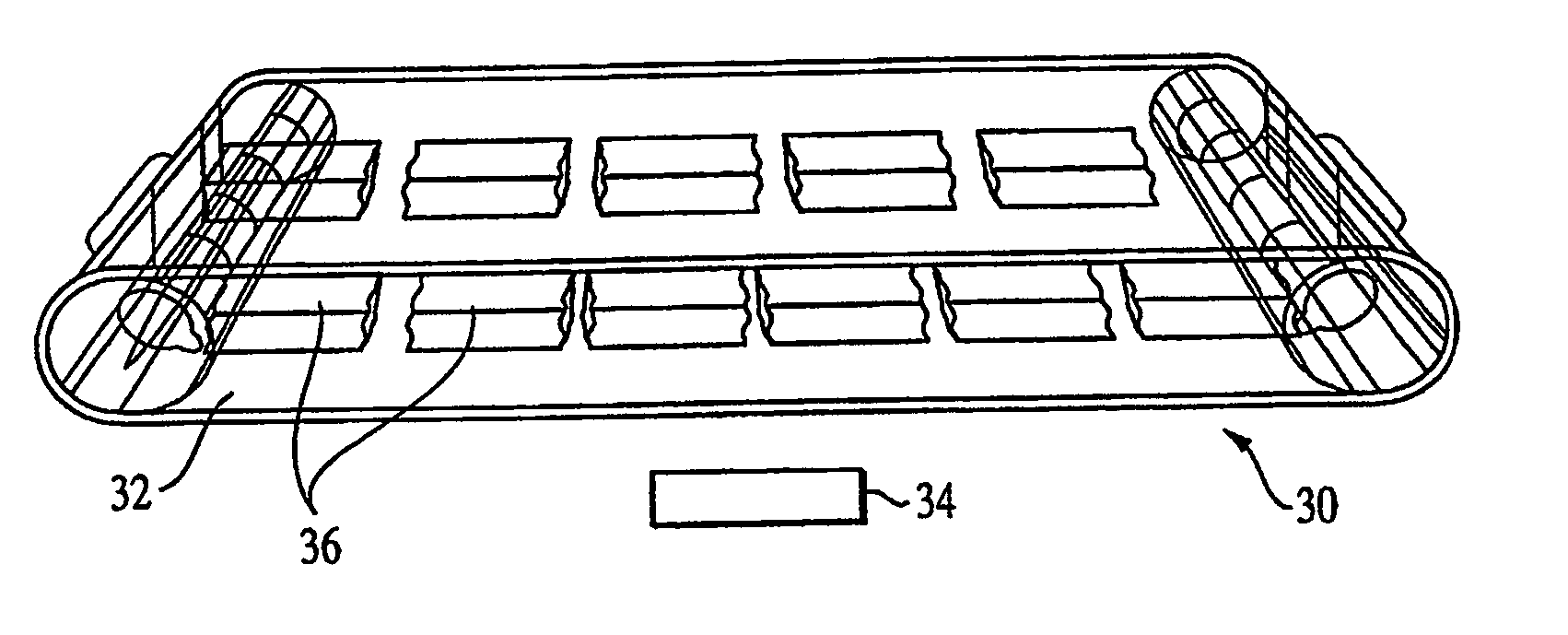
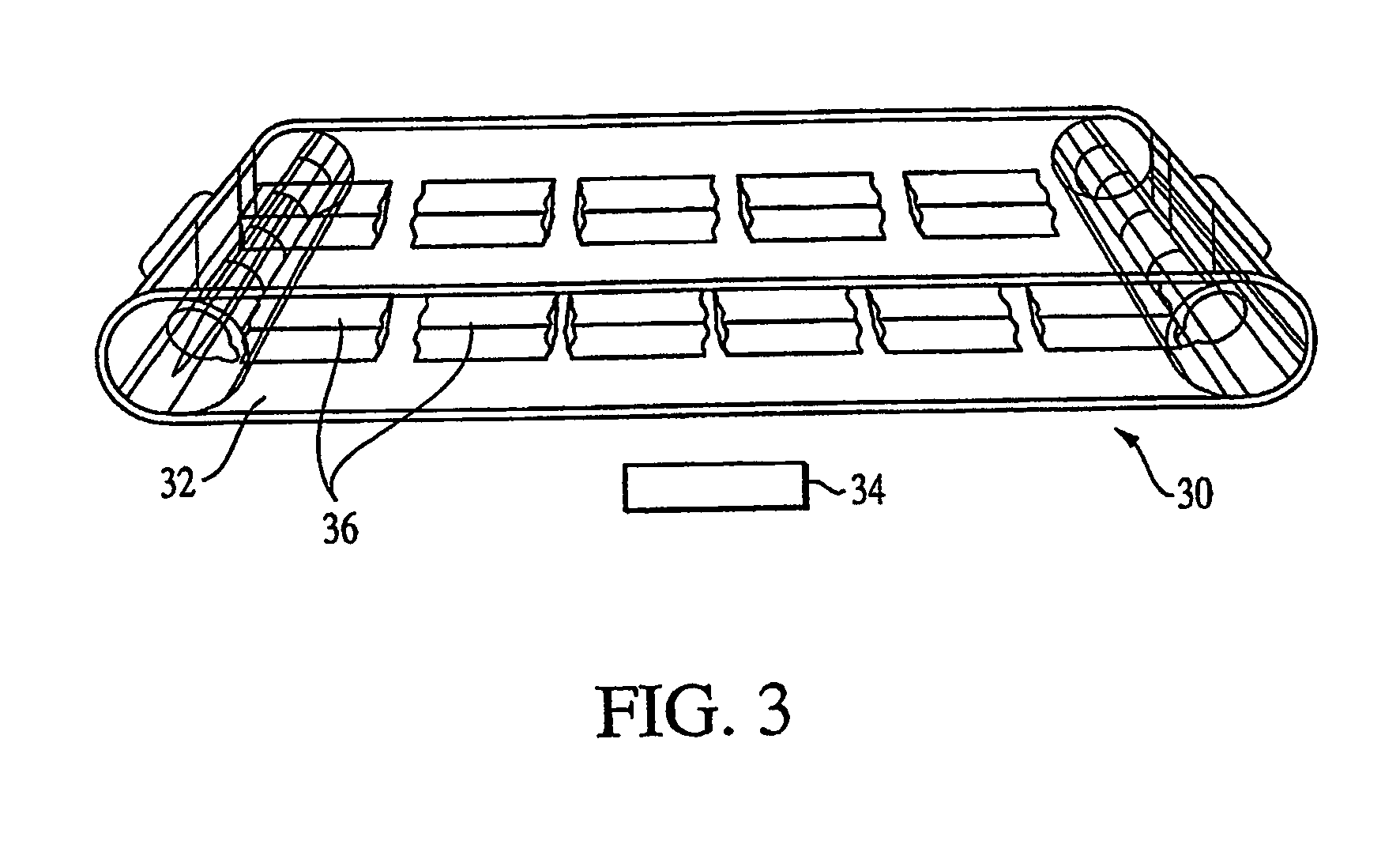
Press section and permeable belt in a paper machine
InactiveUS20100170651A1Large tensionIncrease the opening areaPress sectionDifferential pressureMechanical pressure
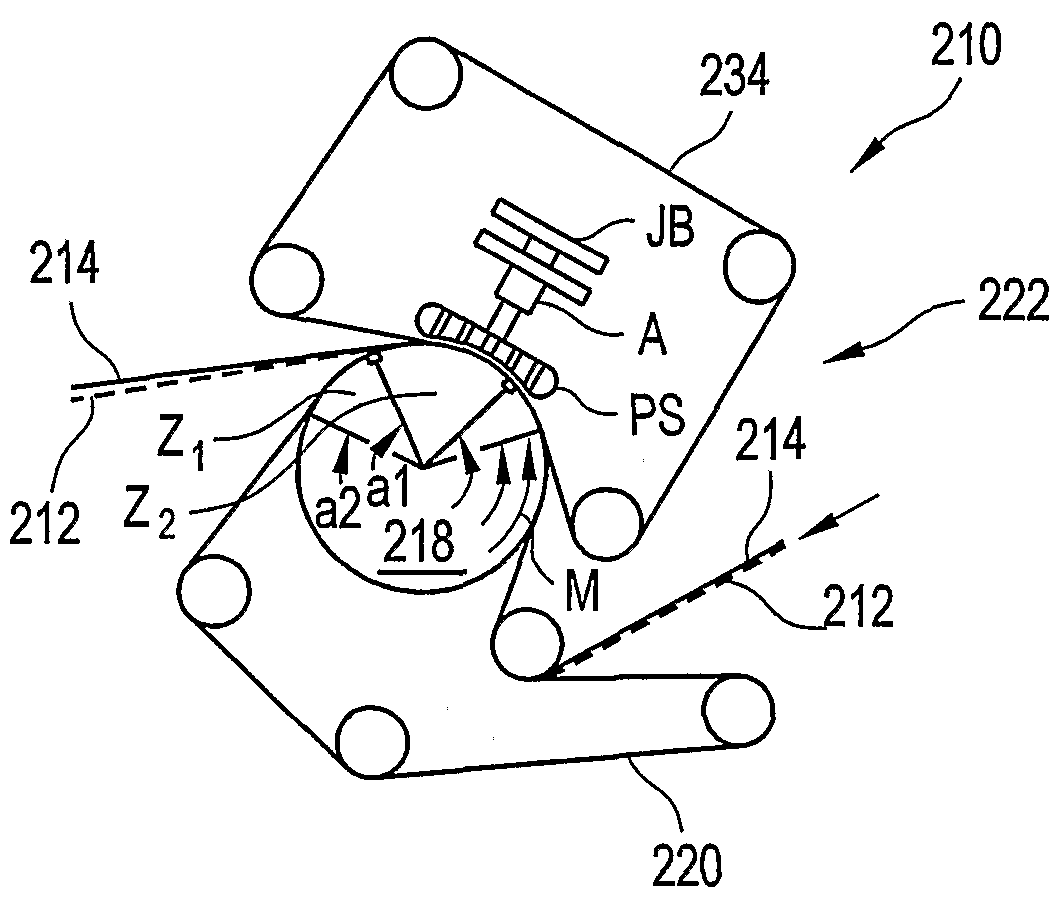
A pressing arrangement including at least one first fabric and second fabric both being permeable. A paper web is disposed between the first fabric and the second fabric. A pressure producing element is in contact with the first fabric. A support surface of a supporting structure is in contact with the second fabric. A differential pressure is provided between the first fabric and the support surface that acts on the first fabric, the paper web, and the second fabric, whereby the paper web is subjected to mechanical pressure and experiences a predetermined hydraulic pressure so as to cause water to be drained from the paper web. The pressing arrangement is structured and arranged to allow air to flow in a direction from the first fabric through the paper web and through the second fabric.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
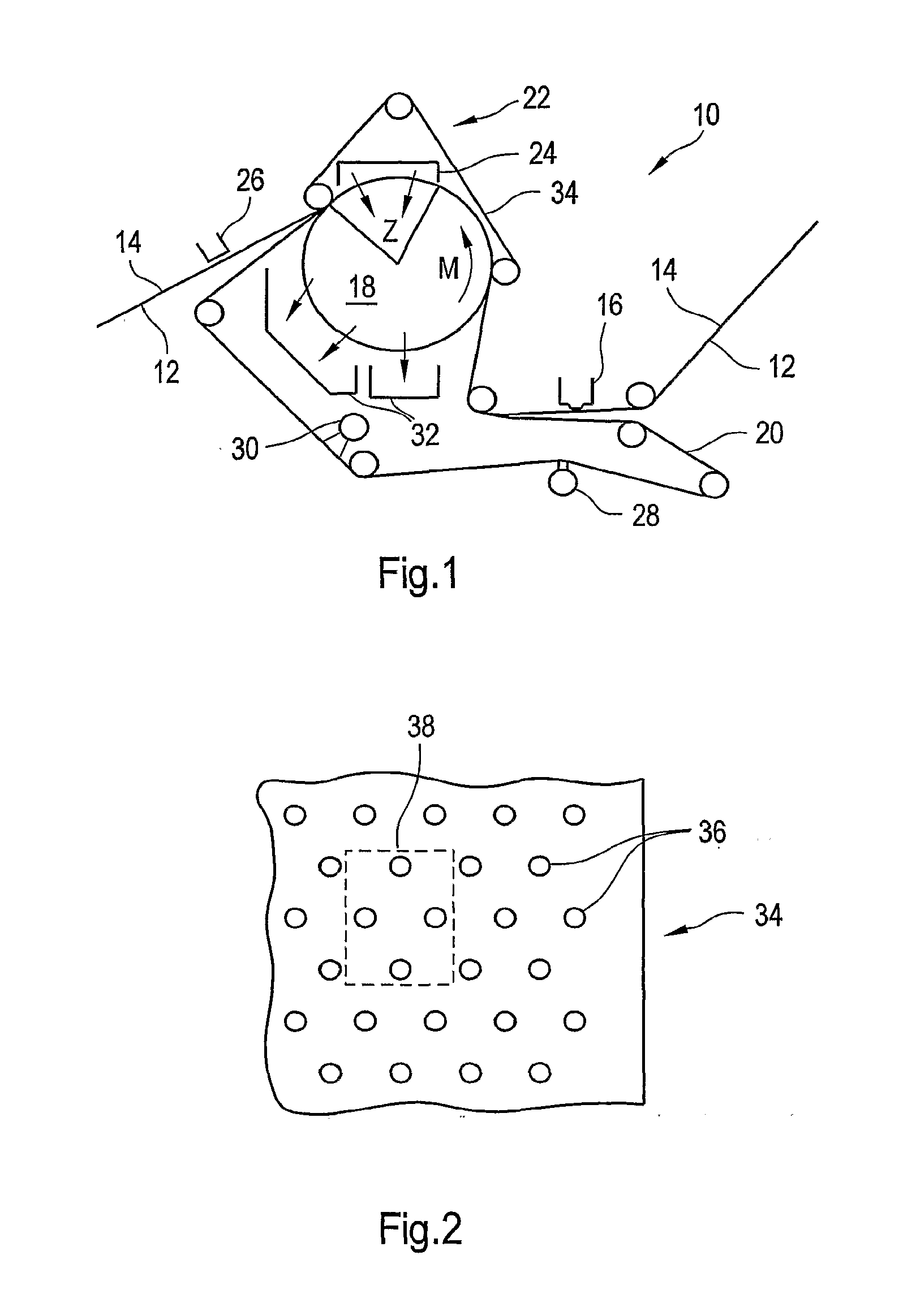
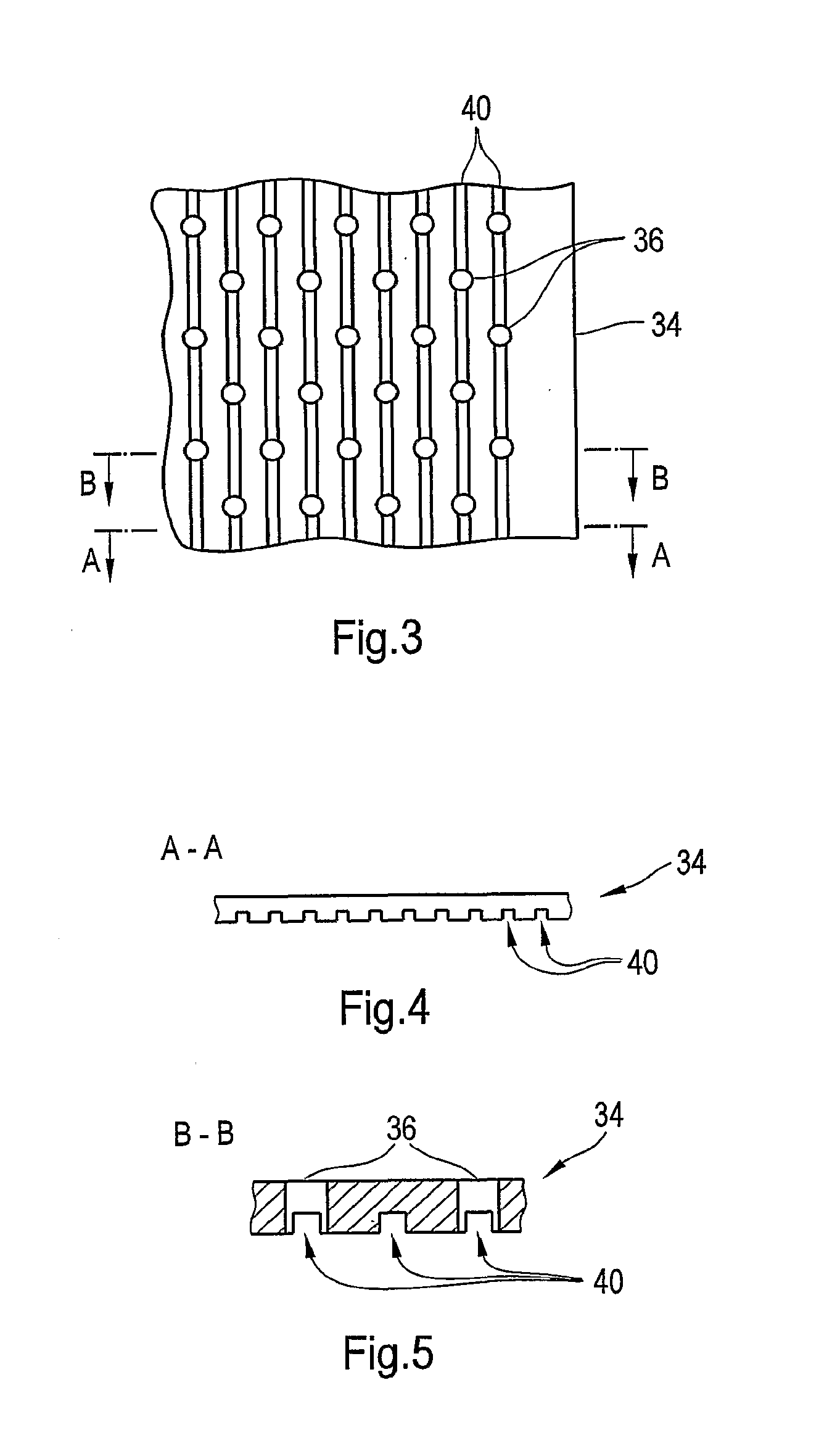
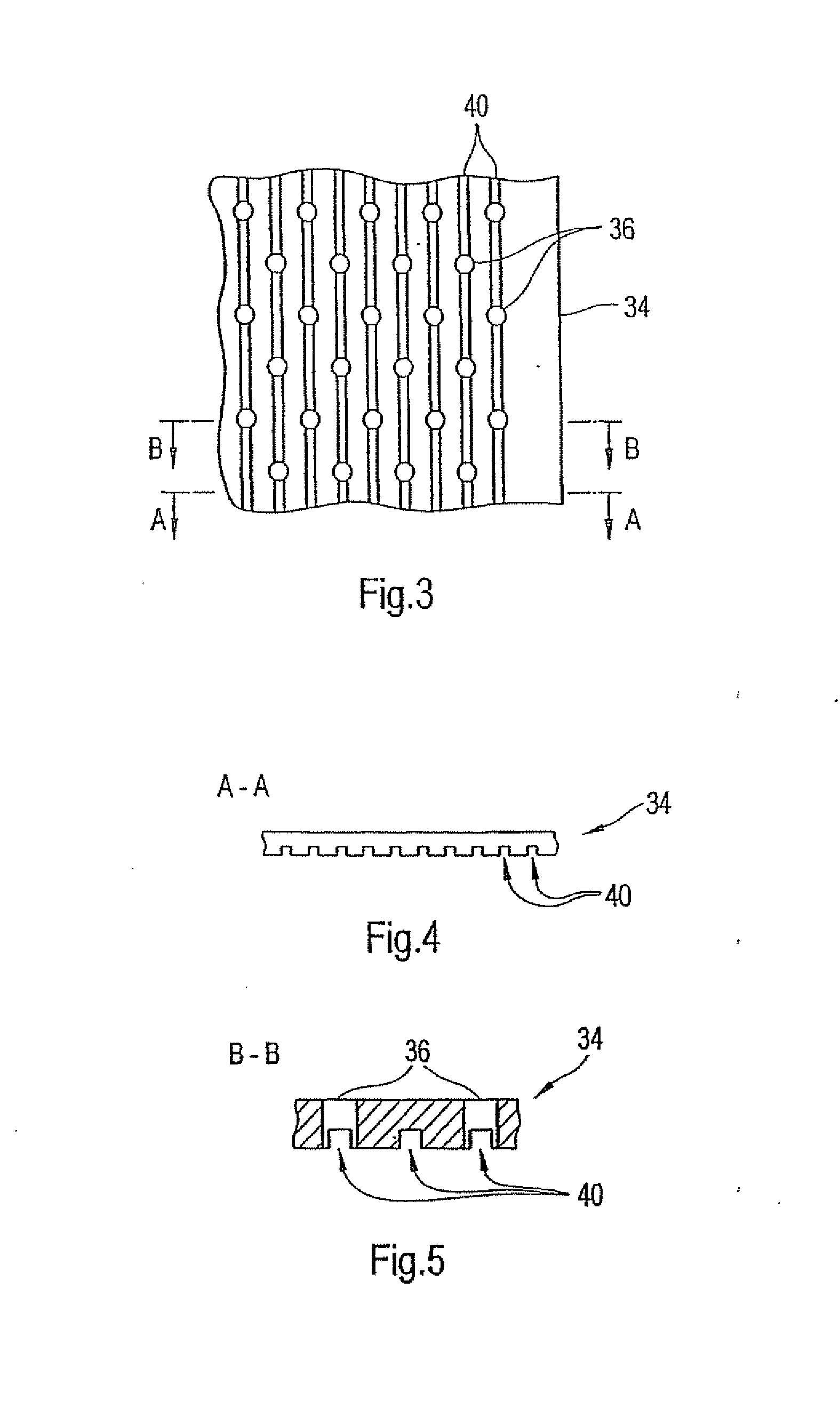
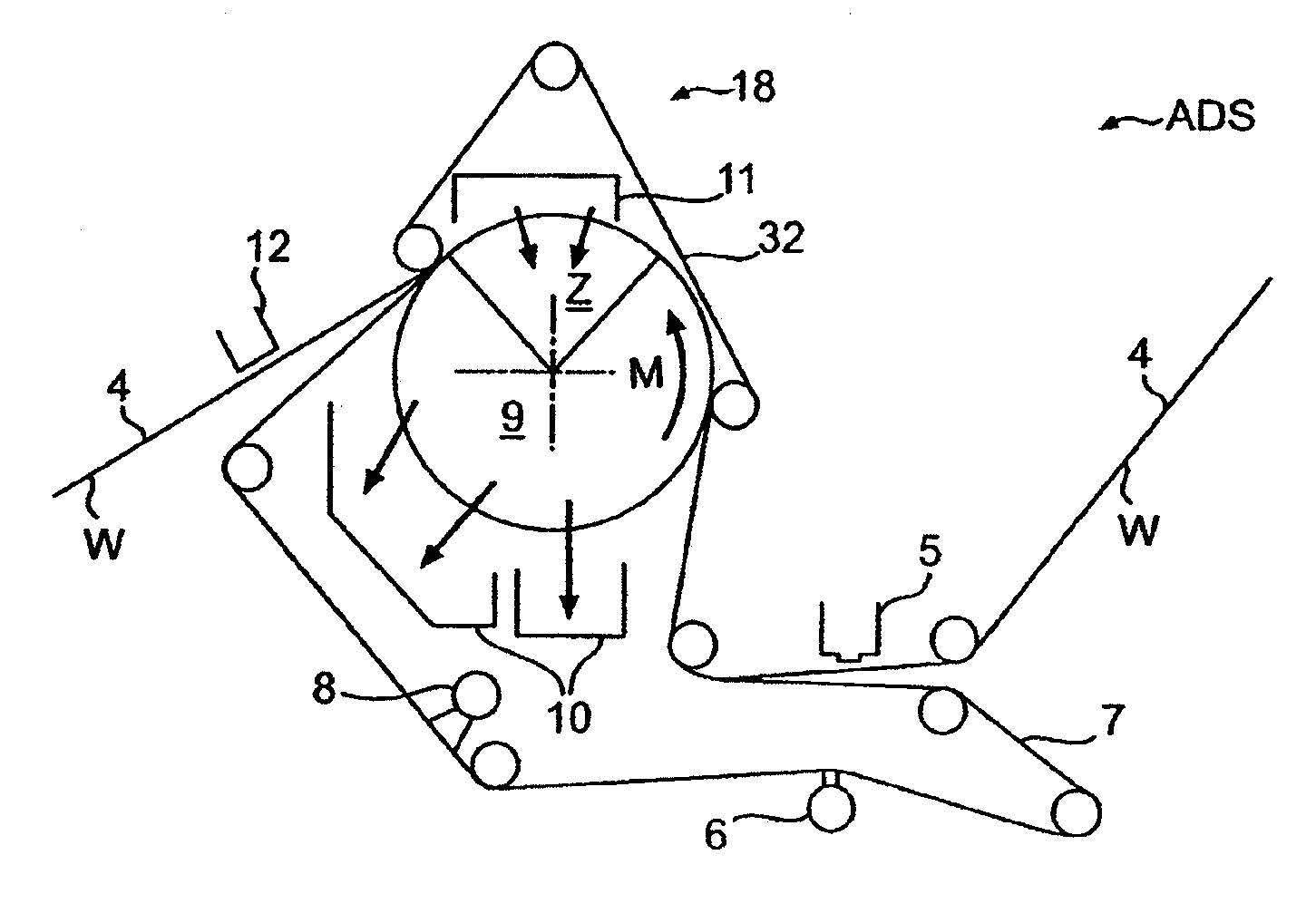
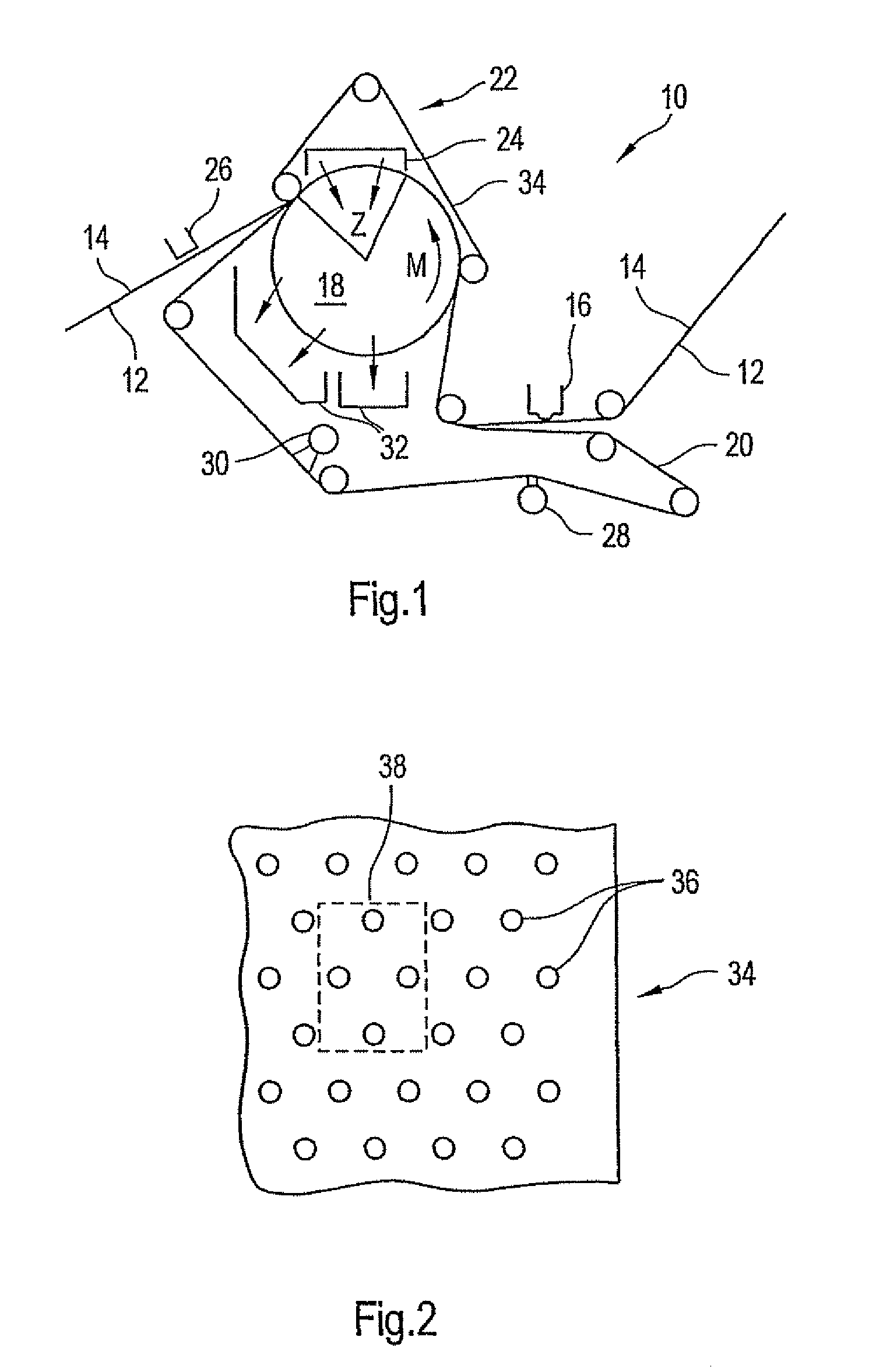
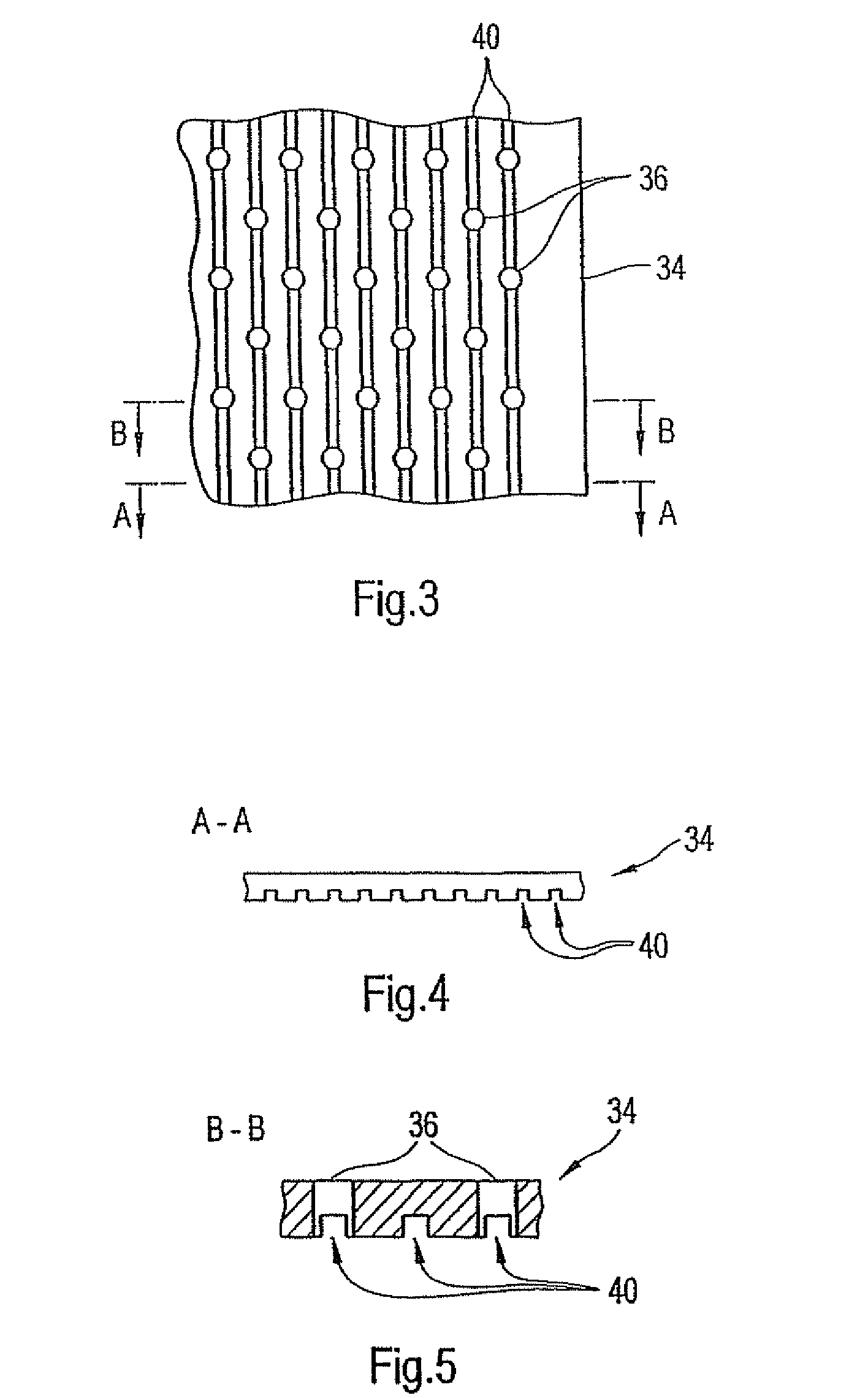
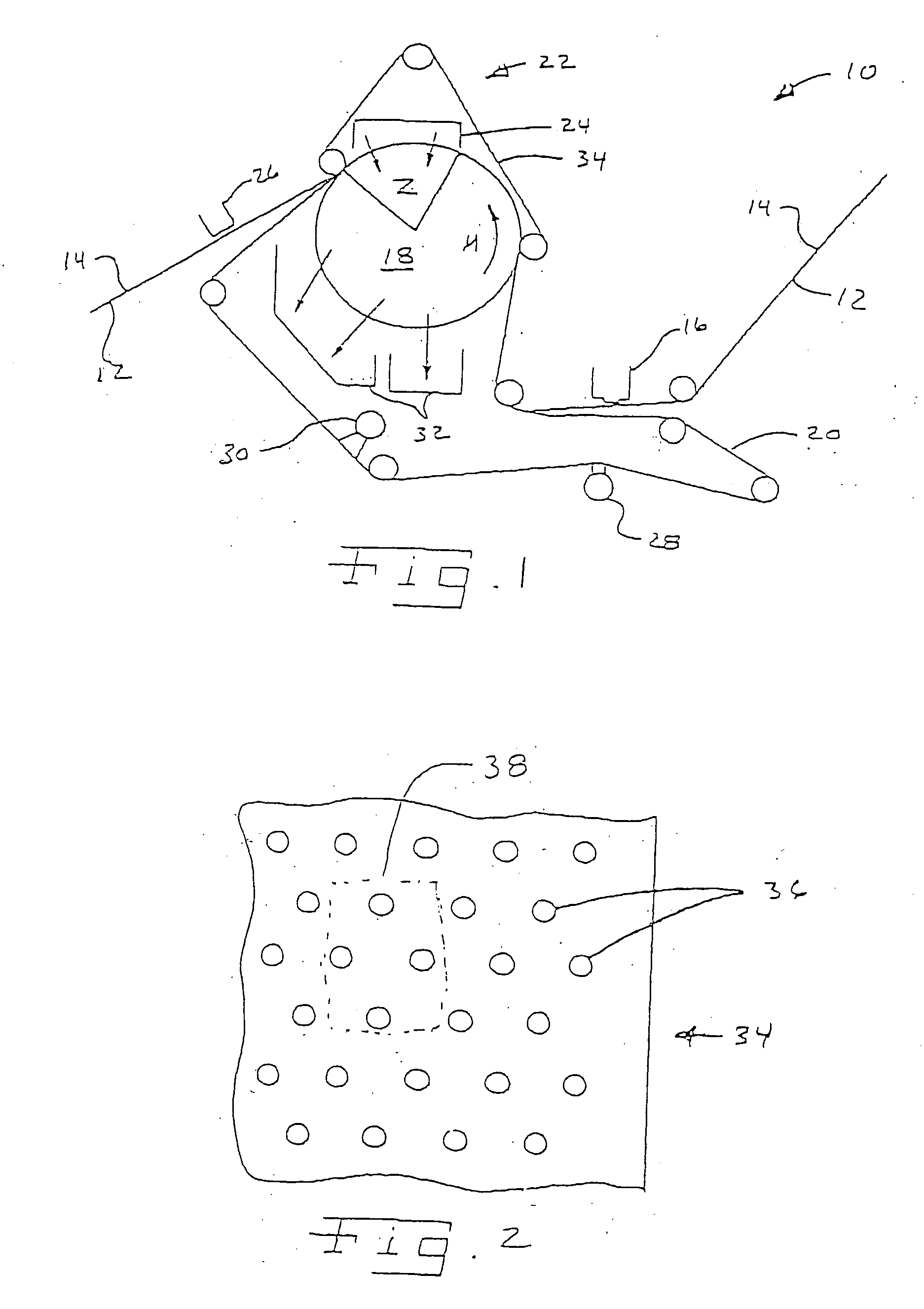
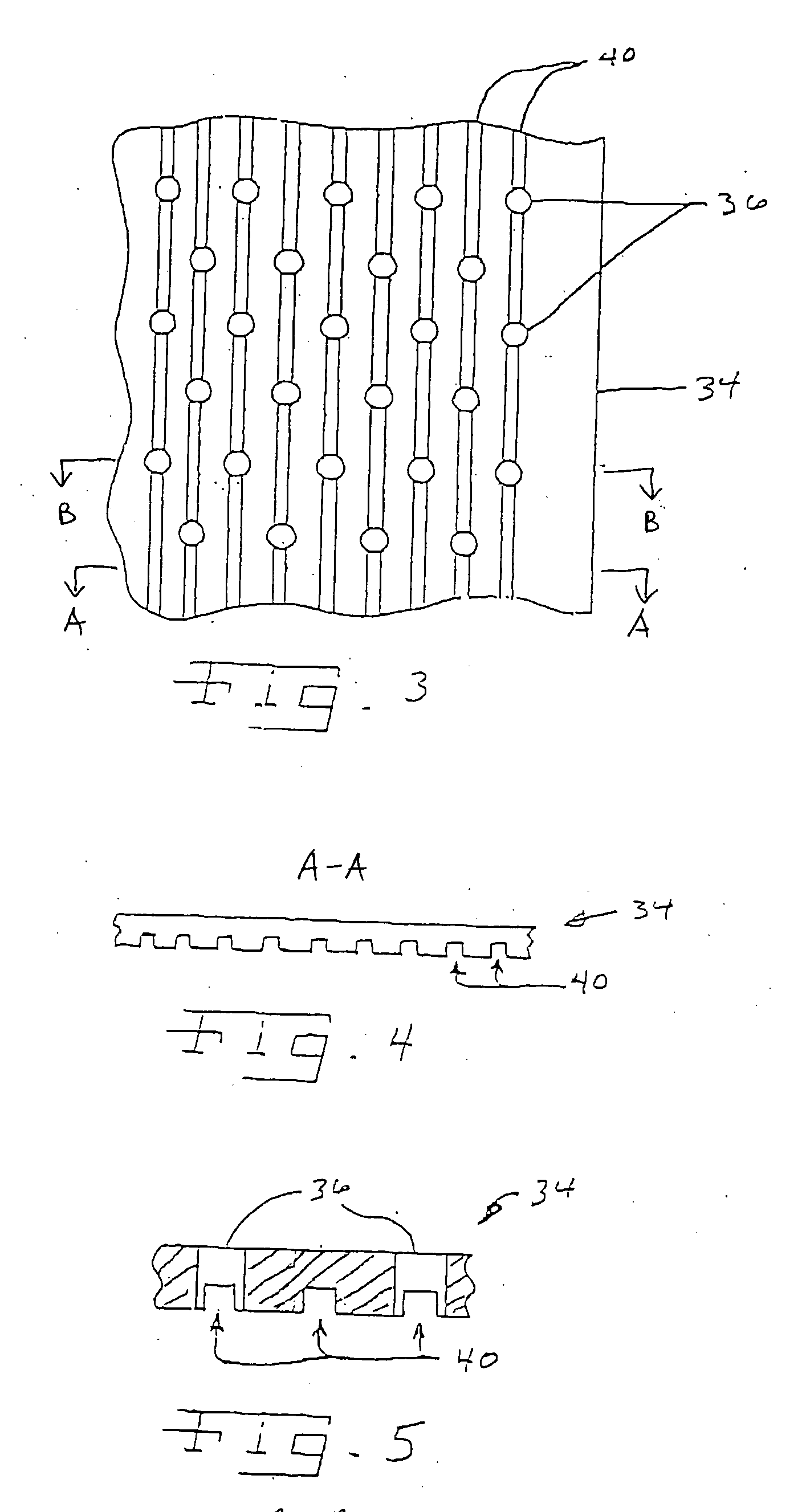
Forming fabric and/or tissue molding belt and/or molding belt for use on an atmos system
ActiveUS20070251659A1Increase the opening areaLong dwell timePaper/cardboardMachine wet endPaper machine
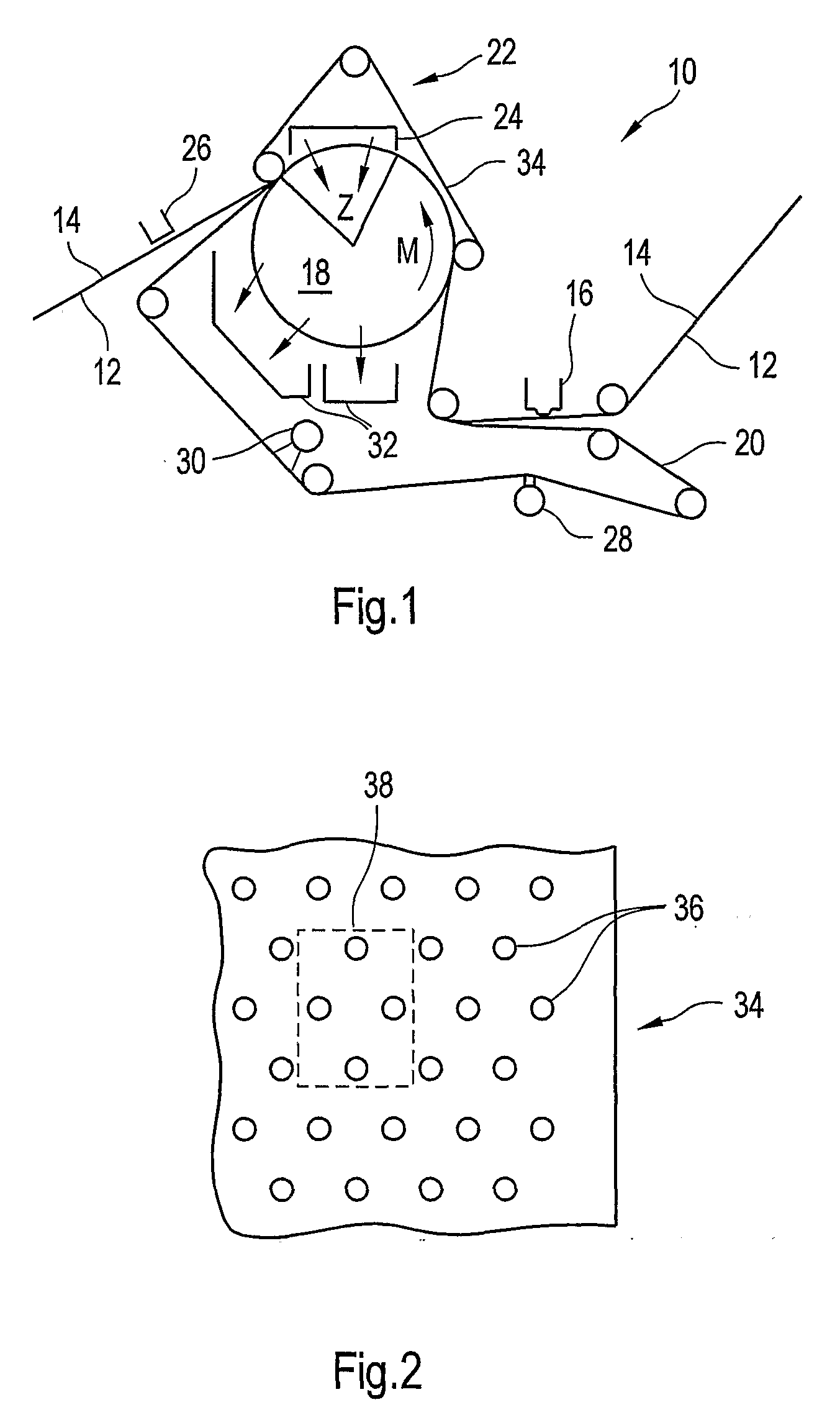
A forming fabric for an ATMOS system or a TAD machine. The forming fabric includes a permeability value of between approximately 100 cfm and approximately 1200 cfm, a paper surface contact area of between approximately 0.5% and approximately 90% when not under pressure and tension, and an open area of between approximately 1.0% and approximately 90%. A belt press for a paper machine can utilize the forming fabric. This Abstract is not intended to define the invention disclosed in the specification, nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
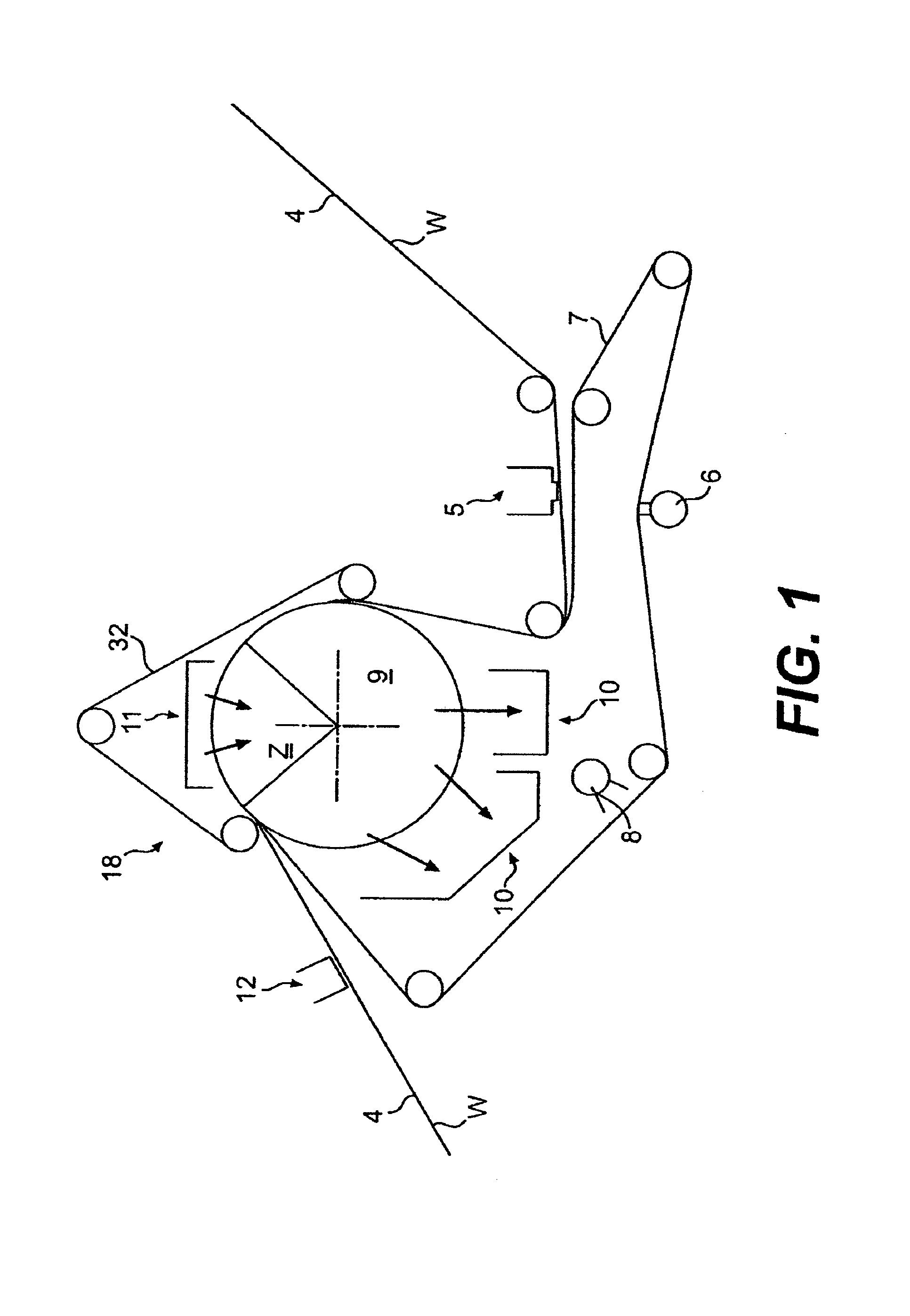
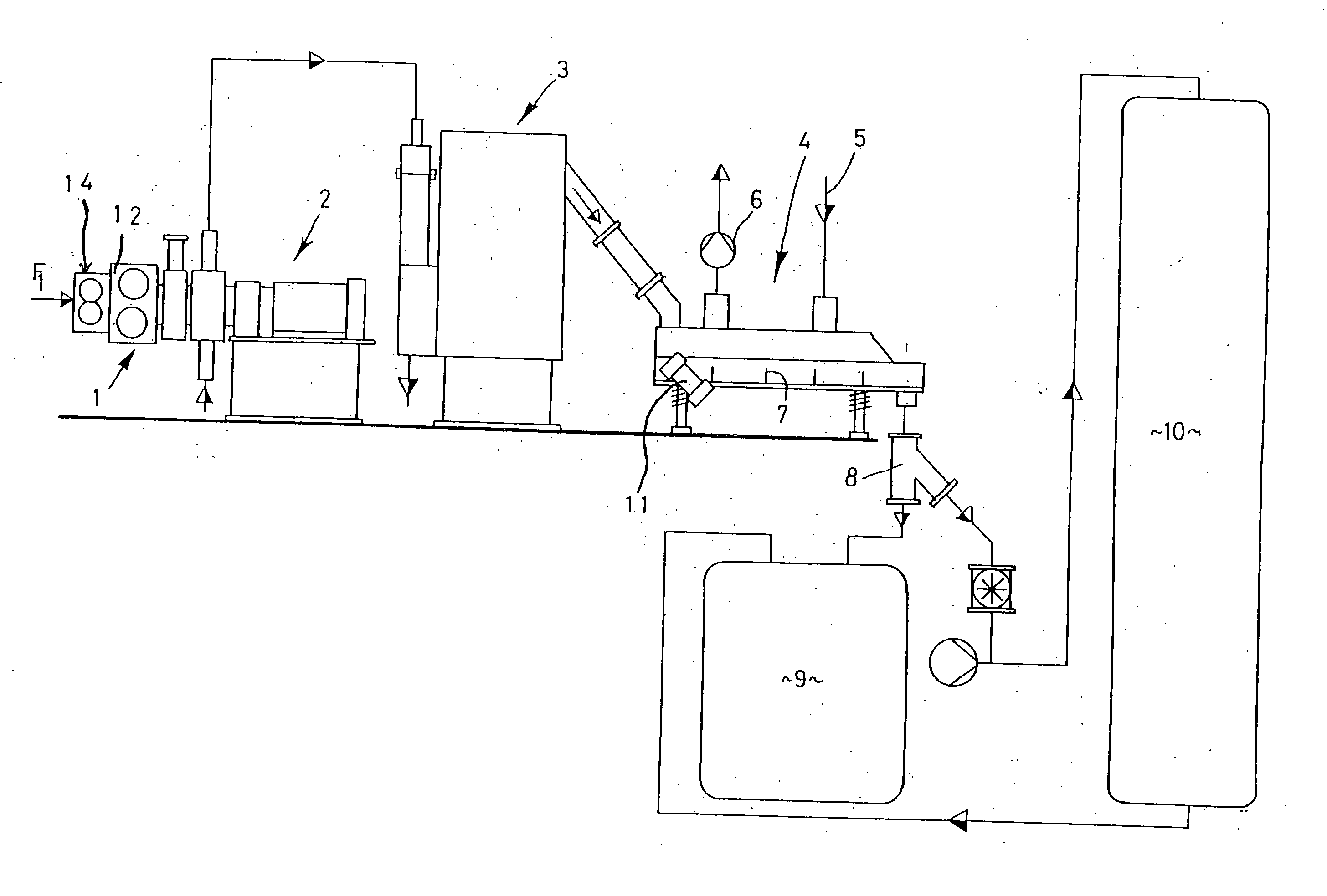
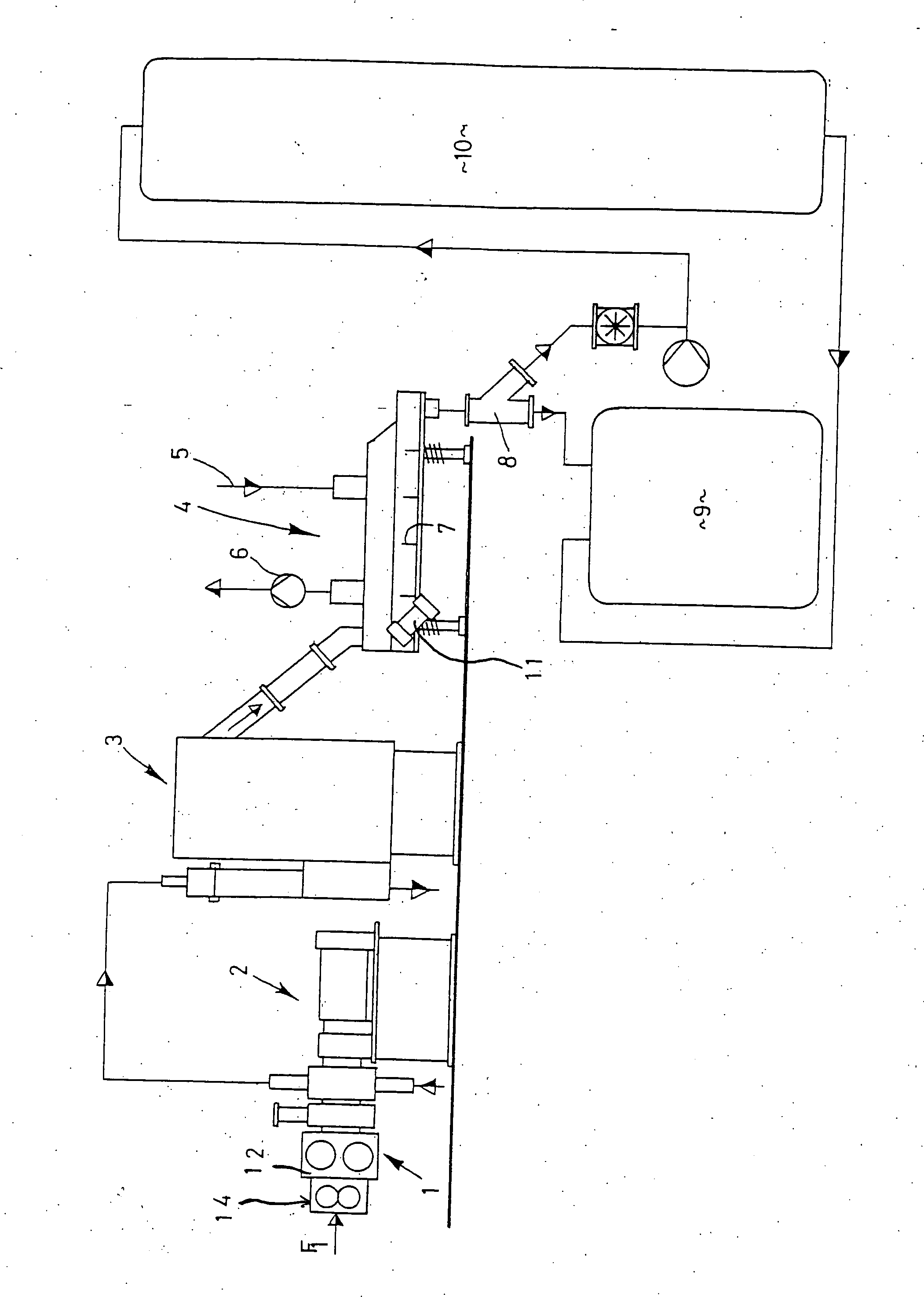
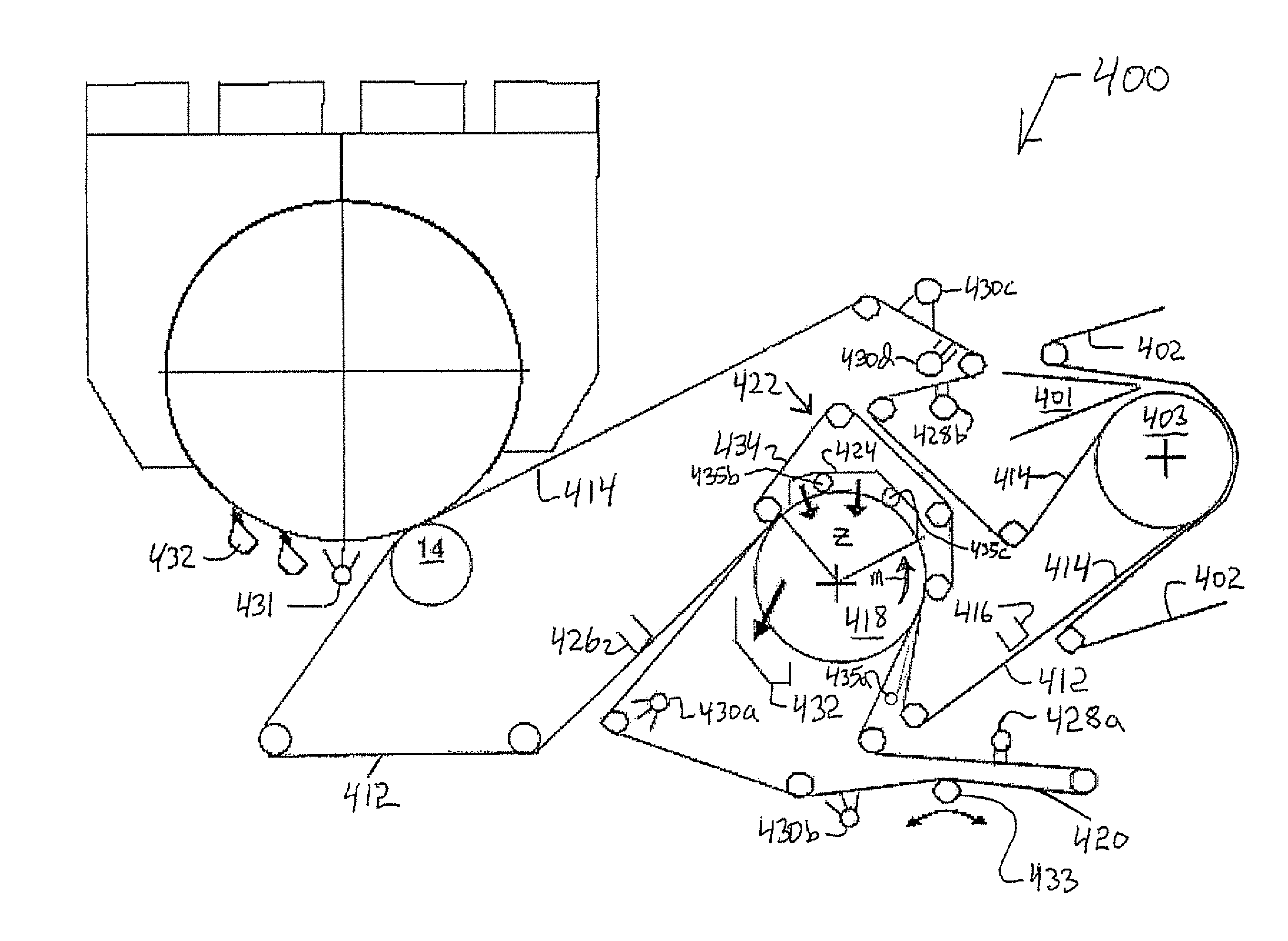
Advanced dewatering system
ActiveUS7510631B2Large tensionIncrease the opening areaDrying solid materials with heatDryer sectionFacial tissueHygiene
System for drying a tissue or hygiene web. The system includes a permeable structured fabric carrying the web over a drying apparatus. A permeable dewatering fabric contacts the web and is guided over the drying apparatus. A mechanism is utilized for applying pressure to the permeable structured fabric, the web, and the permeable dewatering fabric at the drying apparatus. This Abstract is not intended to define the invention disclosed in the specification, nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Method and apparatus for thermally processing polyester pellets
InactiveUS20050085620A1Long dwell timeSmall contact surfaceMouldsConfectioneryPolyesterPolyethylene terephthalate
Method and apparatus for thermally processing polyester pellets, e.g., polyethylene terephthalate pellets, in order to achieve a partial crystallization, whereby the polyester melt is fed to an underwater pelletizer and pelletized, the pellets obtained are fed to a water / solids separating device and the dried pellets are fed at a pellet temperature of greater than 100° C. to an agitation device that the pellets leave at a pellet temperature of over 100° C.
Owner:NORDSON CORP
Dewatering tissue press fabric for an atmos system and press section of a paper machine using the dewatering fabric
A dewatering fabric for an ATMOS system or a TAD machine that includes a caliper of between approximately 0.1 mm and approximately 15 mm, a permeability value of between approximately 1 cfm and approximately 500 cfm, an overall density of between approximately 0.2 g / cm3 and approximately 1.10 g / cm3, and a weight of between approximately 100 g / m2 and approximately 3000 g / m2. A belt press for a paper machine can utilize the dewatering fabric. This Abstract is not intended to define the invention disclosed in the specification, nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in anyway.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Advanced dewatering system
ActiveUS20060085999A1Substantial airflowLarge tensionDrying solid materials with heatDryer sectionHygieneWaste management
System for drying a tissue or hygiene web. The system includes a permeable structured fabric carrying the web over a drying apparatus. A permeable dewatering fabric contacts the web and is guided over the drying apparatus. A mechanism is utilized for applying pressure to the permeable structured fabric, the web, and the permeable dewatering fabric at the drying apparatus. This Abstract is not intended to define the invention disclosed in the specification, nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
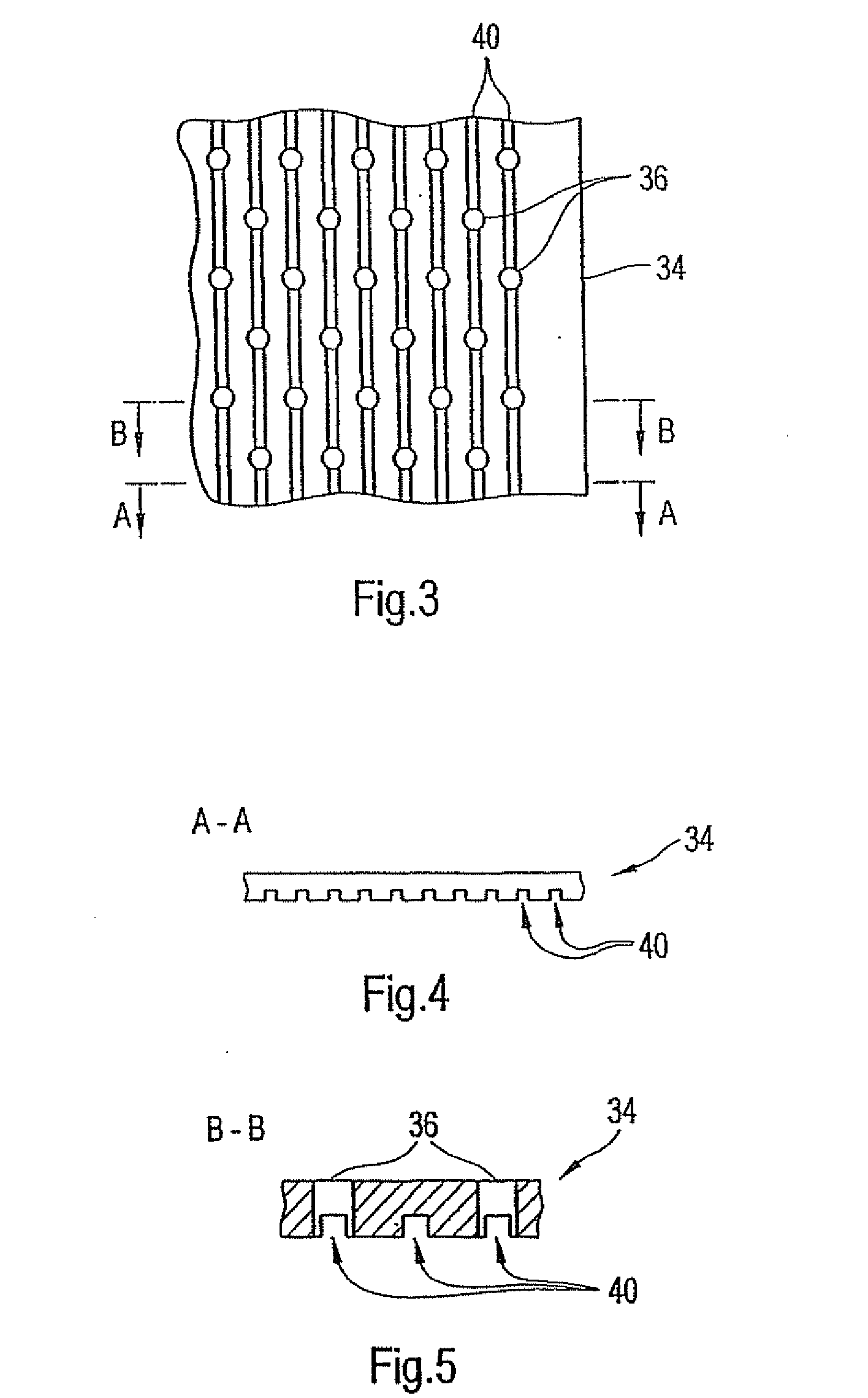
High tension permeable belt for an ATMOS system and press section of paper machine using the permeable belt
ActiveUS7527709B2Large tensionIncrease the opening areaPaper/cardboardPress sectionFiberSupport surface
A permeable belt, a belt press including a roll having an exterior surface and the permeable belt, and a method of drying or pressing a web with the permeable belt. The permeable belt has a paper web facing side and is guided over a support surface. The permeable belt can have a tension of between approximately 20 kN / m and approximately 100 KN / m, a permeability value of between approximately 100 cfm and approximately 1200 cfm, a surface contact area of the paper web side that being between approximately 0.5% and approximately 90% when not under tension, and an open area of between approximately 1.0% and approximately 85%. This Abstract is not intended to define the invention disclosed in the specification, nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Generating sets of tailored laser pulses
ActiveUS20050041976A1Improve removal qualityComplicated processLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAudio power amplifierMaster oscillator
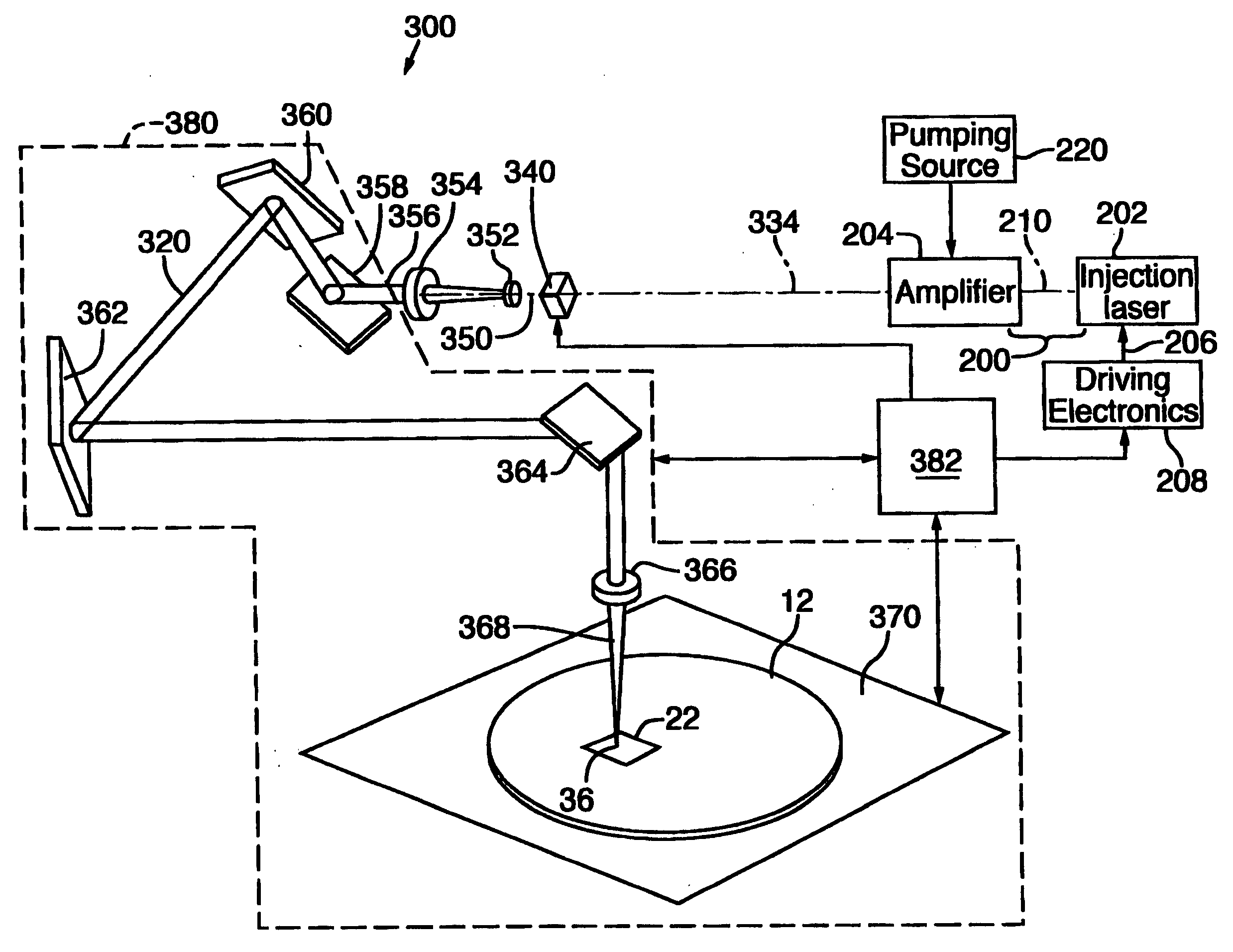
In a master oscillator power amplifier, a driver (208) of a diode laser (202) is specially controlled to generate a set of two or more injection laser pulses that are injected into a power amplifier (204) operated in an unsaturated state to generate a set (50) of laser pulses (52) that replicate the temporal power profile of the injection laser pulses to remove a conductive link (22) and / or its overlying passivation layer (44) in a memory or other IC chip. Each set (50) includes at least one specially tailored pulse (52) and / or two or more pulses (50) having different temporal power profiles. The duration of the set (50) is short enough to be treated as a single “pulse” by conventional positioning systems (380) to perform on-the-fly link removal without stopping.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Dewatering tissue press fabric for an ATMOS system and press section of a paper machine using the dewatering fabric
ActiveUS7550061B2Large tensionIncrease the opening areaPaper/cardboardMachine wet endVolumetric Mass DensityPaper machine
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Press section and permeable belt in a paper machine
InactiveUS8440055B2Large tensionIncrease the opening areaDrying solid materials with heatDrying solid materials without heatDifferential pressureMechanical pressure
A pressing arrangement including at least one first fabric and second fabric both being permeable. A paper web is disposed between the first fabric and the second fabric. A pressure producing element is in contact with the first fabric. A support surface of a supporting structure is in contact with the second fabric. A differential pressure is provided between the first fabric and the support surface that acts on the first fabric, the paper web, and the second fabric, whereby the paper web is subjected to mechanical pressure and experiences a predetermined hydraulic pressure so as to cause water to be drained from the paper web. The pressing arrangement is structured and arranged to allow air to flow in a direction from the first fabric through the paper web and through the second fabric.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
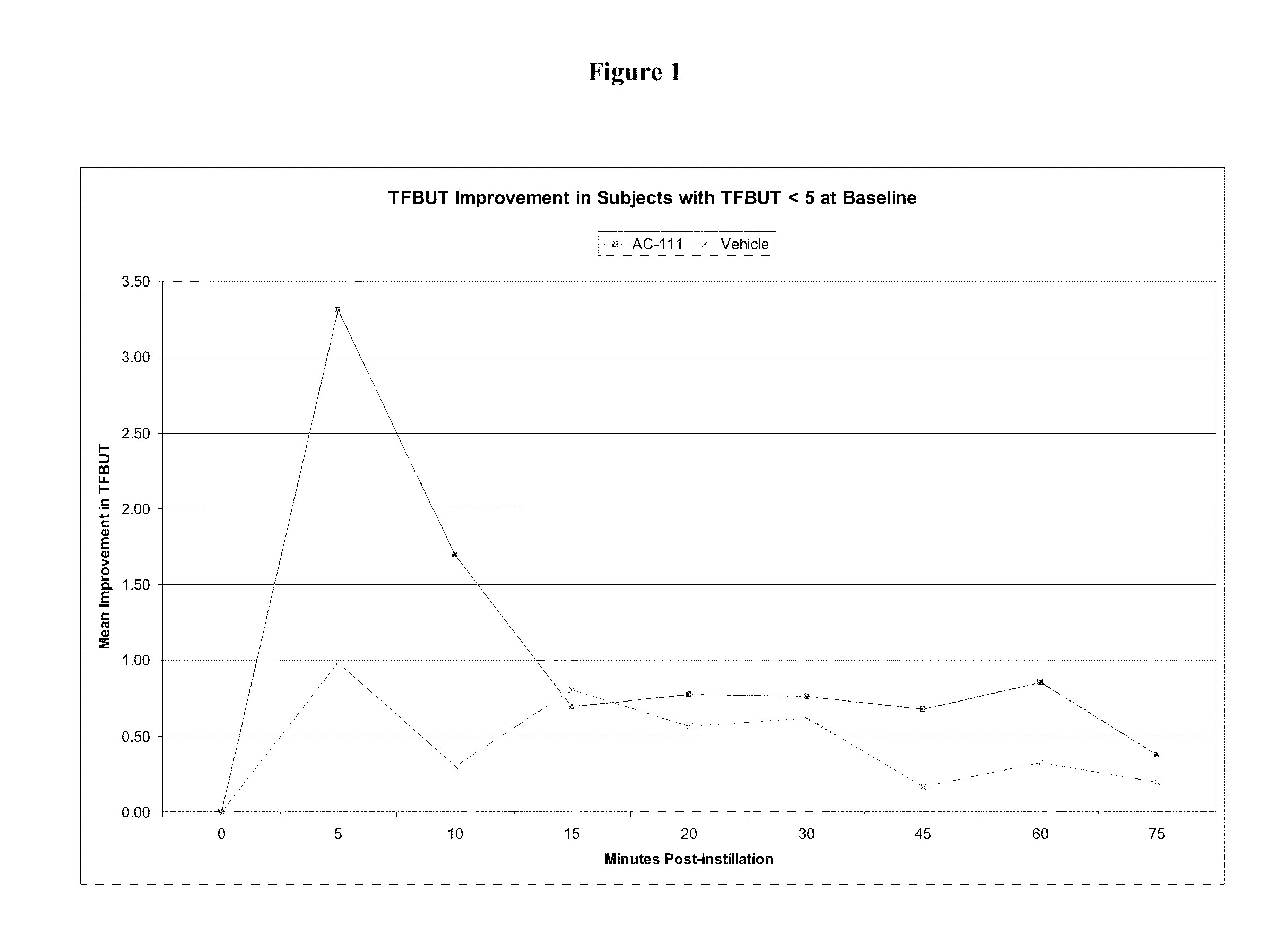
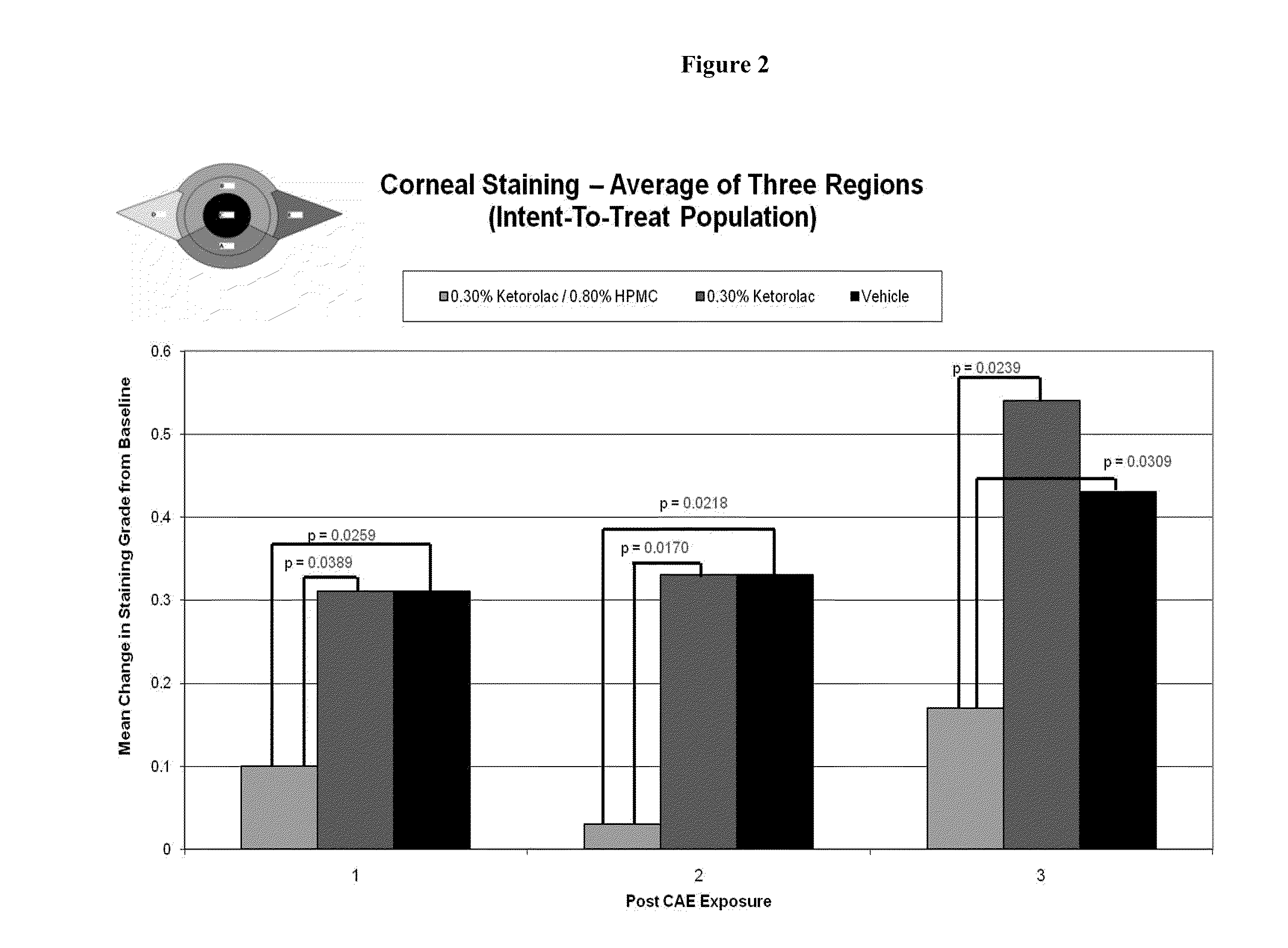
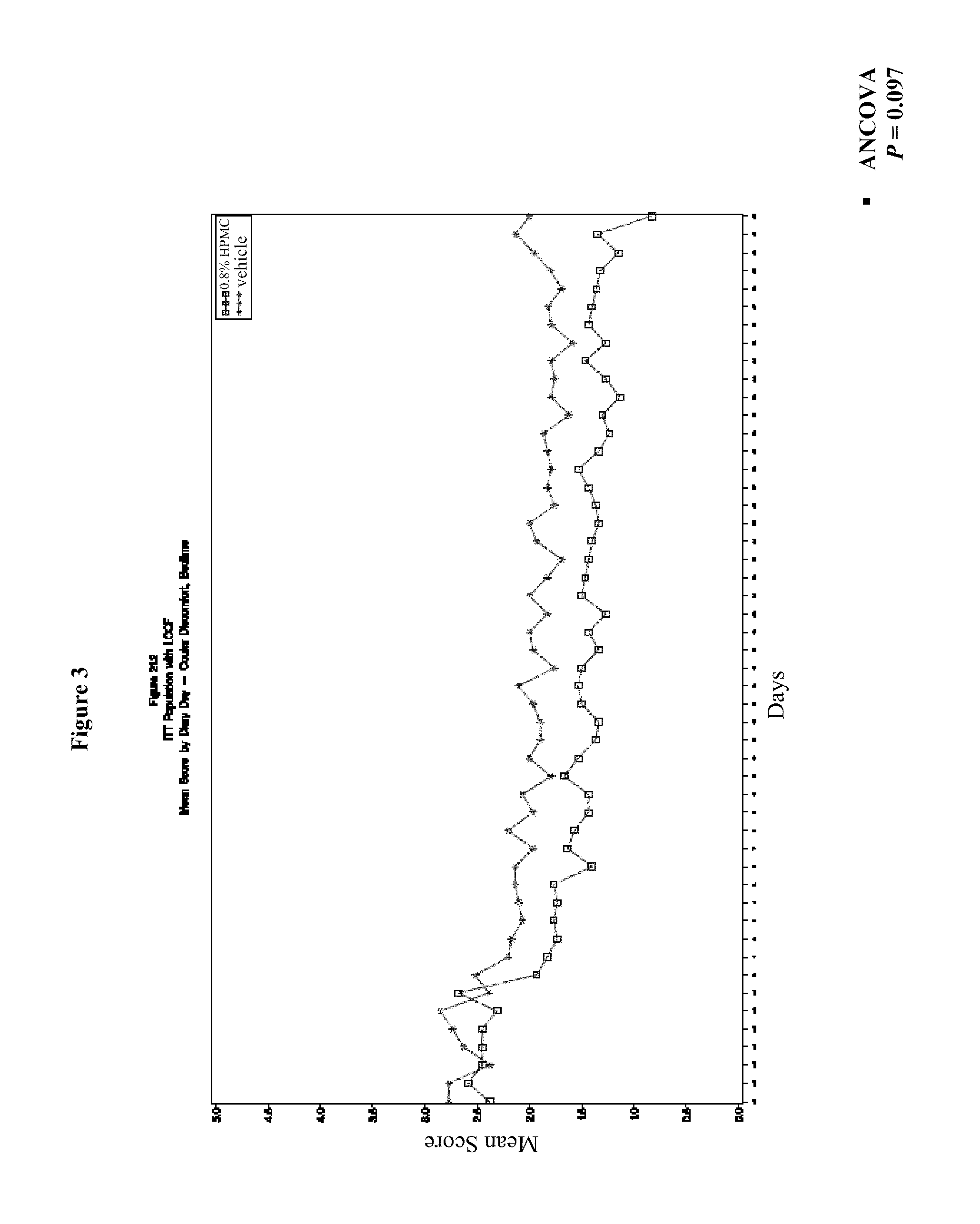
Ophthalmic formulations, methods of manufacture, and methods of using same
InactiveUS20100311688A1Increased tear film stabilityIncreasing tear film break up timeOrganic active ingredientsBiocideOphthalmologyOphthalmic preparations
The present invention provides compositions for treating and / or preventing signs and symptoms associated with dry eye and / or ocular irritation, and methods of use thereof. Such compositions are provided in novel ophthalmic formulations that are comfortable upon instillation in the eye. Methods of manufacture are also provided.
Owner:ACIEX THERAPEUTICS INC
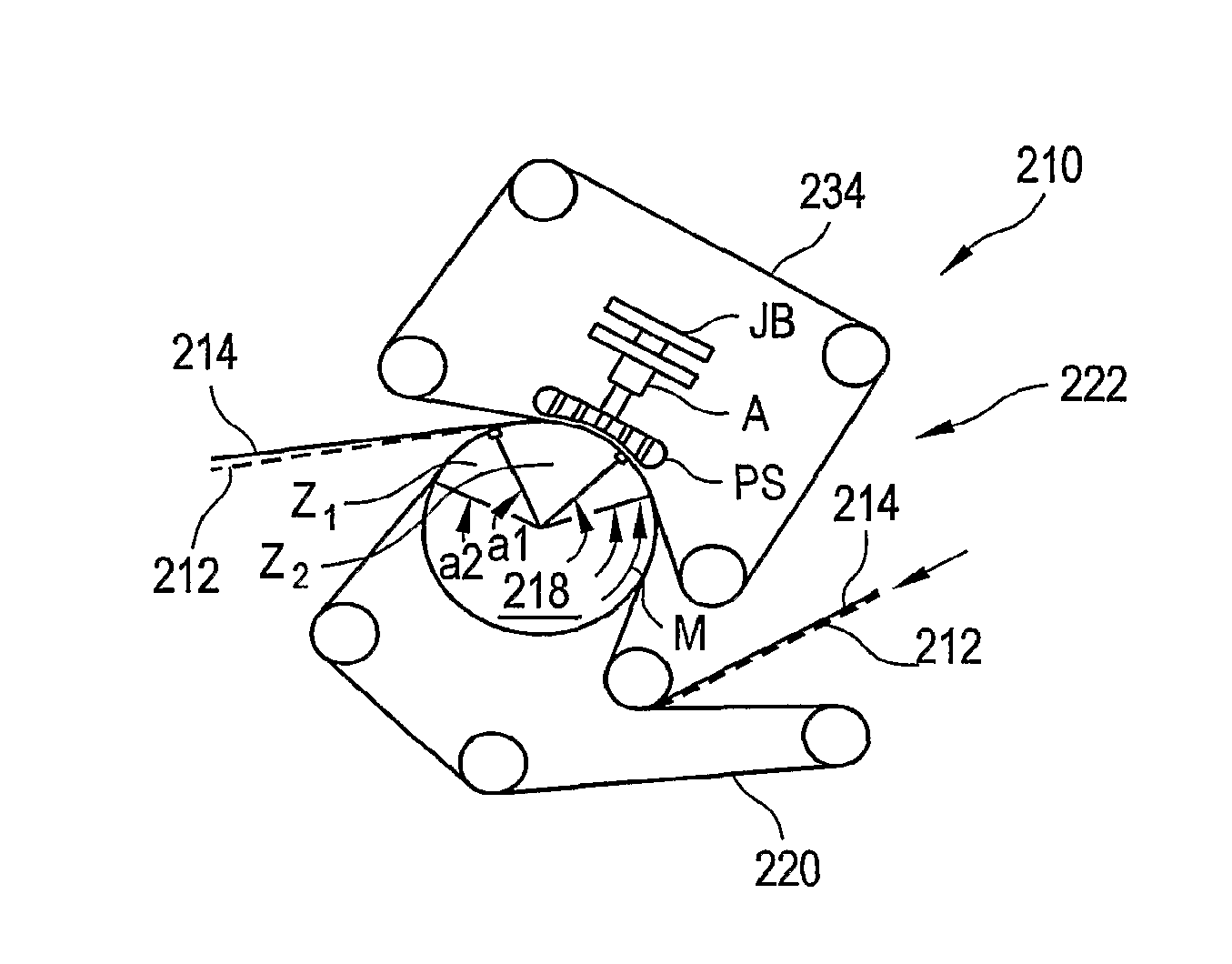
Press section and permeable belt in a paper machine
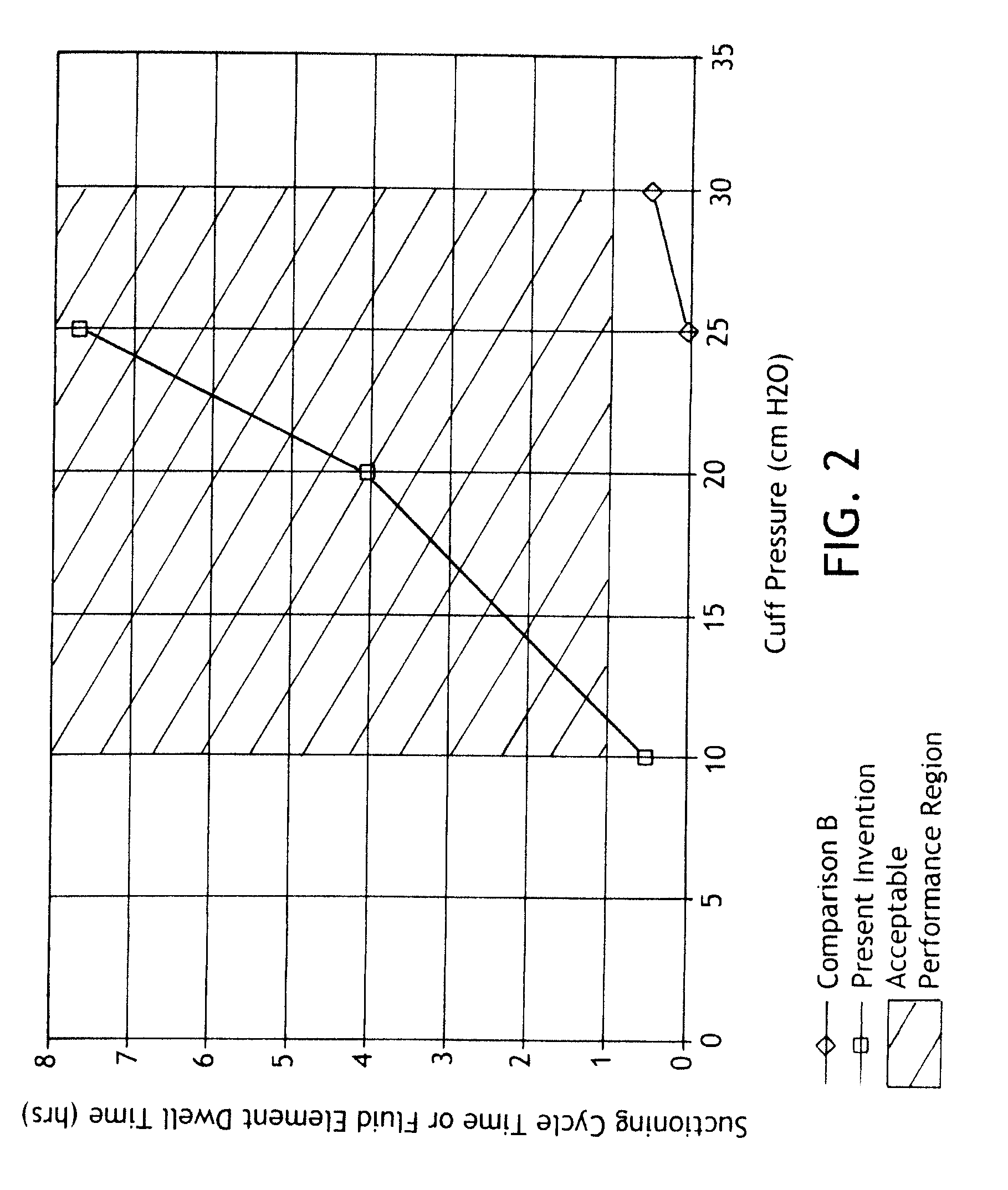
InactiveUS20060086473A1Increase the opening areaLong dwell timeDryer sectionPaper/cardboardPaper machineEngineering
A permeable belt, a belt press including a roll having an exterior surface and the permeable belt, and a method of drying or pressing a web with the permeable belt. The permeable belt can be tensioned to at least 30 KN / m. A side of the permeable belt has an open area of at least approximately 25% and a contact area of at least approximately 25%. This Abstract is not intended to define the invention disclosed in the specification, nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Electro-kinetic air transporter and conditioner device with enhanced housing configuration and enhanced anti-microorganism capability
InactiveUS6911186B2Reduce the amount requiredLong dwell timeMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusParticulatesEmissivity
An electro-kinetic air conditioner for removing particulates from the air creates an airflow using no moving parts. The airflow is subjected to UV radiation from a germicidal lamp within the device. The conditioner includes an ion generator that has an electrode assembly including a first array of emitter electrodes, a second array of collector electrodes, and a high voltage generator. The device can also include a third or leading or focus electrode located upstream of the first array of emitter electrodes, and / or a trailing electrode located downstream of the second array of collector electrodes, and / or an interstitial electrode located between collector electrodes, and / or an enhanced emitter electrode with an enhanced length in order to increase emissivity.
Owner:SHARPER IMAGE ACQUISITION LLC A DELAWARE LIMITED LIABILITY
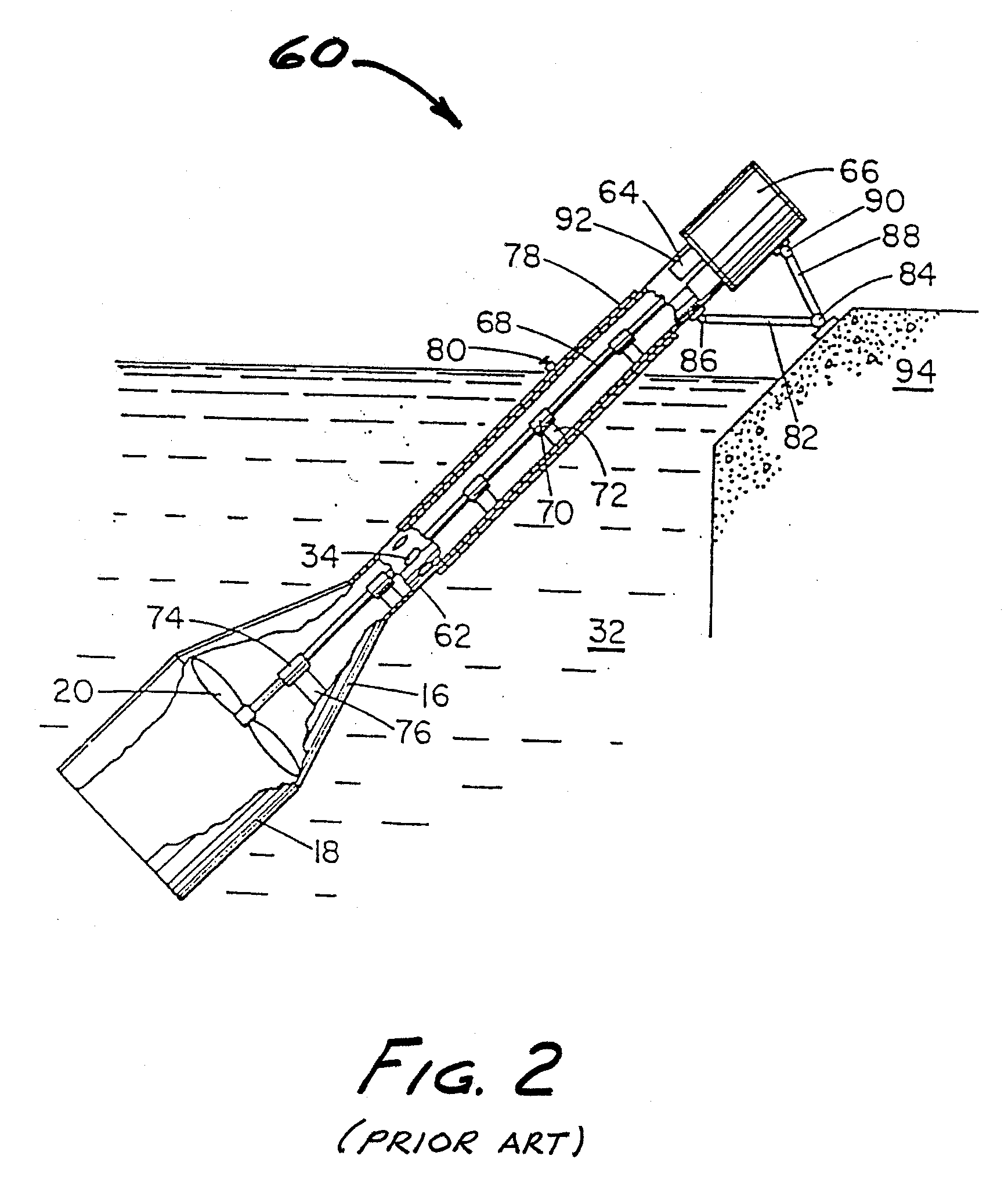
Press section and permeable belt in a paper machine
InactiveUS7476294B2Large tensionIncrease the opening areaDryer sectionPaper/cardboardFiberEngineering
A permeable belt, a belt press including a roll having an exterior surface and the permeable belt, and a method of drying or pressing a web with the permeable belt. The permeable belt can be tensioned to at least 30 KN / m. A side of the permeable belt has an open area of at least approximately 25% and a contact area of at least approximately 25%. This Abstract is not intended to define the invention disclosed in the specification, nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Carbon black
InactiveUS6290767B1Low structural requirementsReduction in carbon black throughputPigmenting treatmentMaterials sciencePigment
Carbon blacks doped with elements that are not carbon, wherein pairs of carbon atoms have been replaced by iso-electronic pairs of elements or combinations of elements. They can be used as a pigment or filler in rubber, plastics, paints, inks or the like.
Owner:UBS AG
Modular multi-stage fusing system
A multi-stage fusing system for fixing toner images to copy substrates of various weights has a primary fuser and a secondary fuser in series with the primary fuser. Various weights of print substrates may have toner images fixed thereon by the primary fuser. The various print substrates are then transmitted to the secondary fuser or directly to a finishing area. The secondary fuser is designed specifically for heavier weight substrates and a bypass paper path is provided for allowing lighter weight substrates to bypass the secondary fuser.
Owner:XEROX CORP
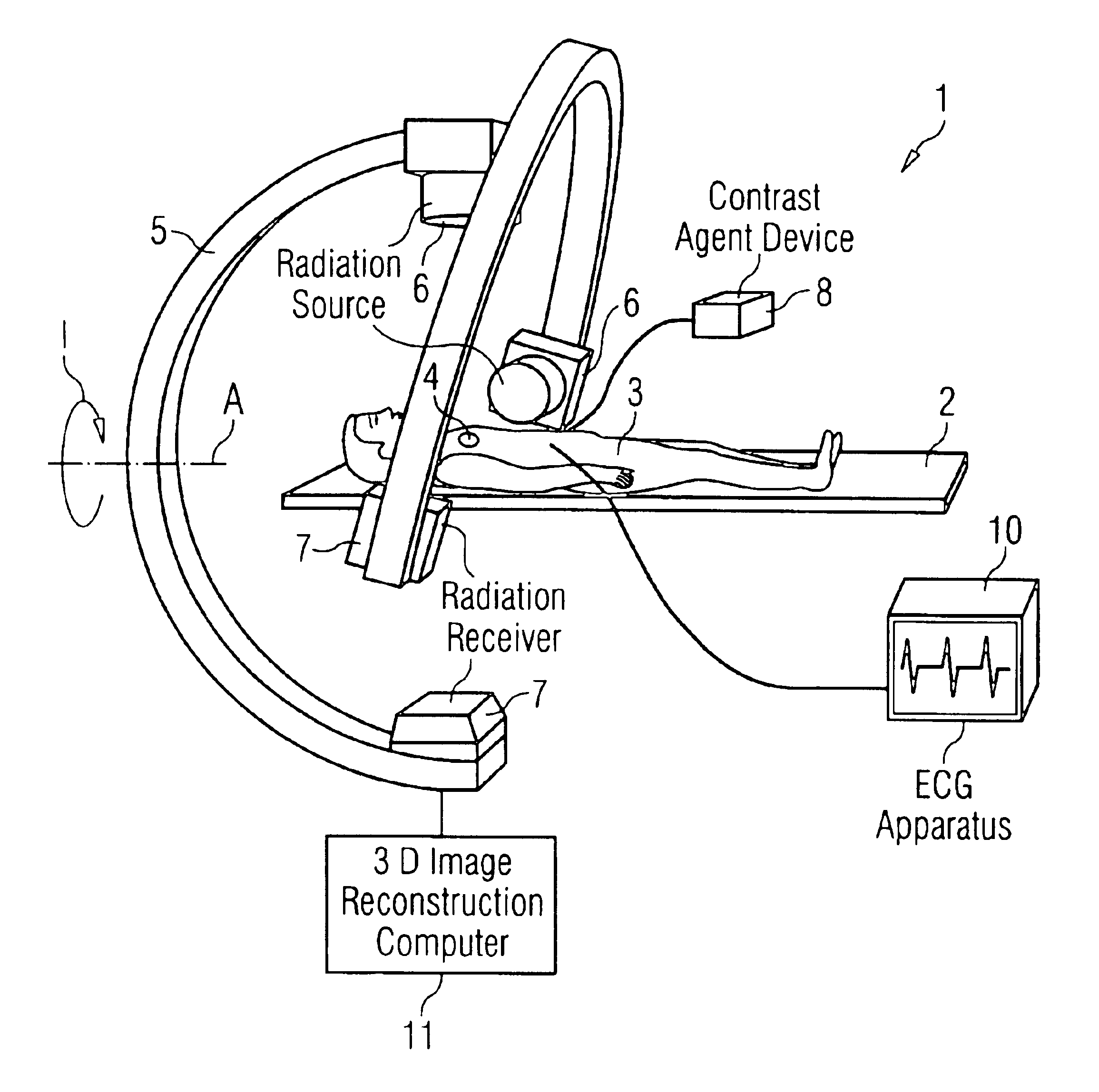
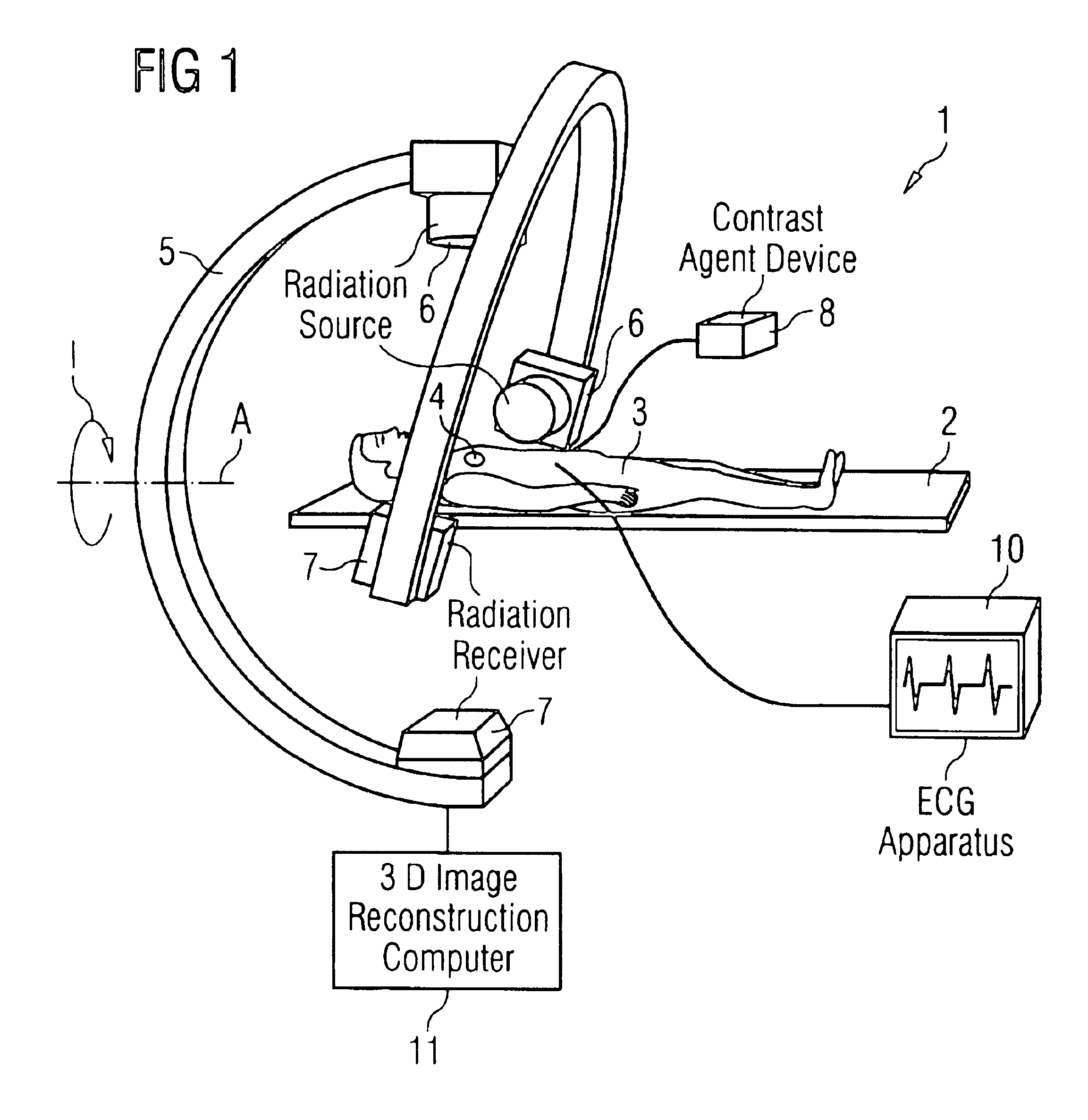
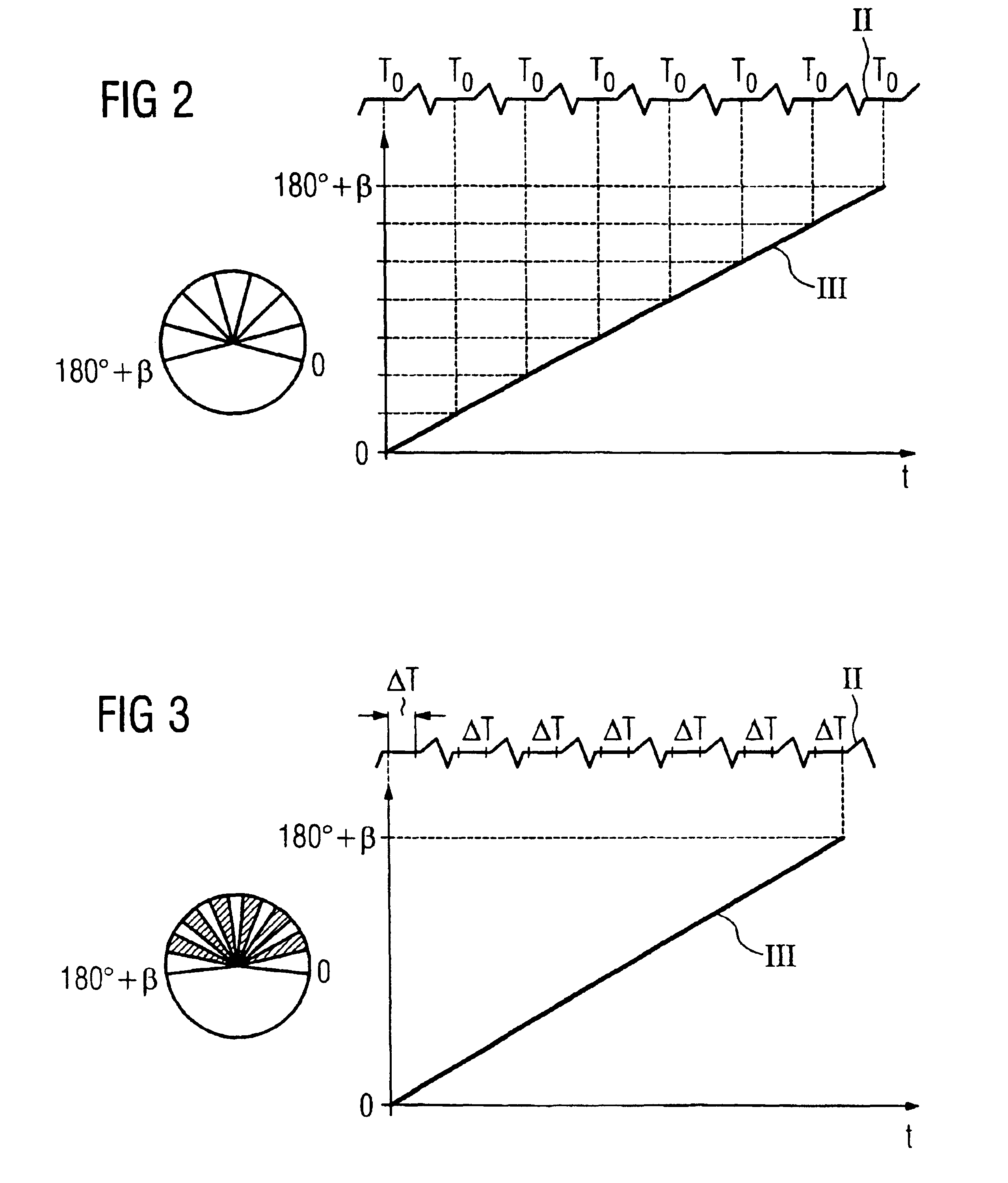
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional imaging of a moving examination subject, particularly for heart imaging
InactiveUS6909769B2Increase speedExtended stayElectrocardiographyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationProjection imageNuclear medicine
In a method and apparatus for three-dimensional imaging of a moving examination subject, particularly heart imaging with an examination apparatus having at least one C-arm with a radiation source and a radiation receiver, the C-arm rotates around the examination subject at least once through 180° plus the radiation fan angle during the time span in which a contrast agent is in the examination subject for the registration of the two-dimensional projection images, on the basis of which a three-dimensional image reconstruction ensues.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Forming fabric and/or tissue molding belt and/or molding belt for use on an ATMOS system
ActiveUS7524403B2Large tensionIncrease the opening areaPaper/cardboardMachine wet endPaper machineTissue paper
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Advanced Dewatering System
InactiveUS20070256806A1Increase the opening areaLong dwell timeDryer sectionMachine wet endEngineeringMechanical engineering
A system for drying one of a tissue and a hygiene web including a drying apparatus, a permeable structured fabric, a permeable dewatering fabric and a mechanism for applying pressure. The permeable structured fabric carries the web over the drying apparatus. The permeable dewatering fabric contacts the web and is guided over the drying apparatus. The mechanism for applying pressure, applies pressure to the permeable structured fabric, the web, and the permeable dewatering fabric at the drying apparatus.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
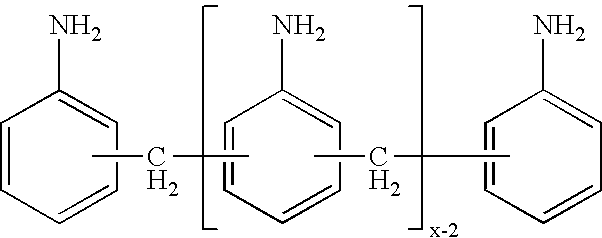
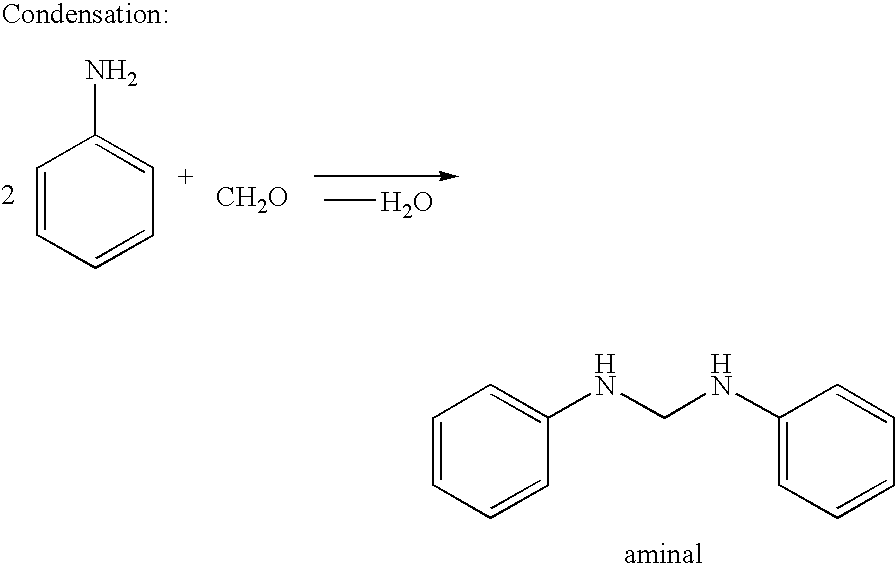
Process for the preparation of polyamines of the diphenylmethane series at a low degree of protonation
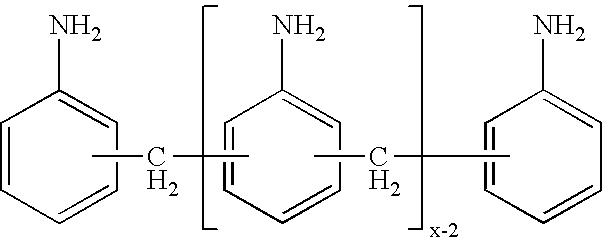
ActiveUS20060287555A1Reduce the probability of reactionLong dwell timeIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationDiphenylmethaneProtonation
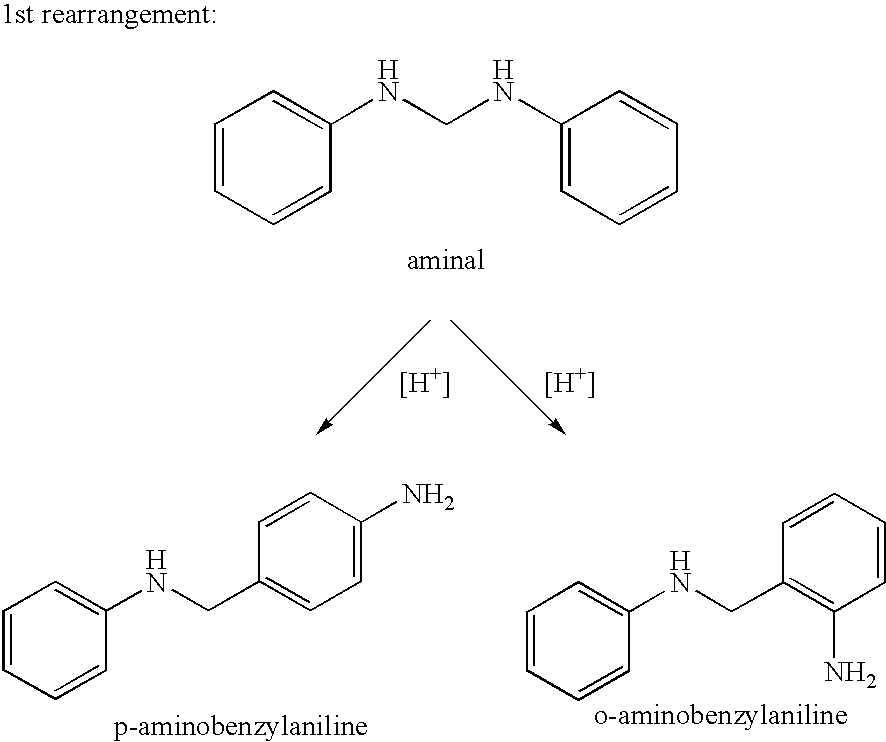
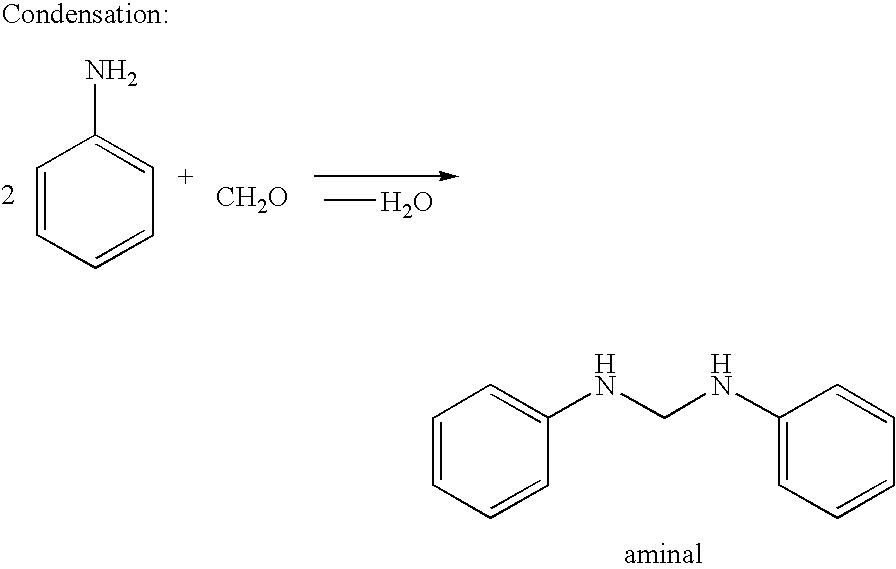
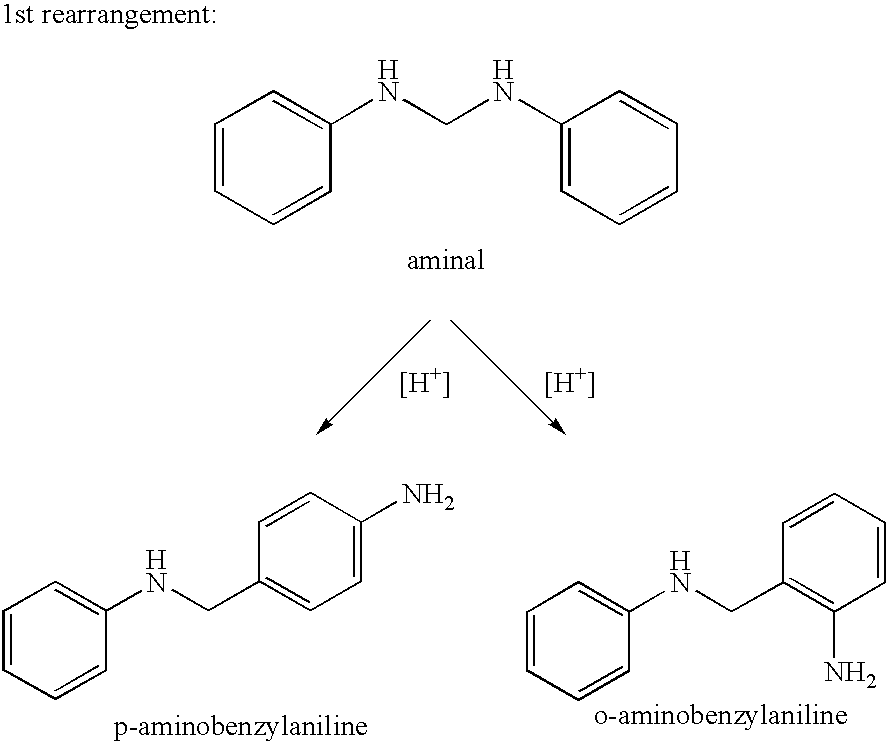
The invention provides a process for the preparation of polyamines of the diphenylmethane series. This process comprises a) reacting aniline and formaldehyde in a molar ratio of 1.5:1 to 6:1, in the presence of an acid catalyst at temperatures of 20° C. to 100° C., in which the water content in the acid reaction mixture is <20 wt. % and a degree of protonation of <15% is established, and b) increasing the temperature of the reaction to a temperature of 110° C. to 250° C. when the ratio of the weight contents of p-aminobenzylaniline to 4,4′-MDA in the reaction mixture falls below a value of 1.00.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Press Section and Permeable Belt in a Paper Machine
InactiveUS20080210397A1Large tensionIncrease the opening areaMachine wet endPaper/cardboardPaper machine
A belt press for a paper machine, the belt press including a roll having an exterior surface and a permeable belt. The permeable belt has a first side and is guided over a portion of the exterior surface of the roll. The permeable belt has a tension of at least approximately 30 KN / m, the first side has an open area of at least approximately 25% and a contact area of at least approximately 10%.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Moving belt sensor
ActiveUS7132943B2Improve system efficiencyReliable classificationDefence devicesMagnetic property measurementsClosed loopEngineering
A detection system is provided which is configured to have a transmitter capable of interacting with an object by generating a field, and a multiplicity of receivers operative to measure changes in the environment caused by the object's response to the generated field and mounted to a closed-looped belt, which is displaceable in a proximity to the object.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Process for the preparation of polyamines of the diphenylmethane series at a low degree of protonation
ActiveUS7253321B2Reduce the probability of reactionLong dwell timeIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationDiphenylmethaneMethylaniline
The invention provides a process for the preparation of polyamines of the diphenylmethane series. This process comprisesa) reacting aniline and formaldehyde in a molar ratio of 1.5:1 to 6:1, in the presence of an acid catalyst at temperatures of 20° C. to 100° C., in which the water content in the acid reaction mixture is <20 wt. % and a degree of protonation of <15% is established, andb) increasing the temperature of the reaction to a temperature of 110° C. to 250° C. when the ratio of the weight contents of p-aminobenzylaniline to 4,4′-MDA in the reaction mixture falls below a value of 1.00.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Process and apparatus for separating hydrocarbons from produced water
InactiveUS20110114566A1Improve uniformityMaximize effectivenessFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater contaminantsHigh concentrationTreated water
A process for removing hydrocarbons such as oil from produced water entrains high concentrations of very small gas bubbles within produced water inside a vertically-oriented primary separation tank by means of aerators immersed in the water inside the tank. Oil droplets coat the gas bubbles which form a buoyant oil-rich froth phase overlying a gas-rich liquid phase. The froth phase flows out through a discharge port in a preferably conical upper section of the primary tank, for disposal or recovery of oil as appropriate. Solid contaminants not borne by the froth phase may be intermittently settled out of the liquid phase and removed for treatment or disposal through a discharge port in a preferably conical lower section of the primary tank. Clean processed water is drawn a medial region of the primary tank for re-use as appropriate. In a preferred embodiment, the froth phase passes into a secondary separation tank for further separation of contaminants by means of gravity and / or supplemental aeration.
Owner:1139076 ALBERTA
Electro-kinetic air transporter and conditioner device with enhanced anti-microorganism capability
InactiveUS6974560B2Reduce the amount requiredLong dwell timeMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusParticulatesEmissivity
An electro-kinetic air conditioner for removing particulates from the air creates an airflow using no moving parts. The airflow is subjected to UV radiation from a germicidal lamp within the device. The conditioner includes an ion generator that has an electrode assembly including a first array of emitter electrodes, a second array of collector electrodes, and a high voltage generator. The device can also include a third or leading or focus electrode located upstream of the first array of emitter electrodes, and / or a trailing electrode located downstream of the second array of collector electrodes, and / or an interstitial electrode located between collector electrodes, and / or an enhanced emitter electrode with an enhanced length in order to increase emissivity.
Owner:SHARPER IMAGE ACQUISITION LLC A DELAWARE LIMITED LIABILITY
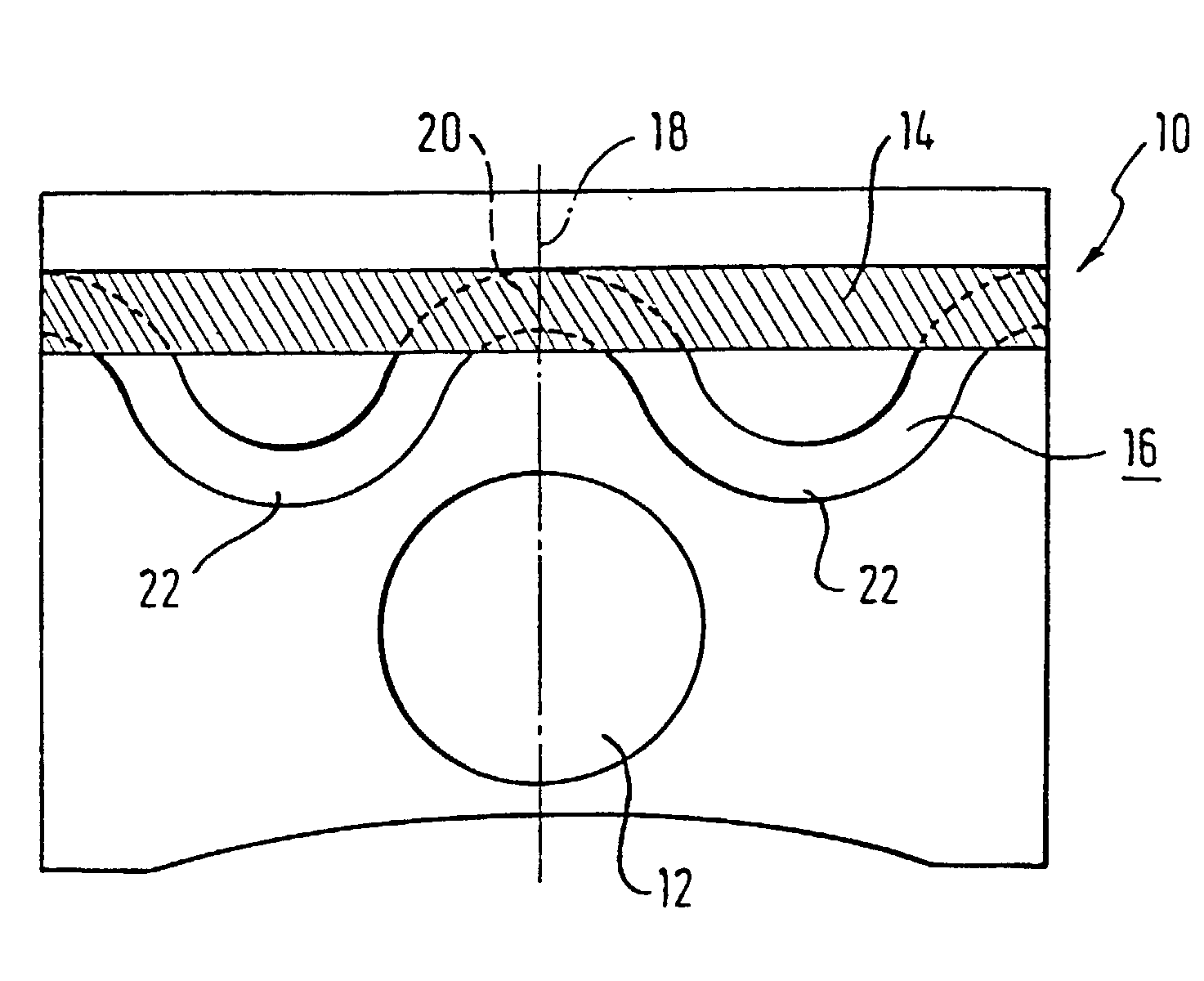
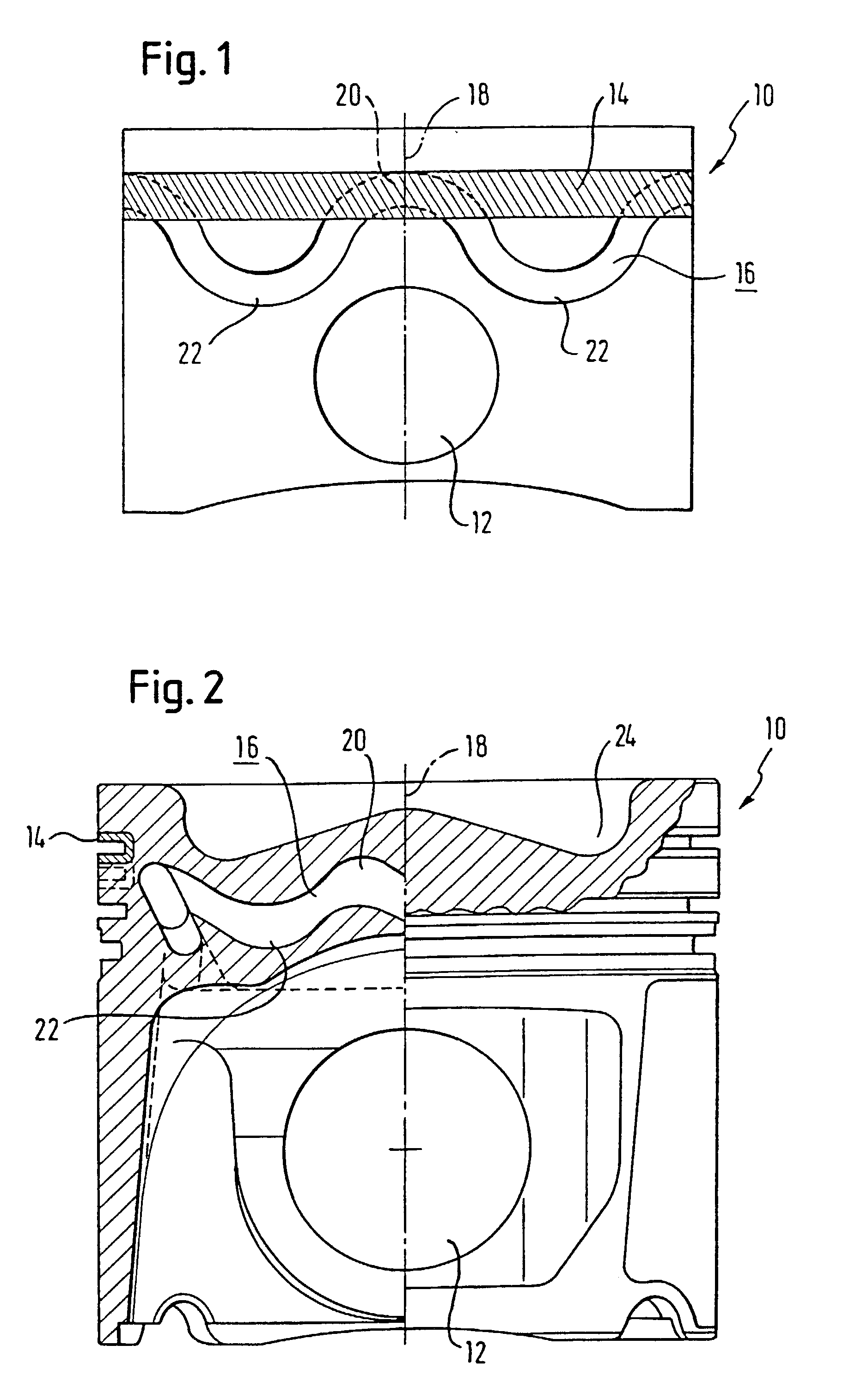
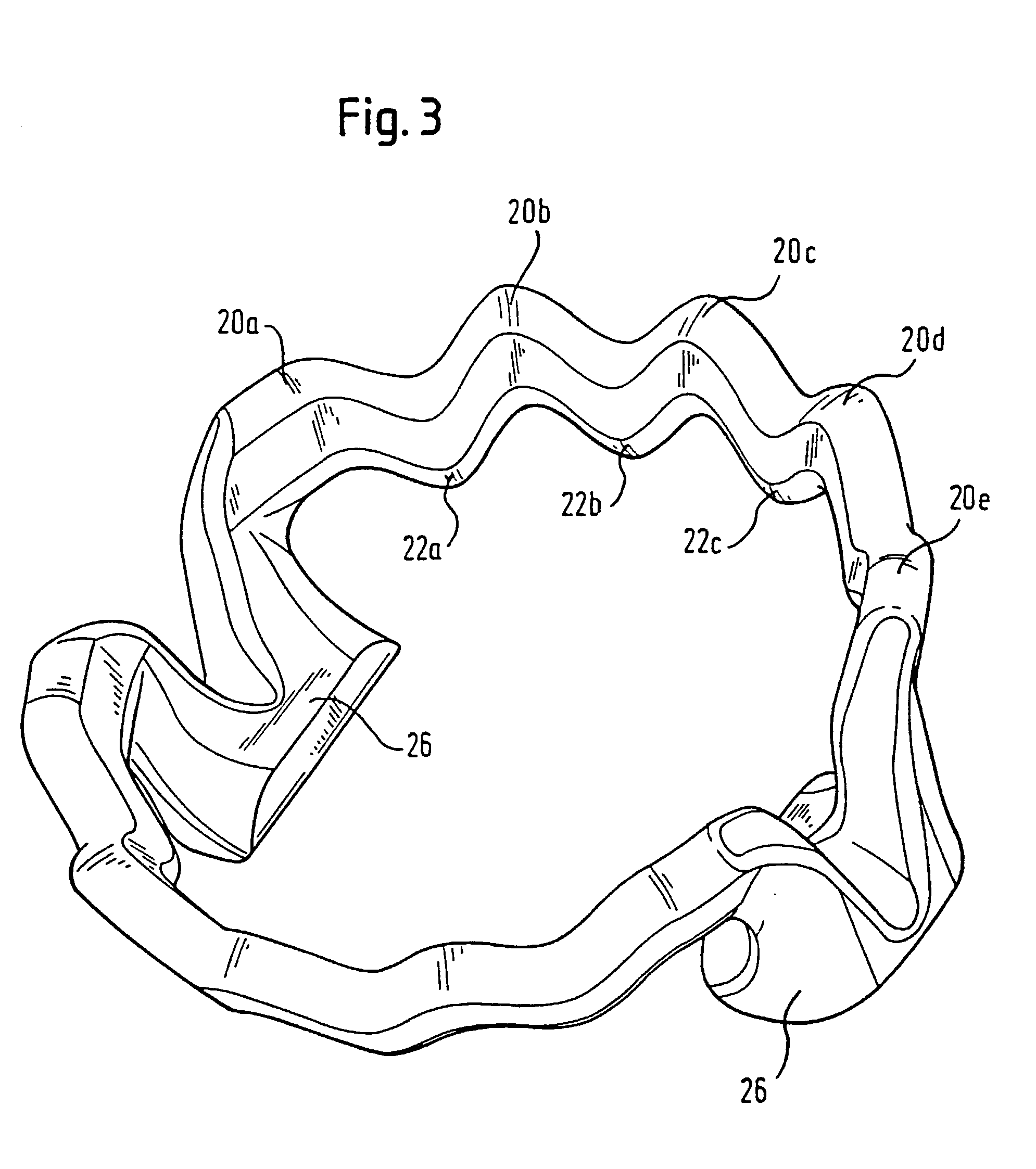
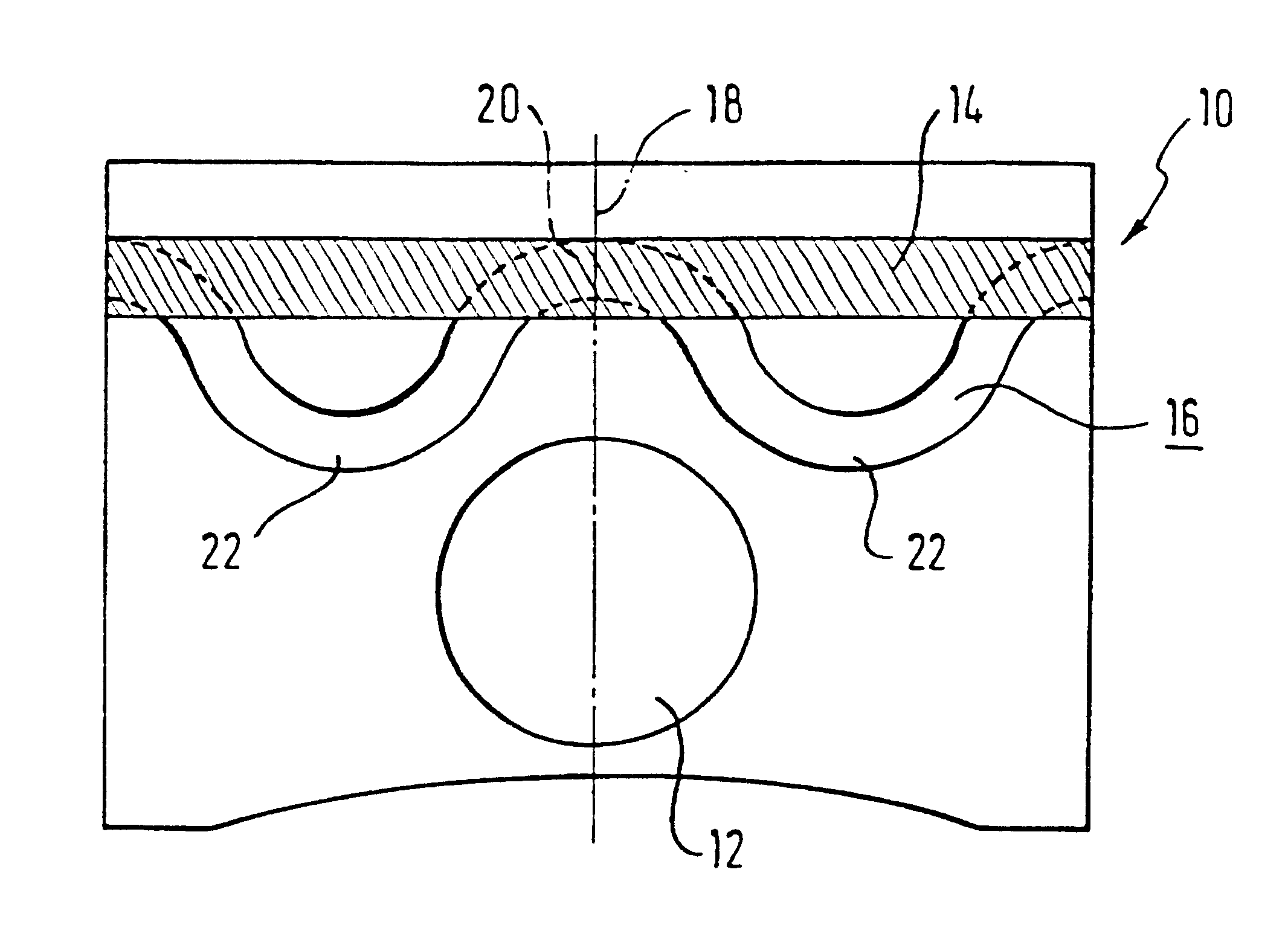
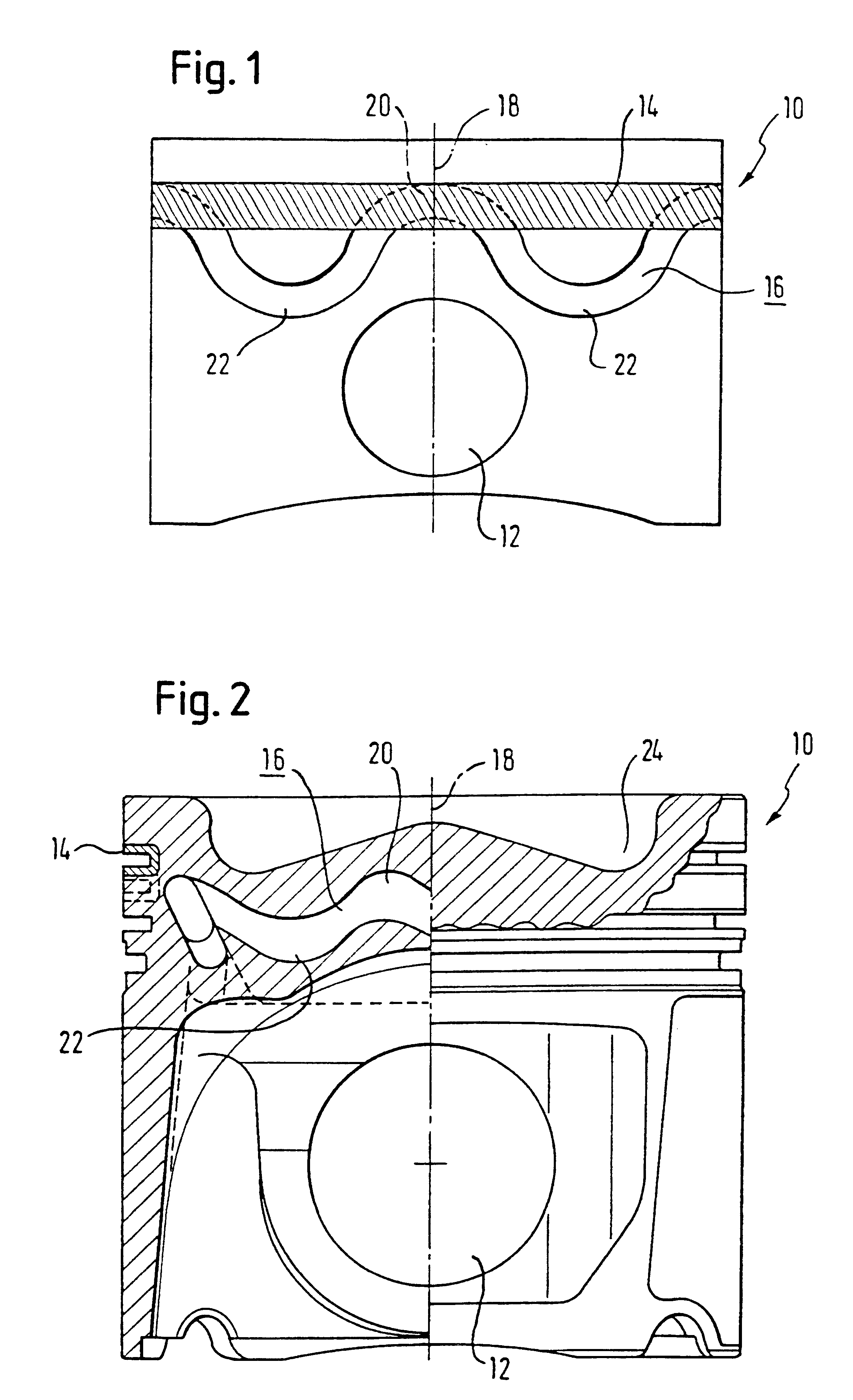
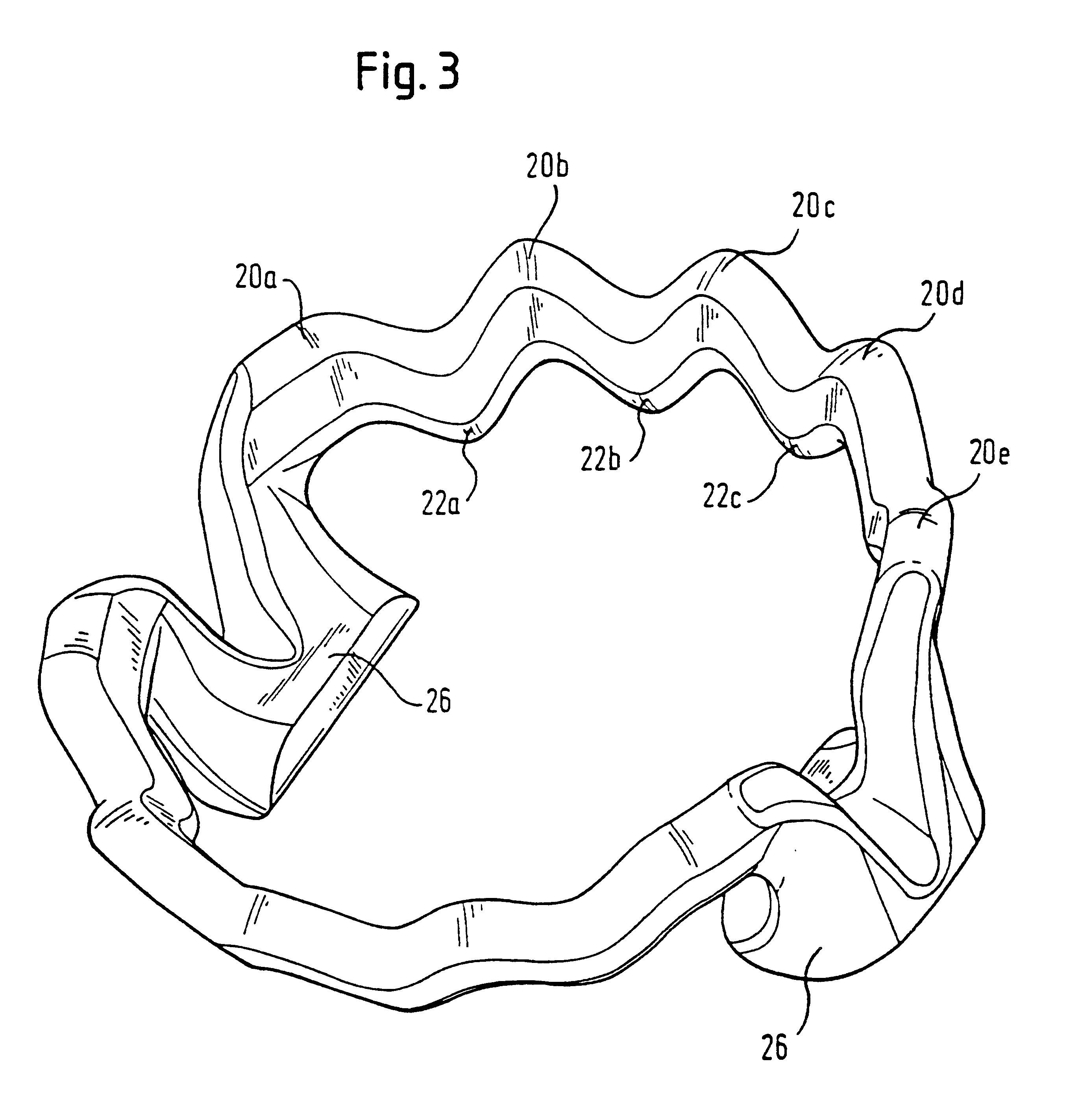
Liquid-cooled piston
InactiveUS20020162448A1Improve cooling effectReduce thicknessPlungersMachines/enginesCombustionEngineering
The invention relates to a liquid-cooled piston (10) for internal combustion engines having a cooling duct (16) that has an annular shape or consists of several annular segments, said duct having a substantially constant cross section along its extension and extending in an undulated manner at least in certain areas in the direction of the axis of the piston (18).
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL NURNBERG GMBH
Air conditioner devices including safety features
InactiveUS20050163669A1Reduce the amount requiredLong dwell timeMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusGermicidal lampElectrical and Electronics engineering
An air conditioner device includes a freestanding housing. An ion generator, which is positioned in the housing, includes at least one removable electrode. A germicidal lamp, which is also within the housing, emits UV radiation upon being energized. A safety mechanism cuts off power to at least one of the lamp and the ion generator when the removable electrode is removed from the housing. A removable panel is adapted to be secured to the housing. A further safety mechanism cuts-off power to at least one of the lamp and the ion generator when the removable panel is removed from the housing.
Owner:THE SHARPER IMAGE
Low-pressure airway management device with active coating and method for patient care
InactiveUS20100051035A1Reduce likelihoodReduce the possibilityTracheal tubesDiagnosticsActive agentCoated surface
An improved endotracheal tube that has a modified surface coating that can elute active agents is described. The coated surface and the use of the device according to a new method or regime for a healthcare worker to care for patients can help reduce the likelihood of ventilator acquire pneumonia or other infections in a patient's respiratory passages.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
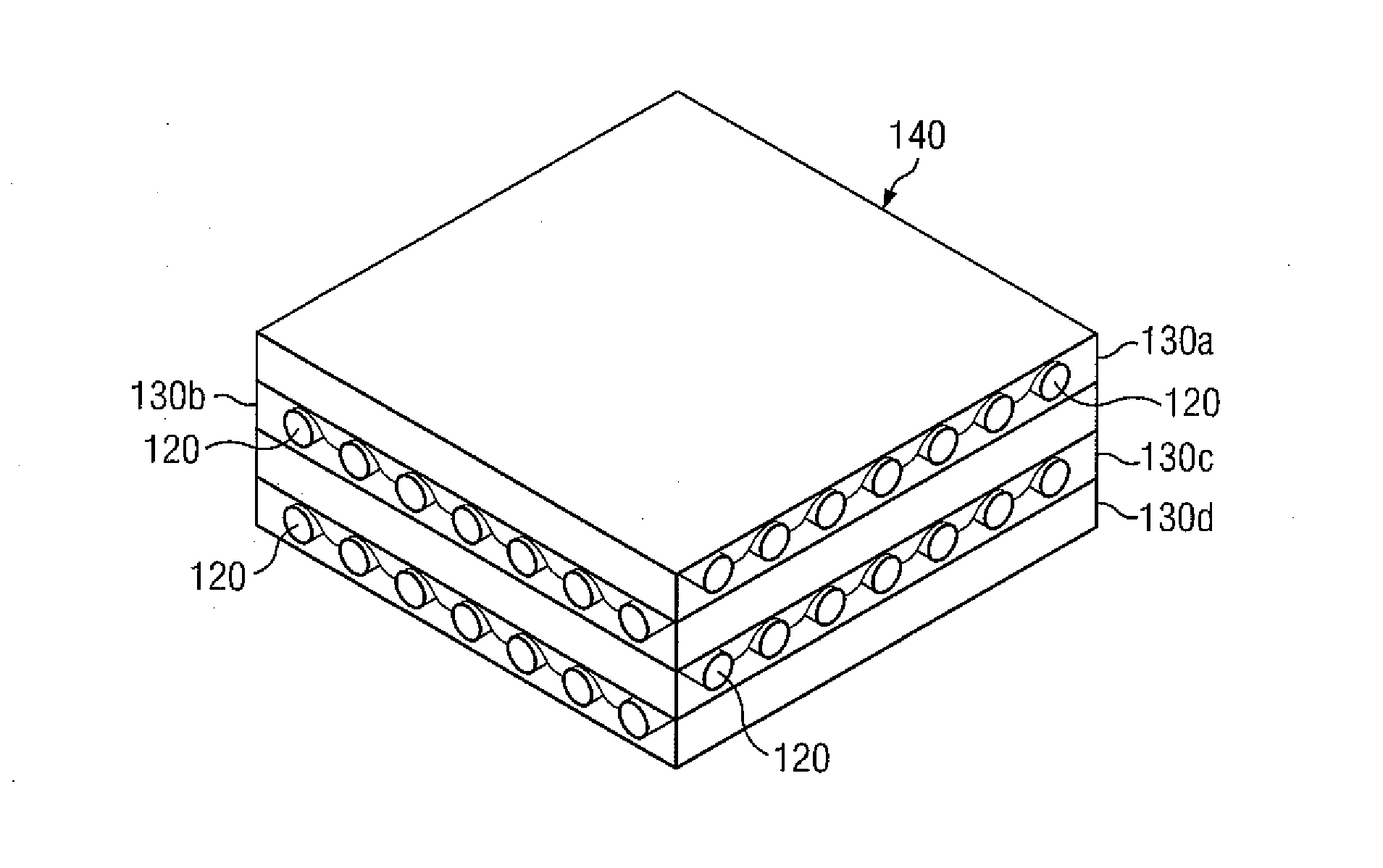
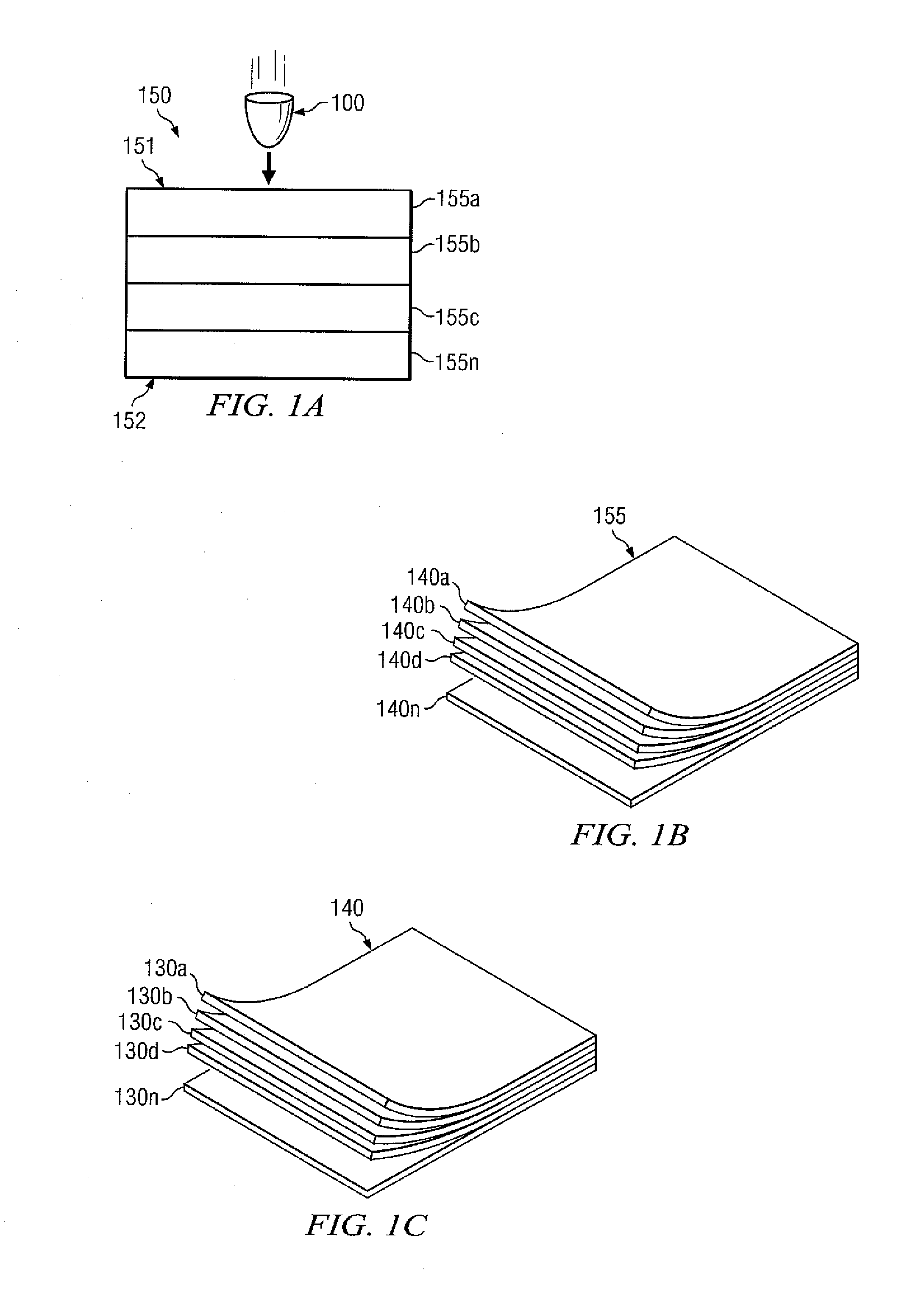
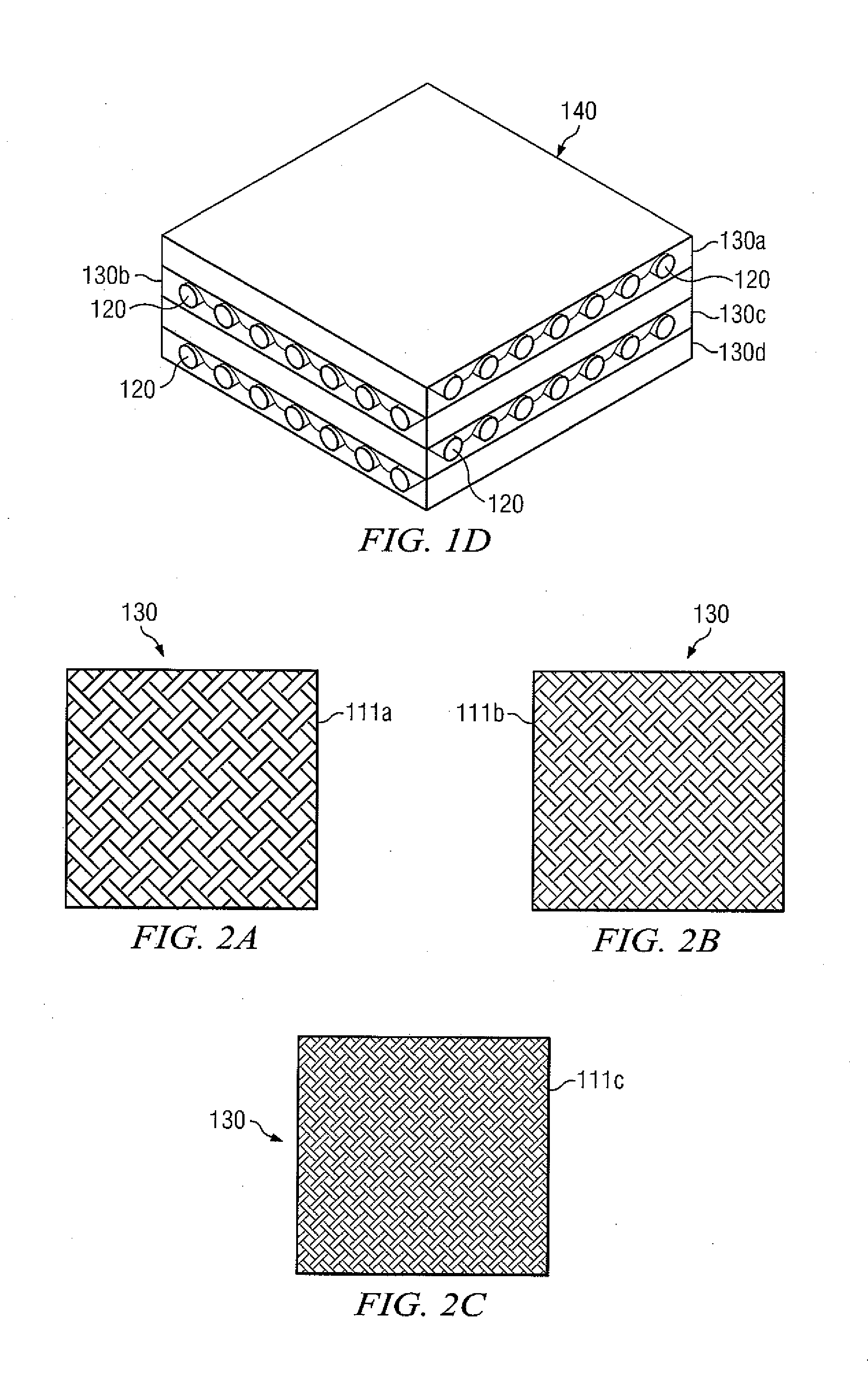
Method of Layering Composite Sheets to Improve Armor Capabilities
According to one embodiment, an armor system comprises a plurality of polylithic composite armor panels. Each of the polylithic composite armor panels comprising a plurality of layers. The plurality of layers comprise at least two layers having a different Young's modulus. Each of the plurality of layers comprising a plurality of sheets. The plurality of sheets comprise one or more fibers. The plurality of sheets have one or more respective weave characteristics.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Liquid-cooled piston
The invention relates to a liquid-cooled piston (10) for internal combustion engines having a cooling duct (16) that has an annular shape or consists of several annular segments, said duct having a substantially constant cross section along its extension and extending in an undulated manner at least in certain areas in the direction of the axis of the piston (18).
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL NURNBERG GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com